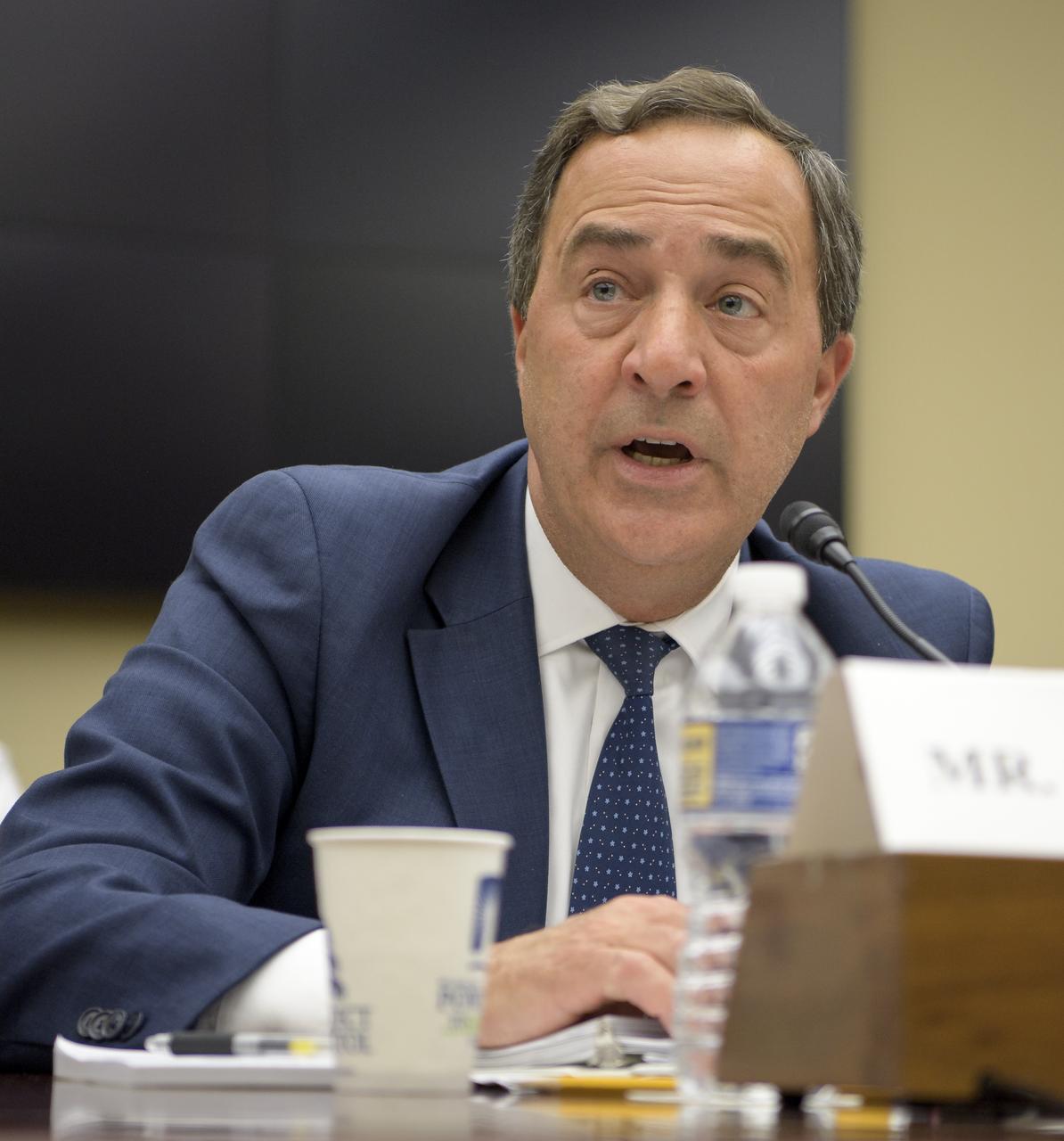

NASA Special Assistant to the Administrator Mark Sirangelo testifies during the House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
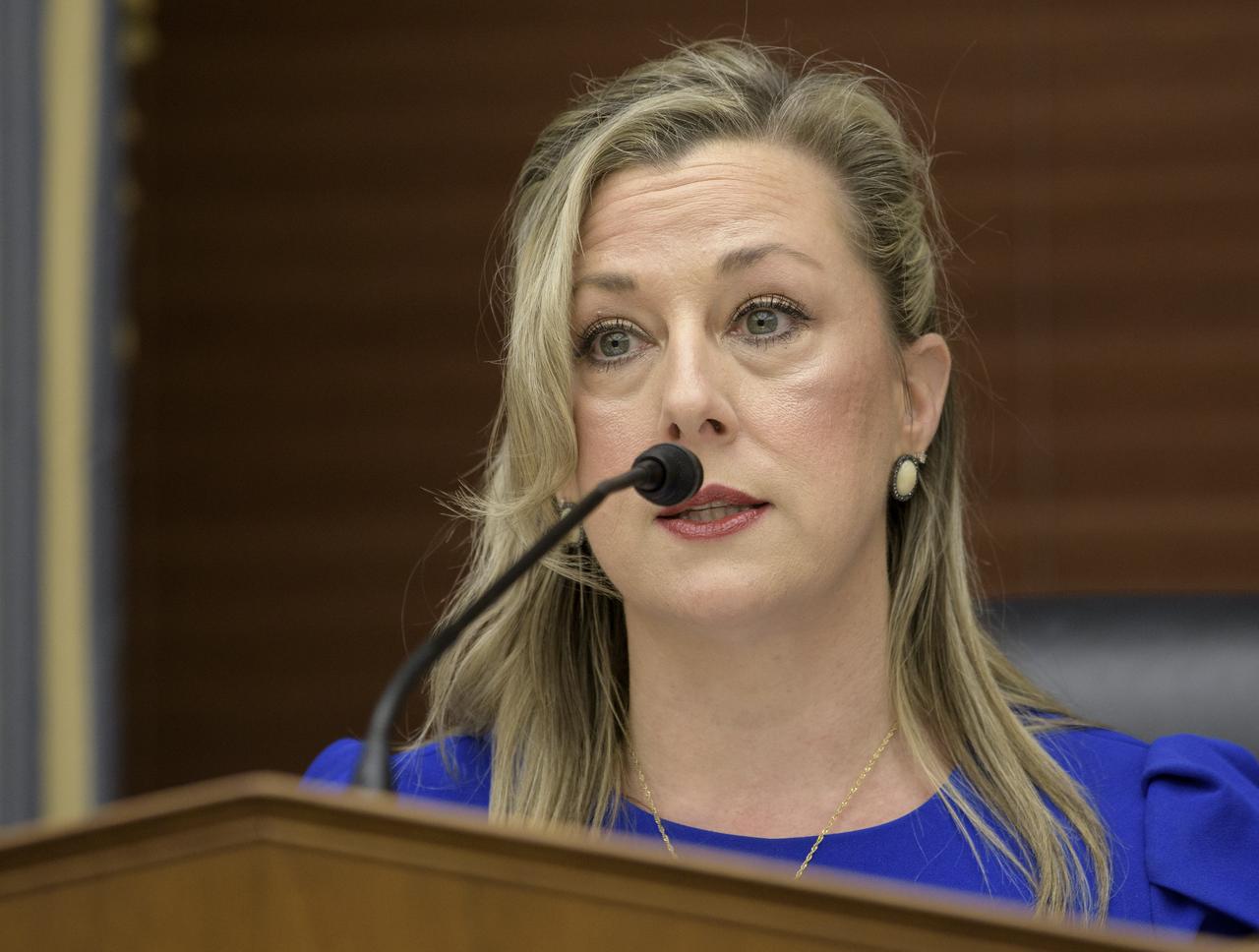

Chair Kendra Horn, D-OK., opens the House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
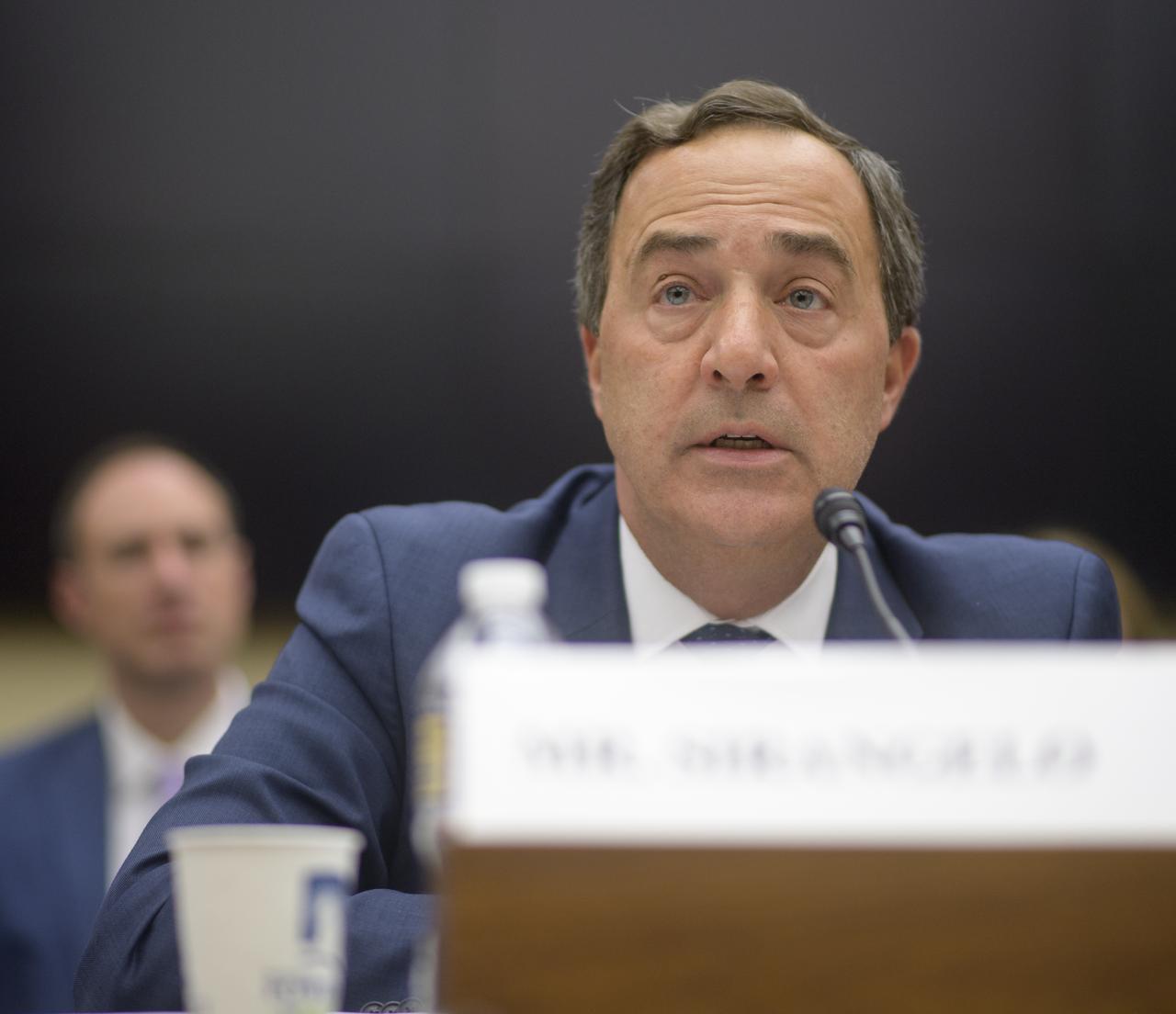

NASA Special Assistant to the Administrator Mark Sirangelo testifies during the House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
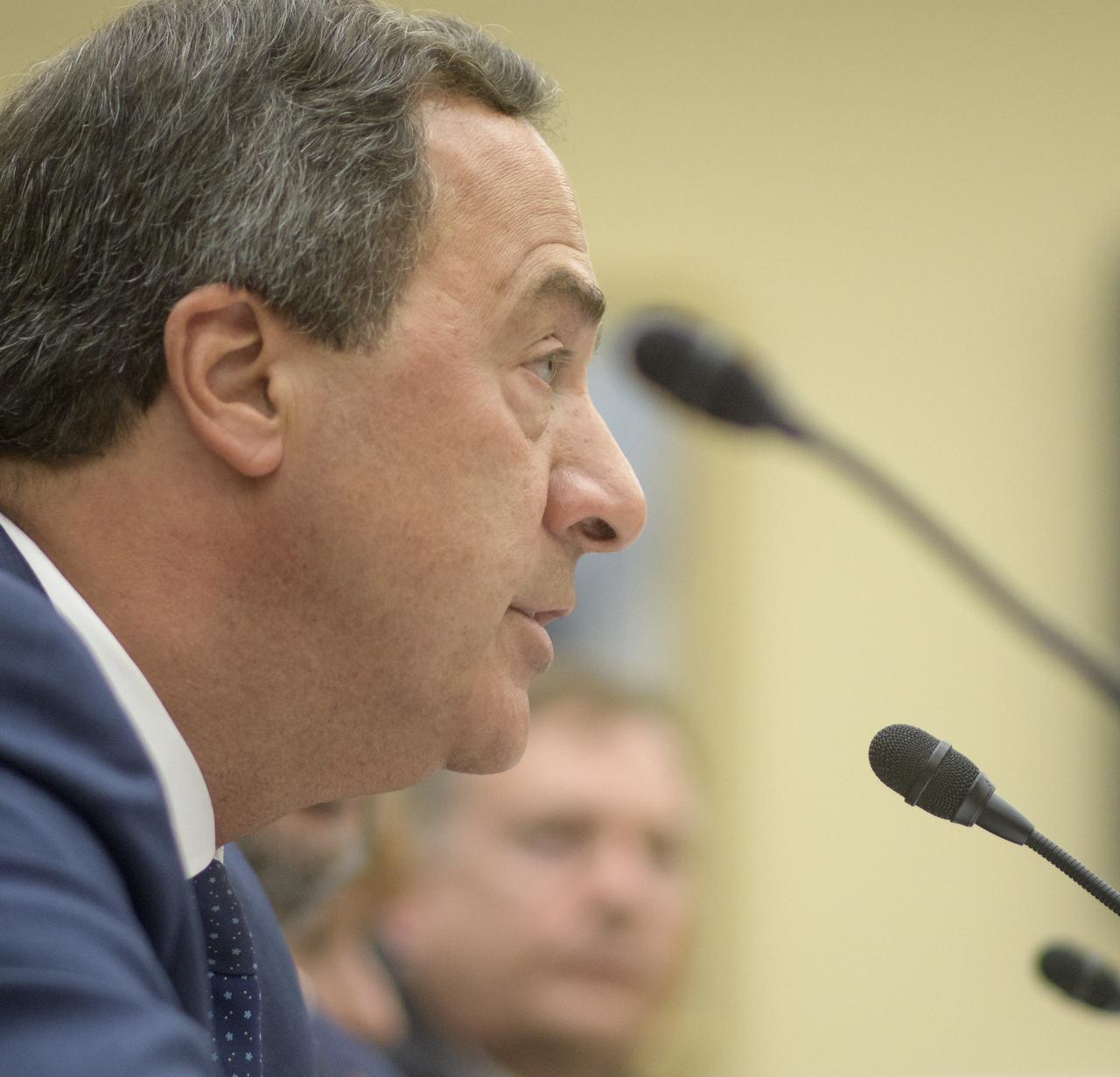

NASA Special Assistant to the Administrator Mark Sirangelo testifies during the House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Special Assistant to the Administrator Mark Sirangelo listens as NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations William Gerstenmaier testifies during the House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Portraits of past House Science and Technology Committee Chairmen, Sherwood Boehlert, left, and Ralph Hall are seen as NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations William Gerstenmaier testifies during a House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
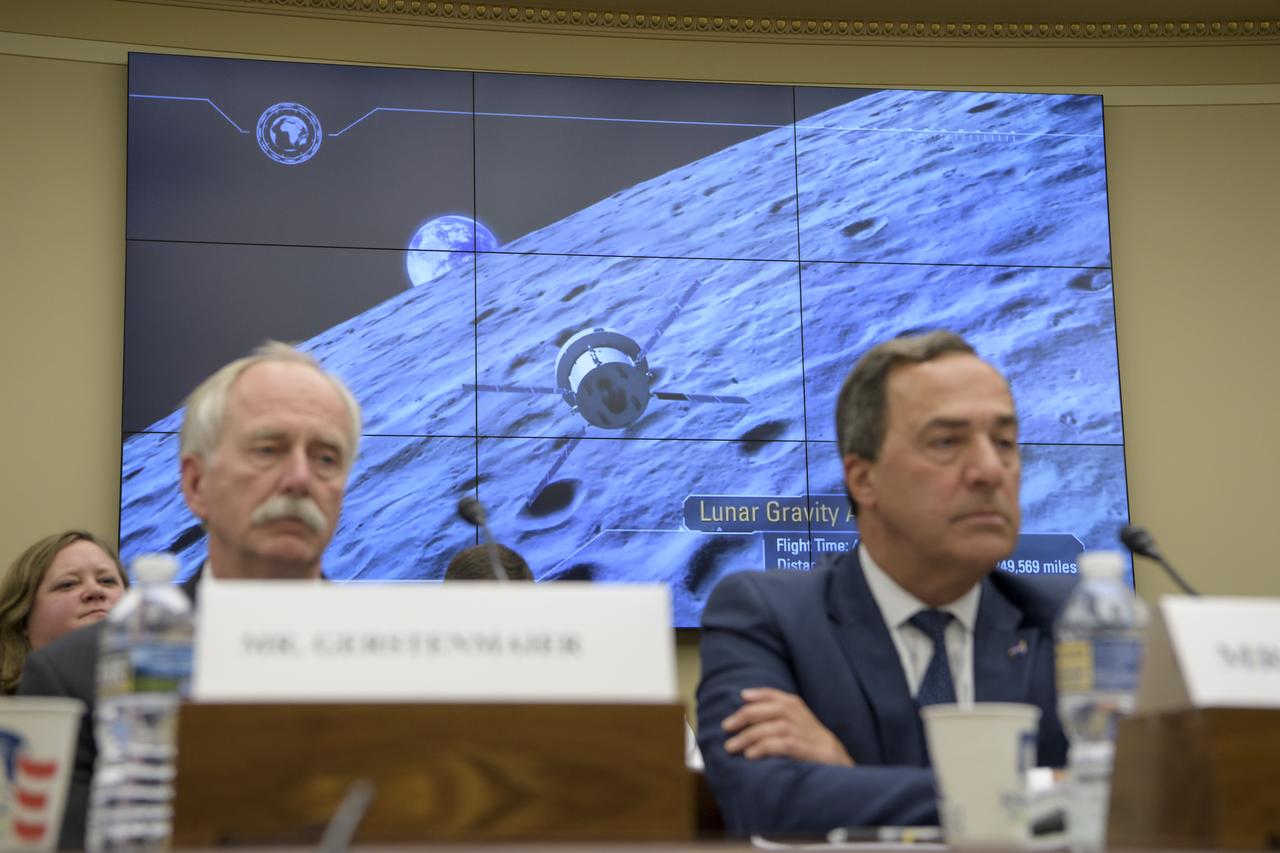

NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations William Gerstenmaier, left, and NASA Special Assistant to the Administrator Mark Sirangelo, watch as a video is played during the House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations William Gerstenmaier testifies during the House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
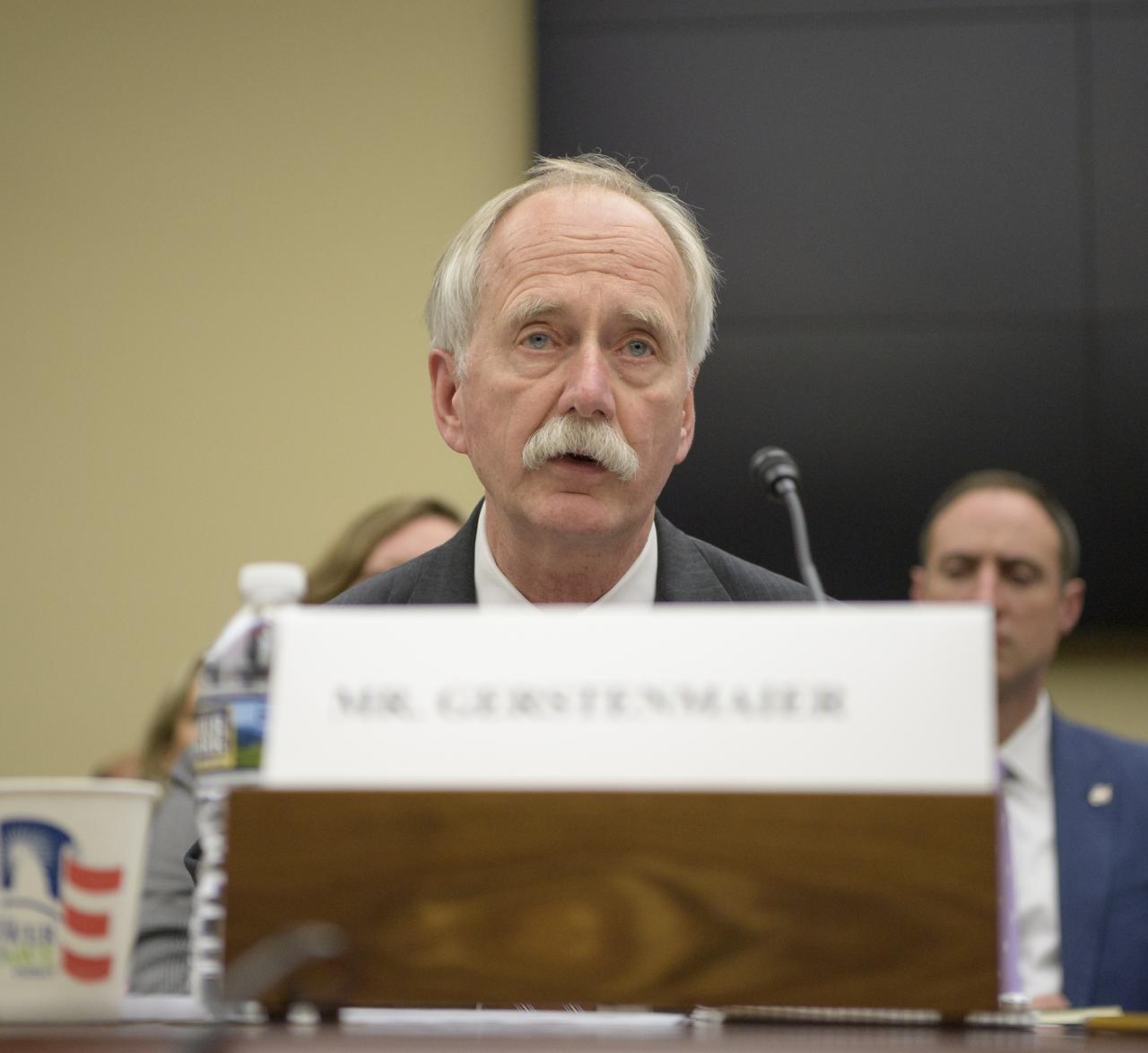

NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations William Gerstenmaier testifies during the House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
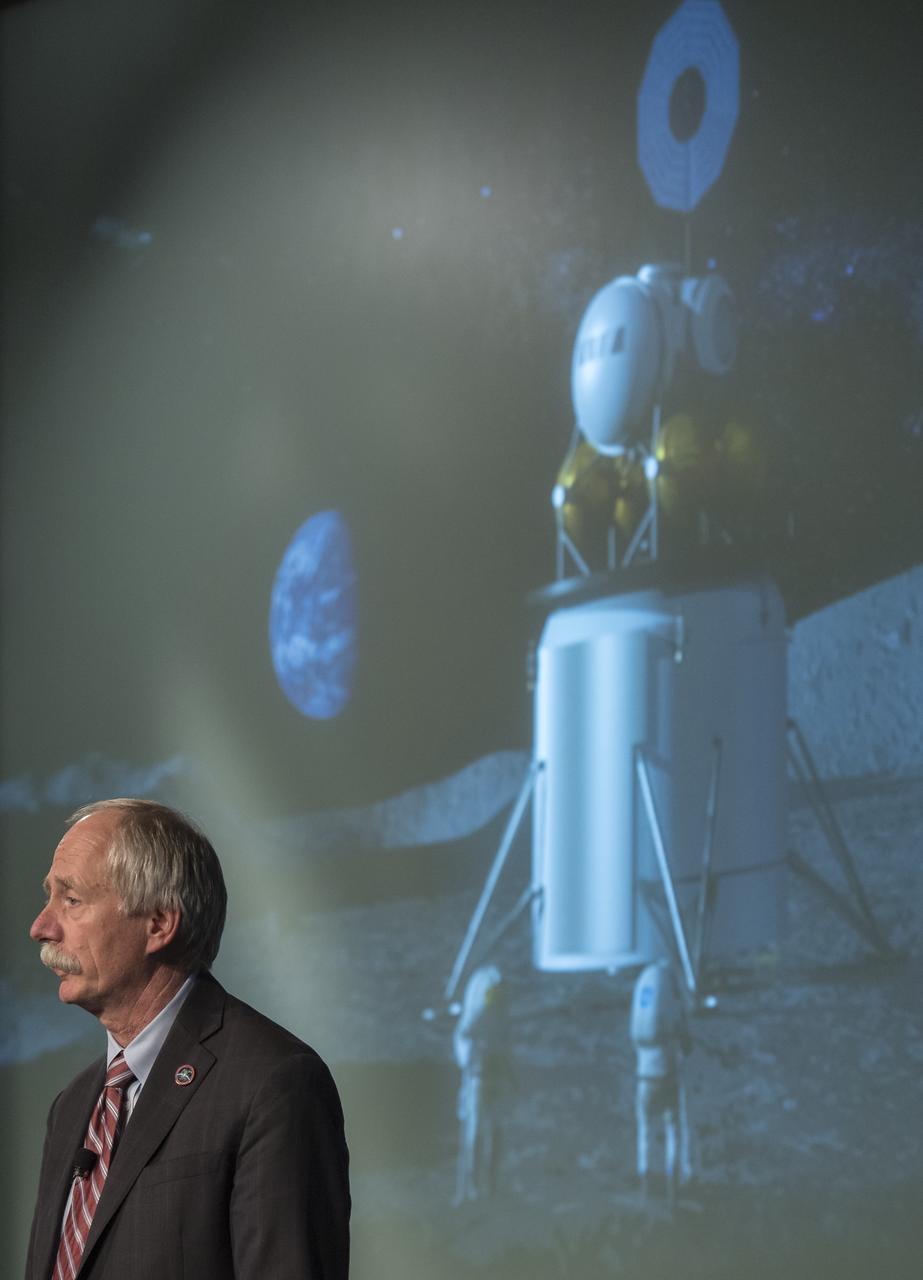

NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate William Gerstenmaier speaks at the opening of an industry forum on the agency's lunar exploration plans, Thursday, Feb. 14, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The agency will work with industry to study and refine the approach to landing on the Moon, which includes a system of three separate elements that will provide astronauts transportation, landing, and safe return. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
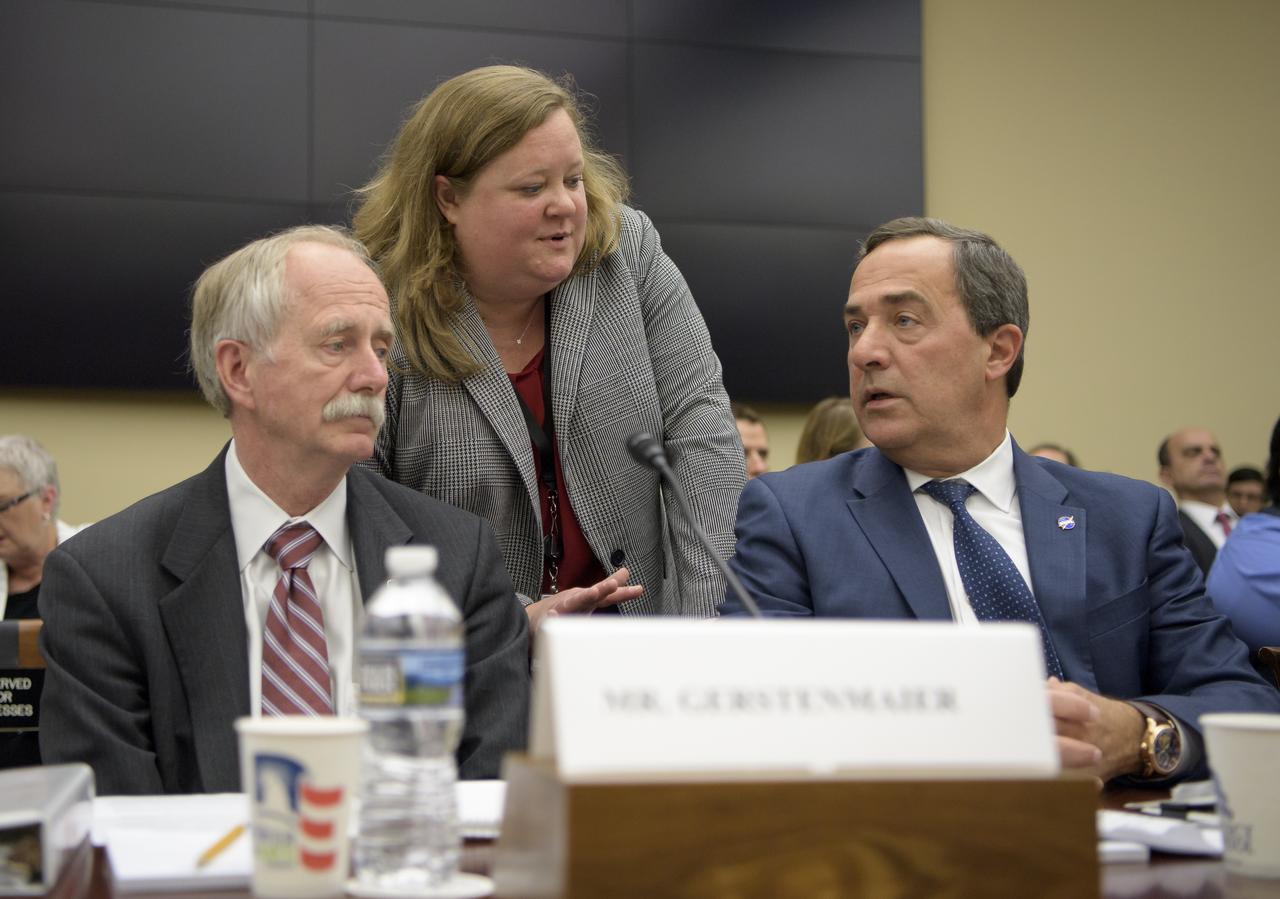

NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations William Gerstenmaier, left, NASA Associate Administrator for Legislative Affairs Suzanne Gillen, center, and NASA Special Assistant to the Administrator Mark Sirangelo, confer prior to the start of the House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
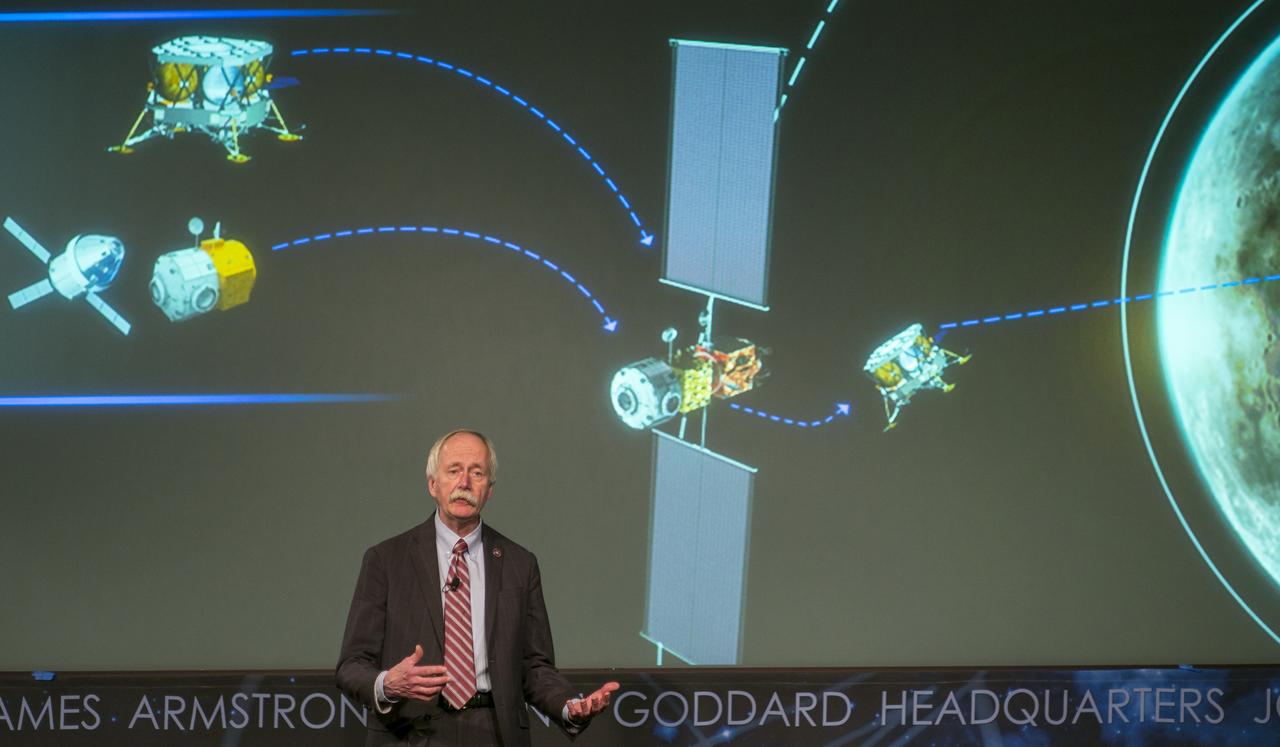
NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate William Gerstenmaier speaks at the opening of an industry forum on the agency's lunar exploration plans, Thursday, Feb. 14, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The agency will work with industry to study and refine the approach to landing on the Moon, which includes a system of three separate elements that will provide astronauts transportation, landing, and safe return. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations William Gerstenmaier testifies during the House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate William Gerstenmaier speaks at the opening of an industry forum on the agency's lunar exploration plans, Thursday, Feb. 14, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The agency will work with industry to study and refine the approach to landing on the Moon, which includes a system of three separate elements that will provide astronauts transportation, landing, and safe return. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
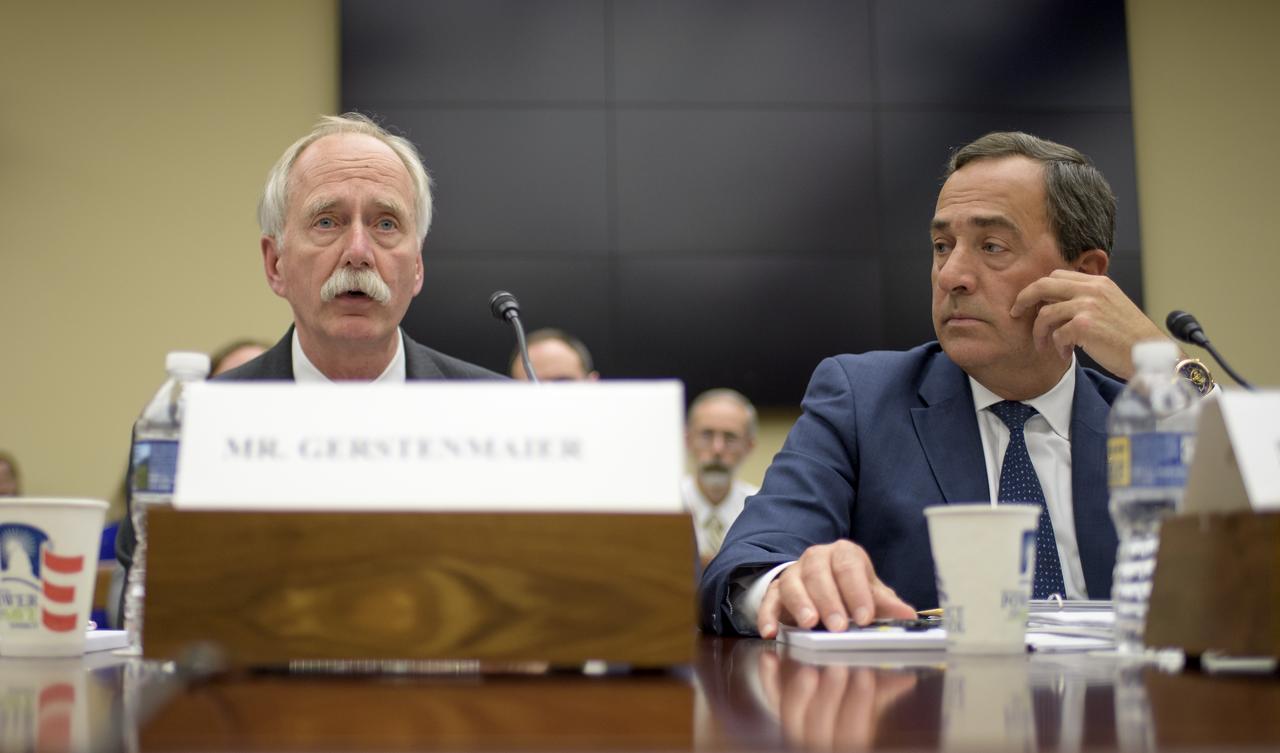

NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations William Gerstenmaier, left, and NASA Special Assistant to the Administrator Mark Sirangelo, testify during the House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
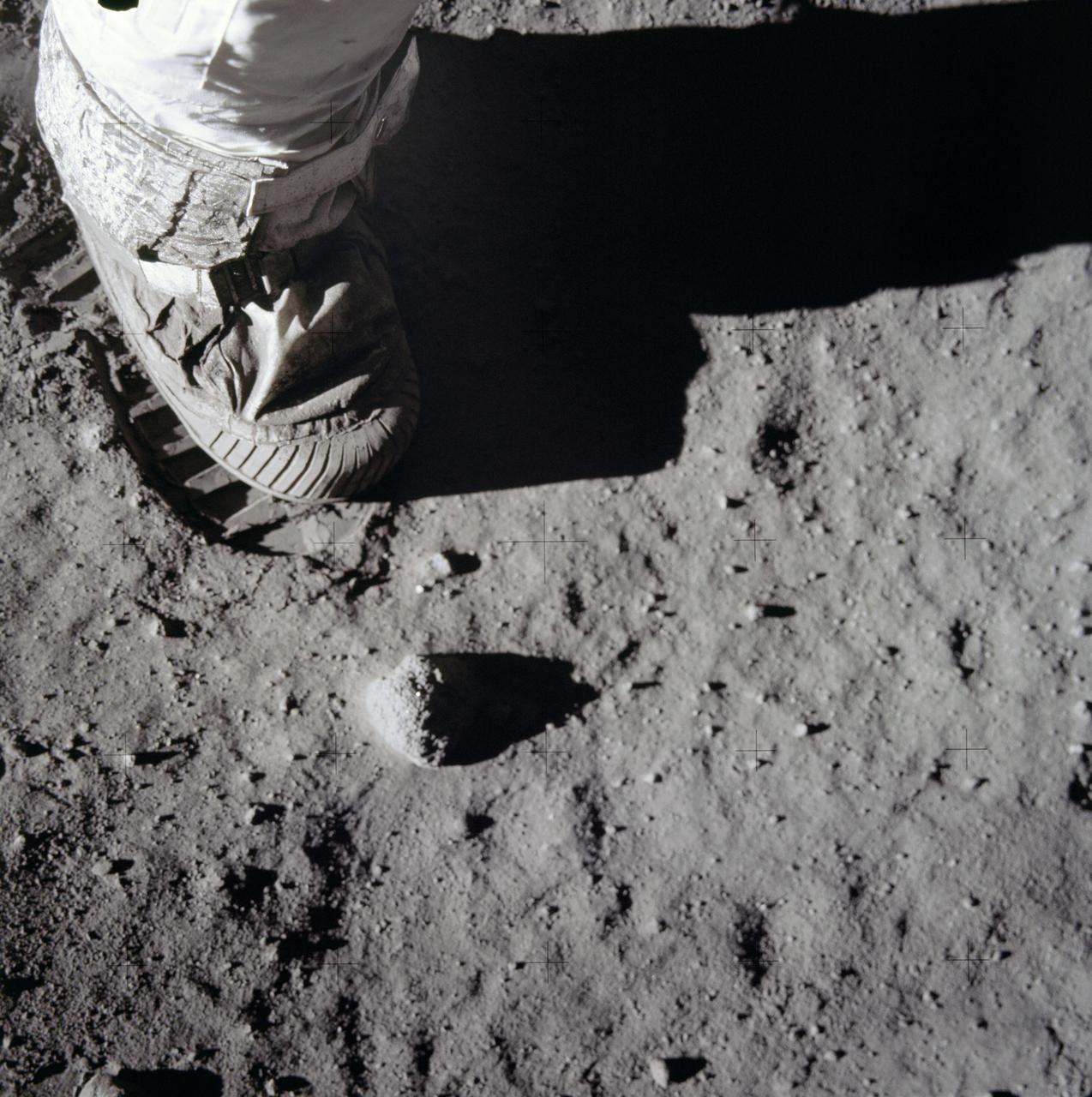

AS11-40-5880 (20 July 1969) --- A close-up view of an astronaut's boot and bootprint in the lunar soil, photographed with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin A. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM)" Columbia" in lunar orbit.
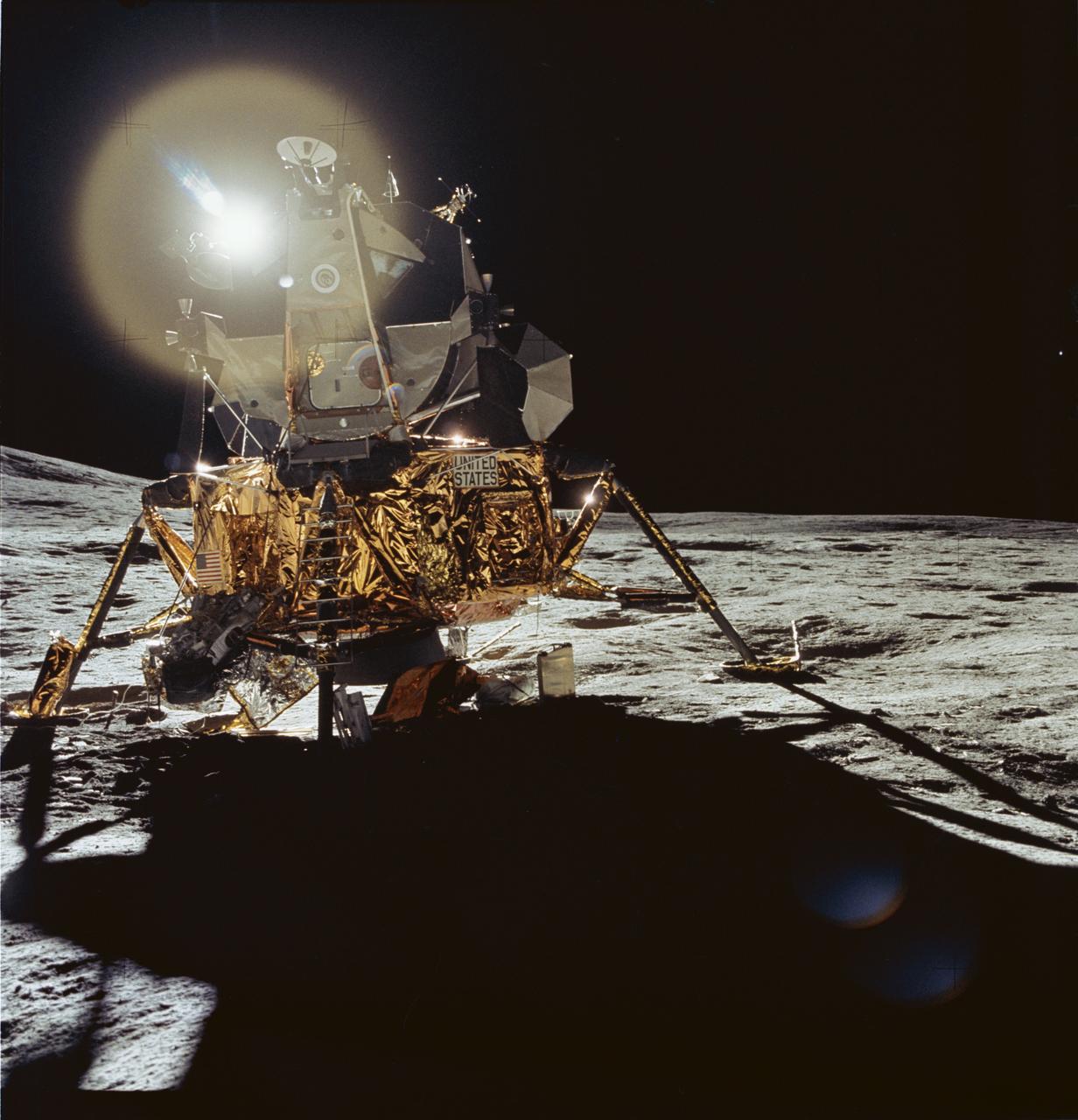

AS14-66-9306 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A front view of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM), which reflects a circular flare caused by the brilliant sun, as seen by the two moon-exploring crew men of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission during their first extravehicular activity (EVA). The unusual ball of light was said by the astronauts to have a jewel-like appearance. At the extreme left the lower slope of Cone Crater can be seen. Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; descended in the LM, while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
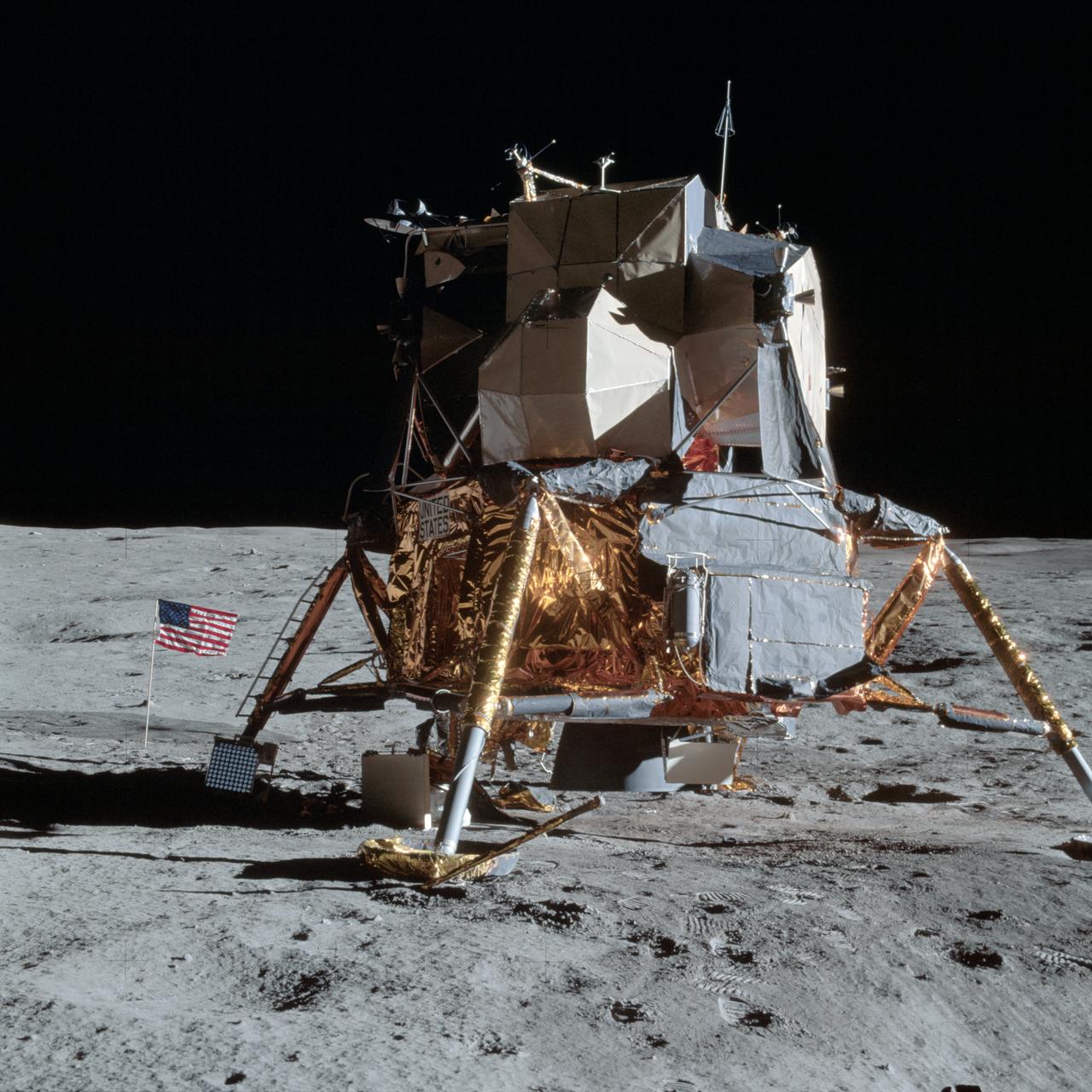
AS14-66-9277 (5 Feb. 1971) --- An excellent view of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) on the moon, as photographed during the first Apollo 14 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The astronauts have already deployed the U.S. flag. Note the laser ranging retro reflector (LR-3) at the foot of the LM ladder. The LR-3 was deployed later. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
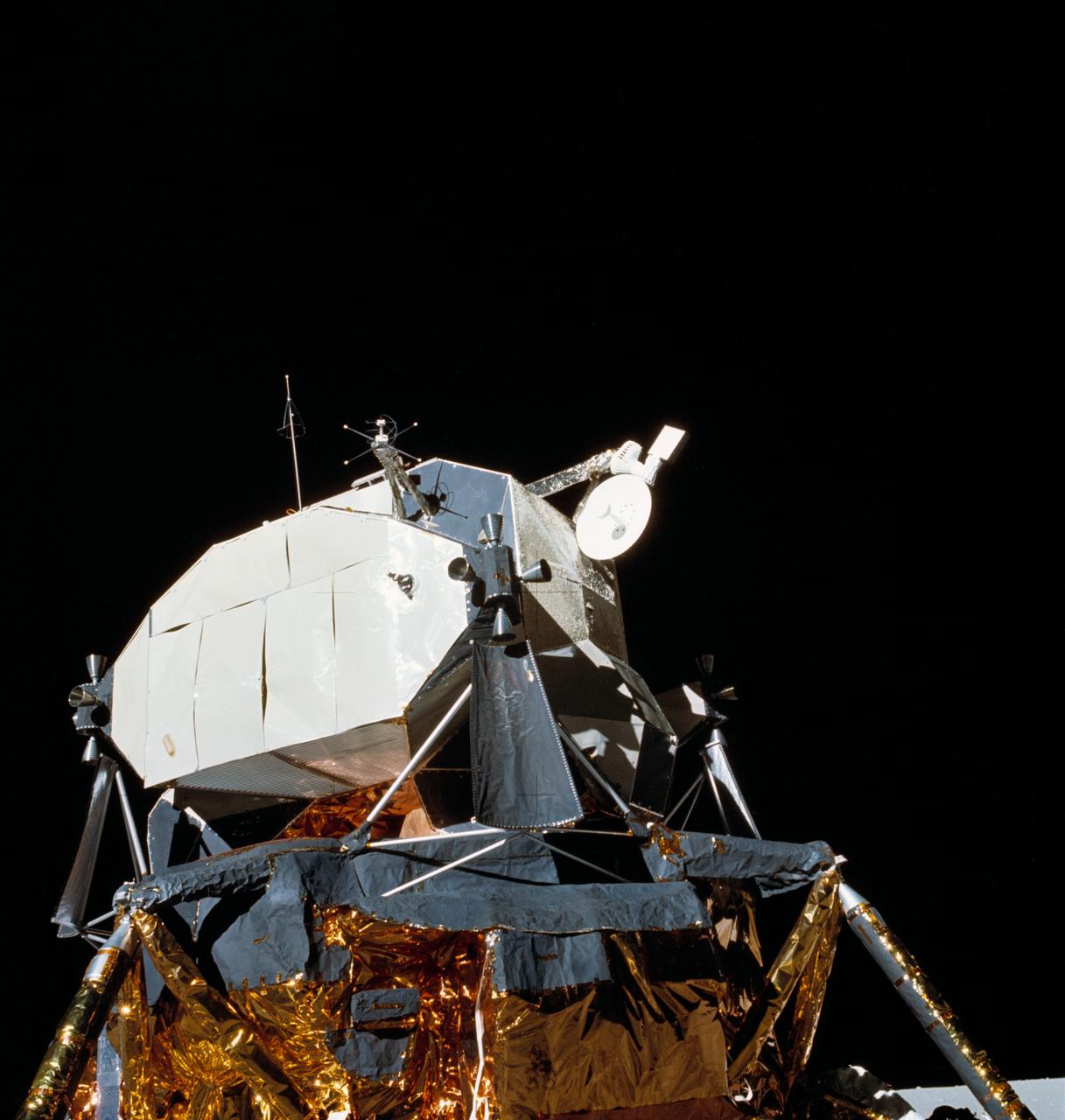

AS16-113-18334 (21 April 1972) --- View of the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" parked on the lunar surface. During their post mission press conference, the Apollo 16 crewmembers called attention to the steerable S-band antenna, which was "frozen" in a yaw axis during much of the flight. This view of the LM was photographed by astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., the lunar module pilot, during the mission's first extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronauts John W. Young, commander, and Duke had earlier descended in the LM to explore the Descartes region of the moon, while astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.

AS11-40-5878 (20 July 1969) --- A close-up view of an astronaut's bootprint in the lunar soil, photographed with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. While astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.

AS11-40-5875 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot of the first lunar landing mission, poses for a photograph beside the deployed United States flag during an Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The Lunar Module (LM) is on the left, and the footprints of the astronauts are clearly visible in the soil of the moon. Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm Hasselblad lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM, the "Eagle", to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit. Photo credit: NASA

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine speaks at the opening of an industry forum on the agency's lunar exploration plans, Thursday, Feb. 14, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The agency will work with industry to study and refine the approach to landing on the Moon, which includes a system of three separate elements that will provide astronauts transportation, landing, and safe return. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
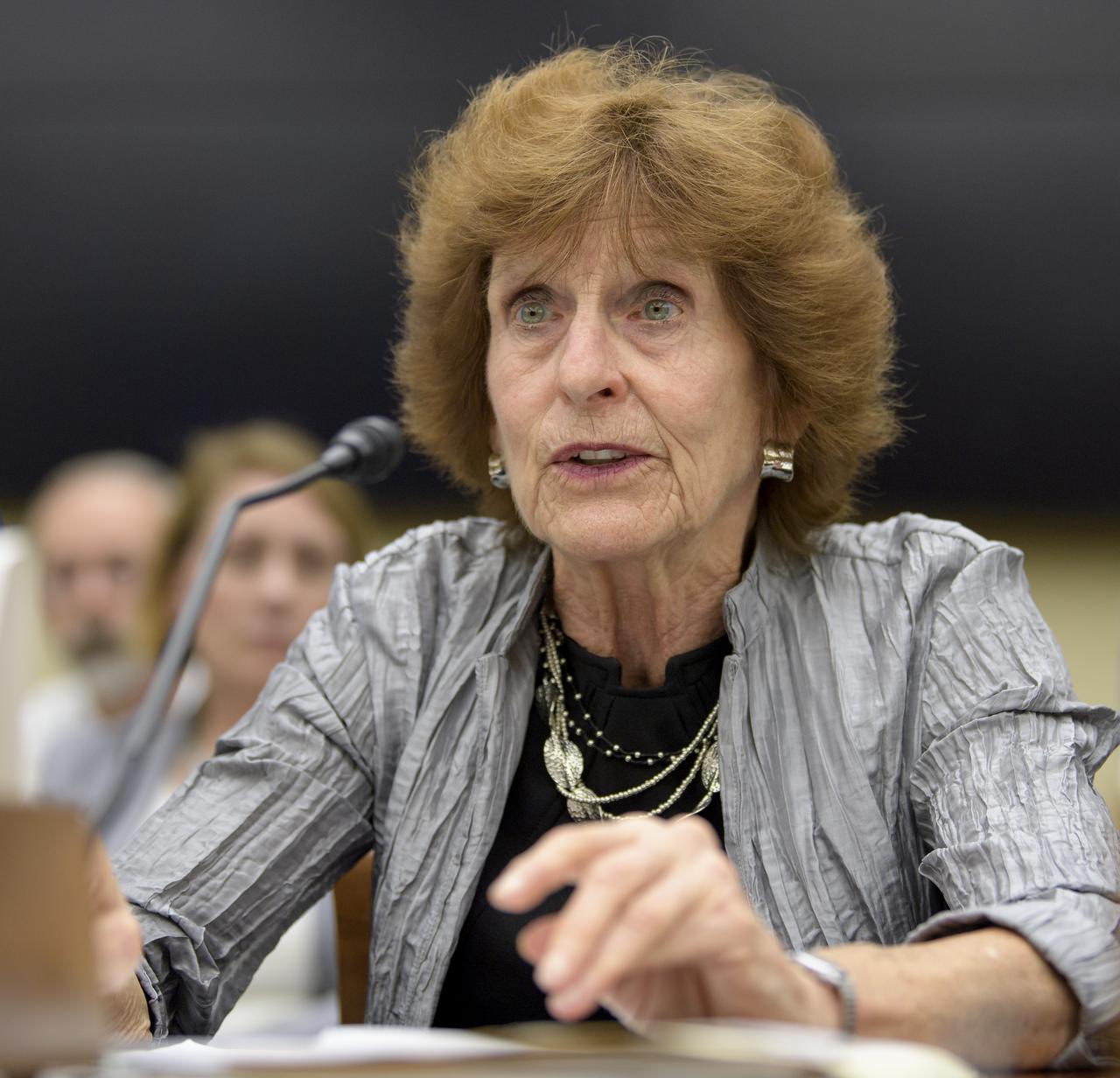

Dr. Patricia Sanders, Chair, Aerospace Safety Advisory Panel testifies during the House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
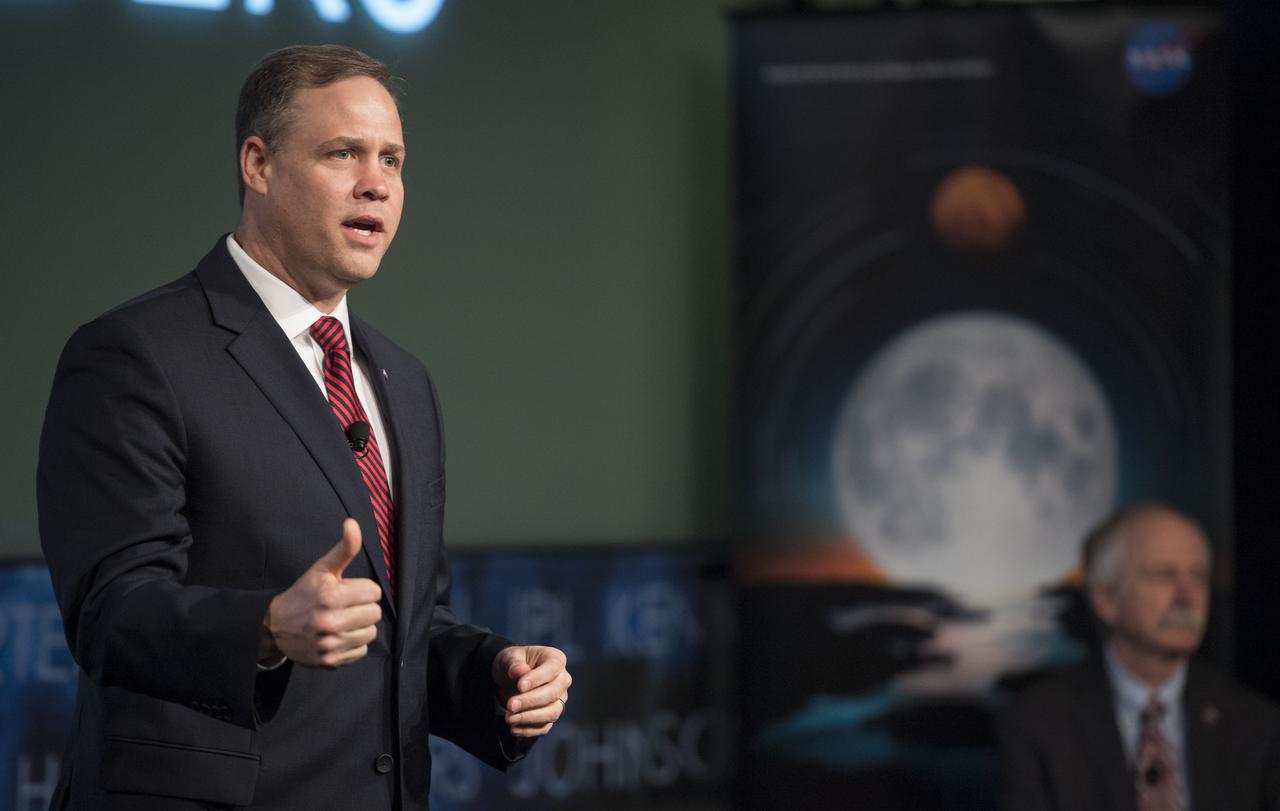

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine speaks at the opening of an industry forum on the agency's lunar exploration plans, Thursday, Feb. 14, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The agency will work with industry to study and refine the approach to landing on the Moon, which includes a system of three separate elements that will provide astronauts transportation, landing, and safe return. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine speaks at the opening of an industry forum on the agency's lunar exploration plans, Thursday, Feb. 14, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The agency will work with industry to study and refine the approach to landing on the Moon, which includes a system of three separate elements that will provide astronauts transportation, landing, and safe return. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
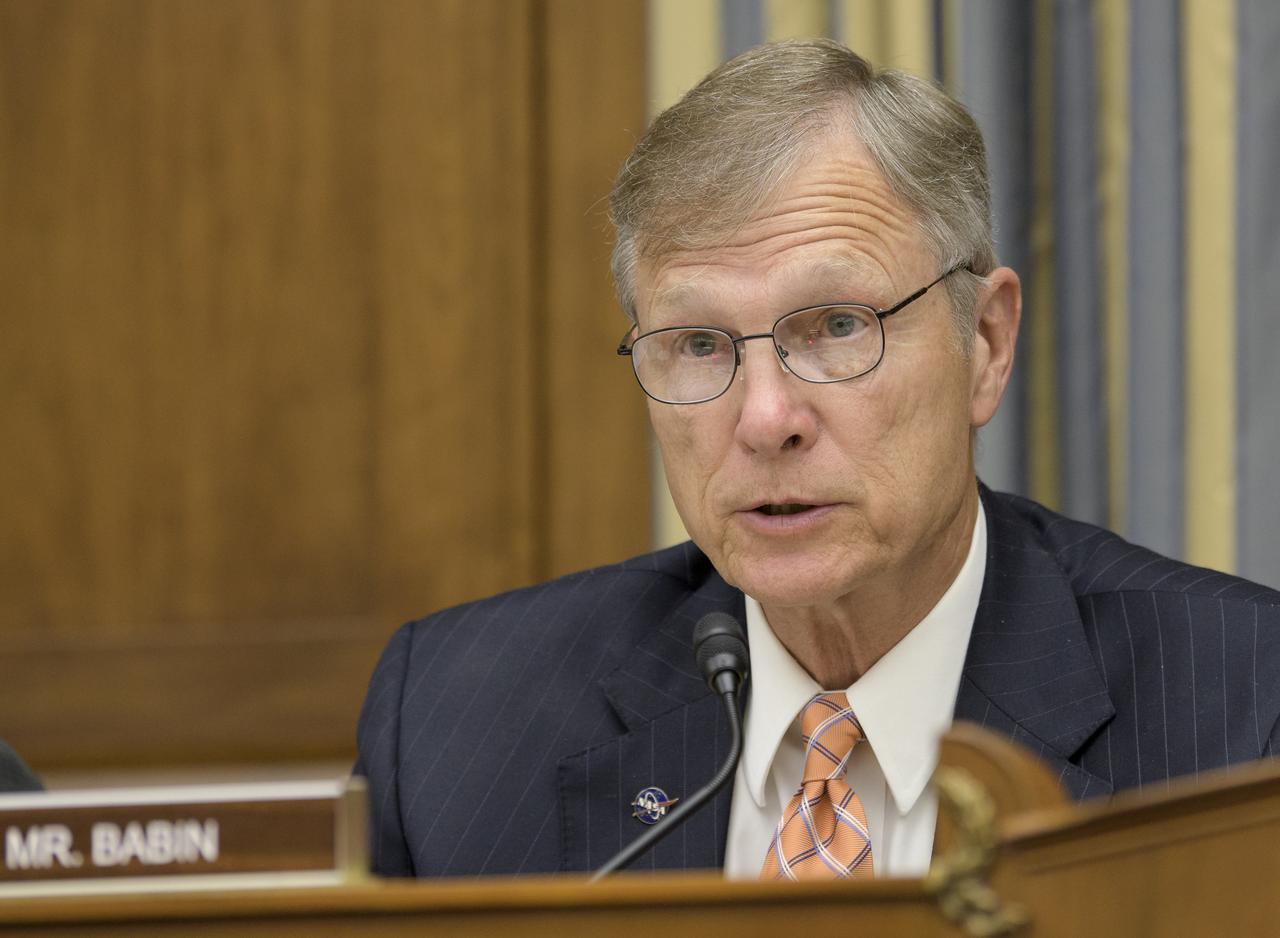
Rep. Brian Babin, R - Texas, gives opening remarks during the House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Associate Administrator for the Office of Communications Bettina Inclán speaks at the opening an industry forum on the agency's lunar exploration plans, Thursday, Feb. 14, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The agency will work with industry to study and refine the approach to landing on the Moon, which includes a system of three separate elements that will provide astronauts transportation, landing, and safe return. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
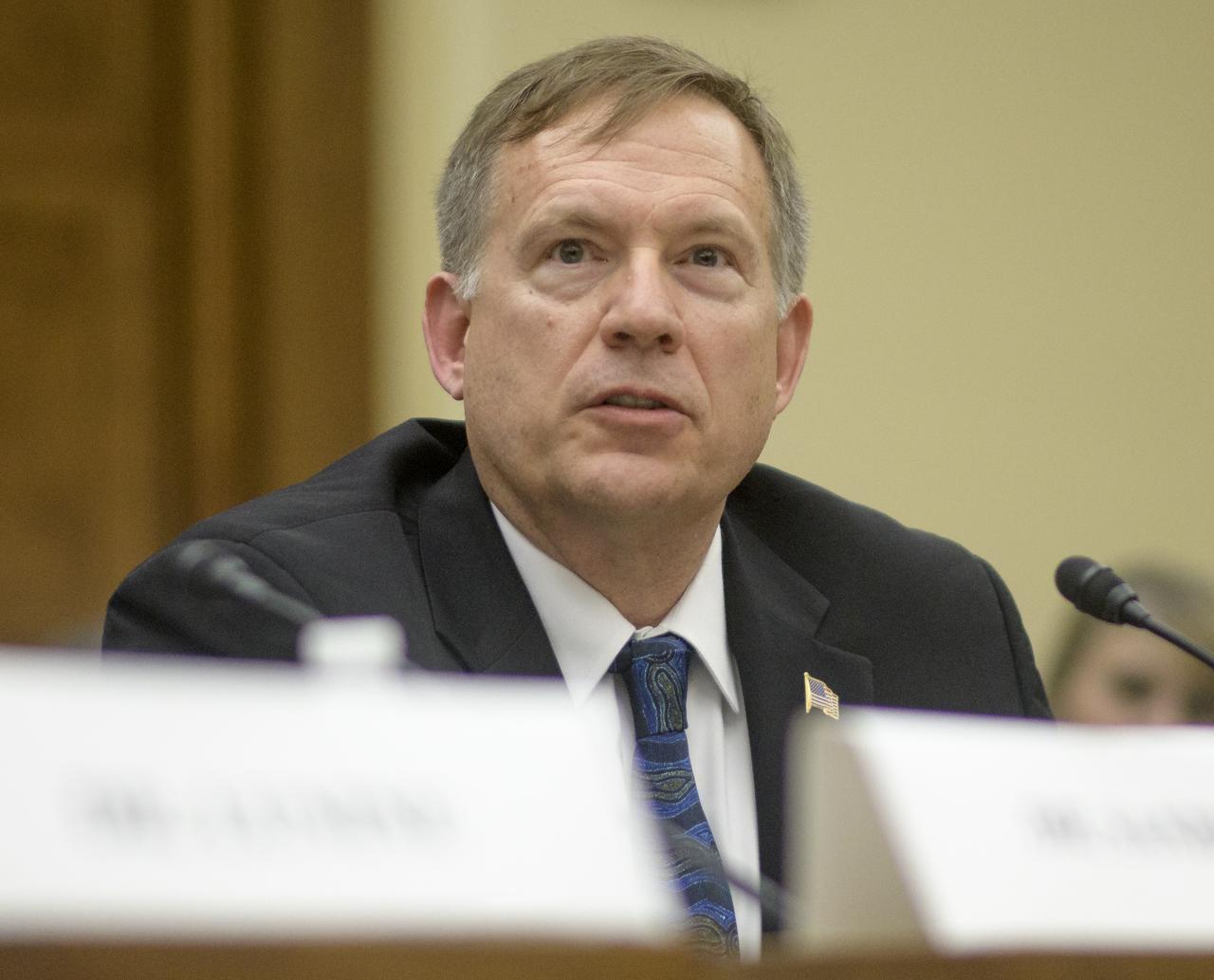

Mr. Walt Faulconer, President, Faulconer Consulting Group, LLC testifies during the House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
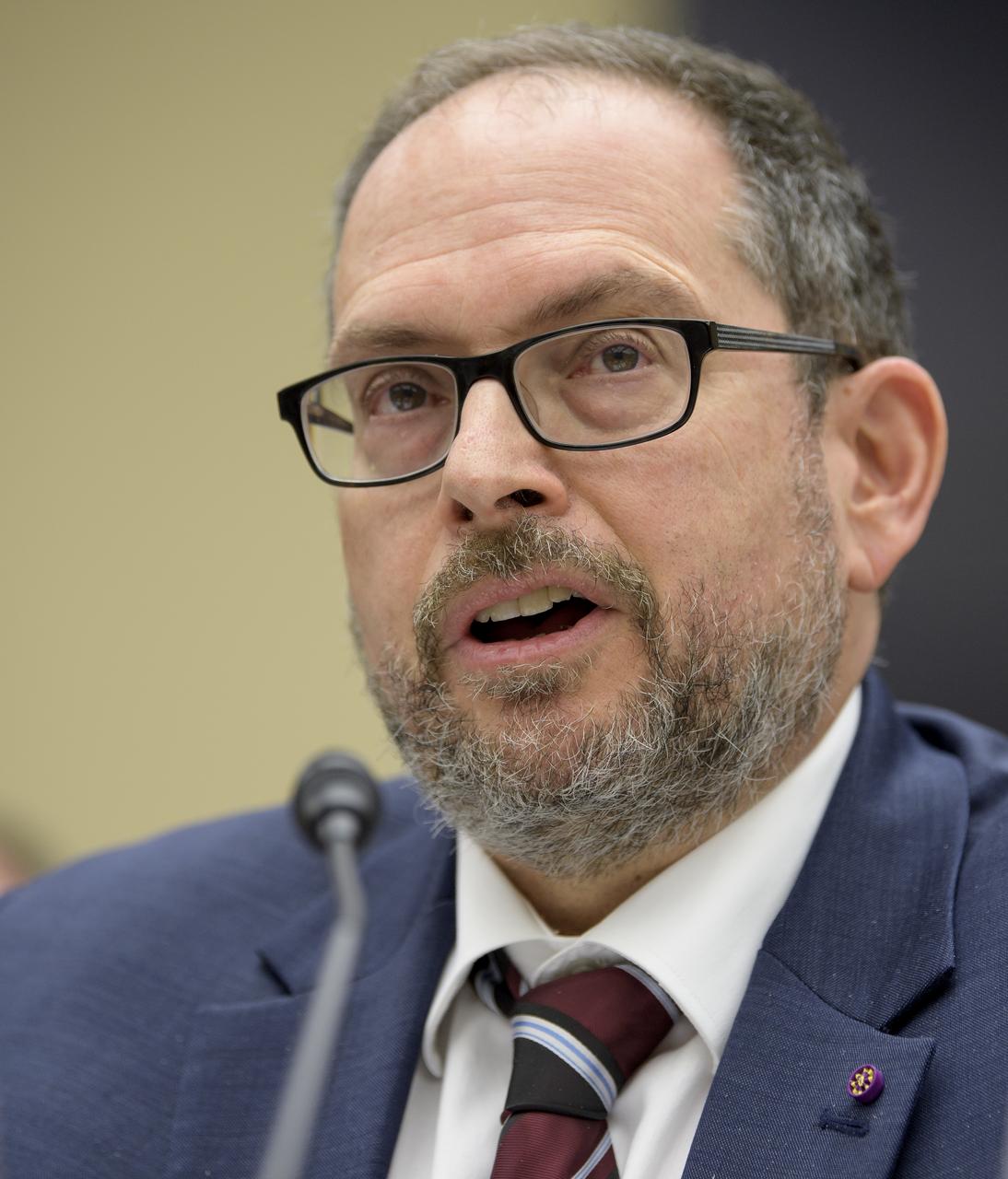

Dr. Jonathan Lunine, Director, Cornell Center for Astrophysics and Planetary Science, Co-Chair of the Former Committee on Human Spaceflight, National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine testifies during the House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
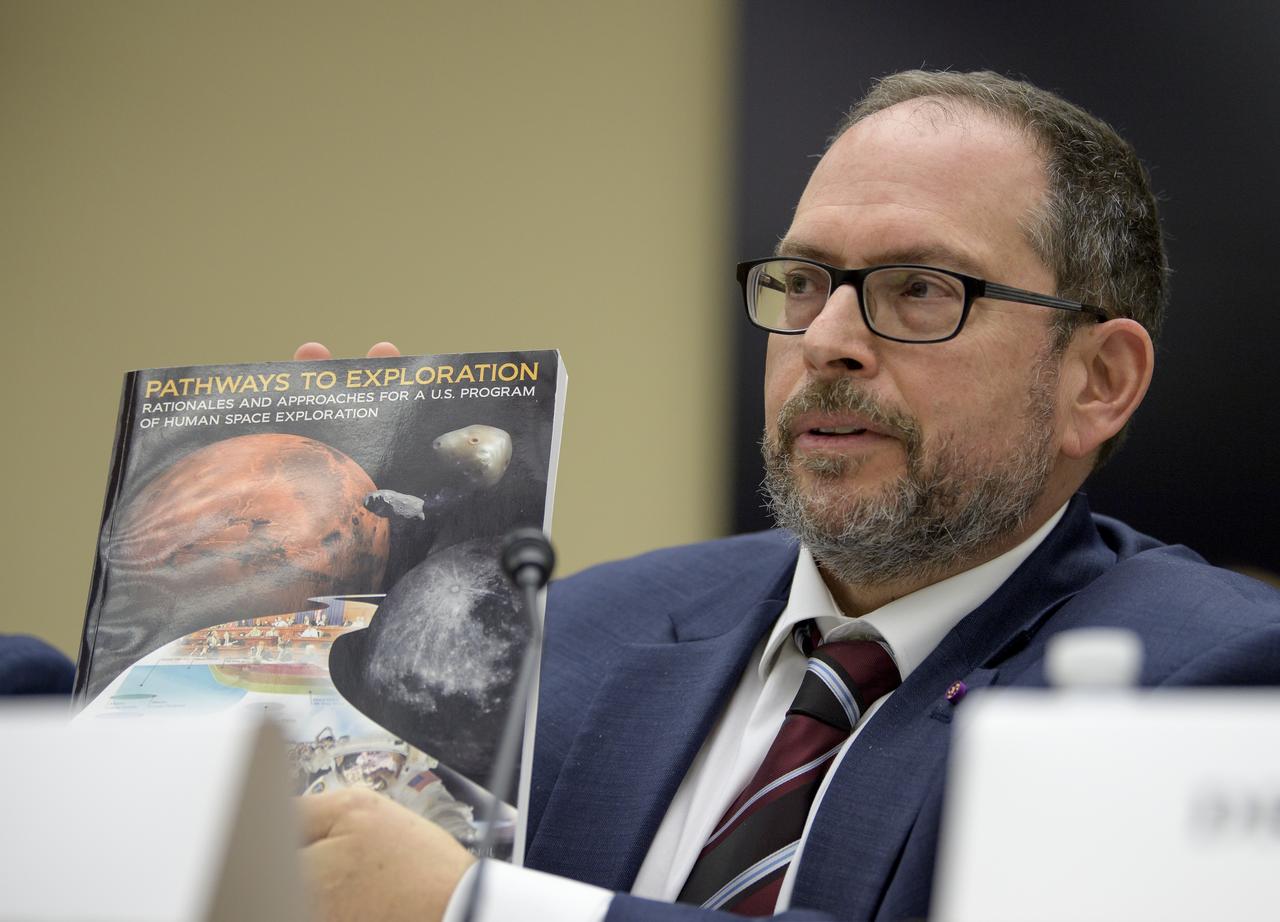

