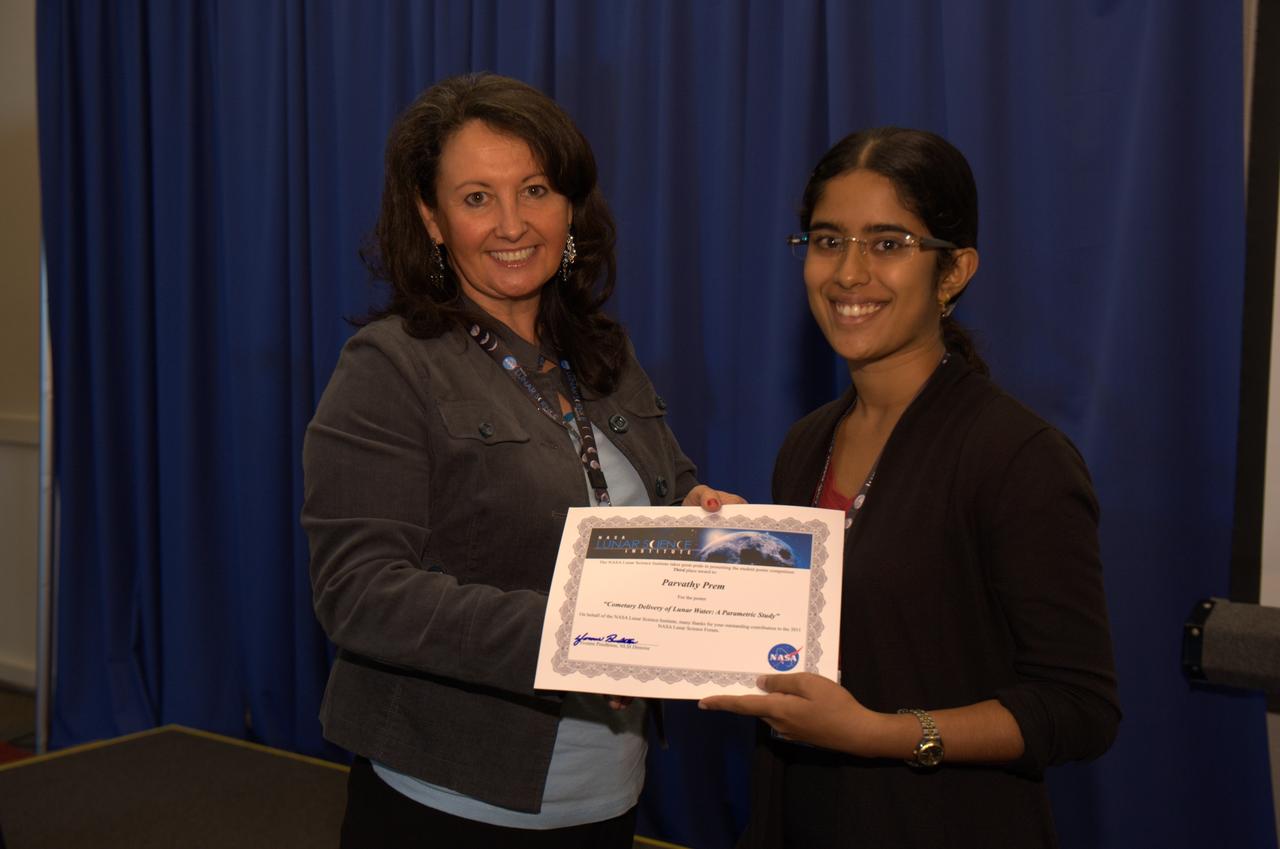

Lunar Science Forum Student Poster competition Third Place award to Parvathy Prem for the poster 'Cometary Delivery of Lunar Water: A Parametric Study'
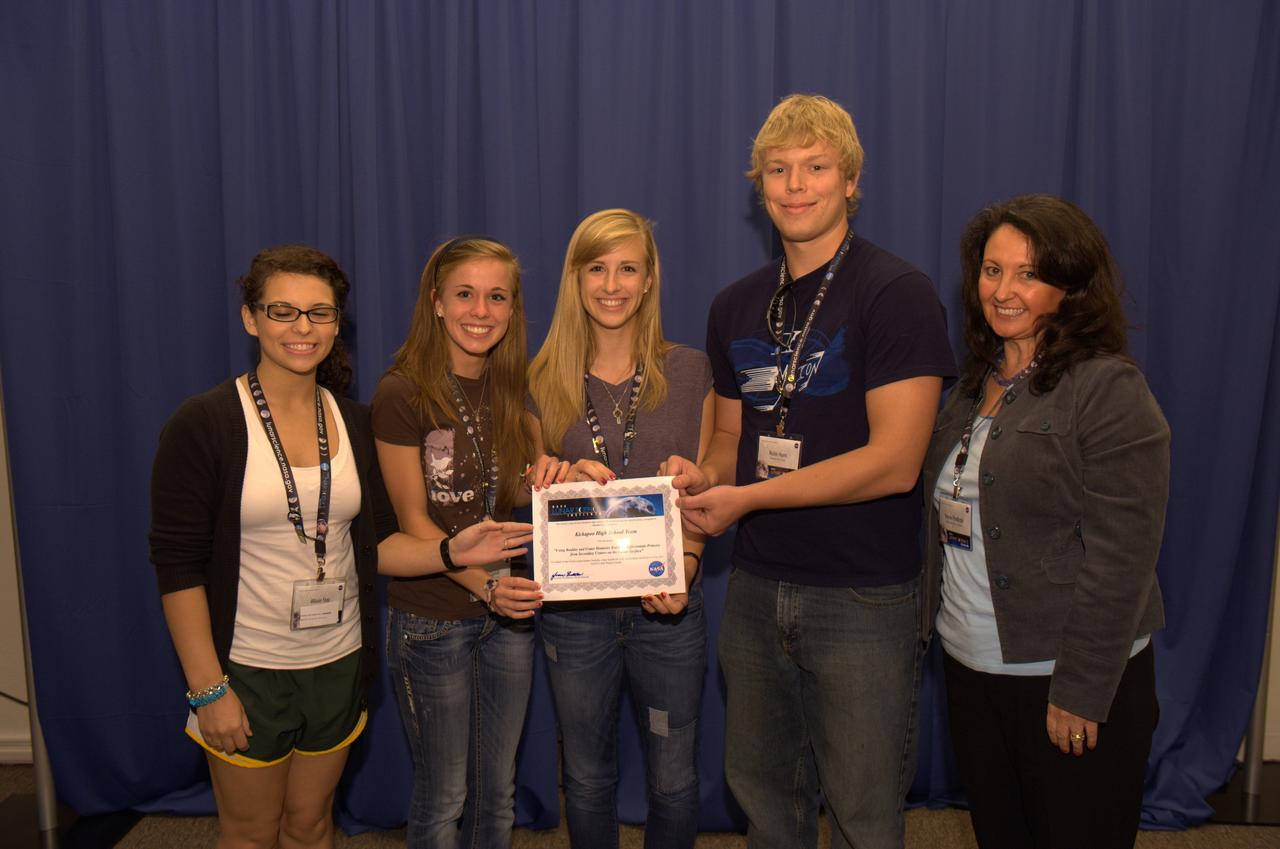

Lunar Science Forum Student Poster competition Second place award to Kickapoo High school Team for the poster 'using Boulder and Crater Diameter Ratios to Differentiate Primary from Secondary Craters and the Lunar Surface'

