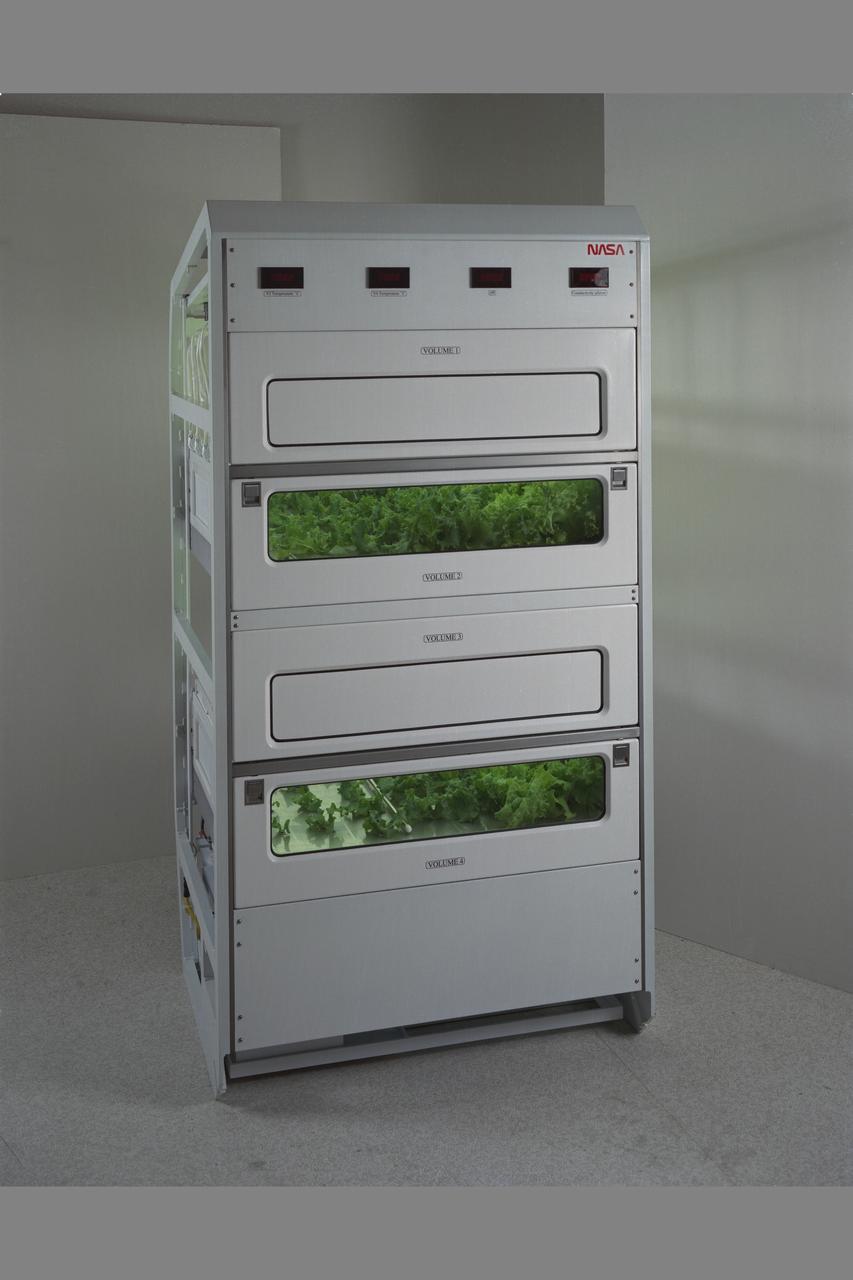

Life Sciences documentation of Salad Machine being developed at NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. for use in long duration space flight or on distant outposts.
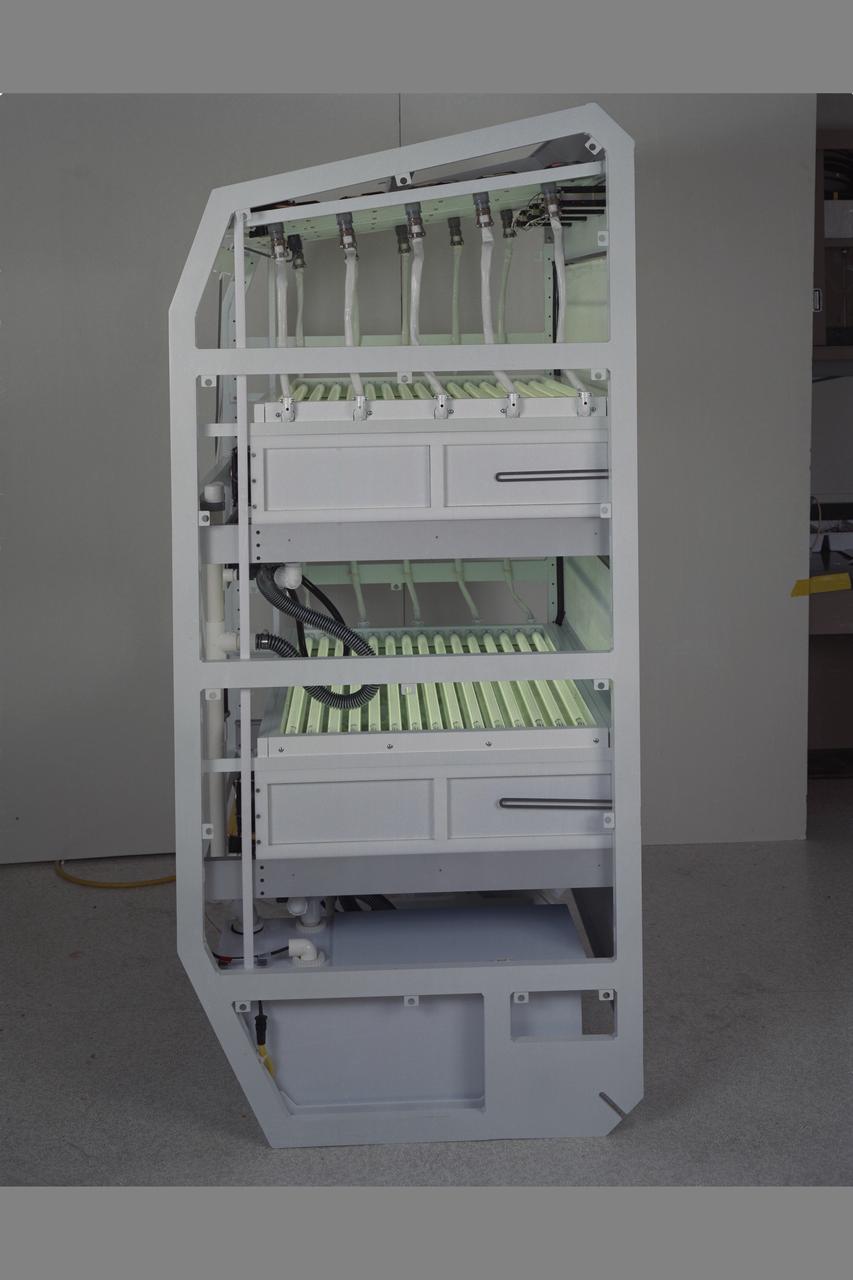

Life Sciences documentation of Salad Machine being developed at NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. for use in long duration space flight or on distant outposts.
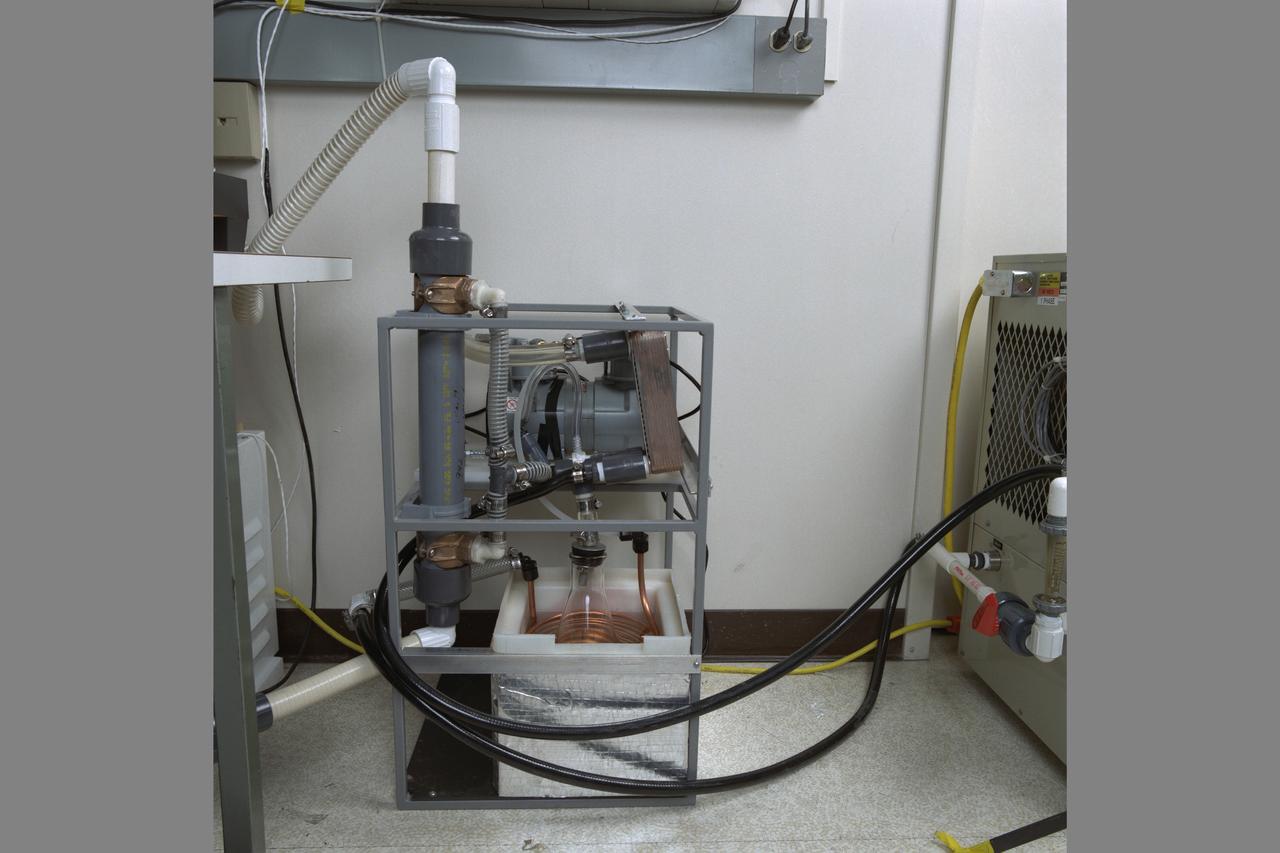
Life Sciences documentation of Salad Machine being developed at NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. for use in long duration space flight or on distant outposts.
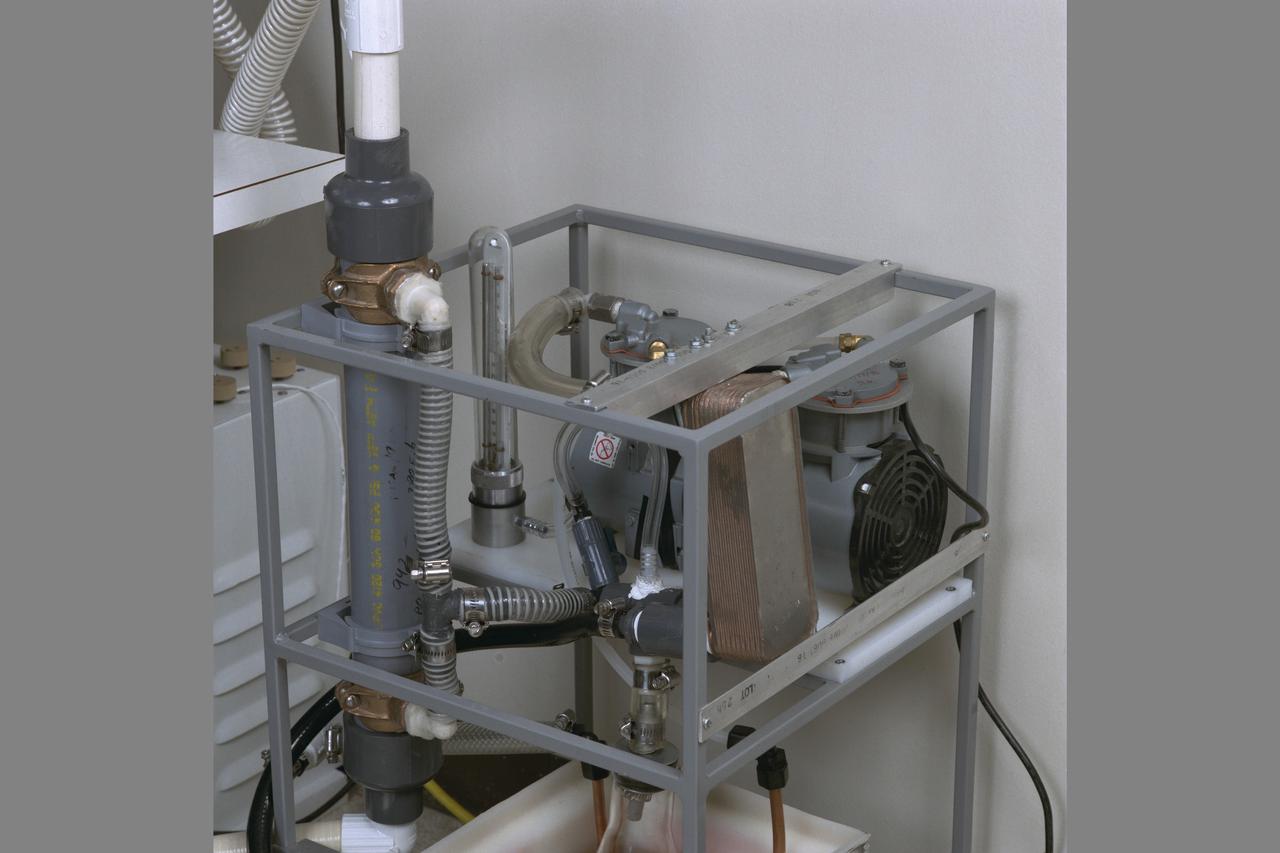
Life Sciences documentation of Salad Machine being developed at NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. for use in long duration space flight or on distant outposts.
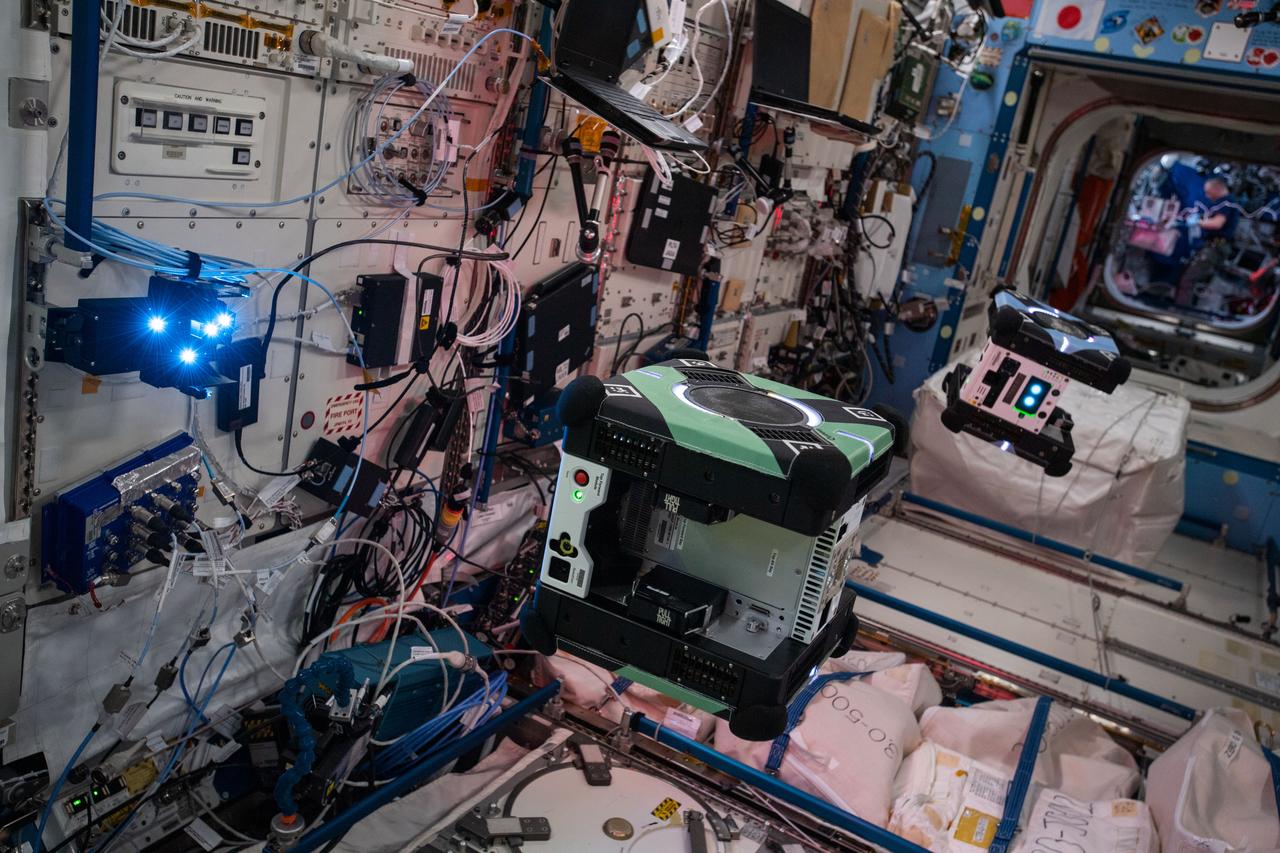

