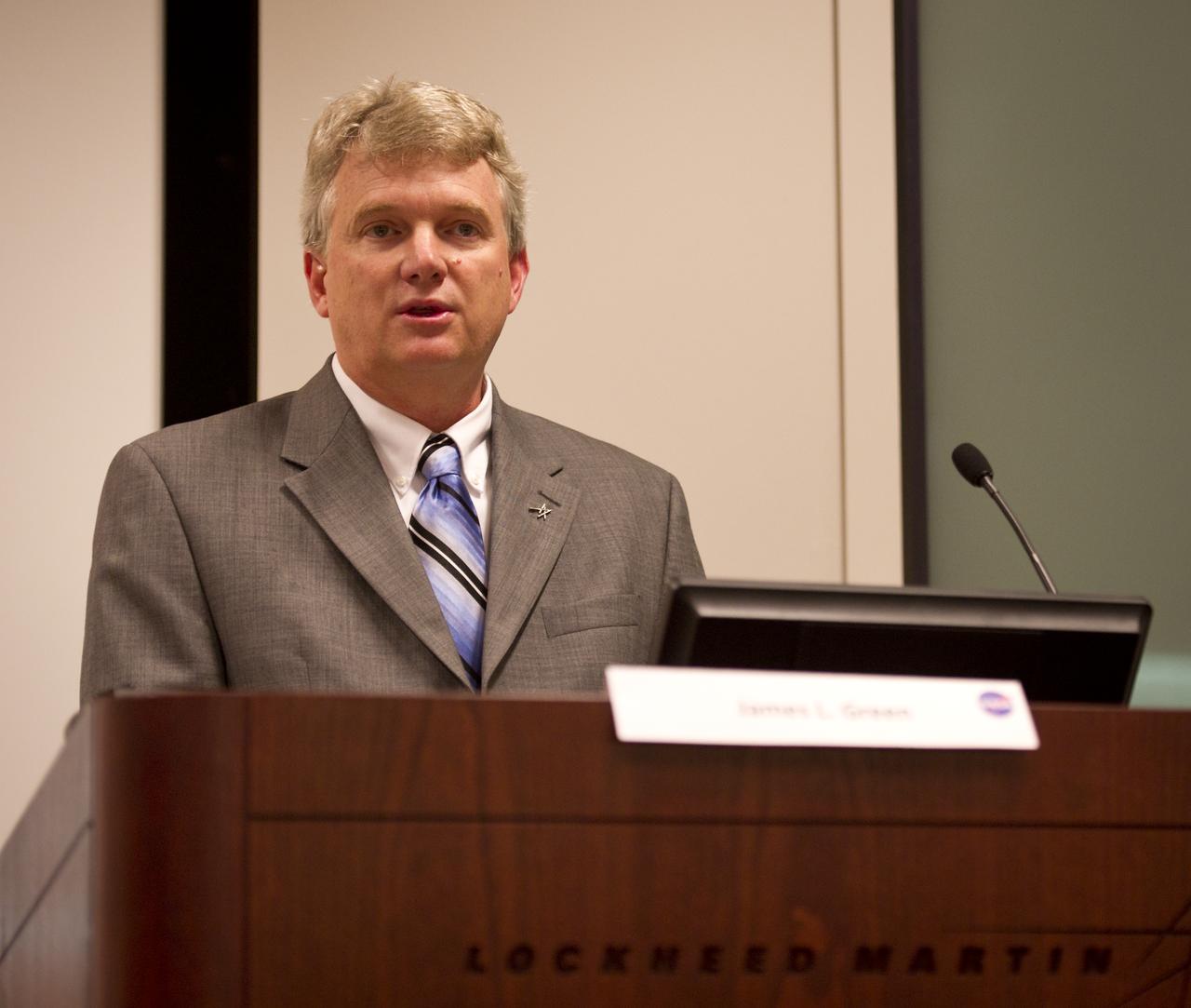

Stephen Price from Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company kicks off the ‚Äö√Ñ√∫Seeking Signs of Life‚Äö√Ñ√π Symposium, celebrating 50 Years of Exobiology and Astrobiology at NASA, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2010, at the Lockheed Martin Global Vision Center in Arlington, Va. NASA has been researching life in the universe since 1959, asking three fundamental questions: "How does life begin and evolve?"‚ "Is there life beyond Earth and, if so, how can we detect it?" and "What is the future of life on Earth and in the universe?" Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
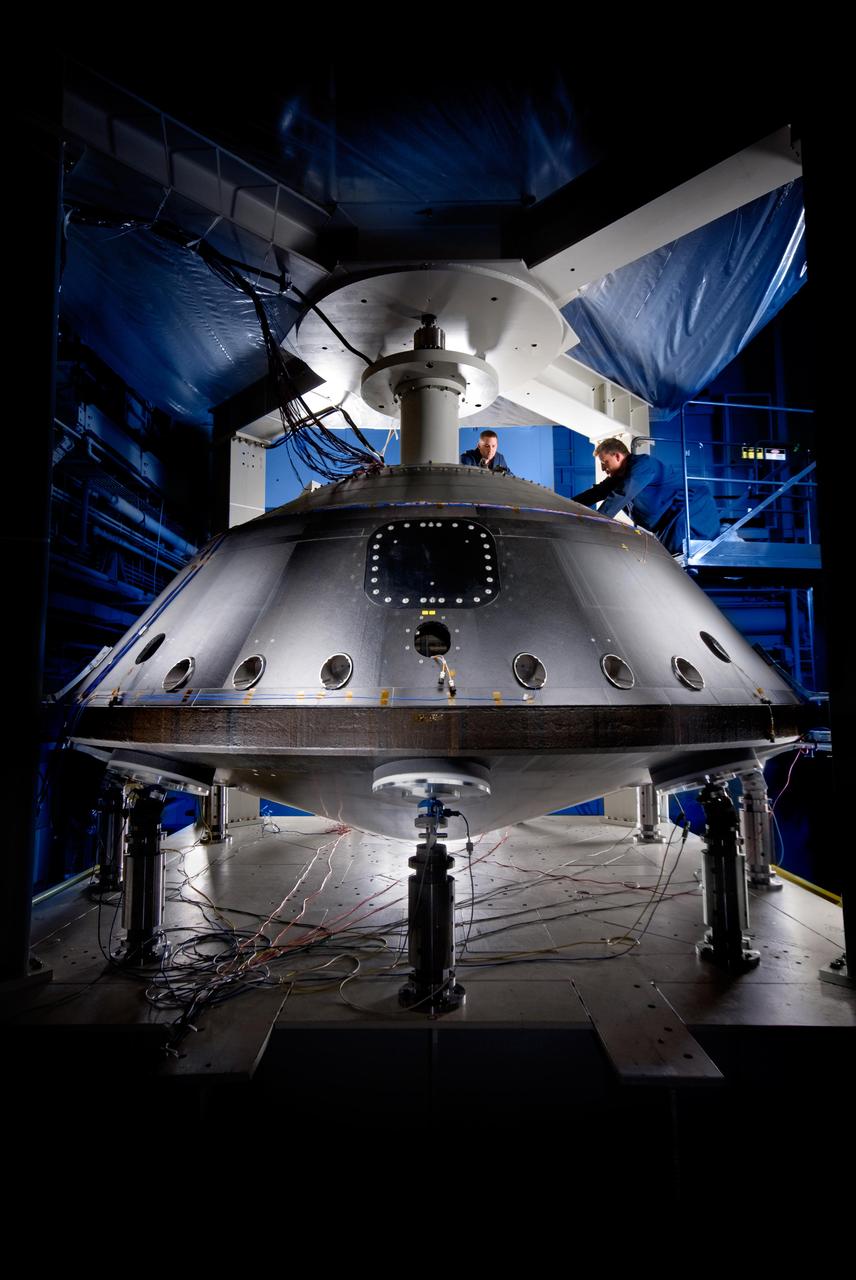

This image from July 2008 shows the aeroshell for NASA Mars Science Laboratory while it was being worked on by spacecraft technicians at Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company near Denver.
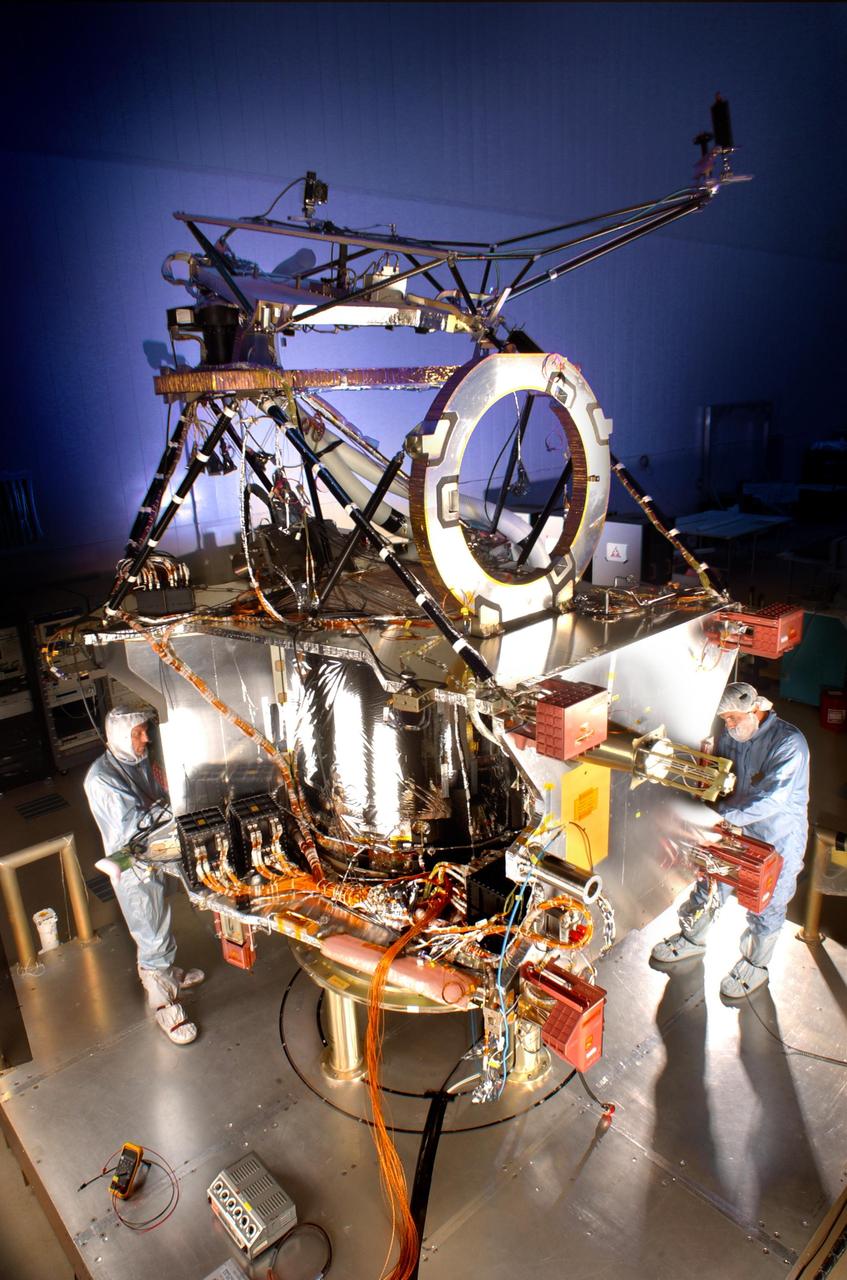
Lockheed Martin Space Systems engineer Terry Kampmann left and lead technician Jack Farmerie work on assembly and test of NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft bus in a cleanroom at the company Denver facility.
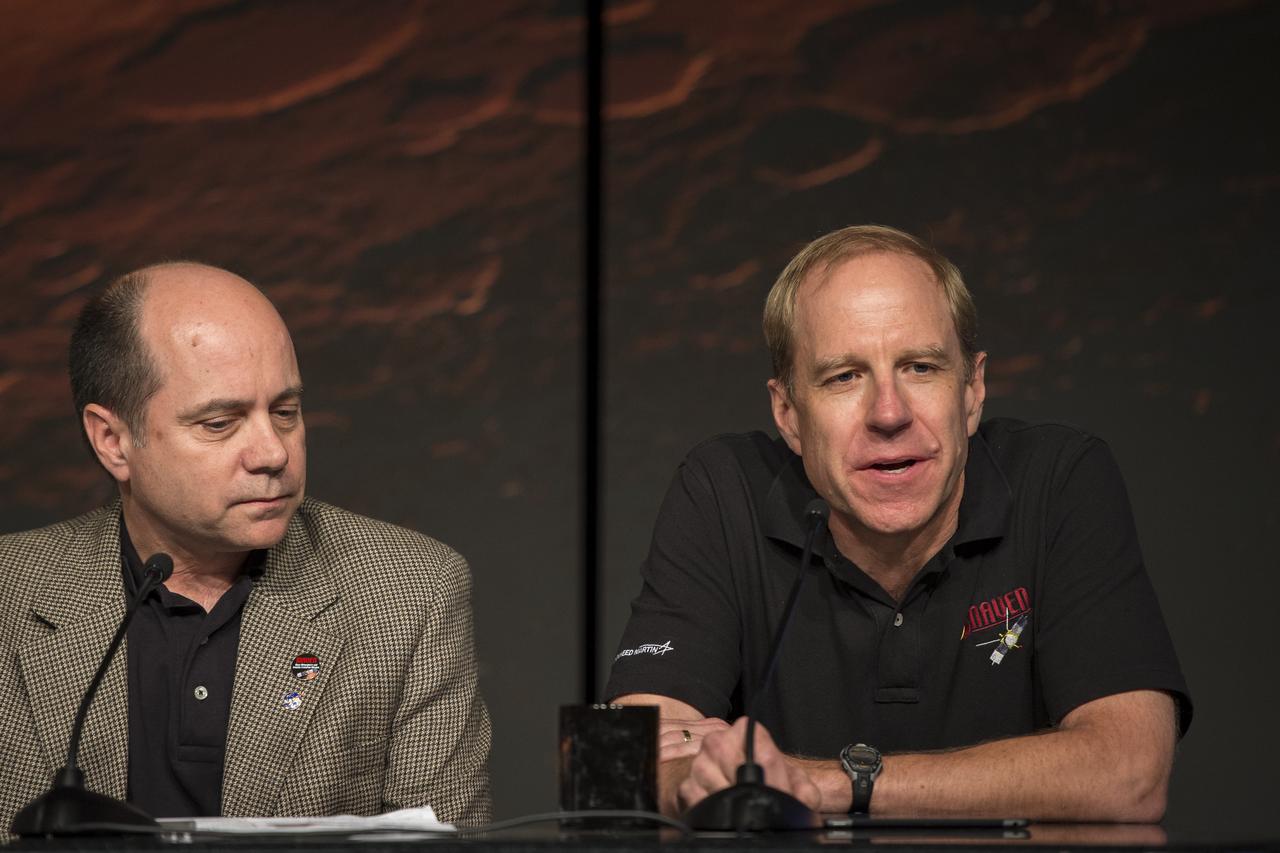

David Mitchell, MAVEN project manager, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland, left, and Guy Beutelschies, Lockheed Martin MAVEN program manager, Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company, Littleton, Colorado are seen during a media briefing where they and other panelist outlined activities around the Sunday, Sept. 21 orbital insertion at Mars of the agency’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft, Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2014 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. (Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Guy Beutelschies, Lockheed Martin MAVEN program manager, Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company, Littleton, Colorado is seen during a media briefing where he and other panelist outlined activities around the Sunday, Sept. 21 orbital insertion at Mars of the agency’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft, Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2014 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. (Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls)
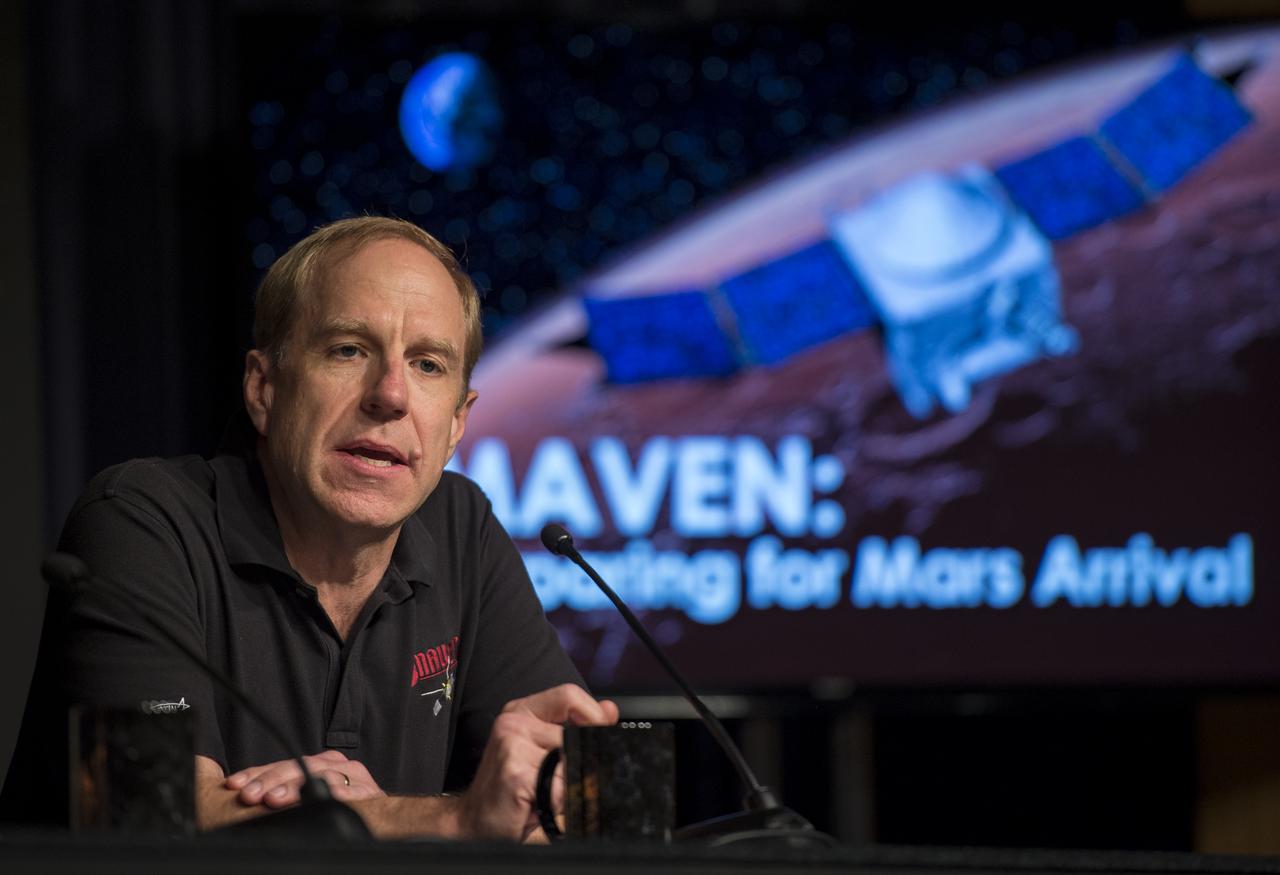

Guy Beutelschies, Lockheed Martin MAVEN program manager, Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company, Littleton, Colorado is seen during a media briefing where he and other panelist outlined activities around the Sunday, Sept. 21 orbital insertion at Mars of the agency’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft, Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2014 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. (Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls)
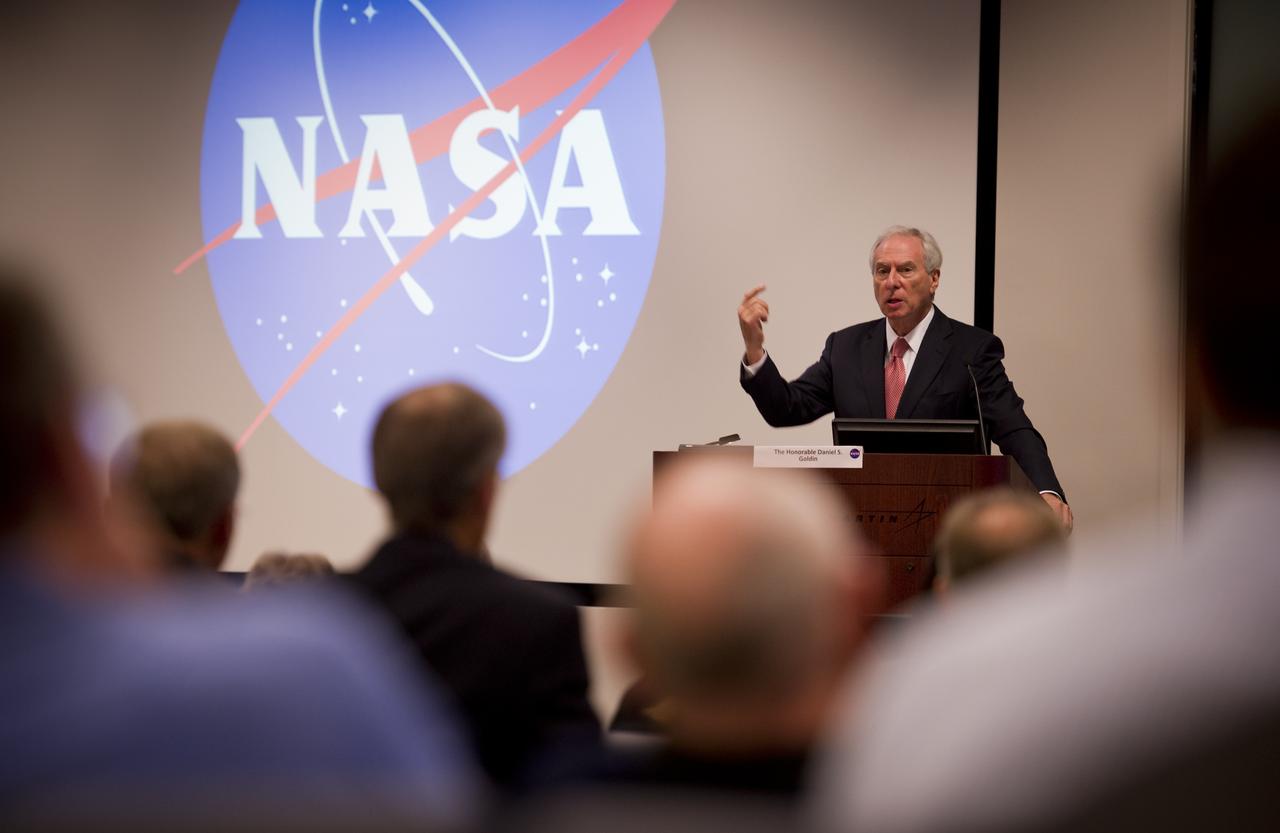

Dan Goldin, NASA's longest serving Administrator from 1992-2001 speaks during the "Seeking Signs of Life" Symposium, celebrating 50 Years of Exobiology and Astrobiology at NASA, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2010, at the Lockheed Martin Global Vision Center in Arlington, Va. NASA has been researching life in the universe since 1959, asking three fundamental questions: ‚"How does life begin and evolve?"‚ "Is there life beyond Earth and, if so, how can we detect it?‚" and "What is the future of life on Earth and in the universe?" Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
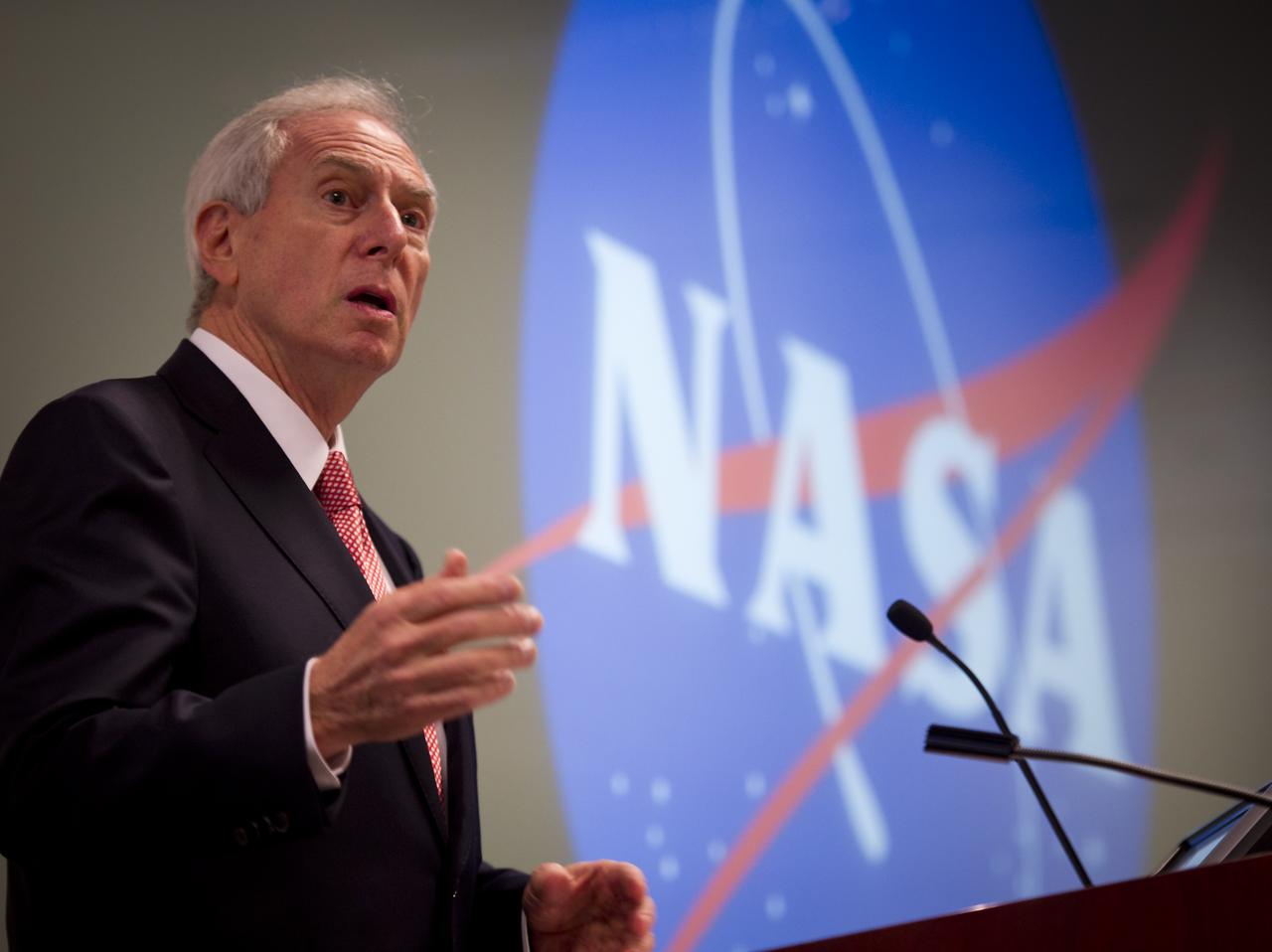

Dan Goldin, NASA's longest serving Administrator from 1992-2001 speaks during the "Seeking Signs of Life" Symposium, celebrating 50 Years of Exobiology and Astrobiology at NASA, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2010, at the Lockheed Martin Global Vision Center in Arlington, Va. NASA has been researching life in the universe since 1959, asking three fundamental questions: ‚"How does life begin and evolve?"‚ "Is there life beyond Earth and, if so, how can we detect it?‚" and "What is the future of life on Earth and in the universe?" Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
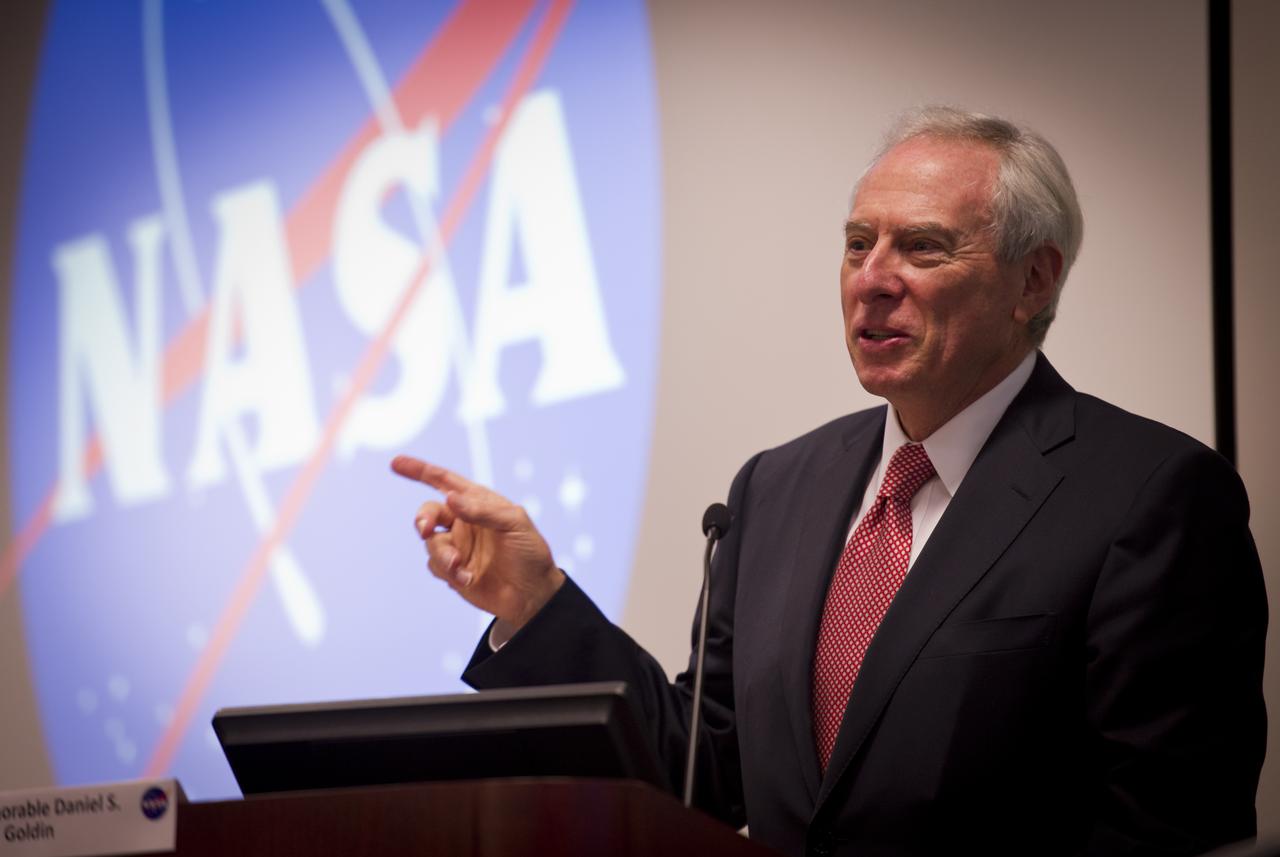

Dan Goldin, NASA's longest serving Administrator from 1992-2001 speaks during the "Seeking Signs of Life" Symposium, celebrating 50 Years of Exobiology and Astrobiology at NASA, Thursday, Oct. 14, 2010, at the Lockheed Martin Global Vision Center in Arlington, Va. NASA has been researching life in the universe since 1959, asking three fundamental questions: ‚"How does life begin and evolve?"‚ "Is there life beyond Earth and, if so, how can we detect it?‚" and "What is the future of life on Earth and in the universe?" Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NEW ORLEANS -- Associate Administrator for Space Operations Bill Gerstenmaier and Manny Zulueta, Lockheed Martin vice president and site executive at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, watch the progress of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, as it is being transported from the facility to the Pegasus Barge. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida secured aboard the barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
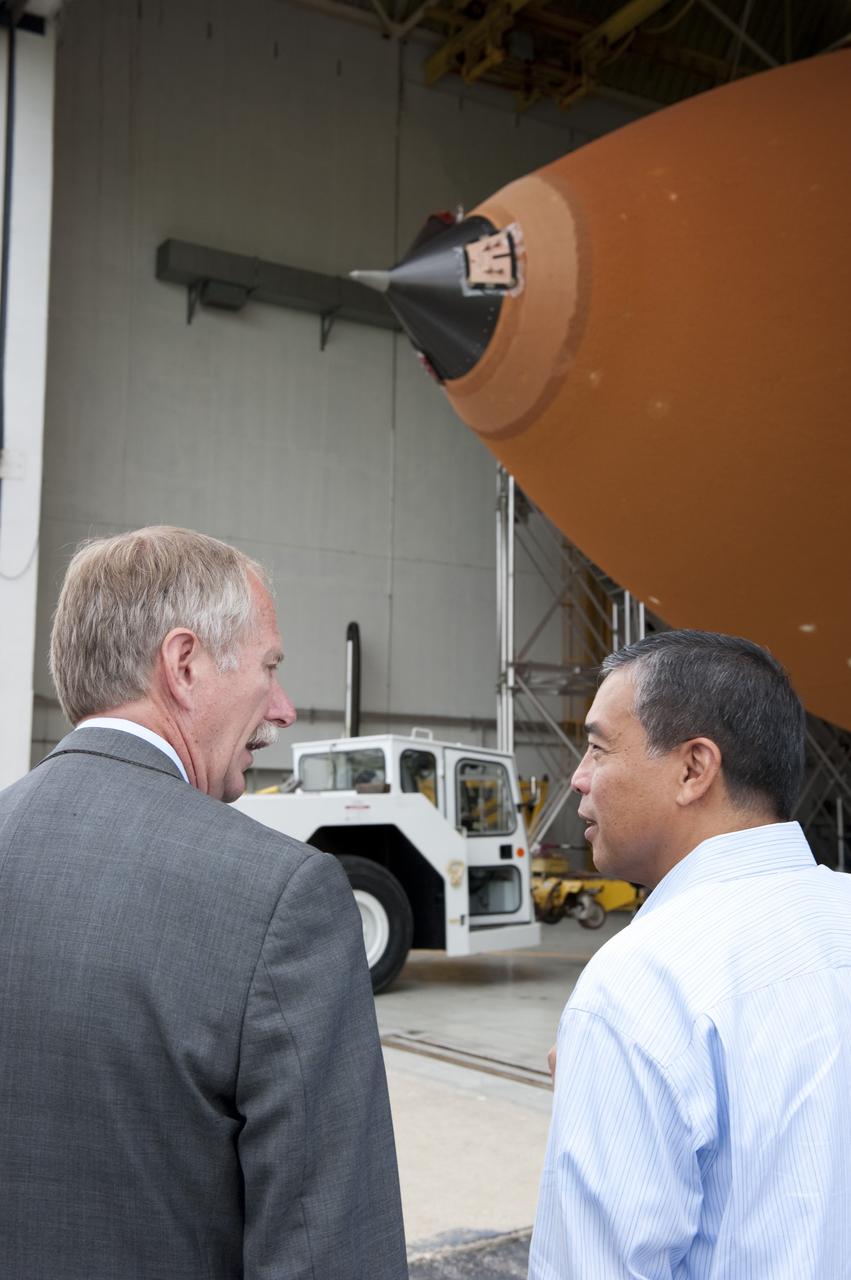

NEW ORLEANS -- Associate Administrator for Space Operations Bill Gerstenmaier and Manny Zulueta, Lockheed Martin vice president and site executive at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, discuss the progress of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, as it is being transported from the facility to the Pegasus Barge. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, secured aboard the barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
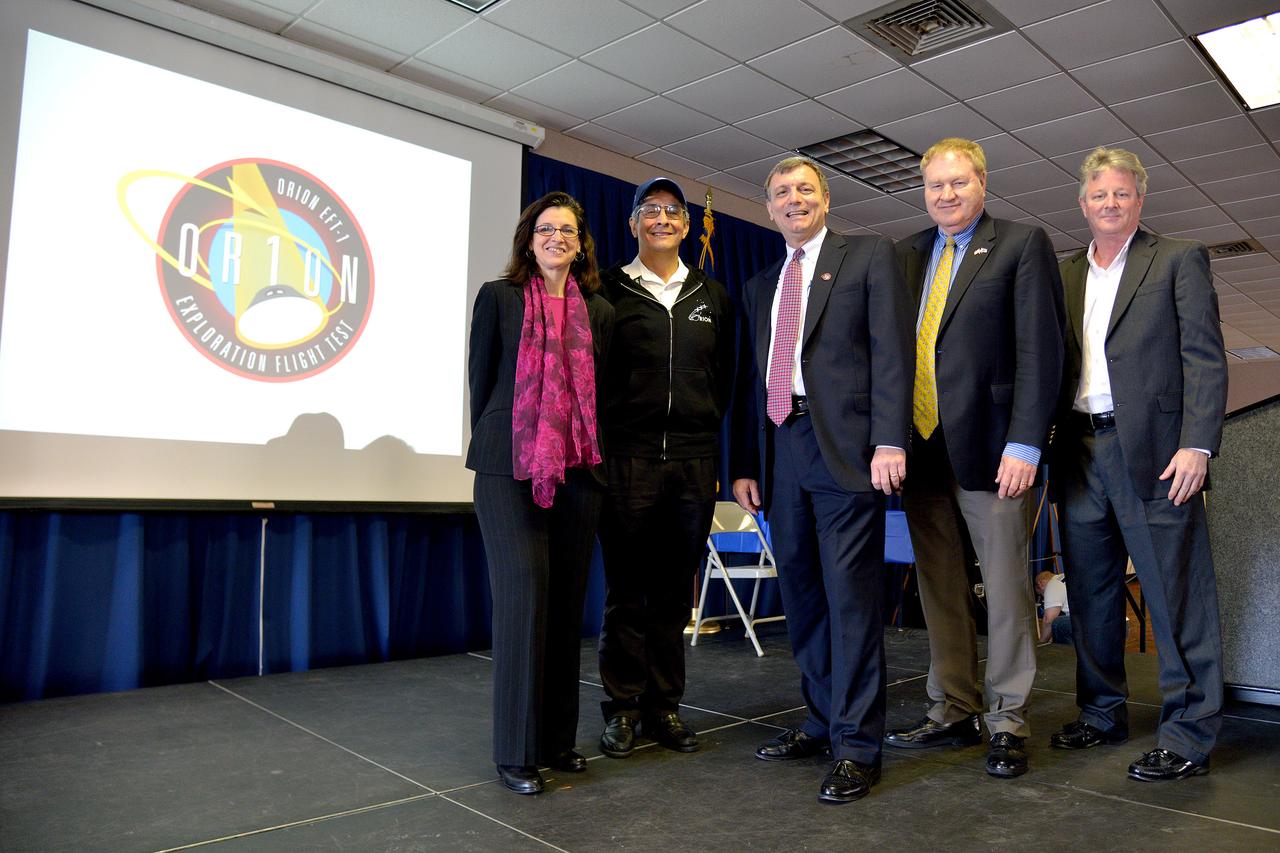

