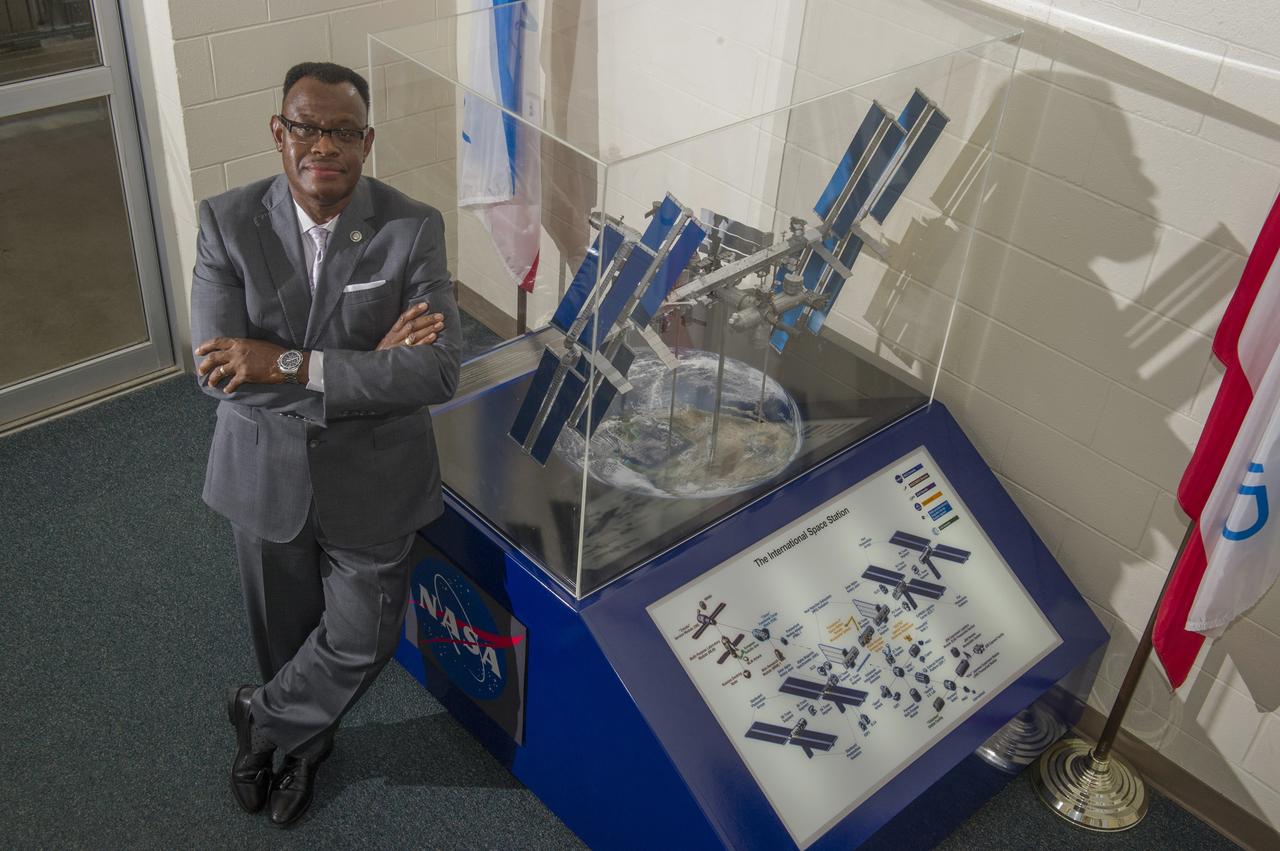

LEWIS WOOTEN MANAGES THE MISSION OPERATIONS LABORATORY. MORE THAN 1600 INVESTIGATIONS AND STUDENT EXPERIMENTS FOR OVER 80 COUNTRIES HAVE BEEN COMPLETED WITH THE HELP OF WOOTEN'S TEAM AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA.
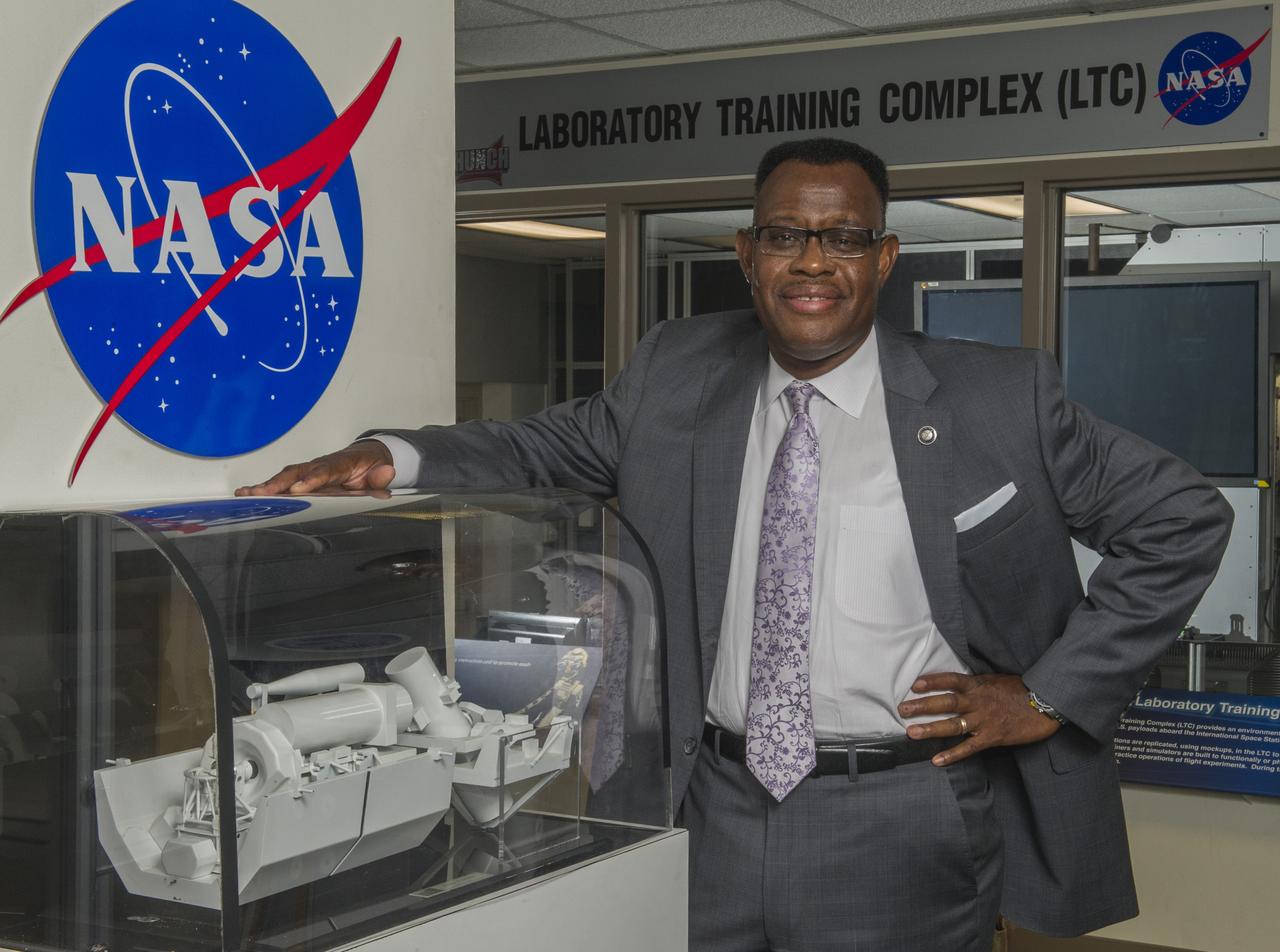

LEWIS WOOTEN MANAGES THE MISSION OPERATIONS LABORATORY. MORE THAN 1600 INVESTIGATIONS AND STUDENT EXPERIMENTS FOR OVER 80 COUNTRIES HAVE BEEN COMPLETED WITH THE HELP OF WOOTEN'S TEAM AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA.
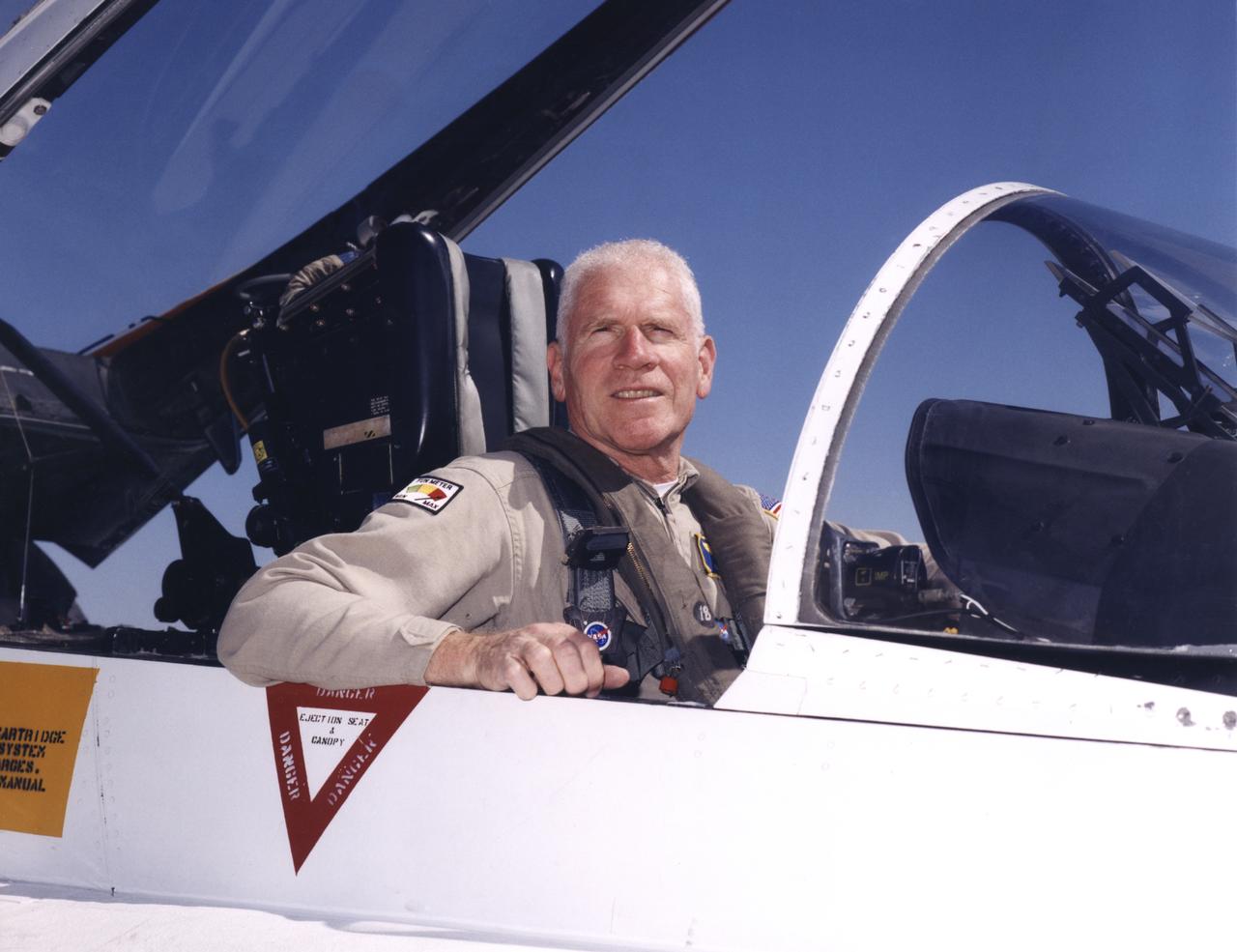

Edwin W. Lewis Jr. is a research pilot in the Airborne Science program, Flight Crew Branch, Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. He currently flies the DC-8, F/A-18, Lear Jet 24, King Air, and T-34C in support of Dryden's flight operations and is mentor pilot for the King Air and the Lear Jet. Prior to accepting this assignment Lewis was a pilot for eight years at NASA's Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California, flying 10 different aircraft C-130B, DC-8-72, UH-1, SH-3, King Air, Lear 24, T-38A, T-39G and YO-3A in support of NASA flight missions. Lewis also flew the Kuiper Airborne Observatory (a modified civilian version of the Lockheed C-141 Starlifter). He was project pilot for Ames' 747 and T-38 programs. Lewis was born in New York City on May 19, 1936, and began flight training as a Civil Air Patrol cadet in 1951, ultimately earning his commercial pilot's certificate in 1958. He received a bachelor of arts degree in biology from Hobart College, Geneva, N.Y., and entered the U.S. Air Force through the Reserve Officer Training Corps. Following pilot training he was assigned to Moody Air Force Base, Ga., as an instructor pilot, for both the T-33 and T-37 aircraft. He served in Vietnam in 1965 and 1966, where he was a forward air controller, instructor and standardization/evaluation pilot, flying more than 1,000 hours in the O-1 "Bird Dog." Lewis separated from the regular Air Force and joined Pan American World Airways and the 129th Air Commando Group, California Air National Guard (ANG) based in Hayward, California. During his 18-year career with the California ANG he flew the U-6, U-10, C-119, HC-130 aircraft and the HH-3 helicopter. He retired as commander, 129th Air Rescue and Recovery Group, a composite combat rescue group, in the grade of colonel. During his 22 years as an airline pilot, he flew the Boeing 707, 727 and 747. He took early retirement from Pan American in 1989 to become a pilot with NASA.
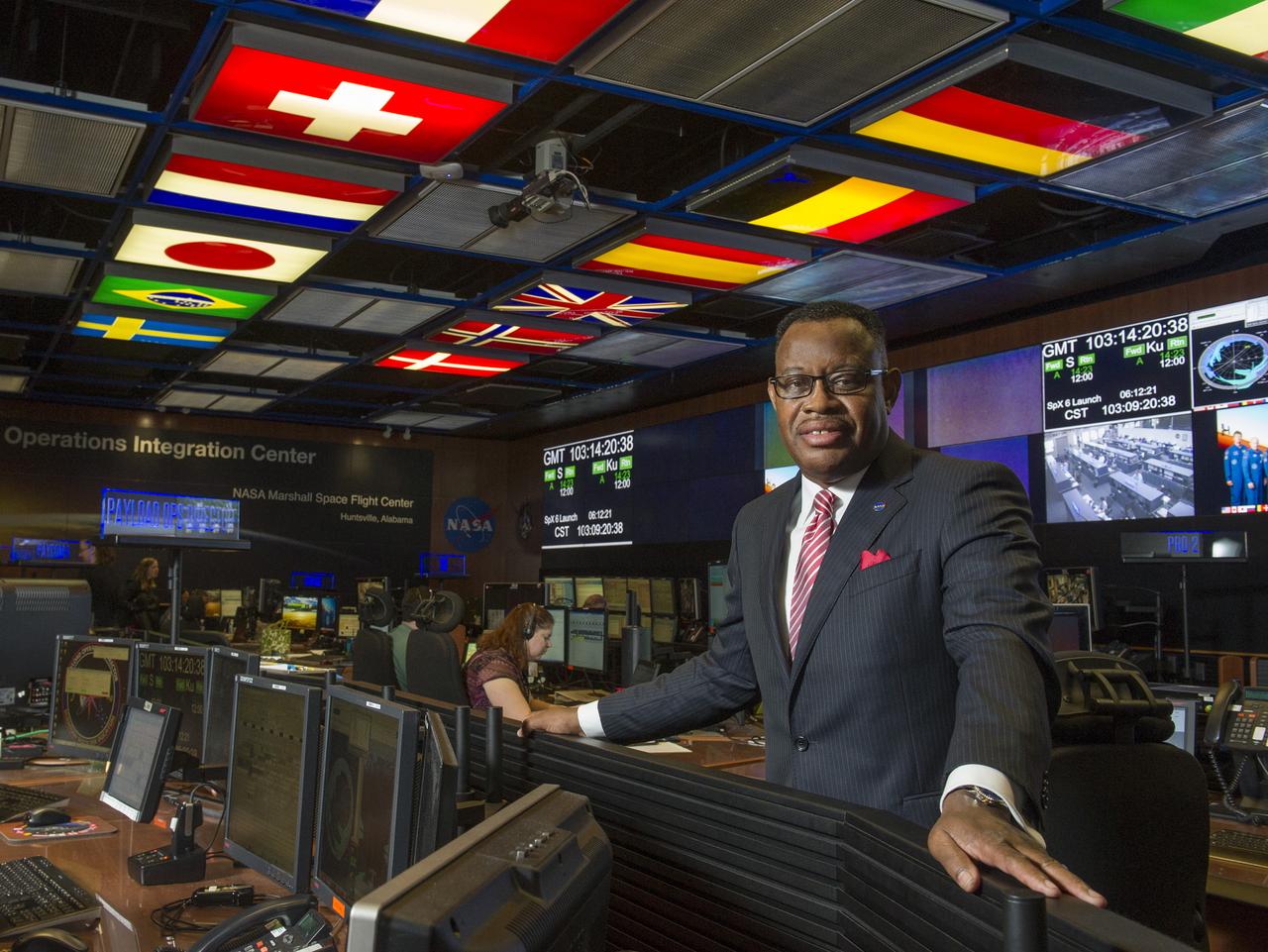

LEWIS WOOTEN, NEW DIRECTOR OF THE MISSION OPERATIONS LABORATORY AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA, MANAGES OPERATIONS IN THE PAYLOAD OPERATIONS INTEGRATION CENTER-THE COMMAND POST FOR ALL SCIENCE AND RESEARCH ACTIVITIES ON THE INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION

NBC Today Show at Lewis Field

Doreen Zudell takes over as the Editor of the Lewis News, Center Newsletter

The newly renovated NASA Glenn Research Center, GRC Lewis Field West Gate at dusk.
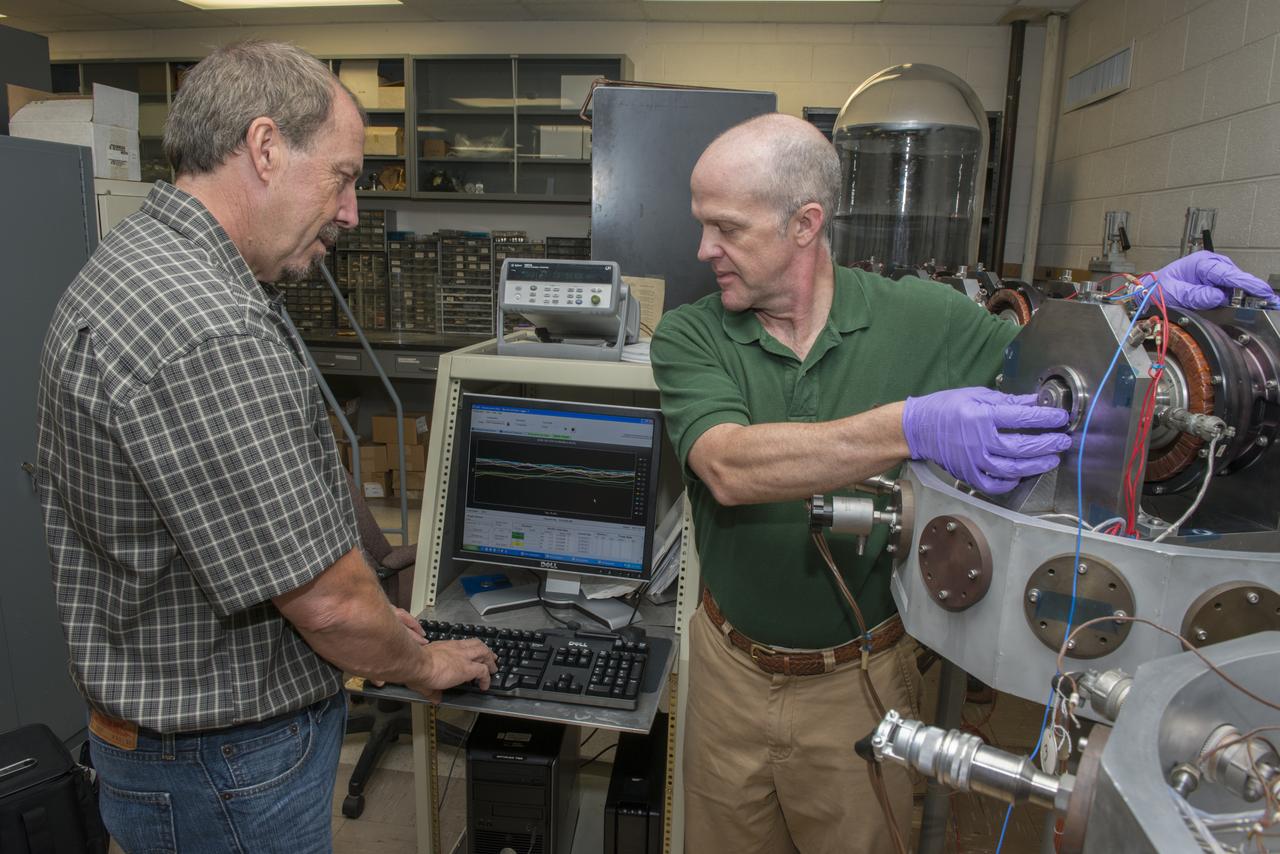

NASA ENGINEERS LEWIS “CHIP” MOORE AND TIM JETT STUDYING BALL BEARING DATA
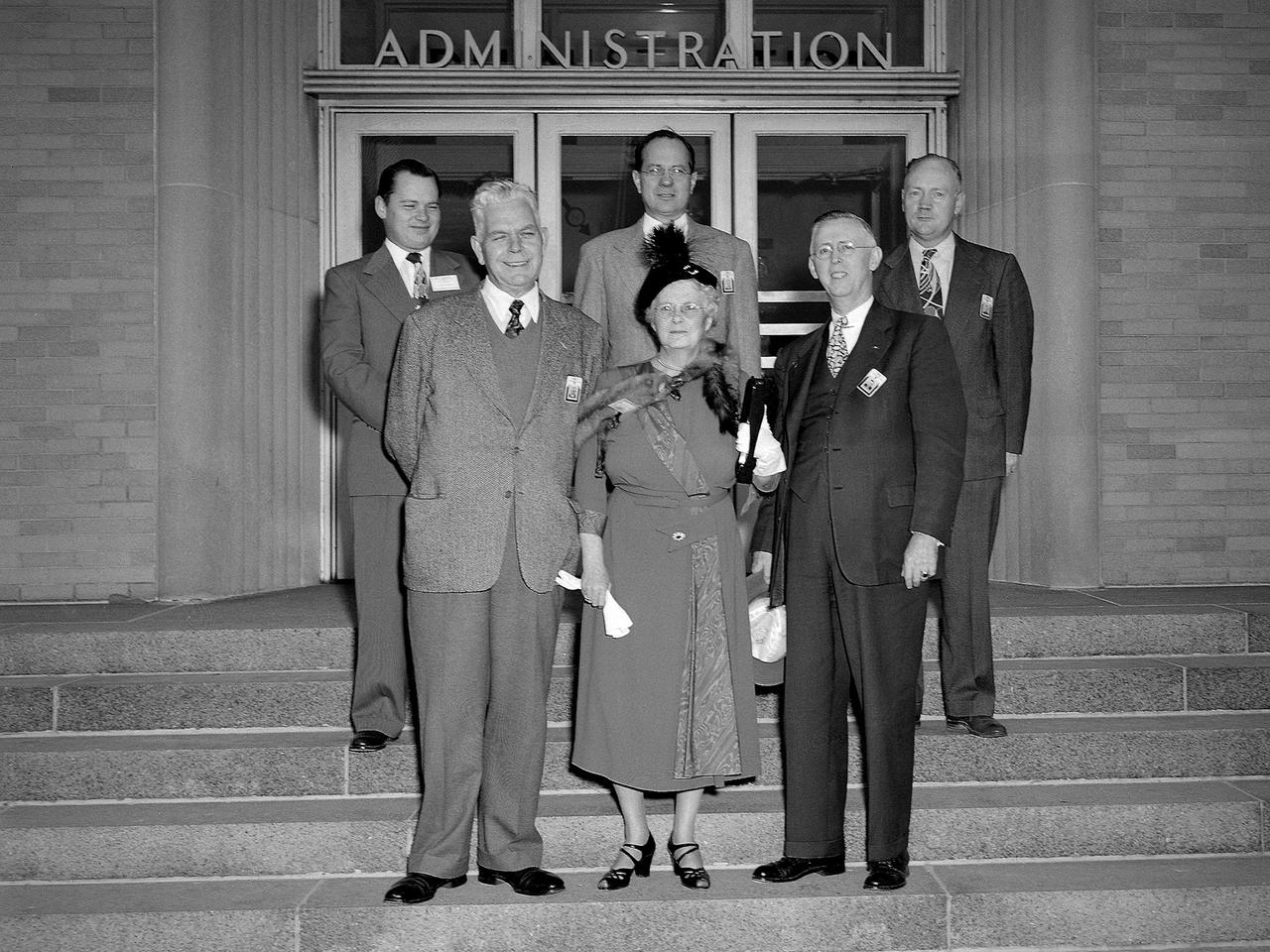

Myrtle Lewis and three of her sons visit the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in Cleveland, Ohio. The Flight Propulsion Research Laboratory was renamed in Lewis’ honor in September 1948. Lewis served as the NACA’s Director of Aeronautical Research for over 20 years. Lewis joined the NACA as Executive Officer in 1919 and was named Director of Aeronautical Research in 1924. In this role Lewis served as the liaison between the Executive Committee and the research laboratories. His most important accomplishment may have been the investigative tours of German research facilities in 1936 and 1939. The visits resulted in the NACA’s physical expansion and the broadening of its scope of research. Lewis did not take a day of leave between the Pearl Harbor attack and the Armistice, but began suffering health problems in 1945. He was forced to retire two years later and passed in July 1948. Front row, left to right: Lewis Director Raymond Sharp, Mrs. Lewis, NACA Executive Secretary John Victory; back row: Executive Officer Robert Sessions, Armand Lewis, Harvey Lewis, and George Lewis II. Harvey and George Lewis II were employed at NACA Lewis in the Instrument Service and Applied Compressor sections, respectively.

A security guard examines the new sign near the entrance to the Lewis Research Center one day after the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) was officially established. NASA came into being on October 1, 1958, and the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory became the NASA Lewis Research Center. Lewis underwent a major reorganization and began concentrating its efforts almost exclusively on the space program. NACA Lewis researchers had been advocating further space research for years. As early as 1955, Lewis management urged the NACA expand its rocket engine research as a logical extension of its aircraft engine work. Lewis management claimed that space exploration was imperative for the nation’s survival during the Cold War. They called for an annual 25-percent increase in the NACA’s staff, a new space laboratory, a launching center, communications center, and other facilities. They were basically outlining what would be needed for the new space agency. During NASA’s first two years of existence, Lewis refocused its efforts almost completely on the space program. Less than 10 percent of the annual budget was dedicated to aeronautics. In the aftermath that followed President Kennedy’s April 1961 “Urgent Needs” address to Congress, NASA was given a seemingly unlimited budget. The Agency reorganized and began swelling its ranks through a massive recruiting effort to accomplish the accelerated lunar landing mission. Lewis personnel increased from approximately 2,700 in 1961 to over 4,800 in 1966.
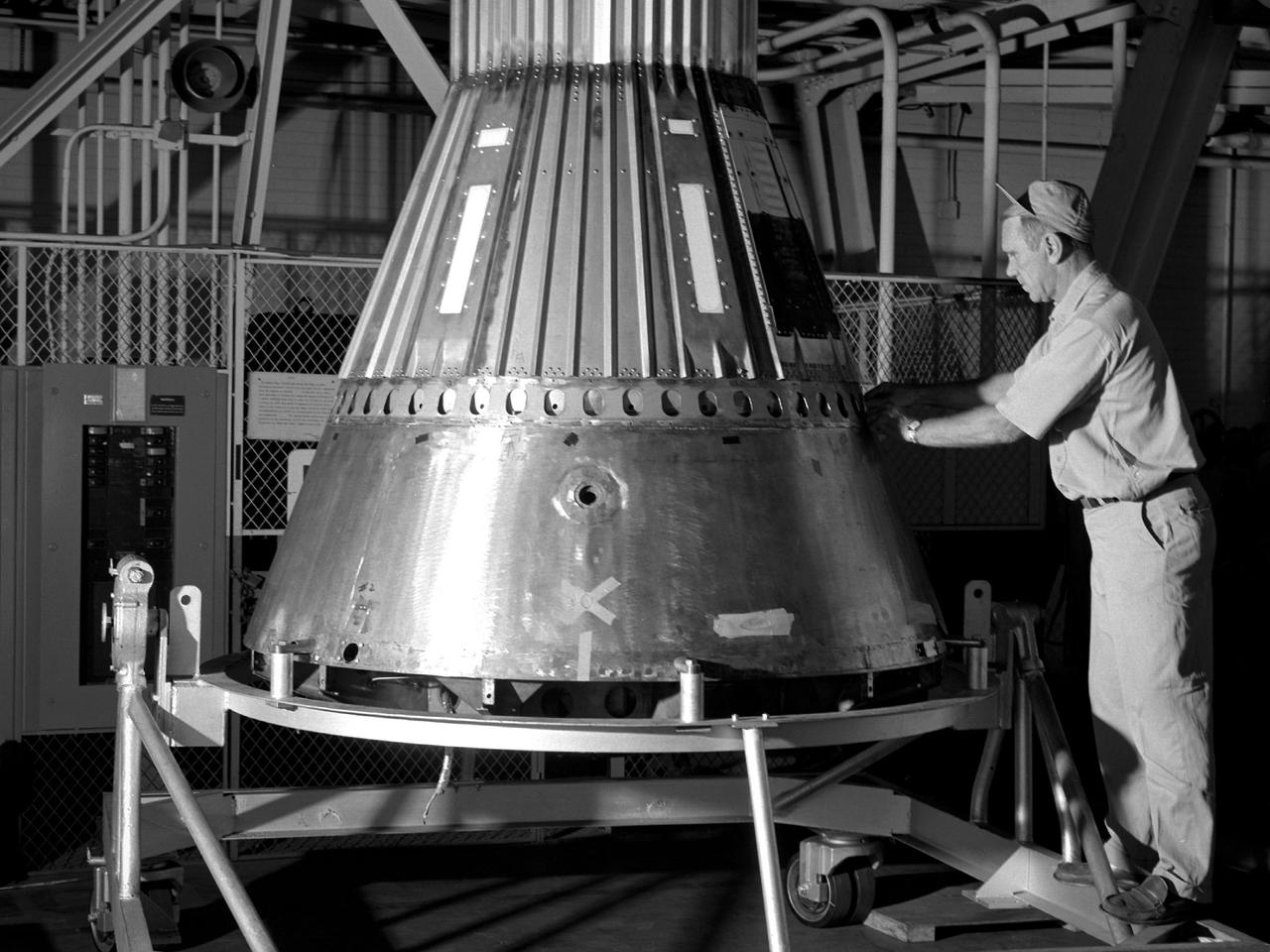

A NASA mechanic secures the afterbody to a Mercury capsule in the hangar at the Lewis Research Center. The capsule was one of two built at Lewis for the “Big Joe” launches scheduled for September 1959. The initial phase of Project Mercury consisted of a series of unmanned launches using the Air Force’s Redstone and Atlas boosters and the Langley-designed Little Joe boosters. The first Atlas launch, referred to as “Big Joe”, was a single attempt early in Project Mercury to use a full-scale Atlas booster to simulate the reentry of a mock-up Mercury capsule without actually placing it in orbit. The overall design of Big Joe had been completed by December 1958, and soon thereafter project manager Aleck Bond assigned NASA Lewis the task of designing the electronic instrumentation and automatic stabilization system. Lewis also constructed the capsule’s lower section, which contained a pressurized area with the electronics and two nitrogen tanks for the retrorockets. Lewis technicians were responsible for assembling the entire capsule: the General Electric heatshield, NASA Langley afterbody and recovery canister, and Lewis electronics and control systems. On June 9, 1959, the capsule was loaded on an air force transport aircraft and flown to Cape Canaveral. A team of 45 test operations personnel from Lewis followed the capsule to Florida and spent the ensuing months preparing it for launch. The launch took place in the early morning hours of September 9, 1959.
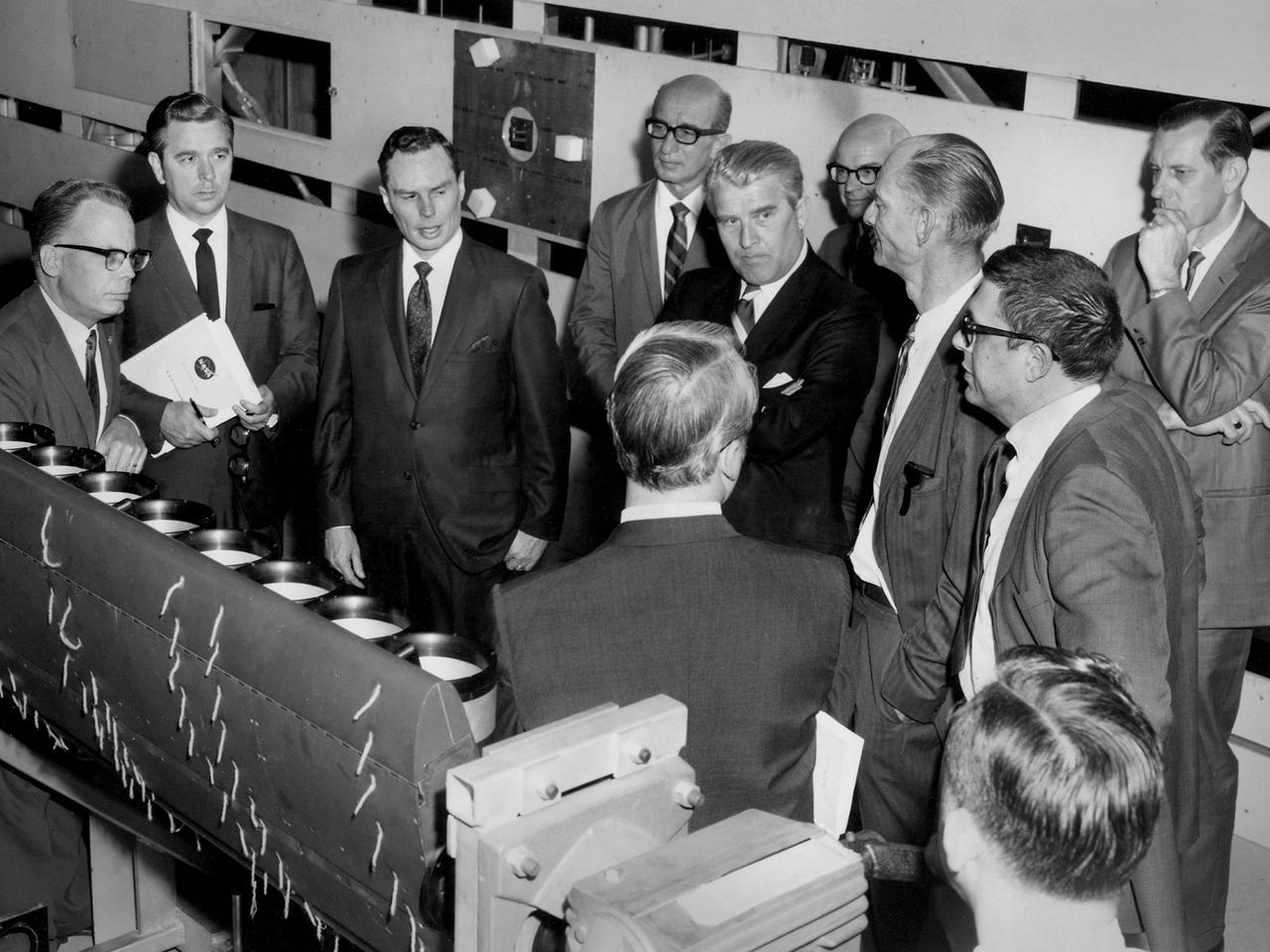

Werner von Braun, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Deputy Associate Administrator for Planning, among a group from Headquarters touring the Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio. Lewis Special Projects Chief Newell Sanders, left, describes a Short Takeoff and Landing wing-propulsion model. Lewis had recently converted the return leg of its 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel into the 9- by 15-Foot Low Speed Wind Tunnel to investigate Vertical and Short Takeoff and Landing propulsion systems. Gathered from the left near Sanders are James Daniels, Headquarters Executive Secretary; Oran Hicks, Acting Associate Administrator for the Headquarters Office of Advanced Research and Technology; Eugene Manganiello, Lewis Deputy Director; von Braun; Dr. Walter Olson, Lewis Assistant Director; Bruce Lundin, Lewis Director and Dr. Bernard Lubarsky, Lewis Assistant Director. Just months before this photograph, NASA asked von Braun to give up his post as Director of the Marshall Space Flight Center after nearly ten years in order to head up the strategic planning effort for the agency from Washington DC. Von Braun retired from NASA two years later.
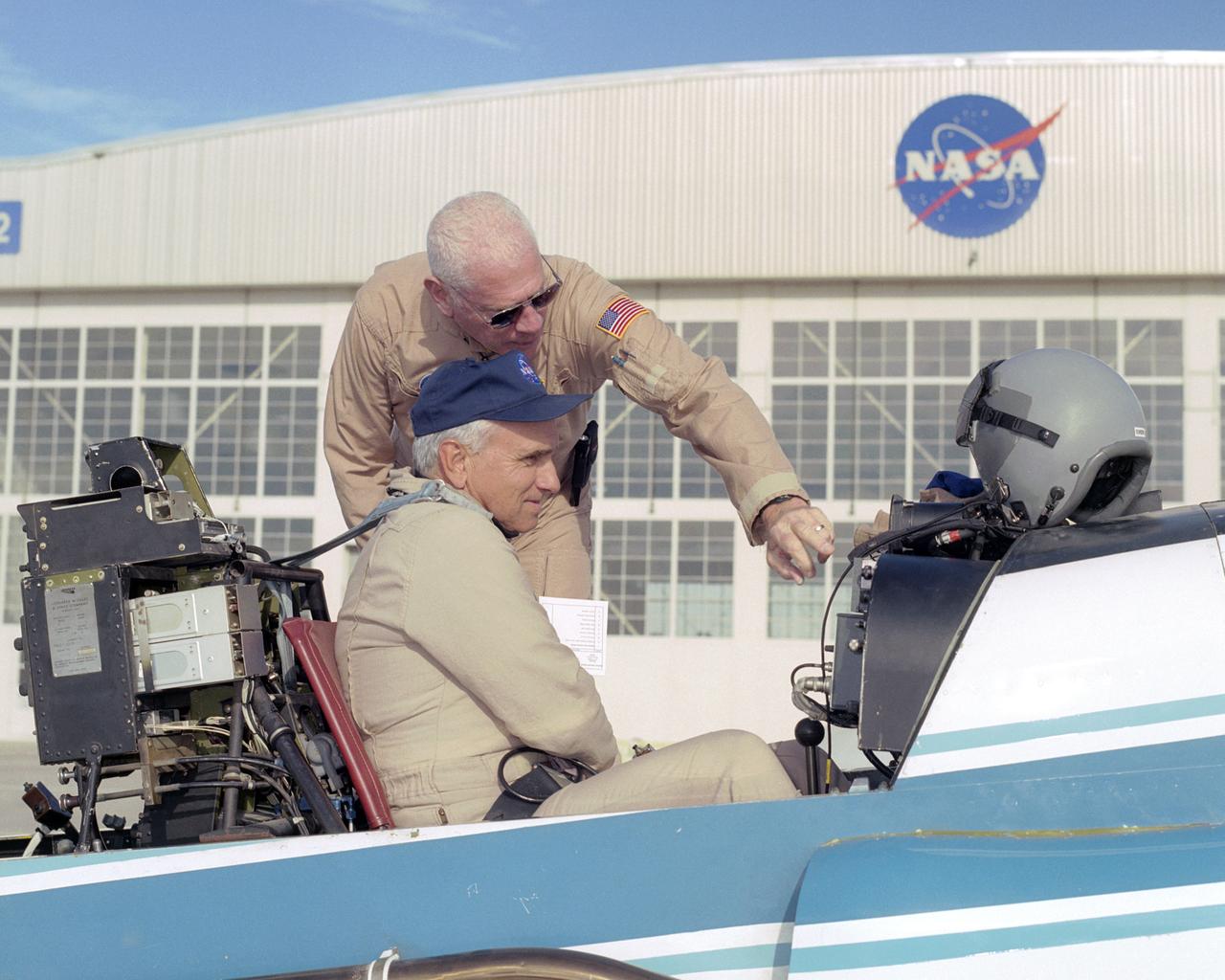

NASA pilot Ed Lewis (rear) briefs NASA test pilot Dick Ewers on the flight instruments of NASA's YO-3A acoustics research aircraft prior to a checkout flight.

