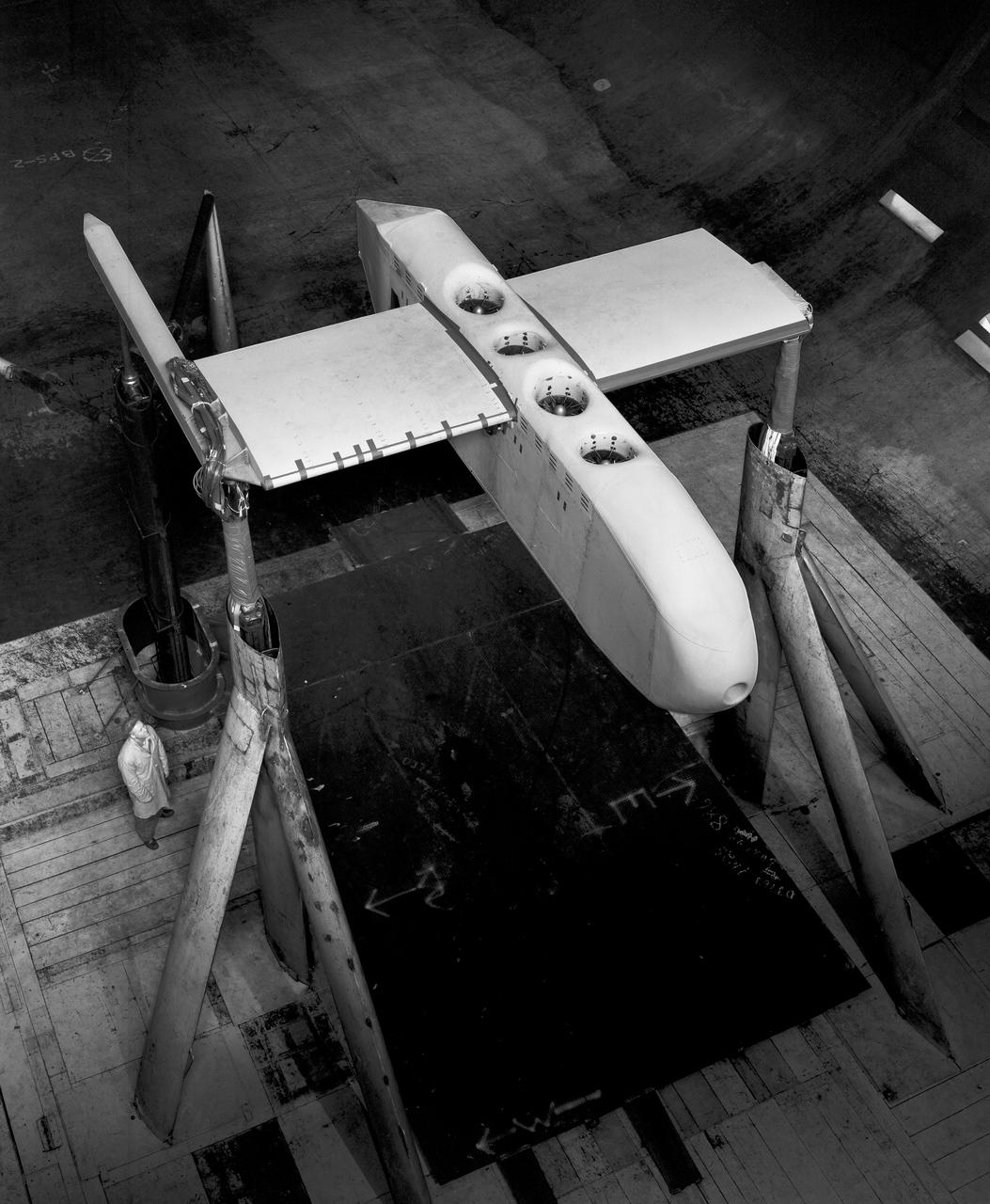

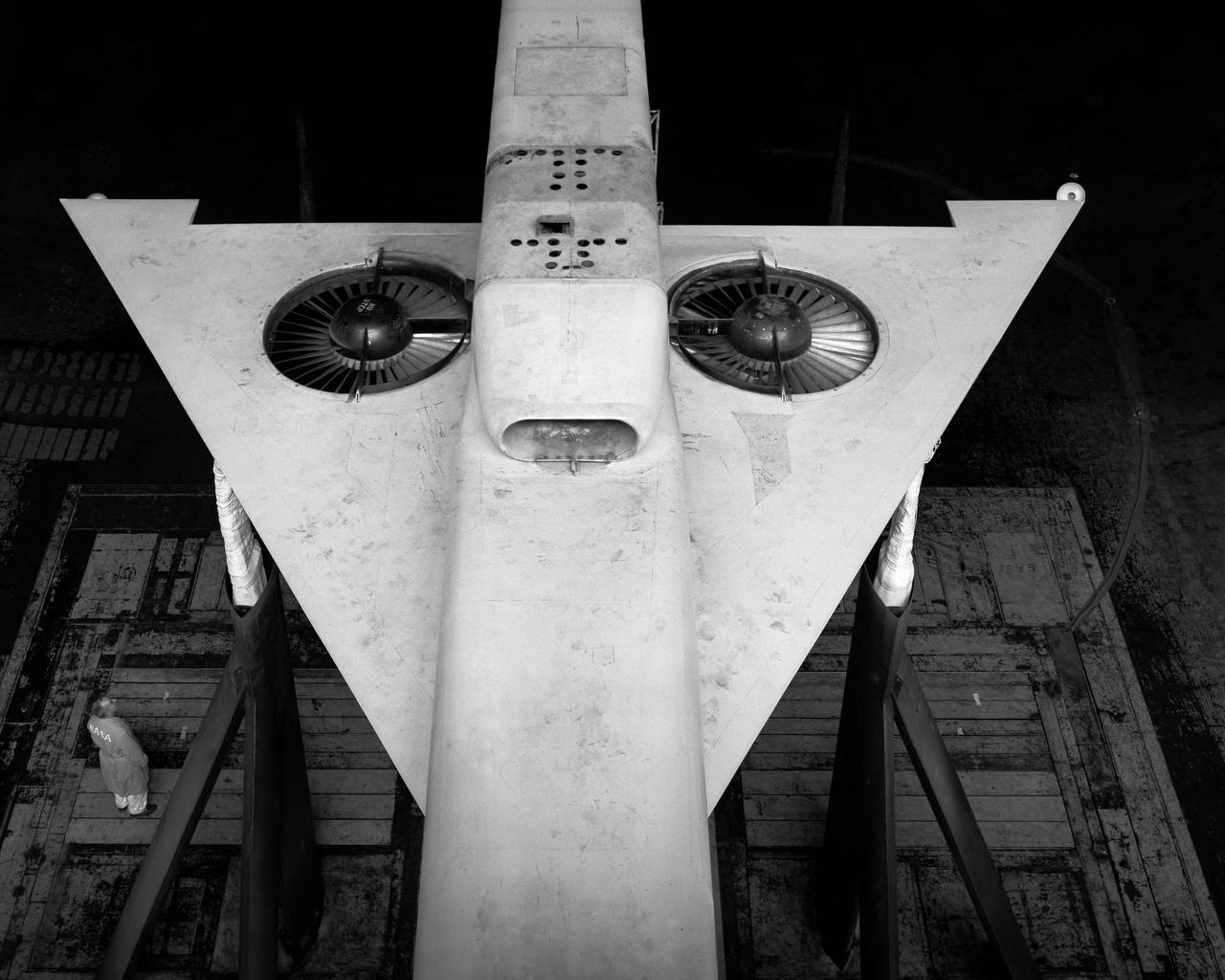
3/4 front, top view of Noriar Lift Engine Pod installation in Ames 40x80 foot wind tunnel
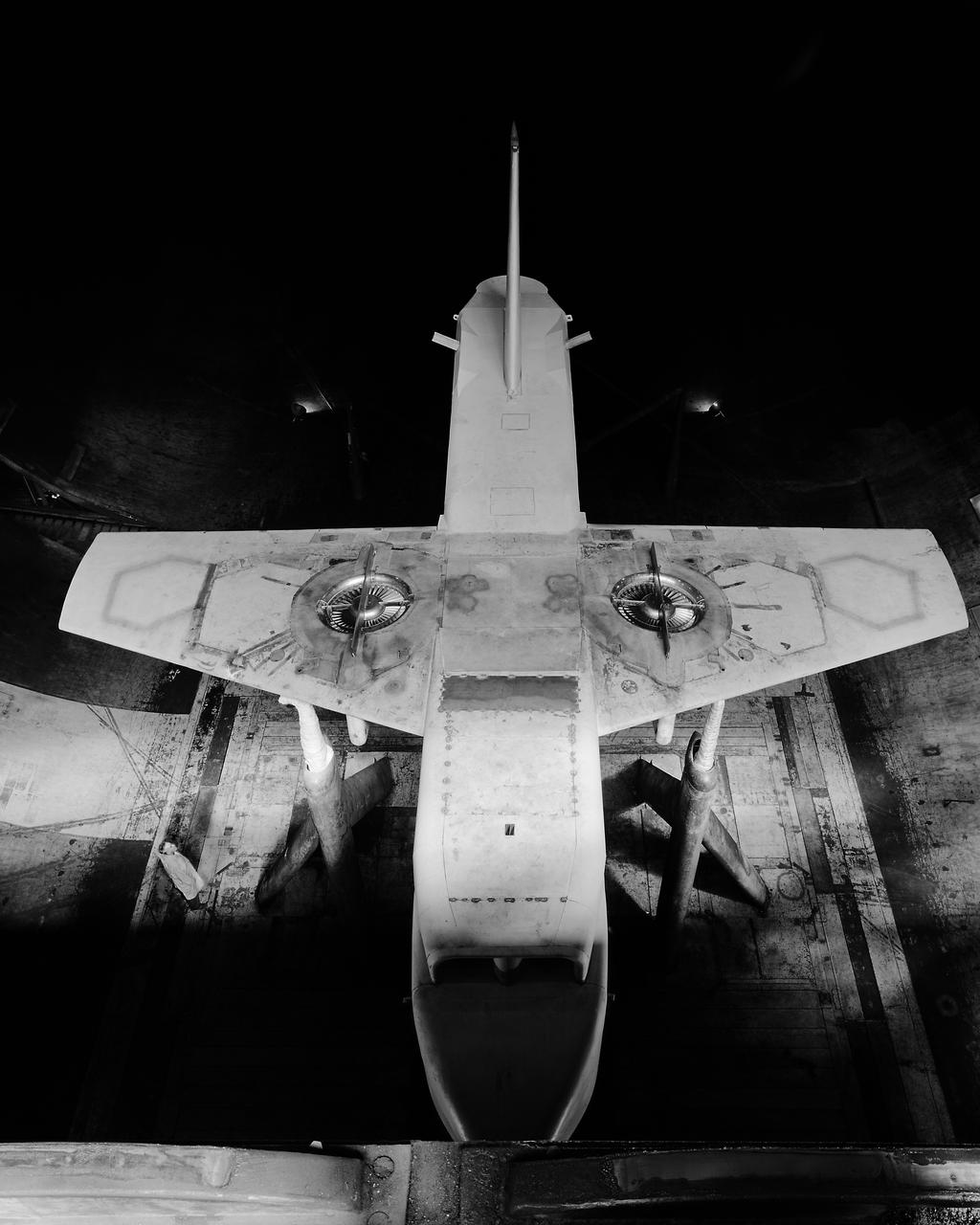

Forward overhead view of lift fan transport model, with two, of a possible six, high pressure ratio wing lift fans. Lift Fan Model In 40 X 80 Wind Tunnel; Test 40-347
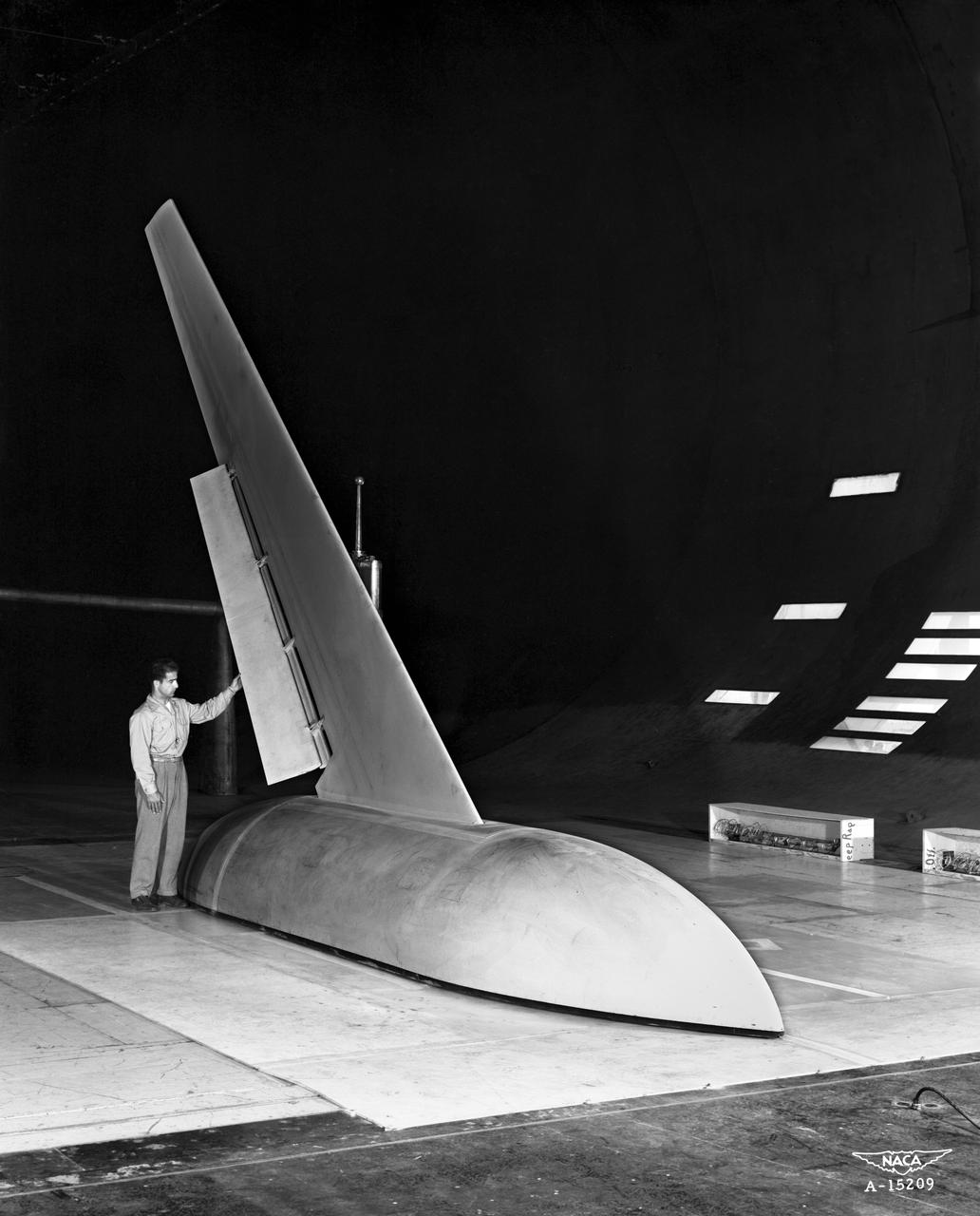

Investigation of High Lift and Stall Control on 45 deg. 3/4 front view Sweptback Cambered and Twisted Wing, in Ames 40x80 foot Wind Tunnel.
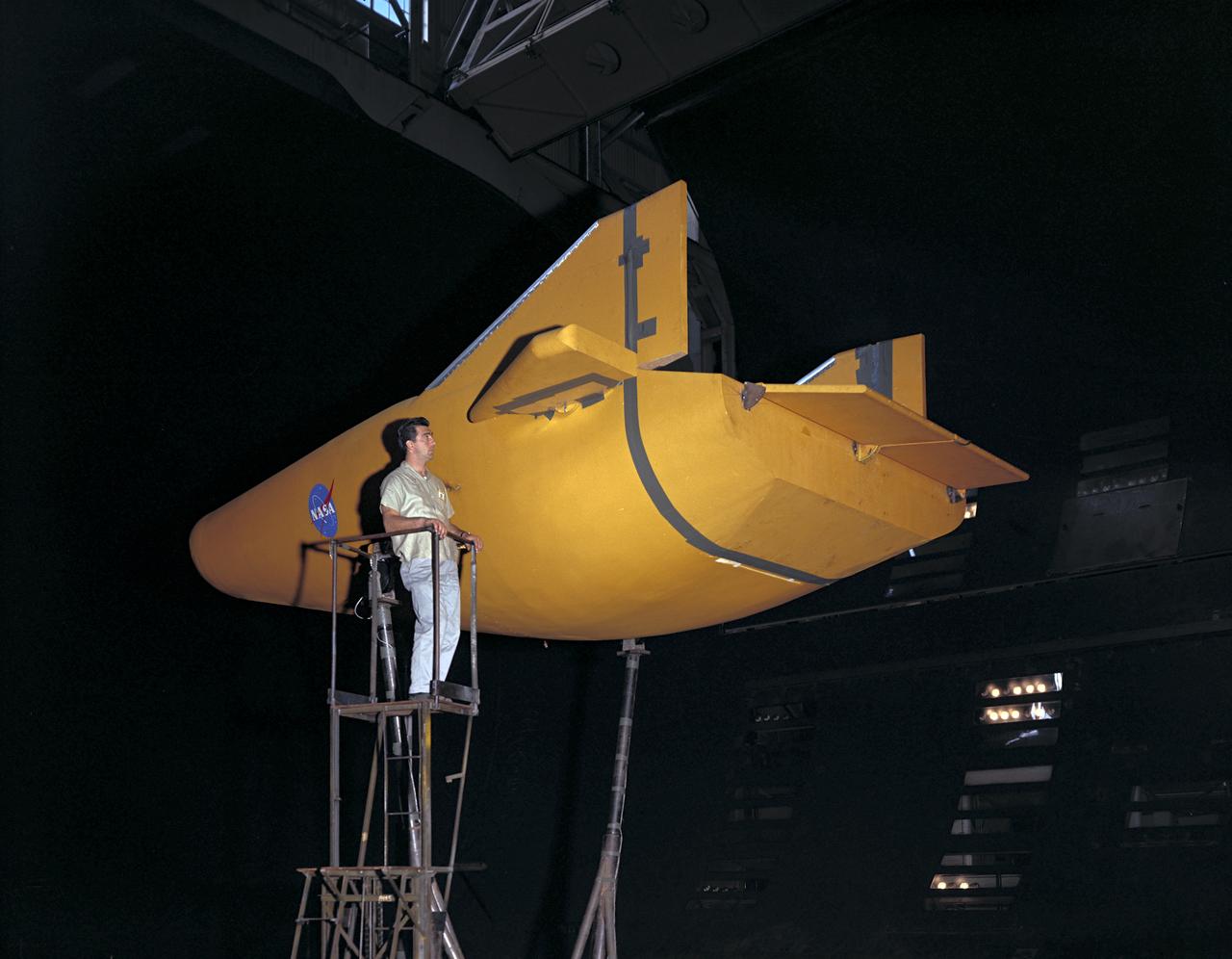

M-2 lifting body wind tunnel model with wind tunnel mechanic Chuck Greco. Model mounted on special support designed for lifting body models. Flaps and elevons visible.

Lifting the Veil of Anonymity

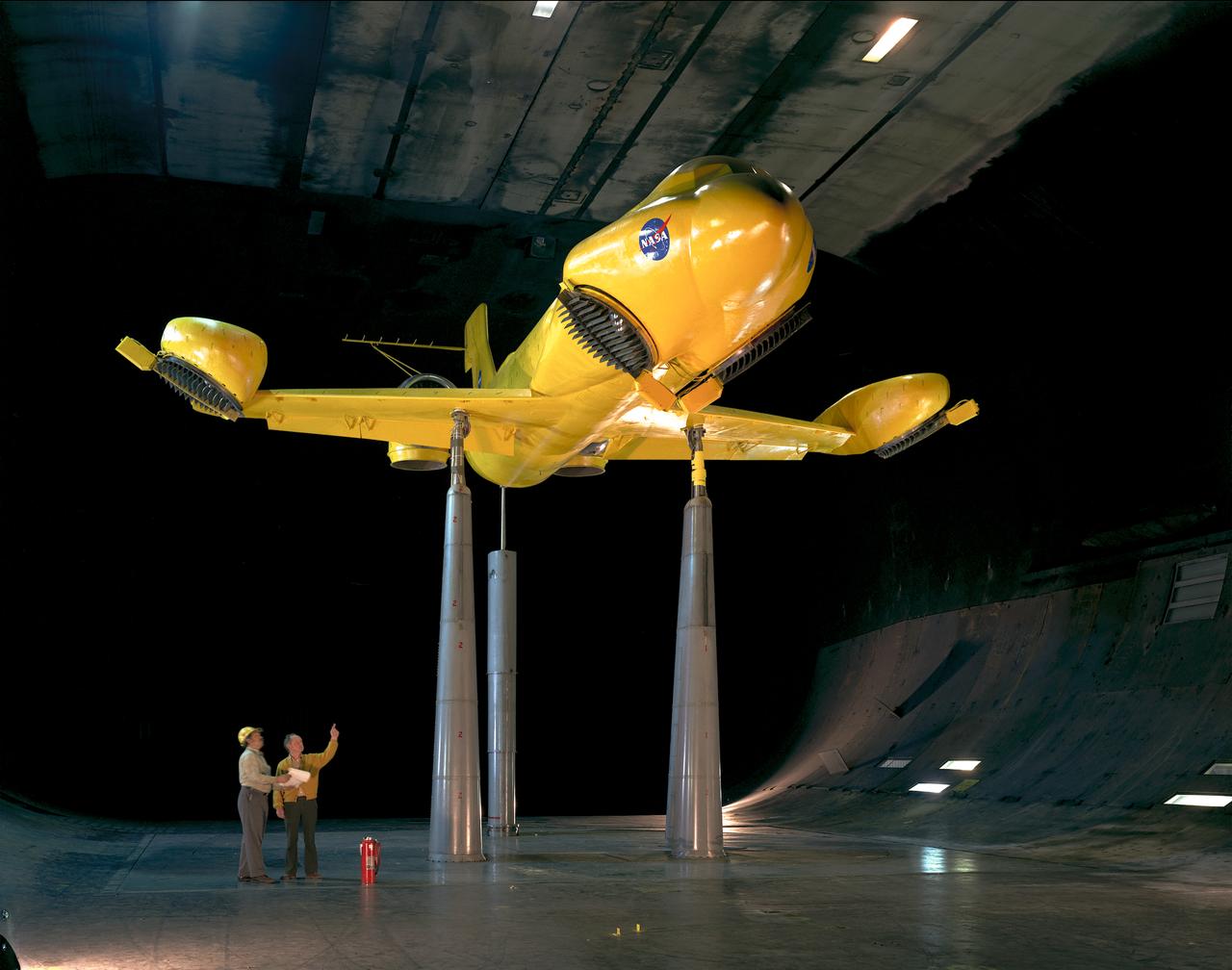
Top front view of Delta wing lift fan fighter model.
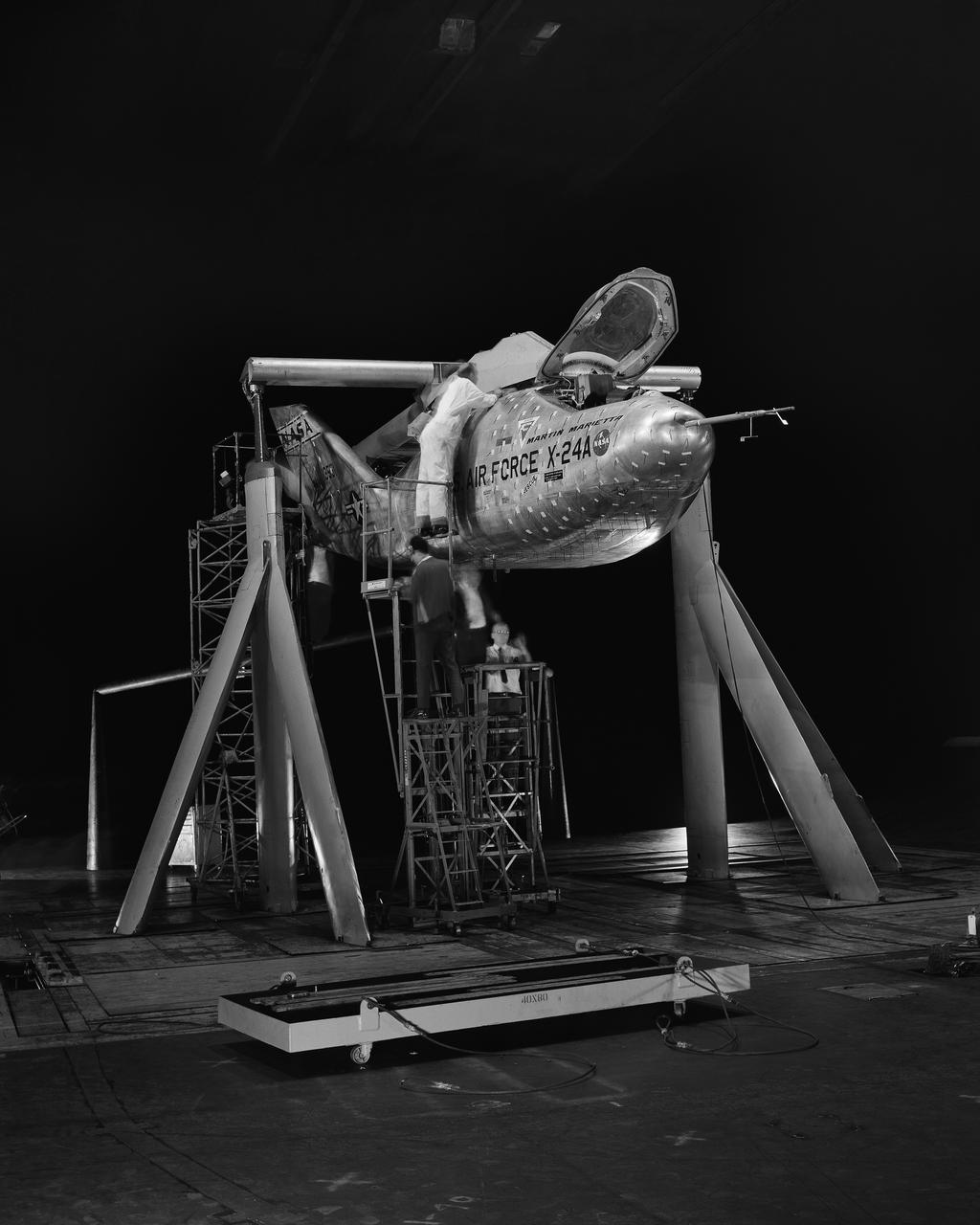

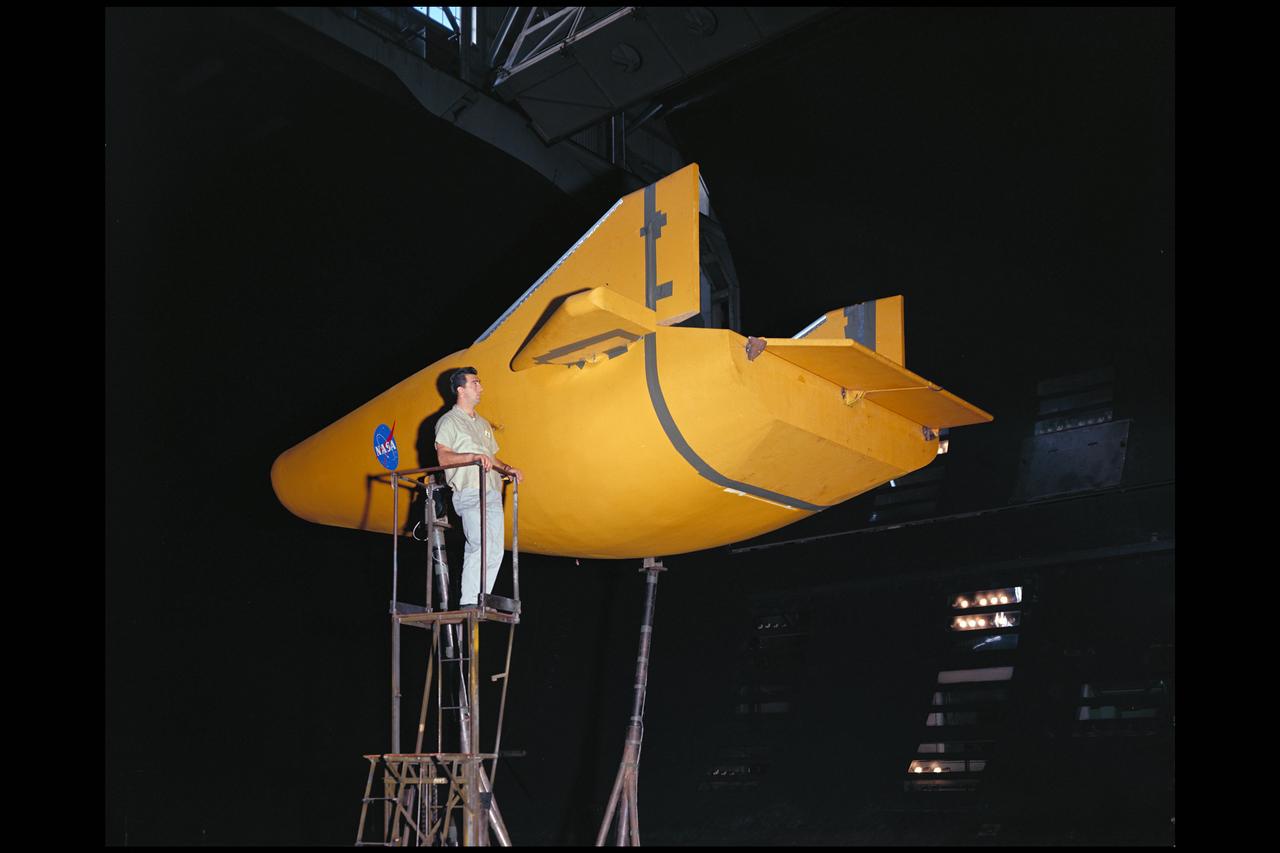
3/4 front view of Martin X-24A lifting body, mounted on B-52 mount.

3/4 lower front view of DC-9 lift/cruz fan transport model. Pictured with Eloy Martinez (left, mechanic) Leo Hall (right, engineer).
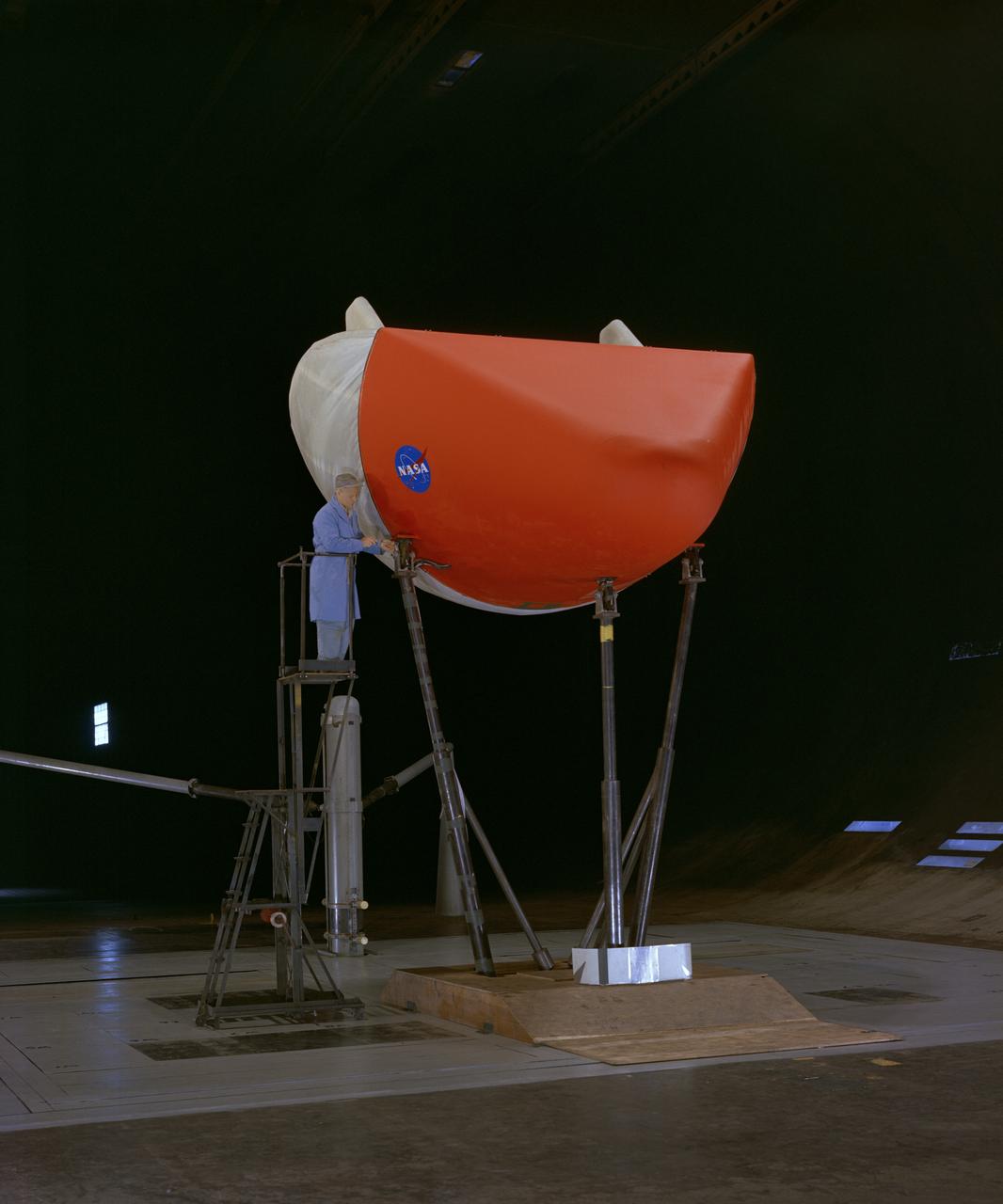

3/4 front view of M-1-L inflatable recovery able lifting body model in Ames 40x80 foot wind tunnel. Mechanic, Ray Schmorance included in picture.
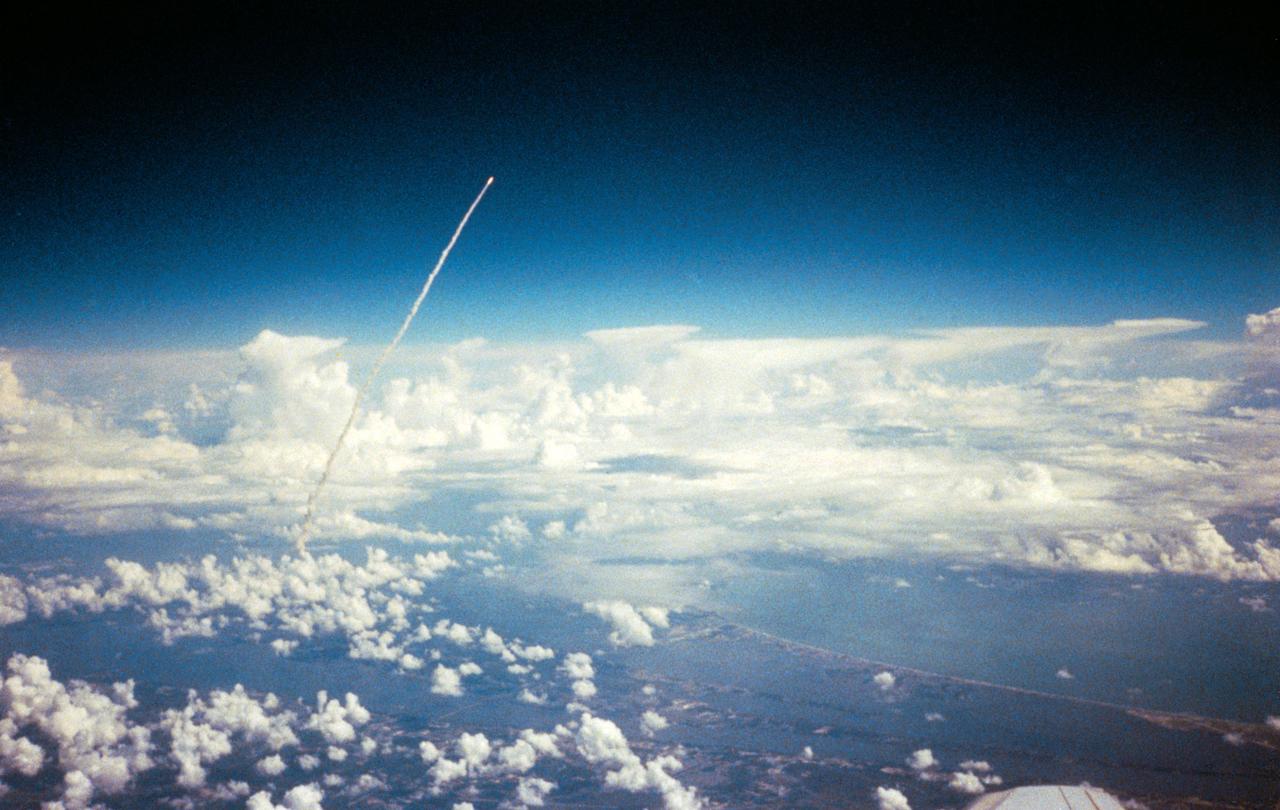

Long range view of an unidentified space shuttle lift off taken from an unidentified high flying aircraft.
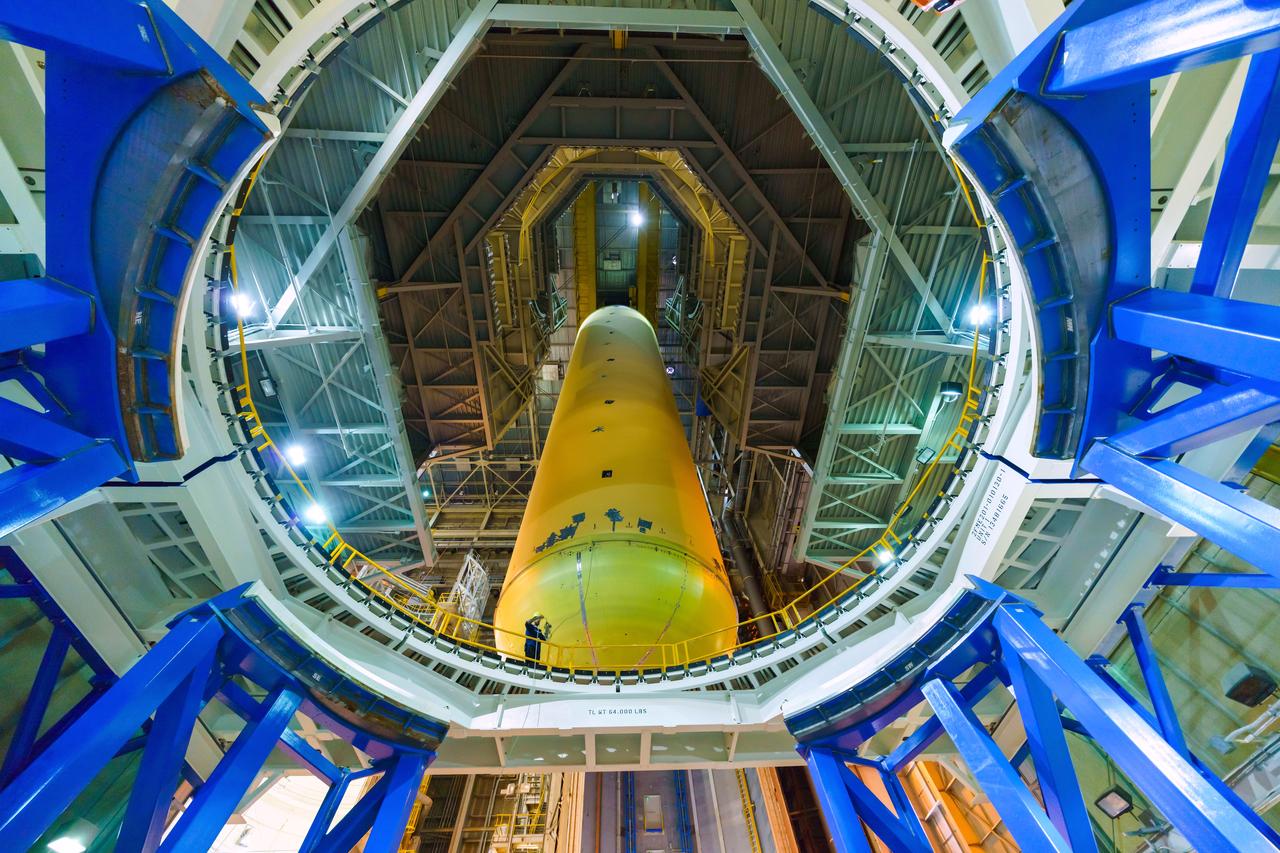

New Orleans, LA - NASA's Space Launch System Liquid Hydrogen(LH2) Stactic Test Article(STA) is lifted into Cell A at the Michoud Assembly Facillty. The tank will be brought to Marshall Space Flight Center for testing.
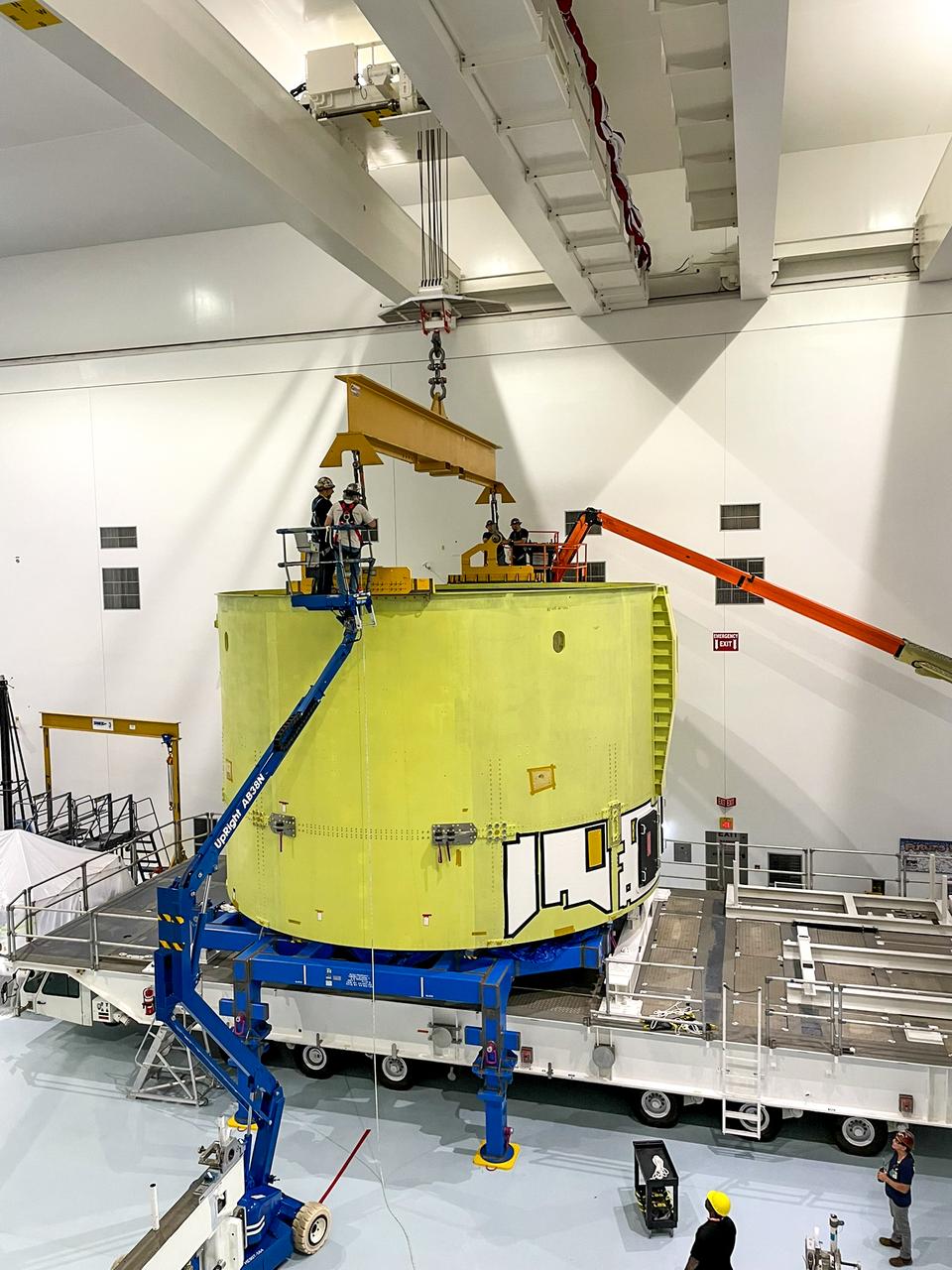

Technicians lift the engine section for NASA’s Artemis IV SLS (Space Launch System) rocket ahead of further processing inside the high bay of the Space Systems Processing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Oct. 21, 2024. The engine section is one of five major elements that makes up the SLS rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, which house the rocket’s four RS-25 engines and vital systems for mounting, controlling, and delivering fuel from the stage’s two massive liquid propellant tanks to the engines.