Documentation of two free-flying Astrobee robots (Queen and Bumble), equipped with LED Targets for the Smartphone Video Guidance Sensor (SVGS) experiment, during SVGS science 3 session. An SVGS LED Target is attached to the Life Sciences Glovebox (LSG) rack, JPM1F5 in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Module (JEM).
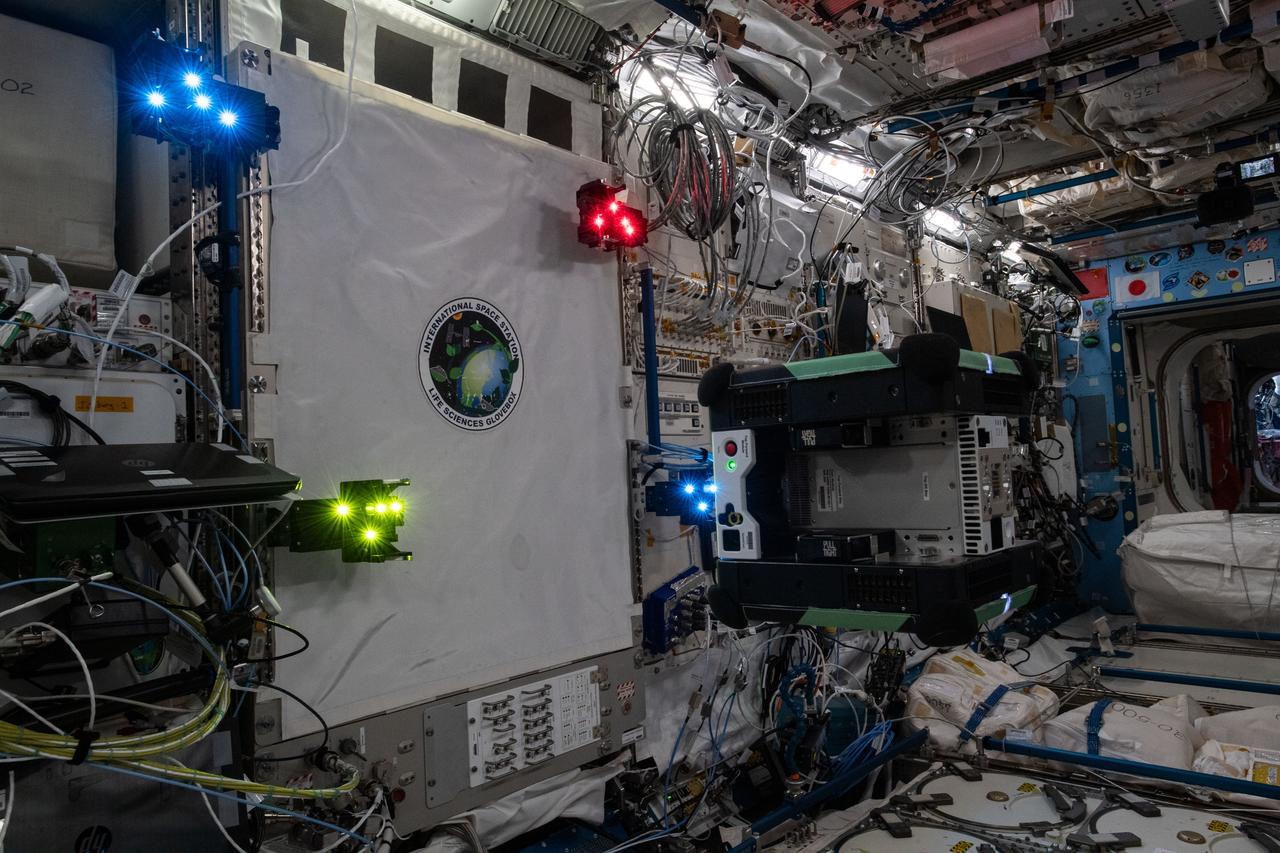

Documentation of a free-flying Astrobee robot (Queen), equipped with an LED Target for the Smartphone Video Guidance Sensor (SVGS) experiment, during SVGS science 3 session. Four SVGS LED Targets are attached to the Life Sciences Glovebox (LSG) rack, JPM1F5 in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Module (JEM).
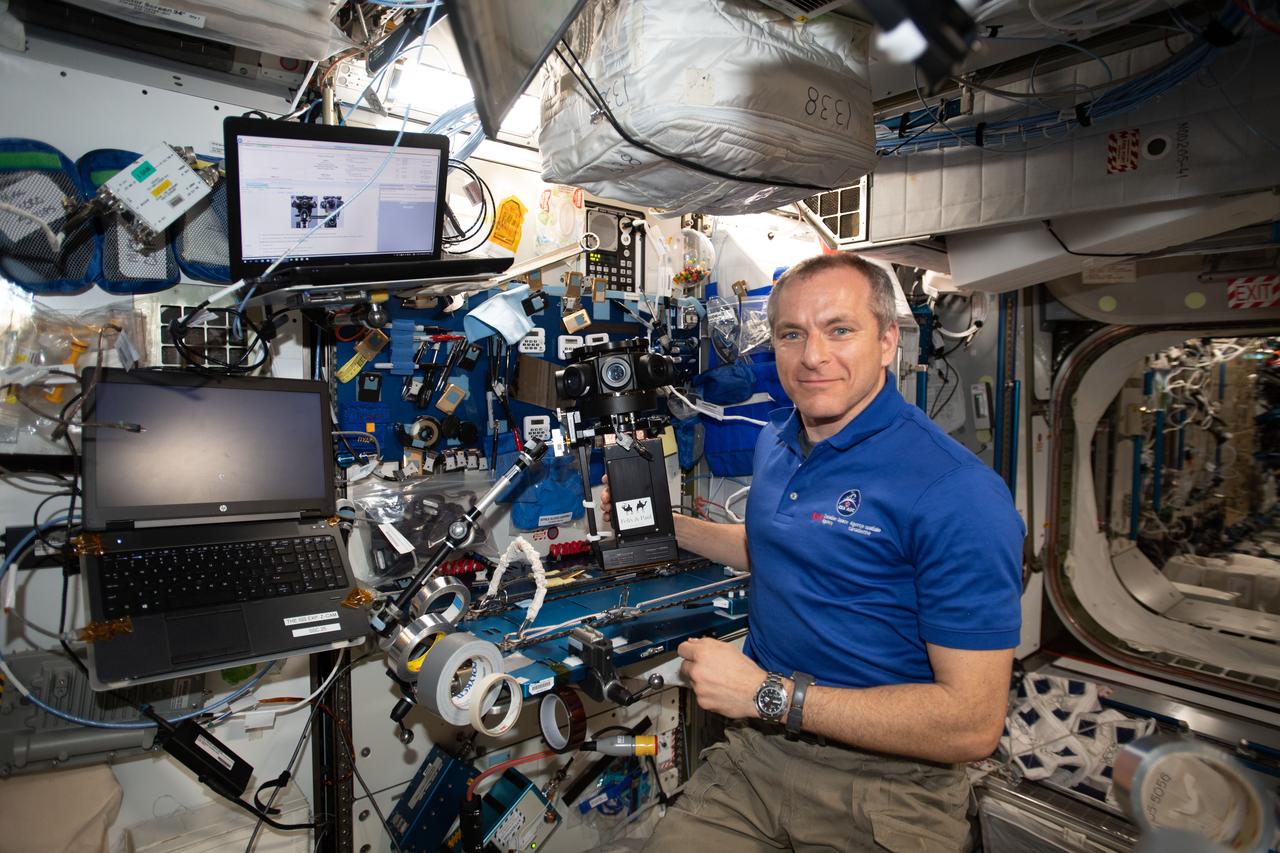

iss058e005160 (1/21/2019) --- A view of Canadian Space Agency (CSA) astronaut David Saint-Jacques setting up the Z-CAM V1 Pro Cinematic camera for the ISS Experience payload. The International Space Station Experience (ISS Experience) creates a virtual reality film documenting daily life aboard the space station. The 8- to 10-minute film created from footage taken during the six-month investigation covers different aspects of crew life, conducting science aboard the station, and the international partnerships involved.
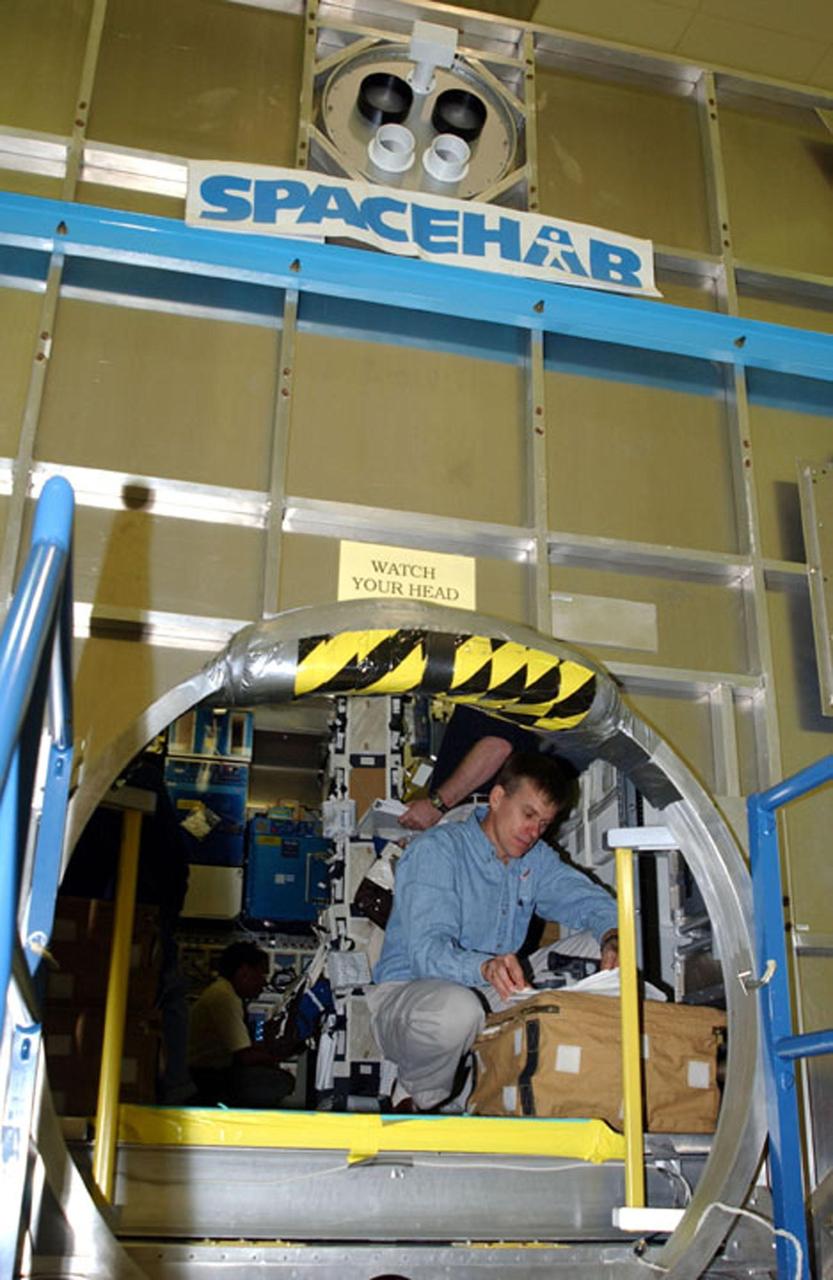