NASA's modified DC-8 now carries the name of the late Edwin W. Lewis below its cockpit window, a tribute to his 18 years piloting the unique science laboratory.
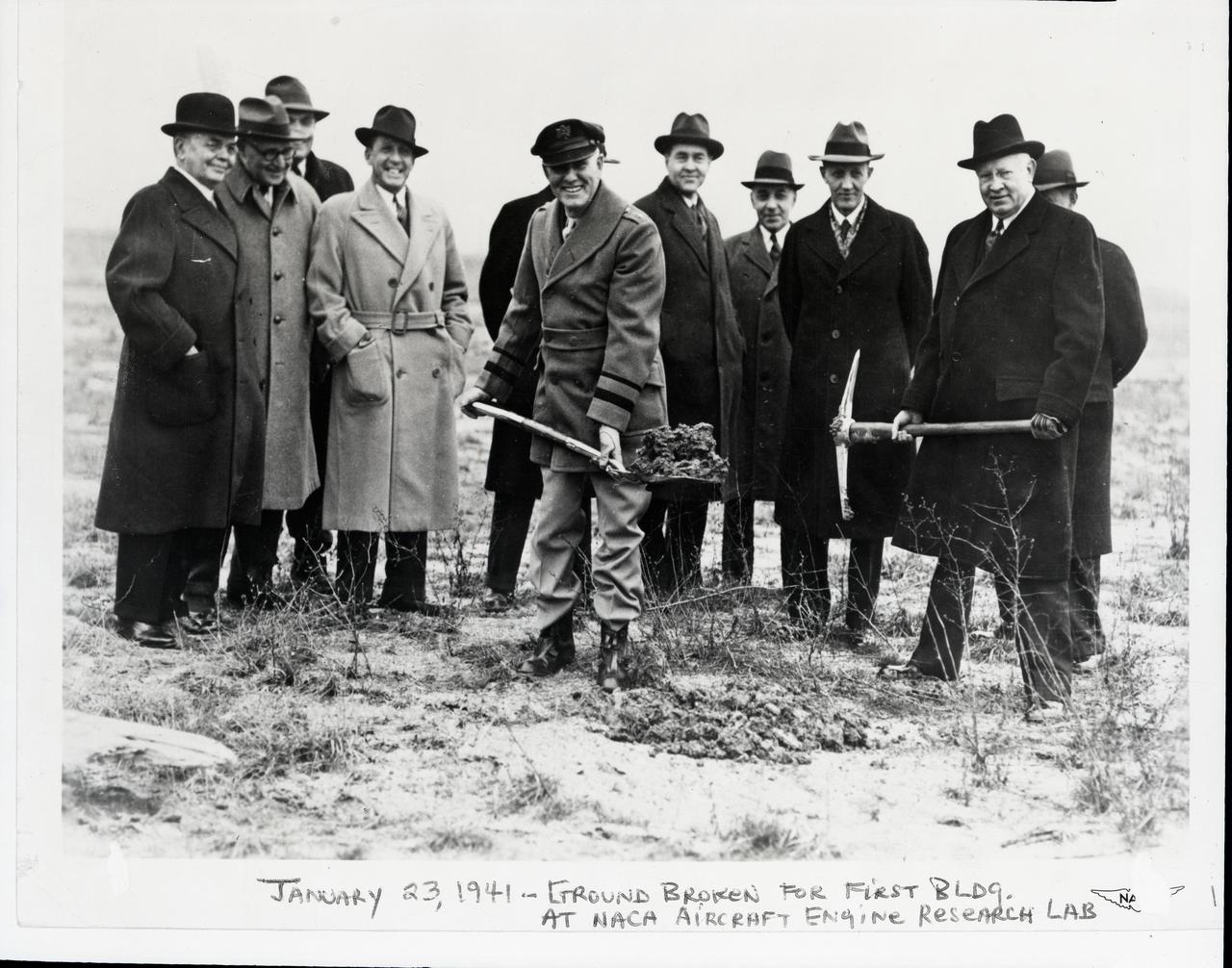

January 23, 1941 groundbreaking ceremony at the NACA Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory: left to right (does not include two individuals obscured from view behind Maj. Brett and Dr. Lewis): • William R. Hopkins – Cleveland City Manager from 1924-1930, was personally responsible for planning and acquiring the land for the Cleveland Airport. The airport’s huge capacity for handling aircraft was one factor in selecting Cleveland for the site of the research center. The Cleveland Airport was renamed Cleveland Hopkins airport in his honor in 1951. • Major John Berry – Cleveland Airport Manager • Edward R. Sharp – GRC’s first director, serving from 1942 to his retirement in 1961. He came to Cleveland in 1941 as the construction manager for the new facility. • Frederick C. Crawford – President of Thompson Products, which became the Thompson-Ramo-Woolridge Corporation (TRW) in 1958. Crawford was, at the time, also president of the Cleveland Chamber of Commerce. He began in 1939 to campaign for Cleveland as the location for the new NACA facility. • Major George H. Brett – A Cleveland native, Brett served in WWI and was commanding officer at Wright Field in Dayton, Ohio before becoming chief of the Army Air Corps. • Dr. Edward P. Warner – Acting chairman of the NACA. • Captain Sydney M. Kraus – Officer in charge of Navy procurement • Edward Blythin – Mayor of Cleveland • Dr. George Lewis – Director of Aeronautical Research for the NACA from 1924-1947, Lewis devoted his life to building a scientific basis for aeronautical engineering. The Cleveland laboratory was renamed the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in his honor in 1948. A description of the event, based on newspaper accounts and later NASA publications is as follows: On January 23, 1941, a brief groundbreaking ceremony at the site marked the start of construction. Dr. George W. Lewis, director of research for the NACA, loosened the soil with a
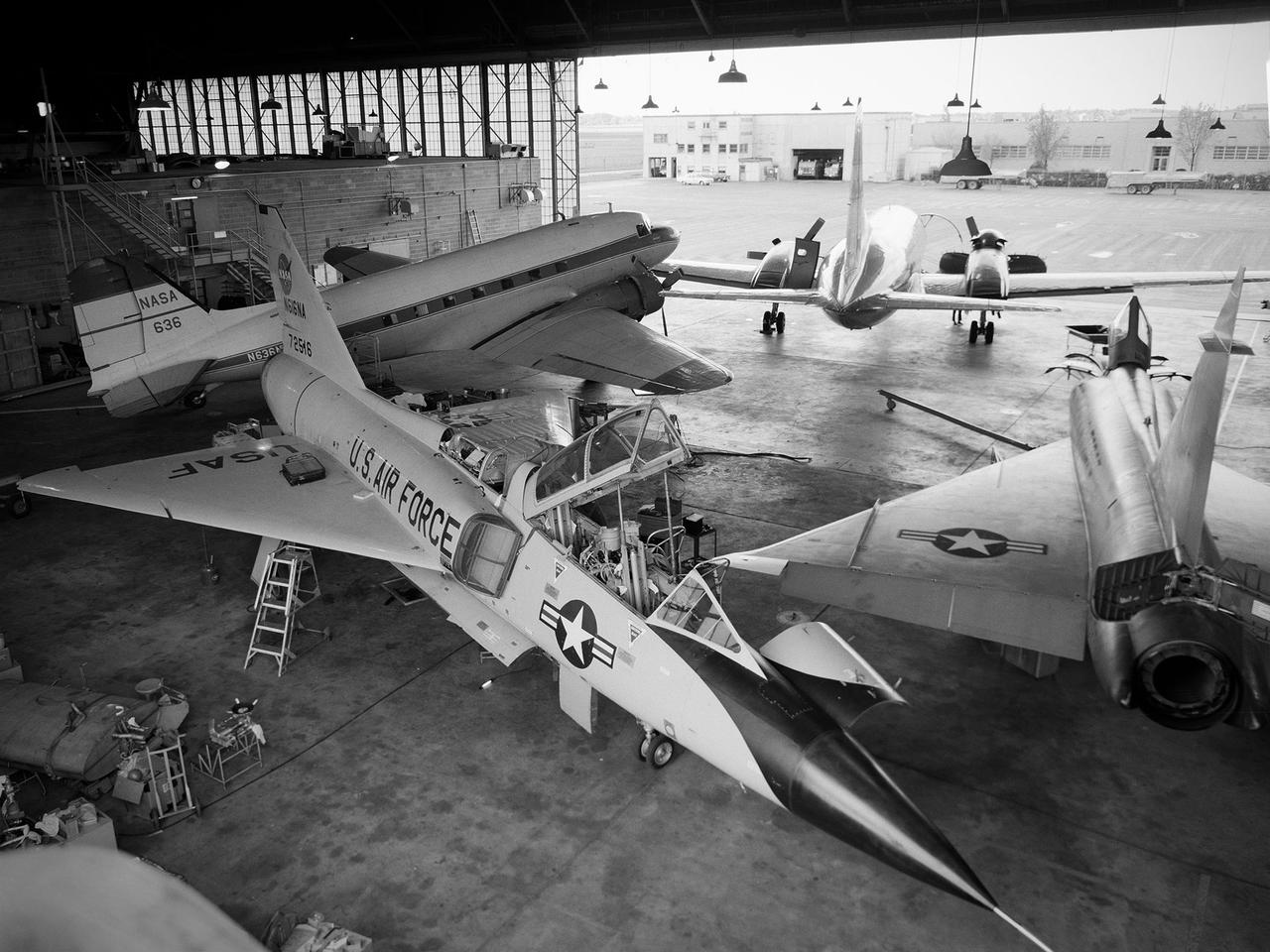

Several aircraft parked inside the Flight Research Building, or hangar, at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio. A Convair F-106B Delta Dart is in the foreground, a Convair F-102A Delta Dagger is to the right, a Douglas DC-3 is in the back to left, and a Convair T-29 is in background. Lewis’ Martin B-57B Canberra is not seen in this photograph. The F-102A had just been acquired by Lewis to serve as a chase plane for the F-106B. The Lewis team removed the weapons system and 700 pounds of wire from the F-106B when it was acquired on October 20, 1966. The staff cut holes in the wings and modified the elevons to mount the test nacelles. A 228-gallon fuel tank was installed in the missile bay, and the existing wing tanks were used for instrumentation. This photograph contains a rare view of the Block House, seen to the left of the aircraft. Lewis acquired three large developmental programs in 1962—the Centaur and Agena rockets and the M-1 engine. The center was short on office space at the time, and its flight research program was temporarily on the wane. Lewis management decided to construct a large cinderblock structure inside one half of the hangar to house the new personnel. This structure was used until 1965 when the new Developmental Engineering Building was built. The Block House was eventually torn down in 1973.
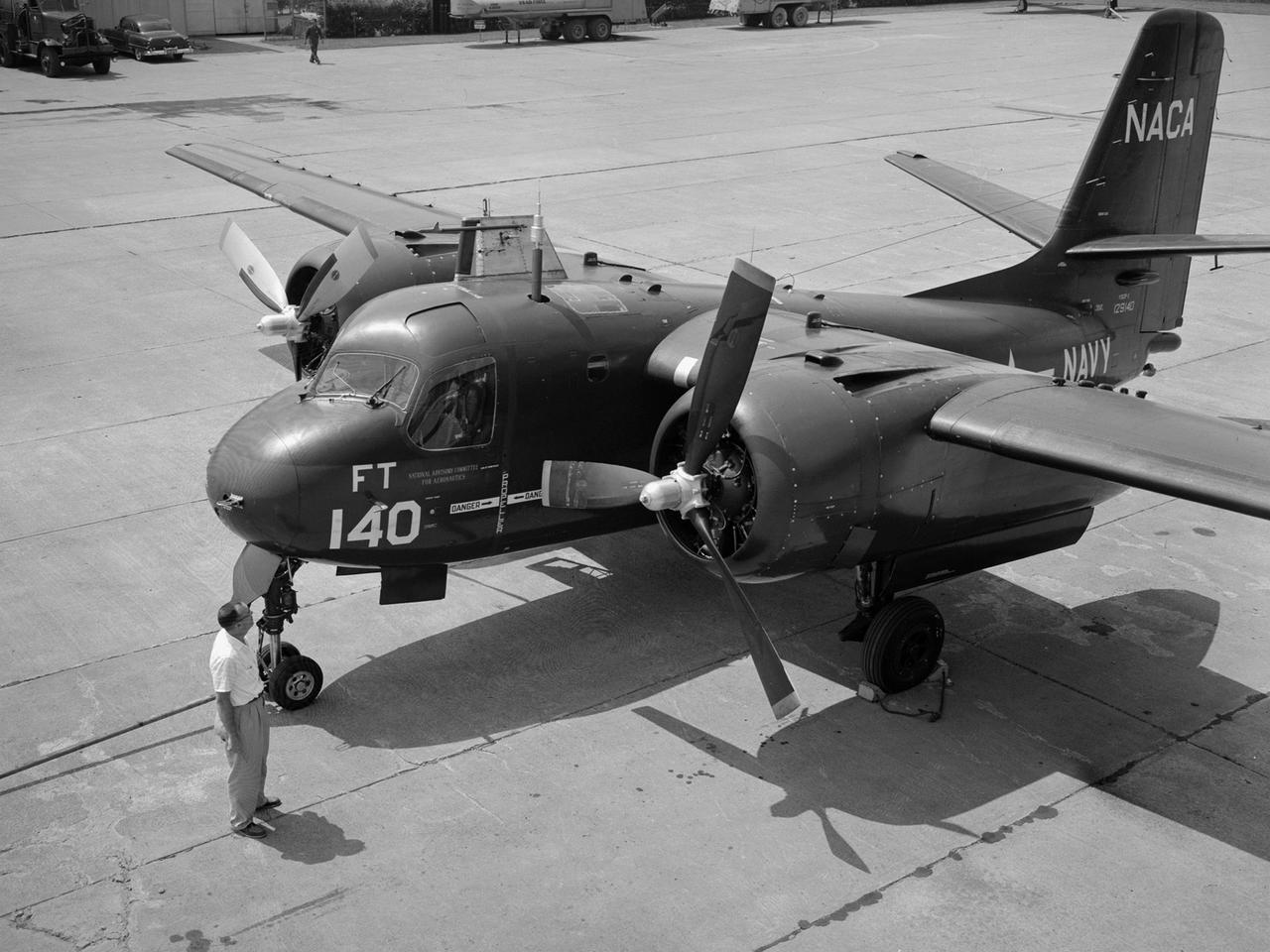

The NACA’s Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory acquired the Grumman S2F-1 Tracker from the Navy in 1955 to study icing instrumentation. Lewis’s icing research program was winding down at the time. The use of jet engines was increasing thus reducing the threat of ice accumulation. Nonetheless Lewis continued research on the instrumentation used to detect icing conditions. The S2F-1 Tracker was a carrier-based submarine hunter for the Navy. Grumman developed the Tracker as a successor to its Korean War-era Guardian patrol aircraft. Prototypes first flew in late 1952 and battle-ready versions entered Naval service in early 1954. The Navy utilized the Trackers to protect fleets from attack.
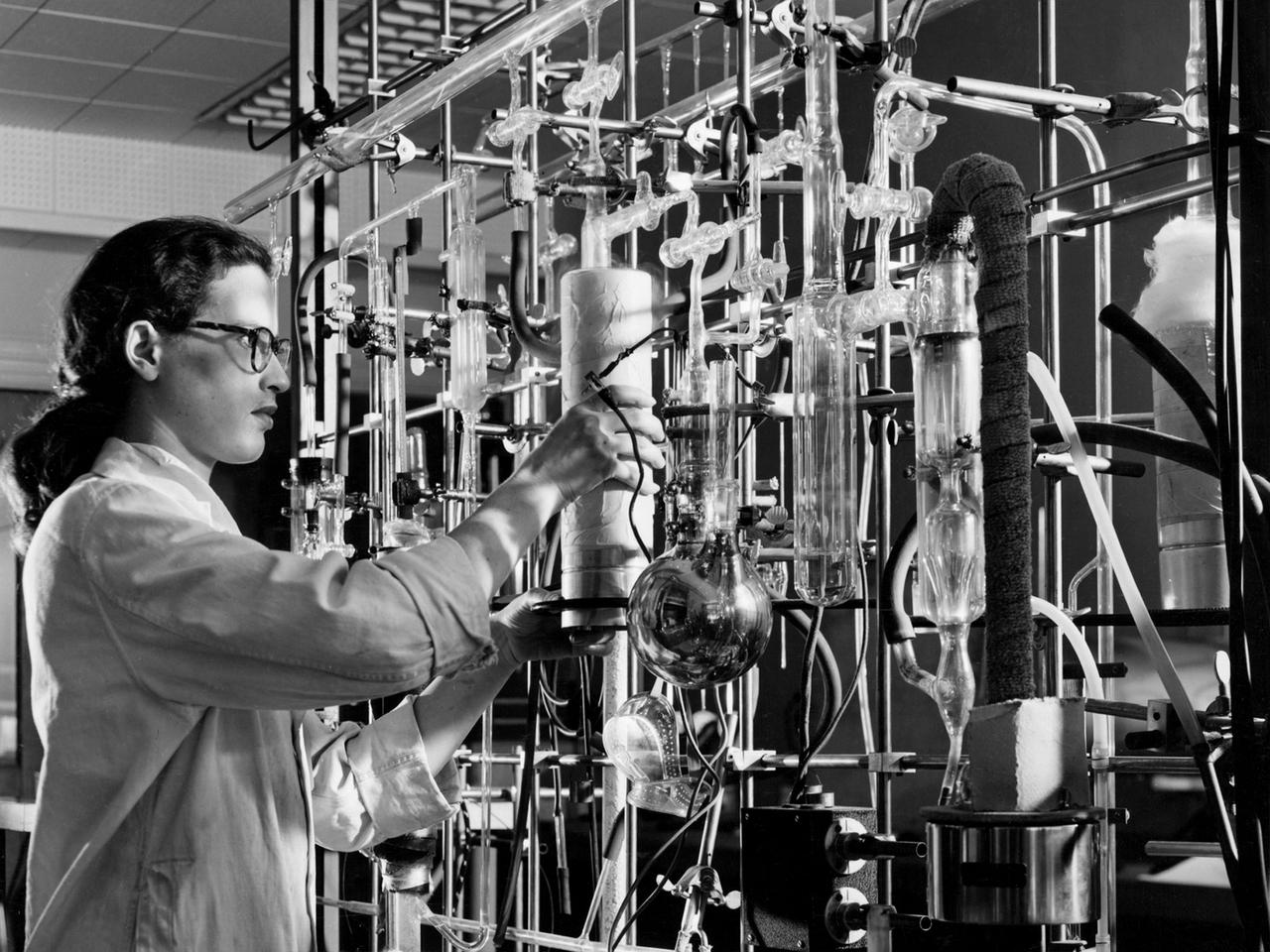

A materials researcher at the NACA’s Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory examines a surface crack detection apparatus in the Materials and Stresses Building during December 1952. Materials research was an important aspect of propulsion technology. Advanced engine systems relied upon alloys, and later composites, that were strong, lightweight, and impervious to high temperatures. Jet engines which became increasingly popular in the late 1940s, produced much higher temperatures than piston engines. These higher temperatures stressed engine components, particularly turbines. Although Lewis materials research began during World War II, the Materials and Thermodynamics Division was not created until 1949. Its primary laboratories were located in the Materials and Stresses Building. The group sought to create new, improved materials and to improve engine design through increased understanding of materials. The Lewis materials researchers of the 1950s made contributions to nickel-aluminum alloys, cermet blades, metal matrix composites, oxide dispersion strengthened superalloys, and universal slopes.
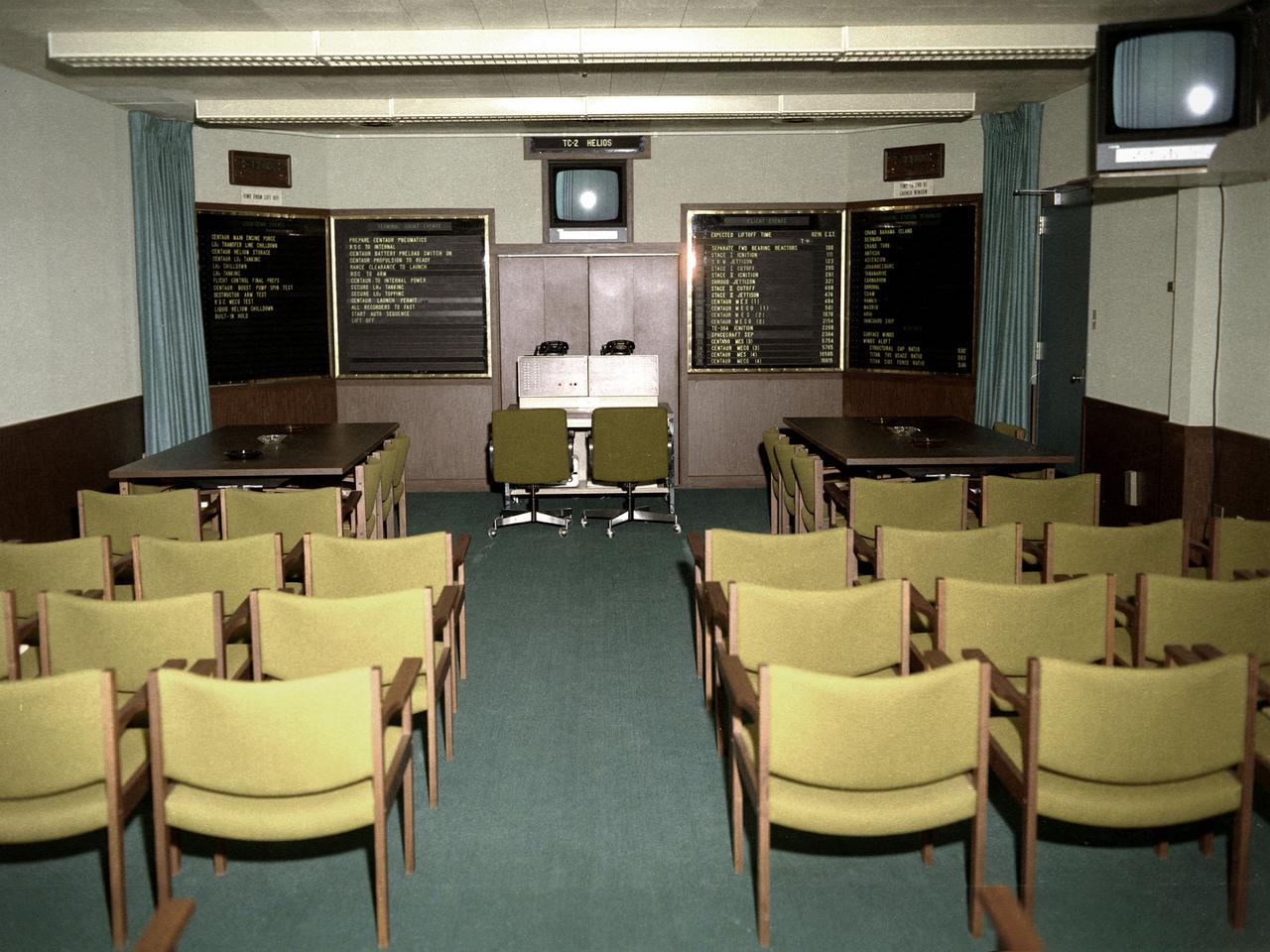

A Centaur rocket control room in the Development Engineering Building (DEB) at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio. The DEB, completed in the mid-1960s, provided office space for several hundred development engineers outside the center’s main gate. The location of the DEB emphasized the development staff’s separation from the research side of the laboratory. This control room at Lewis was directly linked to Cape Kennedy. The Lewis staff in Cleveland could monitor and back up the Lewis launch team in the actual control room at the Cape. This photograph was taken during the preparations for the Titan-Centaur-Helios launch on December 10, 1974. The panels to the left listed the countdown events for the Centaur rocket. The launch countdown clock can be seen above these panels. The two panels on the right listed events predicted to occur during the flight and the availability of the tracking stations. The clock above the panels indicated the time remaining before the launch window expired. The Launch Vehicles Division was created in 1969 to manage the launches of all Centaur and Agena rockets. The Launch Vehicles Division worked with the engineers to design the payload in a manner that ensured that its size and weight were within Centaur’s parameters. They also developed the proper trajectory analysis for the launch. These trajectories often had to be adjusted if the launch did not occur on the planned date.
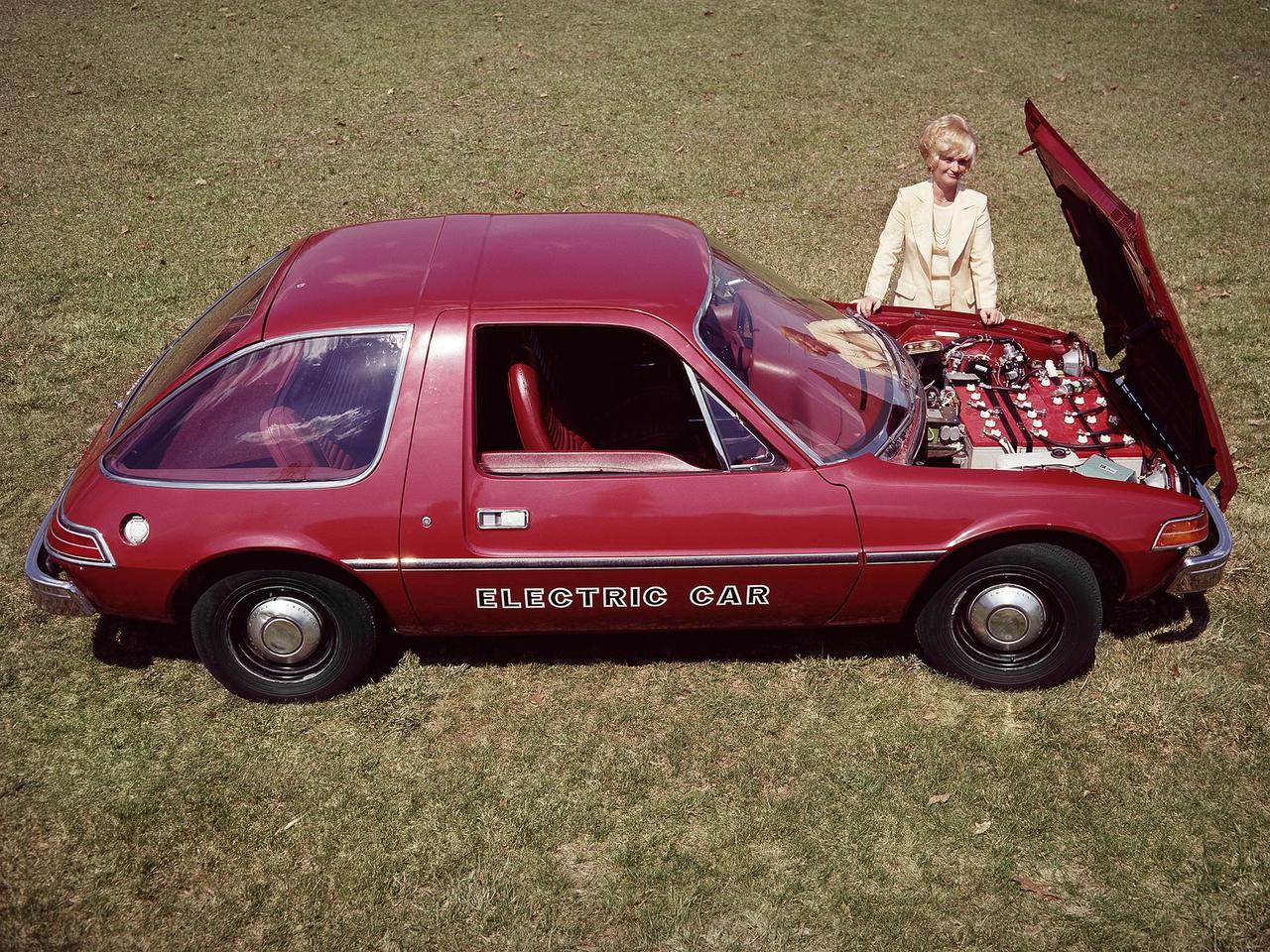

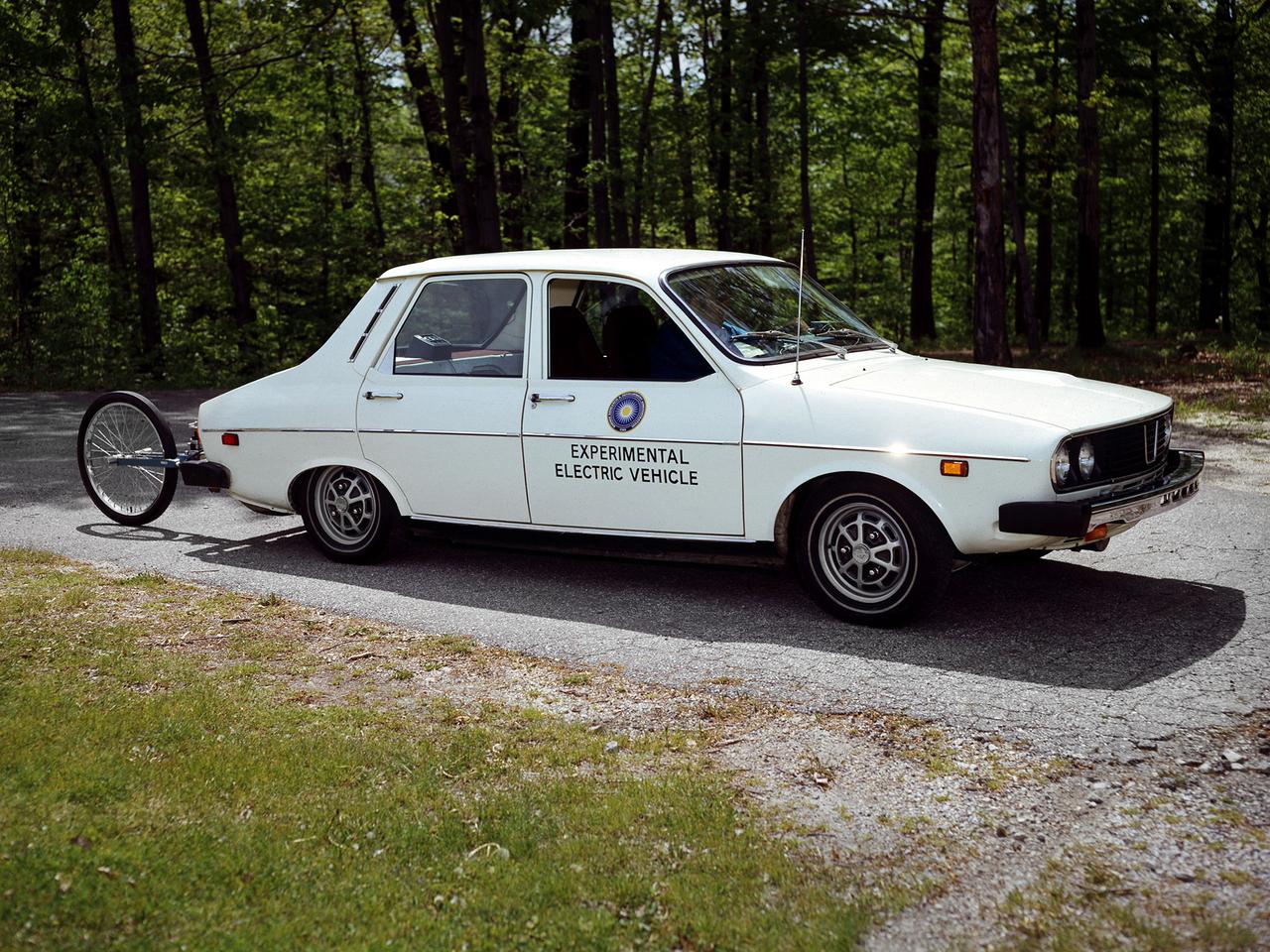
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center tested 16 commercially-manufactured electric vehicles, including this modified Pacer, during the mid-1970s. The Electric Vehicle Project was just one of several energy-related programs that Lewis and the Energy Research and Development Administration (ERDA) undertook in the mid-1970s. NASA and ERDA embarked on this program in 1976 to determine the state of the current electric vehicle technology. As part of the project, Lewis tested a fleet composed of every commercially available electric car. The Cleveland-area Electric Vehicle Associates modified an American Motors Pacer vehicle to create this Change-of-Pace Coupe. It was powered by twenty 6-volt batteries whose voltage could be varied by a foot control. The tests analyzed the vehicle’s range, acceleration, coast-down, braking, and energy consumption. Some of the vehicles had analog data recording systems to measure the battery during operation and sensors to determine speed and distance. Lewis researchers found that the vehicle performance varied significantly from model to model. In general, the range, acceleration, and speed were lower than conventional vehicles. They also found that traditional gasoline-powered vehicles were as efficient as the electric vehicles. The researchers concluded, however, that advances in battery technology and electric drive systems would significantly improve the performance and efficiency.
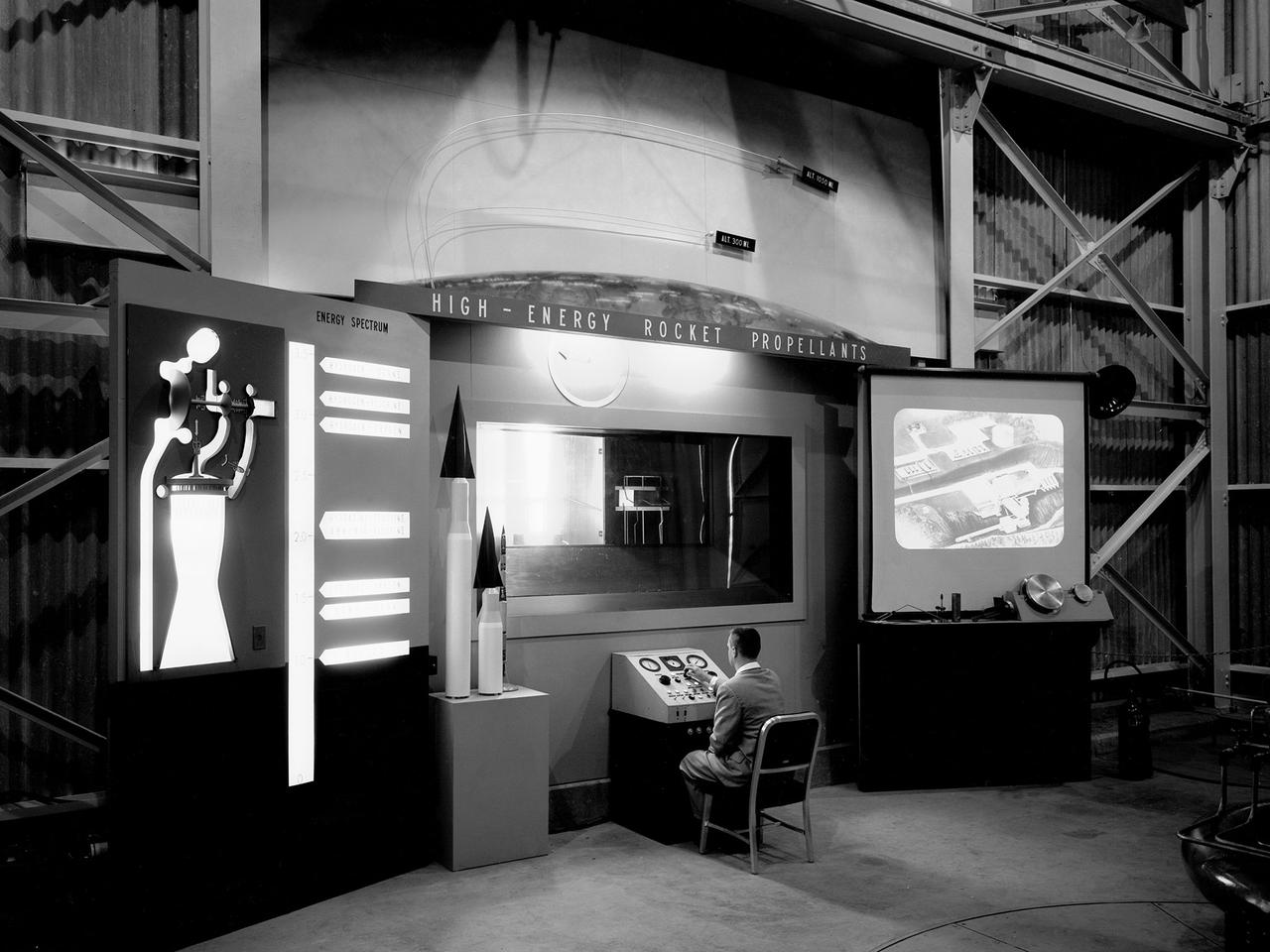

A researcher works a demonstration board in the Rocket Engine Test Facility during the 1957 Inspection of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in Cleveland, Ohio. Representatives from the military, aeronautical industry, universities, and the press were invited to the laboratory to be briefed on the NACA’s latest research efforts and tour the test facilities. Over 1700 people visited the Lewis during the October 7-10, 1957 Inspection. The Soviet Union launched their first Sputnik satellite just days before on October 4. NACA Lewis had been involved in small rockets and propellants research since 1945, but the NACA leadership was wary of involving itself too deeply with the work since ballistics traditionally fell under the military’s purview. The Lewis research was performed by the High Temperature Combustion section in the Fuels and Lubricants Division in a series of small cinderblock test cells. The rocket group was expanded in 1952 and made several test runs in late 1954 using liquid hydrogen as a propellant. A larger test facility, the Rocket Engine Test Facility, was approved and became operational just in time for the Inspection.