Lunar Science Forum 2011 Shoemaker Award reciepiants Gene Shoemaker on left and G. Jeffrey Taylor on right
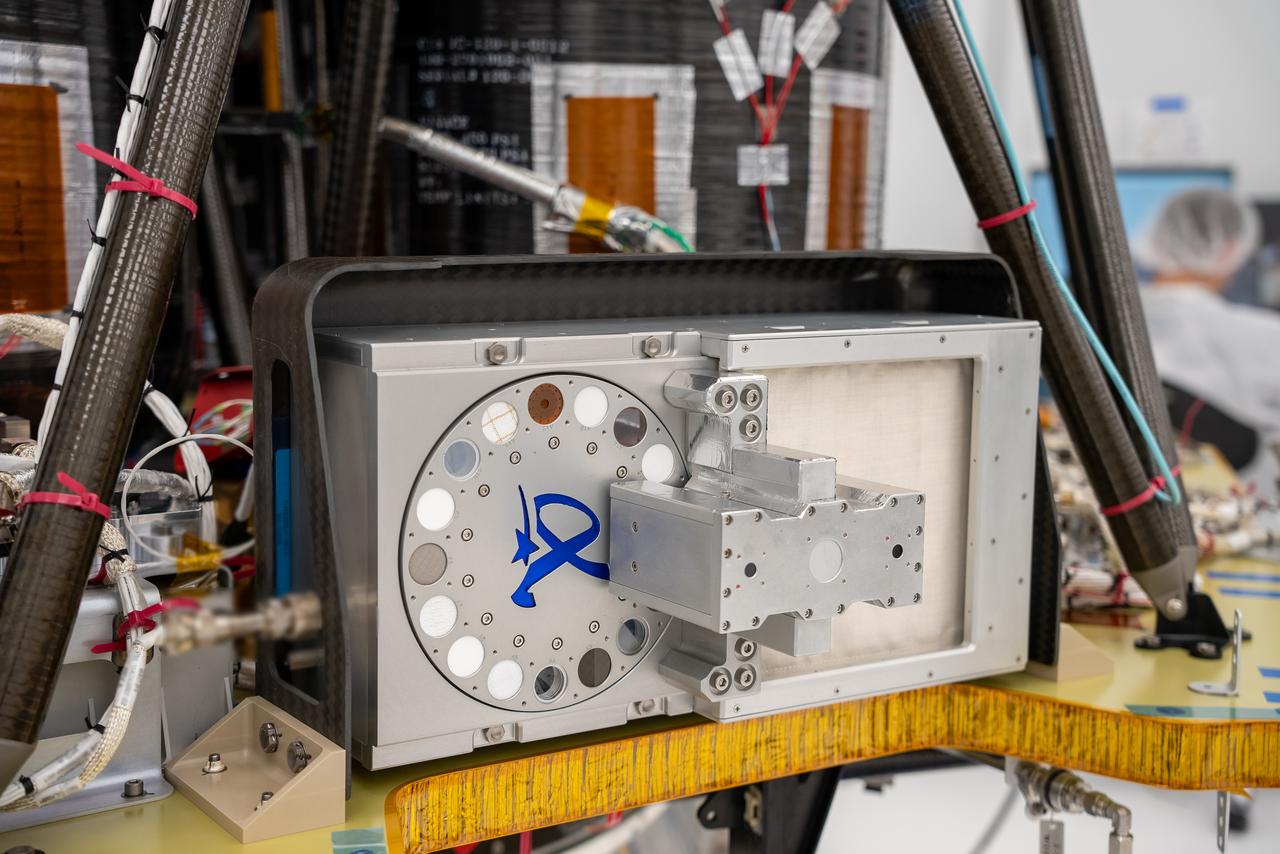
A science instrument flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative is planning to study how different materials react to the lunar environment. Regolith Adherence Characterization, or RAC, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Aegis Aerospace, RAC’s wheels feature a series of different sample materials, helping researchers to better understand how lunar dust repels or attaches to each. Investigations and demonstrations, such as RAC, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
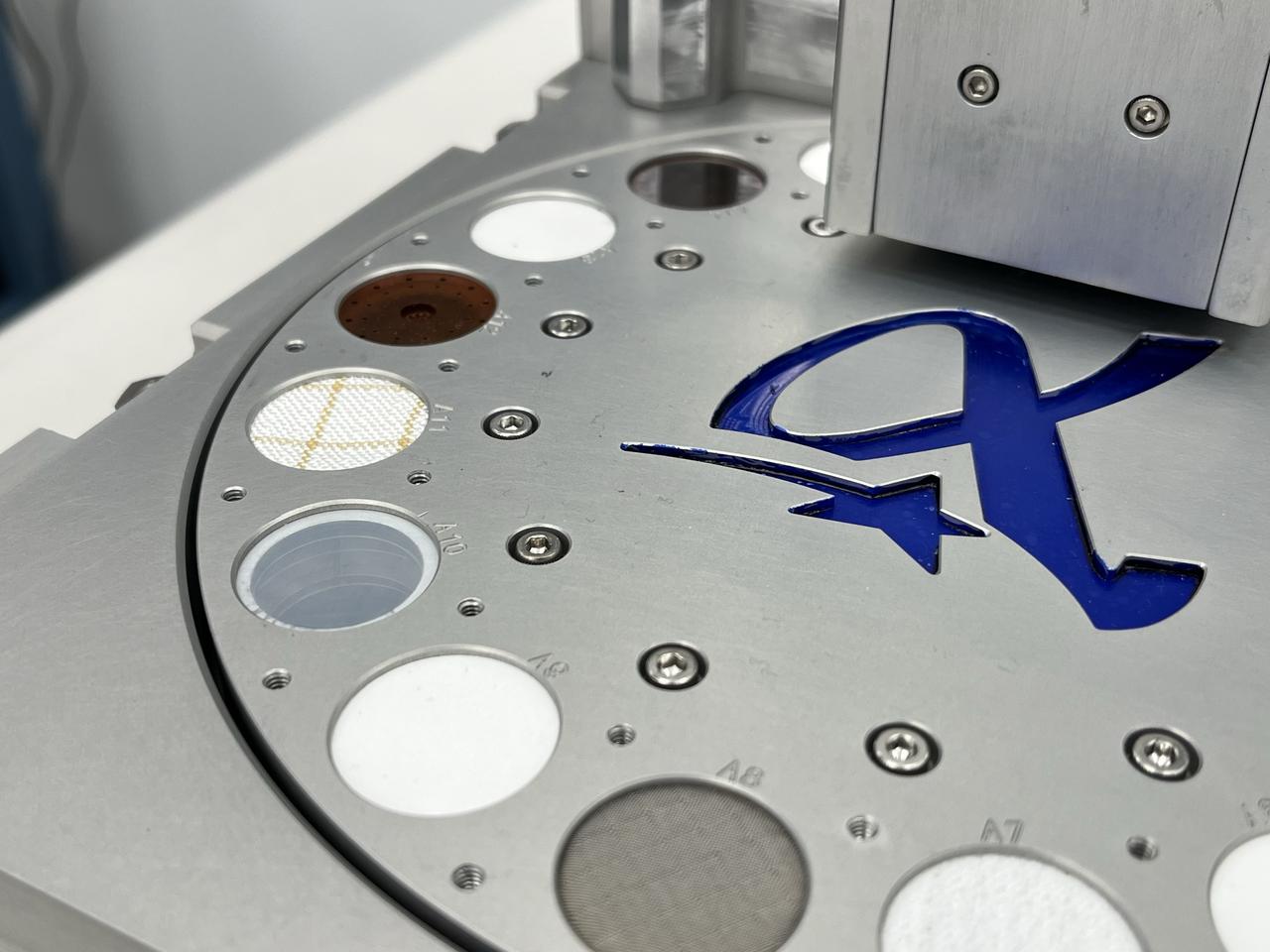
A science instrument flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative is planning to study how different materials react to the lunar environment. Regolith Adherence Characterization, or RAC, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Aegis Aerospace, RAC’s wheels feature a series of different sample materials, helping researchers to better understand how lunar dust repels or attaches to each. Investigations and demonstrations, such as RAC, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
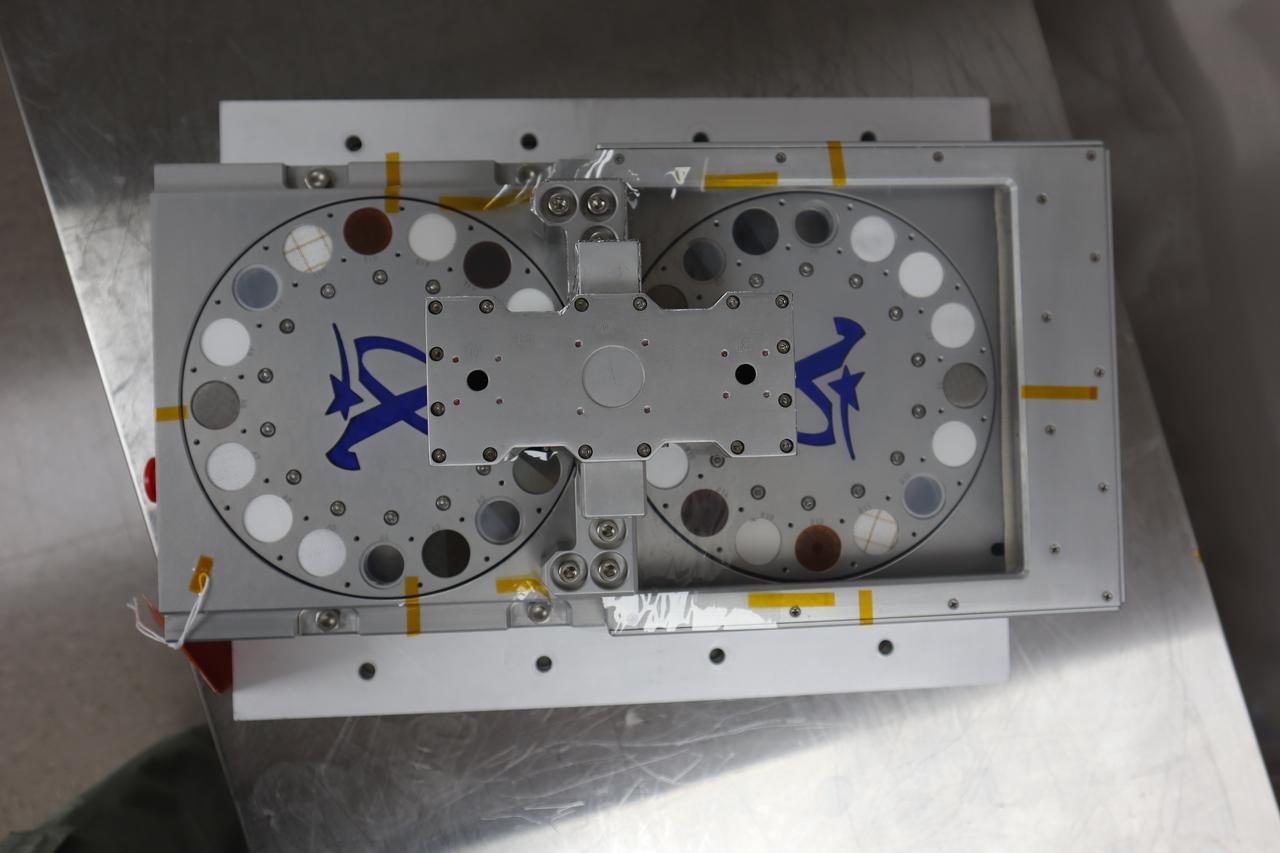
A science instrument flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative is planning to study how different materials react to the lunar environment. Regolith Adherence Characterization, or RAC, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Aegis Aerospace, RAC’s wheels feature a series of different sample materials, helping researchers to better understand how lunar dust repels or attaches to each. Investigations and demonstrations, such as RAC, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
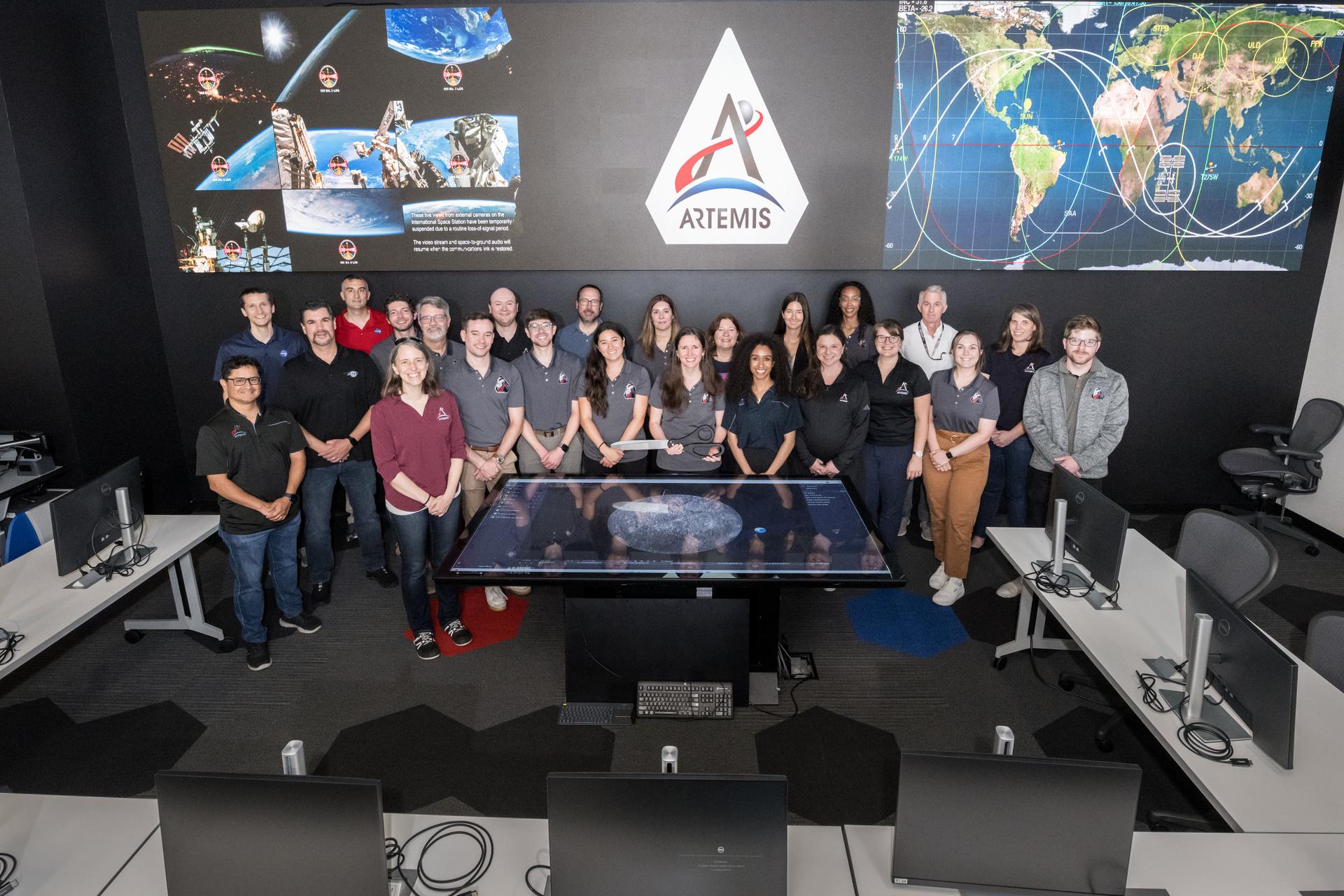

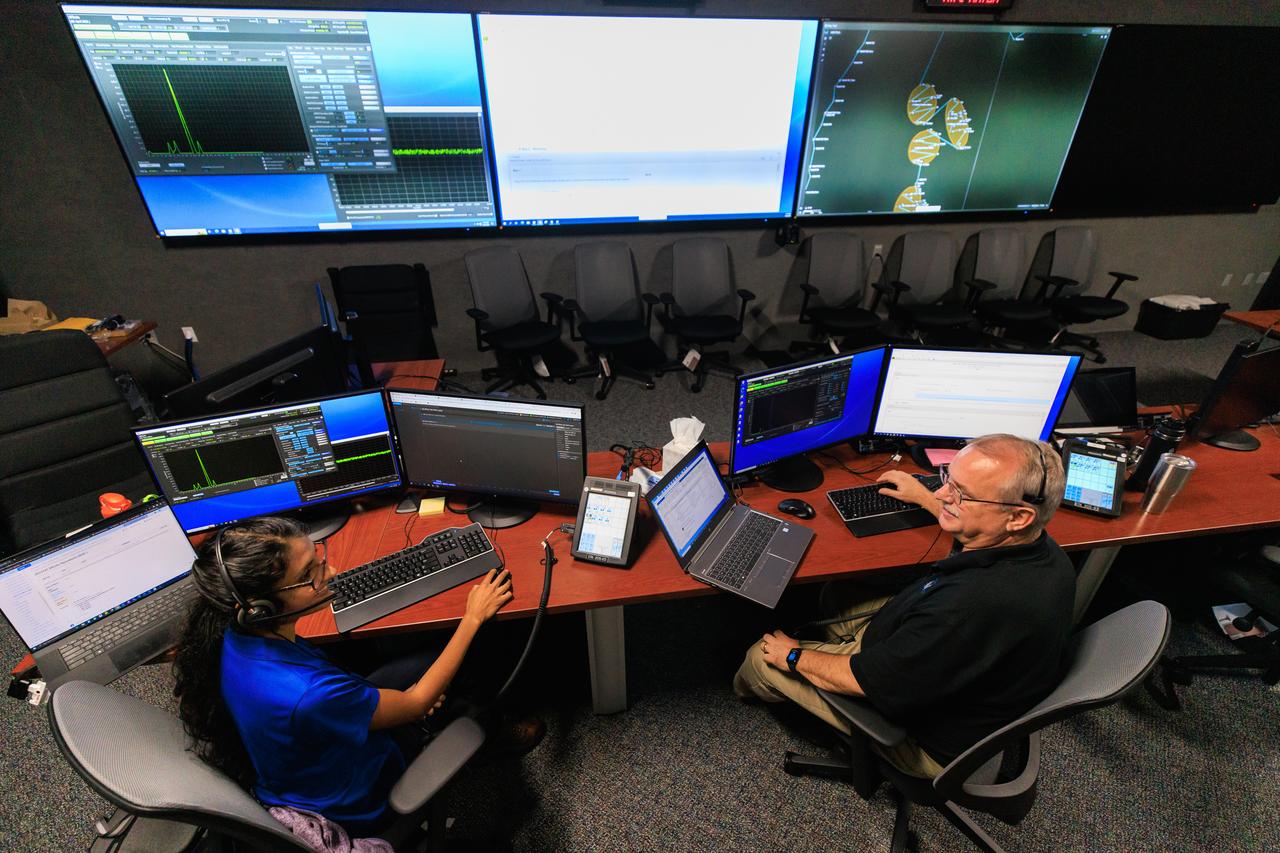
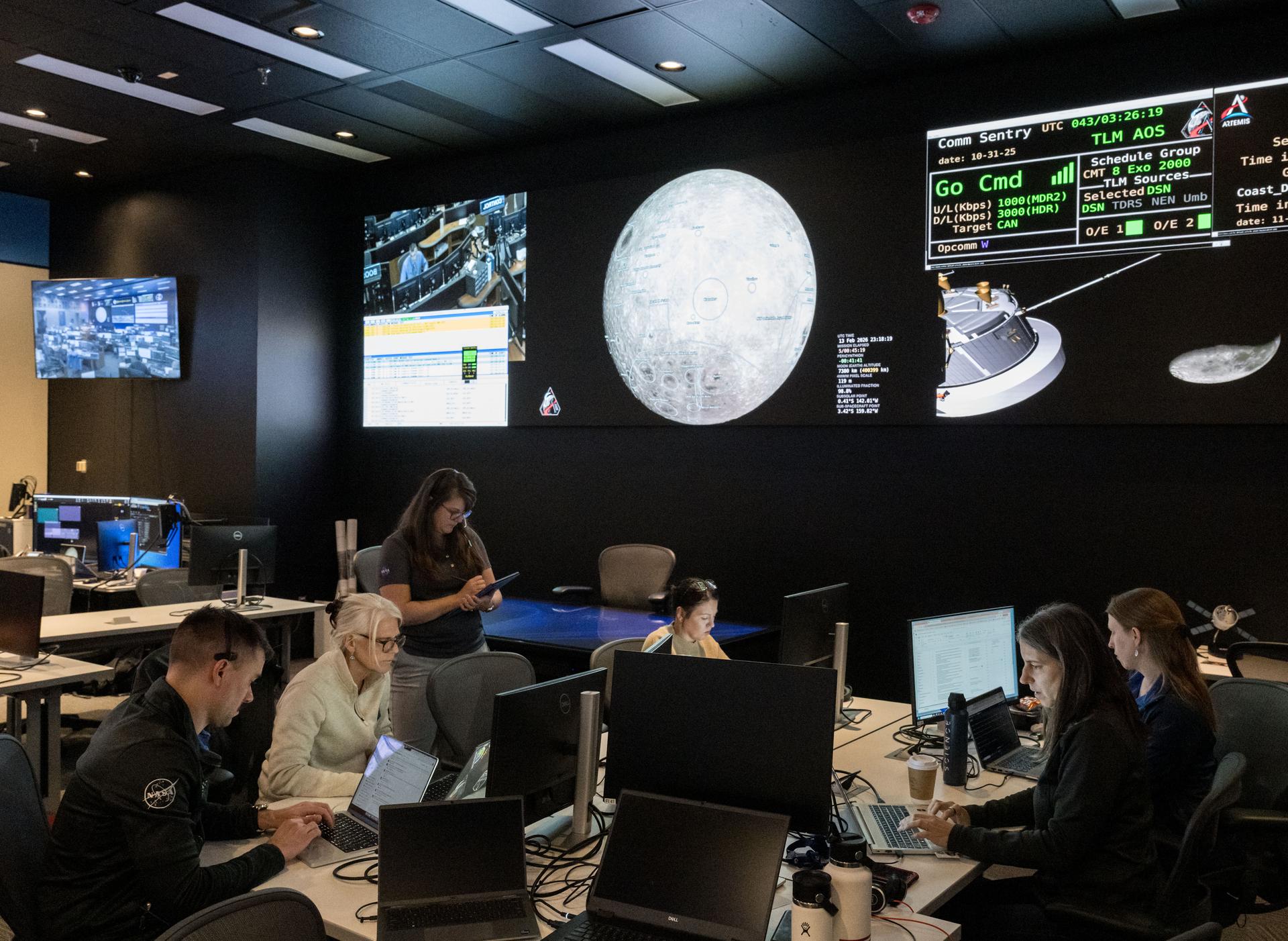
jsc2025e057254 --- NASA’s Artemis II lunar science team is pictured in the Science Evaluation Room (SER) at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Located in the Christopher C. Kraft Jr. Mission Control Center, the SER supports the mission’s main flight control room for lunar science and planetary observations. Built specifically for Artemis missions with these science priorities in mind, the SER is equipped to support rapid data interpretation, collaborative analysis, real-time decision making, and seamless coordination between the science and operations teams.