Dr. Jonathan Lunine, Director, Cornell Center for Astrophysics and Planetary Science, Co-Chair of the Former Committee on Human Spaceflight, National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine testifies during the House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
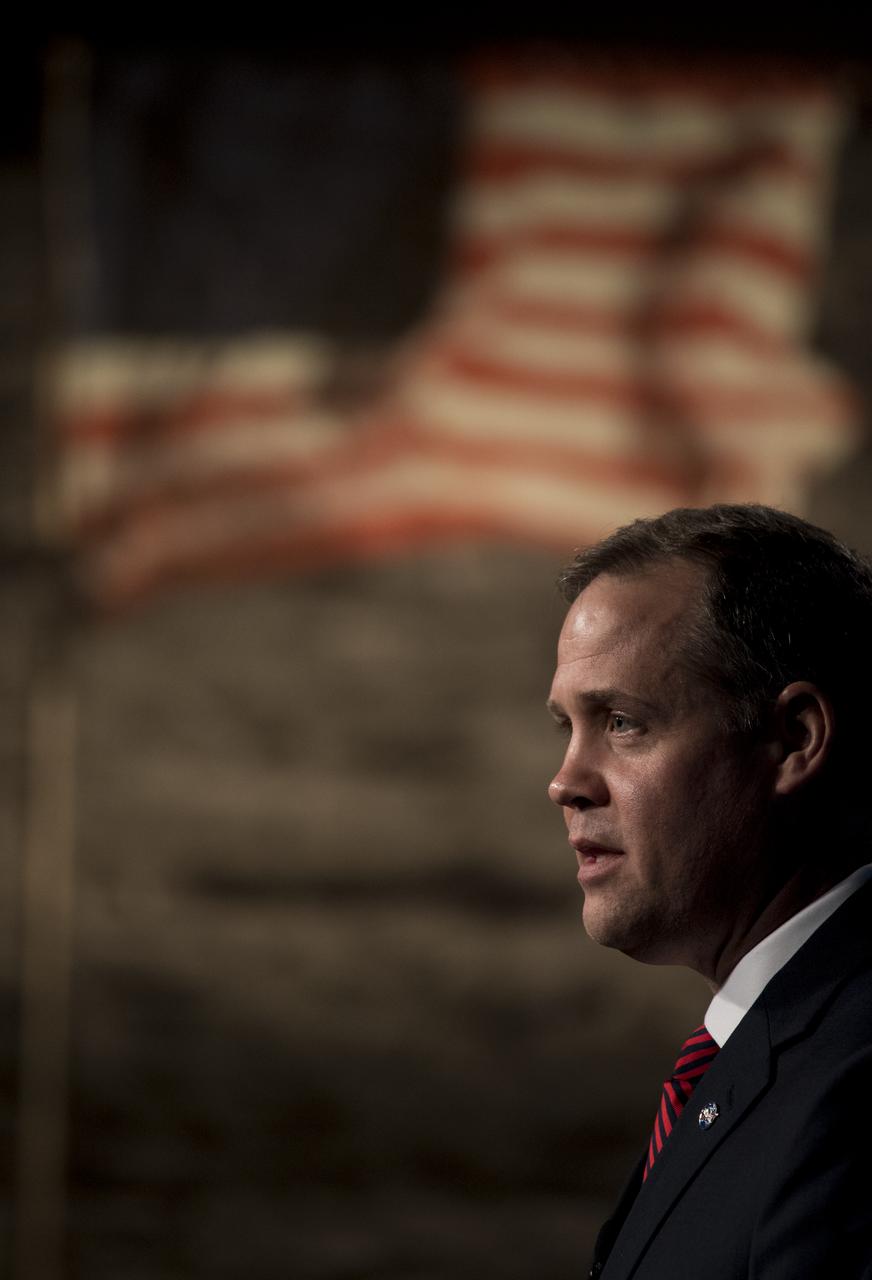

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine speaks at the opening of an industry forum on the agency's lunar exploration plans, Thursday, Feb. 14, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The agency will work with industry to study and refine the approach to landing on the Moon, which includes a system of three separate elements that will provide astronauts transportation, landing, and safe return. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
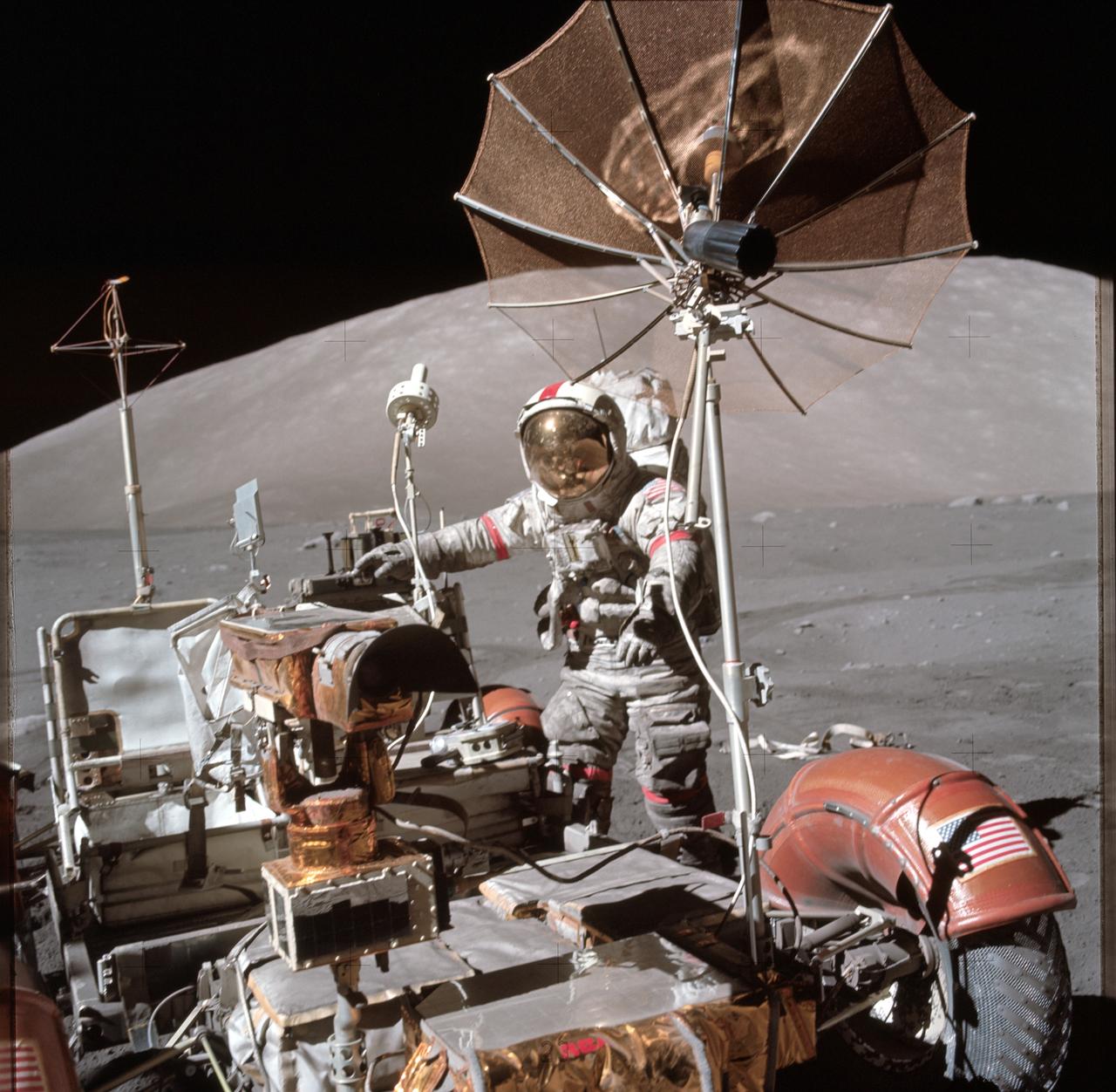

AS17-134-20476 (13 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 commander, approaches the parked Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the lunar surface during the flight's third period of extravehicular activity (EVA). South Massif can be seen in the background. The photograph was taken with a hand-held Hasselblad camera by scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. While the two explored the surface of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
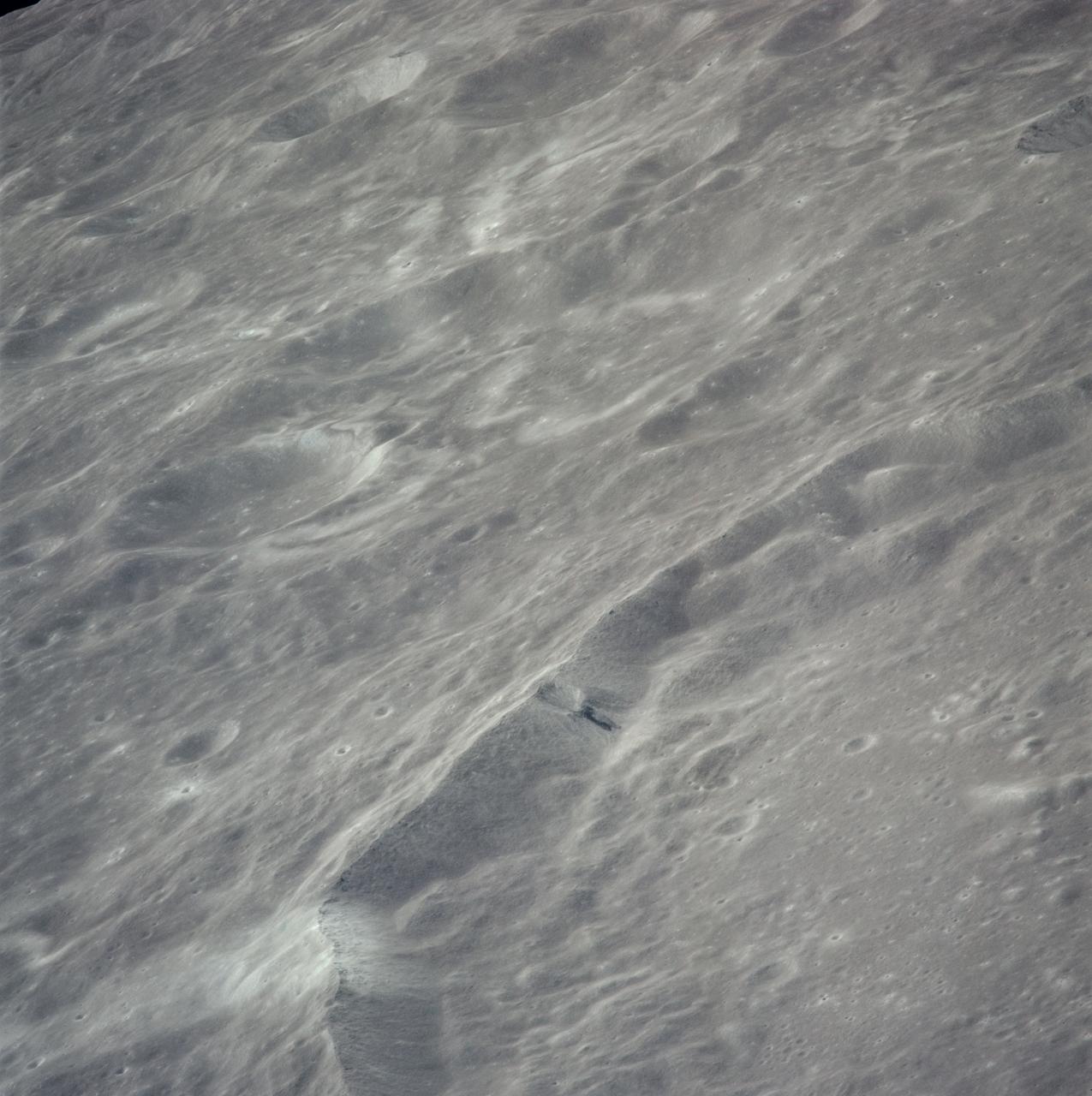

AS16-121-19407 (April 1972) --- An oblique view of a rim of Guyot Crater on the lunar farside, as photographed from the Apollo 16 spacecraft in lunar orbit. The coordinates of the center of Guyot Crater are 116.5 degrees east longitude and 10.5 degrees north latitude. Note the black coloration which appears to be lava flow down the side of the crater rim. While astronauts John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
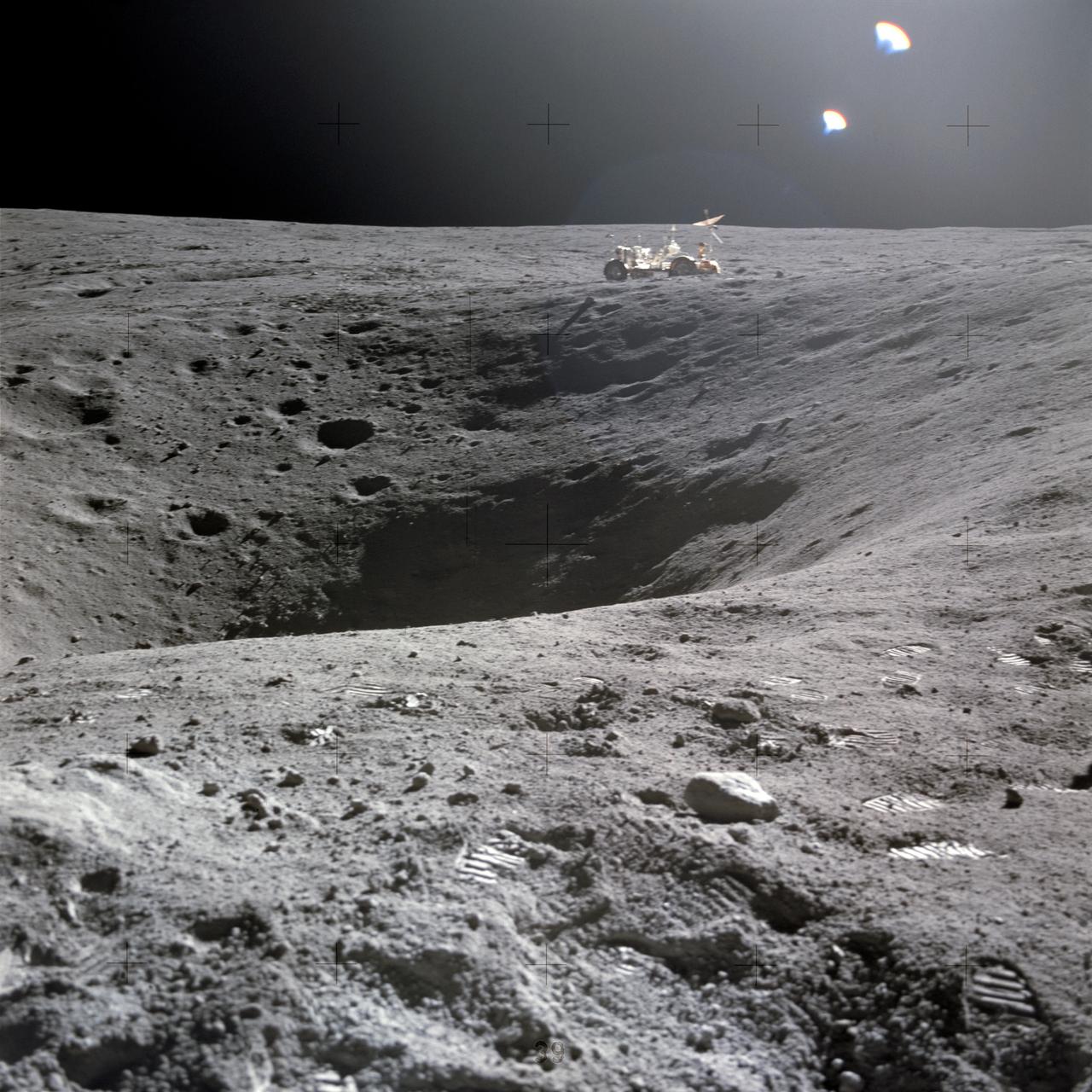

AS16-114-18422 (21 April 1972) --- A view of Plum Crater, which was visited by the two moon-exploring crewmen of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, on their first extravehicular activity (EVA) traverse, April 21, 1972. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is parked on the far side of the crater, which measures approximately 40 meters in diameter. While astronauts John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
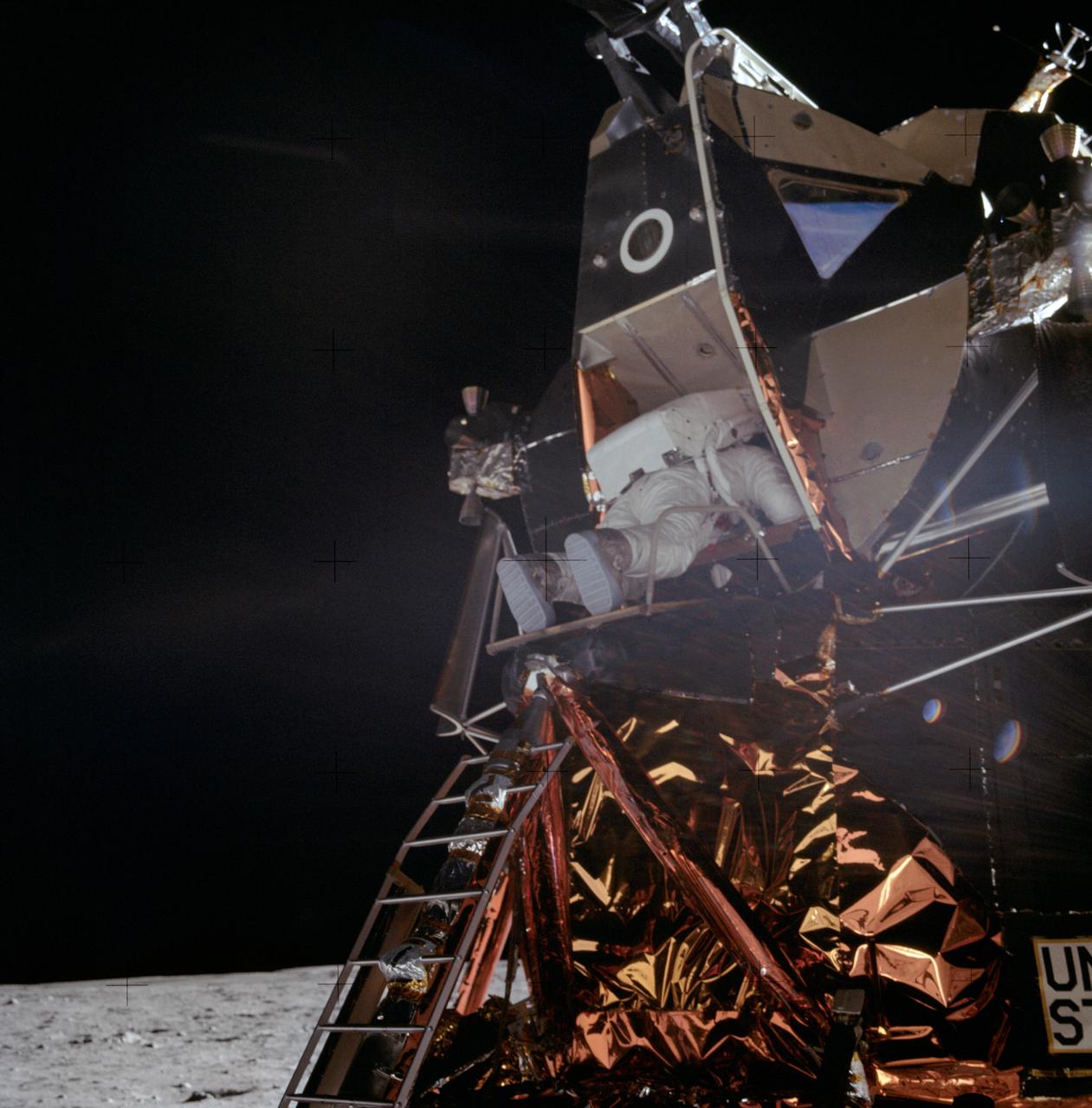

AS11-40-5863 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, is photographed egressing the Lunar Module (LM) during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. This photograph was taken by astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, with a 70mm lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
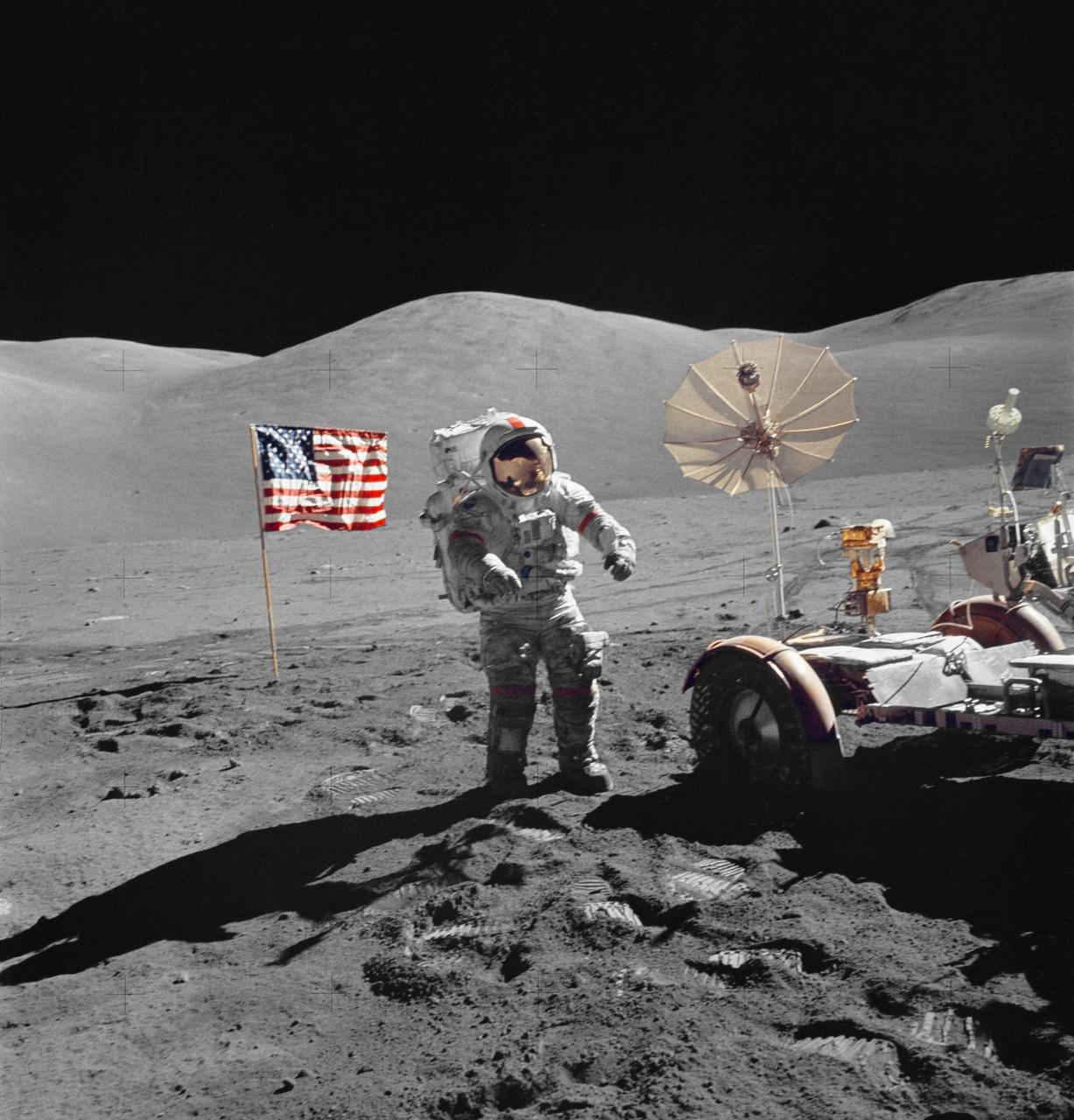

AS17-140-21388 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, mission commander, walks toward the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site of NASA's sixth and final Apollo lunar landing mission. The photograph was taken by astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
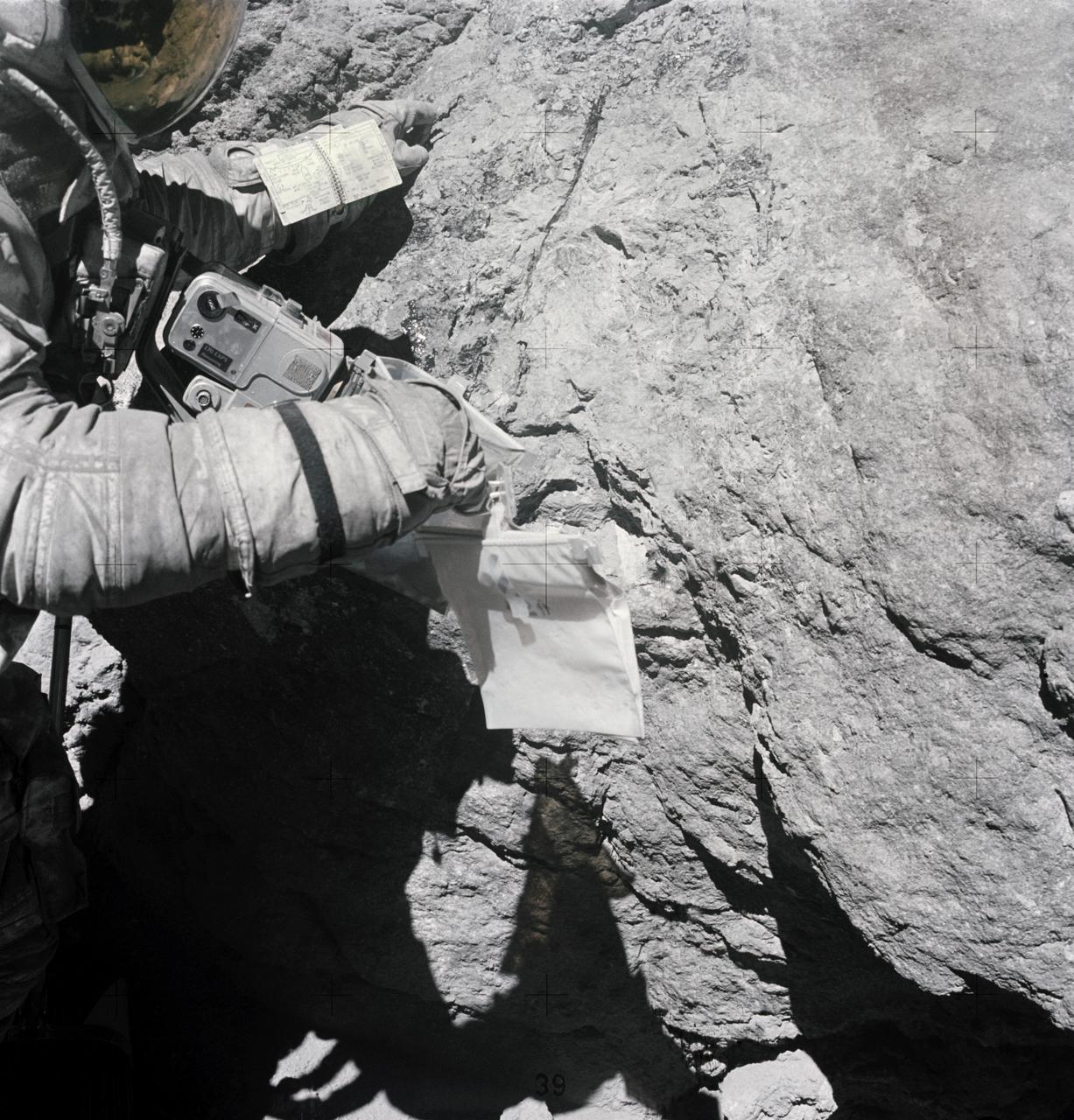

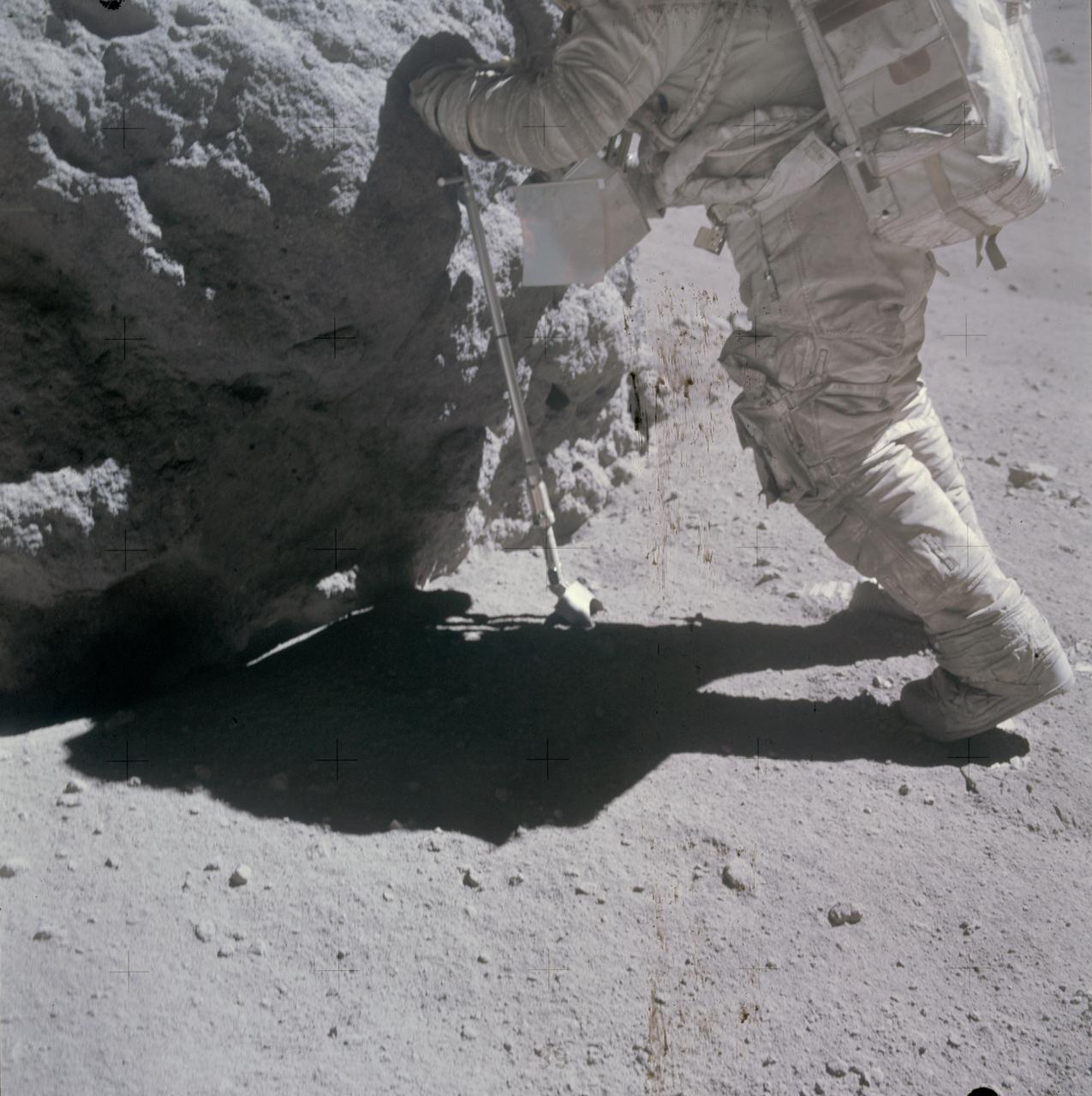
AS16-116-18649 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, examines closely the surface of a large boulder at North Ray Crater during the third Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. This picture was taken by astronaut John W. Young, commander. Note the chest-mounted 70mm Hasselblad camera. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.

AS16-113-18339 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, leaps from the lunar surface as he salutes the United States flag at the Descartes landing site during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, took this picture. The Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" is on the left. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is parked beside the LM. The object behind Young (in the shade of the LM) is the Far Ultraviolet Camera/Spectrograph (FUC/S). Stone Mountain dominates the background in this lunar scene. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the LM to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.

NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations William Gerstenmaier, left, NASA Special Assistant to the Administrator Mark Sirangelo, Director, Cornell Center for Astrophysics and Planetary Science, Co-Chair of the Former Committee on Human Spaceflight, National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine Dr. Jonathan Lunine, Chair, Aerospace Safety Advisory Panel Dr. Patricia Sanders, and, President, Faulconer Consulting Group, LLC Mr. Walt Faulconer, right, are seen during a House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
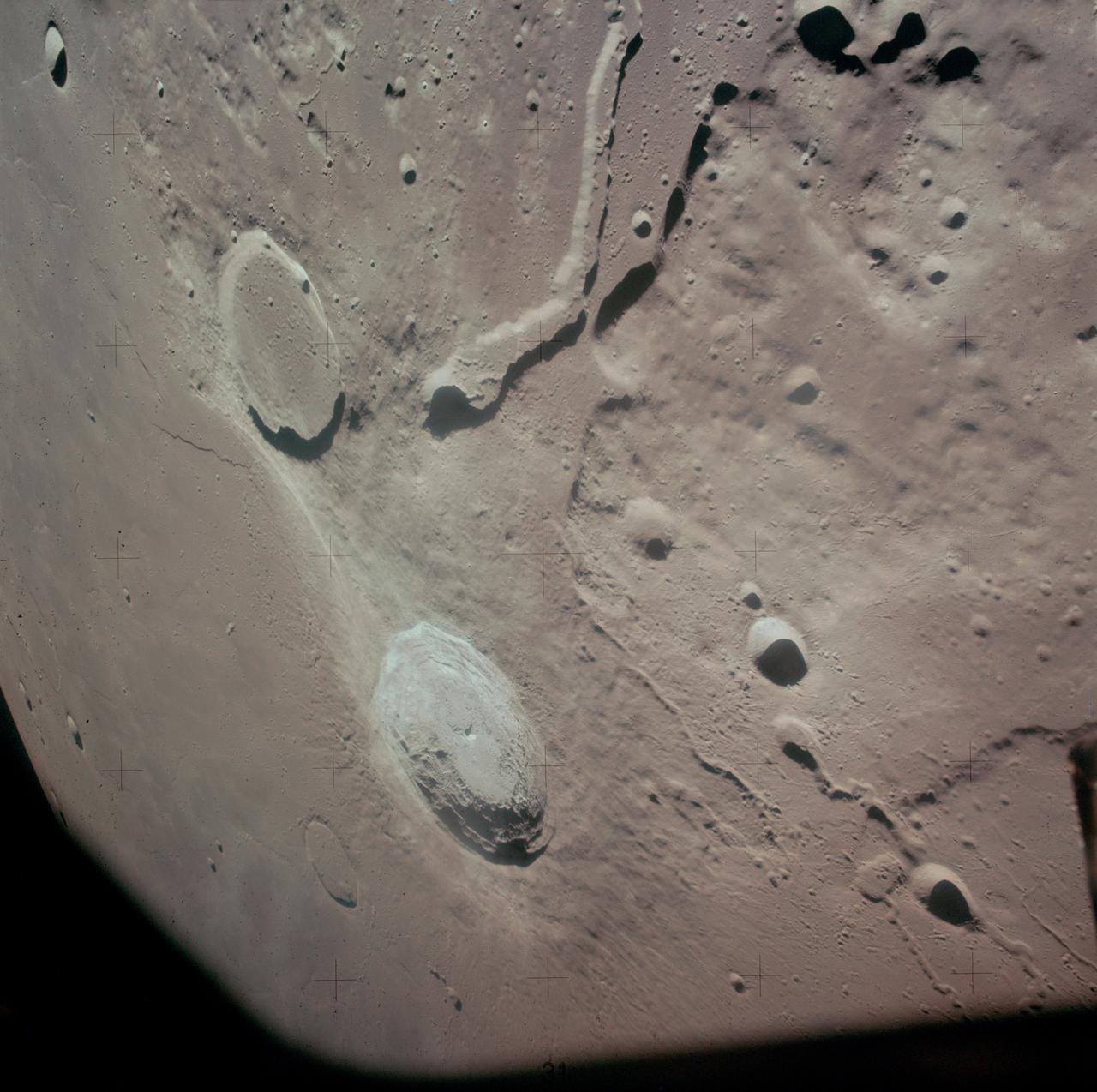

AS15-88-12002 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- An oblique view of a portion of the lunar nearside located near the northeast edge of the Ocean of Storms (Oceanus Procellarum), photographed by astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, from the Apollo 15 spacecraft in lunar orbit, showing the bright-appearing crater Aristarchus on the left, the crater Herodotus on the right, and Schroter's Valley at lower right. This view is looking southward. Aristarchus the head of Schroter's Valley, a sinuous rille in the Aristarchus Plateau, is called Cobra Head. The coordinates of the center of Aristarchus crater are 47.5 degrees west longitude and 23.6 degrees north latitude. While Worden remained in the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit, astronauts David R. Scott, commander; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon.
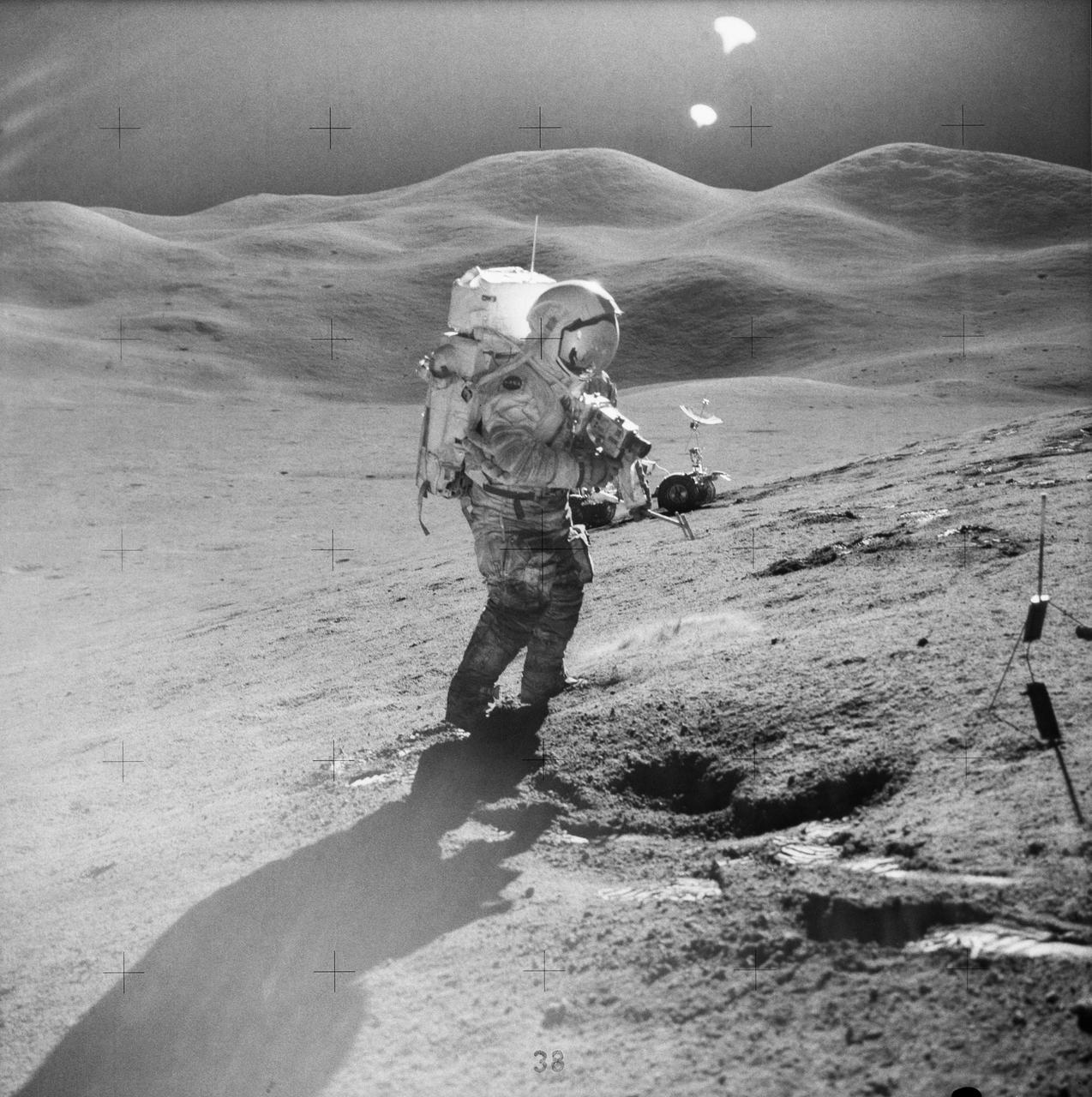