Electrochemistry Branch, Research Contributions to the NASA Mission at the Lewis Research Center
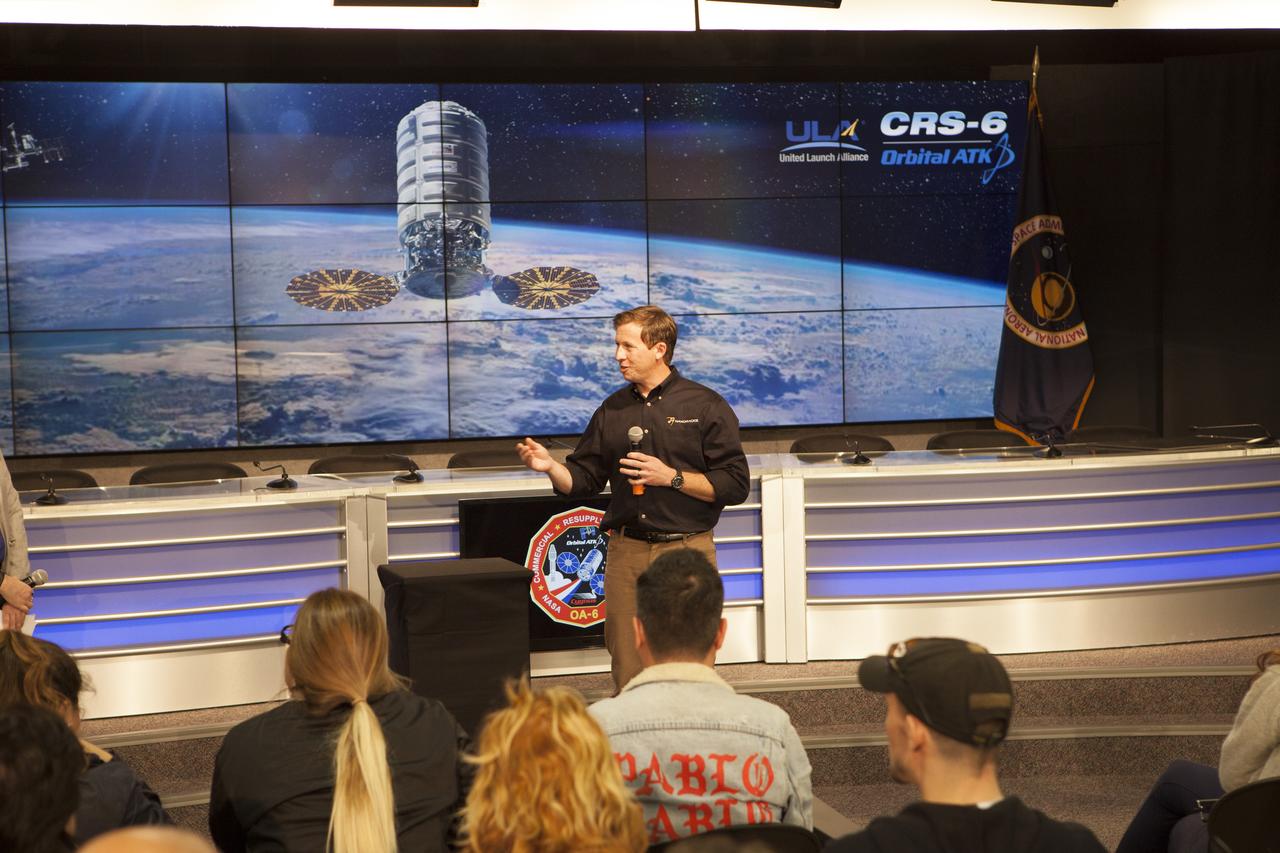

Michael Lewis, chief technology officer for NanoRacks, speaks to members of the media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on science research and technology work planned for the International Space Station, or ISS, following the arrival of a Cygnus spacecraft. The Cygnus is scheduled to be launched March 22 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on the Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission.

NASA pilot Ed Lewis with the T-34C aircraft on the Dryden Flight Research Center Ramp. The aircraft was previously used at the Lewis Research Center in propulsion experiments involving turboprop engines, and was used as a chase aircraft at Dryden for smaller and slower research projects. Chase aircraft accompany research flights for photography and video purposes, and also as support for safety and research. At Dryden, the T-34 is used mainly for smaller remotely piloted vehicles which fly slower than NASA's F-18's, used for larger scale projects. This aircraft was returned to the U.S. Navy in May of 2002.
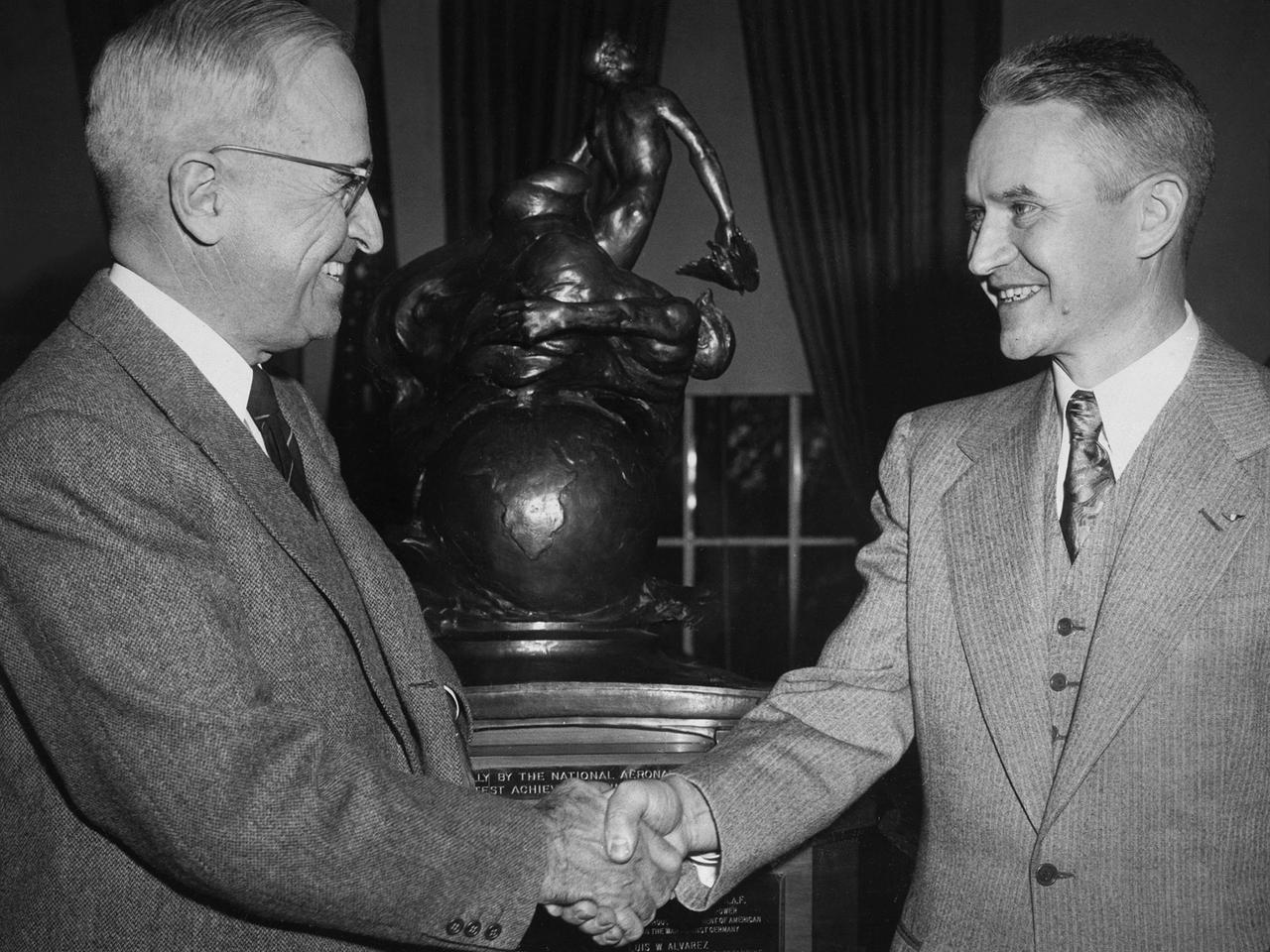

Lewis Rodert, then of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory, receives the Collier Trophy from President Harry Truman for his work in the design and development of an ice prevention system for aircraft. The accumulation of ice on an aircraft had been a critical issue for years. Rodert developed a method of transferring engine heat to the wings and other vulnerable components to prevent ice buildup. Rodert began his icing investigations at Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory in 1936. The NACA ordered a Lockheed 12A aircraft to be built using Rodert’s deicing system. The aircraft successfully flew through icing conditions during the following winter. Soon thereafter the military incorporated the system into a Consolidated B-24D Liberator and several other military aircraft, including a North American XB-25F. Rodert and the NACA icing program transferred to the Lewis lab in Cleveland in 1946. In Cleveland, the focus turned to the study of cloud composition and the causes of icing. Rodert’s role at Lewis diminished over the ensuing years. Rodert was honored in 1947 for his Collier Trophy at ceremonies at Langley, Ames, and then finally Lewis.

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by Mercury 13 Astronaut Trainee, Wally Funk

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by Mercury 13 Astronaut Trainee, Wally Funk
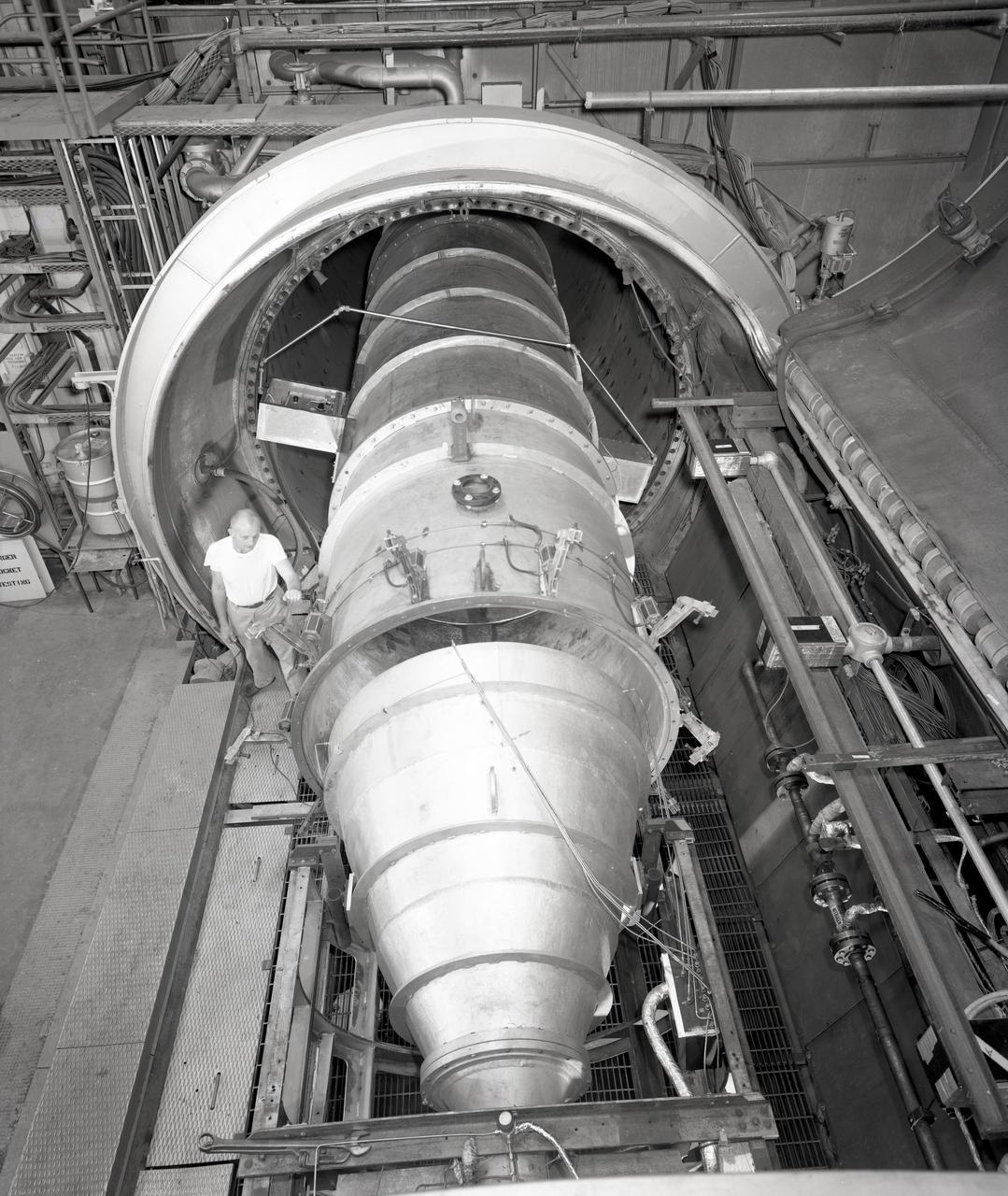
Apollo Contour Engine Model being tested in the NASA Lewis Research Center, Propulsion Systems Laboratory, PSL
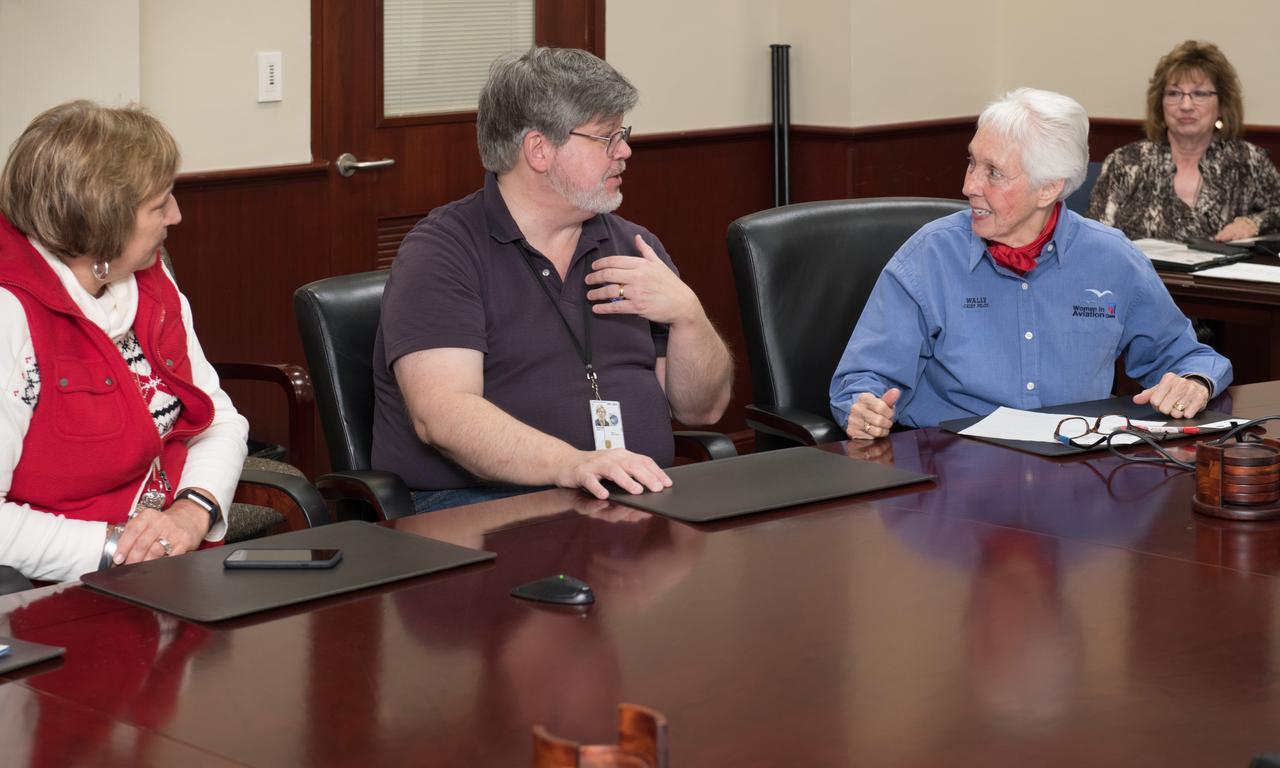

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by Mercury 13 Astronaut Trainee, Wally Funk
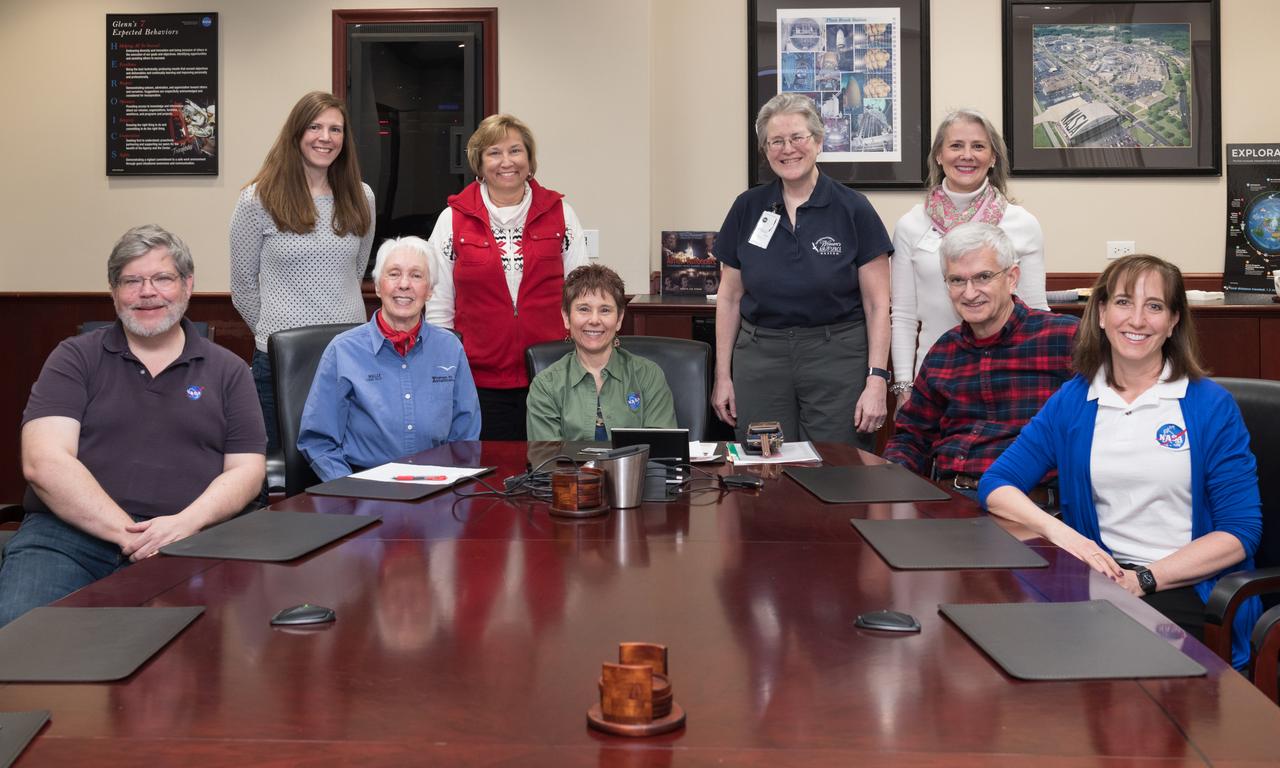

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by Mercury 13 Astronaut Trainee, Wally Funk
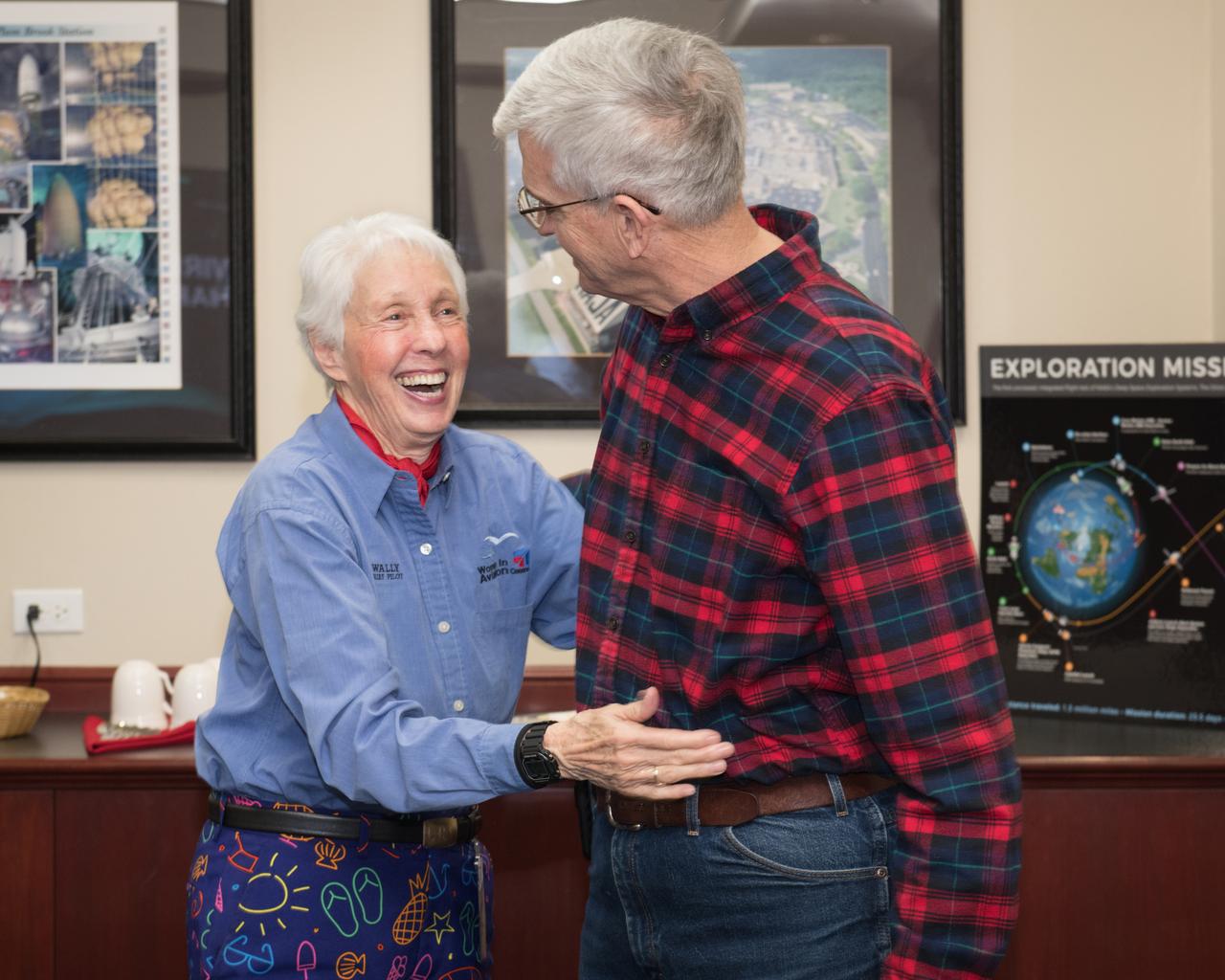

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by Mercury 13 Astronaut Trainee, Wally Funk
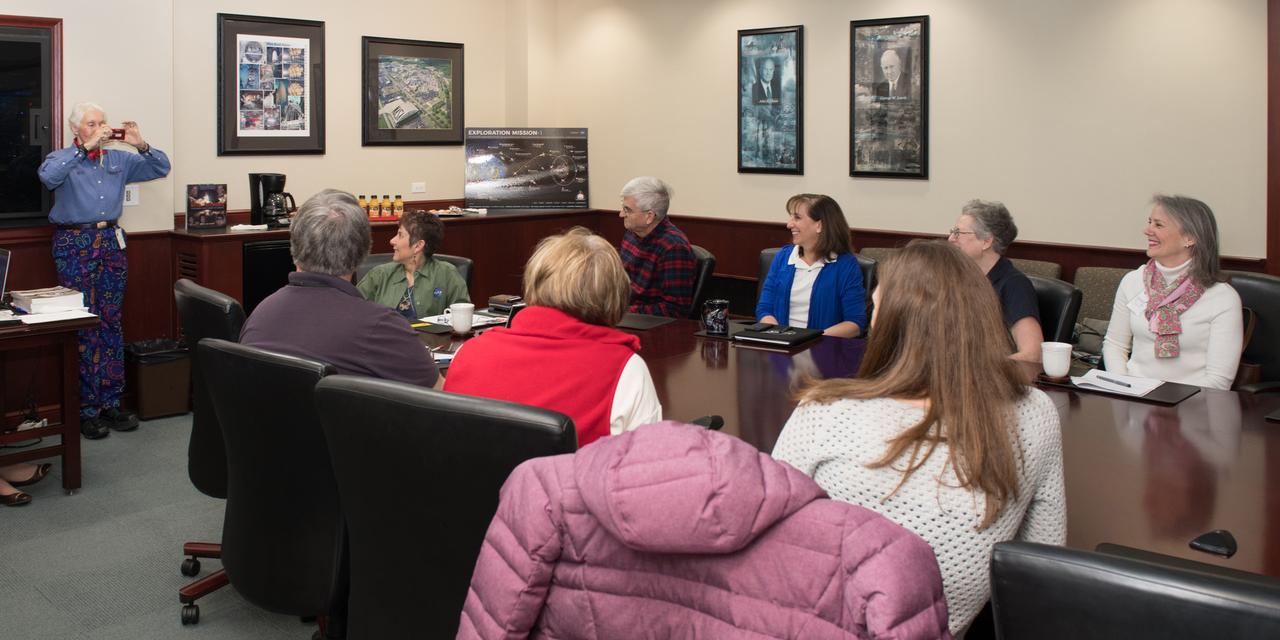

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by Mercury 13 Astronaut Trainee, Wally Funk

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by Mercury 13 Astronaut Trainee, Wally Funk

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by Mercury 13 Astronaut Trainee, Wally Funk

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by Mercury 13 Astronaut Trainee, Wally Funk

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by Mercury 13 Astronaut Trainee, Wally Funk

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by Mercury 13 Astronaut Trainee, Wally Funk

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by Mercury 13 Astronaut Trainee, Wally Funk

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by Mercury 13 Astronaut Trainee, Wally Funk
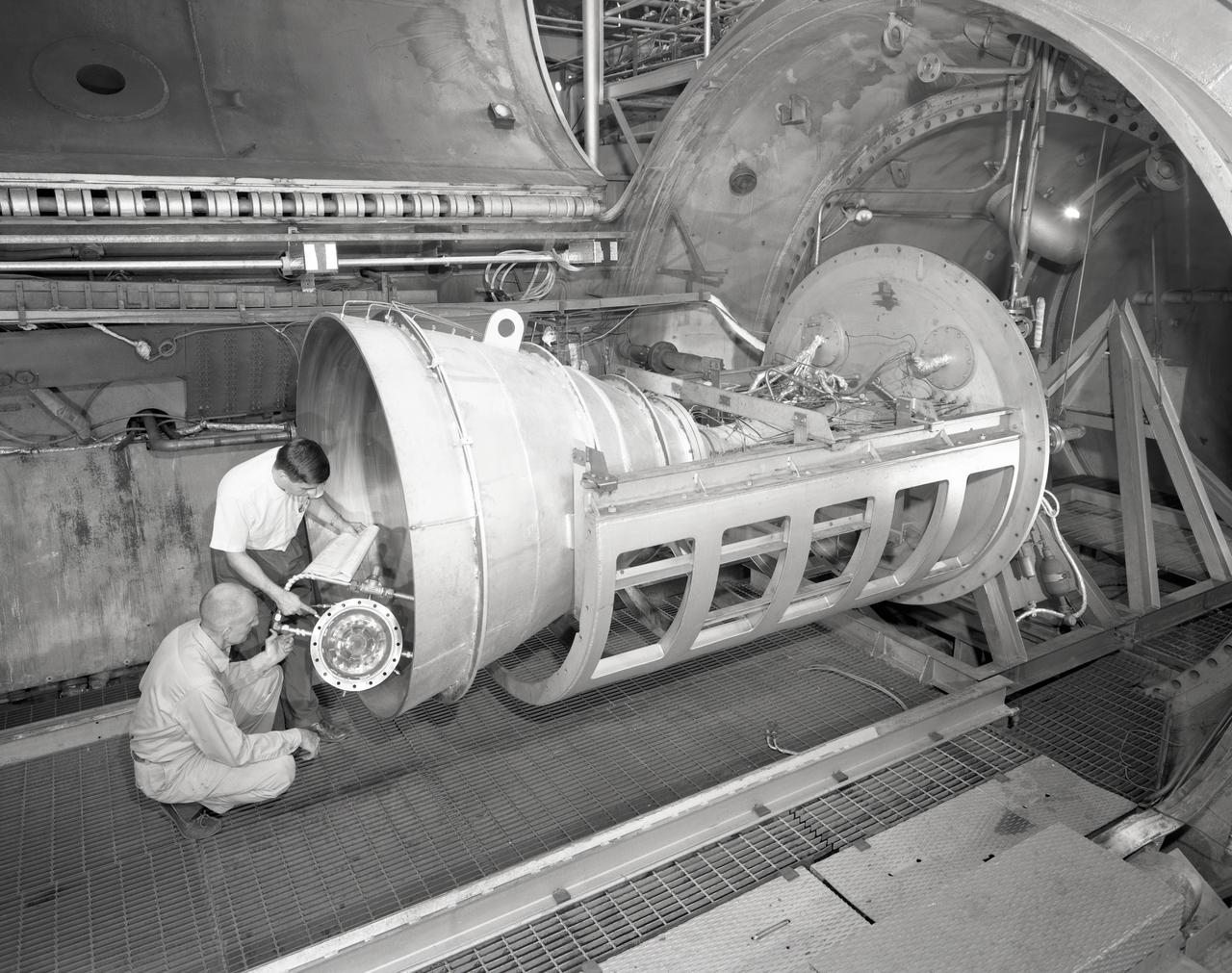
Apollo Contour Engine Model being tested in the NASA Lewis Research Center, Propulsion Systems Laboratory, PSL

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by Mercury 13 Astronaut Trainee, Wally Funk

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by Mercury 13 Astronaut Trainee, Wally Funk

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by Mercury 13 Astronaut Trainee, Wally Funk
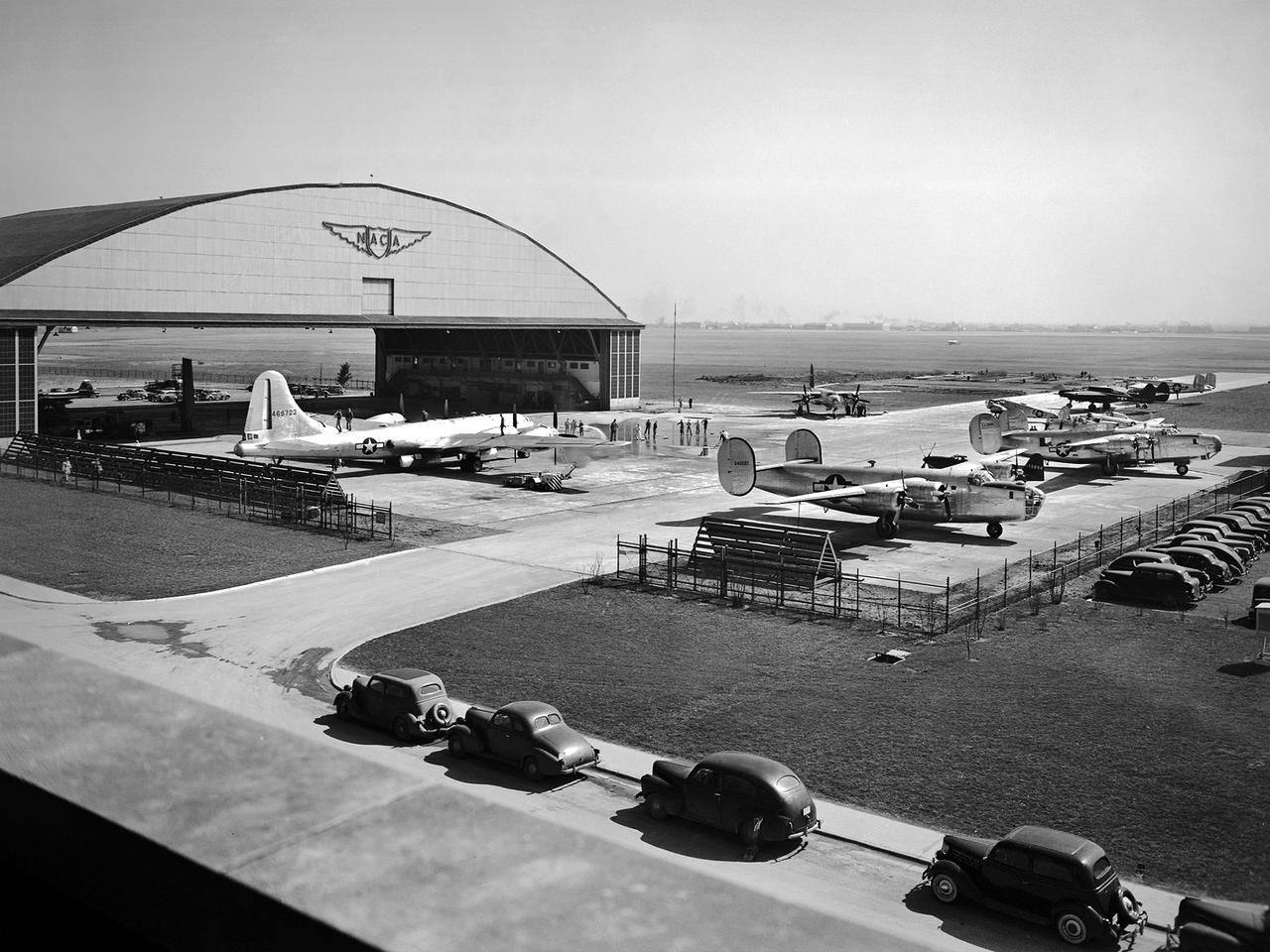