Technicians lift the engine section for NASA’s Artemis IV SLS (Space Launch System) rocket ahead of further processing inside the high bay of the Space Systems Processing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Oct. 21, 2024. The engine section is one of five major elements that makes up the SLS rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage, which house the rocket’s four RS-25 engines and vital systems for mounting, controlling, and delivering fuel from the stage’s two massive liquid propellant tanks to the engines.
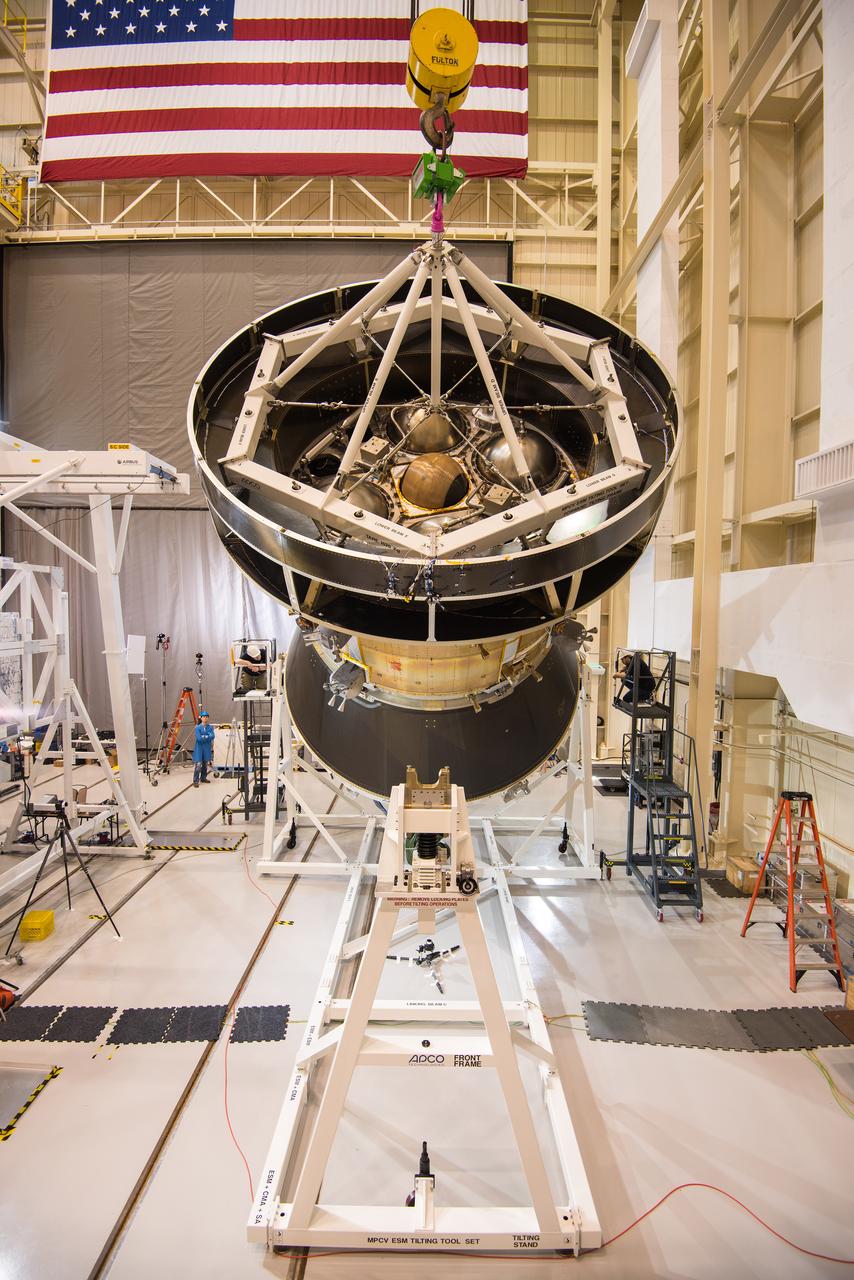

European Service Module Lift and Tilt Operation in the Assembly High Bay at Plum Brook Station’s Space Power Facility (SPF).
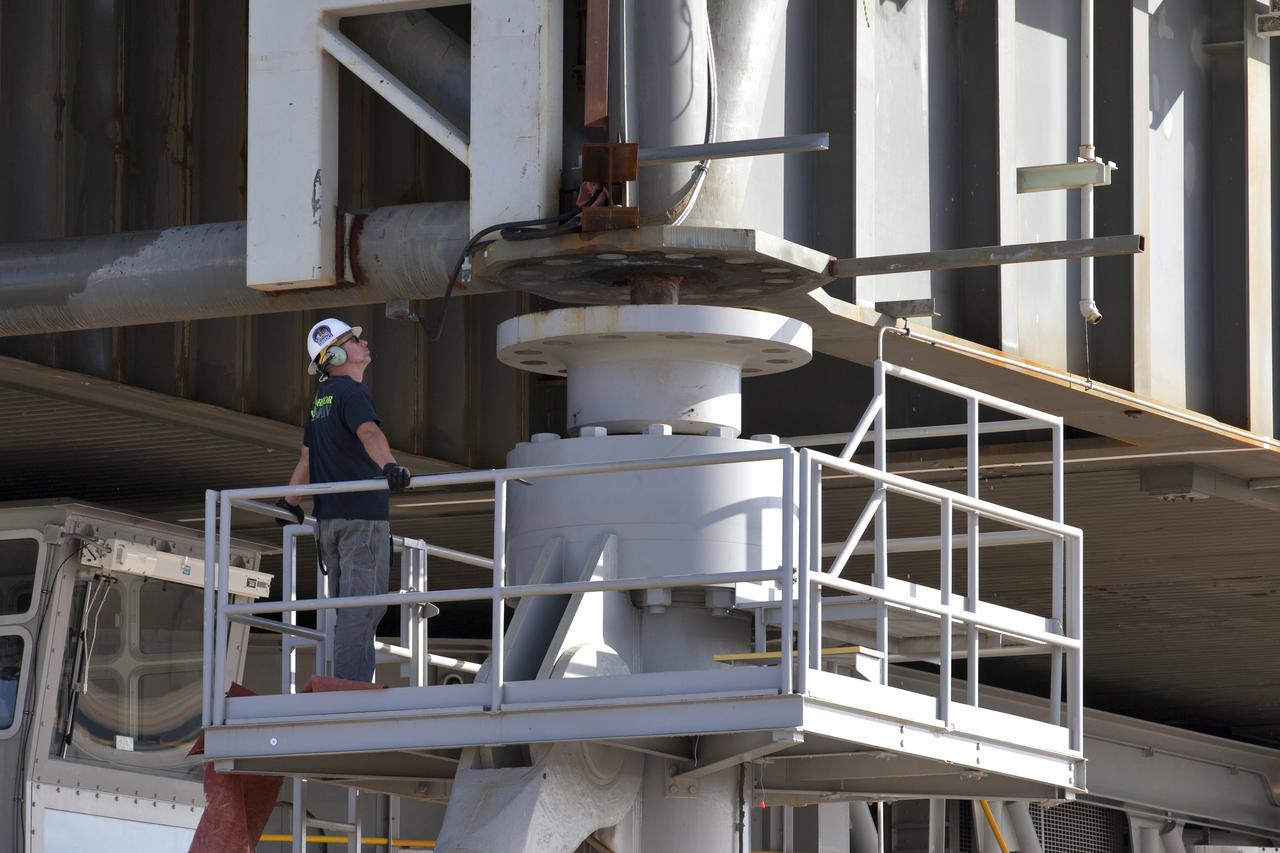

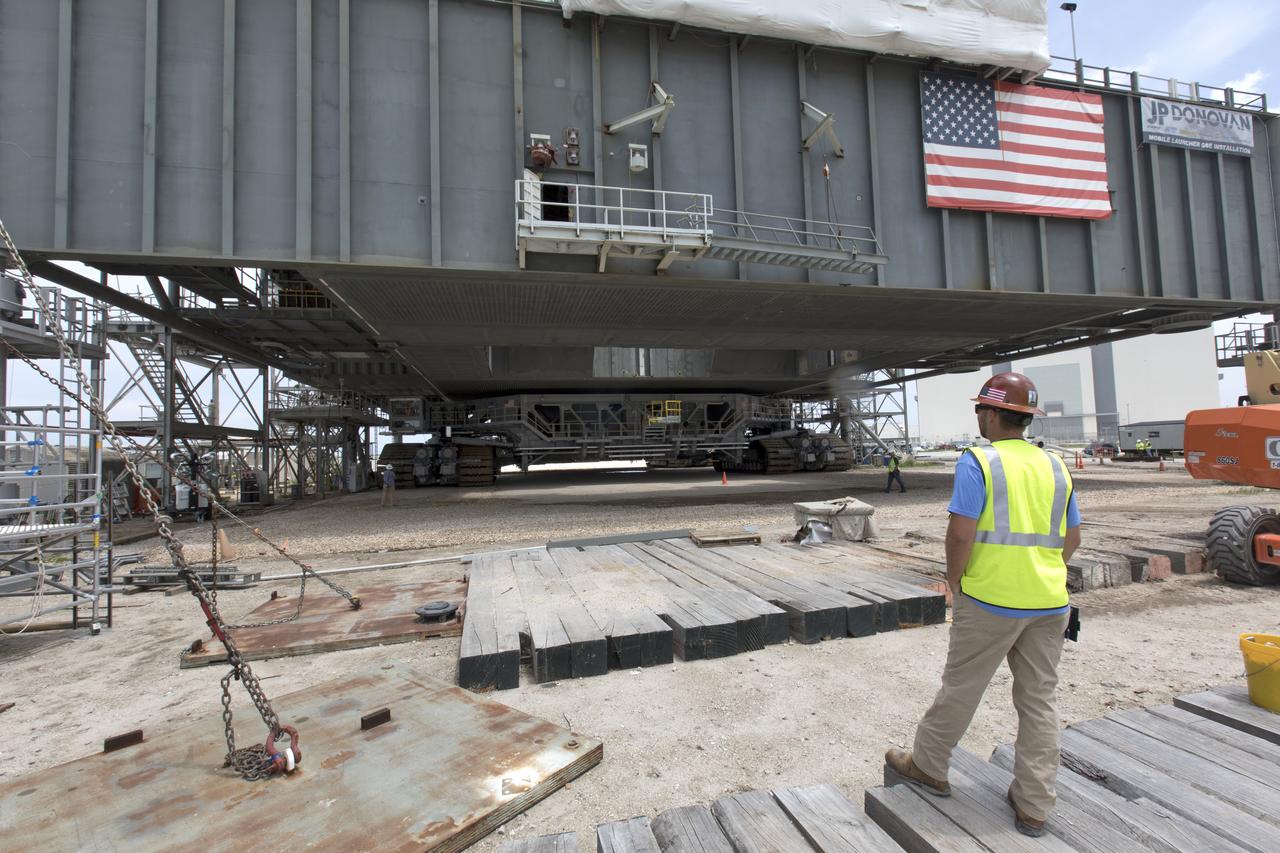
A construction worker monitors the progress as crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) lifts the mobile launcher up a few inches from its support posts June 1, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts were performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. The lift helped to test the capability of the upgraded CT-2 to handle the weight of the mobile launcher. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to support the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.

A construction worker monitors the progress as crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) lifts the mobile launcher up a few inches from its support posts June 1, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts were performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. The lift helped to test the capability of the upgraded CT-2 to handle the weight of the mobile launcher with SLS and Orion atop. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to support the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
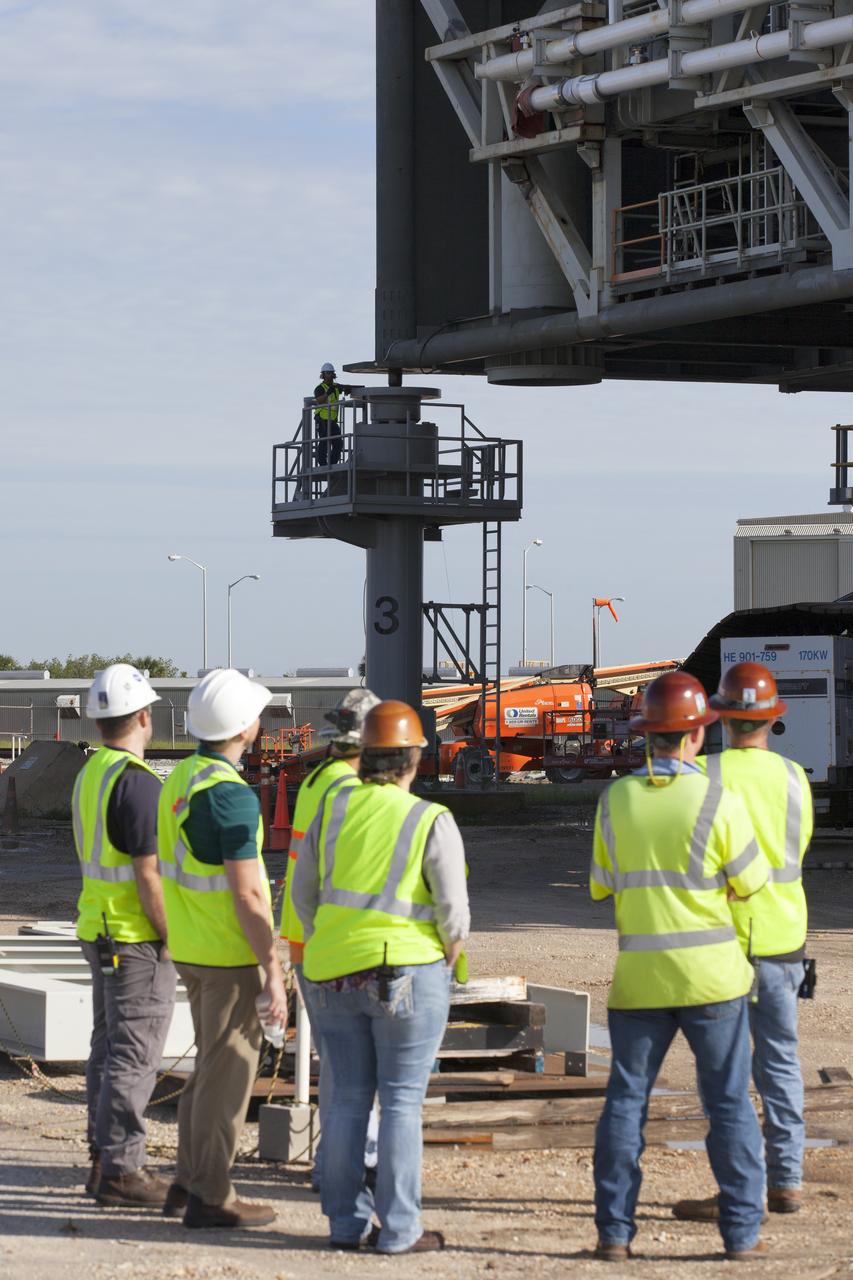

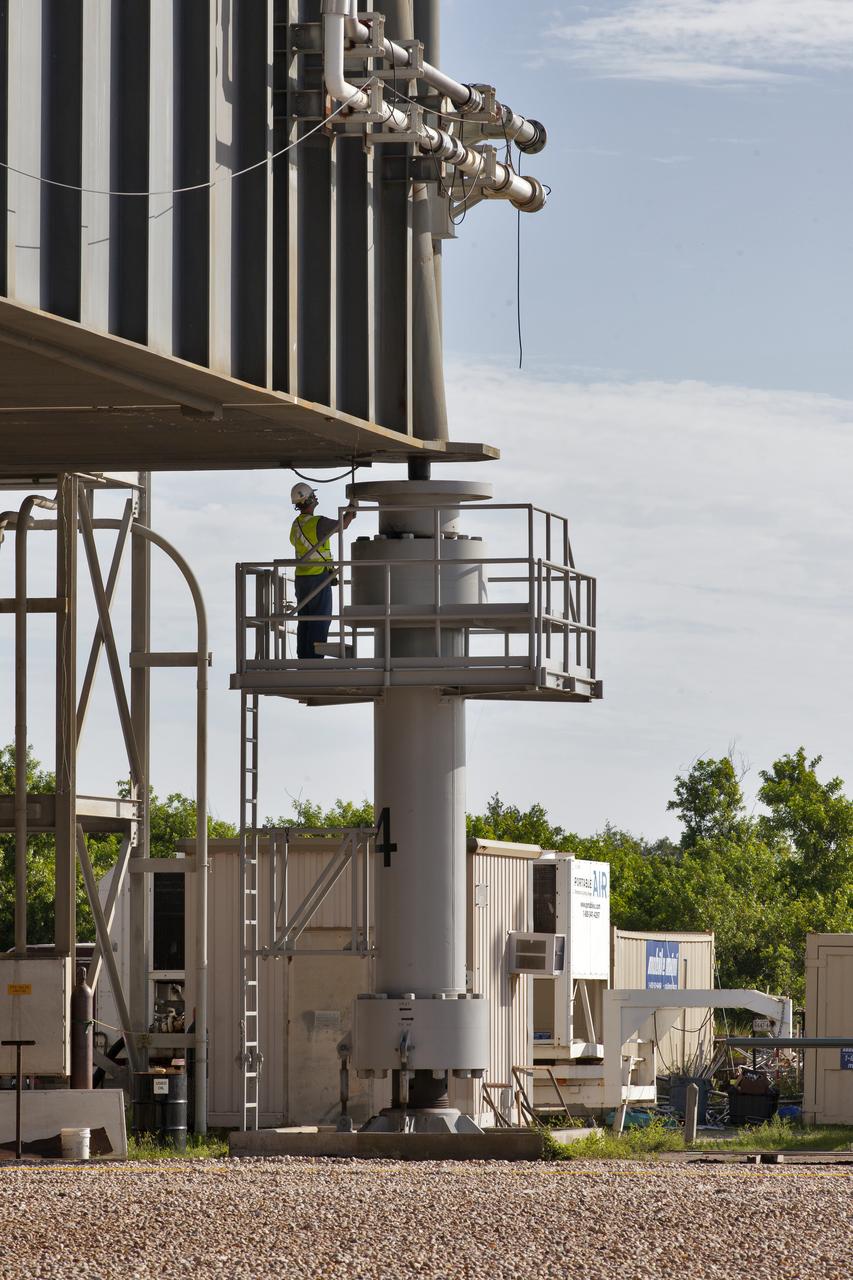
Workers watch as crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) lifts the mobile launcher up a few inches from its support posts June 1, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts were performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. The lift helped to test the capability of the upgraded CT-2 to handle the weight of the mobile launcher. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
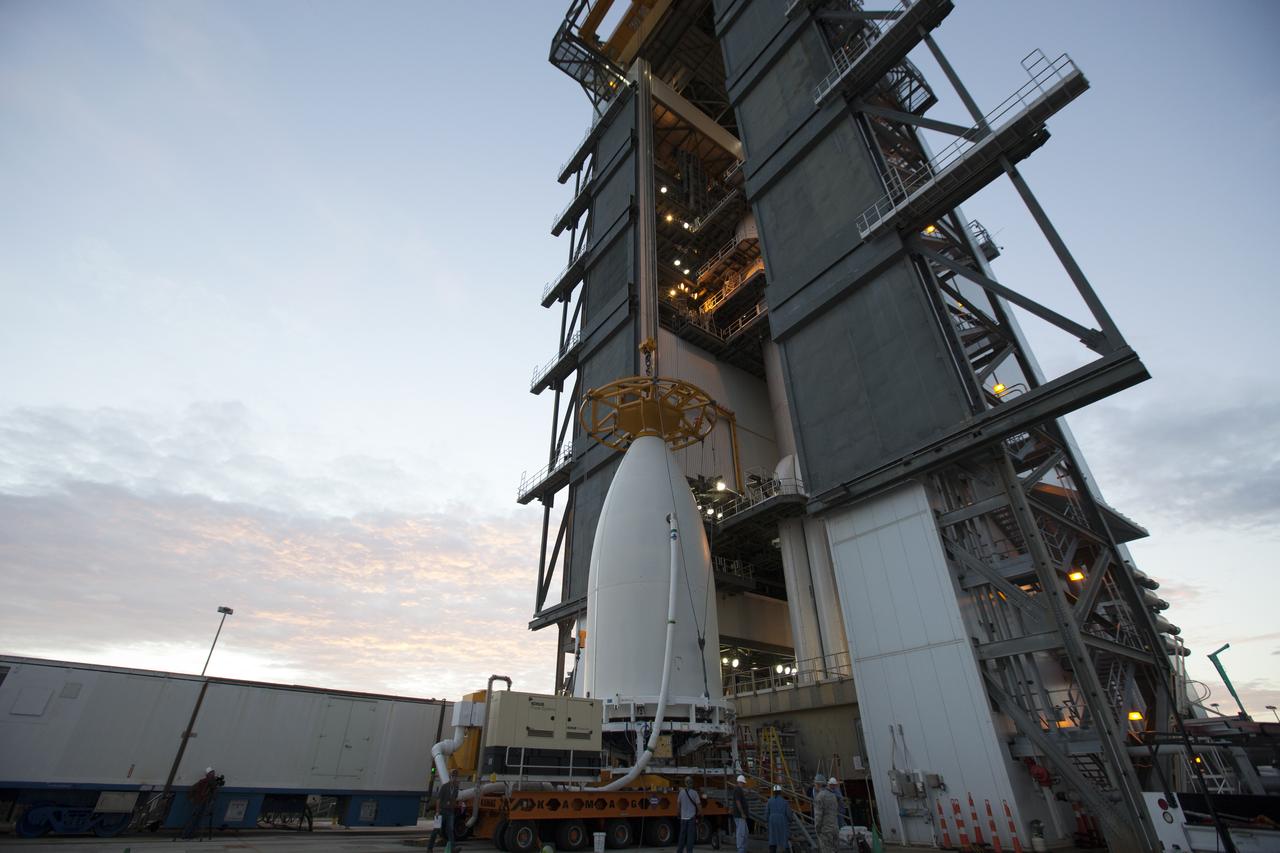

Preparations are underway to lift NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R), enclosed in its payload fairing at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. GOES-R will be mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in preparation for launch in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
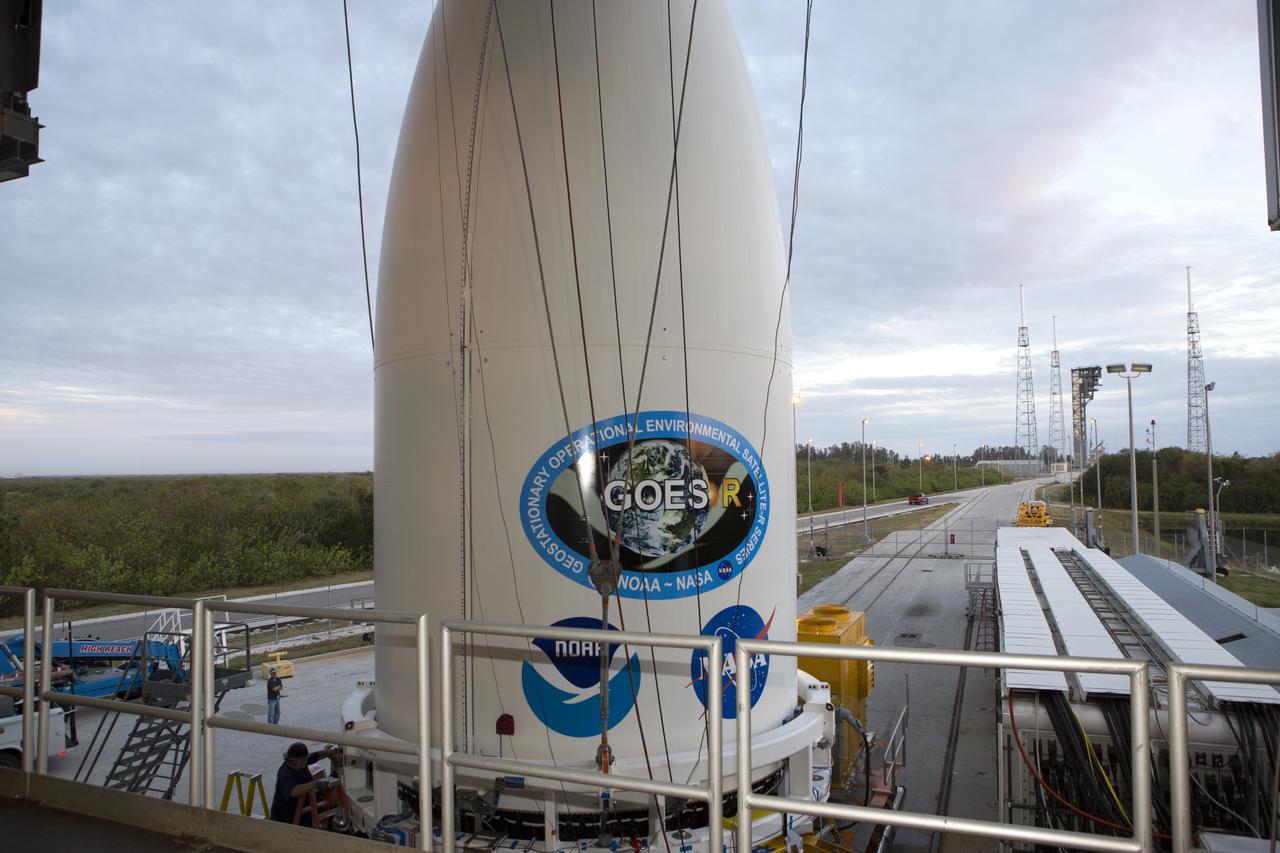

Preparations are underway to lift NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R), enclosed in its payload fairing at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. GOES-R will be mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in preparation for launch in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
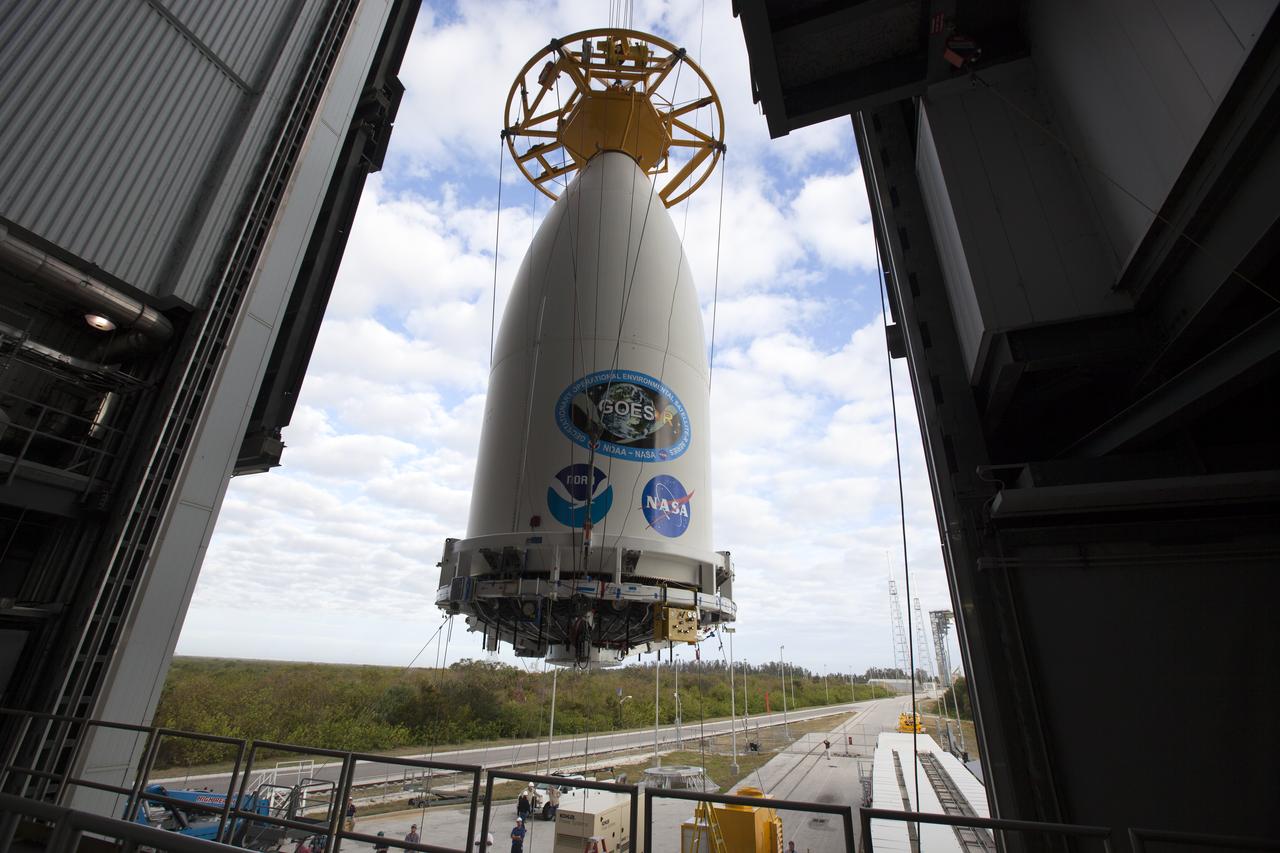

A view from high up inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. A crane lifts the payload fairing containing NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage. The satellite will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
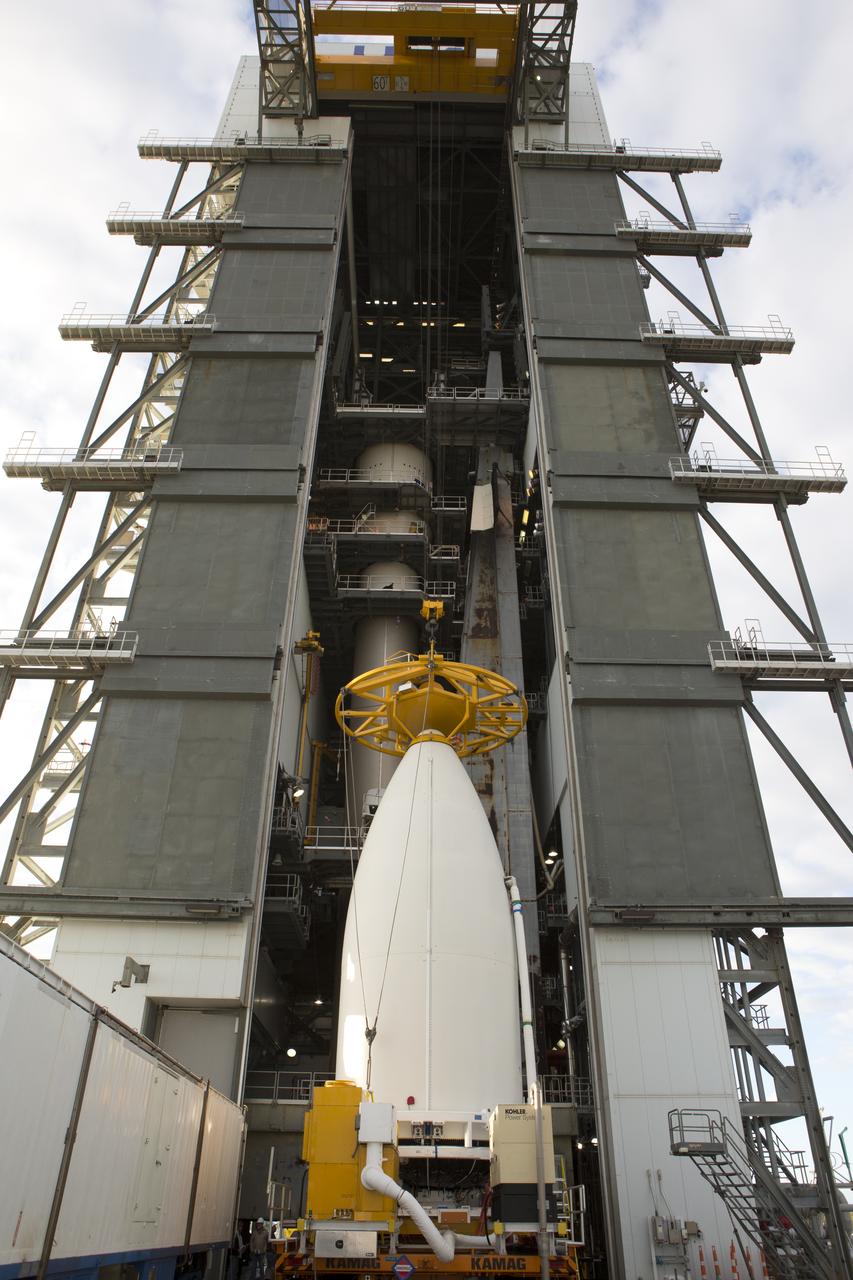

A crane begins to lift the payload fairing containing NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. GOES-R will be mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in preparation for launch in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
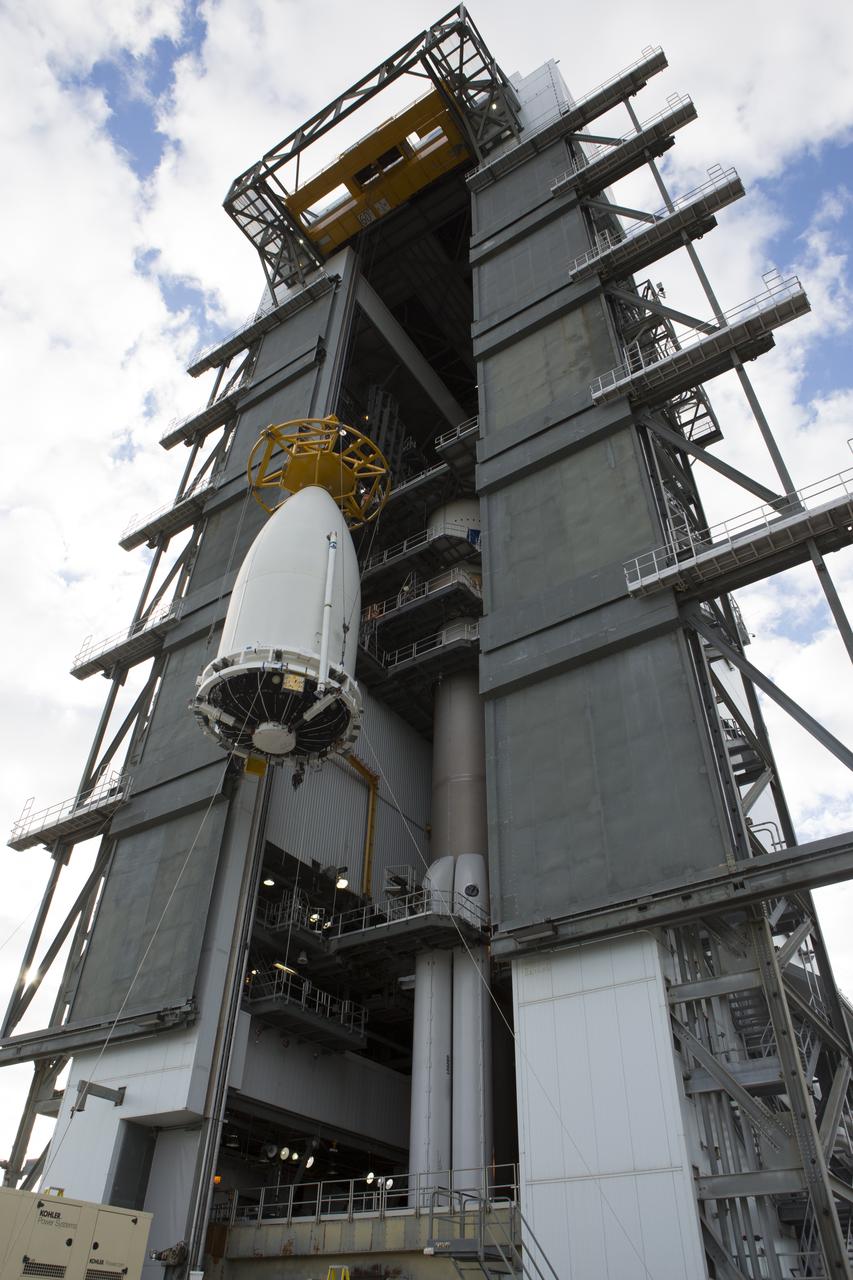

A crane is used to lift the payload fairing containing NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. GOES-R will be mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in preparation for launch in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
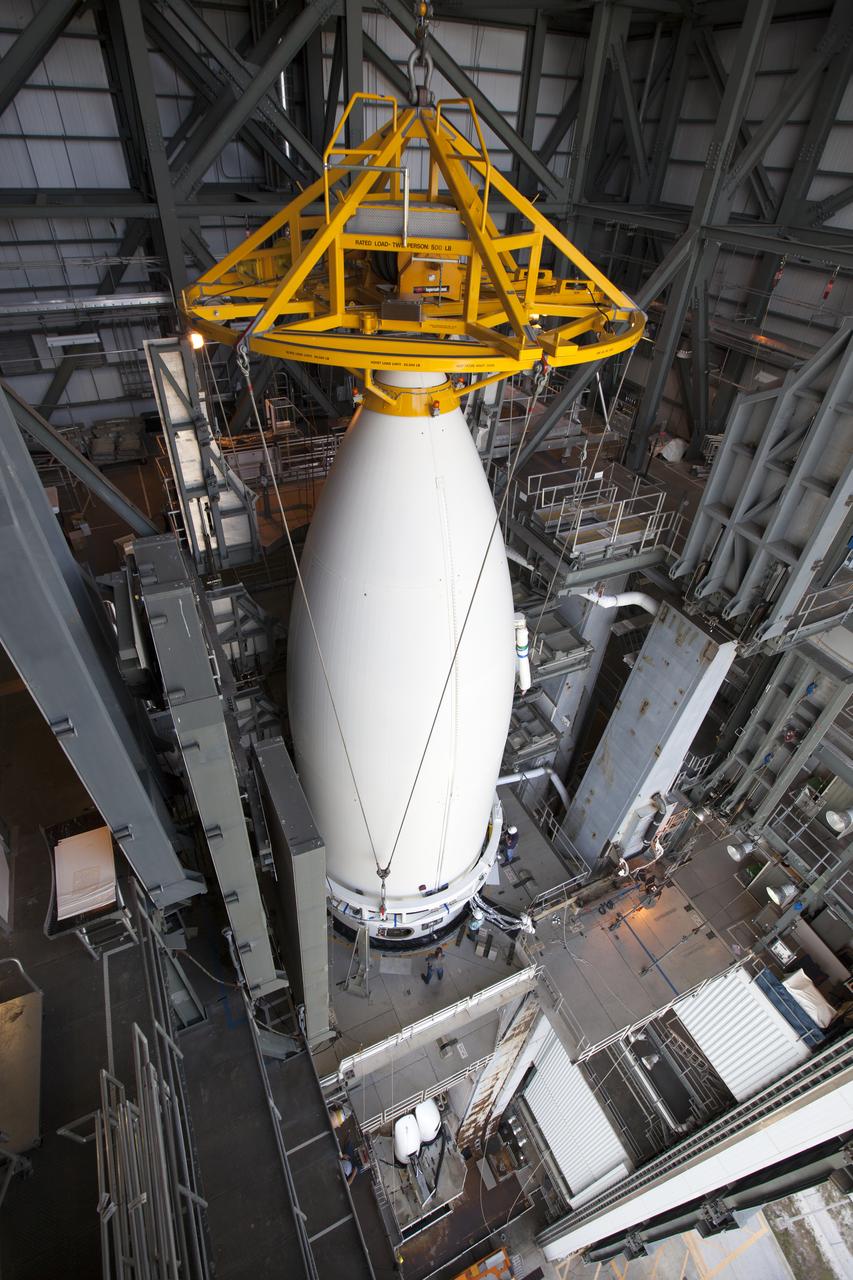