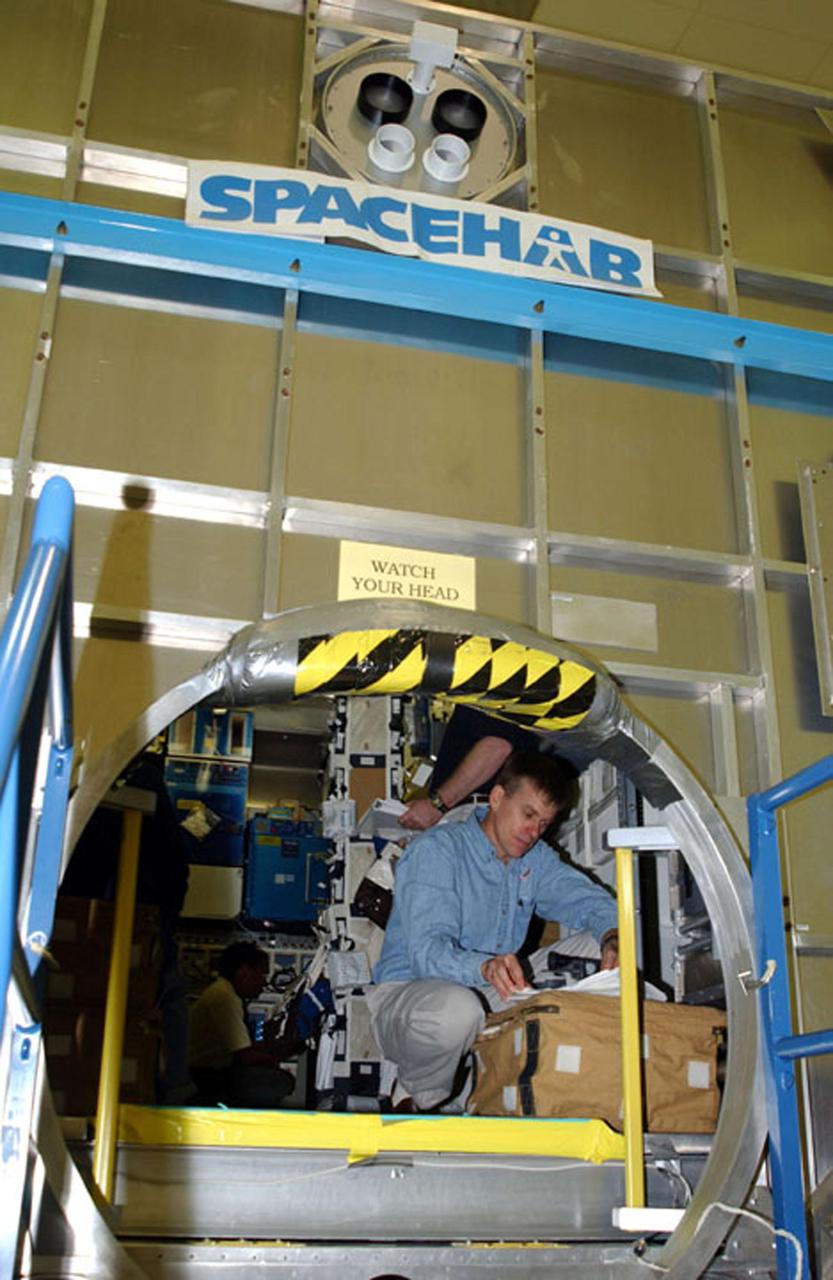
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At SPACEHAB, Cape Canaveral, Fla., members of the STS-107 crew look over equipment. Inside the SPACEHAB module, Pilot William "Willie" McCool scans documents. STS-107 is a research mission, and the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM). The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). Among the experiments is a Hitchhiker carrier system, modular and expandable in accordance with payload requirements. STS-107 is scheduled to launch in June 2002.
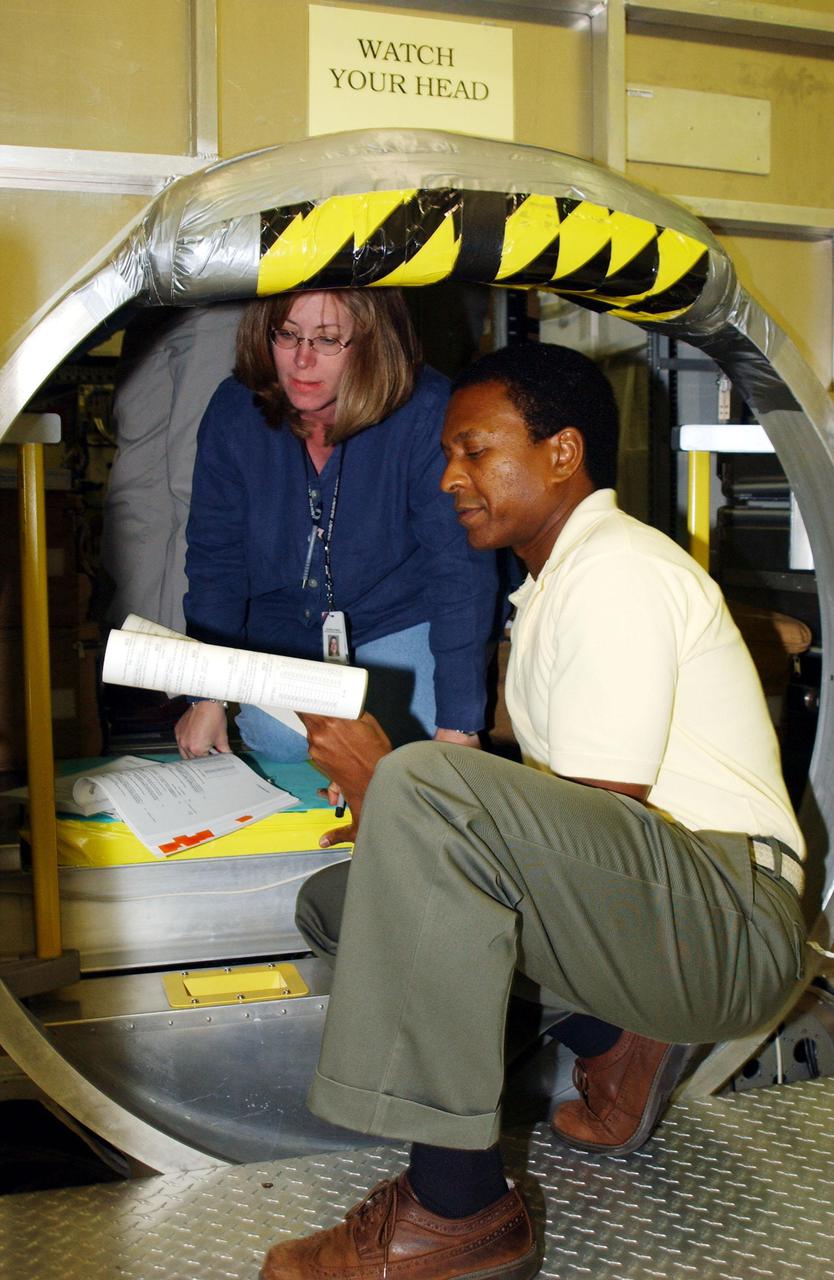

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the SPACEHAB module at SPACEHAB, Cape Canaveral, Fla., Payload Commander Michael Anderson scans documents. STS-107 is a research mission, and the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI_RDM). The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). Among the experiments is a Hitchhiker carrier system, modular and expandable in accordance with payload requirements. STS-107 is scheduled to launch in June 2002.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At SPACEHAB, Cape Canaveral, Fla., members of the STS-107 crew look over equipment. Inside the SPACEHAB module, Pilot William 'Willie' McCool scans documents. STS-107 is a research mission, and the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI_RDM). The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). Among the experiments is a Hitchhiker carrier system, modular and expandable in accordance with payload requirements. STS-107 is scheduled to launch in June 2002.
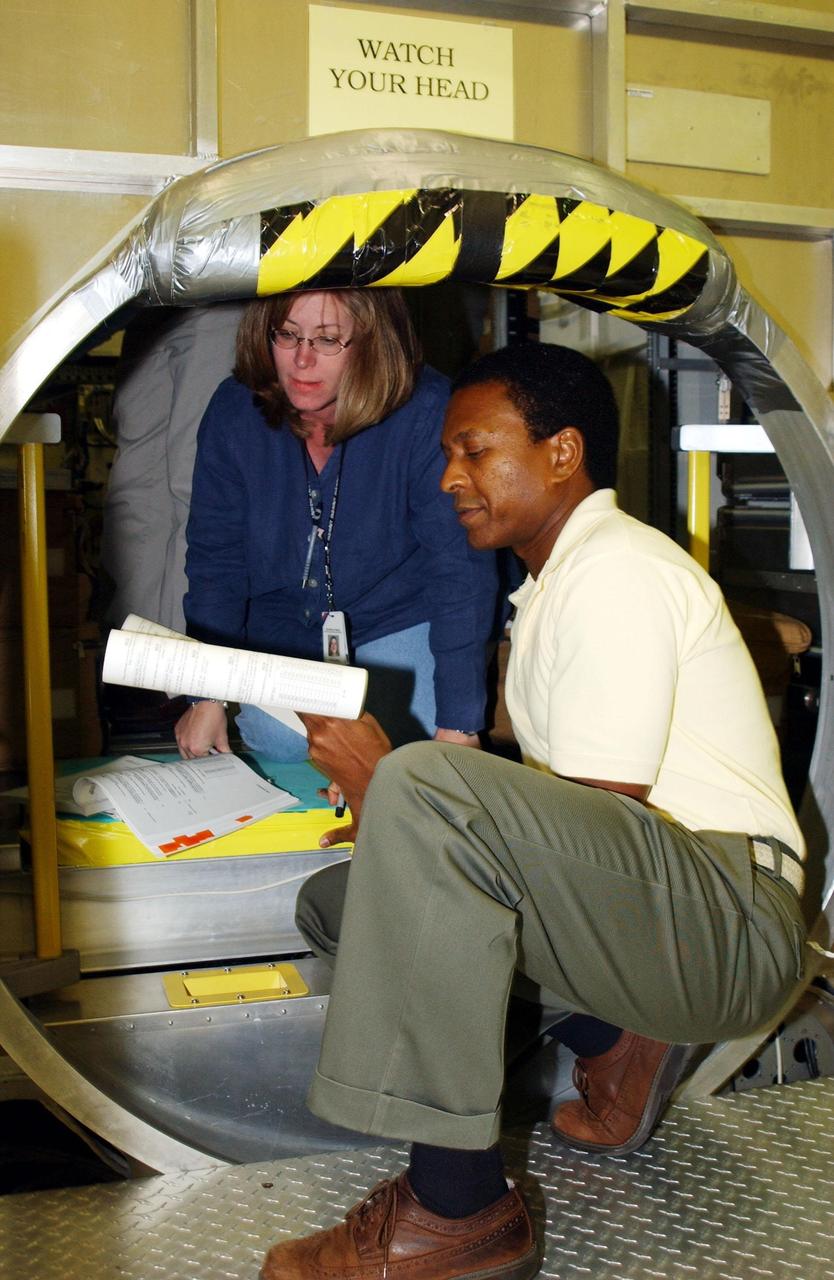

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the SPACEHAB module at SPACEHAB, Cape Canaveral, Fla., Payload Commander Michael Anderson scans documents. STS-107 is a research mission, and the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM). The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). Among the experiments is a Hitchhiker carrier system, modular and expandable in accordance with payload requirements. STS-107 is scheduled to launch in June 2002.
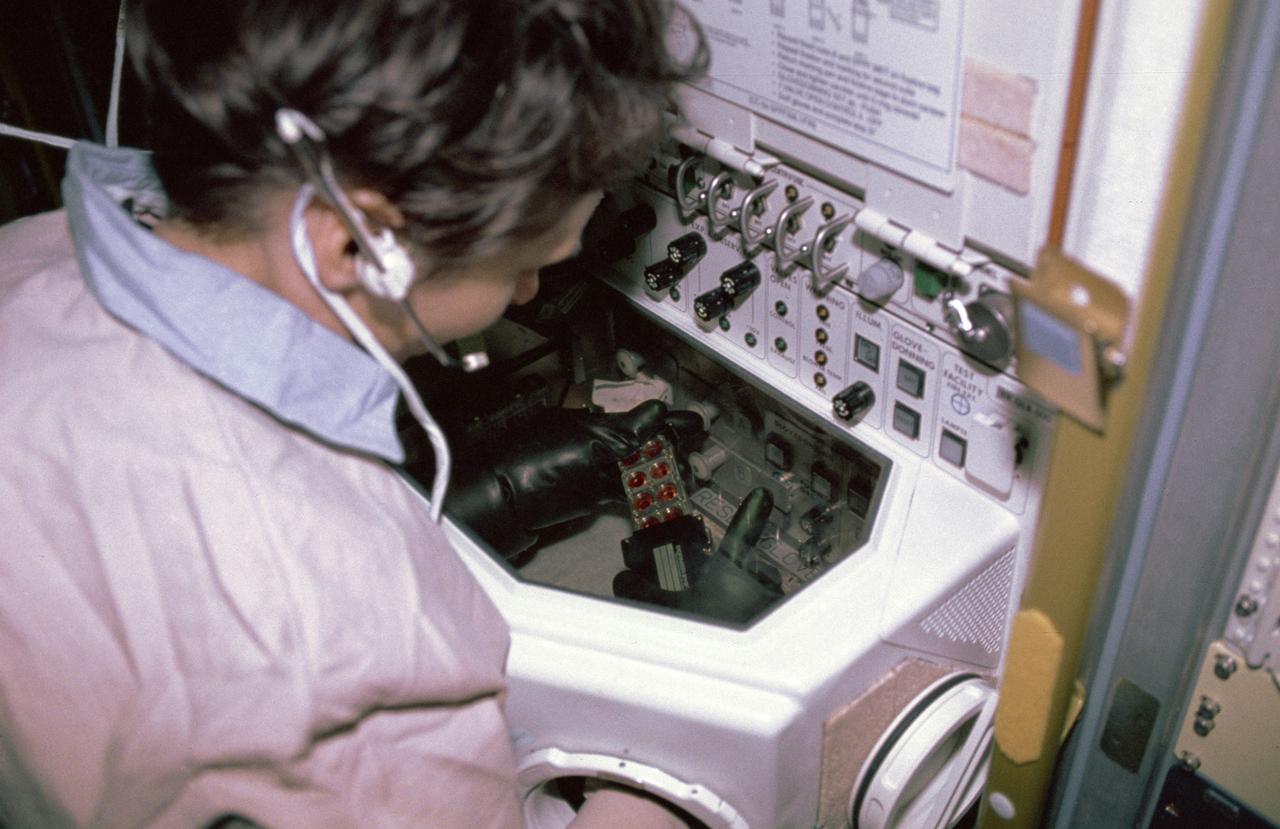

In this photograph, astronaut Roberta Bondar conducts a life science experiment by using the Biorack Glovebox (GBX) during the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1) mission. The Biorack was a large multipurpose facility designed for studying the effects of microgravity and cosmic radiation on numerous small life forms such as cells, tissues, small organisms, and plants. Located at the Biorack, the GBX was an enclosed environment that protected samples from contamination and prevented liquid from escaping. Crewmembers handled the specimens with their hands inside gloves that extended into the sealed work area. A microscope and video camera mounted on the GBX door were used to observe and document experiments. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research and was launched aboard the Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42) on January 22, 1992.
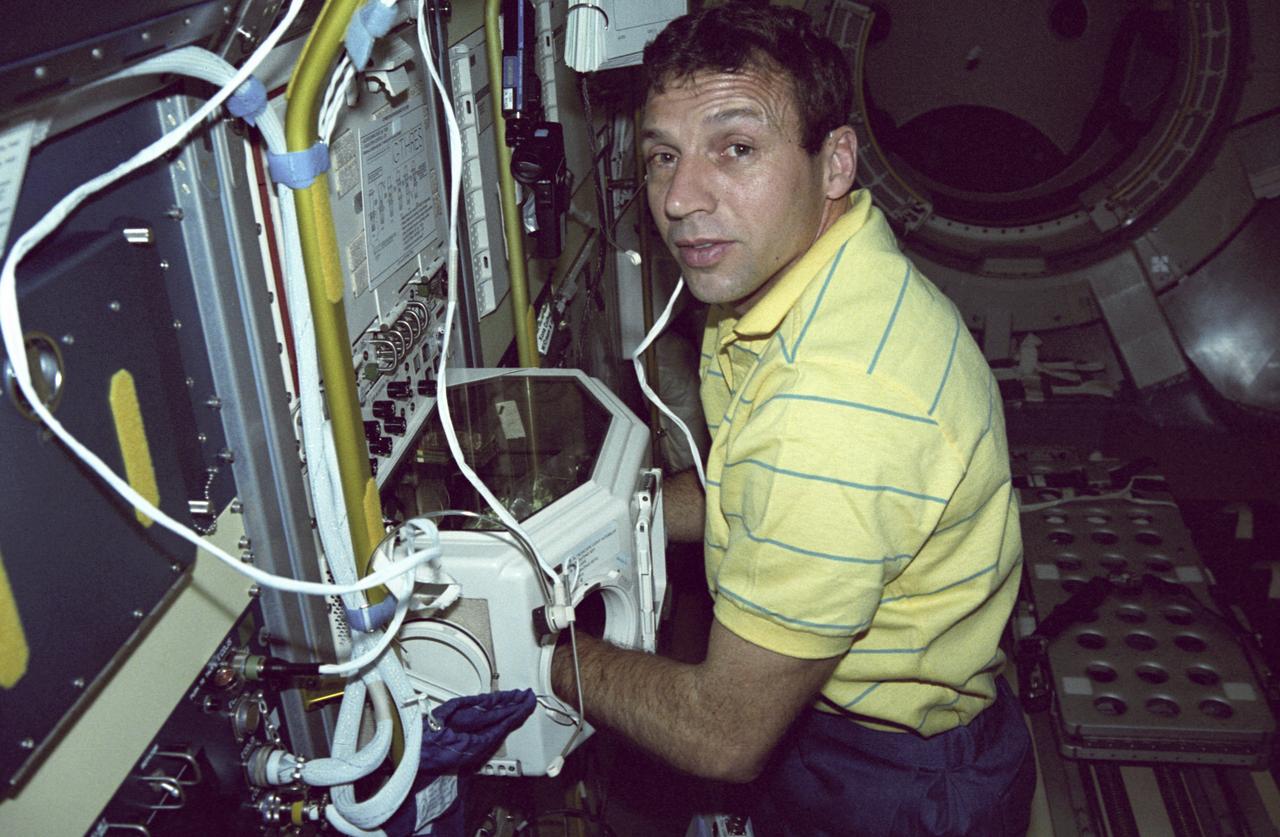

