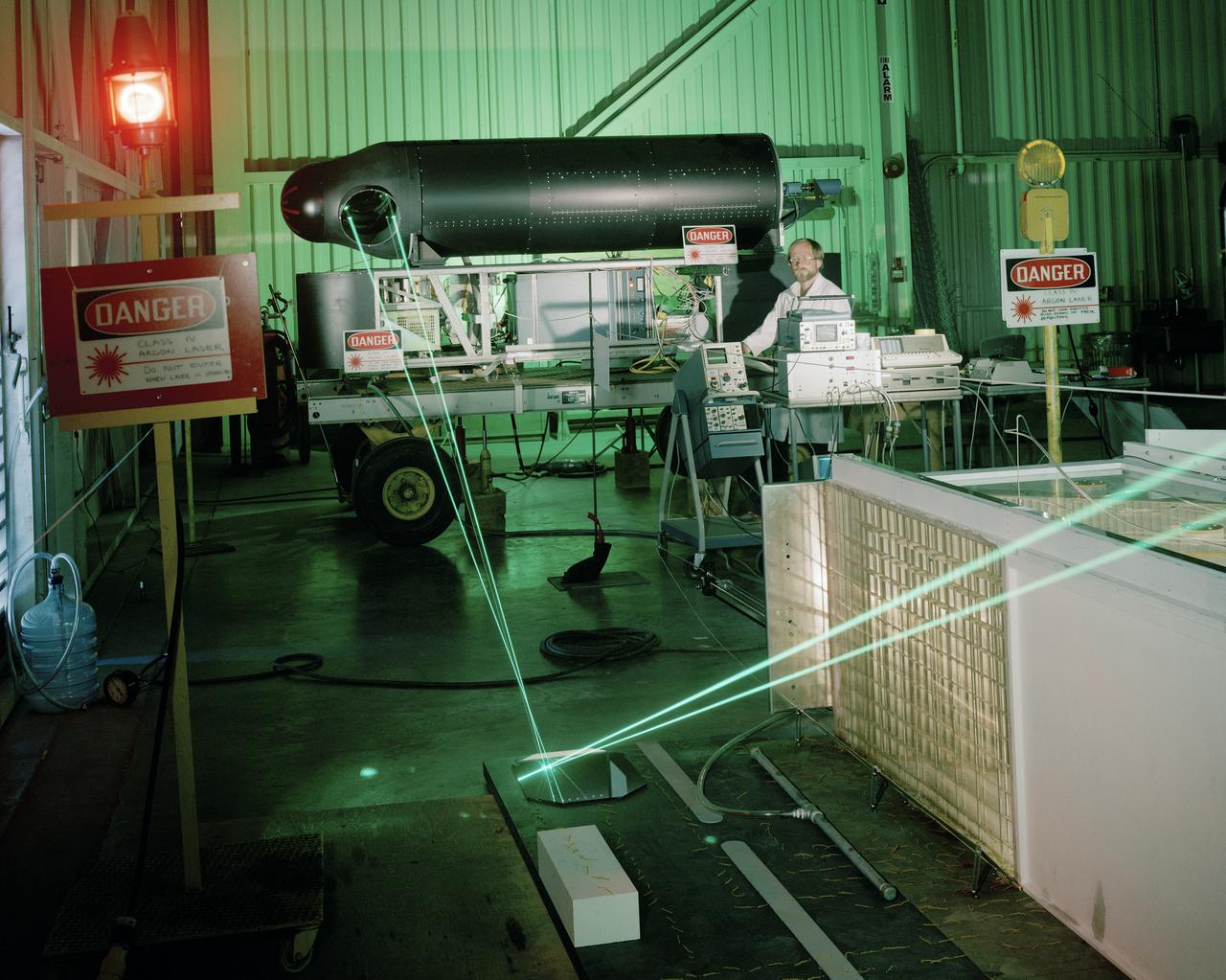
40x80x120 Foot Wind Tunnel at NASA's Ames Research Center Laser Velocimeter (LV) Long Range System. Requesting Organization: Low Speed Aircraft Photographed on May 18, 1983
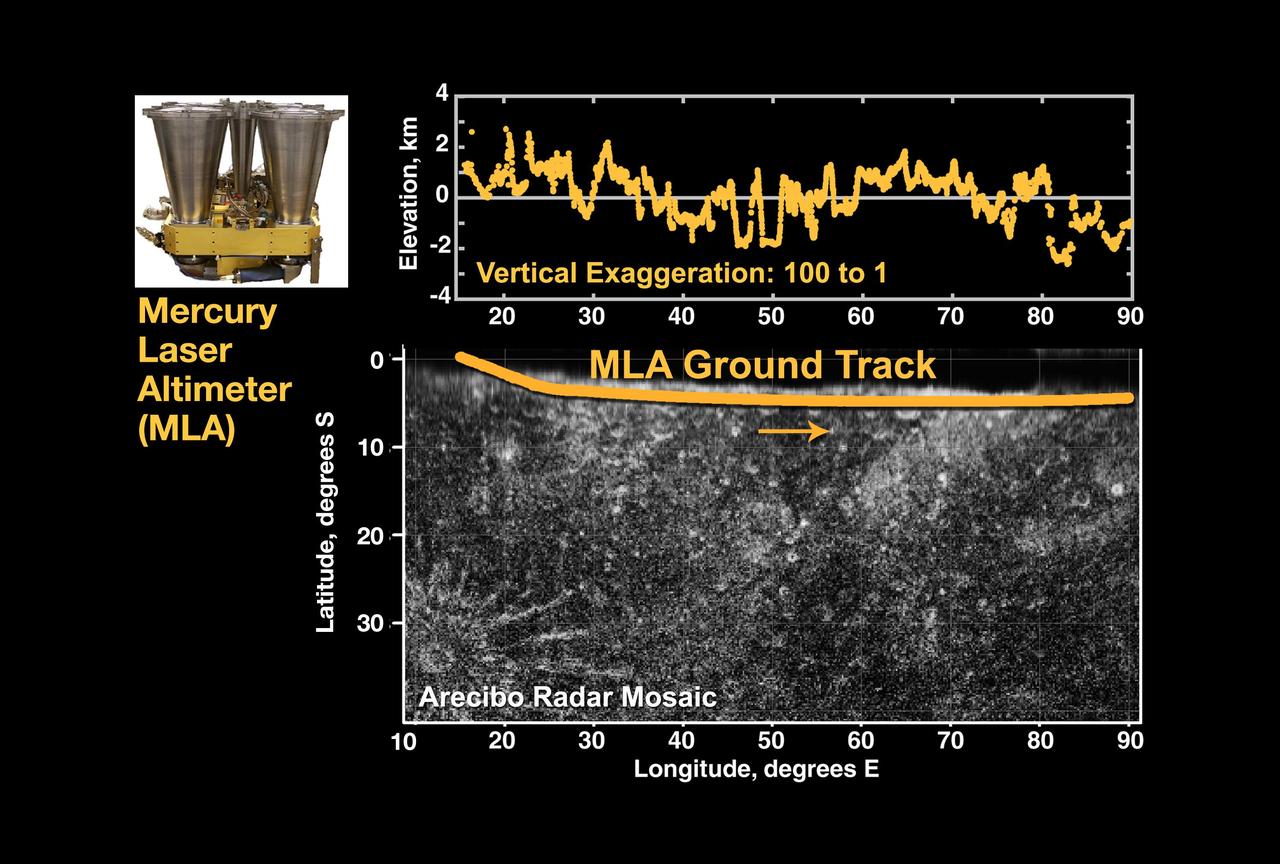
First Laser Altimetry for Mercury
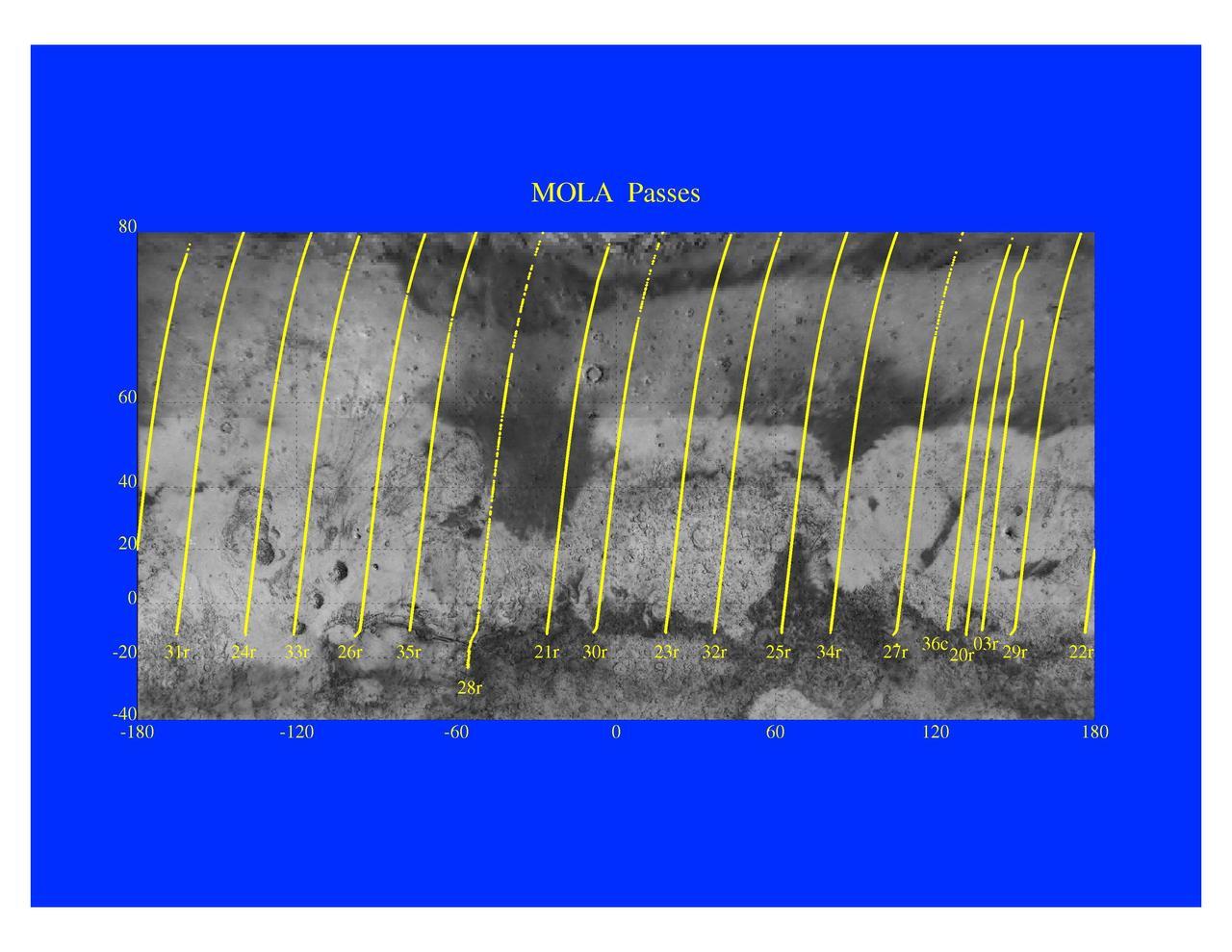
Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter Passes
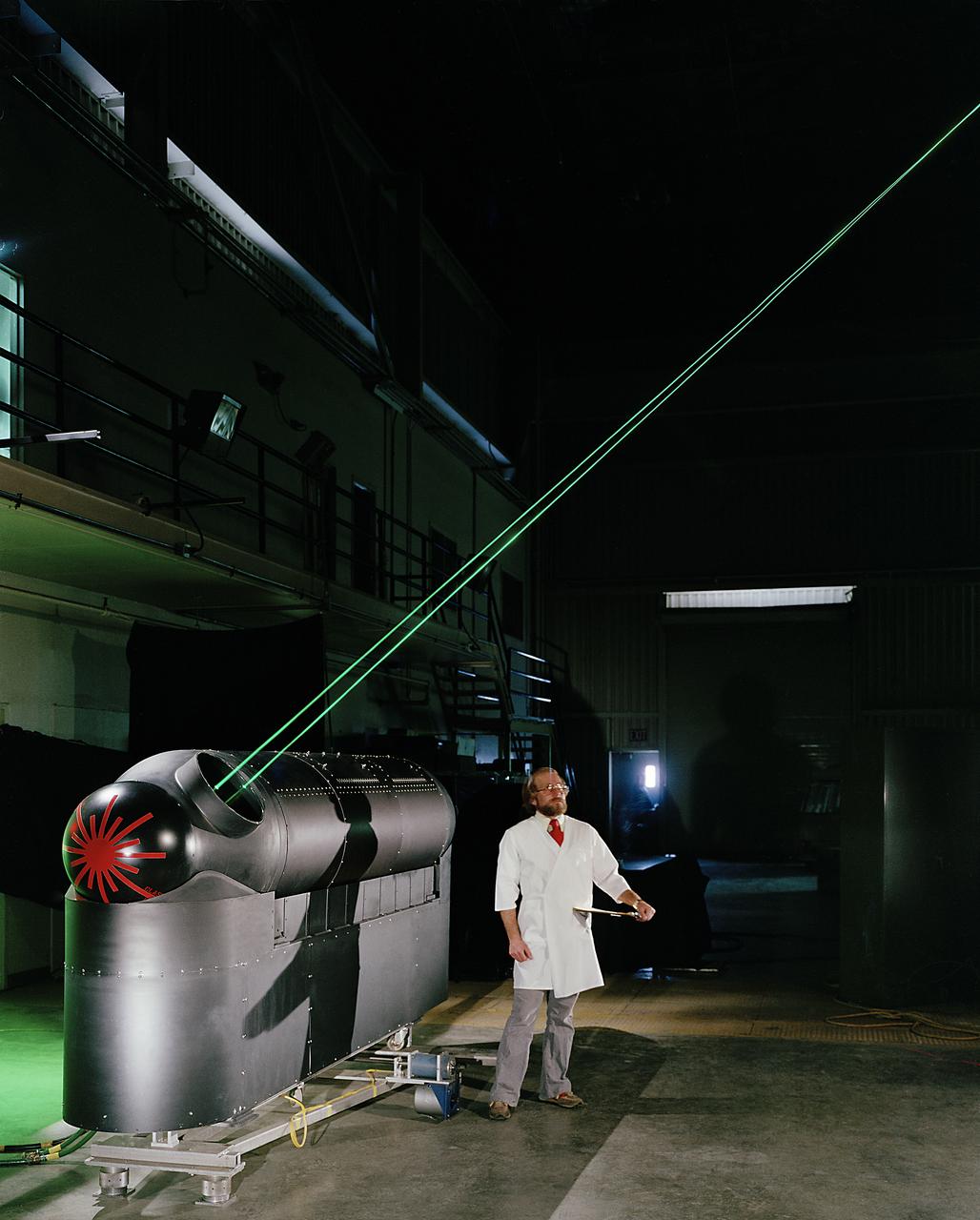

Long Range Laser Velocimeter in 40x80x120 Foot Wind Tunnel at NASA Ames. For use in NFAC.
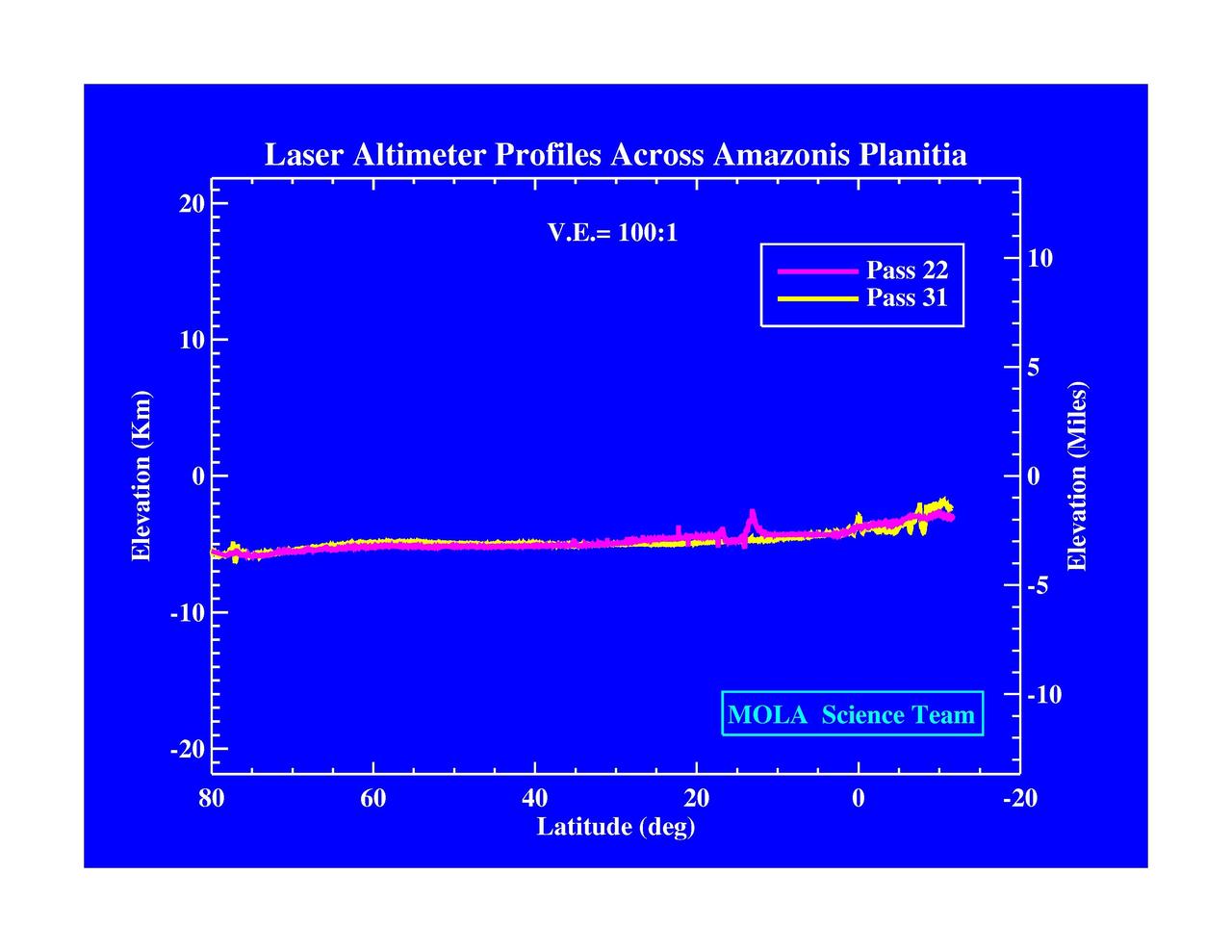
Laser Altimeter Profiles Across Amazonis Planitia
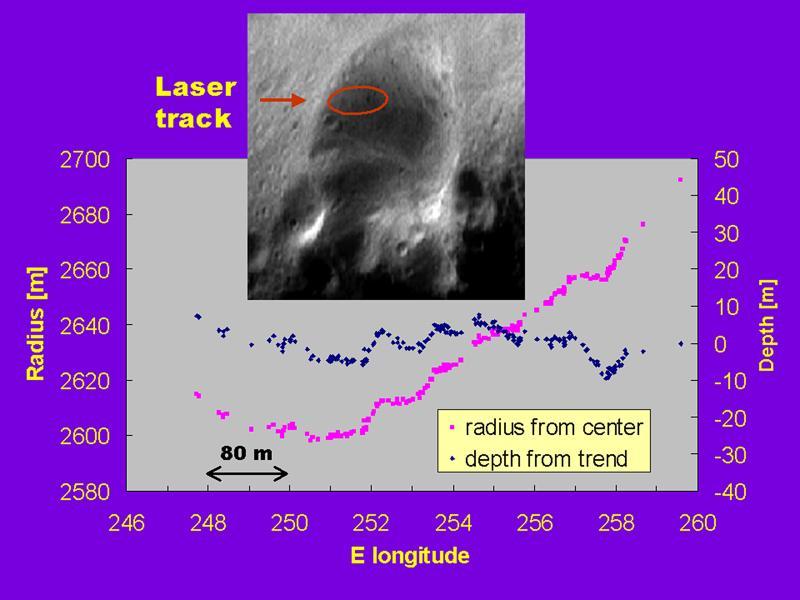
Topographic Profiles from the NEAR Laser Rangefinder
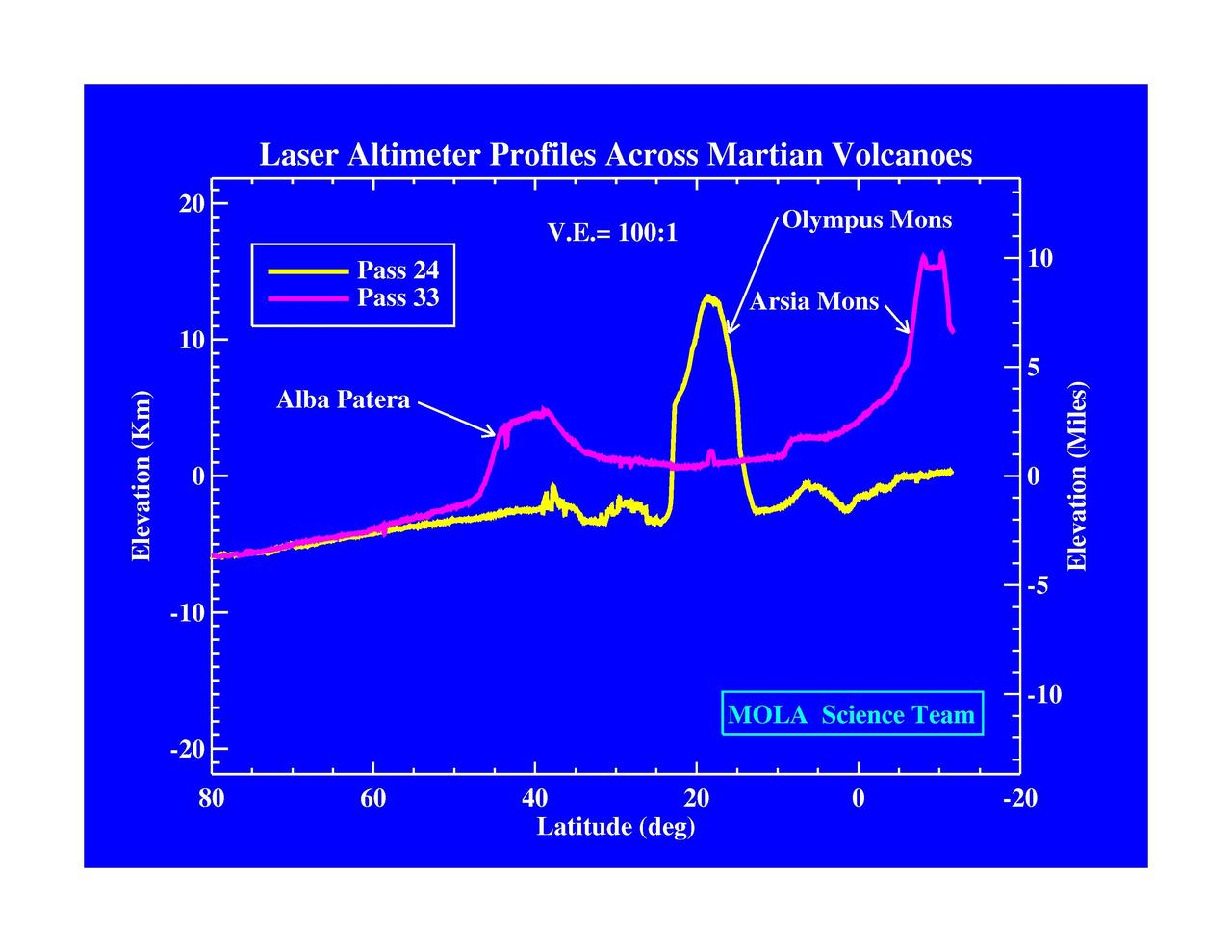
Laser Altimeter Profiles Across Martian Volcanoes
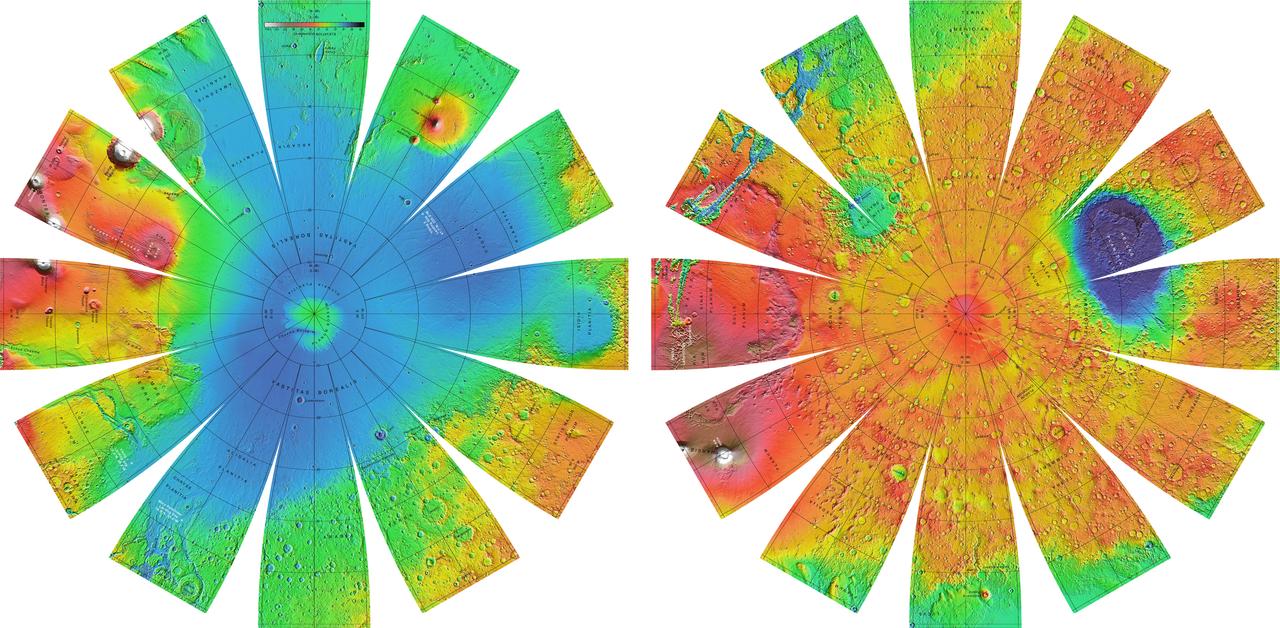
Mars Orbiter Laser Altimiter MOLA Globe

A brief laser flash at the center of the frame was part of an experiment conducted by two NASA CubeSats. In it, one small satellite used a laser to send information to the ISARA CubeSat, managed by JPL. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23117
This picture shows a lab demonstration of the measurement chamber inside the Tunable Laser Spectrometer, an instrument that is part of the Sample Analysis at Mars investigation on NASA Curiosity rover.

ICESat-2 big send off event for the ATLAS laser instrument at the Goddard Recreation Center
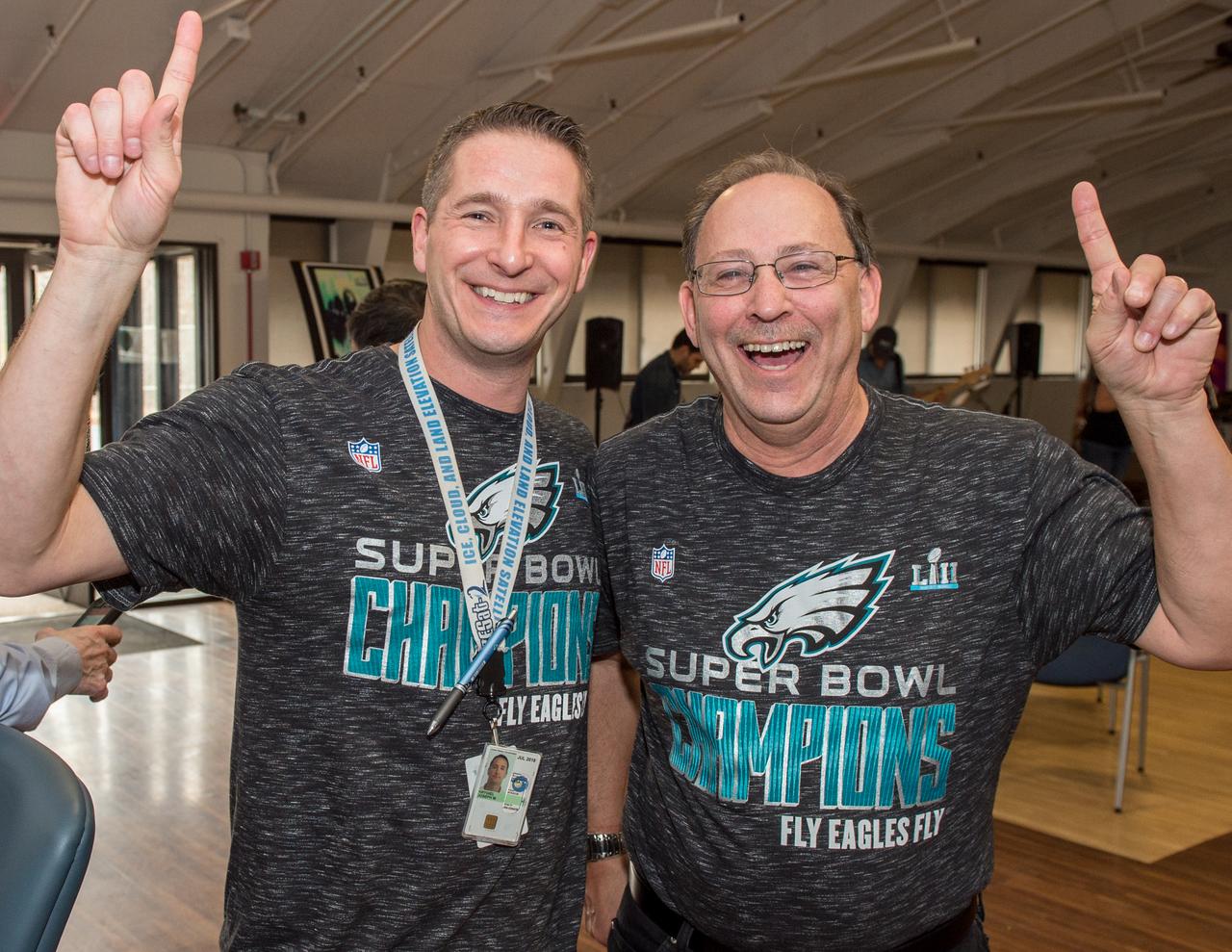