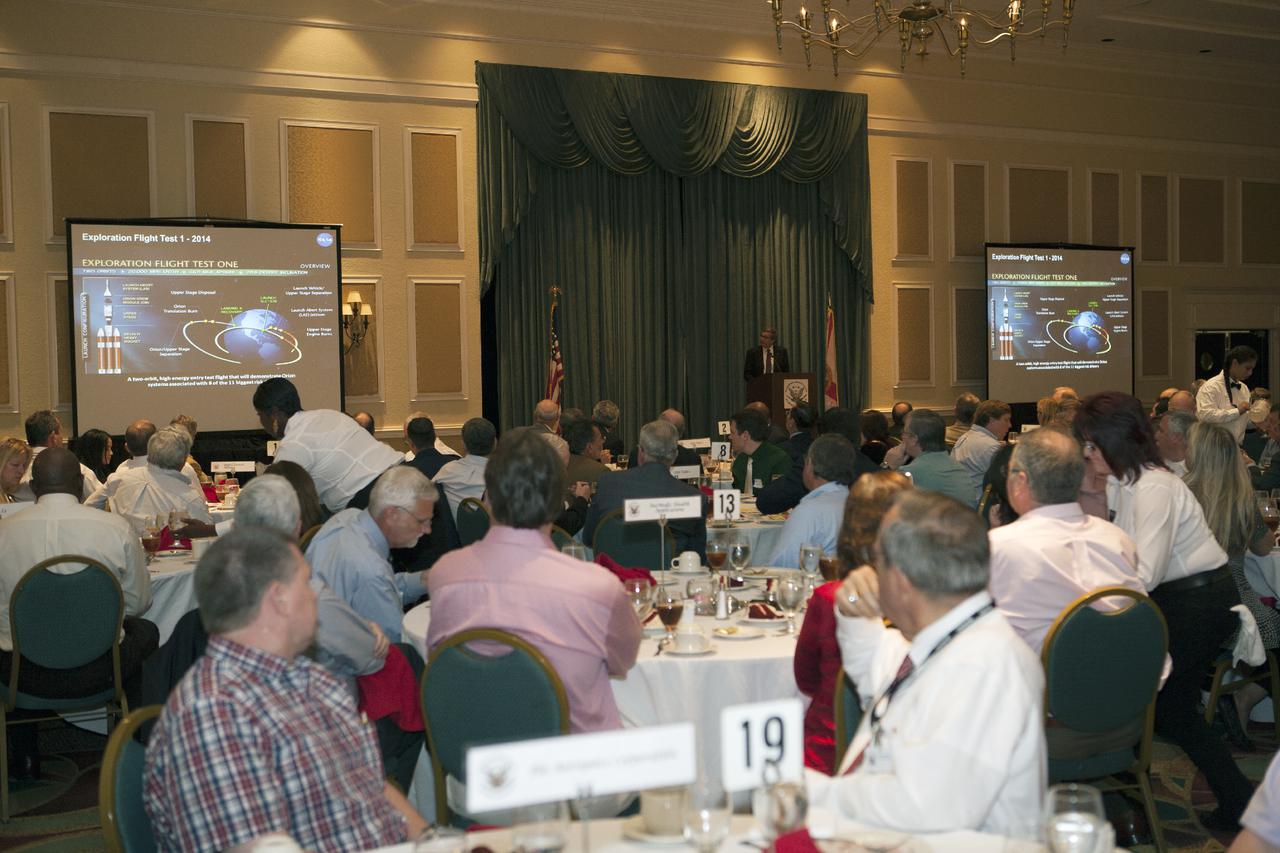
The Michoud Assembly Facility Orion Program Event showcases highlights from the successful Exploration Flight Test-1 mission on March 16, 2015. In addition, the Lockheed Martin and NASA Orion Program Managers will thank the employees and companies for their contribution toward developing the systems needed to enable NASA's future human exploration capabilities in deep space. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
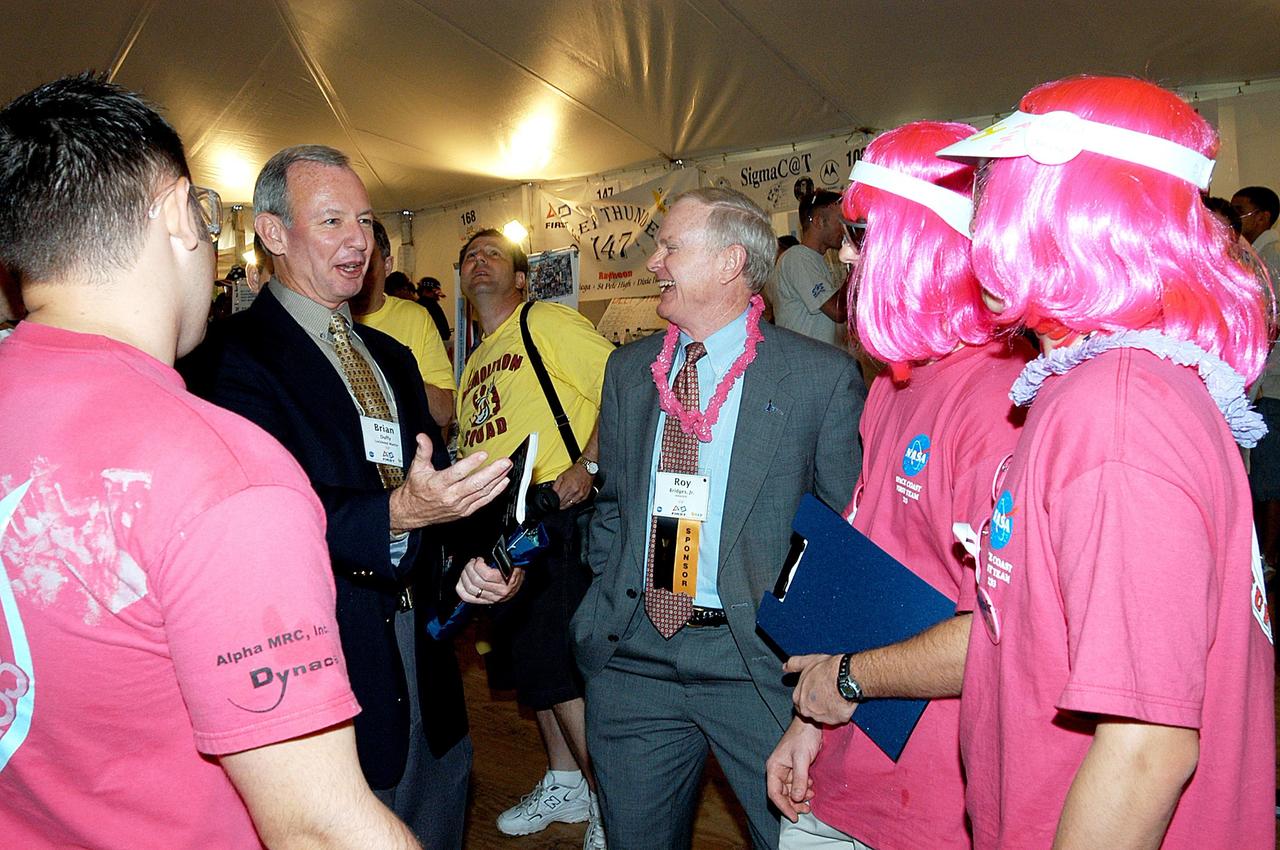

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Lockheed Martin Vice President/Associate Program Manager Brian Duffy (second from left) and NASA/Kennedy Space Center Director Roy Bridges (center) share a laugh with student participants in the 2003 Southeastern Regional FIRST Robotic Competition. The competition is being held at the University of Central Florida (UCF) in Orlando, March 20-23. Forty student teams from around the country are participating in the event that pits team-built gladiator robots against each other in an athletic-style competition. The teams are sponsored by NASA/Kennedy Space Center, The Boeing Company/Brevard Community College, and Lockheed Martin Space Operations/Mission Systems for the nonprofit organization For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology, known as FIRST. The vision of FIRST is to inspire in the youth of our nation an appreciation of science and technology and an understanding that mastering these disciplines can enrich the lives of all mankind.
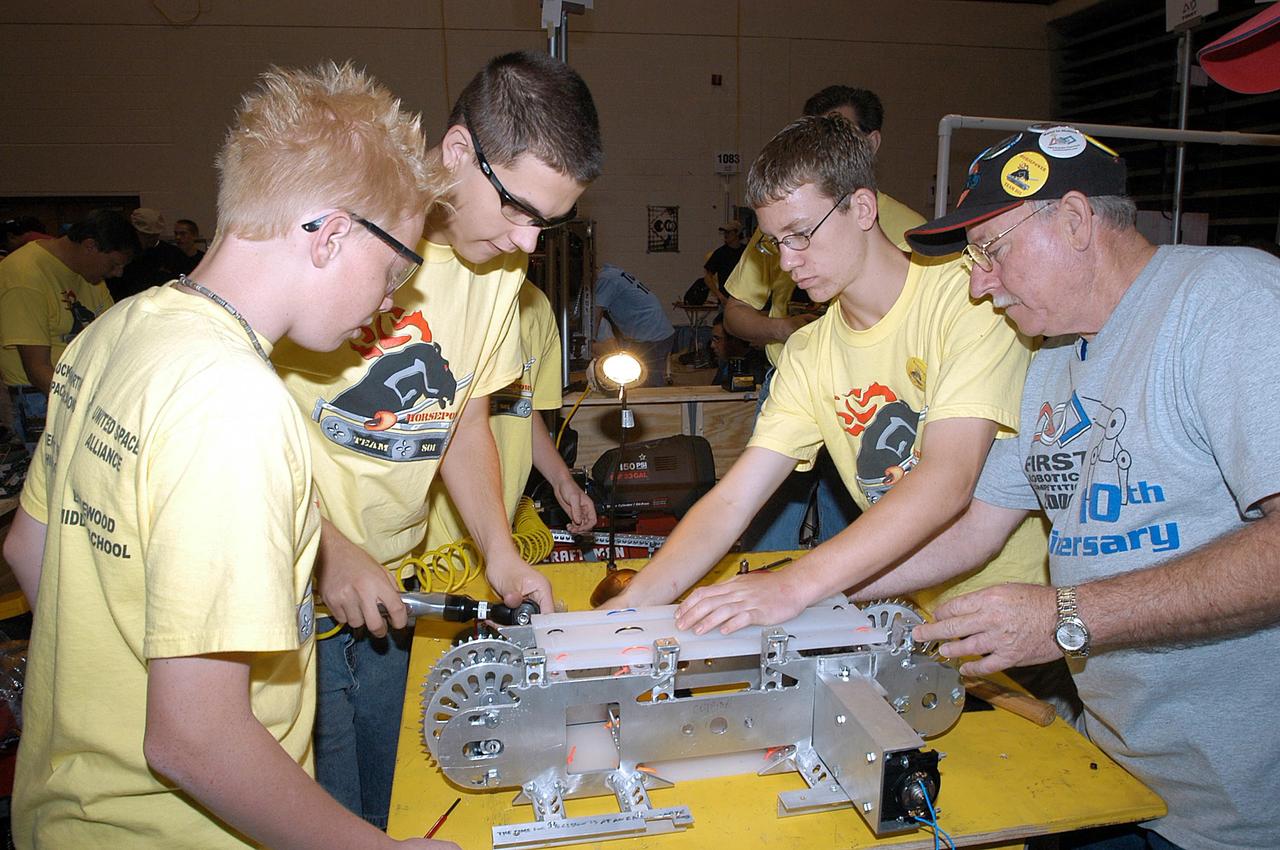

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Merritt Island and Edgewood Middle School students/Lockheed Martin team, participating in the 2003 Southeastern Regional FIRST Robotic Competition, work on their team-built robot. The competition is being held at the University of Central Florida (UCF) in Orlando, March 20-23. Forty teams from around the country are participating in the event that pits team-built gladiator robots against each other in an athletic-style competition. The teams are sponsored by NASA-Kennedy Space Center, The Boeing Company/Brevard Community College, and Lockheed Martin Space Operations/Mission Systems for the nonprofit organization For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology, known as FIRST. The vision of FIRST is to inspire in the youth of our nation an appreciation of science and technology and an understanding that mastering these disciplines can enrich the lives of all mankind.
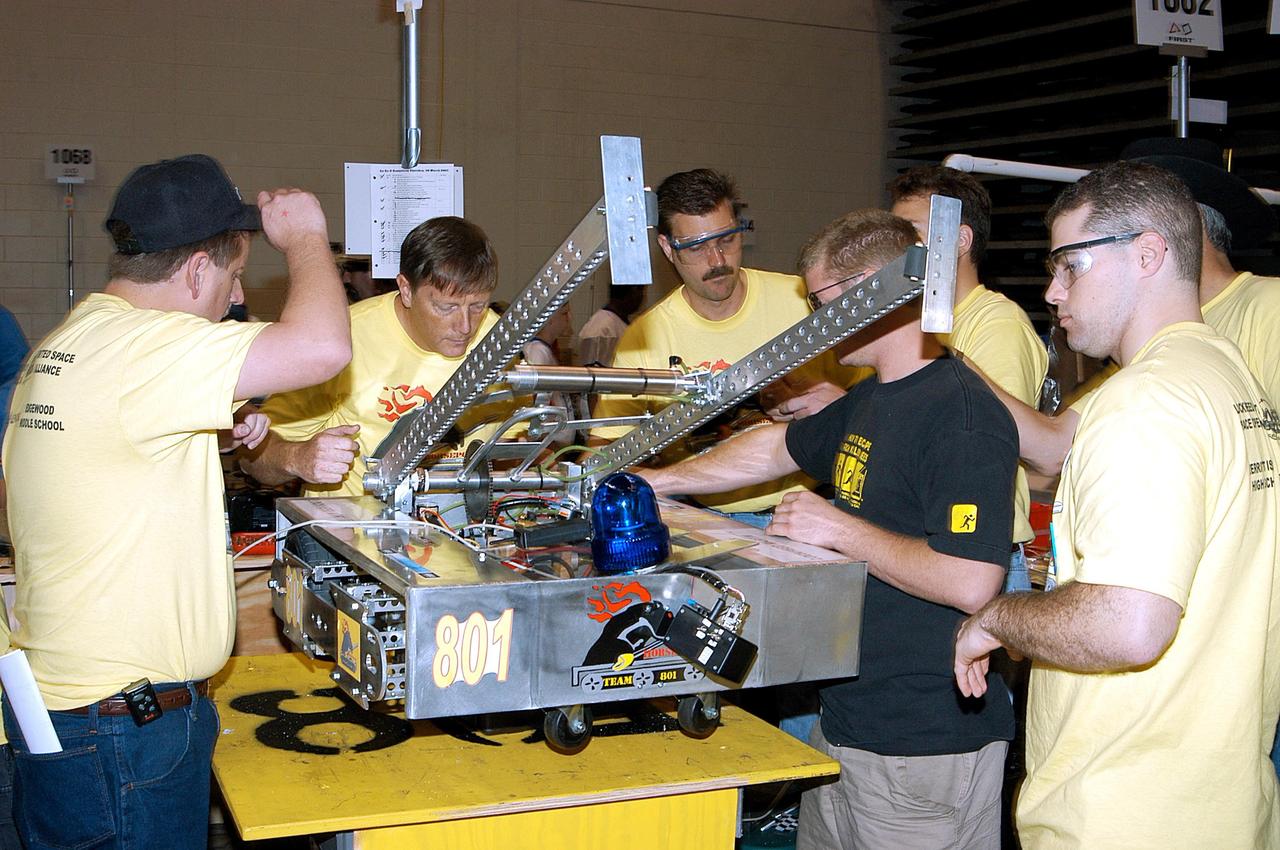

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Members of the Merritt Island and Edgewood Middle School students/Lockheed Martin team look over their robot. They are participating in the 2003 Southeastern Regional FIRST Robotic Competition being held at the University of Central Florida (UCF) in Orlando, March 20-23. Forty teams from around the country are participating in the event that pits team-built gladiator robots against each other in an athletic-style competition. The teams are sponsored by NASA-Kennedy Space Center, The Boeing Company/Brevard Community College, and Lockheed Martin Space Operations/Mission Systems for the nonprofit organization For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology, known as FIRST. The vision of FIRST is to inspire in the youth of our nation an appreciation of science and technology and an understanding that mastering these disciplines can enrich the lives of all mankind.
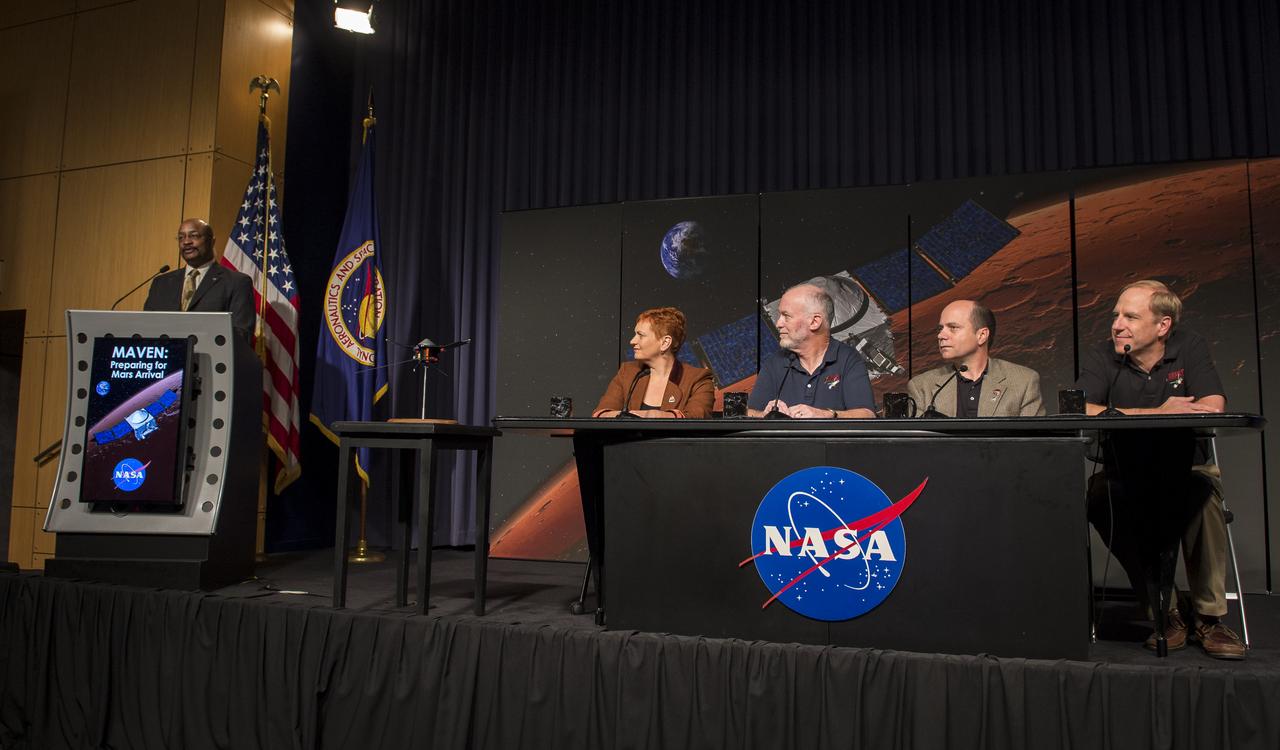

Dwayne Brown, NASA public affairs officer, left, moderates a media briefing where panelist, seated from left, Lisa May, lead program executive, Mars Exploration Program, NASA Headquarters, Washington, Bruce Jakosky, MAVEN principal investigator, Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, University of Colorado, Boulder, David Mitchell, MAVEN project manager, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland, and Guy Beutelschies, Lockheed Martin MAVEN program manager, Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company, Littleton, Colorado, outlined activities around the Sunday, Sept. 21 orbital insertion at Mars of the agency’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft, Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2014 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. (Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls)
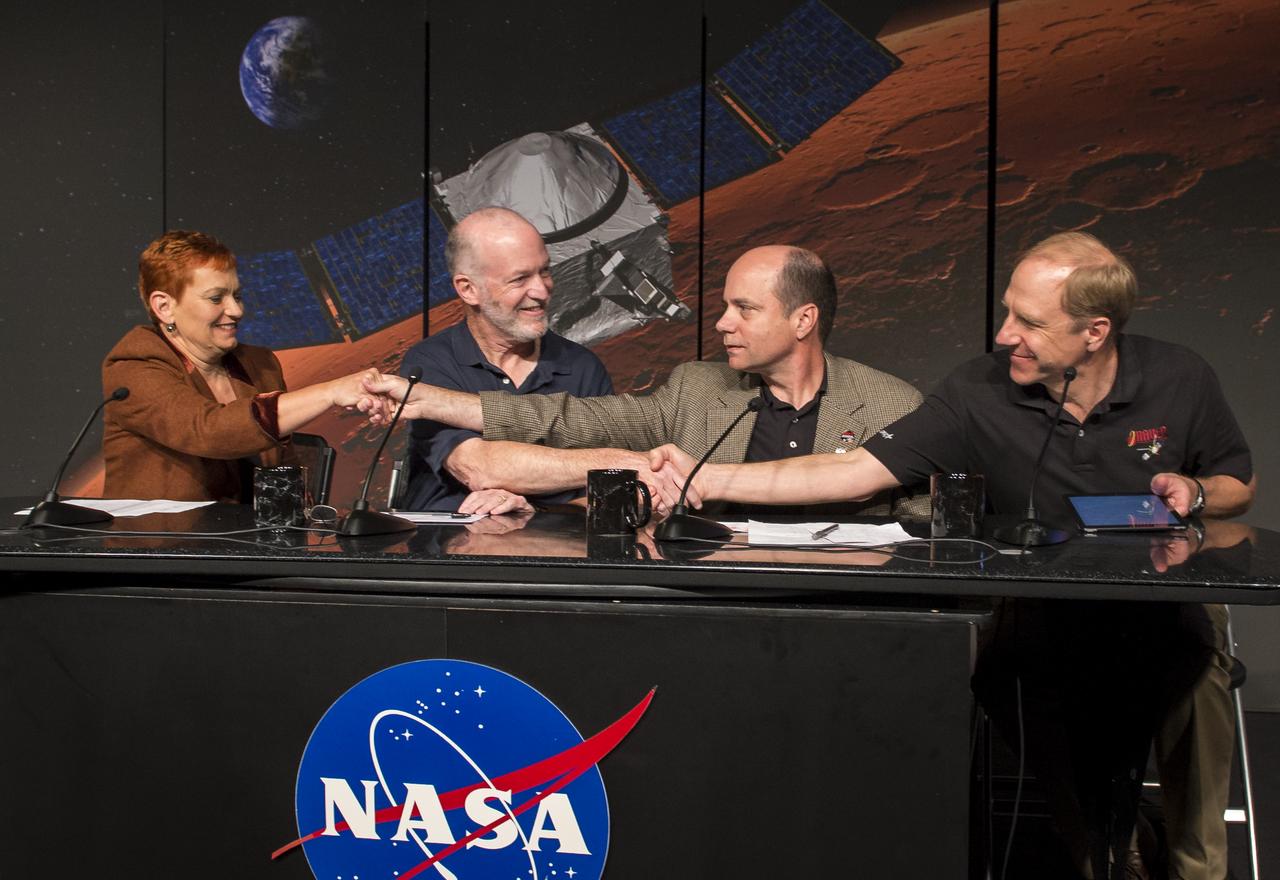

Panelist, from left, Lisa May, lead program executive, Mars Exploration Program, NASA Headquarters, Washington, Bruce Jakosky, MAVEN principal investigator, Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, University of Colorado, Boulder, David Mitchell, MAVEN project manager, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland, and Guy Beutelschies, Lockheed Martin MAVEN program manager, Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company, Littleton, Colorado, all shake hands at the end of a media briefing where they outlined activities around the Sunday, Sept. 21 orbital insertion at Mars of the agency’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) spacecraft, Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2014 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. (Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls)
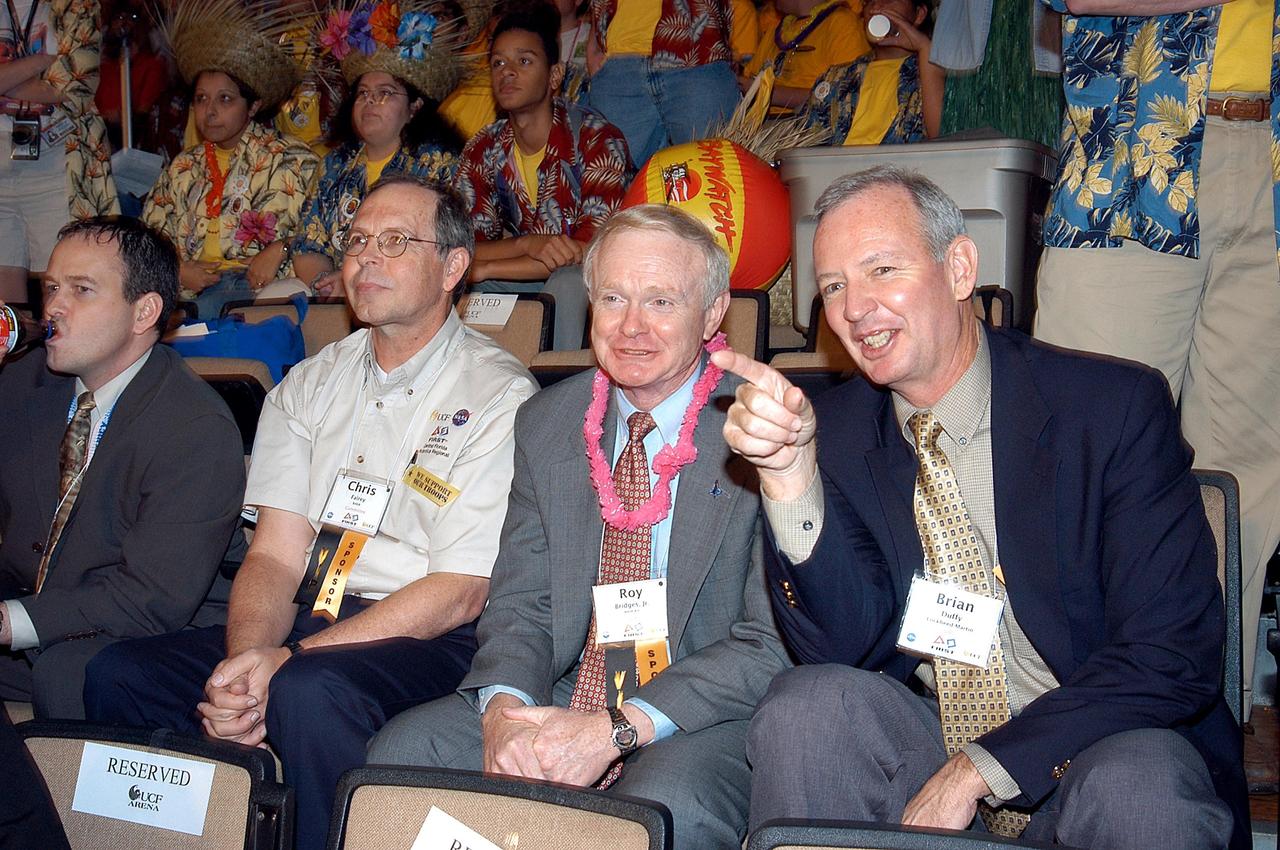

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Observing the festivities at the 2003 Southeastern Regional FIRST Robotic Competition are, from left, David Culp, executive intern to the director of KSC; Chris Fairey, former director of Spaceport Services at KSC; Roy Bridges, KSC director; and Brian Duffy, Lockheed Martin vice president/associate program manager. The competition is being held at the University of Central Florida (UCF) in Orlando, March 20-23. Forty student teams from around the country are participating in the event that pits team-built gladiator robots against each other in an athletic-style competition. The teams are sponsored by NASA/Kennedy Space Center, The Boeing Company/Brevard Community College, and Lockheed Martin Space Operations/Mission Systems for the nonprofit organization For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology, known as FIRST. The vision of FIRST is to inspire in the youth of our nation an appreciation of science and technology and an understanding that mastering these disciplines can enrich the lives of all mankind.
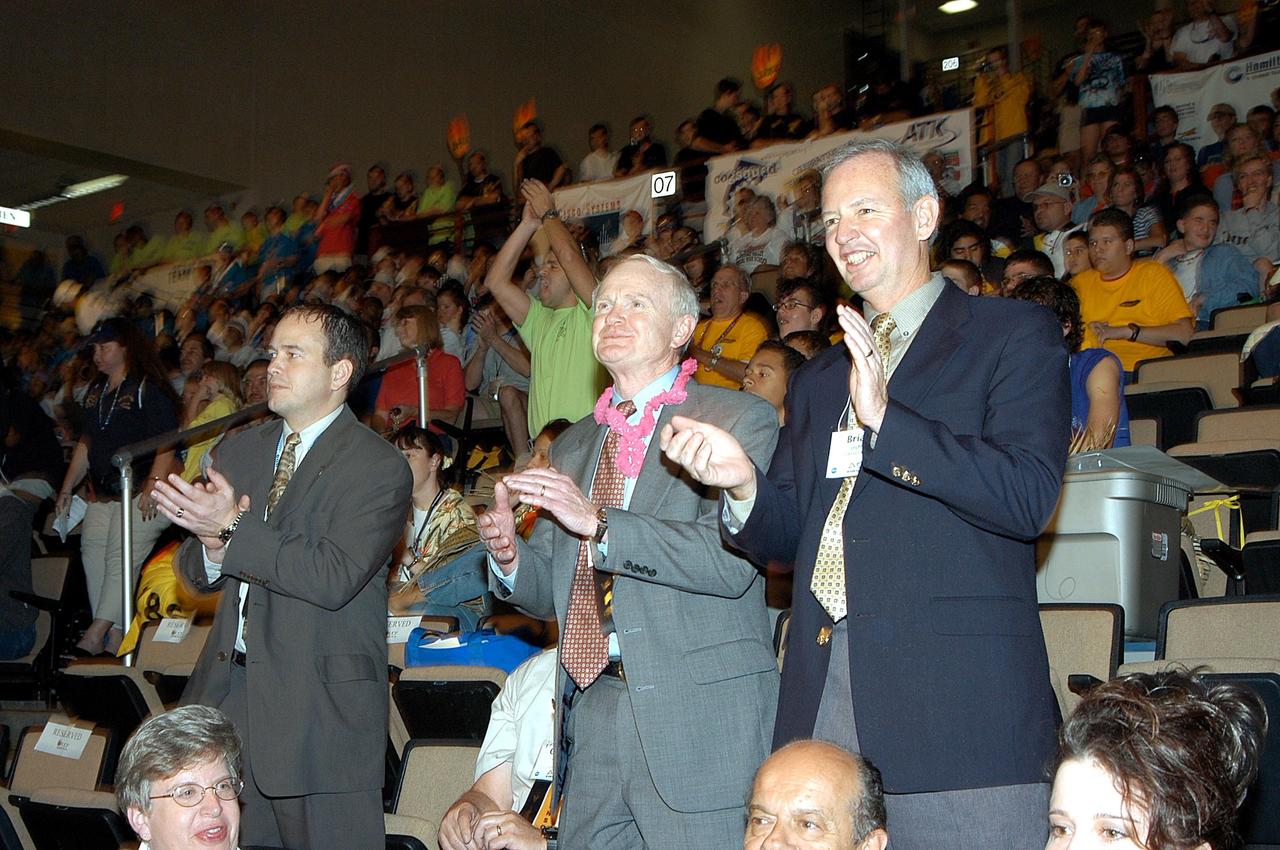

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On their feet, applauding the student participants of the 2003 Southeastern Regional FIRST Robotic Competition are, from left, David Culp, executive intern to the director of KSC; Roy Bridges, KSC director; and Brian Duffy, Lockheed Martin vice president/associate program manager. The competition is being held at the University of Central Florida (UCF) in Orlando, March 20-23. Forty student teams from around the country are participating in the event that pits team-built gladiator robots against each other in an athletic-style competition. The teams are sponsored by NASA/Kennedy Space Center, The Boeing Company/Brevard Community College, and Lockheed Martin Space Operations/Mission Systems for the nonprofit organization For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology, known as FIRST. The vision of FIRST is to inspire in the youth of our nation an appreciation of science and technology and an understanding that mastering these disciplines can enrich the lives of all mankind.
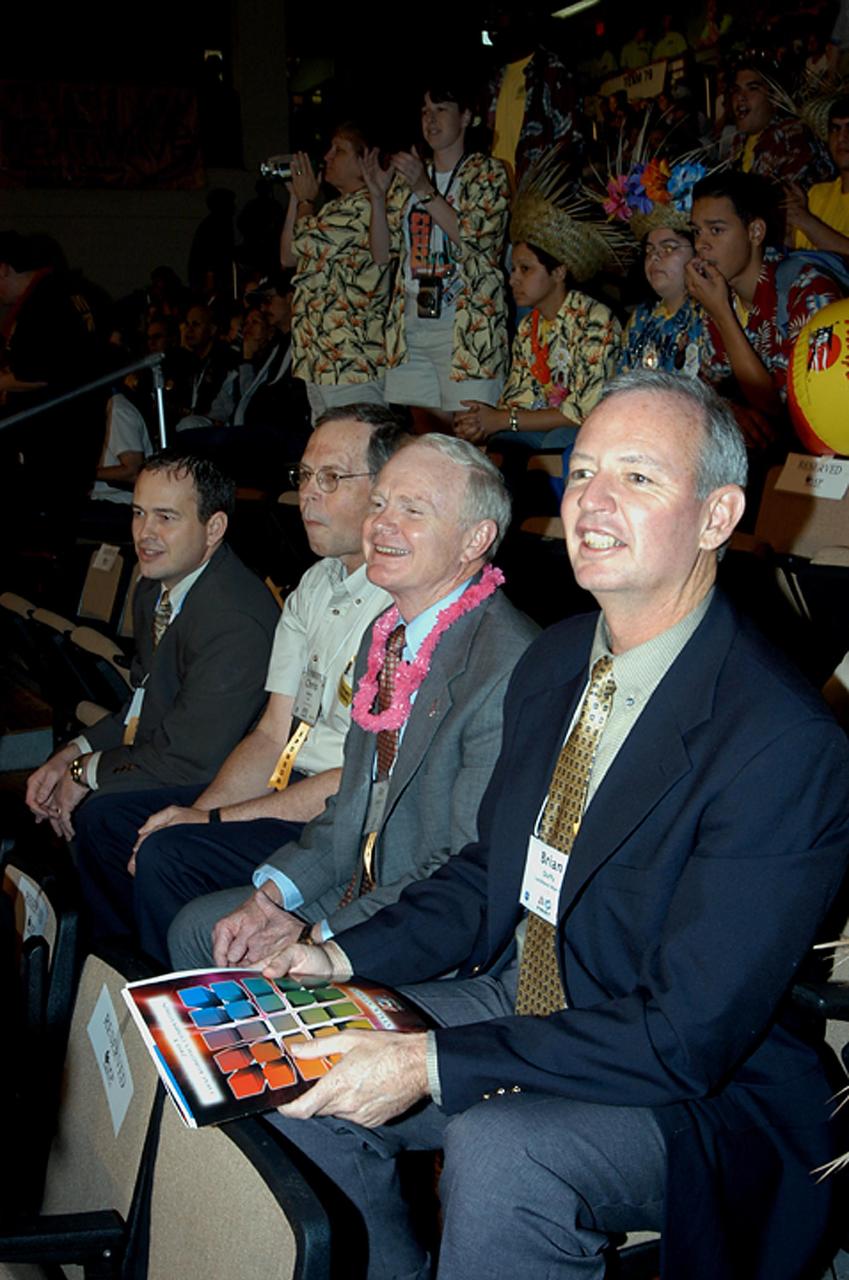

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Observing the festivities at the 2003 Southeastern Regional FIRST Robotic Competition are, from left, David Culp, executive intern to the director of KSC; Chris Fairey, former director of Spaceport Services at KSC; Roy Bridges, KSC director; and Brian Duffy, Lockheed Martin vice president/associate program manager. The competition is being held at the University of Central Florida (UCF) in Orlando, March 20-23. Forty student teams from around the country are participating in the event that pits team-built gladiator robots against each other in an athletic-style competition. The teams are sponsored by NASA/Kennedy Space Center, The Boeing Company/Brevard Community College, and Lockheed Martin Space Operations/Mission Systems for the nonprofit organization For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology, known as FIRST. The vision of FIRST is to inspire in the youth of our nation an appreciation of science and technology and an understanding that mastering these disciplines can enrich the lives of all mankind.
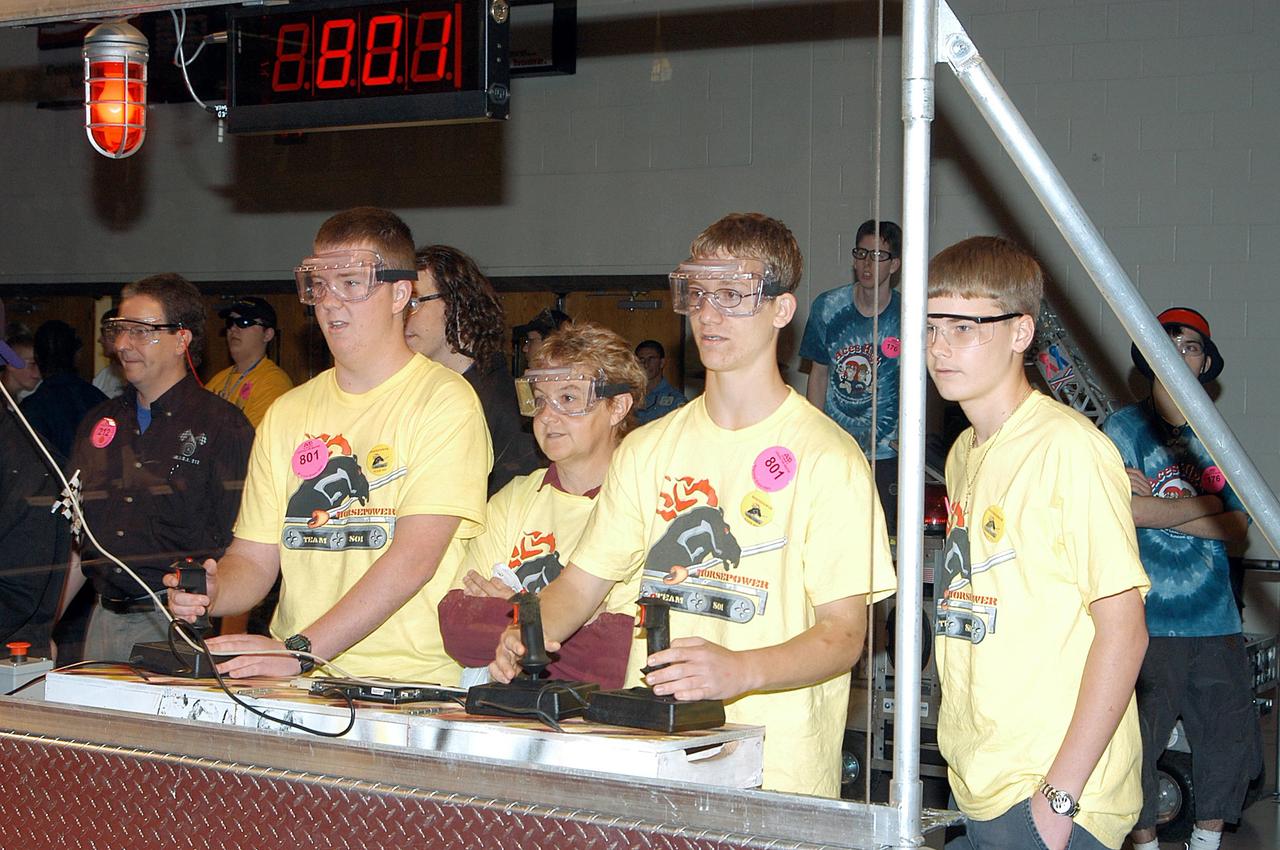

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Members of the Merritt Island and Edgewood Middle School students/Lockheed Martin team maneuver their robot during competition. They are participating in the 2003 Southeastern Regional FIRST Robotic Competition being held at the University of Central Florida (UCF) in Orlando, March 20-23. Forty teams from around the country are participating in the event that pits team-built gladiator robots against each other in an athletic-style competition. The teams are sponsored by NASA-Kennedy Space Center, The Boeing Company/Brevard Community College, and Lockheed Martin Space Operations/Mission Systems for the nonprofit organization For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology, known as FIRST. The vision of FIRST is to inspire in the youth of our nation an appreciation of science and technology and an understanding that mastering these disciplines can enrich the lives of all mankind.