Enclosed in its payload fairing, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) is lifted into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. GOES-R will be mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in preparation for launch aboard the rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
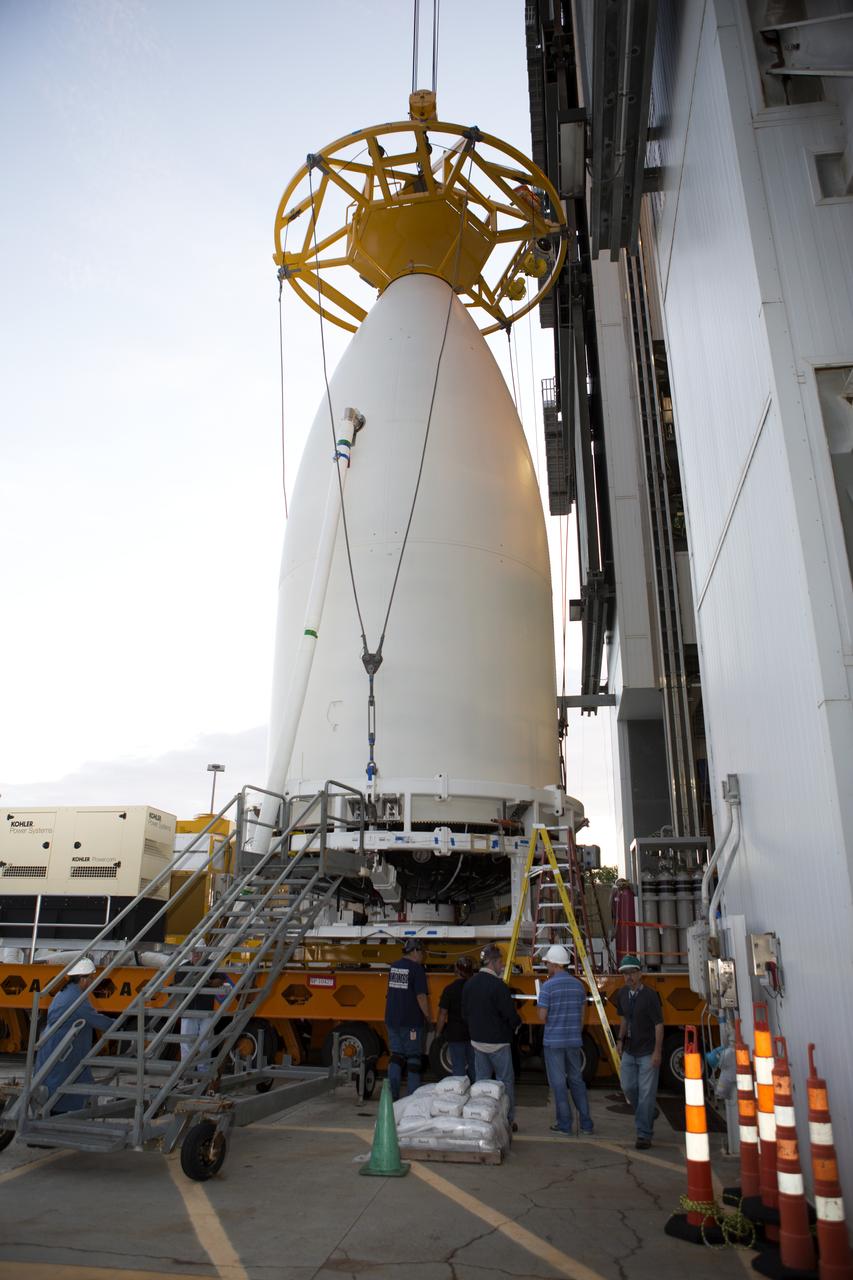

Preparations are underway to lift NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R), enclosed in its payload fairing at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. GOES-R will be mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in preparation for launch in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
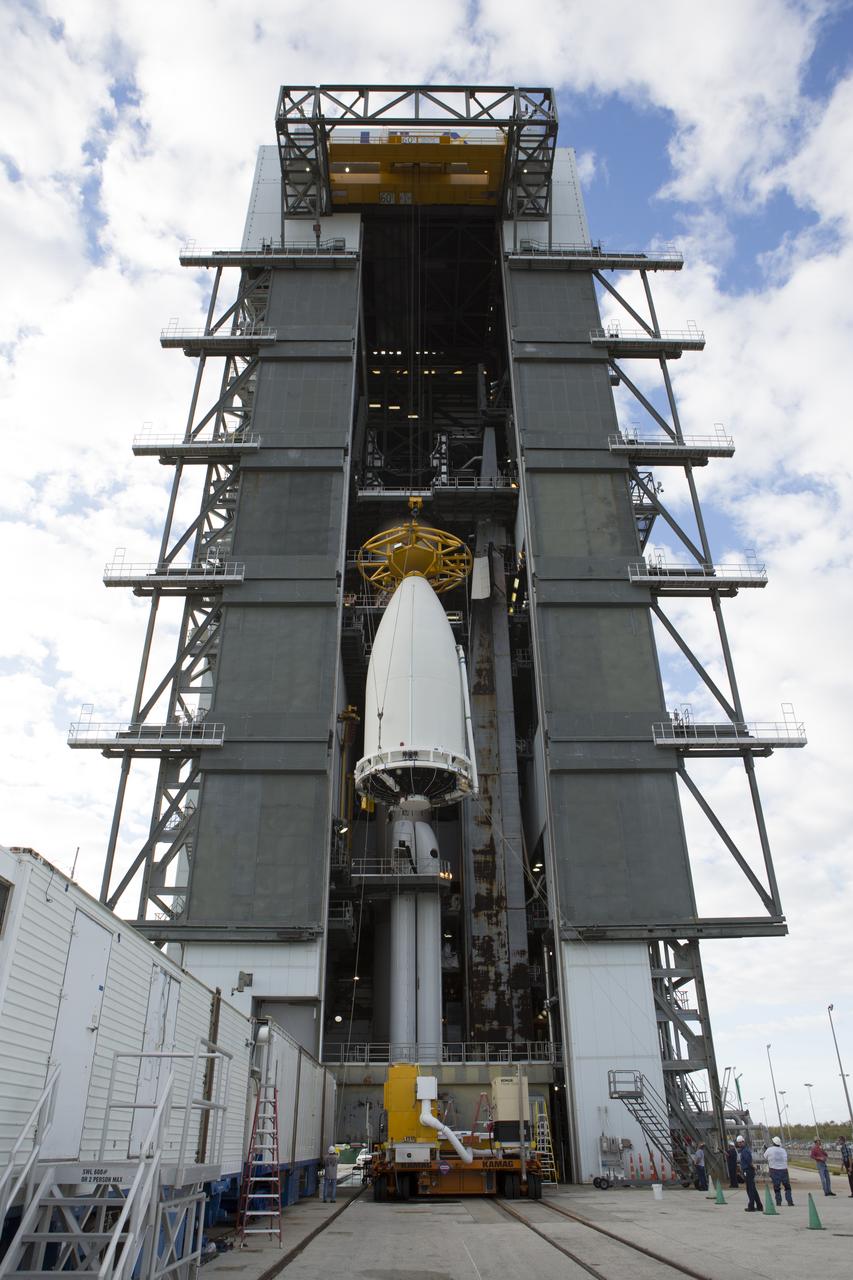

A crane is used to lift the payload fairing containing NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. GOES-R will be mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in preparation for launch in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
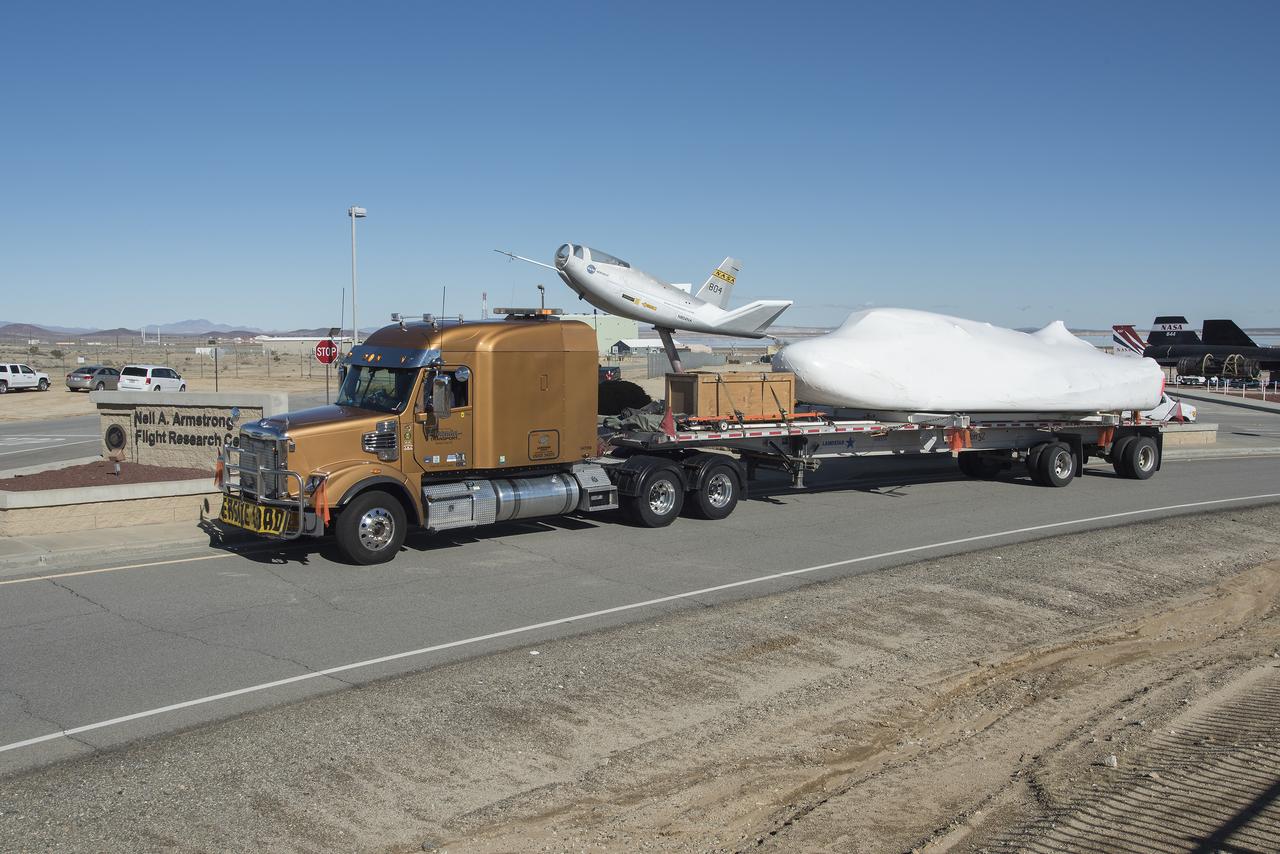

SNC delivers Dream Chaser to NASA Armstrong posing it with the HL-10 lifting body flown the 1960s.
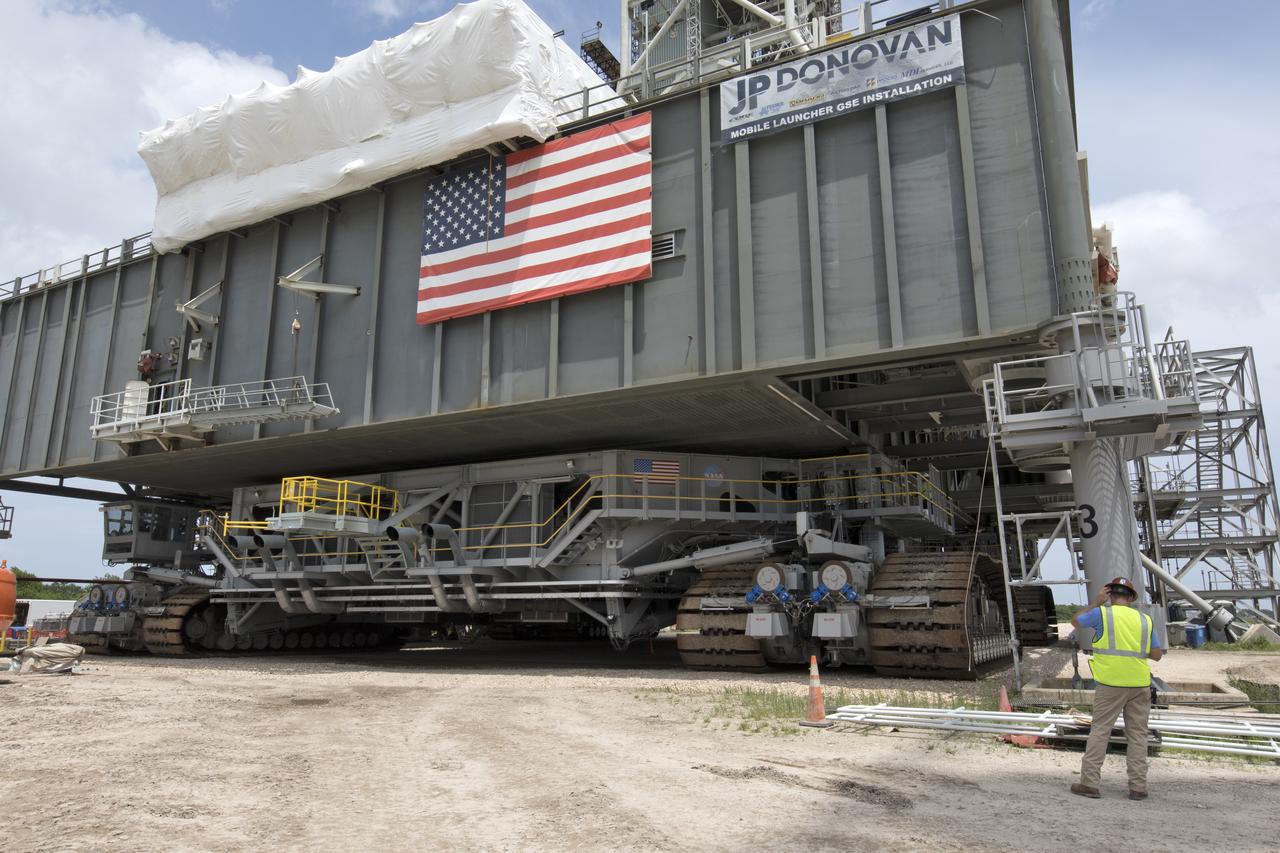

Crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) is underneath the mobile launcher May 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts will be performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. CT-2 has been upgraded to handle the weight of the mobile launcher with SLS and Orion atop. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to support the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.

Crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) is being moved under the mobile launcher May 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts will be performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. CT-2 has been upgraded to handle the weight of the mobile launcher with SLS and Orion atop. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to support the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
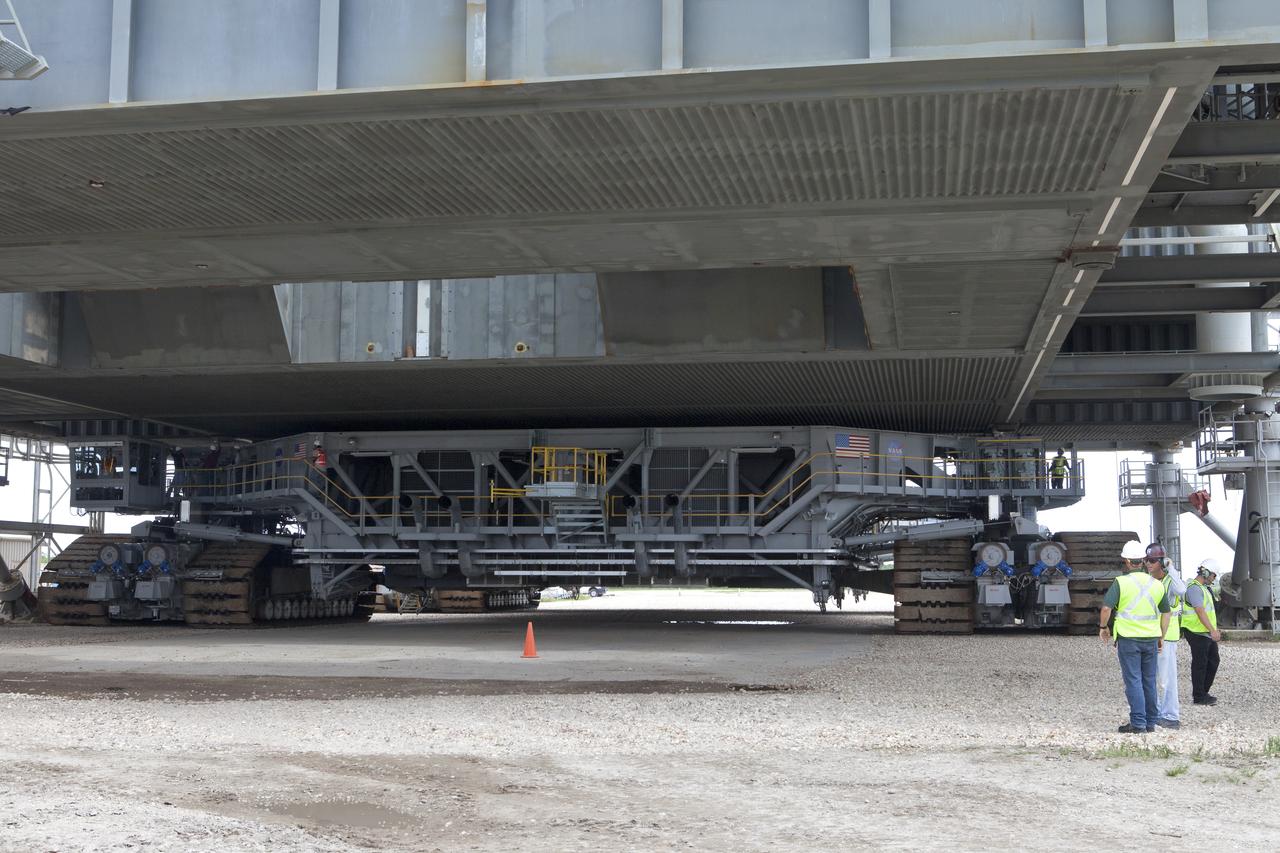

Crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) is moved under the mobile launcher May 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts will be performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. CT-2 has been upgraded to handle the weight of the mobile launcher with SLS and Orion atop. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to support the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
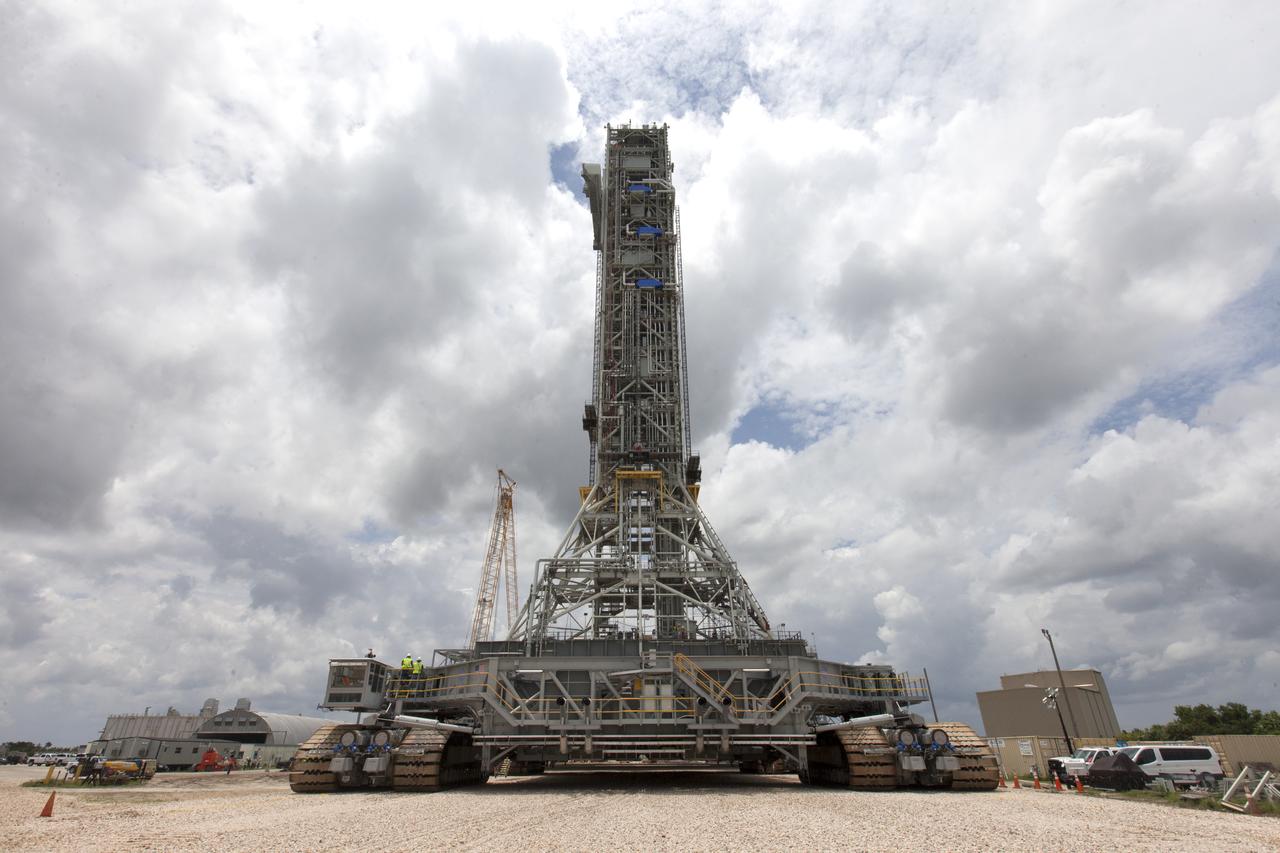

Preparations are underway May 31, 2018, to move crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) under the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts will be performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. CT-2 has been upgraded to handle the weight of the mobile launcher with SLS and Orion atop. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to support the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.

Crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) is underneath the mobile launcher May 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts were performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. CT-2 has been upgraded to handle the weight of the mobile launcher with SLS and Orion atop. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to support the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
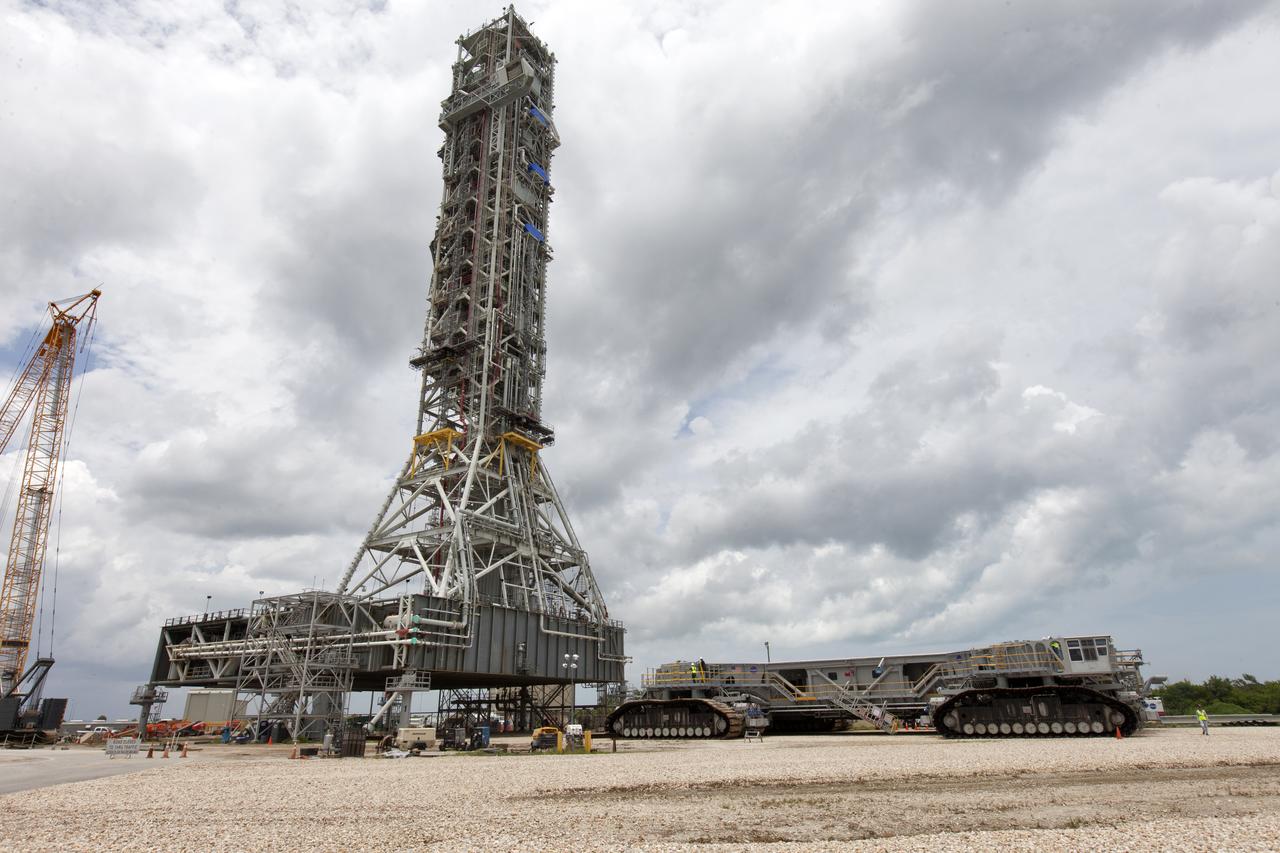

Preparations are underway May 31, 2018, to move crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) under the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts will be performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. CT-2 has been upgraded to handle the weight of the mobile launcher with SLS and Orion atop. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to support the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
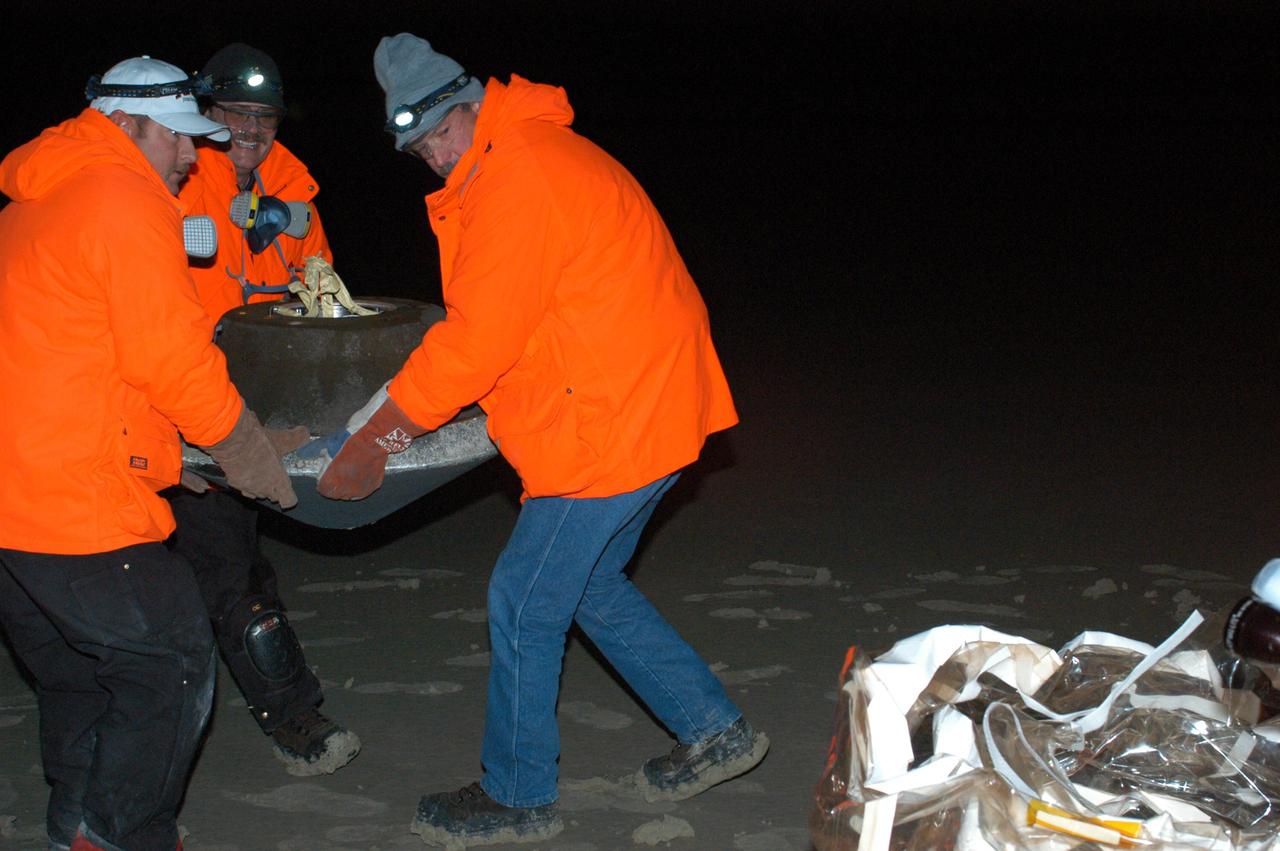

The capsule contains cometary and interstellar samples gathered by NASA Stardust spacecraft. Here, the capsule is being lifted at the landing site.
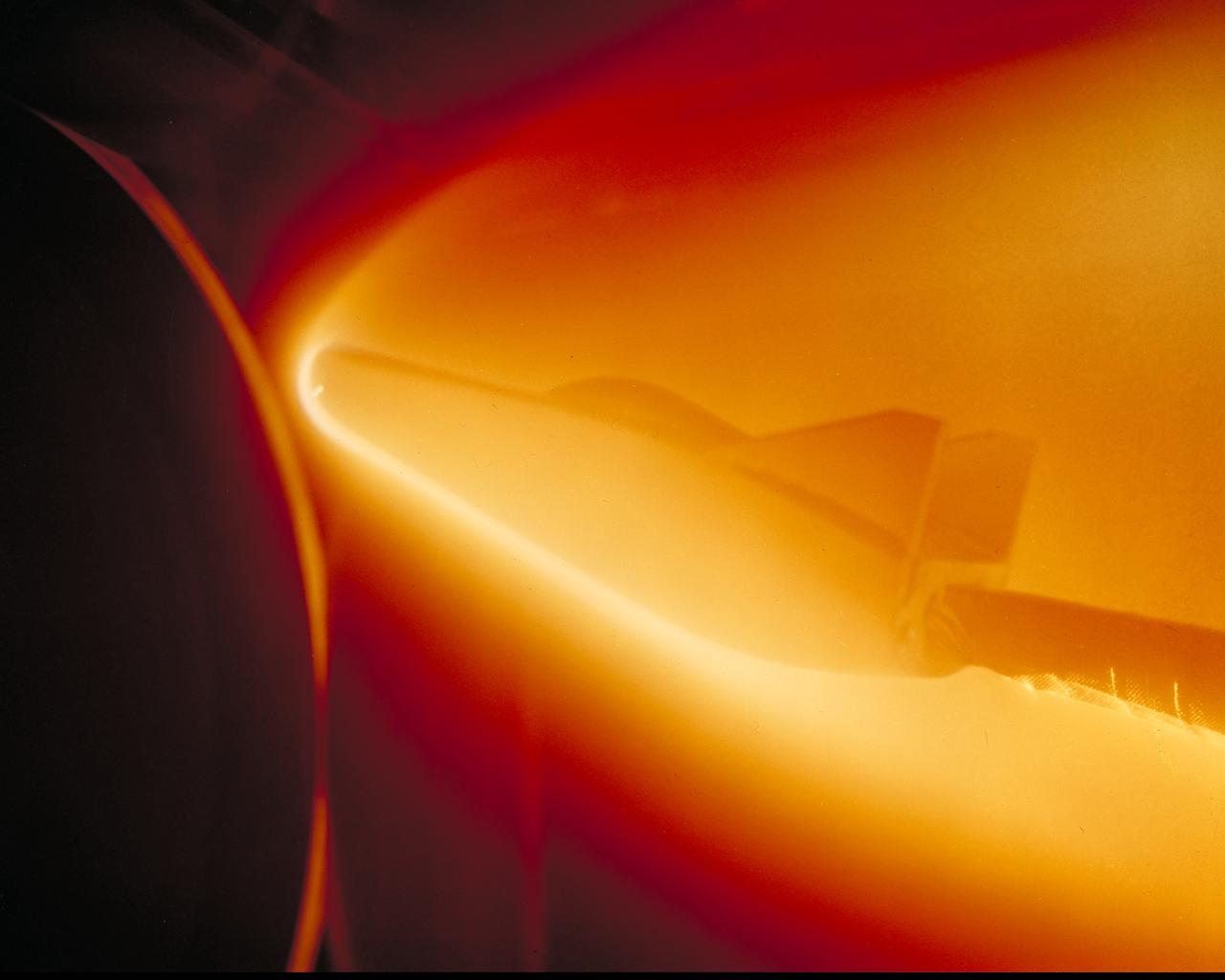

M-2 Lifting Body being tested in Ames atmospheric entry simulator to determine the areas of most intense heat.
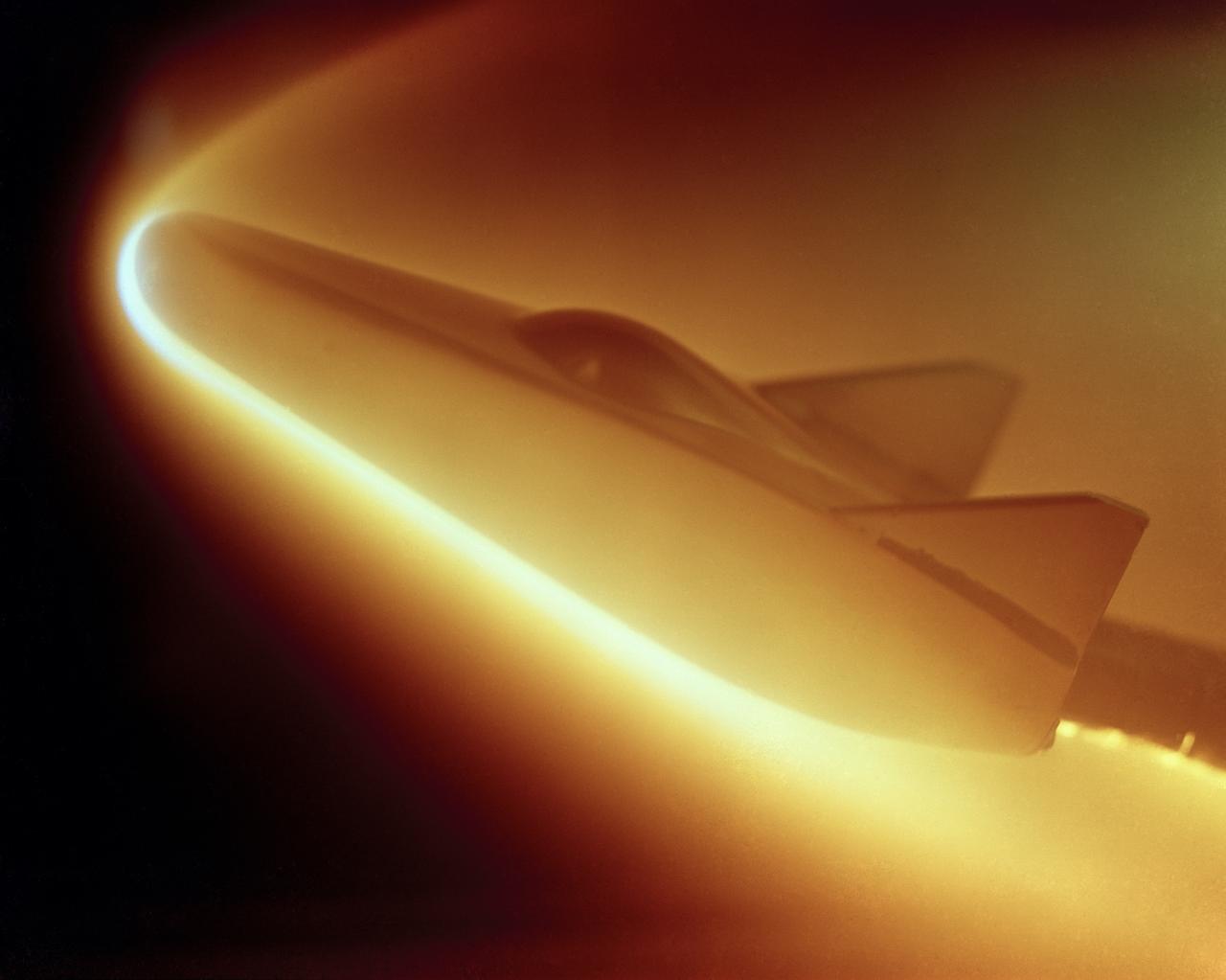

M-2 lifting body; heat transfer distribution test in the 1 ft hypervelocity wind tunnel
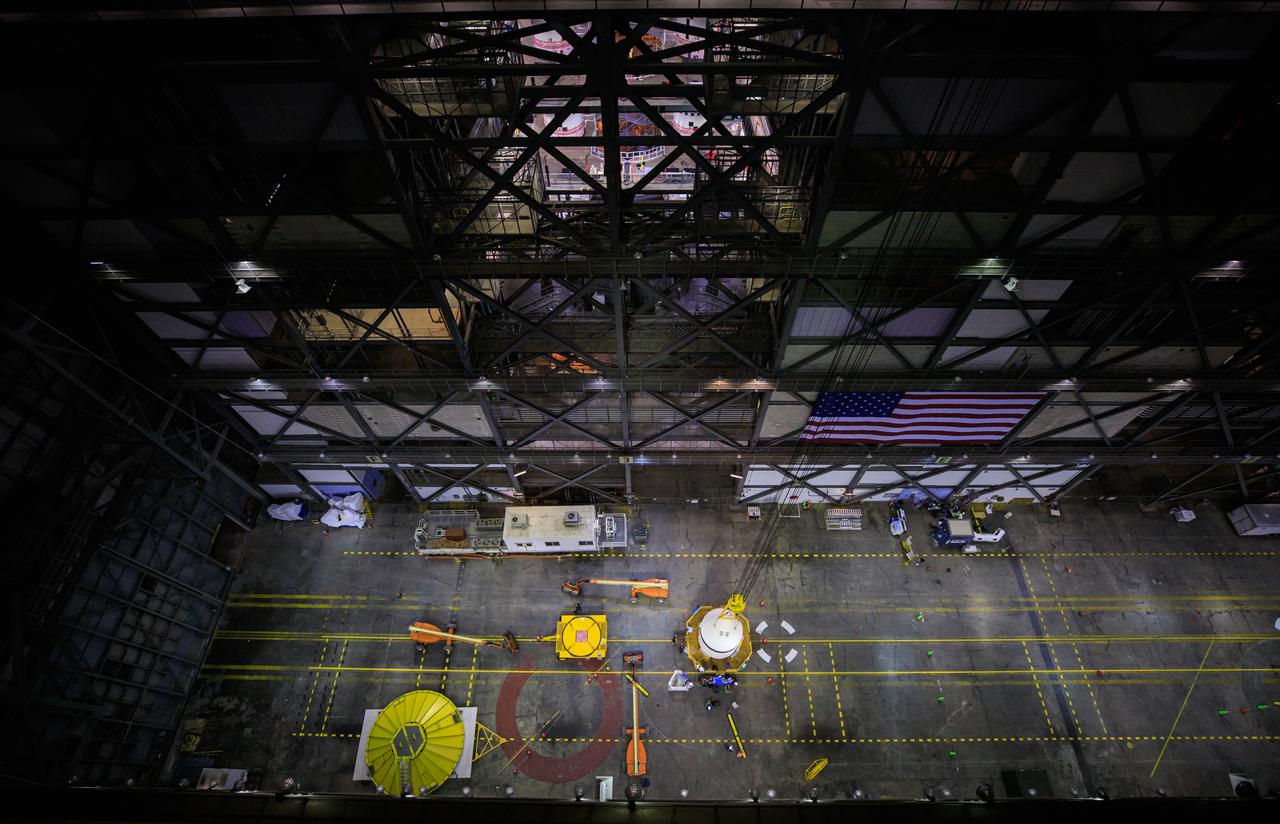

