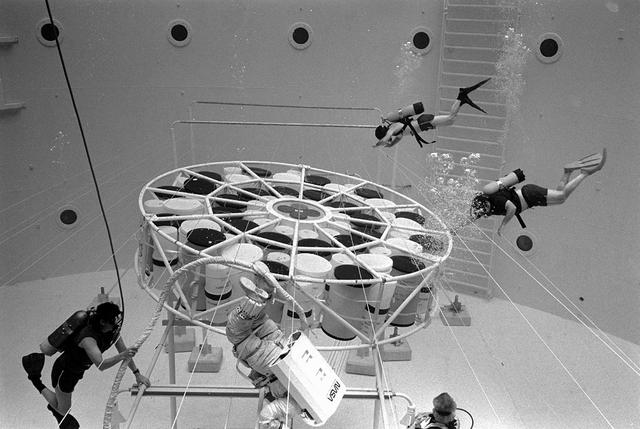

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built.Pictured is an experiment where the astronaut is required to move a large object which weighed 19,000 pounds. It was moved with realitive ease once the astronaut became familiar with his environment and his near weightless condition. Experiments of this nature provided scientists with the information needed regarding weight and mass allowances astronauts could manage in preparation for building a permanent space station in the future.
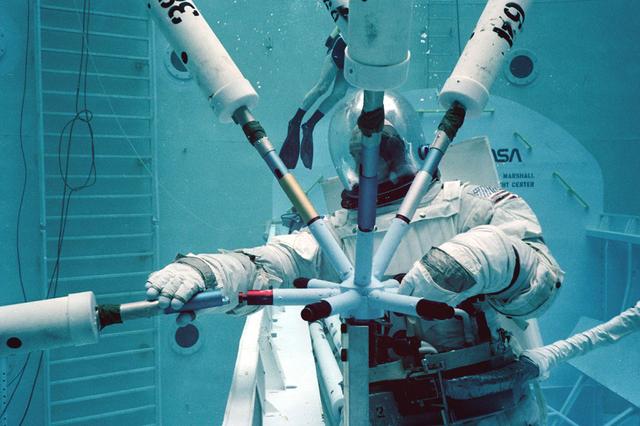

Once the United States' space program had progressed from Earth's orbit into outerspace, the prospect of building and maintaining a permanent presence in space was realized. To accomplish this feat, NASA launched a temporary workstation, Skylab, to discover the effects of low gravity and weightlessness on the human body, and also to develop tools and equipment that would be needed in the future to build and maintain a more permanent space station. The structures, techniques, and work schedules had to be carefully designed to fit this unique construction site. The components had to be lightweight for transport into orbit, yet durable. The station also had to be made with removable parts for easy servicing and repairs by astronauts. All of the tools necessary for service and repairs had to be designed for easy manipulation by a suited astronaut. And construction methods had to be efficient due to limited time the astronauts could remain outside their controlled environment. In lieu of all the specific needs for this project, an environment on Earth had to be developed that could simulate a low gravity atmosphere. A Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) was constructed by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1968. Since then, NASA scientists have used this facility to understand how humans work best in low gravity and also provide information about the different kinds of structures that can be built. Pictured is a Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) student working in a spacesuit on the Experimental Assembly of Structures in Extravehicular Activity (EASE) project which was developed as a joint effort between MFSC and MIT. The EASE experiment required that crew members assemble small components to form larger components, working from the payload bay of the space shuttle.

S-65 Meteor Impact Model set up in the former Altitude Wind Tunnel at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center just days after the September 12, 1962 rededication of the facility as the Space Power Chamber. Although larger test chambers would later be constructed, the rapid conversion of the wind tunnel into two space tanks allowed the facility to play a vital role in the early years of the space program. The eastern section of the tunnel, seen here became a vacuum chamber capable of simulating 100 miles altitude. This space tank was envisioned for the study of small satellites like this one. The transfer of the Centaur Program to Lewis one month late, however, permanently changed this mission. NASA was undertaking an in depth study at the time on the effect of micrometeoroids on satellites. Large space radiators were particularly vulnerable to damage from the small particles of space debris. In order to determine the hazard from meteoroids researchers had to define the flux rate relative to the mass and the velocity distribution because the greater the mass or the velocity of a meteoroid the greater the damage.