ICESat-2 big send off event for the ATLAS laser instrument at the Goddard Recreation Center
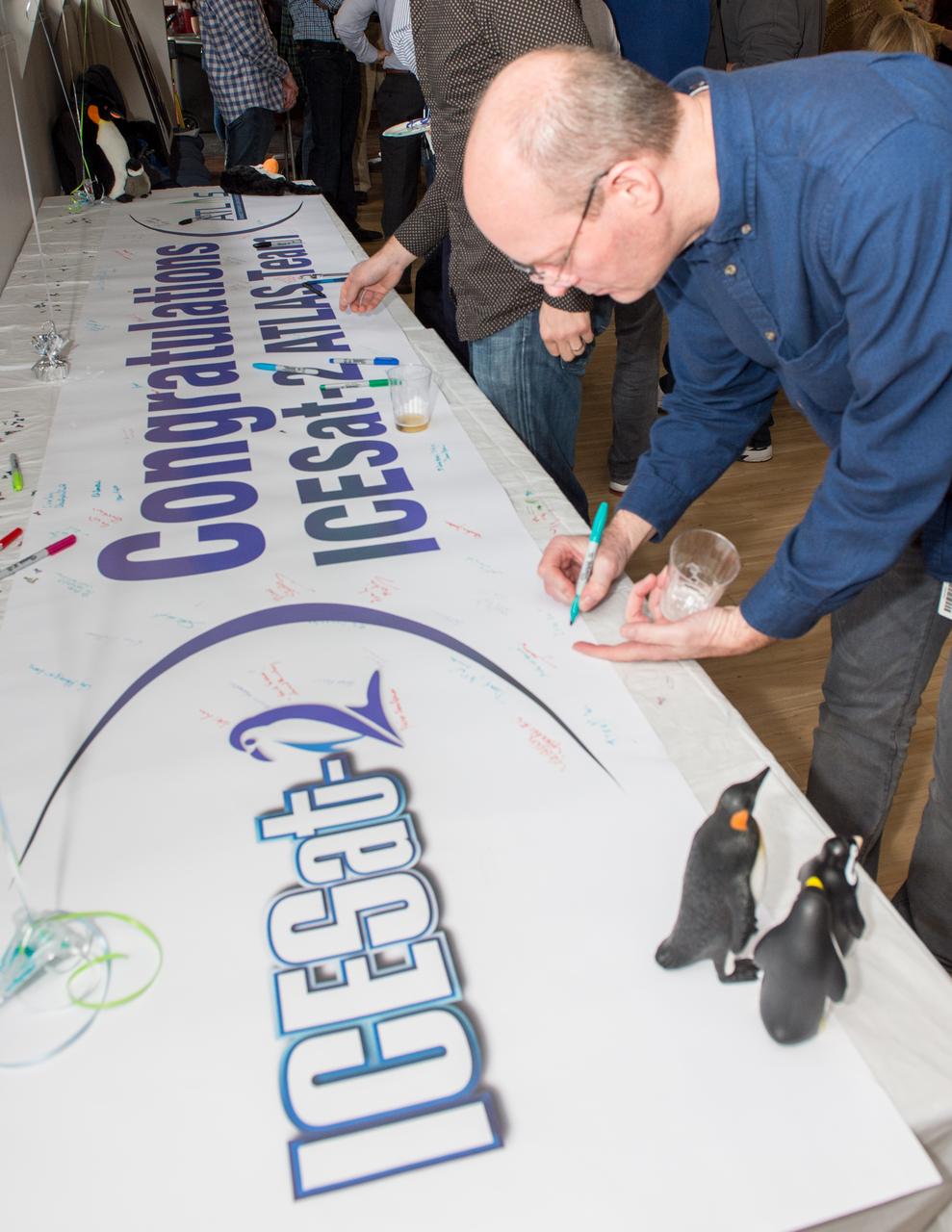

ICESat-2 big send off event for the ATLAS laser instrument at the Goddard Recreation Center
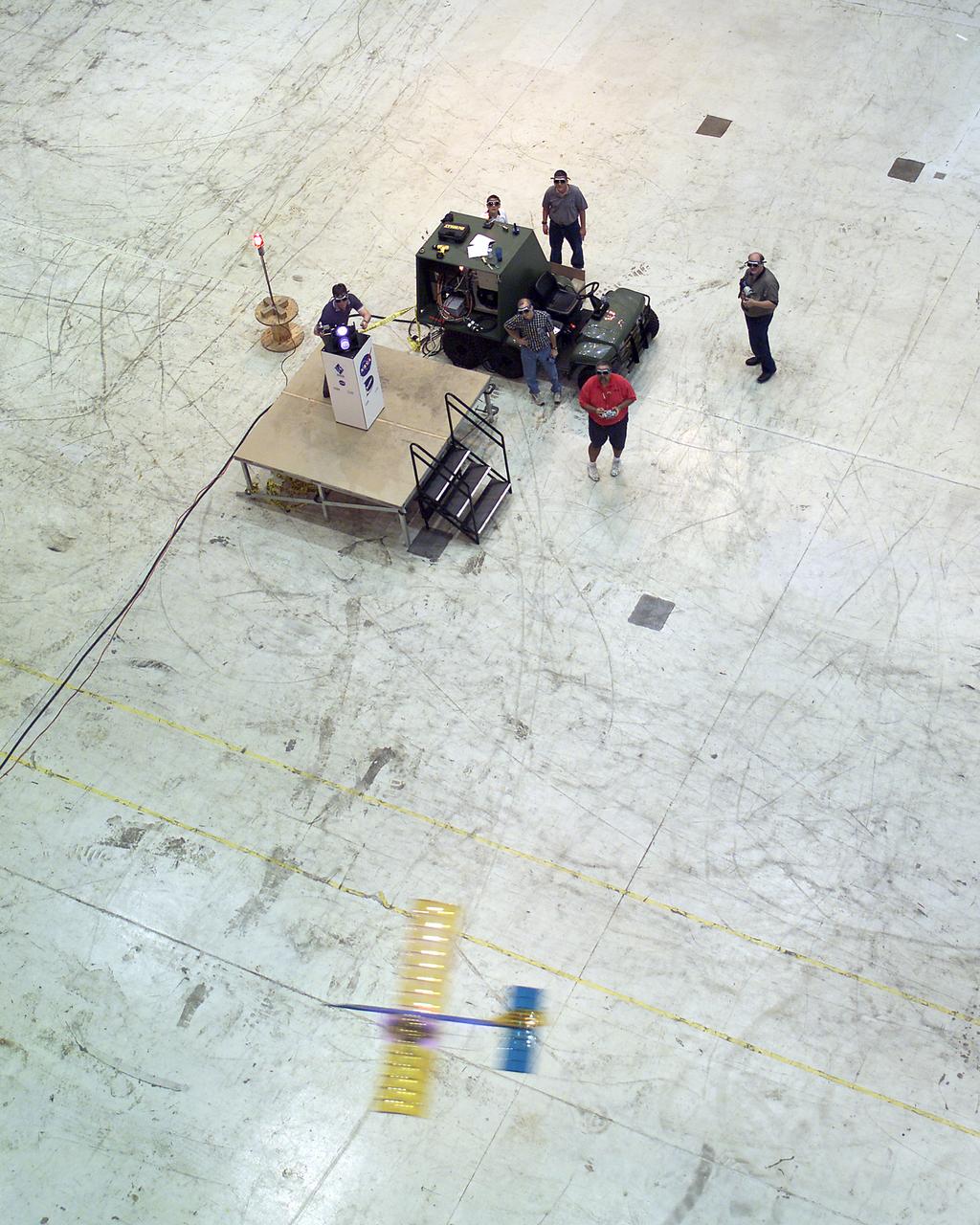

Powered by a laser beam directed at it from a center pedestal, a lightweight model plane makes the first flight of an aircraft powered by laser energy inside a building at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center.
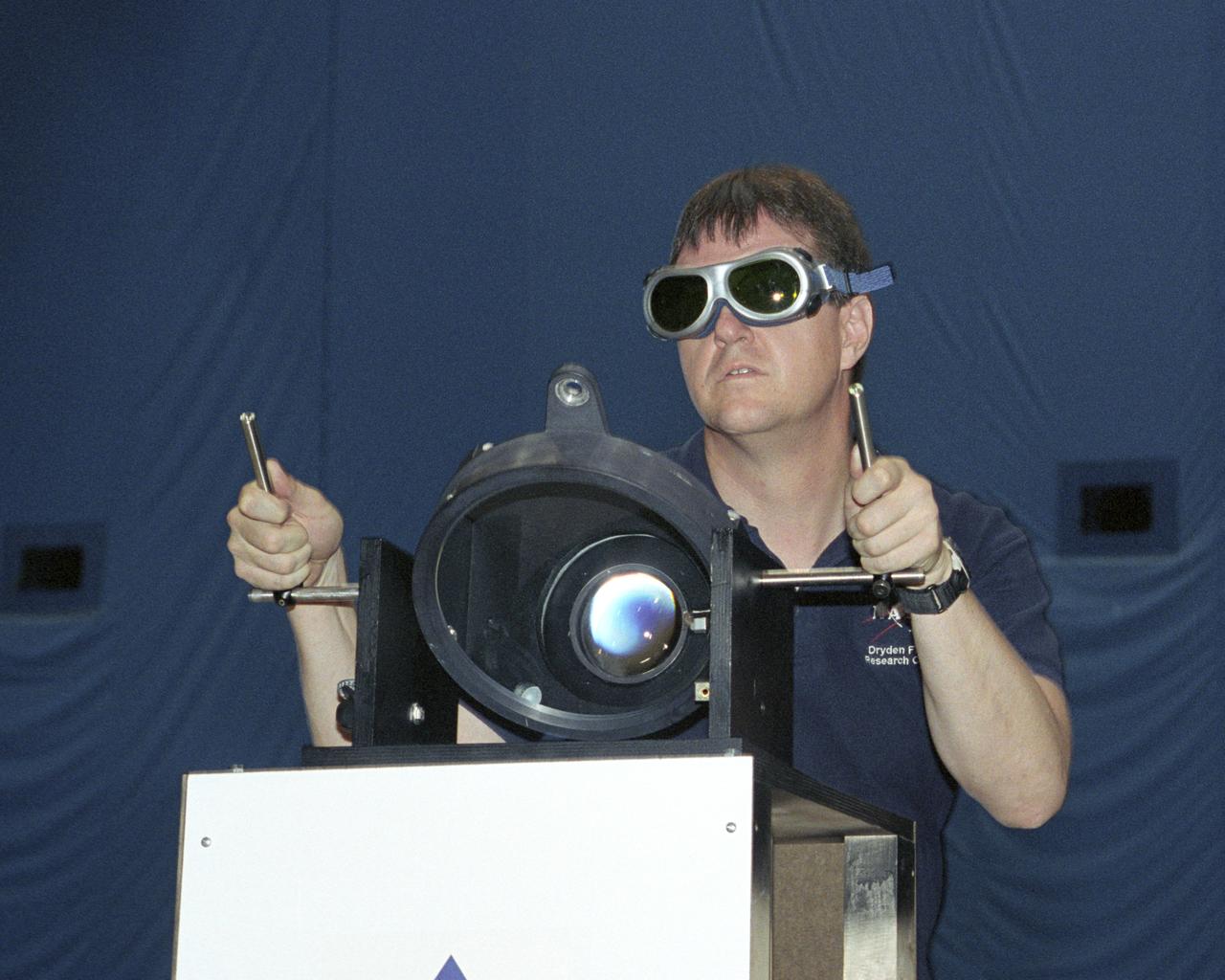

NASA Dryden project engineer Dave Bushman carefully aims the optics of a laser device at a solar cell panel on a model aircraft during the first flight demonstration of an aircraft powered by laser light.
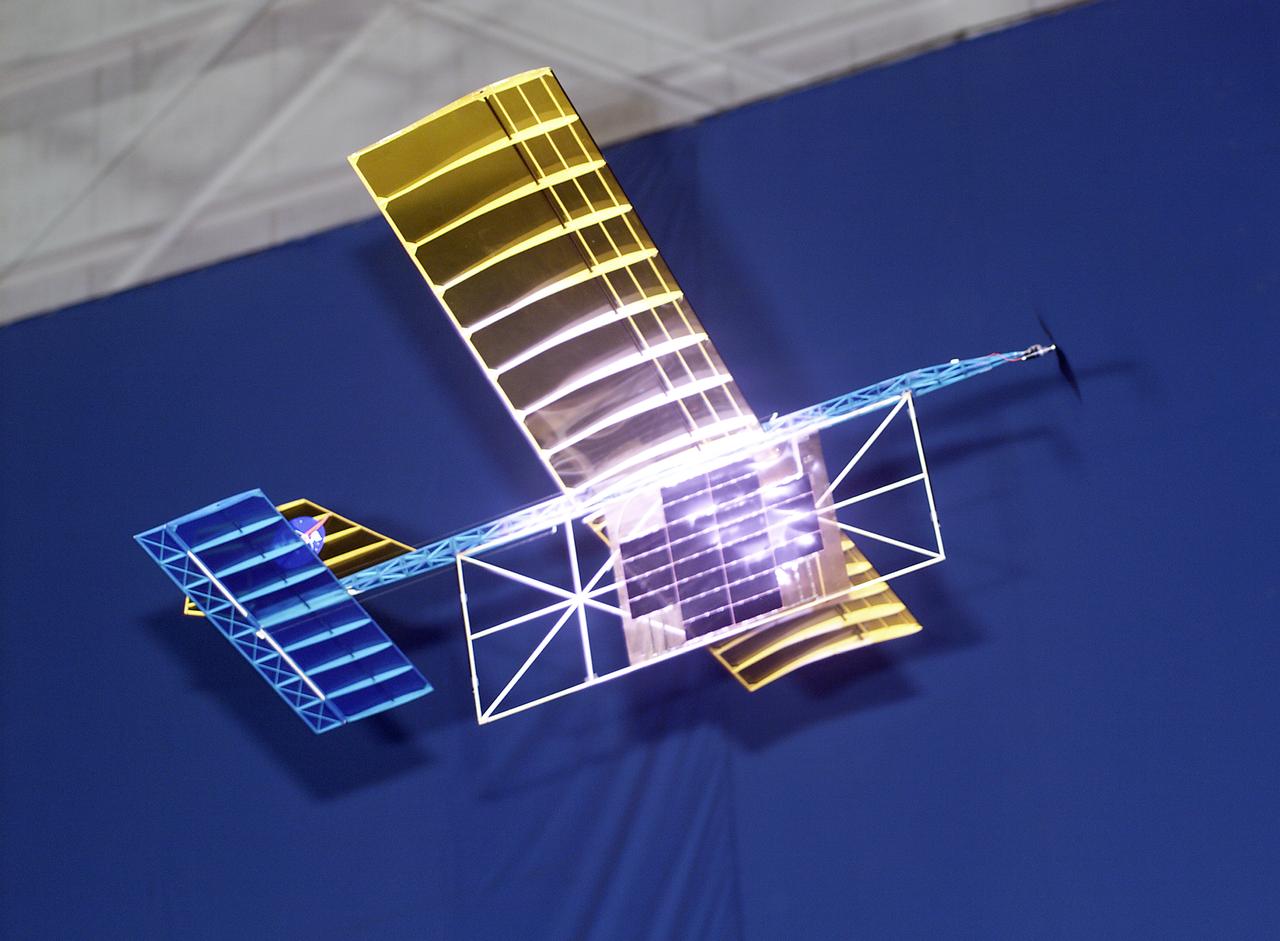
With a laser beam centered on its panel of photovoltaic cells, a lightweight model plane makes the first flight of an aircraft powered by a laser beam inside a building at NASA Marshall Space Flight Center.
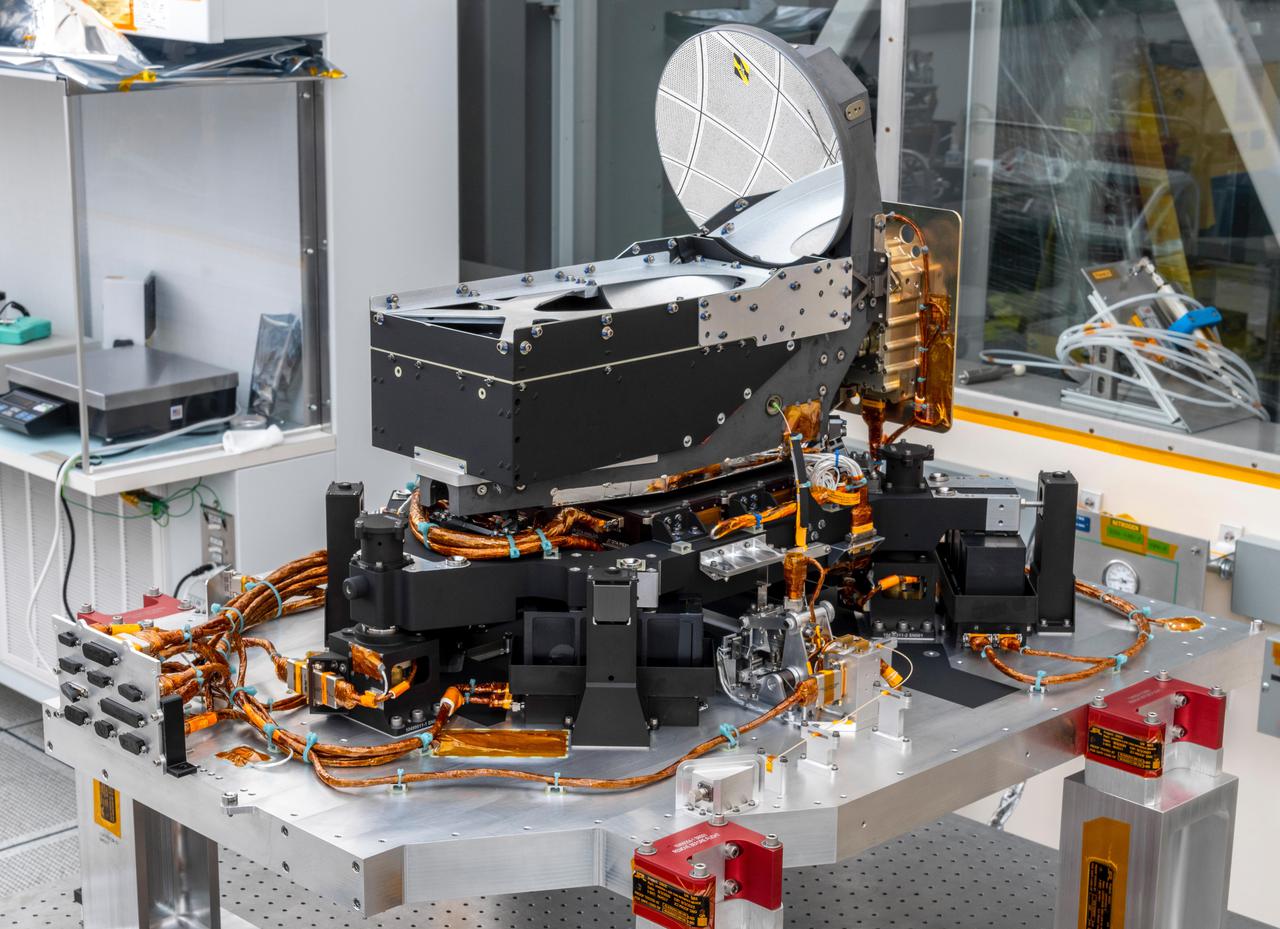
The Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) technology demonstration's flight laser transceiver is shown at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in April 2021, before being installed inside its box-like enclosure that was later integrated with NASA's Psyche spacecraft. The transceiver consists of a near-infrared laser transmitter to send high-rate data to Earth, and a sensitive photon-counting camera to receive ground-transmitted low-rate data. The transceiver is mounted on an assembly of struts and actuators – shown in this photograph – that stabilizes the optics from spacecraft vibrations. The DSOC experiment is the agency's first demonstration of optical communications beyond the Earth-Moon system. DSOC is a system that consists of this flight laser transceiver, a ground laser transmitter, and a ground laser receiver. New advanced technologies have been implemented in each of these elements. The transceiver will "piggyback" on NASA's Psyche spacecraft when it launches in August 2022 to the metal-rich asteroid of the same name. The DSOC technology demonstration will begin shortly after launch and continue as the spacecraft travels from Earth to its gravity-assist flyby of Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24569

Visible near the center of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover in this illustration is the palm-size dome called the Laser Retroreflector Array (LaRA). In the distant future, laser-equipped Mars orbiters could use such a reflector for scientific studies. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24097
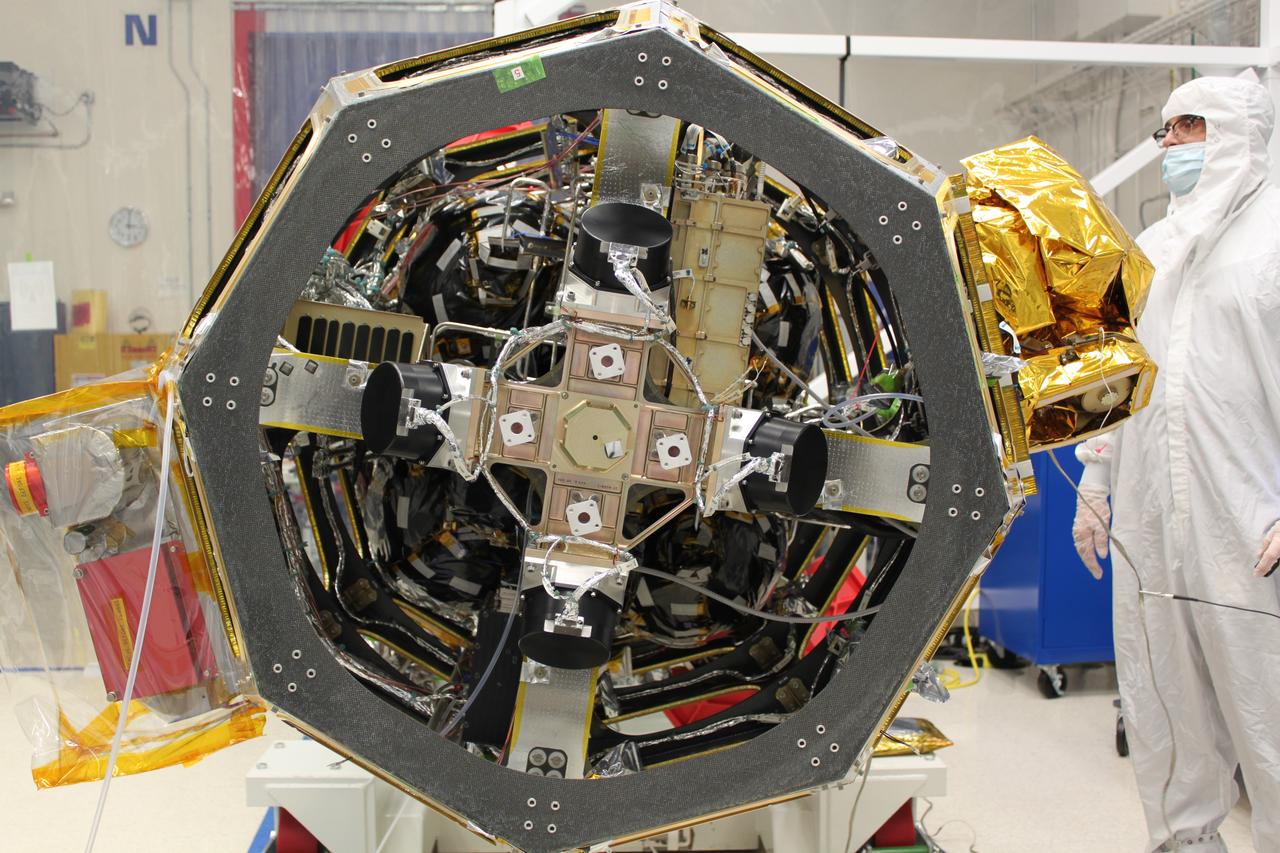
A new NASA-developed, laser-based space communication system will enable higher rates of satellite communications similar in capability to high-speed fiber optic networks on Earth. The space terminal for the Lunar Laser Communication Demonstration (LLCD), NASA's first high-data-rate laser communication system, was recently integrated onto the Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) spacecraft. LLCD will demonstrate laser communications from lunar orbit to Earth at six times the rate of the best modern-day advanced radio communication systems. Credit: NASA ----- What is LADEE? The Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) is designed to study the Moon's thin exosphere and the lunar dust environment. An "exosphere" is an atmosphere that is so thin and tenuous that molecules don't collide with each other. Studying the Moon's exosphere will help scientists understand other planetary bodies with exospheres too, like Mercury and some of Jupiter's bigger moons. The orbiter will determine the density, composition and temporal and spatial variability of the Moon's exosphere to help us understand where the species in the exosphere come from and the role of the solar wind, lunar surface and interior, and meteoric infall as sources. The mission will also examine the density and temporal and spatial variability of dust particles that may get lofted into the atmosphere. The mission also will test several new technologies, including a modular spacecraft bus that may reduce the cost of future deep space missions and demonstrate two-way high rate laser communication for the first time from the Moon. LADEE now is ready to launch when the window opens on Sept. 6, 2013. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/ladee" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/ladee</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
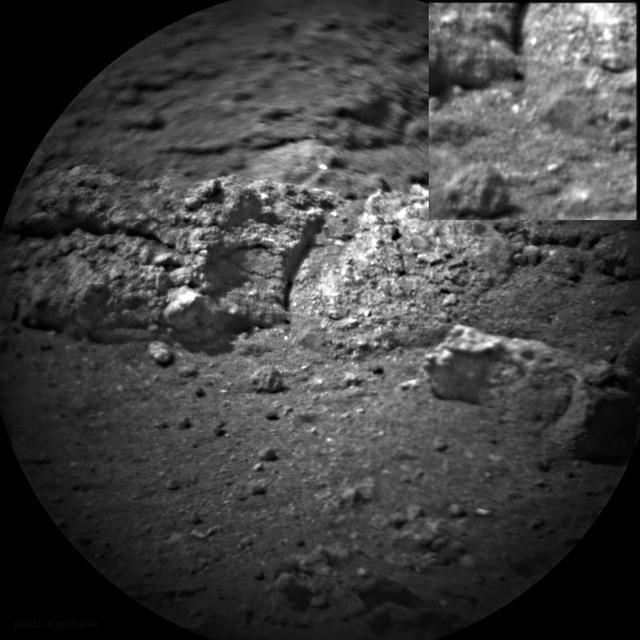

NASA Curiosity rover shot its laser 50 times at rocks exposed by thrusters on the rover sky crane at the scour mark called Goulburn.
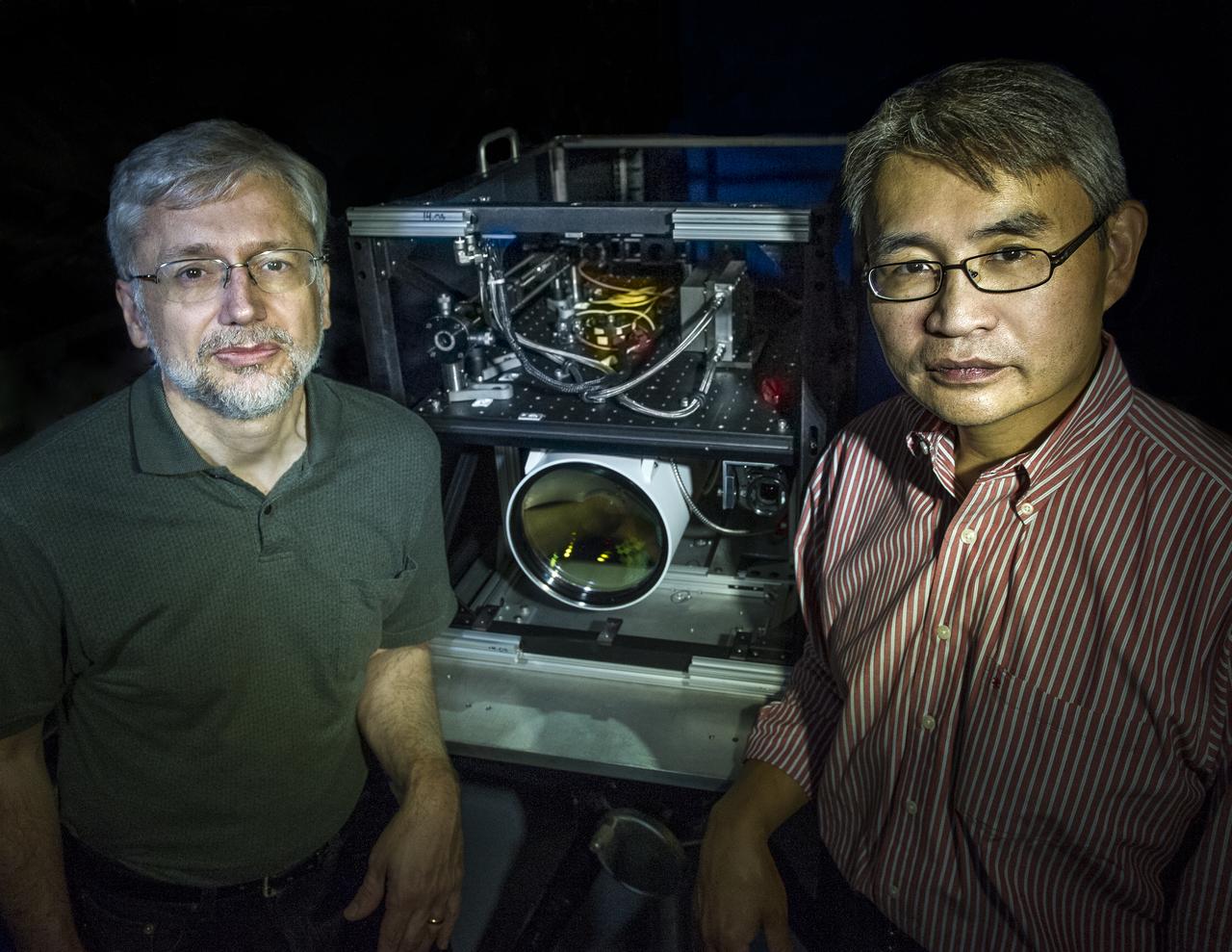
Goddard scientist David Harding and Goddard technologist Tony Yu are developing a lidar system that could meet an ambitious requirement of the proposed LIST mission. ---------- In 2007, the National Research Council threw down a challenge: Design a space-based laser altimeter that could measure the height of Earth's surface everywhere to within a mere 10 centimeters — all at 5-meter resolution. To this day, some believe it can't be done. Goddard scientist Dave Harding begs to differ. He and his team have embraced the challenge and are developing a laser altimeter that could provide the data from a berth onboard the NRC-proposed Lidar Surface Topography, or LIST, mission. It would generate highly detailed maps of topography and vegetation that scientists could use to forecast and respond to natural hazards and study carbon storage in forests. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/17N3Bql" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/17N3Bql</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b> Credit: Bill Hrybck/NASA
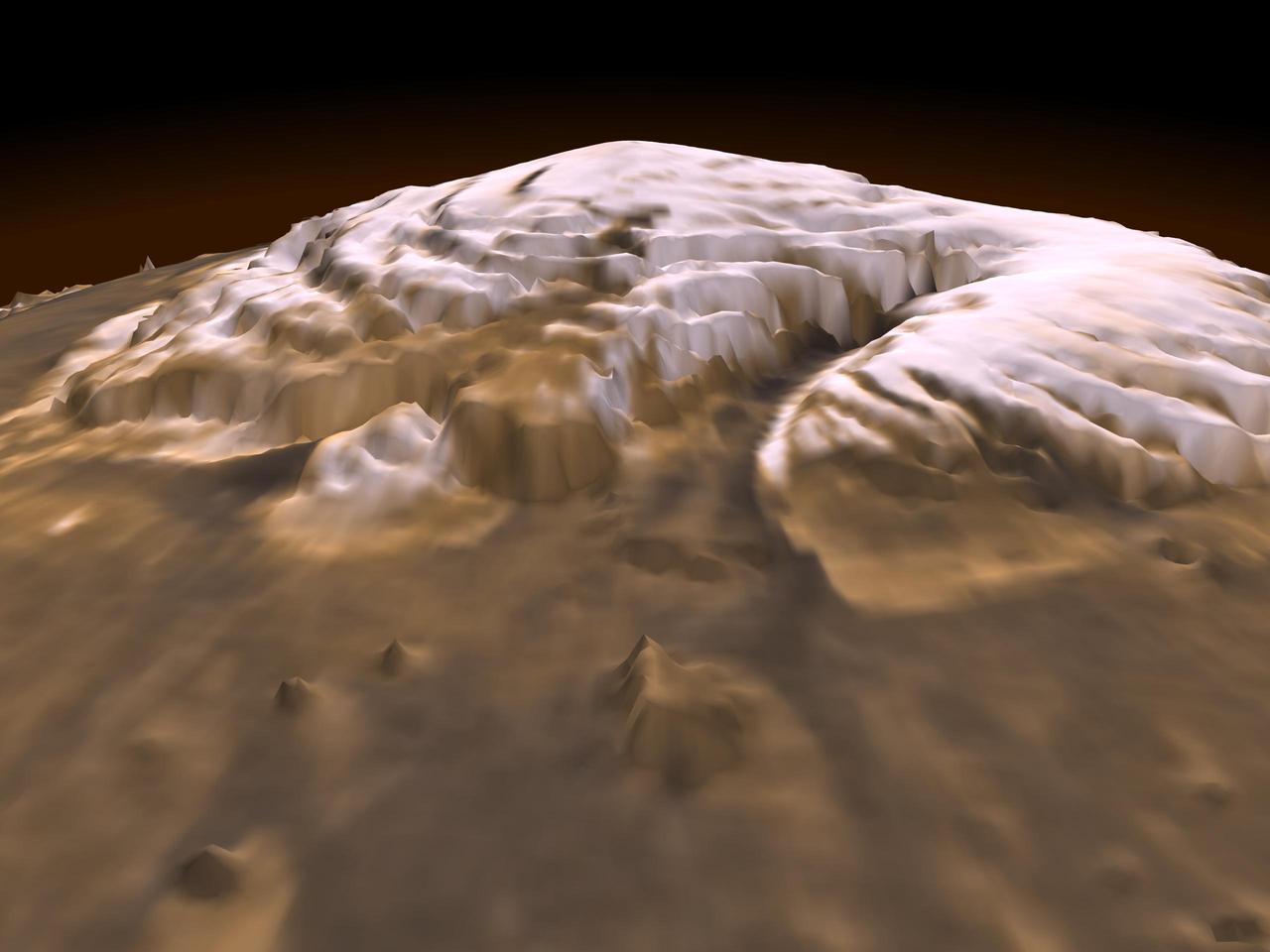
Laser Provides First 3-D View of Mars North Pole

