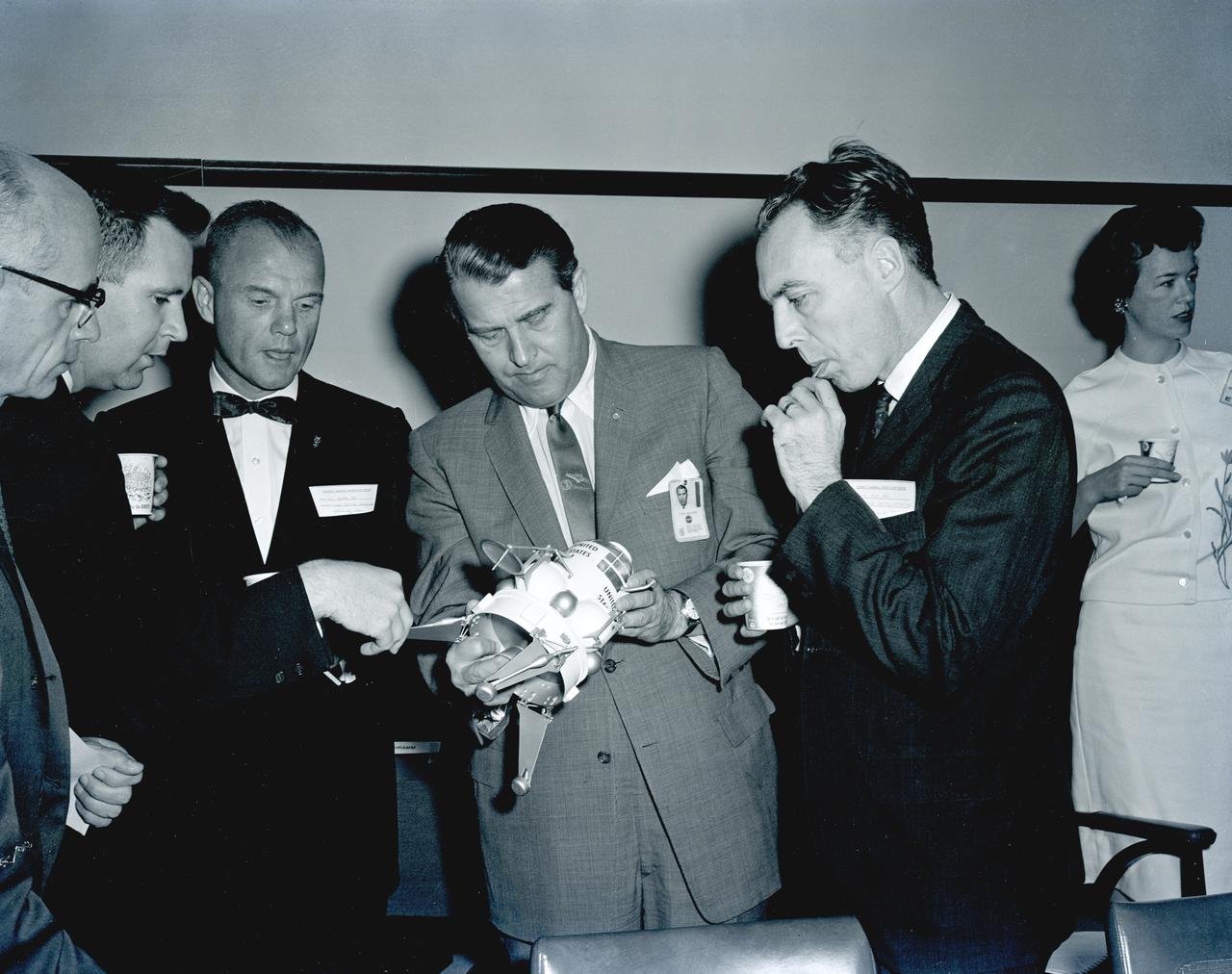

Dr. von Braun (right) and Astronaut John Glenn examine a model of a lunar landing stage during a talk on the manned lunar exploration program by about sixty key officials of the nation's space program at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
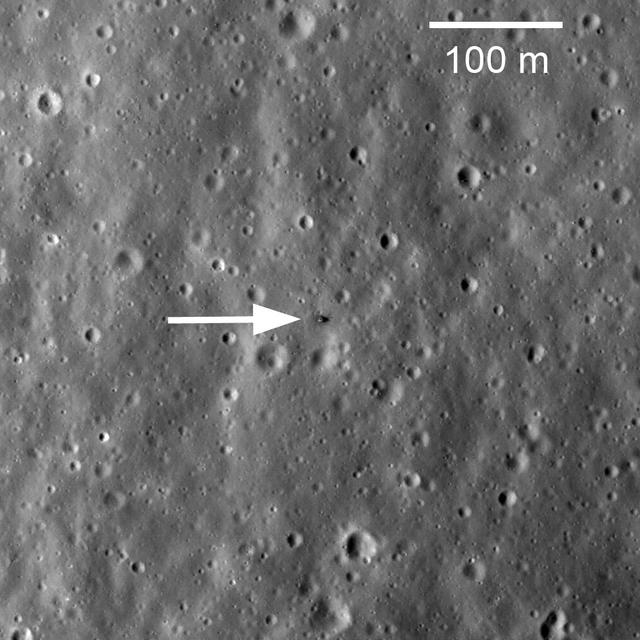

On February 21, 1972, Luna 20 soft landed in the rugged highlands between Mare Fecunditatis and Mare Crisium. The Luna 20 descent stage still sits silently on the Moon, clearly visible in this image taken by NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.

S69-53326 (November 1969) --- Close-up view of a replica of the plaque which the Apollo 12 astronauts will leave on the moon in commemoration of their flight. The plaque will be attached to the ladder on the landing gear strut on the descent stage of the Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM). Apollo 12 will be the United States' second lunar landing mission.
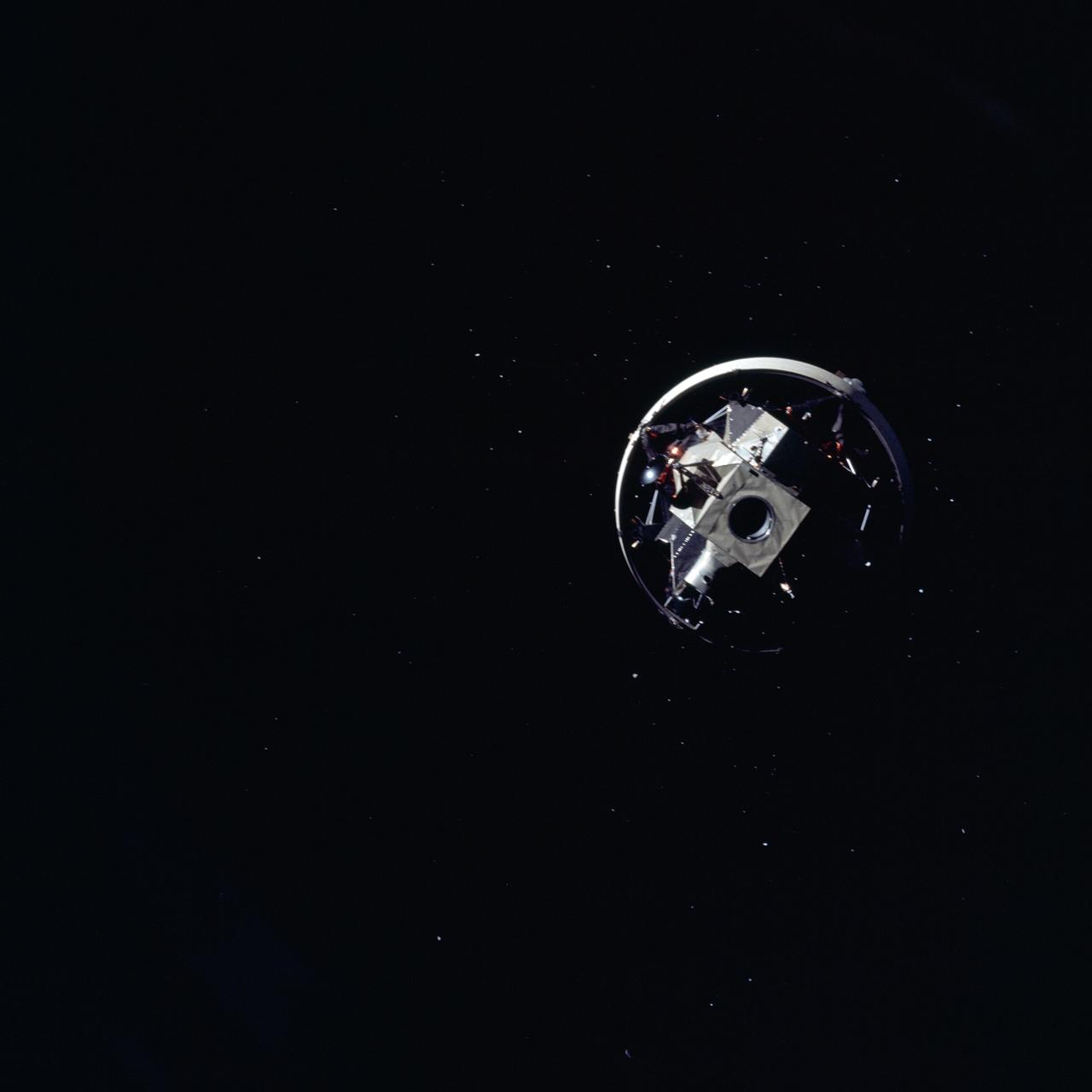

AS12-50-7328 (14 Nov. 1969) --- Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM), still attached to the Saturn V third (S-IVB) stage, is pictured as seen from Apollo 12 Command and Service Modules (CSM) on the first day of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission. This photograph was taken following CSM separation from LM/S-IVB and prior to Lunar Module extraction from the S-IVB stage. The Spacecraft Lunar Module Adapter (SLA) panels have already been jettisoned.
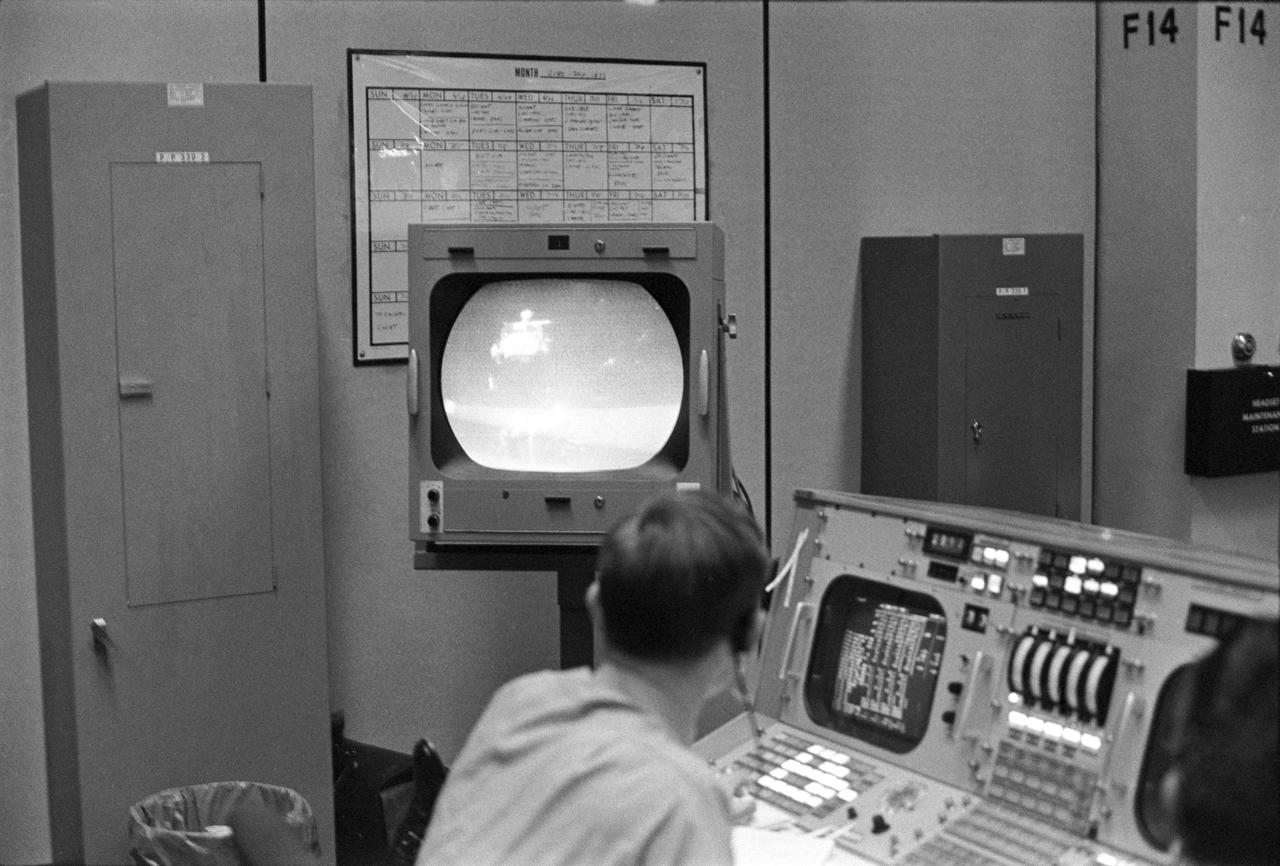

View of a photograph of the television (TV) monitor in the MCC showing a picture being transmitted from the color TV camera mounted on the parked Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) at the Hadley-Apennine Landing Site showing the liftoff of the Apollo 15 Lunar Module (LM) Ascent Stage from the Lunar surface. MSC, Houston, TX
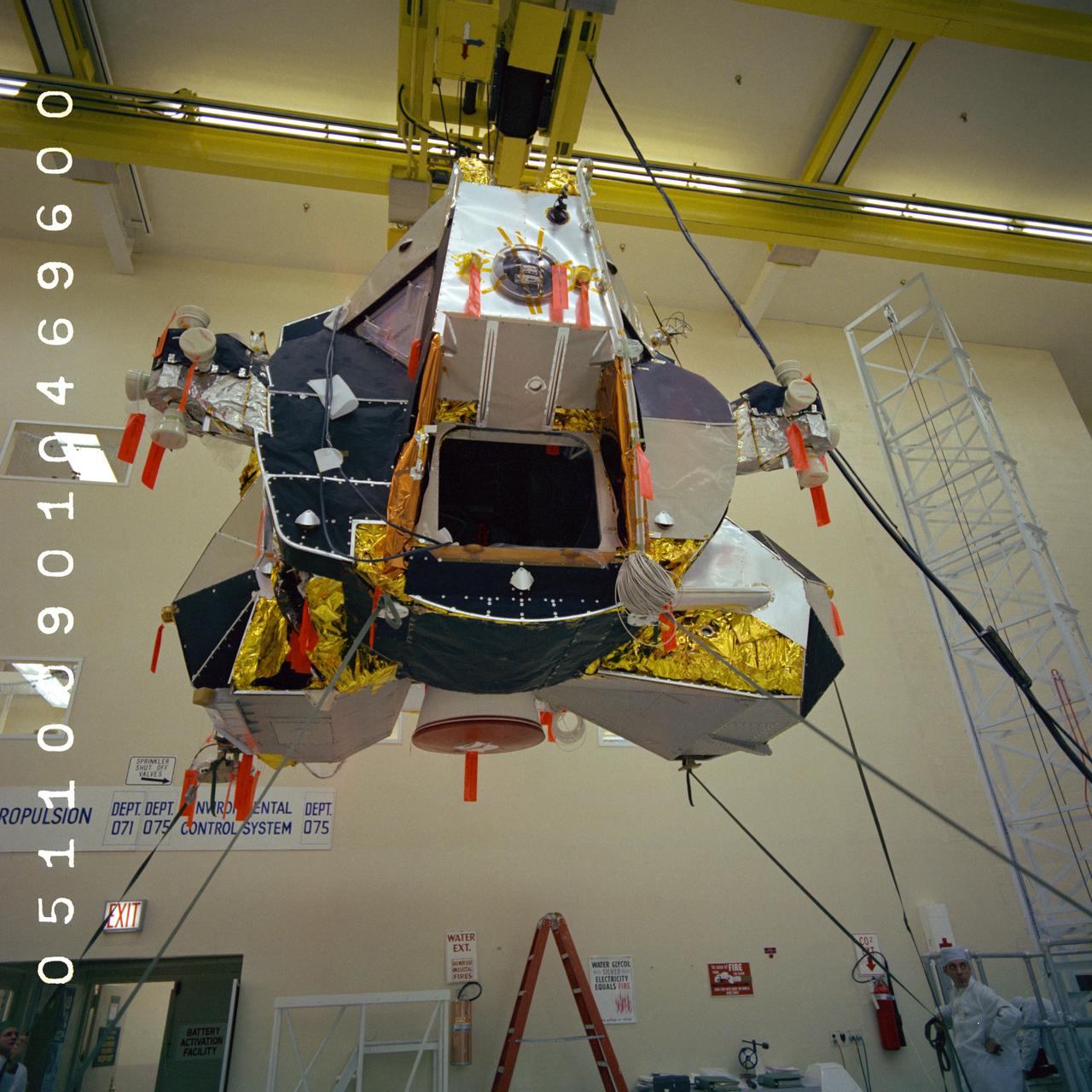

S69-19644 (4 Jan. 1969) --- Lunar Module (LM) 5 ascent stage in Final Assembly Area on overhead hoist being moved to dolly for roll-out inspection. LM-5 will be flown on the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. Photo credit: NASA/Grumman

S71-16637 (January 1971) --- A close-up view of the plaque which the Apollo 14 astronauts will leave behind on the moon during their lunar landing mission. Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, will descend to the lunar surface in the Lunar Module (LM) "Antares". Astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. The seven by nine inch stainless steel plaque will be attached to the ladder on the landing gear strut on the LM's descent stage. Commemorative plaques were also left on the moon by the Apollo 11 and Apollo 12 astronauts.

S71-39357 (July 1971) --- A photographic replica of the plaque which the Apollo 15 astronauts will leave behind on the moon during their lunar landing mission. Astronauts David R. Scott, commander; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot; will descend to the lunar surface in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon". Astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. The seven by nine inch stainless steel plaque will be attached to the ladder on the landing gear strut on the LM's descent stage. Commemorative plaques were also left on the moon by the Apollo 11, Apollo 12 and Apollo 14 astronauts.

S70-34685 (April 1970) --- A photographic replica of the plaque which the Apollo 13 astronauts will leave behind on the moon during their lunar landing mission. Astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, will descend to the lunar surface in the Lunar Module (LM) "Aquarius". Astronaut John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. The plaque will be attached to the ladder of the landing gear strut on the LM?s descent stage. Commemorative plaques were also left on the moon by the Apollo 11 and Apollo 12 astronauts.
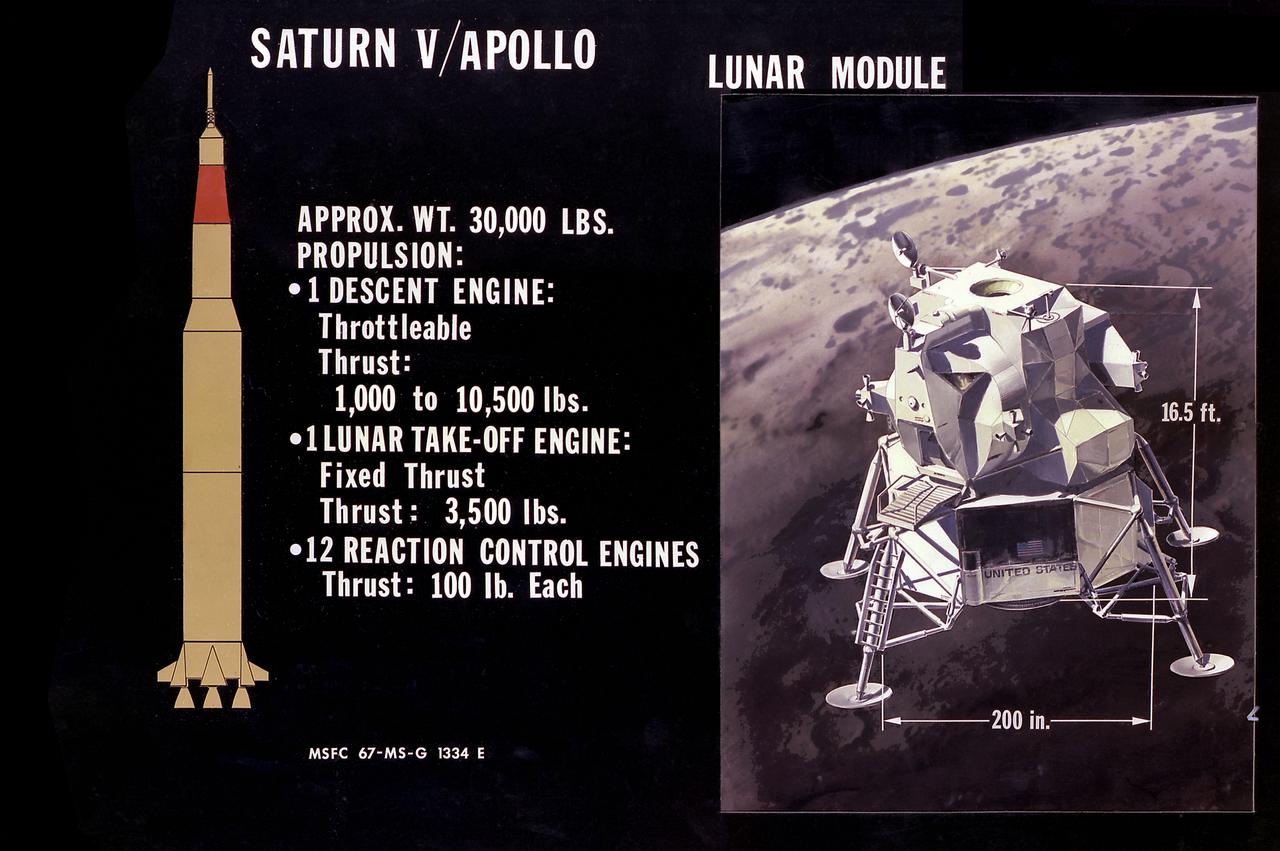
This illustration is the Lunar Module (LM) configuration. The LM was a two part spacecraft. Its lower or descent stage had the landing gear, engines, and fuel needed for the landing. When the LM blasted off the Moon, the descent stage served as the launching pad for its companion ascent stage, which was also home for the two astronauts on the surface of the Moon. The LM was full of gear with which to communicate, navigate, and rendezvous. It also had its own propulsion system, and an engine to lift it off the Moon and send it on a course toward the orbiting Command Module.

S72-55169 (14 Dec. 1972) --- A photographic replica of the plaque which the Apollo 17 astronauts left behind at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. Apollo 17 is the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo program. The commemorative plaque was unveiled at the close of the third extravehicular activity (EVA). The plaque is made of stainless steel measuring nine by seven and five-eighths inches, and one-sixteenth inch thick. It is attached to the ladder on the landing gear strut on the descent stage of Apollo 17 Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger".
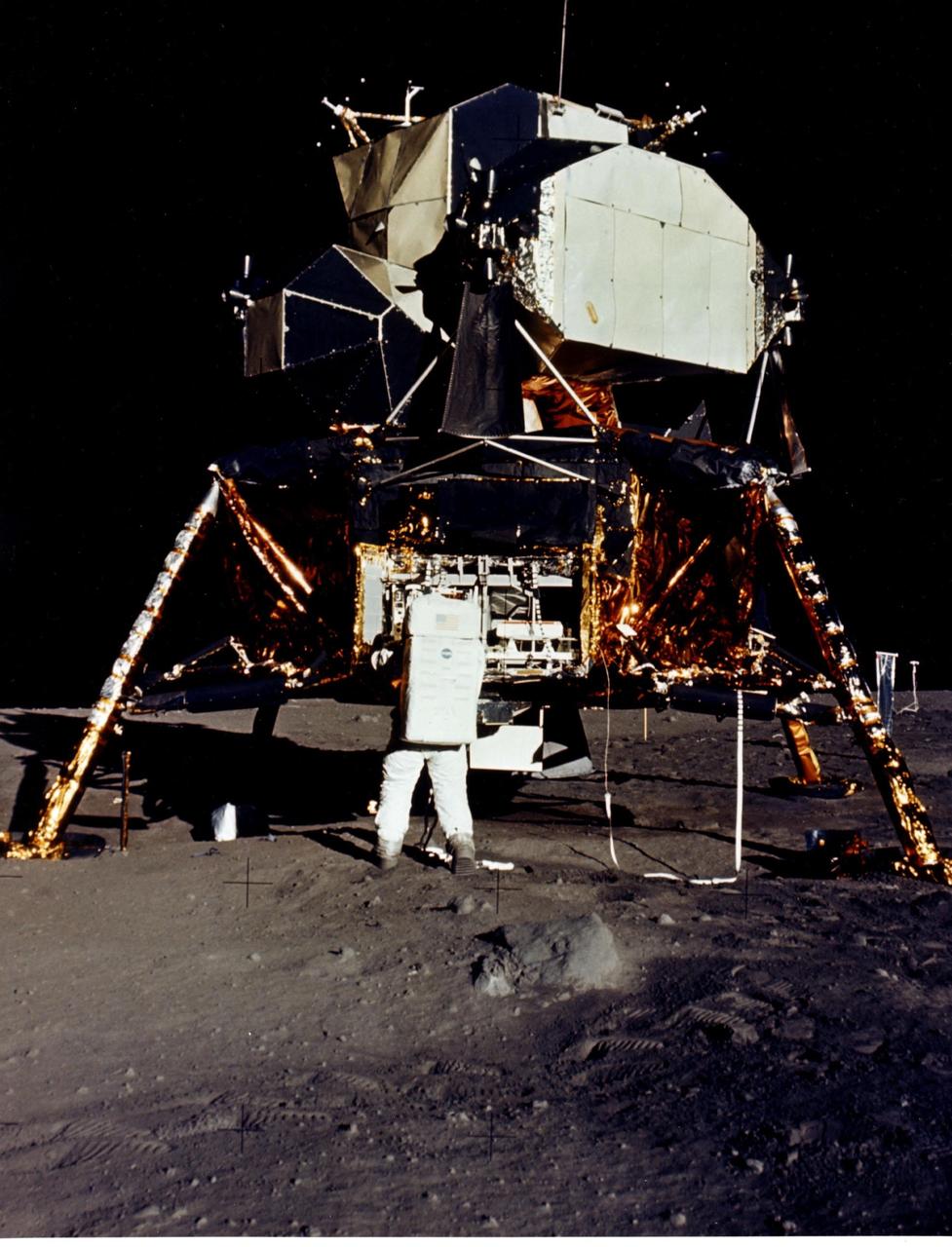

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS - Man's first landing on the Moon was accomplished at 4:17 p.m. today as Lunar Module "Eagle" touched down gently on the Sea of Tranquility on the east side of the Moon. Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module Pilot, removes scientific experiment packages from a stowage area in the Lunar Module's descent stage. Left behind on the lunar surface by Aldrin and Neil A. Armstrong, Apollo 11 commander, were a Passive Seismic Experiments Package and a Laser-Ranging Retro-Reflector.
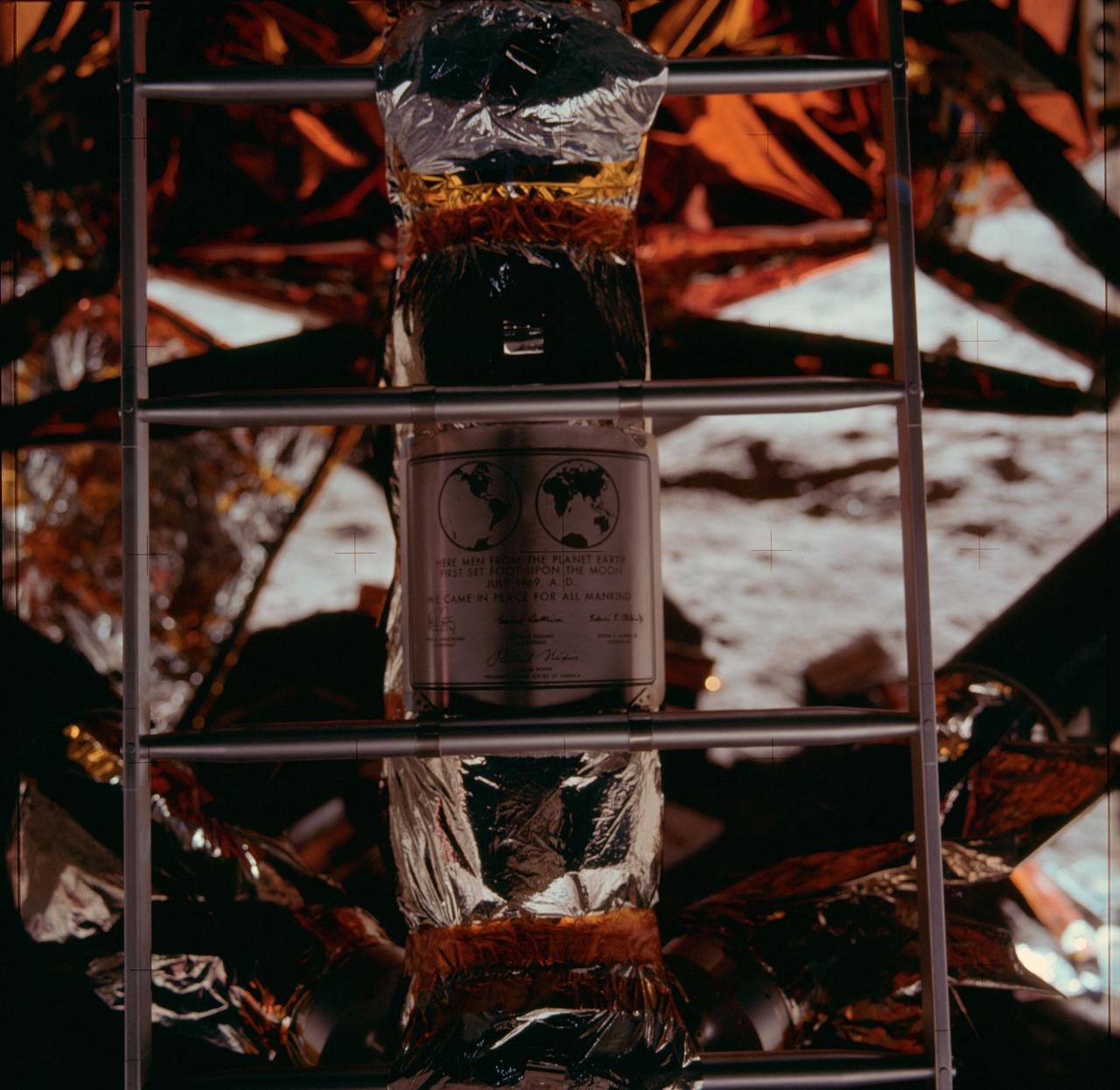

AS11-40-5899 (20 July 1969) --- Close-up view of the plaque which the Apollo 11 astronauts left on the moon in commemoration of the historic lunar landing mission. The plaque was attached to the ladder on the landing gear strut on the descent stage of the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM). The plaque was covered with a thin sheet of stainless steel during flight. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, explored the moon.

This montage depicts the flight crew patches for the manned Apollo 7 thru Apollo 17 missions. The Apollo 7 through 10 missions were basically manned test flights that paved the way for lunar landing missions. Primary objectives met included the demonstration of the Command Service Module (CSM) crew performance; crew/space vehicle/mission support facilities performance and testing during a manned CSM mission; CSM rendezvous capability; translunar injection demonstration; the first manned Apollo docking, the first Apollo Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA), performance of the first manned flight of the lunar module (LM); the CSM-LM docking in translunar trajectory, LM undocking in lunar orbit, LM staging in lunar orbit, and manned LM-CSM docking in lunar orbit. Apollo 11 through 17 were lunar landing missions with the exception of Apollo 13 which was forced to circle the moon without landing due to an onboard explosion. The craft was,however, able to return to Earth safely. Apollo 11 was the first manned lunar landing mission and performed the first lunar surface EVA. Landing site was the Sea of Tranquility. A message for mankind was delivered, the U.S. flag was planted, experiments were set up and 47 pounds of lunar surface material was collected for analysis back on Earth. Apollo 12, the 2nd manned lunar landing mission landed in the Ocean of Storms and retrieved parts of the unmanned Surveyor 3, which had landed on the Moon in April 1967. The Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) was deployed, and 75 pounds of lunar material was gathered. Apollo 14, the 3rd lunar landing mission landed in Fra Mauro. ALSEP and other instruments were deployed, and 94 pounds of lunar materials were gathered, using a hand cart for first time to transport rocks. Apollo 15, the 4th lunar landing mission landed in the Hadley-Apennine region. With the first use of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), the crew was bale to gather 169 pounds of lunar material. Apollo 16, the 5th lunar landing mission, landed in the Descartes Highlands for the first study of highlands area. Selected surface experiments were deployed, the ultraviolet camera/spectrograph was used for first time on the Moon, and the LRV was used for second time for a collection of 213 pounds of lunar material. The Apollo program came to a close with Apollo 17, the 6th and final manned lunar landing mission that landed in the Taurus-Littrow highlands and valley area. This mission hosted the first scientist-astronaut, Schmitt, to land on the Moon. The 6th automated research station was set up, and 243 ponds of lunar material was gathered using the LRV.

S68-19459 (22 Jan. 1968) --- The Apollo 5 (LM-1/Saturn 204) unmanned space mission was launched from the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 37 at 5:48:09 p.m. (EST), Jan. 22, 1968. The Lunar Module-1 payload was boosted into Earth orbit by a launch vehicle composed of a Saturn IB first stage and a Saturn S-IVB second stage. The Apollo lunar module's first flight test was called a complete success. Ascent and descent propulsion systems and the ability to abort a lunar landing and return to orbit were demonstrated.