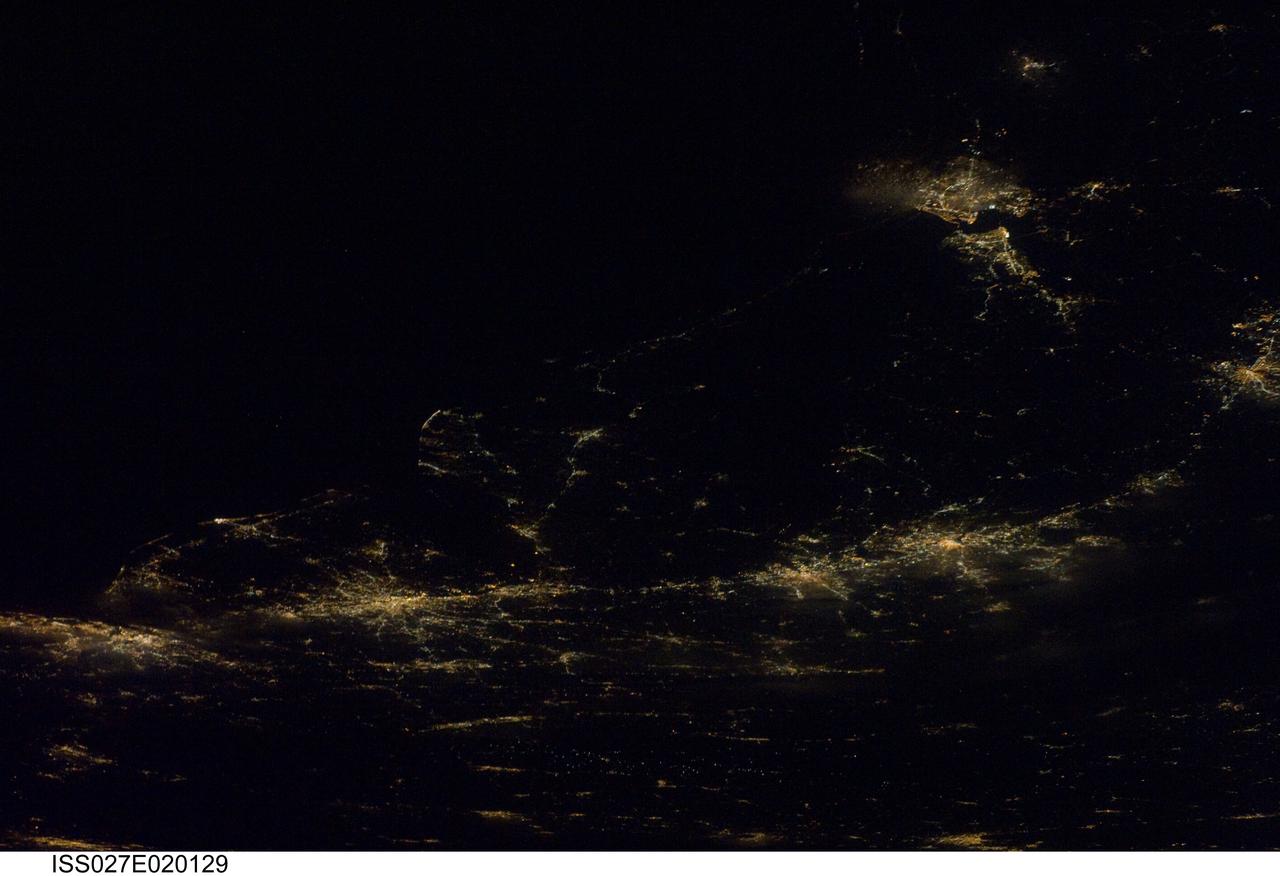

ISS027-E-020129 (6 April 2011) --- A night time view of the Atlantic Seaboard Conurbation, United States of America, is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 27 crew member on the International Space Station. As regional metropolitan areas expand in both physical area and population, they typically aggregate to form economically, politically, and to some extent socially linked entities known as conurbations – the term “megalopolis” has also been used. One of the largest conurbations in the world is located along the eastern coastline of the United States, and has been termed the Atlantic Seaboard Conurbation (ASC). The ASC extends over 1,000 kilometers and includes the major economic, governmental, and cultural centers of Boston, Mass.; New York, N.Y.; Philadelphia, Pa.; Baltimore, Md.; and Washington, D.C. This photograph includes every metropolitan area in the ASC except for Boston, Mass. (located off the image to the northeast of New York, N.Y.). The image was taken during “local night”, which highlights the position and extent of each metropolitan area along the eastern seaboard by their urban lighting patterns. The establishment and growth of the conurbation was facilitated by transportation networks (railroads, highways, and air travel routes) for transfer of goods, materials, and population between the metropolitan areas. Two other large metropolitan areas are visible in the image – Norfolk, Va. and Richmond, Va. at upper right – but these are not considered to be part of the ASC. In contrast to the city lights that mark metropolitan areas and smaller communities along the sea coast and interior, the Atlantic Ocean appears as a featureless dark region occupying the upper left quarter of the image.