MGS Mars Orbiter Laser MOLA Surface Topography of Northern Hemisphere
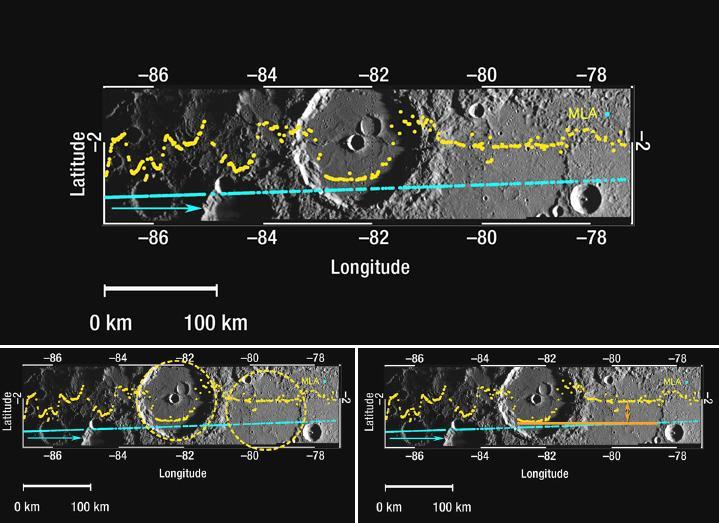
Mercury Laser Altimeter MLA Measures the Depths of Mercury Craters
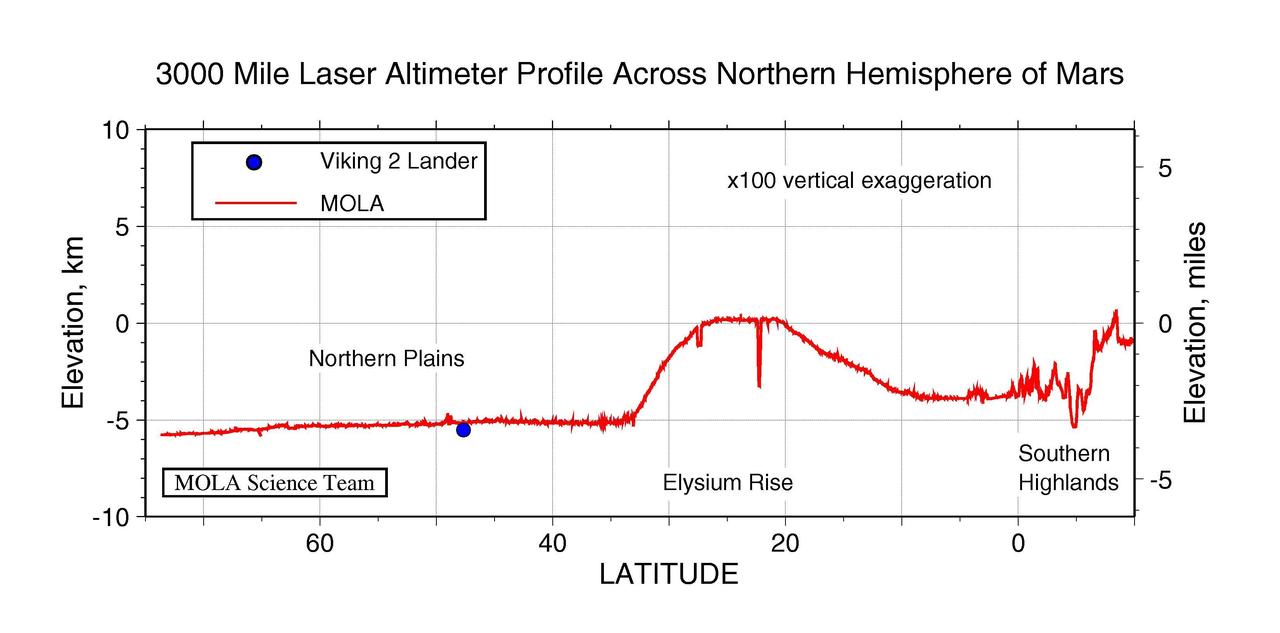
3000 Mile Laser Altimeter Profile Across Northern Hemisphere of Mars
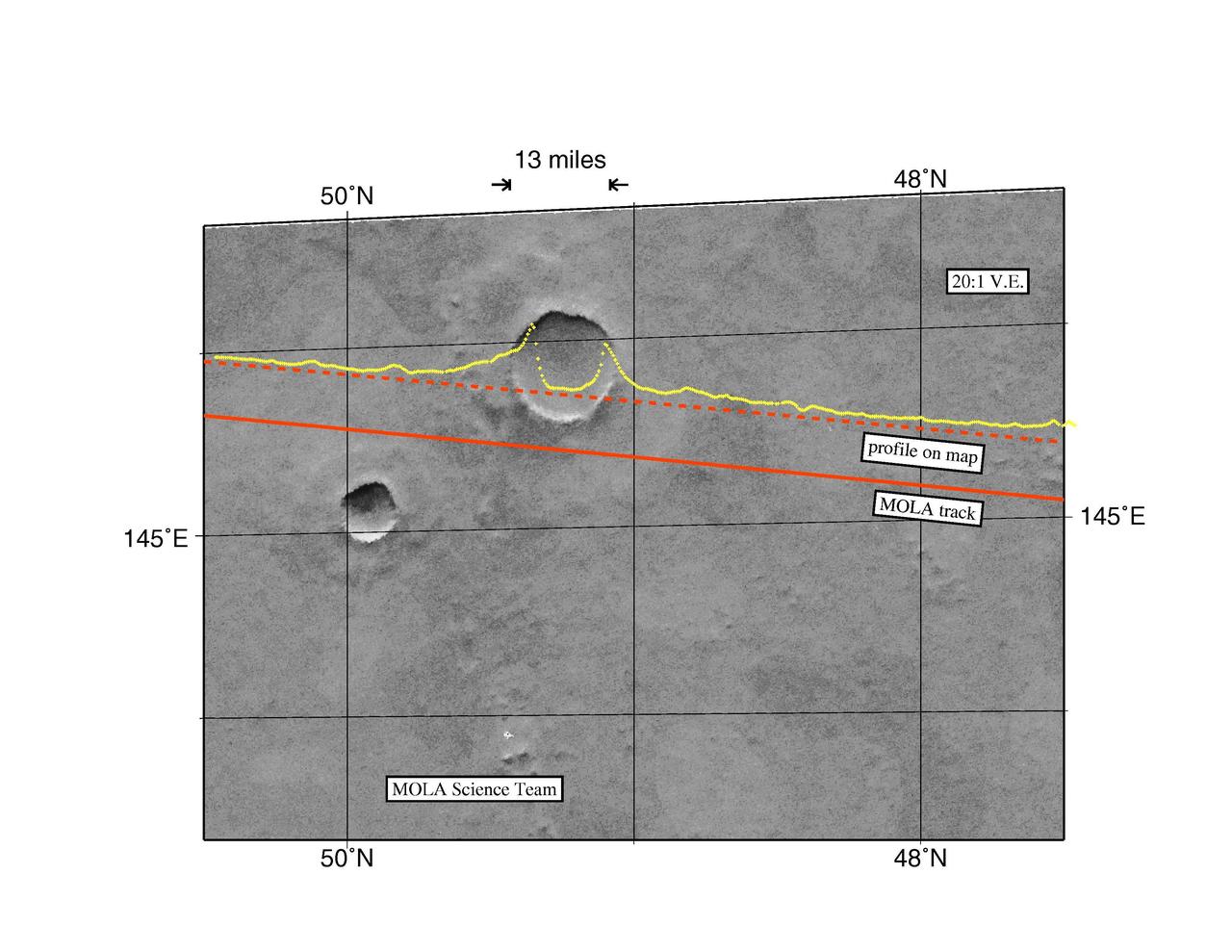
MGS Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter Topographic Profile of Impact Crater
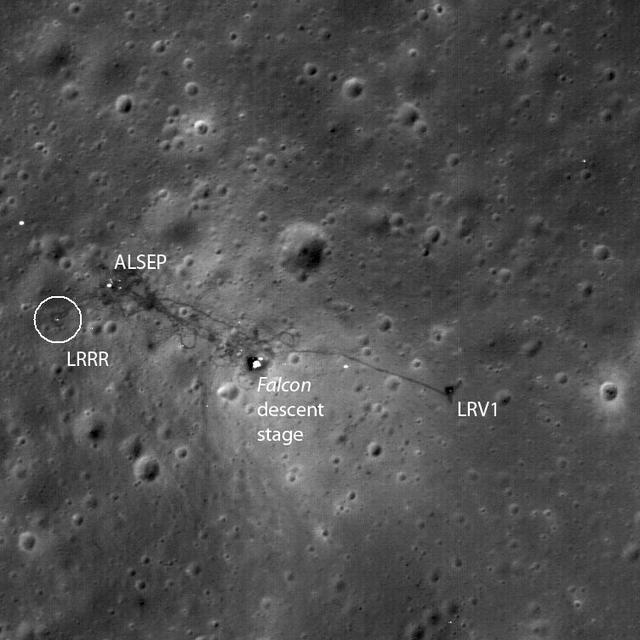

The Apollo 15 Lunar Laser Ranging Retroreflector - A Fundamental Point on the Moon
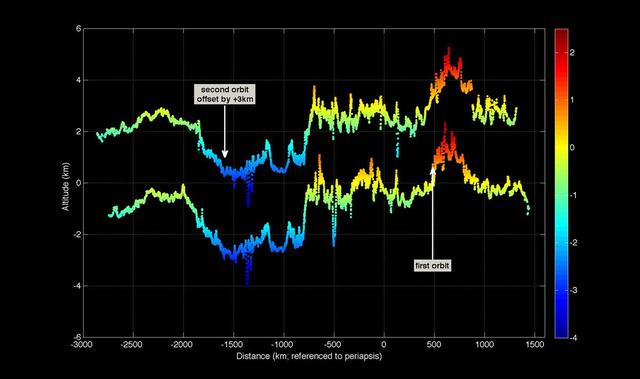
First Mercury Laser Altimeter MLA Results from Orbit

MGS Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter MOLA - Mars/Earth Relief Comparison
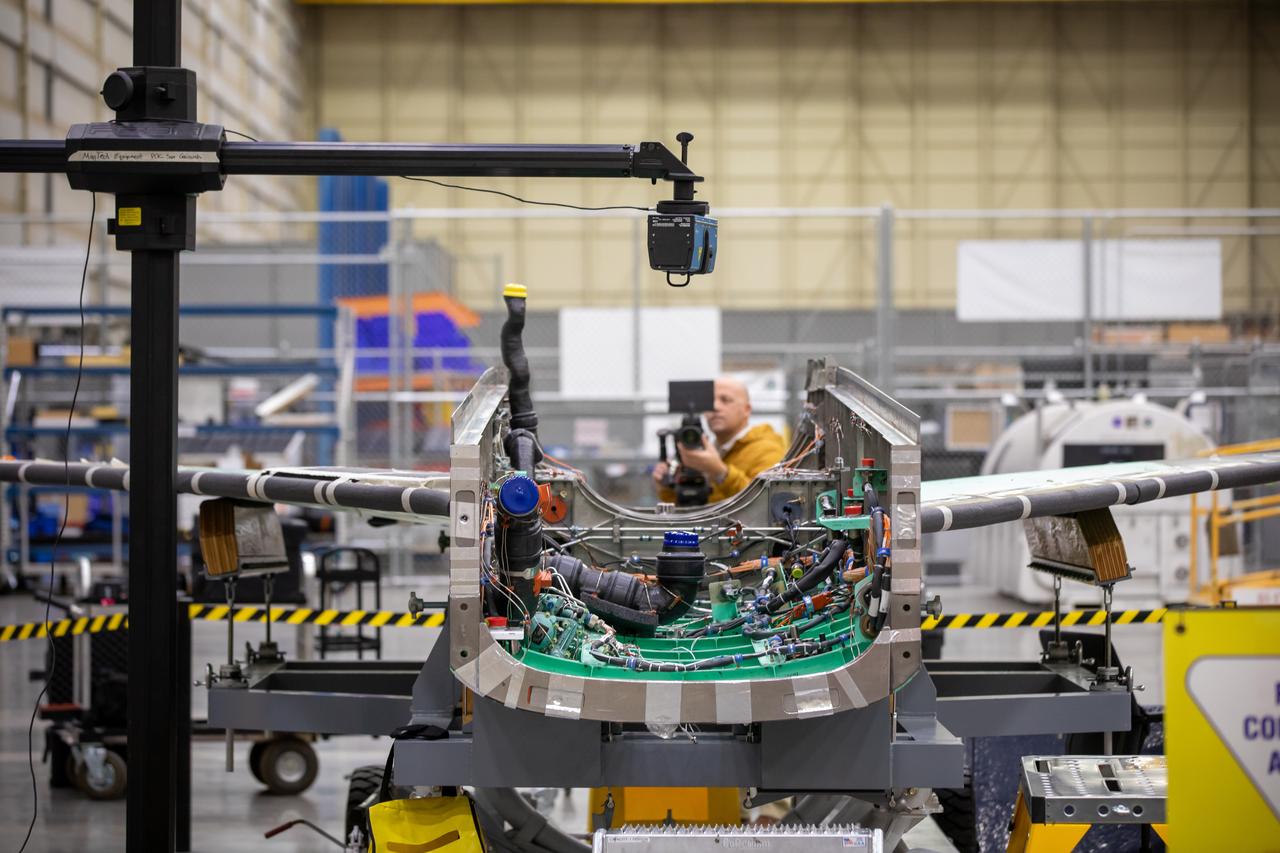

A laser scans the inside of the X-59 aircraft’s lower engine bay at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. These scans can help identify potential hardware or wiring interferences prior to the final installation of the engine and lower tail.
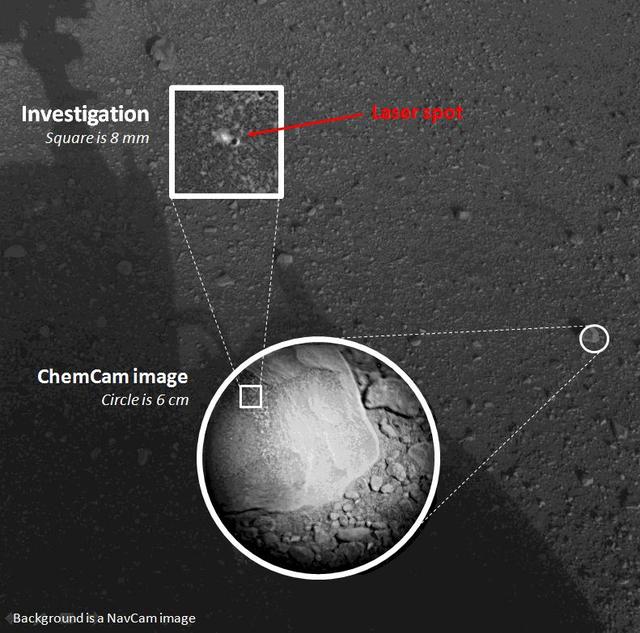
This composite image, with magnified insets, depicts the first laser test by the Chemistry and Camera, or ChemCam, instrument aboard NASA Curiosity Mars rover.
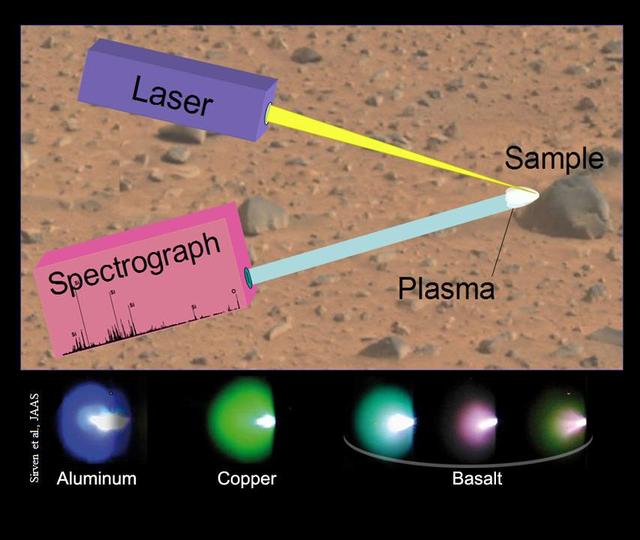
This image illustrates the principals of a technique called laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, which the Chemistry and Camera ChemCam instrument onboard NASA rover, Curiosity, will use on Mars.
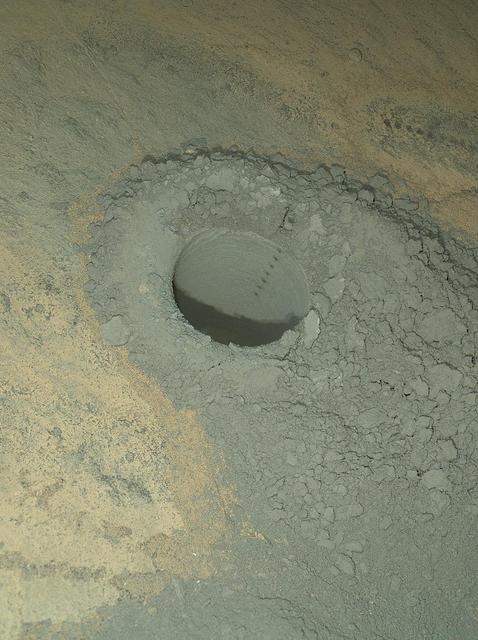

NASA Curiosity Mars rover provided this nighttime view of a hole produced by the rover drill and, inside the hole, a line of scars produced by the rover rock-zapping laser.

This image shows laser plasmas in a test lab at Los Alamos National Laboratory, N.M., under typical atmospheric pressures on Earth and Mars. A plasma is an ionized, glowing gas.
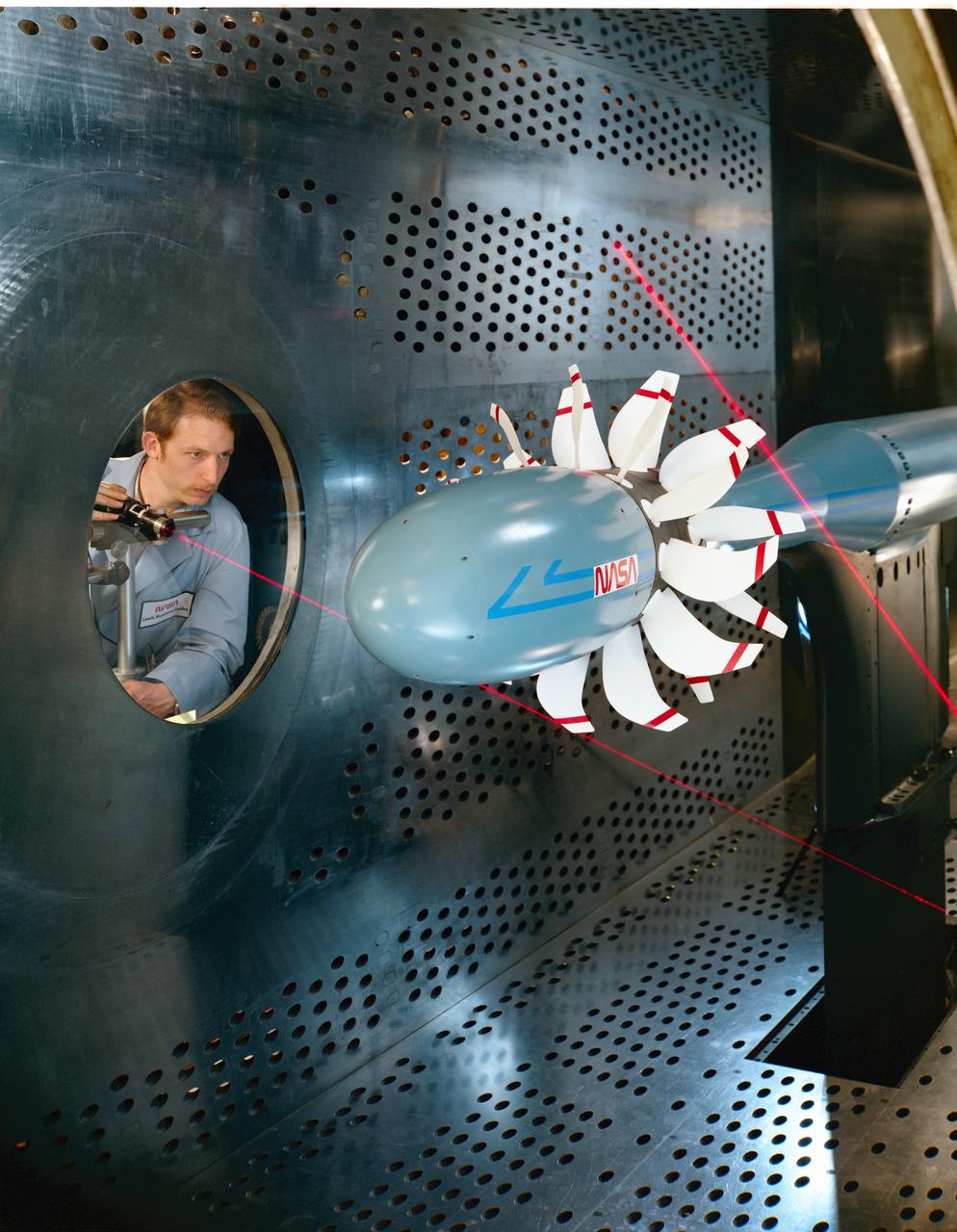
Laser based blade deflection measurement system on Counter Rotation Pusher Propeller model in 8x6 SWT (Supersonic Wind Tunnel)
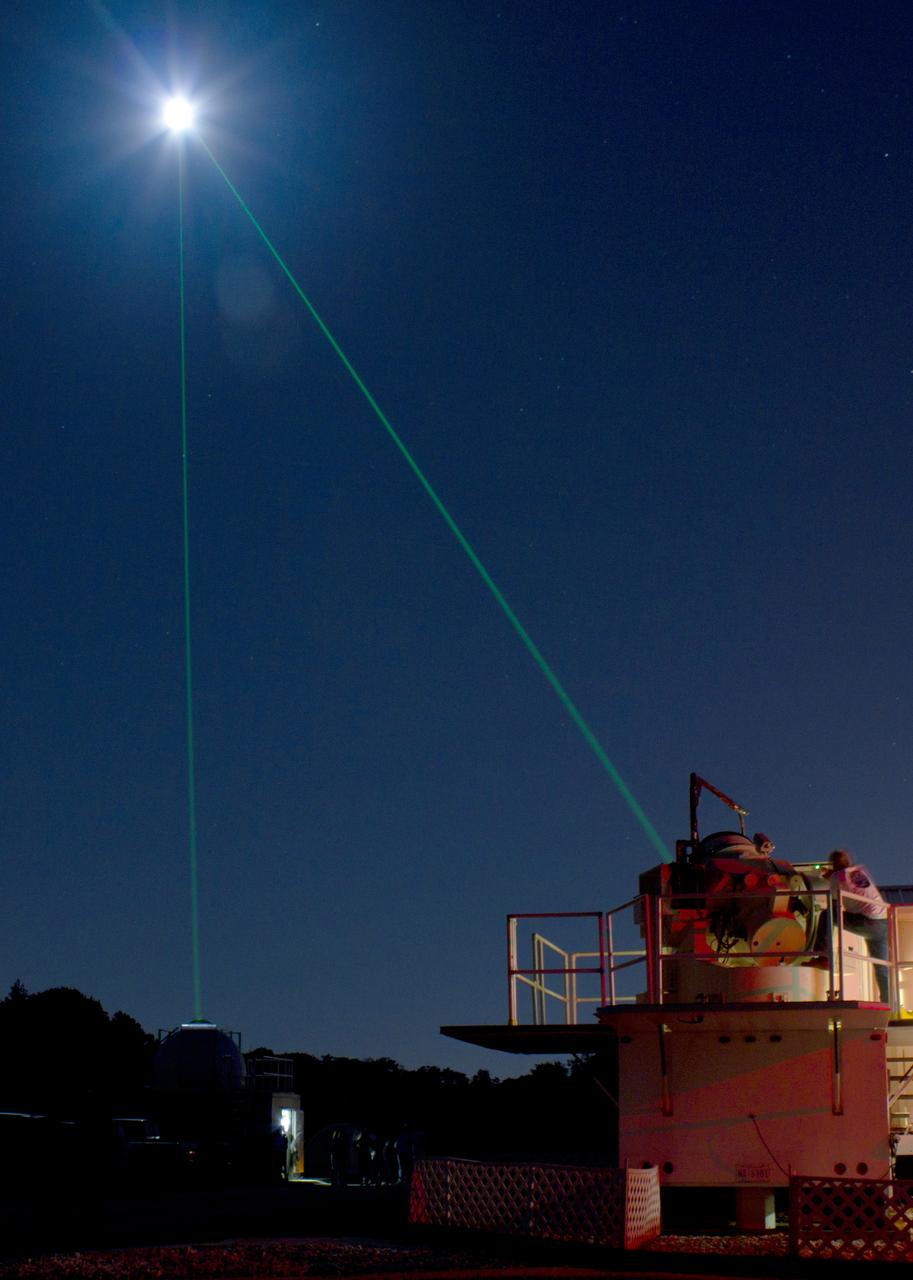

Goddard's Laser Ranging Facility directs a laser toward the Lunar Reconassaince Orbiter on International Observe the Moon Night. (Sept 18, 2010) Background on laser ranging: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/LRO/news/LRO_lr.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/LRO/news/LRO_lr.html</a> Information on inOMN <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/features/2010/moon-night.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/features/2010/moon-nigh...</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> contributes to NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s endeavors by providing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
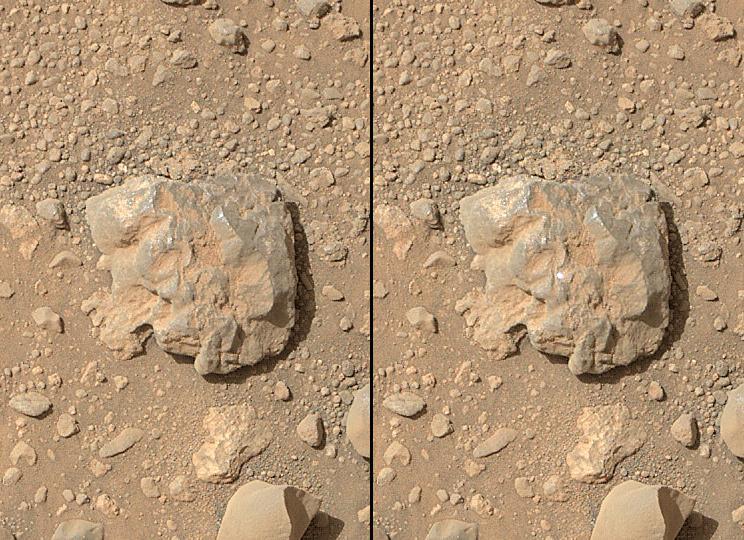

NASA Curiosity Mars rover used the Mars Hand Lens Imager MAHLI camera on its arm to catch the first images of sparks produced by the rover laser being shot at a rock on Mars. The left image is from before the laser zapped this rock, called Nova.

N-213 Laser Optics Laboratory
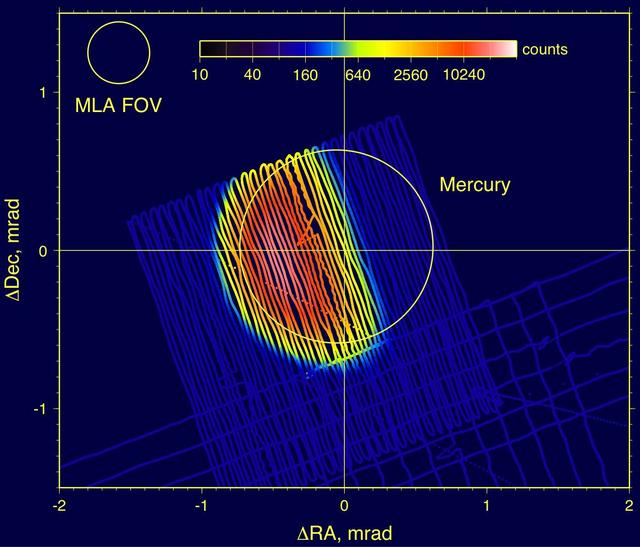
Mercury Laser Altimeter MLA Images Mercury from 4 Million Kilometers http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA10608
N-213 Laser Optics Laboratory with Dana Lynch
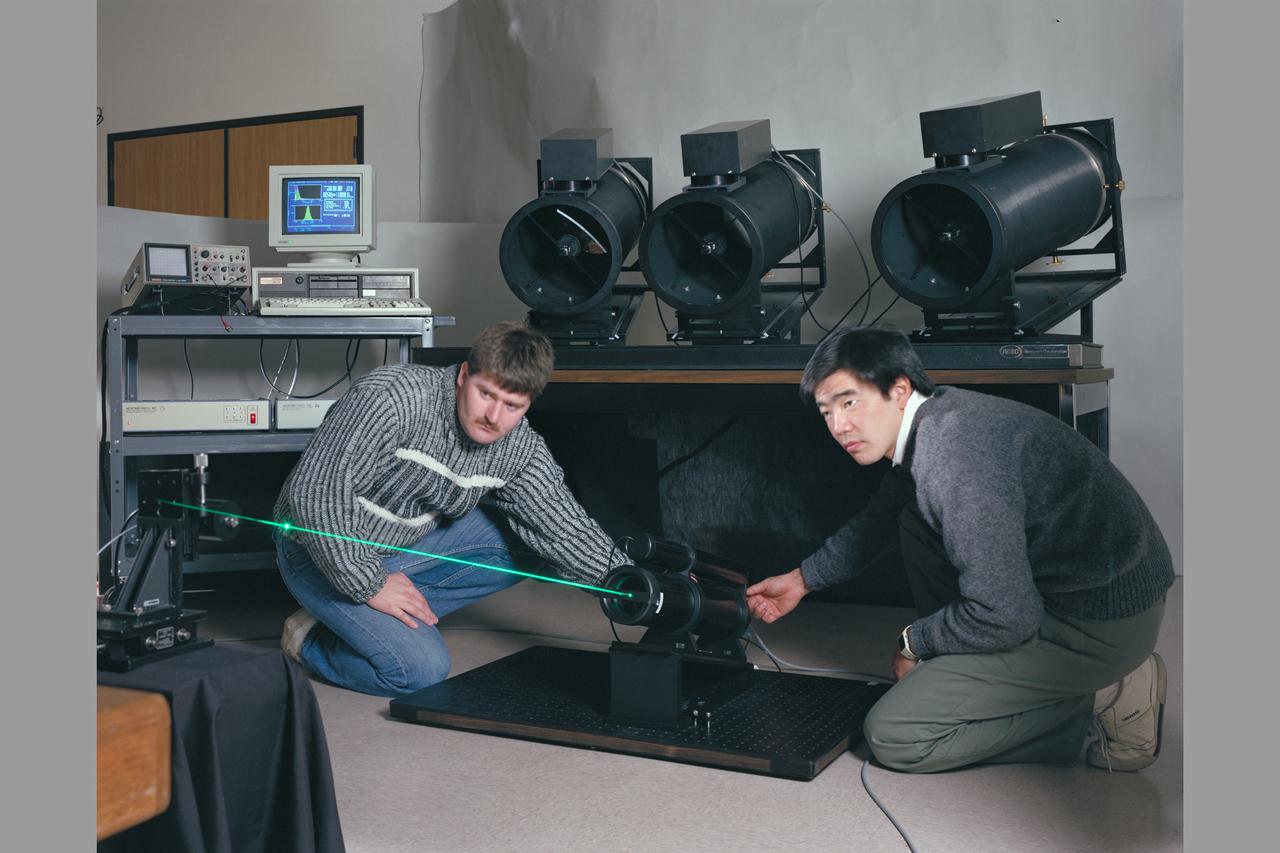

N-213 detector set up for 3d LV (laser velocimeter)

A day after NASA Mars rover Curiosity drilled the first sample-collection hole into a rock on Mars, the rover Chemistry and Camera ChemCam instrument shot laser pulses into the fresh rock powder that the drilling generated.