This fleet of military aircraft was used in the 1940s for research at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in Cleveland, Ohio. The NACA Lewis flight research program was established in March 1943 to augment the lab’s wartime research efforts. NACA Lewis possessed a host of wind tunnels, test stands, and other ground facilities designed to replicate flight conditions, but actual flight tests remained an integral research tool. The military loaned NACA Lewis 15 different aircraft during World War II and six others in the six months following the end of hostilities. During the war these aircraft supported three main efforts: the improved performance of reciprocating engines, better fuel additives and mixtures, and deicing systems. The wartime researchers used the types of aircraft which the studies were intended to improve. After the war the research aircraft served as test beds to investigate engines or systems that often had little to do with the research aircraft. During the war, NACA Lewis’ three pilots were supported by 16 flight engineers, 36 mechanics, and 10 instrumentation specialists. The visible aircraft, from left to right, are a Boeing B-29 Superfortress, a Martin B-26A Marauder, two Consolidated B-24 Liberators, a Cessna UC-78 Bobcat, and a Northrop P-61 Black Widow. Partially obscured are a North American P-51 Mustang, a Bell P-63 King Cobra, a North American AT-6 Texan, and a Lockheed RA-29 Hudson.
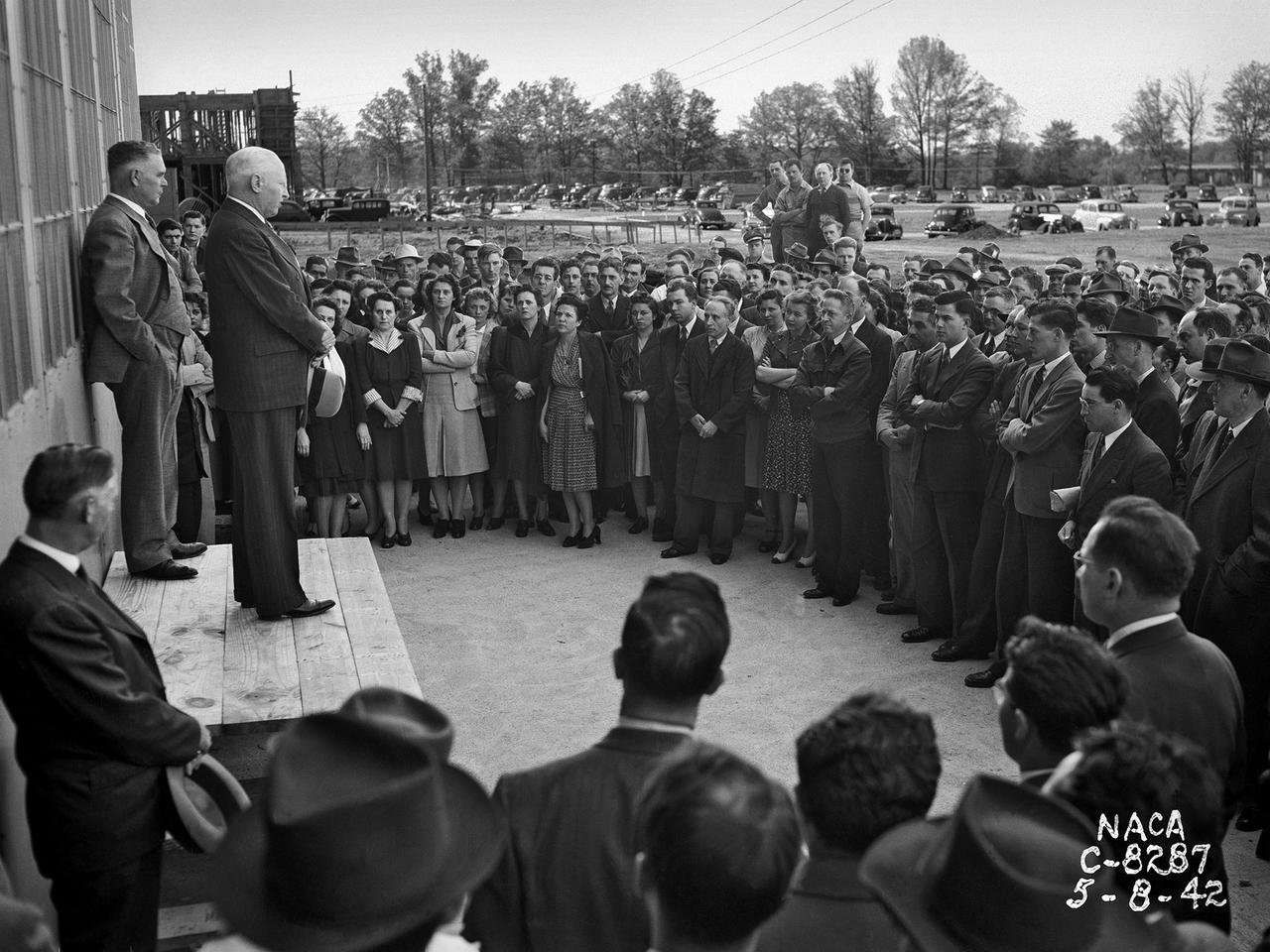

Construction Manager Raymond Sharp and the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Director of Research George Lewis speak to employees during the May 8, 1942, Initiation of Research ceremony at the Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory. The event marked the first operation of a test facility at the new laboratory. The overall laboratory was still under construction, however, and behind schedule. Lewis traveled from his office in Washington, DC every week to personally assess the progress. Drastic measures were undertaken to accelerate the lab’s construction schedule. The military provided special supplies, contractors were given new agreements and pressured to meet deadlines, and Congress approved additional funds. The effort paid off and much of the laboratory was operational in early 1943. George Lewis managed the NACA’s aeronautical research for over 20 years. Lewis joined the NACA as Executive Officer in 1919, and was named Director of Aeronautical Research in 1924. In this role Lewis served as the liaison between the Executive Committee and the research laboratories. His most important accomplishment may have been the investigative tours of the research facilities in Germany in 1936 and 1939. The visits resulted in the NACA’s physical expansion and the broadening of the scope of its research. Lewis did not take a day of leave between the Pearl Harbor attack and the Armistice. He began suffering health problems in 1945 and was forced to retire two years later. The Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory was renamed the NACA Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in September 1948.
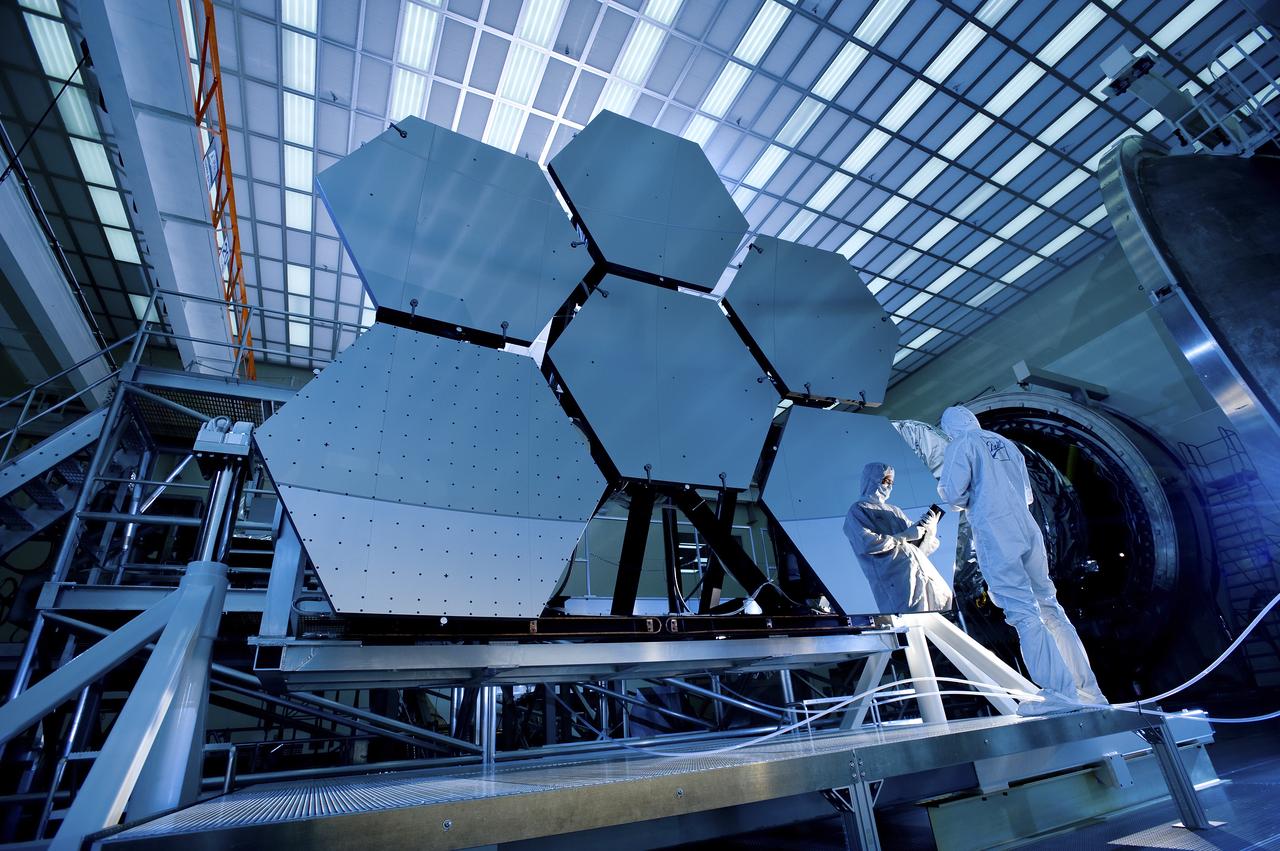

BALL AEROSPACE'S JAKE LEWIS IS REFLECTED IN ONE OF THE MIRRORS ON A JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE ARRAY THAT WAS IN THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING
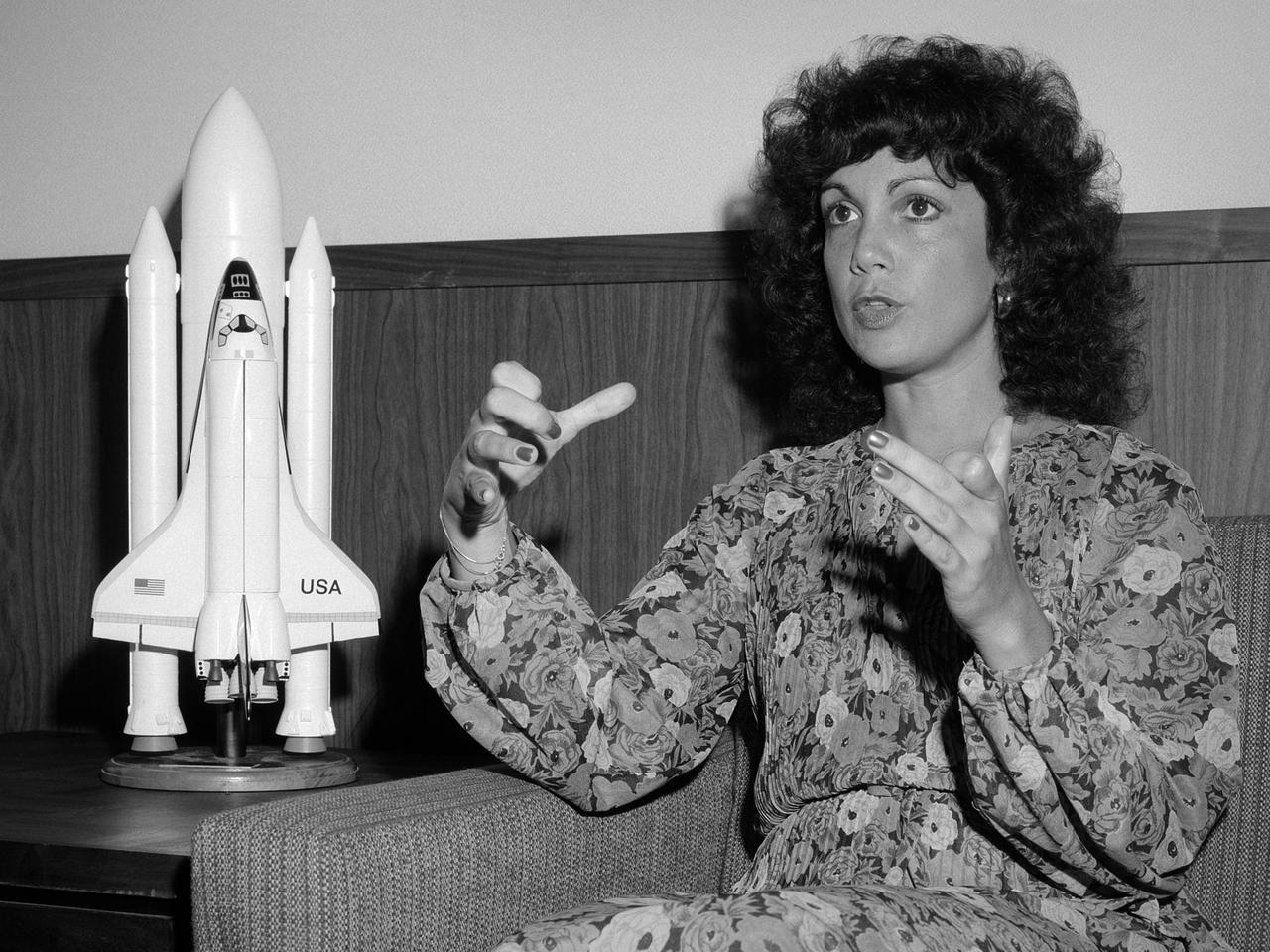

Astronaut Judy Resnik visits the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center on July 18, 1979, the tenth anniversary of the Apollo 11 mission. The event, sponsored by the center’s Public Information Office, was attended by Lewis staff, Cleveland-area media and personalities, and the public. During her time in Cleveland, Resnik appeared on a local television program, gave a press conference, lunched with NASA officials, addressed employees at Lewis, and then met the public at the center’s Visitors Information Center. Resnik related her recent experiences as one of the first US female astronauts and her duties as a mission specialist. The Akron, Ohio native earned a Bachelor’s degree in electrical engineering from Carnegie-Mellon University in 1970 and a doctorate in electrical engineering from the University of Maryland in 1977. Resnik served as a biomedic engineer and staff fellow in the Laboratory of Neurophysiology at the National Institutes of Health from 1974 to 1977, where she performed biological research experiments on visual systems. She served as a senior systems engineer in private industry prior to her selection as an astronaut. Resnik first flew as a mission specialist on STS 41-D, Discovery’s maiden flight, in 1984. Resnik was killed in the January 28, 1986 Challenger accident.

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center tested 16 commercially-manufactured electric vehicles, including this Metro, during the mid-1970s. Lewis and the Energy Research and Development Administration (ERDA) engaged in several energy-related programs in the mid-1970s, including the Electric Vehicle Project. NASA and ERDA undertook the program in 1976 to determine the state of the current electric vehicle technology. As part of the project, Lewis and ERDA tested every commercially available electric car model. Electric Vehicle Associates, located in a Cleveland suburb, modified a Renault 12 vehicle to create this Metro. Its 1040-pound golfcart-type battery provided approximately 106 minutes of operation. The tests analyzed the vehicle’s range, acceleration, coast-down, braking, and energy consumption. Some of the vehicles had analog data recording systems to measure the battery during operation and sensors to determine speed and distance. The researchers found the performance of the different vehicles varied significantly. In general, the range, acceleration, and speed were lower than that found on conventional vehicles. They also found that traditional gasoline-powered vehicles were as efficient as the electric vehicles. The researchers concluded, however, that advances in battery technology and electric drive systems would significantly improve efficiency and performance.
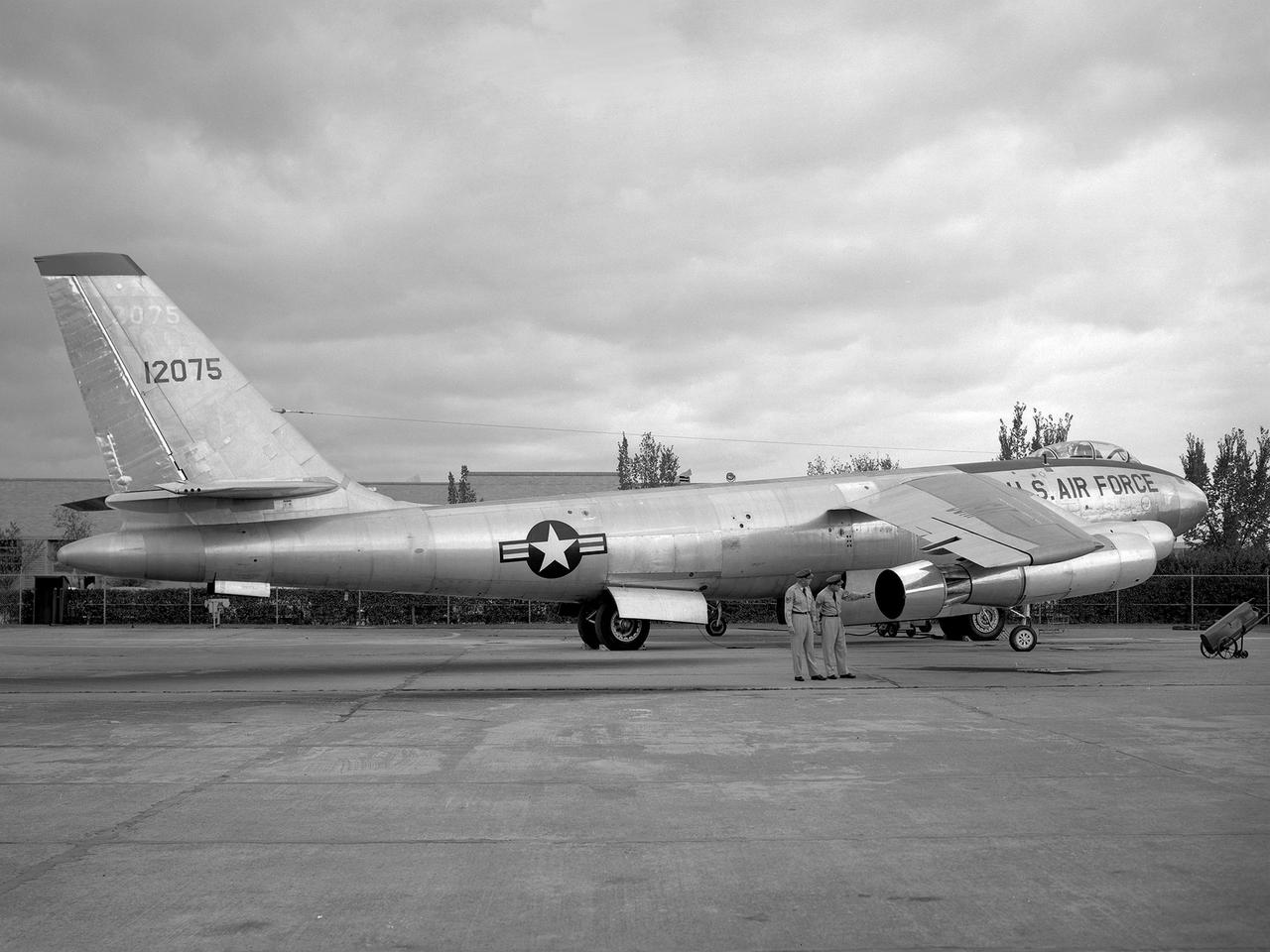

A Boeing B-47 Stratojet bomber with a noise-reducing ejector on its engine at the 1957 Inspection of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. Representatives from the military, aeronautical industry, universities, and the press were invited to the laboratory to be briefed on the NACA’s latest research efforts and tour the state- of- the- art test facilities. Over 1700 people visited the NACA Lewis in Cleveland, Ohio during October 7 - 10, 1957. By the mid-1950s, the aircraft industry was close to introducing jet airliners to the nation’s airways. The noise produced by the large jet engines, however, would pose a considerable problem for communities near airports. This problem was demonstrated at the 1957 Inspection by an NACA Lewis researcher who played longplay (LP) audio records of military jet engines for an audience. Tests showed that the source of the loudest noise was not the engine itself, but the mixing of the engine’s exhaust with the surrounding air in the atmosphere. The pressures resulting from this turbulence produced sound waves. One of Lewis’ first studies sought to design an exhaust nozzle that reduced the turbulence. A Pratt and Whitney J57 was tested in the Altitude Wind Tunnel with many of these nozzle configurations from January to May 1957. Researchers found that the various nozzle types did reduce the noise levels but also reduced the aircraft’s thrust. Afterwards, they determined that the addition of an NACA-developed ejector reduced the noise levels without diminishing thrust.
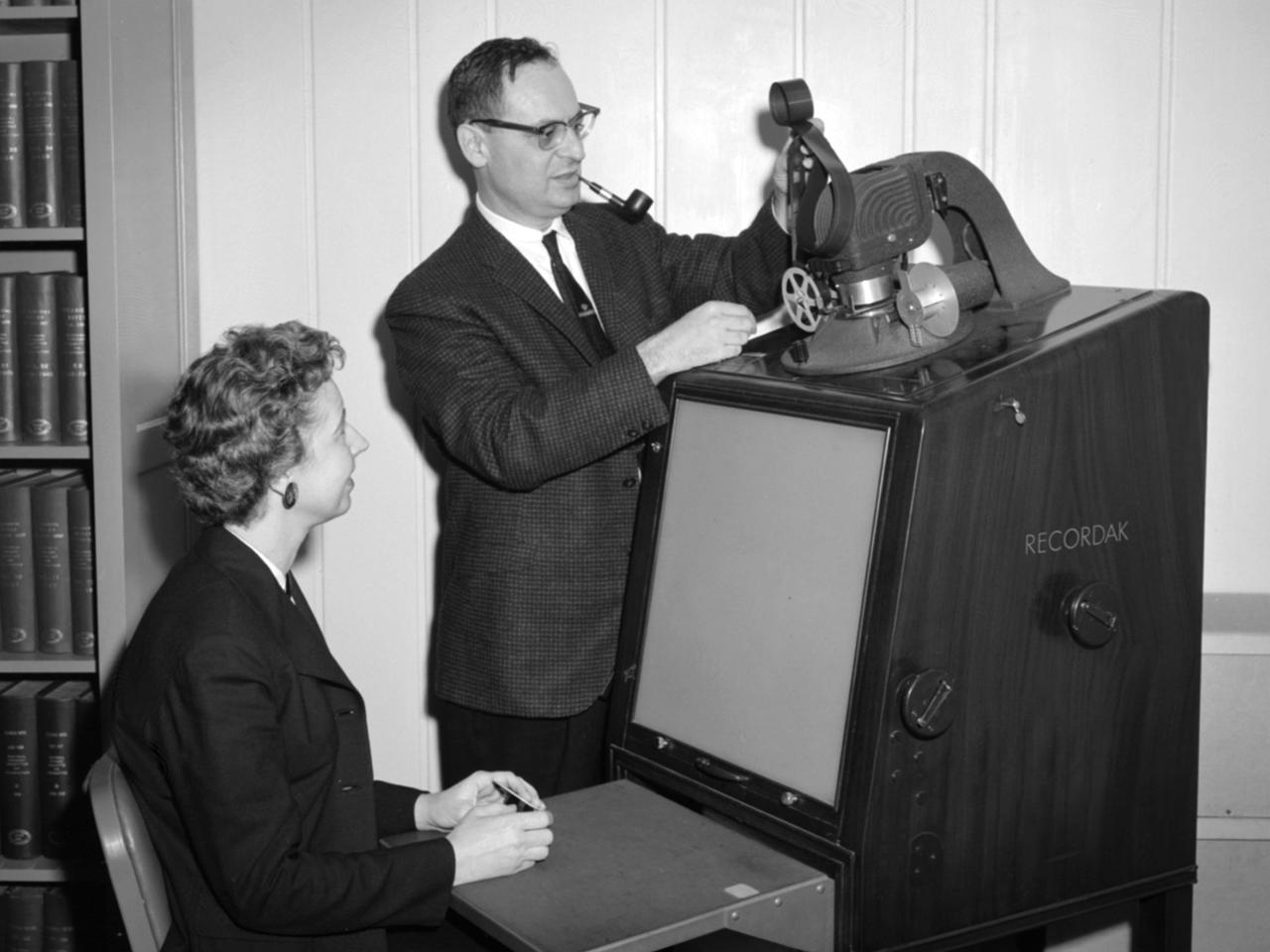

Jean Neidengard and George Mandel operate a Kodak Recordak microfilm reader in the library at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The library was located in the Administration Building until the mid-1960s. It was then moved to the Propulsion Systems Laboratory Office Building. In 2008 the library was moved once again, to the Research Analysis Center. At the time of this photograph, the Lewis library claimed to possess “One of the most complete aero-technical collections in the world.” It was doing a brisk business in the early 1960s. During 1960 alone the library acquired 19,000 new documents and provided 100,000 documents to customers. The library’s eleven-person staff provided reference services, archived technical reports, and supplied periodicals. The staff also included Sam Reiss, a full-time translator who could read 30 languages. He translated technical reports from all over the world for the Lewis research staff. Jean Neidengard oversaw the secret Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) documents in the collection. NASA was partnering with the AEC at the time on Nuclear Engine for Rocket Vehicle Application (NERVA) program. NASA Lewis was the agency’s lead center in the NERVA program. Neidengard’s husband Bill was the head mechanic in the Propulsion Systems Laboratory. George Mandel led the library staff from 1955 to 1968.

Members of Lewis’ Educational Services Office pose with one of the center’s Spacemobile space science demonstration units. Unlike its predecessor, the NACA, the new NASA space agency considered public outreach one of its core tenets. The early astronauts were lionized and new technologies touted. Lewis, which had previously been a closed laboratory, began hosting open houses and elaborate space fairs in the early 1960s. In addition, the center initiated educational programs that worked with local schools and a robust speaker’s bureau that explained NASA activities to the community. One aspect of these efforts was the Spacemobile Program. These vehicles included a delegated speaker, exhibits, models, and other resources. The Spacemobiles, which made forays across the Midwest, were extremely active throughout the 1960s.
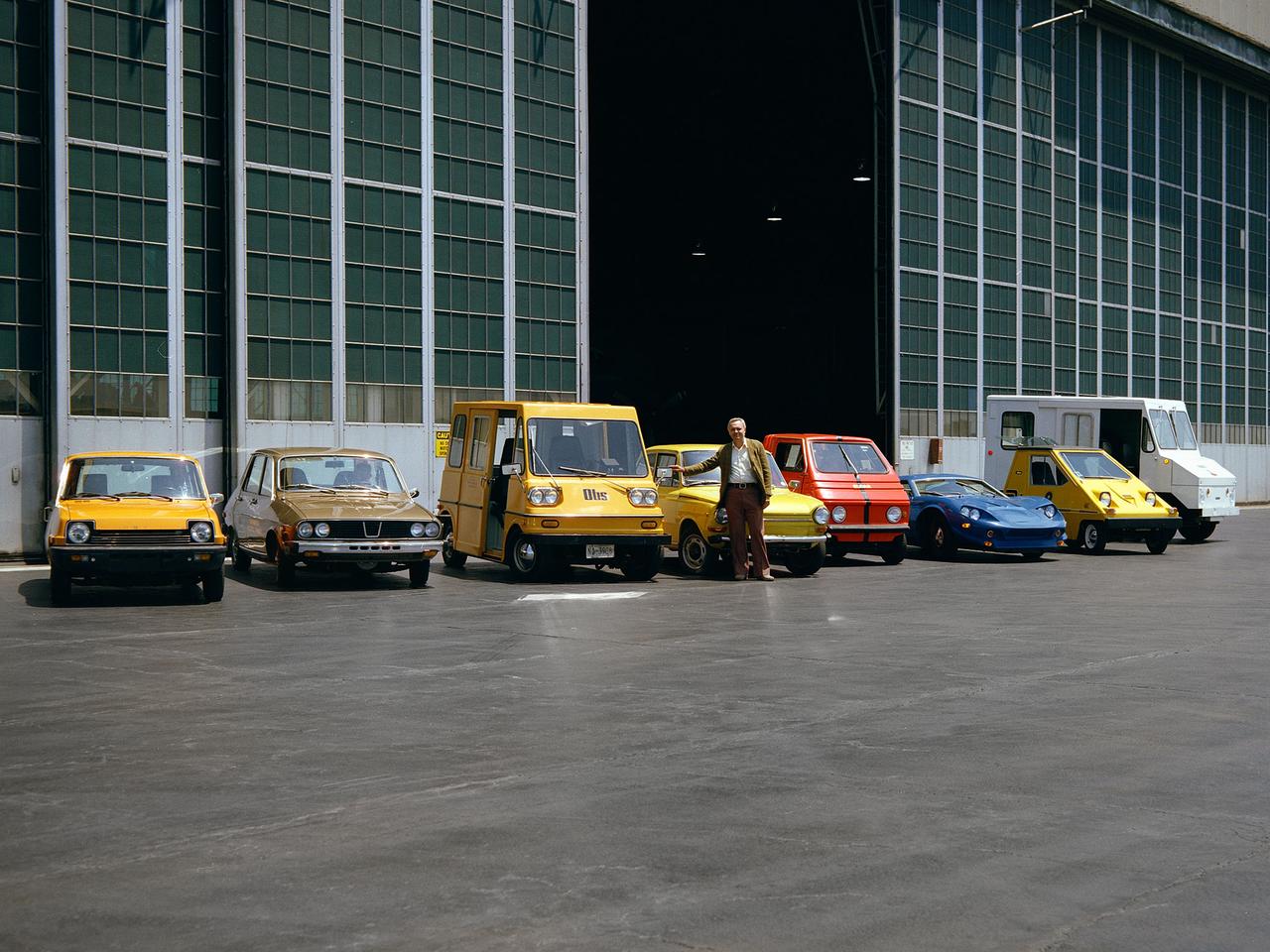

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center tested 16 commercially-manufactured electric vehicles, including these, during the mid-1970s. Lewis and the Energy Research and Development Administration (ERDA) engaged in several energy-related programs in the mid-1970s, including the Electric Vehicle Project. NASA and ERDA undertook the program in 1976 to determine the state of the current electric vehicle technology. The tests were primarily conducted on a 7.5-mile track at the Transportation Research Center located approximately 160 miles southwest of Cleveland, Ohio. Some of the vehicles had analog data recording systems to measure the battery during operation and sensors to determine speed and distance. The tests analyzed the vehicle’s range, acceleration, coast-down, braking, and energy consumption. From left to right: RIPP-Electric, EVA Contactor, Otis P-500, C.H. Waterman DAF, Zagato Elcar, unknown, Sebring-Vanguard Citicar, and Hattronic Minivan
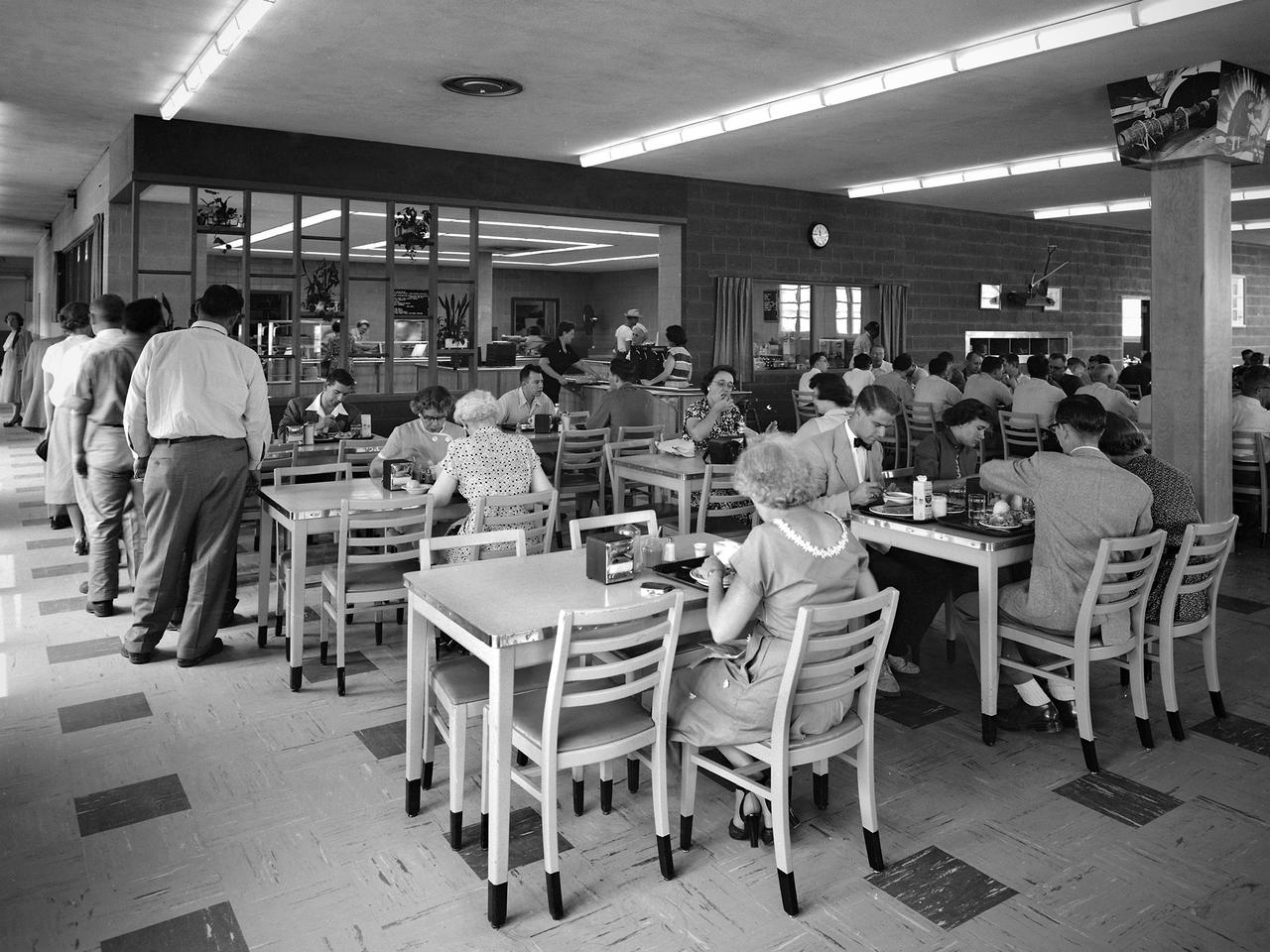