S68-19460 (22 Jan. 1968) --- The Apollo 5 (LM-1/Saturn 204) unmanned space mission was launched from the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 37 at 5:48:09 p.m. (EST), Jan. 22, 1968. The Lunar Module-1 payload was boosted into Earth orbit by a launch vehicle composed of a Saturn IB first stage and a Saturn S-IVB second stage. The Apollo lunar module's first flight test was called a complete success. Ascent and descent propulsion systems and the ability to abort a lunar landing and return to orbit were demonstrated.
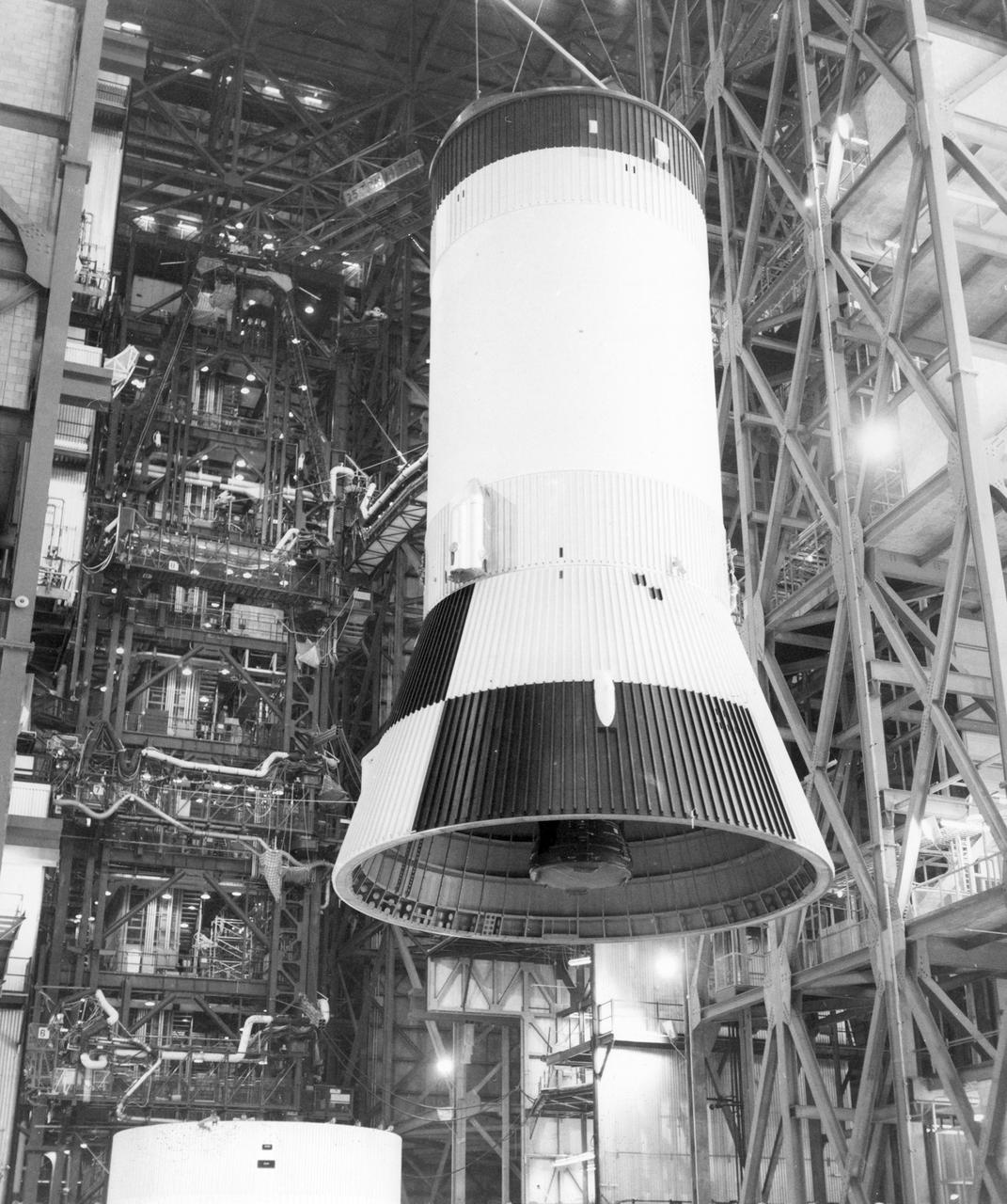

The third stage (S-IVB) of the Saturn V launch vehicle for the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission is hoisted in the vehicle assembly building at the NASA Kennedy Space Center (KSC) for mating with the second stage (S-II). The vehicle, designated as AS-506, projected the first lunar landing mission, Apollo 11, on a trajectory for the Moon. The Apollo 11 mission launched from KSC in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Astronauts onboard included Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin, Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, “Columbia”, piloted by Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon. On July 20, 1969, Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
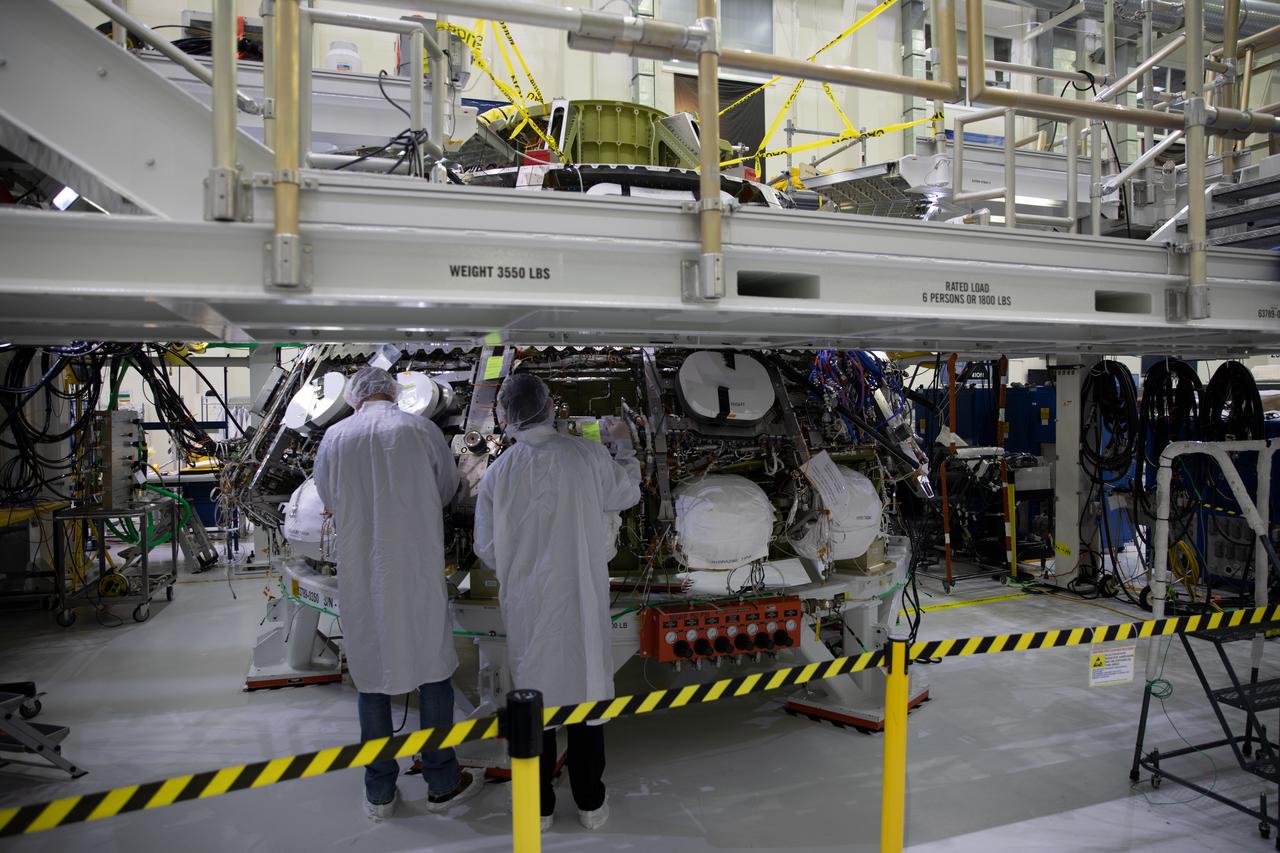

Technicians inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building power on the Orion crew module for the Artemis II mission for the first time at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 27, 2022. The capsule will carry astronauts on a trip around the Moon during the first crewed Artemis flight, helping set the stage for future lunar landings. Through Artemis, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon and establish long-term lunar exploration in preparation for missions to Mars.

This artist's concept illustrates the Module Nova concept - Solid C-3 Basis. From 1960 to 1962, the Marshall Space Flight Center considered the Nova launch vehicle as a means to achieve a marned lunar landing with a direct flight to the Moon. Various configurations of the vehicle were examined. The latest configuration was a five-stage vehicle using eight F-1 engines in the first stage. Although the program was canceled after NASA planners selected the lunar/orbital rendezvous mode, the proposed F-1 engine would eventually be used in the Apollo Program to propel the first stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle.
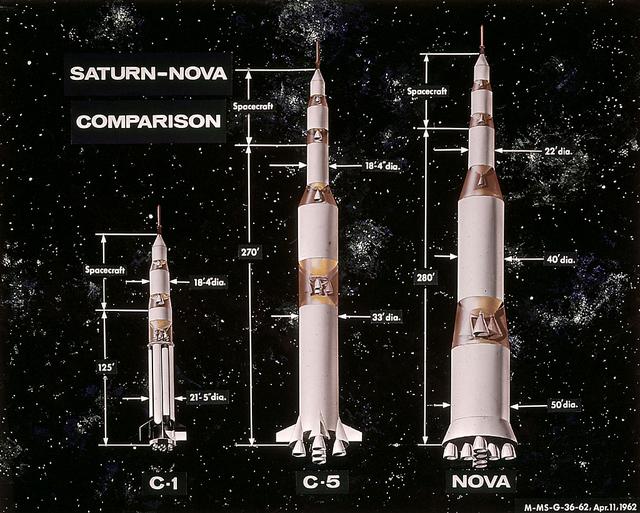

In this 1962 artist's concept , a proposed Nova rocket, shown at right, is compared to a Saturn C-1, left, and a Saturn C-5, center. The Marshall Space Flight Center directed studies of Nova configuration from 1960 to 1962 as a means of achieving a marned lunar landing with a direct flight to the Moon. Various configurations of the vehicle were examined, the largest being a five-stage vehicle using eight F-1 engines in the first stage. Although the program was effectively cancelled in 1962 when NASA planners selected the lunar-orbital rendezvous mode, the proposed F-1 engine was eventually used to propel the first stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle in the Apollo Program.

This artist's concept illustrates the Module Nova concept - Solid C-3 Basis. From 1960 to 1962, the Marshall Space Flight Center considered the Nova launch vehicle as a means to achieve a marned lunar landing with a direct flight to the Moon. Various configurations of the vehicle were examined. The latest configuration was a five-stage vehicle using eight F-1 engines in the first stage. Although the program was canceled after NASA planners selected the lunar/orbital rendezvous mode, the proposed F-1 engine would eventually be used in the Apollo Program to propel the first stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle.
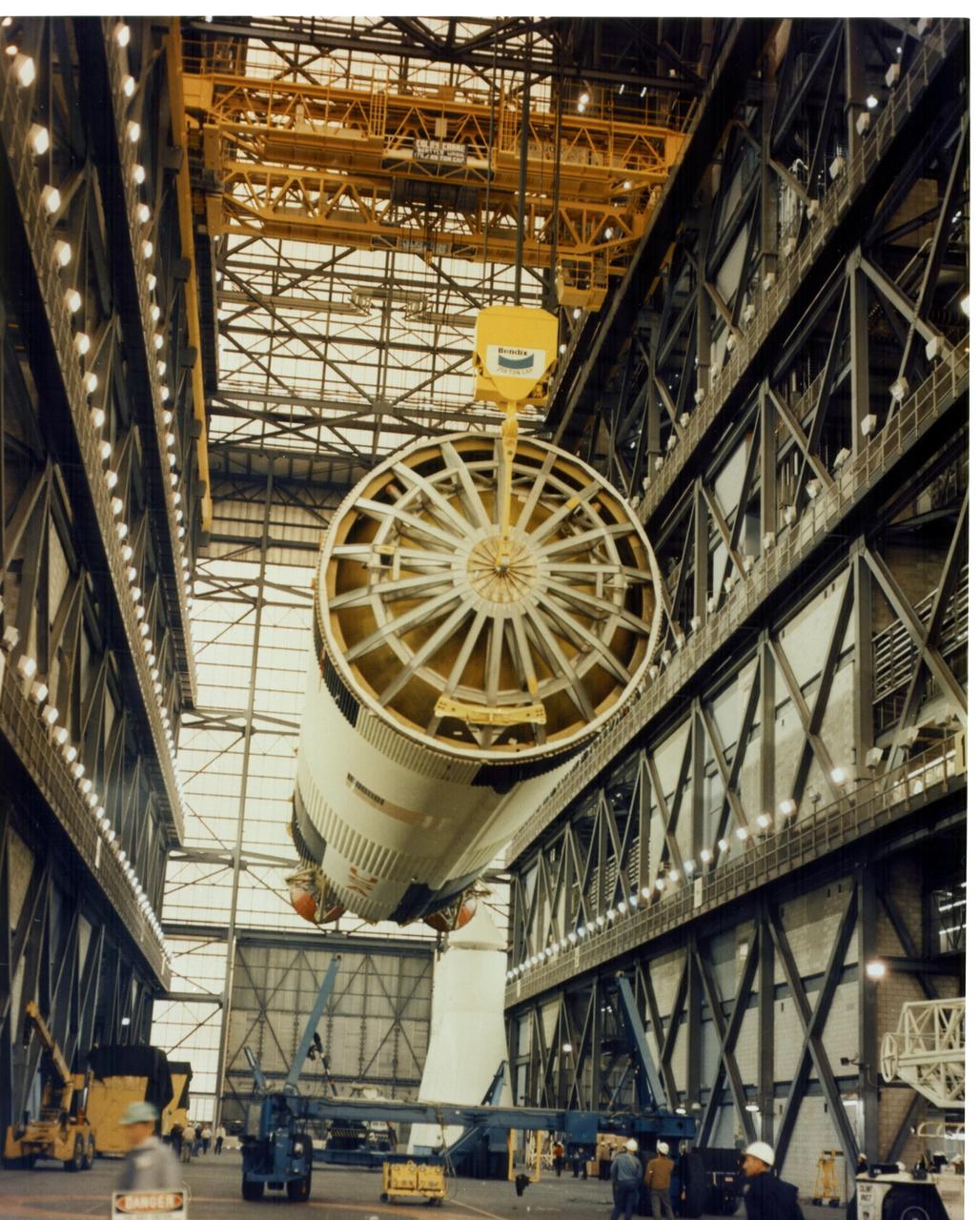

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - An overhead crane lifts the Saturn V first stage for the Apollo 11 mission from the transfer aisle floor in preparation for stacking on a mobile launcher within the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 1. The fully assembled vehicle will be called the Apollo/Saturn 506. The 138-foot-long stage, to which two additional stages -- the instrument unit and the Apollo spacecraft -- will be added, will generate a liftoff thrust of 7.7 million pounds. Astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, Michael Collins and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. will pilot the mission which is to include a lunar landing in the lunar module by Armstrong and Aldrin.
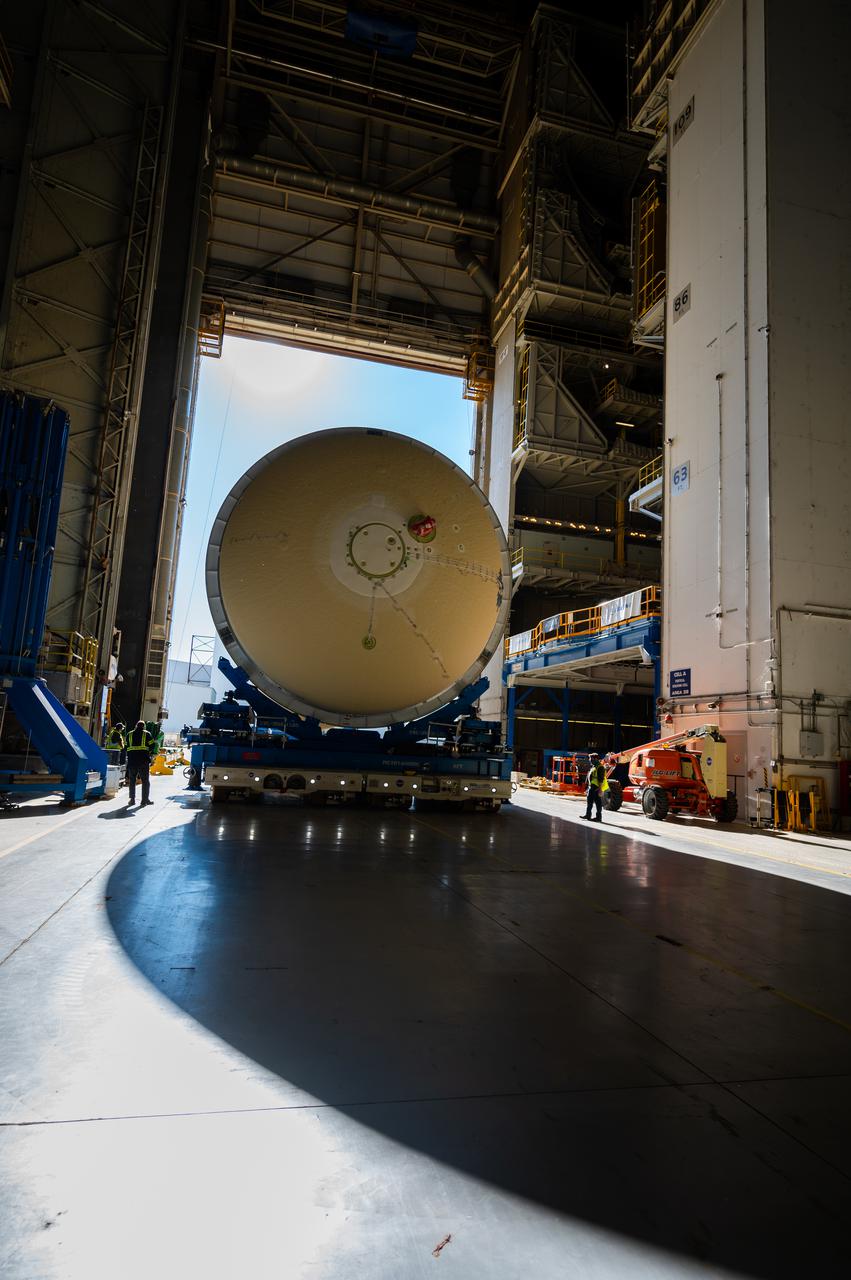

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
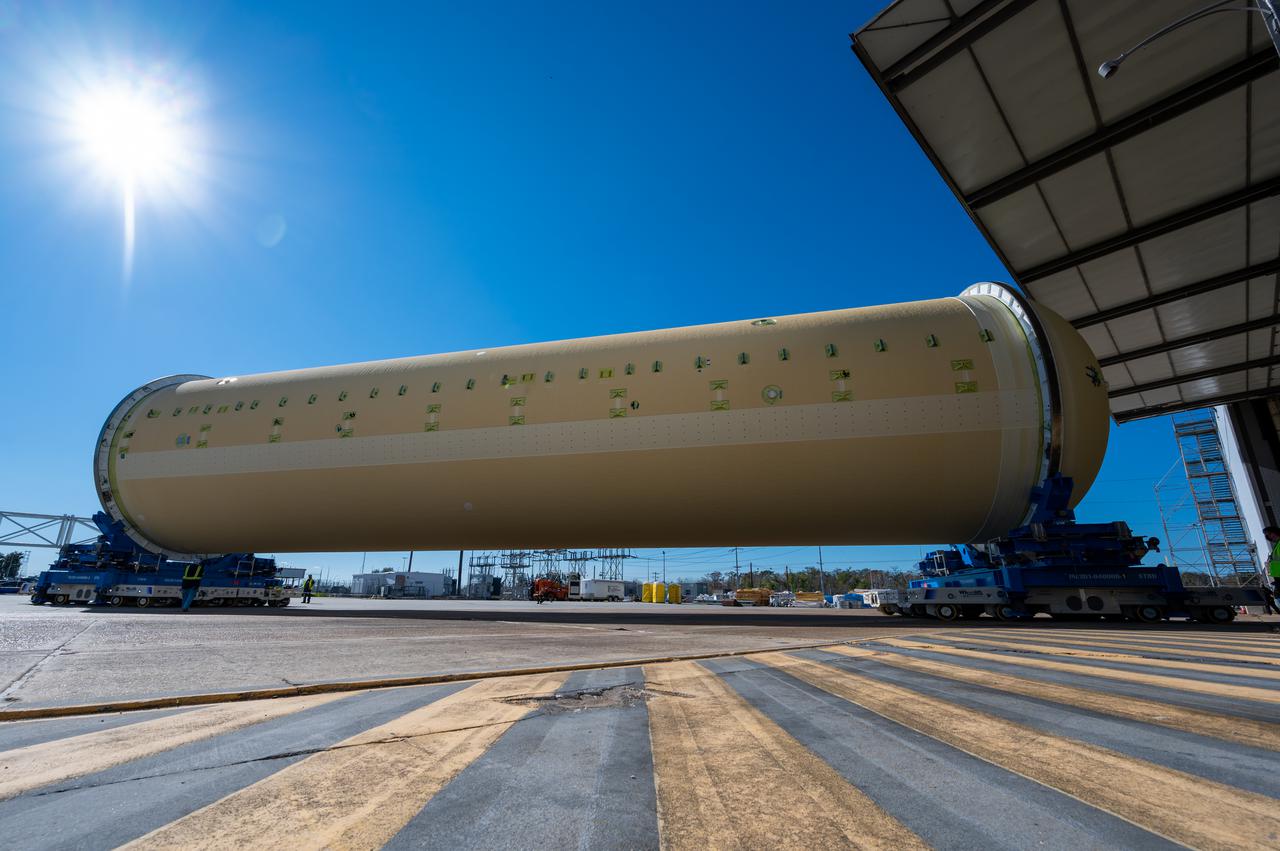

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
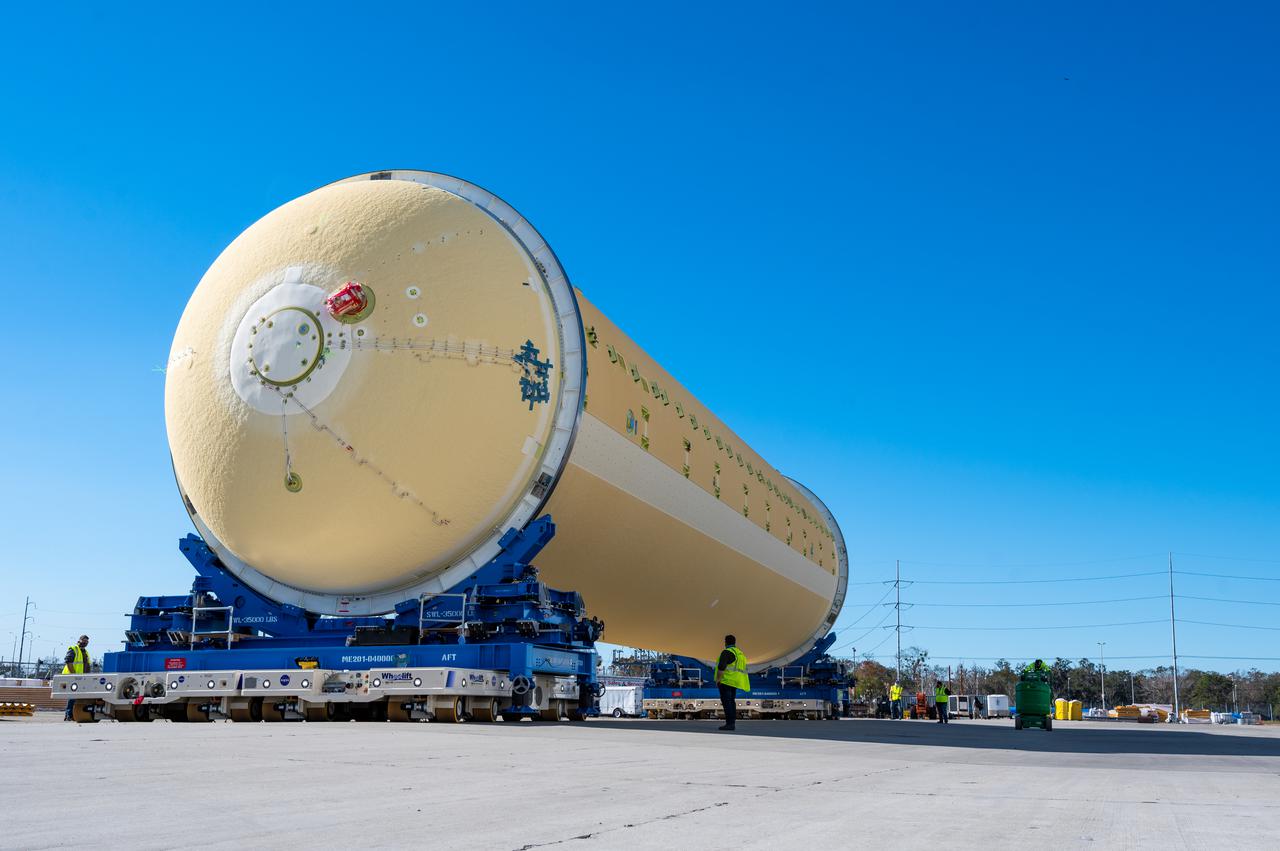

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
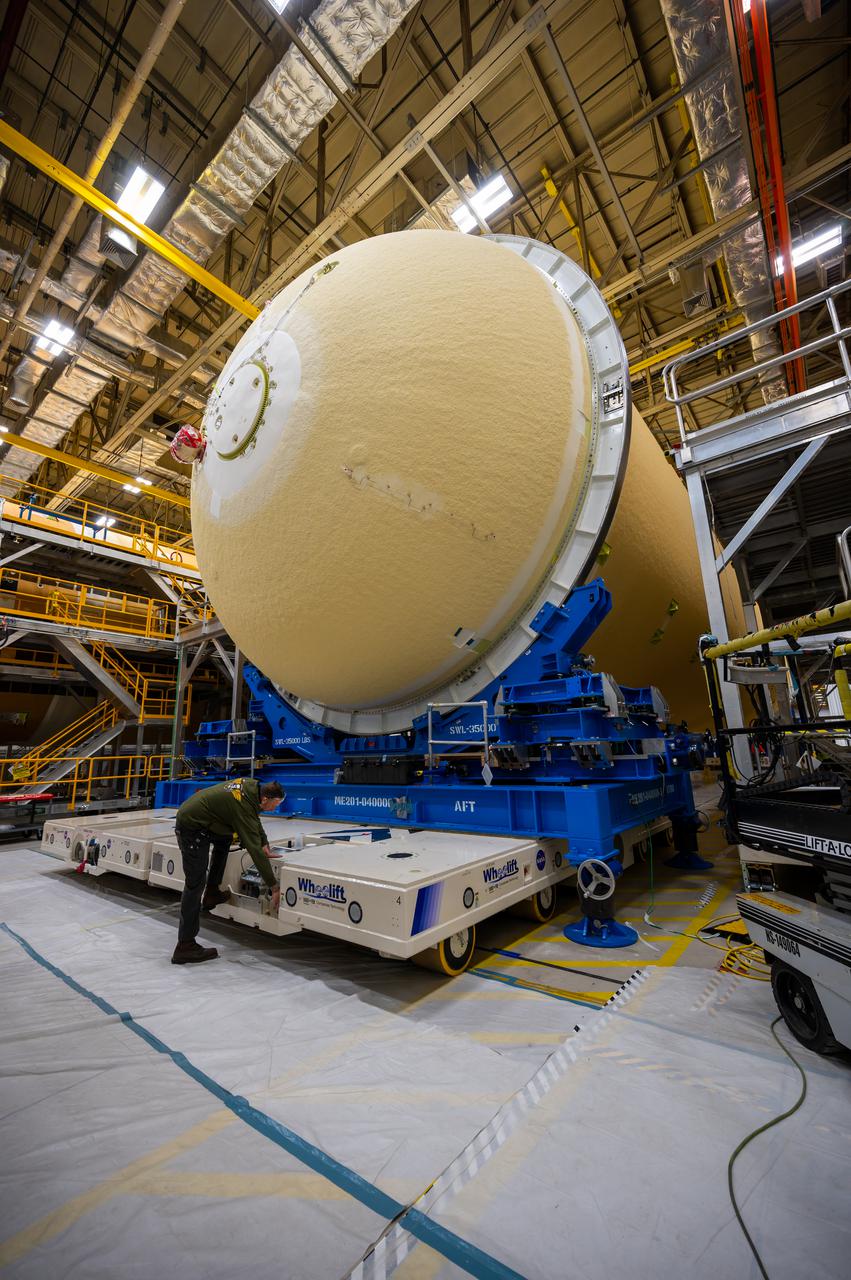

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
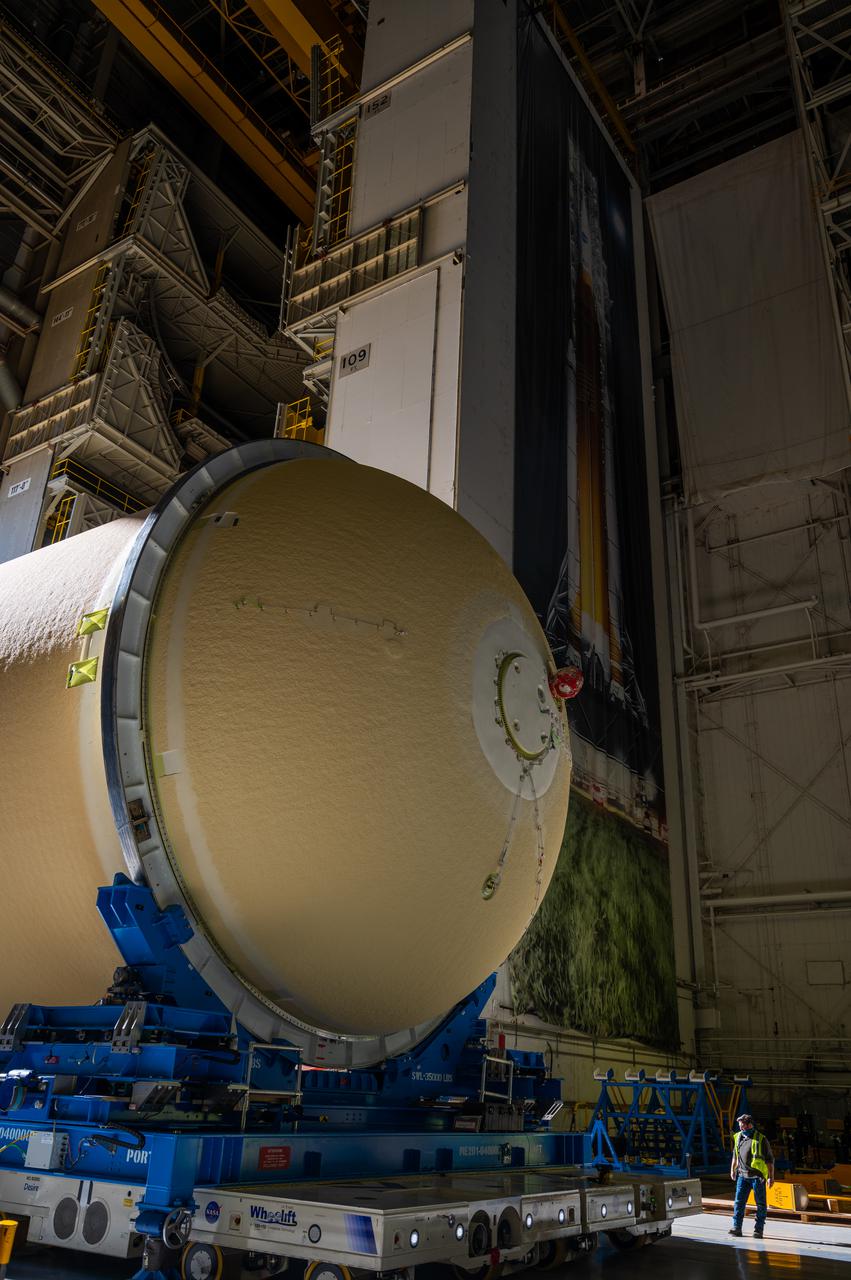

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
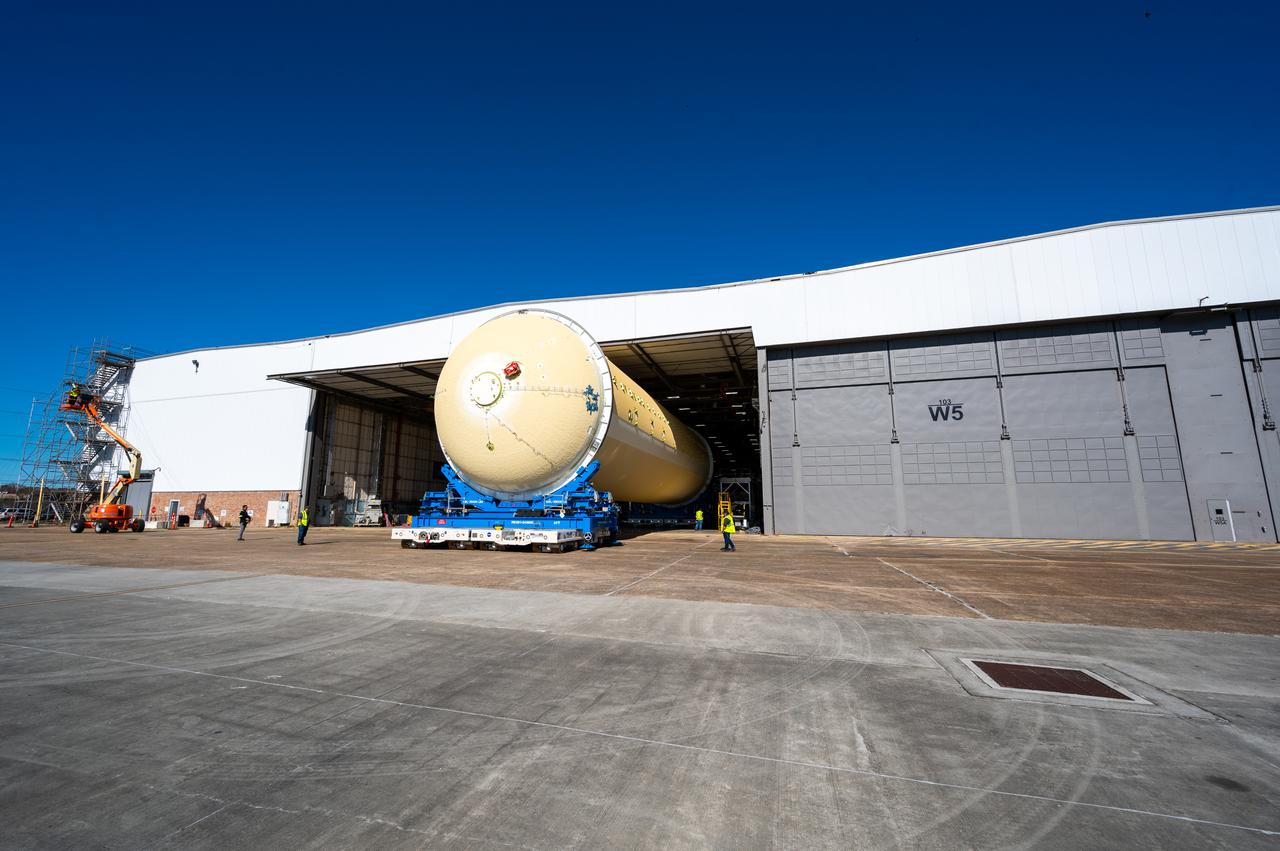

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
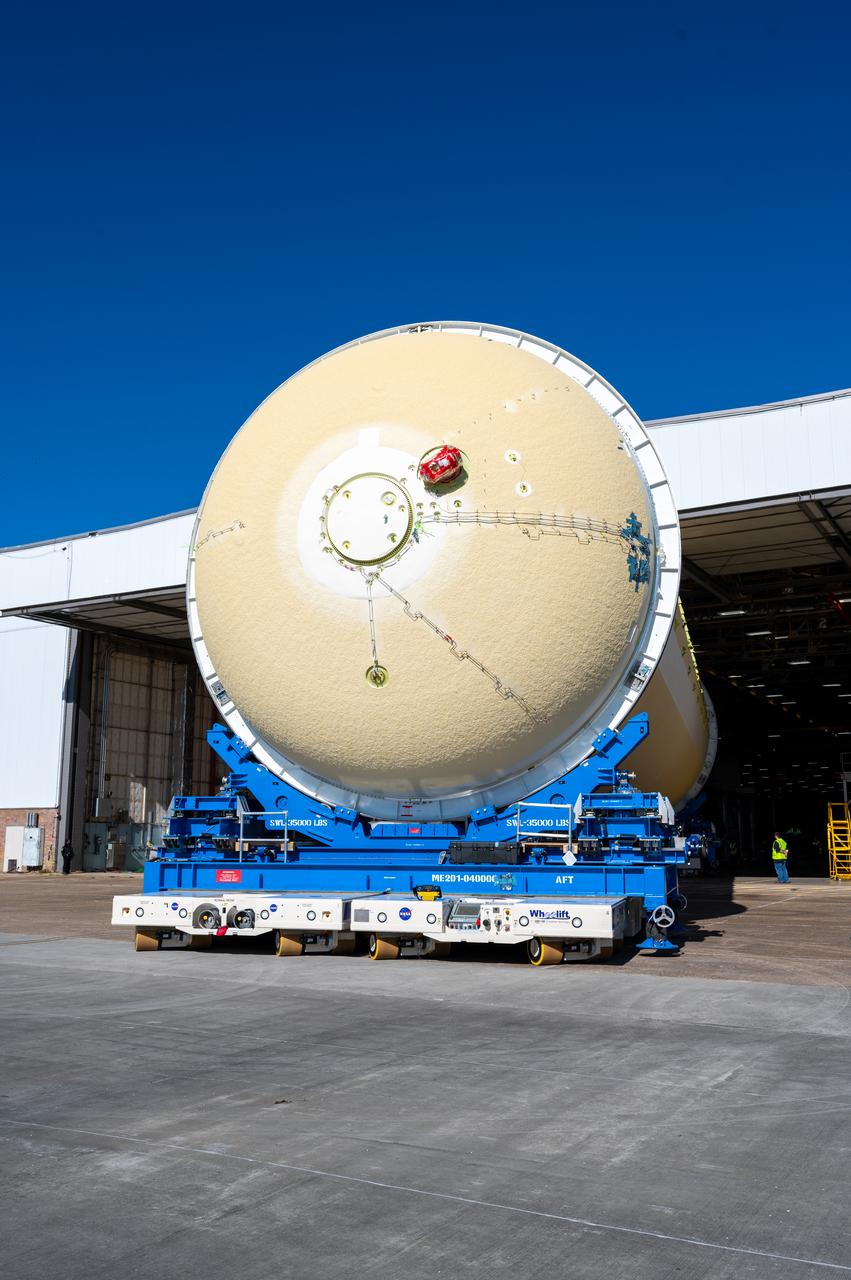

