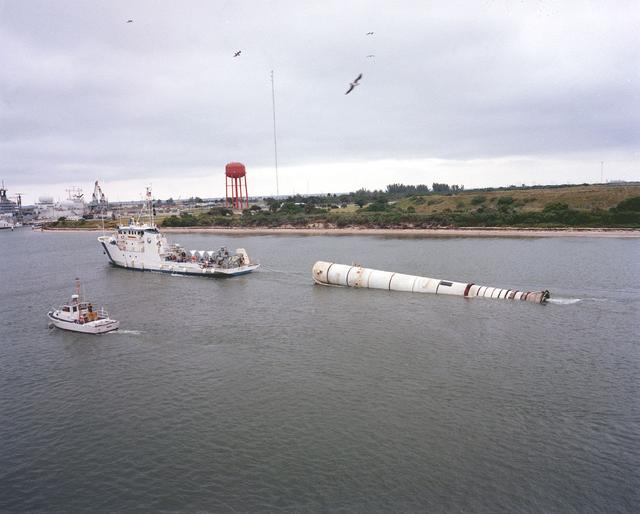

This is a photo of the recovery ship, UTC Liberty, towing the left booster of the STS-5 flight vehicle into Port Canaveral.

This 1967 illustration compares the Apollo Saturn V Spacecraft of the Moon Landing era to the Statue of Liberty located on Liberty Island in New York City. The Apollo Saturn V, at 363 feet towers above Lady Liberty, as the statue is called, standing at 305 feet.
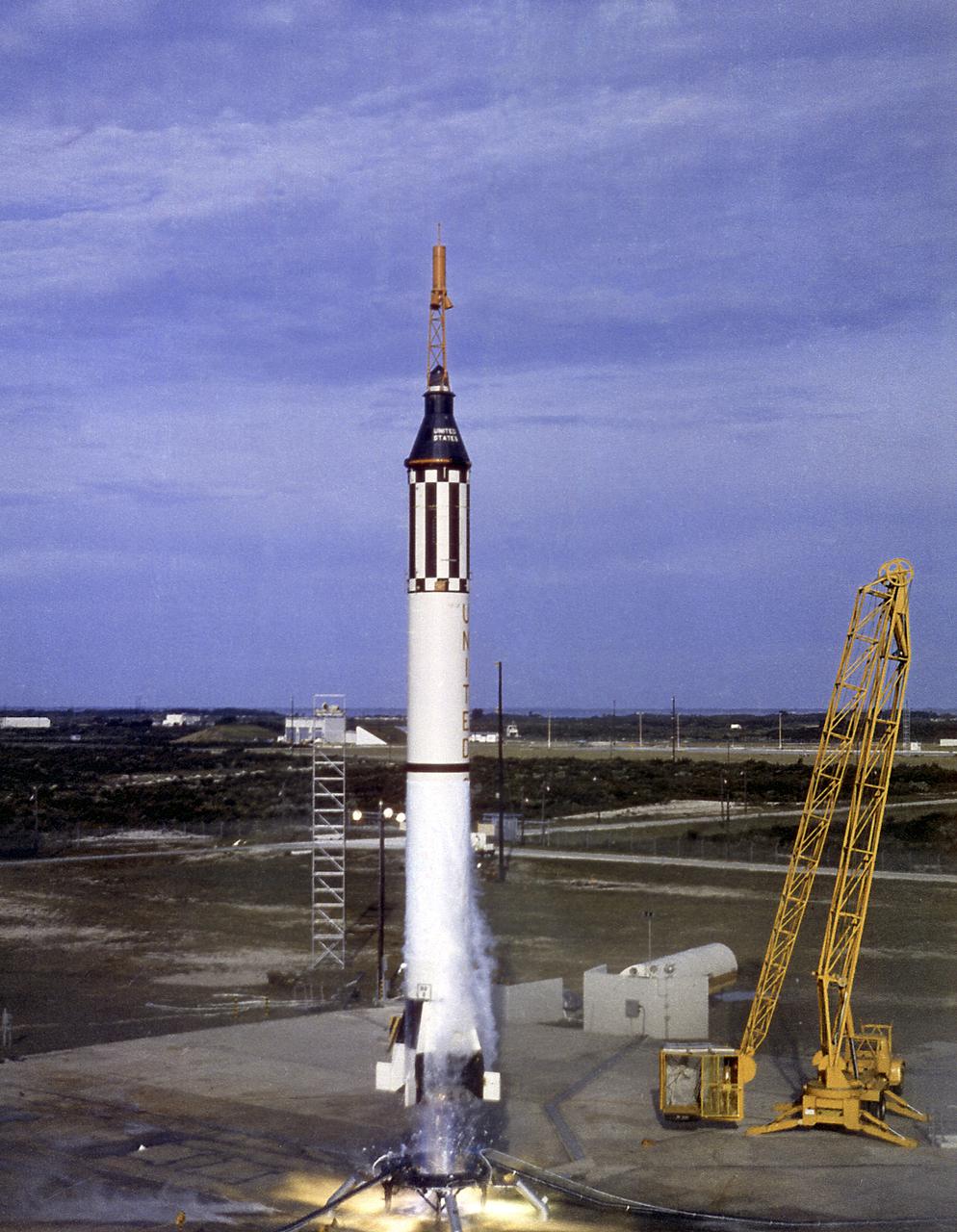
Liftoff of MR-4 (Mercury-Redstone), Liberty Bell 7, on July 21, 1961. MR-4 mission was the second marned suborbital flight and carried Astronaut Virgil Grissom aboard the Liberty Bell 7 spacecraft in space for a duration of 15-1/2 minutes.
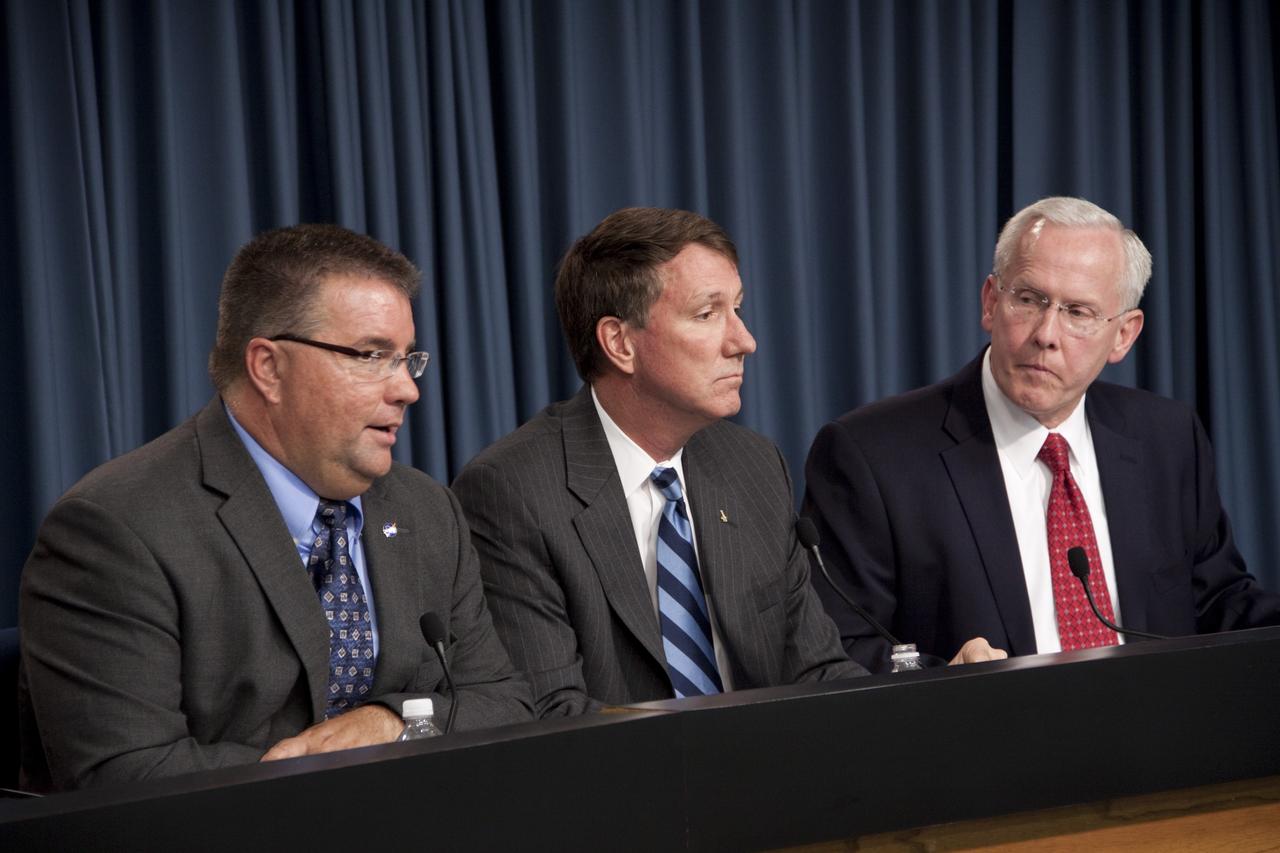

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA and Alliant Techsystems (ATK) managers discuss an agreement that could accelerate the availability of U.S. commercial crew transportation capabilities with media representatives in the Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Ed Mango, Commercial Crew Program manager, NASA; Kent Rominger, vice president, Strategy and Business Development, ATK Aerospace; and John Schumacher, vice president, Space Programs, EADS North America. The unfunded Space Act Agreement (SAA) through NASA's Commercial Crew Program will allow the agency and ATK to review and discuss Liberty system requirements, safety and certification plans, computational models of rocket stage performance, and avionics architecture designs. The agreement outlines key milestones including an Initial System Design review, during which ATK will present to NASA officials the Liberty systems level requirements, preliminary design, and certification process development. For more information about NASA's Commercial Crew Program, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/commercial. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
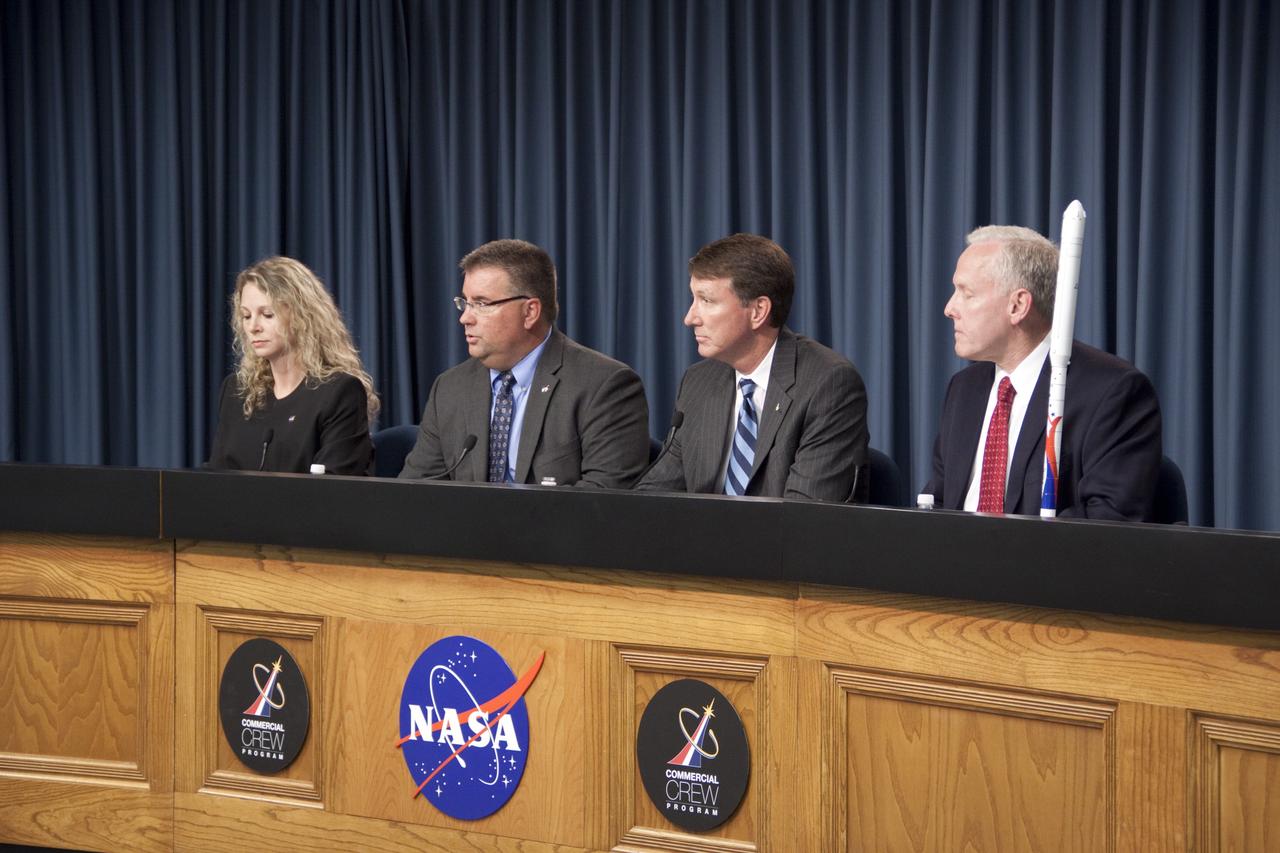

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA and Alliant Techsystems (ATK) managers announce an agreement that could accelerate the availability of U.S. commercial crew transportation capabilities in the Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Candrea Thomas, NASA Public Affairs; Ed Mango, Commercial Crew Program manager, NASA; Kent Rominger, vice president, Strategy and Business Development, ATK Aerospace; and John Schumacher, vice president, Space Programs, EADS North America. The unfunded Space Act Agreement (SAA) through NASA's Commercial Crew Program will allow the agency and ATK to review and discuss Liberty system requirements, safety and certification plans, computational models of rocket stage performance, and avionics architecture designs. The agreement outlines key milestones including an Initial System Design review, during which ATK will present to NASA officials the Liberty systems level requirements, preliminary design, and certification process development. For more information about NASA's Commercial Crew Program, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/commercial. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
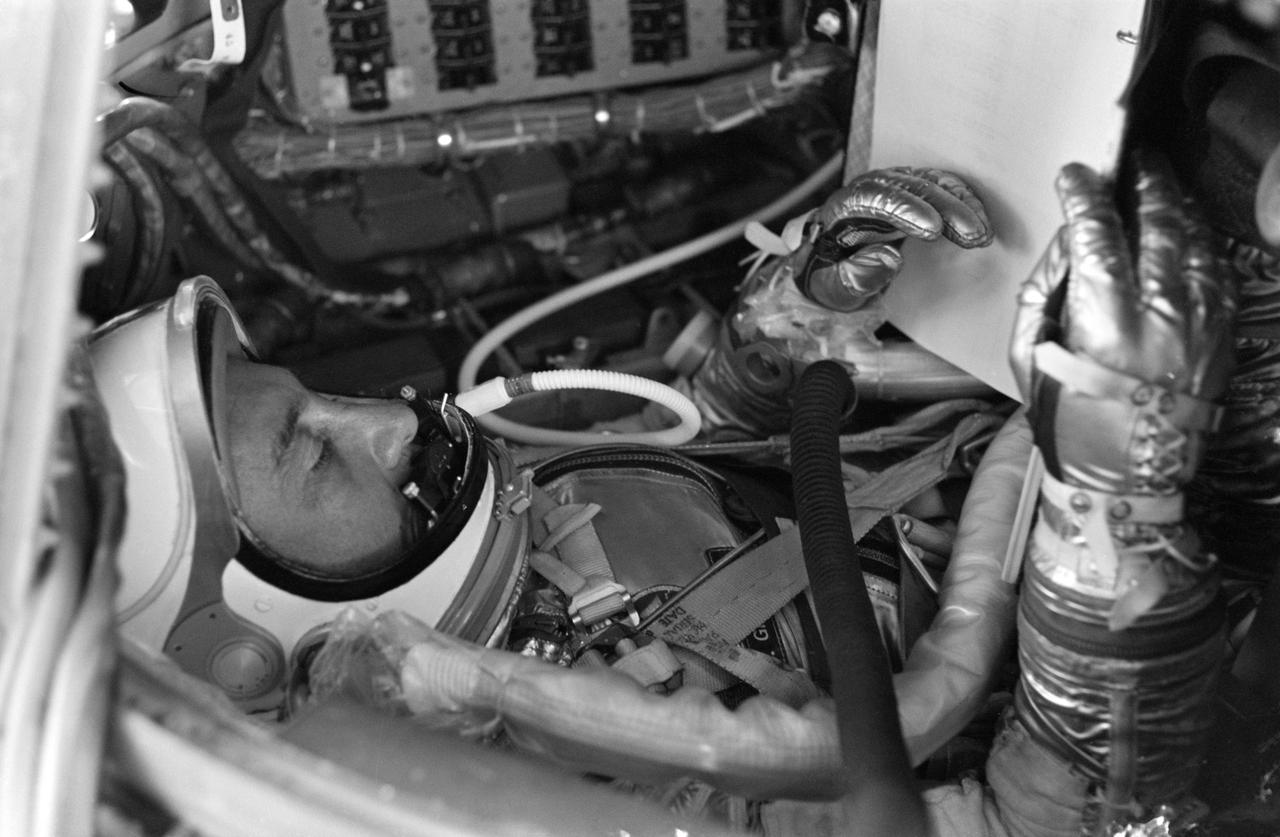

S64-10806 (21 July 1961) --- Astronaut Virgil I. (Gus) Grissom, pilot of the Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) spaceflight, in his Mercury "Liberty Bell 7" spacecraft is checking his flight plan during prelaunch activities. Photo credit: NASA

Assisted by Astronaut John Glenn, Astronaut Virgil Grissom enters the Mercury capsule, Liberty Bell 7, for the MR-4 mission on July 21, 1961. Boosted by the Mercury-Redstone vehicle, the MR-4 mission was the second manned suborbital flight.
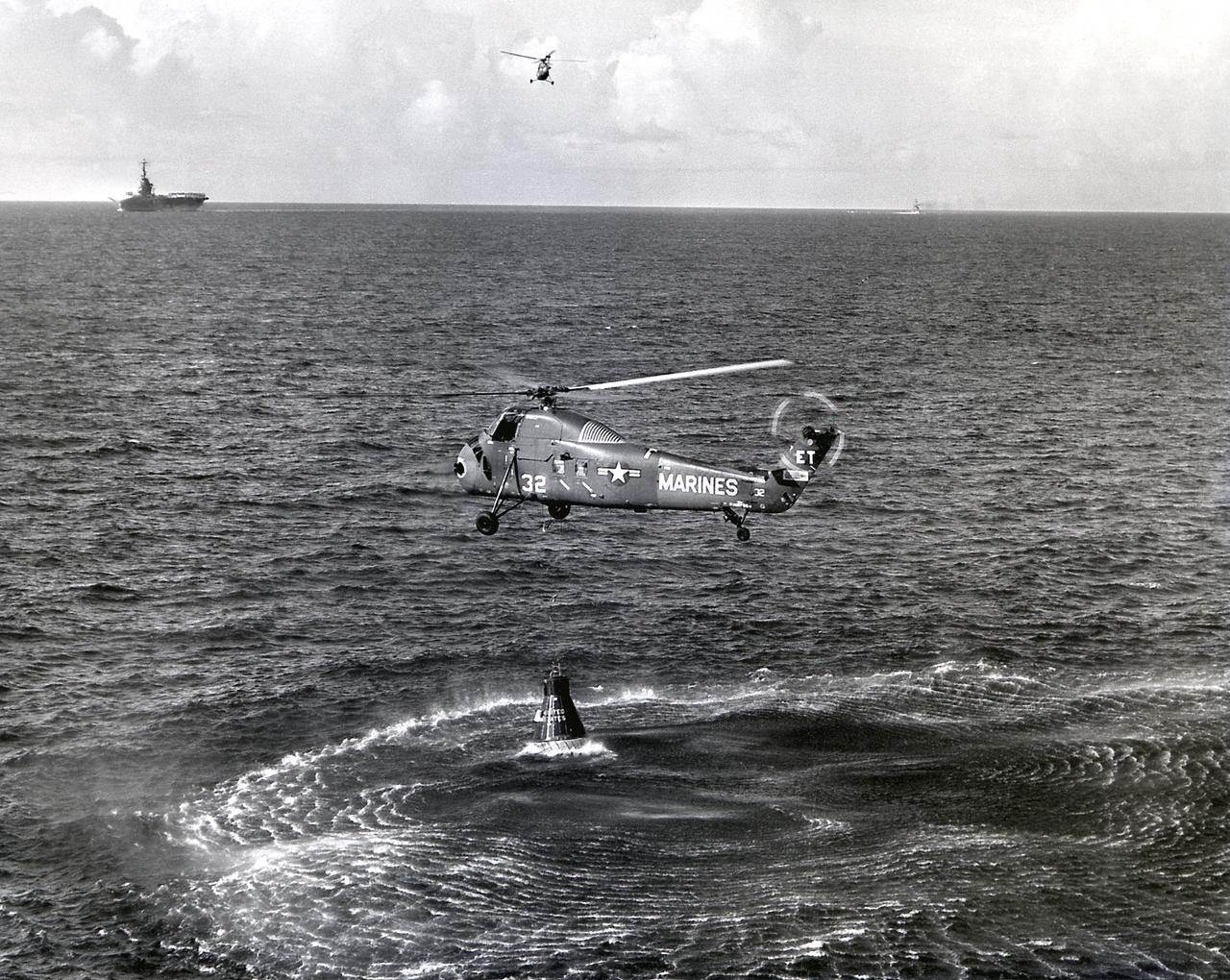

A U.S. Marine helicopter attempts to retrieve the sinking capsule, Liberty Bell 7, of the MR-4 mission. The attempt failed and the capsule sank. The MR-4 mission marned by Astronaut Virgil Grissom was the second manned orbital flight boosted by the Mercury-Redstone vehicle. The Recovery ship is in the background.
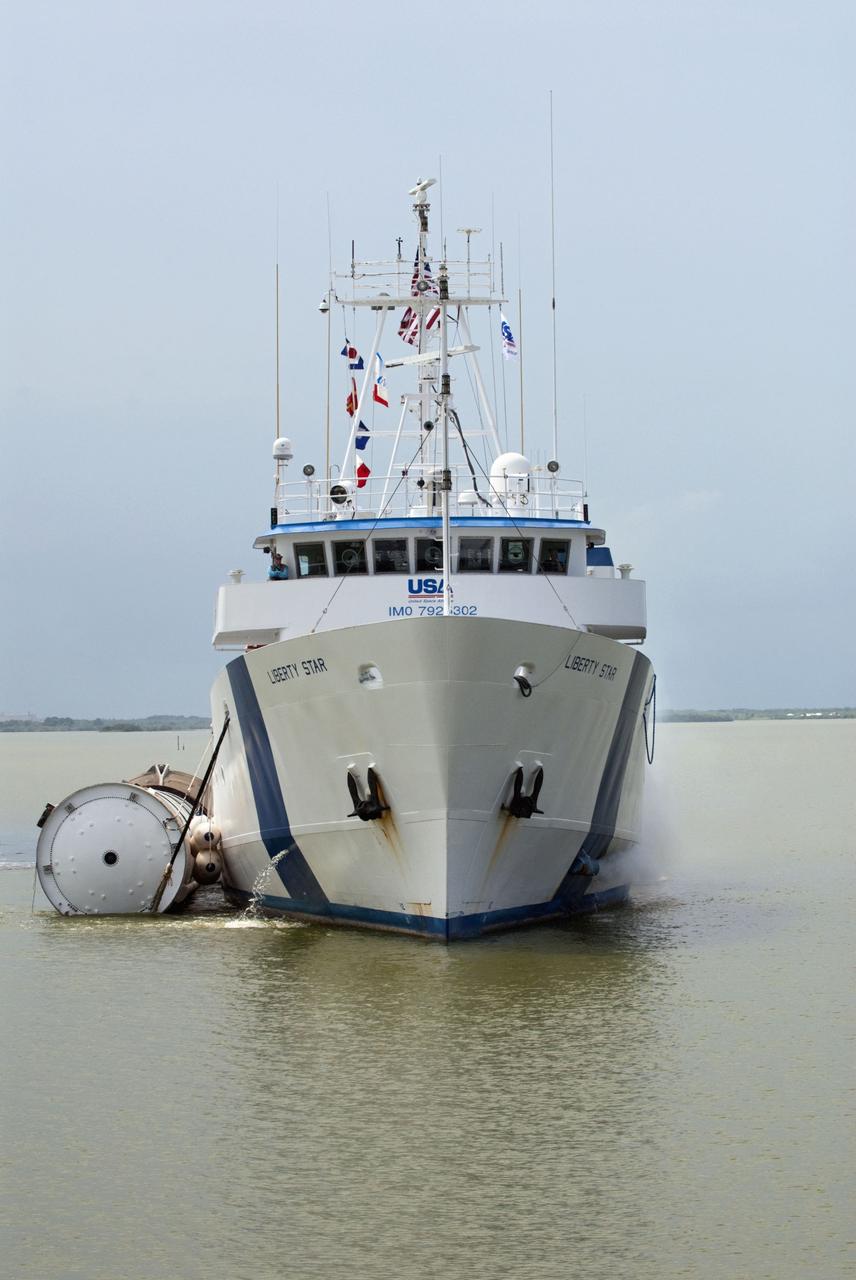

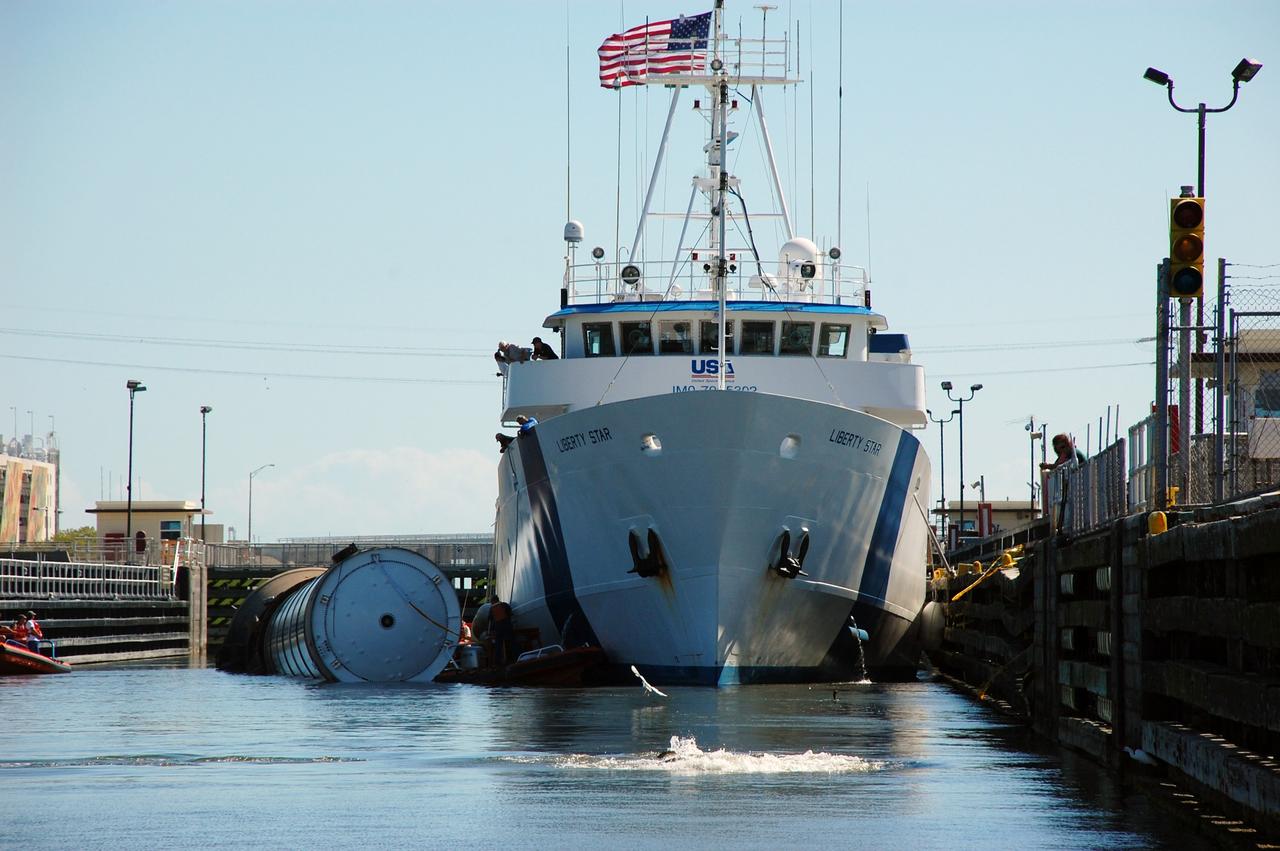
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows a spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
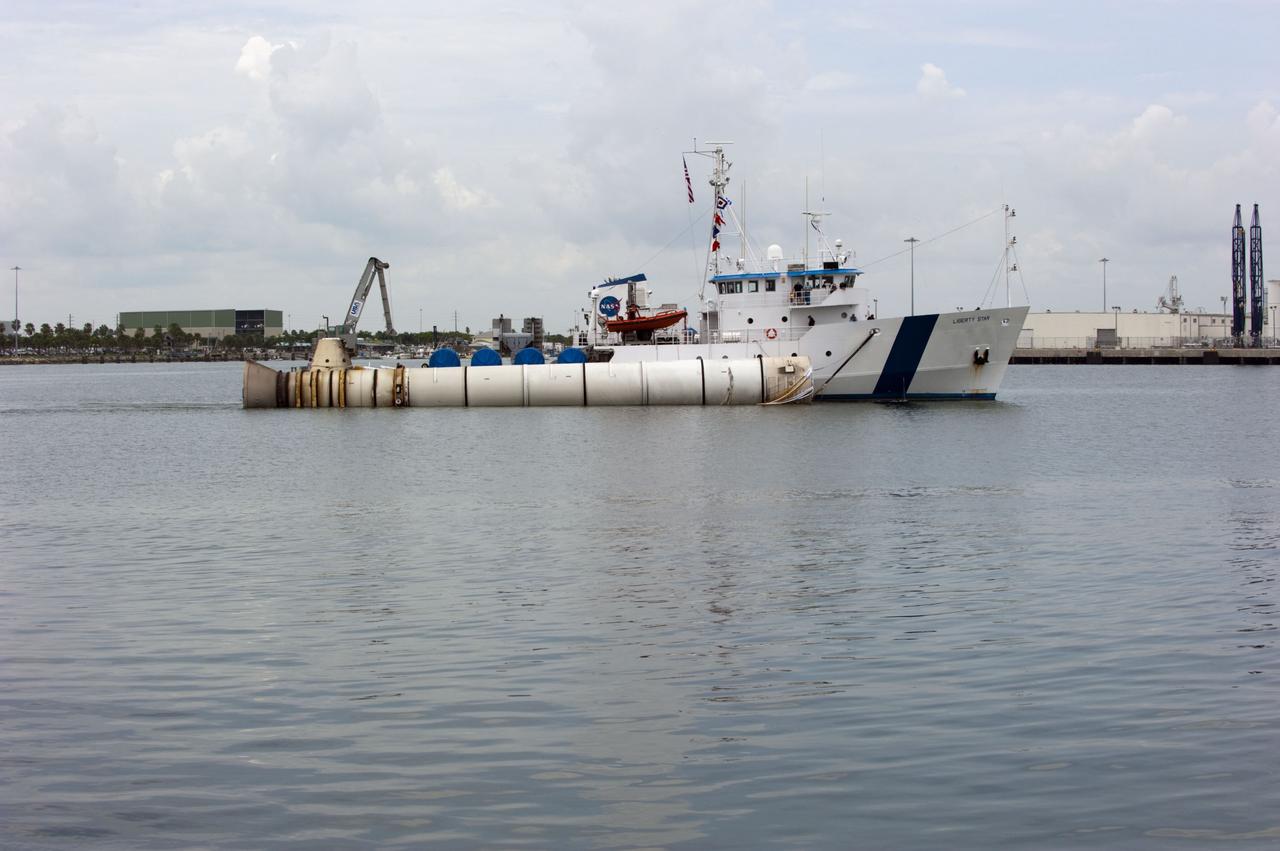

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows a spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8. STS-135 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
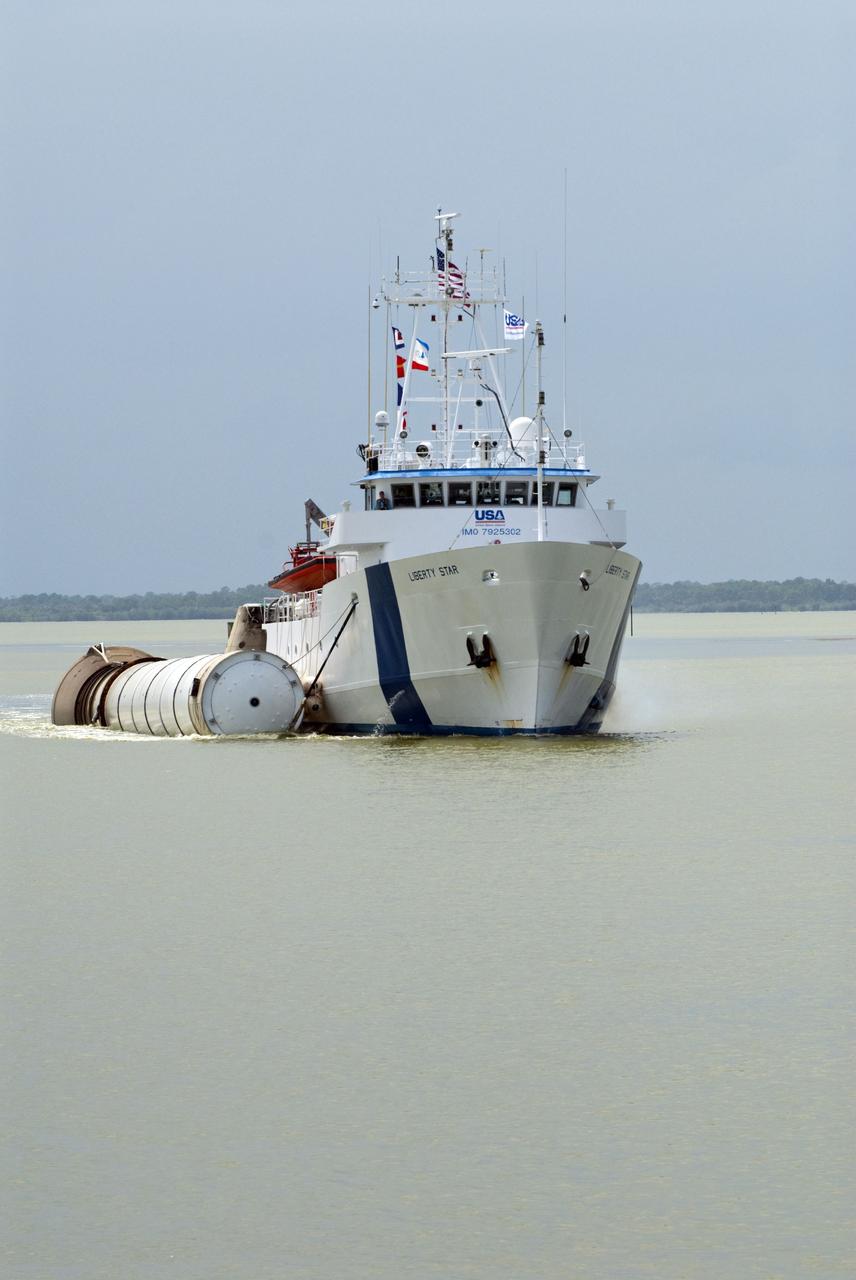

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows a spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
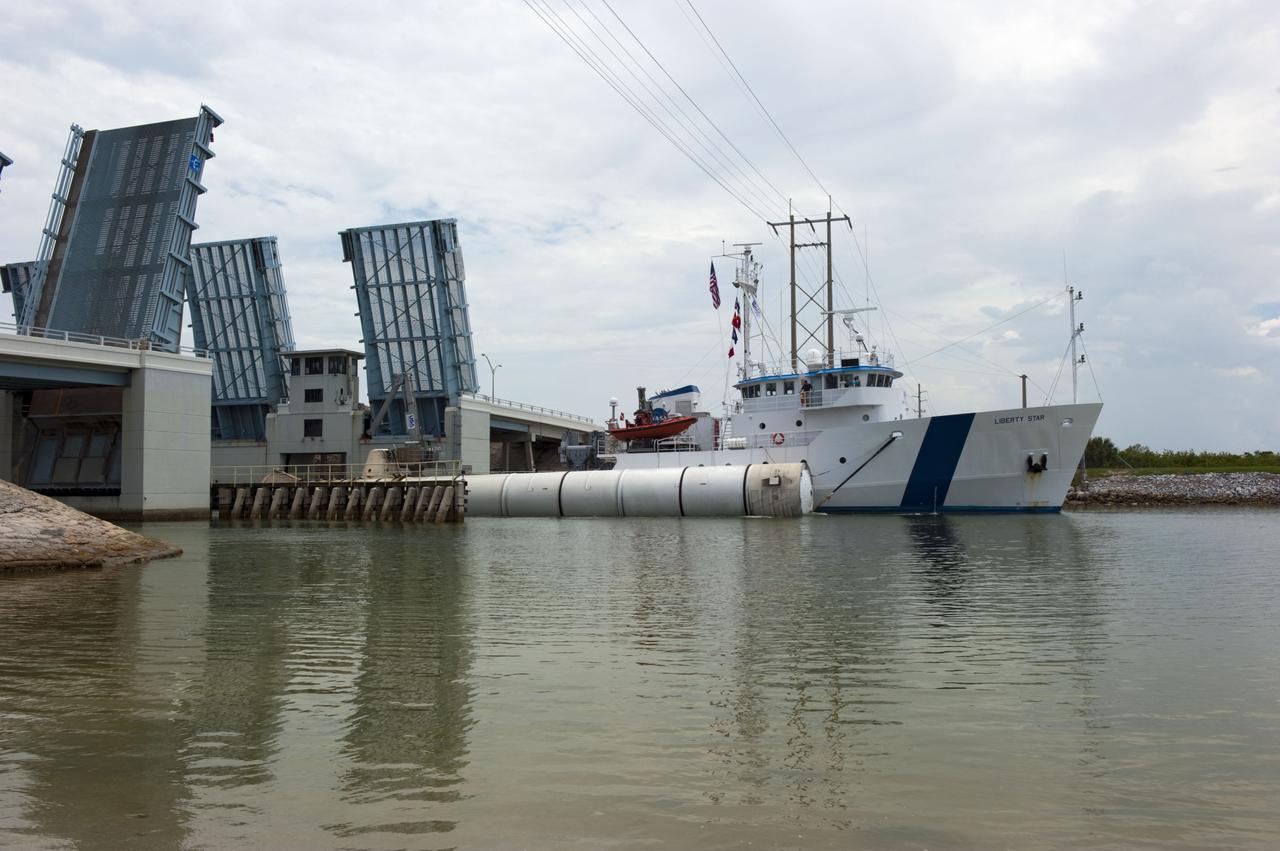