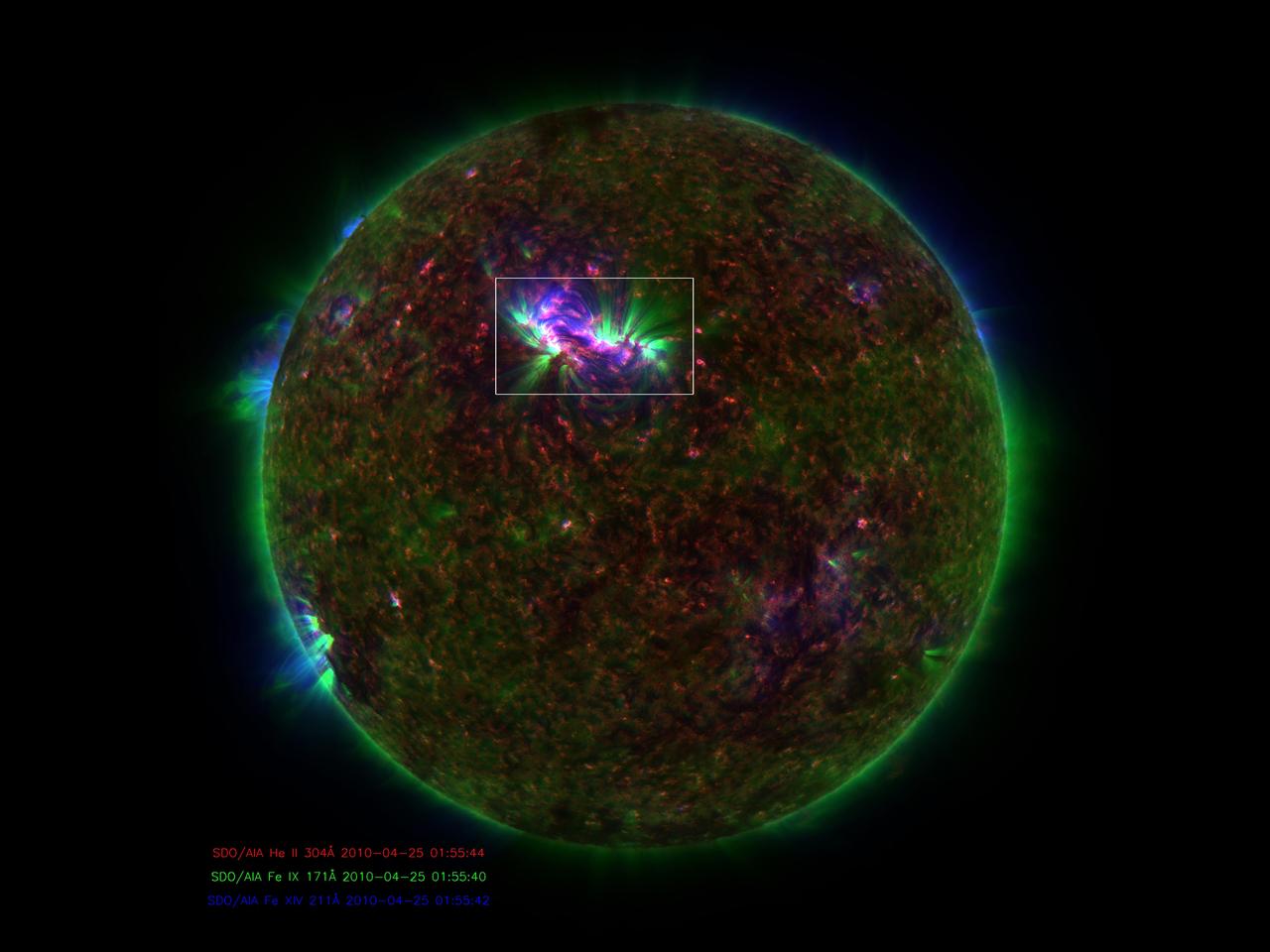
NASA image release January 6, 2010 Caption: Spicules on the sun, as observed by the Solar Dynamics Observatory. These bursts of gas jet off the surface of the sun at 150,000 miles per hour and contain gas that reaches temperatures over a million degrees. GREENBELT, Md. -- Observations from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and the Japanese satellite Hinode show that some gas in the giant, fountain-like jets in the sun's atmosphere known as spicules can reach temperatures of millions of degrees. The finding offers a possible new framework for how the sun's high atmosphere gets so much hotter than the surface of the sun. What makes the high atmosphere, or corona, so hot – over a million degrees, compared to the sun surface's 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit -- remains a poorly understood aspect of the sun's complicated space weather system. That weather system can reach Earth, causing auroral lights and, if strong enough, disrupting Earth's communications and power systems. Understanding such phenomena, therefore, is an important step towards better protecting our satellites and power grids. "The traditional view is that all the heating happens higher up in the corona," says Dean Pesnell, who is SDO's project scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "The suggestion in this paper is that cool gas is being ejected from the sun's surface in spicules and getting heated on its way to the corona." Spicules were first named in the 1940s, but were hard to study in detail until recently, says Bart De Pontieu of Lockheed Martin's Solar and Astrophysics Laboratory, Palo Alto, Calif. who is the lead author on a paper on this subject in the January 7, 2011 issue of Science magazine. In visible light, spicules can be seen to send large masses of so-called plasma – the electromagnetic gas that surrounds the sun – up through the lower solar atmosphere or photosphere. The amount of material sent up is stunning, some 100 times as much as streams away from the sun in the solar wind towards the edges of the solar system. But nobody knew if they contained hot gas. "Heating of spicules to the necessary hot temperatures has never been observed, so their role in coronal heating had been dismissed as unlikely," says De Pontieu. Now, De Pontieu's team -- which included researchers at Lockheed Martin, the High Altitude Observatory of the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) in Colorado and the University of Oslo, Norway -- was able to combine images from SDO and Hinode to produce a more