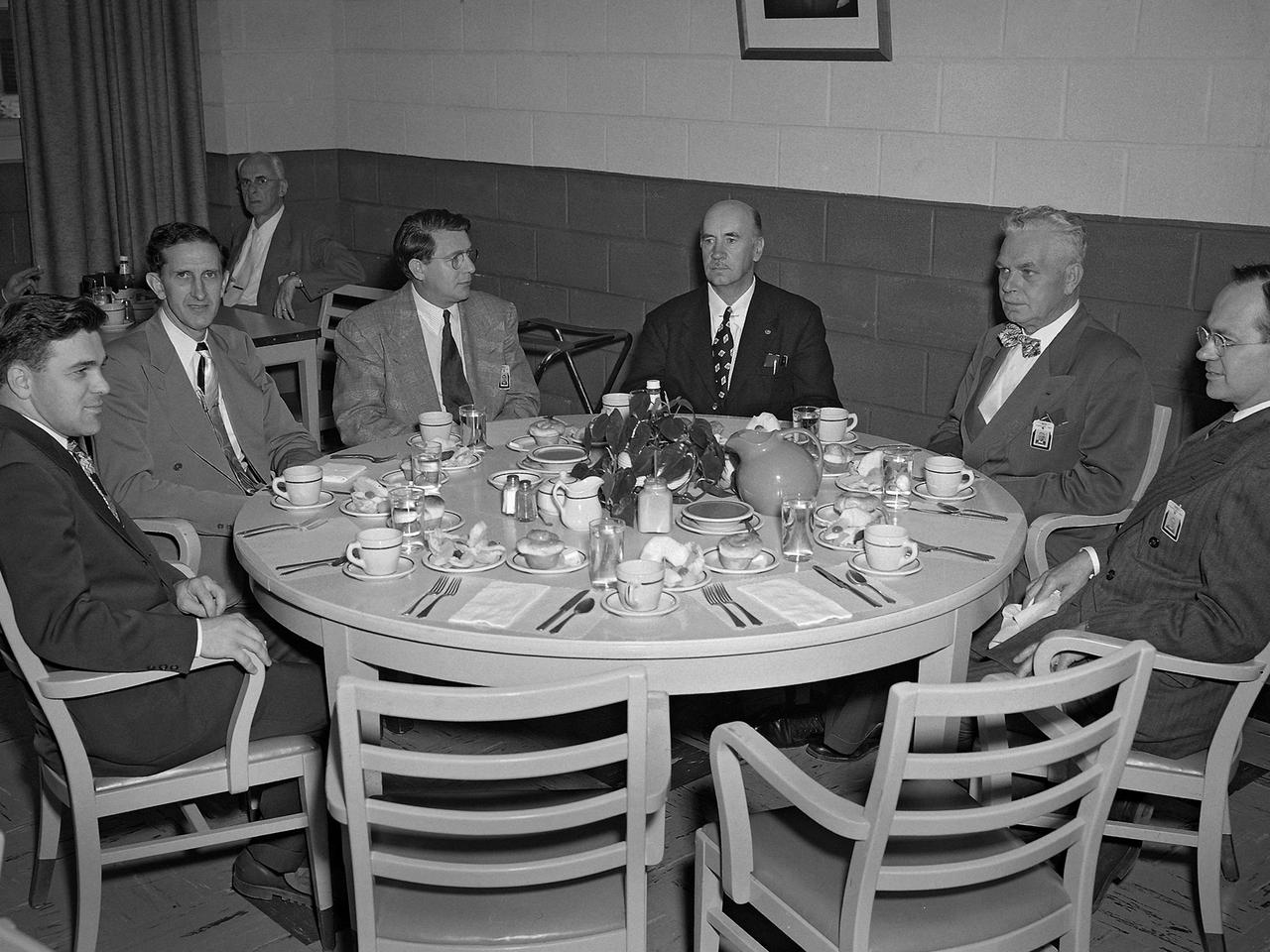
NACA staff members queue up in the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory cafeteria in August 1952. The cafeteria originally opened in November 1942 inside the south end of the Engine Research Building. A non-profit Exchange was established to handle the finances, while Helen Thompson, a German born pastry cook, ran the day-to-day operations. Employees could also purchase her bakery to take home with them. Services were expanded to include a lunch counter and a food cart that ferried meals to the facilities. By the end of World War II the cafeteria was serving nearly 1600 meals daily in a space designed for half of that. In 1951 a new wing was added to the Utilities Building to accommodate an expanded cafeteria, seen in this photograph. In the mid-1960s an auxiliary unit was built in the new Development Engineering Building located across Brookpark Road.
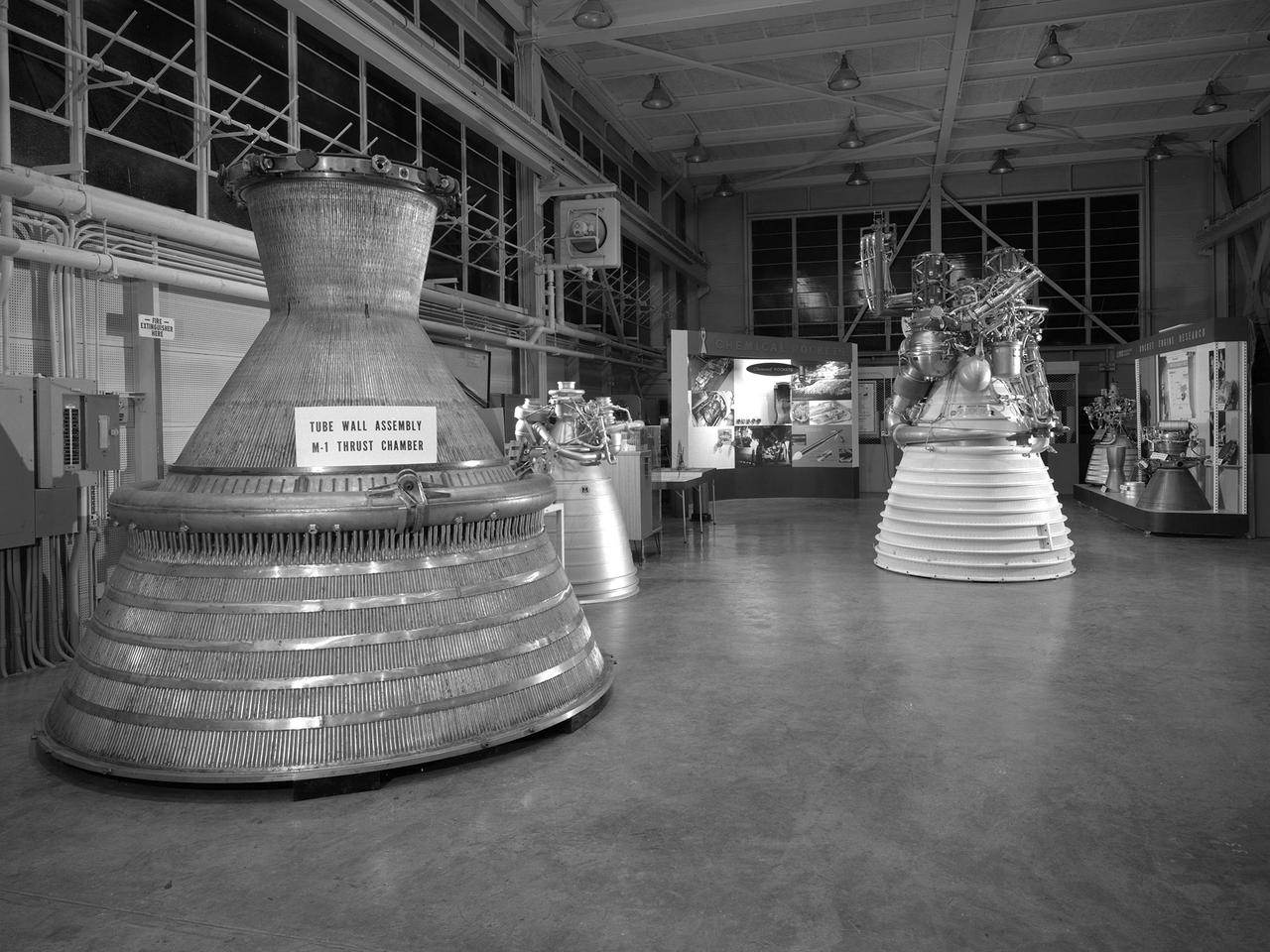

An array of rocket engines displayed in the Propulsion Systems Laboratory for the 1966 Inspection held at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Lewis engineers had been working on chemical, nuclear, and solid rocket engines throughout the 1960s. The engines on display are from left to right: two scale models of the Aerojet M-1, a Rocketdyne J-2, a Pratt and Whitney RL-10, and a Rocketdyne throttleable engine. Also on display are several ejector plates and nozzles. The Chemical Rocket Division resolved issues such as combustion instability and screech, and improved operation of cooling systems and turbopumps. The 1.5-million pound thrust M-1 engine was the largest hydrogen-fueled rocket engine ever created. It was a joint project between NASA Lewis and Aerojet-General. Although much larger in size, the M-1 used technology developed for the RL-10 and J-2. The M-1 program was cancelled in late 1965 due to budget cuts and the lack of a post-Apollo mission. The October 1966 Inspection was the culmination of almost a year of events held to mark the centers’ 25th anniversary. The three‐day Inspection, Lewis’ first since 1957, drew 2000 business, industry, and government executives and included an employee open house. The visitors witnessed presentations at the major facilities and viewed the Gemini VII spacecraft, a Centaur rocket, and other displays in the hangar. In addition, Lewis’ newest facility, the Zero Gravity Facility, was shown off for the first time.
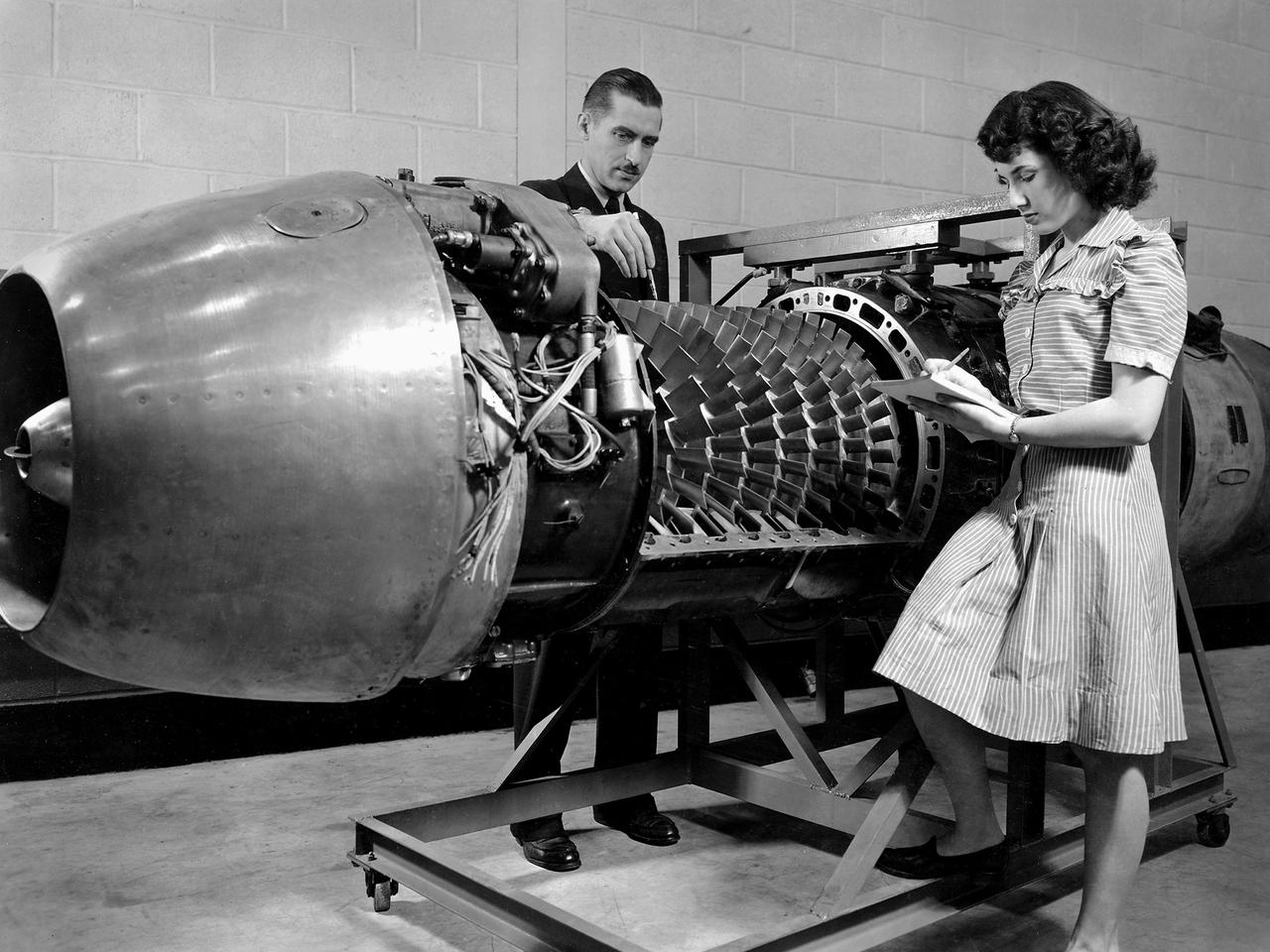

Researcher Robert Miller led an investigation into the combustor performance of a German Jumo 004 engine at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The Jumo 004 powered the world's first operational jet fighter, the Messerschmitt Me 262, beginning in 1942. The Me 262 was the only jet aircraft used in combat during World War II. The eight-stage axial-flow compressor Jumo 004 produced 2000 pounds of thrust. The US Army Air Forces provided the NACA with a Jumo 004 engine in 1945 to study the compressor’s design and performance. Conveniently the engine’s designer Anselm Franz had recently arrived at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in nearby Dayton, Ohio as part of Project Paperclip. The Lewis researchers used a test rig in the Engine Research Building to analyze one of the six combustion chambers. It was difficult to isolate a single combustor’s performance when testing an entire engine. The combustion efficiency, outlet-temperature distribution, and total pressure drop were measured. The researchers determined the Jumo 004’s maximum performance was 5000 revolutions per minute at a 27,000 foot altitude and 11,000 revolutions per minute at a 45,000 foot altitude. The setup in this photograph was created for a tour of NACA Lewis by members of the Institute of Aeronautical Science on March 22, 1945.
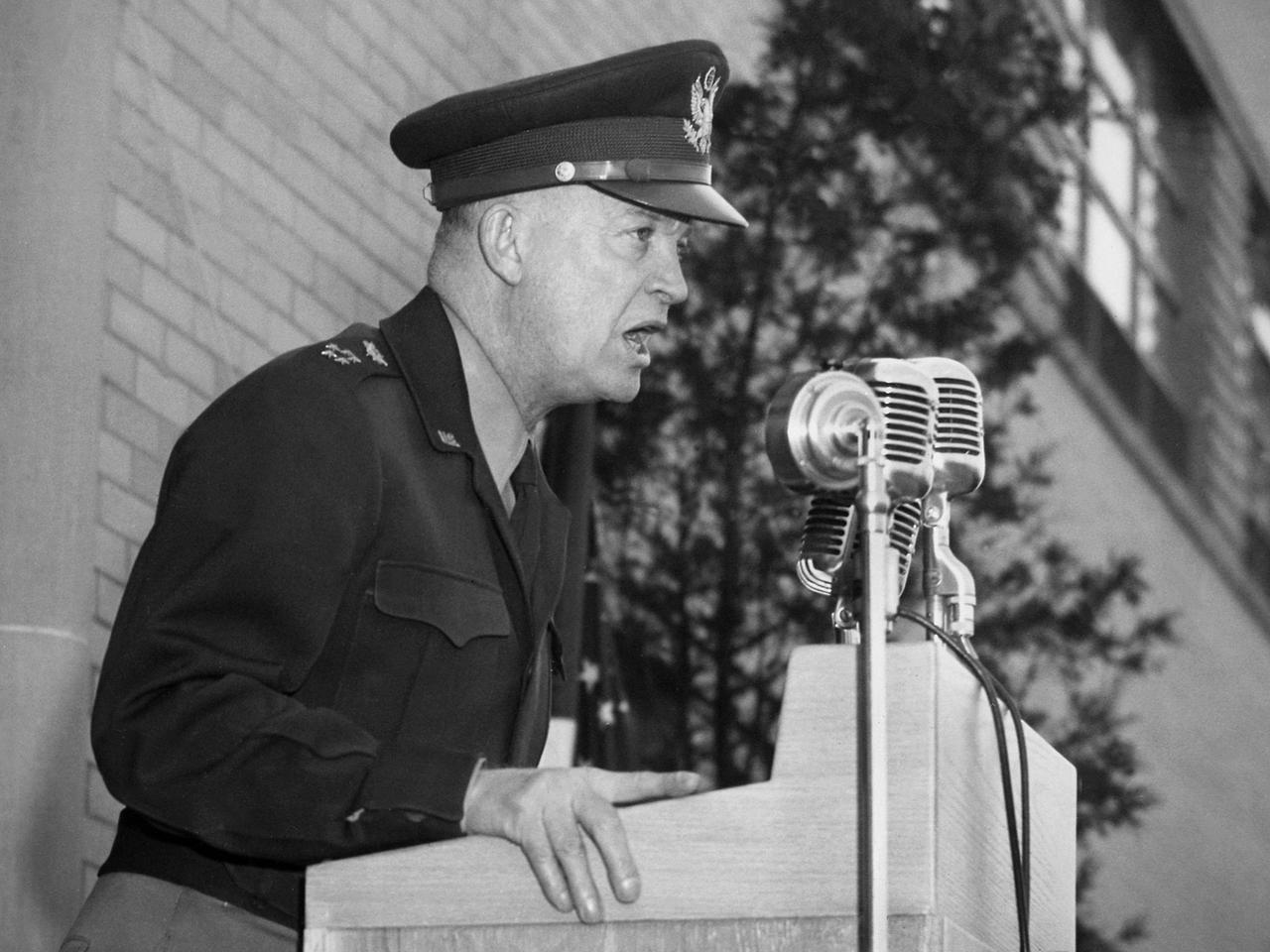

General Dwight Eisenhower addressed the staff of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory during an April 11, 1946 visit to Cleveland. The former supreme commander of Allied Expeditionary Forces in Europe was on a tour of several US cities in the months following the end of World War II. The general arrived in Cleveland on his Douglas C-54 Skymaster, the 'Sunflower II'. Eisenhower employed this aircraft while leading forces during the war. Skymasters, the military version of the DC–4 transport aircraft, were used extensively by both the army and navy throughout the war years. NACA Secretary John Victory, Lewis Director Raymond Sharp, and local politicians formally greeted Eisenhower as he deplaned at the NACA hangar. After patiently posing for the press photographers, Eisenhower accompanied Victory and Sharp to the Administration Building for a press conference. The general made a point of downplaying the prospects for another imminent war. Afterwards Eisenhower was given a tour of the laboratory and addressed the NACA Lewis staff assembled outside the Administration Building on the importance of research and development. Eisenhower left the laboratory in a motorcade for a banquet being held in his honor downtown with the Cleveland Aviation Club.
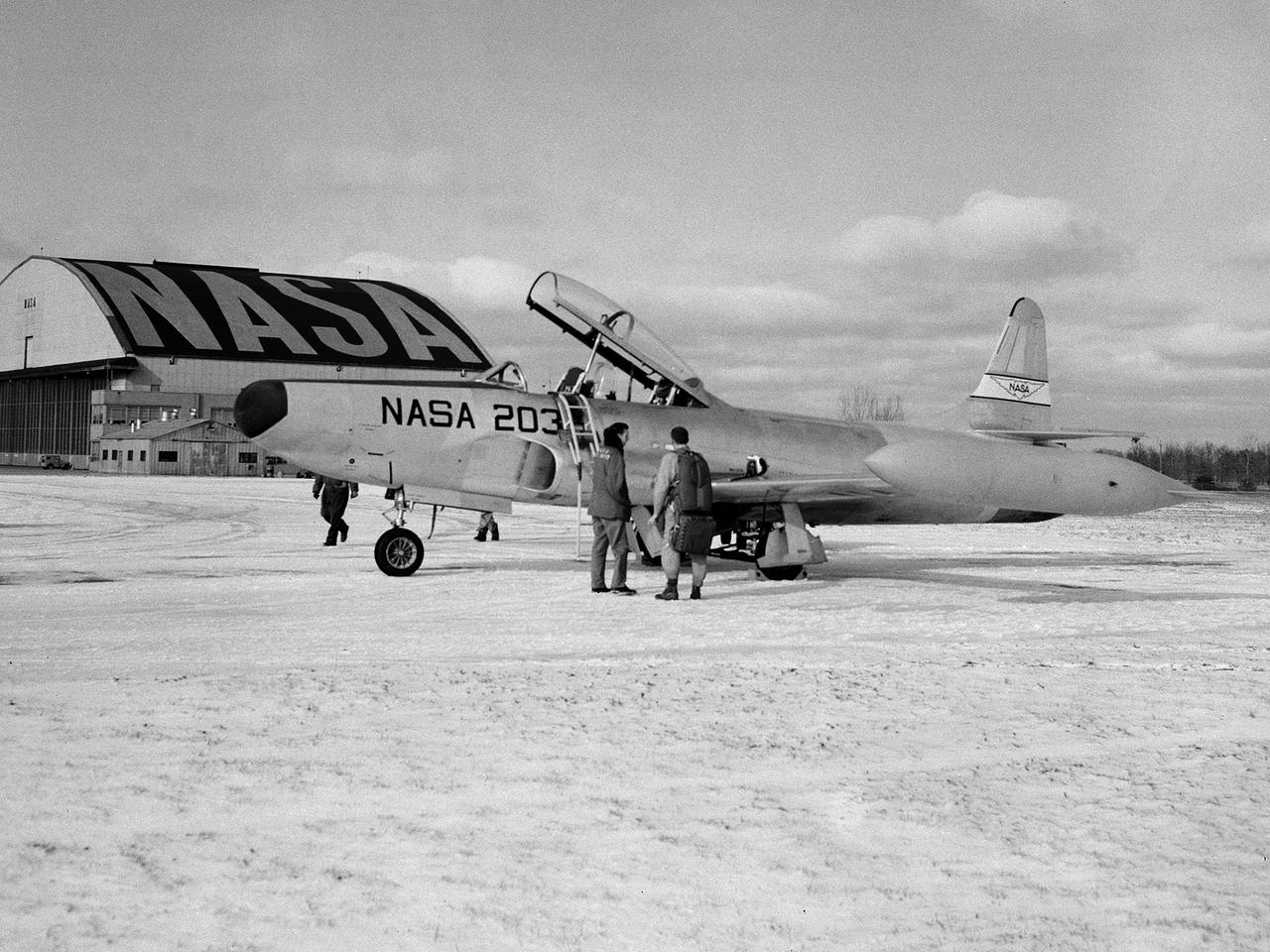

A Lockheed F-94B Starfire on the hangar apron at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio. The Air Force contracted Lockheed in November 1948 to create the new F-94s fighters. The first test flight occurred only months later in April 1949. This quick turnaround was due to the fact that the F-94 was based largely on the TF-80 fighter and constructed with parts from the P-80, including its two General Electric I-40 turbojet engines. The F-94Bs entered the Korean War in late 1951, but were initially prevented from flying over enemy territory due to fear that their fire control system would be copied by the enemy if an F-94B went down. The Starfire went on to perform scores of missions escorting B-29 and B-26 bombers deep into enemy territory and acting as interceptors against enemy fighters. In mid-1954 the F-94s were retired from active military service. Lewis acquired the F-94B Starfire in April 1956. At the time, the aircraft industry was preparing for the first use of jet engines for commercial aviation. The amount of noise generated by the engines was a major obstacle. Lewis undertook an extensive program to understand the causes of the noise and develop methods for reducing it. This program included the study of aerodynamic sound at high speed and altitude using the F-94B.
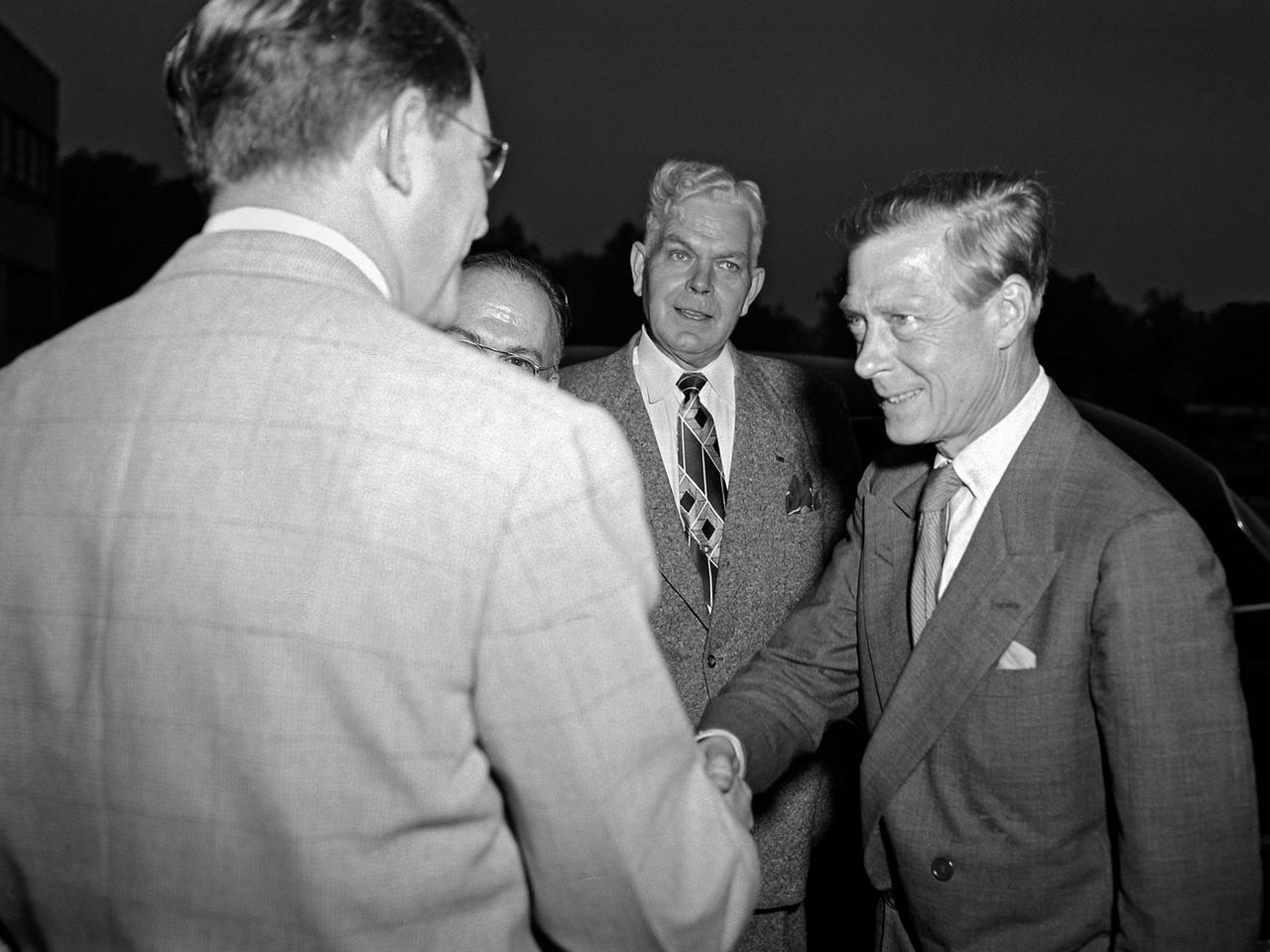

Edward Saxe-Coburg-Gotha, the Duke of Windsor, visits the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in Cleveland, Ohio. He is seen in this photograph shaking hands with Associate Director Abe Silverstein. Lewis Director Ray Sharp is in the background. Cleveland mayor Thomas Burke and other local officials were also on hand to greet Edward. Silverstein led the group on a tour of Lewis’ new 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel where the Duke inquired about the operation of the facility’s flexible walls, the types of components tested, and the generation of airflow. The Duke was in town in 1951 to promote his new autobiography, A King’s Story, at the American Booksellers Convention. Edward had assumed the British throne in January 1936, only to renounce the position less than a year later to controversially marry Wallis Simpson. Ongoing concerns over the couple’s relationship to the German government resulted in his World War II assignment to the Bahamas. Edward spent the remainder of his life in France.
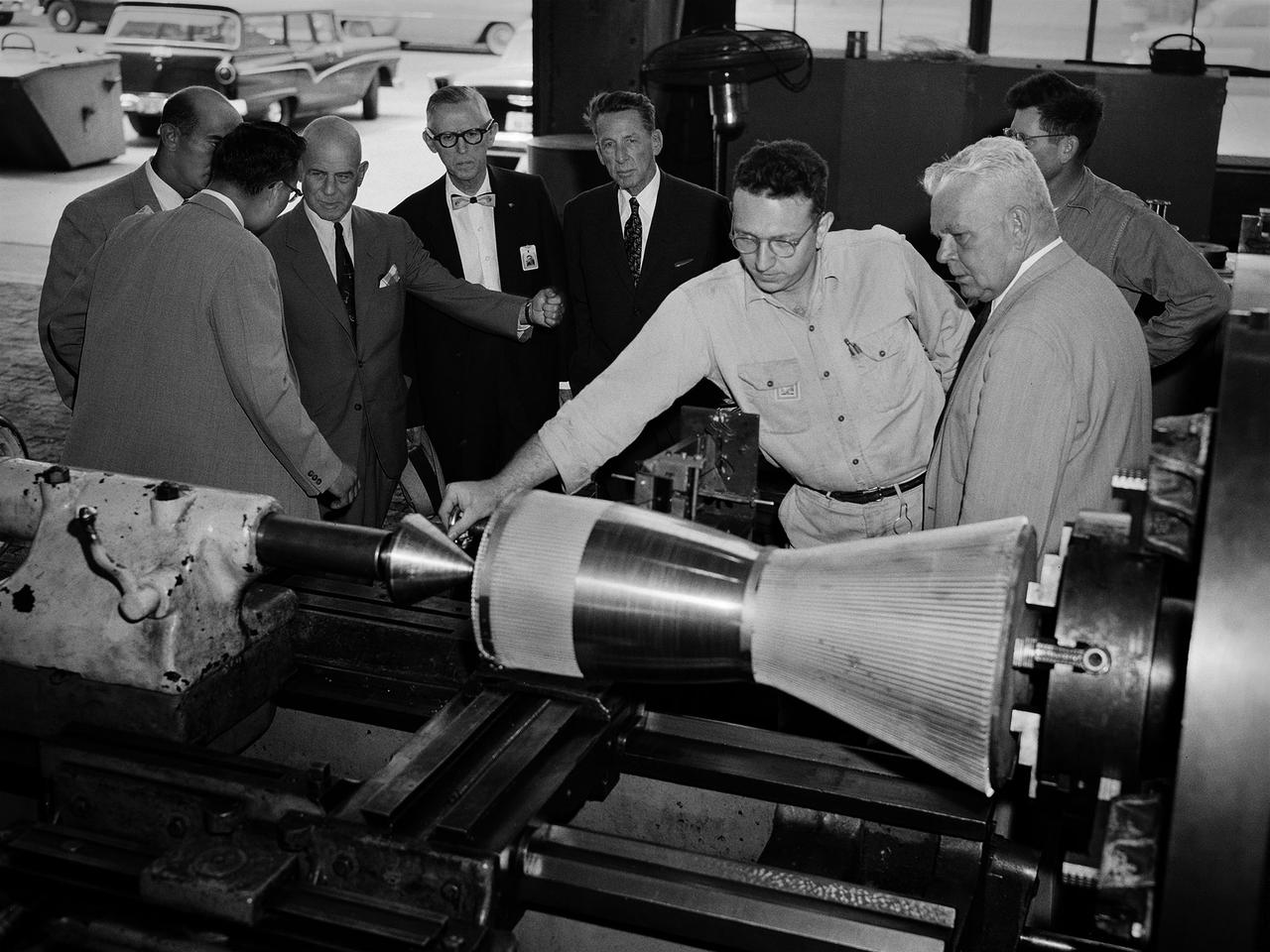

National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Chairman James Doolittle and Thompson Products Chairman of the Board Frederick Crawford receive a tour of the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory during the last few months of the NACA. Lewis mechanic Leonard Tesar demonstrates the machining of a 20,000-pound thrust rocket engine for the group in the Fabrication Shop. From left to right, Associate Director Eugene Manganiello, researcher Edward Baehr, Doolittle, NACA Executive Secretary John Victory, Crawford, Tesar, Lewis Director Raymond Sharp, and mechanic Curtis Strawn. Doolittle began his career as a test pilot and air racer. In 1942 he famously flew a B-25 Mitchell on a daring raid over Tokyo. Doolittle also worked with the aviation industry on the development of aircraft fuels and instrumentation. After the war he served as vice president of Shell Oil and as a key government advisor. In this capacity he also served on the NACA’s Executive Committee for a number of years and served as its Chairman in 1957 and 1958. Tesar was a supervisor at the Sheet Metal Shop in the Fabrication Building. He joined the laboratory in 1948 and enrolled in their Apprentice Program. He graduated from the school three years later as an aviation metalsmith. The Fabrication Branch created a wide variety of hardware for the laboratory’s research projects. Requests from research divisions ranged from sheetmetal manufacturing for aircraft to fabrication of rocket engines. Tesar retired in 1982 after 37 years of service.

Visit to GRC Lewis Field by Joshua Dobbs
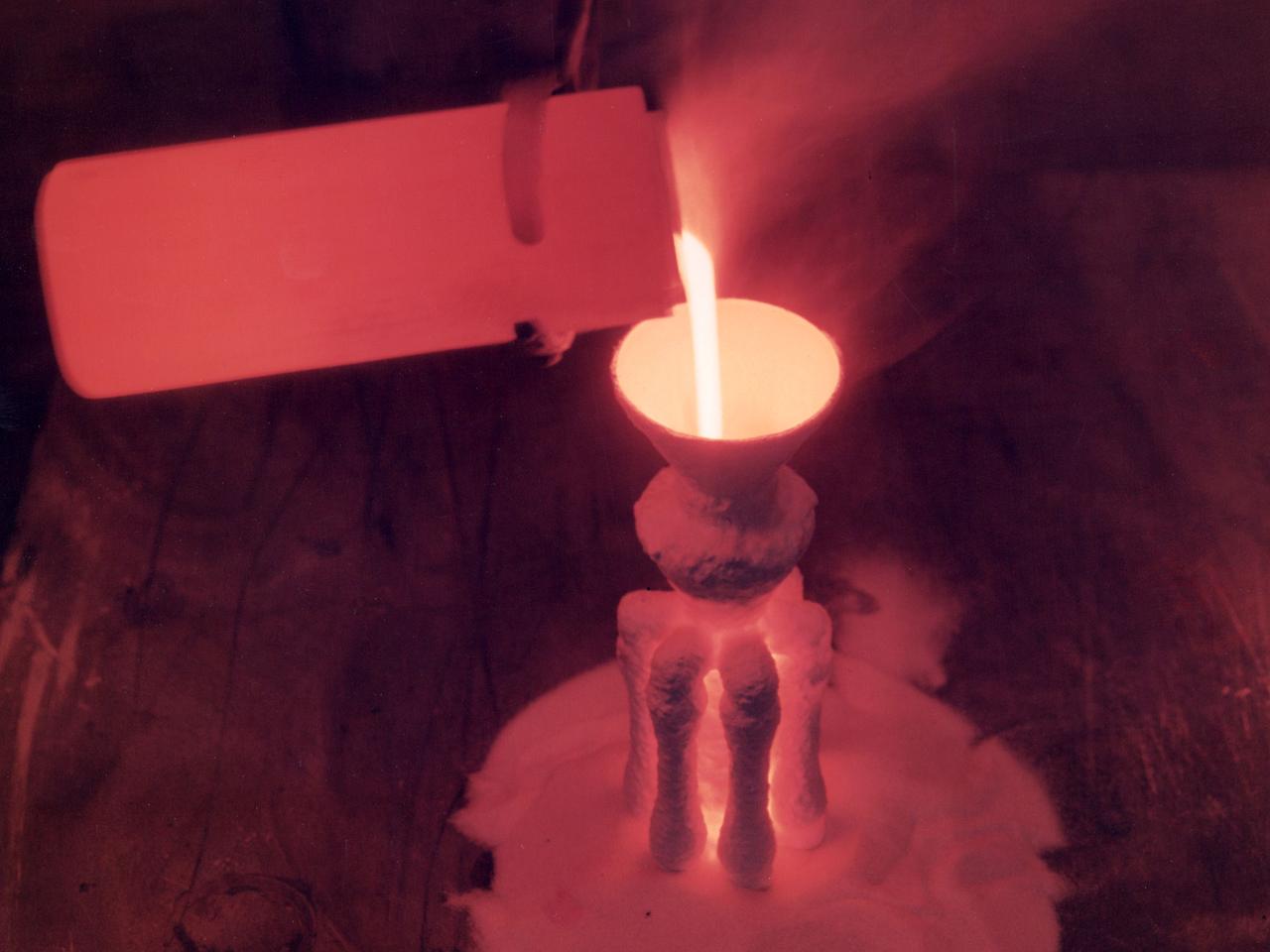

A nickel alloy developed at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center being poured in a shop inside the Technical Services Building. Materials technology is an important element in the successful development of both advanced airbreathing and rocket propulsion systems. An array of dependable materials is needed to build different types of engines for operation in diverse environments. NASA Lewis began investigating the characteristics of different materials shortly after World War II. In 1949 the materials research group was expanded into its own division. The Lewis researchers studied and tested materials in environments that simulated the environment in which they would operate. Lewis created two programs in the early 1960s to create materials for new airbreathing engines. One concentrated on high-temperature alloys and the other on cooling turbine blades. William Klopp, Peter Raffo, Lester Rubenstein, and Walter Witzke developed Tungsten RHC, the highest strength metal at temperatures over 3500⁰ F. The men received an IR-100 Award for their efforts. Similarly a cobalt-tungsten alloy was developed by the Fatigue and Alloys Research Branch. The result was a combination of high temperature strength and magnetic properties that were applicable for generator rotor application. John Freche invented and patented a nickel alloy while searching for high temperature metals for aerospace use. NASA agreed to a three-year deal which granted Union Carbide exclusive use of the new alloy before it became public property.
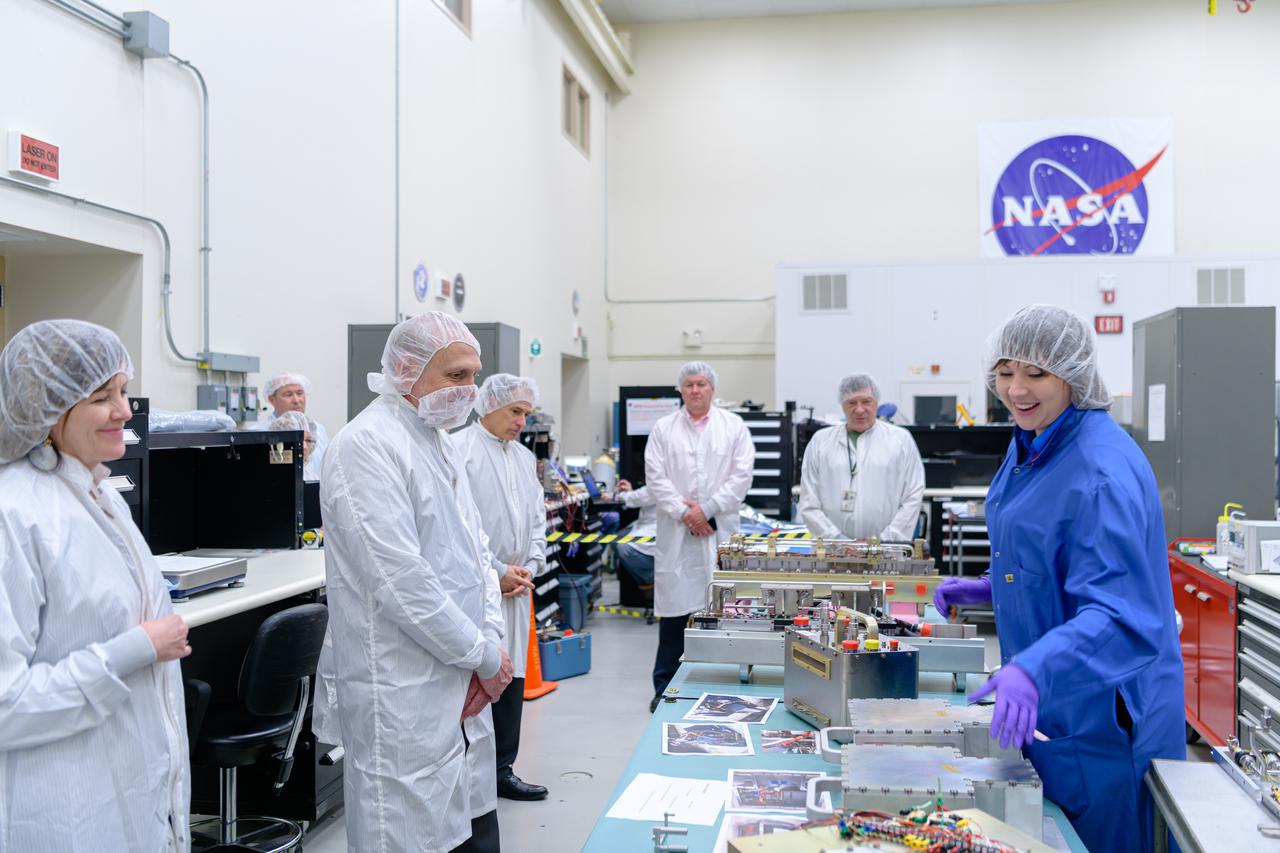