NEW ORLEANS -- Workers escort the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, to the Pegasus Barge at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The tank will travel 900 miles aboard the Pegasus Barge to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
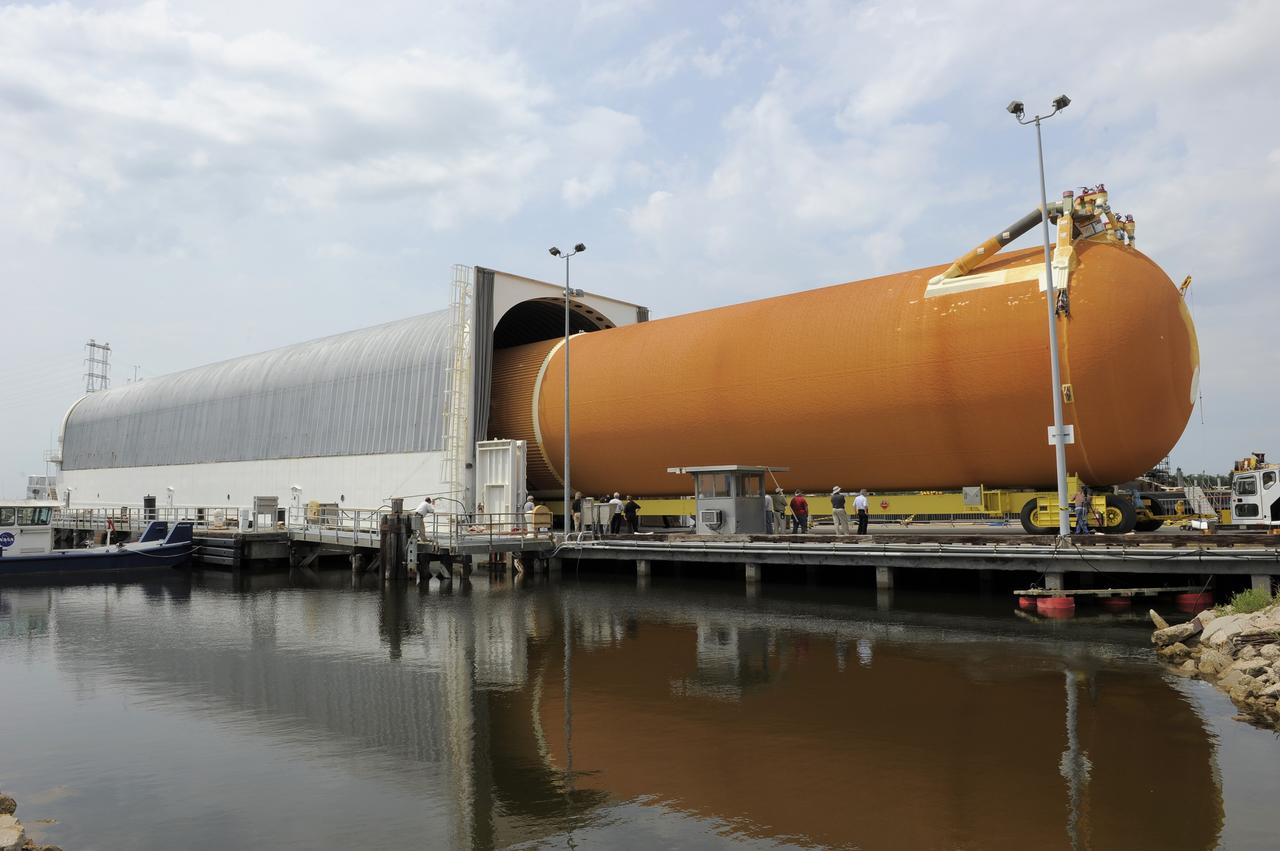

NEW ORLEANS -- The Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, is loaded onto the Pegasus Barge at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The tank will travel 900 miles to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
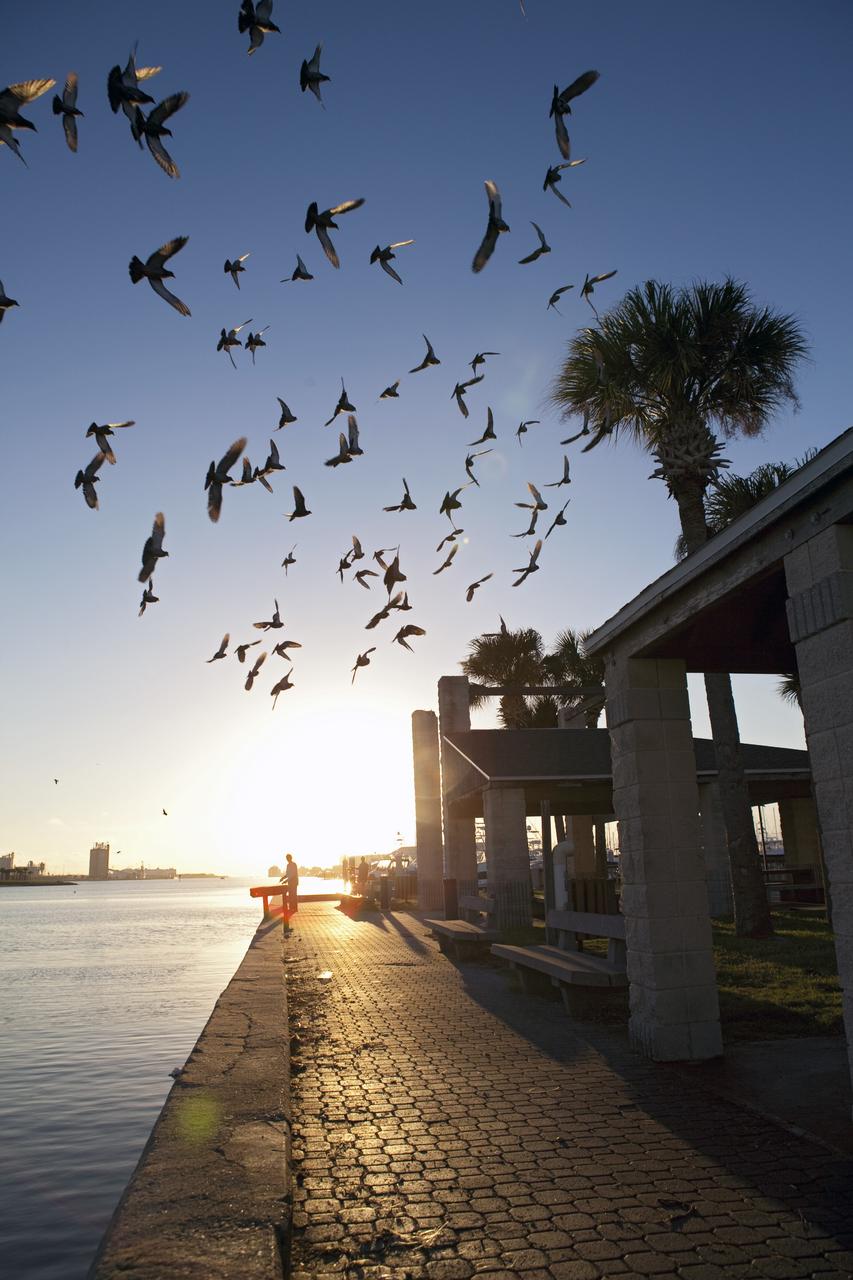

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Space Coast residents watch as the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, approaches NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
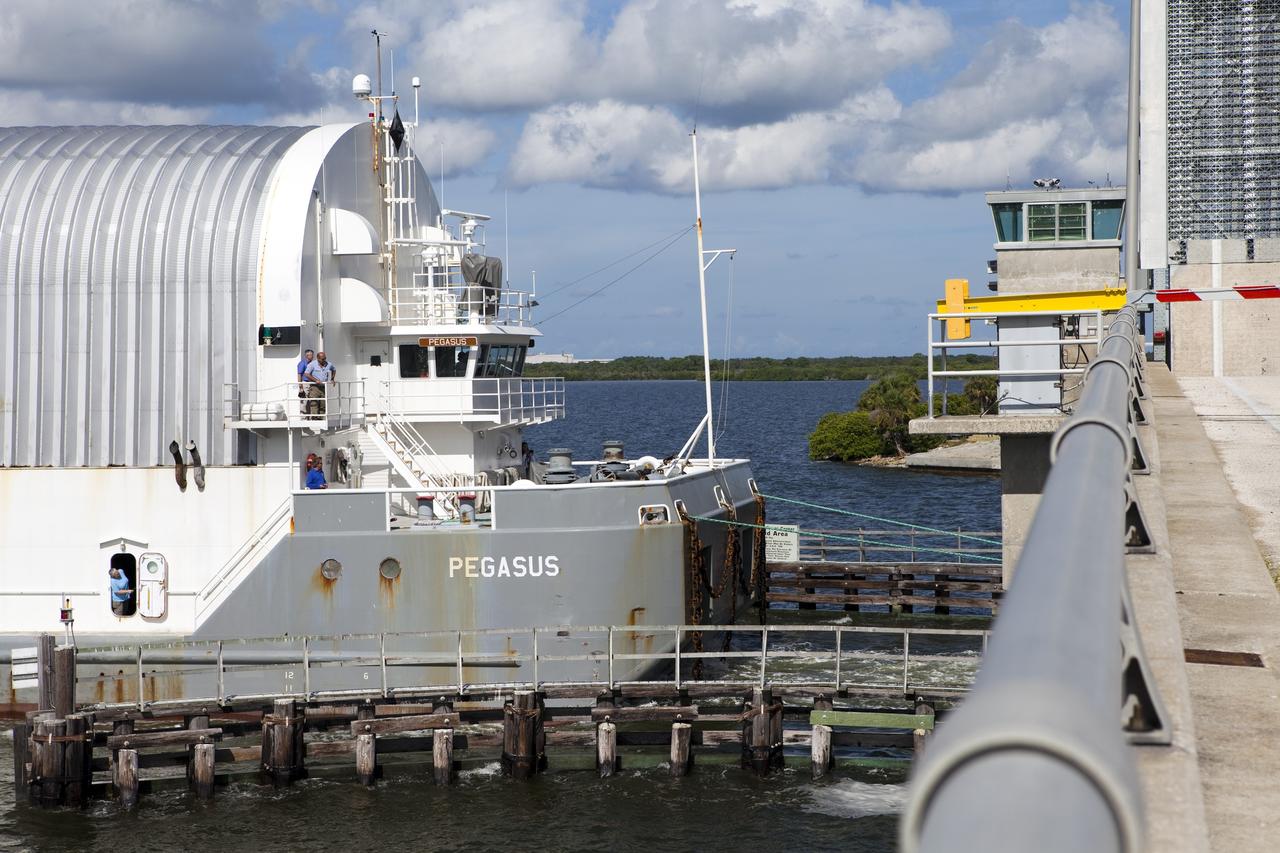

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Pegasus Barge, carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, arrives at the Turn Basin. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
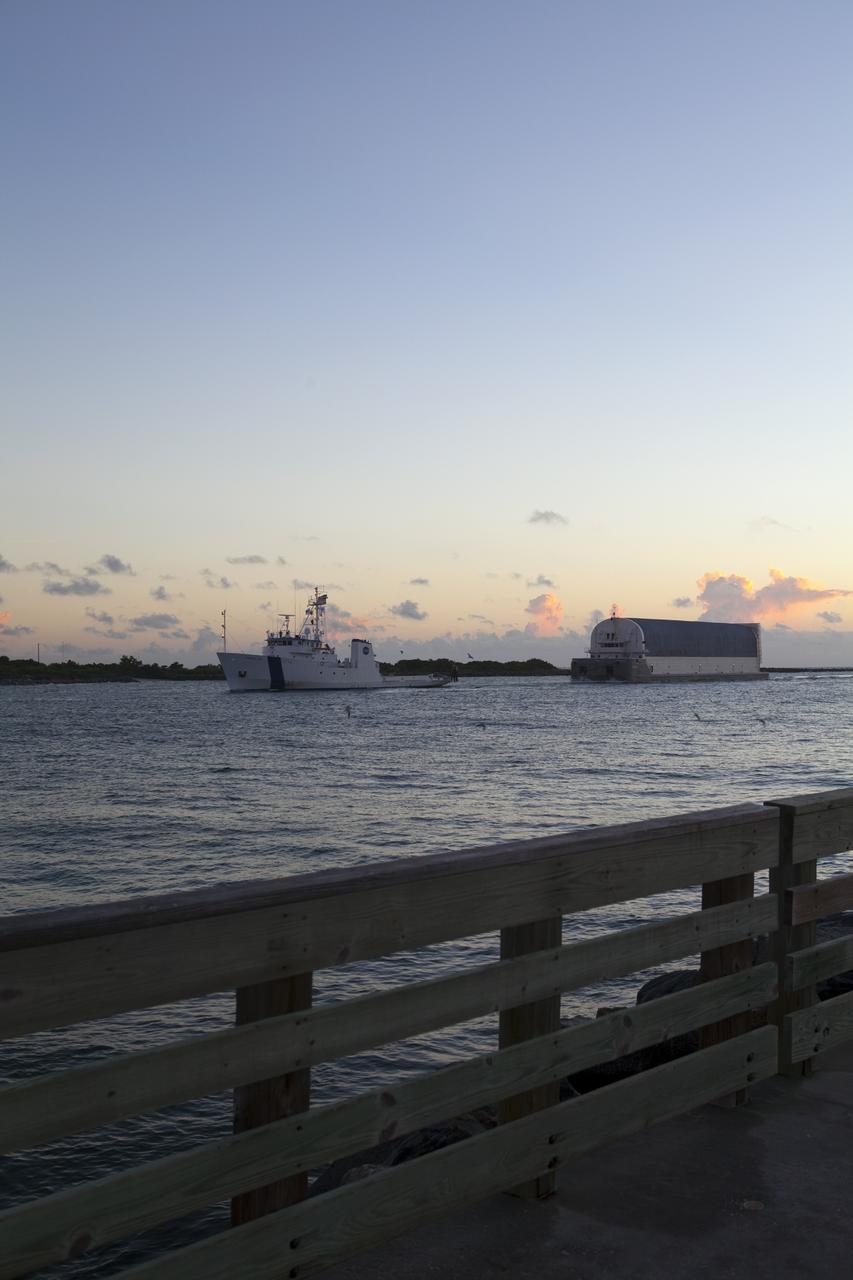

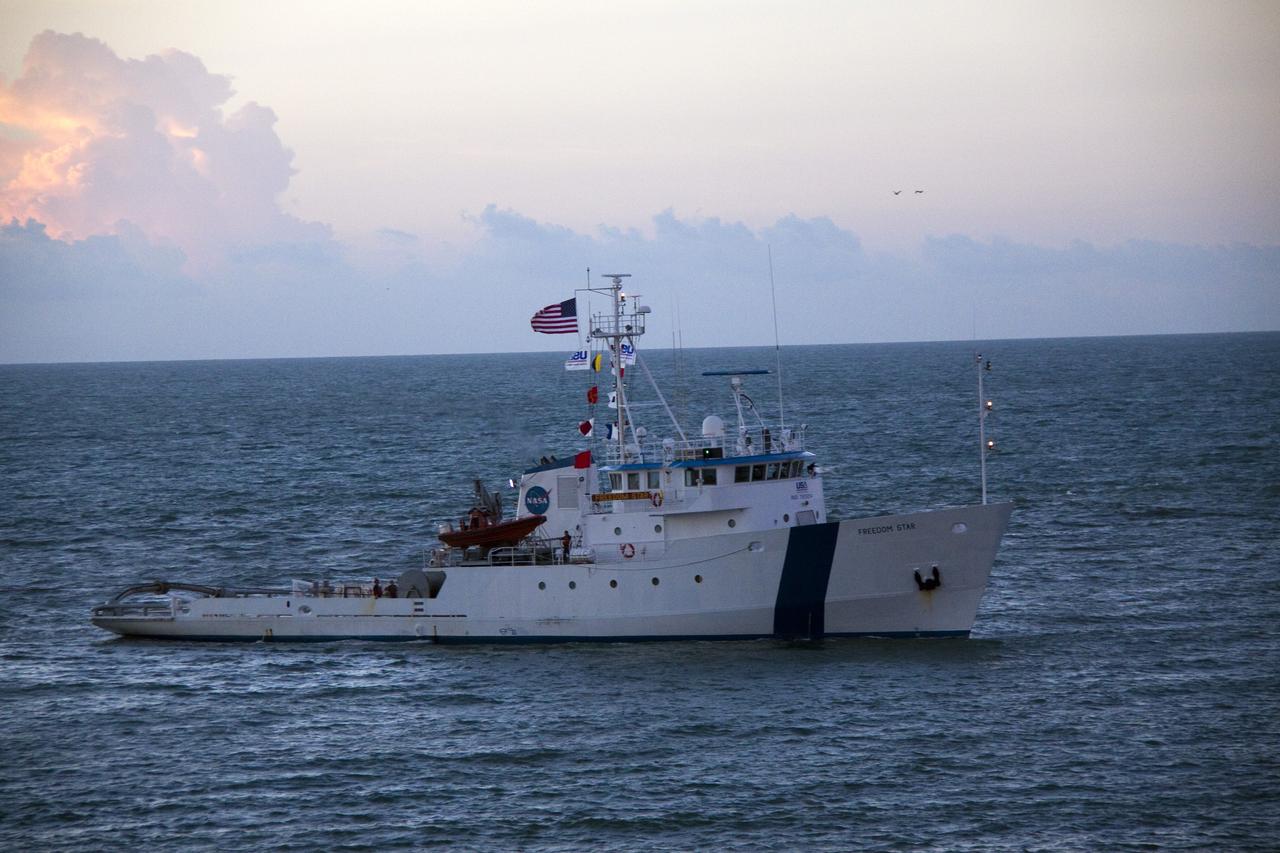
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, ushers the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, ushers the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
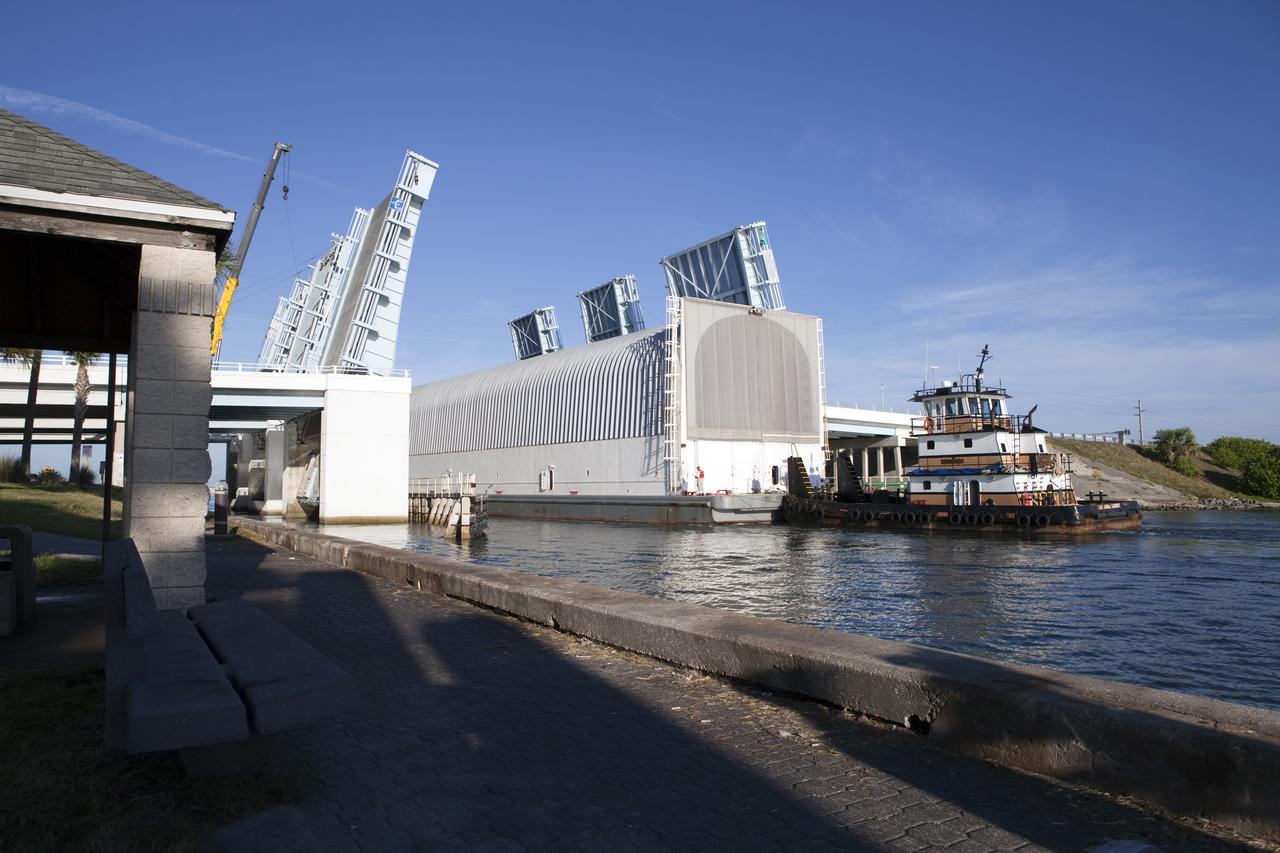

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tug boat pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb., 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
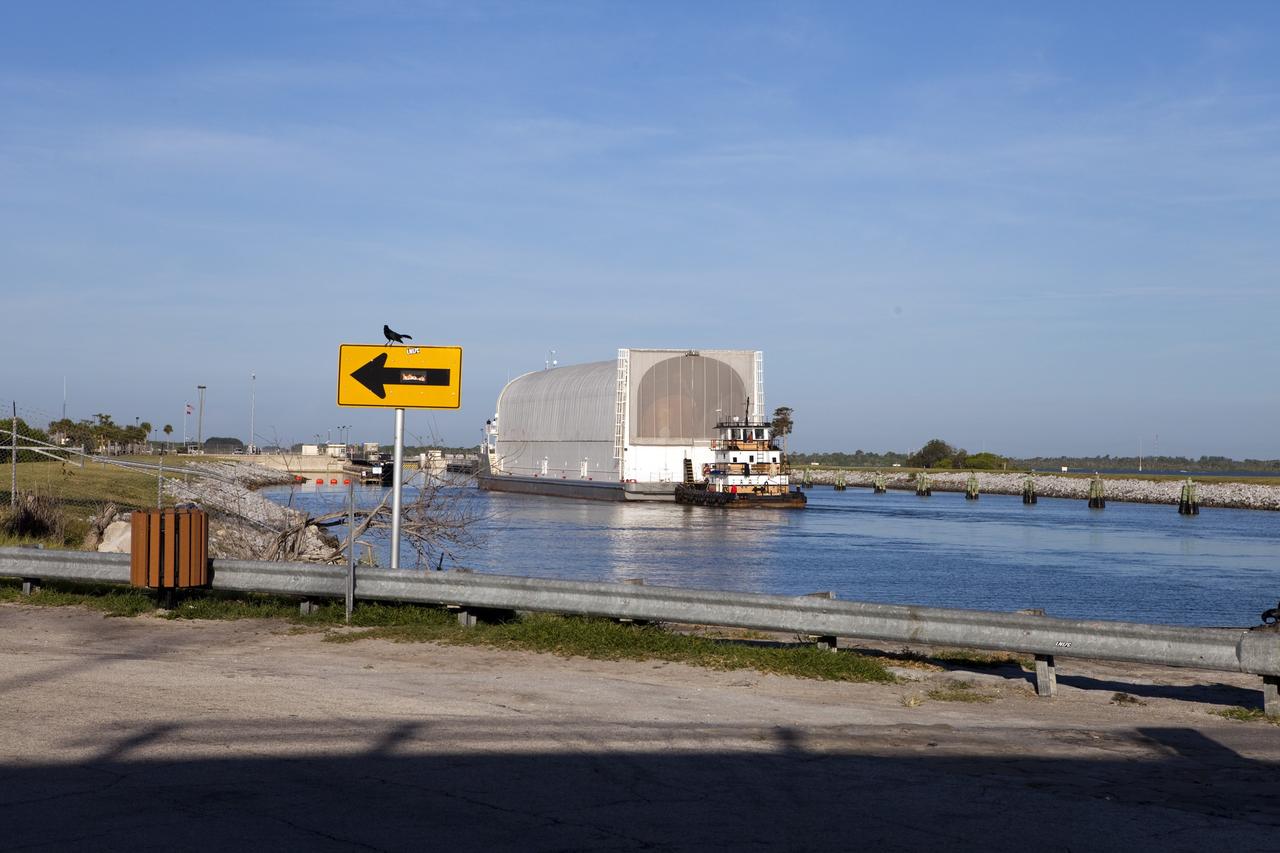

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tug boat pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb., 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
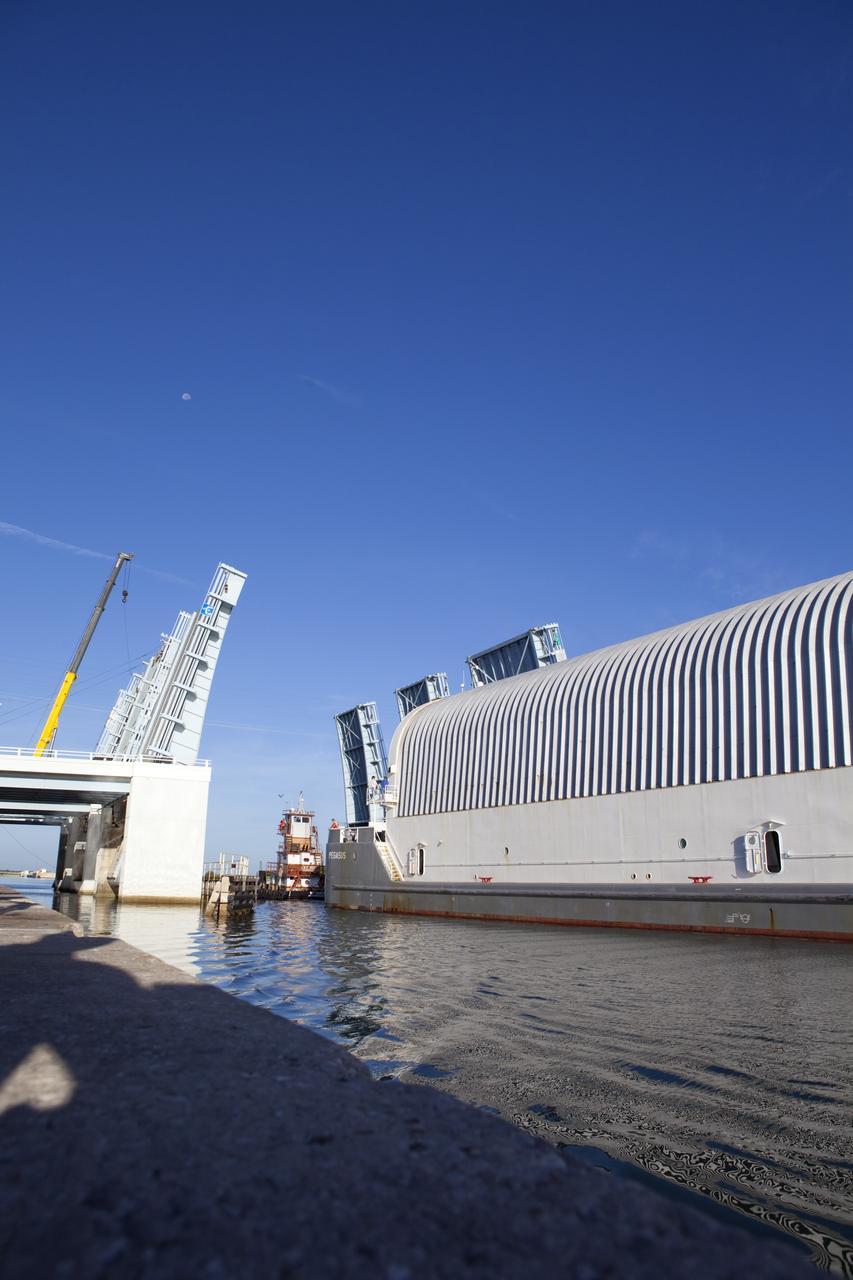

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tug boat pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
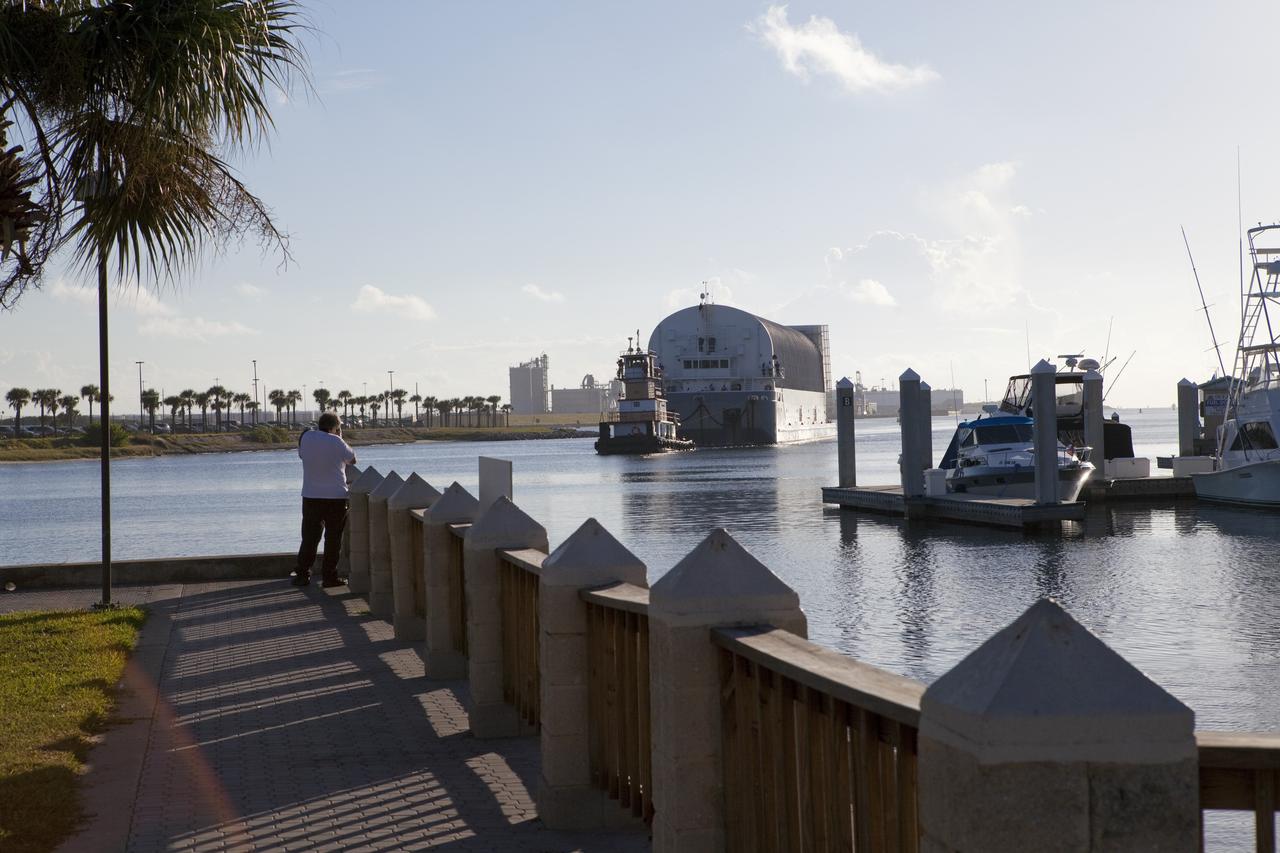

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tug boat pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
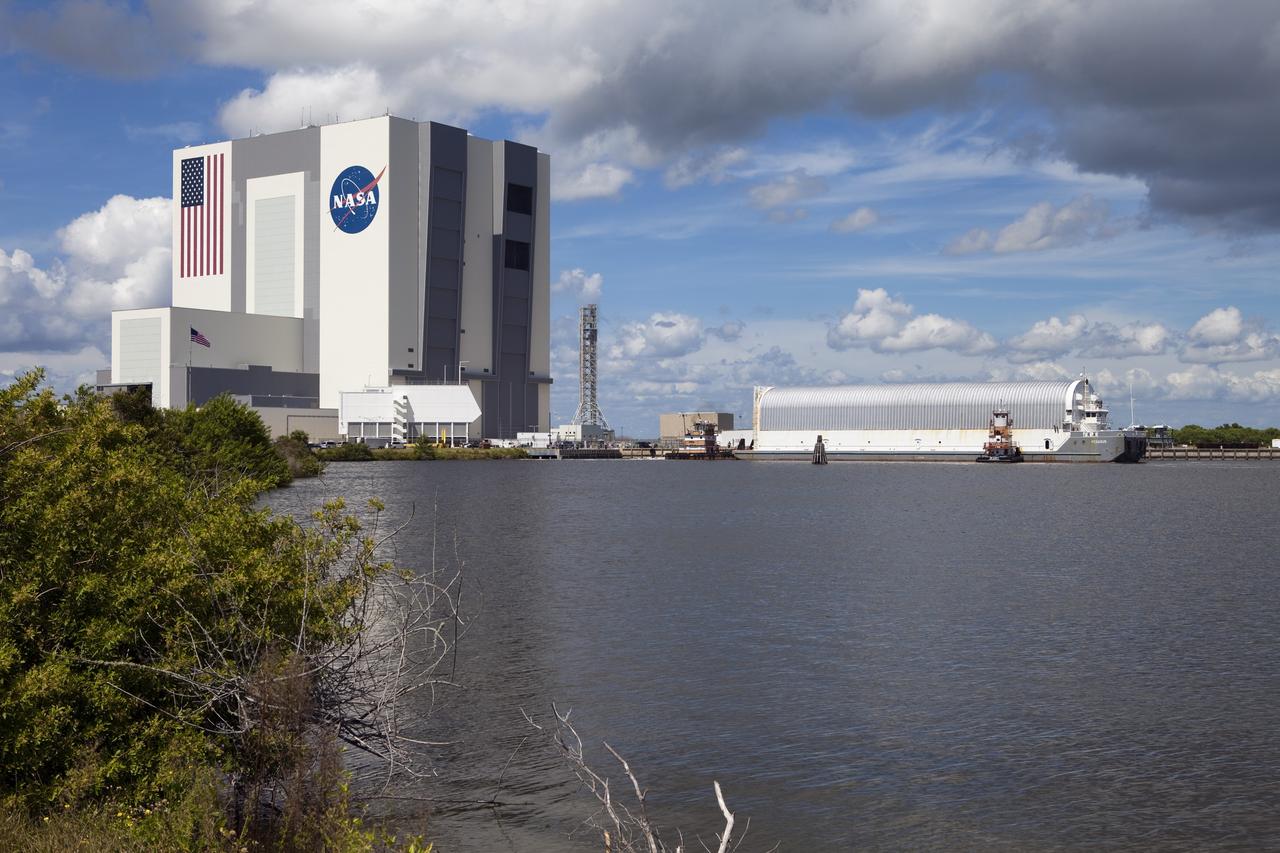

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Pegasus Barge, carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, arrives at the Turn Basin. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
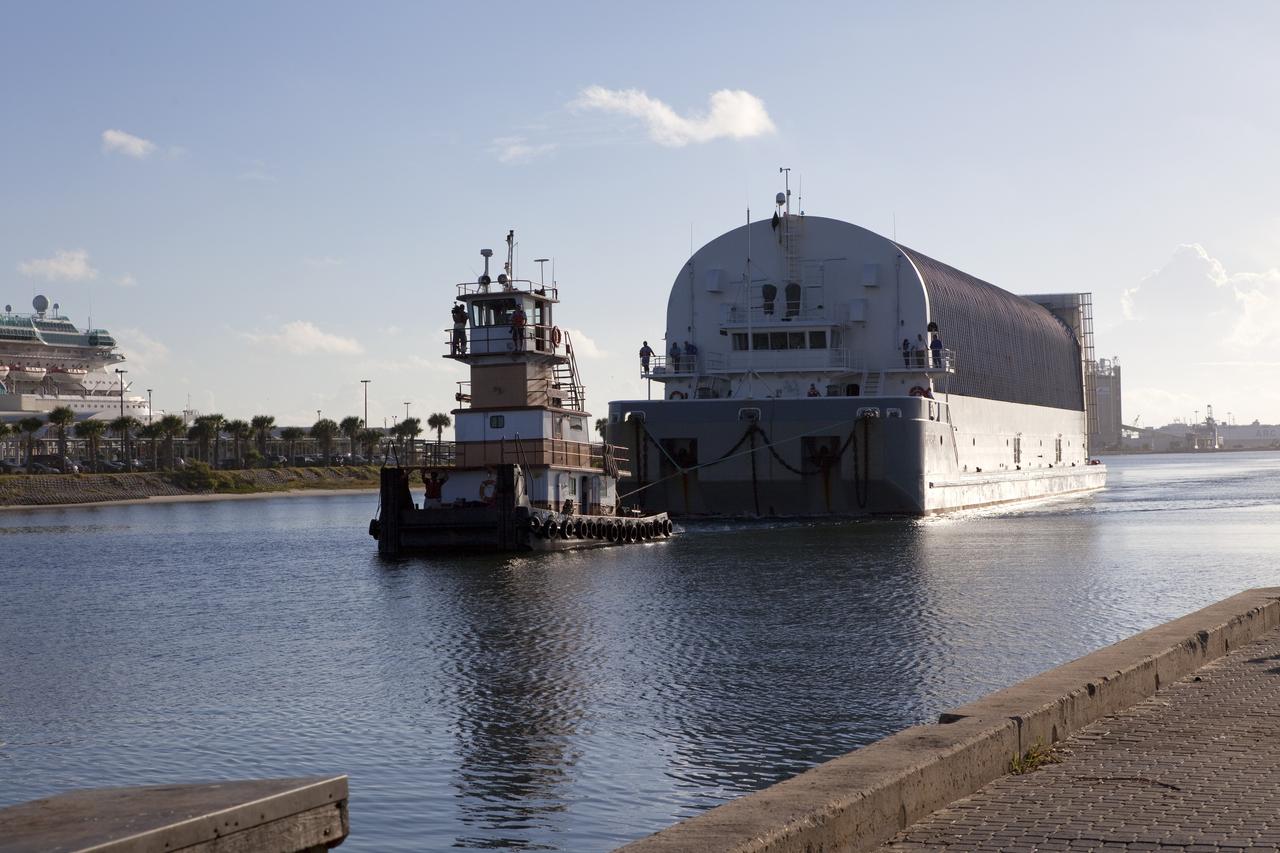

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tug boat pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb., 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
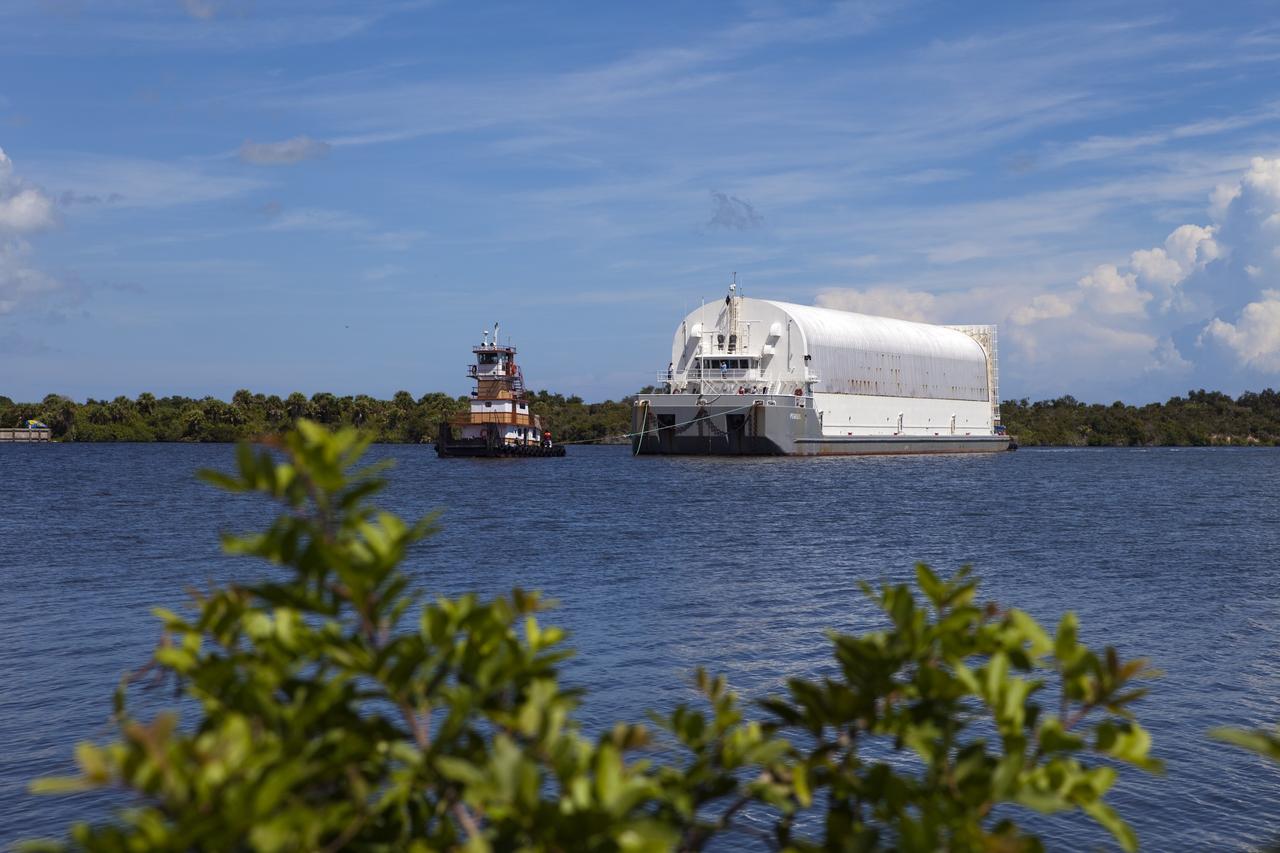

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tug boat pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, to the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
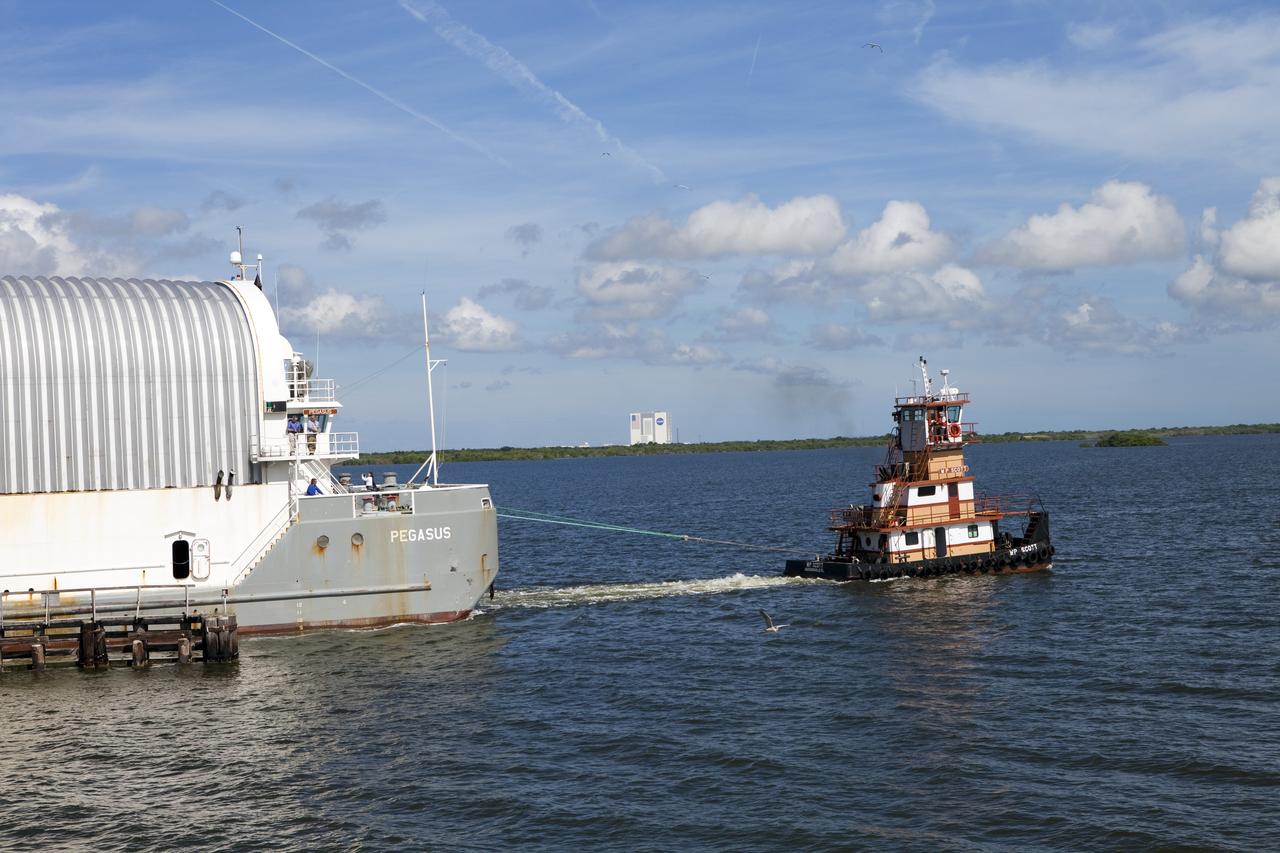