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
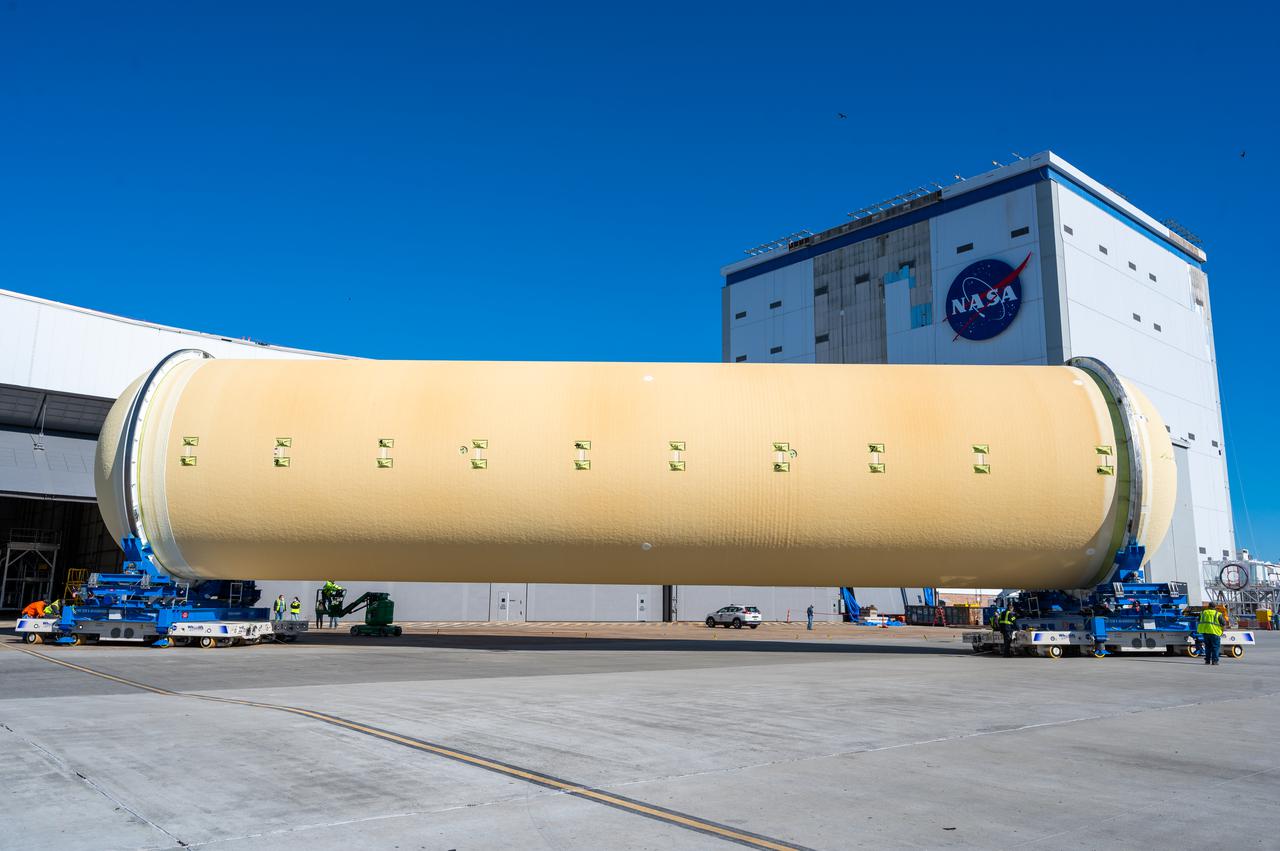

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
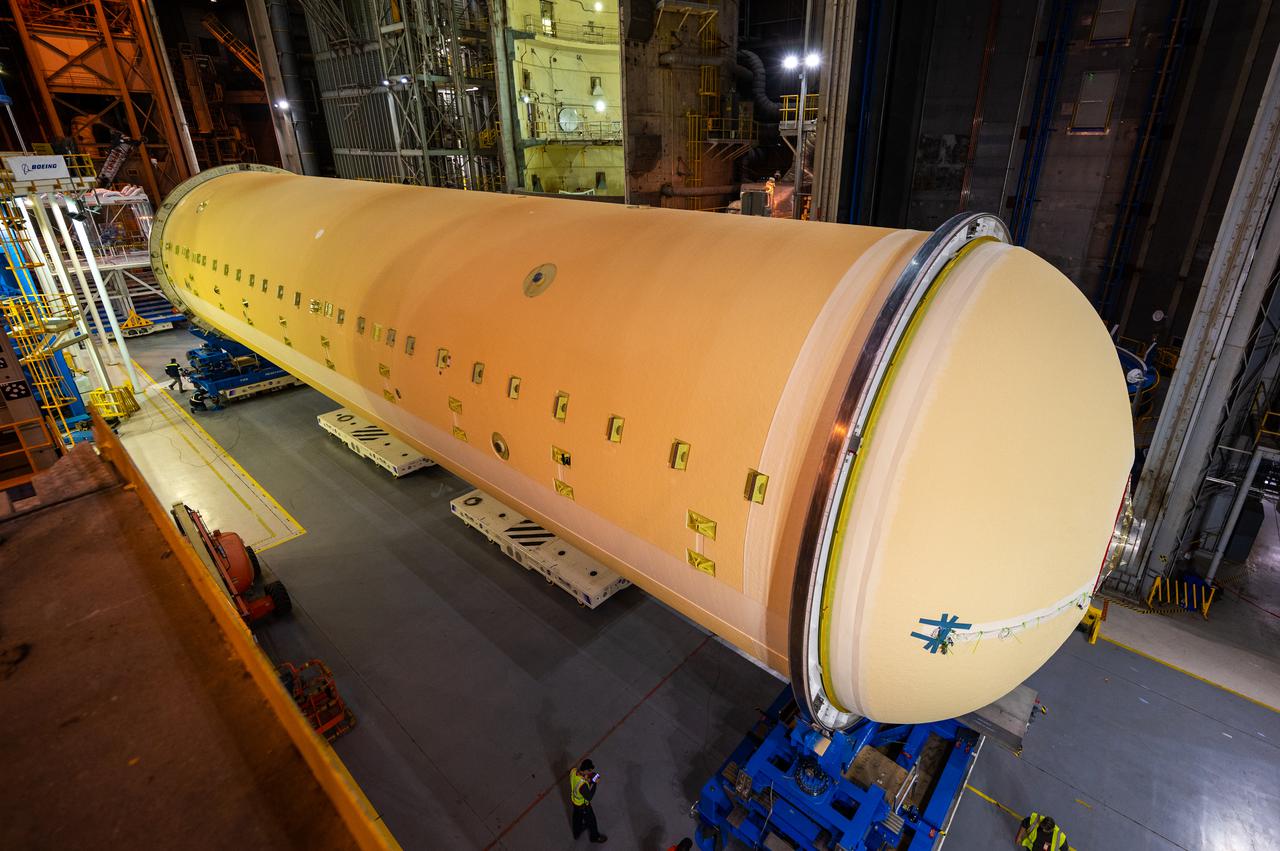

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
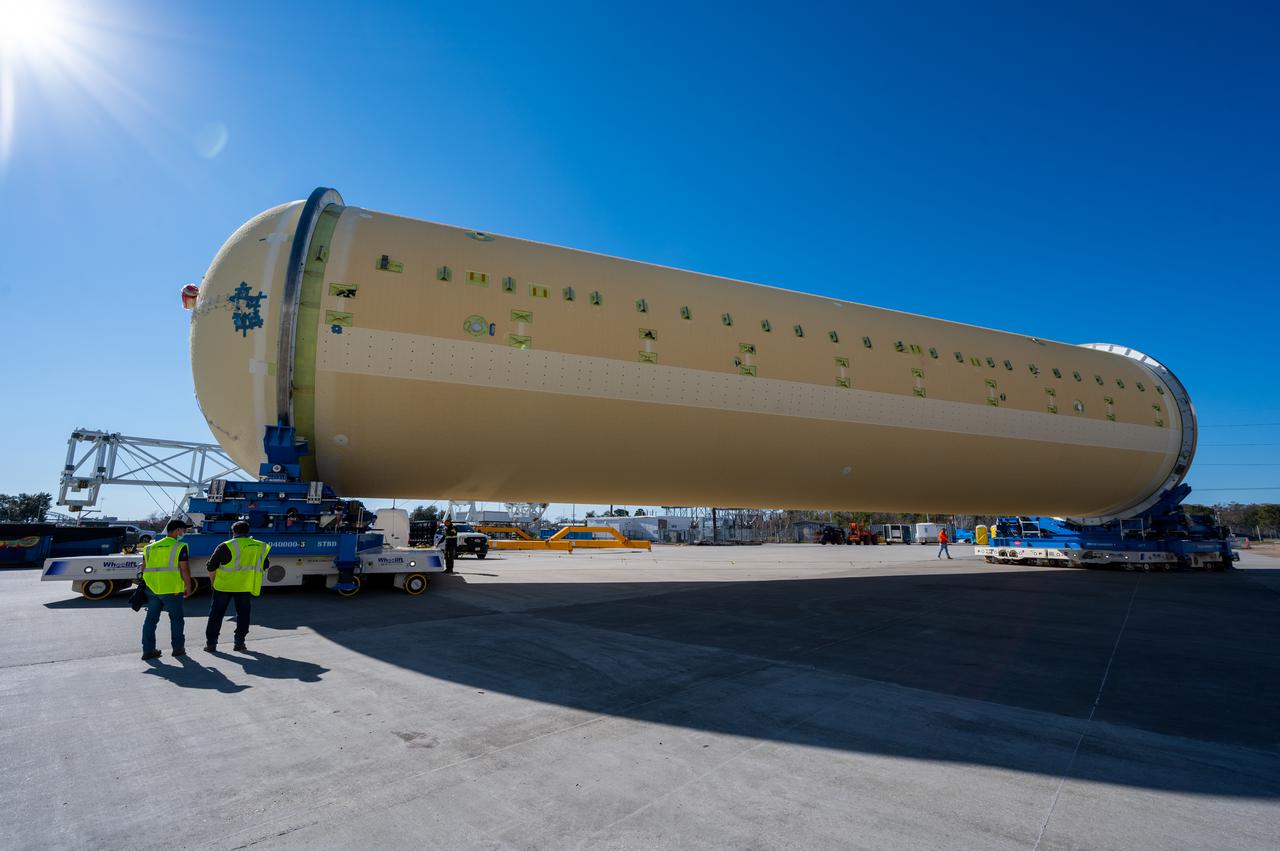

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
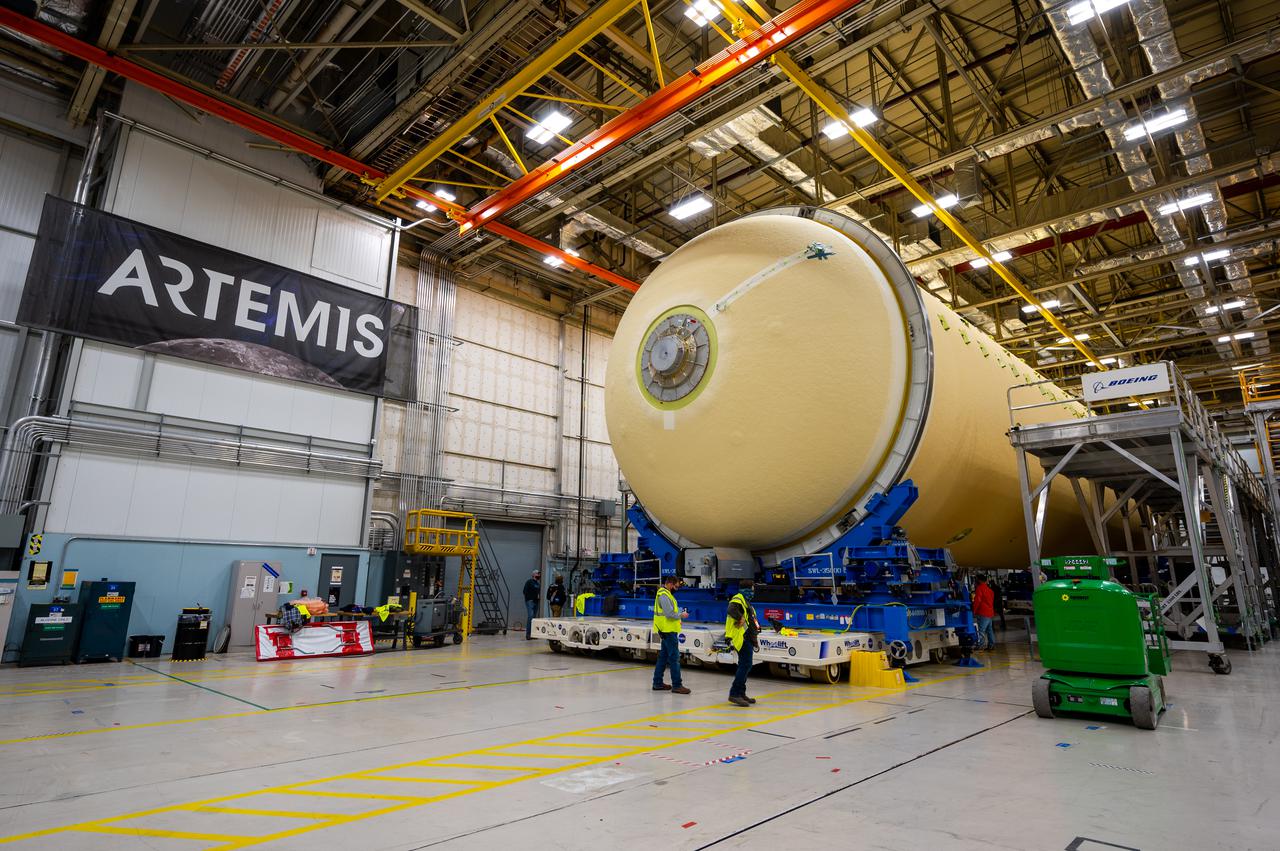

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
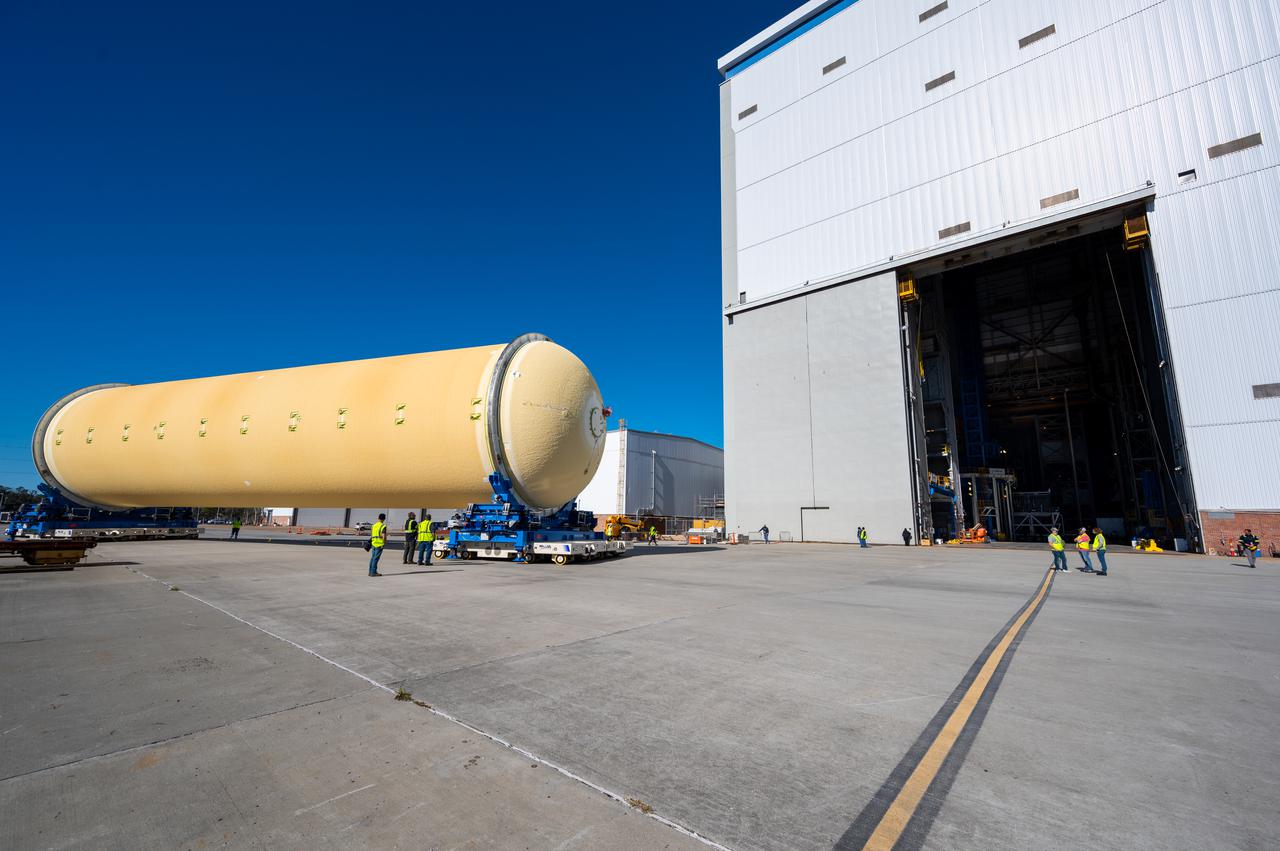

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
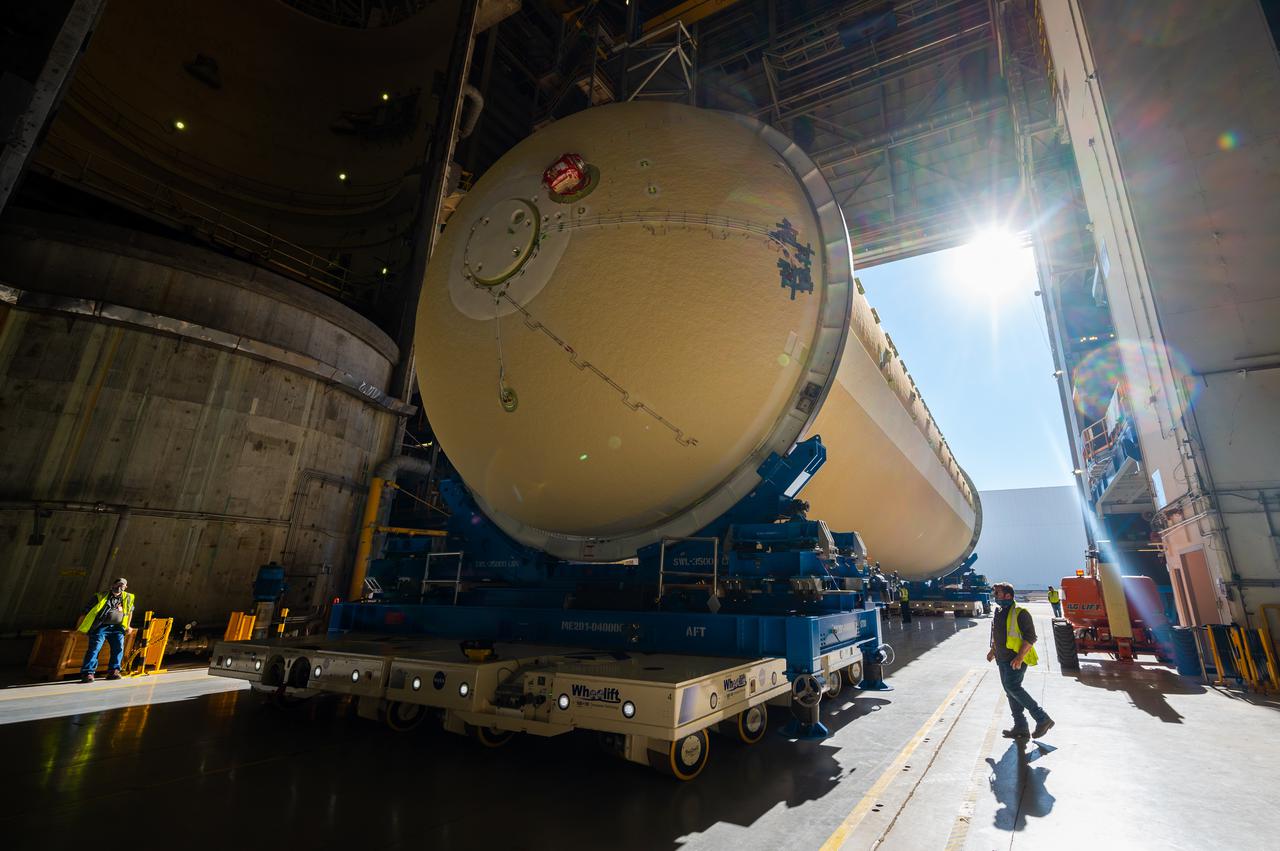

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
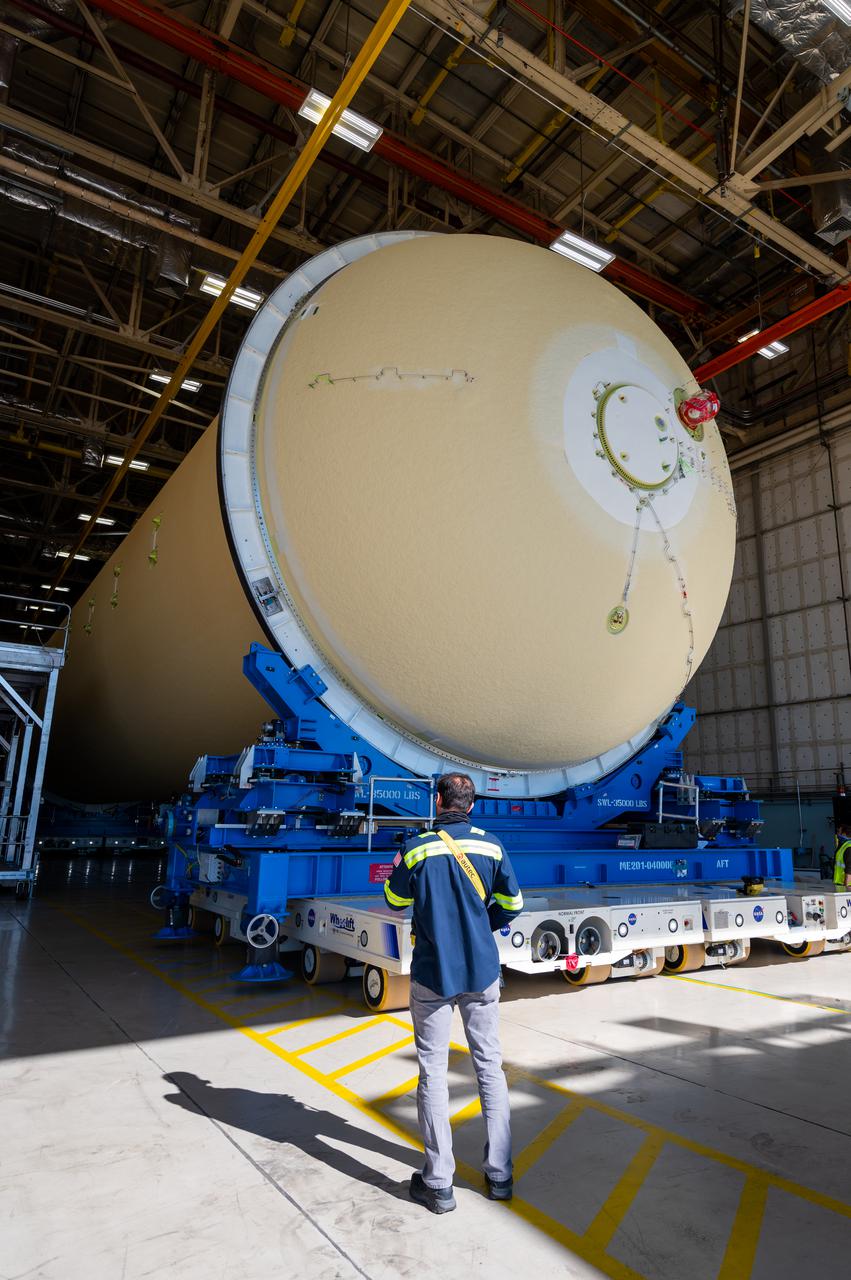

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
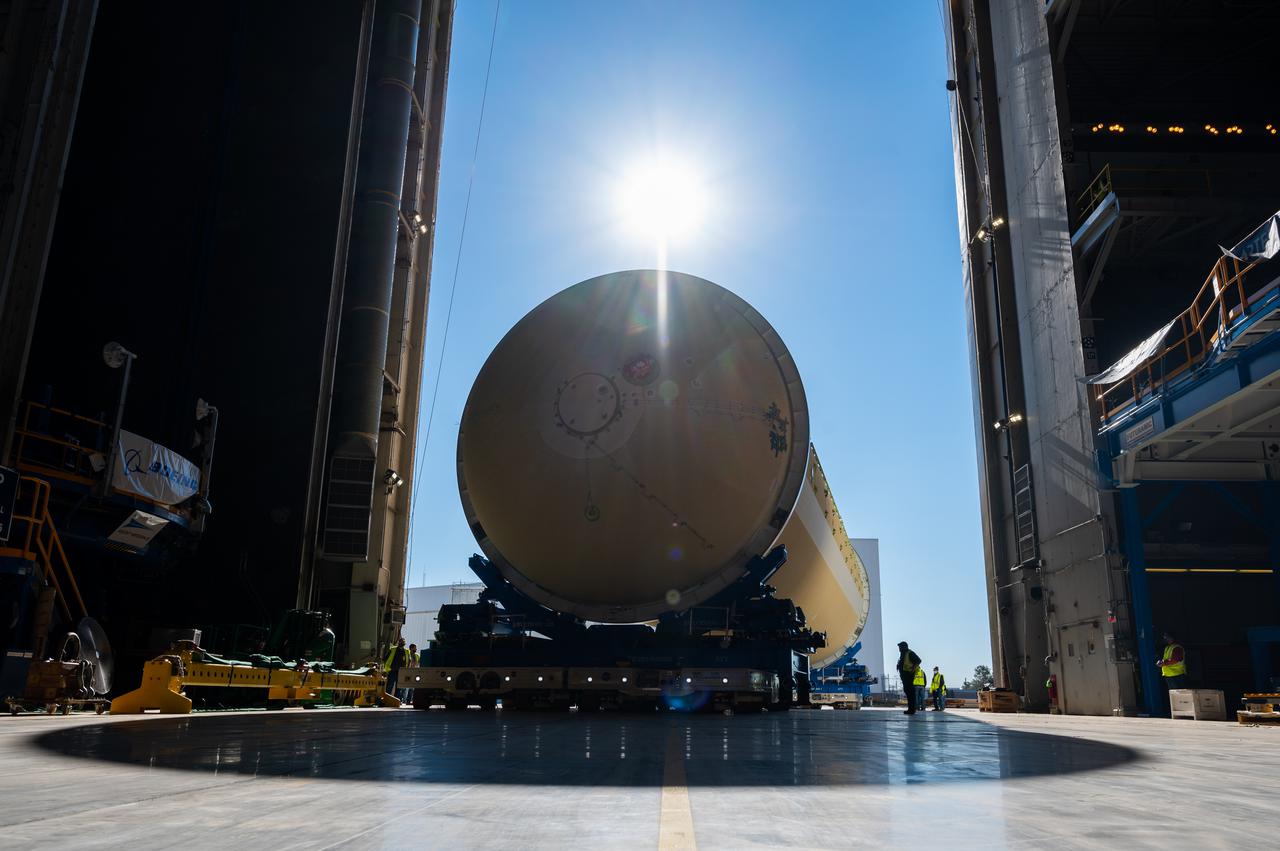

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
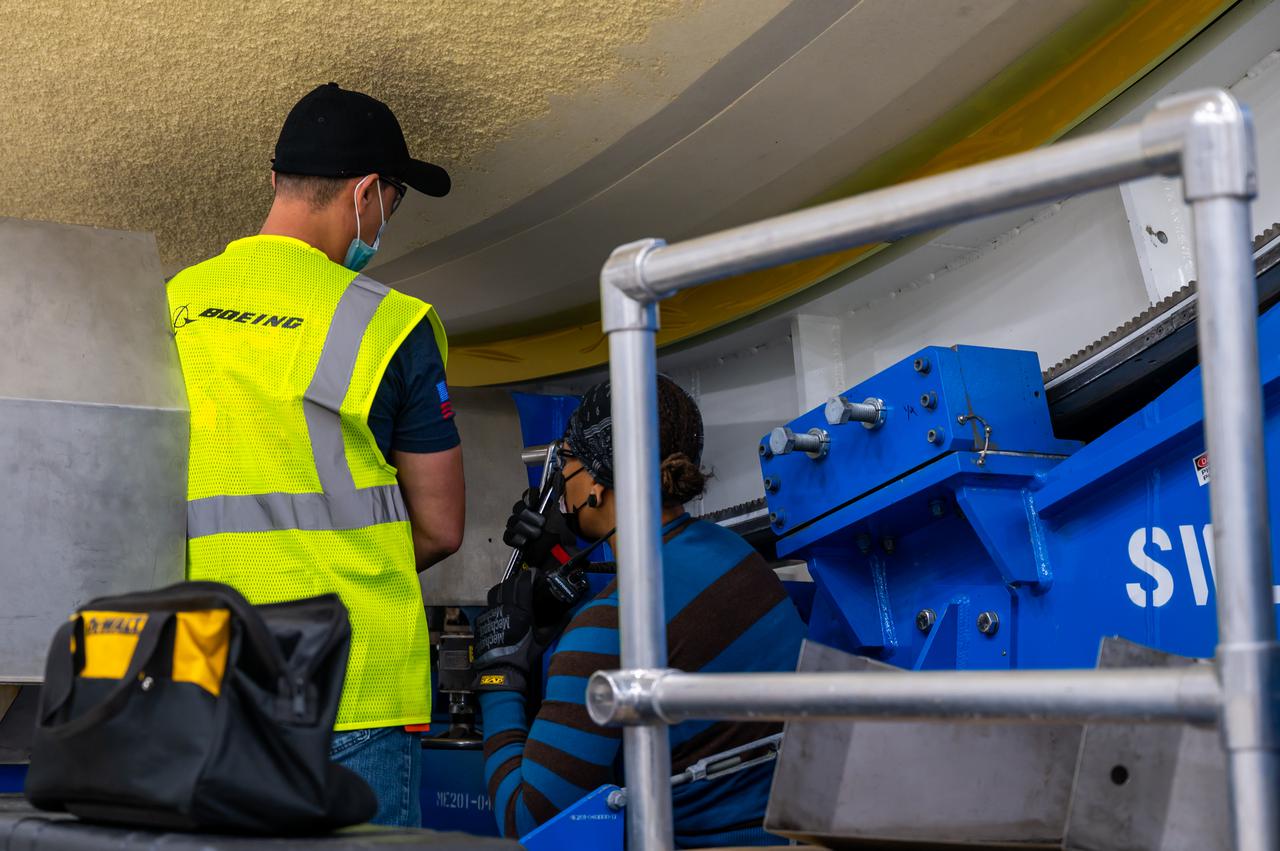

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
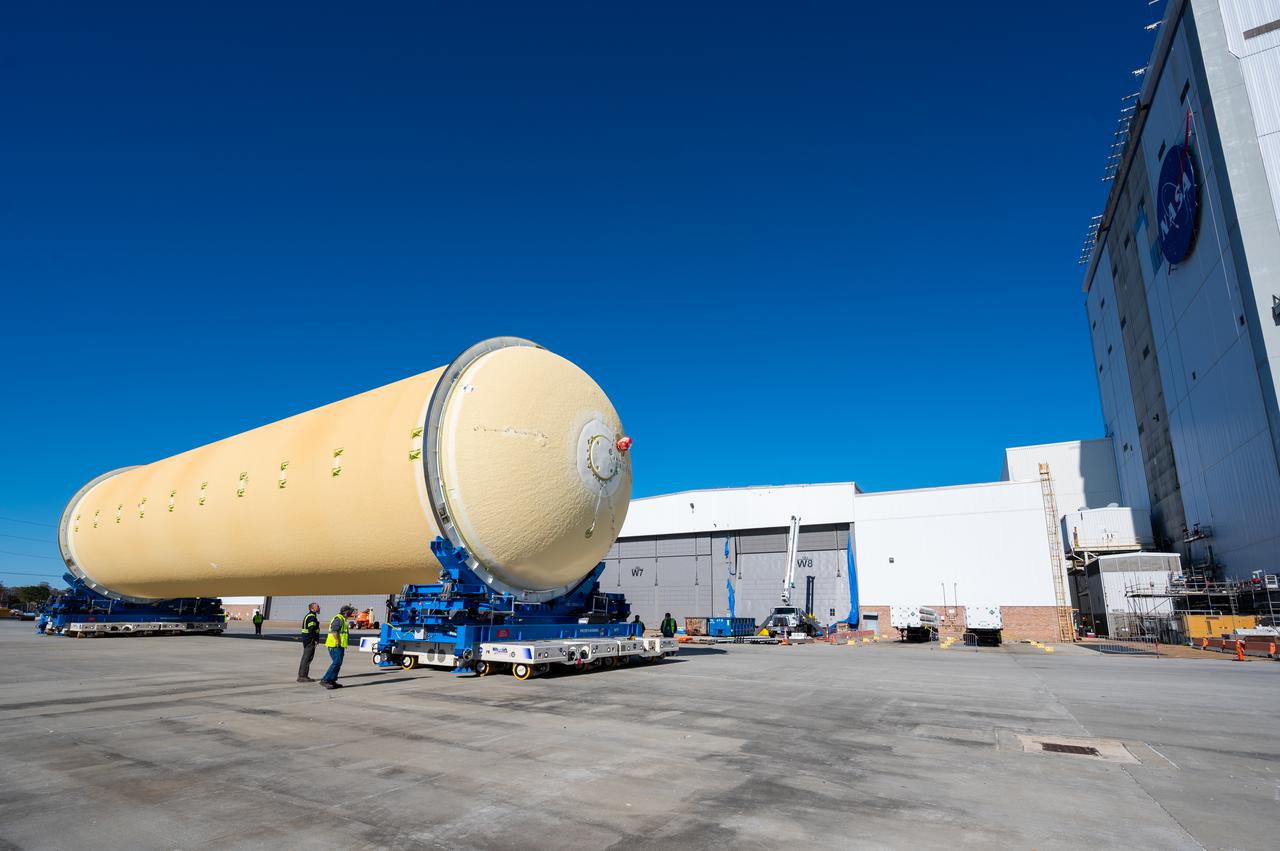

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
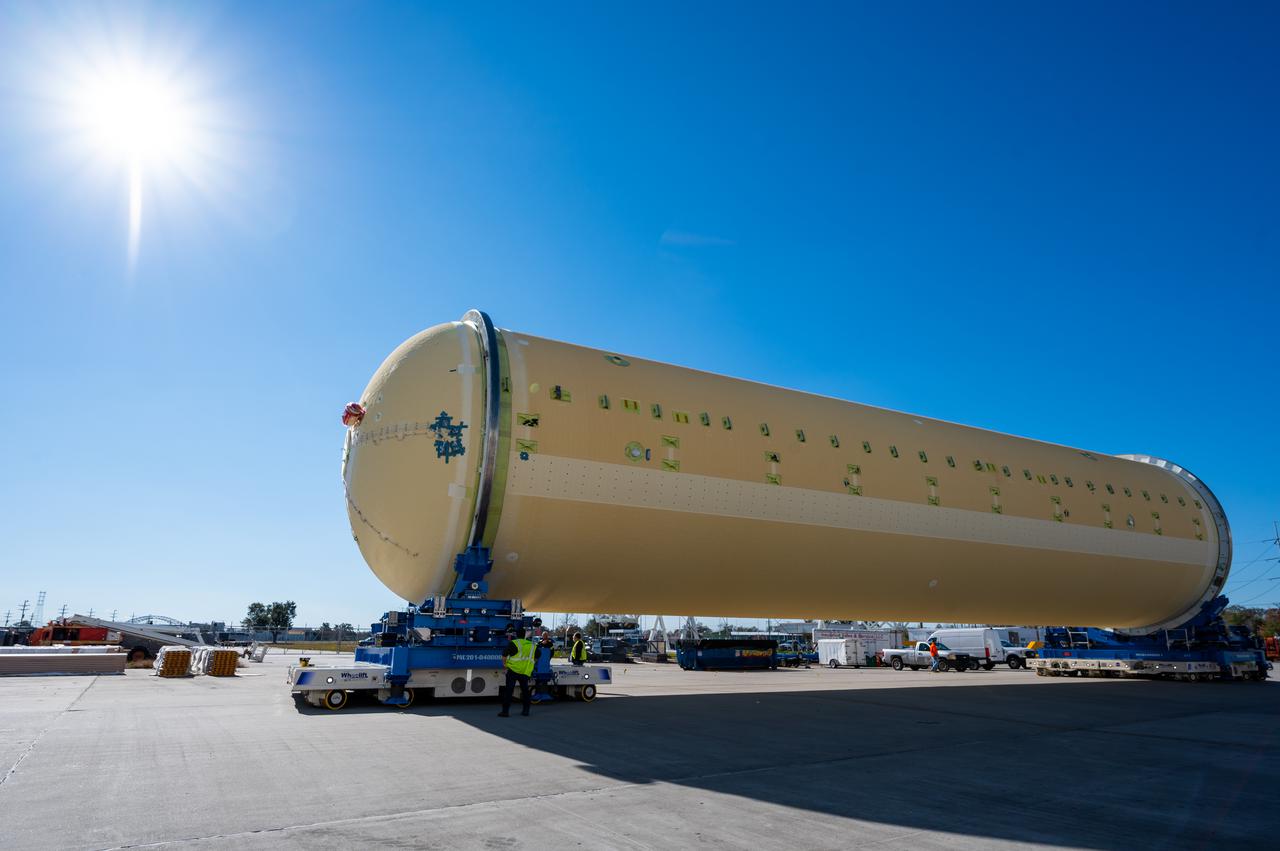