Visit to GRC Lewis Field by the Associate Administrator and Deputy Associate Administrator

The 1969 class of graduating apprentices pose for a group photograph during a rehearsal ceremony at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The 35 men completed four years of classroom and hands-on training in various aerospace research trades. Center Director Bruce Lundin and President of Cuyahoga Community College Dr. Bernard Silk addressed the graduates at the ceremony. The Ohio State Apprenticeship Council officially accredited them as journeymen. The journeymen specialized in one of the following fields: aerospace laboratory mechanic, aerospace service operator, experimental electronic equipment mechanic, experimental facilities electrician, experimental metal modelmaker, experimental metal worker, research equipment mechanic, research instrumentation mechanic, or utilities mechanic.
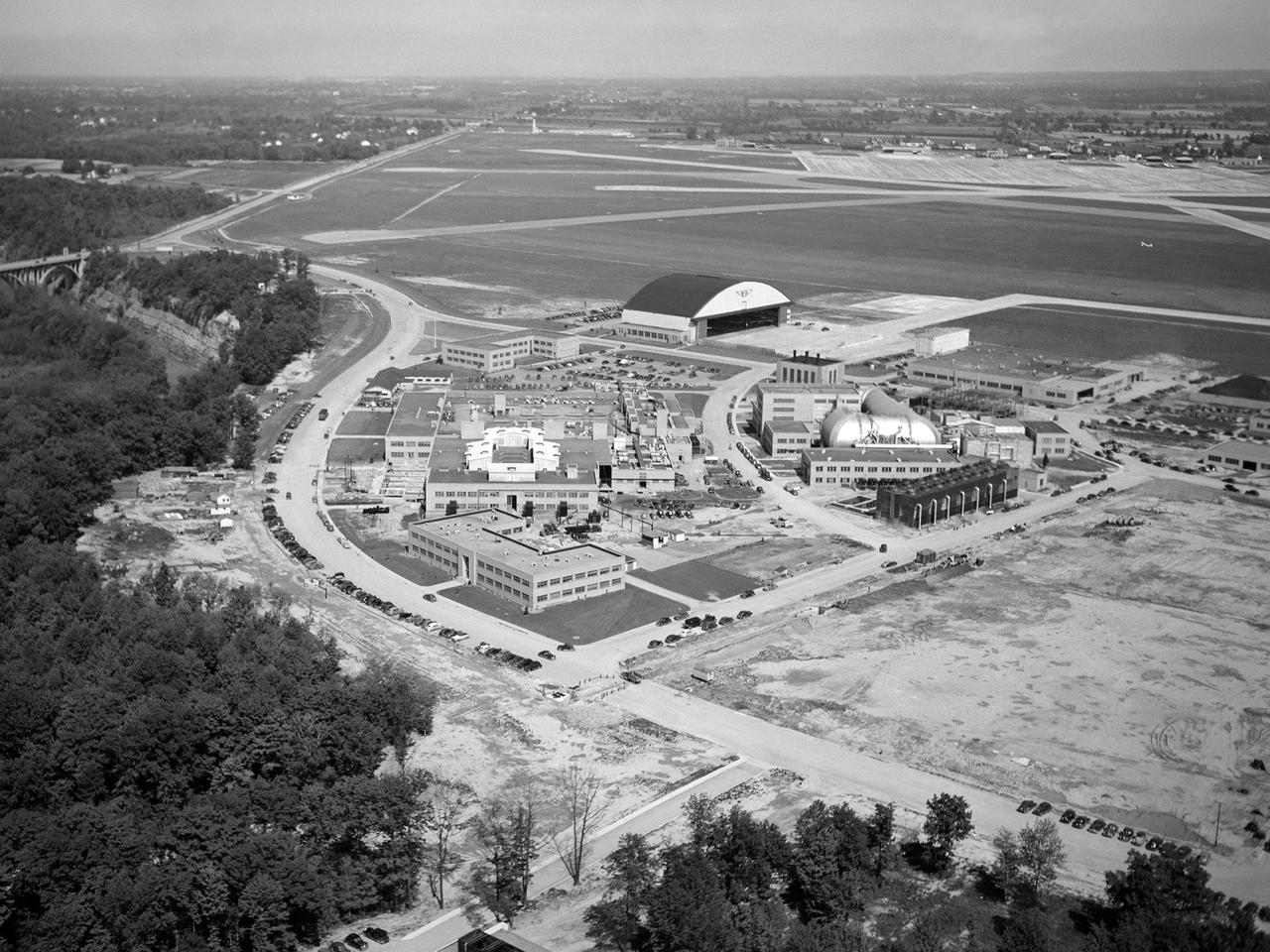

The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in Cleveland, Ohio as seen from the west in May 1946. The Cleveland Municipal Airport is located directly behind. The laboratory was built in the early 1940s to resolve problems associated with aircraft engines. The initial campus contained seven principal buildings: the Engine Research Building, hangar, Fuels and Lubricants Building, Administration Building, Engine Propeller Research Building, Altitude Wind Tunnel, and Icing Research Tunnel. These facilities and their associated support structures were located within an area occupying approximately one-third of the NACA’s property. After World War II ended, the NACA began adding new facilities to address different problems associated with the newer, more powerful engines and high speed flight. Between 1946 and 1955, four new world-class test facilities were built: the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel, the Propulsion Systems Laboratory, the Rocket Engine Test Facility, and the 10- by 10-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel. These large facilities occupied the remainder of the NACA’s semicircular property. The Lewis laboratory expanded again in the late 1950s and early 1960s as the space program commenced. Lewis purchased additional land in areas adjacent to the original laboratory and acquired a large 9000-acre site located 60 miles to the west in Sandusky, Ohio. The new site became known as Plum Brook Station.
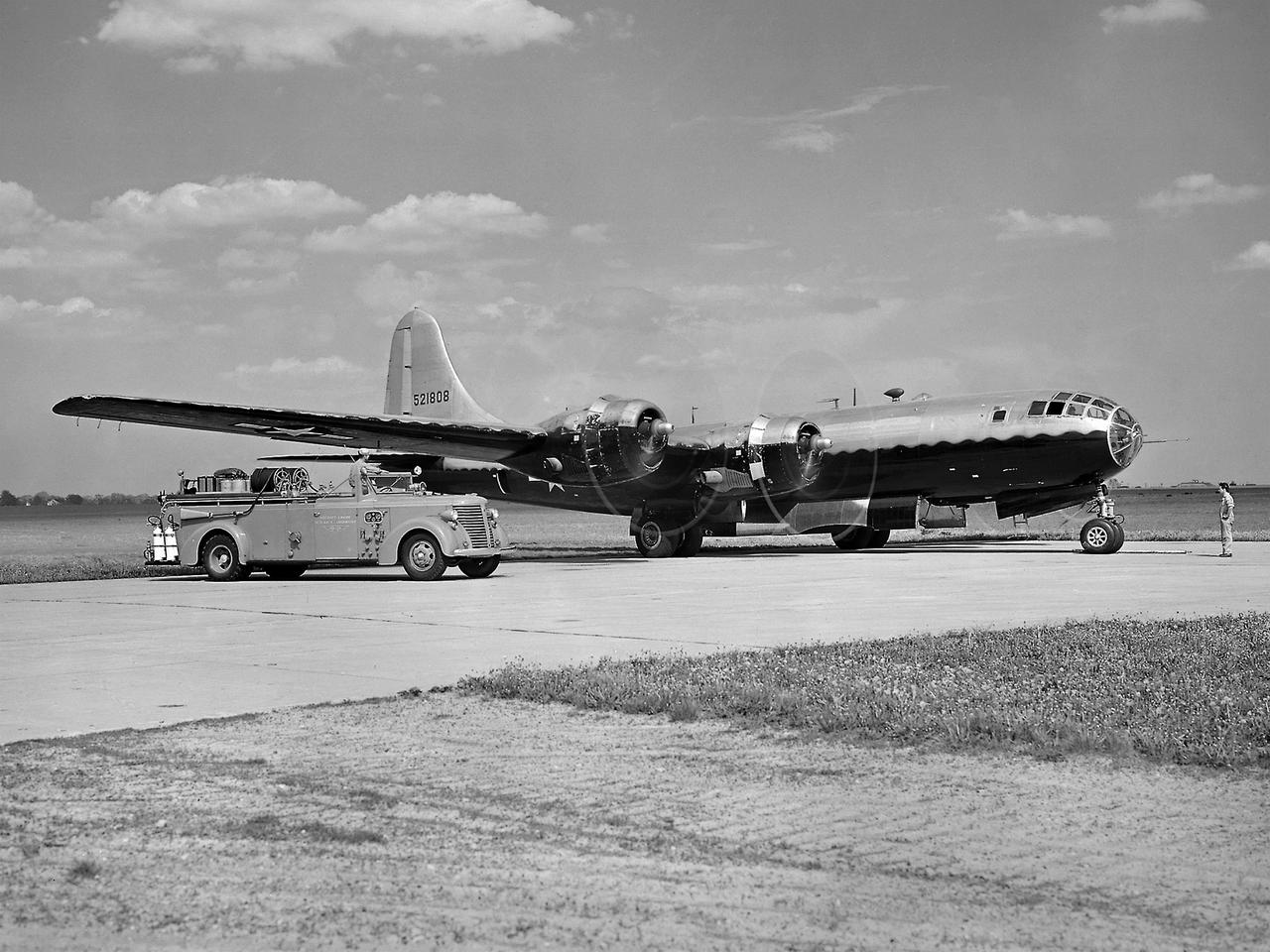

The NACA’s Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory used a Boeing B-29 Superfortress as a testbed for ramjet investigations in the late 1940s. NACA Lewis conducted a wide variety of studies on ramjets to determine basic operational data necessary to design missiles. This information included the relationship between combustion chamber and inlet pressure and temperature, velocity of the fuel-air ratio to the ignition characteristics, and combustion efficiency. Although wind tunnel and test stand studies were important first steps in determining these factors, actual flight tests were required. Lewis engineers modified the B-29 so that the ramjet could be stored in the bomb bay. Once the aircraft reached the desired altitude and speed the ramjet was suspended 52 inches below the bomb bay. The ramjet’s angle-of-attack could be independently adjusted, and a periscope permitted a view of the test article from inside the aircraft. Measurements were taken in free-stream conditions between 5,000 and 30,000 feet. The test flights, which began in April 1947, were flown at speeds up to Mach 0.51 and altitudes of 5,000 to 30,000 feet. The researchers first determined that 14,000 feet was the maximum altitude at which the engine could be ignited by spark. Flares were used to start the engine at altitudes up to 30,000 feet. Overall the ramjet operated well at all speeds and altitudes. Significant changes in fuel flow were successful at lower altitudes, but produced combustion blowout above 20,000 feet.

Dr. Igor Sikorsky, fourth from the left, visits the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in Cleveland, Ohio. The legendary Russian-born aviation pioneer visited NACA Lewis several times during the 1940s and 1950s. In 1946 Sikorsky arrived at Lewis for the 1946 National Air Races, which included demonstrations by five of his helicopters. NACA flight mechanic Joseph Sikosky personally escorted Sikorsky during the visit. Sikorsky frequently addressed local professional organizations, such as the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, during his visits. Sikorsky built and flew the first multi-engine aircraft as a youth in Russia. In his mid-20s Sikorsky designed and oversaw the manufacturing of 75 four-engine bombers. During the Bolshevik Revolution he fled to New York City where he worked jobs outside of aviation. In 1923 Sikorsky obtained funding to build a twin-engine water aircraft. This aircraft was the first US twin-engine flying machine and a world-wide success. In 1939 Sikorsky designed the first successful US helicopter. He then put all of his efforts into helicopters, and built some of the most successful helicopters in use today. Sikorsky passed away in 1972. From left to right: unknown; John Collins, Chief of the Engine Performance and Materials Division; Abe Silverstein, Chief of Research; Sikorsky; lab Director Ray Sharp; and Executive Officer Robert Sessions.
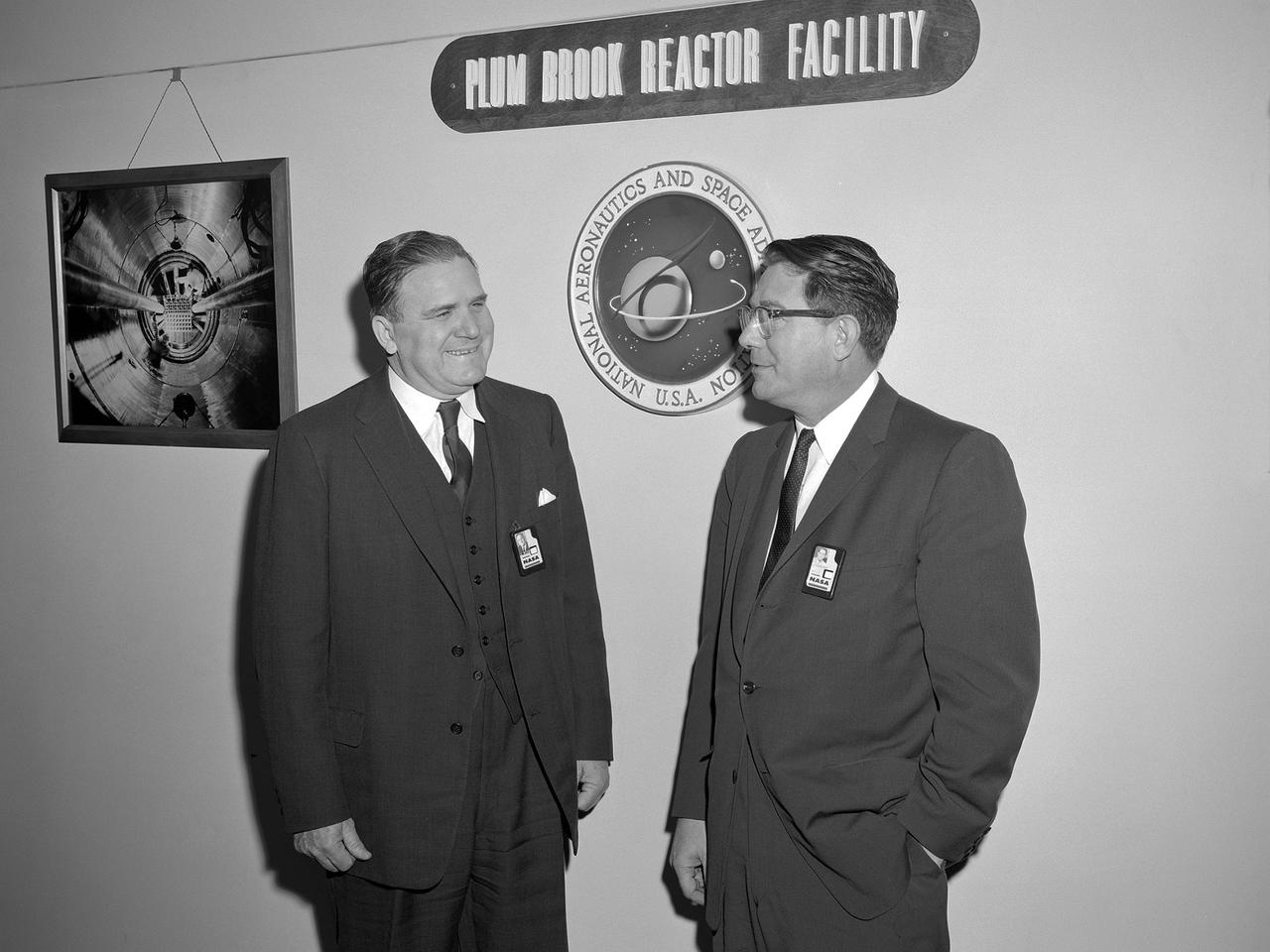

National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Administrator James Webb toured the new Plum Brook Reactor Facility in December 1961 with Abe Silverstein, the newly appointed Director of the Lewis Research Center. The 60-megawatt test reactor was built on 500 acres of the former Plum Brook Ordnance Works in Sandusky, Ohio. After nearly five years of construction, the facility went critical for the first time in June 1961. In late 1957 Hugh Dryden requested Silverstein’s assistance in creating the new space agency. After several months of commuting, Silverstein transferred to Headquarters in May 1958. Silverstein was a critical member of a team that devised a fiscal year 1960 budget and began planning missions. When NASA officially began operation on October 1, 1958, Silverstein was third in command. He directed mission planning, spacecraft design, launch operations, manned space missions, and unmanned probes. James Webb, named NASA administrator on January 7, 1961, sought to have those working on Apollo at the NASA centers report to a new Headquarters program office, not to the head of the Apollo Program. Silverstein requested to be appointed to the vacant center director position in Cleveland. He officially returned as director of the Lewis Research Center on November 1, 1961.

A researcher examines a model being installed in the test section of the 10- by 10-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel during the 1957 Inspection of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The NACA held its annual Inspection at one of its three research laboratories. Representatives from the military, aeronautical industry, universities, and the press were invited to the laboratory to be briefed on the NACA’s latest research efforts and tour the state- of- the- art test facilities. Over 1700 people visited the NACA Lewis in Cleveland, Ohio during the October 7 - 10, 1957 Inspection. NACA researchers Leonard Obery, seen here, James Connors, Leonard, Stitt, David Bowditch gave presentations on high Mach number turbojets at the 10- by 10 tunnel. It had been only 15 years since a jet aircraft had first flown in the US. Since then the sound barrier had been broken and speeds of Mach 2.5 had been achieved. In the late 1950s NACA researchers sought to create an engine that could achieve Mach 4. This type of engine would require an extremely long inlet and nozzle which would have to be capable of adjusting their diameter for different speeds. A Mach 4 engine would require new composite materials to withstand the severe conditions, modified airframes to hold the longer engines, and high temperature seals and lubricants. The 10- by 10-foot tunnel, which had only been in operation for a year and a half, would play a critical role in these studies. NACA researchers at other facilities discussed high energy aircraft fuels and rocket propellants, aircraft noise reduction, hypersonic flight, nuclear propulsion, and high temperature materials.

Raymond Lewis, son-in-law of Mary W. Jackson, takes a picture of the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters sign following a ceremony officially naming the building, Friday, Feb. 26, 2021, at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. Mary W. Jackson, the first African American female engineer at NASA, began her career with the agency in the segregated West Area Computing Unit of NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. The mathematician and aerospace engineer went on to lead programs influencing the hiring and promotion of women in NASA's science, technology, engineering, and mathematics careers. In 2019, she posthumously received the Congressional Gold Medal. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
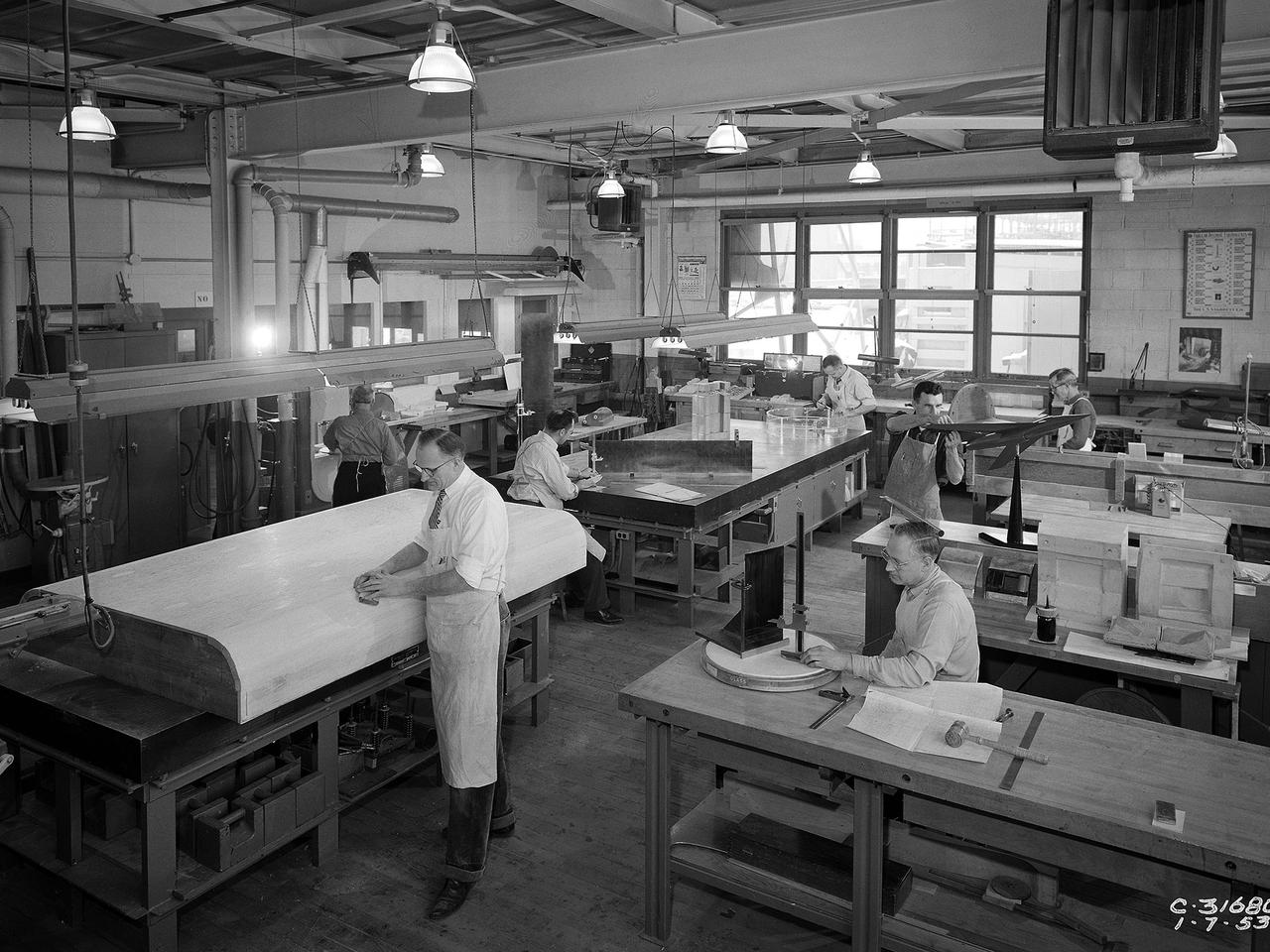

Craftsmen work in the wood model shop at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The Fabrication Division created almost all of the equipment and models used at the laboratory. The Fabrication Shop building contained a number of specialized shops in the 1940s and 1950s. These included a Machine Shop, Sheet Metal Shop, Wood Model and Pattern Shop, Instrument Shop, Thermocouple Shop, Heat Treating Shop, Metallurgical Laboratory, and Fabrication Office. The Wood Model and Pattern Shop created everything from control panels and cabinets to aircraft models molds for sheet metal work.
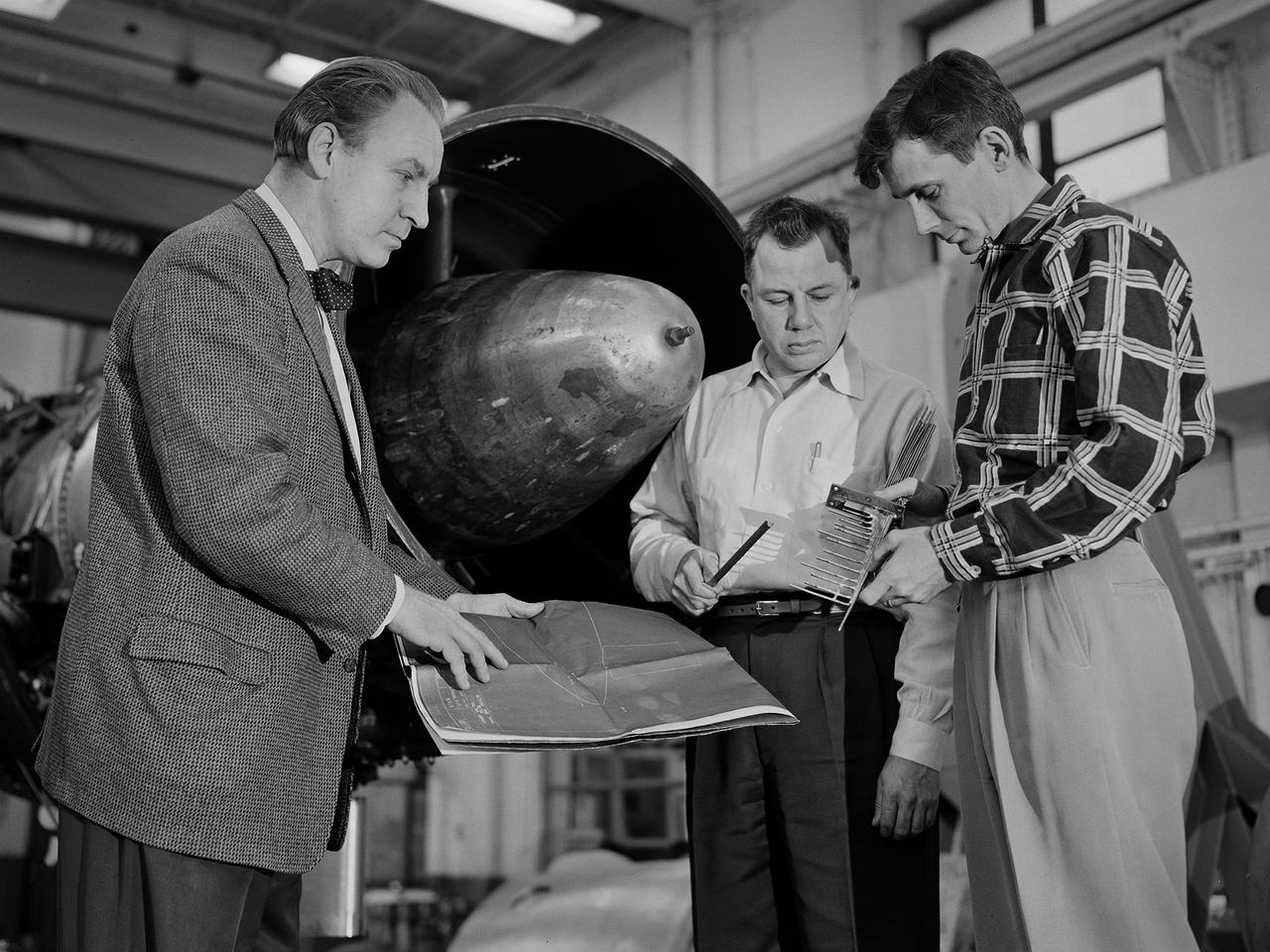

Researcher Bill Reiwaldt discusses the preparations for a test in the Altitude Wind Tunnel with technicians Jack Wagner and Dick Golladay at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. Research engineers developed ideas for tests that were often in response to requests from the military or aircraft industry. Arrangements were made to obtain an engine for the study and to transport it to the Cleveland laboratory. The engine was brought into the facility’s shop area, where it was readied for investigation. It was common for several different engines to be worked on simultaneously in the shop. The researcher would discuss the engine and the test objectives with the Test Installation Division and the facility’s technicians. The operations team would handle the installation of the instrumentation and fitting the test into the facility’s schedule. Upon completion of the previous test, the engine was removed. The next engine was lifted by an overhead crane and transported from the shop to the test section. The engine was connected to the measurement devices and fuel and oil supply lines. Engines were tested over numerous runs under varying conditions and with variations on the configuration. The findings and test procedure were then described in research or technical memorandums and distributed to industry.
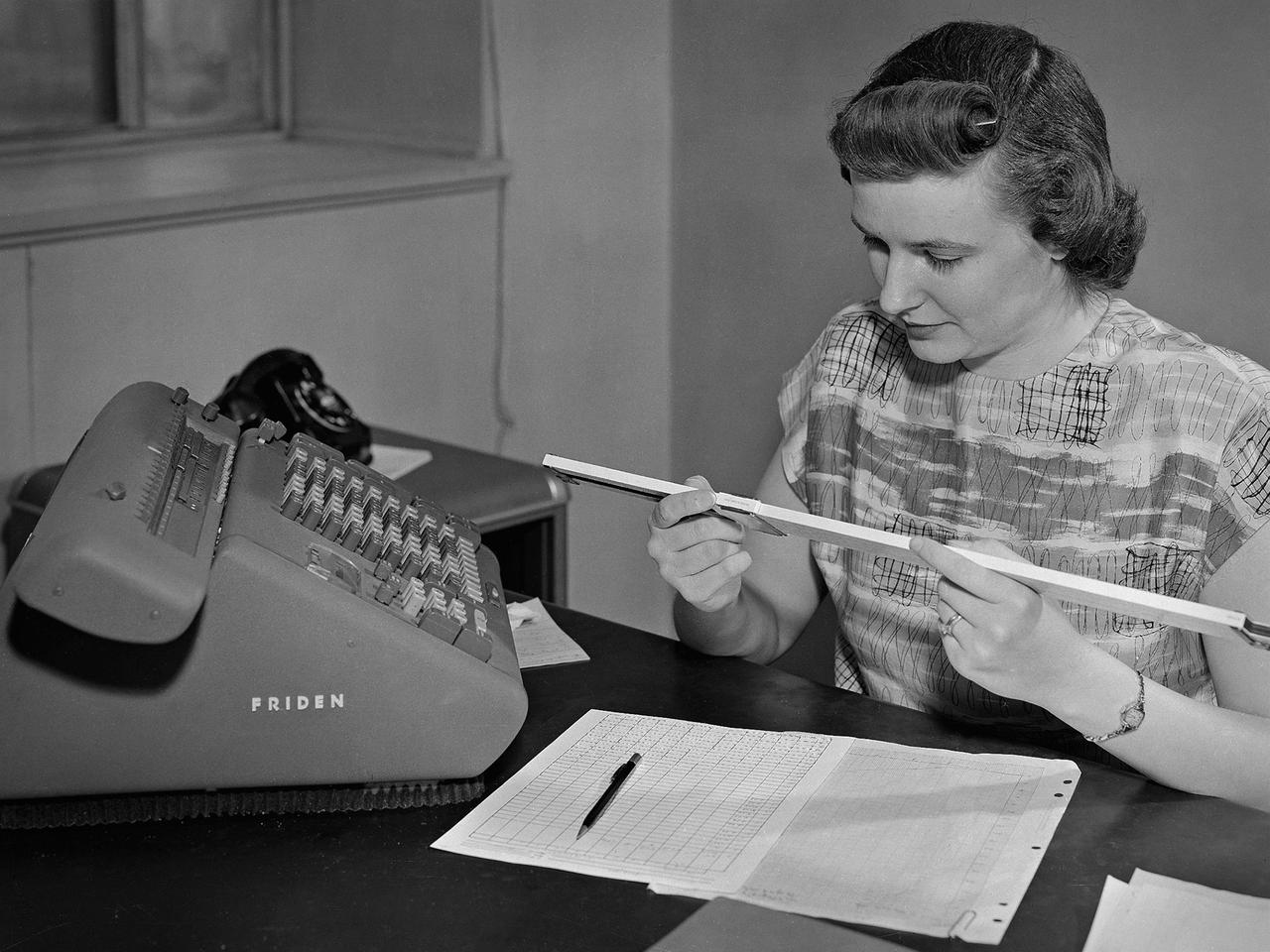

A female computer at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory with a slide rule and Friden adding machine to make computations. The computer staff was introduced during World War II to relieve short-handed research engineers of some of the tedious computational work. The Computing Section was staffed by “computers,” young female employees, who often worked overnight when most of the tests were run. The computers obtained test data from the manometers and other instruments, made the initial computations, and plotted the data graphically. Researchers then analyzed the data and summarized the findings in a report or made modifications and ran the test again. There were over 400 female employees at the laboratory in 1944, including 100 computers. The use of computers was originally planned only for the duration of the war. The system was so successful that it was extended into the 1960s. The computers and analysts were located in the Altitude Wind Tunnel Shop and Office Building office wing during the 1940s and transferred to the new 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel in 1948.
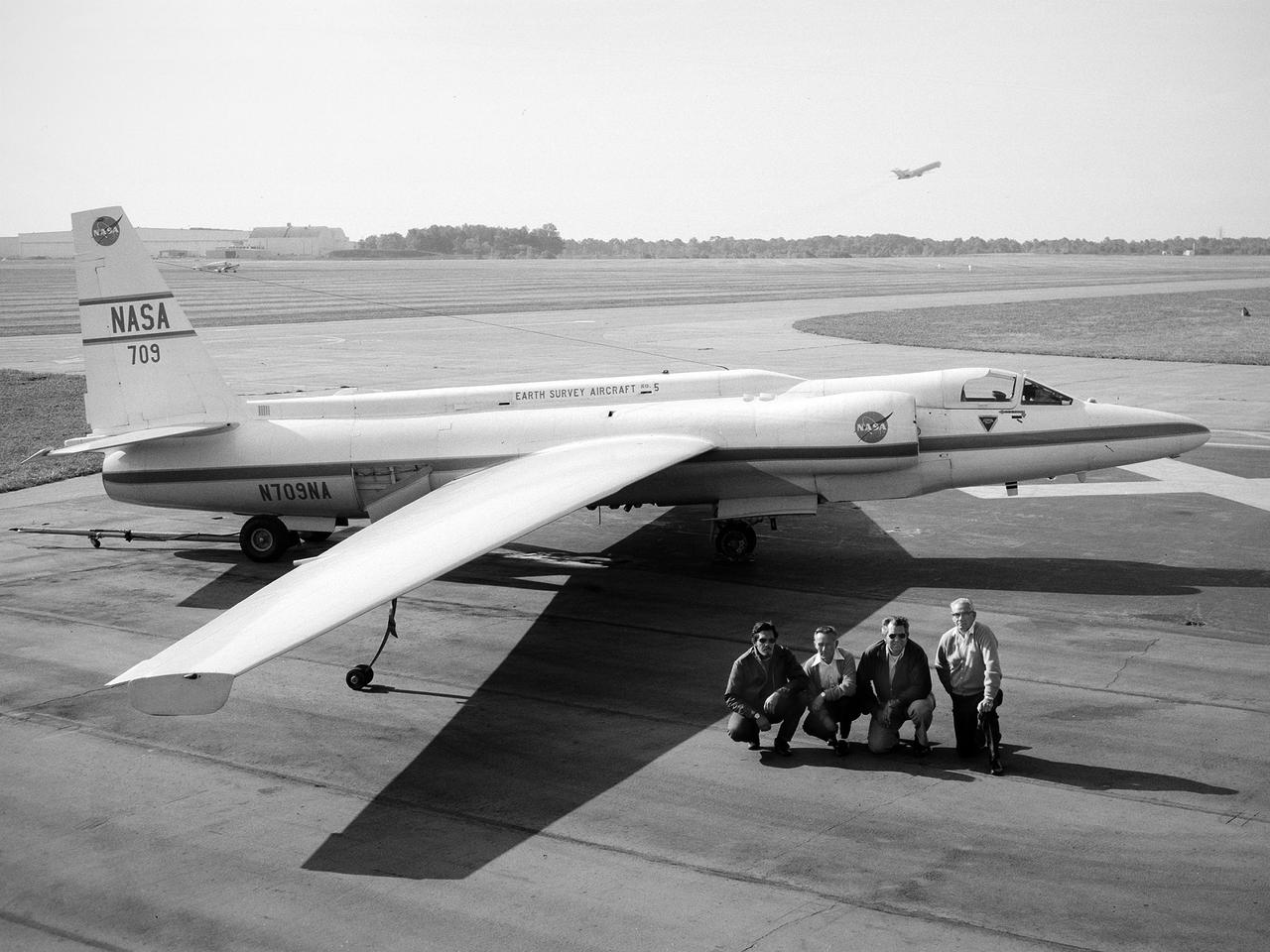

