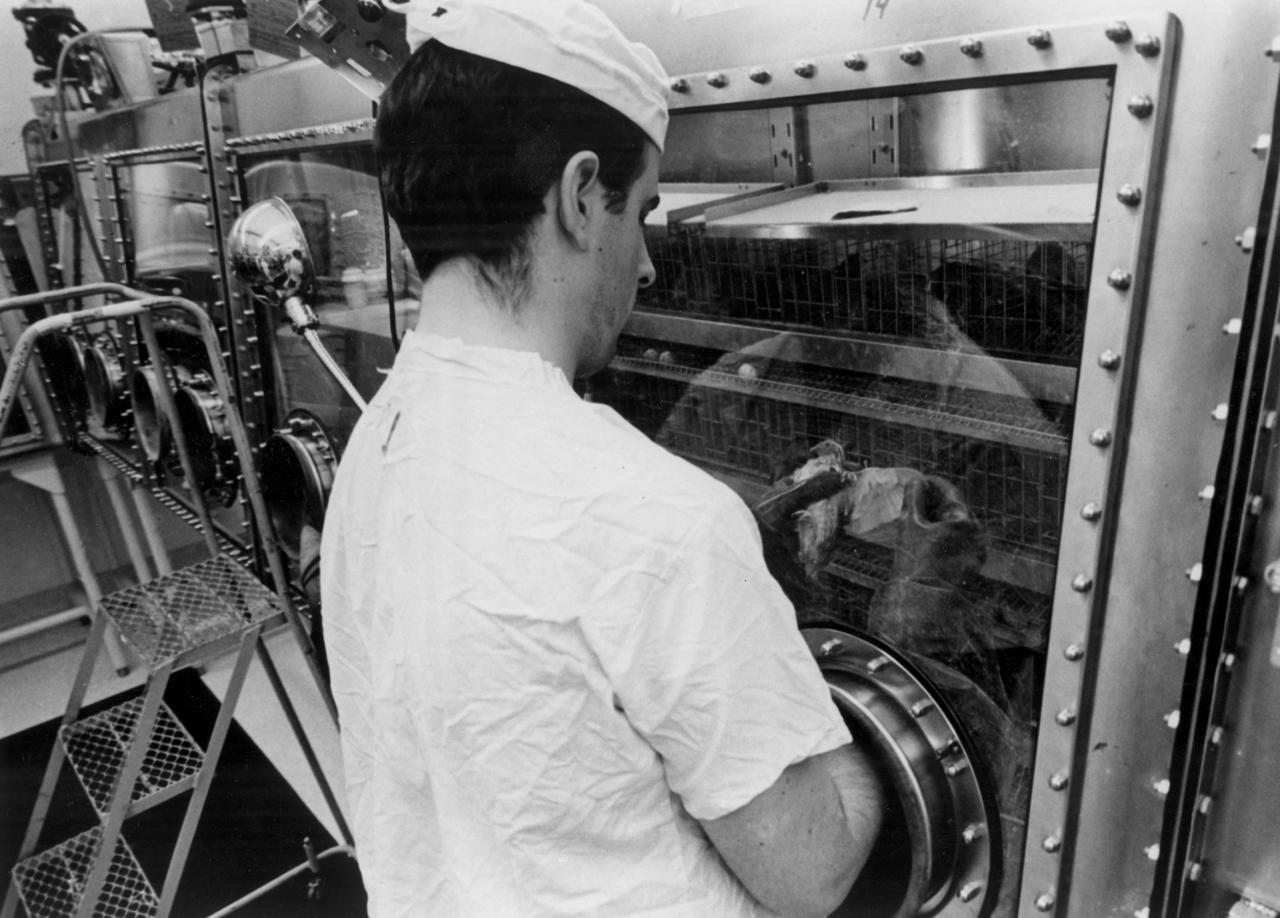

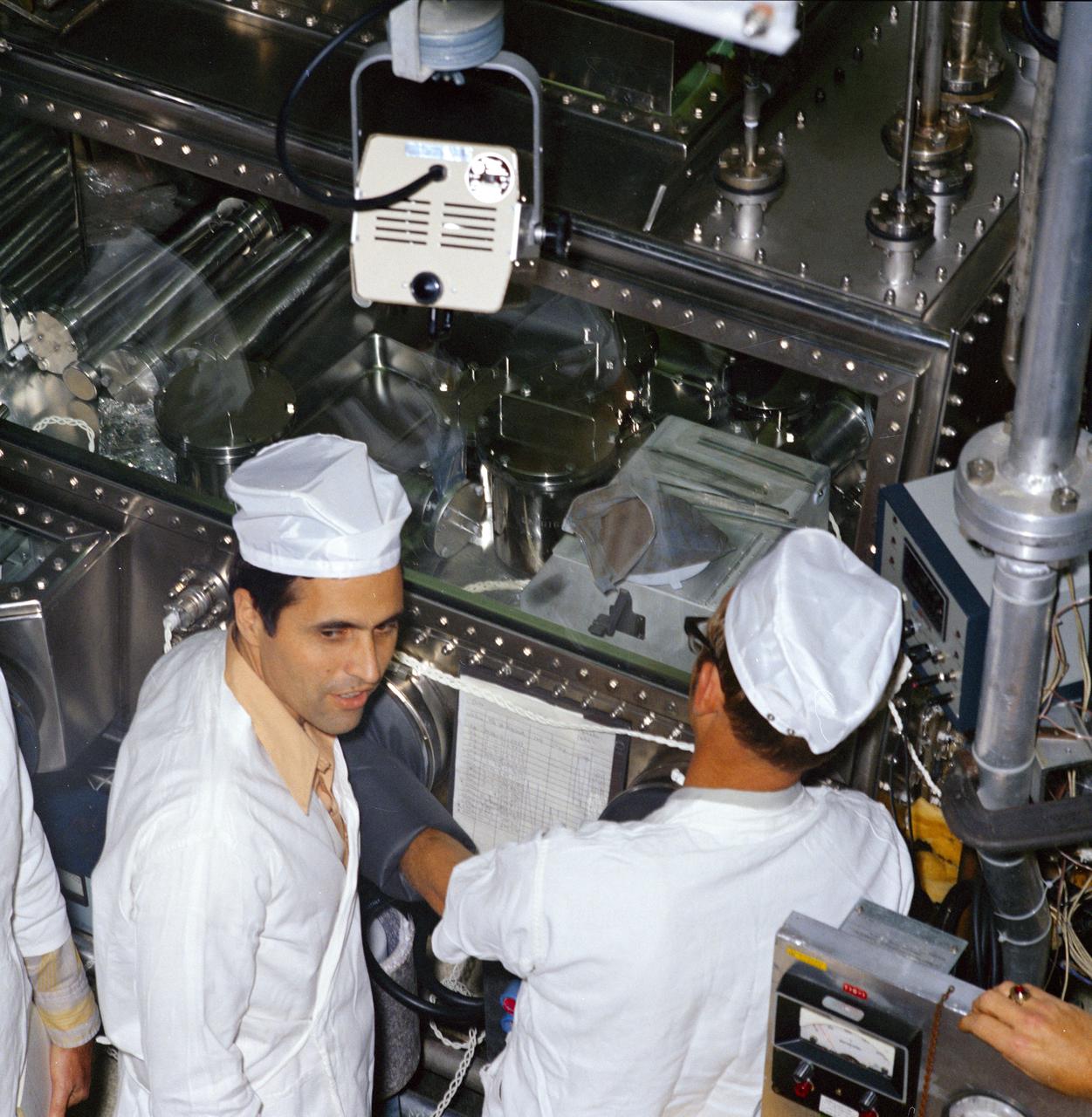
In this photograph, laboratory technician Bart Ruark visually inspects a Japanese Qail confined within a class III cabinet in the Intervertebrae, Aves, and Fish Laboratory of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory, Building 37 of the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) in Houston, Texas. This laboratory was part of the overall physical, chemical, and biological test program of the Apollo 11 returned lunar samples. Aboard the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle, the Apollo 11 mission launched from The Kennedy Space Center, Florida on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The 3-man crew aboard the flight consisted of astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Edwin Aldrin, Lunar Module (LM) pilot; and Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. In 2 1/2 hours, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material which was returned to Earth for analysis.
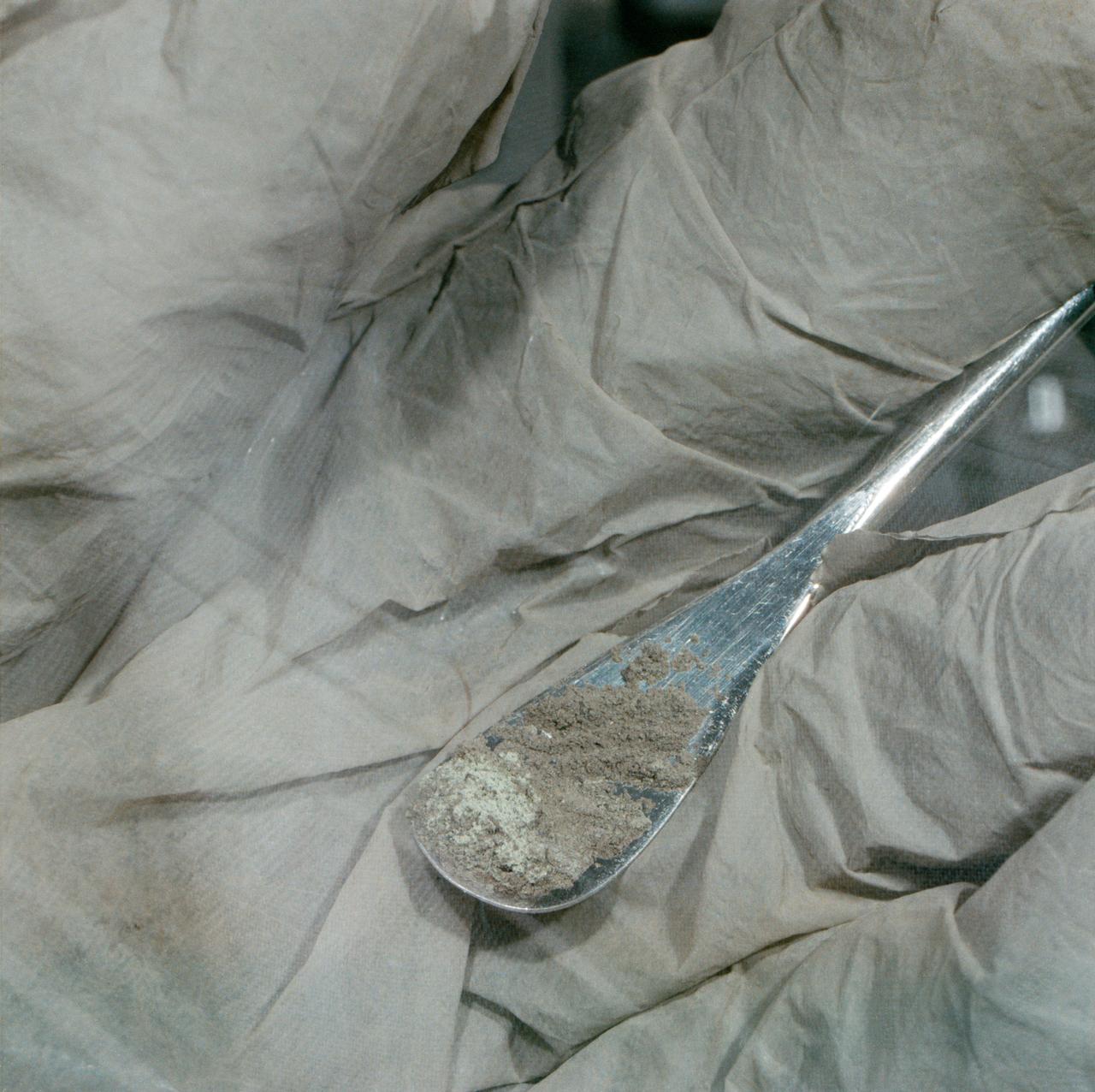

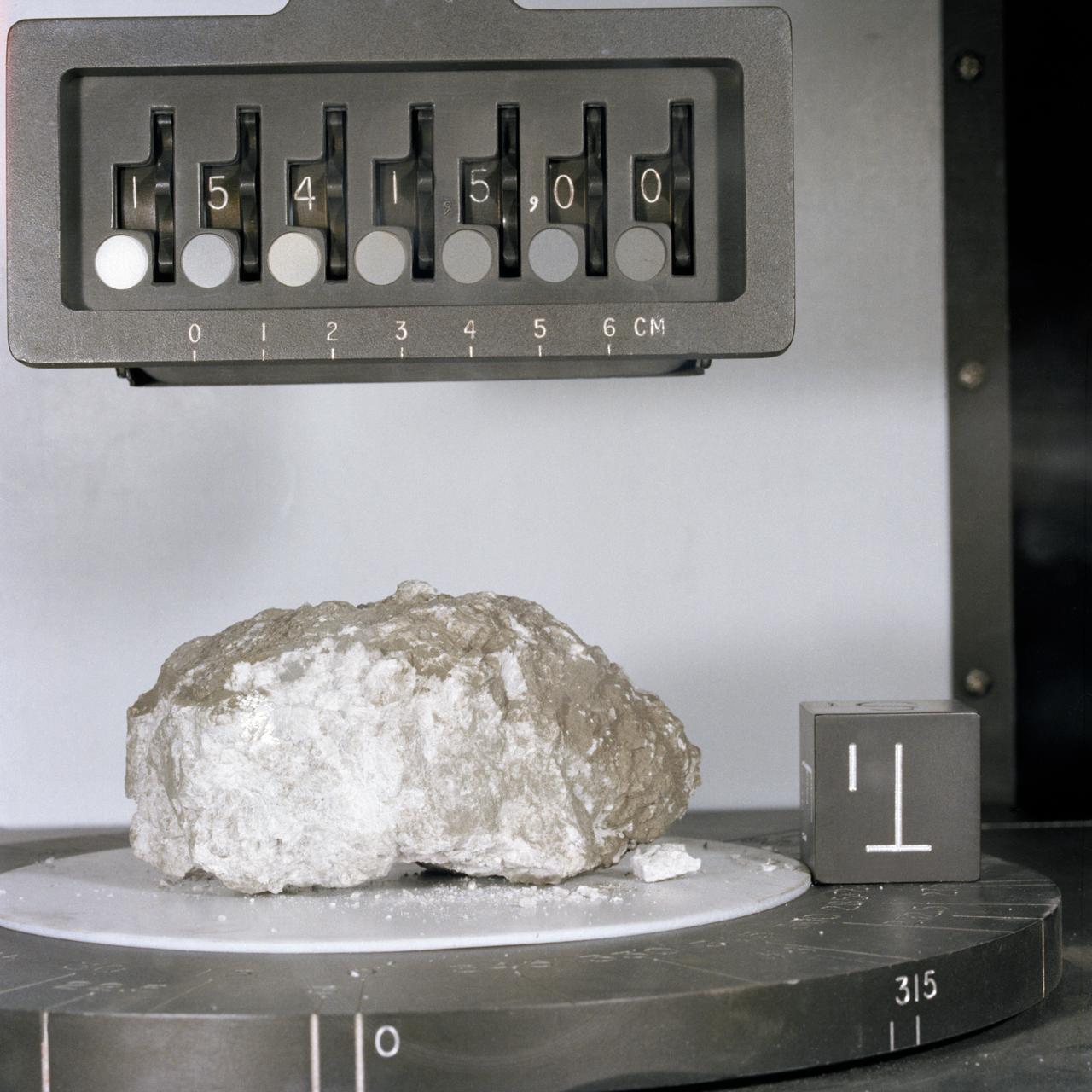
S71-43050 (August 1971) --- A close-up view of Apollo 15 lunar sample No. 15305 in the Non-sterile Nitrogen Processing Line (NNPL) in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). This sample, pictured on a small spatula in a lab technician's glove, is green and is one of six recently taken from container No. 173, made up of comprehensive fines from the Apennine Front, Site No. 7. Astronauts David R. Scott, commander; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, took the sample during their second extravehicular activity (EVA), at a ground elapsed time (GET) of 146:05 to 146:06.

In this photograph, a laboratory technician handles a portion of the more than 20 different plant lines that were used within the Lunar Receiving Laboratory, Building 37 of the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) in Houston, Texas. This laboratory was part of the overall physical, chemical, and biological test program of the Apollo 11 returned lunar samples. Aboard the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle, the Apollo 11 mission launched from The Kennedy Space Center, Florida on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The 3-man crew aboard the flight consisted of astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Edwin Aldrin, Lunar Module (LM) pilot; and Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. In 2 1/2 hours, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material which was returned to Earth for analysis.

S71-43052 (August 1971) --- A close-up view of a container full of green-colored lunar soil in the Non-Sterile Nitrogen Processing Line (NNPL) in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). This sample, broken down into six separate samples after this photo was made, was made up of comprehensive fines from near Spur Crater on the Apennine Front. The numbers assigned to the sample include numbers 15300 through 15305. Astronauts David R. Scott and James B. Irwin took the sample during their second extravehicular activity (EVA) at a ground elapsed time (GET) of 146:05 to 146:06.
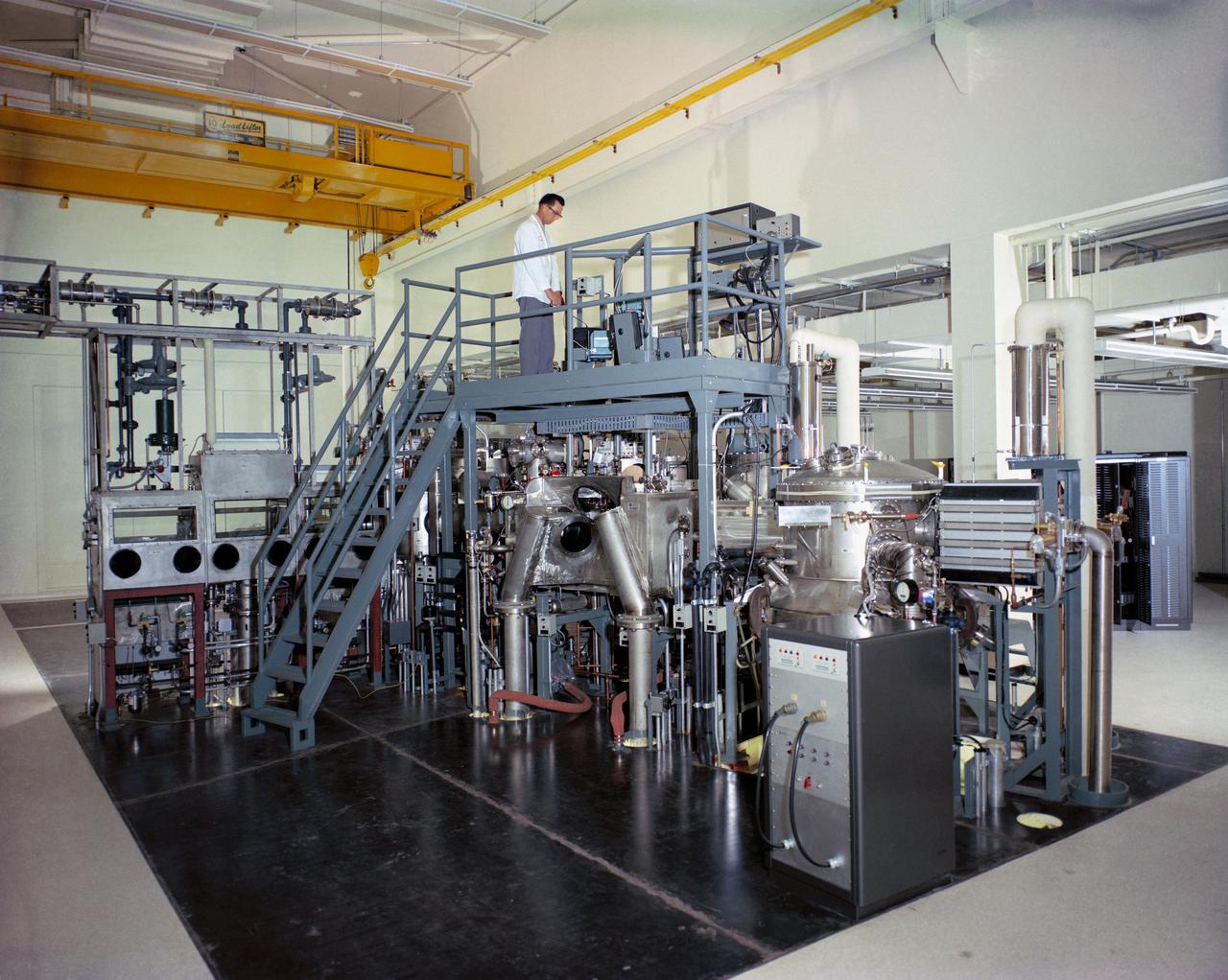
The incubation laboratory of the Sample Operations Area of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory, bldg 37.

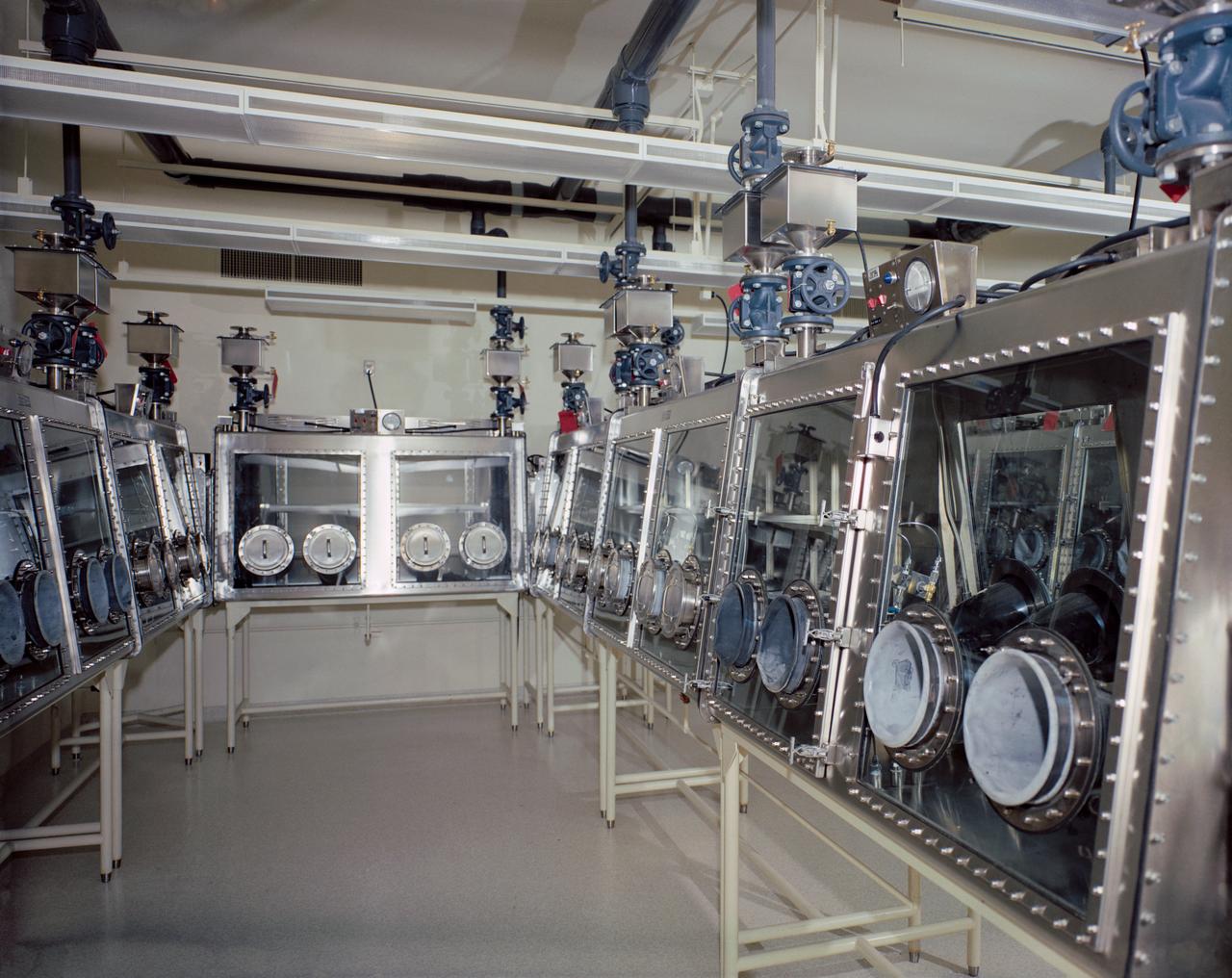
Overall view of the equipment in Room 2-203, Vacuum Laboratory, Sample Operations Area, Lunar Receiving Laboratory, Bldg 37.
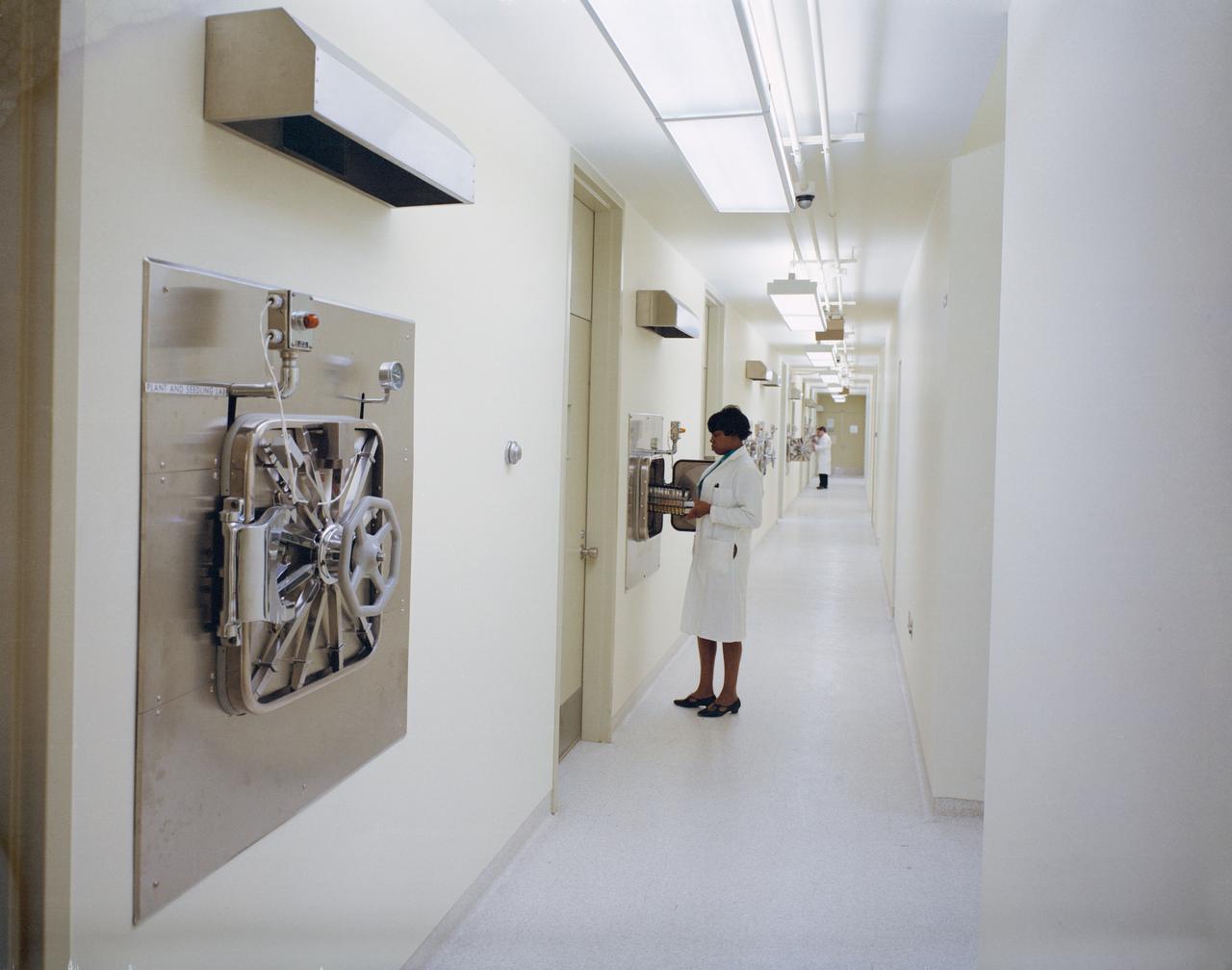

Biological Test Laboratory, Sample Operations Area, Lunar Receiving Laboratory, bldg 37, Manned Spacecraft Center, Houston, Texas.
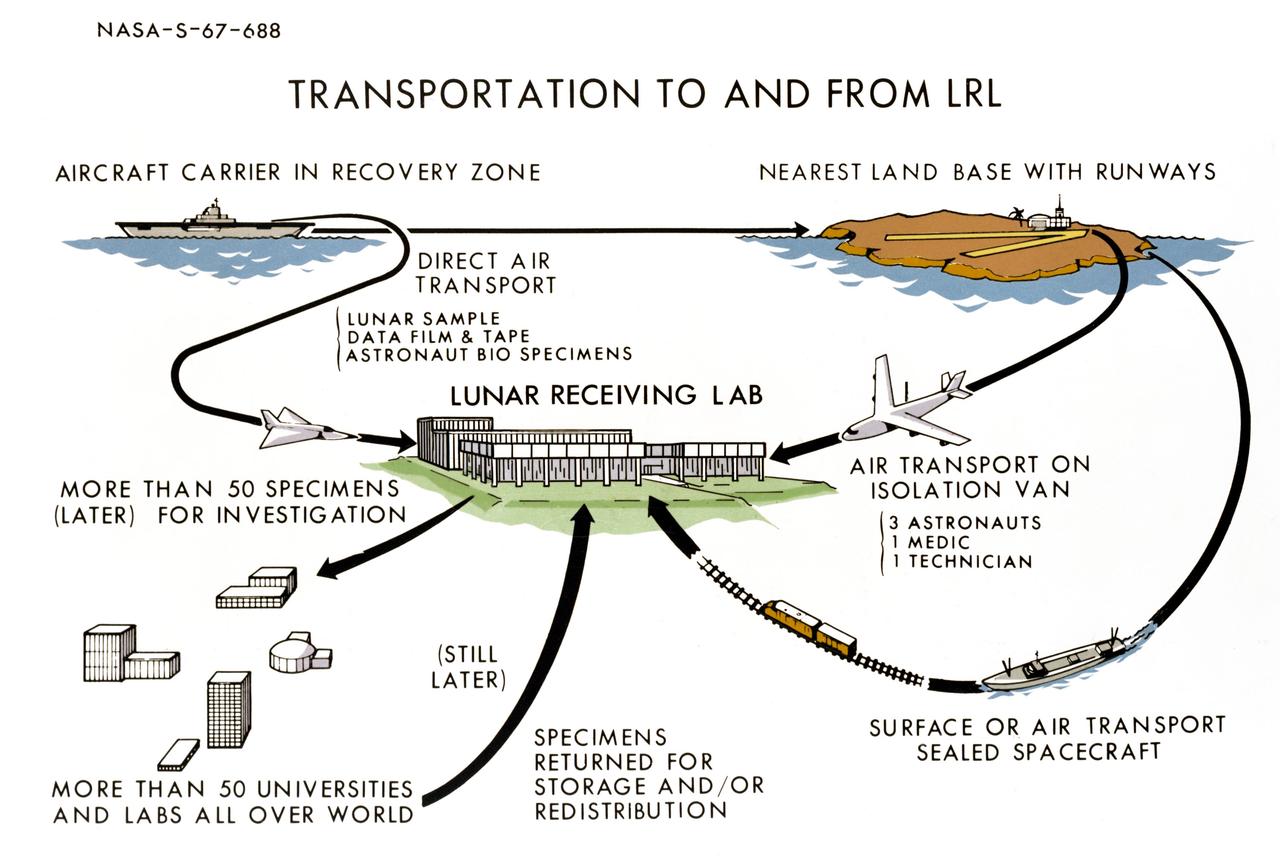
Cutway view illustrating transportation of the LRL to and from MSC. MSC, HOUSTON, TX CN and B&W
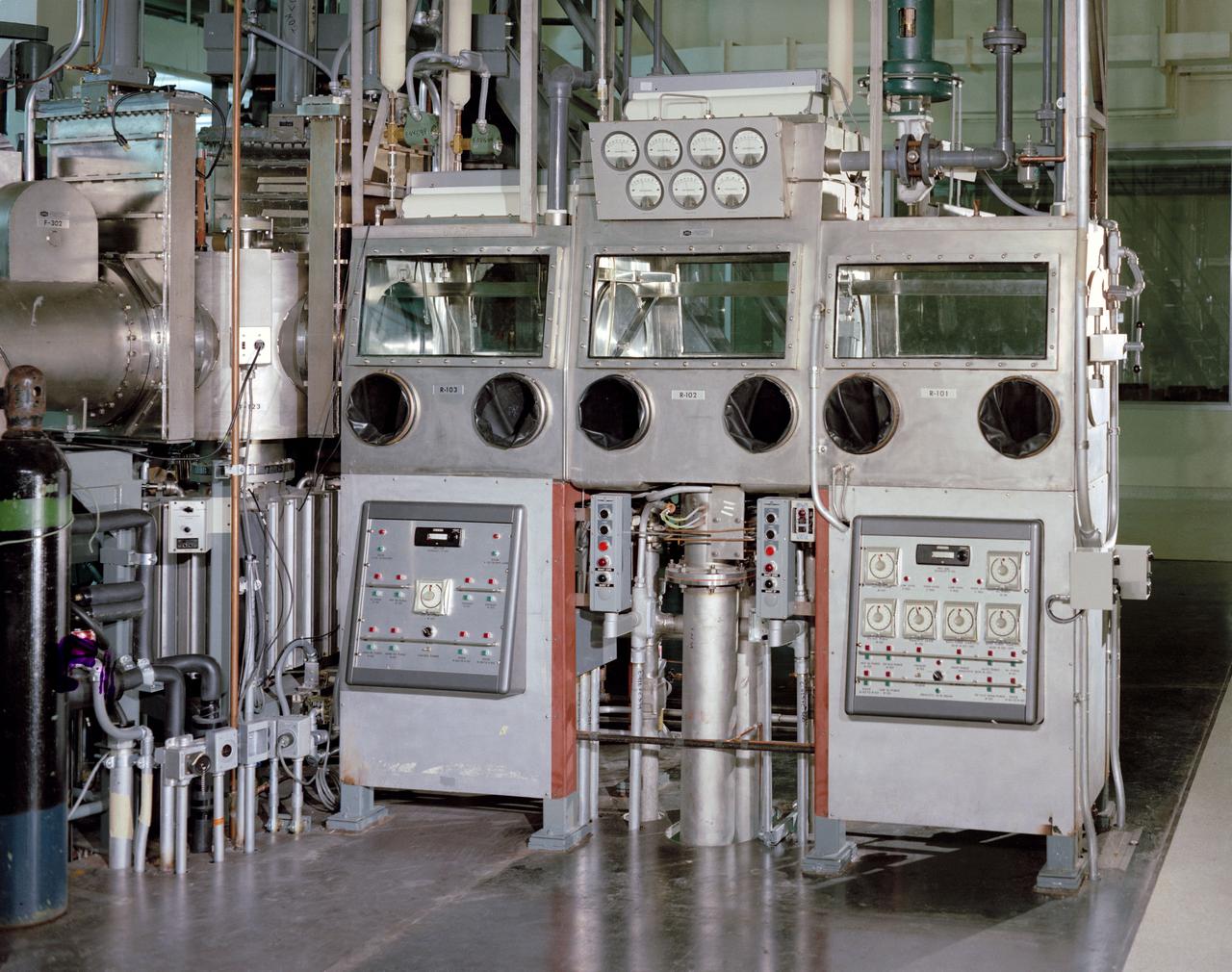