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
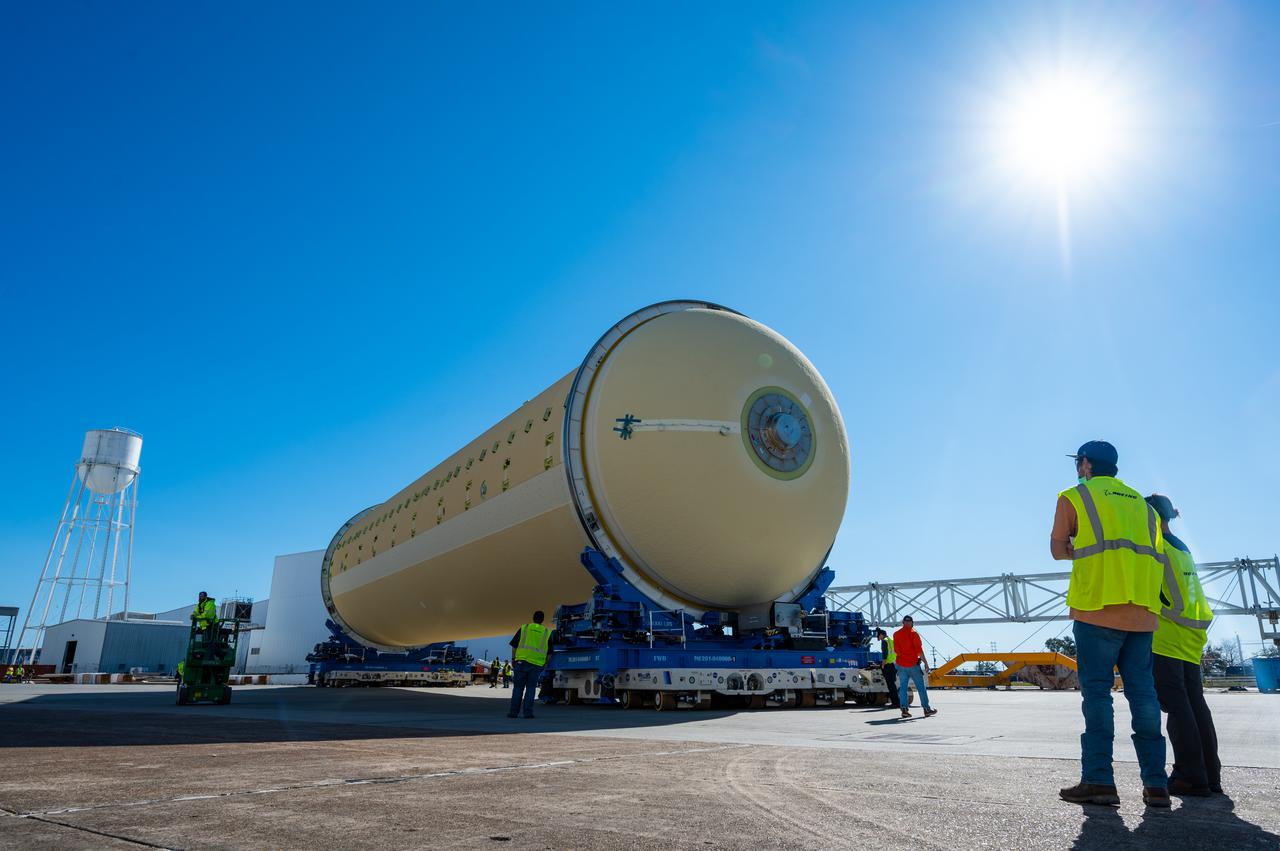

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
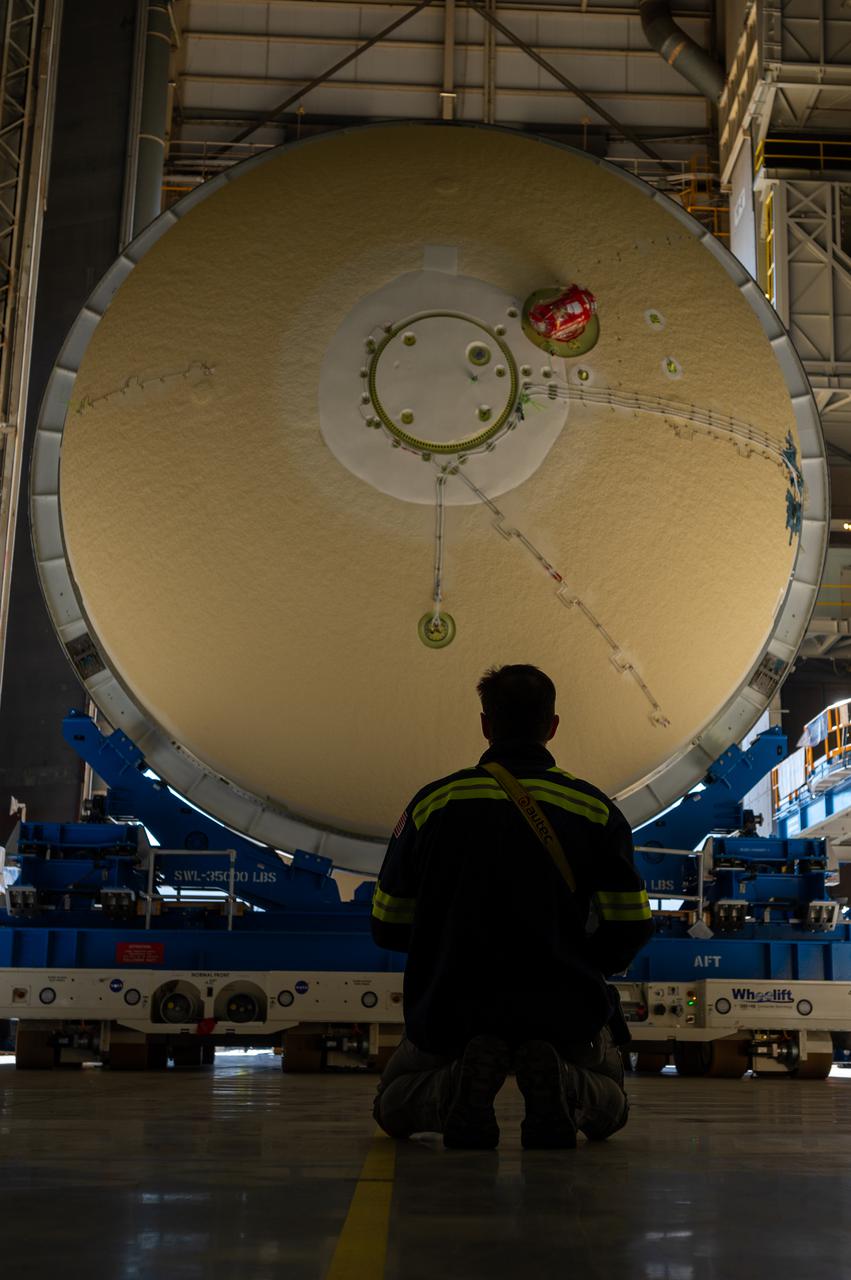

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
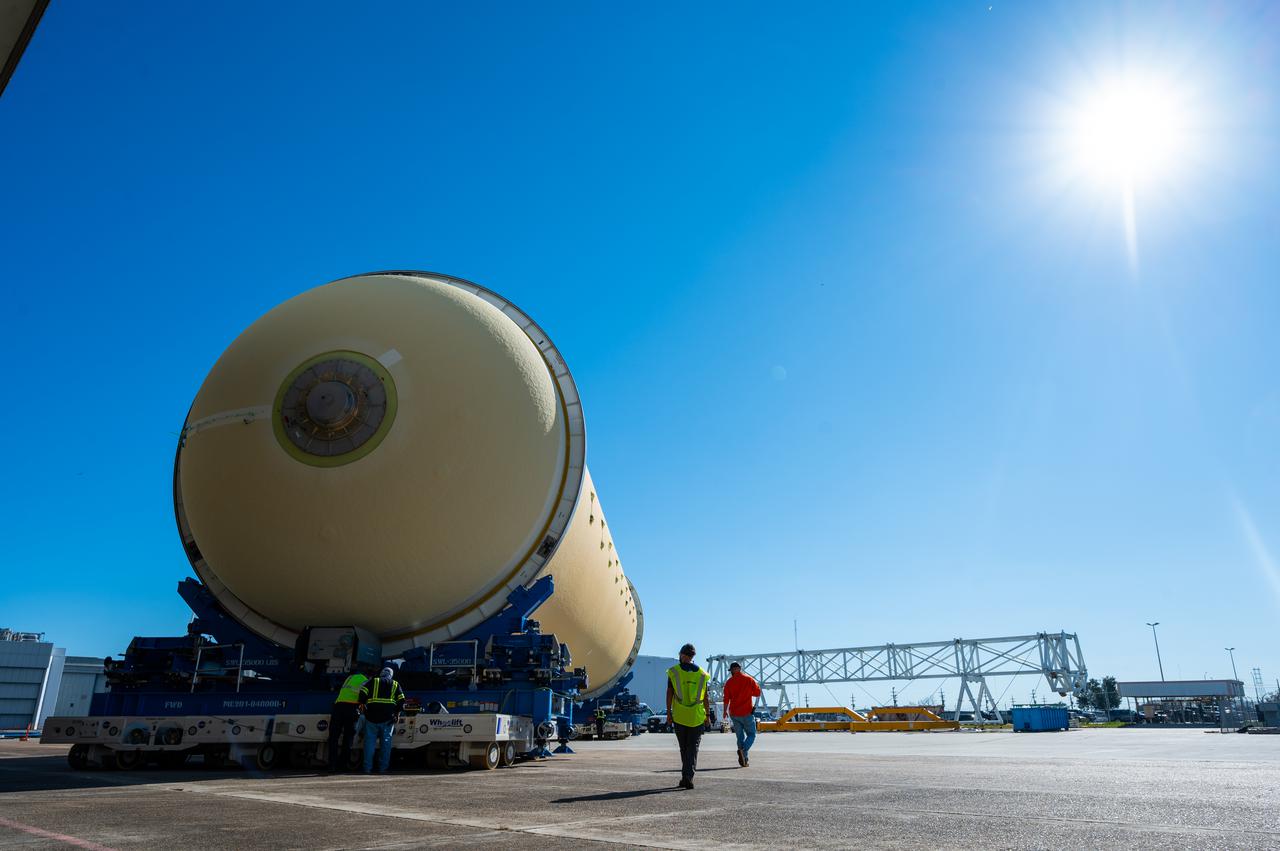

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
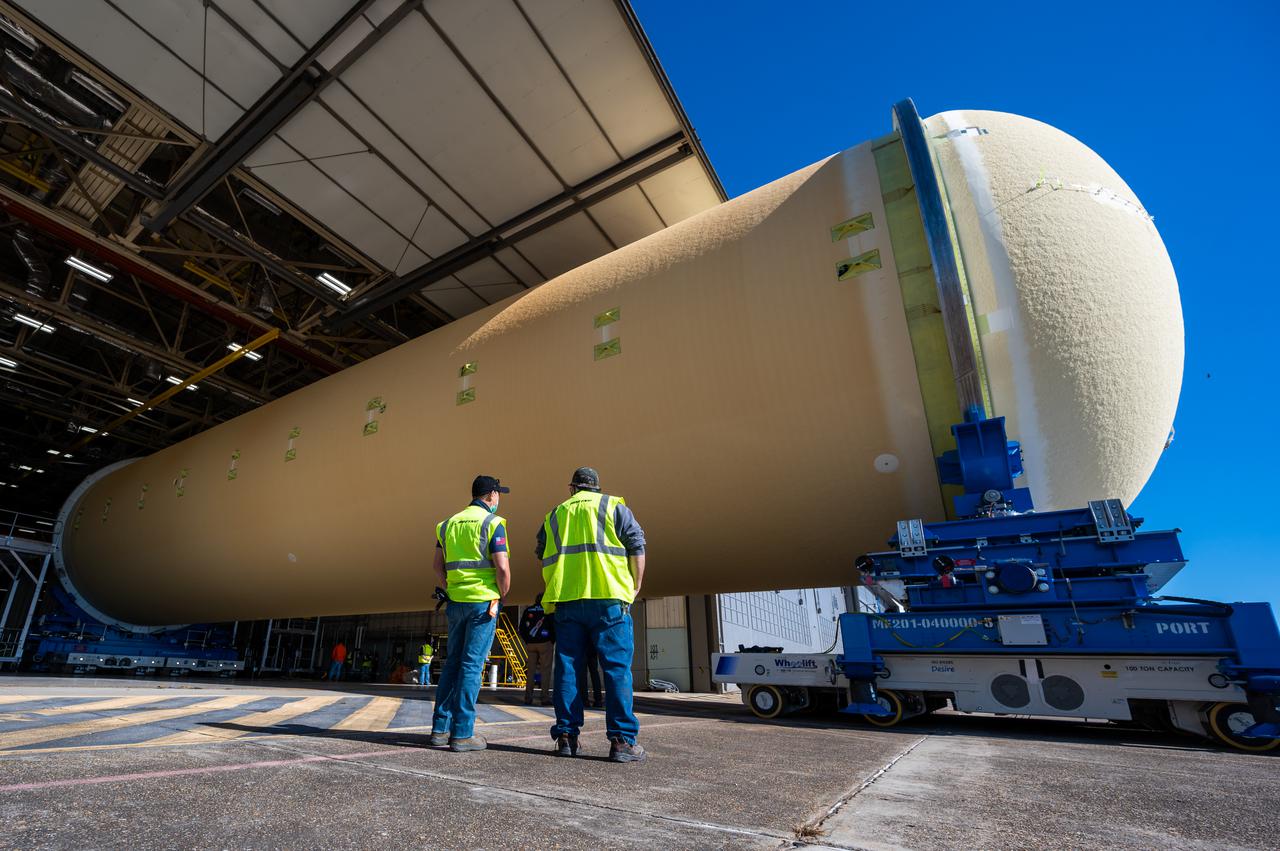

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
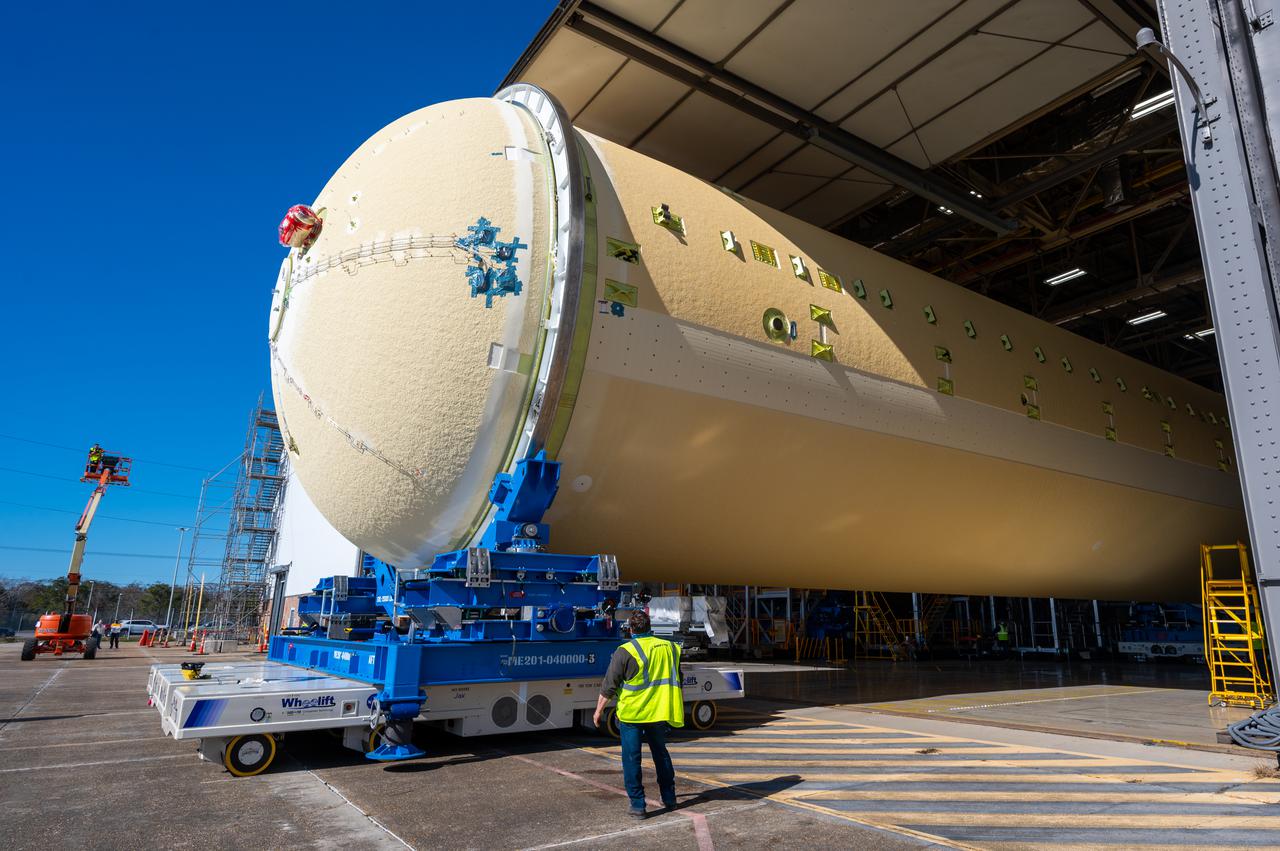

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
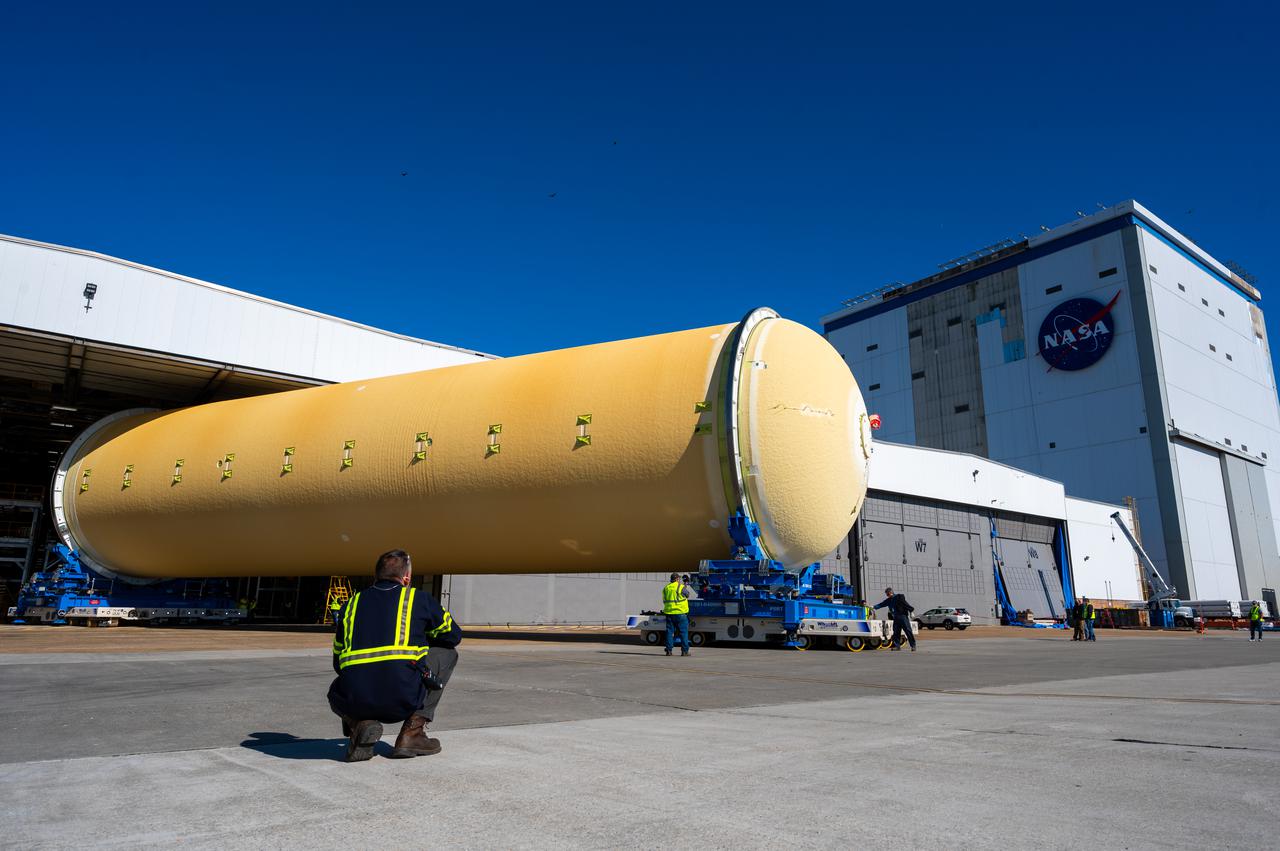

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
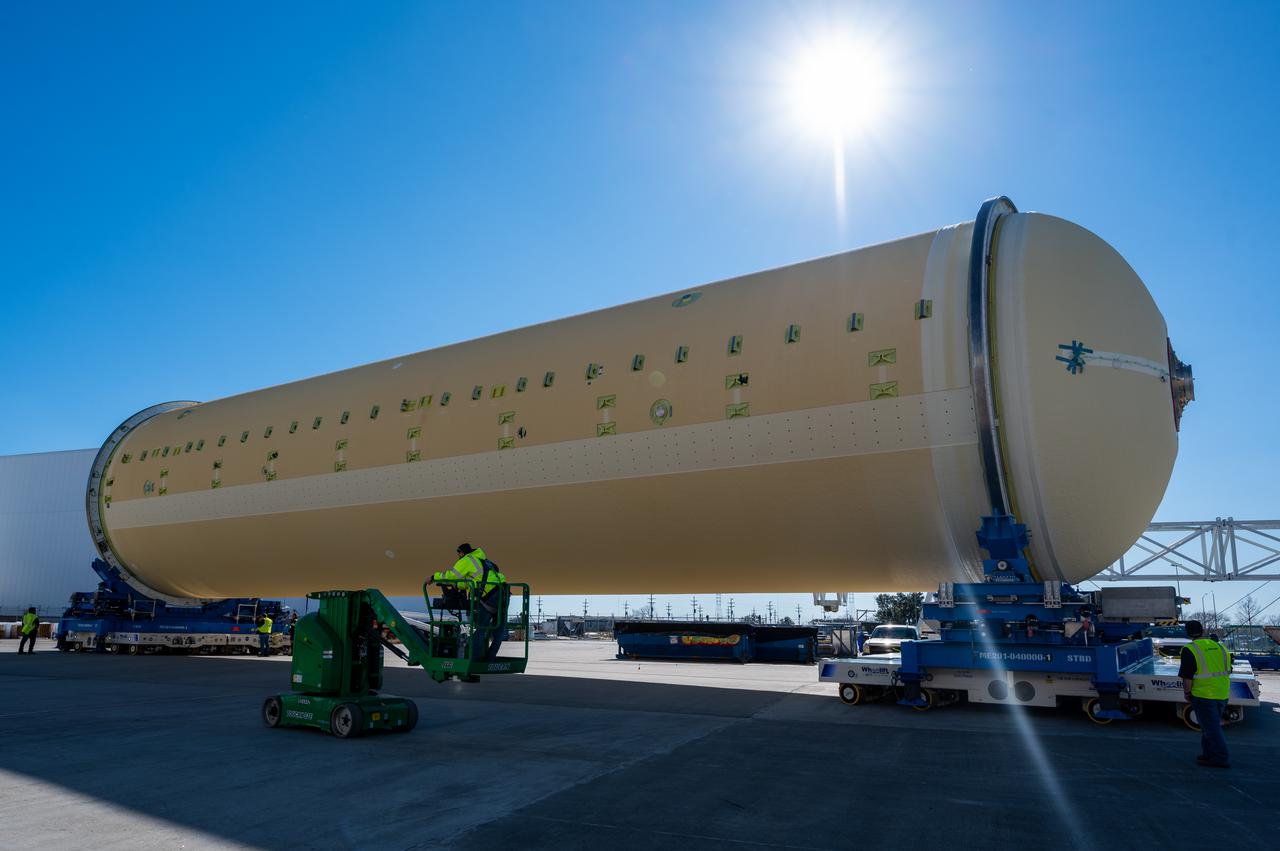

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
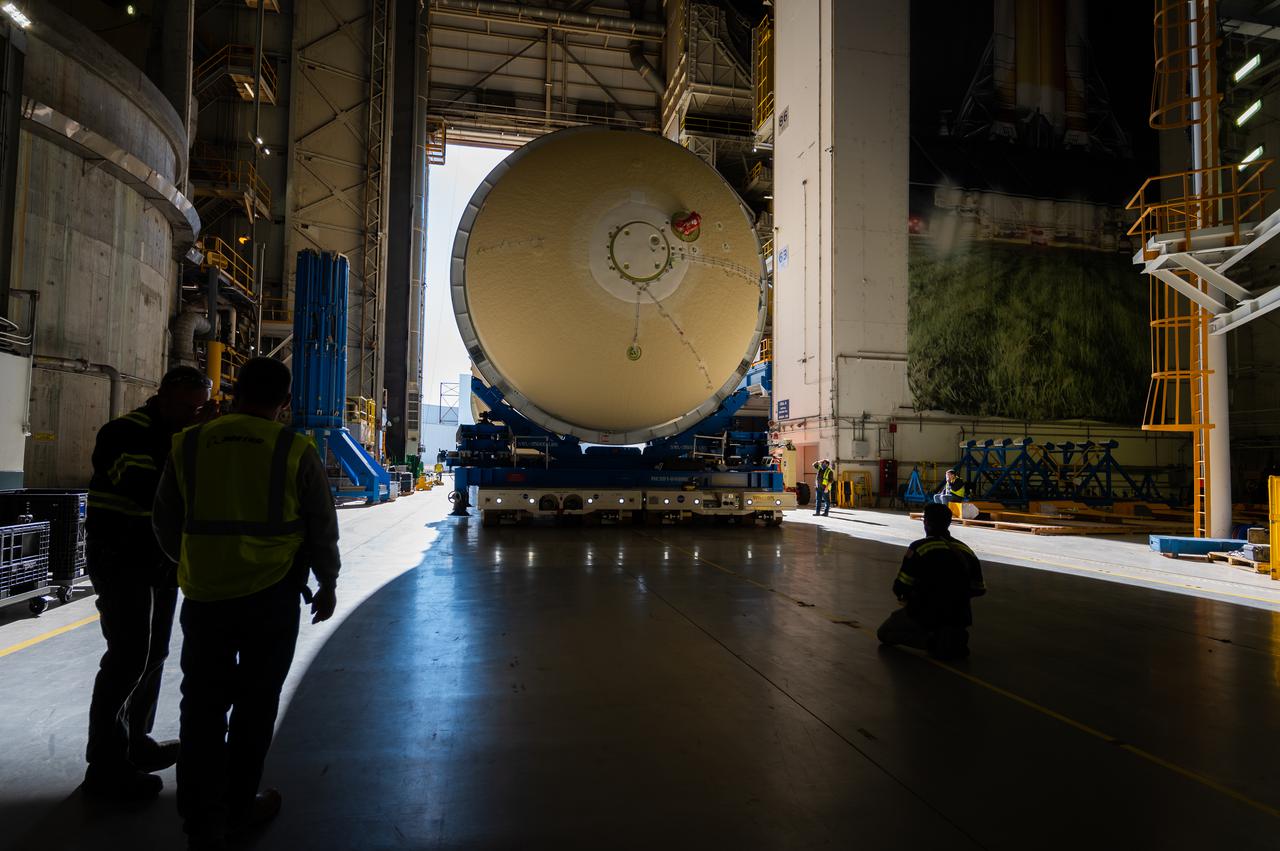

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
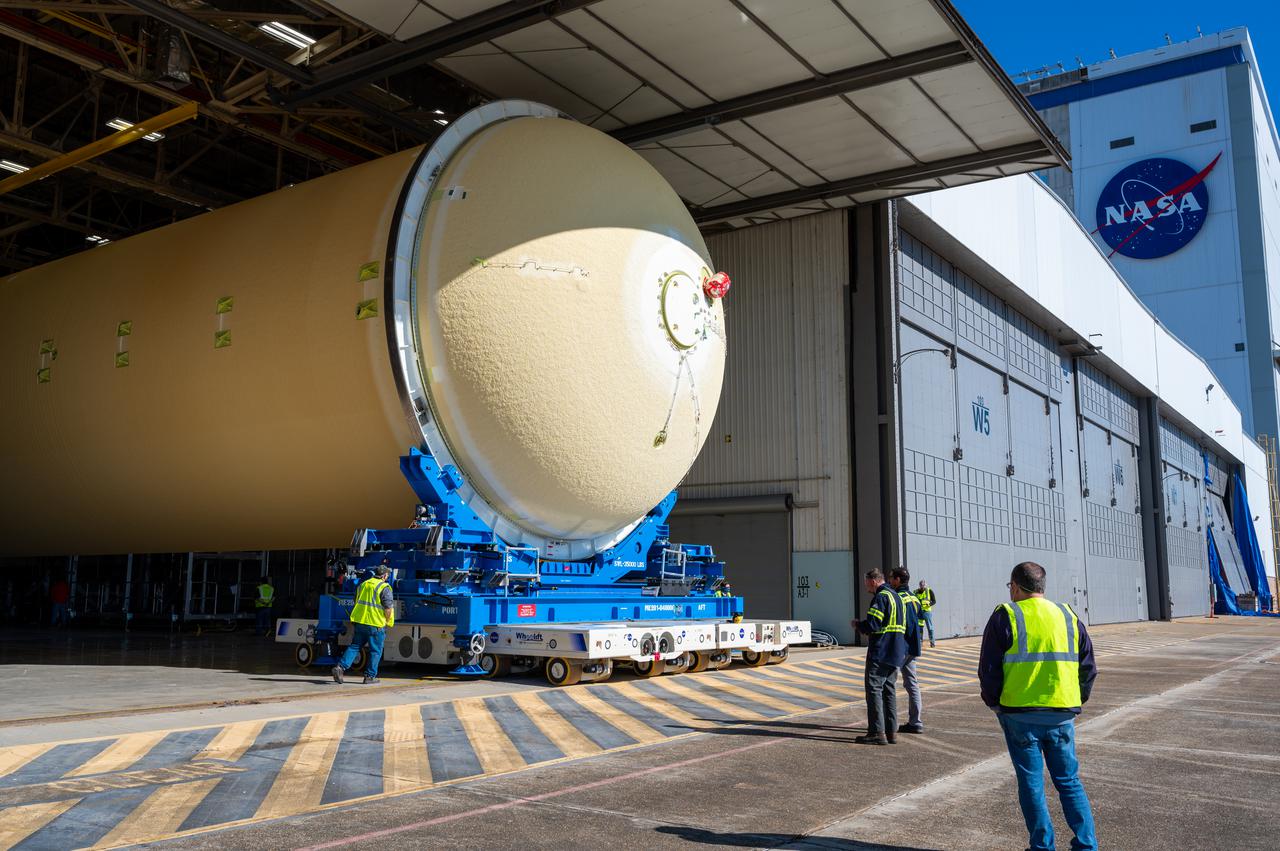

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
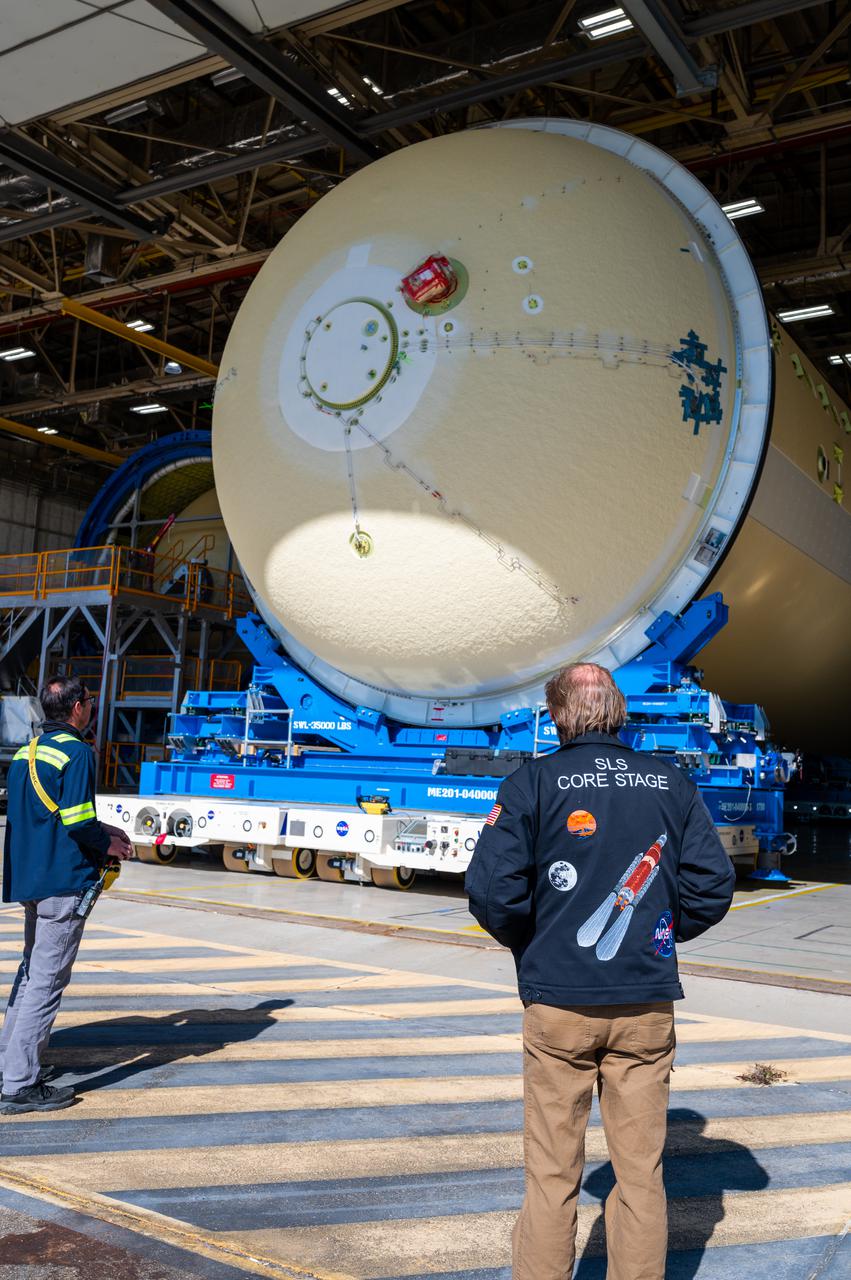

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
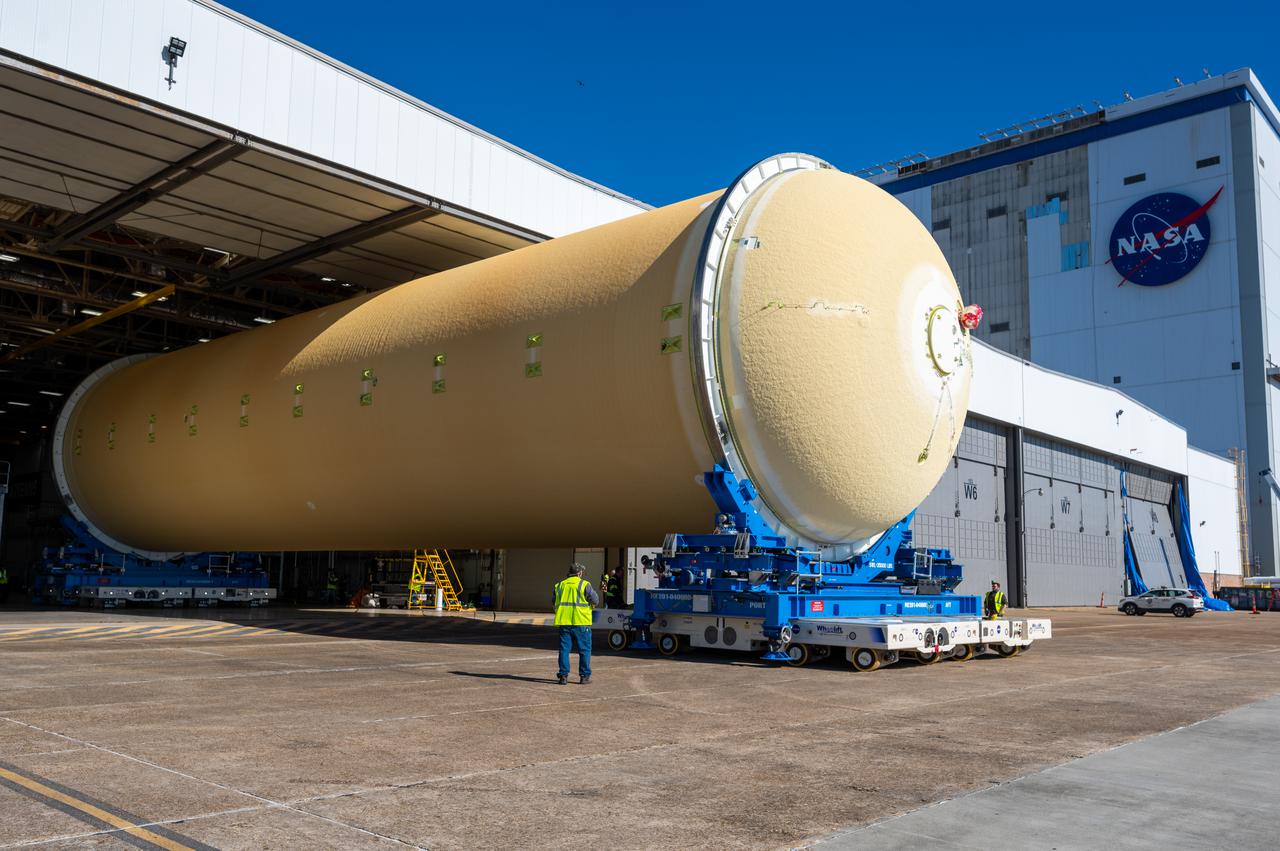