A National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lockheed U-2 aircraft on display at the 1973 Inspection of the Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio. Lockheed developed the U-2 as a high-altitude reconnaissance aircraft in the early 1950s before satellites were available. The U-2 could cruise over enemy territory at 70,000 feet and remain impervious to ground fire, interceptor aircraft, and even radar. An advanced camera system was designed specifically for the aircraft. The pilot is required to use a pressure suit similar to those worn by astronauts. NASA’s Ames Research Center received two U-2 aircraft in April 1971 to conduct high-altitude research. They were used to study and monitor various Earth resources, celestial bodies, atmospheric chemistry, and oceanic processes. NASA replaced its U-2s with ER-2 aircraft in 1981 and 1989. The ER-2s were designed to carry up to 2600 pounds of scientific equipment. The ER-2 program was transferred to Dryden Flight Research Center in 1997. Since the inaugural flight for this program on August 31, 1971, NASA’s U-2 and ER-2 aircraft have flown more than 4500 data missions and test flights for NASA, other federal agencies, states, universities, and the private sector.
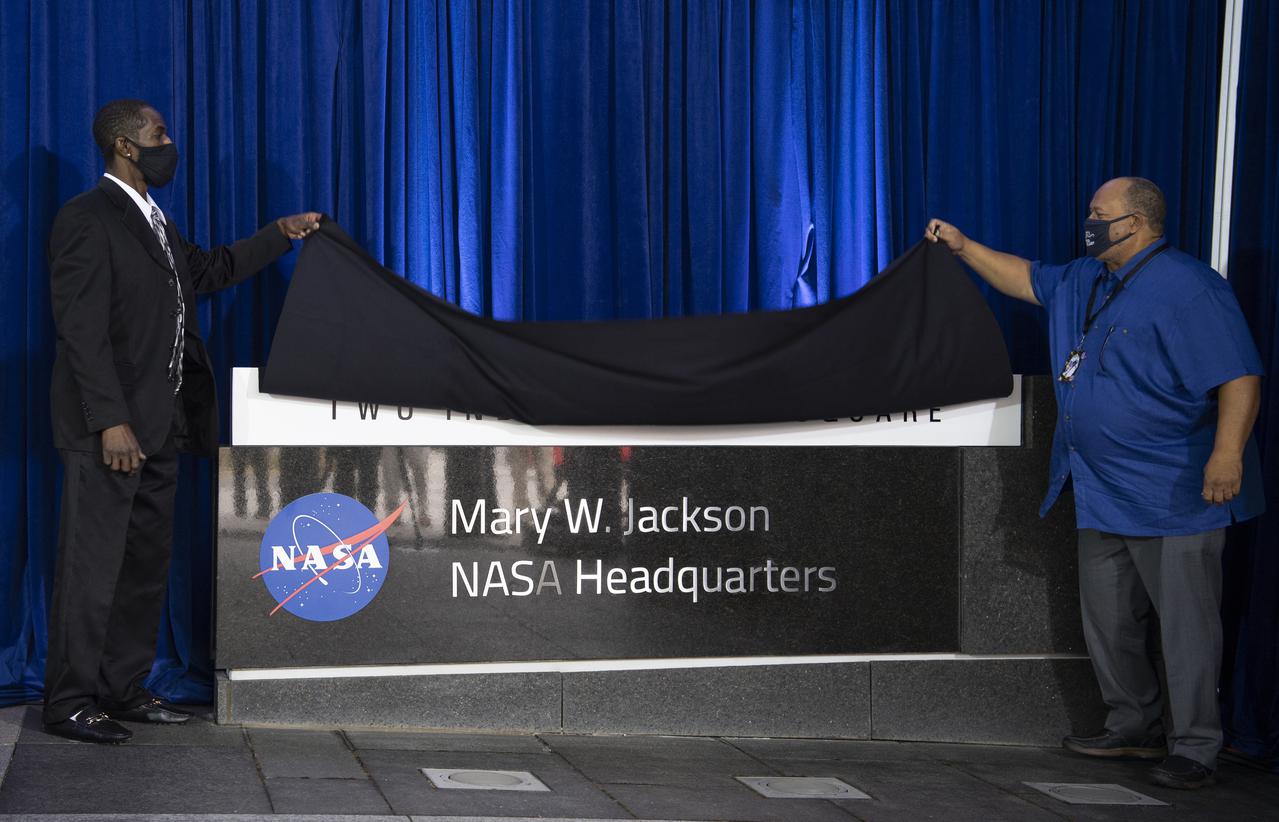

Bryan Jackson, grandson of Mary W. Jackson, left, and Raymond Lewis, son-in-law of Mary W. Jackson, right, unveil the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters sign during a ceremony officially naming the building, Friday, Feb. 26, 2021, at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. Mary W. Jackson, the first African American female engineer at NASA, began her career with the agency in the segregated West Area Computing Unit of NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. The mathematician and aerospace engineer went on to lead programs influencing the hiring and promotion of women in NASA's science, technology, engineering, and mathematics careers. In 2019, she posthumously received the Congressional Gold Medal. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
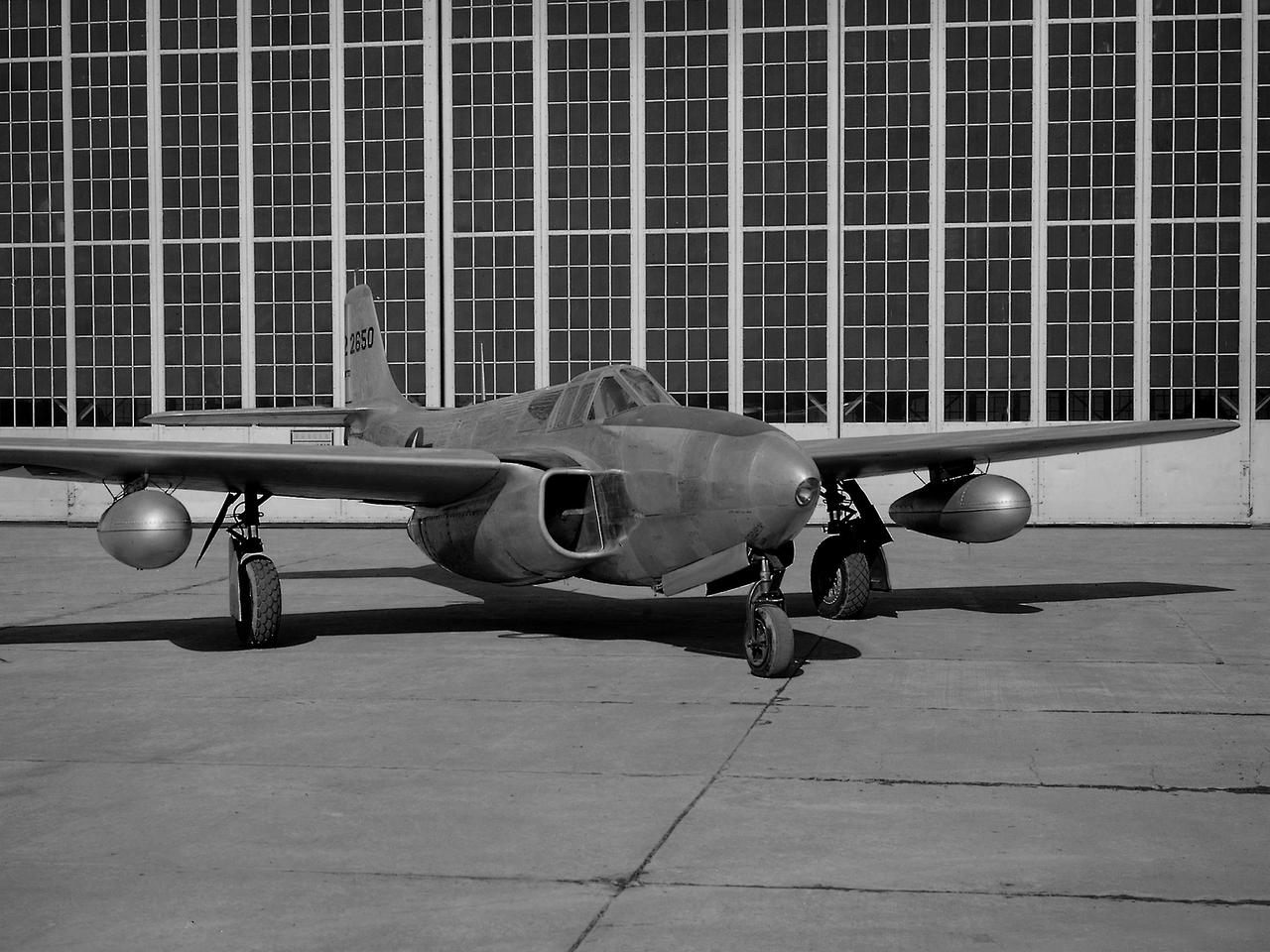

A Bell P-59B Airacomet sits beside the hangar at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. In 1942 the Bell XP-59A Airacomet became the first jet aircraft in the US. The Airacomet incorporated centrifugal turbojet engines that were based on British plans secretly brought to the US in 1941. A Bell test pilot flew the XP-59A for the first time at Muroc Lake, California in October 1942. The General Electric I-16 engines proved to be problematic. In an effort to increase the engine performance, an Airacomet was secretly brought to Cleveland in early 1944 for testing in the Altitude Wind Tunnel. A series of tunnel investigations in February and March resulted in a 25-percent increase in the I-16 engine’s performance. Nonetheless, Bell’s 66 Airacomets never made it into combat. A second, slightly improved Airacomet, a P-59B, was transferred to NACA Lewis just after the war in September 1945. The P-59B was used over the next three years to study general jet thrust performance and thrust augmentation devices such as afterburners and water/alcohol injection. The P-59B flights determined the proper alcohol and water mixture and injection rate to produce a 21-percent increase in thrust. Since the extra boost would be most useful for takeoffs, a series of ground-based tests with the aircraft ensued. It was determined that the runway length for takeoffs could be reduced by as much as 15 percent. The P-59B used for the tests is now on display at the Air Force Museum at Wright Patterson.
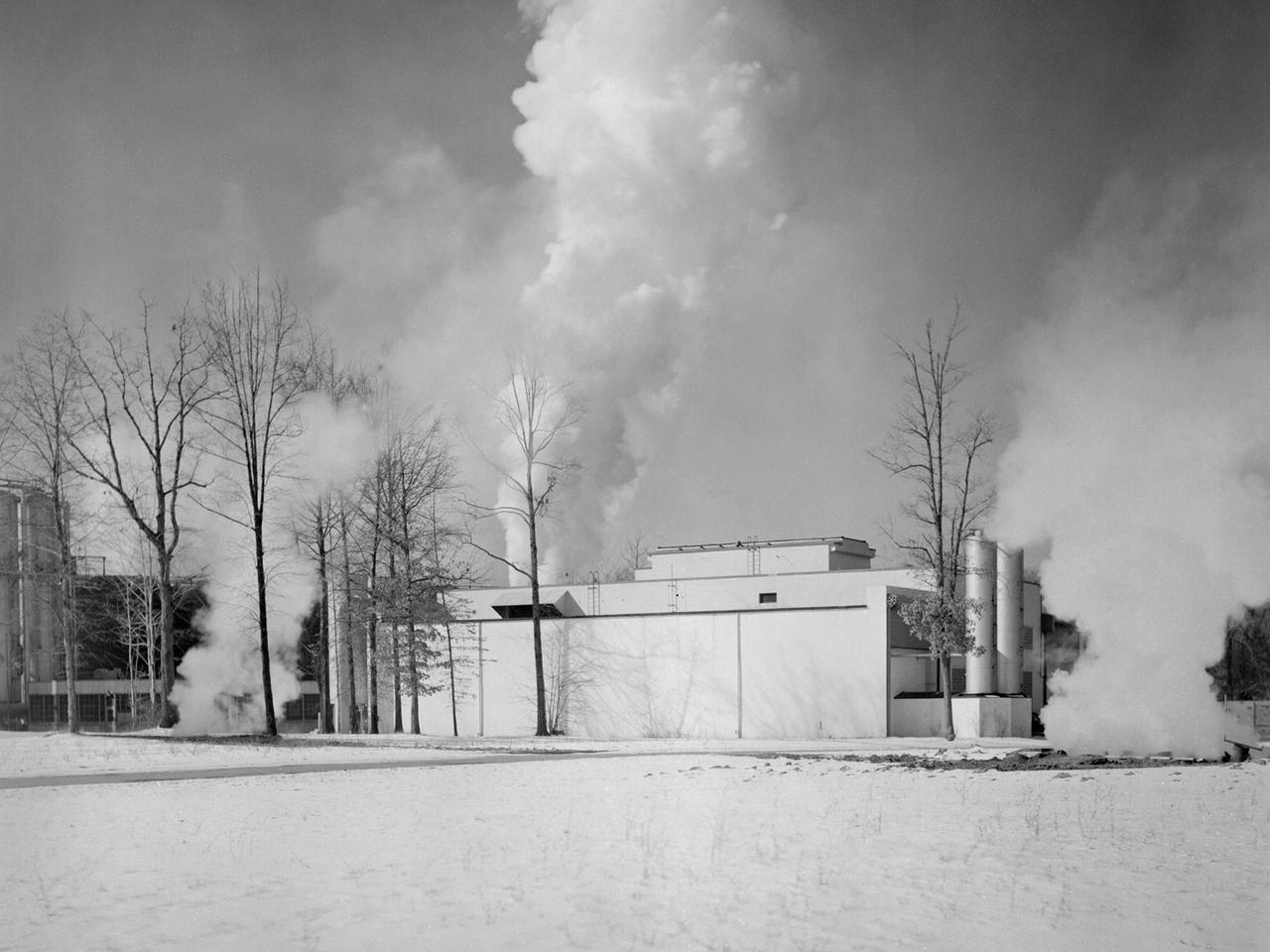

The Engine Propeller Research Building, referred to as the Prop House, emits steam from its acoustic silencers at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. In 1942 the Prop House became the first completed test facility at the new NACA laboratory in Cleveland, Ohio. It contained four test cells designed to study large reciprocating engines. After World War II, the facility was modified to study turbojet engines. Two of the test cells were divided into smaller test chambers, resulting in a total of six engine stands. During this period the NACA Lewis Materials and Thermodynamics Division used four of the test cells to investigate jet engines constructed with alloys and other high temperature materials. The researchers operated the engines at higher temperatures to study stress, fatigue, rupture, and thermal shock. The Compressor and Turbine Division utilized another test cell to study a NACA-designed compressor installed on a full-scale engine. This design sought to increase engine thrust by increasing its airflow capacity. The higher stage pressure ratio resulted in a reduction of the number of required compressor stages. The last test cell was used at the time by the Engine Research Division to study the effect of high inlet densities on a jet engine. Within a couple years of this photograph the Prop House was significantly altered again. By 1960 the facility was renamed the Electric Propulsion Research Building to better describe its new role in electric propulsion.

A mechanic works on a General Electric I-40 turbojet at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The military selected General Electric’s West Lynn facility in 1941 to secretly replicate the centrifugal turbojet engine designed by British engineer Frank Whittle. General Electric’s first attempt, the I-A, was fraught with problems. The design was improved somewhat with the subsequent I-16 engine. It was not until the engine's next reincarnation as the I-40 in 1943 that General Electric’s efforts paid off. The 4000-pound thrust I-40 was incorporated into the Lockheed Shooting Star airframe and successfully flown in June 1944. The Shooting Star became the US’s first successful jet aircraft and the first US aircraft to reach 500 miles per hour. The NACA’s Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory studied all of General Electric’s centrifugal turbojets both during World War II and afterwards. The entire Shooting Star aircraft was investigated in the Altitude Wind Tunnel during 1945. The researchers studied the engine compressor performance, thrust augmentation using a water injection, and compared different fuel blends in a single combustor. The mechanic in this photograph is inserting a combustion liner into one of the 14 combustor cans. The compressor, which is not yet installed in this photograph, pushed high pressure air into these combustors. There the air mixed with the fuel and was heated. The hot air was then forced through a rotating turbine that powered the engine before being expelled out the nozzle to produce thrust.
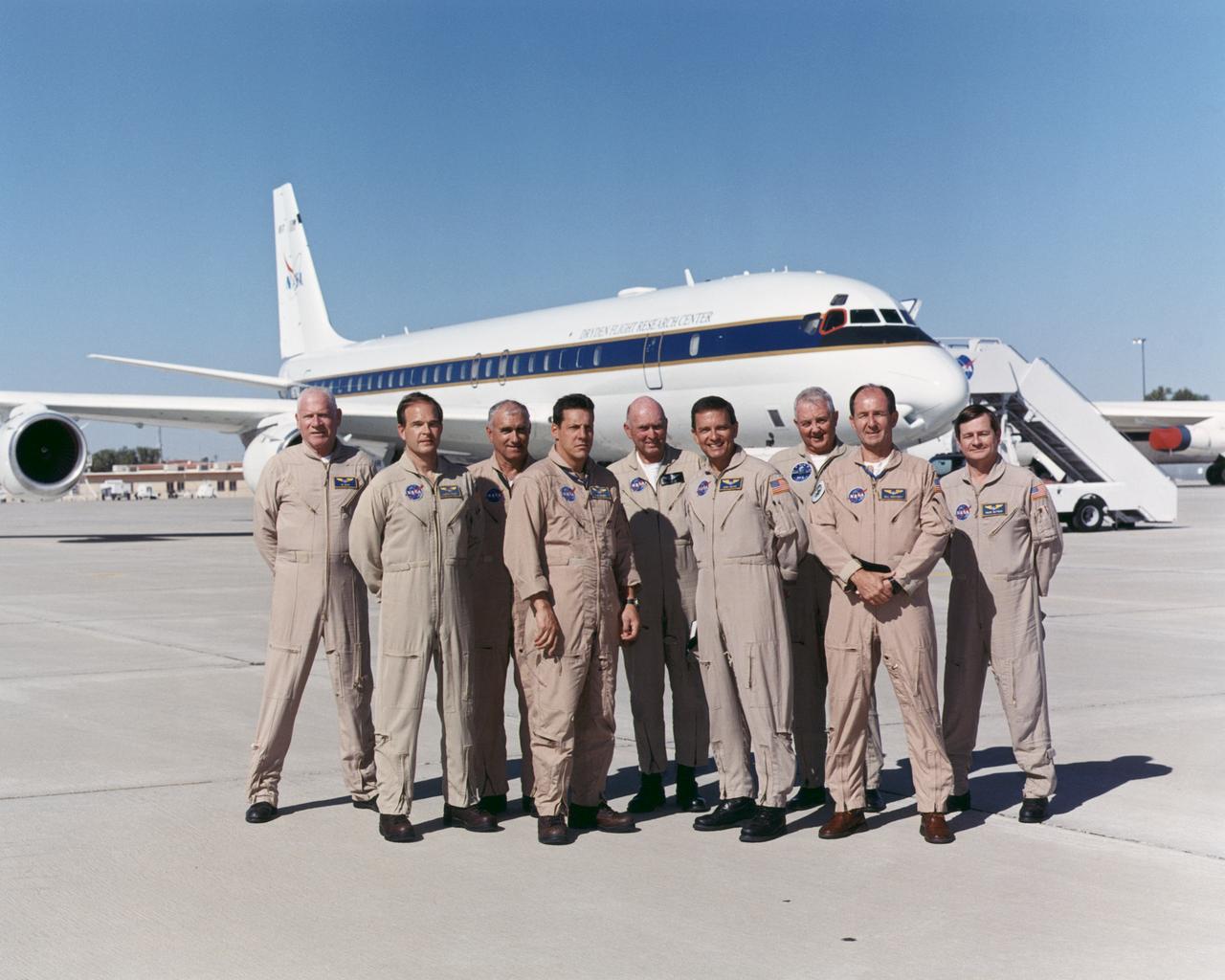

2004 NASA Dryden DC-8 flight crew. Left to Right: Edwin W. Lewis, Jr., Martin J. Trout, Richard G. Ewers, Craig R. Bomben, C. Gordon Fullerton (Chief Pilot), Mark Pestana, Douglas H. Baker, William Frederick Brockett, and Frank Batteas.

Wayne State University professor Shanique Brown, far right, takes part in a panel discussion on diversity and building strong, inclusive teams. She was joined by, from right, Lewis Wooten, associate program manager for the Space Launch System Program Office at Marshall; moderator Lisa Watson-Morgan, deputy director of Marshall's Engineering Directorate; Rick Burt, director of Marshall's Safety & Mission Assurance Directorate; and Bobby Watkins, director of the Human Exploration Development and Operations Office.

LEWIS RESEARCHERS WORKING ON FLUIDS AND COMBUSTION FACILITY COMPONENTS
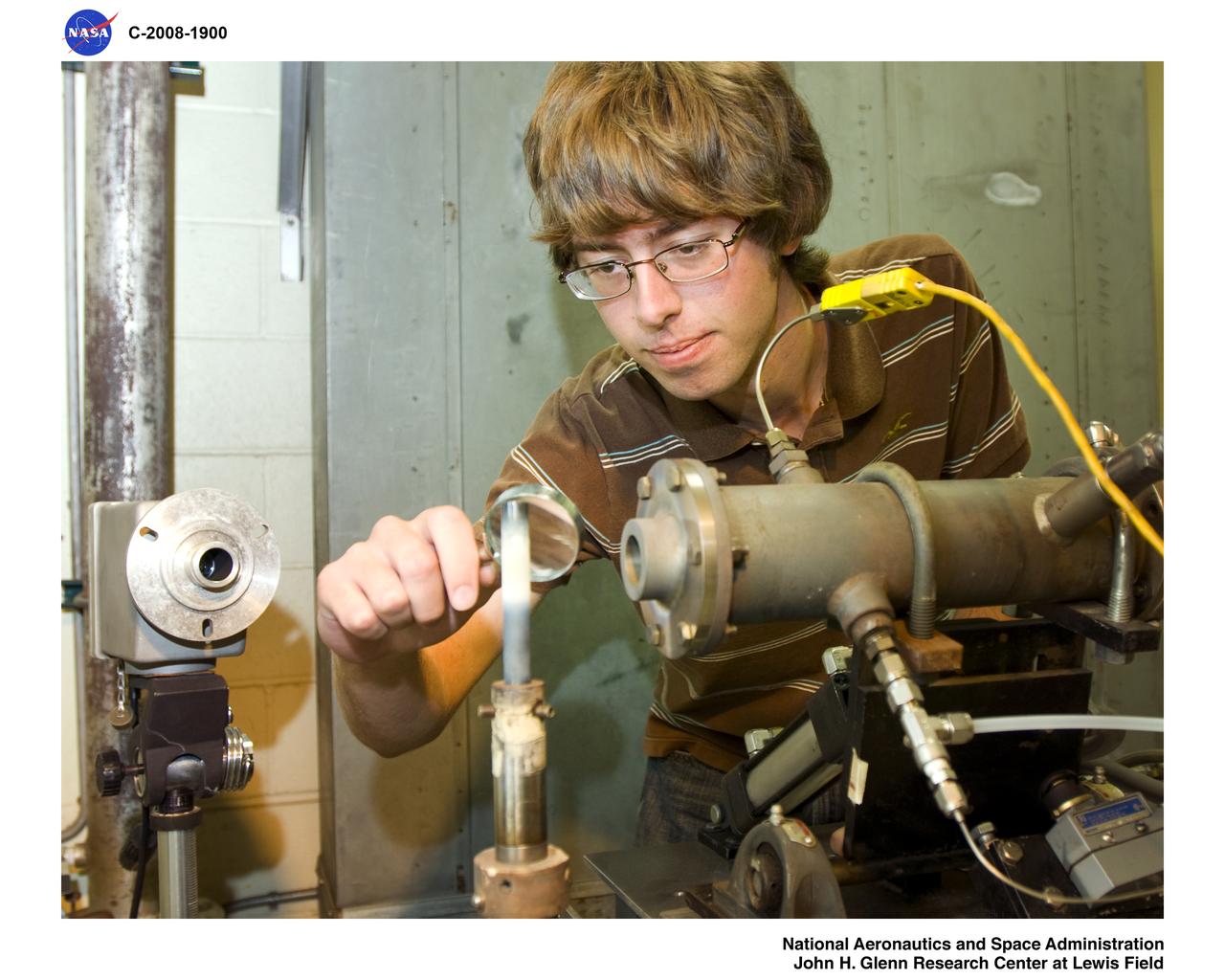

Lewis' Educational and Research Collaborative Intership Program (LERCIP)
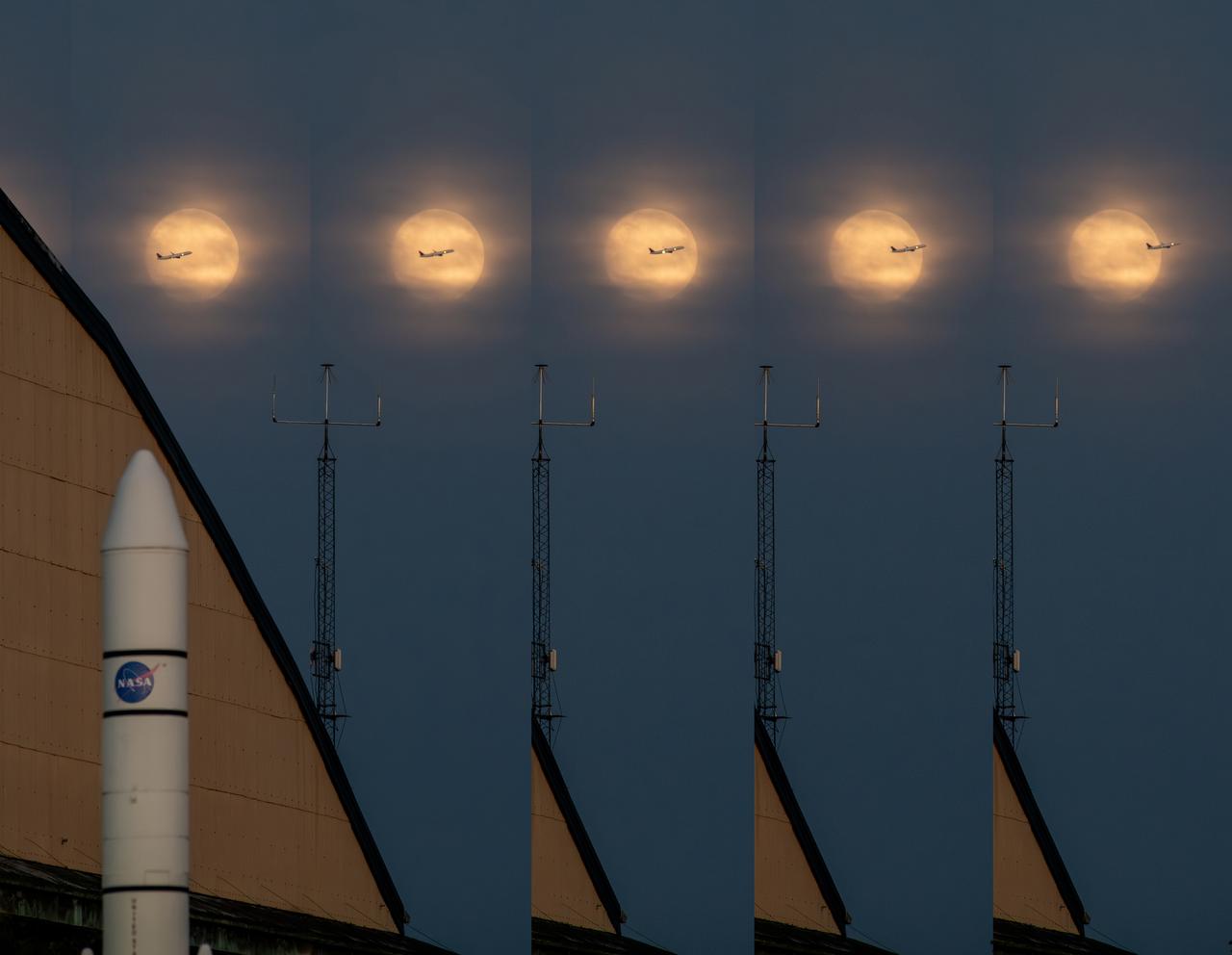

While photographing the Supermoon on September 17, 2024 for a NASA GRC Aerospace Frontiers article on the 2024 Supermoon, a plane departing Cleveland Hopkins Airport flew right through the middle of the moon. The photographer used a portion of the rocket garden’s Ares 1 rocket and a corner of the NASA GRC hangar building to frame the photograph of the moon. When the plane was seen approaching, the photographer used continuous shutter speed in hopes of capturing the plane and the moon together
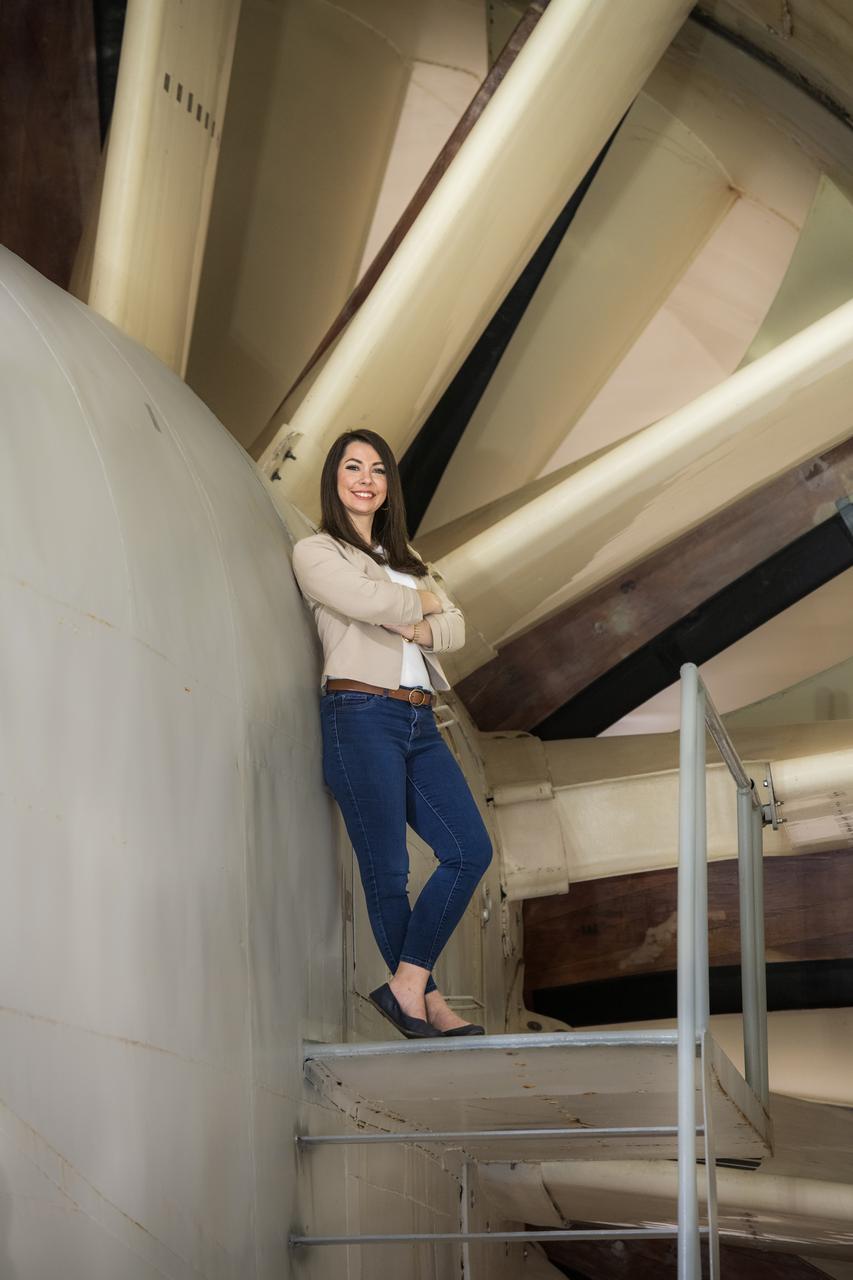

Emily Timko, featured in a Faces of NASA article, poses in the IRT (Icing Research Tunnel) where she works as a “cloud engineer”. She is a Mechanical Test Engineer and works to create unique water spray conditions that simulate icing clouds in the natural aircraft flight environment. Shown in the photo is a portion of the fan drive motor and fan blades that together drive the air through the wind tunnel.
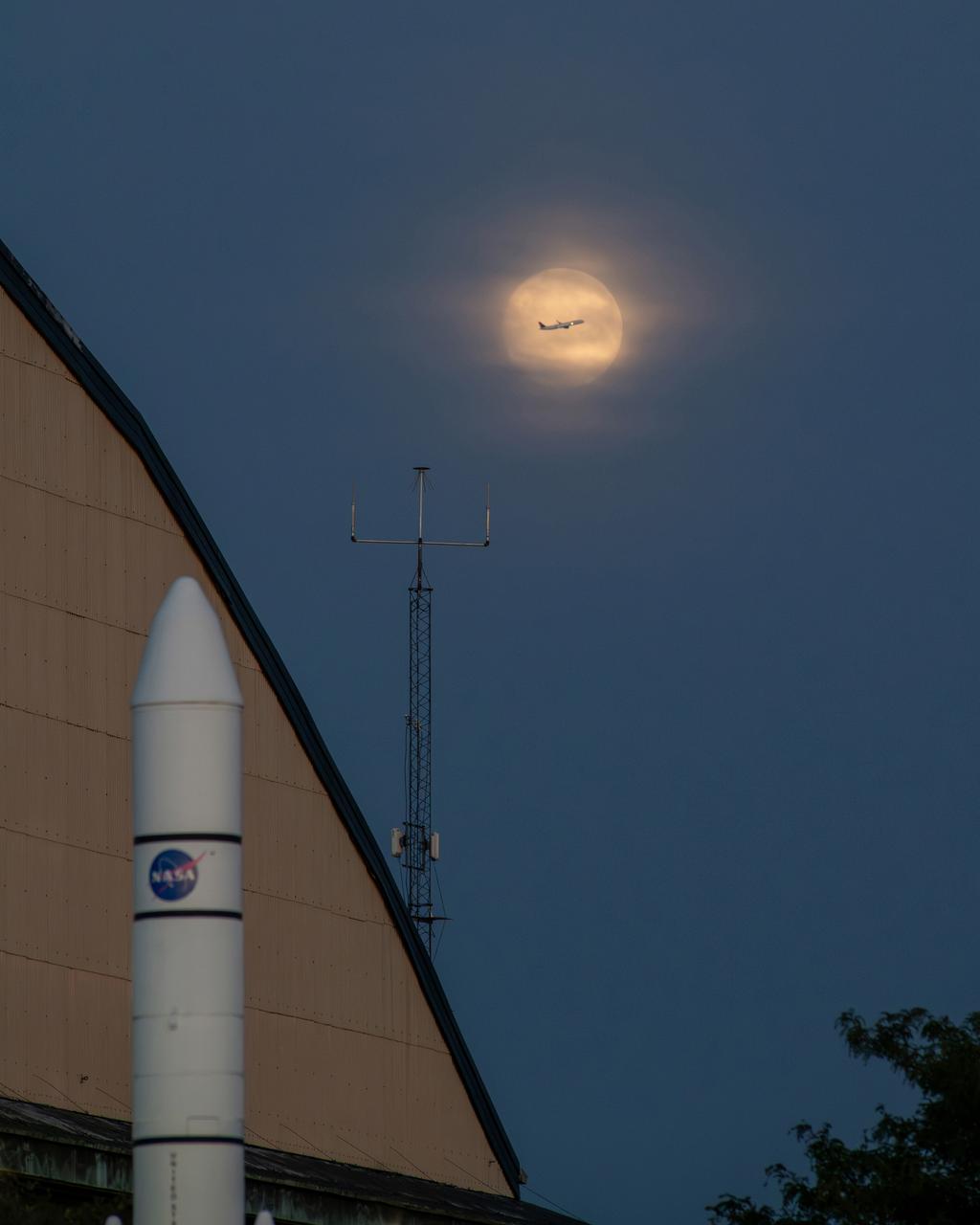