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tug boat pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, to the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
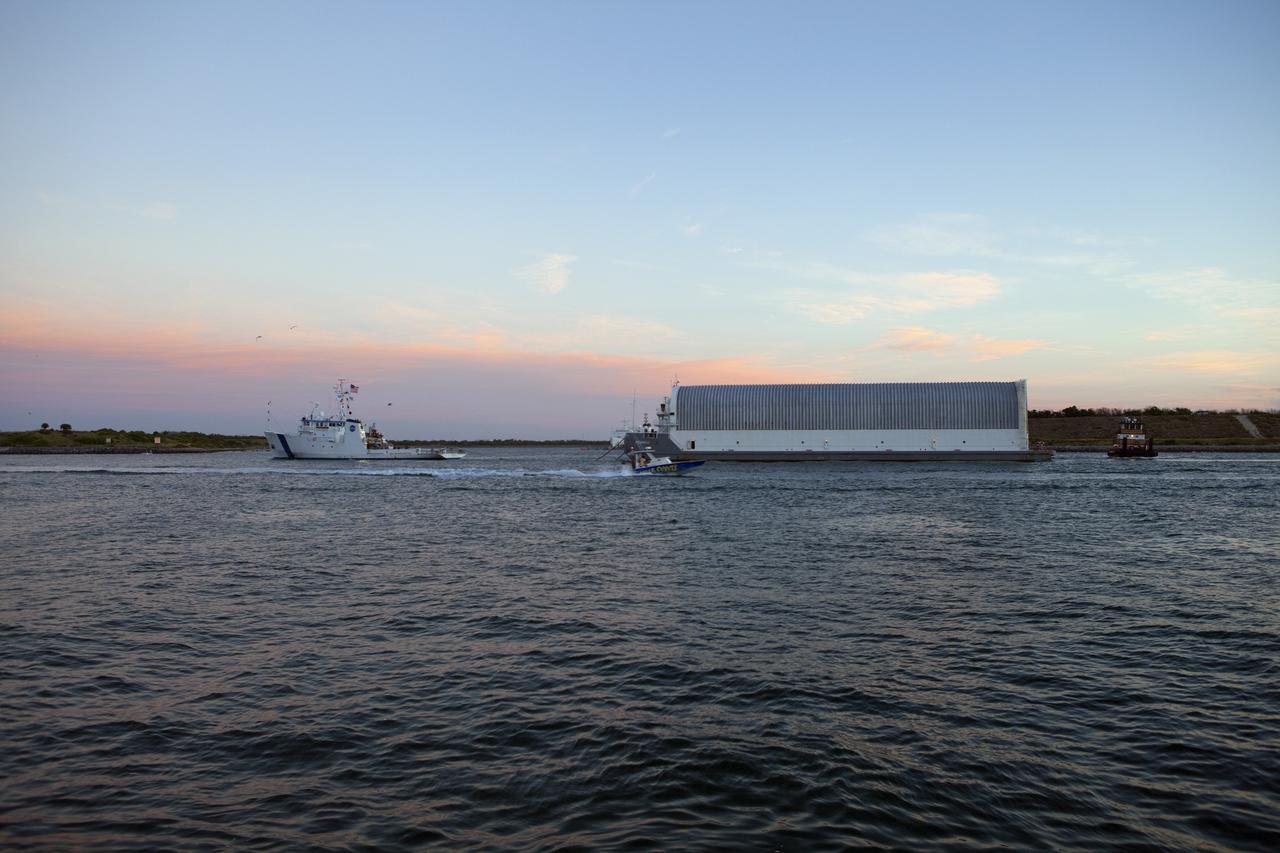

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, ushers the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tug boat pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, to the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

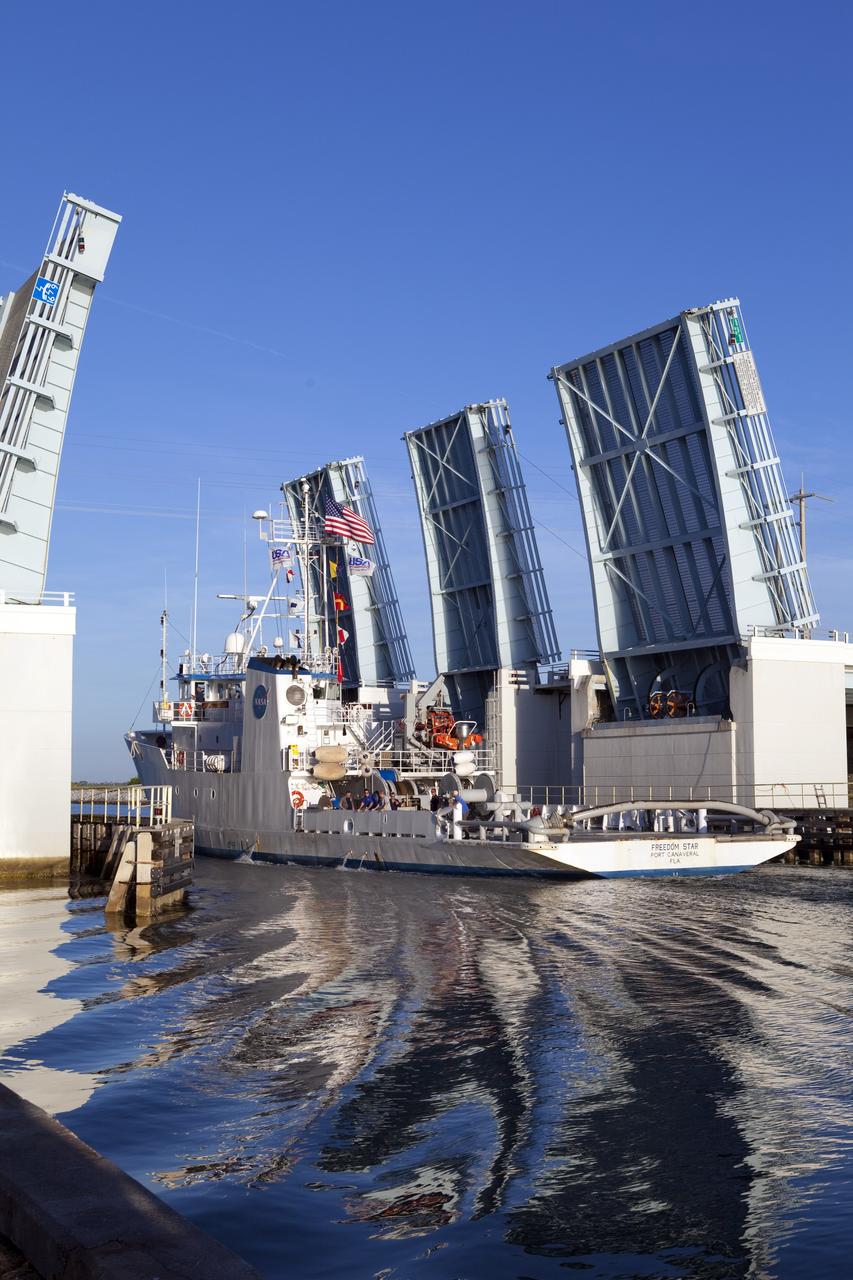
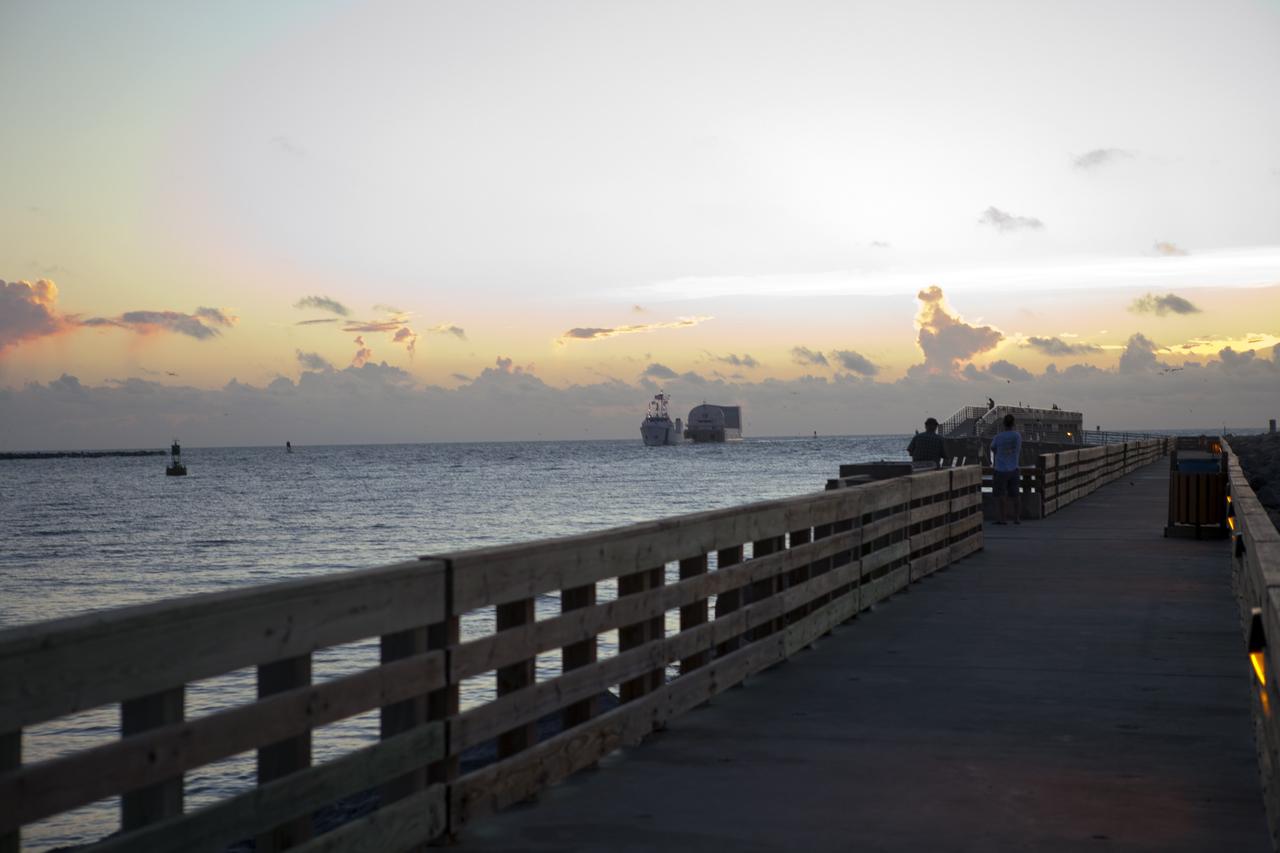
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This panoramic image shows the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, through the Port Canaveral locks on its way to the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Once docked, the tank will be offloaded from the barge and transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The tank traveled 900 miles by sea, carried in the barge, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Once inside the VAB, it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station targeted to launch Feb. 2011. STS-134 currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
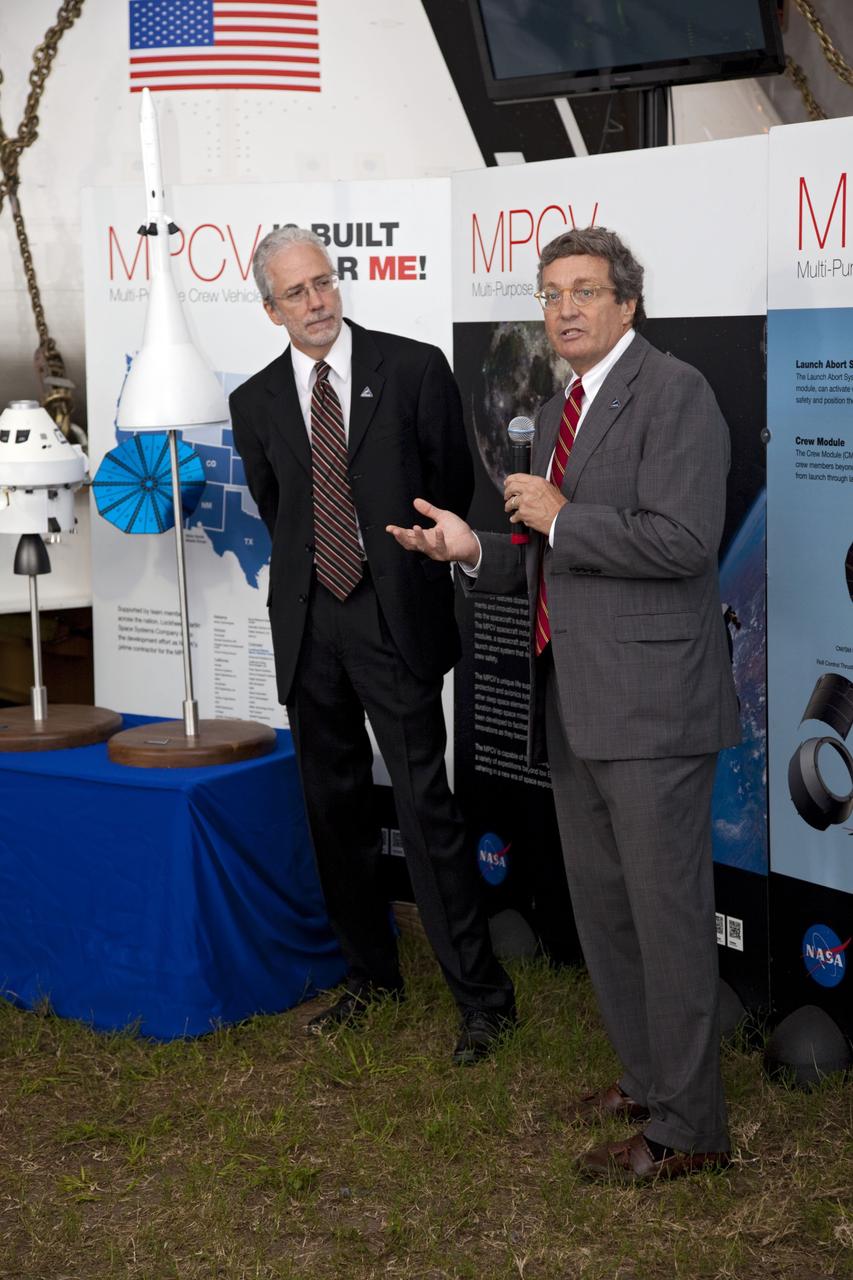

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A media event was held on the grounds near the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida where a Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle (MPCV) is on display. The MPCV is based on the Orion design requirements for traveling beyond low Earth orbit and will serve as the exploration vehicle that will carry the crew to space, provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel, and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Seen here is Mark Geyer, Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle program manager (left) and Laurence A. Price, Orion deputy program manager with Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company speaking to media during a question-and-answer session. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
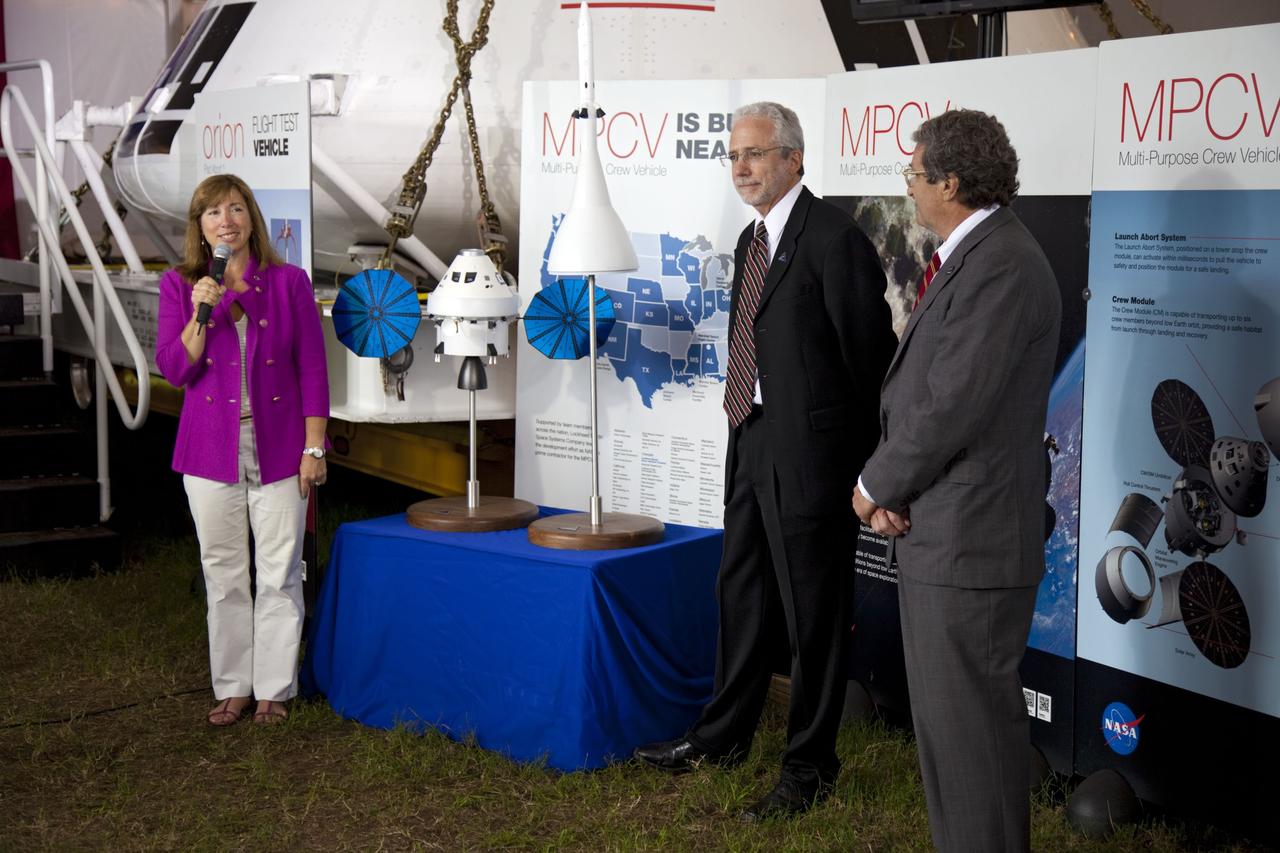

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A media event was held on the grounds near the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida where a Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle (MPCV) is on display. The MPCV is based on the Orion design requirements for traveling beyond low Earth orbit and will serve as the exploration vehicle that will carry the crew to space, provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel, and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Seen here is Lori Garver, NASA deputy administrator, Mark Geyer, Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle program manager and Laurence A. Price, Orion deputy program manager with Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company to talk about the vehicle during a question-and-answer session. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
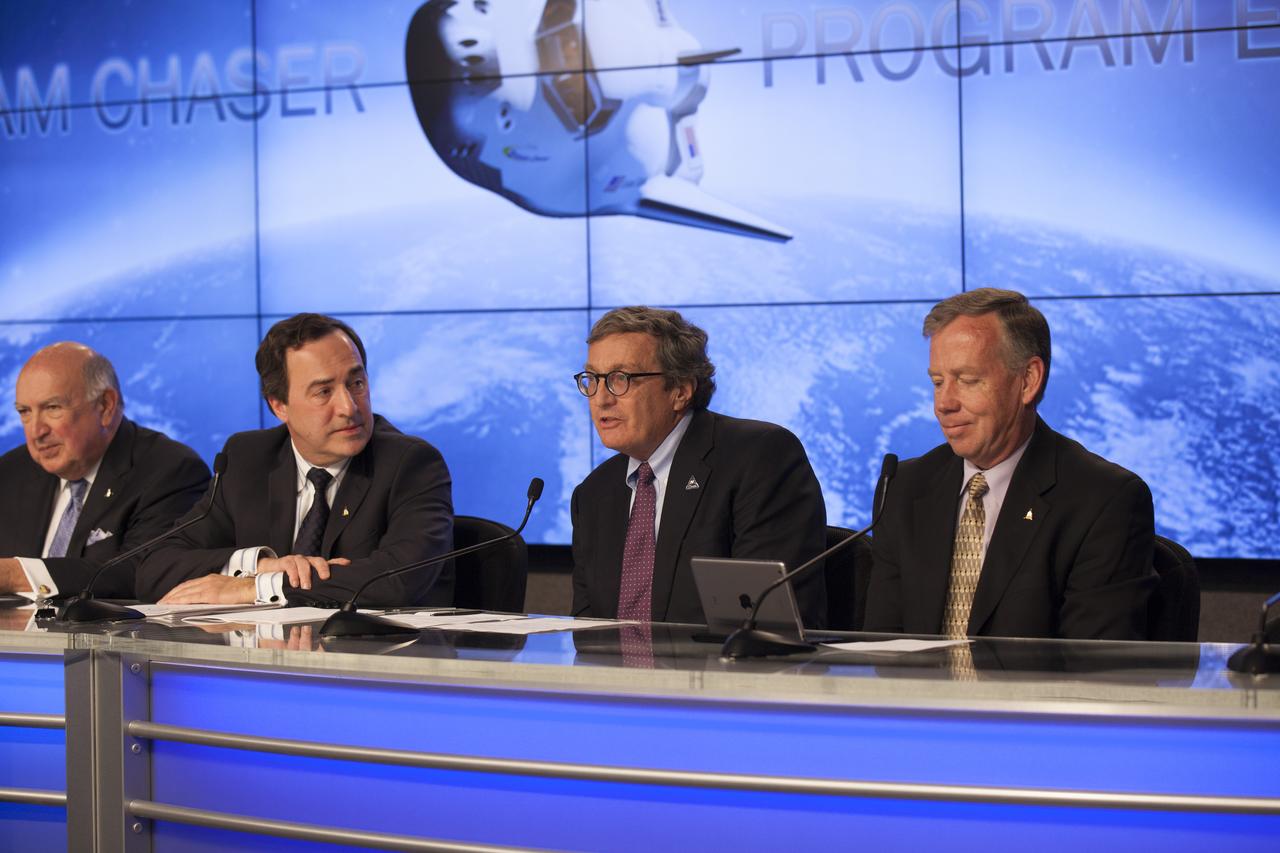

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Larry Price, Lockheed Martin Space Systems deputy program manager for NASA's Orion spacecraft, joins Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Space Systems, as the company announces the steps it will take to prepare for a November 2016 orbital flight of its Dream Chaser spacecraft from Florida’s Space Coast. The steps are considered substantial for SNC and important to plans by NASA and Space Florida for Kennedy Space Center’s transformation into a multi-user spaceport for both commercial and government customers. SNC said it plans to work with United Launch Alliance, or ULA, to launch the Dream Chaser spacecraft into orbit atop an Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station intends to land the winged spacecraft at Kennedy’s 3.5-mile long runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility lease office space at Exploration Park, right outside Kennedy’s gates and process the spacecraft in the high bay of the Operations and Checkout Building at Kennedy, with Lockheed Martin performing the work. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
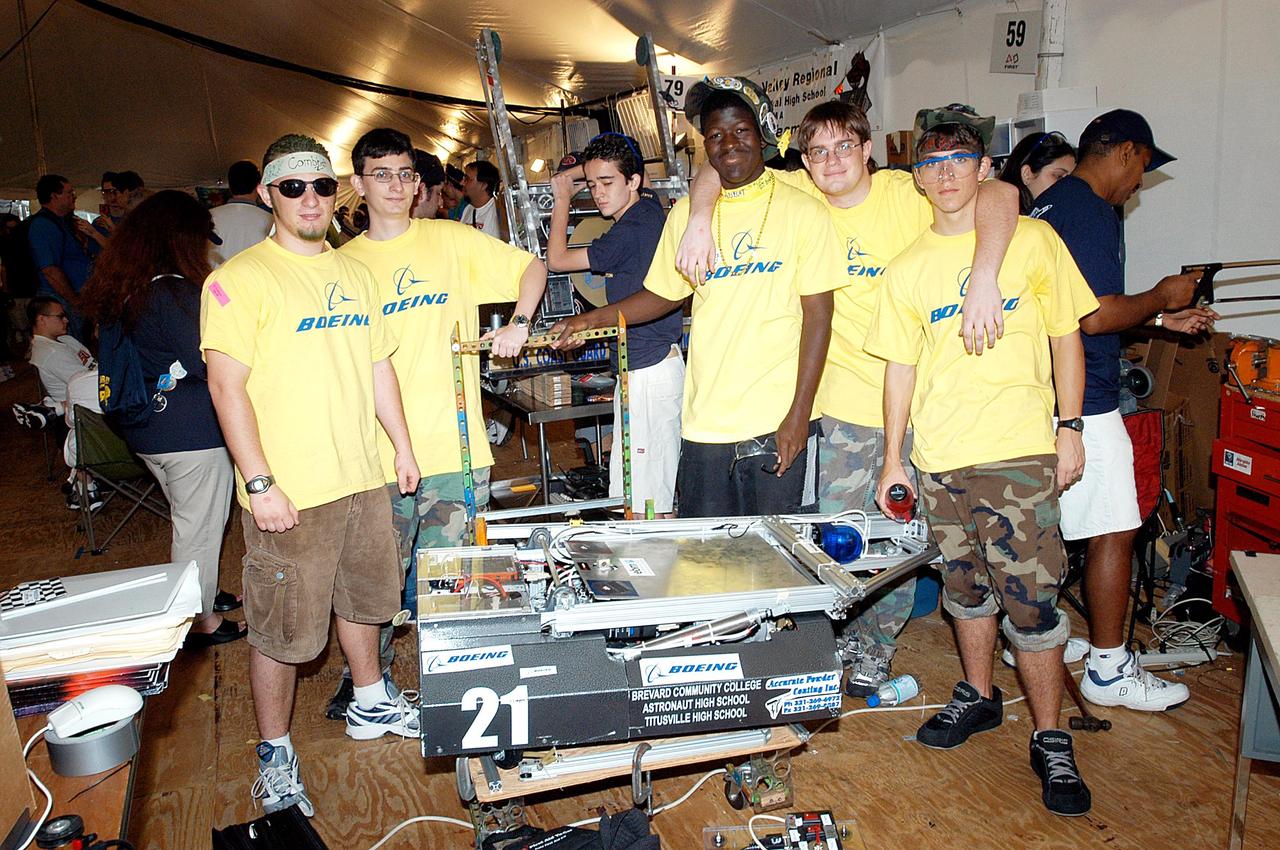

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Boeing Company/Brevard Community College-sponsored students, participating in the 2003 Southeastern Regional FIRST Robotic Competition, pose with their team-built robot. The competition is being held at the University of Central Florida (UCF) in Orlando, March 20-23. Forty teams from around the country are participating in the event that pits team-built gladiator robots against each other in an athletic-style competition. The teams are sponsored by NASA-Kennedy Space Center, The Boeing Company/Brevard Community College, and Lockheed Martin Space Operations/Mission Systems for the nonprofit organization For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology, known as FIRST. The vision of FIRST is to inspire in the youth of our nation an appreciation of science and technology and an understanding that mastering these disciplines can enrich the lives of all mankind.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Boeing Company/Brevard Community College-sponsored student team (in yellow shirts) is congratulated by the judges and support staff of the 2003 Southeastern Regional FIRST Robotic Competition. The competition is being held at the University of Central Florida (UCF) in Orlando, March 20-23. The team won the DaimlerChrysler Team Spirit Award and the Johnson & Johnson Sportsmanship Award. Forty student teams from around the country are participating in the event that pits team-built gladiator robots against each other in an athletic-style competition. The teams are sponsored by NASA/Kennedy Space Center, The Boeing Company/Brevard Community College, and Lockheed Martin Space Operations/Mission Systems for the nonprofit organization For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology, known as FIRST. The vision of FIRST is to inspire in the youth of our nation an appreciation of science and technology and an understanding that mastering these disciplines can enrich the lives of all mankind.
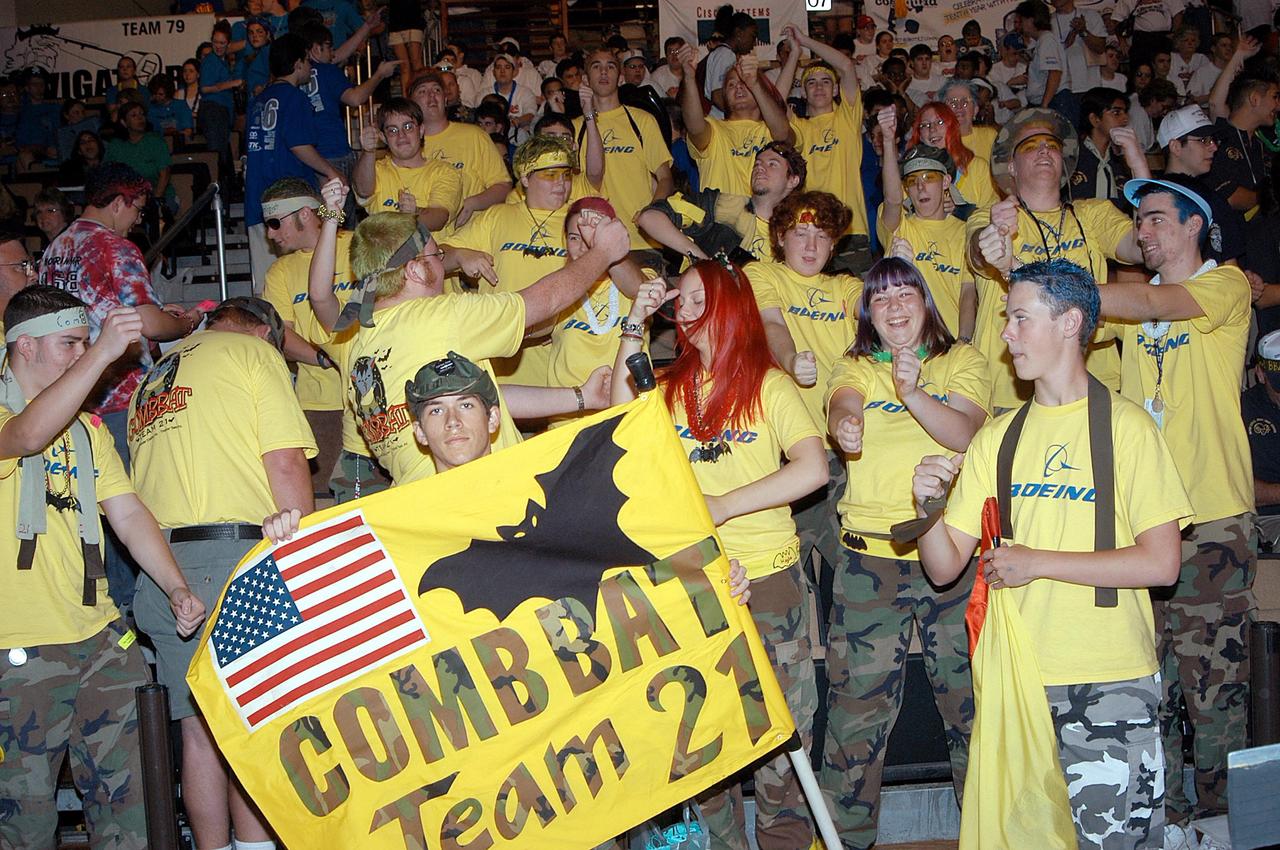

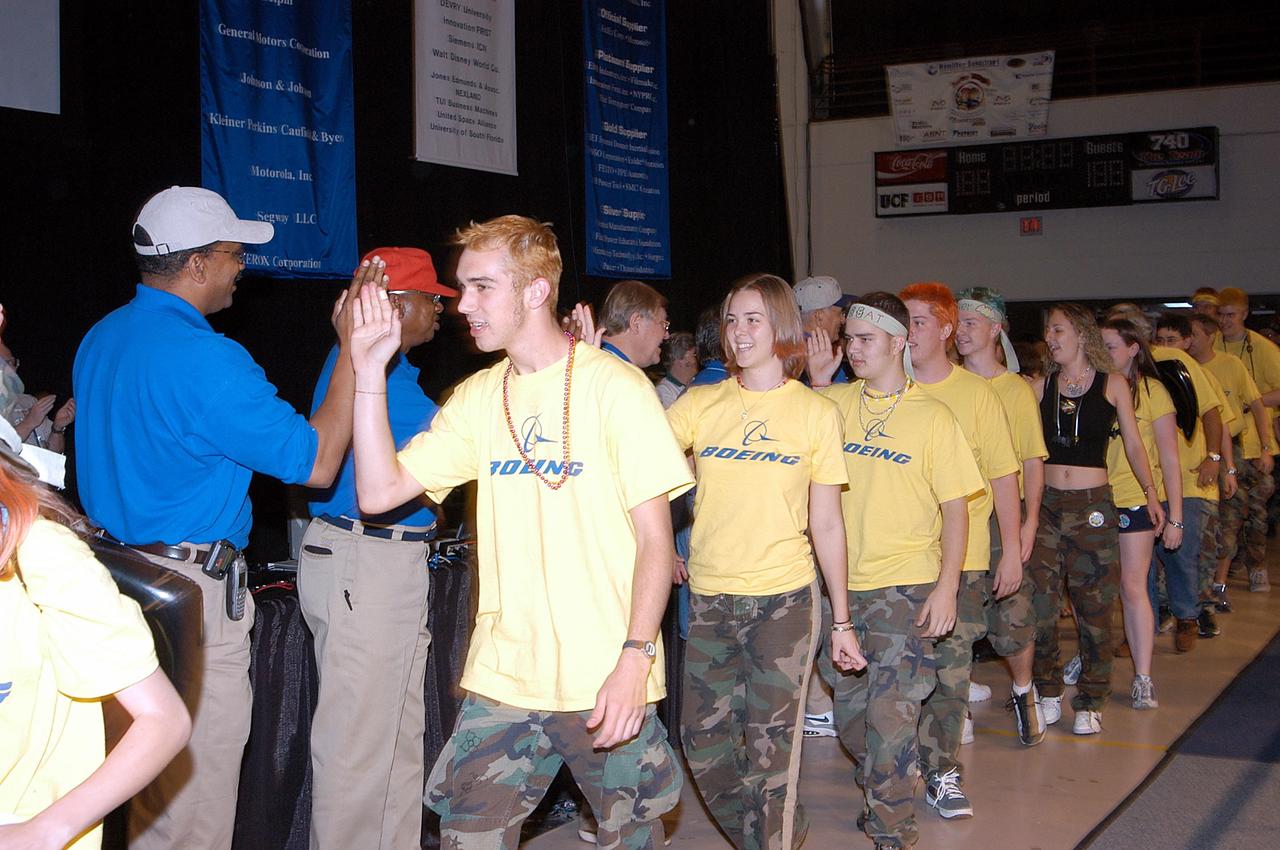
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Boeing Company/Brevard Community College-sponsored students, participating in the 2003 Southeastern Regional FIRST Robotic Competition, demonstrate their team spirit. The competition is being held at the University of Central Florida (UCF) in Orlando, March 20-23. The team won the DaimlerChrysler Team Spirit Award and the Johnson & Johnson Sportsmanship Award. Forty teams from around the country are participating in the event that pits team-built gladiator robots against each other in an athletic-style competition. The teams are sponsored by NASA-Kennedy Space Center, The Boeing Company/Brevard Community College, and Lockheed Martin Space Operations/Mission Systems for the nonprofit organization For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology, known as FIRST. The vision of FIRST is to inspire in the youth of our nation an appreciation of science and technology and an understanding that mastering these disciplines can enrich the lives of all mankind.
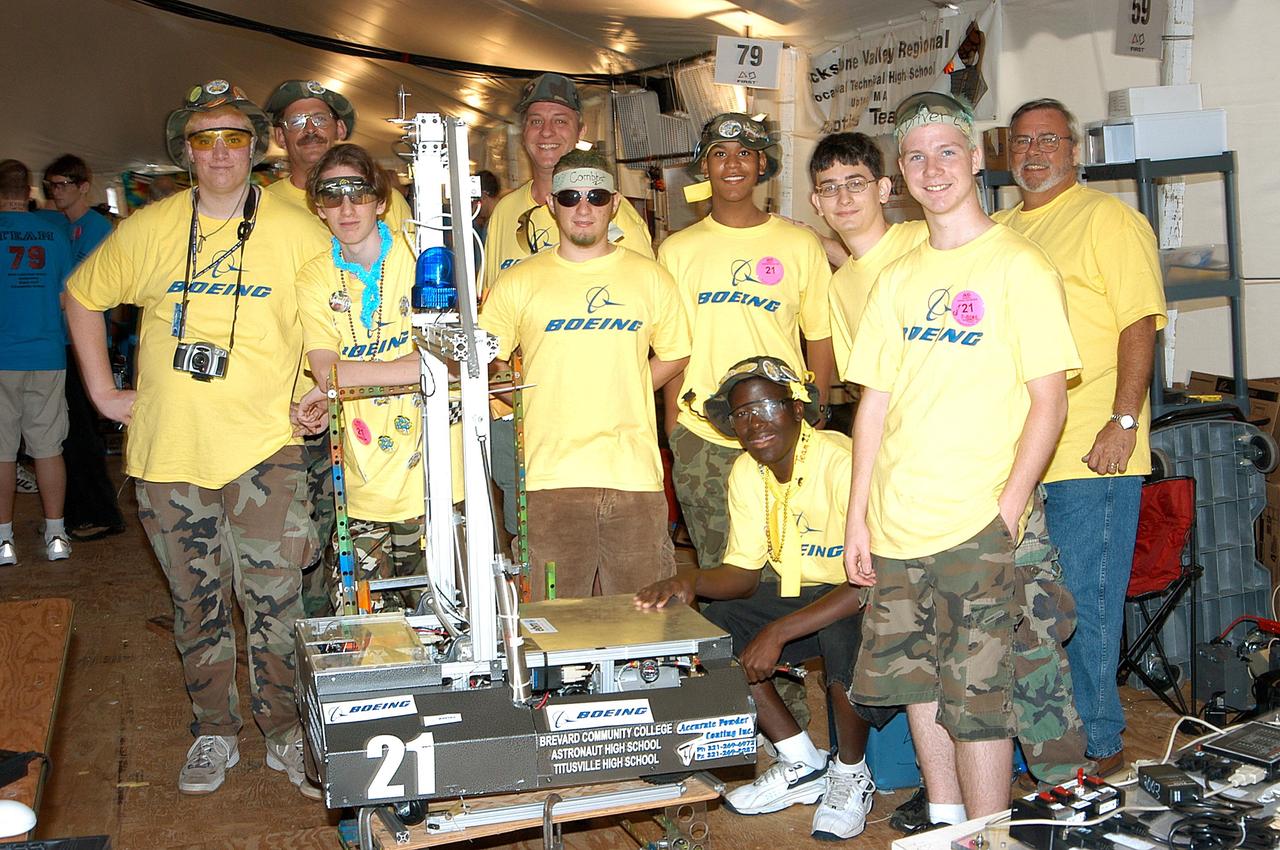

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Boeing Company/Brevard Community College-sponsored students, participating in the 2003 Southeastern Regional FIRST Robotic Competition, pose with their team-built robot. The competition is being held at the University of Central Florida (UCF) in Orlando, March 20-23. Forty teams from around the country are participating in the event that pits team-built gladiator robots against each other in an athletic-style competition. The teams are sponsored by NASA/Kennedy Space Center, The Boeing Company/Brevard Community College, and Lockheed Martin Space Operations/Mission Systems for the nonprofit organization For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology, known as FIRST. The vision of FIRST is to inspire in the youth of our nation an appreciation of science and technology and an understanding that mastering these disciplines can enrich the lives of all mankind.
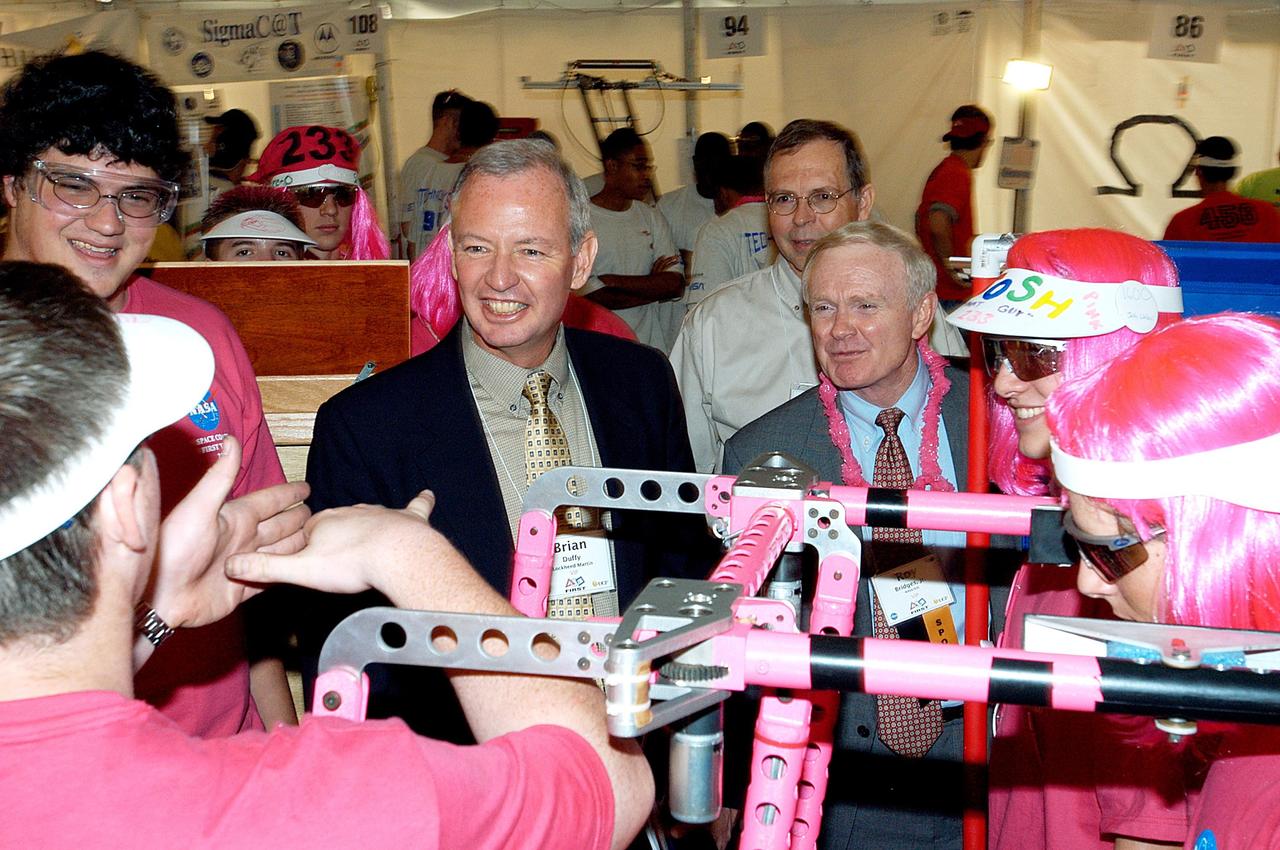