jsc2026e000848 --- Artemis lunar science team members, from left, Jacob Richardson, Marie Henderson, and Kiarre Dumes, monitor a lunar flyby simulation from the Science Evaluation Room (SER) at the NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Located in the Christopher C. Kraft Jr. Mission Control Center, the SER supports the mission’s main flight control room for lunar science and planetary observations. Built specifically for Artemis missions with these science priorities in mind, the SER is equipped to support rapid data interpretation, collaborative analysis, real-time decision making, and seamless coordination between the science and operations teams. Credit: James Blair
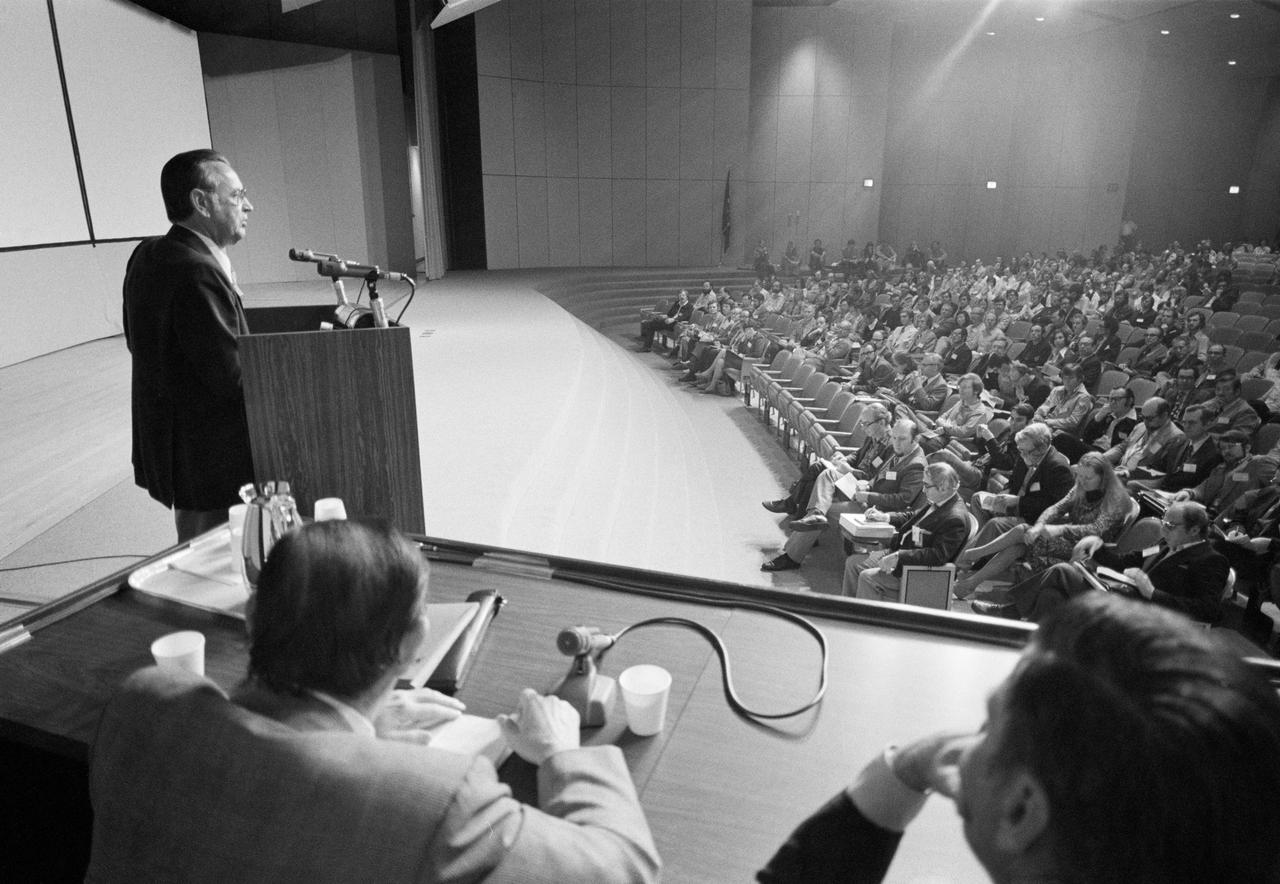

S77-22482 (14 March 1977) --- Johnson Space Center Director Christopher C. Kraft Jr. addresses a crowd of scientists and news media representatives at the opening of the Eighth Annual Lunar Science Conference in the Teague Auditorium. Photo credit: NASA
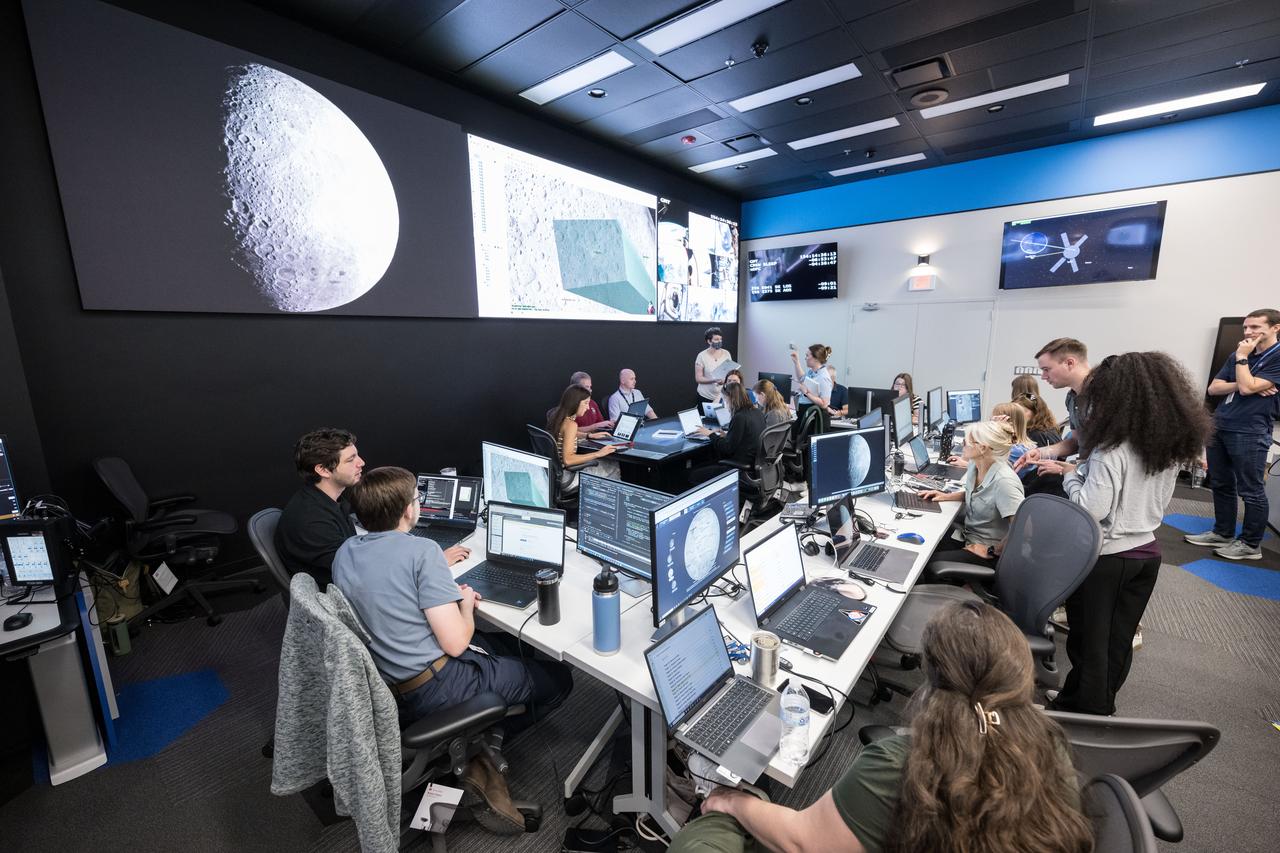

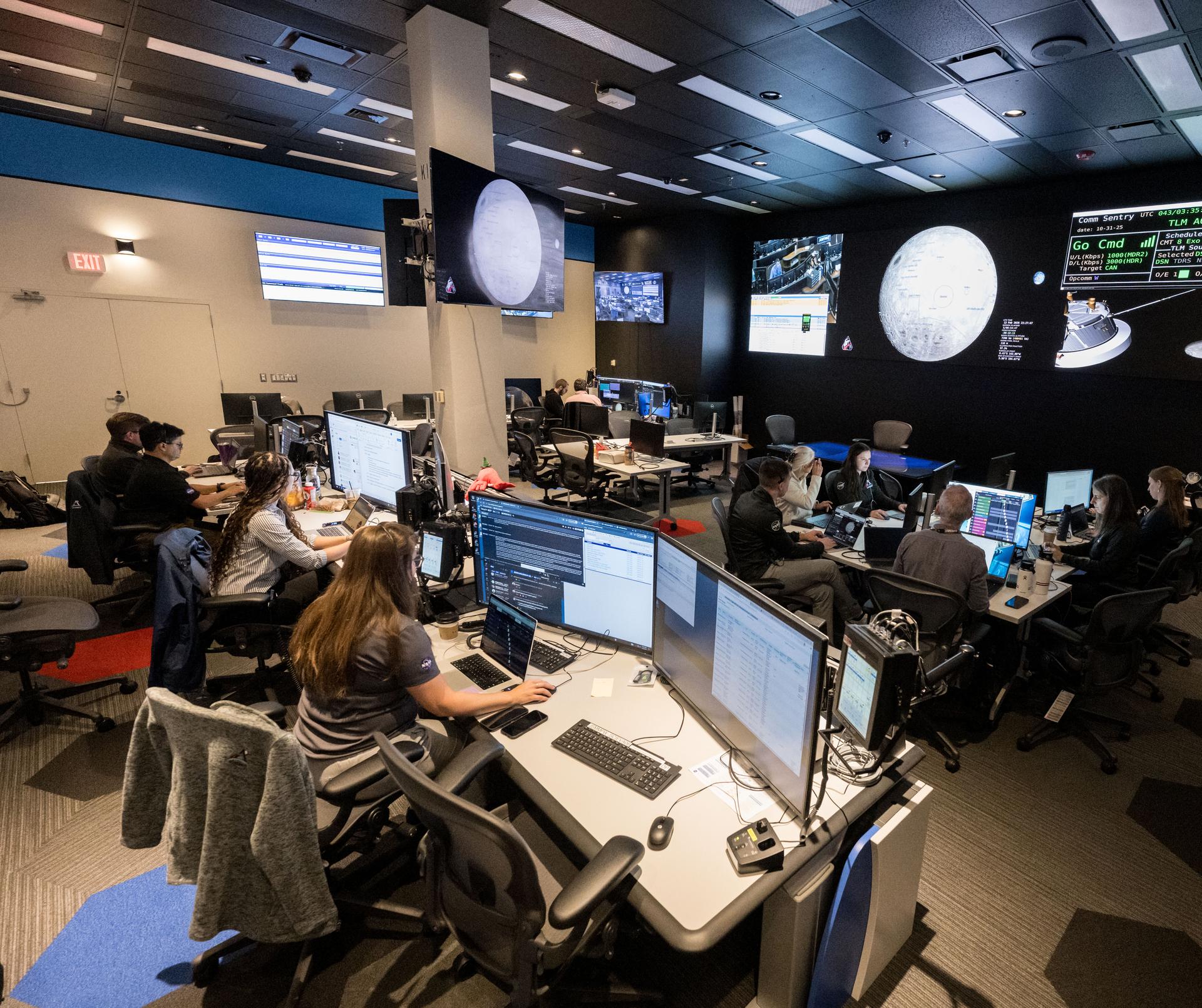
jsc2025e056603 --- The Artemis II Lunar Science Team runs a simulation of lunar observation operations in the new Science Evaluation Room (SER) that serves as a backroom to Mission Control.
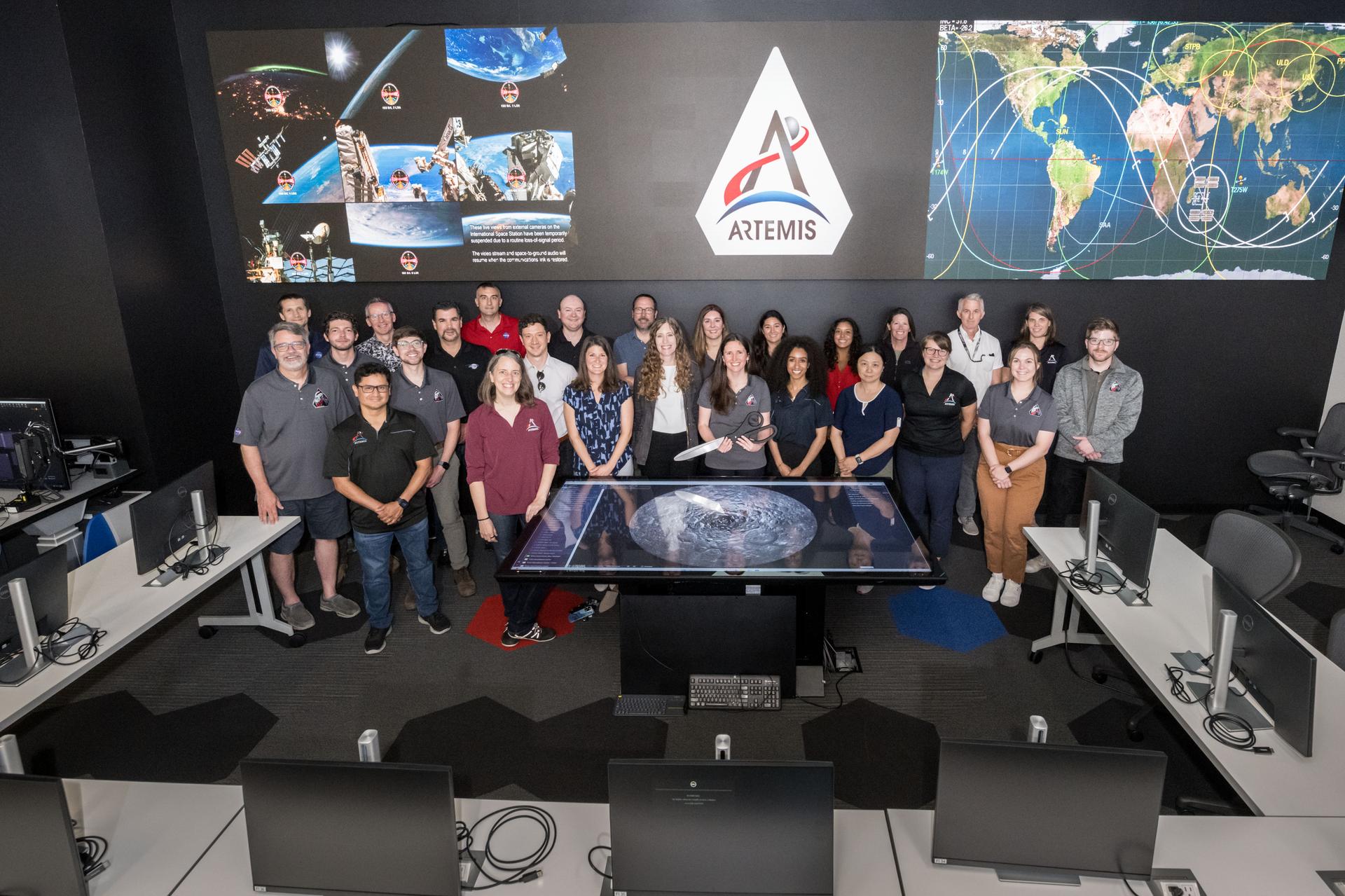

