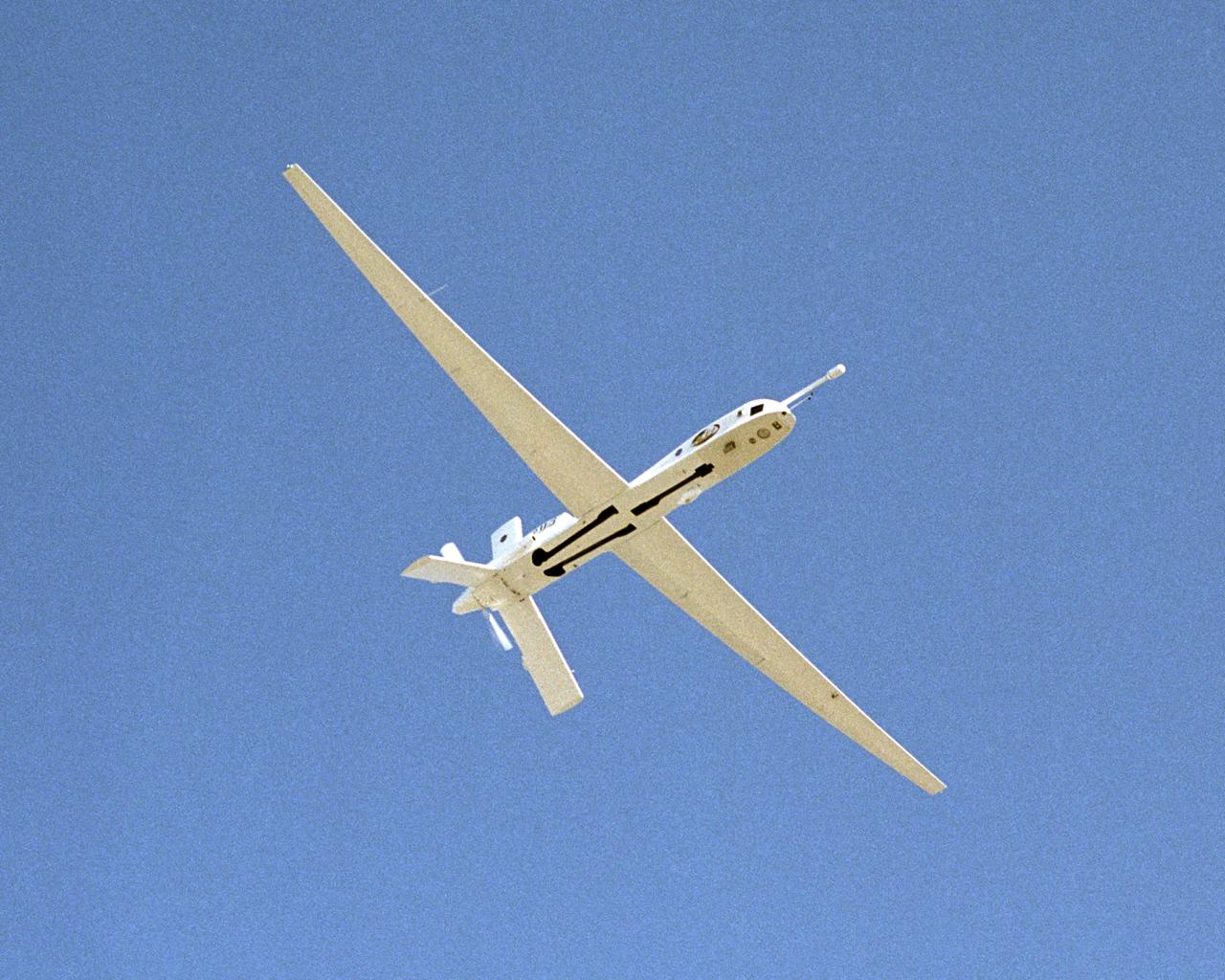

The Altus II remotely piloted aircraft carried a variety of specialized instruments and cameras during a lightning study over Florida during the summer of 2002.
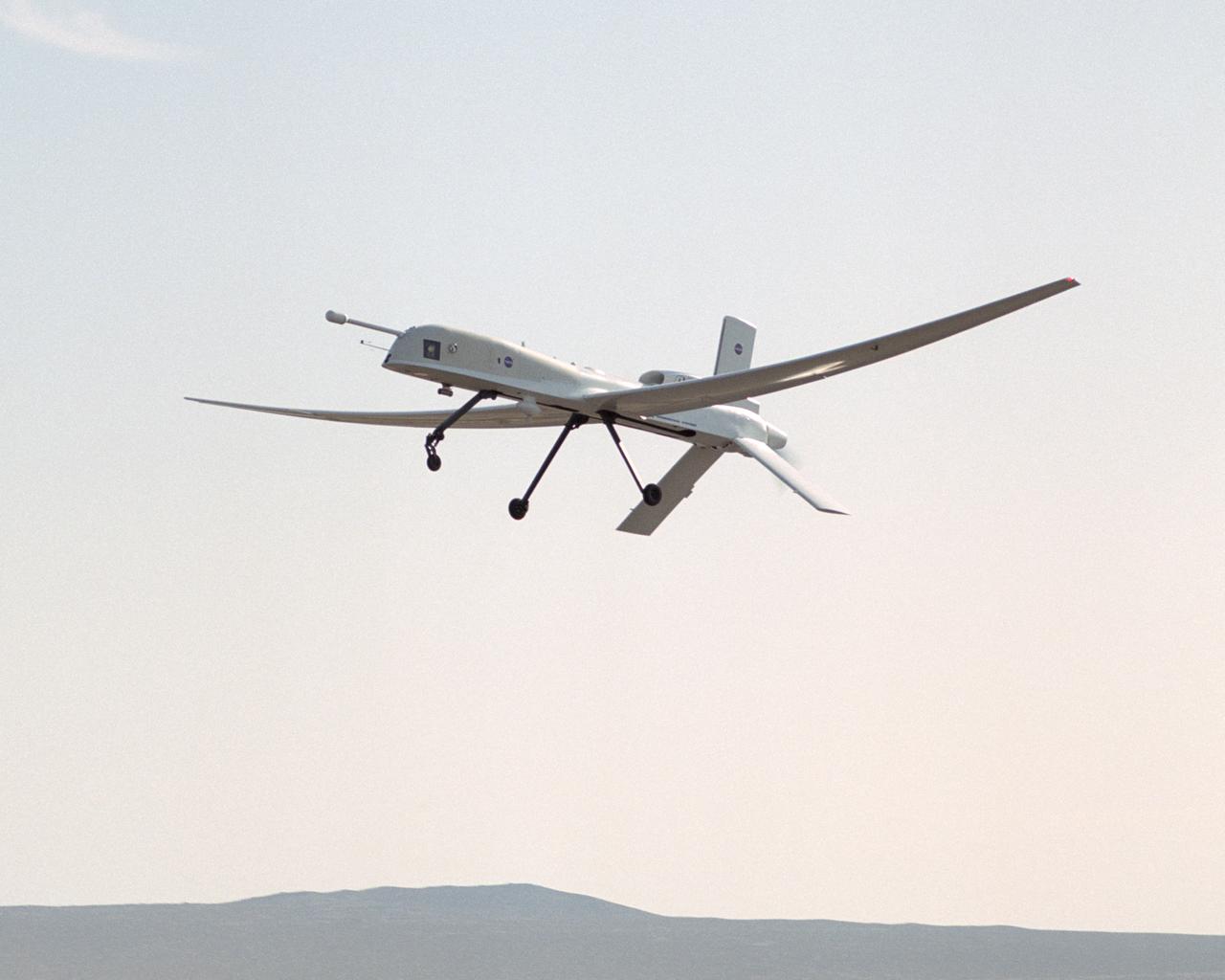

The remotely piloted Altus II aircraft probed lightning development with a variety of specialized instruments and cameras during a month-long study over Florida during the summer of 2002.

Looking ever so much like an alien spacecraft, the Altus II remotely piloted aircraft shows off some of the instruments and camera lenses mounted in its nose for a lightning study over Florida flown during the summer of 2002.

A NASA team studying the causes of electrical storms and their effects on our home planet achieved a milestone on August 21, 2002, completing the study's longest-duration research flight and monitoring four thunderstorms in succession. Based at the Naval Air Station Key West, Florida, researchers with the Altus Cumulus Electrification Study (ACES) used the Altus II remotely-piloted aircraft to study thunderstorms in the Atlantic Ocean off Key West and the west of the Everglades. Using special equipment aboard the Altus II, scientists in ACES will gather electric, magnetic, and optical measurements of the thunderstorms, gauging elements such as lightning activity and the electrical environment in and around the storms. With dual goals of gathering weather data safely and testing the adaptability of the uninhabited aircraft, the ACES study is a collaboration among the Marshall Space Flight Center, the University of Alabama in Huntsville, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Pernsylvania State University in University Park, and General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc.
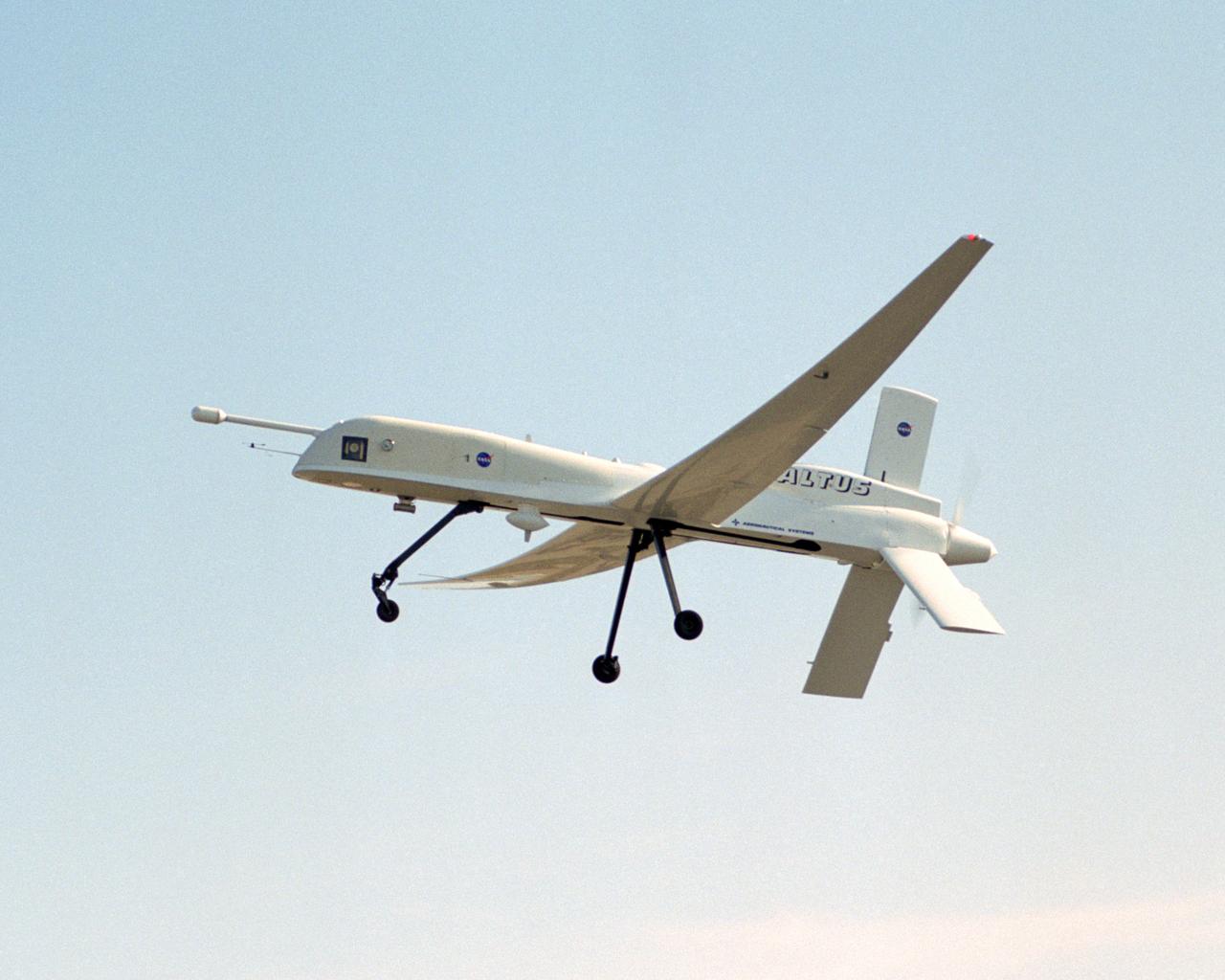

A NASA team studying the causes of electrical storms and their effects on our home planet achieved a milestone on August 21, 2002, completing the study's longest-duration research flight and monitoring four thunderstorms in succession. Based at the Naval Air Station Key West, Florida, researchers with the Altus Cumulus Electrification Study (ACES) used the Altus II remotely-piloted aircraft to study thunderstorms in the Atlantic Ocean off Key West and the west of the Everglades. The ACES lightning study used the Altus II twin turbo uninhabited aerial vehicle, built by General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc. of San Diego. The Altus II was chosen for its slow flight speed of 75 to 100 knots (80 to 115 mph), long endurance, and high-altitude flight (up to 65,000 feet). These qualities gave the Altus II the ability to fly near and around thunderstorms for long periods of time, allowing investigations to be to be conducted over the entire life cycle of storms. The vehicle has a wing span of 55 feet and a payload capacity of over 300 lbs. With dual goals of gathering weather data safely and testing the adaptability of the uninhabited aircraft, the ACES study is a collaboration among the Marshall Space Flight Center, the University of Alabama in Huntsville, NASA,s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Pernsylvania State University in University Park, and General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc.
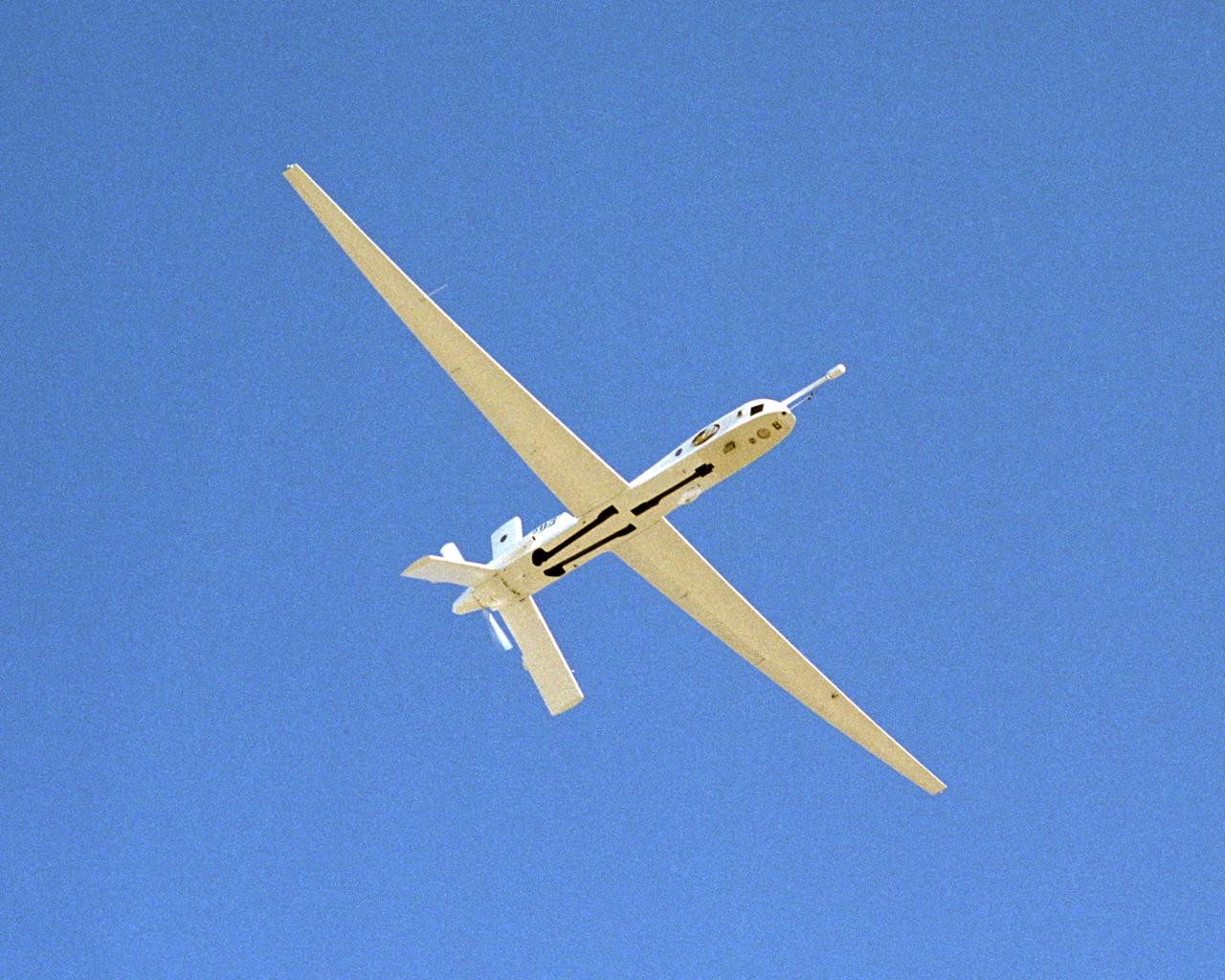

A NASA team studying the causes of electrical storms and their effects on our home planet achieved a milestone on August 21, 2002, completing the study's longest-duration research flight and monitoring four thunderstorms in succession. Based at the Naval Air Station Key West, Florida, researchers with the Altus Cumulus Electrification Study (ACES) used the Altus II remotely piloted aircraft to study thunderstorms in the Atlantic Ocean off Key West and the west of the Everglades. The ACES lightning study used the Altus II twin turbo uninhabited aerial vehicle, built by General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc. of San Diego. The Altus II was chosen for its slow flight speed of 75 to 100 knots (80 to 115 mph), long endurance, and high-altitude flight (up to 65,000 feet). These qualities gave the Altus II the ability to fly near and around thunderstorms for long periods of time, allowing investigations to be conducted over the entire life cycle of storms. The vehicle has a wing span of 55 feet and a payload capacity of over 300 lbs. With dual goals of gathering weather data safely and testing the adaptability of the uninhabited aircraft, the ACES study is a collaboration among the Marshall Space Flight Center, the University of Alabama in Huntsville, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Pernsylvania State University in University Park, and General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc.
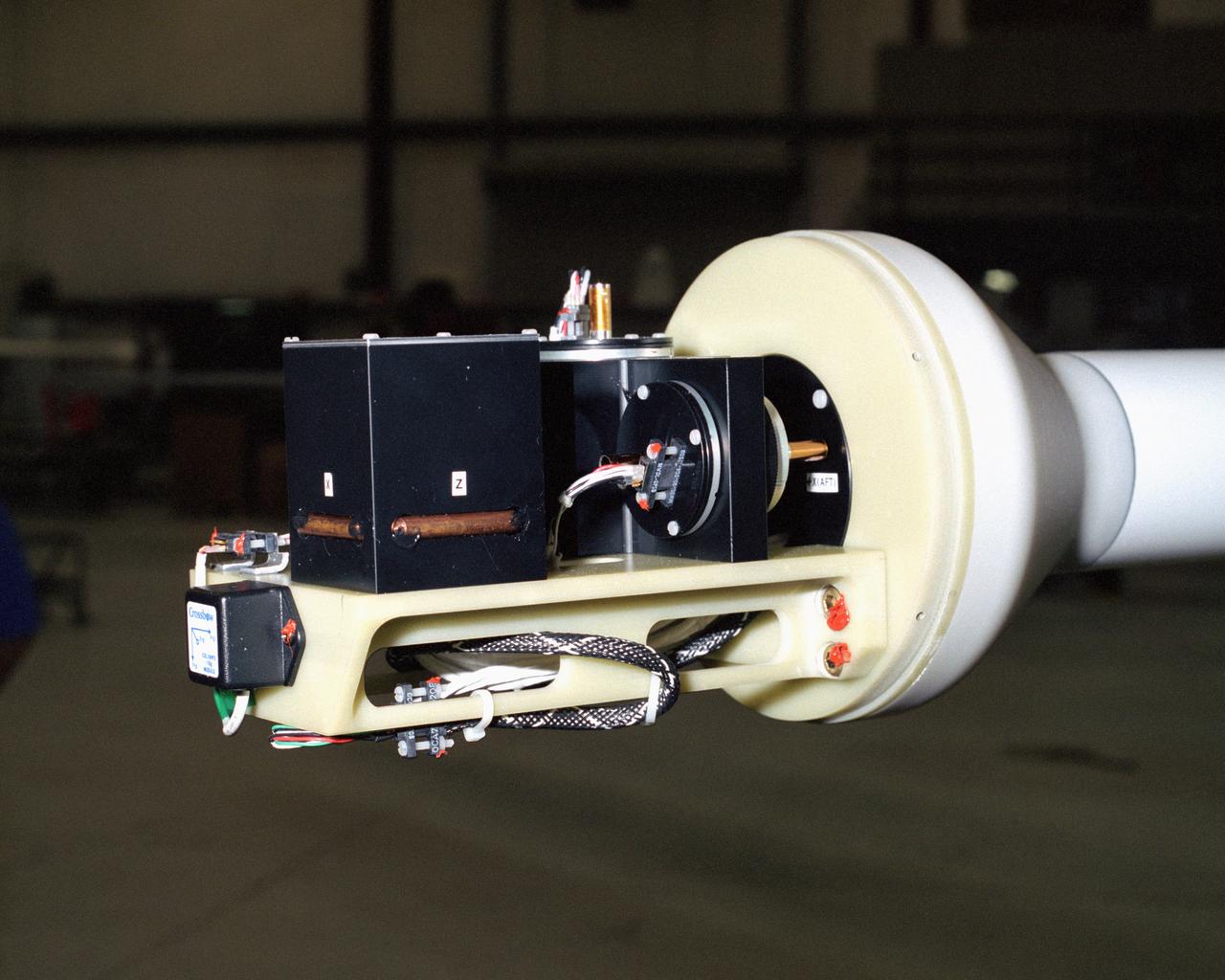
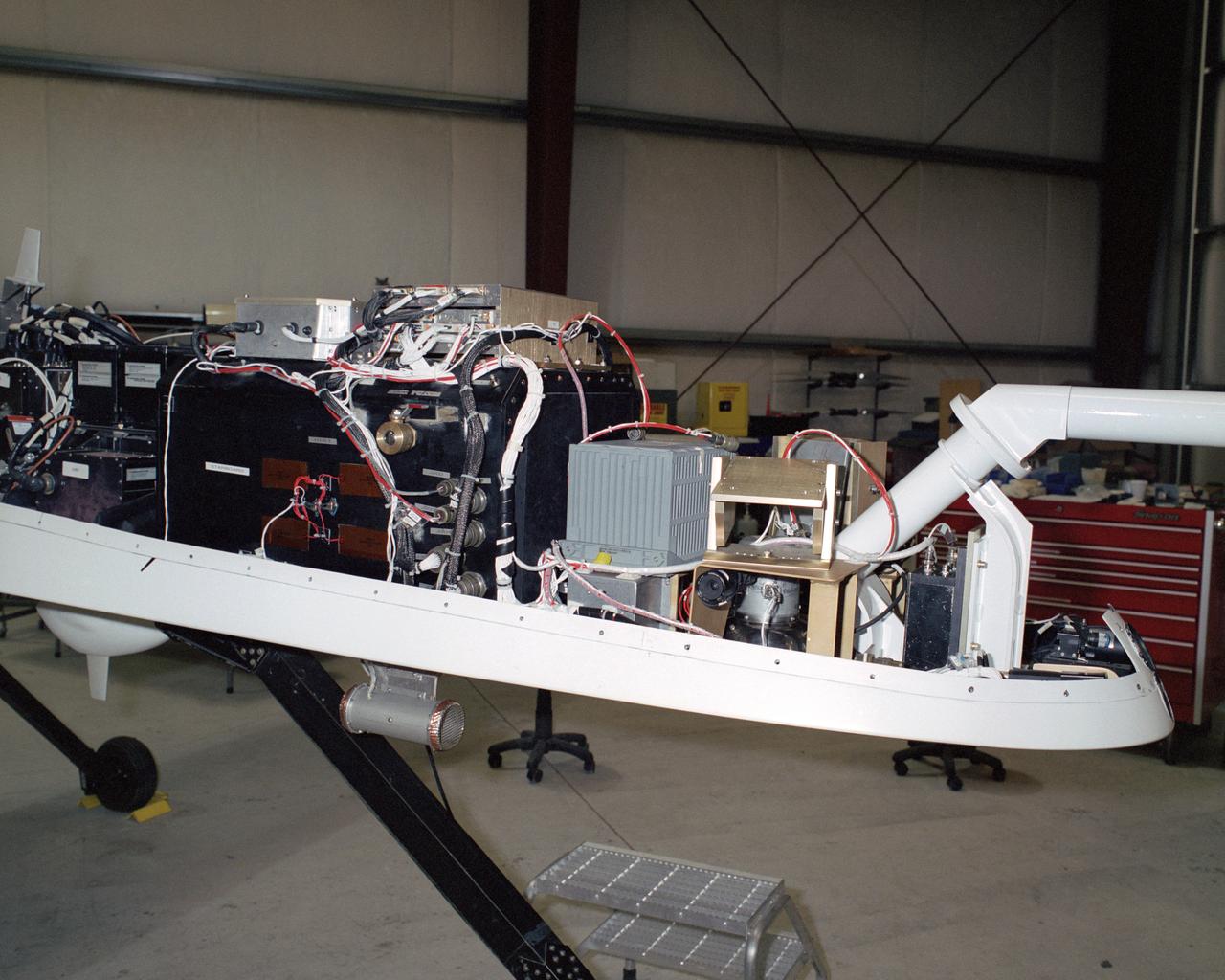
A NASA team studying the causes of electrical storms and their effects on our home planet achieved a milestone on August 21, 2002, completing the study's longest-duration research flight and monitoring four thunderstorms in succession. Based at the Naval Air Station Key West, Florida, researchers with the Altus Cumulus Electrification Study (ACES) used the Altus II remotely-piloted aircraft to study thunderstorms in the Atlantic Ocean off Key West and the west of the Everglades. Data obtained through sensors mounted to the aircraft will allow researchers in ACES to gauge elements such as lightning activity and the electrical environment in and around storms. By learning more about individual storms, scientists hope to better understand the global water and energy cycle, as well as climate variability. Contained in one portion of the aircraft is a three-axis magnetic search coil, which measures the AC magnetic field; a three-axis electric field change sensor; an accelerometer; and a three-axis magnetometer, which measures the DC magnetic field. With dual goals of gathering weather data safely and testing the adaptability of the uninhabited aircraft, the ACES study is a collaboration among the Marshall Space Flight Center, the University of Alabama in Huntsville, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Pernsylvania State University in University Park, and General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc.
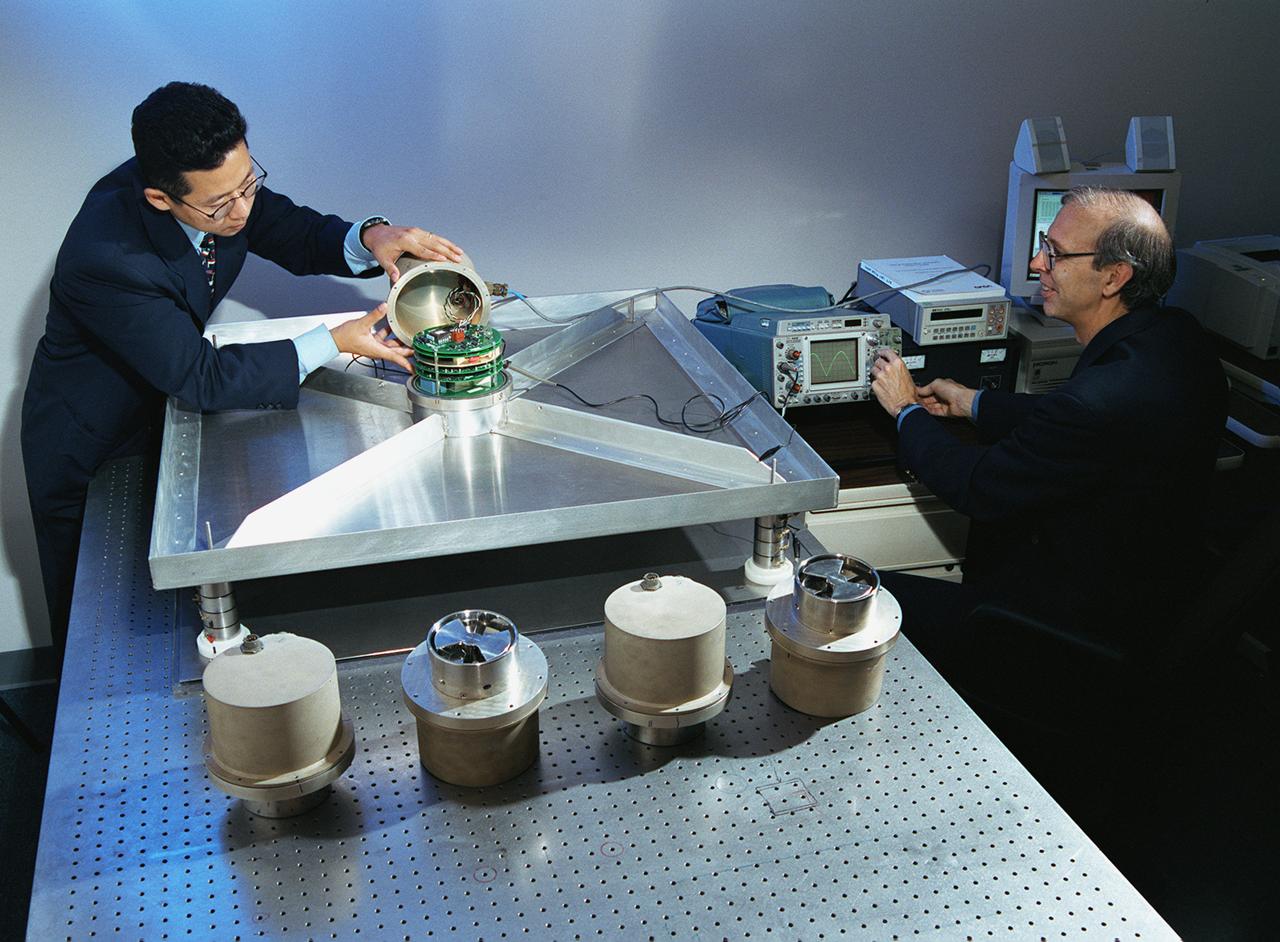