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows a spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
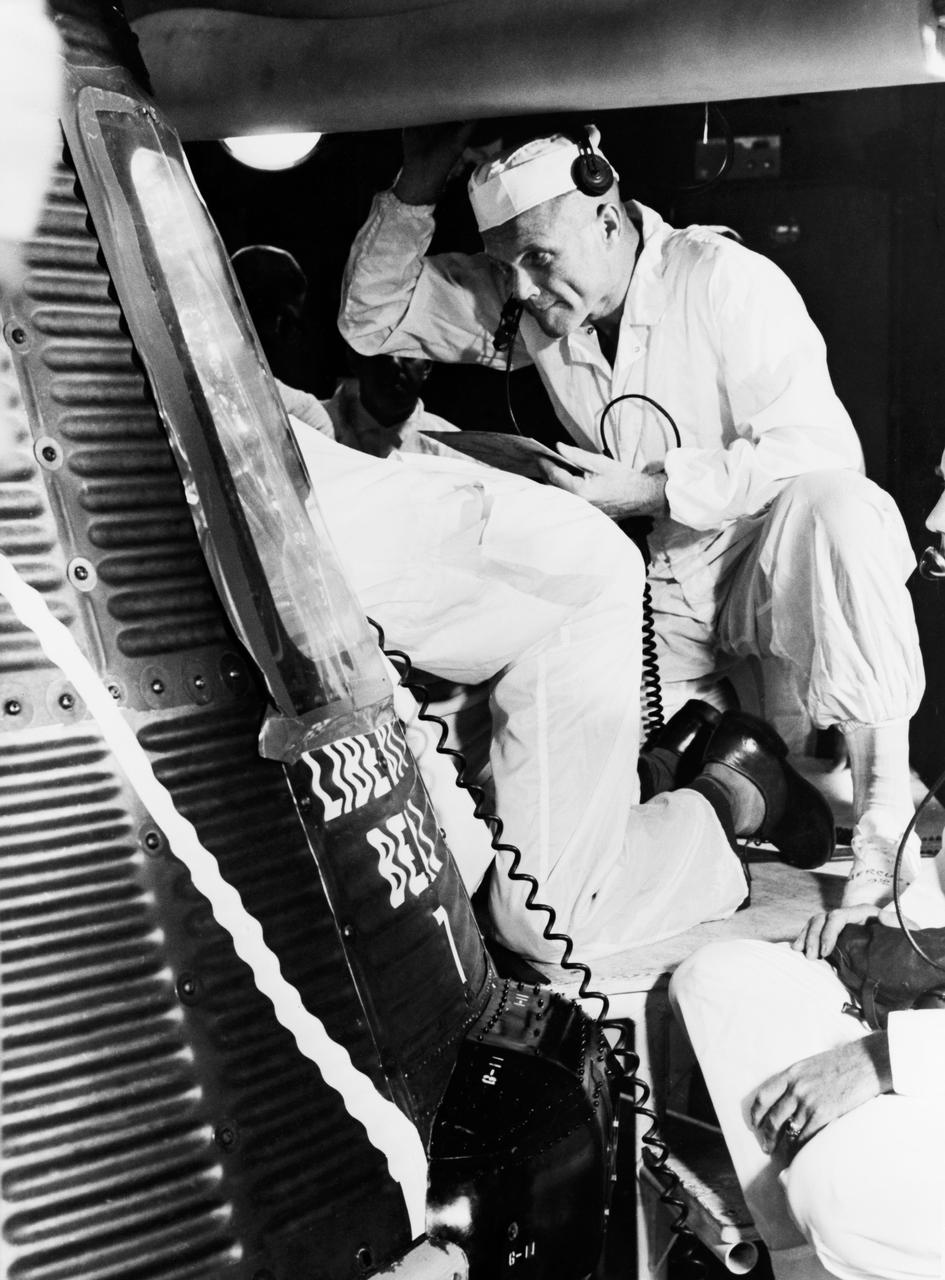

S61-03740 (20 July 1961) --- Astronaut John H. Glenn Jr. and a technician examine the interior of the Liberty Bell 7, the capsule flown a few days later during the Mercury-Redstone 4 mission with astronaut Virgil I. (Gus) Grissom. Photo credit: NASA
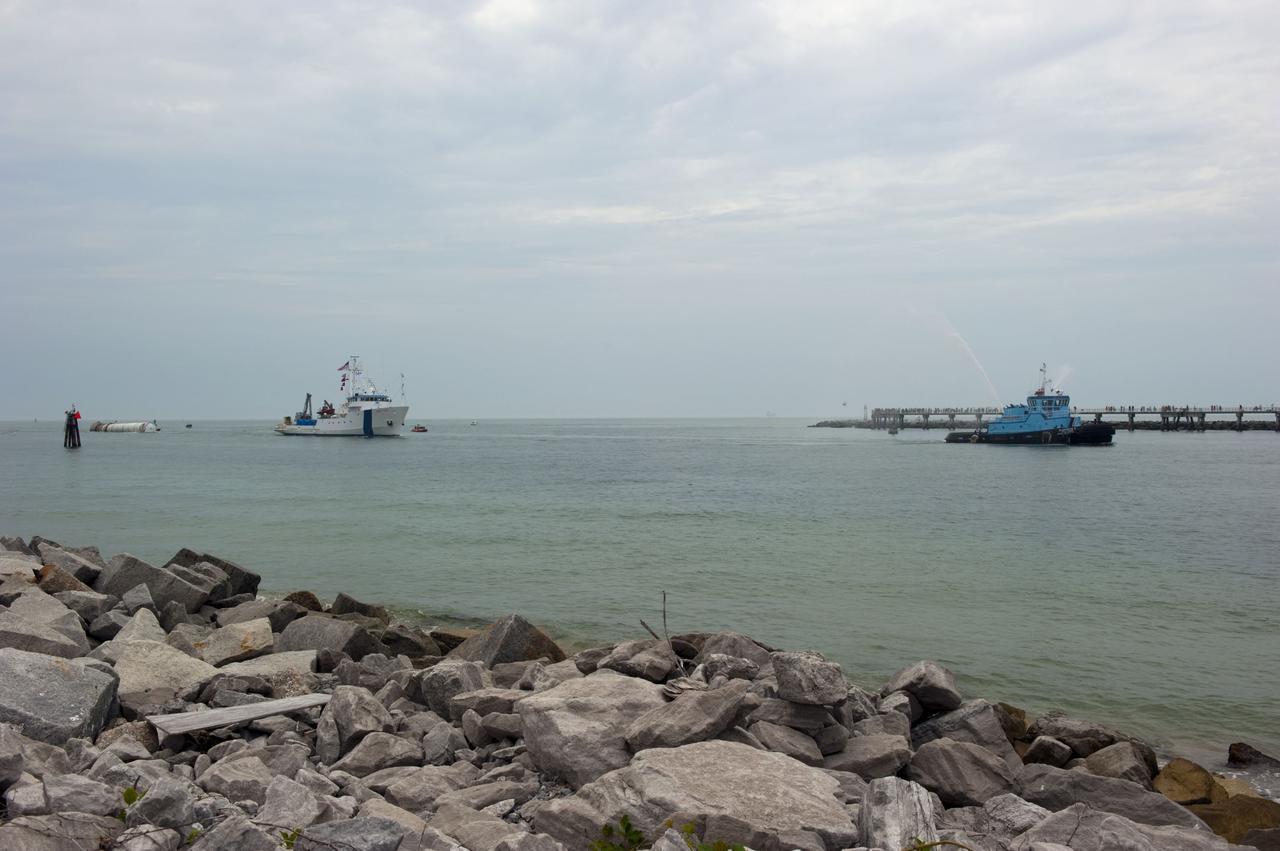

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows a spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. A Cape Canaveral Port Authority tug sends a spray of water through its cannon as a welcome back to the Port. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
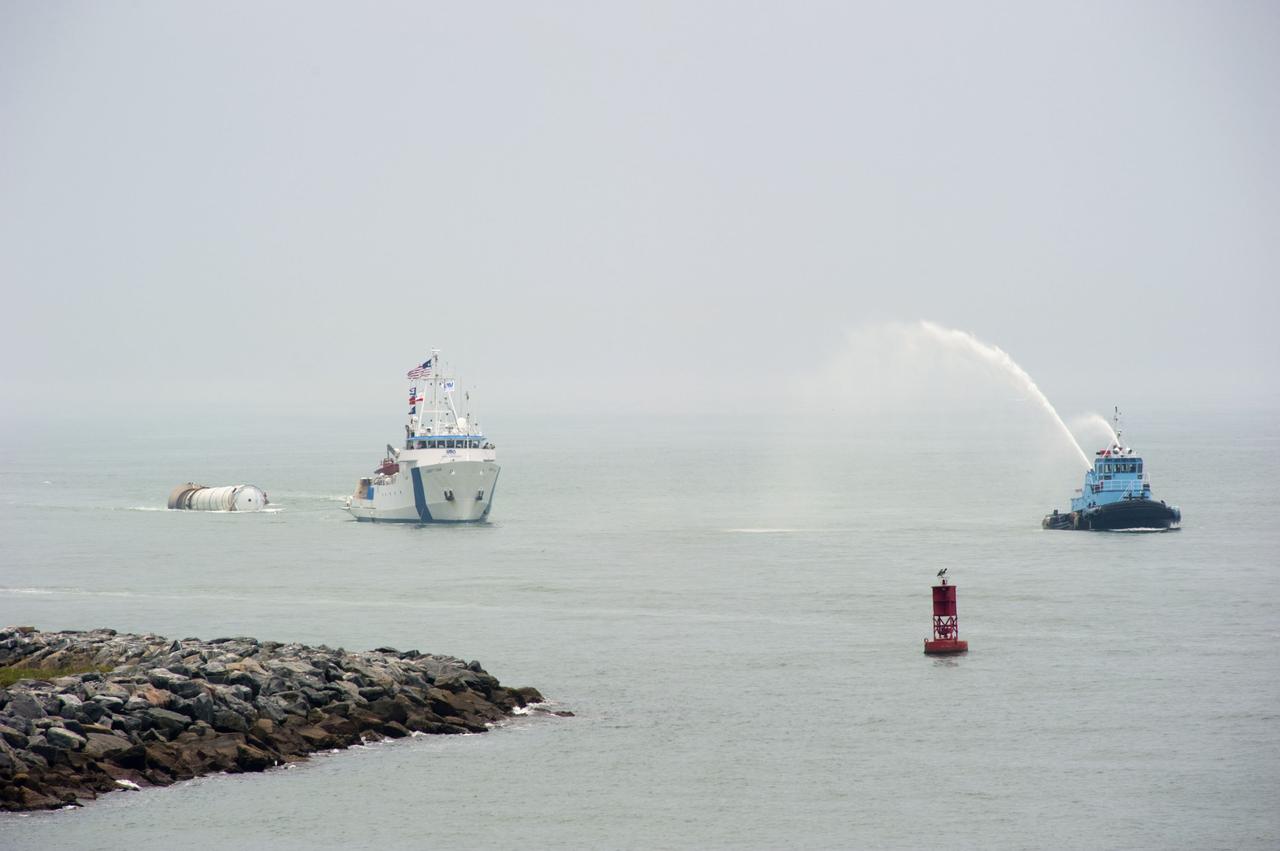

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows a spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. A Cape Canaveral Port Authority tug sends a spray of water through its cannon as a welcome back to the Port. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
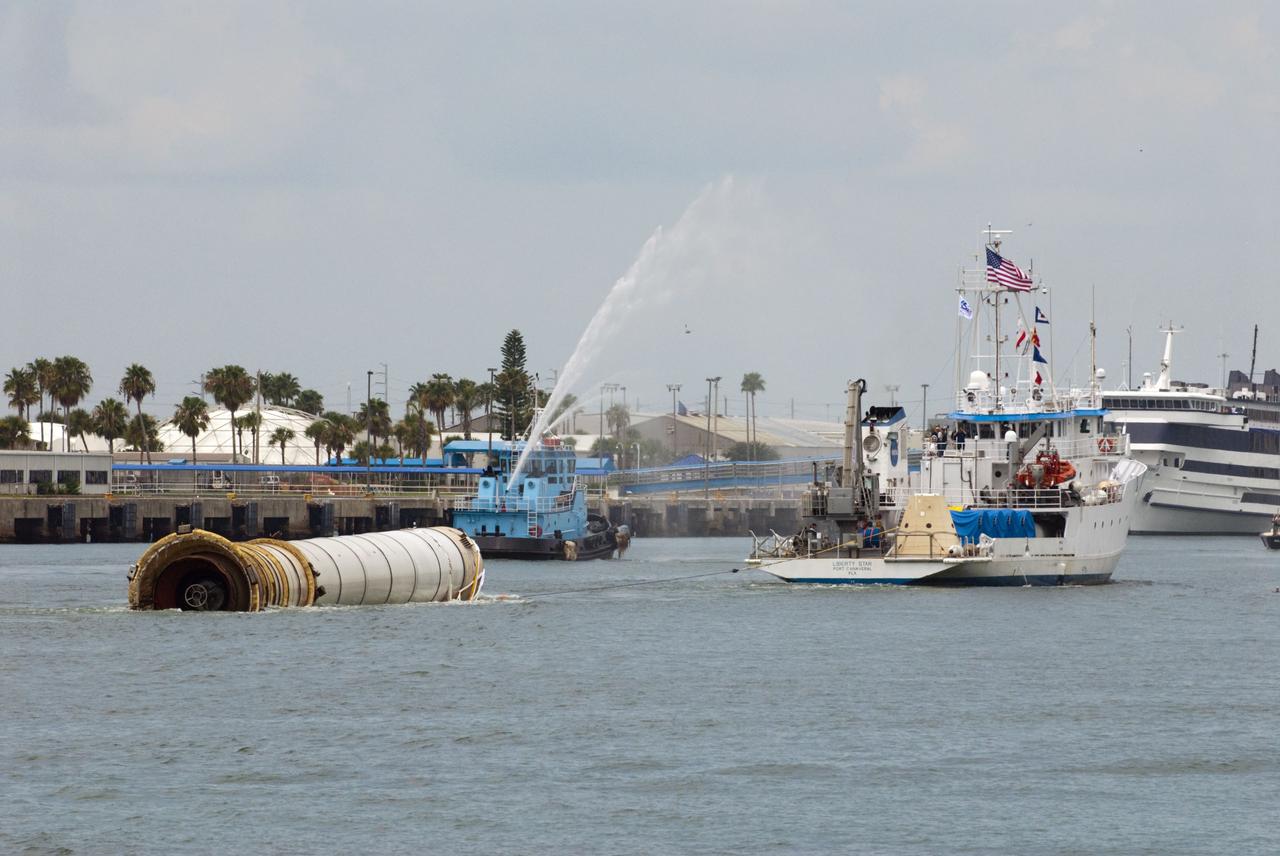

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows a spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. A Cape Canaveral Port Authority tug sends a spray of water through its cannon as a welcome back to the Port. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
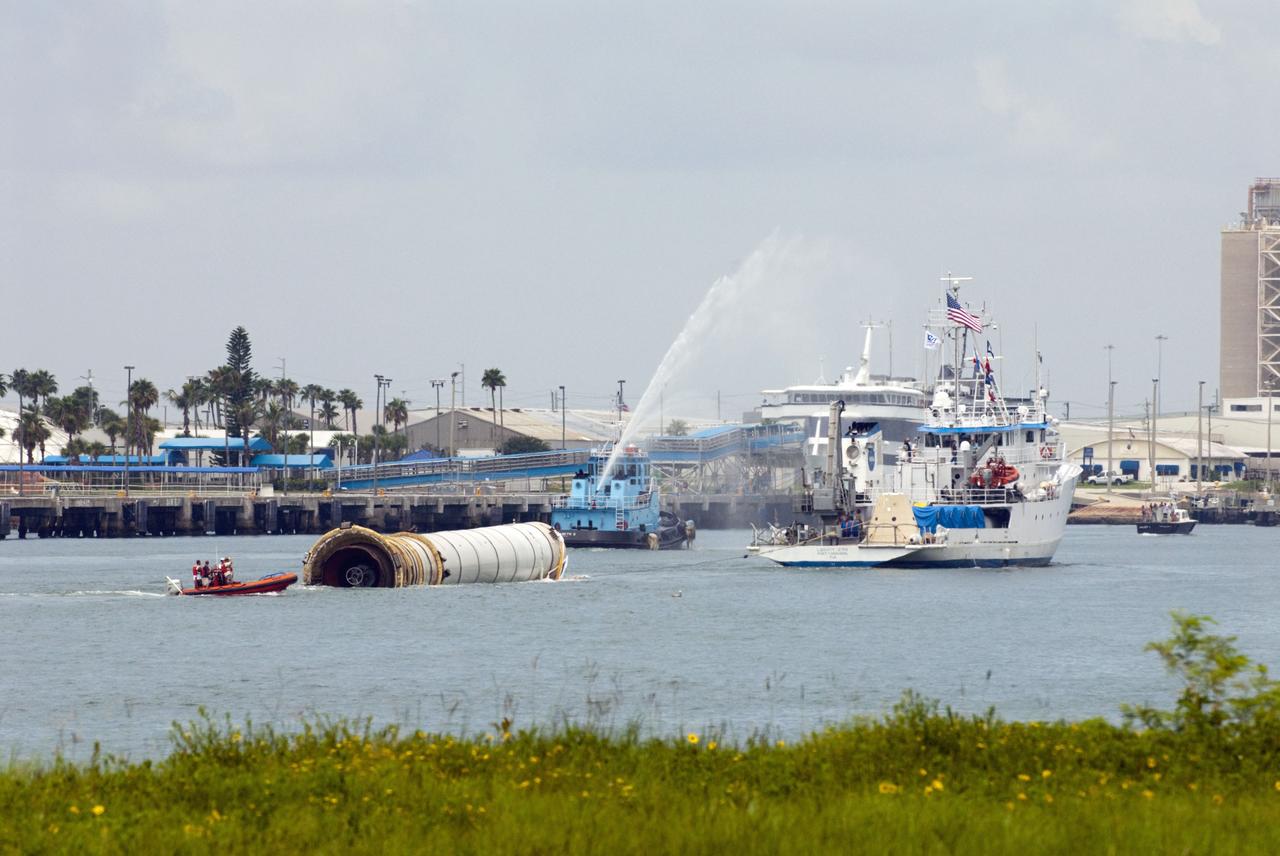

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A water-spraying tugboat escorts the Liberty Star as it tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final to Port Canaveral in Florida. The Liberty Star is one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
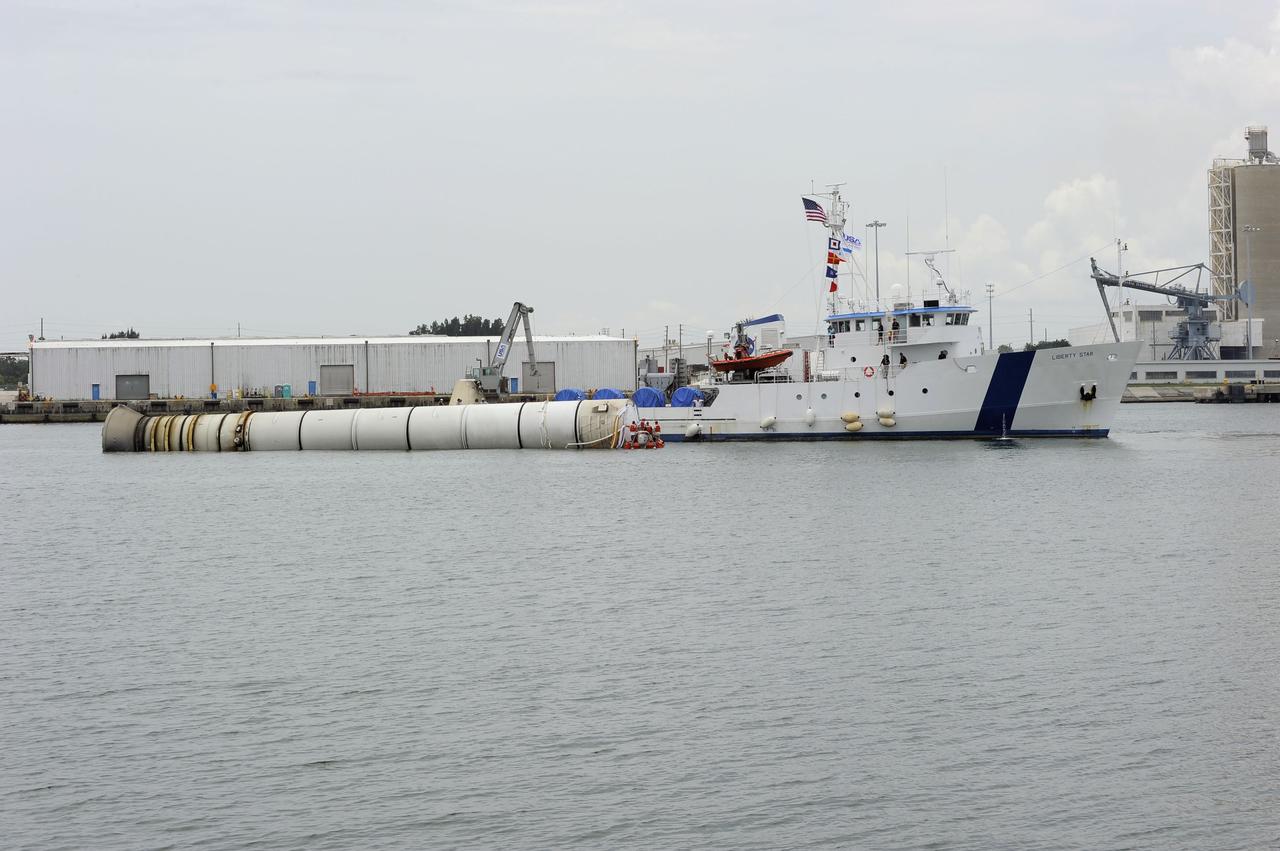

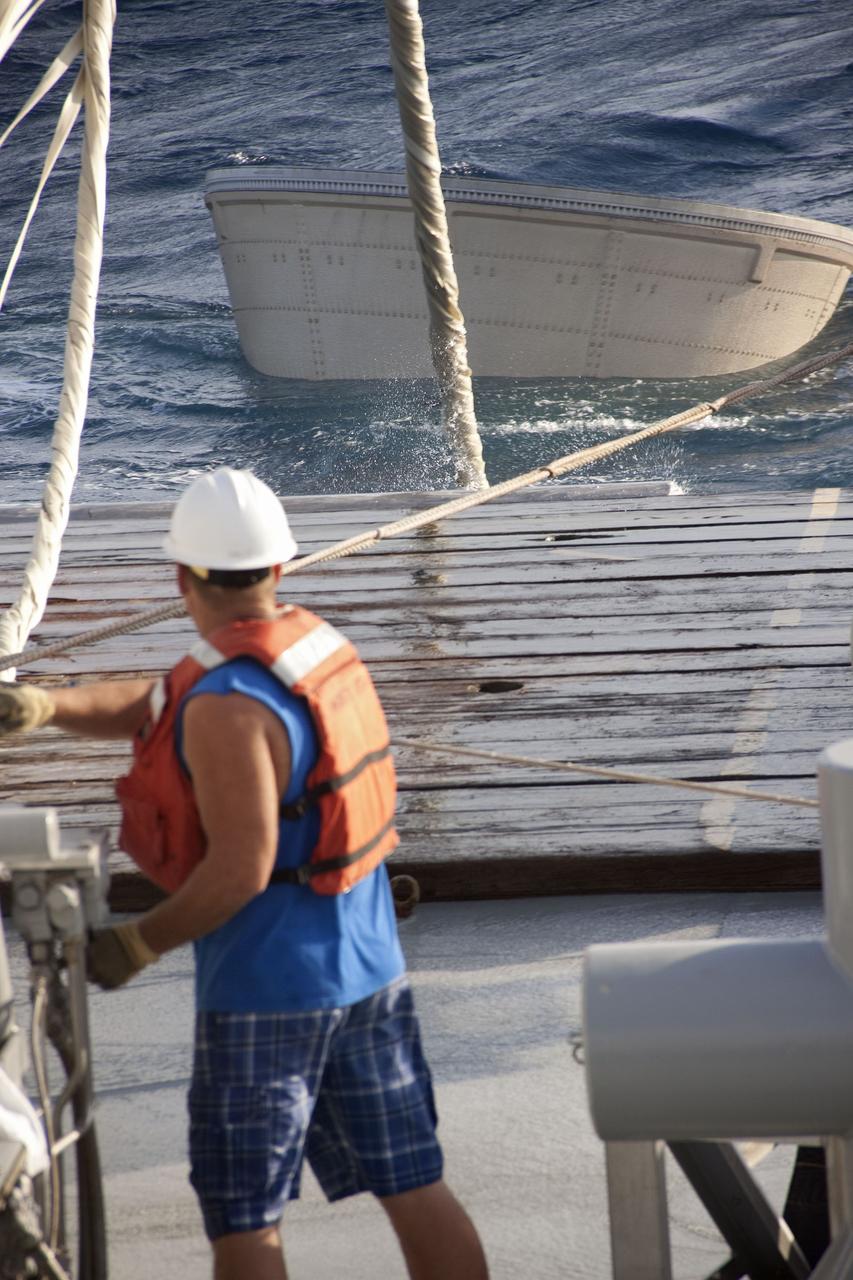
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, maneuvers the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, as it is taken to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
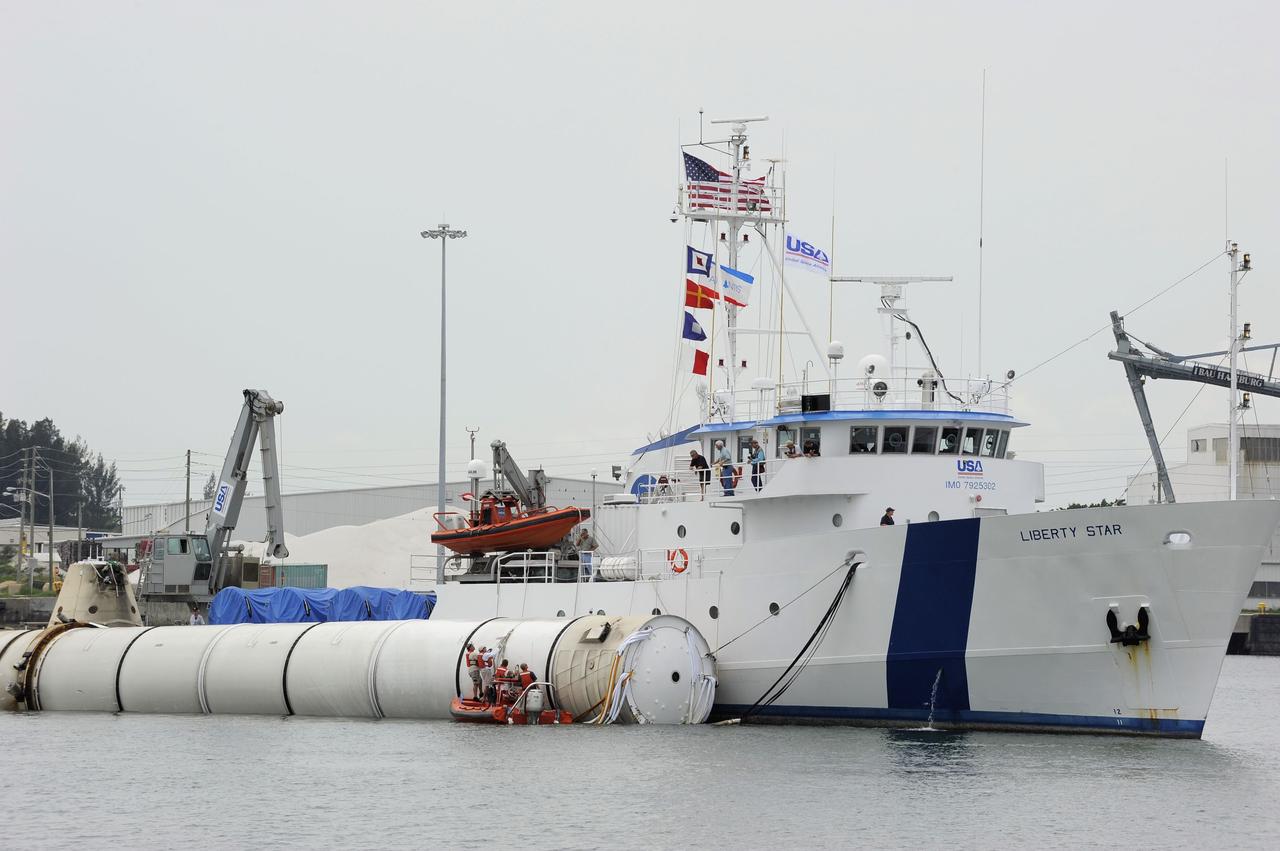

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, maneuvers the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, as it is taken to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
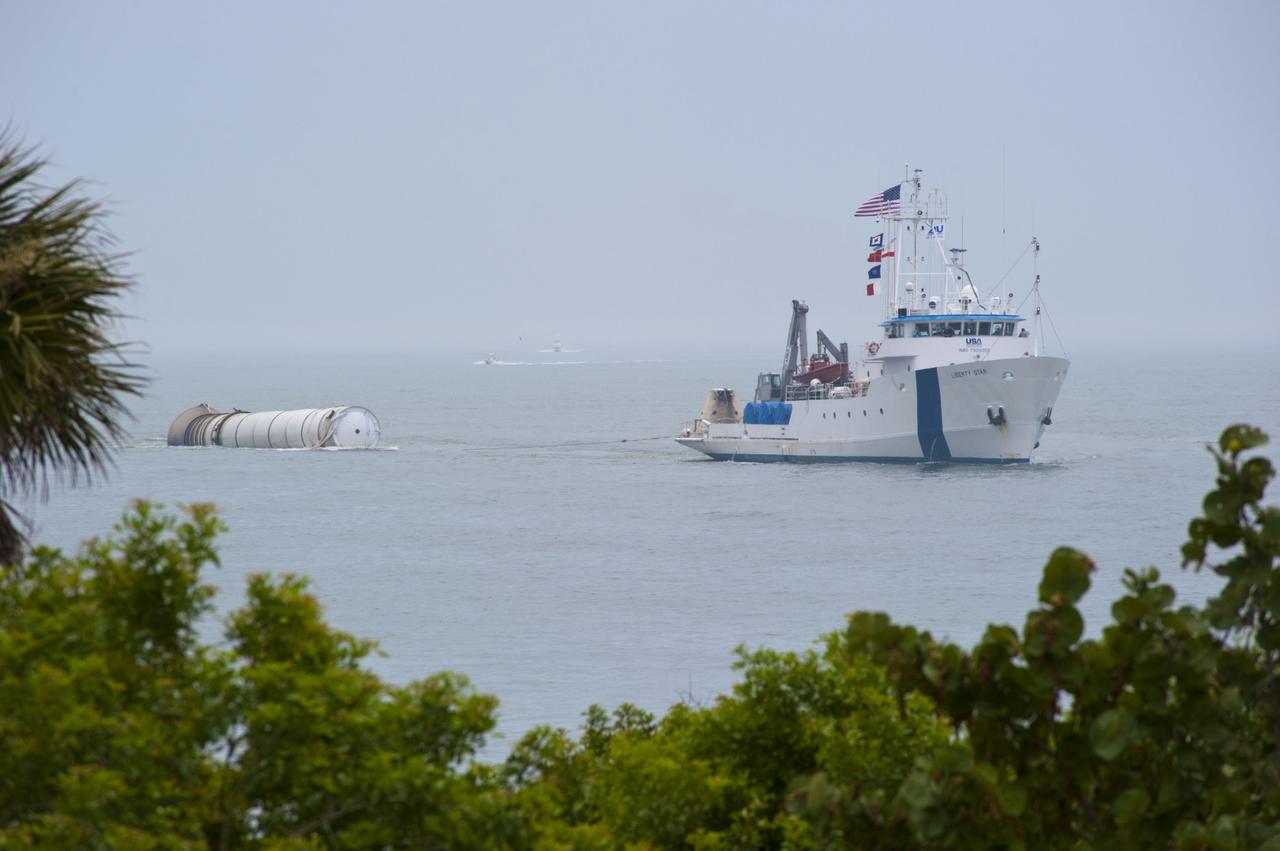

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
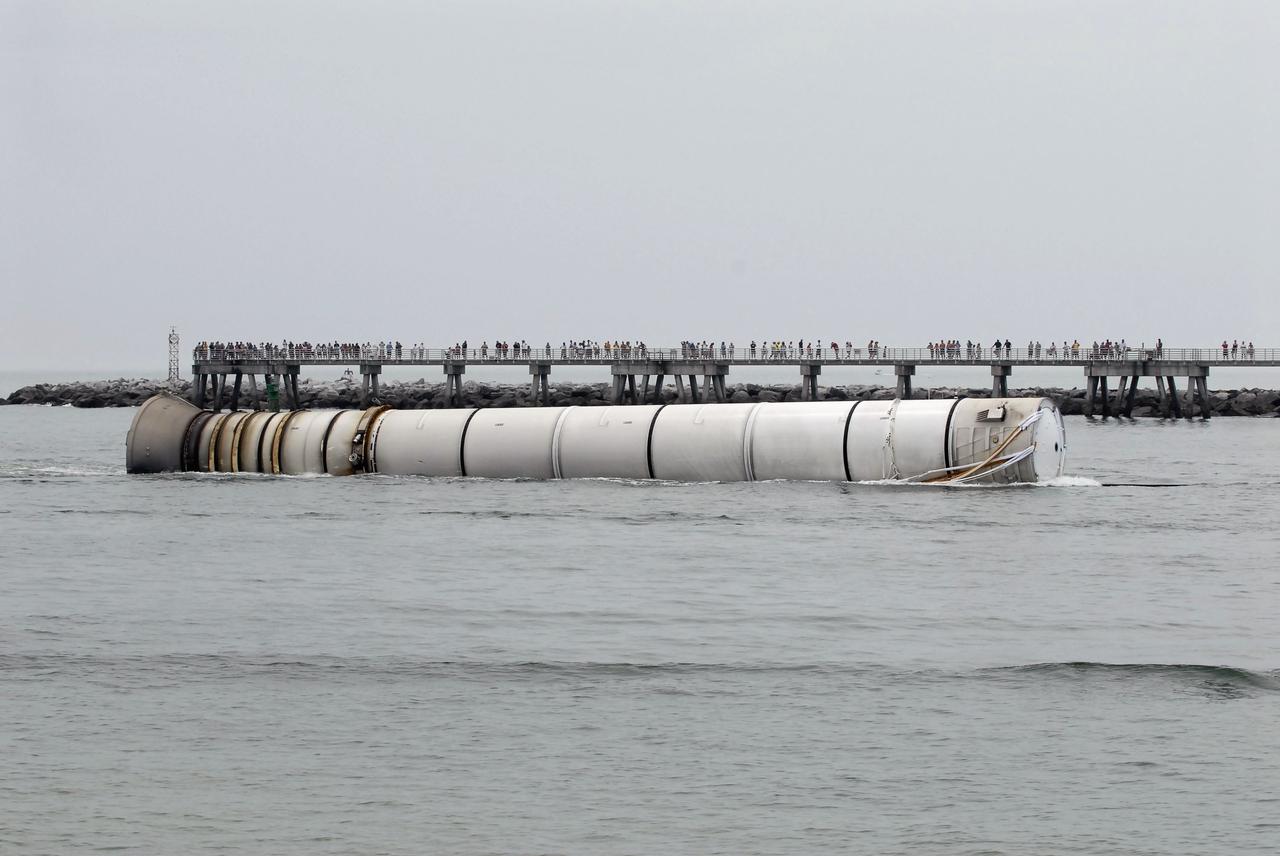

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch is towed by the Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
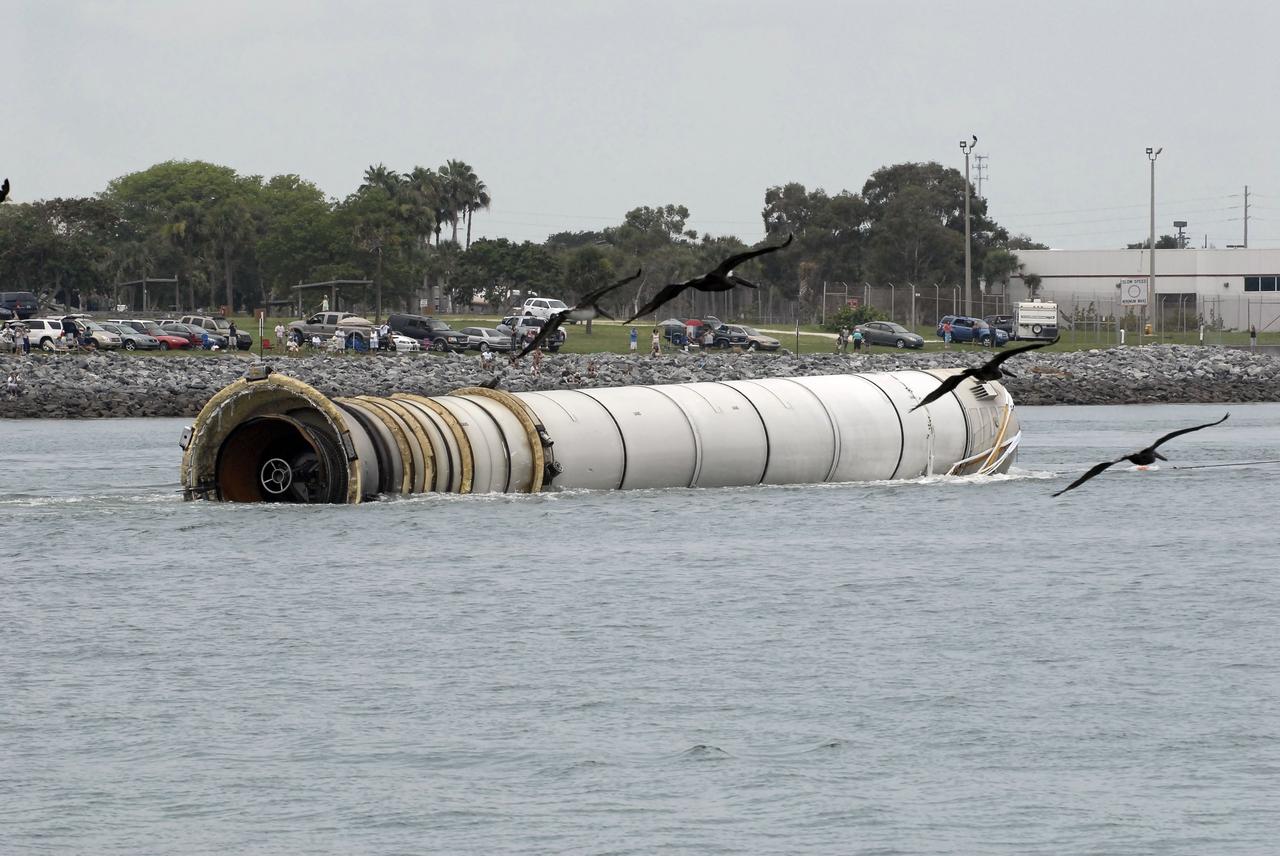

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch is towed by the Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
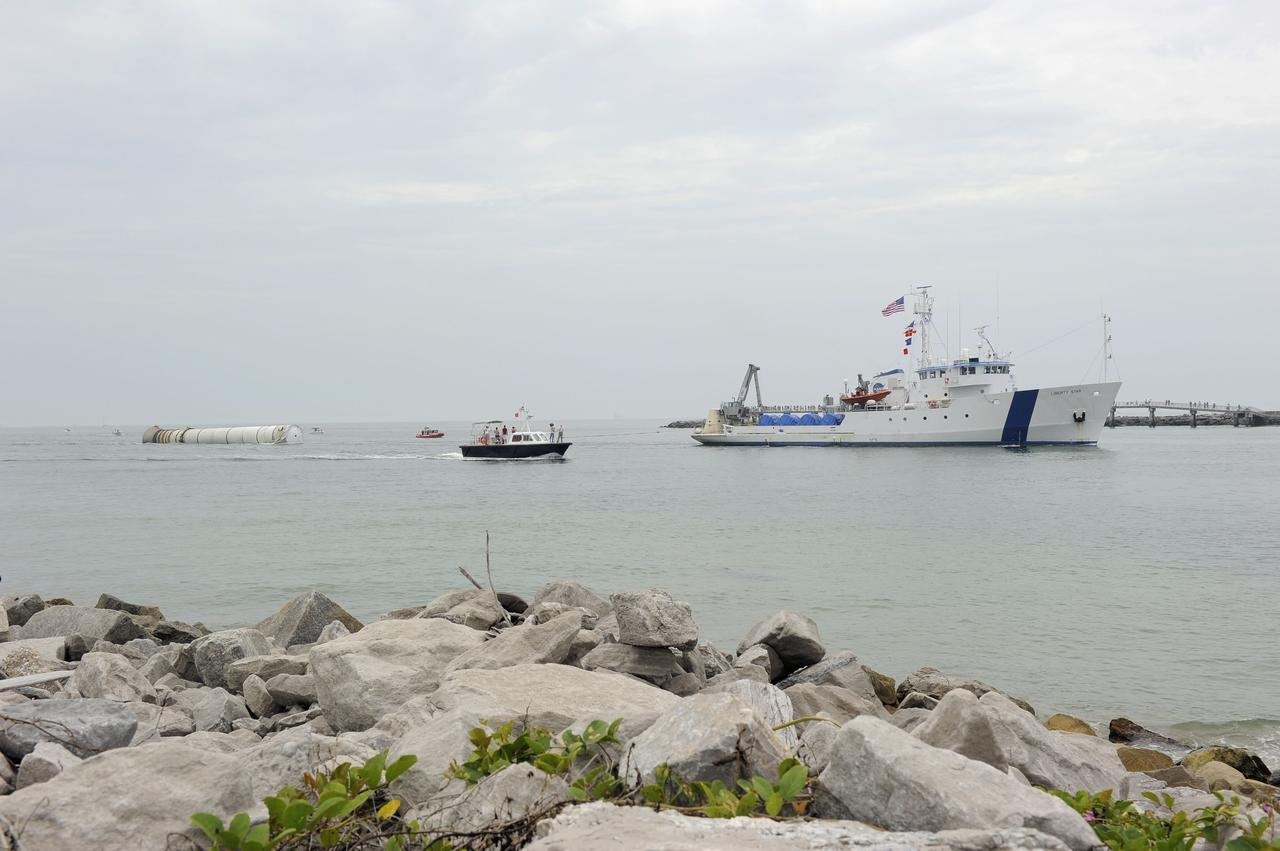