AS15-85-11514 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, commander, standing on the slope of Hadley Delta, uses a 70mm camera during Apollo 15 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. He is 10.5 miles (or 17.5 kilometers) from the base of the Apennine Mountains seen in the background. Scott carries tongs in his left hand. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is in the background. This view is looking east. While astronauts Scott and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

AS15-85-11437 (31 July 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, commander, with tongs and gnomon in hand, studies a boulder on the slope of Hadley Delta during the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission's first extravehicular activity (EVA). The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), "Rover", is in the right foreground. The view is looking slightly south of west. "Bennett Hill" is at extreme right. Astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, took this photograph. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended together in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

Outside a regolith bin at the agency's Kennedy Space center in Florida, an engineer operates controls for a lightweight simulator version of NASA's Resource Prospector during a mobility test. The Resource Prospector mission aims to be the first mining expedition on another world. Operating on the moon’s poles, the robot is designed to use instruments to locate elements at a lunar polar regions, then excavate and sample resources such as hydrogen, oxygen and water. These resources could support human explores on their way to destinations such as farther into the solar system.
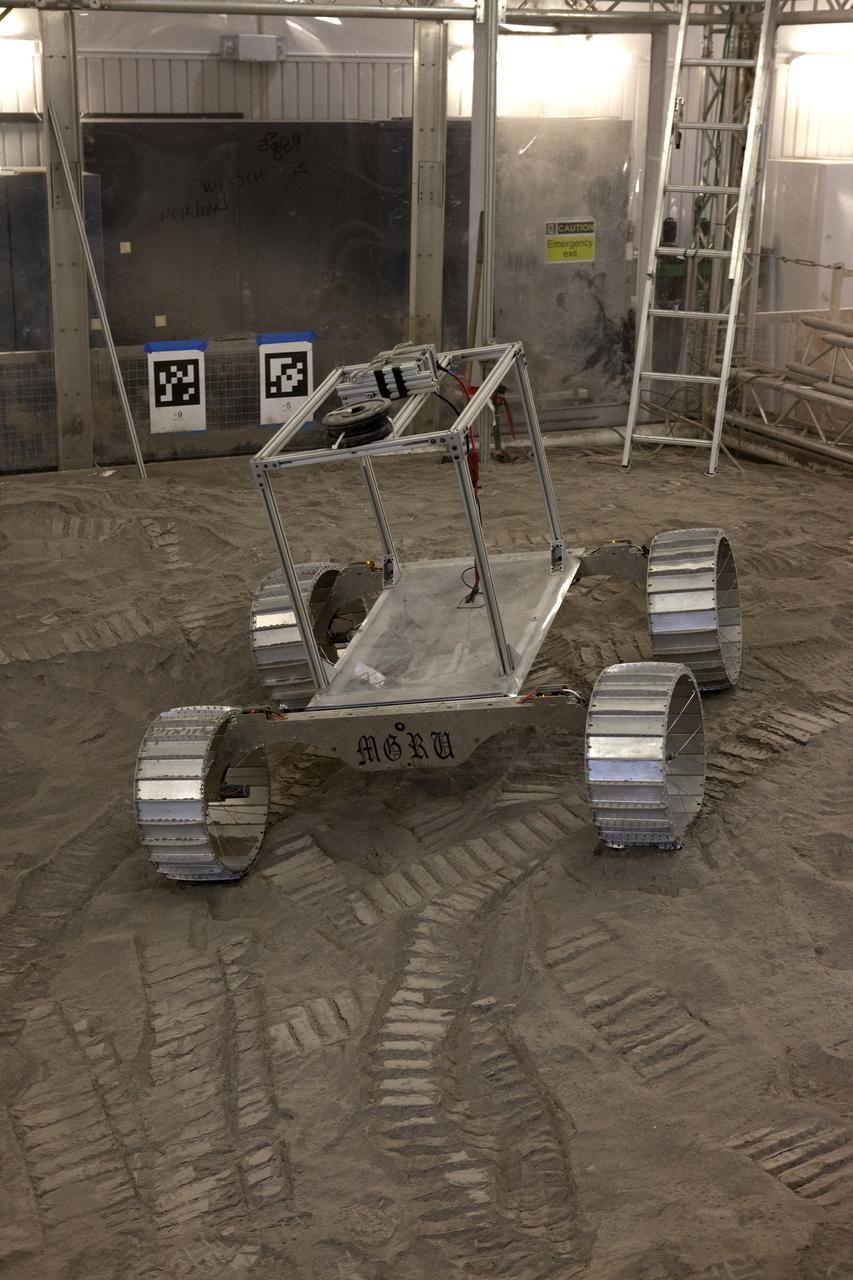

A lightweight simulator version of NASA's Resource Prospector undergoes a mobility test in a regolith bin at the agency's Kennedy Space center in Florida. The Resource Prospector mission aims to be the first mining expedition on another world. Operating on the moon’s poles, the robot is designed to use instruments to locate elements at a lunar polar regions, then excavate and sample resources such as hydrogen, oxygen and water. These resources could support human explores on their way to destinations such as farther into the solar system.

A lightweight simulator version of NASA's Resource Prospector undergoes a mobility test in a regolith bin at the agency's Kennedy Space center in Florida. The Resource Prospector mission aims to be the first mining expedition on another world. Operating on the moon’s poles, the robot is designed to use instruments to locate elements at a lunar polar regions, then excavate and sample resources such as hydrogen, oxygen and water. These resources could support human explores on their way to destinations such as farther into the solar system.
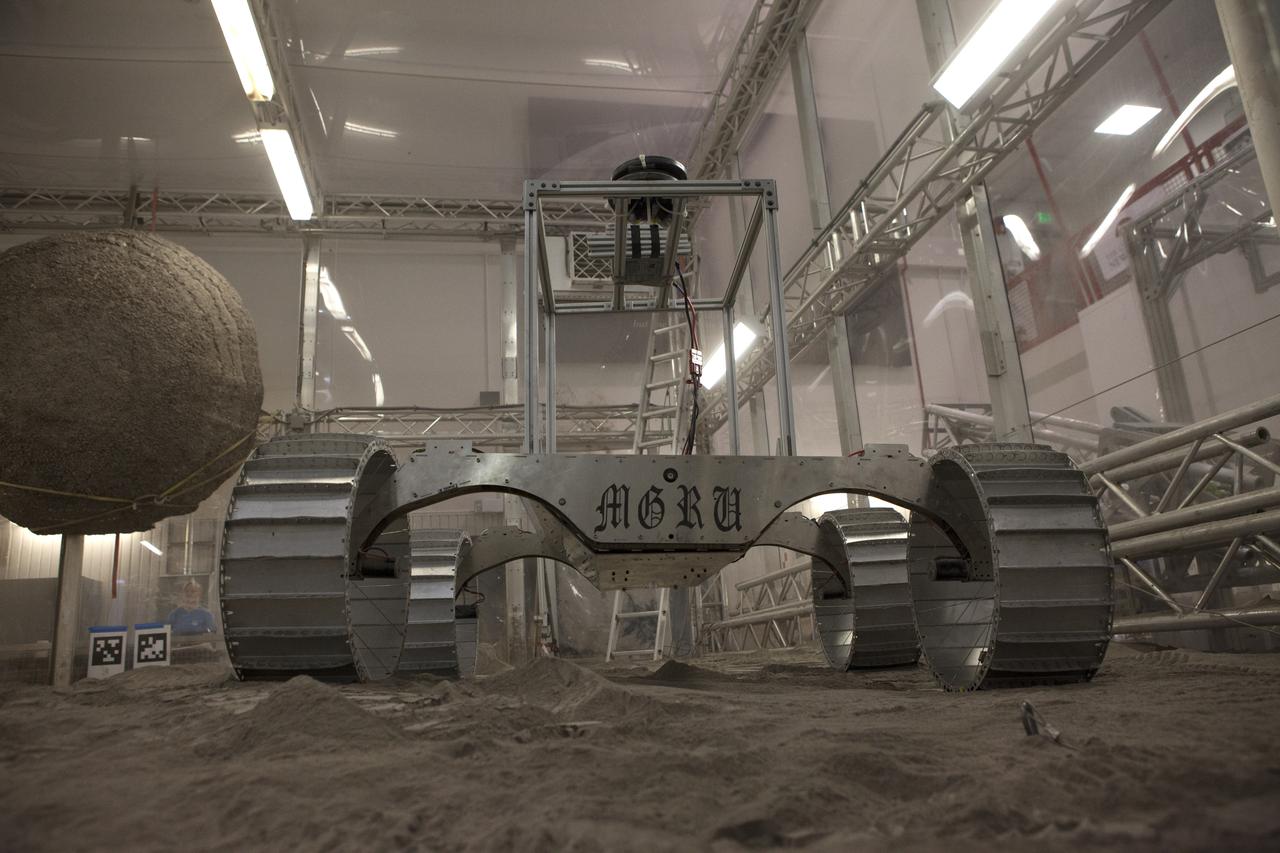

A lightweight simulator version of NASA's Resource Prospector undergoes a mobility test in a regolith bin at the agency's Kennedy Space center in Florida. The Resource Prospector mission aims to be the first mining expedition on another world. Operating on the moon’s poles, the robot is designed to use instruments to locate elements at a lunar polar regions, then excavate and sample resources such as hydrogen, oxygen and water. These resources could support human explores on their way to destinations such as farther into the solar system.
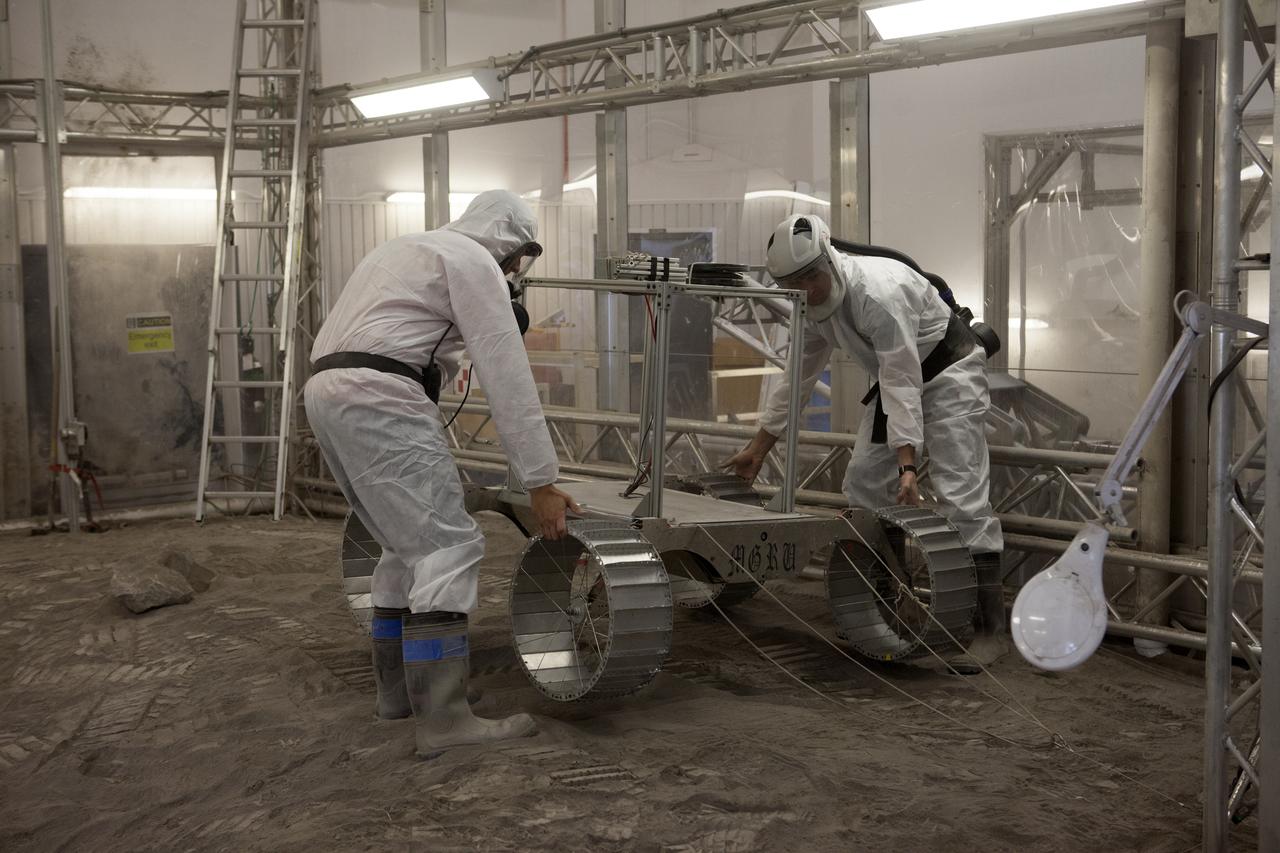

Engineers wearing protecting garb, make adjustments to a lightweight simulator version of NASA's Resource Prospector undergoes a mobility test in a regolith bin at the agency's Kennedy Space center in Florida. The Resource Prospector mission aims to be the first mining expedition on another world. Operating on the moon’s poles, the robot is designed to use instruments to locate elements at a lunar polar regions, then excavate and sample resources such as hydrogen, oxygen and water. These resources could support human explores on their way to destinations such as farther into the solar system.
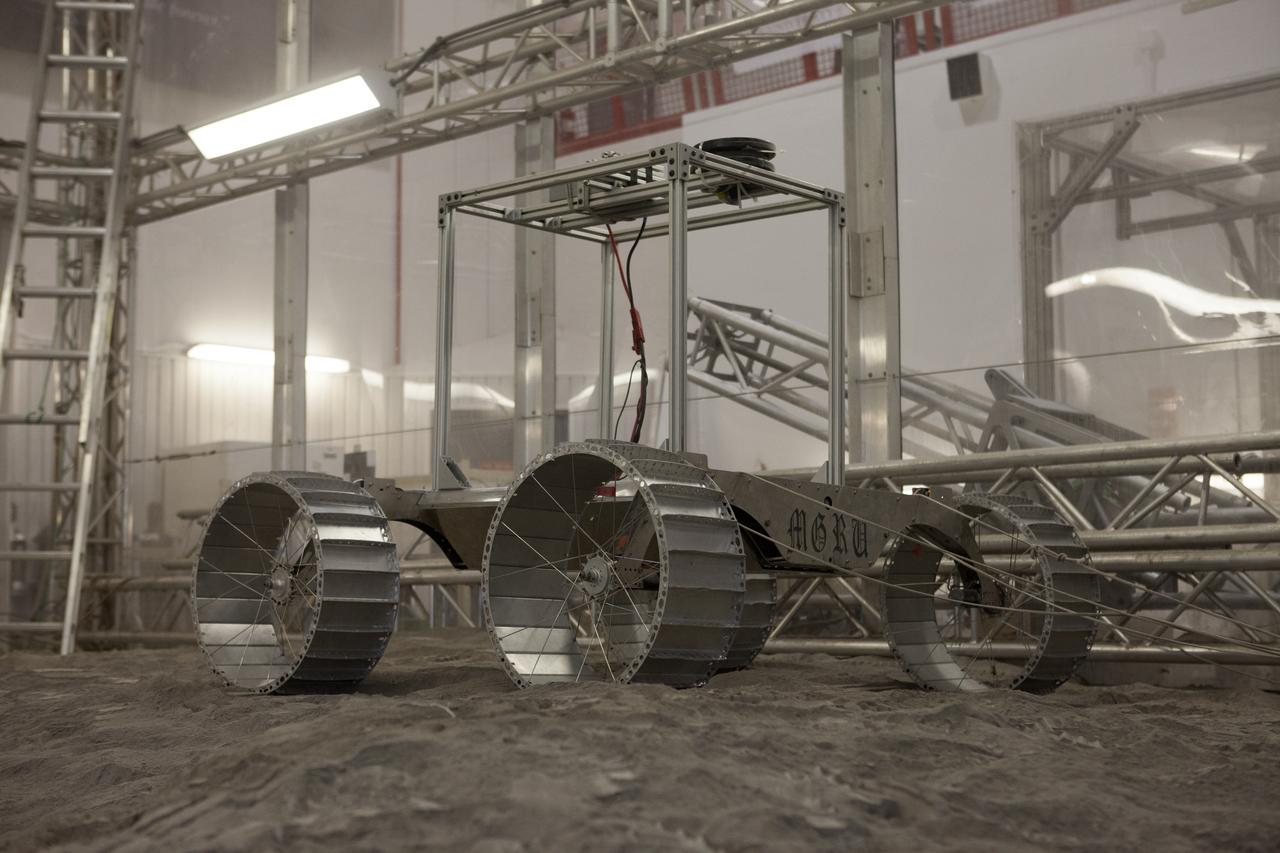

A lightweight simulator version of NASA's Resource Prospector undergoes a mobility test in a regolith bin at the agency's Kennedy Space center in Florida. The Resource Prospector mission aims to be the first mining expedition on another world. Operating on the moon’s poles, the robot is designed to use instruments to locate elements at a lunar polar regions, then excavate and sample resources such as hydrogen, oxygen and water. These resources could support human explores on their way to destinations such as farther into the solar system.
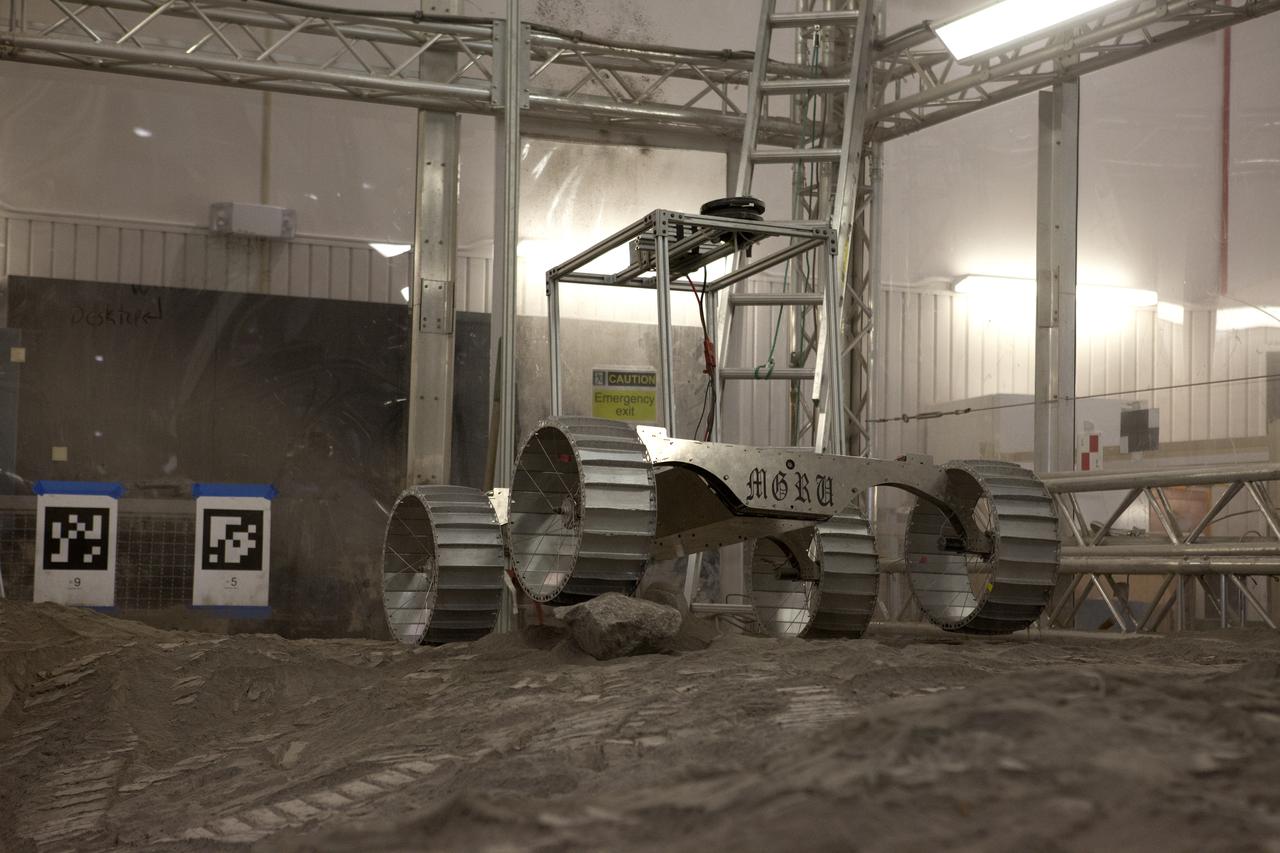

A lightweight simulator version of NASA's Resource Prospector undergoes a mobility test in a regolith bin at the agency's Kennedy Space center in Florida. The Resource Prospector mission aims to be the first mining expedition on another world. Operating on the moon’s poles, the robot is designed to use instruments to locate elements at a lunar polar regions, then excavate and sample resources such as hydrogen, oxygen and water. These resources could support human explores on their way to destinations such as farther into the solar system.
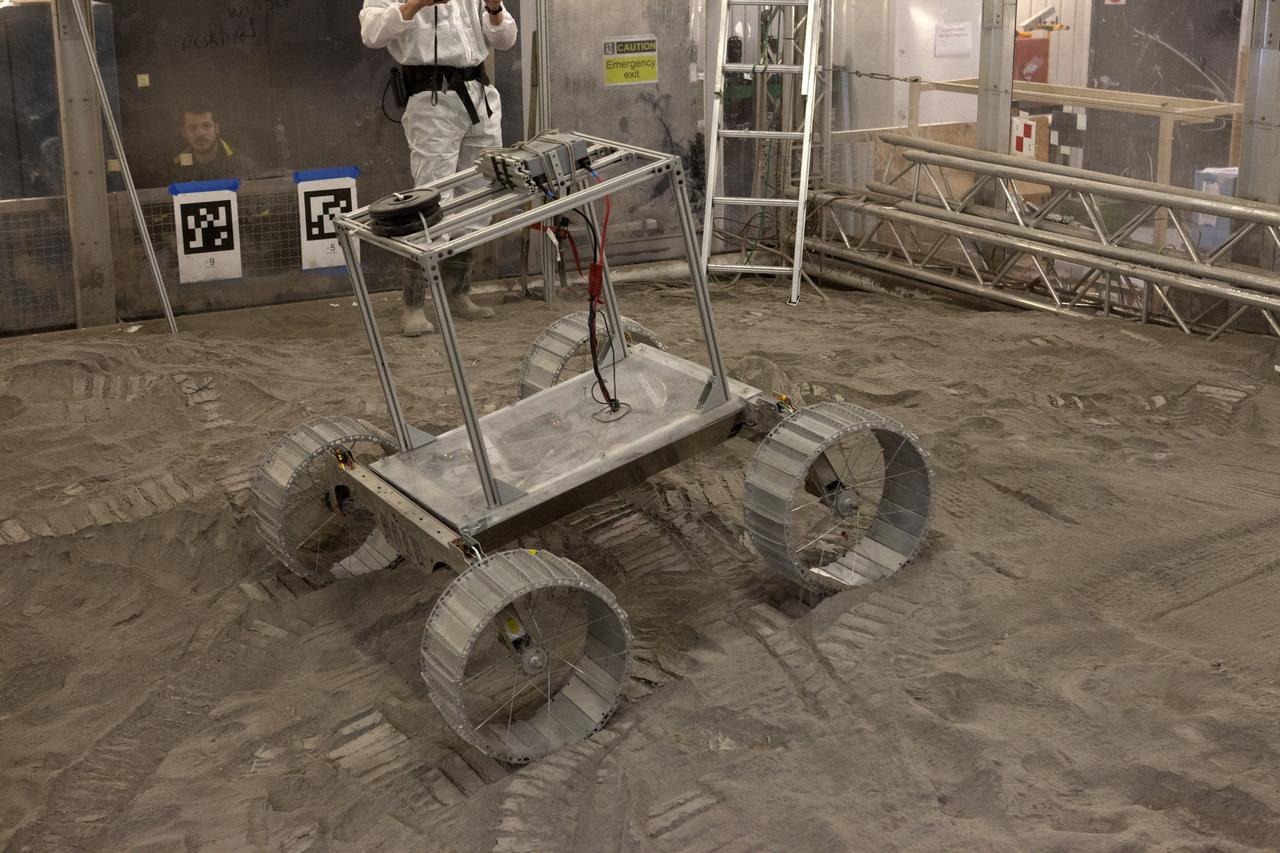

A lightweight simulator version of NASA's Resource Prospector undergoes a mobility test in a regolith bin at the agency's Kennedy Space center in Florida. The Resource Prospector mission aims to be the first mining expedition on another world. Operating on the moon’s poles, the robot is designed to use instruments to locate elements at a lunar polar regions, then excavate and sample resources such as hydrogen, oxygen and water. These resources could support human explores on their way to destinations such as farther into the solar system.

AS16-116-18671 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, works at the "Shadow Rock", discovered during the missions third extravehicular activity (EVA) in the area of North Ray Crater (Station 13), April 23, 1972. The scoop, a geological hand tool, leans against the rock. This view was exposed by astronaut John W. Young, commander. The two moon-exploring crew men sampled this rock, which got its name because of a permanently shadowed area it protected. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
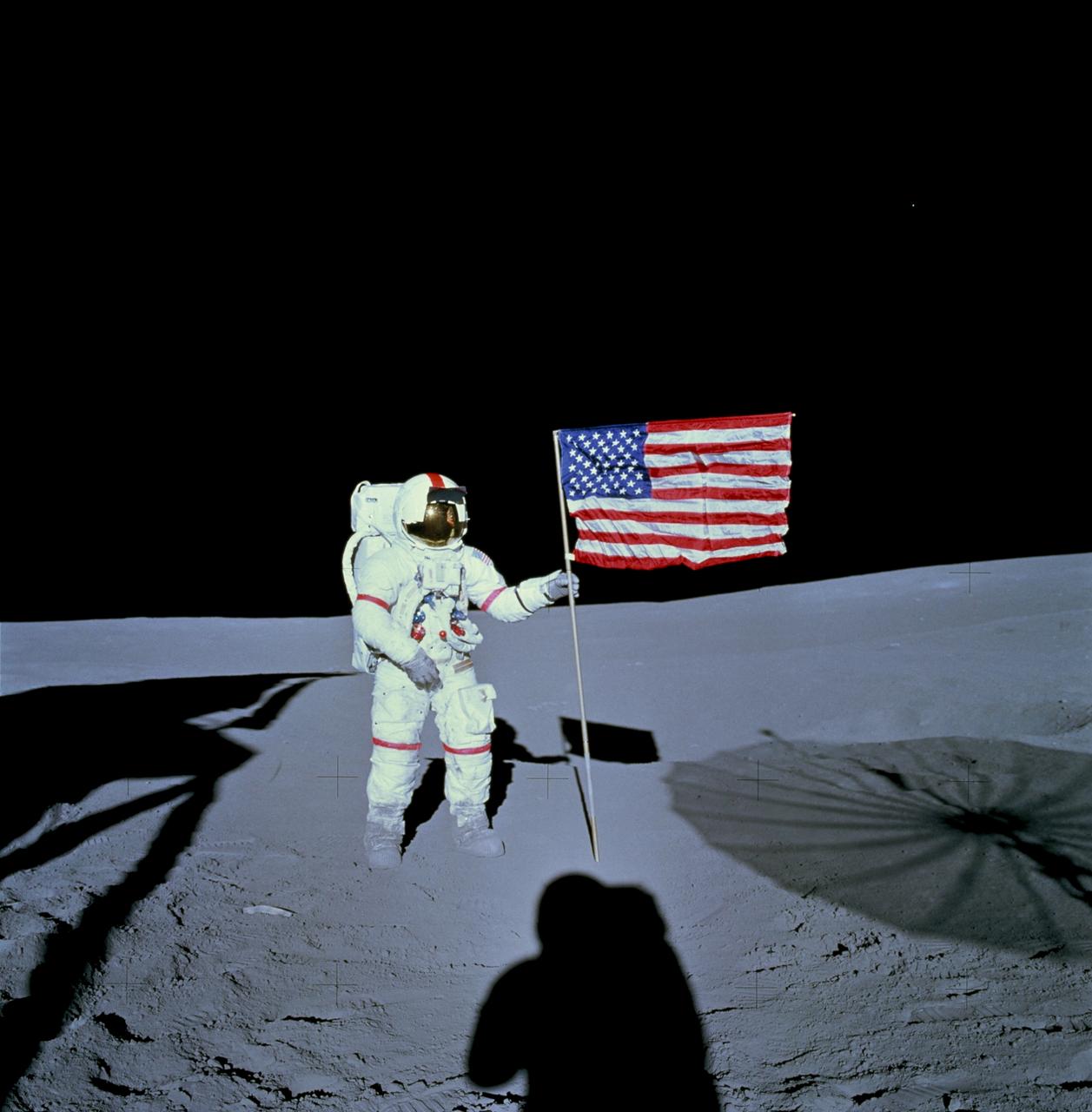

AS14-66-9232 (5 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission, stands by the deployed United States flag on the lunar surface during the early moments of the first extravehicular activity (EVA) of the mission. Shadows of the Lunar Module (LM), astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, and the erectable S-Band Antenna surround the scene of the third flag implanting to be performed on the lunar surface. While astronauts Shepard and Mitchell descended in the LM ?Antares? to explore the Fra Mauro region of the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) ?Kitty Hawk? in lunar orbit.
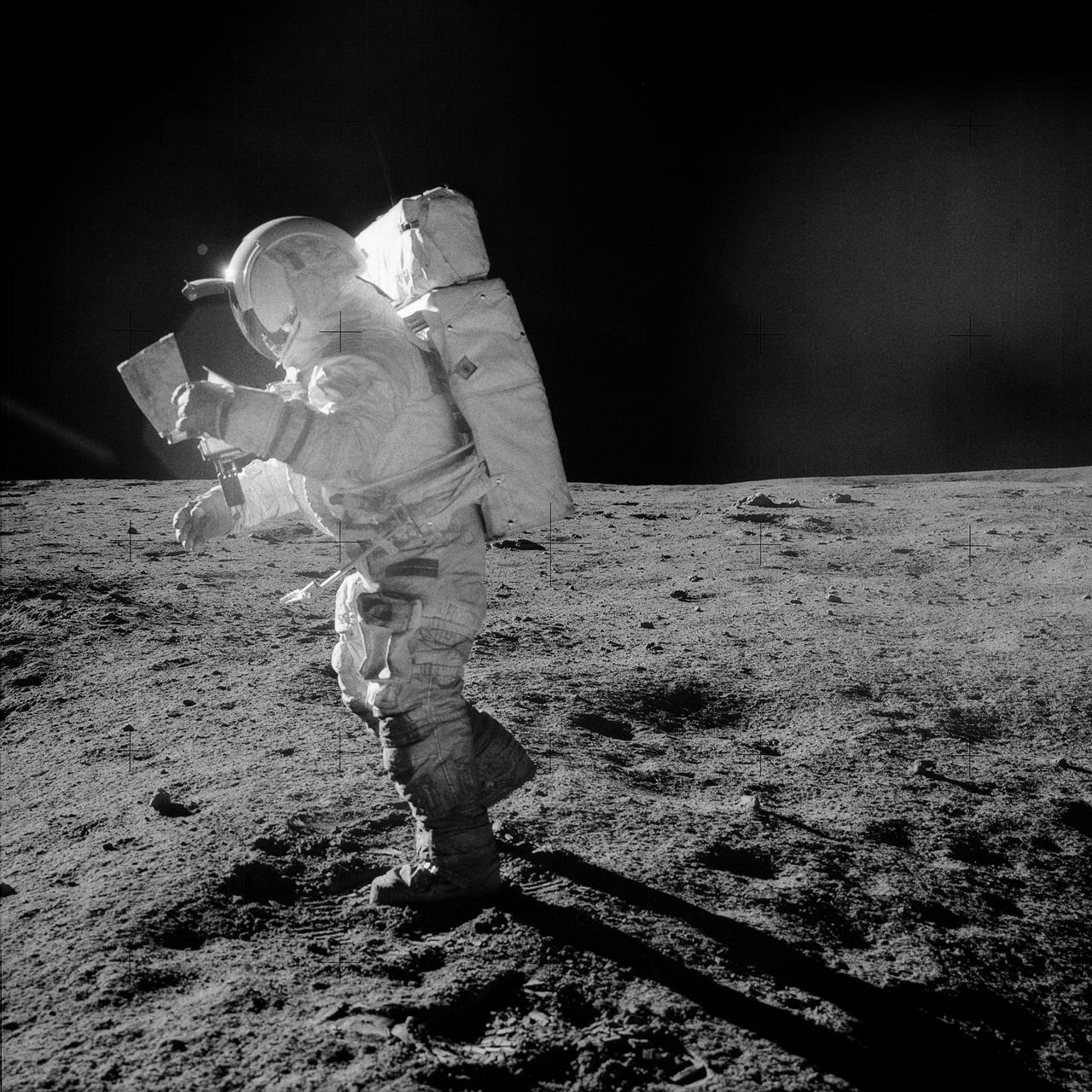

AS14-64-9089 (5-6 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, moves across the lunar surface as he looks over a traverse map during an extravehicular activity (EVA). Lunar dust can be seen clinging to the boots and legs of the space suit. Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Mitchell explored the lunar surface while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, orbited the moon in the Command and Service Modules (CSM).