A NASA team studying the causes of electrical storms and their effects on our home planet achieved a milestone on August 21, 2002, completing the study's longest-duration research flight and monitoring four thunderstorms in succession. Radio news media can talk with Dr. Richard Blakeslee, the project's principal investigator, and Tony Kim, project manager at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), about their results and how their work will help improve future weather forecasting ability. Based at the Naval Air Station Key West, Florida, researchers with the Altus Cumulus Electrification Study (ACES) used the Altus II remotely- piloted aircraft to study a thunderstorm in the Atlantic Ocean off Key West, two storms at the western edge of the Everglades, and a large storm over the northwestern corner of the Everglades. This photograph shows Tony Kim And Dr. Richard Blakeslee of MSFC testing aircraft sensors that would be used to measure the electric fields produced by thunderstorm as part of NASA's ACES. With dual goals of gathering weather data safely and testing the adaptability of the uninhabited aircraft, the ACES study is a collaboration among the MSFC, the University of Alabama in Huntsville, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Pernsylvania State University in University Park, and General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc.
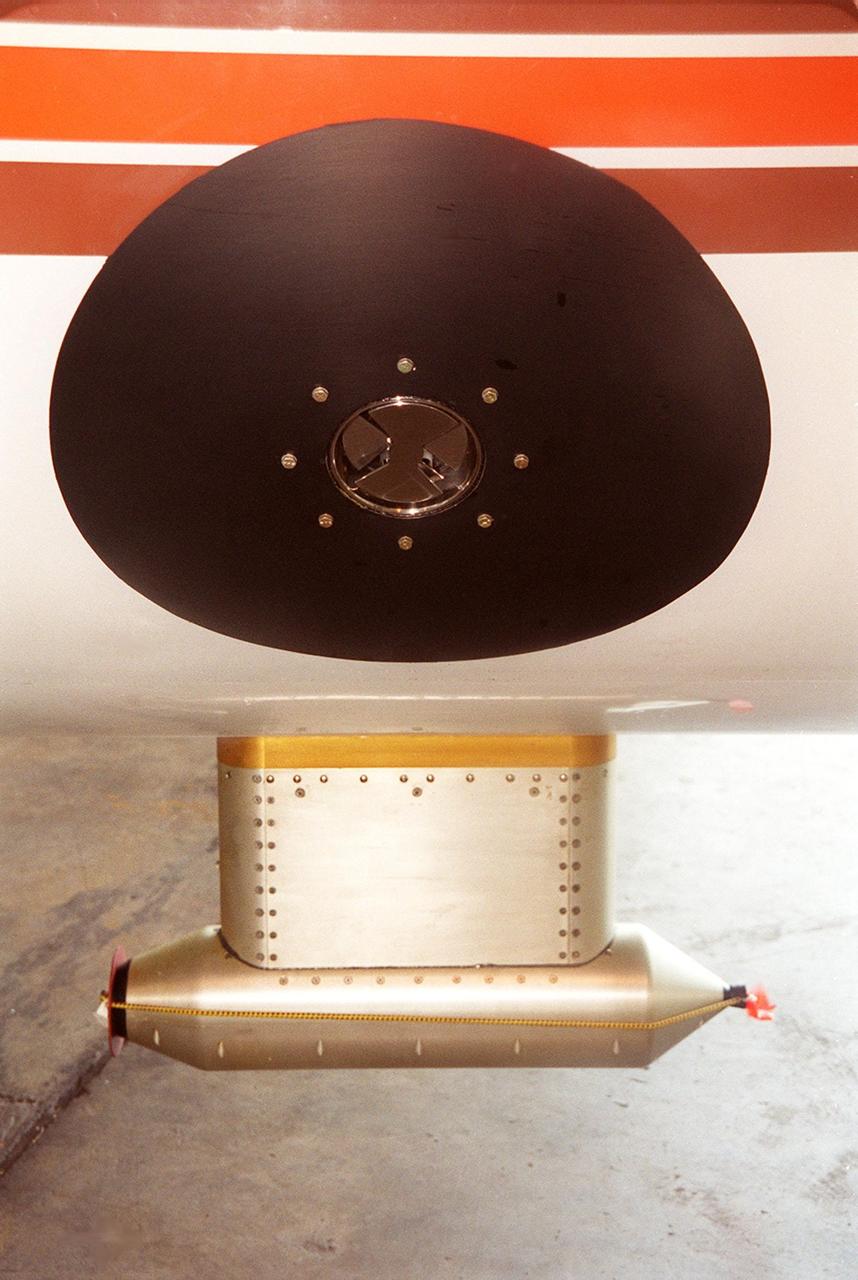
Lightning field study devices are visible on a Cessna Citation aircraft during flight over Central Florida. The center of the black circle contains one of six field mills, used to measure electric fields, located on the body of the plane. Below the circle is one of several cloud physics probes attached to the plane that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The Cessna is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
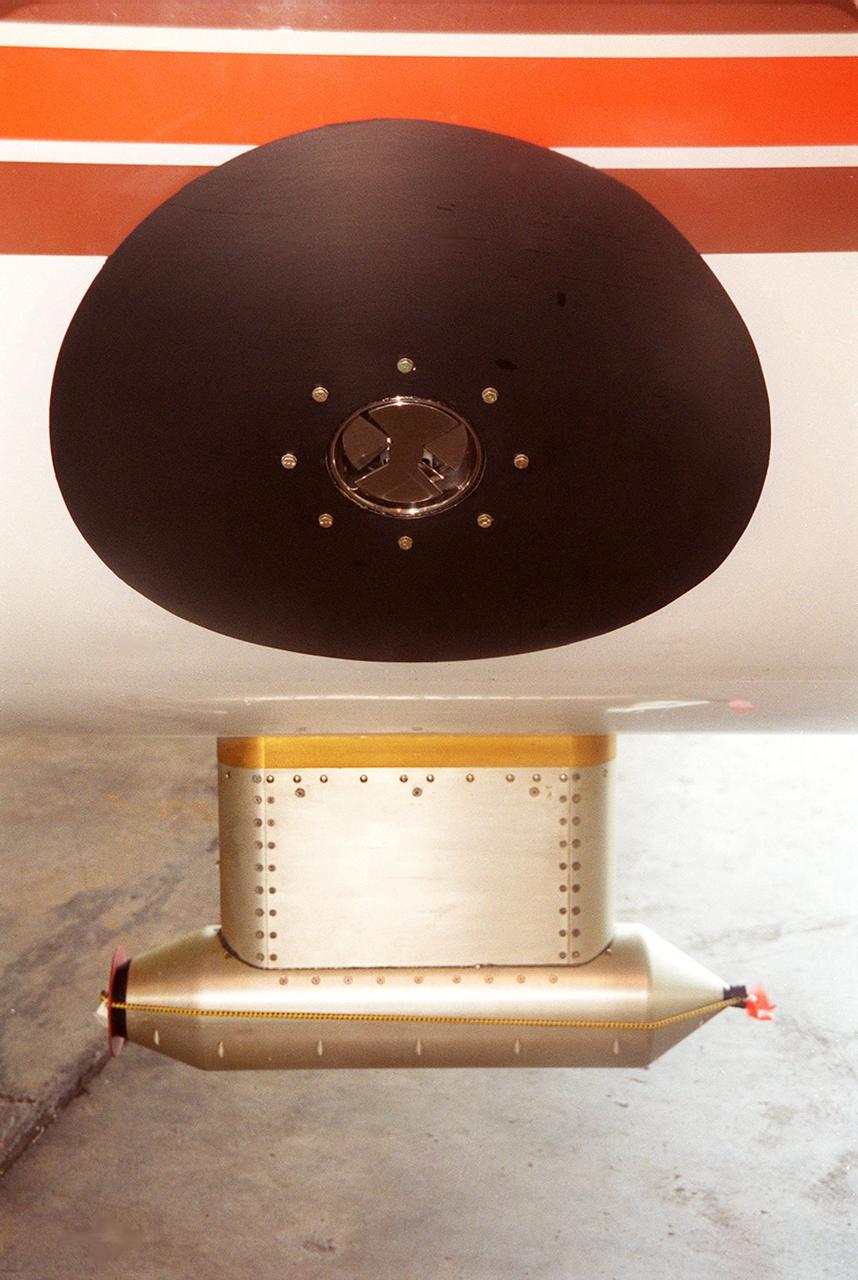
Lightning field study devices are visible on a Cessna Citation aircraft during flight over Central Florida. The center of the black circle contains one of six field mills, used to measure electric fields, located on the body of the plane. Below the circle is one of several cloud physics probes attached to the plane that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The Cessna is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
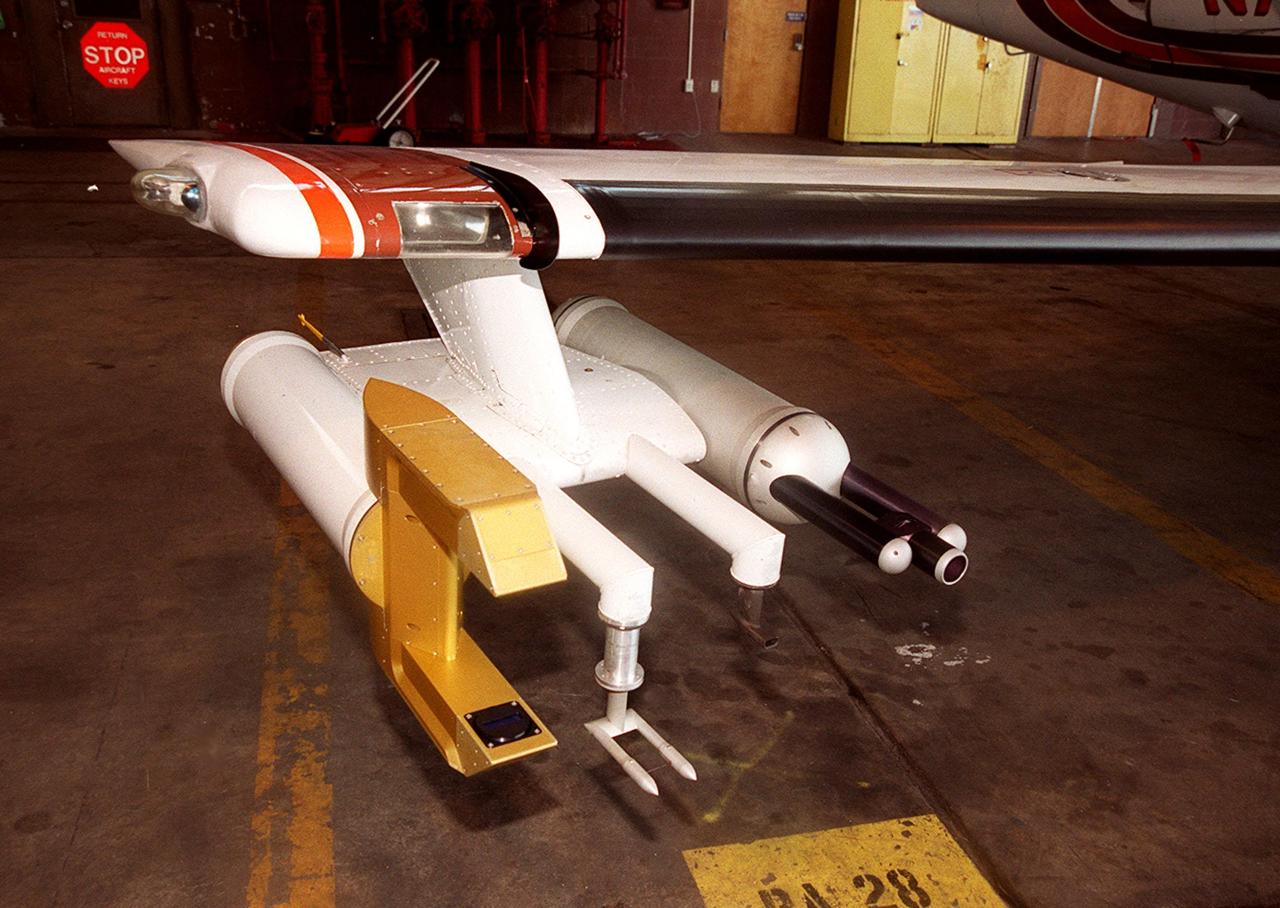

Attached to the wing of a Cessna Citation aircraft are cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is also equipped with field mills, used to measure electric fields. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
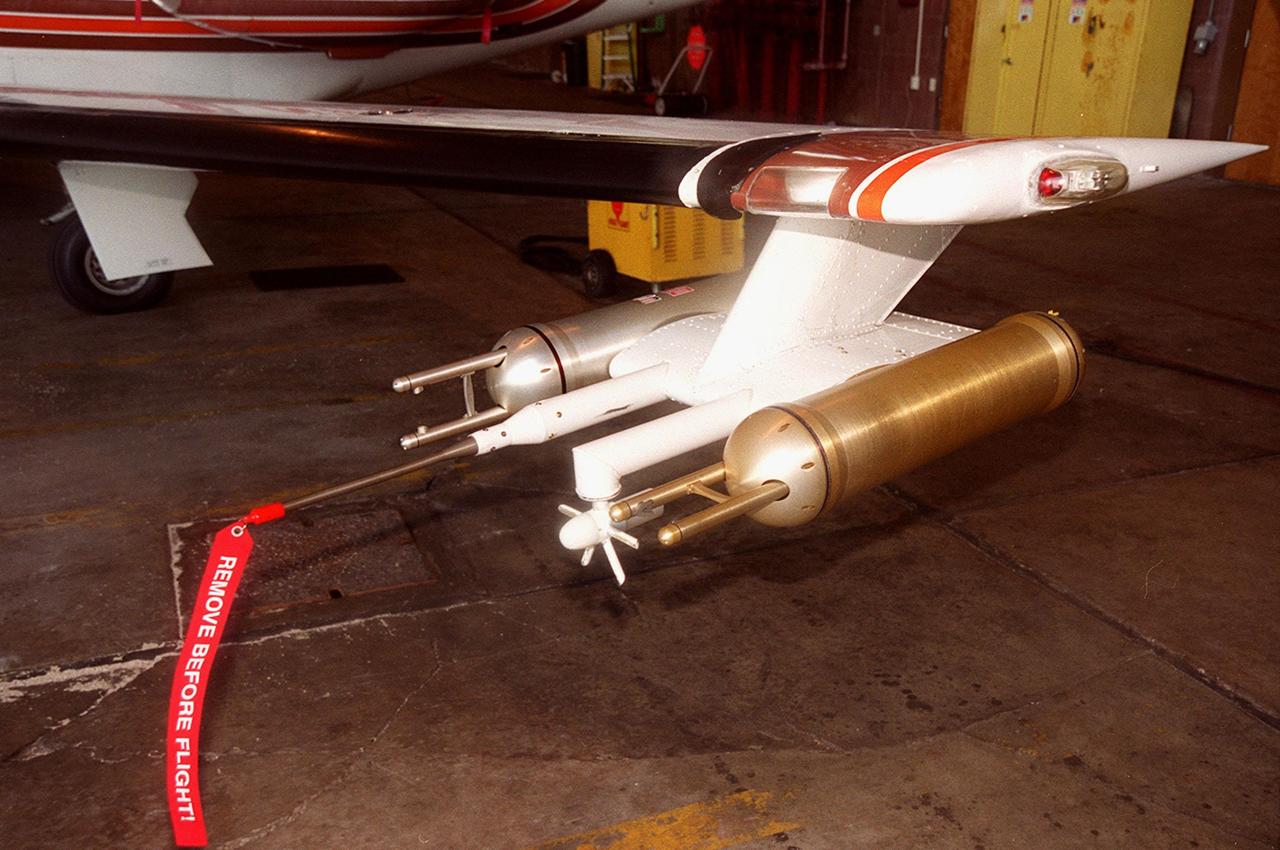

Attached to the wing of a Cessna Citation aircraft are cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is also equipped with field mills, used to measure electric fields. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
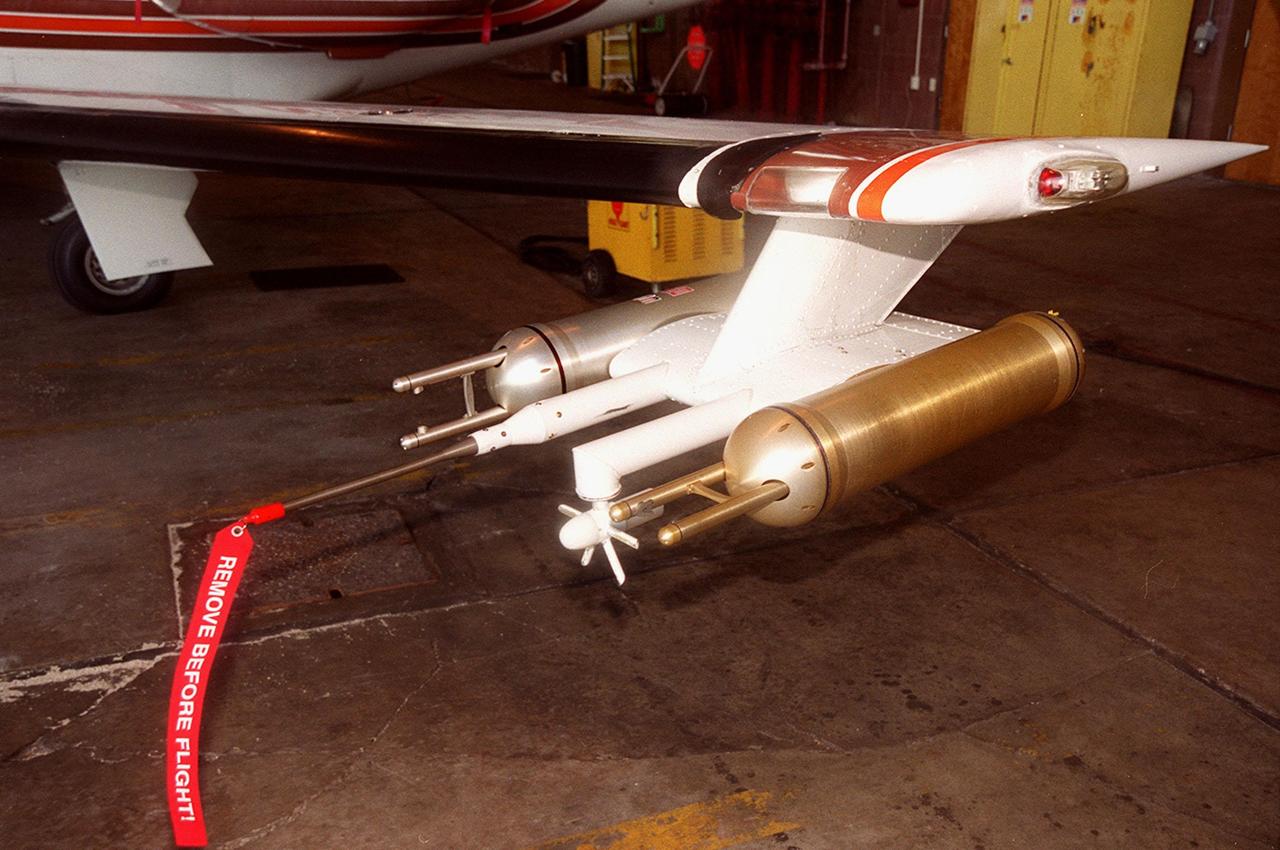

Attached to the wing of a Cessna Citation aircraft are cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is also equipped with field mills, used to measure electric fields. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
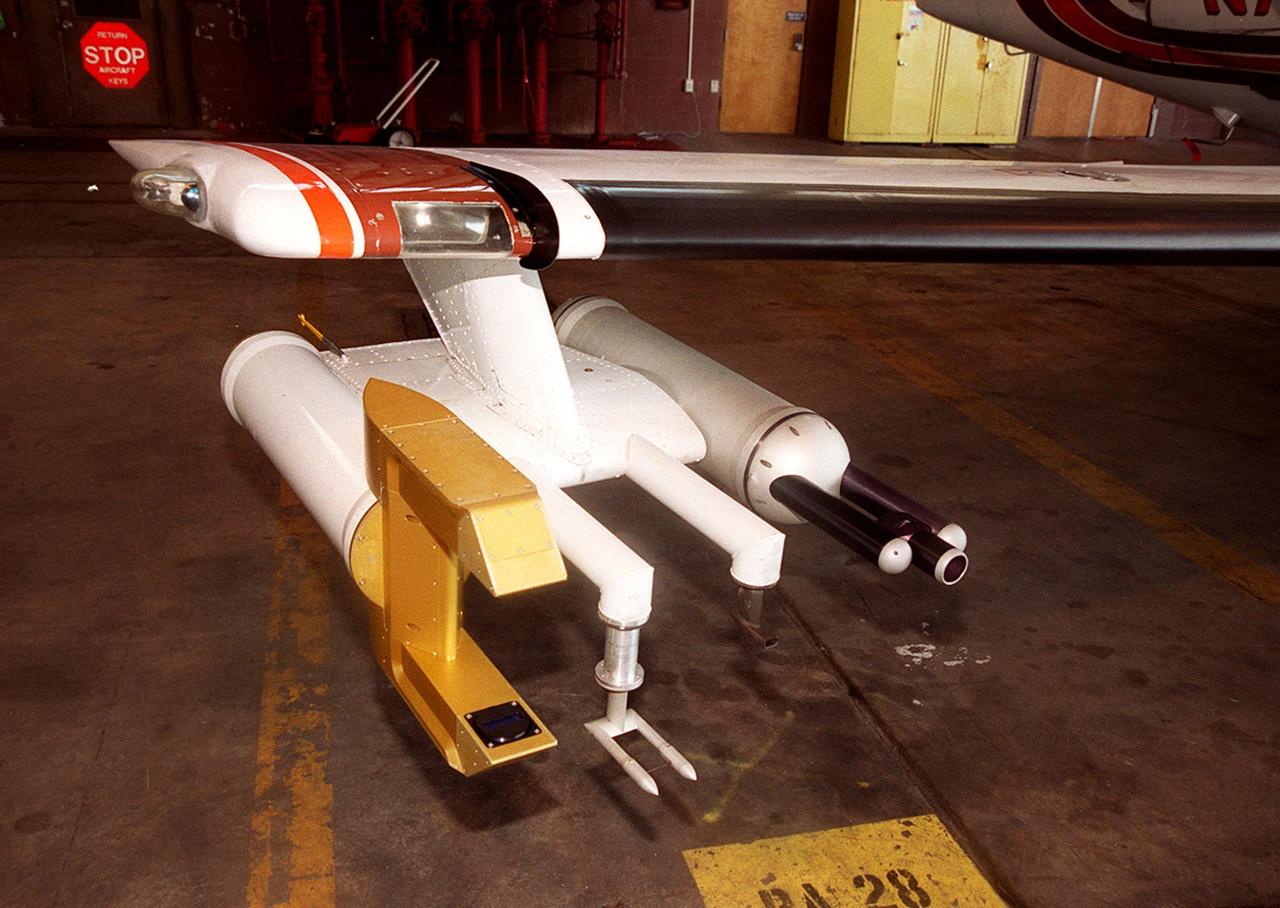