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
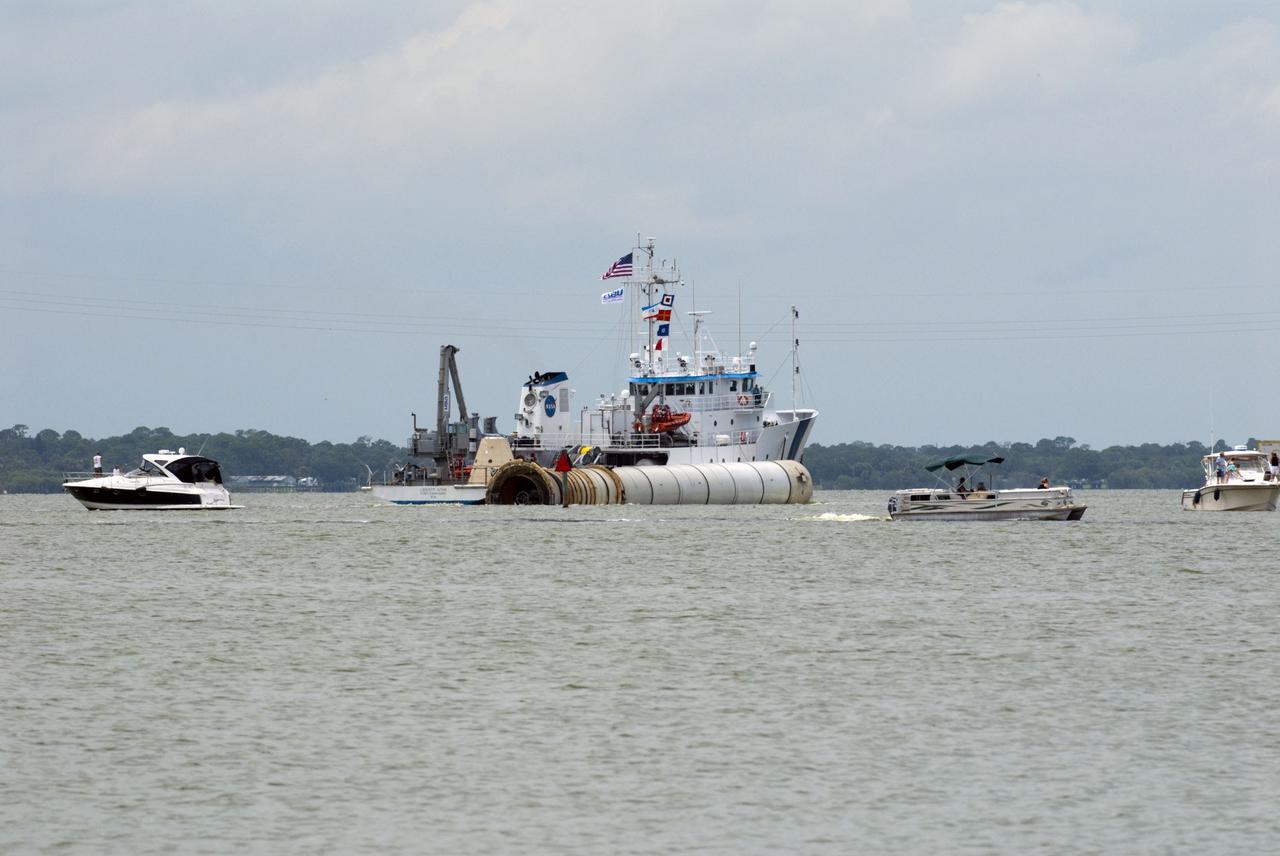

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, as it is taken to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
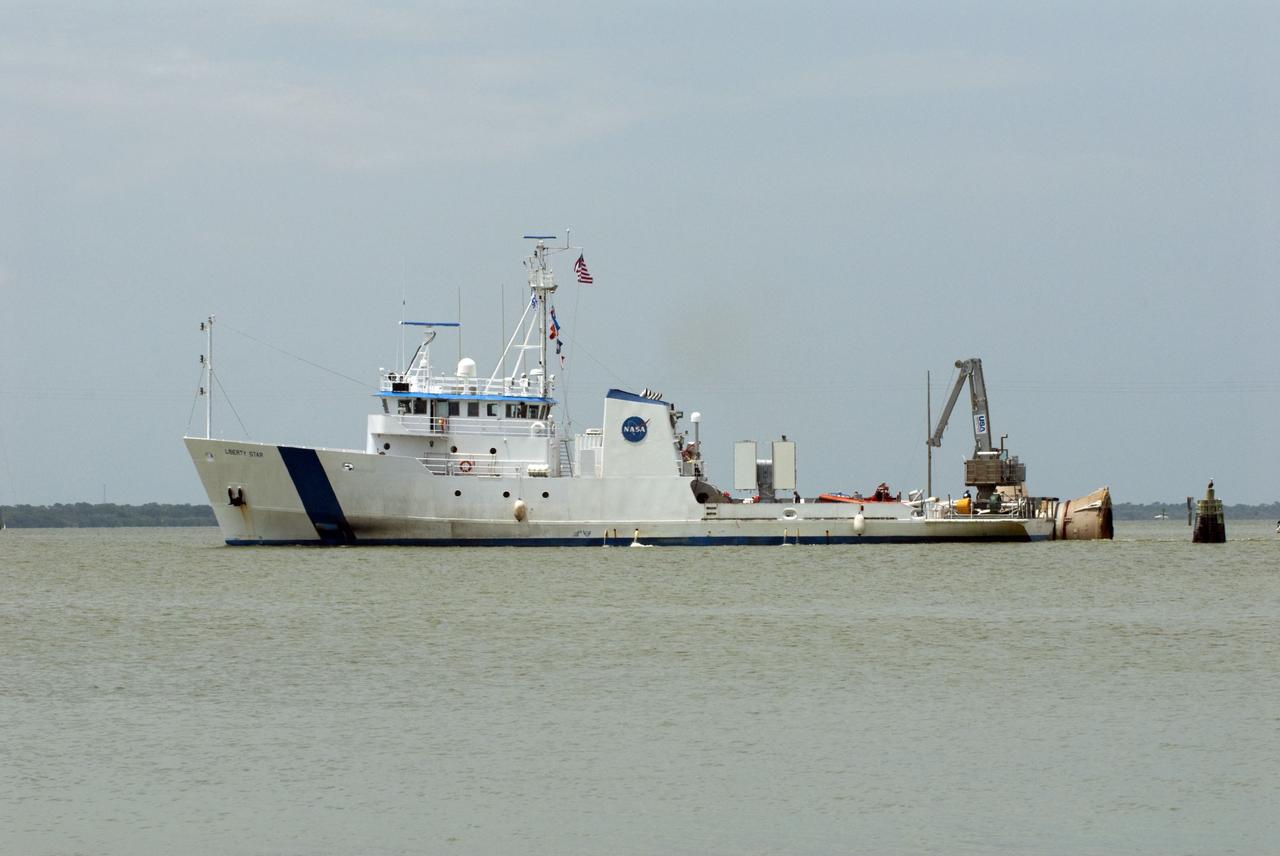

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, as it is taken to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
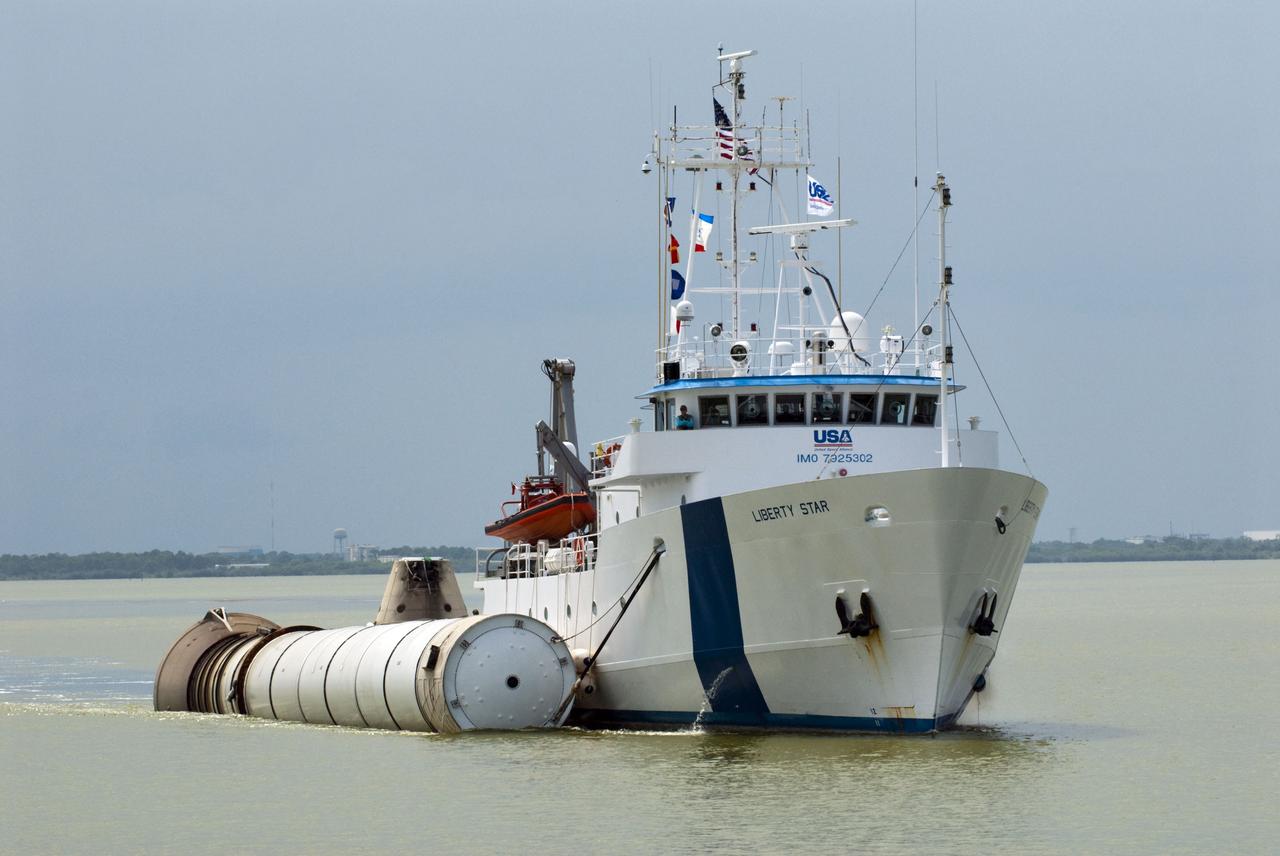

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, as it is taken to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
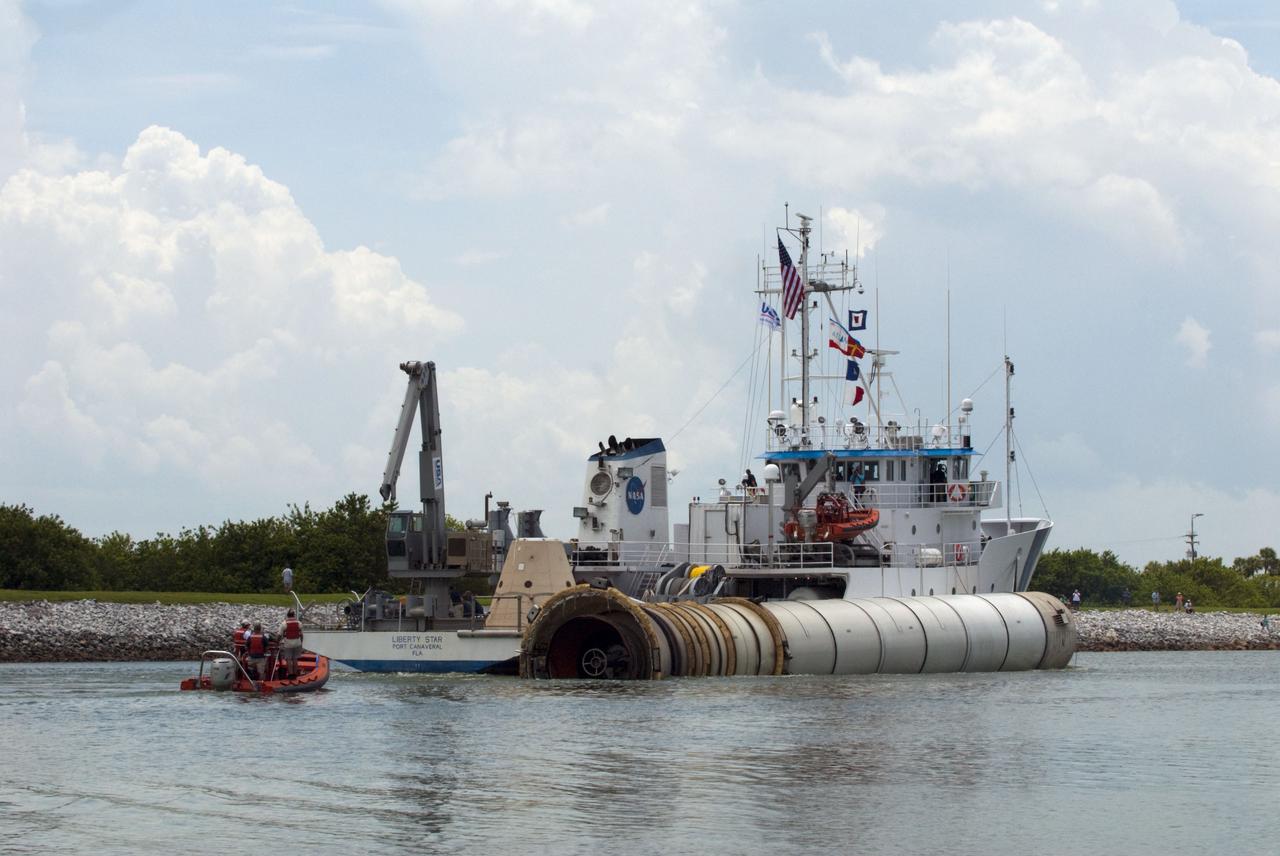

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, as it is taken to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
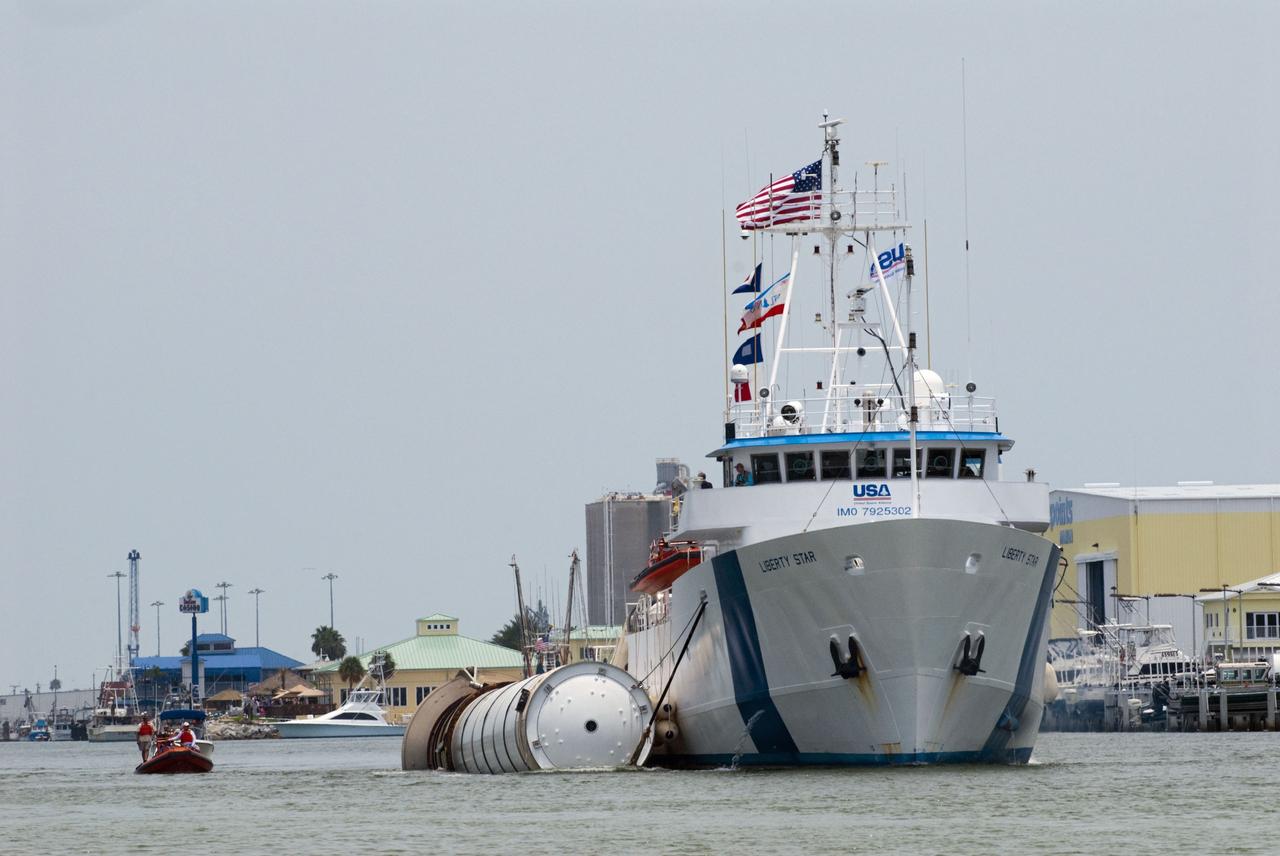

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, as it is taken to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
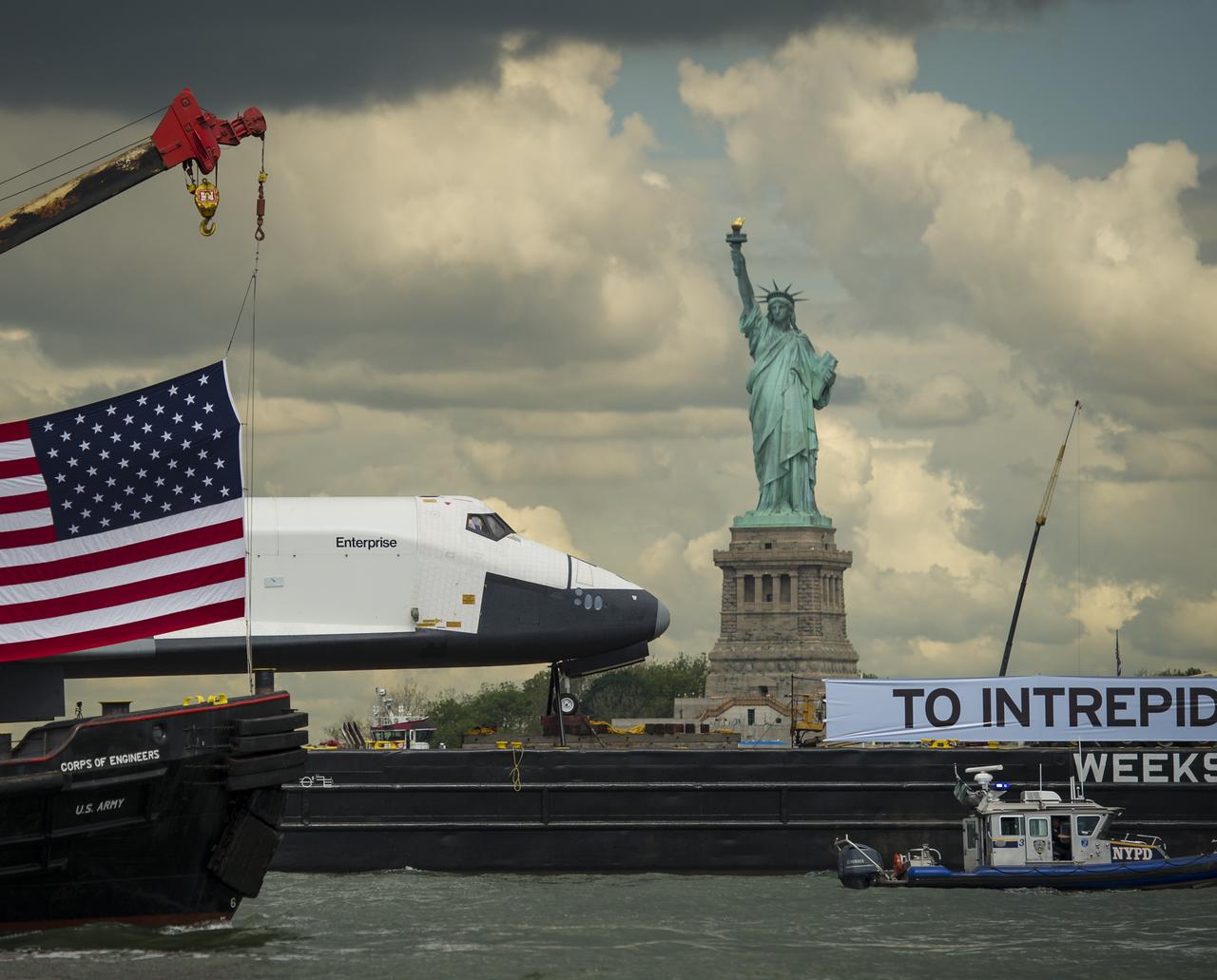

The space shuttle Enterprise, atop a barge, passes the Statue of Liberty in New York on its way to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum where it will be permanently displayed, Wednesday, June 6, 2012. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
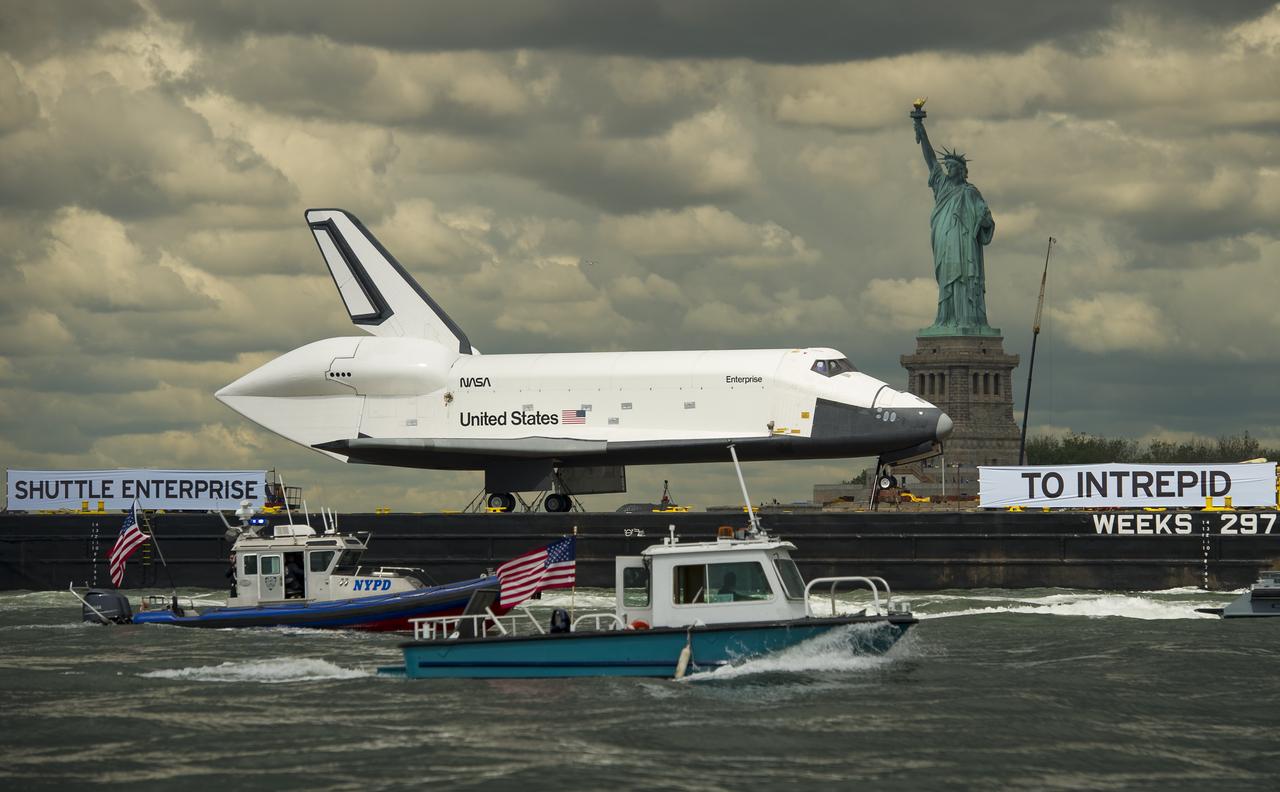

The space shuttle Enterprise, atop a barge, passes the Statue of Liberty in New York on its way to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum where it will be permanently displayed, Wednesday, June 6, 2012. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Astronaut Virgil I. "Gus" Grissom, one of the original seven astronauts for Mercury Project selected by NASA on April 27, 1959. The MR-4 mission, boosted by the Mercury-Redstone vehicle, made the second marned suborbital flight. The capsule, Liberty Bell 7, sank into the sea after the splashdown.
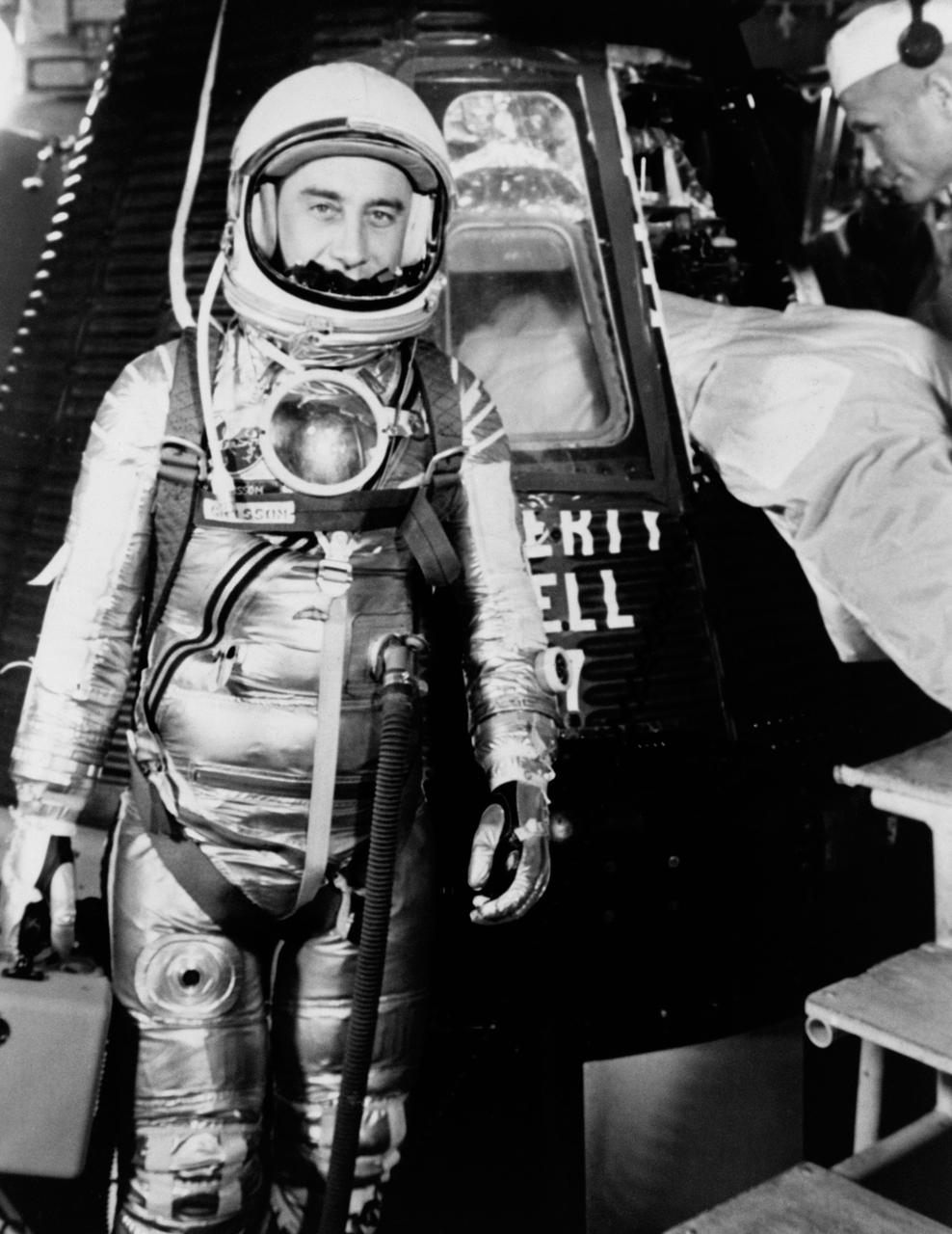

S61-02888 (1961) --- Astronaut Virgil I. (Gus) Grissom, suited up and ready to climb into Liberty Bell 7 spacecraft, stands in front of the capsule for a picture. Backup pilot John Glenn is in the right corner of the view behind Grissom. The Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) mission was scrubbed a few hours later due to unfavorable weather over the launch pad. Photo credit: NASA

S61-03698 (1961) --- Astronaut Virgil I. (Gus) Grissom, suited up and ready to climb into Liberty Bell 7 spacecraft, sits in front of his capsule for a picture. Behind him technicians work inside the capsule. The Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) mission was scrubbed a few hours later due to unfavorable weather over the launch pad. Photo credit: NASA
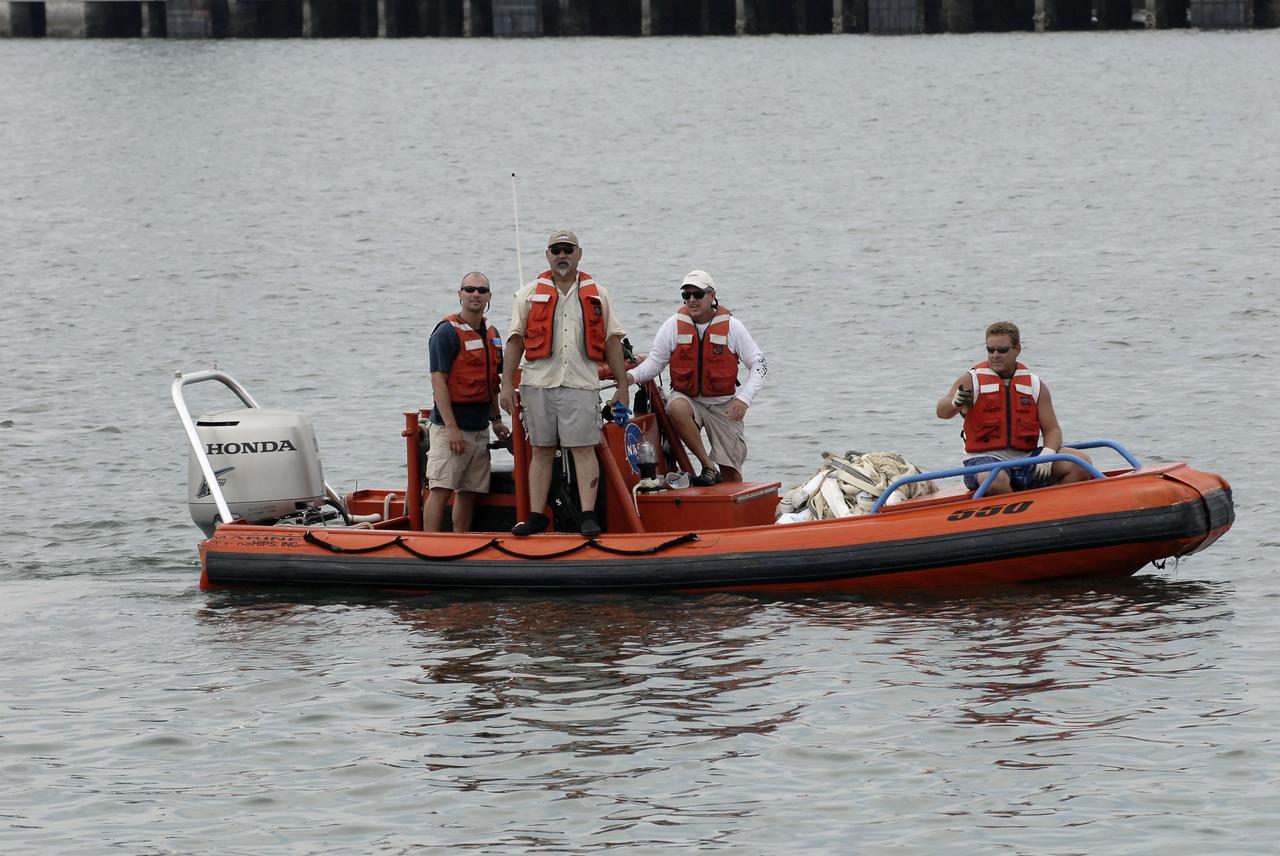

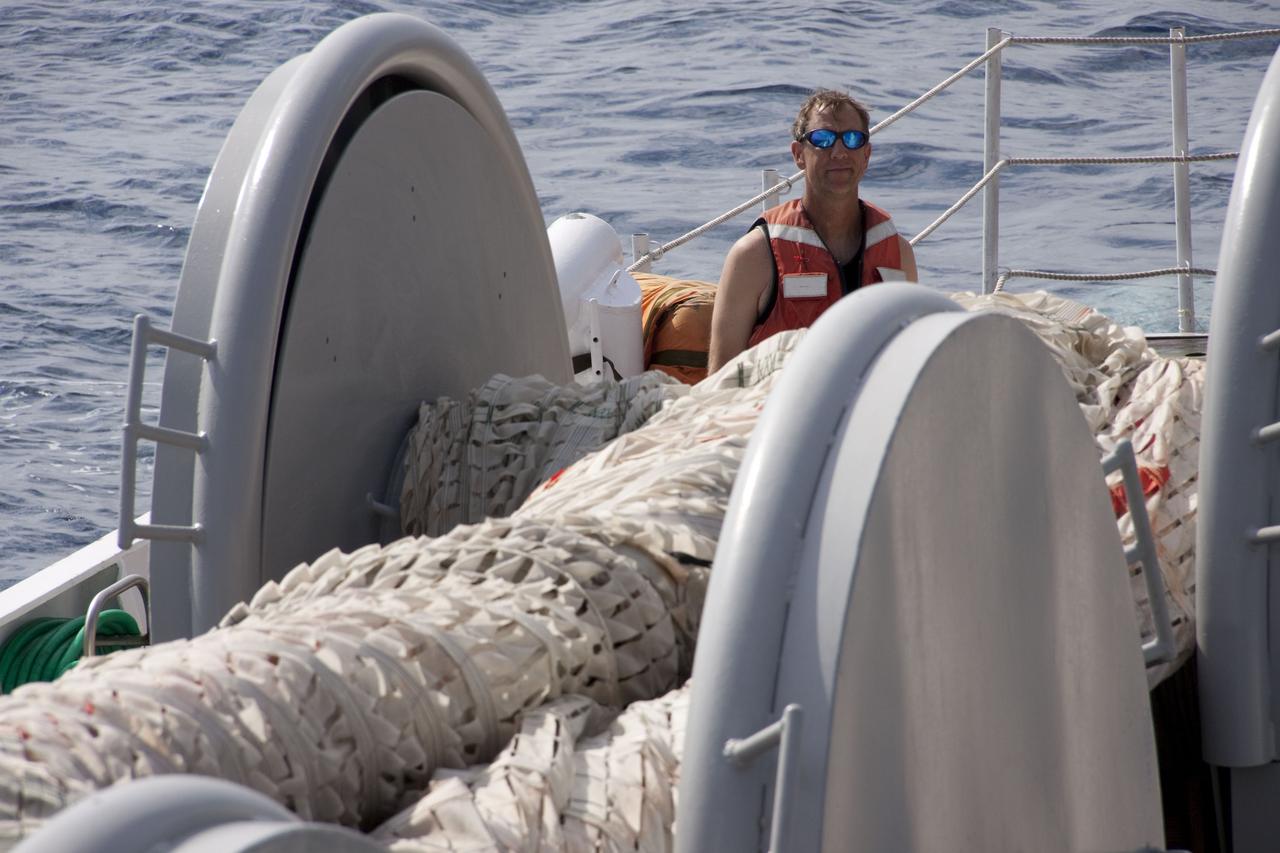
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A team oversees the return of the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final to Port Canaveral in Florida. The boat and team are from the Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
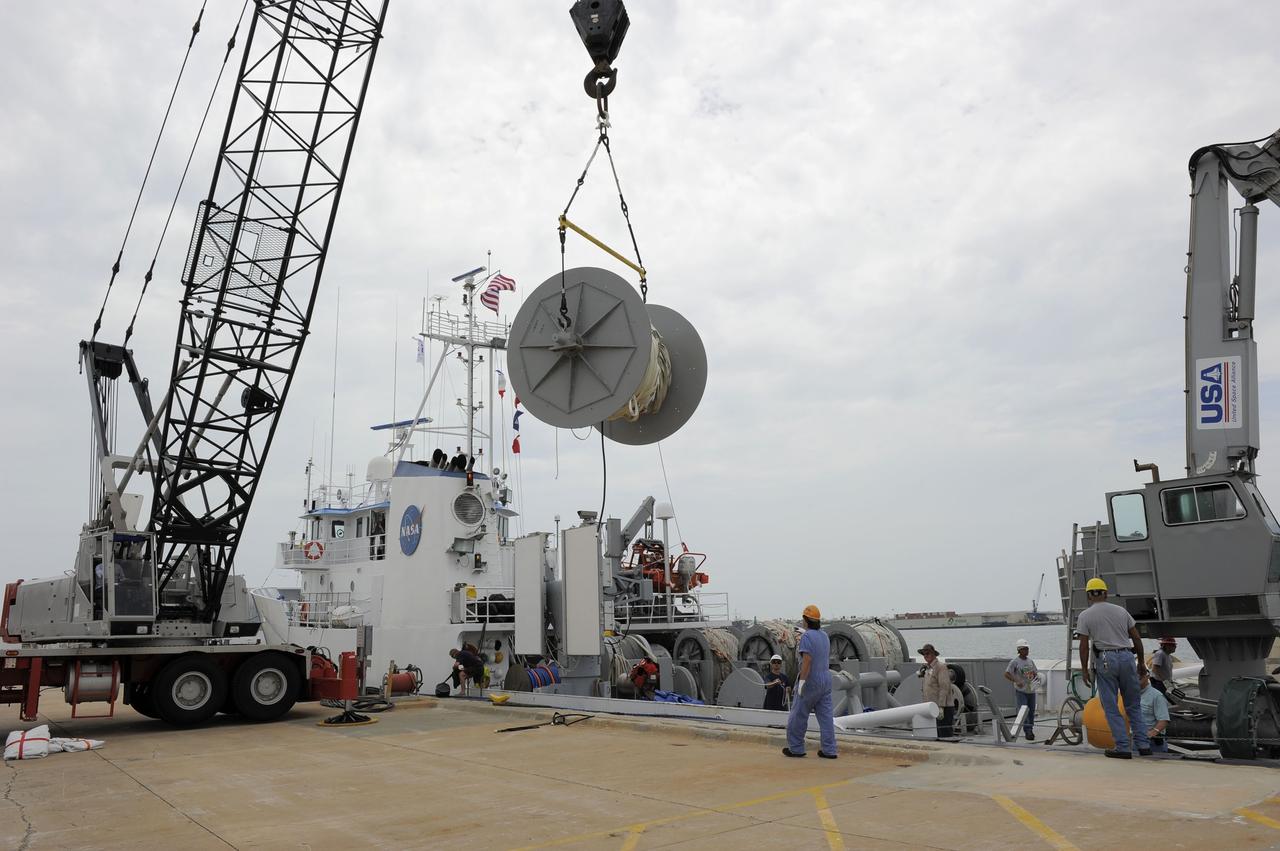

