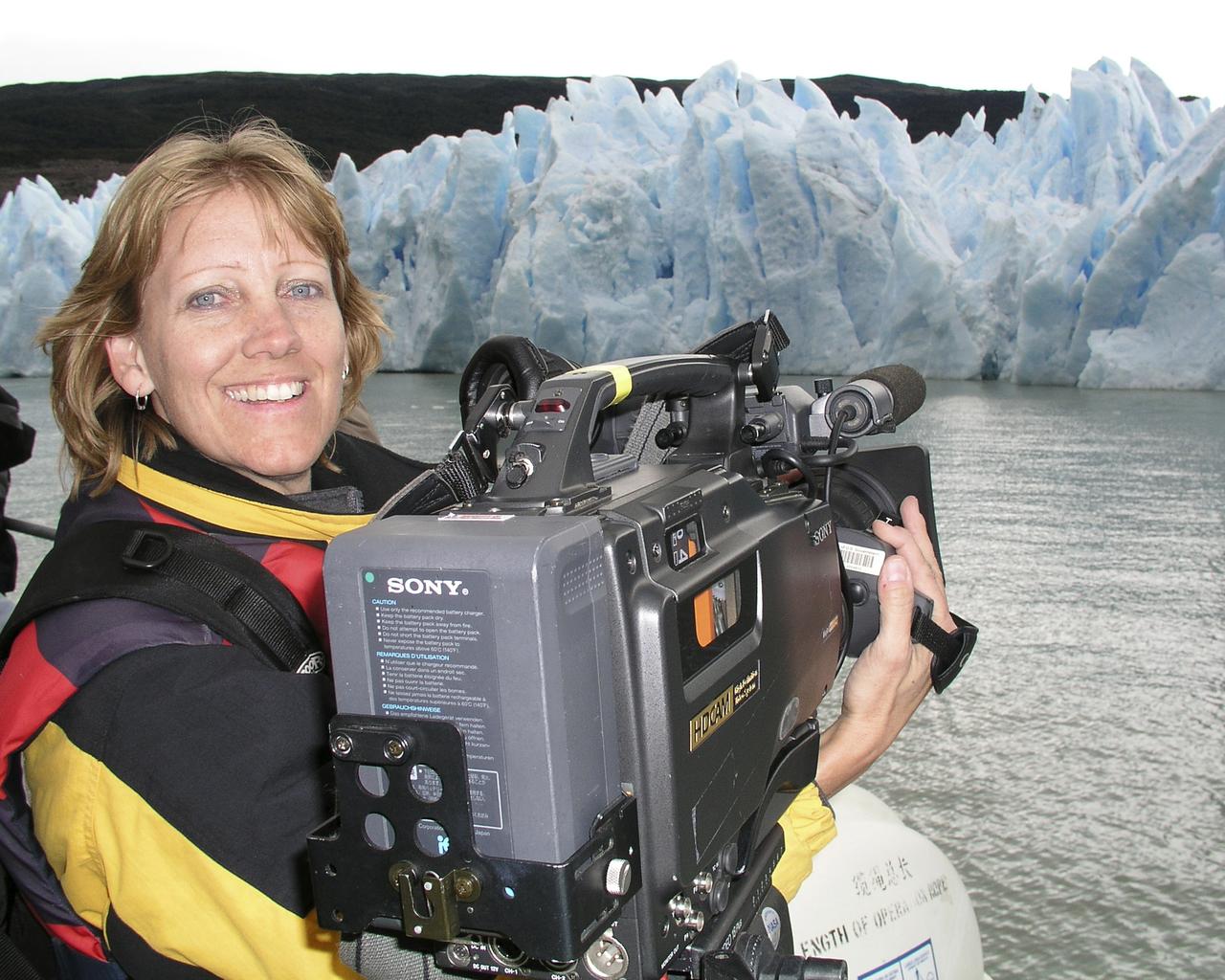
Lori Losey, an employee of Arcata Associates at Dryden, was honored with NASA's 2004 Videographer of the Year award for her work in two of the three categories in the NASA video competition, public affairs and documentation. In the public affairs category, Losey received a first-place citation for her footage of an Earth Science mission that was flown aboard NASA's DC-8 Flying Laboratory in South America last year. Her footage not only depicted the work of the scientists aboard the aircraft and on the ground, but she also obtained spectacular footage of flora and fauna in the mission's target area that helped communicate the environmental research goals of the project. Losey also took first place in the documentation category for her acquisition of technical videography of the X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle flight tests. The video, shot with a hand-held camera from the rear seat of a NASA F/A-18 mission support aircraft, demonstrated her capabilities in recording precise technical visual data in a very challenging airborne environment. The award was presented to Losey during a NASA reception at the National Association of Broadcasters convention in Las Vegas April 19. A three-judge panel evaluated entries for public affairs, documentation and production videography on professional excellence, technical quality, originality, creativity within restrictions of the project, and applicability to NASA and its mission. Entries consisted of a continuous video sequence or three views of the same subject for a maximum of three minutes duration. Linda Peters, Arcata Associates' Video Systems Supervisor at NASA Dryden, noted, "Lori is a talented videographer who has demonstrated extraordinary abilities with the many opportunities she has received in her career at NASA." Losey's award was the second major NASA video award won by members of the Dryden video team in two years. Steve Parcel took first place in the documentation category last year for his camera and editing
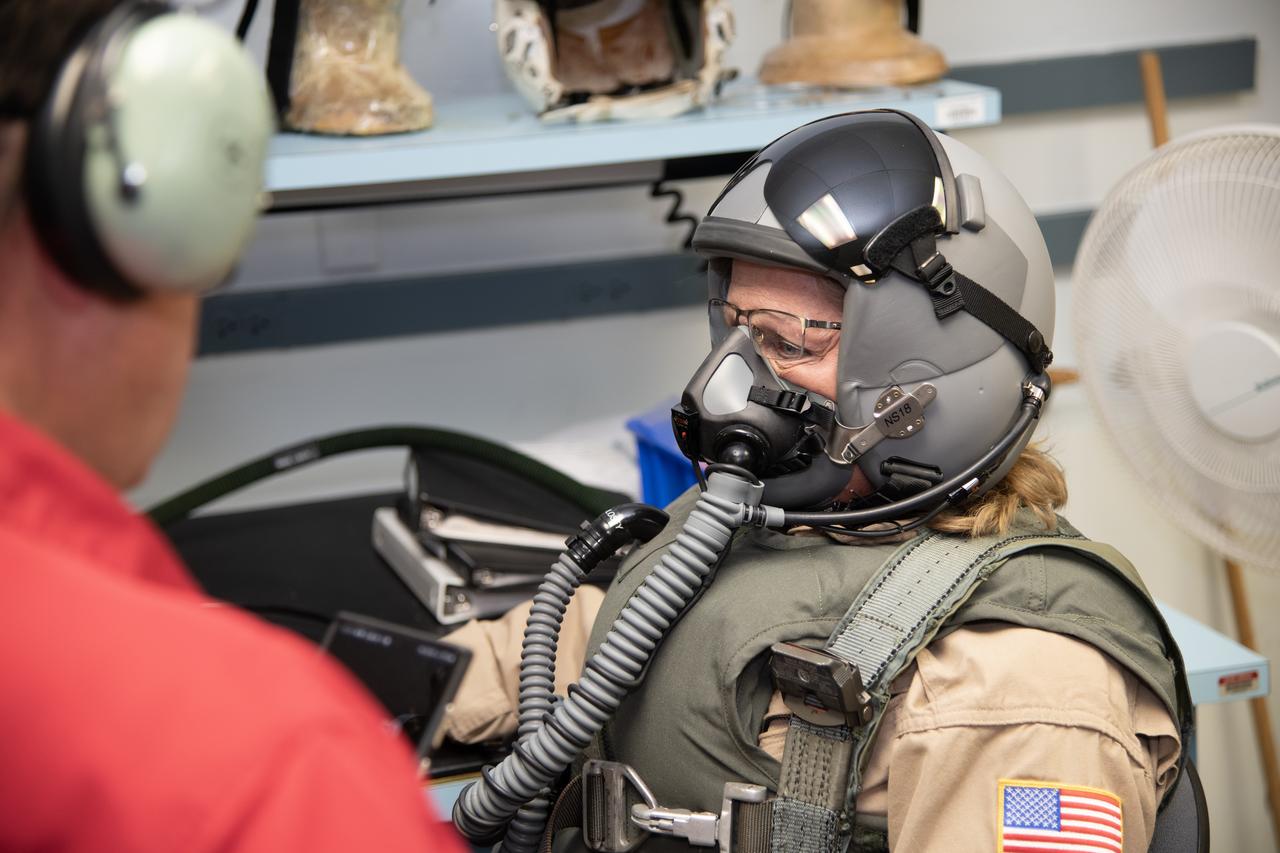

NASA Armstrong videographer Lori Losey undergoes pressure breathing training in San Antonio, Texas. NASA Armstrong aircrews are preparing for high altitude flight tests of the X-59.
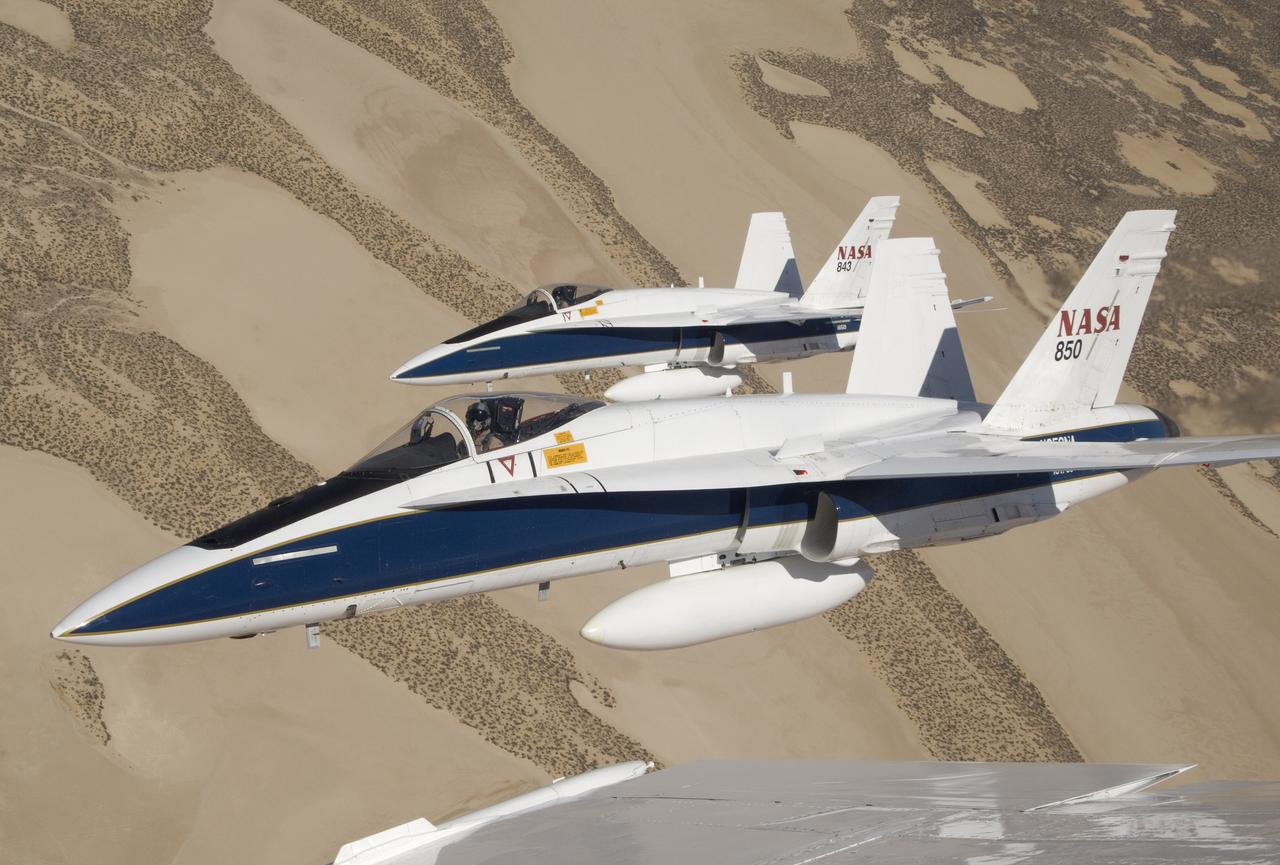

Two NASA Dryden F/A-18s flown by research pilots Frank Batteas and Nils Larson were captured by photographer Lori Losey from a third F/A-18 flown by Dick Ewers as they flew in tight formation over the desert at Edwards Air Force Base.
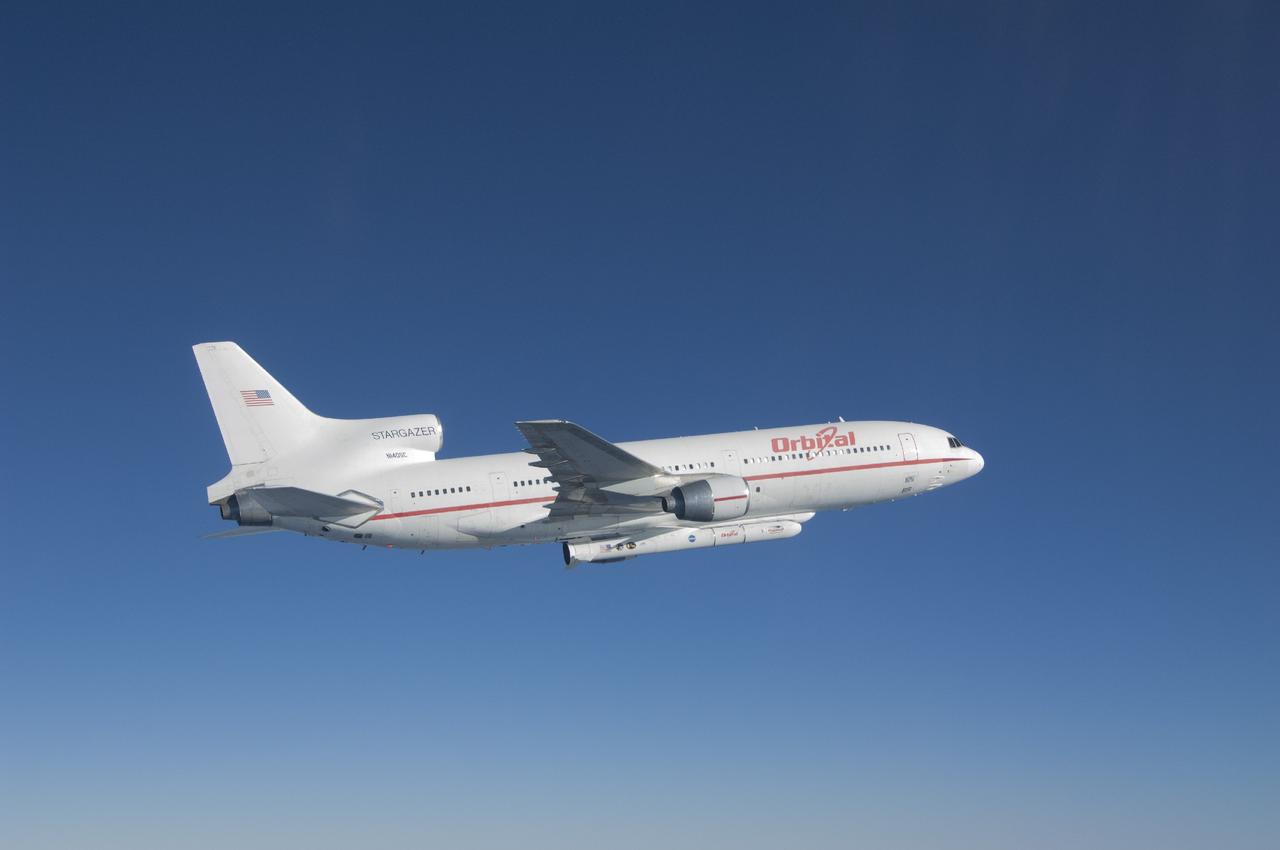

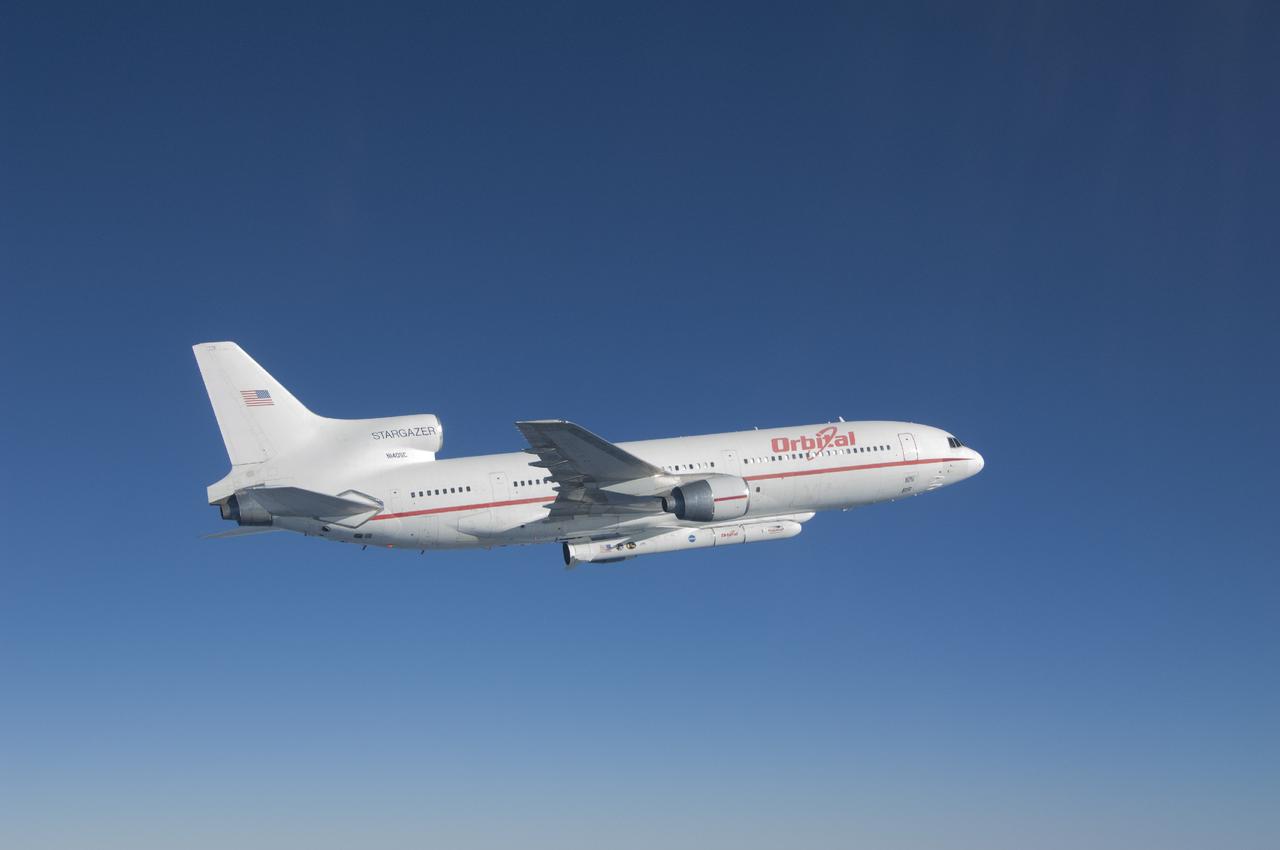
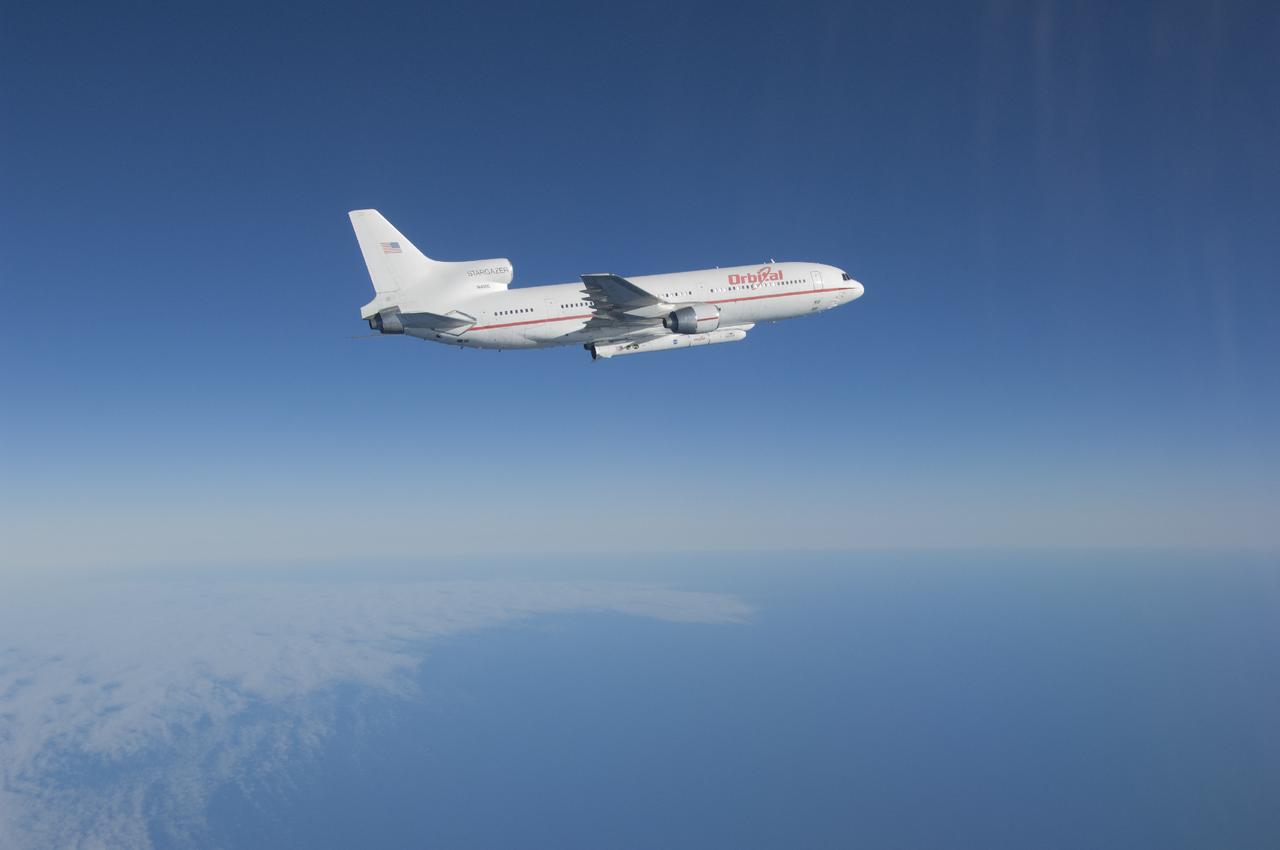
VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – An Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft flies over the Pacific Ocean off the California coast on a mission to launch NASA's IRIS spacecraft into low-Earth orbit. IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, was launched aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket released from the bottom of the L-1011.Photo credit: NASA/Lori Losey
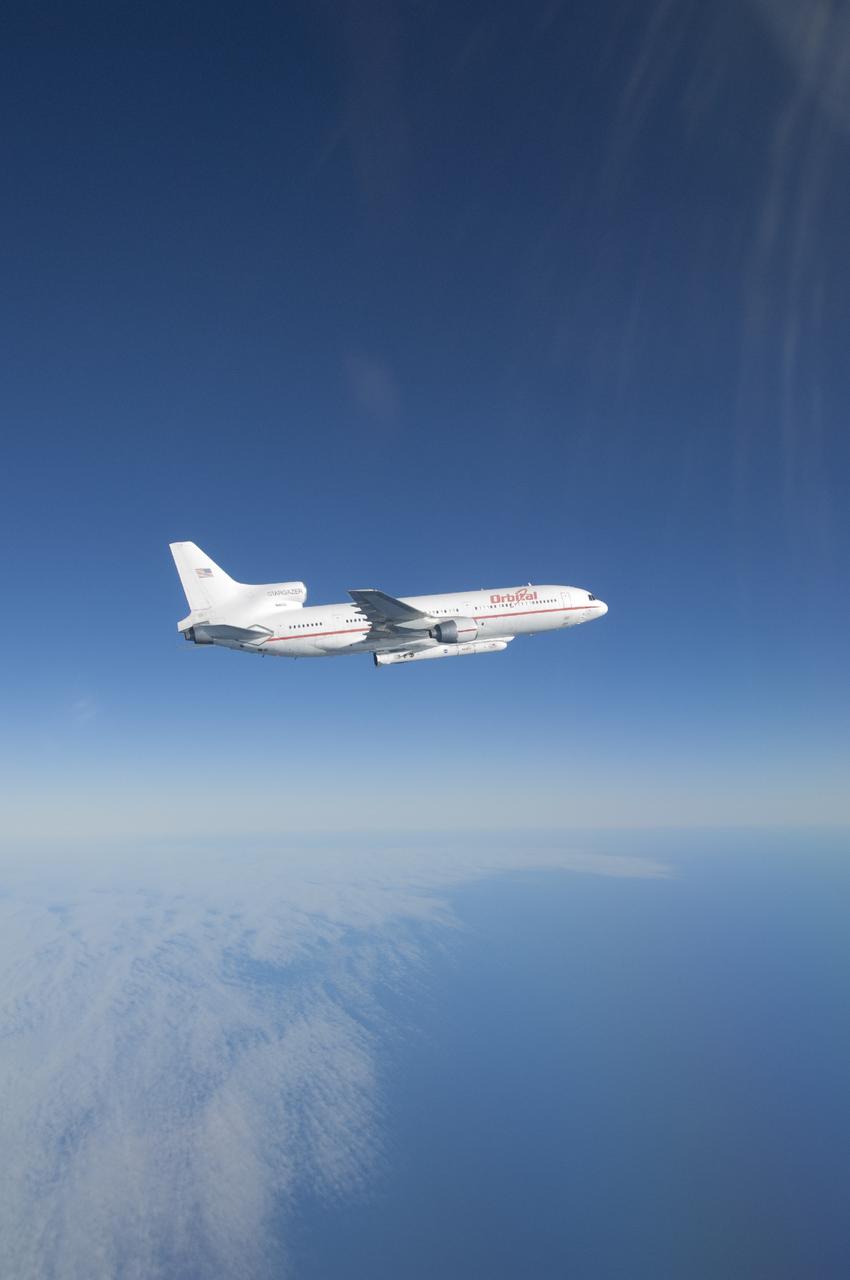

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – An Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft flies over the Pacific Ocean off the California coast on a mission to launch NASA's IRIS spacecraft into low-Earth orbit. IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, was launched aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket released from the bottom of the L-1011.Photo credit: NASA/Lori Losey
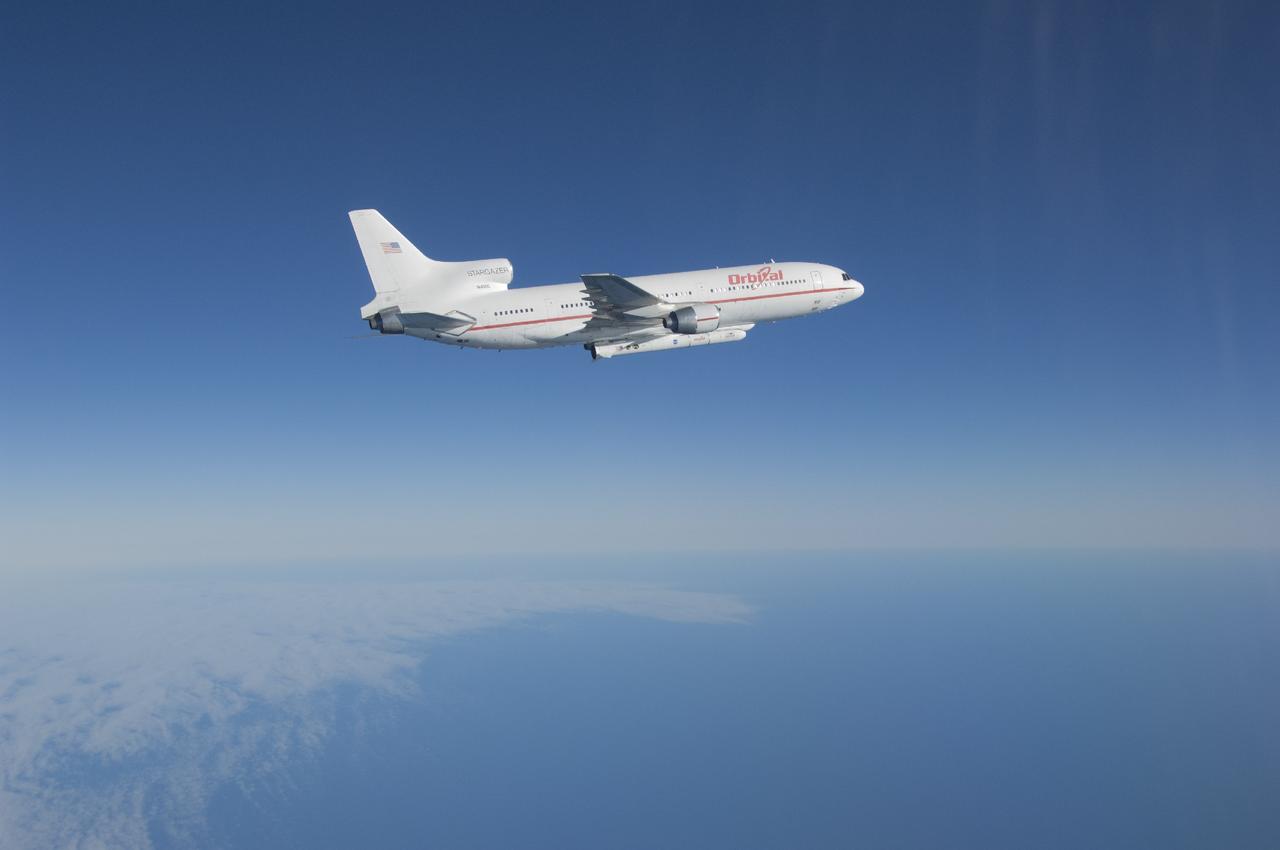

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – An Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft flies over the Pacific Ocean off the California coast on a mission to launch NASA's IRIS spacecraft into low-Earth orbit. IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, was launched aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket released from the bottom of the L-1011.Photo credit: NASA/Lori Losey

From left, pilot Craig Bomben, photographer Carla Thomas, pilot Frank Batteas, and videographer Lori Losey make up the flight crews for two F-18 high-performance jets to document a flight of NASA’s B-52B carrying a Pegasus booster rocket and the X-43A. A dry run, known as a captive carry mission, was conducted to monitor the research hardware in flight for any challenges. The January 2004 X-43A flight was based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.