Atmospheric Decontamination System equipment in Room 2-203, Vacuum Laboratory, Sample Operations Area, Lunar Receiving Laboratory, Bldg 37.
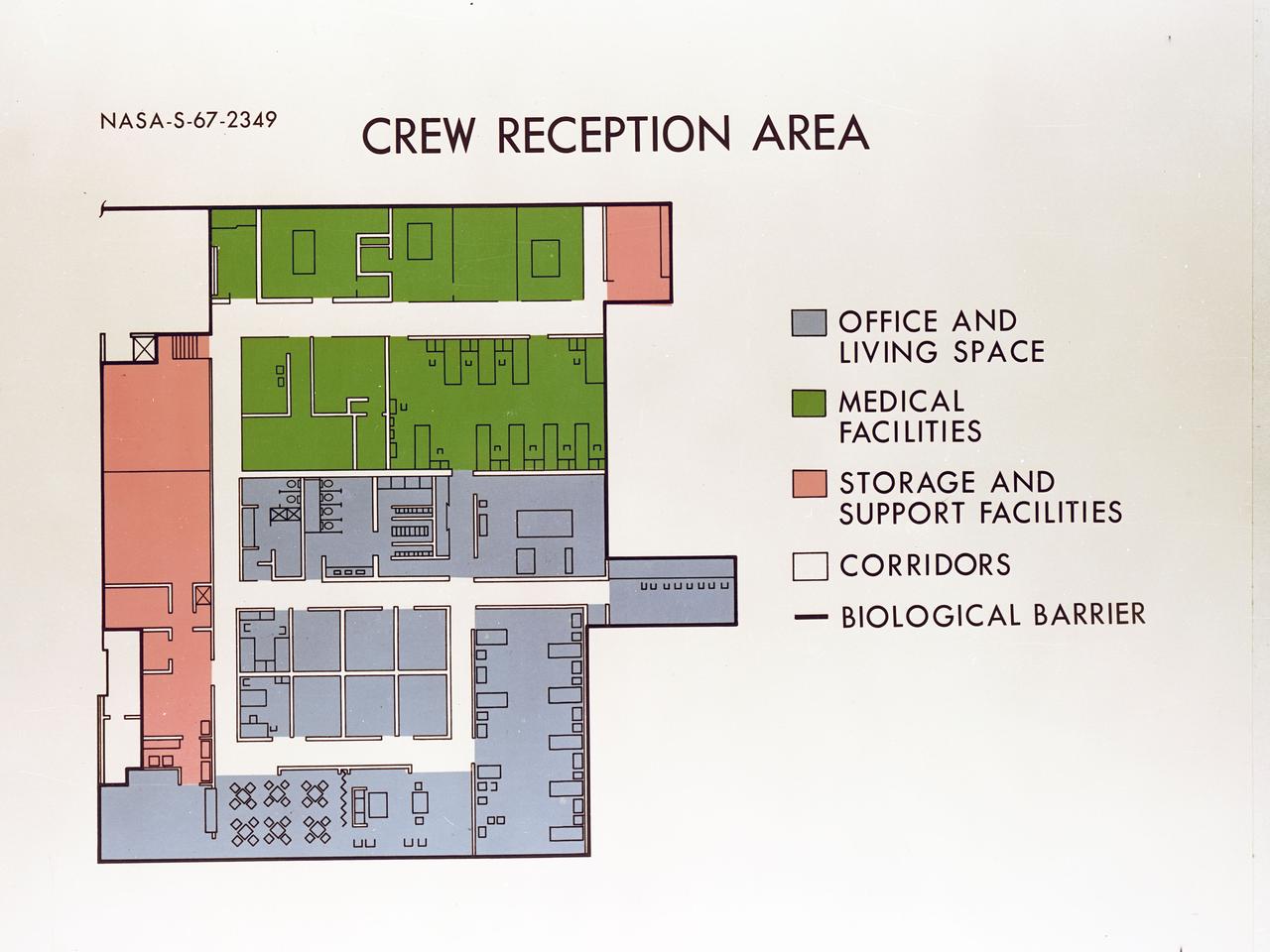
Artist's concept depicting the floor plan of the Crew Reception Area of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL), bldg 37.
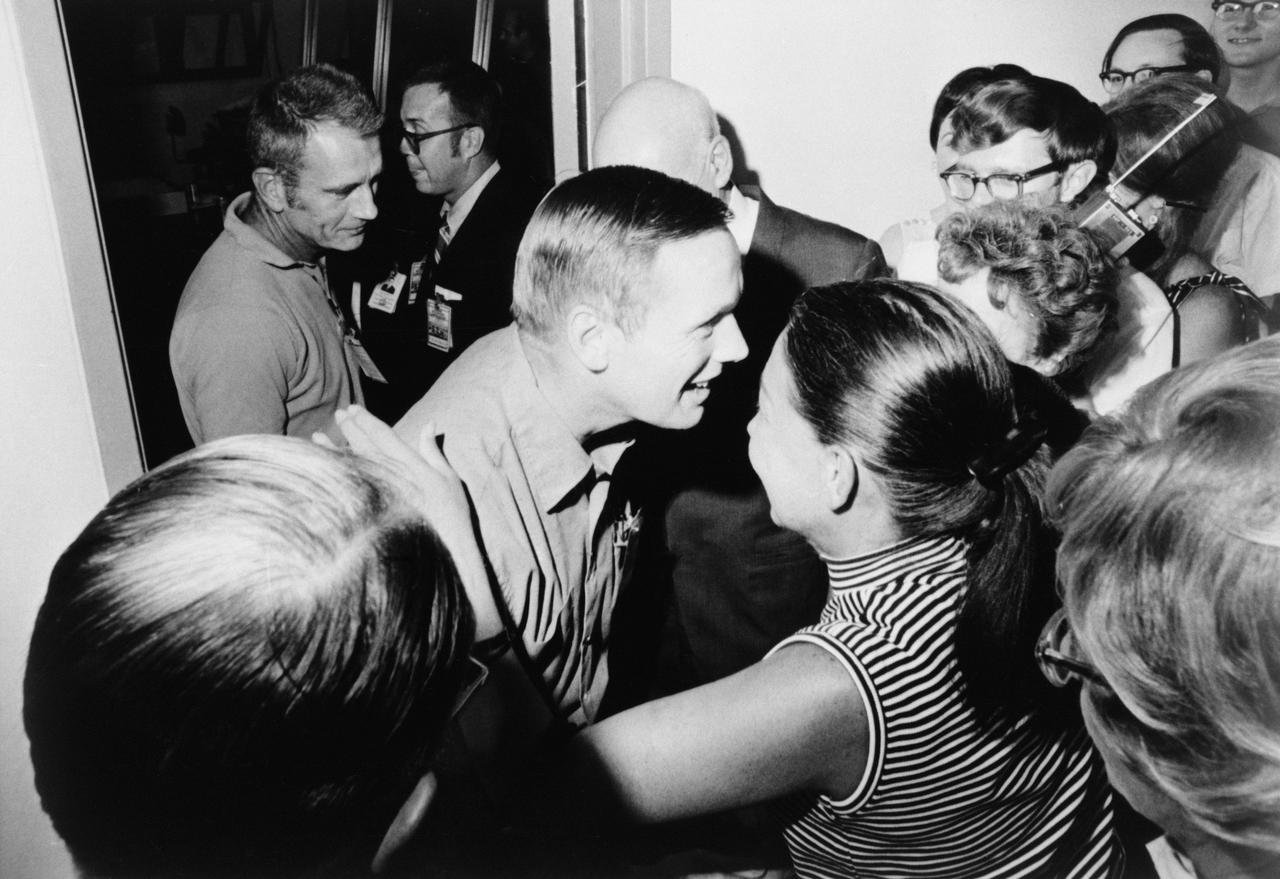

Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong (center), is greeted by friends in the crew reception area of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory. Dr. Gilruth is pictured just to right of Armstrong. Donald K. Slayton, Director of Space Flight Crew Operations, is behind ArmstrongThe Apollo 11 crew left the crew reception area of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at 9 p.m., Aug. 10, 1969.
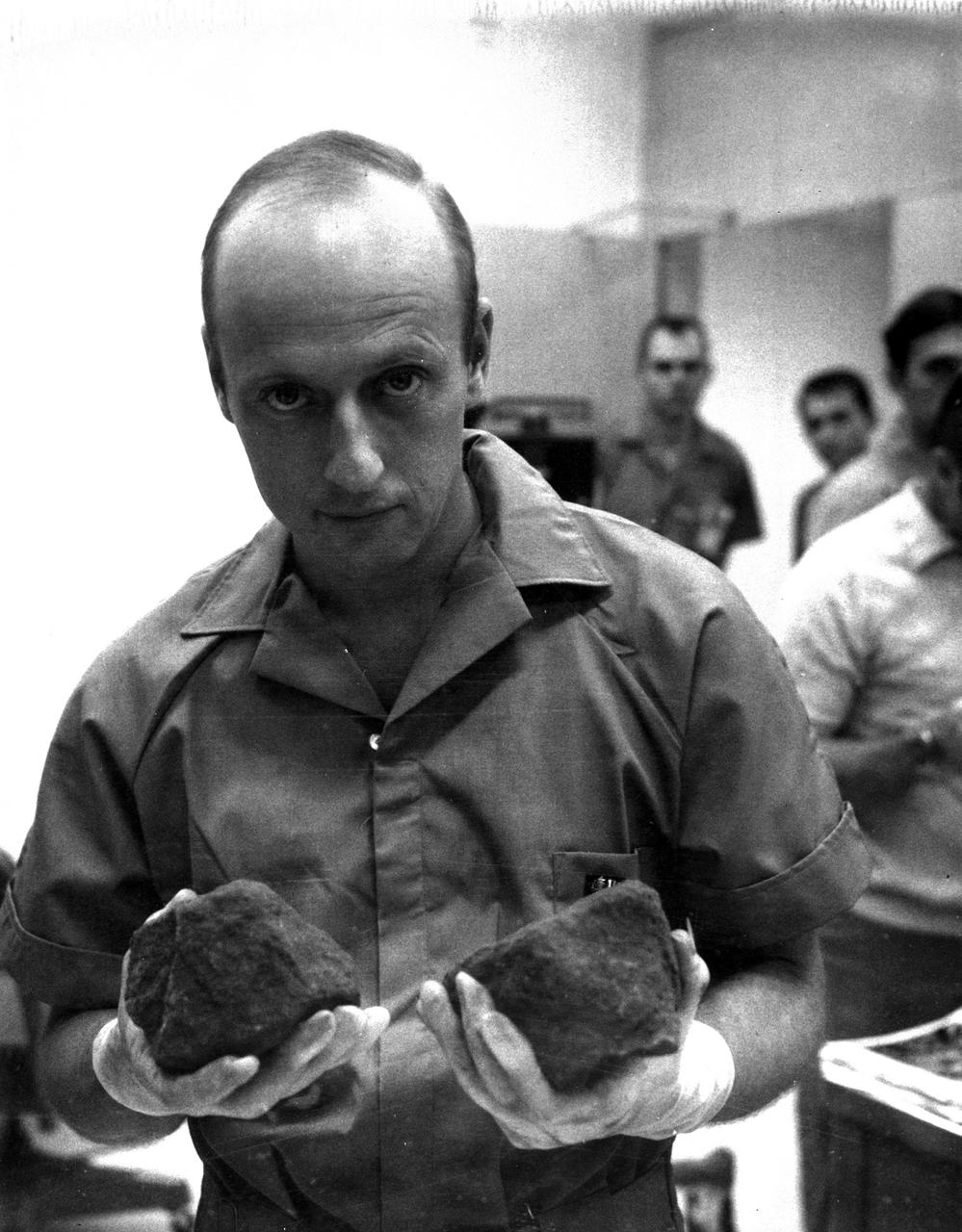

S69-60424 (29 Nov. 1969) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, holds two lunar rocks which were among the samples brought back from the moon by the Apollo 12 astronauts. The samples are under scientific examination in the Manned Spacecraft Center's Lunar Receiving Laboratory.
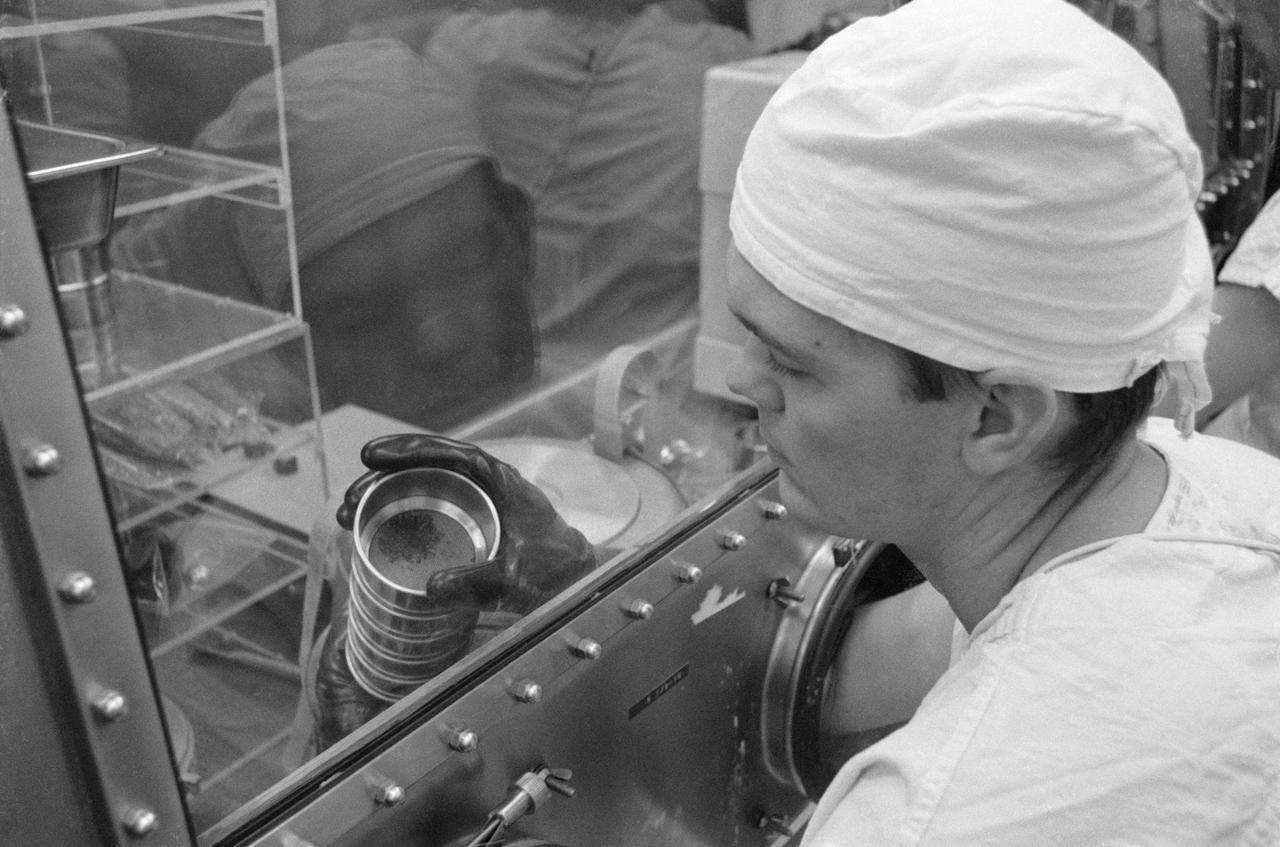

S69-40749 (July 1969) --- Dr. Grant Heikan, MSC and a Lunar Sample Preliminary Examination Team member, examines lunar material in a sieve from the bulk sample container which was opened in the Biopreparation Laboratory of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory. The samples were collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity on July 20, 1969.

S69-40939 (August 1969) --- Landrum Young, Brown and Root - Northrop technician, examines mice in the Animal Laboratory of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) which have been inoculated with lunar sample material. The sample material was collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) on July 20, 1969.
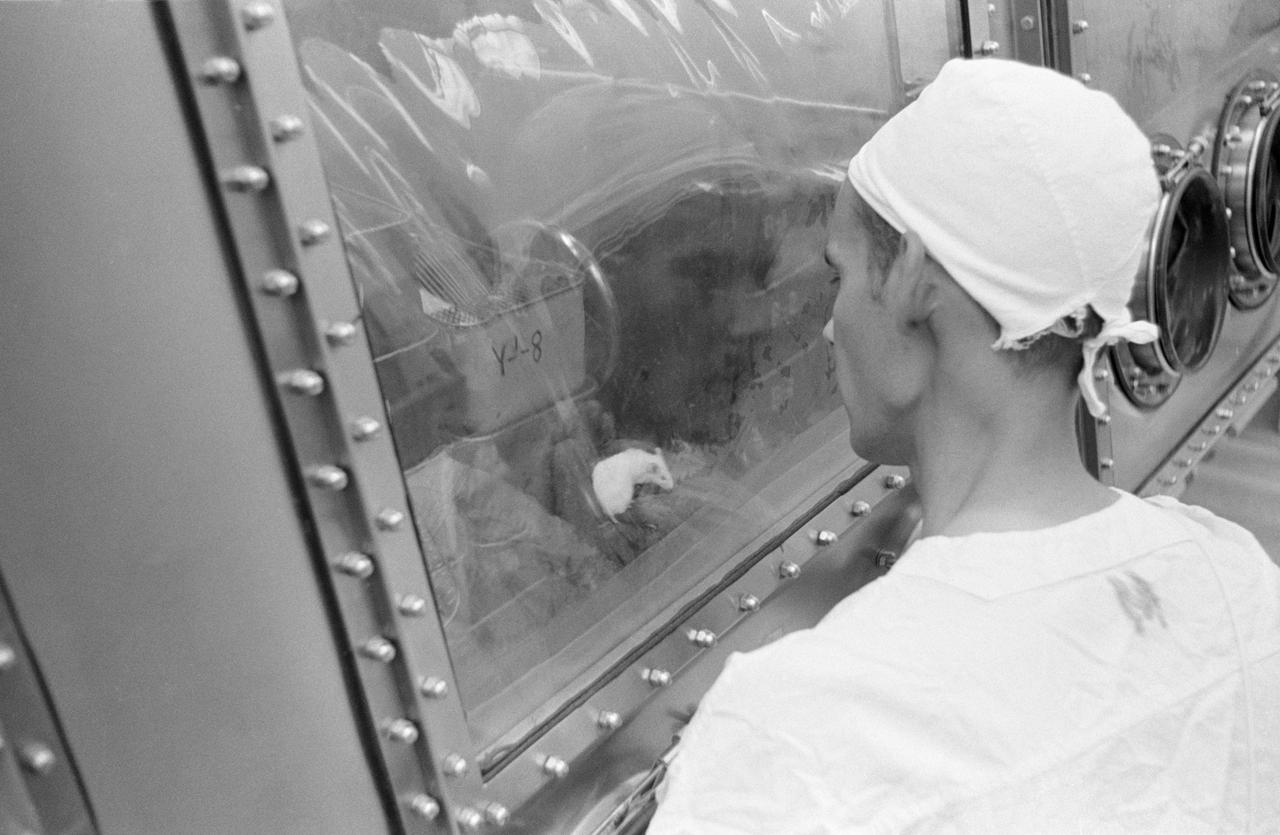

S69-40752 (August 1969) --- Landrum Young, Brown and Root - Northrop technician examines mice in the Animal Laboratory of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) which have been inoculated with lunar sample material. The sample material was collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) on July 20, 1969.
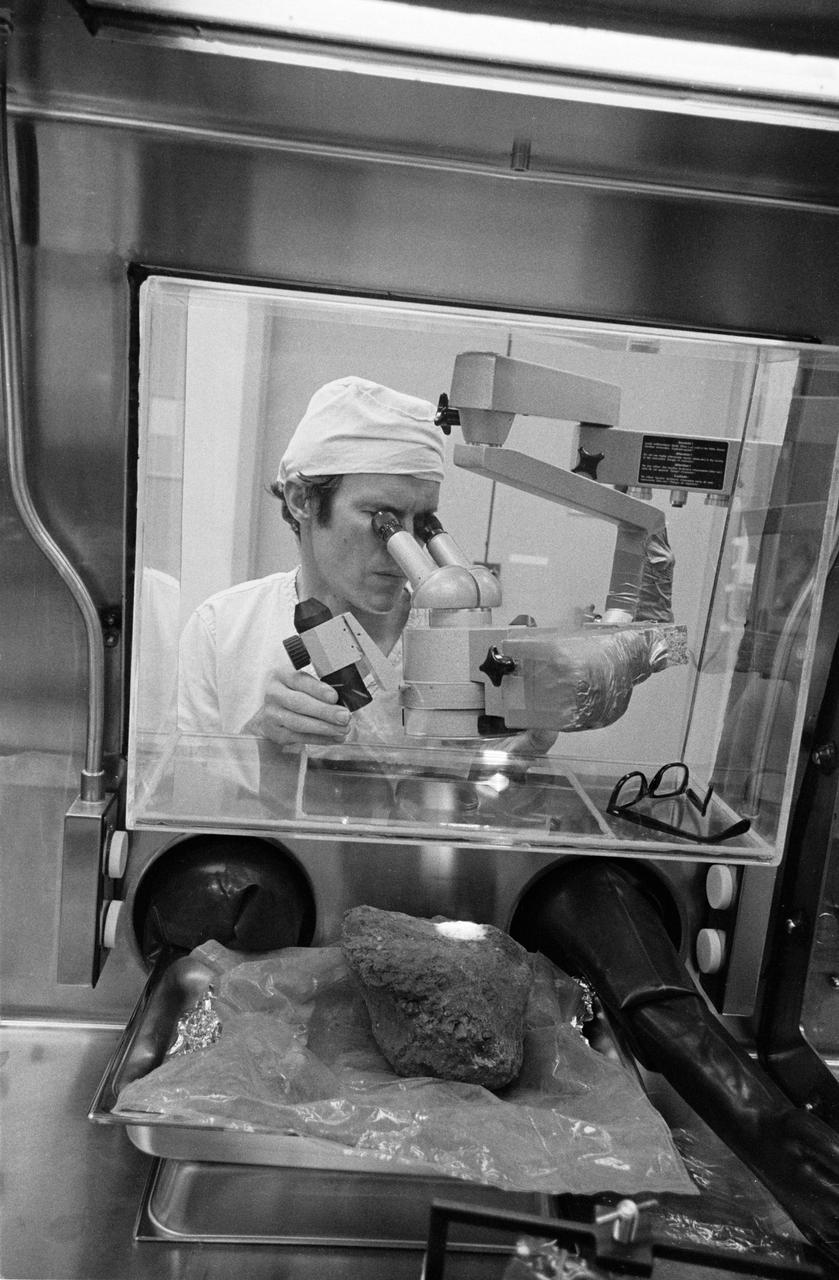

S71-21245 (24 Feb. 1971) --- Dr. Daniel H. Anderson, an aerospace technologist and test director in the Nonsterile Nitrogen Processing Laboratory in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) looks at much-discussed Apollo 14 basketball-size rock through a microscope. The two moon-exploring crew men of Apollo 14 brought back 90-odd pounds of lunar sample material from their two periods of extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface in the Fra Mauro area.
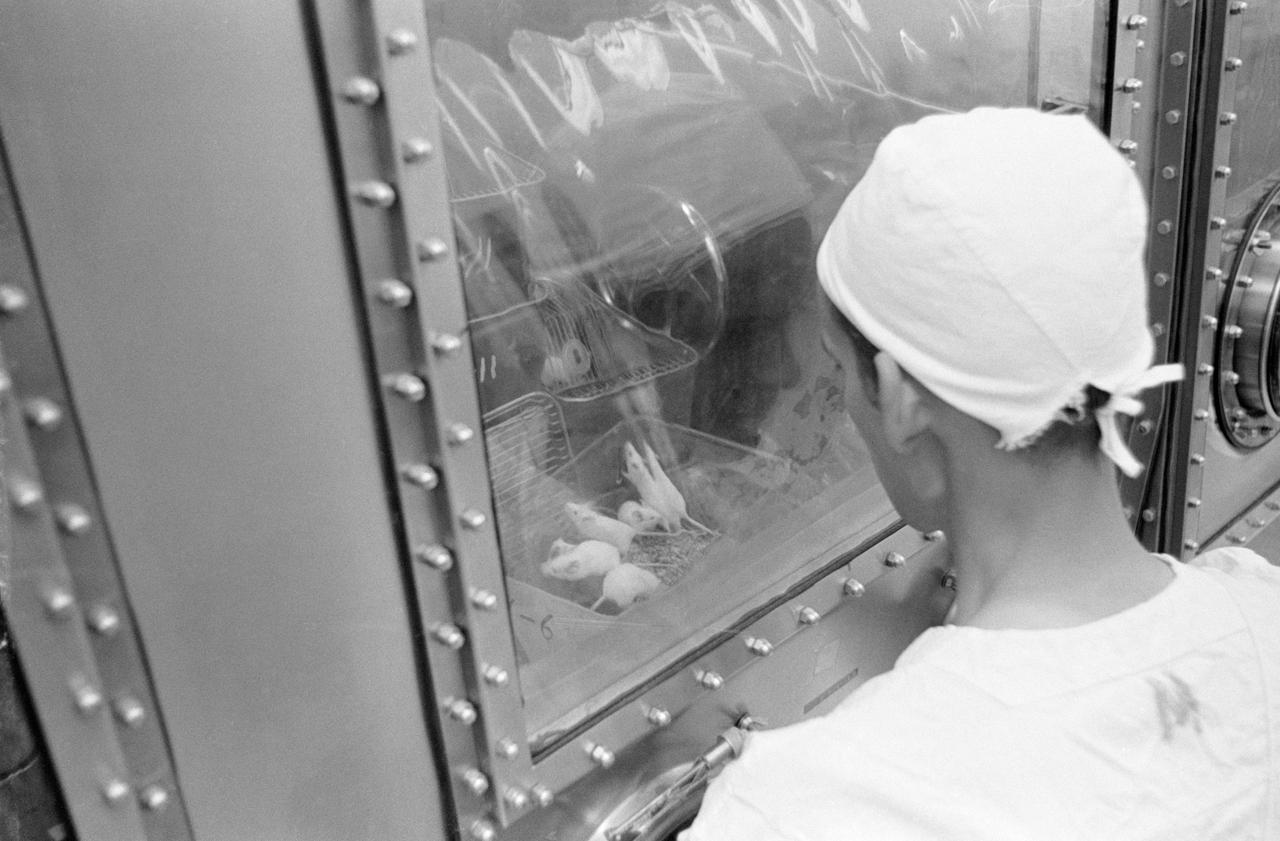

S69-40751 (August 1969) --- Landrum Young, Brown and Root - Northrop technician, examines mice in the Animal Laboratory of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) which have been inoculated with lunar sample material. The sample material was collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) on July 20, 1969.

S69-53894 (October 1969) --- Dr. Charles H. Walkinshaw, Jr., Spaceflight Biotechnology Branch botanist, Preventive Medicine Division, Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), examines sorghum and tobacco plants in lunar (germ free) soil in the Plant Laboratory of the MSC’s Lunar Receiving Laboratory. The soil was brought back from the moon by the crew of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission.
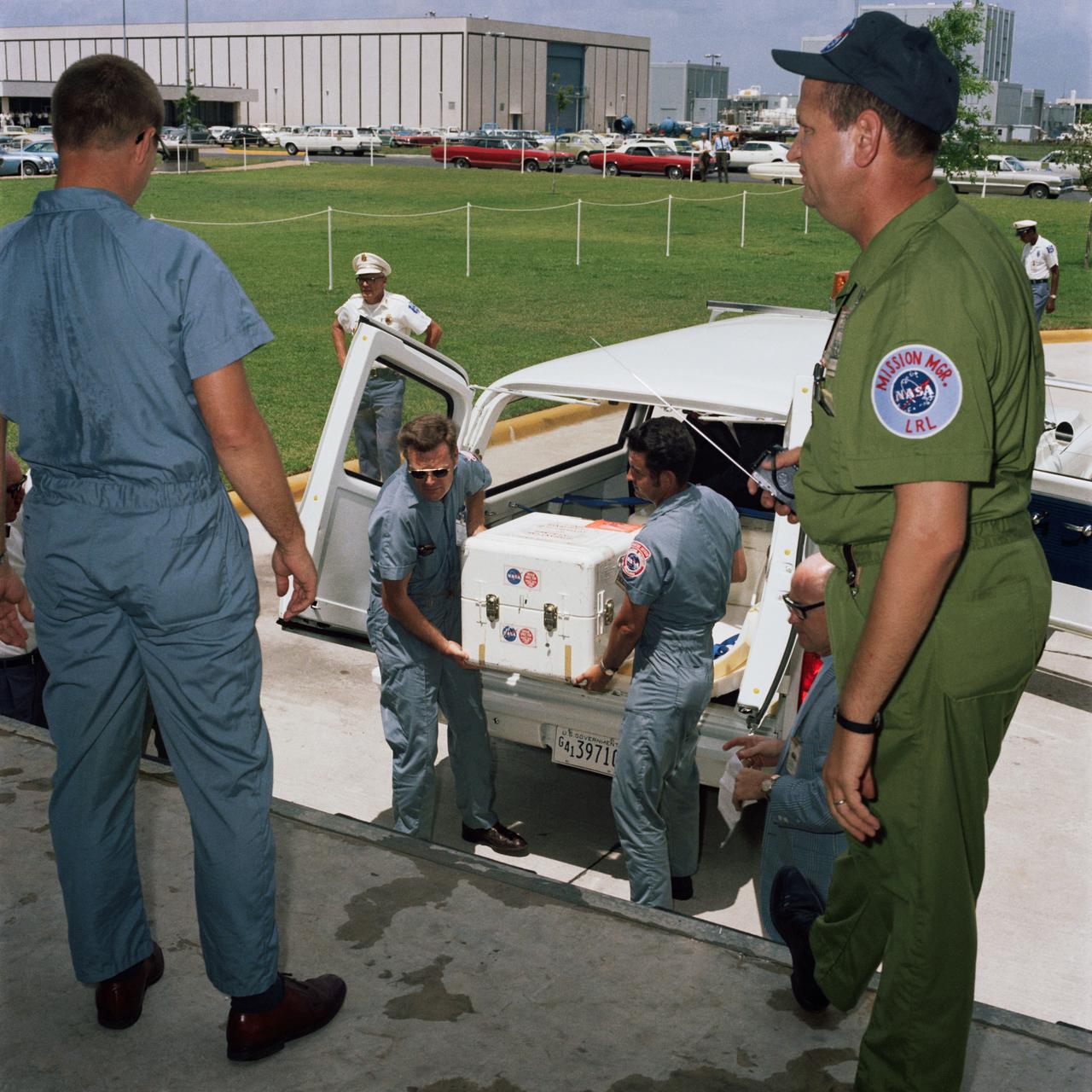

S69-39996 (25 July 1969) --- The first Apollo 11 sample return container, with lunar surface material inside, is unloaded at the Lunar Receiving Laboratory, Building 37, Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The rock box had arrived only minutes earlier at Ellington Air Force Base by air from the Pacific recovery area. The lunar samples were collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity.
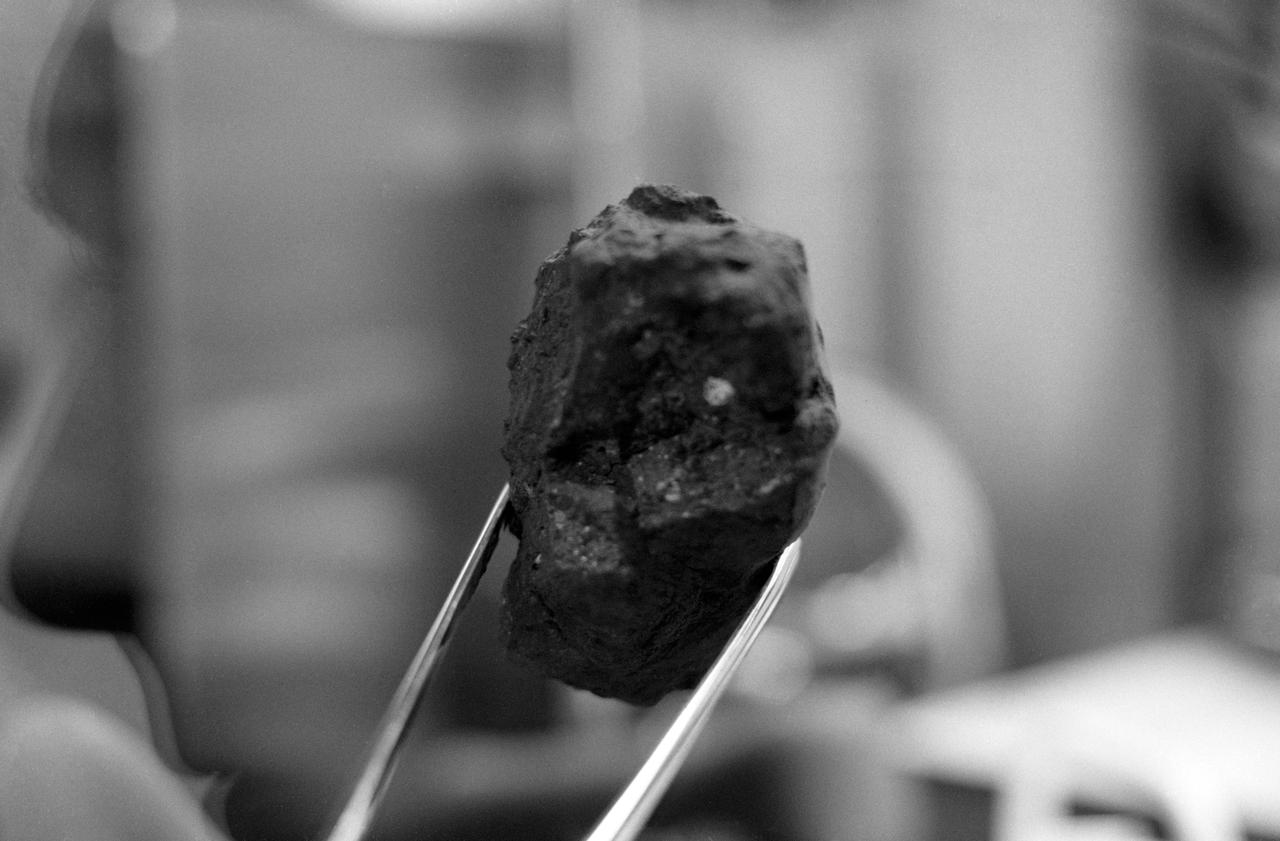