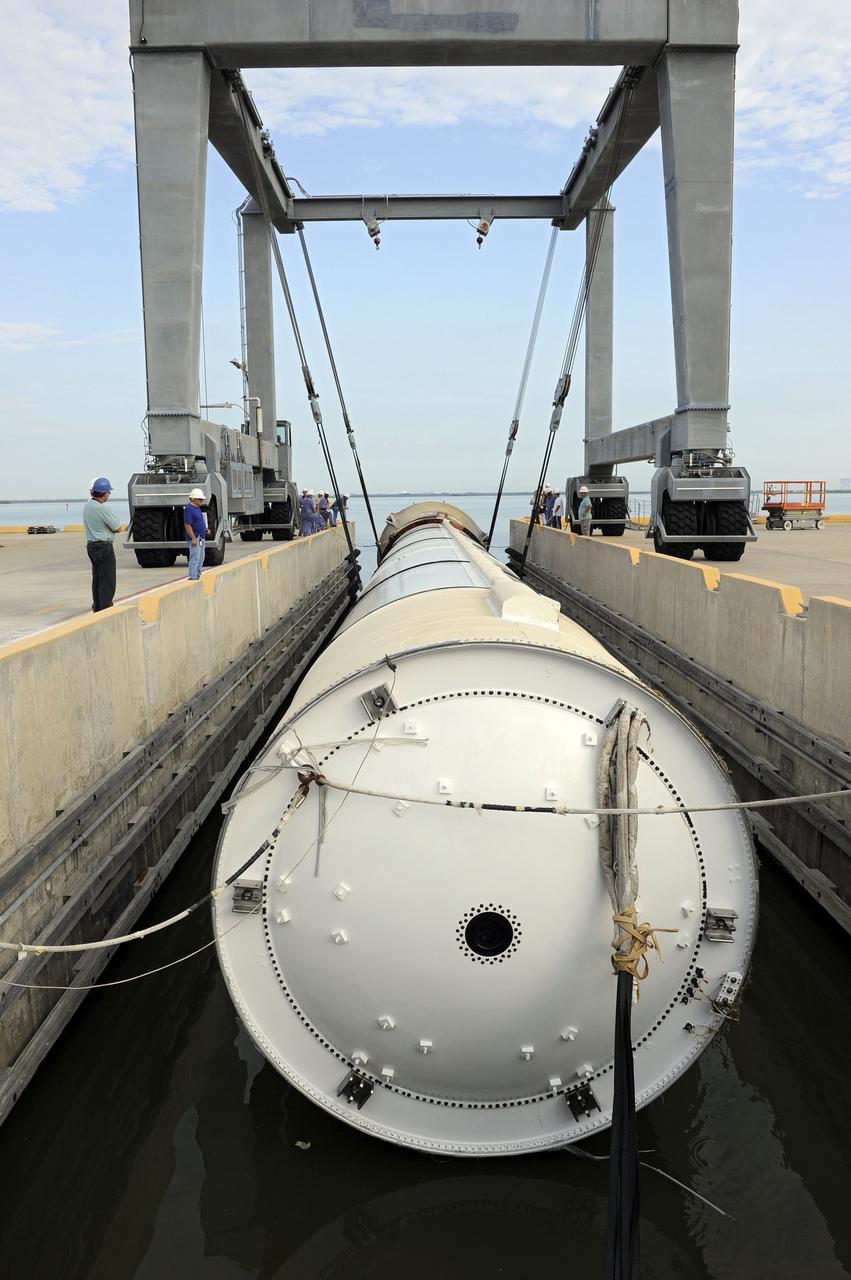
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A crane working from the dock at Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida removes one of the spools holding the parachutes and lines from the right spent boosters from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch. The parachutes and booster were gathered by the crews from the Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
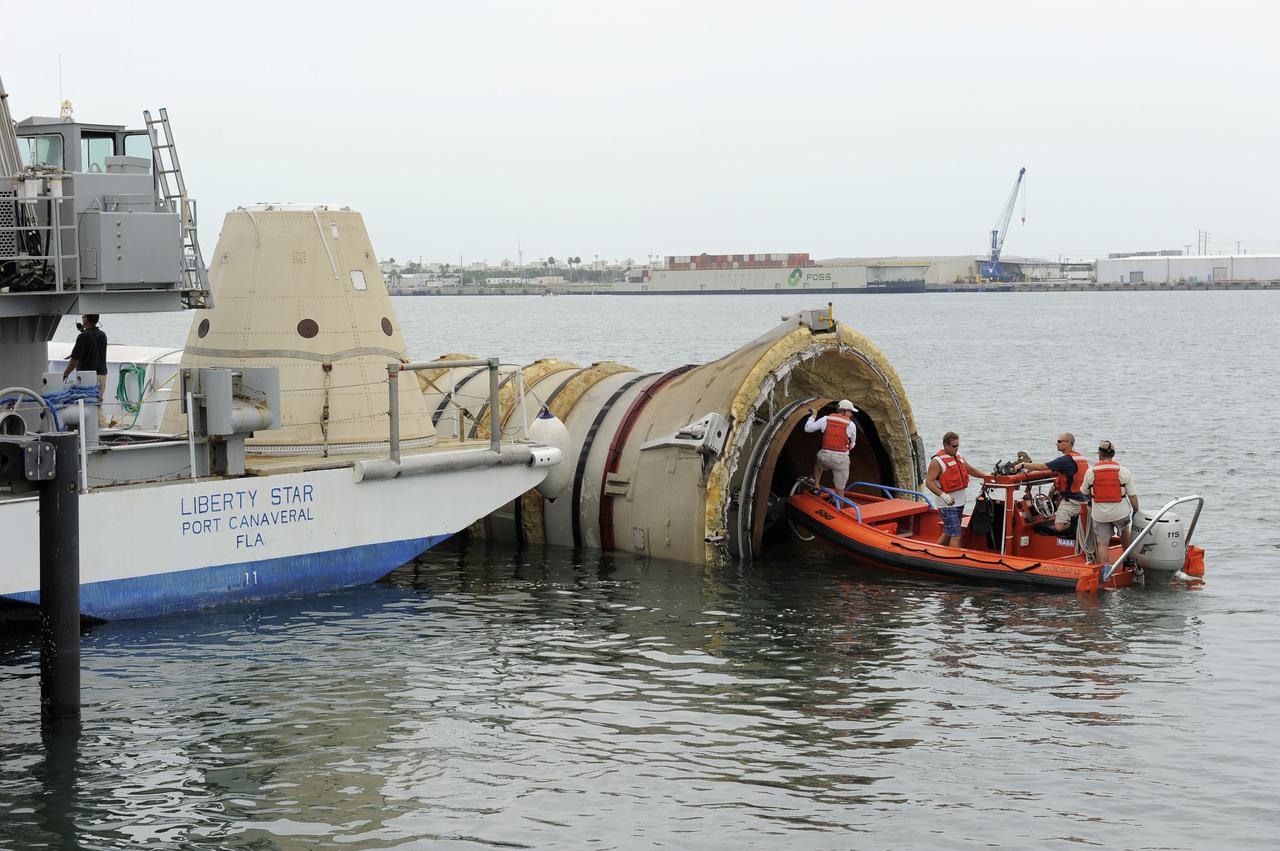

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Crews from the Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, inspect the end of the right spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis' final launch, as it is taken to a berth at Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also delivers the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit to the station. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
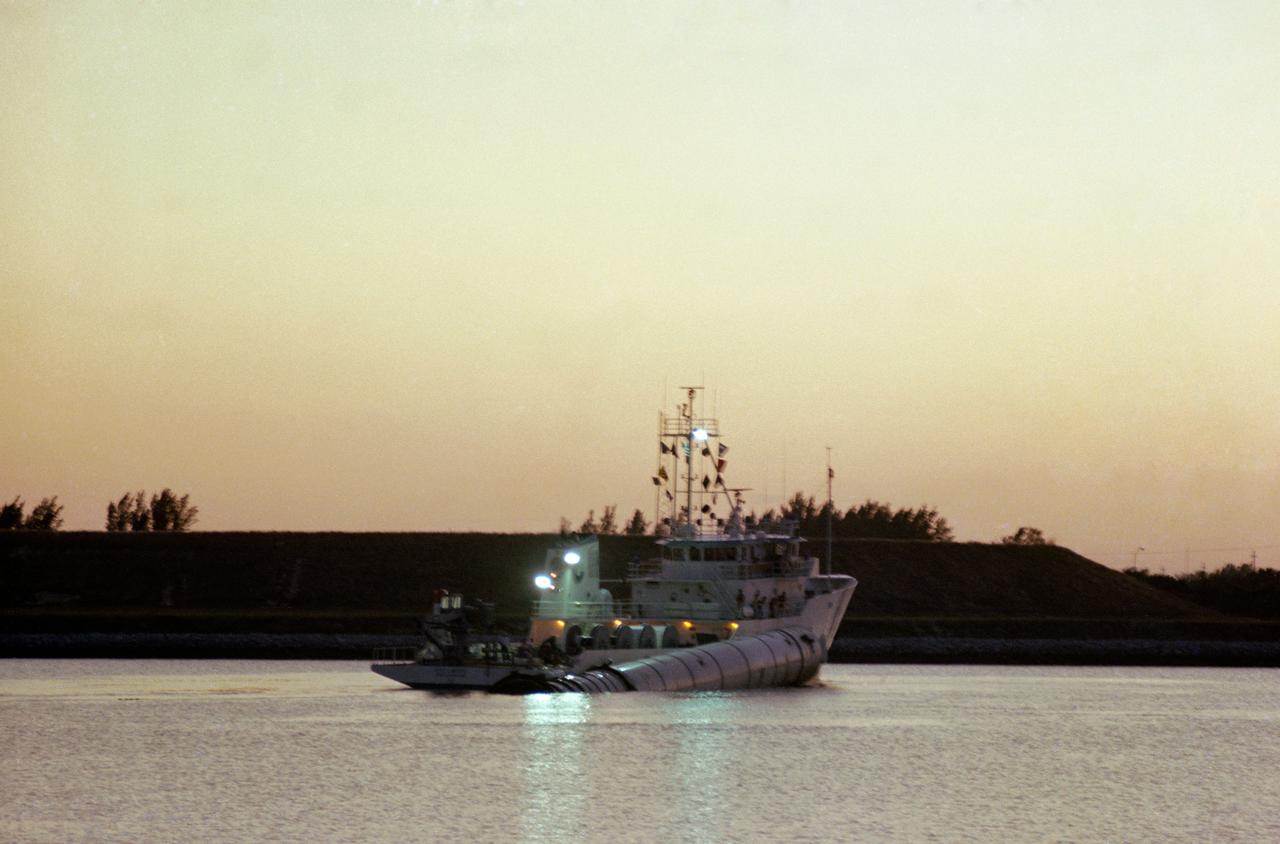

S81-31308 (13 April 1981) --- The solid rocket booster recovery ship UTC Liberty heads for Cape Canaveral Air Force Station after retrieving one of the two booster casings from the launch of Columbia, America?s first space shuttle in orbit. The vessel had been tied up overnight at the Trident Submarine Basin at Port Canaveral, from which point this photograph was made. The boosters and the parachutes that bring them to safe landings in the Atlantic east of NASA's Kennedy Space Center are recovered at sea, dewatered and towed to processing facilities at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA

Space shuttle Enterprise, mounted atop a NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA), is seen as it flies near the Statue of Liberty and the Manhattan skyline, Friday, April 27, 2012, in New York. Enterprise was the first shuttle orbiter built for NASA performing test flights in the atmosphere and was incapable of spaceflight. Originally housed at the Smithsonian's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Enterprise will be demated from the SCA and placed on a barge that will eventually be moved by tugboat up the Hudson River to the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in June. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)

S61-02881 (1961) --- Astronaut Virgil I. (Gus) Grissom, suited up in a newly designed pressure suit, is assisted as he climbs into Liberty Bell 7 spacecraft. Behind him backup pilot John Glenn watches the insertion. The Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) mission was scrubbed a few hours later due to unfavorable weather over the launch pad. Photo credit: NASA

S81-31319 (14 April 1981) --- One of the STS-1 solid rocket boosters (SRB) is towed back to shore after landing in the Atlantic Ocean following the jettisoning of both of Columbia?s SRB en route to her Earth-orbital mission. The UTC Freedom and Liberty (pictured) were involved in the recovery of the reusable boosters. Astronauts John W. Young, commander, and Robert L. Crippen, pilot, are orbiting Earth for approximately two and a third days aboard Columbia. Photo credit: NASA
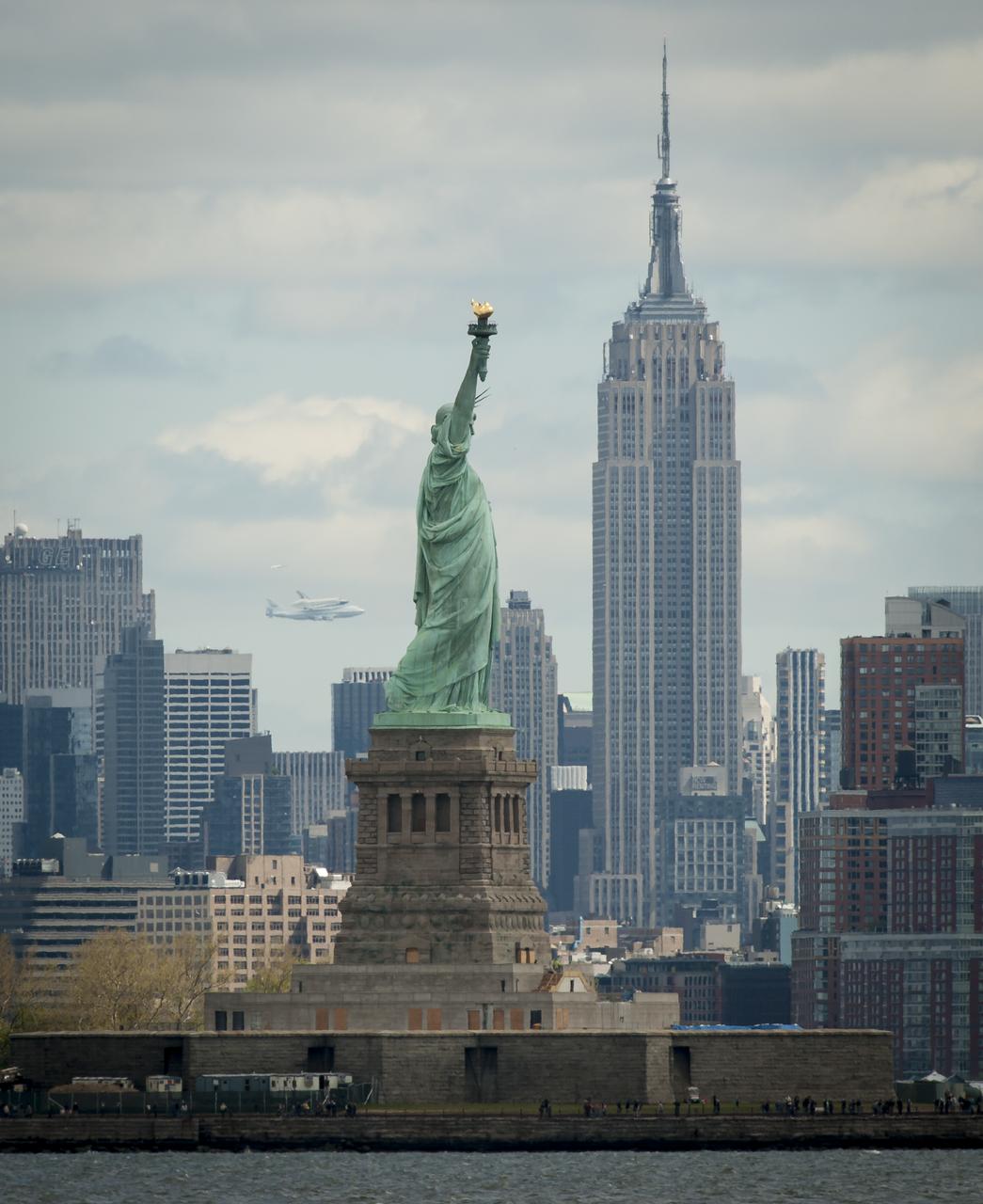

Space shuttle Enterprise, mounted atop a NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA), is seen off in the distance behind the Statue of Liberty, Friday, April 27, 2012, in New York. Enterprise was the first shuttle orbiter built for NASA performing test flights in the atmosphere and was incapable of spaceflight. Originally housed at the Smithsonian's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Enterprise will be demated from the SCA and placed on a barge that will eventually be moved by tugboat up the Hudson River to the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in June. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
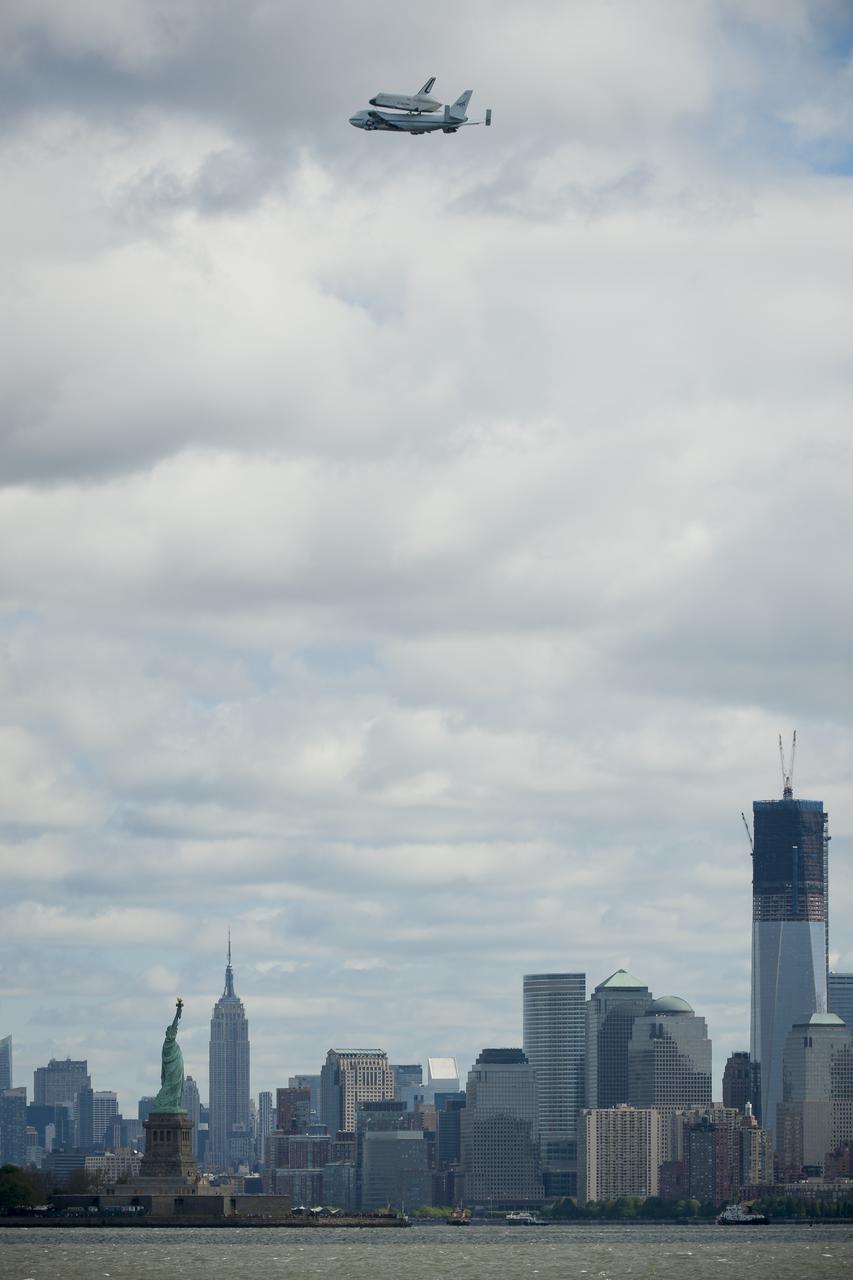

Space shuttle Enterprise, mounted atop a NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA), is seen as it flies near the Statue of Liberty, Friday, April 27, 2012, in New York. Enterprise was the first shuttle orbiter built for NASA performing test flights in the atmosphere and was incapable of spaceflight. Originally housed at the Smithsonian's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Enterprise will be demated from the SCA and placed on a barge that will eventually be moved by tugboat up the Hudson River to the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in June. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
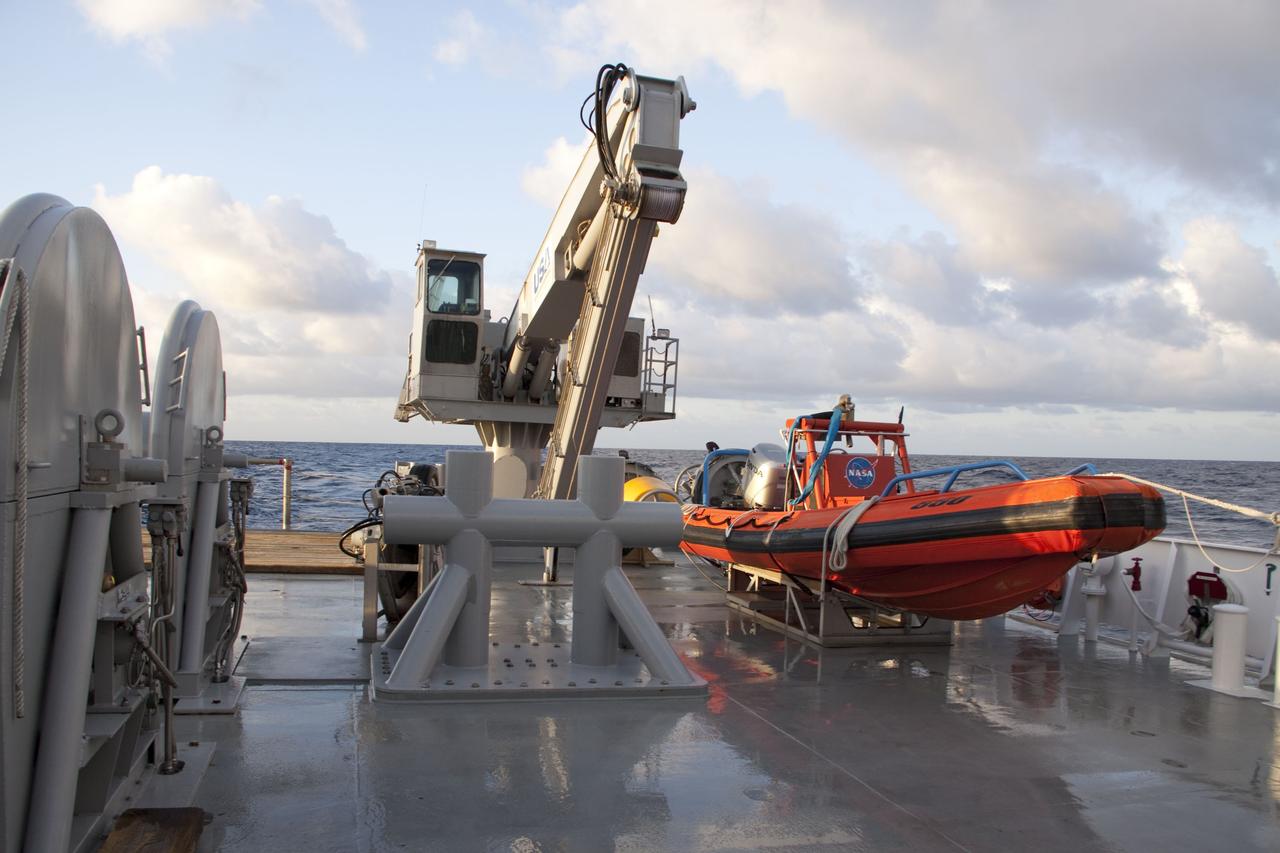

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A crane and a skiff await Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, to reach the splash-down area where the right spent booster from Discovery's final launch has landed. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Liberty Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux

S61-03705 (1961) --- Close-up view of the fueling of the Liberty Bell 7 for the Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) mission. Photo credit: NASA
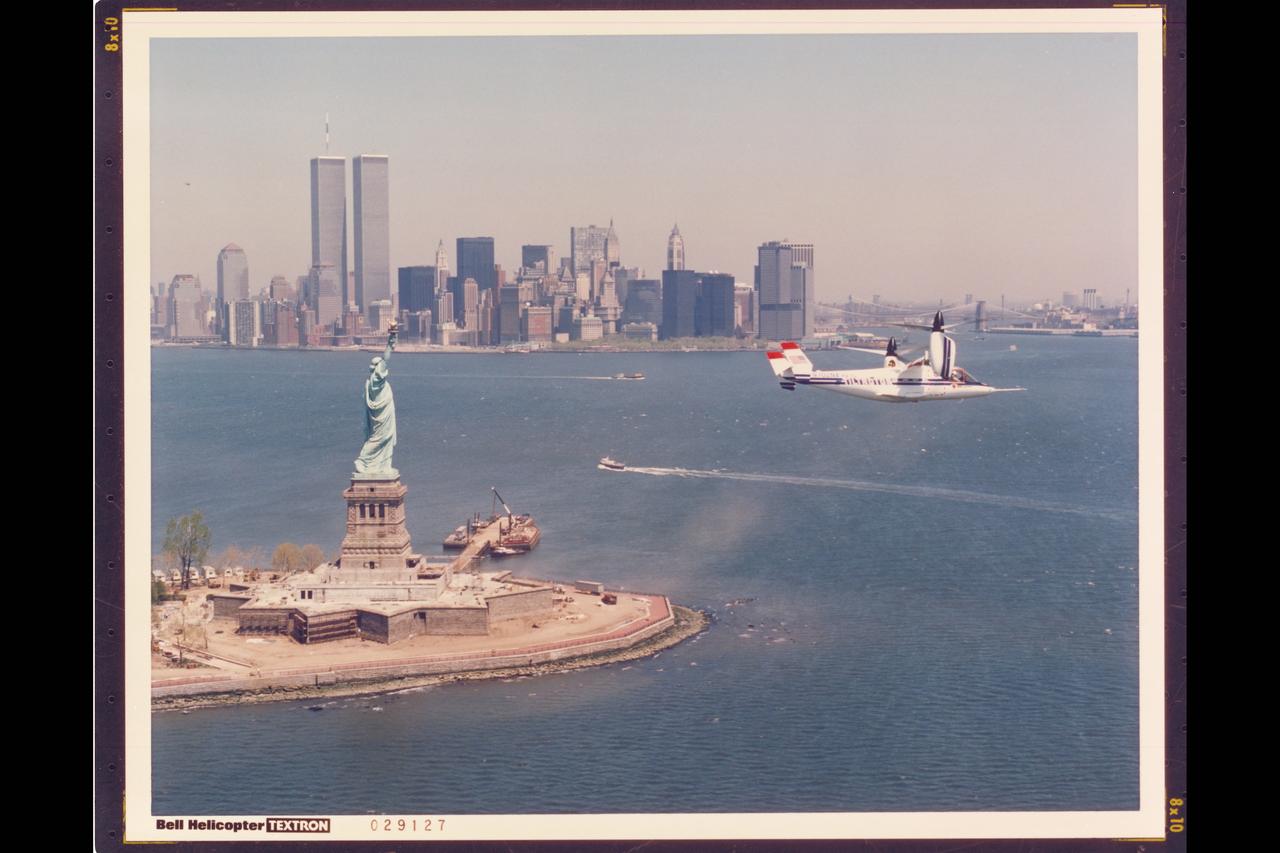

BELL HELICOPTER BELL TEXTRON XV-15 TILT ROTOR AIRCRAFT IN FLIGHT OVER NEW YORK, ELLIS ISLAND AND STATUE OF LIBERTY
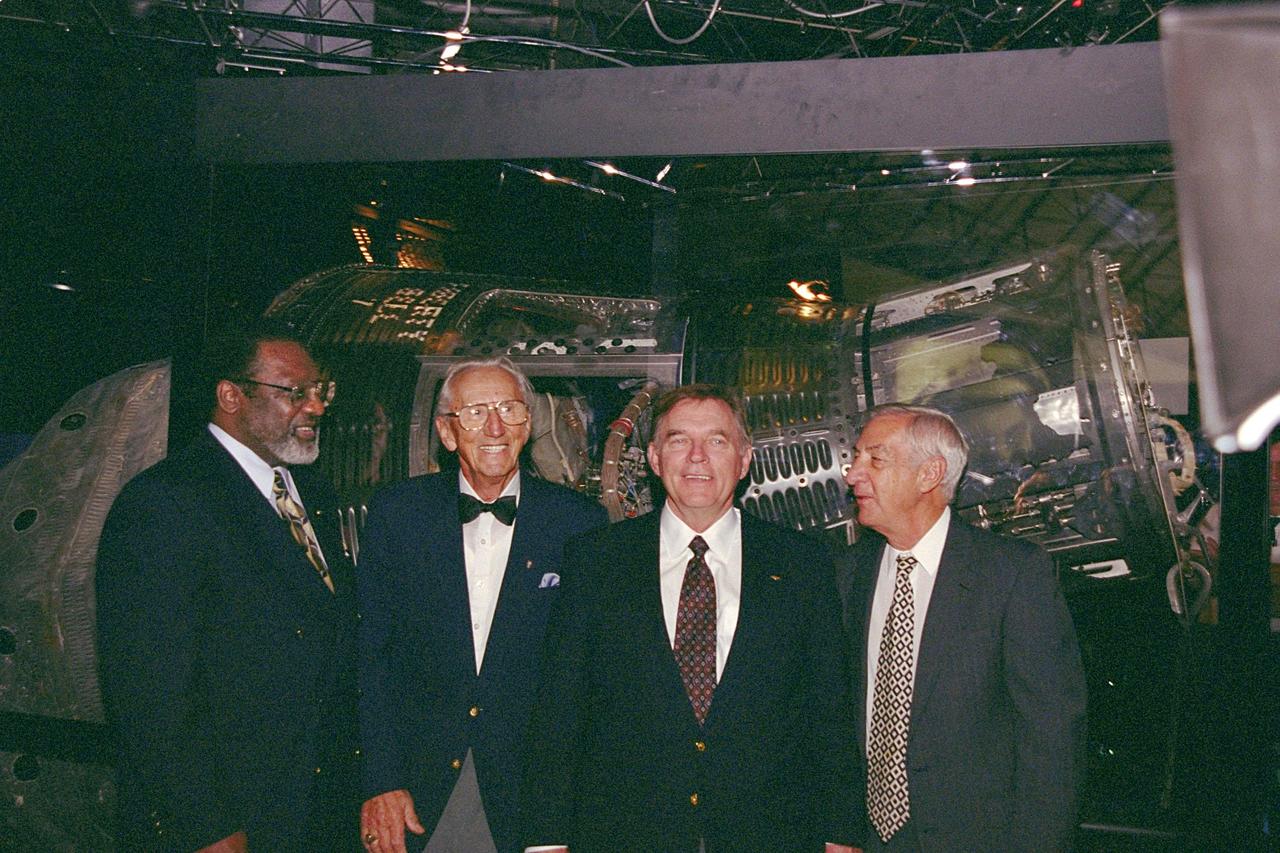

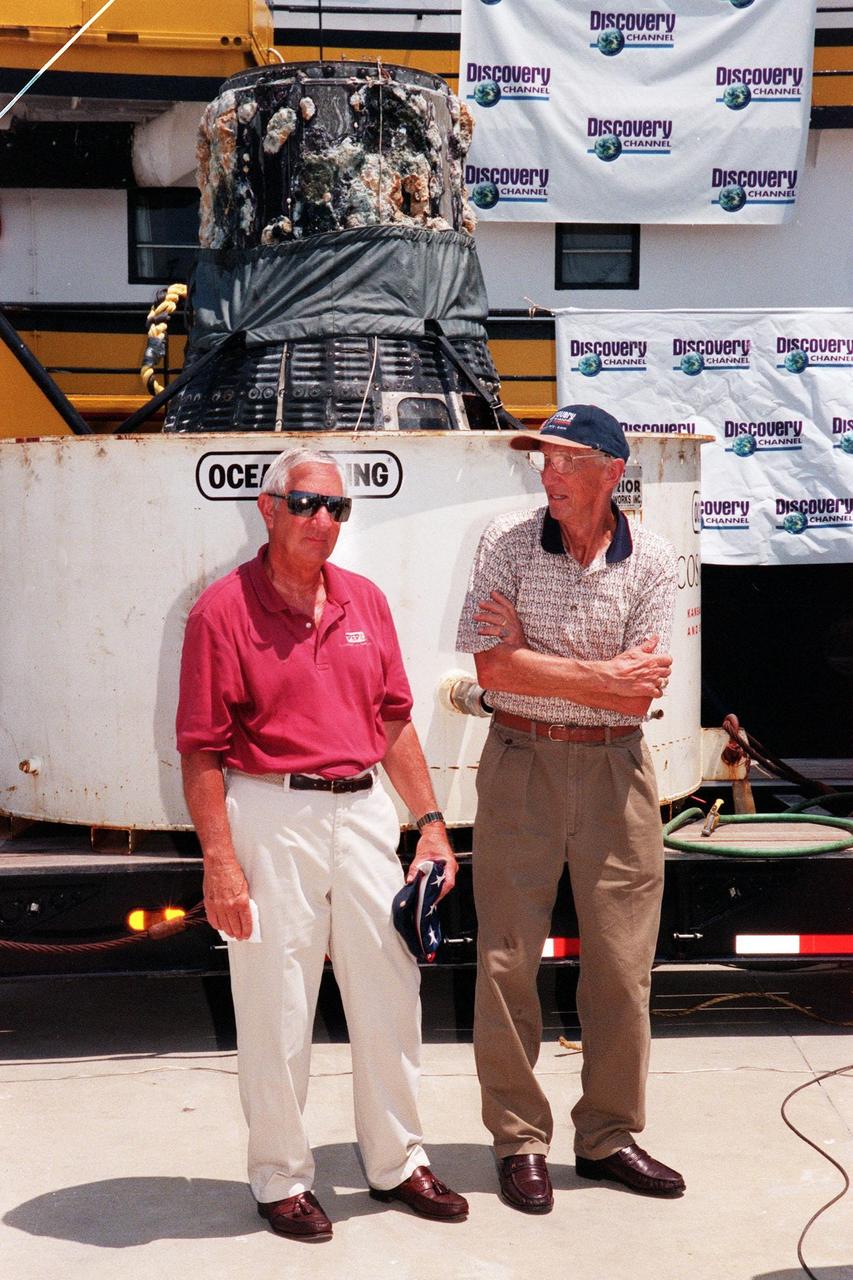
The Discovery Channel’s Liberty Bell 7 Space Capsule Exhibit, which opens to the public at the KSC Visitor Complex on Saturday, June 17, had a preview for the press today. Liberty Bell 7 launched U.S. Air Force Captain Virgil "Gus" Grissom July 21, 1961, on a mission that lasted 15 minutes and 37 seconds before sinking. The capsule lay undetected for nearly four decades before a Discovery Channel expedition located it and recovered it. Standing in front of the restored Liberty Bell 7 capsule are (left to right) KSC’s Deputy Director Jim Jennings; Gunther Wendt, who worked on the Liberty Bell 7 before its launch; Jim Lewis, who piloted the Hunt Club 1 helicopter that rescued Gus Grissom; and Larry Grissom, brother of Gus Grissom. The space capsule, now restored and preserved, is part of an interactive exhibit touring science centers and museums in 12 cities throughout the United States until 2003. The exhibit also includes hands-on elements such as a capsule simulator, a centrifuge, and ROV pilot
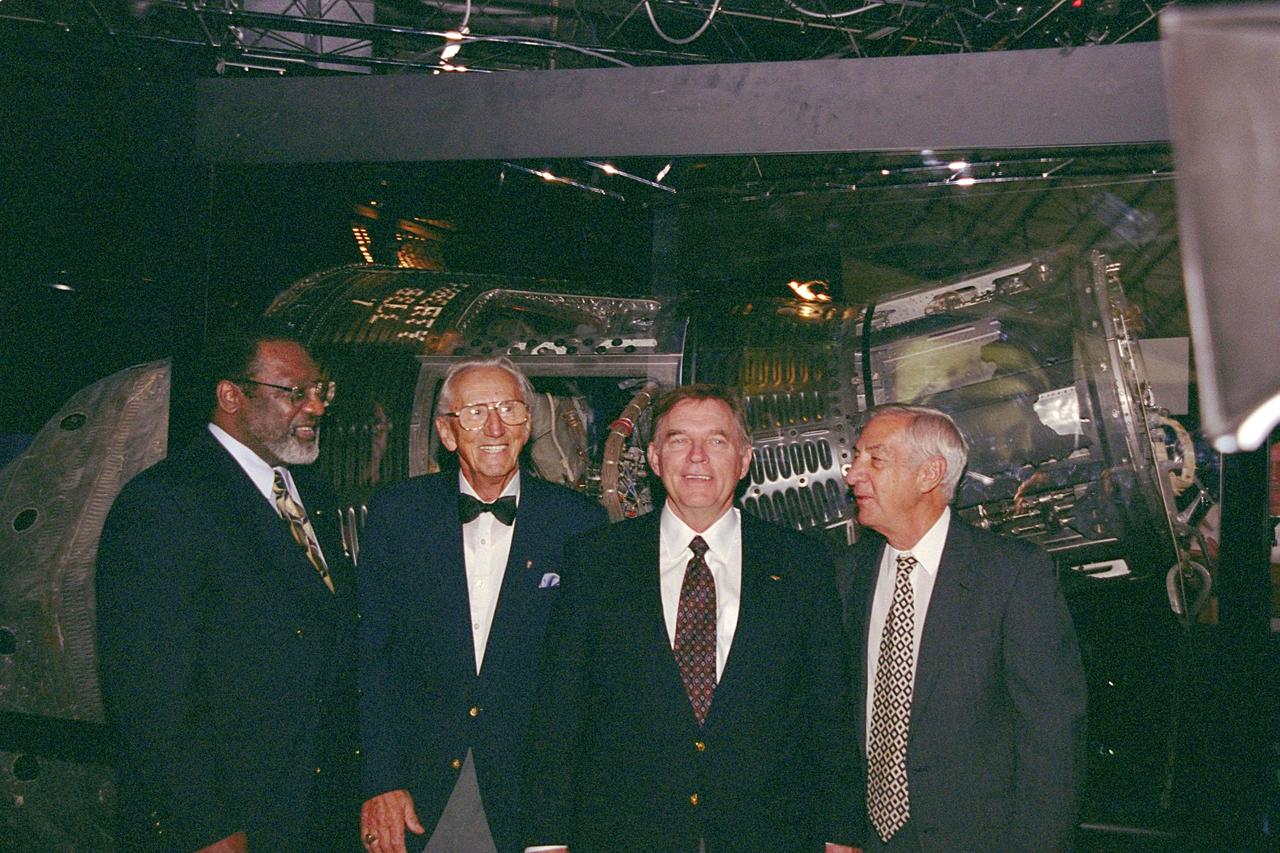