In this photograph, astronaut David Hilmers conducts a life science experiment by using the Biorack Glovebox (GBX) during the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1) mission. The Biorack was a large multipurpose facility designed for studying the effects of microgravity and cosmic radiation on numerous small life forms such as cells, tissues, small organisms, and plants. Located at the Biorack, the GBX was an enclosed environment that protected samples from contamination and prevented liquid from escaping. Crewmembers handled the specimens with their hands inside gloves that extended into the sealed work area. A microscope and video camera mounted on the GBX door were used to observe and document experiments. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research and was launched aboard the Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42) on January 22, 1992.
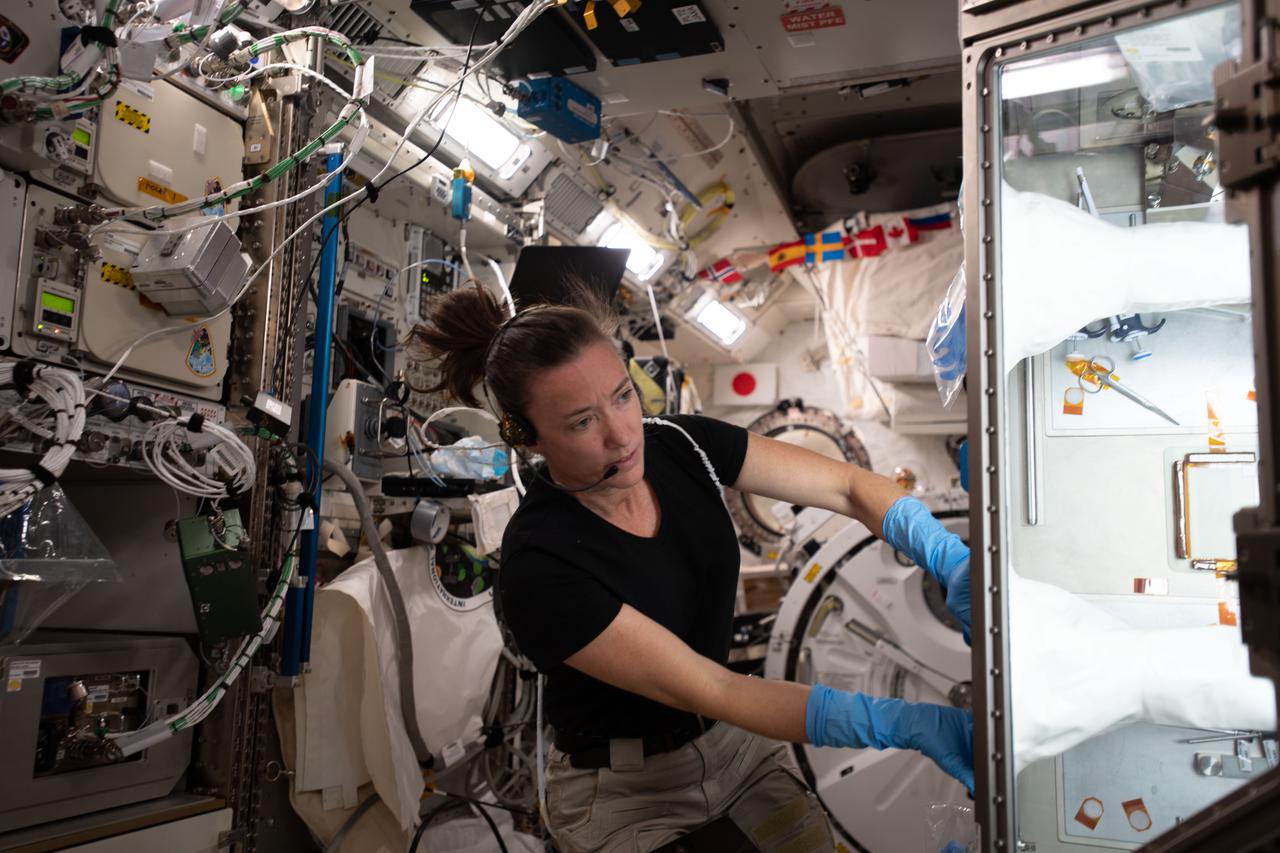

iss065e033958 (May 12, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur services donor cell samples inside the Kibo laboratory module's Life Science Glovebox. The samples are being compared to cells on Earth so scientists can document the significant differences in microgravity. The Celestial Immunity study’s results may provide insights into new vaccines and drugs and advance the commercialization of space.
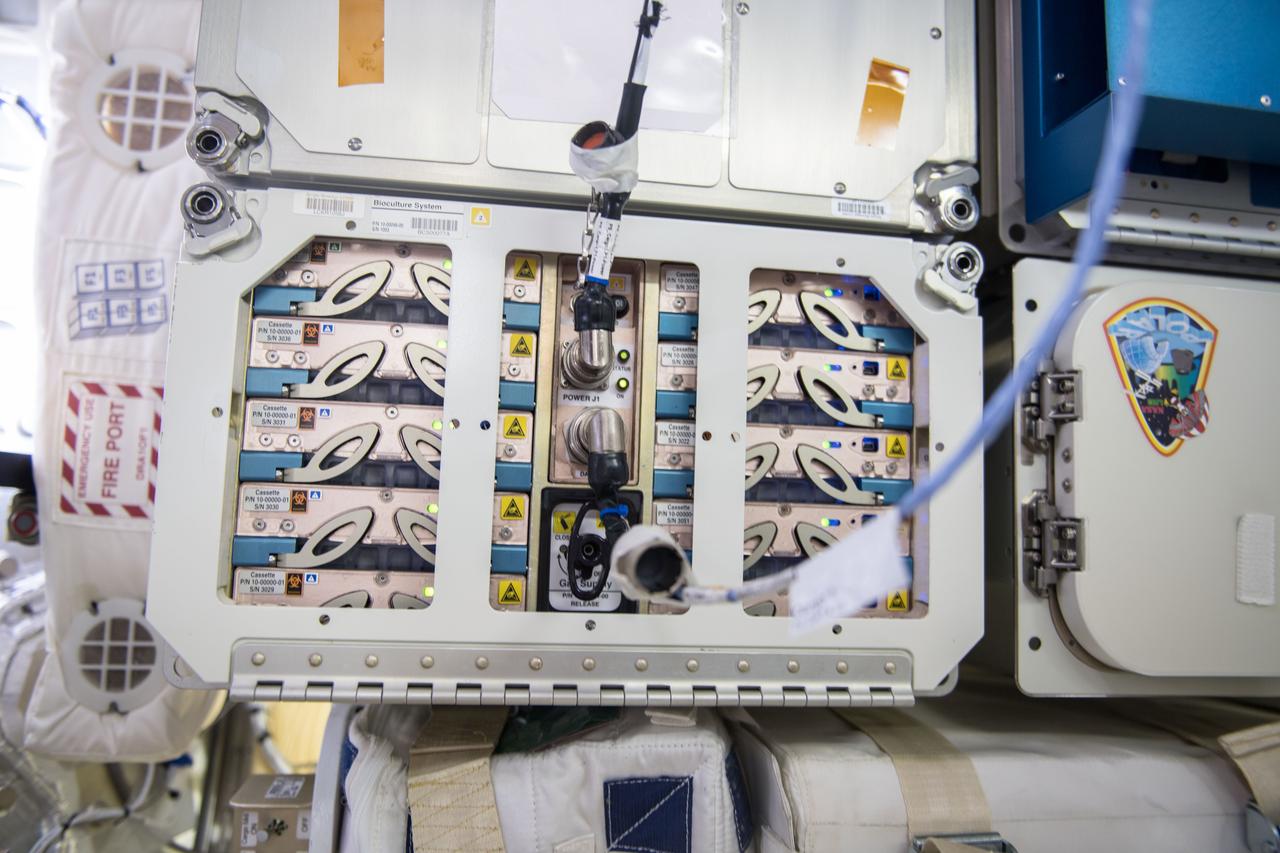
iss054e020928 (1/12/2018) --- Photo documentation of the Bioculture System Facility installed in the SpaceX Dragon Commercial Resupply Services-13 (CRS-13) spacecraft for return to Earth. The Bioculture System Hardware Validation (Cell Science-Validation) tests the performance and life-support capability of a new cell culture hardware system for use aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
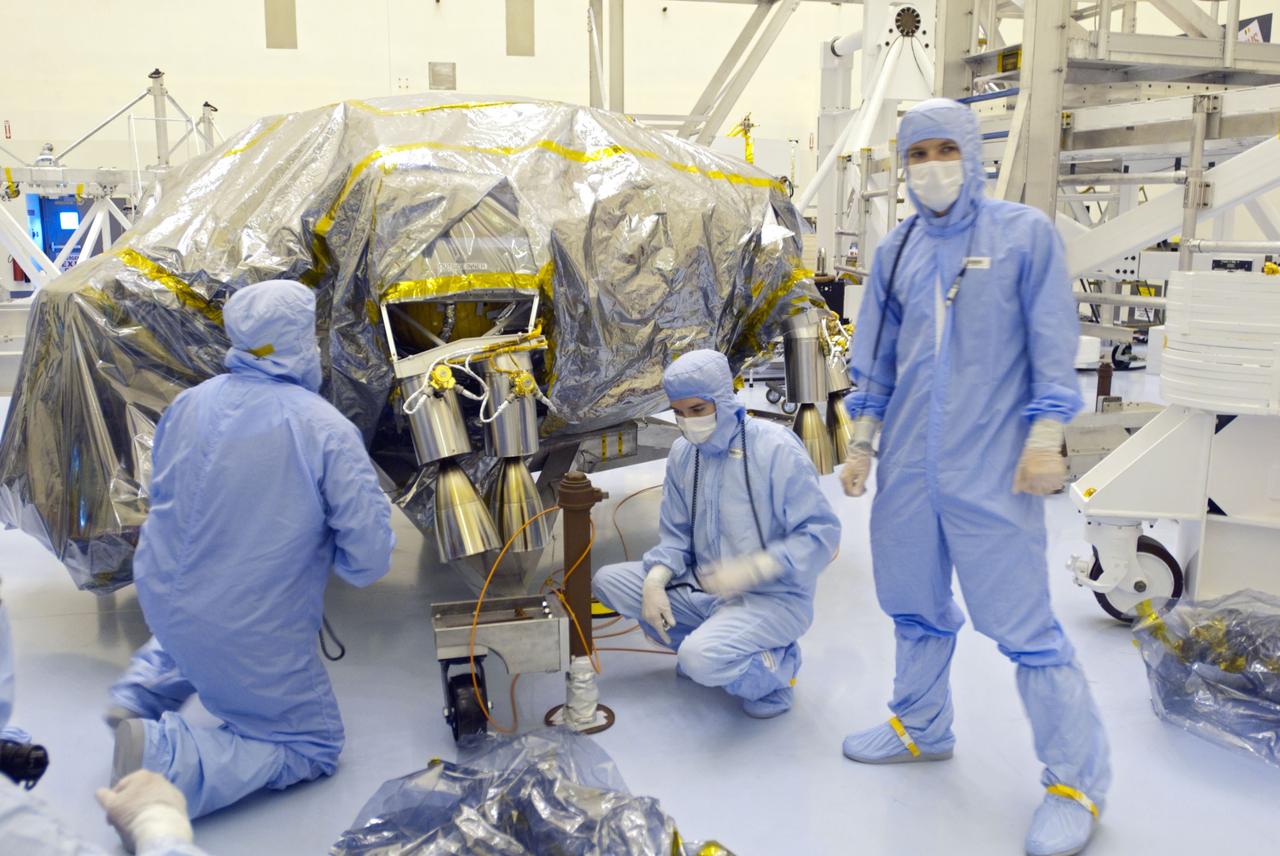

Cape Canaveral, Fla. -- At the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians have unwrapped the protective cover from NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rocket-powered descent stage thrusters for documenting and inspection. The descent stage will fly the MSL rover, Curiosity, during the final moments before landing on Mars. A United Launch Alliance Atlas V-541 configuration will be used to loft MSL into space. Curiosity’s 10 science instruments are designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
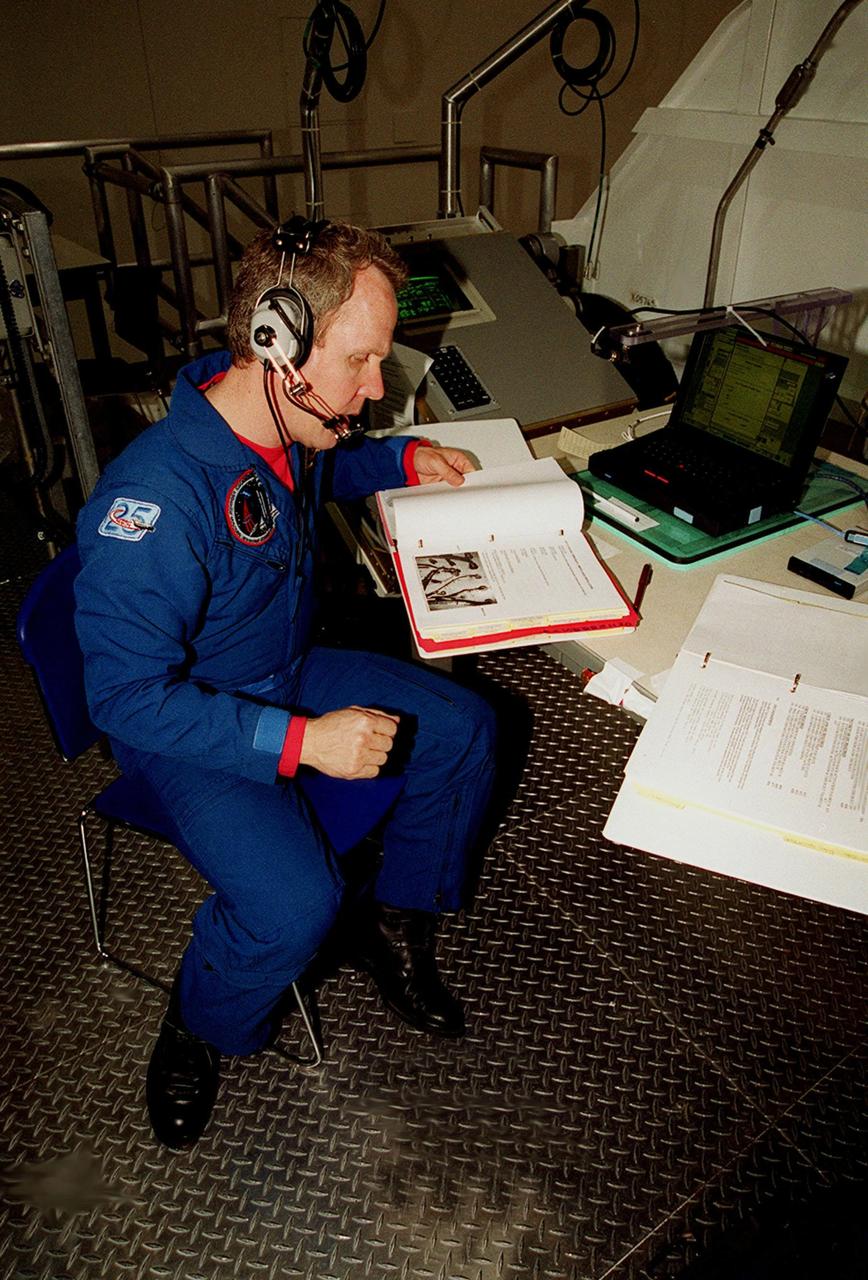