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Lockheed Martin Vice President/Associate Program Manager Brian Duffy (second from left) and NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Roy Bridges (next to Duffy) talk with student participants in the 2003 Southeastern Regional FIRST Robotic Competition. Chris Fairey, the former director of Spaceport Services at KSC, looks on in the background. The competition is being held at the University of Central Florida (UCF) in Orlando, March 20-23. Forty student teams from around the country are participating in the event that pits team-built gladiator robots against each other in an athletic-style competition. The teams are sponsored by NASA/Kennedy Space Center, The Boeing Company/Brevard Community College, and Lockheed Martin Space Operations/Mission Systems for the nonprofit organization For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology, known as FIRST. The vision of FIRST is to inspire in the youth of our nation an appreciation of science and technology and an understanding that mastering these disciplines can enrich the lives of all mankind.
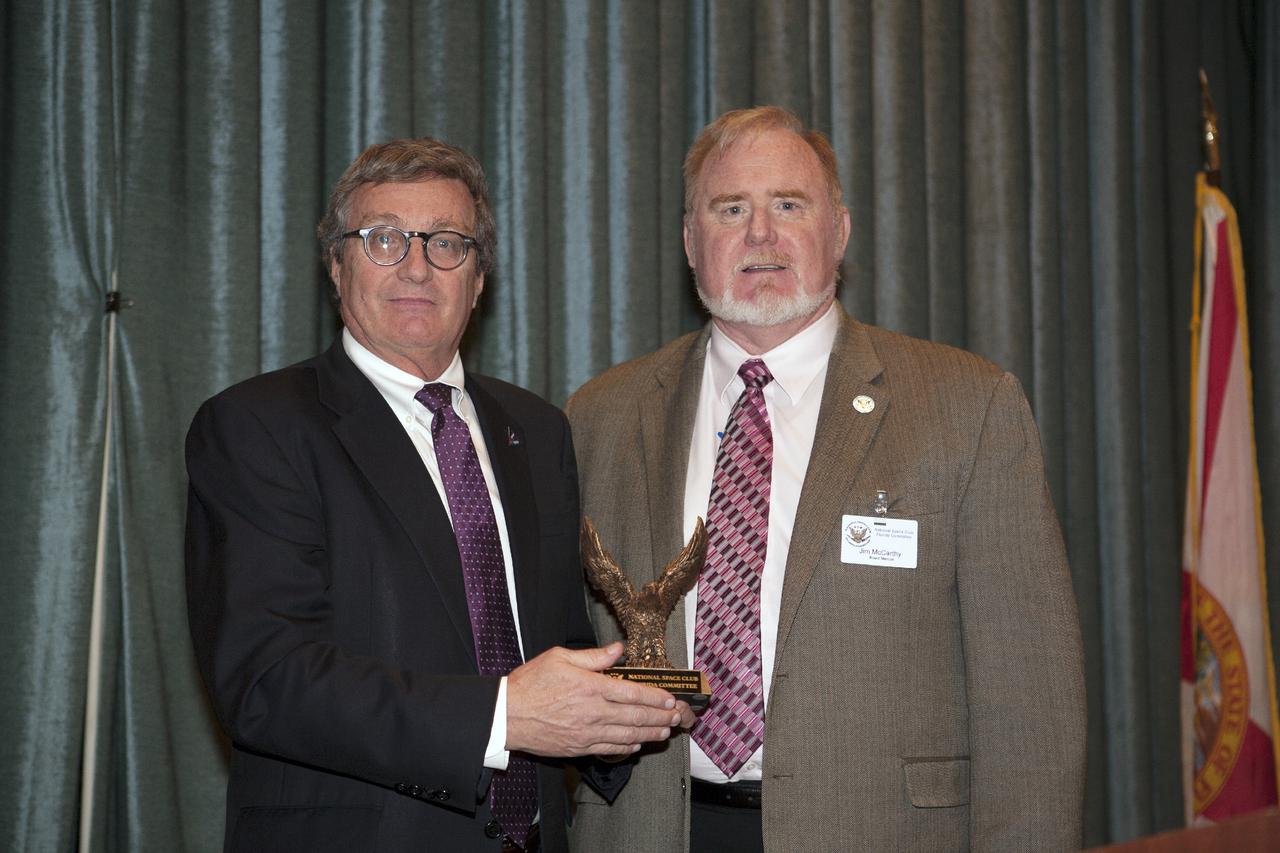

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Jim McCarthy right, president of the National Space Club-Florida Chapter, thanks Larry Price, deputy manager of the Orion Program for the Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company, for his presentation to members and guests at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla. Price’s presentation included an overview of Orion processing, testing and preparations for Exploration Flight Test 1. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Larry Price, deputy manager of the Orion Program for the Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company, speaks to the National Space Club-Florida Chapter members and guests at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla. Price’s presentation included an overview of Orion processing, testing and preparations for Exploration Flight Test 1. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
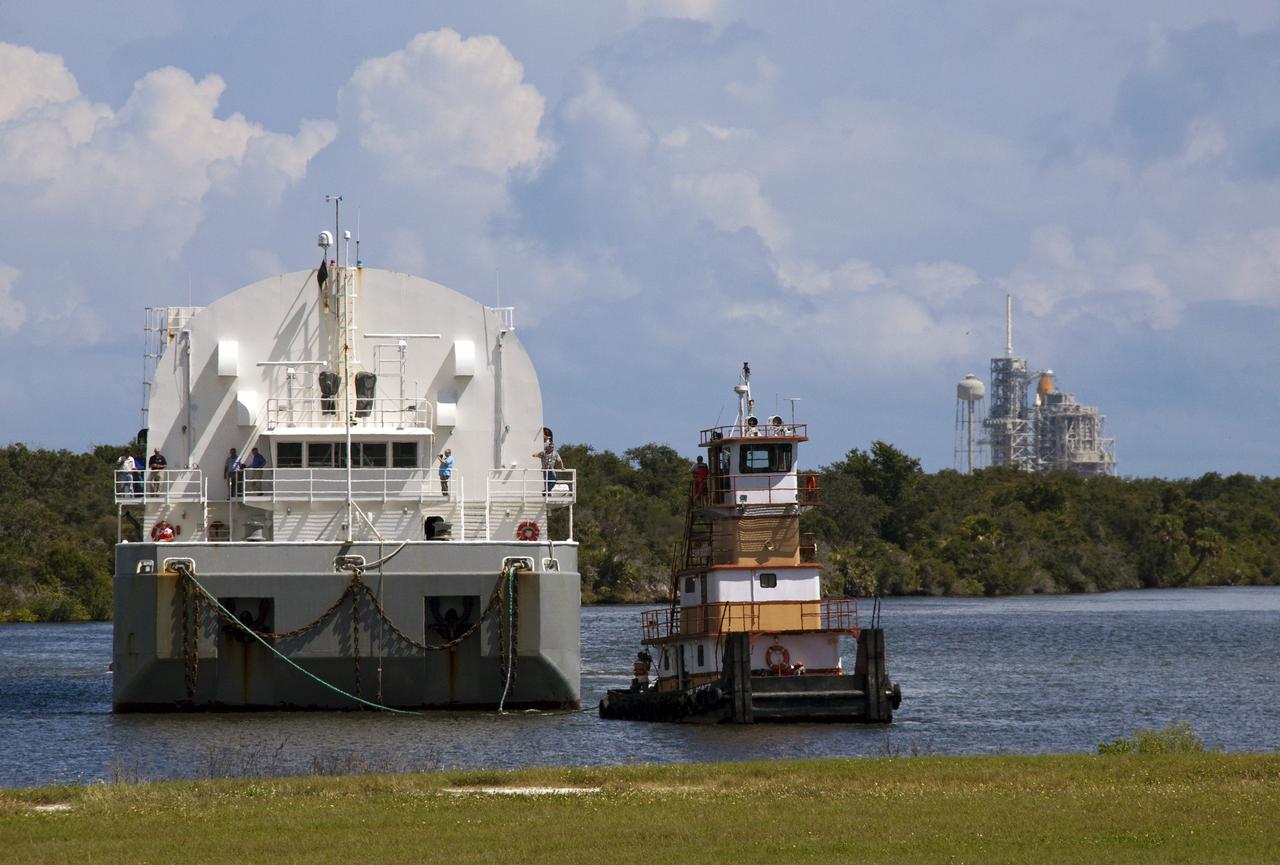

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tugboat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In the background, space shuttle Discovery is on Launch Pad 39A awaiting liftoff on the STS-133 mission to the International Space Station. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

NEW ORLEANS -- At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Associate Administrator for Space Operations Bill Gerstenmaier and a Michoud employee discuss the progress of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, as it is being transported from the facility to the Pegasus Barge. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida secured aboard the barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

NEW ORLEANS -- Workers monitor the progress of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it is being loaded onto the Pegasus BargeThe tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida secured aboard the barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
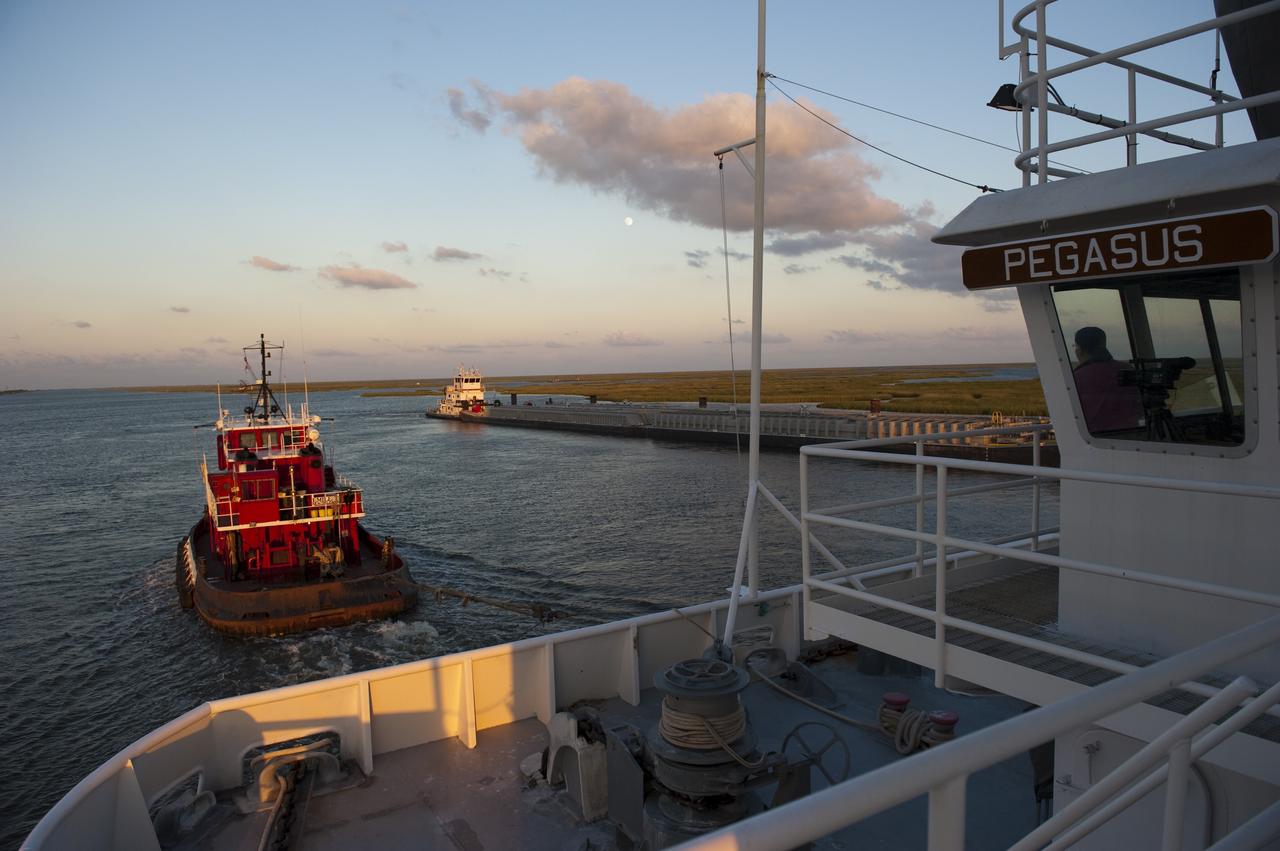

NEW ORLEANS -- A tug boat is pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
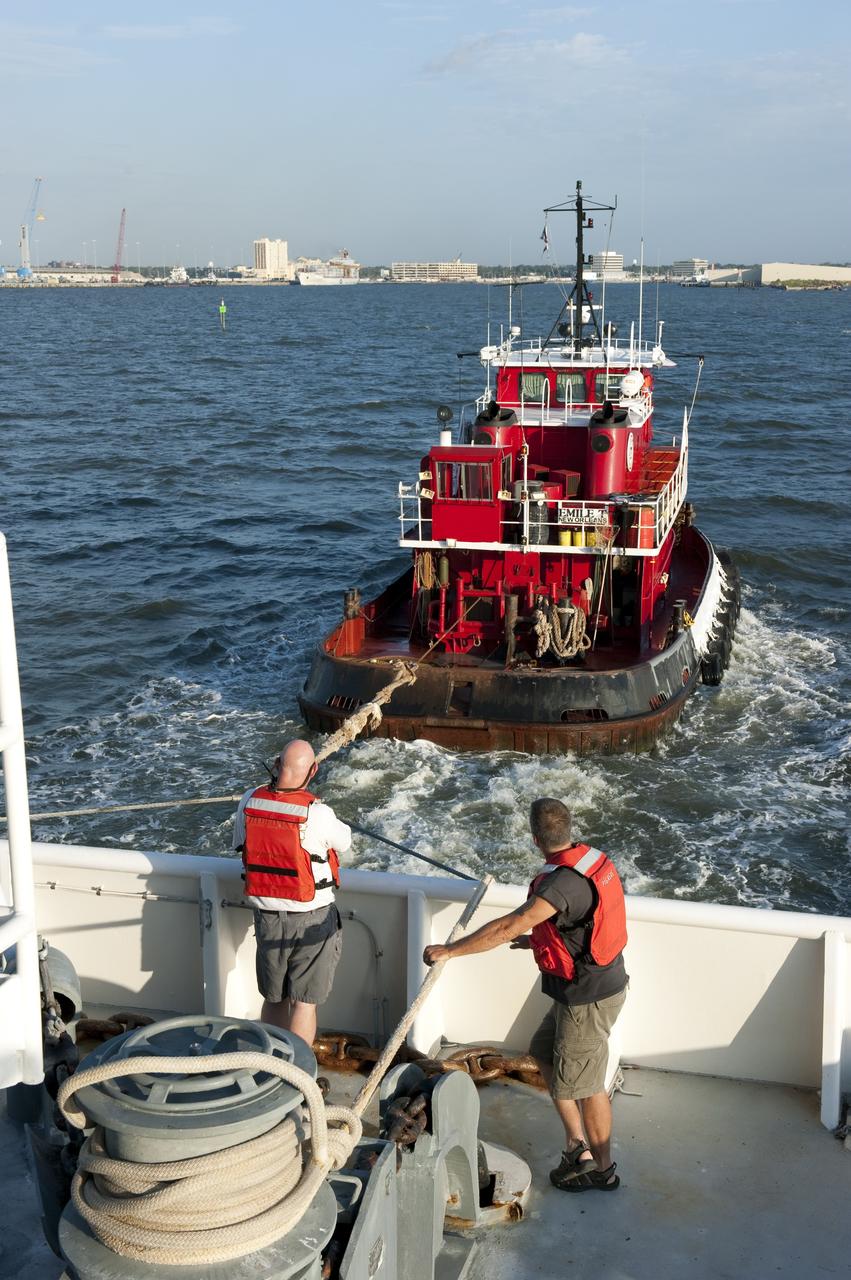

LOUISIANA -- A tug boat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans toward a dock in Gulfport, La. The barge will meet up with Freedom Star, NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ship, which will escort it to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
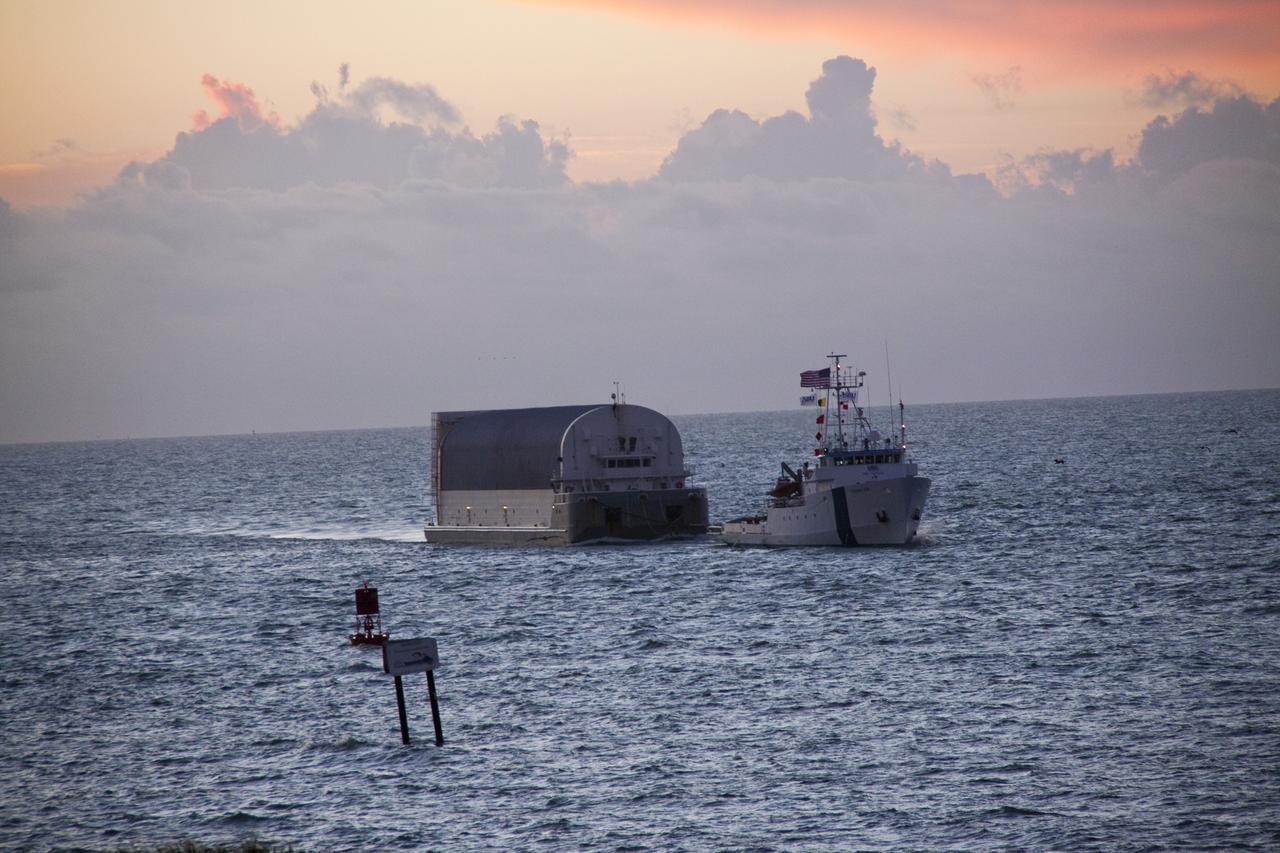

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
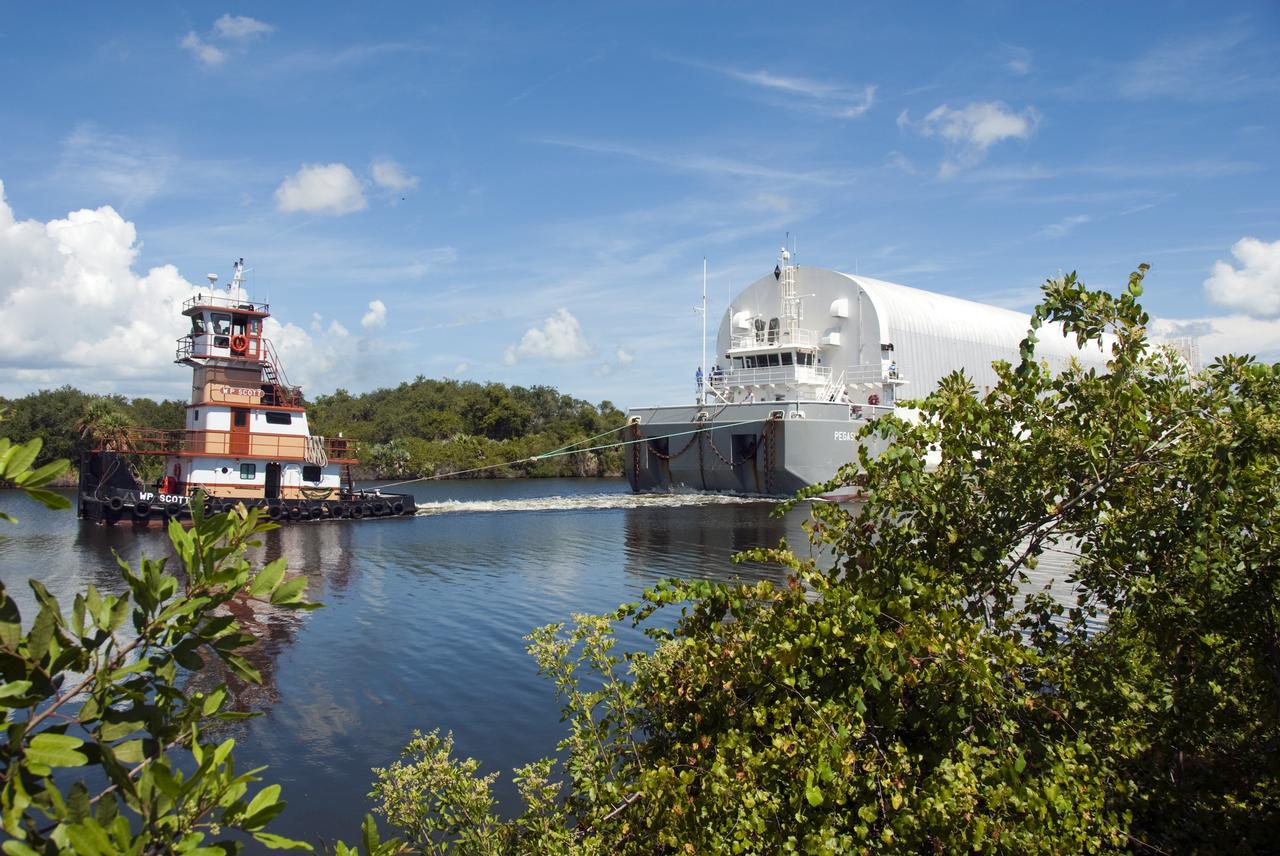

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tugboat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
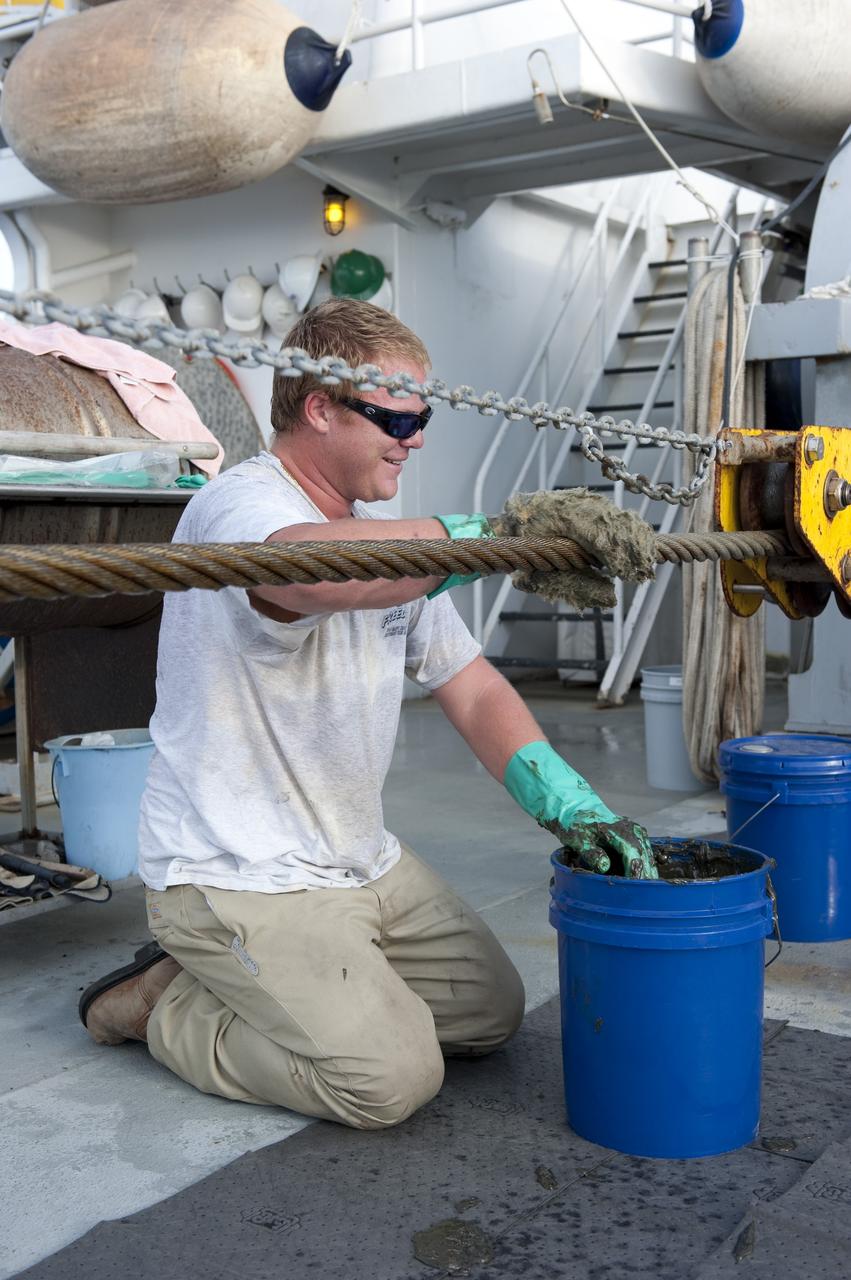

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A deckhand on Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, keeps the ship in good repair as it pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

NEW ORLEANS -- Workers check the progress of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it is being loaded onto the Pegasus Barge. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida secured aboard the barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
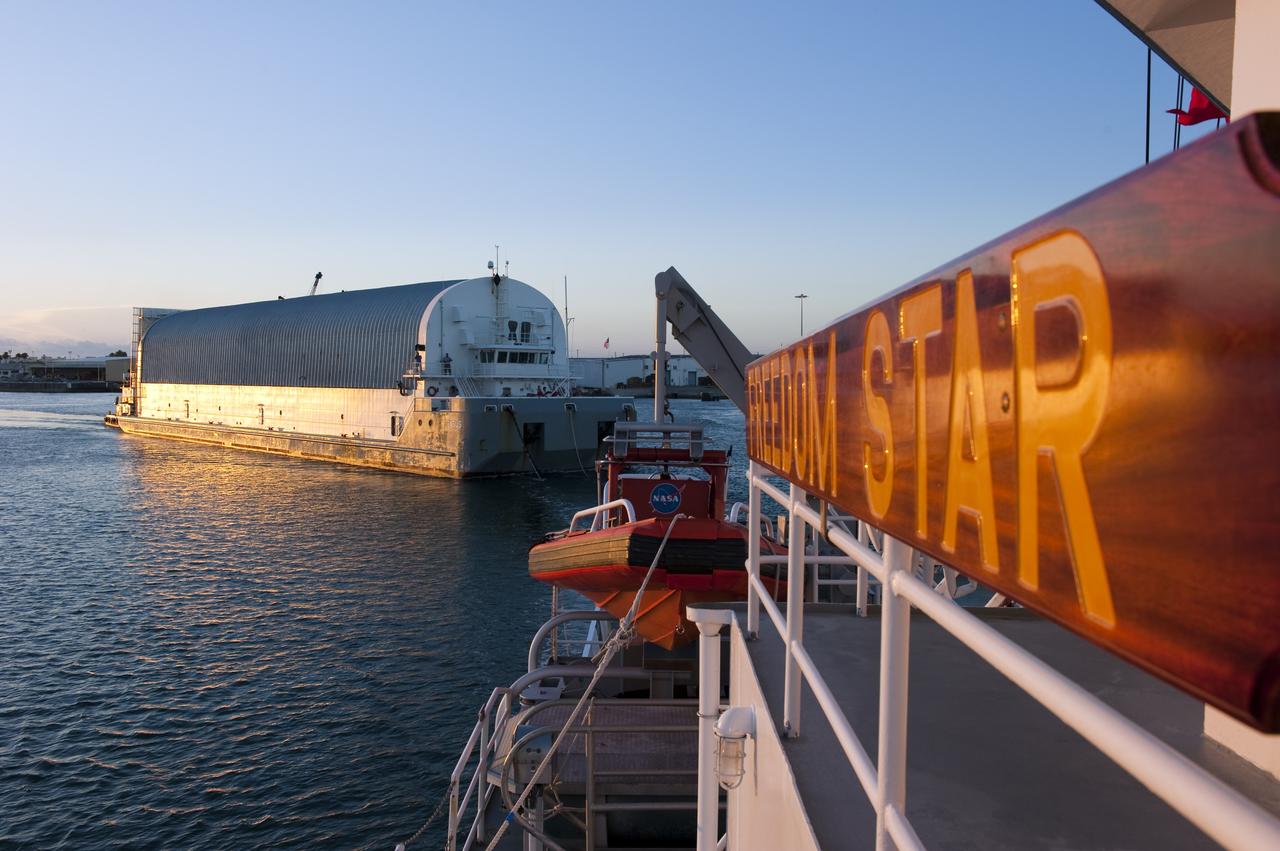

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
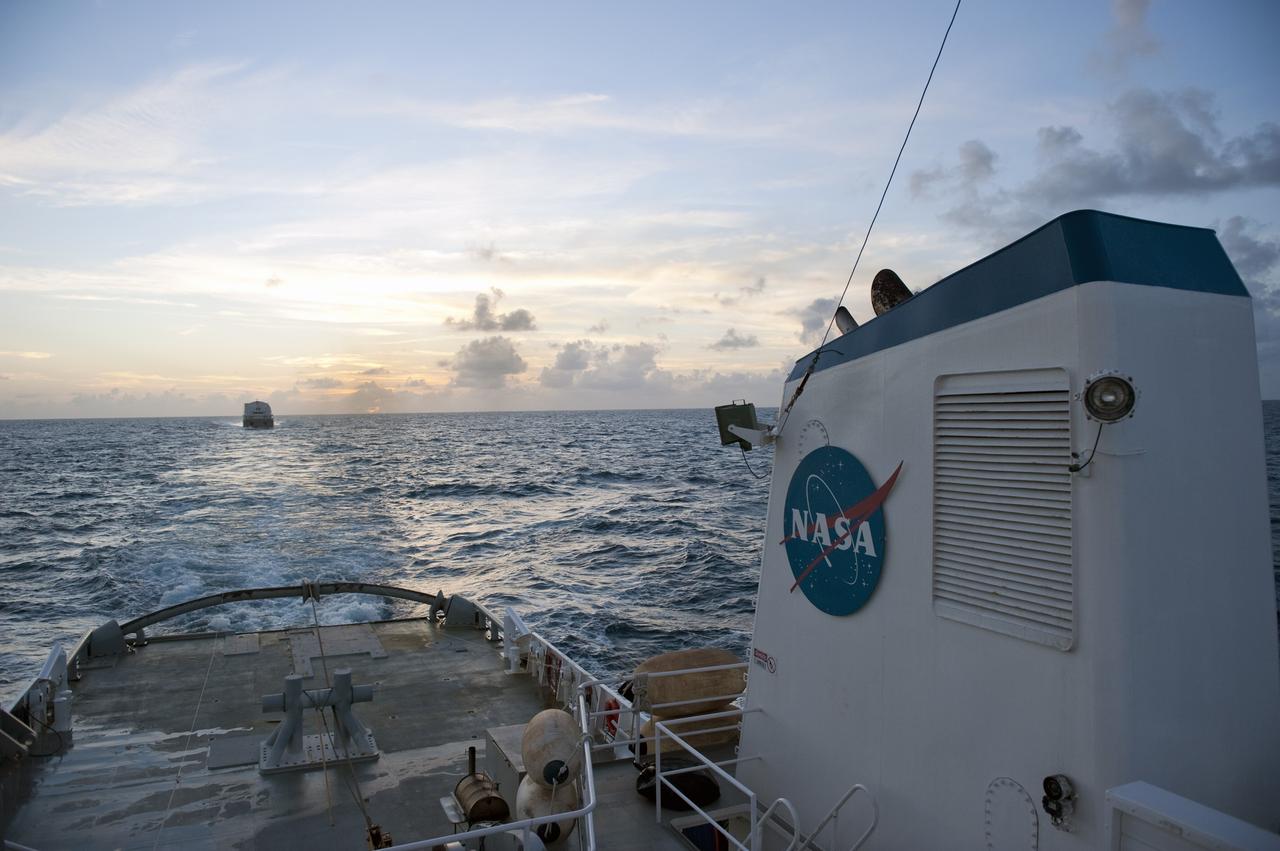

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This view from the stern of Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, shows the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This view from the stern of Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, shows the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, as it is transported to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
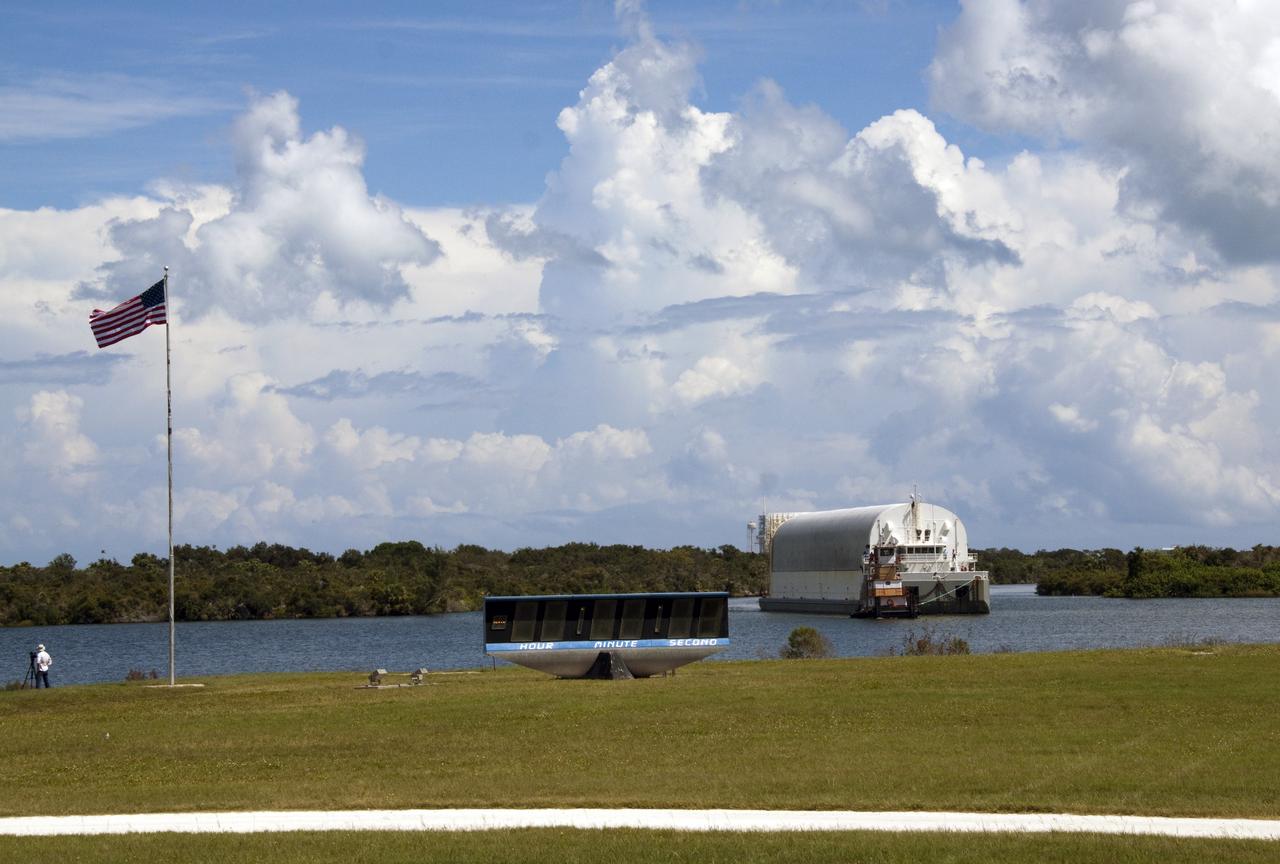

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tugboat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
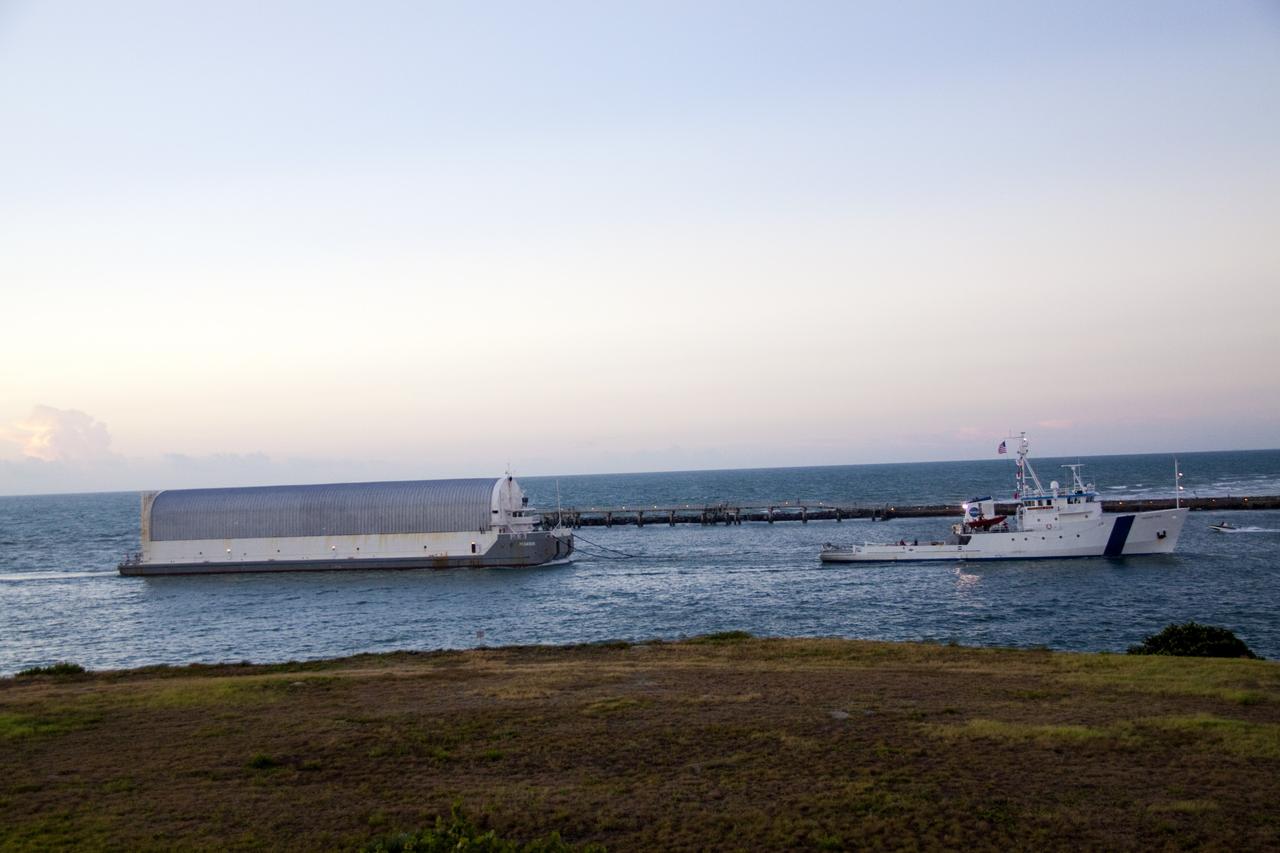