complete picture of the gas inside these gigantic fountains. The scientists found that a large fraction of the gas is heated to a hundred thousand degrees, while a small fraction is heated to millions of degrees. Time-lapsed images show that this material spews up into the corona, with most falling back down towards the surface of the sun. However, the small fraction of the gas that is heated to millions of degrees does not immediately return to the surface. Given the large number of spicules on the Sun, and the amount of material in the spicules, the scientists believe that if even some of that super hot plasma stays aloft it would make a contribution to coronal heating. Astrophysicist Jonathan Cirtain, who is the U.S. project scientist for Hinode at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, Ala., says that incorporating such new information helps address an important question that reaches far beyond the sun. "This breakthrough in our understanding of the mechanisms which transfer energy from the solar photosphere to the corona addresses one of the most compelling questions in stellar astrophysics: How is the atmosphere of a star heated?" he says. "This is a fantastic discovery, and demonstrates the muscle of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, comprised of numerous instruments on multiple observatories." Hinode is the second mission in NASA's Solar Terrestrial Probes program, the goal of which is to improve understanding of fundamental solar and space physics processes. The mission is led by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ). The collaborative mission includes the U.S., the United Kingdom, Norway and Europe. NASA Marshall manages Hinode U.S. science operations and oversaw development of the scientific instrumentation provided for the mission by NASA, academia and industry. The Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center is the lead U.S. investigator for the Solar Optical Telescope on Hinode. SDO is the first mission in a NASA science program called Living With a Star, the goal of which is to develop the scientific understanding necessary to address those aspects of the sun-Earth system that directly affect our lives and society. NASA Goddard built, operates, and manages the SDO spacecraft for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. To learn more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sdo/news/news20110106-spicules.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sdo/news/news20110106-spicules...</a> Credit: NASA Goddard/SDO/AIA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>