S69-60487 (1 Dec. 1969) --- A close-up view of one of the rocks brought back to Earth from the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission. The rock is under examination in the Physical-Chemical Test Laboratory in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL), Building 37, MSC. This rock is one of two breccia found in the contingency collection gathered by astronauts Charles Conrad Jr. and Alan L. Bean during their stay on the lunar surface. The breccia rocks, common in the collection of Apollo 11 lunar samples, have been rare in examinations of the Apollo 12 samples thus far.
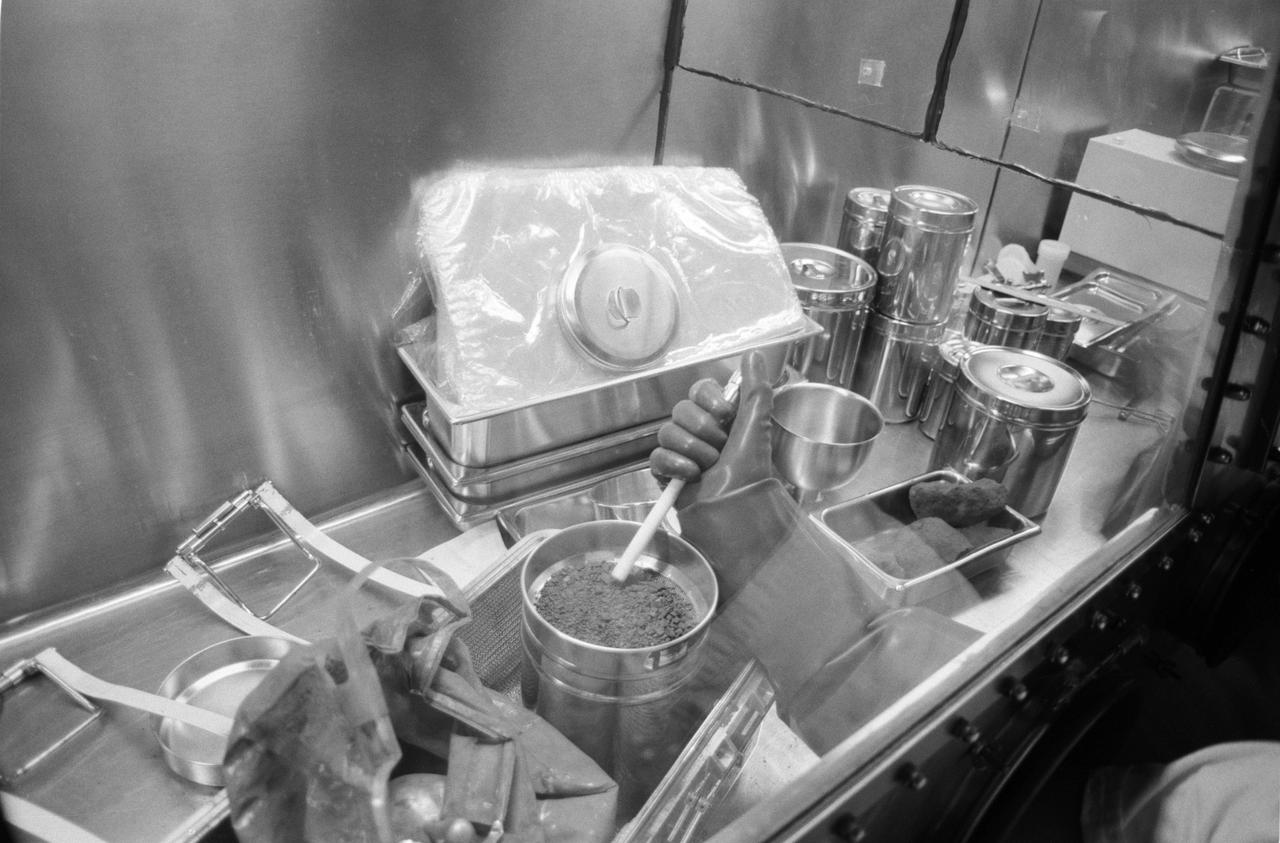

S69-45507 (4 Aug. 1969) --- A close-up of the second Apollo 11 sample return container in the Vacuum Laboratory of the Manned Spacecraft Center’s Lunar Receiving Laboratory, Building 37. This rock box was opened for the first time at 1 p.m. (CDT), Aug. 4, 1969. Some of the material has already been removed from the ALSRC in this view. The stainless steel can contains some course lunar surface material. The lunar samples were collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity on July 20, 1969.
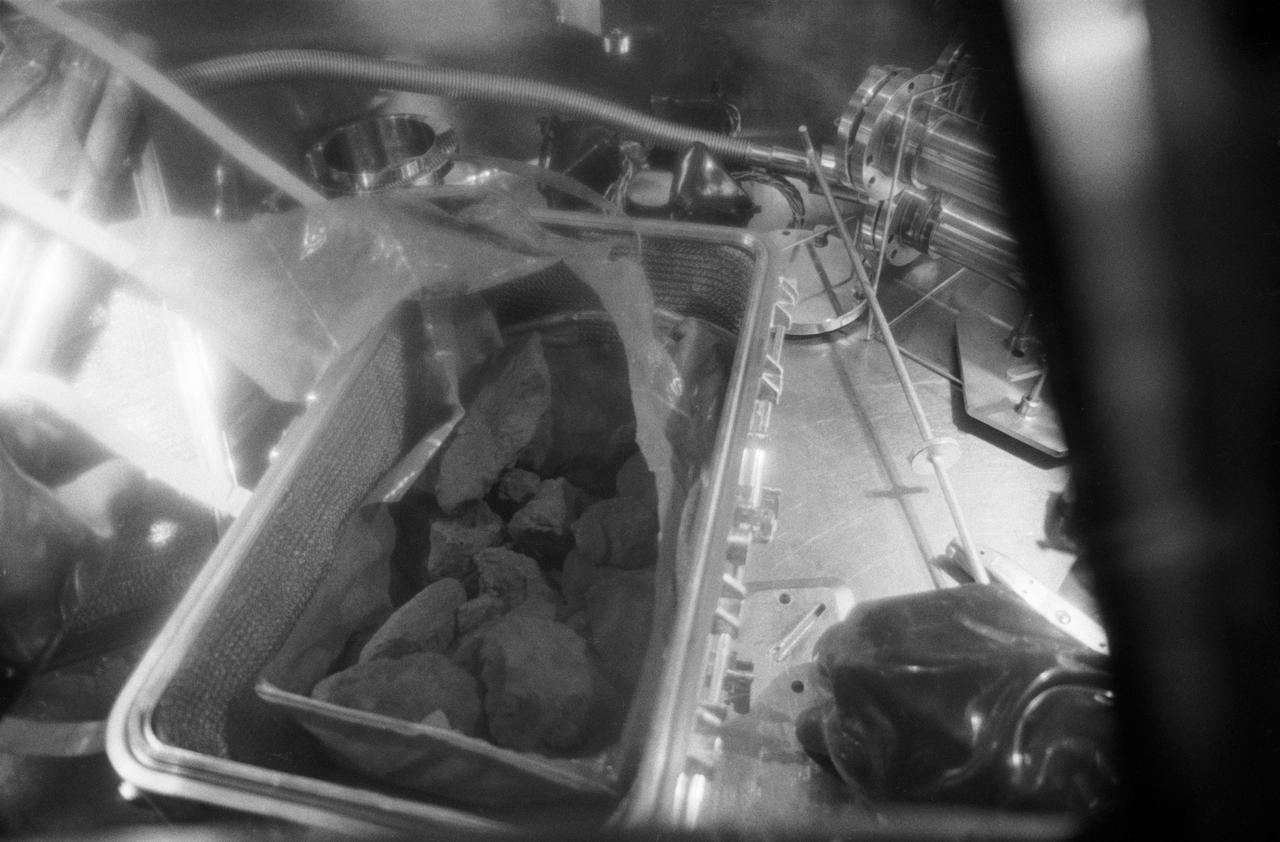

S69-45002 (26 July 1969) --- A close-up view of the lunar rocks contained in the first Apollo 11 sample return container. The rock box was opened for the first time in the Vacuum Laboratory of the Manned Spacecraft Center’s Lunar Receiving Laboratory, Building 37, at 3:55 p.m. (CDT), Saturday, July 26, 1969. The gloved hand gives an indication of size. This box also contained the Solar Wind Composition experiment (not shown) and two core tubes for subsurface samples (not shown). These lunar samples were collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity on July 20, 1969.

S73-36162 (November 1973) --- Dr. Robert S. Clark changes magnetic tape on the Radiation Counting Laboratory's mini-computer. The computer calculates the total content of radioactive isotopes in the lunar materials. Some 120 different samples from the six landings on the moon have been studied by the lab's gamma spectrometer, which generates 65,000 individual data points of each sample. Measurements of radioactive isotopes reveal how long they have been near the surface, and also reflect how much the rocks have been eroded by micrometeorites. Photo credit: NASA
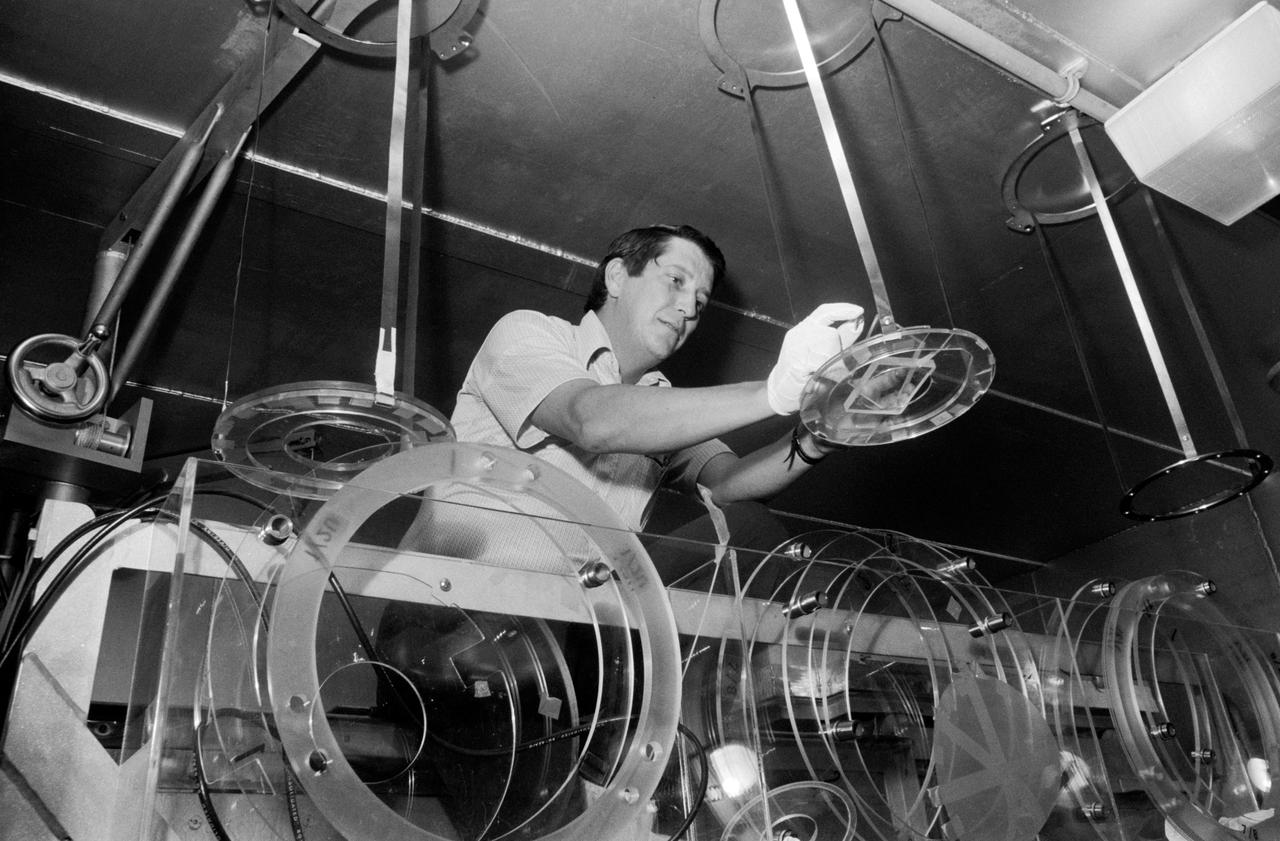

S73-36161 (November 1973) --- In the Radiation Counting Laboratory sixty feet underground at JSC, Dr. Robert S. Clark prepares to load pieces of iridium foil -- sandwiched between plastic sheets -- into the laboratory's radiation detector. The iridium foil strips were worn by the crew of the second Skylab flight in personal radiation dosimeters throughout their 59 1/2 days in space. Inside the radiation detector assembly surrounded by 28 tons of lead shielding, the sample will be tested to determine the total neutron dose to which the astronauts were exposed during their long stay aboard the space station. Photo credit: NASA

S71-21029 (24 Feb. 1971) --- Everett Gibson (left) and Don Morrison with Apollo 14 rocks in the Lunar Receiving Lab (LRL). Photo credit: NASA
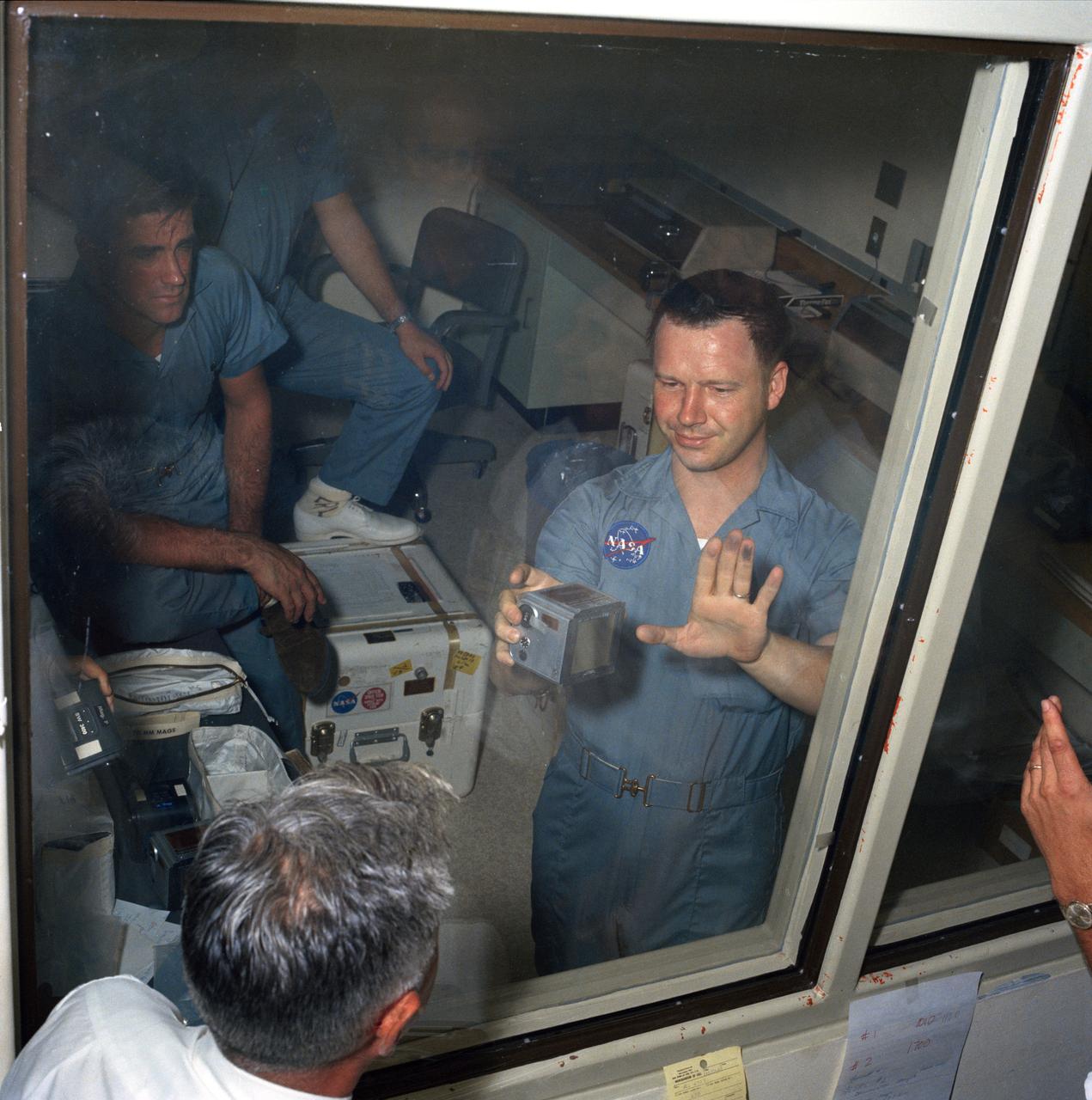

The first direct exposure to Lunar material for Crew Reception Personnel probably happened late Friday, 07/25/1969. Terry Slezak (displaying Moon dust on his left hand fingers), MSC photographic technician, was removing film magazines from the first of two (2) containers when the incident occurred. As he removed the plastic seal from Magazine "S", one of the 70mm magazines taken during Apollo XI Extravehicular Activity (EVA), it was apparent that the exterior of the cassette displayed traces of a black powdery substance. Apollo XI Commander Neil Armstrong reported during the mission that he had retrieved a 70mm cassette which had dropped to the Lunar surface. Seen in the backgound is John H. Boynton. ( S69-40054 ) MSC, Houston, TX
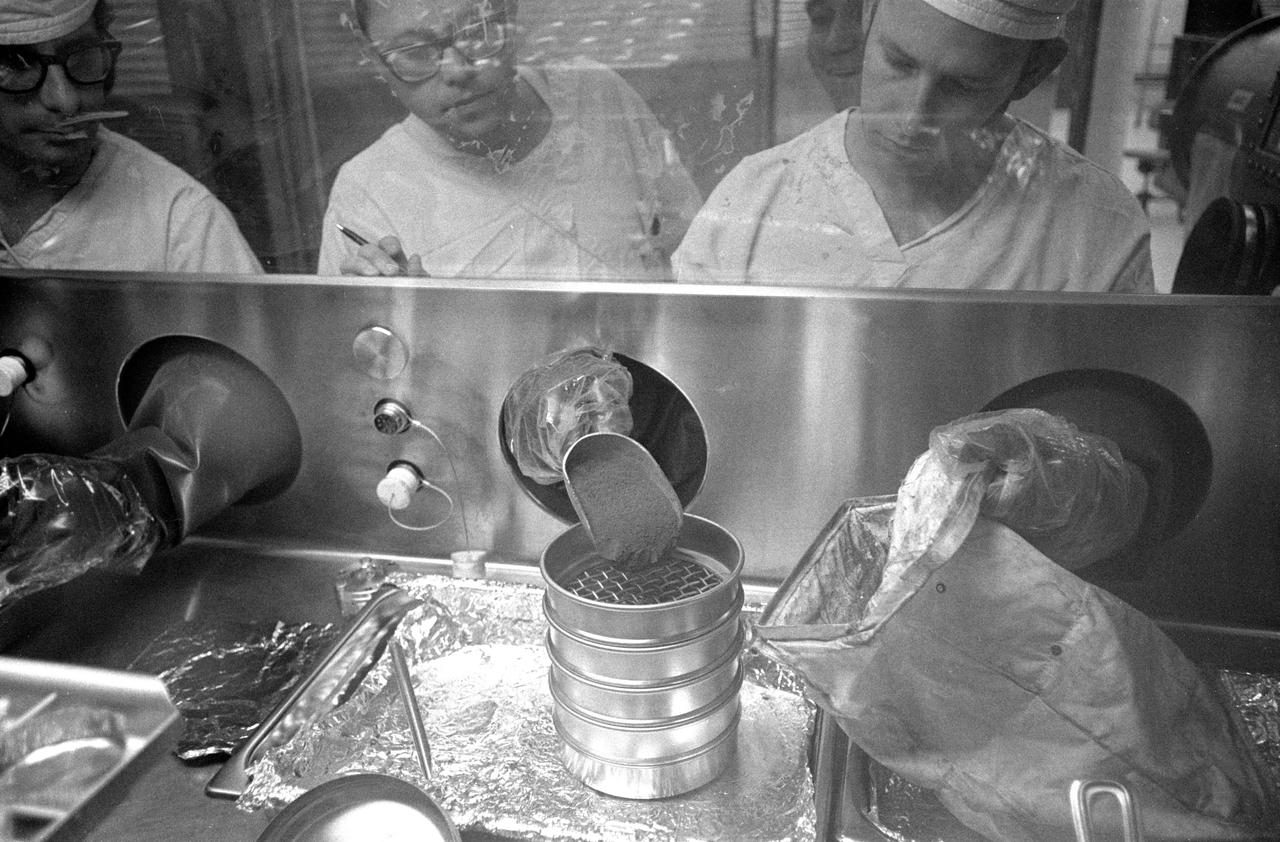

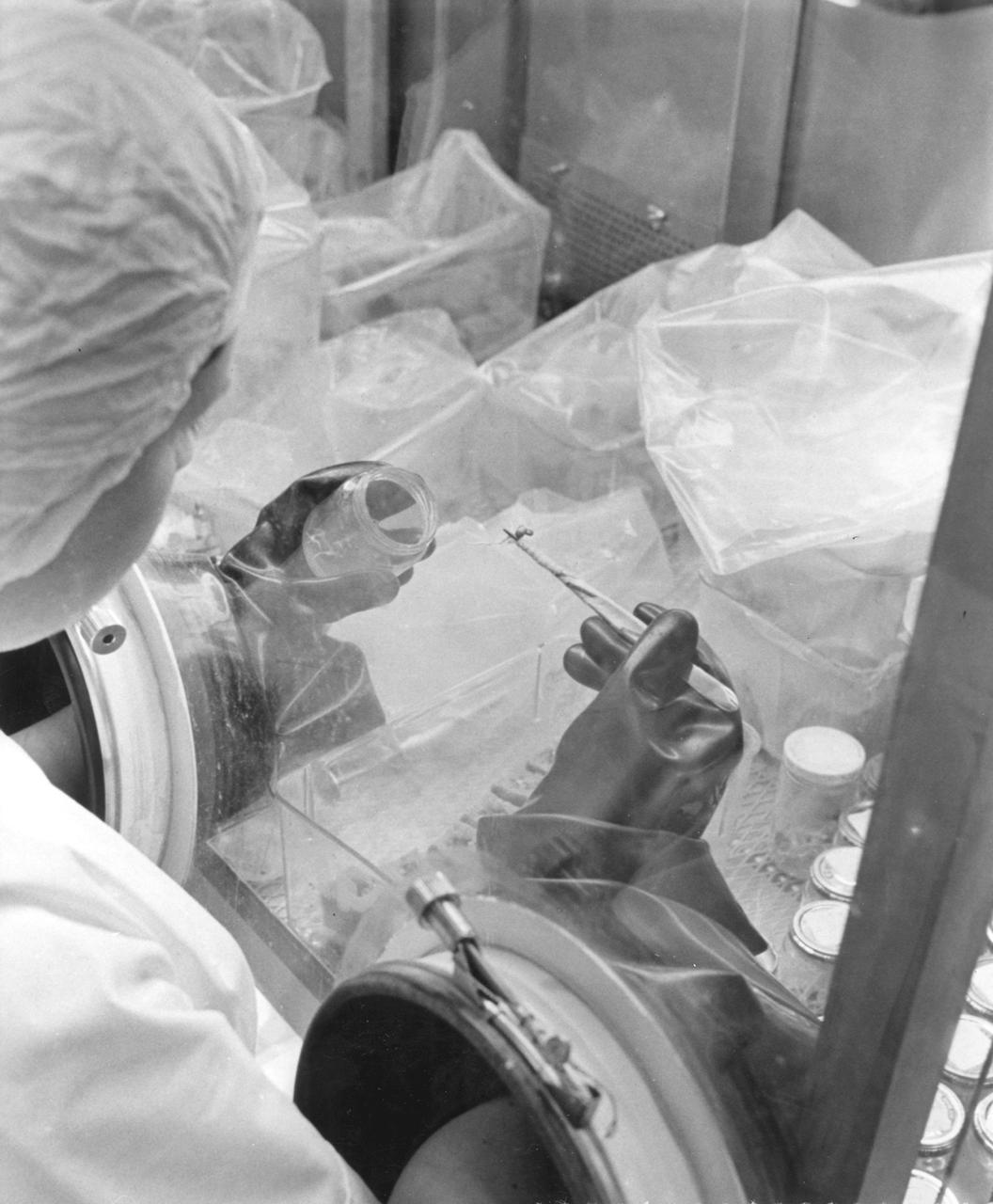
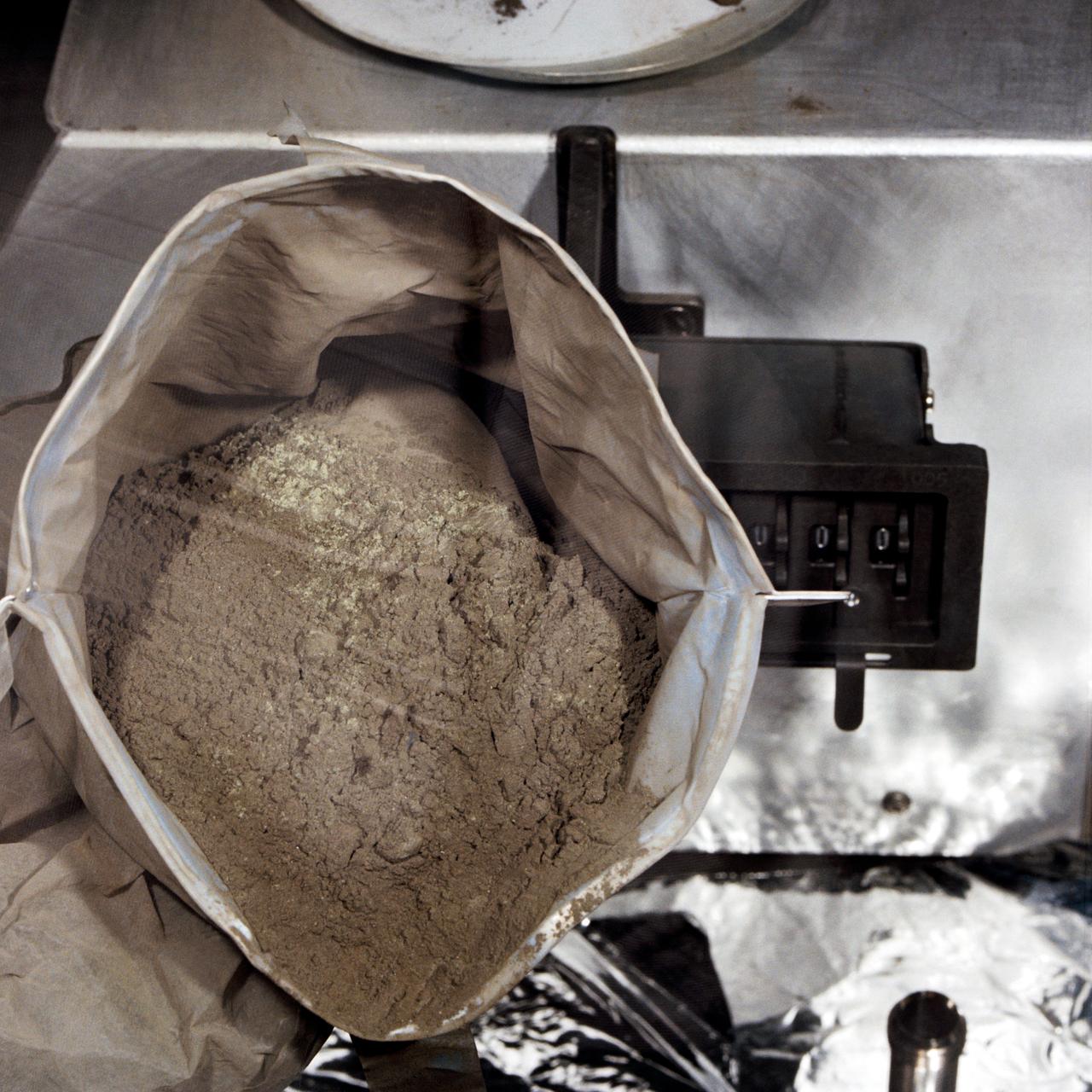
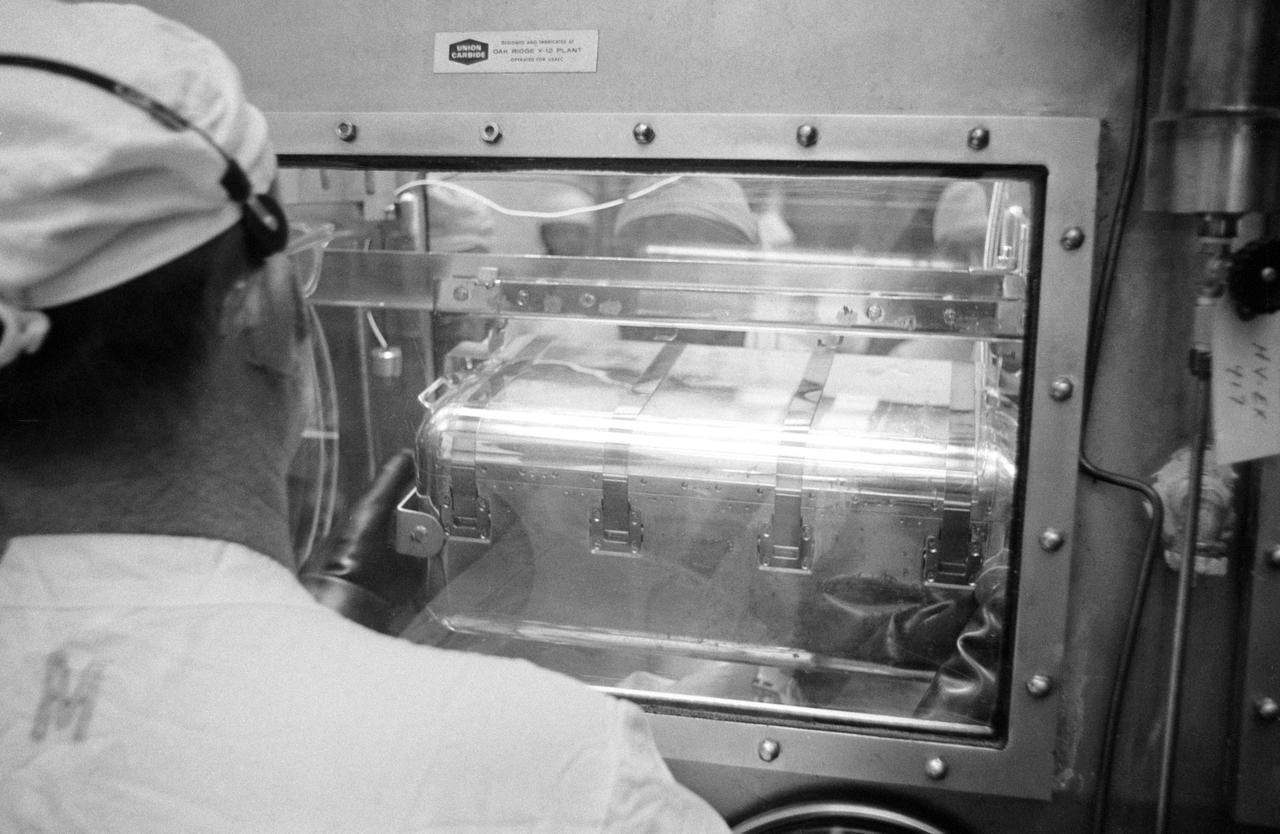
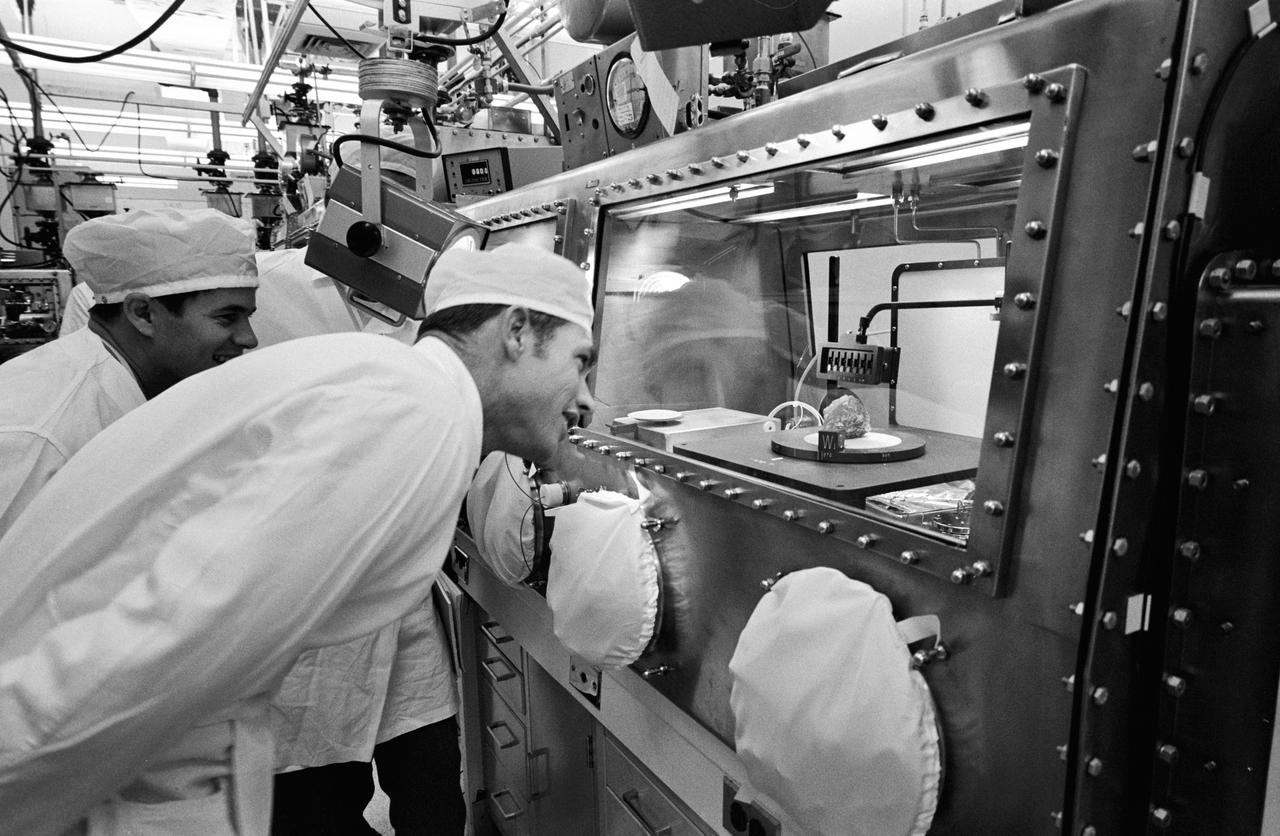
S71-19489 (18 Feb. 1971) --- Glove handlers work with freshly opened Apollo 14 lunar sample material in modularized cabinets in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center. The glove operator on the right starts to pour fine lunar material which he has just taken from a tote bag. The powdery sample was among the last to be revealed of the 90-odd pounds of material brought back to Earth by the Apollo 14 crew members.

S69-40205 (27 July 1969) --- The crewmen of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission go through their post flight debriefing session on Sunday, July 27, 1969. Left to right, are astronauts Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot; Michael Collins, command module pilot; and Neil A. Armstrong, commander. They are seated in the debriefing room of the Crew Reception Area of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center.