AS11-40-5868 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descends the steps of the Lunar Module (LM) ladder as he prepares to walk on the moon. He had just egressed the LM. This photograph was taken by astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA). While Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM "Eagle" to explore the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
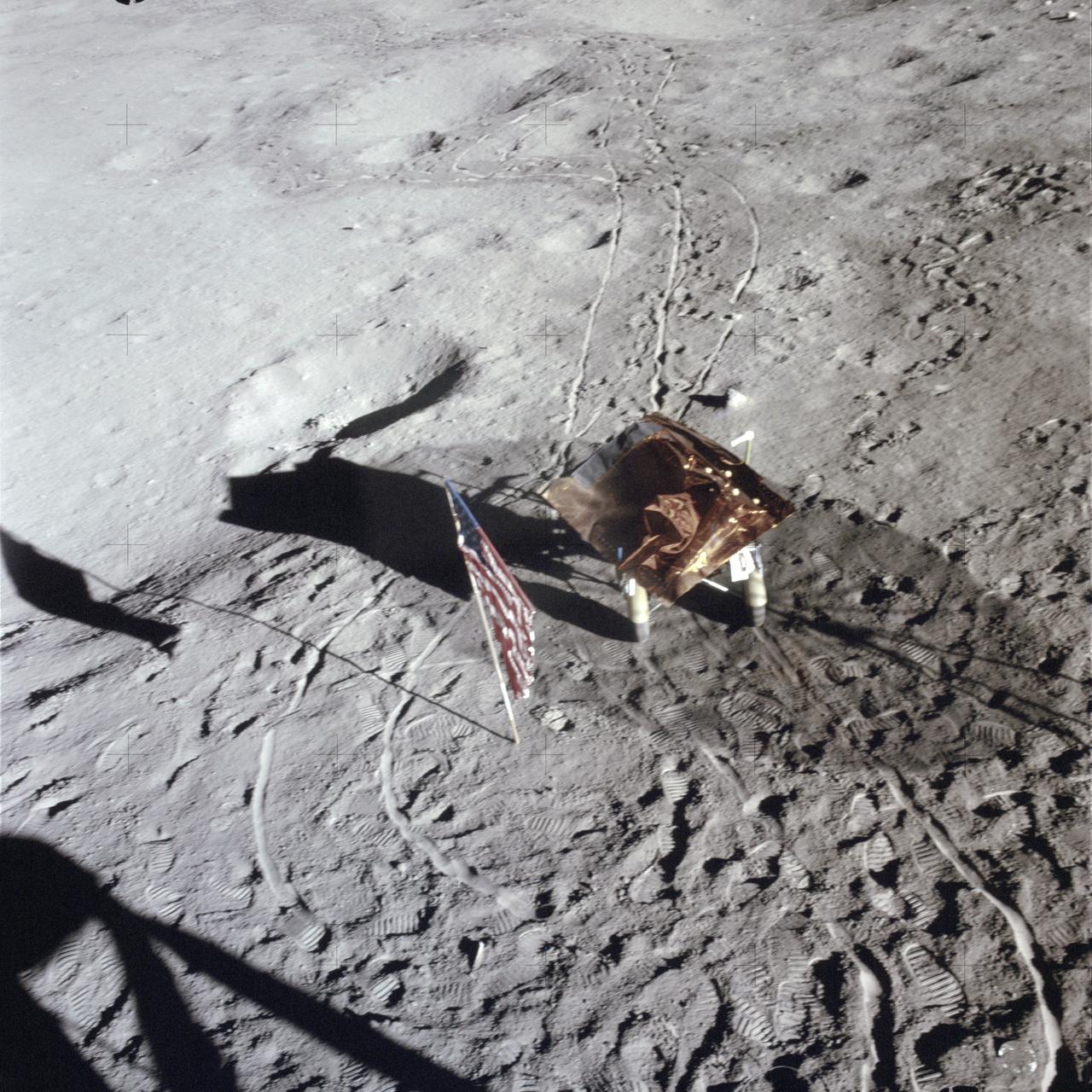

AS14-66-9325 (5 Feb. 1971) --- The third United States flag to be deployed on the lunar surface, footprints, wheel tracks and the "Rickshaw"-type portable workbench, as seen by the two moon-exploring astronauts from inside the Lunar Module (LM), give evidence of a busy first extravehicular activity (EVA) period. The two-wheeled cart is the Apollo modularized equipment transporter (MET), covered with a sheet of foil material to protect the cameras and rock box between EVAs. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
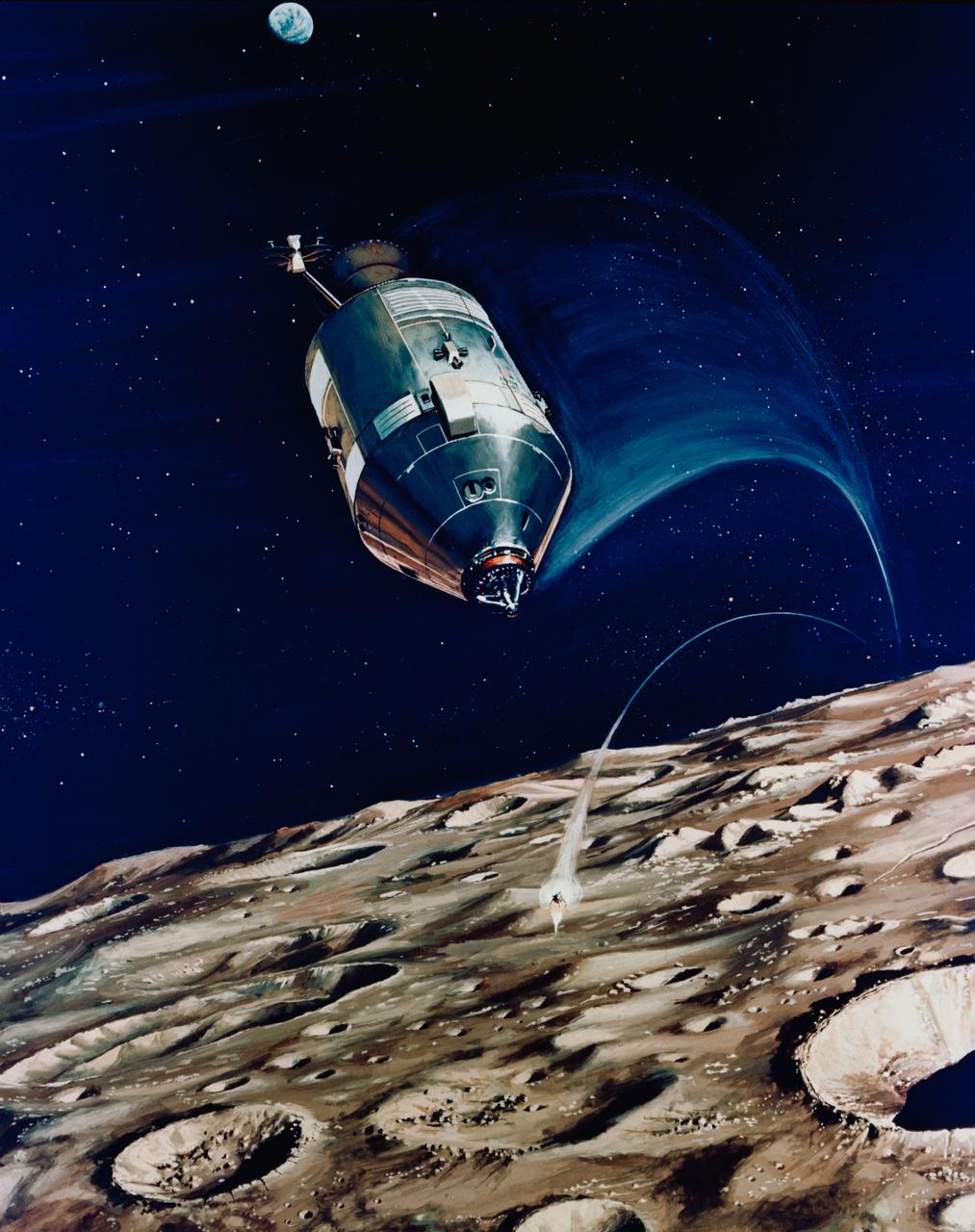

S71-16574 (11 Jan. 1971) --- An artist's concept depicting the Apollo 14 Command and Service Modules (CSM) circling the moon as the Lunar Module (LM) heads toward a lunar landing. While astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remains with the CSM in lunar orbit, astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, will descend in the LM to explore an area in the rugged Fra Mauro highlands.
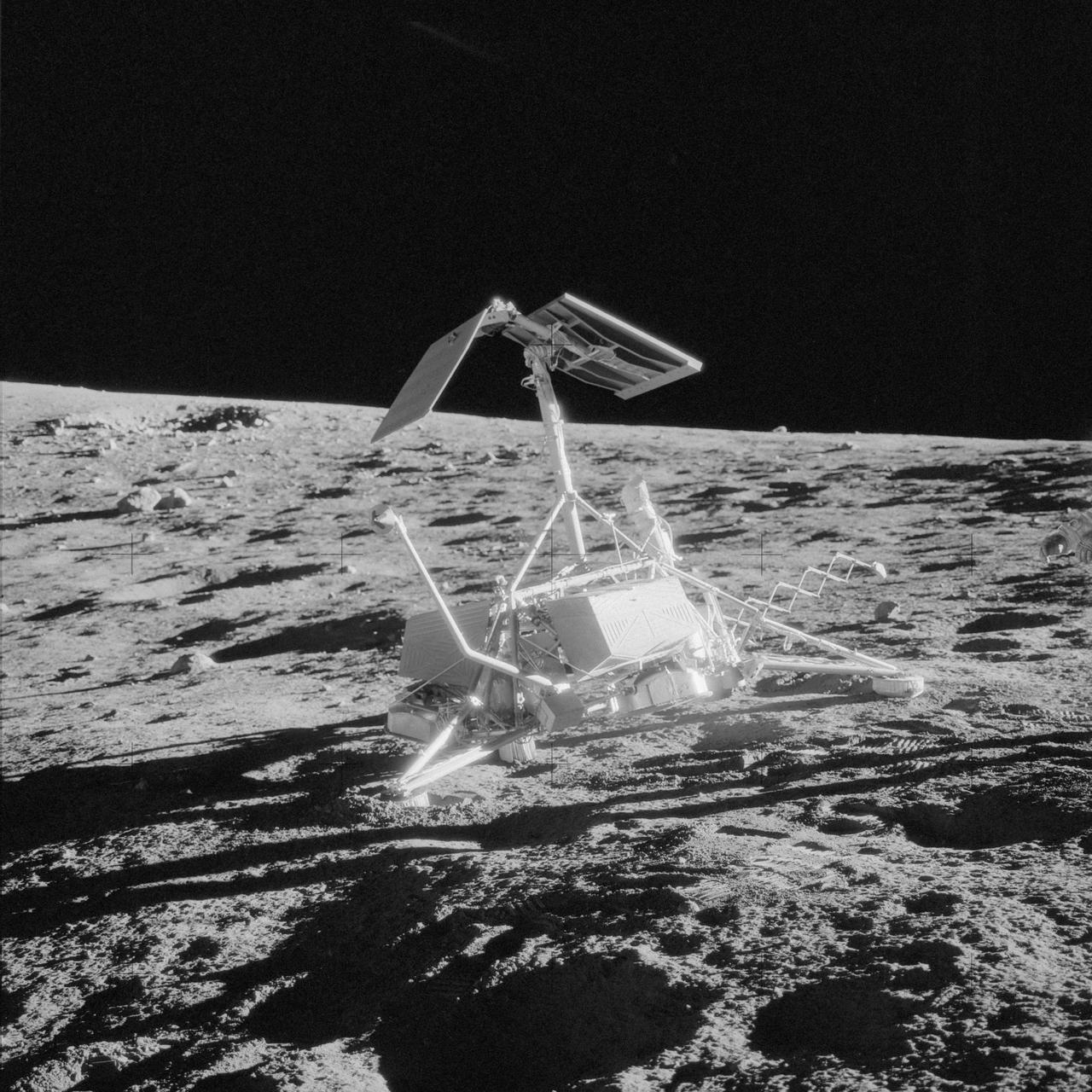

AS12-48-7121 (20 Nov. 1969) --- An excellent view of the unmanned Surveyor 3 spacecraft which was photographed during the Apollo 12 second extravehicular activity (EVA) on the surface of the moon. The Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM), with astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, aboard landed within 600 feet of Surveyor 3 in the Ocean of Storms. The television camera and several other pieces were taken from Surveyor 3 and brought back to Earth for scientific examination. Surveyor 3 landed on the side of this small crater in the Ocean of Storms on April 19, 1967. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 12 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while Conrad and Bean descended to explore the moon.
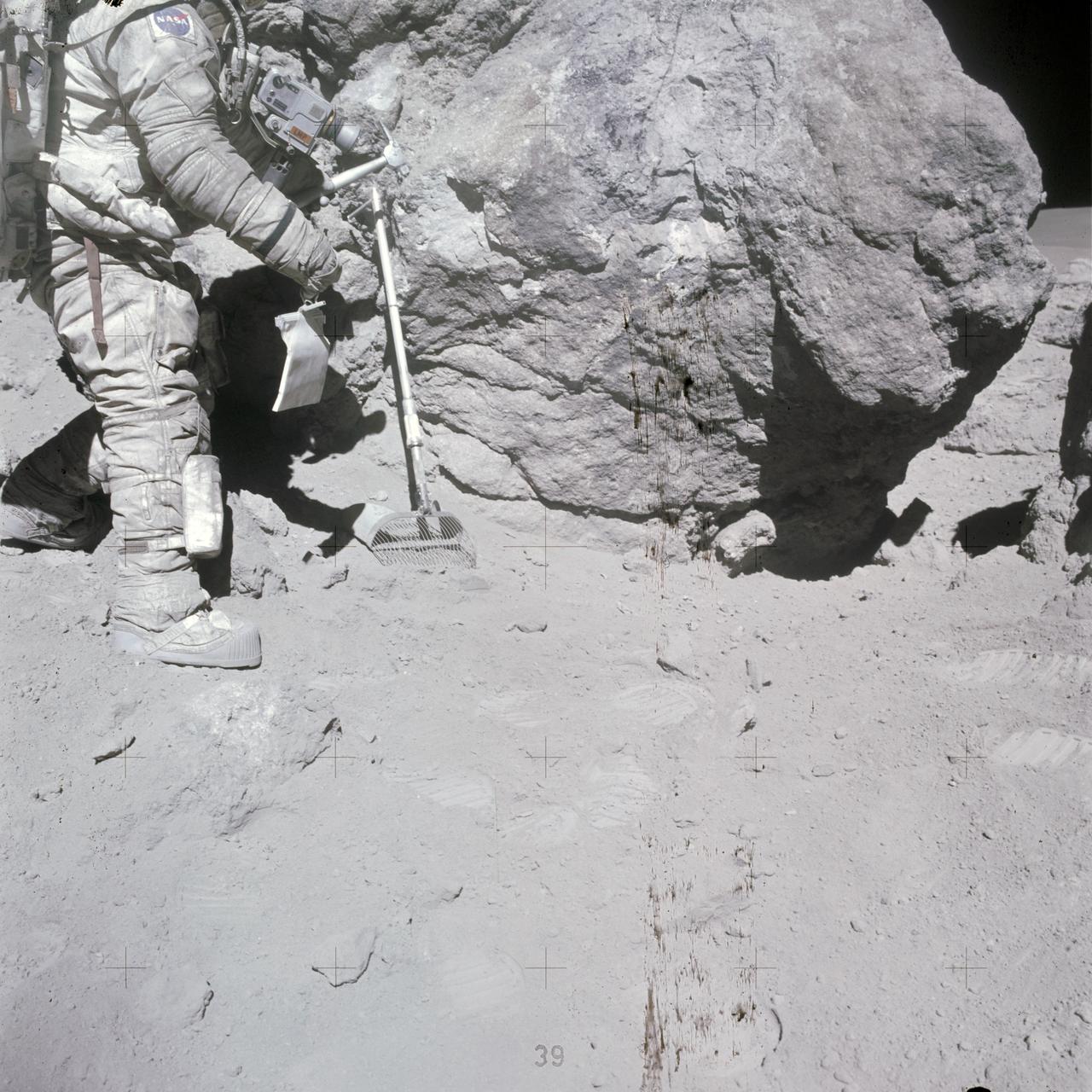

AS16-116-18653 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., Apollo 16 lunar module pilot, stands at a big rock adjacent (south) to the huge "House Rock" (barely out of view at right edge). Note shadow at extreme right center where the two moon-exploring crew members of the mission sampled what they referred to as the "east-by-west split of House Rock" or the open space between this rock and "House Rock". At their post-mission press conference, the crewmen expressed the opinion that this rock was once a part of "House Rock" which had broken away. The two sampled the big boulder seen here also. Duke has a sample bag in his hand, and a lunar surface rake leans against the large boulder. Astronaut John W. Young, commander, exposed this view with a color magazine in his 70mm Hasselblad camera. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
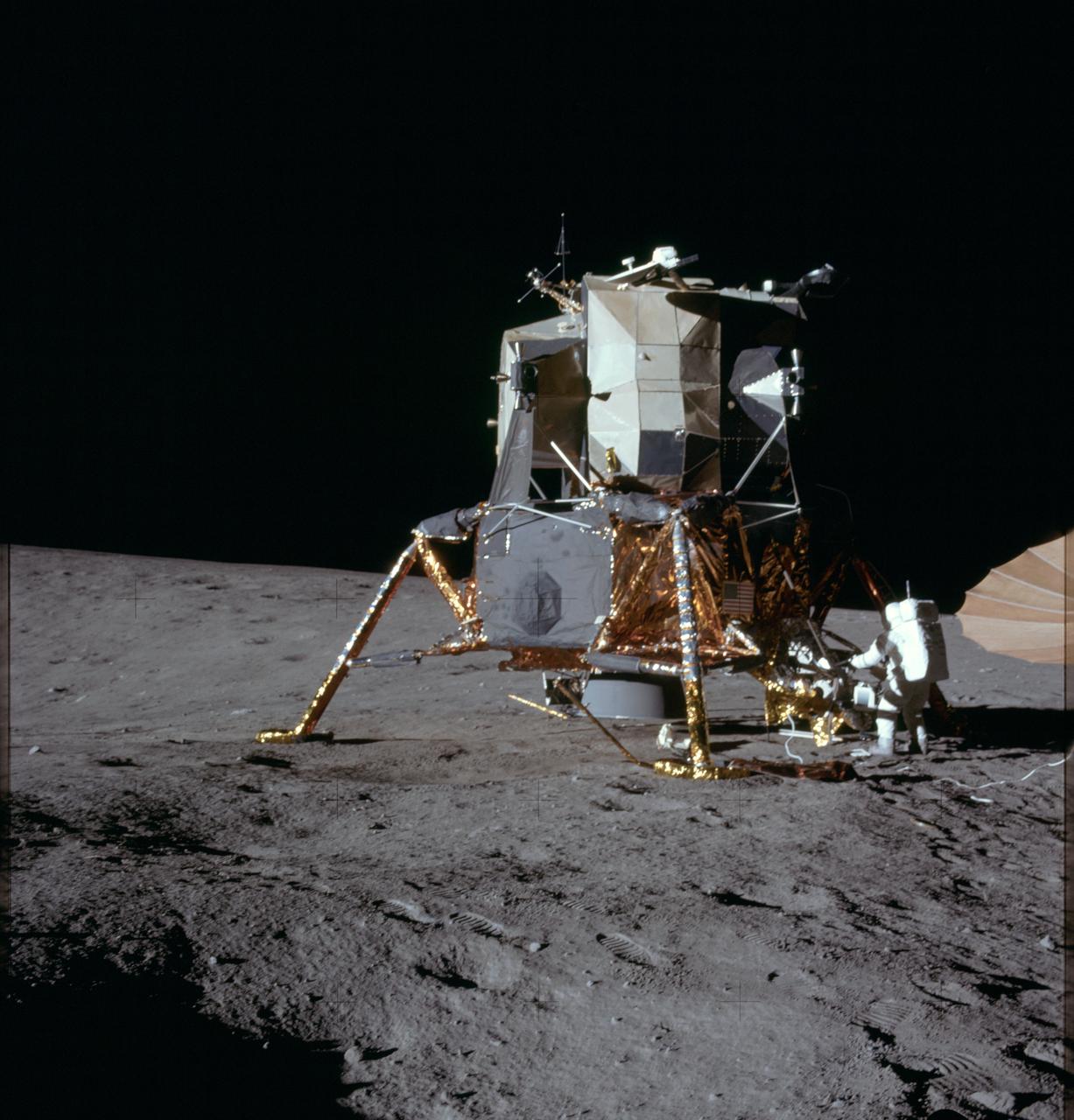

AS12-46-6749 (19 Nov. 1969) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot for the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, works at the Modular Equipment Stowage Assembly (MESA) on the Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM) during the mission's first extravehicular activity, (EVA) on Nov. 19, 1969. Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Bean descended in the Apollo 12 LM to explore the moon while astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
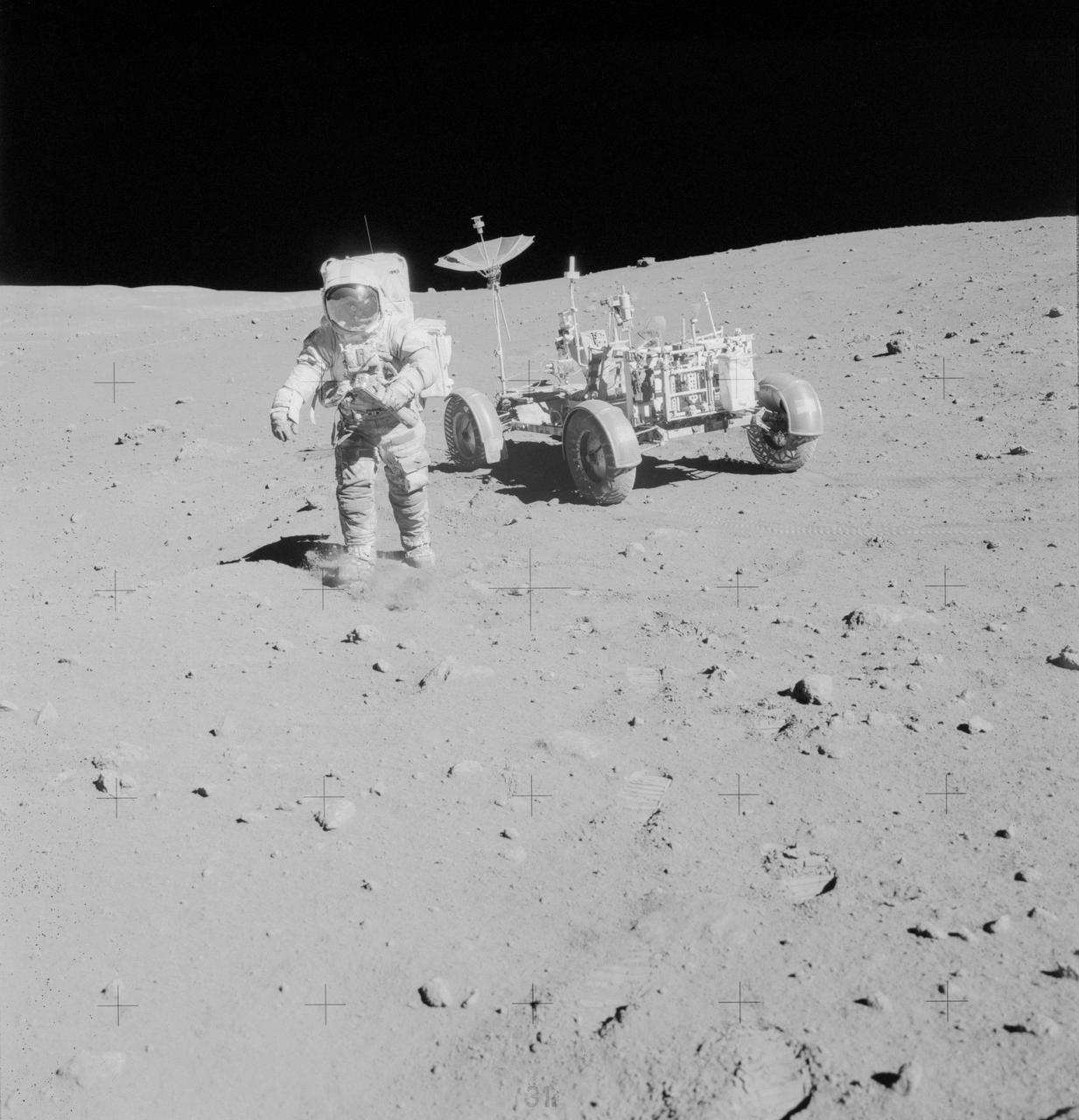

AS15-82-11168 (2 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, walks away from the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during the third Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. The LRV is parked a short distance from the rim of Hadley Rille. The far wall of the rille is in the distance at extreme upper left. Irwin is holding the 500mm Hasselblad camera in his left hand. This photograph was taken by astronaut David R. Scott, commander. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

A model of the Pressurized lunar rover is seen during a briefing discussing the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A model of the Pressurized lunar rover is seen during a briefing discussing the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
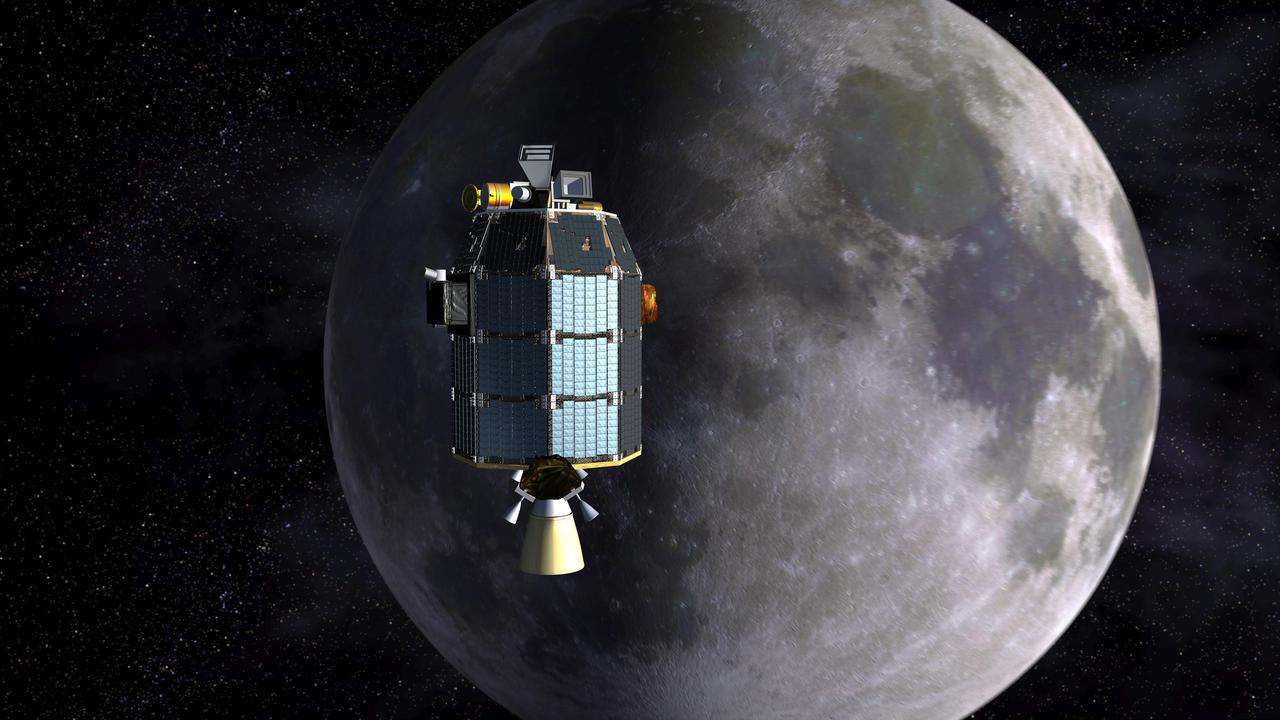

This is an artist depiction of NASA Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer LADEE observatory as it approaches lunar orbit. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18160
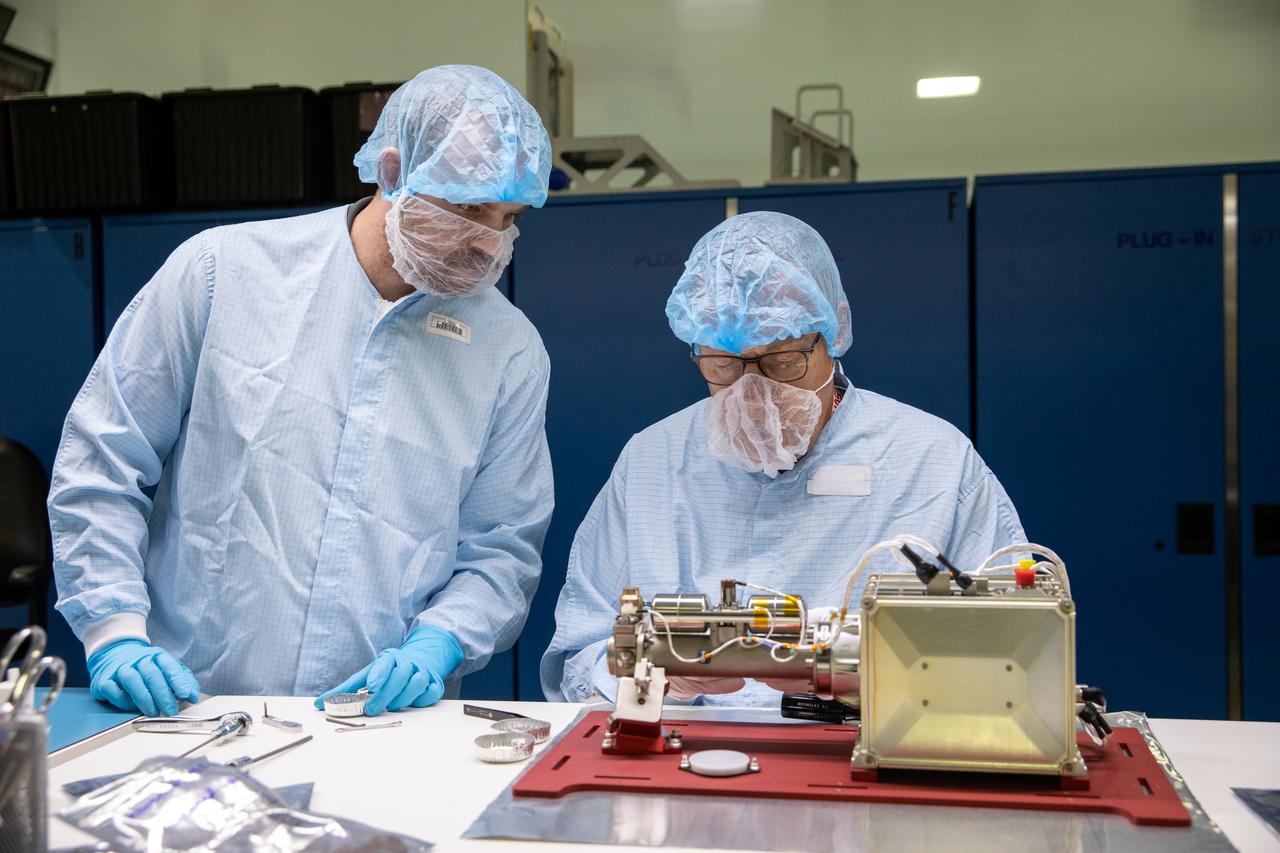

Technicians prepare the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) for NASA’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission for packing inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 21, 2023. MSolo will be shipped to Johnson Space Center in Houston for integration into VIPER. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo will be part of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) mission where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions. VIPER is scheduled to be delivered to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2024 by Astrobotic’s Griffin lander as part of the CLPS initiative.
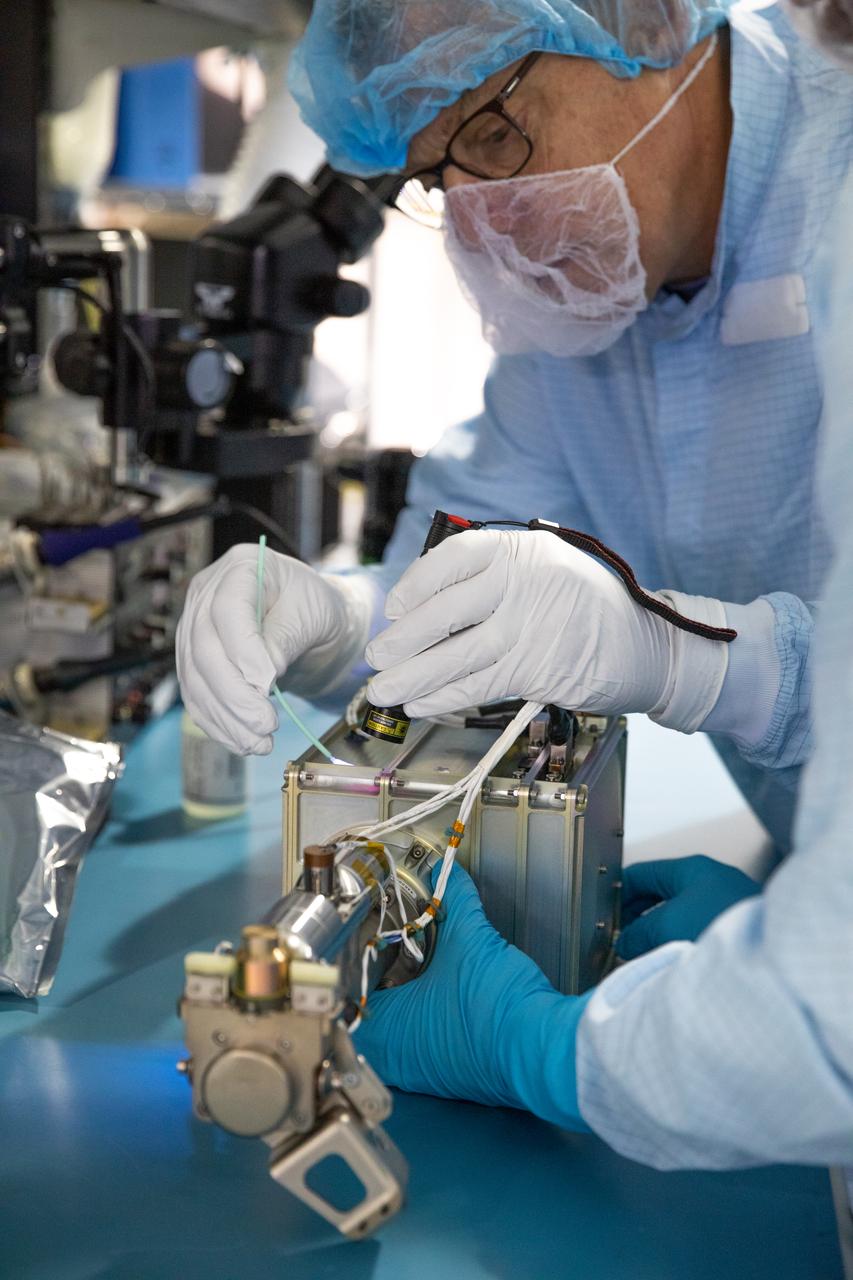

Technicians prepare the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) for NASA’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission for packing inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 21, 2023. MSolo will be shipped to Johnson Space Center in Houston for integration into VIPER. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo will be part of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) mission where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions. VIPER is scheduled to be delivered to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2024 by Astrobotic’s Griffin lander as part of the CLPS initiative.
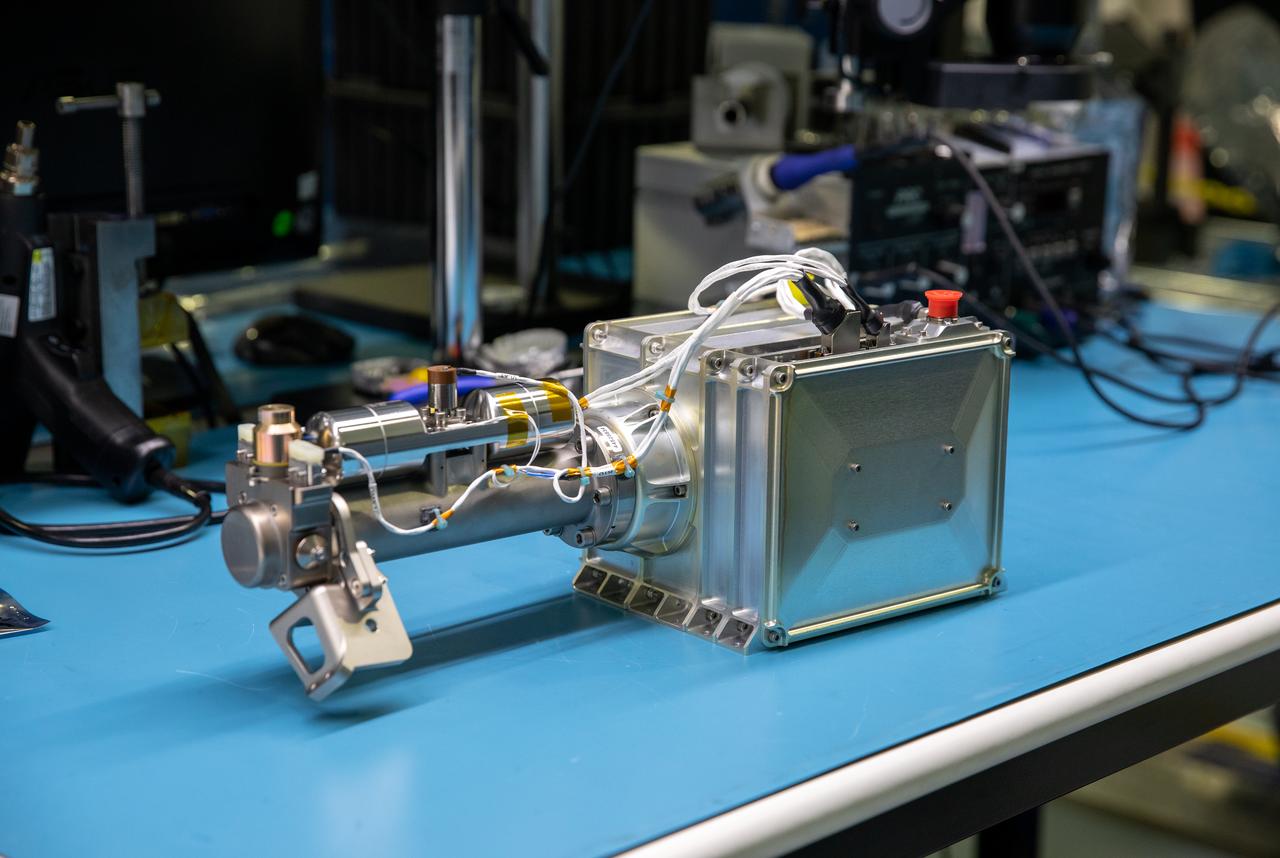
The Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) for NASA’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission is prepared for packing inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 21, 2023. MSolo will be shipped to Johnson Space Center in Houston for integration into VIPER. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo will be part of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) mission where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions. VIPER is scheduled to be delivered to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2024 by Astrobotic’s Griffin lander as part of the CLPS initiative.
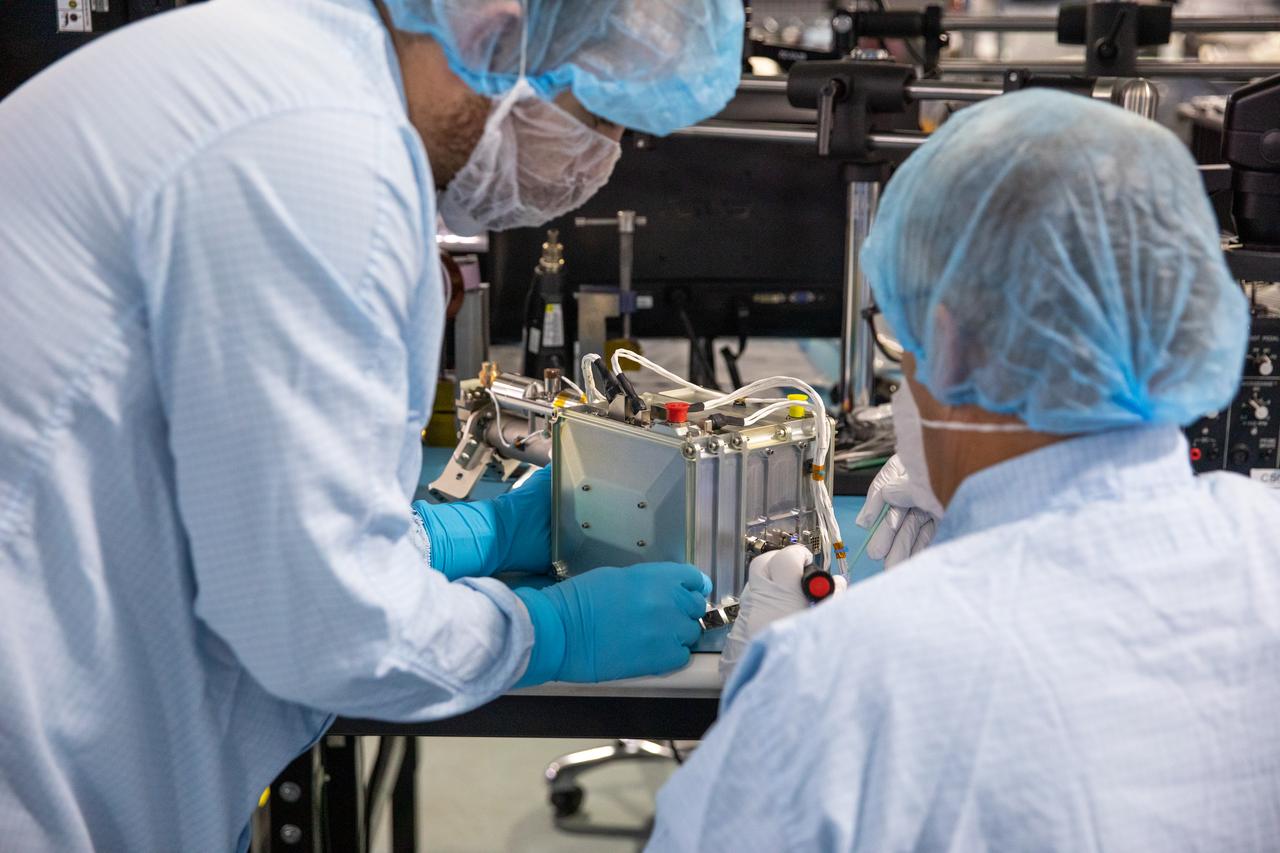