In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-98 Mission Specialist Thomas D. Jones (Ph.D.) looks over documents as part of a Multi-Equipment Interface Test (MEIT) on the U.S. Lab Destiny. Other crew members taking part in the MEIT are Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell and Pilot Mark Polansky. The remaining members of the crew (not present for the MEIT) are and Mission Specialists Robert L. Curbeam Jr. and Marsha S. Ivins. During the STS-98 mission, the crew will install the Lab on the International Space Station during a series of three space walks. The mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Laboratory Module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research. The Lab is planned for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis on the sixth ISS flight, currently targeted no earlier than Aug. 19, 2000
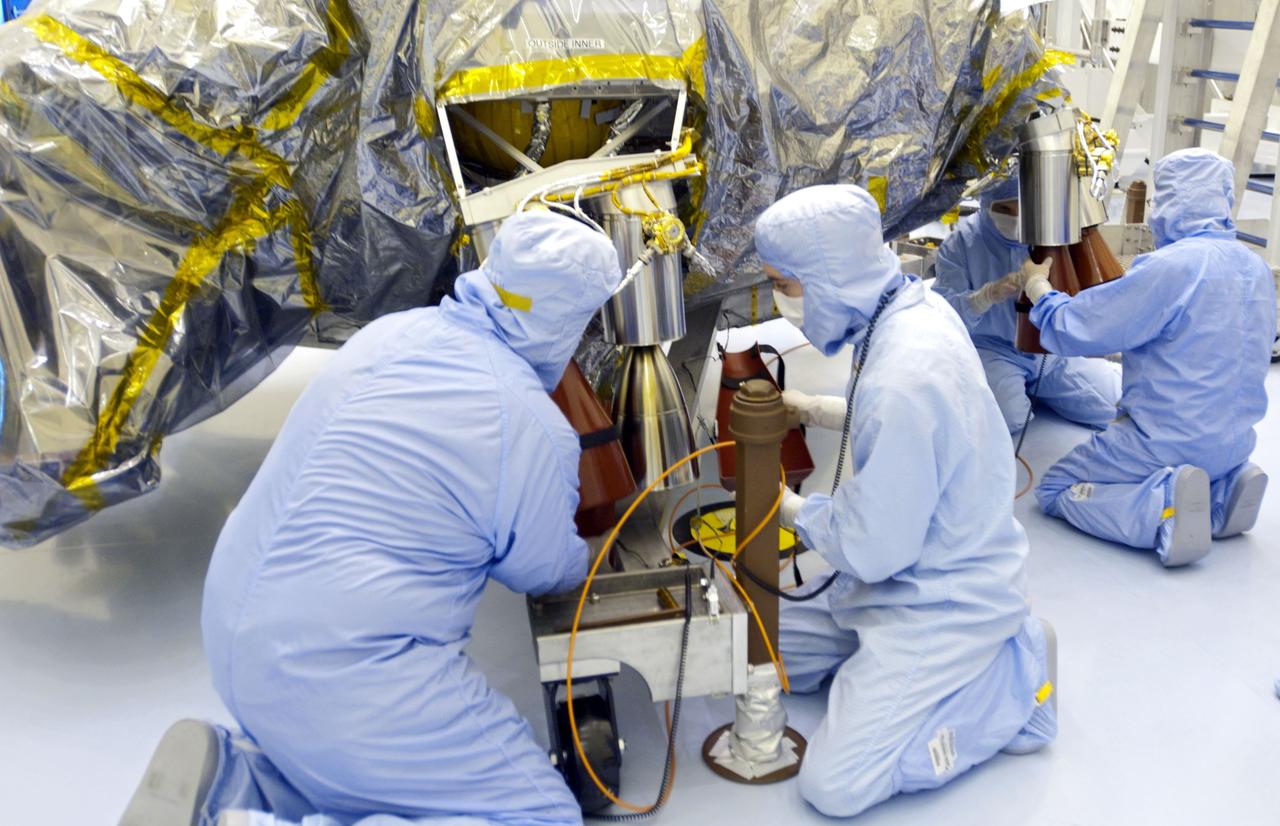

Cape Canaveral, Fla. -- At the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians have unwrapped the protective cover from NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rocket-powered descent stage thrusters for documenting and inspection. The descent stage will fly the MSL rover, Curiosity, during the final moments before landing on Mars. A United Launch Alliance Atlas V-541 configuration will be used to loft MSL into space. Curiosity’s 10 science instruments are designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
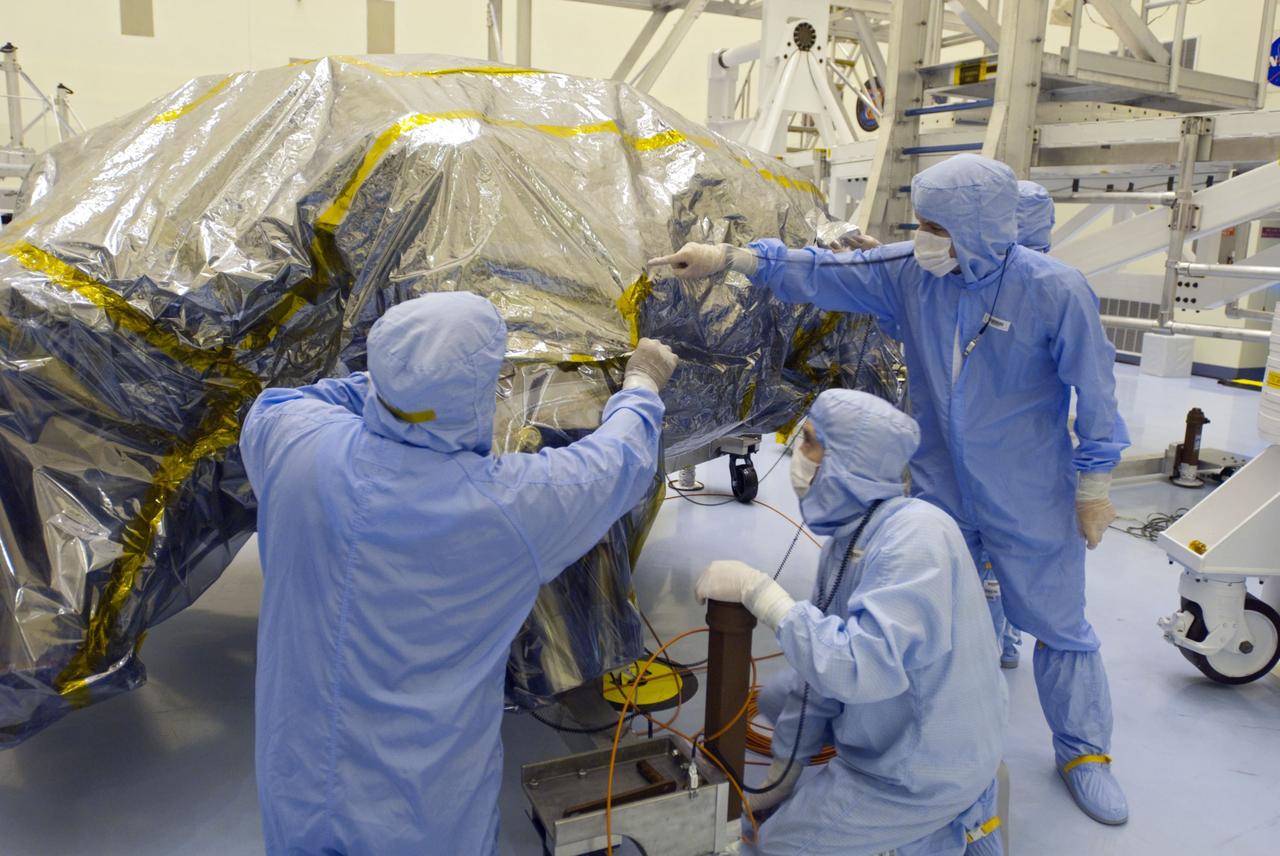

Cape Canaveral, Fla. -- At the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians begin to unwrap the protective cover from NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rocket-powered descent stage thrusters for documenting and inspection. The descent stage will fly the MSL rover, Curiosity, during the final moments before landing on Mars. A United Launch Alliance Atlas V-541 configuration will be used to loft MSL into space. Curiosity’s 10 science instruments are designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

Cape Canaveral, Fla. -- At the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians begin to unwrap the protective cover from NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rocket-powered descent stage thrusters for documenting and inspection. The descent stage will fly the MSL rover, Curiosity, during the final moments before landing on Mars. A United Launch Alliance Atlas V-541 configuration will be used to loft MSL into space. Curiosity’s 10 science instruments are designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
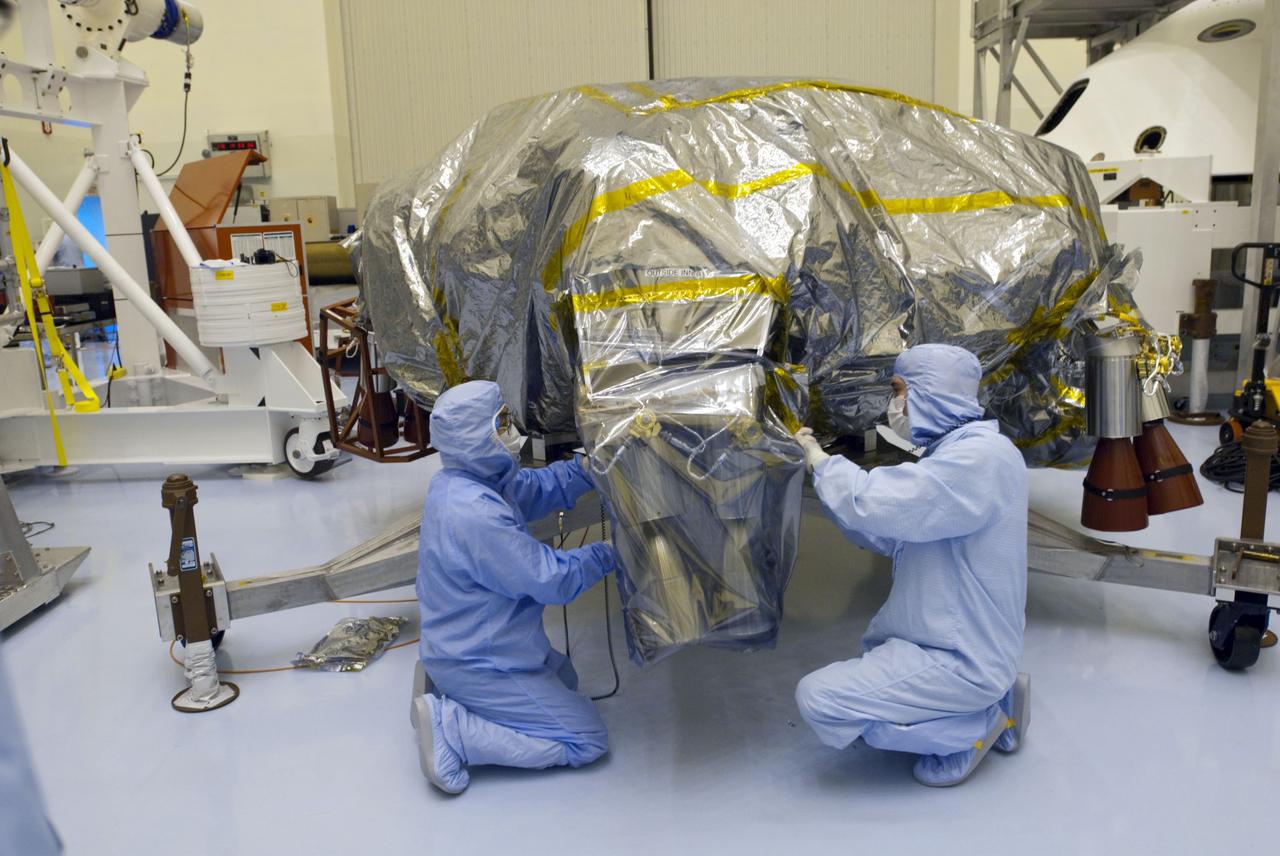

Cape Canaveral, Fla. -- At the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians remove the protective wrapping from the next set of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rocket-powered descent stage thrusters for documenting and inspection. The descent stage will fly the MSL rover, Curiosity, during the final moments before landing on Mars. A United Launch Alliance Atlas V-541 configuration will be used to loft MSL into space. Curiosity’s 10 science instruments are designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
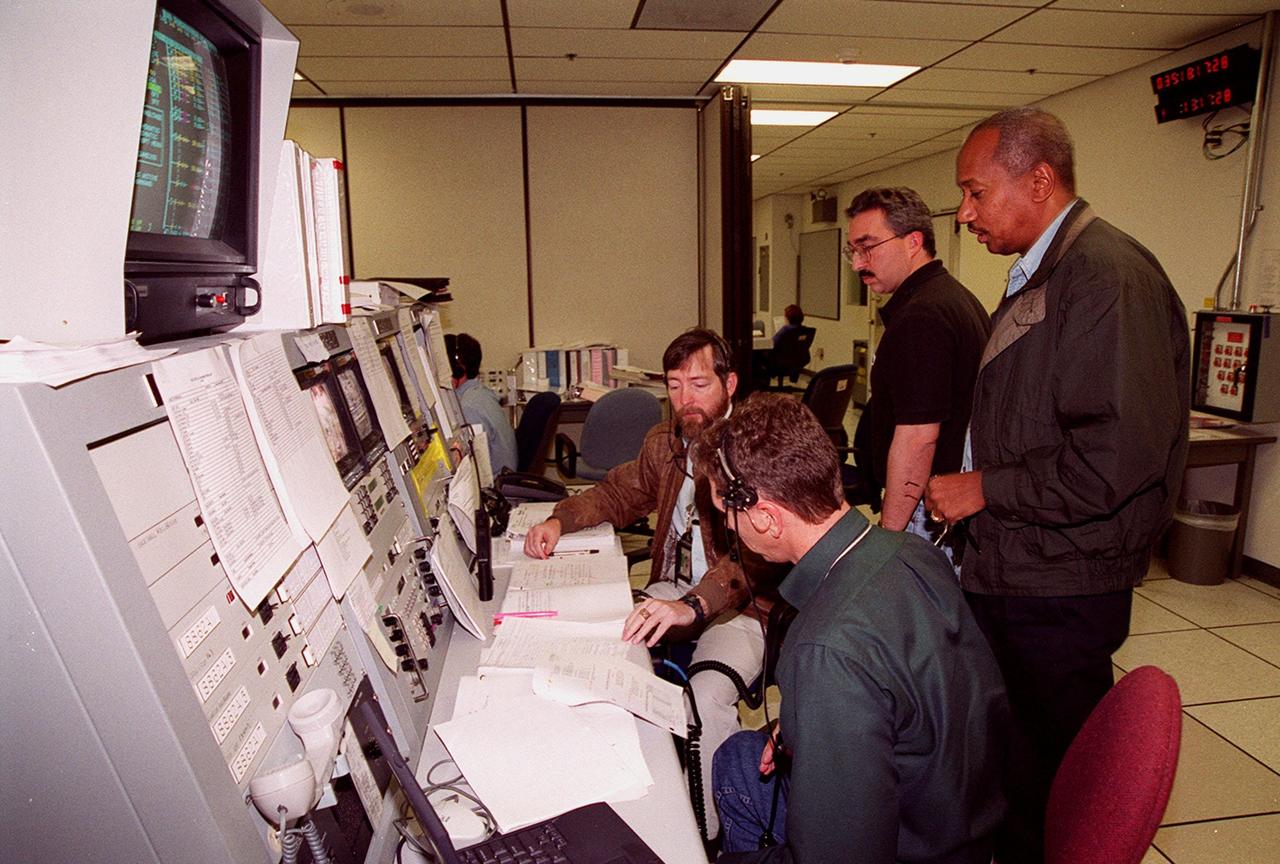

Workers in the Space Station Processing Facility control room check documentation during a Multi-Equipment Interface Test (MEIT) in the U.S. Lab Destiny. Members of the STS-98 crew are taking part in the MEIT checking out some of the equipment in the Lab. During the STS-98 mission, the crew will install the Lab on the station during a series of three space walks. The crew comprises five members: Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell, Pilot Mark L. Polansky, and Mission Specialists Robert L. Curbeam Jr., Thomas D. Jones (Ph.D.) and Marsha S. Ivins. The mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Laboratory Module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research. The Lab is planned for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis on the sixth ISS flight, currently targeted no earlier than Aug. 19, 2000