Attached to the wing of a Cessna Citation aircraft are cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is also equipped with field mills, used to measure electric fields. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
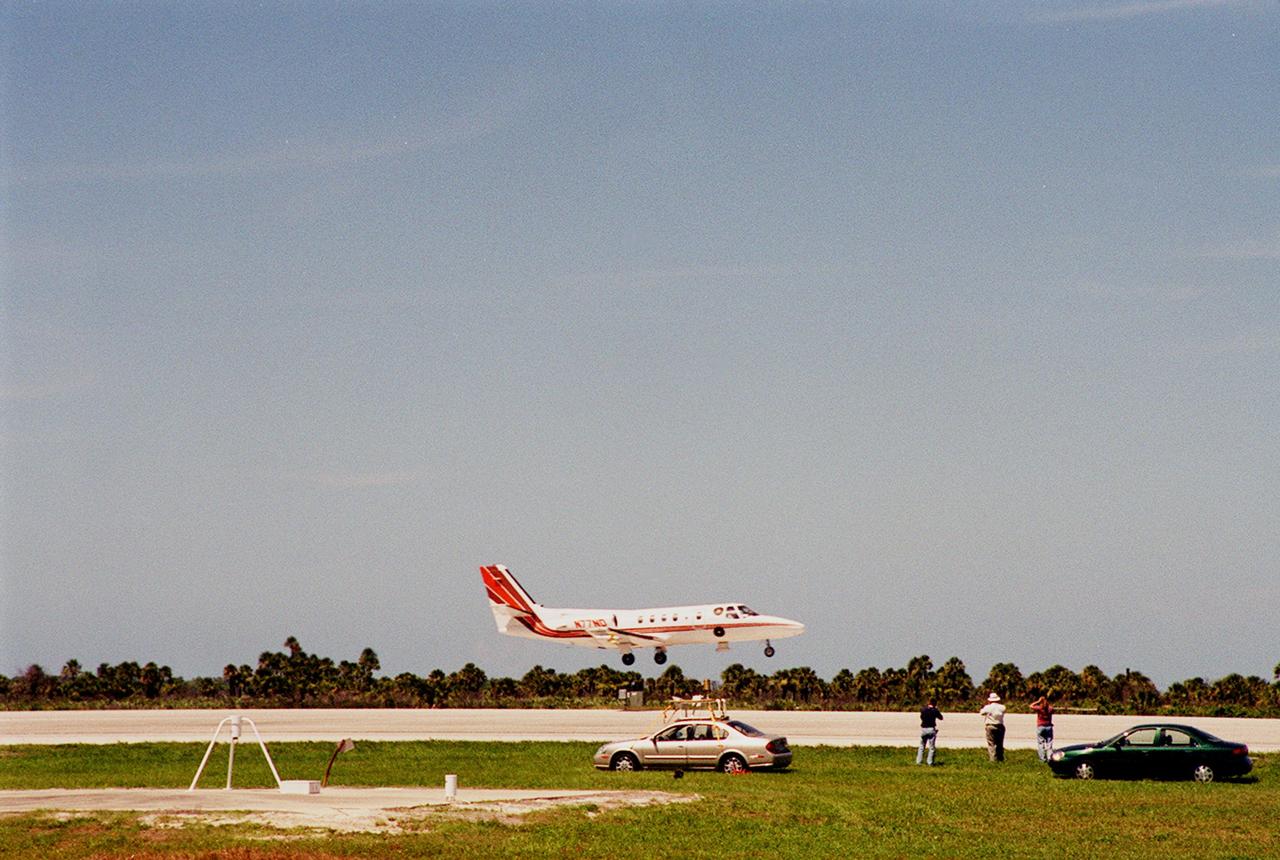

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility, a specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft flies over the runway to calibrate the Cesna's field mills with field mills on the ground (on the tripod at left) and on the car parked nearby (at center). Field mills measure electric fields. The aircraft is also equipped with cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.
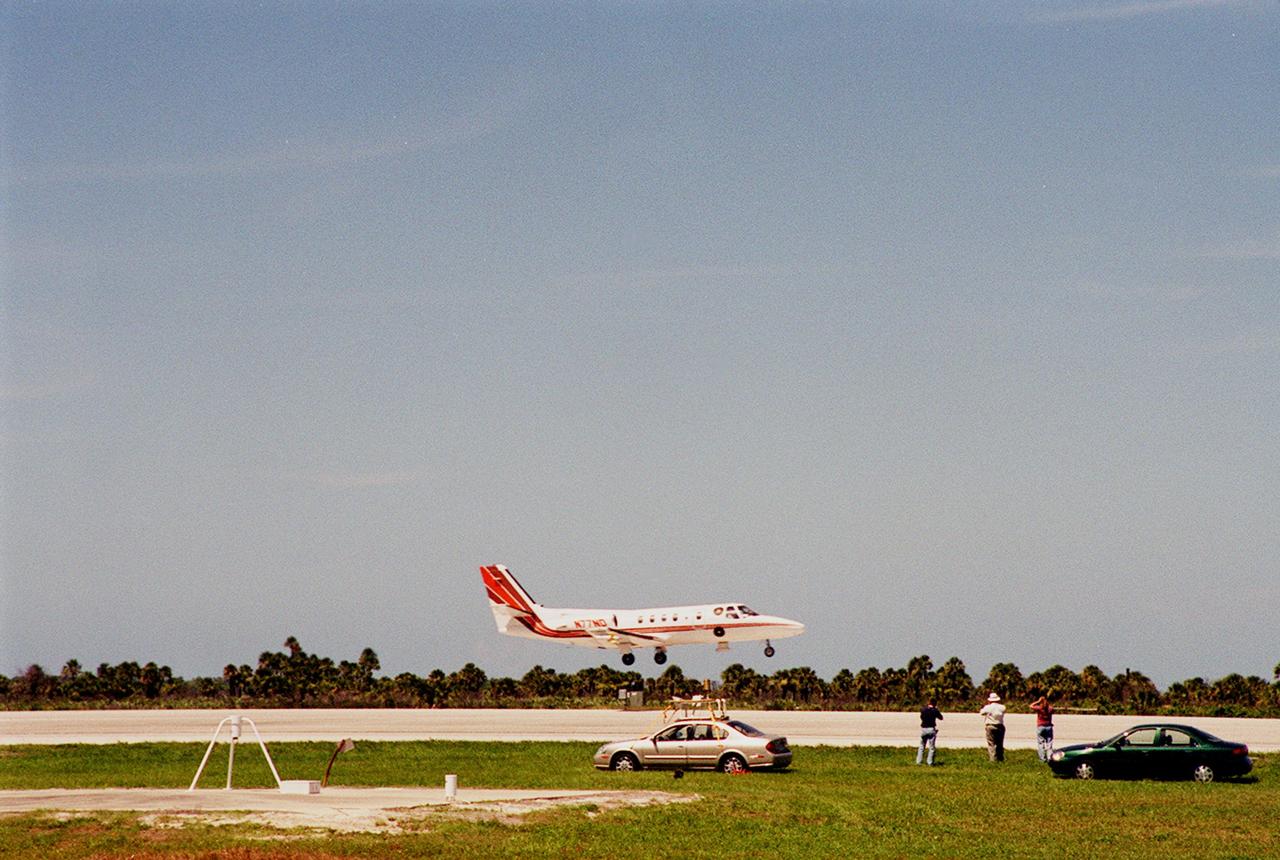

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility, a specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft flies over the runway to calibrate the Cesna's field mills with field mills on the ground (on the tripod at left) and on the car parked nearby (at center). Field mills measure electric fields. The aircraft is also equipped with cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.
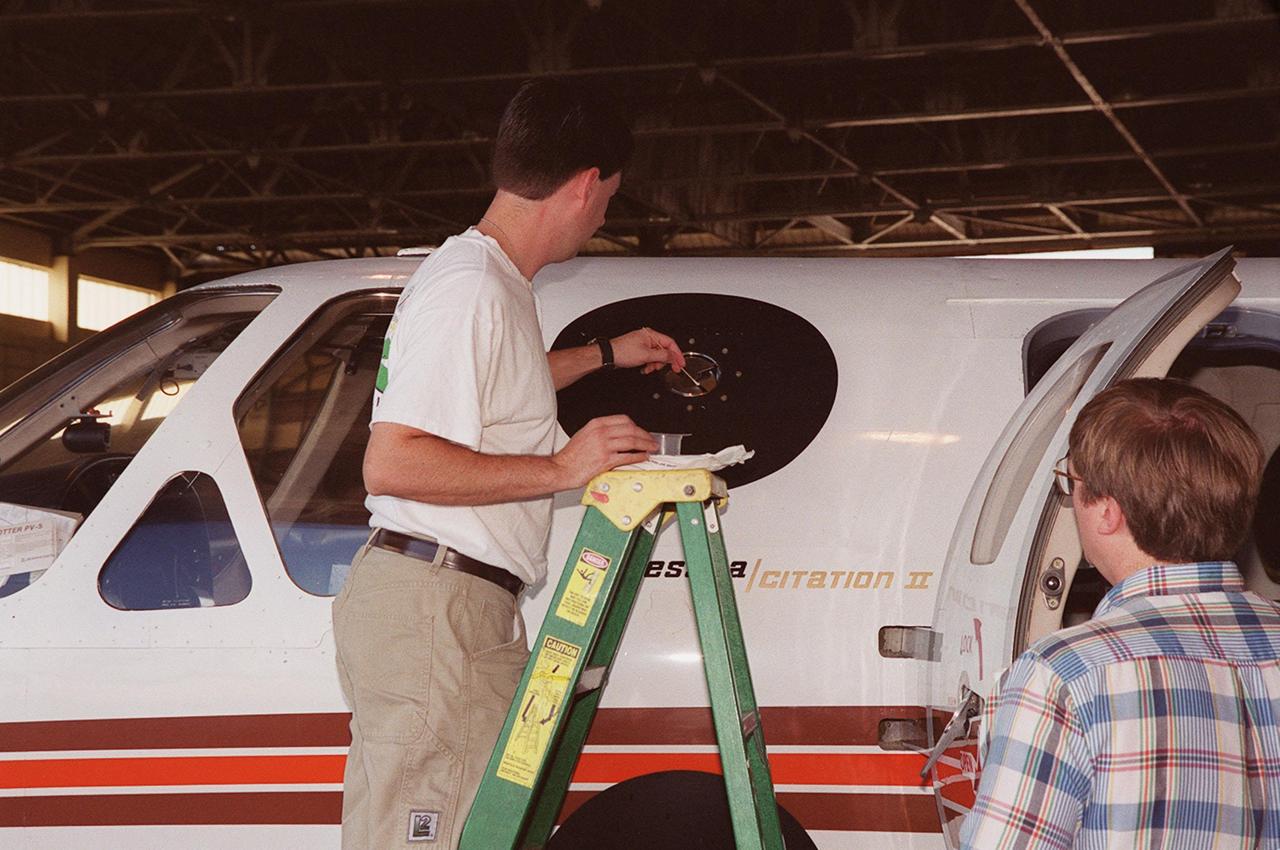

In a hangar at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a weather researcher checks a field mill measuring device on the Cessna Citation. The aircraft is being used for NASA’s airborne field mill study. The plane also carries cloud physics probes (under the body and wings) that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
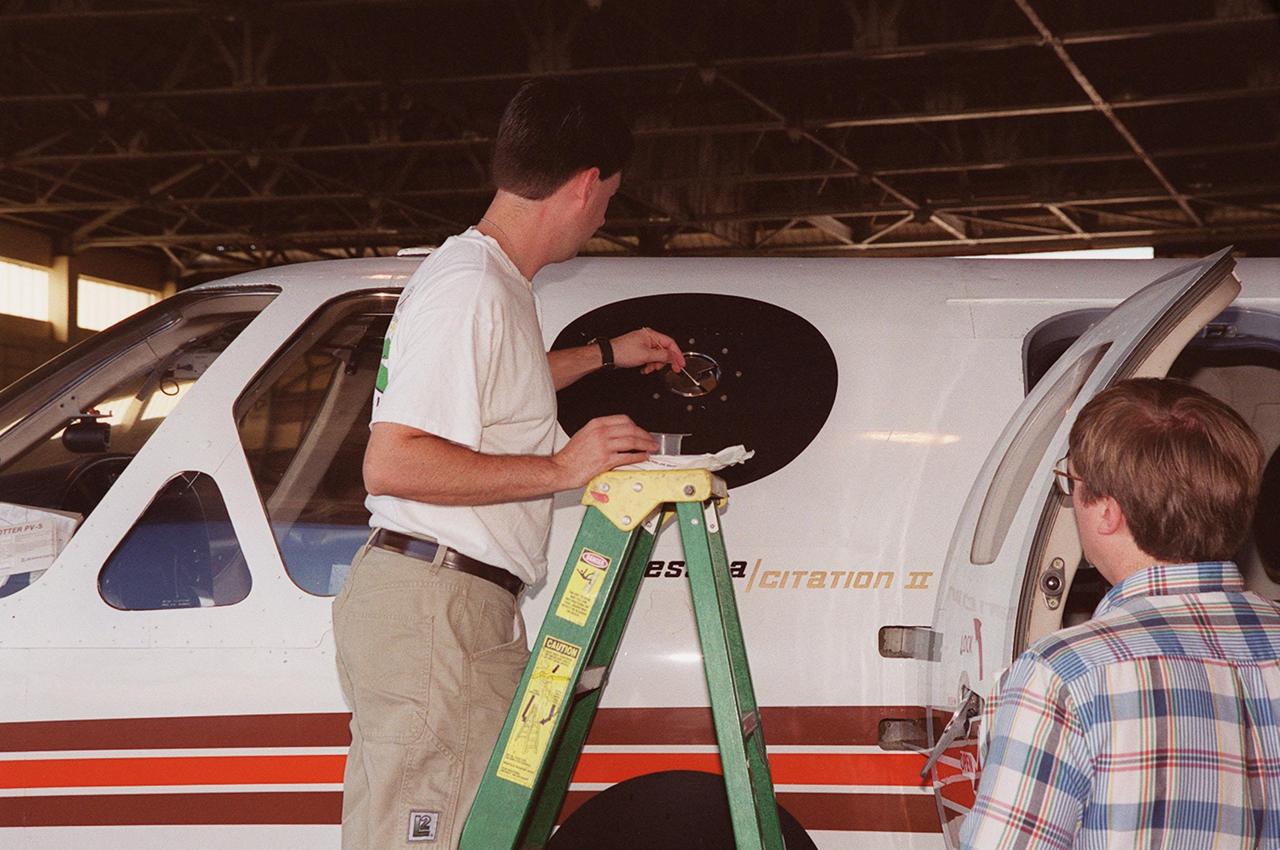

In a hangar at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a weather researcher checks a field mill measuring device on the Cessna Citation. The aircraft is being used for NASA’s airborne field mill study. The plane also carries cloud physics probes (under the body and wings) that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>

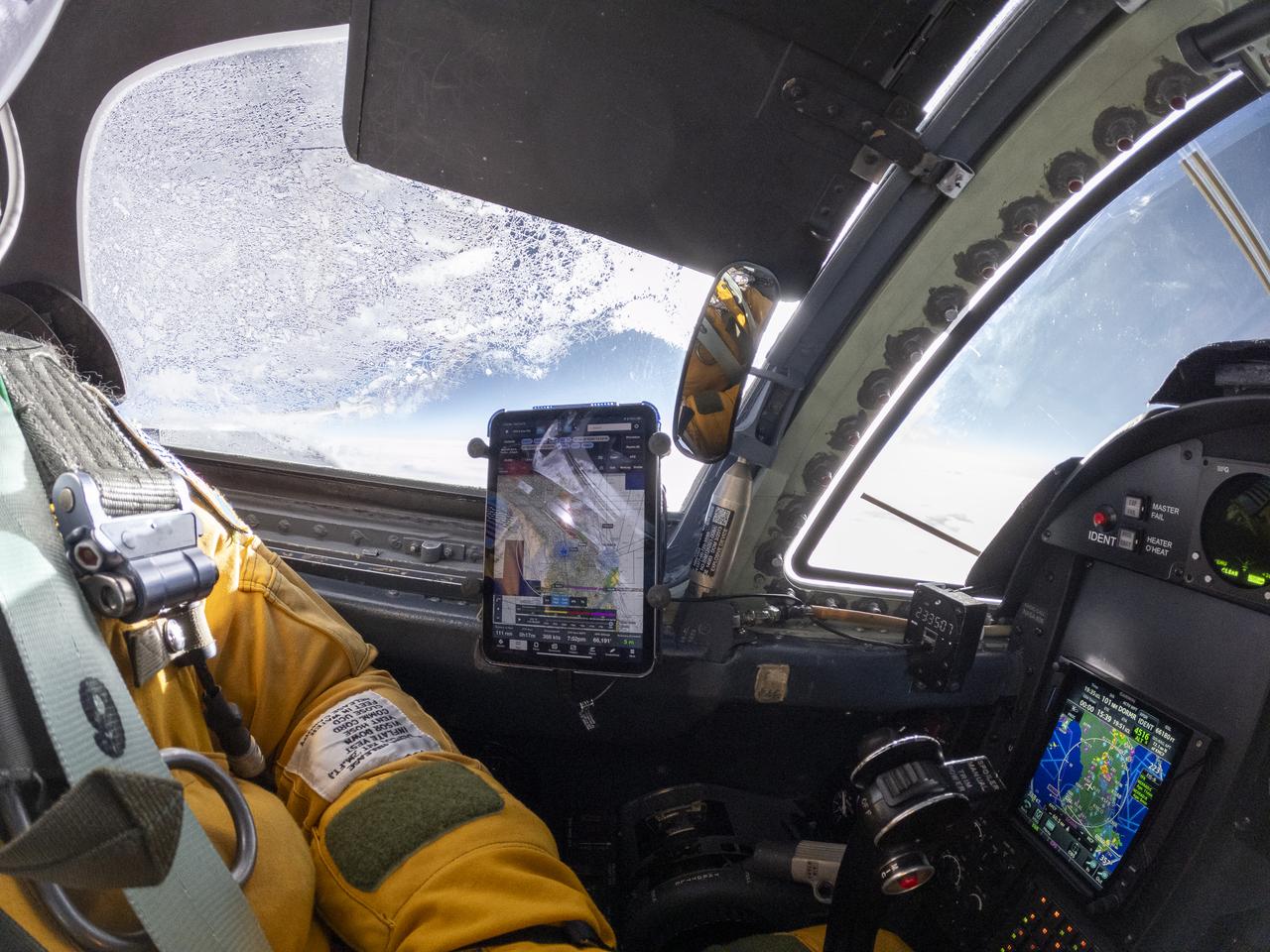
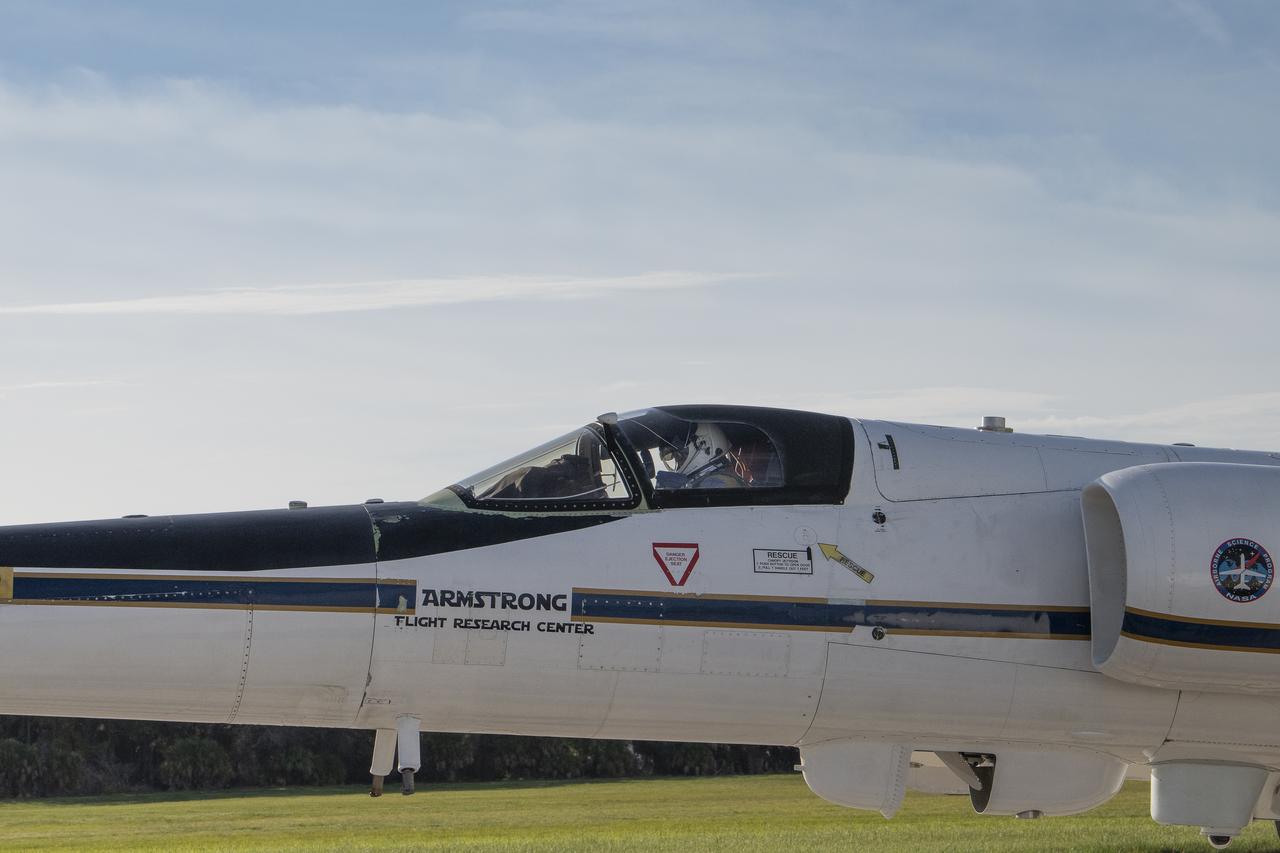
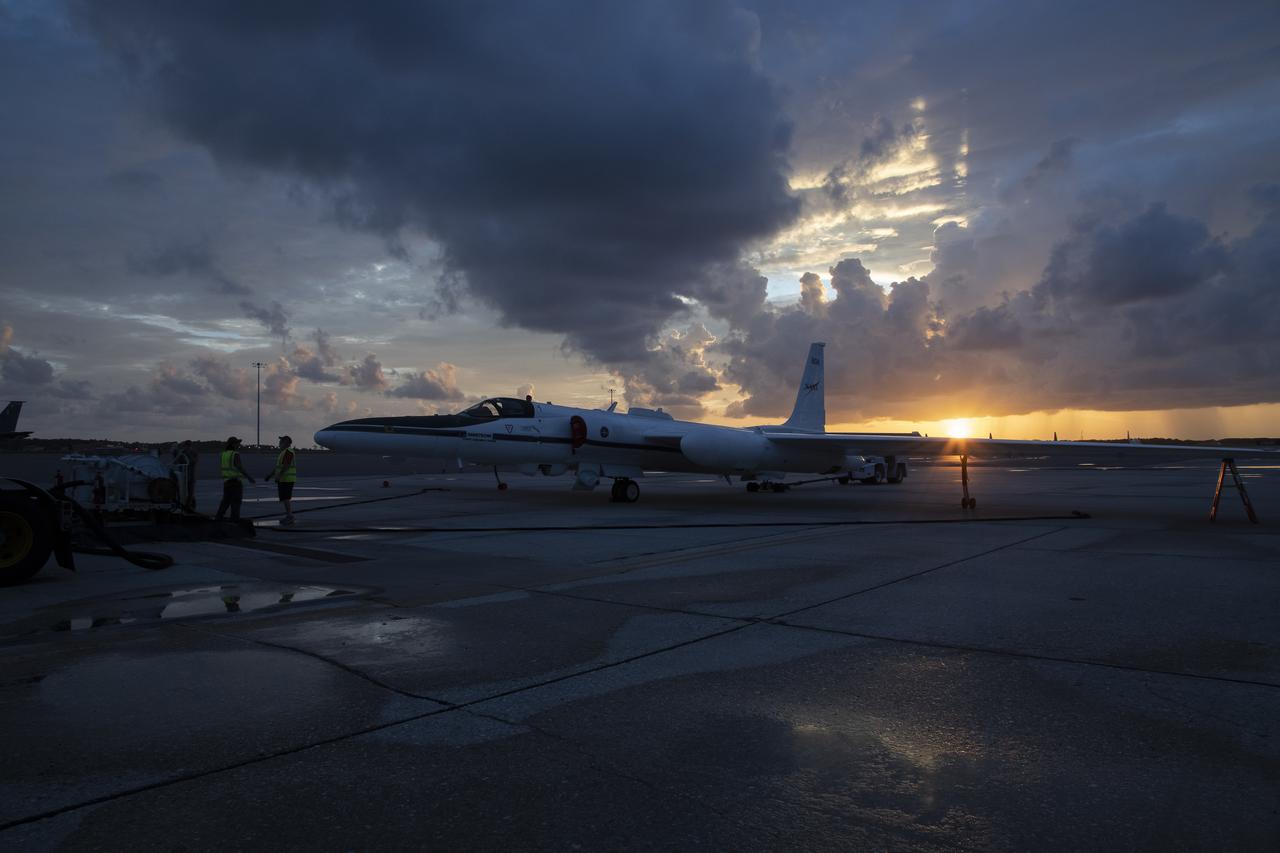
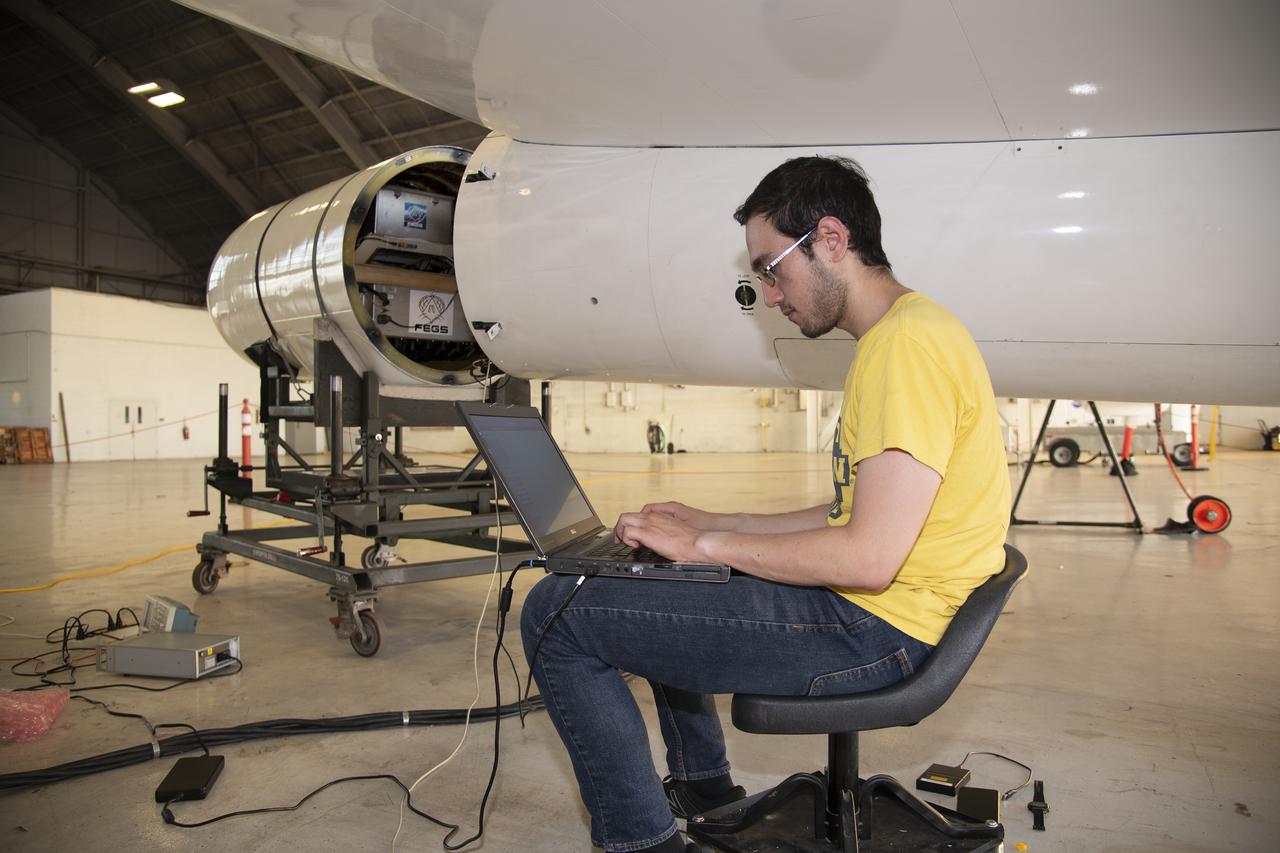
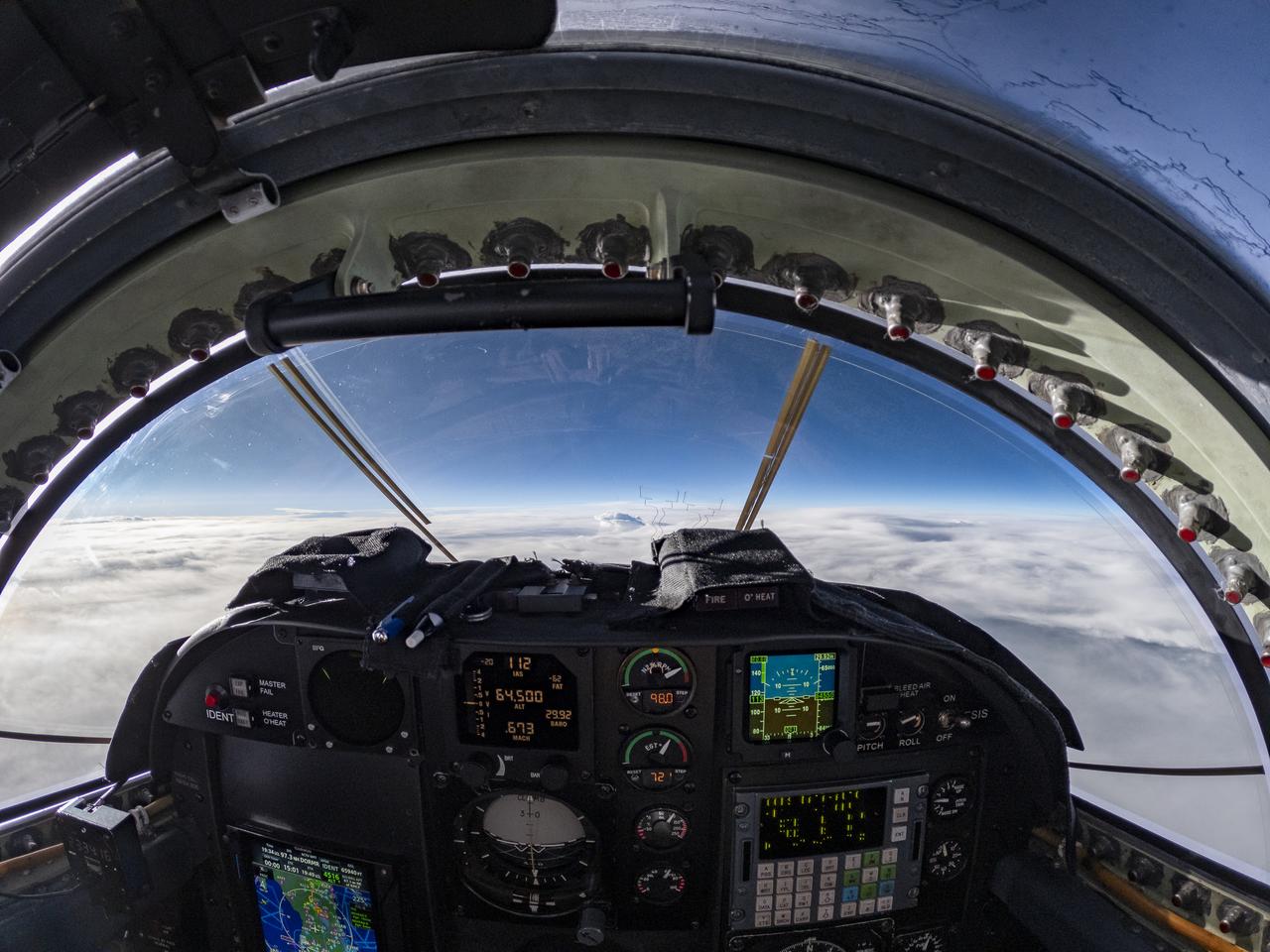
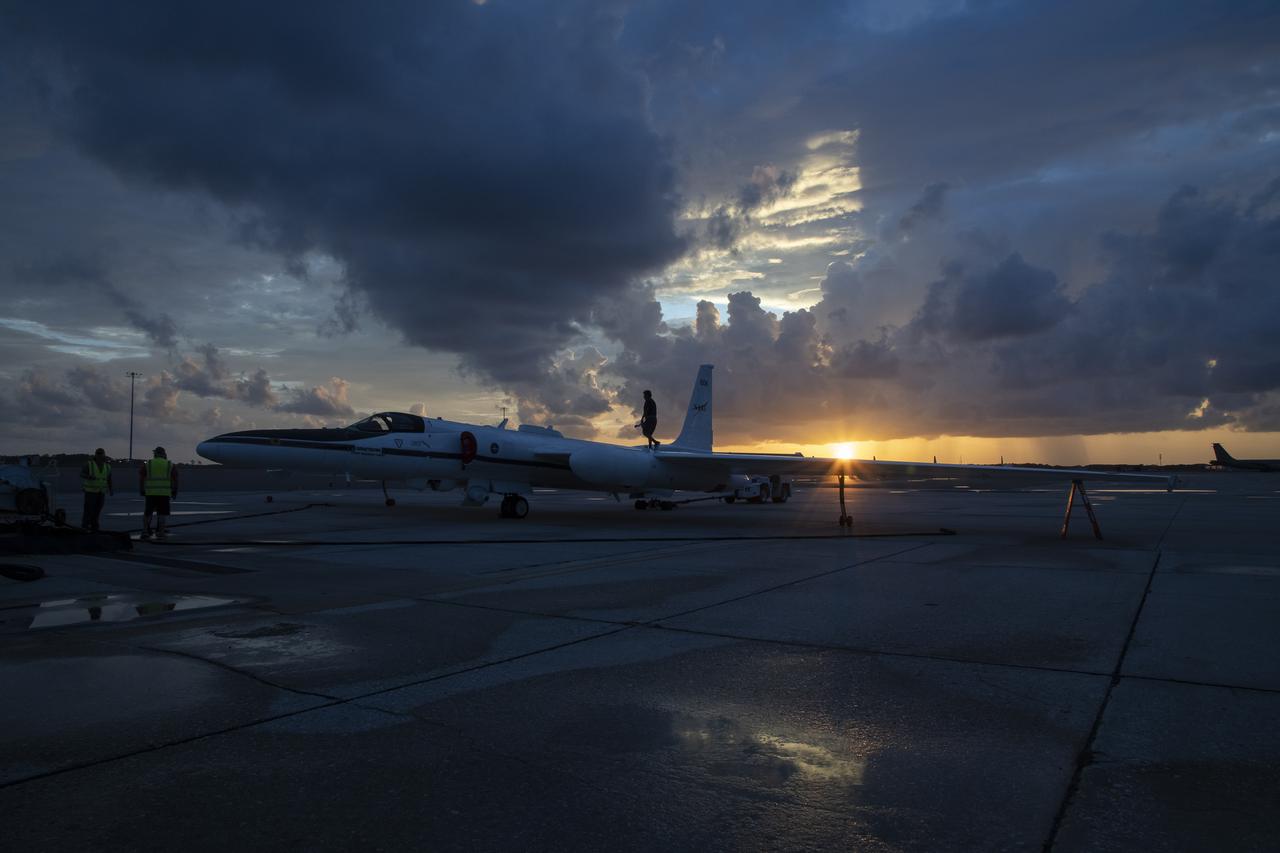
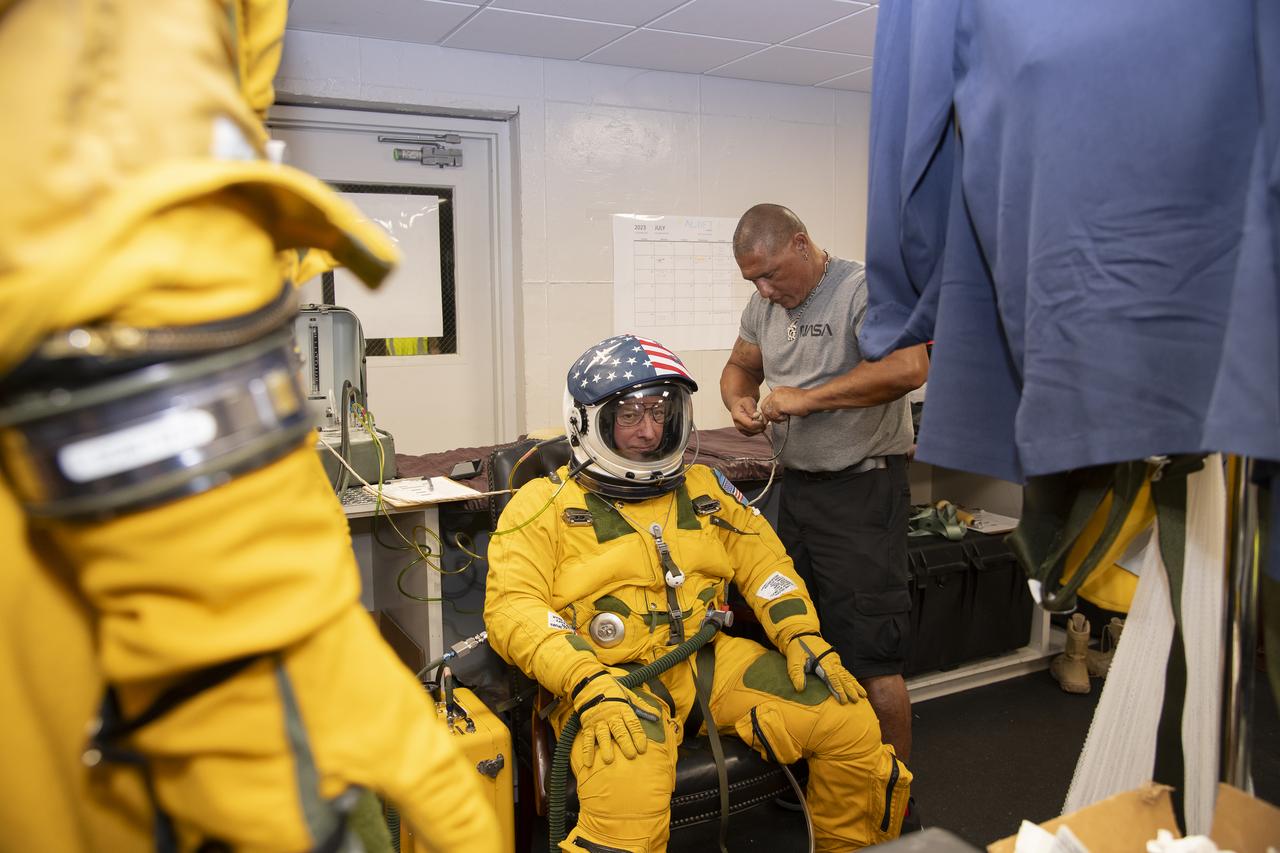
The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
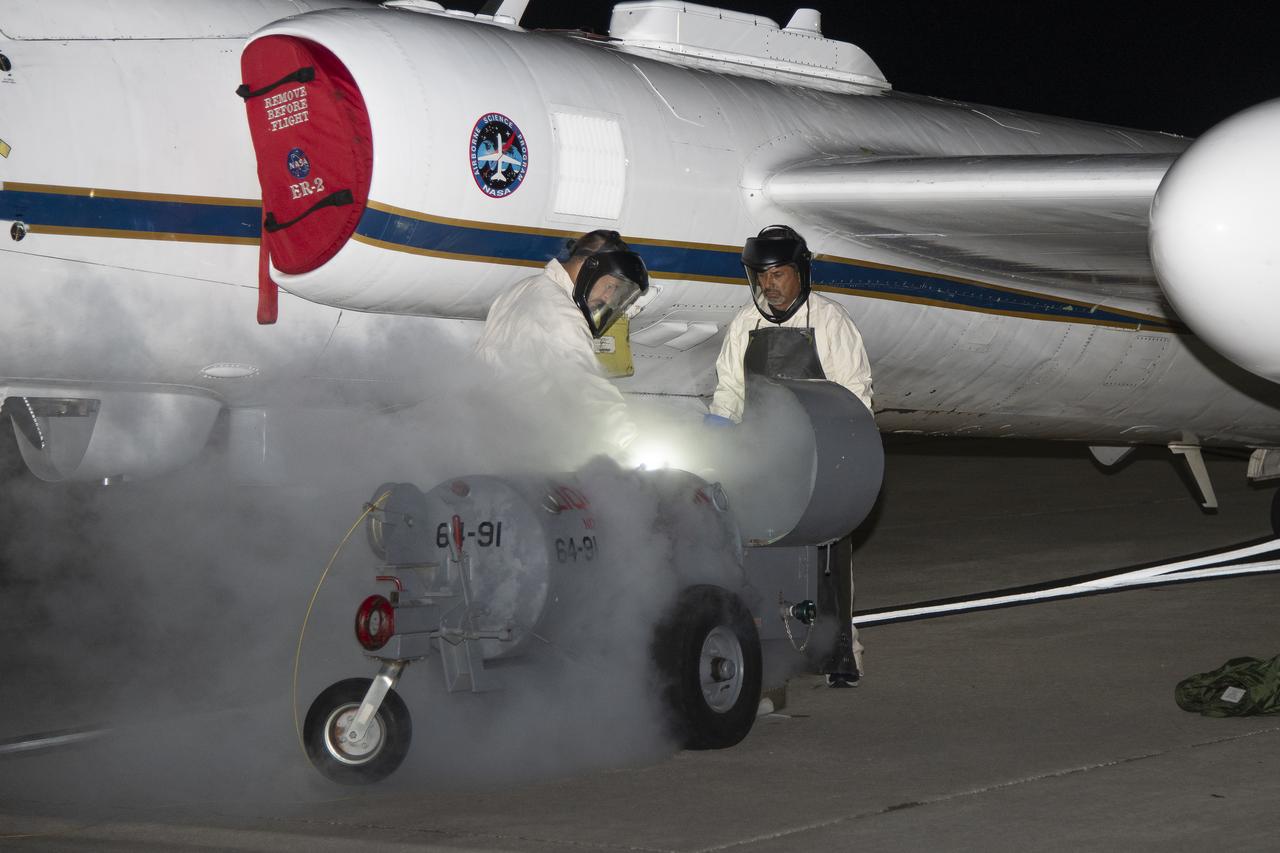