S71-19269 (12 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of Apollo 14 sample number 14414 & 14412, a fine lunar powder-like material under examination in the Sterile Nitrogen Atmospheric Processing (SNAP) line in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Scientists are currently making preliminary analyses of material brought back from the moon by the crew of Apollo 14 lunar landing mission.
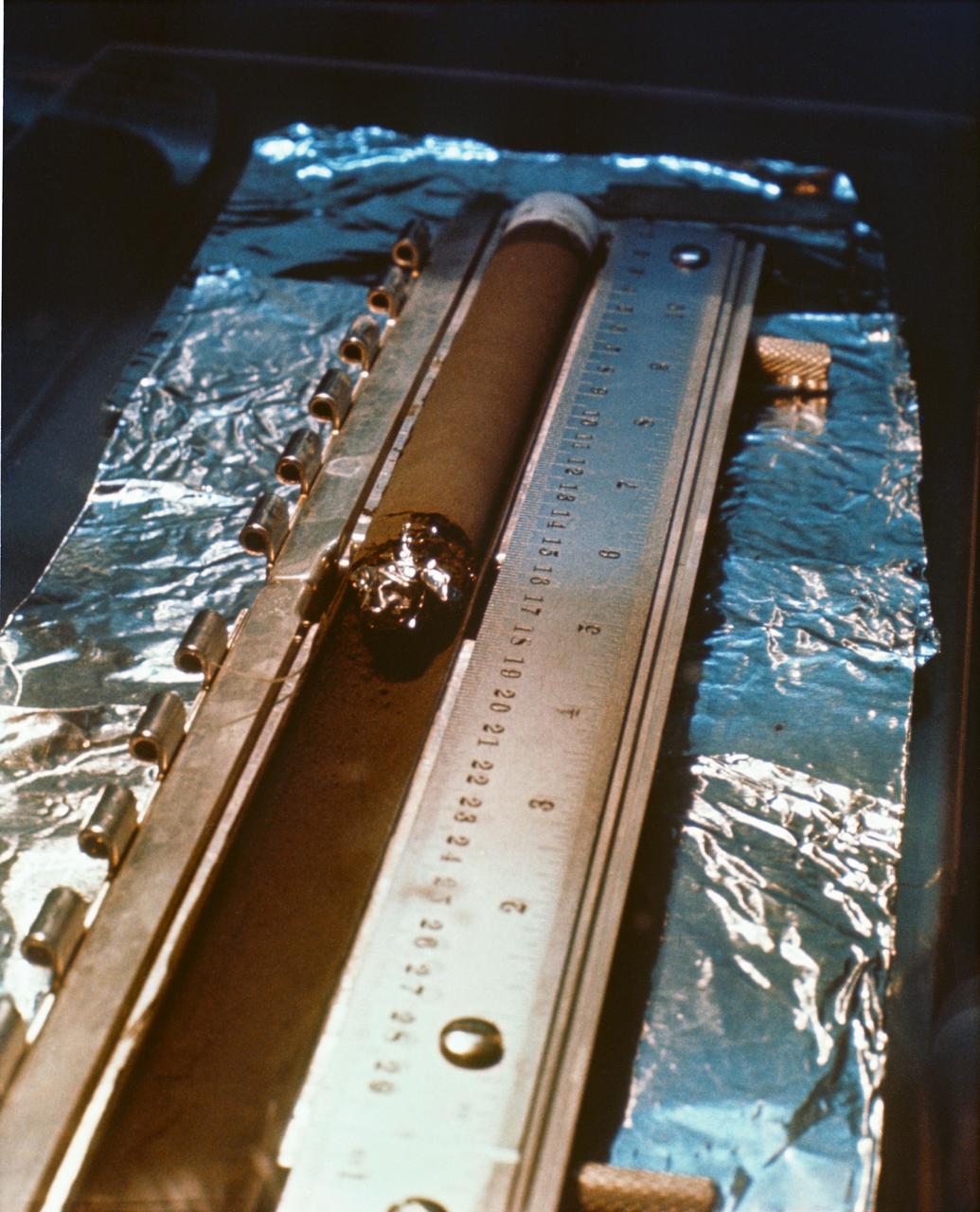
S69-40945 (August 1969) --- This is a core tube sample under study and examination in the Manned Spacecraft Center?s (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL). The sample was among lunar soil and rock samples collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their extravehicular activity (EVA) on July 20, 1969. While astronauts Armstrong, commander; and Aldrin, lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility landing site on the moon. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.

S69-40110 (25 July 1969) --- The first Apollo 11 sample return container, containing lunar surface material, is photographed just after it arrives at the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL), Building 37, Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The box arrived by air at Ellington Air Force Base just before noon on Friday, July 25, 1969, from the Pacific recovery area. It was taken immediately to the Manned Spacecraft Center. The lunar samples were collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA).
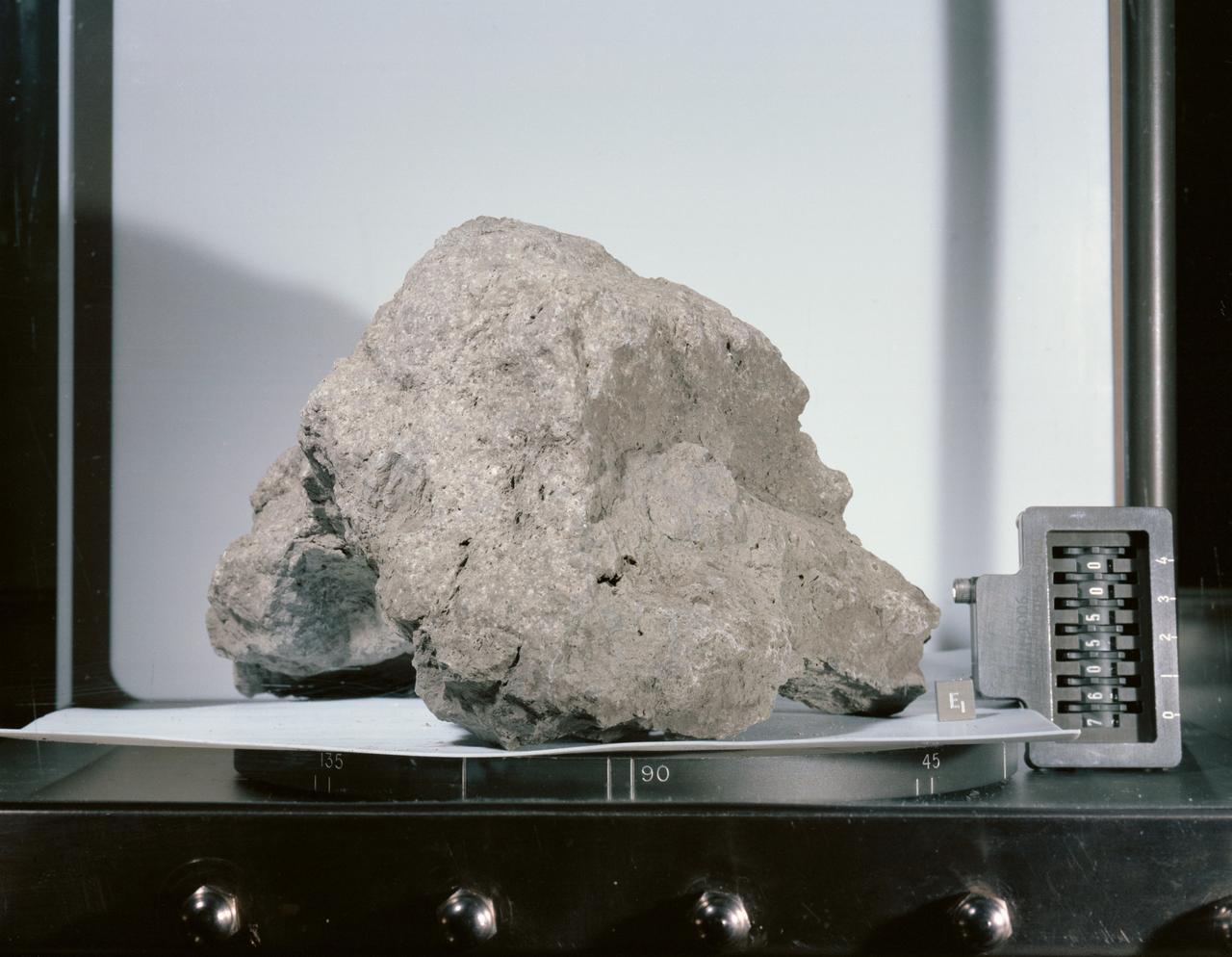

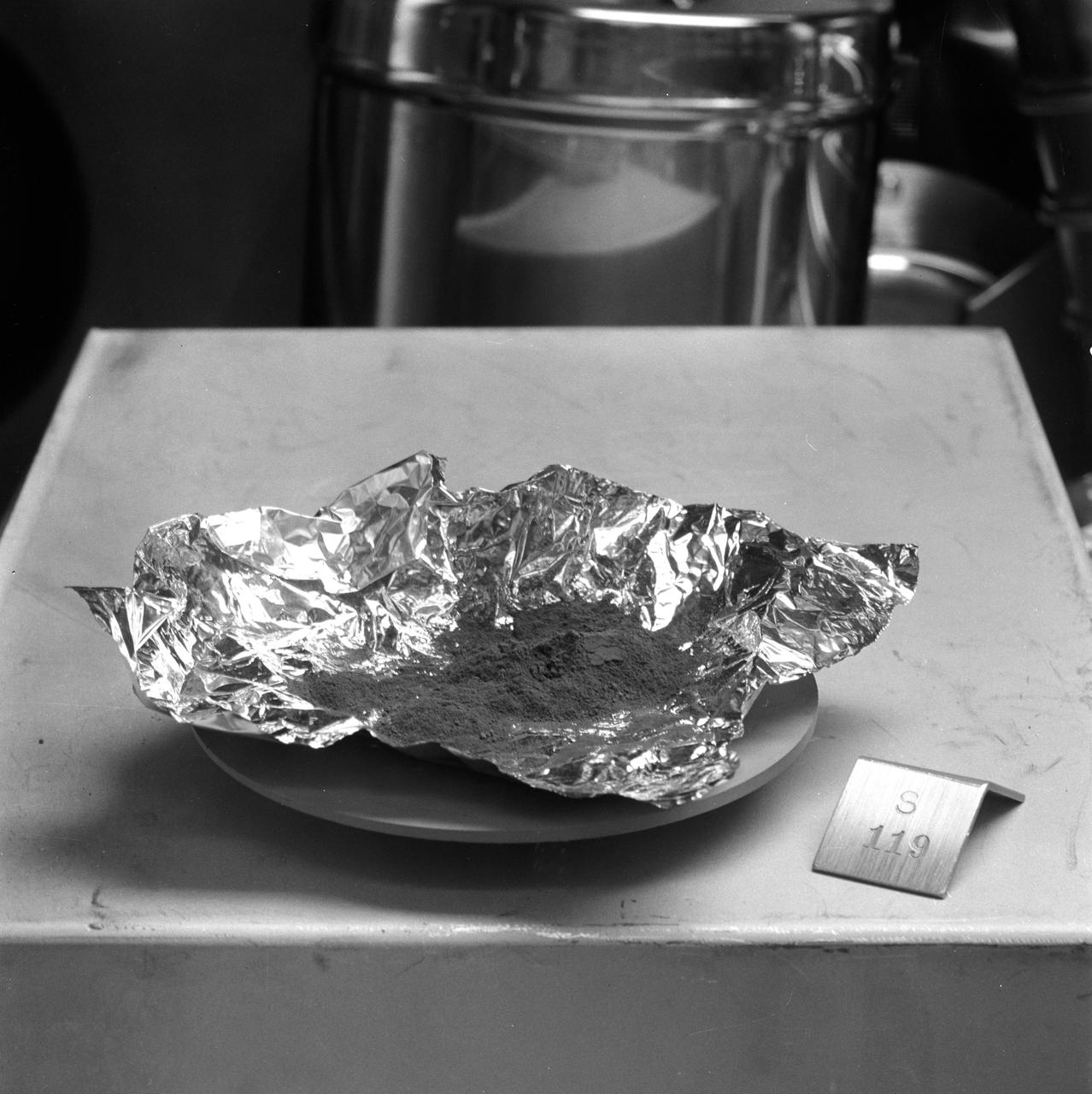
S73-15713 (January 1973) --- A close-up view of Apollo 17 lunar rock sample No. 76055 being studied and analyzed in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center. This tan-gray irregular, rounded breccia was among many lunar samples brought back from the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crew. The rock measures 18 x 20 x 25 centimeters (7.09 x 7.87 x 9.84 inches) and weighs 6,389 grams (14.2554 pounds). The rock was collected from the south side of the lunar roving vehicle while the Apollo 17 astronauts were at Station 7 (base of North Massif).
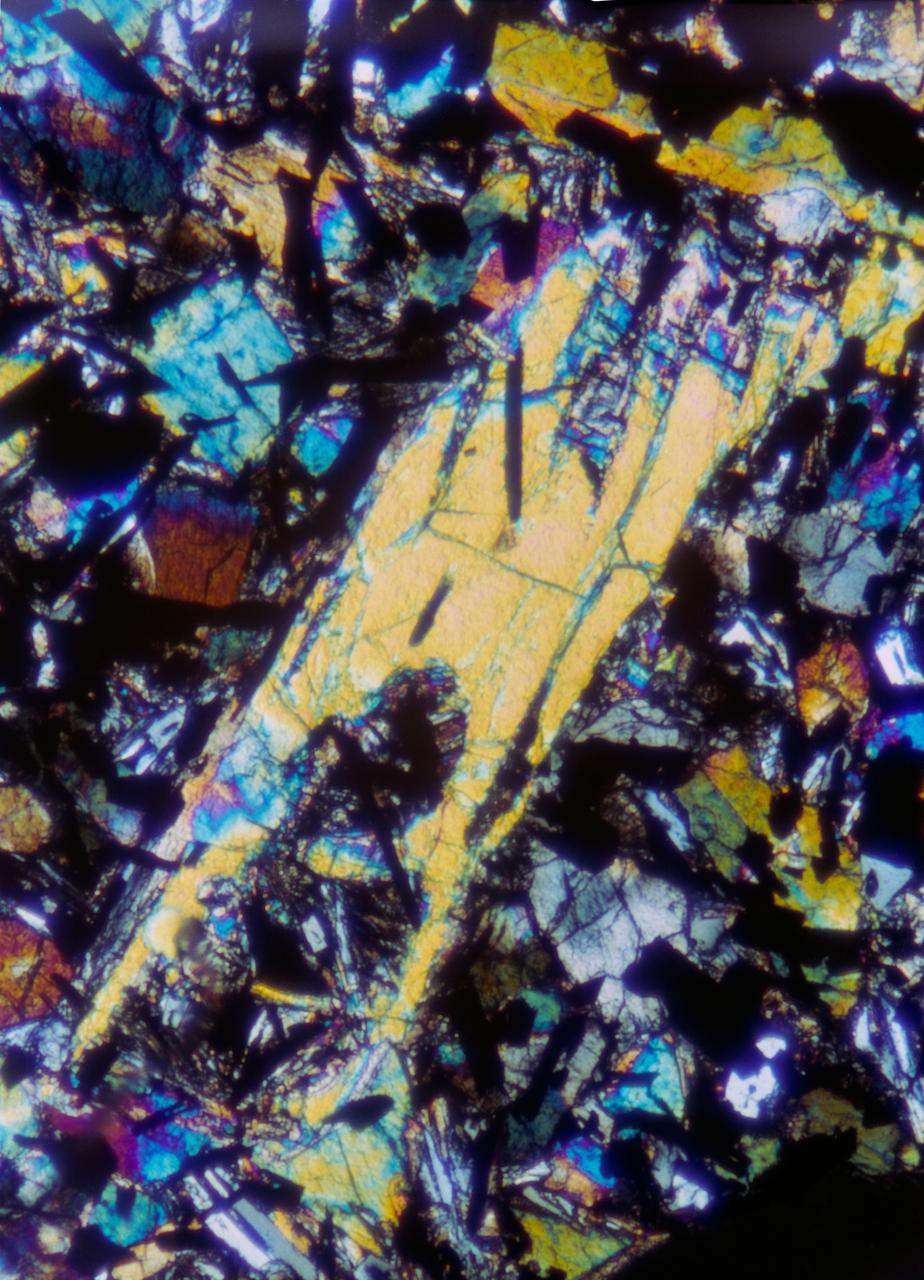
S69-47900 (September 1969) --- This is a photo micrograph of lunar sample 10022. Magnification one inch equals one-tenth millimeter. The light blue and white mineral is plagioclase. The black is ilmenite, and the blue and/or green and/or orange and/or yellow and/or red mineral is pyroxene. The large pyroxene is a phenocryst that had been partially resorbed. The lunar samples collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission have been subjected to extensive tests and examinations at the Manned Spacecraft Center’s Lunar Receiving Laboratory.
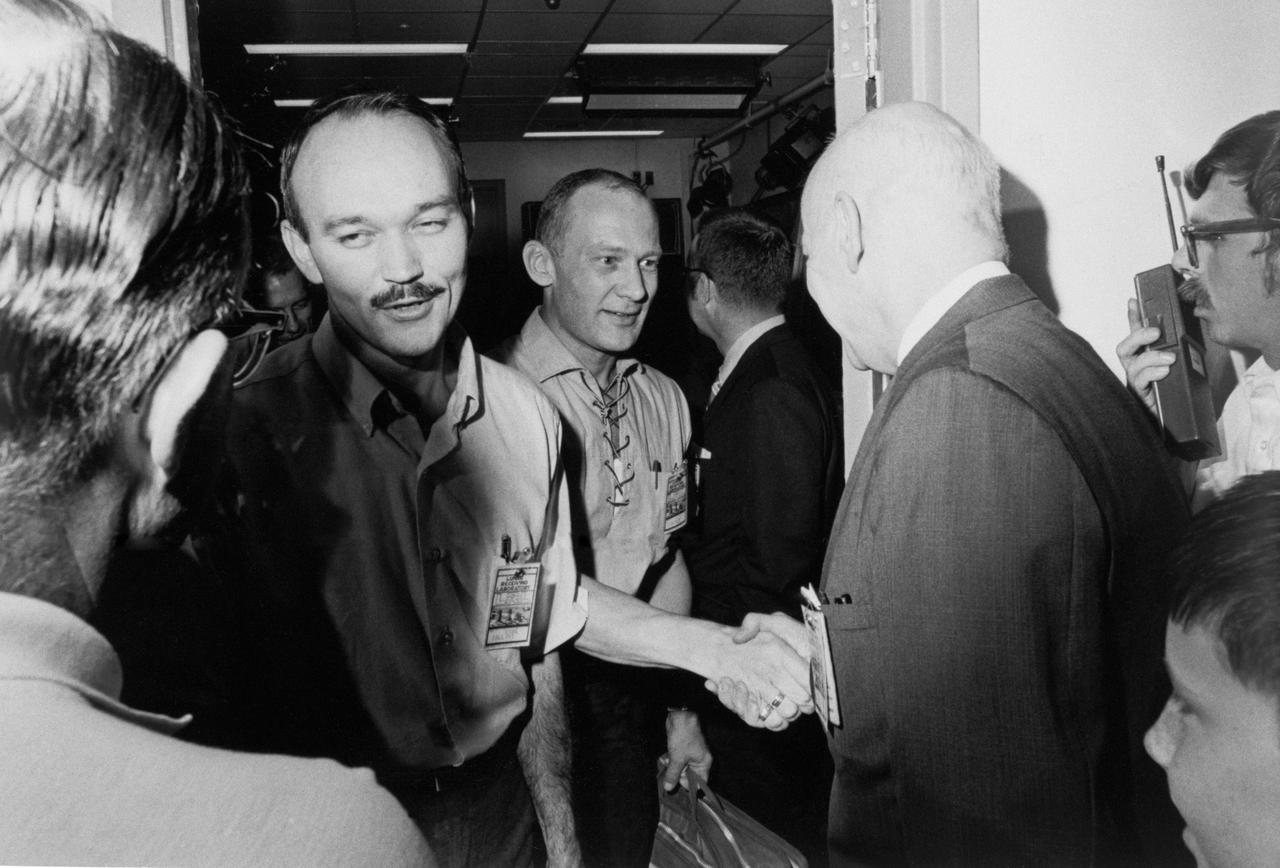

S69-41359 (10 Aug. 1969) --- Astronauts Michael Collins (left) and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., are greeted by Dr. Robert R. Gilruth, director, Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), and others upon their release from quarantine. The Apollo 11 crew left the Crew Reception Area (CRA) of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at 9 p.m., Aug. 10, 1969. While astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Aldrin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
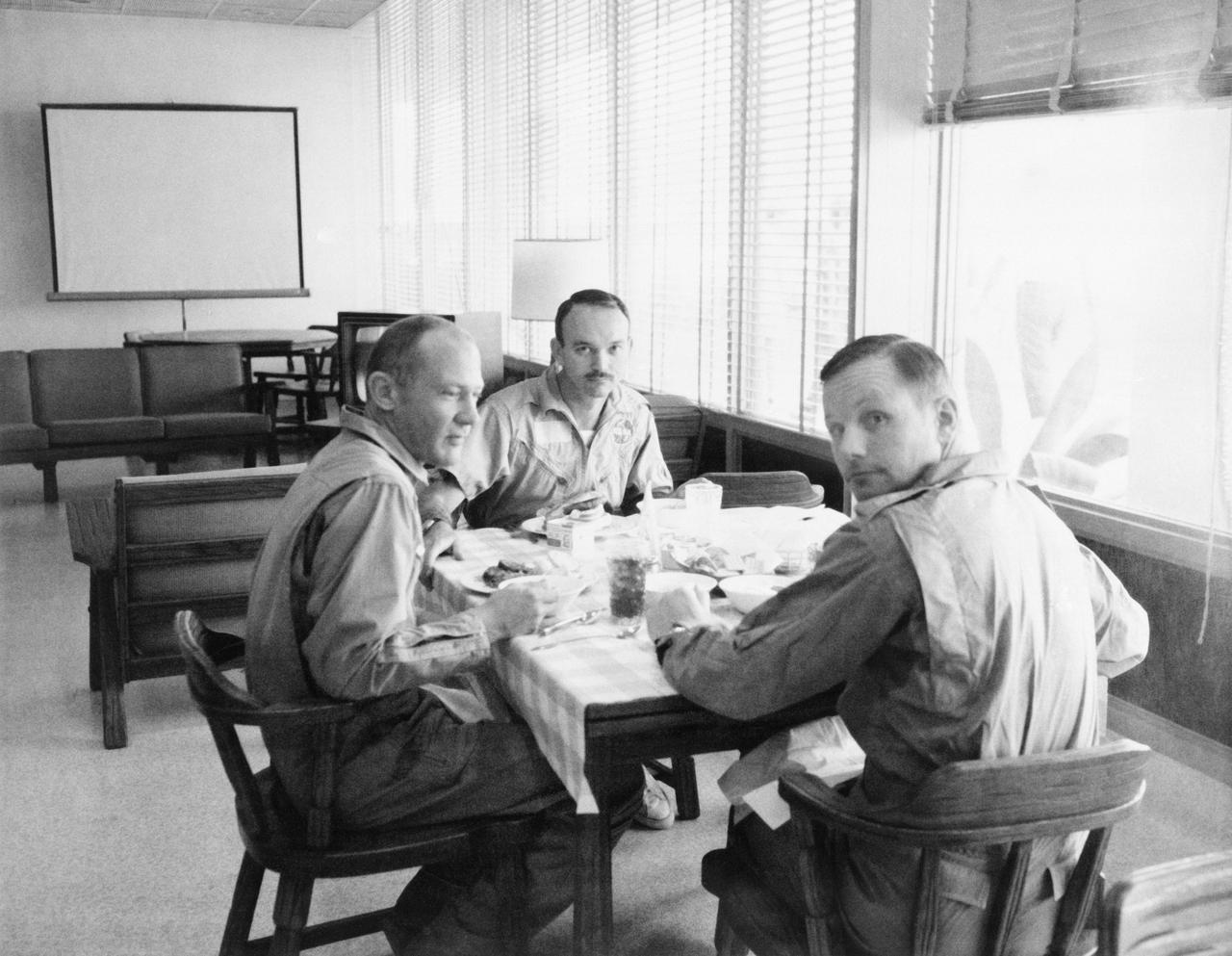

S69-40306 (30 July 1969) --- The crewmen of the historic Apollo 11 lunar landing mission are seen dining in the Crew Reception Area of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory, Building 37, Manned Spacecraft Center. Left to right, are astronauts Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Michael Collins, and Neil A. Armstrong. They are continuing their postflight debriefings. The astronauts will be released from quarantine on Aug. 11, 1969.
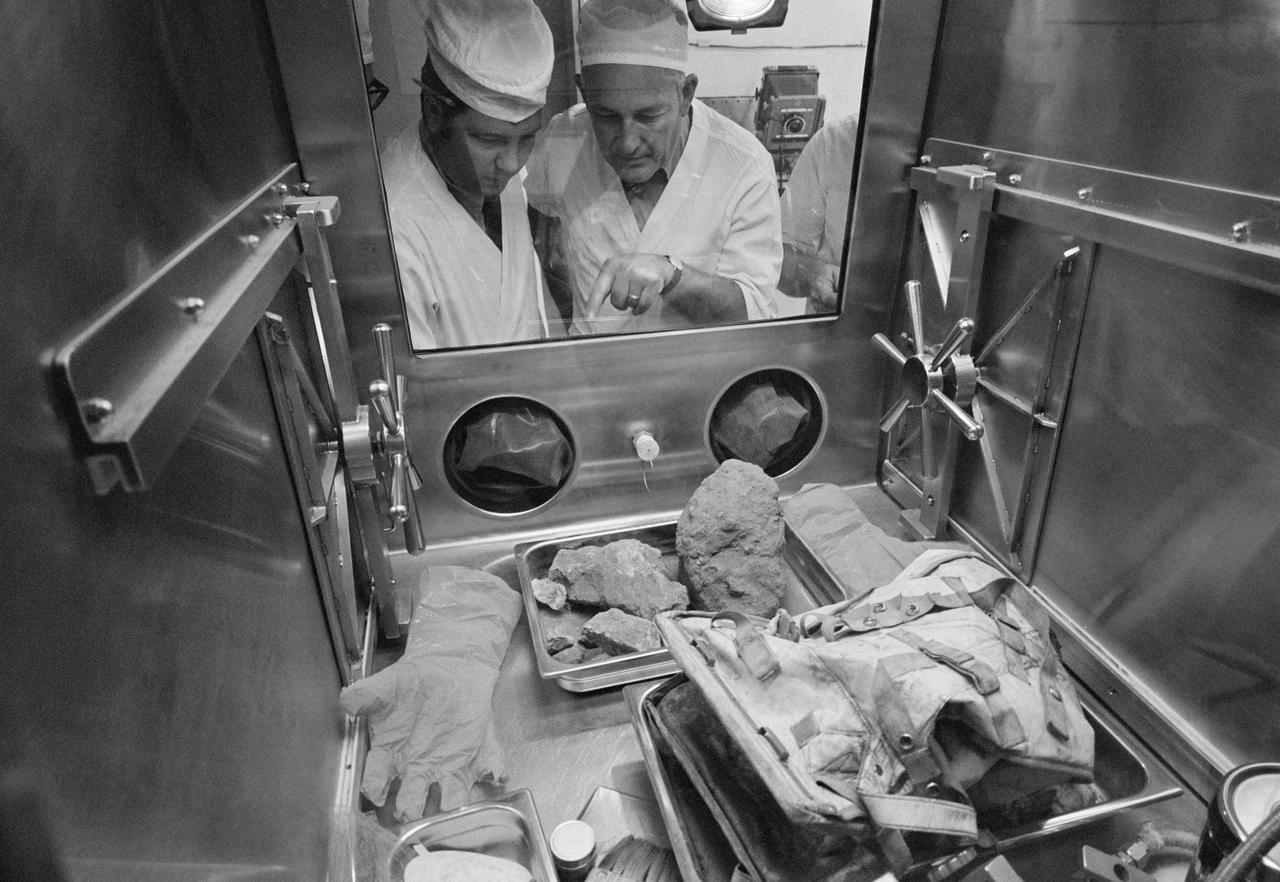
S72-38465 (19 May 1972) --- In an isolated area of the Manned Spacecraft Center's Lunar Receiving Laboratory, engineer David White (left) and University of Texas geologist/professor William Muehlberger look at a "special" rock brought back from the moon recently by the Apollo 16 astronauts. Lunar sample 61016, better known as "Big Muley," is a large breccia sample, the largest moon rock returned by any Apollo crew, which is named after Muehlberger, the Apollo 16 field geology team leader. Photo credit: NASA
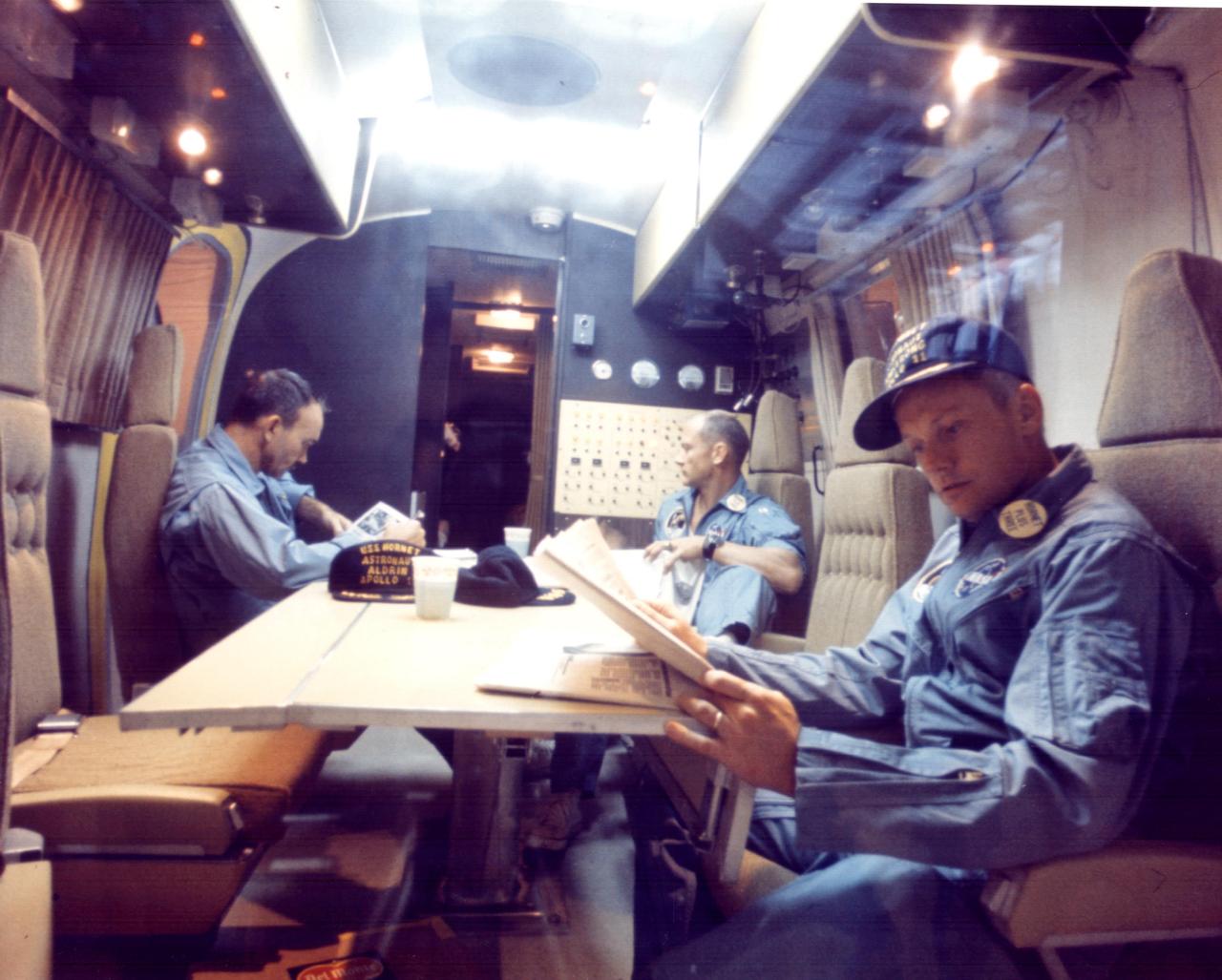

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Within the Mobile Quarantine Facility, Apollo 11 astronauts (left to right) Michael Collins, Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. and Neil A. Armstrong relax following their successful lunar landing mission. They spent two-and-one-half days in the quarantine trailer enroute from the USS Hornet, prime recovery ship, to the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center in Houston. The Hornet docked at Pearl Harbor where the trailer was transferred to a jet aircraft for the flight to Houston.

S71-42955 (August 1971) --- A close-up view of Apollo 15 lunar sample no. 15415 in the Non-Sterile Nitrogen Processing Line (NNPL) in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). This sample is the white anorthositic rock (Genesis Rock) collected by astronauts David R. Scott and James B. Irwin in container no. 196 at Site no. 7 at a Ground Elapsed Time of 145 hours and 42 minutes, on the mission's second extravehicular activity (EVA).