The Chemistry and Camera ChemCam instrument on NASA Mars rover Curiosity used its laser to examine side-by-side points in a target patch of soil, leaving the marks apparent in this before-and-after comparison.
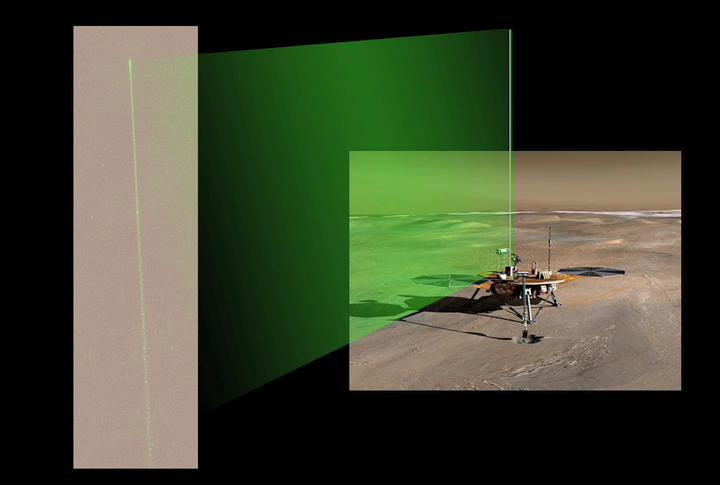
The Surface Stereo Imager camera aboard NASA Phoenix Mars Lander acquired a series of images of the laser beam in the Martian night sky. Bright spots in the beam are reflections from ice crystals in the low level ice-fog.
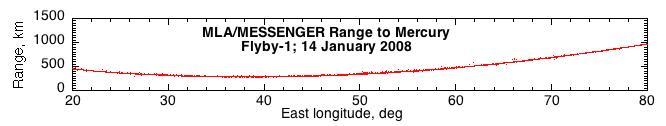
On January 14, 2008, NASA MESSENGER spacecraft Mercury Laser Altimeter MLA became the first instrument to measure the distance between a spacecraft and the surface of Mercury.
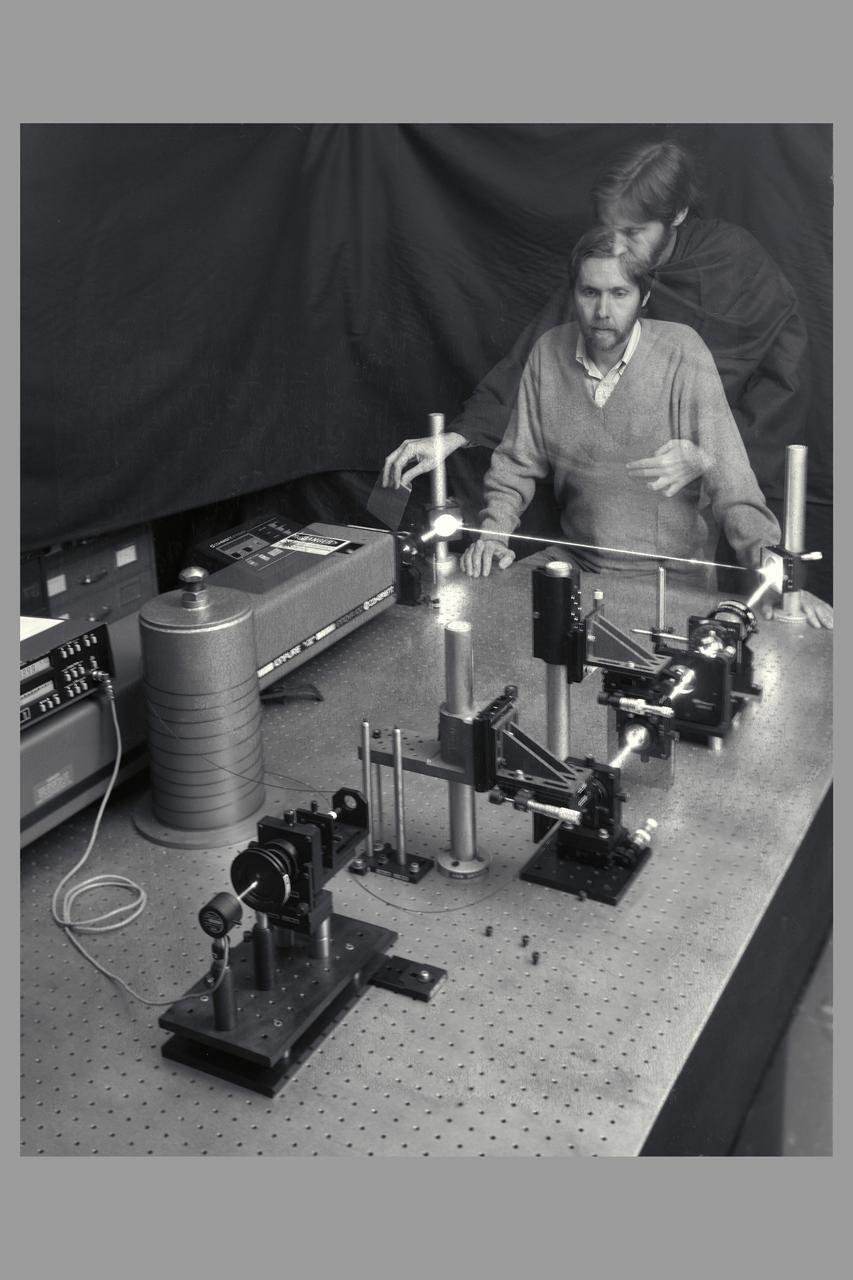
N-213 Laser Optics Laboratory - double exposed polaroid by Ken McAlister (engineer) 3-17-89 with Dana Lynch
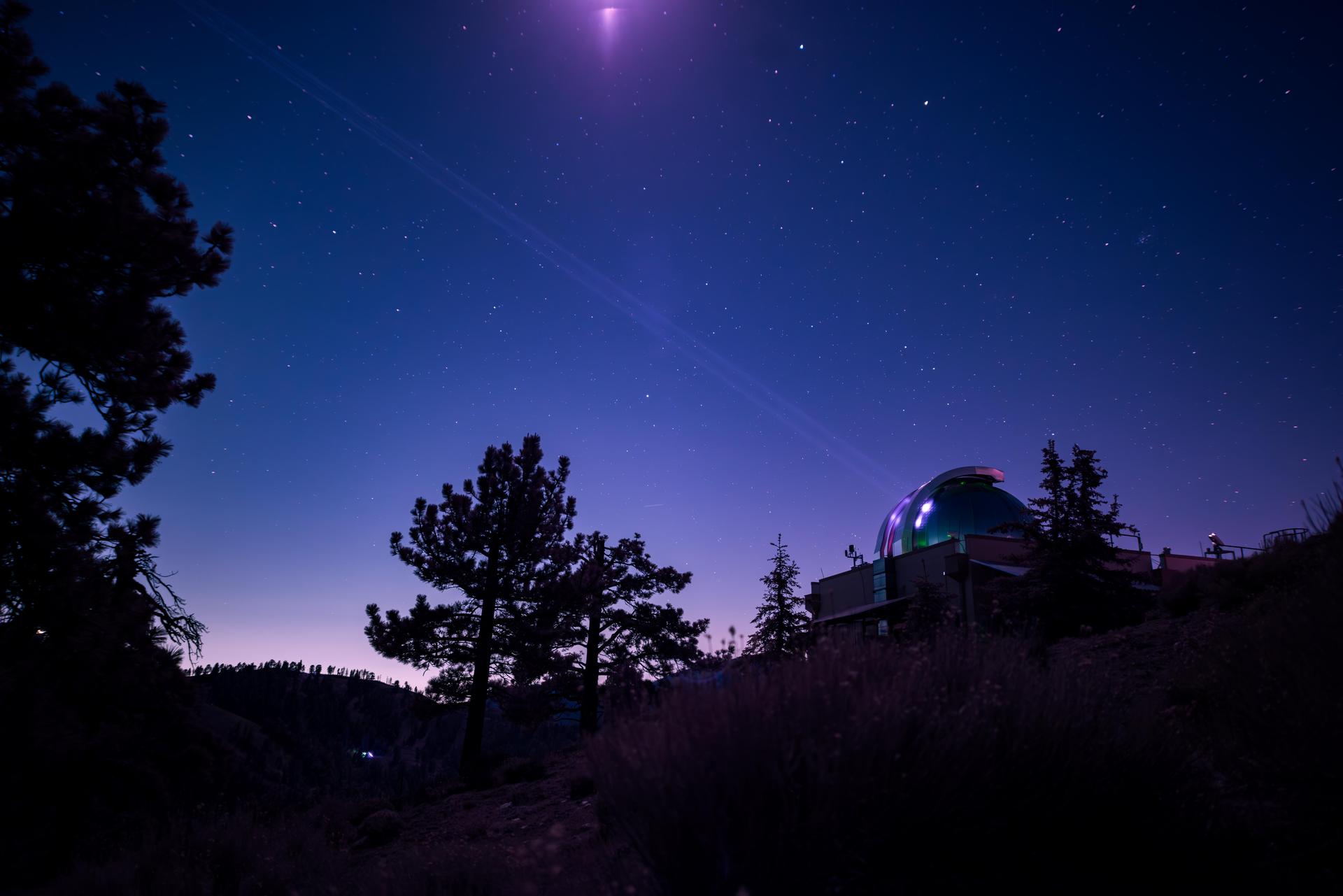

This infrared photograph shows the uplink laser beacon for NASA's Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment beaming into the night sky from the Optical Communications Telescope Laboratory (OCTL) at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Table Mountain Facility near Wrightwood, California. Attached to the agency's Psyche spacecraft, the DSOC flight laser transceiver can receive and send data from Earth in encoded photons. As the experiment's ground laser transmitter, OCTL transmits at an infrared wavelength of 1,064 nanometers from its 3.3-foot-aperture (1-meter) telescope. The telescope can also receive faint infrared photons (at a wavelength of 1,550 nanometers) from the 4-watt flight laser transceiver on Psyche. Neither infrared wavelength is easily absorbed or scattered by Earth's atmosphere, making both ideal for deep space optical communications. To receive the most distant signals from Psyche, the project enlisted the powerful 200-inch-aperture (5-meter) Hale Telescope at Caltech's Palomar Observatory in San Diego County, California, as its primary downlink station, which provided adequate light-collecting area to capture the faintest photons. Those photons were then directed to a cryogenically cooled superconducting high-efficiency detector array at the observatory where the information encoded in the photons could be processed. Managed by JPL, DSOC was designed to demonstrate that data encoded in laser photons could be reliably transmitted, received, and then decoded after traveling millions of miles from Earth out to Mars distances. Nearly two years after launching aboard the agency's Psyche mission in 2023, the demonstration completed its 65th and final "pass" on Sept. 2, 2025, sending a laser signal to Psyche and receiving the return signal from 218 million miles (350 million kilometers) away. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26662
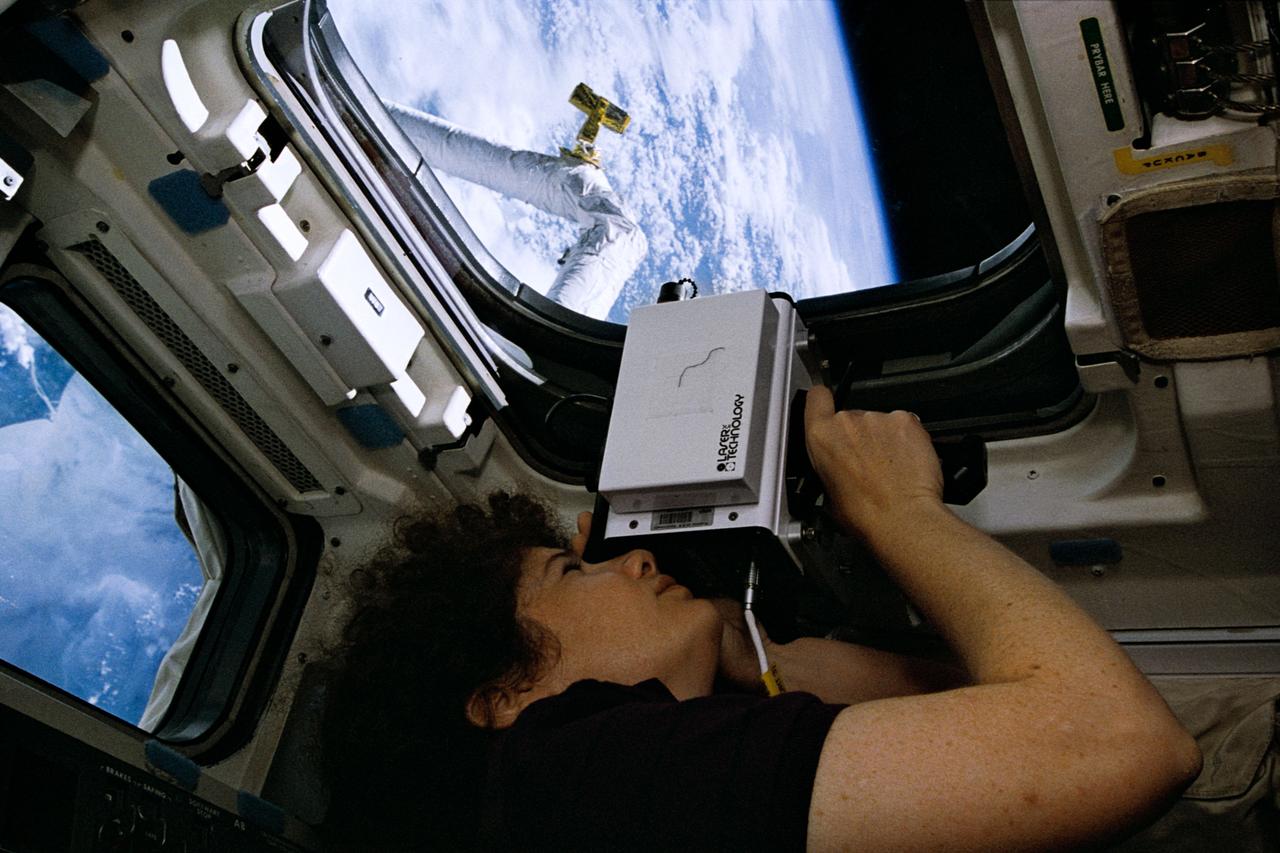

STS064-33-003 (9-20 Sept. 1994) --- Astronaut Susan J. Helms, STS-64 mission specialist, uses a laser instrument during operations with the Shuttle Pointed Autonomous Research Tool for Astronomy 201 (SPARTAN 201). Helms, who spent many mission hours at the controls of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), joined five other NASA astronauts for almost 11 days in Earth orbit aboard the space shuttle Discovery. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
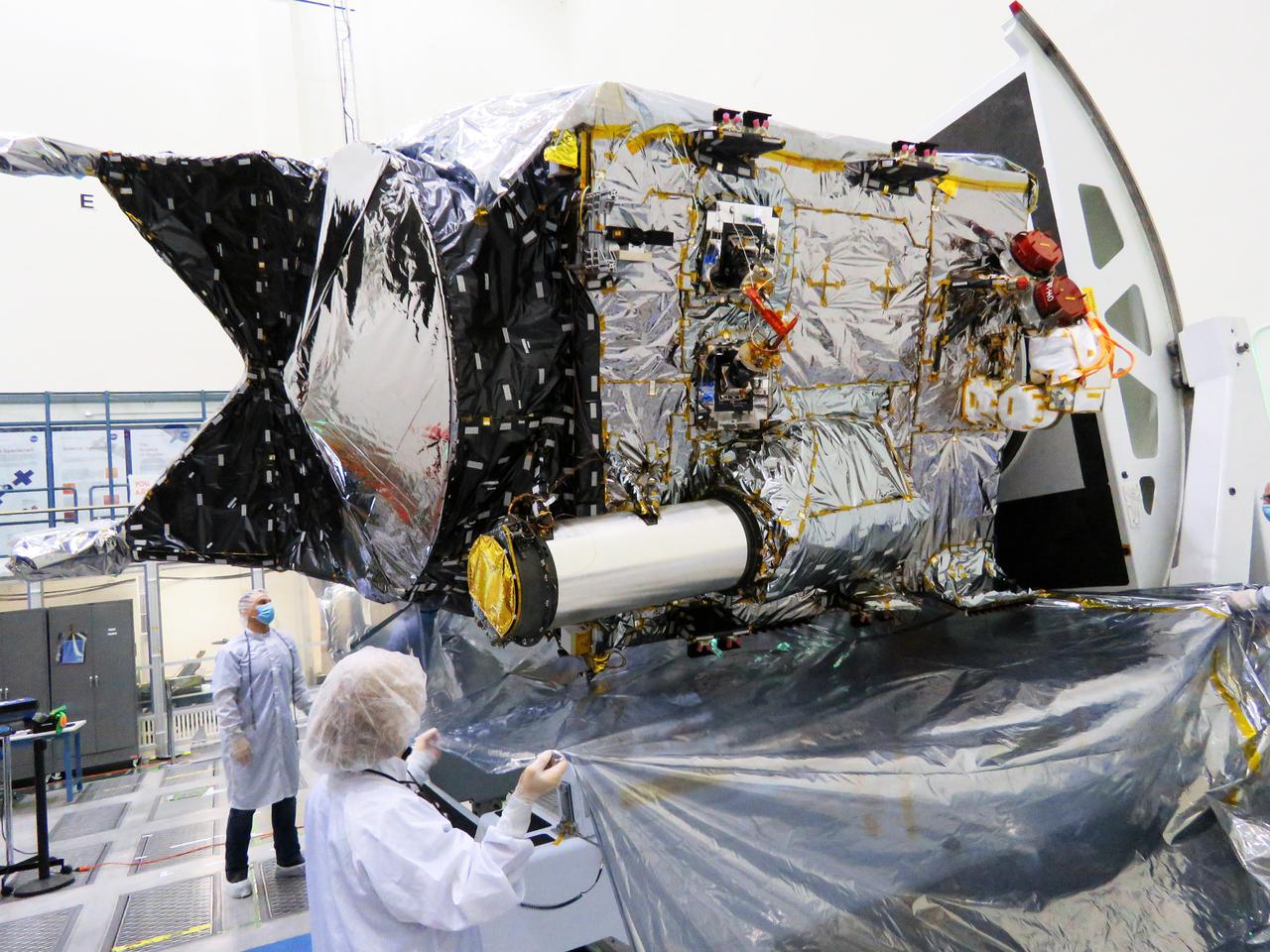

The Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) technology demonstration's flight laser transceiver can be easily identified on NASA's Psyche spacecraft, seen in this December 2021 photograph inside a clean room at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. DSOC's tube-like gray/silver sunshade can be seen protruding from the side of the spacecraft. The bulge to which the sunshade is attached is DSOC's transceiver, which consists of a near-infrared laser transmitter to send high-rate data to Earth and a sensitive photon-counting camera to receive ground-transmitted low-rate data. The DSOC experiment is the agency's first demonstration of optical communications beyond the Earth-Moon system. DSOC is a system that consists of this flight laser transceiver, a ground laser transmitter, and a ground laser receiver. New advanced technologies have been implemented in each of these elements. The transceiver will "piggyback" on NASA's Psyche spacecraft when it launches in August 2022 to the metal-rich asteroid of the same name. The DSOC technology demonstration will begin shortly after launch and continue as the spacecraft travels from Earth to its gravity-assist flyby of Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24570

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover autonomously selects some of the targets for the laser and telescopic camera of the rover's Chemistry and Camera (ChemCam) instrument. For example, on-board software analyzed the image on the left, chose the target highlighted with the yellow dot, and pointed ChemCam to acquire laser analysis and the image on the right. Most ChemCam targets are still selected by scientists discussing rocks or soil seen in images the rover has sent to Earth, but the autonomous targeting provides an added capability. It can offer a head start on acquiring composition information at a location just reached by a drive. The software for target selection and instrument pointing is called AEGIS, for Autonomous Exploration for Gathering Increased Science. The image on the left was taken by the left eye of Curiosity's stereo Navigation Camera (Navcam) a few minutes after the rover completed a drive of about 43 feet (13 meters) on July 14, 2016, during the 1,400th Martian day, or sol, of the rover's work on Mars. Using AEGIS for target selection and pointing based on the Navcam imagery, Curiosity's ChemCam zapped a grid of nine points on a rock chosen for meeting criteria set by the science team. In this run, parameters were set to find bright-toned outcrop rock rather than darker rocks, which in this area tend to be loose on the surface. Within less than 30 minutes after the Navcam image was taken, ChemCam had used its laser on all nine points and had taken before-and-after images of the target area with its remote micro-imager (RMI) camera. The image at right combines those two RMI exposures. The nine laser targets are marked in red at the center. On the Navcam image at left, the yellow dot identifies the selected target area, which is about 2.2 inches (5.6 centimeters) in diameter. An unannotated version of this Sol 1400 Navcam image is available. ChemCam records spectra of glowing plasma generated when the laser hits a target point. These spectra provide information about the chemical elements present in the target. The light-toned patch of bedrock identified by AEGIS on Sol 1400 appears, geochemically, to belong to the "Stimson" sandstone unit of lower Mount Sharp. In mid-2016, Curiosity typically uses AEGIS for selecting a ChemCam target more than once per week. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20762

The ChemCam instrument for NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission uses a pulsed laser beam to vaporize a pinhead-size target, producing a flash of light from the ionized material plasma that can be analyzed to identify chemical elements in the target.
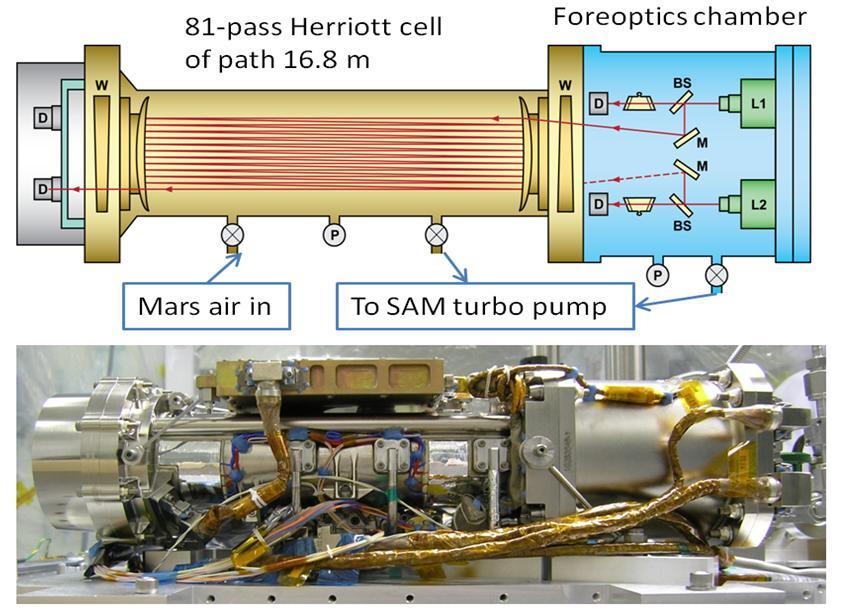
By measuring absorption of light at specific wavelengths, Tunable Laser Spectrometer TLS onboard NASA Curiosity measures concentrations of methane, carbon dioxide and water vapor in Mars atmosphere.

The Chemistry and Camera ChemCam instrument on NASA Mars rover Curiosity used its laser and spectrometers to examine what chemical elements are in a drift of Martian sand during the mission 74th Martian day, or sol Oct. 20, 2012.

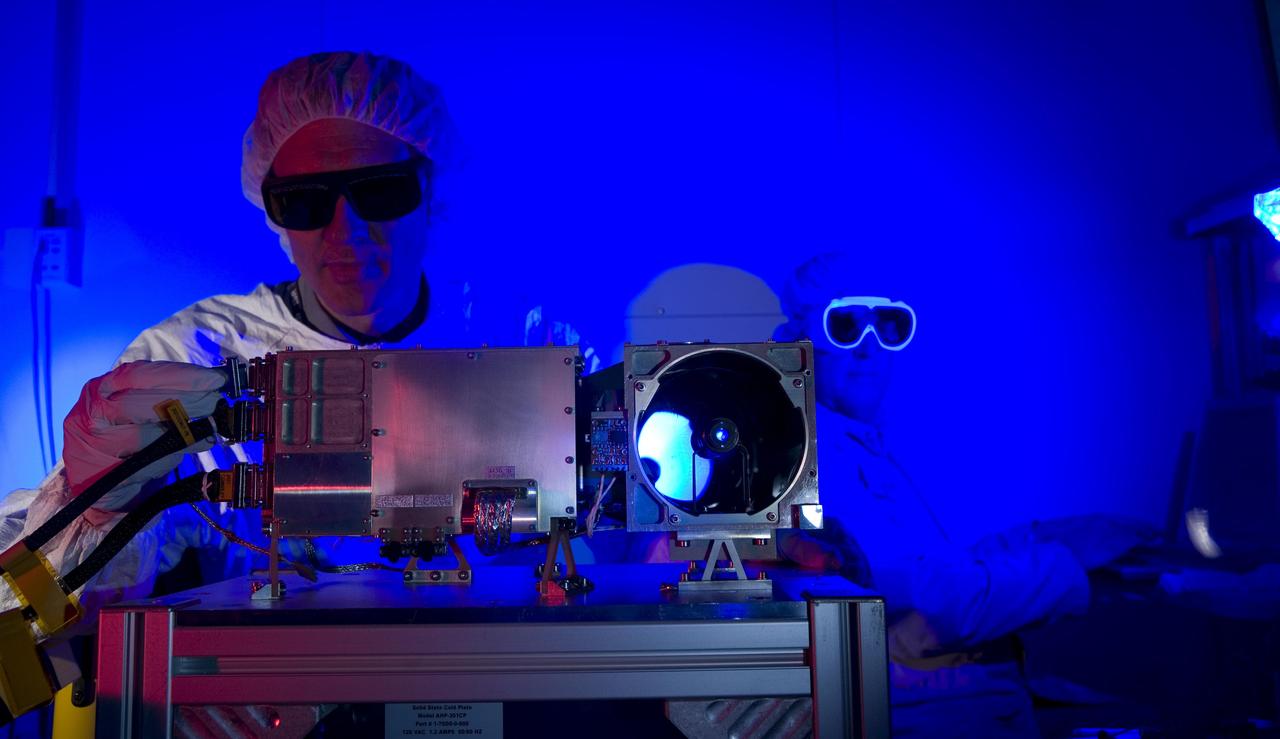
The ChemCam instrument for NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission uses a pulsed laser beam to vaporize a pinhead-size target, producing a flash of light from the ionized material plasma that can be analyzed to identify chemical elements in the target.

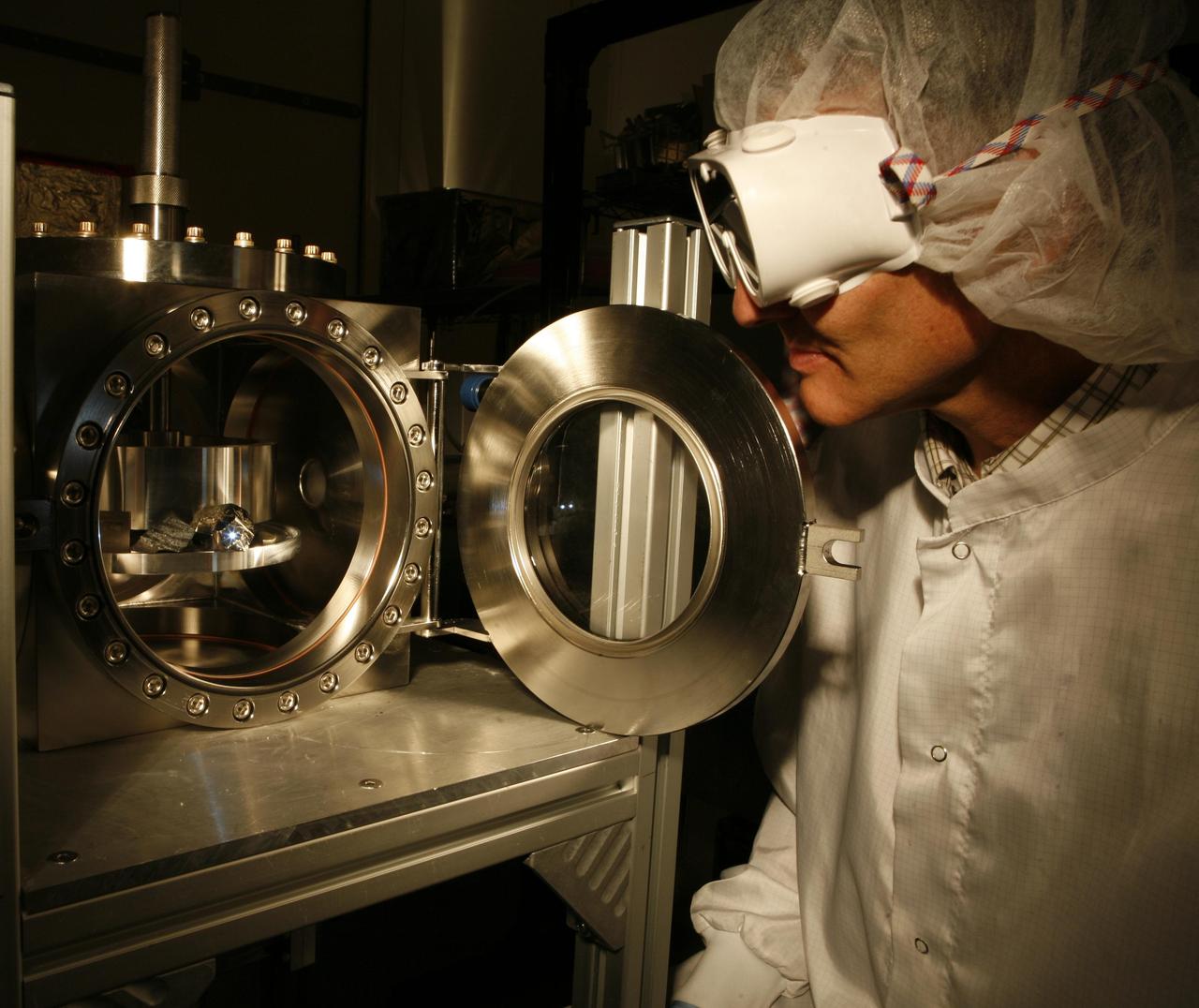
Researchers prepare for a test of the Chemistry and Camera ChemCam instrument that will fly on NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission; researchers are preparing the instrument mast unit for a laser firing test.
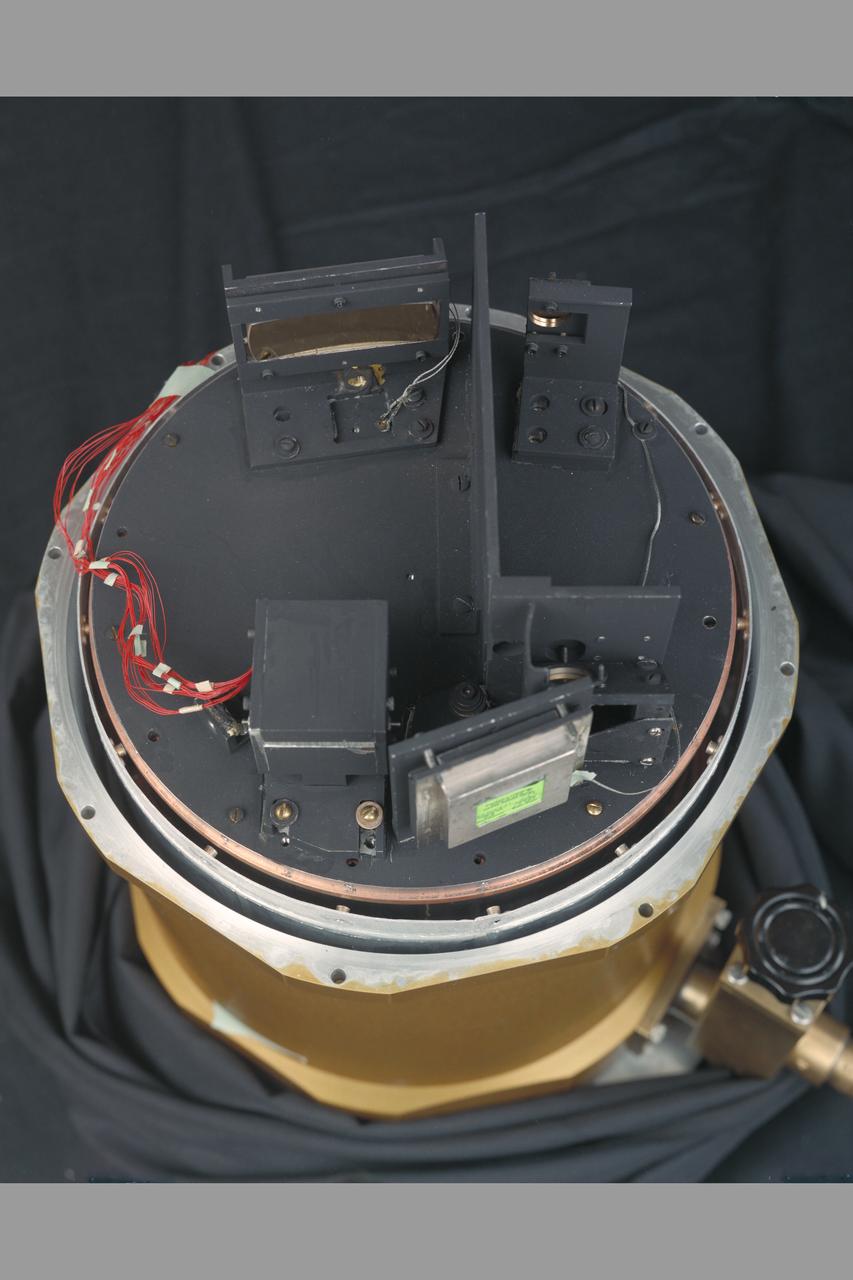

Laser Faint Object Grating Spectrometer (Frogs) with F. Witteborn and Jesse Bregman.