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
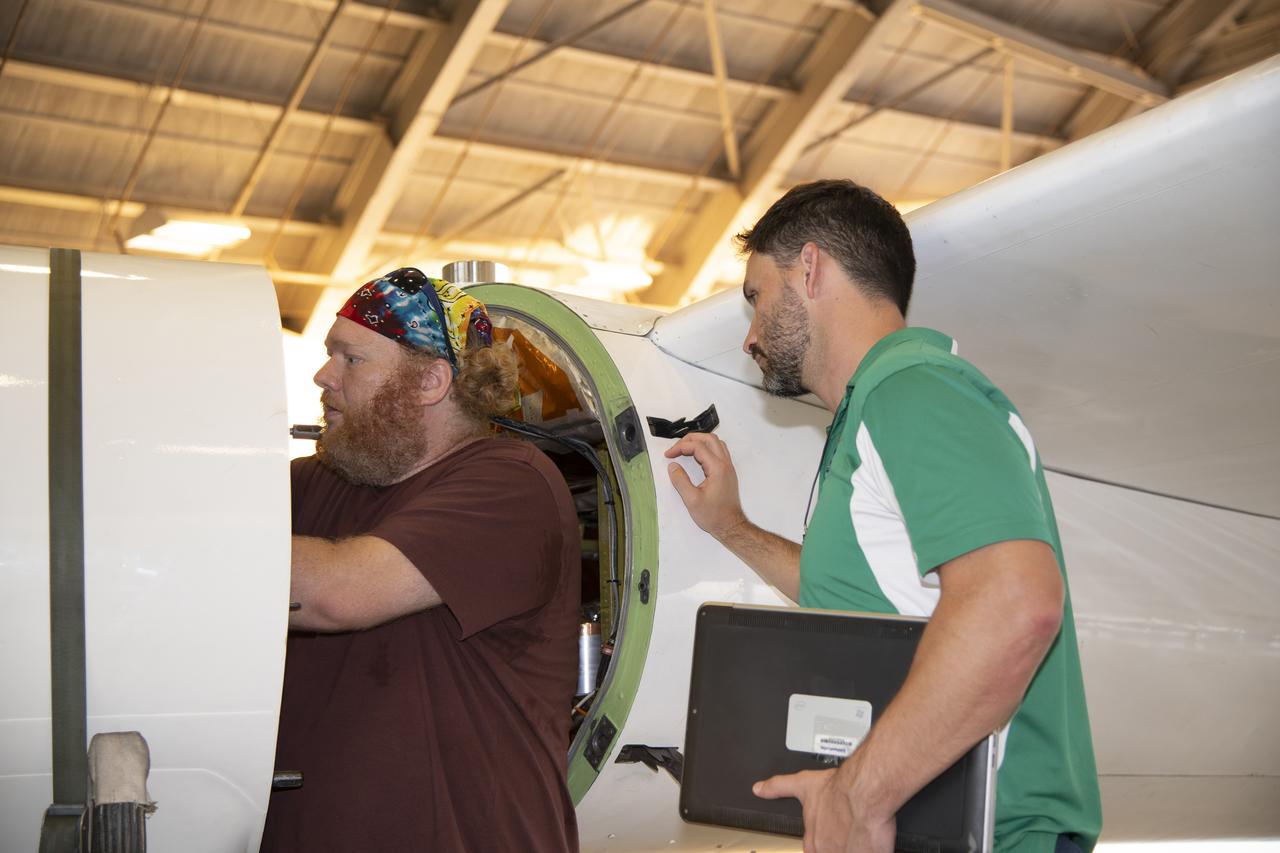

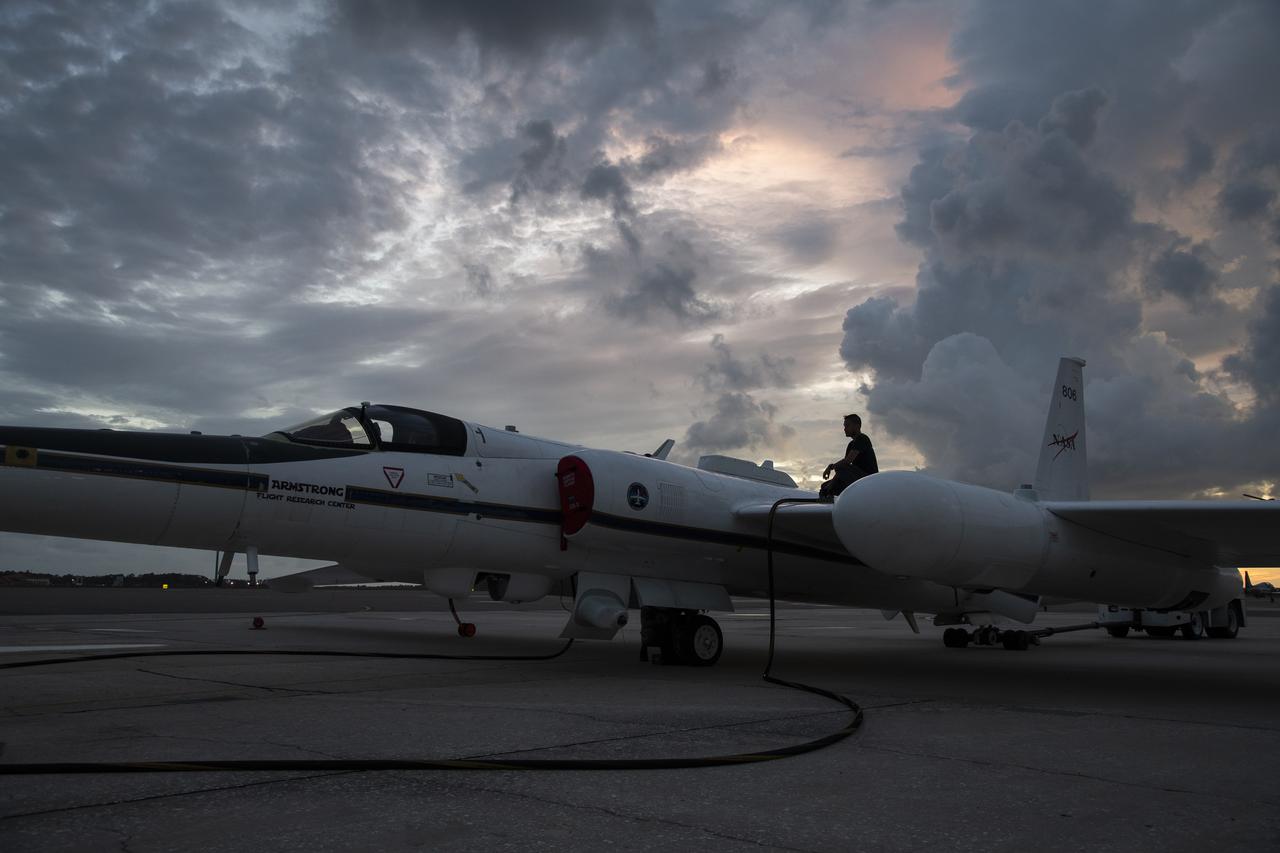
The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
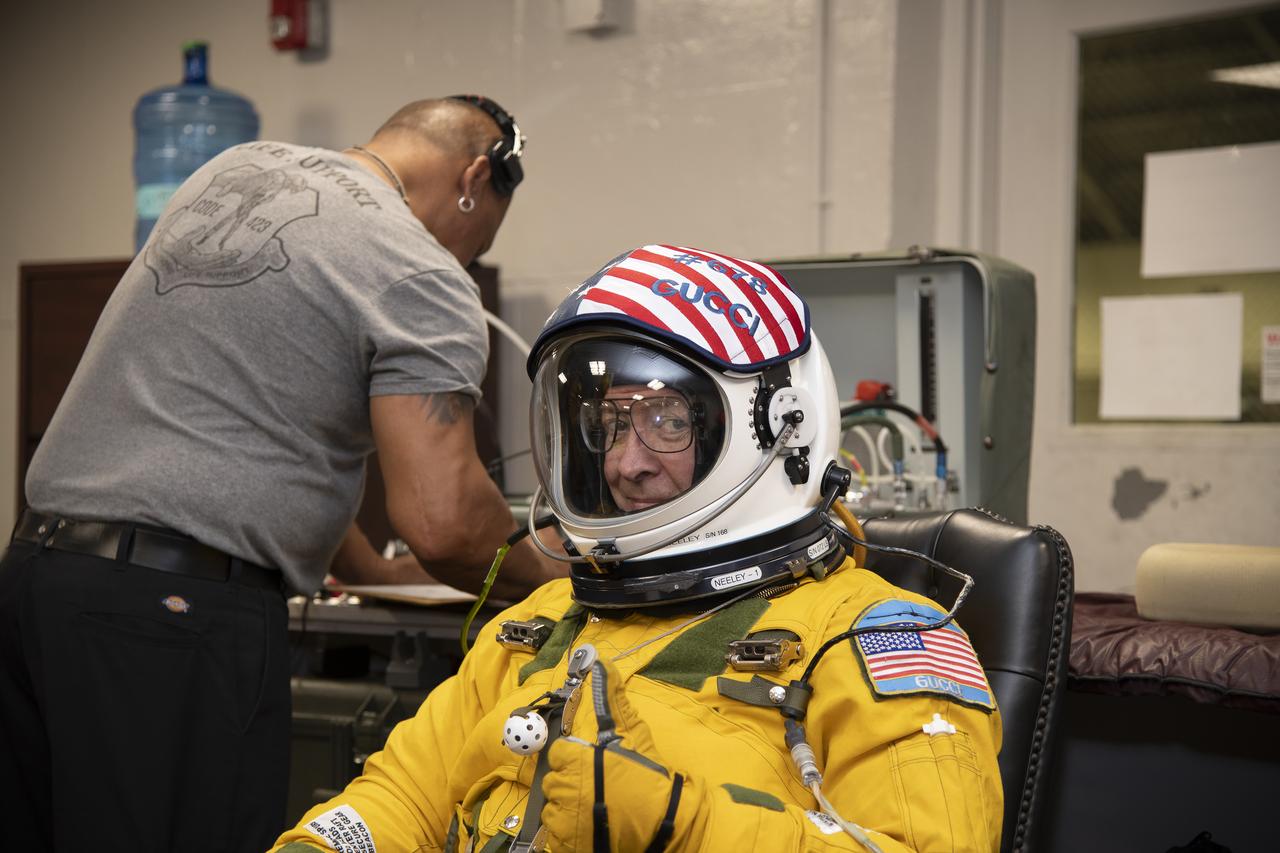