jsc2025e057255 --- NASA’s Artemis III lunar science team is pictured in the Science Evaluation Room (SER) at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Located in the Christopher C. Kraft Jr. Mission Control Center, the SER supports the mission’s main flight control room for lunar science and planetary observations. Built specifically for Artemis missions with these science priorities in mind, the SER is equipped to support rapid data interpretation, collaborative analysis, real-time decision making, and seamless coordination between the science and operations teams.
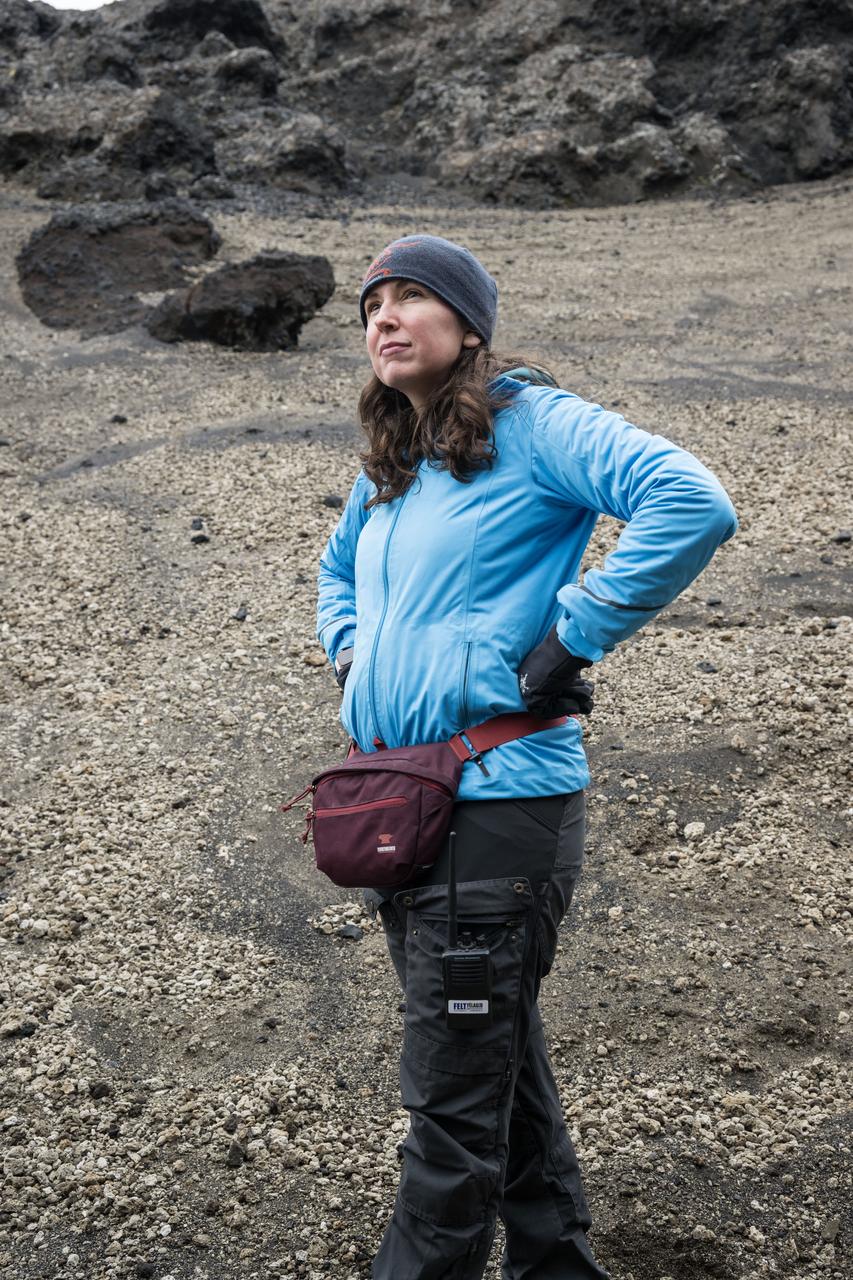

Lunar science lead for Artemis II and Artemis II science officer at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Kelsey Young, stands in the lunar-like landscape of Iceland during an Artemis II crew geology field training.
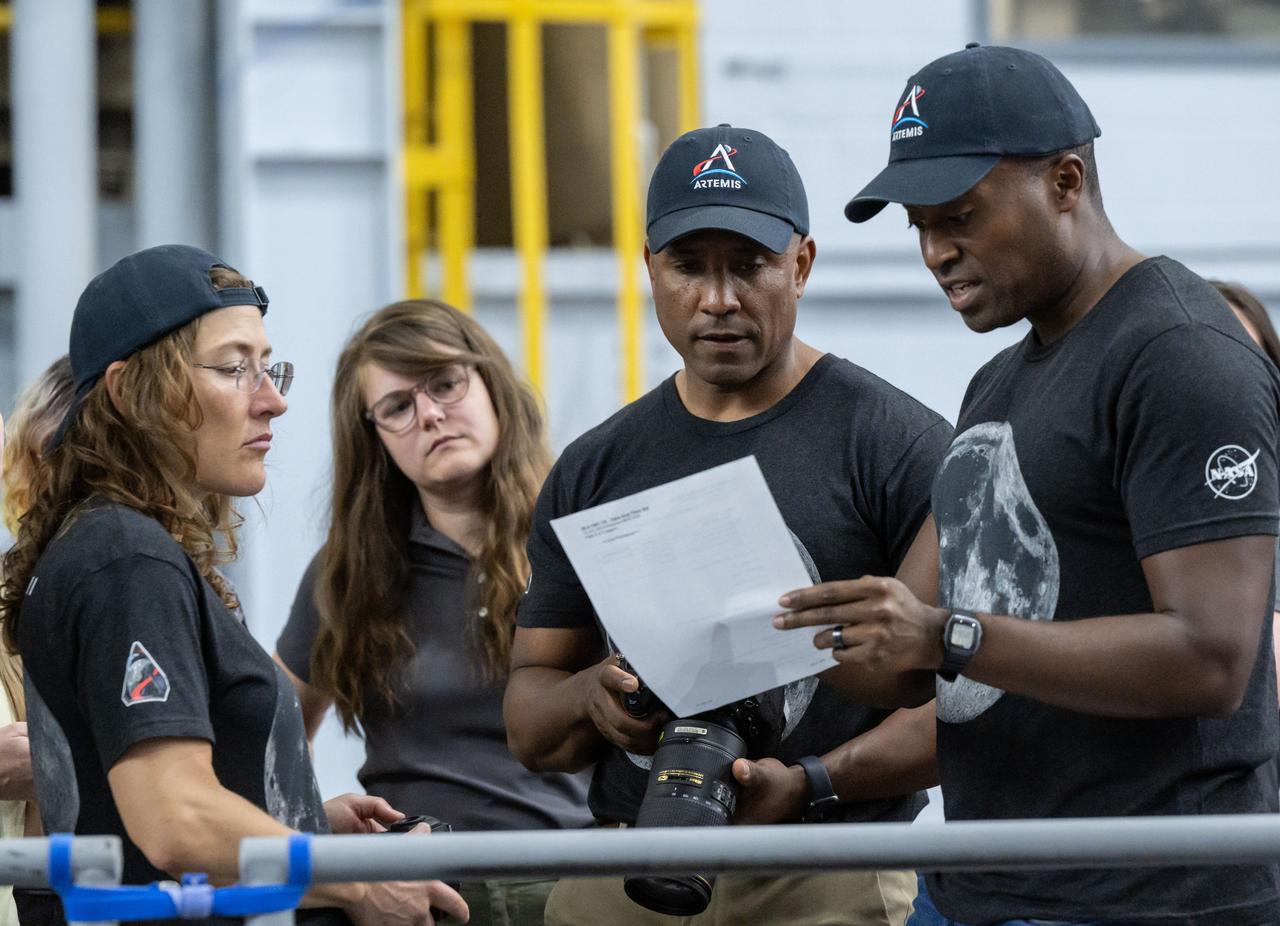

jsc2025e064747 --- Artemis II mission specialist Christina Koch, left, Artemis II lunar science team member Marie Henderson, Artemis II pilot Victor Glover, and Artemis II backup crew member Andre Douglas practice camera setup during crew lunar observations training at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston.
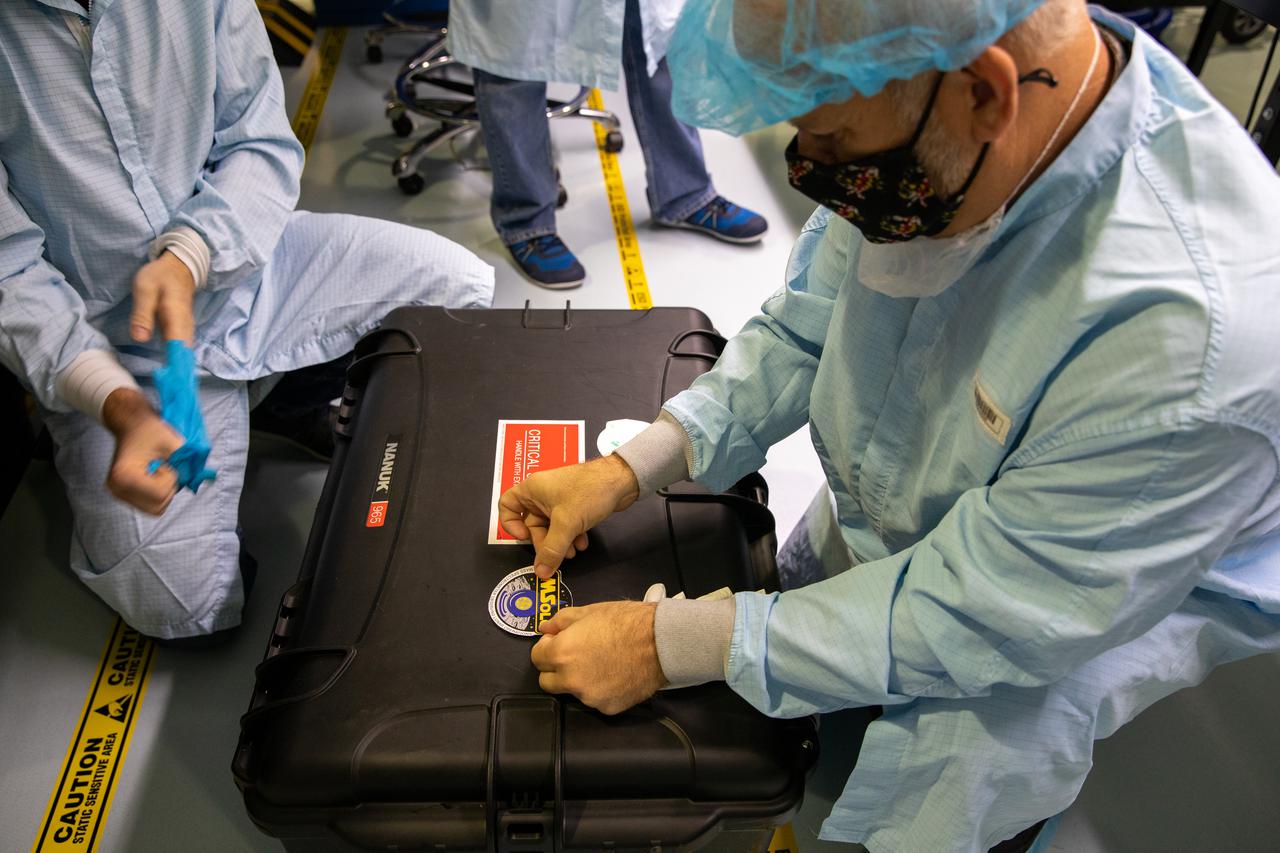