This view from high up in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shows a crane lifting the left-hand forward assembly for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) in the transfer aisle on March 1, 2021. Workers are lifting the segment up for transfer into High Bay 3, where it will be attached to the center forward segment on the mobile launcher (ML). Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs teams have been stacking the twin five-segment boosters on the ML over a number of weeks. When the core stage arrives, it will join the boosters on the mobile launcher, followed by the interim cryogenic propulsion stage and Orion spacecraft. Manufactured by Northrop Grumman in Utah, the twin boosters provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust at launch. Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the SLS. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
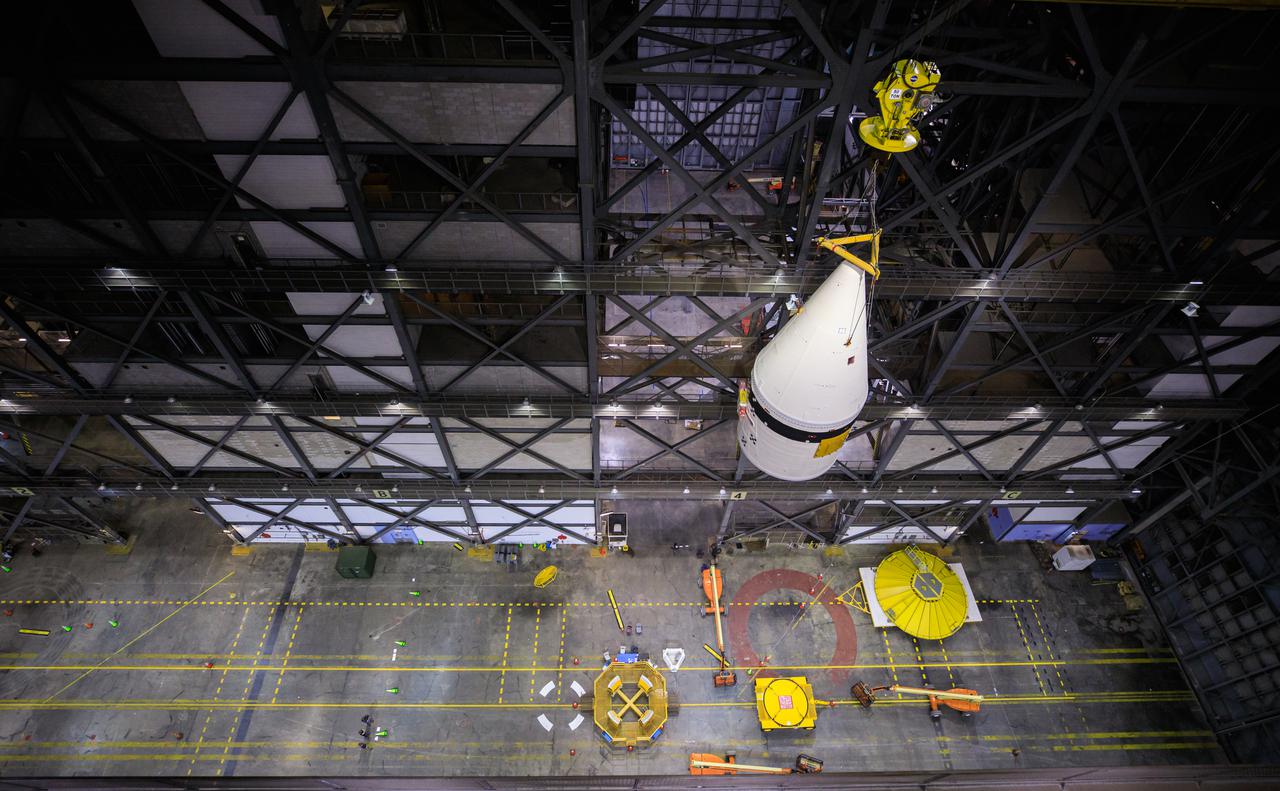

This view from high up in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shows a crane lifting the left-hand forward assembly for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) in the transfer aisle on March 1, 2021. Workers are lifting the segment up for transfer into High Bay 3, where it will be attached to the center forward segment on the mobile launcher (ML). Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs teams have been stacking the twin five-segment boosters on the ML over a number of weeks. When the core stage arrives, it will join the boosters on the mobile launcher, followed by the interim cryogenic propulsion stage and Orion spacecraft. Manufactured by Northrop Grumman in Utah, the twin boosters provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust at launch. Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the SLS. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
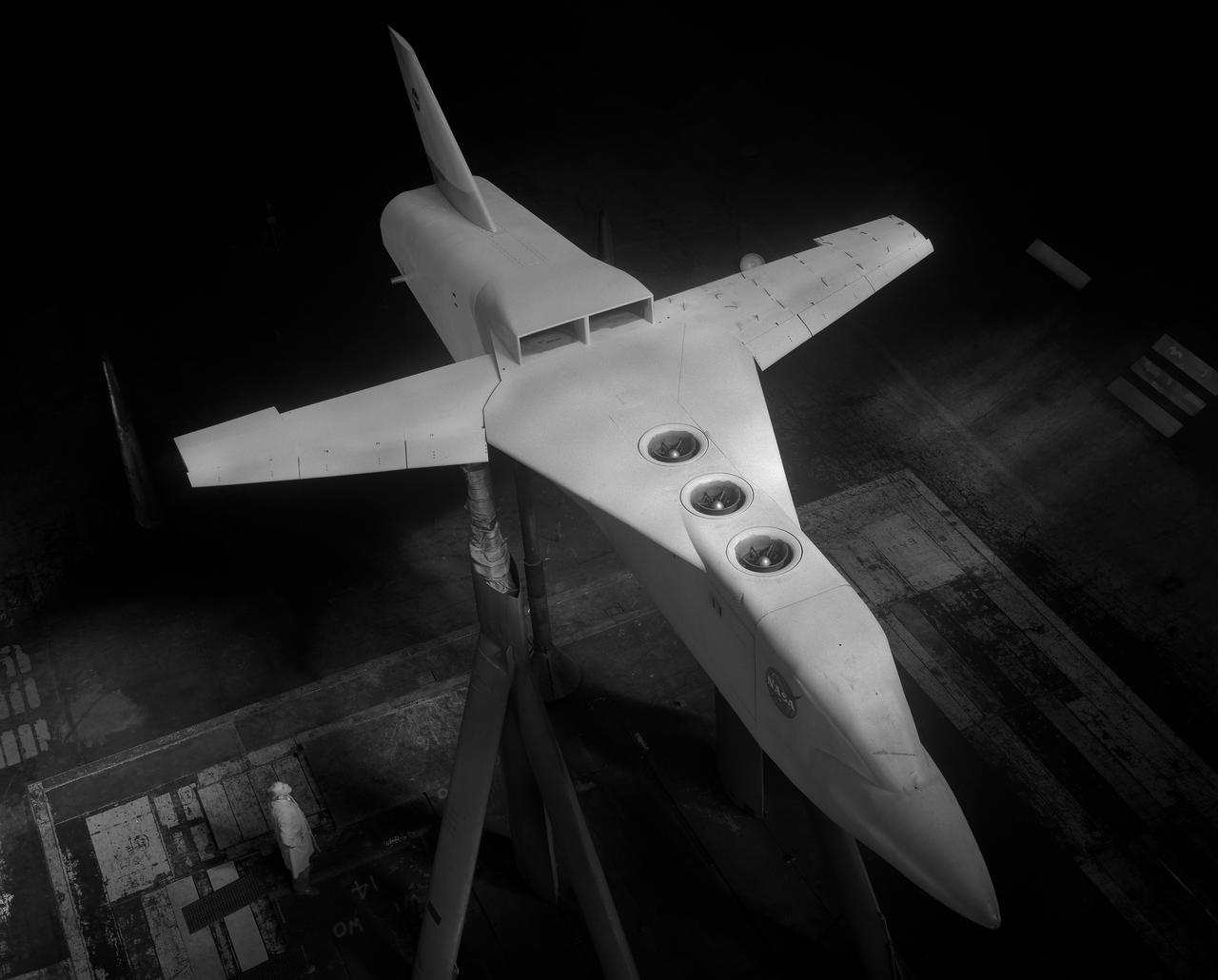

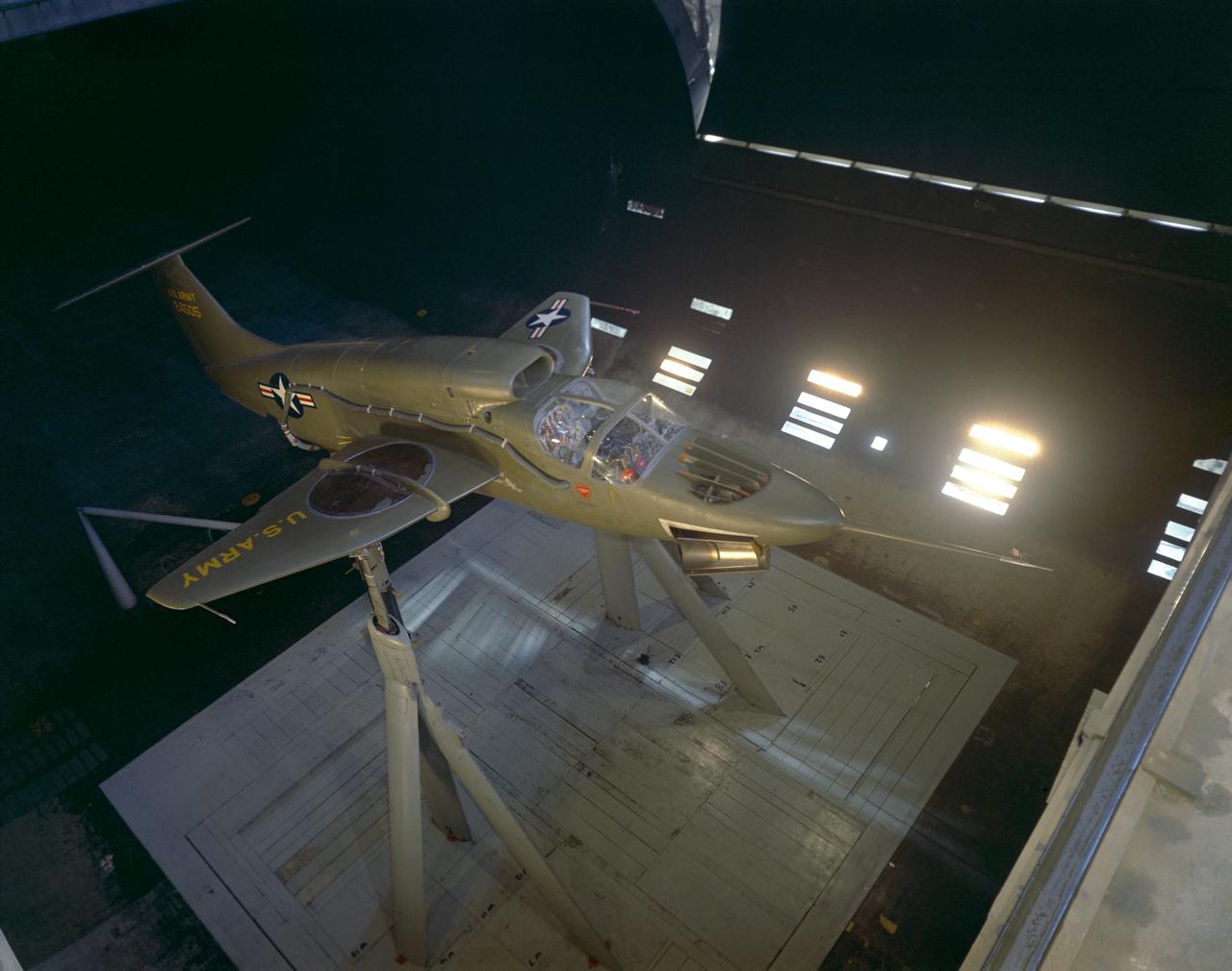
A-38524. Lift engine VSTOL fighter model, 3/4 top front view with jet engines. Edward Varerre, in picture.
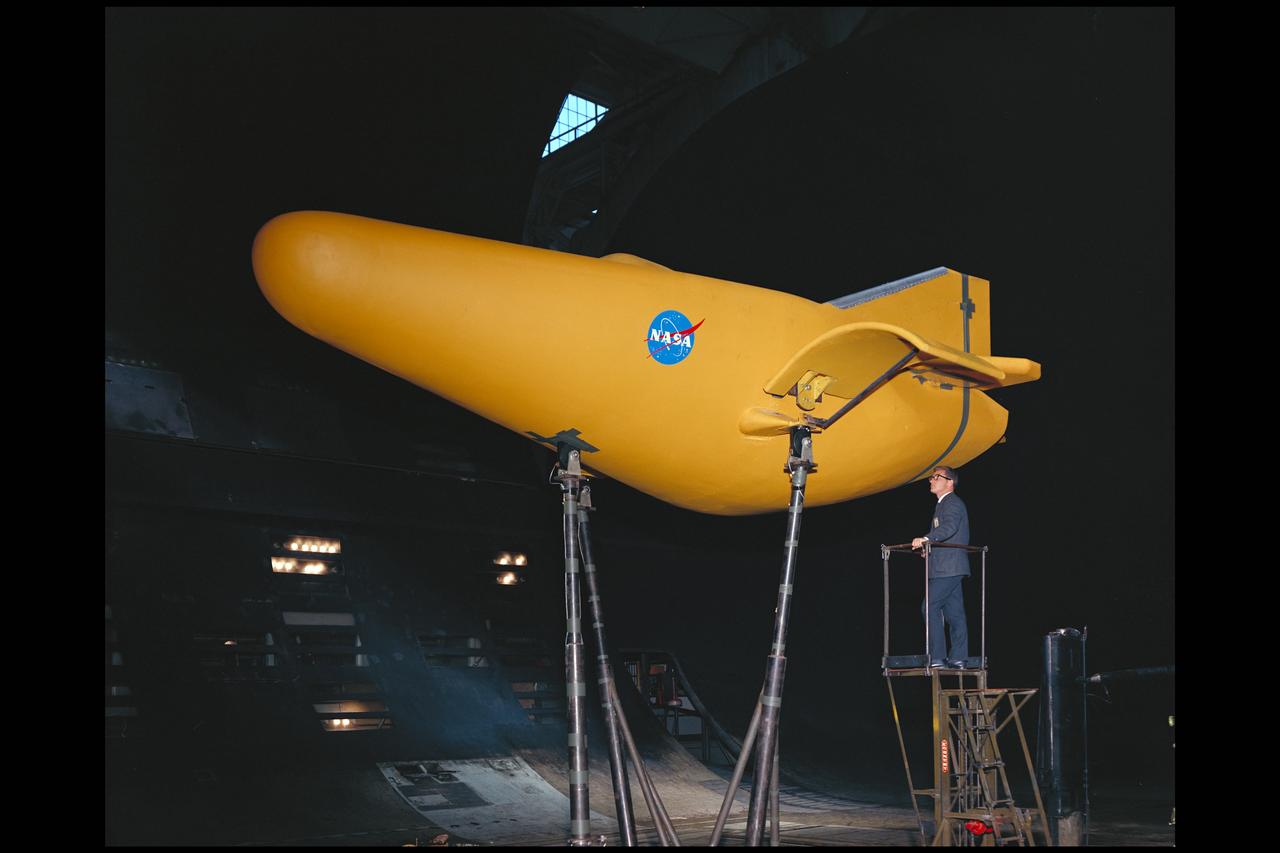

M-2 Lifting body 40x80ft Full Scale Wind Tunnel
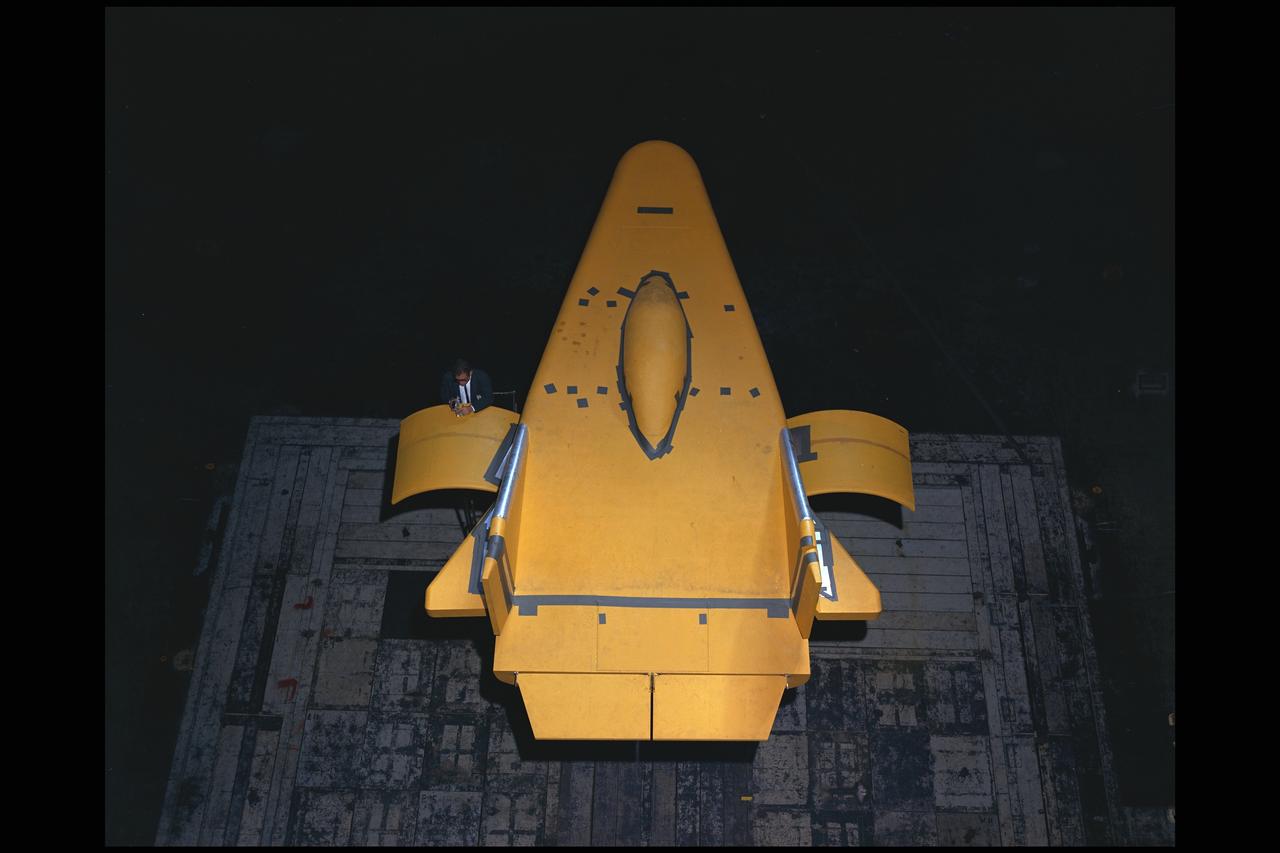

M-2 Lifting body 40x80ft Full Scale Wind Tunnle
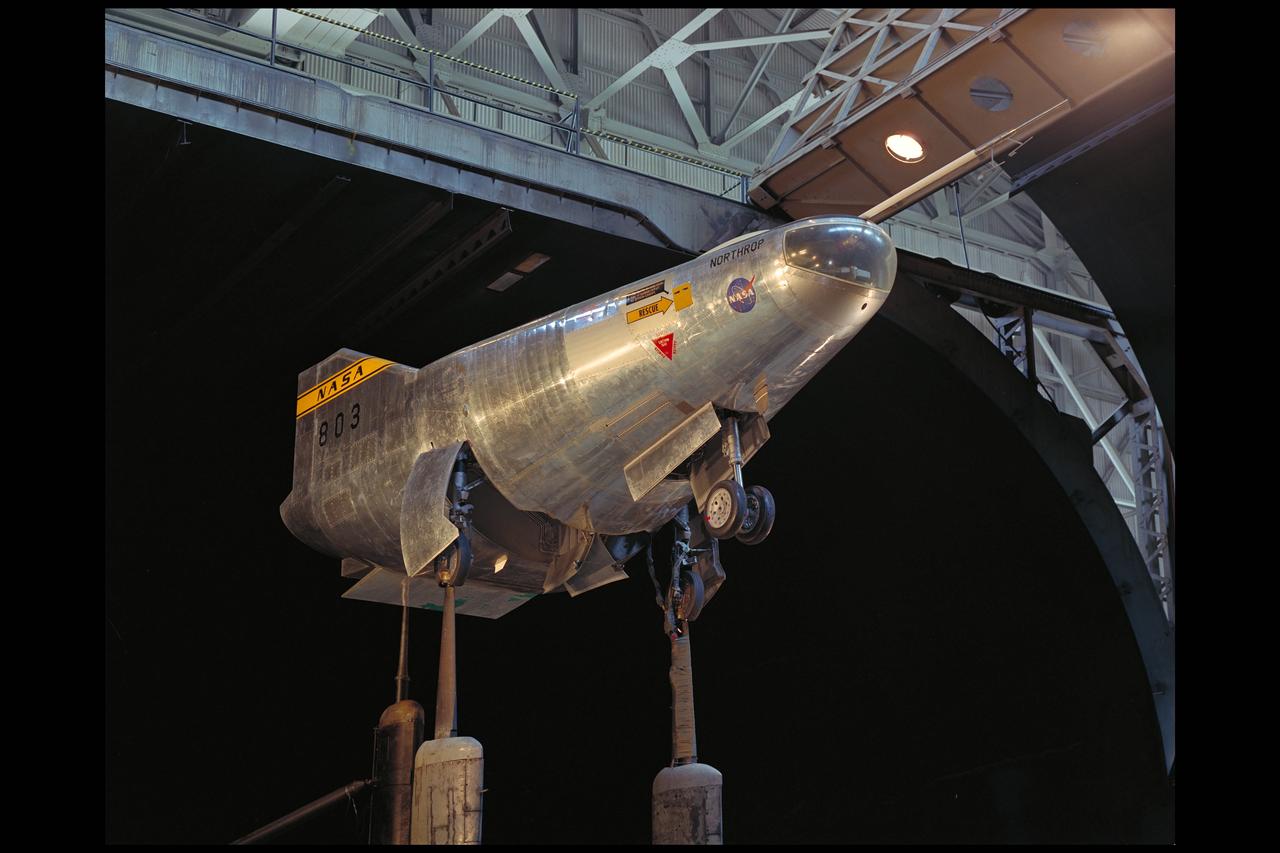

M2-F2 lifting body flight vehicle in 40x80ft w.t.
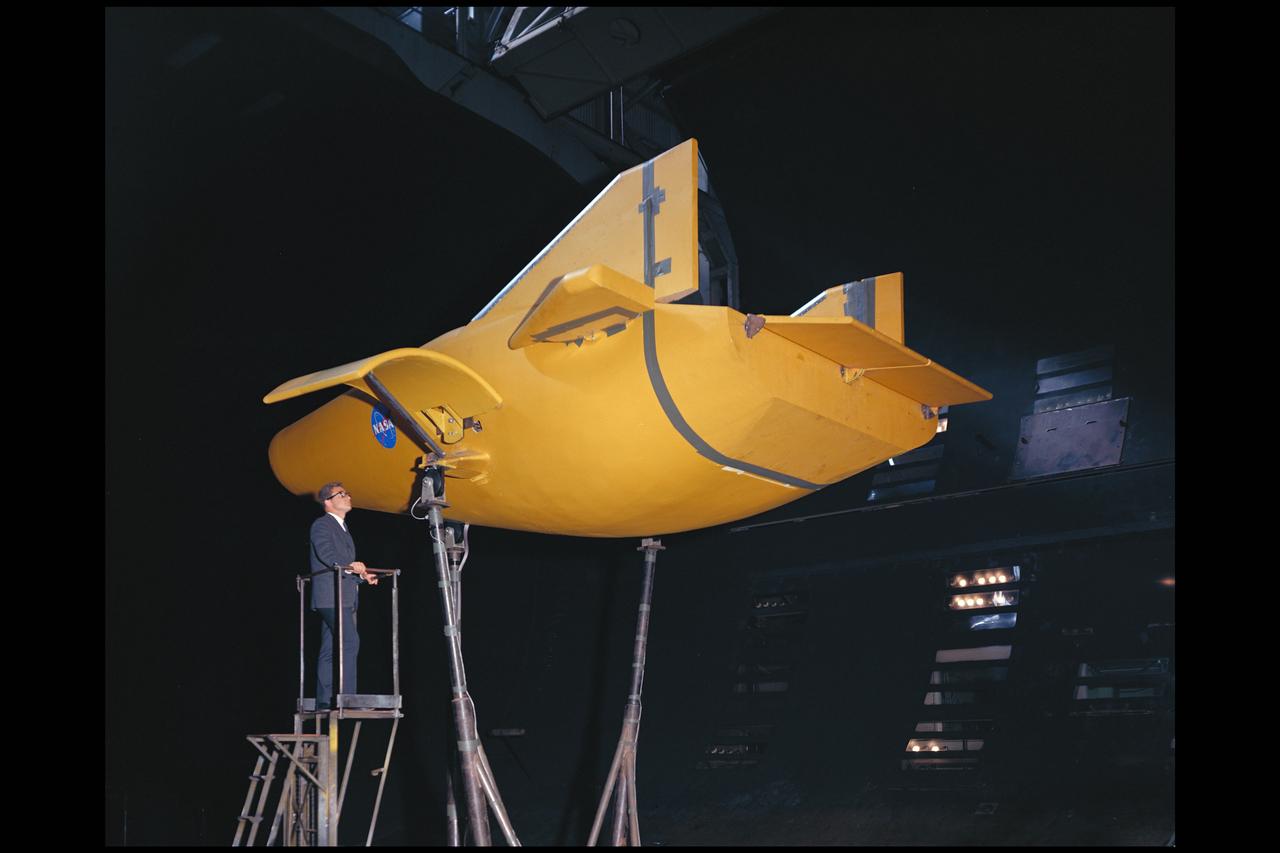

M-2 Lifting body 40x80ft Full Scale Wind Tunnle

M-2 Lifting body 40x80ft Full Scale Wind Tunnle
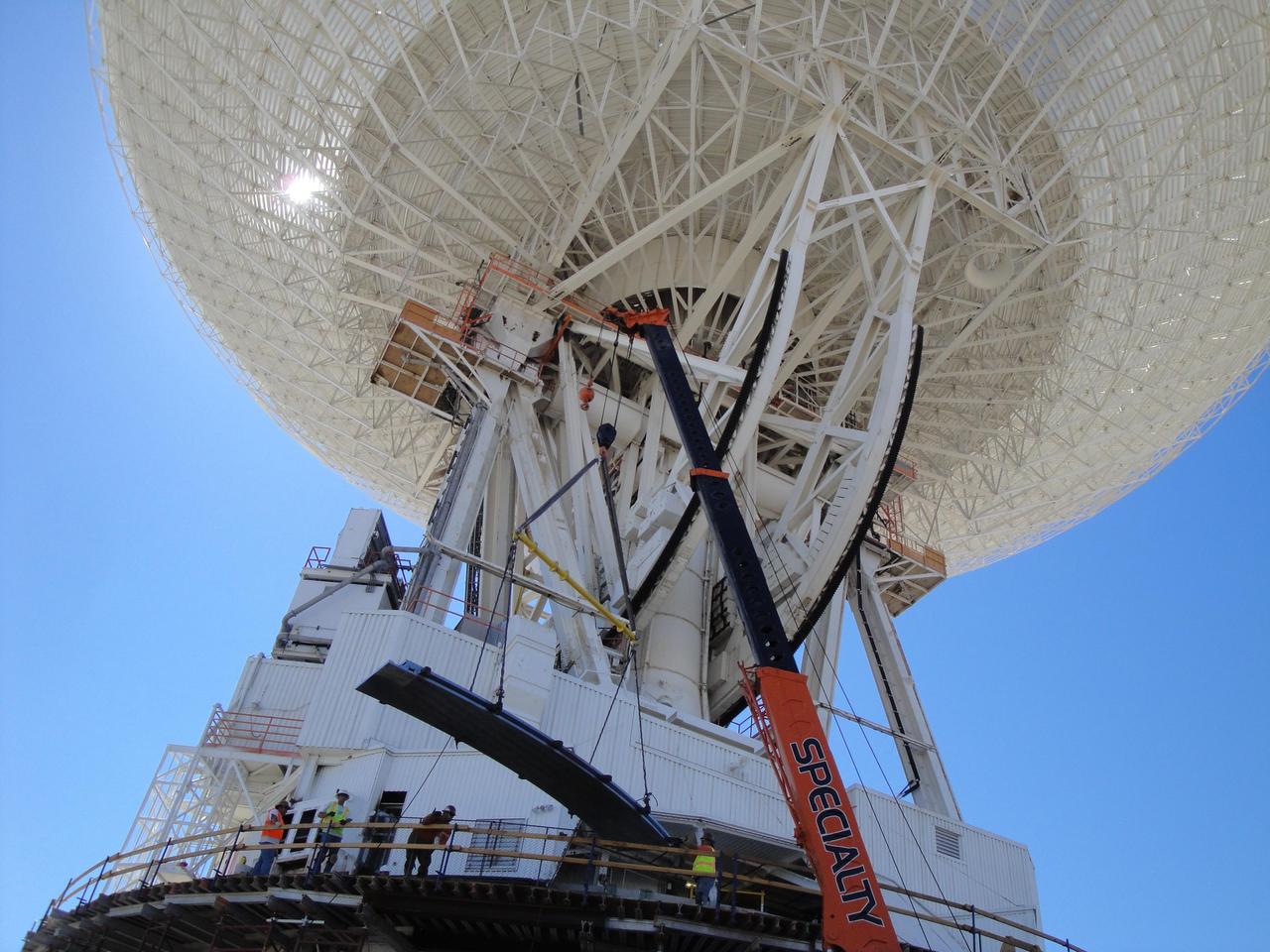

Under the unflinching summer sun, workers at NASA Deep Space Network complex in Goldstone, Calif., use a crane to lift a runner segment that is part of major surgery on a giant, 70-meter-wide antenna.
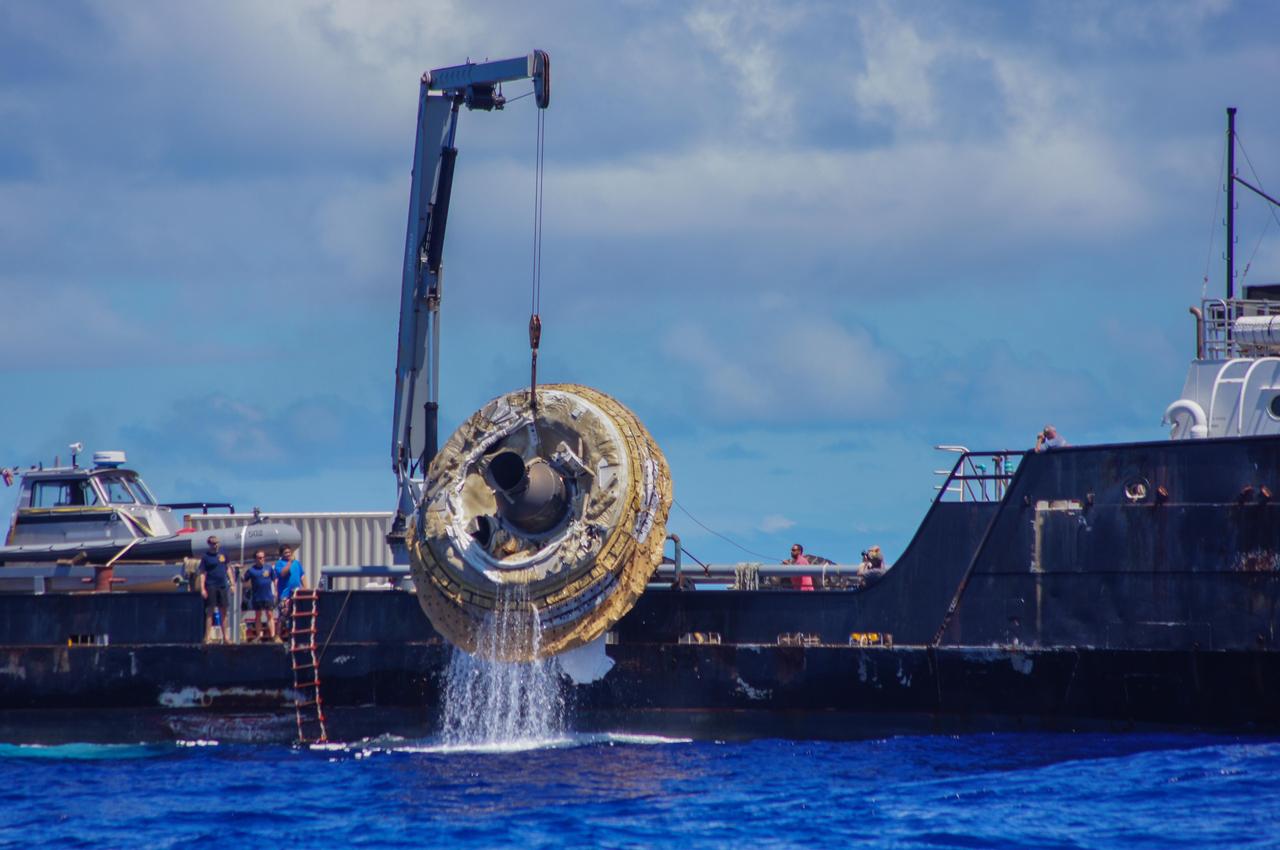

Hours after its successful engineering flight, the first test vehicle for NASA Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator project is lifted aboard the recovery vessel Kahana.

Overhead view of Ryan XV-5A lift-fan VSTOL airplane.
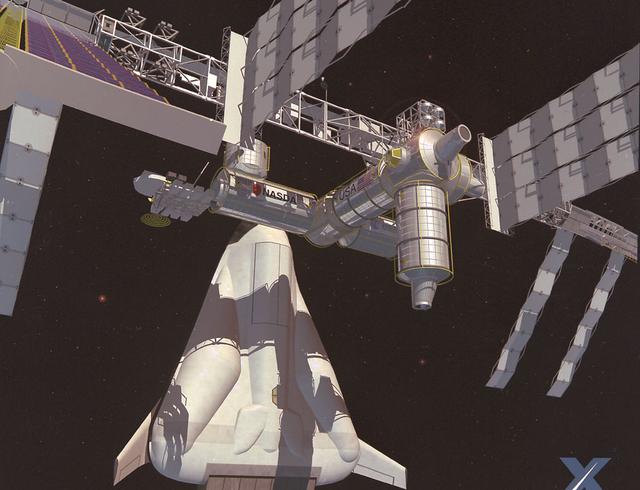

Pictured here is an artist's depiction of Lockheed Martin's Lifting Body Single-Stage-to-Orbit (SSTO) Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) concept servicing the International Space Station. The development of the RLV is essential in the cost reduction of future space travel.
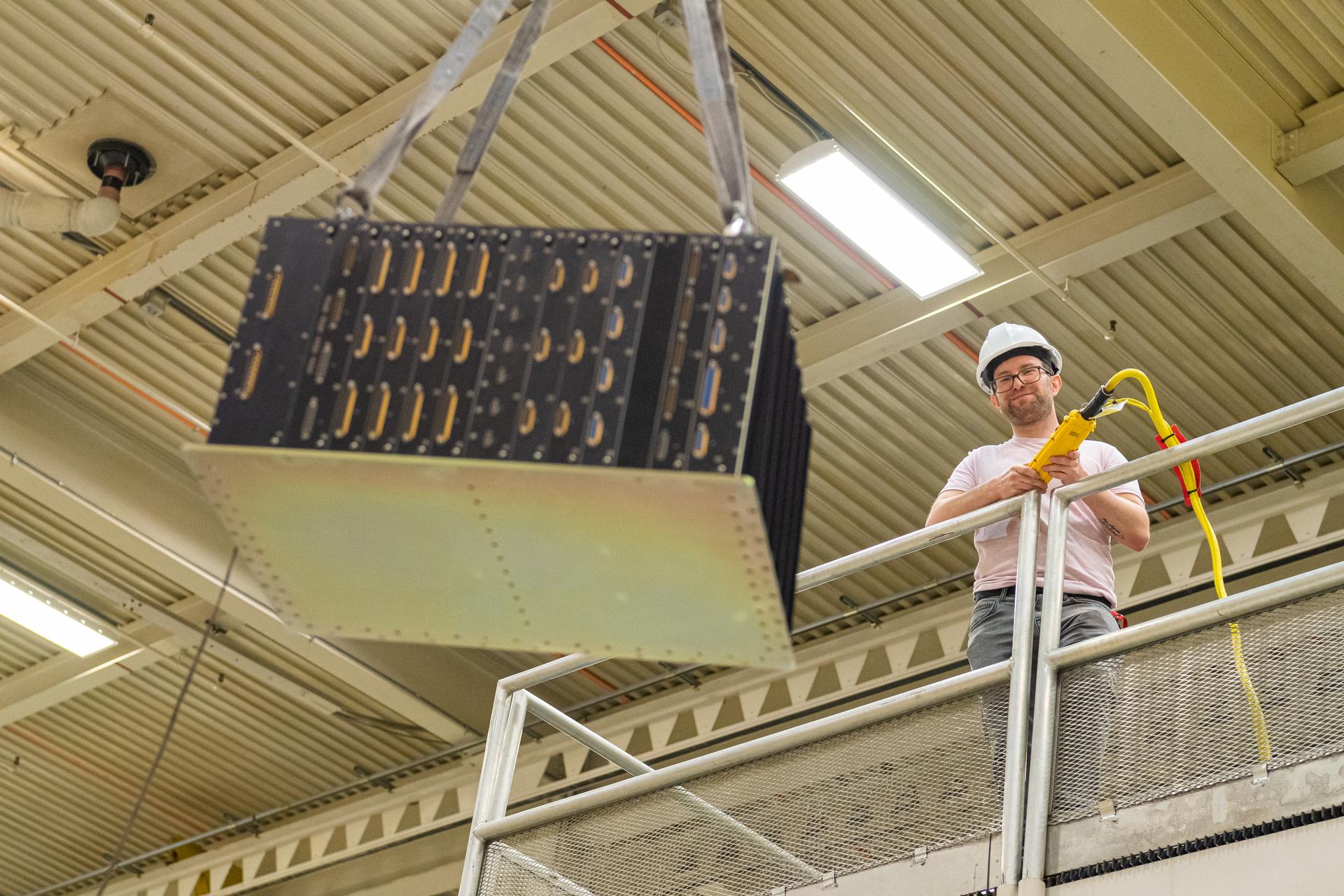

Mechanical engineering and integration technician Seth Alton crane lifts the OSAM-1 power supply unit into the thermal vacuum chamber at Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt Md., April 12, 2023. This photo has been reviewed by OSAM1 project management and the Export Control Office and is released for public view. NASA/Mike Guinto
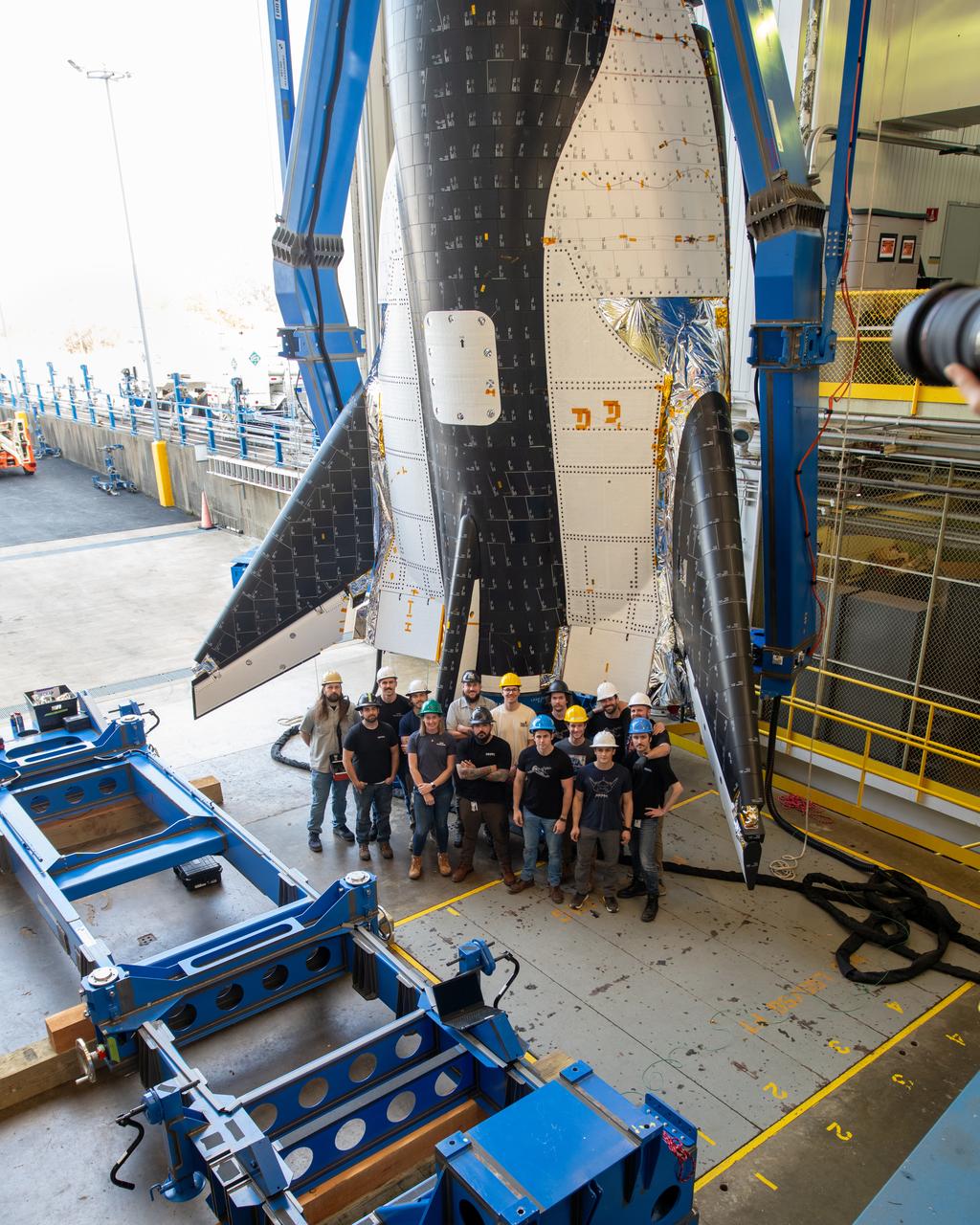