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

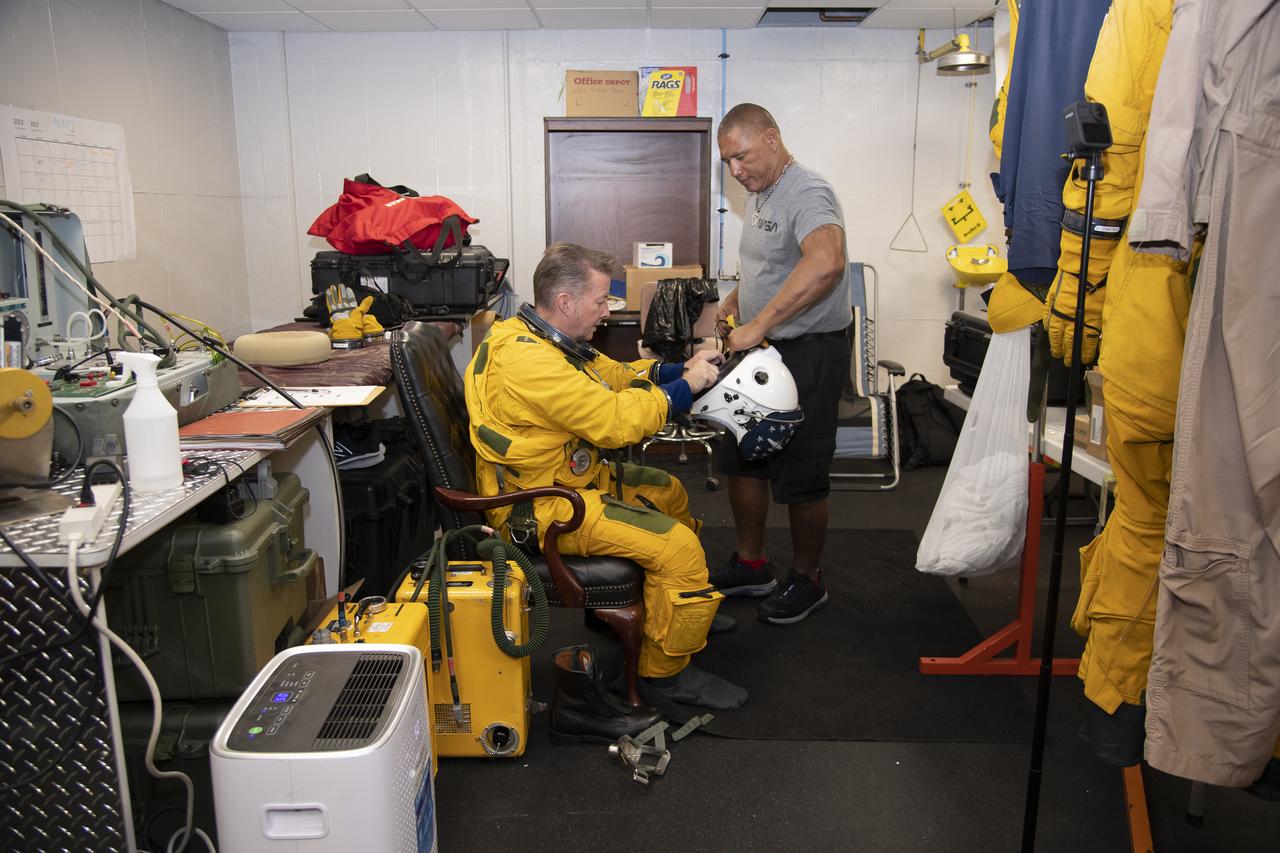
The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
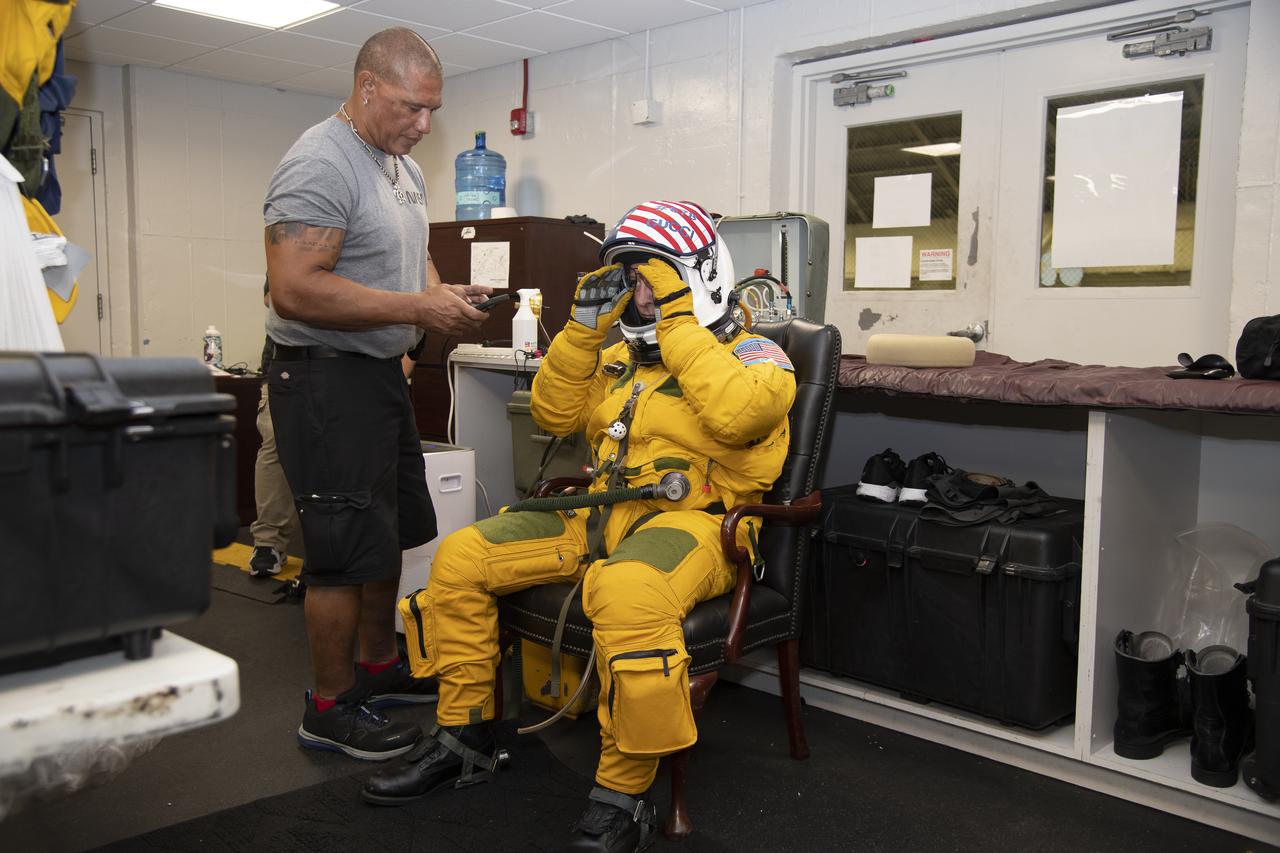

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

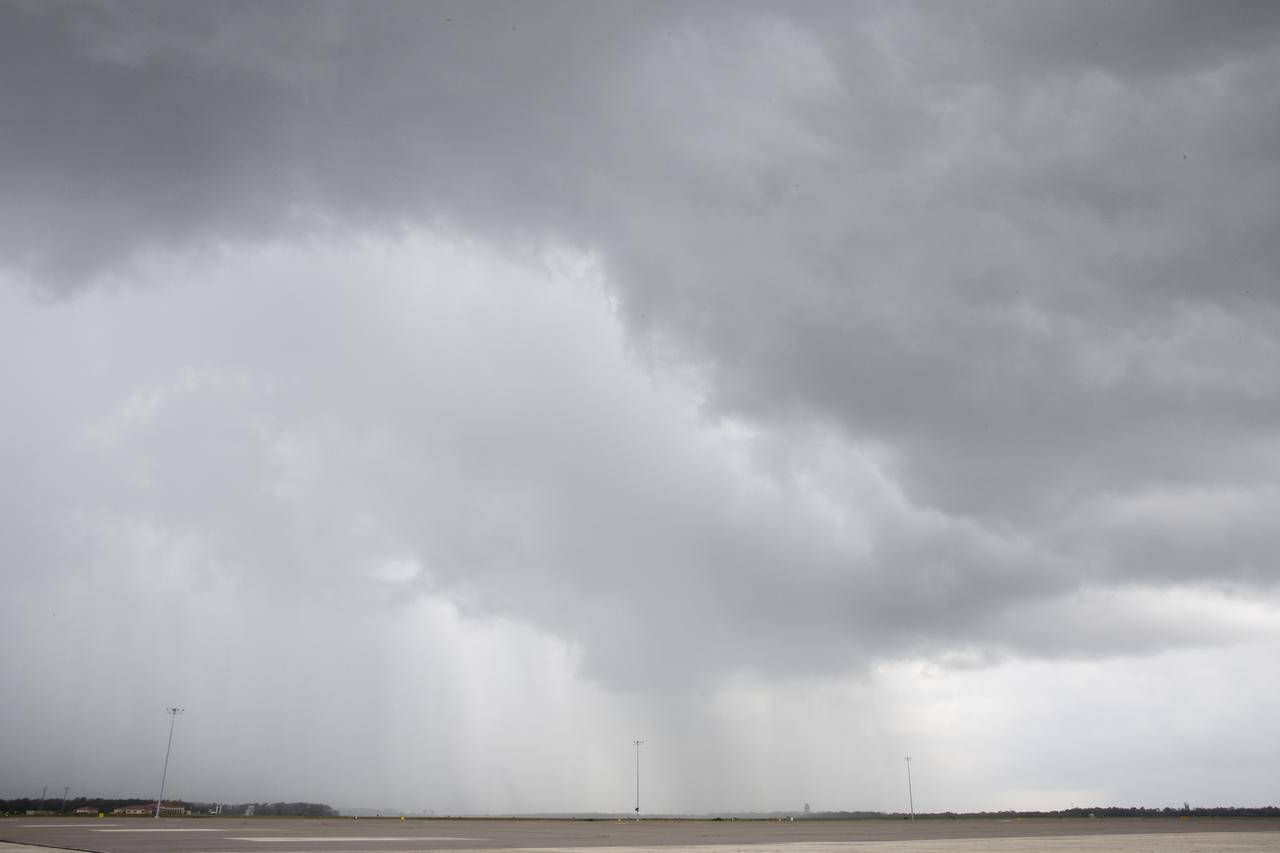
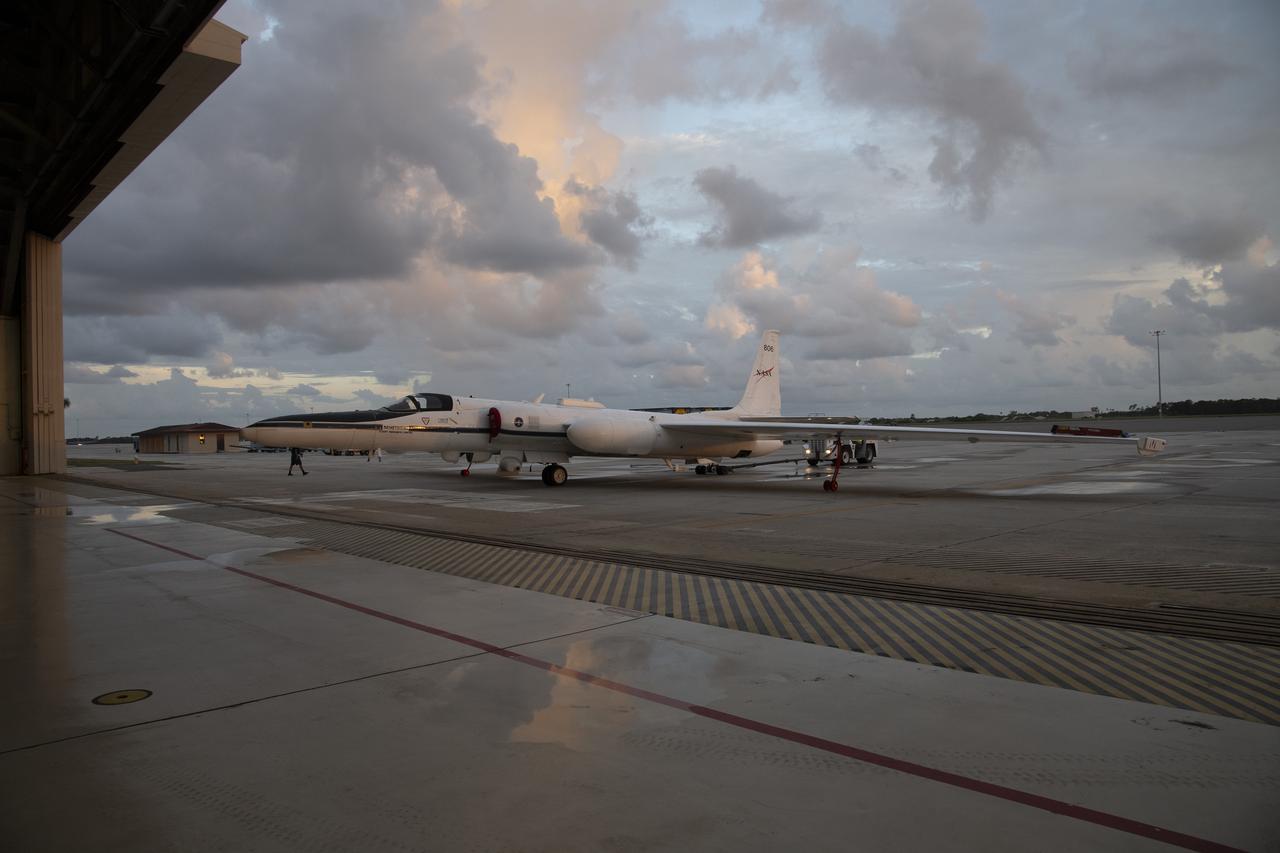
The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
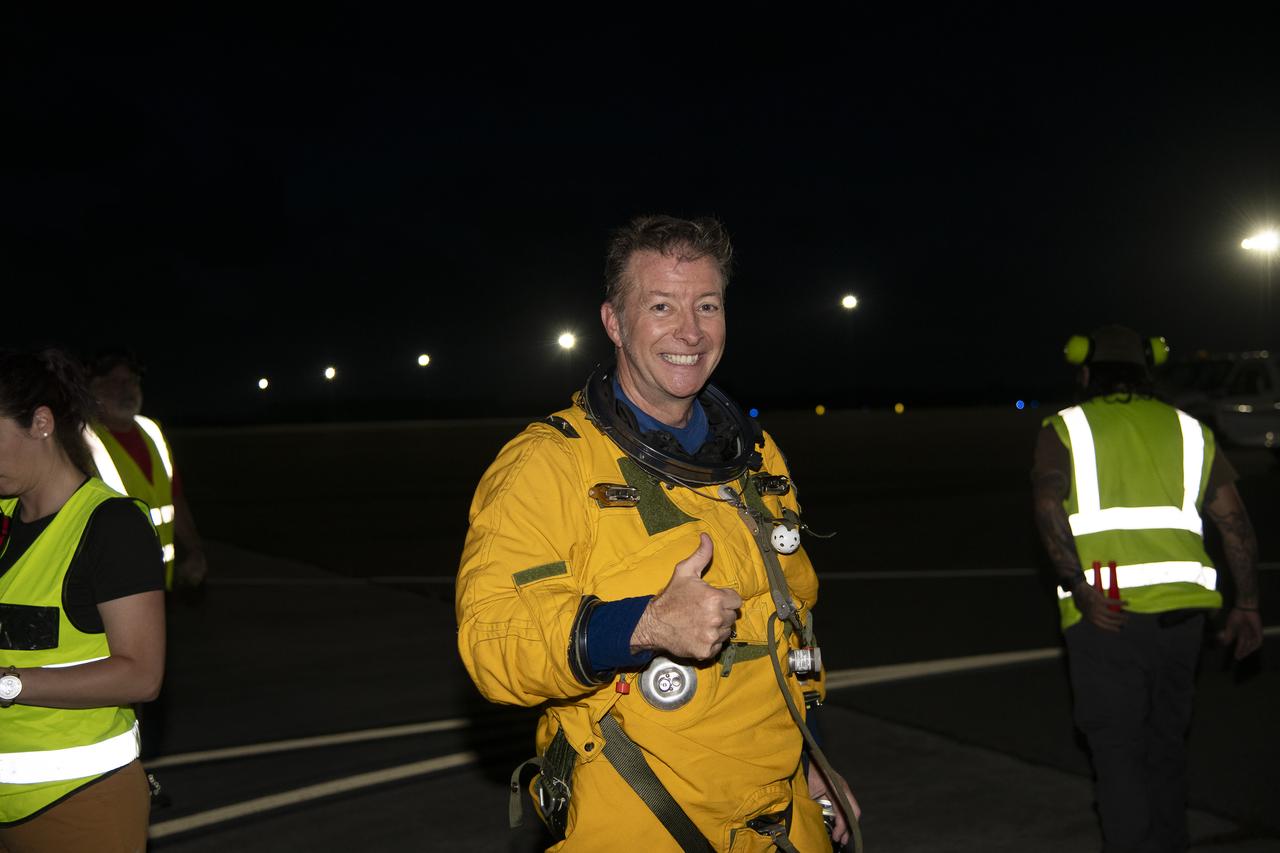

The ALOFT mission, Airborne Lightning Observatory for Fly’s eye simulator and Terrestrial gamma ray flashes, is a collaboration between NASA and the University of Bergen, Norway. NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s ER-2 aircraft flies just above the height of thunderclouds over the Floridian and Caribbean coastlines to collect data about lightning glows and terrestrial gamma ray flashes. Scientists expect to collect more accurate data than ever before that can advance the study of high-energy radiation emissions from thunderstorms.
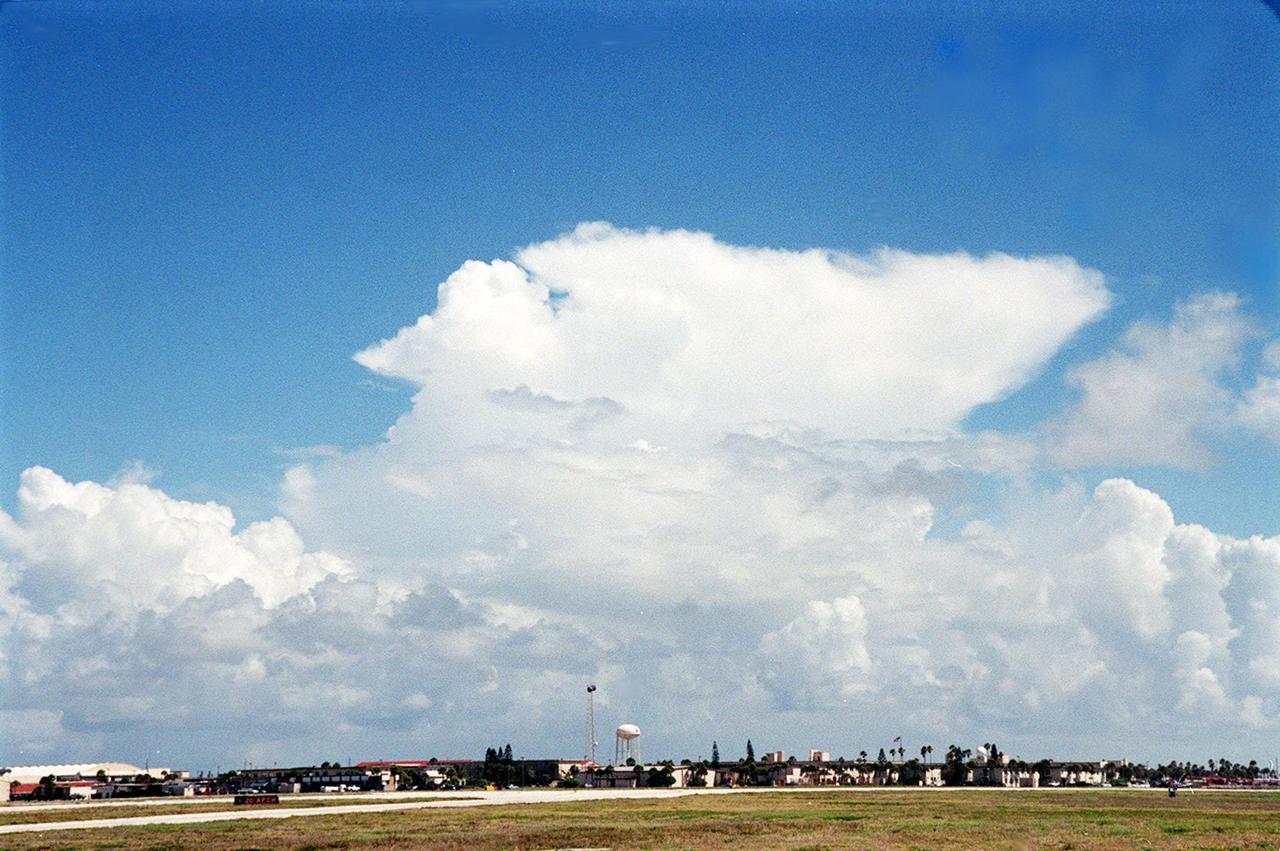

This anvil-shaped cloud over the Central Florida coast is part of a NASA study measuring electric fields in this type of cloud. A specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area . The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
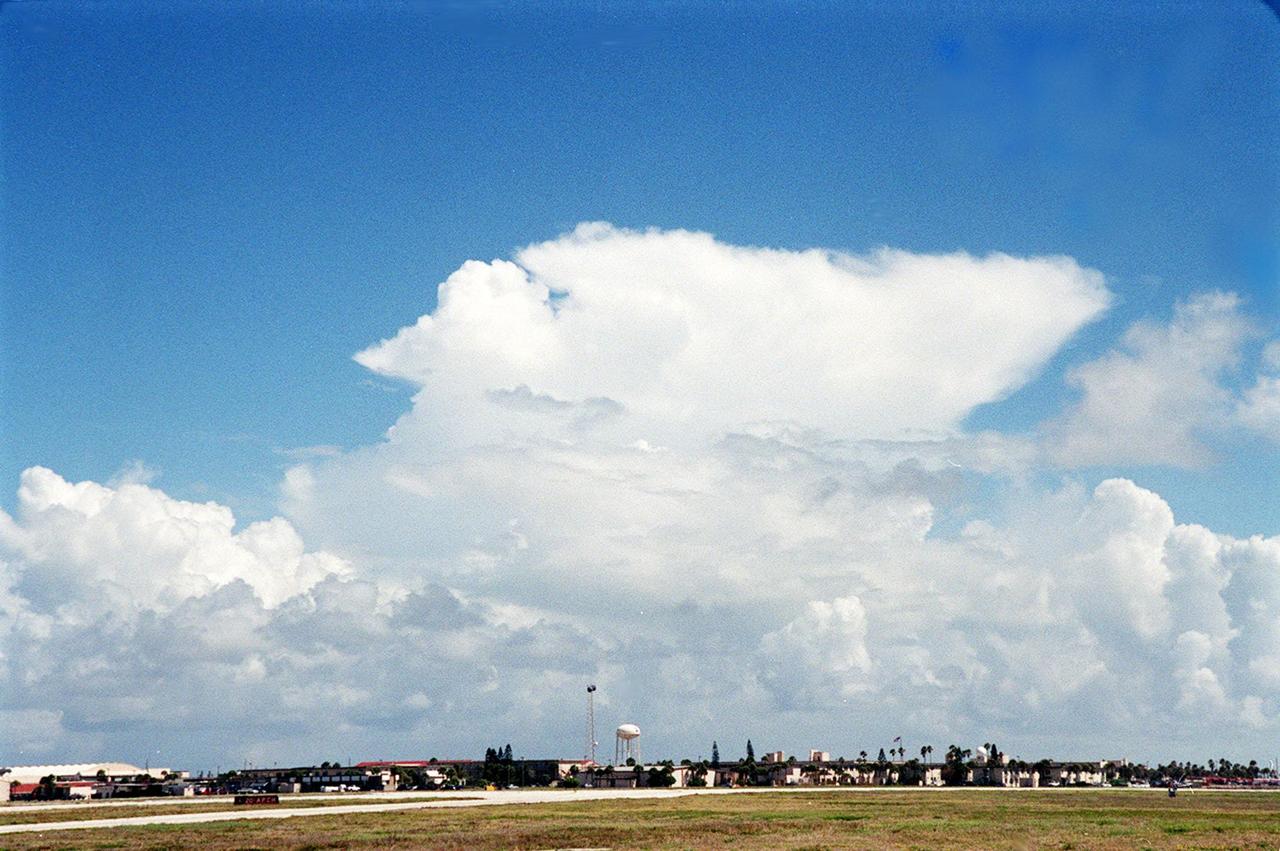

This anvil-shaped cloud over the Central Florida coast is part of a NASA study measuring electric fields in this type of cloud. A specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area . The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
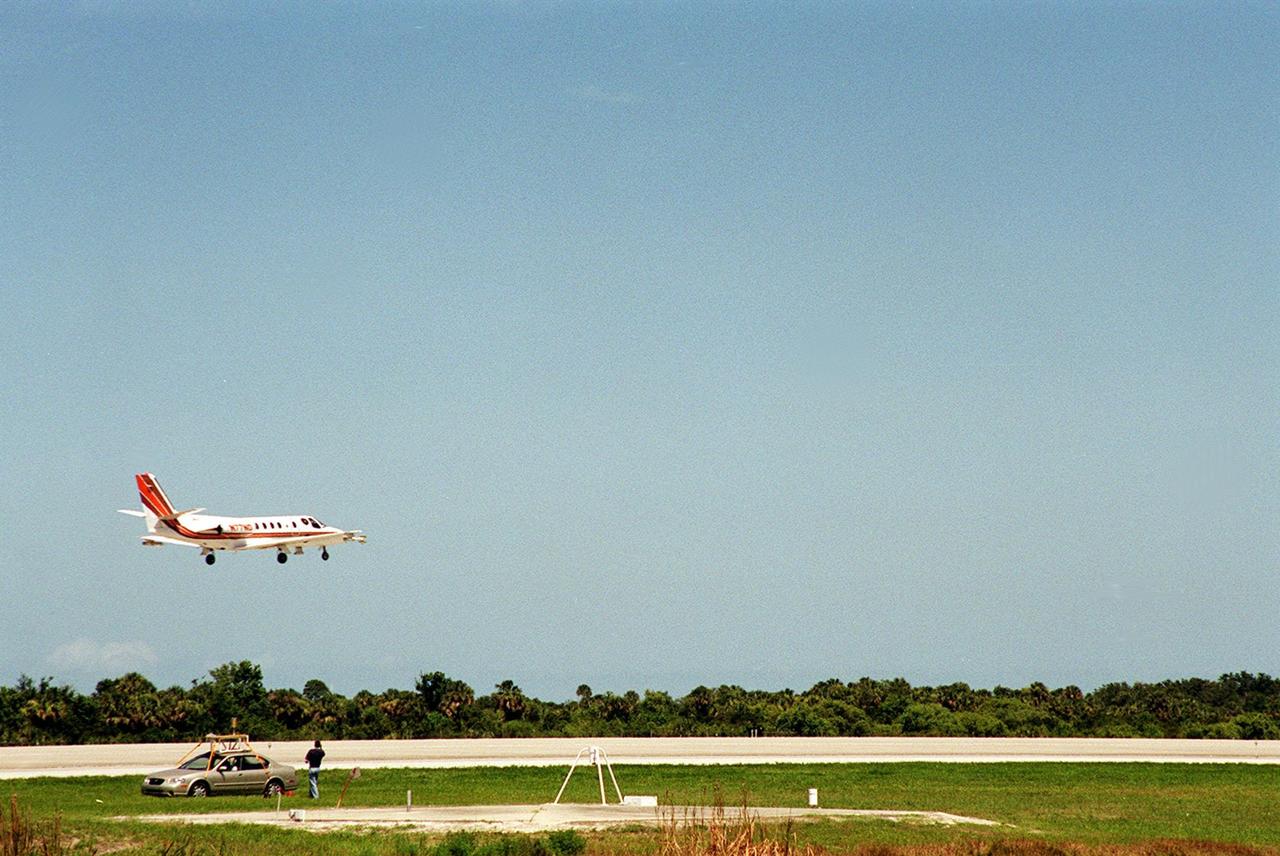

At KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility, a specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft approaches the runway to calibrate the Cessna’s field mills with field mills on the ground (on the tripod at left) and on the car parked nearby (at right). Field mills measure electric fields. The aircraft is also equipped with cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information on this study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
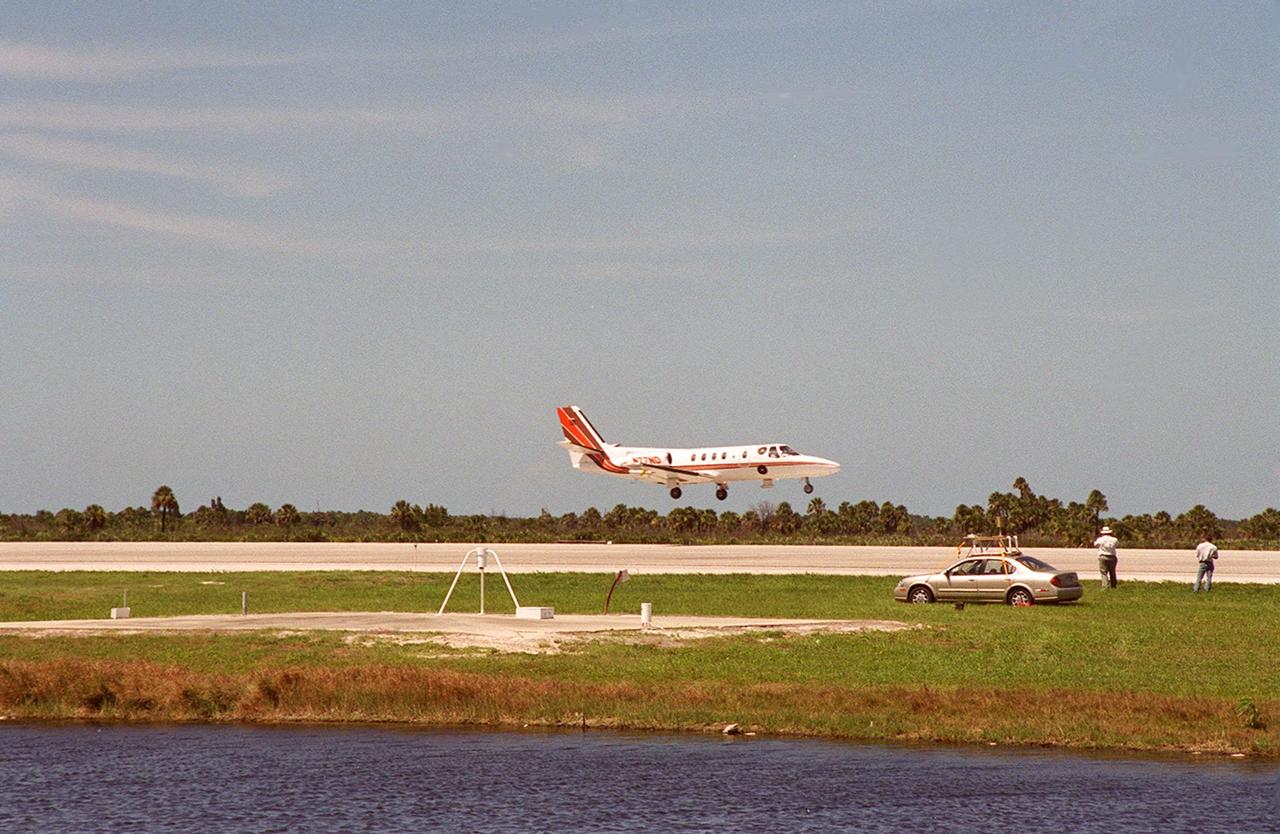

At KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility, a specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft flies over the runway to calibrate the Cessna’s field mills with field mills on the ground (on the tripod at left) and on the car parked nearby (at right). Field mills measure electric fields. The aircraft is also equipped with cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about this study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
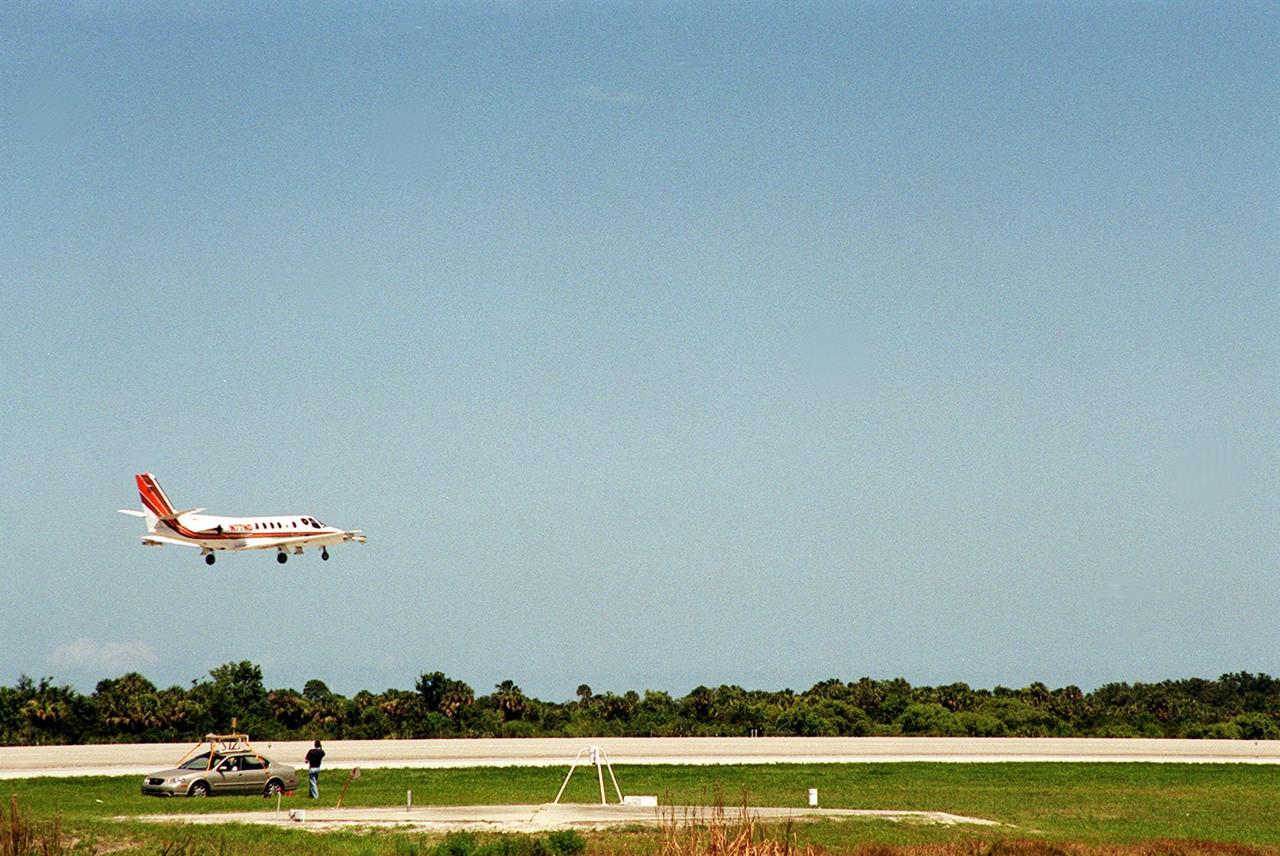

At KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility, a specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft approaches the runway to calibrate the Cessna’s field mills with field mills on the ground (on the tripod at left) and on the car parked nearby (at right). Field mills measure electric fields. The aircraft is also equipped with cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information on this study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
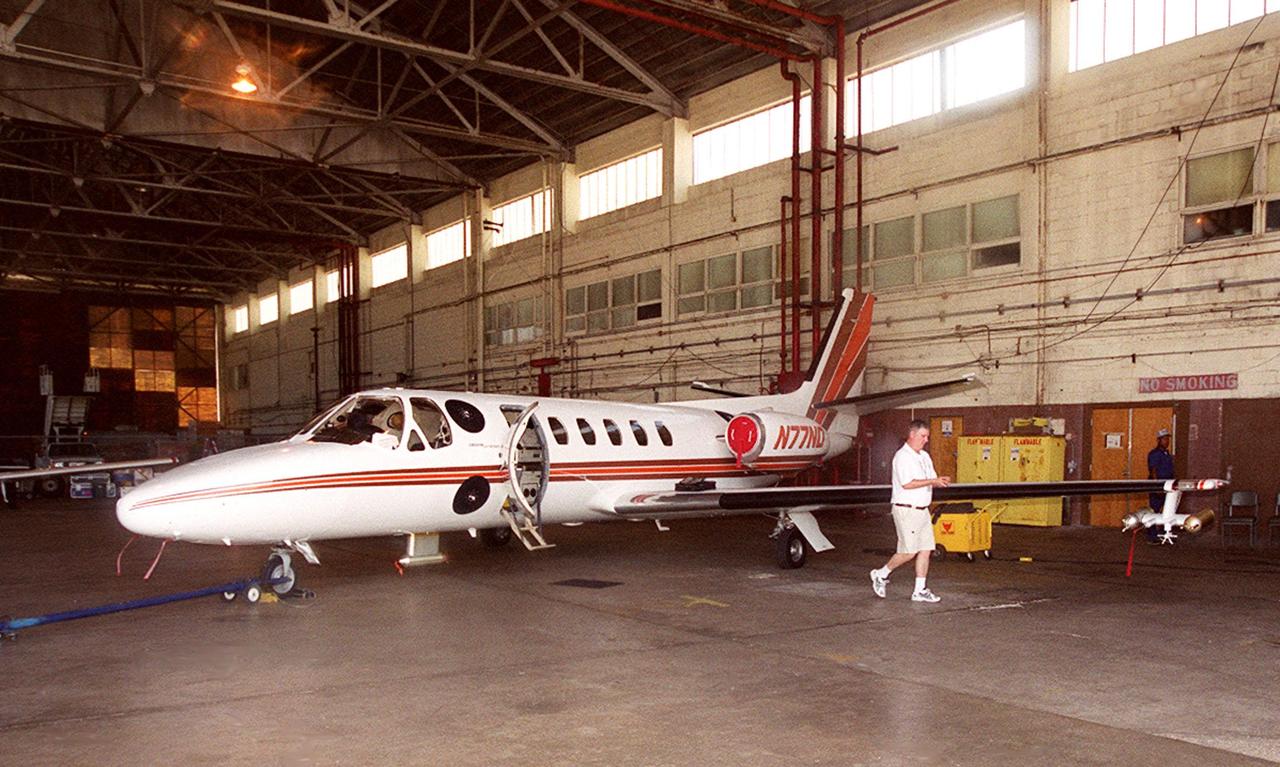

In a hangar at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Cessna Citation aircraft has been fitted on the wings with devices that measure electric fields (black circles shown behind the open door) and with cloud physics probes (under the body and wings) that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
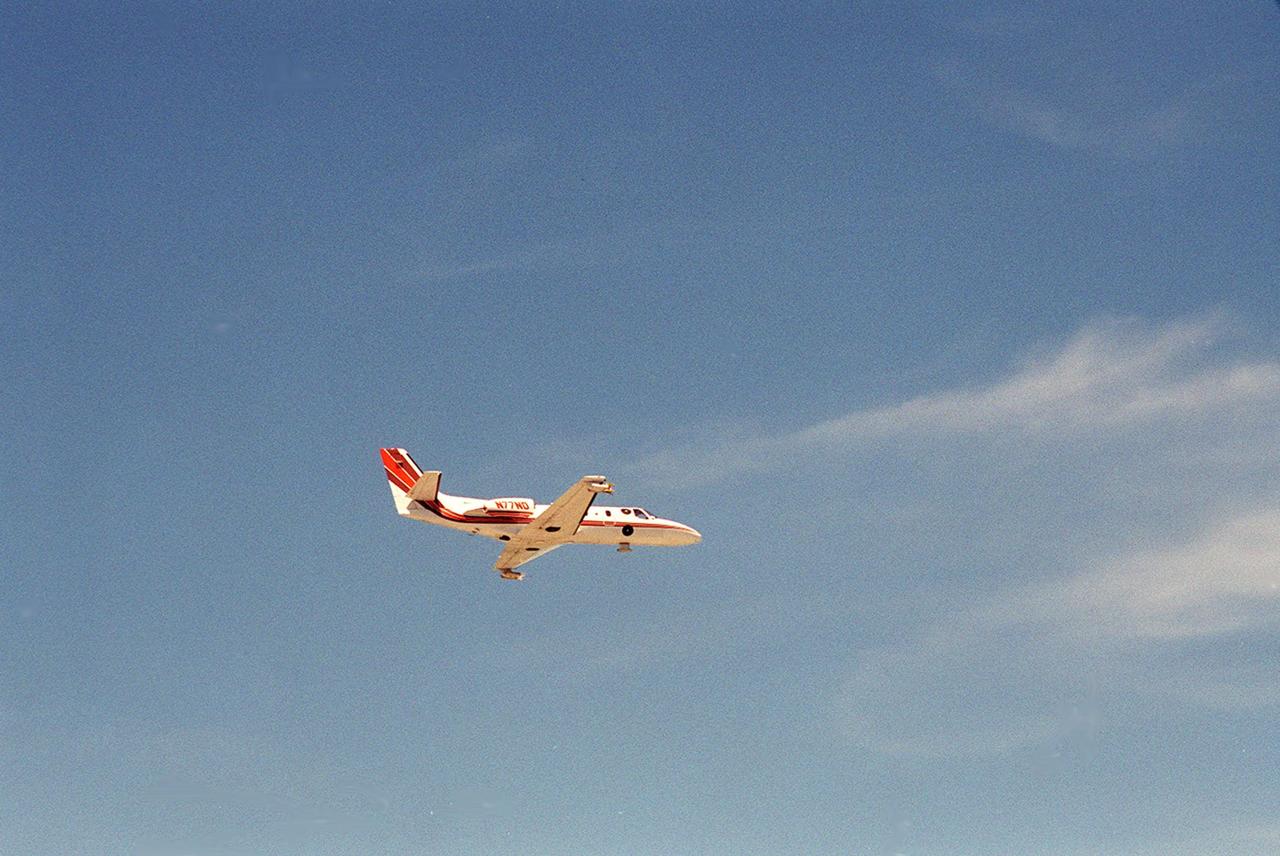

A specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft flies over KSC during a calibration test of field mills used to measure electric fields. The aircraft is also equipped with cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information on this study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
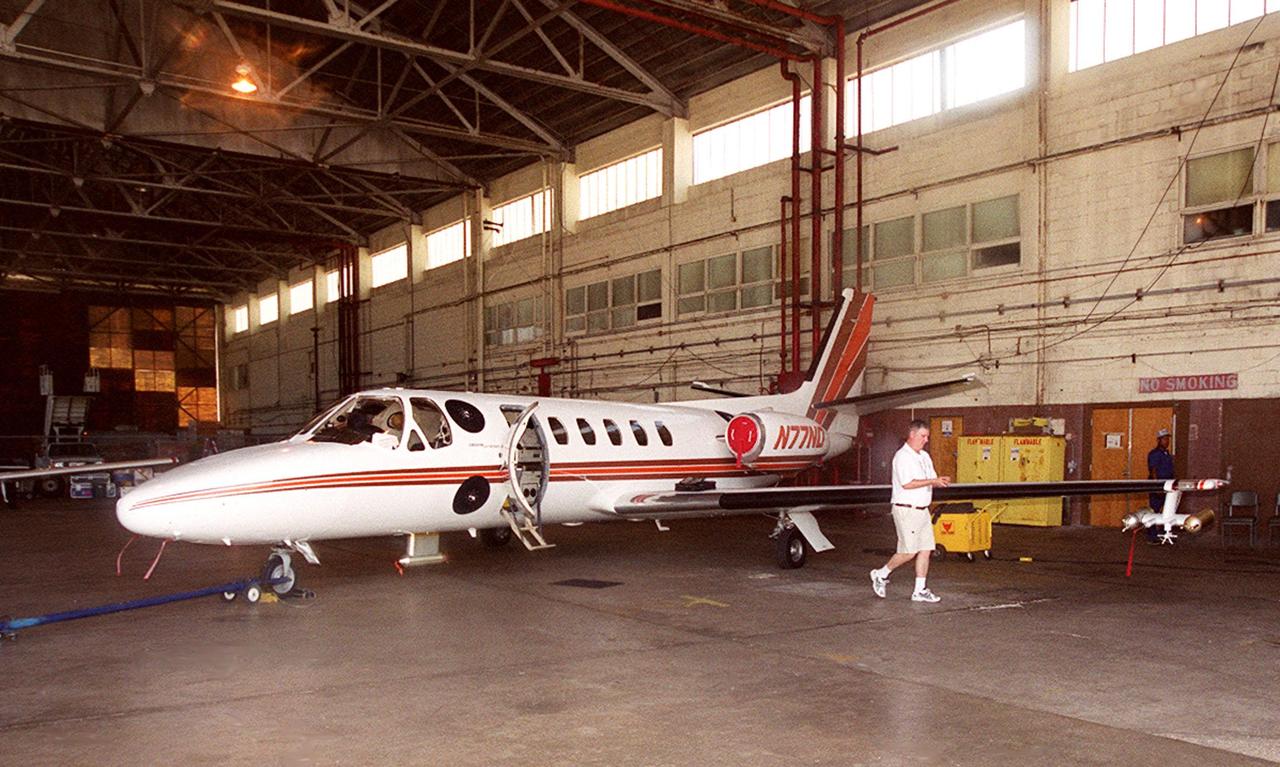

In a hangar at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Cessna Citation aircraft has been fitted on the wings with devices that measure electric fields (black circles shown behind the open door) and with cloud physics probes (under the body and wings) that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about the study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
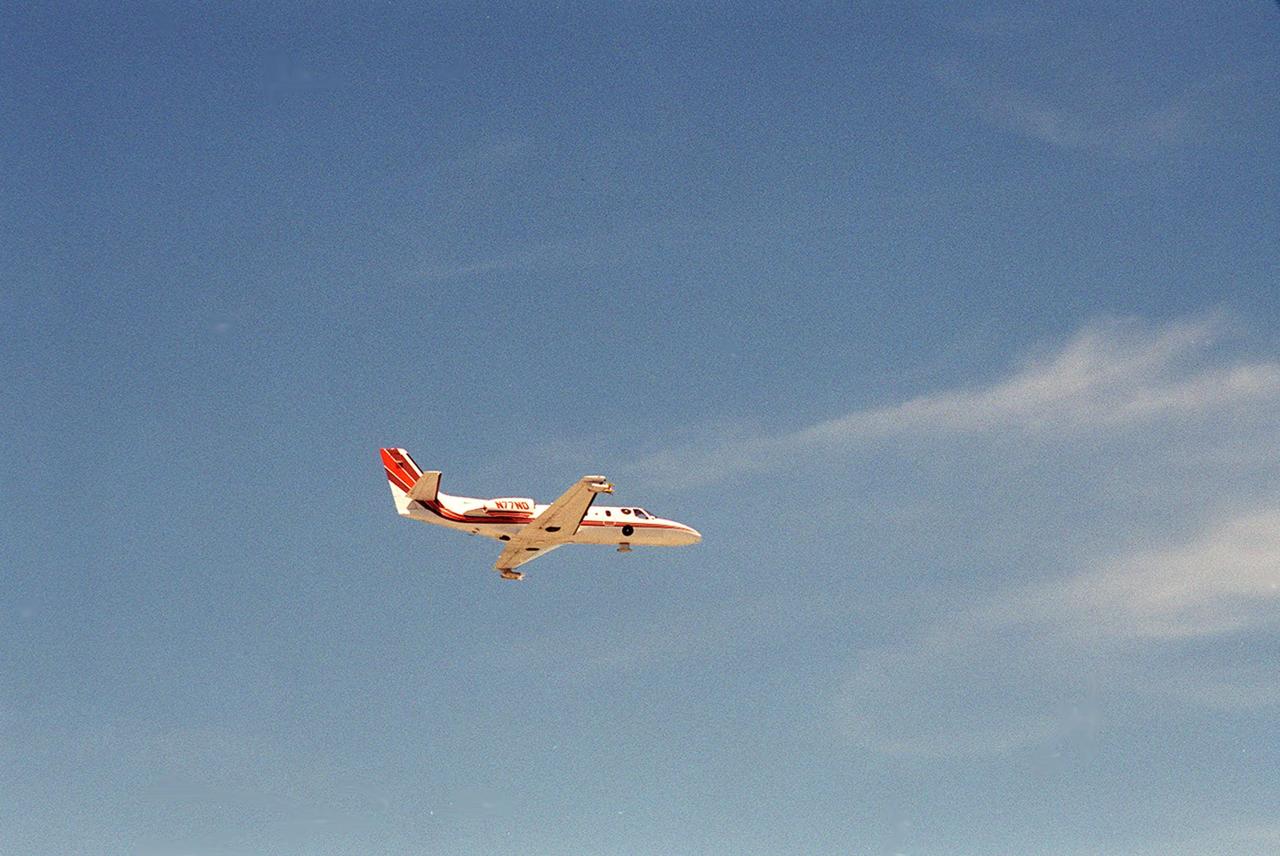

A specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft flies over KSC during a calibration test of field mills used to measure electric fields. The aircraft is also equipped with cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information on this study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
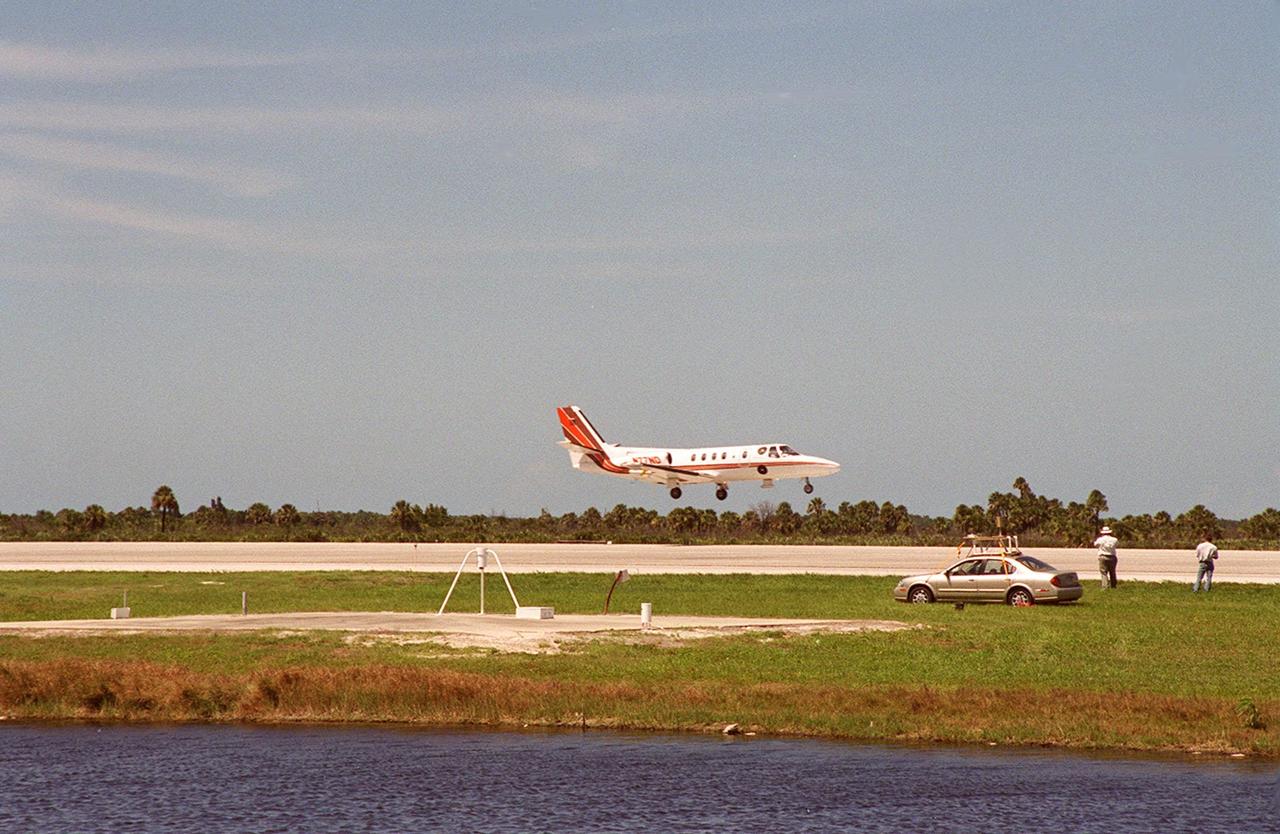

At KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility, a specially equipped Cessna Citation aircraft flies over the runway to calibrate the Cessna’s field mills with field mills on the ground (on the tripod at left) and on the car parked nearby (at right). Field mills measure electric fields. The aircraft is also equipped with cloud physics probes that measure the size, shape and number of ice and water particles in clouds. The plane is being flown into anvil clouds in the KSC area as part of a study to review and possibly modify lightning launch commit criteria. The weather study could lead to improved lightning avoidance rules and fewer launch scrubs for the Space Shuttle and other launch vehicles on the Eastern and Western ranges.; More information about this study can be found in <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/2000/56-00.htm">Release No. 56-00</a>
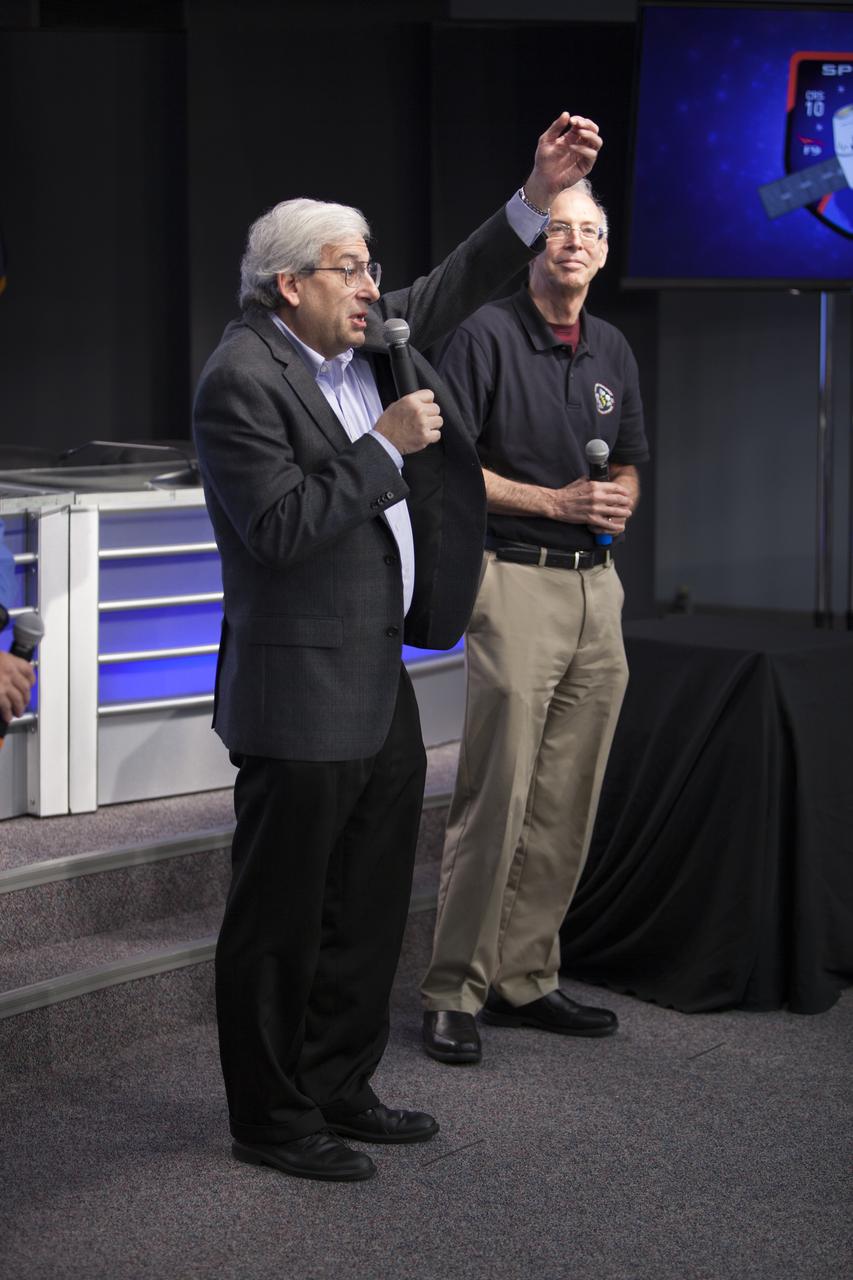