While photographing the Supermoon on September 17, 2024 for a NASA GRC Aerospace Frontiers article on the 2024 Supermoon, a plane departing Cleveland Hopkins Airport flew right through the middle of the moon. The photographer used a portion of the rocket garden’s Ares 1 rocket and a corner of the NASA GRC hangar building to frame the photograph of the moon. When the plane was seen approaching, the photographer used continuous shutter speed in hopes of capturing the plane and the moon together.
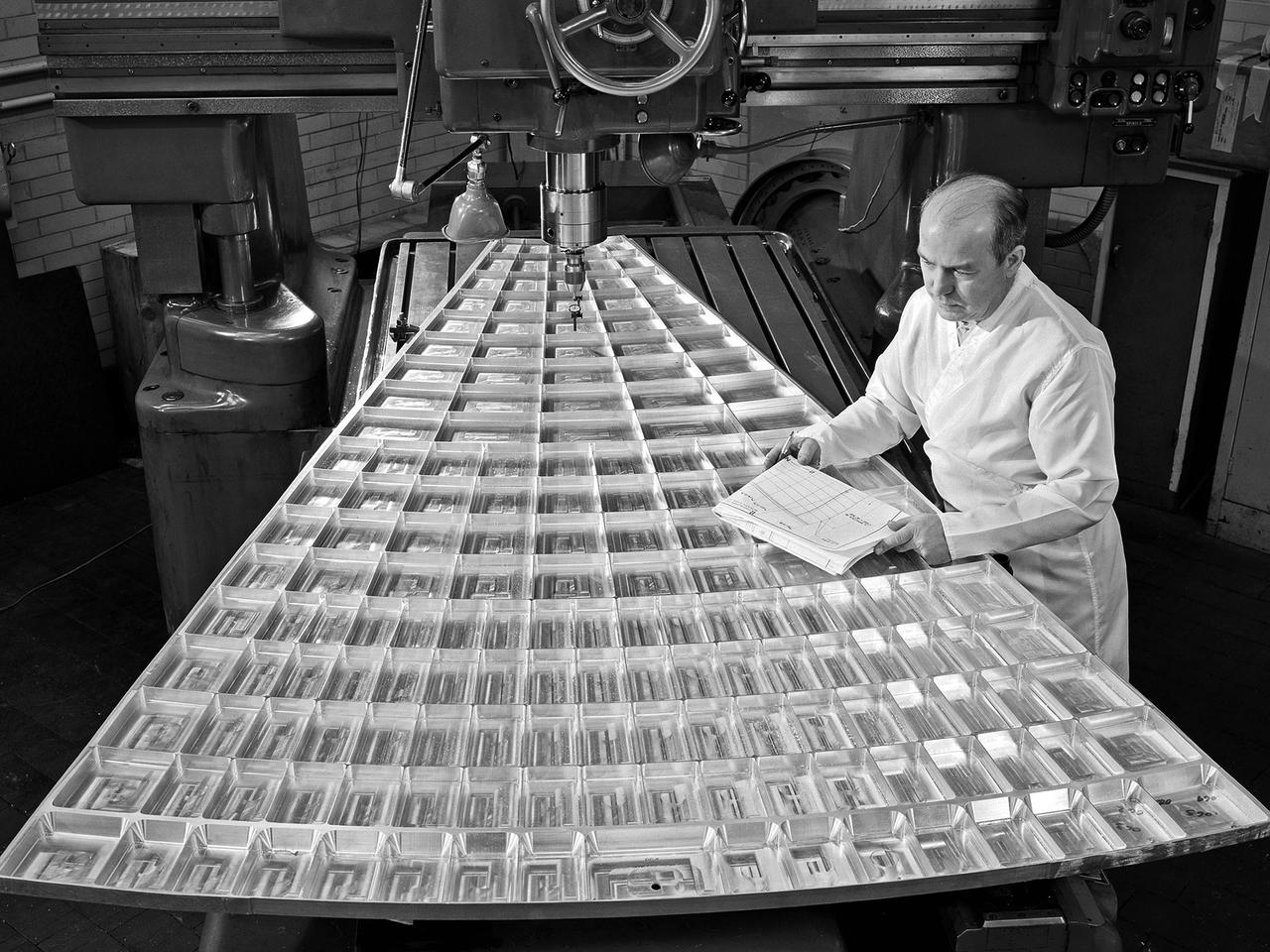

Daniel Bernatowicz, Chief of the Advanced Power Systems Branch at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center, examines a 20-foot section of a solar mirror being fabricated in the Jig Bore Room of the Technical Services Building. NASA Lewis was conducting a wide-ranging effort to explore methods of generating electrical power for spacecraft. One method employed a large parabolic mirror to concentrate the sun’s energy. The mirror had to remain rigid and withstand micrometeoroids, but remain light and compact enough to be easily launched. In 1963 Bernatowicz and his researchers undertook a program to design a solar mirror to work with the Brayton cycle system on a space station. The mirror in this photograph was prepared for a conference on Advanced Technology in Space Power Systems held at Lewis in late August 1966. Lewis experts discussed advances with batteries, fuel cells, isotope and thermoelectric generators, and the SNAP-8 space power system. Lewis was developing several types of solar mirrors to work with a Brayton cycle electric generating system. The mirror’s 12 sections were shaped using a unique forming process developed at Lewis, coated with an epoxy, and plated with aluminum. The mirror concentrated the Sun's rays on a heat storage receiver containing lithium fluoride. This material was heated to produce power in a turbogenerator system, while additional heat was stored for use when the unit was in the Earth's shadow.
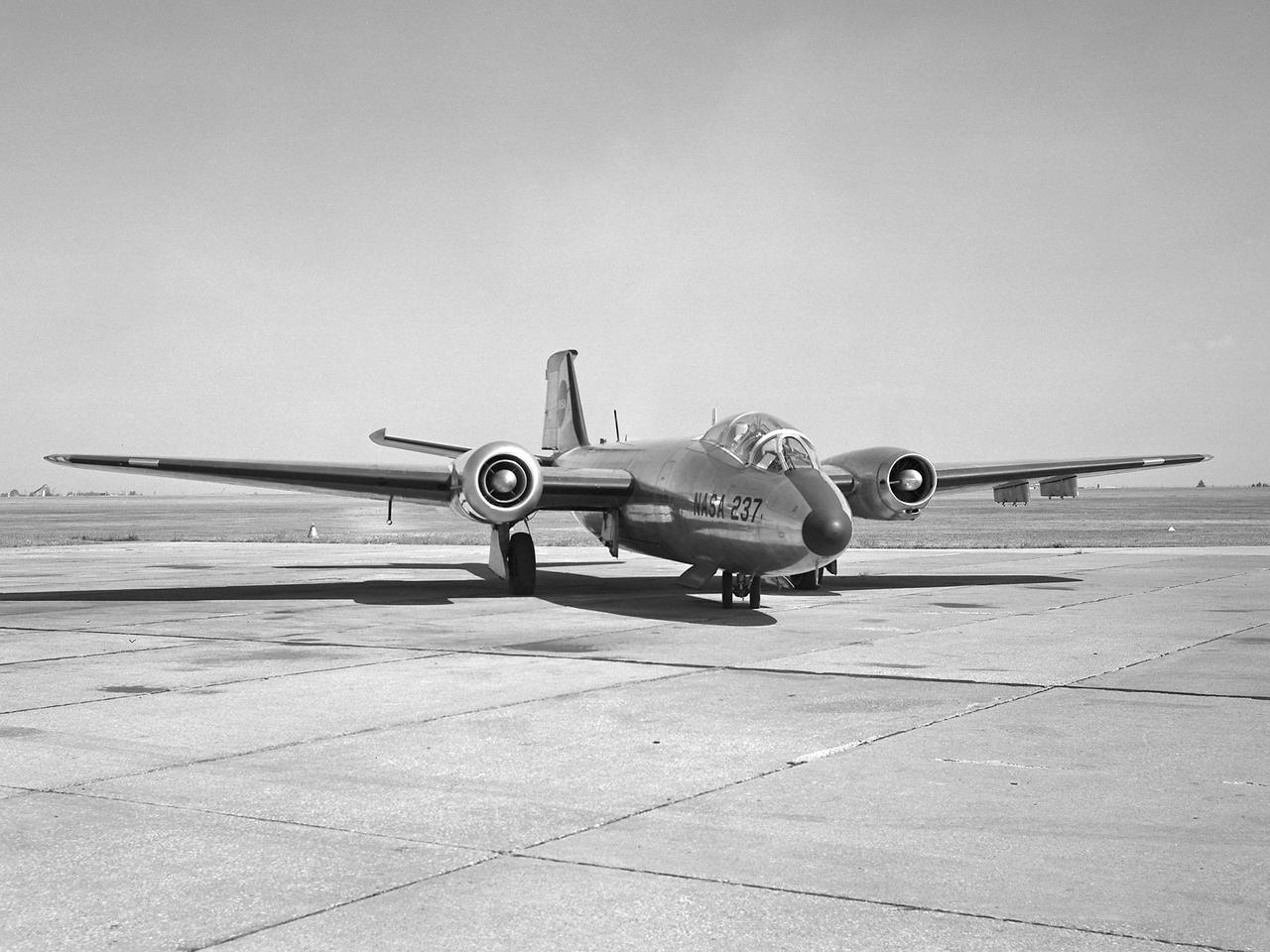

A Martin B-57B Canberra outfitted with a noise suppressor on its right engine at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The aircraft was being prepared for the October 1966 Inspection of the center. The Inspection also marked Lewis’ twentieth anniversary. Lewis researchers had been studying engine noise for almost a decade, but the problem seemed to be increasing in the mid-1960s with heavier airline traffic and larger engines. Researchers discovered early on that the majority of the noise did not emanate from the engine itself, but from the mixing of the hot exhaust gasses with the atmosphere. Attempts to reduce the turbulence using new exhaust nozzles were successful but often resulted in decreased engine performance. The researchers decided to try to lower the jet nozzle exit velocity without decreasing its thrust. The inlet mass air flow had to be increased to accomplish this. The Lewis B-57B was powered by two Wright Aeronautical J65 turbojets. Lewis engineers modified the stators on the two engines to simulate the noise levels from more-modern turbofan engines. A noise suppressor was added to only one of the two engines, seen here on the left. The engines were run one at a time at power levels similar to landing while the aircraft sat on the Lewis hangar apron. A microphone and recording equipment was setup to capture the noise levels. The engine with the suppressor produced 13 fewer decibels than the standard engine.

The sign near the entrance of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Flight Propulsion Research Laboratory. The name was changed several weeks later to the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in honor of the NACA’s former Director of Aeronautical Research, George W. Lewis. The research laboratory has had five different names since its inception in 1941. The Cleveland laboratory was originally known as the NACA Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory. In 1947 it was renamed the NACA Flight Propulsion Research Laboratory to reflect the expansion of the research activities beyond just engines. Following the death of George Lewis, the name was changed to the NACA Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in September 1948. On October 1, 1958, the lab was incorporated into the new NASA space agency, and it was renamed the NASA Lewis Research Center. Following John Glenn’s flight on the space shuttle, the name was changed again to the NASA Glenn Research Center on March 1, 1999. From his office in Washington DC, George Lewis managed the aeronautical research conducted at the NACA for over 20 years. His most important accomplishment, however, may have been an investigative tour of German research facilities in the fall of 1936. The visit resulted in the broadening of the scope of the NACA’s research and the physical expansion that included the new engine laboratory in Cleveland.
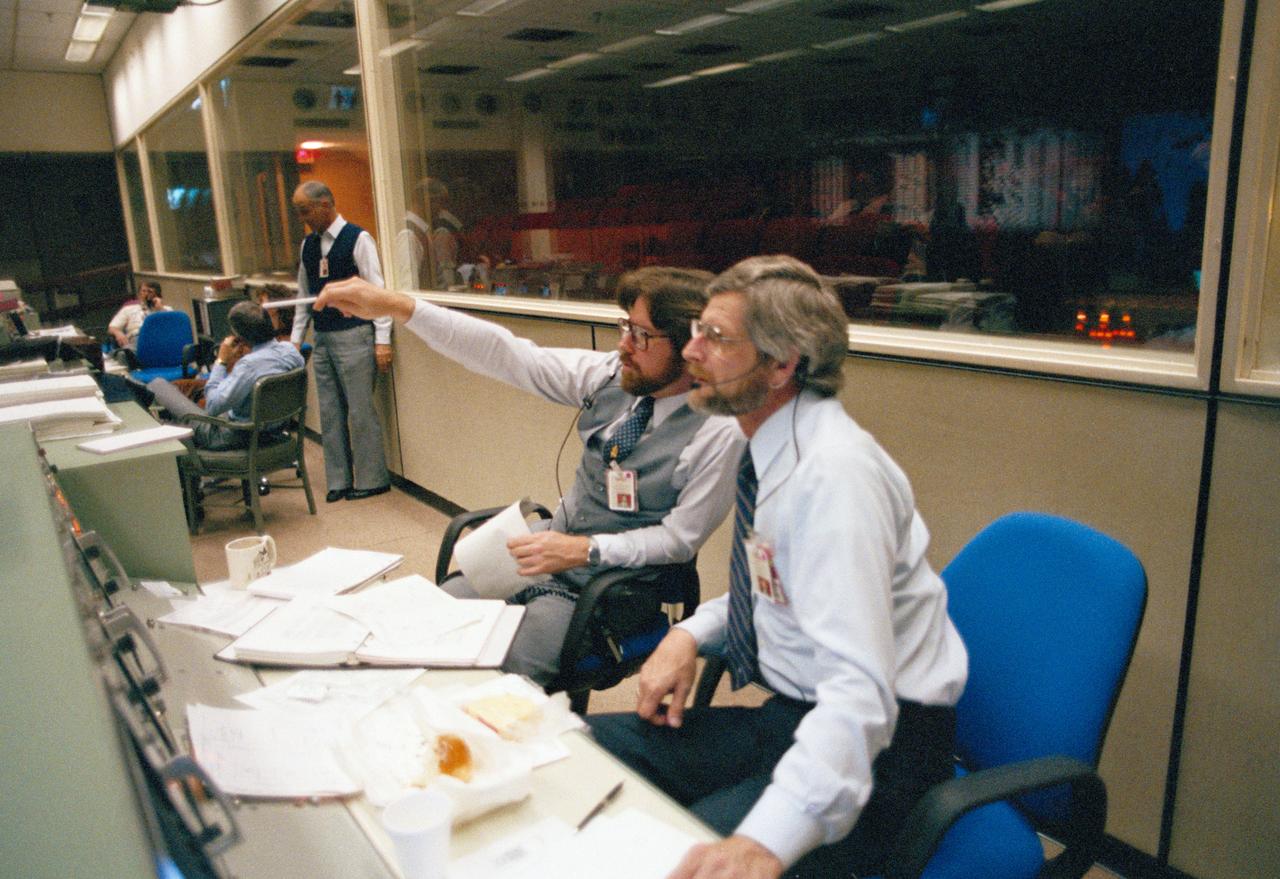

s83-46015 Views of the Mission Control Center activity of Eidophor with STS-9 Landing Data; PAO Console ith Steve Nesbitt and Harold S. Stall; FD Console with Charles Lewis and Ralph Hoodless, Lewis and M.P. "Pete" Frank; and the hanging of the STS-9 Plaque
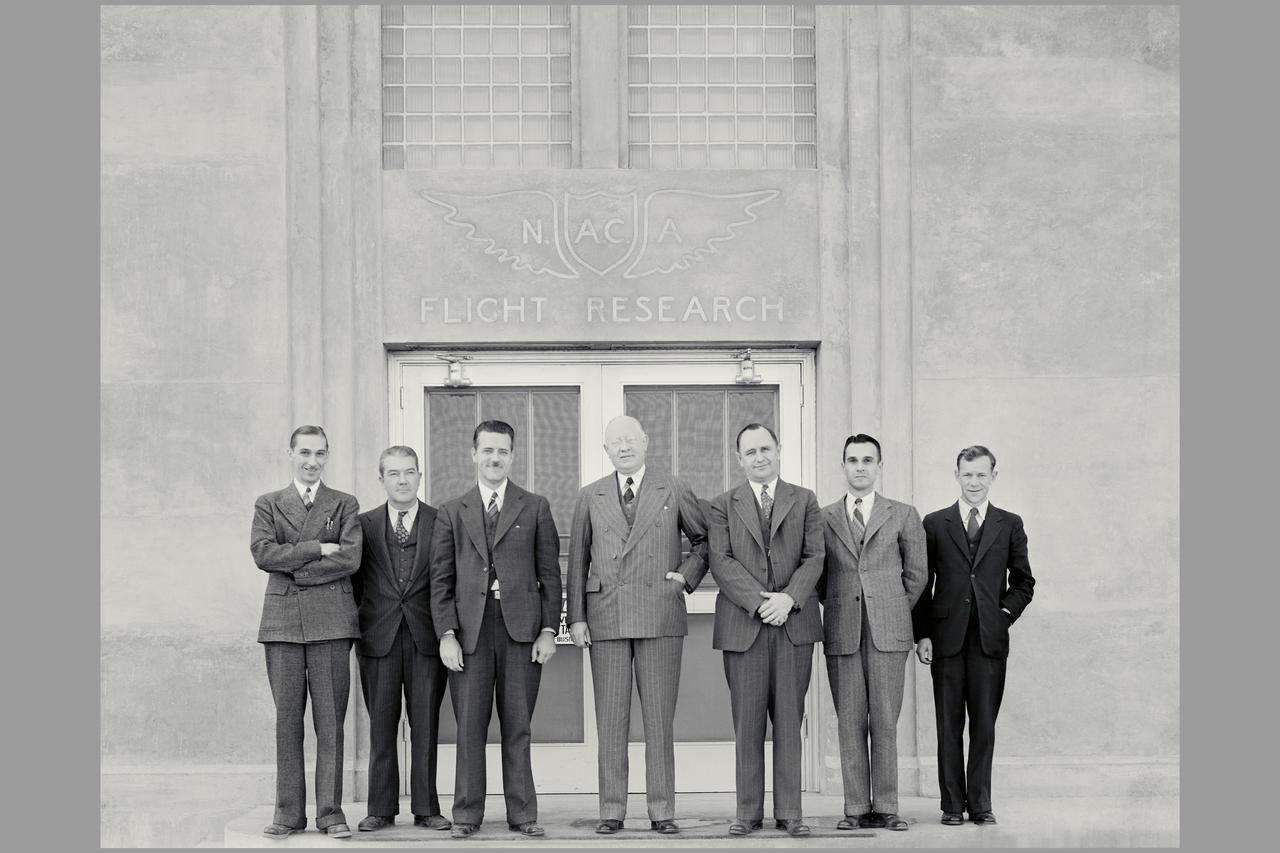

Dr George W. Lewis, NACA Director of Aeronautical Research (1929-1947) first visit to Ames Lab: L-R; John Parsons, William Mc Avoy, Donald H. Wood, Dr. Lewis, S. J. DeFrance, Author B. Freeman, Carlton Bioletti
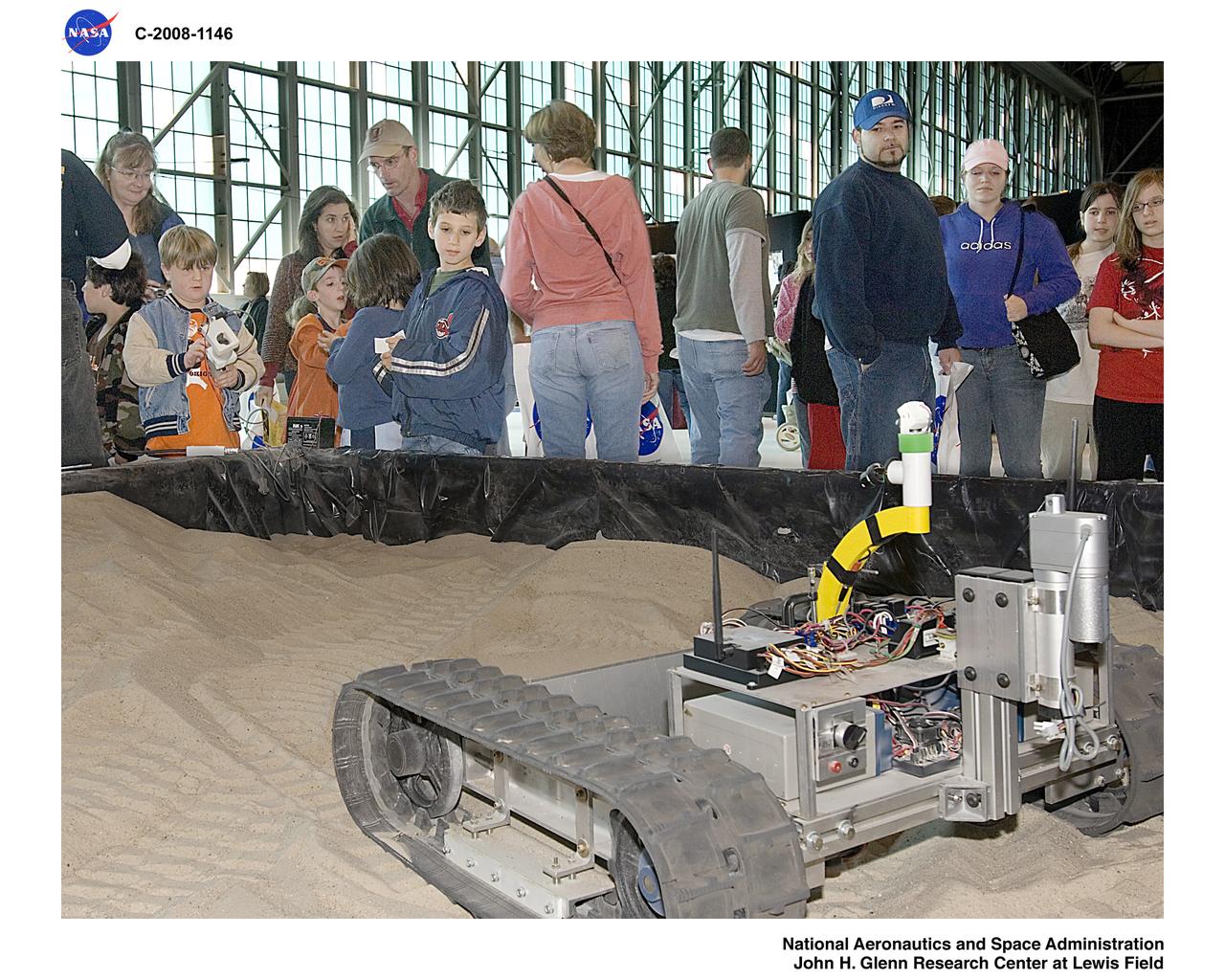

NASA Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field 50th Anniversary Open House

Lewis Educational and Research Collaborative Internship Program, LERCIP - College Student at the Worksite
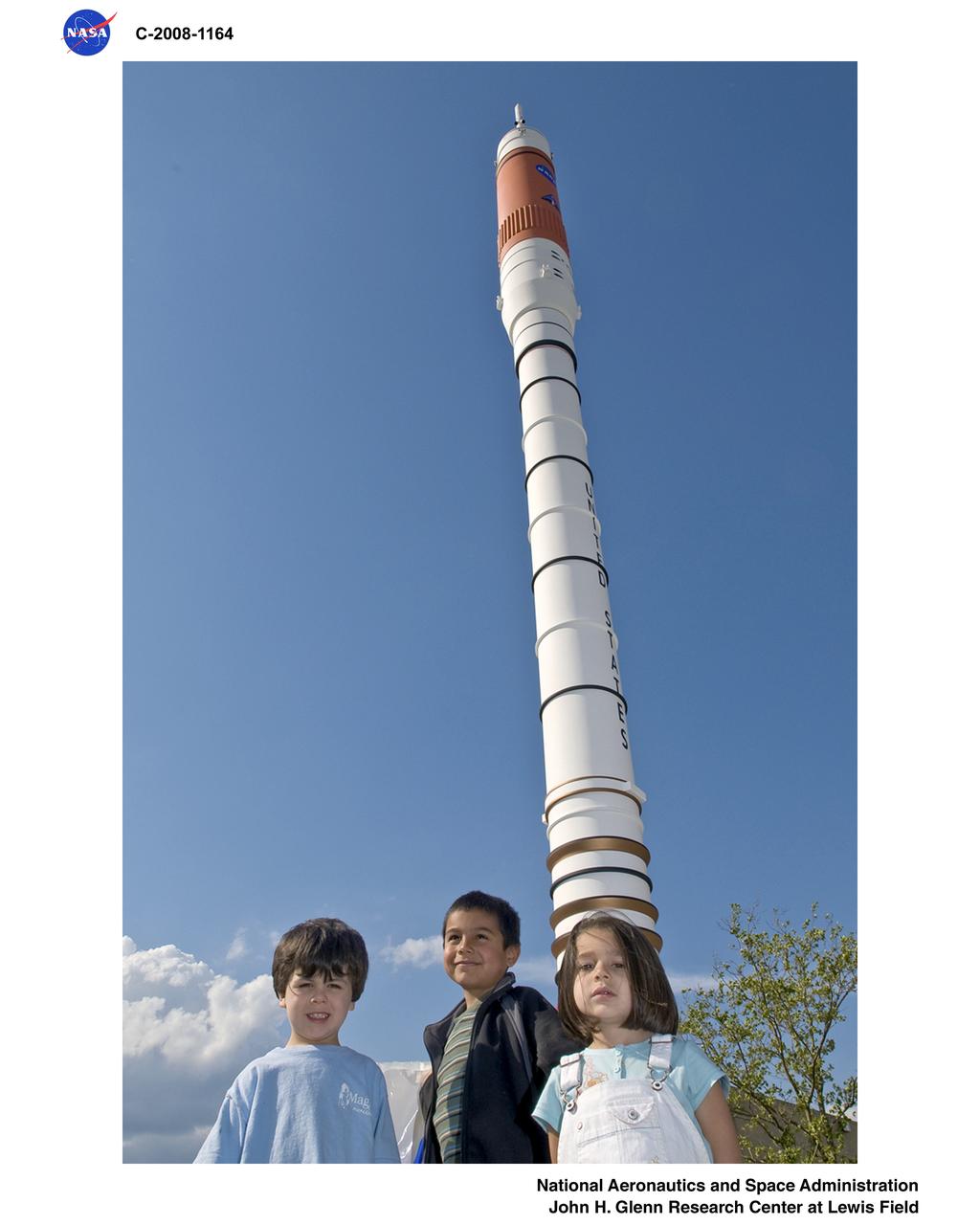

NASA Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field 50th Anniversary Open House

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by NASA Administrator and Deputy Administrator

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by NASA Administrator and Deputy Administrator

Deer in West Area, Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field
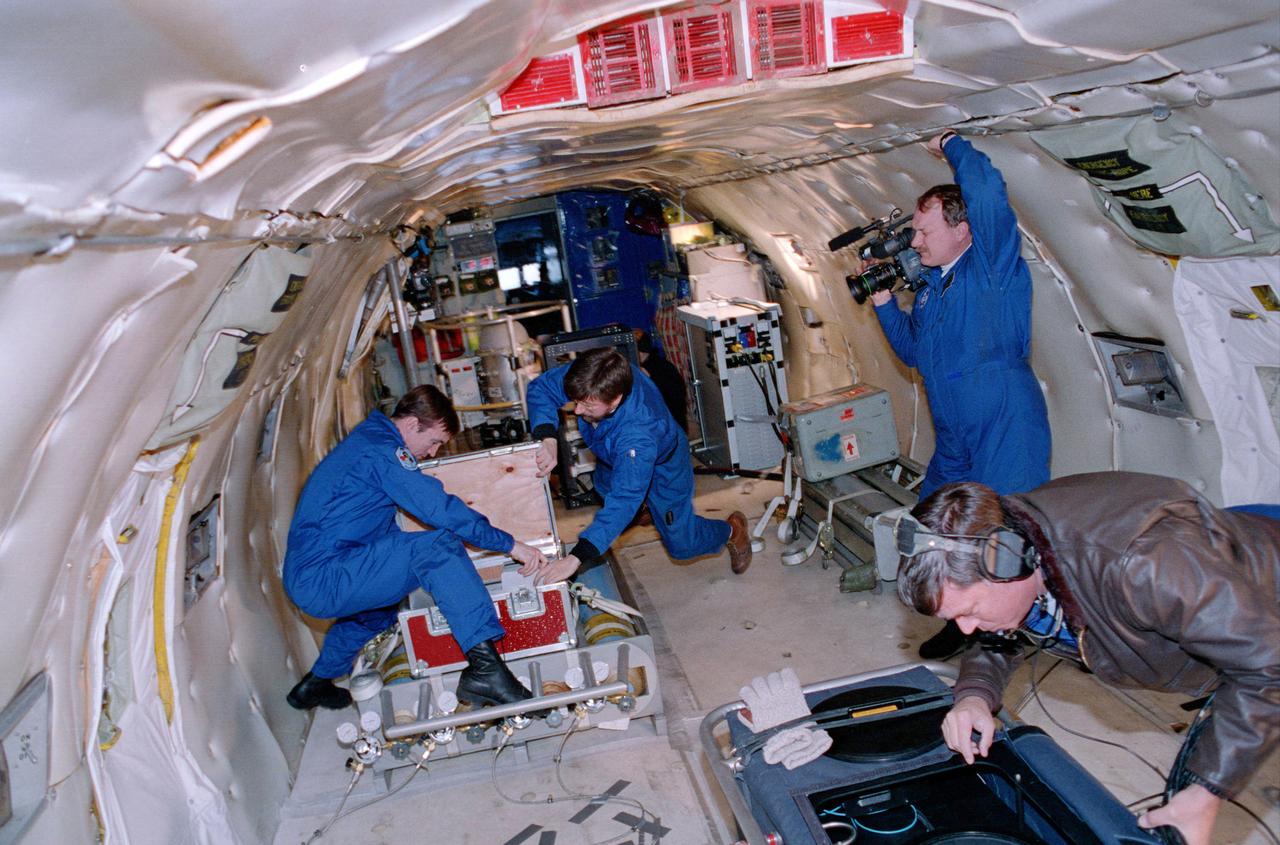

ZERO GRAVITY AIRCRAFT KC135 FLIGHTS AT LEWIS RESEARCH CENTER

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field, GRC, by Astronaut Steve Swanson

Visit to Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field by NASA Administrator and Deputy Administrator
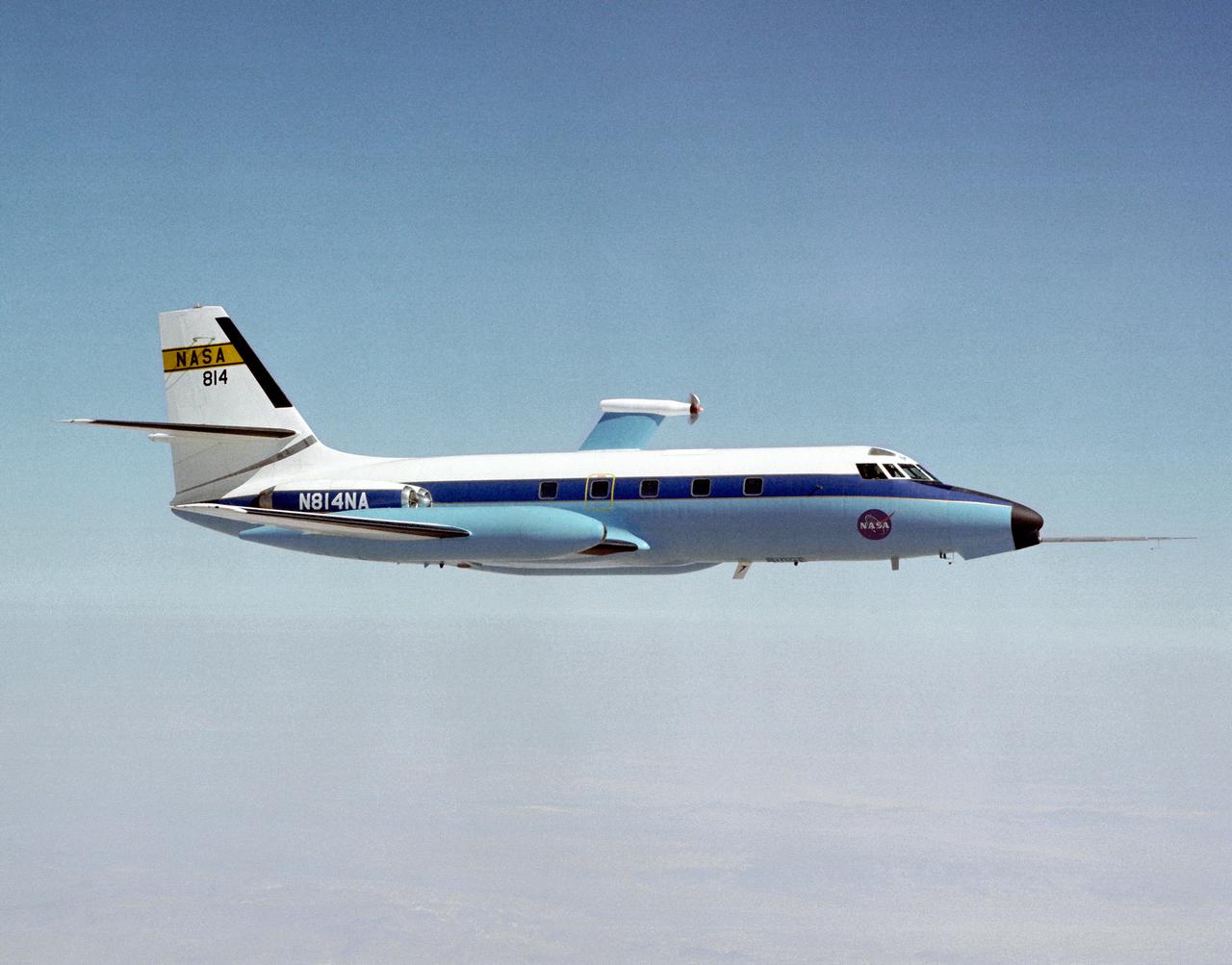

The Dryden C-140 JetStar during testing of advanced propfan designs. Dryden conducted flight research in 1981-1982 on several designs. The technology was developed under the direction of the Lewis Research Center (today the Glenn Research Center, Cleveland, OH) under the Advanced Turboprop Program. Under that program, Langley Research Center in Virginia oversaw work on accoustics and noise reduction. These efforts were intended to develop a high-speed and fuel-efficient turboprop system.
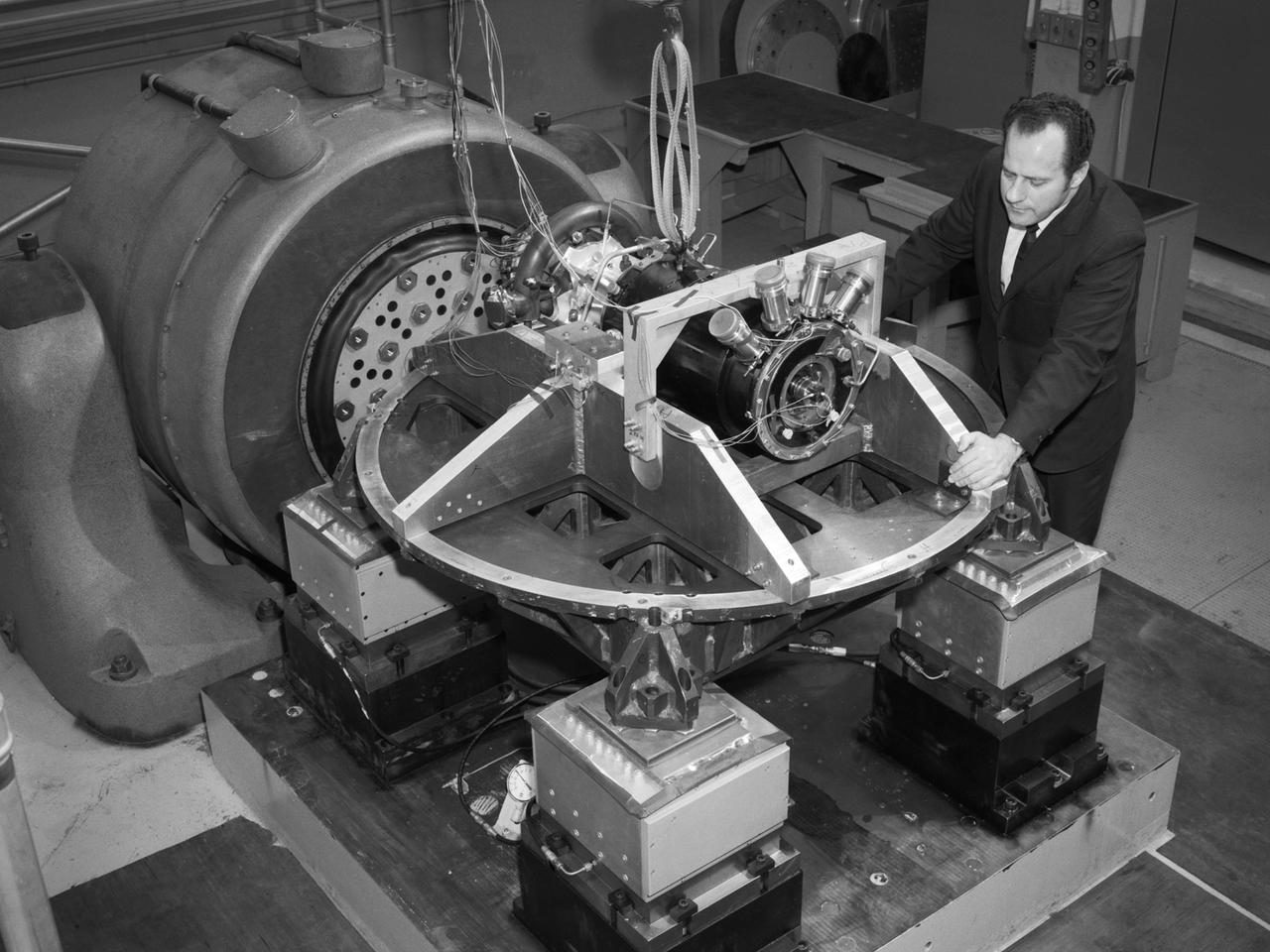

Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Aerojet General was contracted to design the SNAP-8 generator which employed a mercury Rankine system to convert the reactor’s heat into electrical power. The hermetically-sealed pump was designed to generate from 35 to 90 kilowatts of electrical power. In 1964 a SNAP-8 test rig with a mercury boiler and condenser was set up in cell W-1 of Lewis’ Engine Research Building to study the transients in the system’s three loops. In 1967 a complete Rankine system was operated for 60 days in W-1 to verify the integrity of the Lewis-developed mercury boiler. Further tests in 1969 verified the shutdown and startup of the system under normal and emergency conditions. Aerojet operated the first full-Rankine system in June 1966 and completed a 2500-hour endurance test in early 1969. Lewis and Aerojet’s success on the Rankine system was acknowledged with NASA Group Achievement Award in November 1970. The 1970 vibration tests, seen here, were conducted in Lewis’ Engine Research Building’s environmental laboratory. The testing replicated the shock and vibration expected to occur during the launch into space and subsequent maneuvering. The pump was analyzed on each of its major axes.