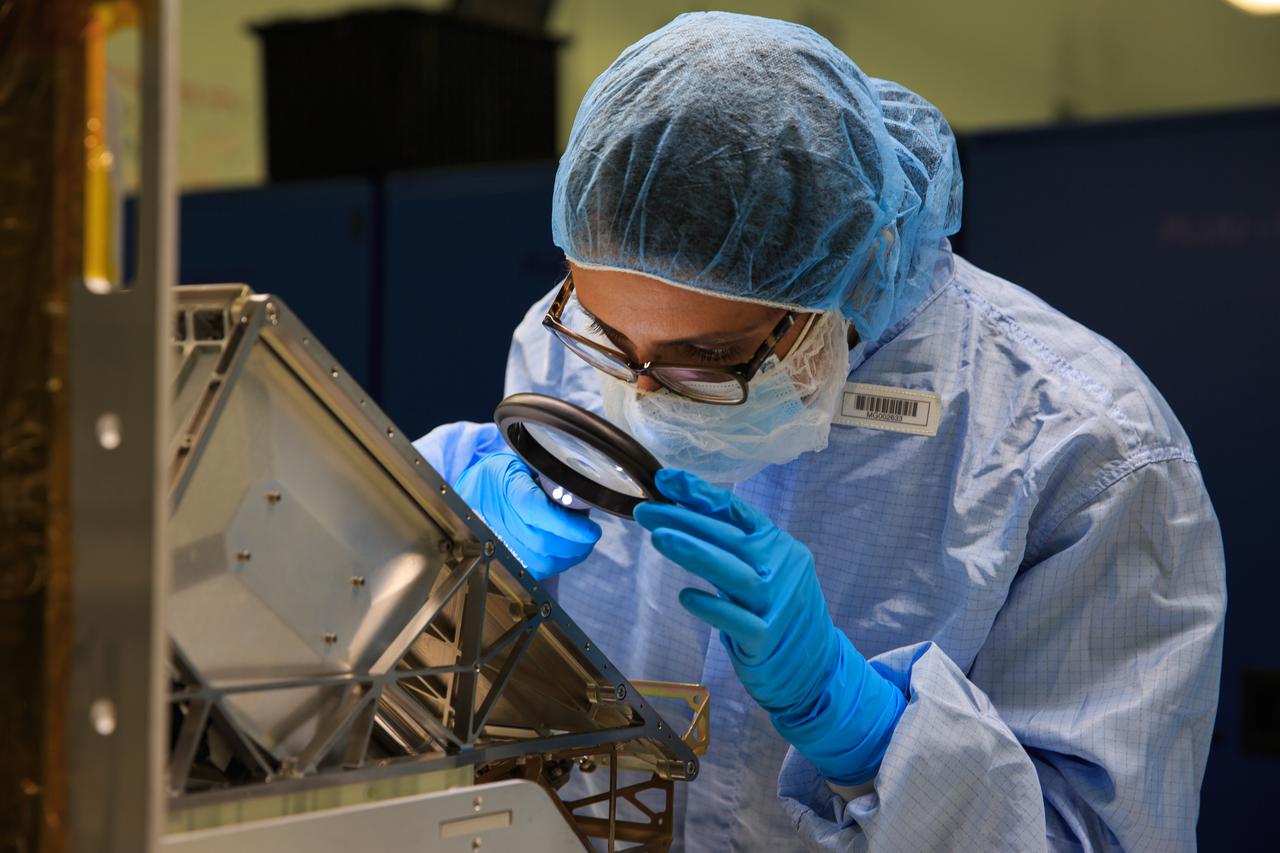
Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) team prepare MSolo flight hardware for shipment in preparation for launch in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2022 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
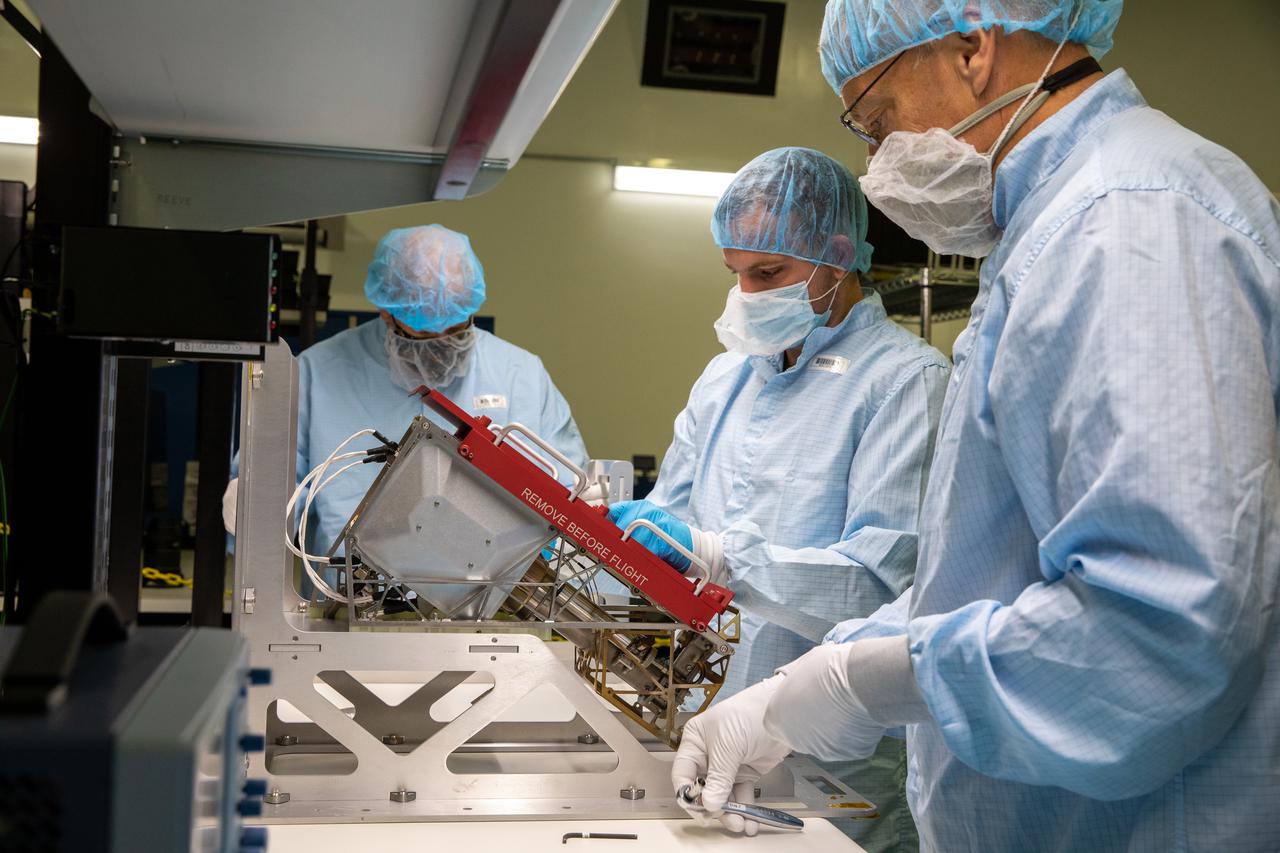

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) team prepare MSolo flight hardware for shipment in preparation for launch in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2022 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) team prepare MSolo flight hardware for shipment in preparation for launch in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2022 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
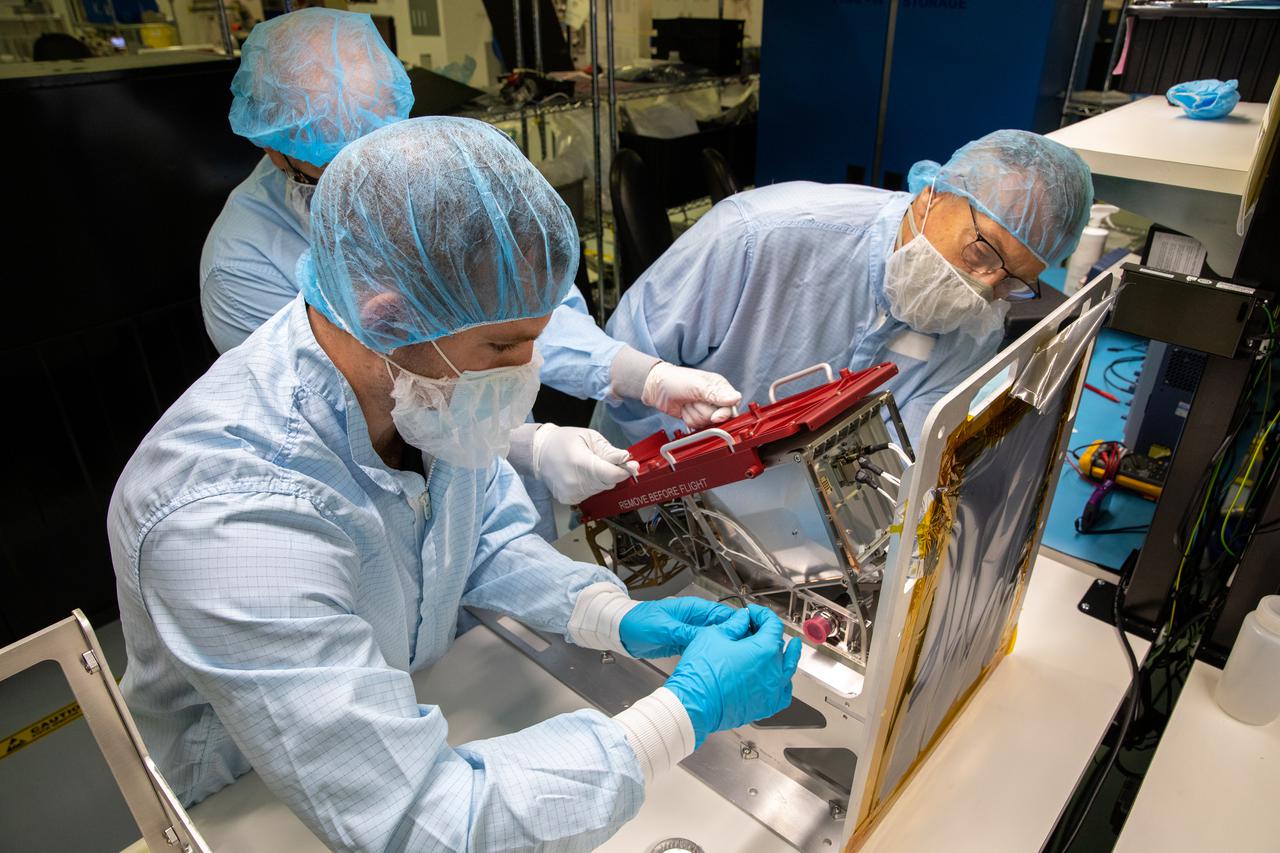

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) team prepare MSolo flight hardware for shipment in preparation for launch in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2022 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.

Preparations are underway to conduct a vibration test on the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) for NASA’s VIPER mission inside a laboratory in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 8, 2022. Exposing the instrument to vibration environments that it might see during launch helps engineers to find issues prior to liftoff. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo will be part of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) mission where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
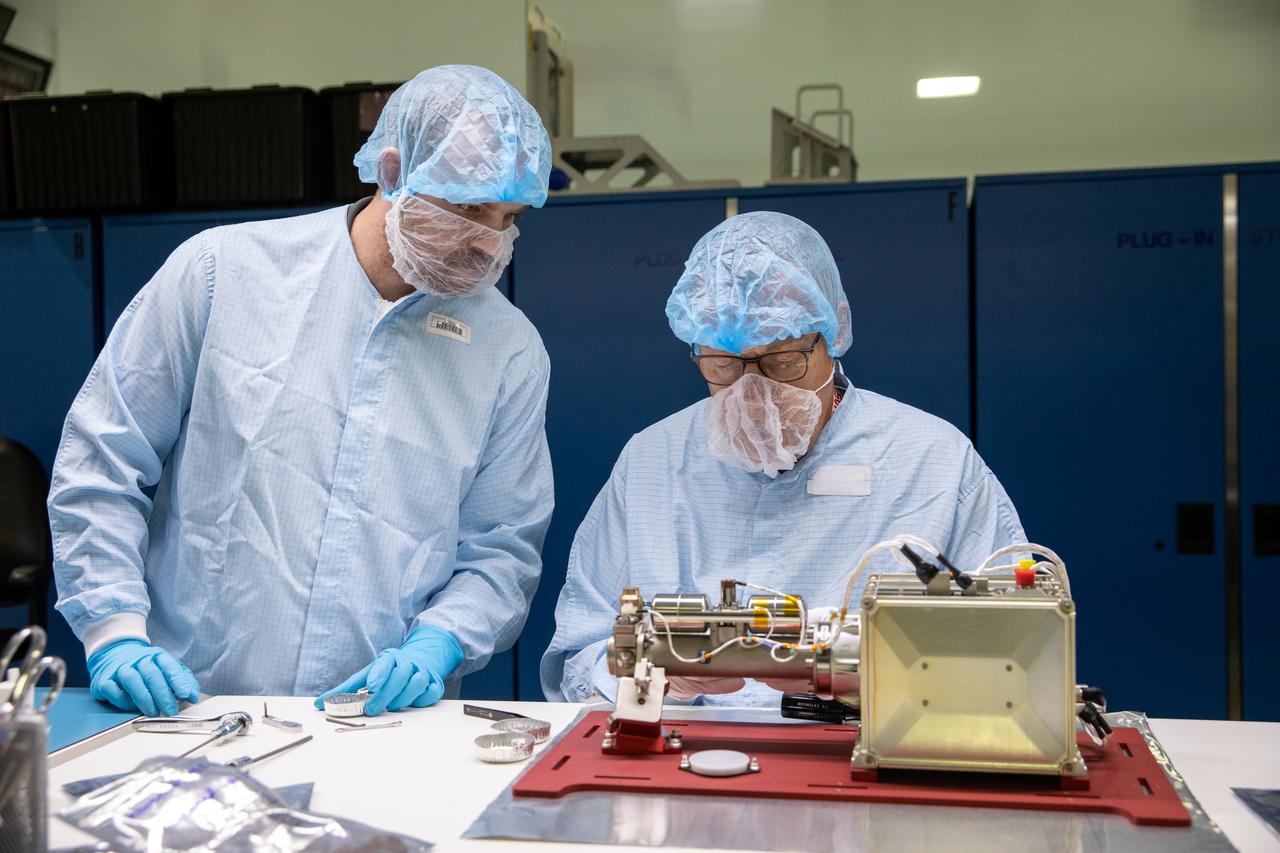

Technicians prepare the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) for NASA’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission for packing inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 21, 2023. MSolo will be shipped to Johnson Space Center in Houston for integration into VIPER. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo will be part of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) mission where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions. VIPER is scheduled to be delivered to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2024 by Astrobotic’s Griffin lander as part of the CLPS initiative.
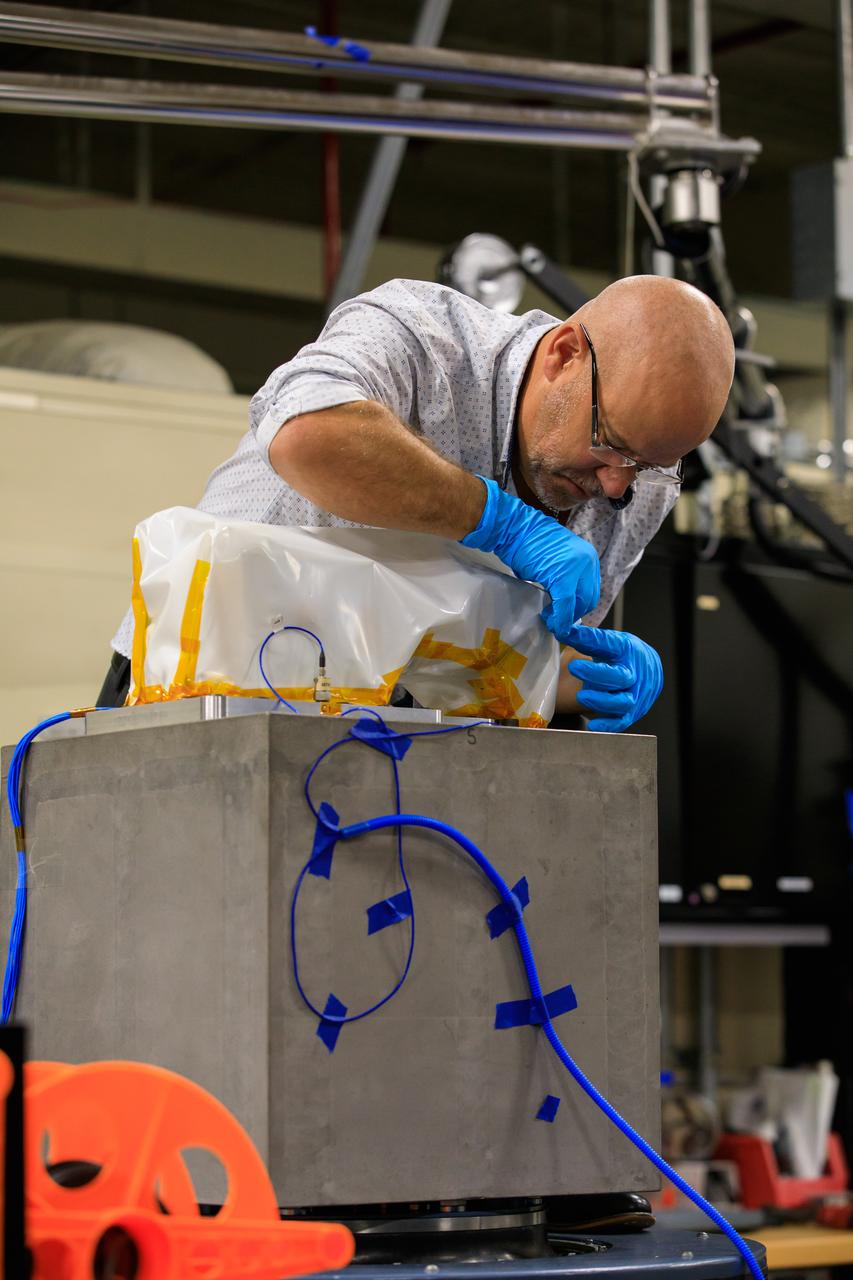