IRIS launch from Orbital Sciences Corporation Pegasus XL rocket
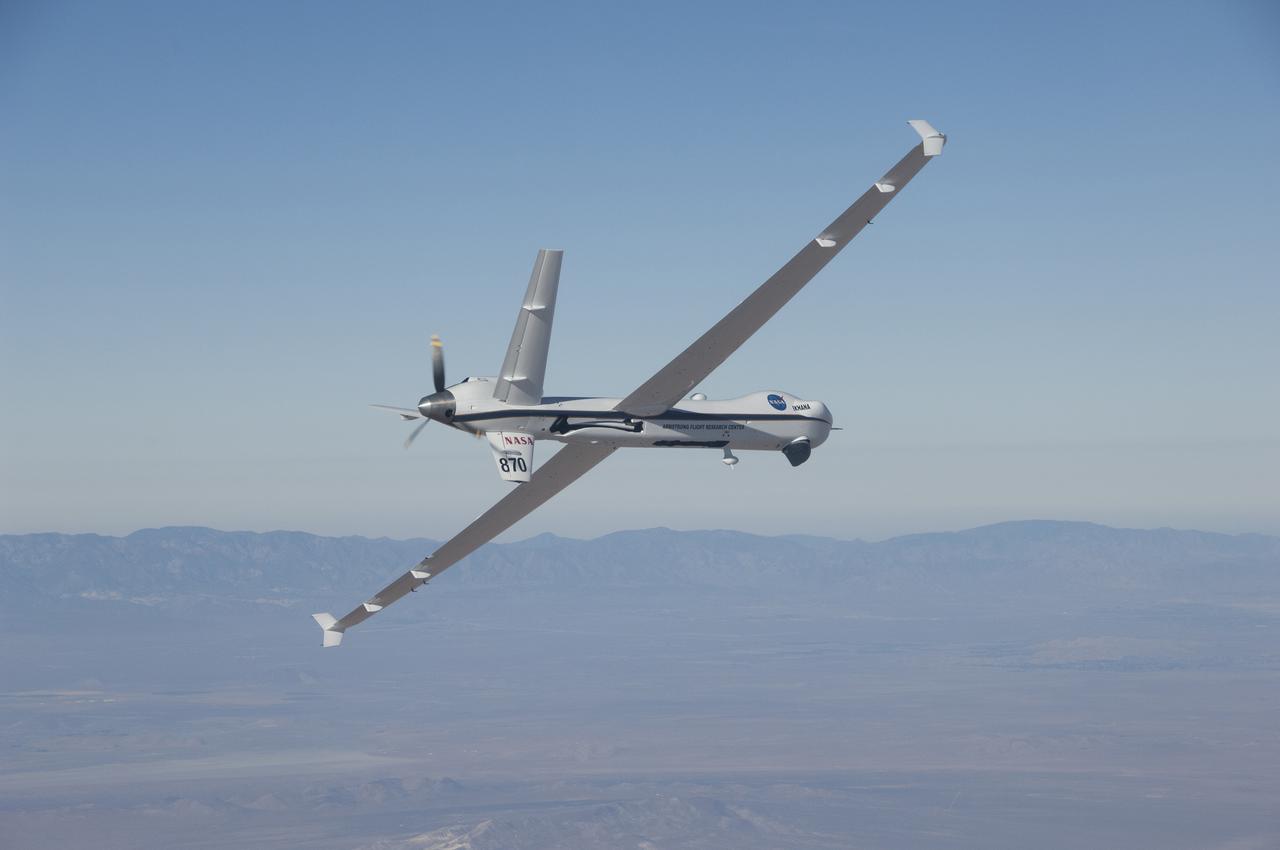

The Ikhana aircraft is flying a TAMDAR Edge probe that could significantly improve weather models and forecasts.
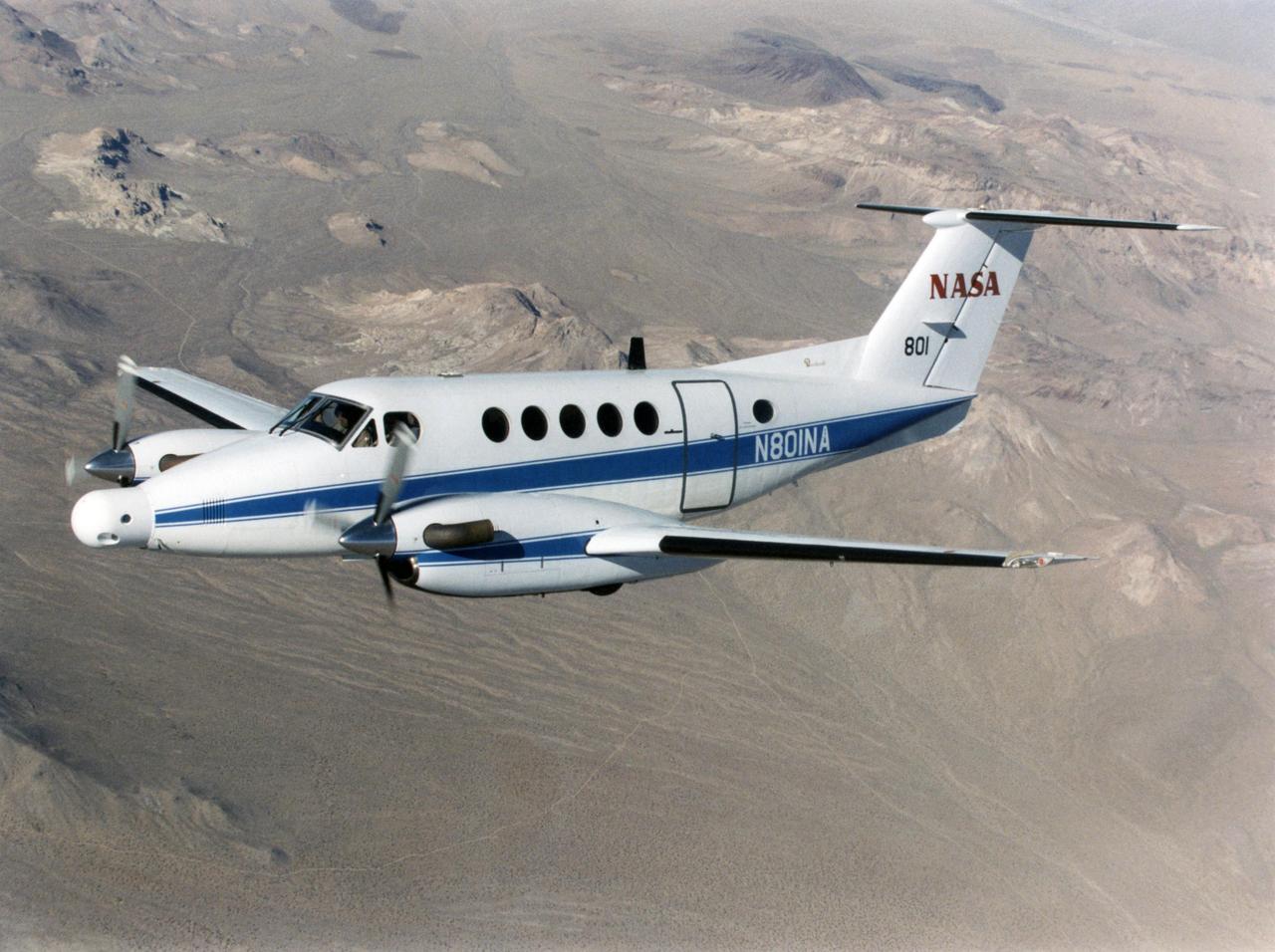

A NASA King Air successfully tested the Advanced Data Acquisition and Telemetry System during a recent series of three research flights.

IRIS launch from Orbital Sciences Corporation Pegasus XL rocket
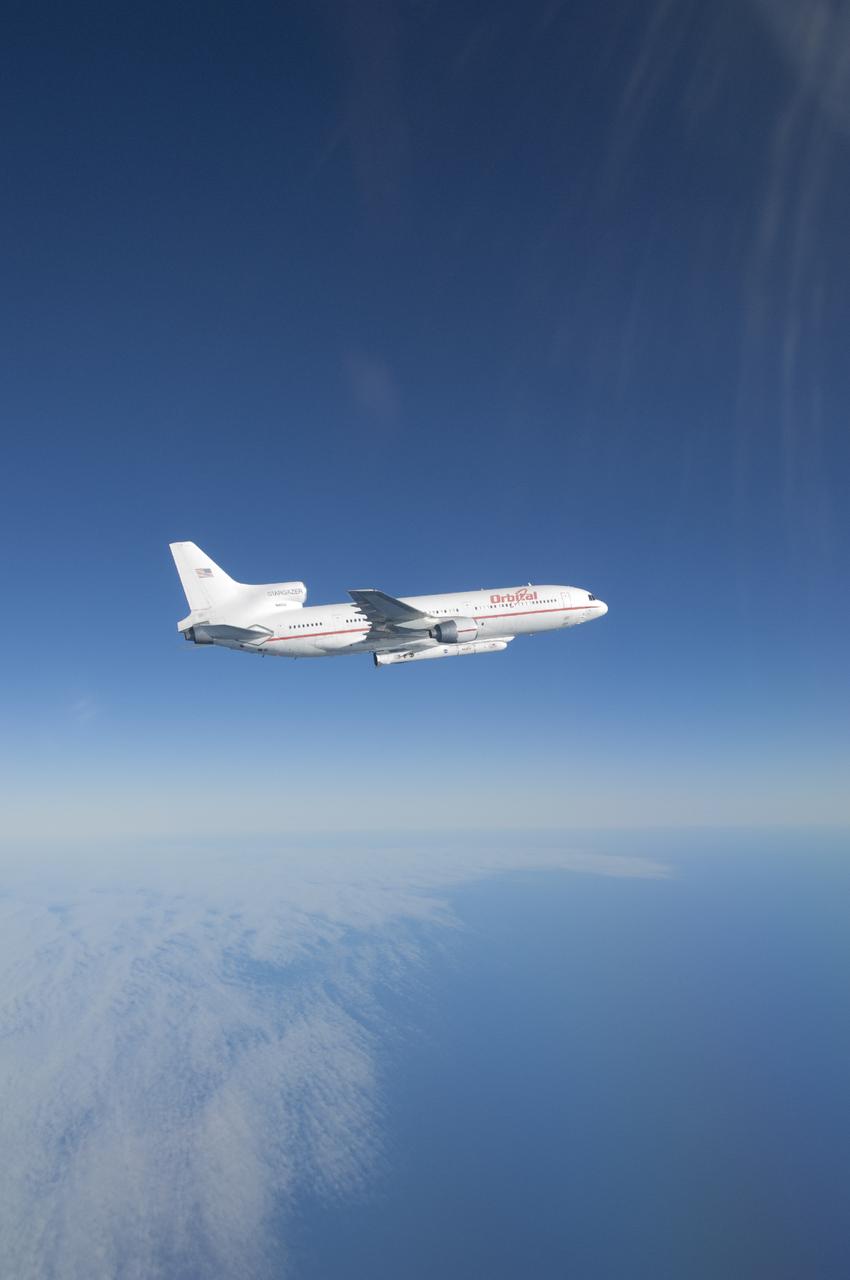

IRIS launch from Orbital Sciences Corporation Pegasus XL rocket

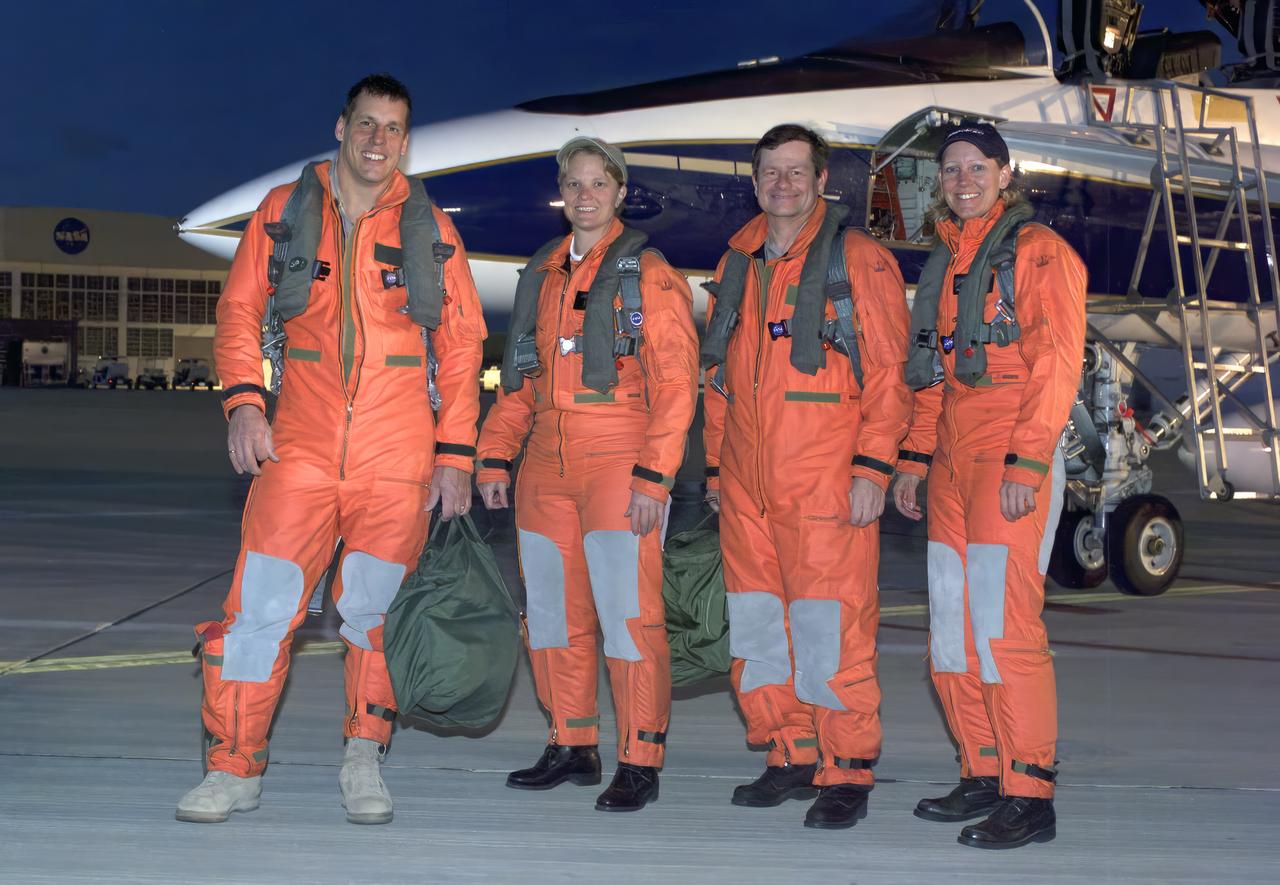
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Videographer Lori Losey, back seat, and pilot Jim Less board an F-18 aircraft at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The F-18 will be the "chase plane" for the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft transporting the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to orbit. Release of the rocket from under the wing of the L-1011 is scheduled for 10:27 p.m. EDT. IRIS will open a new window of discovery using spectrometry and imaging to trace the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona. The spacecraft will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. This interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and its upper atmosphere, is where most of its ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. NASA's Launch Services Program at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is managing the countdown and launch. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Videographer Lori Losey boards an F-18 aircraft at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The F-18 "chase plane" will accompany the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft as it transports the Pegasus XL rocket carrying NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory over the Pacific Ocean. Release of the rocket from under the wing of the L-1011 is scheduled for 10:27 p.m. EDT. IRIS will open a new window of discovery using spectrometry and imaging to trace the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona. The spacecraft will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. This interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and its upper atmosphere, is where most of its ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. NASA's Launch Services Program at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is managing the countdown and launch. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
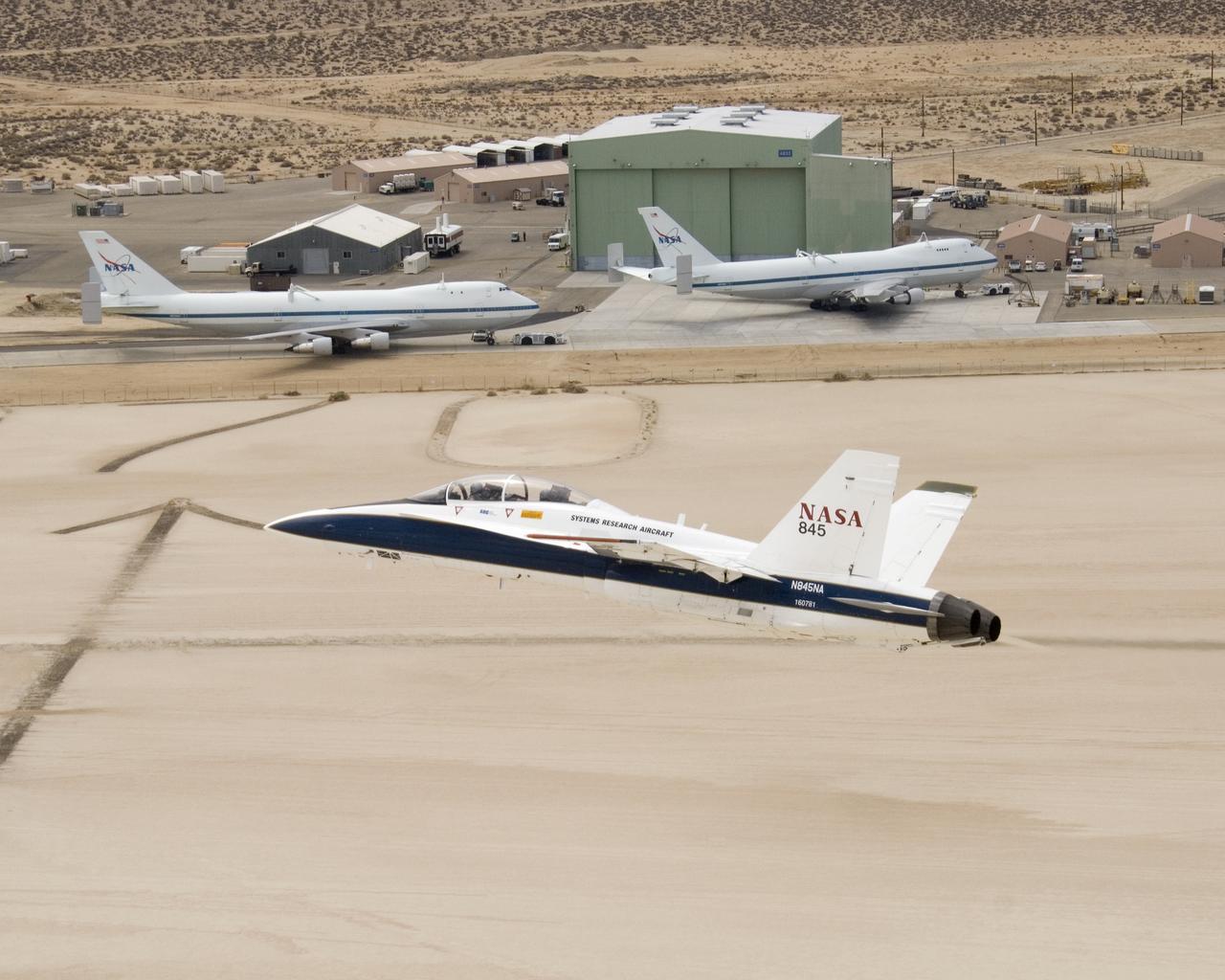

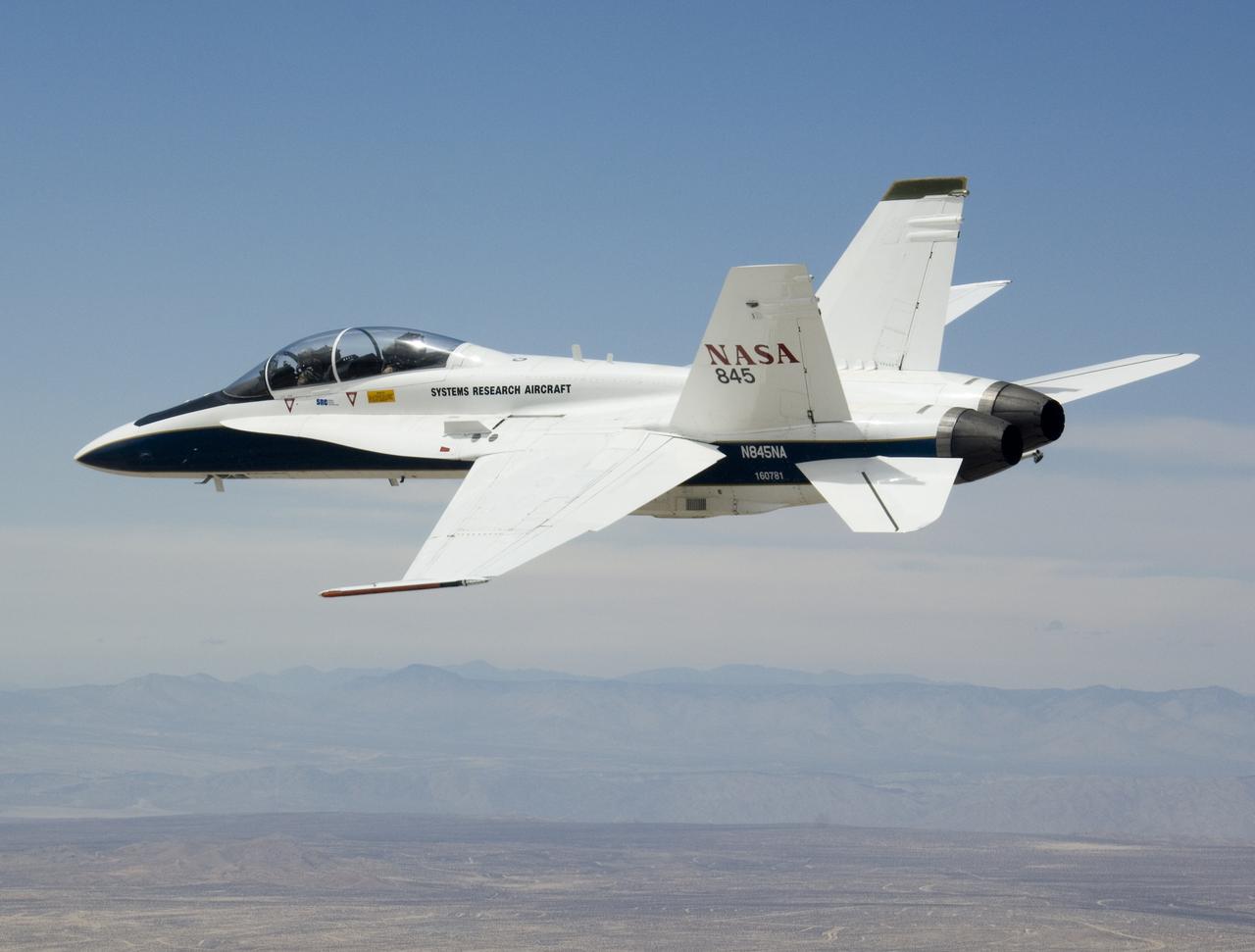
NASA's two Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft form the backdrop as pilot Dick Ewers banks NASA F/A-18 #845 low over Rogers Dry Lake to end a research flight.
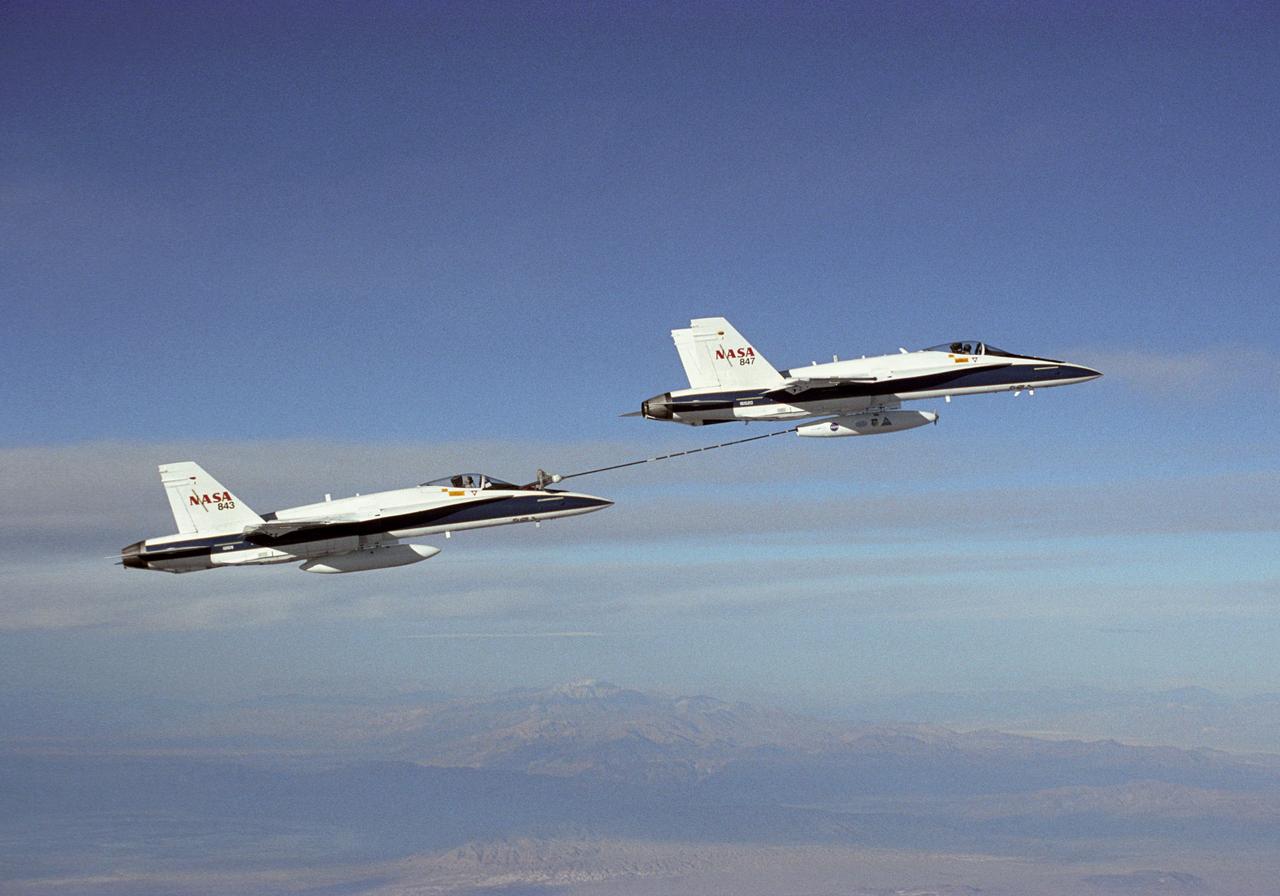

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft (No. 843) flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.