Laser Faint Object Grating Spectrometer (Frogs) with F. Witteborn and Jesse Bregman.
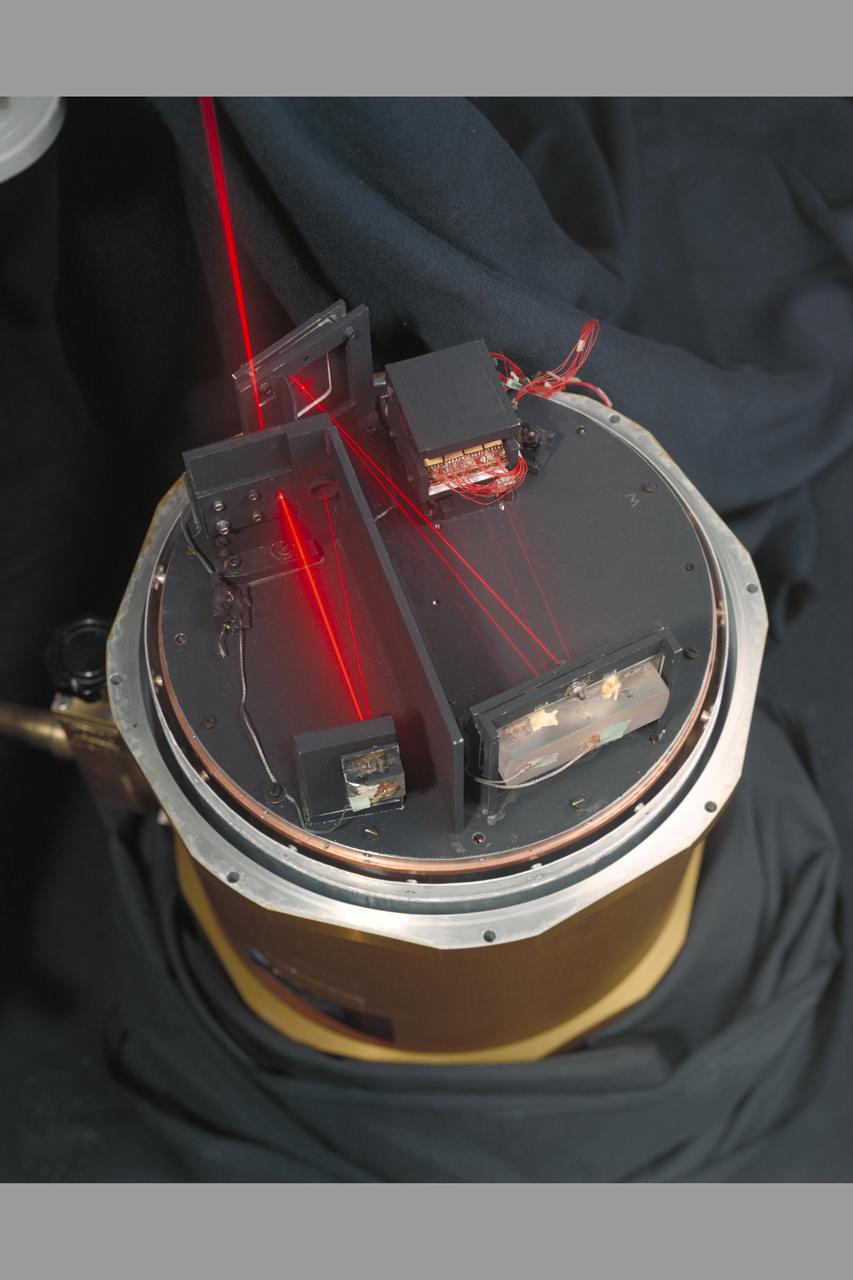
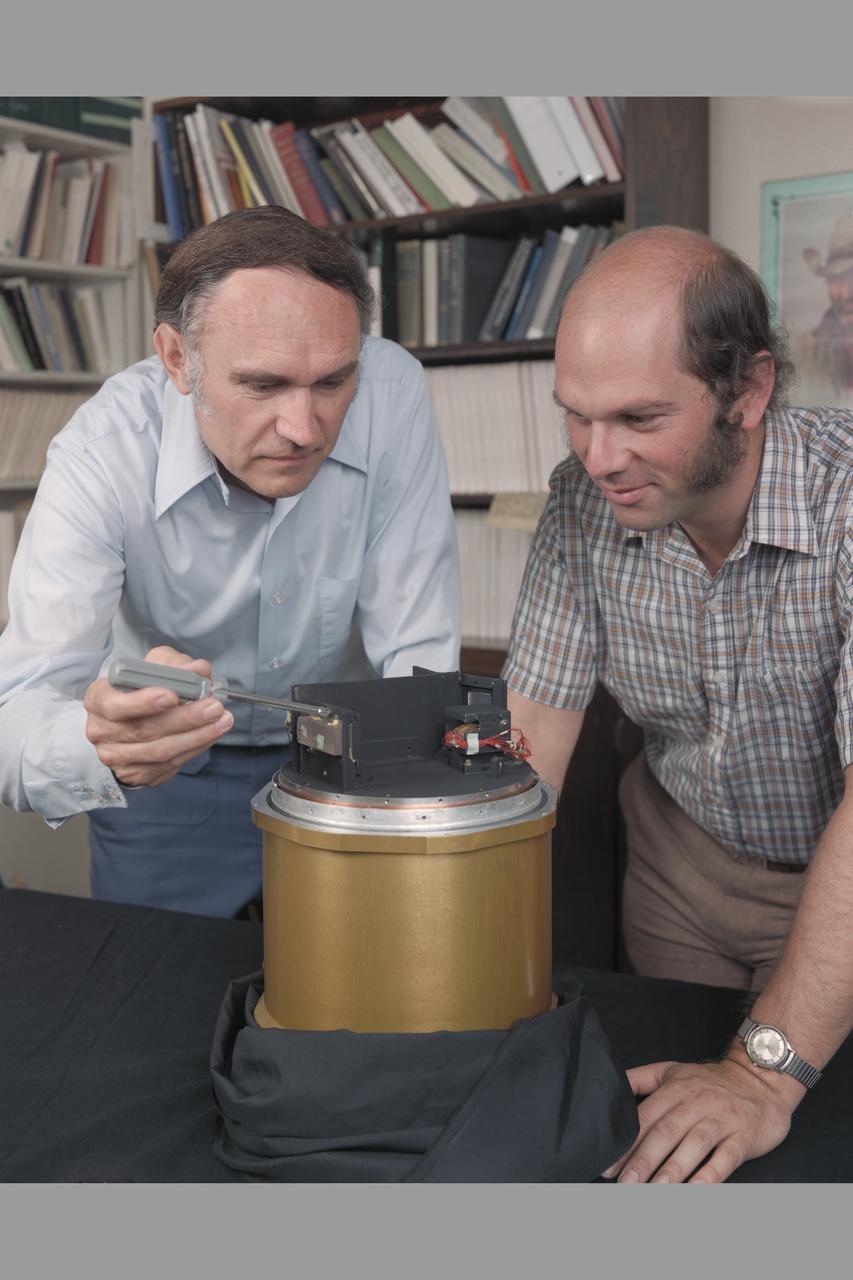
Laser Faint Object Grating Spectrometer (Frogs) with F. Witteborn and Jesse Bregman.
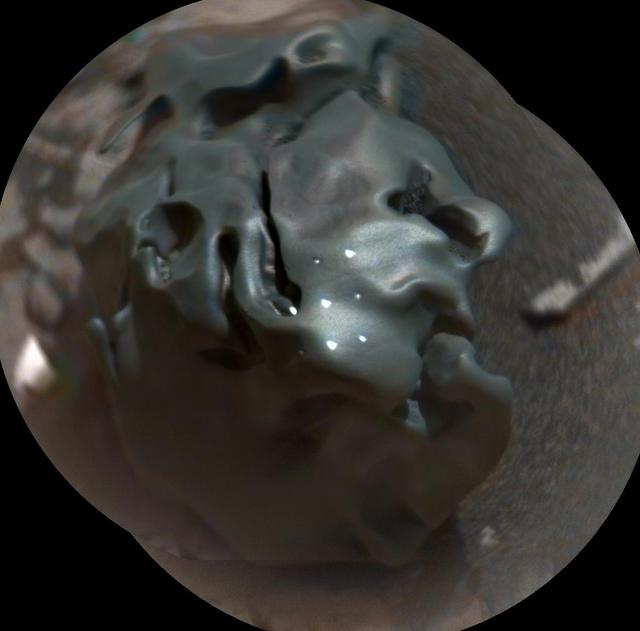
The dark, golf-ball-size object in this composite, colorized view from the Chemistry and Camera (ChemCam) instrument on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover shows a grid of shiny dots where ChemCam had fired laser pulses used for determining the chemical elements in the target's composition. The analysis confirmed that this object, informally named "Egg Rock," is an iron-nickel meteorite. Iron-nickel meteorites are a common class of space rocks found on Earth, and previous examples have been found on Mars, but Egg Rock is the first on Mars to be examined with a laser-firing spectrometer. The laser pulses on Oct. 30, 2016, induced bursts of glowing gas at the target, and ChemCam's spectrometer read the wavelengths of light from those bursts to gain information about the target's composition. The laser pulses also burned through the dark outer surface, exposing bright interior material. This view combines two images taken later the same day by ChemCam's remote micro-imager (RMI) camera, with color added from an image taken by Curiosity's Mast Camera (Mastcam). A Mastcam image of Egg Rock is at PIA21134. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21133
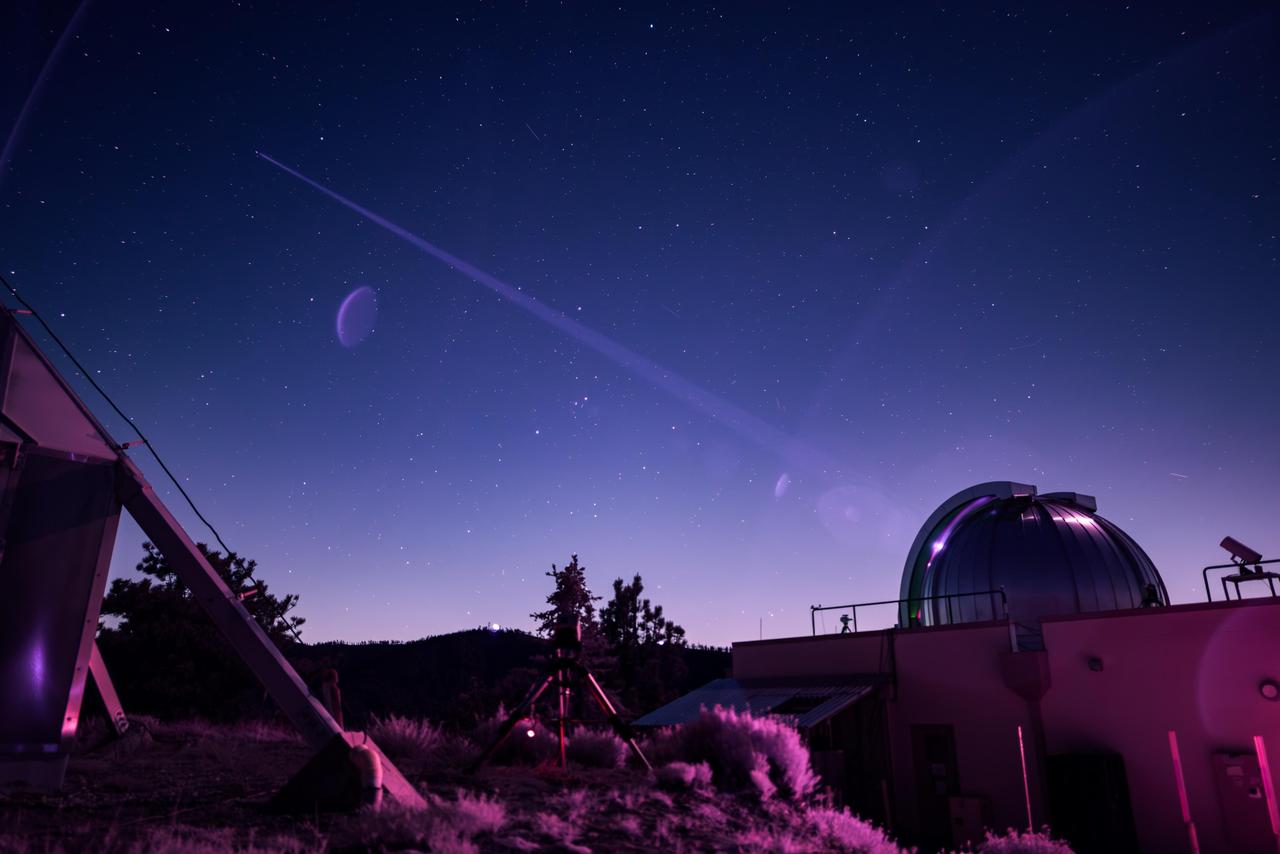

In this infrared photograph, the Optical Communications Telescope Laboratory (OCTL) at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Table Mountain Facility near Wrightwood, California, beams its eight-laser beacon (at a total power of 1.4 kilowatts) to the Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) flight laser transceiver aboard NASA's Psyche spacecraft. The photo was taken on June 2, 2025, when Psyche was about 143 million miles (230 million kilometers) from Earth. The faint purple crescent just left of center and near the laser beam is a lens flare caused by a bright light (out of frame) reflecting inside the camera lens. As the experiment's ground laser transmitter, OCTL transmits at an infrared wavelength of 1,064 nanometers from its 3.3-foot-aperture (1-meter) telescope. The telescope can also receive faint infrared photons (at a wavelength of 1,550 nanometers) from the 4-watt flight laser transceiver on Psyche. Neither infrared wavelength is easily absorbed or scattered by Earth's atmosphere, making both ideal for deep space optical communications. To receive the most distant signals from Psyche, the project enlisted the powerful 200-inch-aperture (5-meter) Hale Telescope at Caltech's Palomar Observatory in San Diego County, California, as its primary downlink station, which provided adequate light-collecting area to capture the faintest photons. Those photons were then directed to a cryogenically cooled superconducting high-efficiency detector array at the observatory where the information encoded in the photons could be processed. Managed by JPL, DSOC was designed to demonstrate that data encoded in laser photons could be reliably transmitted, received, and then decoded after traveling millions of miles from Earth out to Mars distances. Nearly two years after launching aboard the agency's Psyche mission in 2023, the demonstration completed its 65th and final "pass" on Sept. 2, 2025, sending a laser signal to Psyche and receiving the return signal from 218 million miles (350 million kilometers) away. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26661

A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Pictured from Left to Right: James Demers, Adam Wroblewski, Shaun McKeehan, Kurt Blankenship. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data.
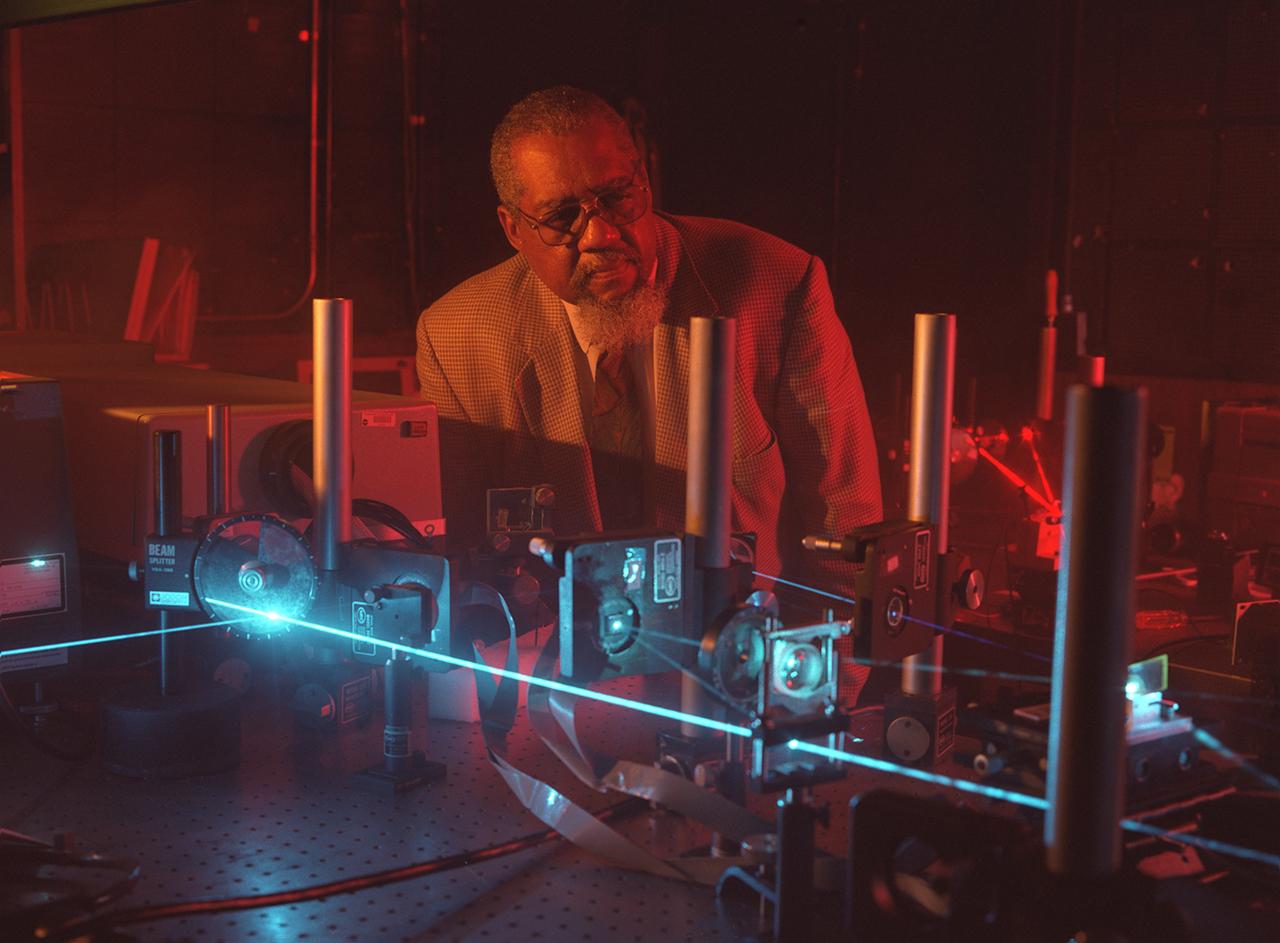

NASA researcher Dr. Donald Frazier uses a blue laser shining through a quartz window into a special mix of chemicals to generate a polymer film on the inside quartz surface. As the chemicals respond to the laser light, they adhere to the glass surface, forming optical films. Dr. Frazier and Dr. Mark S. Paley developed the process in the Space Sciences Laboratory at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, AL. Working aboard the Space Shuttle, a science team led by Dr. Frazier formed thin-films potentially useful in optical computers with fewer impurities than those formed on Earth. Patterns of these films can be traced onto the quartz surface. In the optical computers of the future, thee films could replace electronic circuits and wires, making the systems more efficient and cost-effective, as well as lighter and more compact. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center
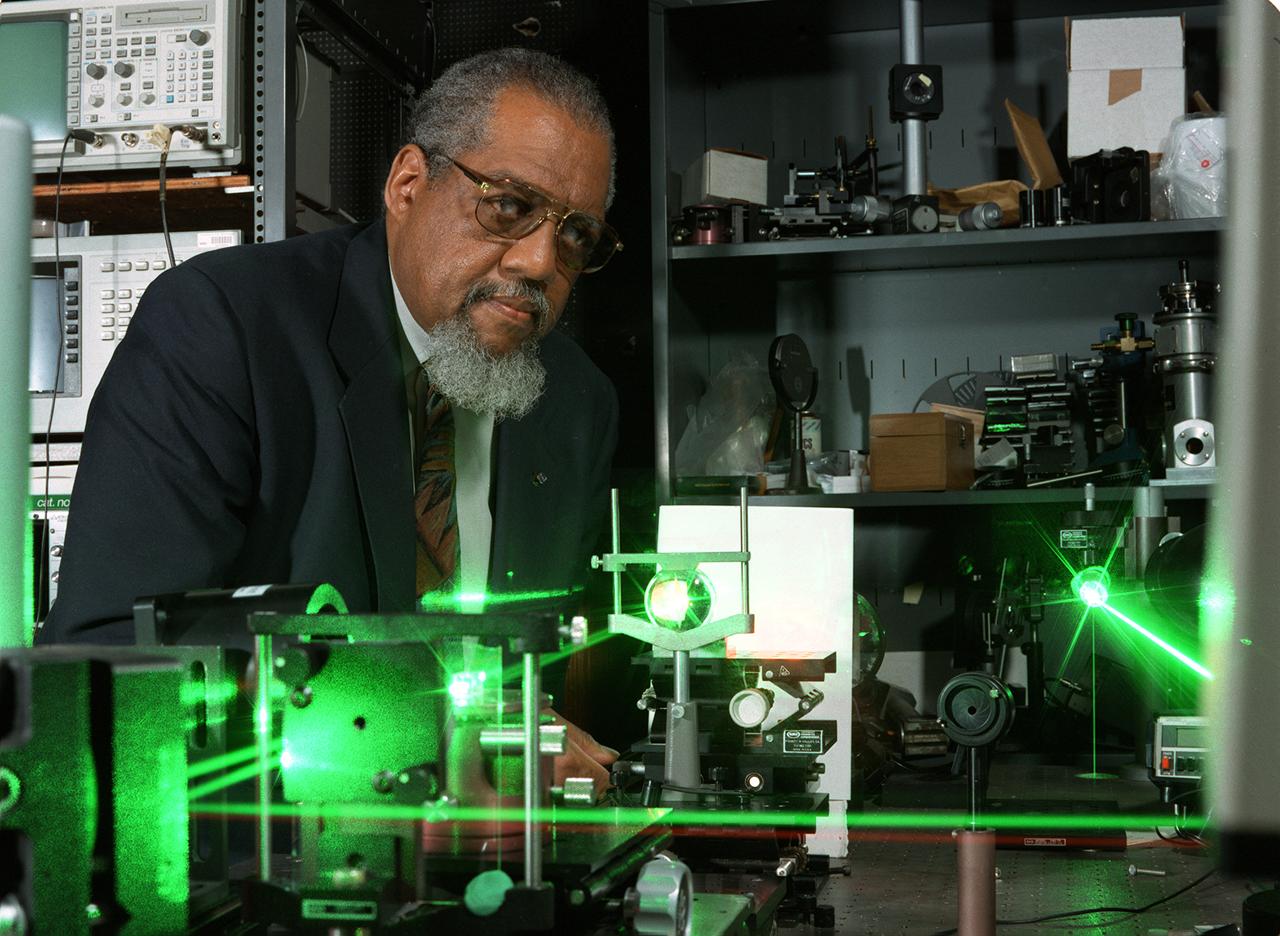

NASA research Dr. Donald Frazier uses a blue laser shining through a quartz window into a special mix of chemicals to generate a polymer film on the inside quartz surface. As the chemicals respond to the laser light, they adhere to the glass surface, forming opticl films. Dr. Frazier and Dr. Mark S. Paley developed the process in the Space Sciences Laboratory at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, AL. Working aboard the Space Shuttle, a science team led by Dr. Frazier formed thin-films potentially useful in optical computers with fewer impurities than those formed on Earth. Patterns of these films can be traced onto the quartz surface. In the optical computers on the future, these films could replace electronic circuits and wires, making the systems more efficient and cost-effective, as well as lighter and more compact. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center
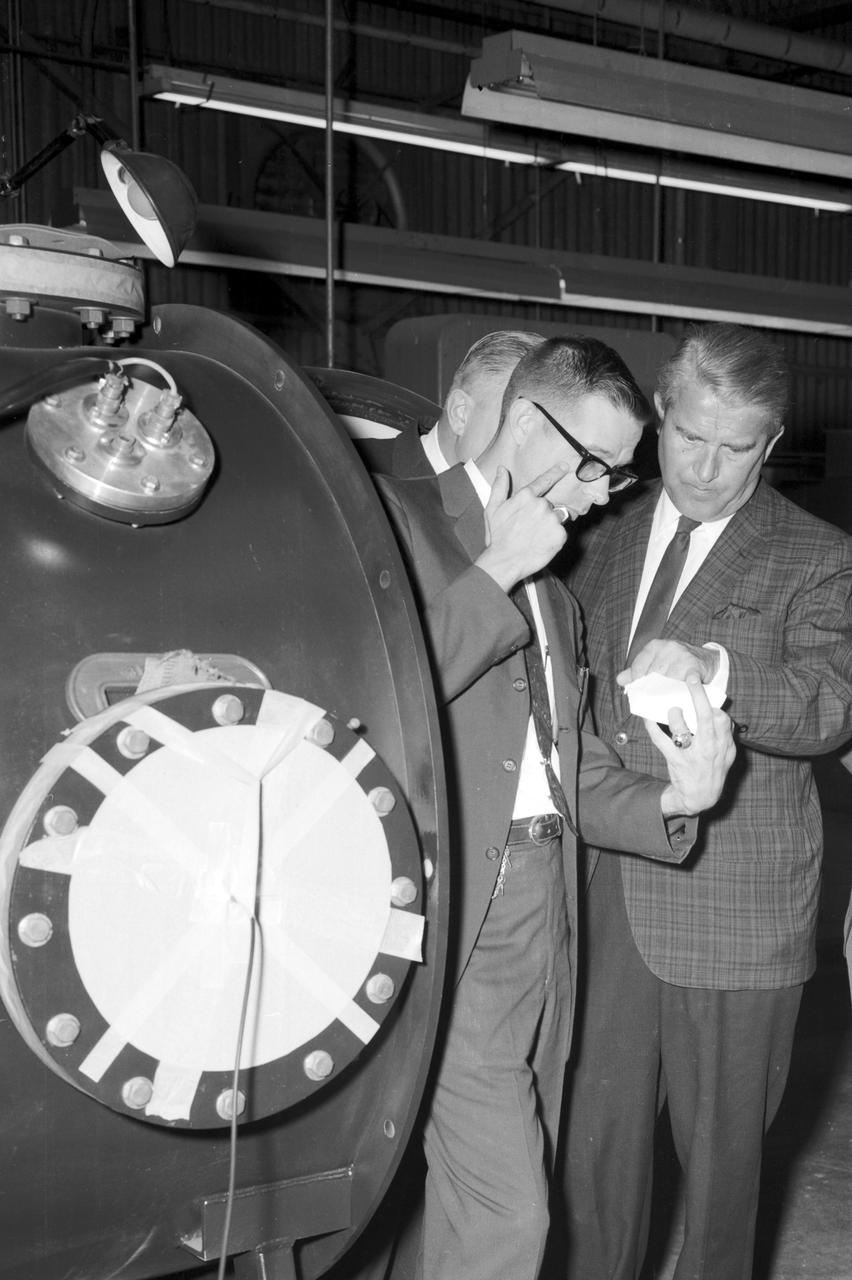

Dr. von Braun and party look at a laser beam component during a visit at the Marshall Space Flight Center Space Science Laboratory on August 28, 1967.