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
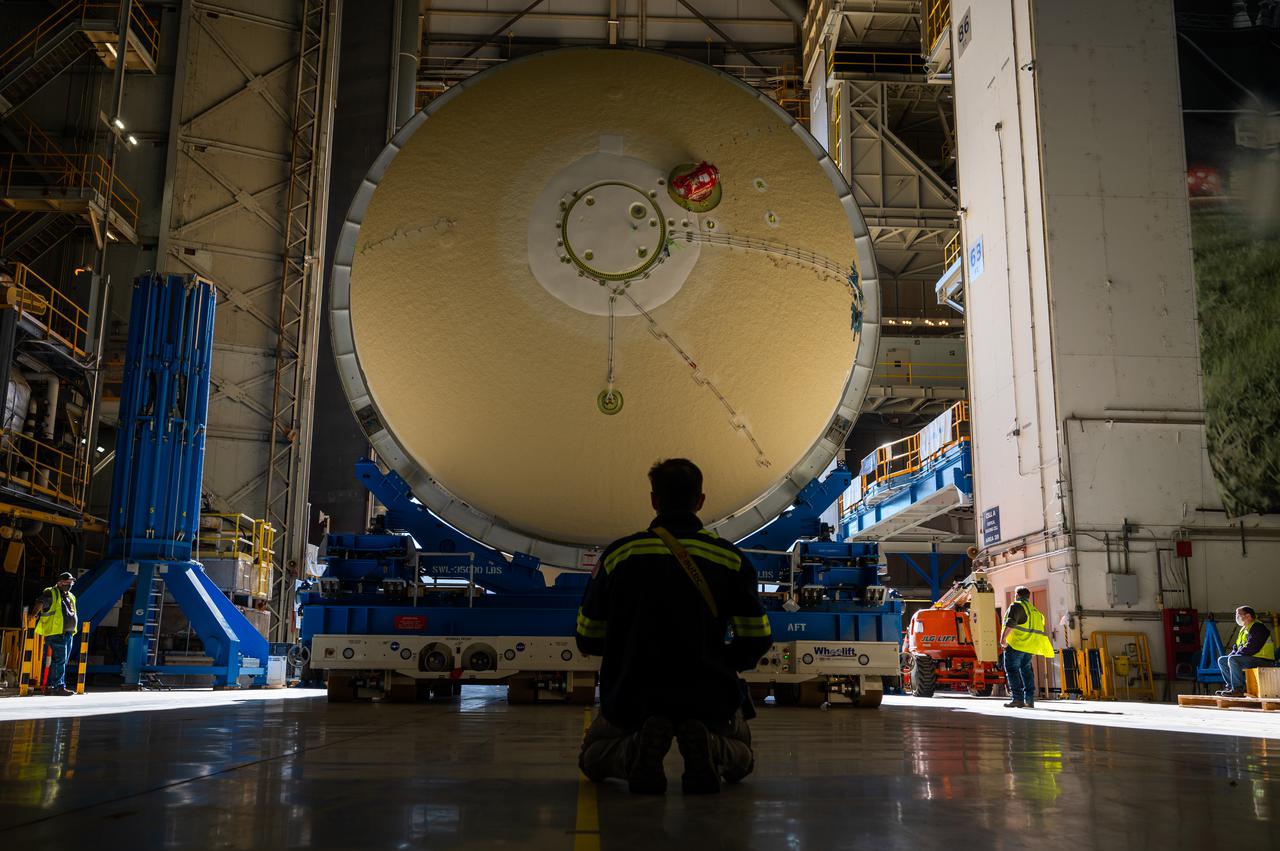

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
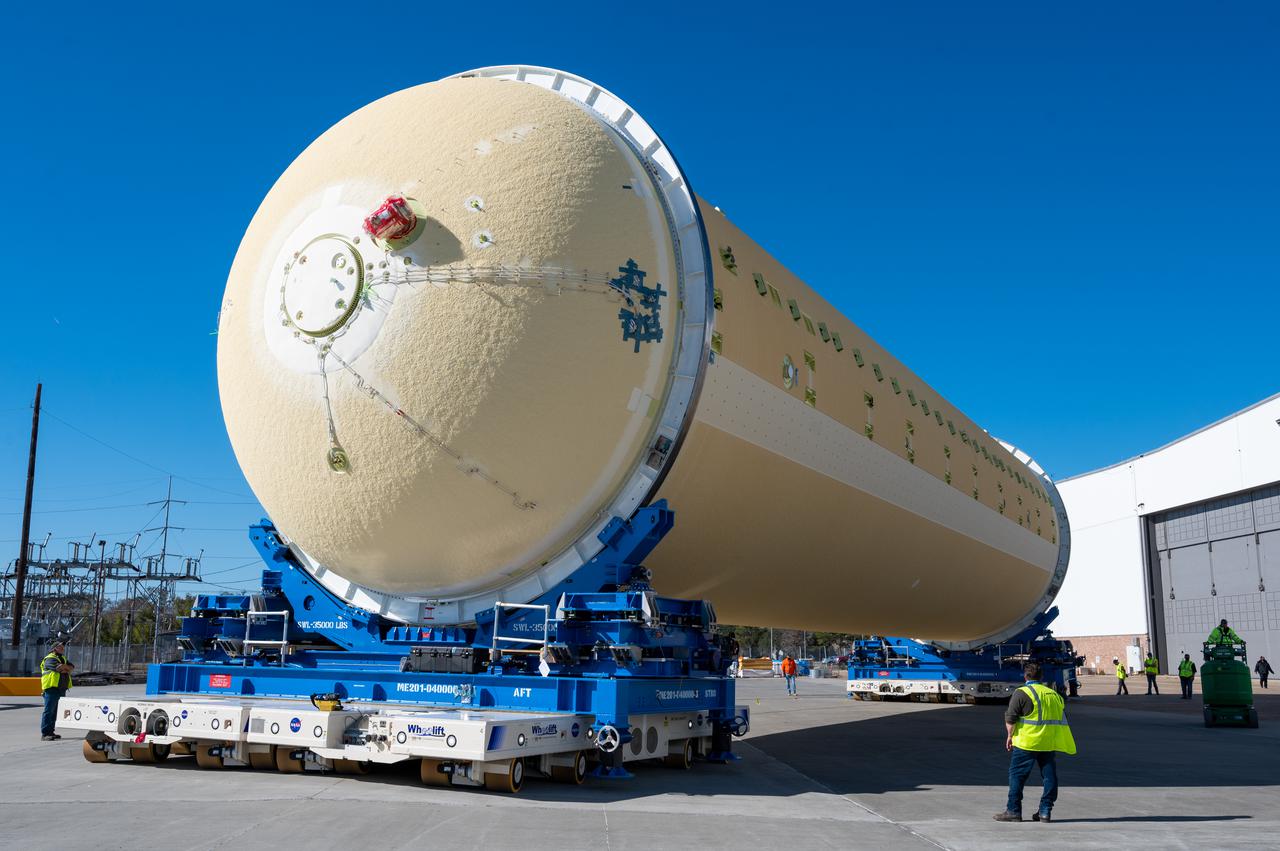

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
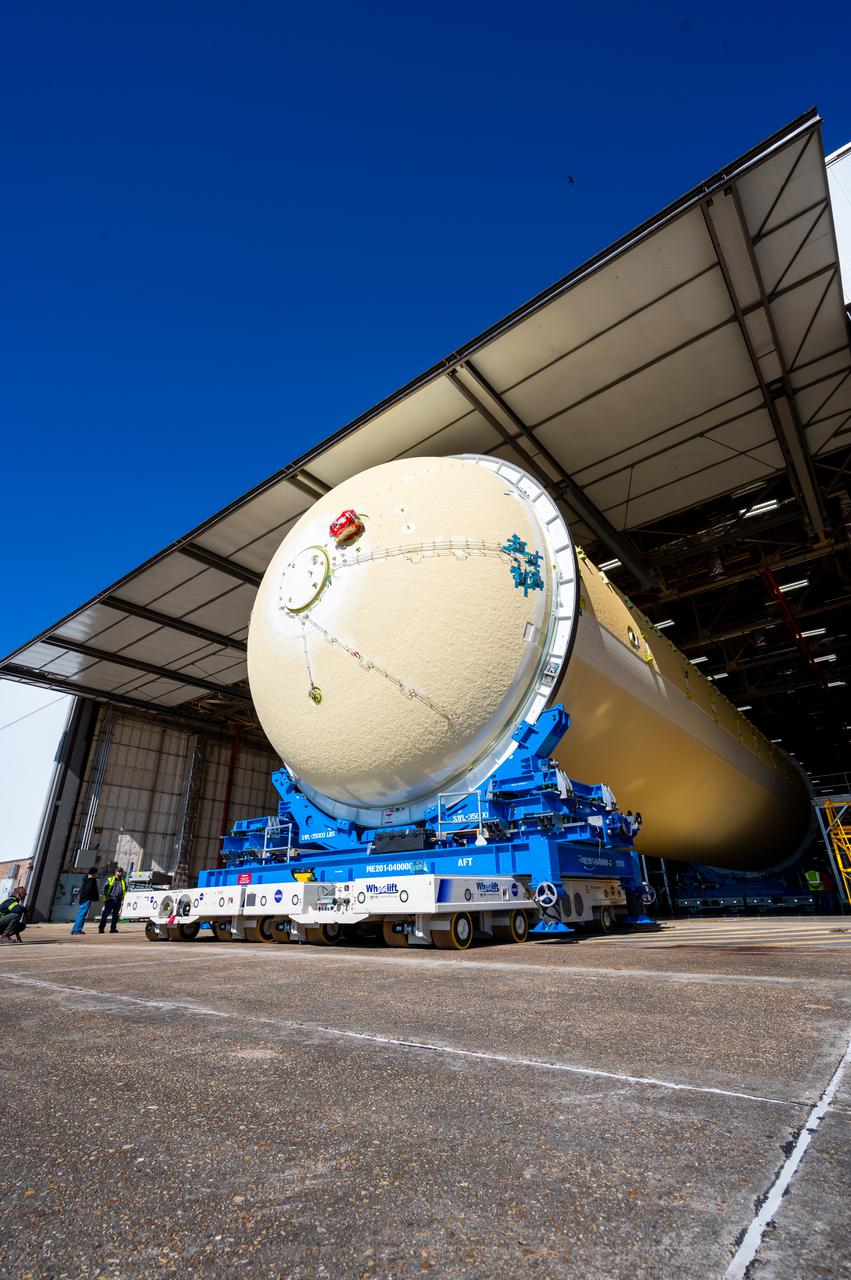

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
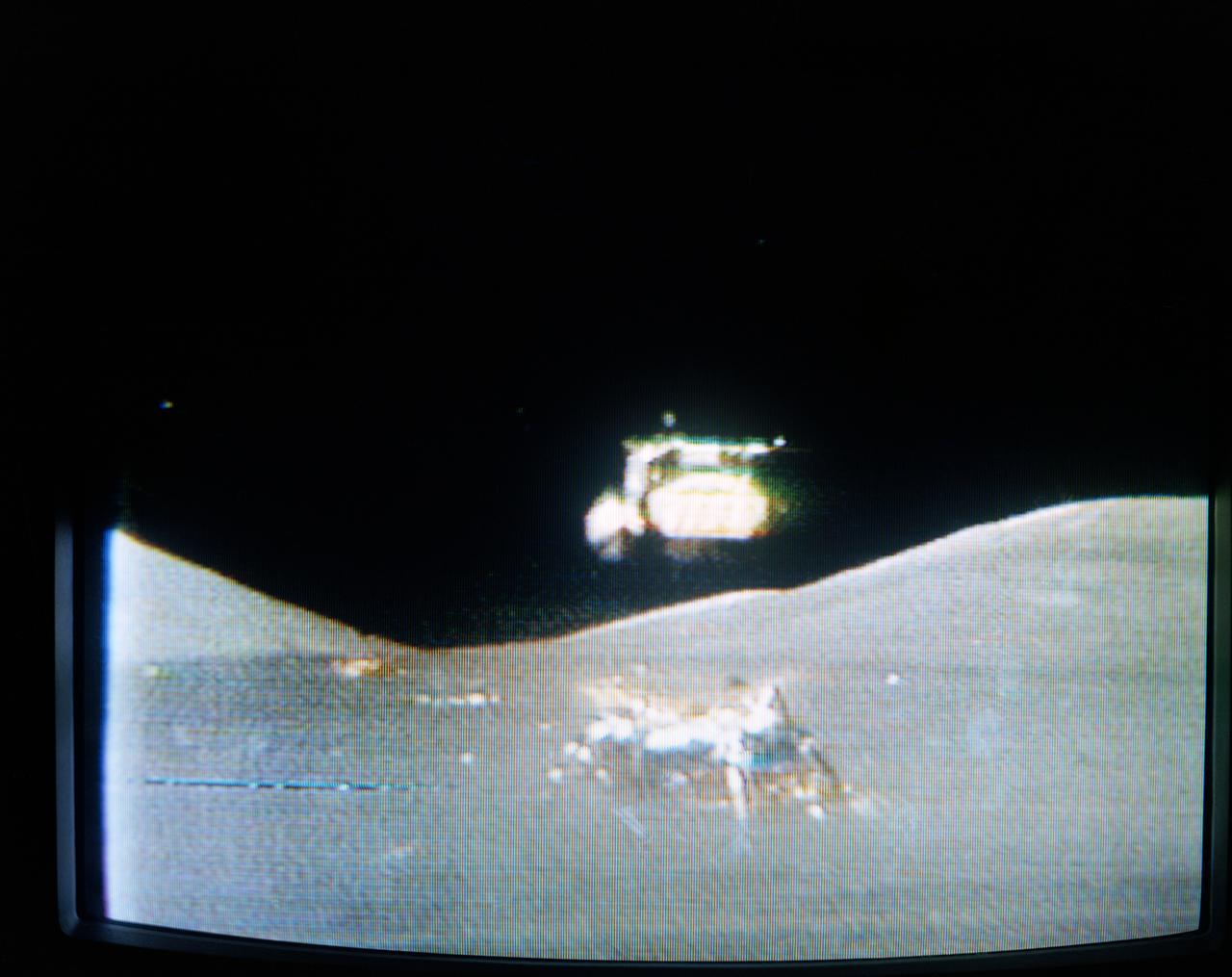

S72-55421 (14 Dec. 1972) --- The Apollo 17 Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" ascent stage leaves the Taurus-Littrow landing site as it makes its spectacular liftoff from the lunar surface, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV-mounted TV camera, remotely controlled from the Mission Control Center (MCC) in Houston, made it possible for people on Earth to watch the fantastic event. The LM liftoff was at 188:01:36 ground elapsed time, 4:54:36 p.m. (CST), Thursday, Dec. 14, 1972. The LM ascent stage, with astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt aboard, returned from the lunar surface to rejoin the Command and Service Modules (CSM) orbiting the moon. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the CSM in lunar orbit while Cernan and Schmitt explored the moon. The LM descent stage is used as a launching platform and remains behind on the moon. Here, the two stages have completely separated and the ascent stage is headed skyward.
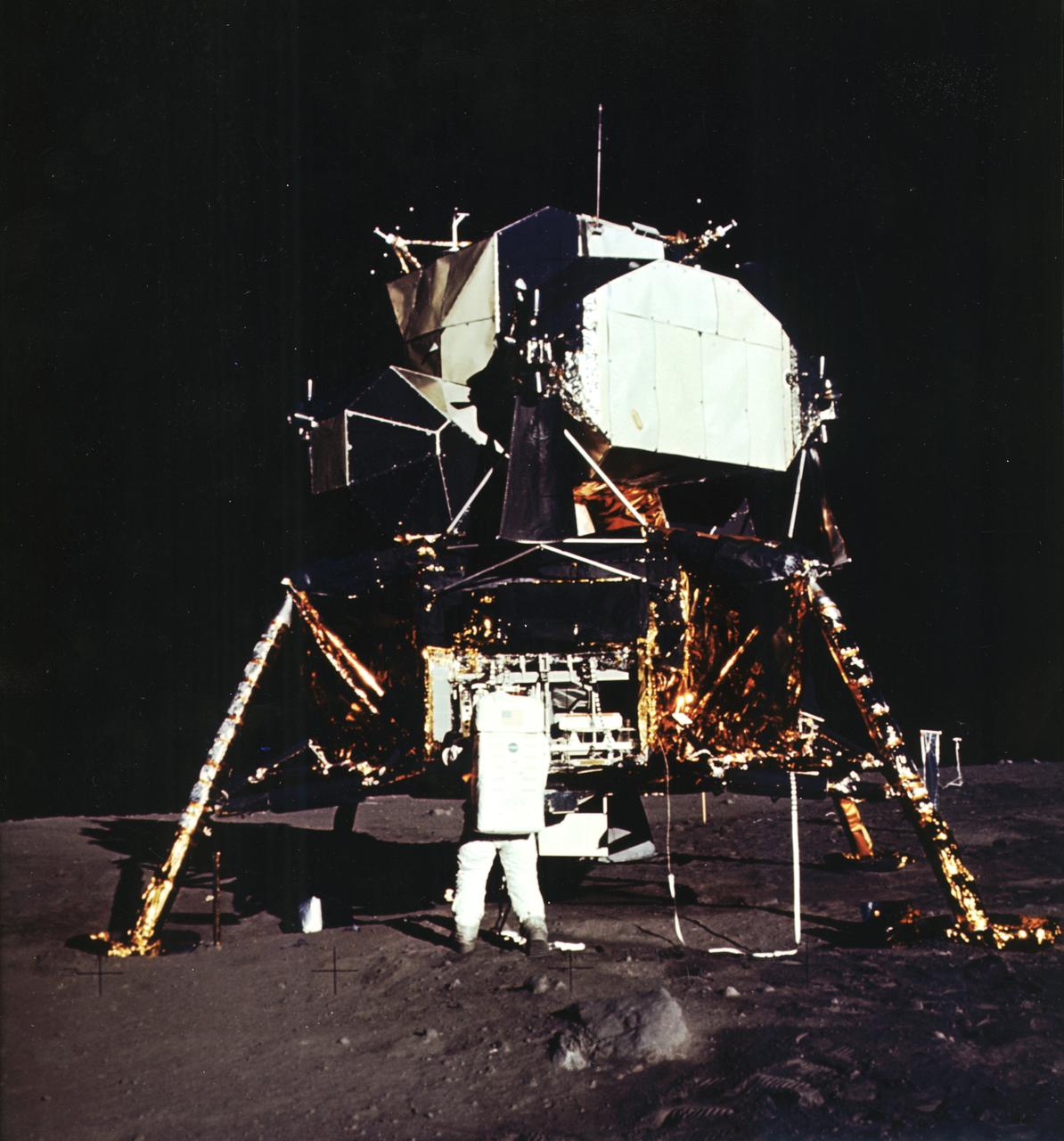
The first manned lunar landing mission, Apollo 11, launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon in the Sea of Tranquility. The LM was a two part spacecraft. Its lower or descent stage had the landing gear, engines, and fuel needed for the landing. When the LM blasted off the Moon, the descent stage served as the launching pad for its companion ascent stage, which was also home for the two astronauts on the surface of the Moon. The LM was full of gear with which to communicate, navigate, and rendezvous. It also had its own propulsion system, and an engine to lift it off the Moon and send it on a course toward the orbiting CM. Aldrin is pictured here next to the LM on the lunar surface.
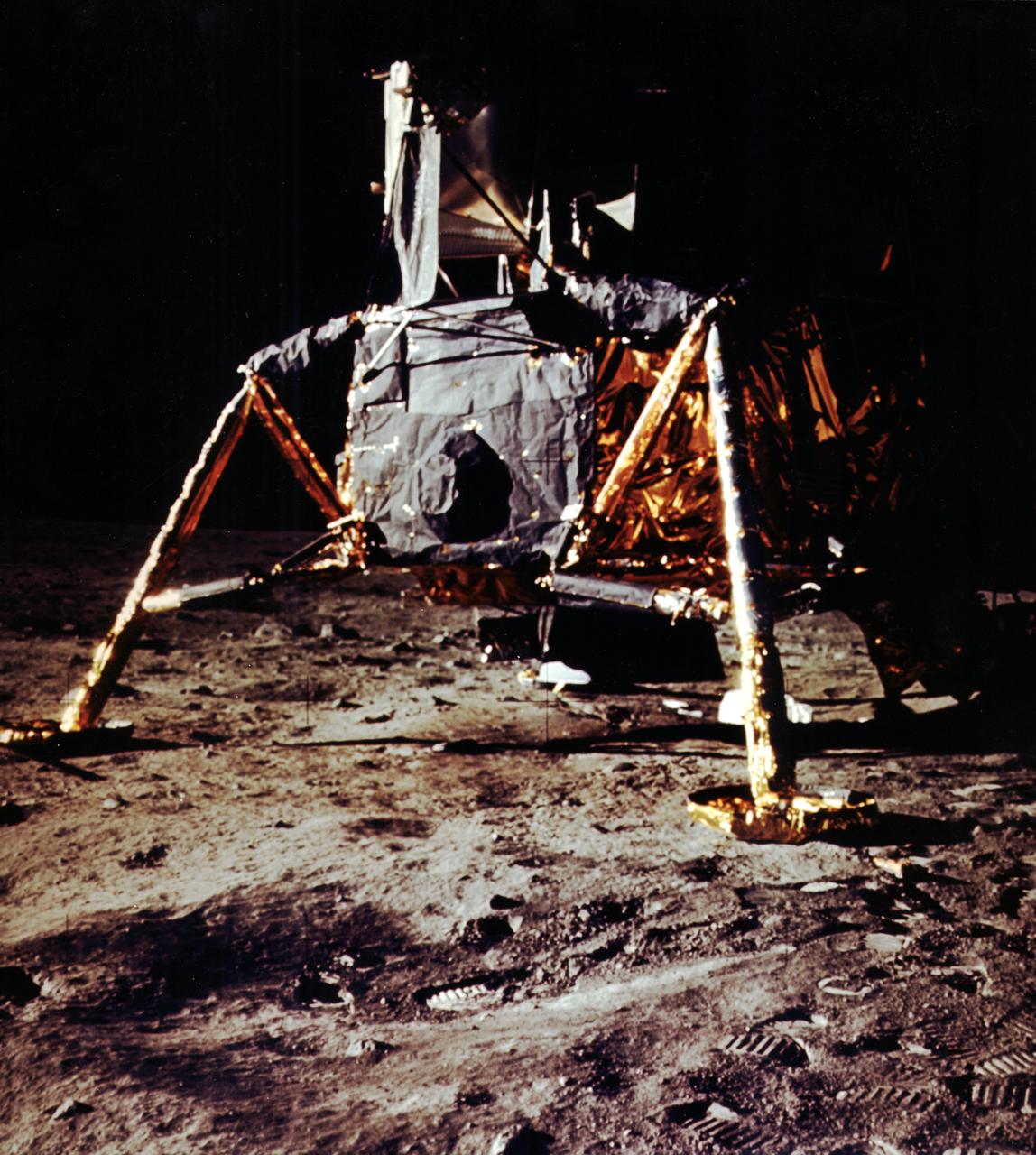

The first manned lunar landing mission, Apollo 11, launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon in the Sea of Tranquility. The LM was a two part spacecraft. Its lower or descent stage had the landing gear, engines, and fuel needed for the landing. When the LM blasted off the Moon, the descent stage served as the launching pad for its companion ascent stage, which was also home for the two astronauts on the surface of the Moon. The LM was full of gear with which to communicate, navigate, and rendezvous. It also had its own propulsion system, and an engine to lift it off the Moon and send it on a course toward the orbiting CM. This photograph shows a close up of the LM on the Lunar surface.
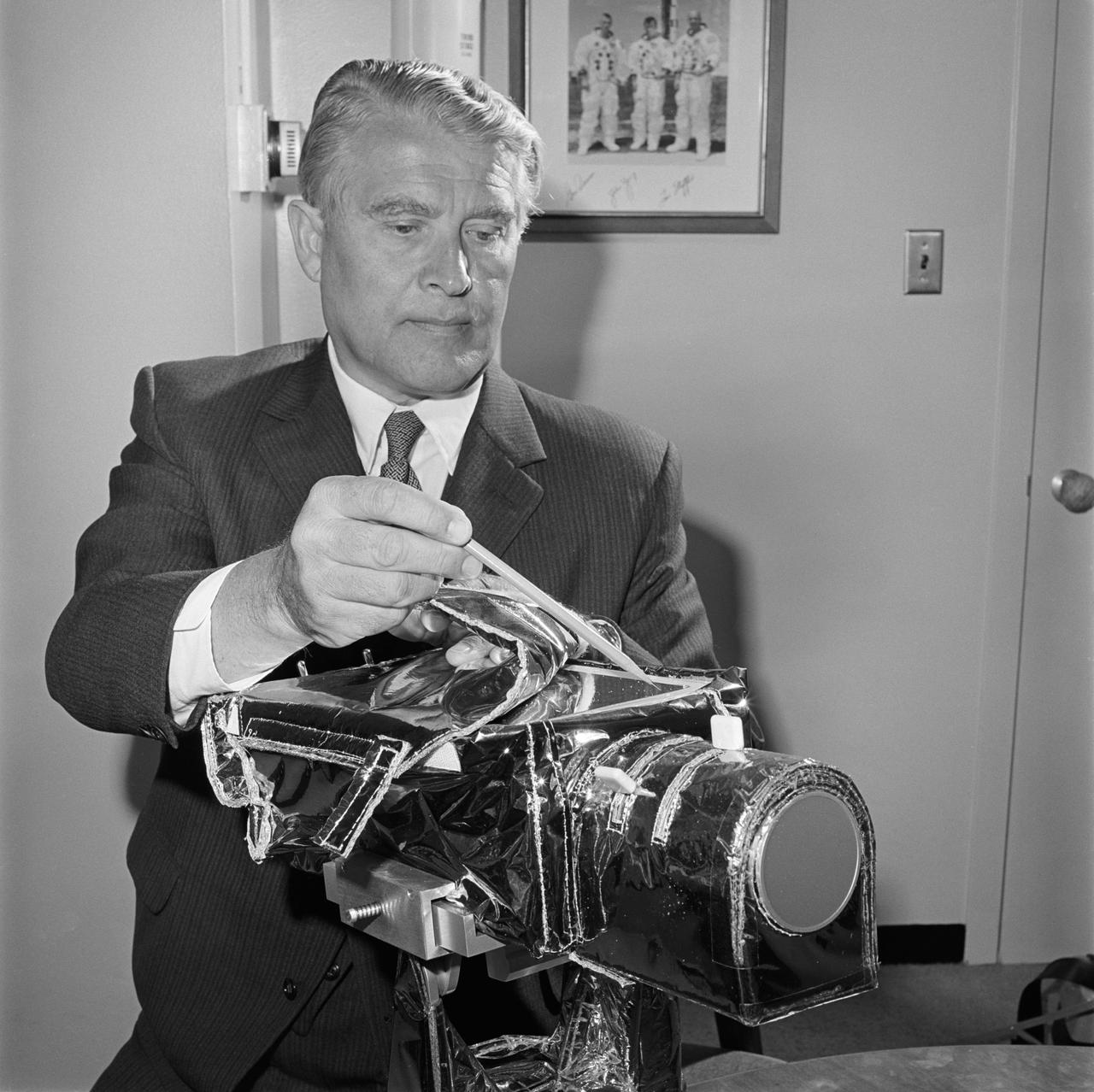

S71-35169 (June 1971) --- The color television camera for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Apollo 15 lunar landing mission is examined by NASA's Deputy Associate Director Dr. Wernher von Braun. The camera will be mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) and will be operated by the flight crew astronauts, David R. Scott and James B. Irwin, or by ground command from the Mission Control Center (MCC) in Houston during the three lunar traverses. It will also be used to show the astronauts whenever they leave the LRV, and for the first time it will make possible the viewing of the Lunar Module (LM) ascent stage as it lifts off the moon.
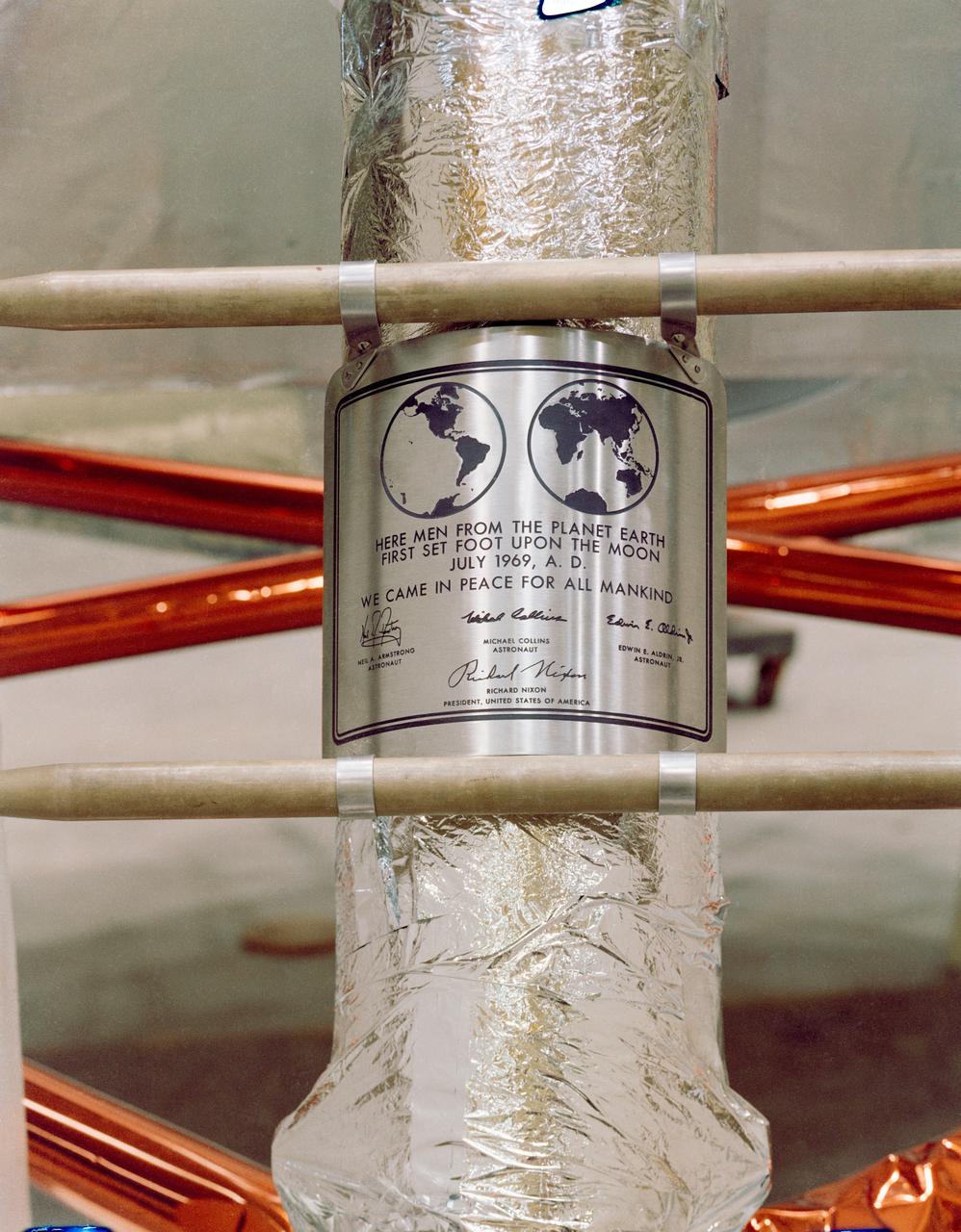

S69-38749 (July 1969) --- Close-up view of the plaque which the Apollo 11 astronauts will leave behind on the moon in commemoration of the historic event. The plaque is made of stainless steel measuring nine by seven and five-eighths inches, and one-sixteenth inch thick. The plaque will be attached to the ladder on the landing gear strut on the descent stage of the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM). Covering the plaque during flight will be a thin sheet of stainless steel which will be removed on the lunar surface.