S69-40307 (30 July 1969) --- The crewmen of the historic Apollo 11 lunar landing mission stand in the serving line as they prepare to dine in the Crew Reception Area of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory, Building 37, Manned Spacecraft Center. Left to right, are astronauts Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Michael Collins, and Neil A. Armstrong. They are continuing their postflight debriefings. The three astronauts will be released from quarantine on Aug. 11, 1969.
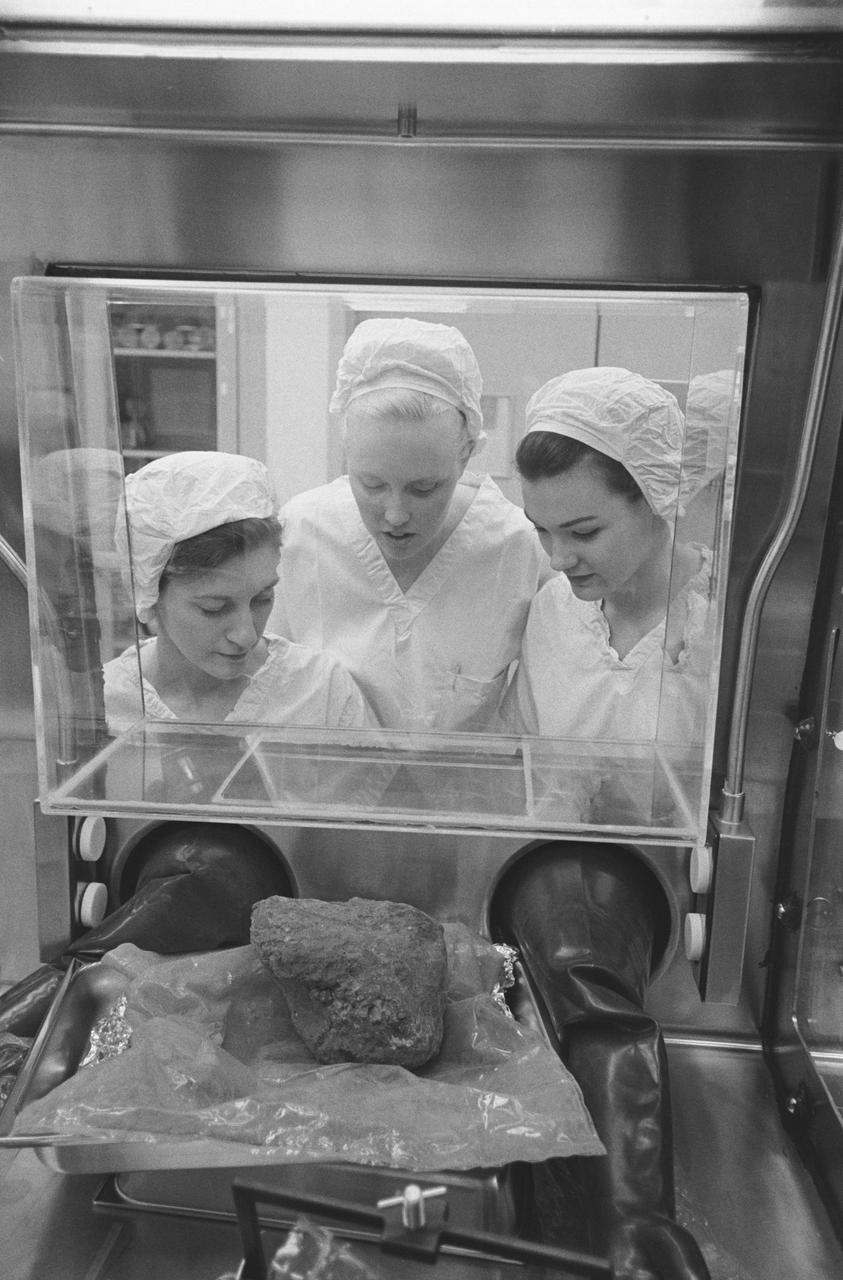

S71-21244 (24 Feb. 1971) --- Three Brown and Root/Northrop technicians in the Nonsterile Nitrogen Laboratory in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) peer through glass at the much-discussed basketball size rock which Apollo 14 crewmen brought back from the Fra Mauro area of the moon. They are, left to right, Linda Tyler, Nancy L. Trent and Sandra Richards.
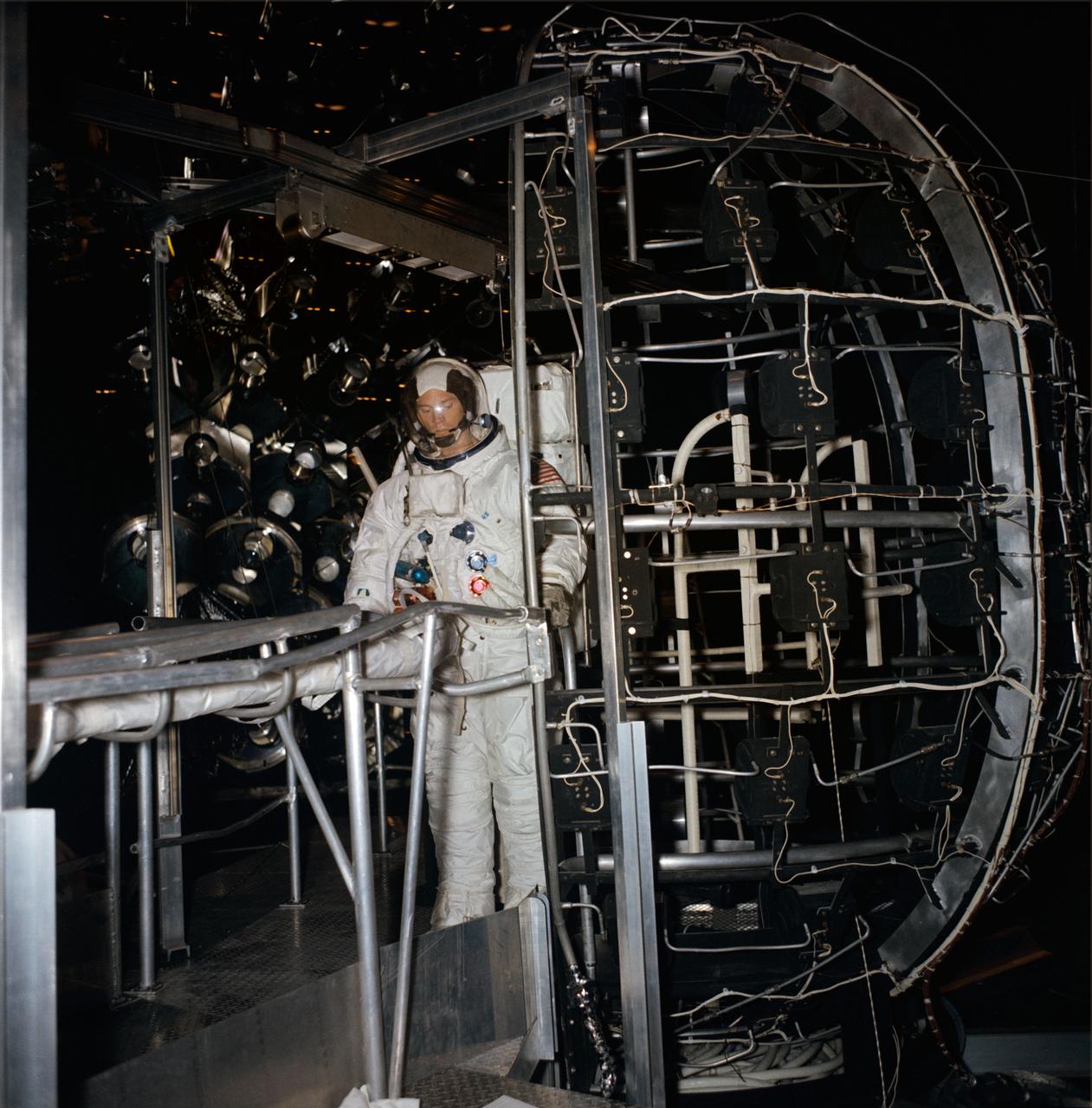

S68-55391 (11 Dec. 1968) --- Astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot of the Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/Saturn 504) space mission, is seen inside Chamber "A," Space Environment Simulation Laboratory, Building 32, participating in dry run activity in preparation for extravehicular activity which is scheduled in Chamber "A." The purpose of the scheduled training is to familiarize the crewmen with the operation of EVA equipment in a simulated space environment. In addition, metabolic and workload profiles will be simulated on each crewman. Astronauts Schweickart and Alan L. Bean, backup lunar module pilot, are scheduled to receive thermal-vacuum training simulating Earth-orbital EVA.

S69-45009 (27 July 1969) --- This is the first lunar sample that was photographed in detail in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The photograph shows a granular, fine-grained, mafic (iron magnesium rich) rock. At this early stage of the examination, this rock appears similar to several igneous rock types found on Earth. The scale is printed backwards due to the photographic configuration in the Vacuum Chamber. The sample number is 10003. This rock was among the samples collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) on July 20, 1969.
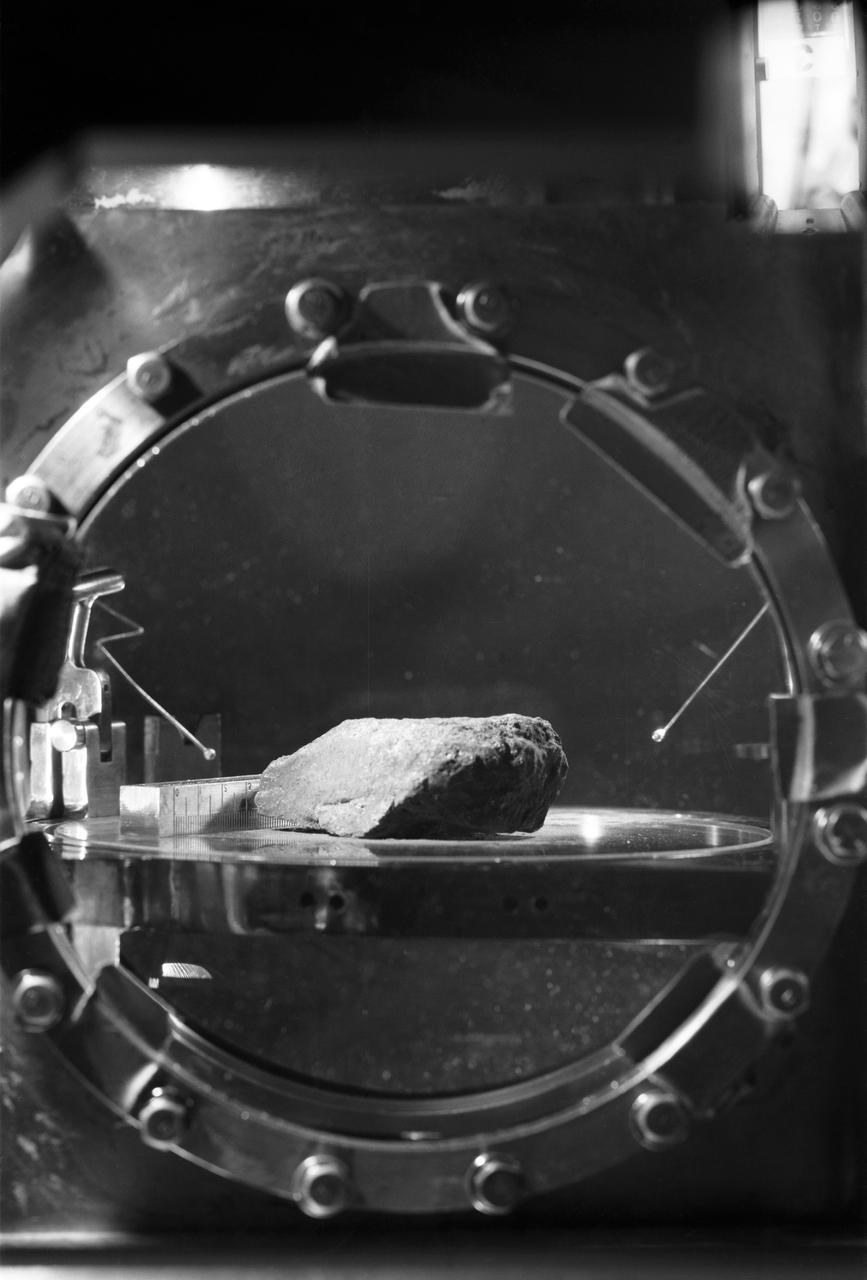

S69-45025 (27 July 1969) --- This is the first lunar sample that was photographed in detail in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center. The photograph shows a granular, fine-grained, mafic (iron magnesium rich) rock. At this early stage of the examination, this rock appears similar to several igneous rock types found on Earth. The scale is printed backwards due to the photographic configuration in the Vacuum Chamber. The sample number is 10003. This rock was among the samples collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity on July 20, 1969.
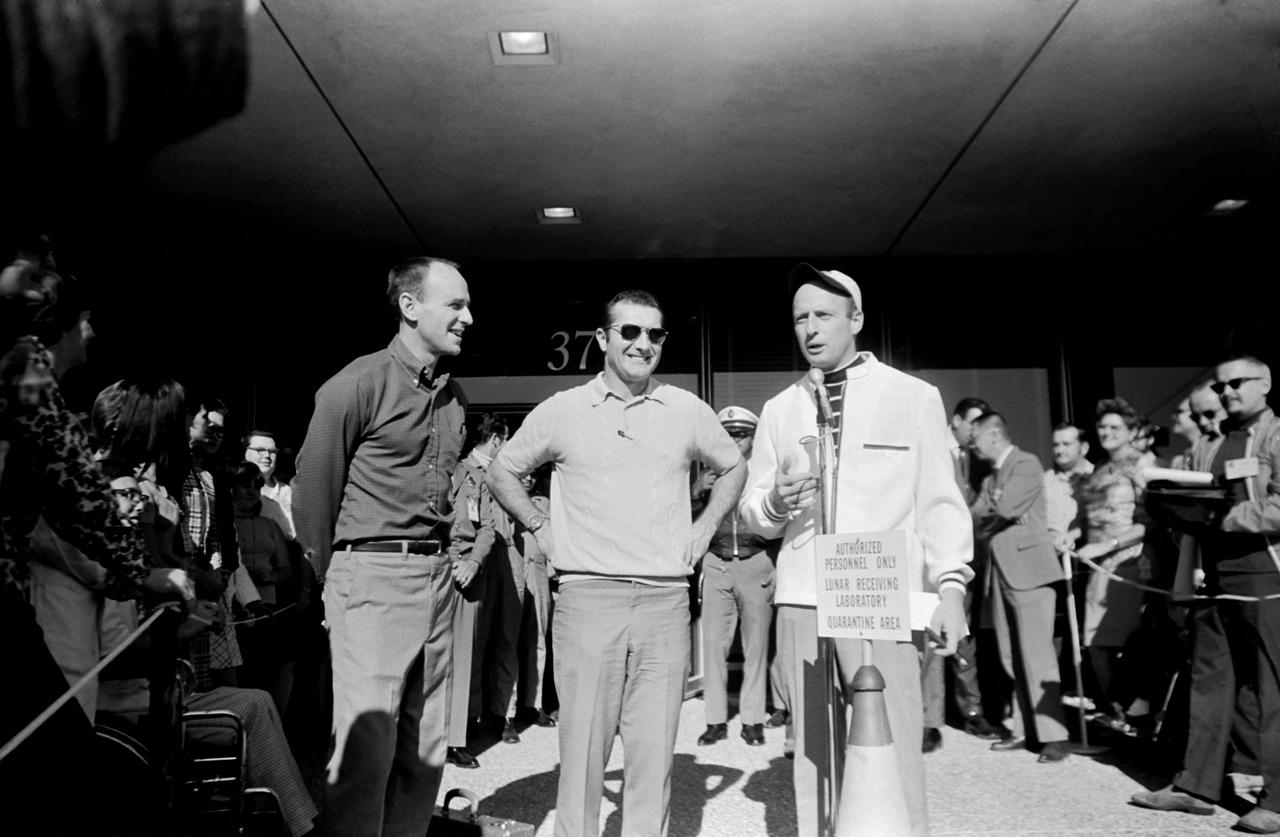

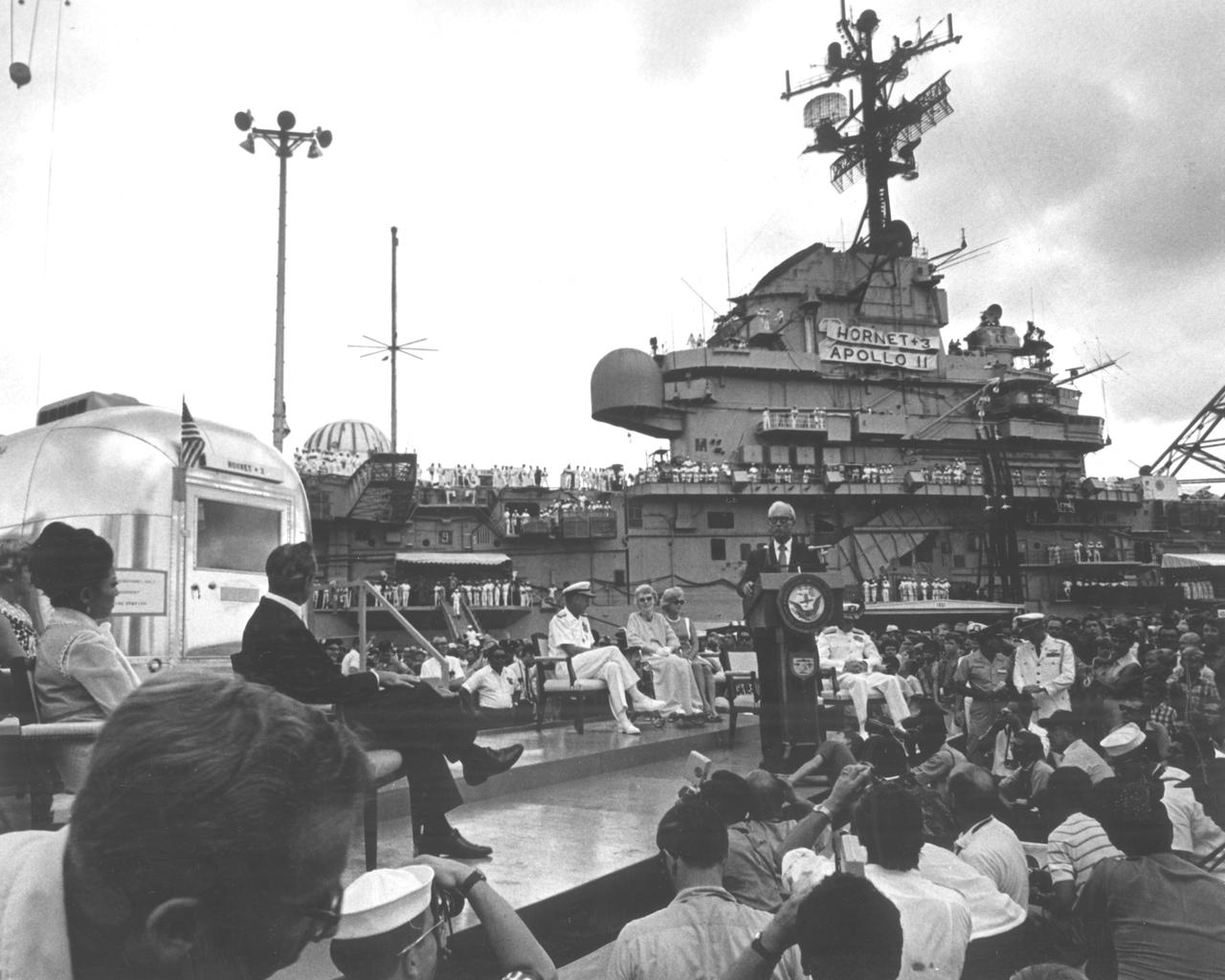
S69-62884 (10 Dec. 1969) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, makes several remarks publicly in response to the welcome given him and other members of the Apollo 12 crew upon their release from post-mission isolation in the Manned Spacecraft Center's (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL). Pictured with Conrad outside Building 37, which houses the LRL, are his fellow crewmembers for the Apollo 12 mission, astronauts Alan L. Bean (left), lunar module pilot; and Richard F. Gordon Jr. (center), command module pilot.
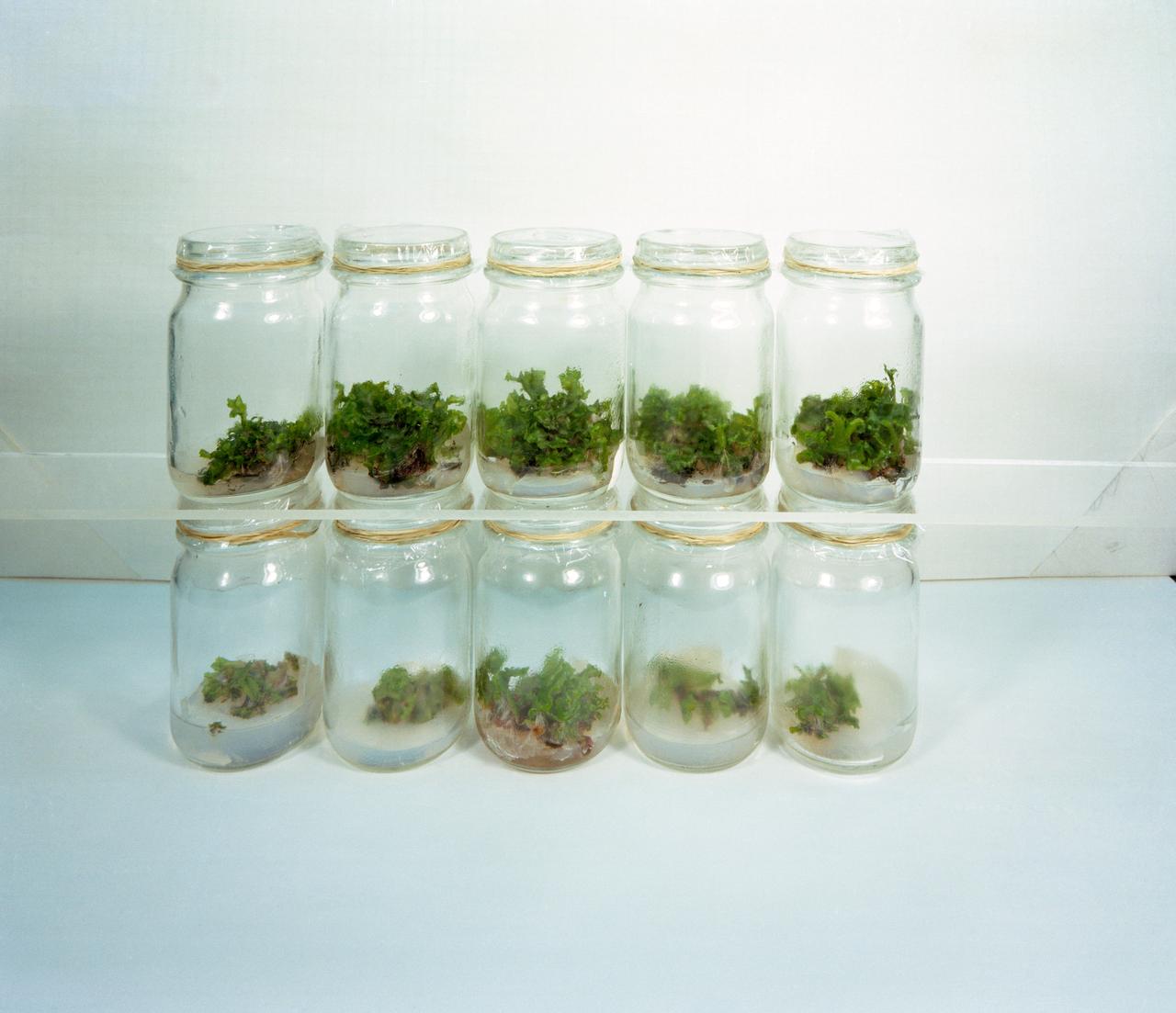

S69-53126 (30 Sept. 1969) --- A progress photograph of sample experiments being conducted in the Manned Spacecraft Center?s Lunar Receiving Laboratory with lunar material brought back to Earth by the crew of the Apollo 11 mission. Aseptic cultures of liverwort (Marchantia polymorpha) - a species of plant commonly found growing on rocks or in wooded areas - are shown in two rows of sample containers. Seven weeks or some 50 days prior to this photograph 0.22 grams of finely ground lunar material was added to each of the upper samples of cultures. The lower cultures were untreated, and a noted difference can be seen in the upper row and the lower one, both in color and size of the cultures.
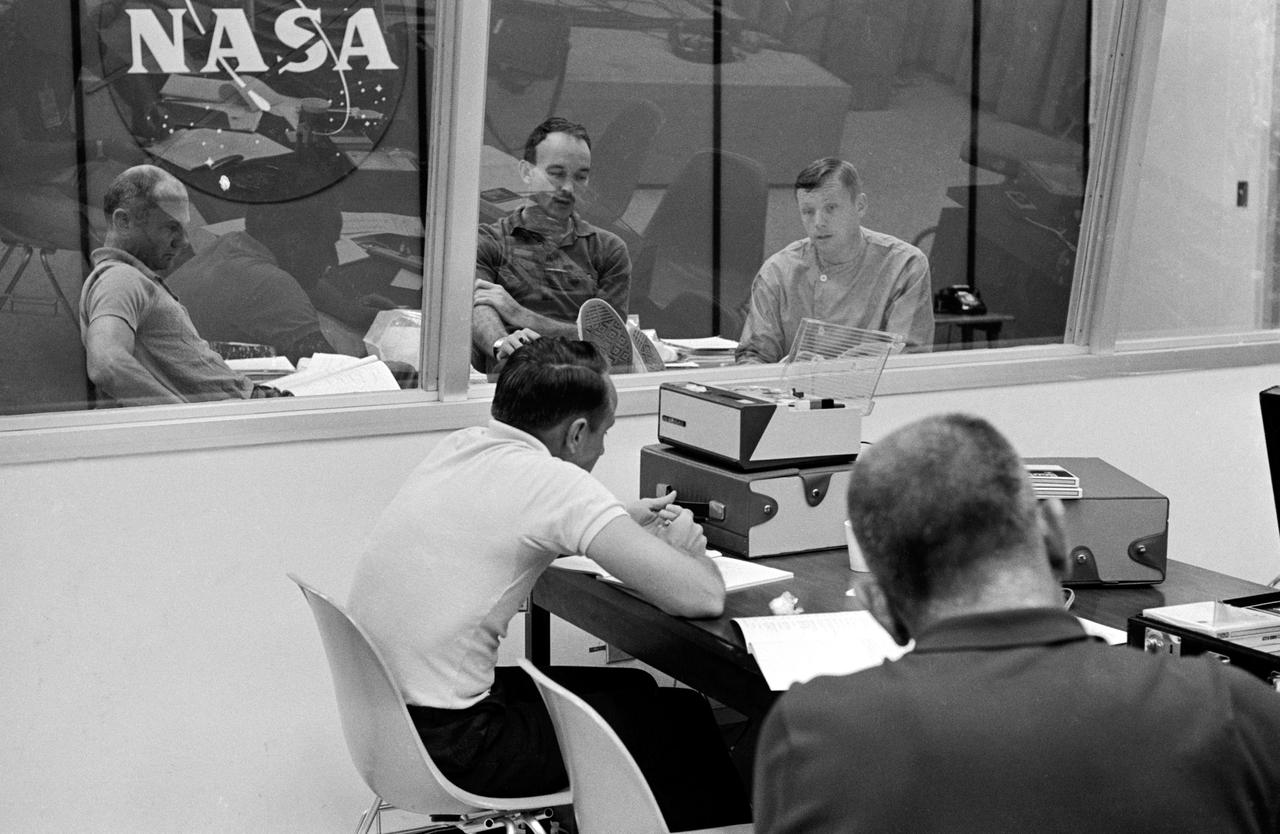

S69-40209 (27 July 1969) --- The crewmen of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission go through their post flight debriefing session on Sunday, July 27, 1969. Left to right, are astronauts Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot; Michael Collins, command module pilot; and Neil A. Armstrong, commander. They are seated in the debriefing room of the Crew Reception Area of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). In the foreground are Donald K. Slayton (right), MSC Director of Flight Crew Operations; and Lloyd Reeder, training coordinator.

The two moon-exploring crewmen of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission show off some of the largest of the lunar rocks they collected on their mission, during a through-the-glass meeting with newsmen in the Crew Reception Area of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell (left), lunar module pilot, holds up a tote bag in which some of the lunar samples were stowed, while astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, looks on. The largest sample brought back on the mission, a basketball-size rock (nicknamed "Big Bertha"), is said to be the largest lunar rock collected in three lunar landing missions for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
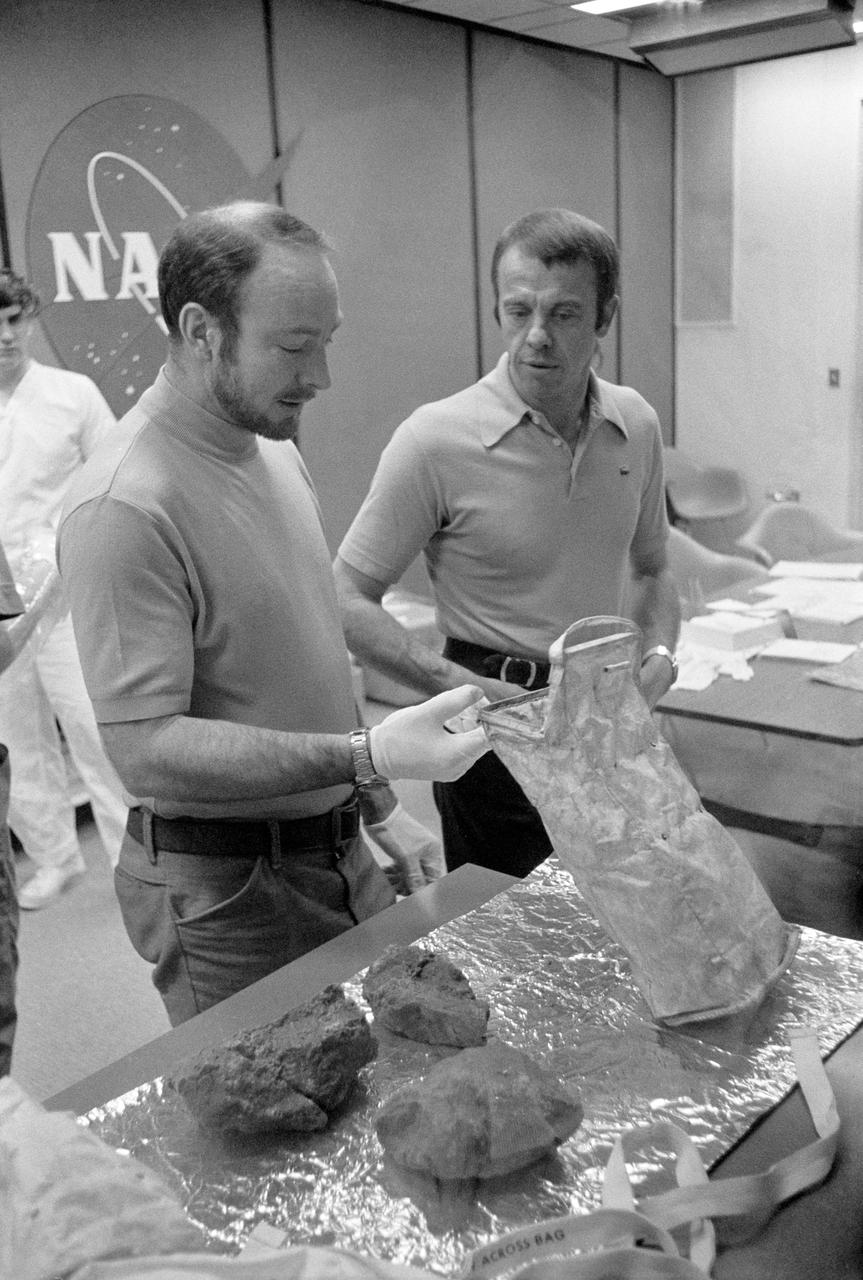

S71-20375 (19 Feb. 1971) --- The two moon-exploring crewmen of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission show off some of the largest of the lunar rocks they collected on their mission, during a through-the-glass meeting with newsmen in the Crew Reception Area of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell (left), lunar module pilot, holds up a tote bag in which some of the lunar samples were stowed, while astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, looks on. The largest sample brought back on the mission, a basketball-size rock (nicknamed "Big Bertha"), is said to be the largest lunar rock collected in three lunar landing missions for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).

S69-60644 (29 Nov. 1969) --- A Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF), with the crew men of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission aboard, arrived at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Saturday morning, Nov. 29, 1969. Astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., Richard F. Gordon Jr., and Alan L. Bean were on their way to the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) where they will remain in quarantines until Dec. 10, 1969. Minutes earlier the three astronauts had arrived at Ellington Air Force Base from Hawaii aboard a U.S. Air Force C-141 transport. The crewmen were confined to the MQF from splashdown until they arrived at the LRL.
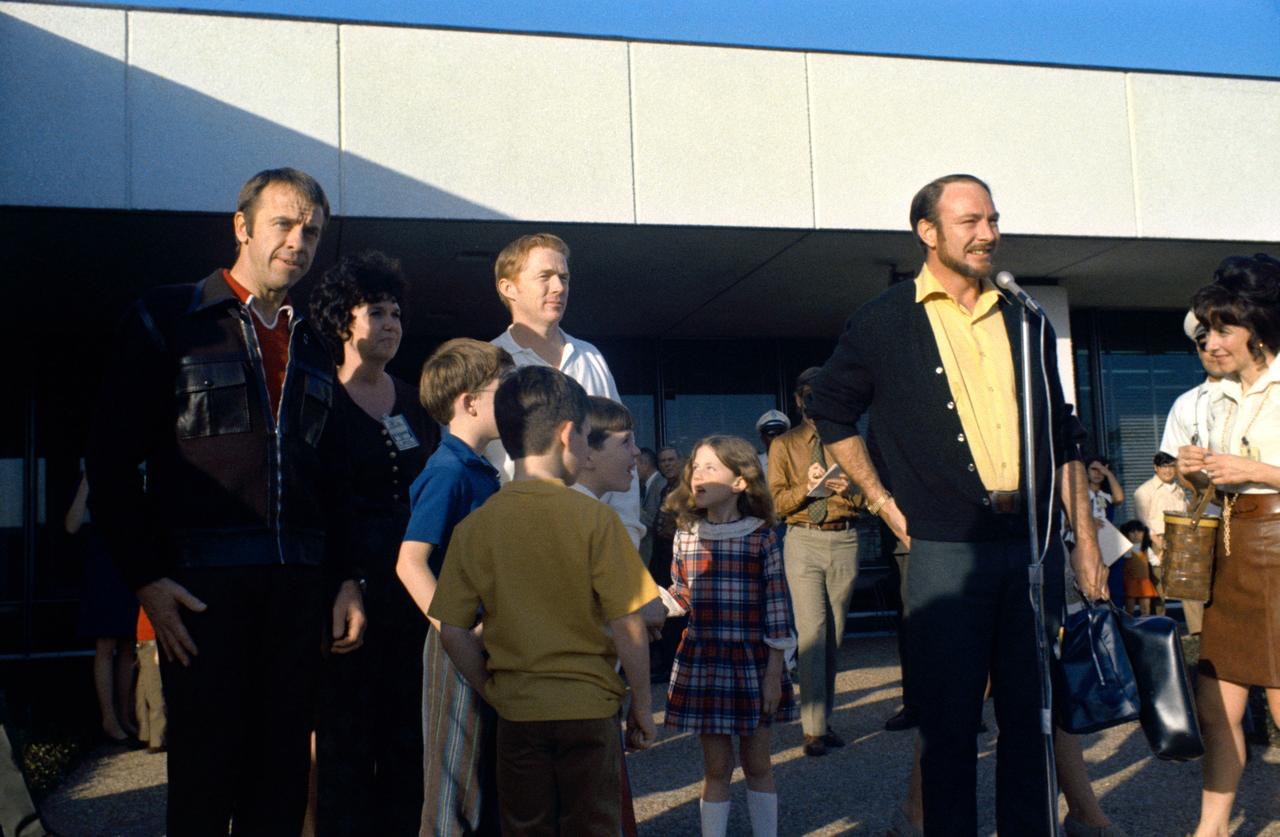

S71-22028 (26 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, right, the Apollo 14 lunar module pilot, addresses NASA-MSC personnel and news media representatives and other visitors soon after he and his fellow crewmen were released from a 15-day confinement period in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory. Pictured with Mitchell in front of the LRL, MSC Building 37, are astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., left, commander; and Stuart A Roosa, command module pilot, Mrs. Mitchell is at right and Mrs. Roosa, near left. Roosa is flanked by his four children, left to right, Christopher A., Stuart A. Roosa Jr., John D. and Rosemary D.