ER-2 tail number 809, is one of two Airborne Science ER-2s used as science platforms by Dryden. The aircraft are platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They are also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation. The ER-2s are capable of carrying a maximum payload of 2,600 pounds of experiments in a nose bay, the main equipment bay behind the cockpit, two wing-mounted superpods and small underbody and trailing edges. Most ER-2 missions last about six hours with ranges of about 2,200 nautical miles. The aircraft typically fly at altitudes above 65,000 feet. On November 19, 1998, the ER-2 set a world record for medium weight aircraft reaching an altitude of 68,700 feet. The aircraft is 63 feet long, with a wingspan of 104 feet. The top of the vertical tail is 16 feet above ground when the aircraft is on the bicycle-type landing gear. Cruising speeds are 410 knots, or 467 miles per hour, at altitude. A single General Electric F118 turbofan engine rated at 17,000 pounds thrust powers the ER-2.

New range safety and range user system antennas for the ECANS project can be seen just behind and to the left of the cockpit on NASA's NF-15B research aircraft.

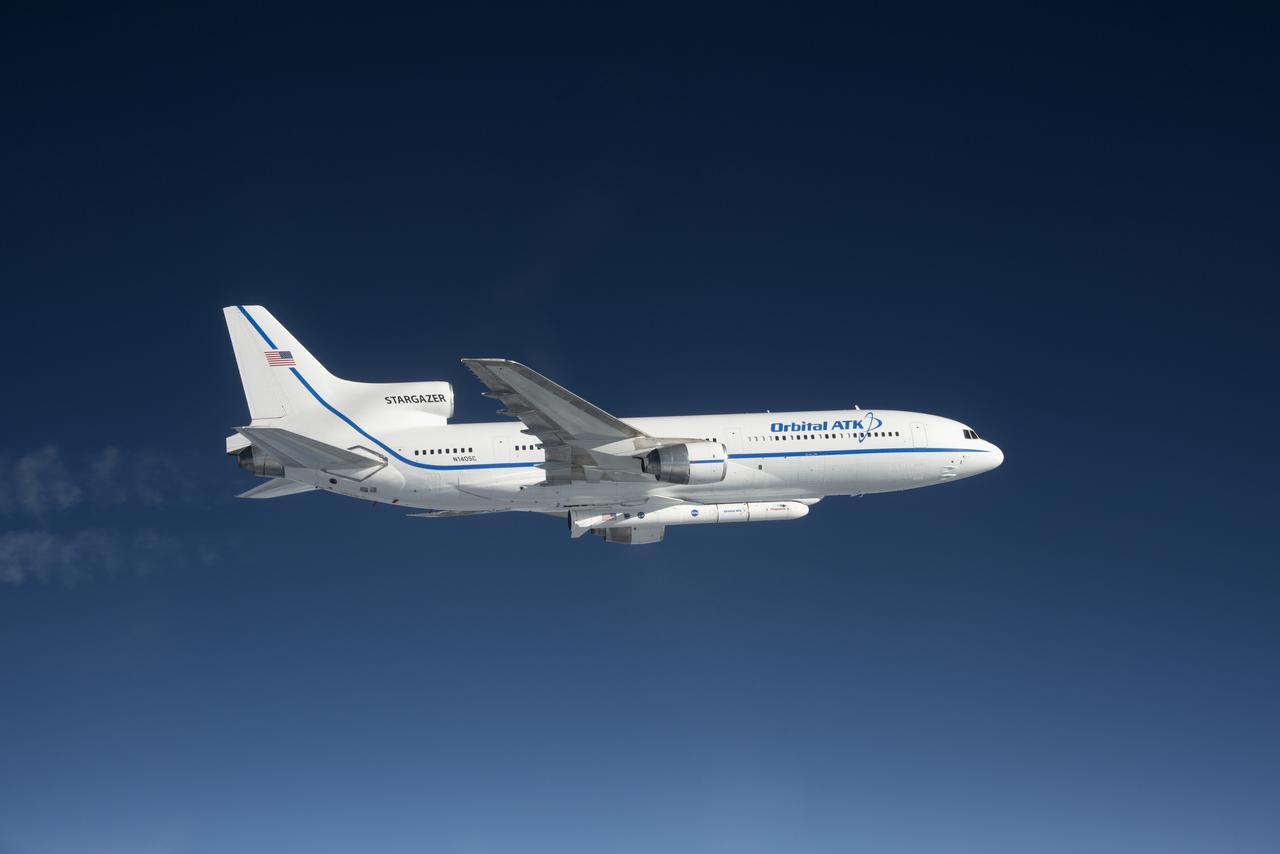
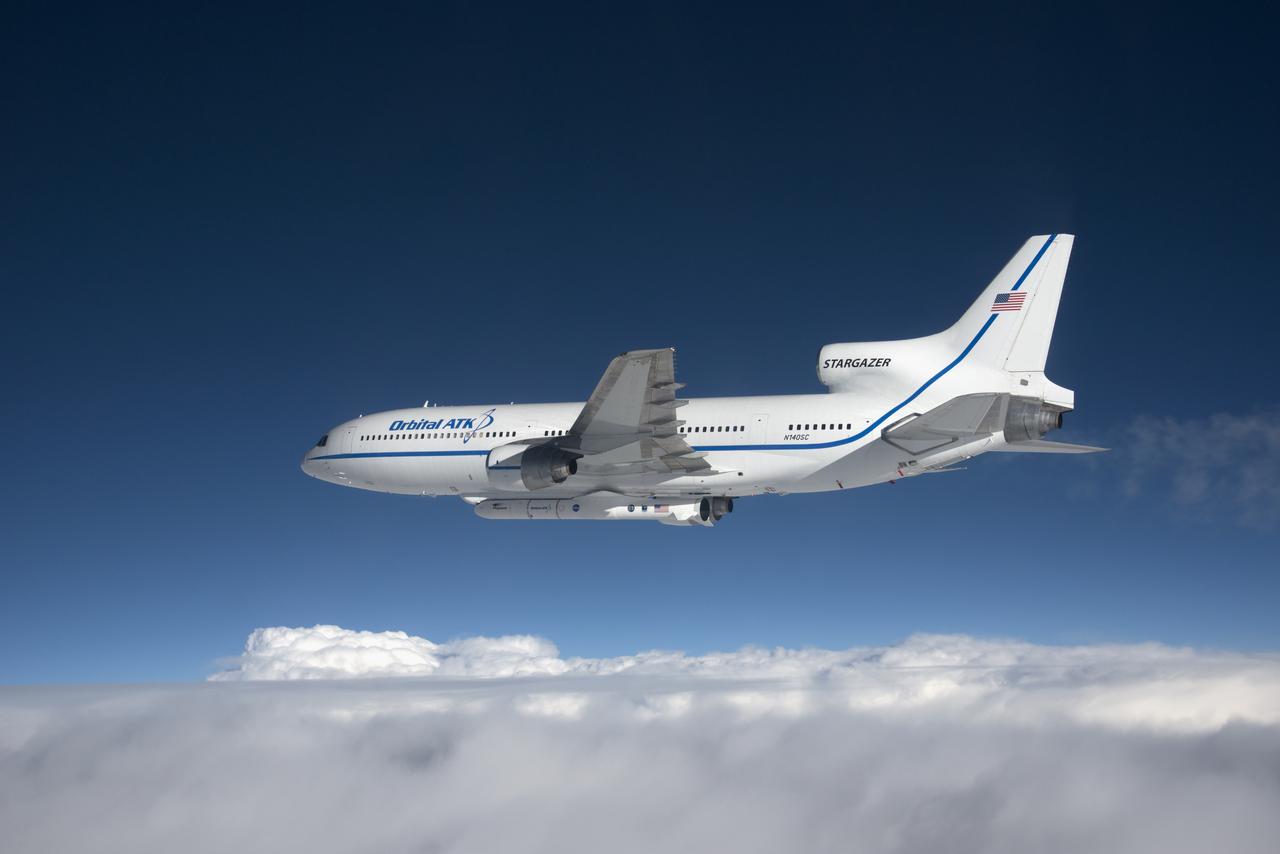
The Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket carrying NASA's Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft is released and the first stage ignites at 8:37 a.m. EST. The rocket was released from the Orbital ATK L-1011 Stargazer aircraft flying over the Atlantic Ocean offshore from Daytona Beach, Florida following takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. This image was taken from a NASA F-18 chase plane provided by Armstrong Flight Research Center in California. The CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes.
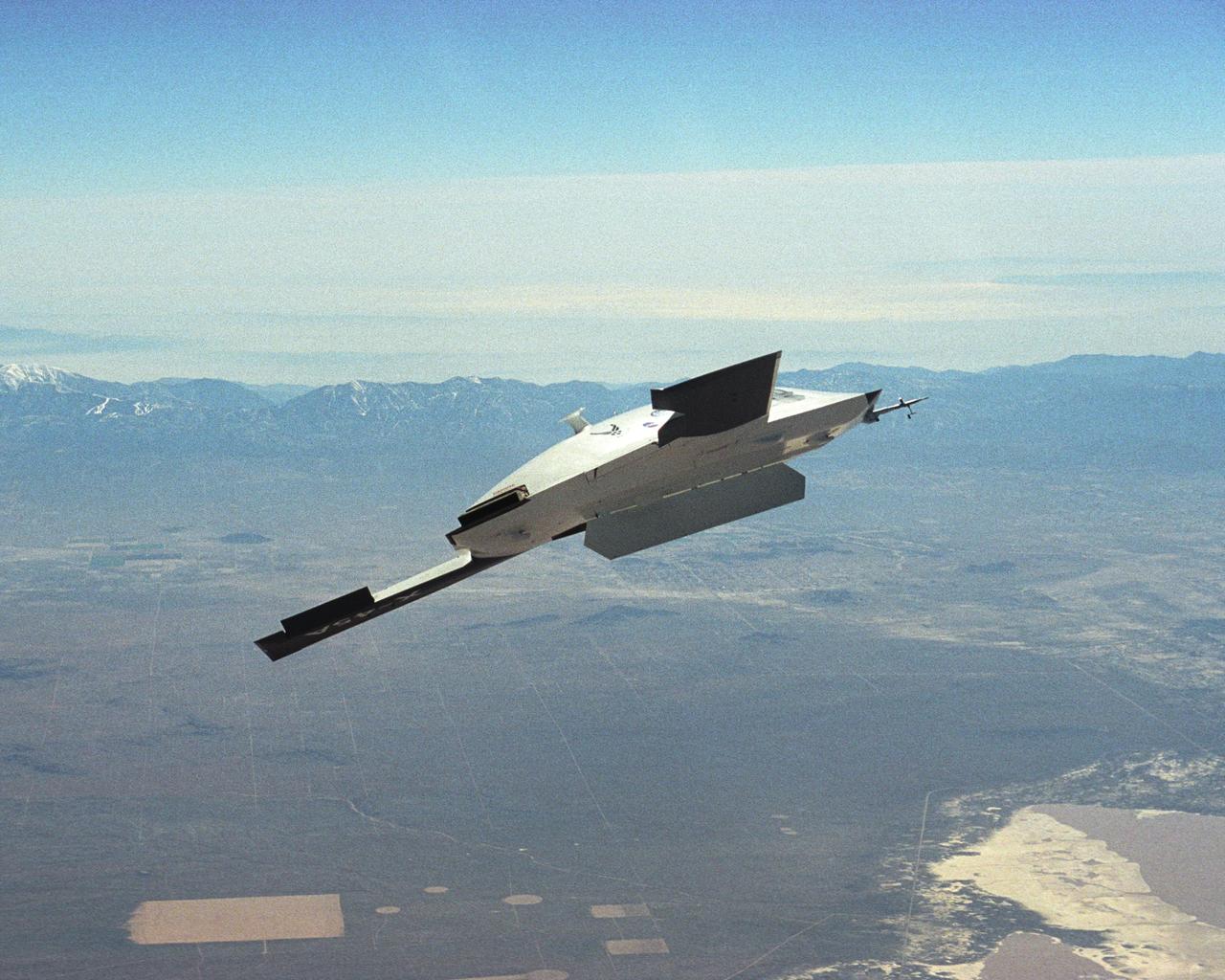

The DARPA/U.S. Air Force X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) system demonstration program completed the first phase of demonstrations, known as Block I, on Feb. 28, 2003. The final Block I activities included two flights at Dryden, during which safe operation of the weapons bay door was verified at 35,000 feet and speeds of Mach 0.75, the maximum planned altitude and speed for the two X-45A demonstrator vehicles.
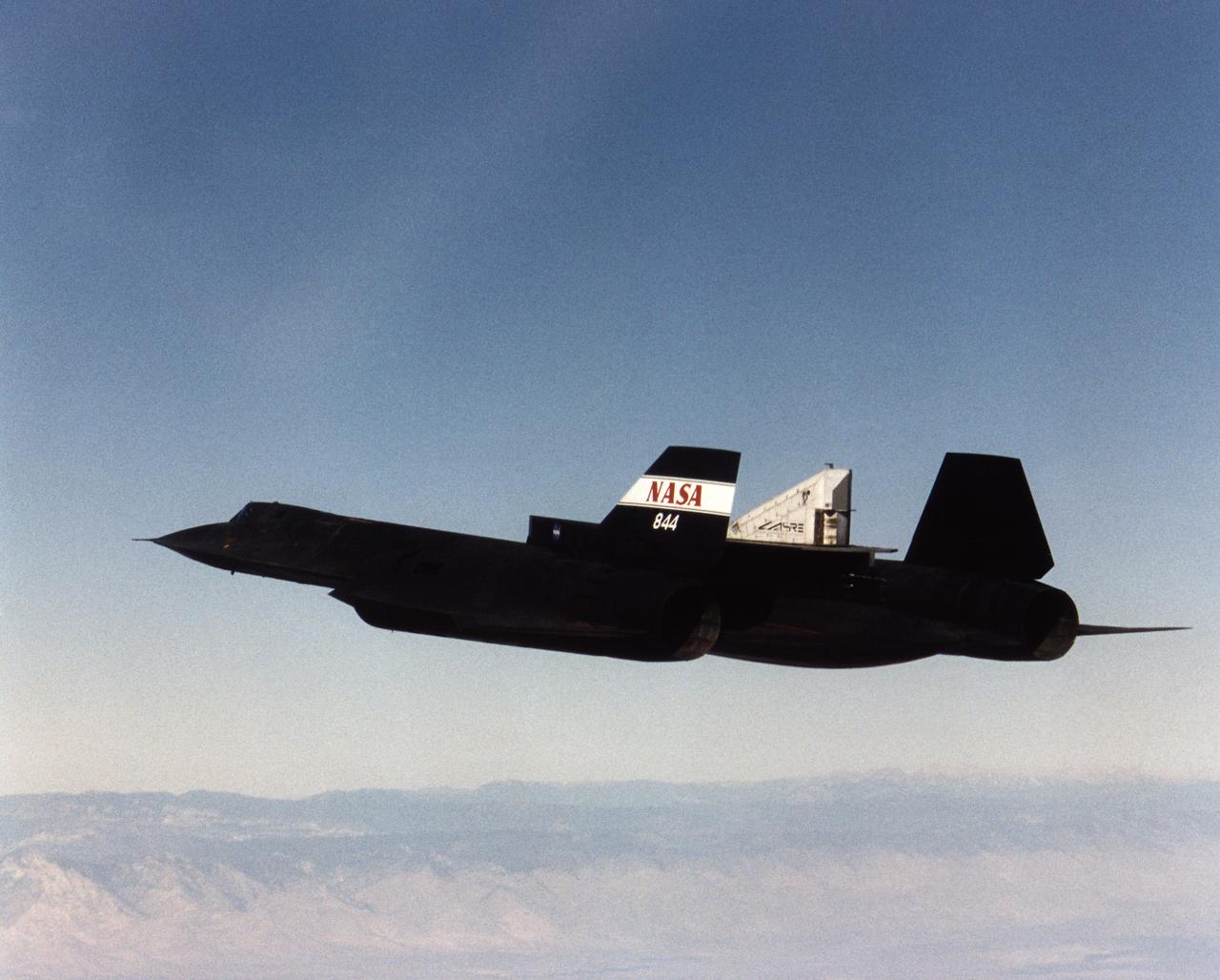

A NASA SR-71 successfully completed its first flight 31 October 1997 as part of the NASA/Rocketdyne/Lockheed Martin Linear Aerospike SR-71 Experiment (LASRE) at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The SR-71 took off at 8:31 a.m. PST. The aircraft flew for one hour and fifty minutes, reaching a maximum speed of Mach 1.2 before landing at Edwards at 10:21 a.m. PST, successfully validating the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The goal of the first flight was to evaluate the aerodynamic characteristics and the handling of the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The engine was not fired during the flight.

The Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket carrying NASA's Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft is released and the first stage ignites at 8:37 a.m. EST. The rocket was released from the Orbital ATK L-1011 Stargazer aircraft flying over the Atlantic Ocean offshore from Daytona Beach, Florida following takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. This image was taken from a NASA F-18 chase plane provided by Armstrong Flight Research Center in California. The CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes.

NASA's Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) Boeing 747SP flies over NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center after a ferry flight from Waco, Texas. NASA's Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, or SOFIA, arrived at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. on May 31, 2007. The heavily modified Boeing 747SP was ferried to Dryden from Waco, Texas, where L-3 Communications Integrated Systems installed a German-built 2.5-meter infrared telescope and made other major modifications over the past several years. SOFIA is scheduled to undergo installation and integration of mission systems and a multi-phase flight test program at Dryden over the next three years that is expected to lead to a full operational capability to conduct astronomy missions in about 2010. During its expected 20-year lifetime, SOFIA will be capable of "Great Observatory" class astronomical science, providing astronomers with access to the visible, infrared and sub-millimeter spectrum with optimized performance in the mid-infrared to sub-millimeter range.

The Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket carrying NASA's Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft is released and the first stage ignites at 8:37 a.m. EST. The rocket was released from the Orbital ATK L-1011 Stargazer aircraft flying over the Atlantic Ocean offshore from Daytona Beach, Florida following takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. This image was taken from a NASA F-18 chase plane provided by Armstrong Flight Research Center in California. The CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes.

The UAVSAR underbelly pod is in clear view as NASA's Gulfstream-III research aircraft banks away over Edwards AFB during aerodynamic clearance flights.

The effect of the underbelly UAVSAR pod on the aerodynamics of NASA's Gulfstream-III research aircraft was evaluated during several check flights in early 2007.

NASA's F/A-18B #845 was captured by the photographer as it returned from its final flight in the Autonomous Airborne Refueling Demonstration research project.

The jagged ridges of Southern California's Tehachapi Mountains form the backdrop to NASA's brightly-colored NF-15B testbed aircraft during a research mission.
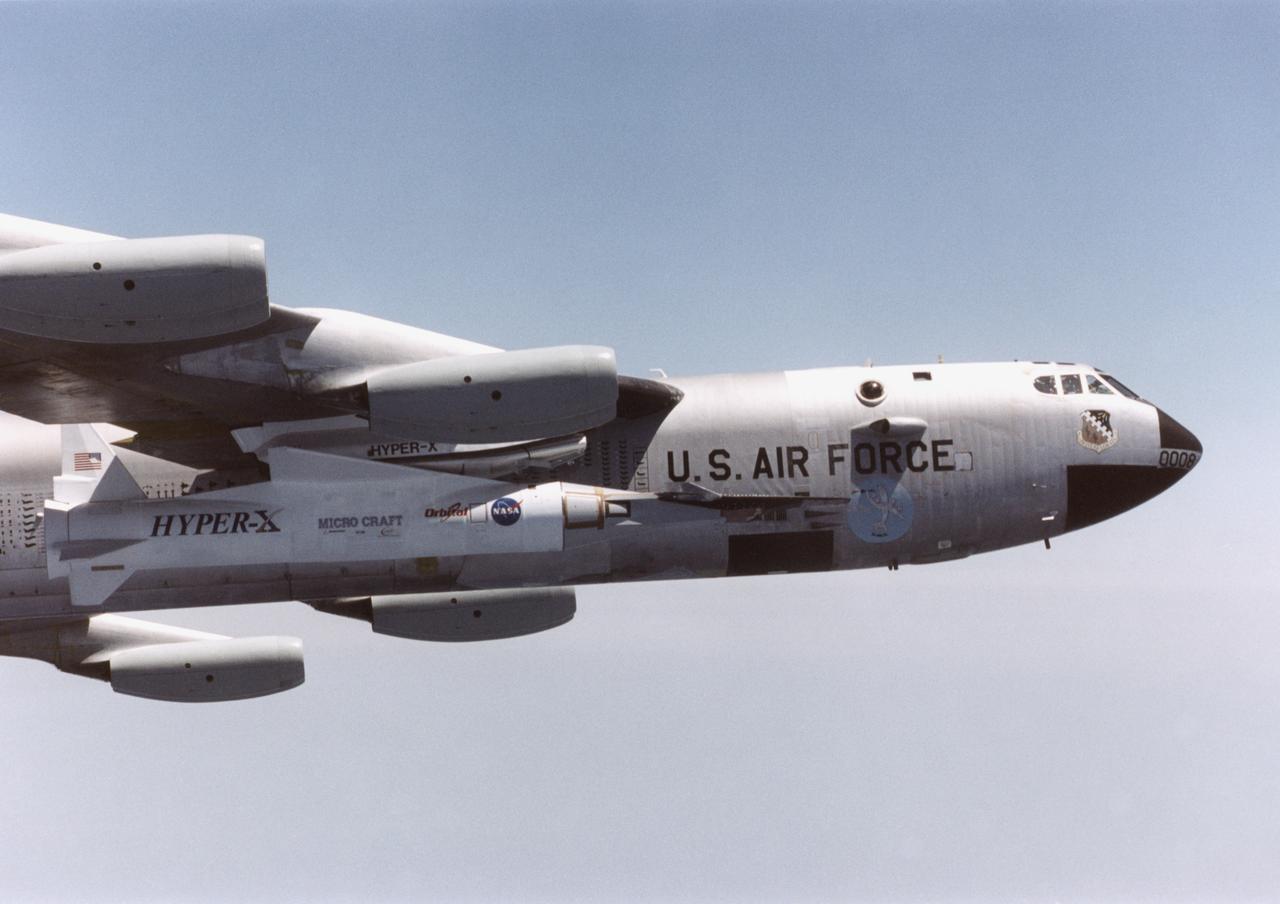