The Discovery Channel’s Liberty Bell 7 Space Capsule Exhibit, which opens to the public at the KSC Visitor Complex on Saturday, June 17, had a preview for the press today. Liberty Bell 7 launched U.S. Air Force Captain Virgil "Gus" Grissom July 21, 1961, on a mission that lasted 15 minutes and 37 seconds before sinking. The capsule lay undetected for nearly four decades before a Discovery Channel expedition located it and recovered it. Standing in front of the restored Liberty Bell 7 capsule are (left to right) KSC’s Deputy Director Jim Jennings; Gunther Wendt, who worked on the Liberty Bell 7 before its launch; Jim Lewis, who piloted the Hunt Club 1 helicopter that rescued Gus Grissom; and Larry Grissom, brother of Gus Grissom. The space capsule, now restored and preserved, is part of an interactive exhibit touring science centers and museums in 12 cities throughout the United States until 2003. The exhibit also includes hands-on elements such as a capsule simulator, a centrifuge, and ROV pilot
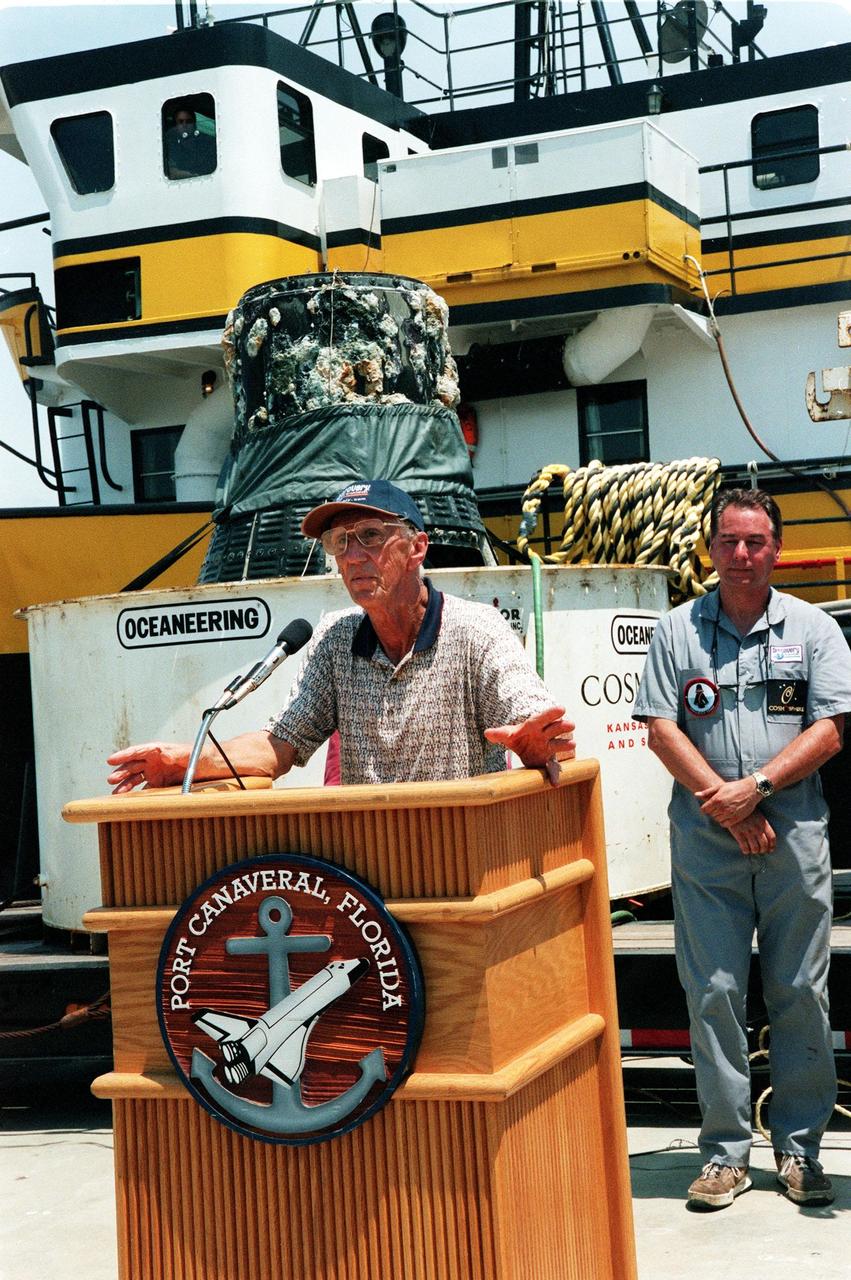

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Gunther Wendt takes a turn at the podium after viewing the recovered Liberty Bell 7 Project Mercury capsule, seen in the background. At right is Curt Newport who led the expedition to find and retrieve the capsule. The expedition was sponsored by the Discovery Channel. Wendt worked on the Liberty Bell 7 before its launch July 21, 1961. After its successful 16-minute suborbital flight, the Liberty Bell 7, with astronaut Virgil "Gus" Grissom aboard, splashed down in the Atlantic Ocean. A prematurely jettisoned hatch caused the capsule to flood and a Marine rescue helicopter was unable to lift it. It quickly sank to a three-mile depth. Grissom was rescued but his spacecraft remained lost on the ocean floor, until now. An underwater salvage expert, Newport located the capsule through modern technology, and after one abortive attempt, successfully raised it and brought it to Port Canaveral. The recovery of Liberty Bell 7 fulfilled a 14-year dream for the expedition leader. The capsule is being moved to the Kansas Cosmosphere and Space Center in Hutchinson, Kansas, where it will be restored for eventual public display. Newport has also been involved in salvage operations of the Space Shuttle Challenger and TWA Flight 800 that crashed off the coast of Long Island, N.Y

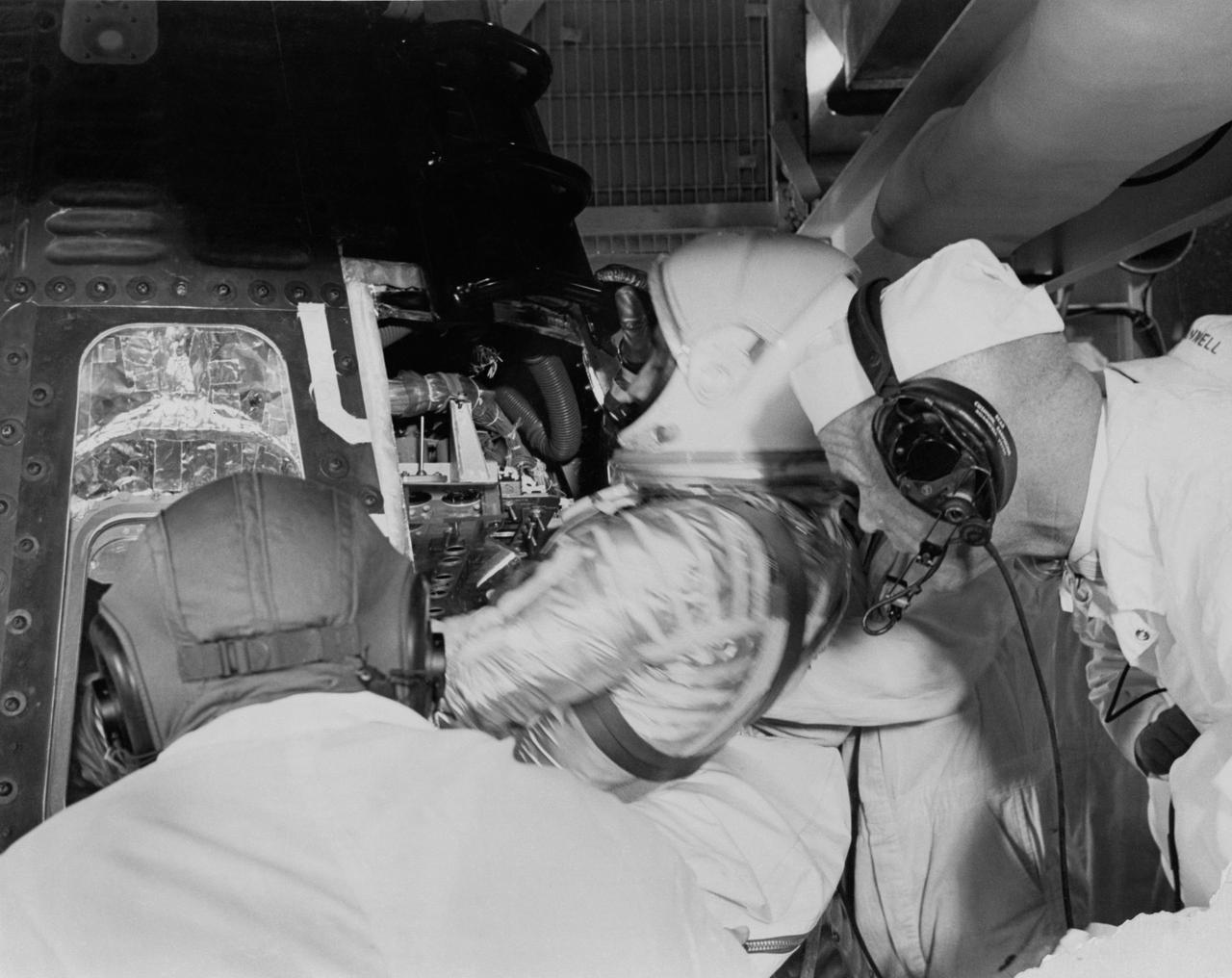
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- CHAMBER TEST - Project Mercury astronaut Virgil I. 'Gus' Grissom, assisted by McDonnell technicians, leaves Mercury spacecraft, dubbed Liberty Bell 7, following simulated flight.
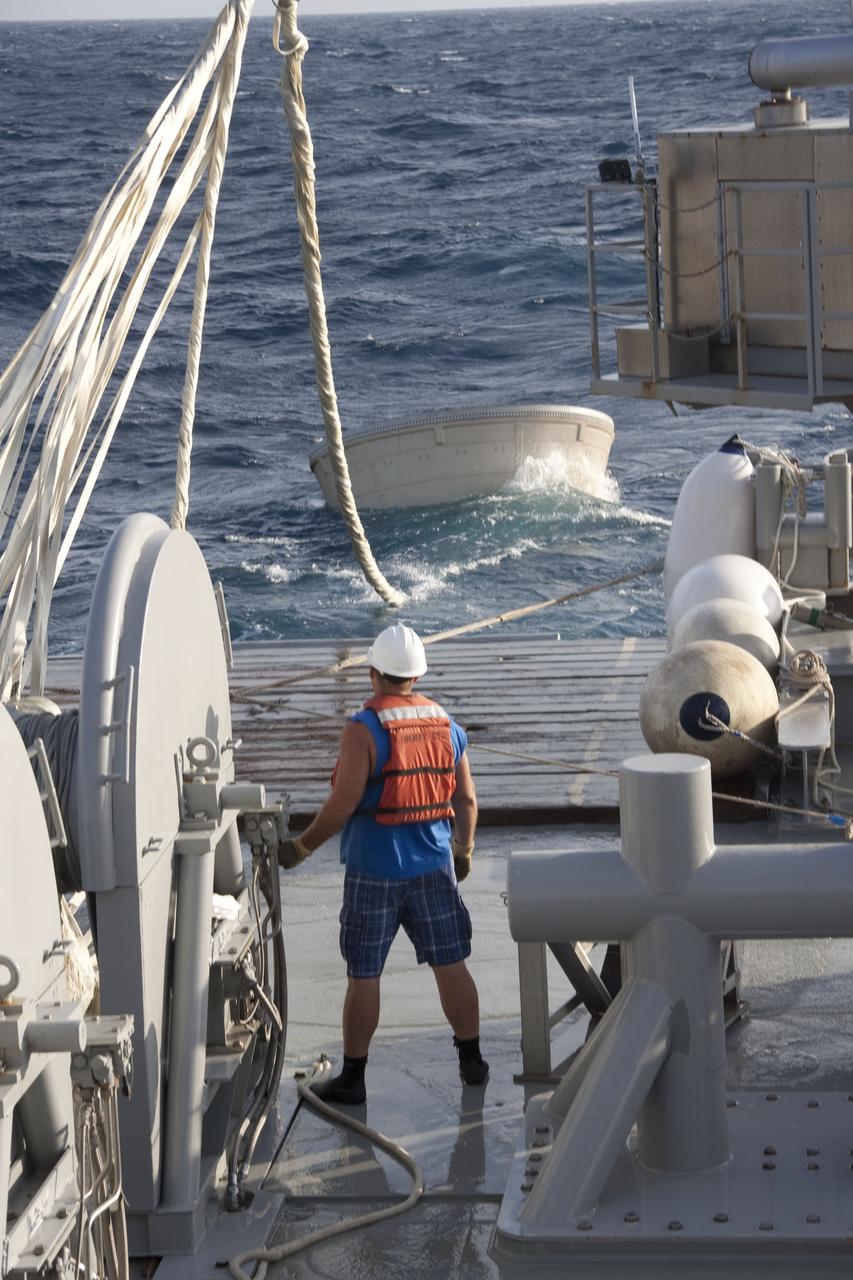

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A crew member on Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, uses a crane to haul the right booster nose cap out of the Atlantic Ocean that splashed down after Discovery's final launch. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
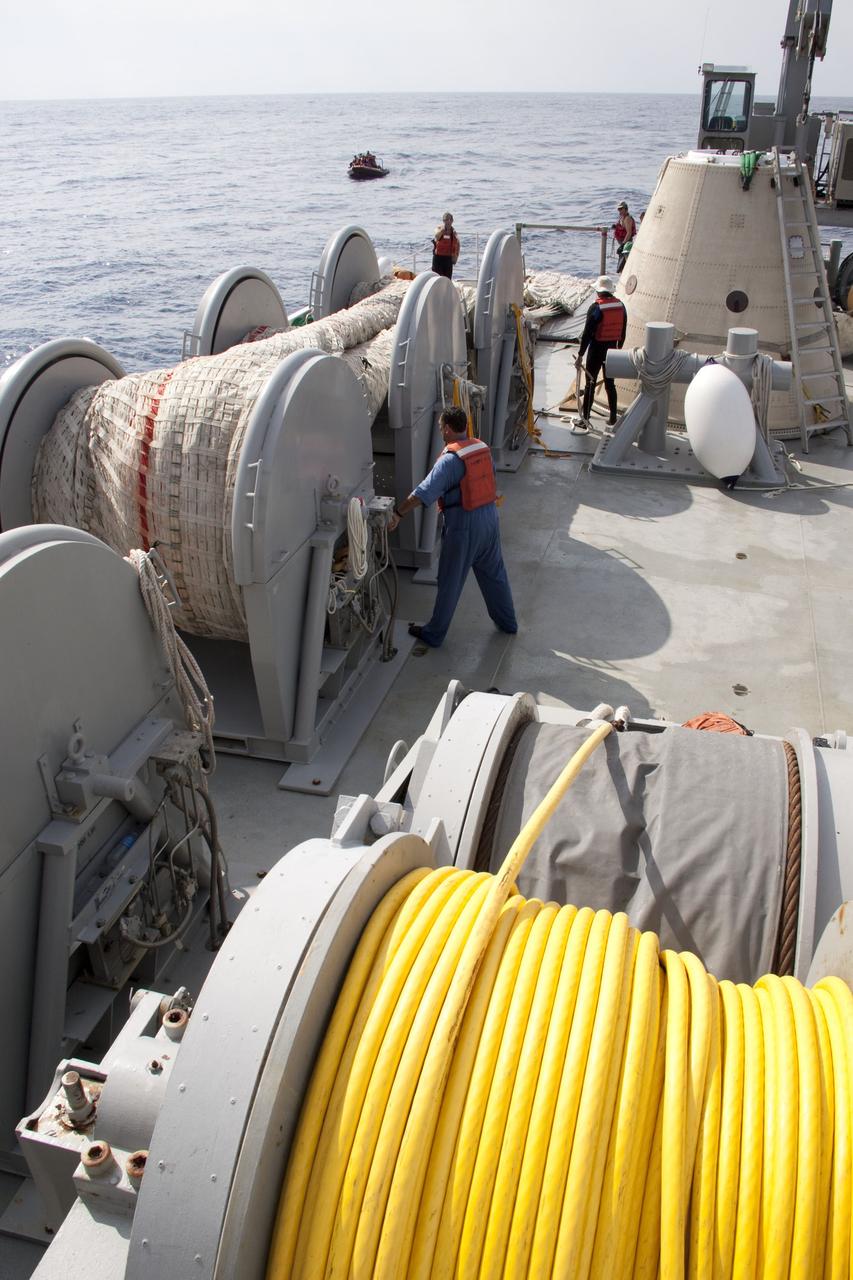

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Crew members on board Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, haul in the massive parachute from the right spent booster from space shuttle Discovery's final launch. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Waiting for the arrival of the Liberty Bell 7 after its raising from the ocean floor. Liberty Bell 7 launched U.S. Air Force Captain Virgil "Gus" Grissom July 21, 1961 on a mission that lasted 15 minutes and 37 seconds before sinking to the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, three miles deep. It lay undetected for nearly four decades before a Discovery Channel expedition located it and recovered it. The space capsule is now restored and preserved, and part of an interactive exhibit touring science centers and museums in 12 cities throughout the United States until 2003. The exhibit includes hands-on elements such as a capsule simulator, a centrifuge, and ROV pilot.
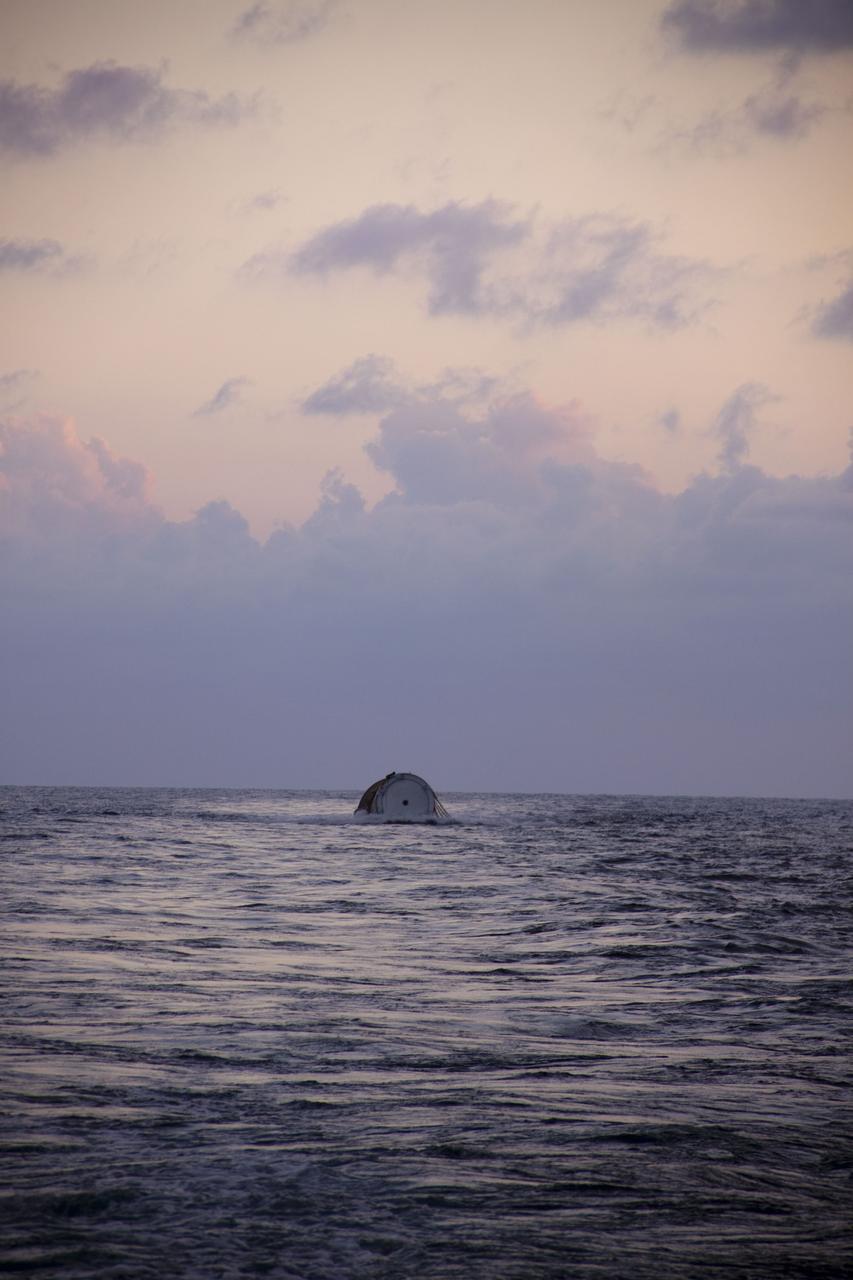

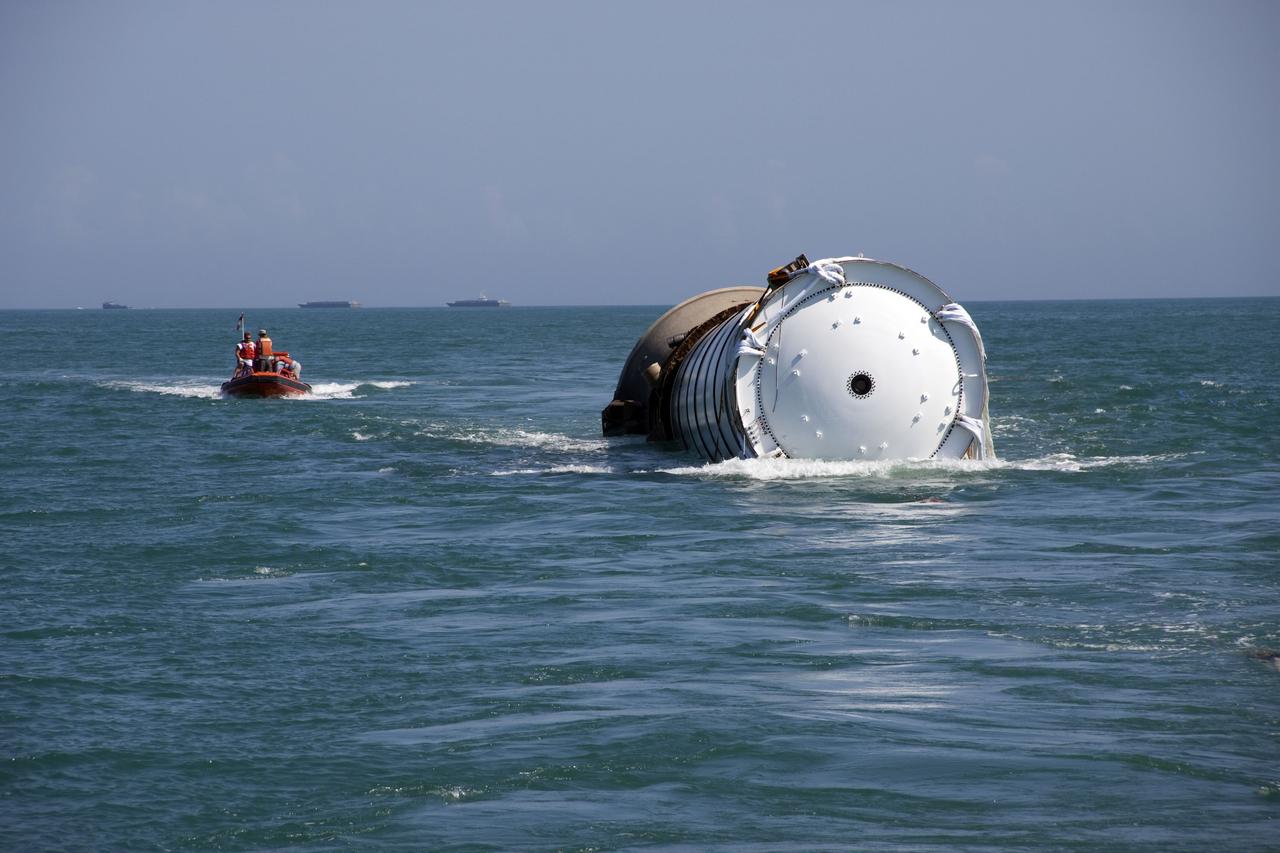
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Discovery's final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
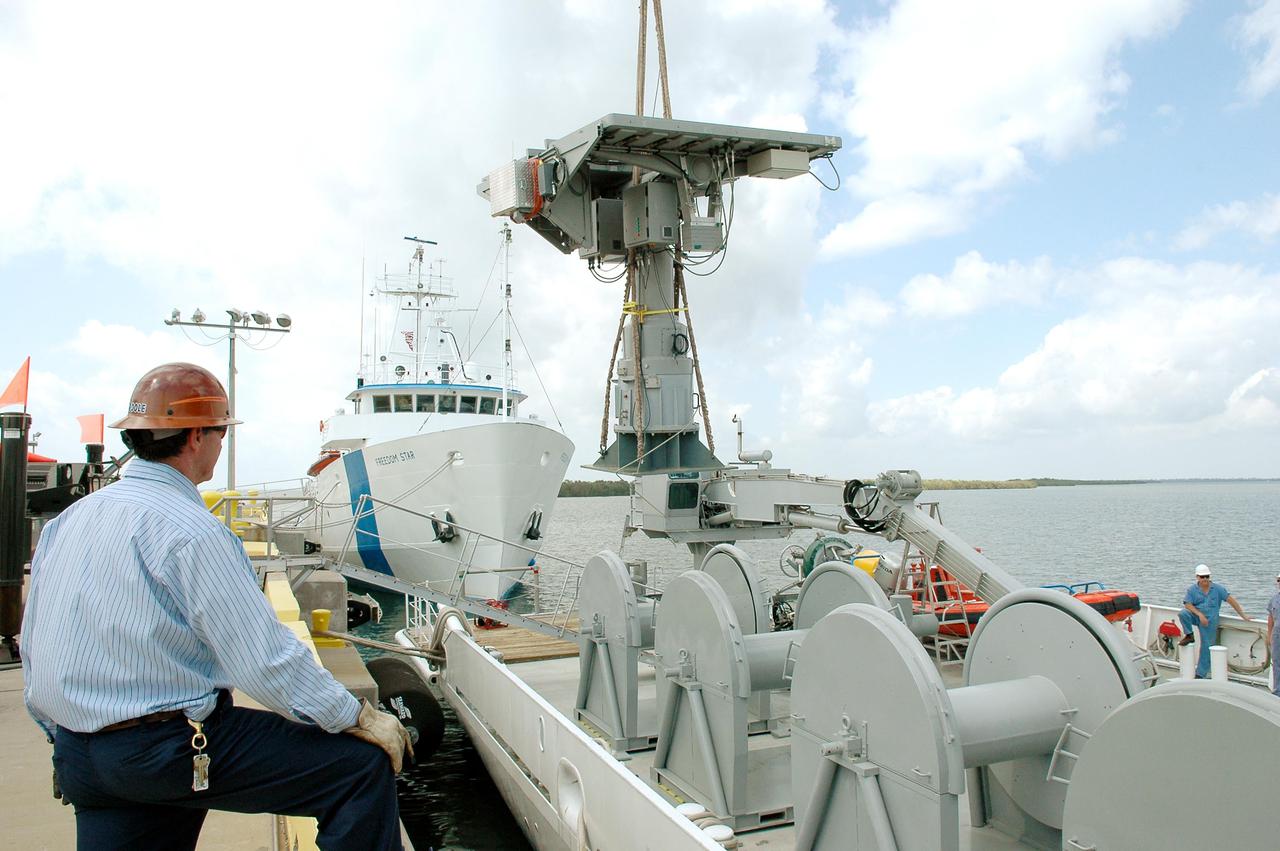

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - An X-band Doppler radar array is lowered toward the deck of the Liberty Star, one of the two SRB Retrieval Ships, at Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The other retrieval ship, Freedom Star, is aft of the Liberty Star. The radar will be used for tracking support on NASA’s Return to Flight mission, STS-114, on Space Shuttle Discovery. Launch is targeted for May 15 with a launch window that extends to June 3. During its 12-day mission, Discovery’s seven-member crew will test new hardware and techniques to improve Shuttle safety, as well as deliver supplies to the International Space Station.
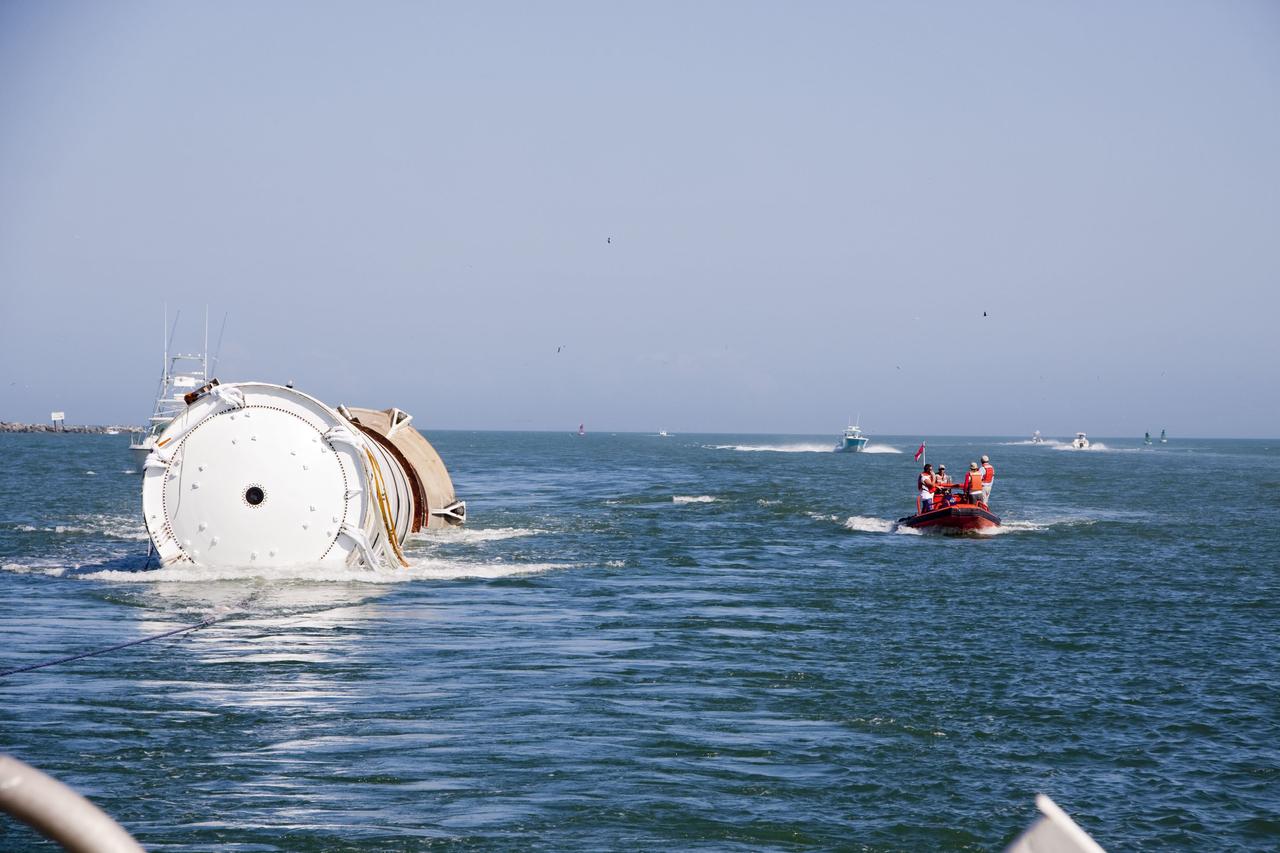

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Discovery's final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
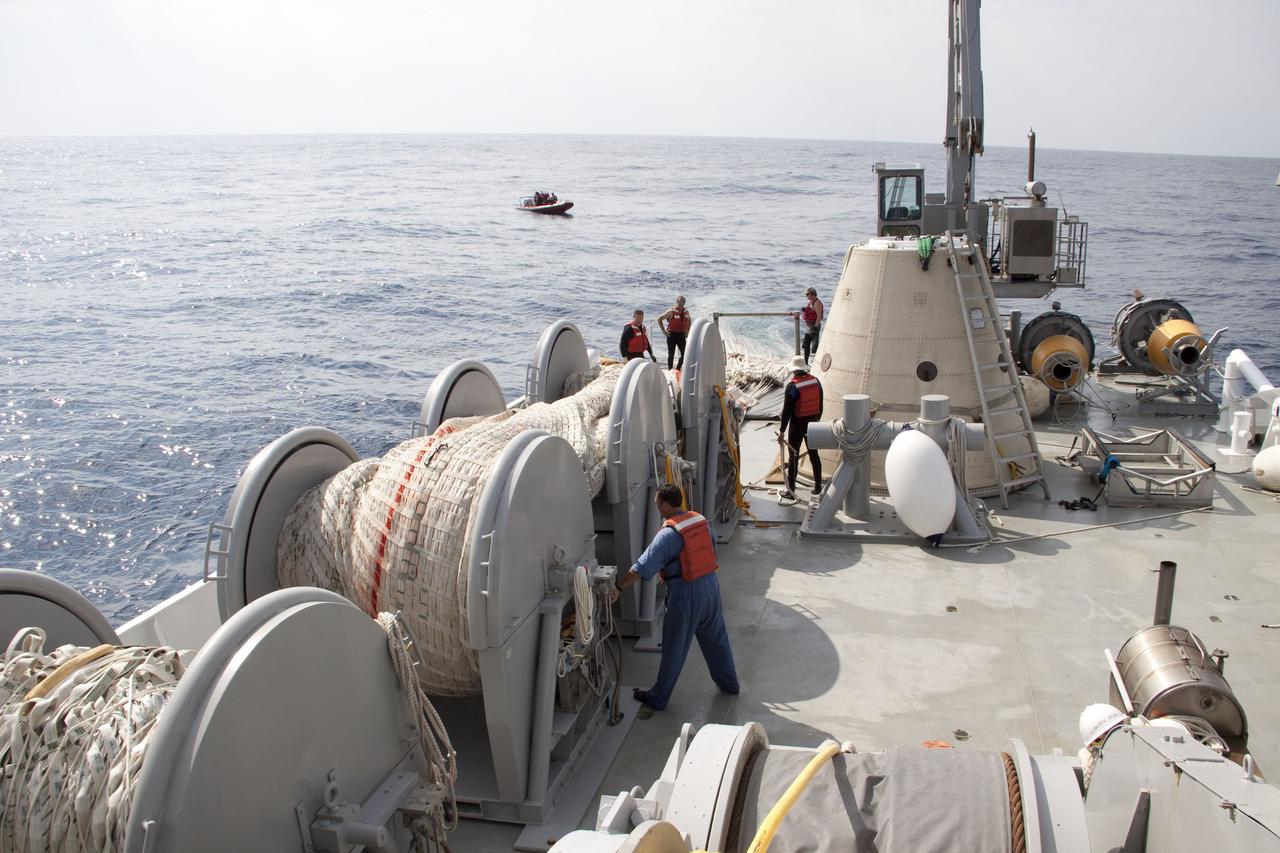

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Crew members on board Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, haul in the massive parachute from the right spent booster from space shuttle Discovery's final launch. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A crew member on Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, uses a crane to haul the right booster nose cap out of the Atlantic Ocean that splashed down after Discovery's final launch. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A crew member on Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, monitors the progress as the massive parachute from the right spent booster from space shuttle Discovery's final launch is hauled on board. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows the right spent booster from space shuttle Discovery's final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A nose cap from the right spent booster can be seen bobbing in the Atlantic Ocean, waiting to be recovered by the crew members of Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
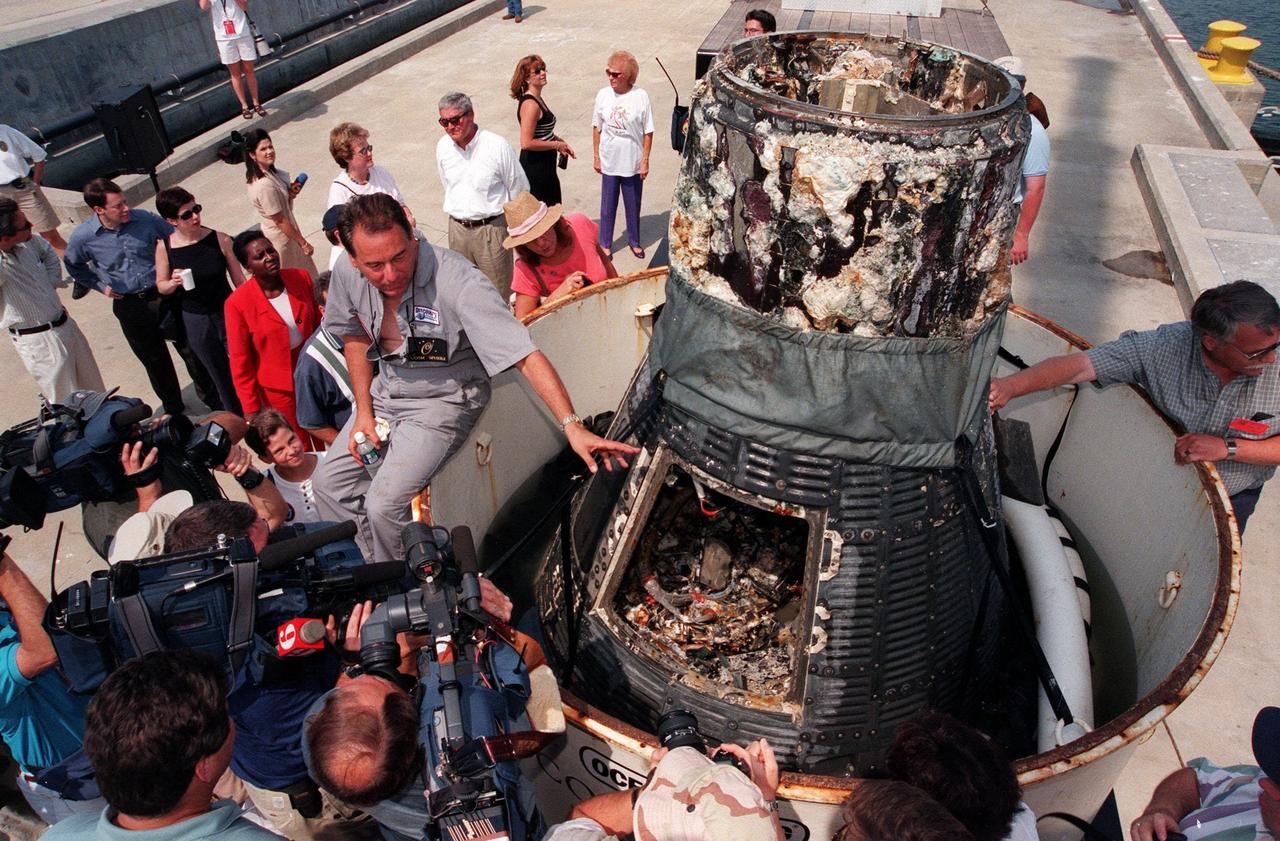

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Retrieved from the ocean floor three miles deep, the Liberty Bell 7 Project Mercury capsule is revealed to photographers and the media in Port Canaveral, Fla. The capsule was found and raised by Curt Newport (left), leading an expedition sponsored by the Discovery Channel. After its successful 16-minute suborbital flight on July 21, 1961, the Liberty Bell 7, with astronaut Virgil "Gus" Grissom aboard, splashed down in the Atlantic Ocean. A prematurely jettisoned hatch caused the capsule to flood and a Marine rescue helicopter was unable to lift it. It quickly sank to a three-mile depth. Grissom was rescued but his spacecraft remained lost on the ocean floor, until now. An underwater salvage expert, Newport located the capsule through modern technology, and after one abortive attempt, successfully raised it and brought it to Port Canaveral. The recovery of Liberty Bell 7 fulfilled a 14-year dream for the expedition leader. The capsule is being moved to the Kansas Cosmosphere and Space Center in Hutchinson, Kansas, where it will be restored for eventual public display. Newport has also been involved in salvage operations of the Space Shuttle Challenger and TWA Flight 800 that crashed off the coast of Long Island, N.Y
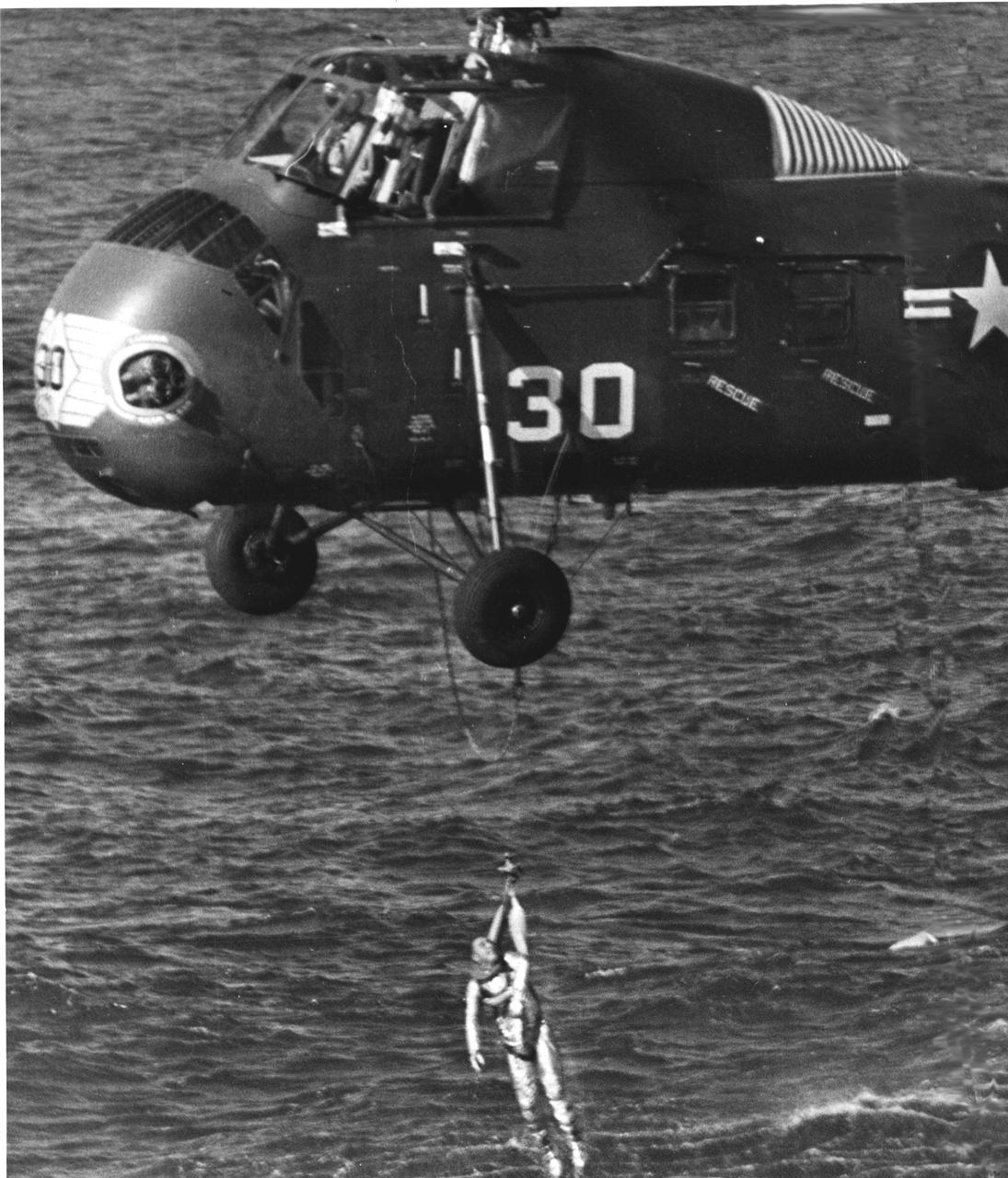

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Marine helicopter has astronaut Virgil I. Grissom in harness and is bringing him up out of the water. The Liberty Bell 7 spacecraft has just sunk below the water. His Mercury-Redstone 4 launch was the second in the U.S. manned space effort.