This composite image, made from four taken by the SuperCam instrument aboard NASA's Perseverance rover on August 8, 2021, shows the hole in a Martian rock where the rover attempted to collect its first sample; the small pits within it were created by laser zaps from SuperCam during subsequent efforts to analyze the rock's composition. The rover science team has nicknamed the drill hole "Roubion." The team believes that because of this rock's unusual composition, the process of extracting a core created a significant pile of tailings (or cuttings) around the coring hole. Eight pits produced by 30 laser shots each are seen in two columns inside the drill hole. The SuperCam team's analysis suggests that the top six pits penetrated the compacted mound of tailings around the hole, while the bottom two pits in the hole interrogated material below the rock surface. Two additional laser pits can be seen in the tailings at the near side of the hole. Two vertical ridges inside the hole – one on each side of the laser pits – were produced as the drill was removed, prior to laser analysis. Some bright mineral grains can be seen as glints in the tailings and in the drill hole. A few clumps or larger pieces of material are seen at the top of the tailings pile just to the left of the hole. The SuperCam images were taken from a distance of 7.32 feet (2.23 meters). A scale bar is included in this image. Perseverance landed in Mars' Jezero Crater on February 18, 2021, and has been exploring the floor of the crater since. At the time these images were taken, Perseverance was in an area nicknamed the "Crater Floor Fractured Rough" area. SuperCam is led by Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico, where the instrument's Body Unit was developed. That part of the instrument includes several spectrometers as well as control electronics and software. The Mast Unit, including the Remote Microscopic Imager used for these images, was developed and built by several laboratories of the CNRS (the French research center) and French universities under the contracting authority of Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES, the French space agency). A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24749

This timelapse video shows the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Table Mountain Facility near Wrightwood, California, transmitting its 3-kilowatt laser beacon to the agency's Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment aboard NASA's Psyche mission on June 2, 2025; the spacecraft was about 143 million miles (230 million kilometers) from Earth at the time. Managed by JPL, DSOC was designed to demonstrate that data encoded in laser photons could be reliably transmitted, received, and then decoded after traveling millions of miles from Earth out to Mars distances. Nearly two years after launching aboard the agency's Psyche mission in 2023, the demonstration completed its 65th and final "pass" on Sept. 2, 2025, sending a laser signal to Psyche and receiving the return signal from 218 million miles (350 million kilometers) away. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26663
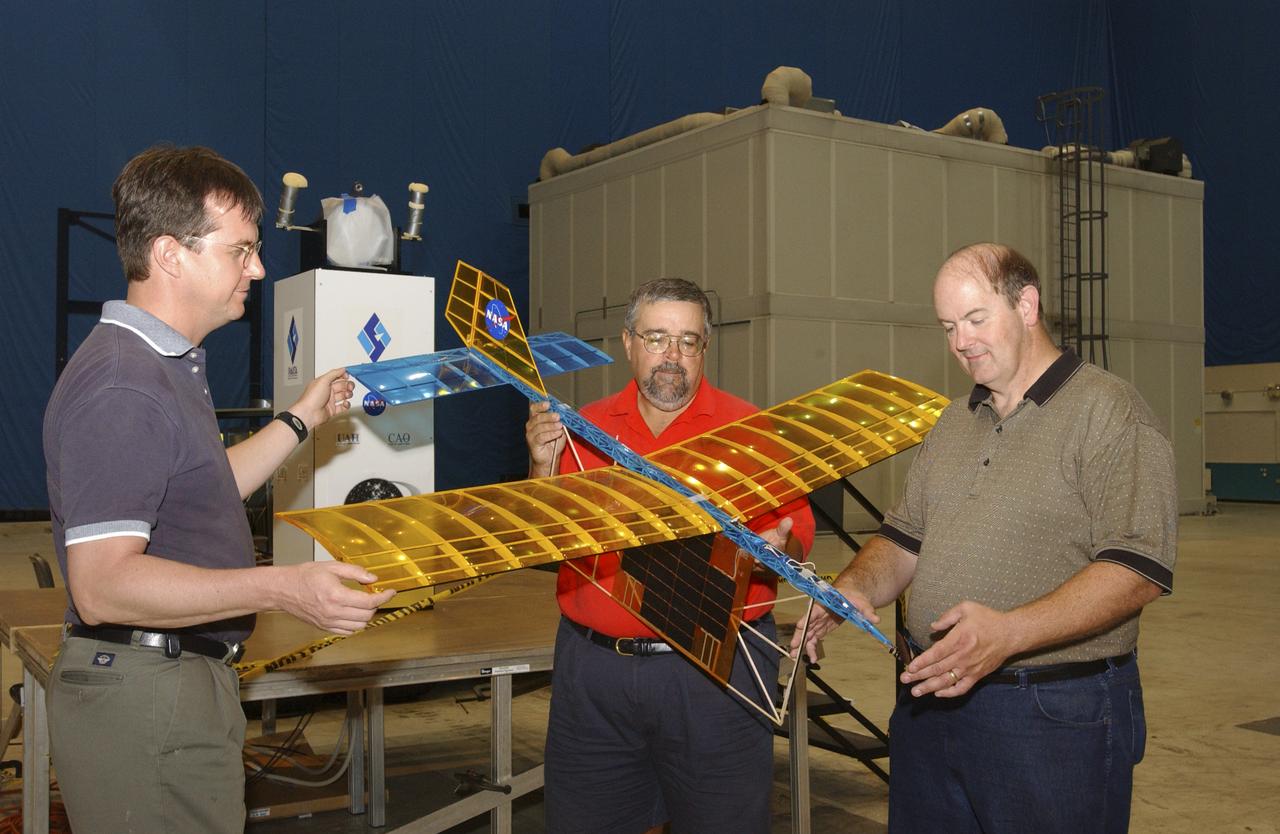

A team of NASA researchers from Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and Dryden Flight Research center have proven that beamed light can be used to power an aircraft, a first-in-the-world accomplishment to the best of their knowledge. Using an experimental custom built radio-controlled model aircraft, the team has demonstrated a system that beams enough light energy from the ground to power the propeller of an aircraft and sustain it in flight. Special photovoltaic arrays on the plane, similar to solar cells, receive the light energy and convert it to electric current to drive the propeller motor. In a series of indoor flights this week at MSFC, a lightweight custom built laser beam was aimed at the airplane `s solar panels. The laser tracks the plane, maintaining power on its cells until the end of the flight when the laser is turned off and the airplane glides to a landing. The laser source demonstration represents the capability to beam more power to a plane so that it can reach higher altitudes and have a greater flight range without having to carry fuel or batteries, enabling an indefinite flight time. The demonstration was a collaborative effort between the Dryden Center at Edward's, California, where the aircraft was designed and built, and MSFC, where integration and testing of the laser and photovoltaic cells was done. Laser power beaming is a promising technology for consideration in new aircraft design and operation, and supports NASA's goals in the development of revolutionary aerospace technologies. Photographed with their invention are (from left to right): David Bushman and Tony Frackowiak, both of Dryden; and MSFC's Robert Burdine.
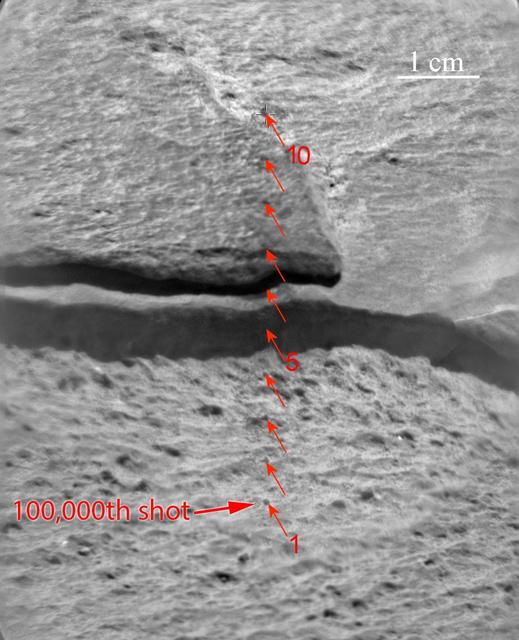

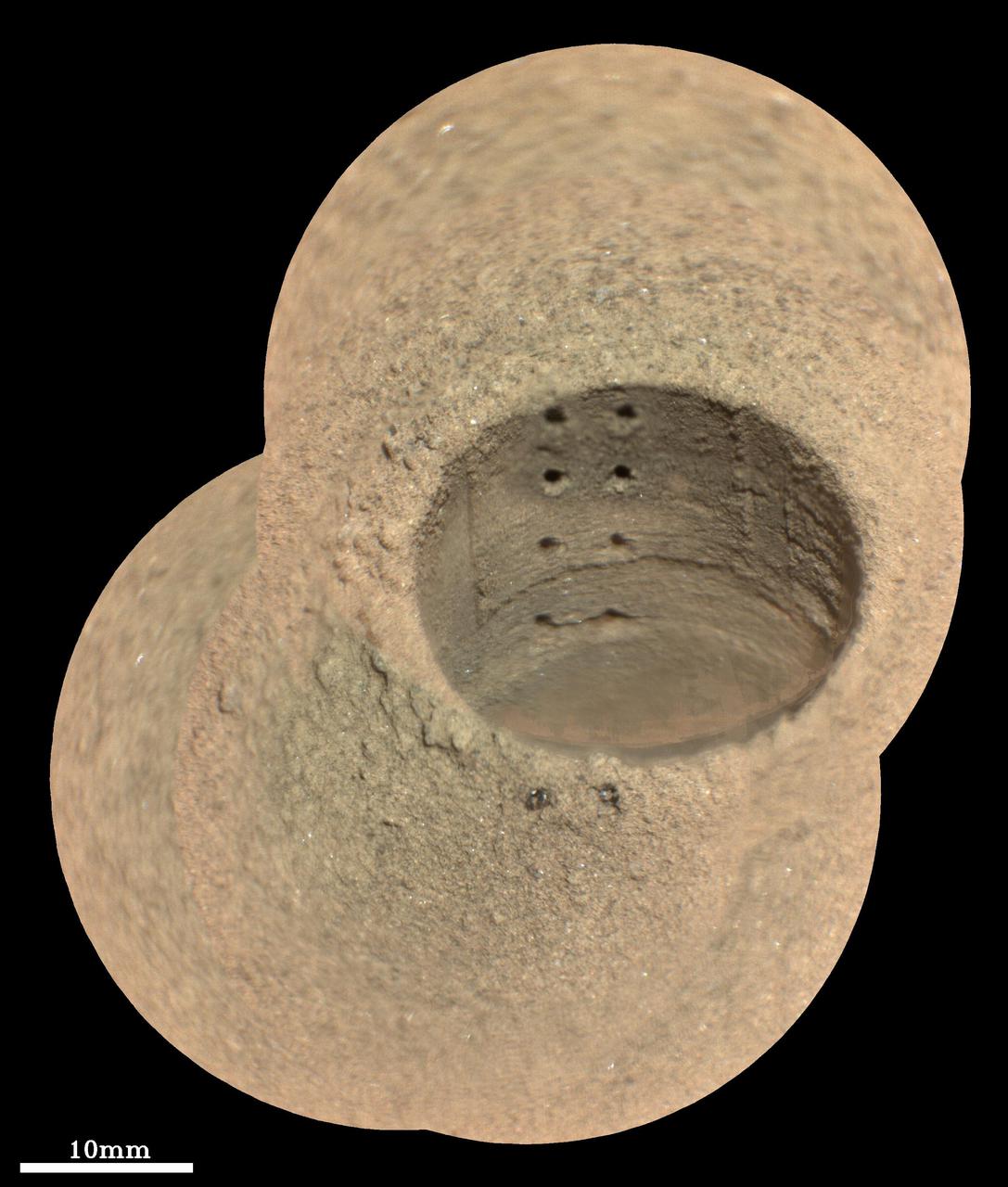
Since landing on Mars in August 2012, NASA Curiosity Mars rover has fired the laser on its Chemistry and Camera ChemCam instrument more than 100,000 times at rock and soil targets up to about 23 feet 7 meters away.
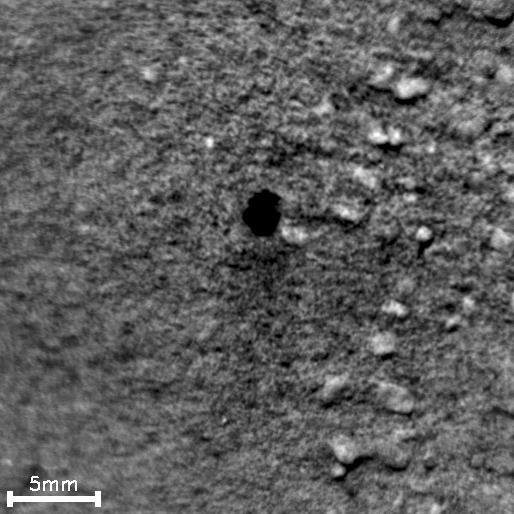

This image from an animation shows how repeated laser shots from the ChemCam instrument on NASA Mars rover Curiosity cause a pit to form at the target point in Martian soil.
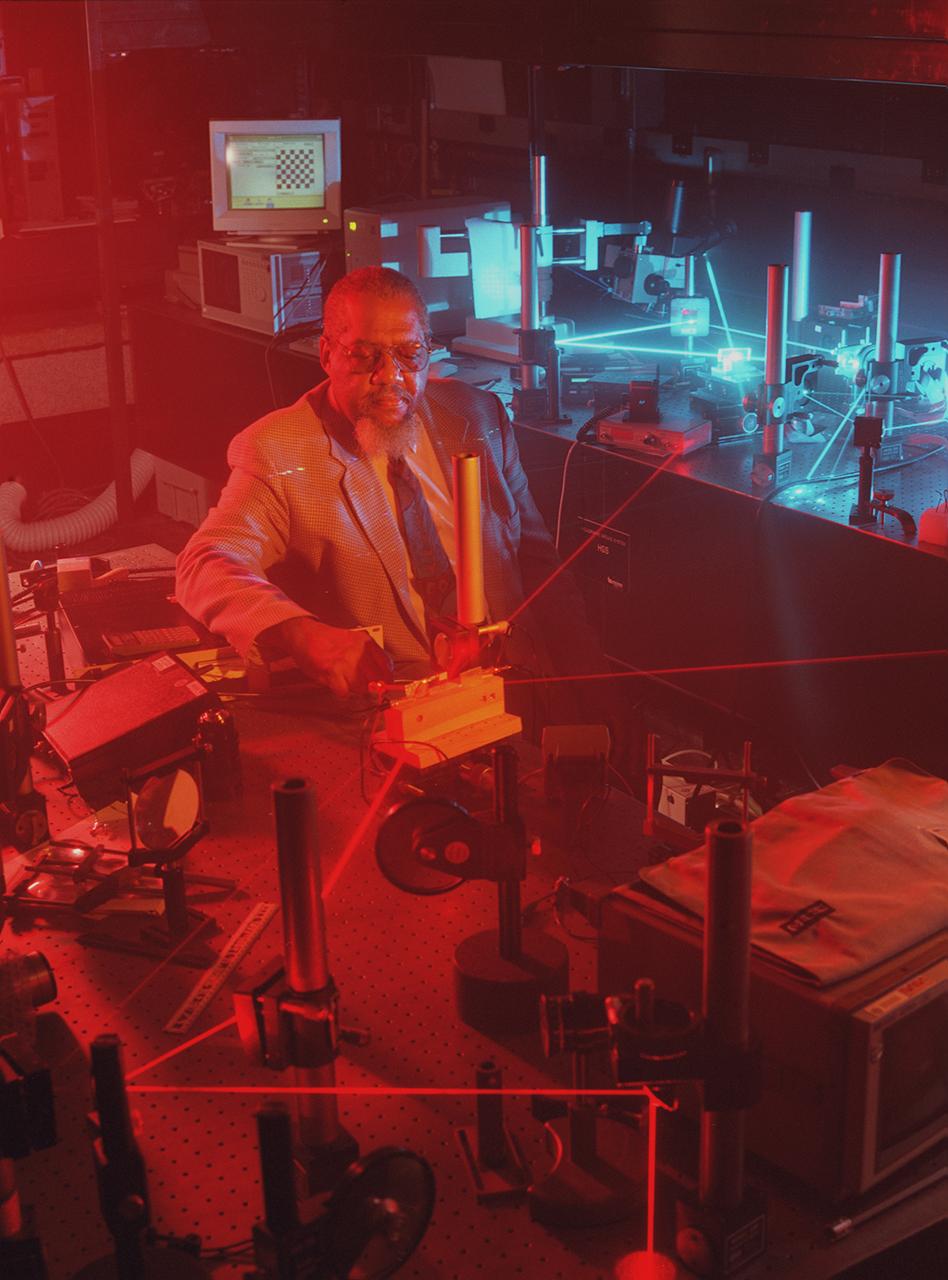

Dr. Donald Frazier works with a laser imaging system designed by Dr. Hossin Abdeldayem for pattern recognition applications. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)
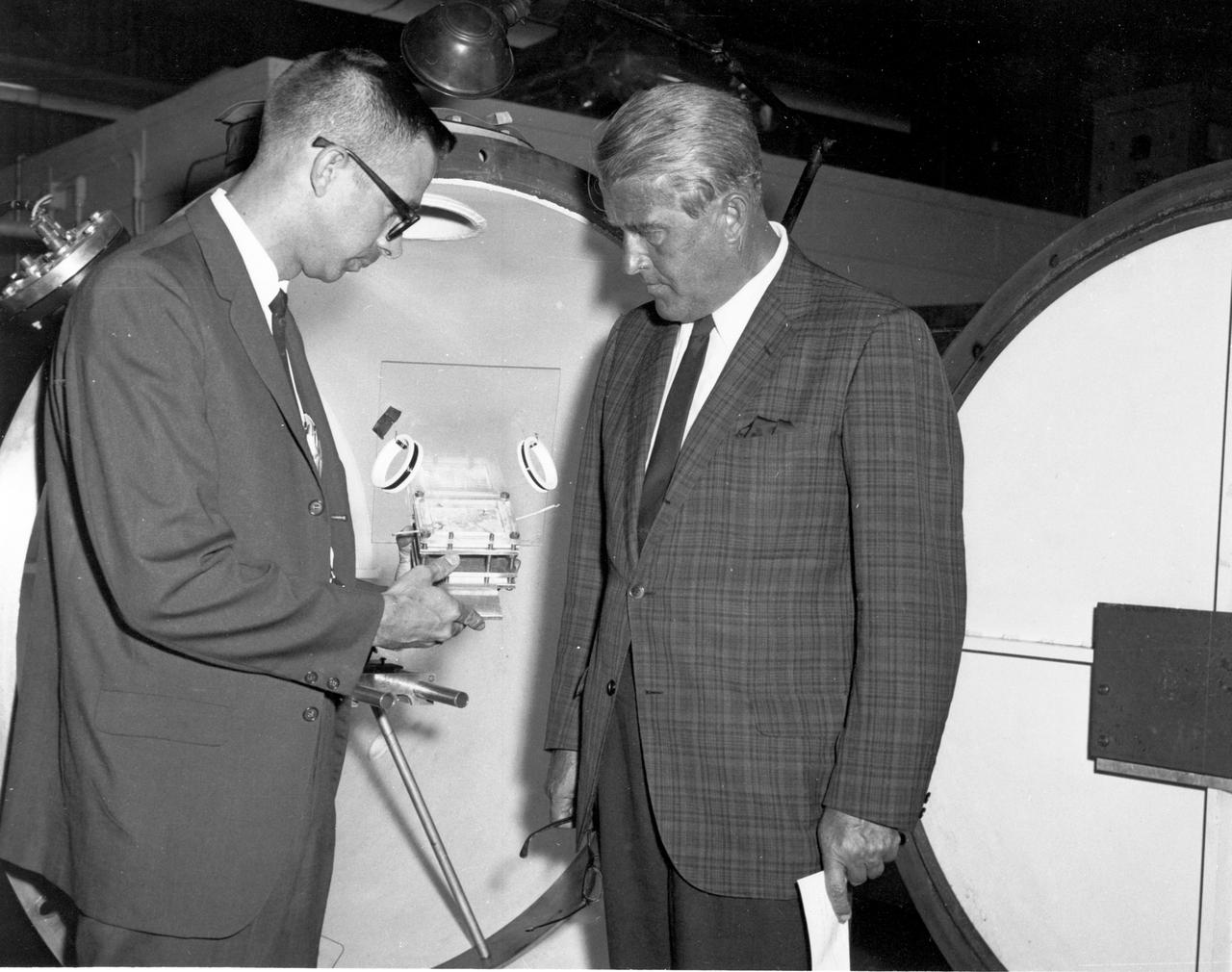

Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC) director, Dr. Wernher von Braun (right), inspects a component of a laser experiment being conducted in MSFC’s Space Sciences Laboratory during a tour on August 28, 1967.
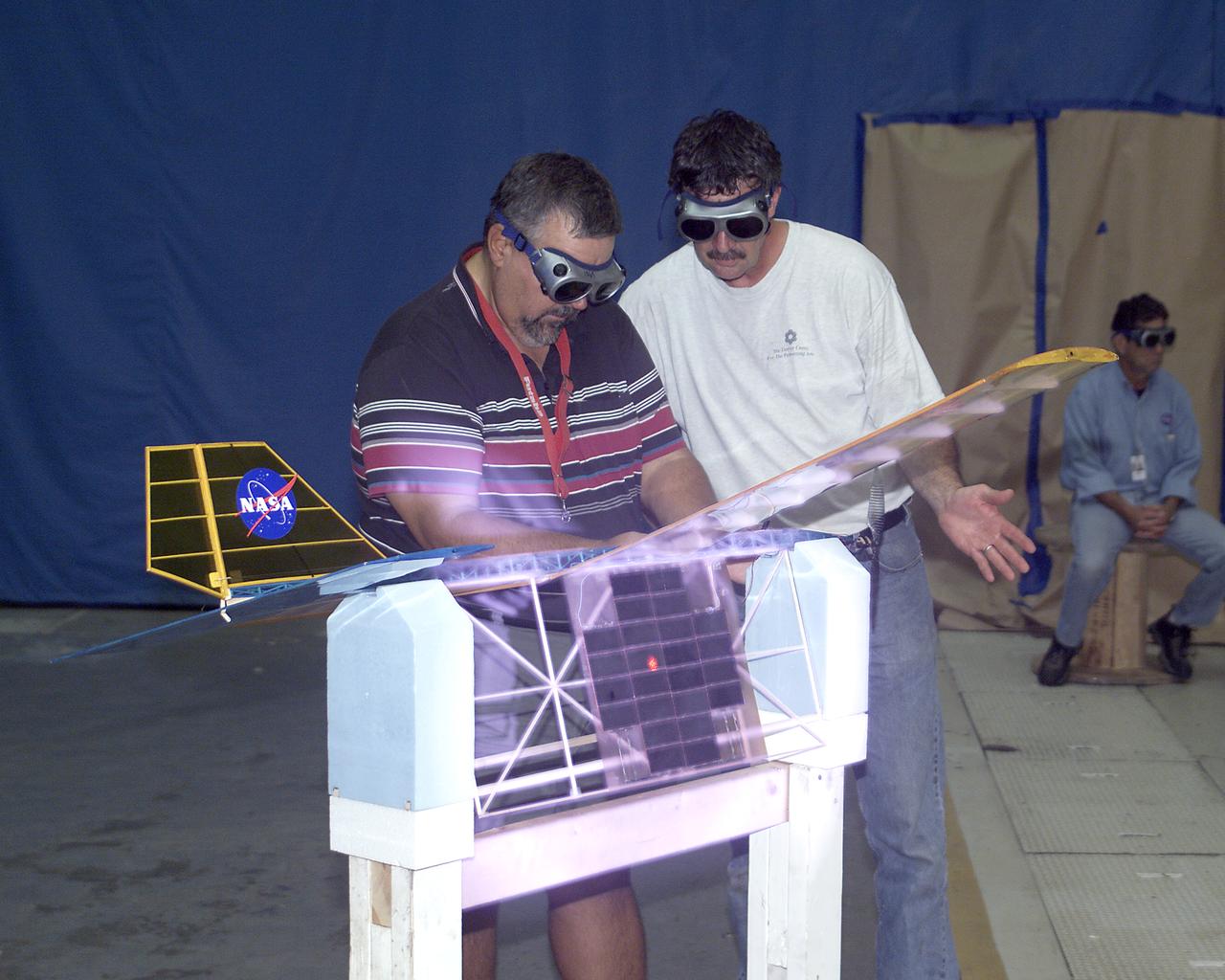

With a laser beam centered on its solar panel, a lightweight model aircraft is checked out by technician Tony Frakowiak and researcher Tim Blackwell before its power-beamed demonstration flight.
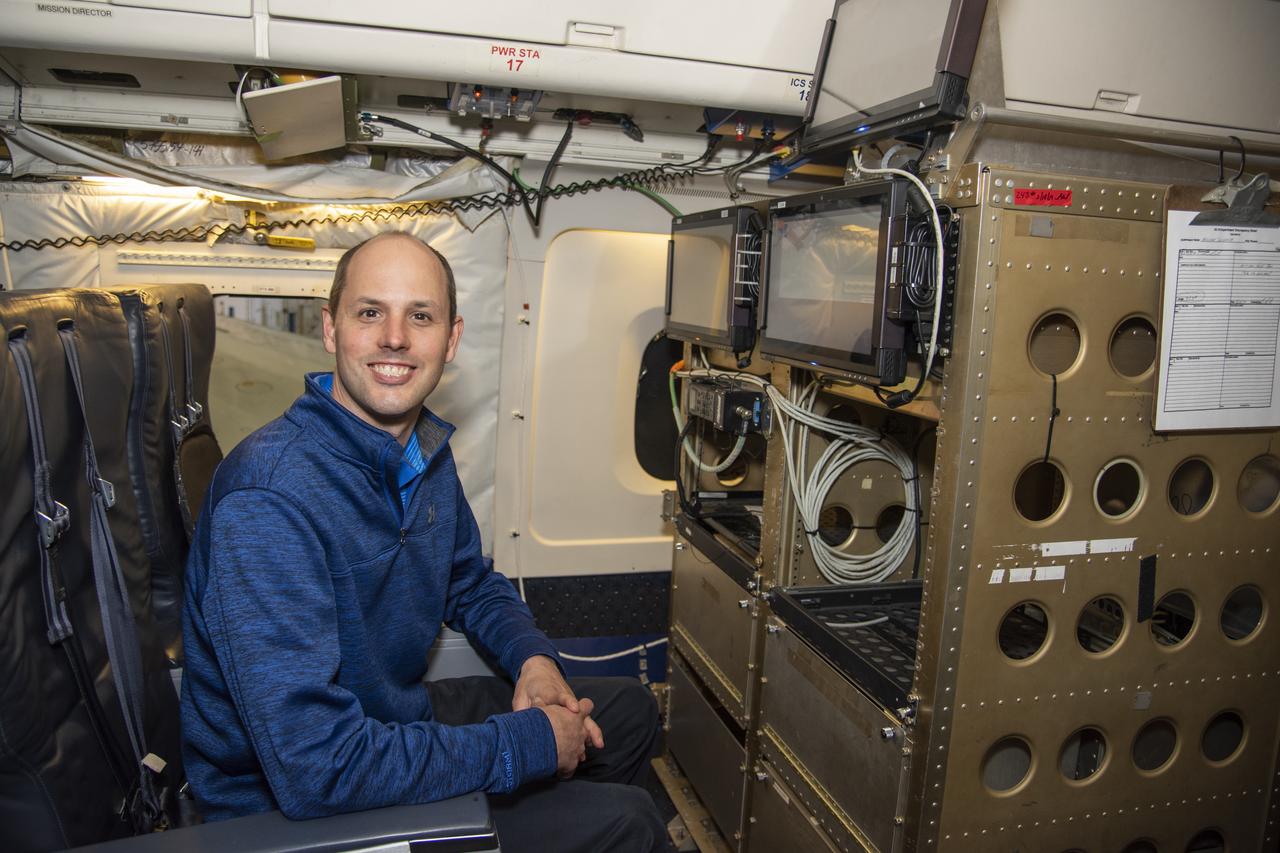

NASA Langley Research Center's Kris Bedka, pictured here on the DC-8 flying laboratory, is the lead for an airborne mission called Aeoulus that is advancing laser-based technologies for measuring winds in the lower atmosphere.
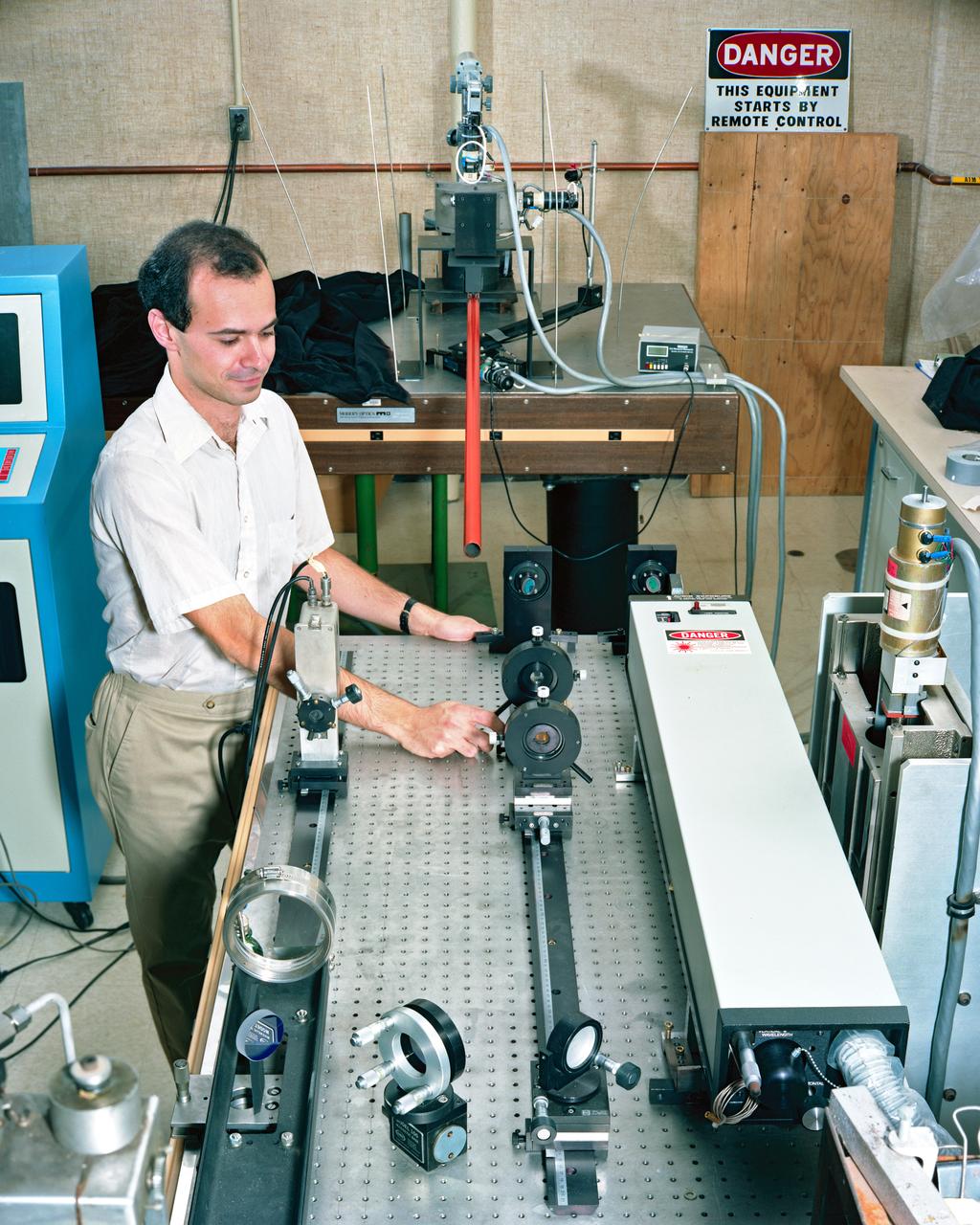

LASER EXPERIMENT IN REAR PORTION OF CE-13 IN ENGINE RESEARCH BUILDING

Looking for a faster computer? How about an optical computer that processes data streams simultaneously and works with the speed of light? In space, NASA researchers have formed optical thin-film. By turning these thin-films into very fast optical computer components, scientists could improve computer tasks, such as pattern recognition. Dr. Hossin Abdeldayem, physicist at NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Huntsville, Al, is working with lasers as part of an optical system for pattern recognition. These systems can be used for automated fingerprinting, photographic scarning and the development of sophisticated artificial intelligence systems that can learn and evolve. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)
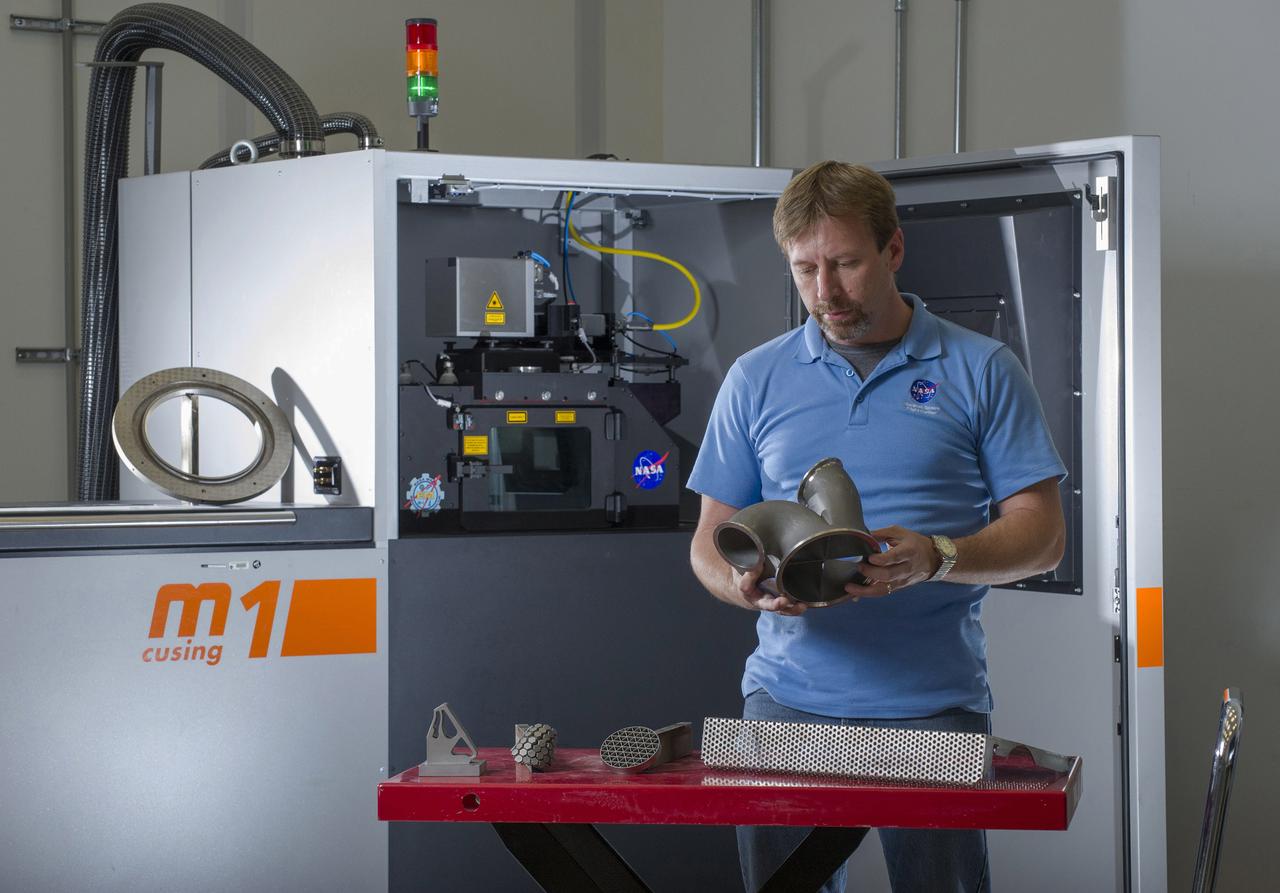