Group photo of the crew just before the critical lift of Dream Chaser into the chamber at ISP (In Space Propulsion) NASA GRC-ATF. Once lifted and lowered into the test chamber, it will be exposed to the harsh cold conditions of space for extended periods of time. Sierra Space Dream Chaser space plane will be lifted into the chamber at ISP (In Space Propulsion) facility, building 3211 at ATF (Armstrong Test Facility) for environmental testing
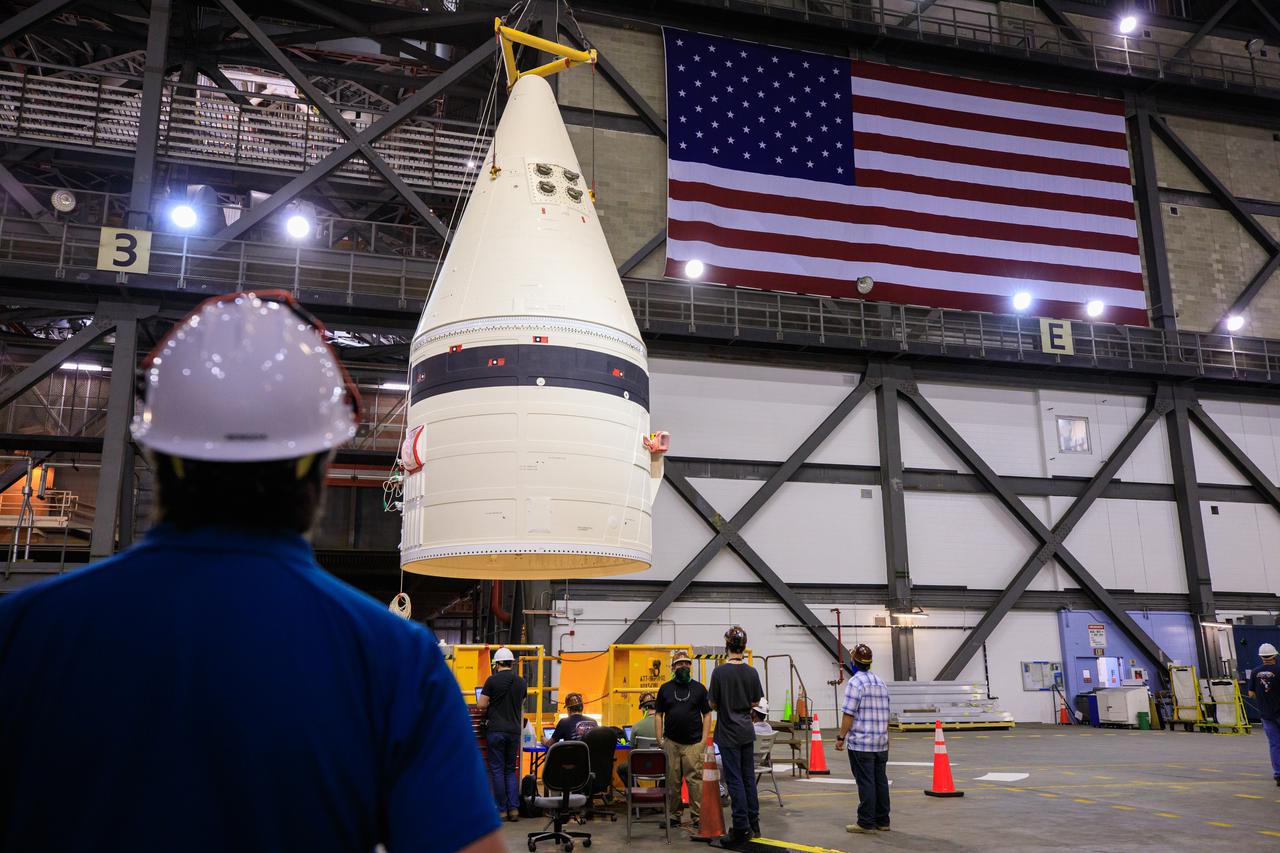

In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers use a crane to lift up the left-hand booster forward assembly for the agency’s Space Launch System for transfer into High Bay 3 on March 1, 2021. The forward assembly will be attached to the center forward segment on the mobile launcher (ML). Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs teams have been stacking the twin five-segment boosters on the ML over a number of weeks. When the core stage arrives, it will join the boosters on the mobile launcher, followed by the interim cryogenic propulsion stage and Orion spacecraft. Manufactured by Northrop Grumman in Utah, the twin boosters provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust at launch. Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the SLS. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
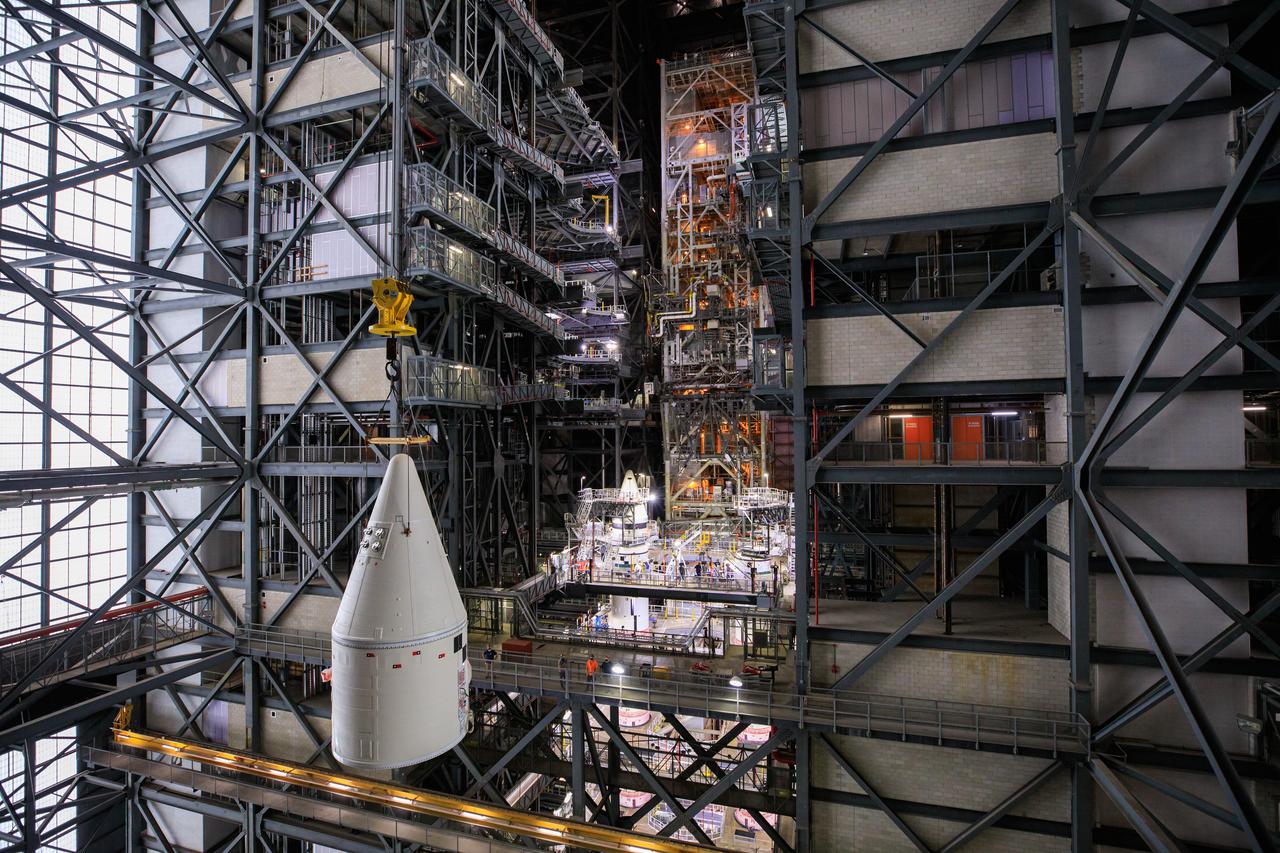

In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers use a crane to lift the right-hand forward assembly for the Space Launch System (SLS) high up for transfer into High Bay 3 on March 2, 2021. The forward assembly will be attached to the center forward segment on the mobile launcher (ML). Workers with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs teams are stacking the twin five-segment boosters on the ML over a number of weeks. When the core stage arrives, it will join the boosters on the mobile launcher, followed by the interim cryogenic propulsion stage and Orion spacecraft. Manufactured by Northrop Grumman in Utah, the twin boosters provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust at launch. Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the SLS. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
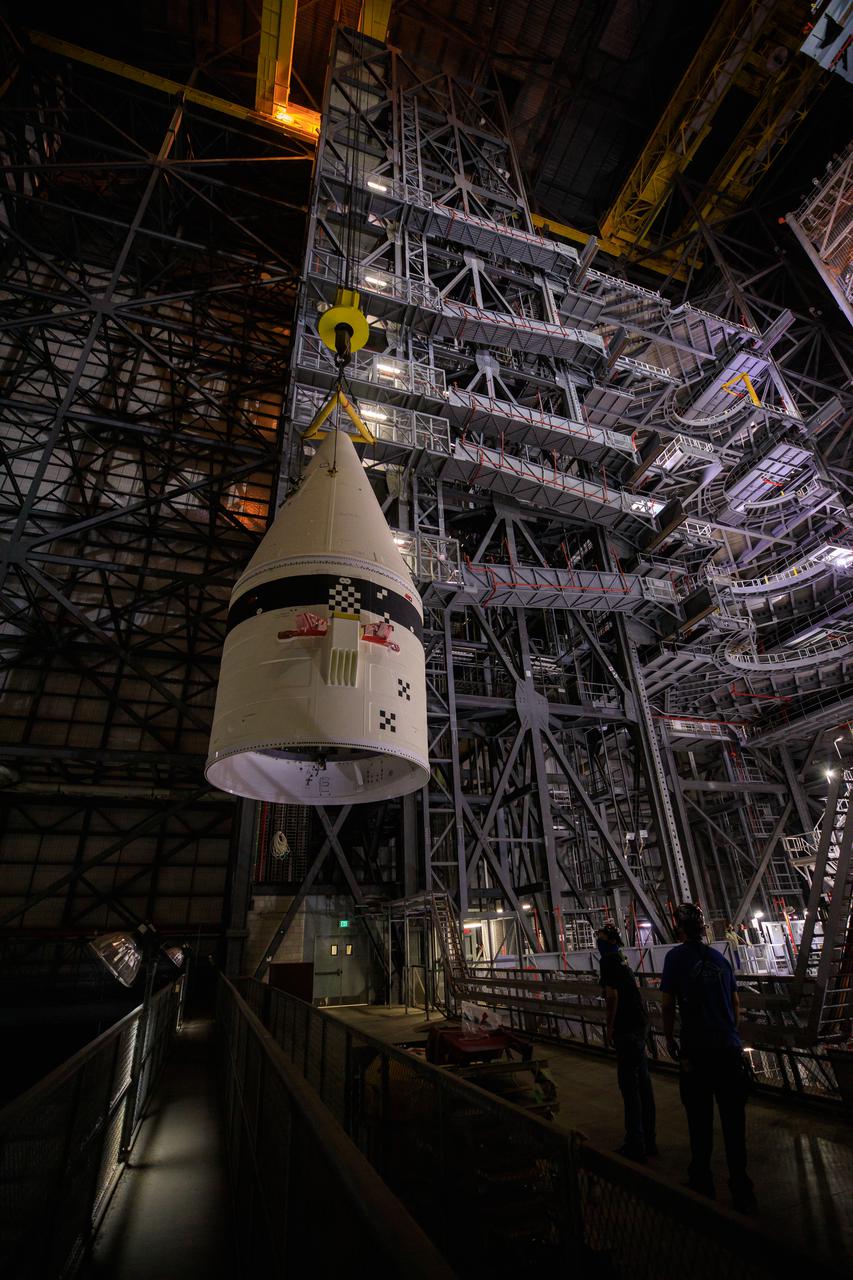

In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers use a crane to lift up the left-hand booster forward assembly for the agency’s Space Launch System for transfer into High Bay 3 on March 1, 2021. The forward assembly will be attached to the center forward segment on the mobile launcher (ML). Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs teams have been stacking the twin five-segment boosters on the ML over a number of weeks. When the core stage arrives, it will join the boosters on the mobile launcher, followed by the interim cryogenic propulsion stage and Orion spacecraft. Manufactured by Northrop Grumman in Utah, the twin boosters provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust at launch. Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the SLS. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
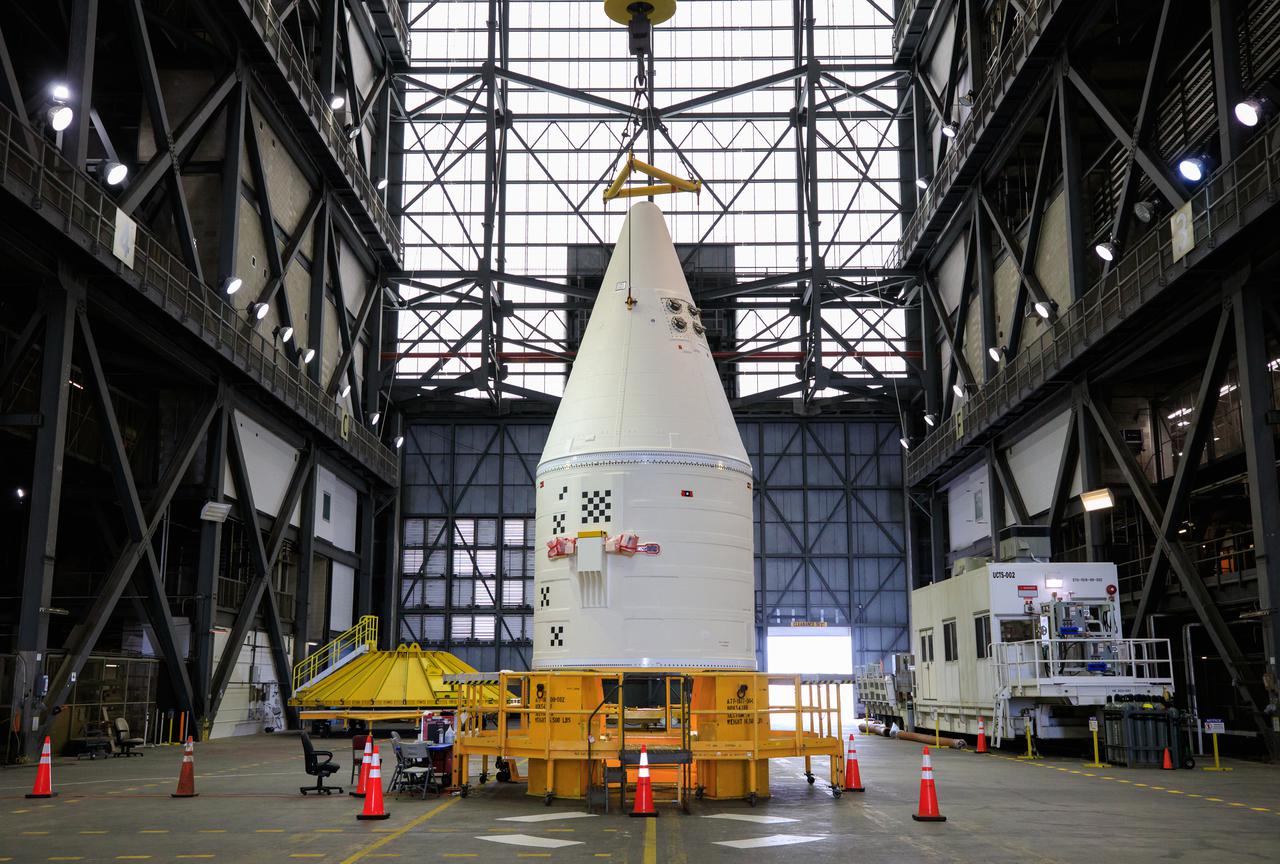

In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers use a crane to lift the right-hand forward assembly up for transfer into High Bay 3 for the Space Launch System (SLS) on March 2, 2021. The forward assembly will be attached to the center forward segment on the mobile launcher (ML). Workers with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs teams are stacking the twin five-segment boosters on the ML over a number of weeks. When the core stage arrives, it will join the boosters on the mobile launcher, followed by the interim cryogenic propulsion stage and Orion spacecraft. Manufactured by Northrop Grumman in Utah, the twin boosters provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust at launch. Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the SLS. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
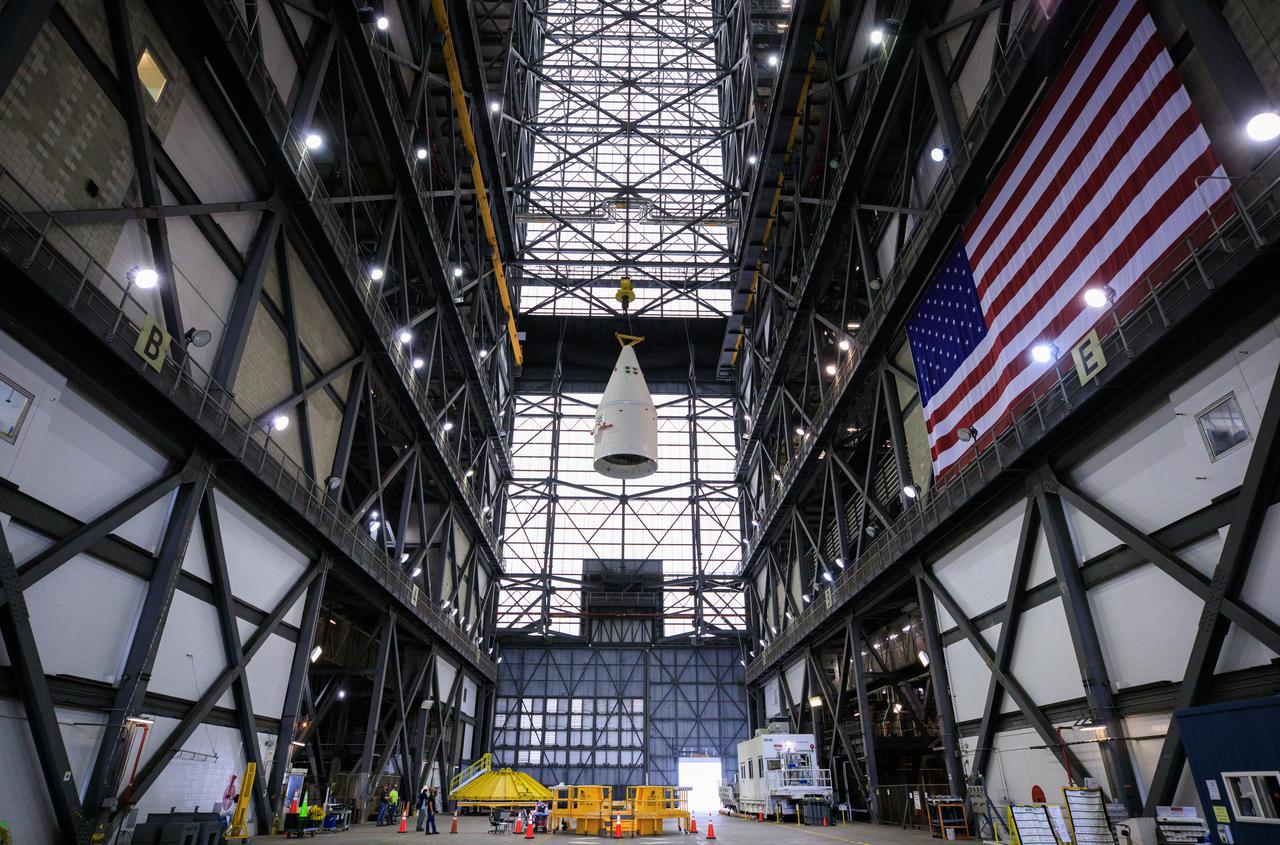

In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers use a crane to lift the right-hand forward assembly for the Space Launch System (SLS) high up for transfer into High Bay 3 on March 2, 2021. The forward assembly will be attached to the center forward segment on the mobile launcher (ML). Workers with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs teams are stacking the twin five-segment boosters on the ML over a number of weeks. When the core stage arrives, it will join the boosters on the mobile launcher, followed by the interim cryogenic propulsion stage and Orion spacecraft. Manufactured by Northrop Grumman in Utah, the twin boosters provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust at launch. Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the SLS. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
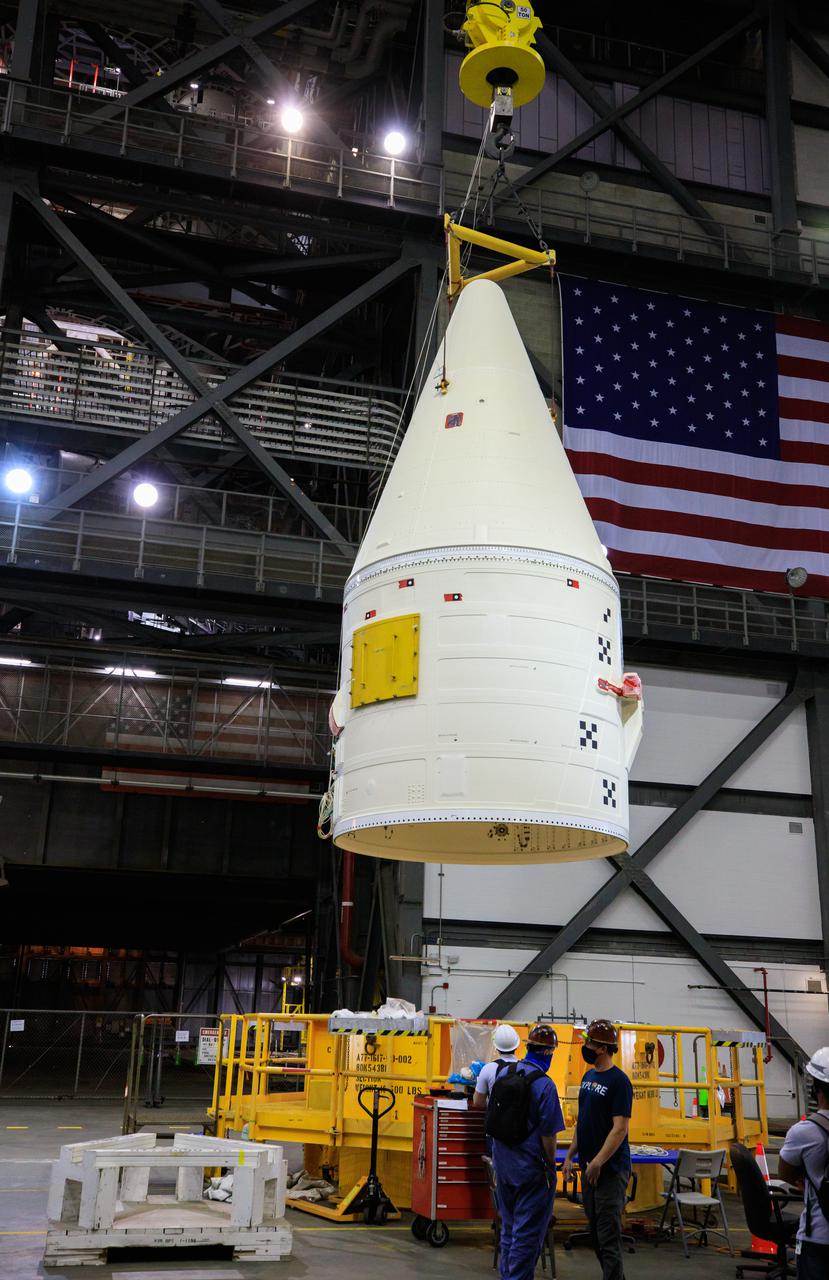

In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers use a crane to lift the right-hand forward assembly up for transfer into High Bay 3 for the Space Launch System (SLS) on March 2, 2021. The forward assembly will be attached to the center forward segment on the mobile launcher (ML). Workers with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs teams are stacking the twin five-segment boosters on the ML over a number of weeks. When the core stage arrives, it will join the boosters on the mobile launcher, followed by the interim cryogenic propulsion stage and Orion spacecraft. Manufactured by Northrop Grumman in Utah, the twin boosters provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust at launch. Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the SLS. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
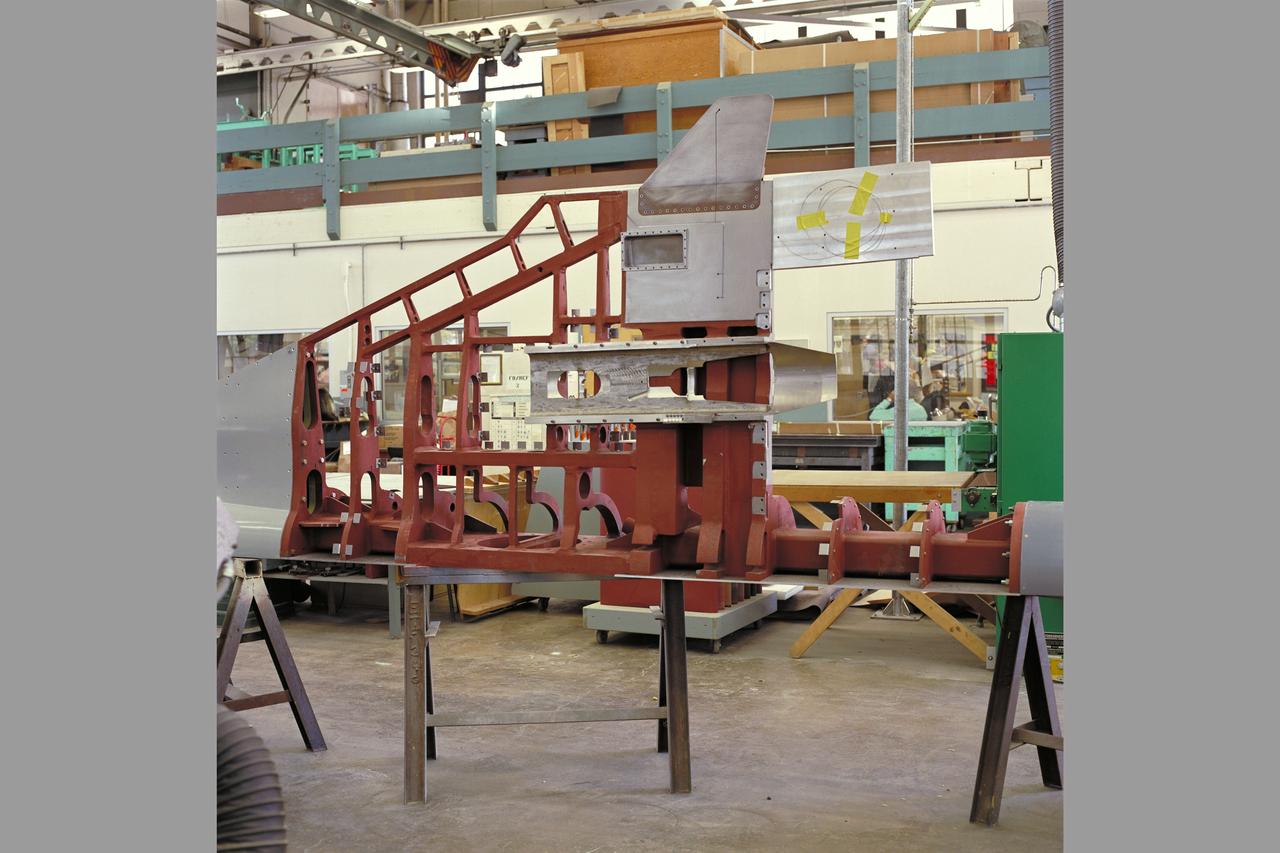

HEAT Project (High-Lift Engine Aeroacustics Technology) model assembly
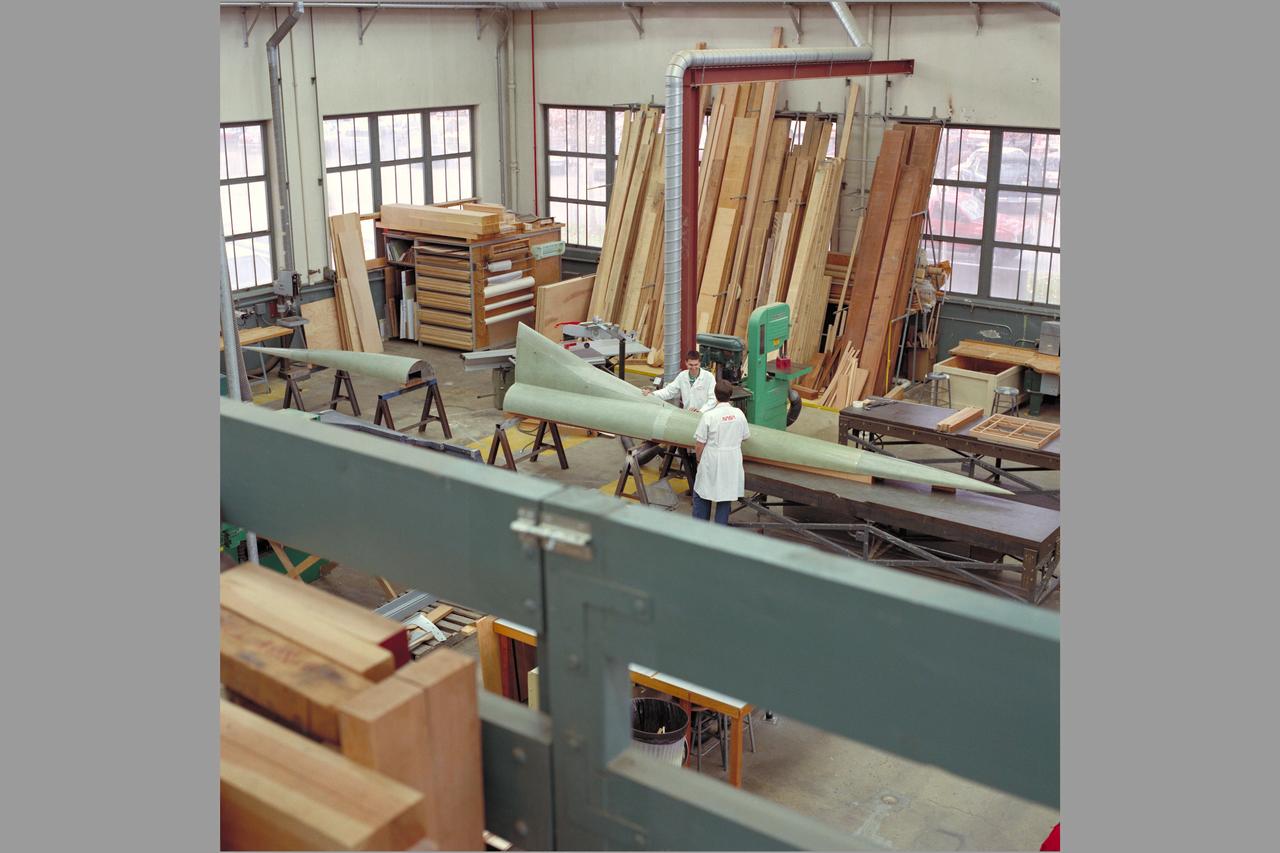

HEAT Project (High-Lift Engine Aeroacustics Technology) model assembly
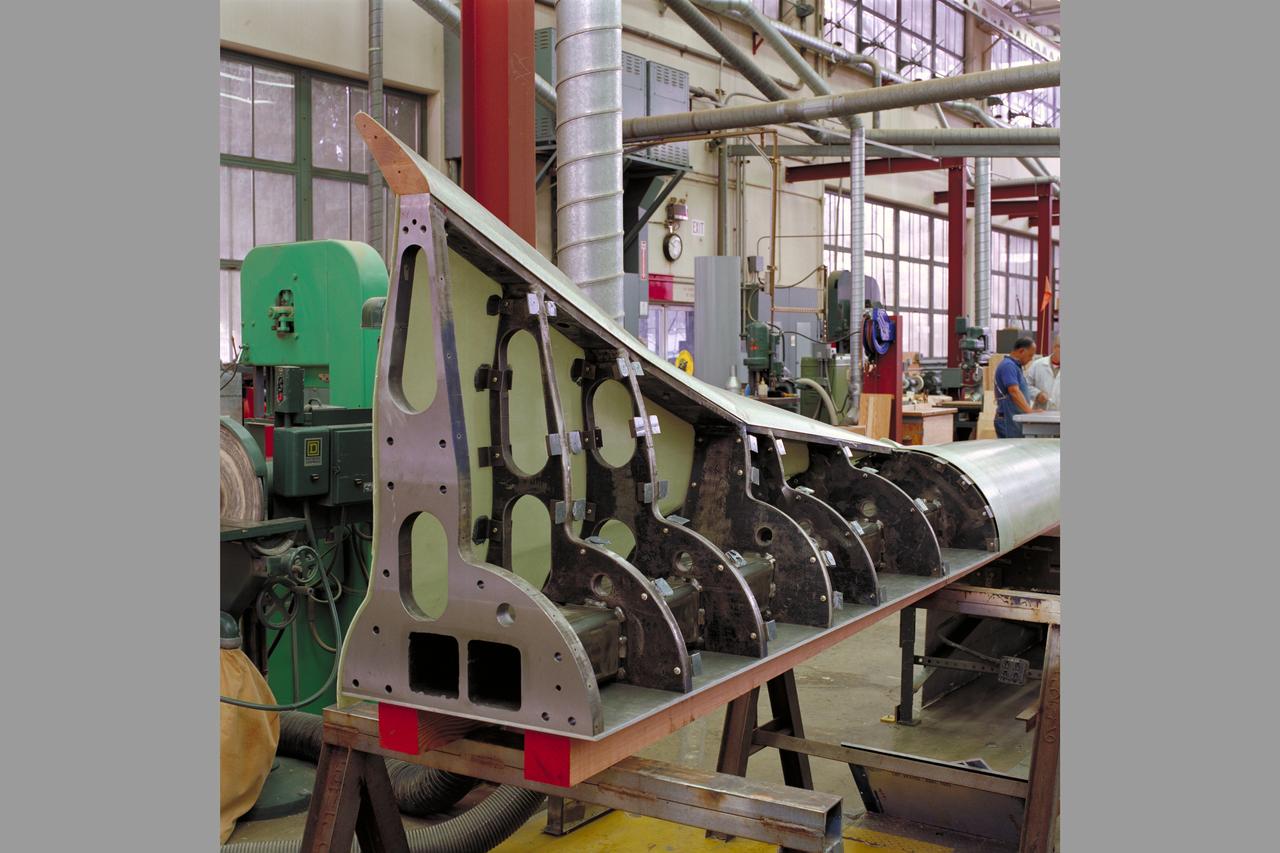

HEAT Project (High-Lift Engine Aeroacustics Technology) model assembly
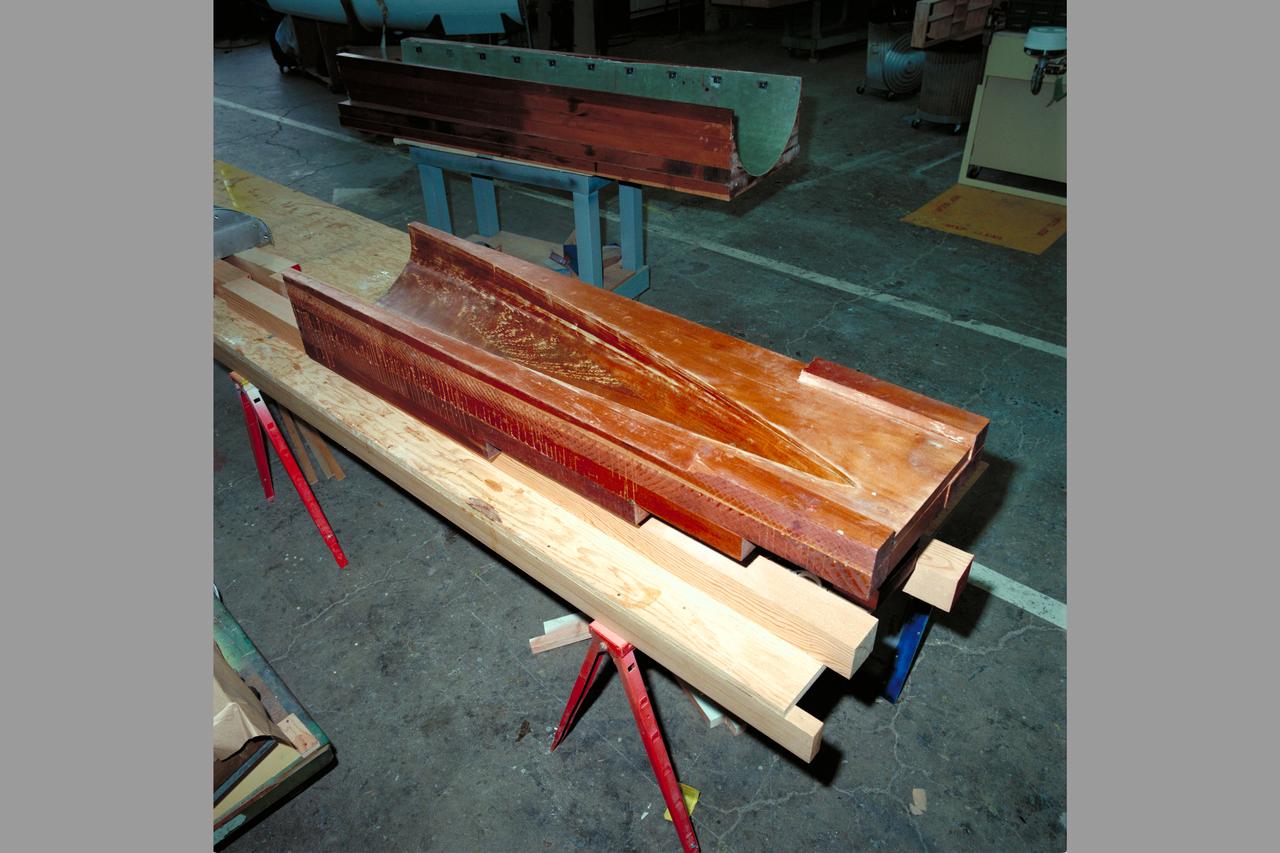

HEAT Project (High-Lift Engine Aeroacustics Technology) model assembly
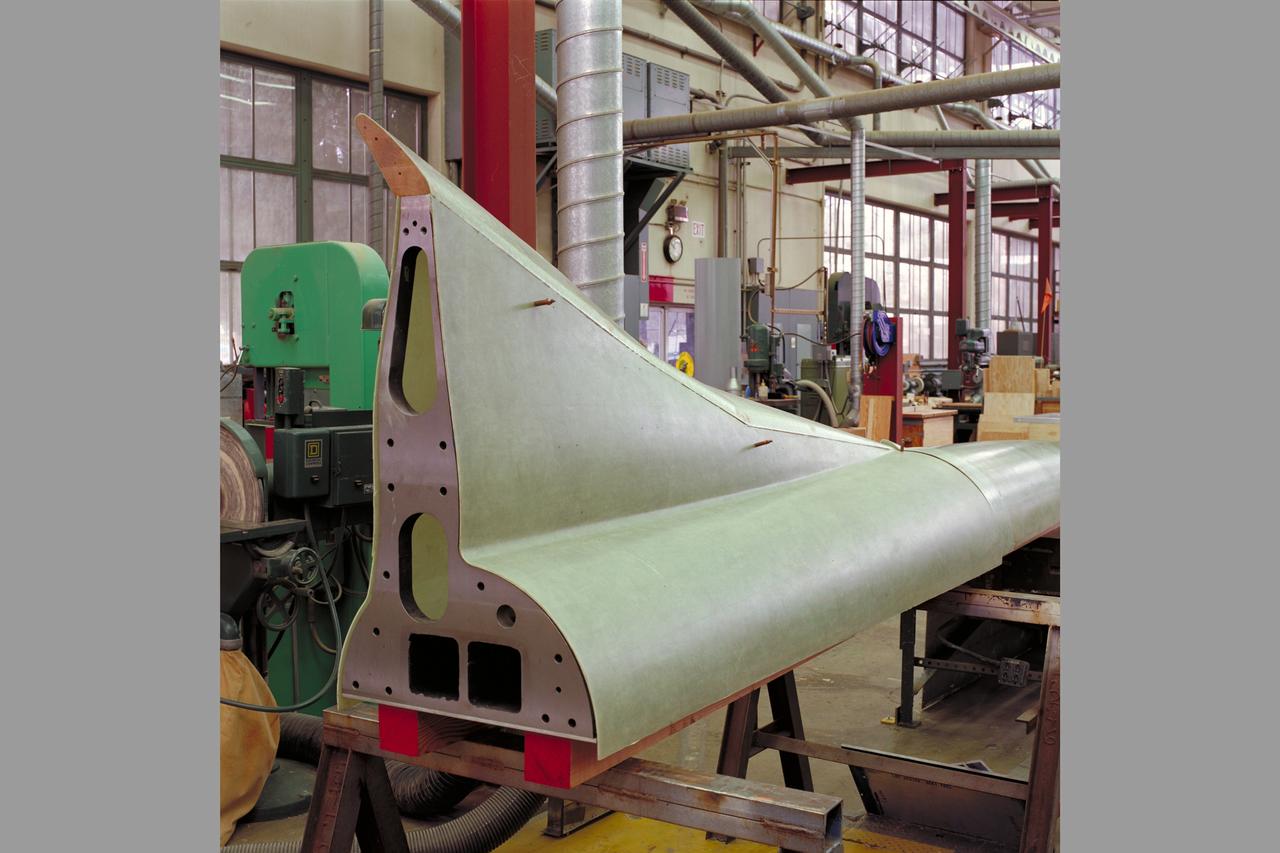