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
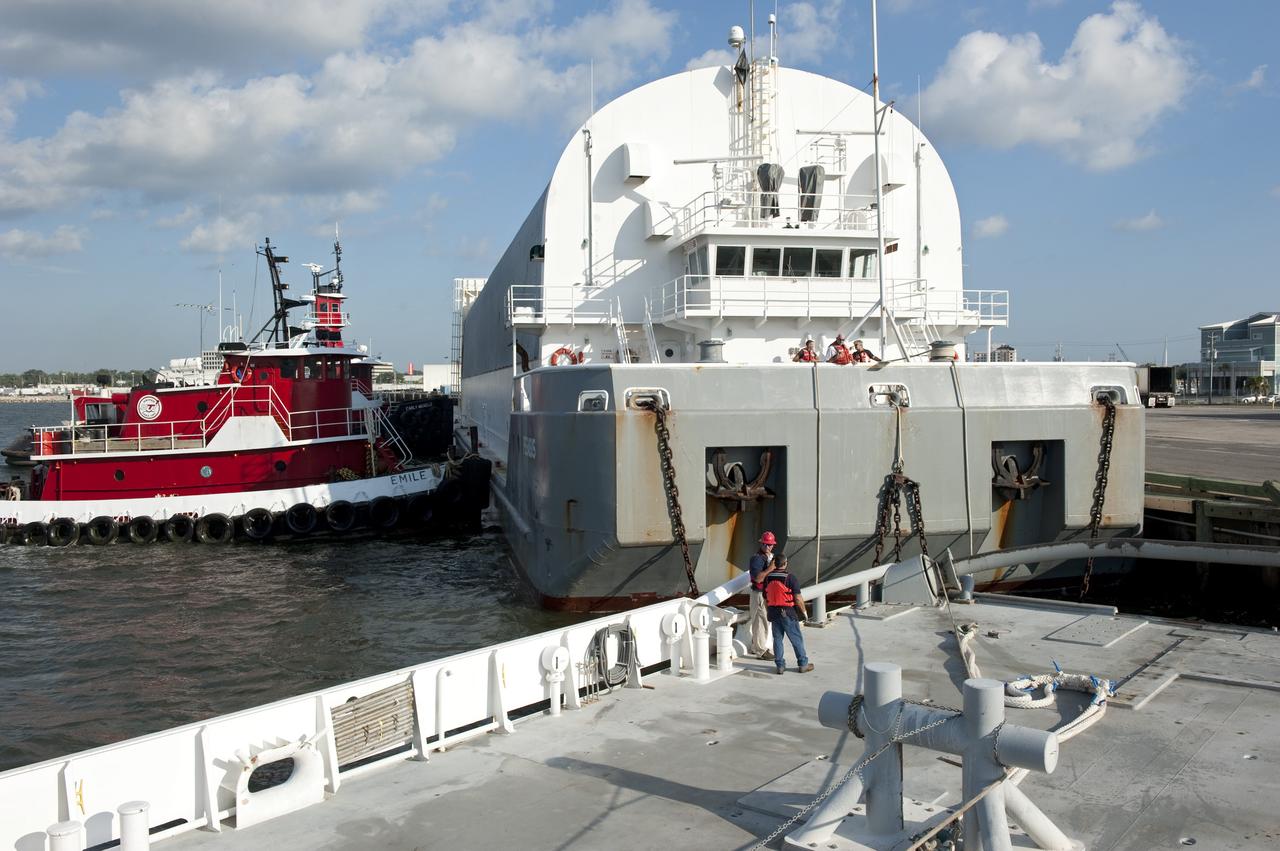

LOUISIANA -- In Gulfport, La., workers connect the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, to Freedom Star, NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ship. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
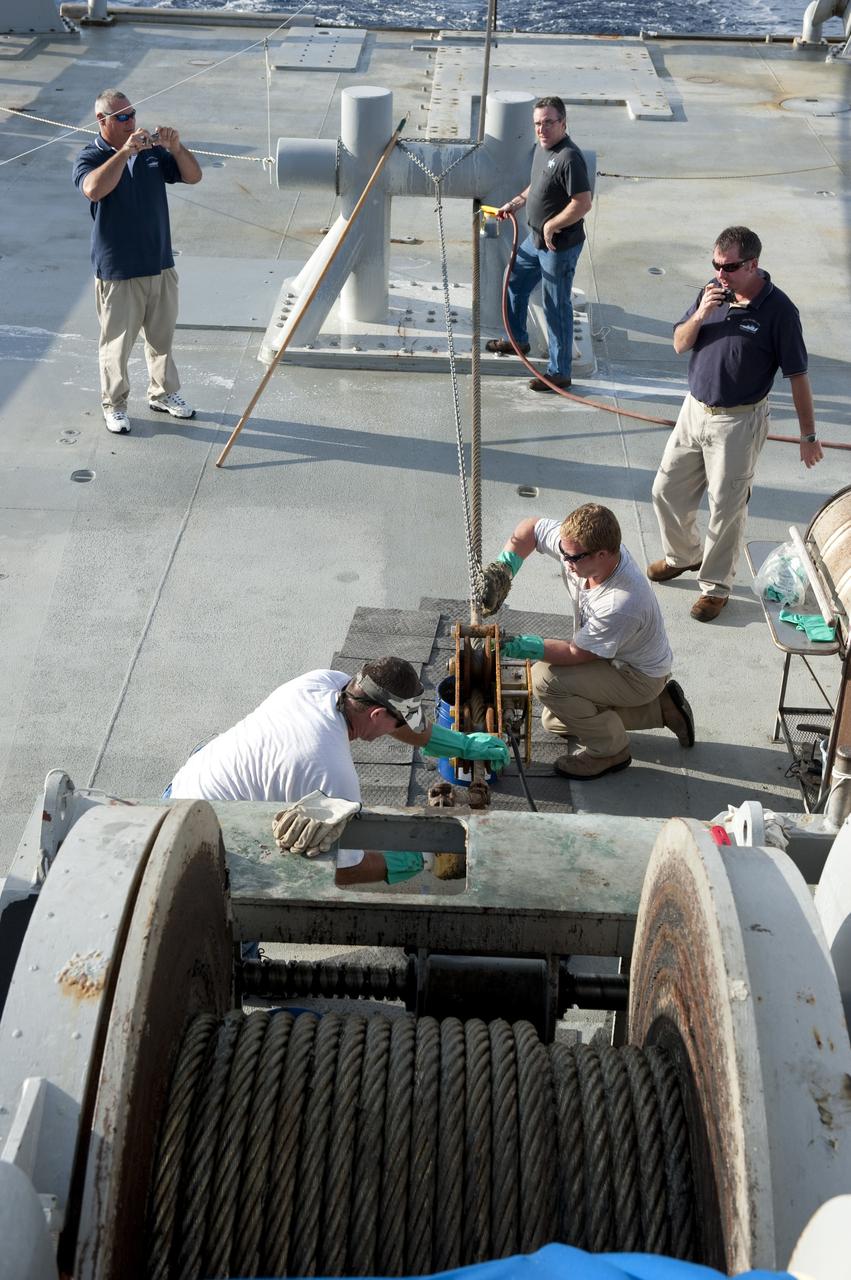

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Deckhands on Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, keep the ship in good repair as it pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
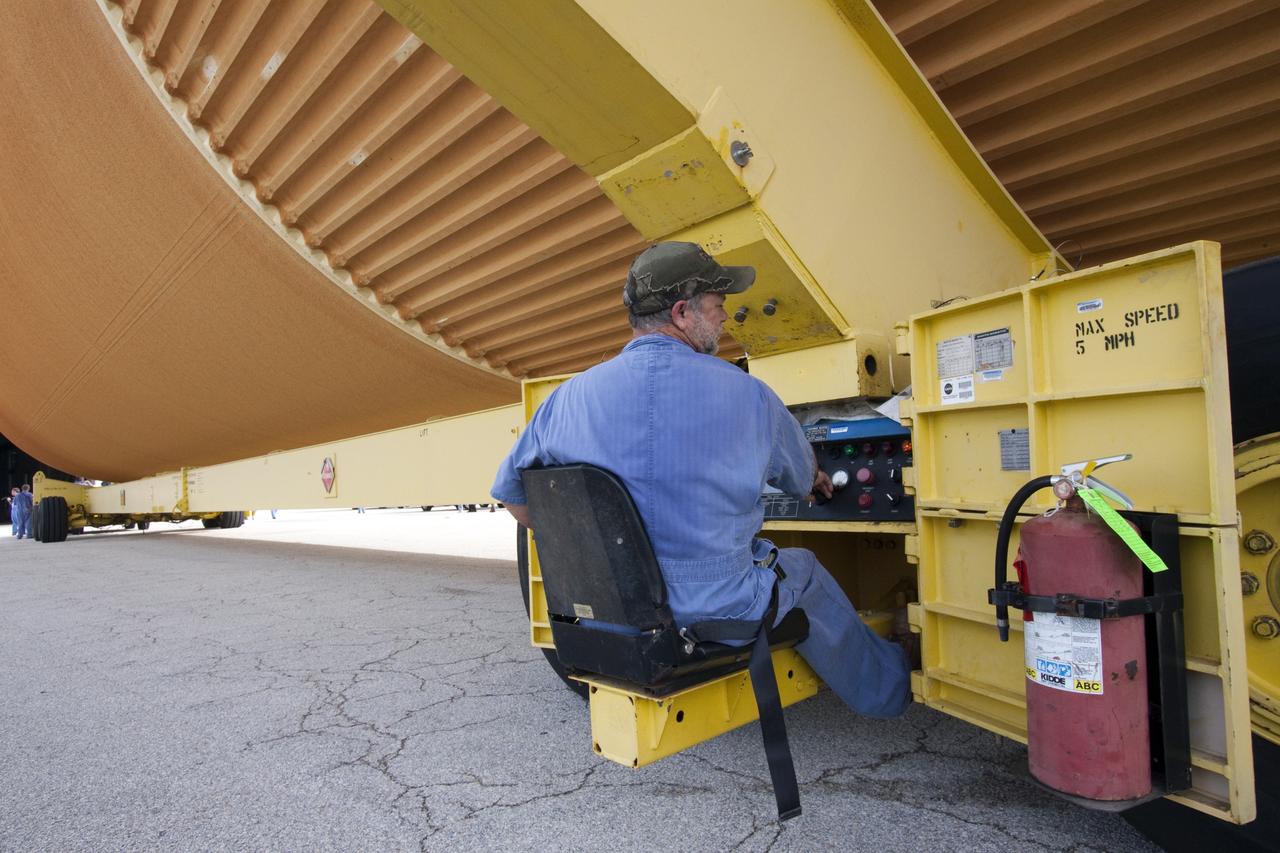

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A United Space Alliance technician monitors the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, as it moves from the Turn Basin to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. Once inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
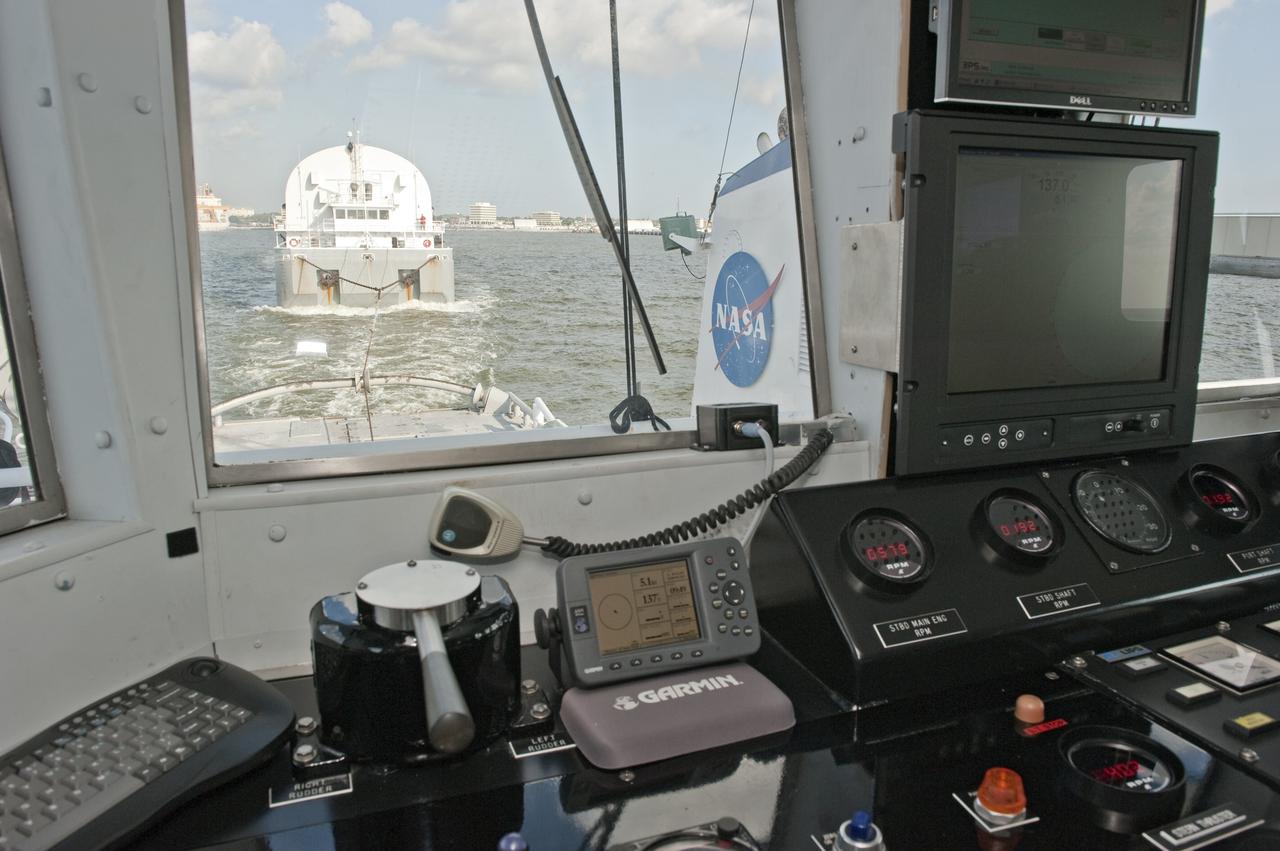

GULFPORT, La. -- This view from the captain's deck of Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, shows the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, as it is escorted from Gulfport, La., to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
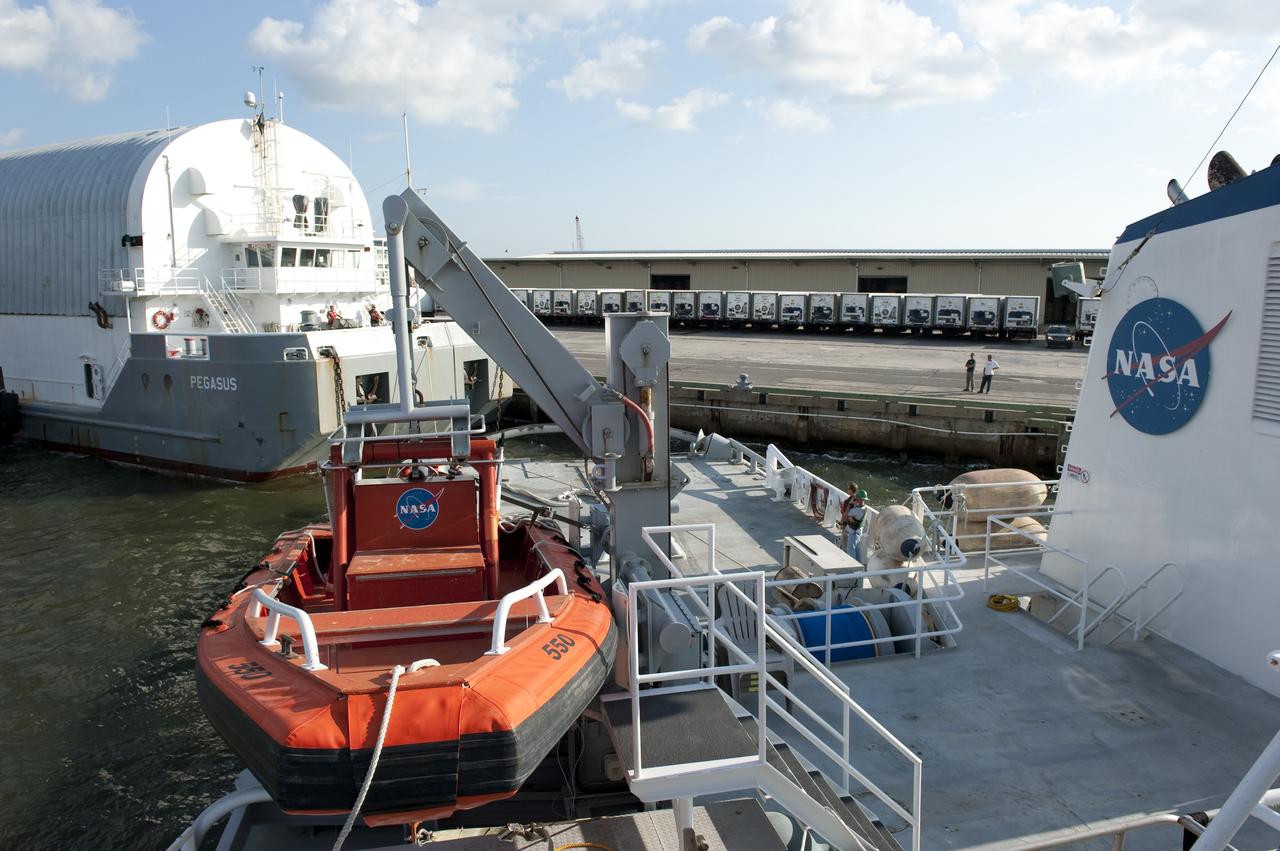

LOUISIANA -- In Gulfport, La., workers connect the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, to Freedom Star, NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ship. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
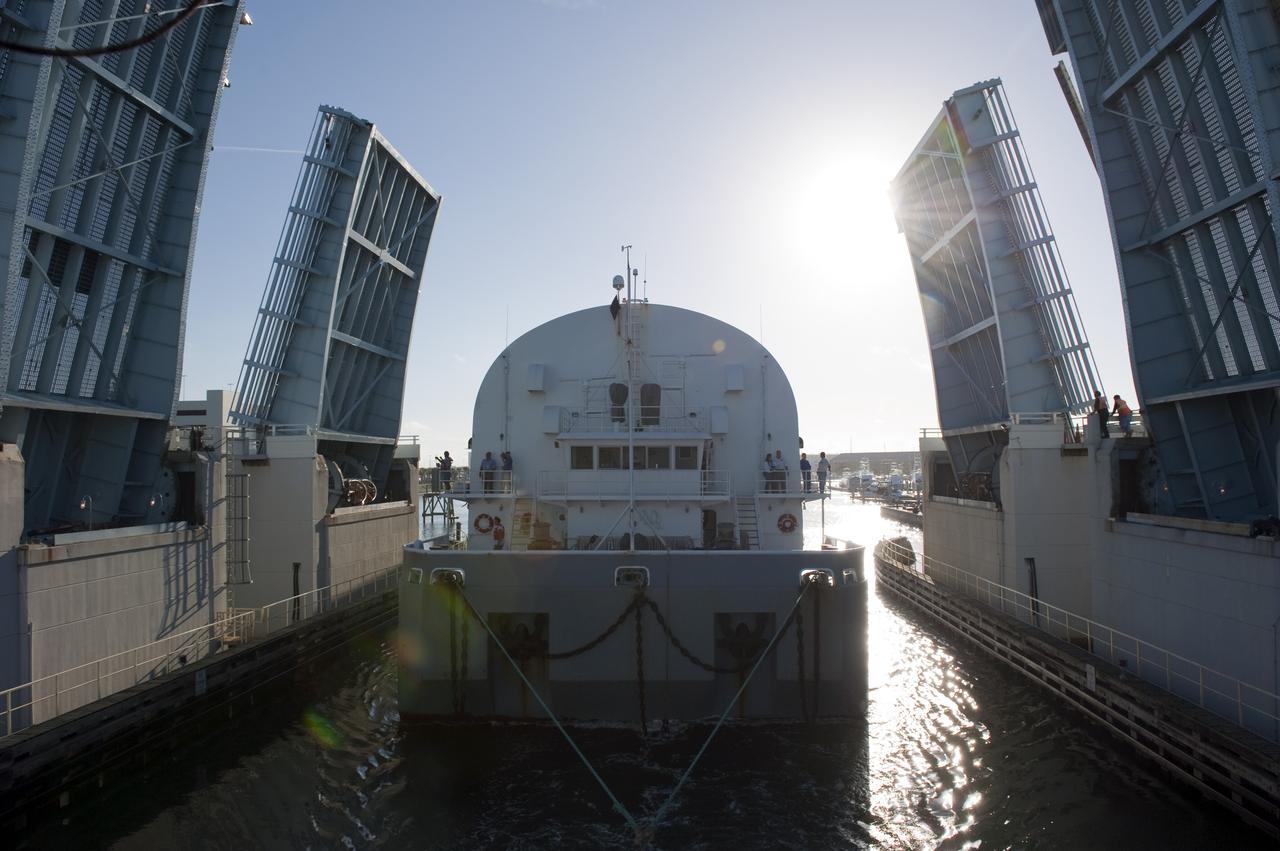

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Pegasus barge moves through the bridge at Port Canaveral, Fla. The barge is carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
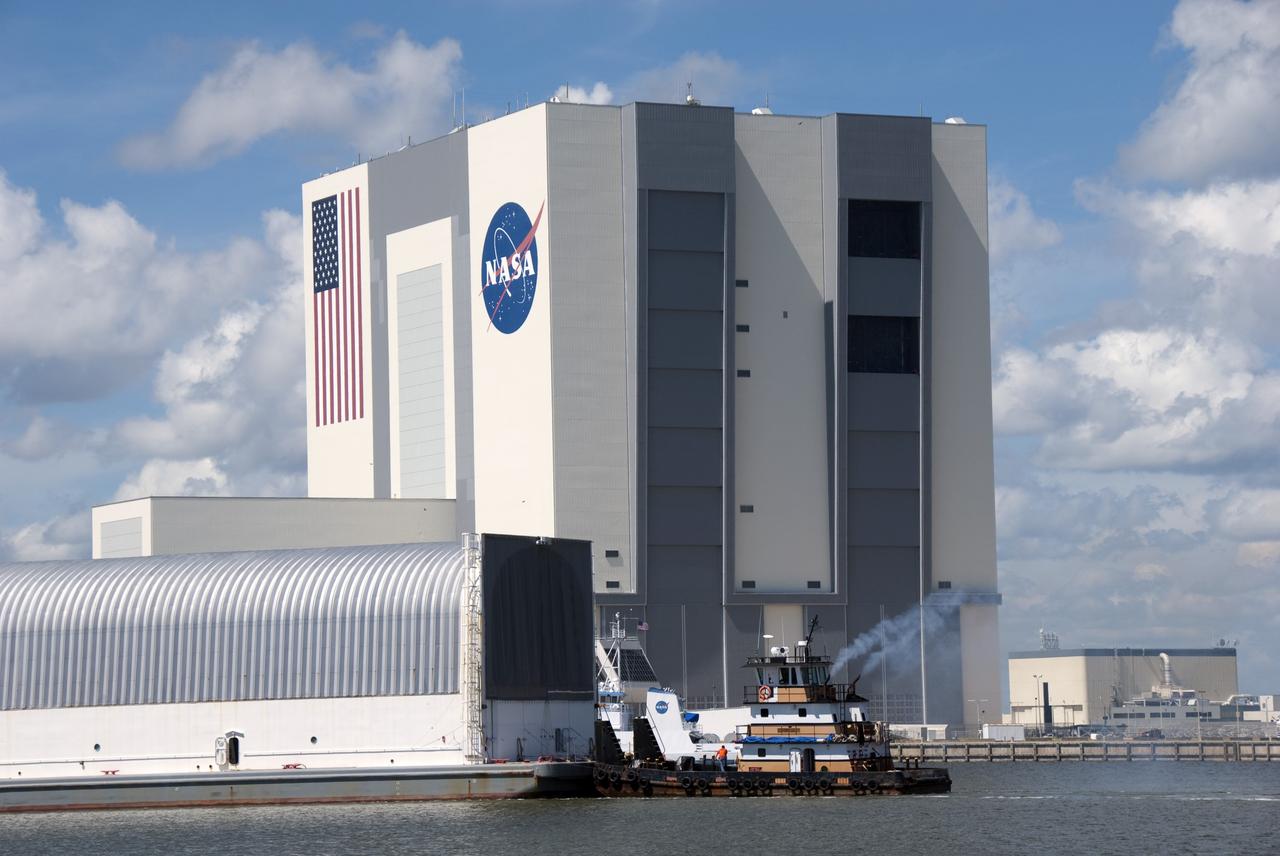

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tugboat pushes the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
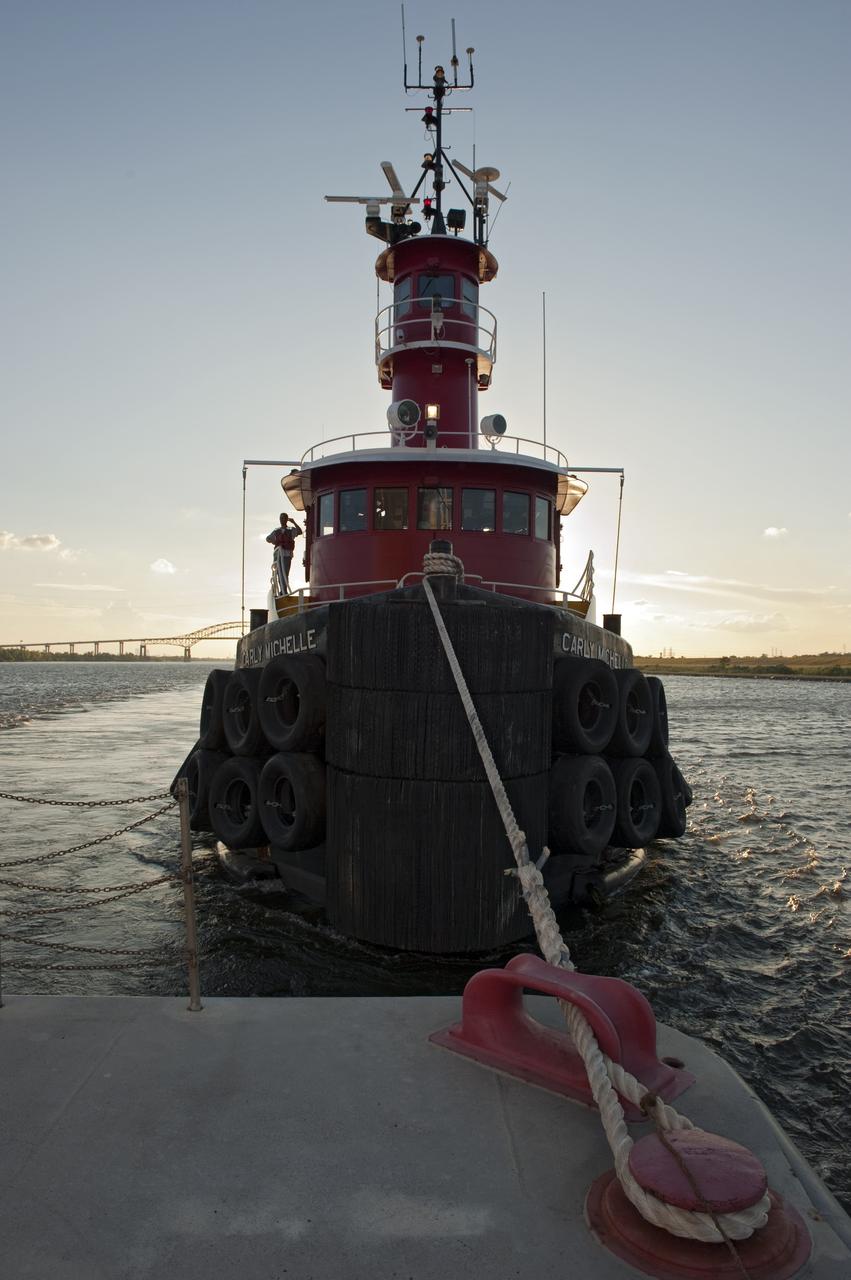

NEW ORLEANS -- A tug boat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
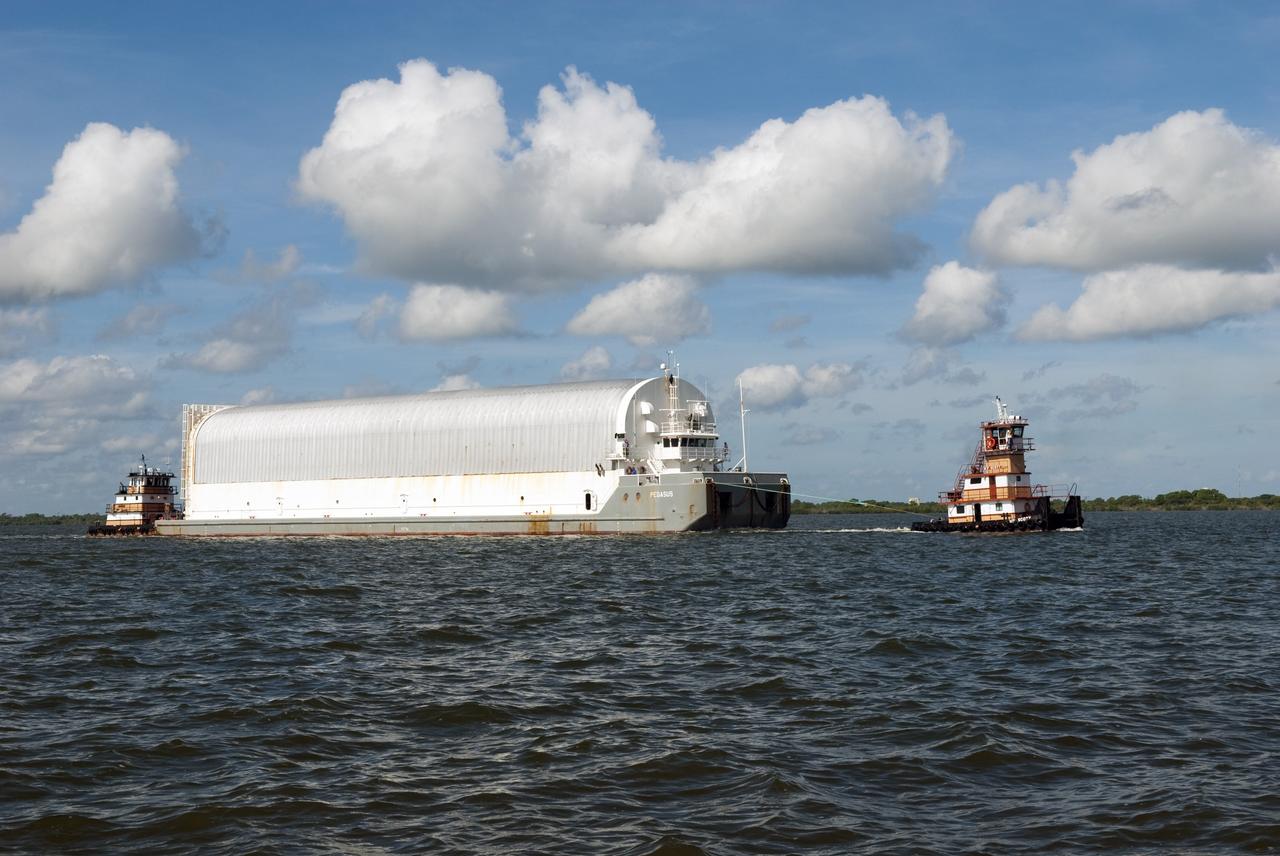

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- One tugboat pulls while another pushes the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
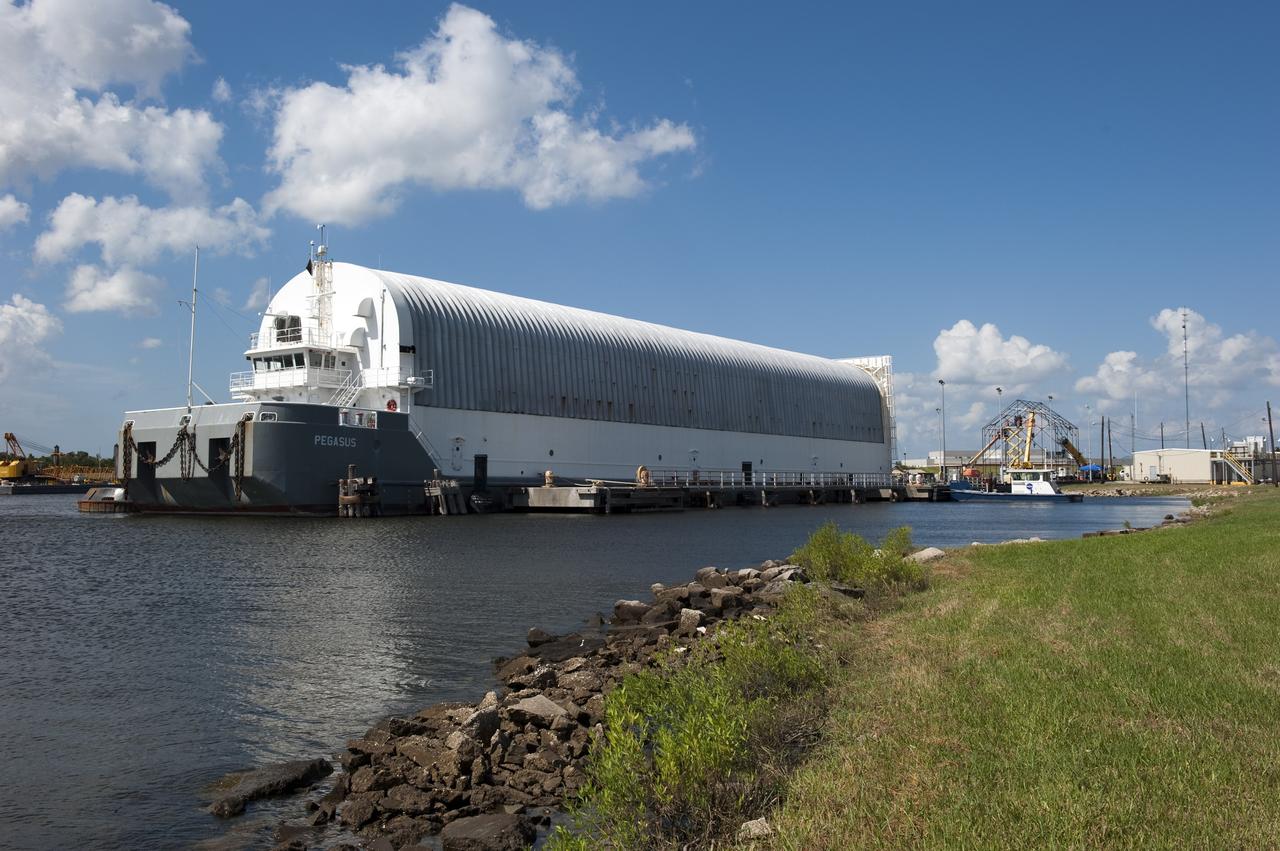

NEW ORLEANS -- At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, is ready for transportation to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Secured aboard the Pegasus Barge the tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
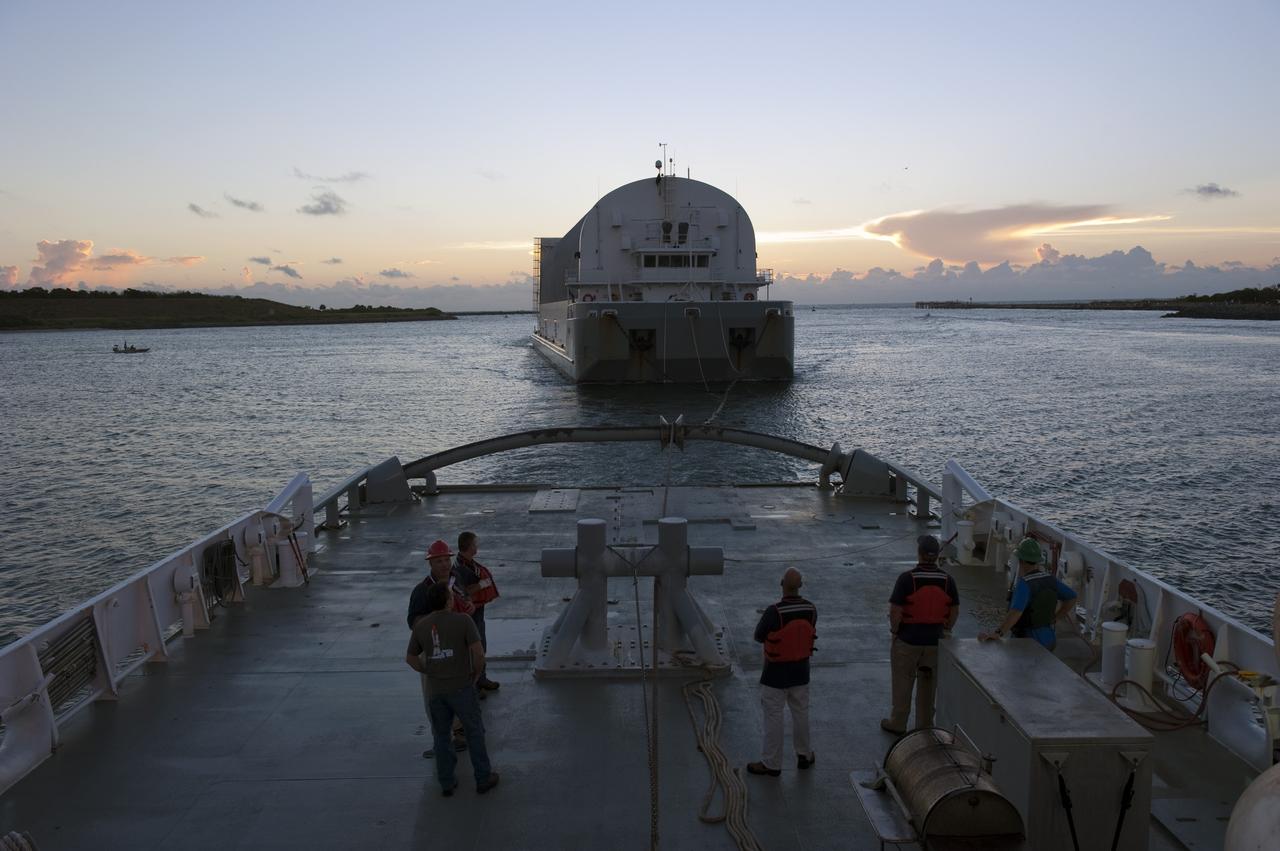