The 51-J mission insignia, designed by Atlantis's first crew, pays tribute to the Statue of Liberty and the ideas it symbolizes. The historical gateway figure bears additional significance for Astronauts Karol J. Bobko, mission commander; and Ronald J. Grabe, pilot, both New Your Natives.
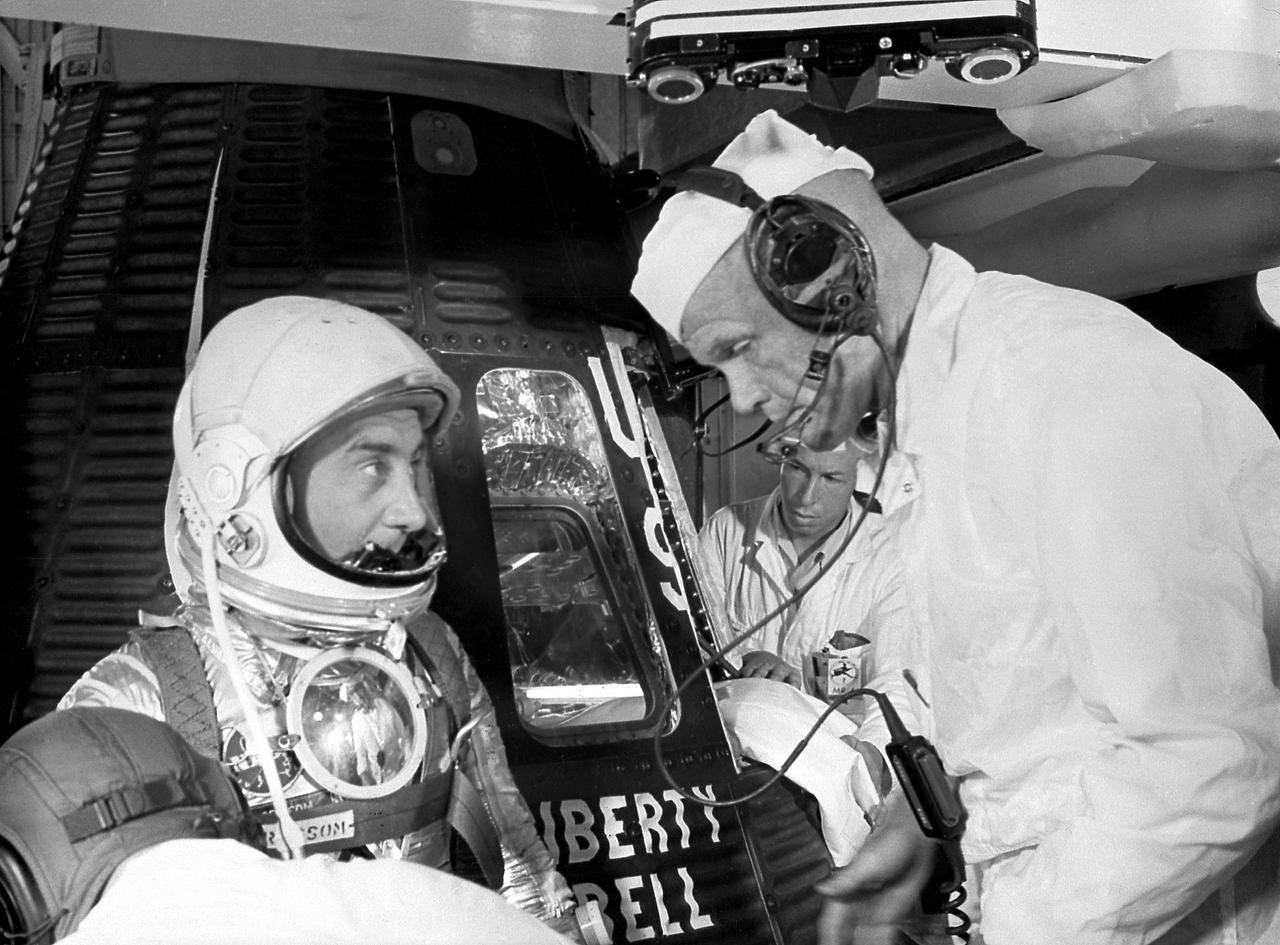

Astronaut Virgil Grissom chats with Astronaut John Glenn prior to entering the Liberty Bell 7 capsule for the MR-4 Mission. The MR-4 mission was the second manned suborbital flight using the Mercury-Redstone booster, which was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center.
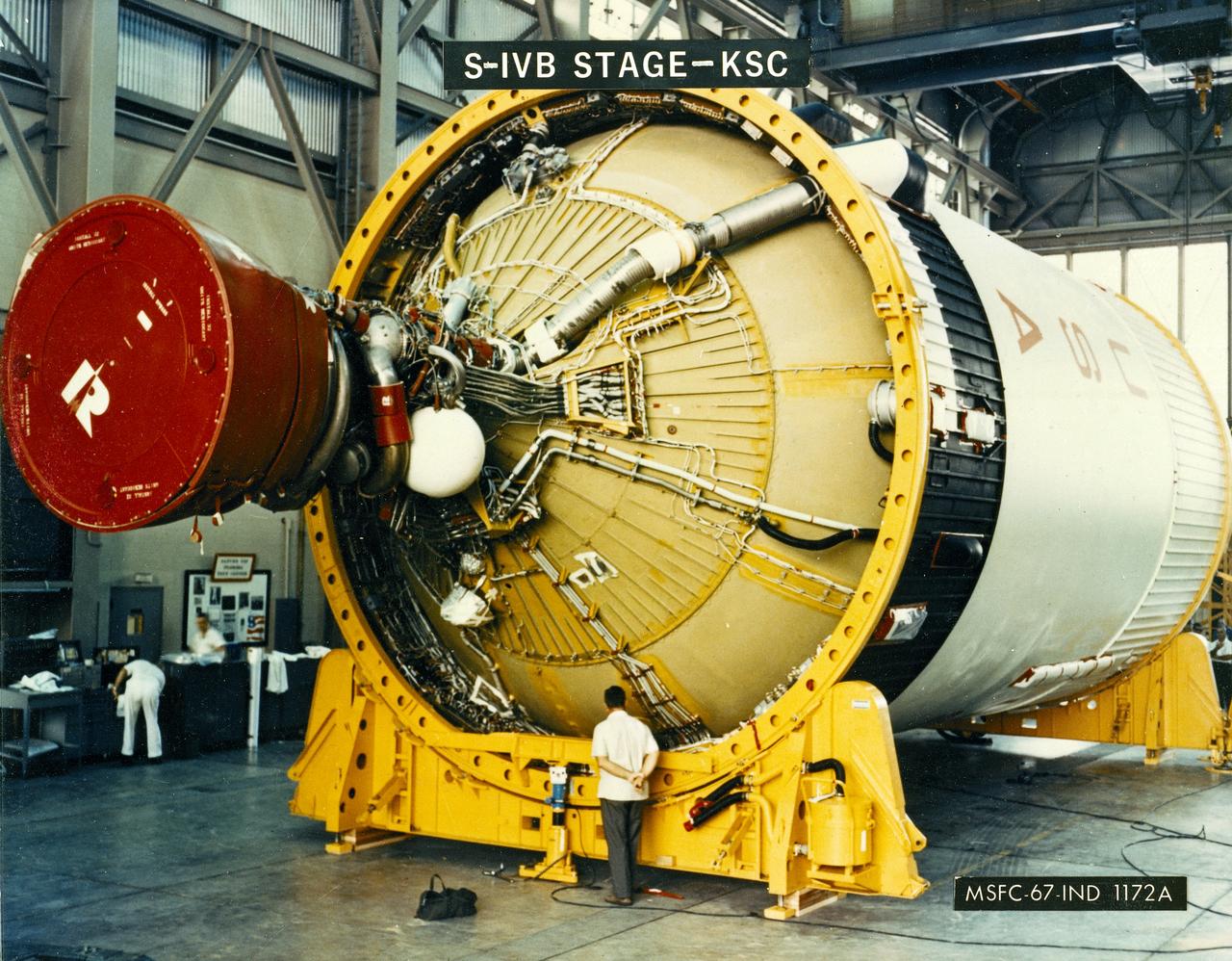
A NASA technician is dwarfed by the gigantic Third Stage (S-IVB) as it rests on supports in a facility at KSC. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
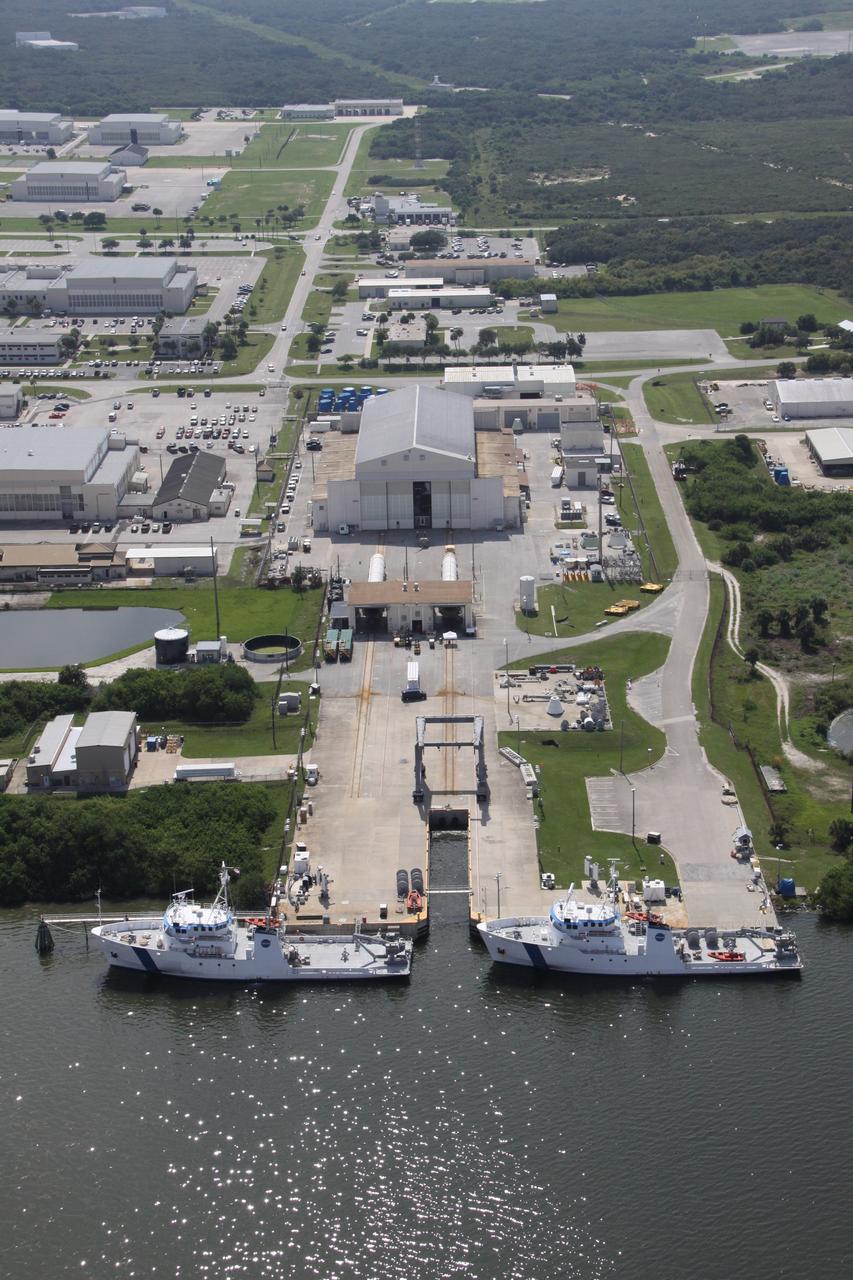

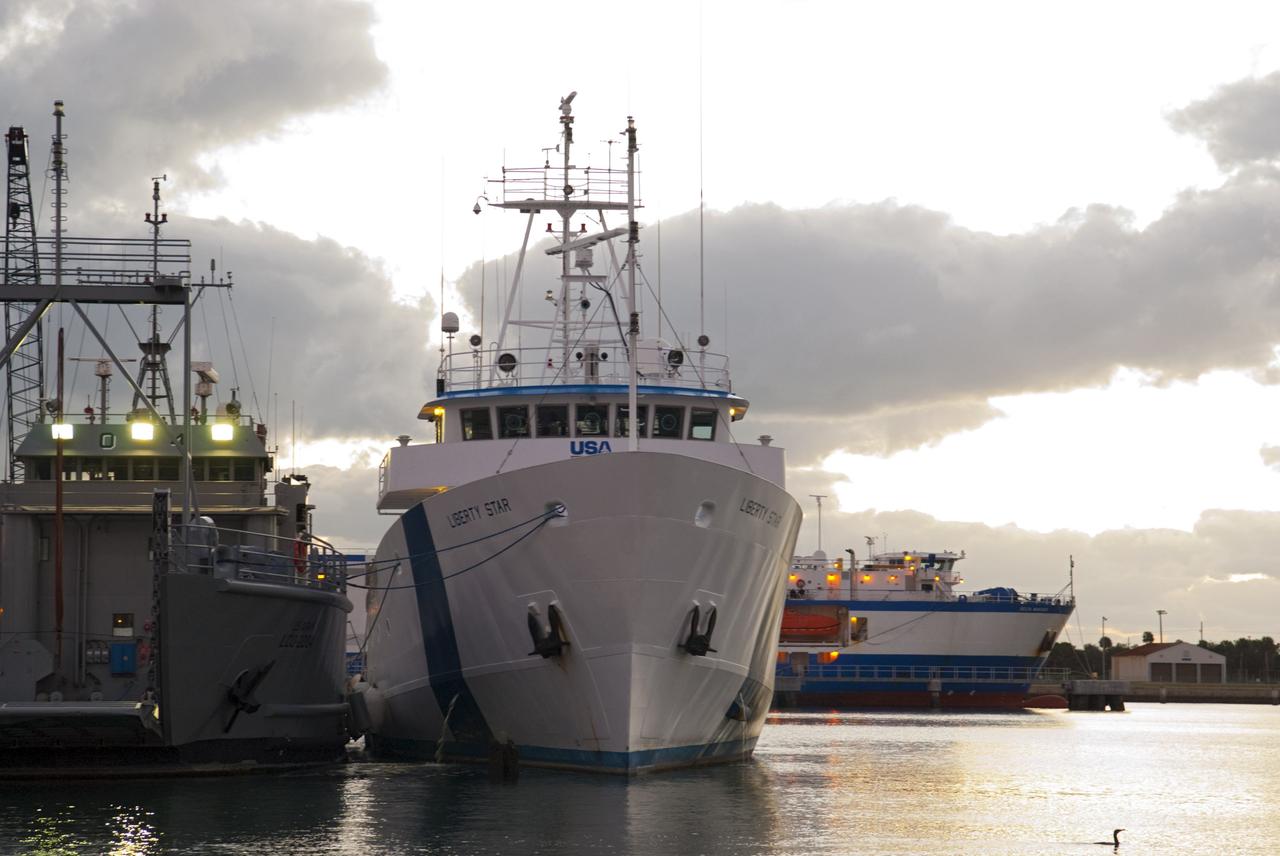
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of the Solid Rocket Booster Recovery Ships Liberty Star and Freedom Star at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Hangar AF. The ships recently returned from recovering the boosters from space shuttle Discovery's launch on the STS-128 mission. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
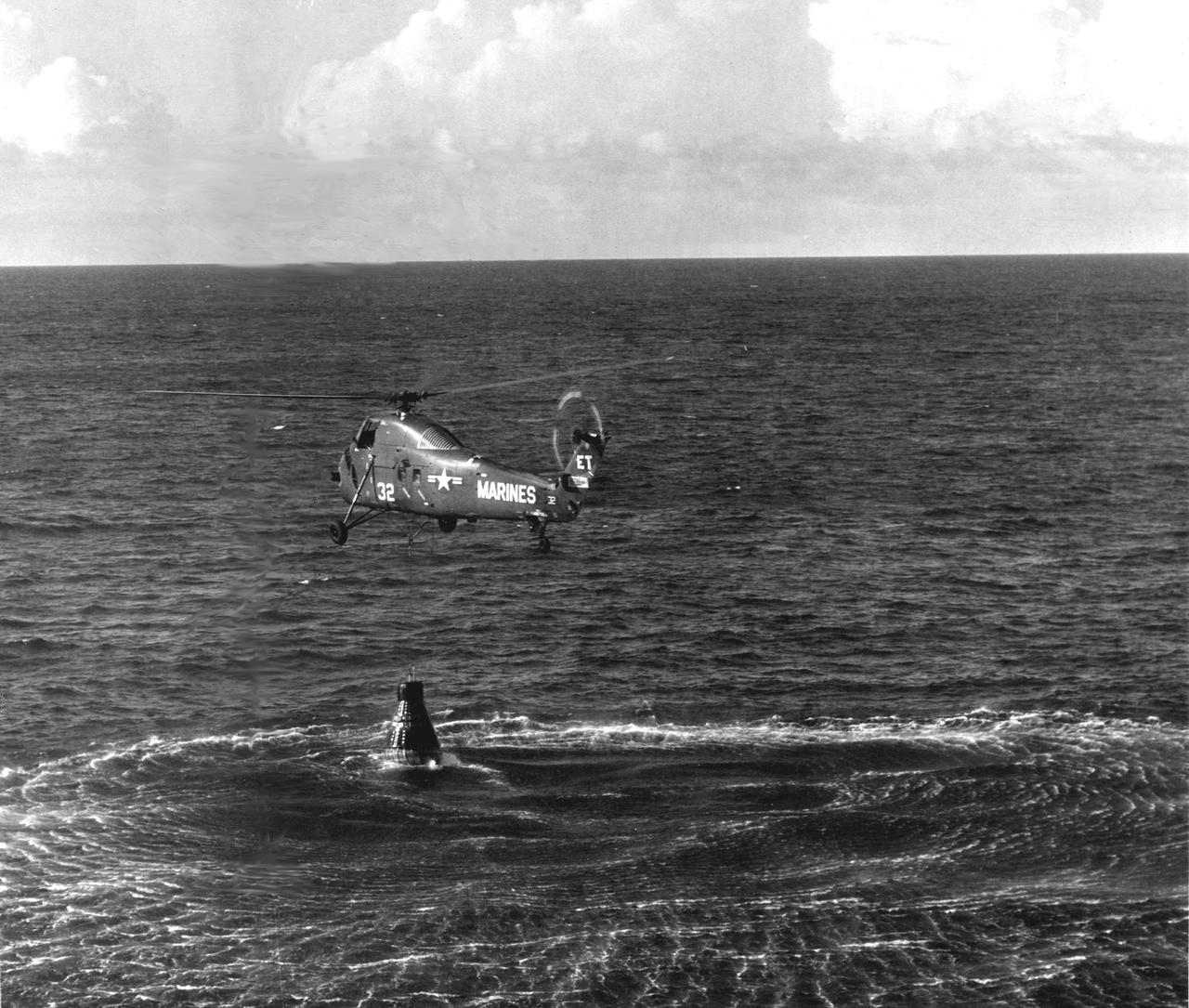

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Marine helicopter appears to have Liberty Bell 7 in tow after Virgil I. Grissom's successful flight of 305 miles down the Atlantic Missile Range. Minutes after 'Gus' Grissom got out of the spacecraft, it sank. (NASA Photo
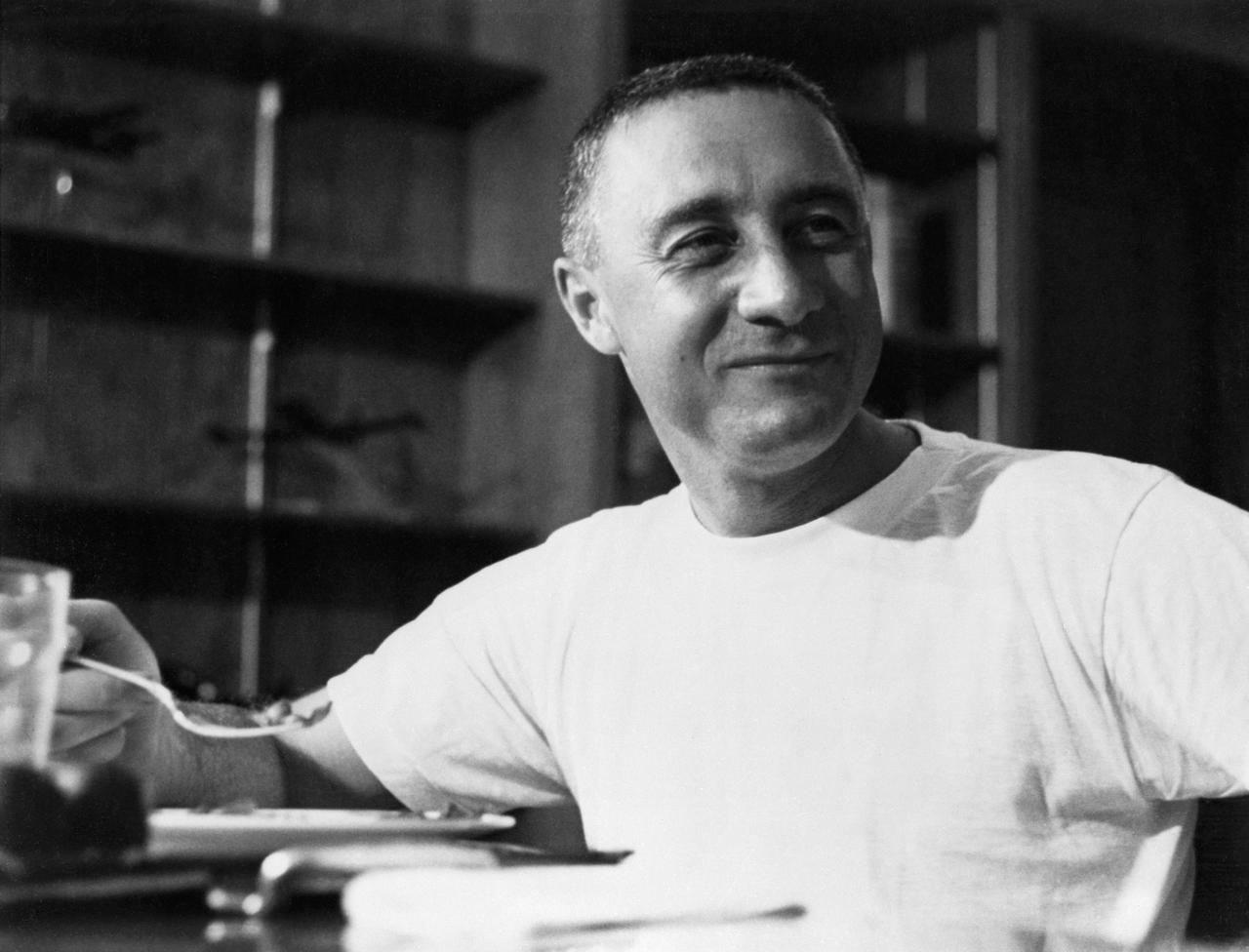

S61-02898 (21 July 1961) --- Virgil I. (Gus) Grissom, pilot of the Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) ?Liberty Bell 7? spaceflight, enjoys a meal aboard the recovery ship, USS Randolph, following his 15-minute, 37-second suborbital space mission. Photo credit: NASA
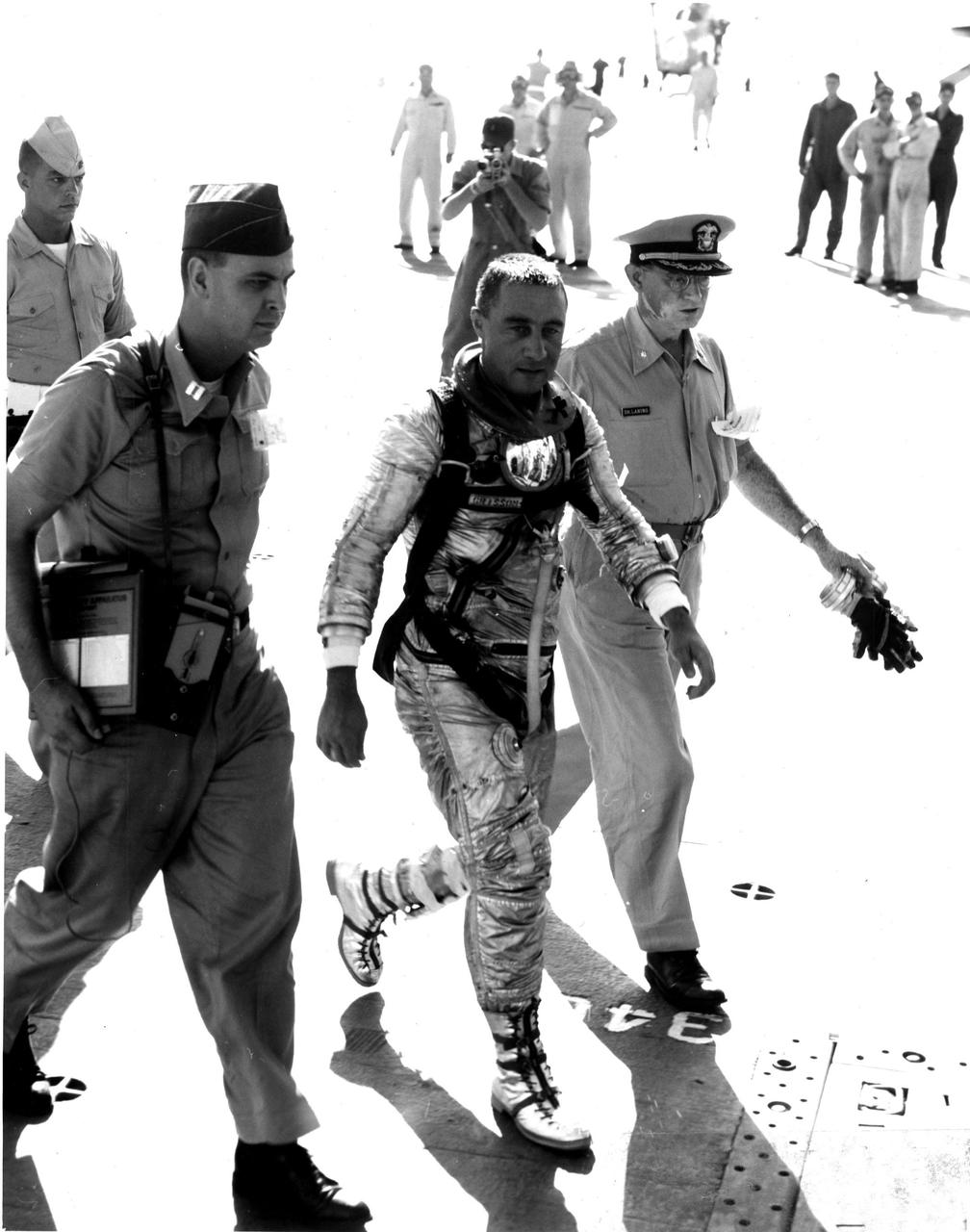

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Astronaut Virgil I. Grissom walks across the deck of the U.S.S. Randolph after being airlifted by helicopter from the Liberty Bell 7 impact area. 'Gus' Grissom was the second U.S. man in space. (NASA Photo)
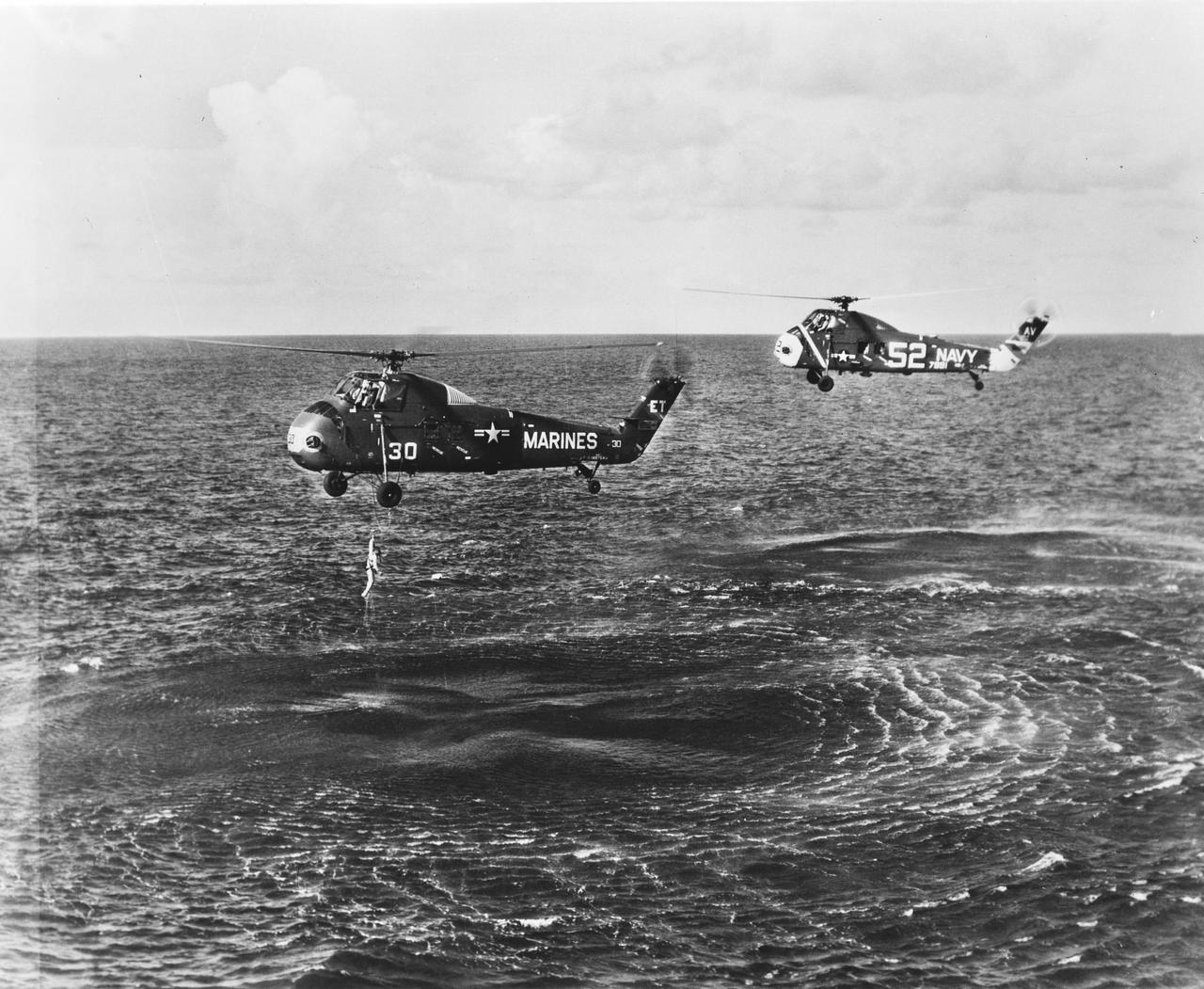

S61-02819 (21 July 1961) --- A U.S. Marine Corps helicopter retrieves astronaut Virgil I. Grissom from the Atlantic Ocean following the Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) spaceflight. Grissom's "Liberty Bell" Mercury spacecraft sank to the bottom of the ocean and was not recovered. Photo credit: NASA

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of the Solid Rocket Booster Recovery Ships Liberty Star and Freedom Star at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Hangar AF. The ships recently returned from recovering the boosters from space shuttle Discovery's launch on the STS-128 mission. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
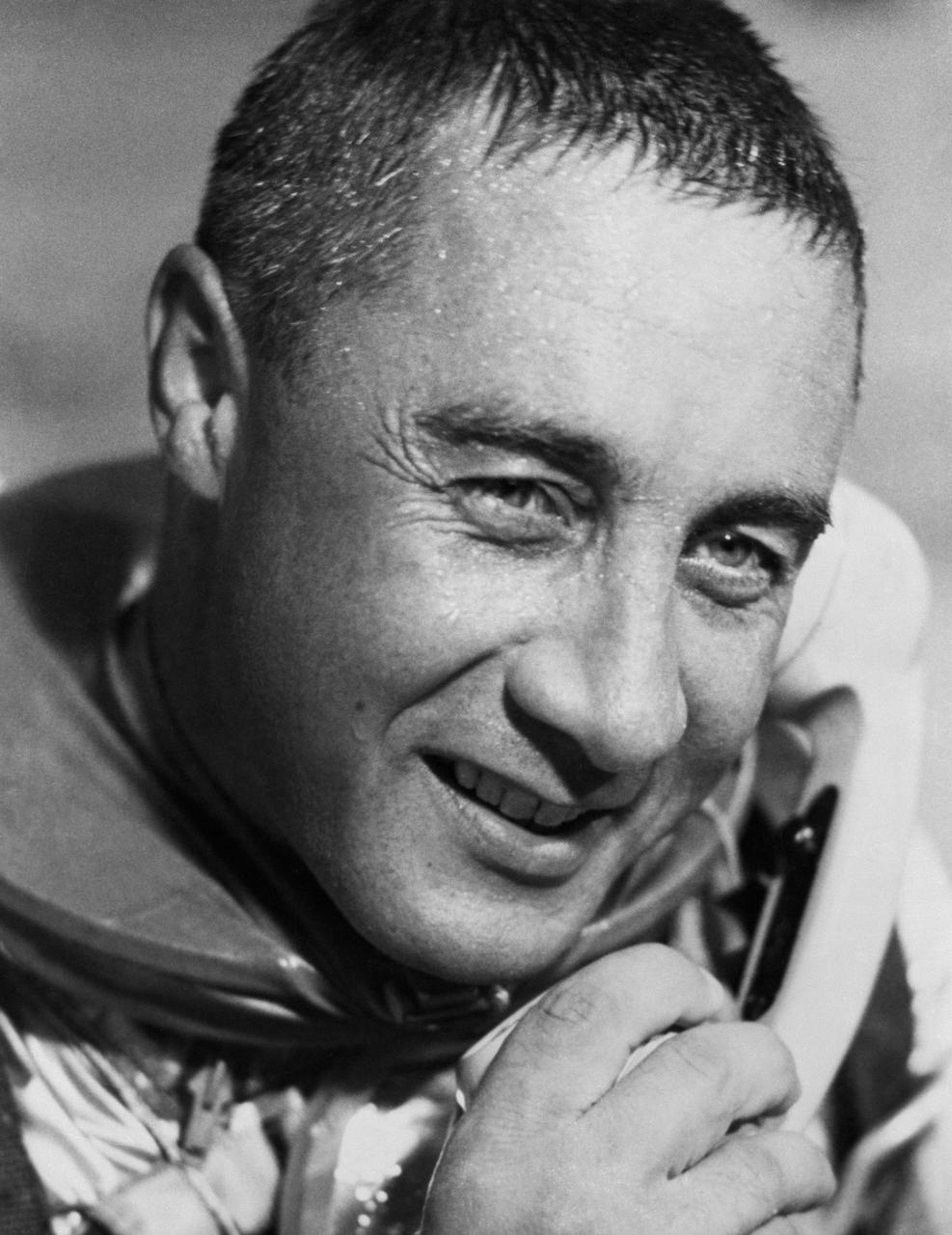

S61-02897 (21 July 1961) --- Virgil I. (Gus) Grissom, pilot of the Mercury-Redstone 4 (MR-4) ?Liberty Bell 7? spaceflight, talking on the phone with President Kennedy. Grissom is still wearing his pressure suit. Photo credit: NASA
/61-mr4-65(s)~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This is MR-4 in the final minutes of the mission countdown on July 19. In the background is the rocket's service structure, which was moved to the edge of the pad at T-60. Shortly thereafter the 'cherry picker' was stationed at the spacecraft's hatch to permit emergency egress of the pilot, if necessary. The spacecraft is known as Liberty Bell 7
/61-mr4-72(s)~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Astronaut Virgil I. Grissom, suited up and ready to climb into Liberty Bell 7 spacecraft, talks with backup astronaut John Glenn prior to insertion. The Mercury-Redstone 4 mission was scrubbed a few hours later due to unfavorable weather over the launch area. (NASA Photo)