S69-39334 (July 1969) --- This is a replica of the plaque which the Apollo 11 astronauts will leave behind on the moon in commemoration of the historic event. The plaque is made of stainless steel, measuring nine by seven and five-eighths inches, and one-sixteenth inch thick. The plaque will be attached to the ladder on the landing gear strut on the descent stage of the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM). Covering the plaque during the flight will be a thin sheet of stainless steel which will be removed on the lunar surface.
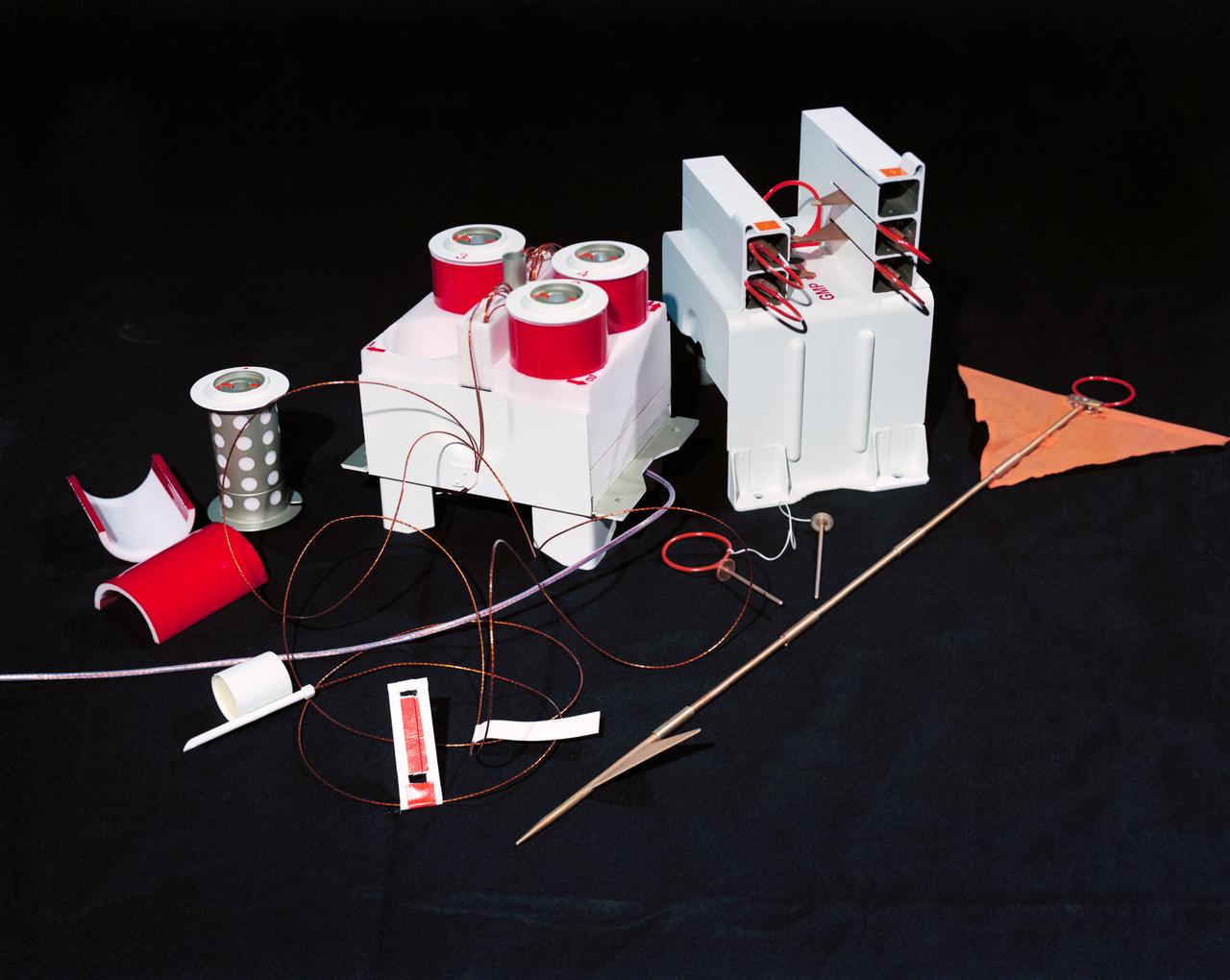
S72-37259 (November 1972) --- The Geophone Module and Cable Reels of the Lunar Seismic Profiling Experiment (S-203), a component of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package which will be carried on the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. LSPE components are four geophones similar to those used in an earlier active seismic experiment, an electronics package in the ALSEP central station, and eight explosive packages which will be deployed during the geology traverse. The four geophones will be placed one in the center and one at each corner of a 90-meter equilateral triangle. Explosive charges placed on the surface will generate seismic waves of varying strengths to provide data on the structural profile of the landing site. After the charges have been fired by ground command, the experiment will settle down into a passive listening mode, detecting moonquakes, meteorite impacts and the thump caused by the Lunar Module ascent stage impact.
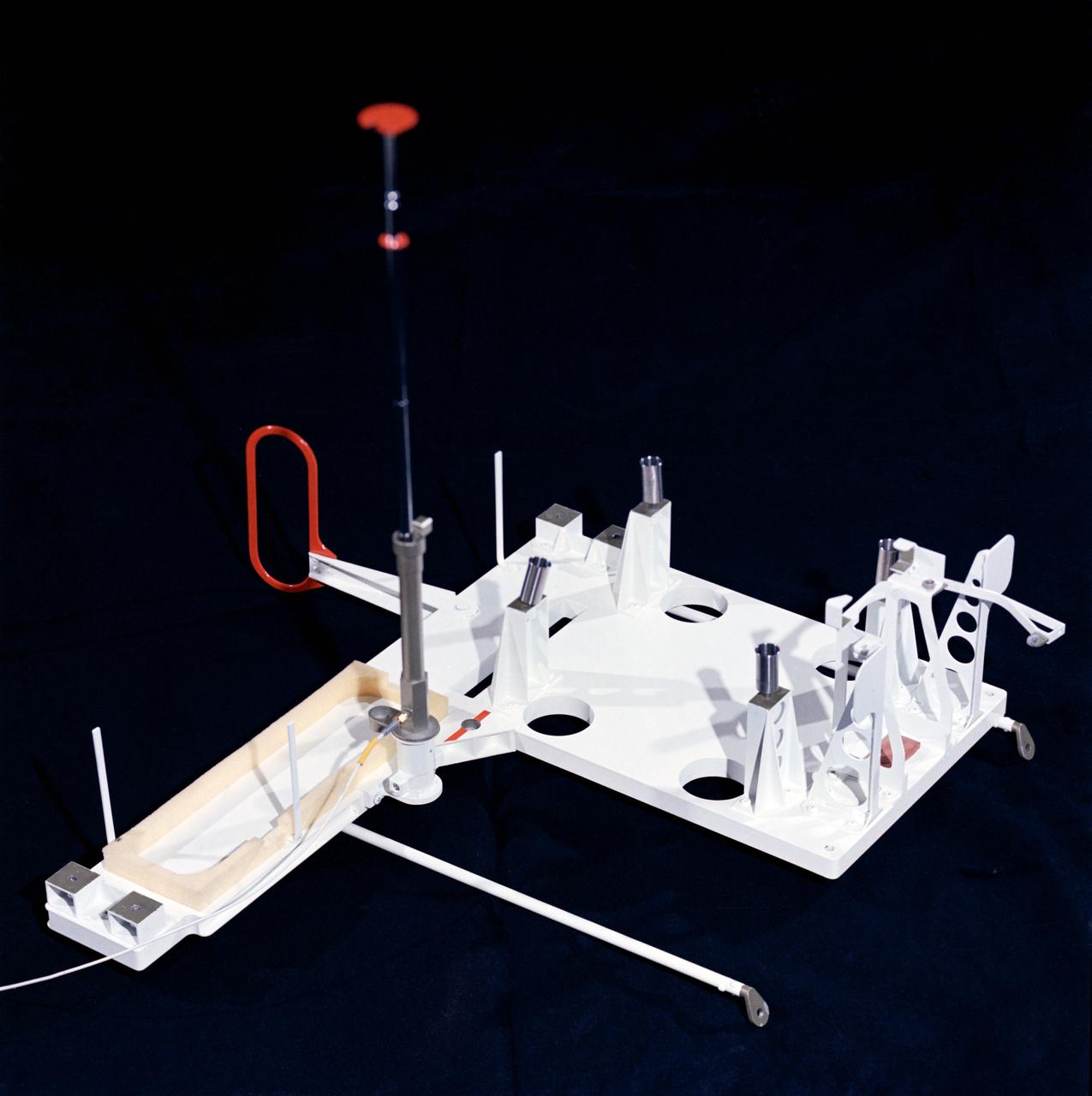

S72-37260 (November 1972) --- The remote antenna for the Lunar Seismic Profiling Experiment, Numbered S-203, a component of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package which will be carried on the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. LSPE components are four geophones similar to those used in earlier active seismic experiments an electronics package in the ALSEP central station, and eight explosive packages which will be deployed during the geology traverse. The four geophones will be placed one in the center and at each corner of a 90-meter equilateral triangle. Explosive charges placed on the surface will generate seismic waves of varying strengths to provide data on the structural profile of the landing site. After the charges have been fired by ground command, the experiment will settle down into a passive listening mode, detecting moonquakes, meteorite impacts and the thump caused by the Lunar Module ascent stage impact. The antenna is of the telescoping type.
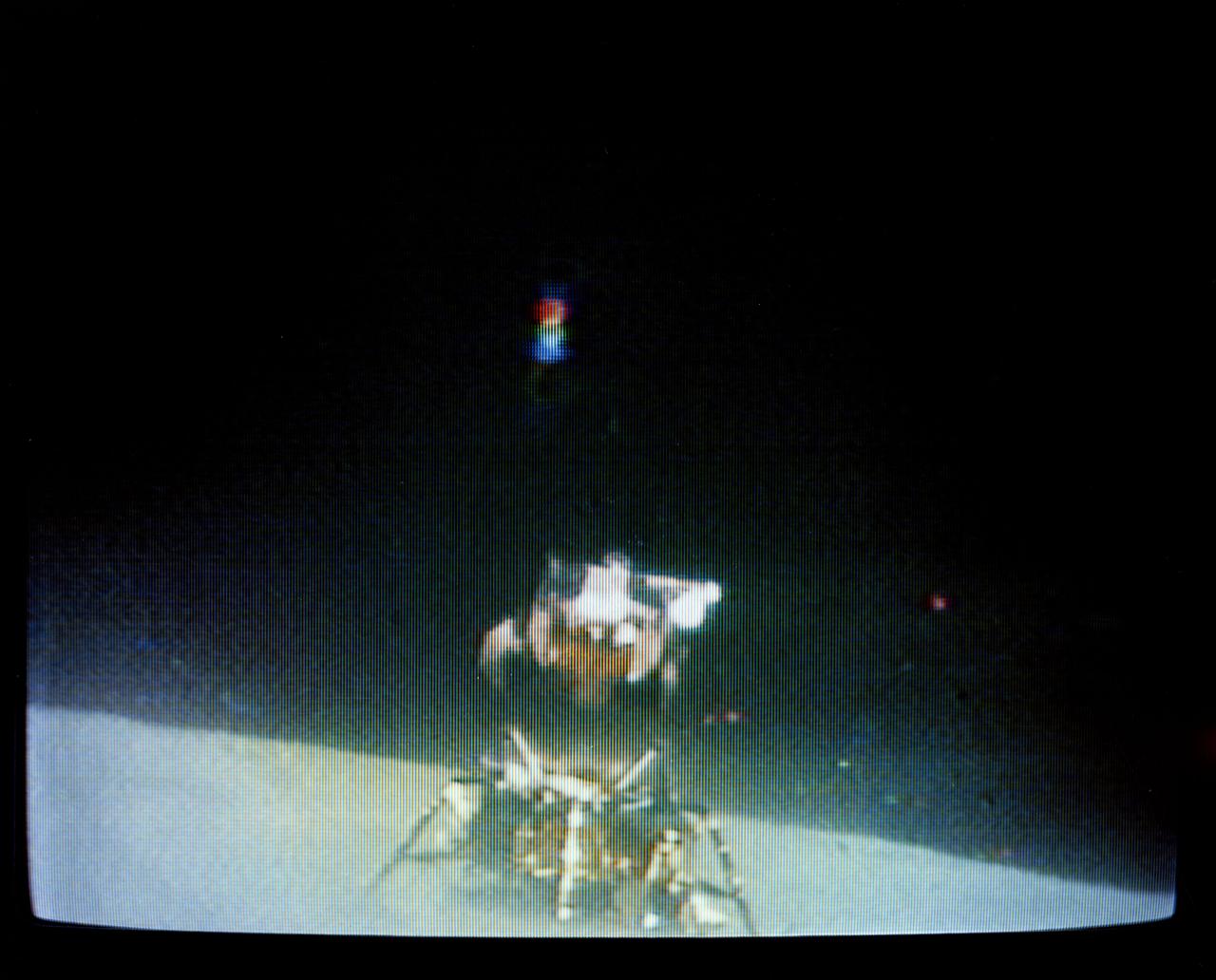

S72-35614 (23 April 1972) --- The Apollo 16 Lunar Module "Orion" ascent stage makes its liftoff from the lunar surface in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the RCA color TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). Remotely controlled from NASA's Mission Control Center (MCC) in Houston, the LRV-mounted camera made it possible for persons on Earth to watch the LM's launch from the moon. Liftoff occurred at 175:44 ground elapsed time, 7:26 p.m. (CST), April 23, 1972. The "Orion" ascent stage, with astronauts John W. Young and Charles M. Duke Jr. aboard, returned from the lunar surface to rejoin the Command and Service Modules (CSM) orbiting the moon. Astronaut Thomas K. (Ken) Mattingly II remained with the CSM in lunar orbit while Young and Duke descended in the LM to explore the Descartes landing site. The LM descent stage is used as a launching platform and remains behind on the moon.
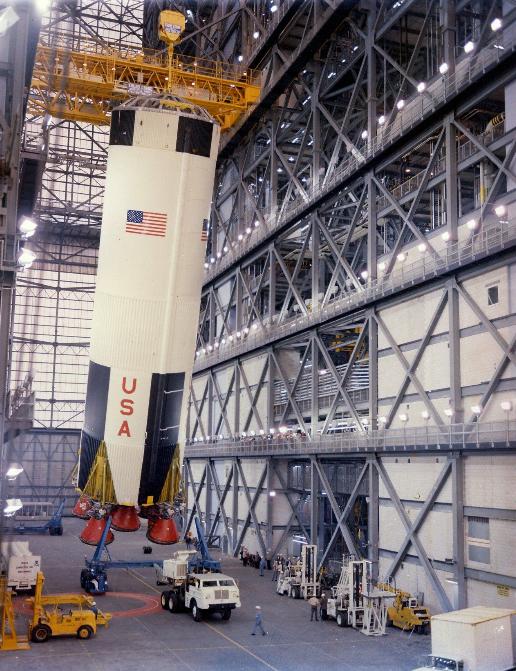

Teams lift the first stage of the Apollo 8 Saturn V rocket inside the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 1, 1968, and prepare to place it atop the mobile launcher. Apollo 8 was the first crewed spacecraft to successfully orbit the Moon and return to Earth, setting the stage for Apollo 11 – the first crewed lunar landing. Apollo 8 launched on Dec. 21, 1968, and the crew members consisted of Frank Borman, William A. Anders, and James A. Lovell Jr.

The upper stage for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will power the agency’s Artemis III mission and send astronauts on to the Moon for a lunar landing arrived at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station Poseidon Wharf in Florida on Aug. 9, 2023. Known as the SLS ICPS (interim cryogenic propulsion stage), it will undergo final checkouts by contractors Boeing and ULA (United Launch Alliance) at ULA’s facilities before it is delivered to NASA’s nearby Kennedy Space Center.
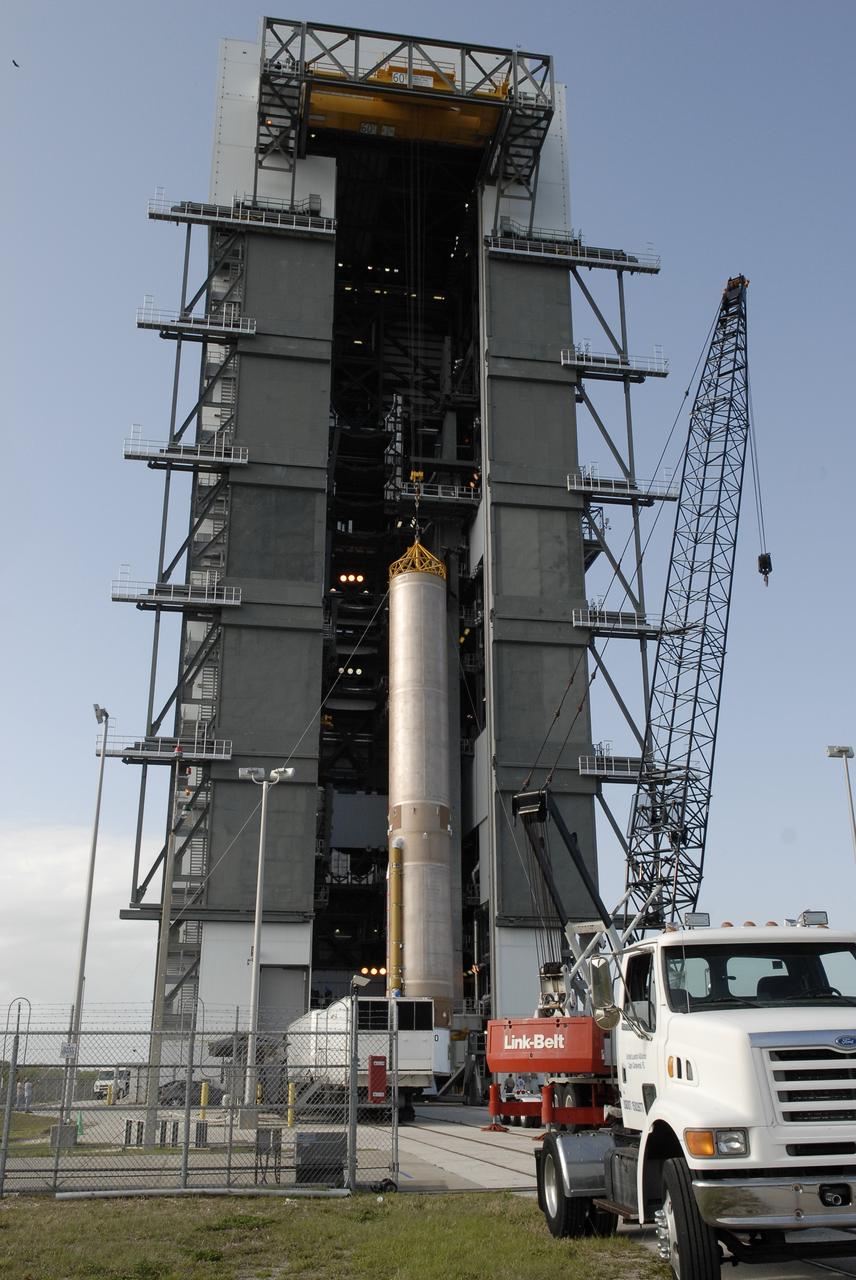

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the Atlas V first stage is being moved into the Vertical Integration Facility. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
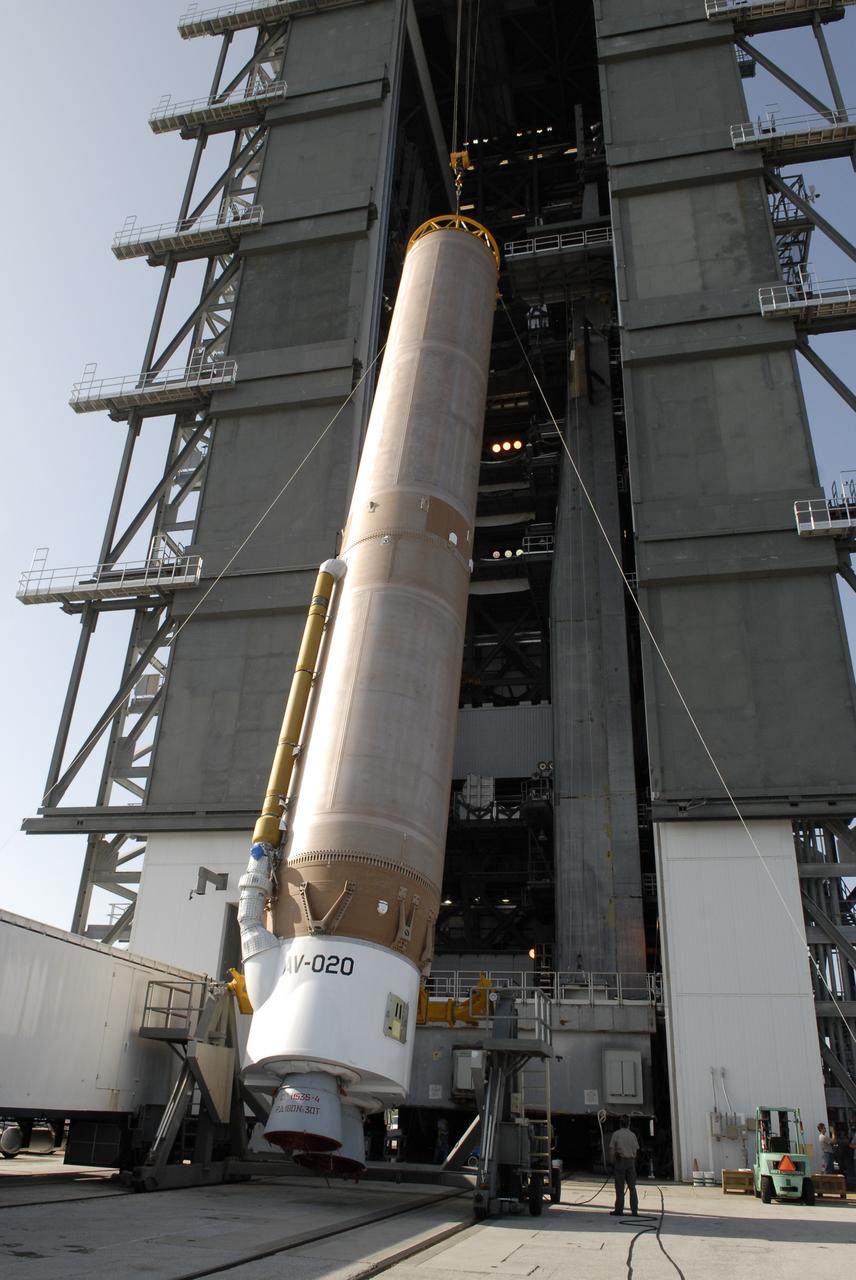

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– When the Atlas V first stage is raised to vertical, it will be lifted into the Vertical Integration Facility on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
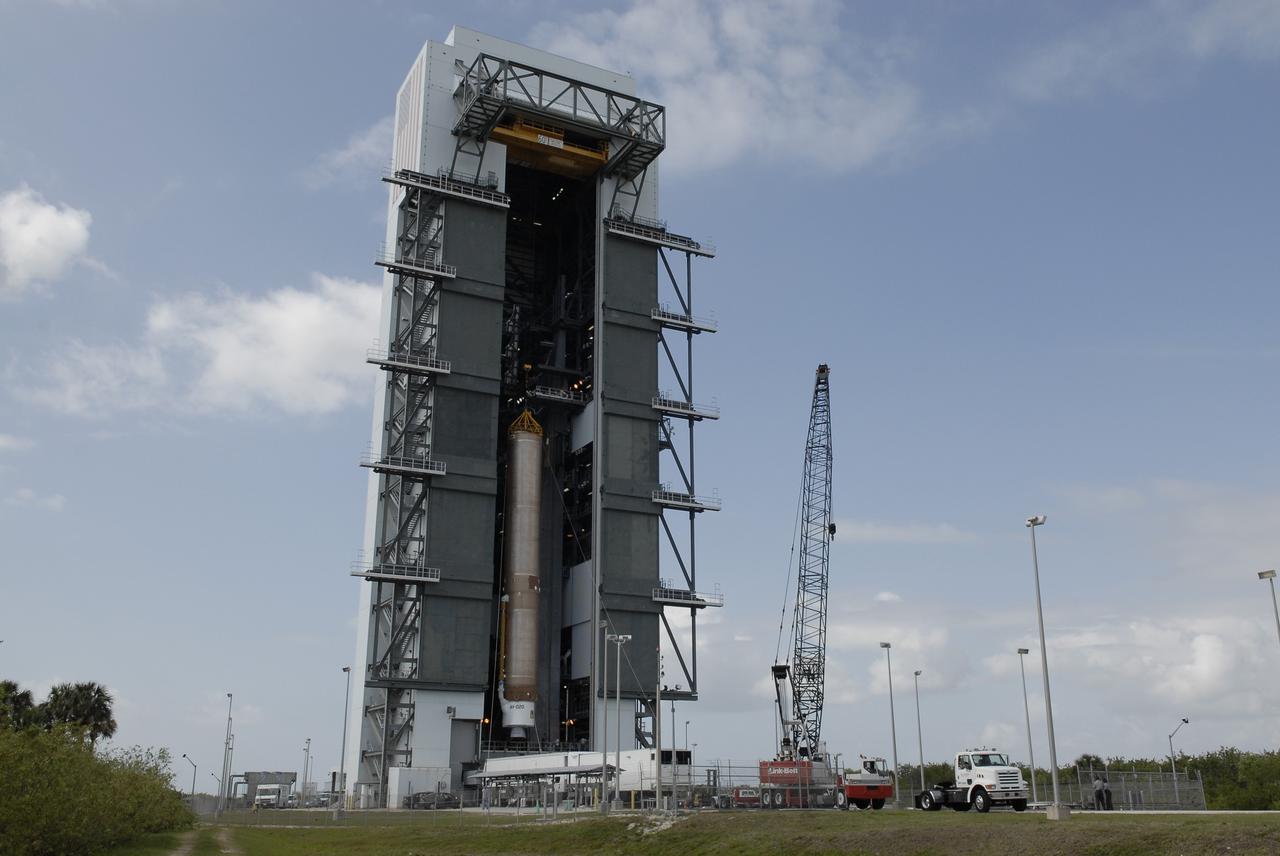

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the Atlas V first stage is being moved into the Vertical Integration Facility. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
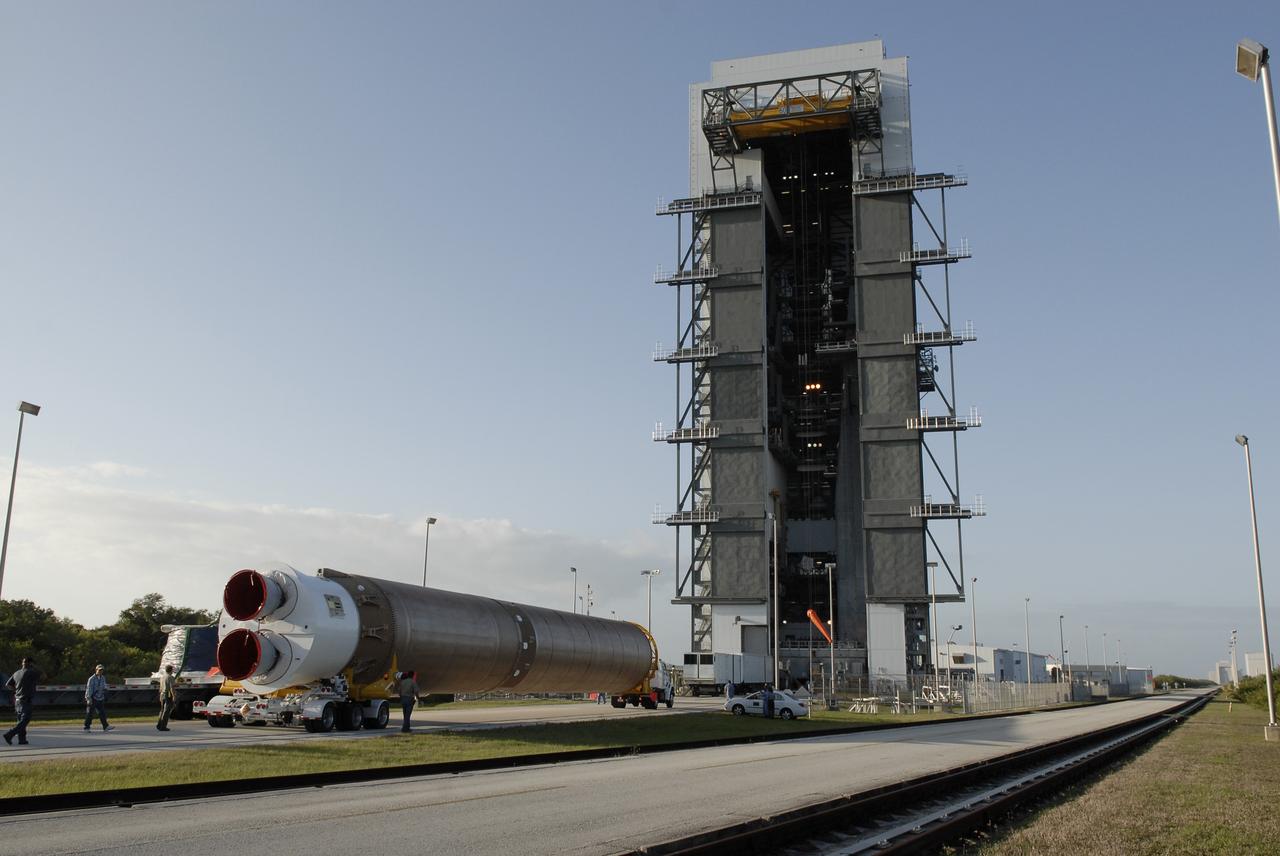

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– The Atlas V first stage arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
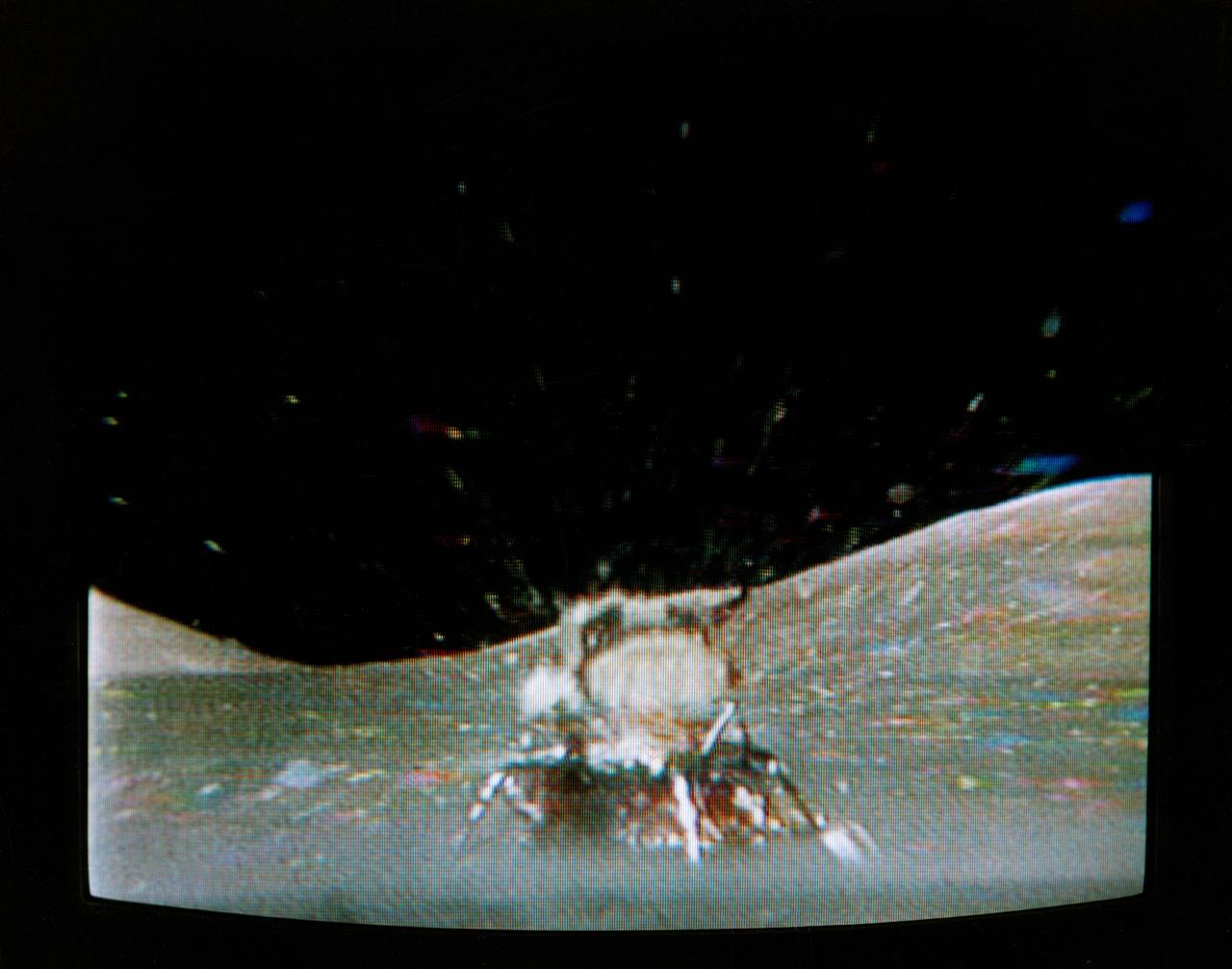
The Apollo 17 Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" ascent stage leaves the Taurus-Littrow landing site as it makes its spectacular liftoff from the lunar surface, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV-mounted TV camera, remotely controlled from the Mission Control Center (MCC) in Houston, made it possible for people on Earth to watch the fantastic event. The LM liftoff was at 188:01:36 ground elapsed time, 4:54:36 p.m. (CST), Thursday, December 14, 1972.
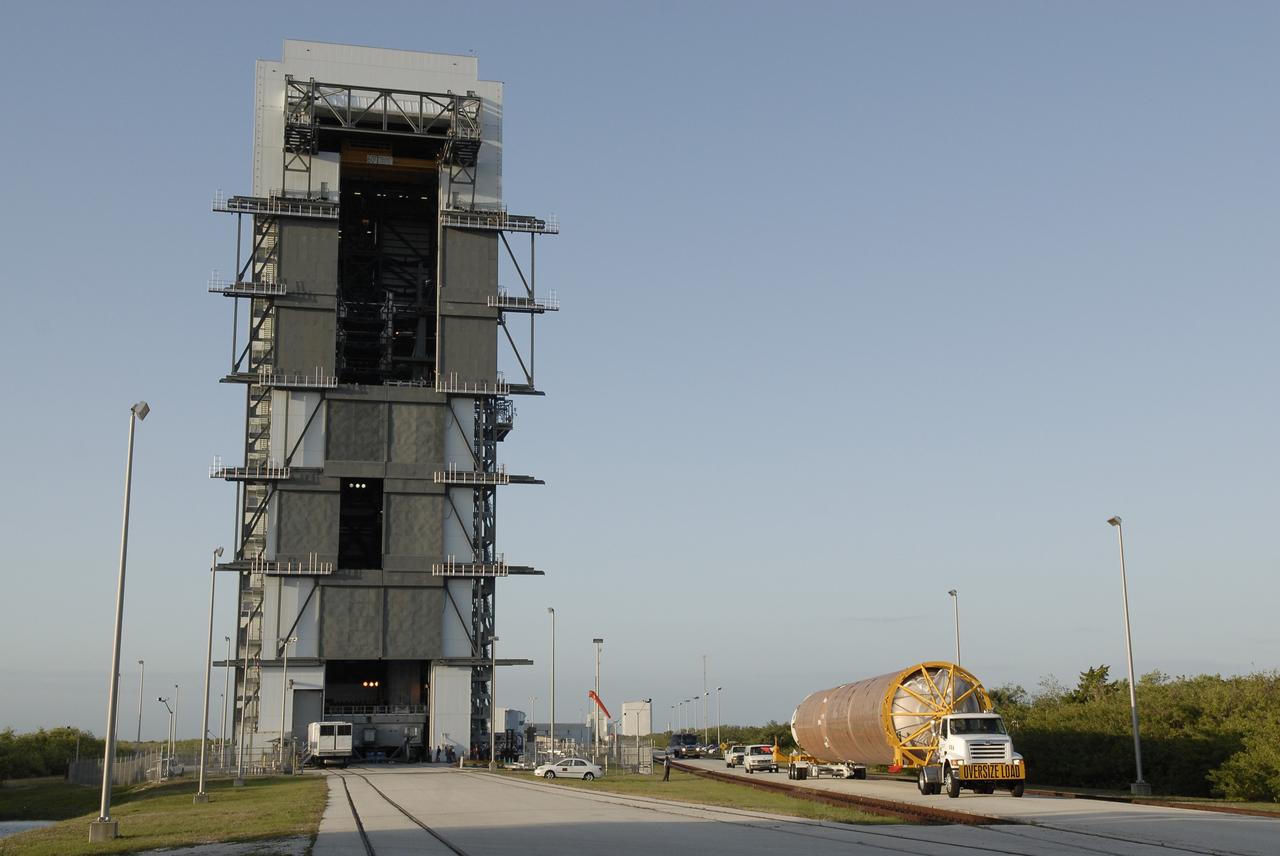

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– The Atlas V first stage arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
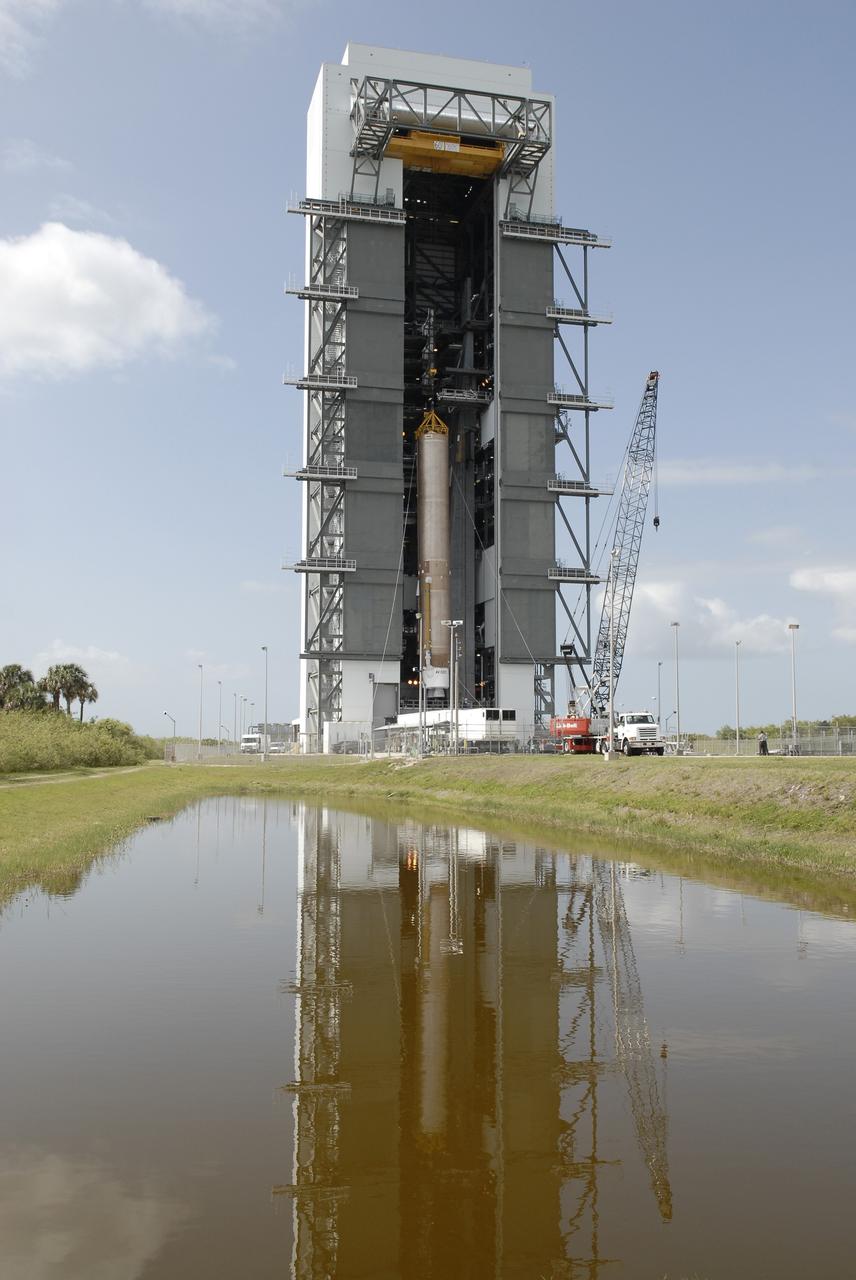