Cape Canaveral, Fla. -- At the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians have removed the protective wrapping from all of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rocket-powered descent stage thrusters for documenting and inspection. The descent stage will fly the MSL rover, Curiosity, during the final moments before landing on Mars. A United Launch Alliance Atlas V-541 configuration will be used to loft MSL into space. Curiosity’s 10 science instruments are designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
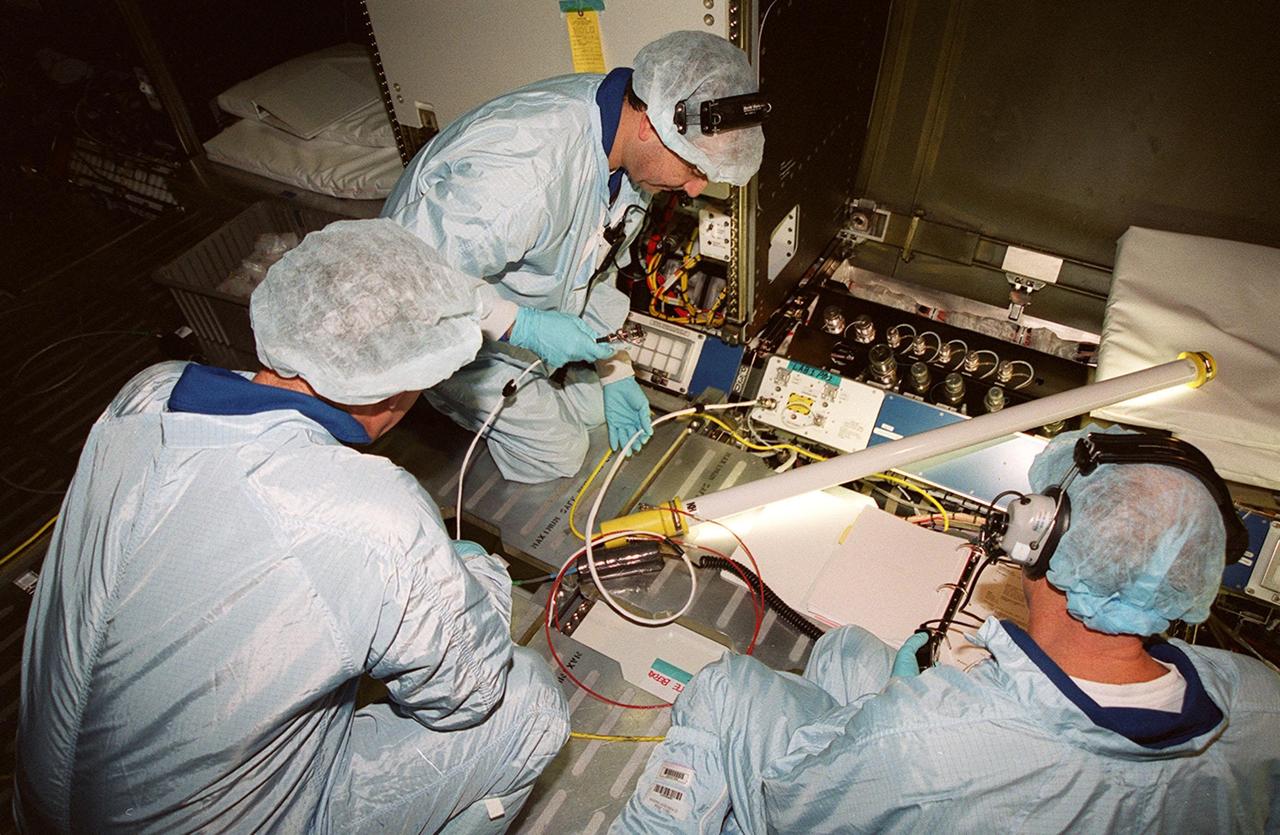
During a Multi-Equipment Interface Test (MEIT) in the U.S. Lab Destiny, which is in the Space Station Processing Facility, astronaut James Voss (left) joins STS-98 Pilot Mark Polansky (center) and Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell (right) in checking wiring against documentation on the floor. Also participating in the MEIT is Mission Specialist Thomas D. Jones (Ph.D.). Voss is assigned to mission STS-102 as part of the second crew to occupy the International Space Station. During the STS-98 mission, the crew will install the Lab on the station during a series of three space walks. The mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Laboratory Module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research. The Lab is planned for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis on the sixth ISS flight, currently targeted no earlier than Aug. 19, 2000
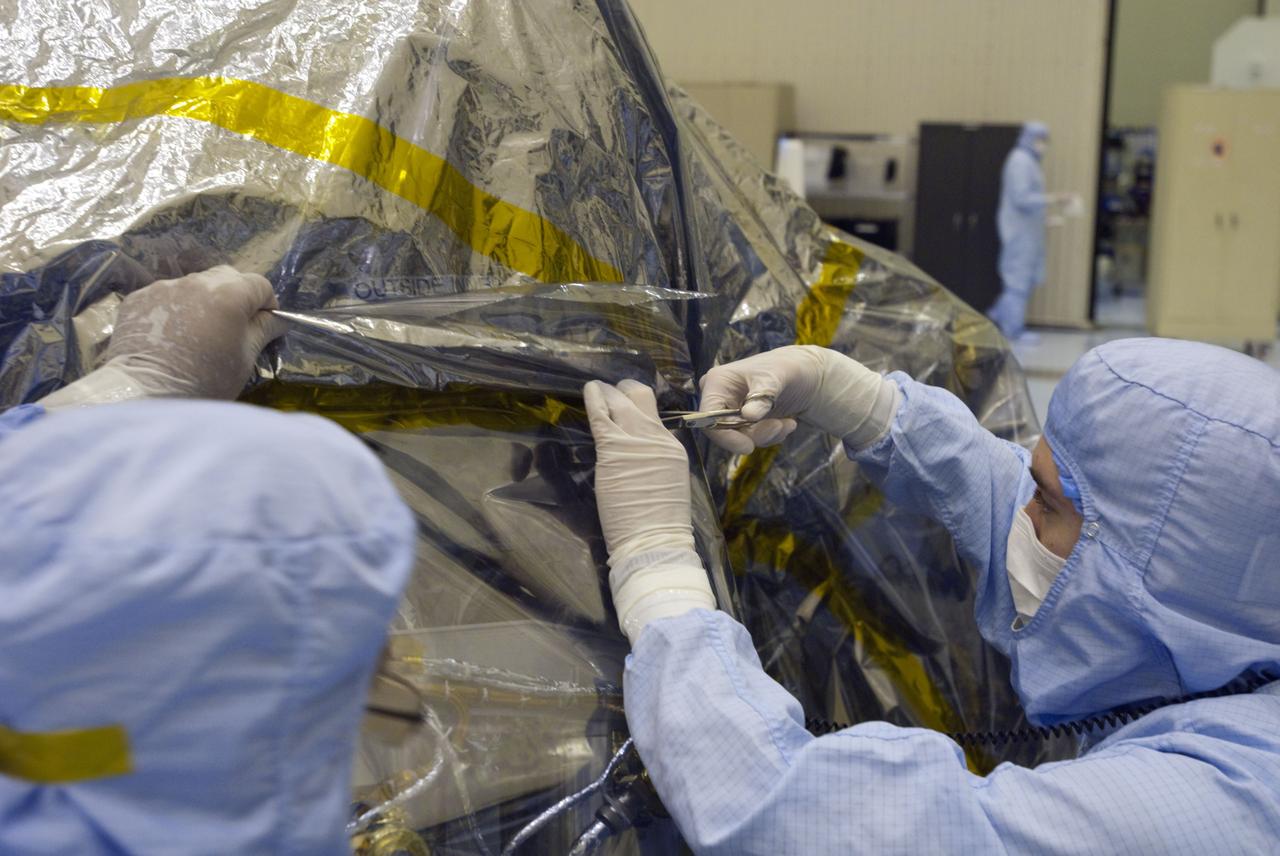

Cape Canaveral, Fla. -- At the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians remove the protective wrapping from the next set of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rocket-powered descent stage thrusters for documenting and inspection. The descent stage will fly the MSL rover, Curiosity, during the final moments before landing on Mars. A United Launch Alliance Atlas V-541 configuration will be used to loft MSL into space. Curiosity’s 10 science instruments are designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
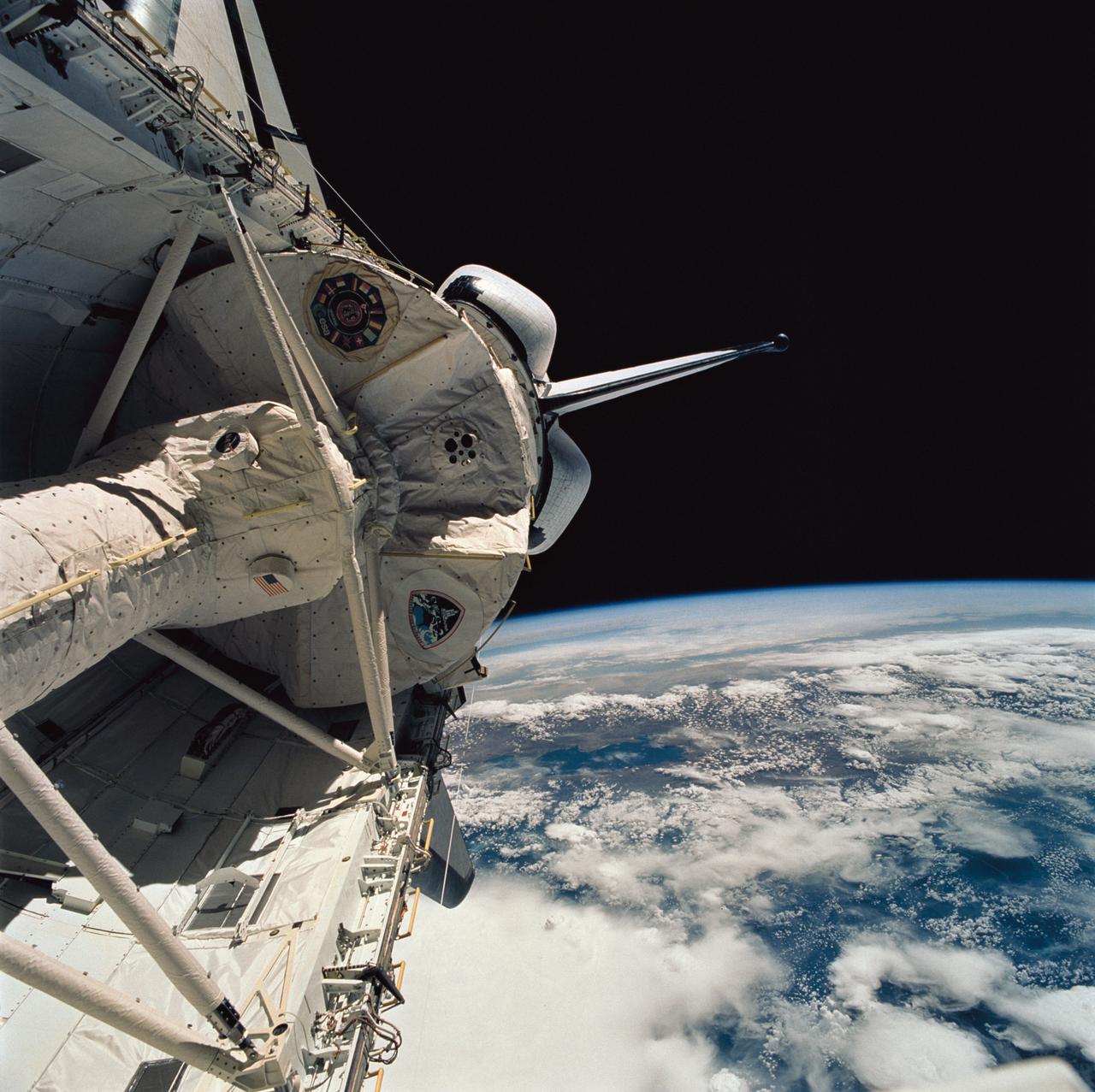

STS058-76-041 (18 Oct-1 Nov 1993) --- Backdropped against the Peru-Bolivia border and part of the Amazon basin, the Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-2) laboratory module was captured with a 70mm camera, by one of the seven crew members inside the Space Shuttle Columbia's cabin. Part of the tunnel-like passageway is visible in the foreground. Six NASA astronauts and a veterinarian from the private sector spent two weeks devoted to medical research in Earth-orbit. Lake Titicaca, the largest high-altitude lake in the world lies in the Altiplano of Bolivia and Peru. Space Shuttle photography has been used to document fluctuations of several meters of the level of Lake Titicaca during the past decade, as well as to document the eutrophication of the north end of the lake, which is primarily due to increased population in the Peruvian shoreline areas. This view shows the effect of abnormally heavy precipitation of the region for the third successive year. Meteorologists feel this precipitation increase, which may portend another increase of the lake level, is due to the third successive El Nino - Southern Oscillation phenomenon in the 1993 - 94 southern hemisphere summertime. This global phenomenon is now resulting in major weather disturbances in Indonesia, California, Texas and elsewhere.
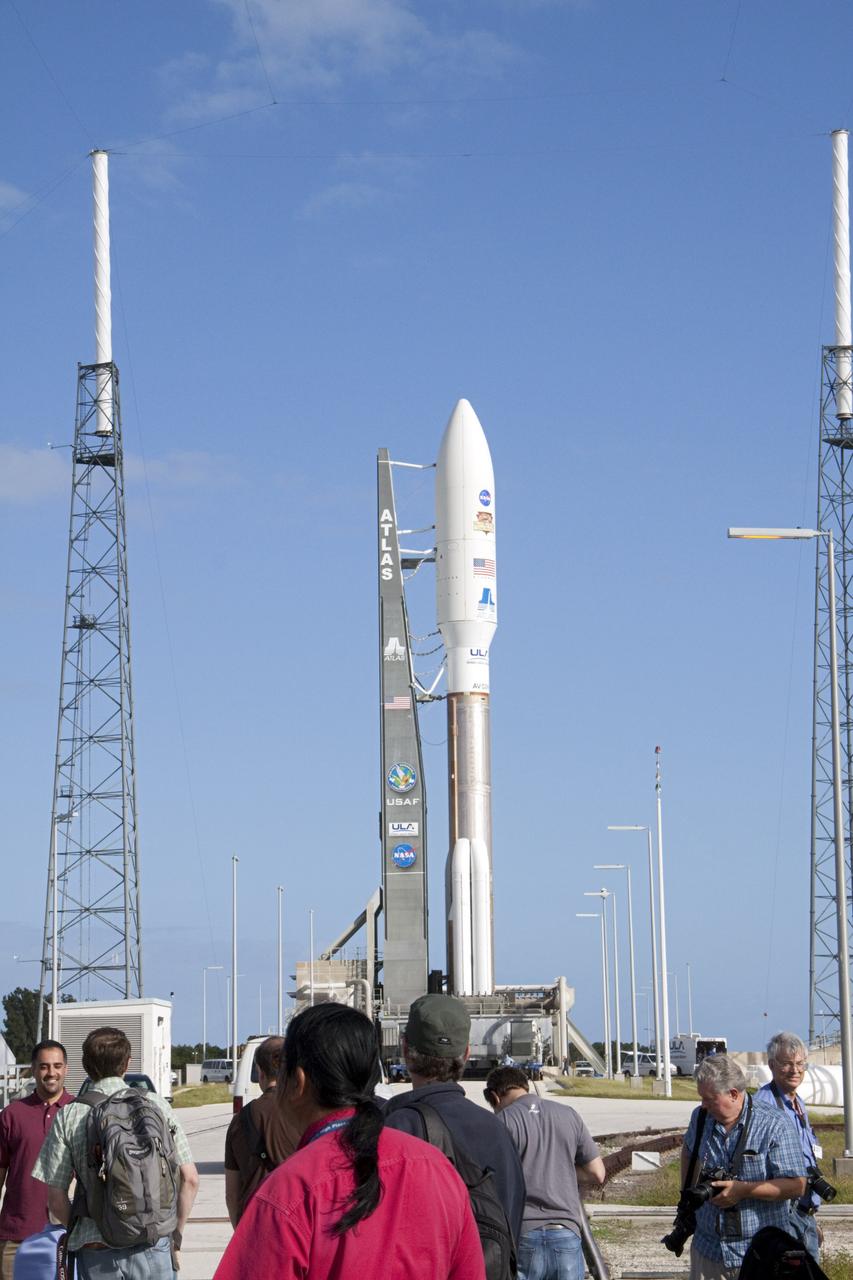