Preparations are underway to conduct a vibration test on the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) for NASA’s VIPER mission inside a laboratory in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 8, 2022. Exposing the instrument to vibration environments that it might see during launch helps engineers to find issues prior to liftoff. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo will be part of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) mission where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
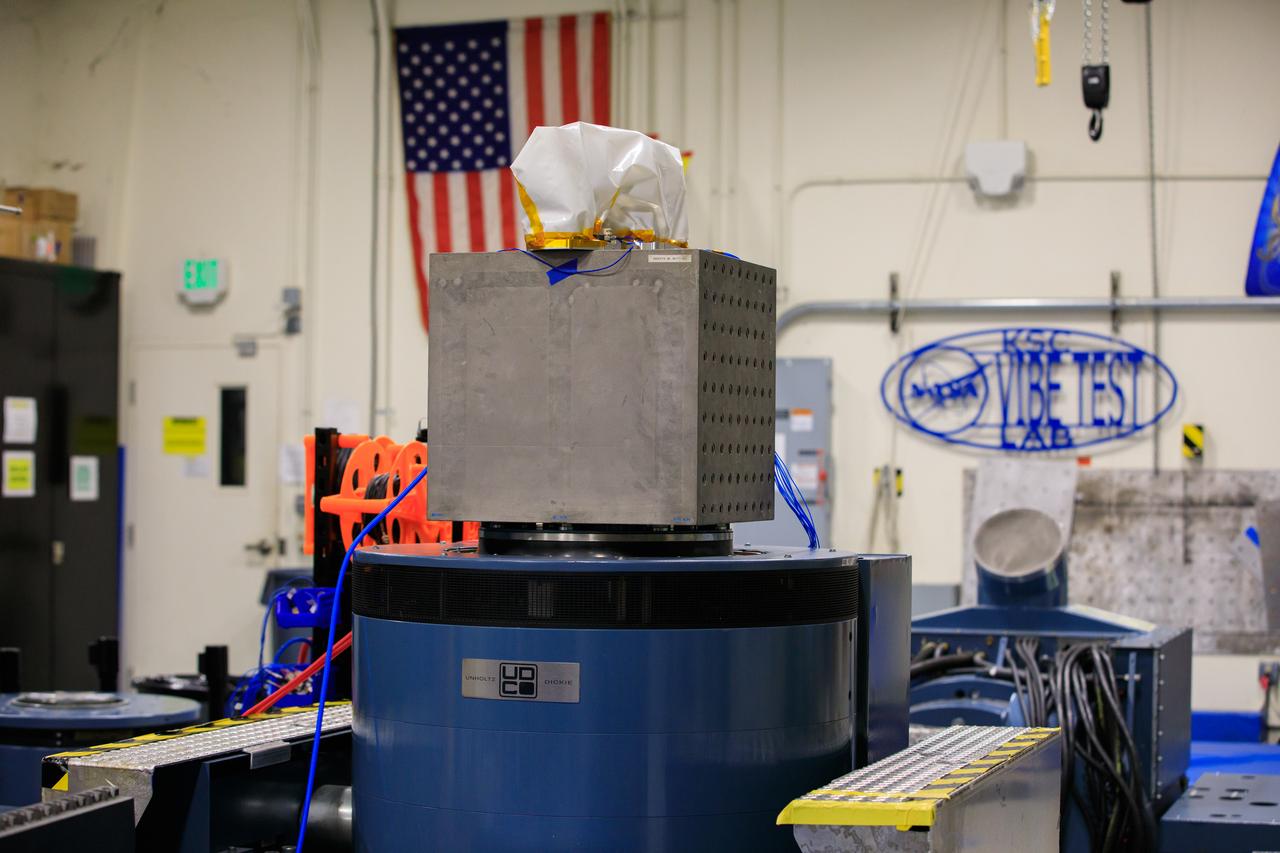

The Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) for NASA’s VIPER mission is being prepared for a vibration test inside a laboratory in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 8, 2022. Exposing the instrument to vibration environments that it might see during launch helps engineers to find issues prior to liftoff. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo will be part of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) mission where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.

Technicians prepare the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) for NASA’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission for packing inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 21, 2023. MSolo will be shipped to Johnson Space Center in Houston for integration into VIPER. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo will be part of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) mission where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions. VIPER is scheduled to be delivered to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2024 by Astrobotic’s Griffin lander as part of the CLPS initiative.
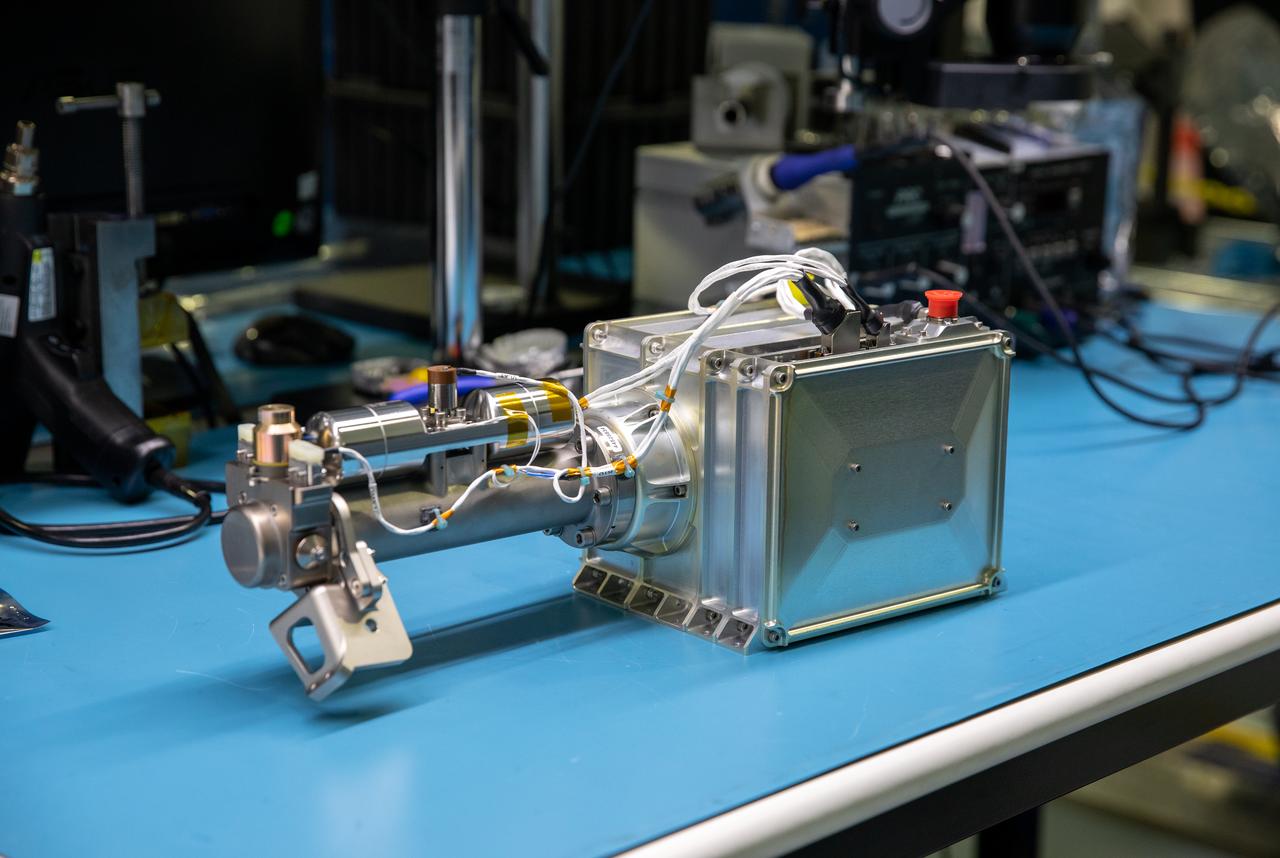
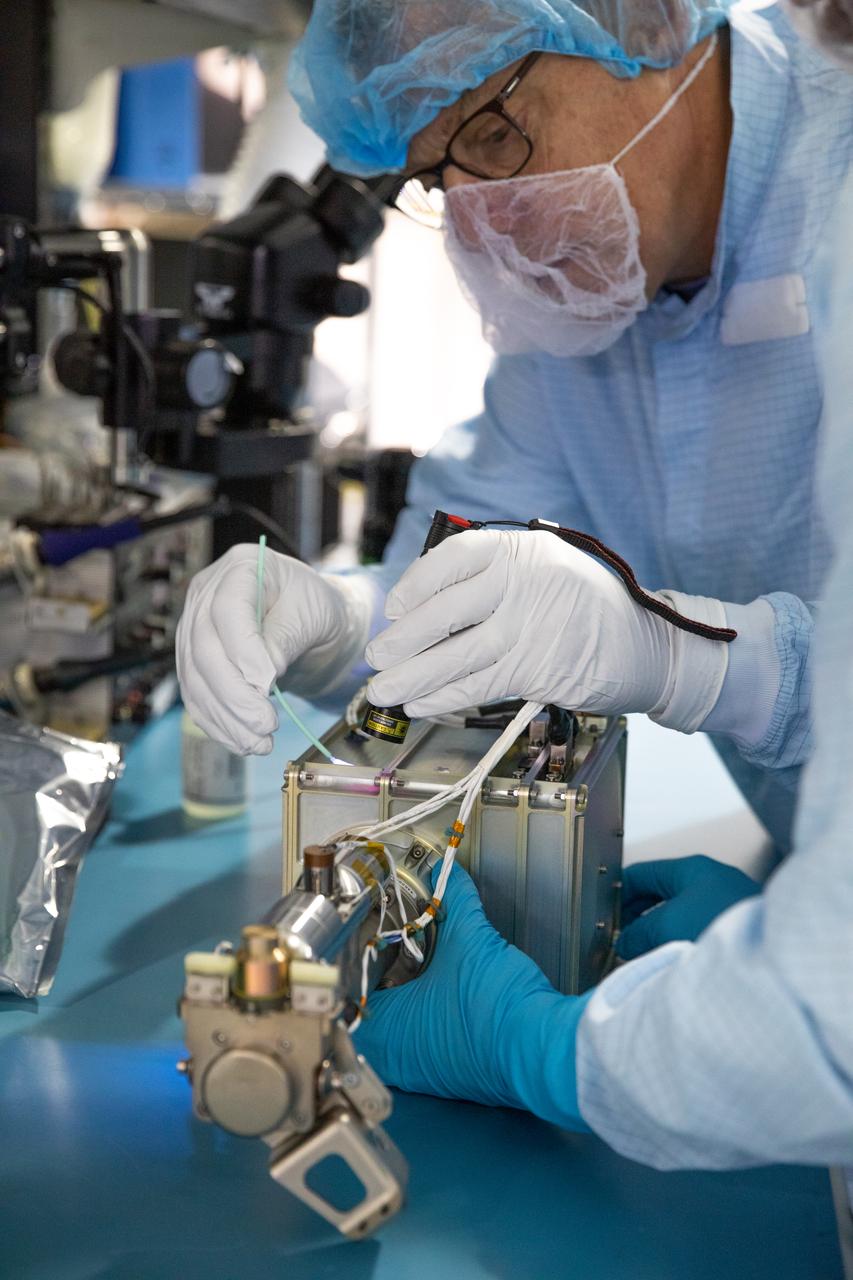
The Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) for NASA’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission is prepared for packing inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 21, 2023. MSolo will be shipped to Johnson Space Center in Houston for integration into VIPER. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo will be part of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) mission where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions. VIPER is scheduled to be delivered to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2024 by Astrobotic’s Griffin lander as part of the CLPS initiative.
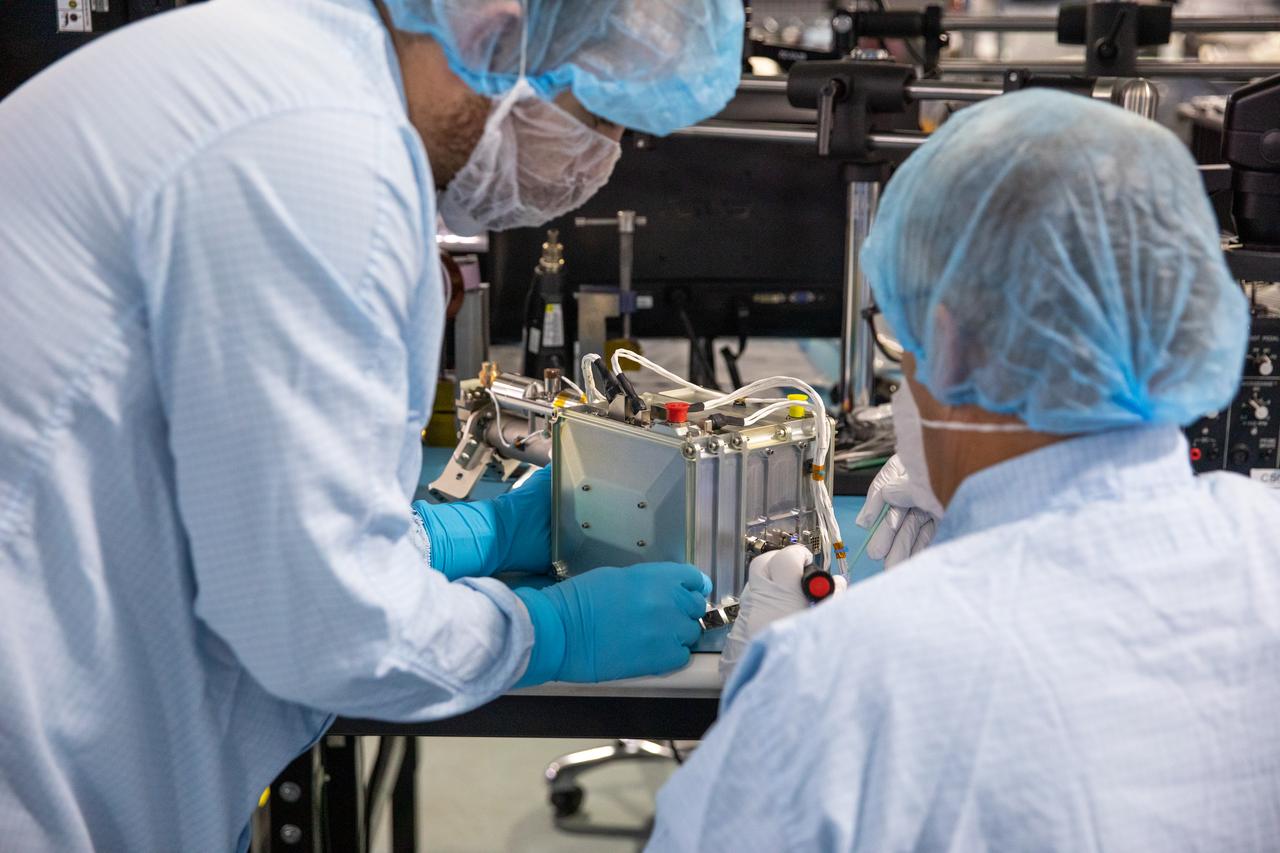