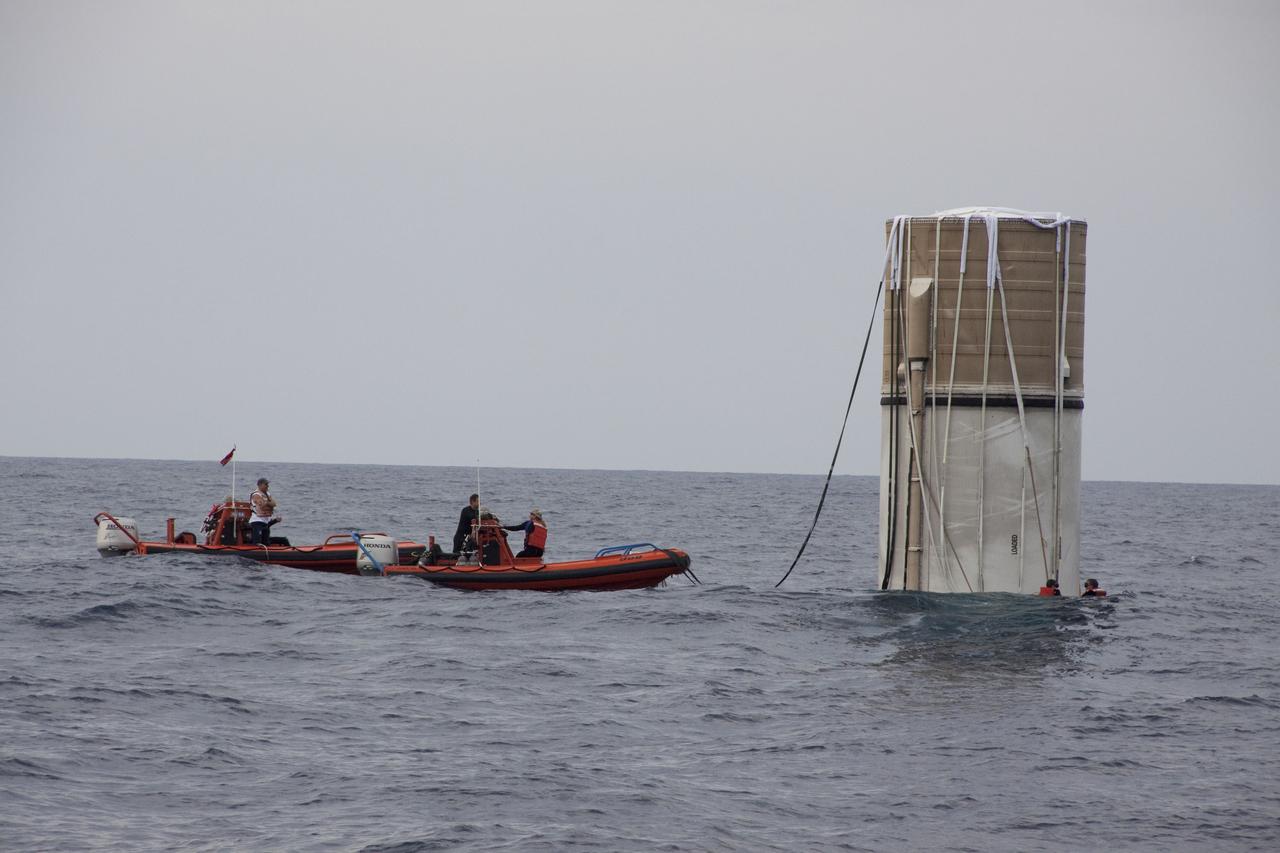
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers help secure one of two solid rocket boosters to a mooring at Port Canaveral in Florida. Liberty Star, one of NASA’s two booster retrieval ships, towed the spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis’ final launch to the port. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff, and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight, STS-135, at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Crew members from Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, use skiffs to approach the right spent booster bobbing in the Atlantic Ocean after space shuttle Discovery's final launch. Divers are already in the water. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, ushers a spent shuttle booster to Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The booster was used during space shuttle Discovery's STS-133 launch from NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A on Feb. 24. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – One of two solid rocket boosters is secured to a mooring at Port Canaveral in Florida. Liberty Star, one of NASA’s two booster retrieval ships, towed the spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis’ final launch to the port. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff, and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight, STS-135, at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Preparations are under way at Port Canaveral in Florida for the early-morning departure of NASA's Liberty Star ship. Liberty Star has been enlisted to support the Crew Module Recovery Attach Fitting Test (CRAFT) which began at-sea operations Nov. 29. Multiple attach clips are being evaluated against the current recovery cleat configuration by U.S. Air Force pararescue jumpers (PJs) and a U.S. Navy diver. The 21st Century Ground Systems Program will use data collected from the tests to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft being developed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
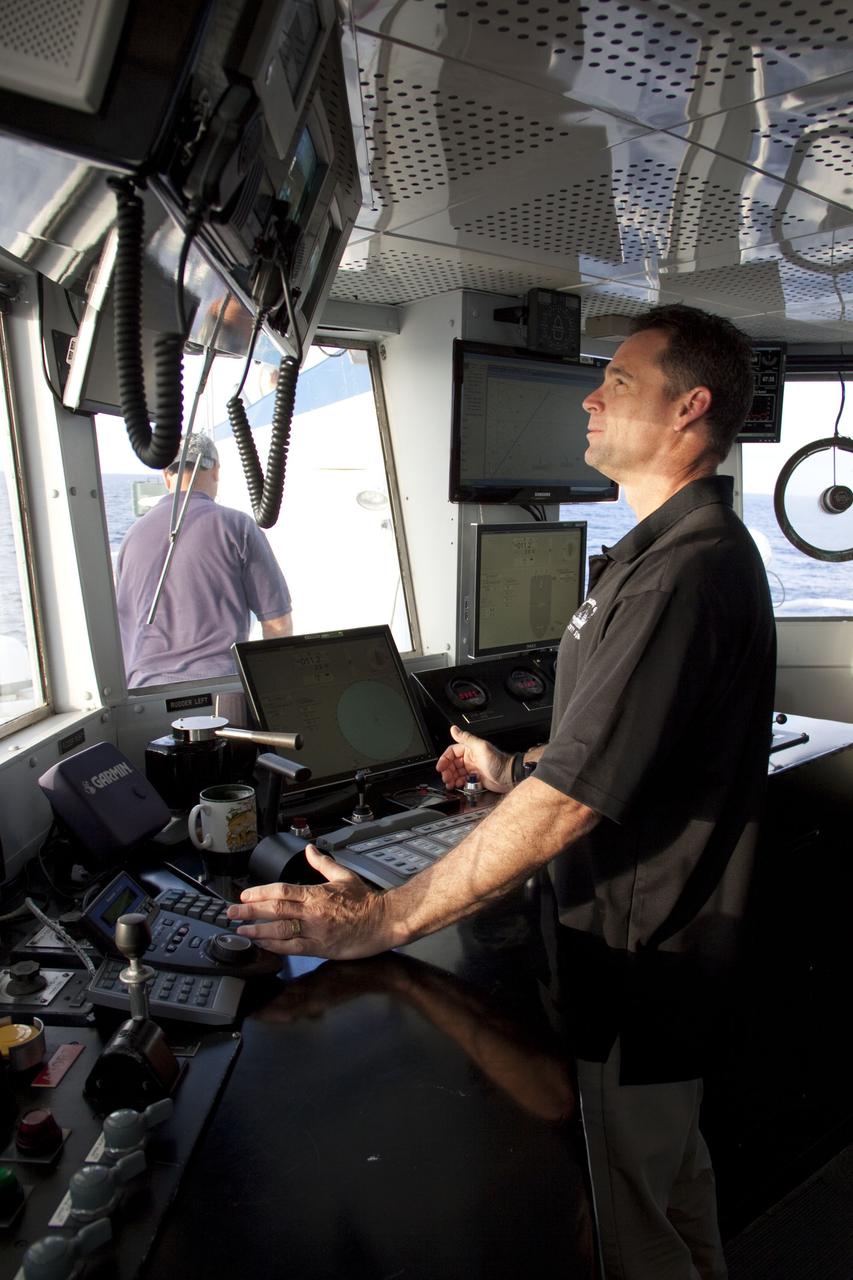

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Captain Bren Wade is steering Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships in the direction of the right spent booster that splashed down into the Atlantic Ocean after space shuttle Discovery's STS-133 launch. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
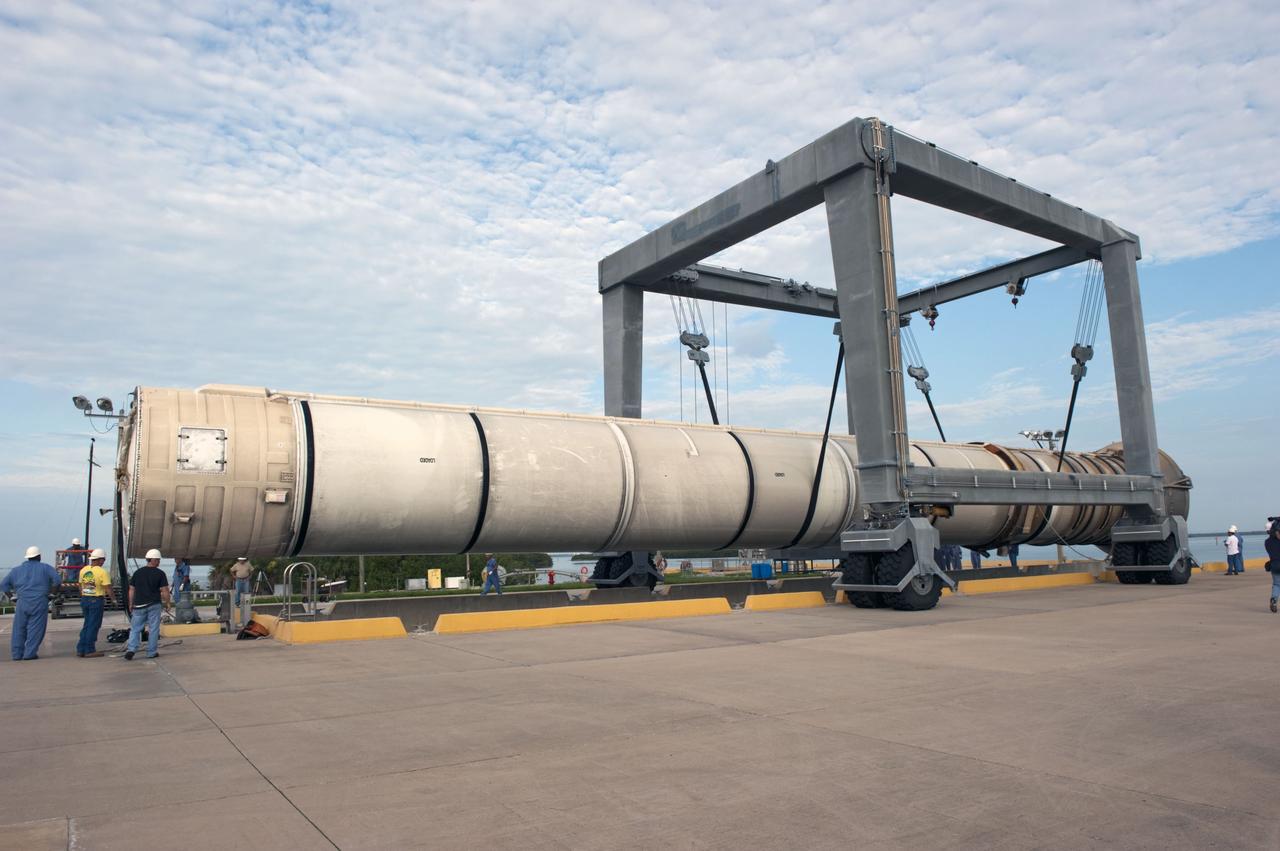

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – One of two solid rocket boosters is lifted above a mooring at Port Canaveral in Florida. Liberty Star, one of NASA’s two booster retrieval ships, towed the spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis’ final launch to the port. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff, and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight, STS-135, at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
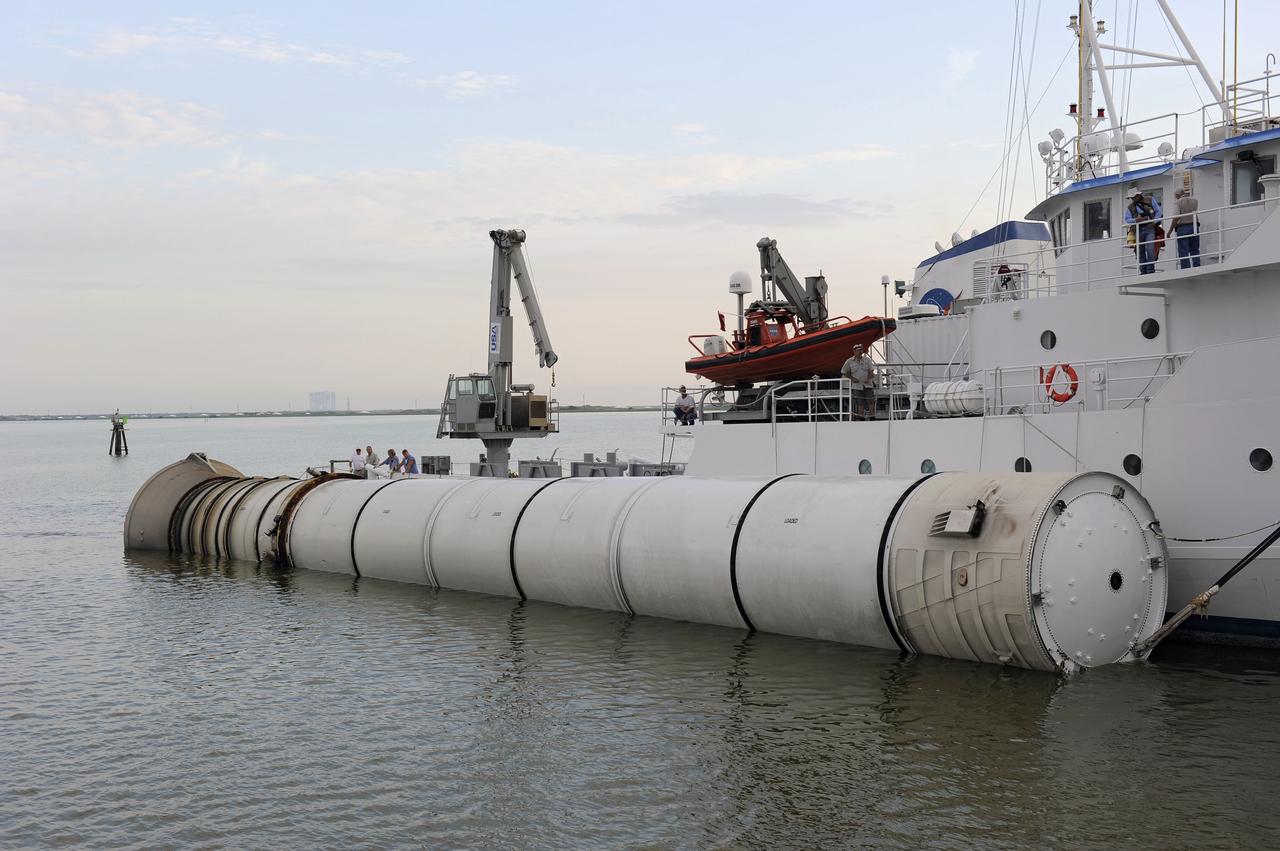

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Liberty Star, one of NASA’s solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows a spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis’ final launch, to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight, STS-135, at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
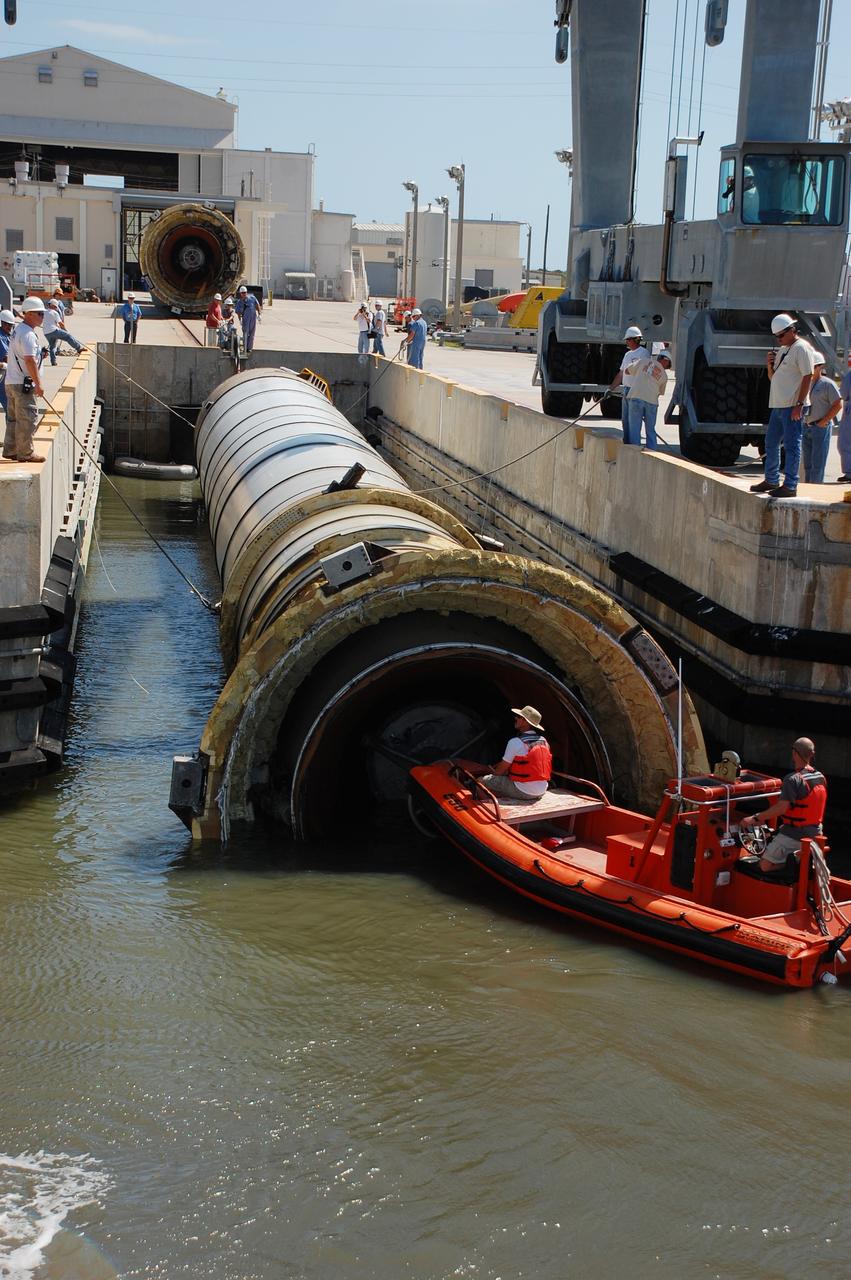

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Crew members in a skiff from Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, usher a spent shuttle booster to Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The booster was used during space shuttle Discovery's STS-133 launch from NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A on Feb. 24. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
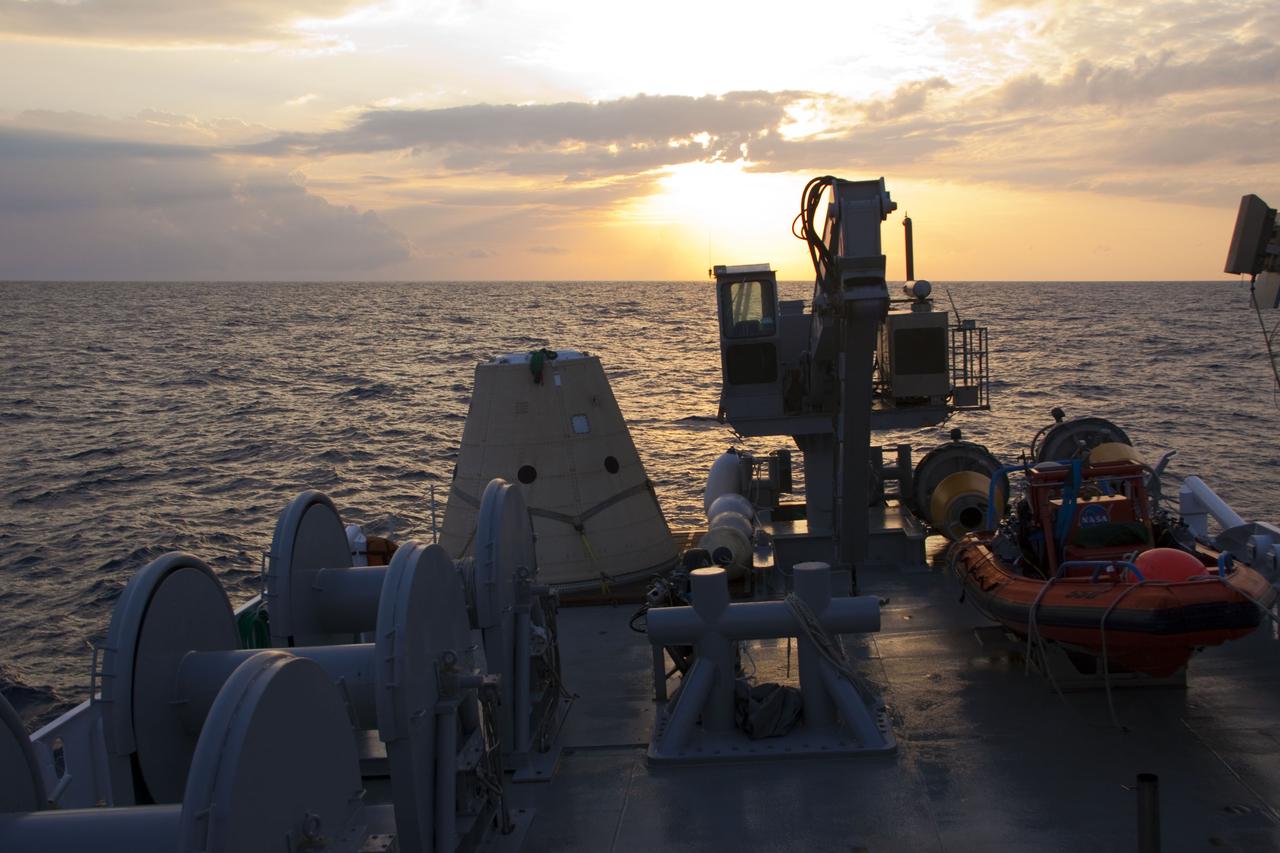

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The sun dawns over the Atlantic Ocean and Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, stationed in the Atlantic Ocean, to recover the right spent booster after it splashed down following space shuttle Discovery's final launch. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
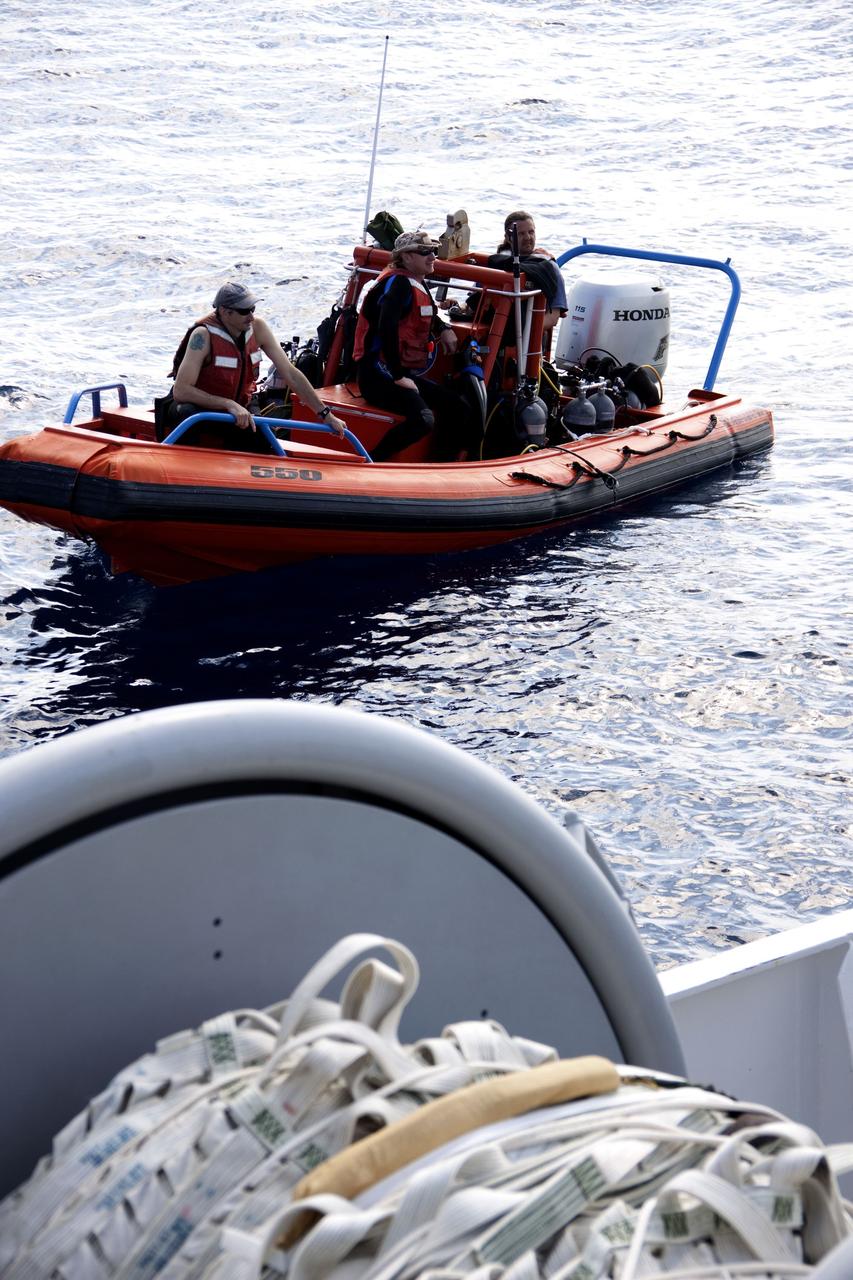

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Crew members return to Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, in a skiff after the massive parachute from the right spent booster has been hauled on board from space shuttle Discovery's final launch. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Crew members in a skiff from Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, attach a tow rope to the parachute lines from the right spent booster bobbing in the Atlantic Ocean from space shuttle Discovery's final launch. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
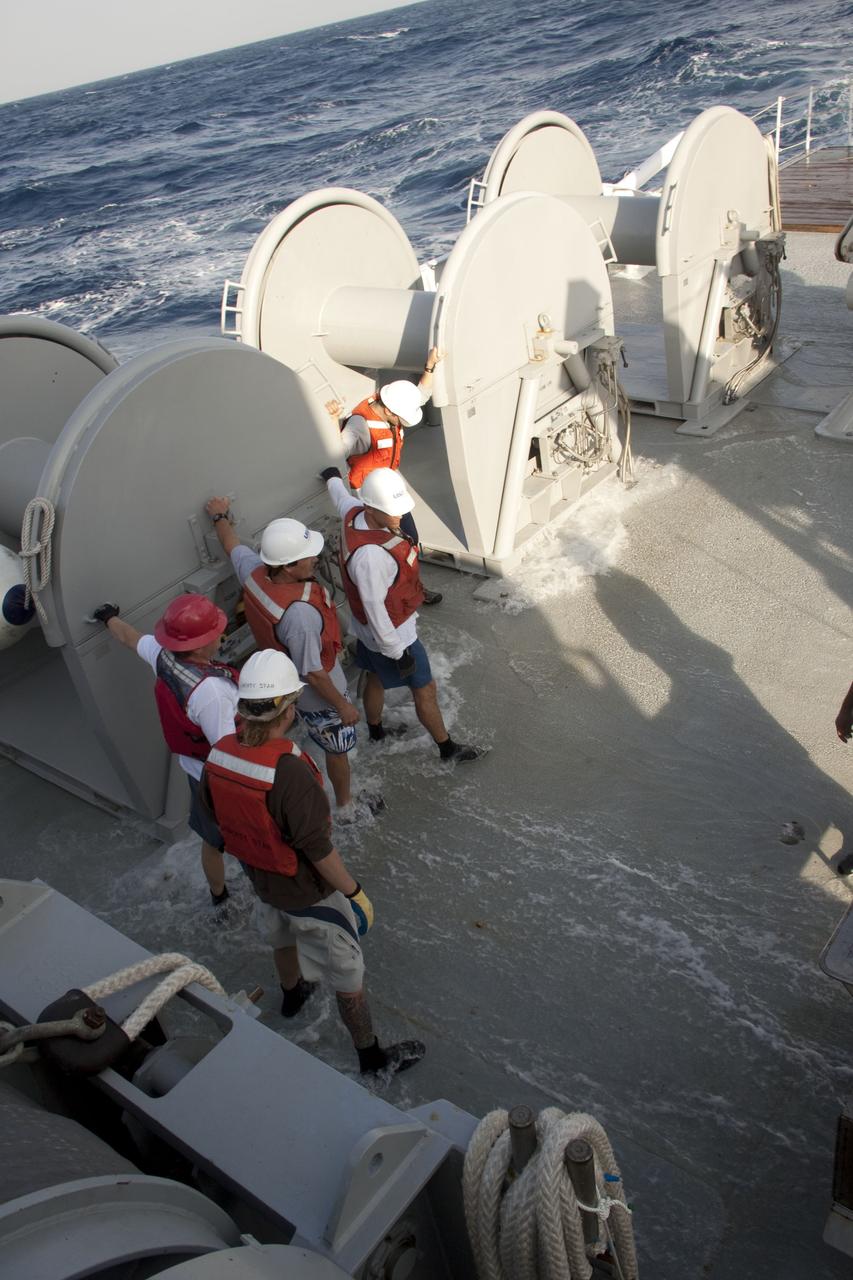

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Crew members of Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, hold on tightly to handle grips as the swells of the Atlantic Ocean cause the vessel to pitch and roll while heading toward the recovery area where the right spent booster splashed down after Discovery's final launch. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
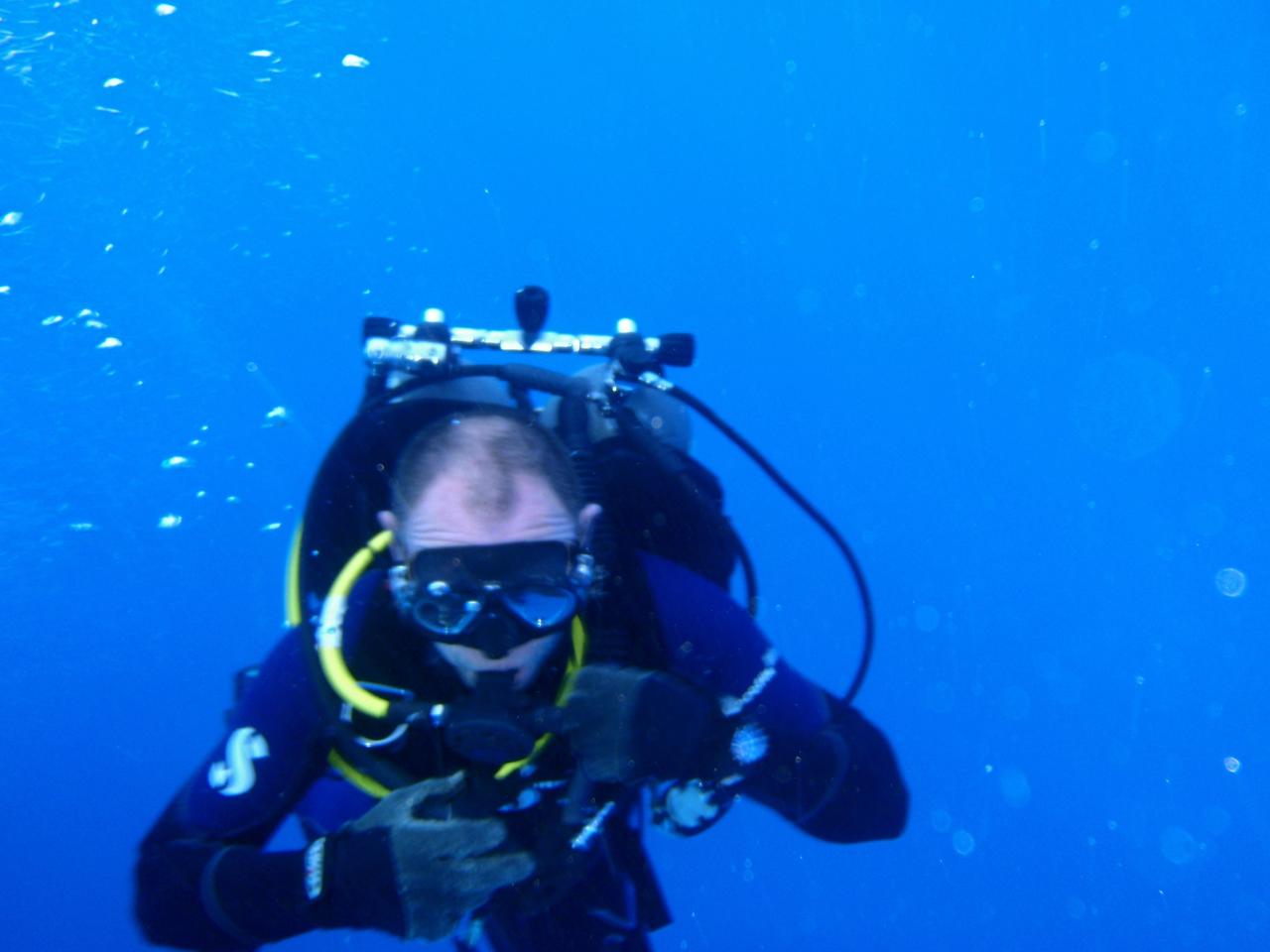

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A diver from Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, helps retrieve a spent shuttle booster in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Florida. The booster, which was used during space shuttle Discovery's STS-133 launch from NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A on Feb. 24, will be transported to Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered after every launch by Liberty Star and Freedom Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
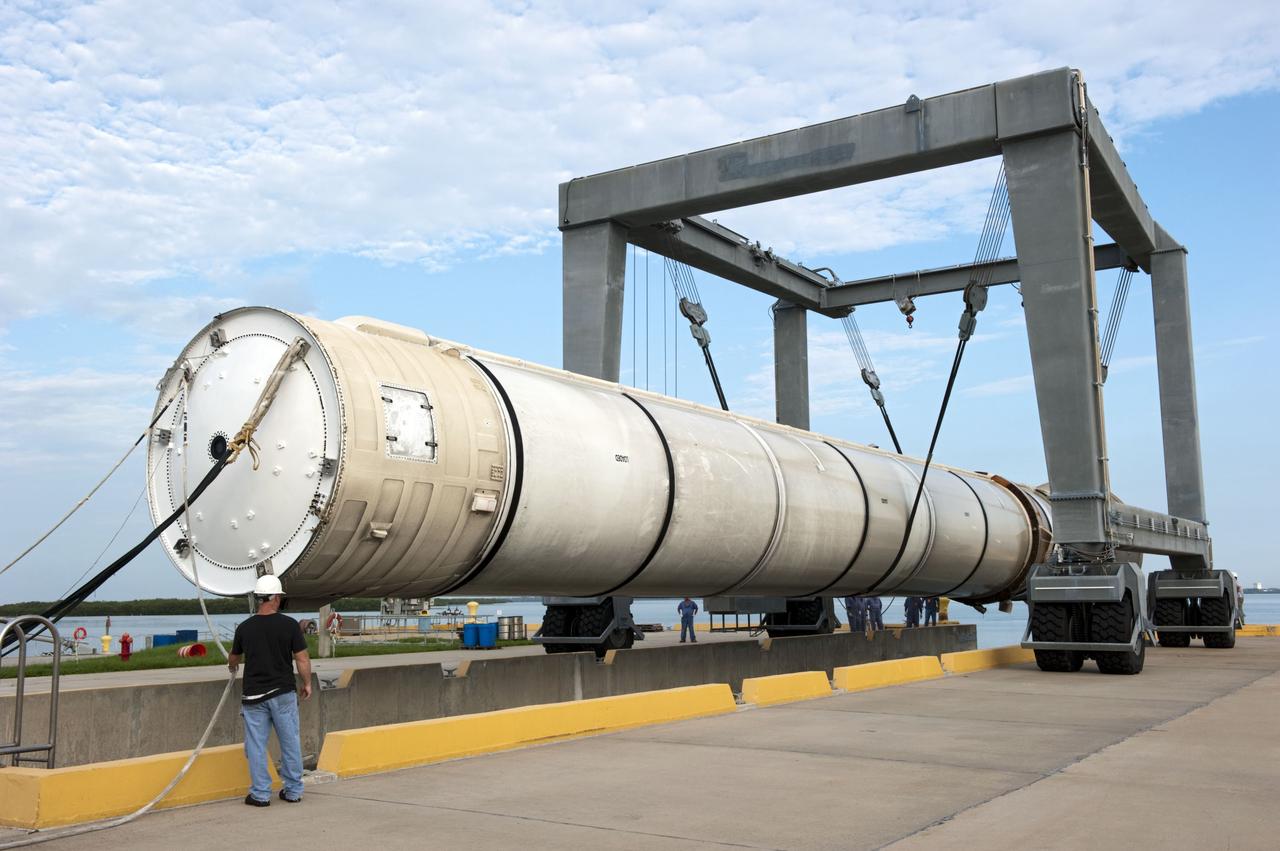

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – One of two solid rocket boosters is lifted above a mooring at Port Canaveral in Florida. Liberty Star, one of NASA’s two booster retrieval ships, towed the spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis’ final launch to the port. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff, and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight, STS-135, at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
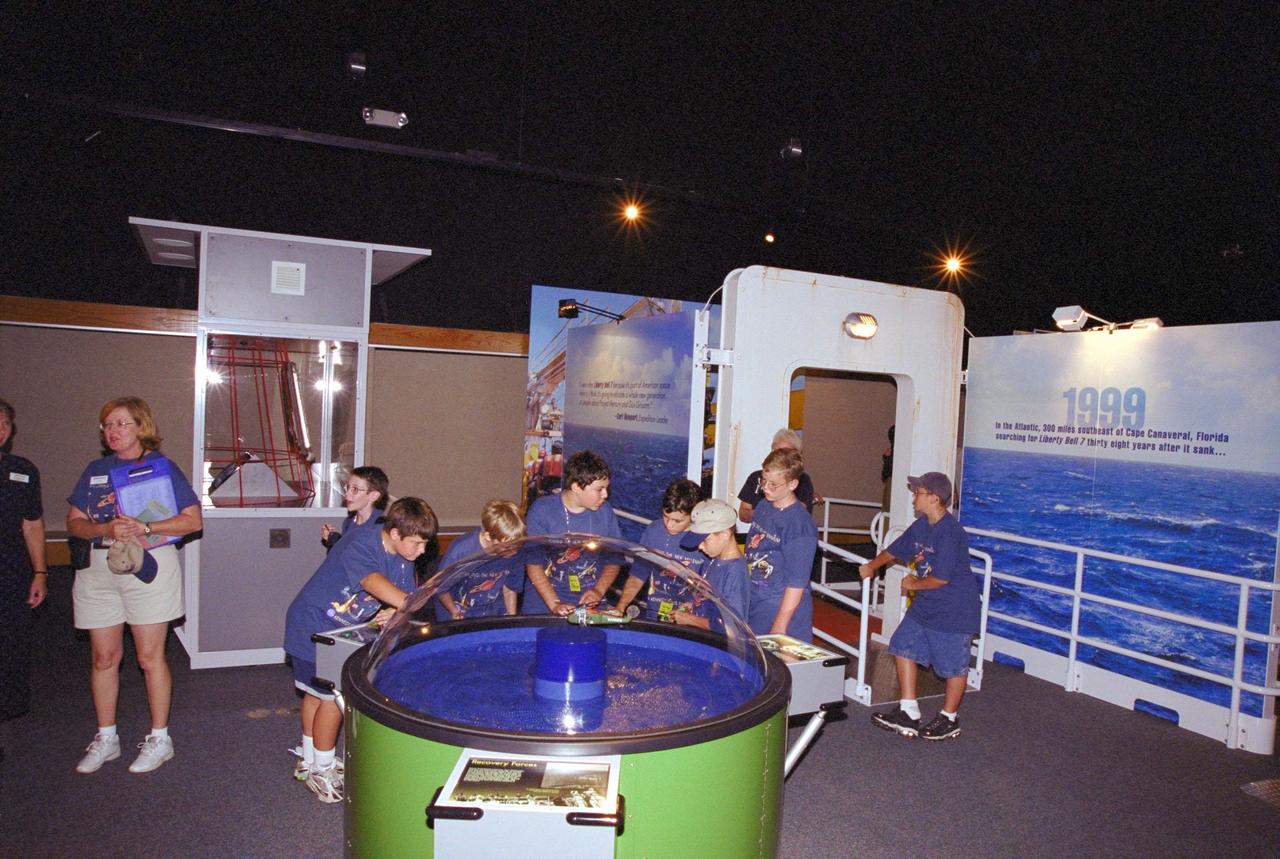