Technicians prepare the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) for NASA’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission for packing inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 21, 2023. MSolo will be shipped to Johnson Space Center in Houston for integration into VIPER. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo will be part of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) mission where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions. VIPER is scheduled to be delivered to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2024 by Astrobotic’s Griffin lander as part of the CLPS initiative.
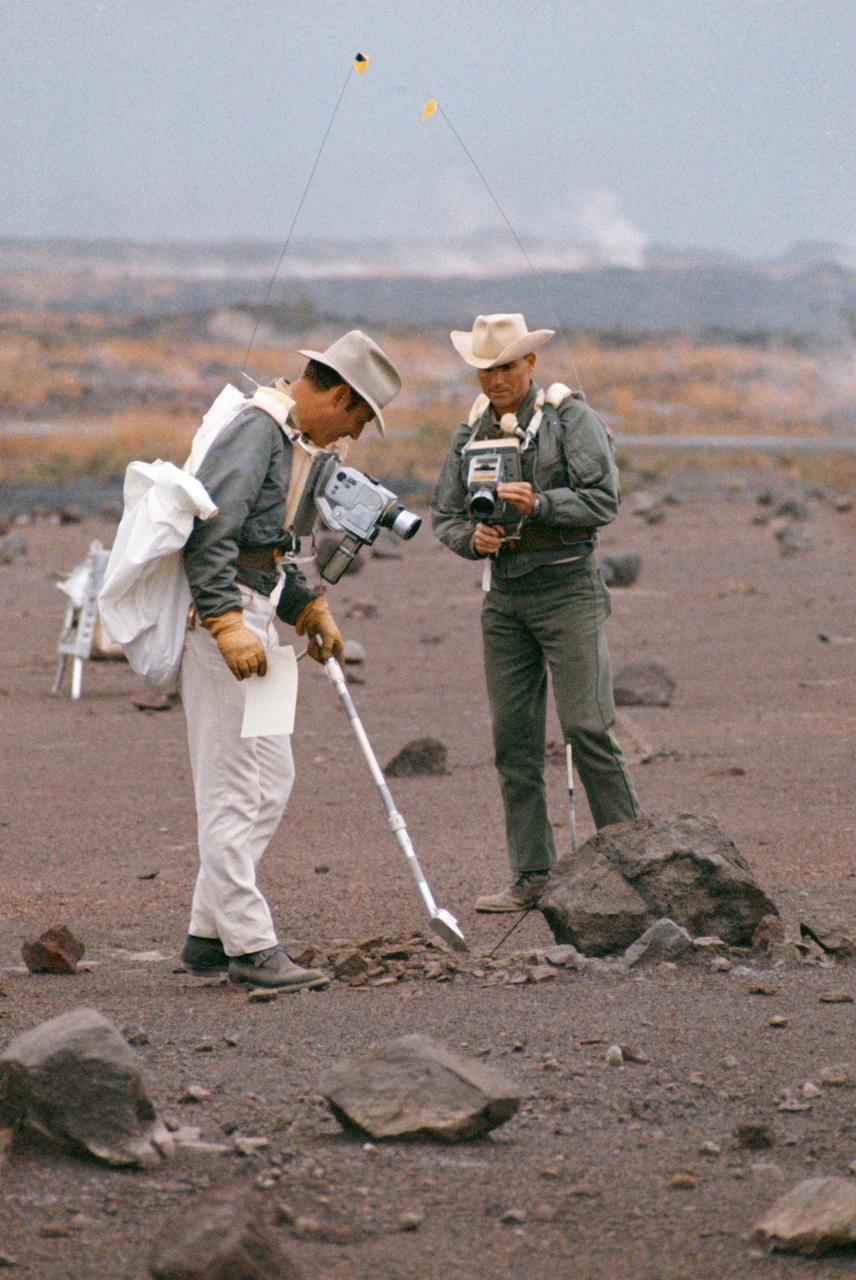

S70-20253 (December 1969) --- Astronauts James A. Lovell Jr. (left) commander, and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, carry out a simulation of a lunar traverse at Kilauea, Hawaii, site. Both crew members of NASA's third team of moon explorers were carrying cameras and communications equipment during the simulated traverse. They maintained contact with men in the roles of spacecraft throughout the traverse. Lovell holds a scoop for the Apollo Lunar Hand Tools (ALHT) and a gnomon, also for the ALHT is deployed in front of Haise. The ALHT carrier is at left background, (almost obscured by Lovell).
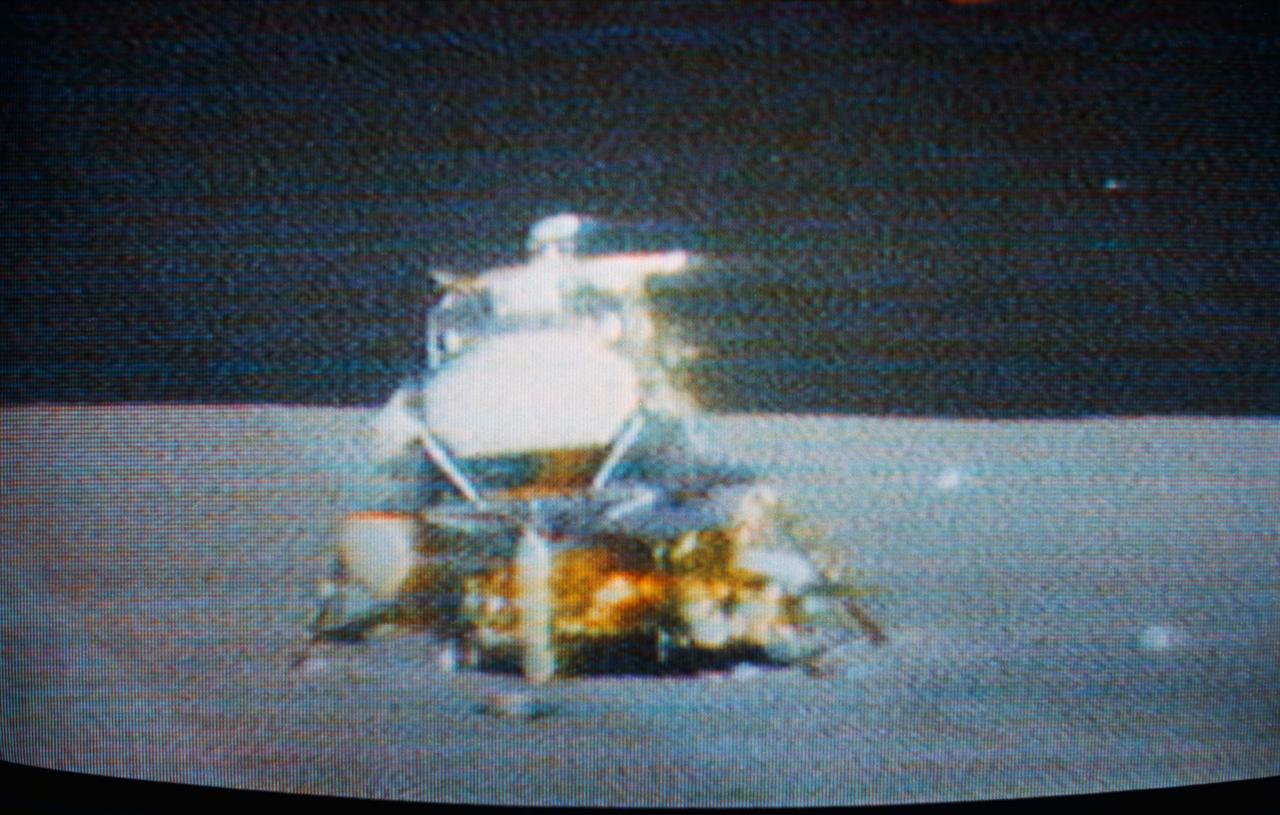

S71-41511 (2 Aug. 1971) --- The Apollo 15 Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" is seen only seconds before ascent stage liftoff in this color reproduction taken from a transmission made by the RCA color television camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV was parked about 300 feet east of the LM. The LRV-mounted TV camera, remotely controlled from the Mission Control Center (MCC), made it possible for people on Earth to watch the LM's launch from the moon. The LM liftoff was at 171:37 ground elapsed time. The "Falcon" ascent stage, with astronauts David R. Scott, commander; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, aboard, returned from the lunar surface to rejoin the Command and Service Modules (CSM) orbiting the moon. Astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the CSM in lunar orbit while Scott and Irwin explored the moon. The LM descent stage is used as a launching platform and remains behind on the moon. This is part one of a four-part sequence.
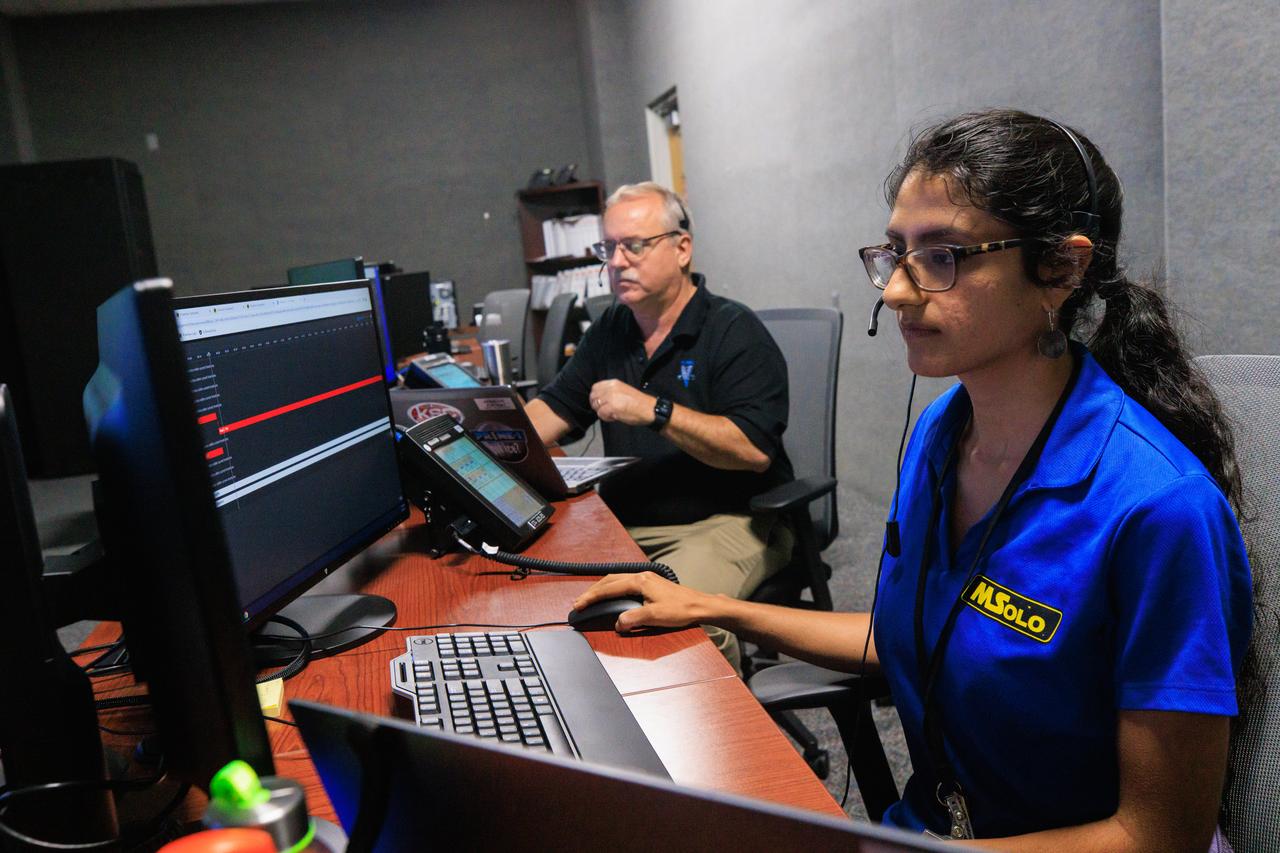

Jim Kania (left), Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSOLO) software engineering lead, and Pri Johnson, MSOLO systems engineer, participate in simulation training at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 25, 2023, in preparation for the agency’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission. The purpose of the training was to get the integrated VIPER team – a mix of engineers from Kennedy and NASA’s Ames Research Center in California – accustomed to operating together during phases of the mission where the rover will be driving. MSOLO is a modified commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer that will help the agency analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon and study water on the lunar surface. MSOLO, as part of VIPER, is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) initiative in late 2024, landing at the Moon’s South Pole aboard Astrobotic’s Griffin lander. Through Artemis missions, CLPS deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human deep space exploration missions.
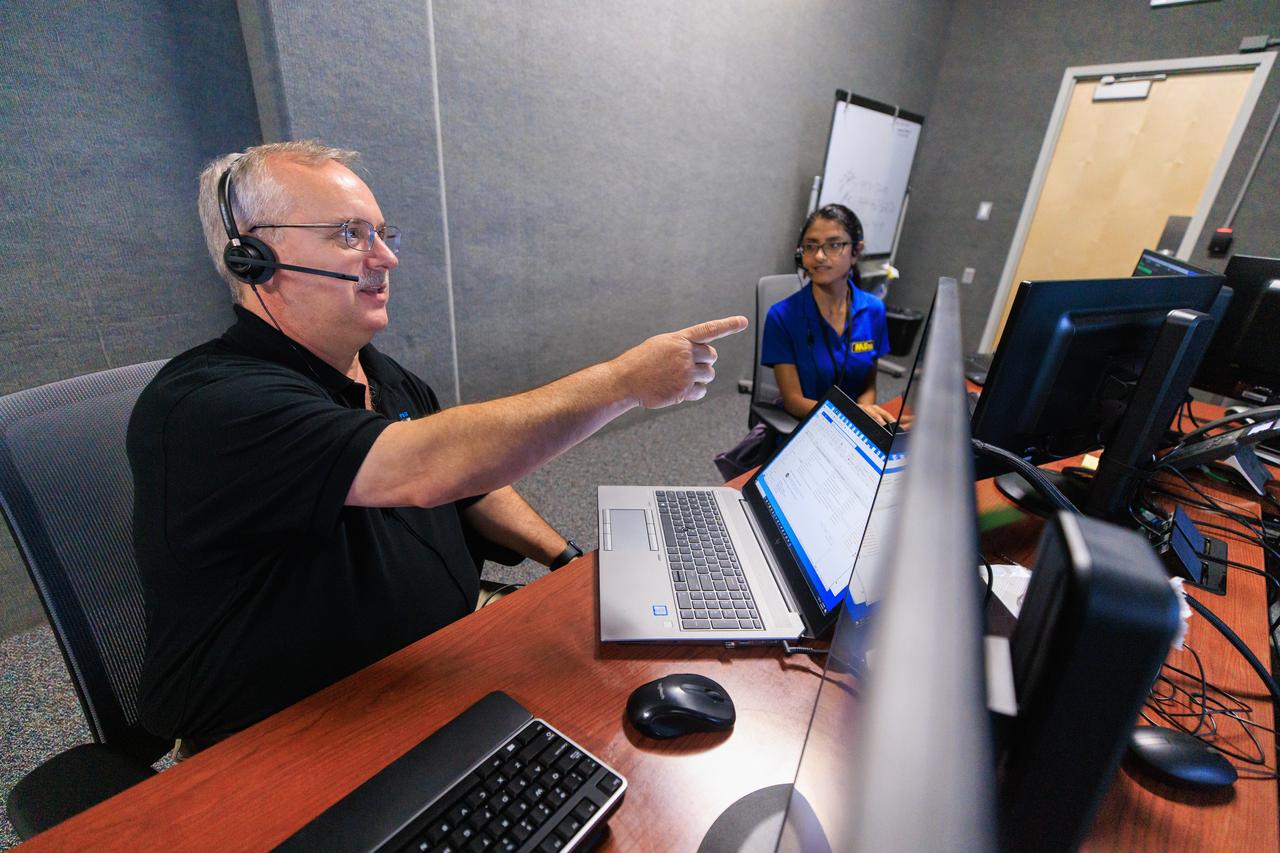

Jim Kania (left), Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSOLO) software engineering lead, and Pri Johnson, MSOLO systems engineer, participate in simulation training at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 25, 2023, in preparation for the agency’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission. The purpose of the training was to get the integrated VIPER team – a mix of engineers from Kennedy and NASA’s Ames Research Center in California – accustomed to operating together during phases of the mission where the rover will be driving. MSOLO is a modified commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer that will help the agency analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon and study water on the lunar surface. MSOLO, as part of VIPER, is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) initiative in late 2024, landing at the Moon’s South Pole aboard Astrobotic’s Griffin lander. Through Artemis missions, CLPS deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human deep space exploration missions.
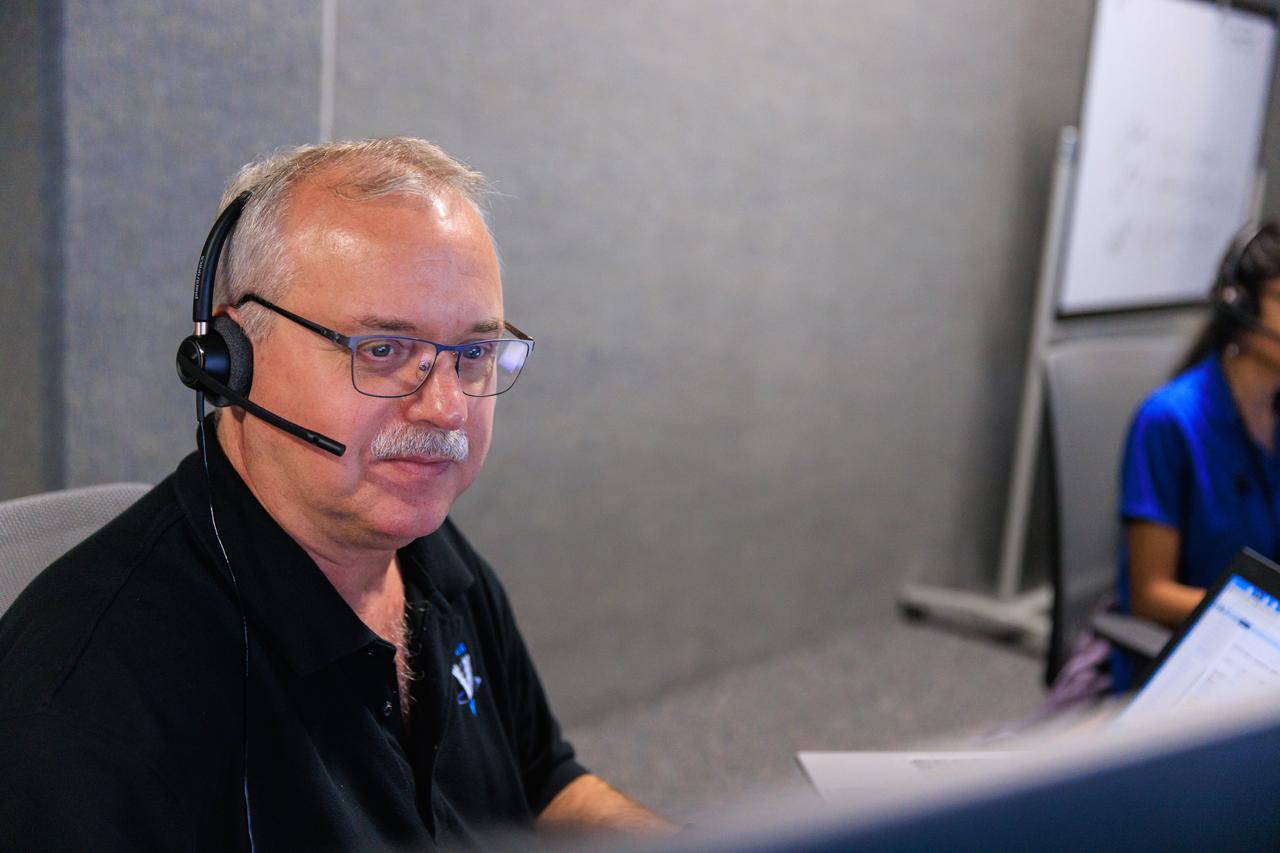

Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSOLO) Software Engineering Lead Jim Kania participates in simulation training at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 25, 2023, in preparation for the agency’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission. The purpose of the training was to get the integrated VIPER team – a mix of engineers from Kennedy and NASA’s Ames Research Center in California – accustomed to operating together during phases of the mission where the rover will be driving. MSOLO is a modified commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer that will help the agency analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon and study water on the lunar surface. MSOLO, as part of VIPER, is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) initiative in late 2024, landing at the Moon’s South Pole aboard Astrobotic’s Griffin lander. Through Artemis missions, CLPS deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human deep space exploration missions.
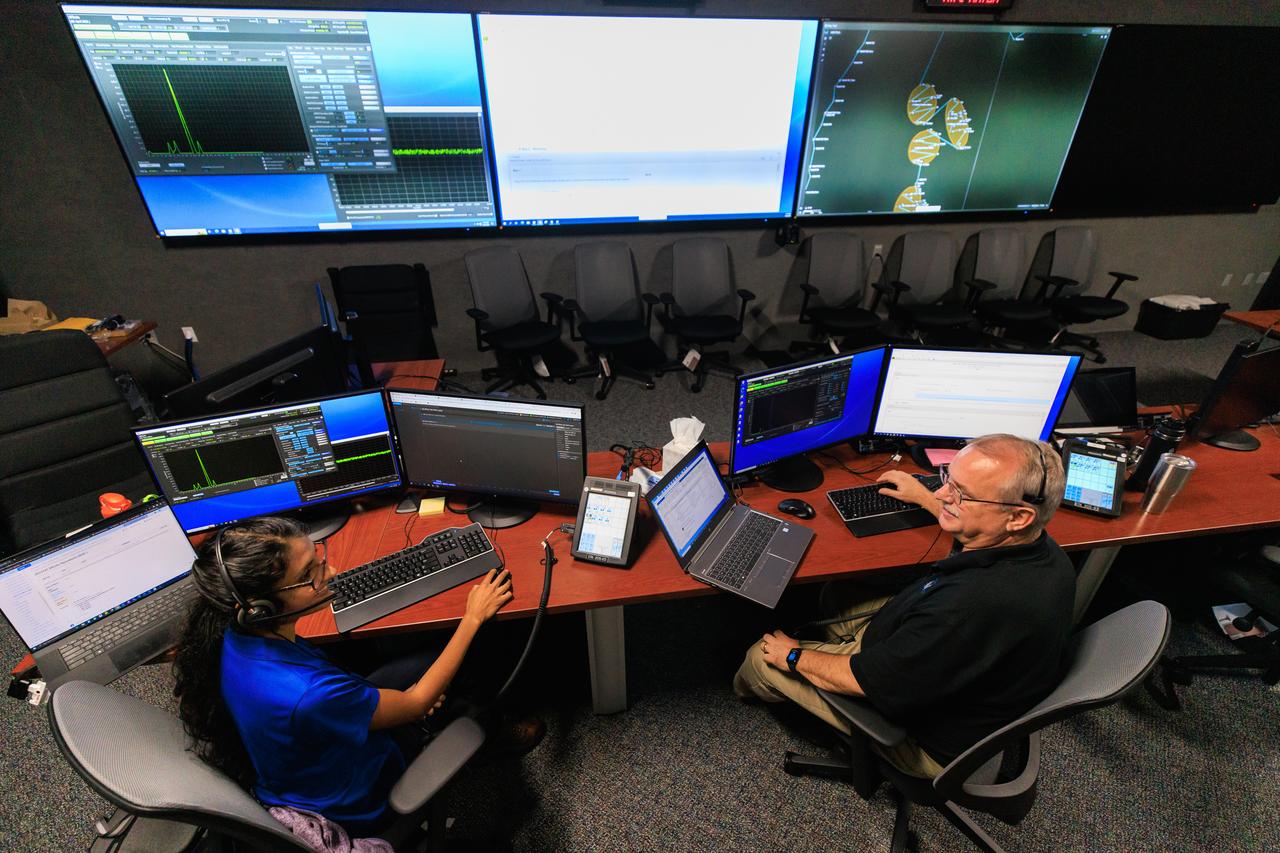

Pri Johnson (left), Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSOLO) systems engineer, and Jim Kania, MSOLO software engineering lead, participate in simulation training at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 25, 2023, in preparation for the agency’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission. The purpose of the training was to get the integrated VIPER team – a mix of engineers from Kennedy and NASA’s Ames Research Center in California – accustomed to operating together during phases of the mission where the rover will be driving. MSOLO is a modified commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer that will help the agency analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon and study water on the lunar surface. MSOLO, as part of VIPER, is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) initiative in late 2024, landing at the Moon’s South Pole aboard Astrobotic’s Griffin lander. Through Artemis missions, CLPS deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human deep space exploration missions.
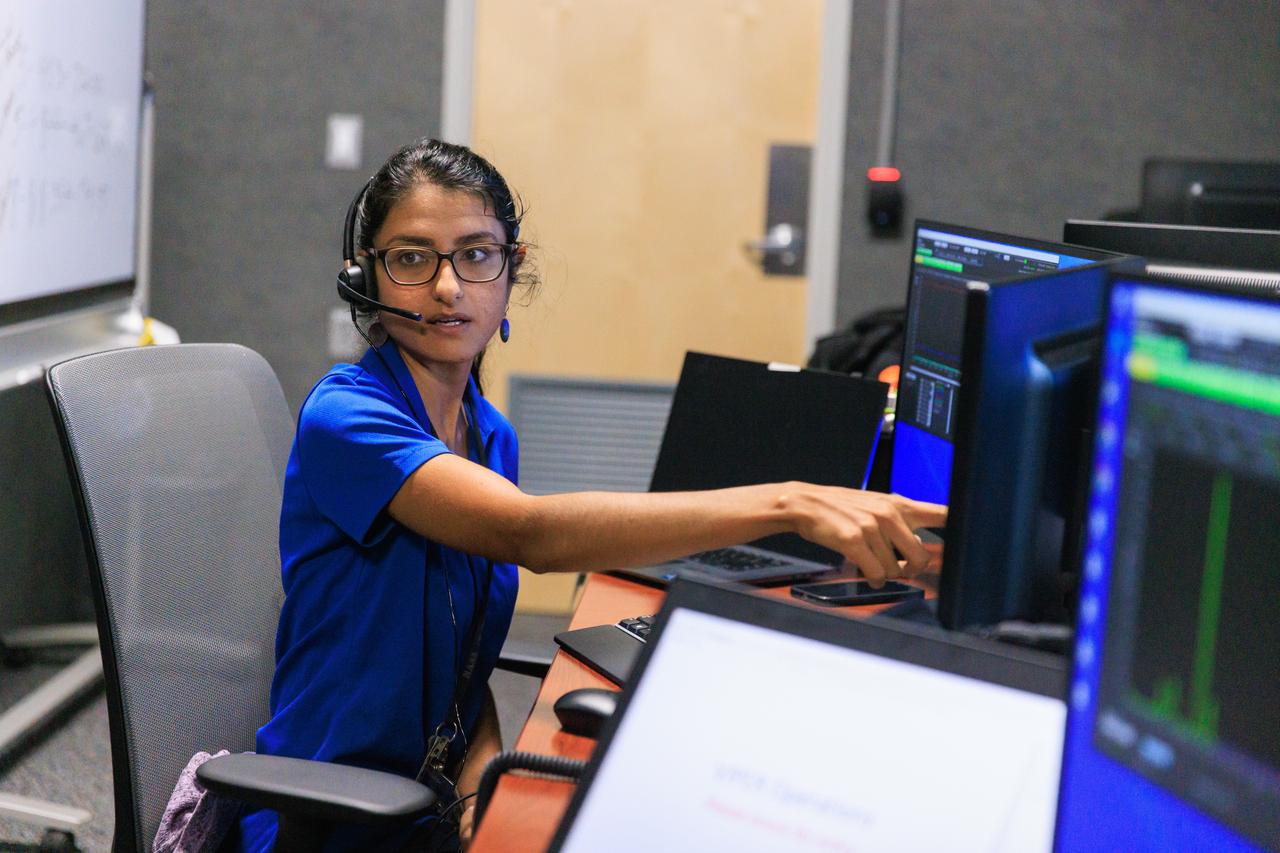

Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSOLO) Systems Engineer Pri Johnson participates in simulation training at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 25, 2023, in preparation for the agency’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission. The purpose of the training was to get the integrated VIPER team – a mix of engineers from Kennedy and NASA’s Ames Research Center in California – accustomed to operating together during phases of the mission where the rover will be driving. MSOLO is a modified commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer that will help the agency analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon and study water on the lunar surface. MSOLO, as part of VIPER, is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) initiative in late 2024, landing at the Moon’s South Pole aboard Astrobotic’s Griffin lander. Through Artemis missions, CLPS deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human deep space exploration missions.
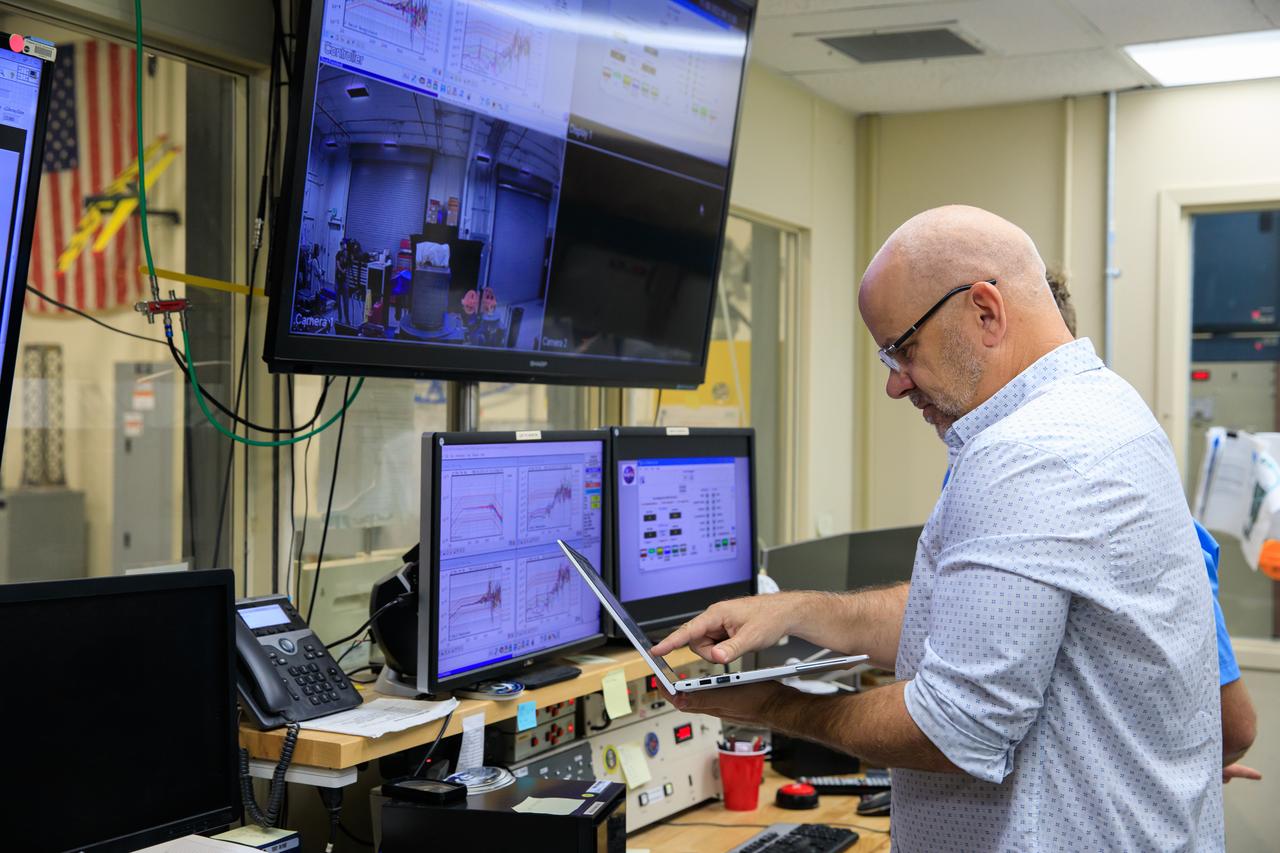

Preparations are underway to conduct a vibration test on the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) for NASA’s VIPER mission inside a laboratory in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 8, 2022. Exposing the instrument to vibration environments that it might see during launch helps engineers to find issues prior to liftoff. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo will be part of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) mission where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
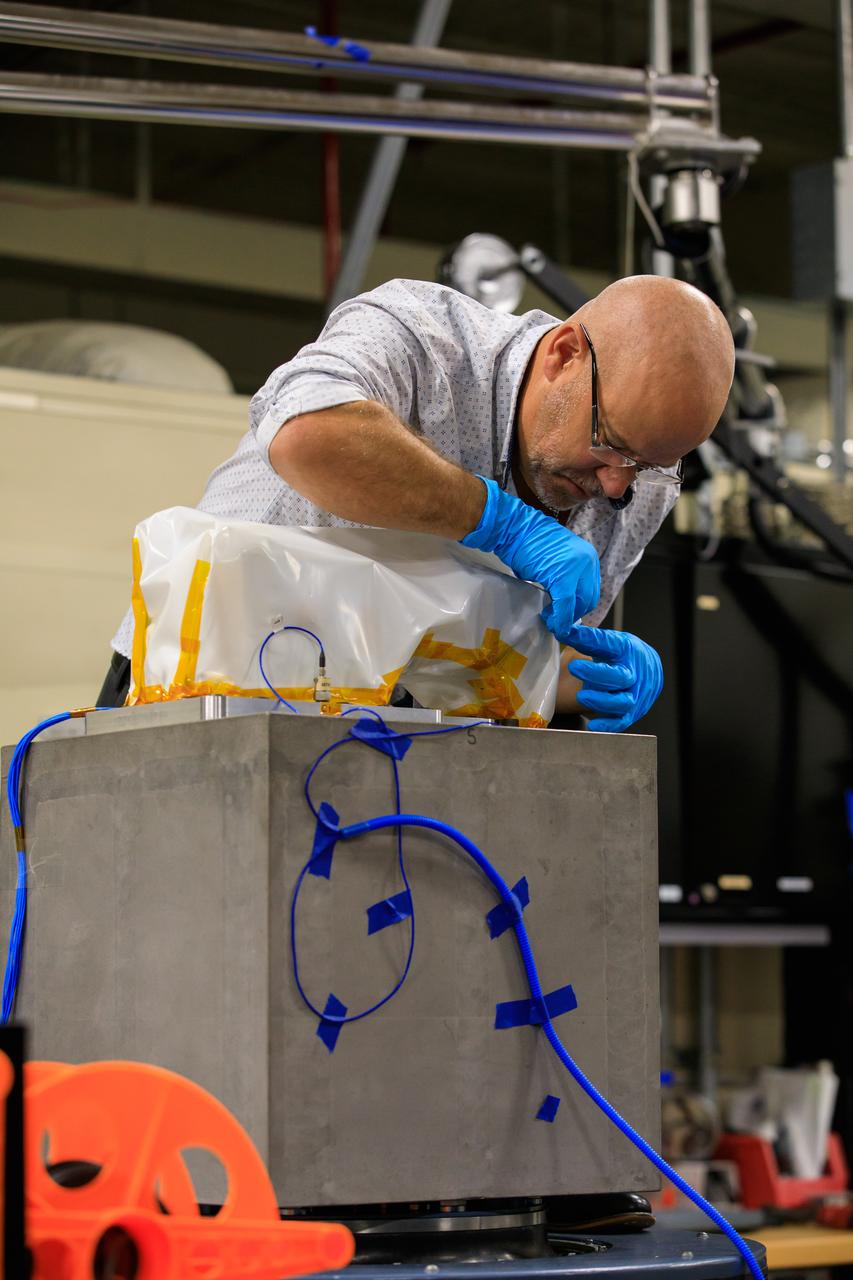

Preparations are underway to conduct a vibration test on the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) for NASA’s VIPER mission inside a laboratory in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 8, 2022. Exposing the instrument to vibration environments that it might see during launch helps engineers to find issues prior to liftoff. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo will be part of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) mission where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
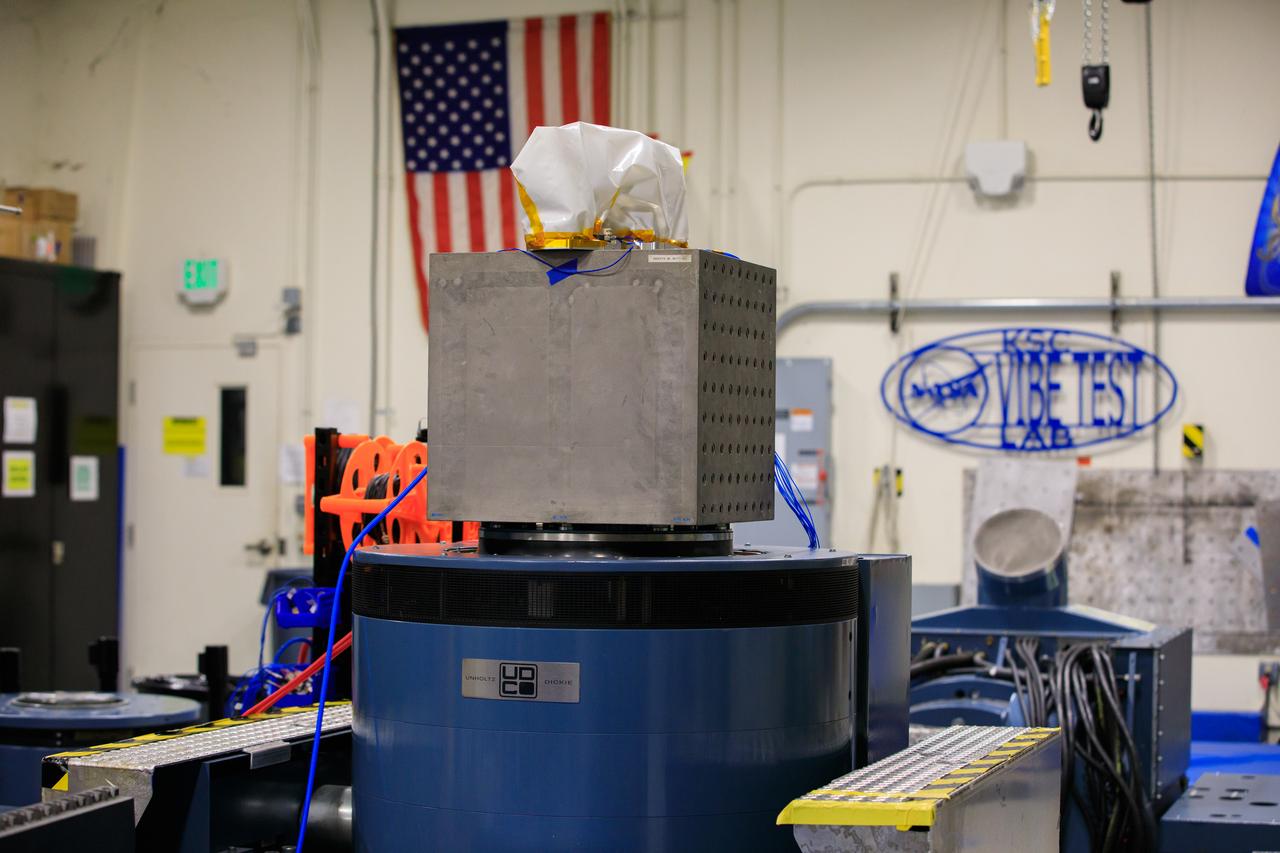

The Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) for NASA’s VIPER mission is being prepared for a vibration test inside a laboratory in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 8, 2022. Exposing the instrument to vibration environments that it might see during launch helps engineers to find issues prior to liftoff. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo will be part of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) mission where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
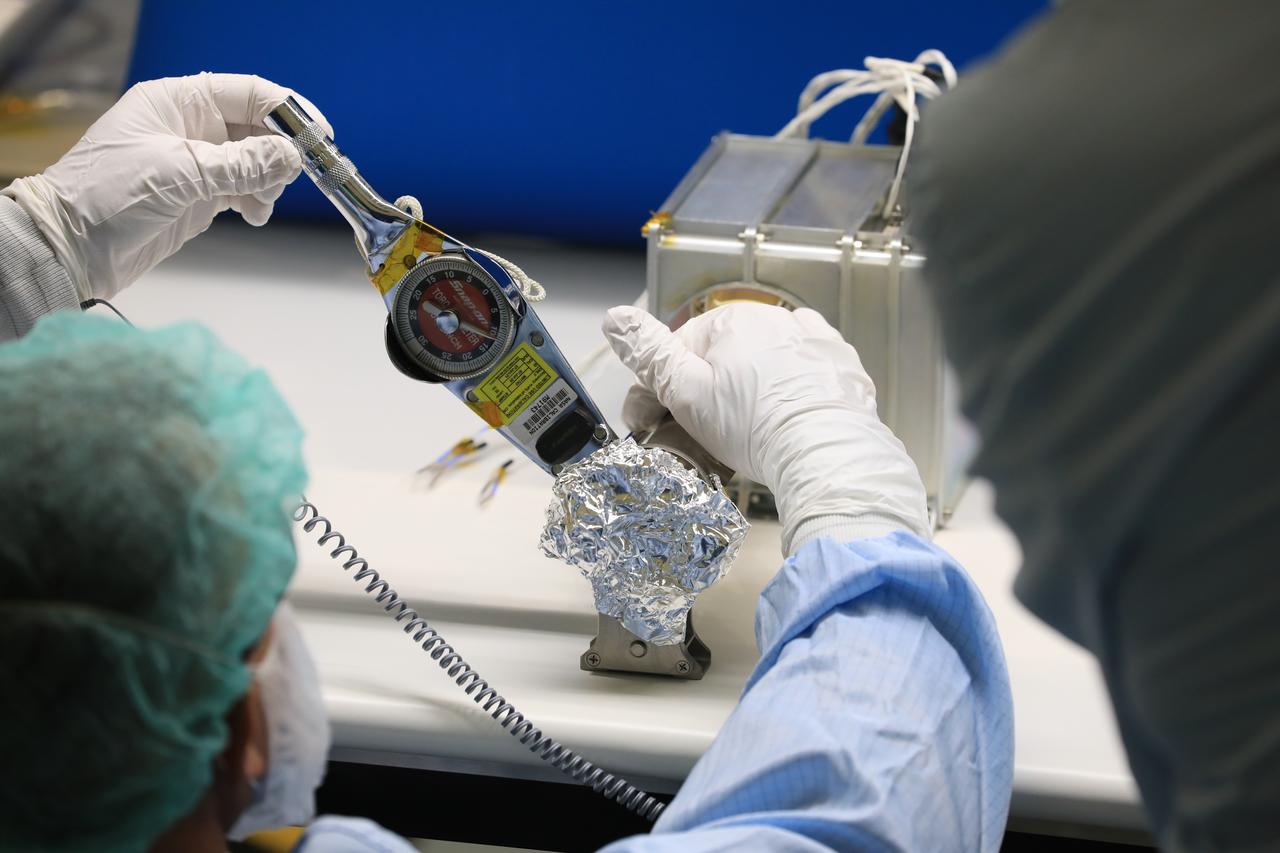

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work with instruments for Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) inside the Space Station Processing on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This work is preparing MSolo hardware for a robotic mission as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).
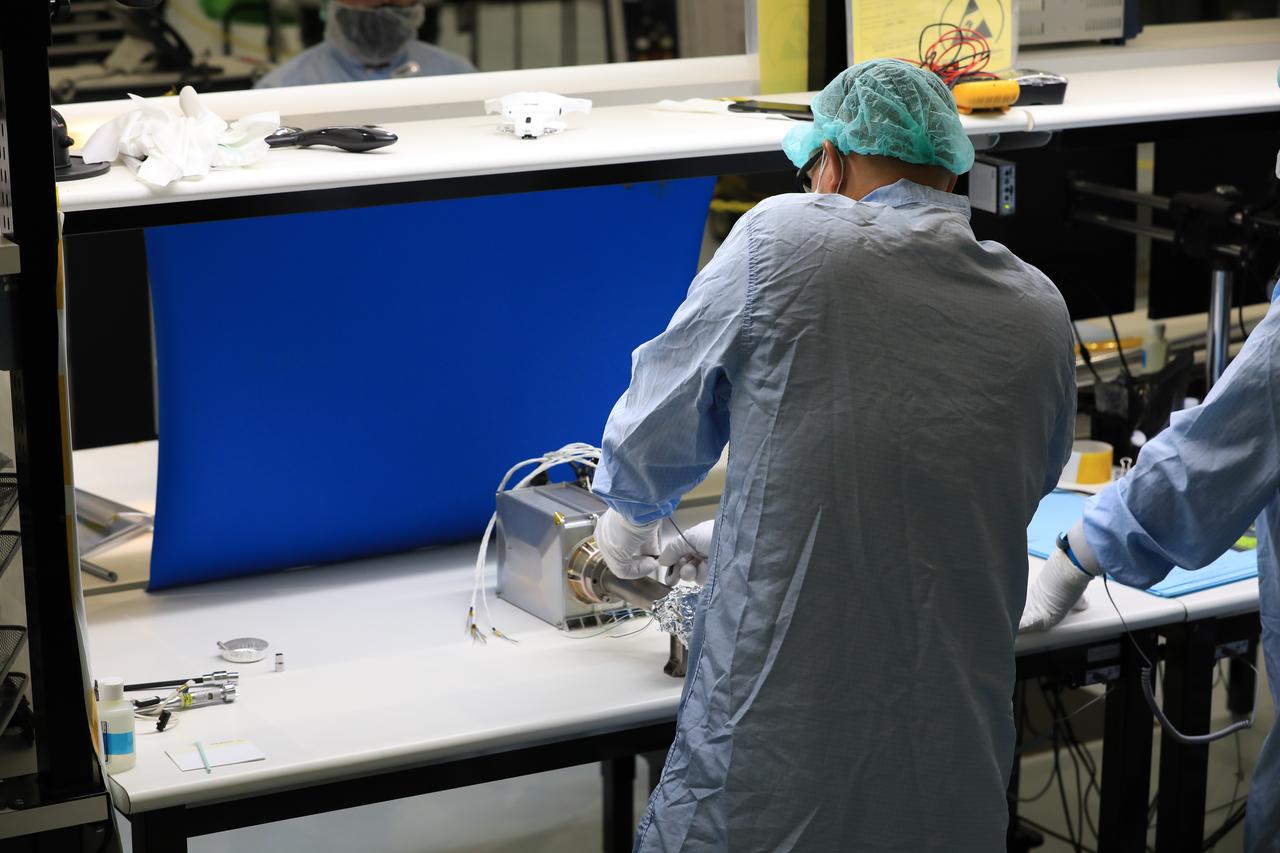

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work with instruments for Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) inside the Space Station Processing on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This work is preparing MSolo hardware for a robotic mission as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).
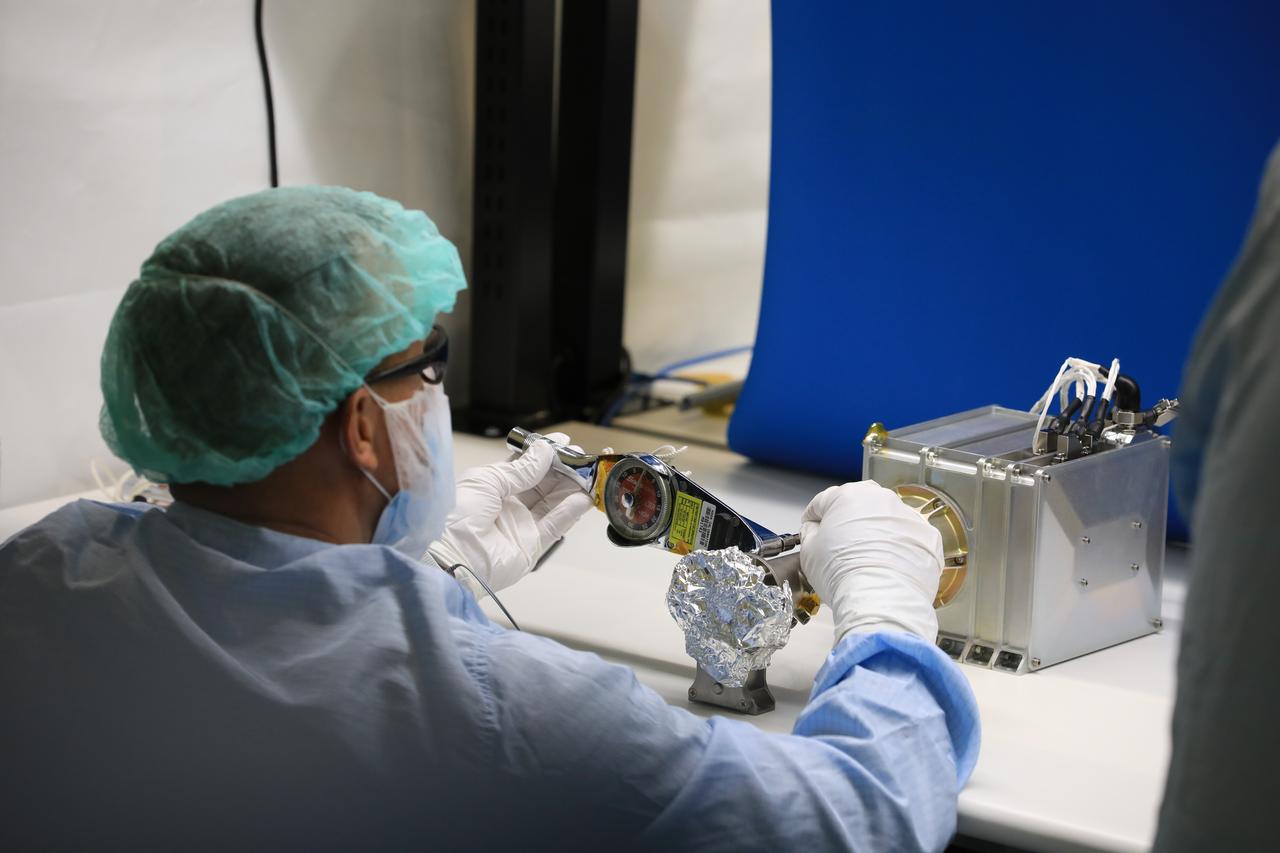

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work with instruments for Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) inside the Space Station Processing on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This work is preparing MSolo hardware for a robotic mission as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).
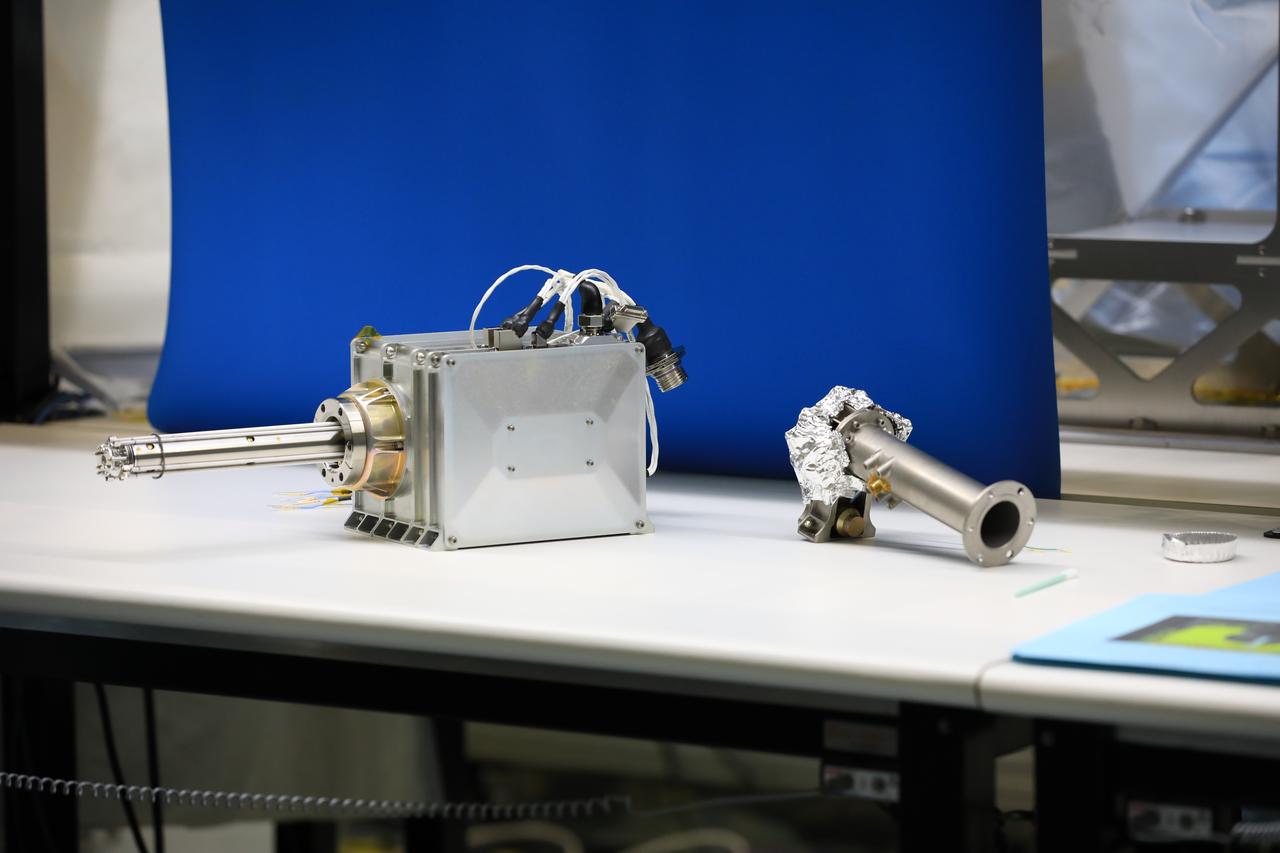
Instruments for the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) are in view inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This work is preparing MSolo hardware for a robotic mission as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).
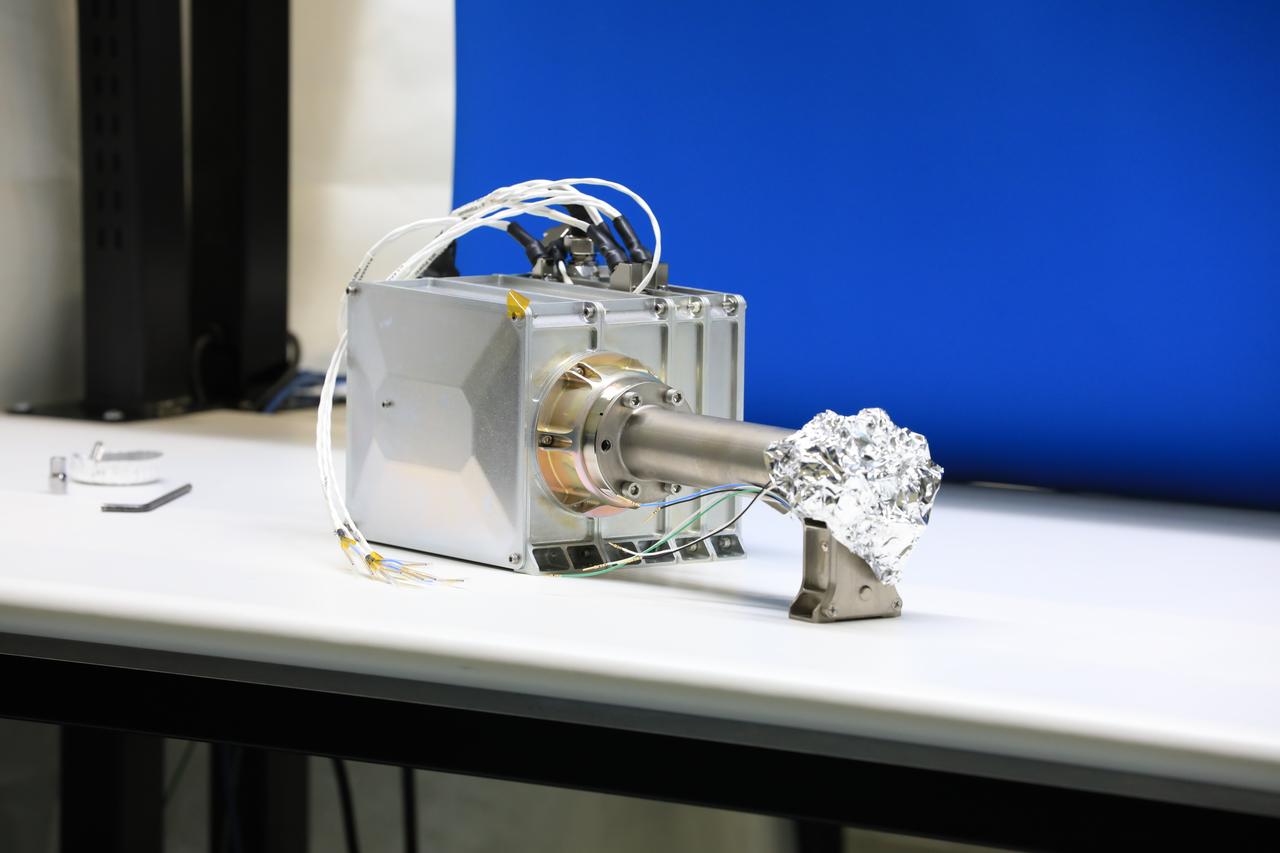
Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida are preparing the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) for launch inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo hardware is a payload for a robotic mission to the Moon as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).
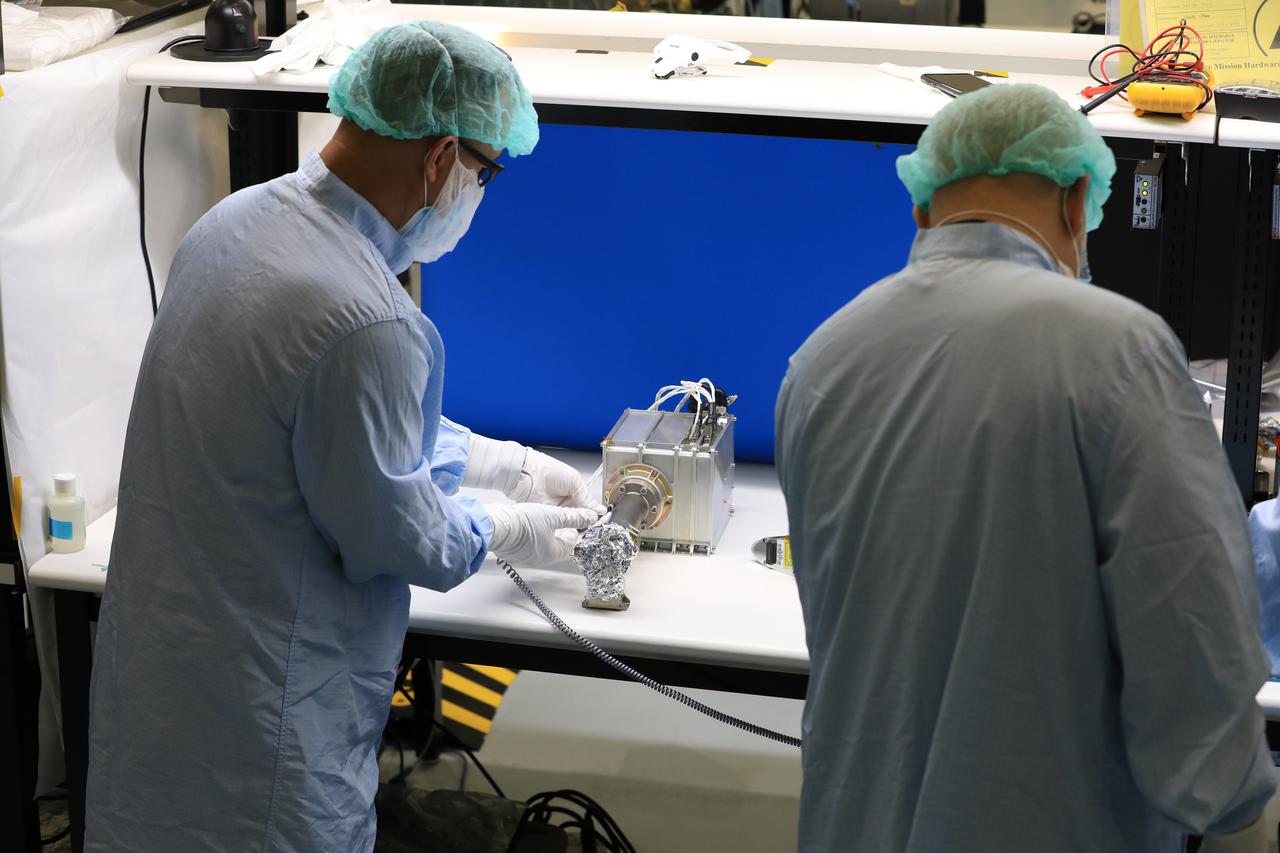

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work with instruments for Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) inside the Space Station Processing on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This work is preparing MSolo hardware for a robotic mission as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).
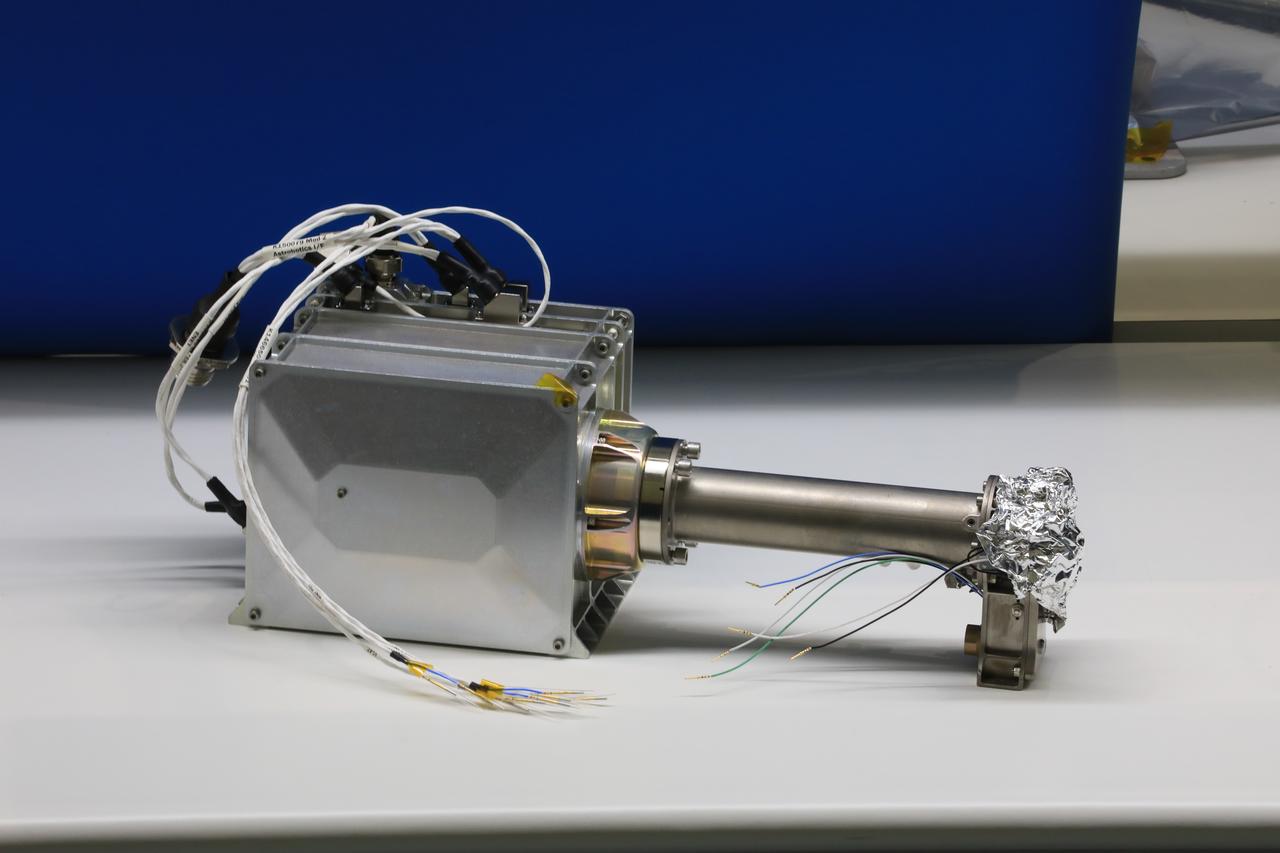
Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida are preparing the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) for launch inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo hardware is a payload for a robotic mission to the Moon as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).
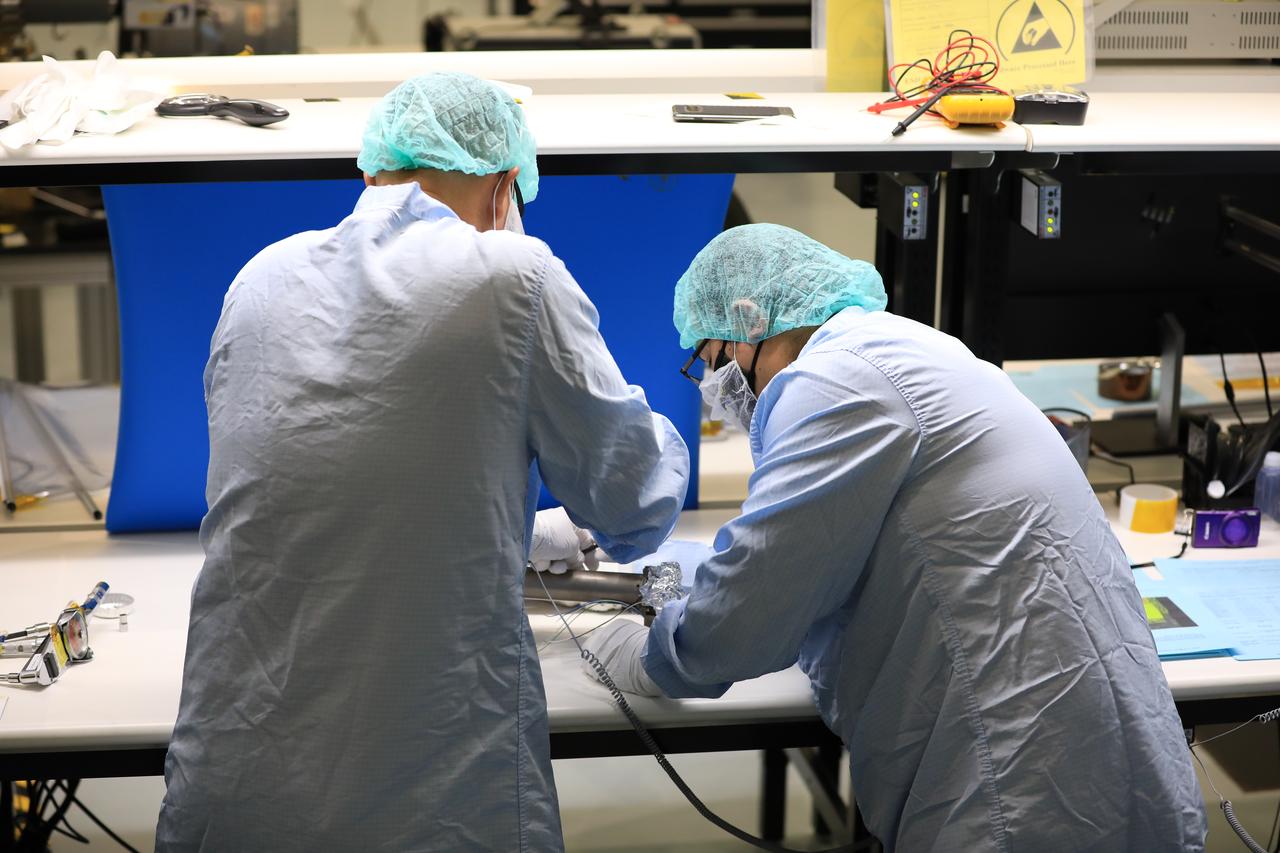

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work with instruments for Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) inside the Space Station Processing on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This work is preparing MSolo hardware for a robotic mission as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).
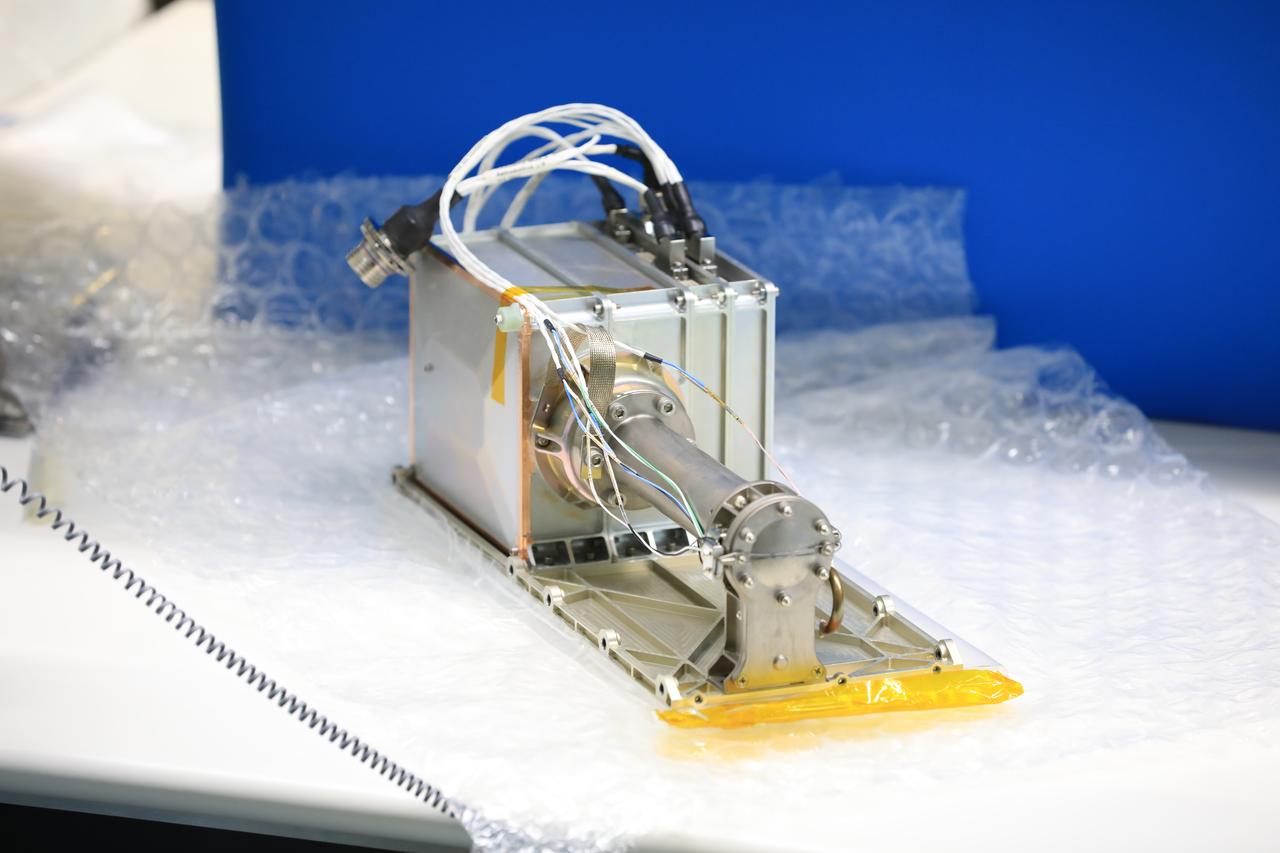

The Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument is photographed inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida following installation of its radiator on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
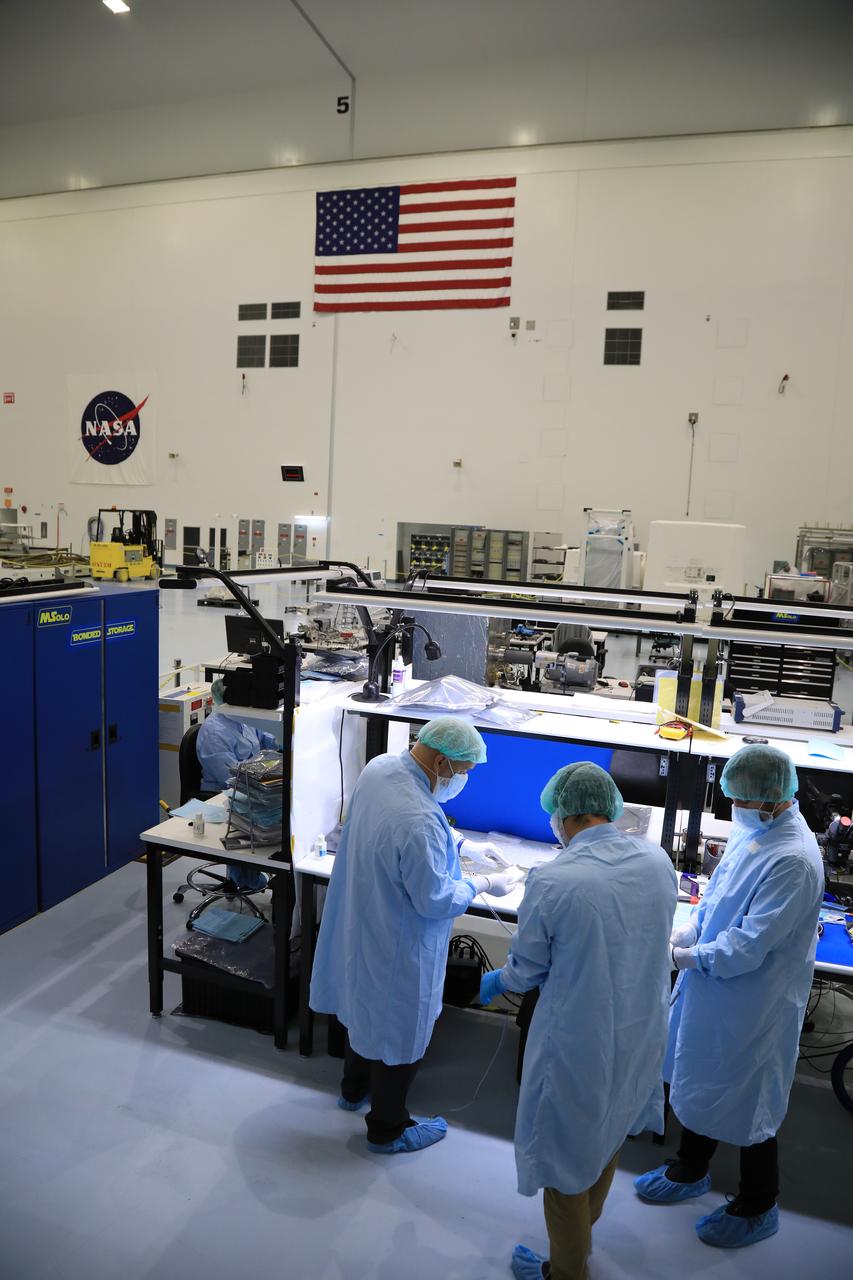