The NASA X-43A hypersonic research vehicle and its Pegasus booster rocket, mounted beneath the wing of their B-52 mothership, had a successful first captive-carry flight on April 28, 2001, Basically a dress rehearsal for a subsequent free flight, the captive-carry flight kept the X-43A-and-Pegasus combination attached to the B-52's wing pylon throughout the almost two-hour mission from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif., over the Pacific Missile Test Range, and back to Dryden.
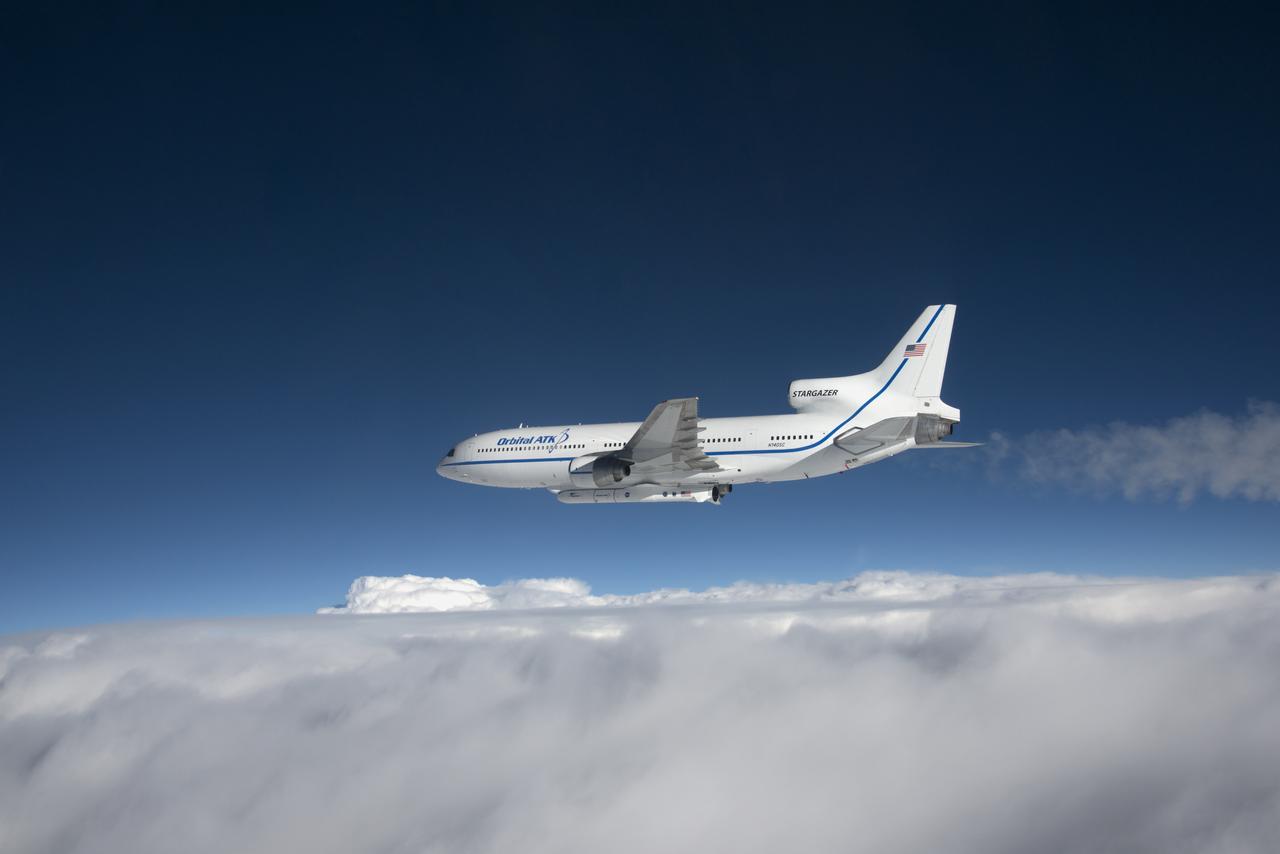

Photographed from the F-18 pathfinder aircraft, the Orbital ATK L-1011 Stargazer aircraft is seen flying over the Atlantic Ocean offshore from Daytona Beach, Florida. Attached beneath the aircraft is the Pegasus XL rocket with eight Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft. The CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a crucial role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes. NOTE: The Dec. 12, 2016 launch attempt was postponed due to a hydraulic pump aboard the Orbital ATK L-1011 aircraft which is required to release the latches holding Pegasus in place, is not receiving power.
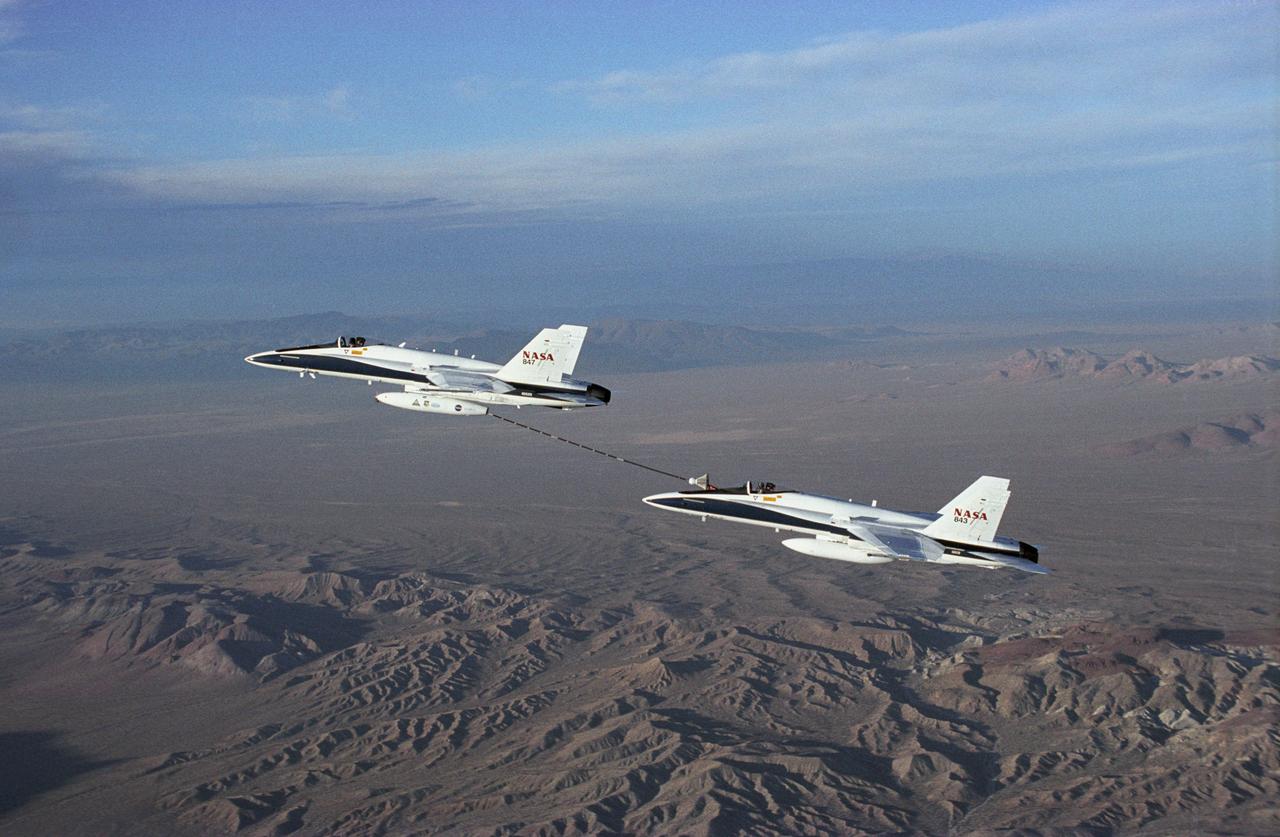

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft (No. 843) flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.
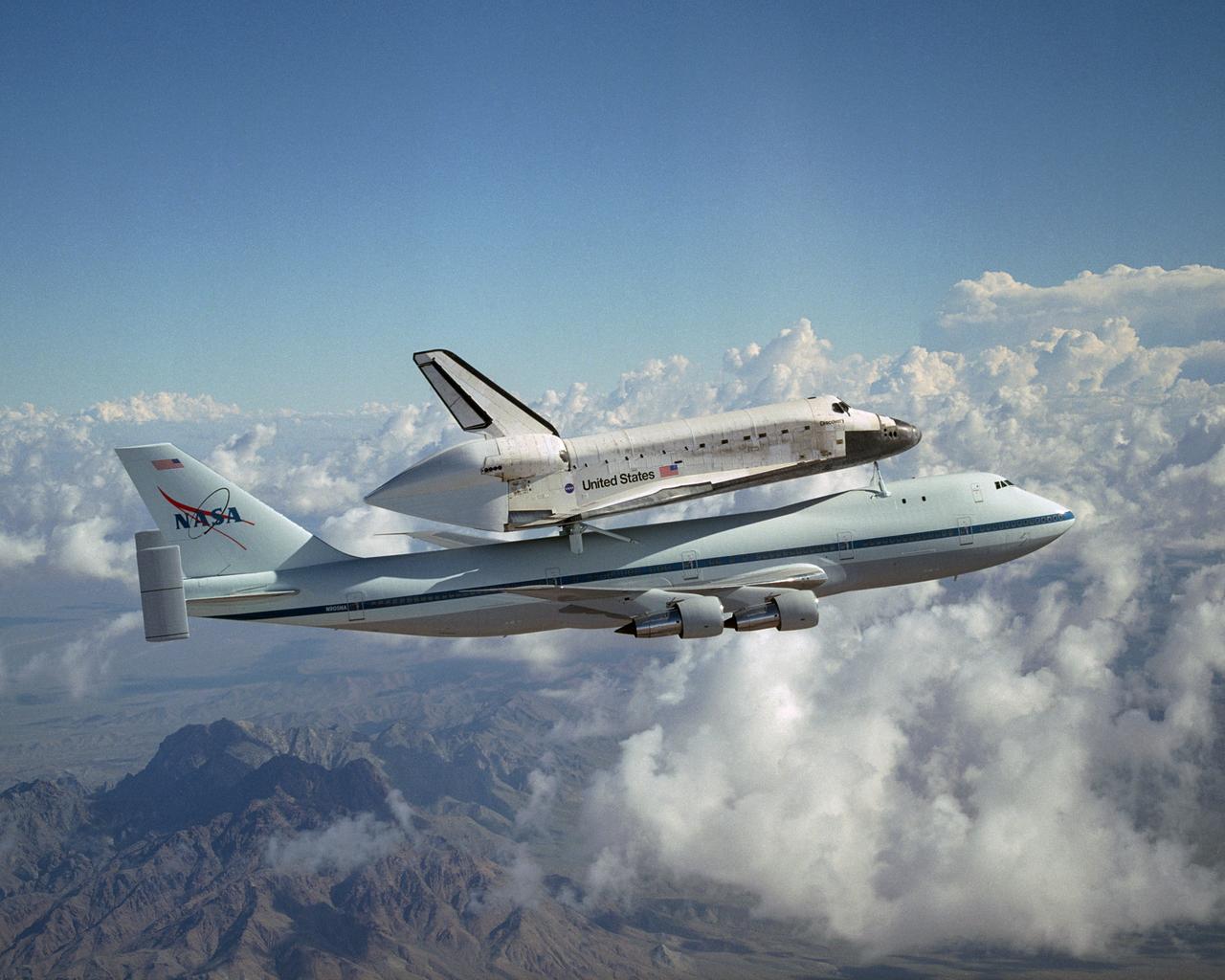

The Space Shuttle Discovery hitched a ride on NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft for the flight from the Dryden Flight Research Center in California, to Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on August 19, 2005. The cross-country ferry flight to return Discovery to Florida after it's landing in California will take two days, with stops at several intermediate points for refueling. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
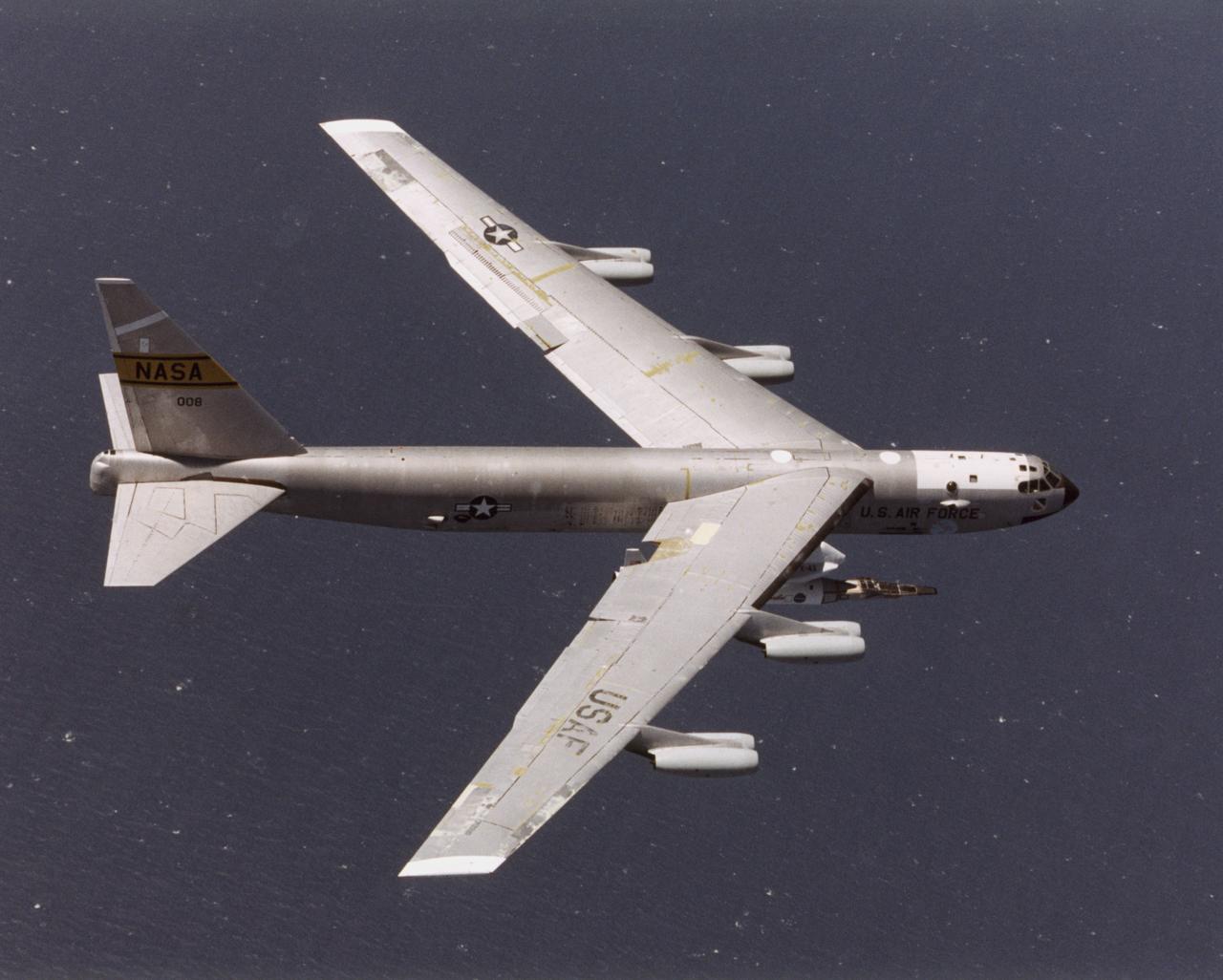

The NASA X-43A hypersonic research vehicle and its Pegasus booster rocket, mounted beneath the wing of their B-52 mothership, had a successful first captive-carry flight on April 28, 2001, Basically a dress rehearsal for a subsequent free flight, the captive-carry flight kept the X-43A-and-Pegasus combination attached to the B-52's wing pylon throughout the almost two-hour mission from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif., over the Pacific Missile Test Range, and back to Dryden.

Range safety and phased-array range user system antennas validated in the ECANS project can be seen just behind the cockpit on NASA's NF-15B research aircraft.
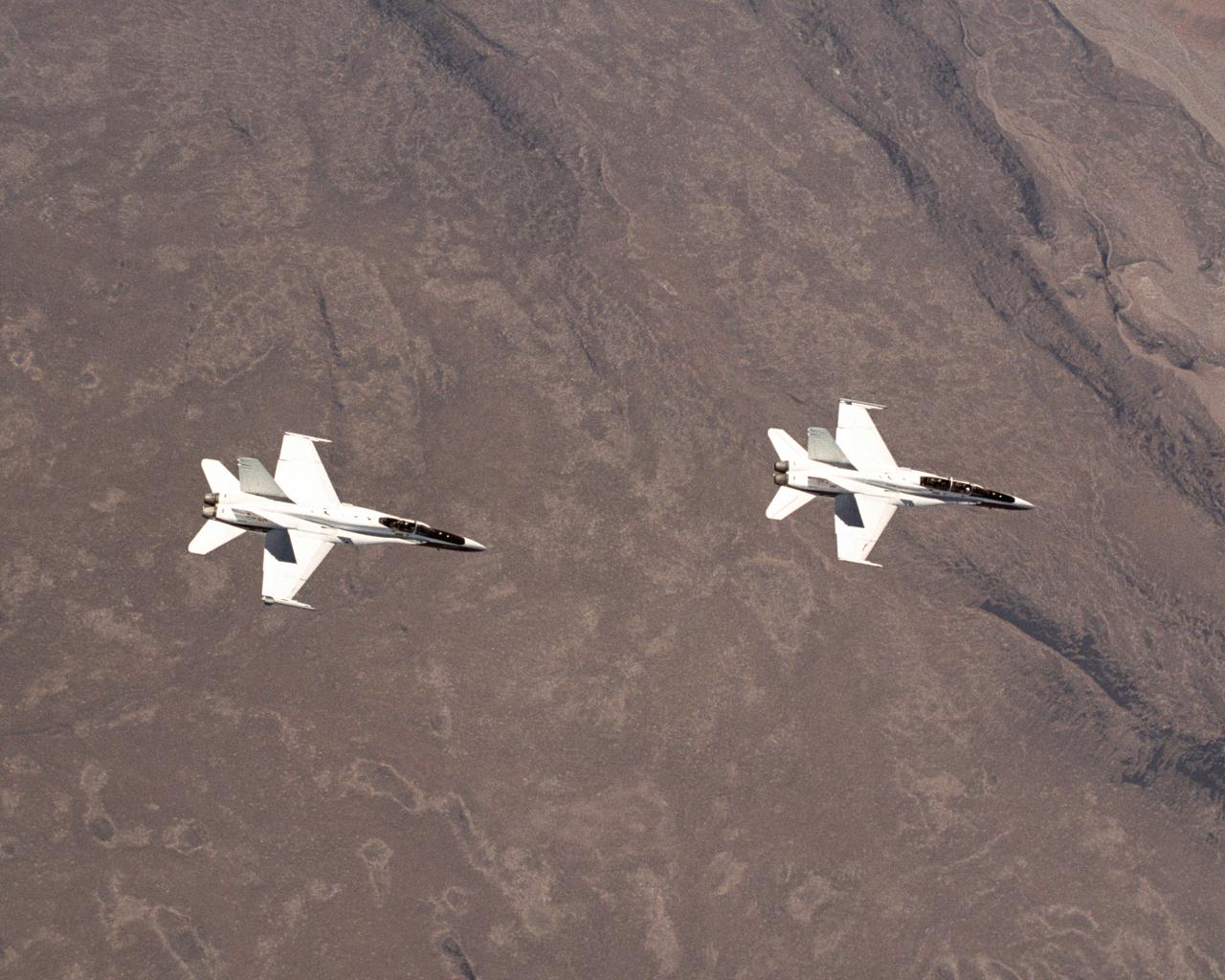

These two NASA F/A-18 aircraft are flying a test point for the Autonomous Formation Flight project over California's Mojave Desert.
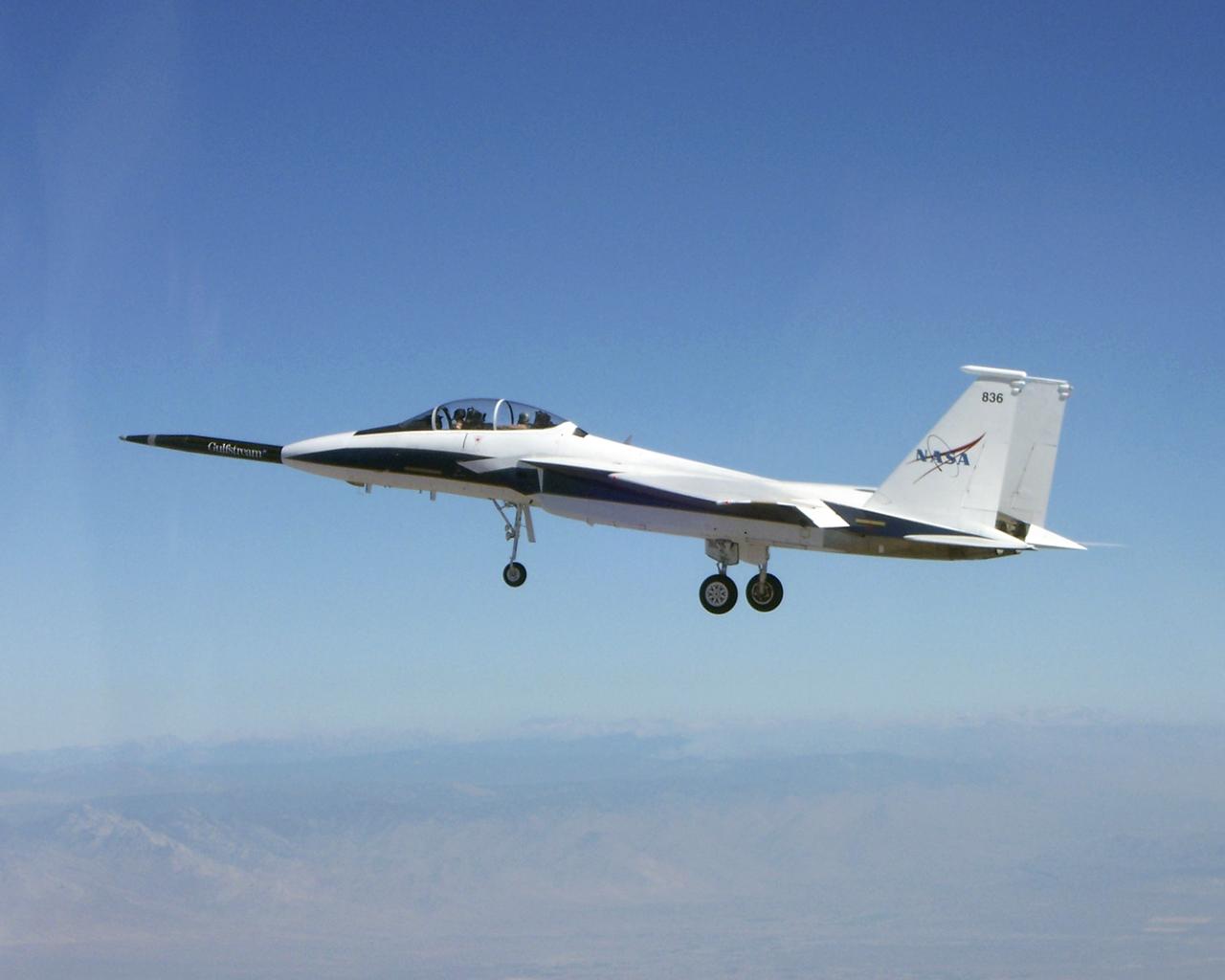

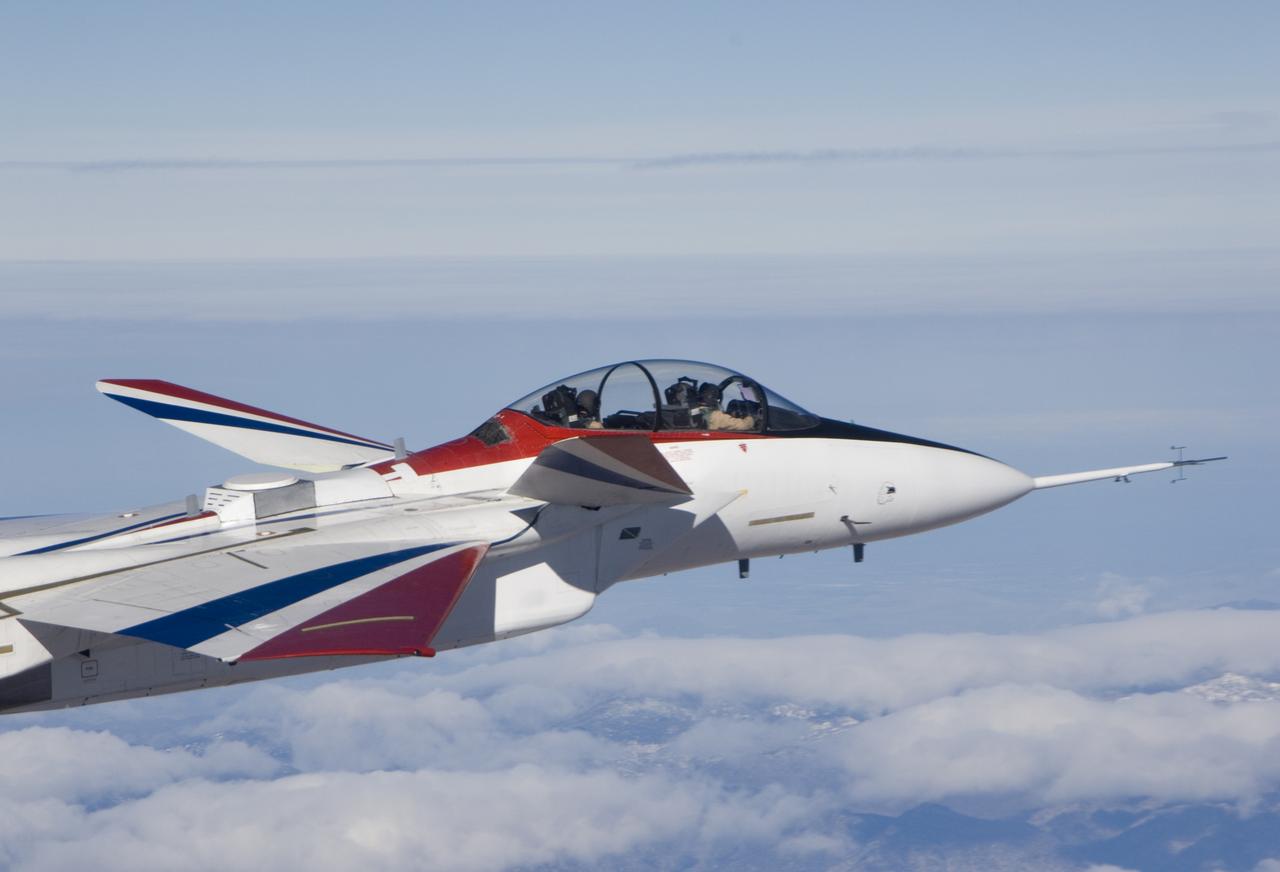
NASA's F-15B testbed aircraft in flight during the first evaluation flight of the joint NASA/Gulfstream Quiet Spike project. The project seeks to verify the structural integrity of the multi-segmented, articulating spike attachment designed to reduce and control a sonic boom.
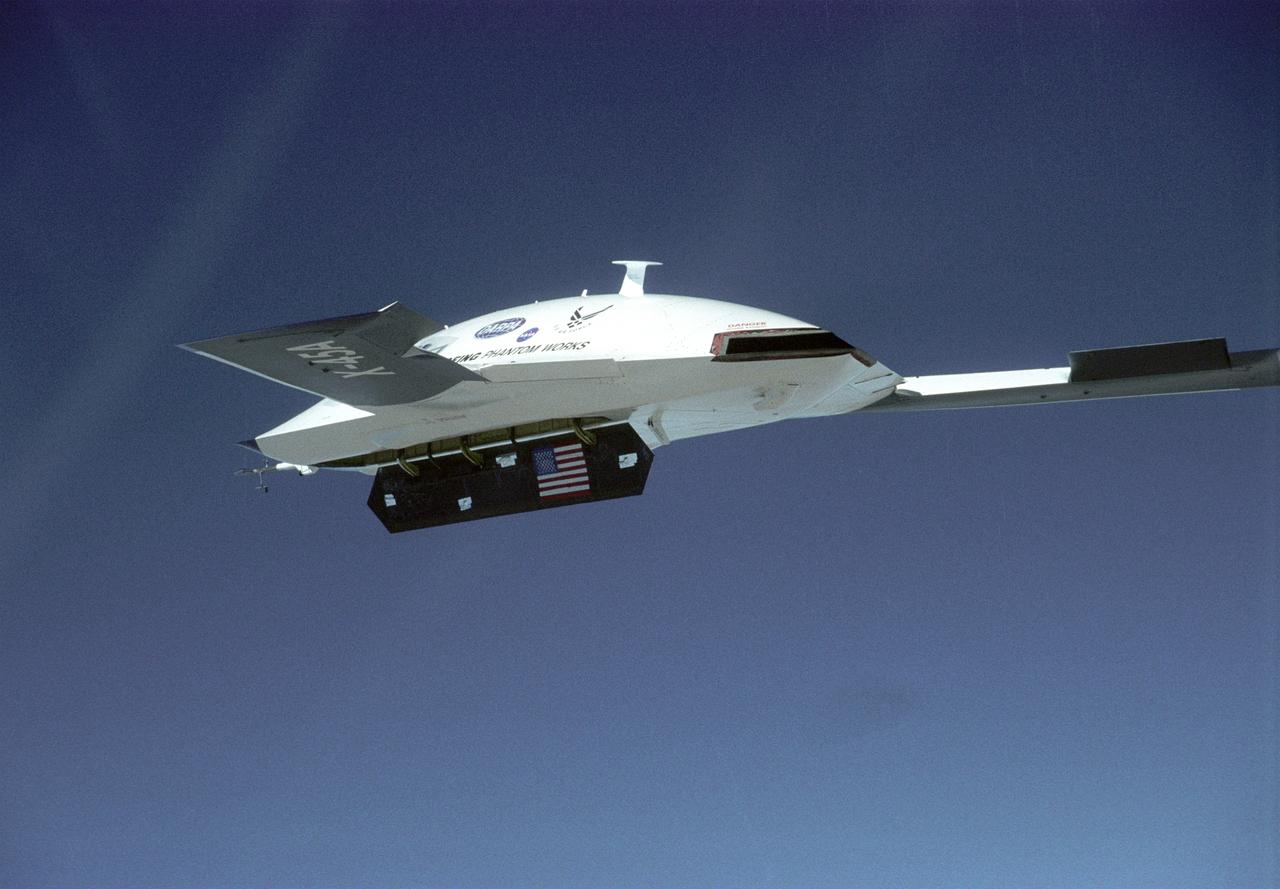