S69-40152 (27 July 1969) --- A Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF), with the three Apollo 11 crewmen inside, is unloaded from a United States Air Force C-141 transport at Ellington Air Force Base very early Sunday after a flight from Hawaii. A large crowd was present to welcome astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. back to Houston following their historic lunar landing mission. The crew remained in the MQF until they arrived at the Crew Reception Area of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The crew will be released from quarantine on Aug. 11, 1969.
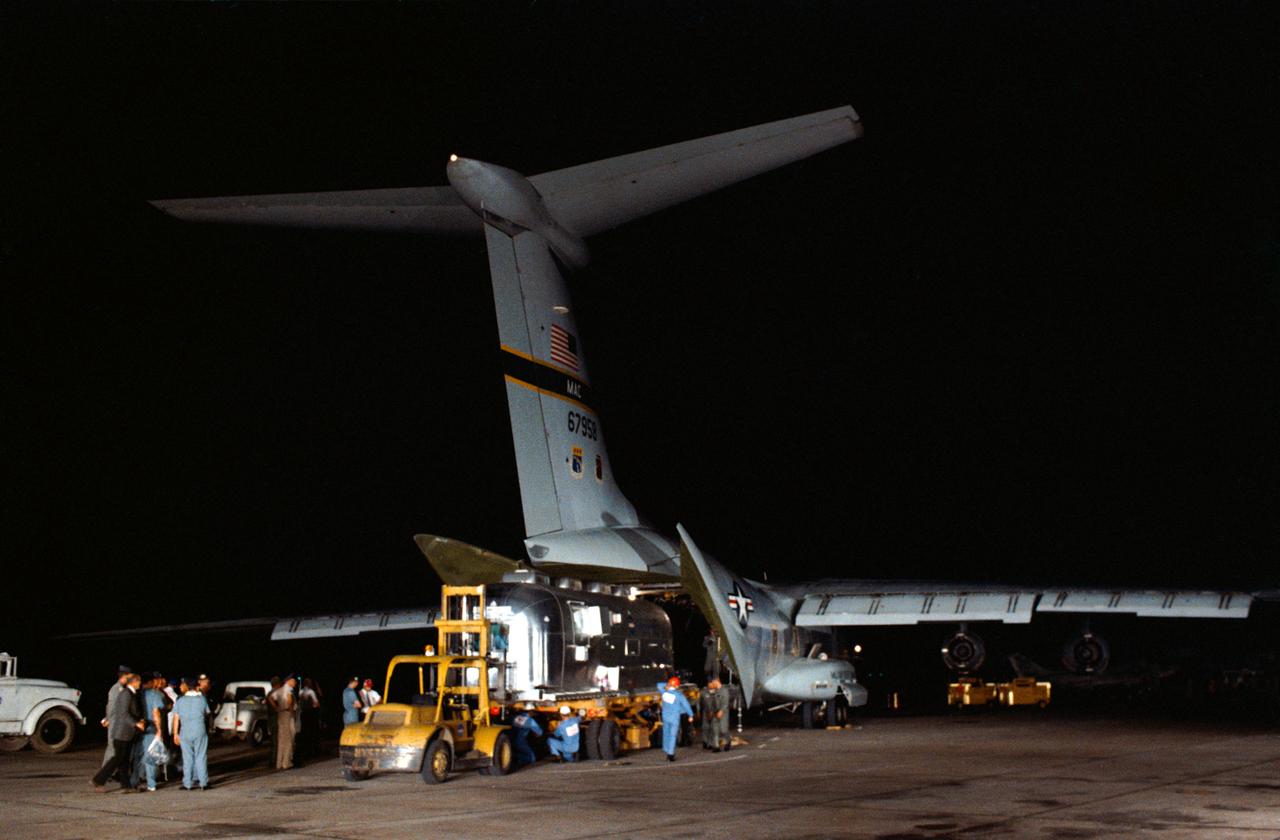

S69-40132 (27 July 1969) --- A Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF), with the three Apollo 11 crewmembers inside, is unloaded from a United States Air Force C-141 transport at Ellington Air Force Base very early Sunday after a flight from Hawaii. A large crowd was present to welcome astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. back to Houston following their historic lunar landing mission. The crew remained in the MQF until they arrived at the Crew Reception Area of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The crew will be released from quarantine on Aug. 11, 1969.

S72-38463 (19 May 1972) --- In an isolated area of the Manned Spacecraft Center's Lunar Receiving Laboratory, geologists Don Morrison (left) and Fred Horz flank University of Texas geologist/professor William (Bill) Muehlberger as the three look at a "special" rock brought back from the moon recently by the Apollo 16 astronauts. Lunar sample 61016, better known as "Big Muley," is a large breccia sample, the largest moon rock returned by any Apollo crew, which is named after Muehlberger, the Apollo 16 field geology team leader. Photo credit: NASA
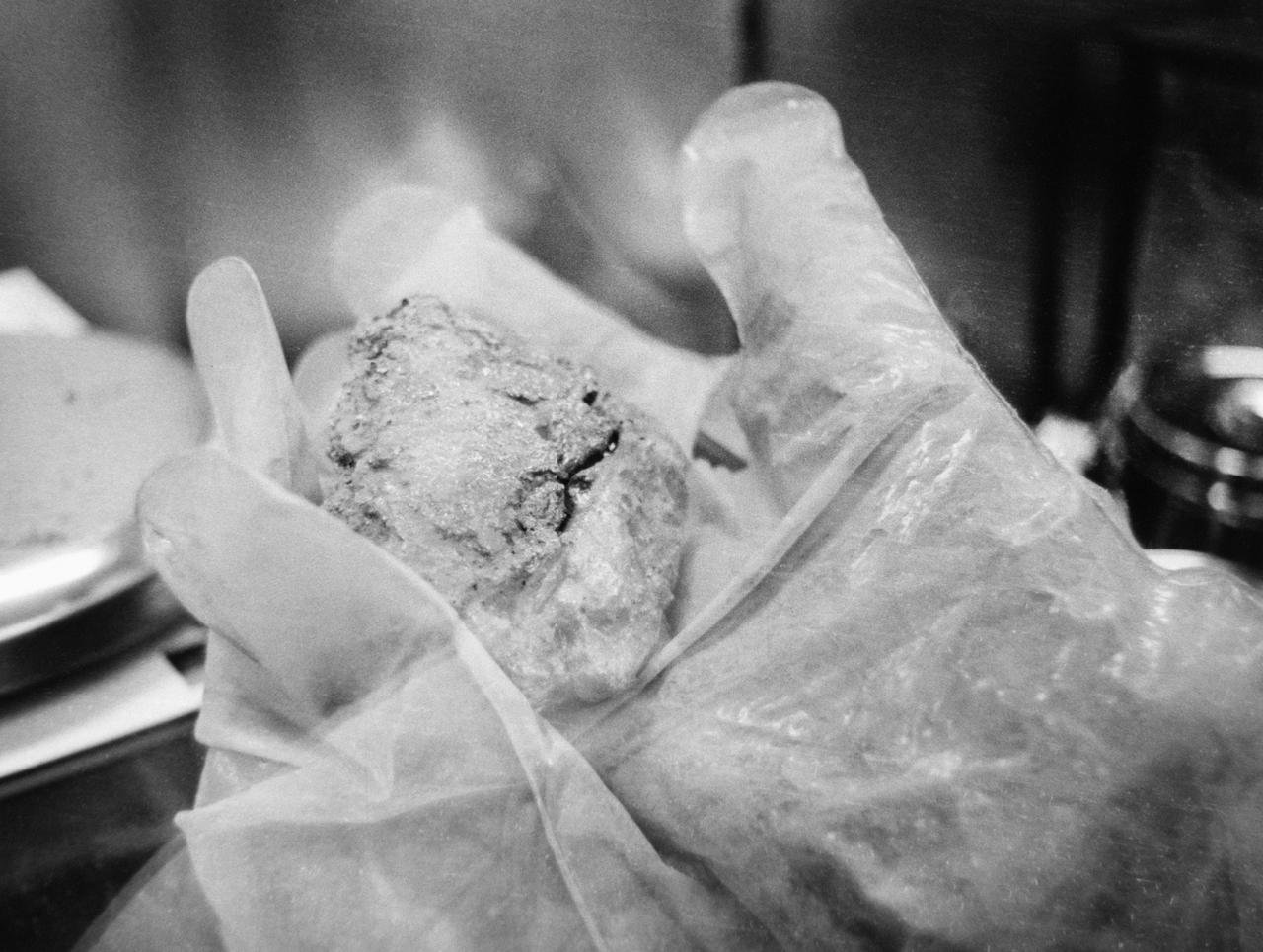
S69-60354 (29 Nov. 1969) --- A scientist's gloved hand holds one of the numerous rock samples brought back to Earth from the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission. The rocks are under thorough examination in the Manned Spacecraft Center's (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL). This sample is a highly shattered basaltic rock with a thin black-glass coating on five of its six sides. Glass fills fractures and cements the rock together. The rock appears to have been shattered and thrown out by a meteorite impact explosion and coated with molten rock material before the rock fell to the surface.

S71-43477 (12 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, right, commander of the Apollo 15 mission, gets a close look at the sample referred to as "Genesis rock" in the Non-Sterile Nitrogen Processing Line (NNPL) in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Allen IV, left, an Apollo 15 spacecraft communicator, looks on with interest. The white-colored rock has been given the permanent identification of 15415.
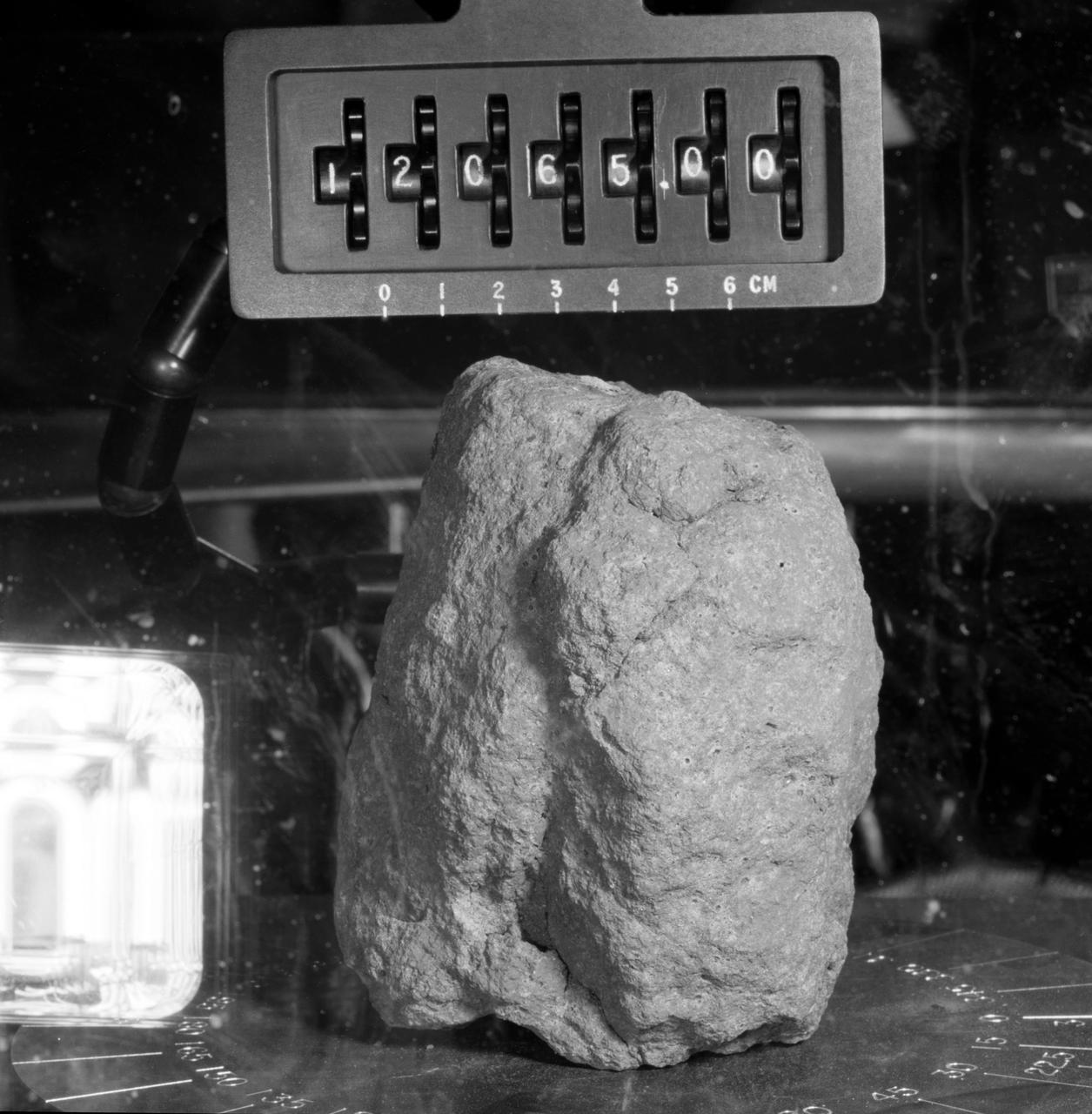

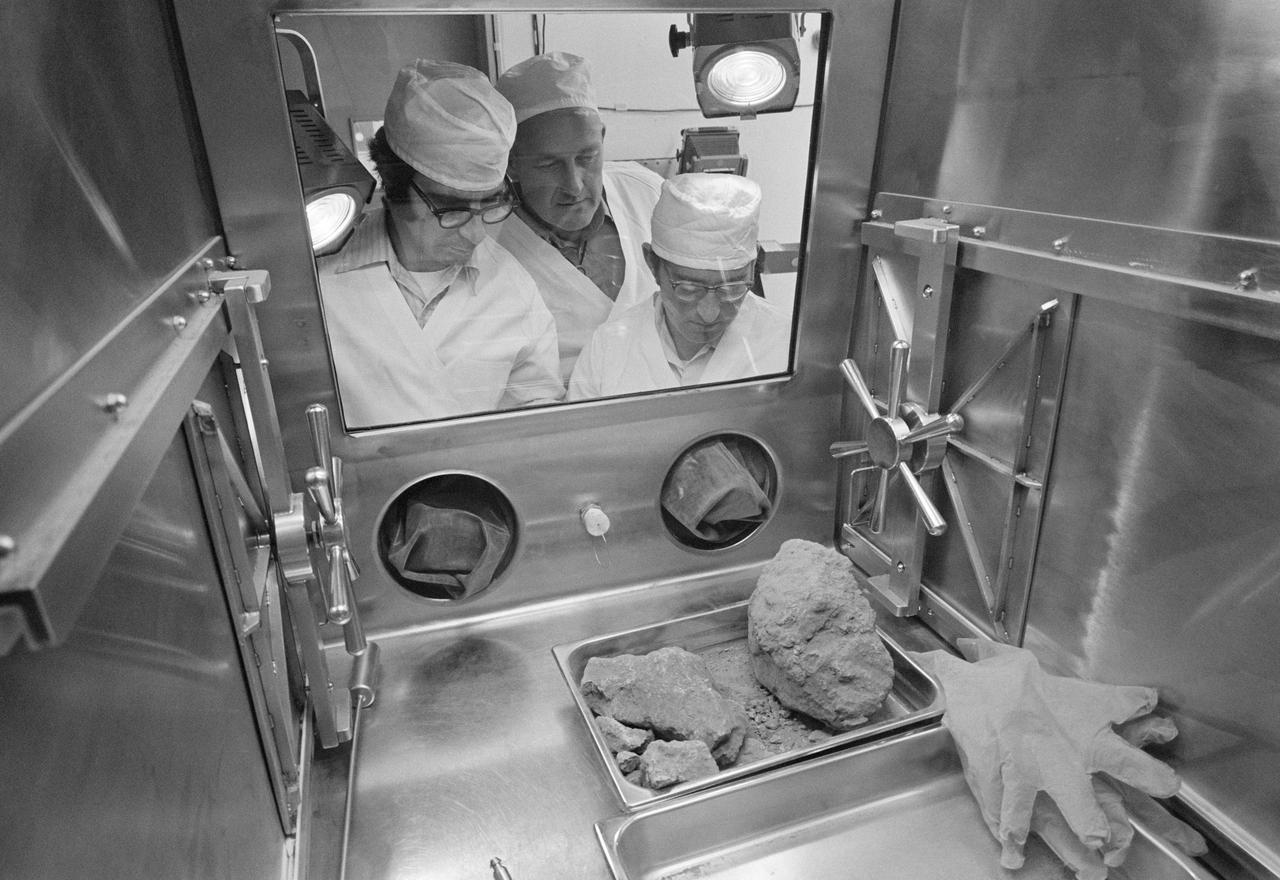
S69-60580 (November 1969) --- Close-up view of Apollo 12 sample 12,065 under observation in the Manned Spacecraft Center's (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL). This sample, collected during the second Apollo 12 extravehicular activity (EVA) of astronauts Charles Conrad Jr. and Alan L. Bean, is a fine-grained rock. Note the glass-lined pits. Viewer can gain an idea of the size of the rock by reference to the gauge on the bottom portion of the number meter.
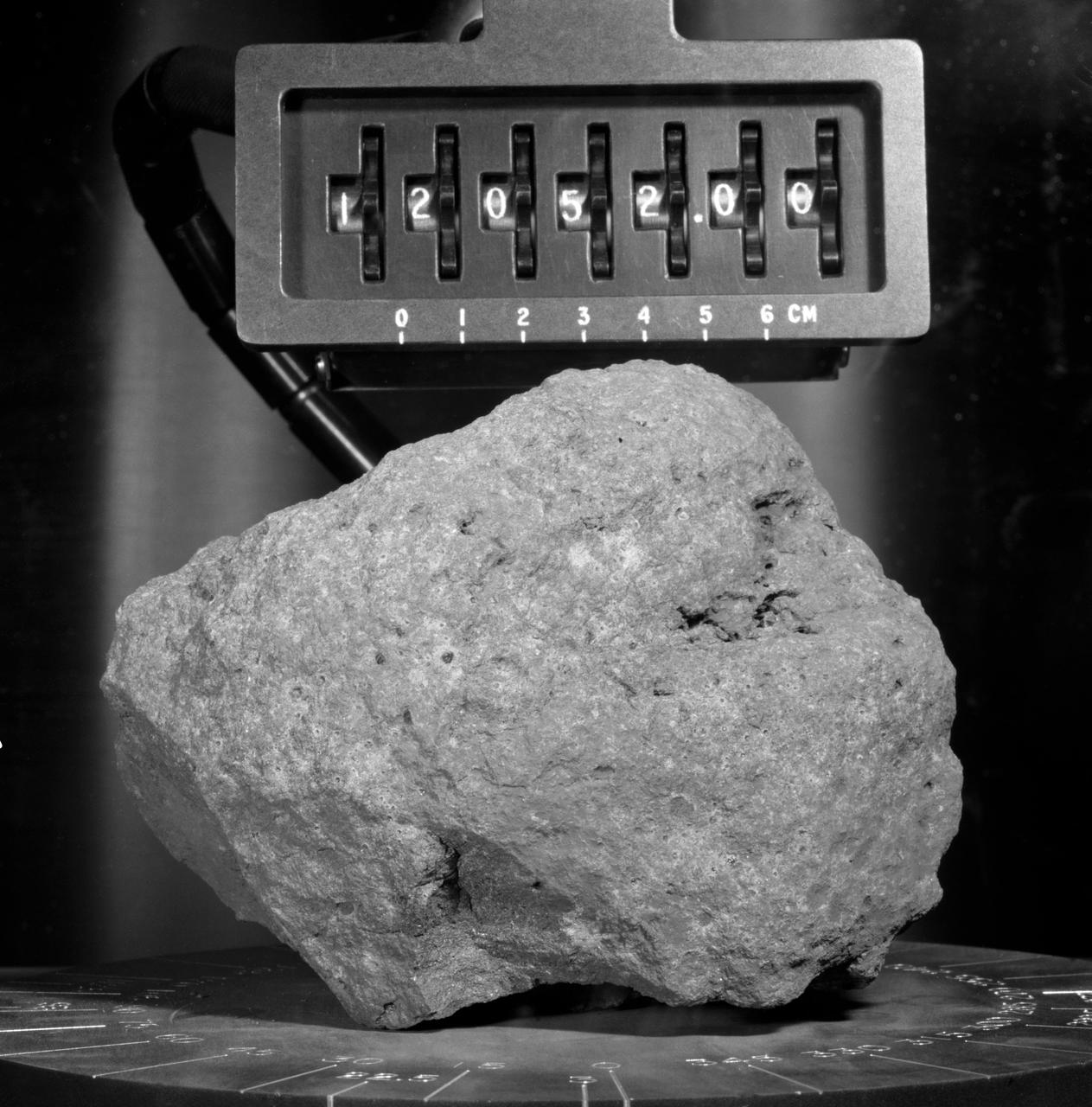

S69-60909 (November 1969) --- A close-up view of lunar sample 12,052 under observation in the Manned Spacecraft Center's Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL). Astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., and Alan L. Bean collected several rocks and samples of finer lunar matter during their Apollo 12 lunar landing mission extravehicular activity (EVA). This particular sample was picked up during the second space walk (EVA) on Nov. 20, 1969. It is a typically fine-grained crystalline rock with a concentration of holes on the left part of the exposed side. These holes are called vesicles and have been identified as gas bubbles formed during the crystallization of the rock. Several glass-lined pits can be seen on the surface of the rock.

S69-40753 (24 July 1969) --- The Apollo 11 crewmen, wearing biological isolation garments, arrive aboard the USS Hornet during recovery operations in the central Pacific. They are walking toward the Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF), in which they will be confined until they arrive at the Manned Spacecraft Center's (MSC), Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL). Apollo 11, with astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, command module pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, onboard, splashed down at 11:49 a.m. (CDT), July 24, 1969, about 812 nautical miles southwest of Hawaii and only 12 nautical miles from the USS Hornet to conclude their historic lunar landing mission.
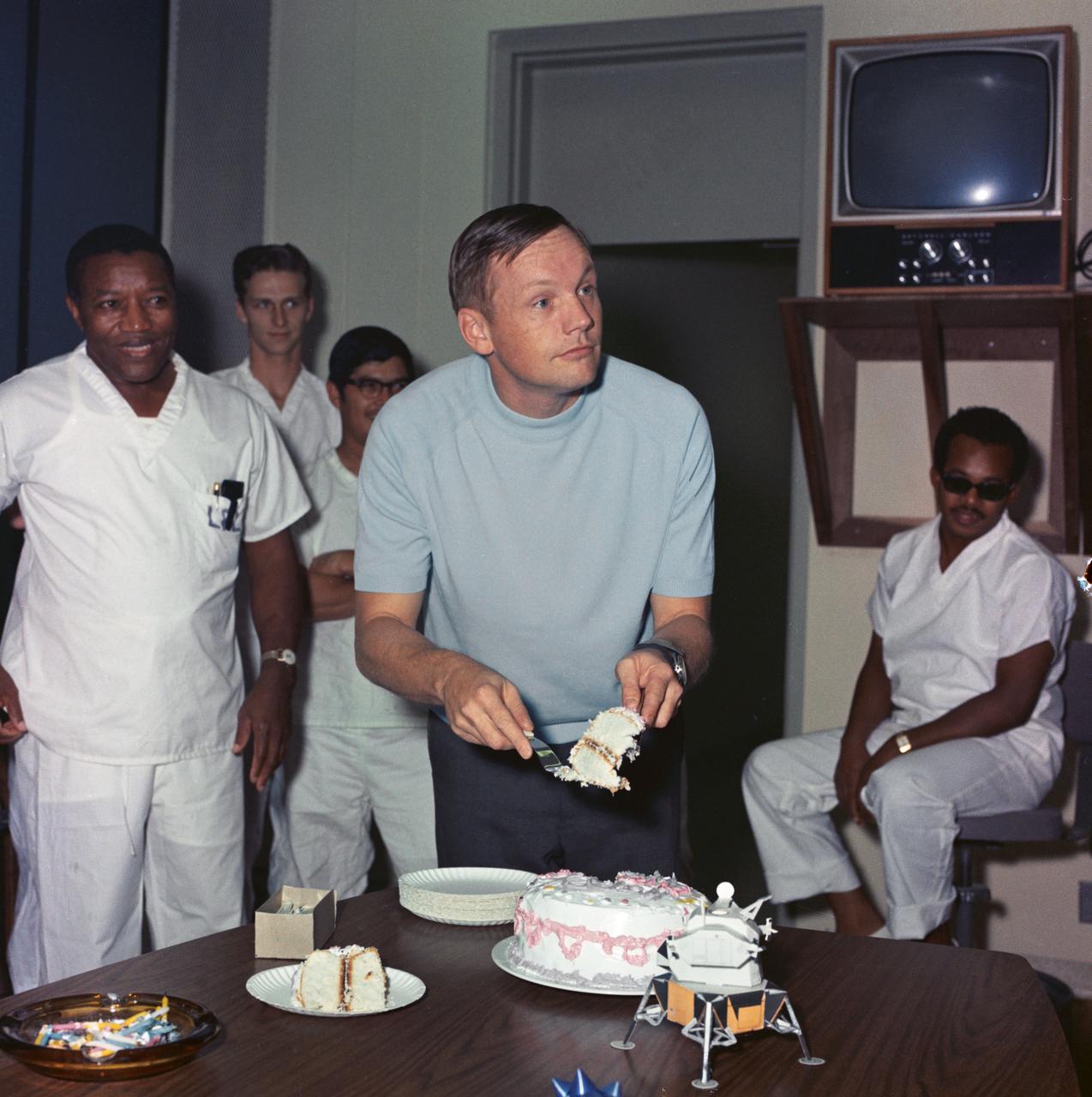
S69-40958 (5 August 1969) --- Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander of the historic Apollo 11 lunar landing mission, and the first man to set foot on the Moon, cuts his birthday cake as he celebrated his 39th birthday. The crew still confined to the Crew Reception Area (CRA) of the Manned Spacecraft Center's (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL). Armstrong was born on August 5, 1930, in Wapakoneta, Ohio. The cake was described as "standard two-layer, plain vanilla" on which was placed 39 candles. Eighteen of the persons quarantined with Armstrong assembled and sang happy birthday; and a champagne toast was offered. CRA support personnel are in the background. Astronauts Armstrong; Michael Collins, command module pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, will be released from quarantine on August 11, 1969.
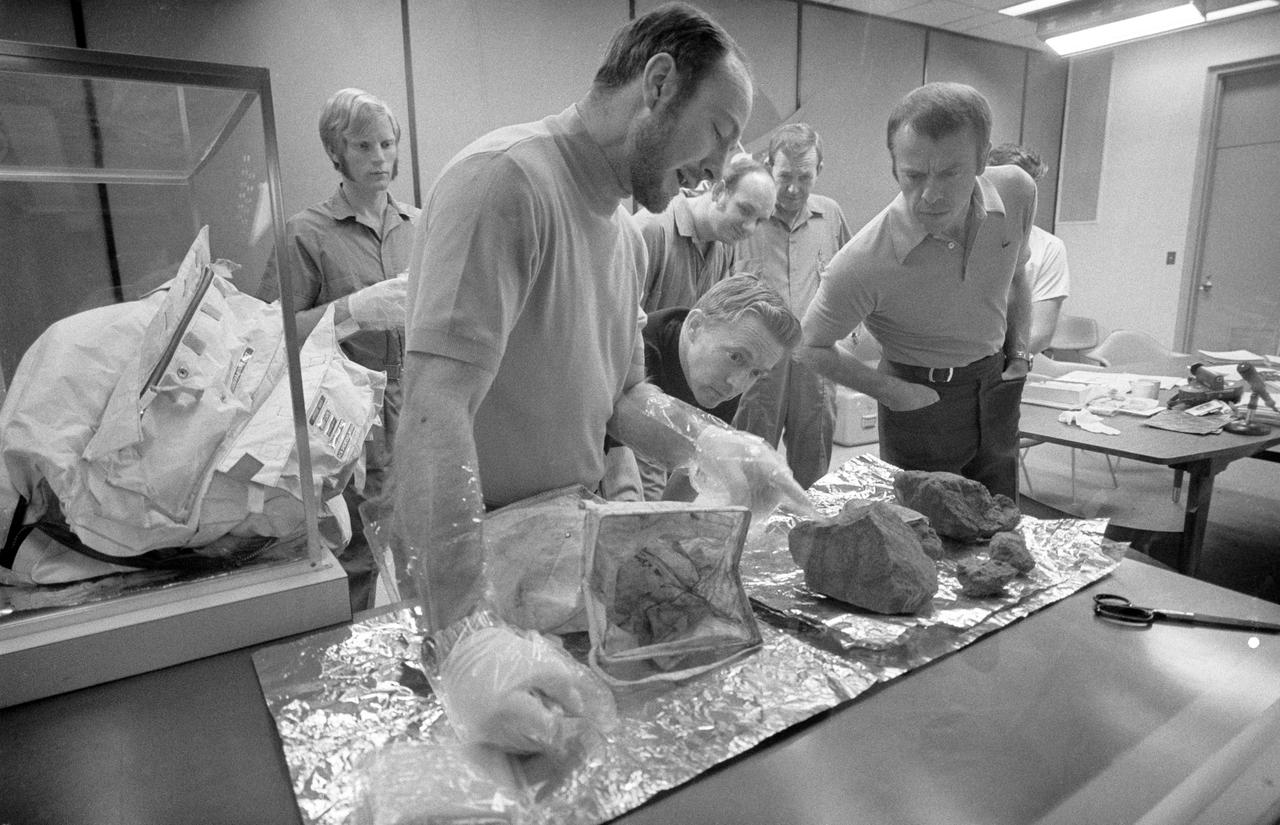
S71-20373 (19 Feb. 1971) --- The Apollo 14 crew men show off some of the largest of the lunar rocks which they brought back from the moon during a through-the-glass meeting with news men in the Crew Reception Area of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr. (right), mission commander, leans over to view a large basketball-size rock which astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, points out. Astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, who circled the moon in the Command and Service Modules (CSM) while his two fellow crewmembers explored the moon, looks on (near the center of the photograph). Four of the 14 men quarantined with the Apollo 14 crew look on in the background.
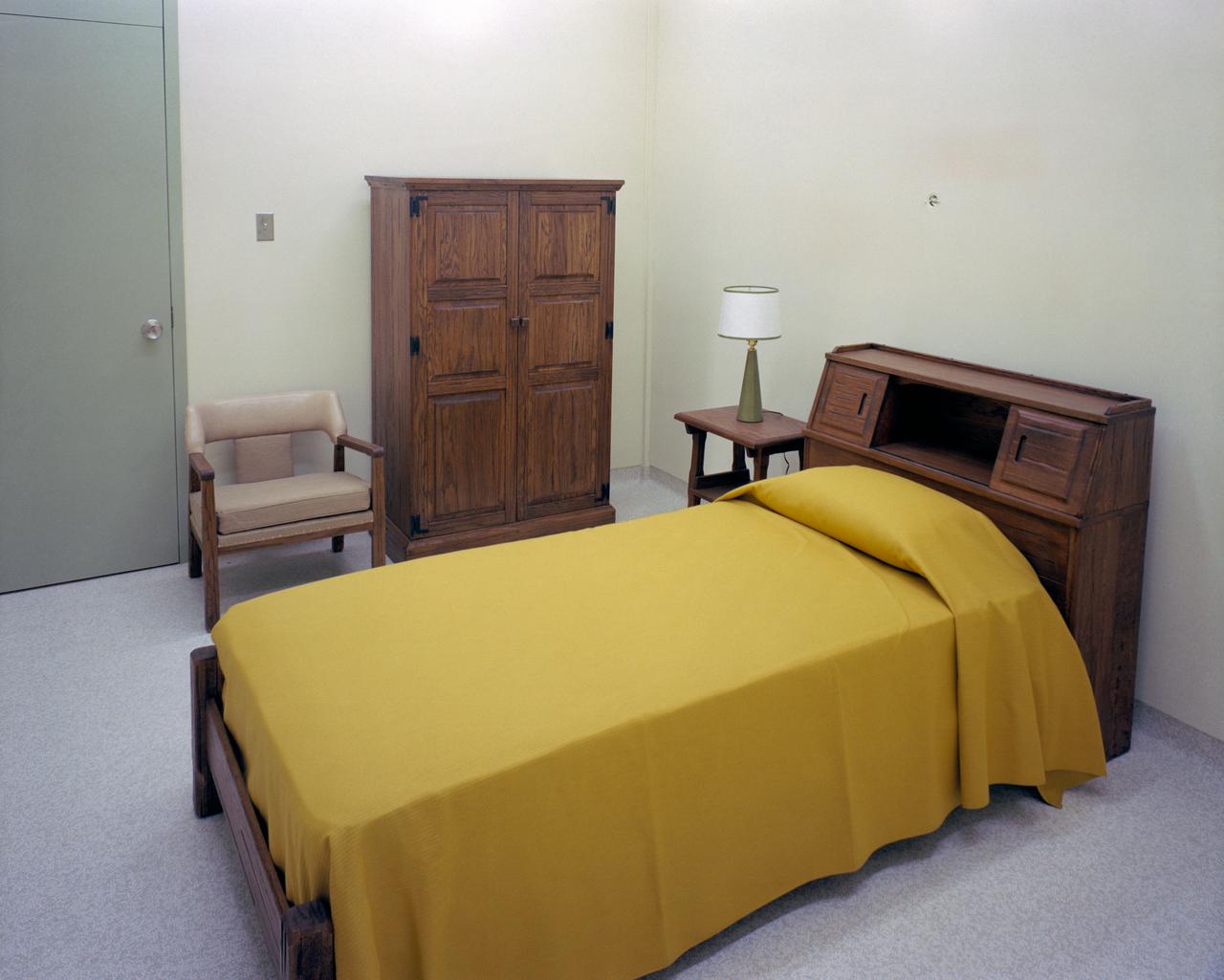

Typical Astronaut living quarters in the Crew Reception Area of the LRL, Bldg. 37, MSC, Houston, TX
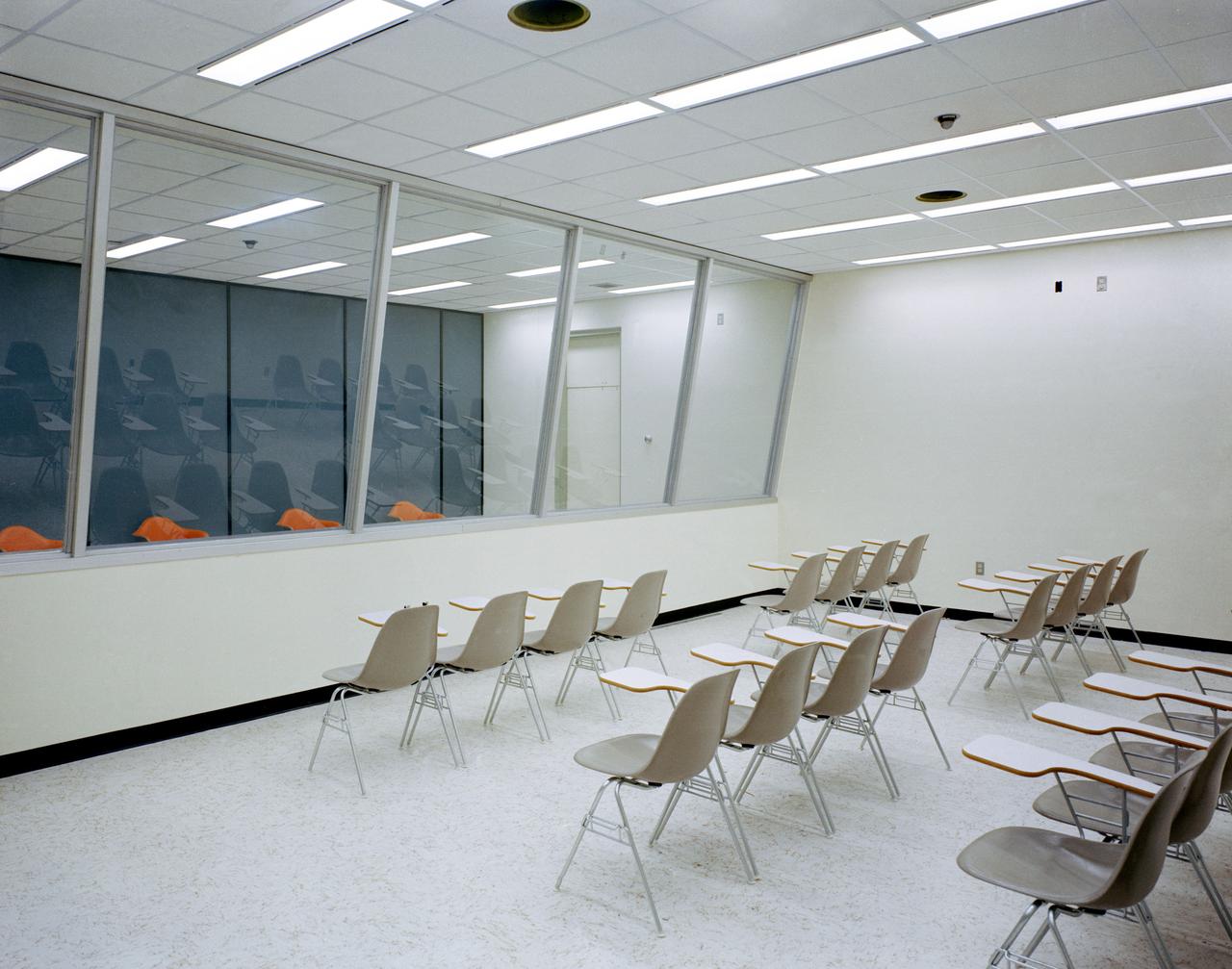