Technicians prepare the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) for NASA’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission for packing inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 21, 2023. MSolo will be shipped to Johnson Space Center in Houston for integration into VIPER. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo will be part of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) mission where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions. VIPER is scheduled to be delivered to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2024 by Astrobotic’s Griffin lander as part of the CLPS initiative.
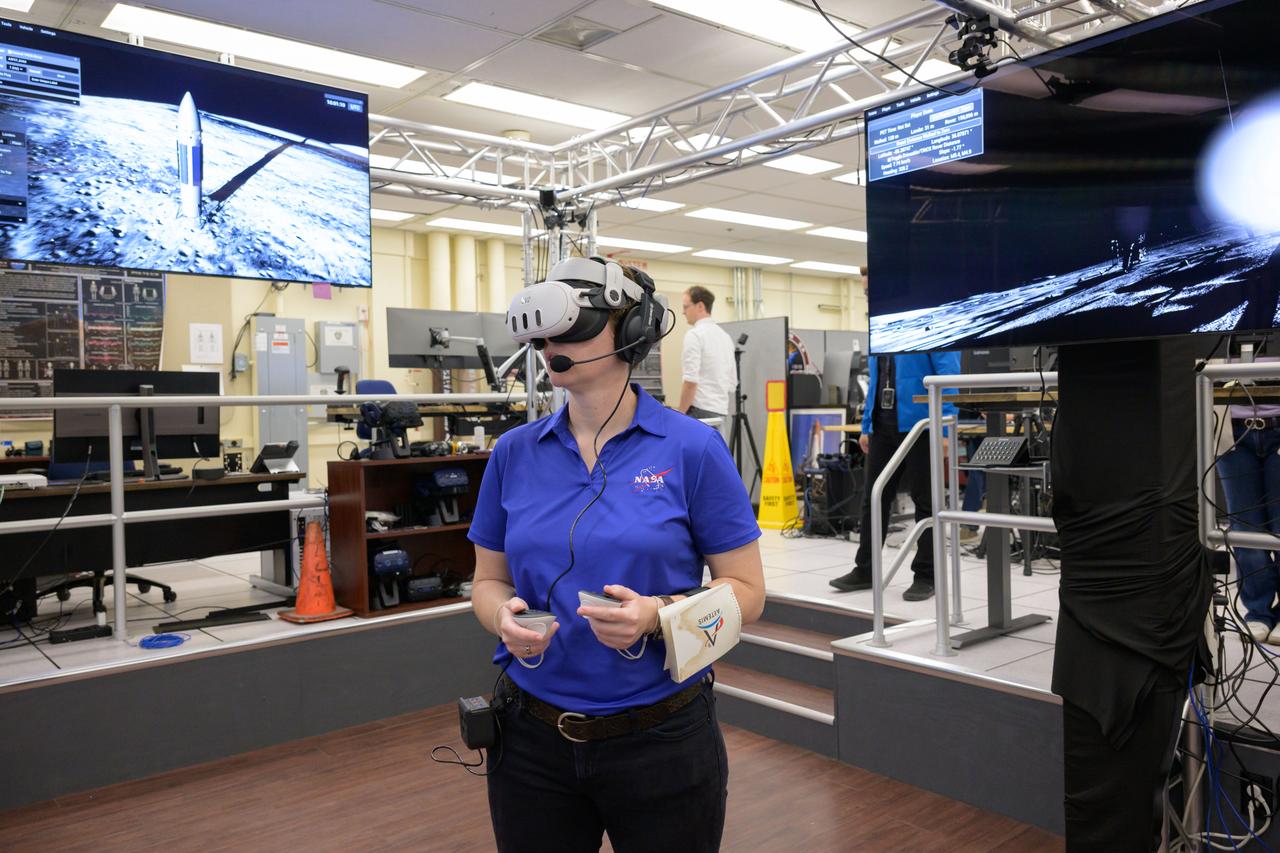

jsc2024e076628 – Tess Caswell, a crew stand-in for the Artemis III Virtual Reality Mini-Simulation, executes a moonwalk in the Prototype Immersive Technology (PIT) lab at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. The simulation was a test of using VR as a training method for flight controllers and science teams’ collaboration on science-focused traverses on the lunar surface. Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
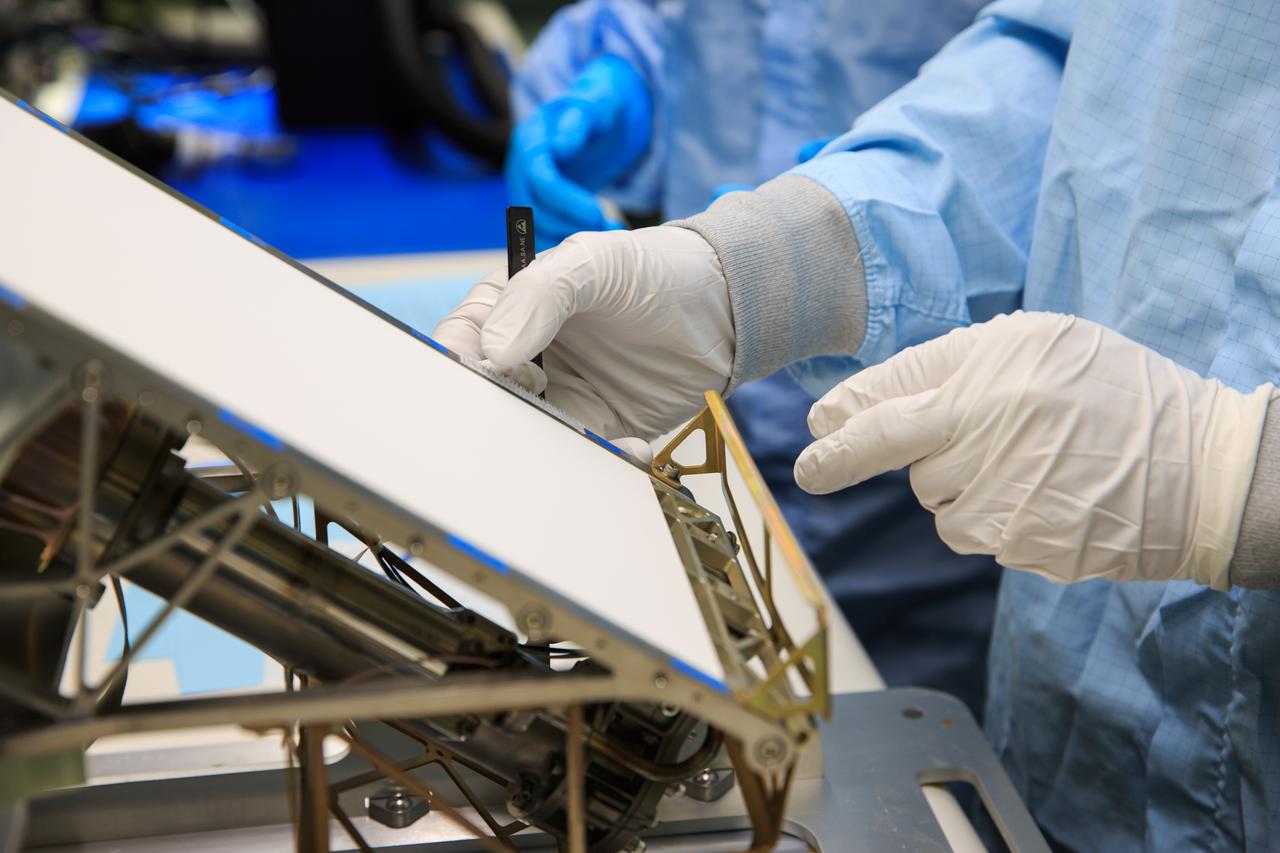

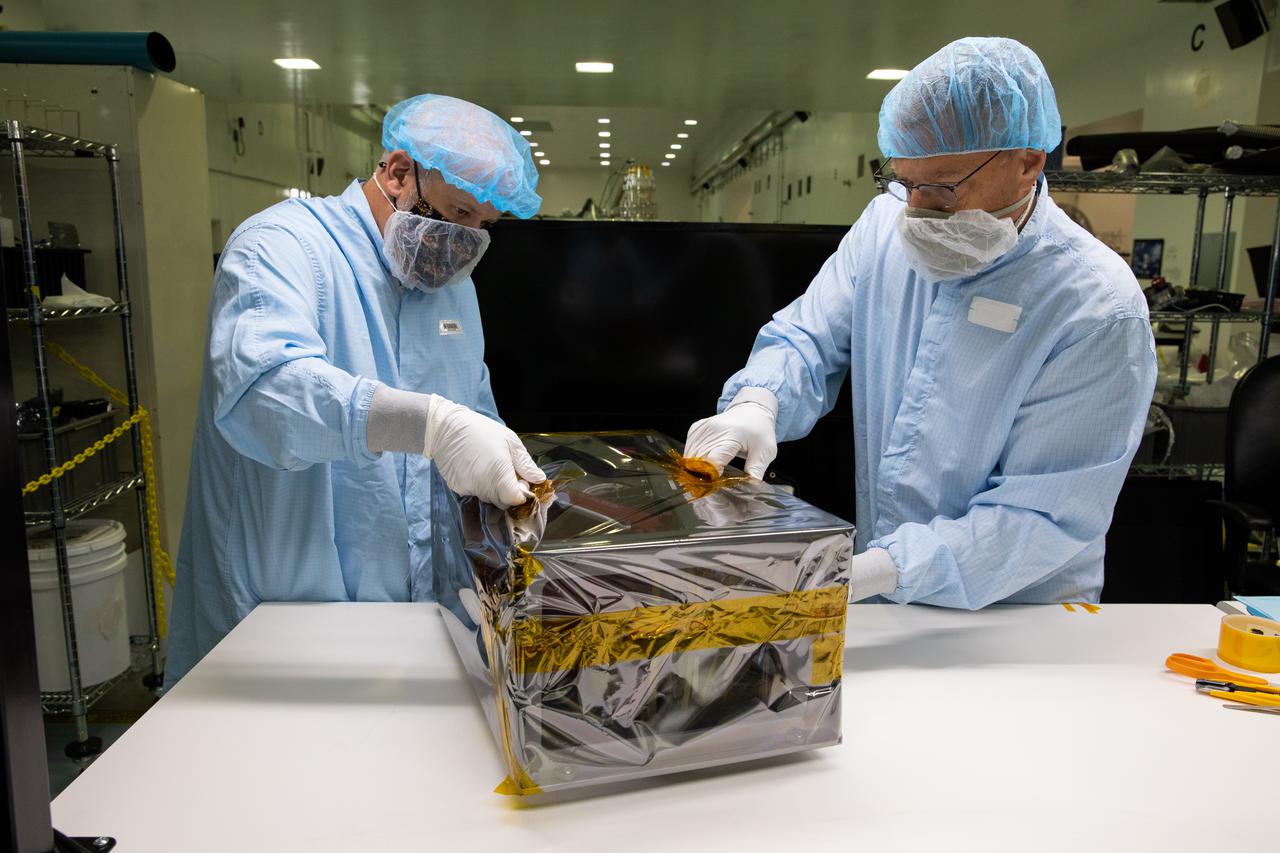
Team members working inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Sept. 23, 2021, meticulously assemble ground support equipment that will protect shipment of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) flight hardware for preparations before it launches in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo, scheduled to first launch in 2022, is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will include science experiments, testing of technologies and demonstrations of capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.

Team members working inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Sept. 23, 2021, meticulously assemble ground support equipment that will protect shipment of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) flight hardware for preparations before it launches in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo, scheduled to first launch in 2022, is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will include science experiments, testing of technologies and demonstrations of capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
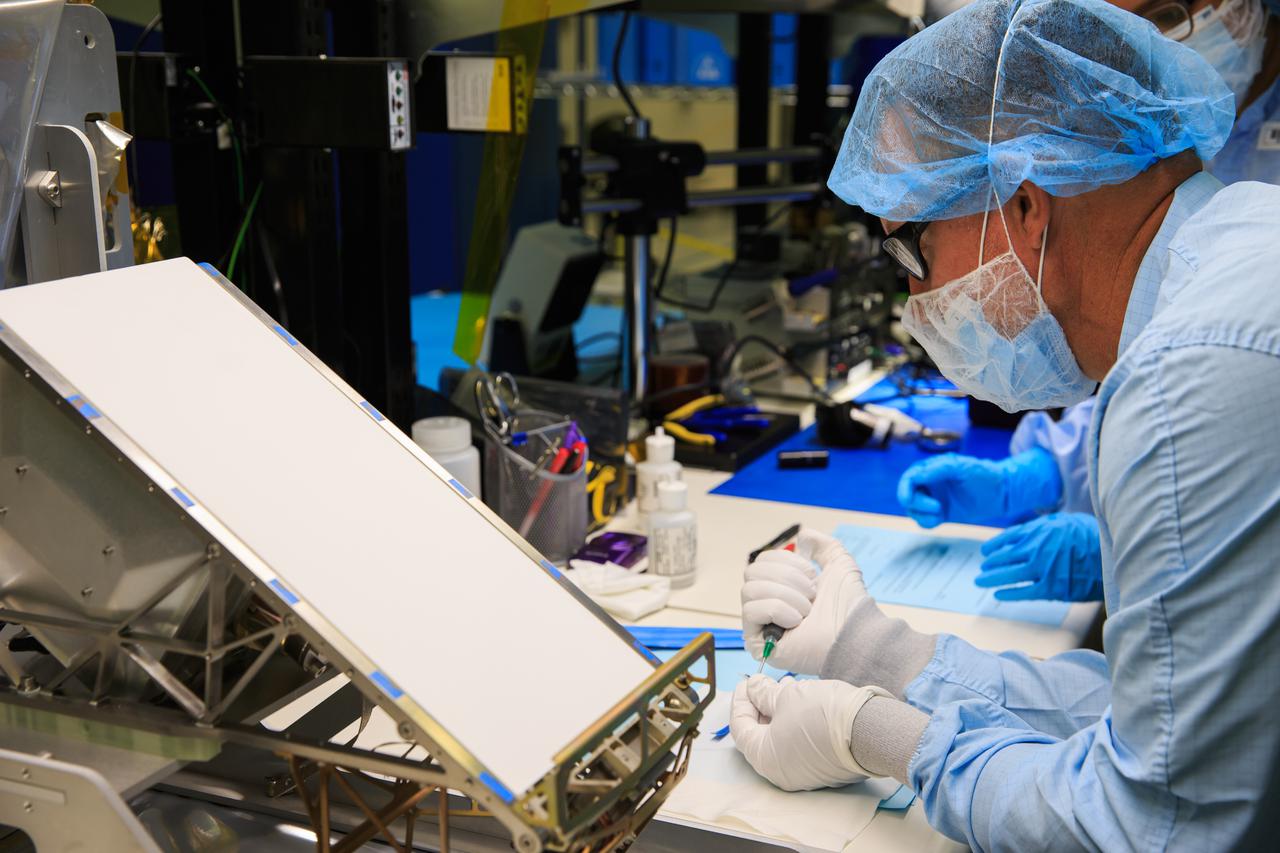