Speaking to members of the media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, Dr. Michael Freilich of the Earth Science Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington, D.C., left, and Dr. Richard Blakeslee of NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, discussed instruments to be delivered to the International Space Station on the SpaceX CRS-10 mission. The Lightning Imaging Sensor (LIS) is to measure the amount, rate and energy of lightning around the world. The SAGE III instrument is designed to study ozone in the atmosphere. A Dragon spacecraft is scheduled to be launched from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A on Feb. 18 atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on the company's 10th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
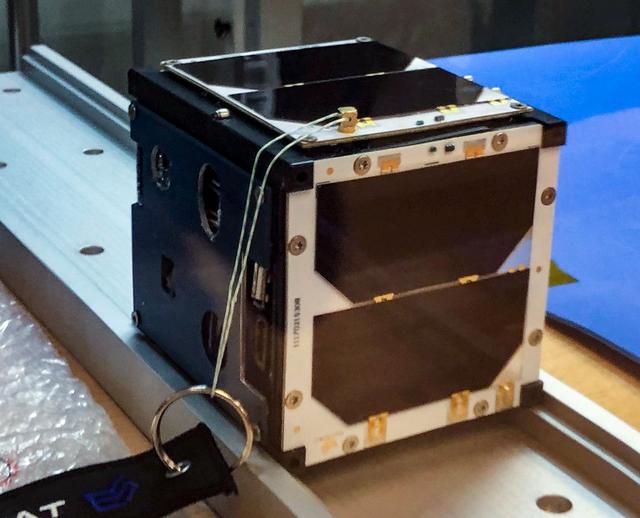
jsc2019e056550 (9/27/2019) --- Preflight view of Argus-02 awaiting integration at the NanoRacks facility. Argus-02 has two objectives: to examine the effect of space radiation on electronics and to test machine-learning algorithms that identify natural events. Memory cards loaded with known images are exposed to space radiation to further study radiation-induced effects. Simultaneously, the CubeSat images the Earth limb and uses algorithms to identify events such as lightning strikes and auroras; false-positive identification of events leads to modification of algorithms. Argus-02 results may help improve electronics and software for future space travel. Image courtesy of: Saint Louis University
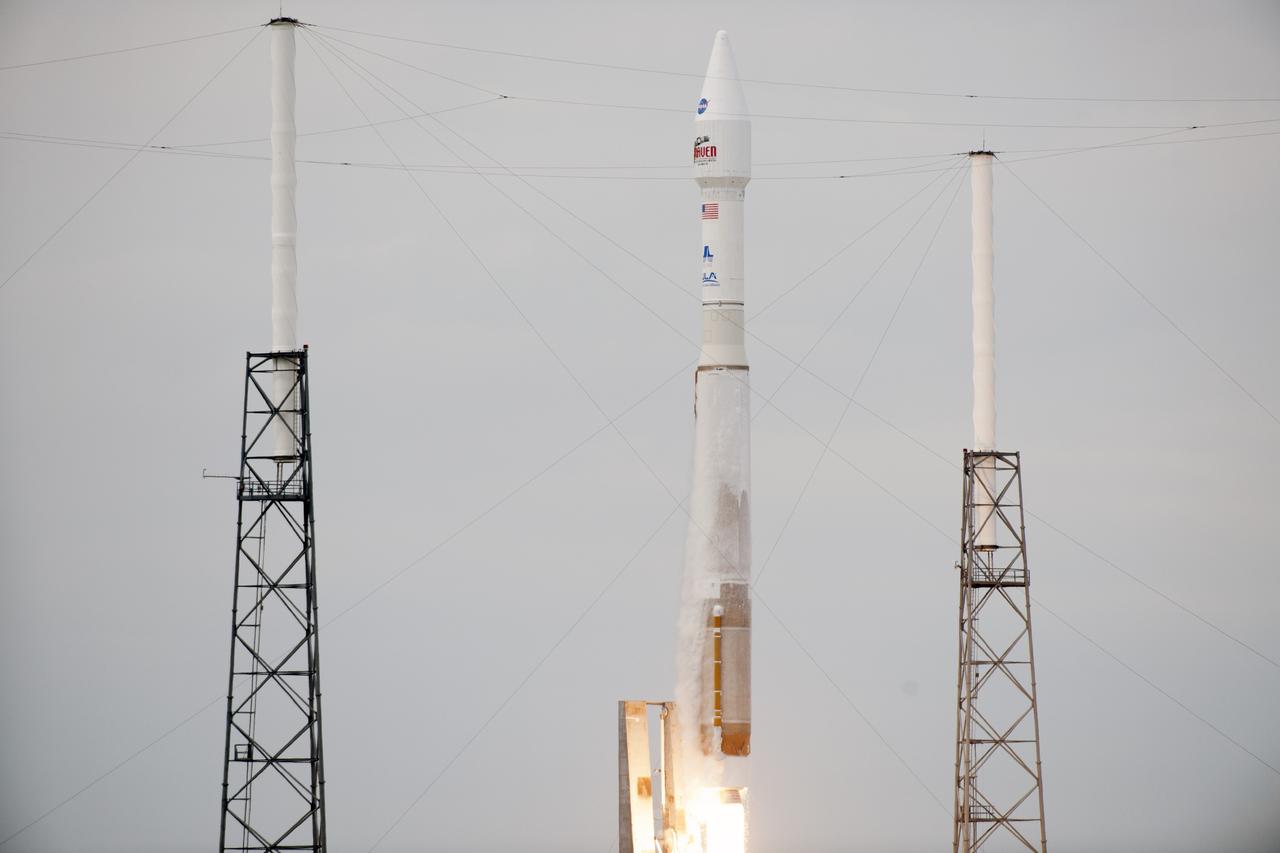

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off past the lightning masts on Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying NASA's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN, or MAVEN, spacecraft. Launch was on schedule at 1:28 p.m. EST Nov. 18 at the opening of a two-hour launch window. After a 10-month journey to the Red Planet, MAVEN will study its upper atmosphere in unprecedented detail from orbit above the planet. Built by Lockheed Martin in Littleton, Colo., MAVEN will arrive at Mars in September 2014 and will be inserted into an elliptical orbit with a high point of 3,900 miles, swooping down to as close as 93 miles above the planet's surface. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Rusty Backer
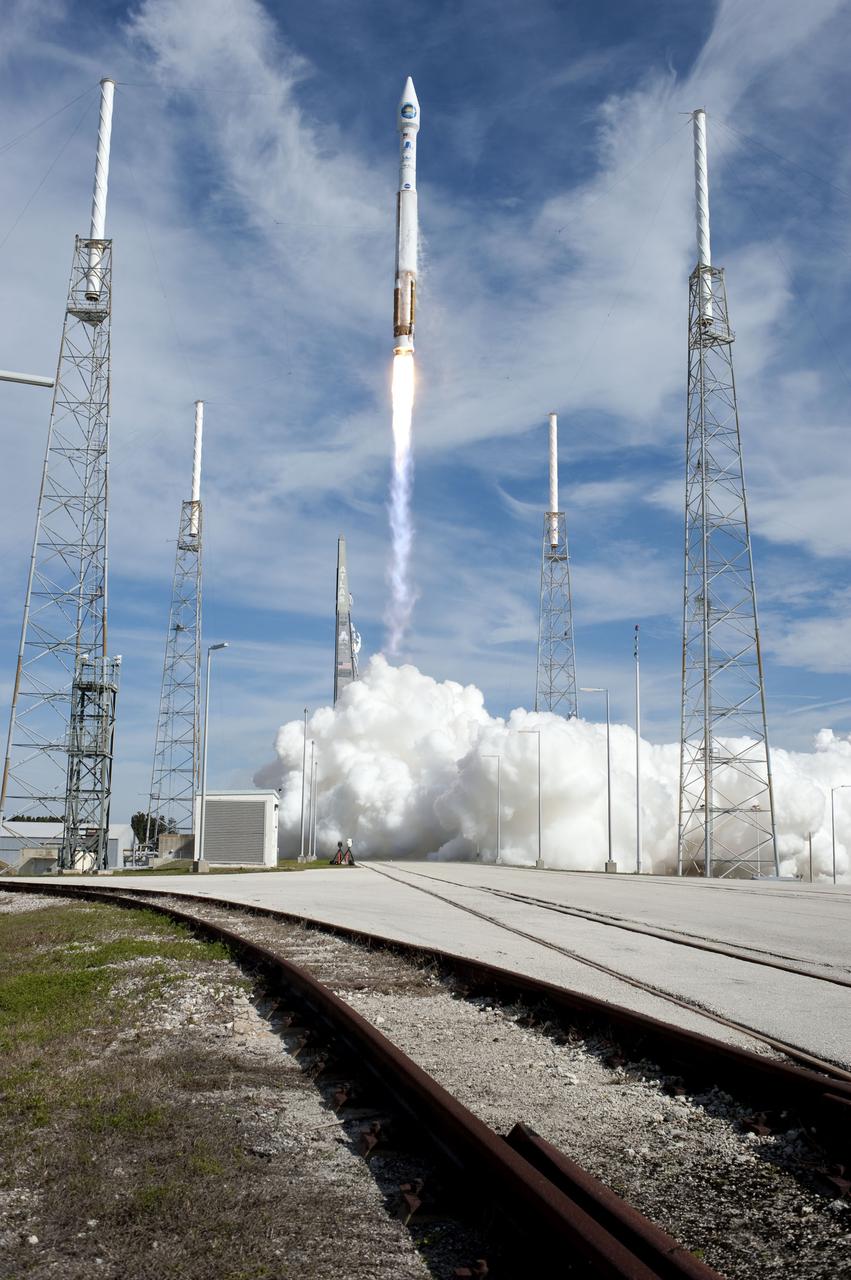

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket lifts off between the towers of the lightning protection system at Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 10:23 a.m. EST Feb. 11 carrying NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory to orbit. This is the 100th launch of a commercial Atlas_Centaur rocket. The observatory, known as SDO, is the first mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program and is designed to study the causes of solar variability and its impacts on Earth. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information to help characterize the interior of the Sun, the Sun's magnetic field, the hot plasma of the solar corona, and the density of radiation that creates the ionosphere of the planets. The information will be used to create better forecasts of space weather needed to protect the aircraft, satellites and astronauts living and working in space. For information on SDO, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_sdo. Photo credit: NASA_Sandra Joseph and Tony Gray
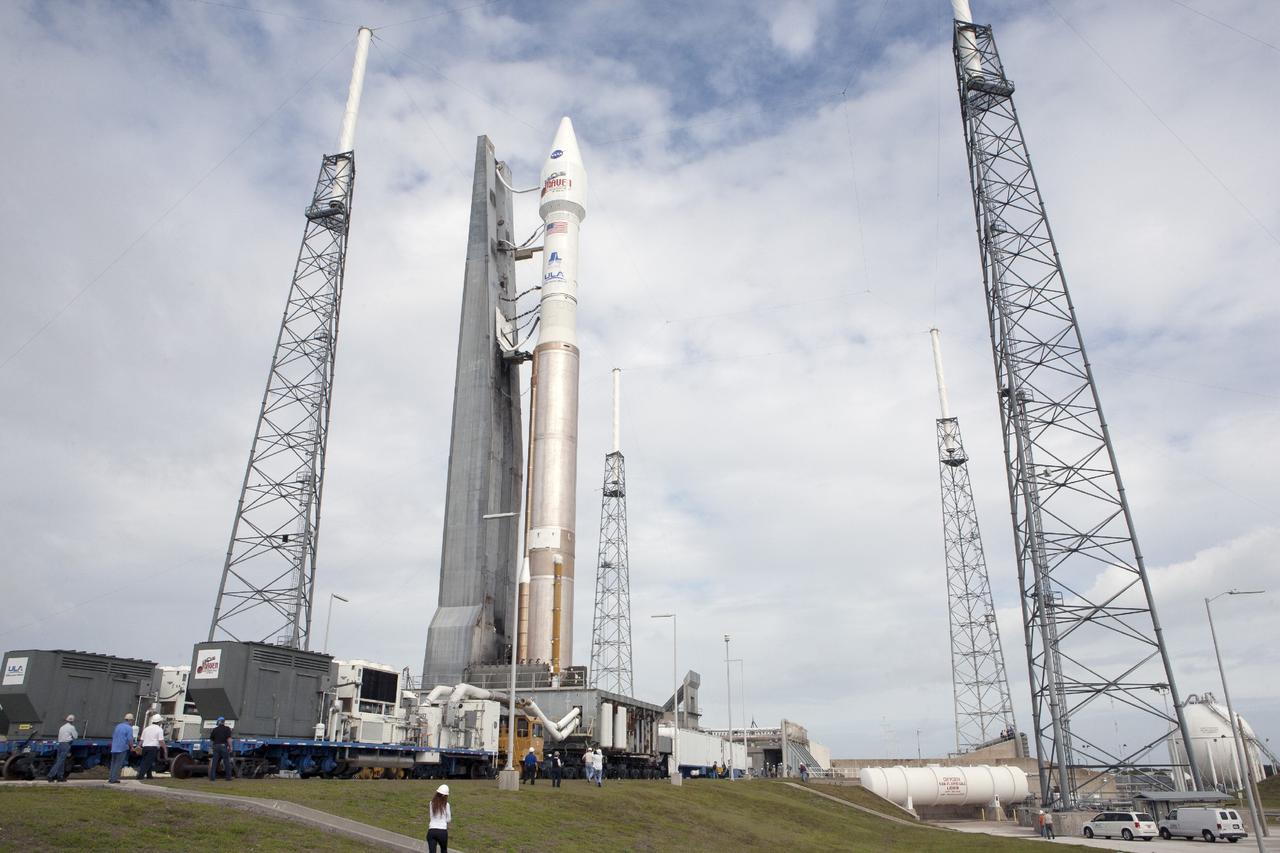

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket carrying NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN, or MAVEN, spacecraft moves between the lightning masts at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida following a 20-minute journey from the Vertical Integration Facility. Rollout began on schedule with first motion at 9:57 a.m. EST. Launch is scheduled for Nov. 18 during a window that extends from 1:28 to 3:28 p.m. Once positioned in orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study its upper atmosphere in unprecedented detail. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
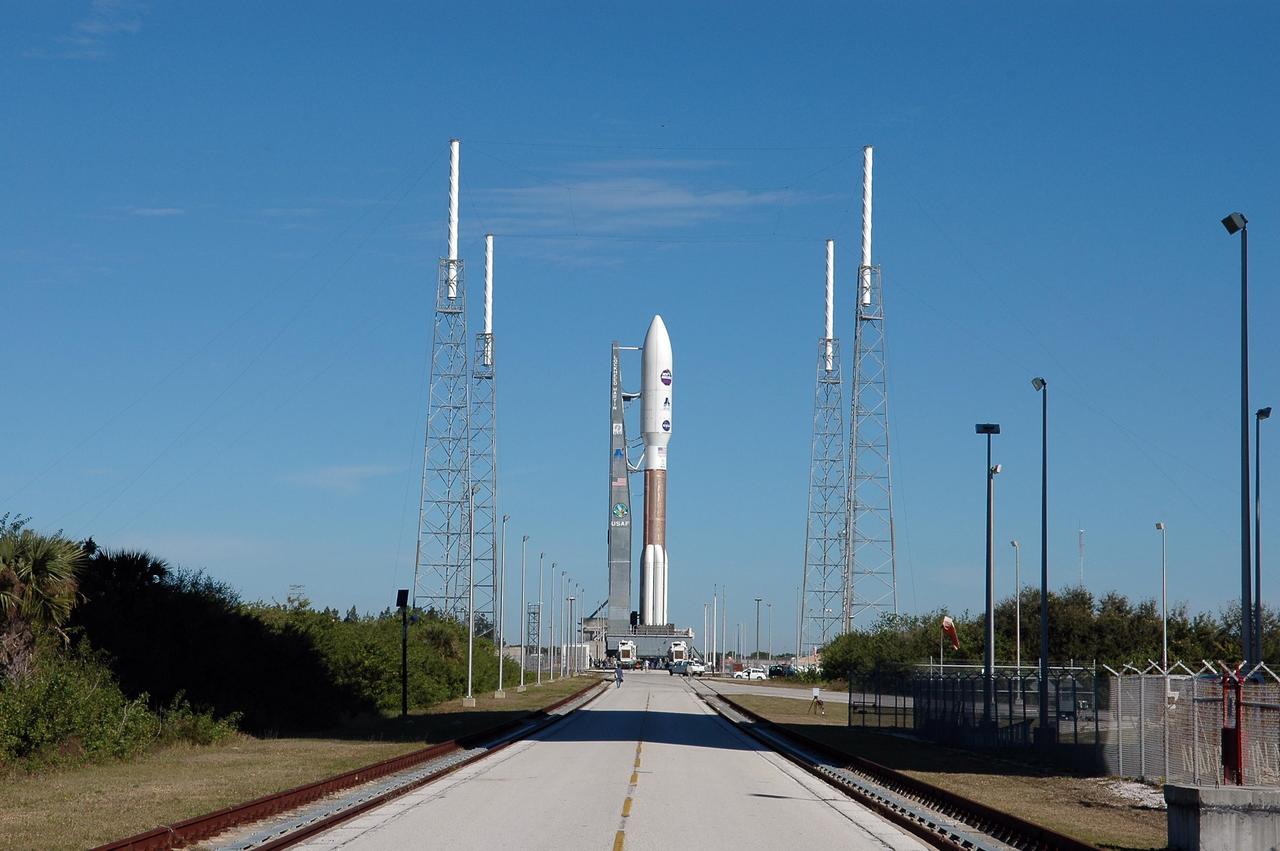

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Atlas V expendable launch vehicle with the New Horizons spacecraft has been moved to the pad. Umbilicals have been attached. Seen near the rocket are lightning masts that support the catenary wire used to provide lightning protection. Liftoff is scheduled for 1:24 p.m. EST Jan. 17. After its launch aboard the Atlas V, the compact, 1,050-pound piano-sized probe will get a boost from a kick-stage solid propellant motor for its journey to Pluto. New Horizons will be the fastest spacecraft ever launched, reaching lunar orbit distance in just nine hours and passing Jupiter 13 months later. The New Horizons science payload, developed under direction of Southwest Research Institute, includes imaging infrared and ultraviolet spectrometers, a multi-color camera, a long-range telescopic camera, two particle spectrometers, a space-dust detector and a radio science experiment. The dust counter was designed and built by students at the University of Colorado, Boulder. A launch before Feb. 3 allows New Horizons to fly past Jupiter in early 2007 and use the planet’s gravity as a slingshot toward Pluto. The Jupiter flyby trims the trip to Pluto by as many as five years and provides opportunities to test the spacecraft’s instruments and flyby capabilities on the Jupiter system. New Horizons could reach the Pluto system as early as mid-2015, conducting a five-month-long study possible only from the close-up vantage of a spacecraft.
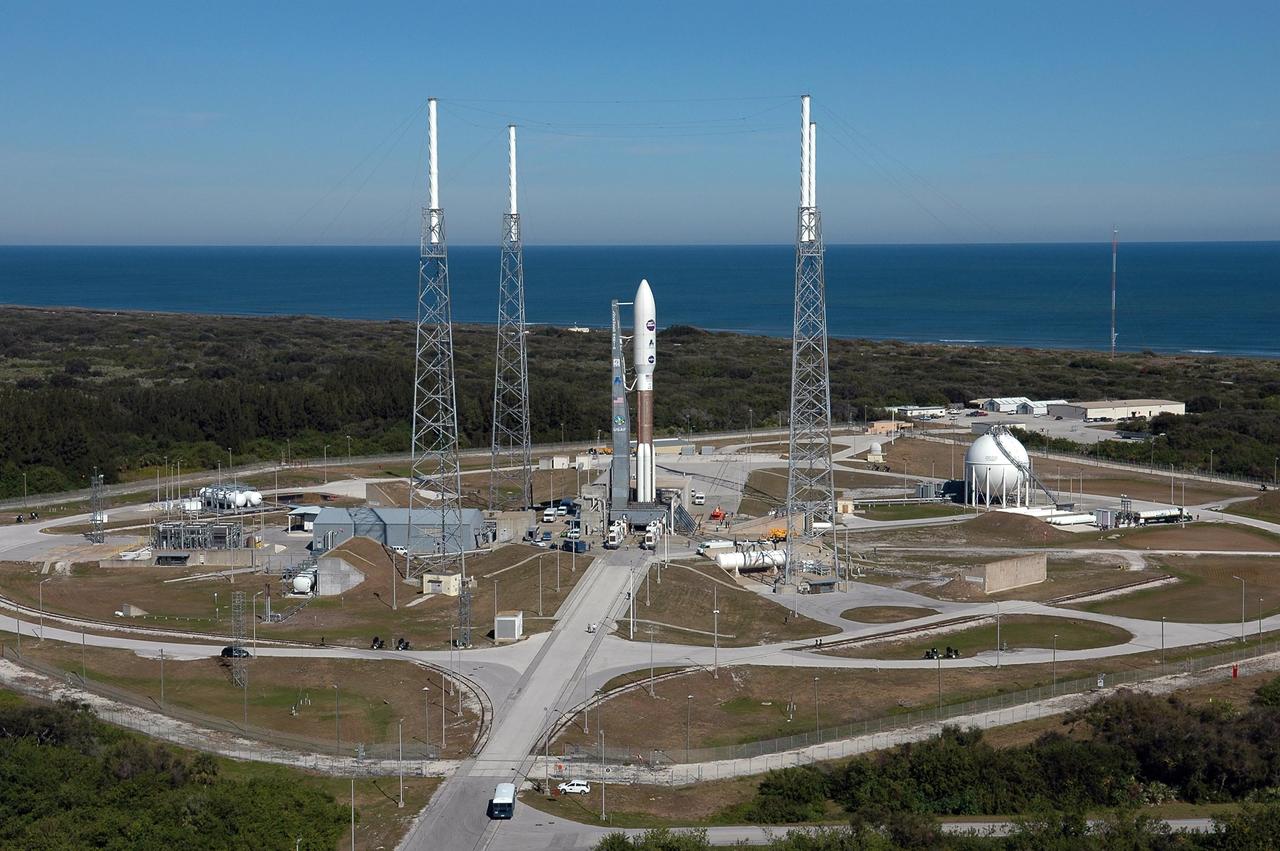

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - With the backdrop of blue sky and blue water of the Atlantic Ocean, the Atlas V expendable launch vehicle with the New Horizons spacecraft (center) is nearly ready for launch. Surrounding the rocket are lightning masts that support the catenary wire used to provide lightning protection. The liftoff is scheduled for 1:24 p.m. EST Jan. 17. After its launch aboard the Atlas V, the compact, 1,050-pound piano-sized probe will get a boost from a kick-stage solid propellant motor for its journey to Pluto. New Horizons will be the fastest spacecraft ever launched, reaching lunar orbit distance in just nine hours and passing Jupiter 13 months later. The New Horizons science payload, developed under direction of Southwest Research Institute, includes imaging infrared and ultraviolet spectrometers, a multi-color camera, a long-range telescopic camera, two particle spectrometers, a space-dust detector and a radio science experiment. The dust counter was designed and built by students at the University of Colorado, Boulder. A launch before Feb. 3 allows New Horizons to fly past Jupiter in early 2007 and use the planet’s gravity as a slingshot toward Pluto. The Jupiter flyby trims the trip to Pluto by as many as five years and provides opportunities to test the spacecraft’s instruments and flyby capabilities on the Jupiter system. New Horizons could reach the Pluto system as early as mid-2015, conducting a five-month-long study possible only from the close-up vantage of a spacecraft.
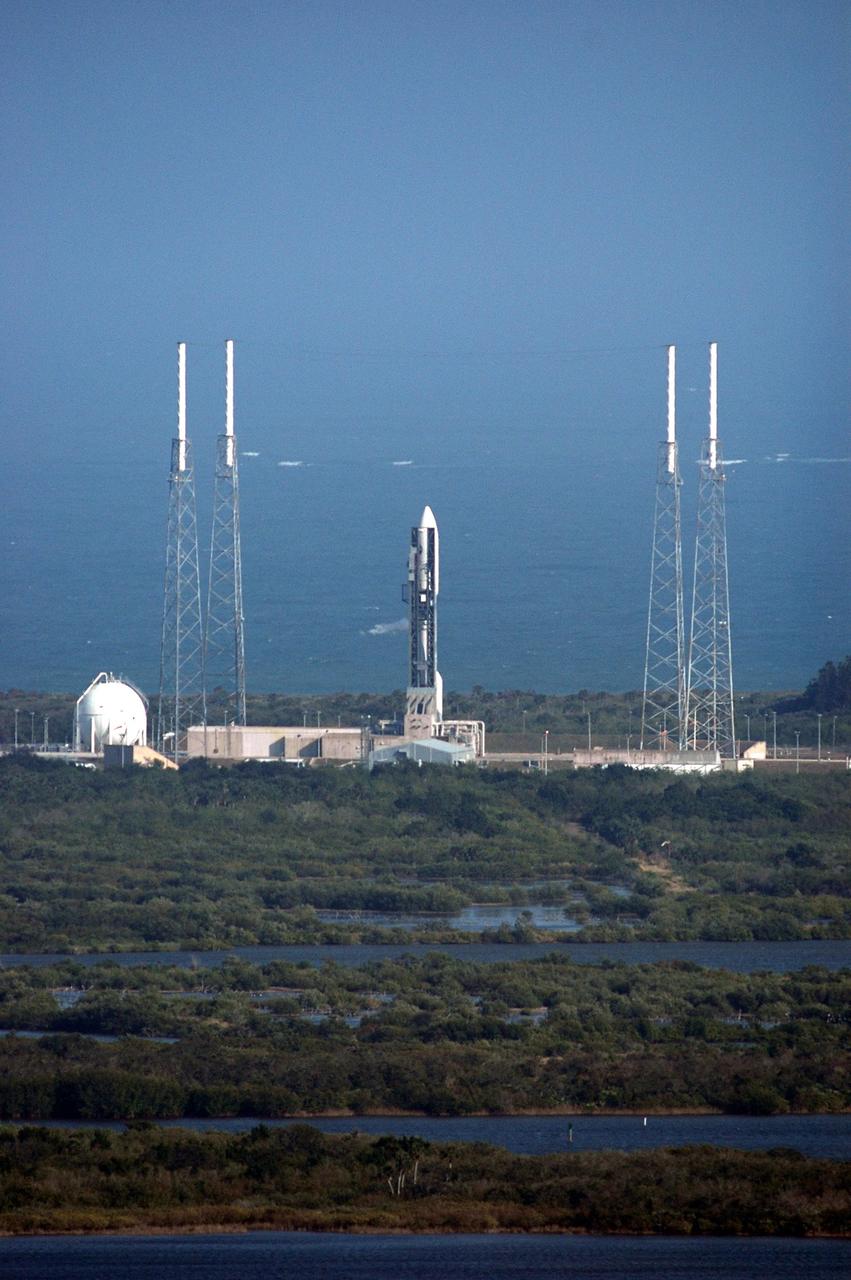