Room 190 of the Support and Administrative Facilities, CRA, LRL, Bldg 37. The room is a debriefing room which facilitates indirect contact with the Astronauts and CRA Medical Staff during quarantine periods. Also called the Press Room. MSC, Houston, TX

S69-40217 (27 July 1969) --- Neil A. Armstrong, commander of the Apollo 11 flight, greets his son Mark, on telephone intercom system, while his wife Jan and another son Eric look on. Armstrong had just arrived in early morning with the Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) at Ellington Air Force Base. Armstrong and fellow astronauts will remain in the MQF until arrival and confinement in the Crew Reception Area (CRA) of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Quarantine period will end on Aug. 11, 1969.
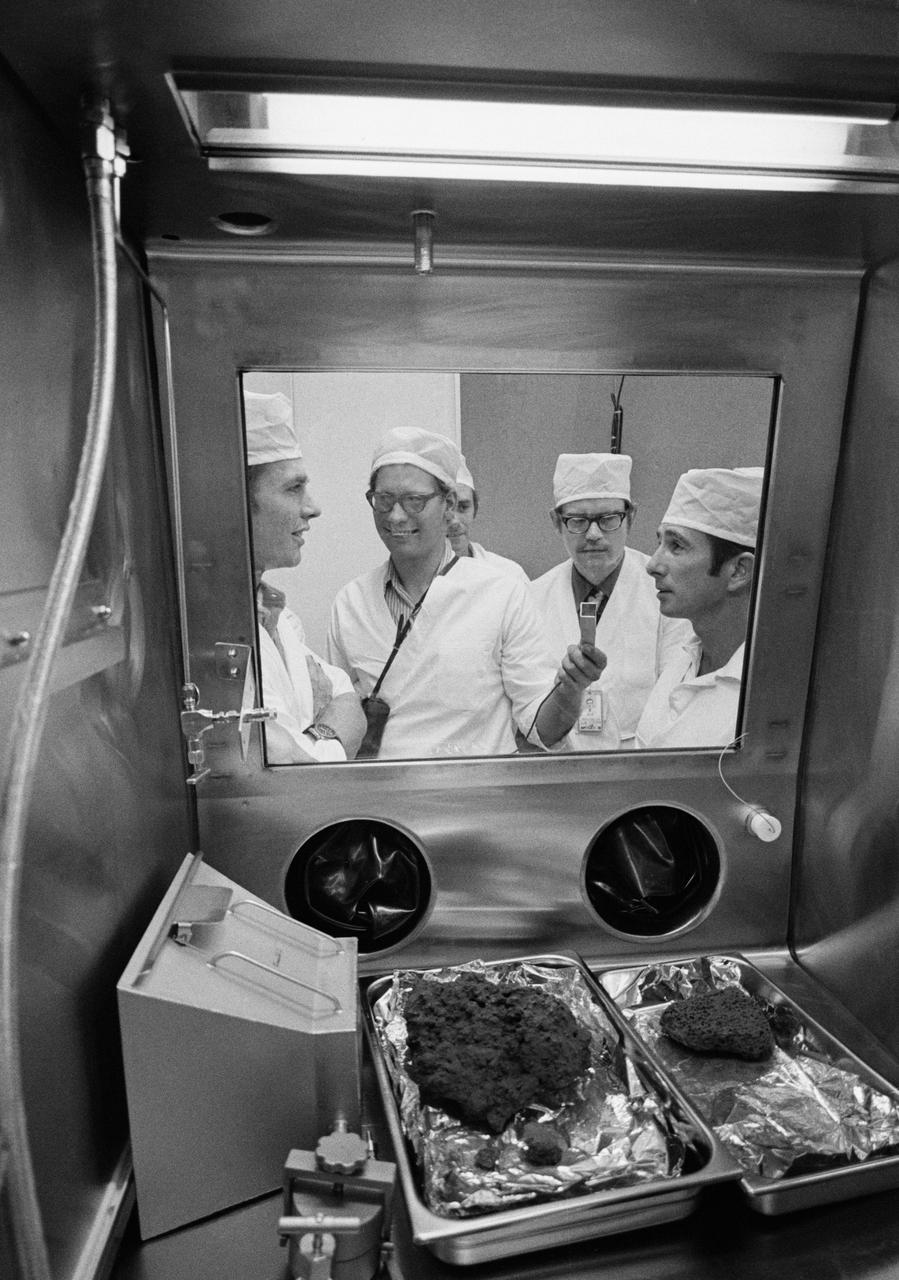

S71-43203 (9 Aug. 1971) --- Astronauts David R. Scott, left foreground, and James B. Irwin, right foreground, join the Manned Spacecraft Center's (MSC) geologists in getting first looks at some of the first Apollo 15 samples to be opened in the Non-Sterile Nitrogen Processing Line (NNPL) in the MSC Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL). Holding the microphone and making recorded tapes of the two Apollo 15 crew men's comments is Dr. Gary Lofgren. Partially obscured, near center of photo is Dr. William Phinney, and to his left is Dr. James W. Head.
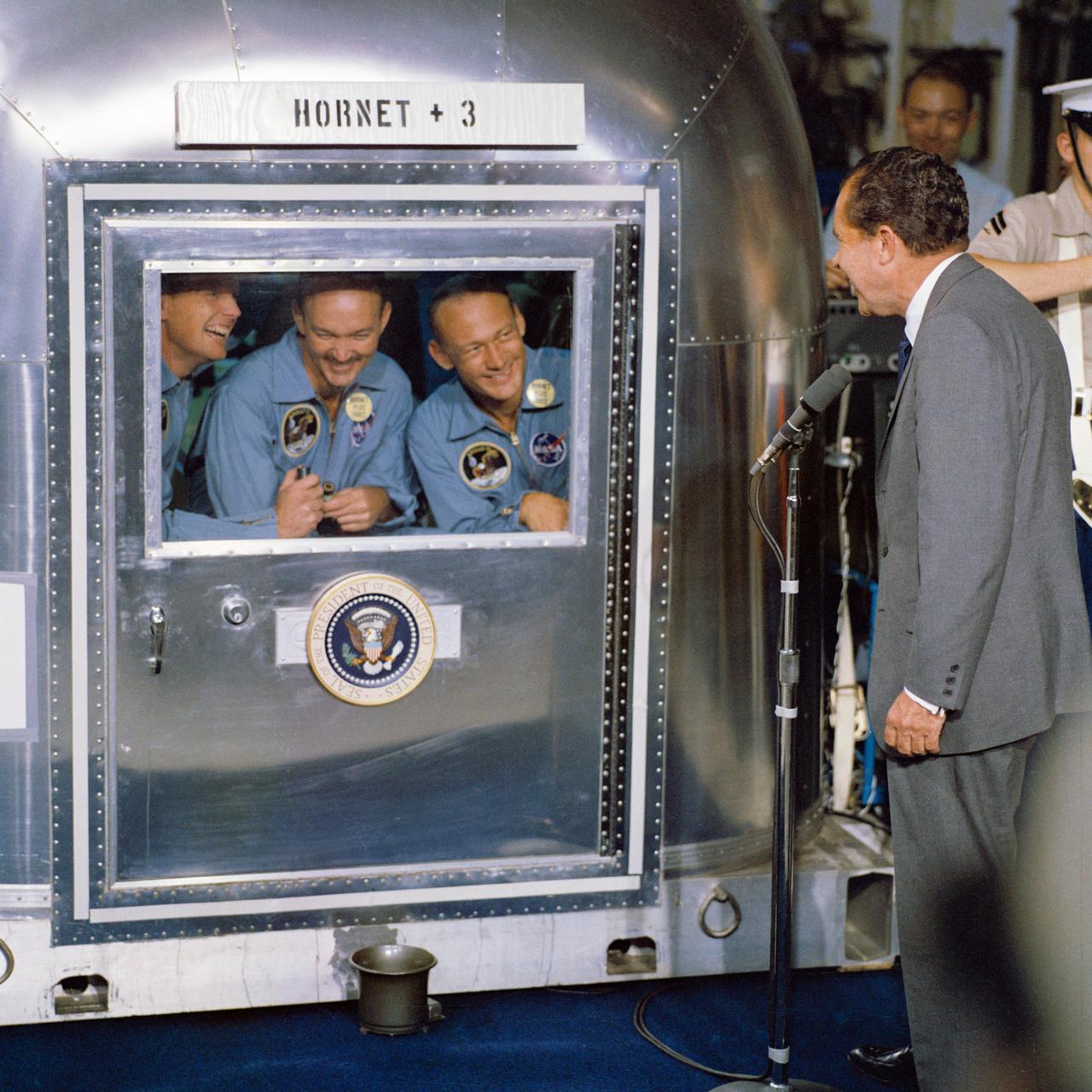

S69-21365 (24 July 1969) --- United States President Richard M. Nixon was in the central Pacific recovery area to welcome the Apollo 11 astronauts aboard the USS Hornet, prime recovery ship for the historic Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. Already confined to the Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) are (left to right) Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, command module pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot. Apollo 11 splashed down at 11:49 a.m. (CDT), July 24, 1969, about 812 nautical miles southwest of Hawaii and only 12 nautical miles from the USS Hornet. The three crewmen will remain in the MQF until they arrive at the Manned Spacecraft Center's (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL). While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Collins remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit. Photo credit: NASA
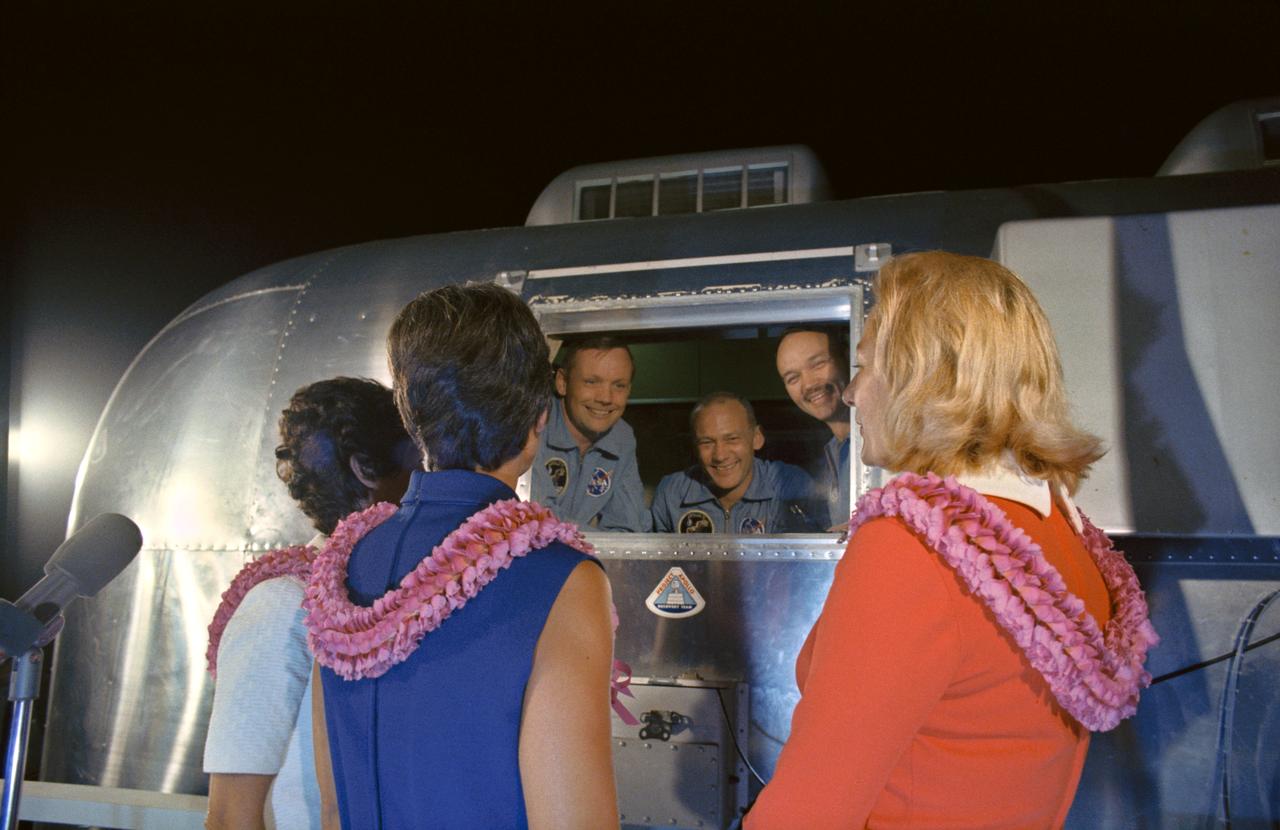

S69-40147 (27 July 1969) --- The Apollo 11 crewmen, still under a 21-day quarantine, are greeted by their wives. They arrived at Ellington Air Force Base very early Sunday after a flight aboard a U.S. Air Force C-141 transport from Hawaii. Looking through the window of a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) are (left to right) astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., and Michael Collins. The wives are (left to right) Mrs. Pat Collins, Mrs. Jan Armstrong, and Mrs. Joan Aldrin. The crew of the historic Apollo 11 lunar landing mission remained in the MQF until they arrived to the Crew Reception Area of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The astronauts will be released from quarantine on Aug. 11, 1969.

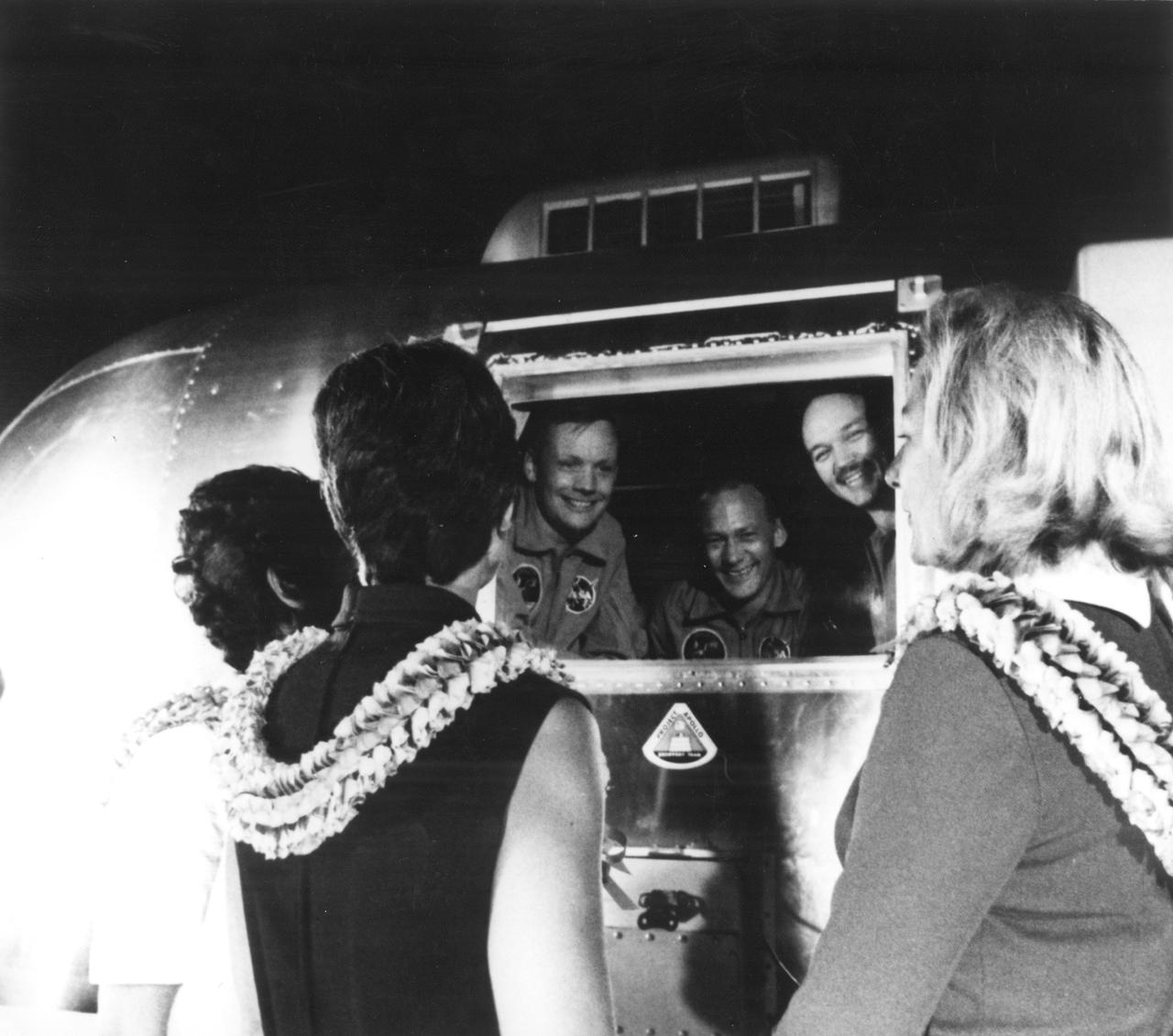
The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) which served as their home until they reached the NASA Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory in Houston, Texas. The three are seen here at the MSC, still inside the MQF, undergoing their first debriefing on Sunday, August 3, 1969. Behind the glass are (L-R): Edwin Aldrin, Michael Collins, and Neil Armstrong.

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet recovery ship, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) for 21 days. The recovery vessel docked in Pearl Harbor Hawaii, where the occupied MQF was transferred for transport to the to NASA Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory in Houston, Texas. In this photo the quarantined astronauts are addressed by Hawaiian Governor John Burns upon their arrival at Pearl Harbor.

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) which served as their home until they reached the NASA Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory in Houston, Texas. In this close up of the MQF, commander Armstrong can be seen through the facility window after its arrival at the MSC.
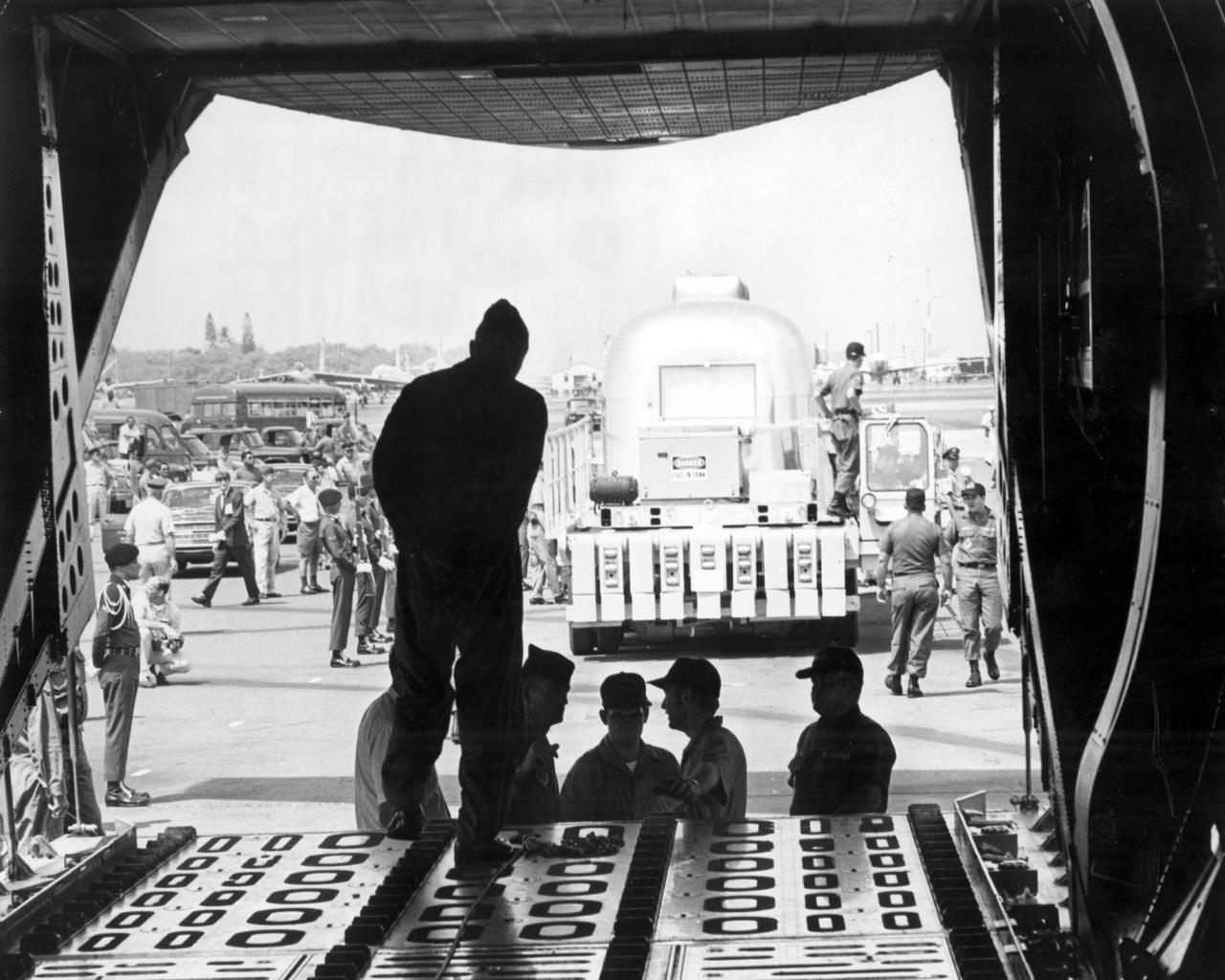

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) which served as their home until they reached the NASA Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory in Houston, Texas. In this photo taken at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, the inhabited MQF is prepared for loading into an Air Force C-141 jet transport for the flight back to Ellington Air Force Base Texas and then on to the MSC.

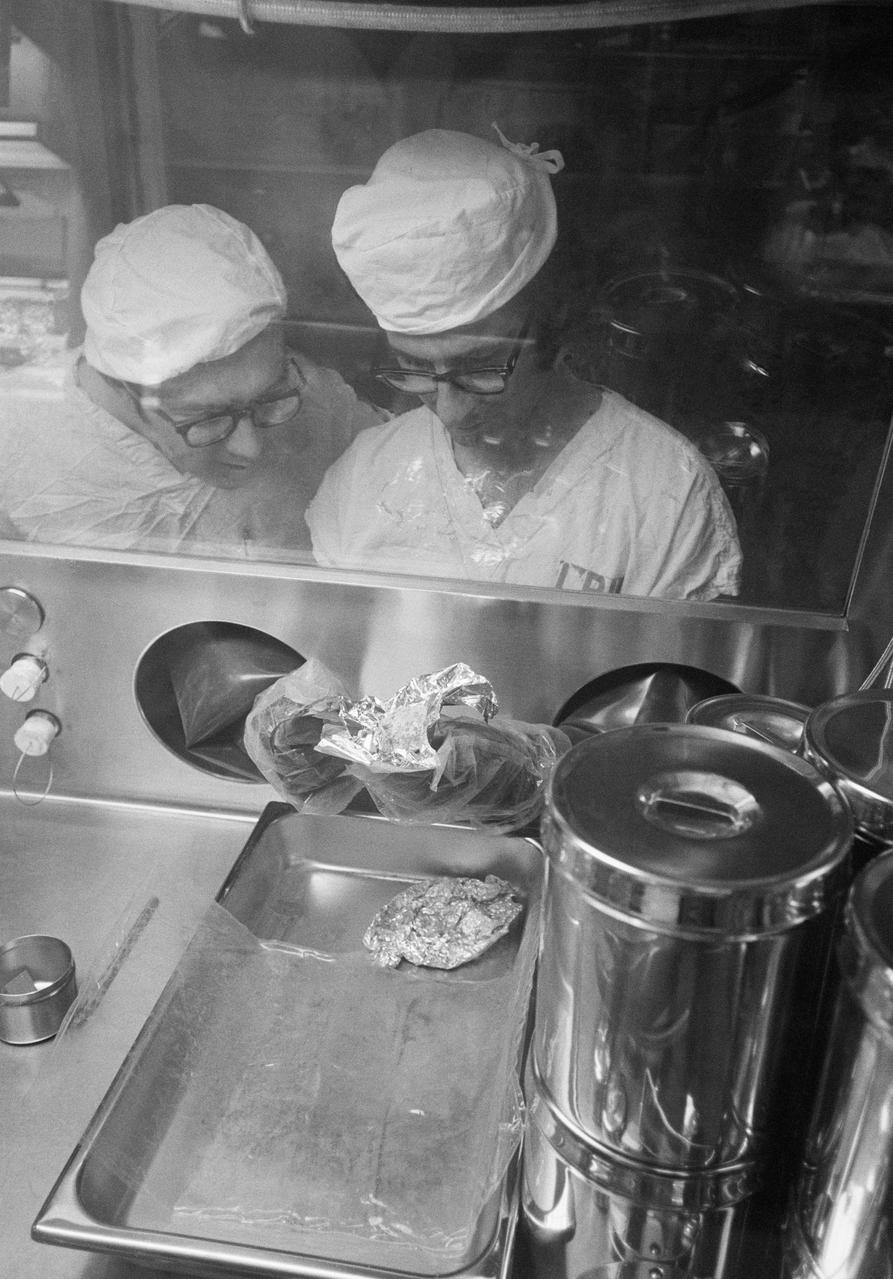
S72-56362 (27 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. "Jack" Schmitt (facing camera), Apollo 17 lunar module pilot, was one of the first to look at the sample of "orange" soil which was brought back from the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crewmen. Schmitt discovered the material at Shorty Crater during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA). The "orange" sample, which was opened Wednesday, Dec. 27, 1972, is in the bag on a weighing platform in the sealed nitrogen cabinet in the upstairs processing line in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center. Just before, the sample was removed from one of the bolt-top cans visible to the left in the cabinet. The first reaction of Schmitt was "It doesn't look the same." Most of the geologists and staff viewing the sample agreed that it was more tan and brown than orange. Closer comparison with color charts showed that the sample had a definite orange cast, according the MSC geology branch Chief William Phinney. After closer investigation and sieving, it was discovered that the orange color was caused by very fine spheres and fragments of orange glass in the midst of darker colored, larger grain material. Earlier in the day the "orange" soil was taken from the Apollo Lunar Sample Return Container No. 2 and placed in the bolt-top can (as was all the material in the ALSRC "rock box").
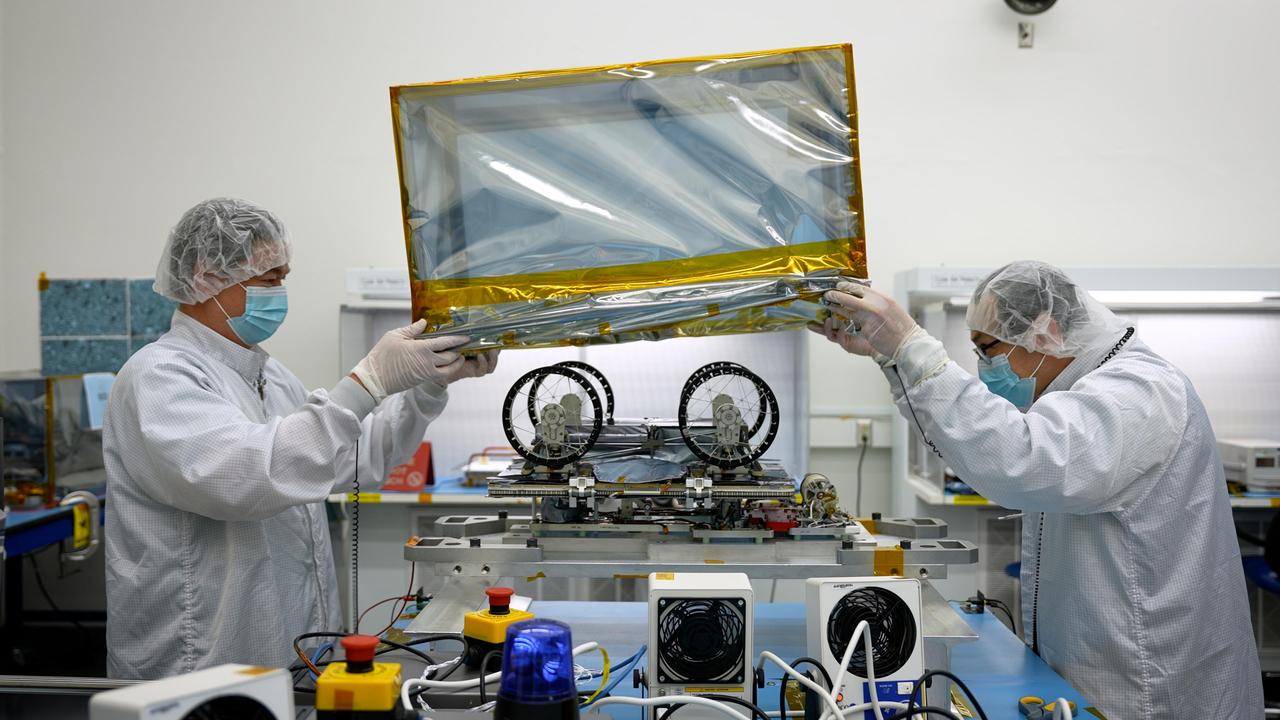

Engineers and technicians prepare one of three small lunar rovers that are part of a NASA technology demonstration called CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration). Mechanical engineer Kristopher Sherrill, left, and technician Leroy Montalvo lower an enclosure over the upside-down rover in a clean room at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Jan. 29, 2025. CADRE aims to prove that a group of robots can collaborate to gather data without receiving direct commands from mission controllers on Earth. Its trio of rovers will use their cameras and ground-penetrating radars to send back imagery of the lunar surface and subsurface while testing out the novel software systems that enable them to work together as a team autonomously. Before embarking on the first leg of a multistage journey to the Moon, each rover was mated to its deployer system, which will lower it via tether from an Intuitive Machines lander onto the dusty lunar surface. Engineers flipped each rover-deployer pair over and attached it to an aluminum plate for safe transit. The rovers were then sealed into protective metal-frame enclosures that were fitted snuggly into metal shipping containers and loaded onto a truck for the drive to Intuitive Machines' Houston facility. A division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, JPL manages CADRE for the Game Changing Development program within NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate in Washington. The technology demonstration was selected under the agency's Lunar Surface Innovation Initiative, which was established to expedite the development of technologies for sustained presence on the lunar surface. CADRE will launch as a payload on the third lunar lander mission by Intuitive Machines, called IM-3, under NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, which is managed by the agency's Science Mission Directorate, also in Washington. The agency's Glenn Research Center in Cleveland and its Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley, California, both supported the project. Motiv Space Systems designed and built key hardware elements at the company's Pasadena facility. Clemson University in South Carolina contributed research in support of the project. For more about CADRE, go to: https://go.nasa.gov/cadre https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26426
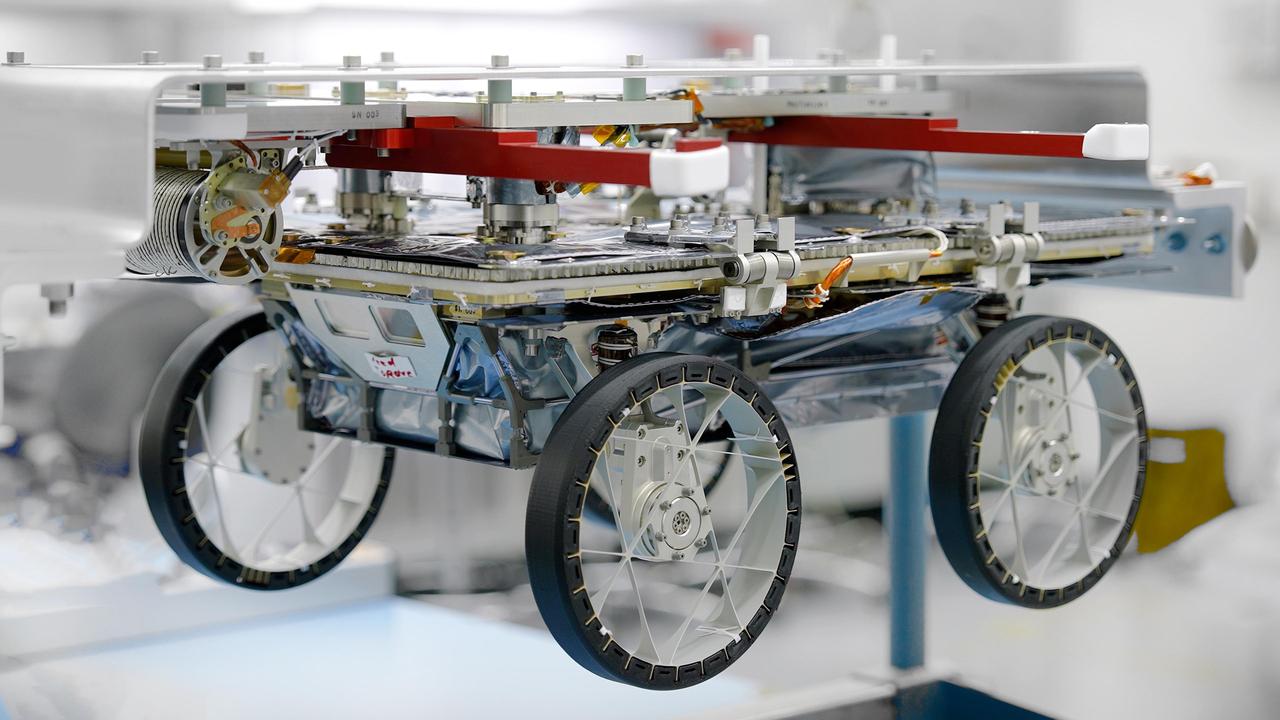
One of three small lunar rovers that are part of a NASA technology demonstration called CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration) is attached to a fixture in a clean room at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Jan. 29, 2025. Less than two weeks later, the rover had been packed up and shipped off in preparation for launch. CADRE aims to prove that a group of robots can collaborate to gather data without receiving direct commands from mission controllers on Earth. Its trio of rovers will use their cameras and ground-penetrating radars to send back imagery of the lunar surface and subsurface while testing out the novel software systems that enable them to work together as a team autonomously. Before embarking on the first leg of a multistage journey to the Moon, each rover was mated to its deployer system, which will lower it via tether from an Intuitive Machines lander onto the dusty lunar surface. Engineers flipped each rover-deployer pair over and attached it to an aluminum plate for safe transit. The rovers were then sealed into protective metal-frame enclosures that were fitted snuggly into metal shipping containers and loaded onto a truck for the drive to Intuitive Machines' Houston facility. A division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, JPL manages CADRE for the Game Changing Development program within NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate in Washington. The technology demonstration was selected under the agency's Lunar Surface Innovation Initiative, which was established to expedite the development of technologies for sustained presence on the lunar surface. CADRE will launch as a payload on the third lunar lander mission by Intuitive Machines, called IM-3, under NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, which is managed by the agency's Science Mission Directorate, also in Washington. The agency's Glenn Research Center in Cleveland and its Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley, California, both supported the project. Motiv Space Systems designed and built key hardware elements at the company's Pasadena facility. Clemson University in South Carolina contributed research in support of the project. For more about CADRE, go to: https://go.nasa.gov/cadre https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26428
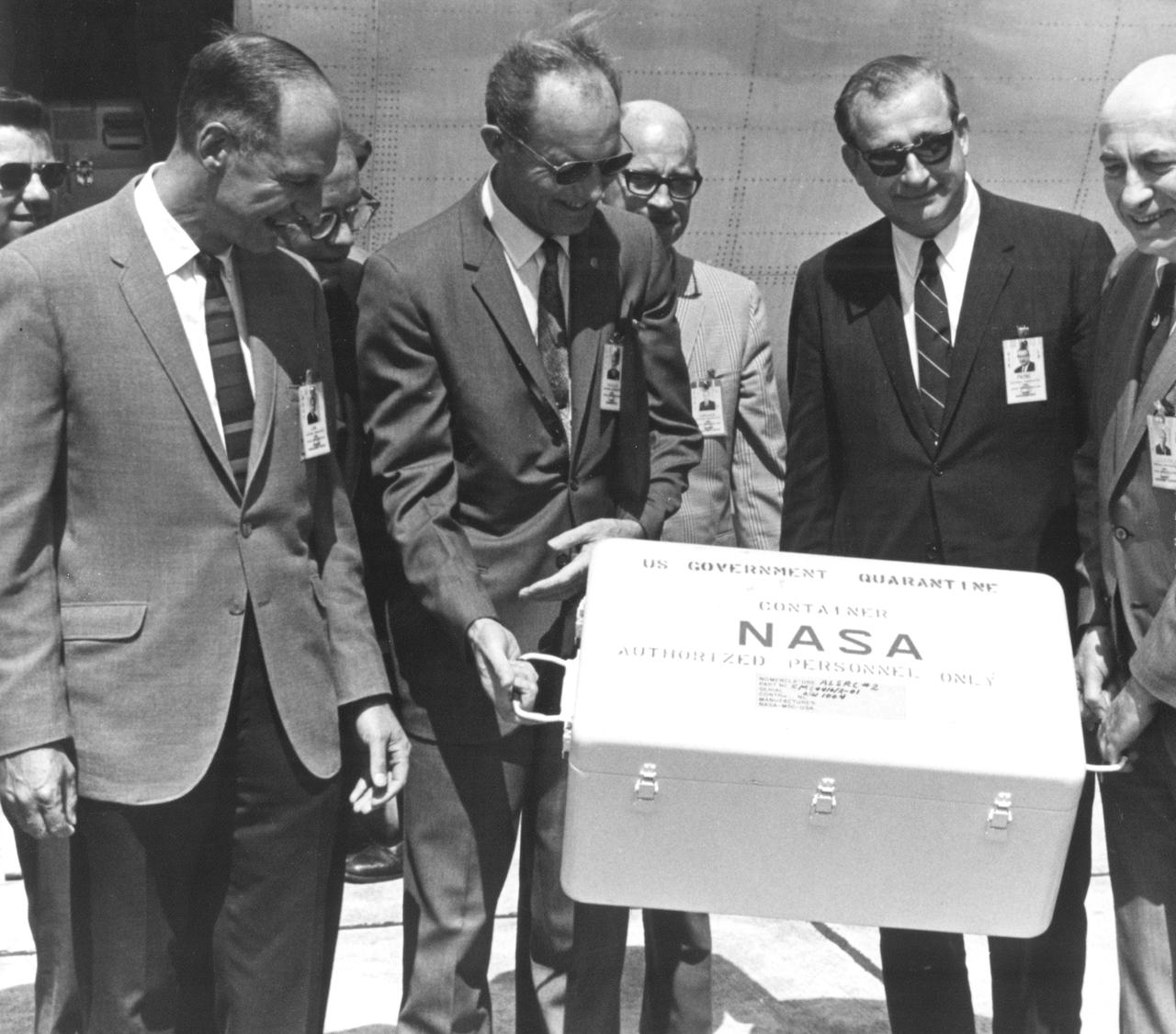