HEAT Project (High-Lift Engine Aeroacustics Technology) model assembly
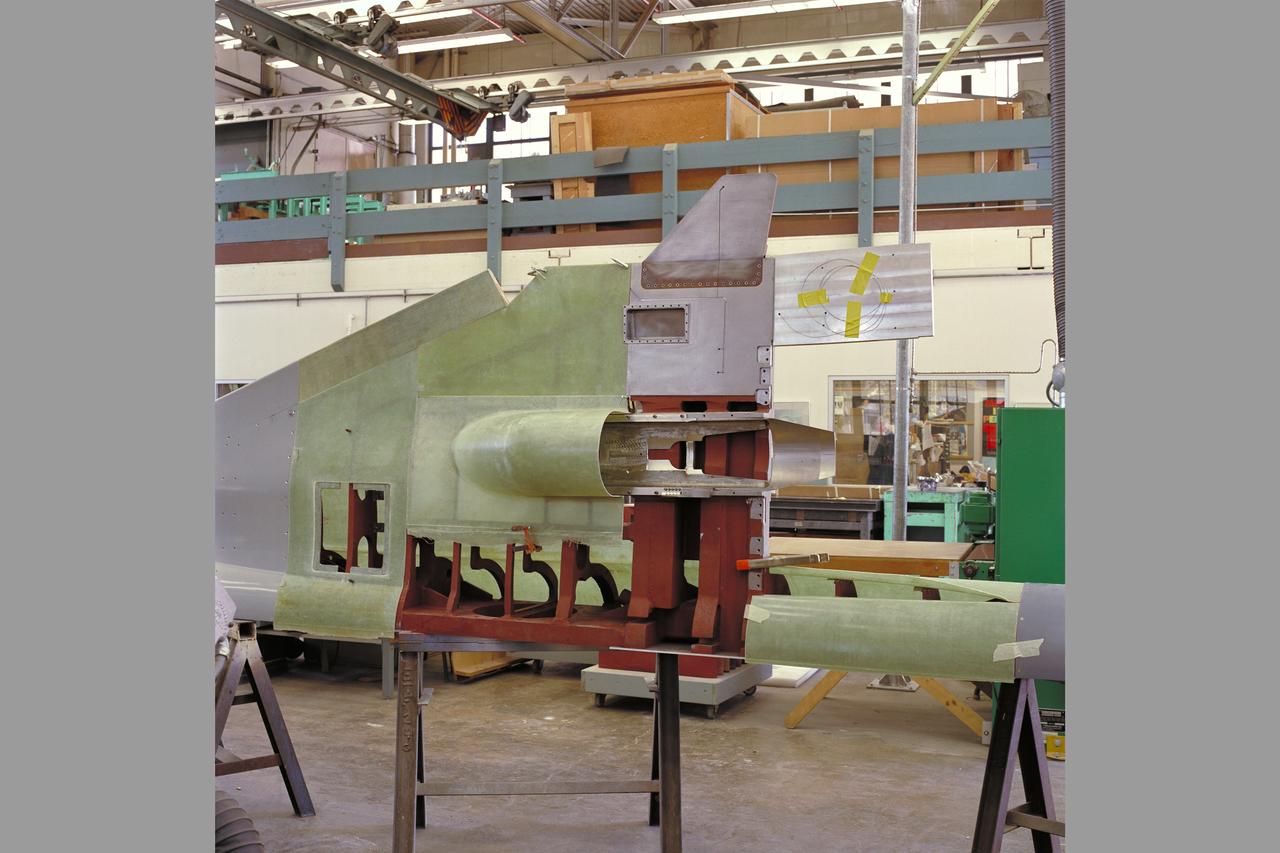

HEAT Project (High-Lift Engine Aeroacustics Technology) model assembly
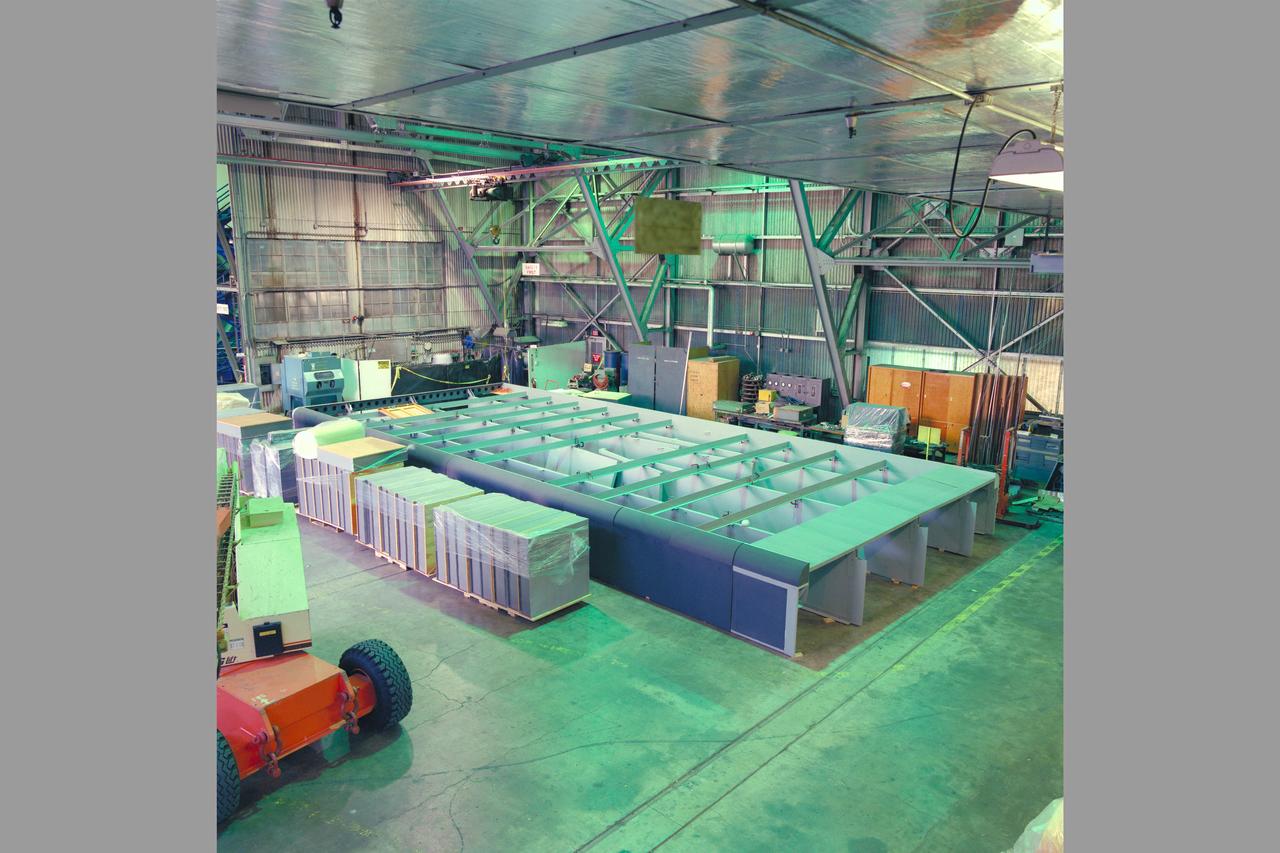

HEAT Project (High-Lift Engine Aeroacustics Technology) model assembly
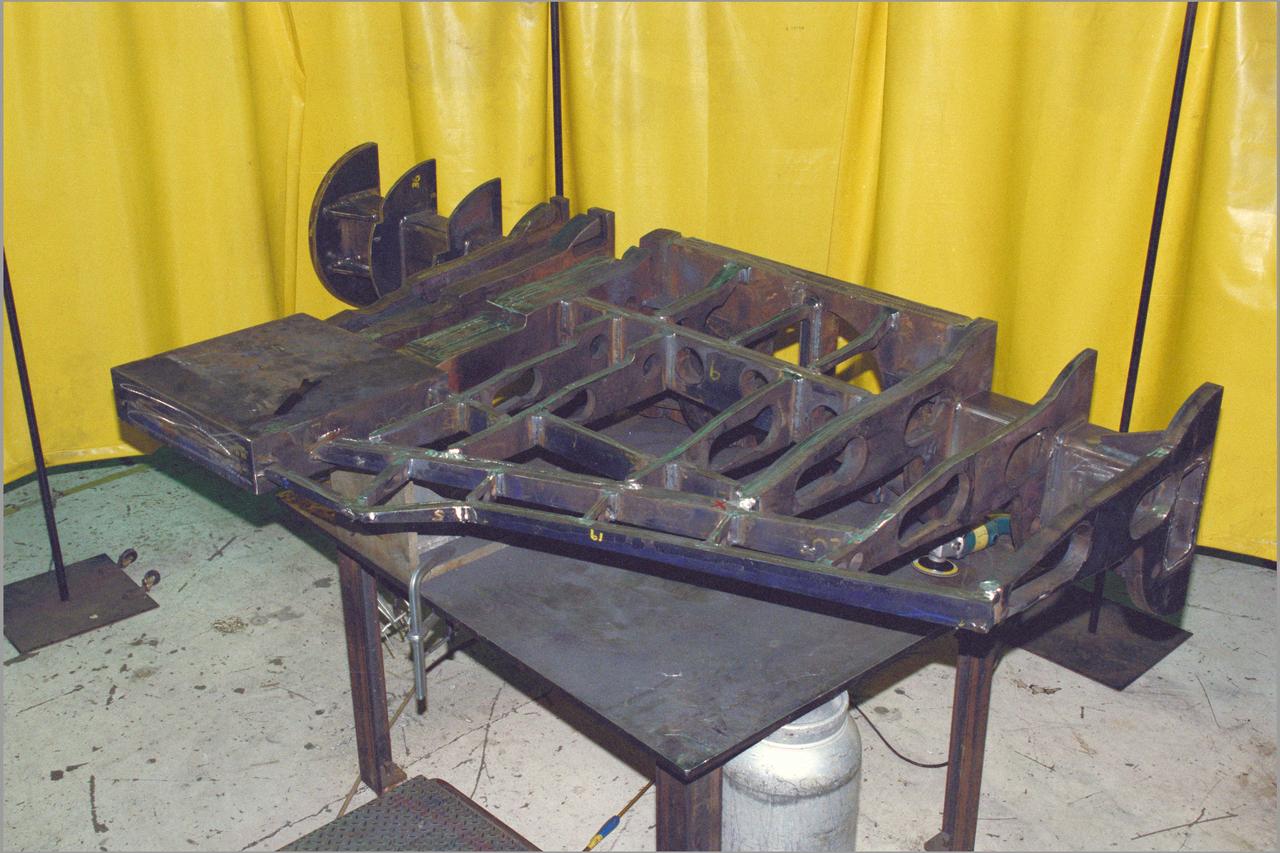

HEAT Project (High-Lift Engine Aeroacustics Technology) model assembly
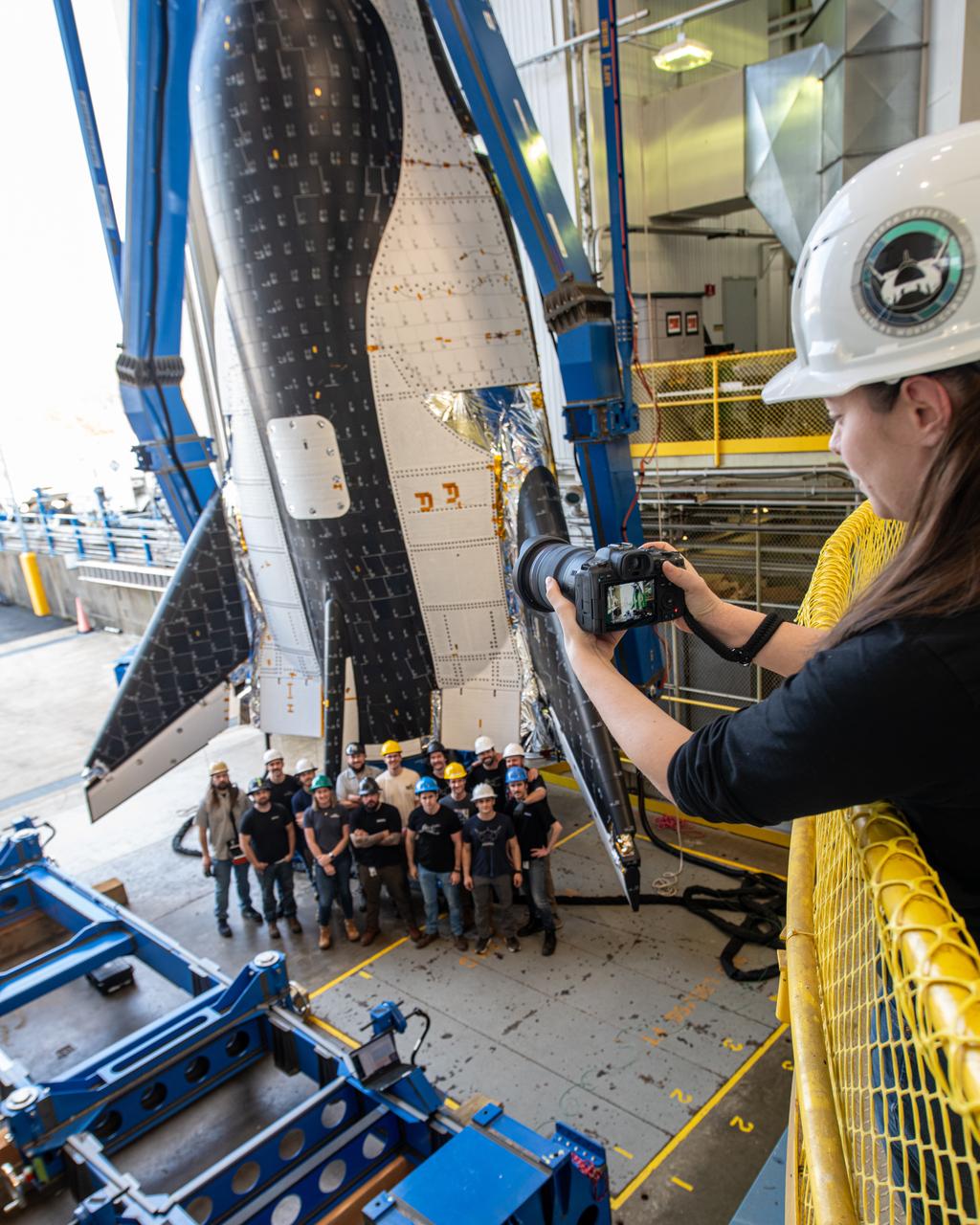

Sierra Space photographer, Shay Saldana is photographed taking a group photo of the crew just before the critical lift of Dream Chaser into the chamber at ISP (In Space Propulsion) NASA GRC-ATF. Once lifted and lowered into the test chamber, it will be exposed to the harsh cold conditions of space for extended periods of time
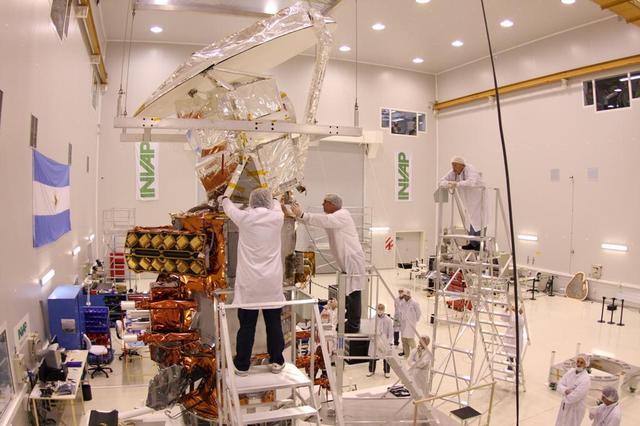

NASA Aquarius instrument is lifted upright onto the SAC-D service platform at the INVAP high bay facility in Bariloche, Argentina.
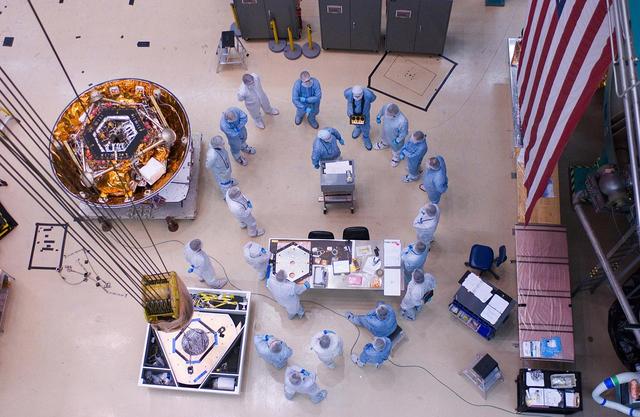

Spacecraft specialists huddle to discuss the critical lift of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander into a thermal vacuum chamber
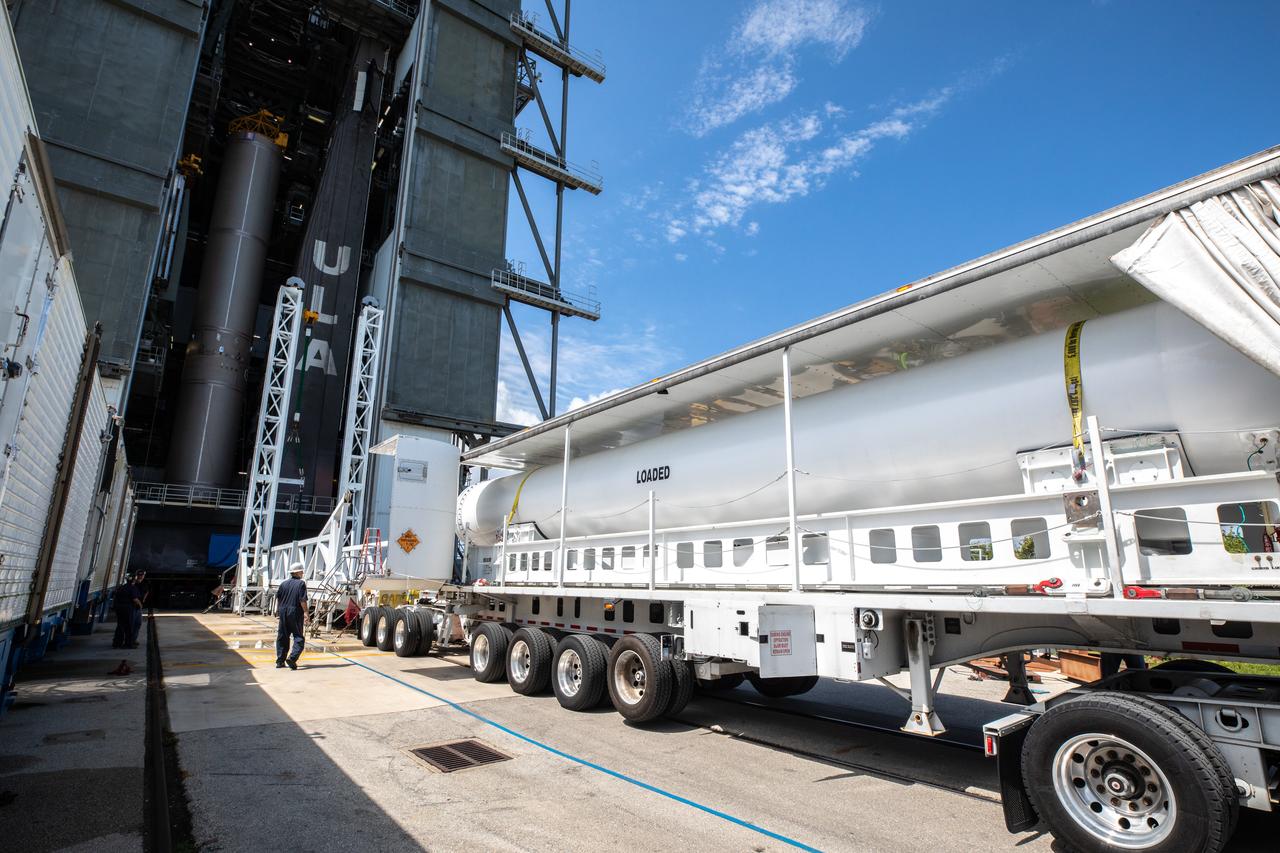

The first solid rocket booster (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket for NASA’s Mars 2020 mission with the Perseverance rover arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on May 29, 2020. The SRB will be prepared for lift and mating to the Atlas V booster in the VIF. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch in mid-July atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
The first solid rocket booster (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket for NASA’s Mars 2020 mission with the Perseverance rover departs for the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on May 29, 2020. The SRB will be prepared for lift and mating to the Atlas V booster in the VIF. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch in mid-July atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
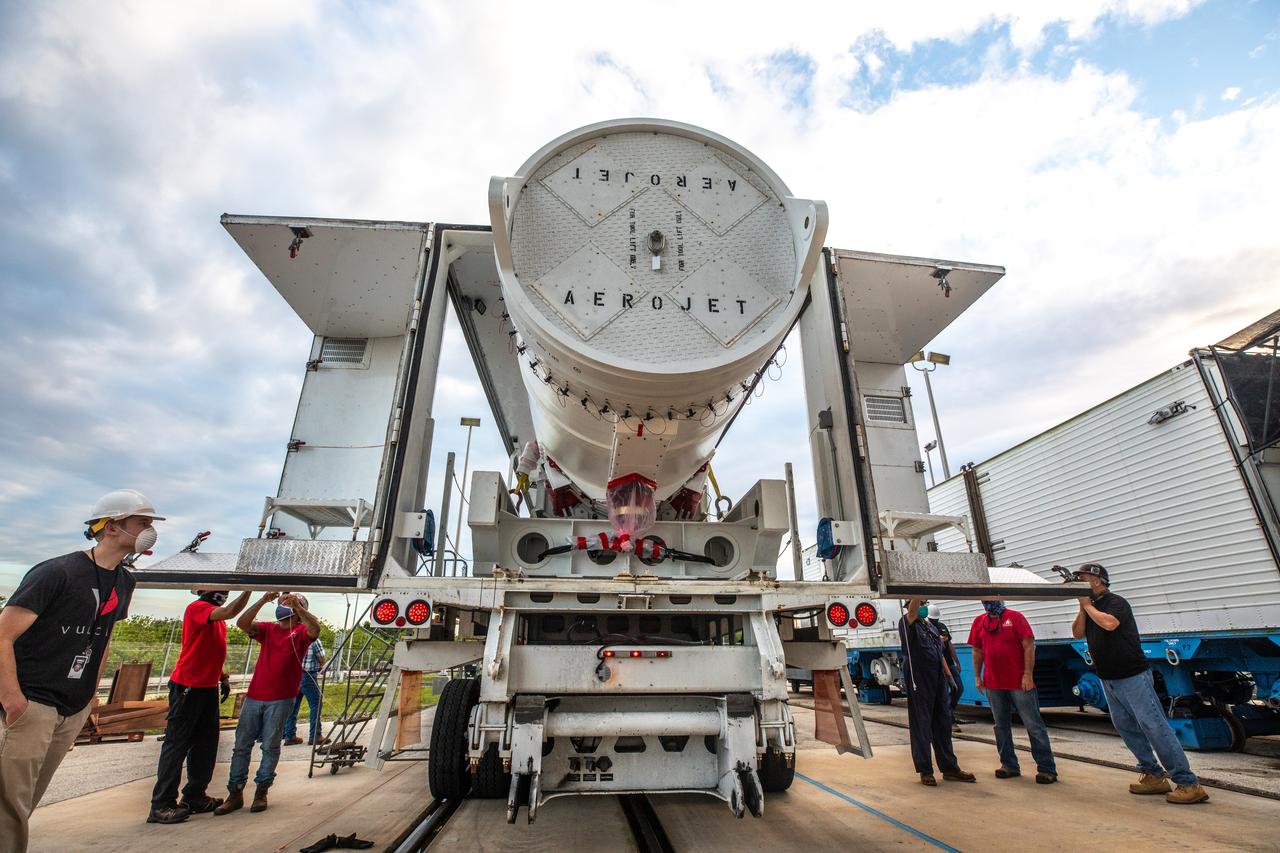

The first solid rocket booster (SRB) for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket for NASA’s Mars 2020 mission with the Perseverance rover arrives near the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on May 29, 2020. The SRB will be prepared for lift and mating to the Atlas V booster in the VIF. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch in mid-July atop the Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
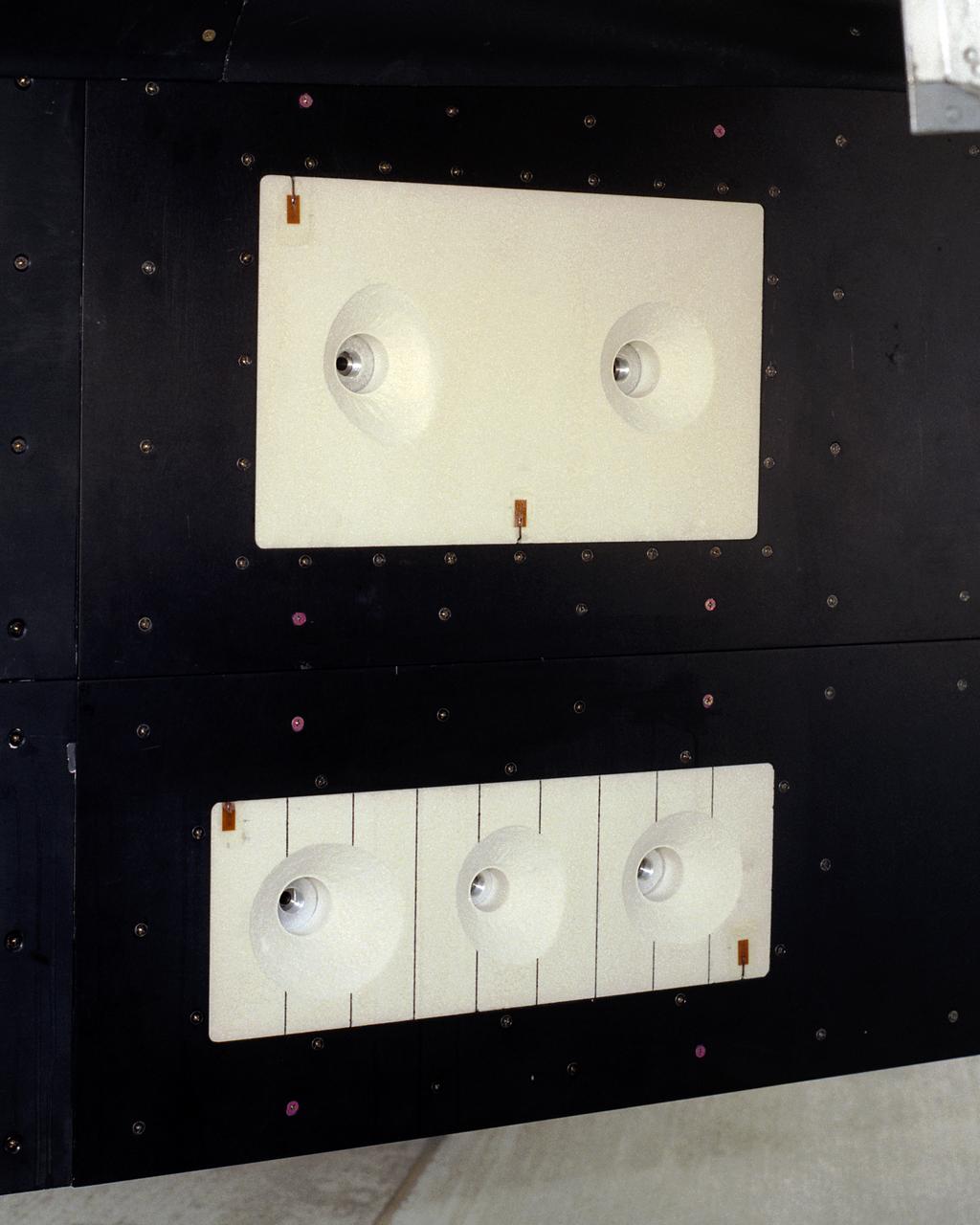

A close-up of the panels on the F-15B's flight test fixture shows five divots of TPS foam were successfully ejected during the LIFT experiment flight #2, the first flight with TPS foam.
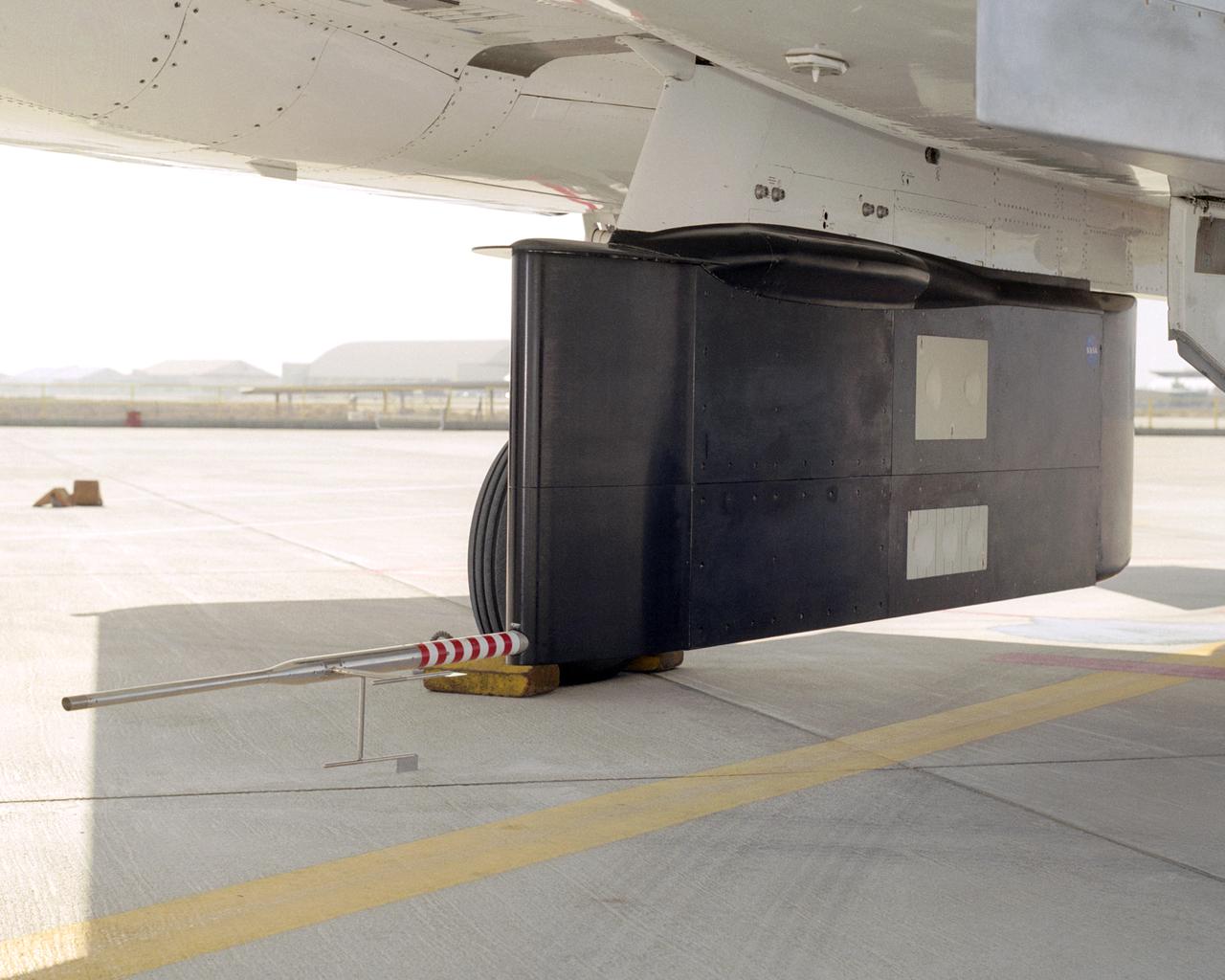

A post-flight inspection of the panels on the F-15B's flight test fixture shows five divots of TPS foam were successfully ejected during the LIFT experiment flight #2, the first flight with TPS foam.
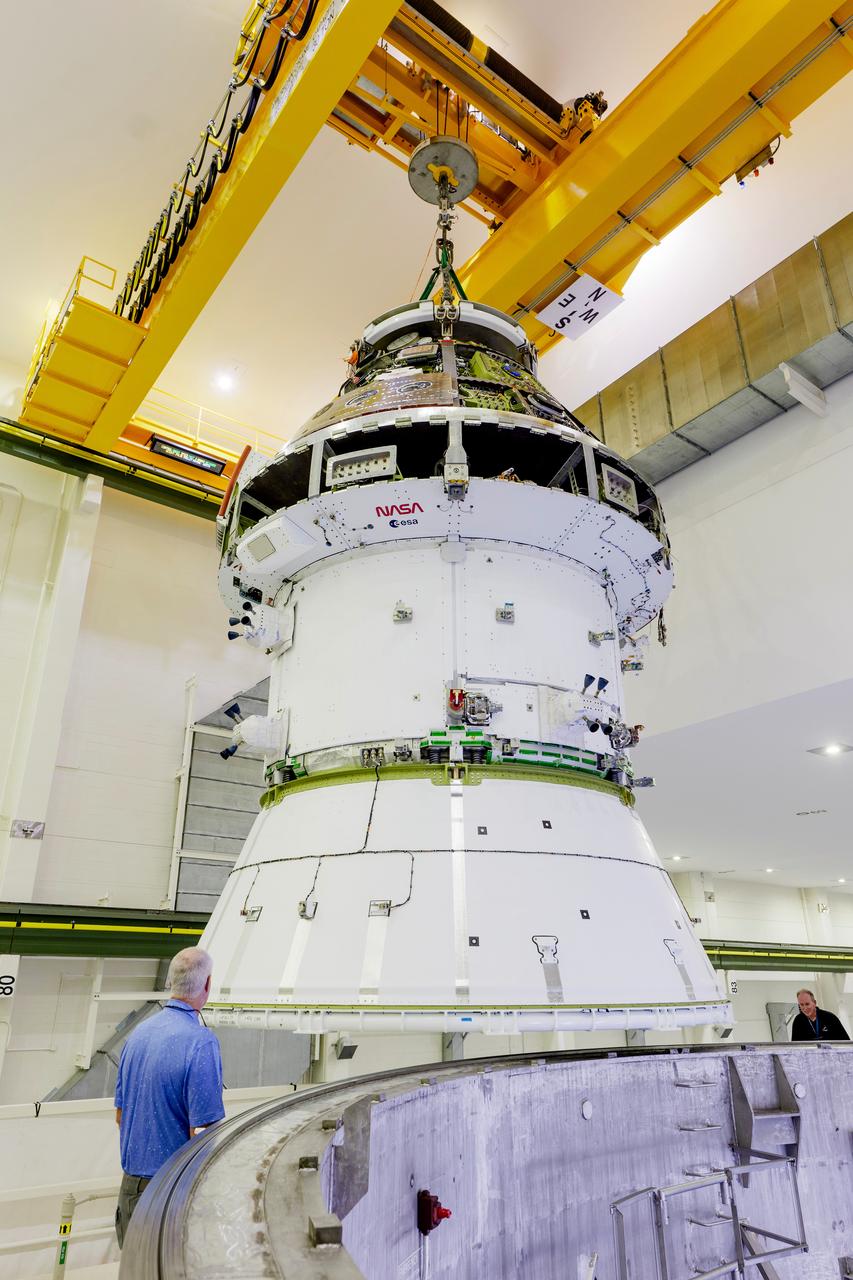

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
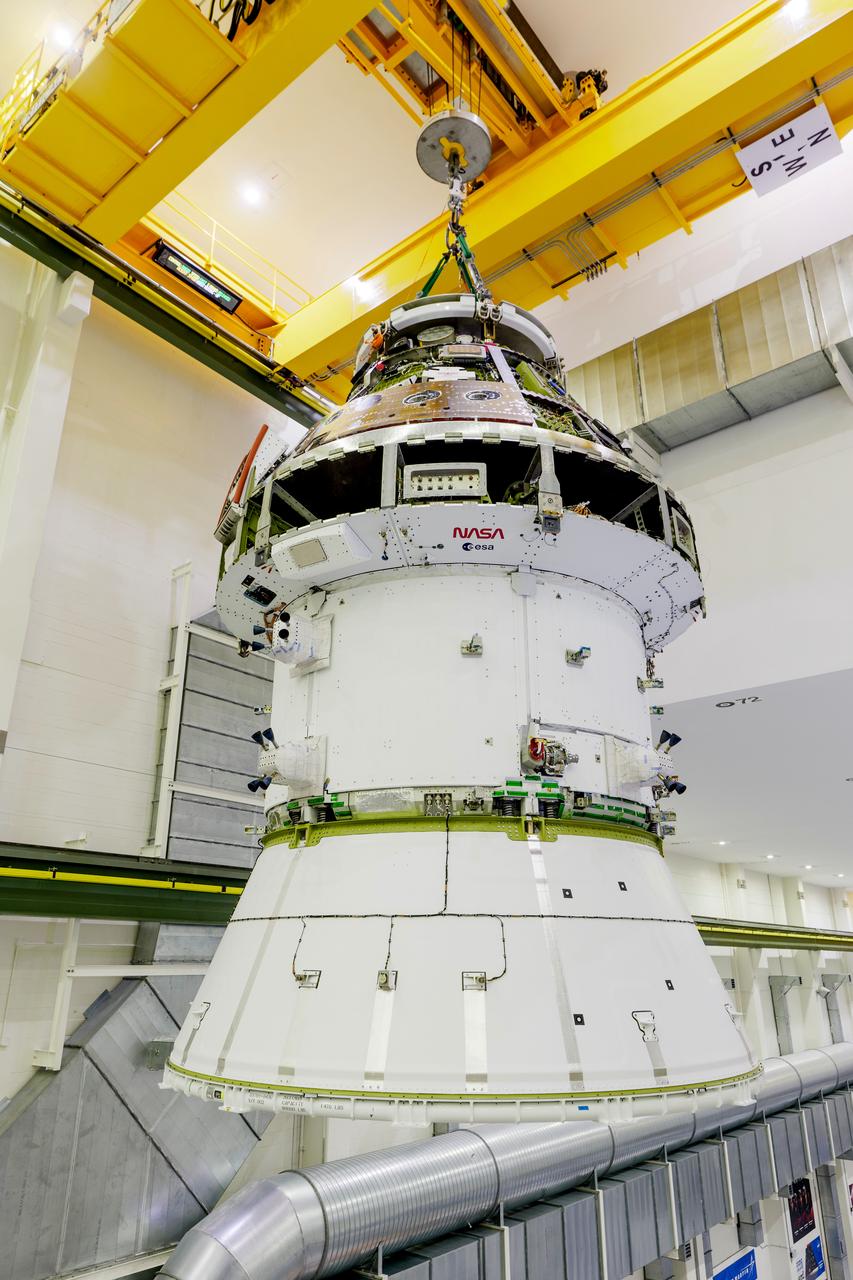

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
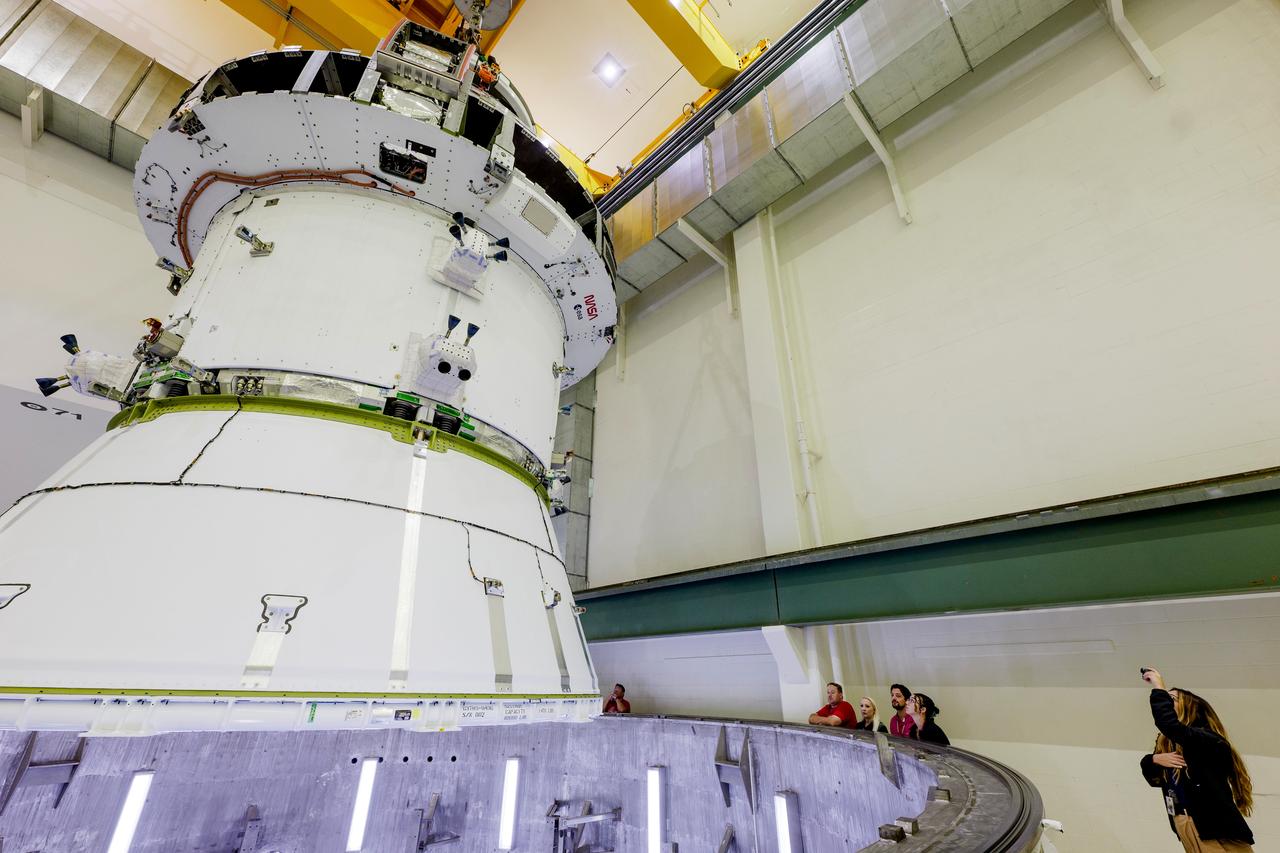