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

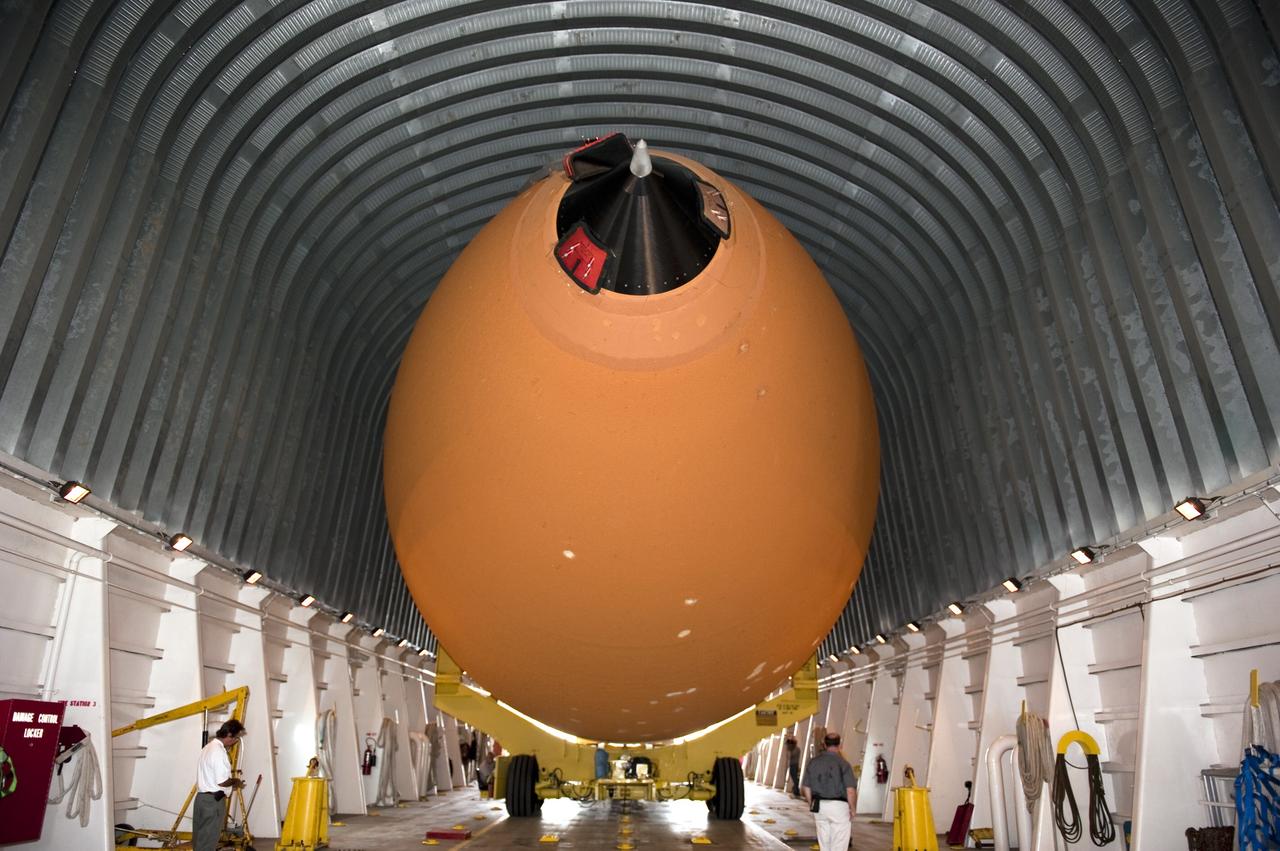
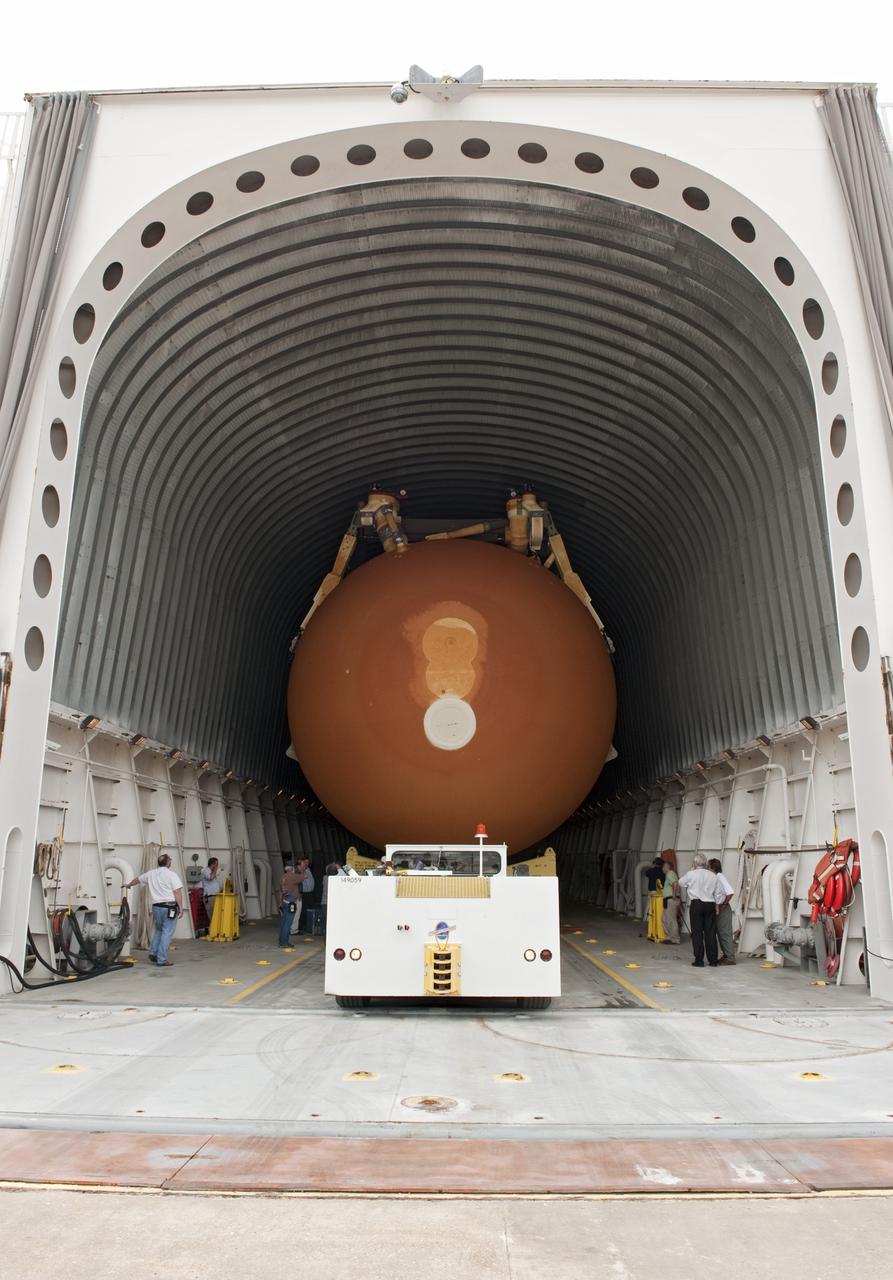
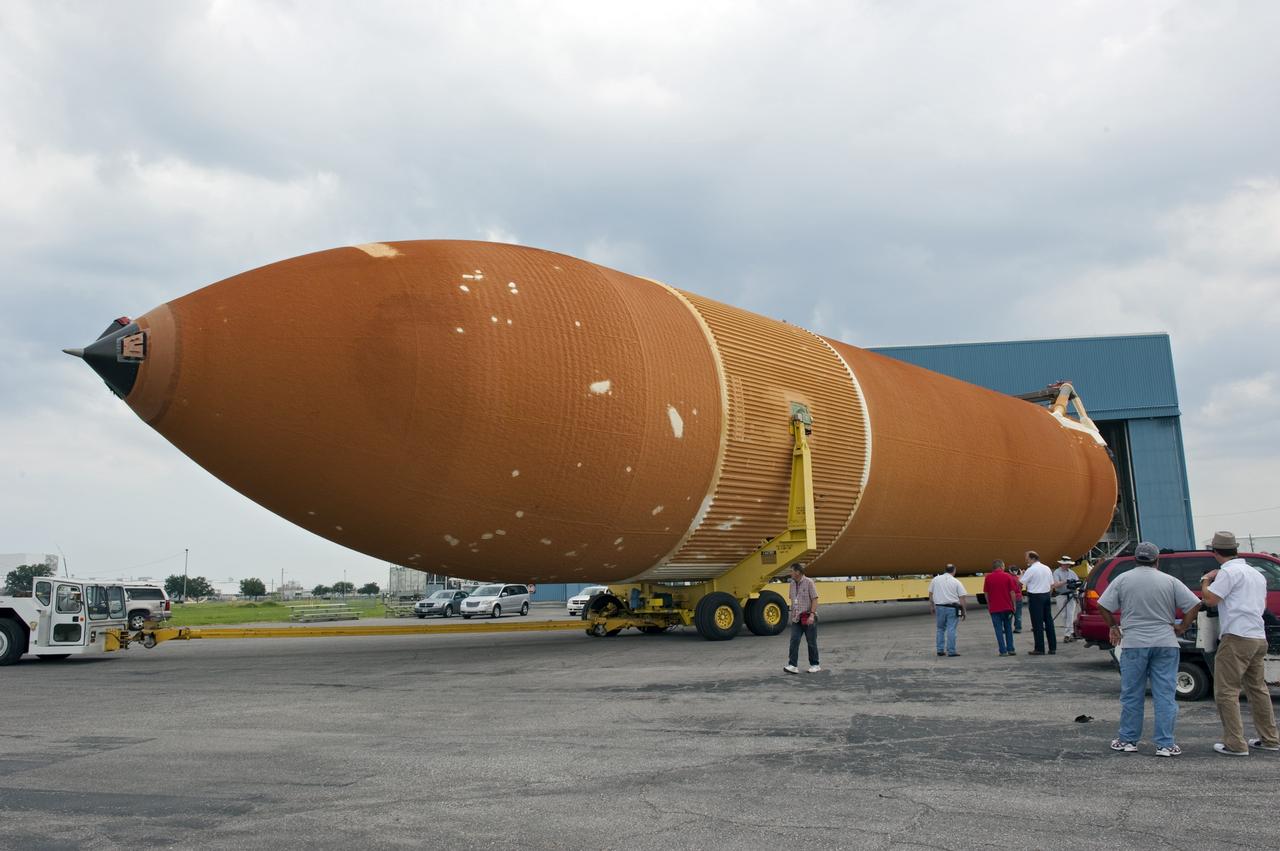
NEW ORLEANS -- To commemorate the history of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, its intertank door is emblazoned with an ET-122 insignia. The external tank will travel 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida secured aboard the Pegasus Barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
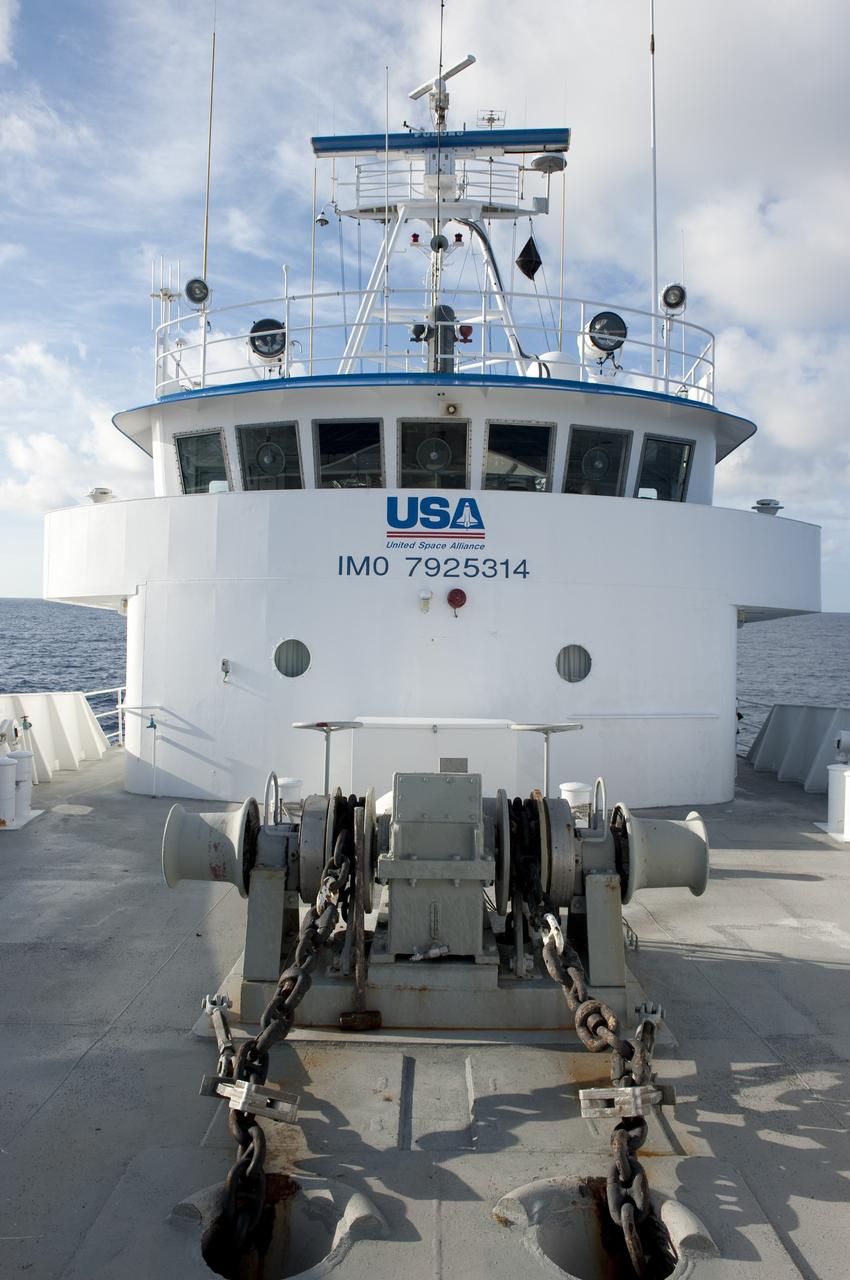

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This view is from the deck of Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, as it pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
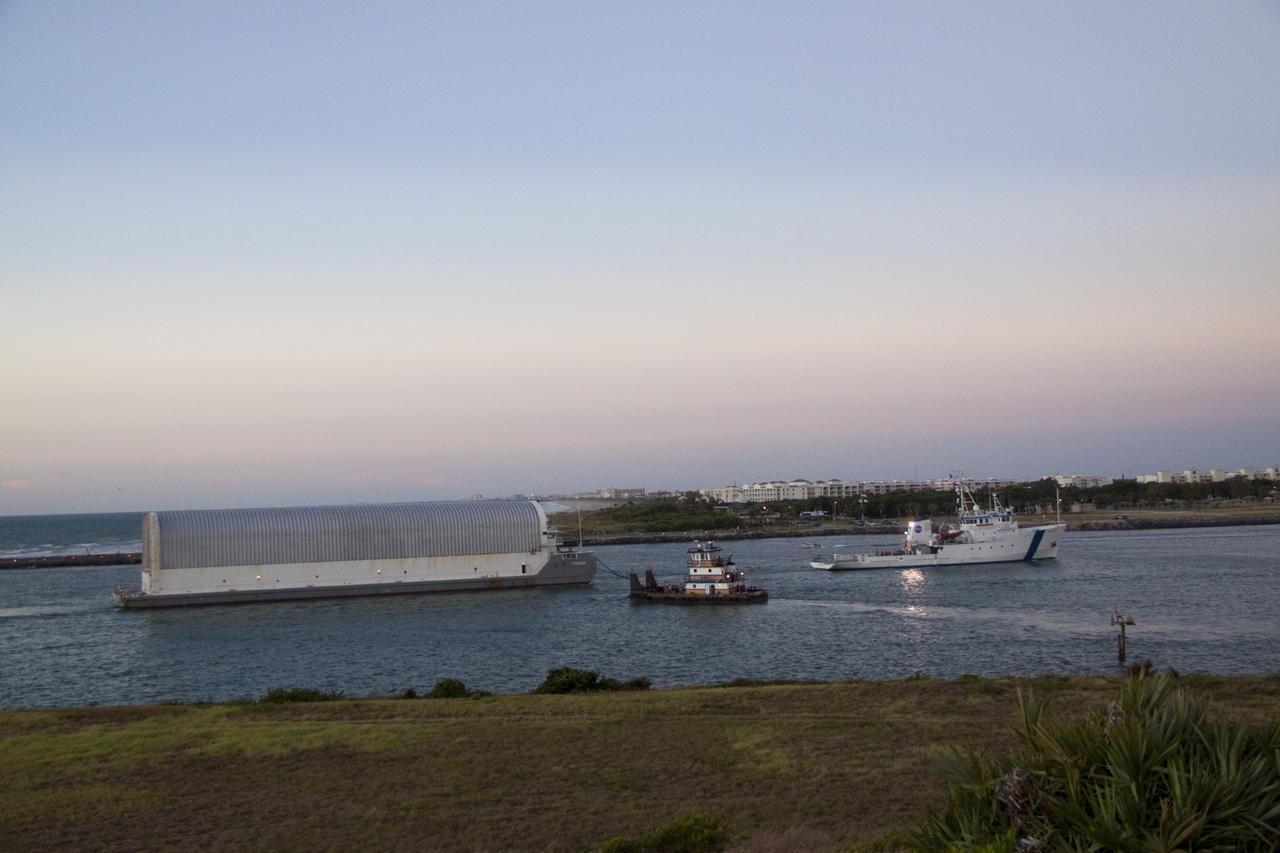

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
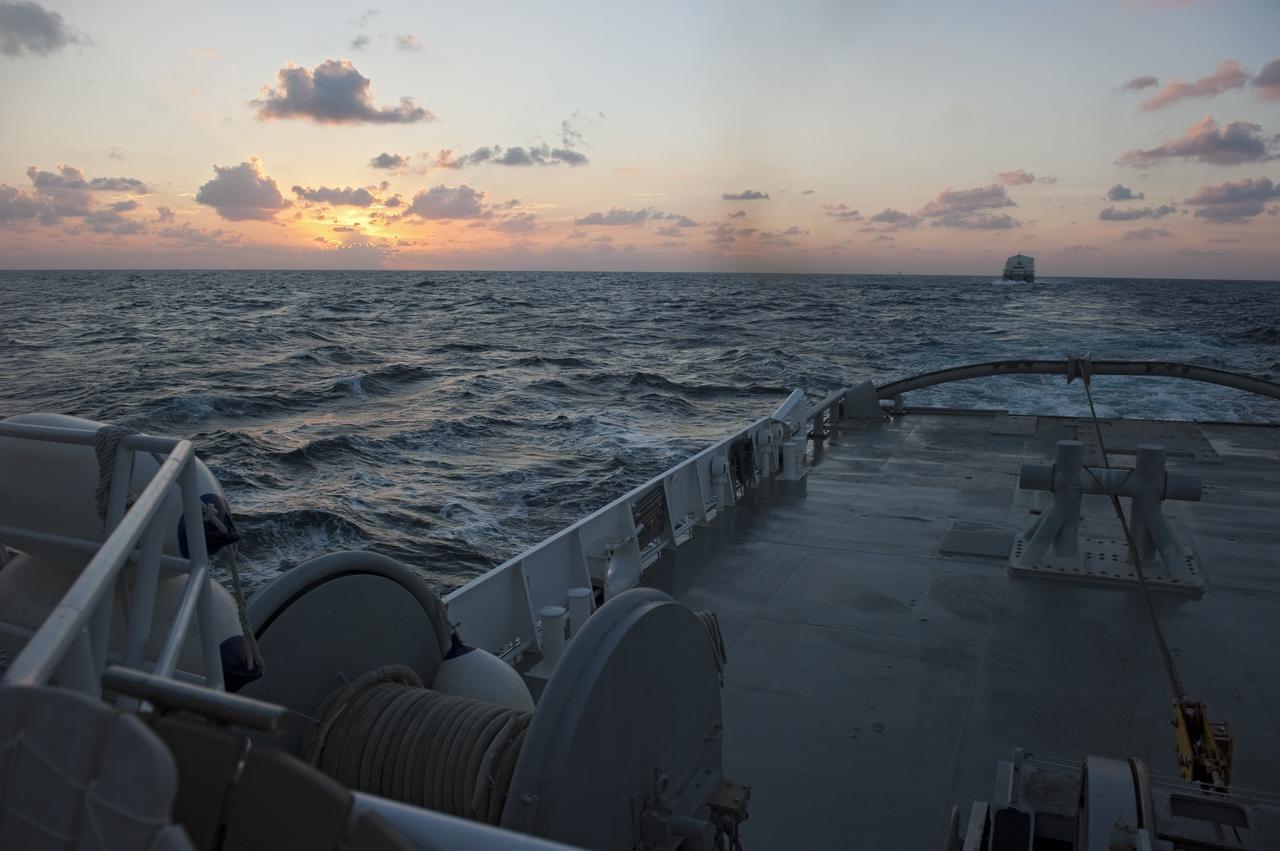

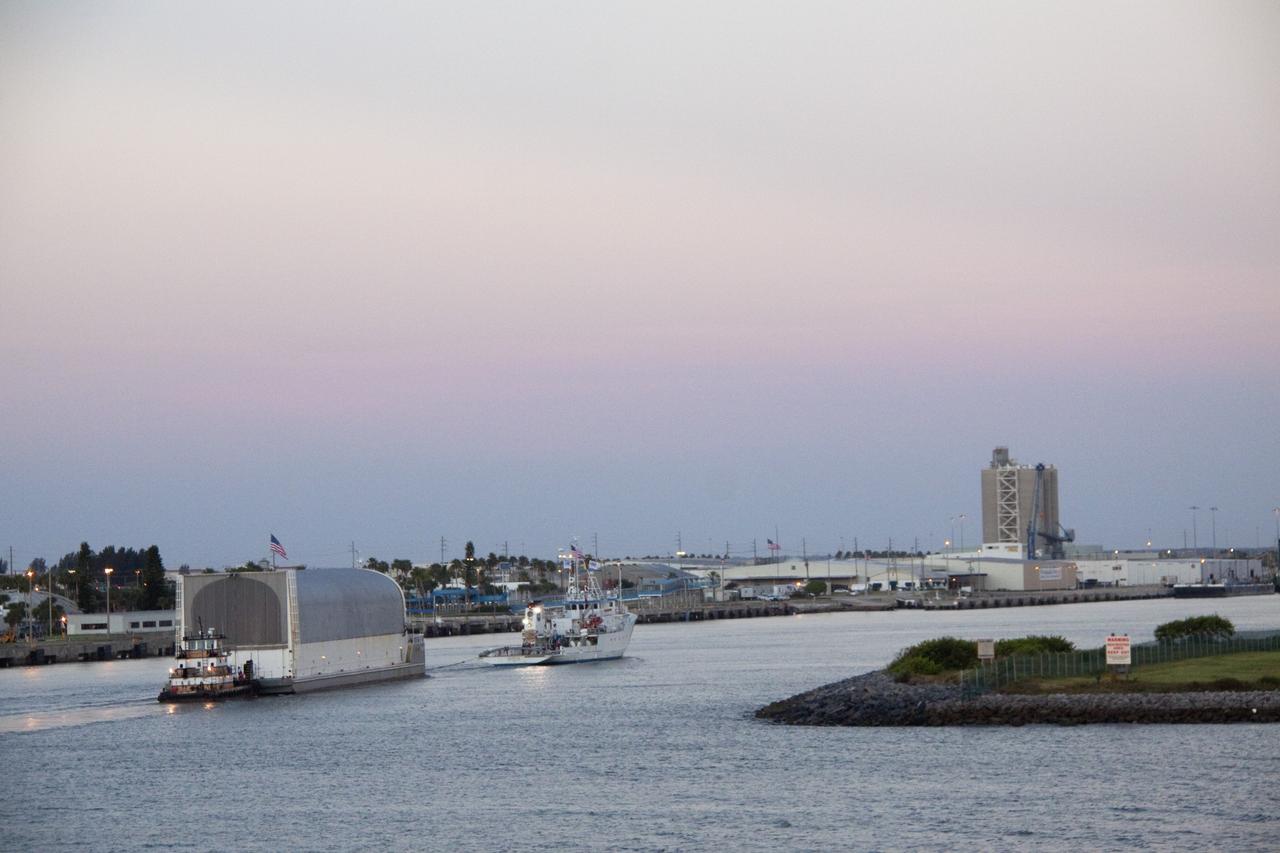
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This view at dusk from the stern of Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, shows the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, as it is transported to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
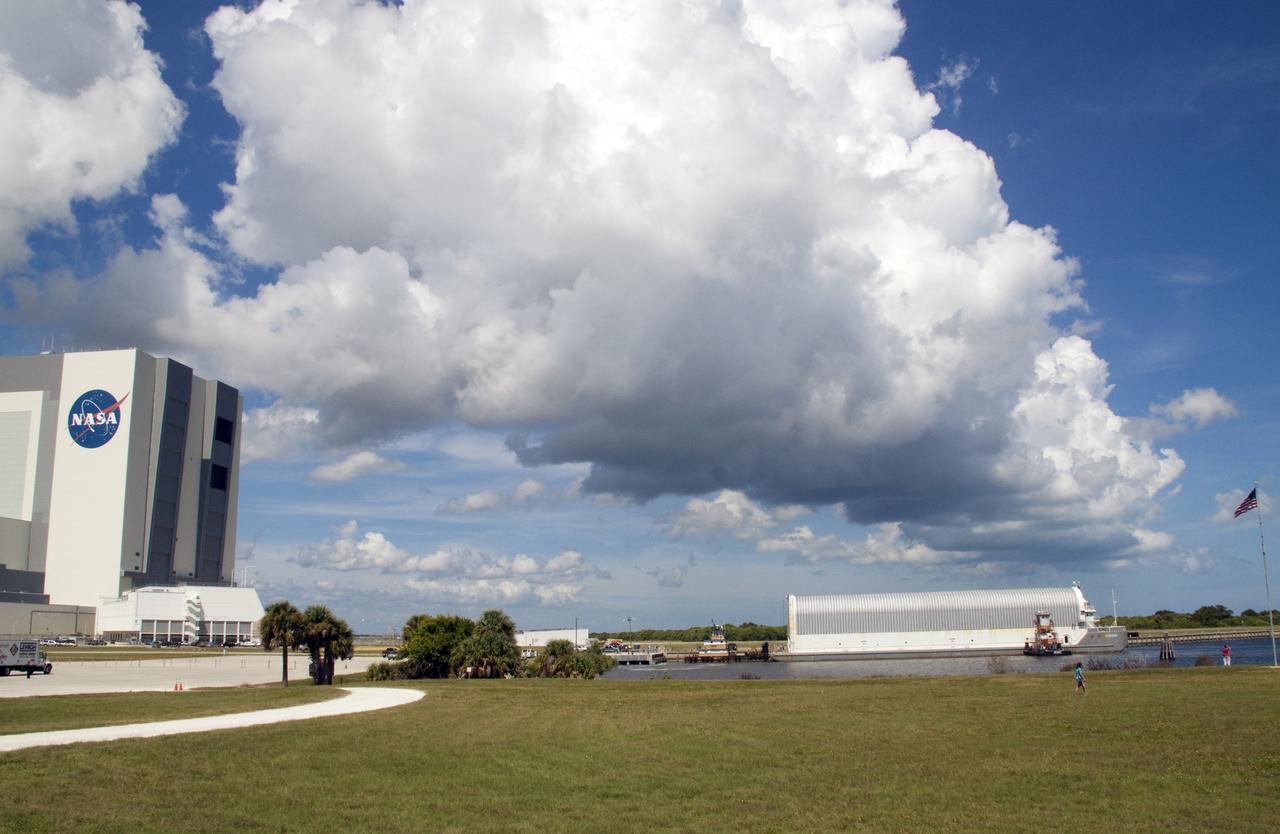

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, arrives at the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
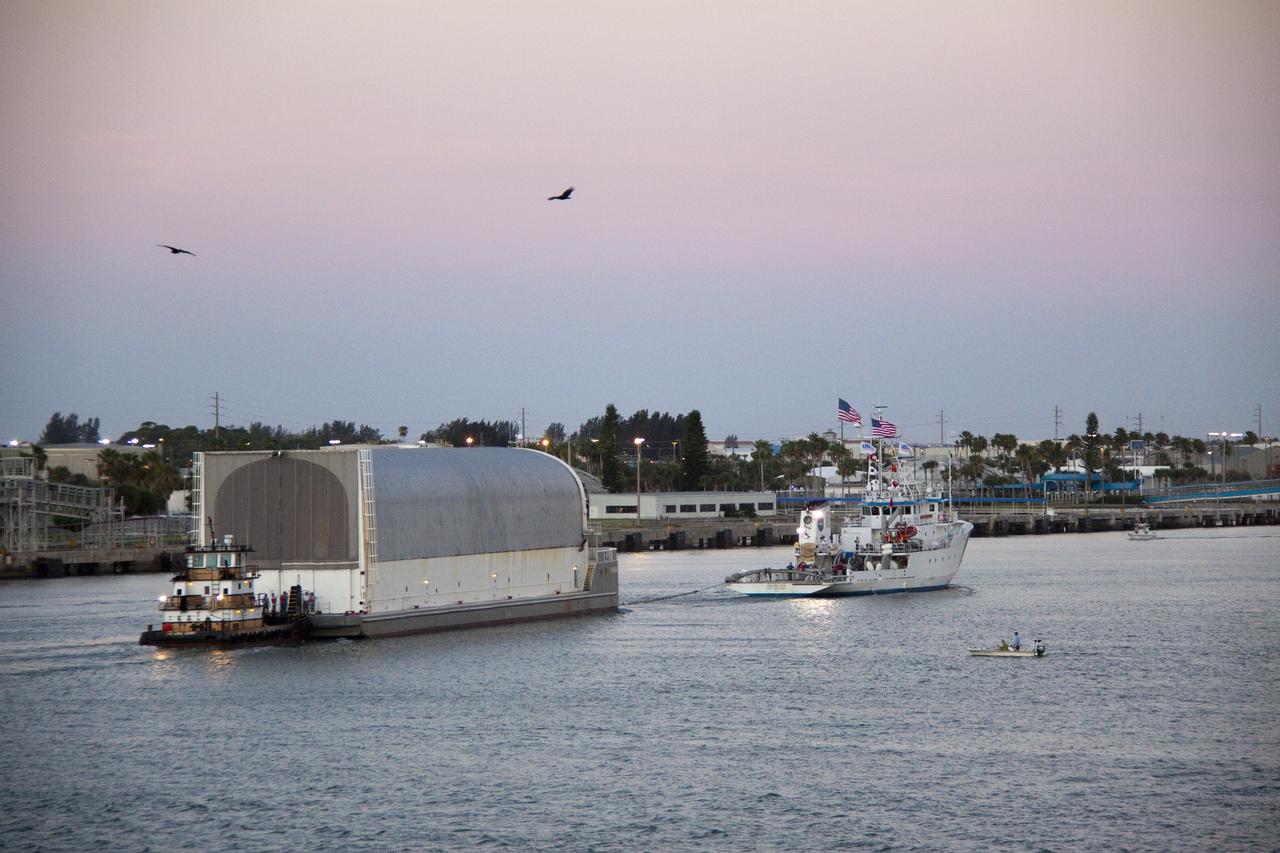

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Boaters watch as Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

LOUISIANA -- In Gulfport, La., tugboats are preparing the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, for connection to Freedom Star, NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ship. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
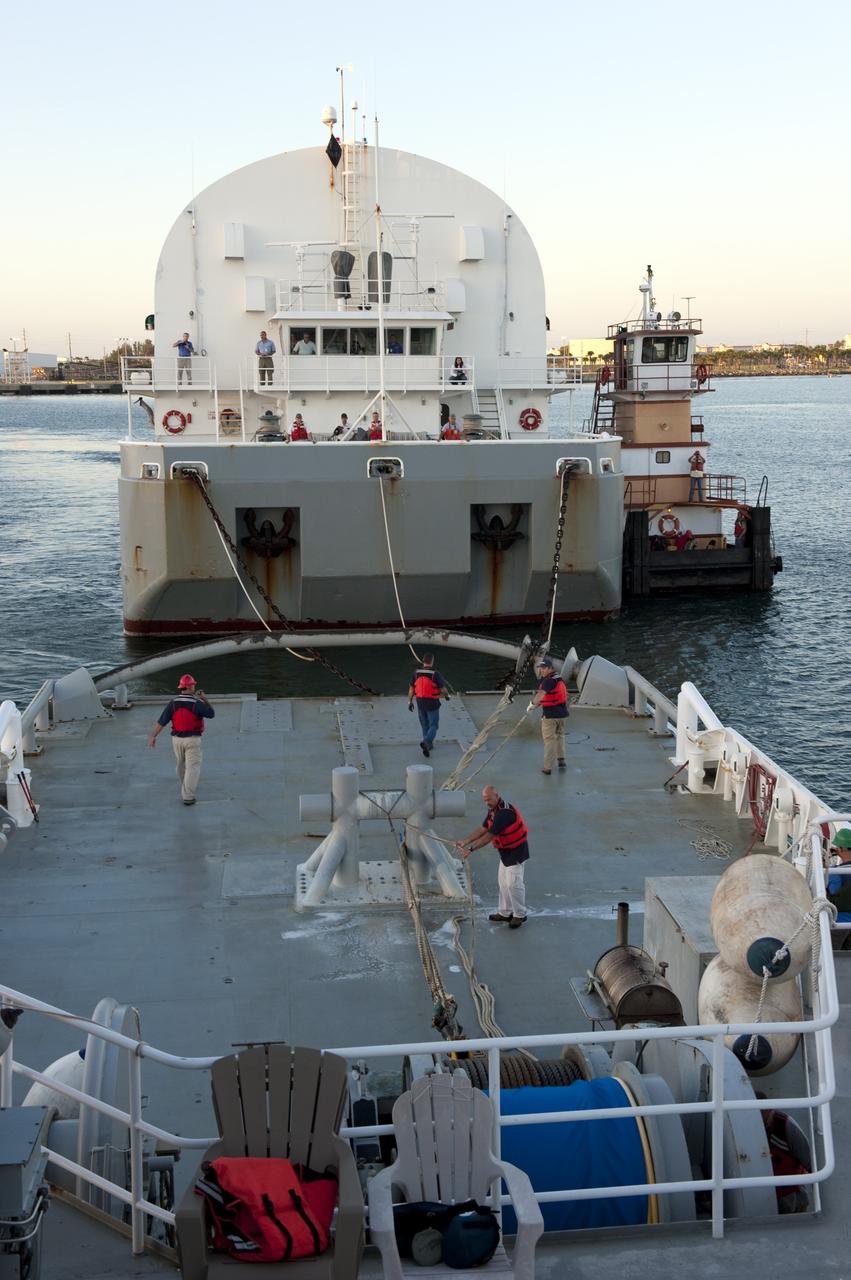

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers aboard Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, disconnect their ship from the Pegasus Barge, which is carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
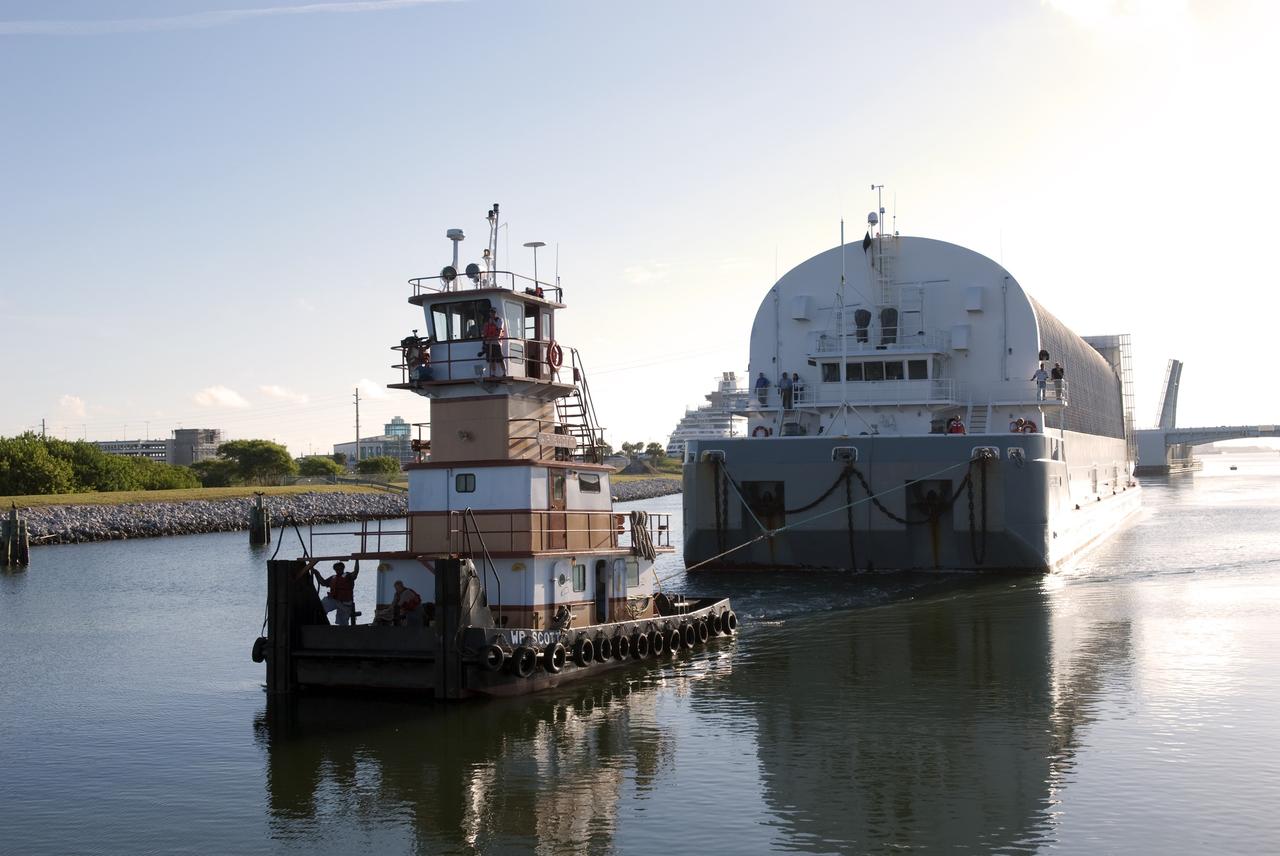

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tugboat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
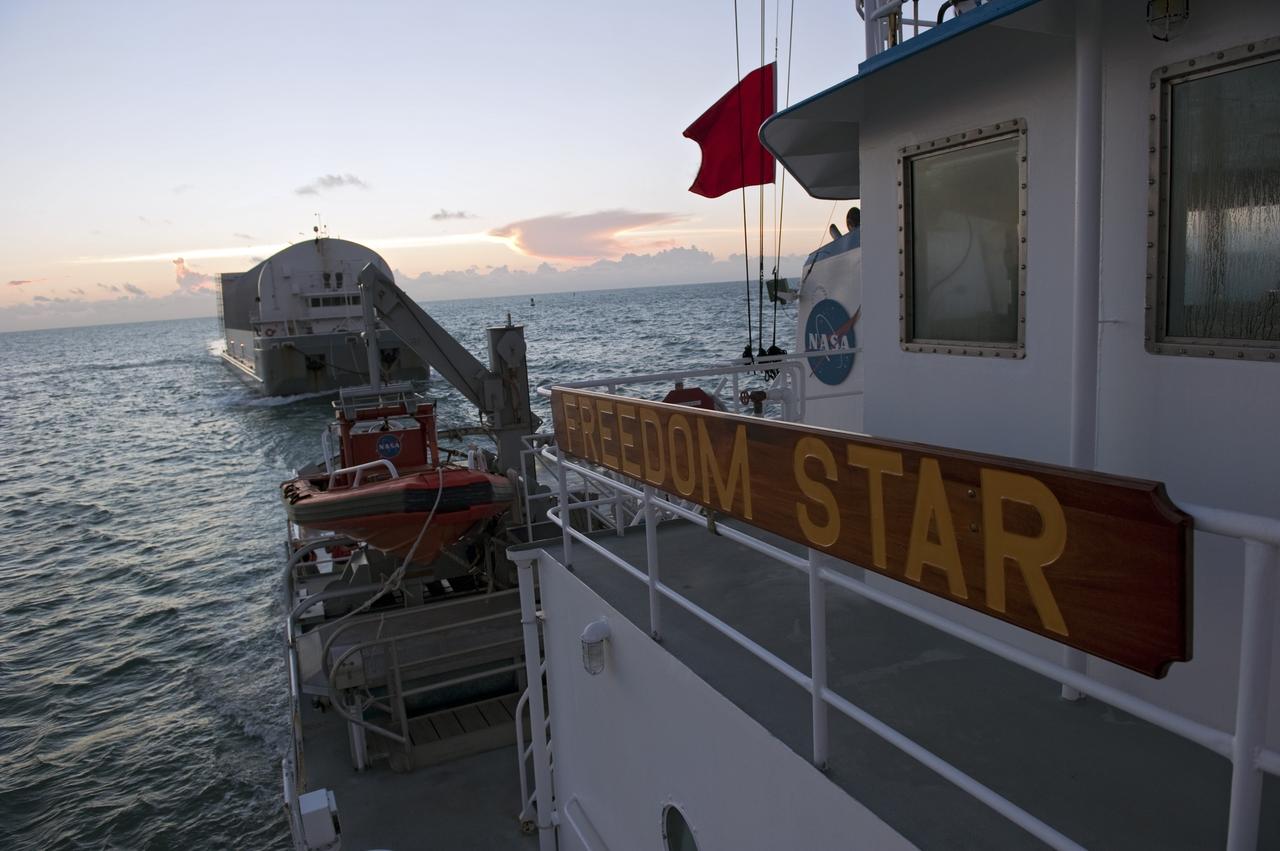

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, pulls the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

NEW ORLEANS -- Workers escort the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans onto the Pegasus Barge. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida secured aboard the barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
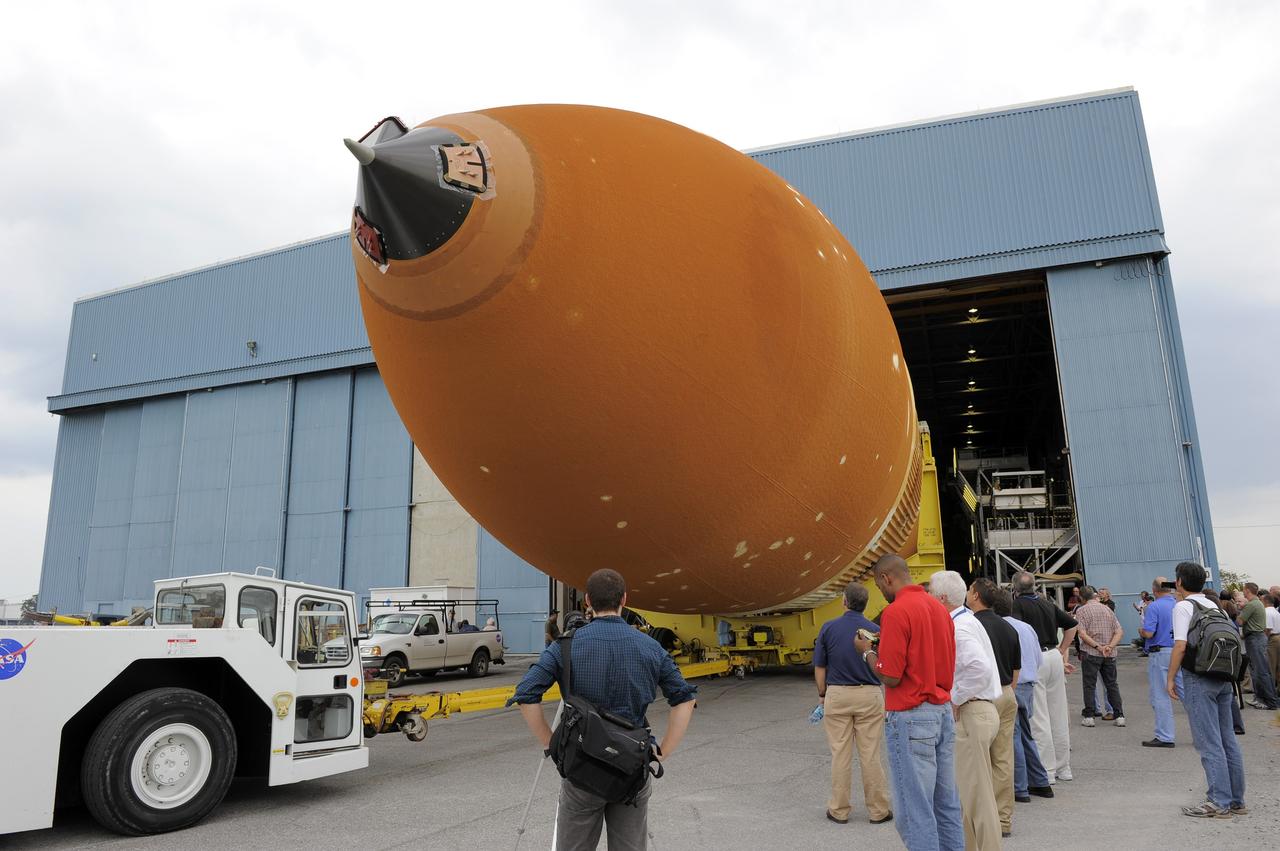