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the Atlas V first stage is being moved into the Vertical Integration Facility. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
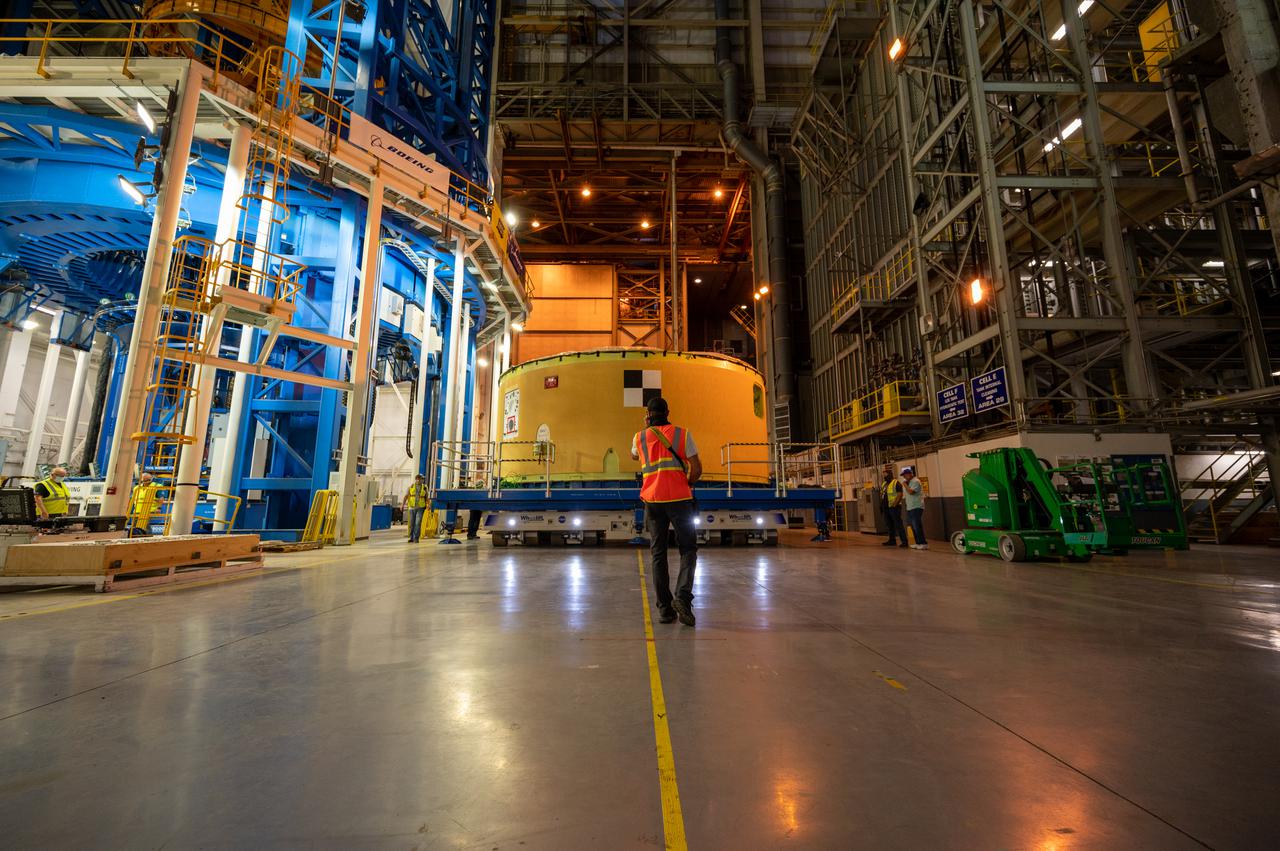

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
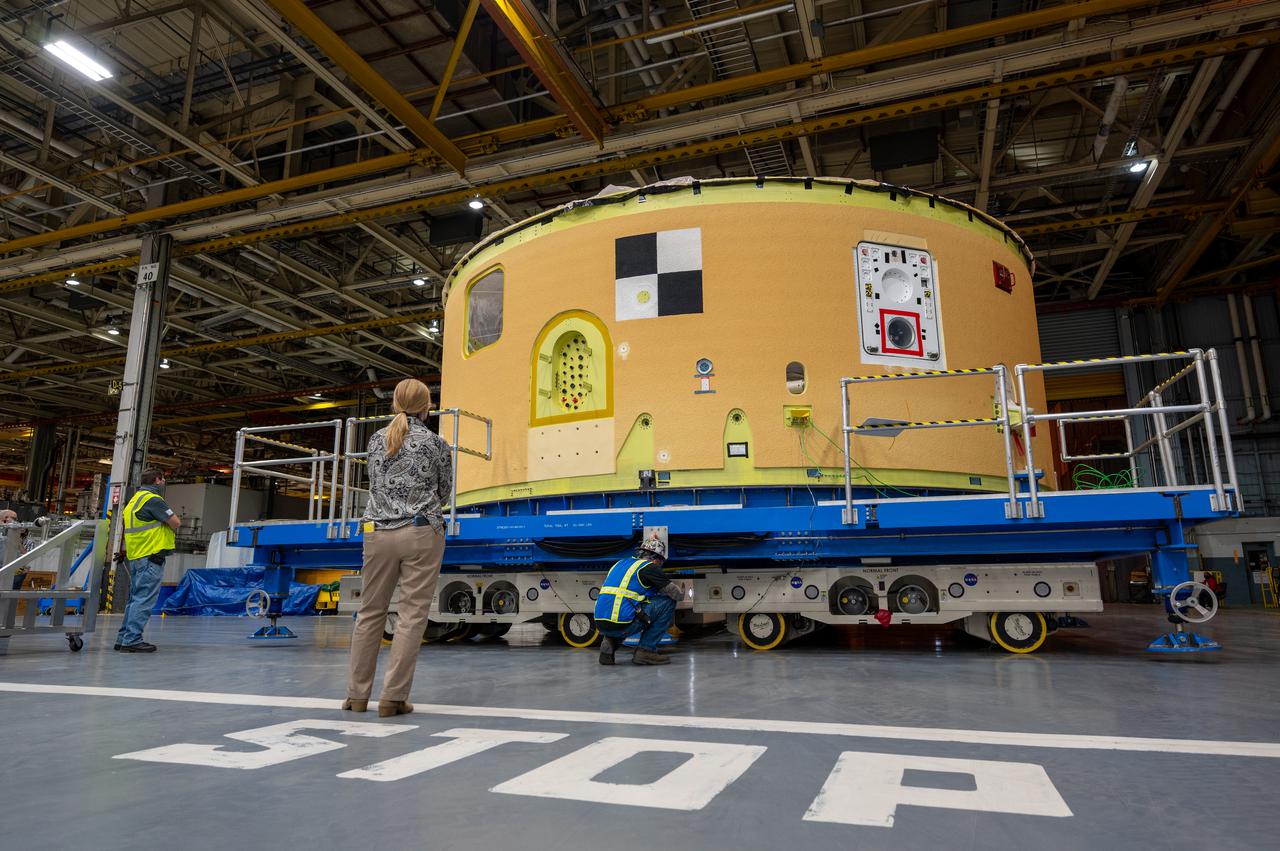

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
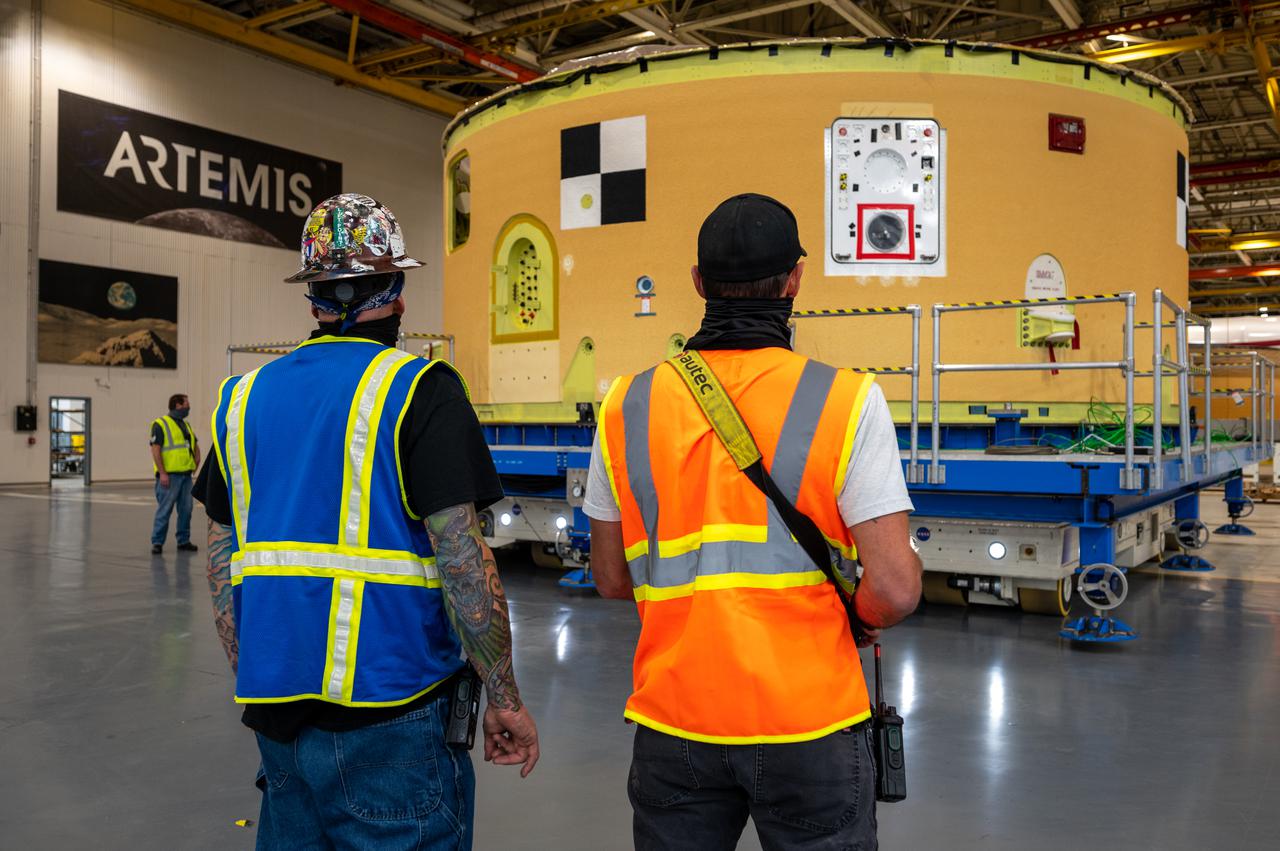

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
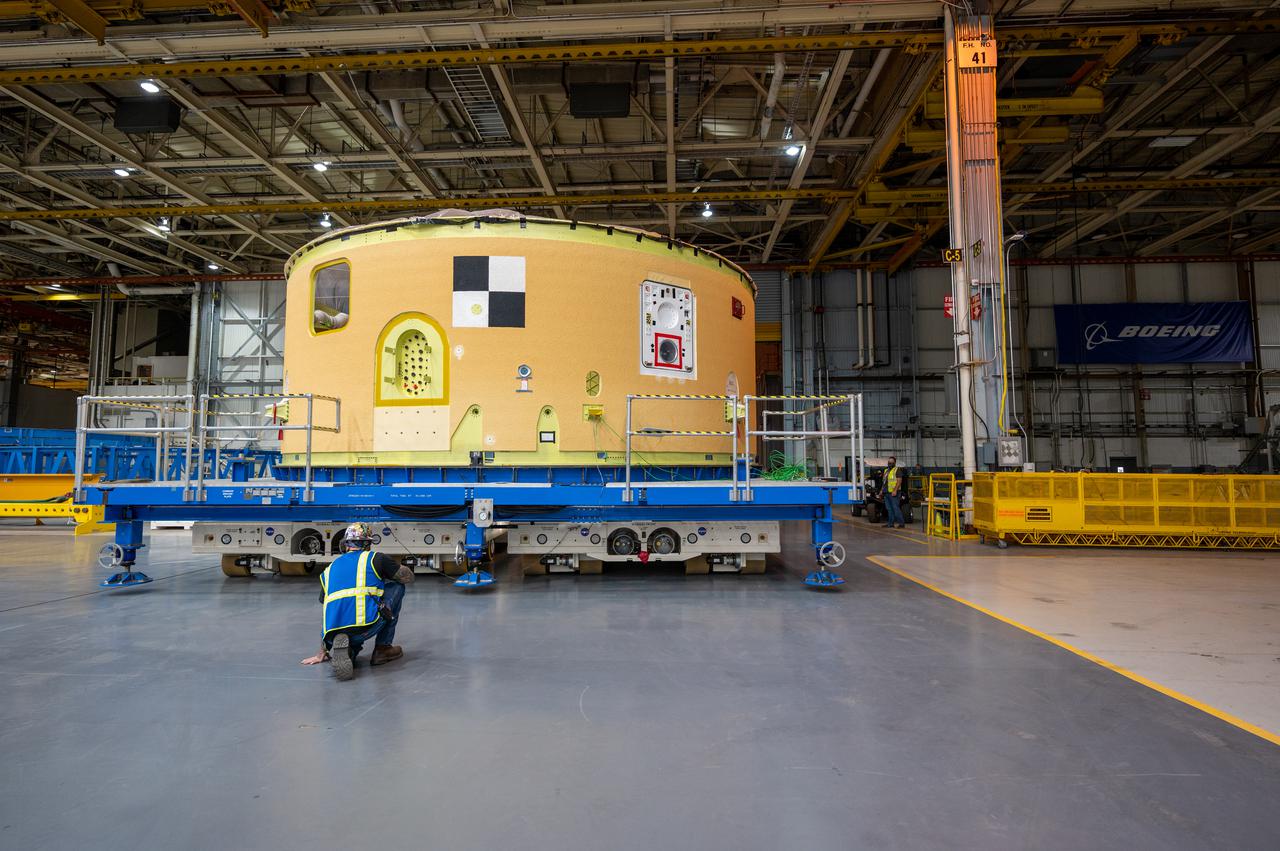

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
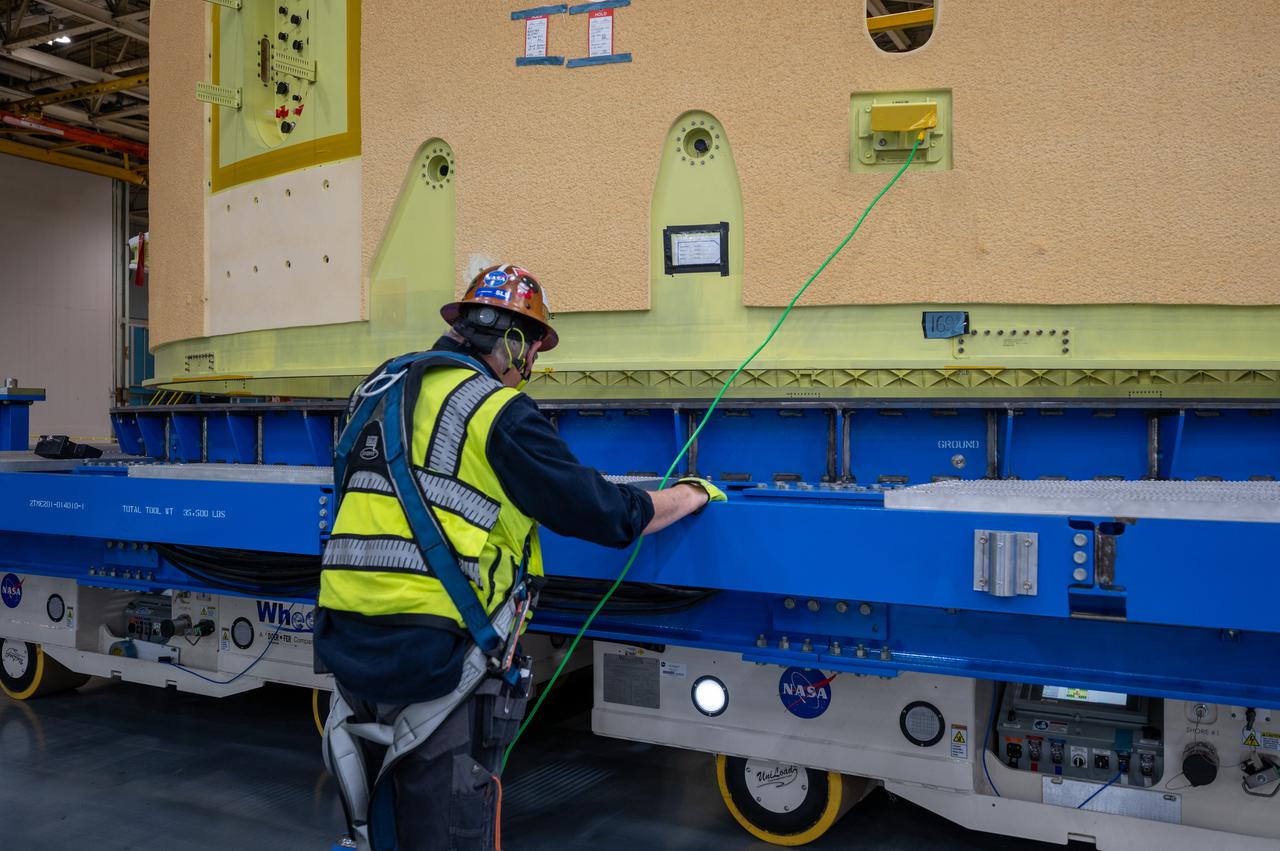

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
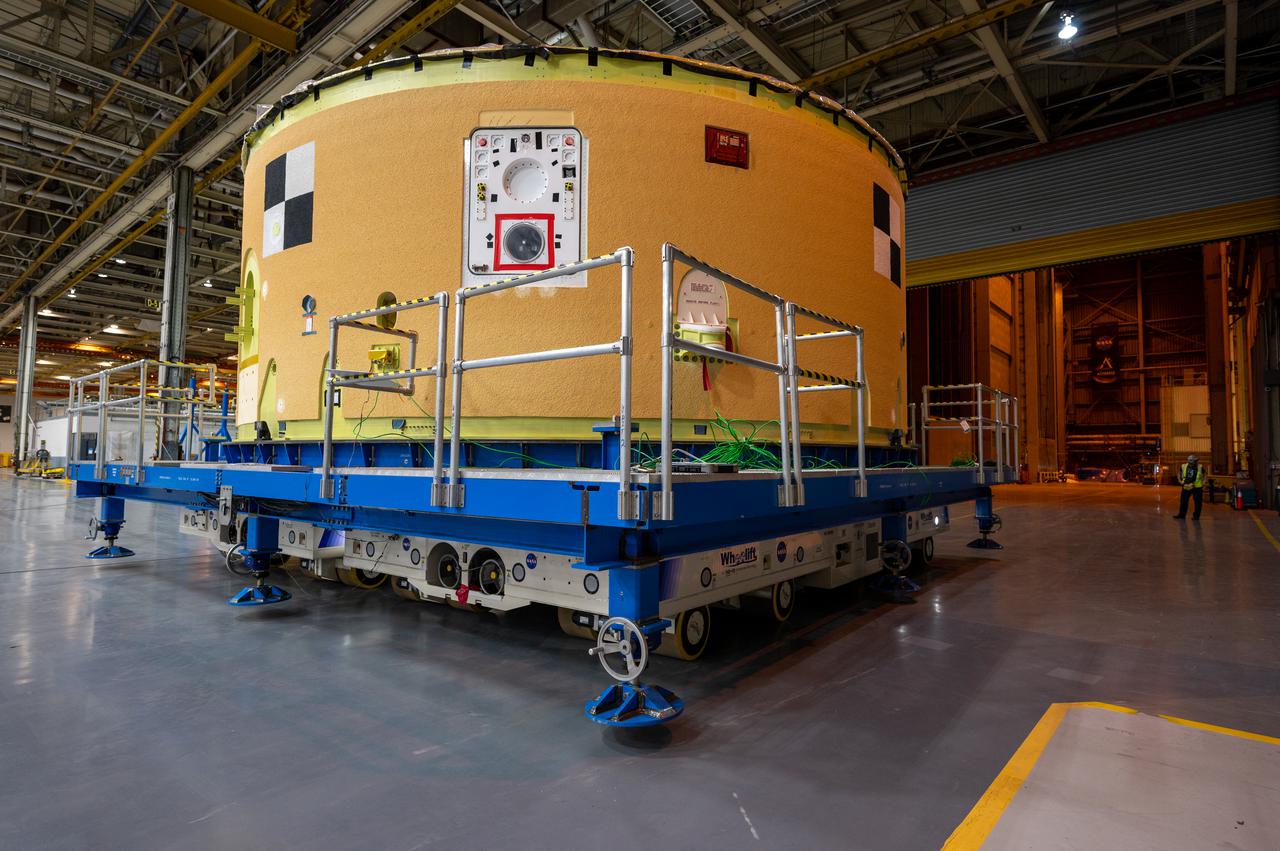

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
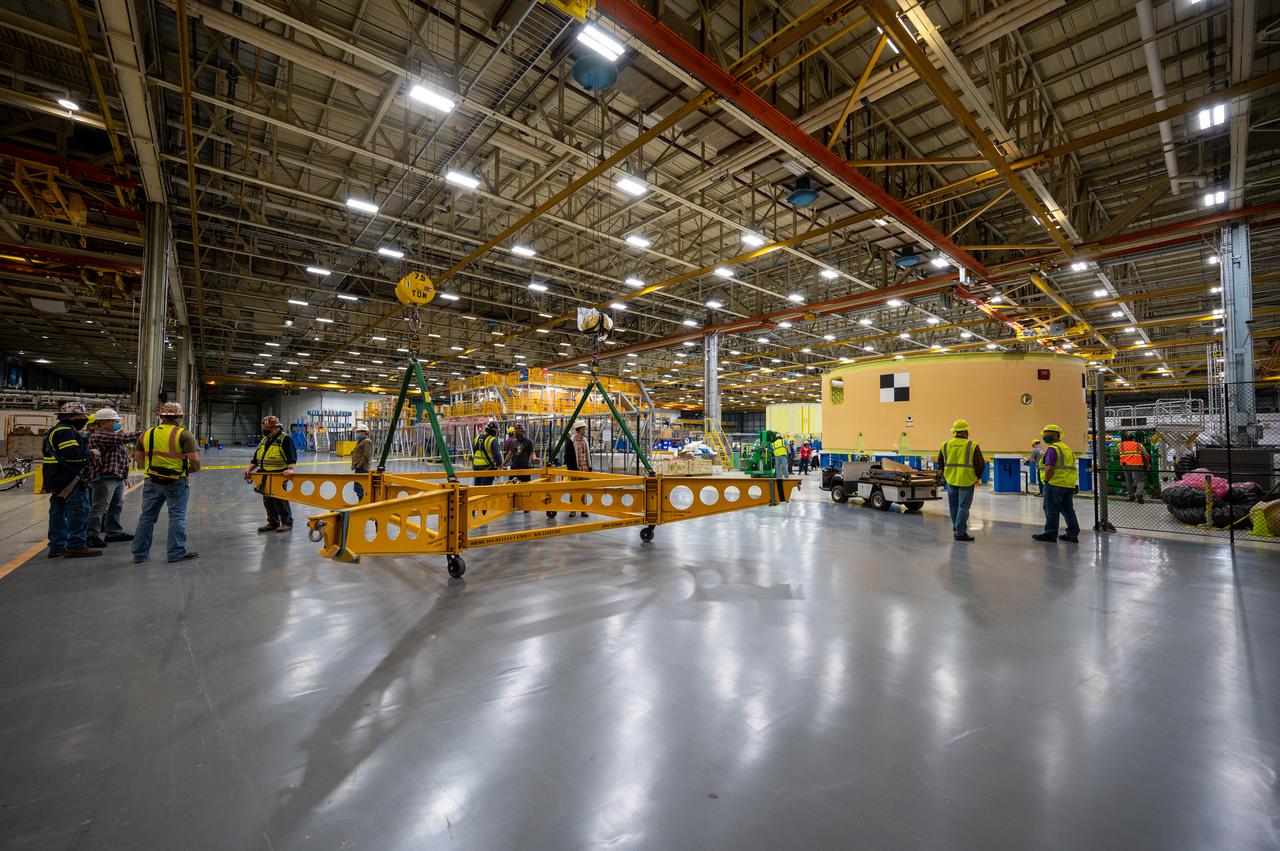

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
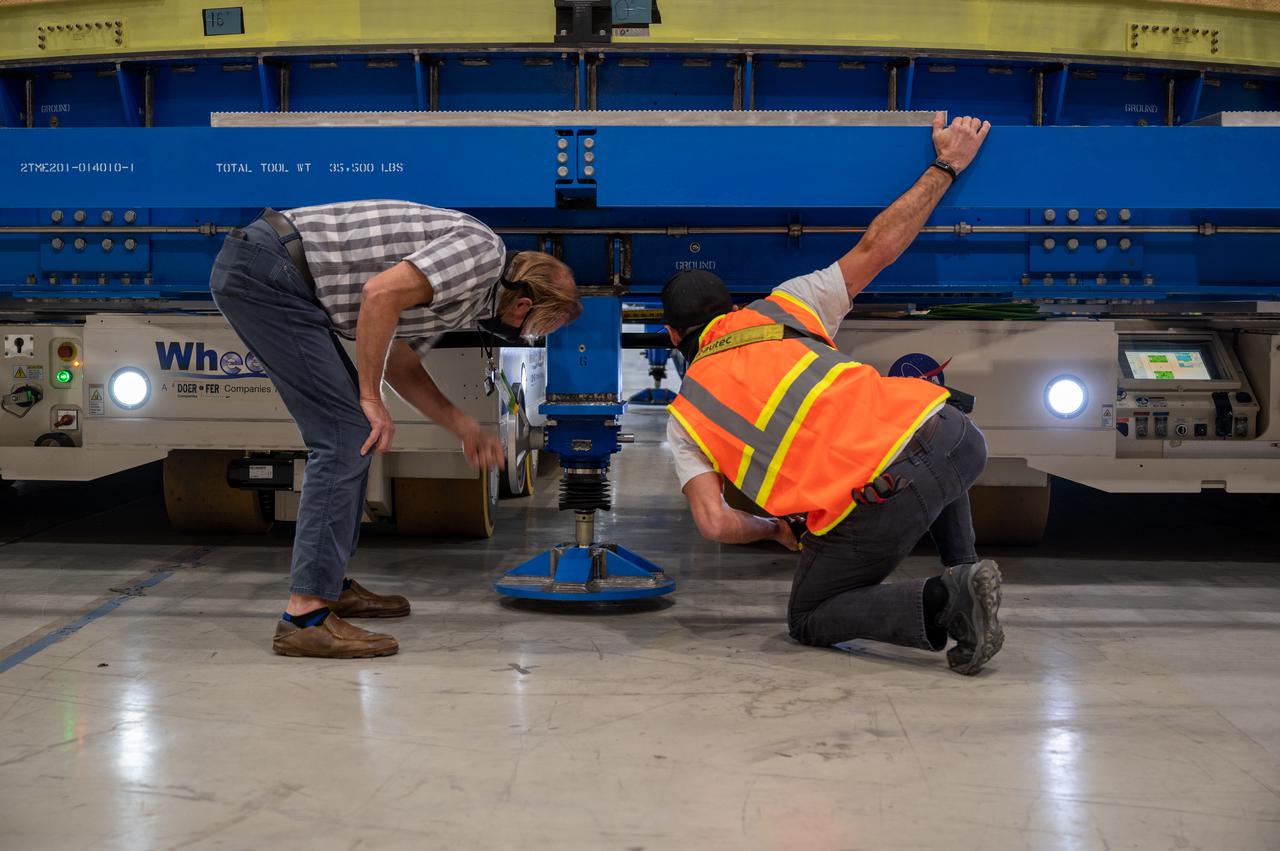

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
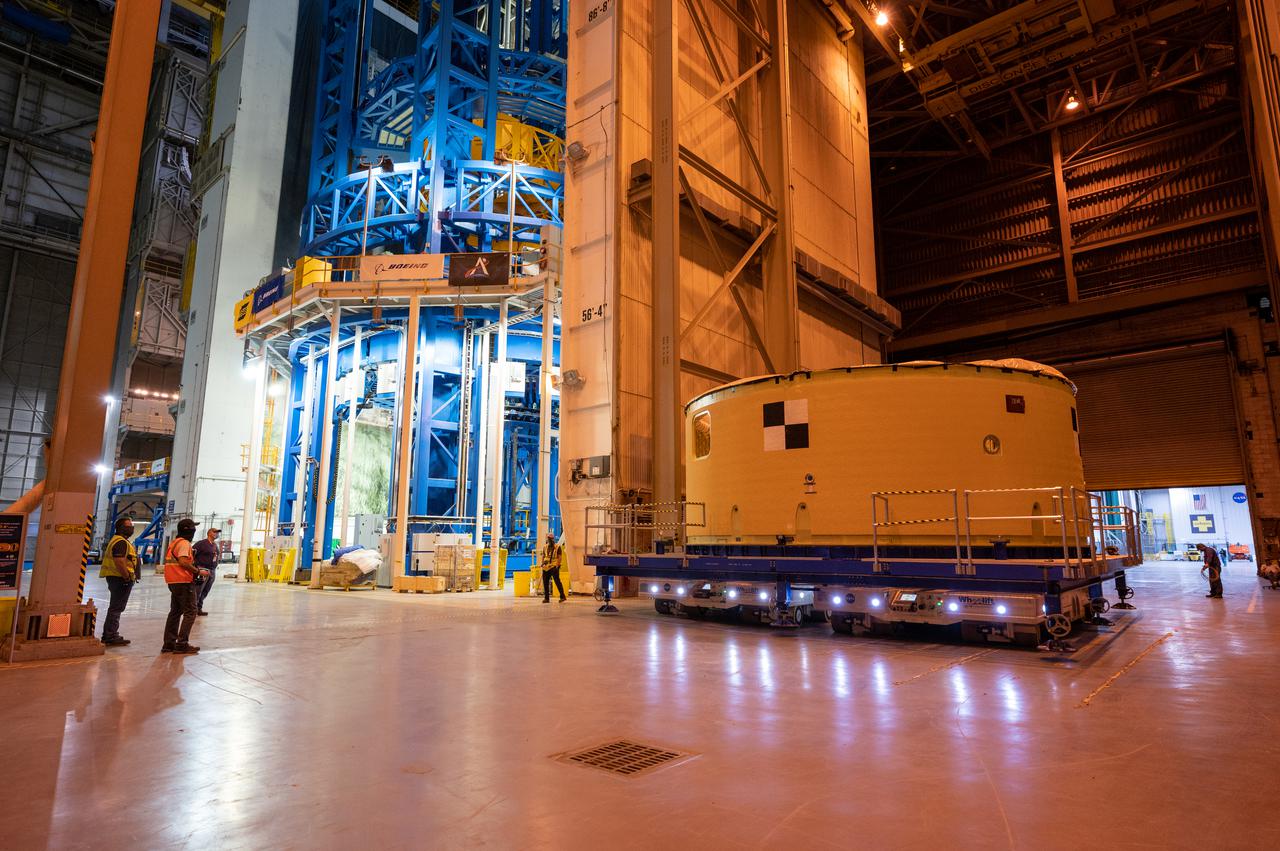

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
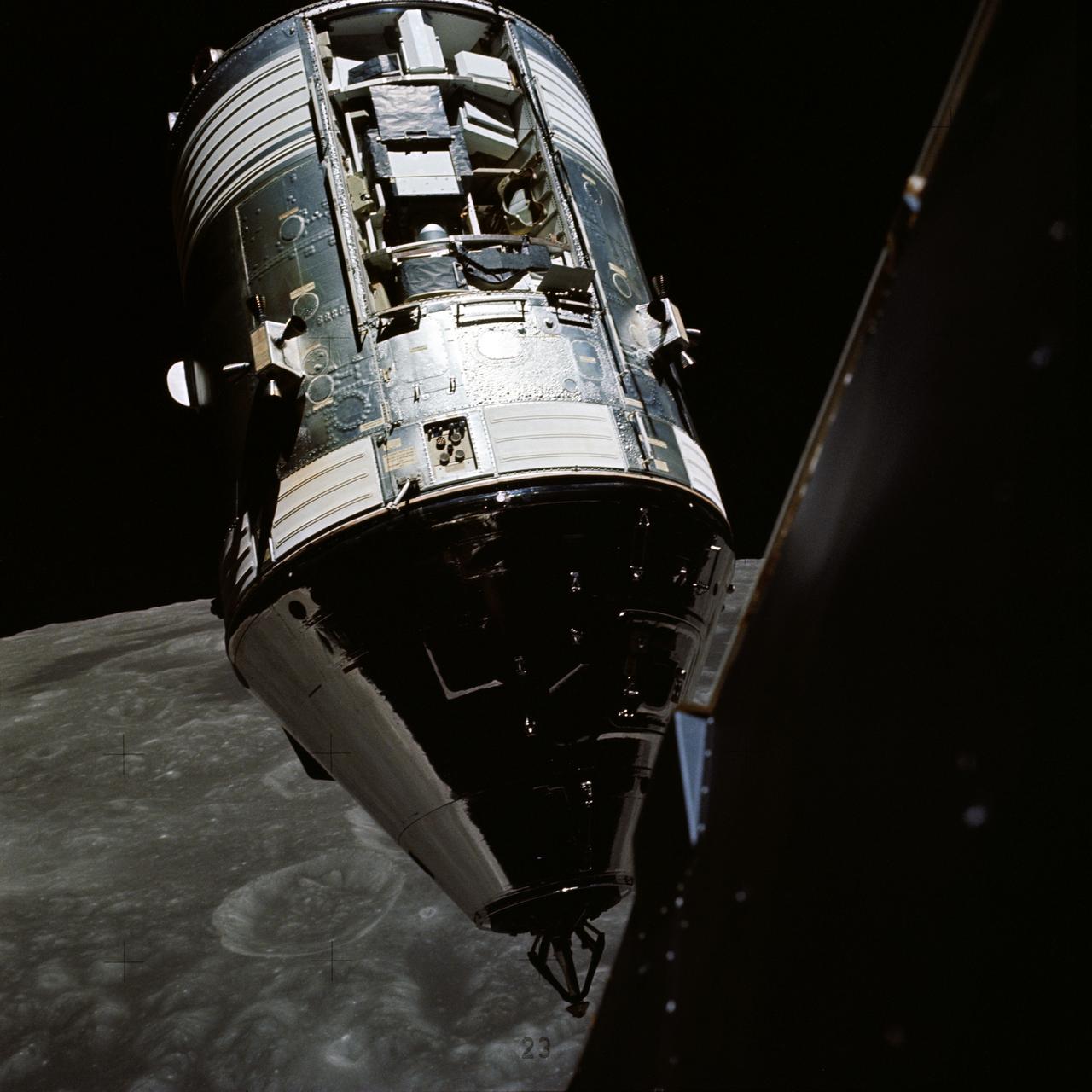

AS17-145-22254 (14 Dec. 1972) --- An excellent view of the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules (CSM) photographed from the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" during rendezvous and docking maneuvers in lunar orbit. The LM ascent stage, with astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt aboard, had just returned from the Taurus-Littrow landing site on the lunar surface. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the CSM in lunar orbit. Note the exposed Scientific Instrument Module (SIM) Bay in Sector 1 of the Service Module (SM). Three experiments are carried in the SIM bay: S-209 lunar sounder, S-171 infrared scanning spectrometer, and the S-169 far-ultraviolet spectrometer. Also mounted in the SIM bay are the panoramic camera, mapping camera and laser altimeter used in service module photographic tasks. A portion of the LM is on the right.
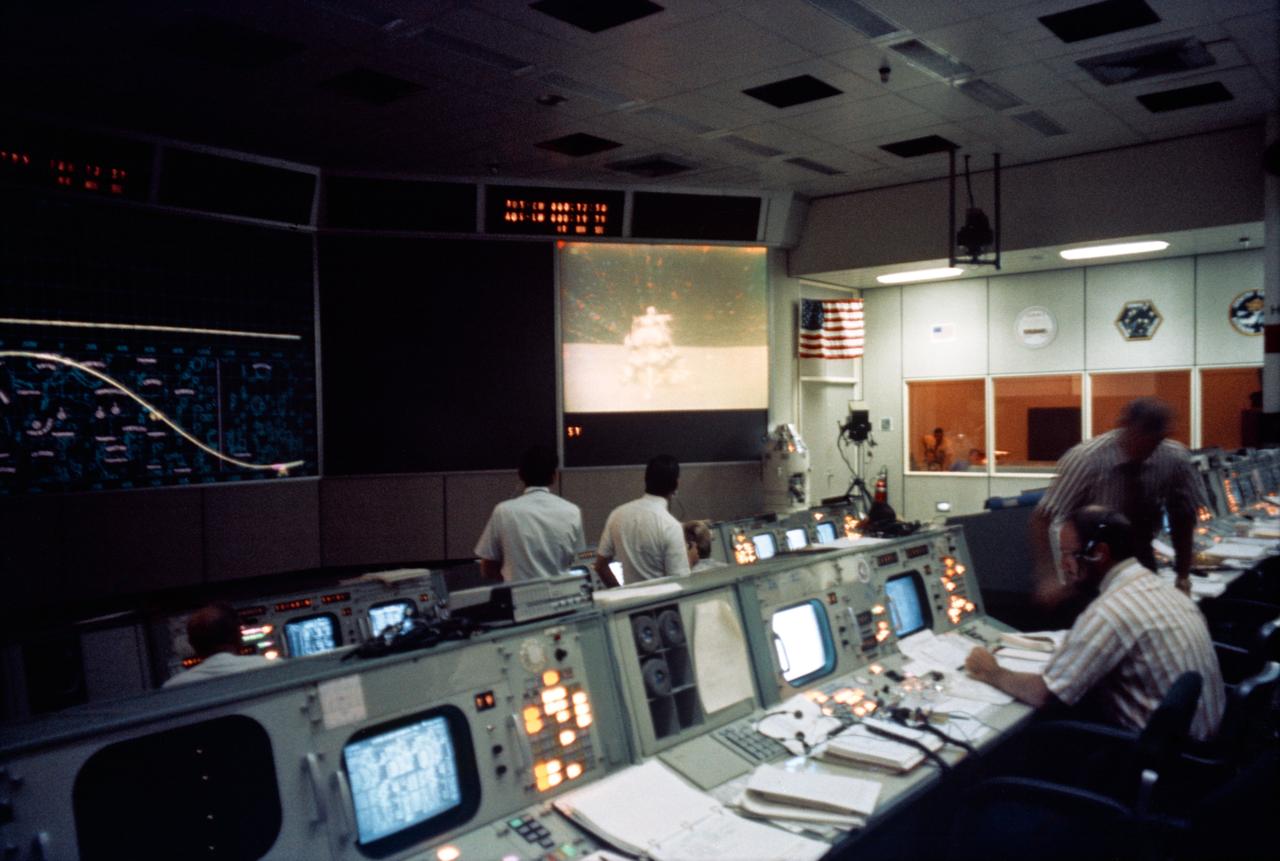