The DARPA/U.S. Air Force X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) system demonstration program completed the first phase of demonstrations, known as Block I, on Feb. 28, 2003. The final Block I activities included two flights at Dryden, during which safe operation of the weapons bay door was verified at 35,000 feet and speeds of Mach 0.75, the maximum planned altitude and speed for the two X-45A demonstrator vehicles.
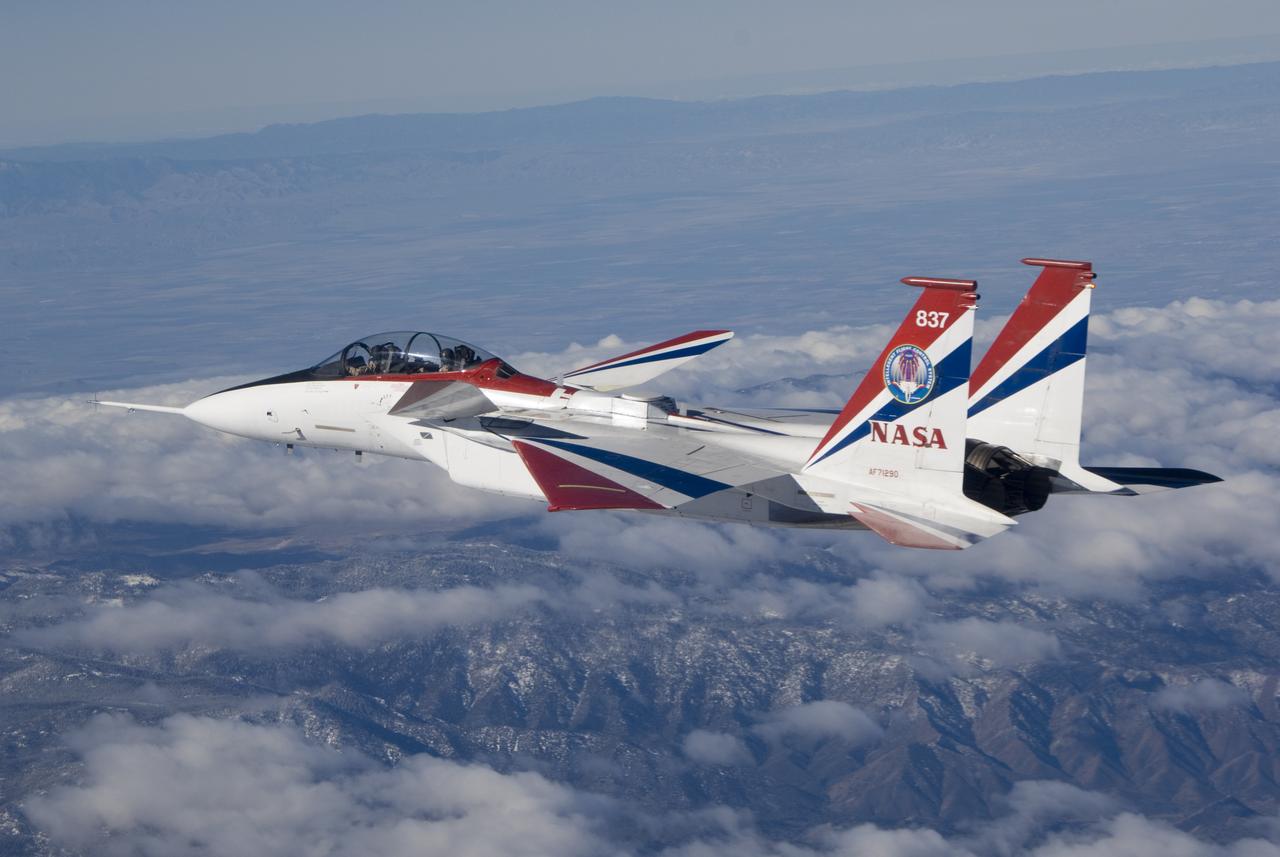

Antennas used for the Space-Based Range Demonstration and Certification project protrude from the top of NASA's NF-15B testbed during a research flight.
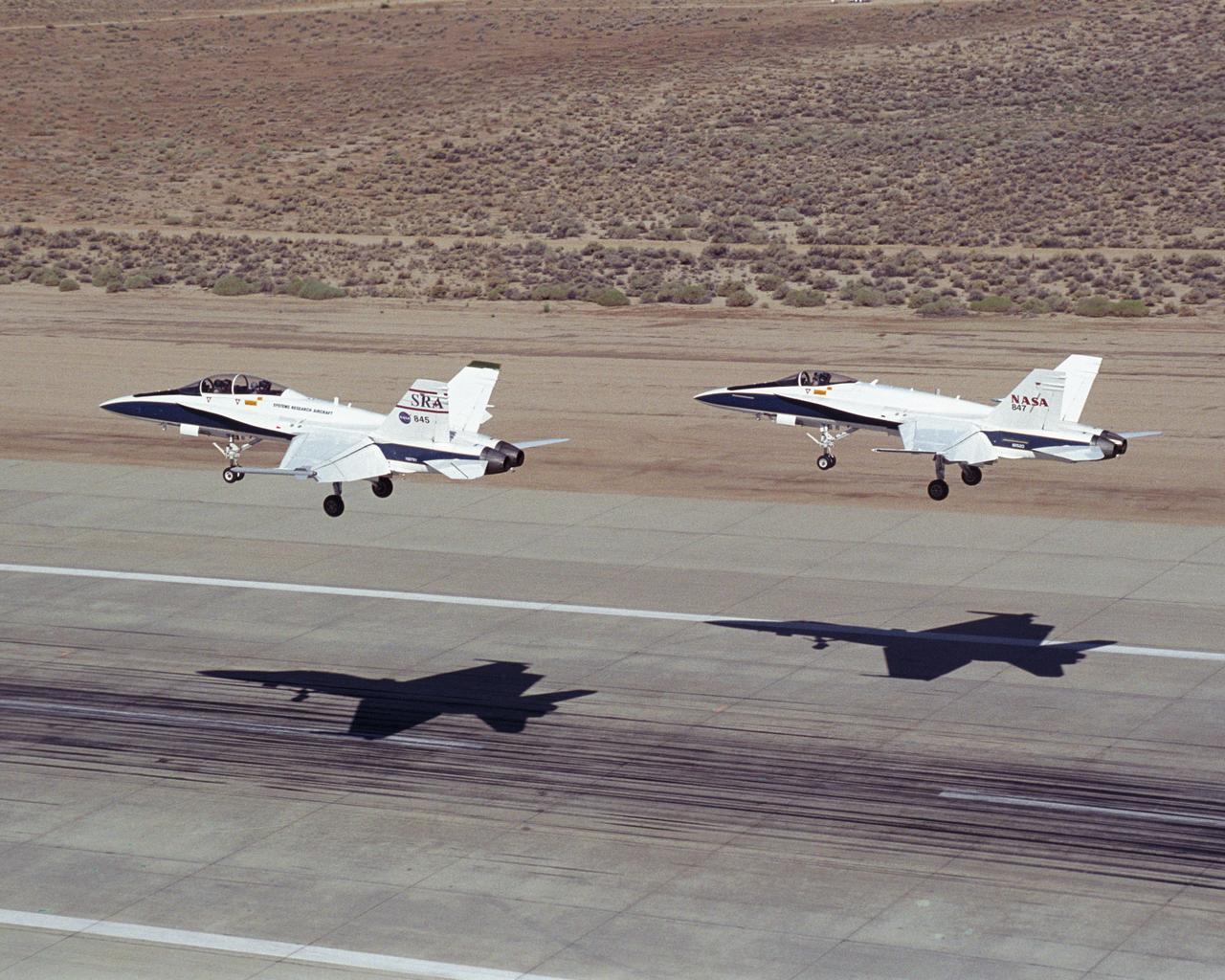

Two NASA Dryden F/A-18's land on the Edwards Air Force Base runway after completion of an Autonomous Formation Flight (AFF) mission.

Photographed from the F-18 pathfinder aircraft, the Orbital ATK L-1011 Stargazer aircraft is seen flying over the Atlantic Ocean offshore from Daytona Beach, Florida. Attached beneath the aircraft is the Pegasus XL rocket with eight Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft. The CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a crucial role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
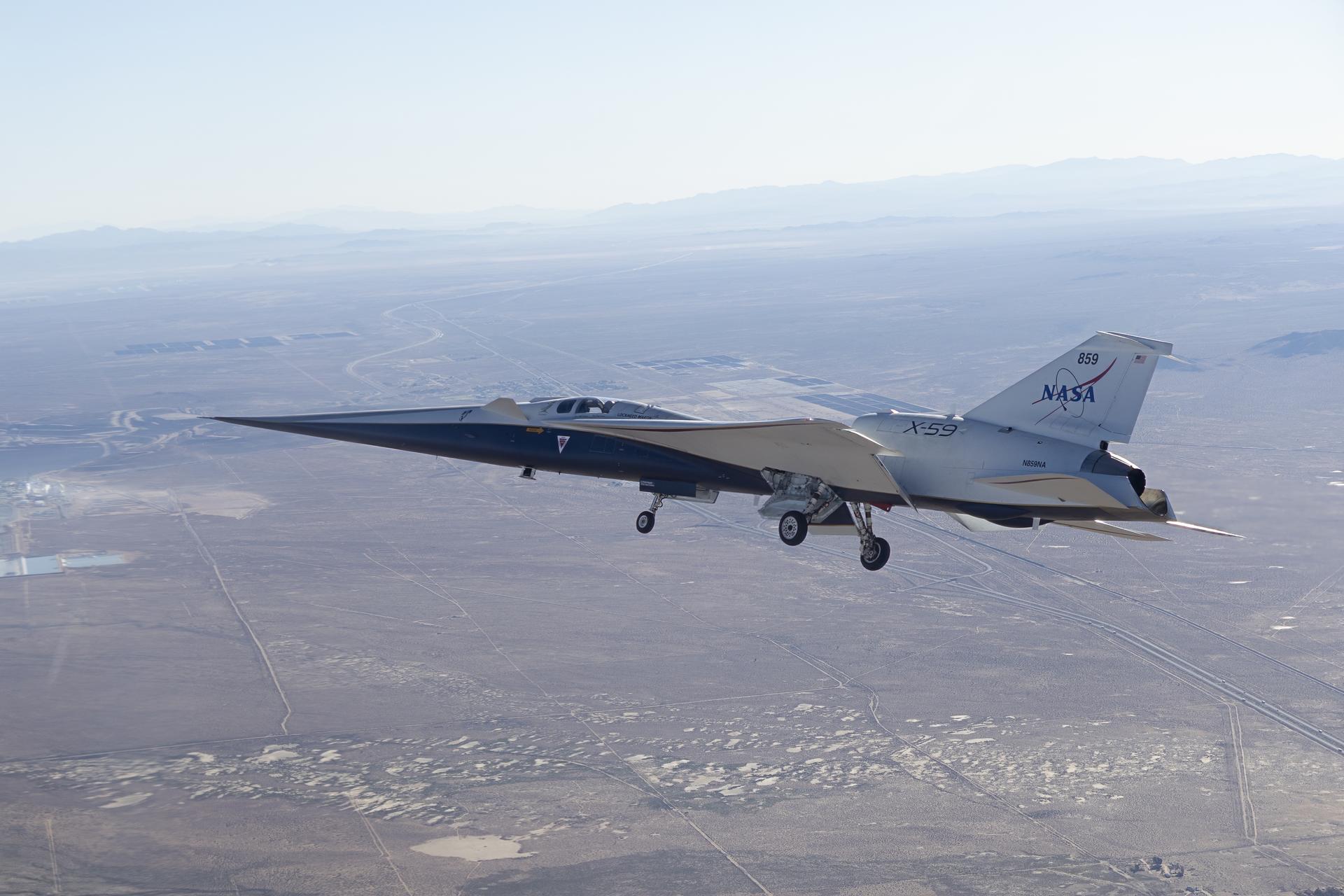

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft cruises above Palmdale and Edwards, California, during its first flight, Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025. The aircraft traveled to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
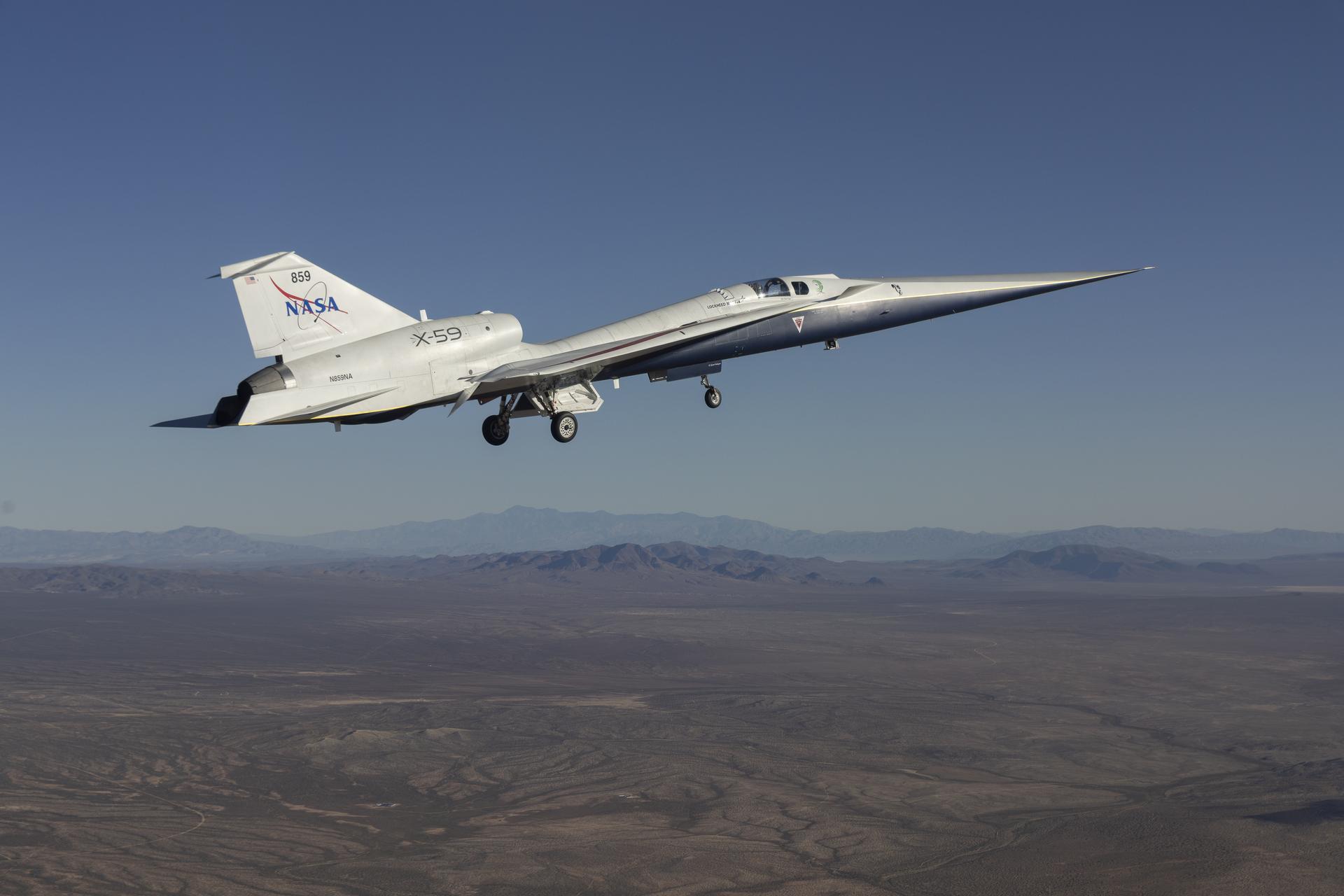

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft lifts off for its first flight Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025, from U.S. Air Force Plant 42 in Palmdale, California. The aircraft’s first flight marks the start of flight testing for NASA’s Quesst mission, the result of years of design, integration, and ground testing and begins a new chapter in NASA’s aeronautics research legacy.

NASA F-15B #836 in flight with Quiet Spike attached. The project seeks to verify the structural integrity of the multi-segmented, articulating spike attachment designed to reduce and control a sonic boom.
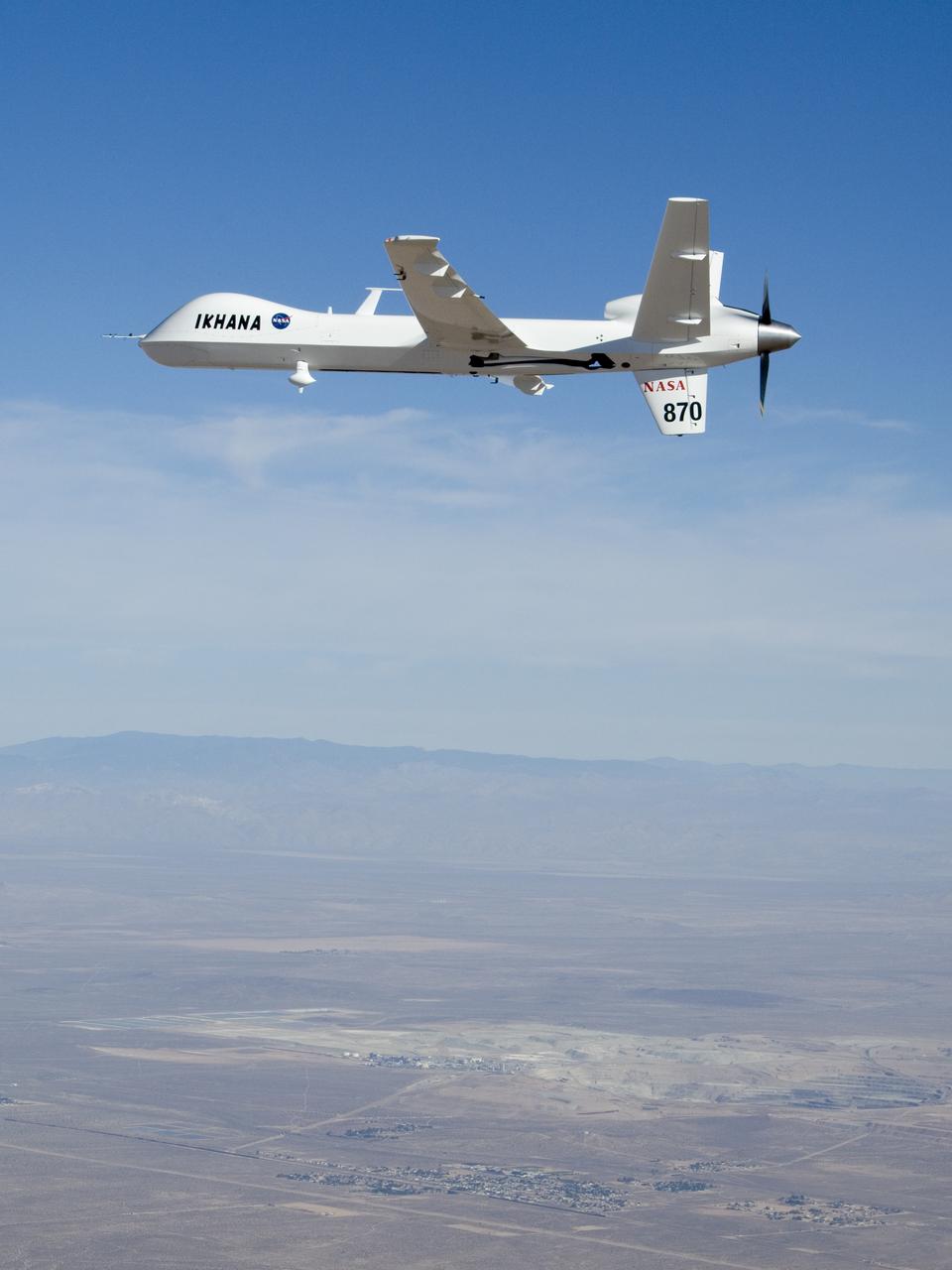

NASA's Ikhana unmanned science demonstration aircraft over the U.S. Borax mine, Boron, California, near the Dryden/Edwards Air Force Base complex. NASA took possession of the new aircraft in November, 2006, and it arrived at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards AFB, Calif., on June 23, 2007.
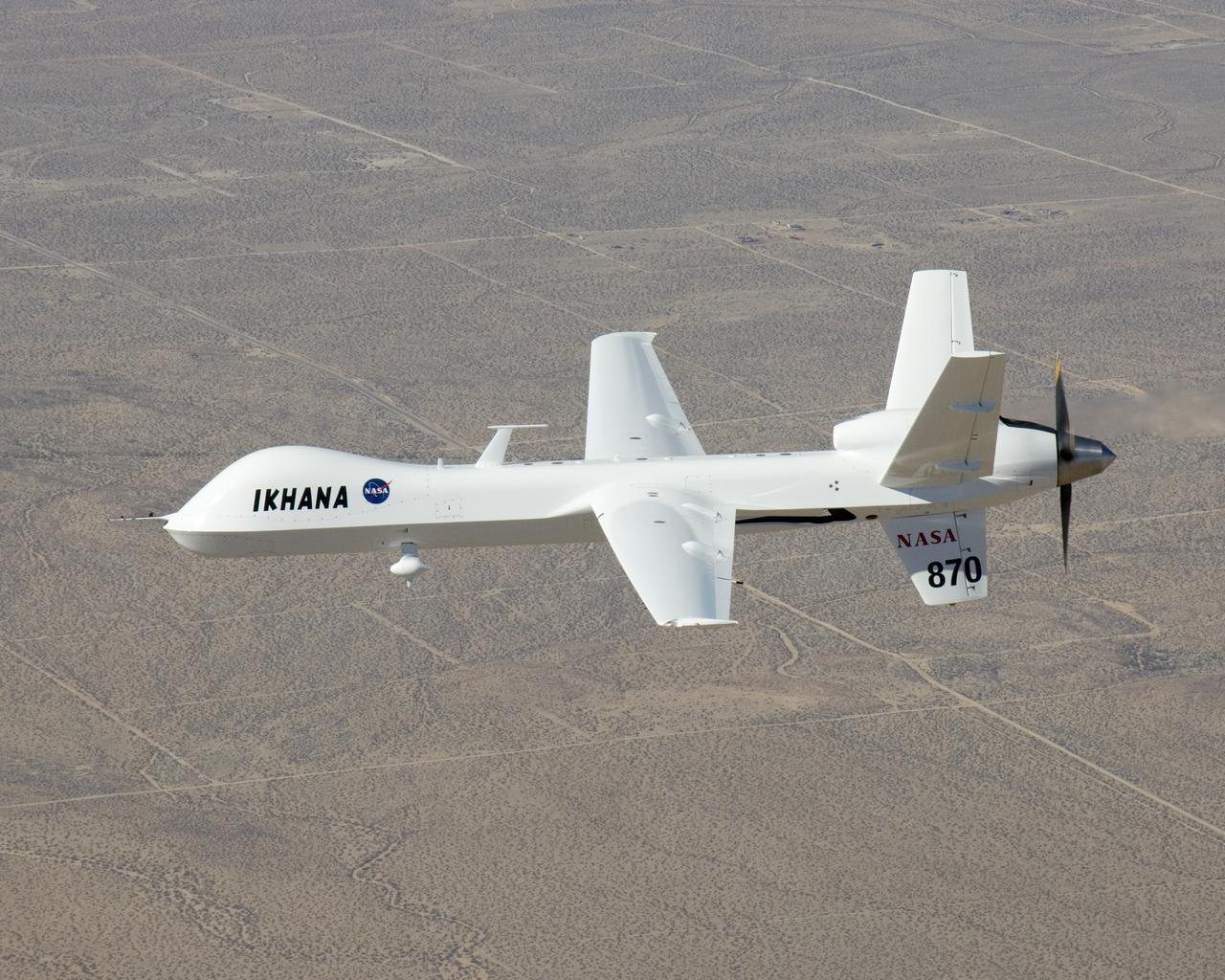

NASA's Ikhana unmanned science demonstration aircraft over Southern California's high desert during the ferry flight to its new home at the Dryden Flight Research Center. NASA took possession of the new aircraft in November, 2006, and it arrived at DFRC at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., on June 23, 2007.
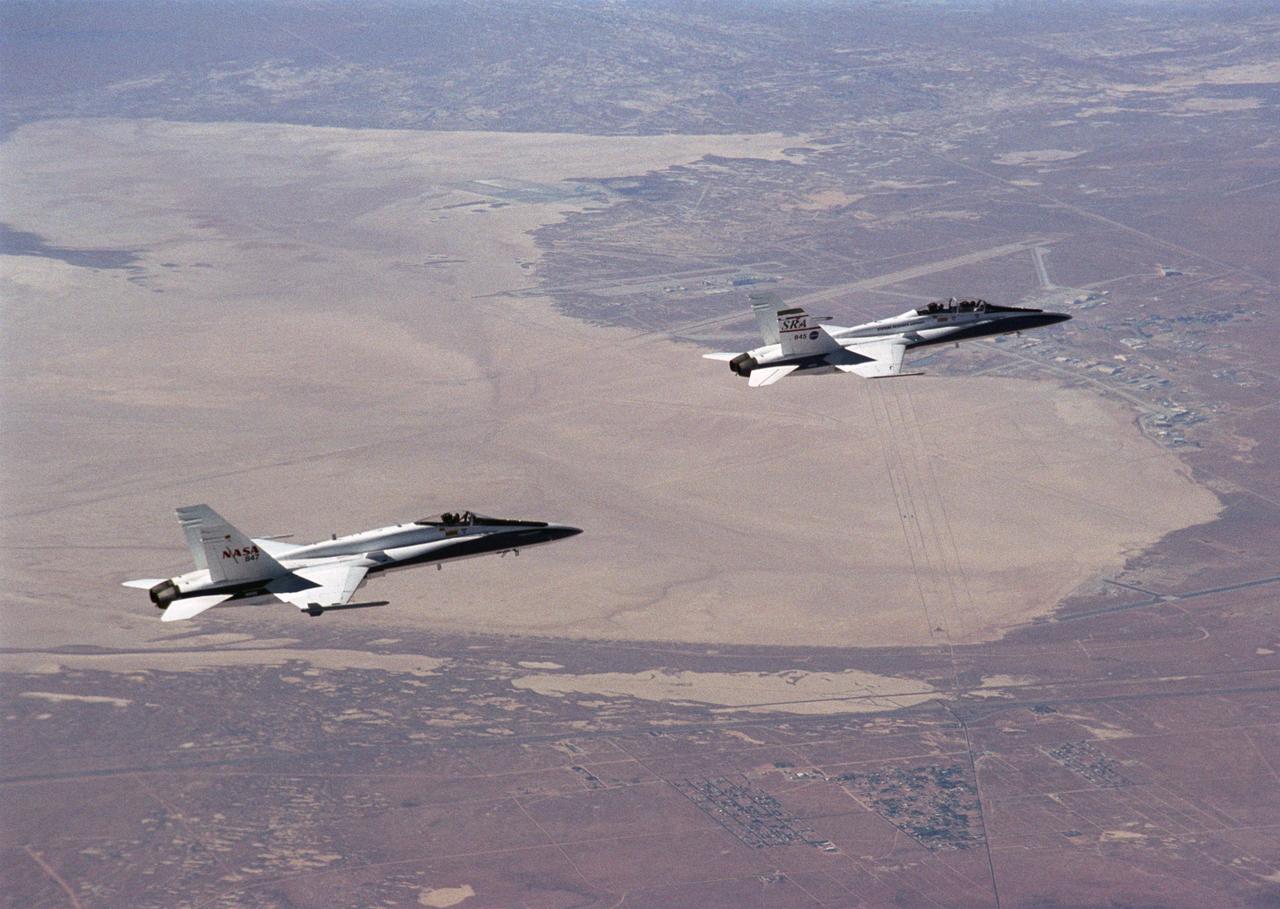

Flying an Autonomous Formation Flight mission, two F/A-18s from the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, gain altitude near Rogers Dry Lake.

The Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket carrying NASA's Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft is released and the first stage ignites at 8:37 a.m. EST. The rocket was released from the Orbital ATK L-1011 Stargazer aircraft flying over the Atlantic Ocean offshore from Daytona Beach, Florida following takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. This image was taken from a NASA F-18 chase plane provided by Armstrong Flight Research Center in California. The CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes.
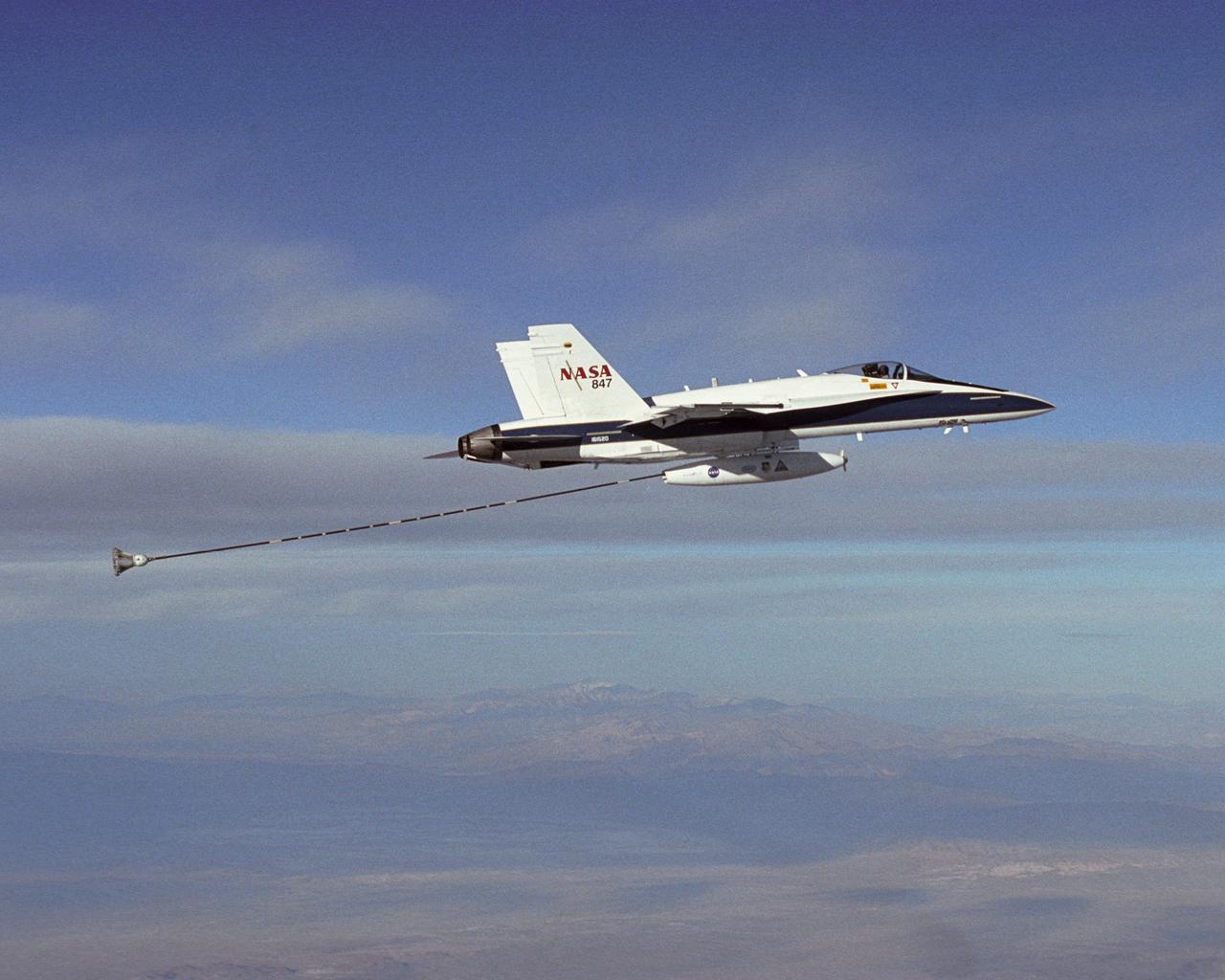

NASA Dryden's Automated Aerial Refueling (AAR) project evaluated the capability of an F/A-18A aircraft as an in-flight refueling tanker with the objective of developing analytical models for an automated aerial refueling system for unmanned air vehicles. The F/A-18 "tanker" aircraft (No. 847) underwent flight test envelope expansion with an aerodynamic pod containing air-refueling equipment carried beneath the fuselage. The second aircraft (No. 843) flew as the receiver aircraft during the study to assess the free-stream hose and drogue dynamics on the F/A-18A.

Photographed from the F-18 pathfinder aircraft, the Orbital ATK L-1011 Stargazer aircraft is seen flying over the Atlantic Ocean offshore from Daytona Beach, Florida. Attached beneath the aircraft is the Pegasus XL rocket with eight Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft. The CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a crucial role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.

Photographed from the F-18 pathfinder aircraft, the Orbital ATK L-1011 Stargazer aircraft is seen flying over the Atlantic Ocean offshore from Daytona Beach, Florida. Attached beneath the aircraft is the Pegasus XL rocket with eight Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft. The CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a crucial role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes. NOTE: The Dec. 12, 2016 launch attempt was postponed due to a hydraulic pump aboard the Orbital ATK L-1011 aircraft which is required to release the latches holding Pegasus in place, is not receiving power.

Photographed from the F-18 pathfinder aircraft, the Orbital ATK L-1011 Stargazer aircraft is seen flying over the Atlantic Ocean offshore from Daytona Beach, Florida. Attached beneath the aircraft is the Pegasus XL rocket with eight Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft. The CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a crucial role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes. NOTE: The Dec. 12, 2016 launch attempt was postponed due to a hydraulic pump aboard the Orbital ATK L-1011 aircraft which is required to release the latches holding Pegasus in place, is not receiving power.
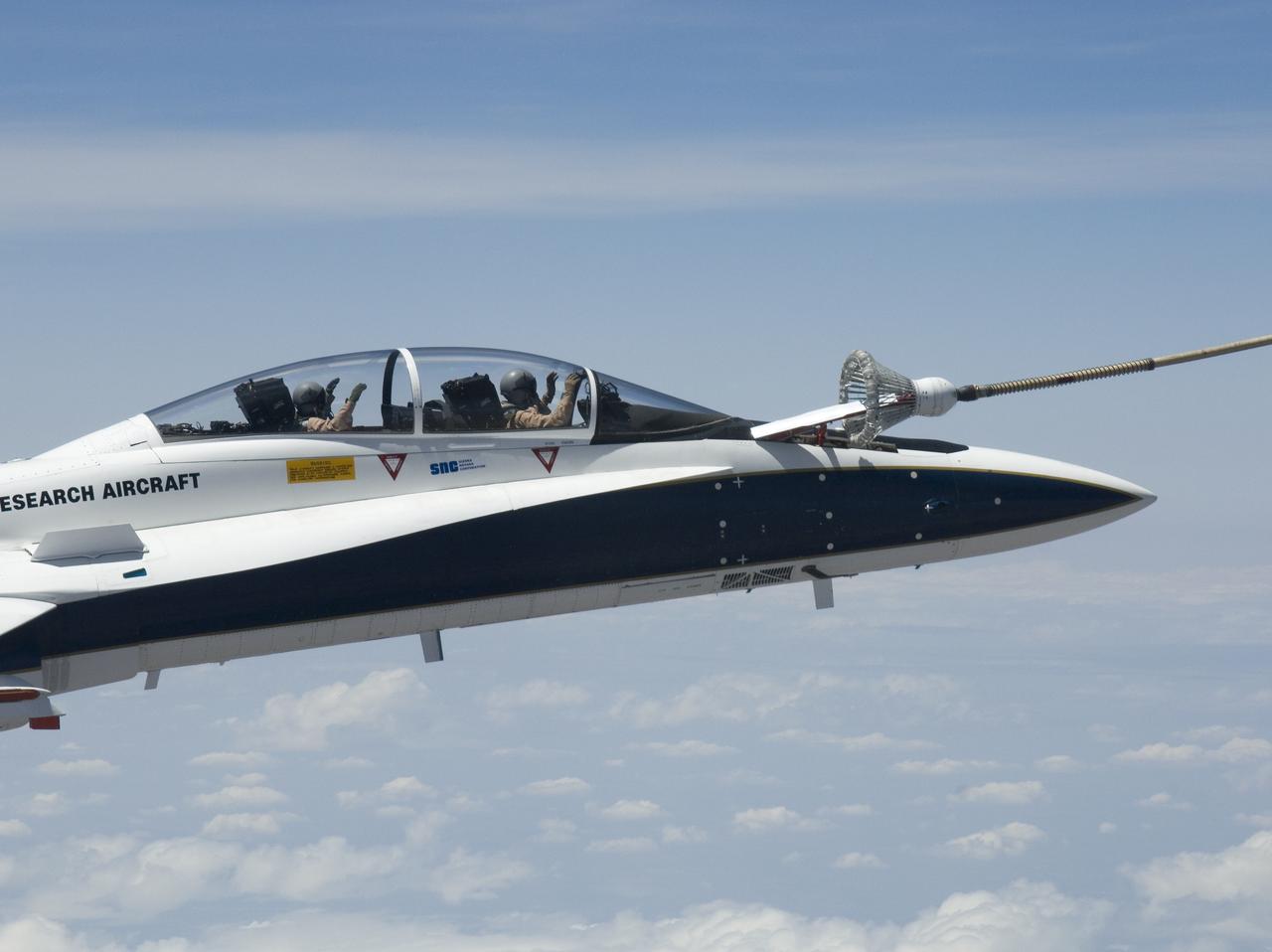

Pilot Dick Ewers and flight test engineer Leslie Molzahn were hands-off as NASA F/A-18 #845 flew itself into the drogue on an autonomous refueling demonstration.
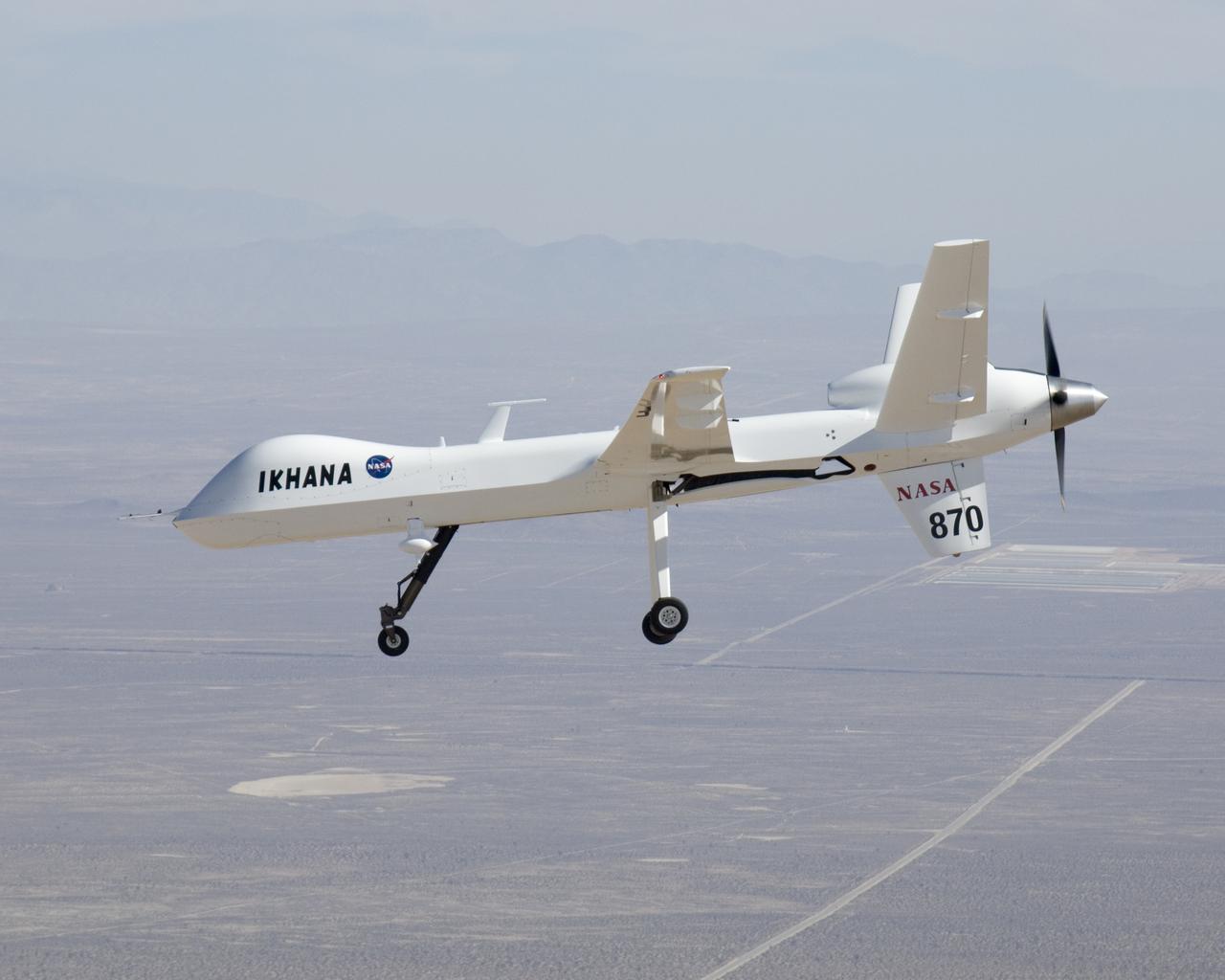

NASA's Ikhana unmanned science demonstration aircraft prepares for landing as it arrives at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. NASA took possession of the new aircraft in November, 2006, and it arrived at its new home at NASA's Dryden Flight Reseach Center at Edwards AFB, on June 23, 2007.
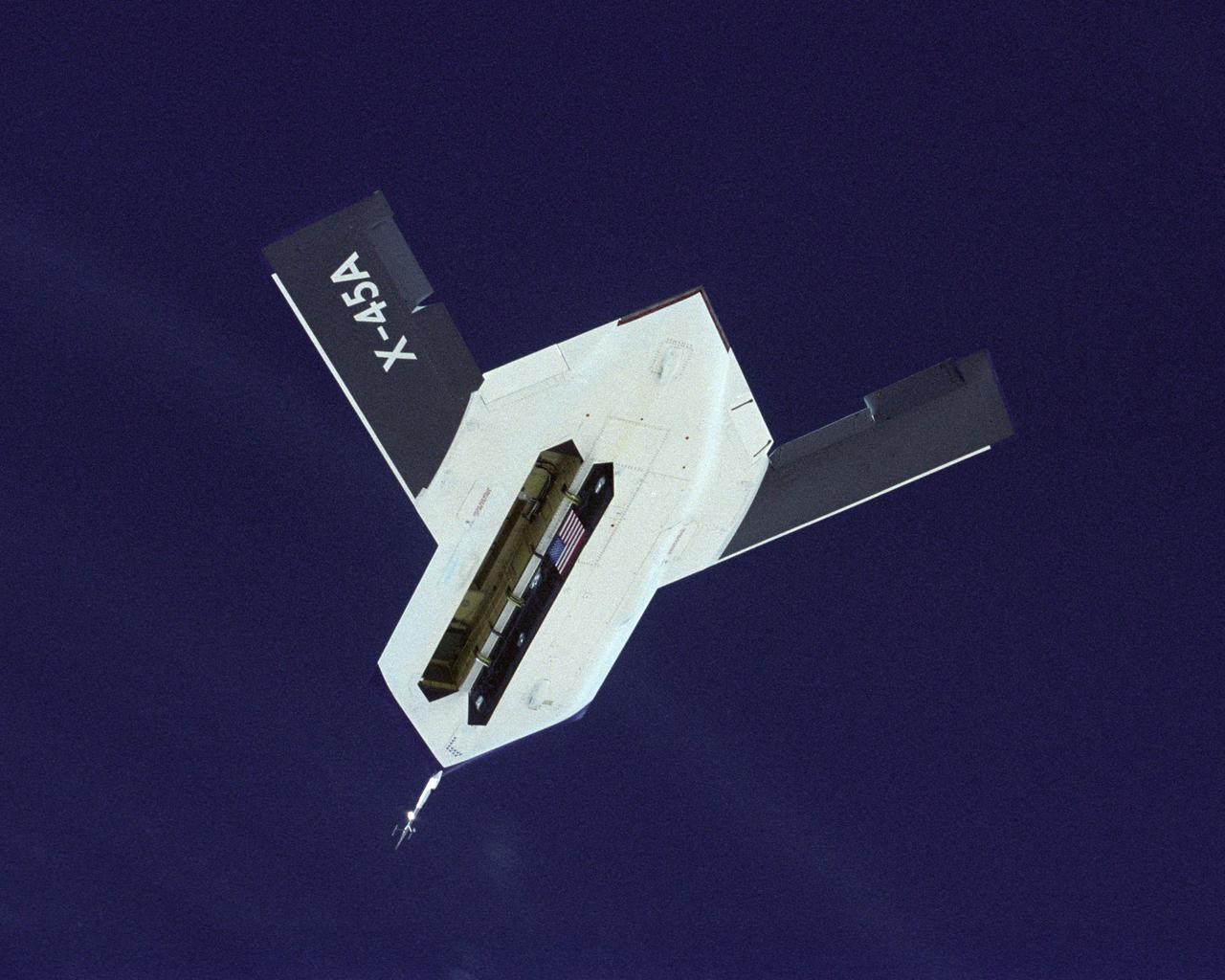
The DARPA/U.S. Air Force X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) system demonstration program completed the first phase of demonstrations, known as Block I, on Feb. 28, 2003. The final Block I activities included two flights at Dryden, during which safe operation of the weapons bay door was verified at 35,000 feet and speeds of Mach 0.75, the maximum planned altitude and speed for the two X-45A demonstrator vehicles.
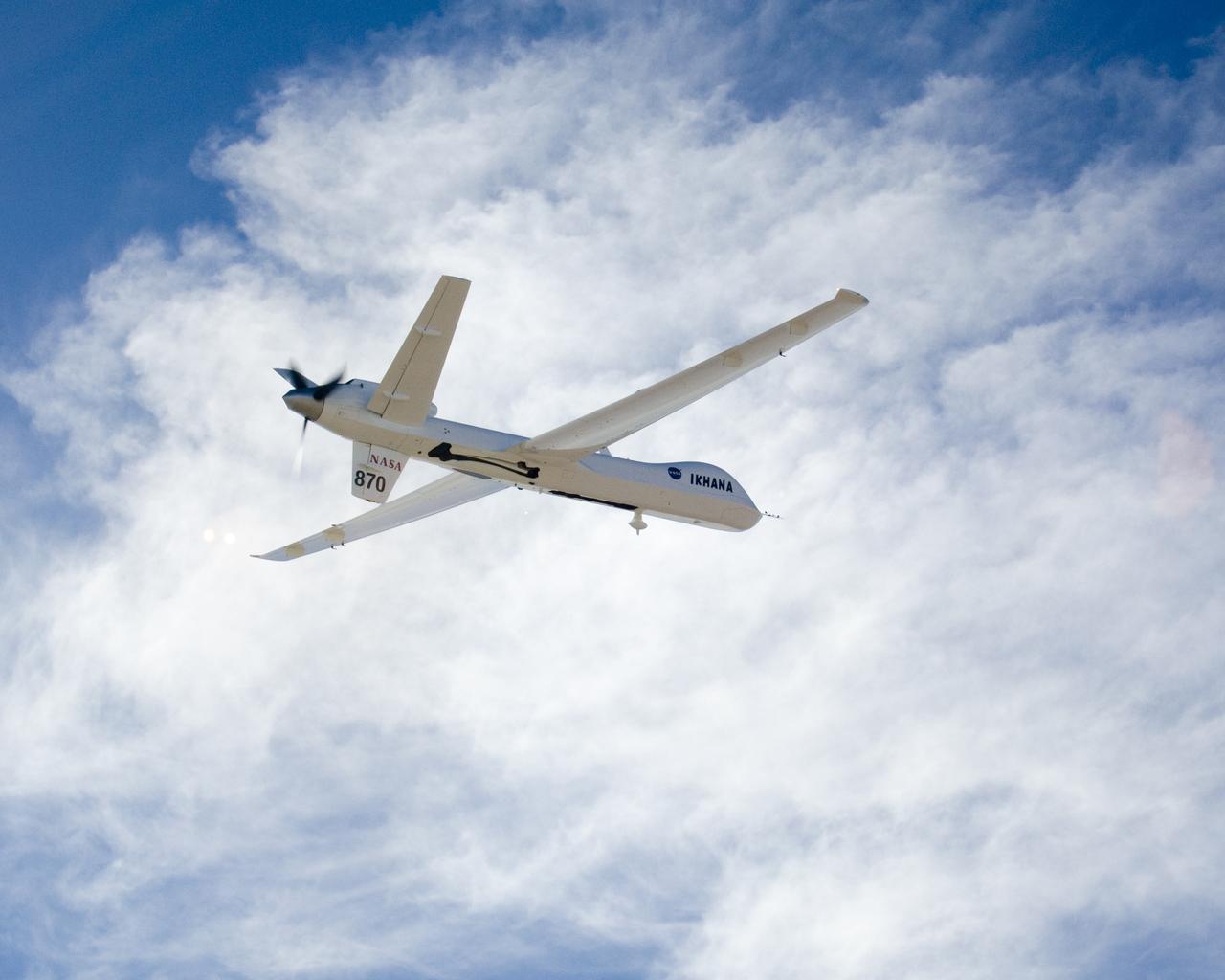

NASA's Ikhana unmanned science demonstration aircraft in flight during the ferry flight to its new home at the Dryden Flight Research Center. NASA took possession of the new aircraft in November, 2006, and it arrived at the NASA center at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., on June 23, 2007.
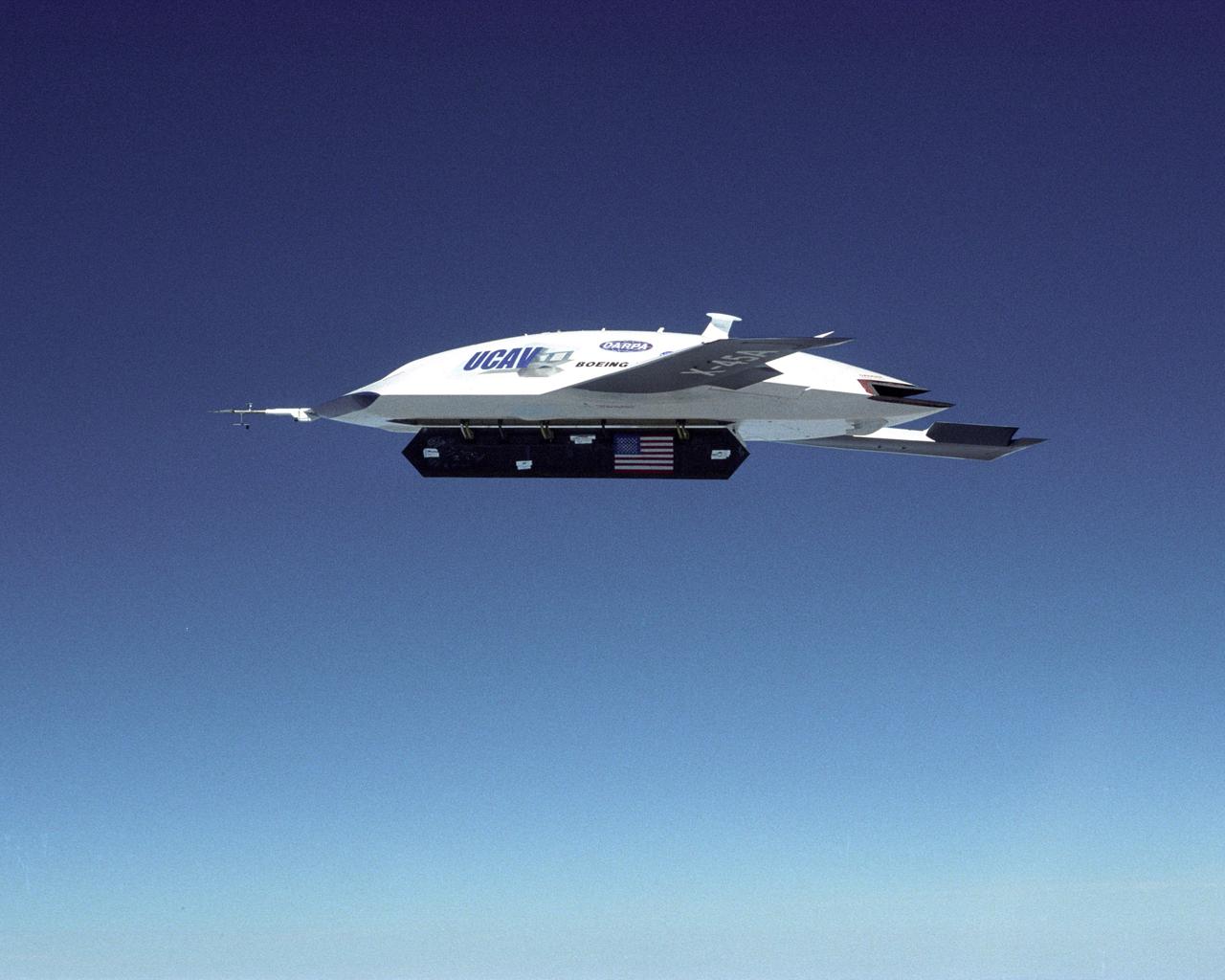