NEW ORLEANS -- Workers watch as the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, rolls out of its processing hangar at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The tank will travel 900 miles aboard the Pegasus Barge to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
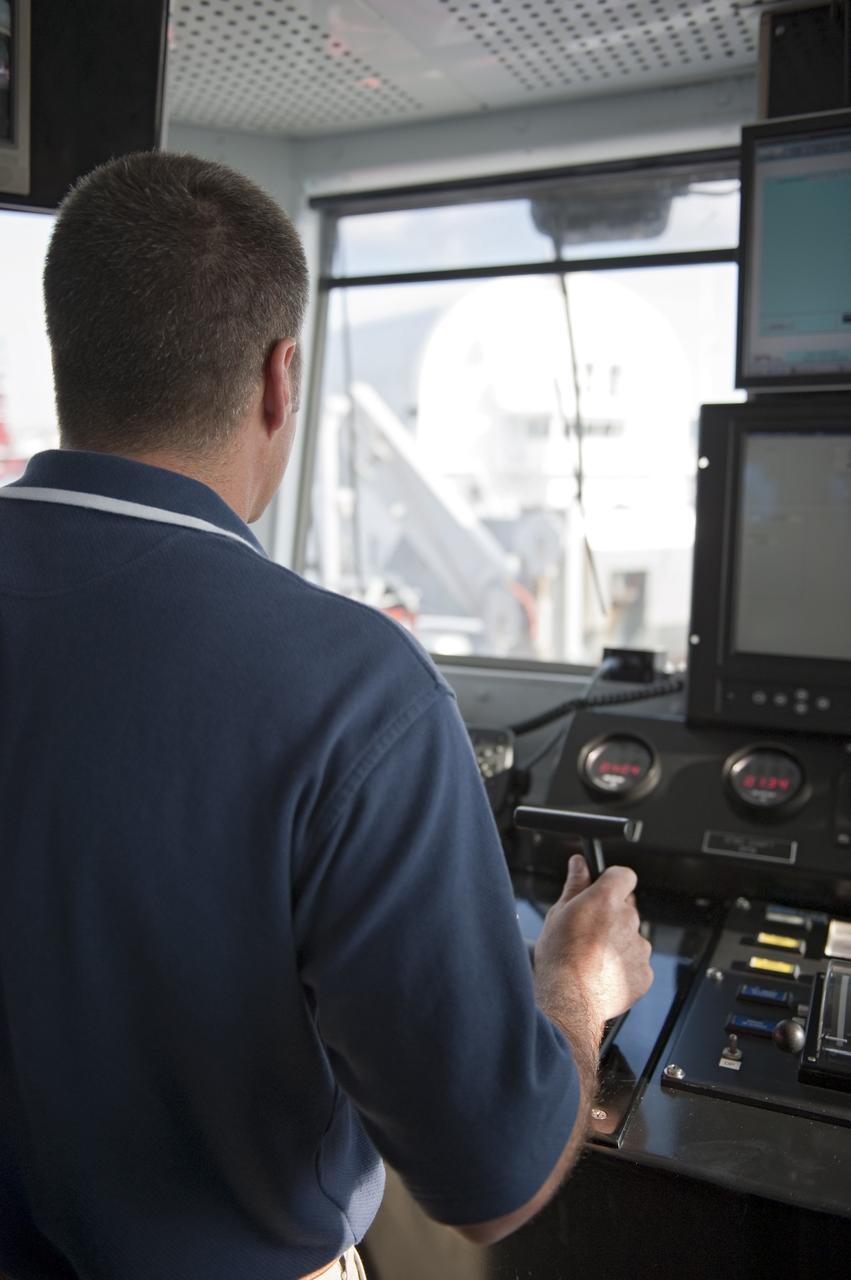

GULFPORT, La. -- At Gulfport, La., Michael Nicholas, captain M/V Freedom Star, guides NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ship out of port pulling the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
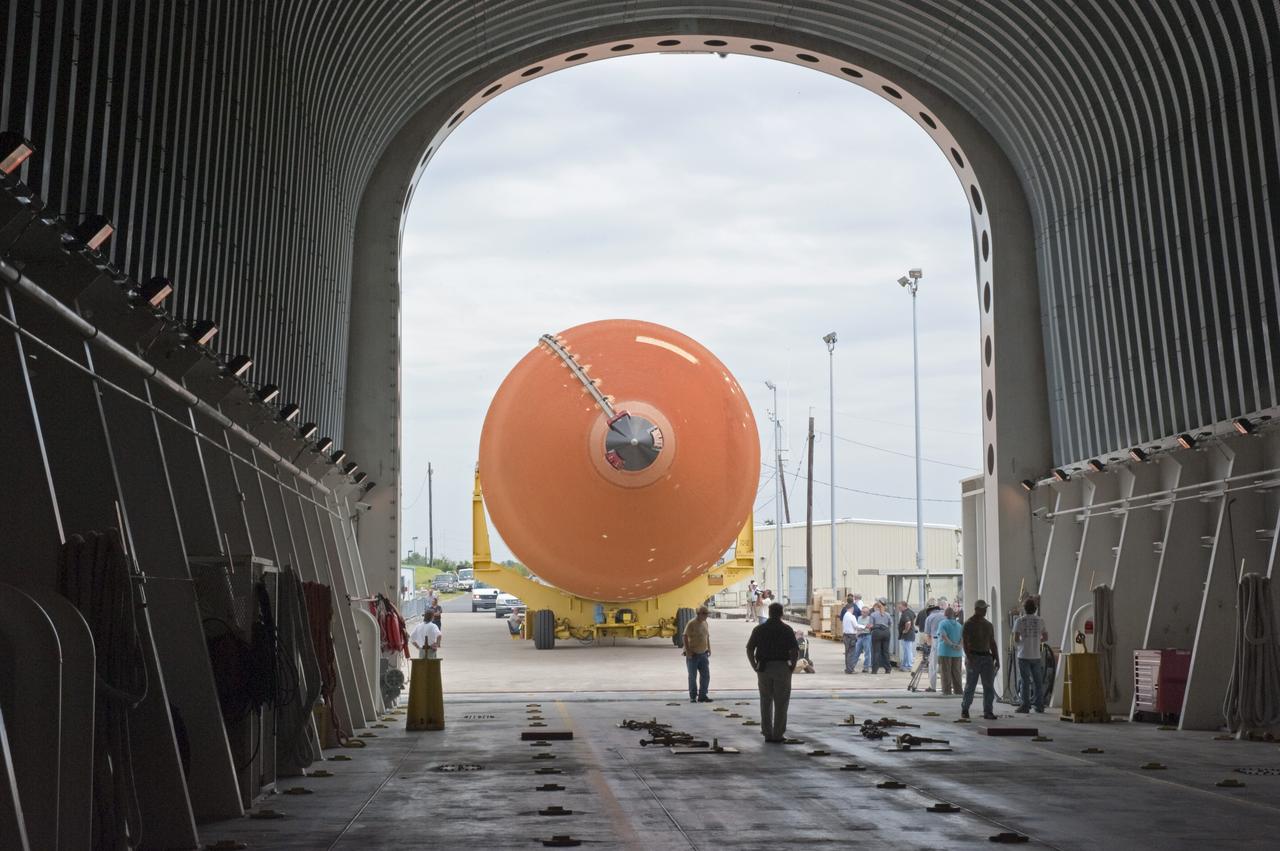

NEW ORLEANS -- Workers monitor the progress of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it is being loaded onto the Pegasus Barge. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida secured aboard the barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

NEW ORLEANS -- A tug boat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
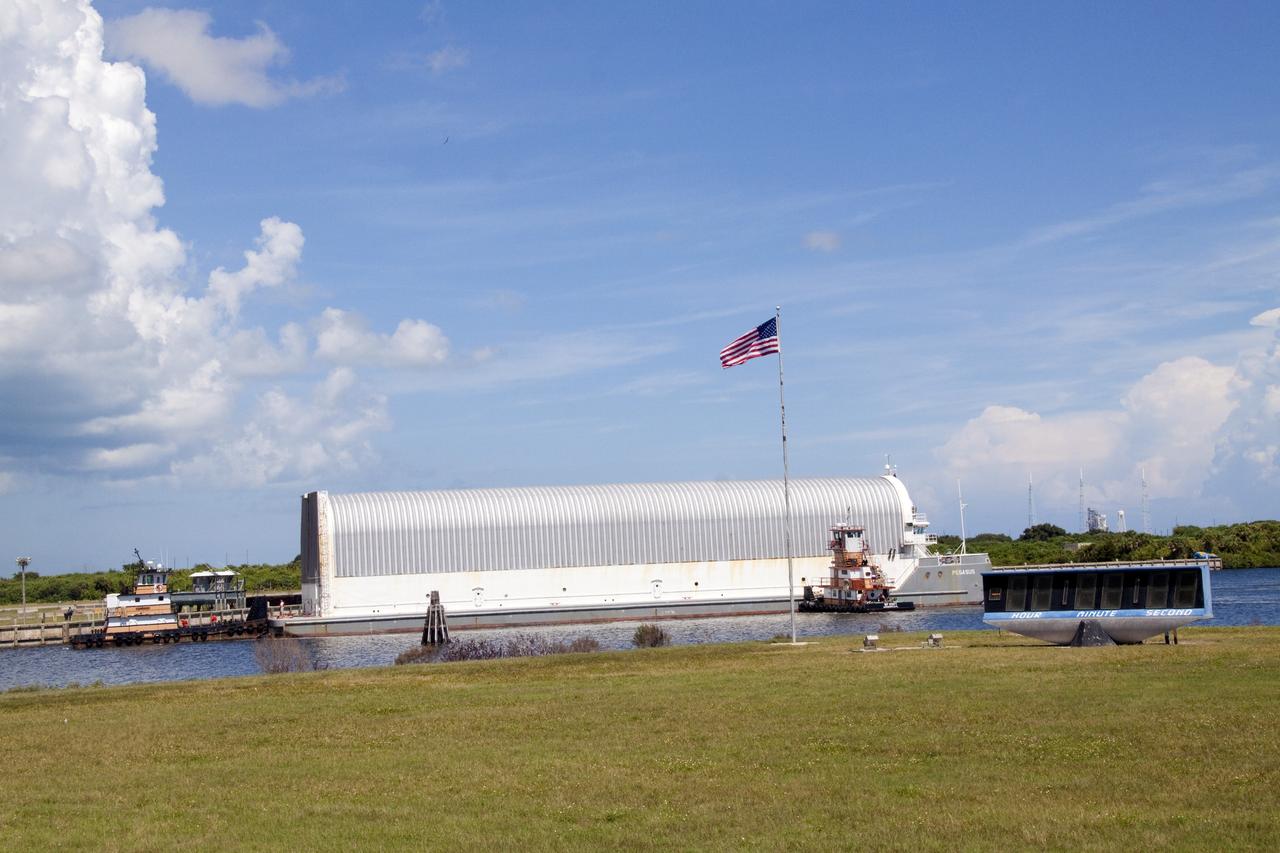

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, arrives at the Turn Basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
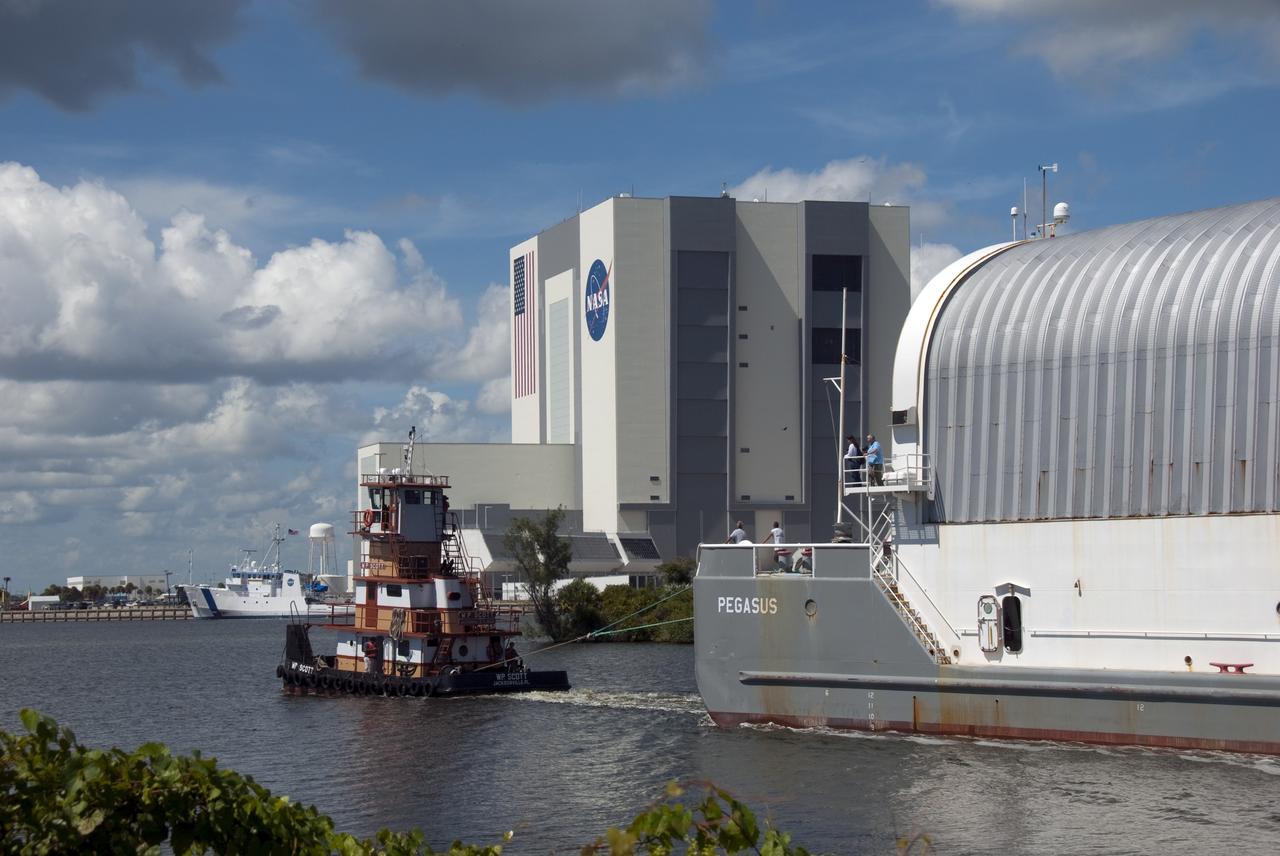

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A tugboat pulls the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, toward NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. After reaching the Turn Basin at Kennedy, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
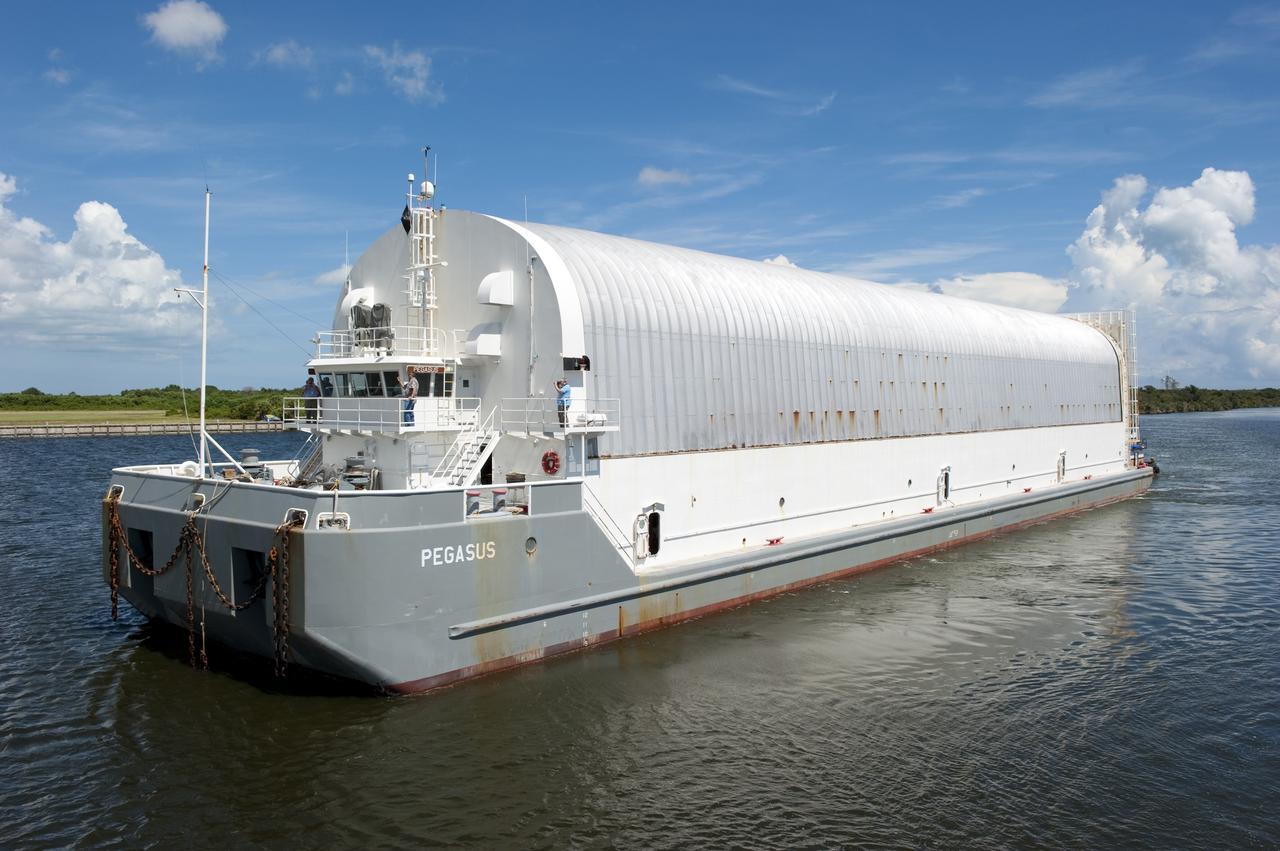

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Pegasus barge, carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, arrives at the Turn Basin of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
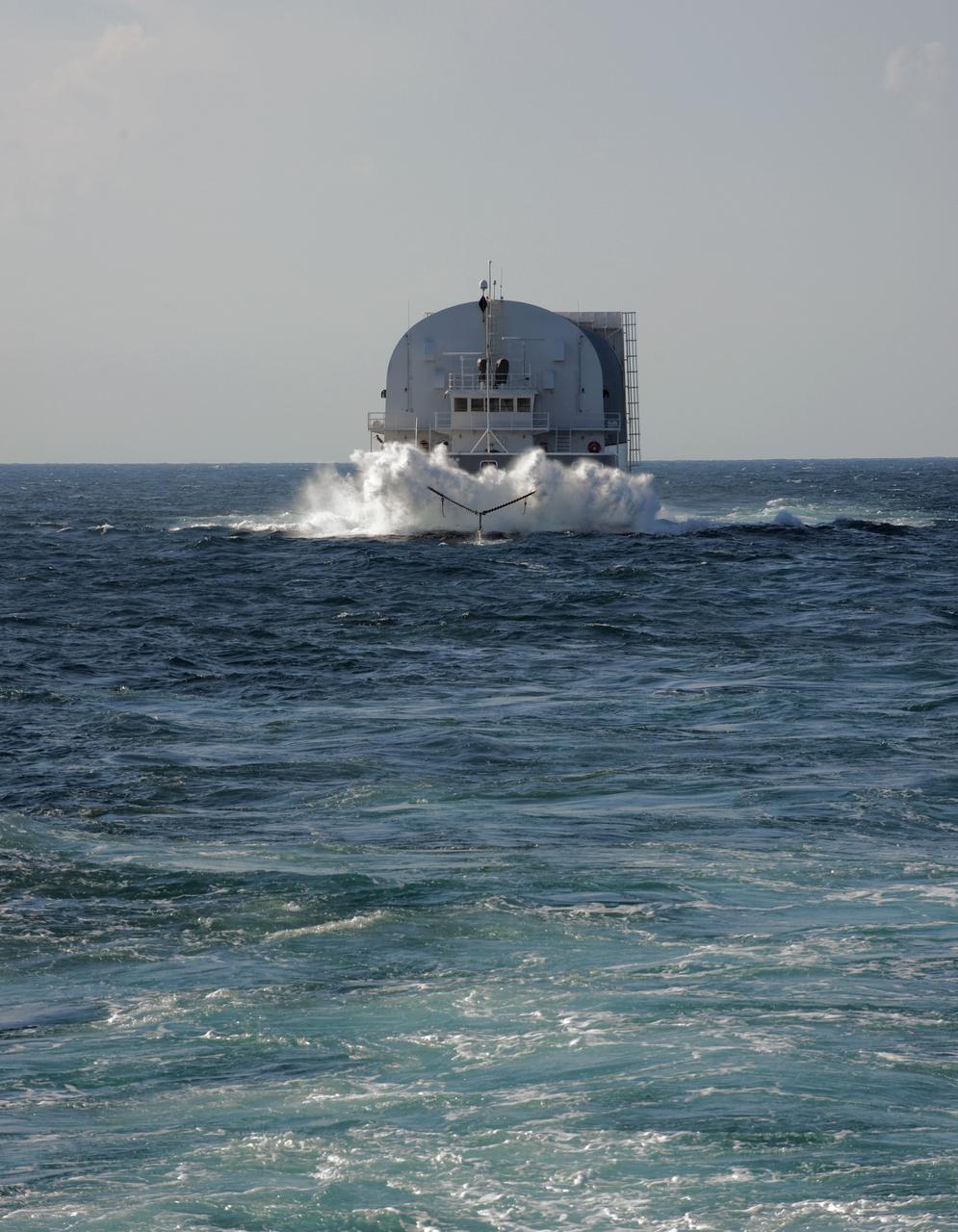

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This view from Freedom Star, one NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, shows the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, as it is transported to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
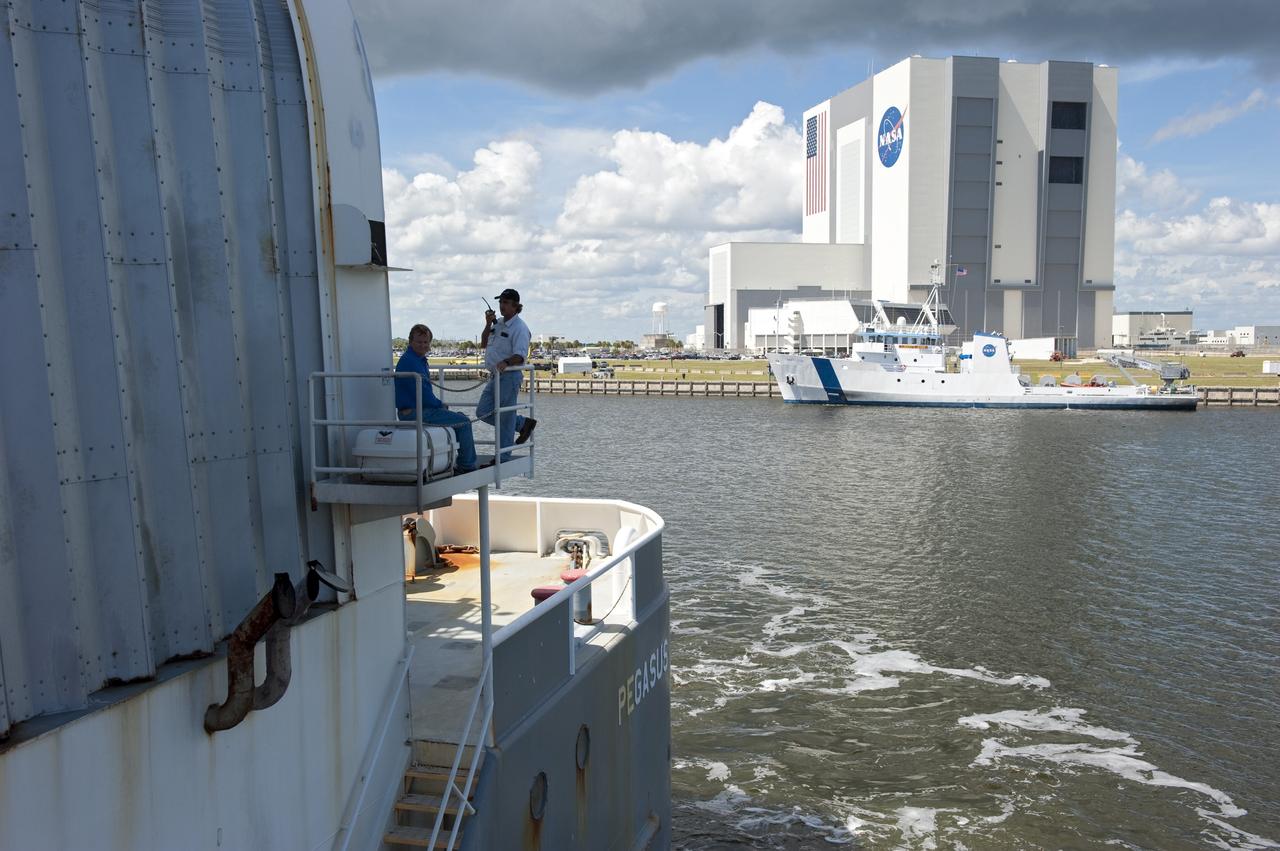

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Pegasus barge, carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, arrives at the Turn Basin of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank traveled 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Next, the tank will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
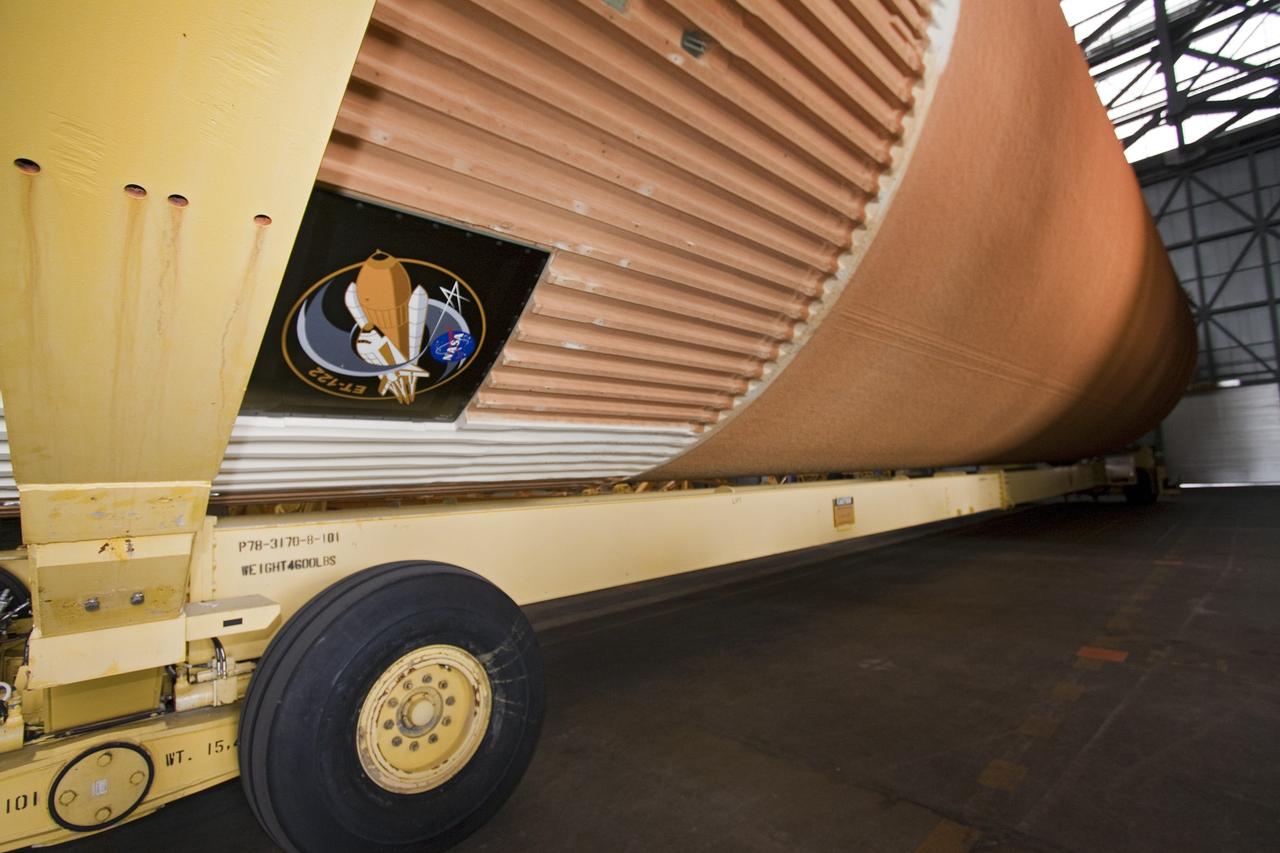

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- To commemorate the history of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, its intertank door is emblazoned with an ET-122 insignia. The tank is in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after traveling 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. It eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was completed in 2002, modified during Return to Flight operations in 2003 and 2004, damaged during Hurricane Katrina in 2005, and then restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees in 2008 at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
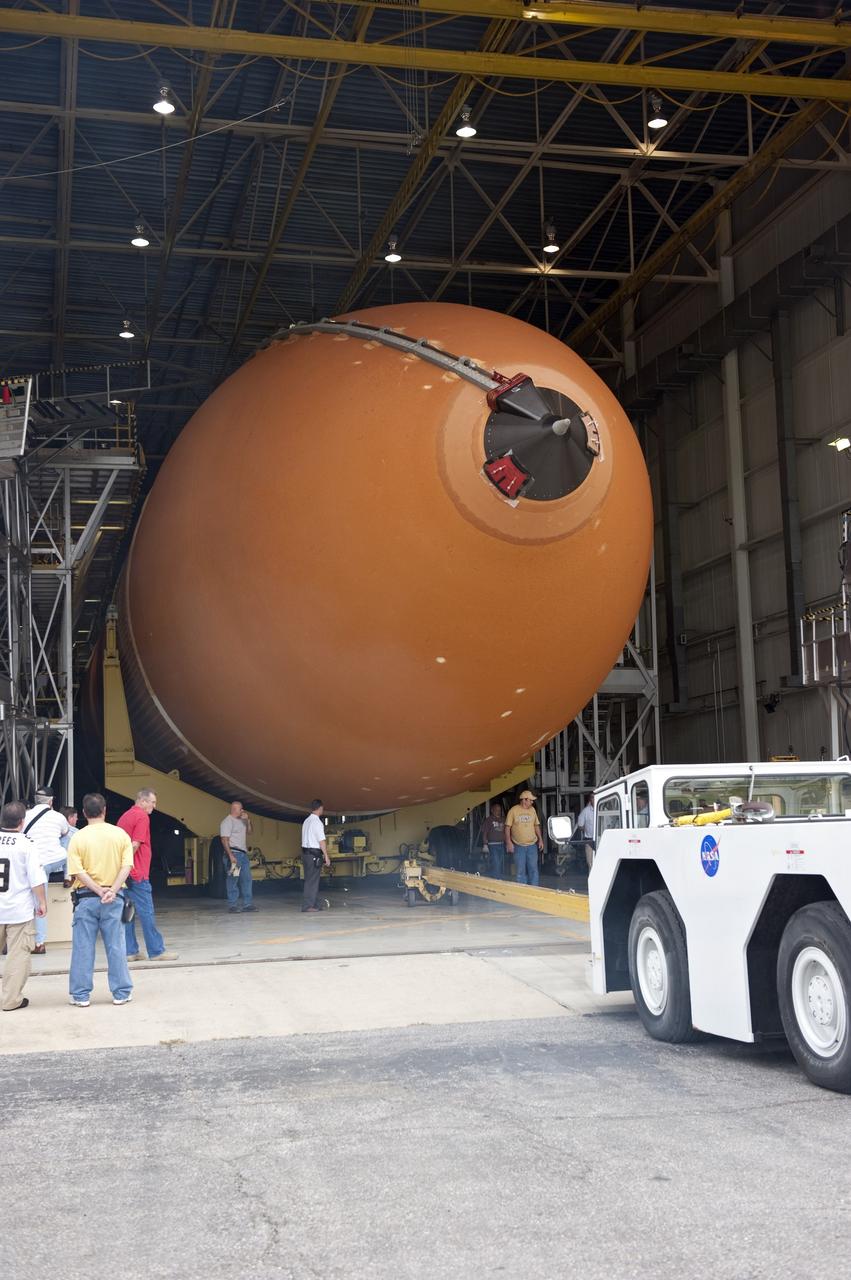

NEW ORLEANS -- Workers escort the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122, from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans for transportation to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea secured aboard the Pegasus Barge, offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
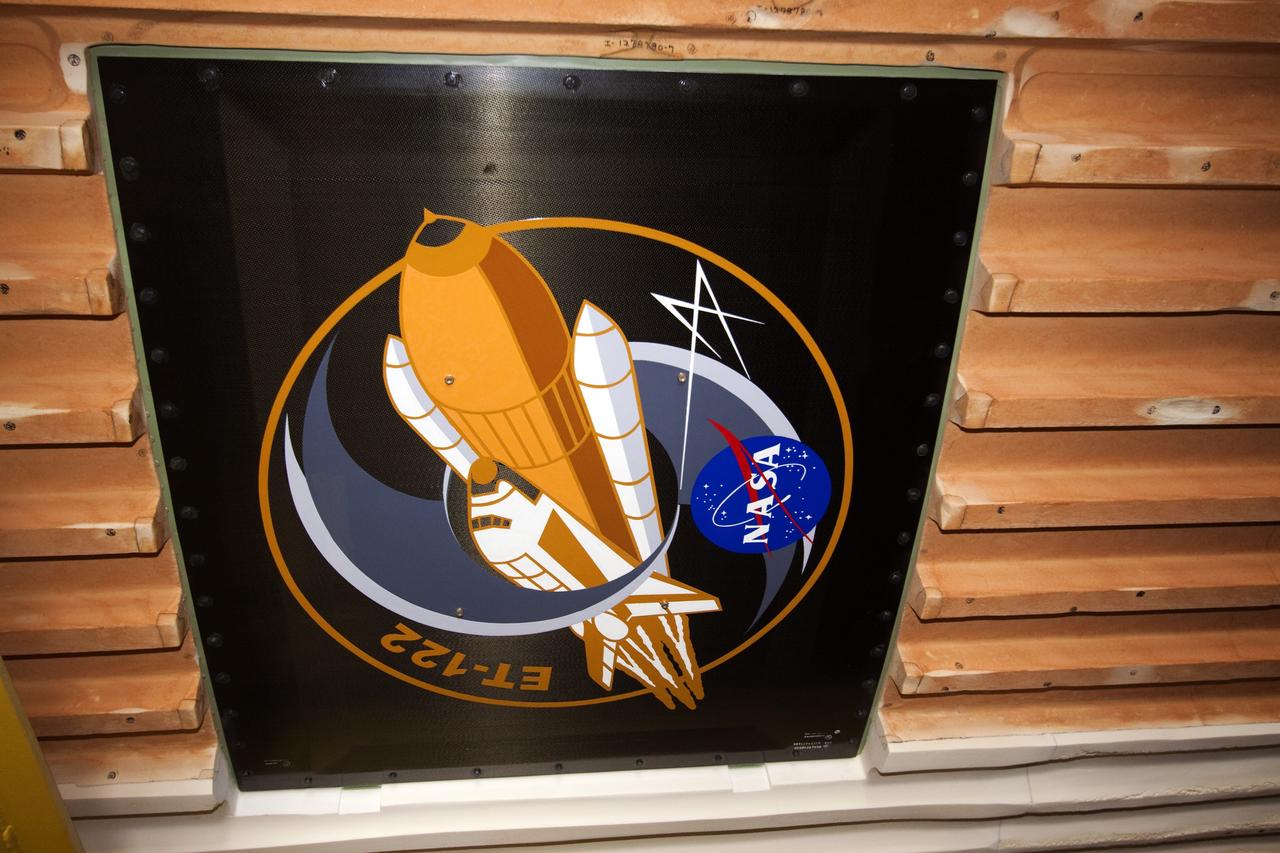

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- To commemorate the history of the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, its intertank door is emblazoned with an ET-122 insignia. The tank is in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after traveling 900 miles by sea from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans aboard the Pegasus Barge. It eventually will be attached to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. STS-134, targeted to launch in Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the shuttle program. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was completed in 2002, modified during Return to Flight operations in 2003 and 2004, damaged during Hurricane Katrina in 2005, and then restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees in 2008 at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
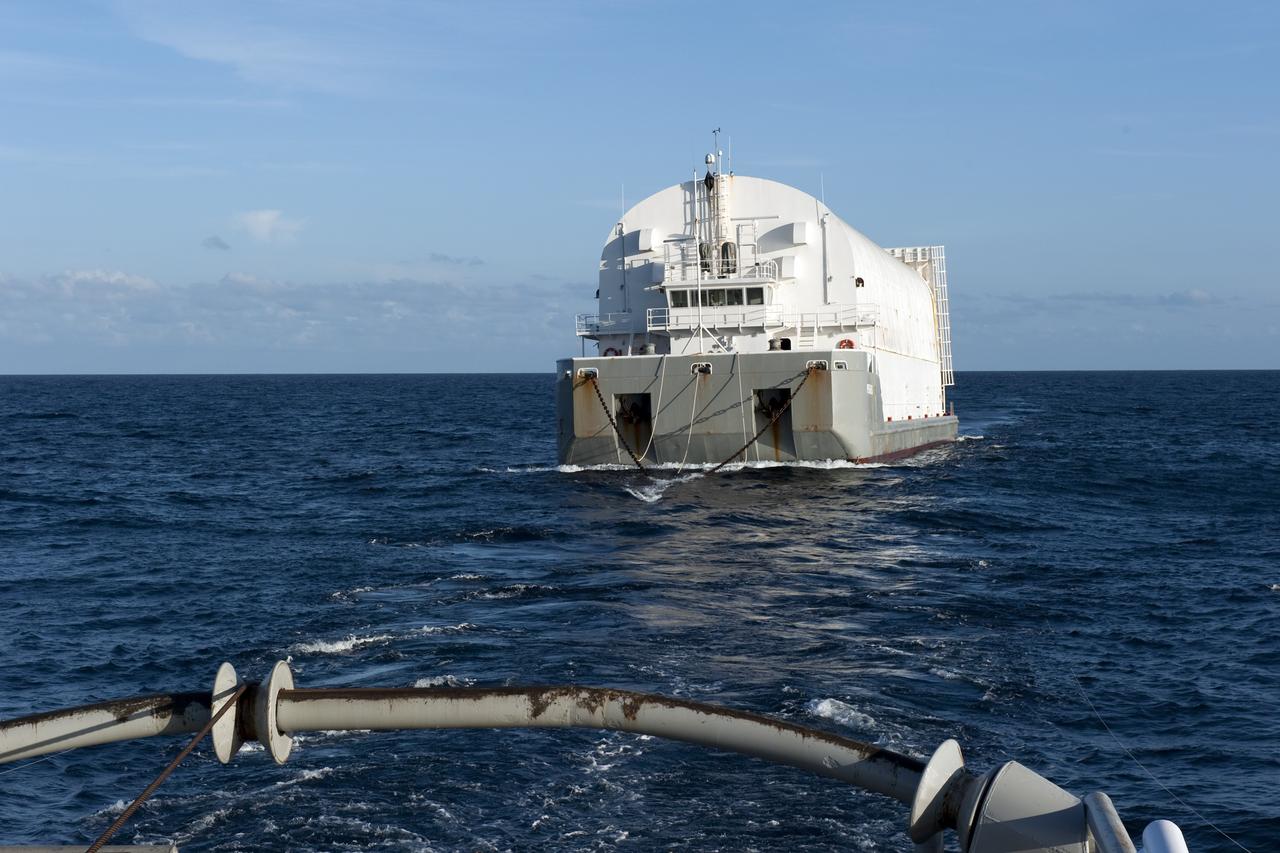

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This view from the stern of Freedom Star, one of NASA's solid rocket booster retrieval ships, shows the Pegasus Barge carrying the Space Shuttle Program's last external fuel tank, ET-122. The tank will travel 900 miles by sea to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before being offloaded and moved to Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be integrated to space shuttle Endeavour for the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The tank, which is the largest element of the space shuttle stack, was damaged during Hurricane Katrina in August 2005 and restored to flight configuration by Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company employees. STS-134, targeted to launch Feb. 2011, currently is scheduled to be the last mission in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett