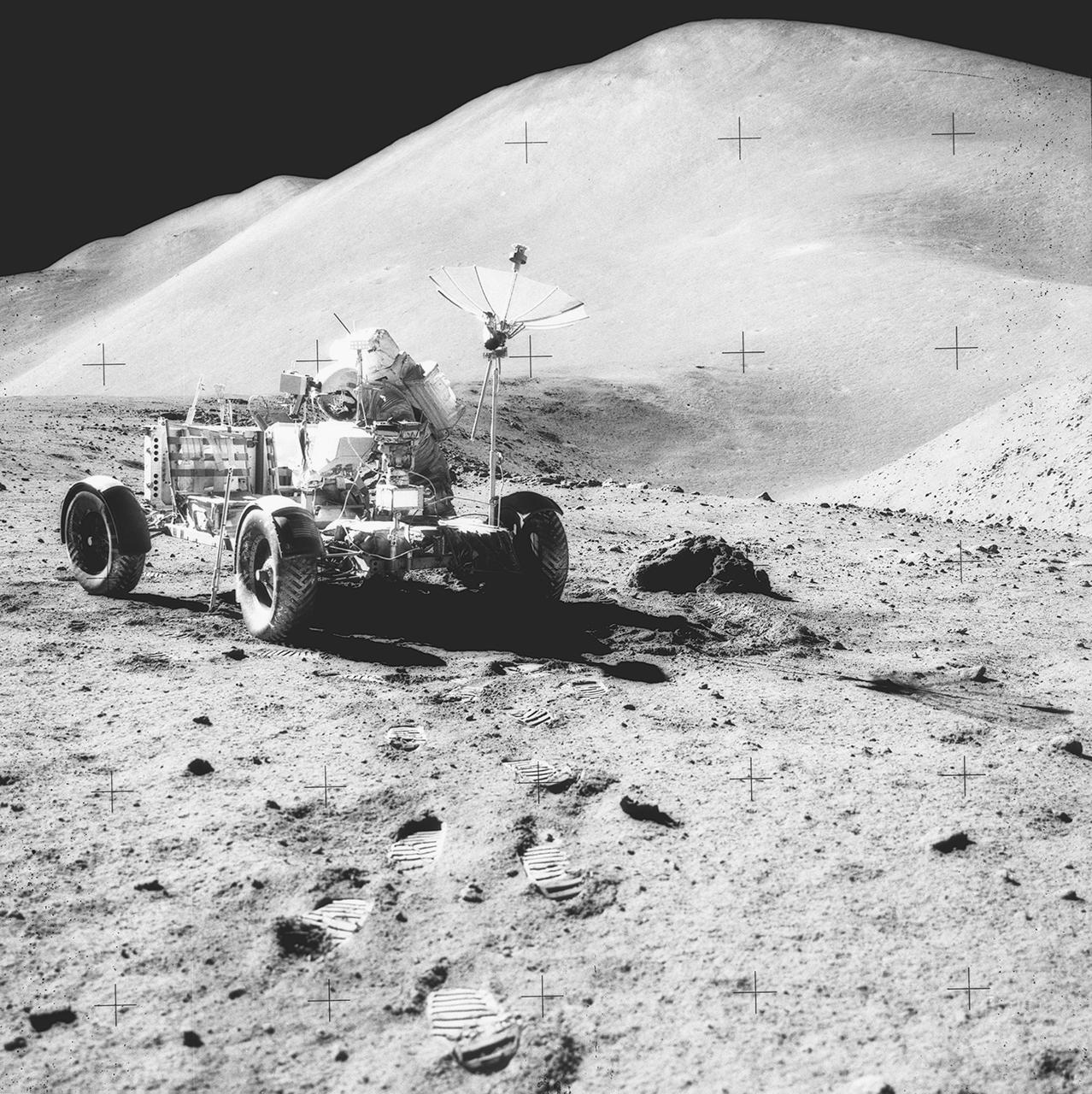

The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions, Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17, in 1971 and 1972 to permit the crew to travel several miles from the lunar landing site. This photograph was taken during the Apollo 15 mission.
This photograph shows a rear view of a folded configuration of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) No. 2. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration. It was an open-space and collapsible vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and camera. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was built by the Boeing Company under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
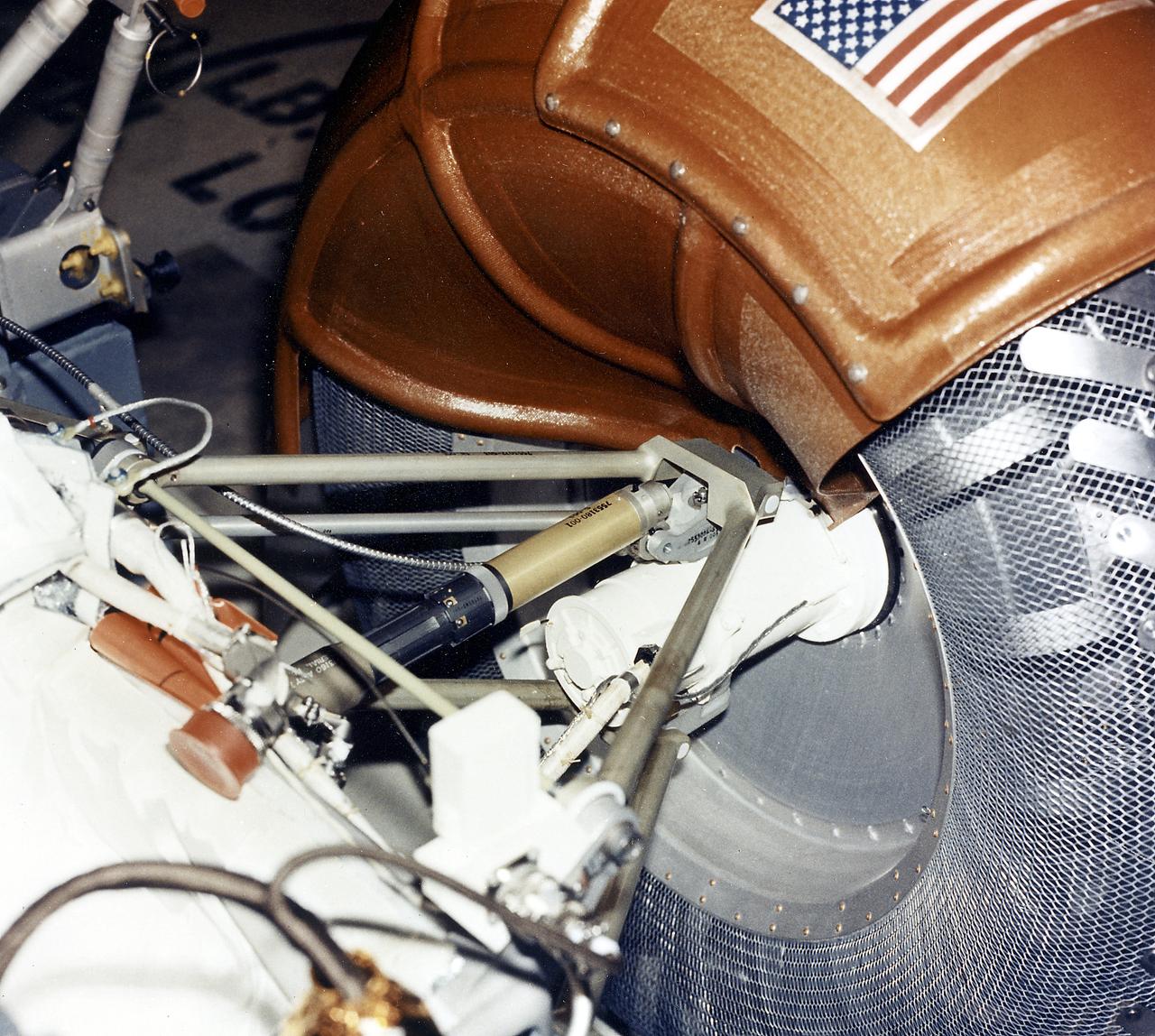
This is a close-up inboard view of a left front wheel of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) No. 1. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater Range of mobility during lunar exploration. It was an open-space and collapsible vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and camera. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was built by the Boeing Company under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
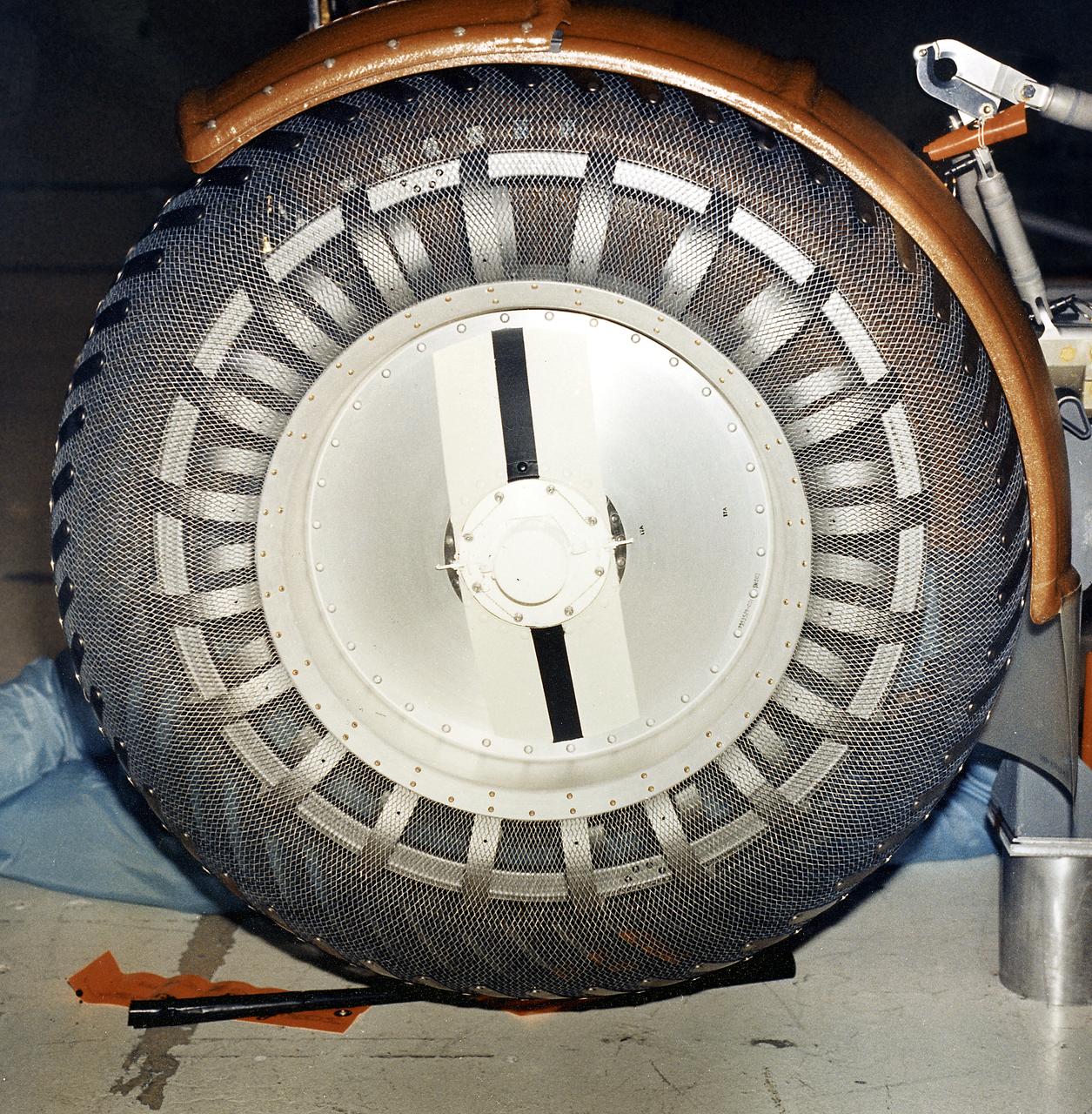

This is a close-up view of a left front wheel of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) No. 1. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration. It was an open-space and collapsible vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and camera. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was built by the Boeing Company under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
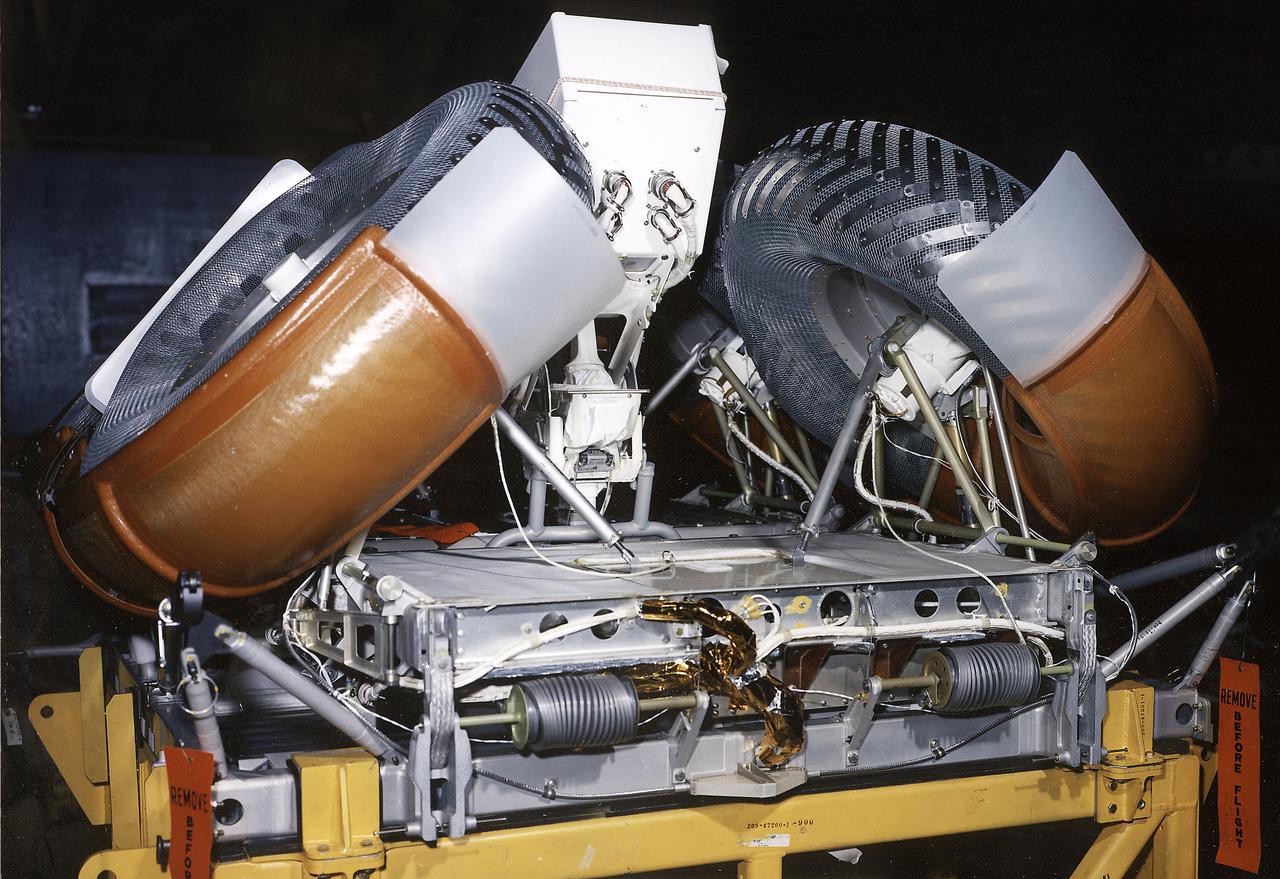
This photograph shows a front view of a folded configuration of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) No. 2. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration. It was an open-space and collapsible vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and camera. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was built by the Boeing Company under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
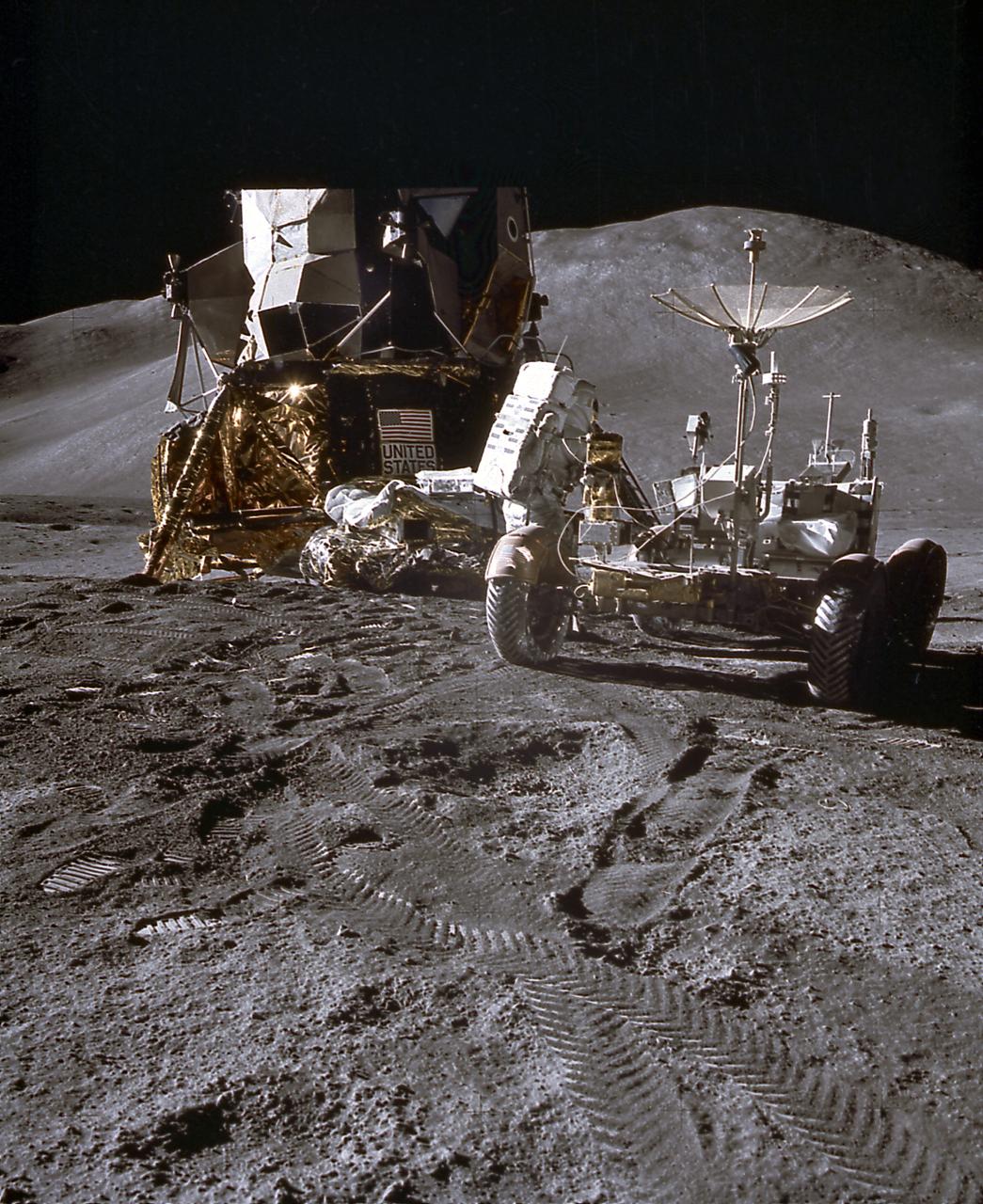

This photograph of an astronaut getting the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) ready for exploration of the lunar surface was taken during activities of the Apollo 15 mission. Designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company, the LRV was first used on the Apollo 15 mission and increased the range of astronauts' mobility and productivity on the lunar surface.
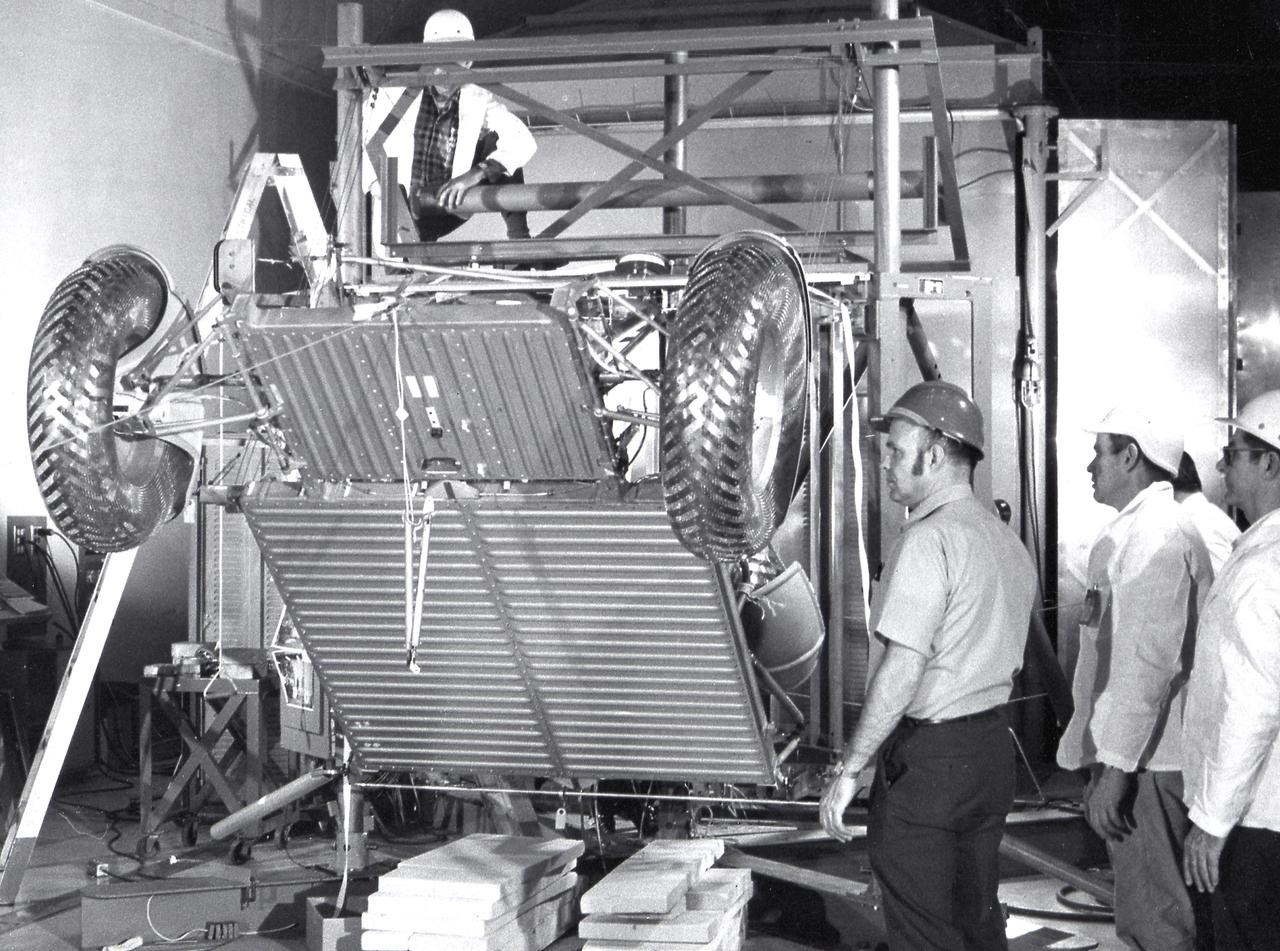
This photograph shows workmen at the Boeing plant in Kent, Washington, performing deployment tests on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility on the lunar surface during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.

The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crew to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.
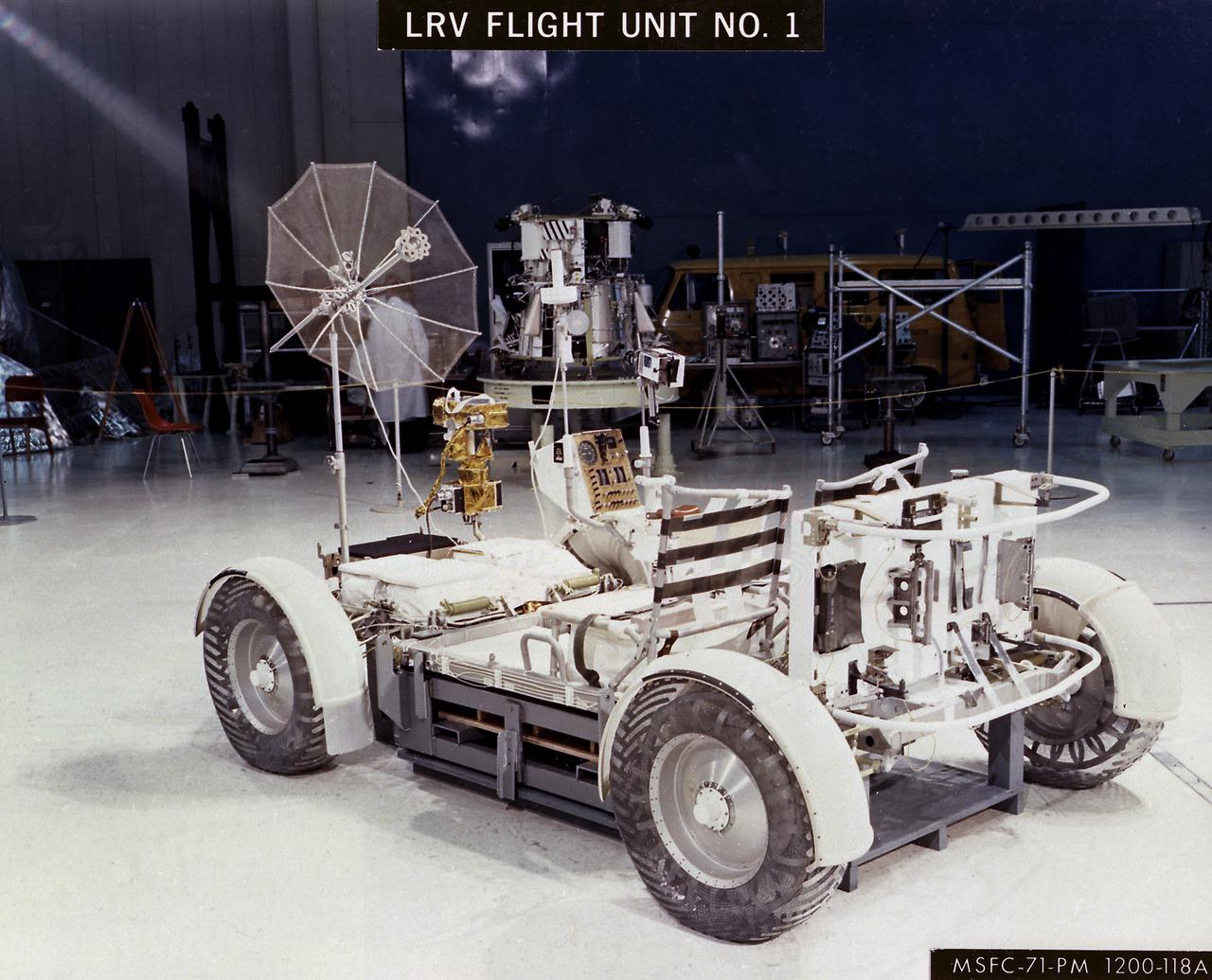
The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crews to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.
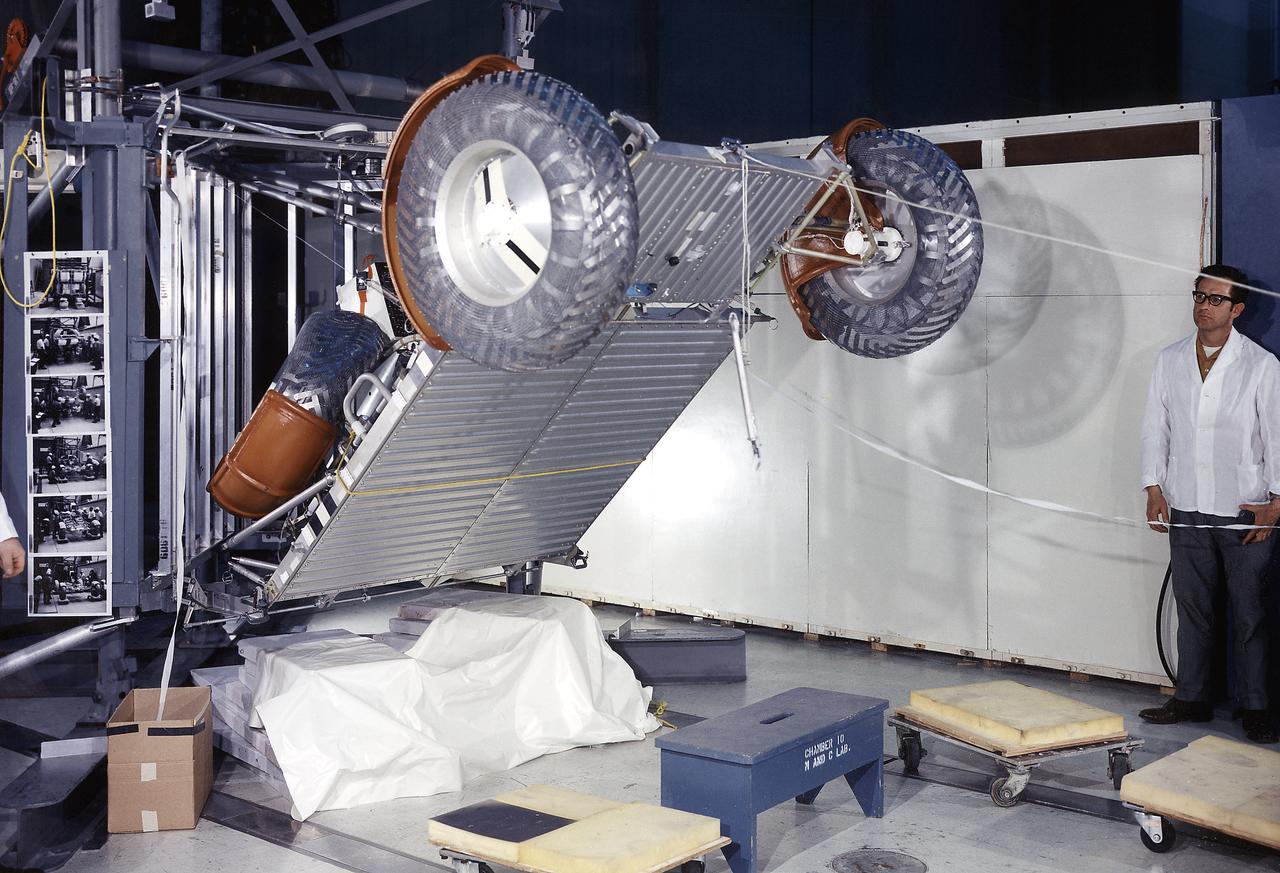
This photograph was taken during a deployment simulation of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
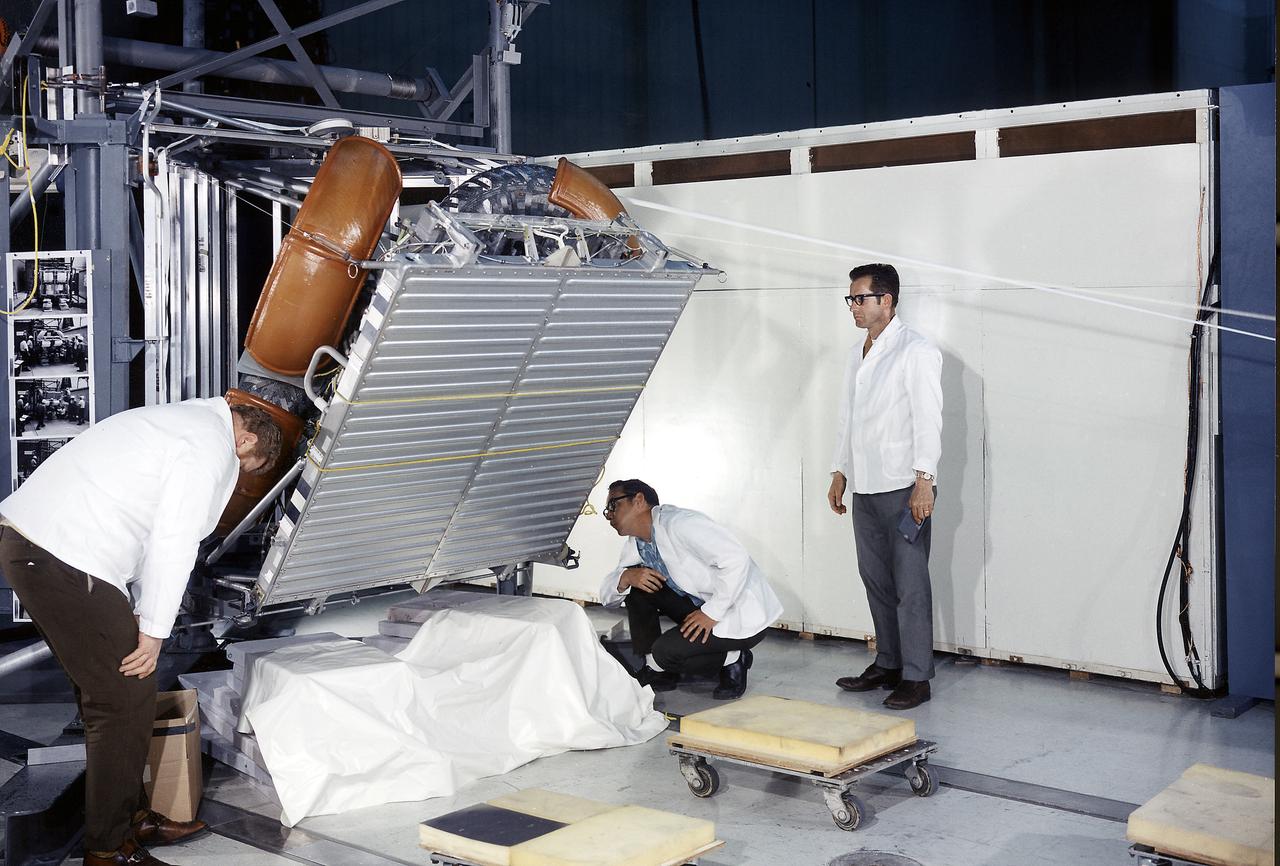

This photograph was taken during a deployment simulation of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
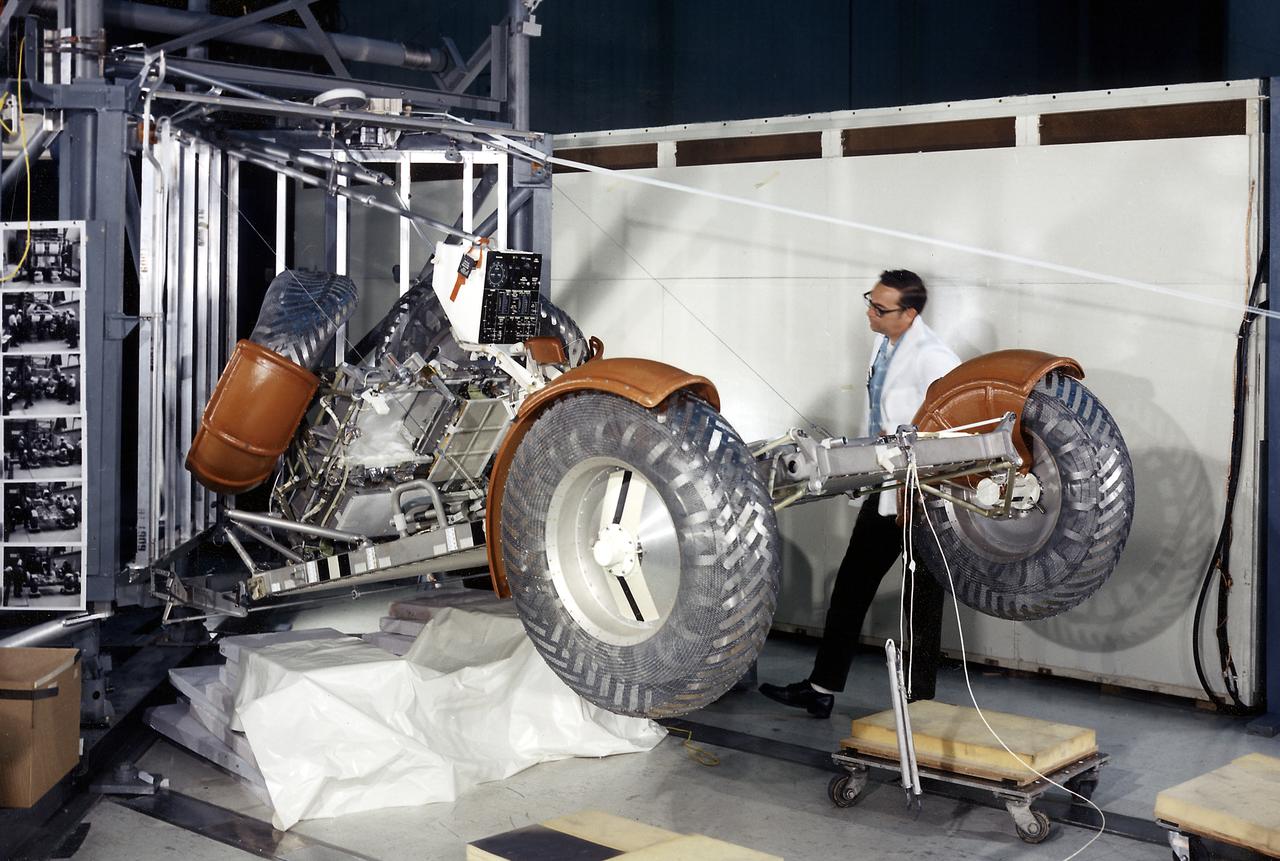

This photograph was taken during a deployment simulation of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.

This in an aerial view (looking north) of a Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), often referrd to as “Moonbuggy”, simulator area built at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) where tesing was performed. The LRV was developed under the direction of MSFC to provide astronauts with greater mobility on the lunar surface.
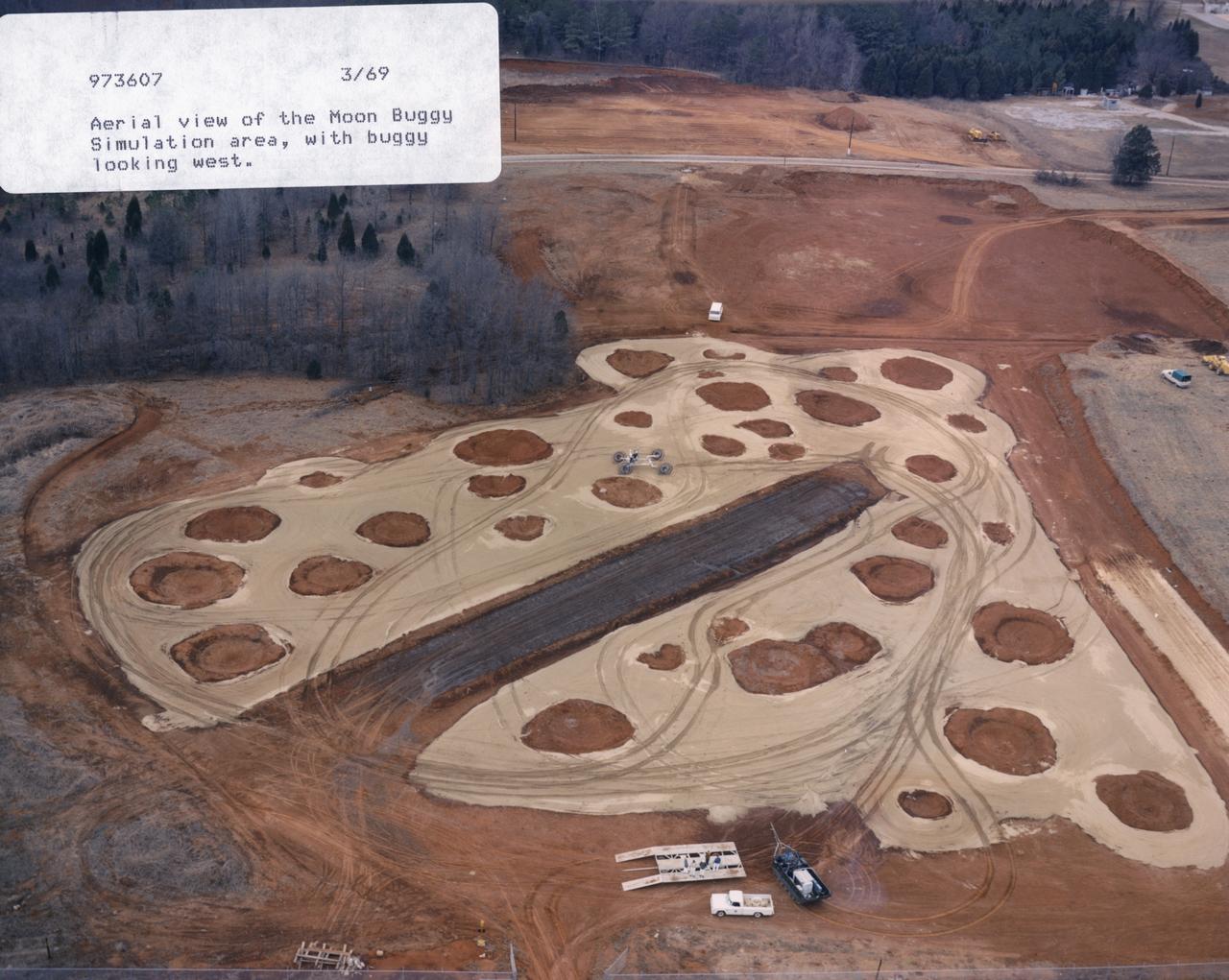

This in an aerial view (looking west) of a Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), often referred to as “Moonbuggy”, simulator area built at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) where tesing was performed. The LRV was developed under the direction of MSFC to provide astronauts with greater mobility on the lunar surface.
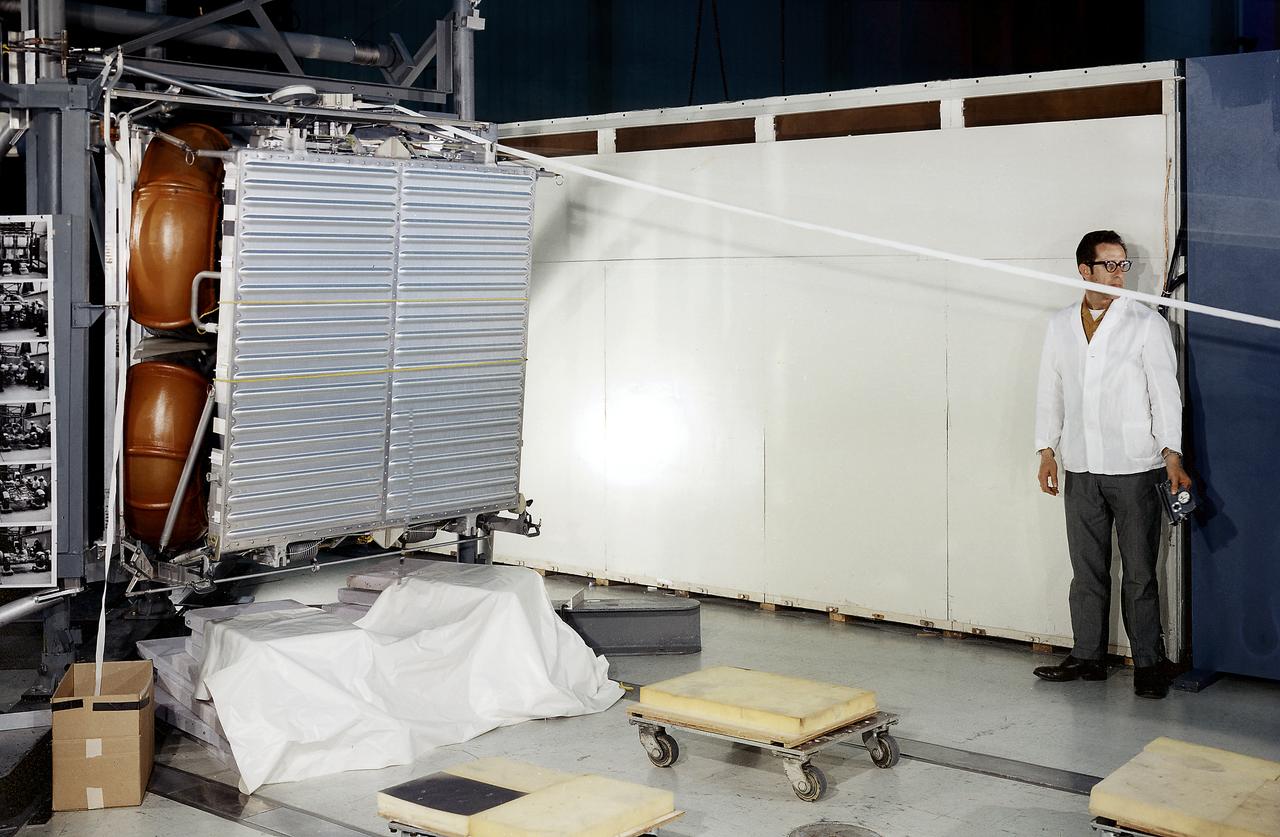

This photograph was taken during a deployment simulation of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
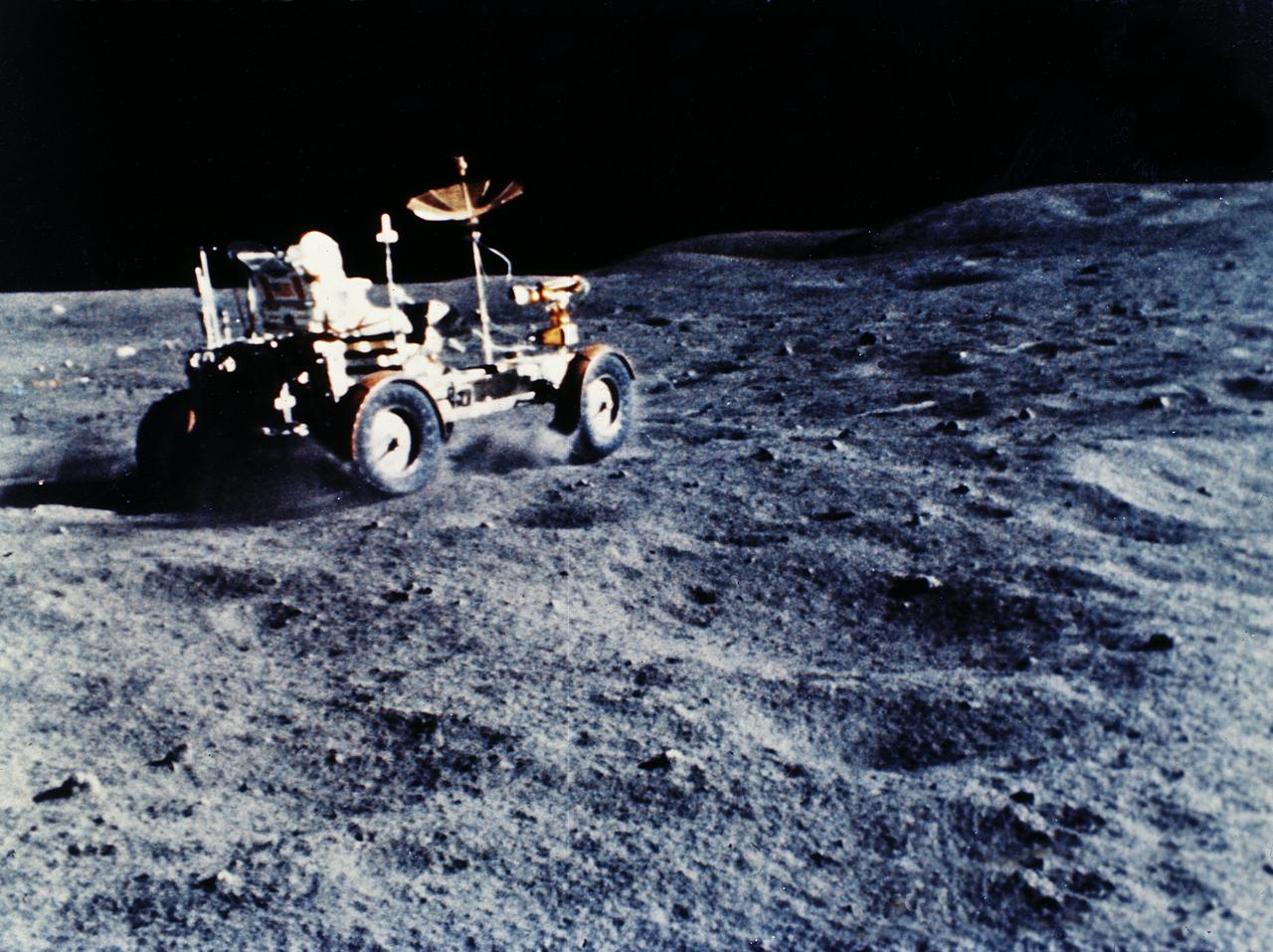
The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17, in 1971 and 1972, to permit the crew to travel several miles from the lunar landing site. This photograph was taken during the Apollo 16 mission.
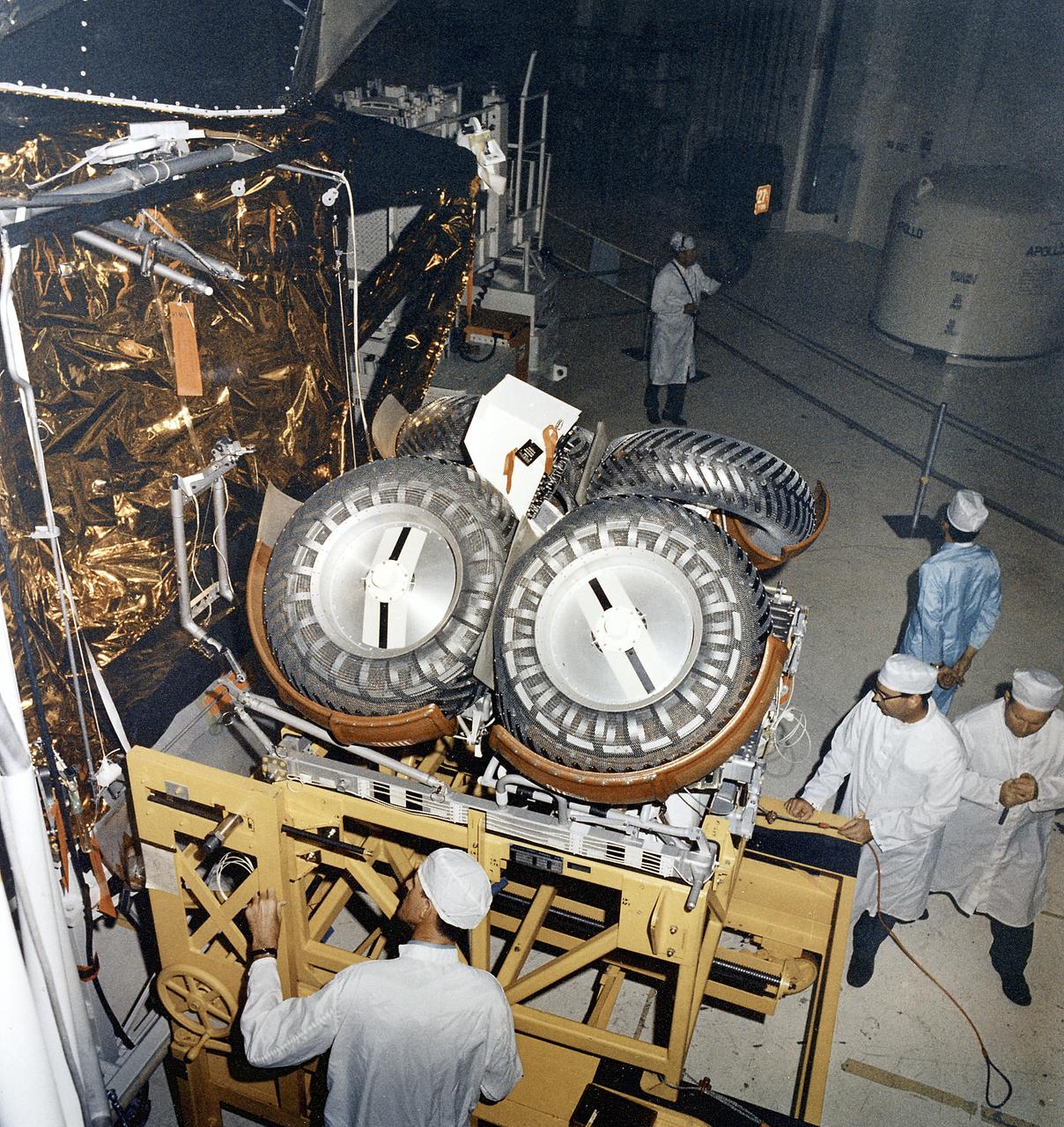
This photograph was taken during the installation of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) in the Lunar Module at the Kennedy Space Center. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.

This photograph shows the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) being prepared for installation in the Lunar Module at the Kennedy Space Center. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
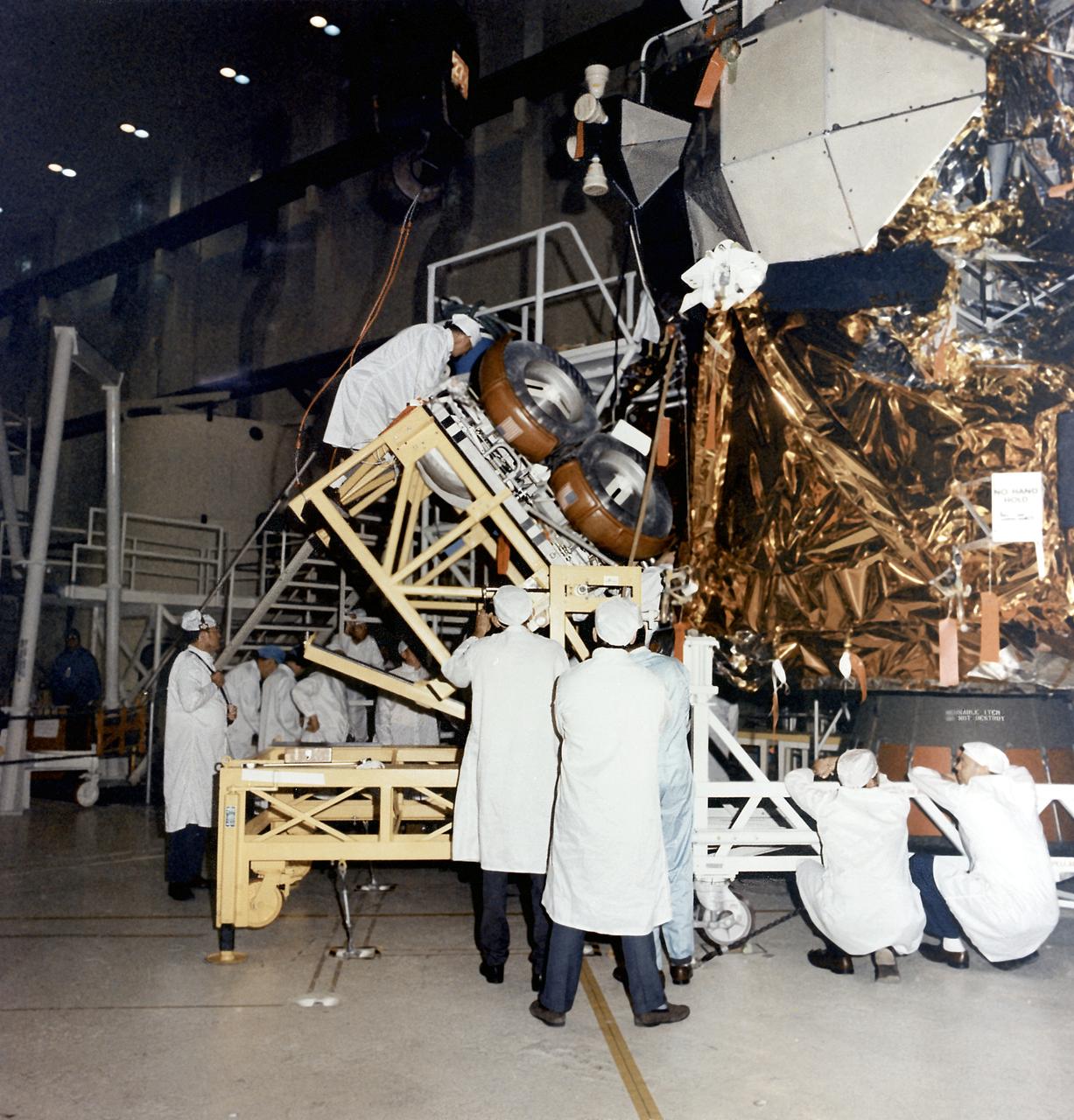

This photograph was taken during the installation of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) in the Lunar Module at the Kennedy Space Center. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
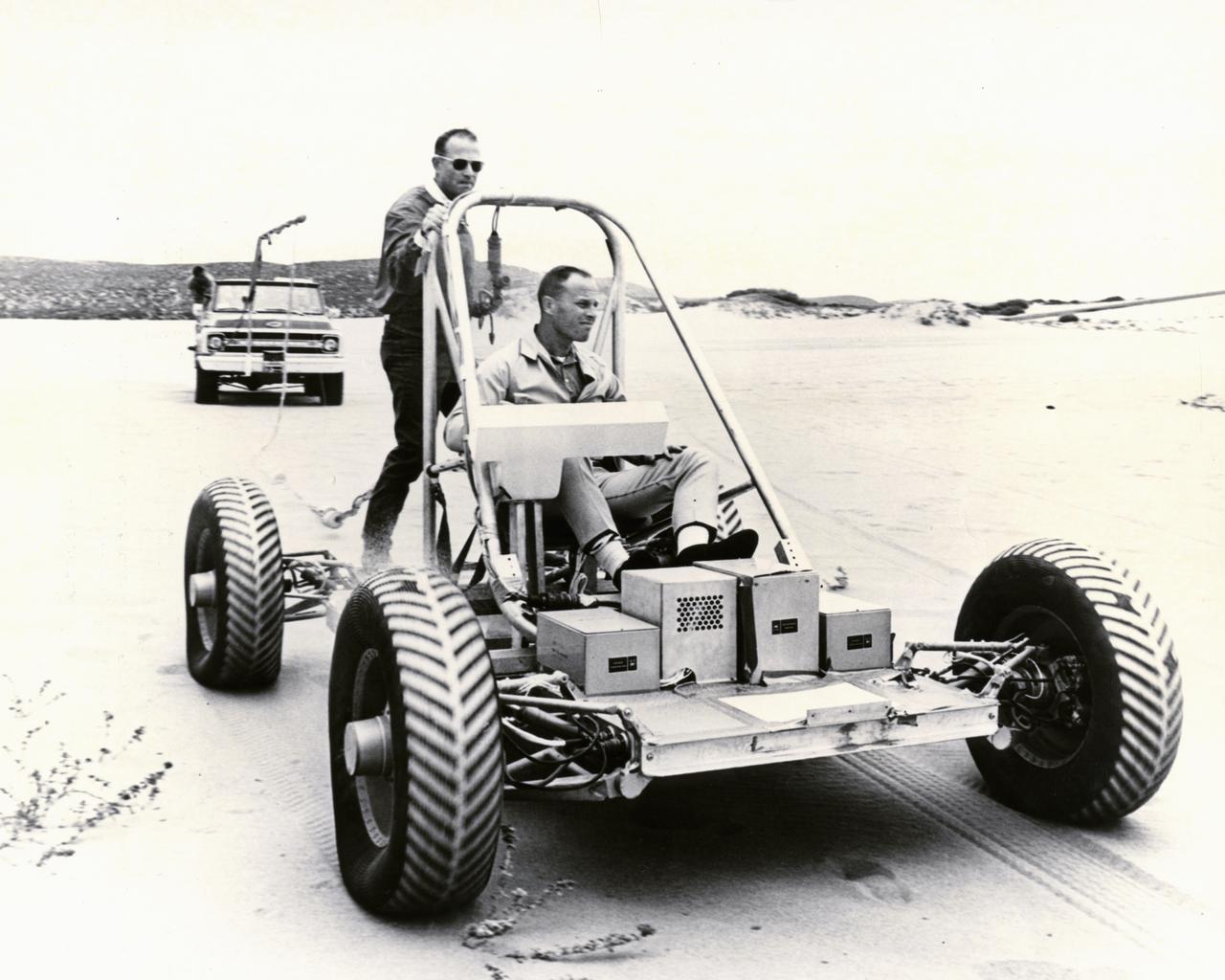

Astronauts Jack Lousma (seated) and Gerald Carr tested the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) training unit on the sands near Pismo Beach. The vehicle was built by the AC Delco electronics division of General Motors Corporation. Under the direction of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions. The LRVs were deployed during the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.
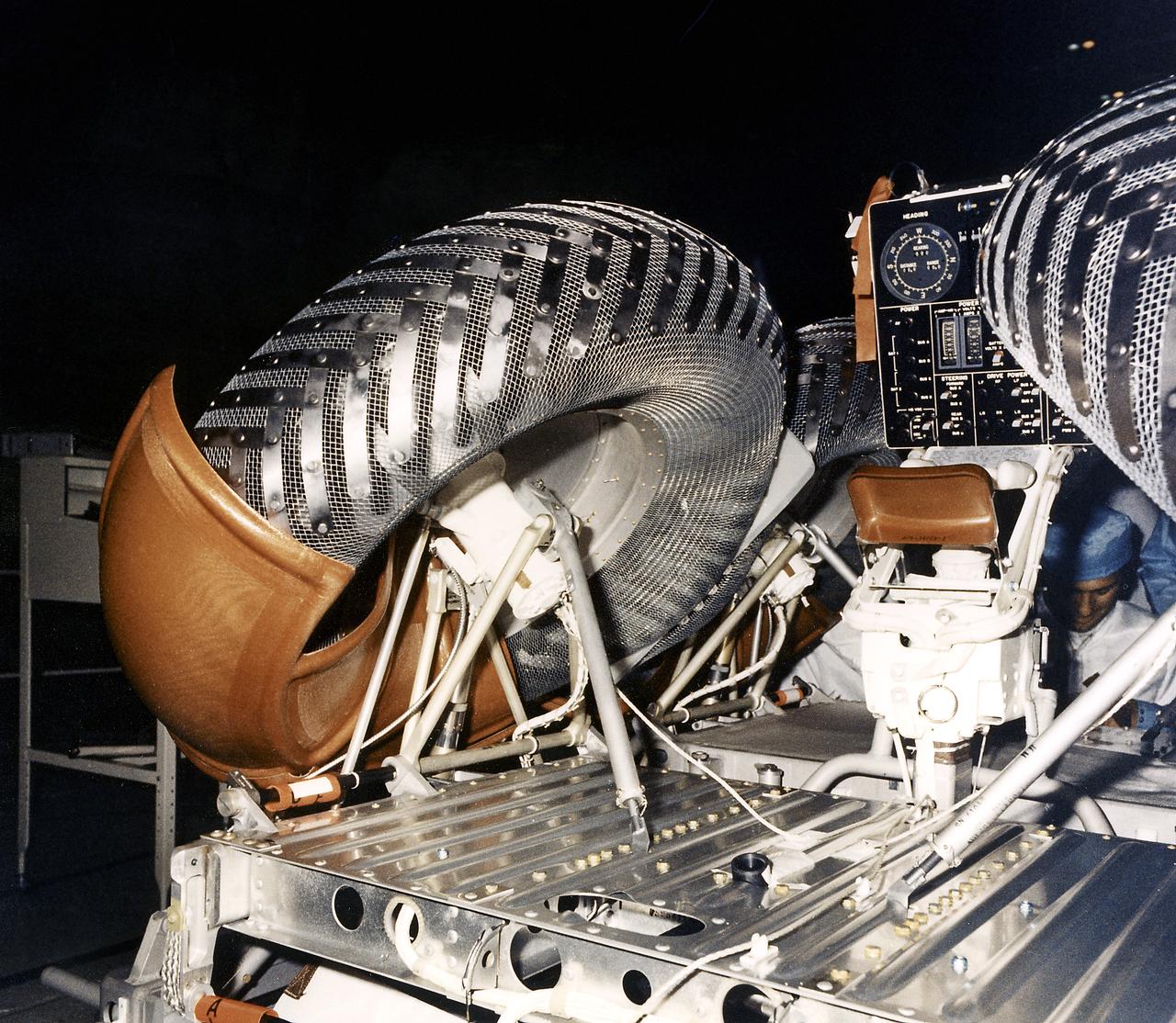
This is a close-up view of a right rear wheel strut of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) No. 1. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration. It was an open-space and collapsible vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and camera. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was built by the Boeing Company under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
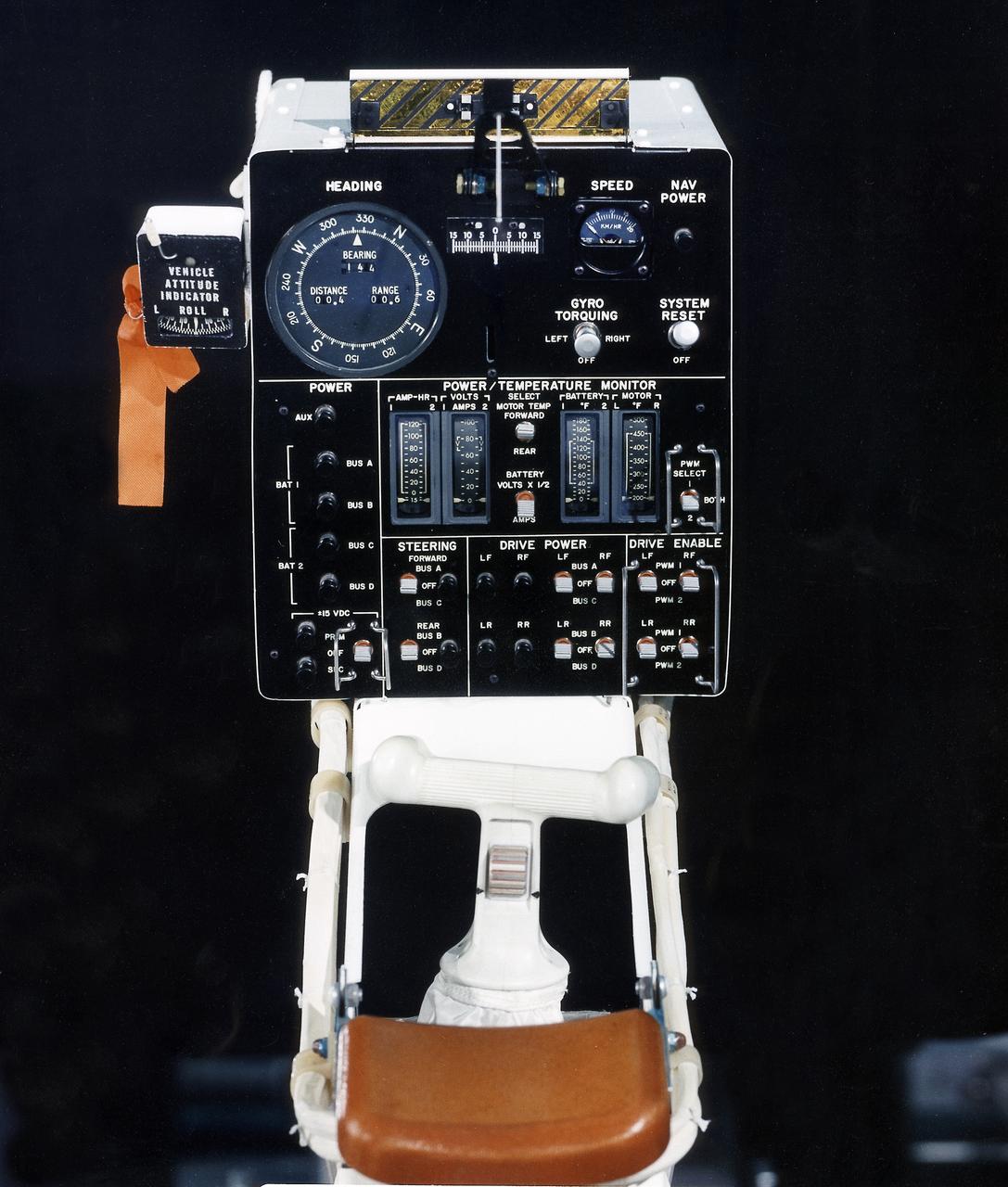
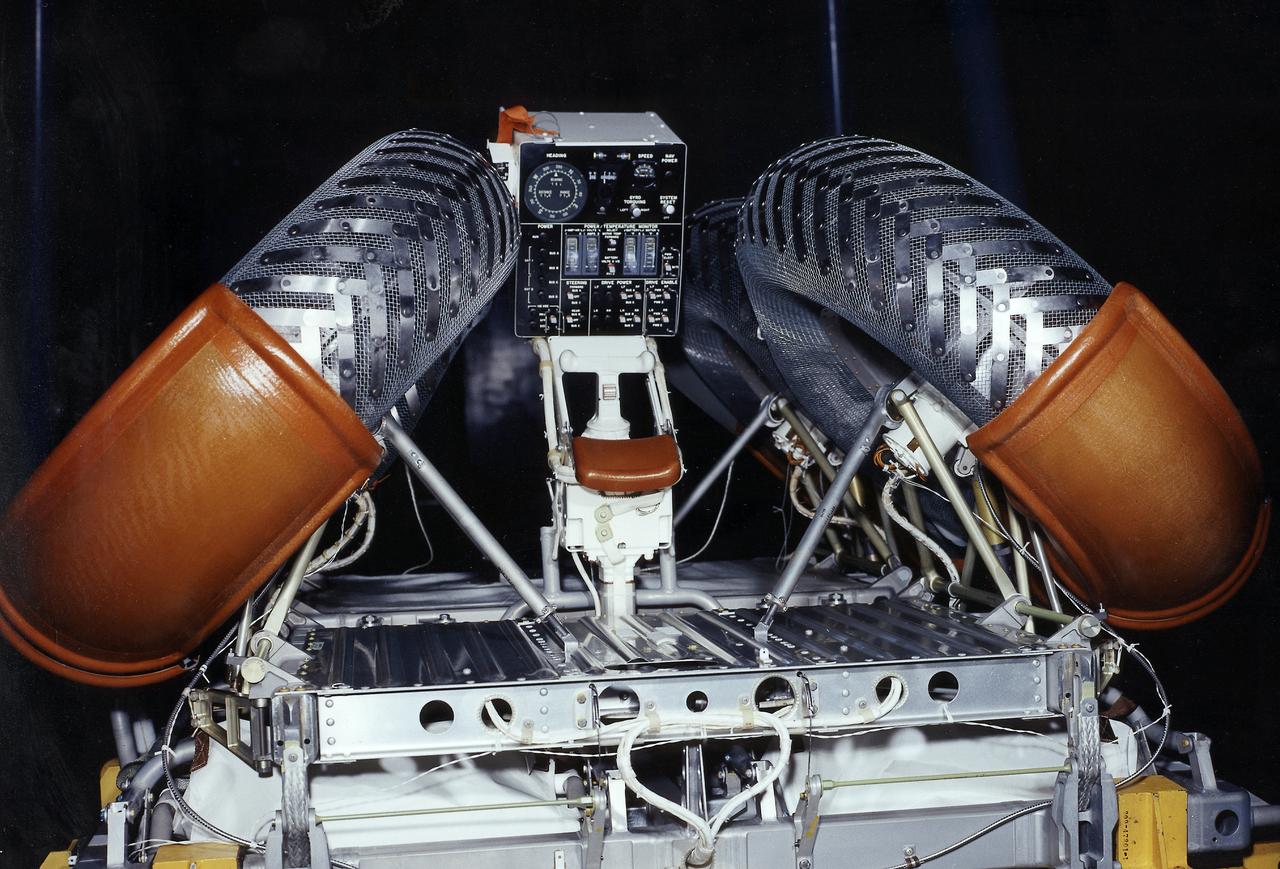
This photograph is a view of a display, control console, and hand controller for the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) No. 2. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration. It was an open-space and collapsible vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and camera. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was built by the Boeing Company under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
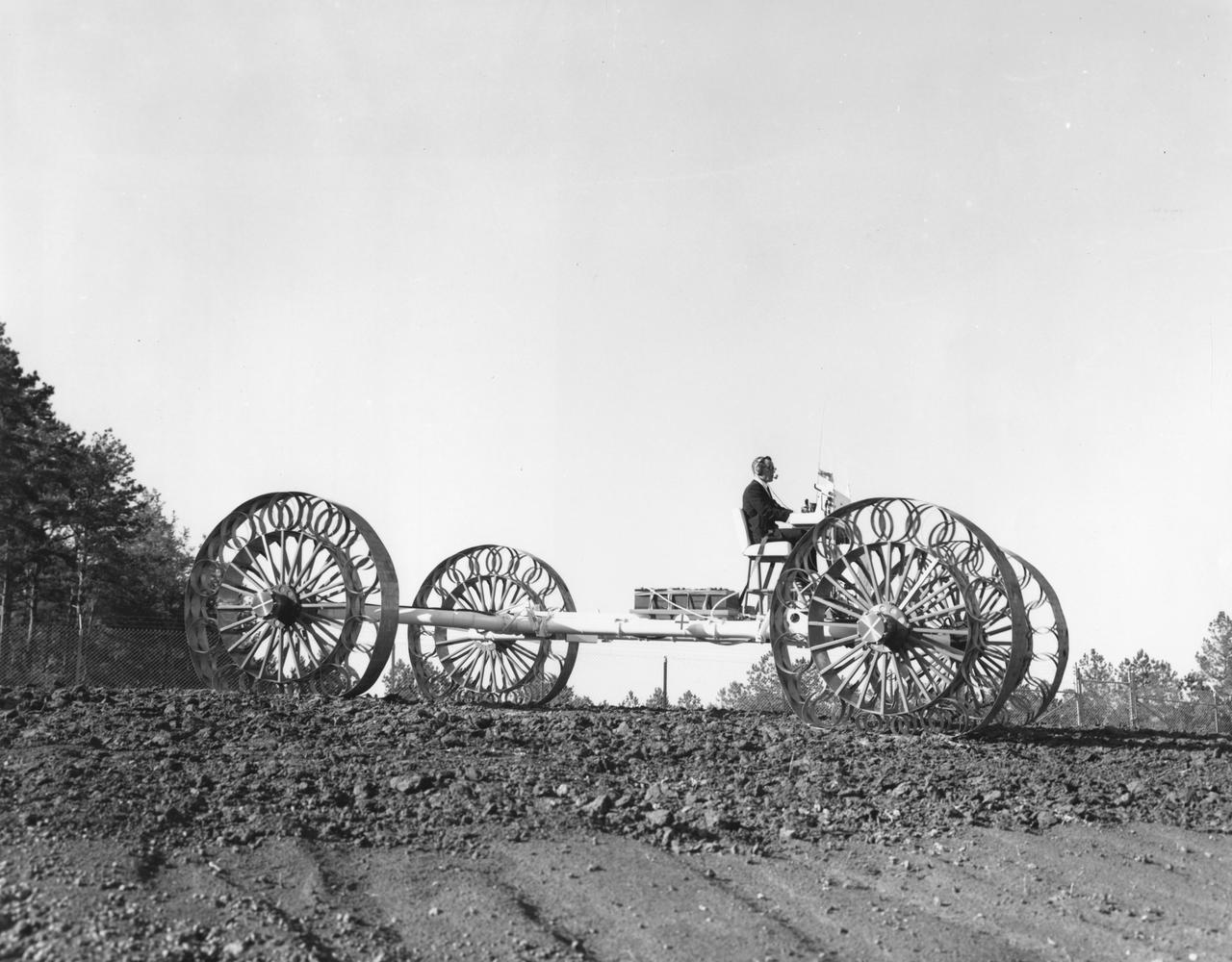

An engineer demonstrates a Mobility Test Article (MTA) at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). This unit, weighing 1/6th as much as an actual vehicle, was built by the Bendix Corporation and was one of the concepts of a possible Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
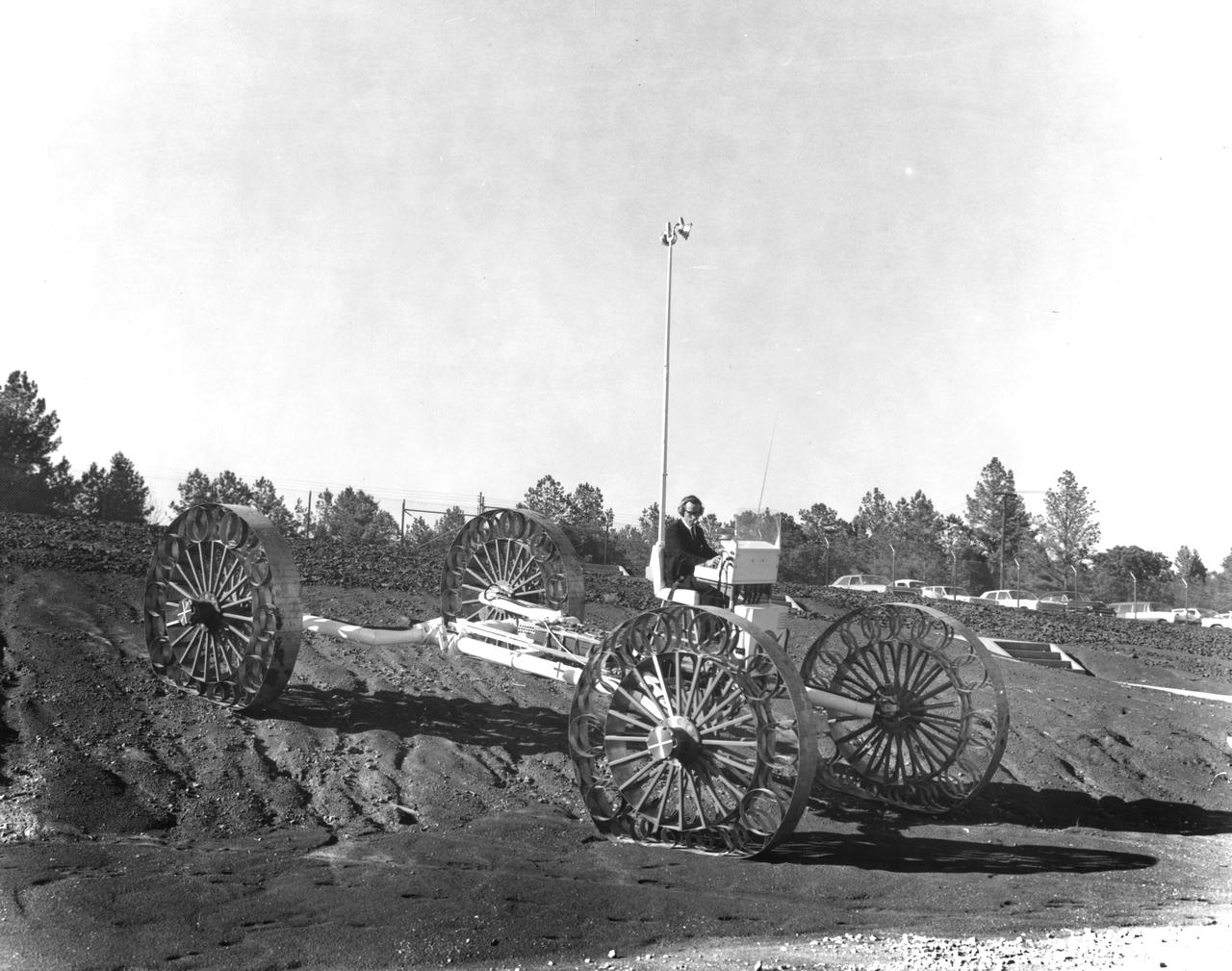

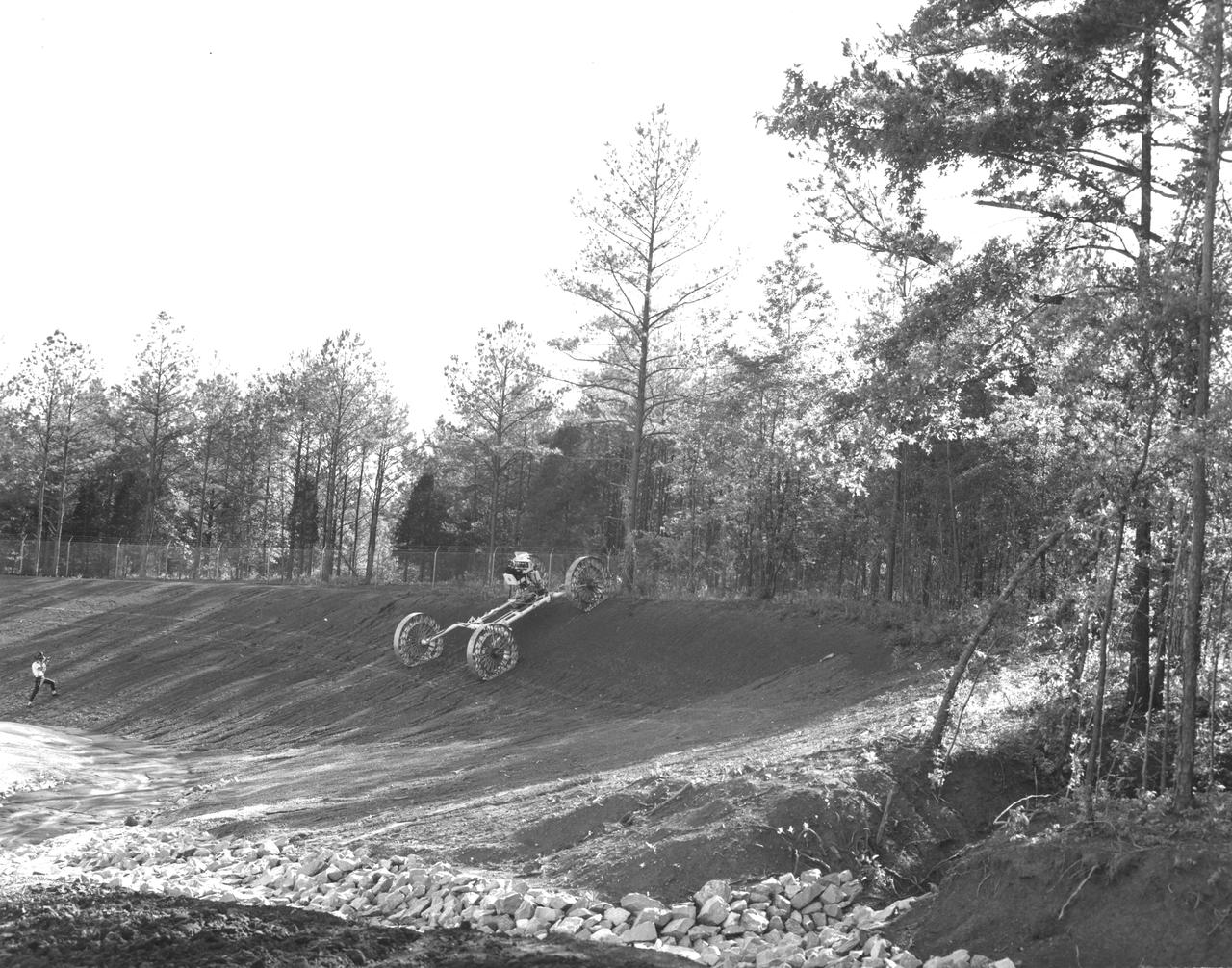
An engineer demonstrates a Mobility Test Article (MTA) at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as he goes down a slope onto soft earth. This unit, weighing 1/6th as much as an actual vehicle, was built by the Bendix Corporation and was one of the concepts of a possible Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
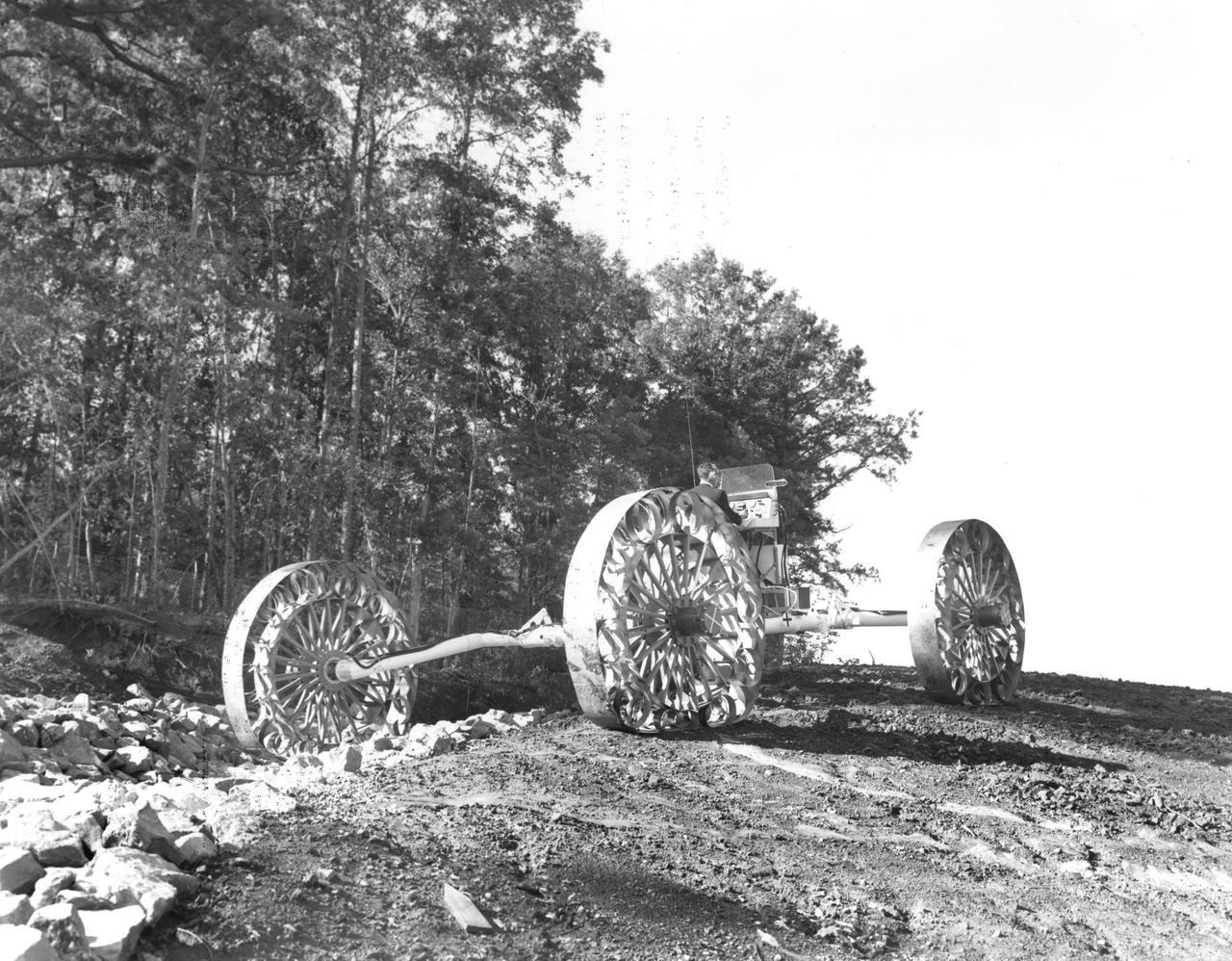

An engineer demonstrates a Mobility Test Article (MTA) at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). This unit, weighing 1/6th as much as an actual vehicle, was built by the Bendix Corporation and was one of the concepts of a possible Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
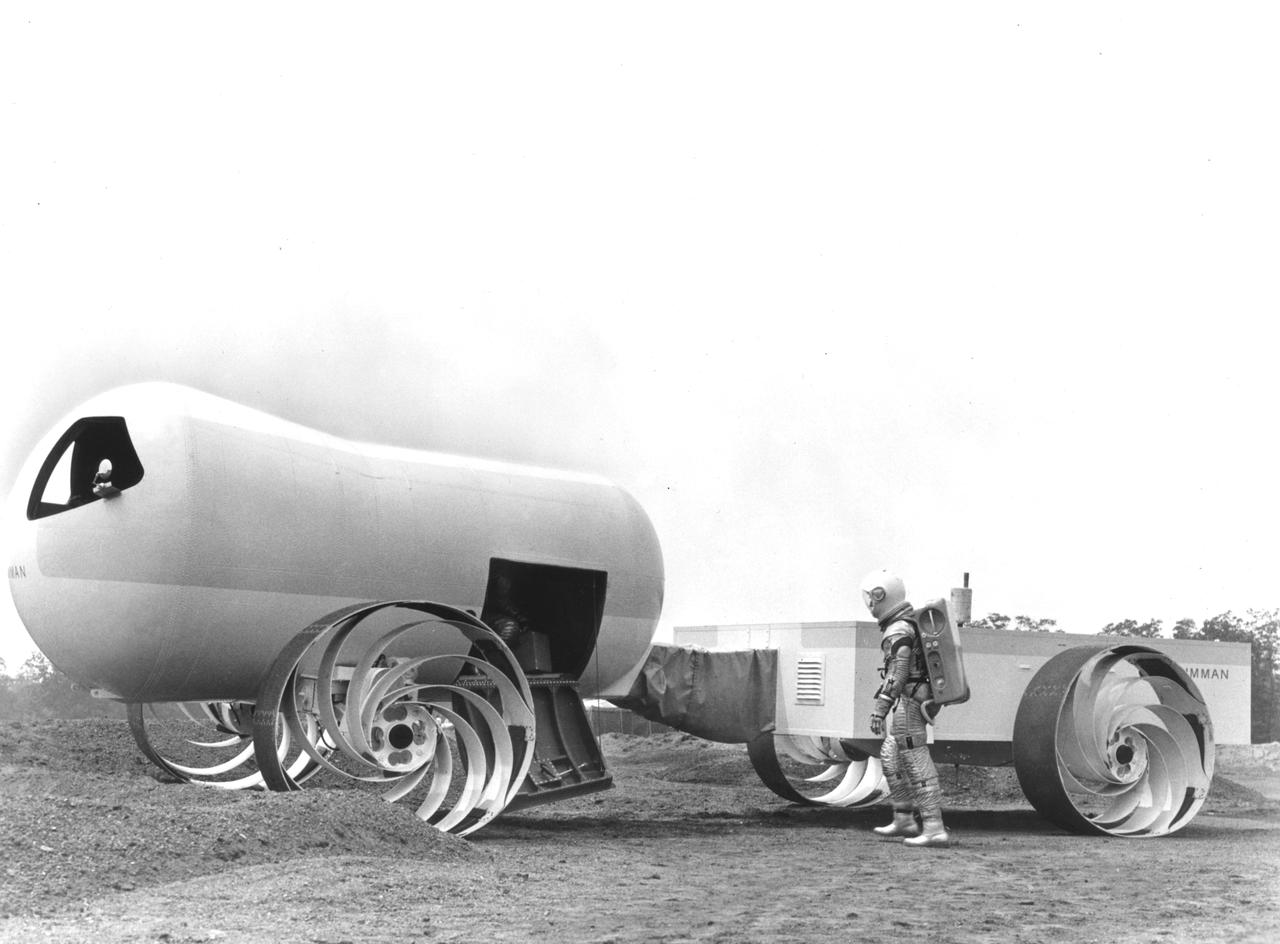

This Mobility Test Article (MTA) was a concept of a possible dual mode Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) built by the Grumman Industries for NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
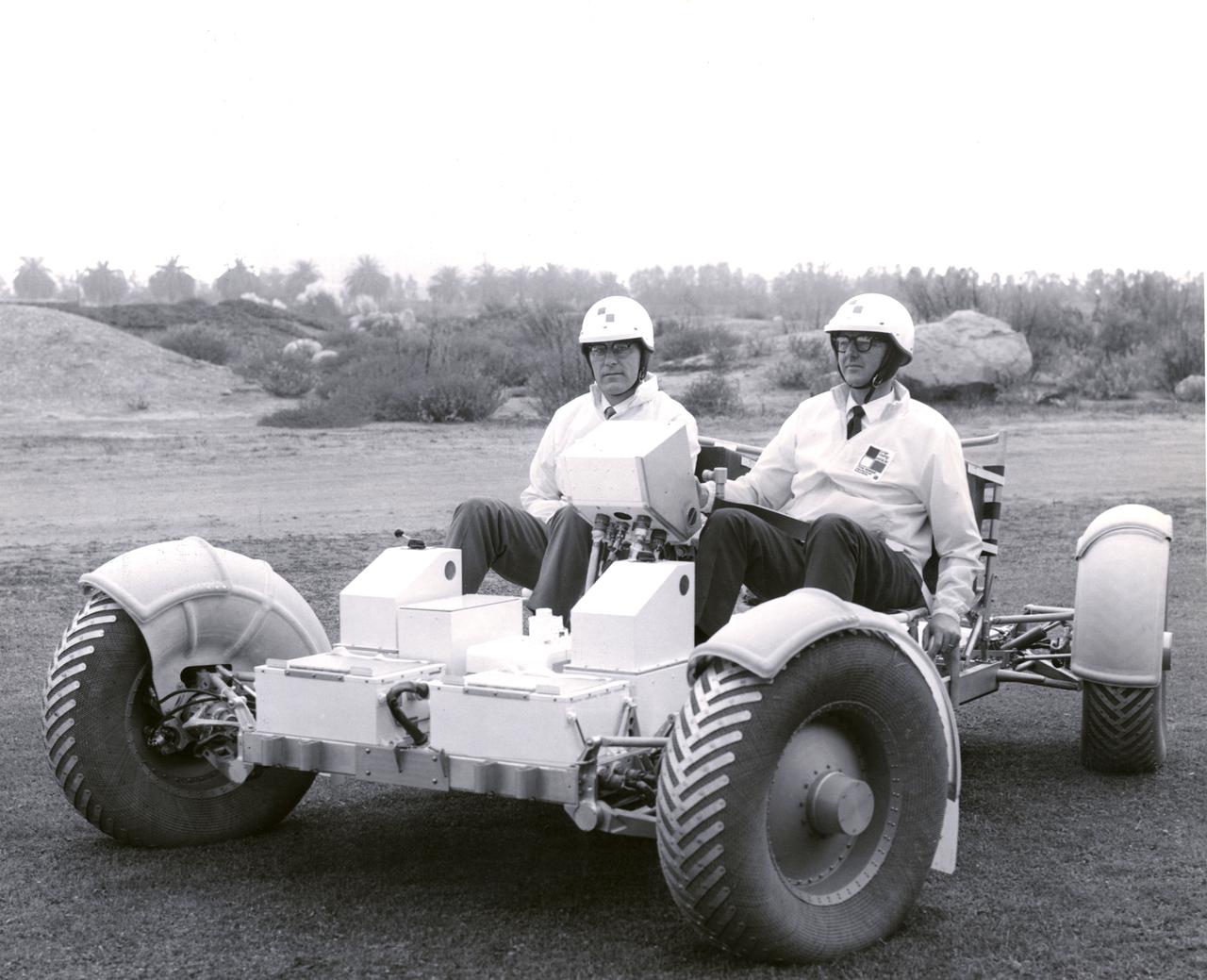

Delco engineers are operating this Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) Trainer. Built by by Delco Electronics Division of the General Motors Corporation, the trainer was shipped to NASA’s Manned Spacecraft Center in Houston, Texas for an astronaut training program. Under the direction of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions. The LRVs were deployed during the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.
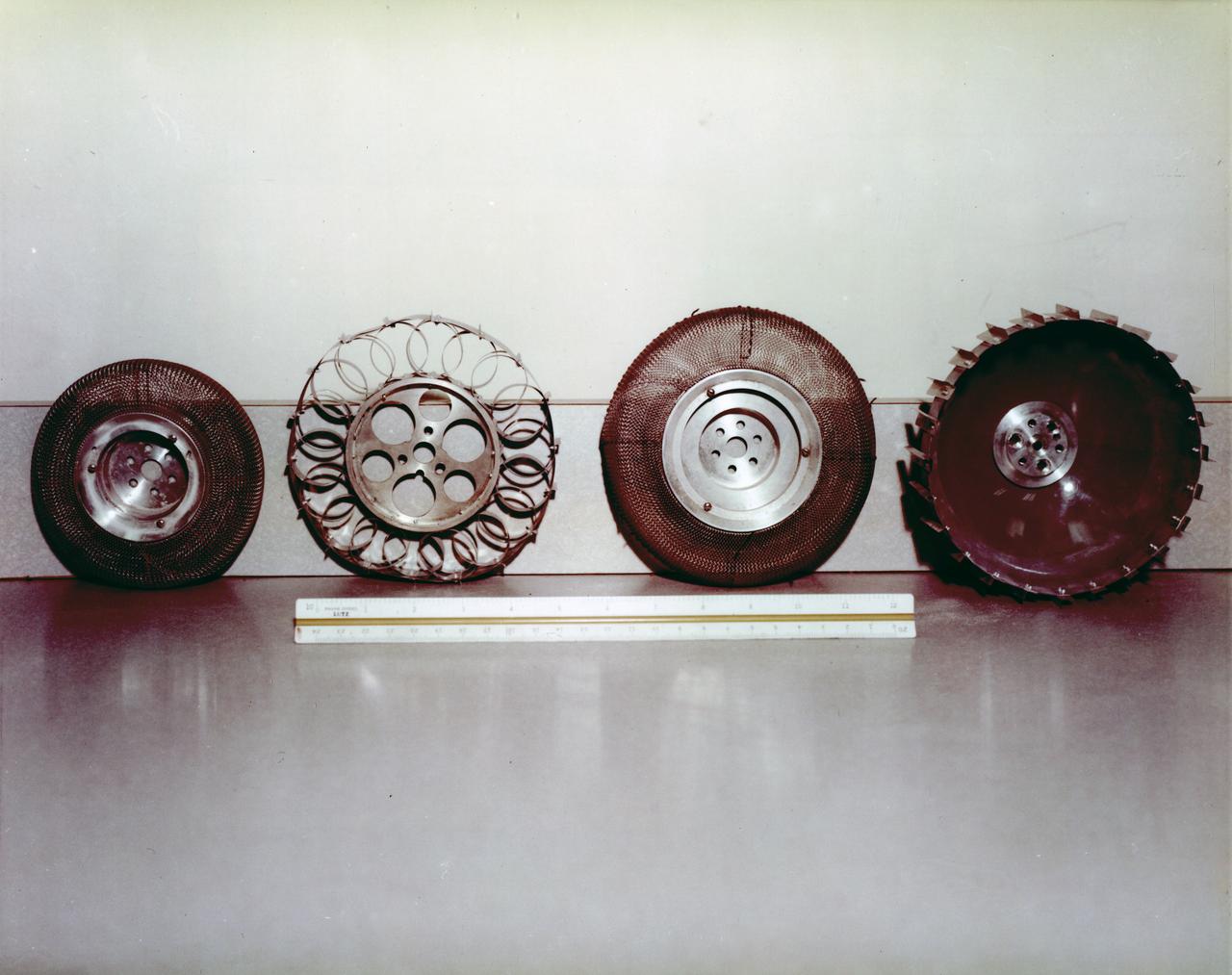

Under the direction of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions. During the development process, LRV prototype wheels underwent soil tests in building 4481 at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Pictured from left to right are the wheels for: LRV, Bendix Corporation, Local Scientific Survey Module (LSSM), and Grumman Industries.

Artist’s concept of a Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) Mobility Test Article (MTA) on the Lunar surface. The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the LRV, developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
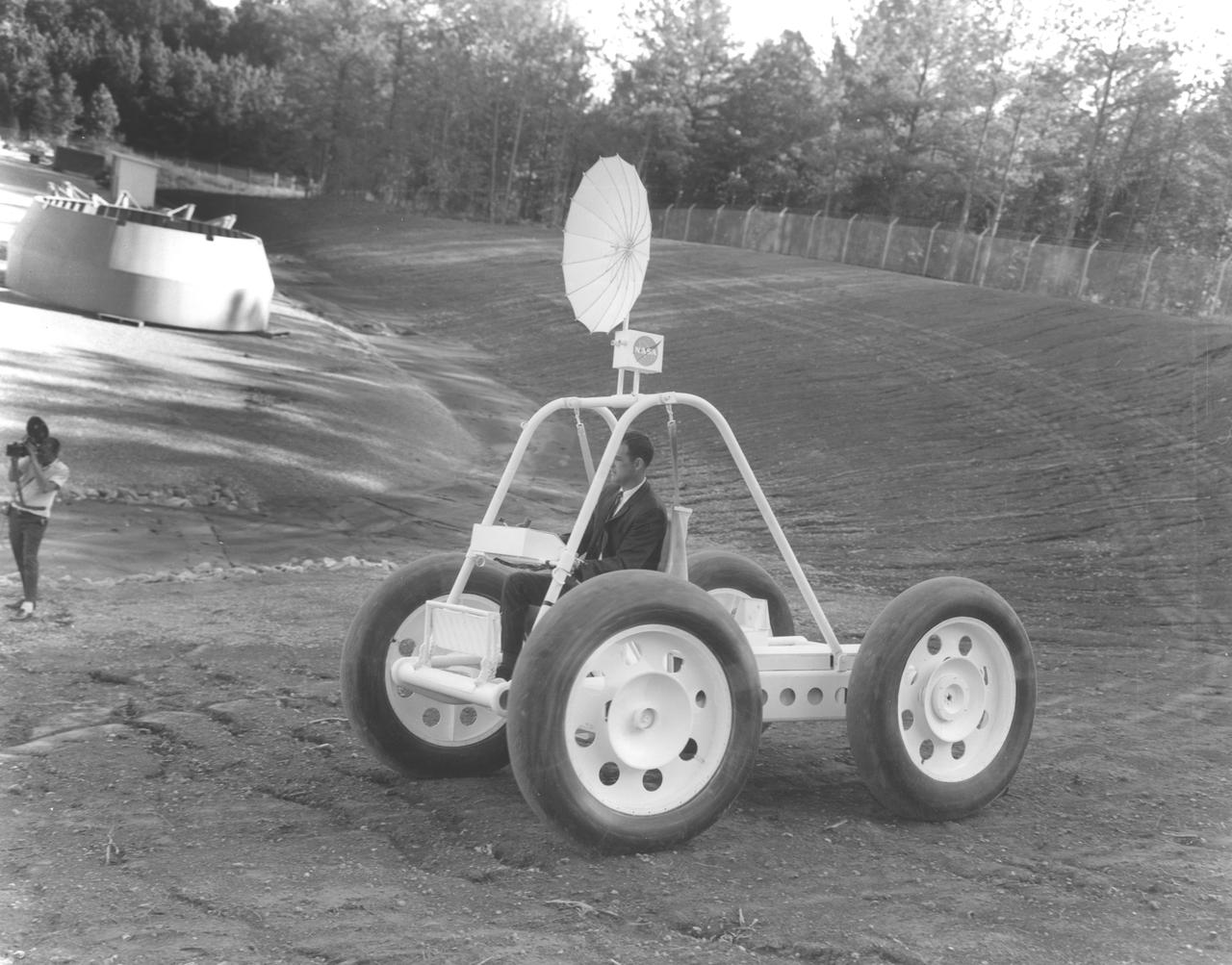

Built by Brown Engineering company of Huntsville, Alabama, a motorized mockup of a small Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is being demonstrated at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). This particular vehicle weighed about 1200 pounds and is almost 10 feet long, 7-feet and 2-inches wide, and 7-feet and 8-inches high. The LRV was developed under the direction of MSFC to provide astronauts with greater mobility on the lunar surface.
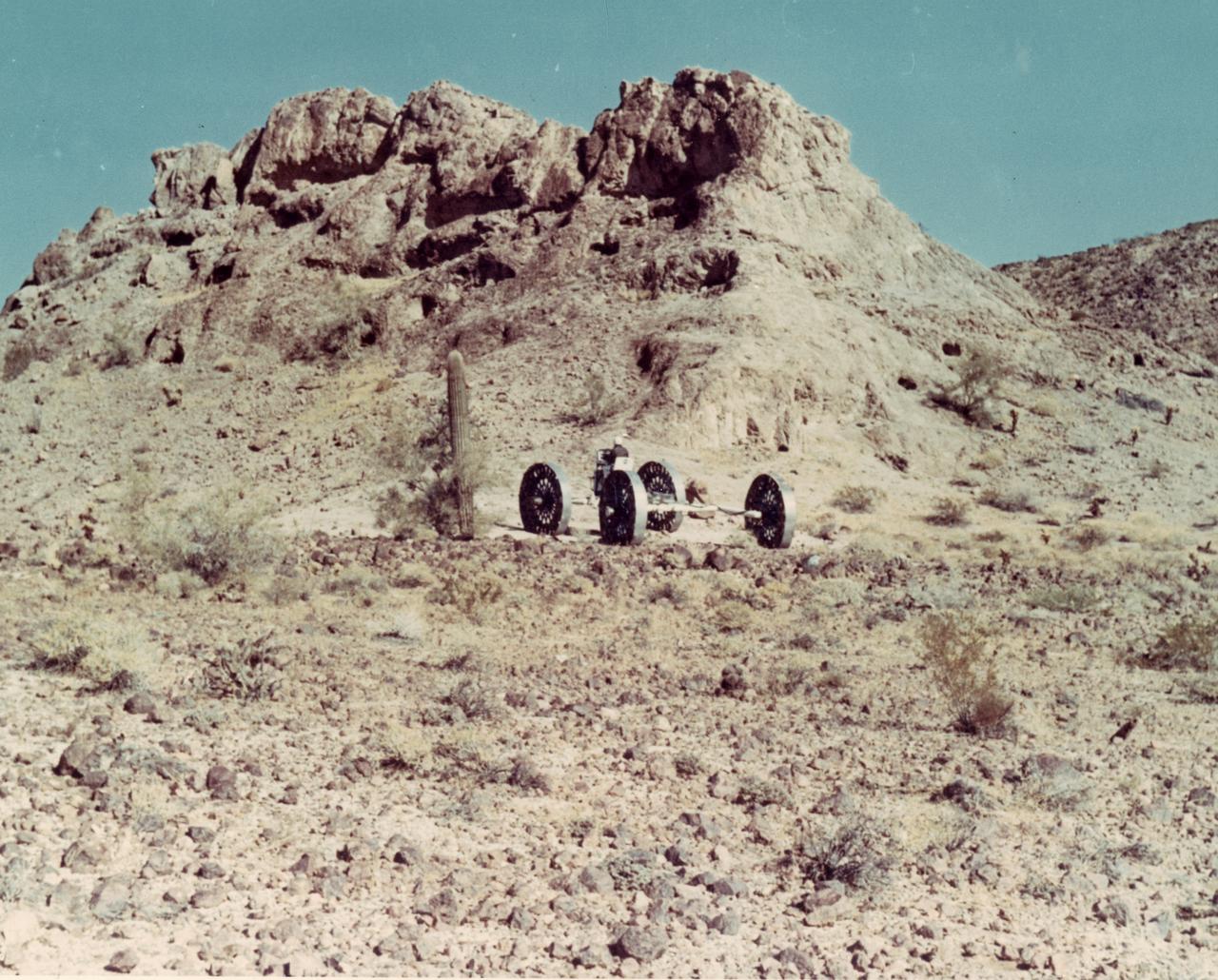

A test engineer drives a Mobility Test Article (MTA) during a test of a Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) concept through the mountains of Arizona. The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the LRV, developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
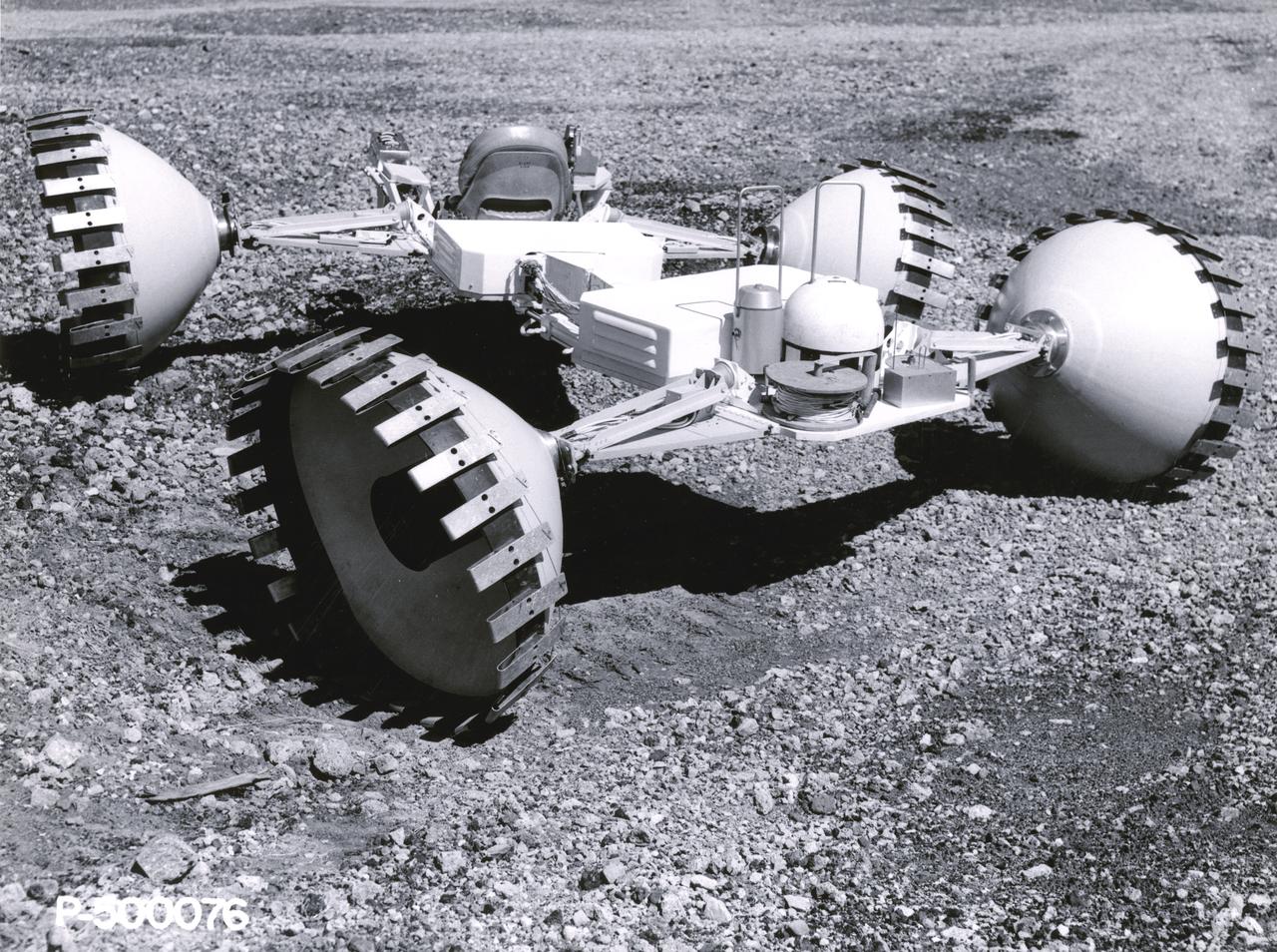
A concept of a possible Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) built for NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). This Mobility Test Article (MTA) is one of many that provided data contributing to the design of the LRV, developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
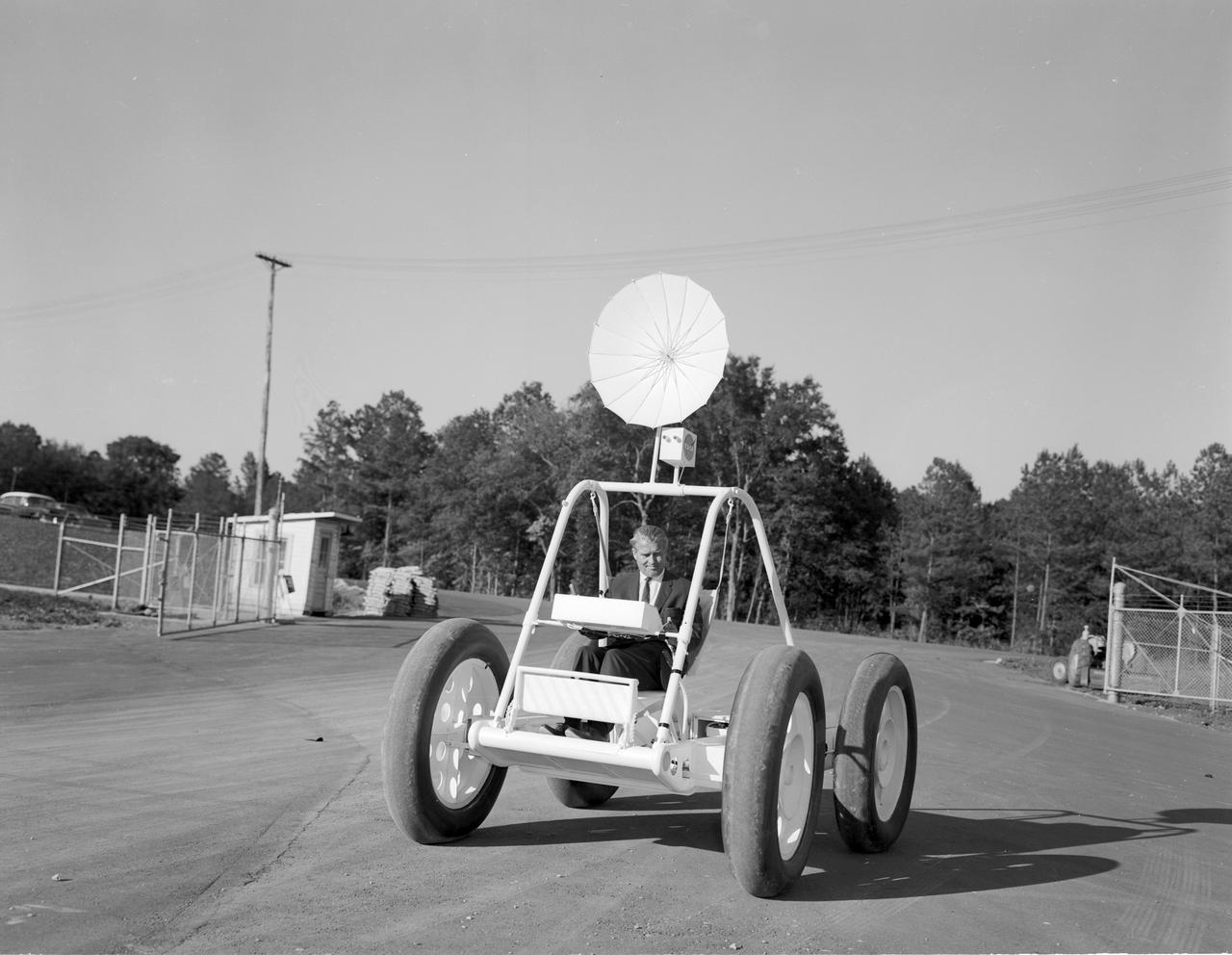

Dr. von Braun, director of NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), is driving a small vehicle used in the studies of modes for transportation on the moon’s surface. From those studies evolved the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV).
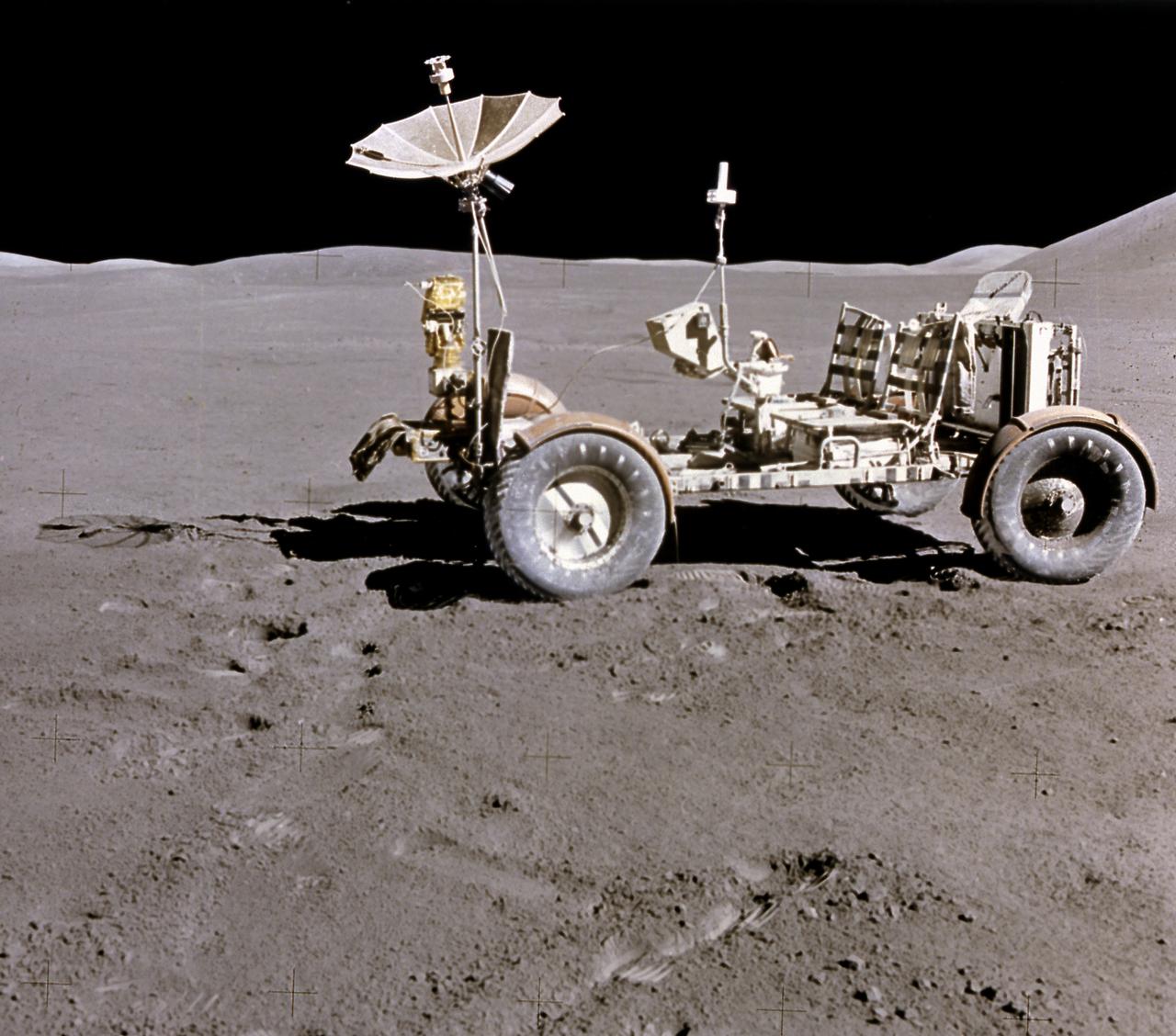
This photograph of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was taken during the Apollo 15 mission. Powered by battery, the lightweight electric car greatly increased the range of mobility and productivity on the scientific traverses for astronauts. It weighed 462 pounds (77 pounds on the Moon) and could carry two suited astronauts, their gear and cameras, and several hundred pounds of bagged samples. The LRV's mobility was quite high. It could climb and descend slopes of about 25 degrees. The LRV was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.

Artist’s concept of a dual mode Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the Lunar surface. This represents the Grumman version in an unmanned configuration. The LRV was developed under the direction of MSFC to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
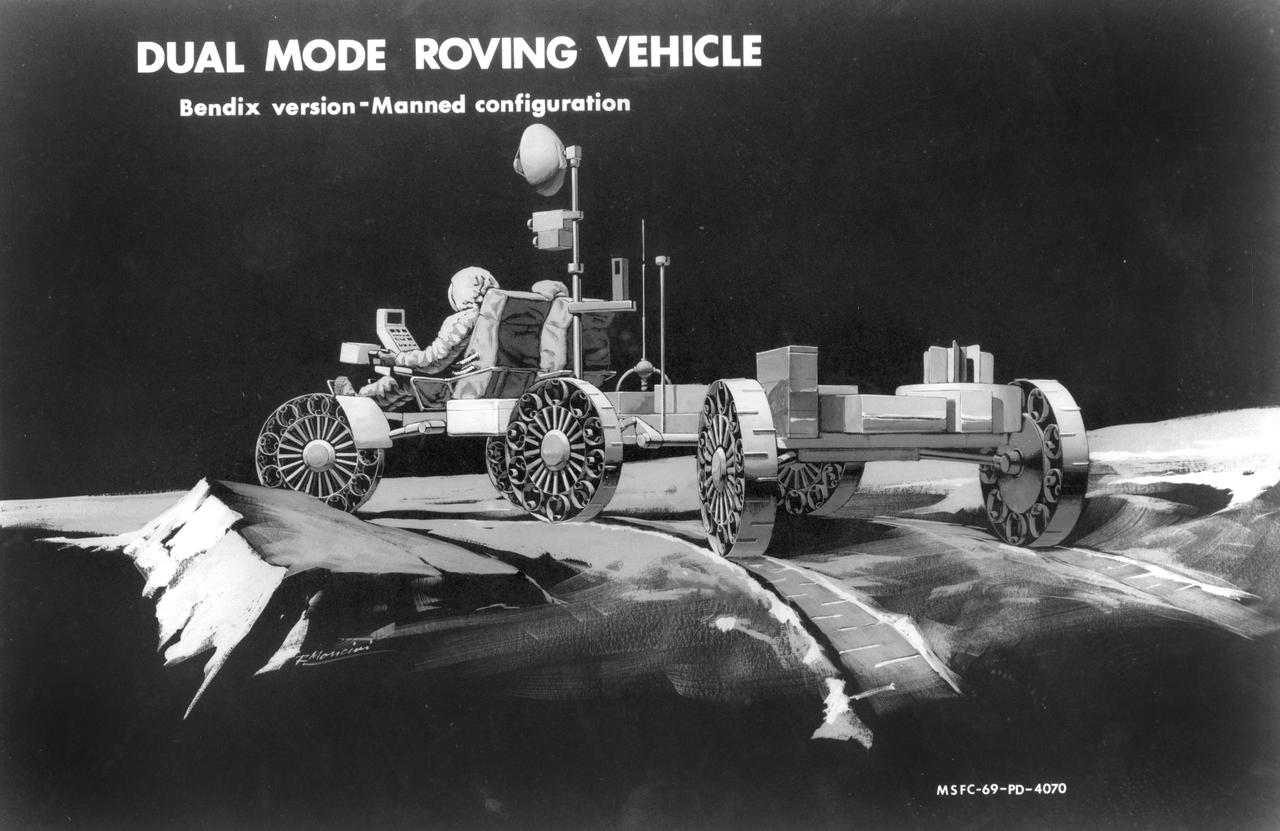
Artist’s concept of a dual mode Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the Lunar surface. This represents the Bendix version in an unmanned configuration. The LRV was developed under the direction of MSFC to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
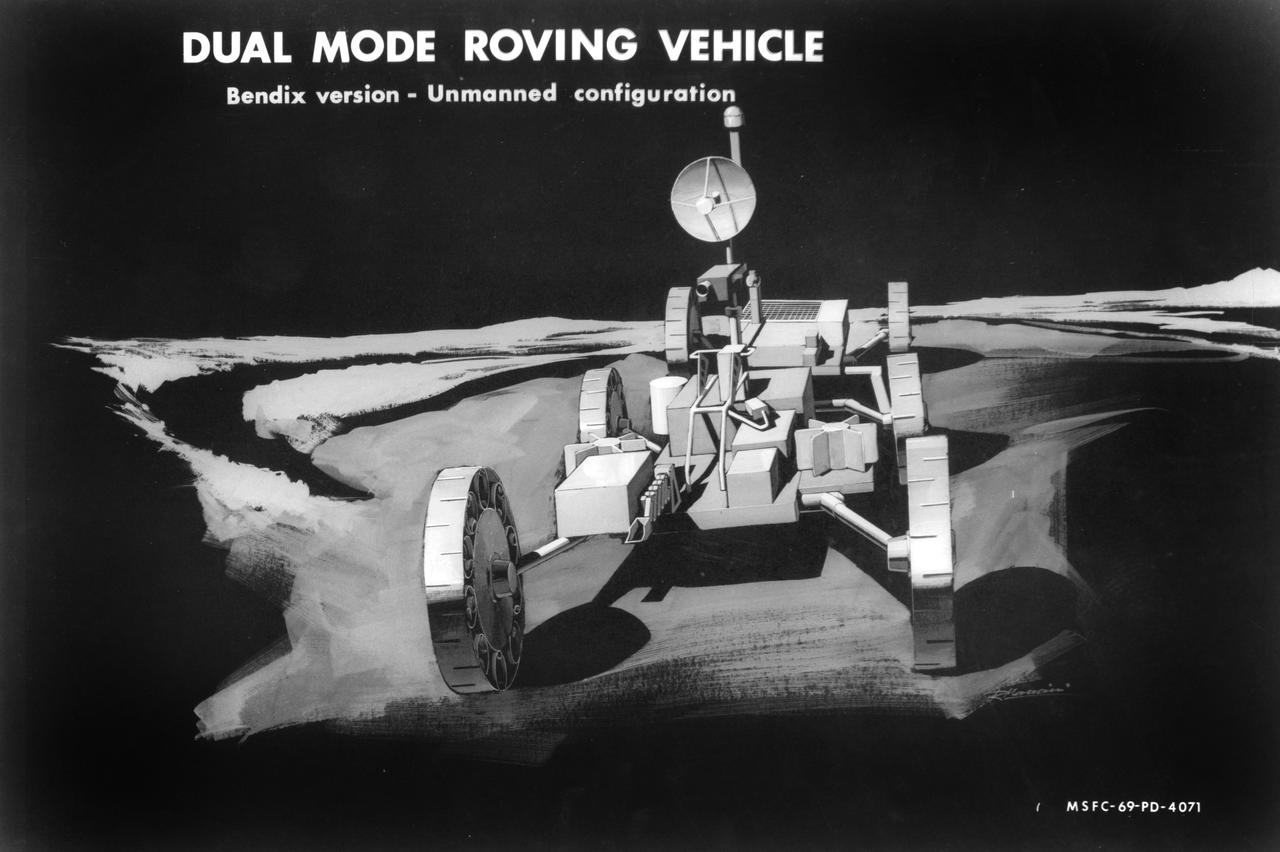
Artist’s concept of a dual mode Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the Lunar surface. This represents the Bendix version in an unmanned configuration. The LRV was developed under the direction of MSFC to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.

Artist’s concept of a manned Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) depicting two-man operation on the Lunar surface. The LRV was developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) to provide Apollo astronauts with a greater range of mobility on the lunar surface.
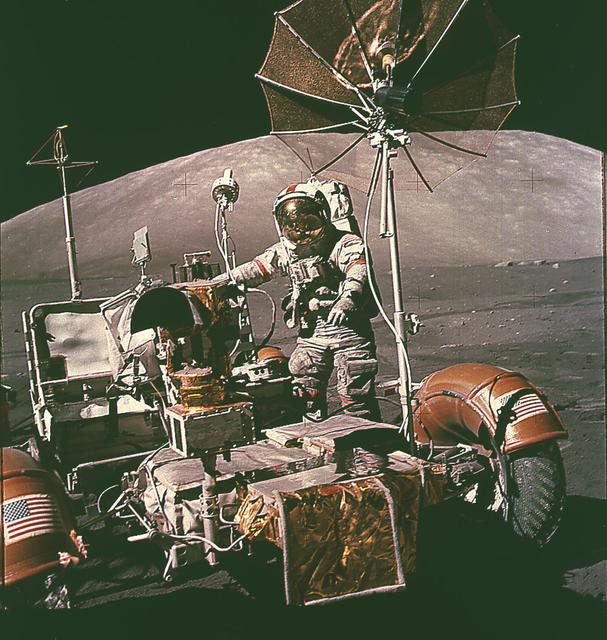

This is an Apollo 17 onboard photo of an astronaut beside the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the lunar surface. Designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company, the LRV was first used on the Apollo 15 mission and increased the range of astronauts' mobility and productivity on the lunar surface. This lightweight electric car had battery power sufficient for about 55 miles. It weighed 462 pounds (77 pounds on the Moon) and could carry two suited astronauts, their gear, cameras, and several hundred pounds of bagged samples. The LRV's mobility was quite high. It could climb and descend slopes of about 25 degrees.
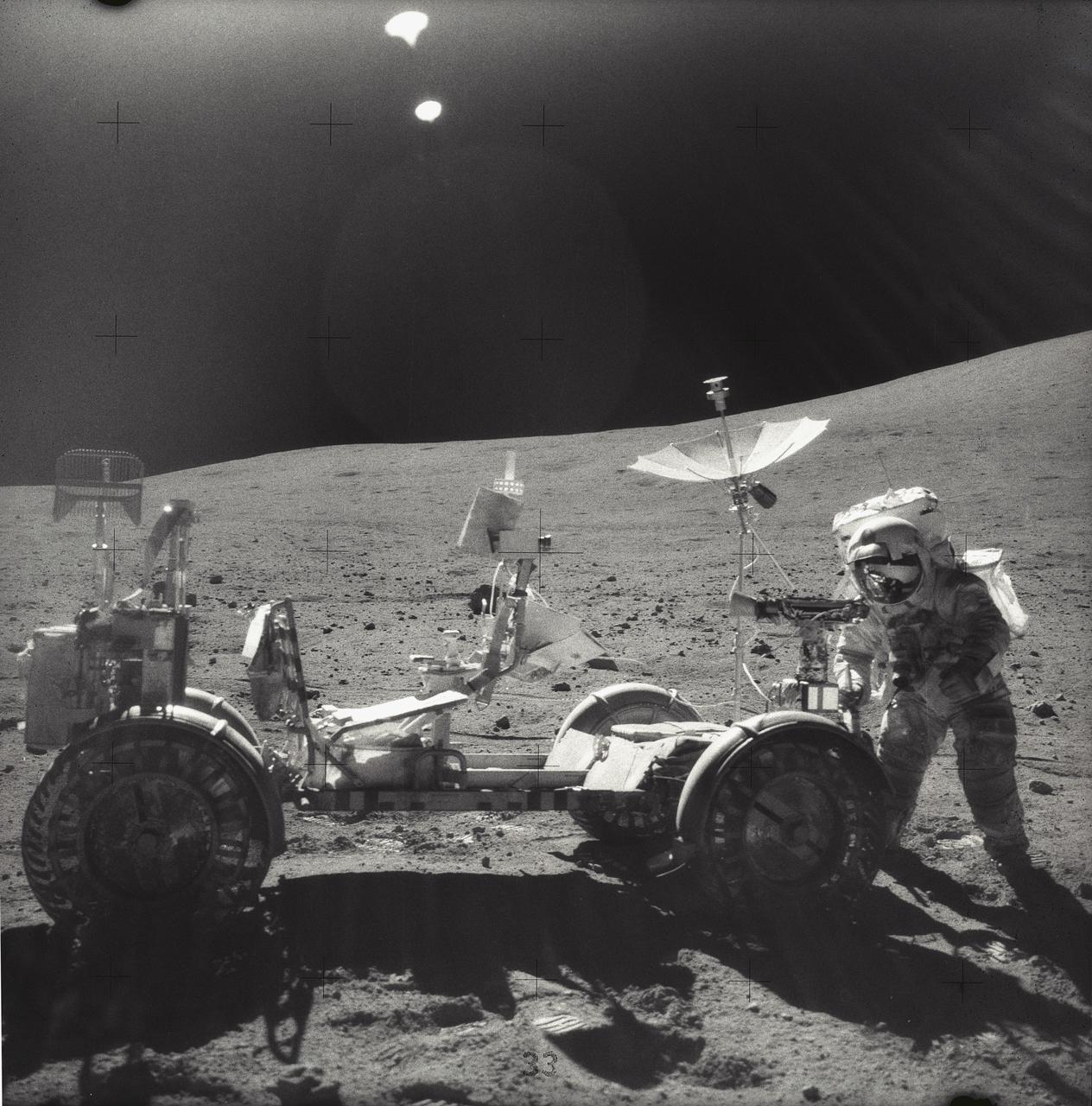

The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed by Marshall Space Flight Center to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17, in 1971 and 1972, to permit the crew to travel several miles from the lunar landing site. This photograph was taken during the Apollo 16 mission in 1972.
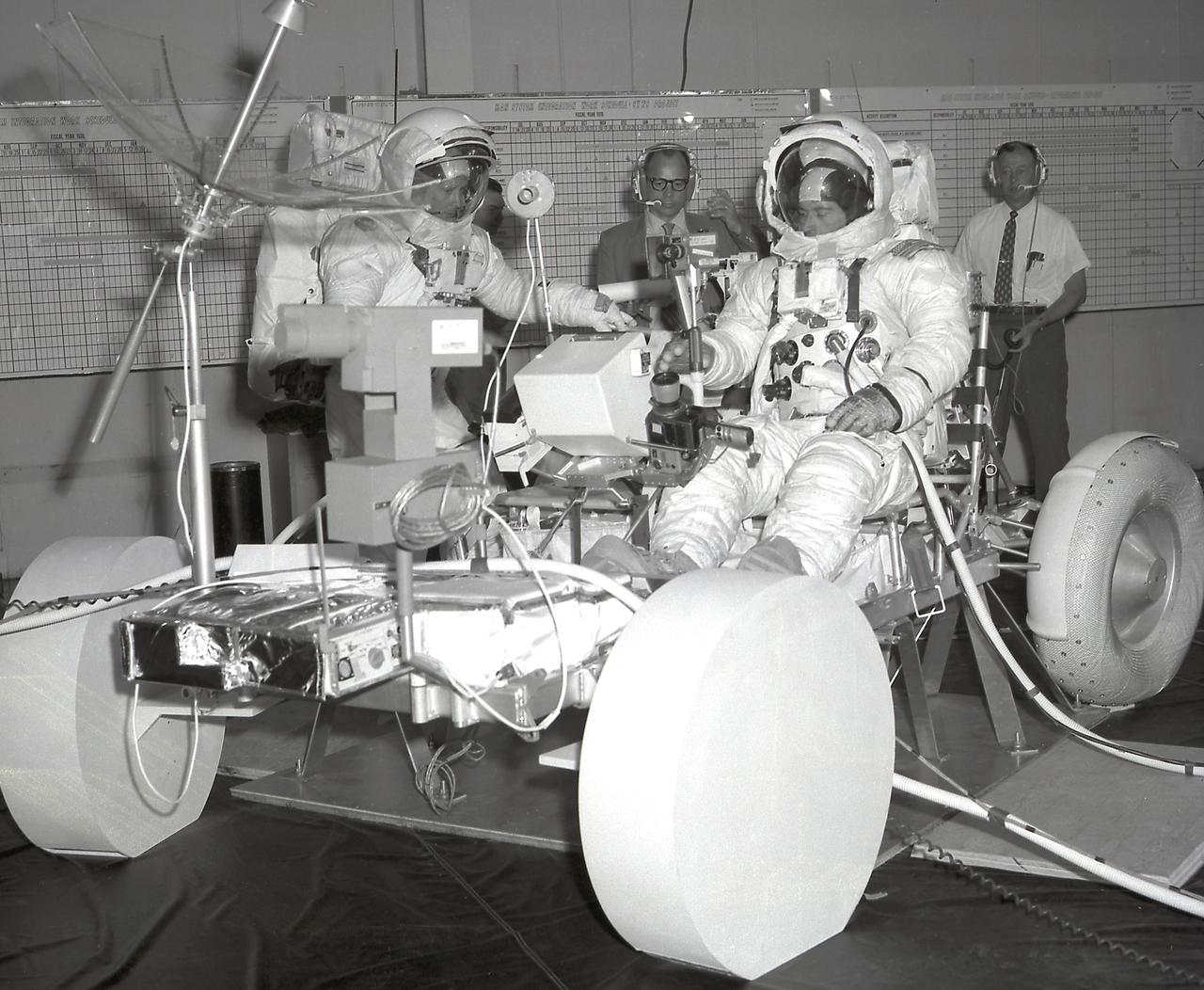
This image depicts the Apollo 16 mission astronauts John Young (right) and Charles Duke (left) in pressure suits during a final crew training on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), building 4619. Developed by the MSFC, the LRV was the lightweight electric car designed to increase the range of mobility and productivity of astronauts on the lunar surface. It was used on the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.
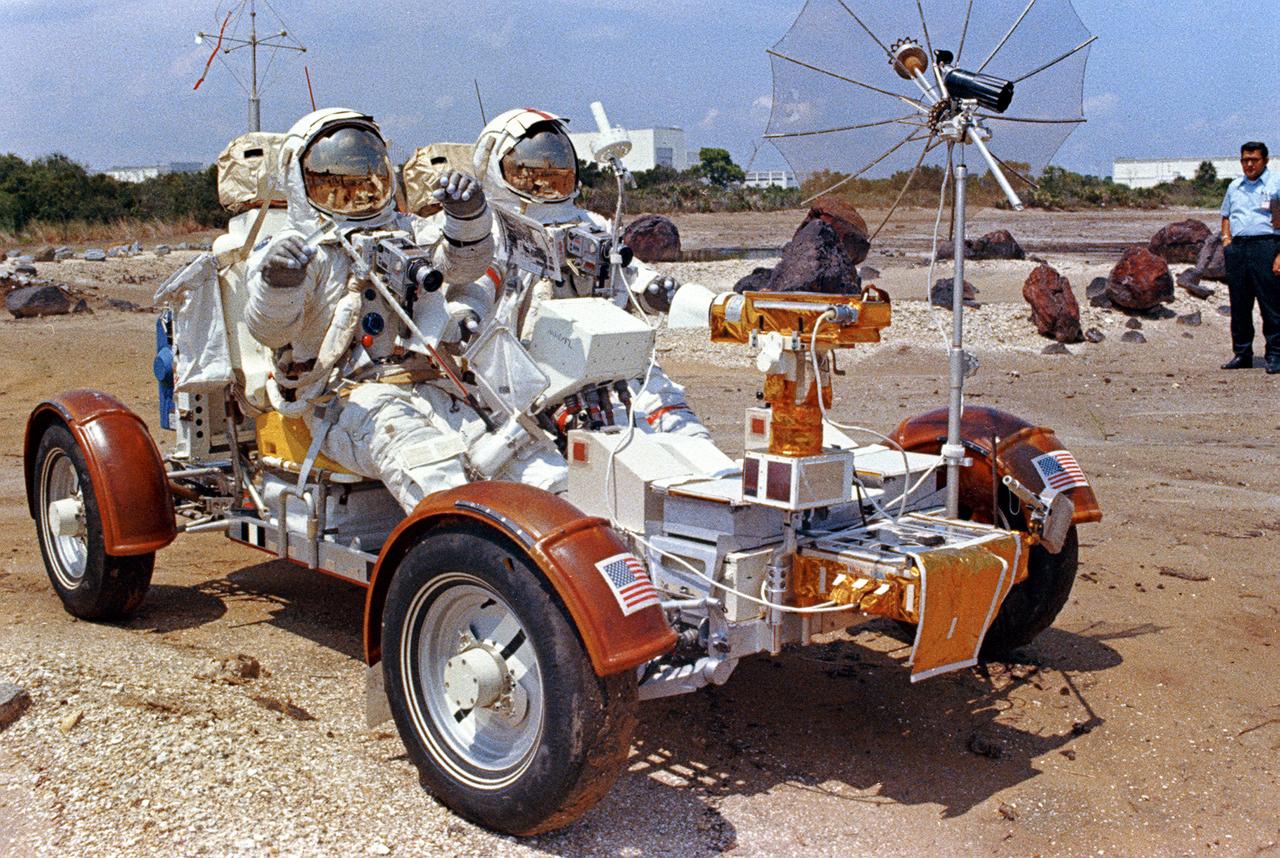
This photograph was taken during the testing of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) at the Johnson Space Center. Developed by the MSFC, the LRV was the lightweight electric car designed to increase the range of mobility and productivity of astronauts on the lunar surface. It was used on the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.
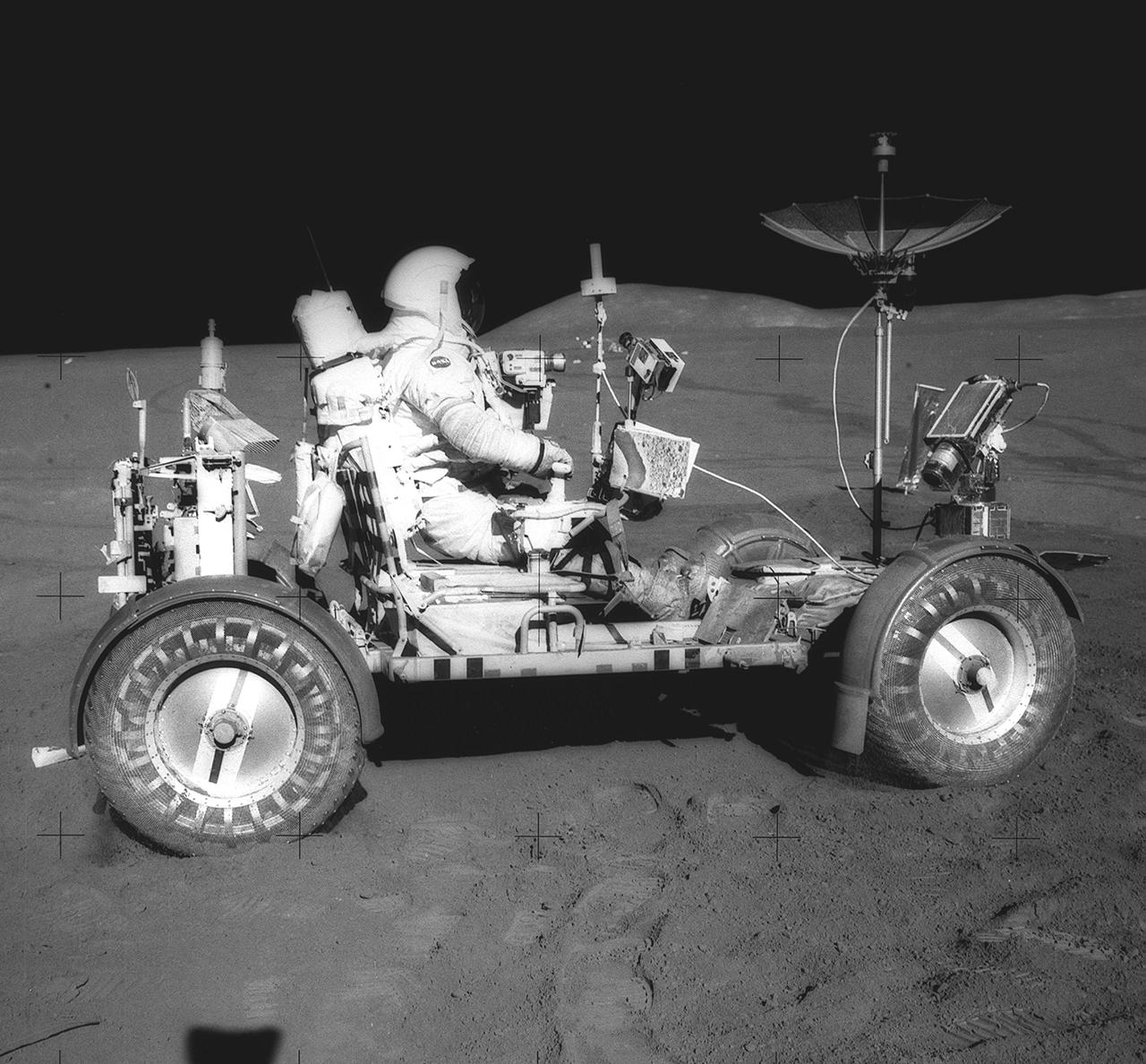

This photograph was taken during the Apollo 15 mission on the lunar surface. Astronaut David R. Scott waits in the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) for astronaut James Irwin for the return trip to the Lunar Module, Falcon, with rocks and soil collected near the Hadley-Apernine landing site. The Apollo 15 was the first mission to use the LRV. Powered by battery, the lightweight electric car greatly increased the range of mobility and productivity on the scientific traverses for astronauts. It weighed 462 pounds (77 pounds on the Moon) and could carry two suited astronauts, their gear and cameras, and several hundred pounds of bagged samples. The LRV's mobility was quite high. It could climb and descend slopes of about 25 degrees. The LRV was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.

An engineer demonstrates a Mobility Test Article (MTA) at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). This unit, weighing 1/6th as much as an actual vehicle, was built by the Bendix Corporation and was one of the concepts of a possible Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the LRV, developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.

An engineer demonstrates a Mobility Test Article (MTA) at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as he crosses a soft clay strip onto rocky ground. This unit, weighing 1/6th as much as an actual vehicle, was built by the Bendix Corporation and was one of the concepts of a possible Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the LRV, developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
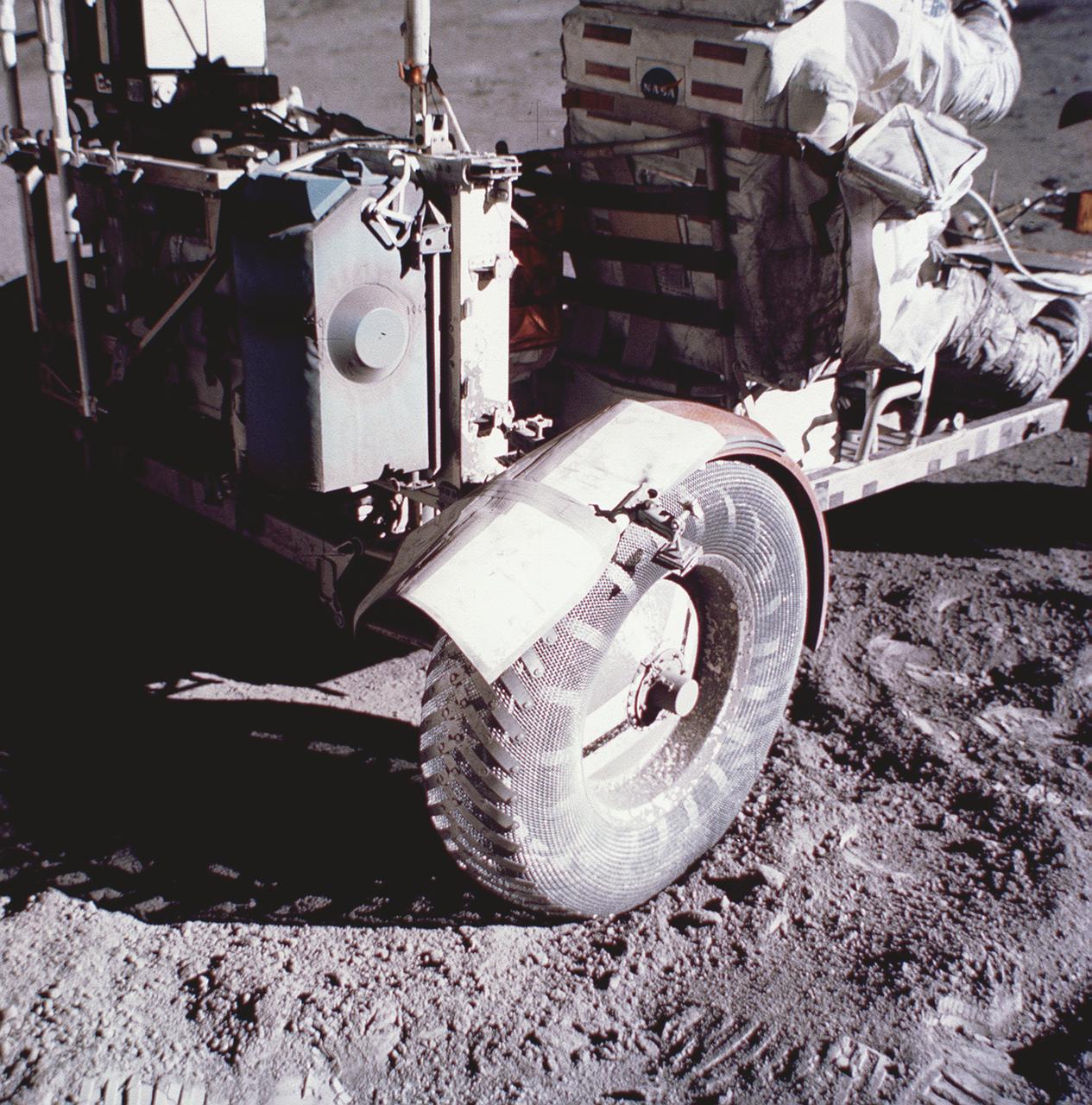

This photograph taken during the Apollo 17 mission (the last mission of the Apollo Program), depicts stiff plasticized maps being taped together and fastened by clamps to patch a broken fender of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). Powered by battery, the lightweight electric car greatly increased the range of mobility and productivity on the scientific traverses for astronauts. It weighed 462 pounds (77 pounds on the Moon) and could carry two suited astronauts, their gear and cameras, and several hundred pounds of bagged samples. The LRV's mobility was quite high. It could climb and descend slopes of about 25 degrees. The LRV was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
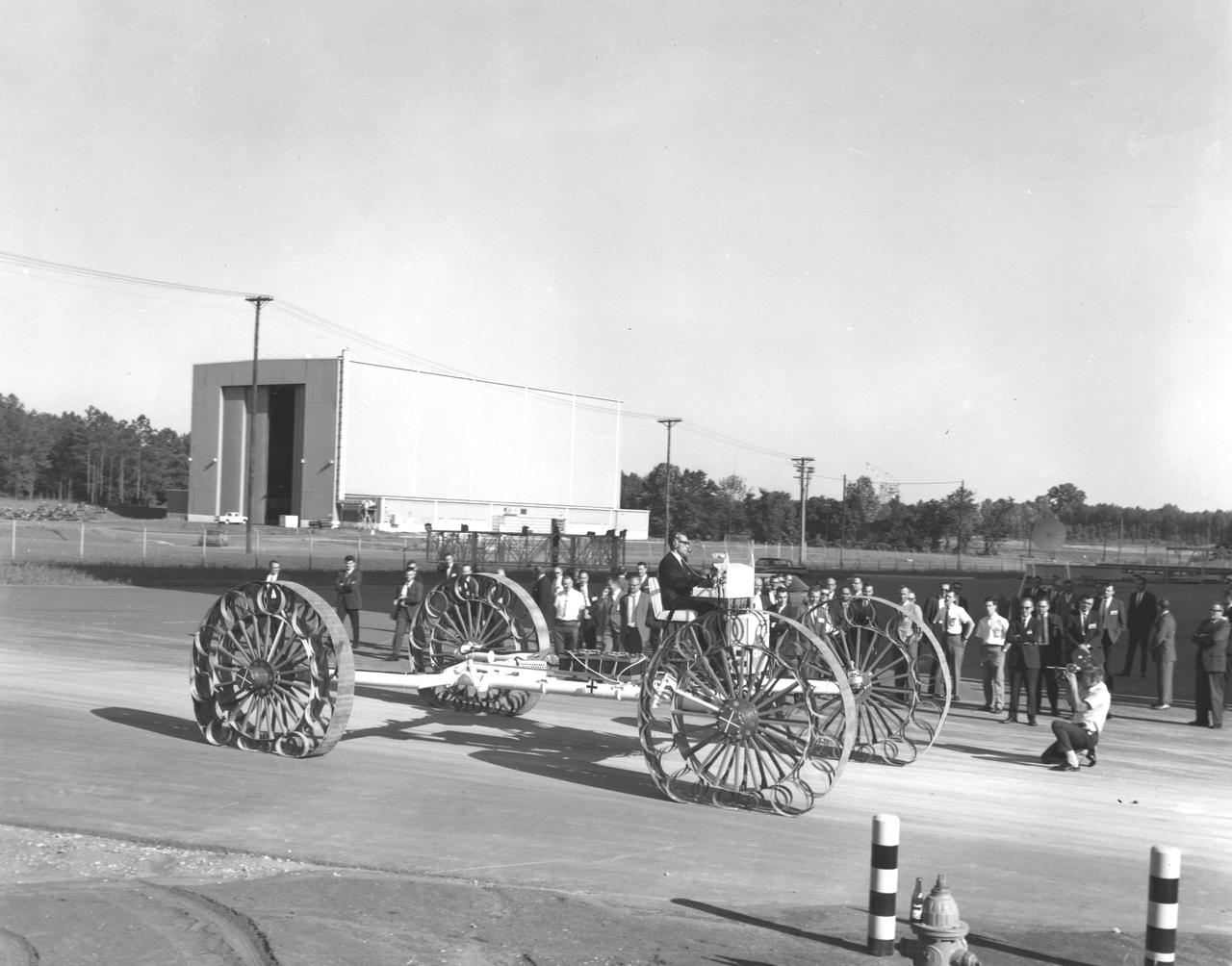

Newsmen watch a test engineer drive a Mobility Test Article (MTA) demonstrated at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). This unit, built by the Bendix Corporation, was one of the concepts of a possible Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the LRV, developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
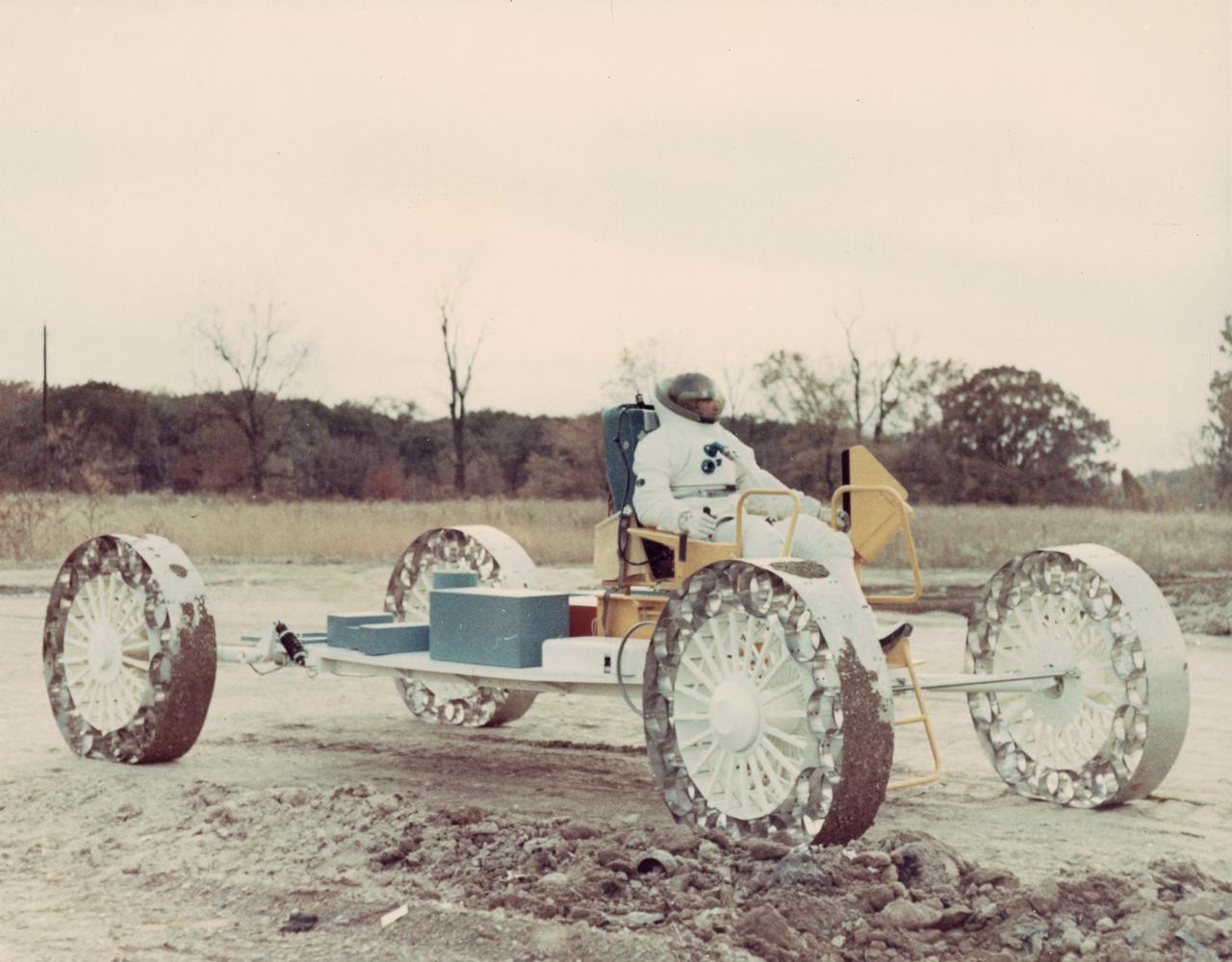
A concept of a possible Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) built by the Grumman Industries for NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), this Mobility Test Article (MTA) is undergoing a full fledged test, complete with space suit attire. The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the LRV, developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
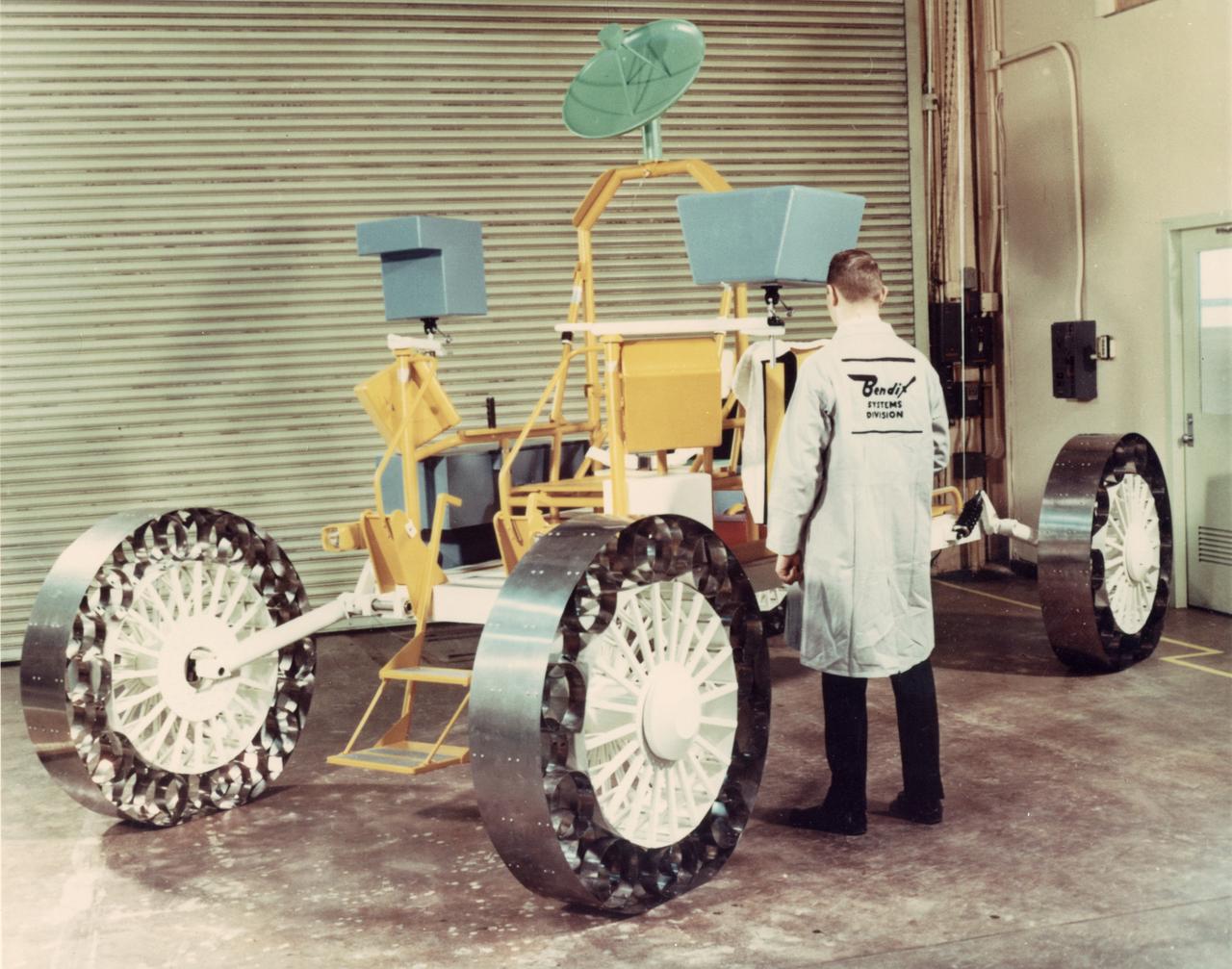

A concept of a possible Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) built by the Bendix Corporation for NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). This Mobility Test Article (MTA) is being inspected by a Bendix technician. The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the LRV, developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
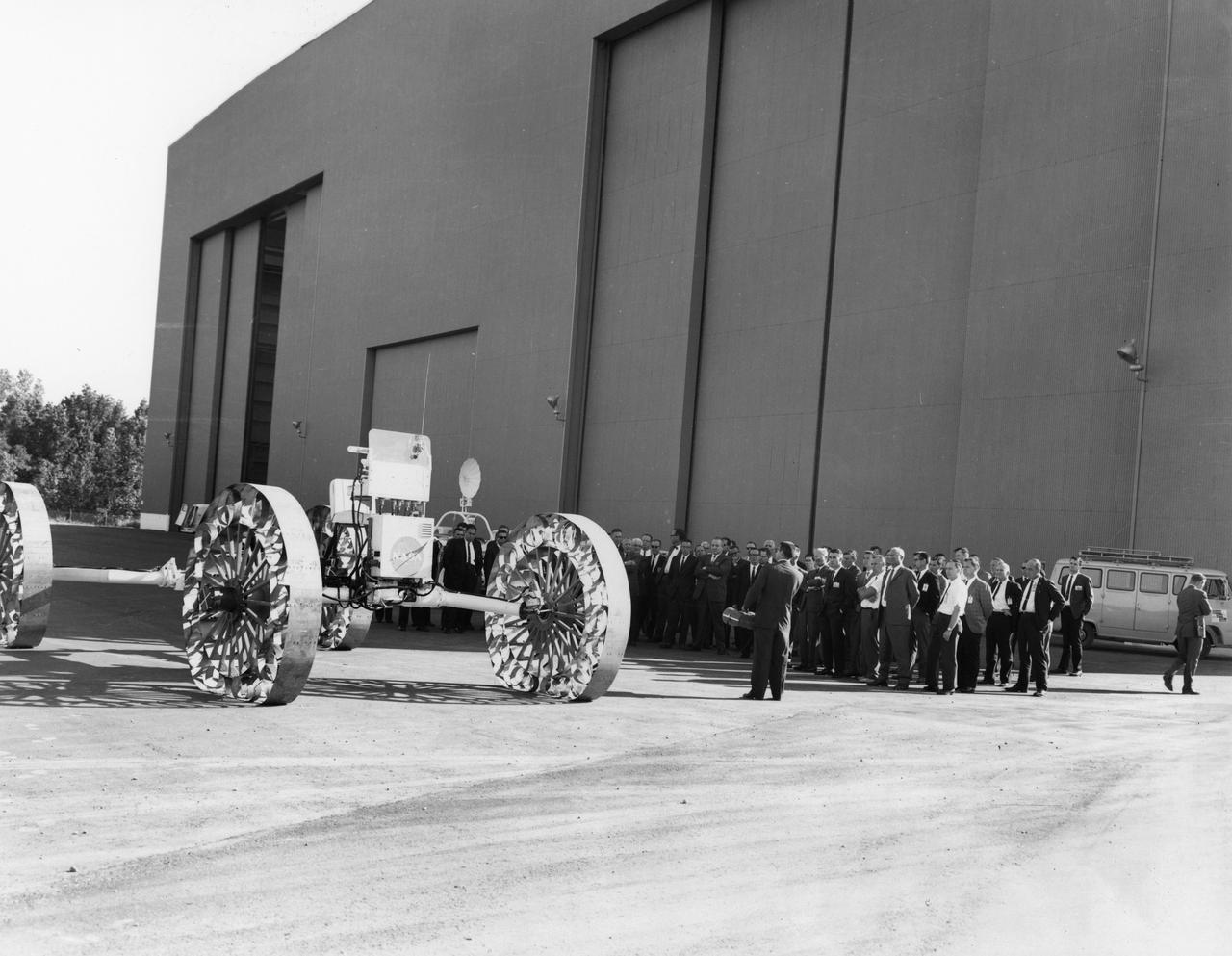

Newsmen listen as an engineer explains operations and capabilities of a Mobility Test Article (MTA) demonstrated at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). This unit, built by the Bendix Corporation, was one of the concepts of a possible Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the LRV, developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
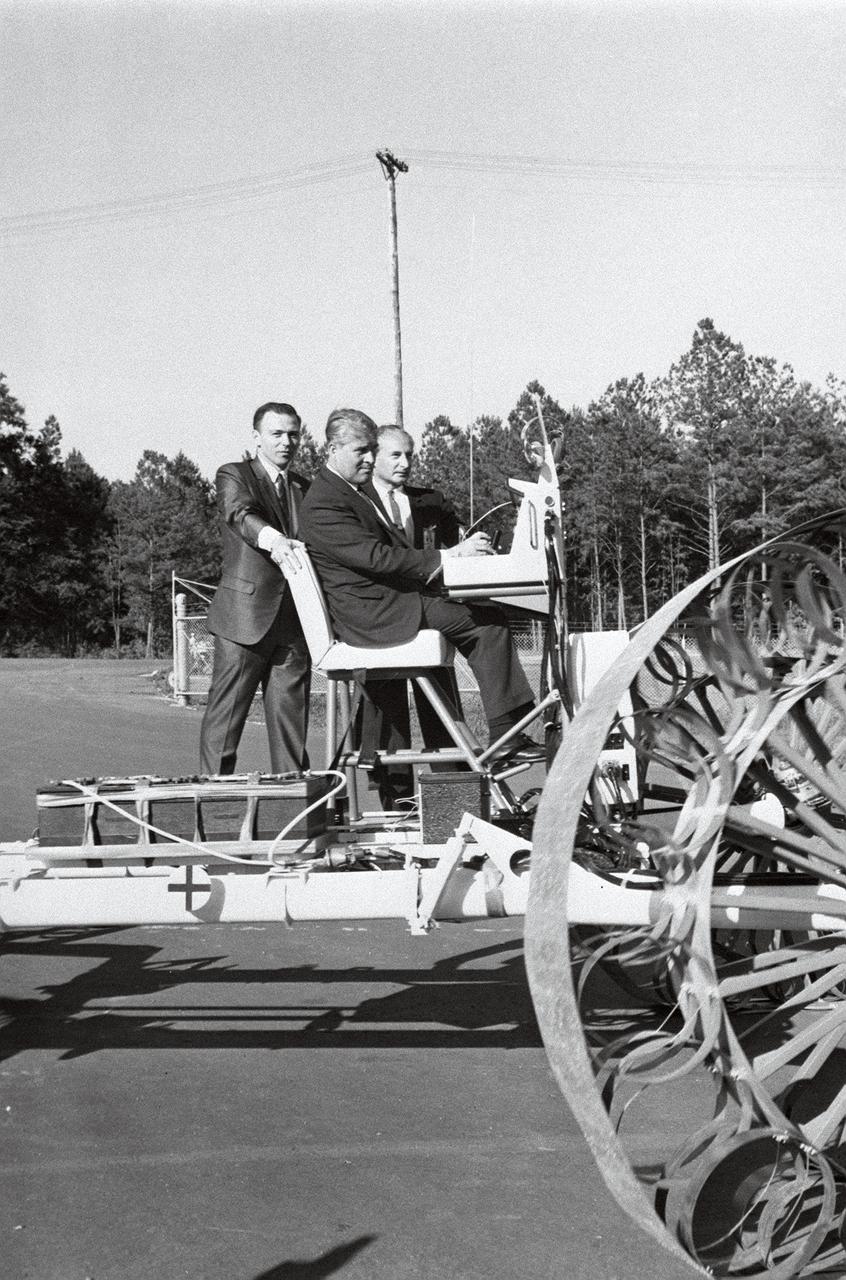

In this June 1966 photograph, Marshall Space Flight Center Director Dr. Wernher von Braun test-drives the Mobility Test Article (MTA), a developmental vehicle built by the Bendix Corporation to test lunar mobility vehicle concepts. The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), developed under the direction of the MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions. The LRVs were deployed during the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.
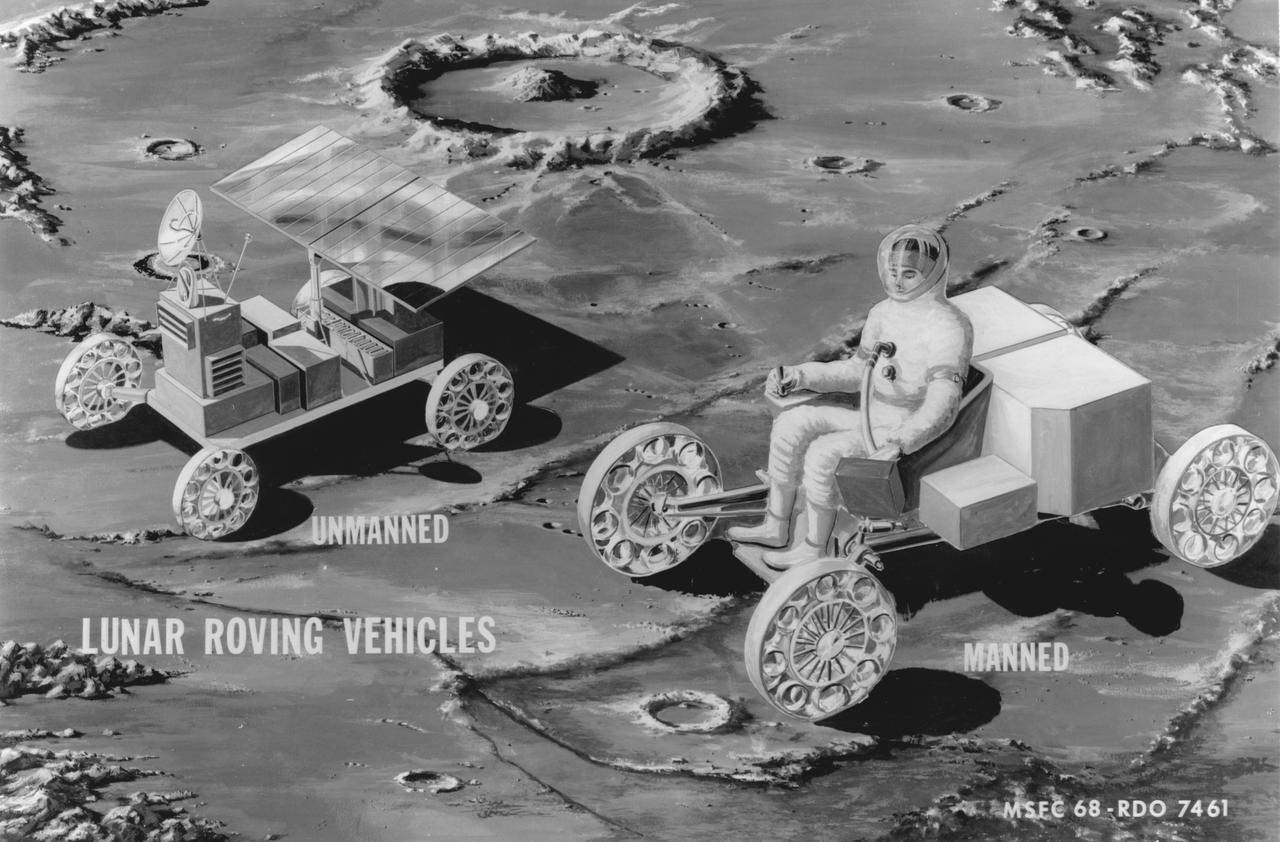
Artist’s manned and unmanned concepts of a Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) Mobility Test Article (MTA) on the Lunar surface. The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the LRV, developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
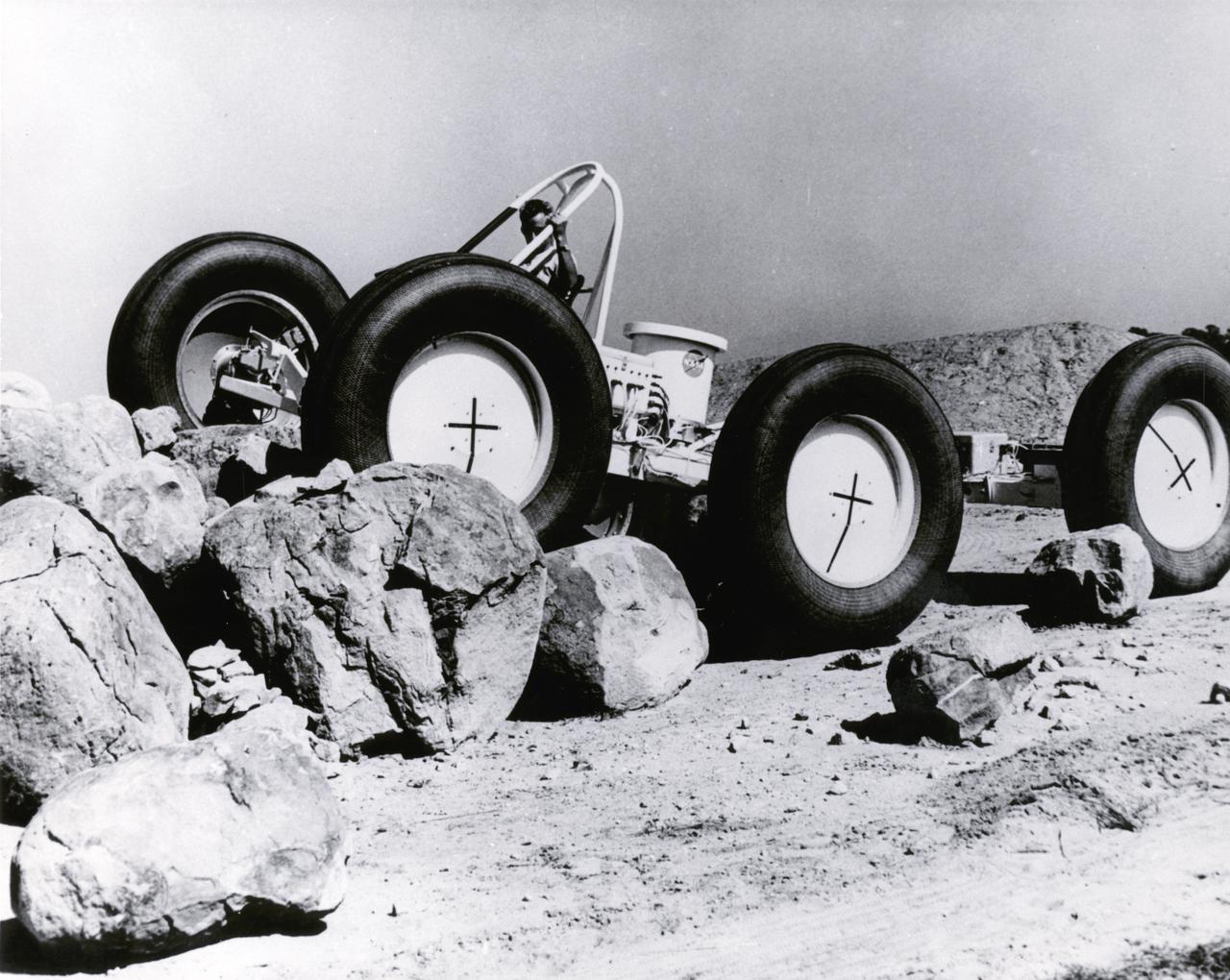

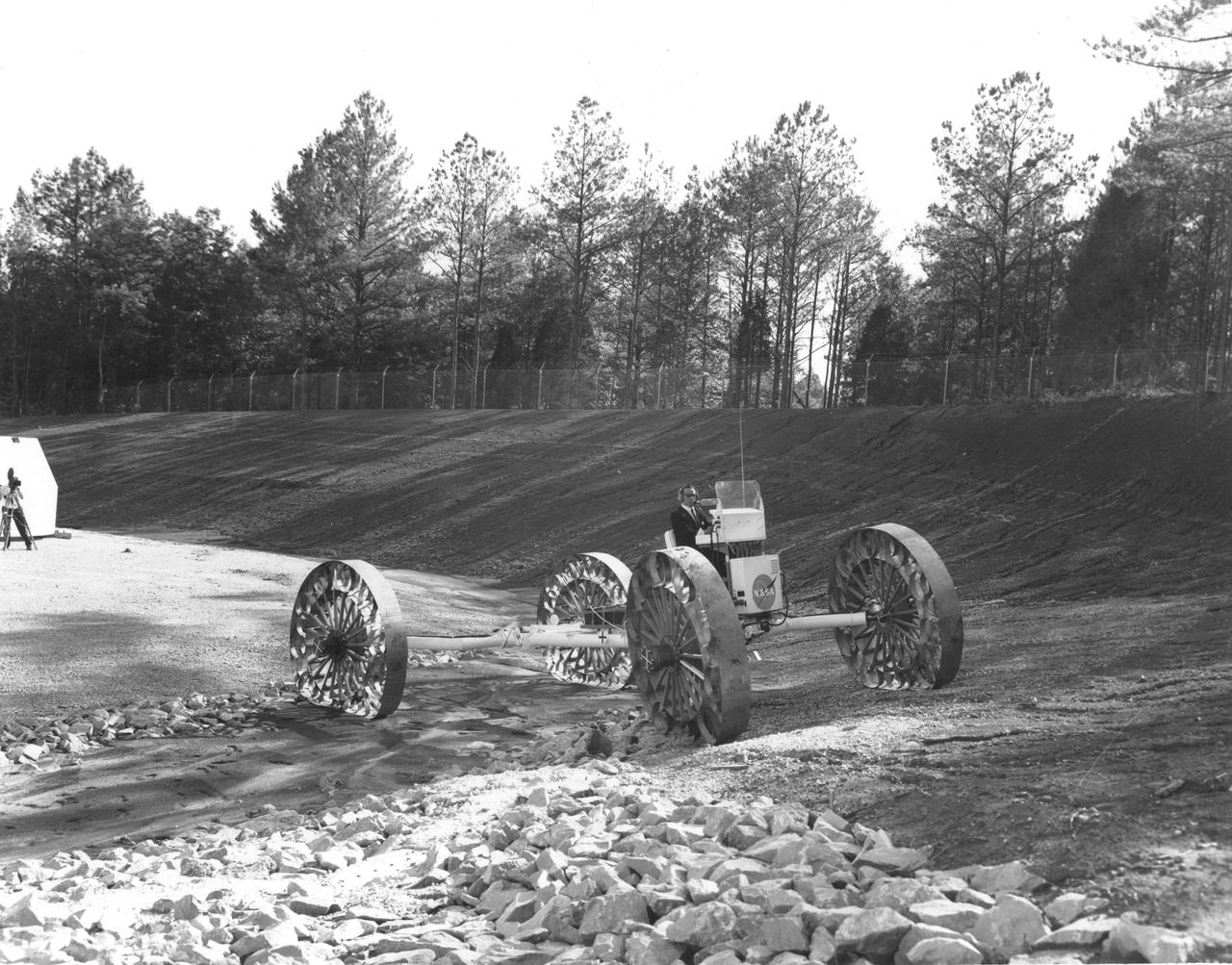
A test engineer drove a Mobility Test Article (MTA) of a possible future Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) over rocks during tests in Arizona. The machine was built by General Motors for NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Under the direction of MSFC, the LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
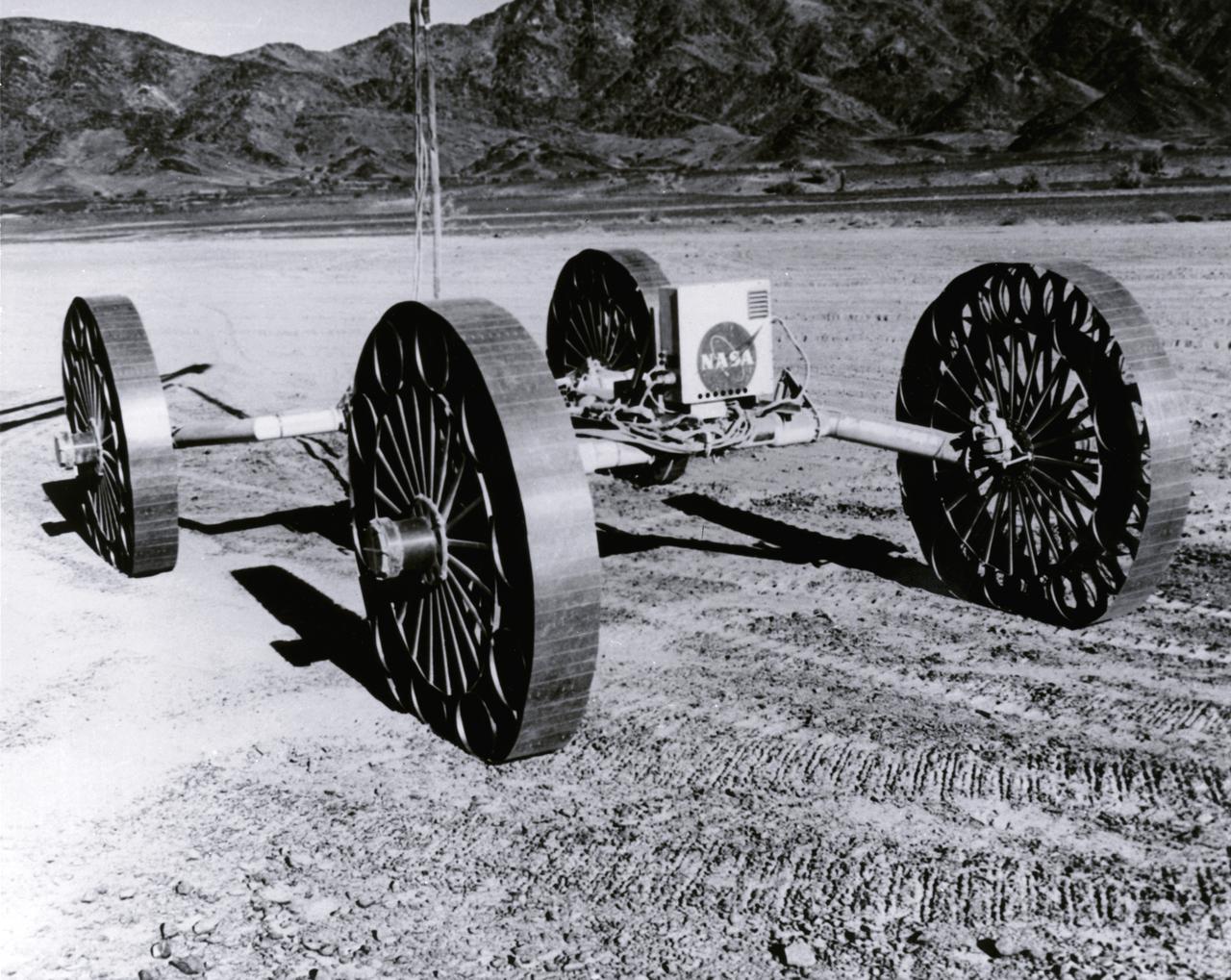
This Mobility Test Article (MTA), built by the Bendix Corporation for NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), was driven over rocks in Arizona. The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), developed under the direction of the MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
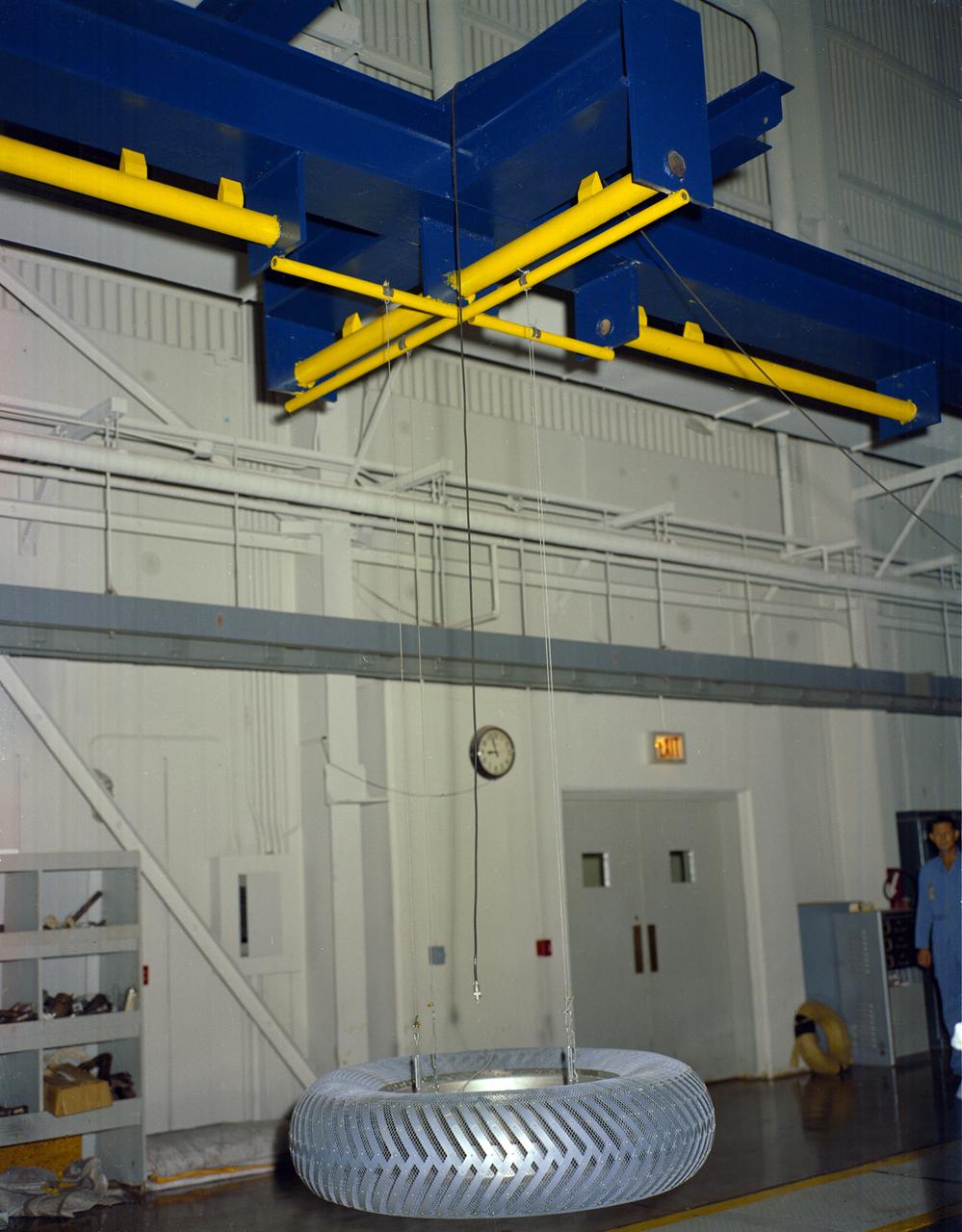

Under the direction of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions. During the development process, LRV prototype wheels underwent soil tests in building 4481 at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Pictured is the GM wheel design.
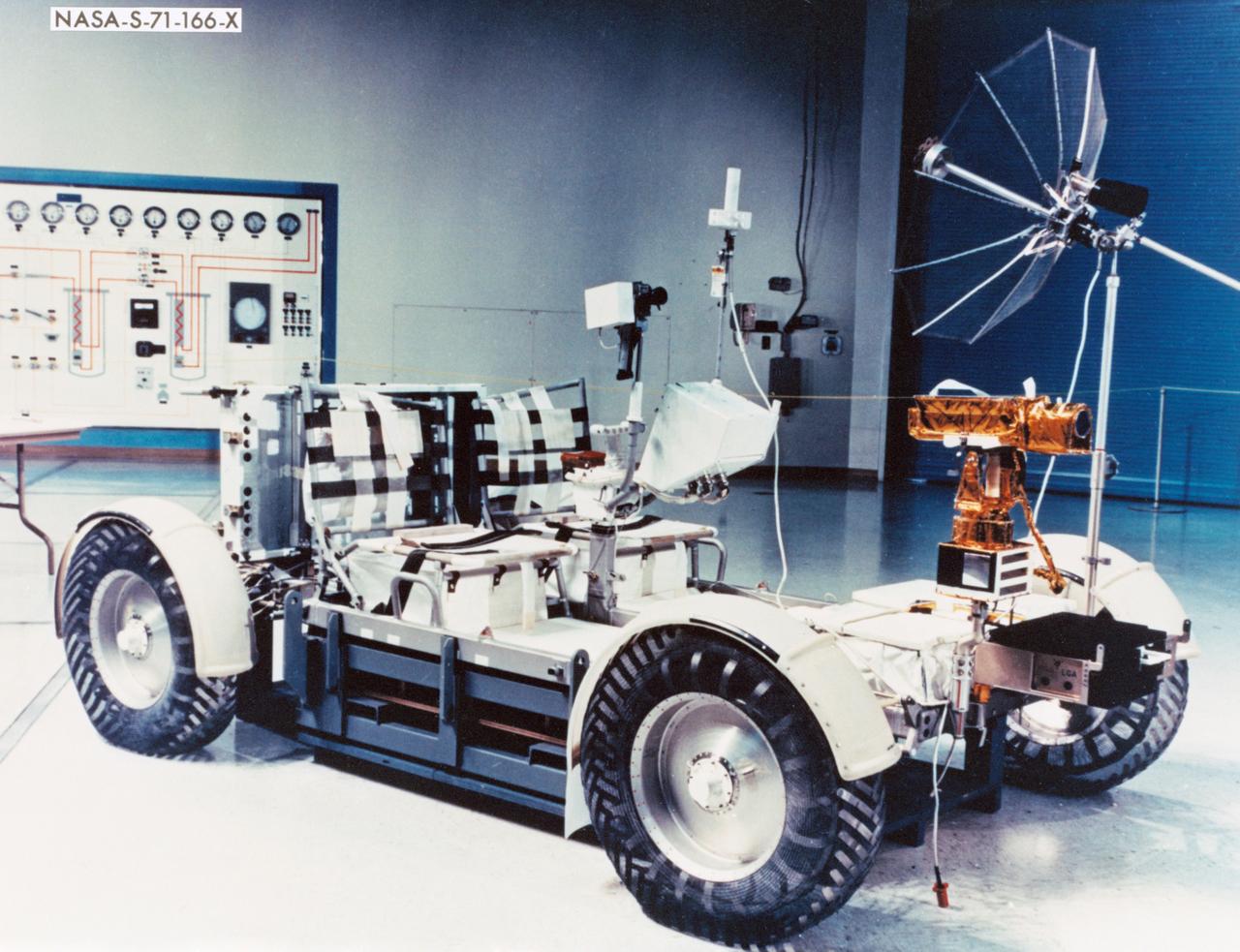
S71-00166 (June 1971) --- A close-up view of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). Apollo 15 will be the first mission to employ the services of the LRV. Astronauts David R. Scott, commander; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, will move about the lunar surface in the Hadley-Apennine region in their four-wheeled vehicle while astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remains with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. A television camera, which can be controlled remotely from the ground (front), and a motion picture camera (rear) are among the gear on the LRV.
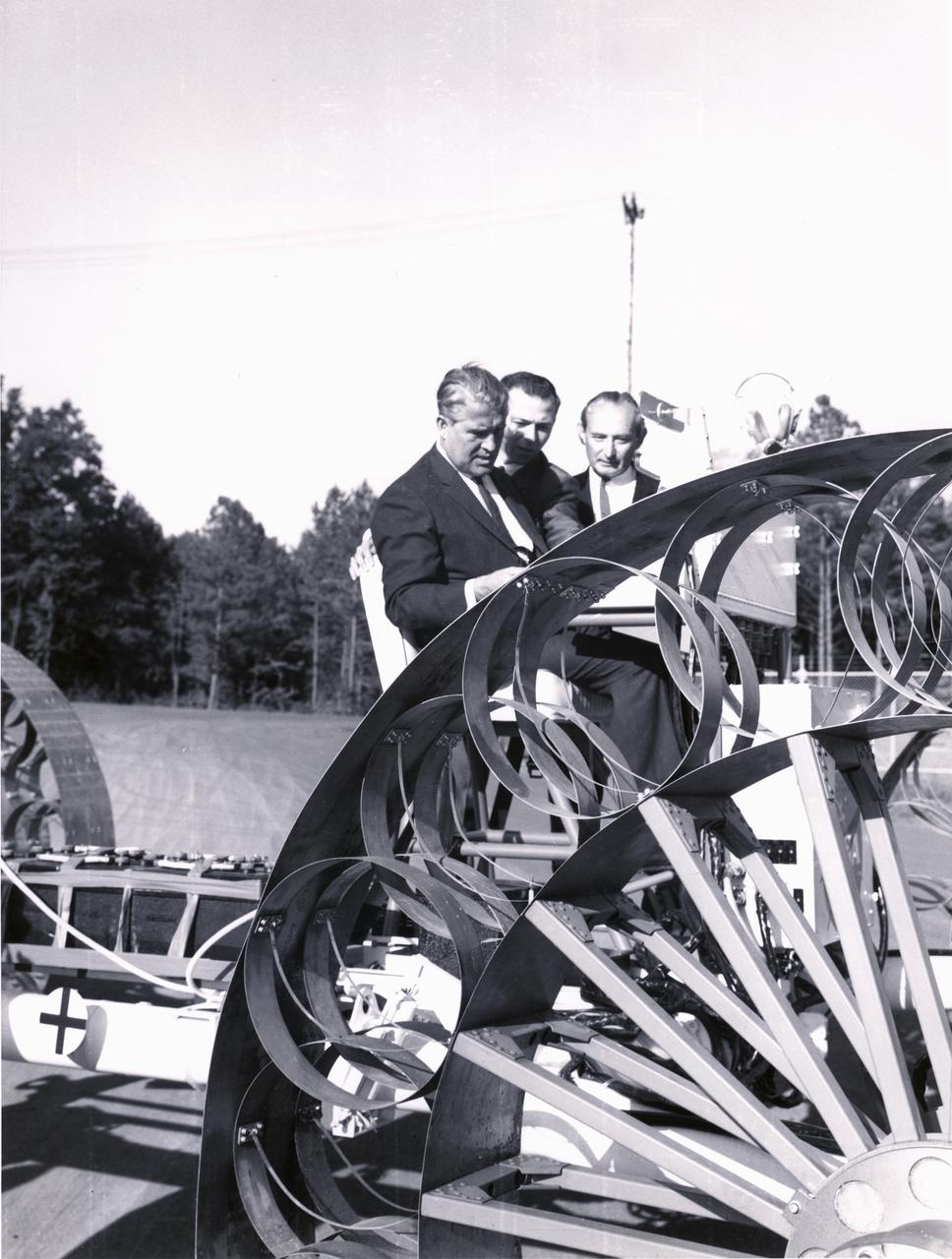

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) director, Wernher von Braun, and others examine one concept of a possible Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) built by the Bendix Corporation. The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the LRV, developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
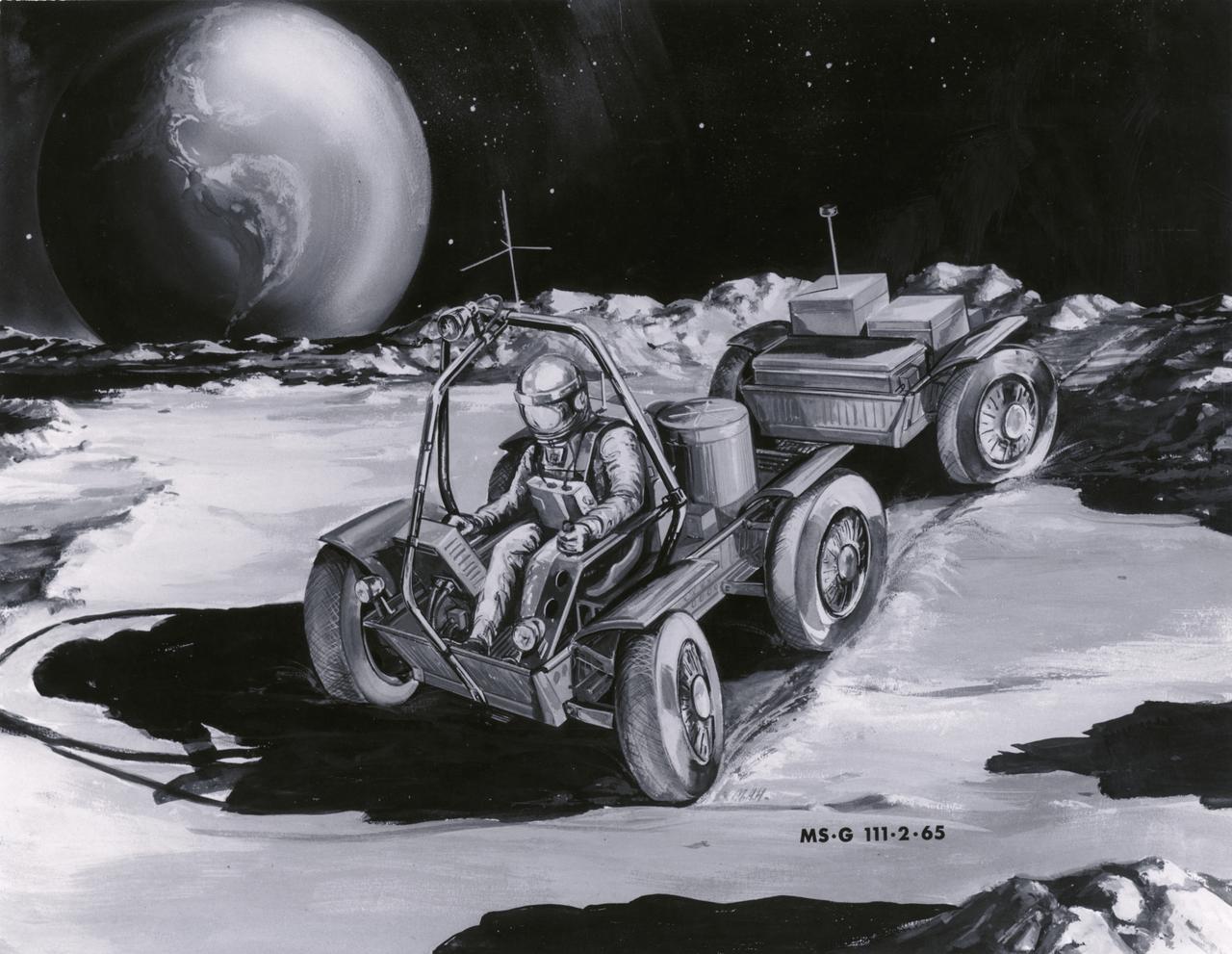
Artist’s concept of the Local Scientific Survey Module (LSSM), one of two designs for a Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), depicted on the lunar surface A Bendix Corporation concept, this configuration weighs more than 8,000 pounds, is 21-feet long, 15-feet wide and has 6 wheels with 5-foot diameters. The LRV was developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) to give Apollo astronauts a wider range of mobility on the lunar surface.
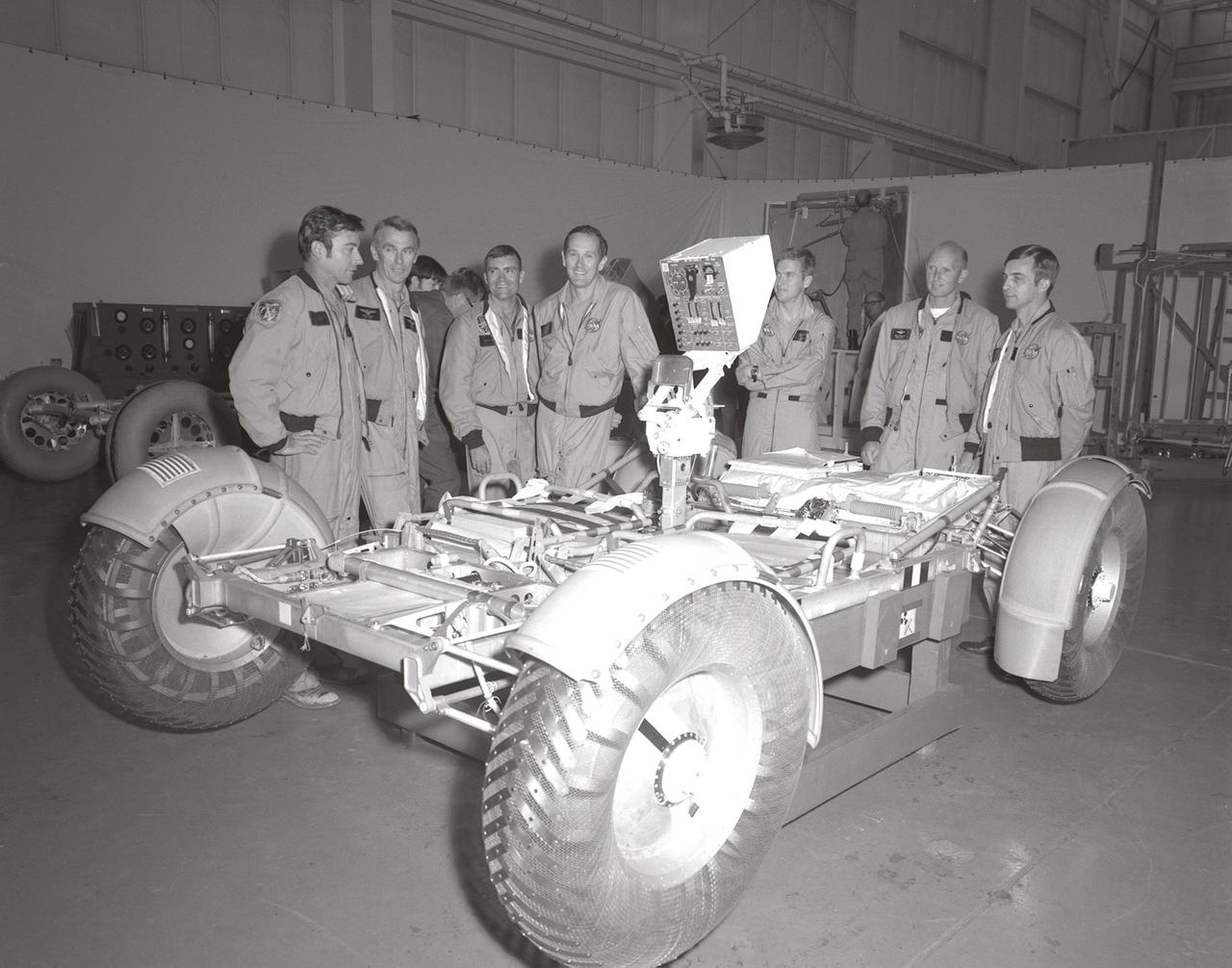

In this November 1971 photograph, (from left to right) Astronauts John Young, Eugene Cernan, Charles Duke, Fred Haise, Anthony England, Charles Fullerton, and Donald Peterson await deployment tests of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) qualification test unit in building 4649 at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The LRV, developed under the direction of the MSFC, was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility on the lunar surface during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.
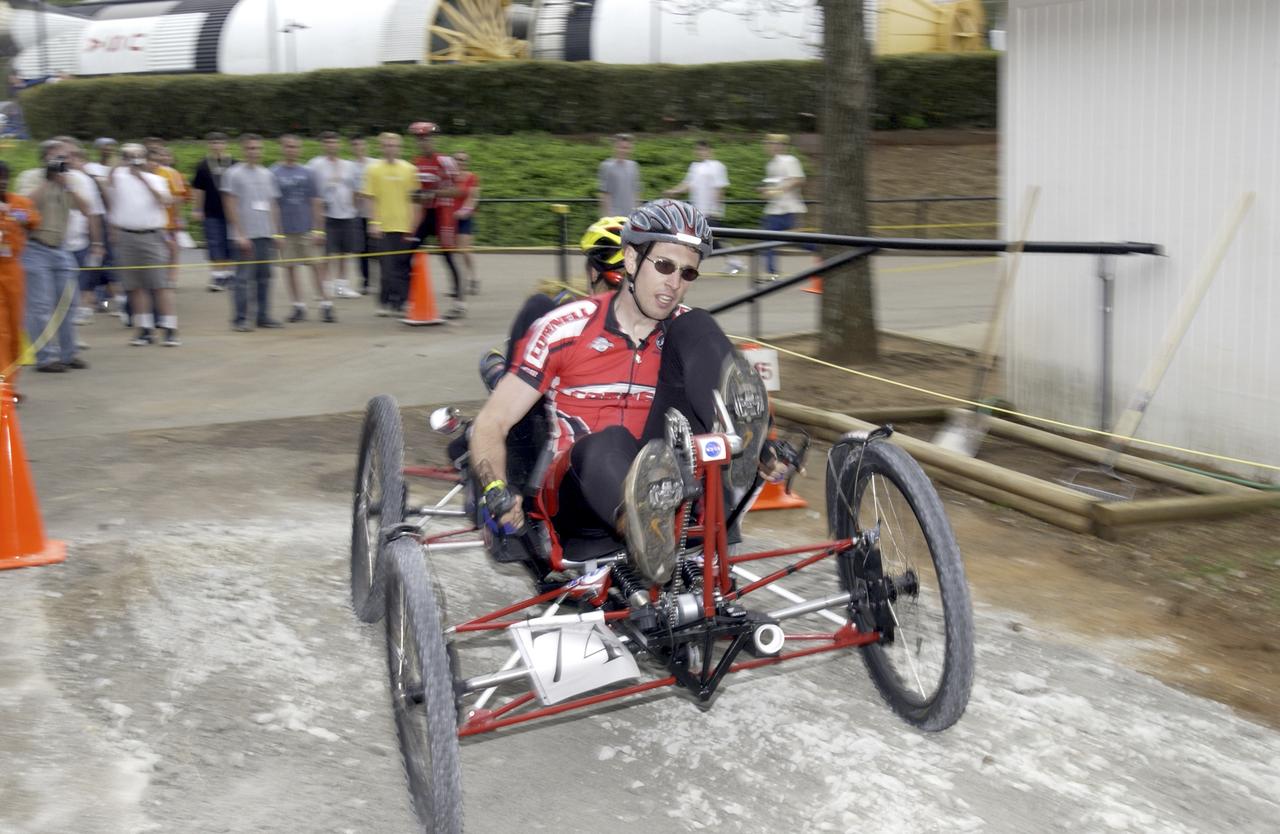

Students from across the United States and as far away as Puerto Rico and South America came to Huntsville, Alabama for the 9th annual Great Moonbuggy Race at the U.S. Space Rocket Center. Seventy-seven teams, representing high schools and colleges from 21 states, Puerto Rico, and Columbia, raced human powered vehicles over a lunar-like terrain. A team from Cornell University in Ithaca, New York, took the first place honor in the college division. In this photograph, the Cornell #1 team, the collegiate first place winner, maneuvers their vehicle through the course. Vehicles powered by two team members, one male and one female, raced one at a time over a half-mile obstacle course of simulated moonscape terrain. The competition is inspired by development, some 30 years ago, of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), a program managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The LRV team had to design a compact, lightweight, all-terrain vehicle that could be transported to the Moon in the small Apollo spacecraft. The Great Moonbuggy Race challenges students to design and build a humanpowered vehicle so they will learn how to deal with real-world engineering problems similar to those faced by the actual NASA LRV team.
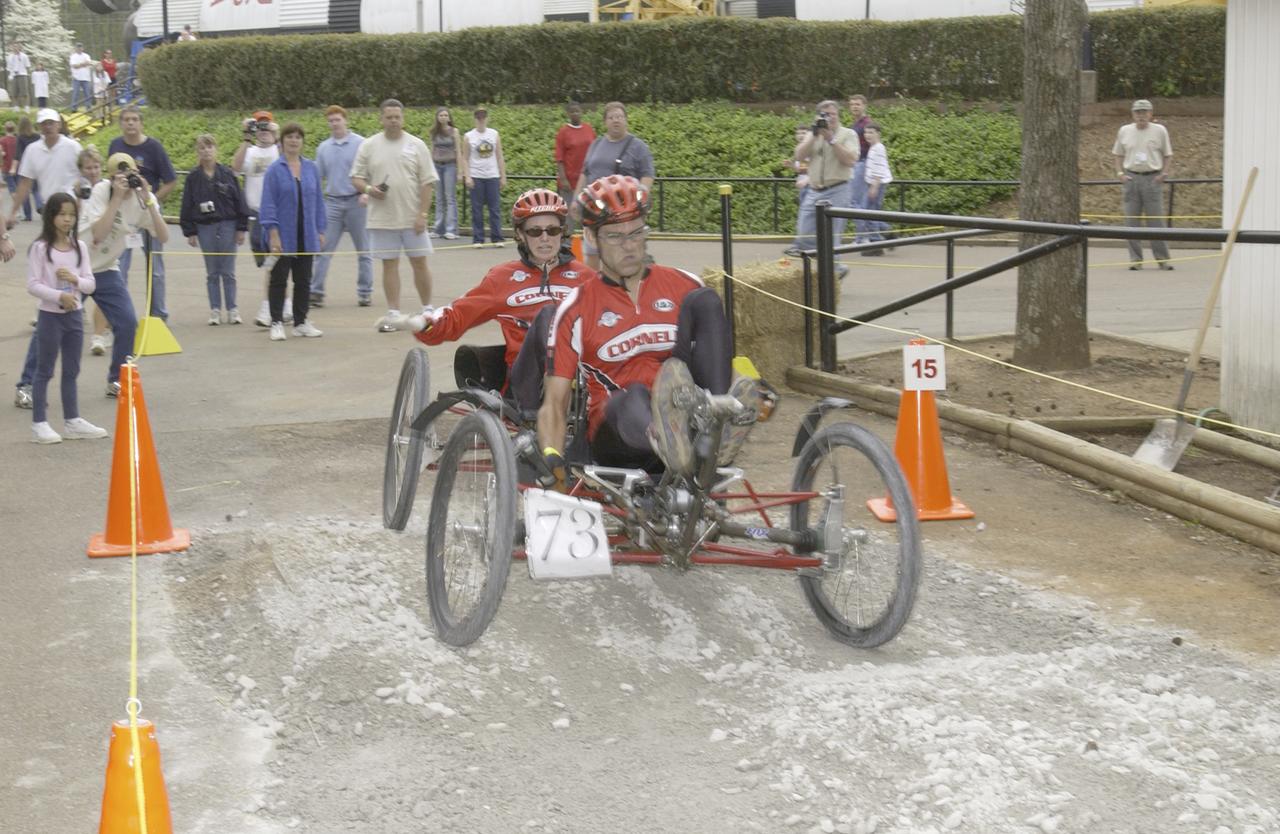

Students from across the United States and as far away as Puerto Rico and South America came to Huntsville, Alabama for the 9th annual Great Moonbuggy Race at the U.S. Space Rocket Center. Seventy-seven teams, representing high schools and colleges from 21 states, Puerto Rico, and Columbia, raced human powered vehicles over a lunar-like terrain. A team from Cornell University in Ithaca, New York, took the first place honor in the college division. This photograph shows the Cornell #2 team driving their vehicle through the course. The team finished the race in second place in the college division. Vehicles powered by two team members, one male and one female, raced one at a time over a half-mile obstacle course of simulated moonscape terrain. The competition is inspired by development, some 30 years ago, of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), a program managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The LRV team had to design a compact, lightweight, all-terrain vehicle, that could be transported to the Moon in the small Apollo spacecraft. The Great Moonbuggy Race challenges students to design and build a human powered vehicle so they will learn how to deal with real-world engineering problems, similar to those faced by the actual NASA LRV team.

This in an aerial view (looking east) of a Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), often referred to as “Moonbuggy”, simulator area built at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) where testing was performed. The LRV was developed under the direction of MSFC to provide astronauts with greater mobility on the lunar surface. Visible in the background is the 18-acre facility known as the Random Motion/ Lift-Off Simulator or ‘Arm Farm’ which was developed to test the Saturn swingarm mechanisms that were used to hold the rocket in position until lift-off.
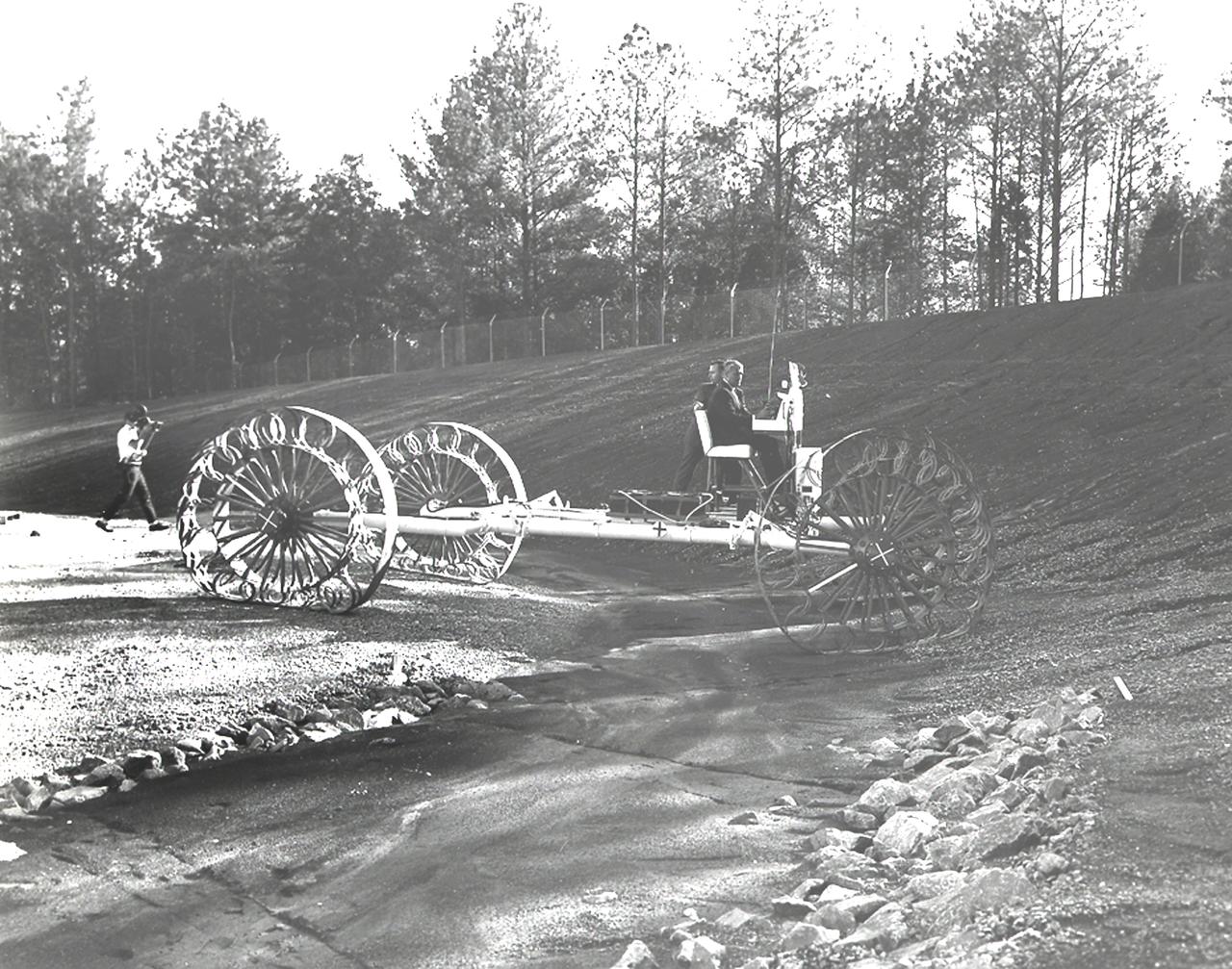

In this June, 1966 photograph, Marshall Space Flight Center Director, Dr. Wernher von Braun test drives the Mobility Test Article (MTA), a developmental vehicle built by the Bendix Corporation to test lunar mobility concepts. The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range during lunar exploration missions and served its purpose during the last three Apollo lunar missions in 1971 and 1972.
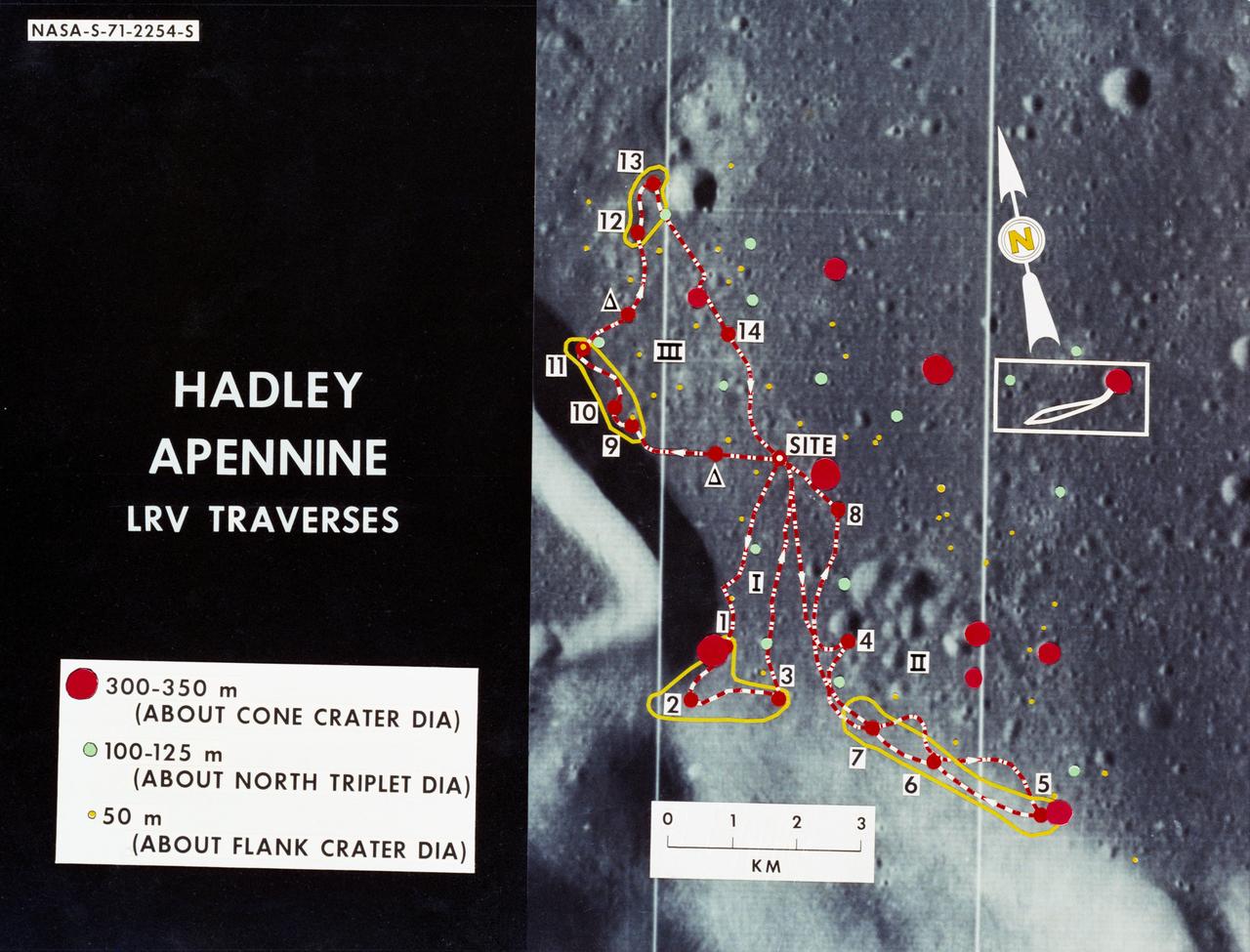
S71-02254 (June 1971) --- An enlarged Lunar Orbiter photograph showing the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) traverse routes overlaid on the Hadley-Apennine landing site. Apollo 15 is to land at the point labeled "site," and a comparison of Apollo 14 crater sizes with those of Apollo 15 is included, also. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descend in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
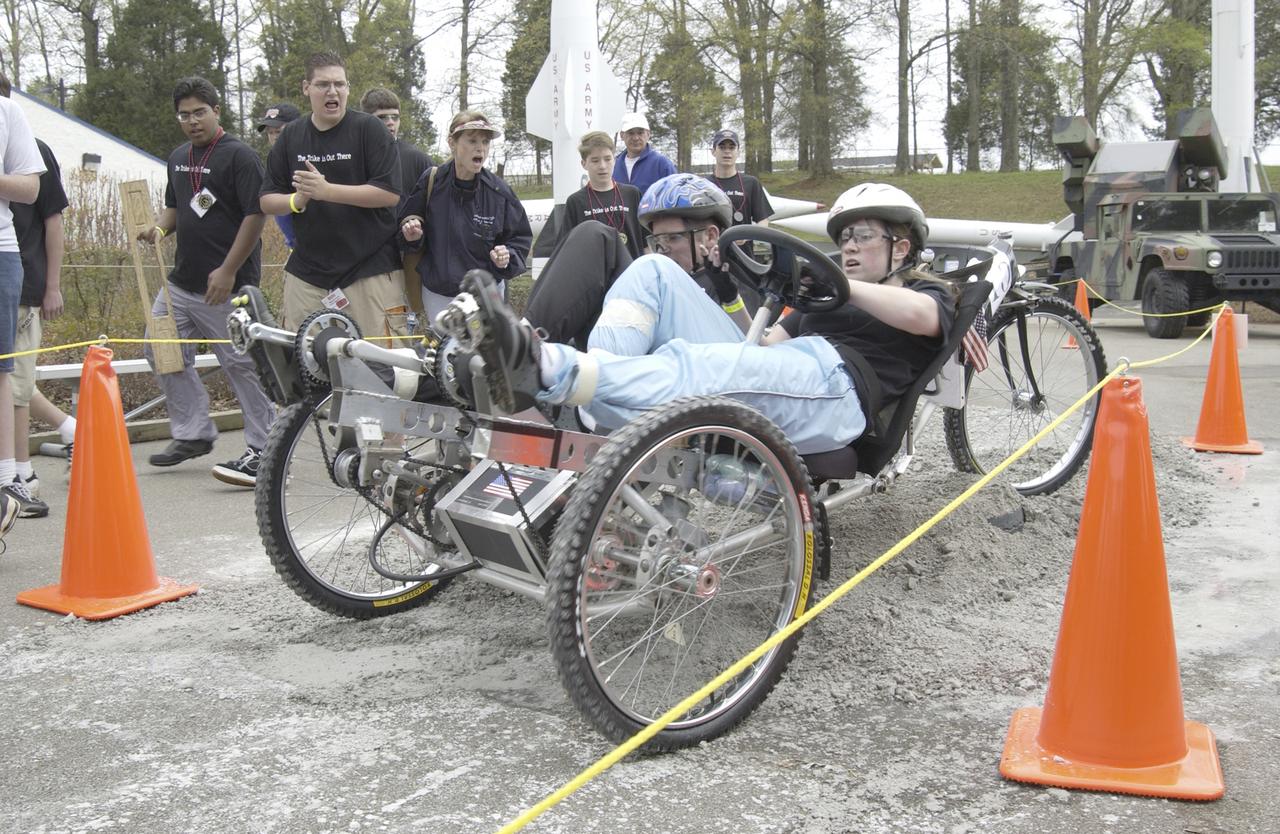

Students from across the United States and as far away as Puerto Rico and South America came to Huntsville, Alabama for the 9th annual Great Moonbuggy Race at the U.S. Space Rocket Center. Seventy-seven teams, representing high schools and colleges from 21 states, Puerto Rico, and Columbia, raced human powered vehicles over a lunar-like terrain. In this photograph, the New Orleans area schools team #2 from New Orleans, Louisiana maneuvers through an obstacle course. The team captured second place in the high school division competition. Vehicles powered by two team members, one male and one female, raced one at a time over a half-mile obstacle course of simulated moonscape terrain. The competition is inspired by the development, some 30 years ago, of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), a program managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The LRV team had to design a compact, lightweight, all-terrain vehicle that could be transported to the Moon in the small Apollo spacecraft. The Great Moonbuggy Race challenges students to design and build a human powered vehicle so they will learn how to deal with real-world engineering problems, similar to those faced by the actual NASA LRV team.
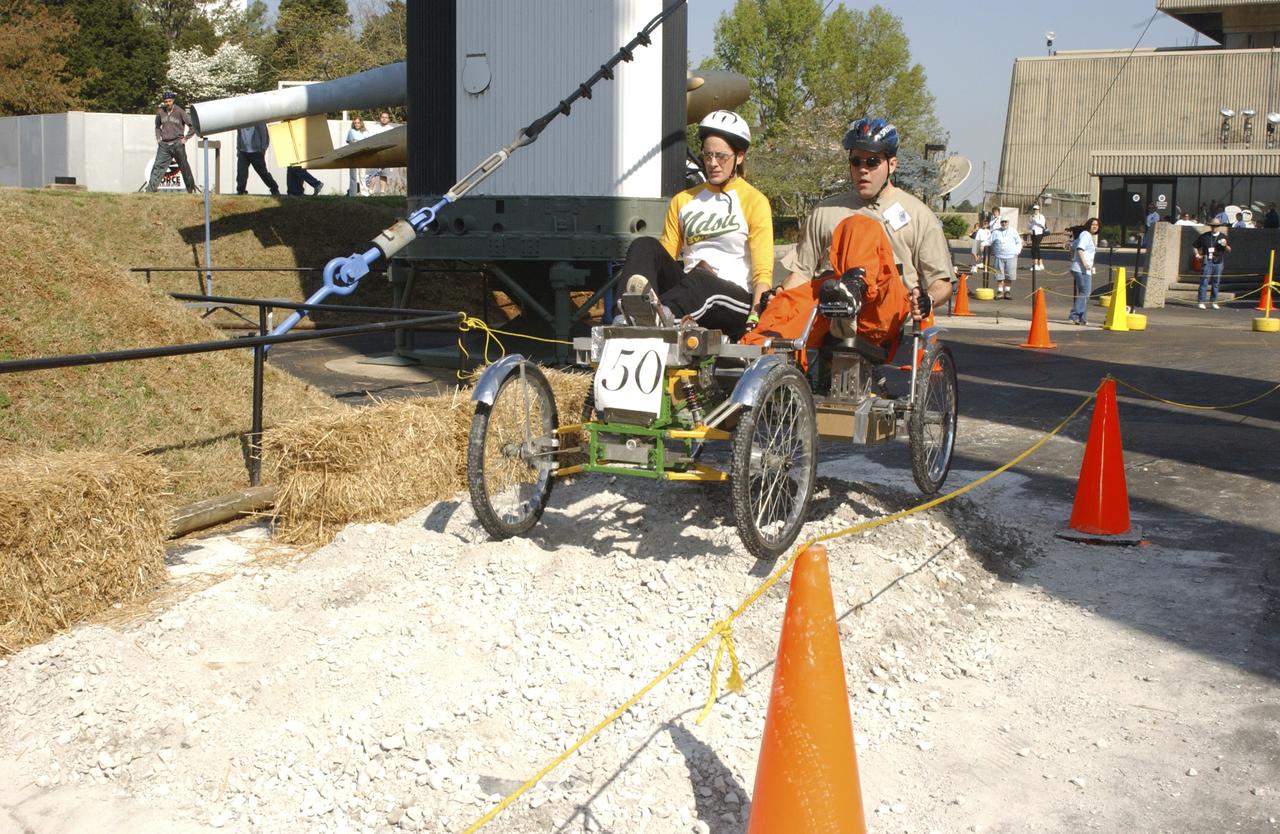

Students from across the United States and as far away as Puerto Rico came to Huntsville, Alabama for the 10th annual Great Moonbuggy Race at the U.S. Space Rocket Center. Sixty-eight teams, representing high schools and colleges from all over the United States, and Puerto Rico, raced human powered vehicles over a lunar-like terrain. Vehicles powered by two team members, one male and one female, raced one at a time over a half-mile obstacle course of simulated moonscape terrain. The competition is inspired by development, some 30 years ago, of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), a program managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The LRV team had to design a compact, lightweight, all-terrain vehicle that could be transported to the Moon in the small Apollo spacecraft. The Great Moonbuggy Race challenges students to design and build a human powered vehicle so they will learn how to deal with real-world engineering problems similar to those faced by the actual NASA LRV team. In this photograph, Team No. 1 from North Dakota State University in Fargo conquers one of several obstacles on their way to victory. The team captured first place honors in the college level competition.
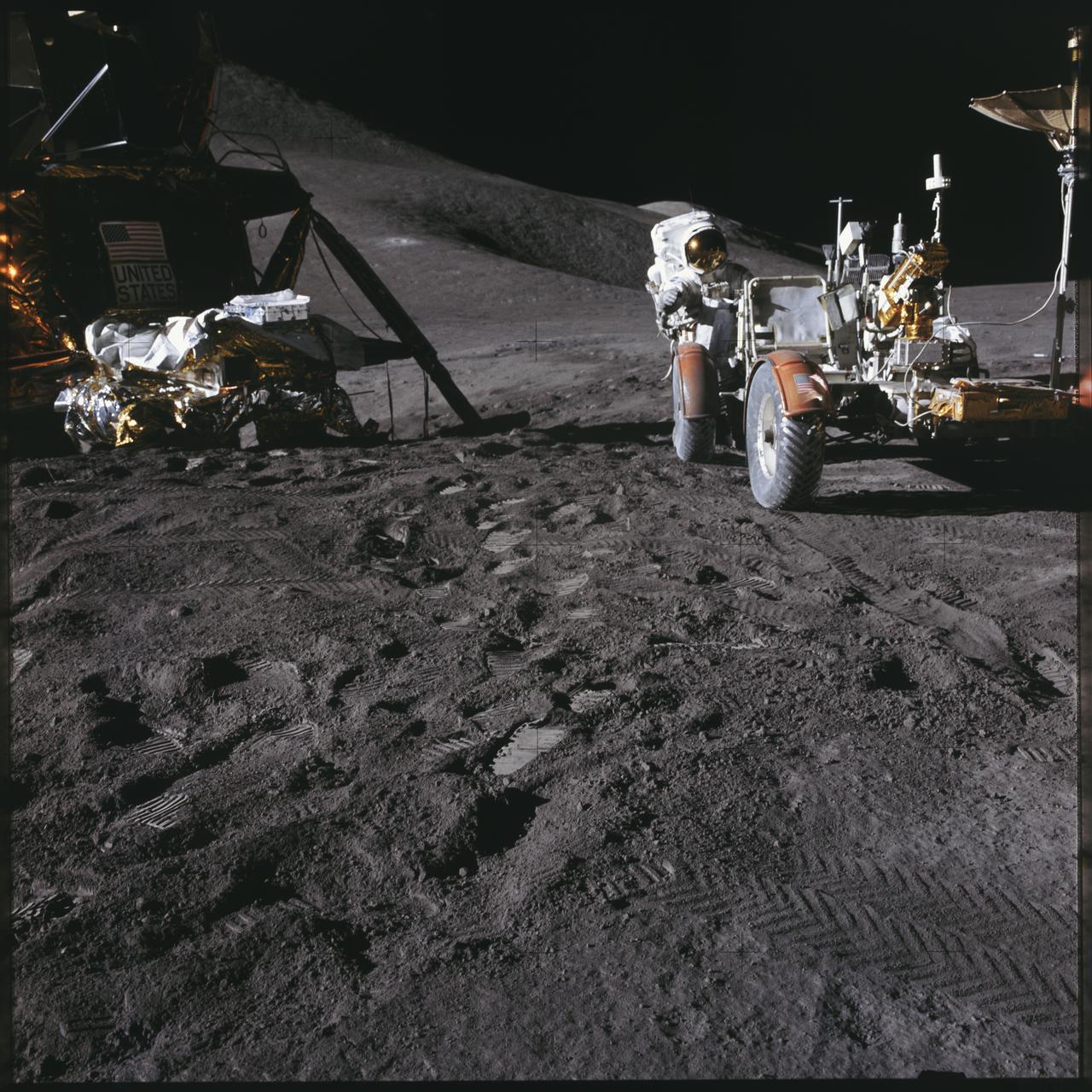

AS15-86-11601 (31 July 1971) --- Astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, works at the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during the first Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. The Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" is on the left. The undeployed Laser Ranging Retro Reflector (LR-3) lies atop the LM's modular equipment stowage assembly (MESA). This view is looking slightly west of south. Hadley Delta and the Apennine Front are in the background to the left. St. George crater is approximately five kilometers (about three statute miles) in the distance behind Irwin's head. This photograph was taken by astronaut David R. Scott, commander. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
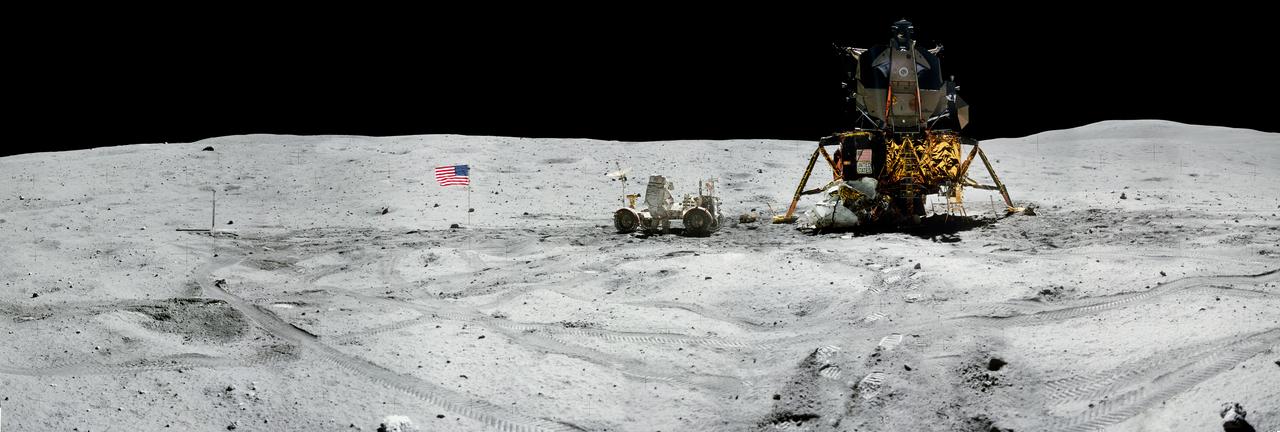

jsc2011e118363 - Panorama view of Apollo 16 commander Astronaut John W. Young, working at the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) just prior to deployment of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) during the first moonwalk of the mission on April 21, 1972. The panoramas were built by combining Apollo 16 images starting with frame AS16-116-18573 thru end frame AS16-116-18581. The panoramic images received minimal retouching by NASA imagery specialists, including the removal of lens flares that were problematic in stitching together the individual frames and blacking out the sky to the lunar horizon. These adjustments were made based on observations of the Moon walkers who reported that there are no stars visible in the sky due to the bright lunar surface reflection of the Sun.
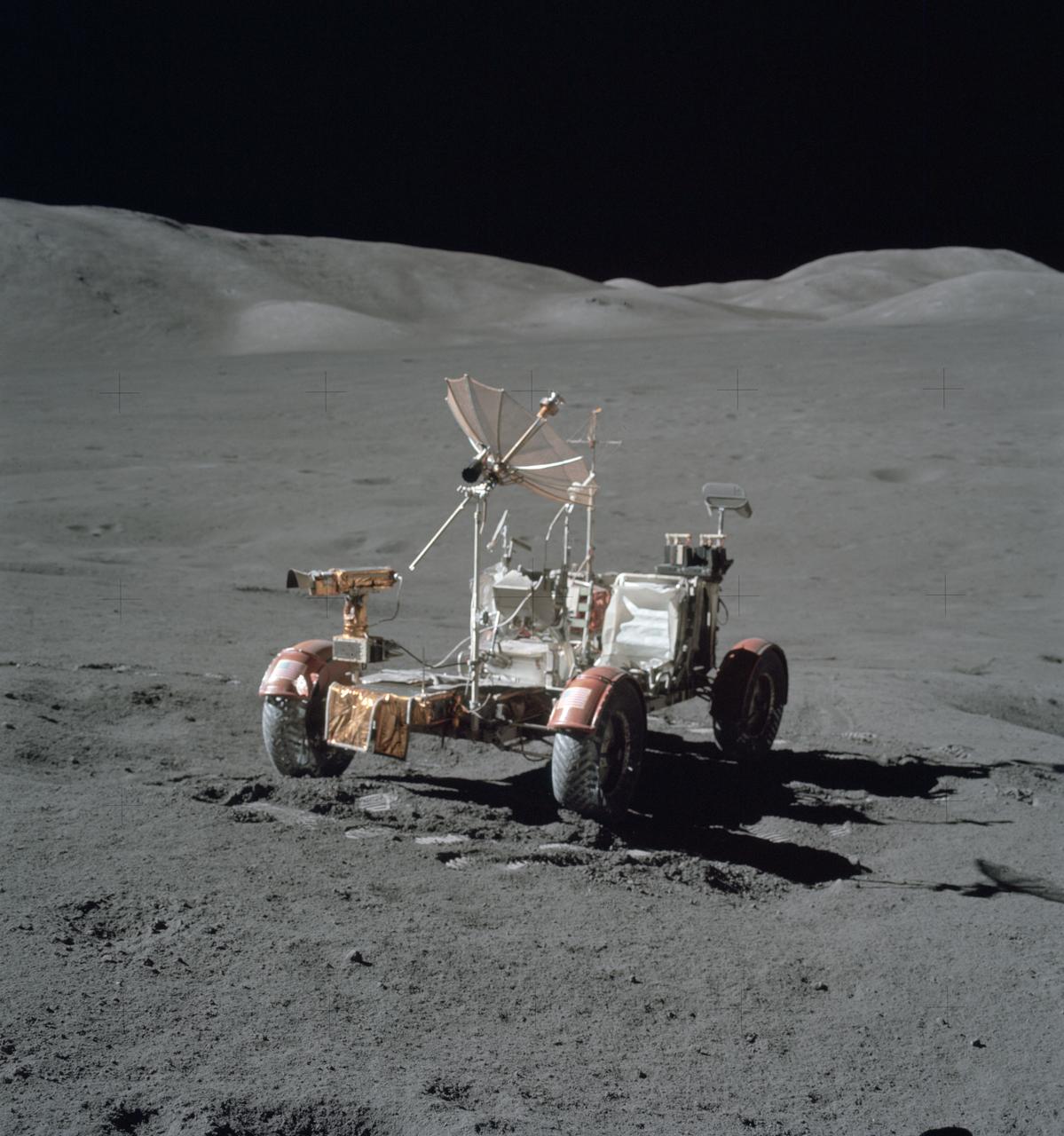

AS17-146-22367 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- This is an excellent view of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) which was used extensively by astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt at the Taurus-Littrow landing site.
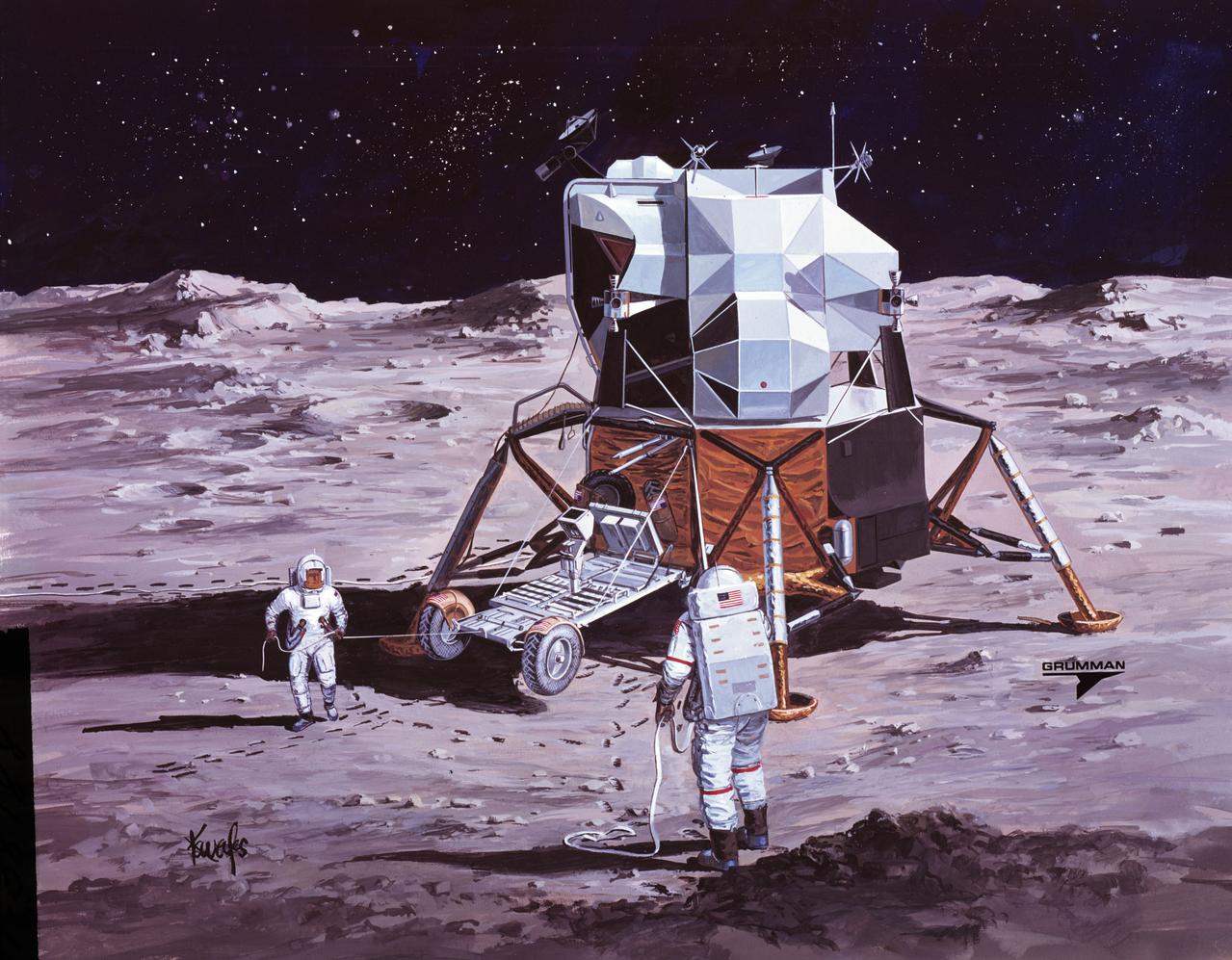
S71-38188 (26 June 1971) --- An artist's concept showing the Apollo 15 mission commander and the lunar module pilot performing deployment of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the lunar surface. The figure on the left represents astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, who here is maintaining a constant pull on the deployment cable to help the LRV unfold, while astronaut David R. Scott (right), commander, pulls the tapes that lower the LRV to the surface. (This is the third in a series of Grumman Aerospace Corporation artist's concepts telling the lunar surface LRV deployment story of the Apollo 15 mission).
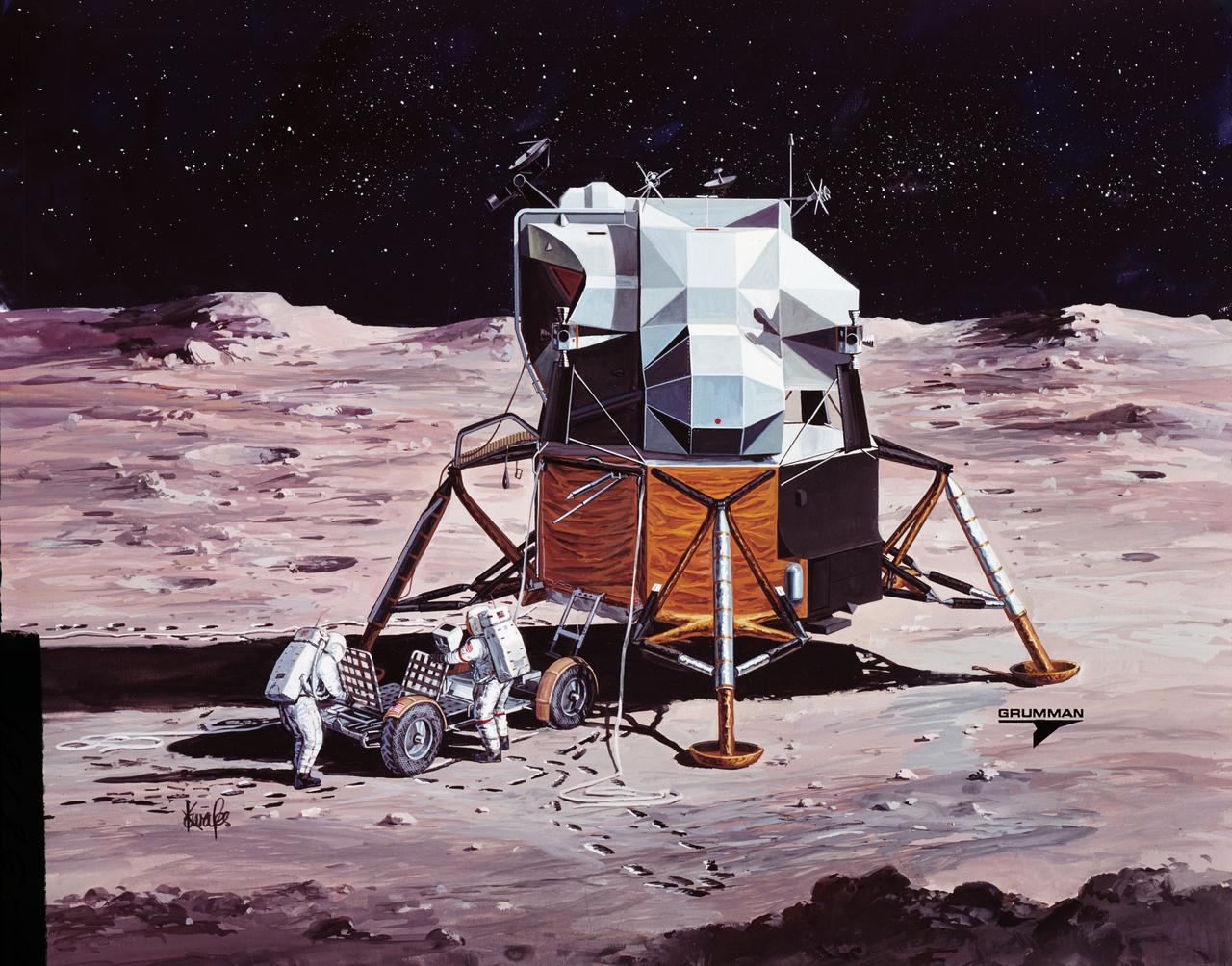

S71-38189 (26 June 1971) --- An artist's concept showing the final steps of readying the Apollo 15 Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) or Rover 1 for mobility on the lunar surface. Performing the last few LRV deployment tasks here are, left to right, astronauts James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, and David R. Scott, commander. More specifically the tasks depicted here include the setting up of the seats and the total releasing of the LRV from the LM. (This is the fourth in a series of four Grumman Aerospace Corporation artist's concepts telling the lunar surface LRV deployment story for Apollo 15).
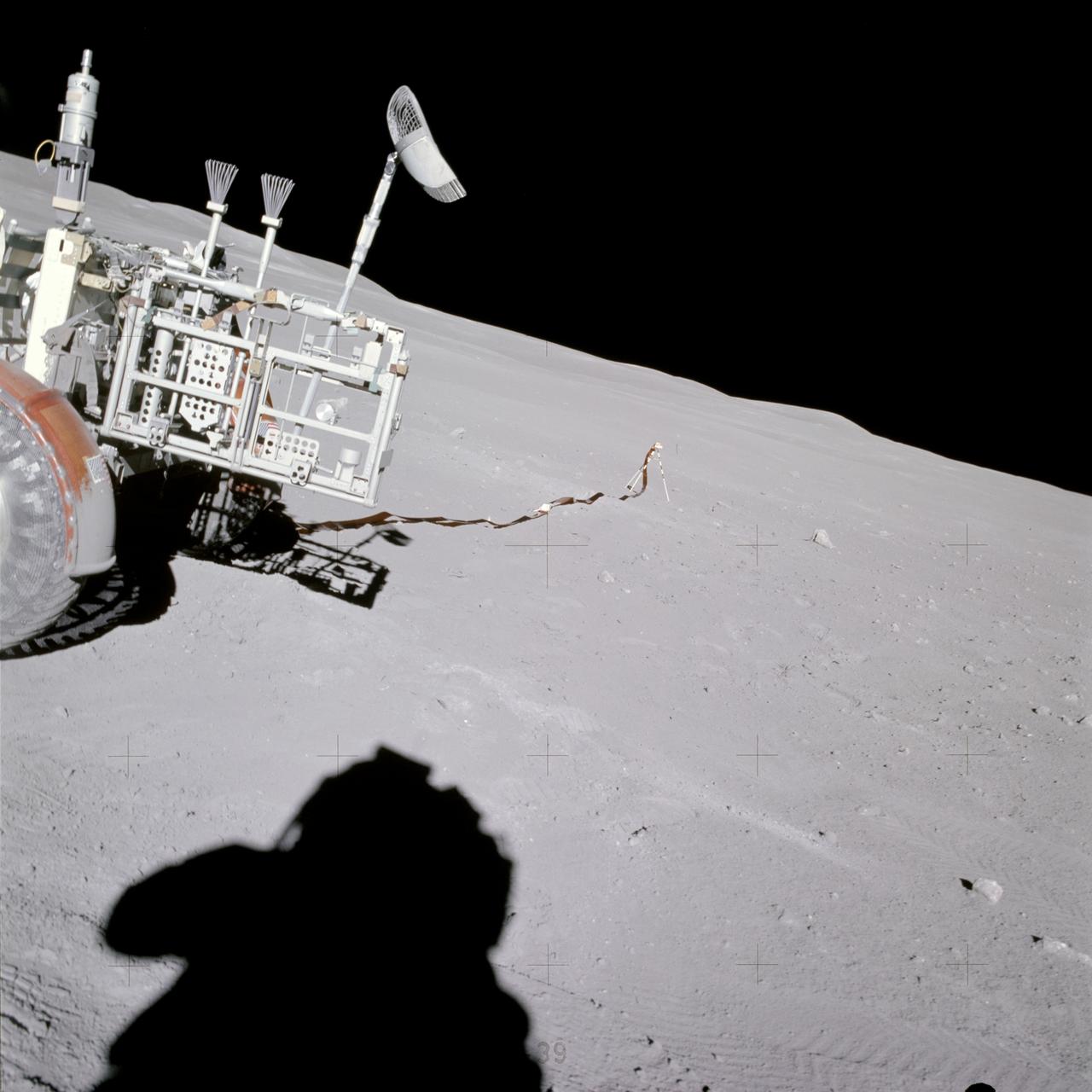

AS16-114-18433 (22 April 1972) --- View of the Lunar Portable Magnetometer mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) which was parked at Station No. 2 on the Descartes lunar landing site. The Apollo 16 crew photographed it during their second extravehicular activity (EVA). Note the shadow of the astronaut taking the photograph in the left foreground.
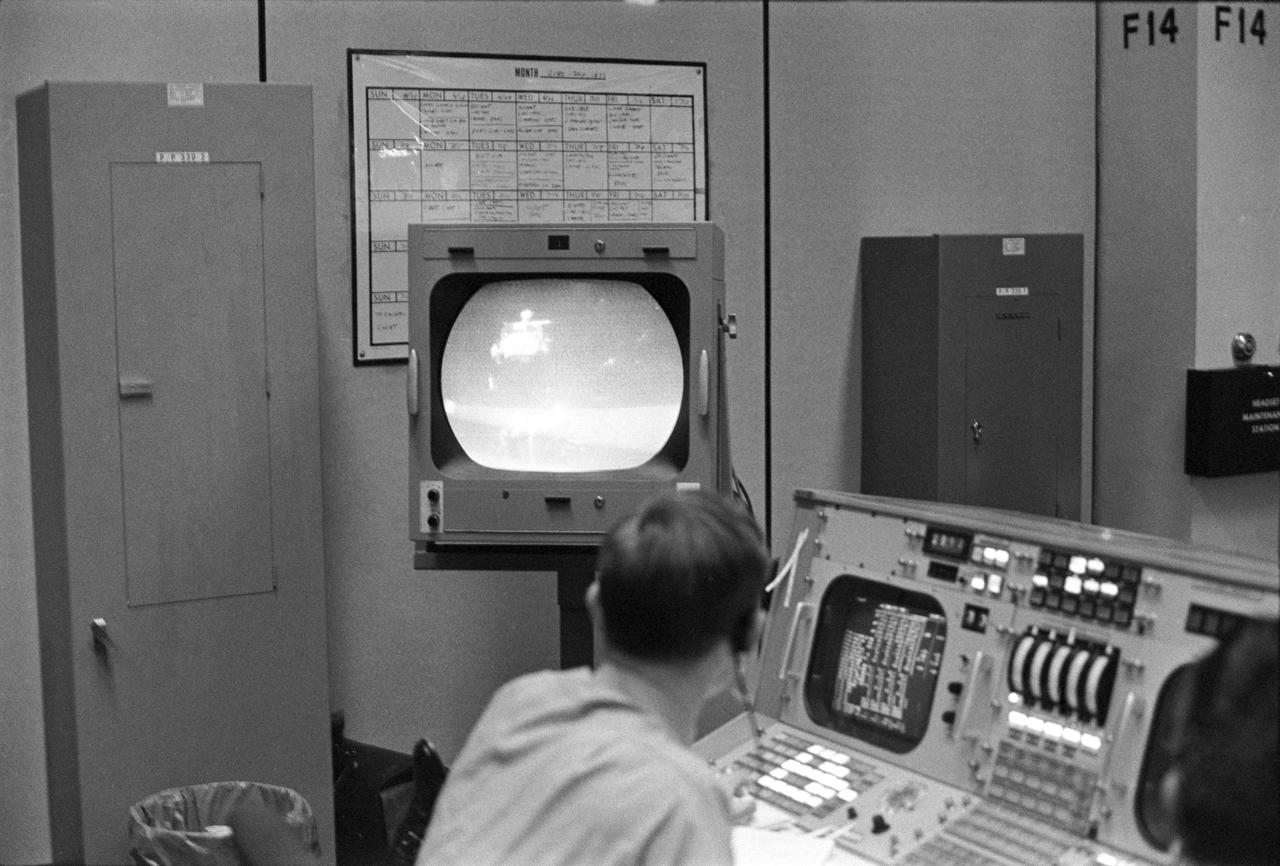

View of a photograph of the television (TV) monitor in the MCC showing a picture being transmitted from the color TV camera mounted on the parked Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) at the Hadley-Apennine Landing Site showing the liftoff of the Apollo 15 Lunar Module (LM) Ascent Stage from the Lunar surface. MSC, Houston, TX
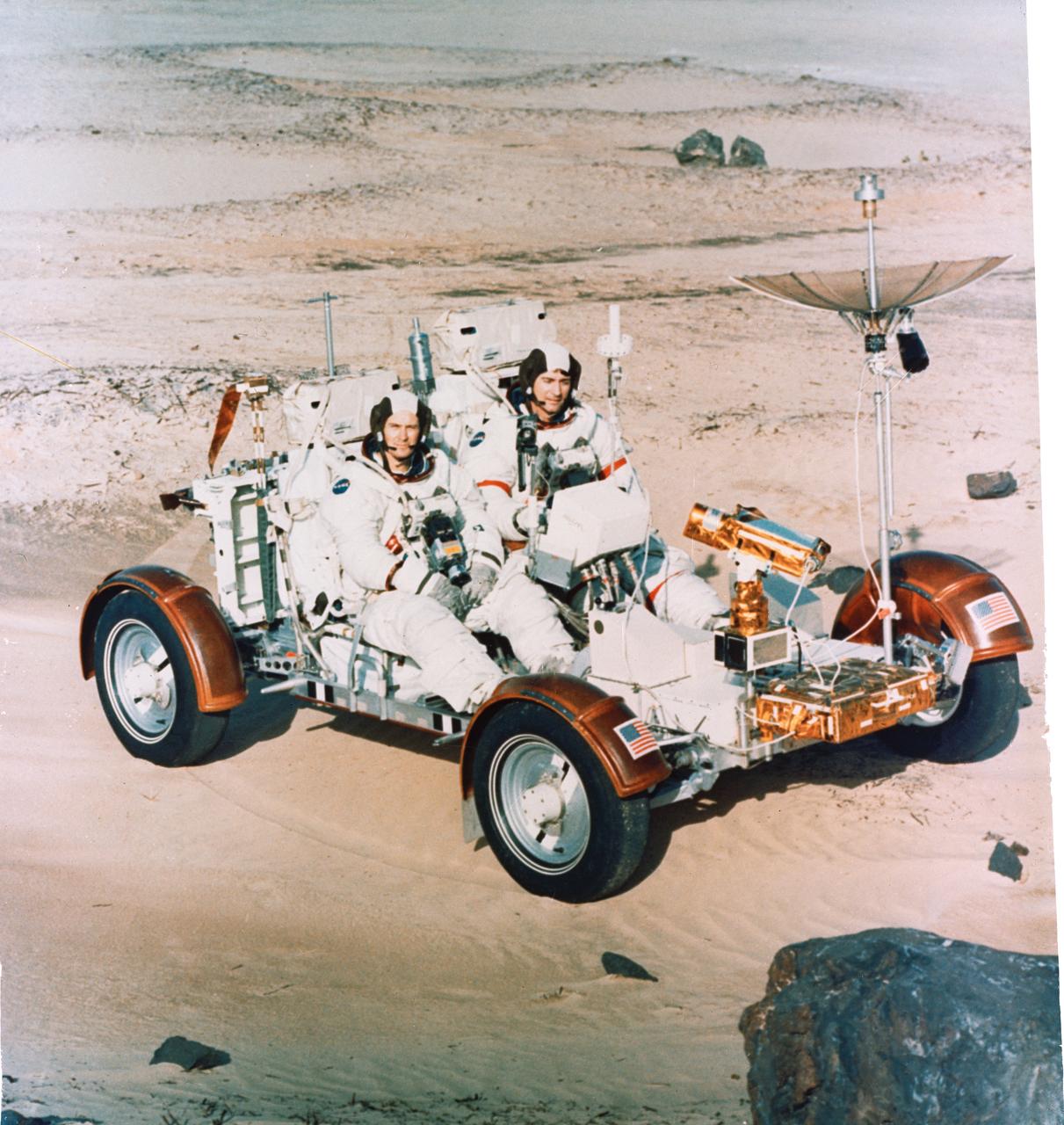

S72-30695 (22 Dec. 1971) --- Astronauts John W. Young, right, Apollo 16 commander, and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, maneuver a training version of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) about a field at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) simulated to represent the lunar surface. The LRV is planned to transport the two crew men around the Descartes area on the lunar surface while astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, orbits the moon in the Command and Service Modules (CSM).
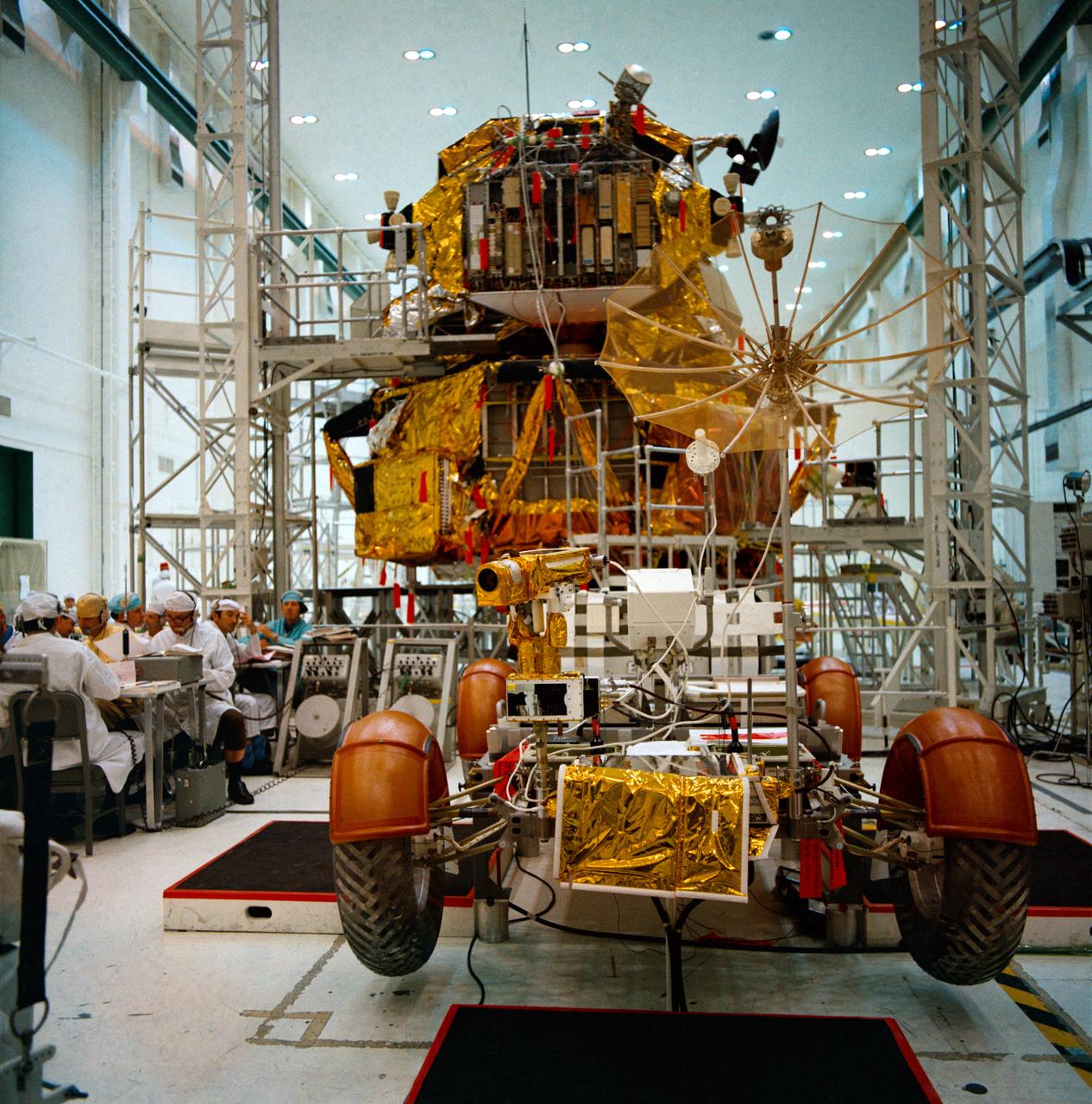

S71-30542 (21 April 1971) --- An overall view of the Apollo 15 Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) and the Lunar Module (LM) during simulations at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, will man the LRV on the lunar surface during their August 1971 traverses. Rover 1 will permit the astronauts to cover a larger area of the moon for exploration and sample collecting than on previous missions.
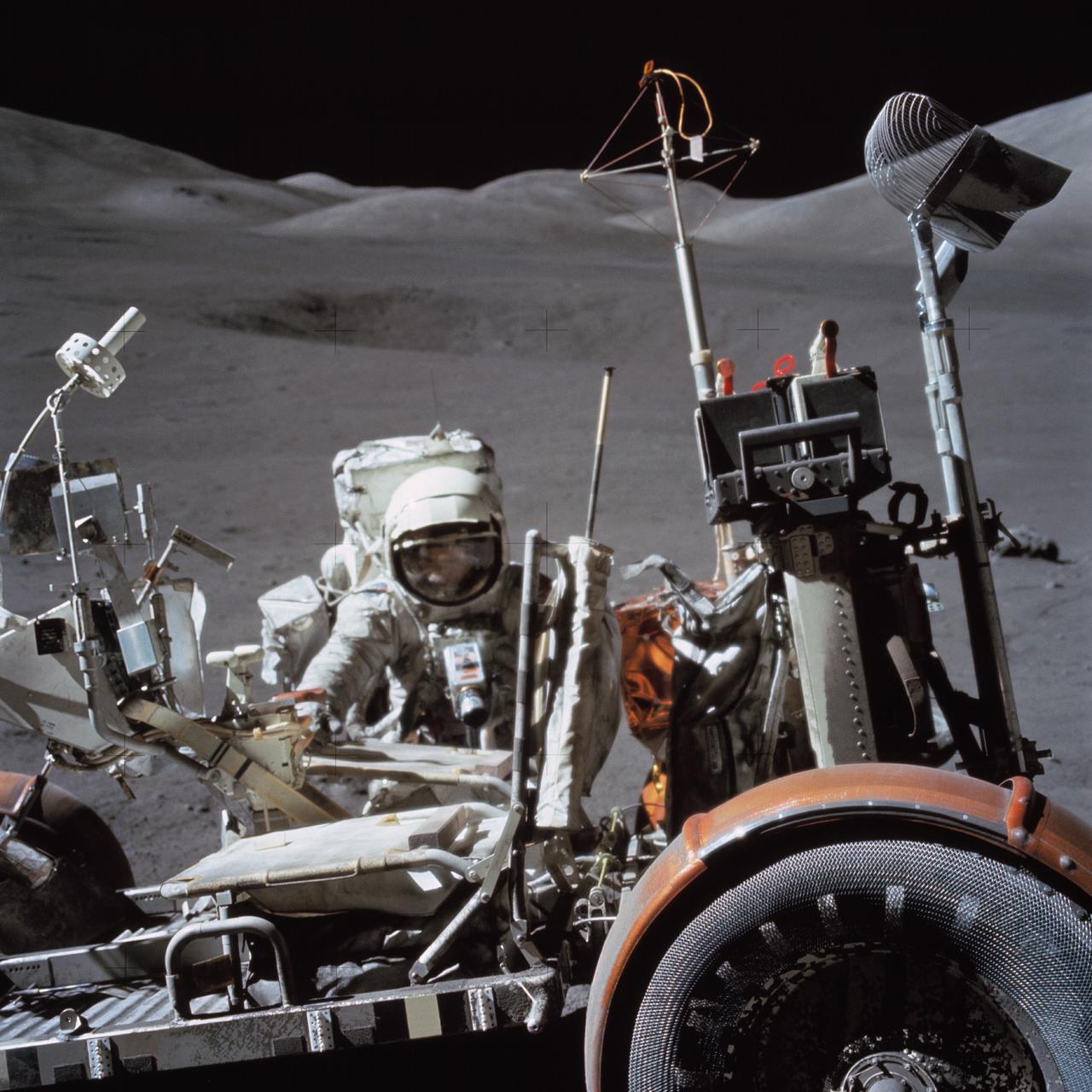
AS17-146-22296 (13 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, works near the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during the third Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow site on the lunar surface. The front part of the LRV is out of frame at left, but the seats and several geological tools can be seen. The photo was taken by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, mission commander.
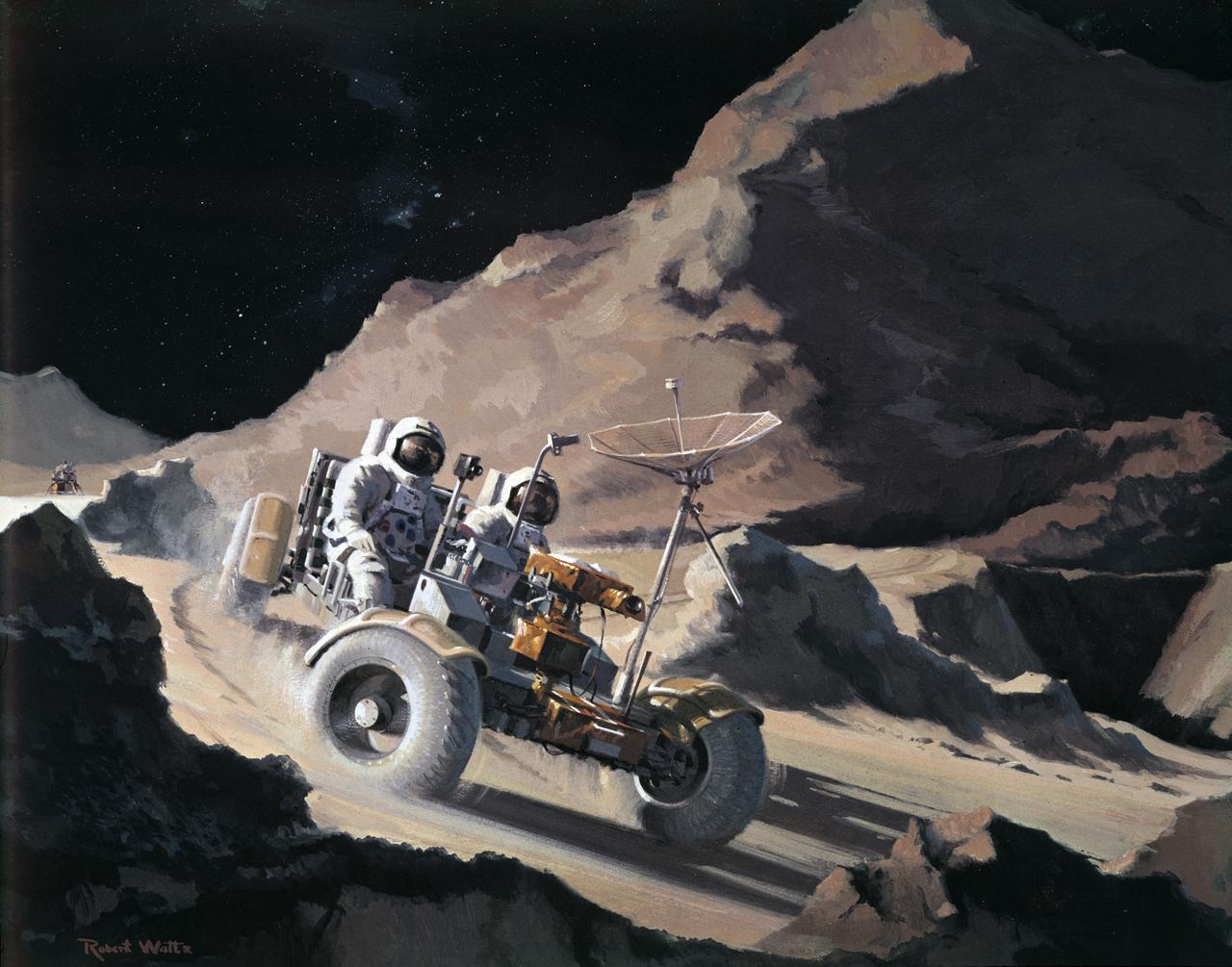

S71-39868 (July 1971) --- An artist's concept of the Apollo 15 Hadley-Apennine landing area showing the two moon-exploring crewmen on a traverse in their Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The two figures represent astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. The artwork is by Teledyne Ryan.

Astronaut John W. Young, Apollo 16 prime crew commander (right), takes a drive in the One-G Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) trainer in the Lunar Topgraphic Simulation area at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). He is accompanied by John Omstead, with General Electric, MSC.
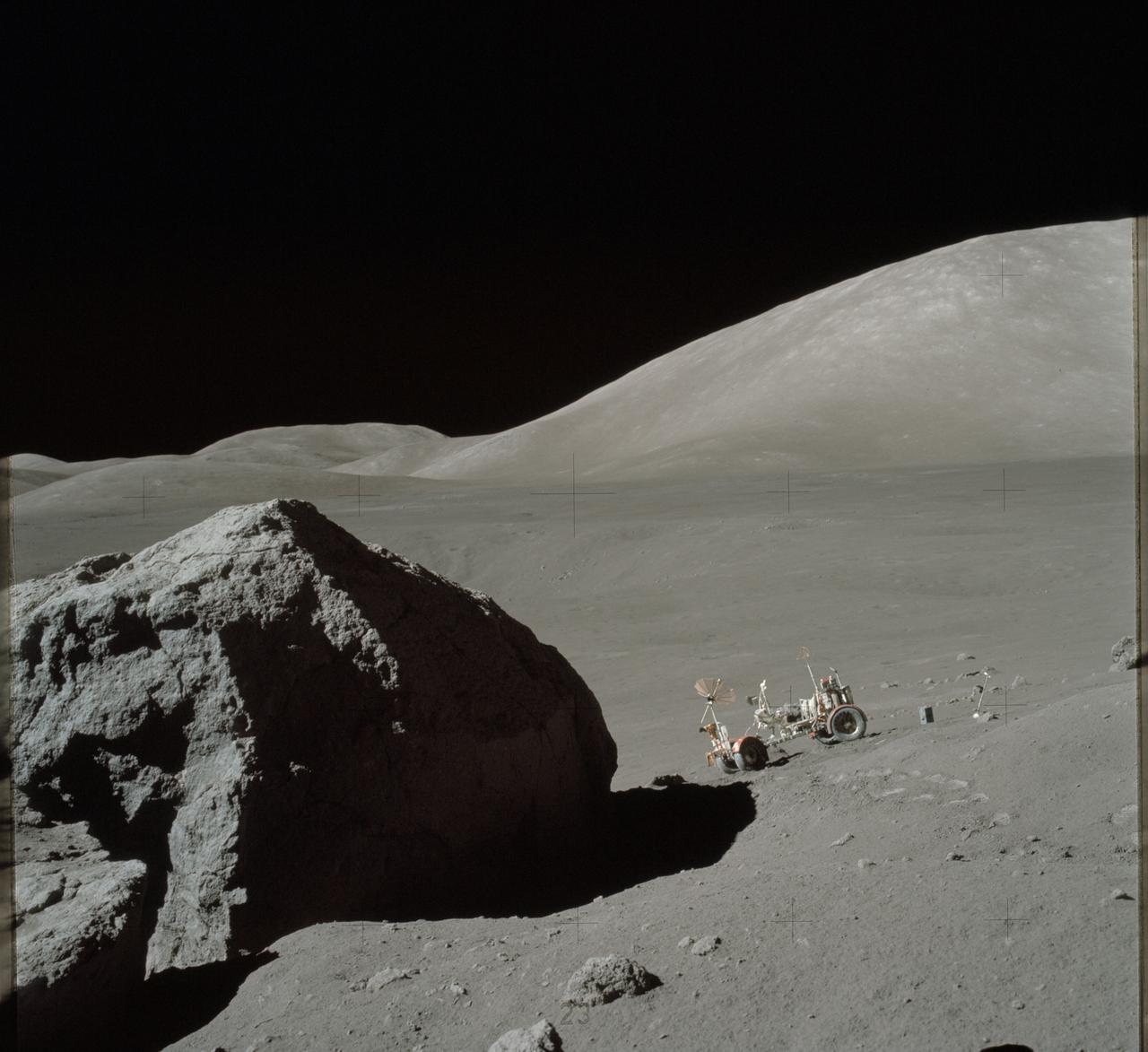

AS17-140-21494 (13 Dec. 1972) --- This view shows the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) parked by an outcrop of rocks by astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. (Jack) Schmitt during their visit to extravehicular activity Station 6 (Henry Crater).

AS16-107-17436 (21 April 1972) --- An excellent view of the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" and Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), as photographed by astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. Astronaut John W. Young, commander, can be seen directly behind the LRV. The lunar surface feature in the left background is Stone Mountain. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the LM to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
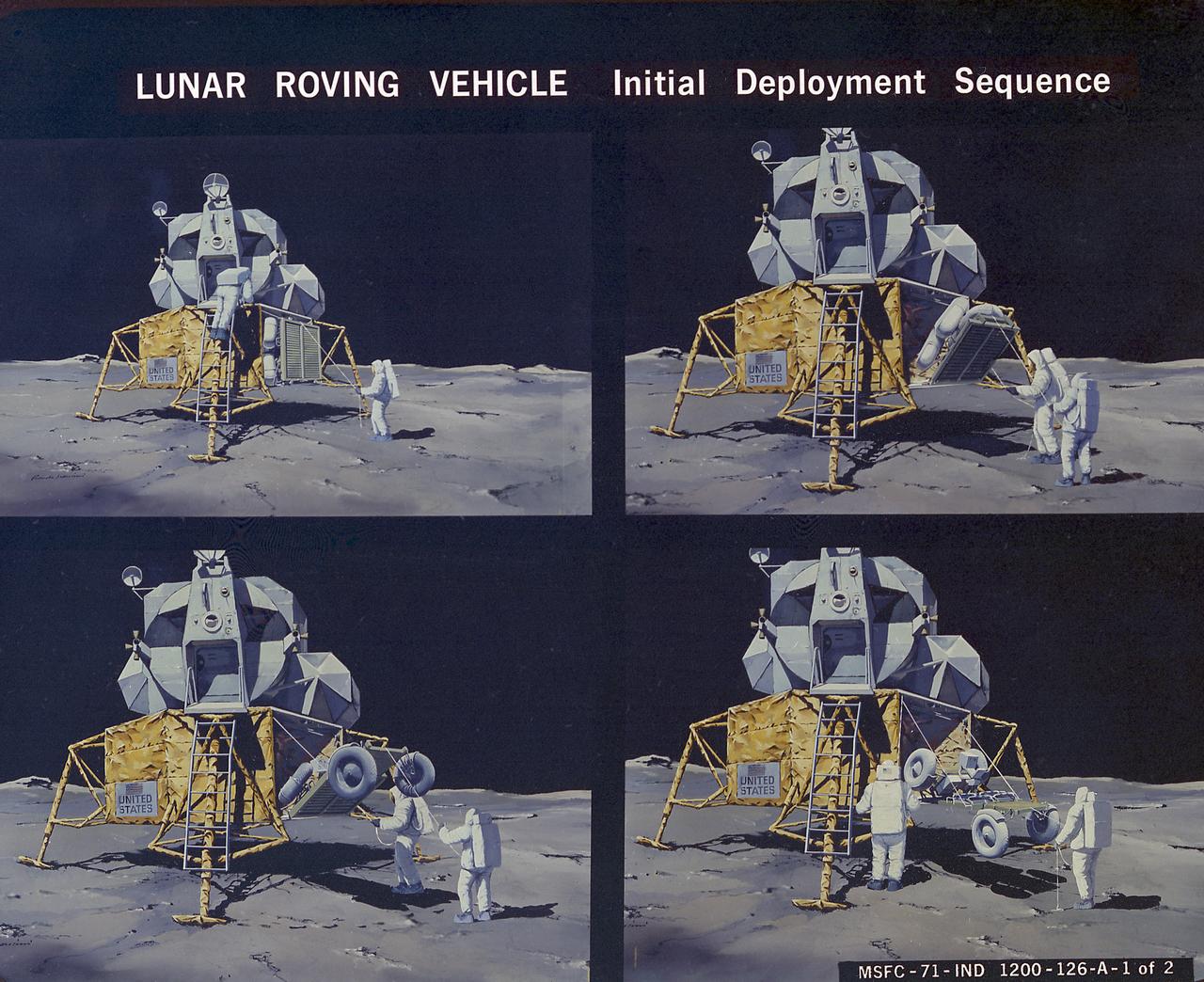
This artist's concept illustrates the deployment sequence of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the Moon. The LRV was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crew to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.
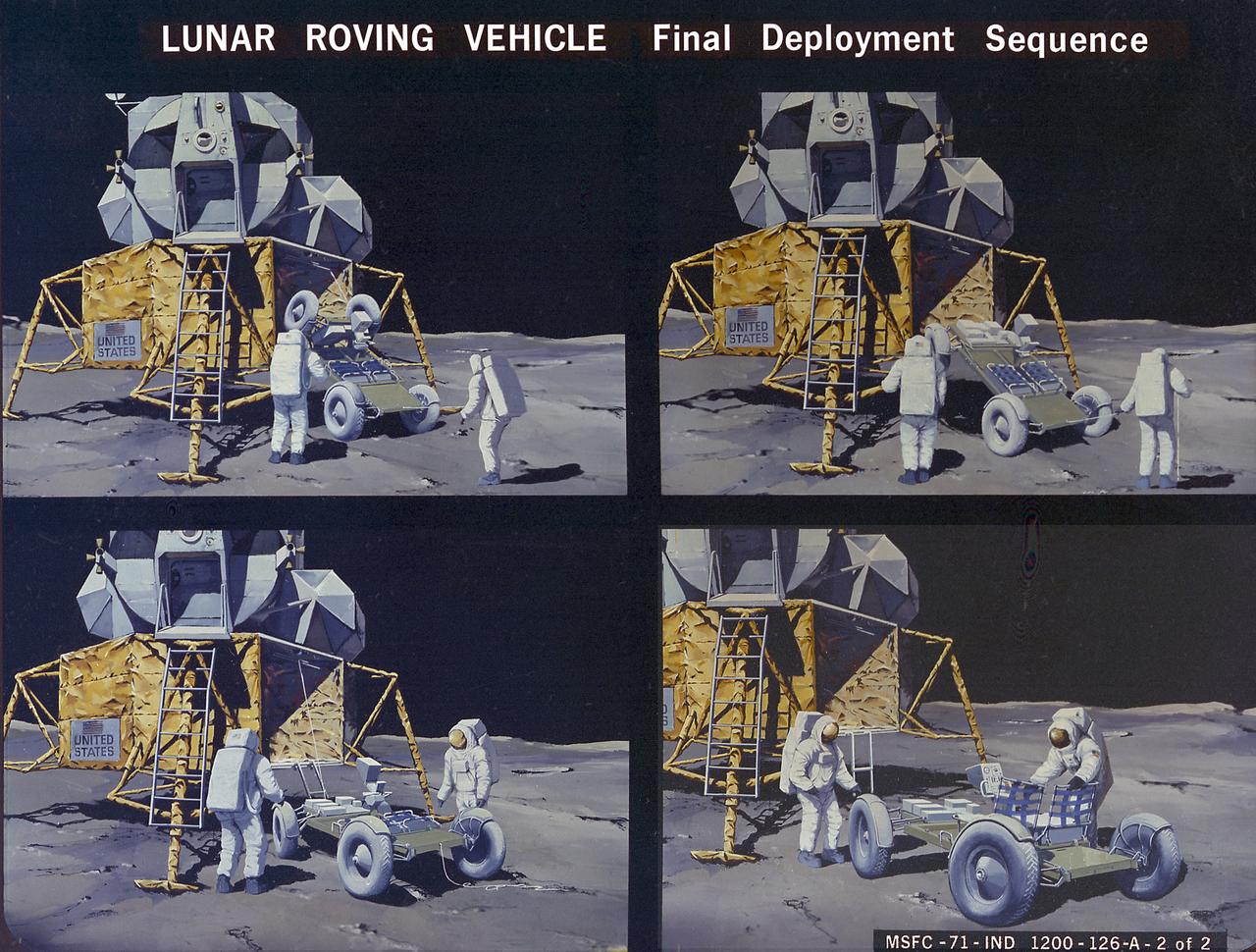
This artist's concept illustrates the deployment sequence of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the Moon. The LRV was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crew to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.
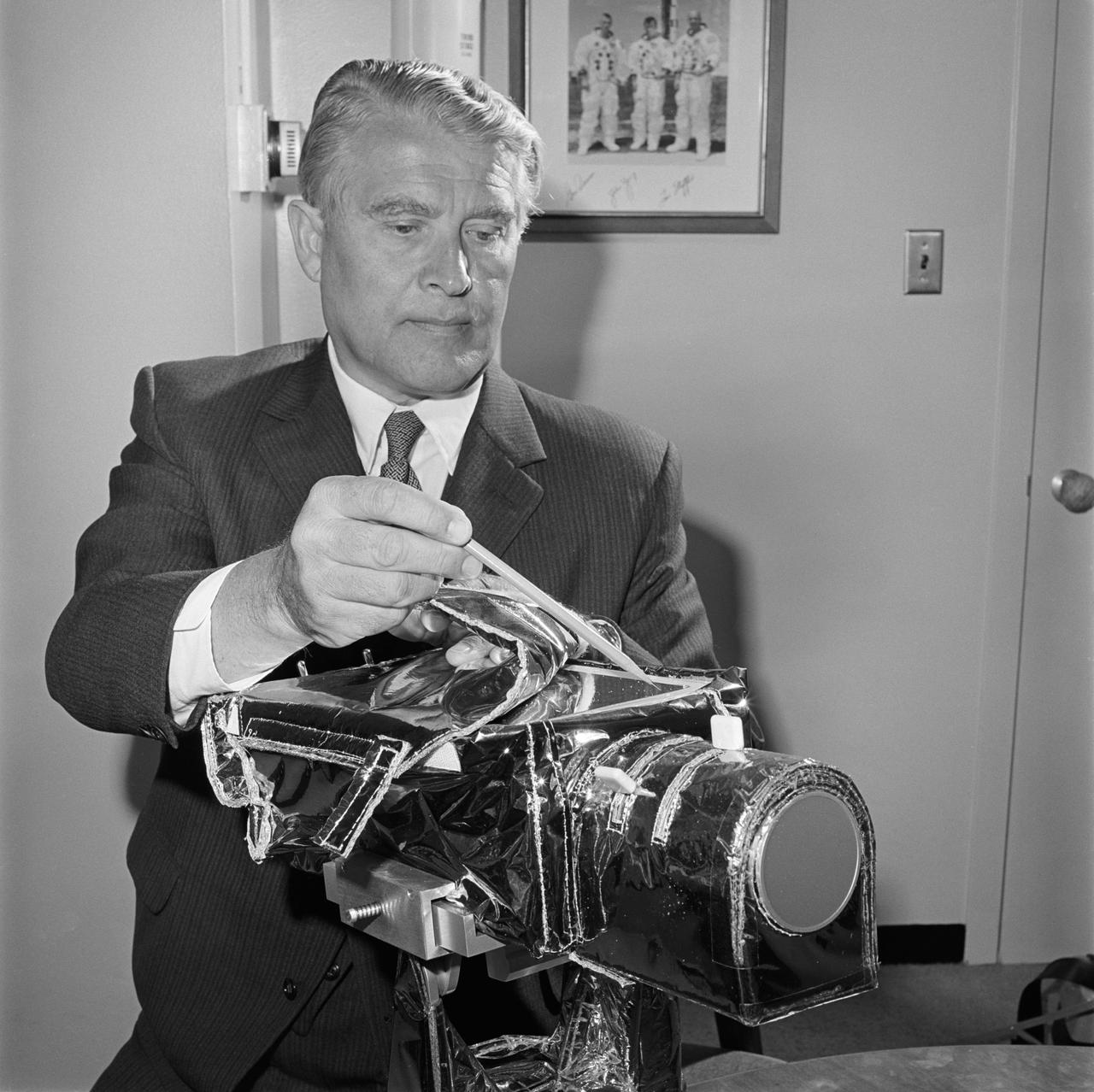

S71-35169 (June 1971) --- The color television camera for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Apollo 15 lunar landing mission is examined by NASA's Deputy Associate Director Dr. Wernher von Braun. The camera will be mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) and will be operated by the flight crew astronauts, David R. Scott and James B. Irwin, or by ground command from the Mission Control Center (MCC) in Houston during the three lunar traverses. It will also be used to show the astronauts whenever they leave the LRV, and for the first time it will make possible the viewing of the Lunar Module (LM) ascent stage as it lifts off the moon.

S71-39867 (June 1971) --- Astronauts David R. Scott (right), commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, are shown on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida, during Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) simulations. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descend in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
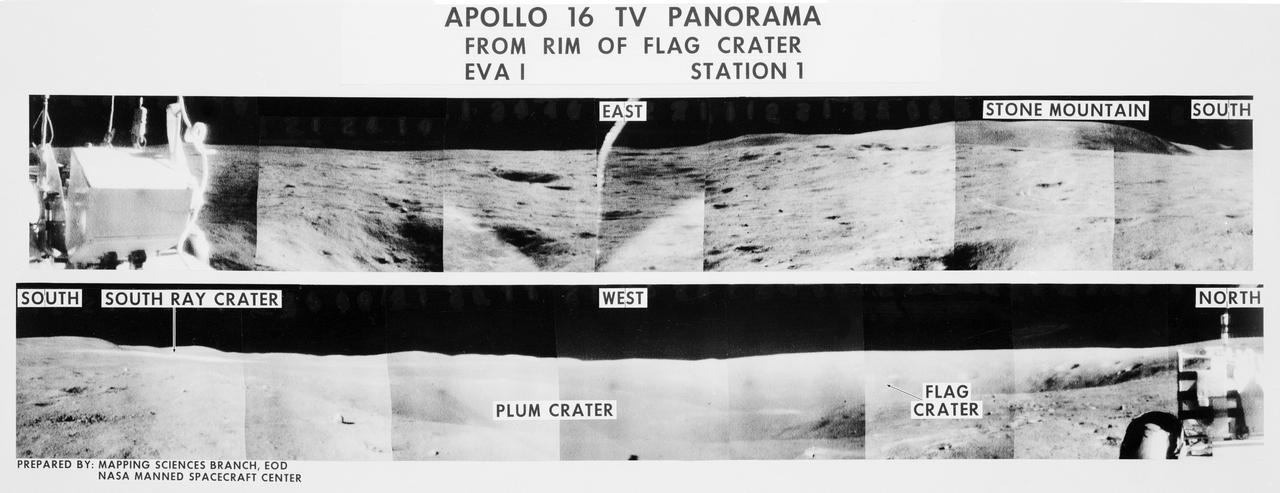
S72-35970 (21 April 1972) --- A 360-degree field of view of the Apollo 16 Descartes landing site area composed of individual scenes taken from color transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). This panorama was made while the LRV was parked at the rim of Flag Crater (Station 1) during the first Apollo 16 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) by astronauts John W. Young and Charles M. Duke Jr. The overlay identifies the directions and the key lunar terrain features. The camera panned across the rear portion of the LRV in its 360-degree sweep. Astronauts Young, commander; and Duke, lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon. Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
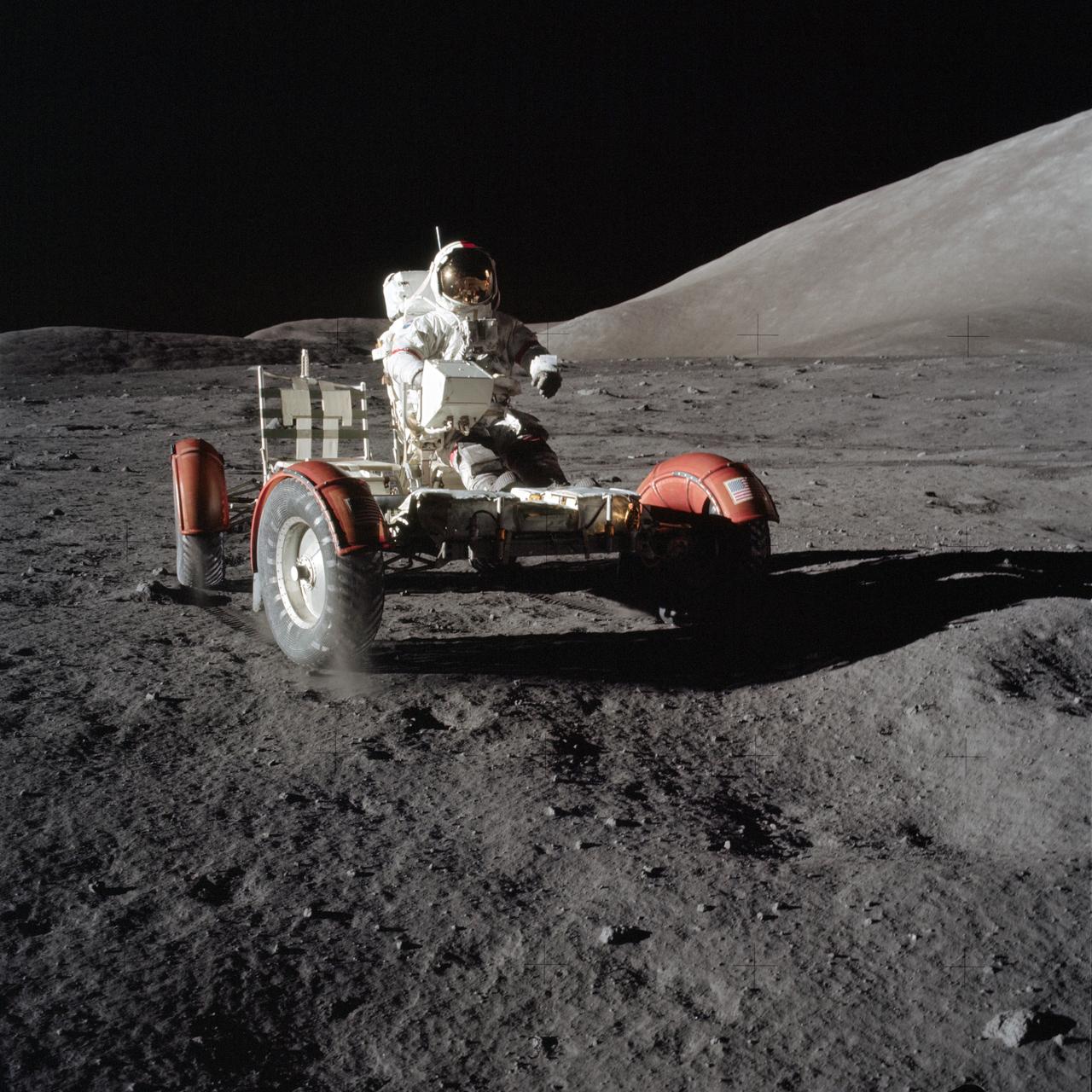

AS17-147-22526 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, commander, makes a short checkout of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during the early part of the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. This view of the "stripped down" LRV is prior to loading up. Equipment later loaded onto the LRV included the ground-controlled television assembly, the lunar communications relay unit, hi-gain antenna, low-gain antenna, aft tool pallet, lunar tools and scientific gear. This photograph was taken by scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. The mountain in the right background is the east end of South Massif. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
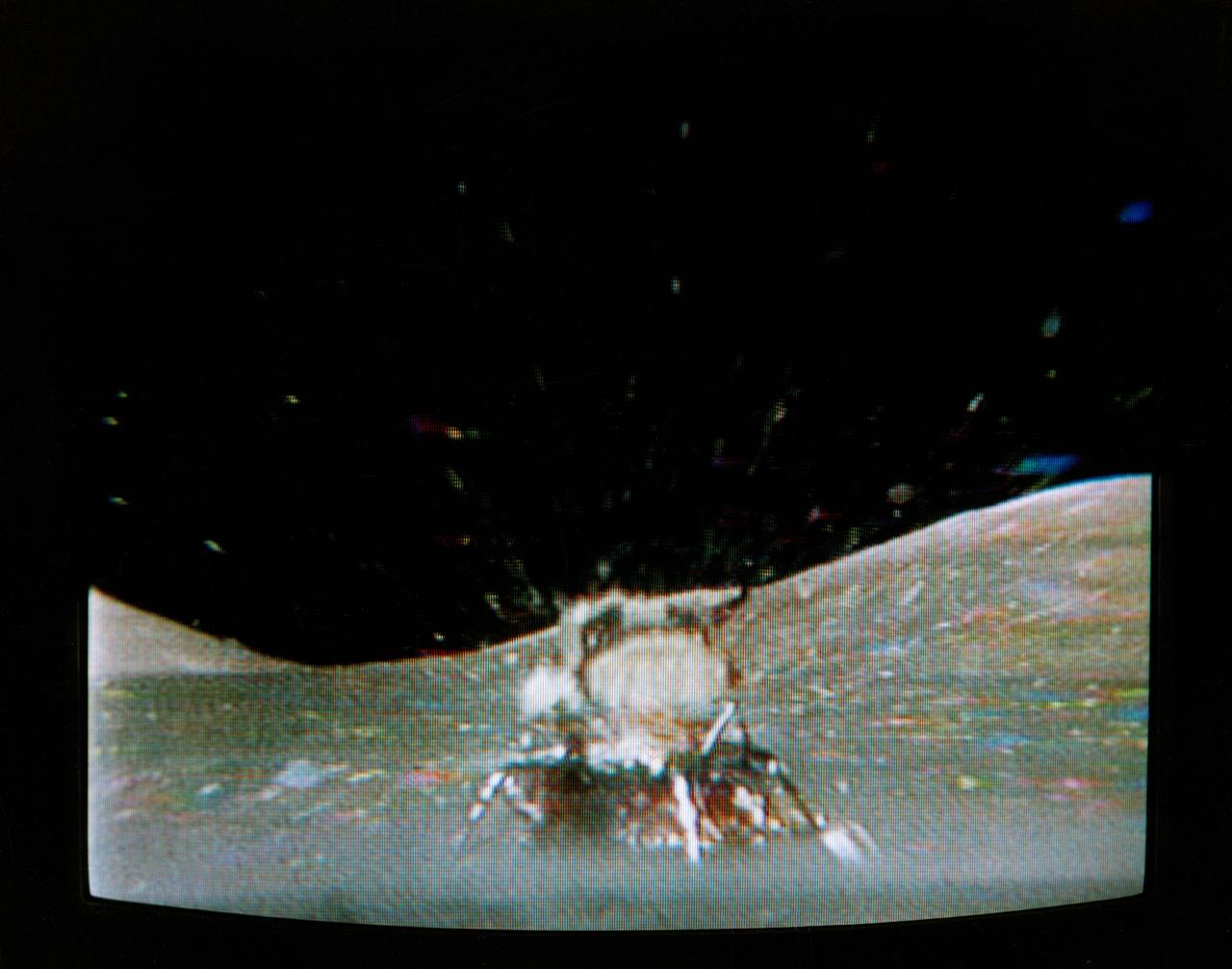
The Apollo 17 Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" ascent stage leaves the Taurus-Littrow landing site as it makes its spectacular liftoff from the lunar surface, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV-mounted TV camera, remotely controlled from the Mission Control Center (MCC) in Houston, made it possible for people on Earth to watch the fantastic event. The LM liftoff was at 188:01:36 ground elapsed time, 4:54:36 p.m. (CST), Thursday, December 14, 1972.
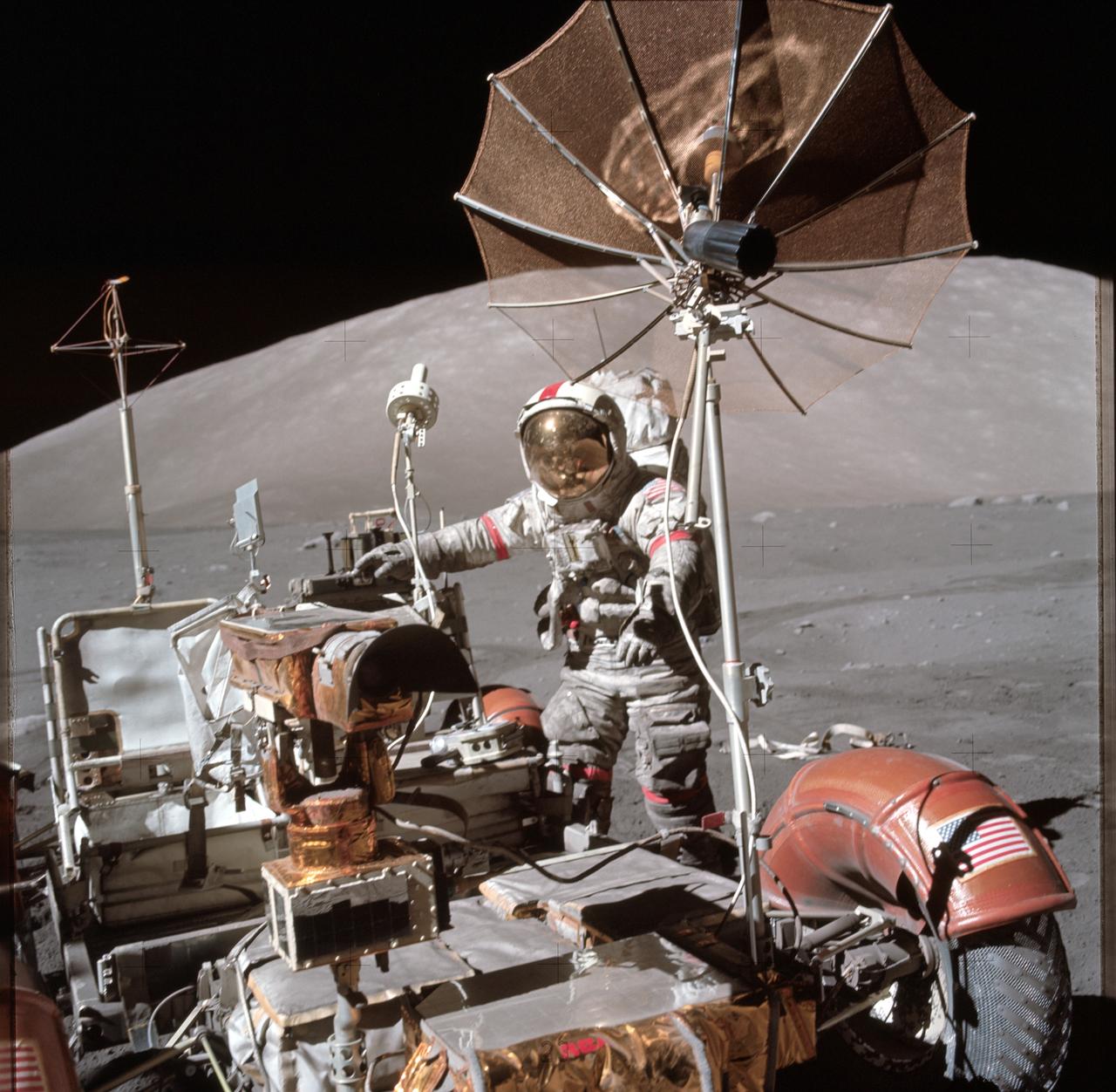

AS17-134-20476 (13 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 commander, approaches the parked Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the lunar surface during the flight's third period of extravehicular activity (EVA). South Massif can be seen in the background. The photograph was taken with a hand-held Hasselblad camera by scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. While the two explored the surface of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
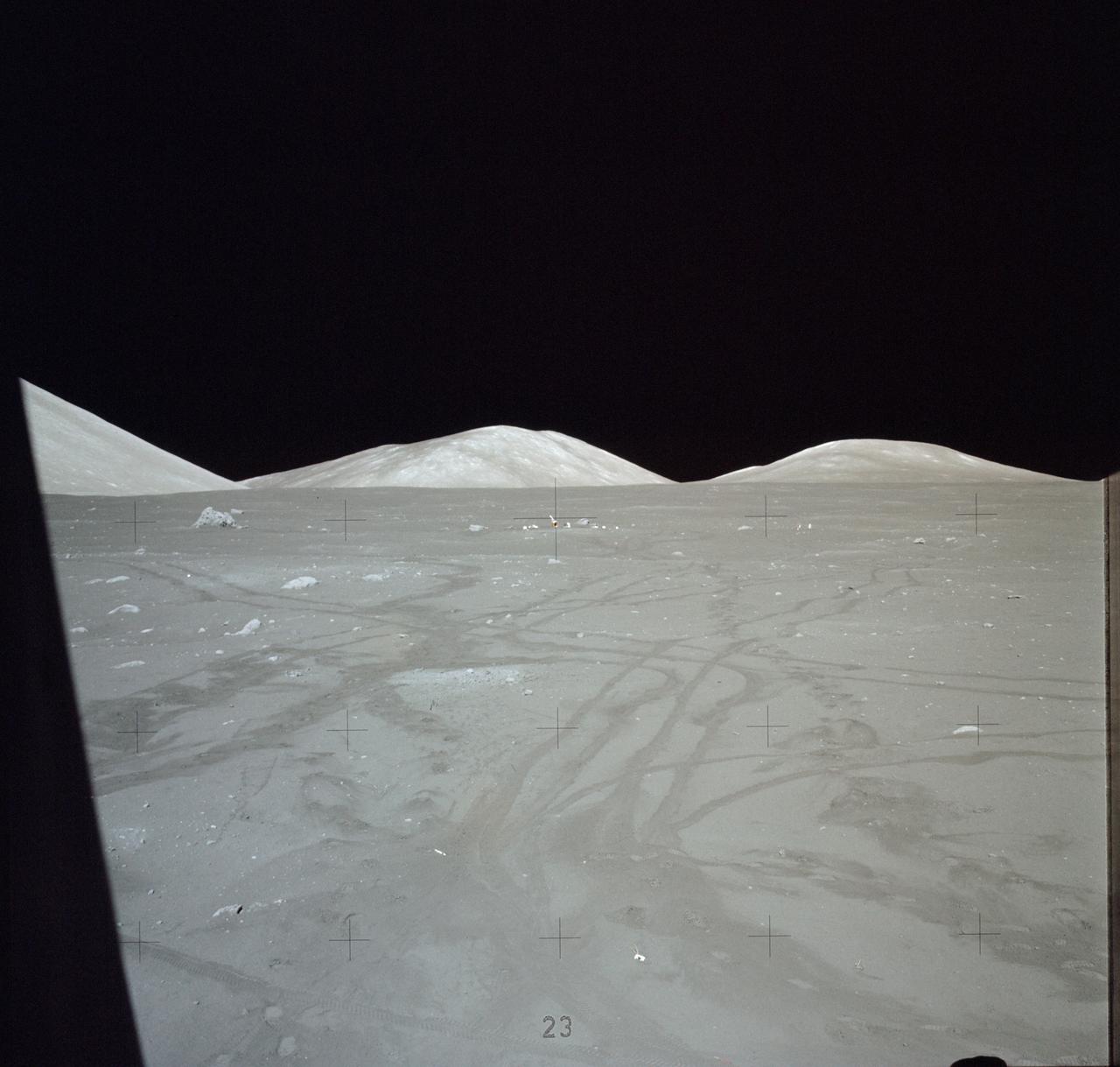