Children on a tour at the KSC Visitor Complex get an early look at the Discovery Channel's Liberty Bell 7 Space Capsule Exhibit, which opens to the public on Saturday, June 17. They are on a re-creation of the deck of Ocean Project, the ship that located and recovered the space capsule from the floor of the Atlantic Ocean. Liberty Bell 7 launched U.S. Air Force Captain Virgil “Gus” Grissom July 21, 1961, on a mission that lasted 15 minutes and 37 seconds before sinking. It lay undetected for nearly four decades before a Discovery Channel expedition located it and recovered it. The space capsule, now restored and preserved, is part of an interactive exhibit touring science centers and museums in 12 cities throughout the United States until 2003. The exhibit also includes hands-on elements such as a capsule simulator, a centrifuge, and ROV pilot
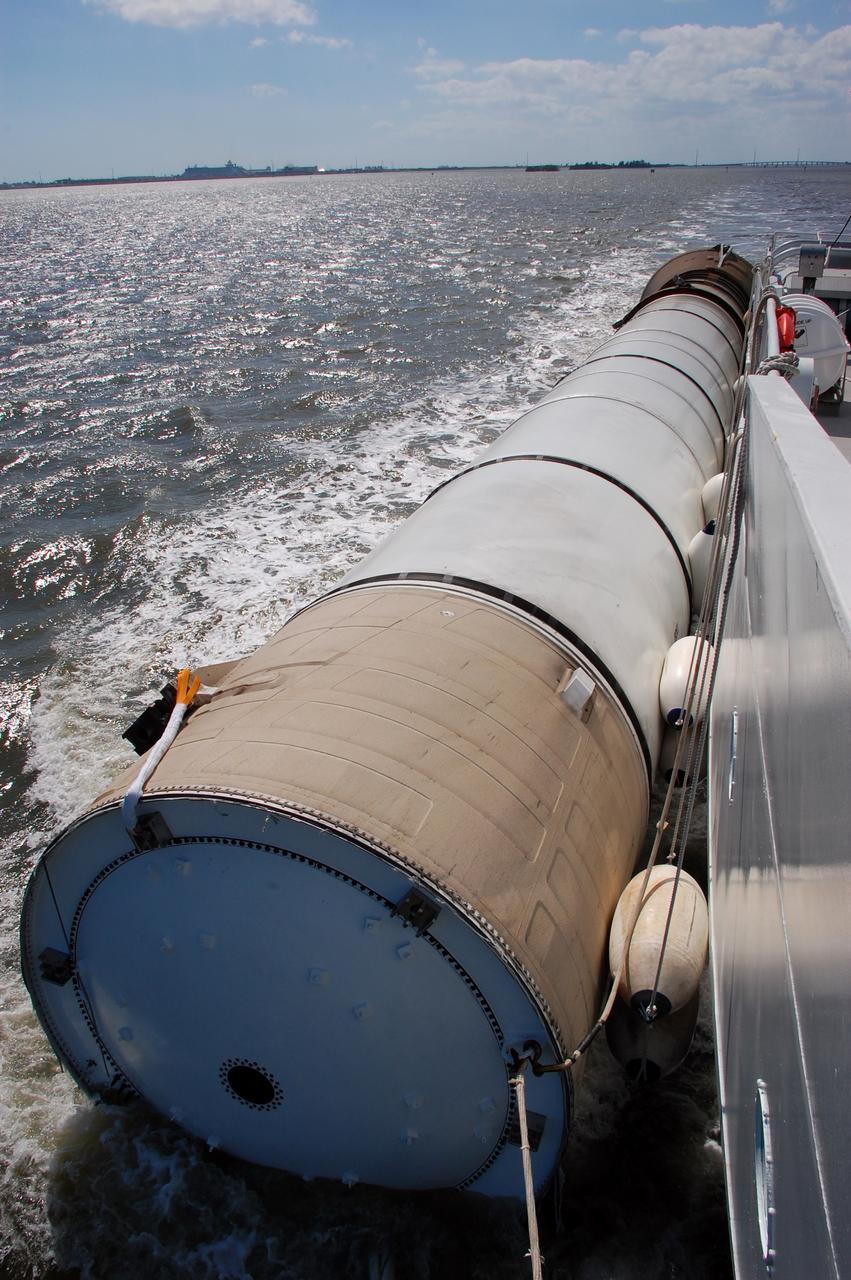

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, ushers a spent shuttle booster to Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The booster was used during space shuttle Discovery's STS-133 launch from NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A on Feb. 24. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
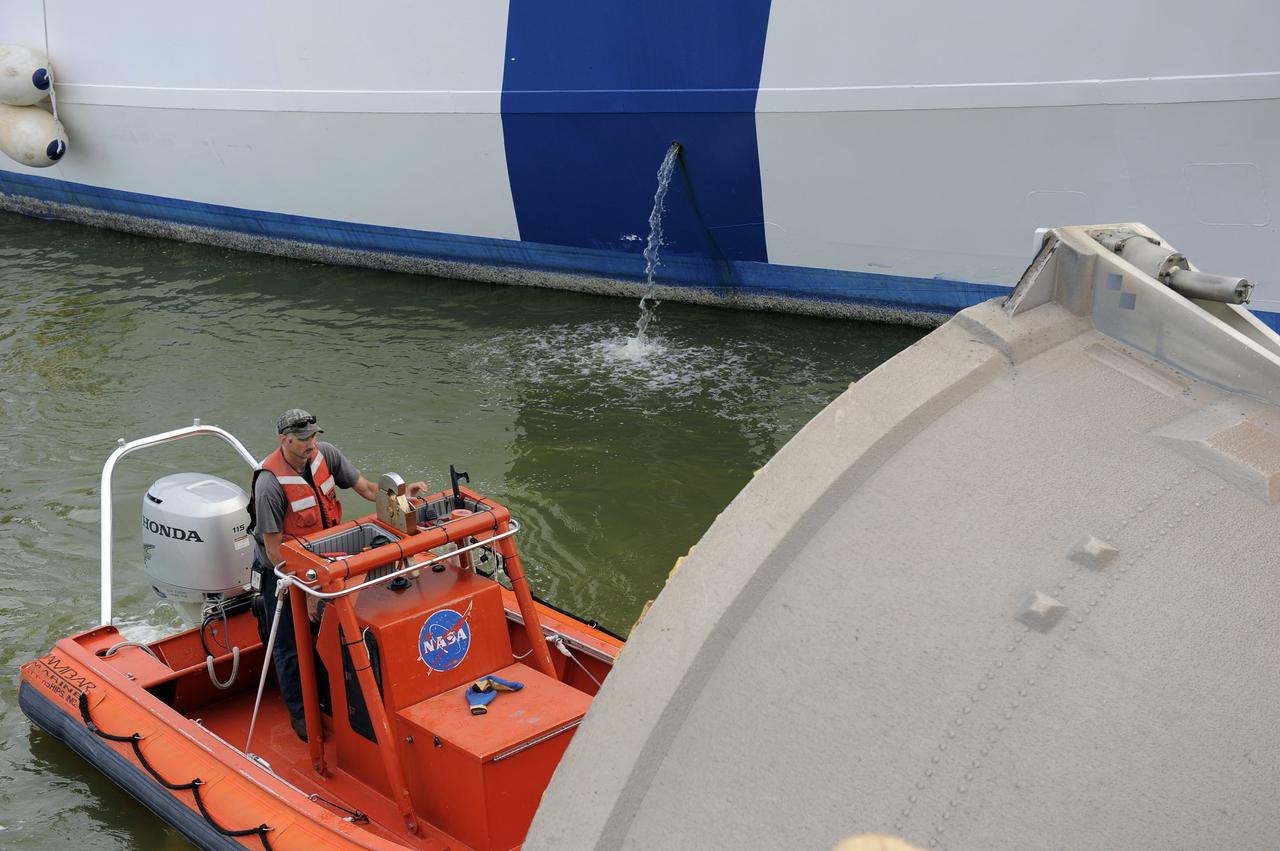

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A United Space Alliance tugboat driver monitors the progress as Liberty Star, one of NASA’s solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows a spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis’ final launch to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff, and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight, STS-135, at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
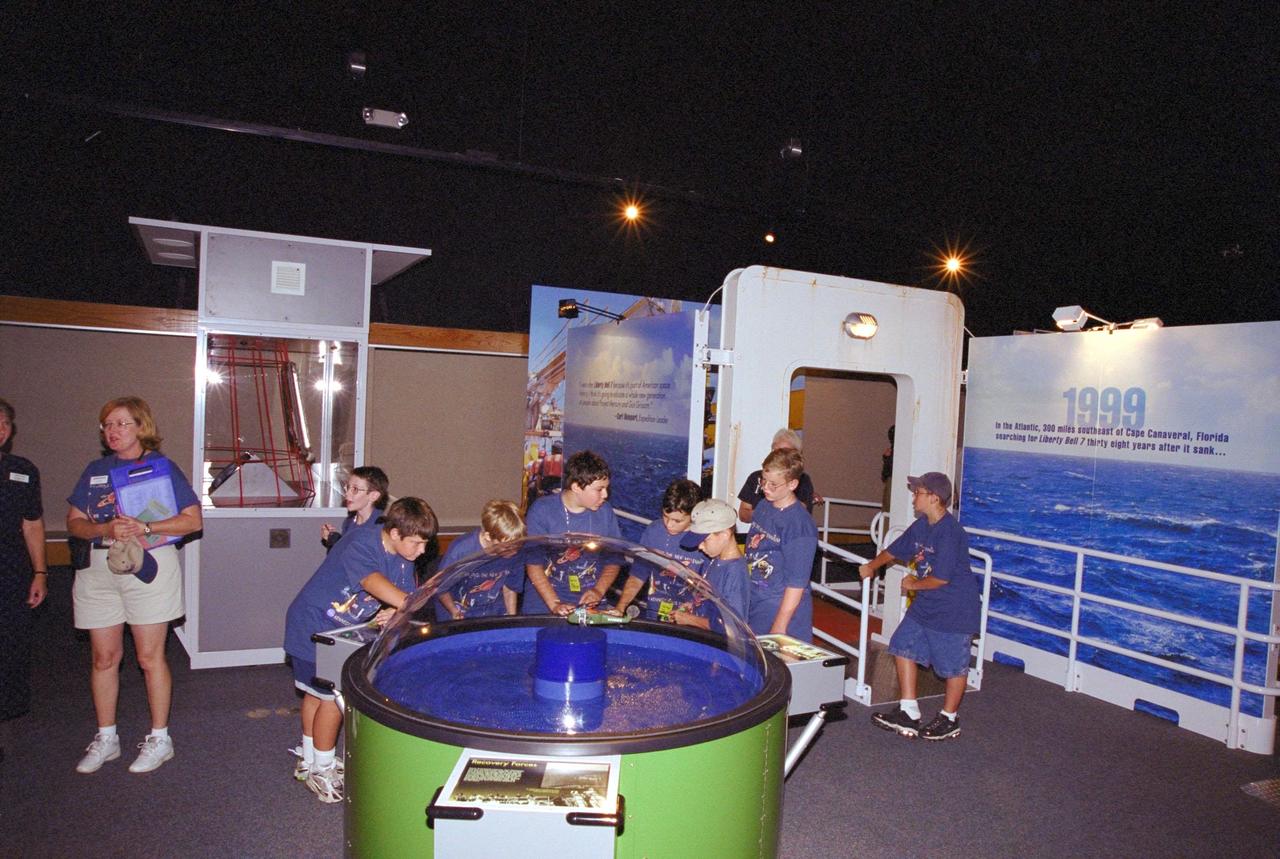

Children on a tour at the KSC Visitor Complex get an early look at the Discovery Channel's Liberty Bell 7 Space Capsule Exhibit, which opens to the public on Saturday, June 17. They are on a re-creation of the deck of Ocean Project, the ship that located and recovered the space capsule from the floor of the Atlantic Ocean. Liberty Bell 7 launched U.S. Air Force Captain Virgil “Gus” Grissom July 21, 1961, on a mission that lasted 15 minutes and 37 seconds before sinking. It lay undetected for nearly four decades before a Discovery Channel expedition located it and recovered it. The space capsule, now restored and preserved, is part of an interactive exhibit touring science centers and museums in 12 cities throughout the United States until 2003. The exhibit also includes hands-on elements such as a capsule simulator, a centrifuge, and ROV pilot
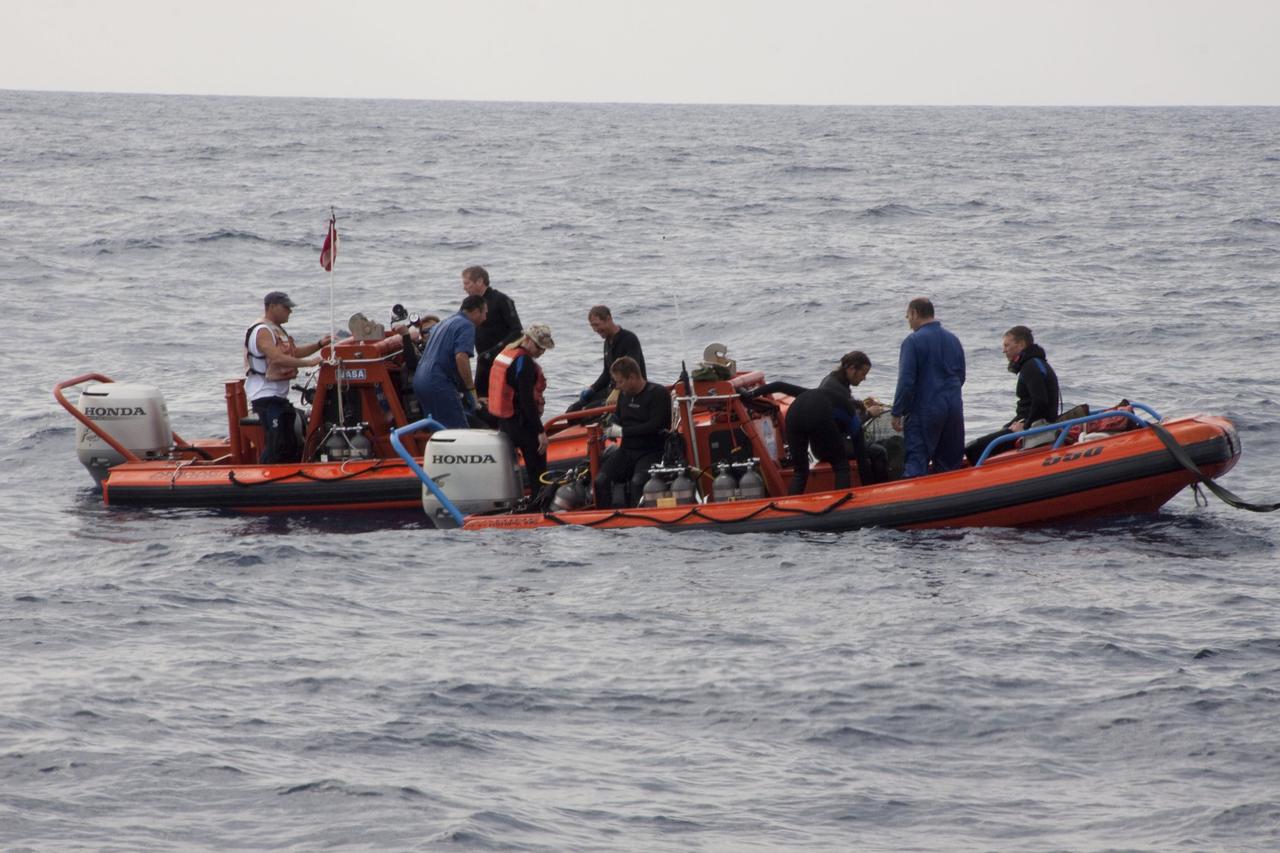

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Crew members and divers in skiffs from Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, are prepared to retrieve the parachute lines from the right spent booster bobbing in the Atlantic Ocean from space shuttle Discovery's final launch. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
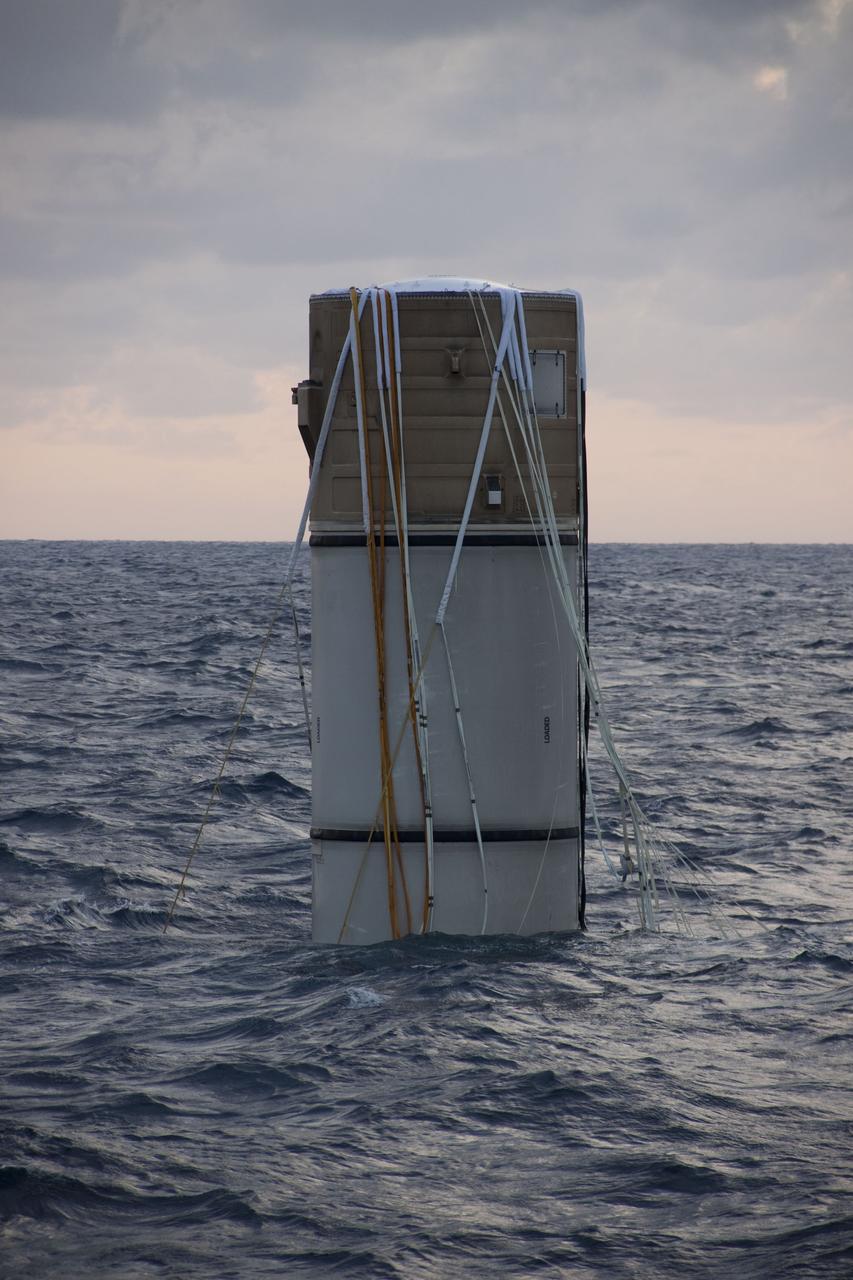

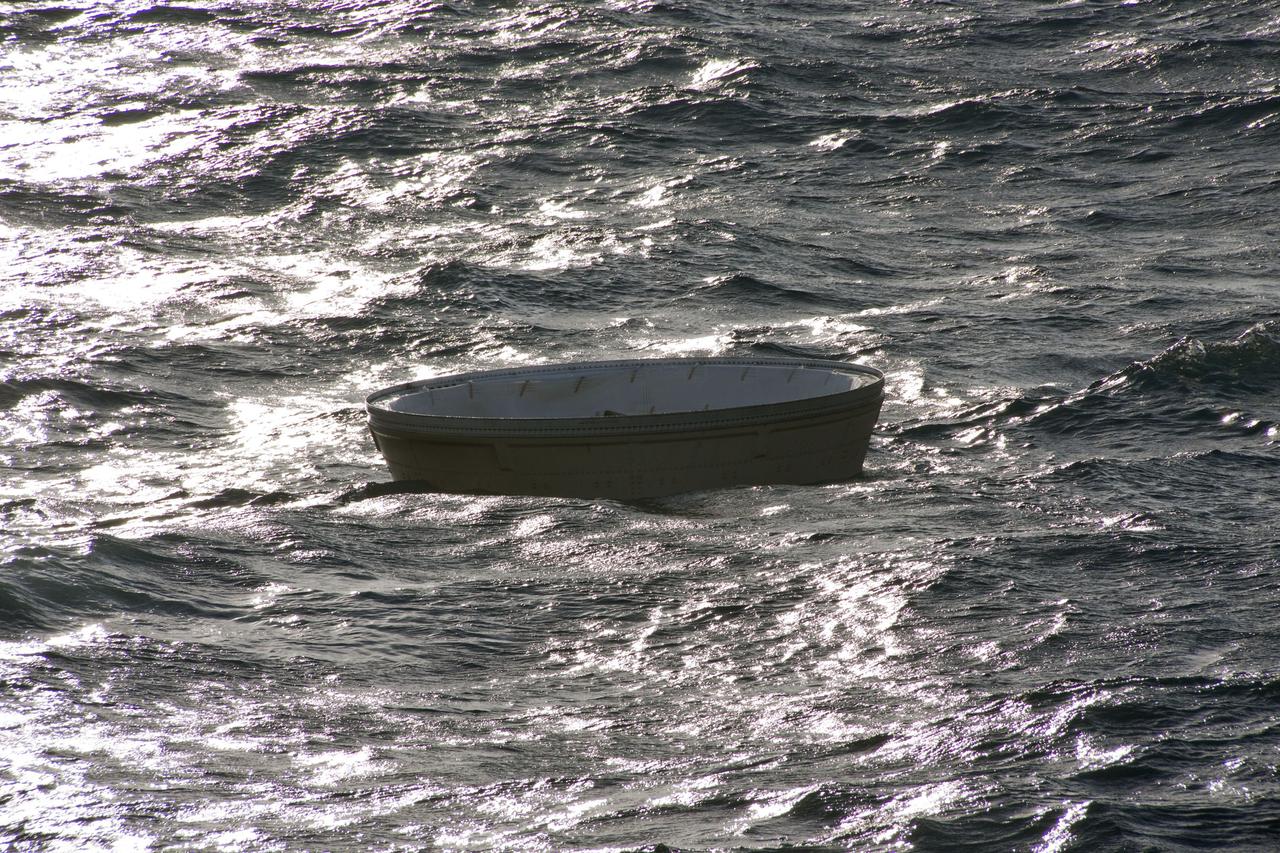
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The right spent booster from shuttle Discovery's final launch is seen bobbing in the Atlantic Ocean. Crew members from Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, will recover the parachute and tow the booster back to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
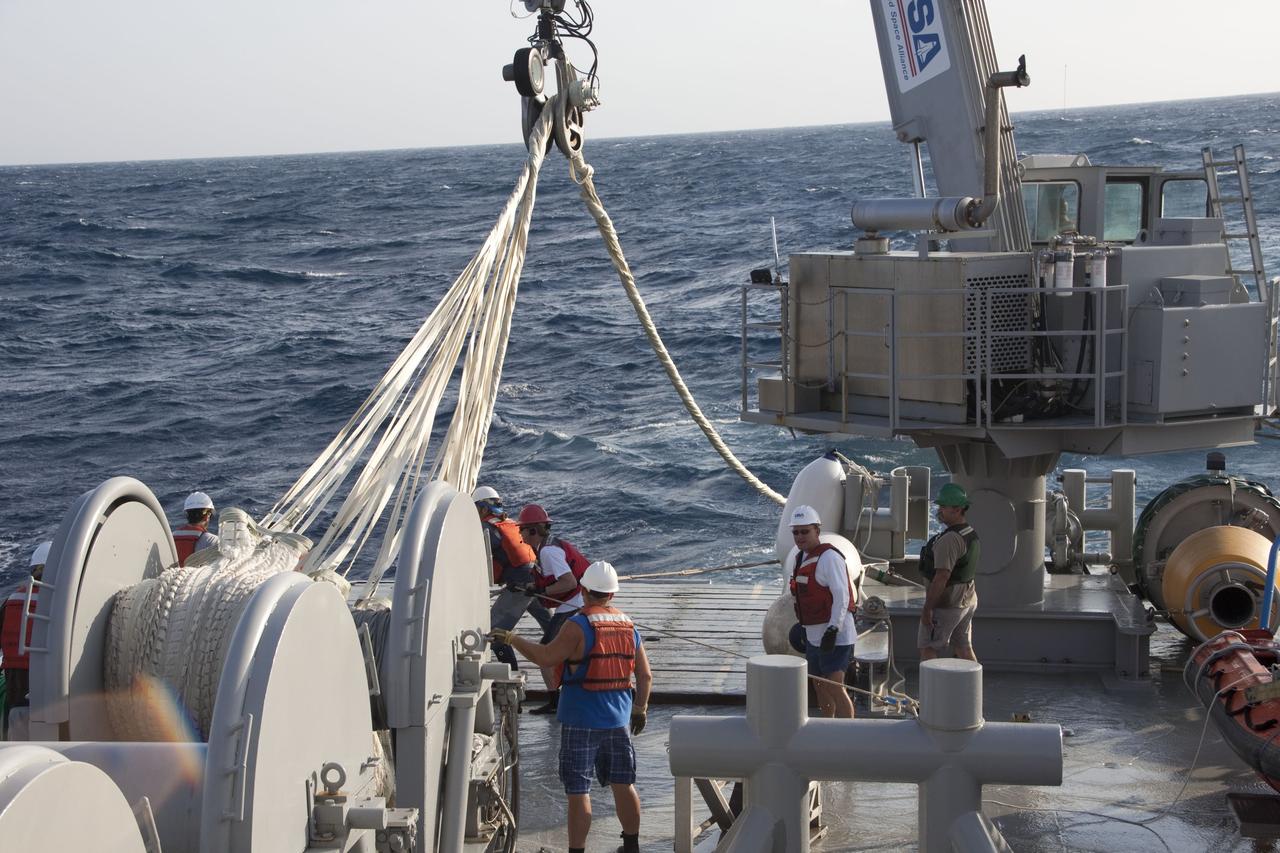

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Crew members on Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, use a crane to haul the parachute from the right spent booster onto the ship after it splashed down in the Atlantic Ocean after Discovery's final launch. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
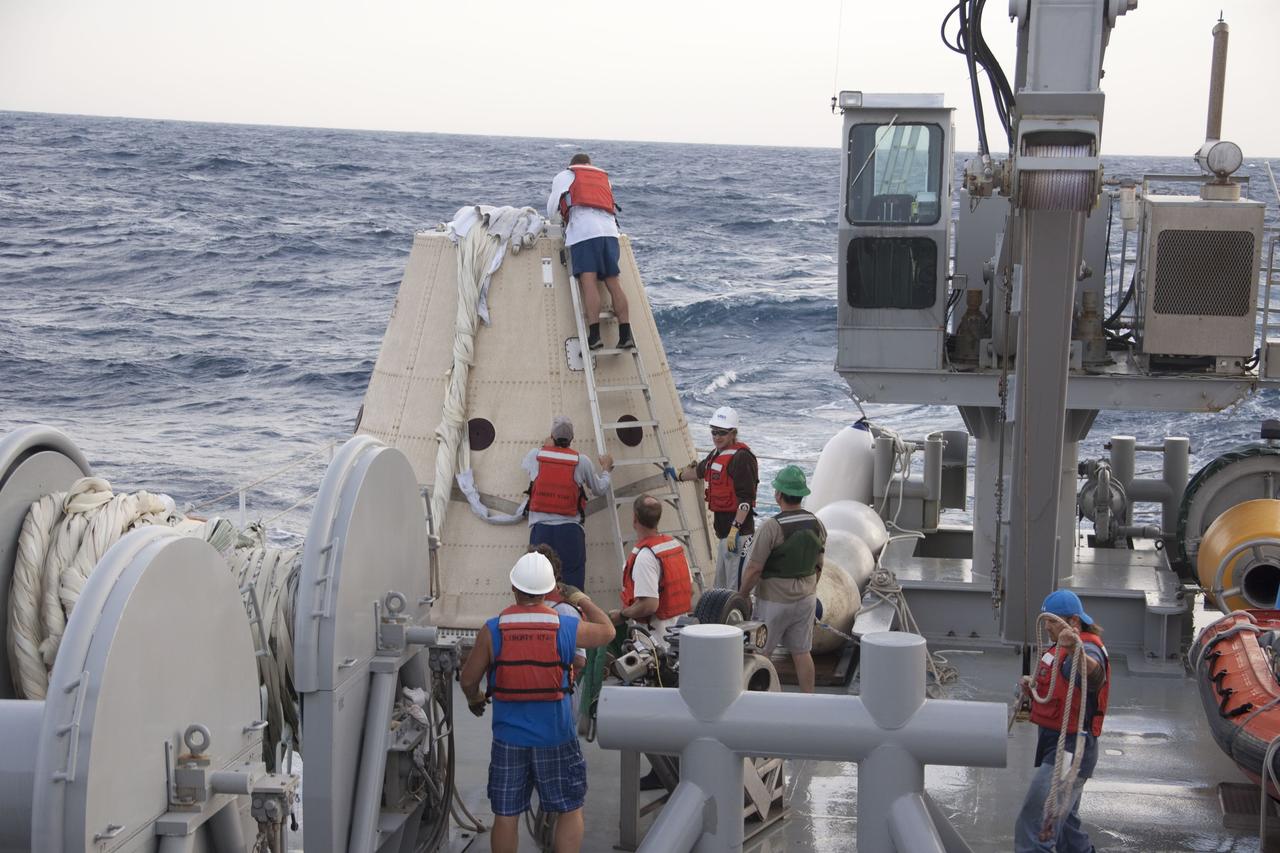

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Crew members from Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, work on the parachute from the right spent booster nose cap that splashed down in the Atlantic Ocean after Discovery's final launch. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
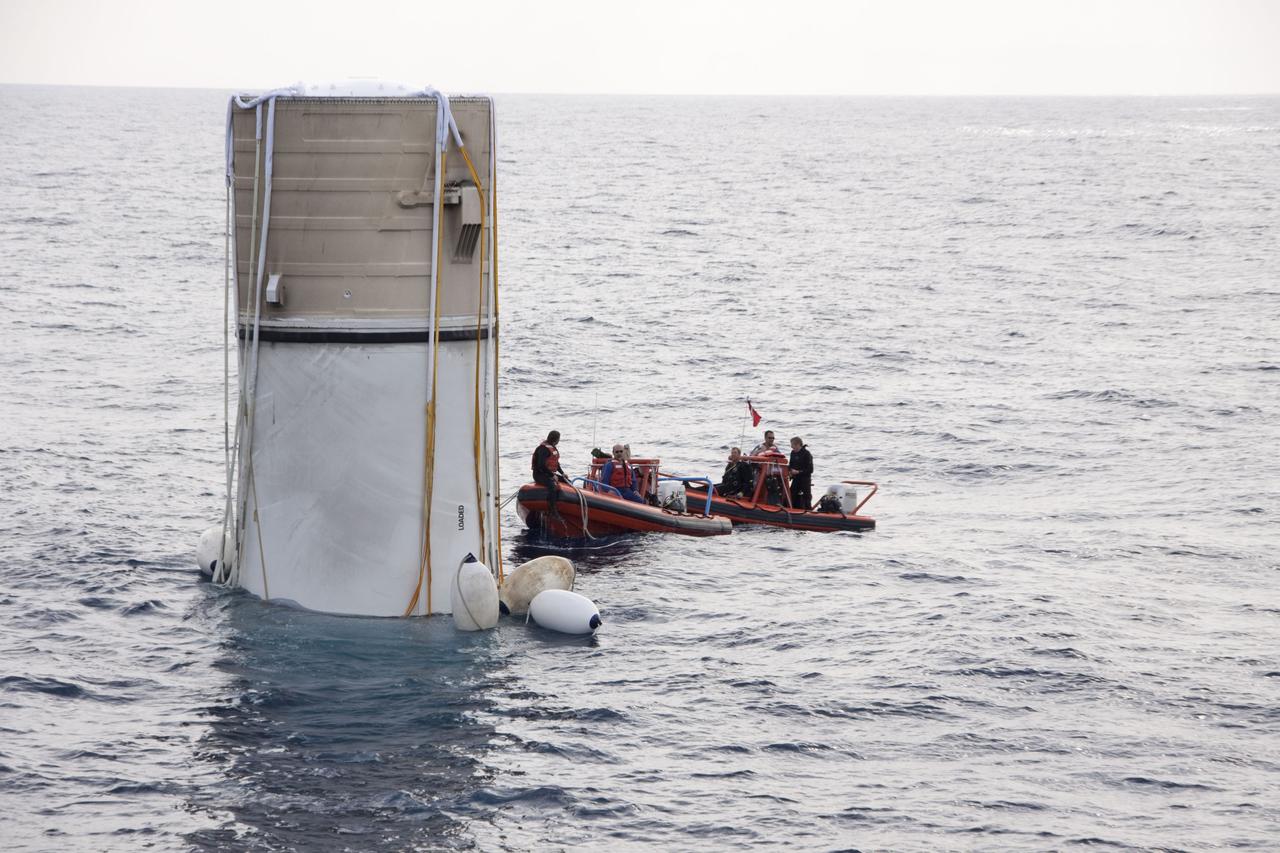

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Crew members in a skiff from Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, attach flotation devices, or buoys, to the parachute lines from the right spent booster from space shuttle Discovery's final launch. The shuttle's two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux
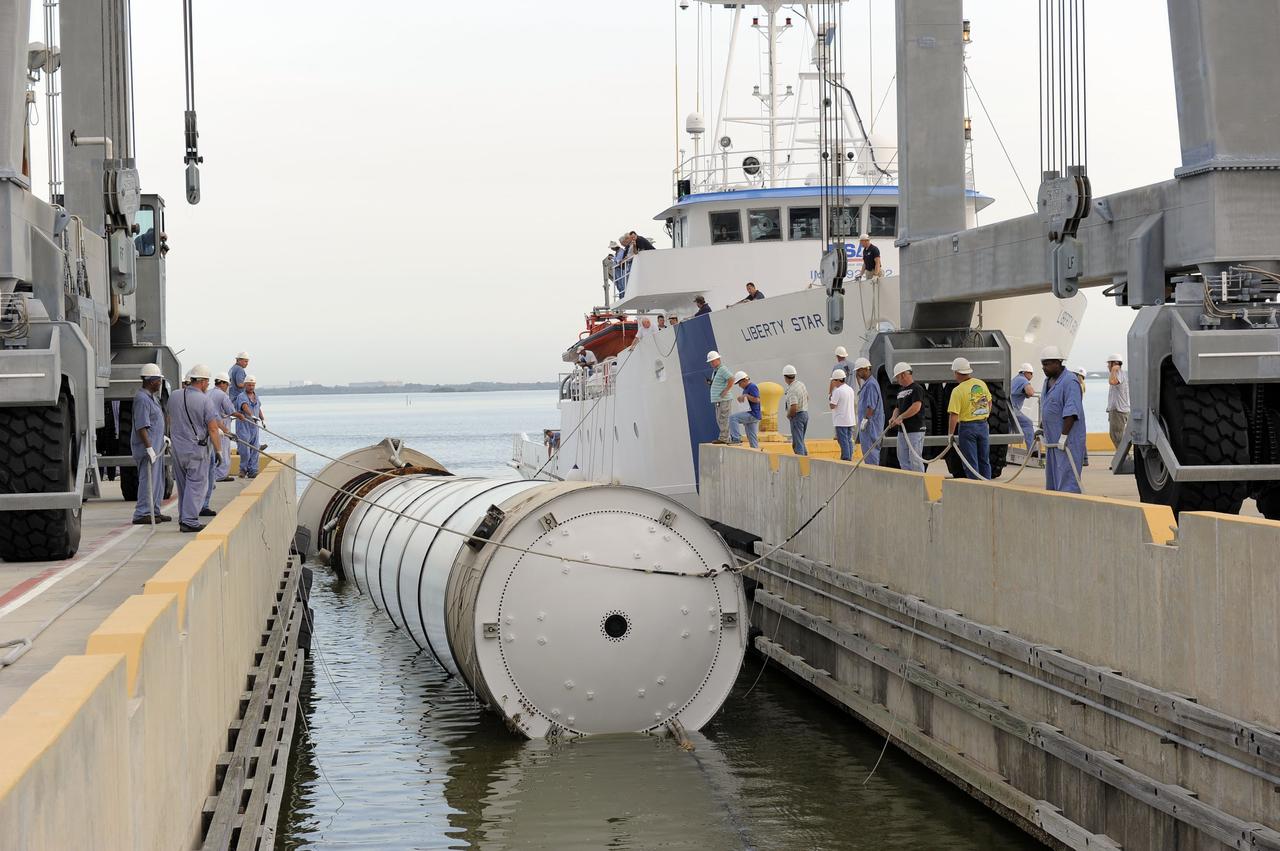

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers assist as Liberty Star, one of NASA’s solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tows a spent booster from space shuttle Atlantis’ final launch to Port Canaveral in Florida. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff, and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be deserviced and stored, if needed. Atlantis began its final flight, STS-135, at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
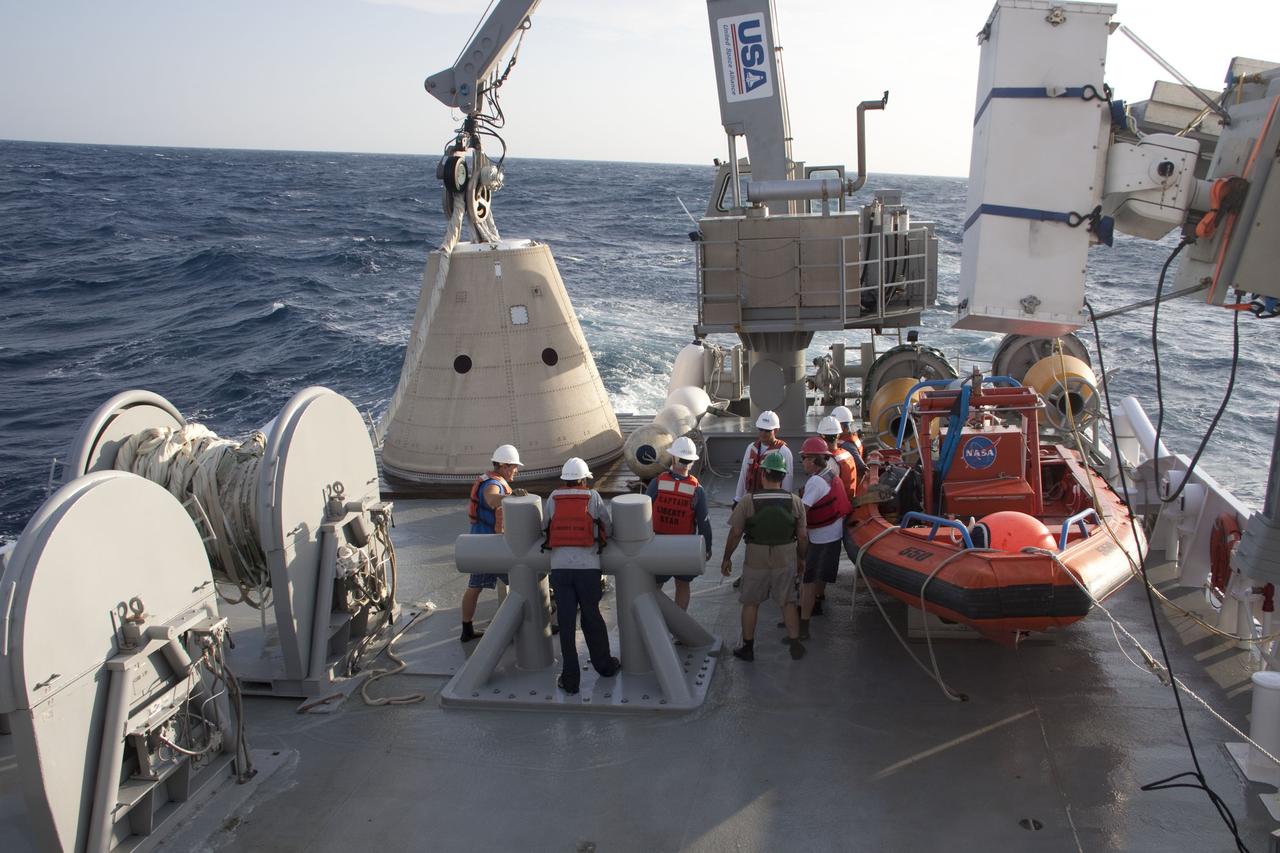

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Crew members from Liberty Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, have recovered and secured the right spent booster nose cap to a pallet on the ship's deck that was recovered from the Atlantic Ocean after Discovery's final launch. The shuttle’s two solid rocket booster casings and associated flight hardware are recovered in the Atlantic Ocean after every launch by Freedom Star and Liberty Star. The boosters impact the Atlantic about seven minutes after liftoff and the retrieval ships are stationed about 10 miles from the impact area at the time of splashdown. After the spent segments are processed, they will be transported to Utah, where they will be refurbished and stored, if needed. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Michaux