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prepare to install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
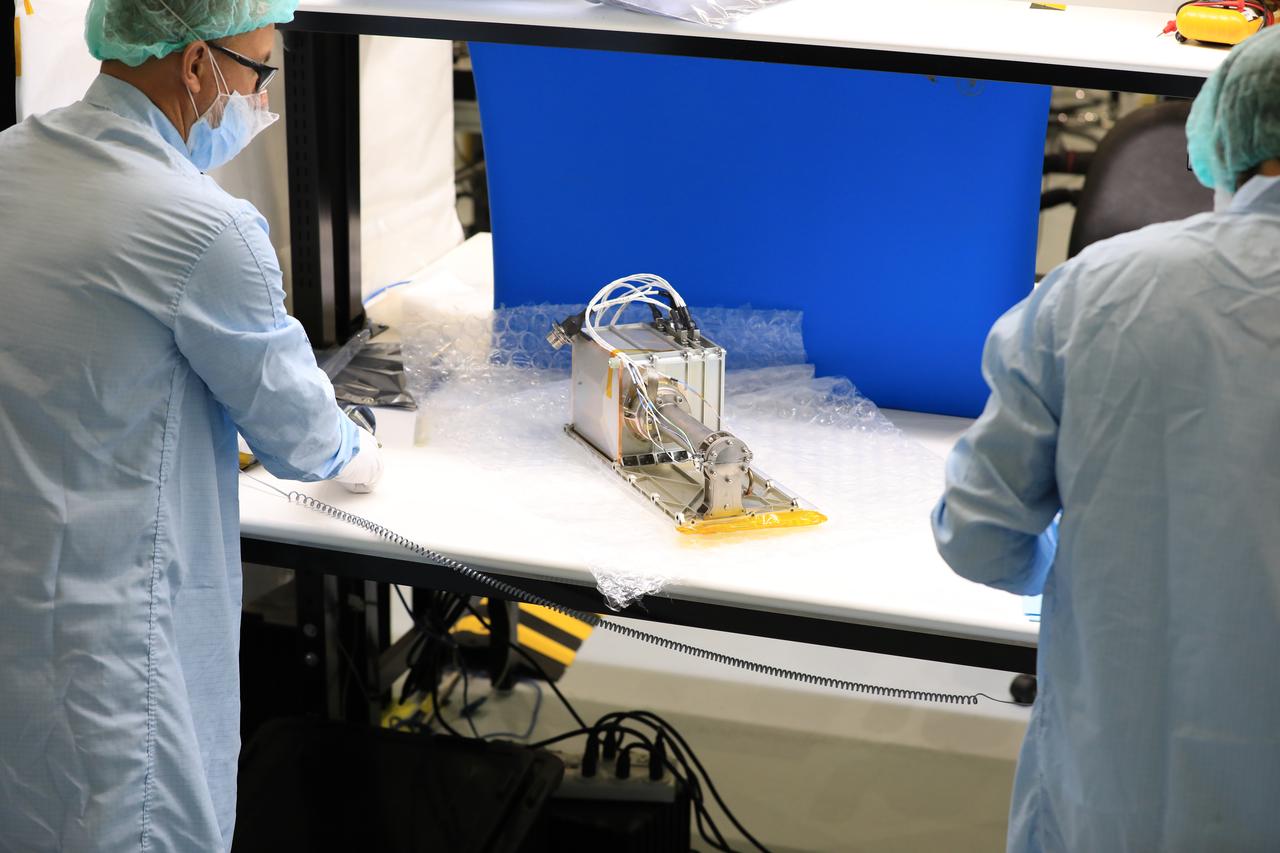
Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
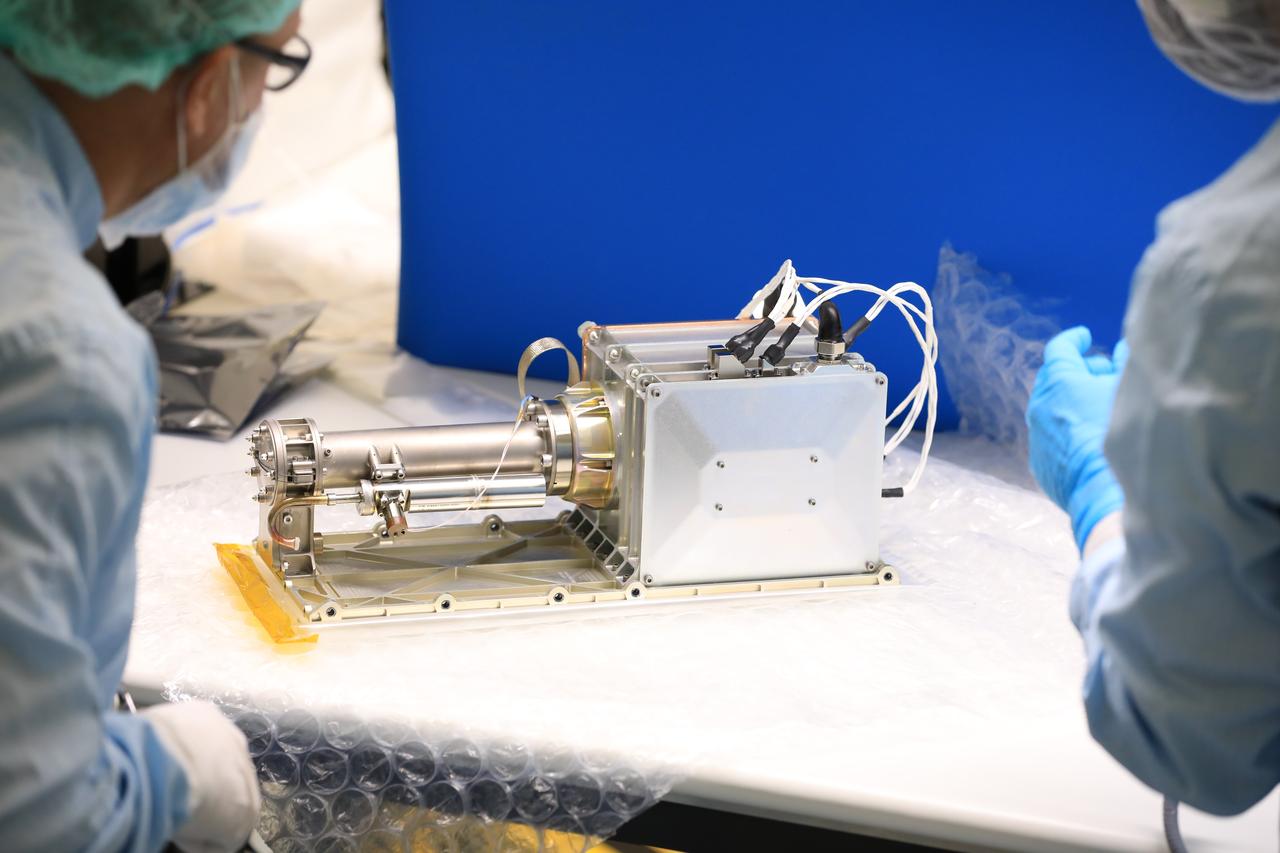

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
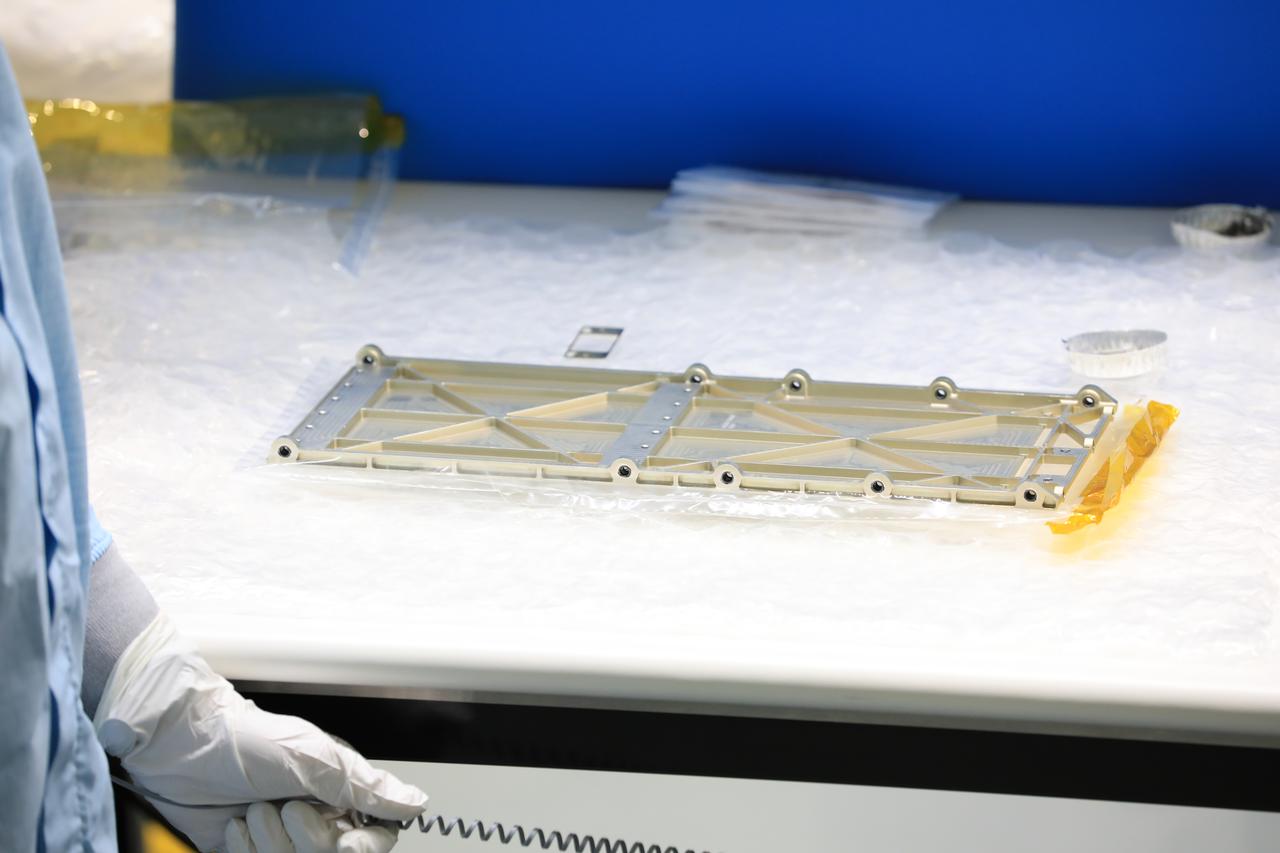
Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida have prepped the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument’s radiator for installation inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
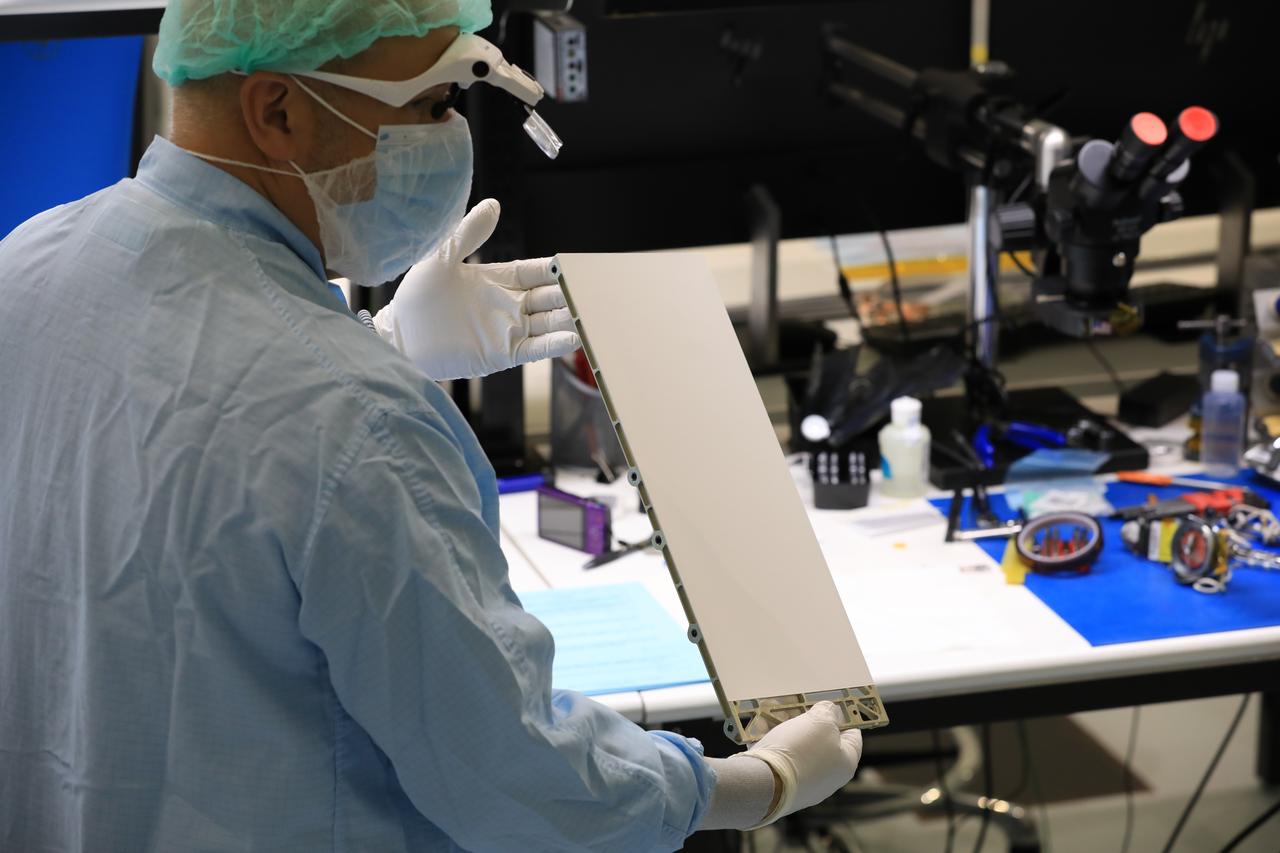

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prepare to install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
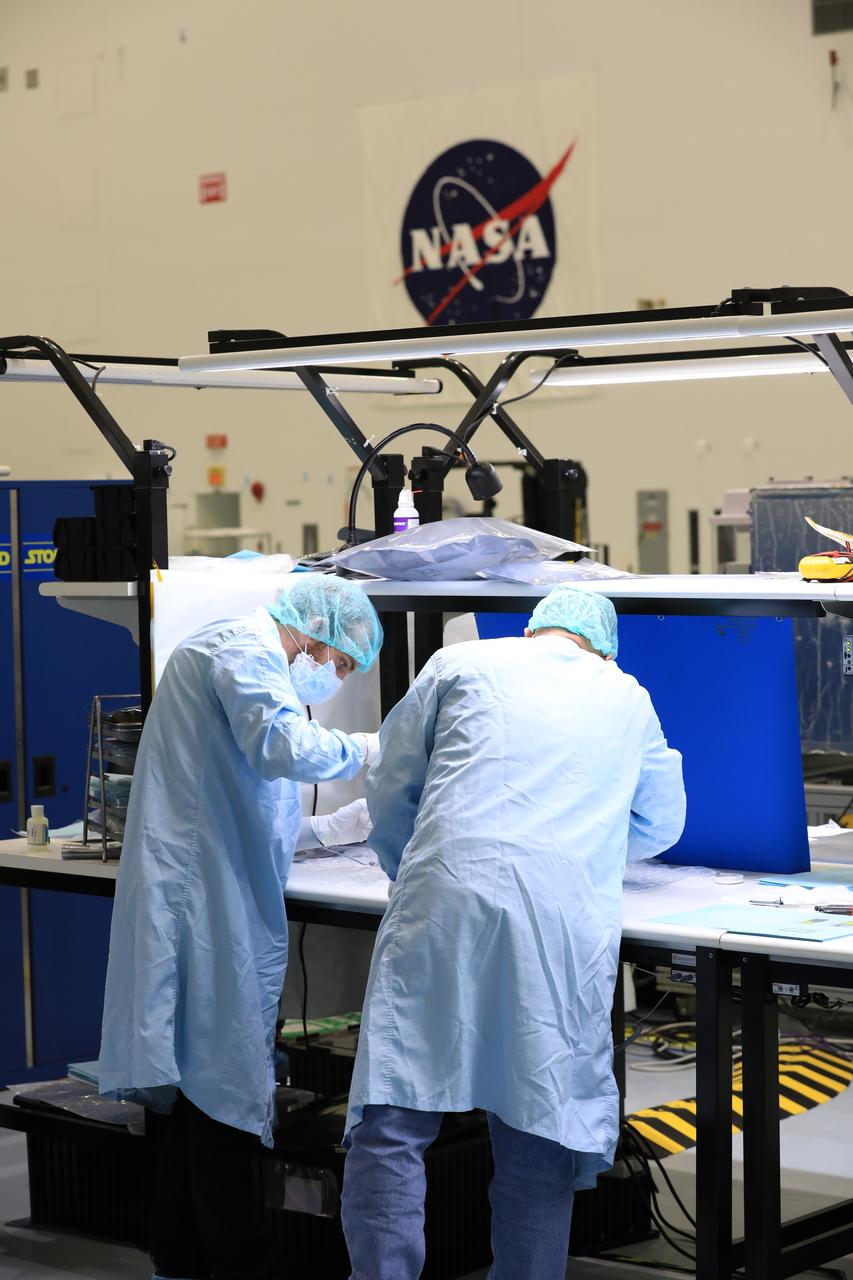

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
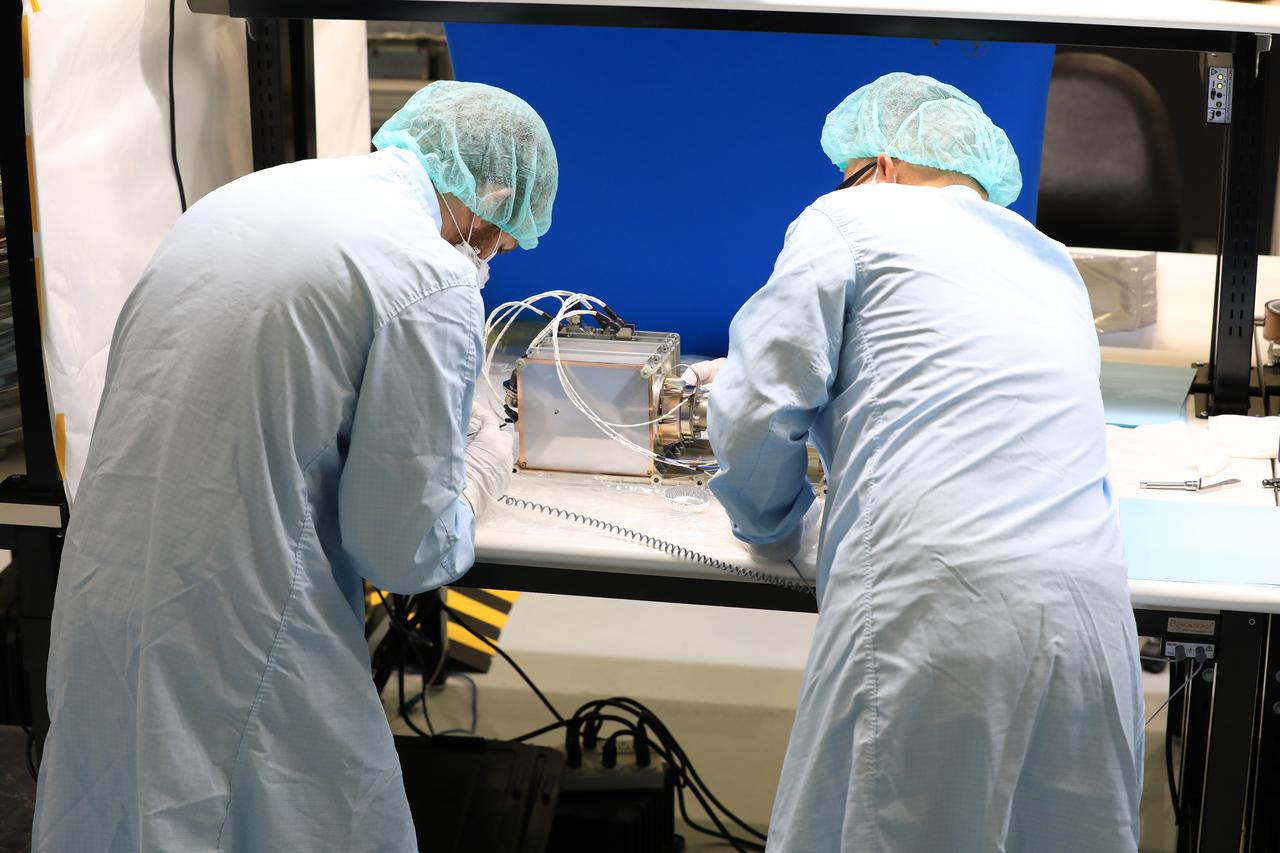

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
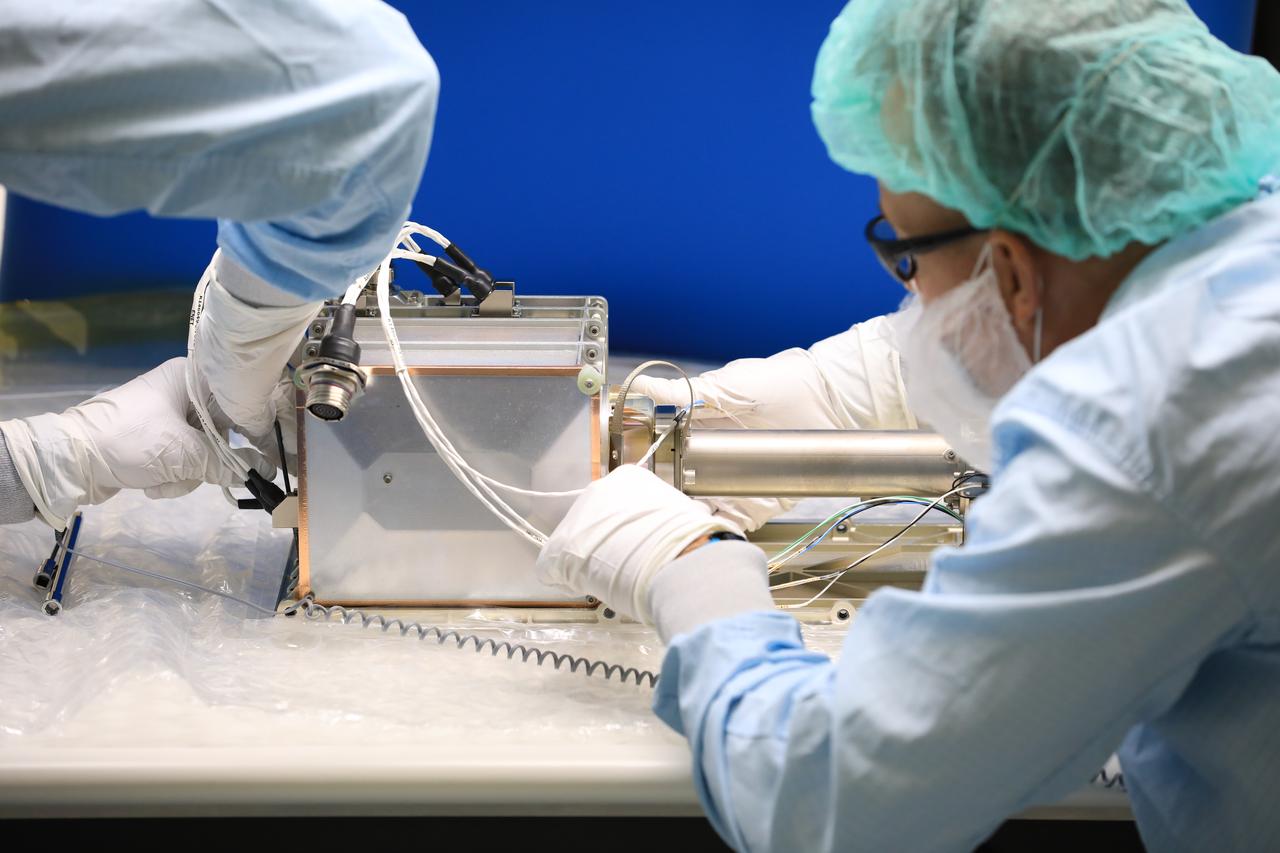

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
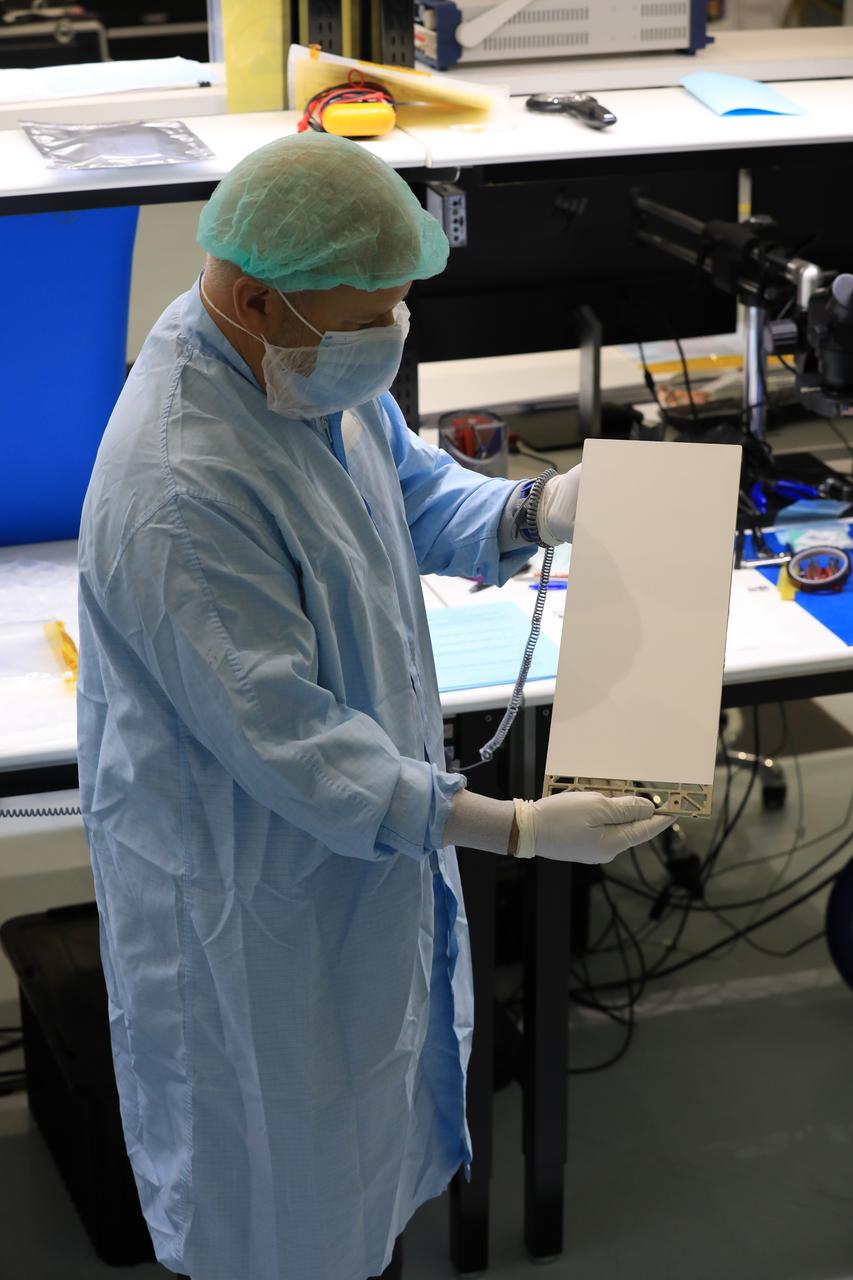

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prepare to install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
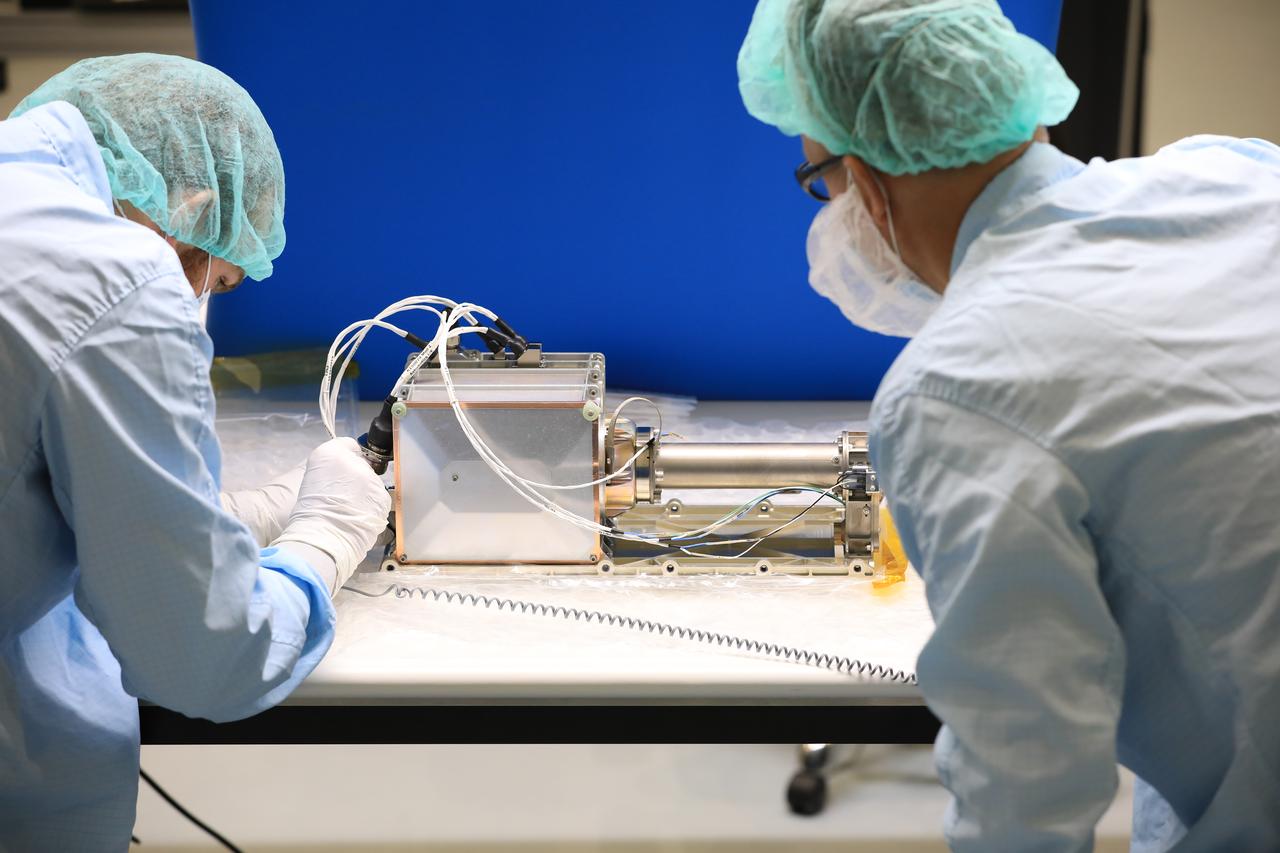

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
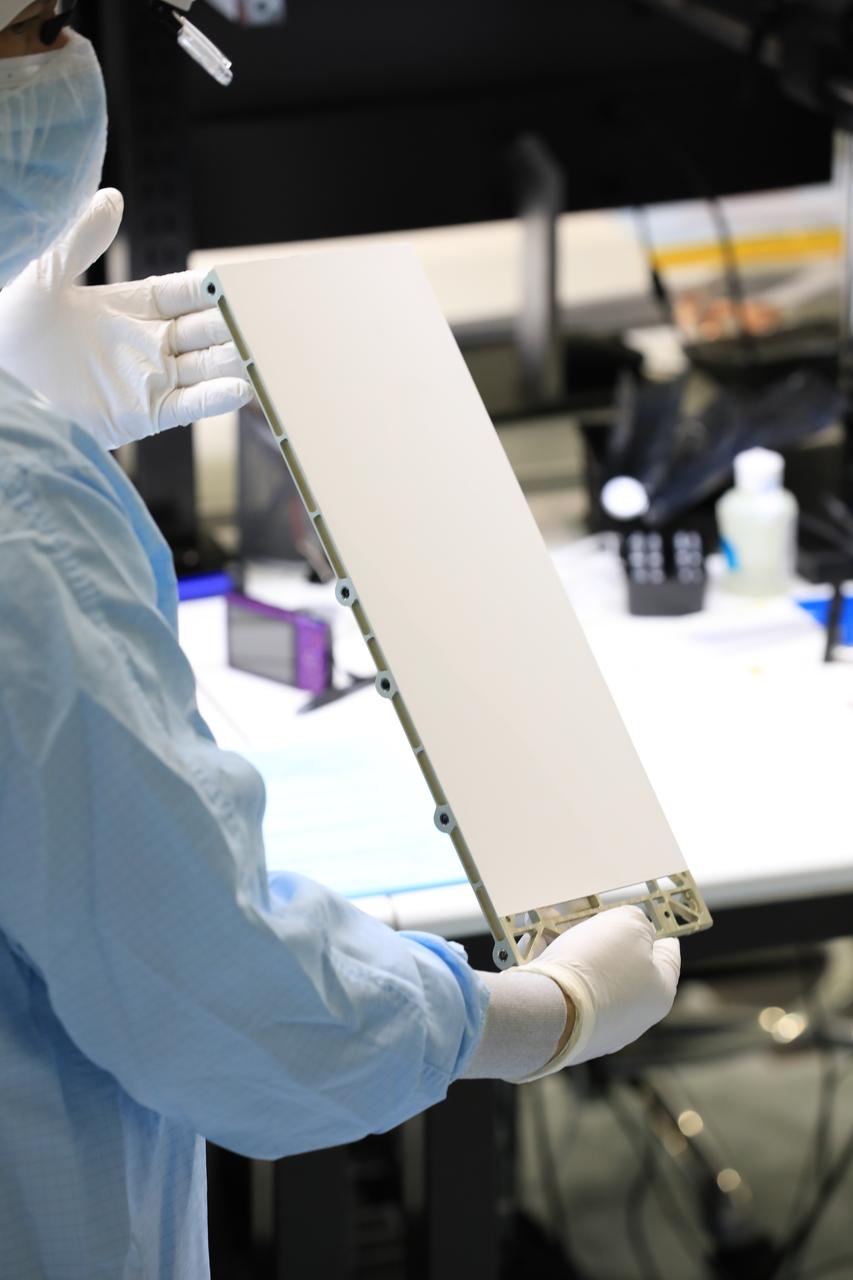

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prepare to install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
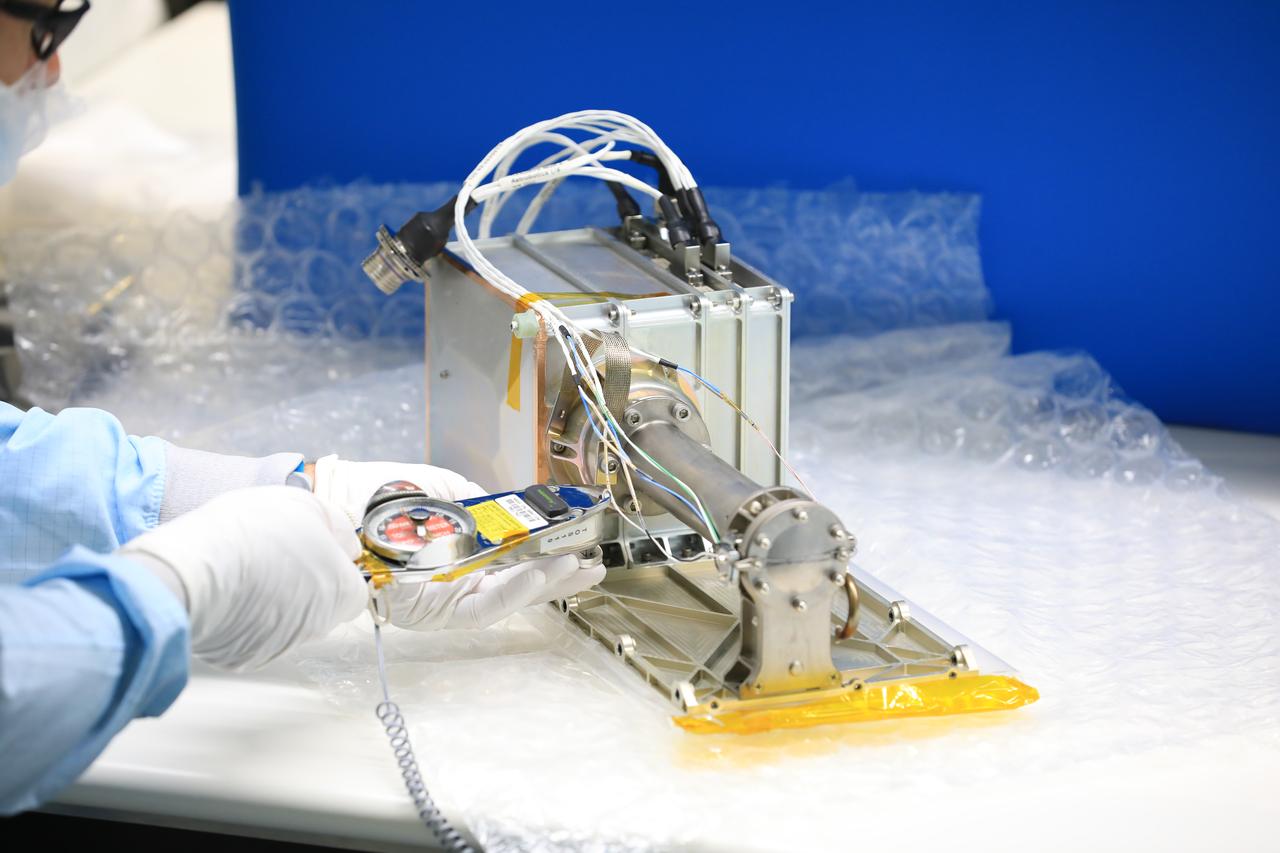

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
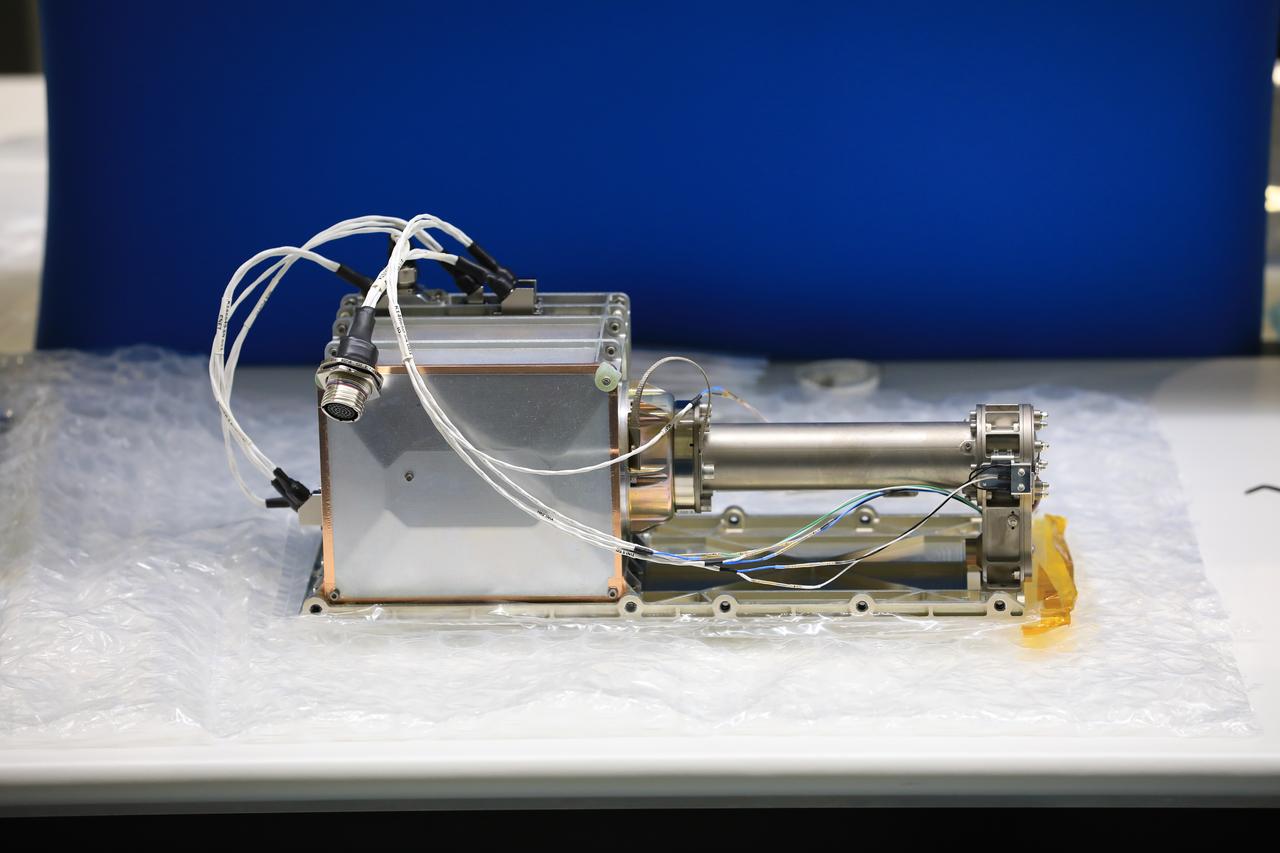
The Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument is photographed inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida following installation of its radiator on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.