AS17-140-21355 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- This picture of the lunar surface was taken from the window of the lunar module at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. Astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt were inside the lunar module preparing for the mission's third spacewalk. Tracks made by lunar roving vehicle (LRV) and the astronauts' bootprints from earlier spacewalks are seen in the foreground.
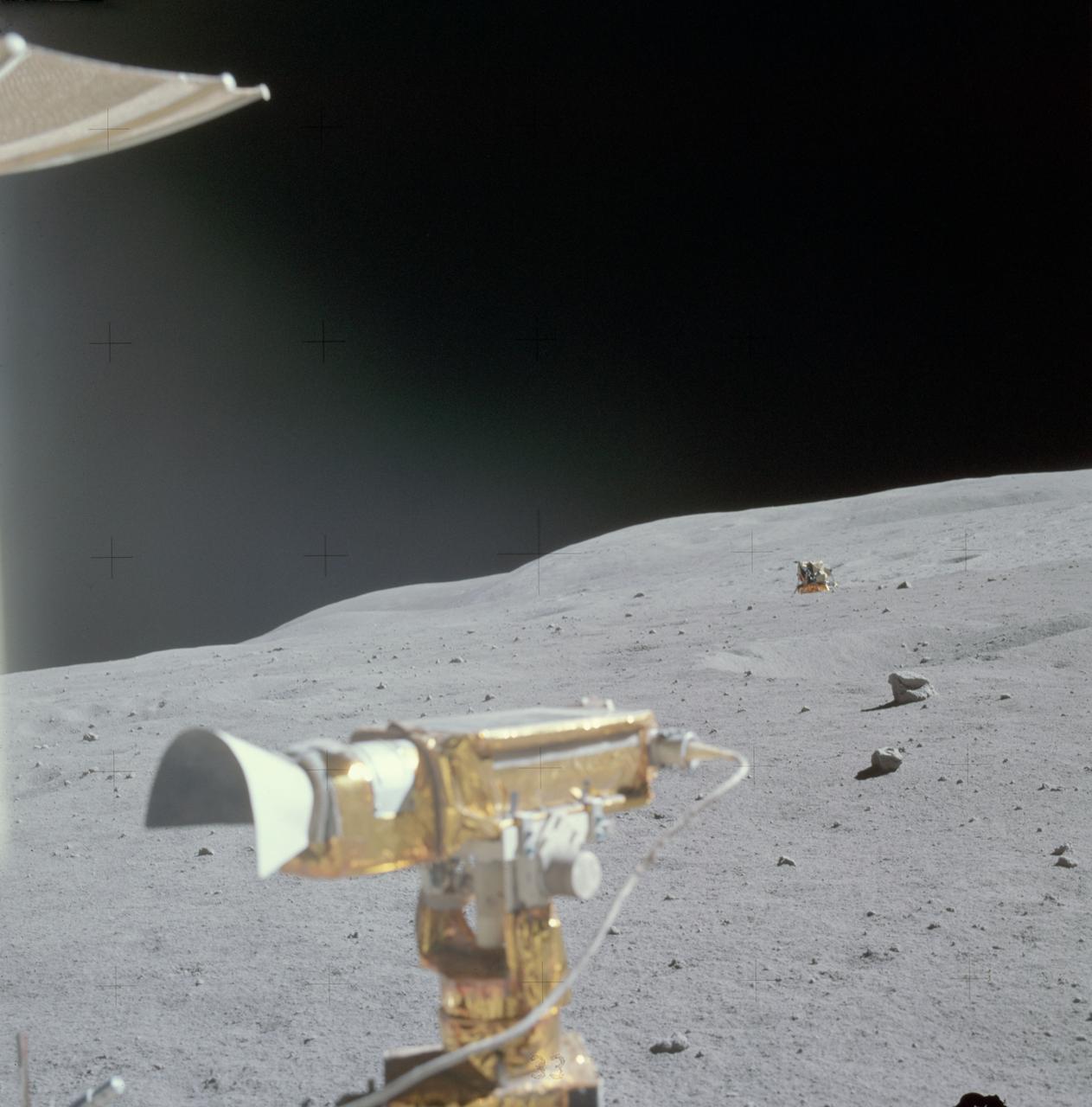
AS16-115-18549 (22 April 1972) --- The Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" is photographed from a distance by astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, aboard the moving Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). Astronauts Duke and John W. Young, commander, were returning from their excursion to Stone Mountain during the second Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA). The RCA color television camera mounted on the LRV is in the foreground. A portion of the LRV's high-gain antenna is at top left. Smoky Mountain rises behind the LM in this north-looking view at the Descartes landing site. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
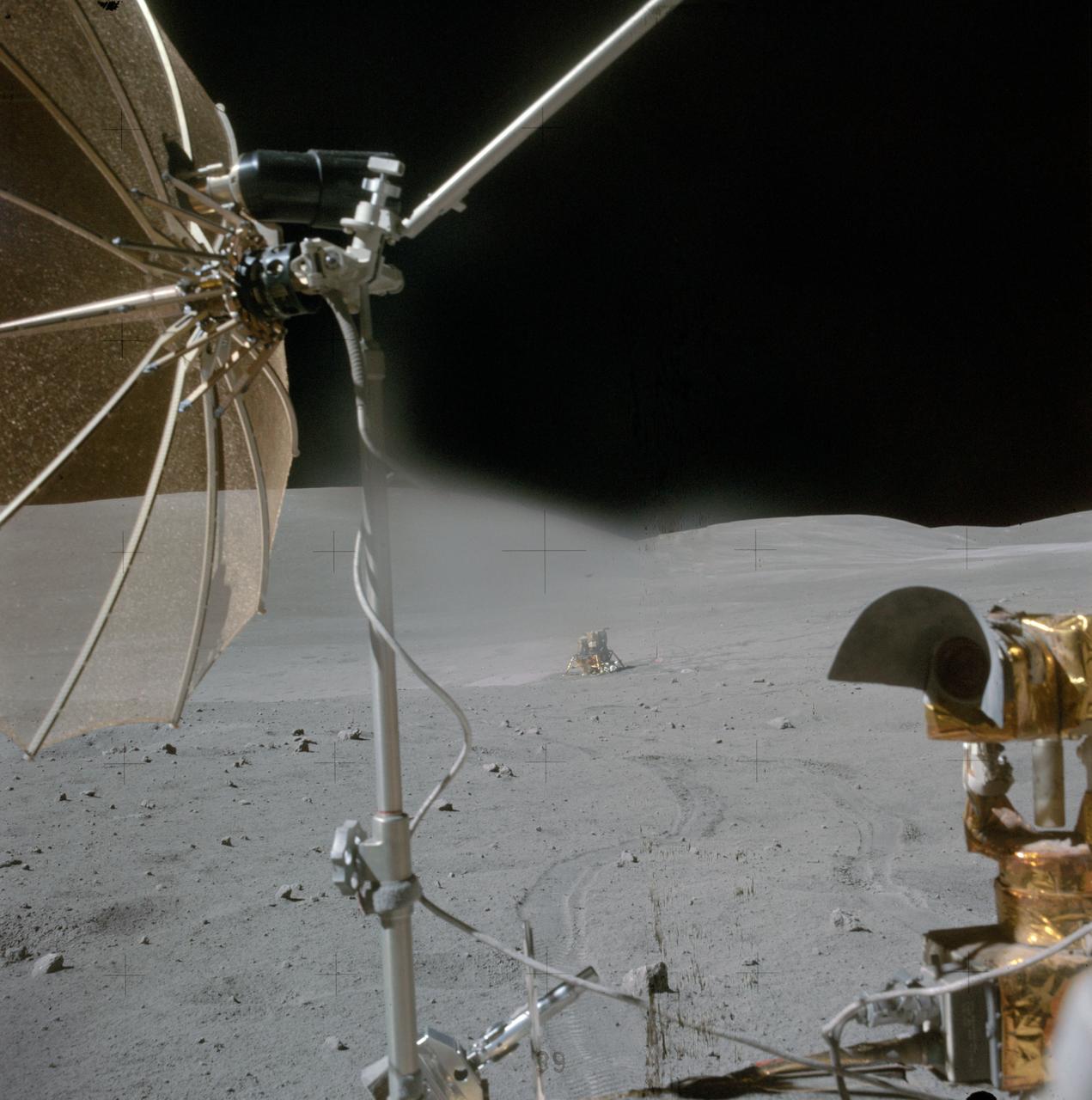
AS16-116-18678 (23 April 1972) --- A view from the moving Apollo 16 Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) as the crew men headed "home" at the end of the mission's third and final extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut John W. Young called attention to the series of block fields between the Lunar Module (LM) and LRV. Young also noted that, "The LM was obviously sitting in the only flat place around." Stone Mountain stretches about half way across the background. The high gain antenna and the RCA television camera on the LRV are in the foreground. While astronauts Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 LM "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
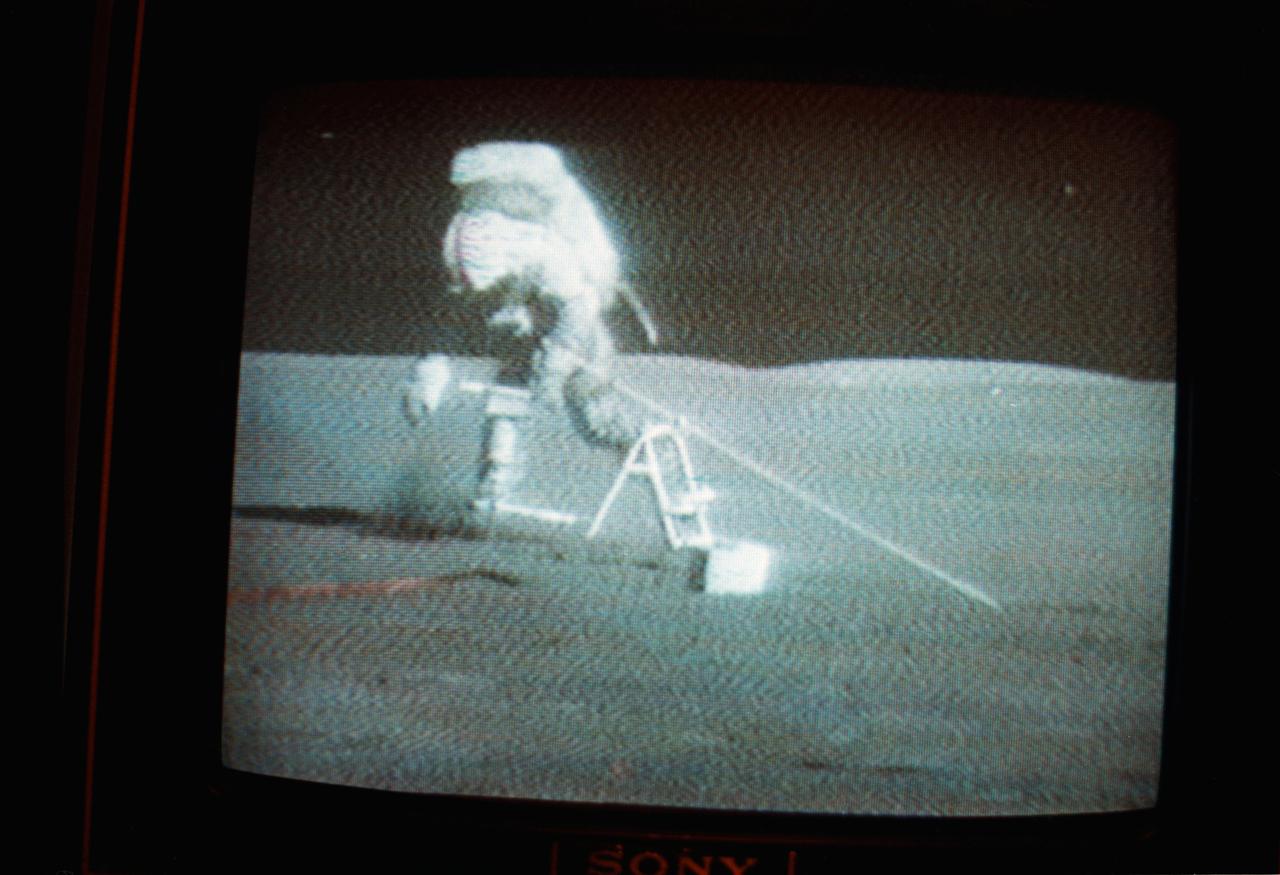

S71-41501 (1 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, Apollo 15 commander, is seen carrying the Apollo Lunar Surface Drill (ALSD) during the second lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) in this black and white reproduction taken from a color transmission made by the RCA color television camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). This transmission was the fourth made during the mission.
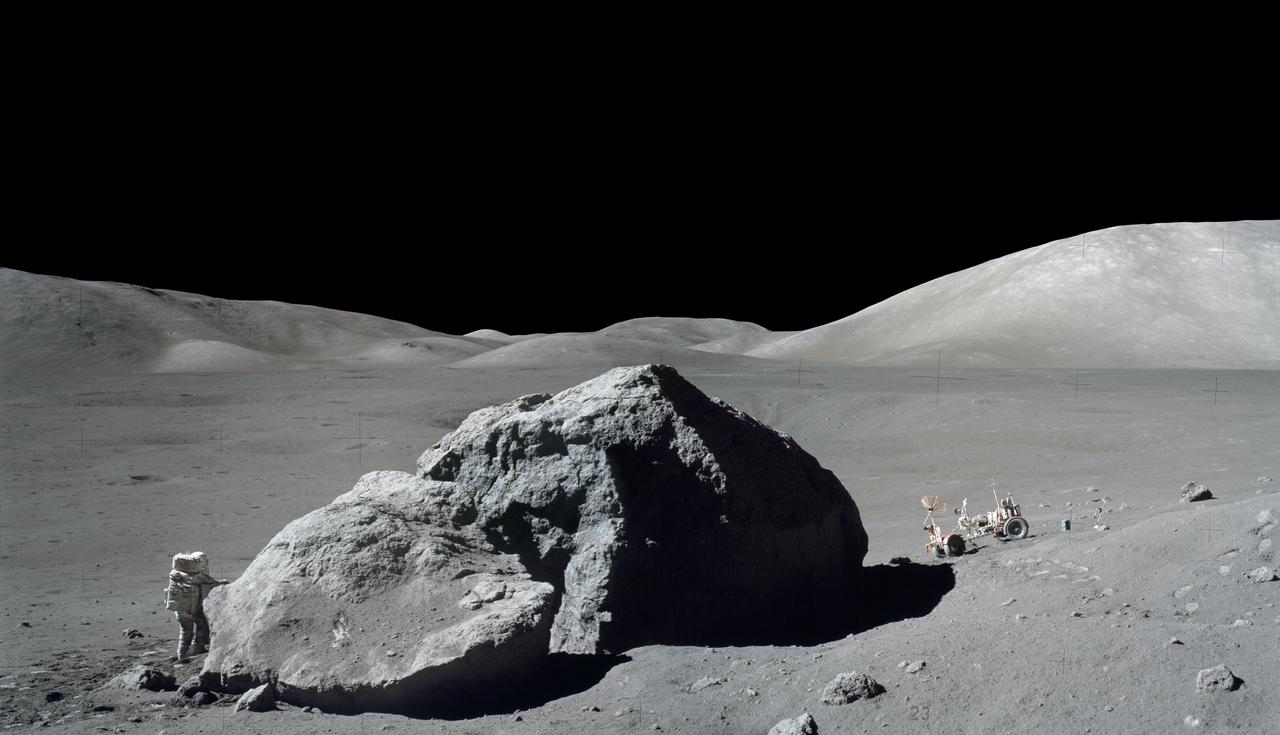

S73-22871 (13 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt is photographed standing next to a huge, split lunar boulder during the third Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), which transported Schmitt and Eugene A. Cernan to this extravehicular station from their Lunar Module (LM), is seen in the background. The mosaic is made from two frames from Apollo 17 Hasselblad magazine 140. The two frames were photographed by Cernan.
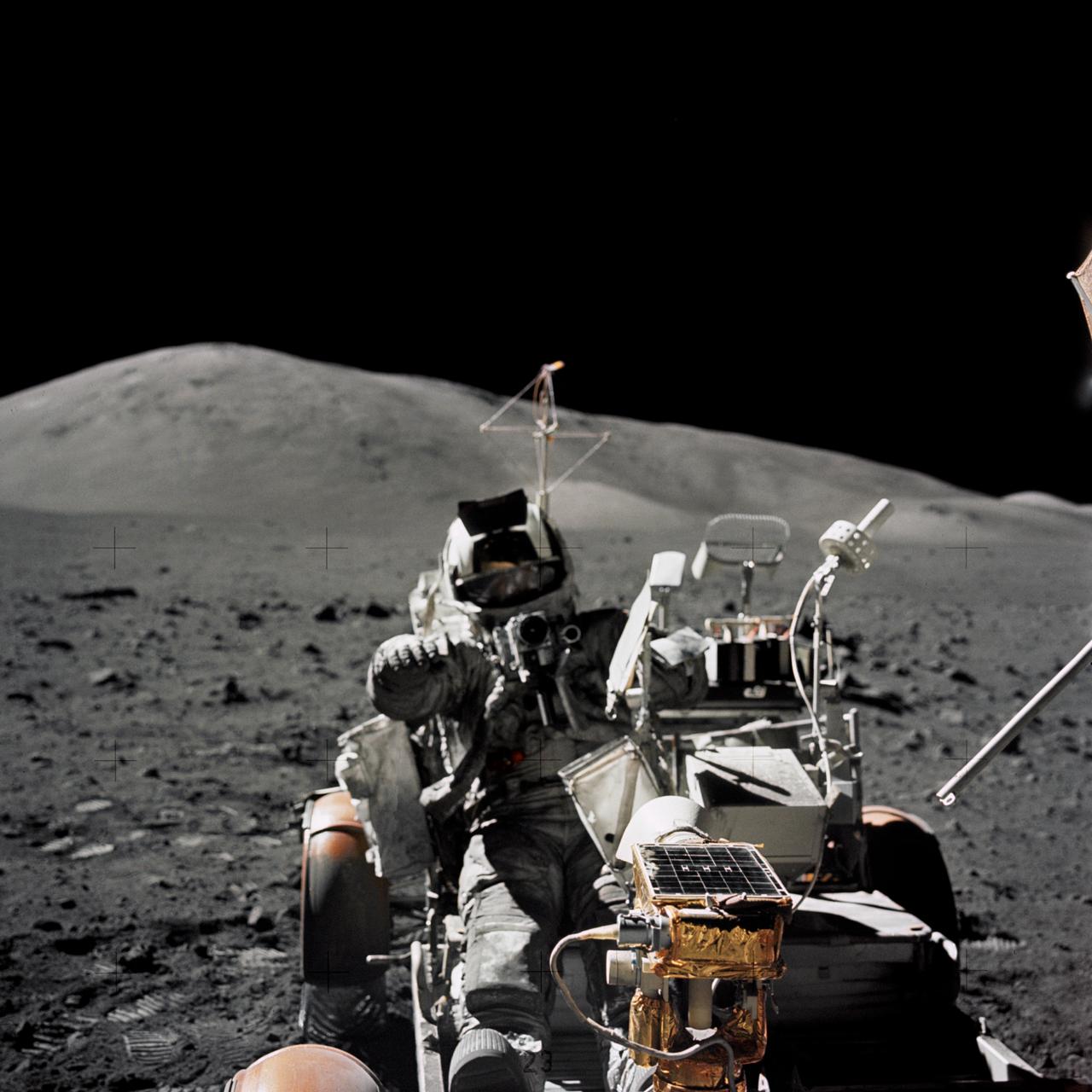

AS17-134-20454 (13 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt is photographed seated in the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) at Station 9 (Van Serg Crater) during the third Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. This photograph was taken by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, commander. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, and Cernan explored the moon while astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit.
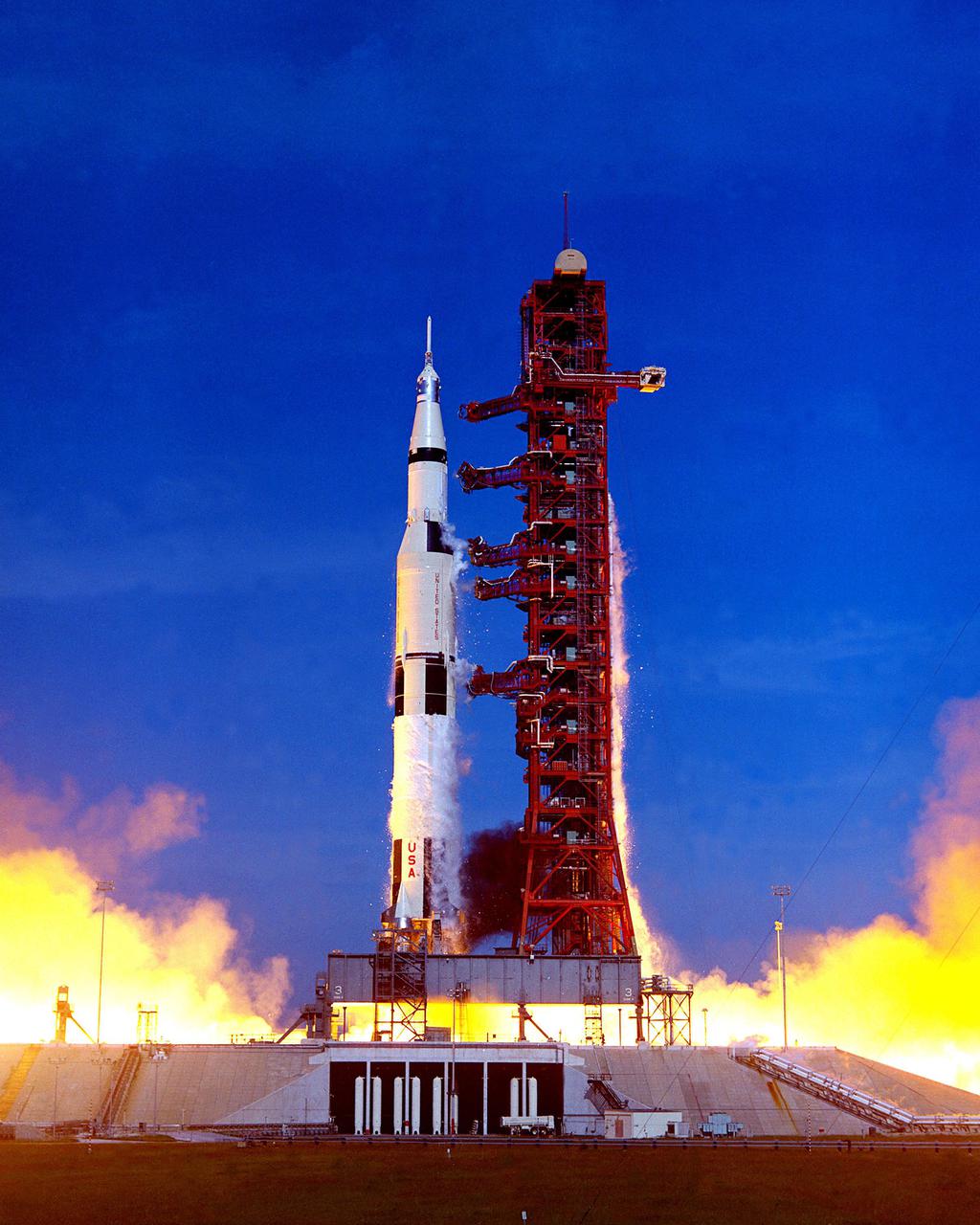

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Apollo 15 Saturn V Space Vehicle soars into the skies after liftoff at Launch Pad 39A marking the beginning of NASA's fourth Manned Lunar Landing Mission. The astronauts aboard are David R. Scott, commander; James B. Irwin, Lunar Module pilot; and Alfred M. Worden Jr., Command Module pilot. The landing site for the Lunar Module is the Hadley-Apennine area of the Moon, about 465 miles north of the Lunar Equator. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) will be used for the first time.
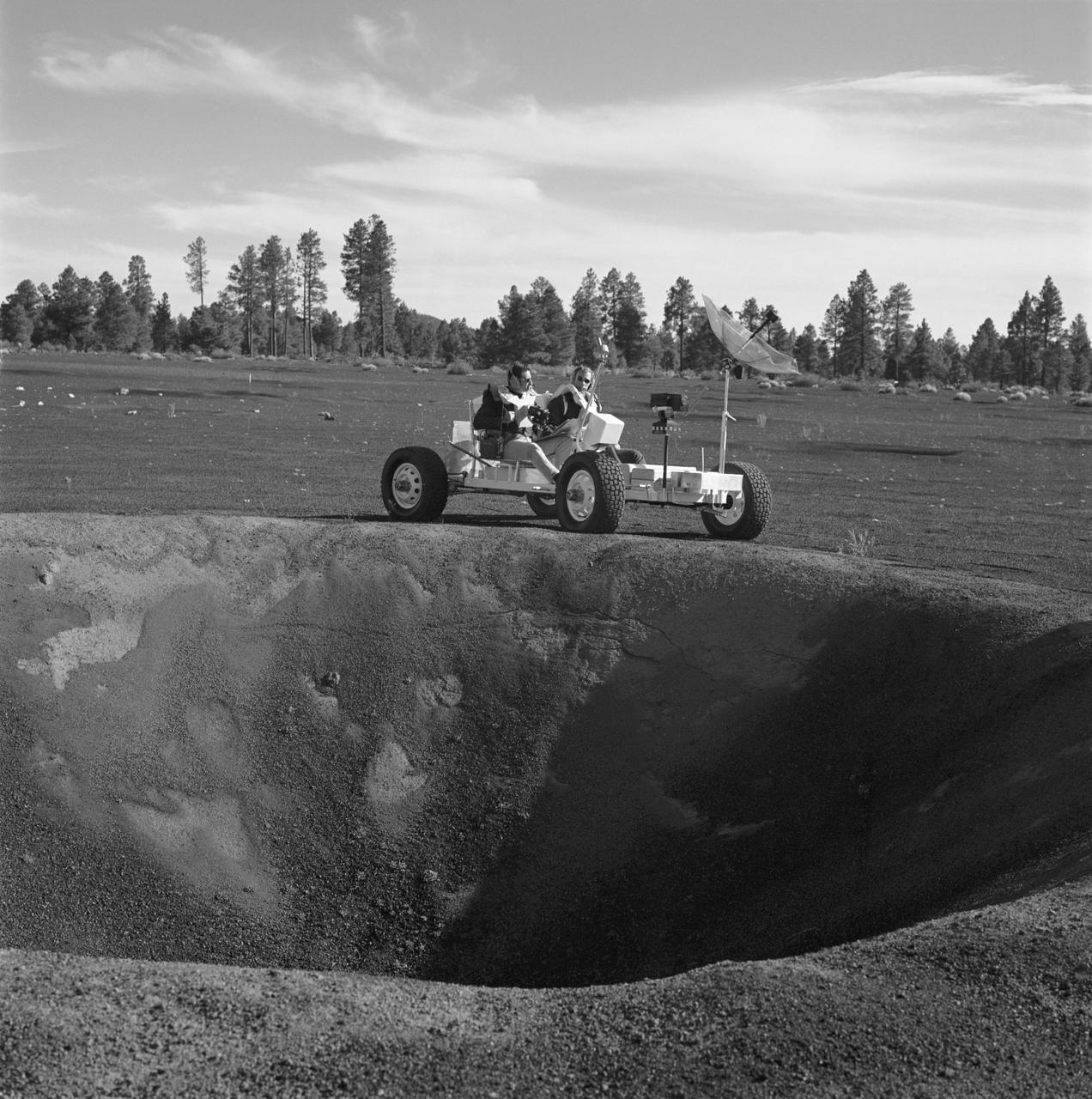

S70-53300 (2-3 Nov. 1970) --- Two Apollo 15 crew members, riding a Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) simulator, participate in geology training at the Cinder Lake crater field in Arizona. Astronaut David R. Scott, Apollo 15 commander, seated on the left; and to Scott's right is astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. They have stopped at the rim of a 30-feet deep crater to look over the terrain. The simulator, called "Grover", was built by the United States Geological Survey.
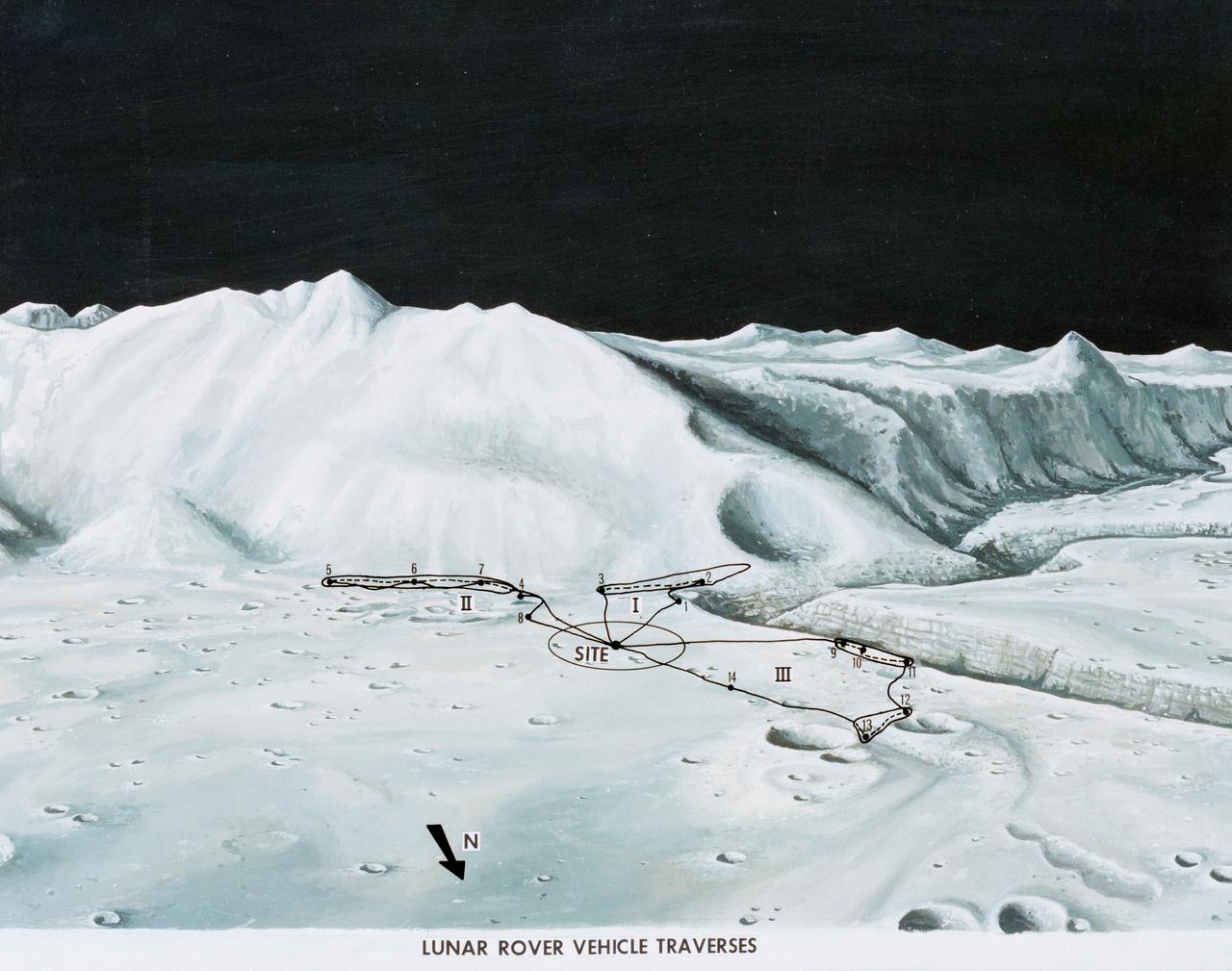

S71-33433 (1 July 1971) --- An artist's concept of the Hadley-Apennine landing site, depicting the traverses planned on the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission using the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The Roman numerals indicate the three periods of extravehicular activity (EVA). The Arabic numbers represent the station stops. This artist's concept was excerpted from "On the Moon with Apollo 15: A Guidebook to Hadley Rille and the Apennine Mountains," by Gene Simmons. The station stops indicated here are keyed to information given in the publication. Artwork by Jerry Elmore.
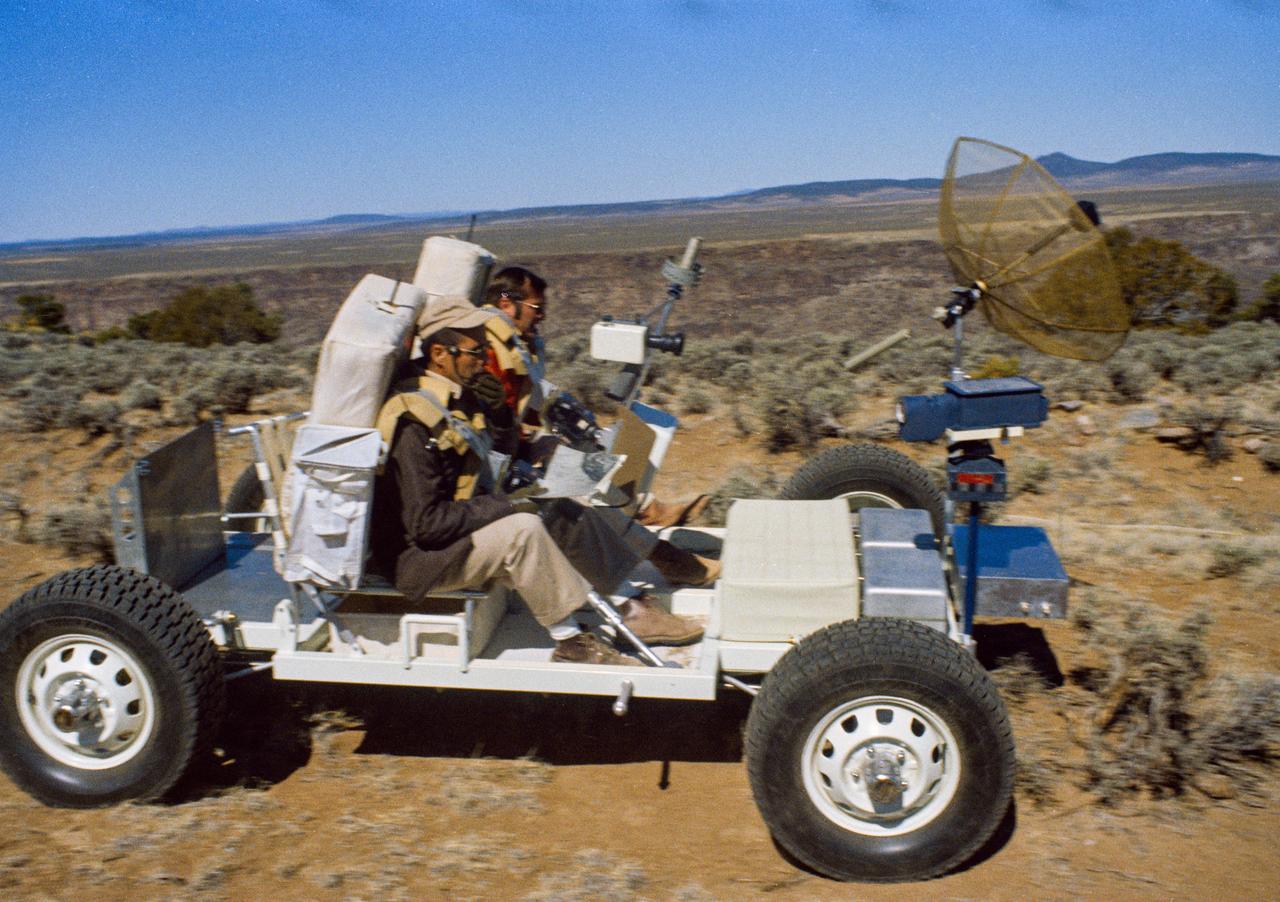

S71-24079 (1971) --- Astronauts Richard F. Gordon Jr., right, and Harrison H. Schmitt ? back-up crew members for the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission -- traverse in an Earth-bound training version of the Apollo Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV or Rover) during geology training in Hawaii. Photo credit: NASA Note: There are elements of this description that have not been confimred. Please hold any release of descriptive information until such can be confirmed.
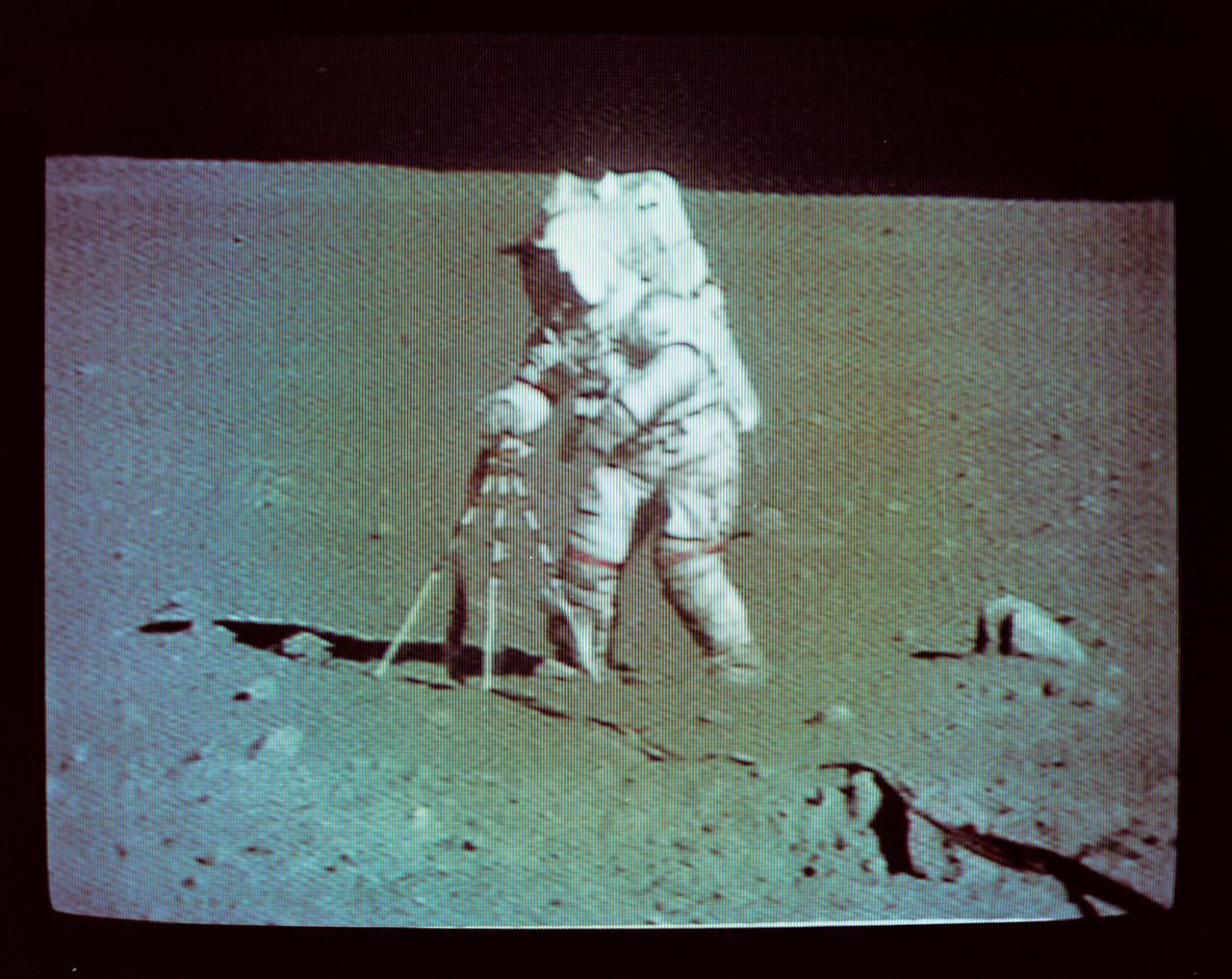

S72-35610 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, deploys the lunar Portable Magnetometer during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color television camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). While astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit, astronauts Young and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the Descartes landing site.
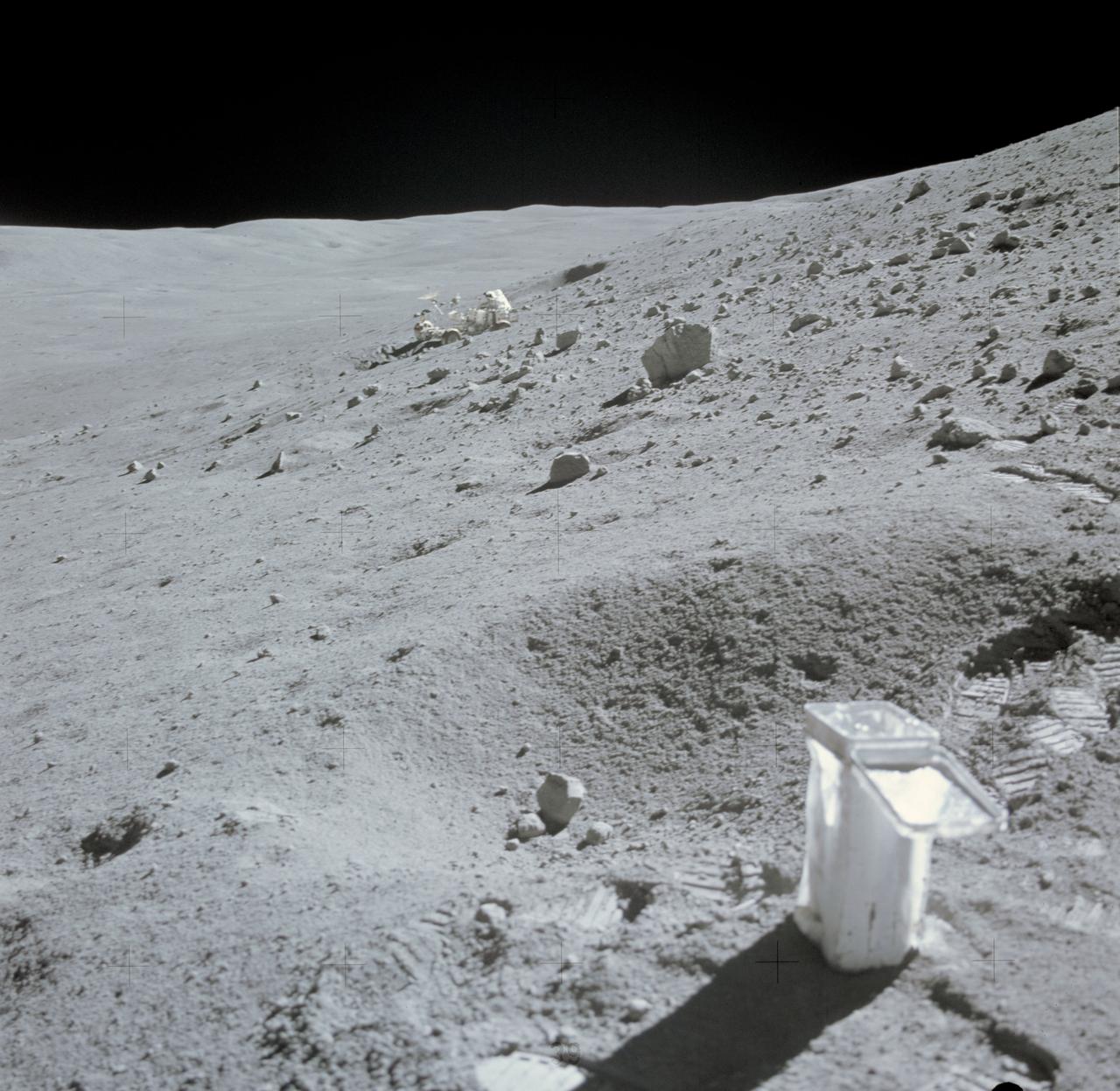

AS16-107-17473 (22 April 1972) --- The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) appears to be parked in a deep lunar depression, on the slope of Stone Mountain. This photograph of the lunar scene at Station No. 4 was taken during the second Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. A sample collection bag is in the right foreground. Note field of small boulders at upper right. While astronauts John W. Young, commander, and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.