KEN COOPER, TEAM LEAD OF MSFC’S ADVANCED MANUFACTURING TEAM, WITH NICKEL ALLOY 718 PARTS FABRICATED USING THE M1 SELECTIVE LASER MELTING SYSTEM. THE M1 MACHINE IS DEDICATED TO BUILDING QUALIFICATION SAMPLES AND HARDWARE DEMONSTRATORS FOR THE RS25 ENGINE PROJECT.
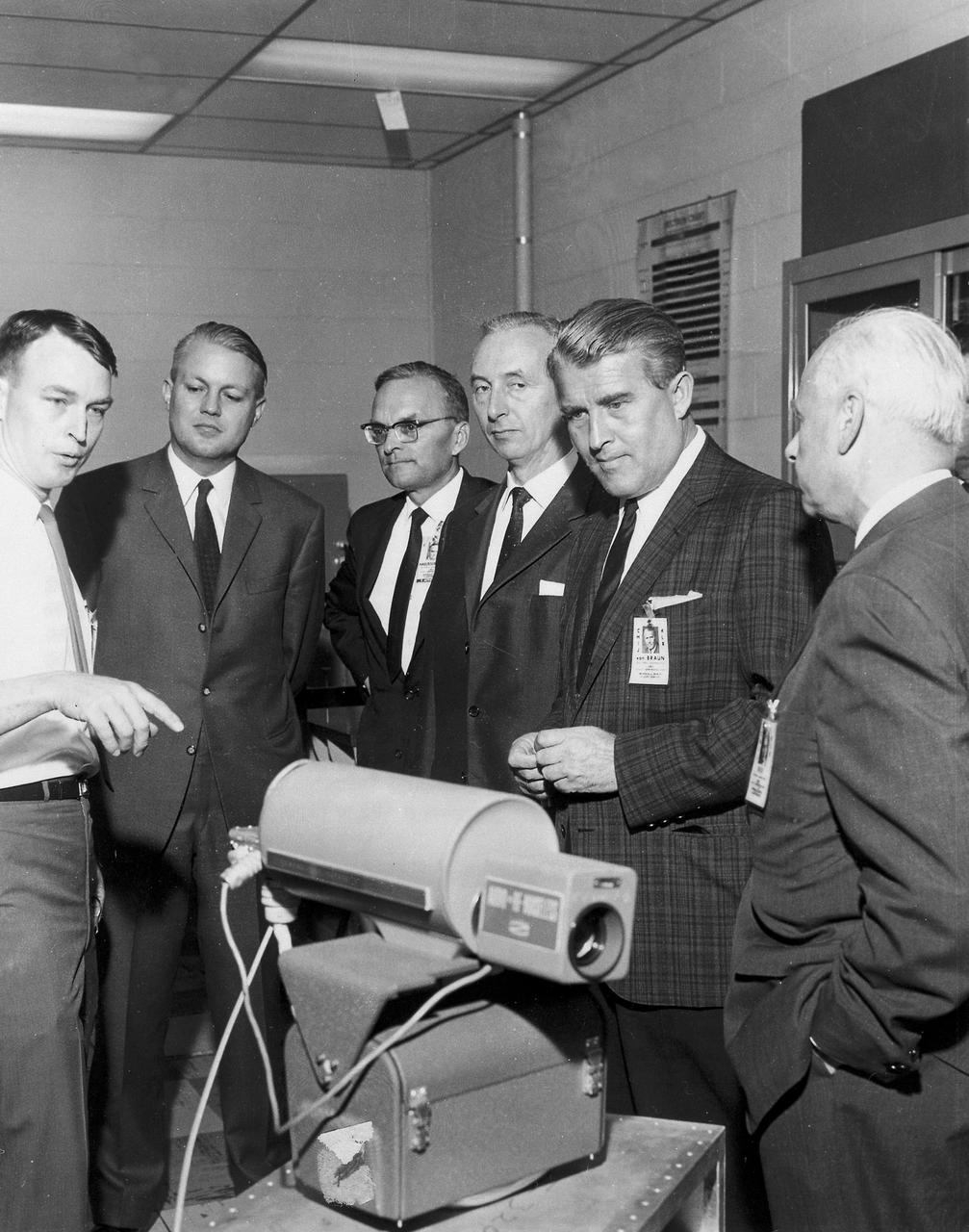

Dr. Joseph Randall, a laser expert at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), explains one of the projects he is working on to a group composed of Federal Republic of Germany and MSFC officials. From left are: Dr. Randall; Minister for Scientific Research of Federal Republic of Germany, Dr. Gerhard Stolenberg; Director of MSFC Astrionics Lab, Dr. Walter Haeusserman; Head of Space Research Federal Republic of Germany, Max Mayer; MSFC Director Dr. von Braun; MSFC Deputy Director Dr. Elberhard Rees.
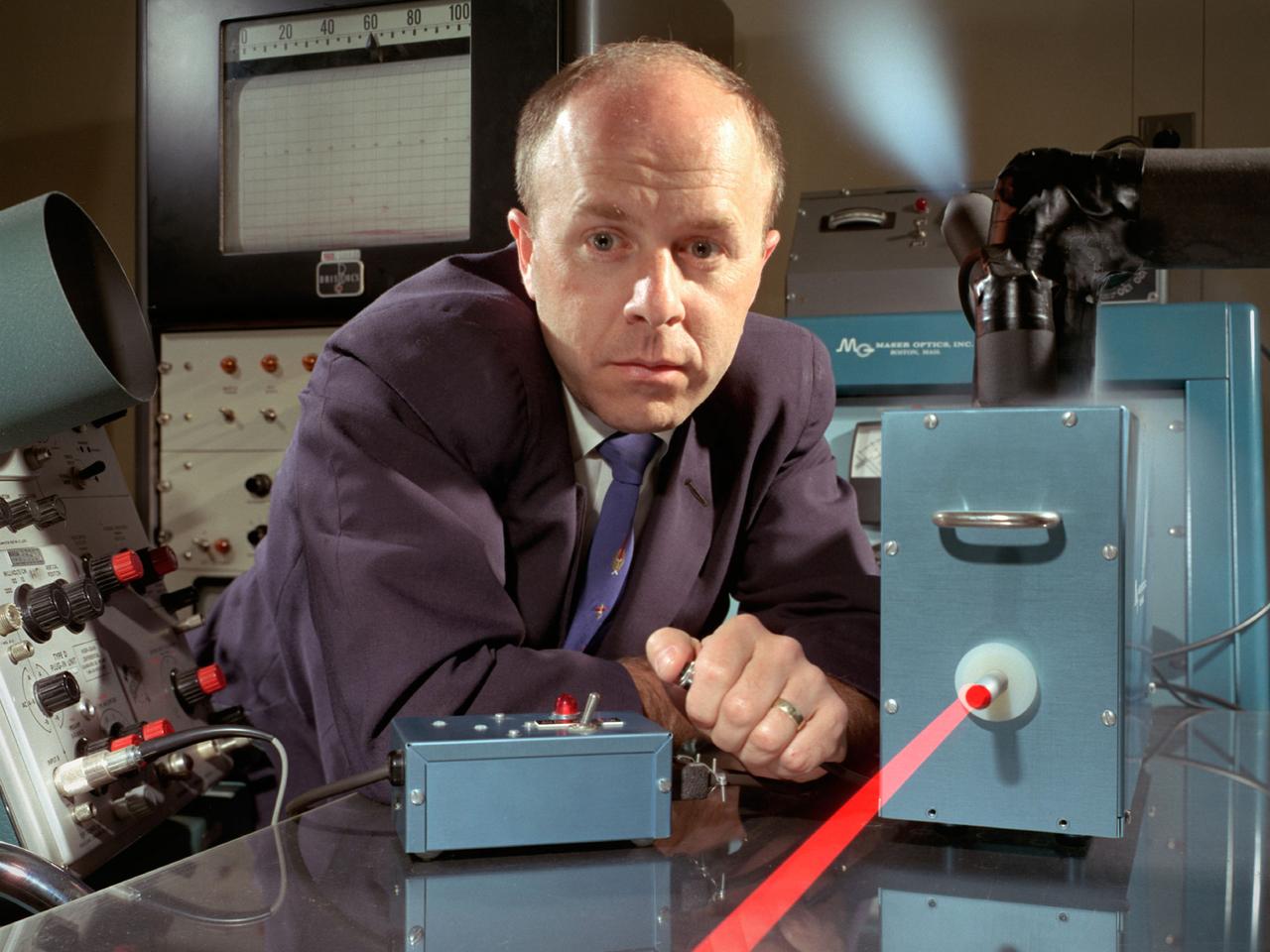

National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center researcher Americo Forestieri aims a ruby laser beam at a crystal to determine the effects of its radiation. Forestieri was a researcher in the Electric Component Experiment Section of the Space Power System Division. Lewis was in the midst of a long-term effort to develop methods of delivering electrical power to spacecraft using nuclear, solar, or electrochemical technologies. Ruby lasers contain a ruby crystal with mirrors on either side. The laser action is created when a high-intensity lamp shines around the ruby and excites the electrons in the ruby’s chromium atoms. After the excitation, the electrons emit their ruby-red light. The mirrors reflect some of this red light back and forth inside the ruby which causes other excited chromium atoms to produce additional red light. This continues until the light pulse reaches high power levels and consumes all of the energy stored in the crystal. Forestieri used optical absorption and electron paramagnetic resonance techniques to study the extent and manner in which the radiation interacted with the samples. He determined that individual bands were assigned to specific electronic transitions. He also studied the atomic changes in the ruby crystals after irradiation. He found that complex interactions depend on the crystal pretreatment, purity, and irradiation dose.
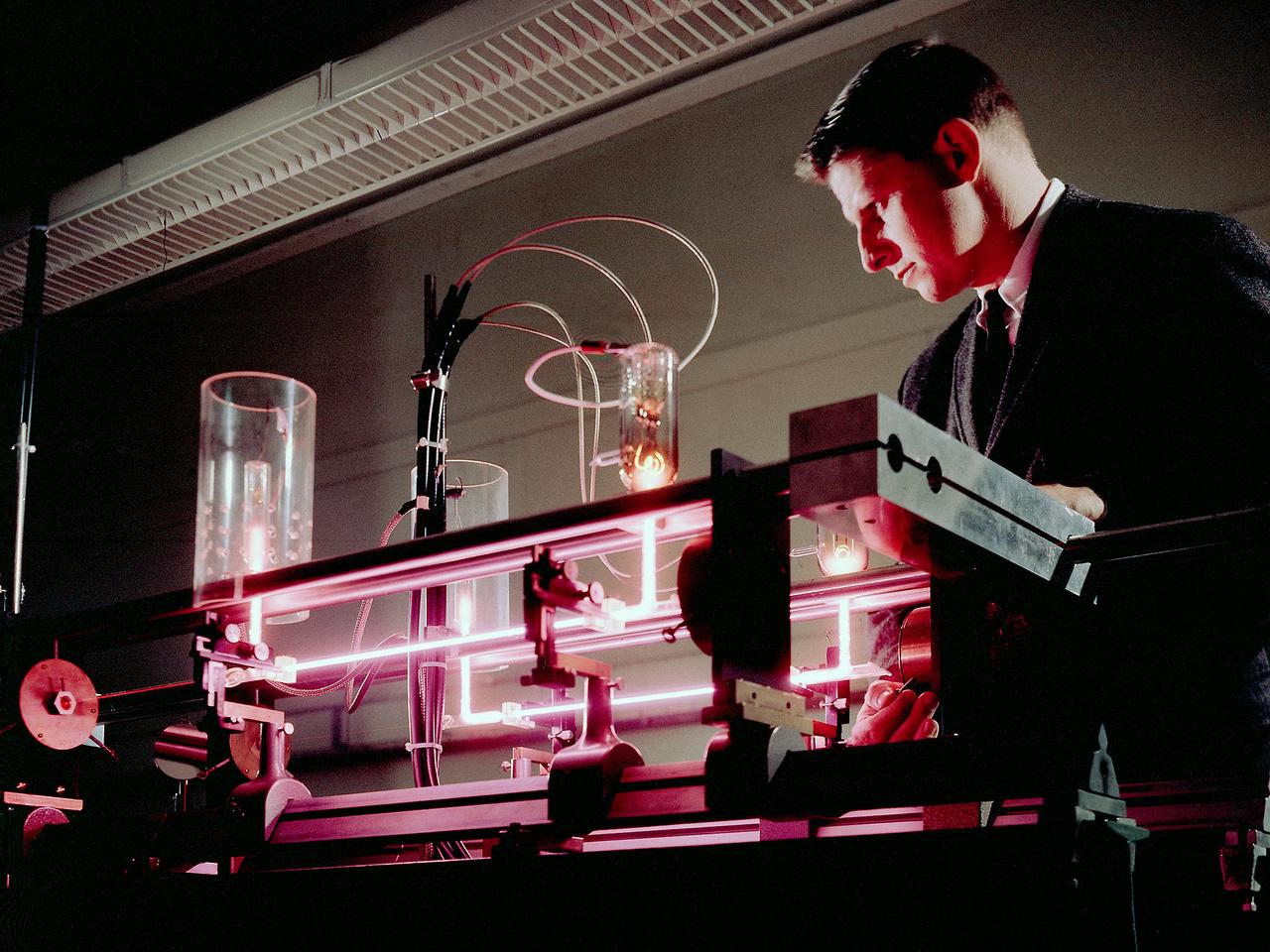
Richard Lancashire operates a gas laser interferometer in the Electric Conversion Laboratory at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Lewis was in the midst of a long-term effort to develop methods of delivering electrical power to spacecraft using nuclear, solar, or electrochemical technologies. Lancashire was measuring the thermionic diode’s plasma particle density. The thermionic diodes were being studied for possible use in radioisotope thermoelectric generators for use in space. Microwave interferometry was one method of measuring transient plasmas. The interferometer measured the difference between the frequencies of two laser beams, one of which passed through the diode. The electron density was measured by revealing the phase shift of the transmitted microwave beam brought about by a change in the plasma refraction. Microwave interferometry, however, offers poor spatial resolution and has limited range of applicability.

Deep Space Station 13 (DSS-13) at NASA's Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex near Barstow, California – part of the agency's Deep Space Network – is a 34-meter (112-foot) experimental antenna that has been retrofitted with an optical terminal (the boxy instrument below the center of the antenna's dish). Since November 2023, DSS-13 has been tracking the downlink laser of the Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment that is aboard NASA's Psyche mission, which launched on Oct. 13, 2023. In a first, the antenna also synchronously received radio-frequency signals from the spacecraft as it travels through deep space on its way to investigate the metal-rich asteroid Psyche. The laser signal collected by the camera is then transmitted through optical fiber that feeds into a cryogenically cooled semiconducting nanowire single photon detector. Designed and built by JPL's Microdevices Laboratory, the detector is identical to the one used at Caltech's Palomar Observatory, in San Diego County, California, that acts as DSOC's downlink ground station. Goldstone is one of three complexes that comprise NASA's Deep Space Network, which provides radio communications for all of the agency's interplanetary spacecraft and is also utilized for radio astronomy and radar observations of the solar system and the universe. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the DSN for the agency. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26148

Howard University student Nathan Roseboro gives NASA astronaut Jessica Watkins a demonstration of his work with lasers during a tour of the Laser Spectroscopy Laboratory at Howard University, Friday, March 31, 2023, in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Howard University student Miles Phillips gives NASA astronaut Jessica Watkins a demonstration of his work with lasers during a tour of the Laser Spectroscopy Laboratory at Howard University, Friday, March 31, 2023, in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Howard University student Nathan Roseboro gives NASA astronaut Jessica Watkins a demonstration of his work with lasers during a tour of the Laser Spectroscopy Laboratory at Howard University, Friday, March 31, 2023, in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Howard University student Miles Phillips gives NASA astronaut Jessica Watkins a demonstration of his work with lasers during a tour of the Laser Spectroscopy Laboratory at Howard University, Friday, March 31, 2023, in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA astronaut Jessica Watkins asks a question after a demonstration by Howard University student Nathan Roseboro of his work with lasers during a tour of the Laser Spectroscopy Laboratory at Howard University, Friday, March 31, 2023, in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
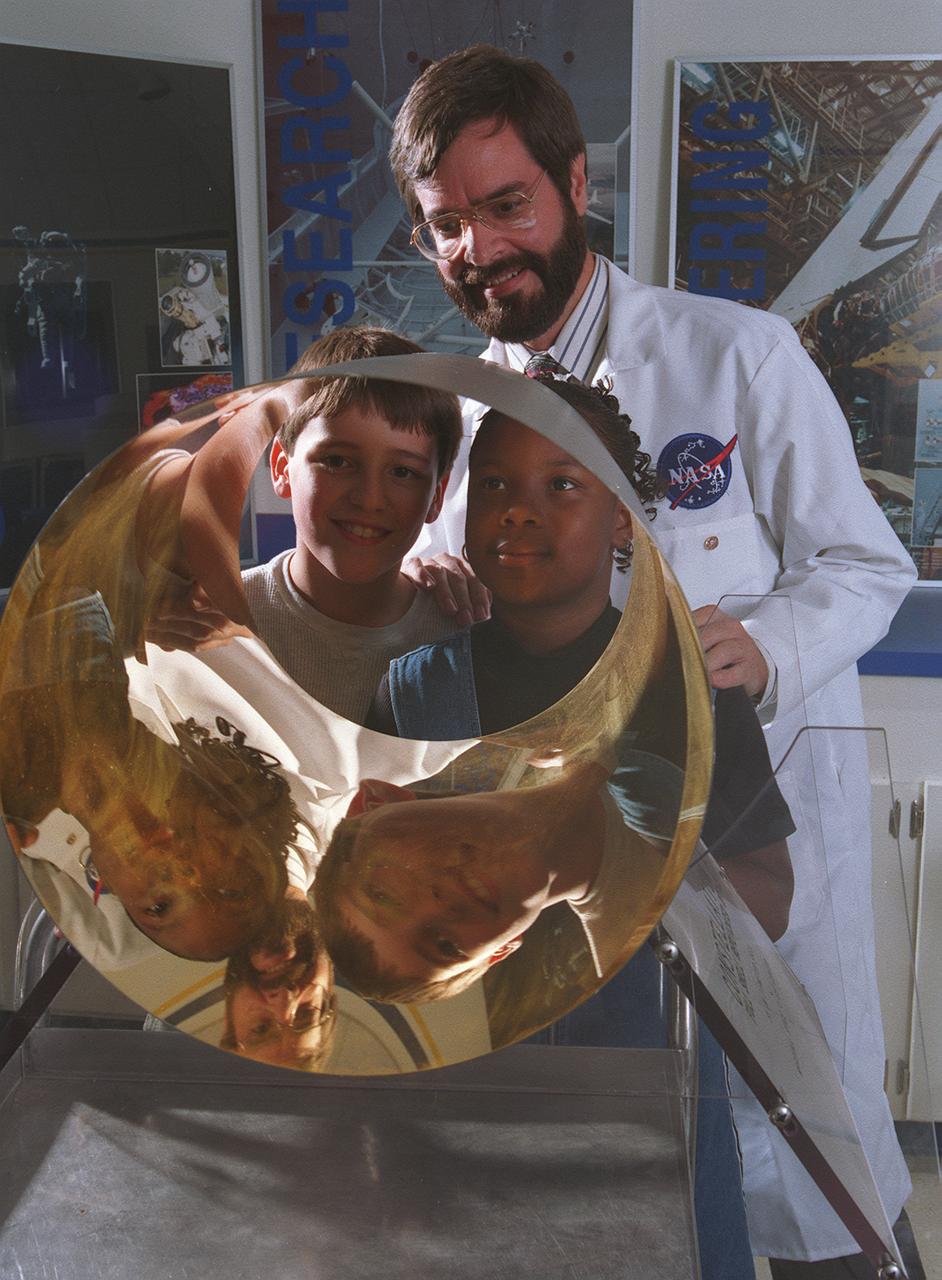

Through Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Education Department, over 400 MSFC employees have volunteered to support educational program during regular work hours. Project LASER (Learning About Science, Engineering, and Research) provides support for mentor/tutor requests, education tours, classroom presentations, and curriculum development. This program is available to teachers and students living within commuting distance of the NASA/MSFC in Huntsville, Alabama (approximately 50-miles radius). This image depicts students viewing their reflections in an x-ray mirror with Marshall optic engineer Vince Huegele at the Discovery Laboratory, which is an onsite MSFC laboratory facility that provides hands-on educational workshop sessions for teachers and students learning activities.
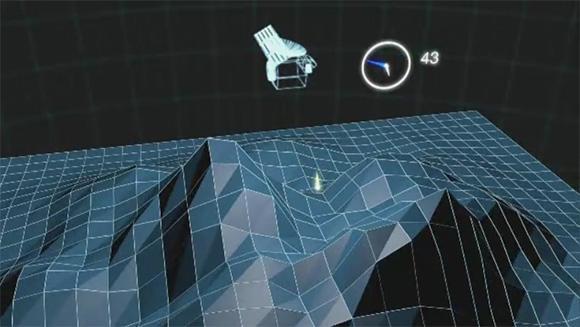
NASA Mercury Laser Altimeter MLA is shown ranging to Mercury surface from orbit. In this animation, yellow flashes represent near-infrared laser pulses that can reflect off terrain in shadow as well as in sunlight.

This mosaic image shows the first target NASA Curiosity rover aims to zap ChemCam instrument. ChemCam will be firing a laser at this rock, provisionally named N165, and analyzing the glowing, ionized gas, called plasma, that the laser excites.
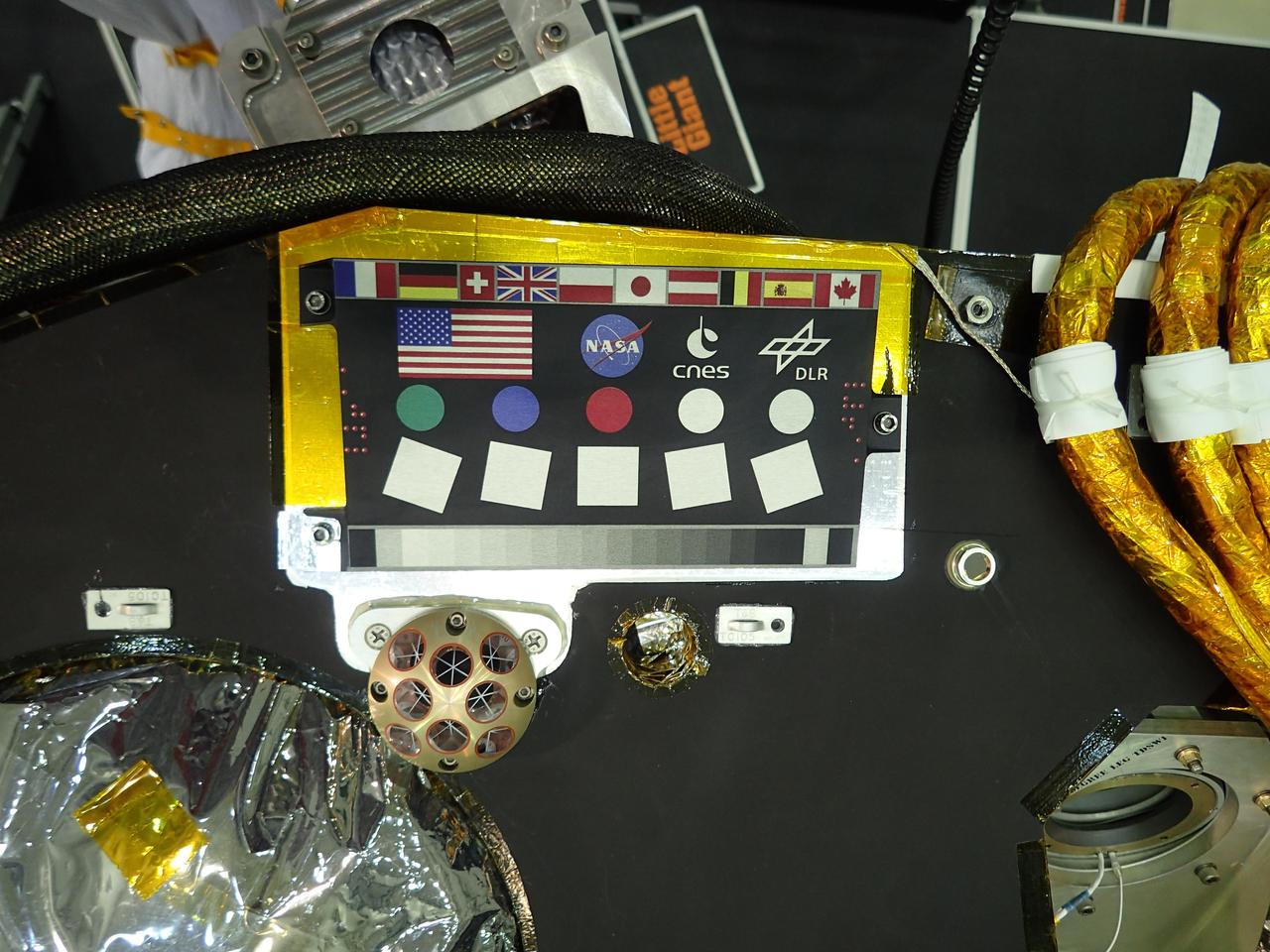

A camera calibration target sits on the deck of the NASA's InSight lander, adorned with the flags of the countries participating in the mission. The target, which will be viewed by InSight's cameras, provides a variety of colors and shapes to help calibrate the lander's cameras. It also shows off international flags representing the agencies, institutions and participating scientists of the mission as of late 2014 (since that time, Italy has contributed an experiment). In the second row are the United States flag and the logos of NASA, the French space agency CNES, which provided InSight's seismometer; and the German Aerospace Center DLR, which provided InSight's heat flow probe. Below the target in the photo is an Italian experiment called the Laser Retroreflector for InSight (LaRRI). LaRRI is the small, copper-colored dome covered with circles just below the calibration target; it won't actually play a role in InSight's mission. The national space agency of Italy (ASI, for Agenzia Spaziale Italiana) provided LaRRI to be used by a possible future Mars orbiter mission with a laser altimeter making extremely precise measurements of the lander's location for fundamental physics studies and precision cartography. A microchip bearing the names of nearly a million members of the public is visible in this image to the right of the calibration target. A second microchip with more than a million additional names was added after this photo was taken. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22540
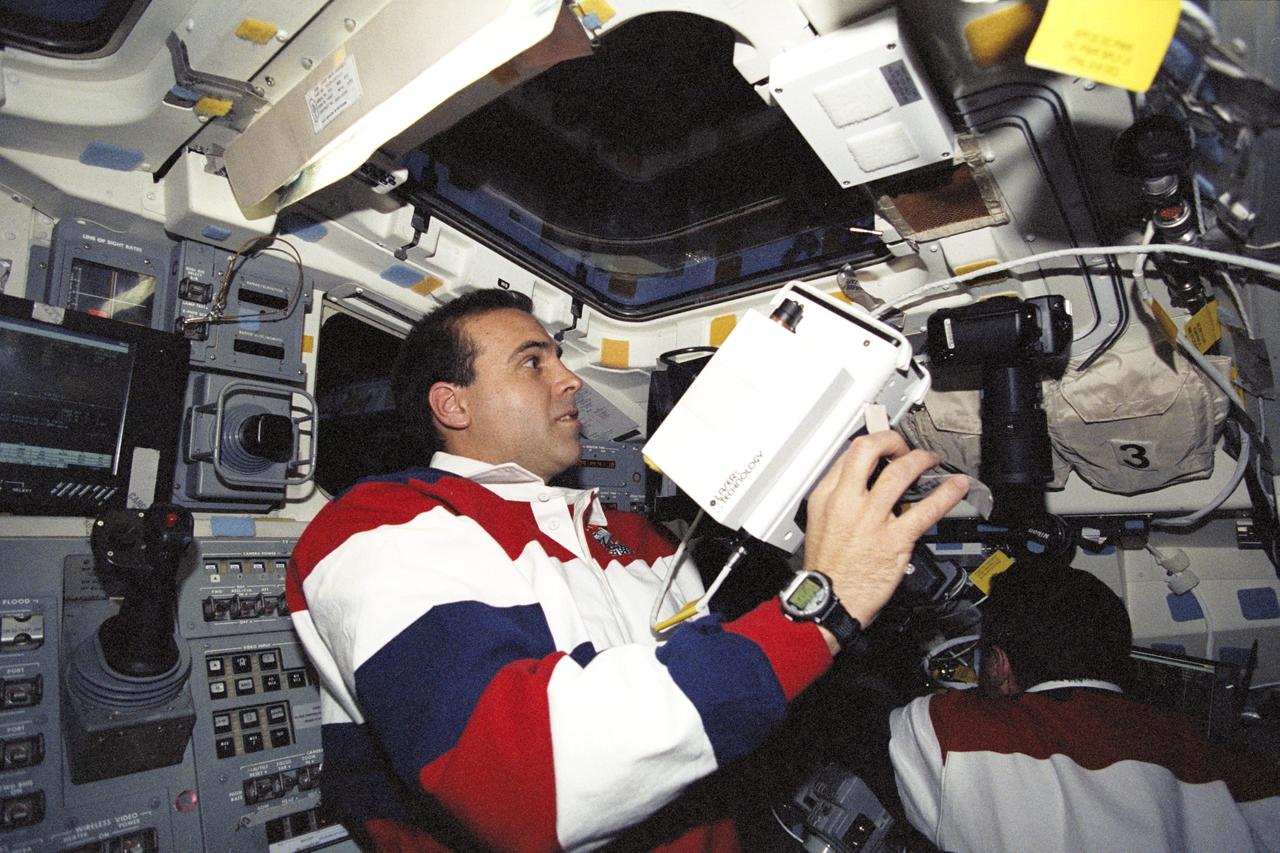