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. This photograph was taken as the mission’s first loaded sample return container arrived at Ellington Air Force Base by air from the Pacific recovery area. The rock box was immediately taken to the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) in Houston, Texas. Happily posing for the photograph with the rock container are (L-R) Richard S. Johnston (back), special assistant to the MSC Director; George M. Low, MSC Apollo Spacecraft Program manager; George S. Trimble (back), MSC Deputy Director; Lt. General Samuel C. Phillips, Apollo Program Director, Office of Manned Spaceflight at NASA headquarters; Eugene G. Edmonds, MSC Photographic Technology Laboratory; Dr. Thomas O. Paine, NASA Administrator; and Dr. Robert R. Gilruth, MSC Director.
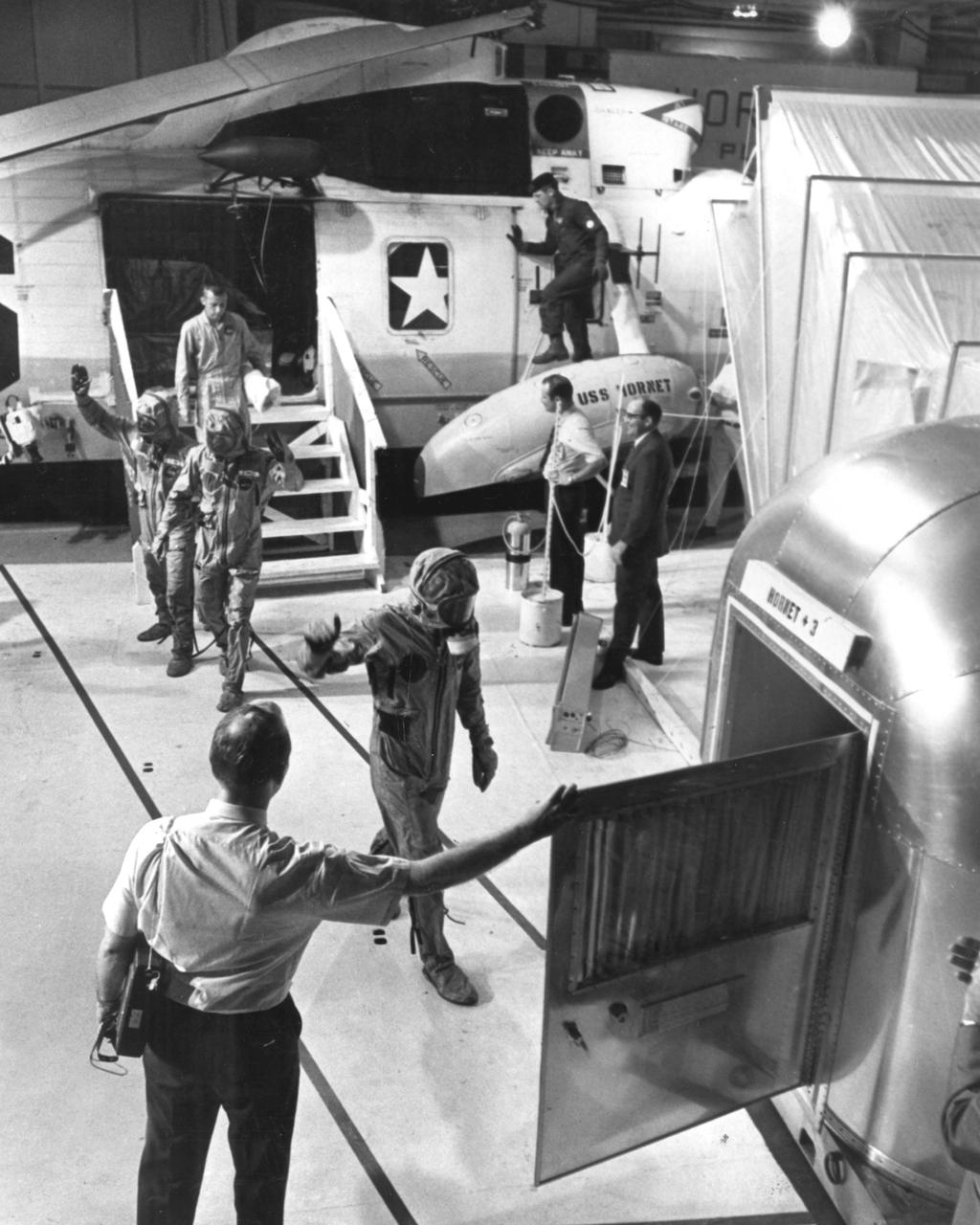

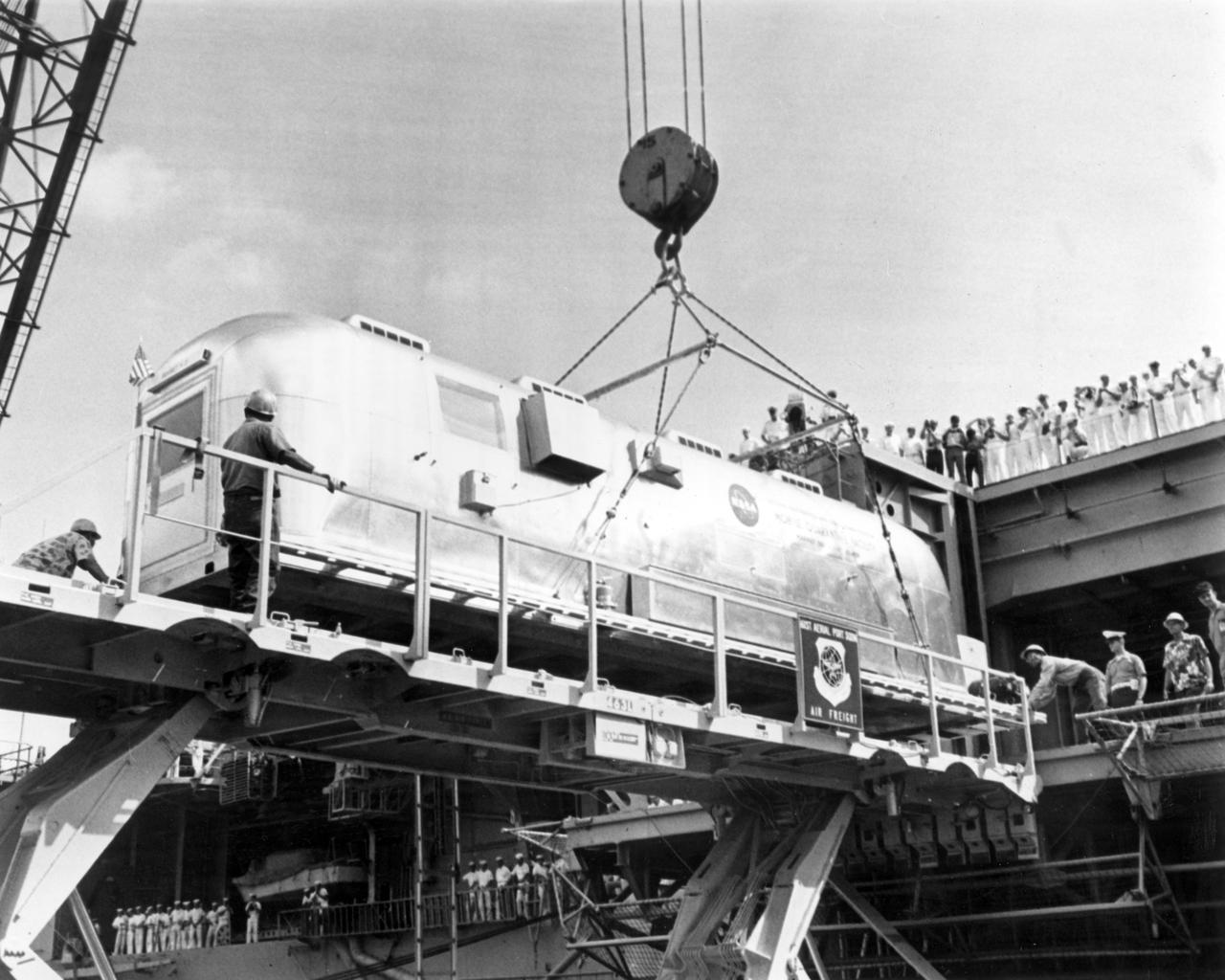
The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard the craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface followed by Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF). Donned in biological isolation garments, the Apollo 11 crew members (front to rear) Armstrong, Collins, and Aldrin leave the pick up helicopter making their way to the MQF. This portable facility served as their home until they reached the NASA Manned Spacecraft Center Lunar Receiving Laboratory in Houston, Texas. With the success of Apollo 11 mission the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
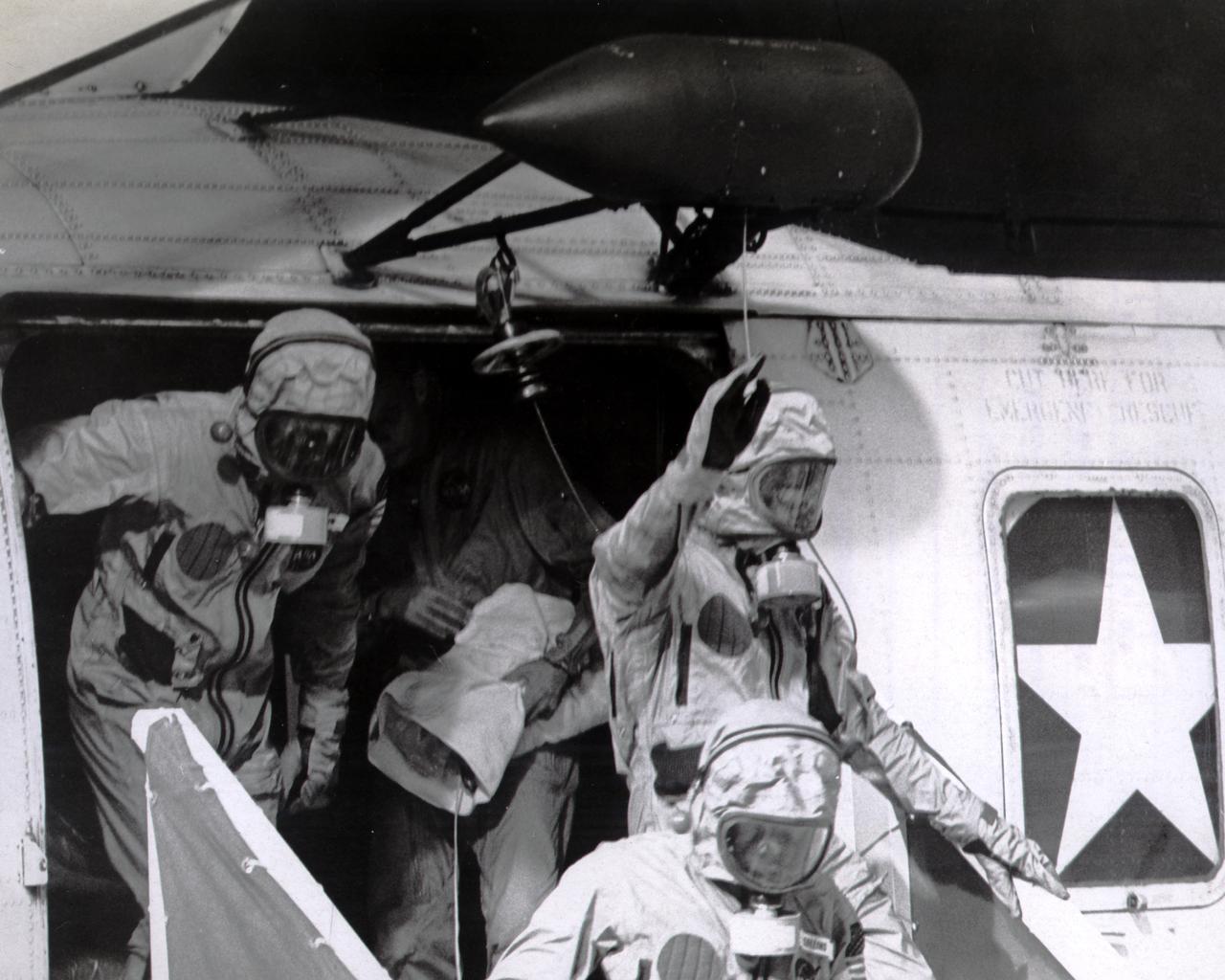
Donned in biological isolation garments, the Apollo 11 crew members, (L-R) Edwin Aldrin, Neil Armstrong (waving), and Michael Collins exit the recovery pick up helicopter to board the U.S.S. Hornet aircraft carrier after splashdown. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF). This portable facility served as their home until they reached the NASA Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory in Houston, Texas. The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida via the Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard were Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Werher von Braun.
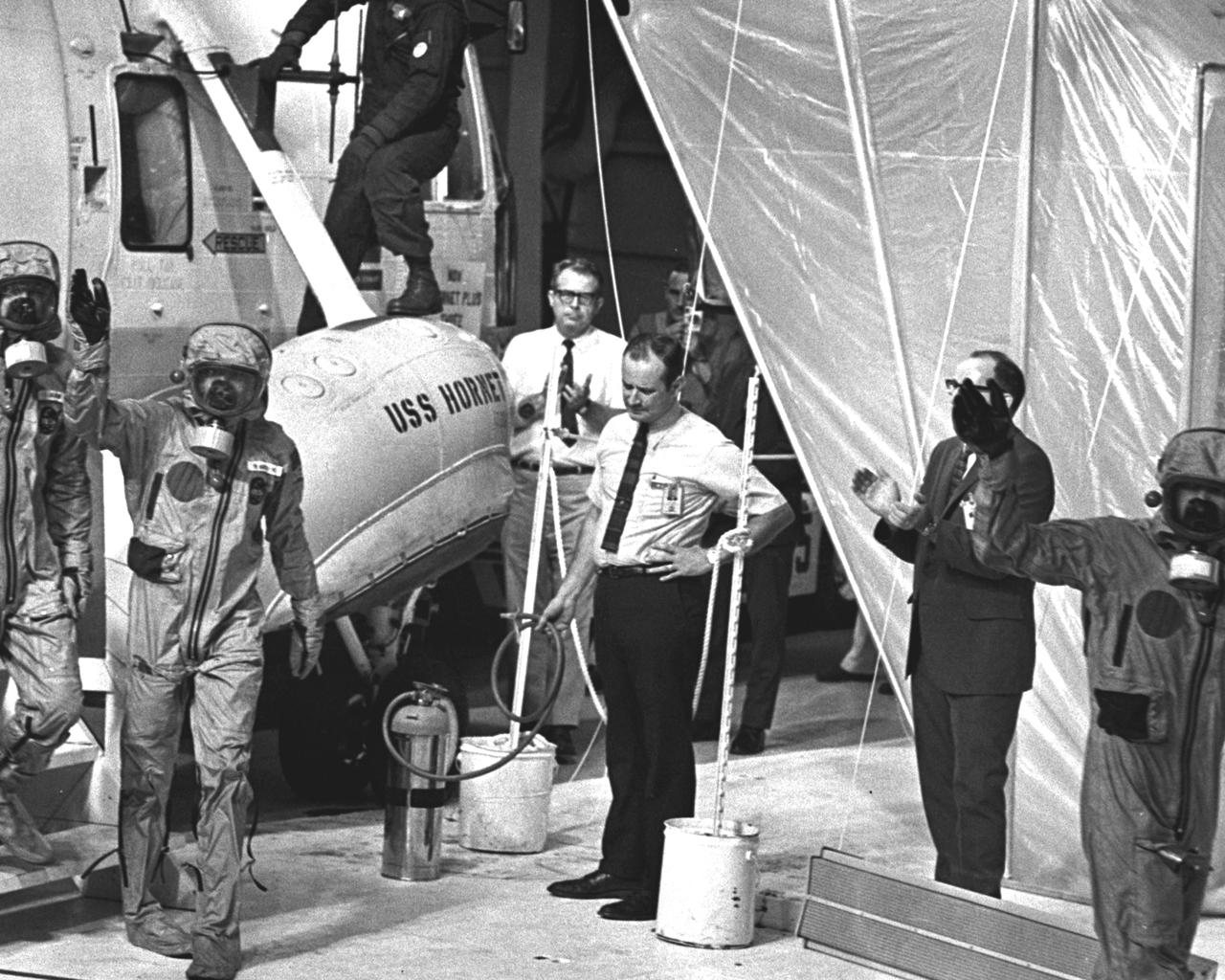

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard were Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF). Donned in biological isolation garments, the Apollo 11 crew members wave to well wishers as they leave the pick up helicopter making their way to the MQF. This portable facility served as their home until they reached the NASA Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory in Houston, Texas. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
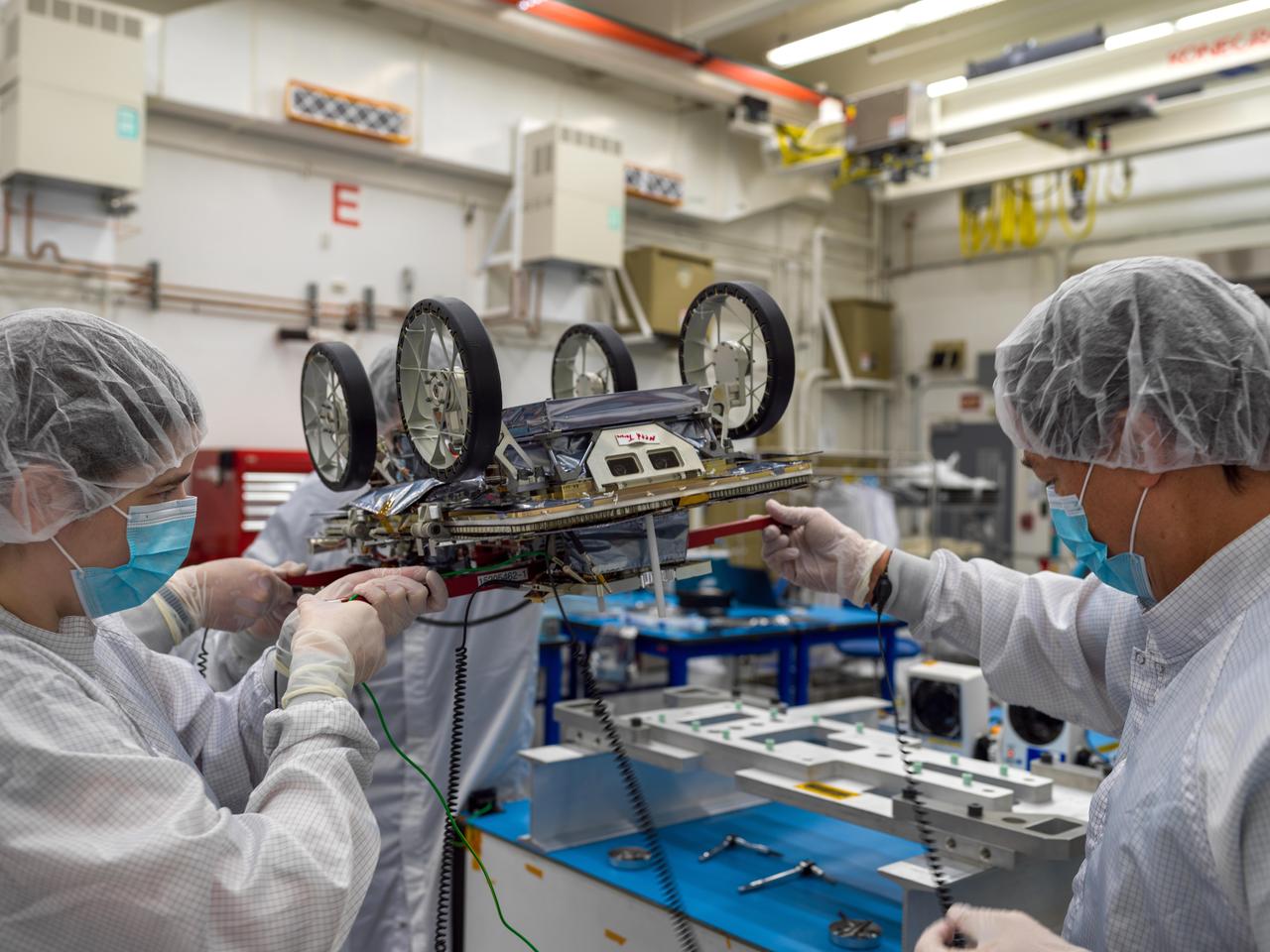

One of three small lunar rovers that are part of a NASA technology demonstration called CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration) is prepared for shipping in a clean room at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Jan. 29, 2025. CADRE aims to prove that a group of robots can collaborate to gather data without receiving direct commands from mission controllers on Earth. Its trio of rovers will use their cameras and ground-penetrating radars to send back imagery of the lunar surface and subsurface while testing out the novel software systems that enable them to work together as a team autonomously. Before embarking on the first leg of a multistage journey to the Moon, each rover was mated to its deployer system, which will lower it via tether from an Intuitive Machines lander onto the dusty lunar surface. Engineers flipped each rover-deployer pair over and attached it to an aluminum plate for safe transit. The rovers were then sealed into protective metal-frame enclosures that were fitted snuggly into metal shipping containers and loaded onto a truck for the drive to Intuitive Machines' Houston facility. Here, members of the project's assembly, test, and launch operations team hold the upside-down rover by temporary red handles in order to move it to a table where they'll attach it to the aluminum plate. A division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, JPL manages CADRE for the Game Changing Development program within NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate in Washington. The technology demonstration was selected under the agency's Lunar Surface Innovation Initiative, which was established to expedite the development of technologies for sustained presence on the lunar surface. CADRE will launch as a payload on the third lunar lander mission by Intuitive Machines, called IM-3, under NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, which is managed by the agency's Science Mission Directorate, also in Washington. The agency's Glenn Research Center in Cleveland and its Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley, California, both supported the project. Motiv Space Systems designed and built key hardware elements at the company's Pasadena facility. Clemson University in South Carolina contributed research in support of the project. For more about CADRE, go to: https://go.nasa.gov/cadre https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26427

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet recovery ship, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) which served as their home until they reached the NASA Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory in Houston, Texas. The occupied MQF was unloaded from the U.S.S. Hornet in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. In this photo, the facility is moved from the Hornet’s dock enroute to Hickam Field where it was loaded aboard an Air Force C-141 jet transport for the flight back to Ellington Air Force Base Texas, and then on to the MSC.
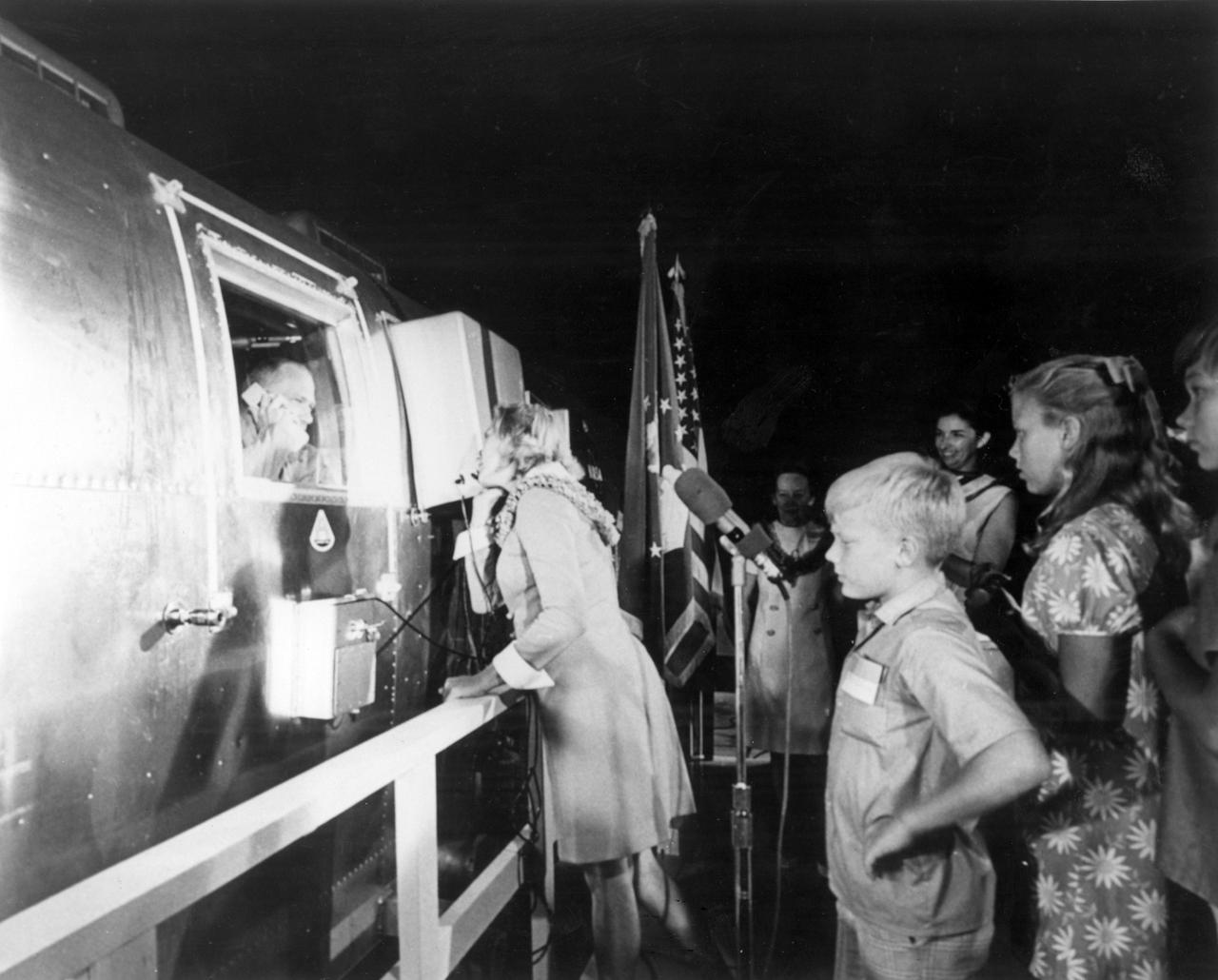

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) which served as their home until they reached the NASA Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory in Houston, Texas. On arrival at Ellington Air Force base near the MSC, the crew, still under a 21 day quarantine in the MQF, were greeted by their wives. Pictured here is Joan Aldrin, wife of Buzz Aldrin, speaking with her husband via telephone patch.

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) which served as their home until they reached the NASA Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory in Houston, Texas. On arrival at Ellington Air Force base near the MSC, the crew, still under a 21 day quarantine in the MQF are greeted by their wives. Looking out of the facility are (L-R) Armstrong, Aldrin, and Collins. Wives are (L-R) Pat Collins, Jan Armstrong, and Joan Aldrin.

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet recovery ship, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) which served as their home for 21 days. In this photo taken at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, the quarantined housing facility is being lowered from the U.S.S. Hornet, onto a trailer for transport to Hickam Field. From there, it was loaded aboard an Air Force C-141 jet and flown back to Ellington Air Force Base Texas, and then on to the NASA Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory in Houston, Texas.
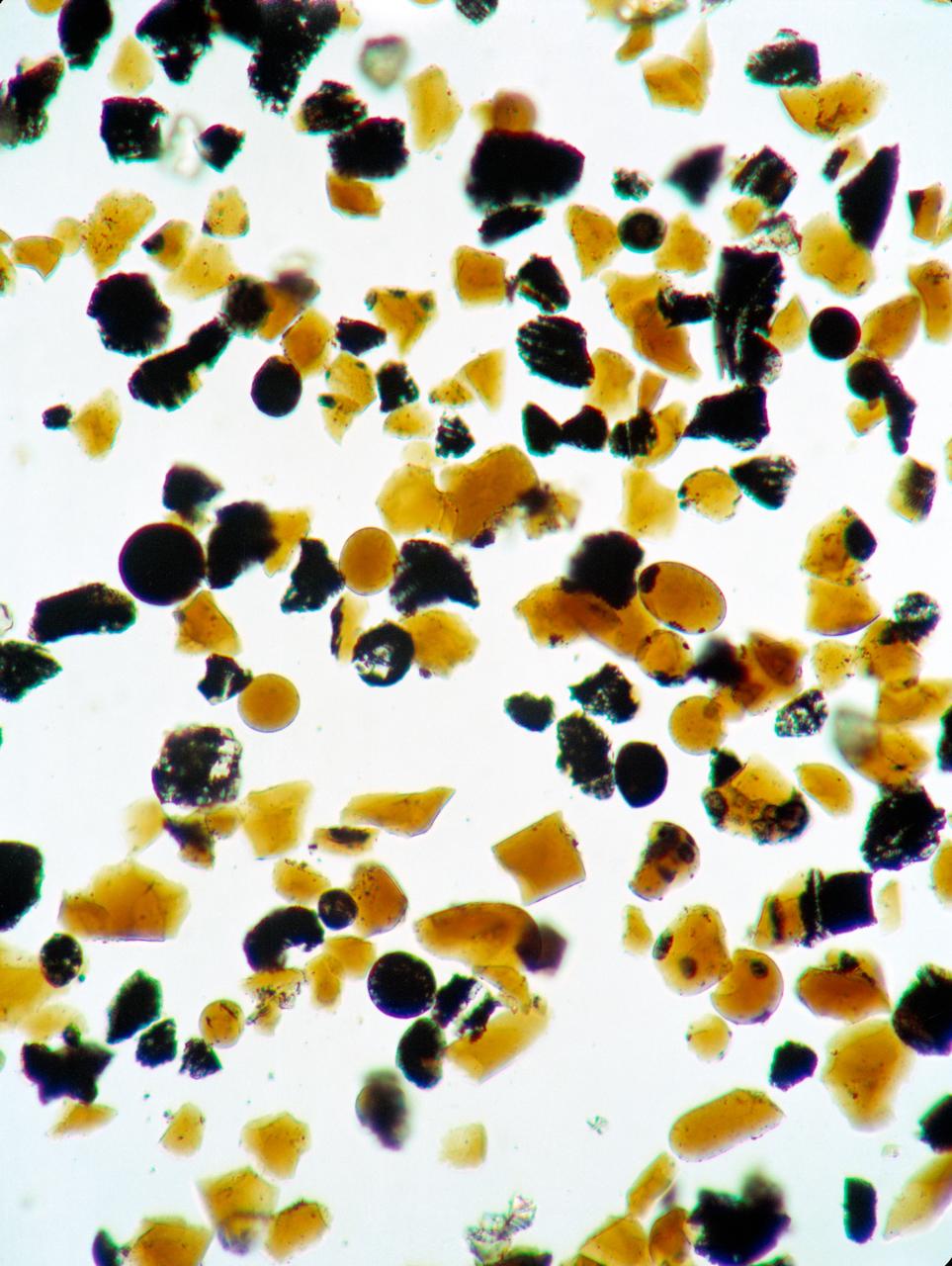
S73-15171 (4 Jan. 1973) --- These orange glass spheres and fragments are the finest particles ever brought back from the moon. Ranging in size from 20 to 45 microns (about 1/1000 of an inch) the particles are magnified 160 times in this photomicrograph made in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center. The orange soil was brought back from the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crewmen. Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. "Jack" Schmitt discovered the orange soil at Shorty Crater during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA). This lunar material is being studied and analyzed by scientists in the LRL. The orange particles in this photomicrograph, which are intermixed with black and black-speckled grains, are about the same size as the particles that compose silt on Earth. Chemical analysis of the orange soil material has shown the sample to be similar to some of the samples brought back from the Apollo 11 (Sea of Tranquility) site several hundred miles to the southwest. Like those samples, it is rich in titanium (8%) and iron oxide (22%). But unlike the Apollo 11 samples, the orange soil is unexplainably rich in zinc ? an anomaly that has scientists in a quandary. This Apollo 17 sample is not high in volatile elements, nor do the minerals contain substantial amounts of water. These would have provided strong evidence of volcanic activity. On the other hand, the lack of agglutinates (rocks made up of a variety of minerals cemented together) indicates that the orange glass is probably not the product of meteorite impact -- strengthening the argument that the glass was produced by volcanic activity.