S71-41759 (2 Aug. 1971) --- A partial view of activity in the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center during the liftoff of the Apollo 15 Lunar Module "Falcon" ascent stage from the lunar surface. An RCA color television camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle made it possible for people on Earth to watch the LM's spectacular launch from the moon. The LM liftoff was at 171:37 ground elapsed time. The LRV was parked about 300 feet east of the LM. The TV camera was remotely controlled from a console in the MOCR. Seated in the right foreground is astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, a spacecraft communicator. Mitchell was lunar module pilot of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission. Note liftoff on the television monitor in the center background.
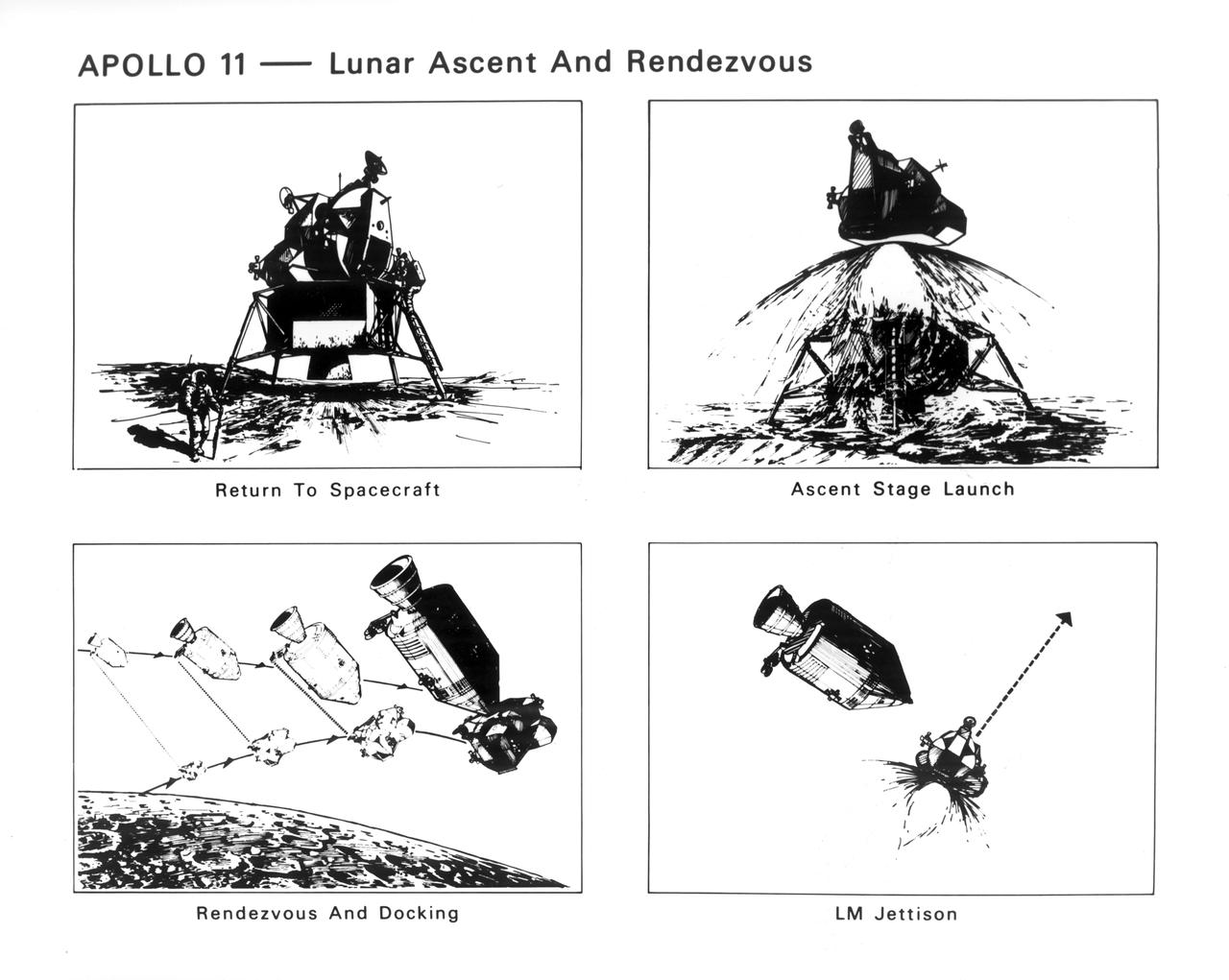
The Apollo 11 mission launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished. These sketches illustrate the steps taken when the astronauts left the Moon. After 2½ hours of surface exploration, astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin returned to the Lunar Module (LM) “Eagle” for rest, eating, and checkout of the vehicle in preparation for liftoff. The ascent stage lifted off, using the descent stage as a launch pad. The ascent stage went into lunar orbit and moved in to dock with the orbiting CM “Columbia”. After Armstrong and Aldrin joined Collins in the CM, the engine of the LM ascent stage was fired to move it out of the same orbit.
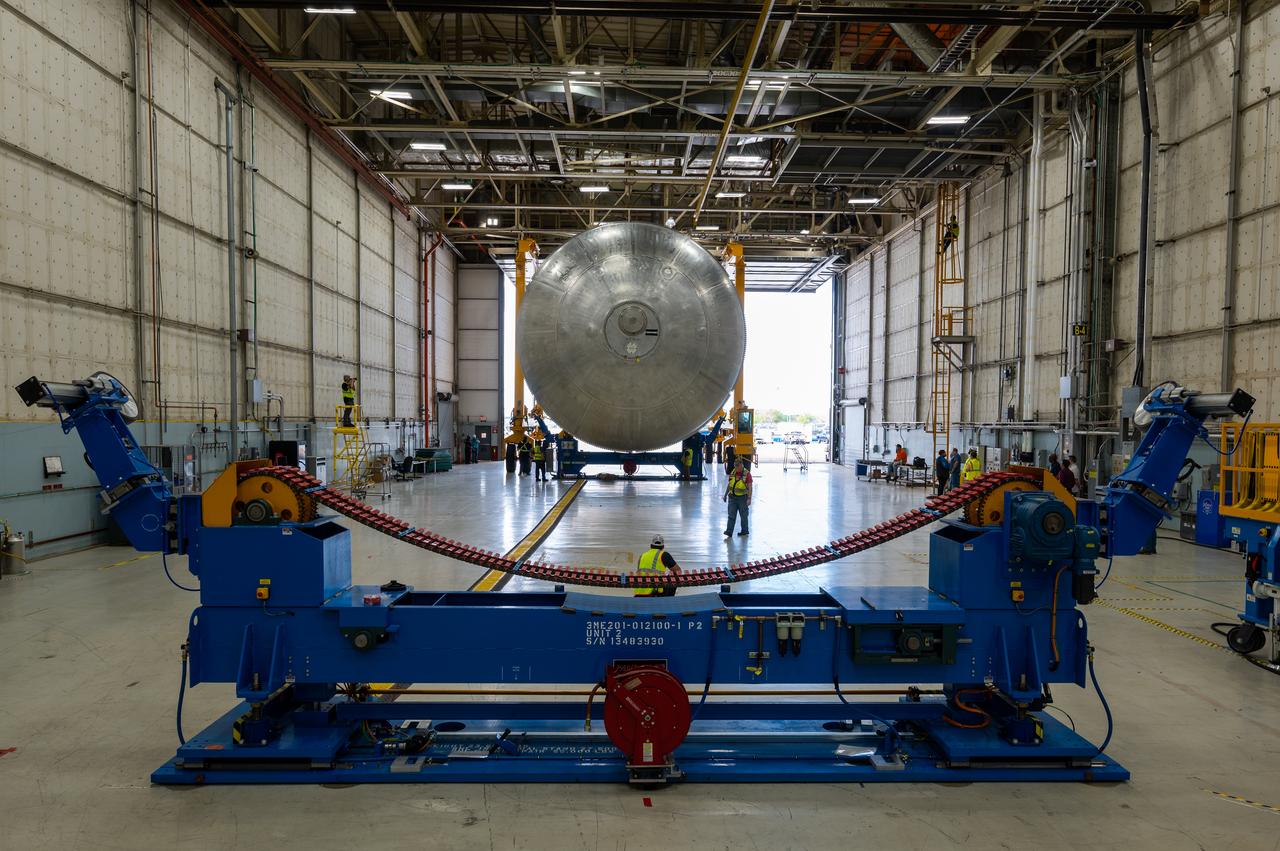

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface.
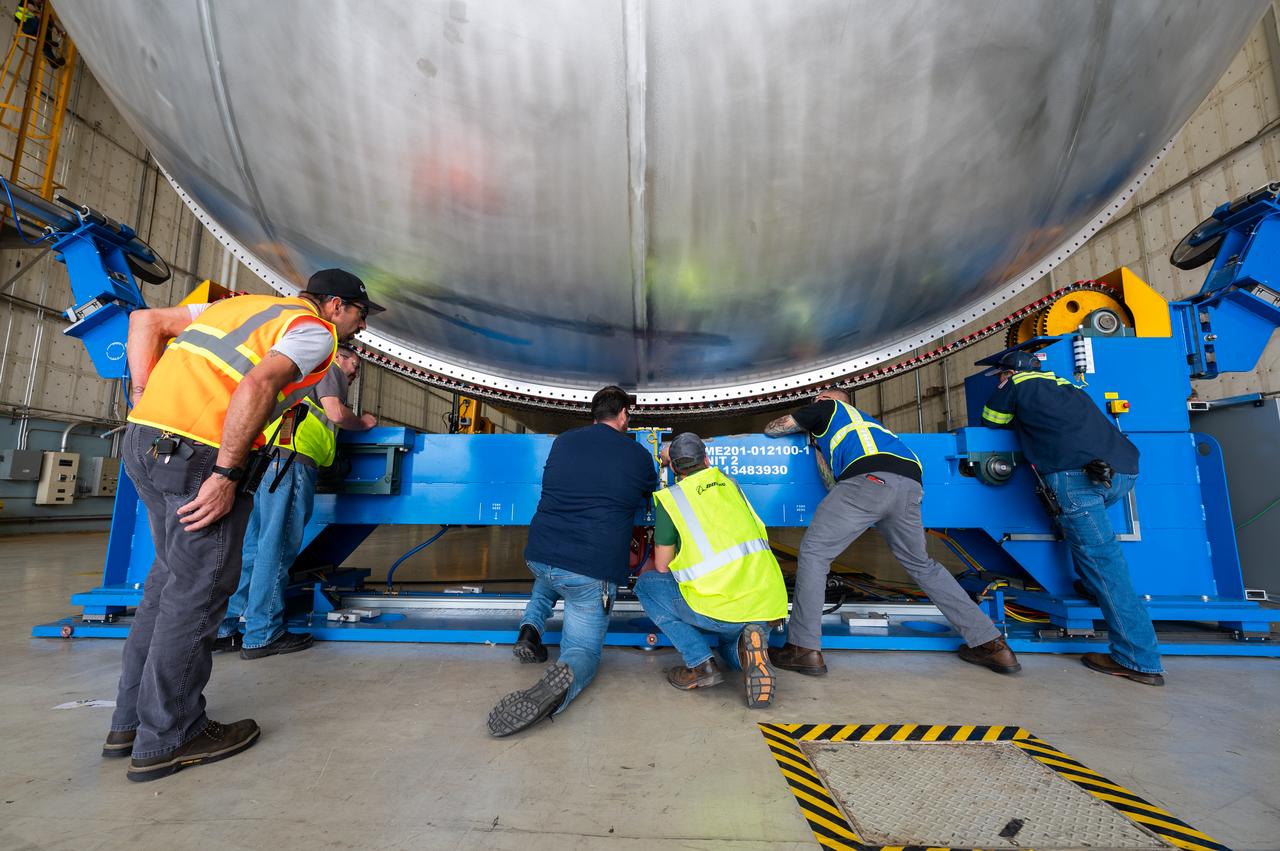

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface.
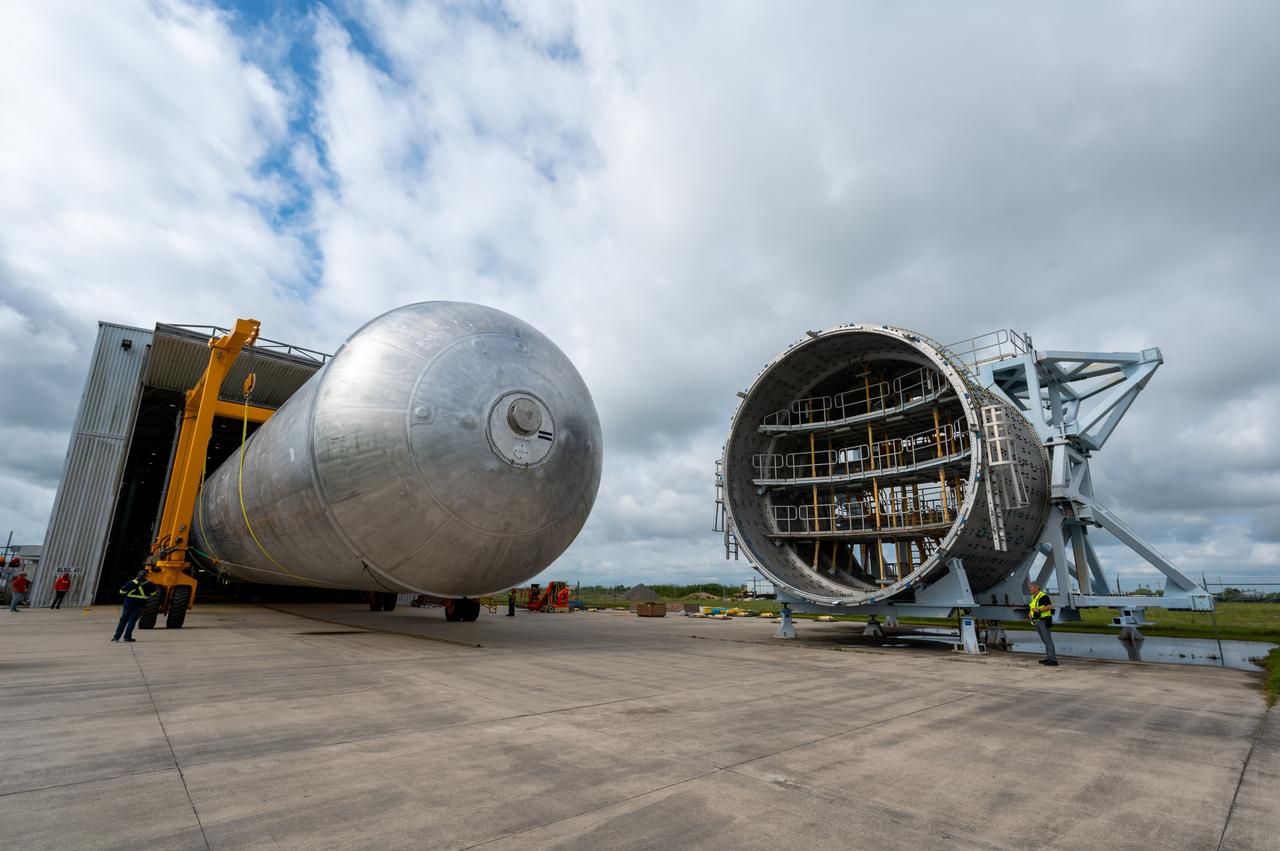

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface.
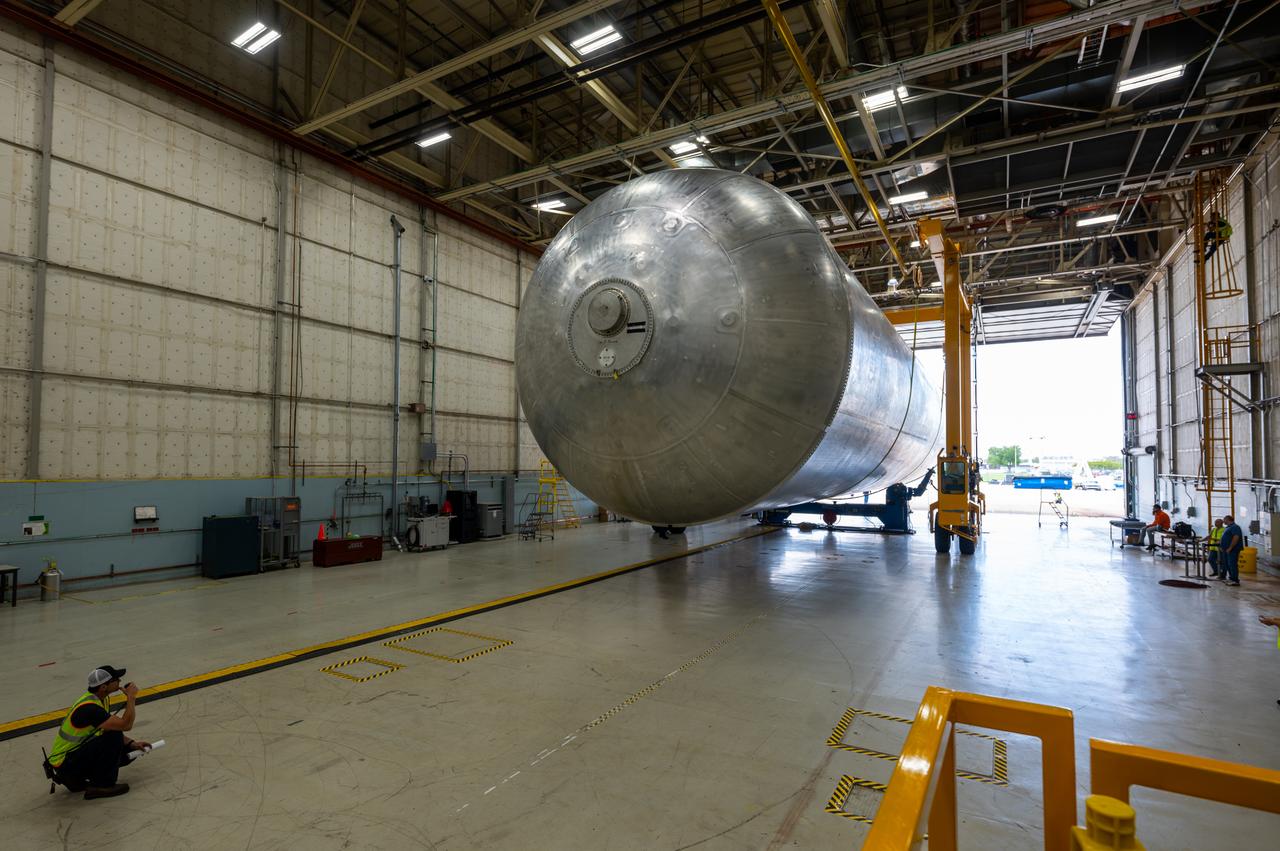

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface.
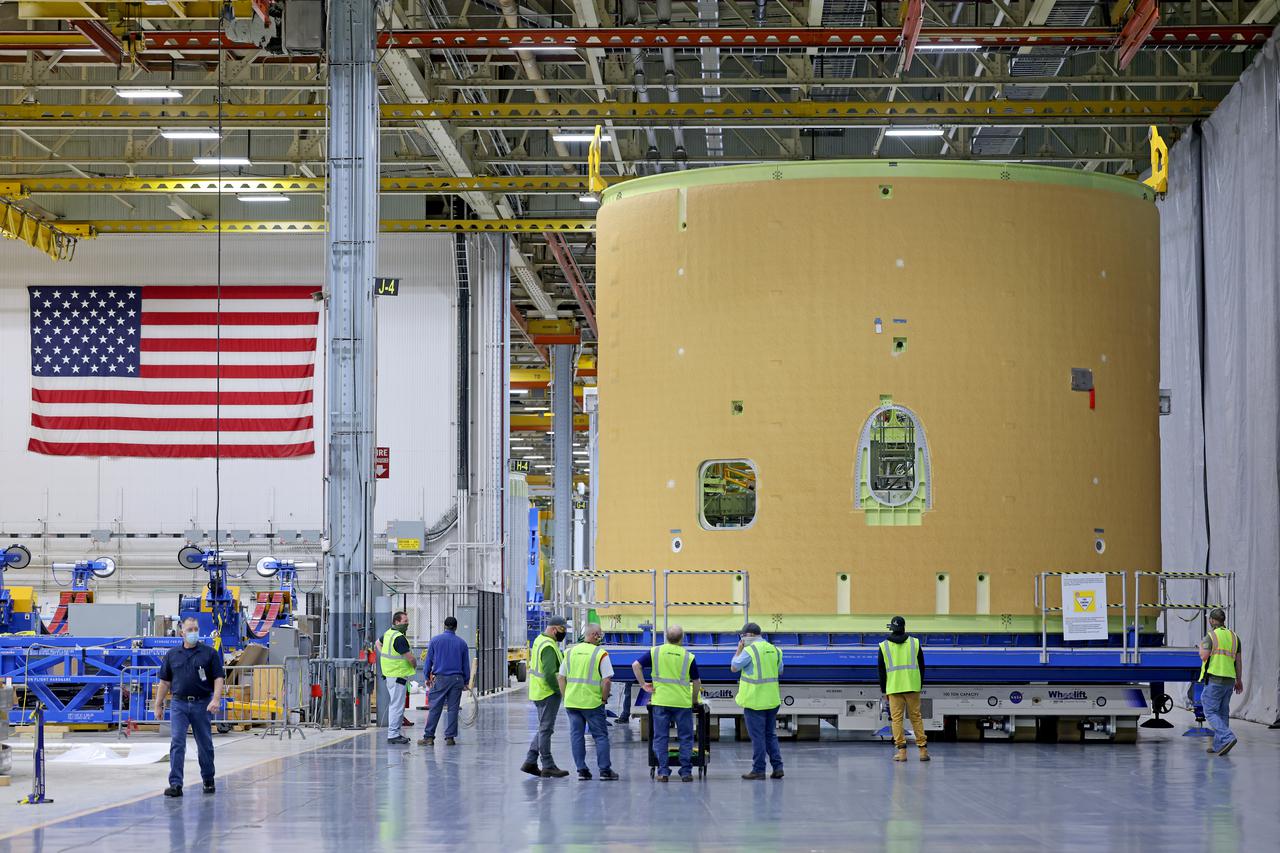

This image shows technicians and engineers beginning the process of the forward join on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The forward join connects the forward skirt, the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) and the intertank structures to form the top part of the SLS rocket’s core stage. Now, NASA and Boeing, the SLS prime contractor, will continue to integrate various systems inside the forward part of the core stage and prepare for structural joining of the liquid hydrogen tank and engine section to form the bottom of the stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
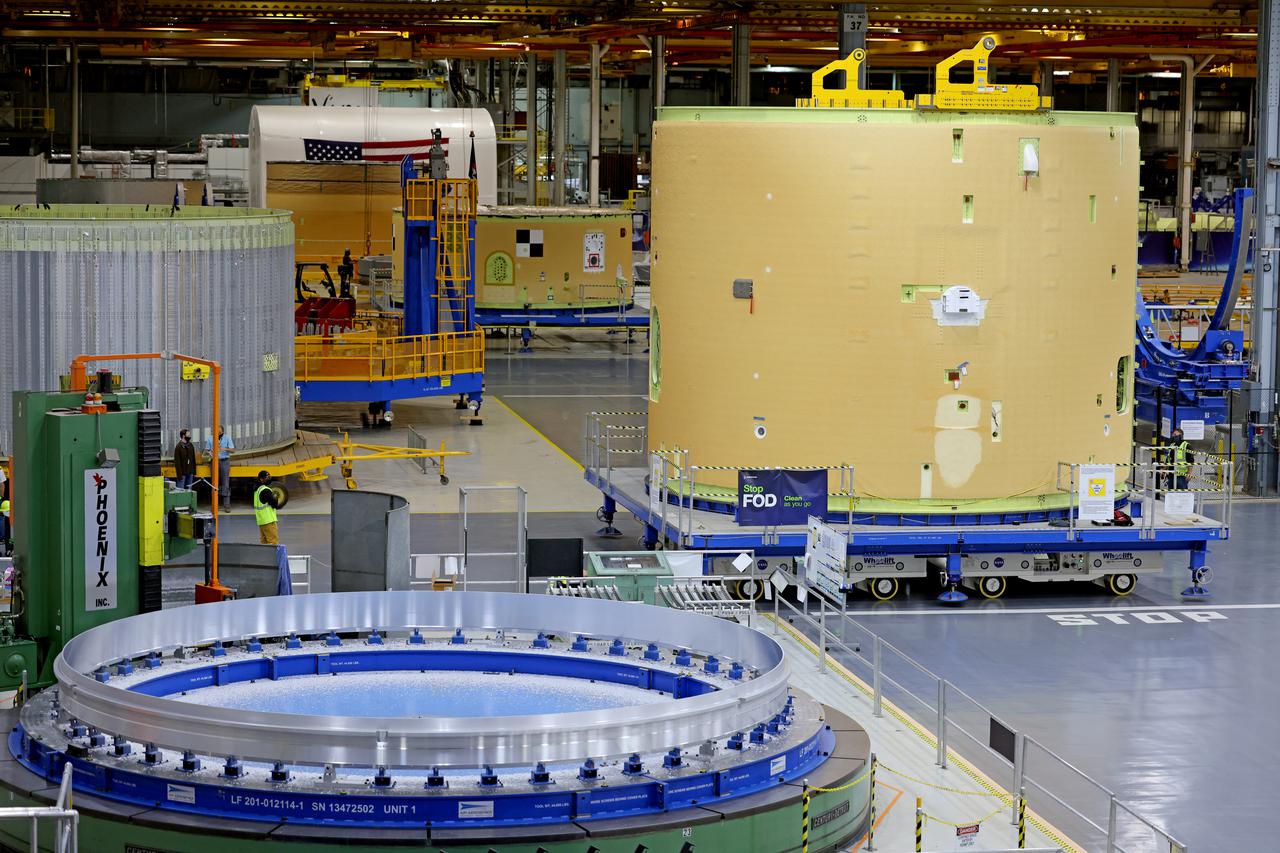

This image shows technicians and engineers beginning the process of the forward join on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The forward join connects the forward skirt, the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) and the intertank structures to form the top part of the SLS rocket’s core stage. Now, NASA and Boeing, the SLS prime contractor, will continue to integrate various systems inside the forward part of the core stage and prepare for structural joining of the liquid hydrogen tank and engine section to form the bottom of the stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

This image shows technicians and engineers move and connect the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) to the intertank as they continue the process of the forward join on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The forward join connects the forward skirt, the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) and the intertank structures to form the top part of the SLS rocket’s core stage. Now, NASA and Boeing, the SLS prime contractor, will continue to integrate various systems inside the forward part of the core stage and prepare for structural joining of the liquid hydrogen tank and engine section to form the bottom of the stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
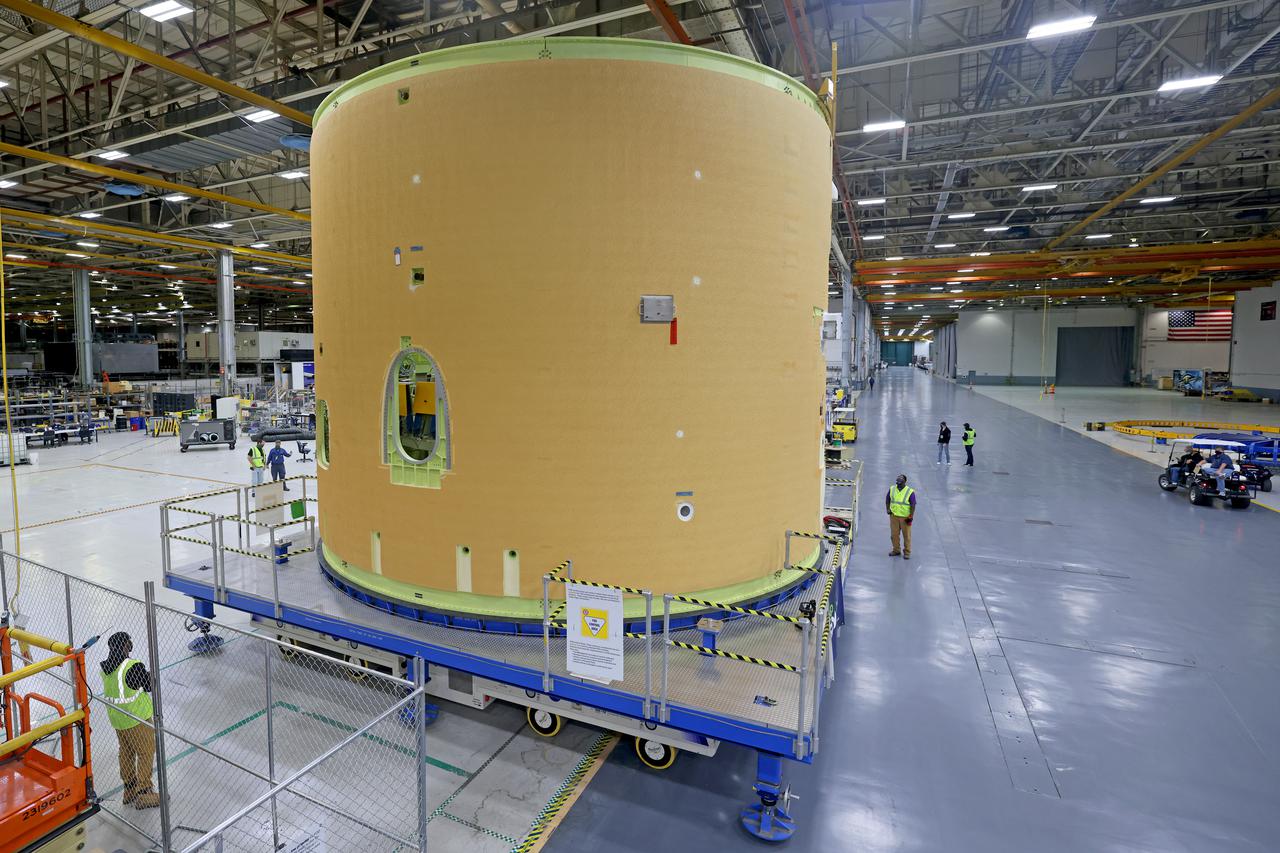

This image shows technicians and engineers beginning the process of the forward join on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The forward join connects the forward skirt, the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) and the intertank structures to form the top part of the SLS rocket’s core stage. Now, NASA and Boeing, the SLS prime contractor, will continue to integrate various systems inside the forward part of the core stage and prepare for structural joining of the liquid hydrogen tank and engine section to form the bottom of the stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

This image shows technicians and engineers beginning the process of the forward join on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The forward join connects the forward skirt, the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) and the intertank structures to form the top part of the SLS rocket’s core stage. Now, NASA and Boeing, the SLS prime contractor, will continue to integrate various systems inside the forward part of the core stage and prepare for structural joining of the liquid hydrogen tank and engine section to form the bottom of the stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
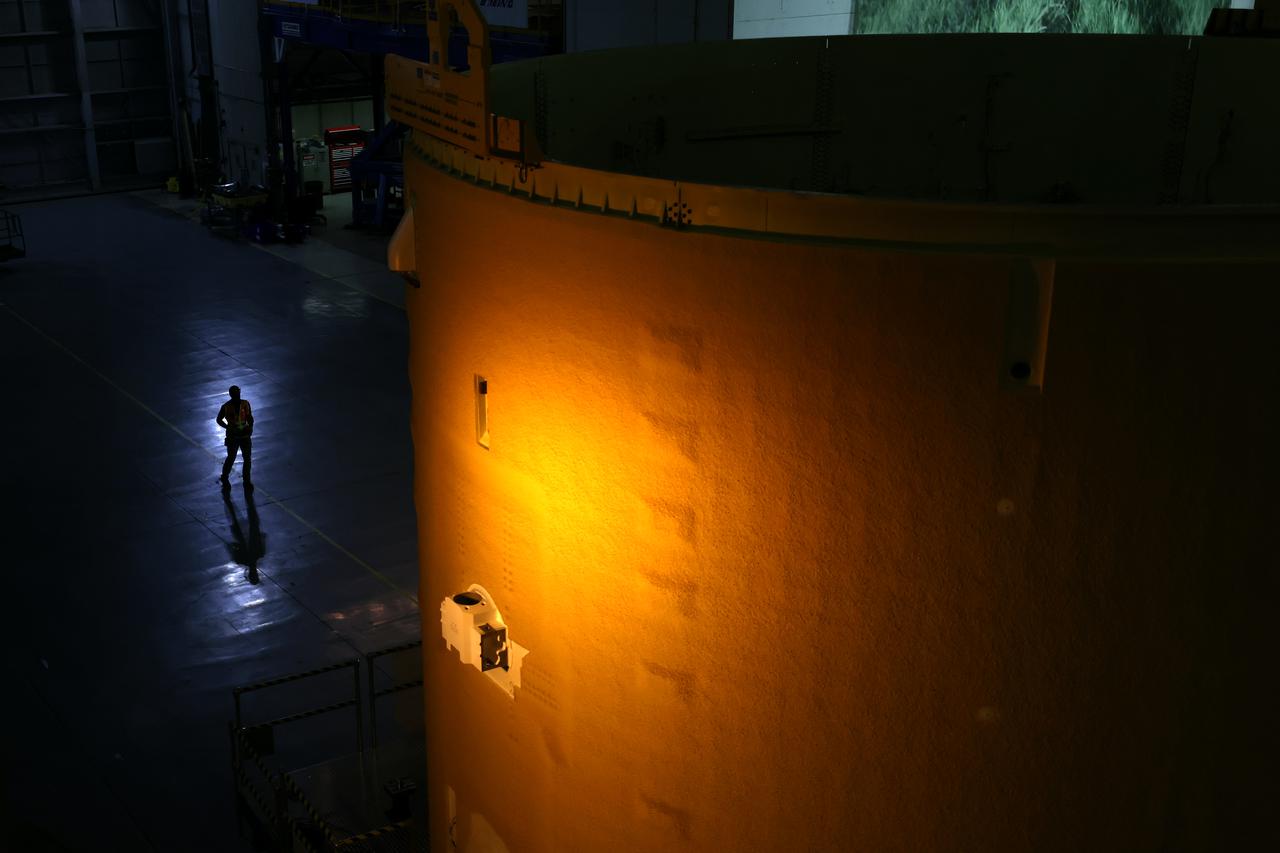

This image shows technicians and engineers beginning the process of the forward join on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The forward join connects the forward skirt, the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) and the intertank structures to form the top part of the SLS rocket’s core stage. Now, NASA and Boeing, the SLS prime contractor, will continue to integrate various systems inside the forward part of the core stage and prepare for structural joining of the liquid hydrogen tank and engine section to form the bottom of the stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

This image shows technicians and engineers move and connect the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) to the intertank as they continue the process of the forward join on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The forward join connects the forward skirt, the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) and the intertank structures to form the top part of the SLS rocket’s core stage. Now, NASA and Boeing, the SLS prime contractor, will continue to integrate various systems inside the forward part of the core stage and prepare for structural joining of the liquid hydrogen tank and engine section to form the bottom of the stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.