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Members of the media gather near the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, documenting the arrival of the 197-foot-tall United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket after its early morning move from the nearby Vertical Integration Facility (VIF). Atop the rocket is NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL), enclosed in its payload fairing. The rocket began its move from the VIF at 8 a.m. EST and reached the launch pad at 8:40 a.m. Liftoff is planned during a launch window which extends from 10:02 a.m. to 11:45 a.m. EST on Nov. 26. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley
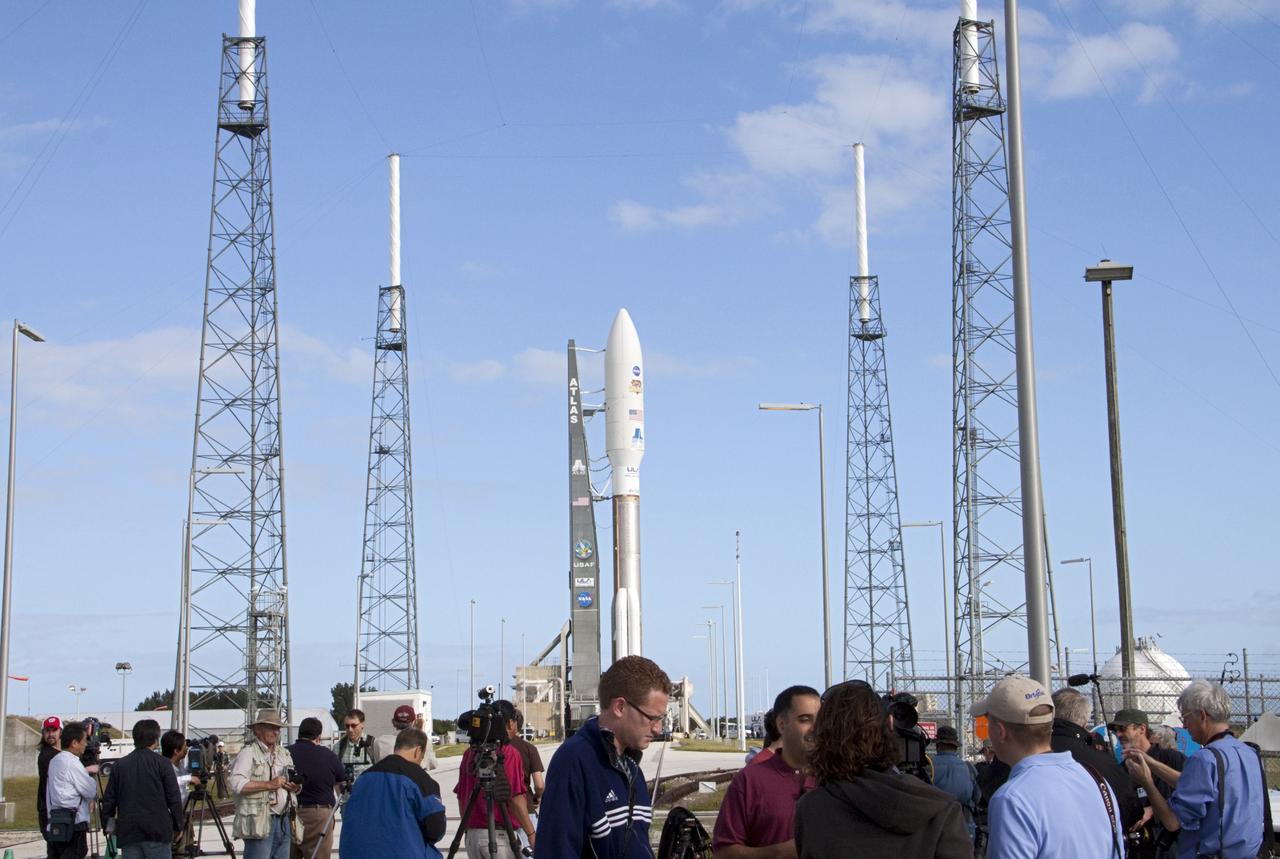

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, members of the media gather near the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 to document the arrival of the 197-foot-tall United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket after an early morning move from the nearby Vertical Integration Facility (VIF). Atop the rocket is NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL), enclosed in its payload fairing. The rocket began its move from the VIF at 8 a.m. EST and reached the launch pad at 8:40 a.m. Liftoff is planned during a launch window which extends from 10:02 a.m. to 11:45 a.m. EST on Nov. 26. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley
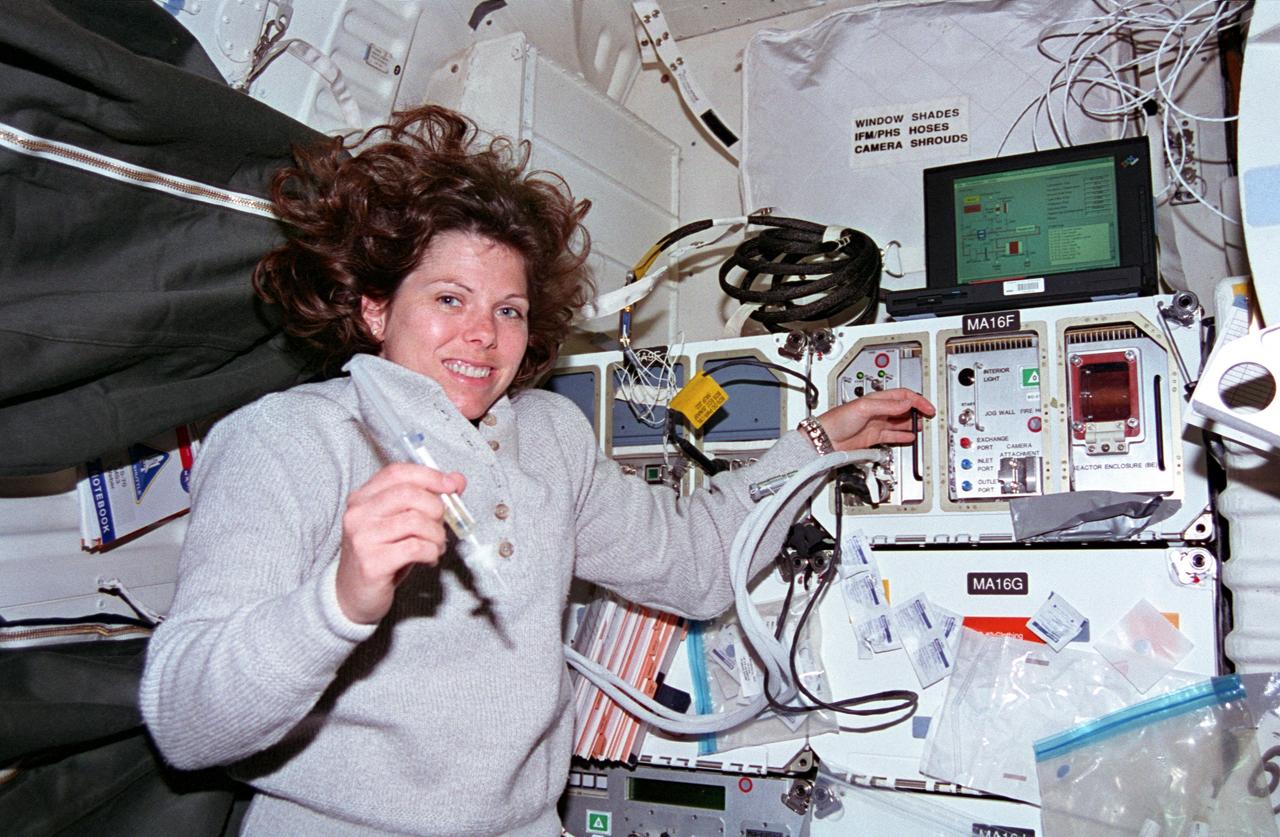

STS070-301-025 (13-22 July 1995) --- Astronaut Mary Ellen Weber works with a syringe related to the Bioreactor Development System (BDS). The almost weightless state of space travel provides life science researchers with the opportunity to grow cells into three-dimensional tissue pieces that are not achievable using conventional tissue culture methods on Earth. At specified times during the STS-70 mission, crew members injected color producing substances to document fluid movement in the reactor, and various-sized beads to estimate the tissue size that could be supported in the Bioreactor. The photo was among NASA's first release of still photography from the STS-70 mission. The mission was launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) on July 13, 1995, and ended when Discovery landed on Runway 33 there on July 22, 1995. The crew members were astronauts Terence T. (Tom) Henricks, commander; Kevin R. Kregel, pilot; and Donald A. Thomas, Nancy J. Currie and Weber, all mission specialists.
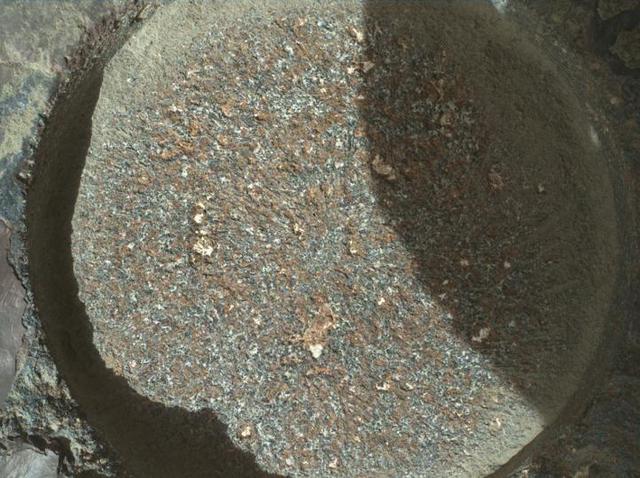