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
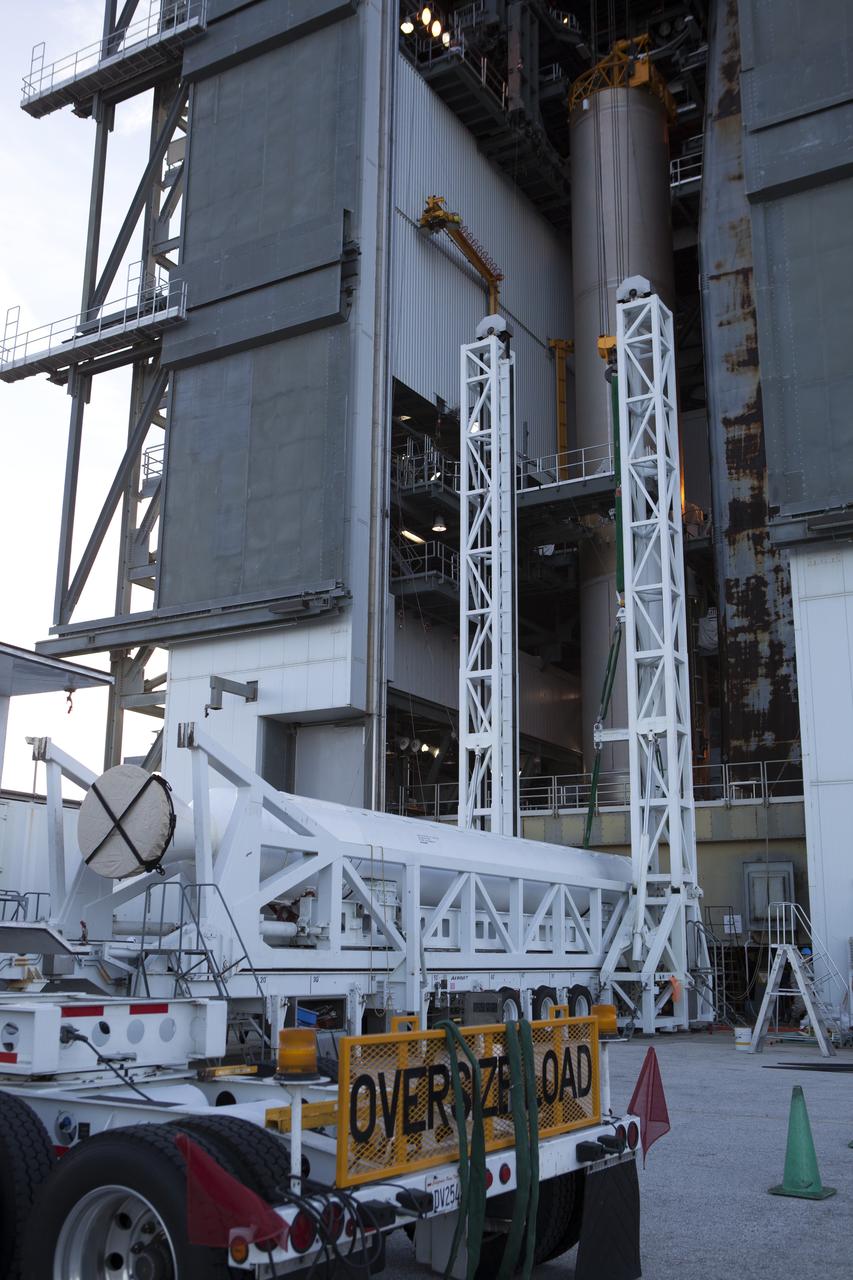

Preparations are underway to lift the solid rocket motor up from its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
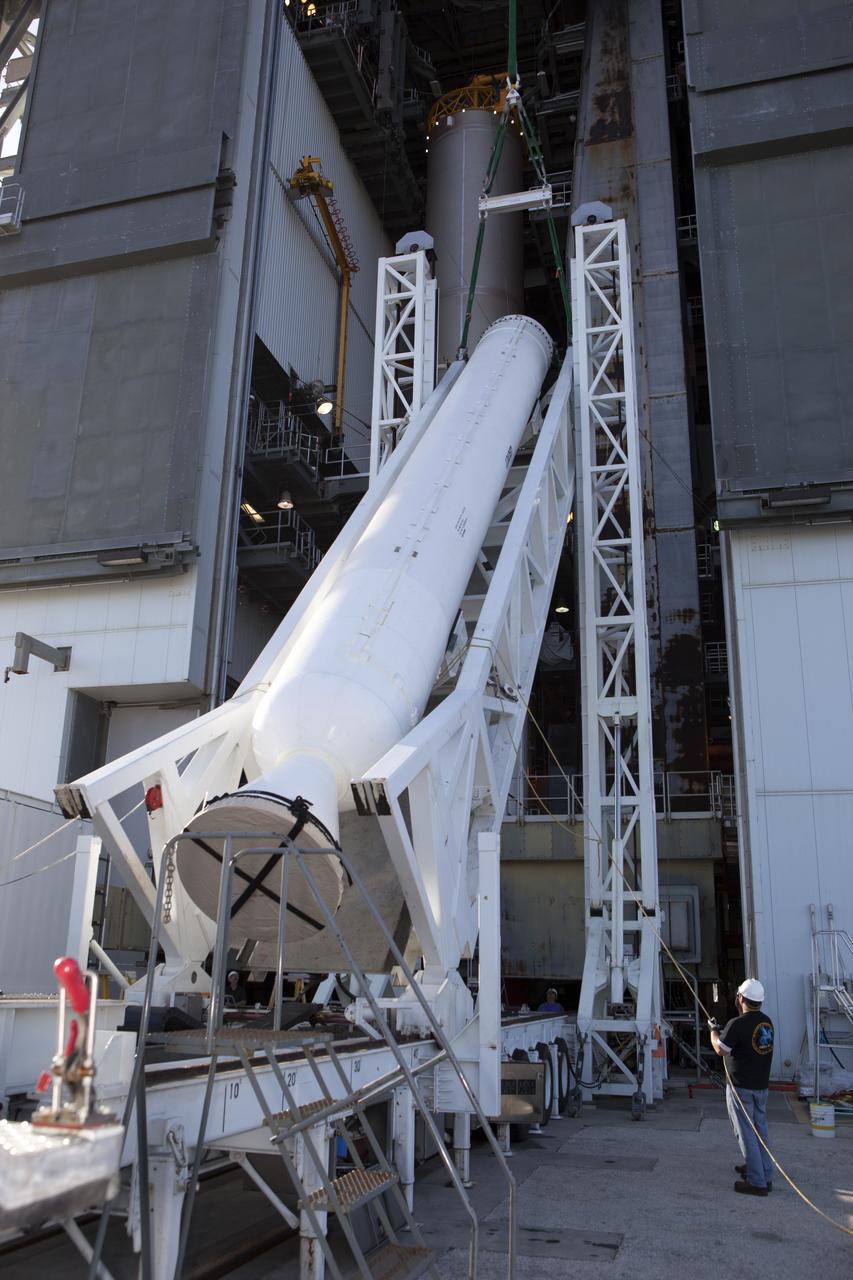

The solid rocket motor is lifted on its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
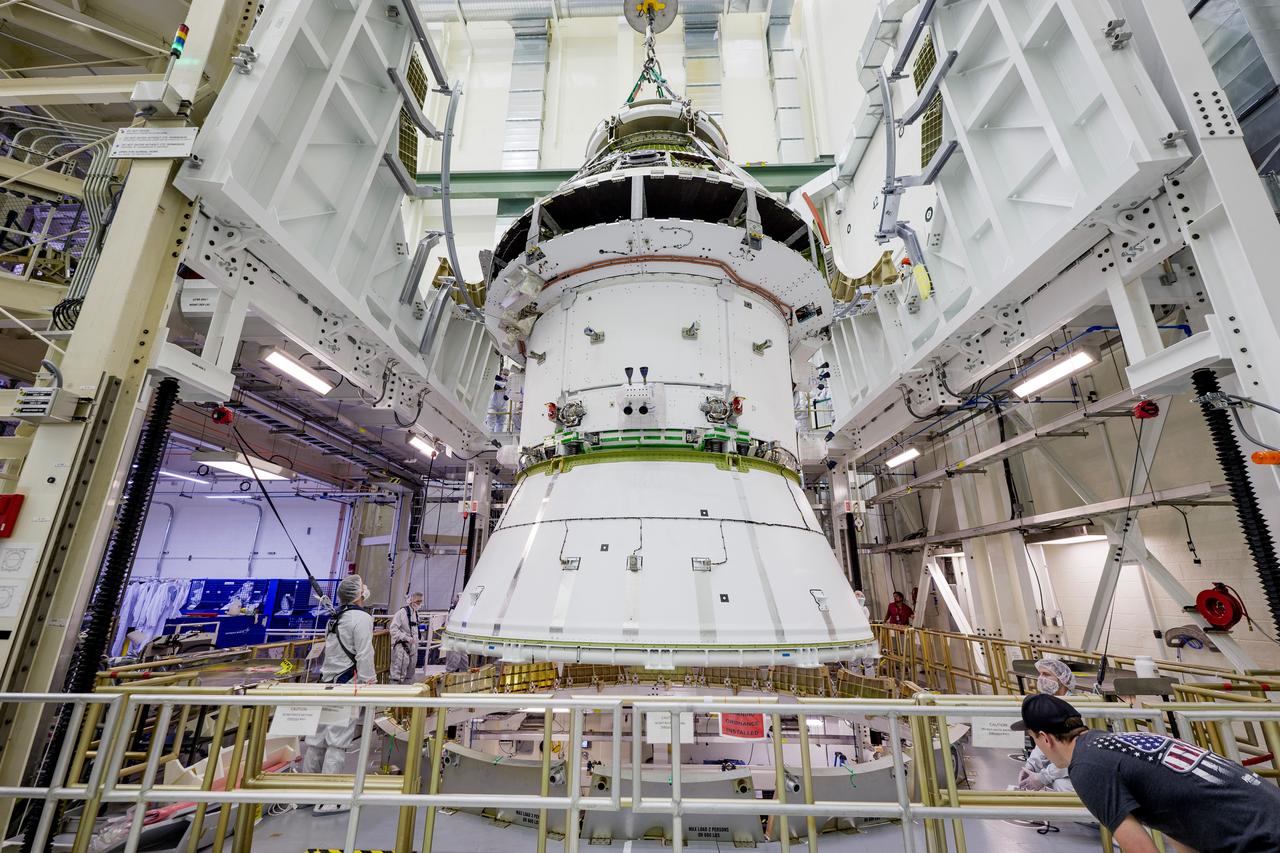

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
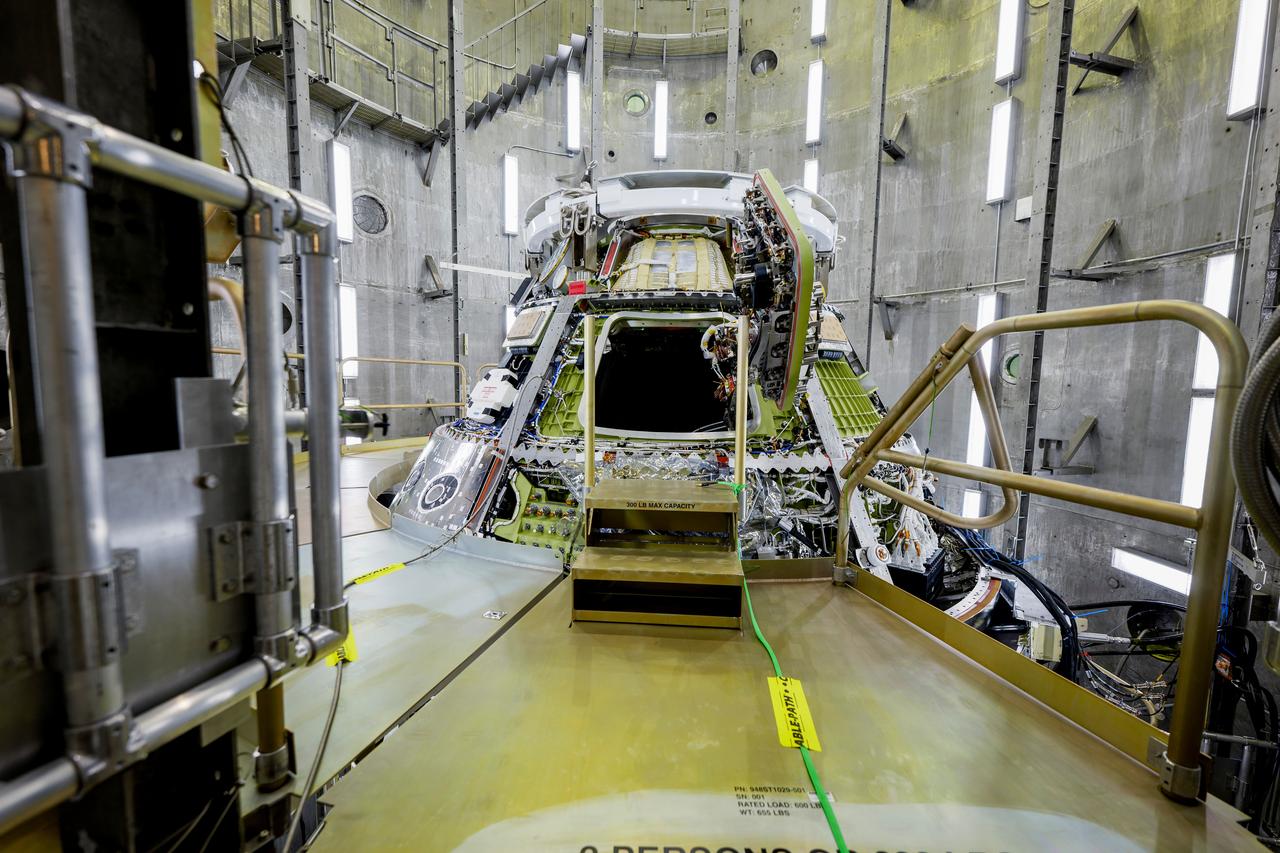

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
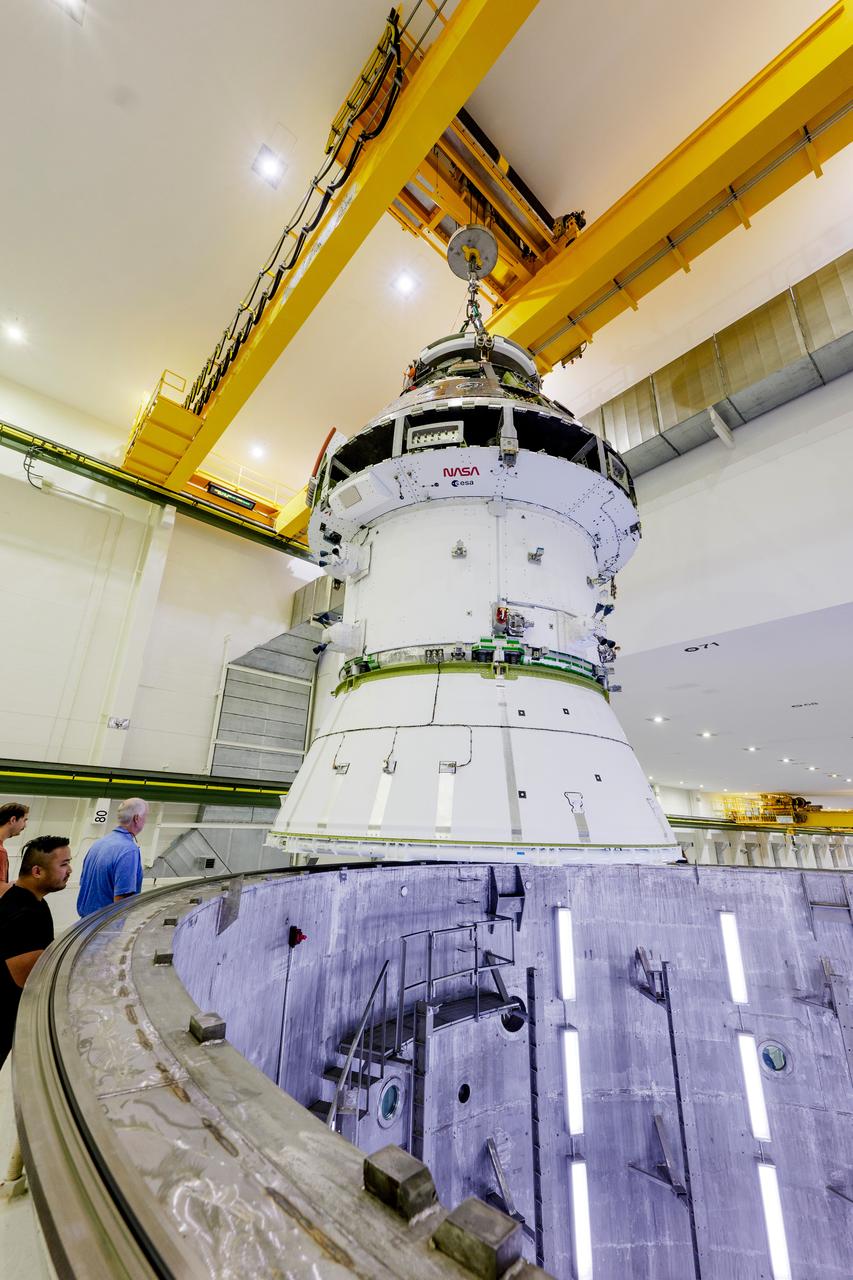

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
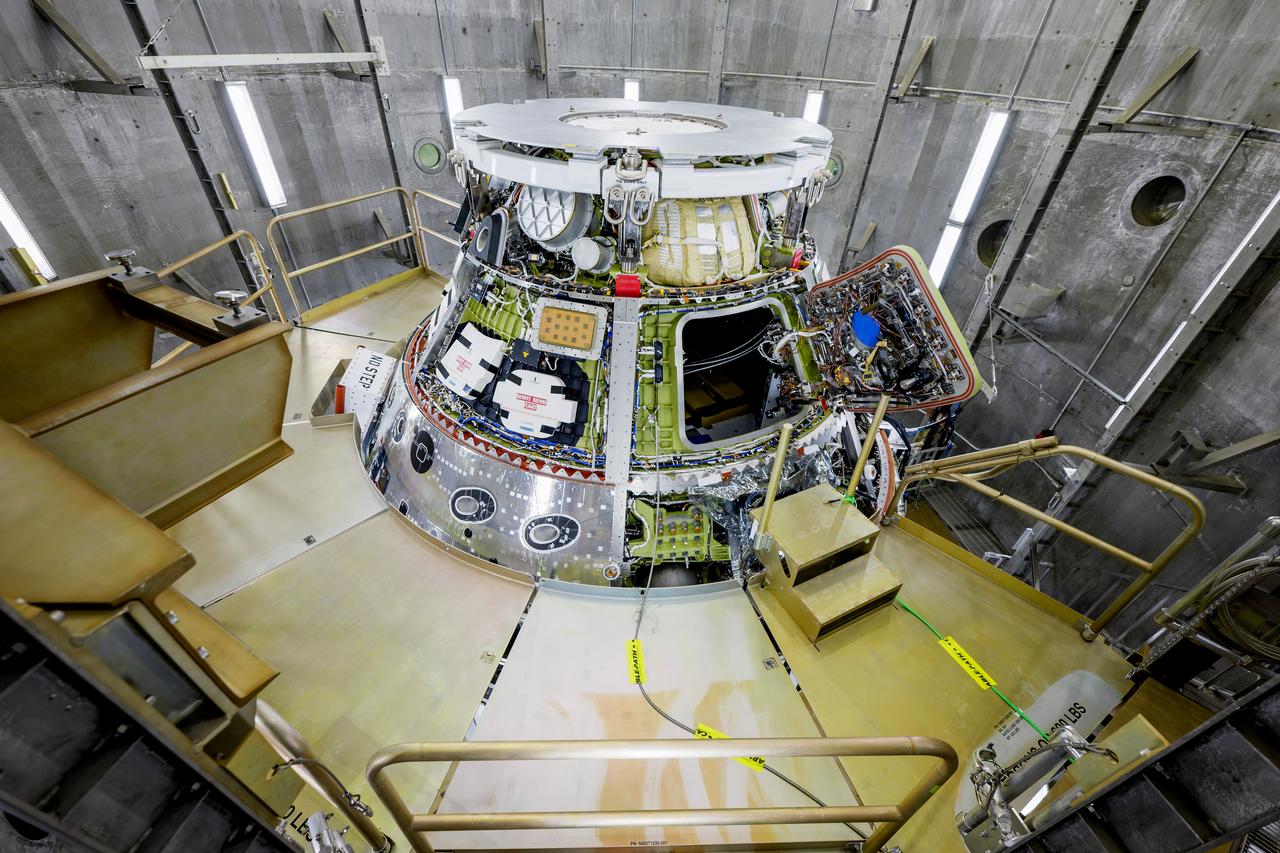

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
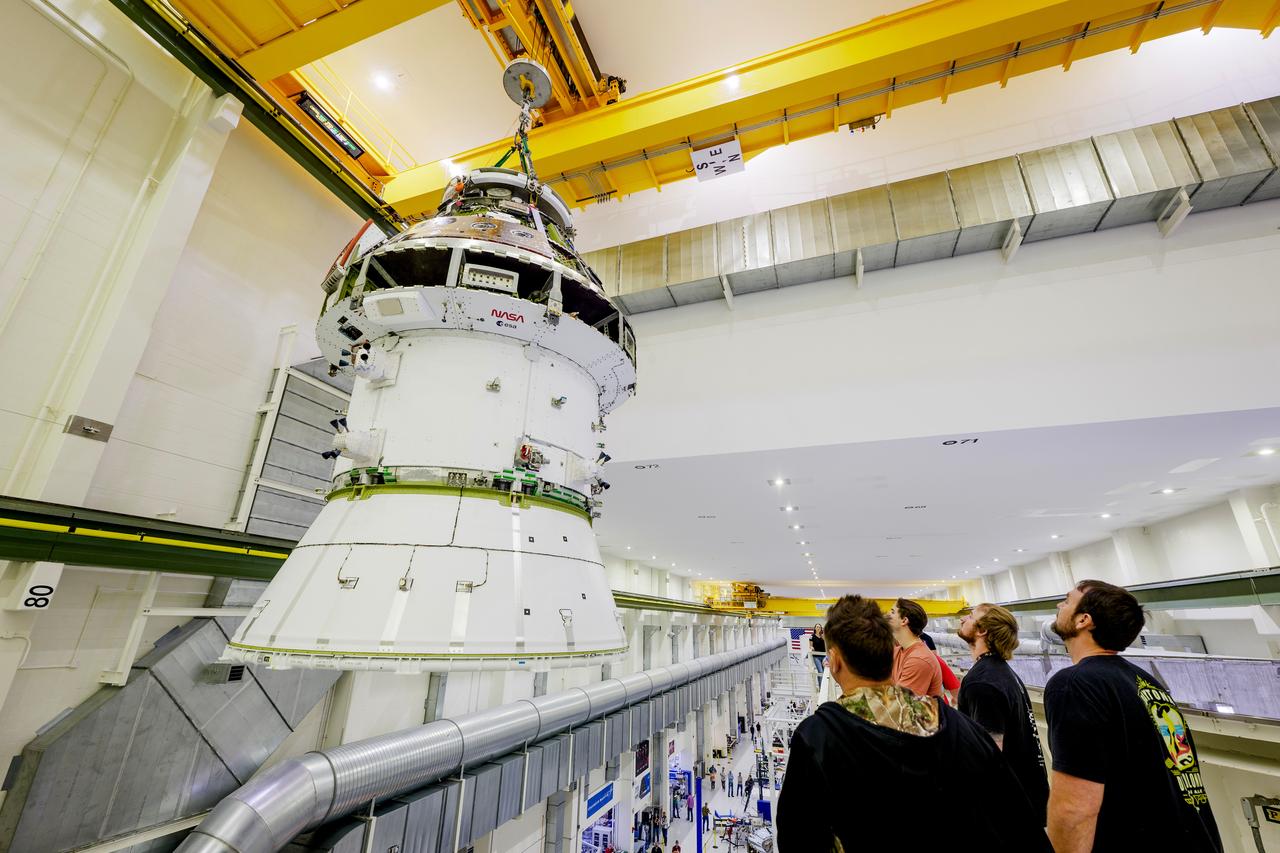

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
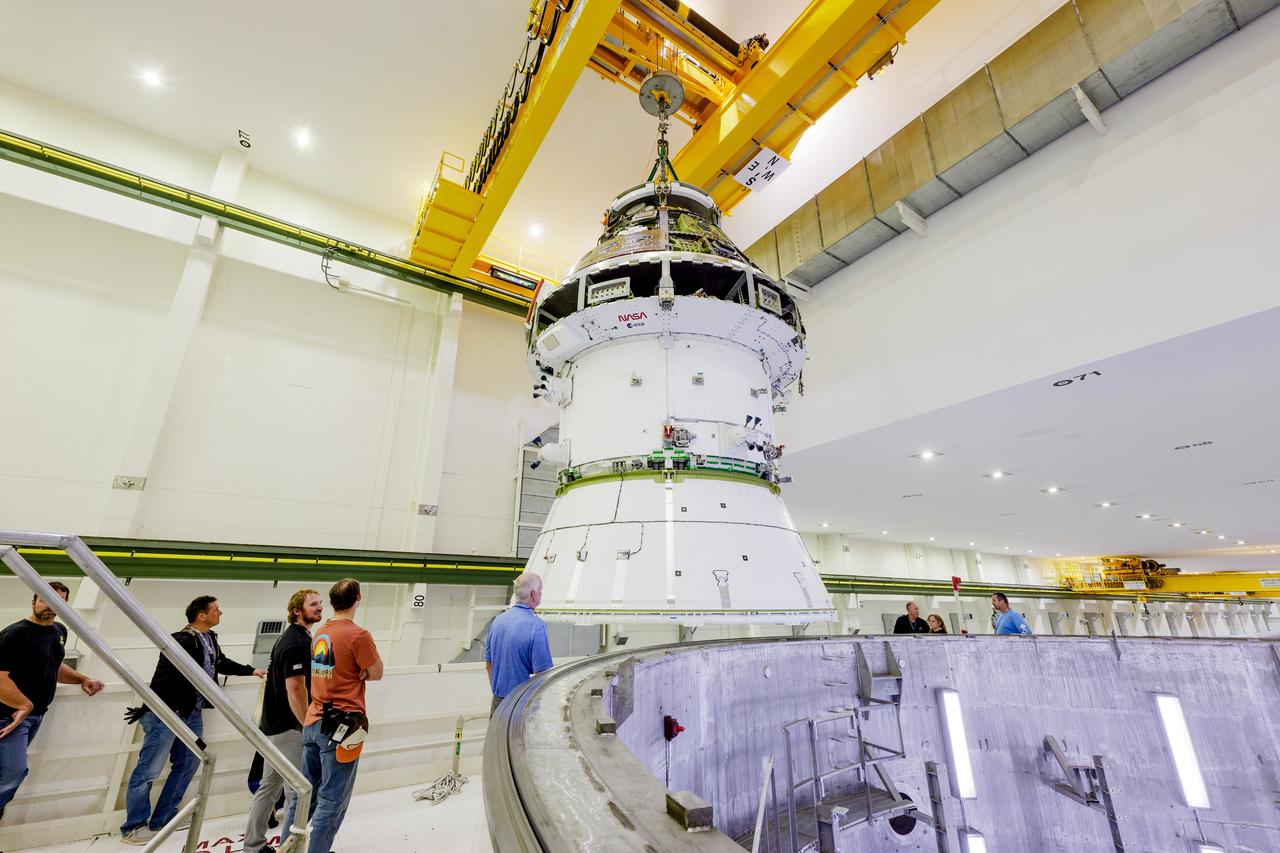

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
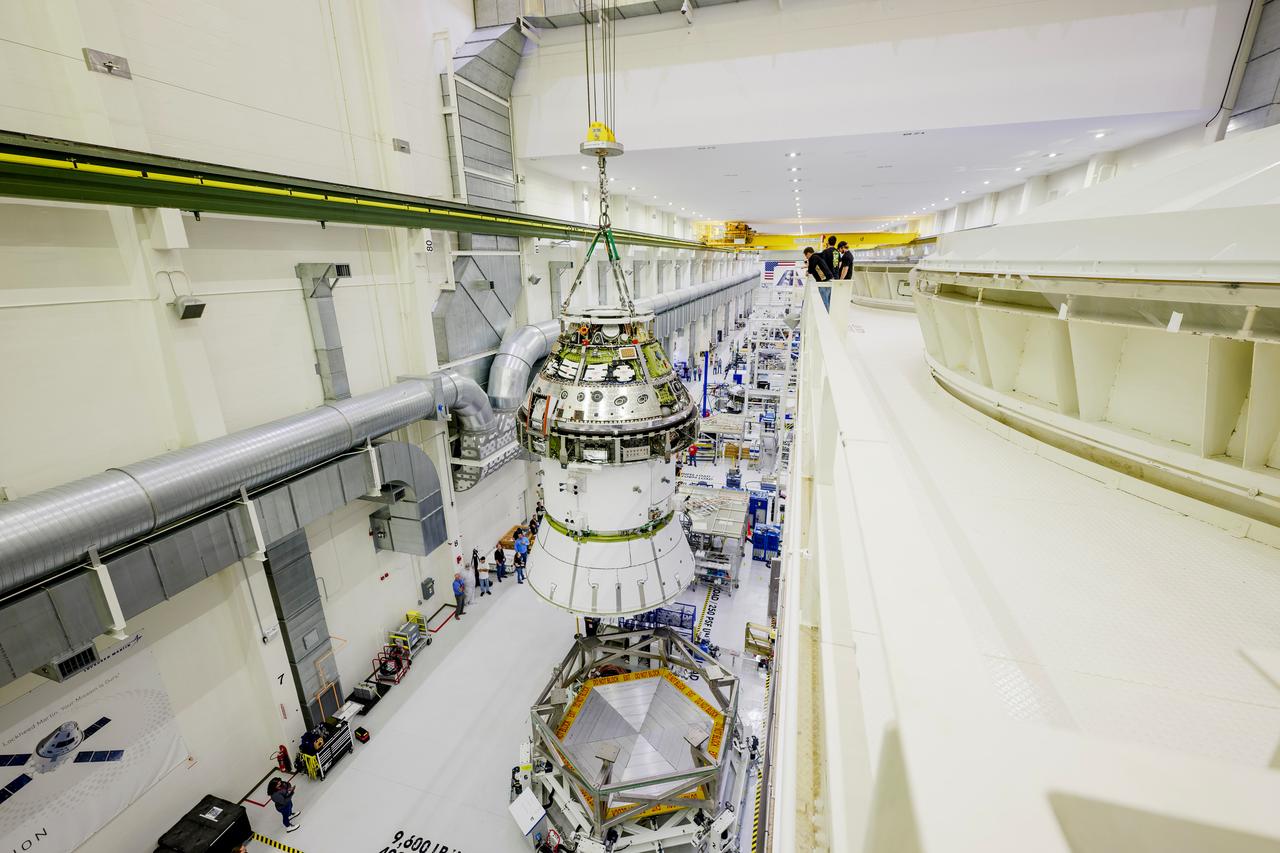

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
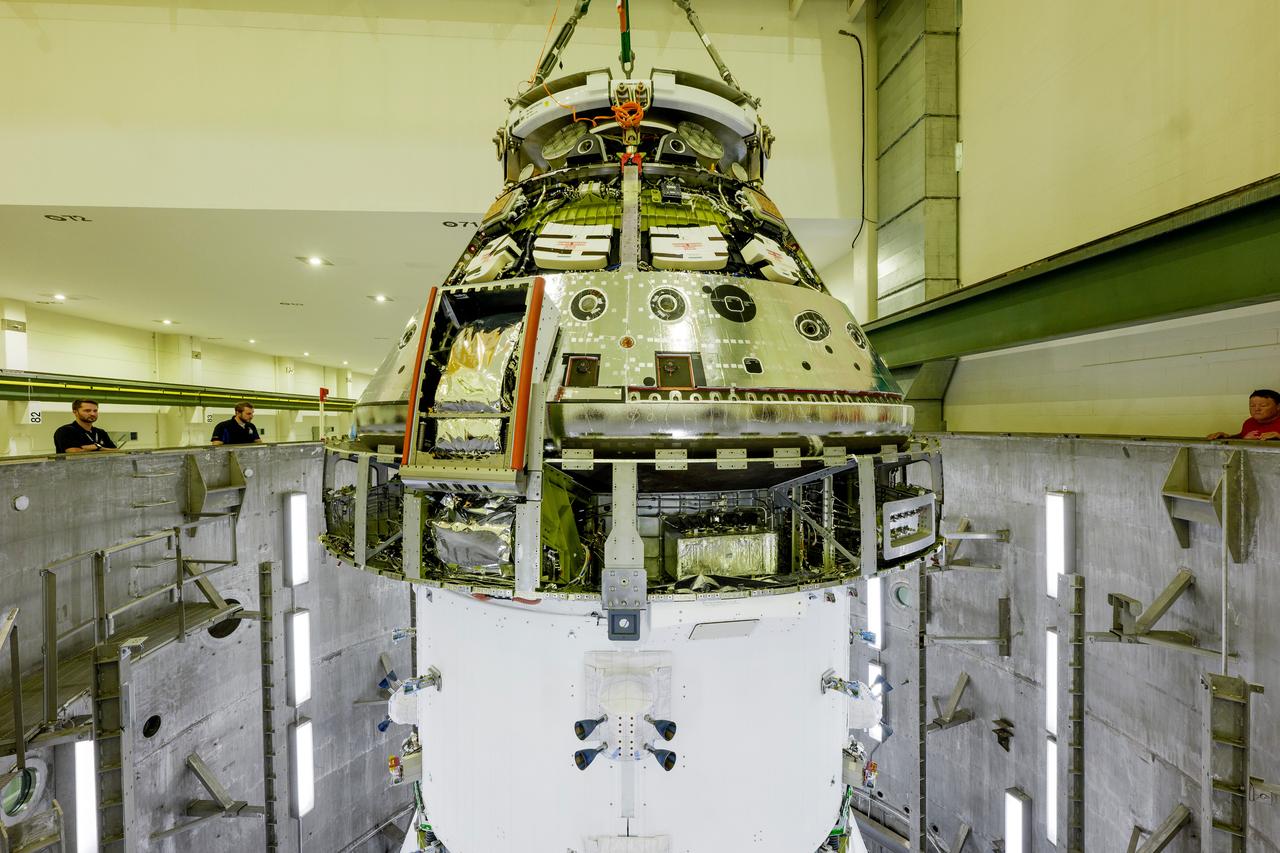

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
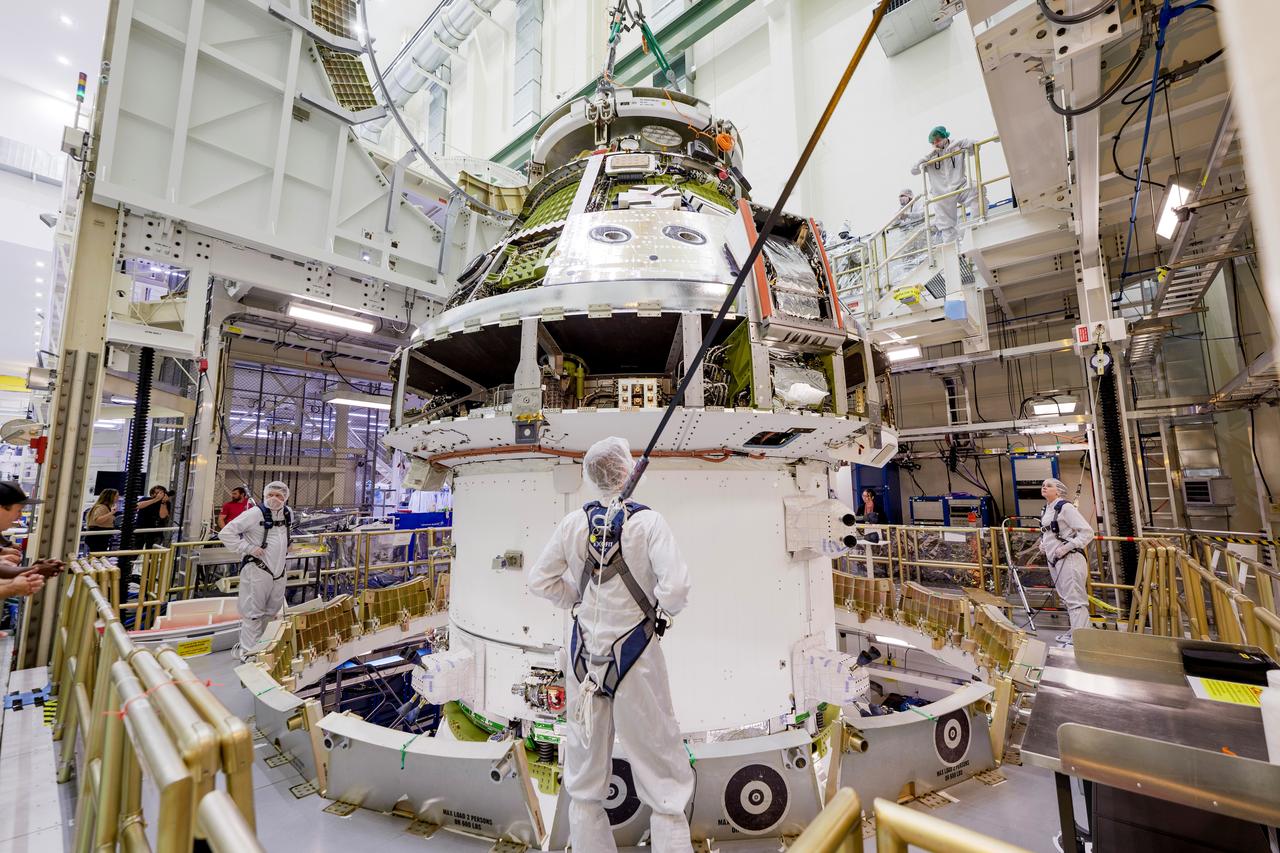

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
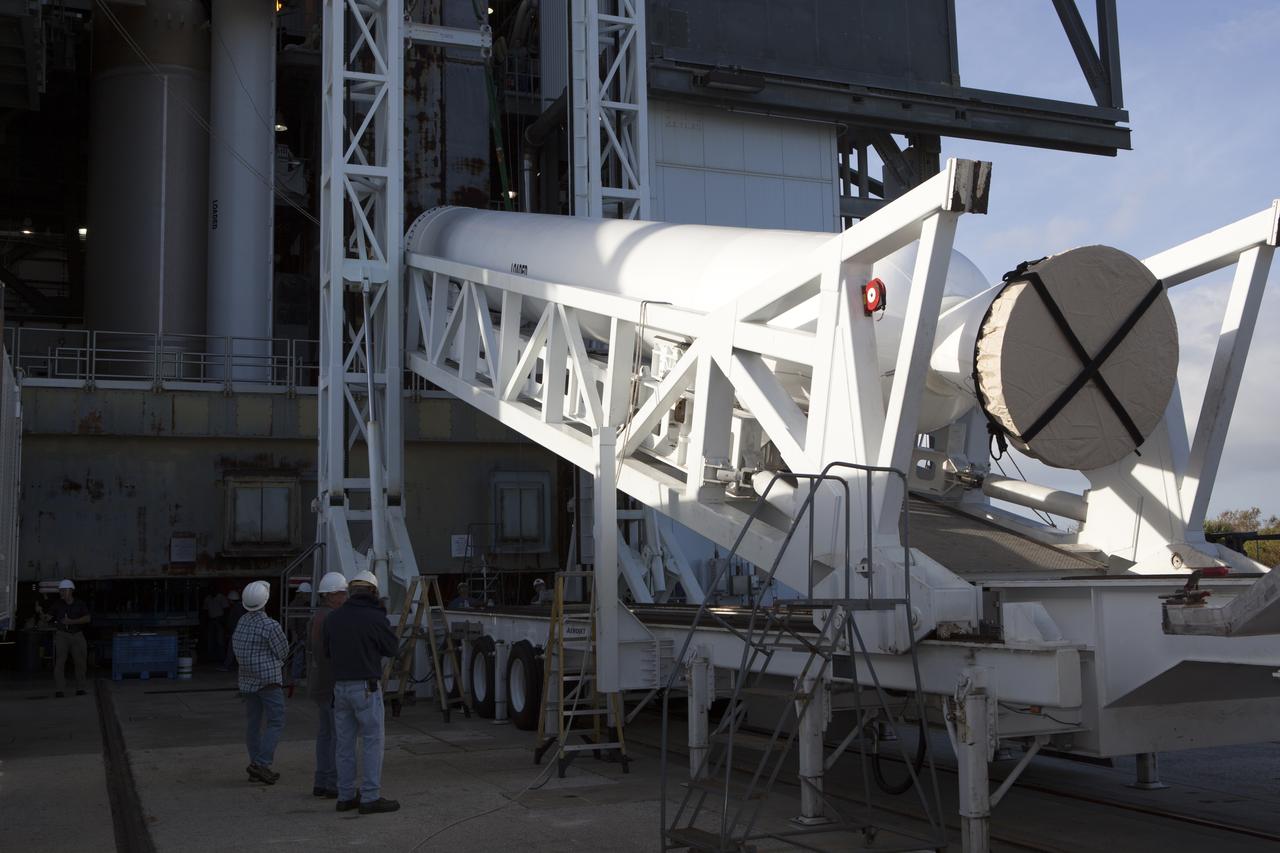