The DARPA/U.S. Air Force X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) system demonstration program completed the first phase of demonstrations, known as Block I, on Feb. 28, 2003. The final Block I activities included two flights at Dryden, during which safe operation of the weapons bay door was verified at 35,000 feet and speeds of Mach 0.75, the maximum planned altitude and speed for the two X-45A demonstrator vehicles.
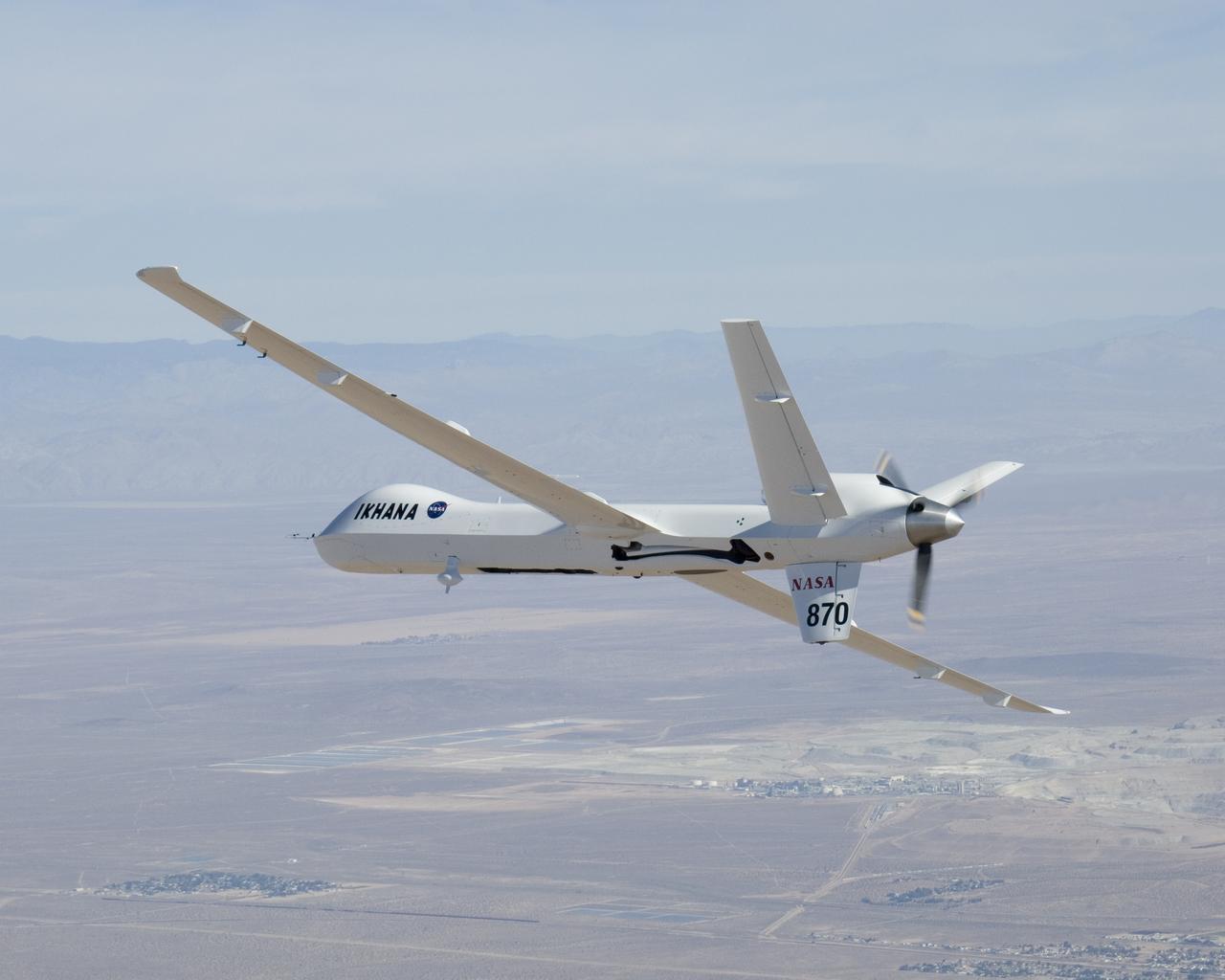

NASA's Ikhana unmanned science demonstration aircraft over the U.S. Borax mine, Boron, California, near the Dryden/Edwards Air Force Base complex. NASA took possession of the new aircraft in November, 2006, and it arrived at the NASA center at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., on June 23, 2007.
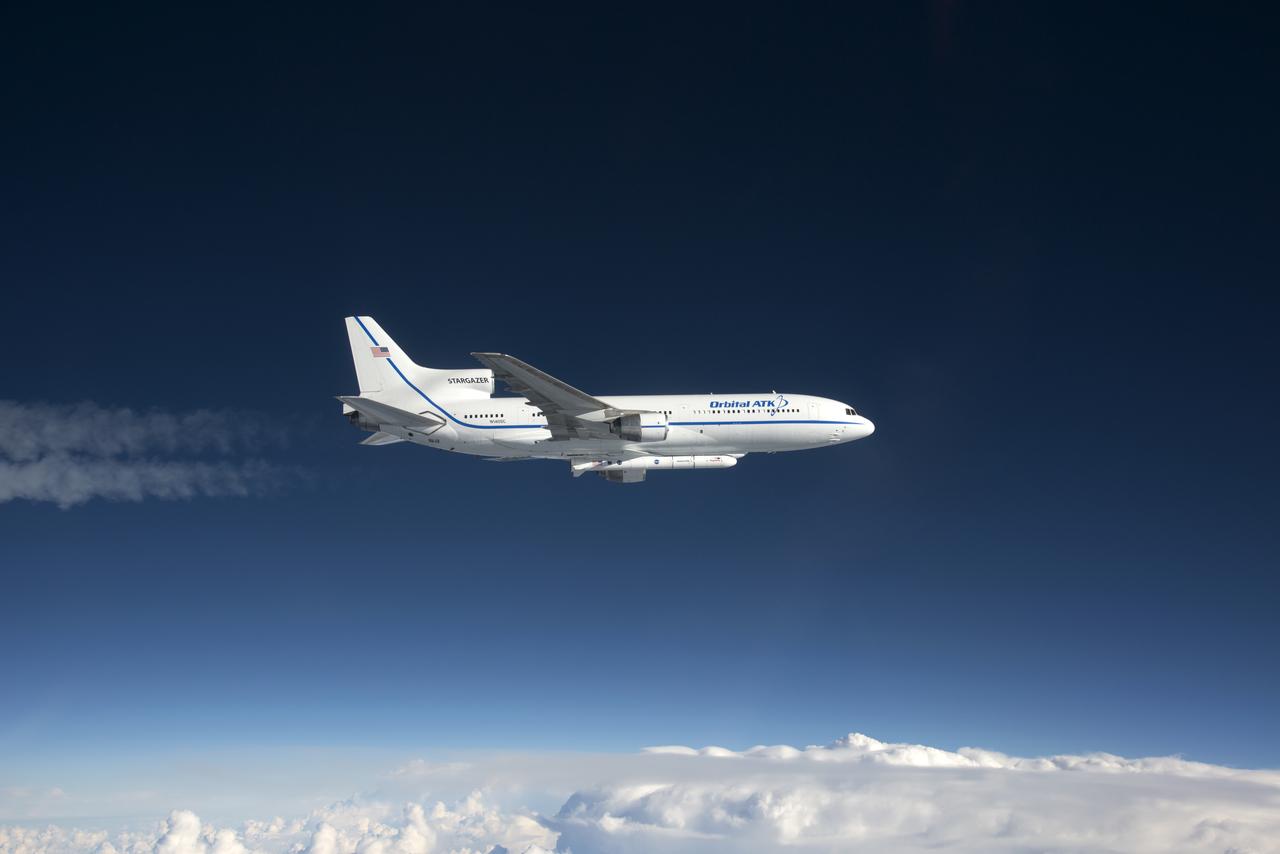

Photographed from the F-18 pathfinder aircraft, the Orbital ATK L-1011 Stargazer aircraft is seen flying over the Atlantic Ocean offshore from Daytona Beach, Florida. Attached beneath the aircraft is the Pegasus XL rocket with eight Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft. The CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a crucial role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes. NOTE: The Dec. 12, 2016 launch attempt was postponed due to a hydraulic pump aboard the Orbital ATK L-1011 aircraft which is required to release the latches holding Pegasus in place, is not receiving power.
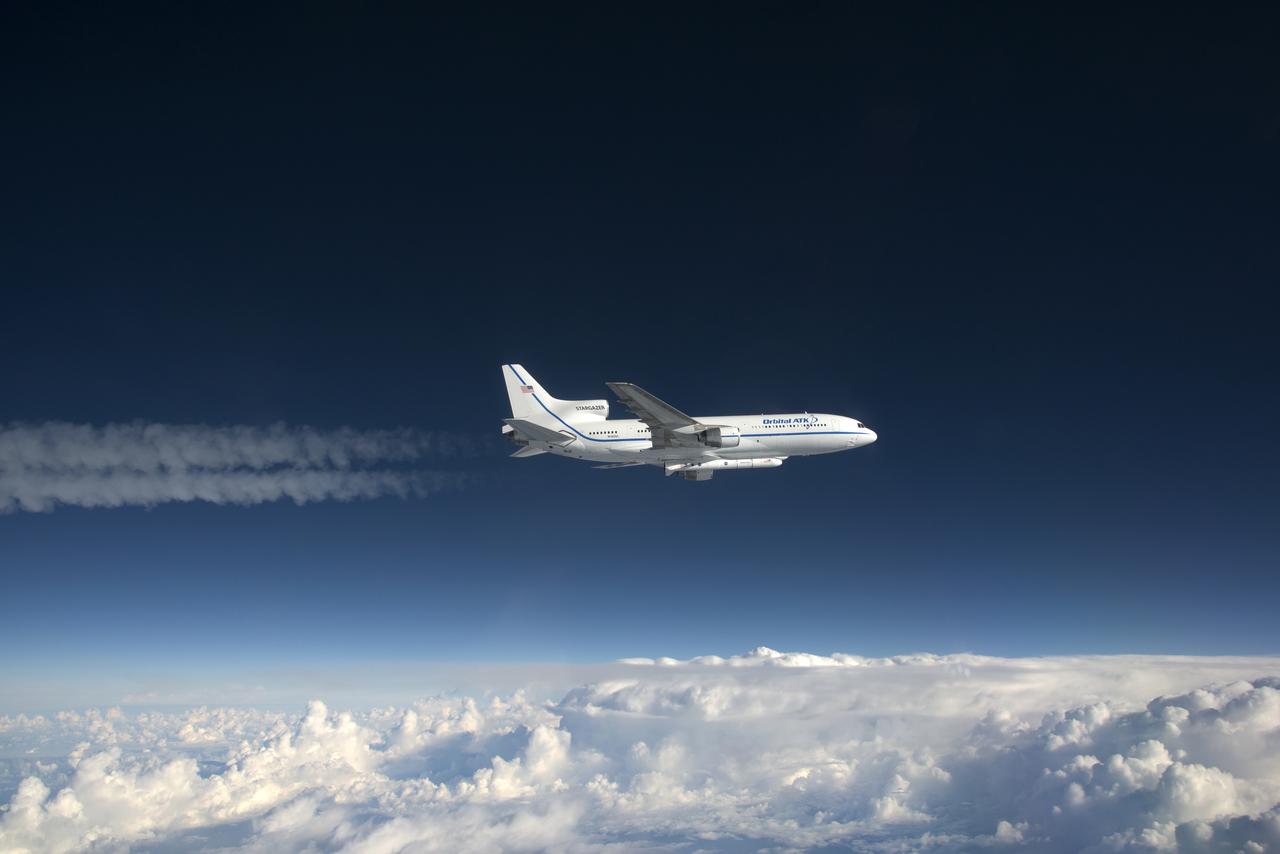

Photographed from the F-18 pathfinder aircraft, the Orbital ATK L-1011 Stargazer aircraft is seen flying over the Atlantic Ocean offshore from Daytona Beach, Florida. Attached beneath the aircraft is the Pegasus XL rocket with eight Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft. The CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a crucial role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes. NOTE: The Dec. 12, 2016 launch attempt was postponed due to a hydraulic pump aboard the Orbital ATK L-1011 aircraft which is required to release the latches holding Pegasus in place, is not receiving power.
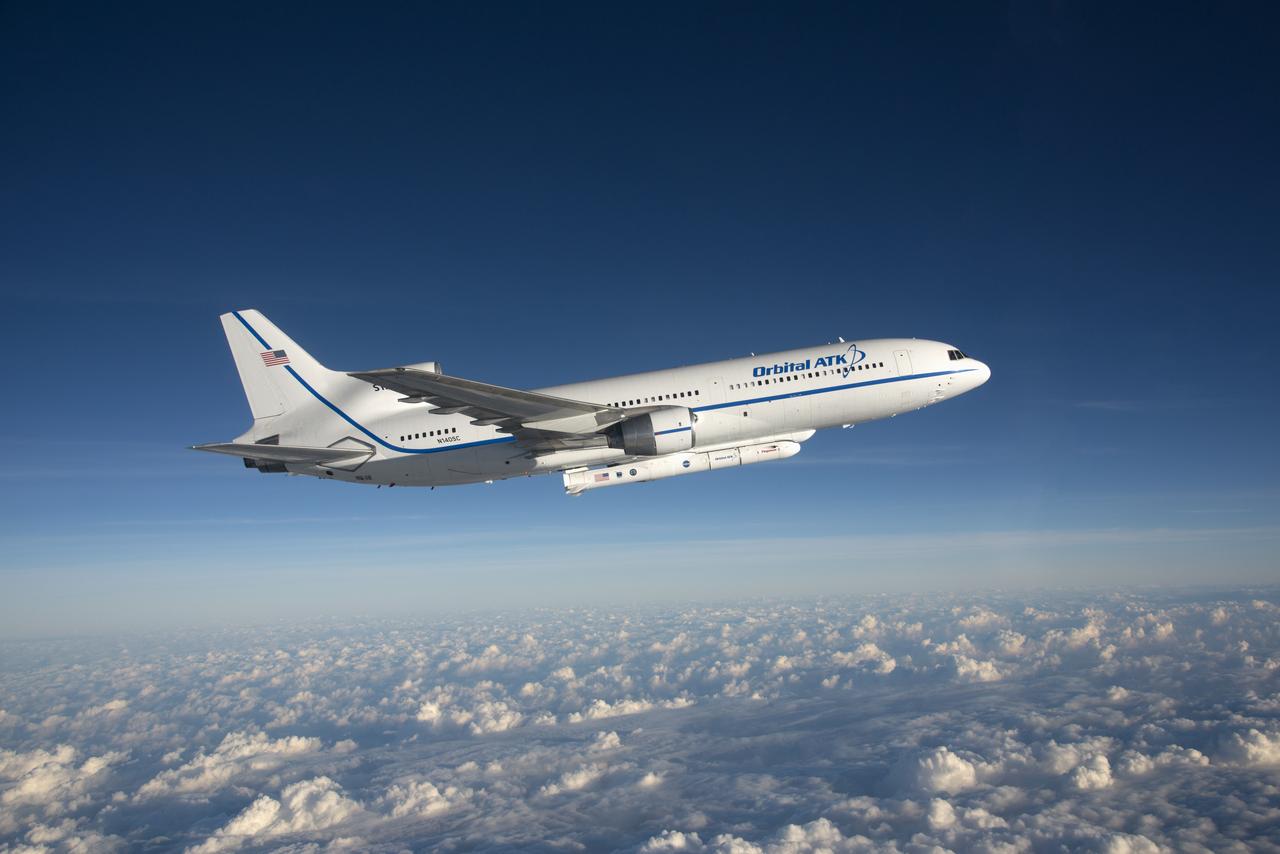

Photographed from the F-18 pathfinder aircraft, the Orbital ATK L-1011 Stargazer aircraft is seen flying over the Atlantic Ocean offshore from Daytona Beach, Florida. Attached beneath the aircraft is the Pegasus XL rocket with eight Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft. The CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a crucial role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
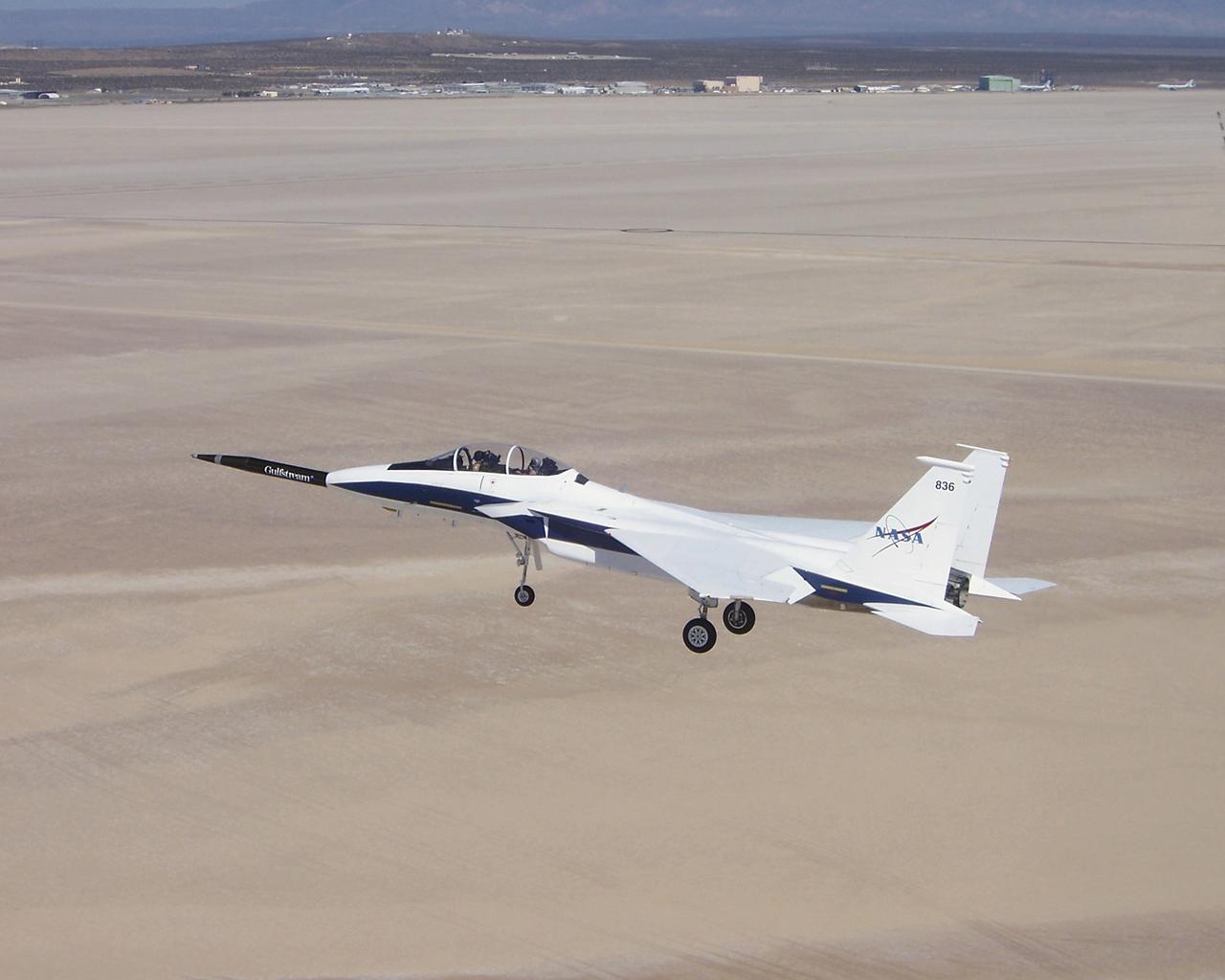

Approaching the runway after the first evaluation flight of the Quiet Spike project, NASA's F-15B testbed aircraft cruises over Roger's Dry Lakebed near the Dryden Flight Research Center. The Quiet Spike was developed by Gulfstream Aerospace as a means of controlling and reducing the sonic boom caused by an aircraft 'breaking' the sound barrier.
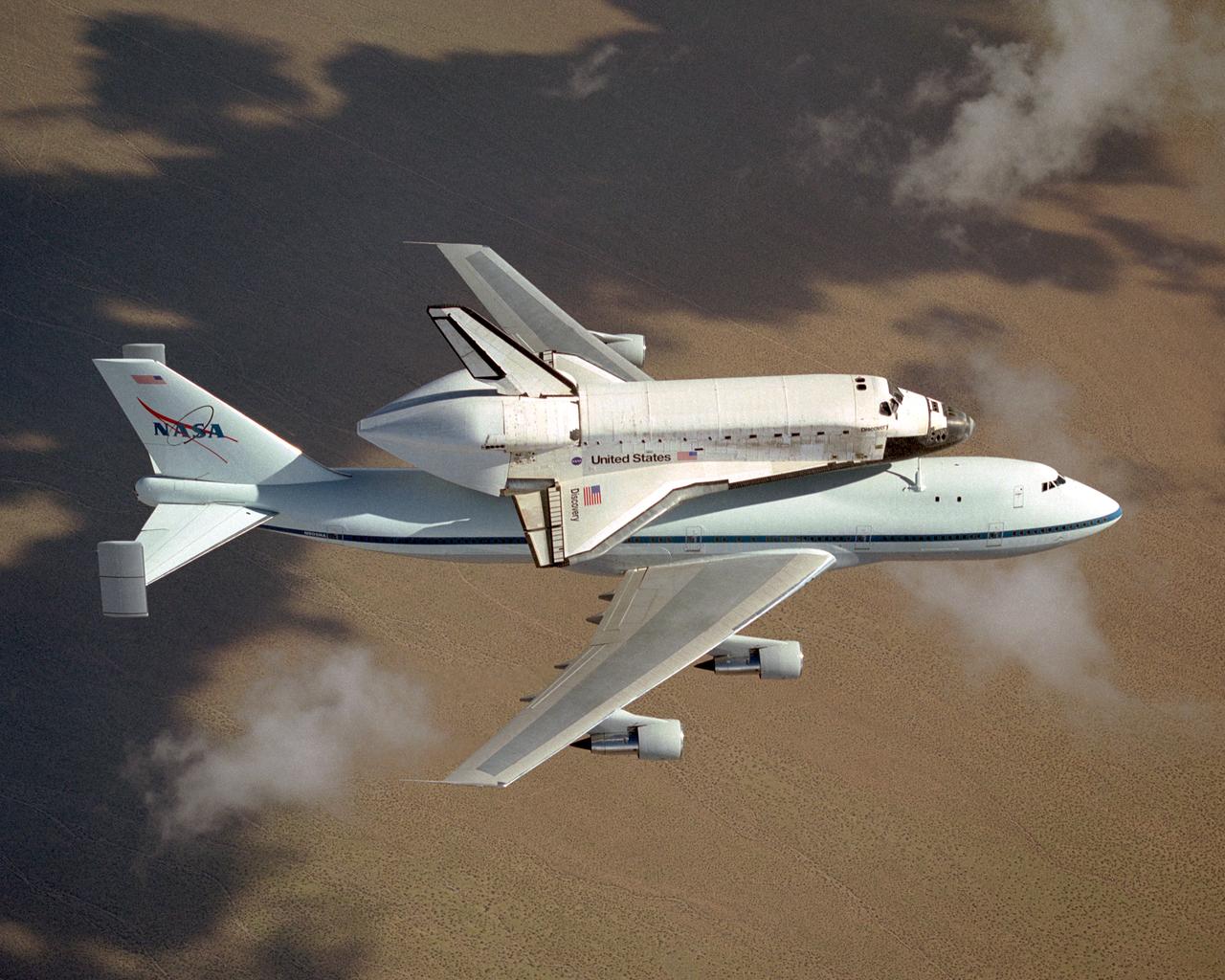