STS106-320-014 (10 September 2000) --- Astronaut Richard A. Mastracchio, mission specialist, uses a handheld laser device on the aft flight deck of the Space Shuttle Atlantis to track the range of the International Space Station during rendezvous operations.
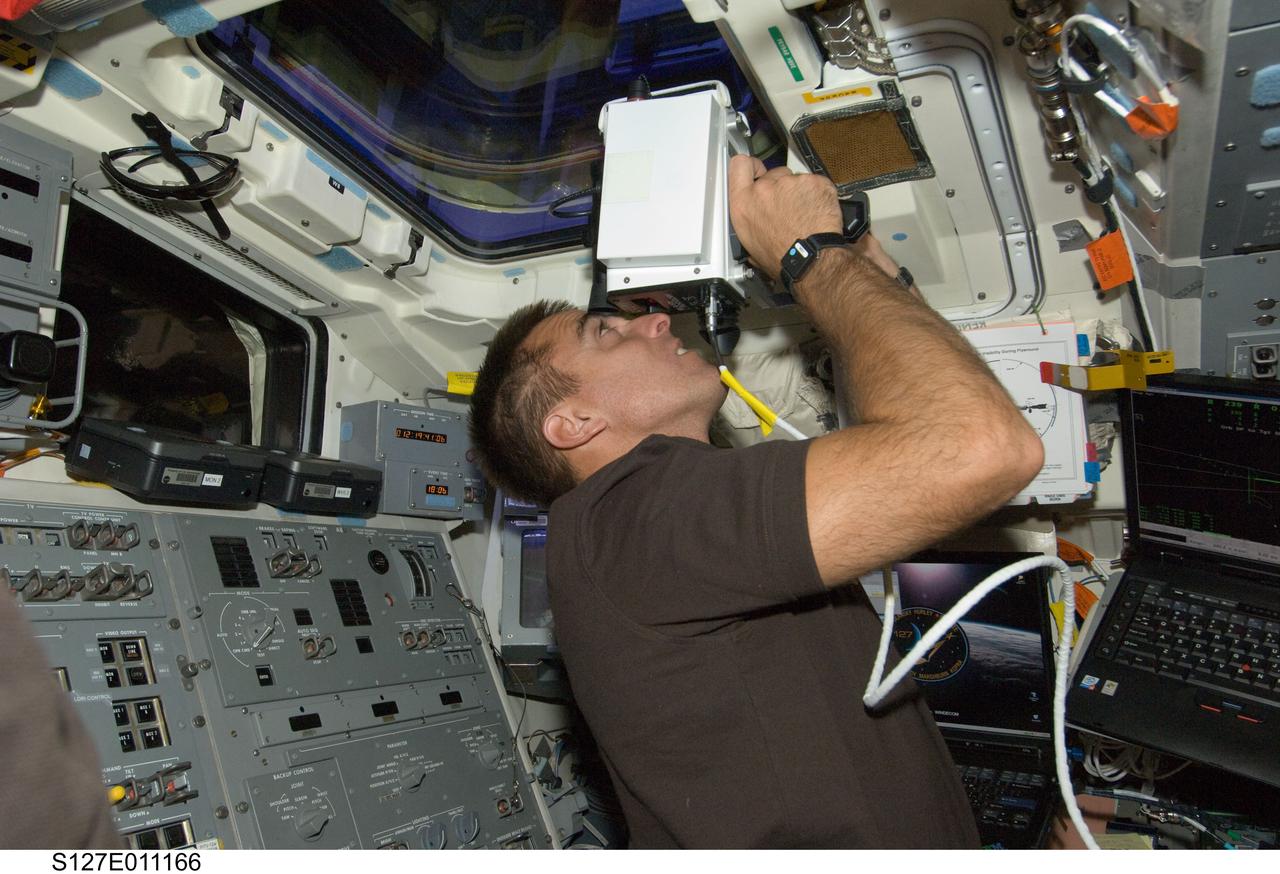

S127-E-011166 (28 July 2009) --- Astronaut Christopher Cassidy, STS-127 mission specialist, uses a handheld laser ranging device -- designed to measure the range between two spacecraft -- through one of the overhead windows on the aft flight deck of Space Shuttle Endeavour after undocking from the International Space Station.
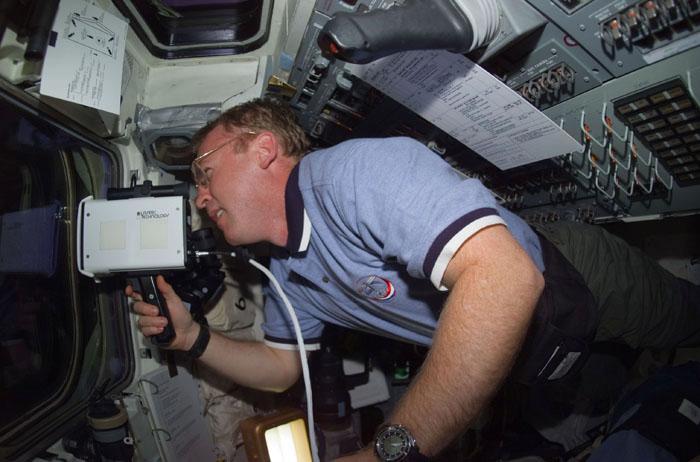

STS102-E-5064 (10 March 2001) --- Astronaut Andrew S.W. Thomas, STS-102 mission specialist, uses a laser ranging device on aft flight deck of the Space Shuttle Discovery. This instrument is a regularly called-on tool during rendezvous operations with the International Space Station (ISS). The photograph was recorded with a digital still camera.
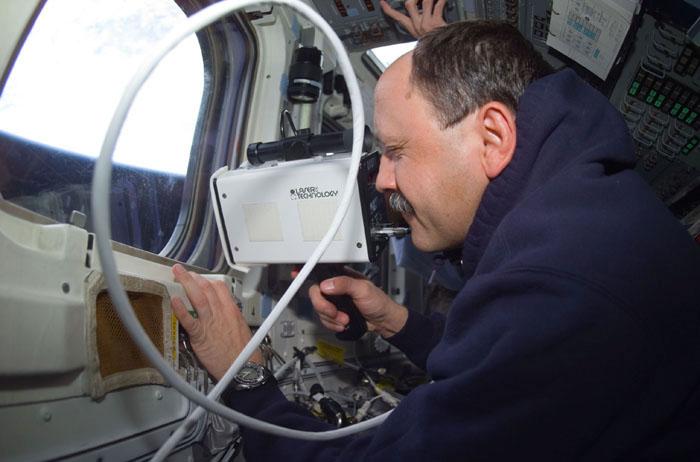

STS102-E-5085 (10 March 2001) --- Cosmonaut Yury V. Usachev, STS-102 mission specialist, uses a laser ranging device on Discovery's aft flight deck during rendezvous operations. The photograph was recorded with a digital still camera.
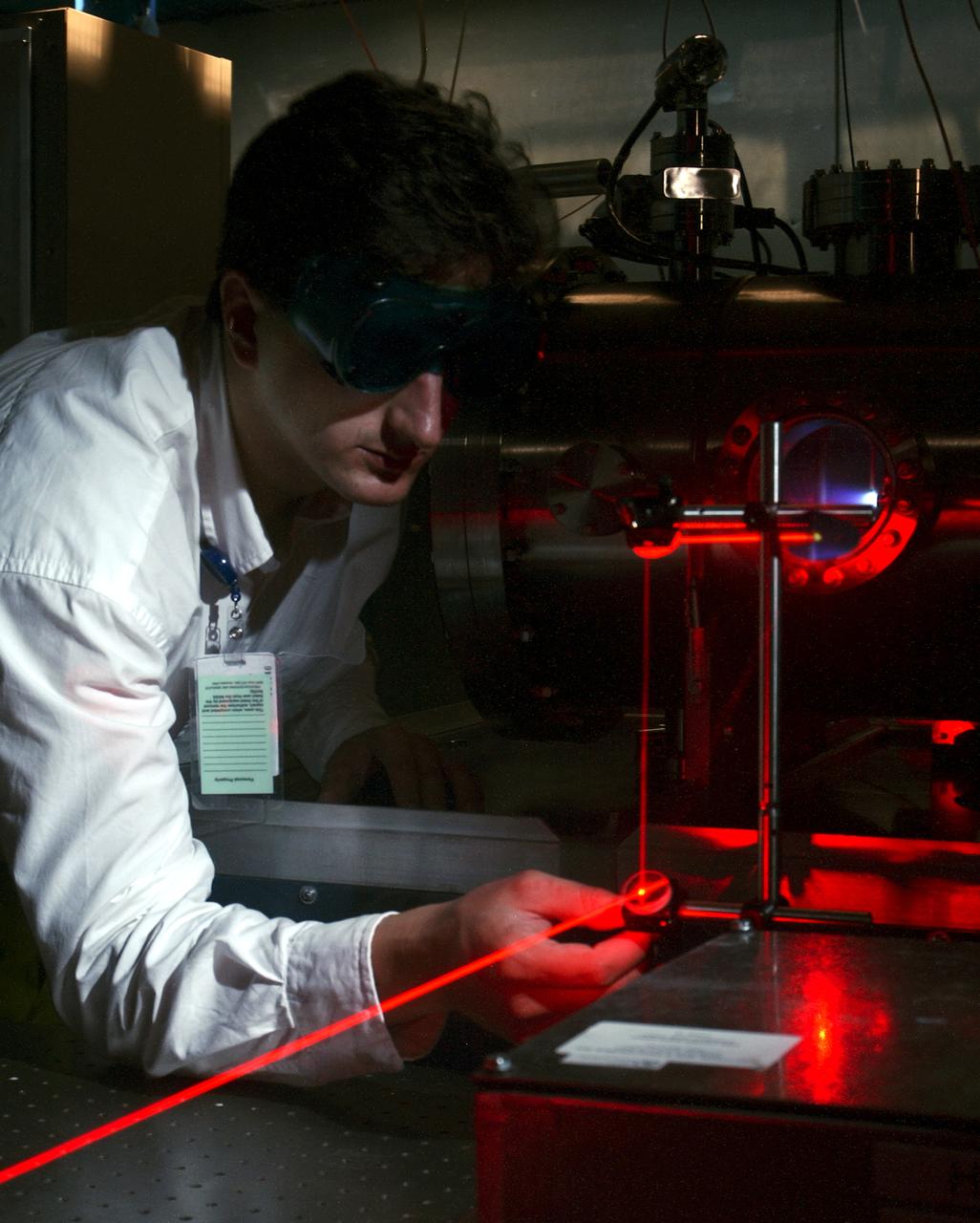

Dr. Tom Markusic, a propulsion research engineer at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), adjusts a diagnostic laser while a pulsed plasma thruster (PPT) fires in a vacuum chamber in the background. NASA/MSFC's Propulsion Research Center (PRC) is presently investigating plasma propulsion for potential use on future nuclear-powered spacecraft missions, such as human exploration of Mars.
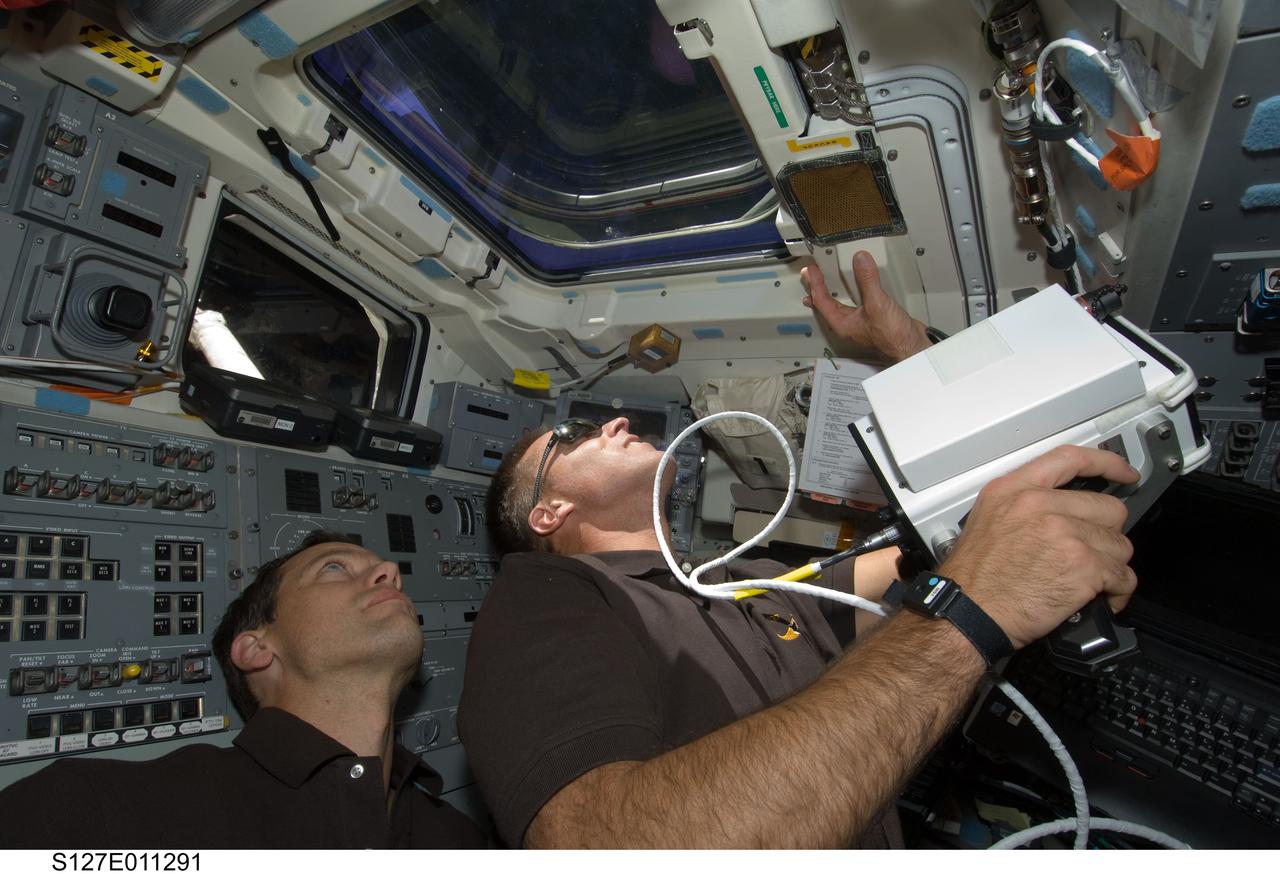

S127-E-011291 (28 July 2009) --- Astronauts Tom Marshburn (left) and Christopher Cassidy, both STS-127 mission specialists, look through an overhead window on the aft flight deck of Space Shuttle Endeavour during flight day 14 activities. Cassidy is holding a handheld laser ranging device -- designed to measure the range between two spacecraft.
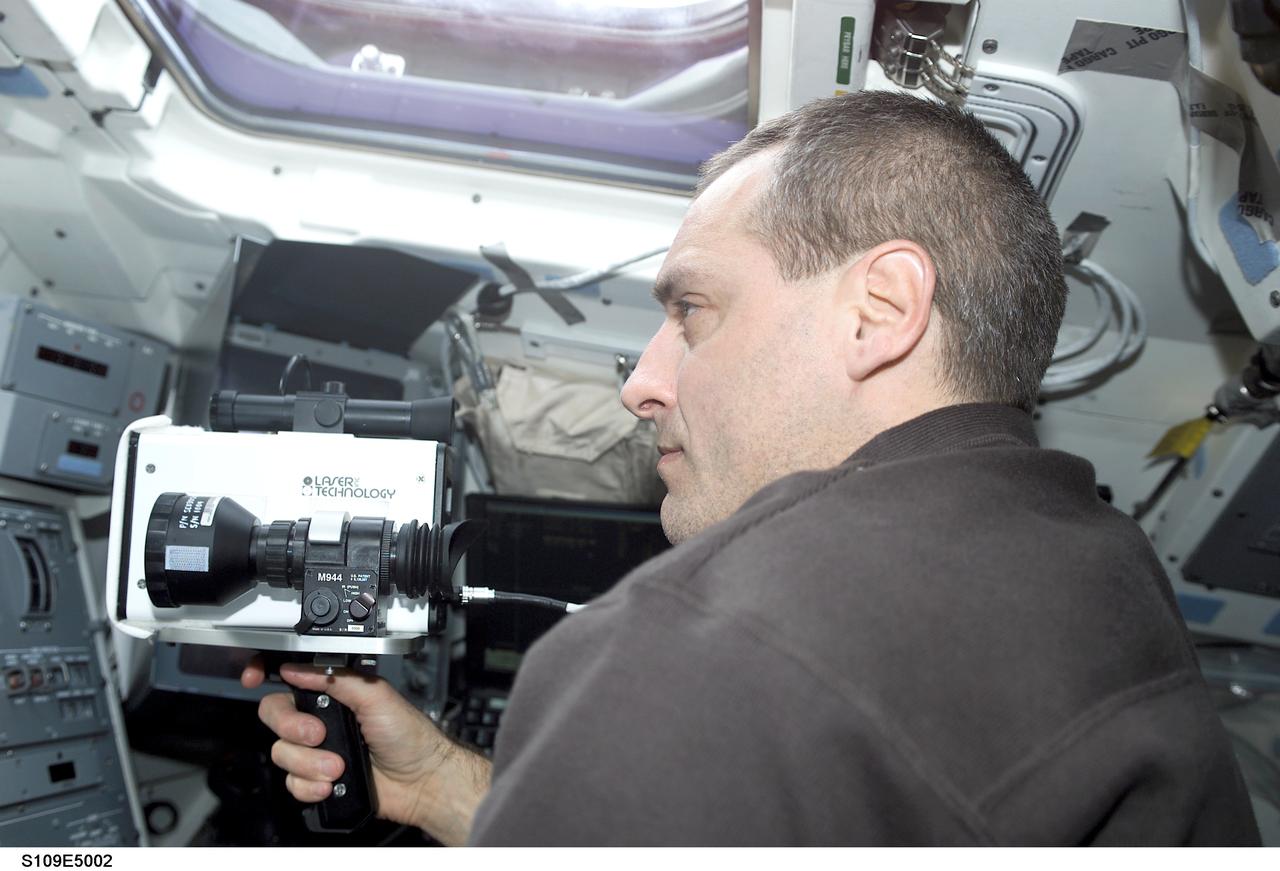

STS109-E-5002 (3 March 2002) --- Astronaut Richard M. Linnehan, mission specialist, uses a laser ranging device designed to measure the range between two spacecraft. Linnehan positioned himself on the cabin's aft flight deck as the Space Shuttle Columbia approached the Hubble Space Telescope. A short time later, the STS-109 crew captured and latched down the giant telescope in the vehicle's cargo bay for several days of work on the Hubble. The image was recorded with a digital still camera.
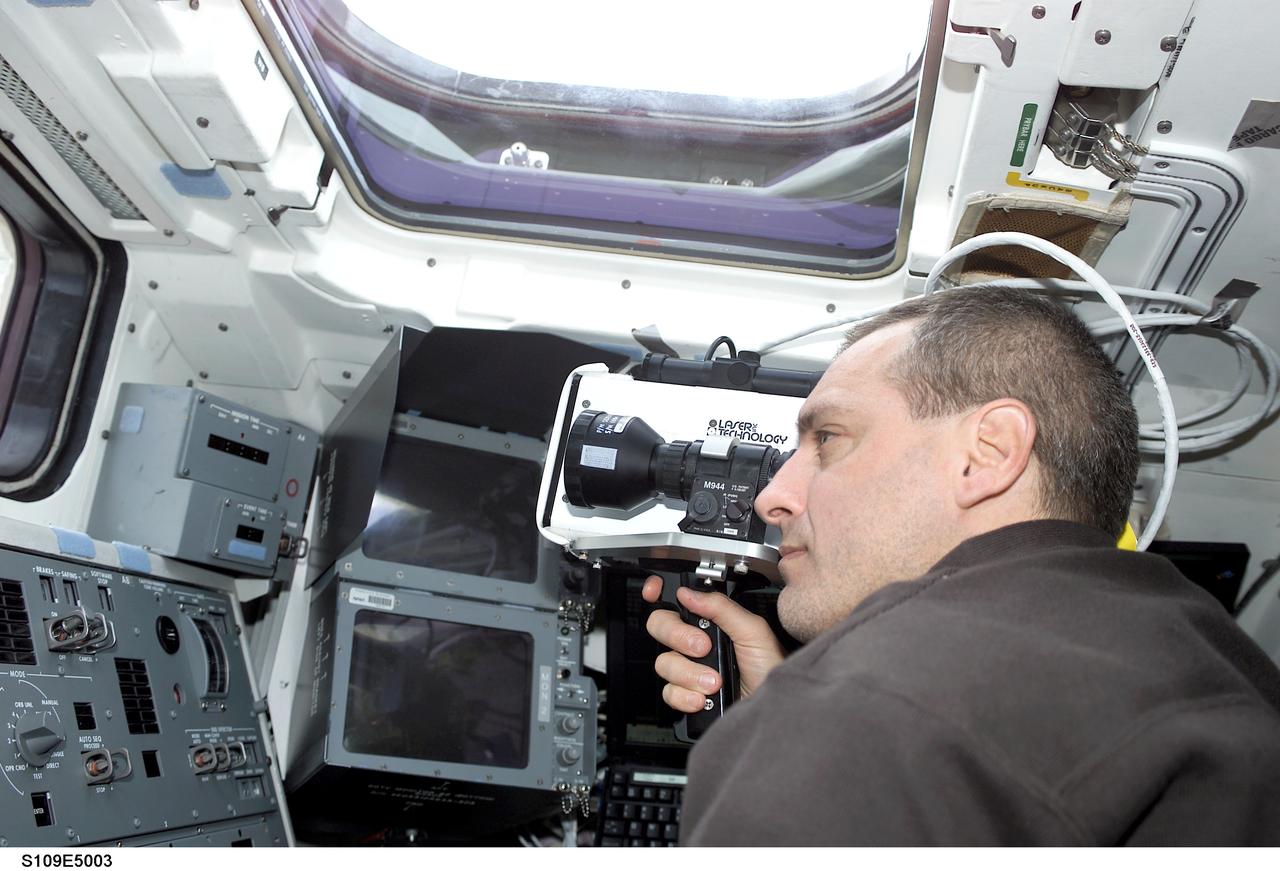

STS109-E-5003 (3 March 2002) --- Astronaut Richard M. Linnehan, mission specialist, uses a laser ranging device designed to measure the range between two spacecraft. Linnehan positioned himself on the cabin's aft flight deck as the Space Shuttle Columbia approached the Hubble Space Telescope. A short time later, the STS-109 crew captured and latched down the giant telescope in the vehicle's cargo bay for several days of work on the Hubble. The image was recorded with a digital still camera.
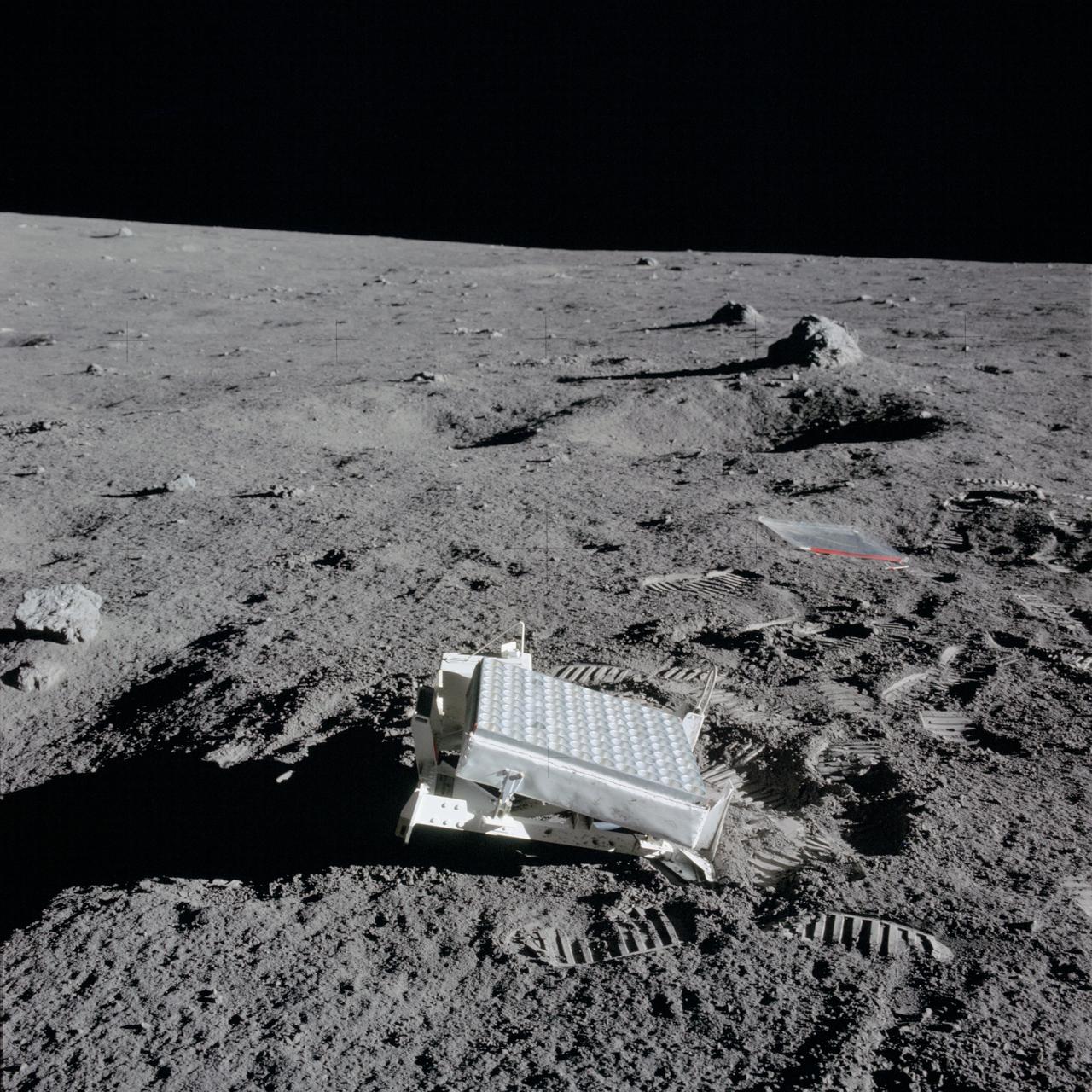
AS14-67-9386 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of the laser ranging retro reflector (LR3) which the Apollo 14 astronauts deployed on the moon during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
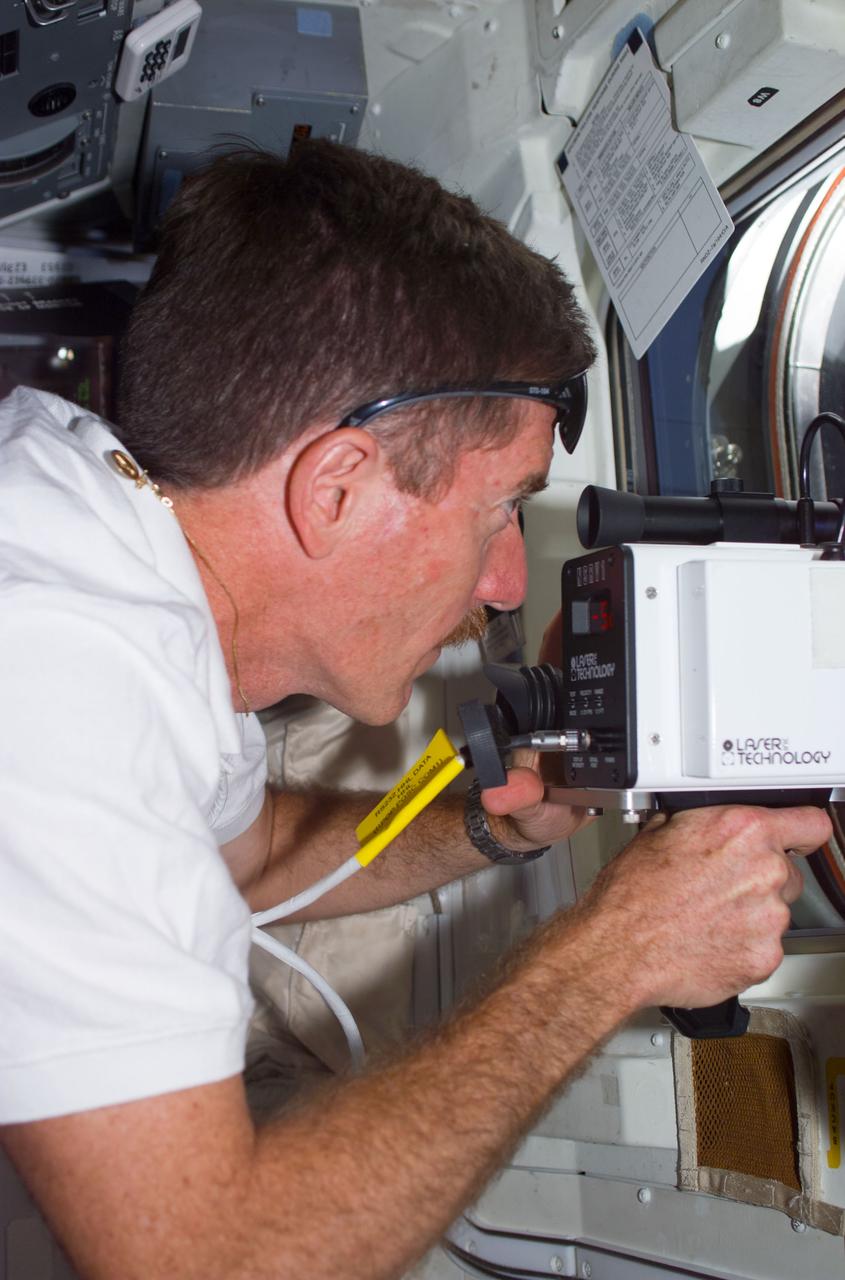

STS104-E-5026 (14 July 2001) --- Positioned near a window on the aft flight deck of the Space Shuttle Atlantis, astronaut James F. Reilly, STS-104 mission specialist, uses a laser ranging device to hone in on the International Space Station (ISS) during pre-docking operations about 237 miles above Earth.
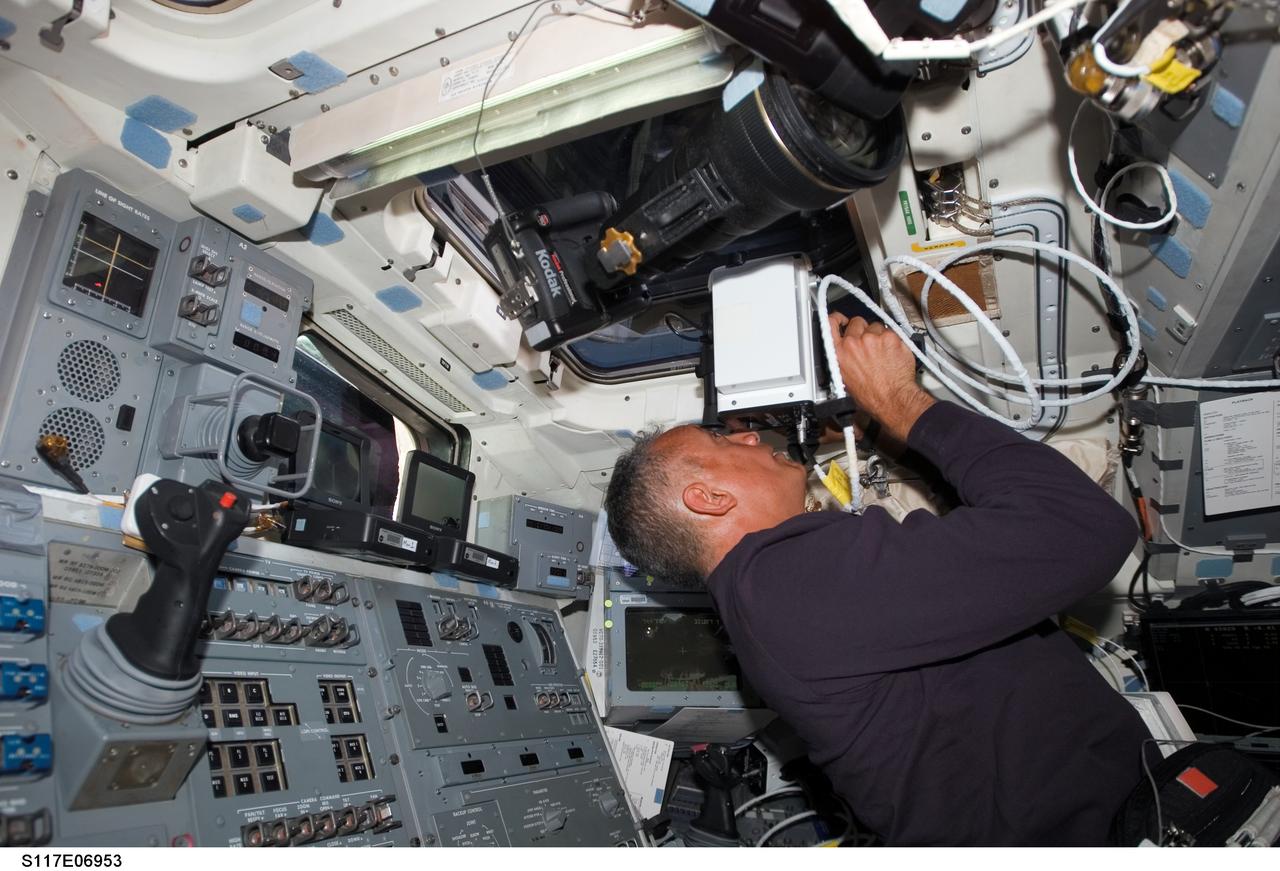

S117-E-06953 (10 June 2007) --- Astronaut John "Danny" Olivas, STS-117 mission specialist, aims a laser range finder through one of the overhead windows on the aft flight deck of the Space Shuttle Atlantis at it approaches the International Space Station. This instrument is a regularly called-on tool during rendezvous operations with the station. The subsequent docking will allow the STS-117 astronauts and the Expedition 15 crew to team up for several days of key tasks in space.