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its WATSON (Wide Angle Topographic Sensor for Operations and eNgineering) camera to take eight images – combined here into the single composite image – of a rock abraded by a tool on the rover's robotic arm. The images were taken on Aug. 27, 2021 (the 185th Martian day, or sol, of the mission). Nicknamed "Bellegarde," the abraded target is 0.4 inches (5 centimeters) in diameter. A subsystem of SHERLOC, WATSON can document the structure and texture within a drilled or abraded target, and its data can be used to derive depth measurements. The area within the blue box is roughly 6.5 millimeters squared. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory built and manages operations of Perseverance and Ingenuity for the agency. Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages JPL for NASA. WATSON was built by Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) in San Diego and is operated jointly by MSSS and JPL. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24770
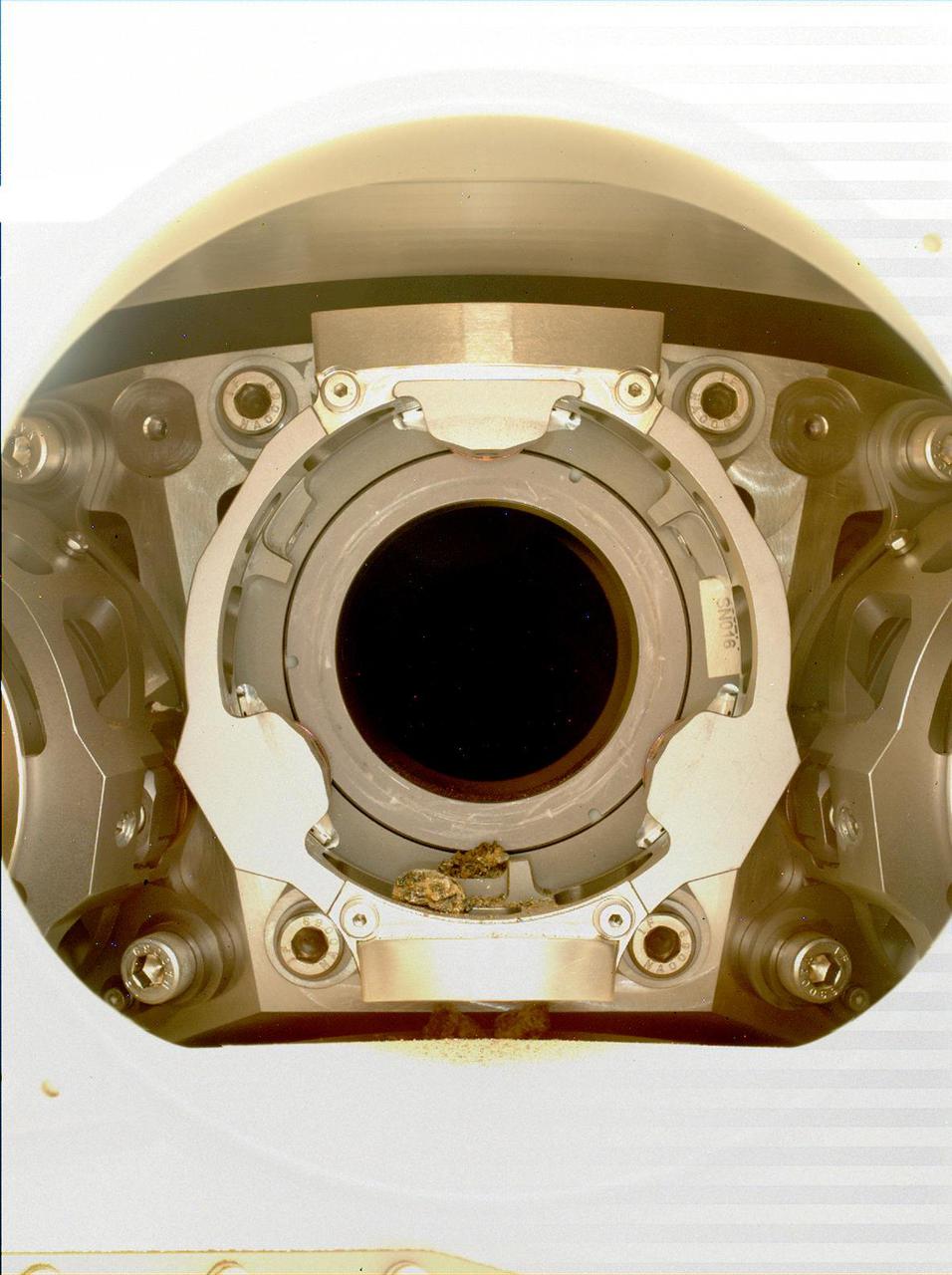
This image of pebble-sized debris in the bit carousel on NASA's Perseverance Mars rover was acquired on Jan. 7, 2022, by the WATSON camera. The image was taken to assist the Perseverance team in diagnosing an anomaly that occurred during a rock sampling on Dec. 29, 2021. A subsystem of the SHERLOC (Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals) instrument, WATSON can document the structure and texture within a drilled or abraded target, and its data can be used to derive depth measurements. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory built and manages operations of Perseverance and Ingenuity for the agency. Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages JPL for NASA. WATSON was built by Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) in San Diego and is operated jointly by MSSS and JPL. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25066
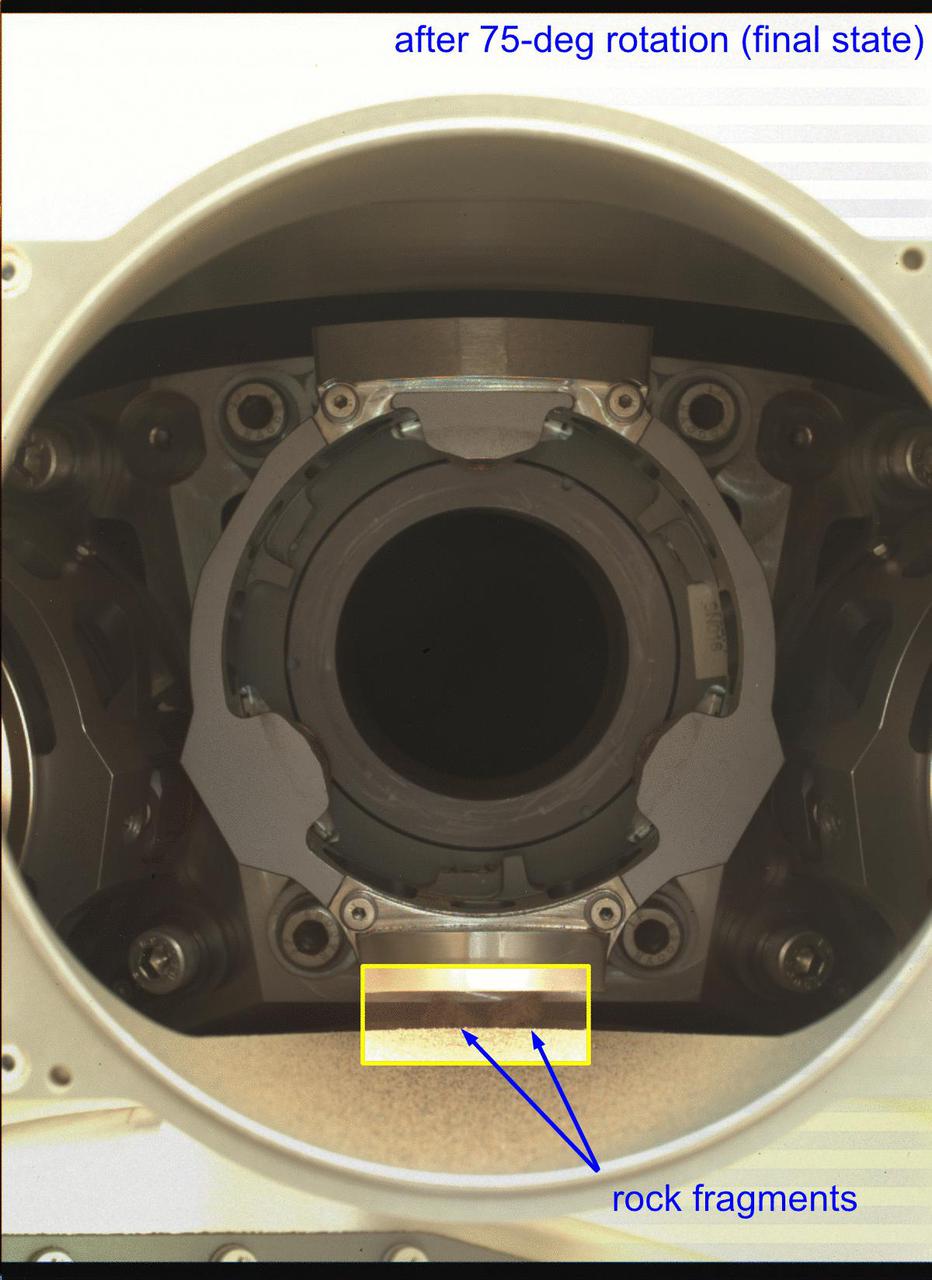
In this annotated animated GIF, the bit carousel on NASA's Perseverance Mars rover can be seen rotating during a test of the component on Jan. 17, 2022, the 325th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The carousel was rotated about 75 degrees during the test, then was returned back to its original position. The five images that compose this animated GIF were captured to determine the status – after the test – of four fragments of the cored rock that fell out of the sample tube during Perseverance sampling activity on Dec. 29, 2021. After completion of the test, the upper two rock fragments (seen in the first image) have disappeared, having been ejected during the rotation. However, the lower two rock fragments, located below the bit carousel housing, remain. The five images that make up the GIF were obtained by the WATSON (Wide Angle Topographic Sensor for Operations and eNgineering) camera. Located in the turret at the end of the rover's robotic arm, WATSON can document the structure and texture within a drilled or abraded target, and its data can be used to derive depth measurements. The camera is a subsystem of the SHERLOC (Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals) instrument. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory built and manages operations of Perseverance and Ingenuity for the agency. Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages JPL for NASA. WATSON was built by Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) in San Diego and is operated jointly by MSSS and JPL. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25071
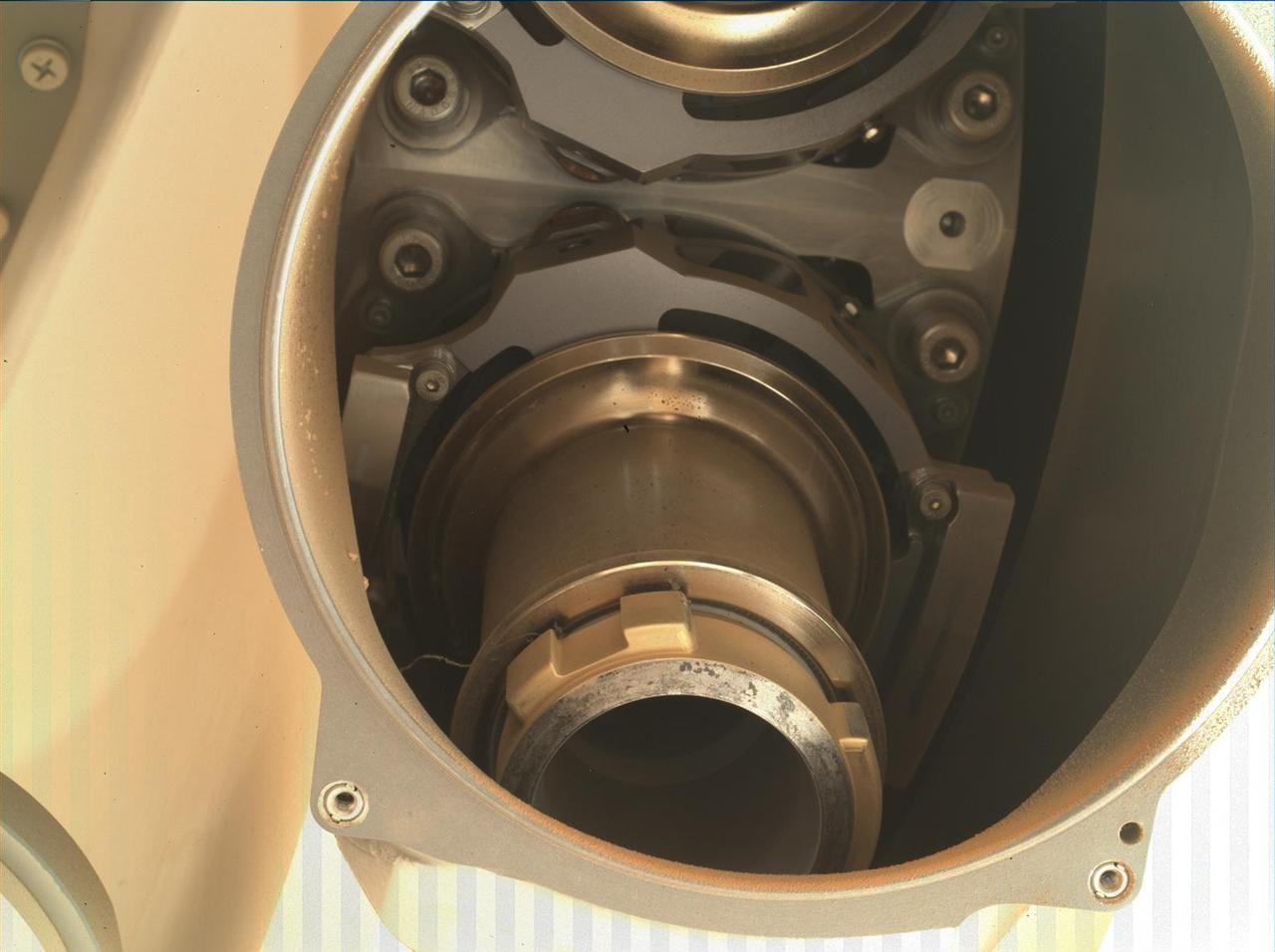
This image shows the back of Coring Bit 2 in the bit carousel of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. A wavy, stringlike piece of foreign object debris (FOD) can be seen on the left side of the bit (the lower center of image). Coring Bit 2 was recently used to sample the sedimentary rock at "Wildcat Ridge." The image was obtained by the WATSON (Wide Angle Topographic Sensor for Operations and eNgineering) camera on Aug. 17, 2022, the 531st Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Located in the turret at the end of the rover's robotic arm, WATSON can document the structure and texture within a natural (intact), drilled, or abraded target, and its data can be used to derive depth measurements. The camera is a subsystem of the SHERLOC (Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals) instrument. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory built and manages operations of Perseverance and Ingenuity for the agency. Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages JPL for NASA. WATSON was built by Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) in San Diego and is operated jointly by MSSS and JPL. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25327
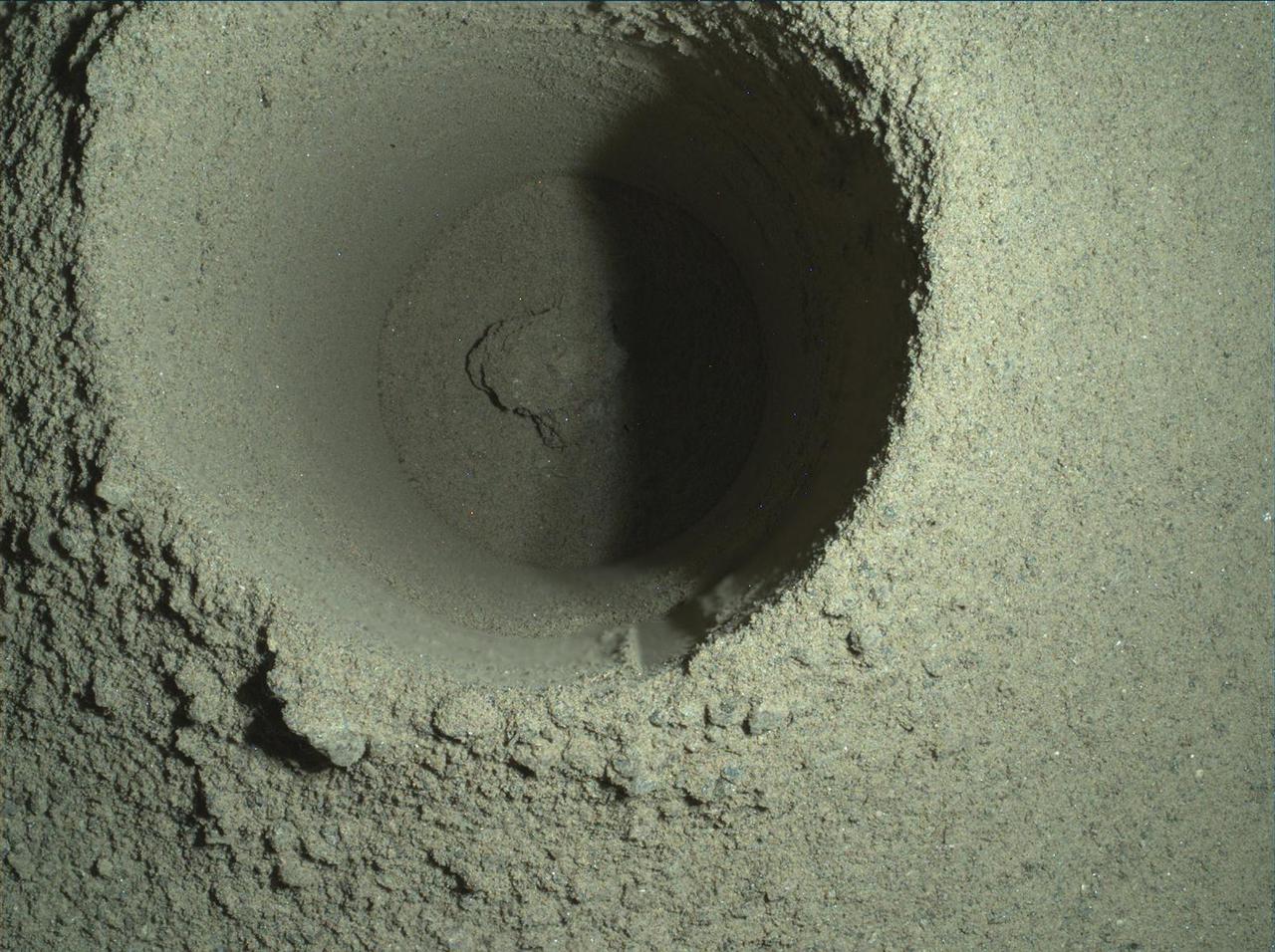

This composite image of the first borehole drilled by NASA's Perseverance rover on Mars was generated using multiple images taken by the rover's WATSON (Wide Angle Topographic Sensor for Operations and eNgineering) imager. The borehole is 1.06 inches (2.7 centimeters) in diameter. A subsystem of the SHERLOC (Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals) instrument, WATSON can document the structure and texture within a drilled target, and its data can be used to derive depth measurements. The image was taken on the mission's 165th Martian day, or sol, at night in order to reduce self-shadowing within the borehole that can occur during daylight imaging. Some of WATSON's white LEDs illuminated the borehole. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory built and manages operations of Perseverance and Ingenuity for the agency. Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages JPL for NASA. WATSON was built by Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) in San Diego and is operated jointly by MSSS and JPL. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24796
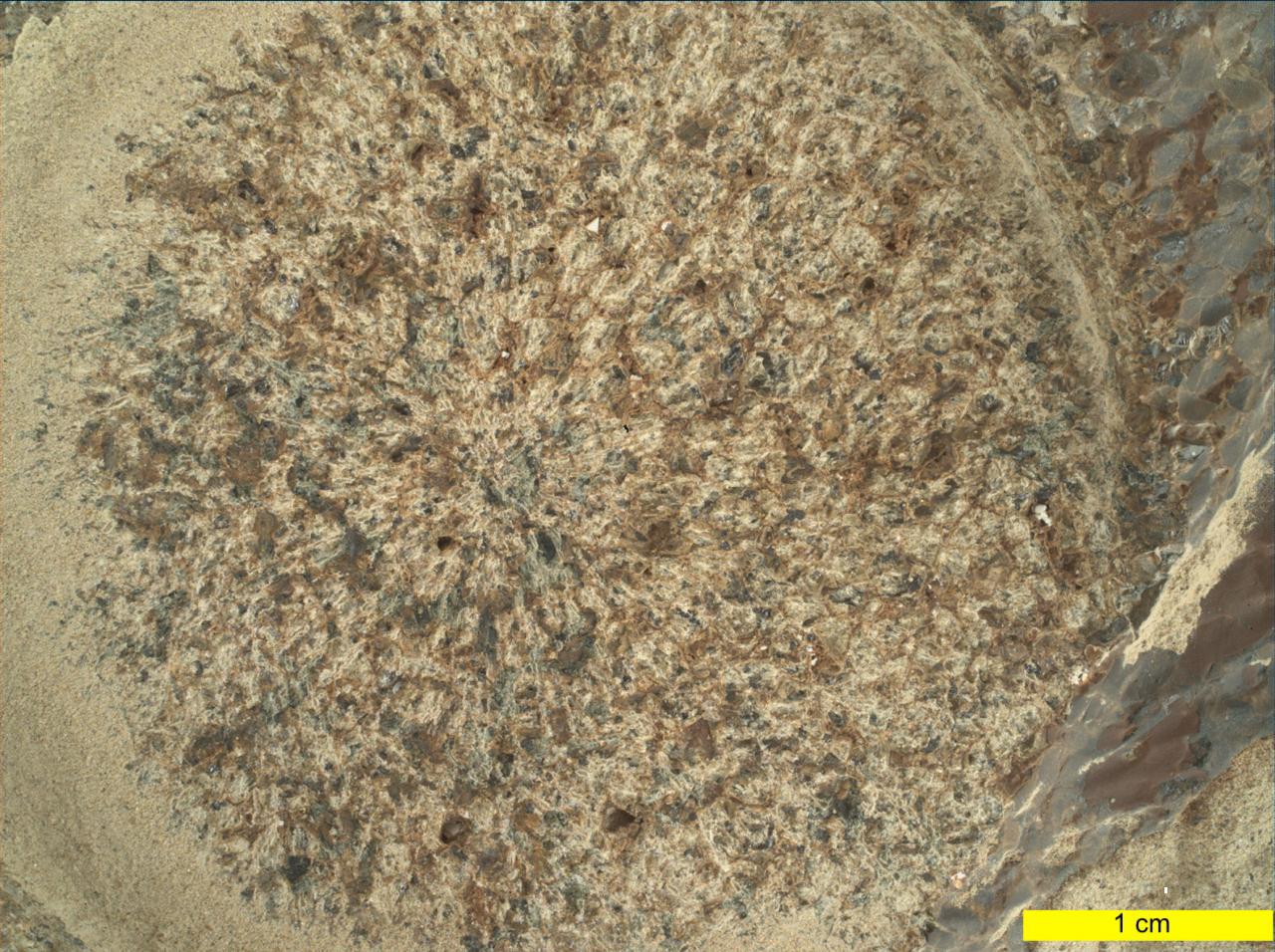
This close-up view of a rock target named "Dourbes" was provided by the WATSON (Wide Angle Topographic Sensor for Operations and eNgineering) camera on the end of the robotic arm aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. WATSON took a series of eight fully-shadowed images on Nov. 5, 2021, the 253rd Martian day, or sol, of the mission, and the images were subsequently merged to create this view. Before drilling rocks, the rover abrades the rock surface using a tool on its robotic arm to clear away dust and weathering rinds, allowing other instruments to study the rocks in detail. The abraded patch is 2 inches (5 centimeters) in diameter. Perseverance subsequently acquired two rock core samples from this outcrop, called "Brac," which forms part of the "South Séítah" geologic unit of Jezero Crater. The WATSON image shows that the abrasion patch is dominated by discrete areas of light-toned material, with subordinate brown, dark-toned interstitial areas. The chemistry and mineralogy of the abrasion patch was analysed by a series of co-registered observations using the SuperCam, Mastcam-Z, PIXL (Planetary Instrument for X-ray Lithochemistry), and SHERLOC (Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals) instruments. A subsystem of an instrument called SHERLOC (Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals), WATSON can document the structure and texture within a drilled or abraded target, and its data can be used to derive depth measurements. WATSON was built by Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) in San Diego and is operated jointly by MSSS and JPL. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24940