The space shuttle Discovery atop NASA's modified 747 is captured over the Mojave Desert while being ferried from NASA Dryden to the Kennedy Space Center. NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft with the Space Shuttle Discovery on top lifts off from Edwards Air Force Base to begin its ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cross-country journey will take two days, with stops at several intermediate points for refueling. Space shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14 days on orbit.
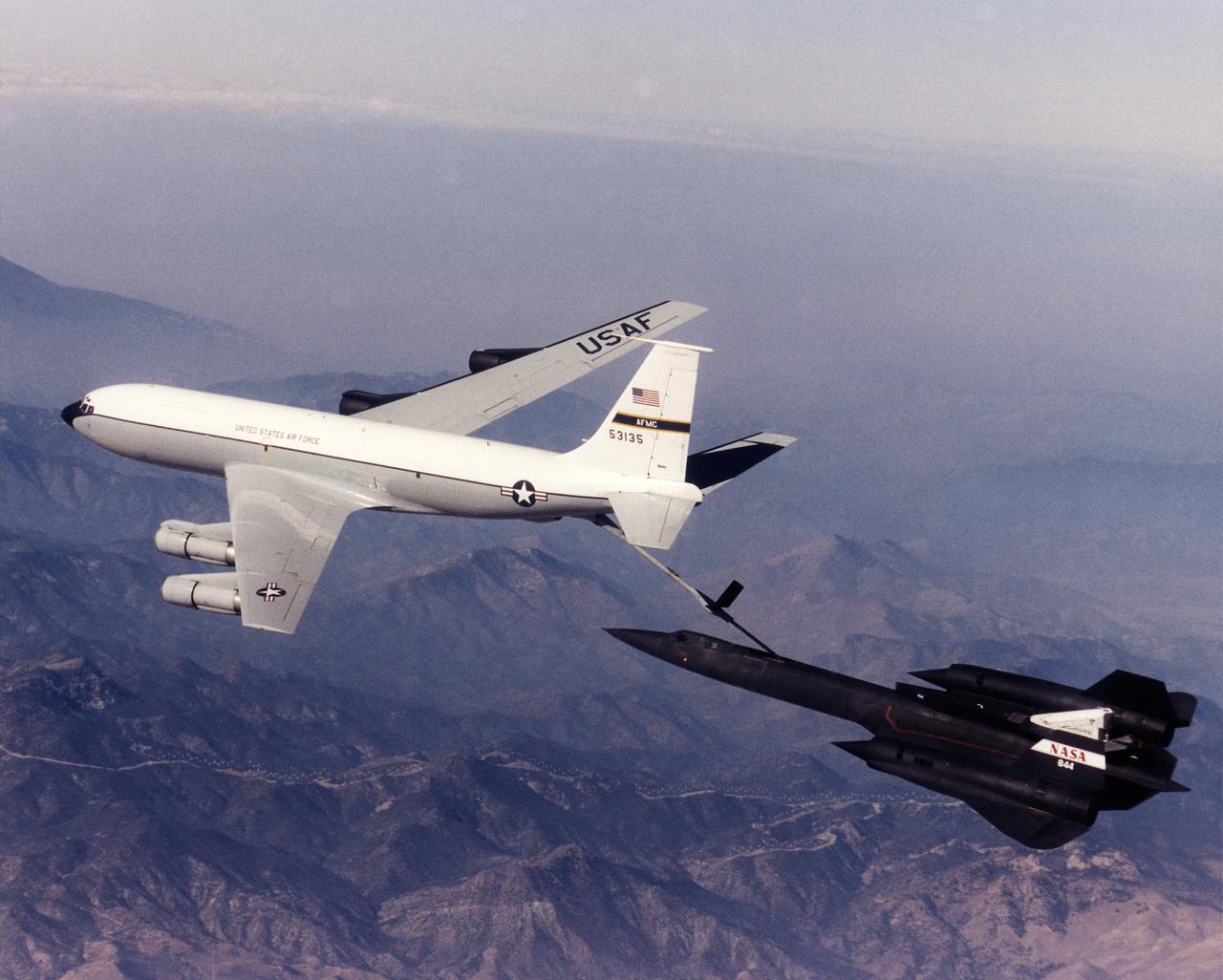

A NASA SR-71 refuels with an Edwards Air Force Base KC-135 during the first flight of the NASA/Rocketdyne/ Lockheed Martin Linear Aerospike SR-71 Experiment (LASRE). The flight took place Oct. 31 at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The SR-71 took off at 8:31 a.m. PST. The aircraft flew for one hour and fifty minutes, reaching a maximum speed of Mach 1.2 before landing at Edwards at 10:21 a.m. PST, successfully validating the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The goal of the first flight was to evaluate the aerodynamic characteristics and the handling of the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The engine was not fired during the flight.
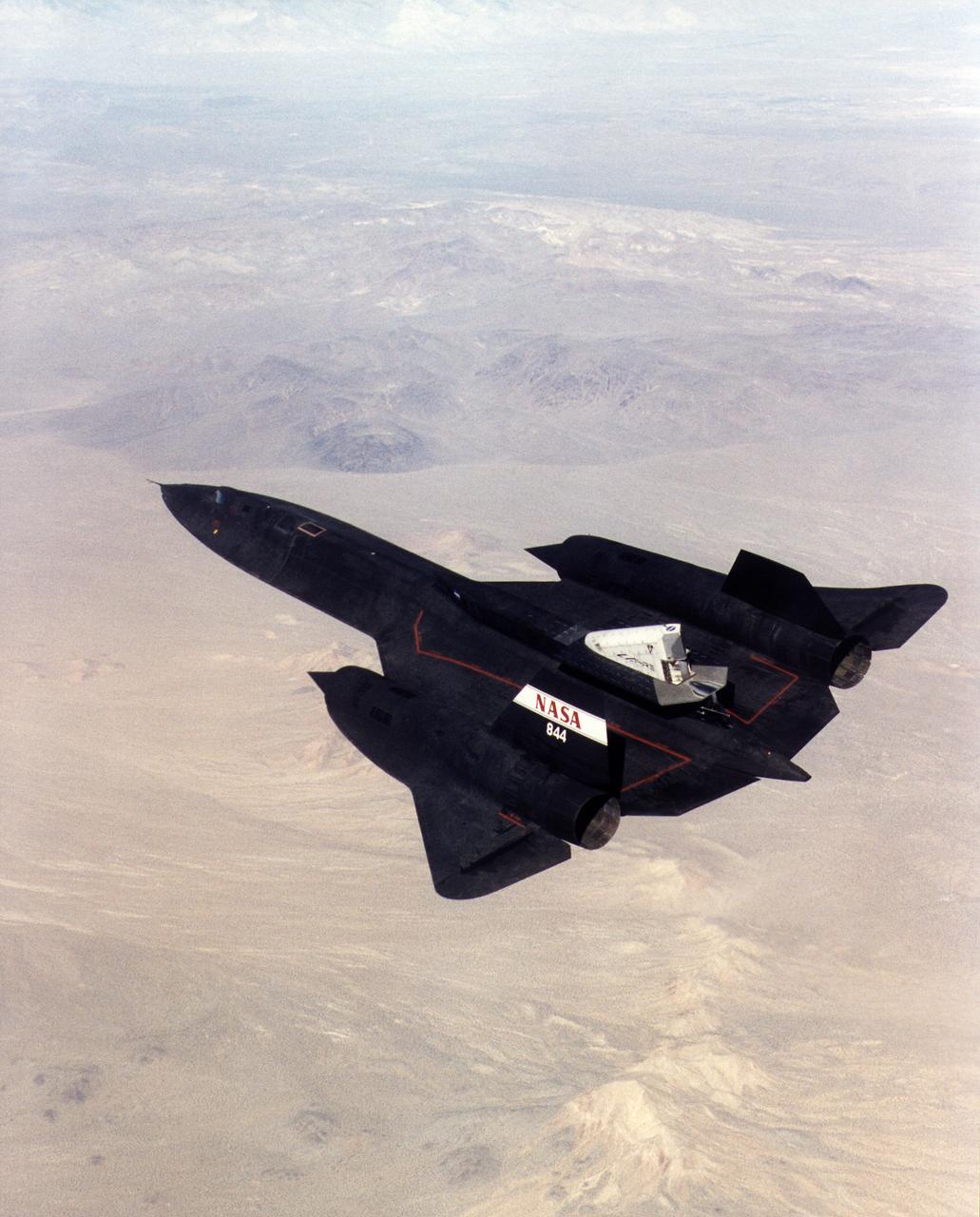

A NASA SR-71 successfully completed its first flight 31 October 1997 as part of the NASA/Rocketdyne/Lockheed Martin Linear Aerospike SR-71 Experiment (LASRE) at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The SR-71 took off at 8:31 a.m. PST. The aircraft flew for one hour and fifty minutes, reaching a maximum speed of Mach 1.2 before landing at Edwards at 10:21 a.m. PST, successfully validating the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The goal of the first flight was to evaluate the aerodynamic characteristics and the handling of the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The engine was not fired during the flight.
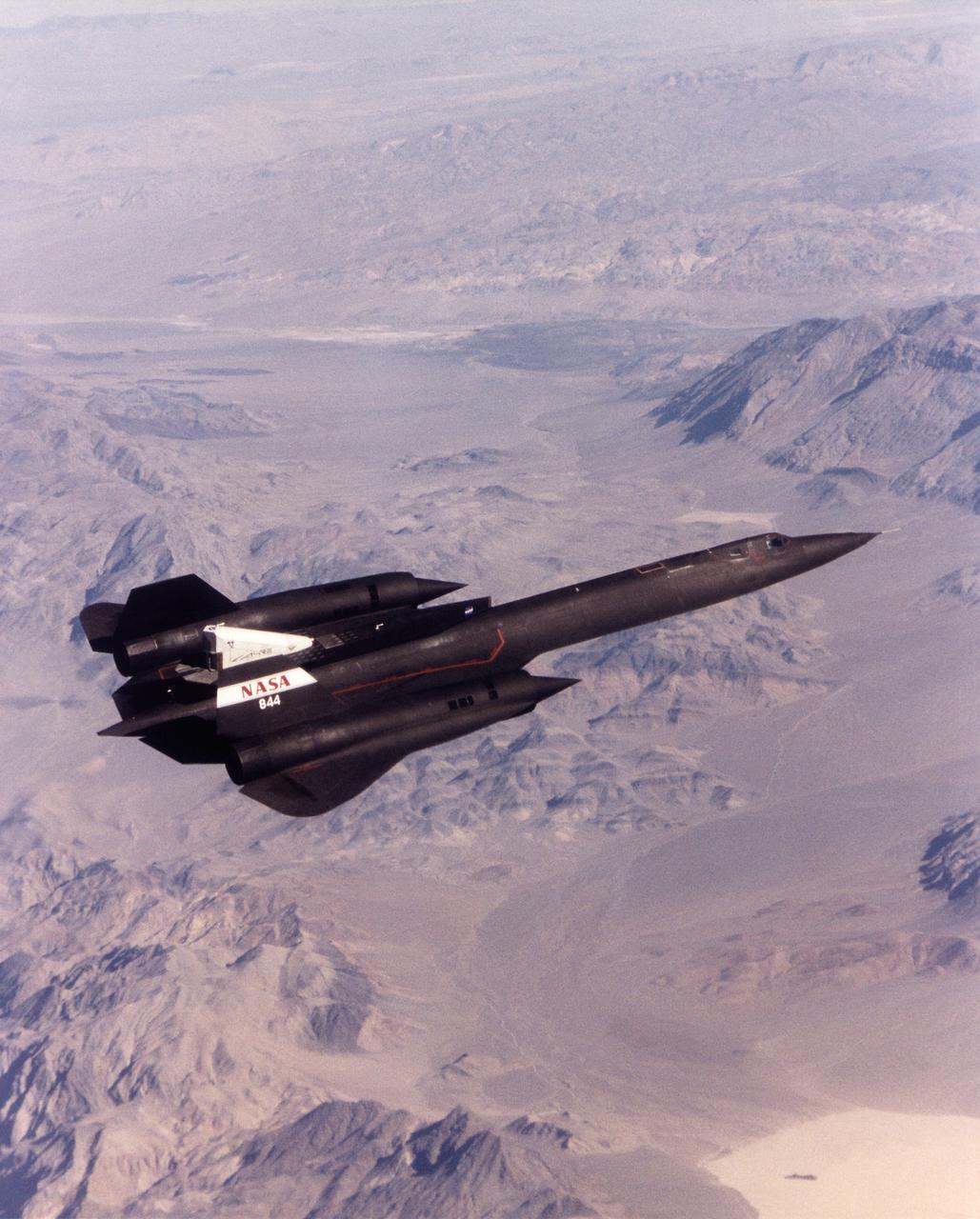

A NASA SR-71 made its successful first flight Oct. 31 as part of the NASA/Rocketdyne/ Lockheed Martin Linear Aerospike SR-71 Experiment (LASRE) at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The SR-71 took off at 8:31 a.m. PST. The aircraft flew for one hour and fifty minutes, reaching a maximum speed of Mach 1.2 before landing at Edwards at 10:21 a.m. PST, successfully validating the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The goal of the first flight was to evaluate the aerodynamic characteristics and the handling of the SR-71/linear aerospike experiment configuration. The engine was not fired during the flight.
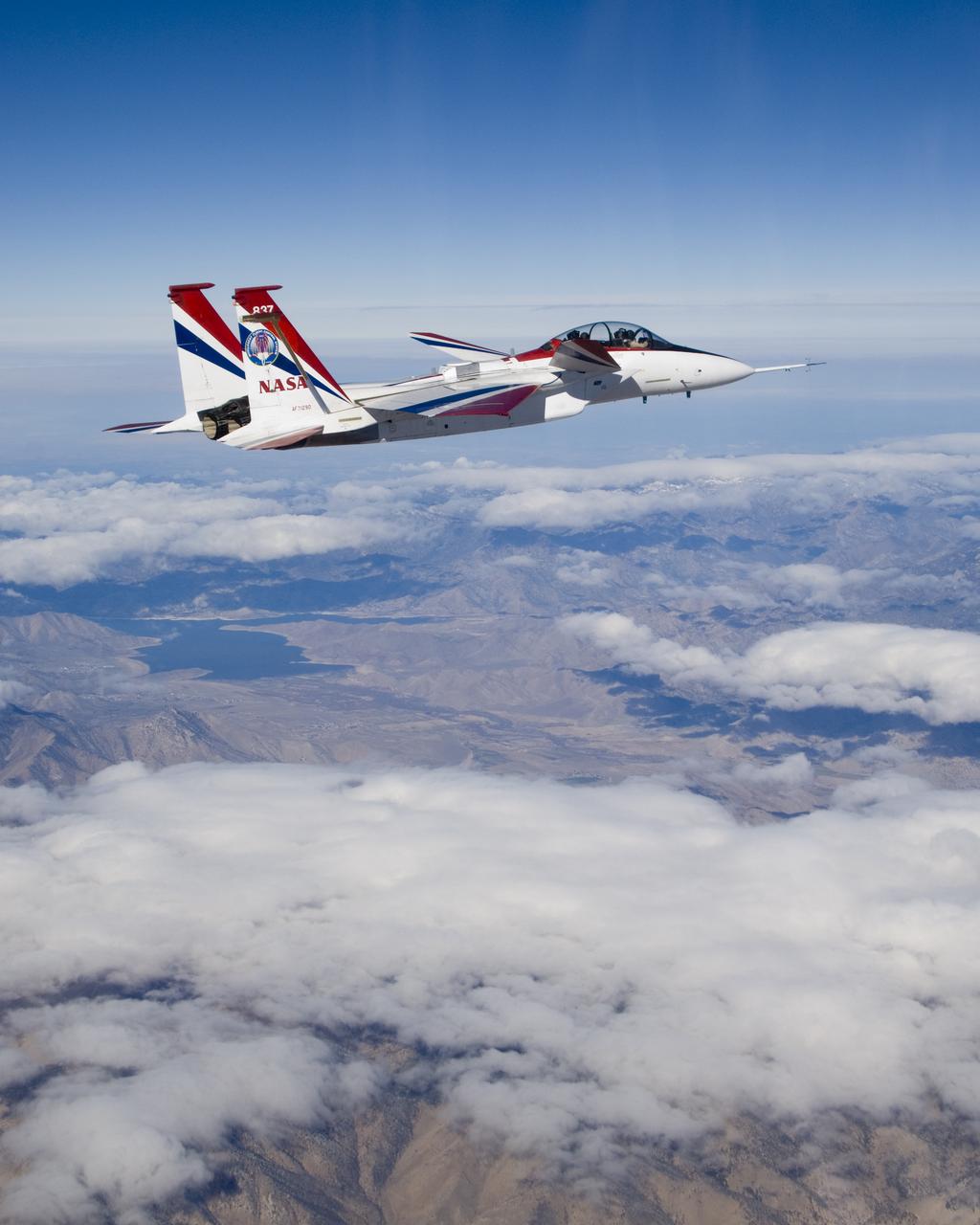

NASA's highly modified NF-15B research aircraft cruises over Southern California's Tehachapi Mountains near Lake Isabella during a research mission.
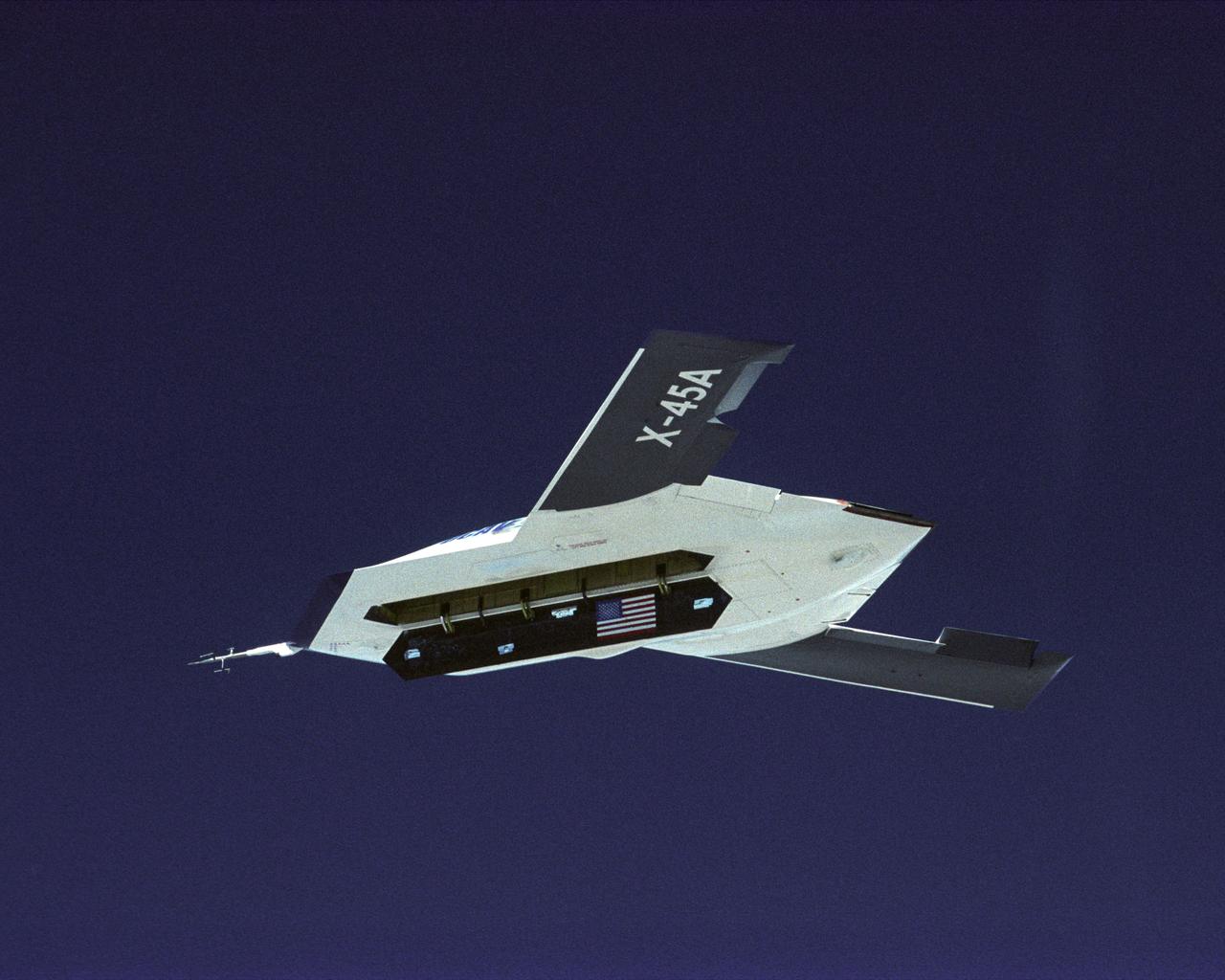

The DARPA/U.S. Air Force X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle (UCAV) system demonstration program completed the first phase of demonstrations, known as Block I, on Feb. 28, 2003. The final Block I activities included two flights at Dryden, during which safe operation of the weapons bay door was verified at 35,000 feet and speeds of Mach 0.75, the maximum planned altitude and speed for the two X-45A demonstrator vehicles.
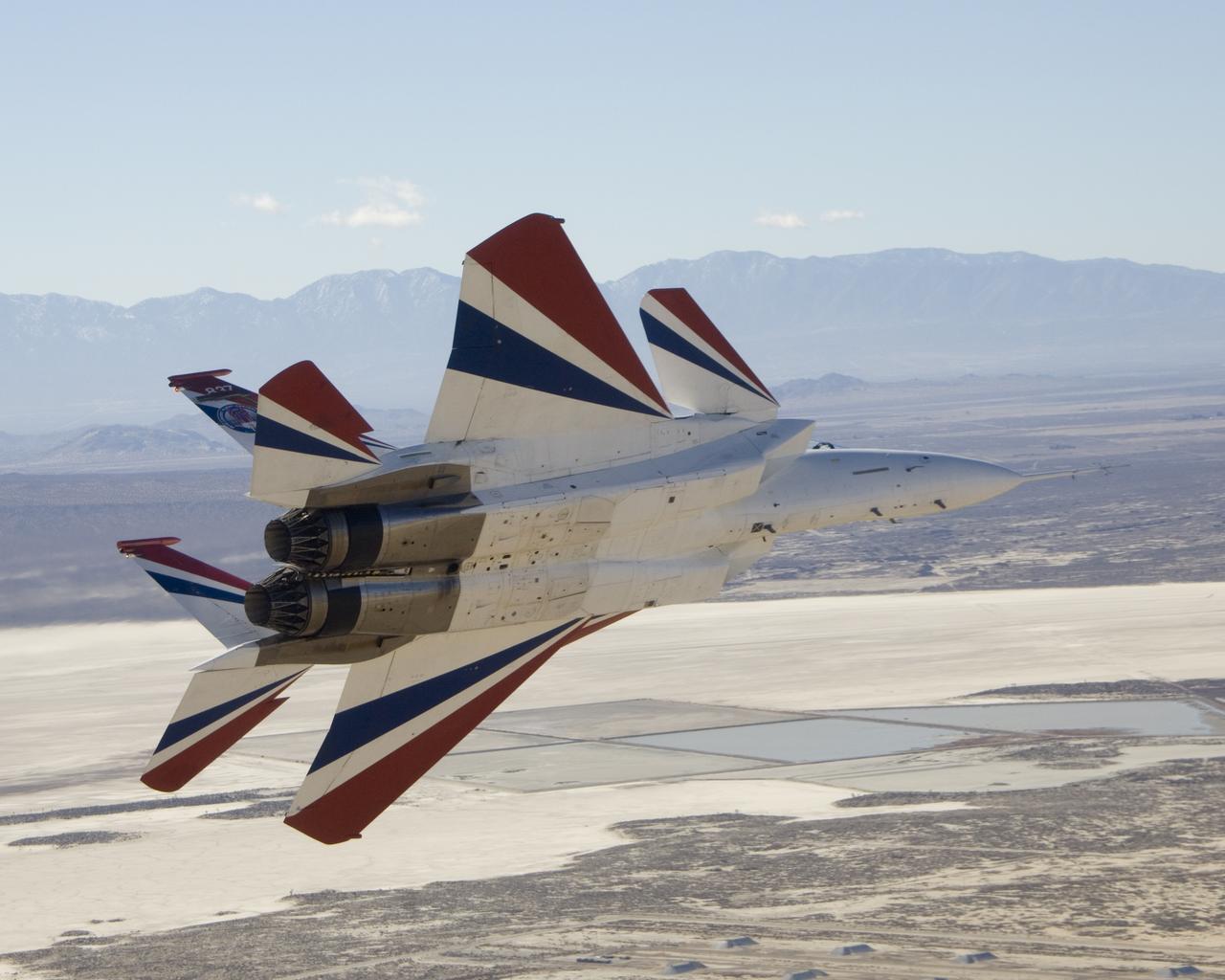

Two small Range Safety System antennas are located just behind the engine inlets of NASA's NF-15B research aircraft as it banks away from the chase plane.
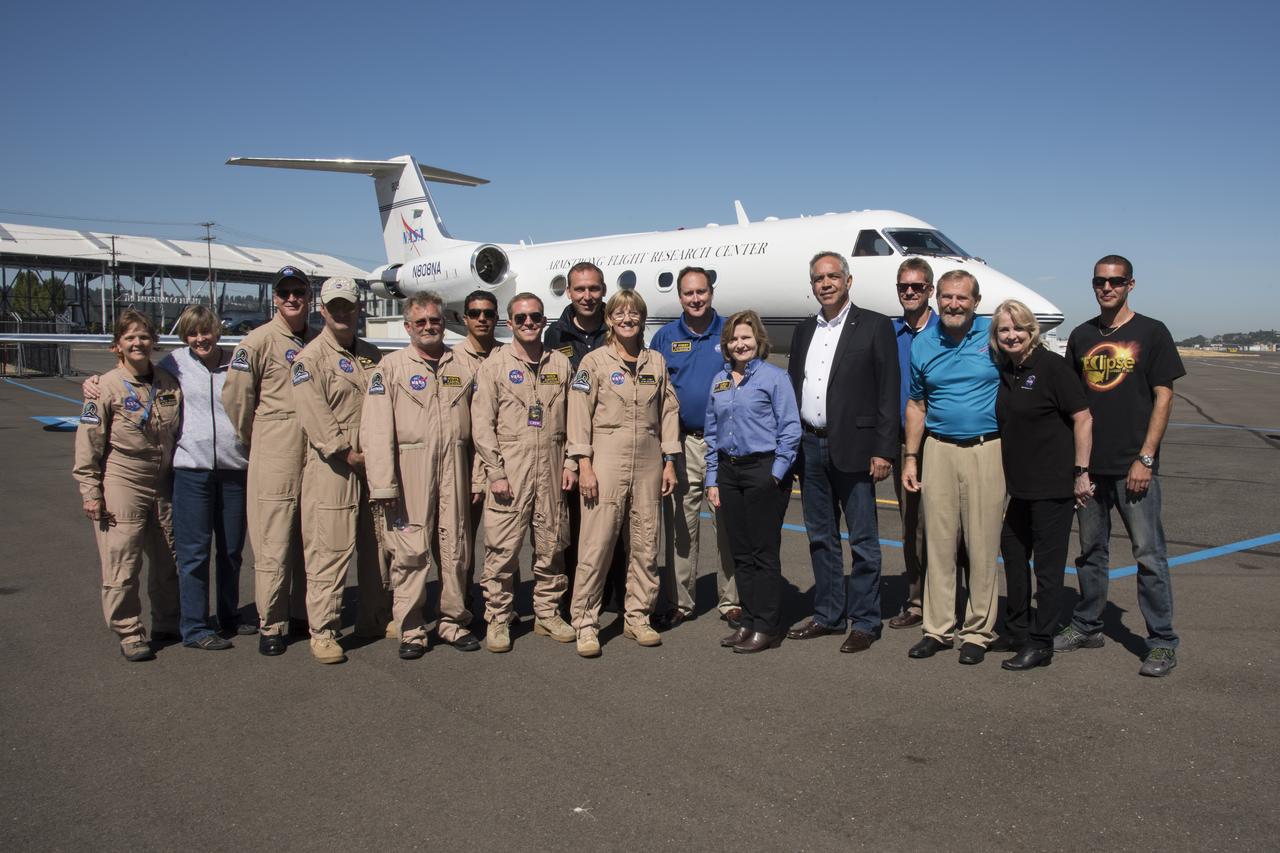

NASA Armstrong and NASA senior management Gulfstream III team pose for group shot by aircraft after return from covering Total solar eclipse. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Thomas)