The solid rocket motor is lifted on its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
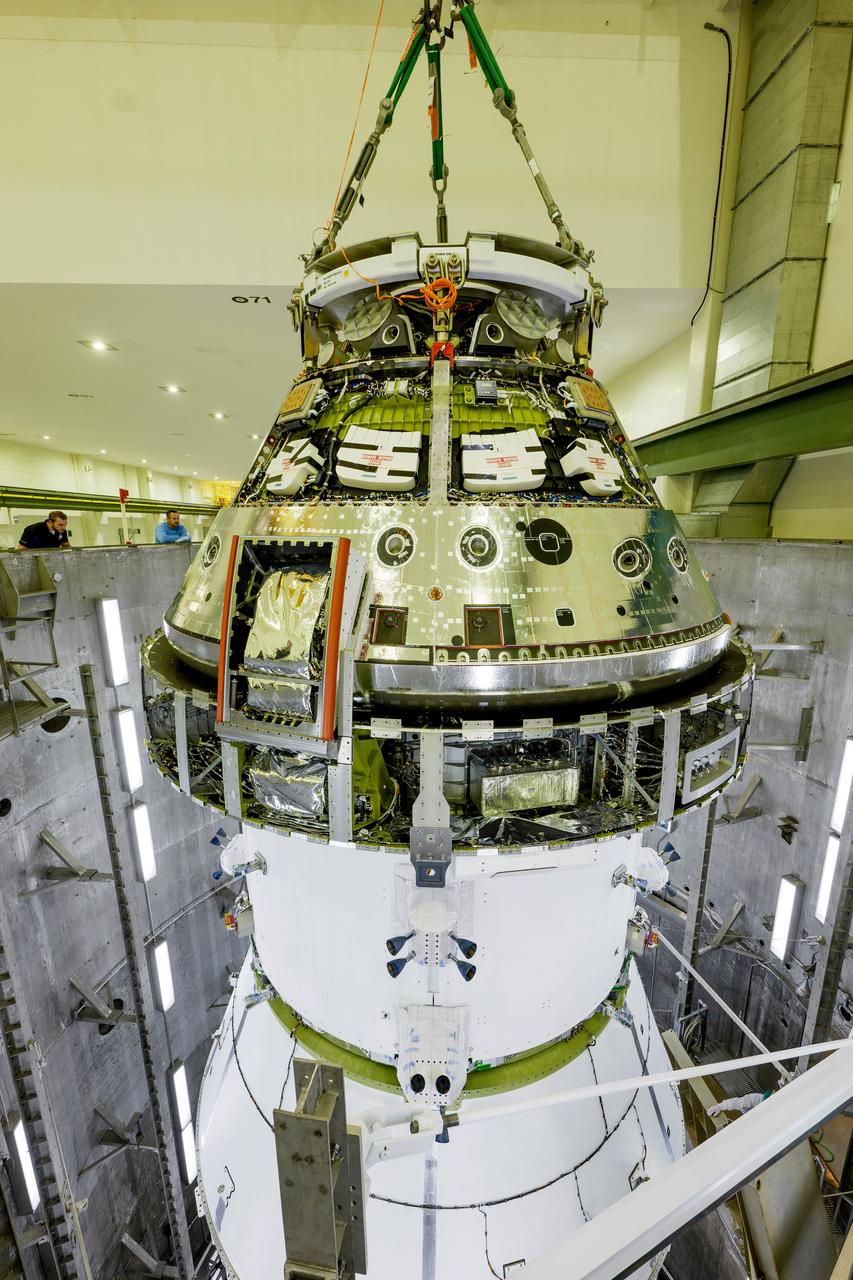

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
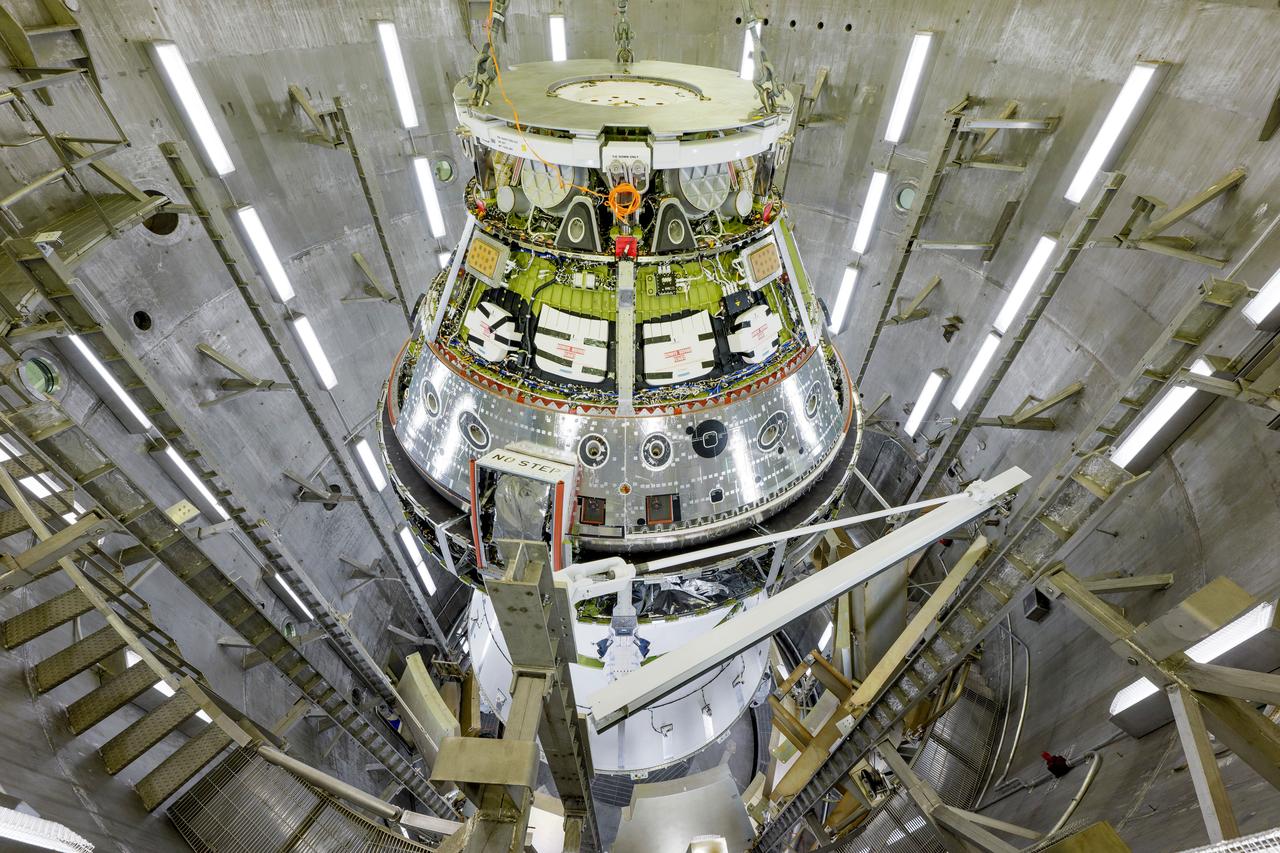

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
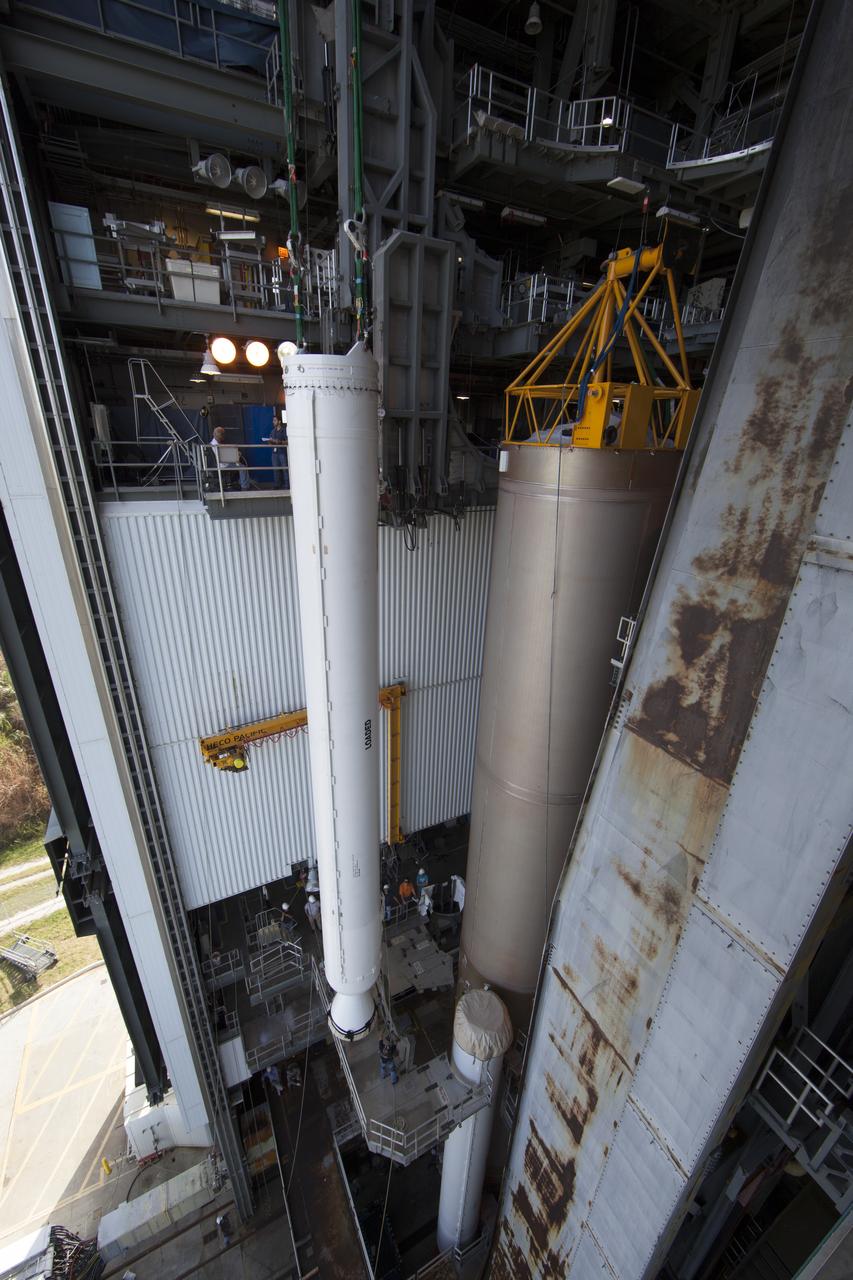

The solid rocket motor has been lifted to the vertical position and moved into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
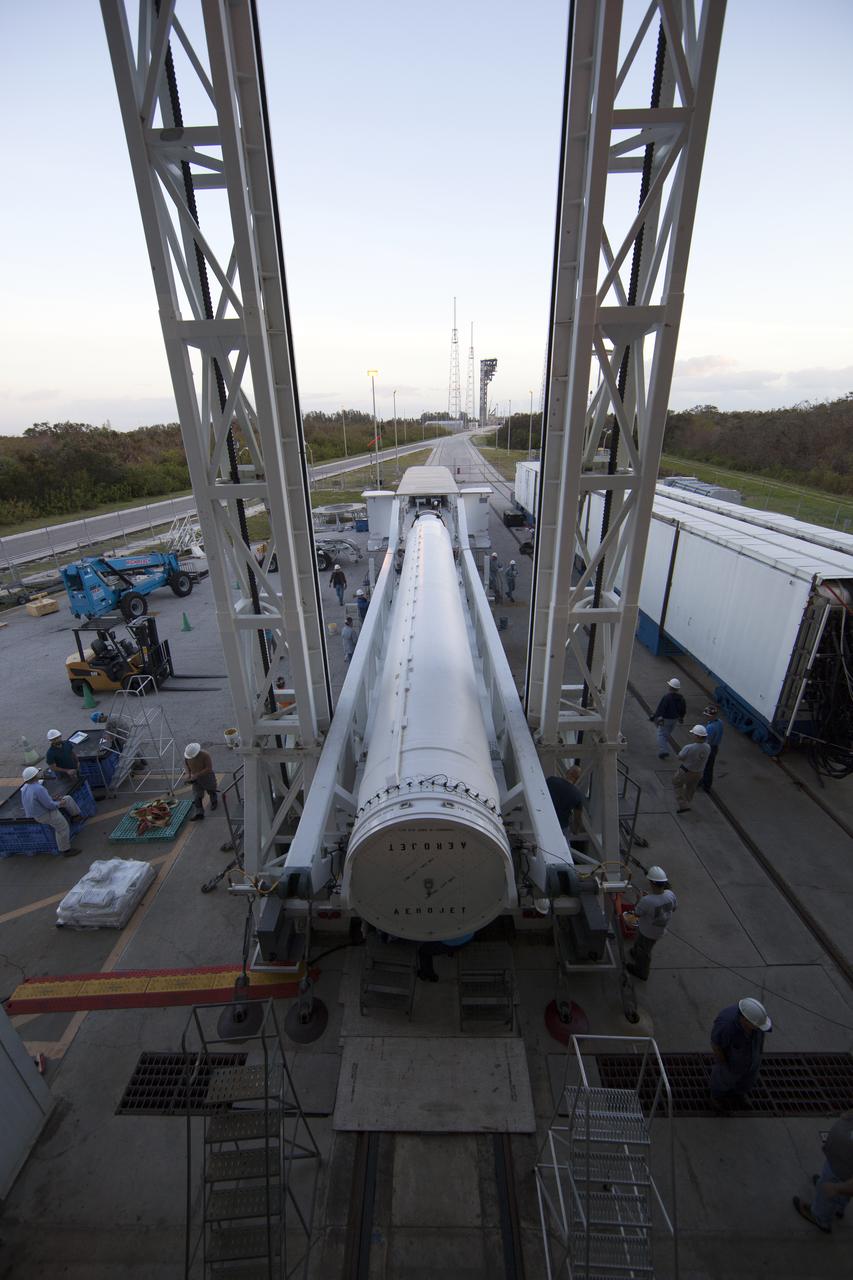

Preparations are underway to lift the solid rocket motor up from its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
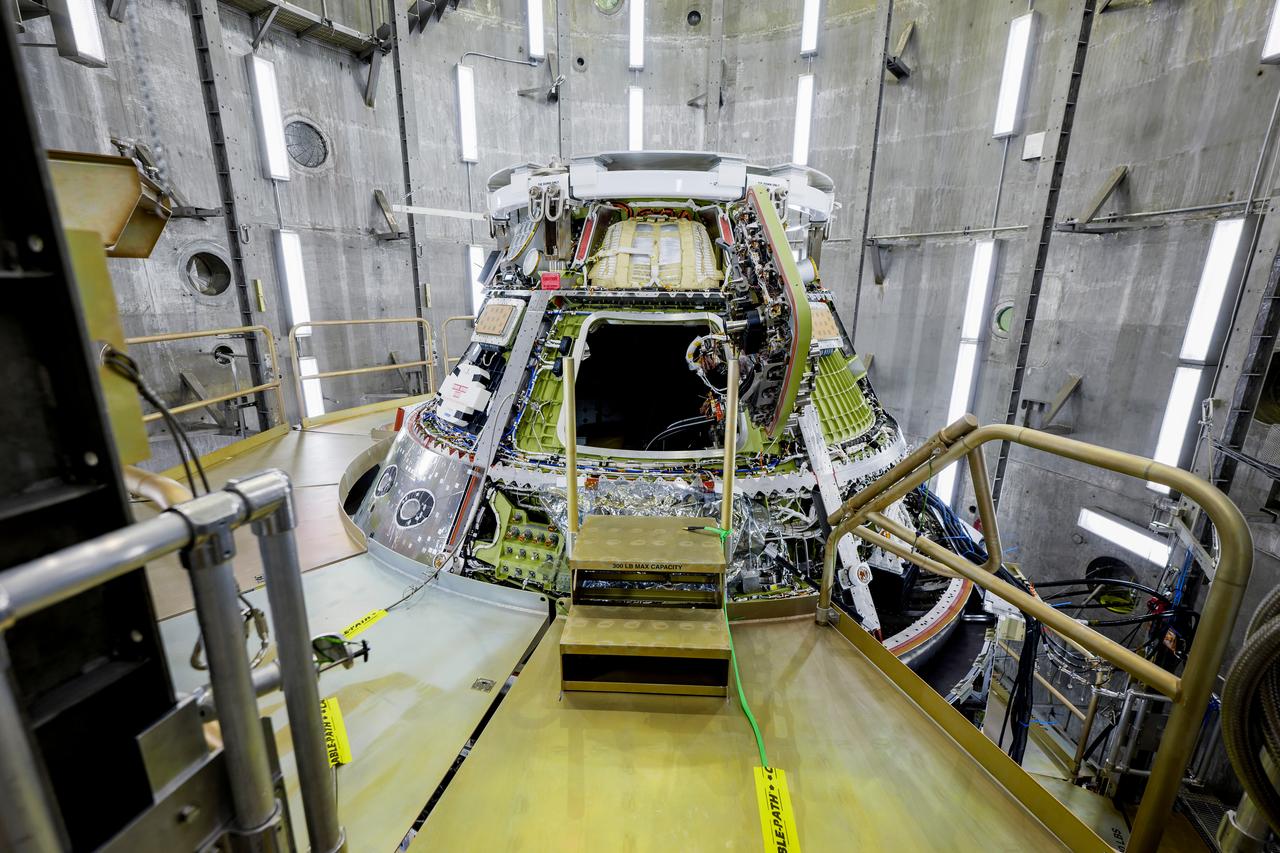

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
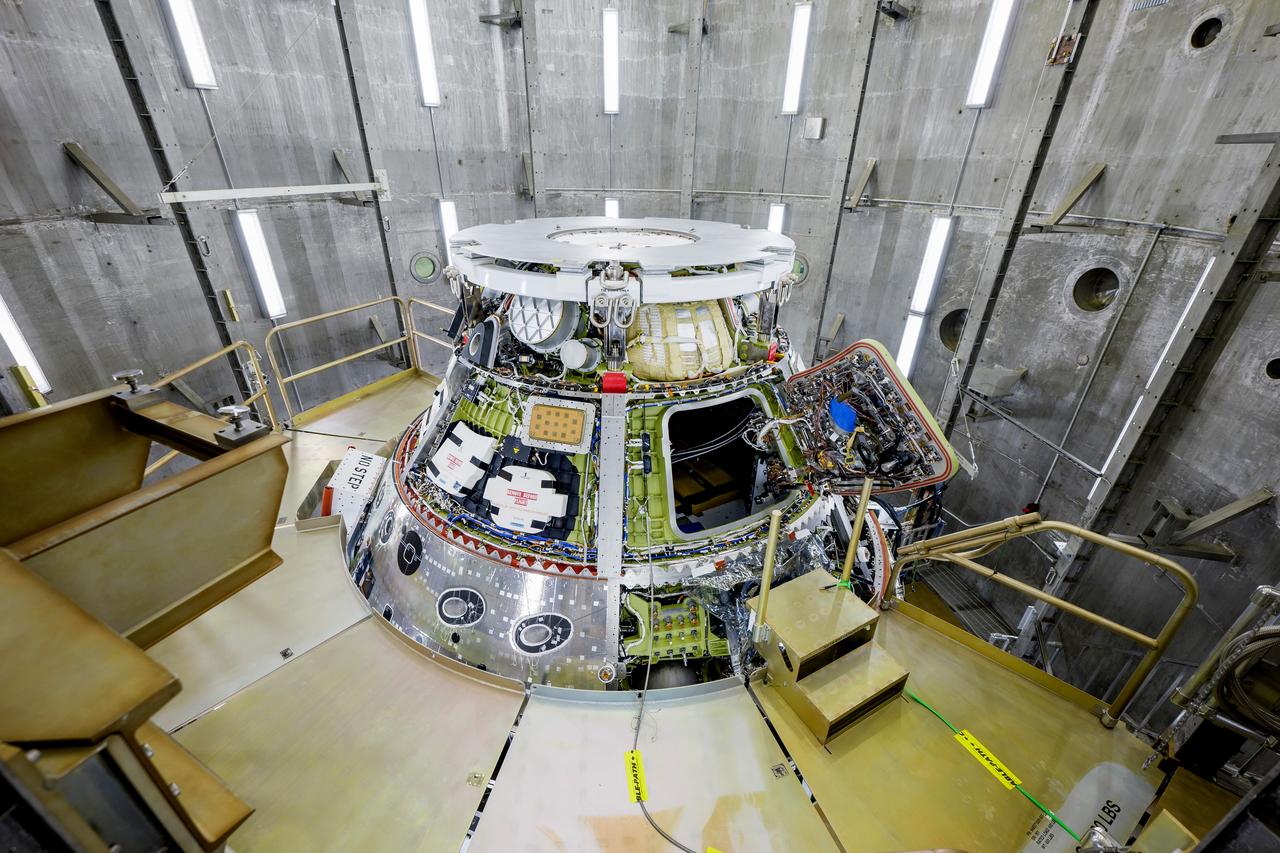

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
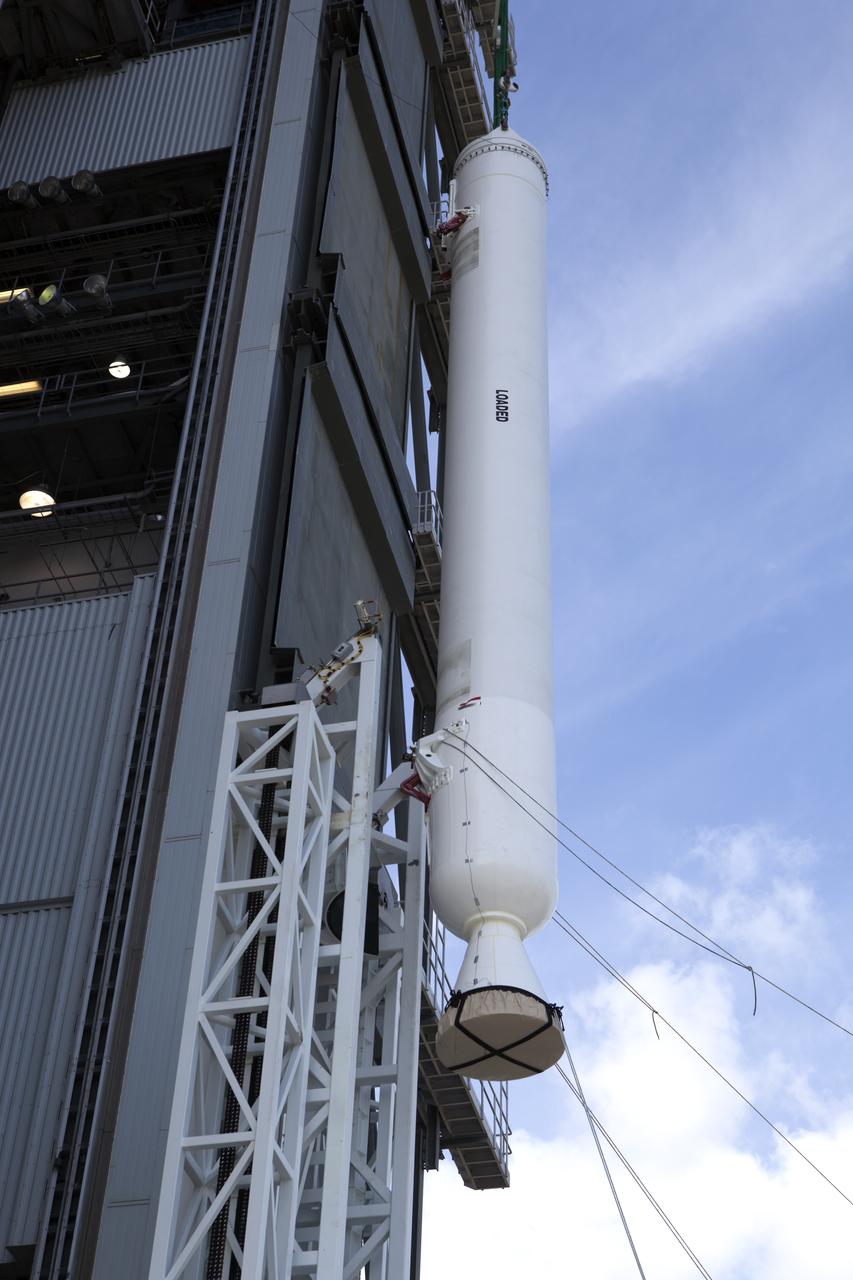

The solid rocket motor has been lifted to the vertical position for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
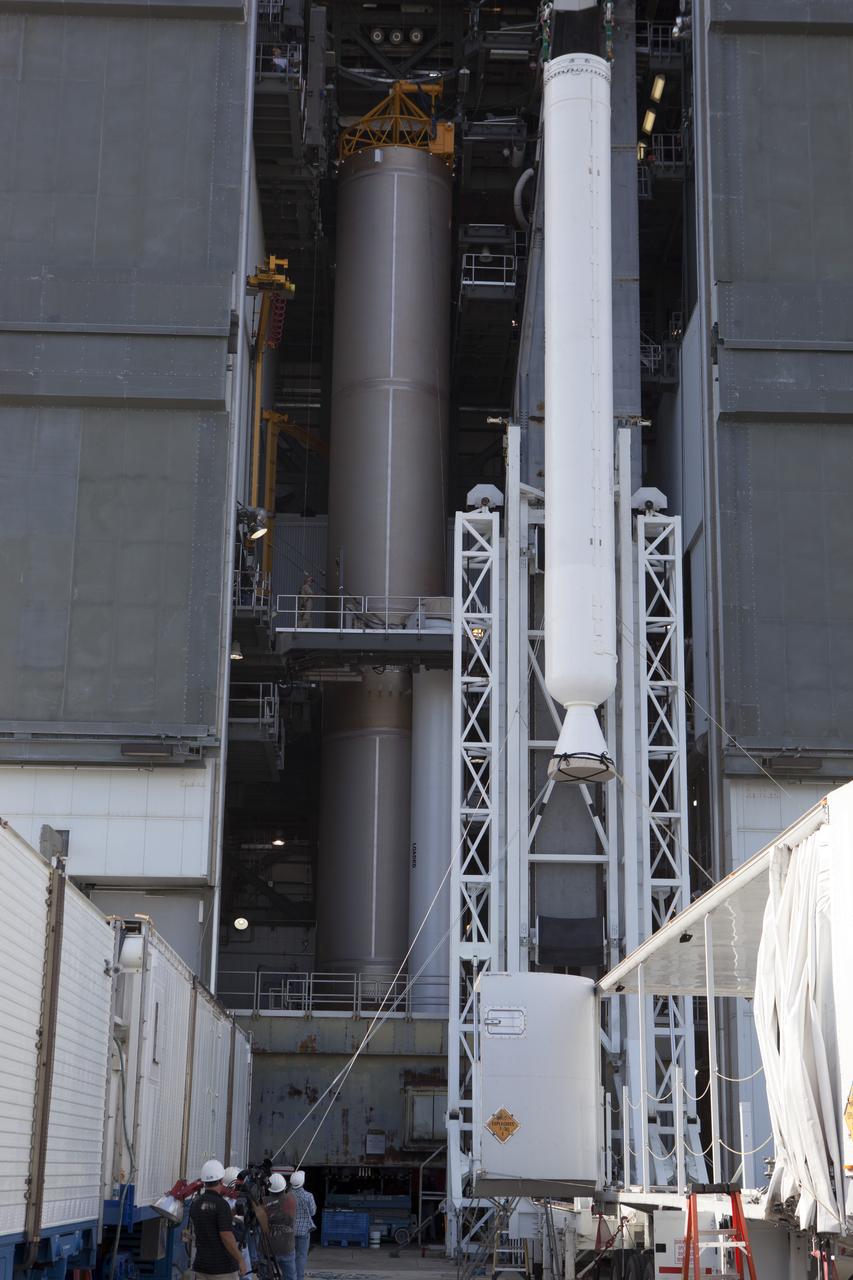

The solid rocket motor has been lifted to the vertical position on its transporter for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
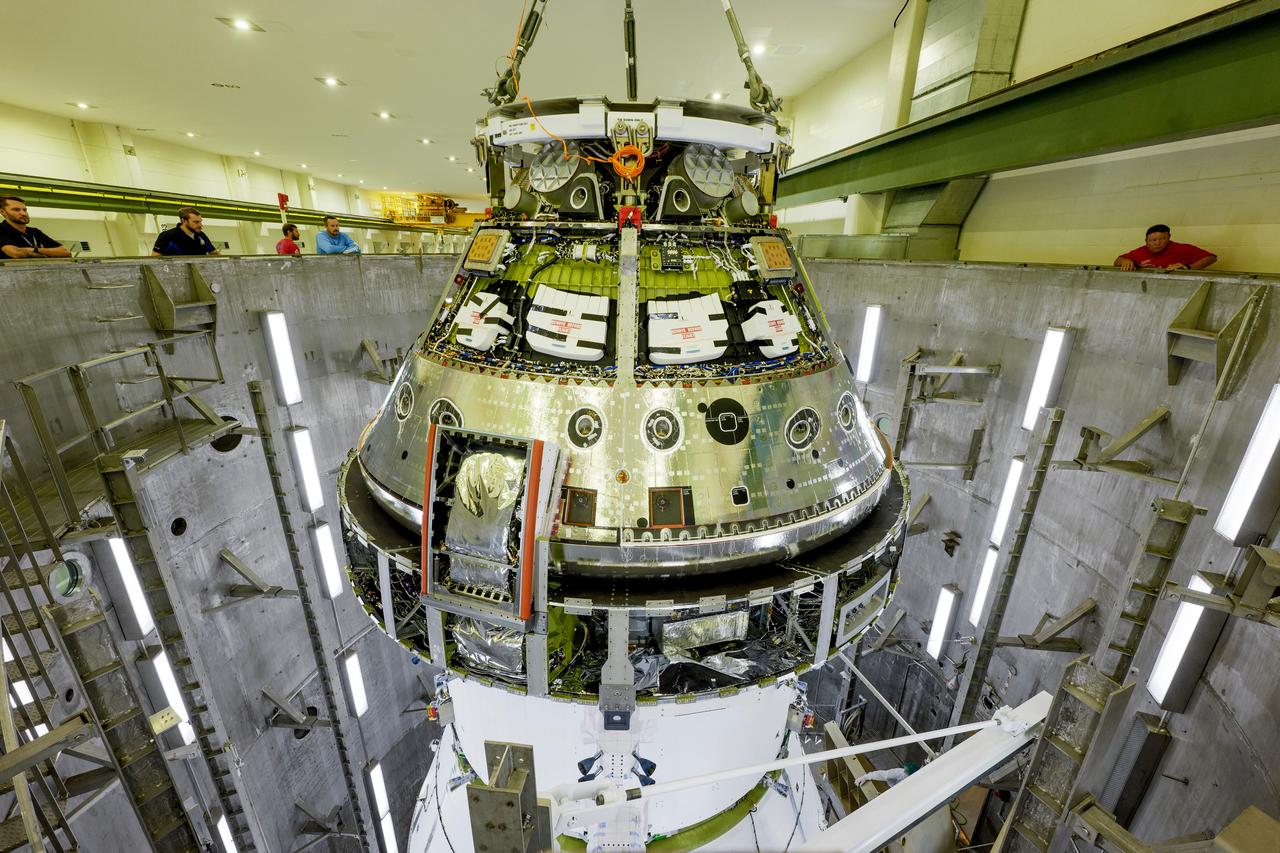

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) technician inspects the solid rocket motor for the ULA Atlas V rocket on its transporter near the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The solid rocket motor will be lifted and mated to the rocket in preparation for the launch of NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) this month. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
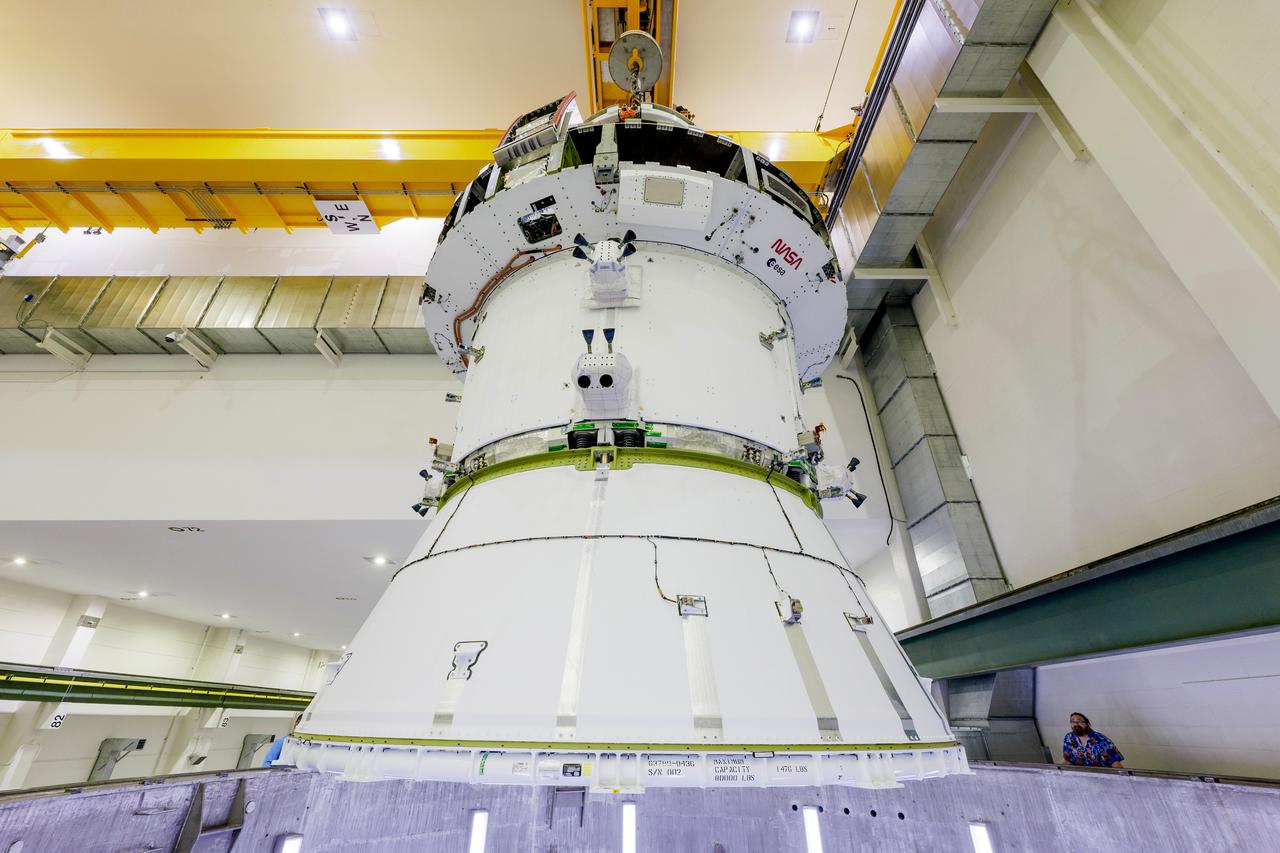

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
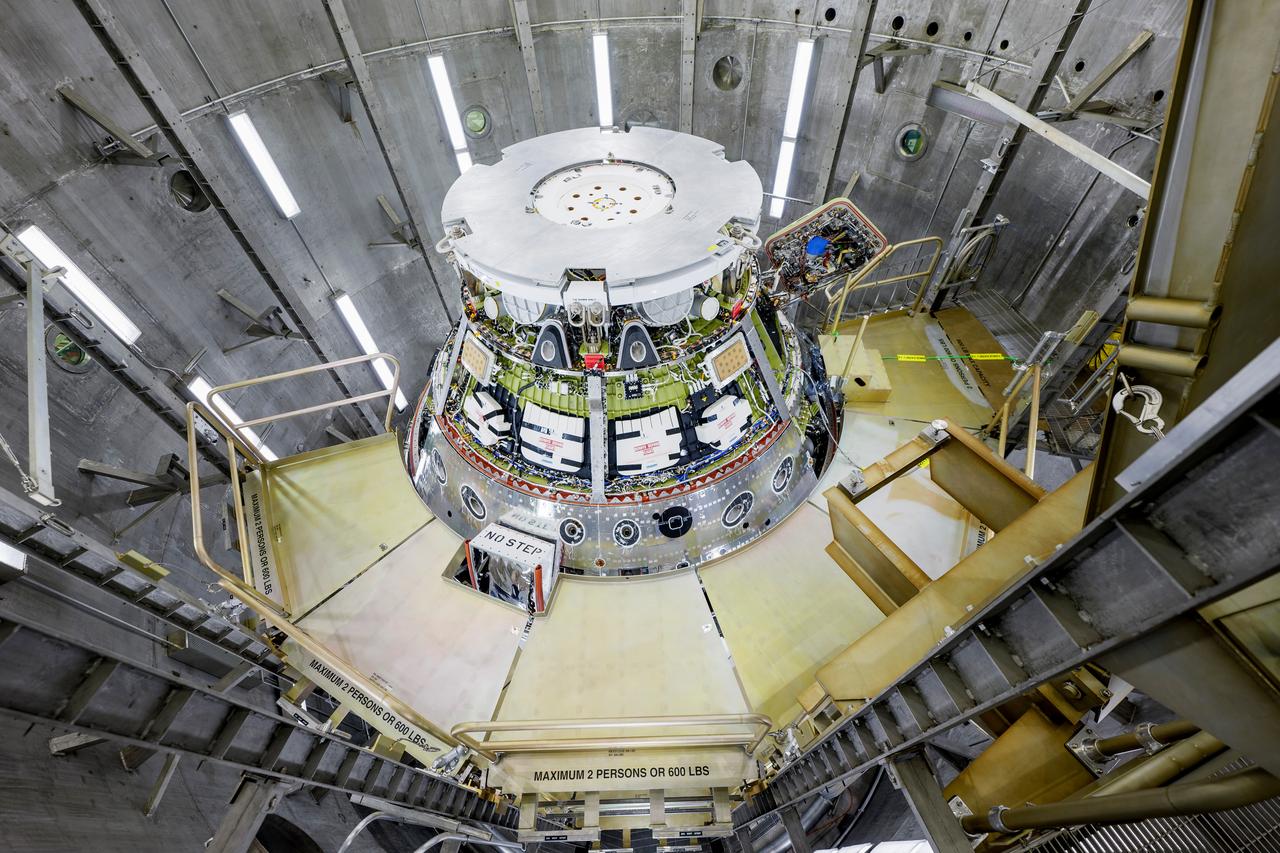

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
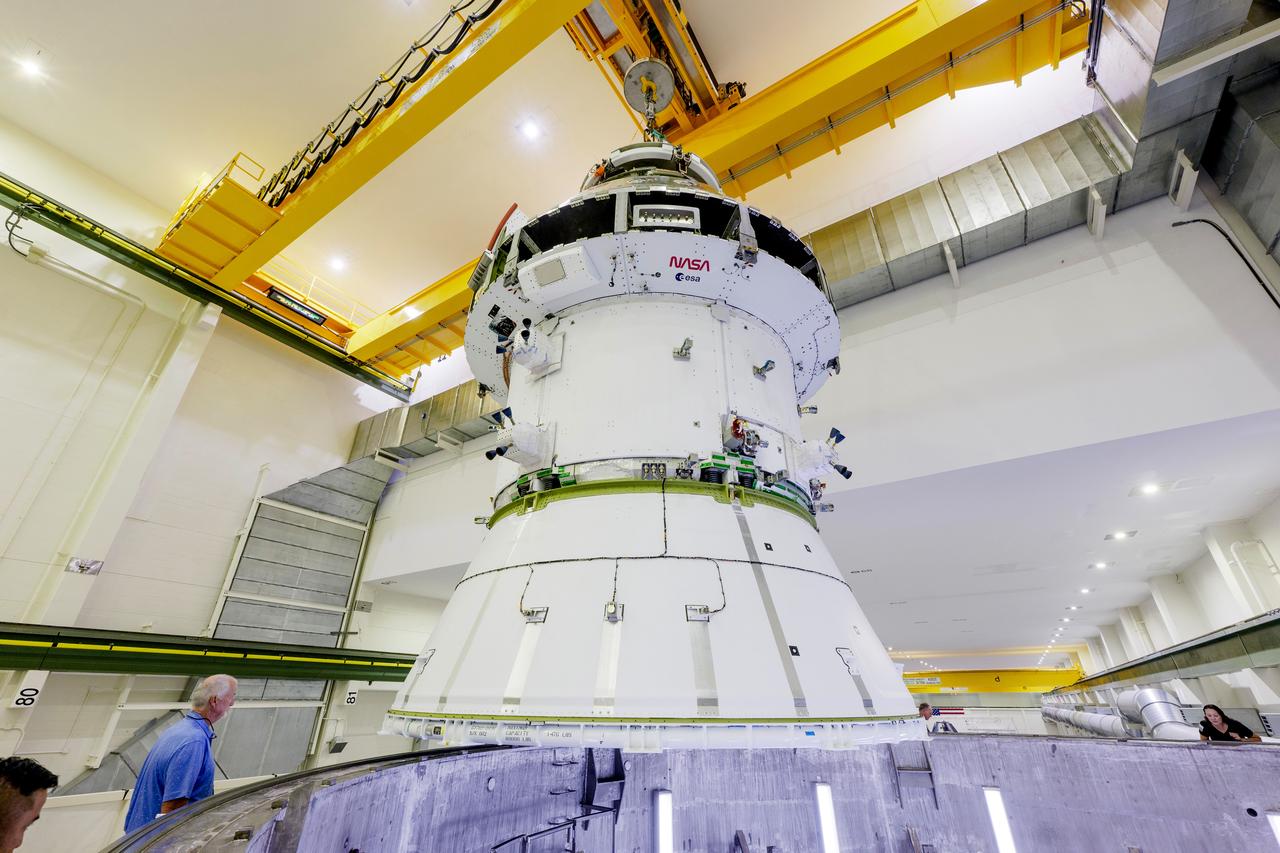

The Artemis II Orion spacecraft is lifted from the Final Assembly and Testing (FAST) Cell and placed in the west altitude chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’S Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 28, 2024. Inside the altitude chamber, the spacecraft underwent a series of tests simulating deep space vacuum conditions. Photo Credit: NASA / Rad Sinyak
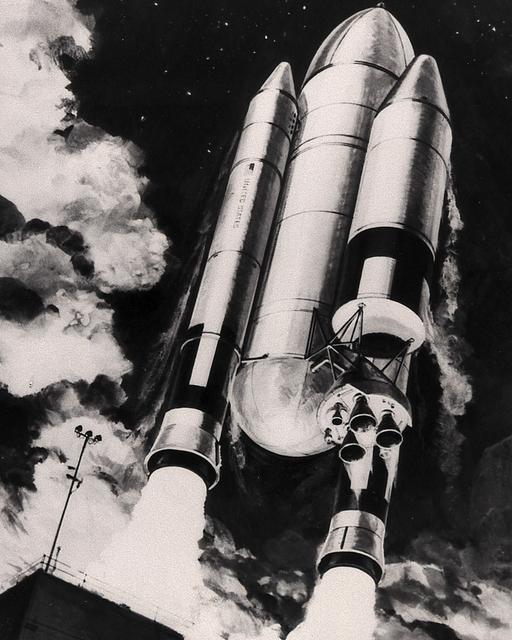

During the Space Shuttle development phase, Marshall plarners concluded a Heavy Lift Launch Vehicle (HLLV) would be needed for successful Space Industrialization. Shown here in this 1976's artist's conception is an early version of the HLLV during launch.