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Atlas V rocket with the New Horizons spacecraft on top sits waiting on the launch pad at Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The view is from the top of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA Kennedy Space Center. Surrounding the launch vehicle are four lightning masts. The launch on this date was scrubbed due to high surface winds in the area and has been rescheduled for 1:16 p.m. EST Jan. 18. The compact, 1,050-pound piano-sized probe will get a boost from a kick-stage solid propellant motor for its journey to Pluto. New Horizons will be the fastest spacecraft ever launched, reaching lunar orbit distance in just nine hours and passing Jupiter 13 months later. The launch at this time allows New Horizons to fly past Jupiter in early 2007 and use the planet’s gravity as a slingshot toward Pluto. The Jupiter flyby trims the trip to Pluto by as many as five years and provides opportunities to test the spacecraft’s instruments and flyby capabilities on the Jupiter system. New Horizons could reach the Pluto system as early as mid-2015, conducting a five-month-long study possible only from the close-up vantage of a spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-115 Commander Brent Jett studies the controls in the cockpit of the Shuttle Training Aircraft before a practice session of landing the shuttle. STA practice is part of launch preparations. The STA is a Grumman American Aviation-built Gulf Stream II jet that was modified to simulate an orbiter’s cockpit, motion and visual cues, and handling qualities. In flight, the STA duplicates the orbiter’s atmospheric descent trajectory from approximately 35,000 feet altitude to landing on a runway. Because the orbiter is unpowered during re-entry and landing, its high-speed glide must be perfectly executed the first time. Mission STS-115 is scheduled to lift off about 12:29 p.m. Sept. 6. Mission managers cancelled Atlantis' first launch campaign due to a lightning strike at the pad and the passage of Tropical Storm Ernesto along Florida's east coast. The mission will deliver and install the 17-and-a-half-ton P3/P4 truss segment to the port side of the integrated truss system on the orbital outpost. The truss includes a new set of photovoltaic solar arrays. When unfurled to their full length of 240 feet, the arrays will provide additional power for the station in preparation for the delivery of international science modules over the next two years. STS-115 is expected to last 11 days and includes three scheduled spacewalks. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
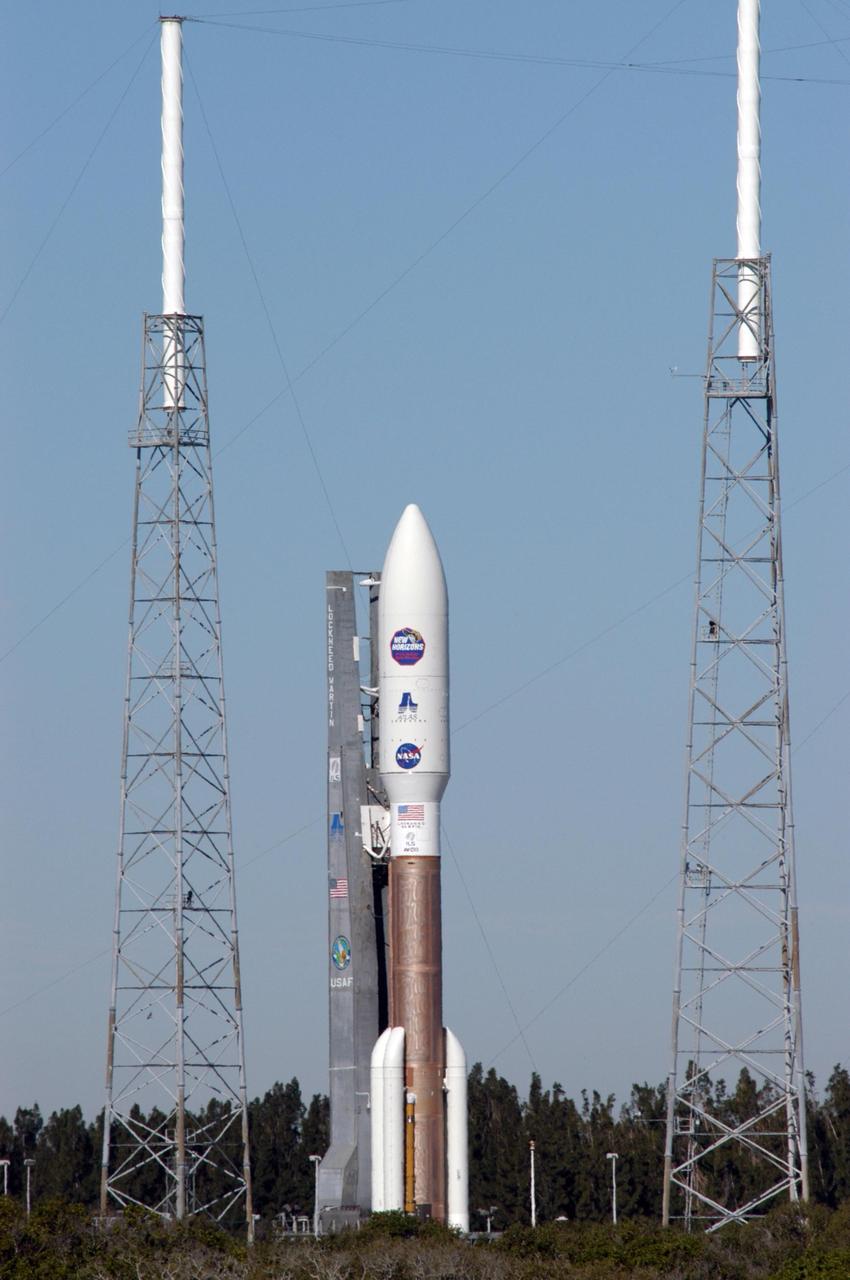

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Atlas V expendable launch vehicle with the New Horizons spacecraft moves with the launcher umbilical tower between lightning masts on its way to the launch pad. The liftoff is scheduled for 1:24 p.m. EST Jan. 17. After its launch aboard the Atlas V, the compact, 1,050-pound piano-sized probe will get a boost from a kick-stage solid propellant motor for its journey to Pluto. New Horizons will be the fastest spacecraft ever launched, reaching lunar orbit distance in just nine hours and passing Jupiter 13 months later. The New Horizons science payload, developed under direction of Southwest Research Institute, includes imaging infrared and ultraviolet spectrometers, a multi-color camera, a long-range telescopic camera, two particle spectrometers, a space-dust detector and a radio science experiment. The dust counter was designed and built by students at the University of Colorado, Boulder. A launch before Feb. 3 allows New Horizons to fly past Jupiter in early 2007 and use the planet’s gravity as a slingshot toward Pluto. The Jupiter flyby trims the trip to Pluto by as many as five years and provides opportunities to test the spacecraft’s instruments and flyby capabilities on the Jupiter system. New Horizons could reach the Pluto system as early as mid-2015, conducting a five-month-long study possible only from the close-up vantage of a spacecraft.
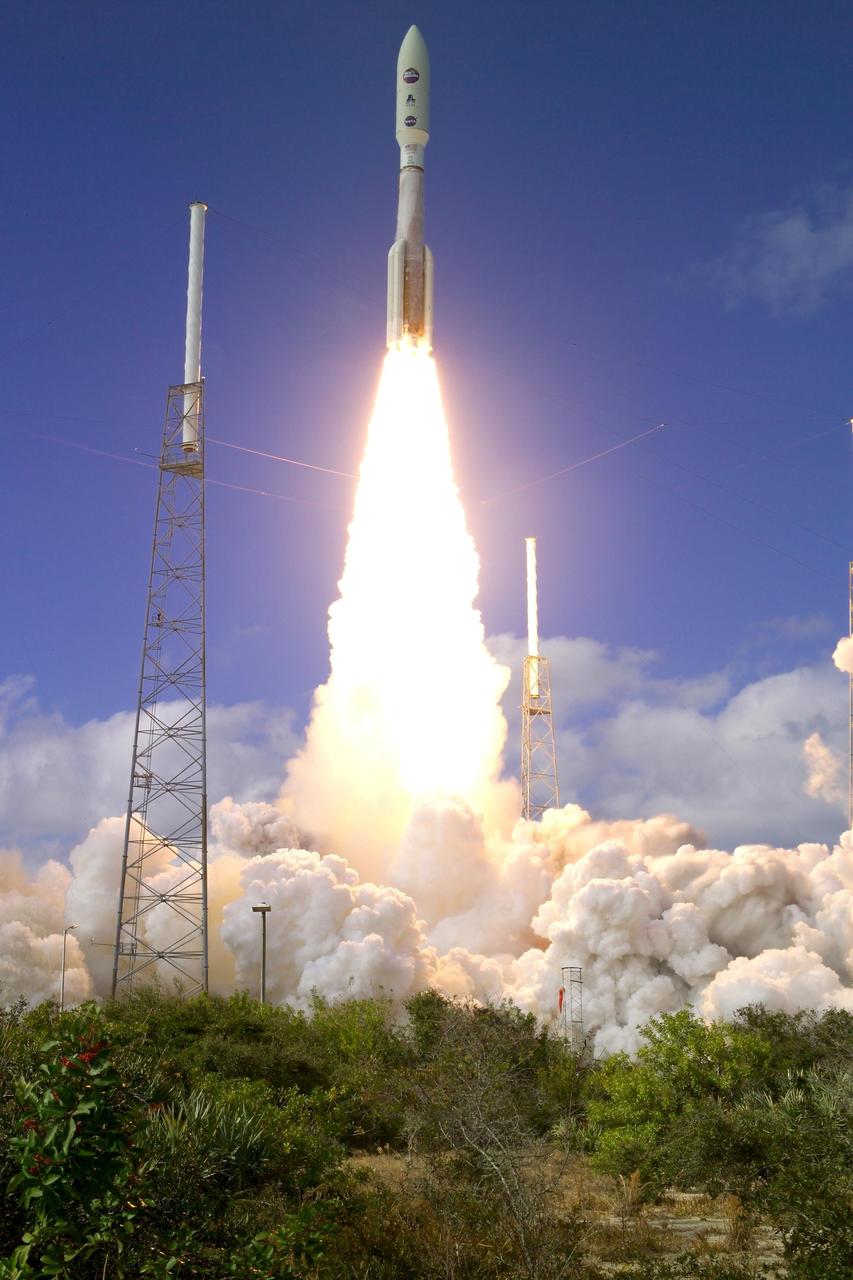

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — From between lightning masts surrounding the launch pad, NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft roars into the blue sky aboard an Atlas V rocket spewing flames and smoke. Liftoff was on time at 2 p.m. EST from Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. This was the third launch attempt in as many days after scrubs due to weather concerns. The compact, 1,050-pound piano-sized probe will get a boost from a kick-stage solid propellant motor for its journey to Pluto. New Horizons will be the fastest spacecraft ever launched, reaching lunar orbit distance in just nine hours and passing Jupiter 13 months later. The New Horizons science payload, developed under direction of Southwest Research Institute, includes imaging infrared and ultraviolet spectrometers, a multi-color camera, a long-range telescopic camera, two particle spectrometers, a space-dust detector and a radio science experiment. The dust counter was designed and built by students at the University of Colorado, Boulder. The launch at this time allows New Horizons to fly past Jupiter in early 2007 and use the planet’s gravity as a slingshot toward Pluto. The Jupiter flyby trims the trip to Pluto by as many as five years and provides opportunities to test the spacecraft’s instruments and flyby capabilities on the Jupiter system. New Horizons could reach the Pluto system as early as mid-2015, conducting a five-month-long study possible only from the close-up vantage of a spacecraft.
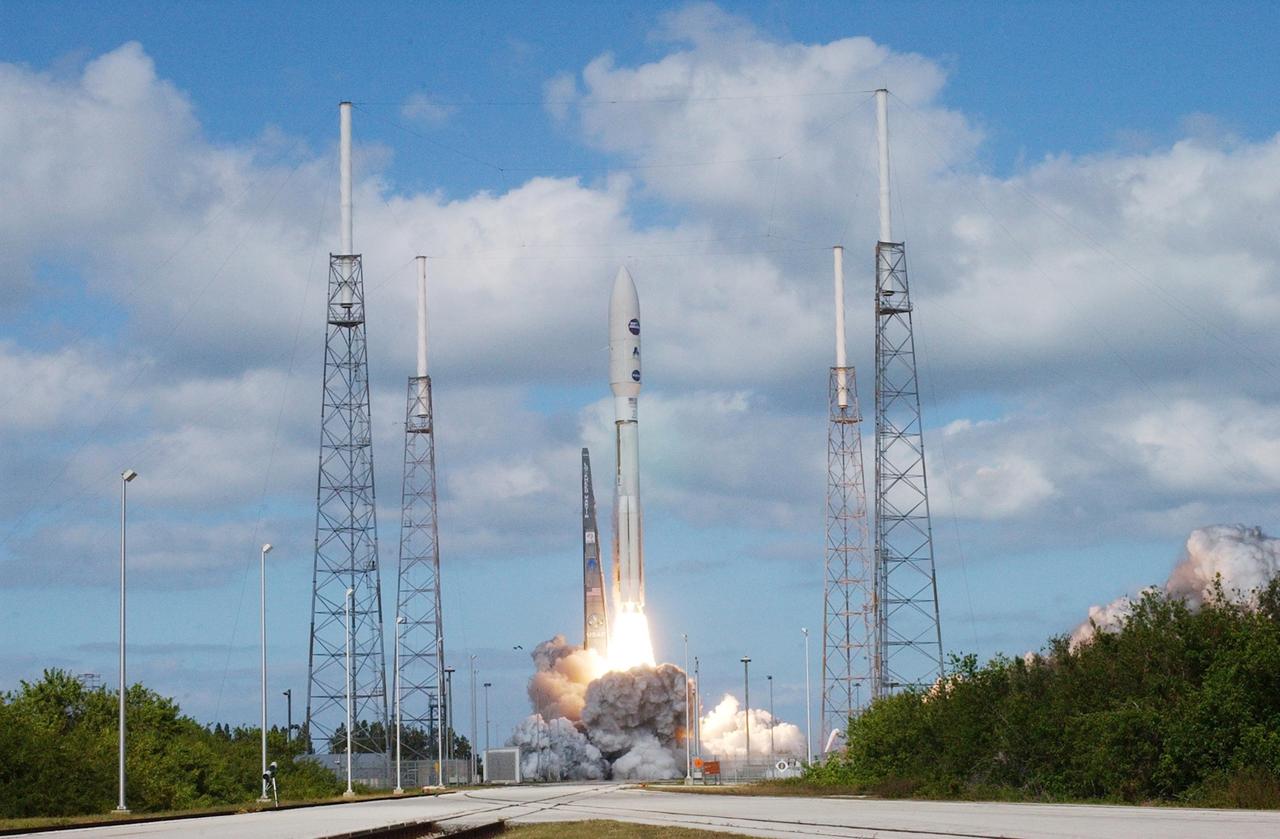

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — From among four lightning masts surrounding the launch pad, NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft lifts off the launch pad aboard an Atlas V rocket spewing flames and smoke. Liftoff was on time at 2 p.m. EST from Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. This was the third launch attempt in as many days after scrubs due to weather concerns. The compact, 1,050-pound piano-sized probe will get a boost from a kick-stage solid propellant motor for its journey to Pluto. New Horizons will be the fastest spacecraft ever launched, reaching lunar orbit distance in just nine hours and passing Jupiter 13 months later. The New Horizons science payload, developed under direction of Southwest Research Institute, includes imaging infrared and ultraviolet spectrometers, a multi-color camera, a long-range telescopic camera, two particle spectrometers, a space-dust detector and a radio science experiment. The dust counter was designed and built by students at the University of Colorado, Boulder. The launch at this time allows New Horizons to fly past Jupiter in early 2007 and use the planet’s gravity as a slingshot toward Pluto. The Jupiter flyby trims the trip to Pluto by as many as five years and provides opportunities to test the spacecraft’s instruments and flyby capabilities on the Jupiter system. New Horizons could reach the Pluto system as early as mid-2015, conducting a five-month-long study possible only from the close-up vantage of a spacecraft.
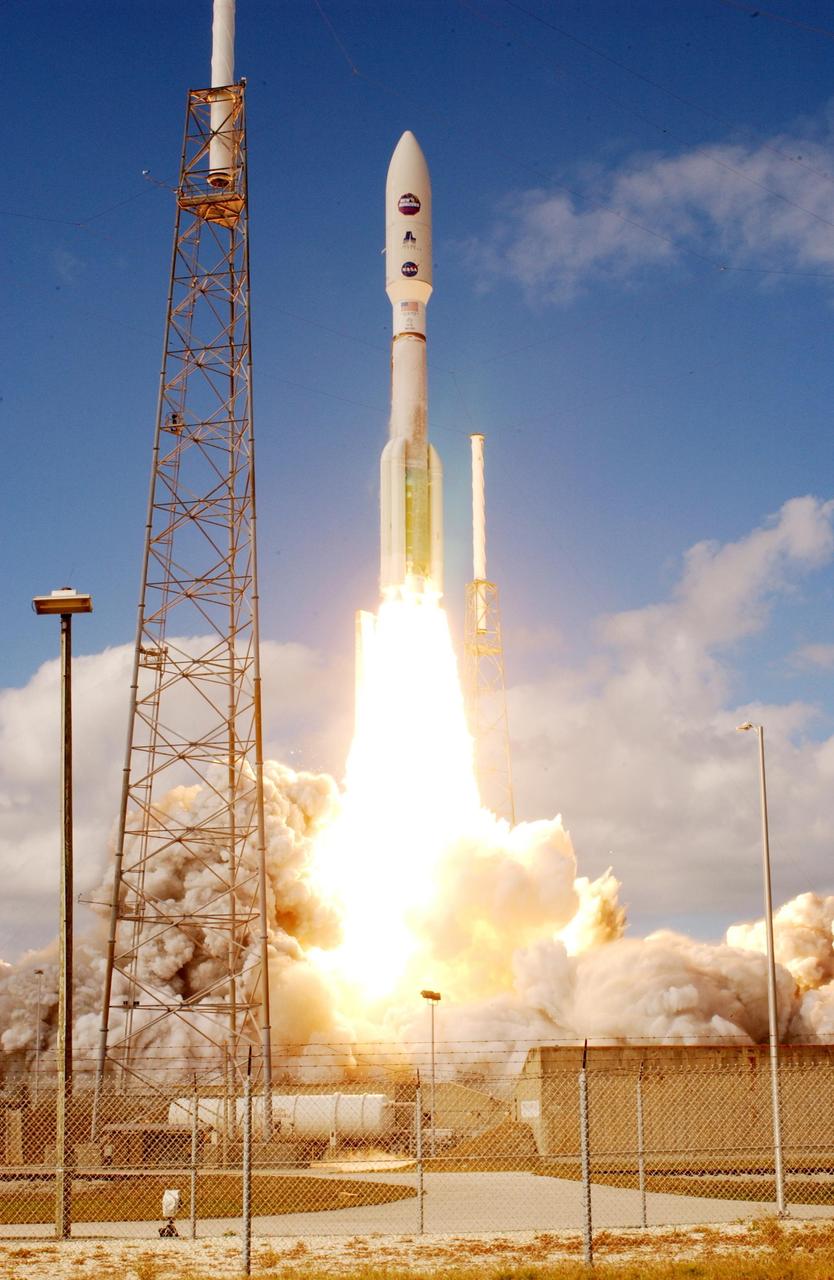

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — From between lightning masts surrounding the launch pad, NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft roars into the blue sky aboard an Atlas V rocket spewing flames and smoke. Liftoff was on time at 2 p.m. EST from Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. This was the third launch attempt in as many days after scrubs due to weather concerns. The compact, 1,050-pound piano-sized probe will get a boost from a kick-stage solid propellant motor for its journey to Pluto. New Horizons will be the fastest spacecraft ever launched, reaching lunar orbit distance in just nine hours and passing Jupiter 13 months later. The New Horizons science payload, developed under direction of Southwest Research Institute, includes imaging infrared and ultraviolet spectrometers, a multi-color camera, a long-range telescopic camera, two particle spectrometers, a space-dust detector and a radio science experiment. The dust counter was designed and built by students at the University of Colorado, Boulder. The launch at this time allows New Horizons to fly past Jupiter in early 2007 and use the planet’s gravity as a slingshot toward Pluto. The Jupiter flyby trims the trip to Pluto by as many as five years and provides opportunities to test the spacecraft’s instruments and flyby capabilities on the Jupiter system. New Horizons could reach the Pluto system as early as mid-2015, conducting a five-month-long study possible only from the close-up vantage of a spacecraft.
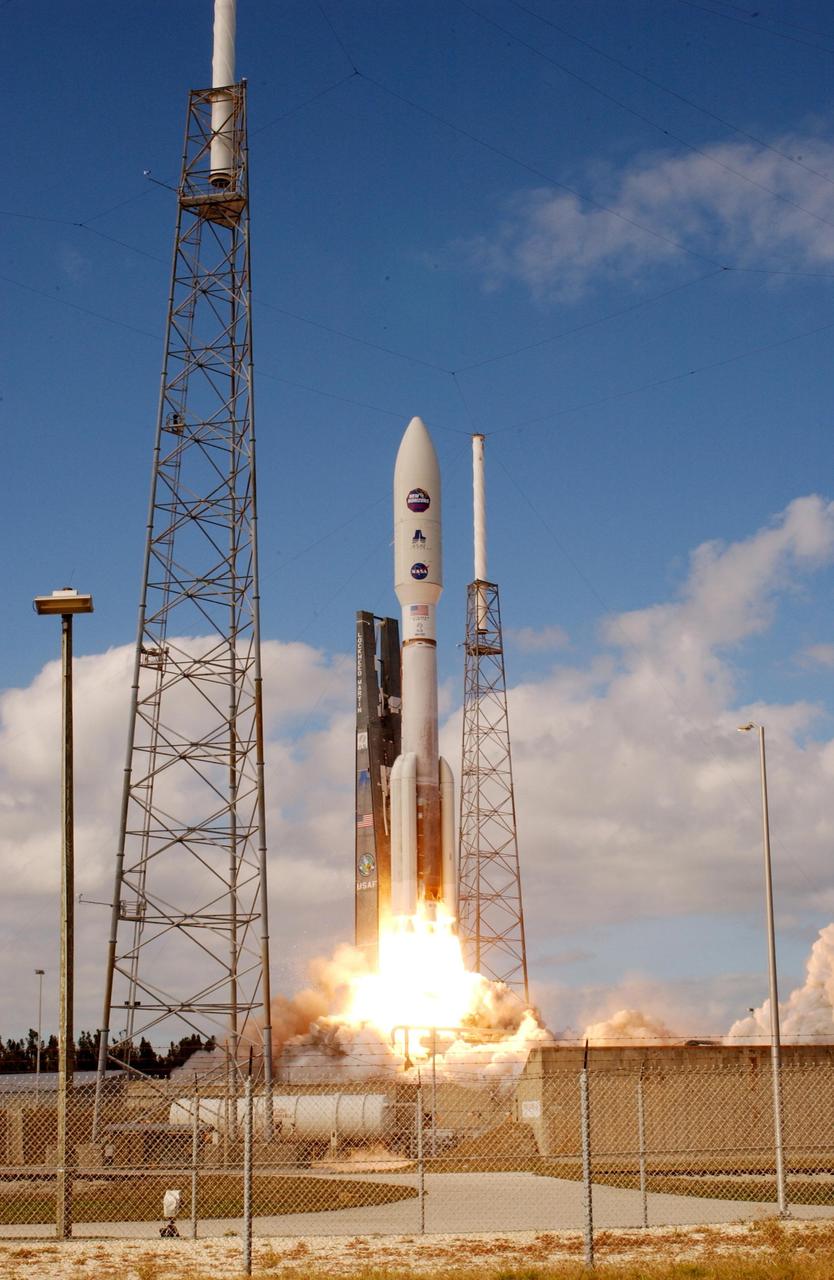

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — From between lightning masts surrounding the launch pad, NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft roars into the blue sky aboard an Atlas V rocket spewing flames and smoke. Liftoff was on time at 2 p.m. EST from Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. This was the third launch attempt in as many days after scrubs due to weather concerns. The compact, 1,050-pound piano-sized probe will get a boost from a kick-stage solid propellant motor for its journey to Pluto. New Horizons will be the fastest spacecraft ever launched, reaching lunar orbit distance in just nine hours and passing Jupiter 13 months later. The New Horizons science payload, developed under direction of Southwest Research Institute, includes imaging infrared and ultraviolet spectrometers, a multi-color camera, a long-range telescopic camera, two particle spectrometers, a space-dust detector and a radio science experiment. The dust counter was designed and built by students at the University of Colorado, Boulder. The launch at this time allows New Horizons to fly past Jupiter in early 2007 and use the planet’s gravity as a slingshot toward Pluto. The Jupiter flyby trims the trip to Pluto by as many as five years and provides opportunities to test the spacecraft’s instruments and flyby capabilities on the Jupiter system. New Horizons could reach the Pluto system as early as mid-2015, conducting a five-month-long study possible only from the close-up vantage of a spacecraft.
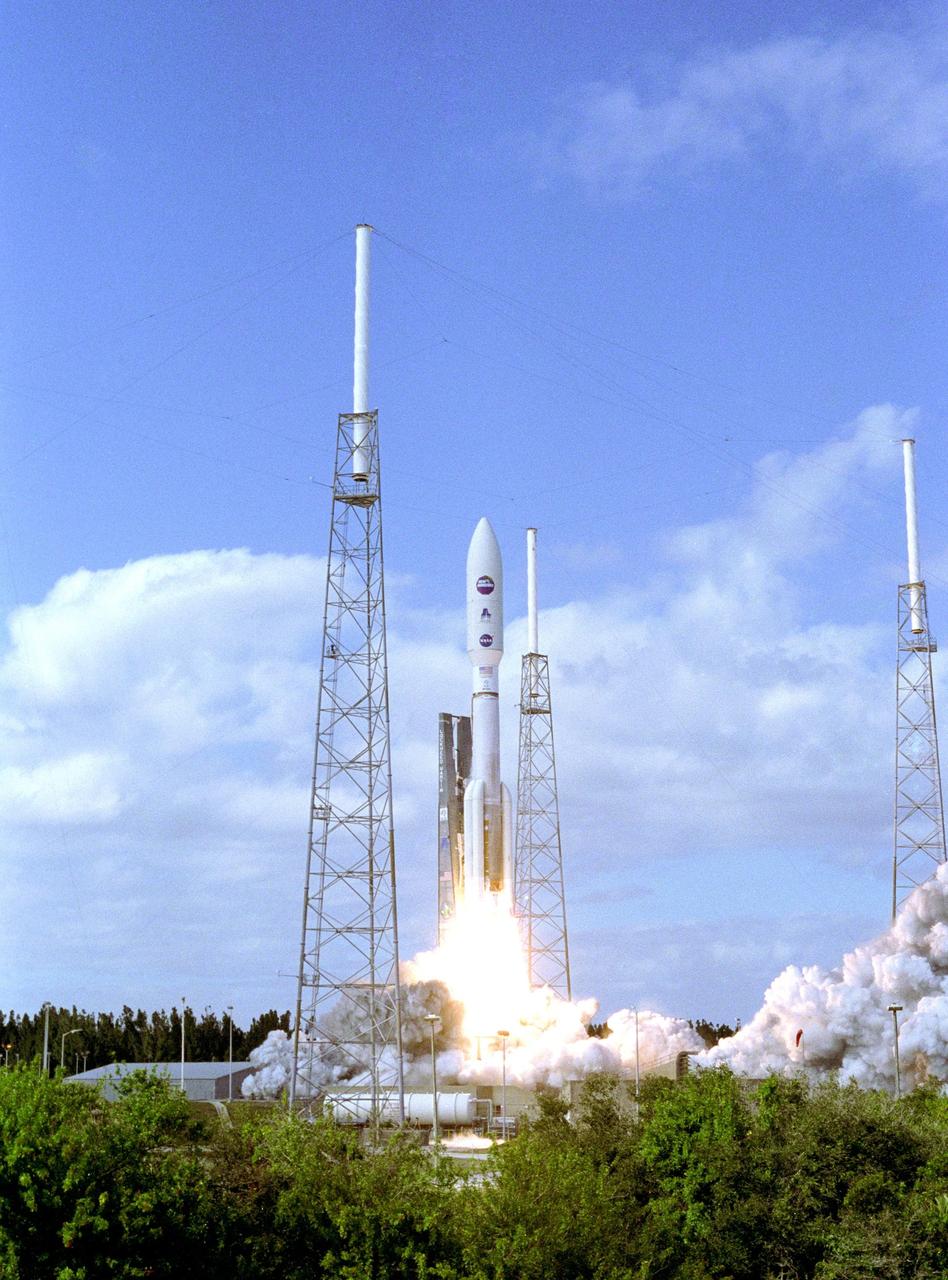

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — From between lightning masts surrounding the launch pad, NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft roars into the blue sky aboard an Atlas V rocket spewing flames and smoke. Liftoff was on time at 2 p.m. EST from Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. This was the third launch attempt in as many days after scrubs due to weather concerns. The compact, 1,050-pound piano-sized probe will get a boost from a kick-stage solid propellant motor for its journey to Pluto. New Horizons will be the fastest spacecraft ever launched, reaching lunar orbit distance in just nine hours and passing Jupiter 13 months later. The New Horizons science payload, developed under direction of Southwest Research Institute, includes imaging infrared and ultraviolet spectrometers, a multi-color camera, a long-range telescopic camera, two particle spectrometers, a space-dust detector and a radio science experiment. The dust counter was designed and built by students at the University of Colorado, Boulder. The launch at this time allows New Horizons to fly past Jupiter in early 2007 and use the planet’s gravity as a slingshot toward Pluto. The Jupiter flyby trims the trip to Pluto by as many as five years and provides opportunities to test the spacecraft’s instruments and flyby capabilities on the Jupiter system. New Horizons could reach the Pluto system as early as mid-2015, conducting a five-month-long study possible only from the close-up vantage of a spacecraft.