Team members working inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Sept. 23, 2021, meticulously assemble ground support equipment that will protect shipment of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) flight hardware for preparations before it launches in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo, scheduled to first launch in 2022, is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will include science experiments, testing of technologies and demonstrations of capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
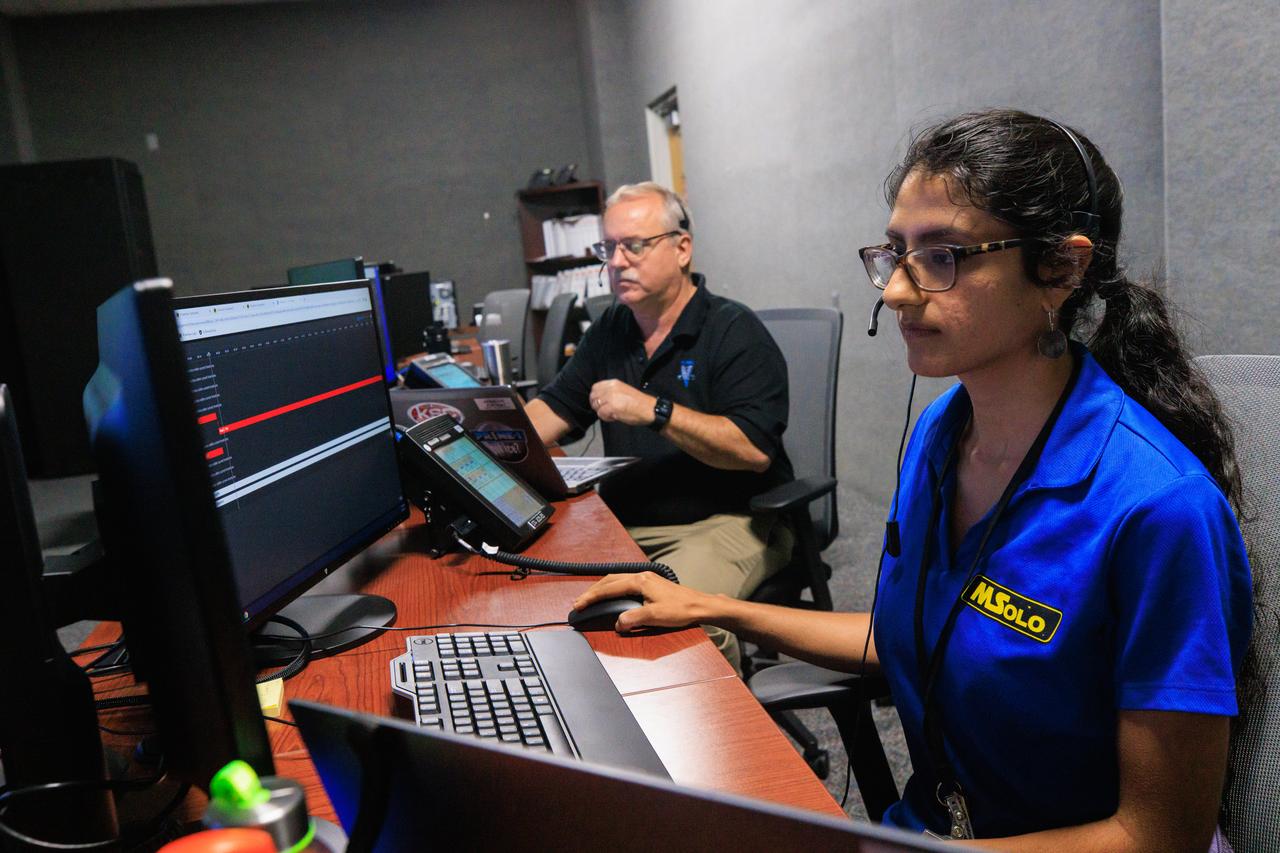

Jim Kania (left), Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSOLO) software engineering lead, and Pri Johnson, MSOLO systems engineer, participate in simulation training at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 25, 2023, in preparation for the agency’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission. The purpose of the training was to get the integrated VIPER team – a mix of engineers from Kennedy and NASA’s Ames Research Center in California – accustomed to operating together during phases of the mission where the rover will be driving. MSOLO is a modified commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer that will help the agency analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon and study water on the lunar surface. MSOLO, as part of VIPER, is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) initiative in late 2024, landing at the Moon’s South Pole aboard Astrobotic’s Griffin lander. Through Artemis missions, CLPS deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human deep space exploration missions.
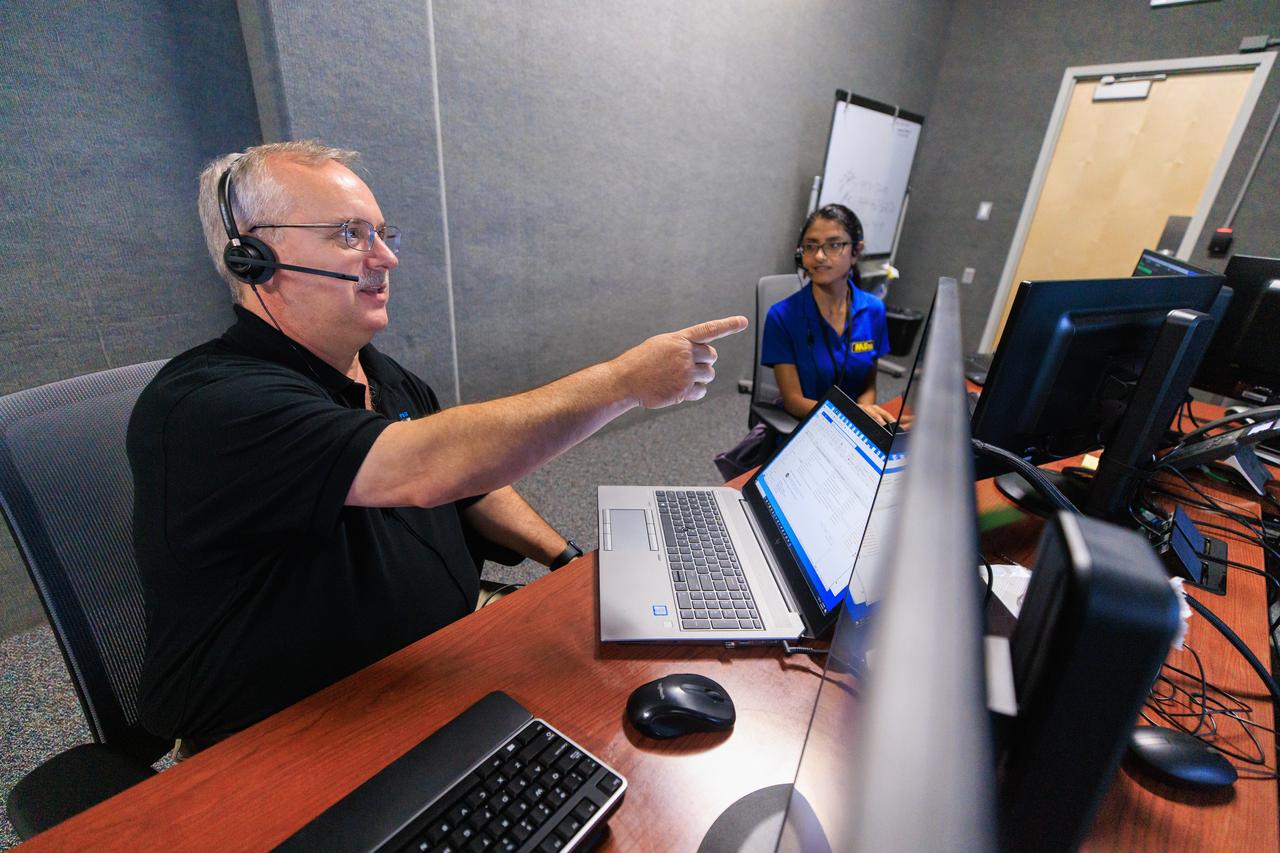

Jim Kania (left), Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSOLO) software engineering lead, and Pri Johnson, MSOLO systems engineer, participate in simulation training at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 25, 2023, in preparation for the agency’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission. The purpose of the training was to get the integrated VIPER team – a mix of engineers from Kennedy and NASA’s Ames Research Center in California – accustomed to operating together during phases of the mission where the rover will be driving. MSOLO is a modified commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer that will help the agency analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon and study water on the lunar surface. MSOLO, as part of VIPER, is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) initiative in late 2024, landing at the Moon’s South Pole aboard Astrobotic’s Griffin lander. Through Artemis missions, CLPS deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human deep space exploration missions.
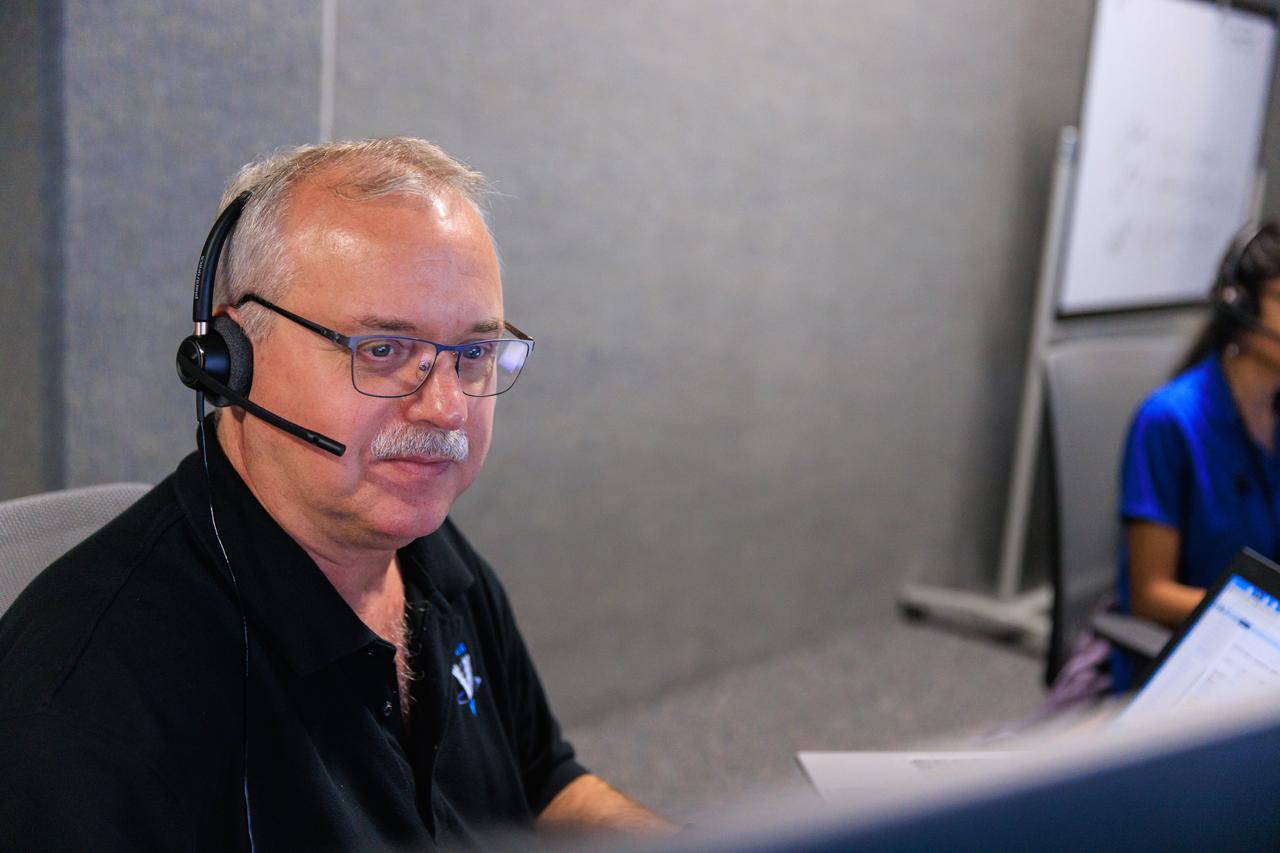

Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSOLO) Software Engineering Lead Jim Kania participates in simulation training at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 25, 2023, in preparation for the agency’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission. The purpose of the training was to get the integrated VIPER team – a mix of engineers from Kennedy and NASA’s Ames Research Center in California – accustomed to operating together during phases of the mission where the rover will be driving. MSOLO is a modified commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer that will help the agency analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon and study water on the lunar surface. MSOLO, as part of VIPER, is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) initiative in late 2024, landing at the Moon’s South Pole aboard Astrobotic’s Griffin lander. Through Artemis missions, CLPS deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human deep space exploration missions.

Pri Johnson (left), Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSOLO) systems engineer, and Jim Kania, MSOLO software engineering lead, participate in simulation training at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 25, 2023, in preparation for the agency’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission. The purpose of the training was to get the integrated VIPER team – a mix of engineers from Kennedy and NASA’s Ames Research Center in California – accustomed to operating together during phases of the mission where the rover will be driving. MSOLO is a modified commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer that will help the agency analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon and study water on the lunar surface. MSOLO, as part of VIPER, is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) initiative in late 2024, landing at the Moon’s South Pole aboard Astrobotic’s Griffin lander. Through Artemis missions, CLPS deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human deep space exploration missions.

Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSOLO) Systems Engineer Pri Johnson participates in simulation training at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 25, 2023, in preparation for the agency’s Volatile Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission. The purpose of the training was to get the integrated VIPER team – a mix of engineers from Kennedy and NASA’s Ames Research Center in California – accustomed to operating together during phases of the mission where the rover will be driving. MSOLO is a modified commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer that will help the agency analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon and study water on the lunar surface. MSOLO, as part of VIPER, is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) initiative in late 2024, landing at the Moon’s South Pole aboard Astrobotic’s Griffin lander. Through Artemis missions, CLPS deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human deep space exploration missions.
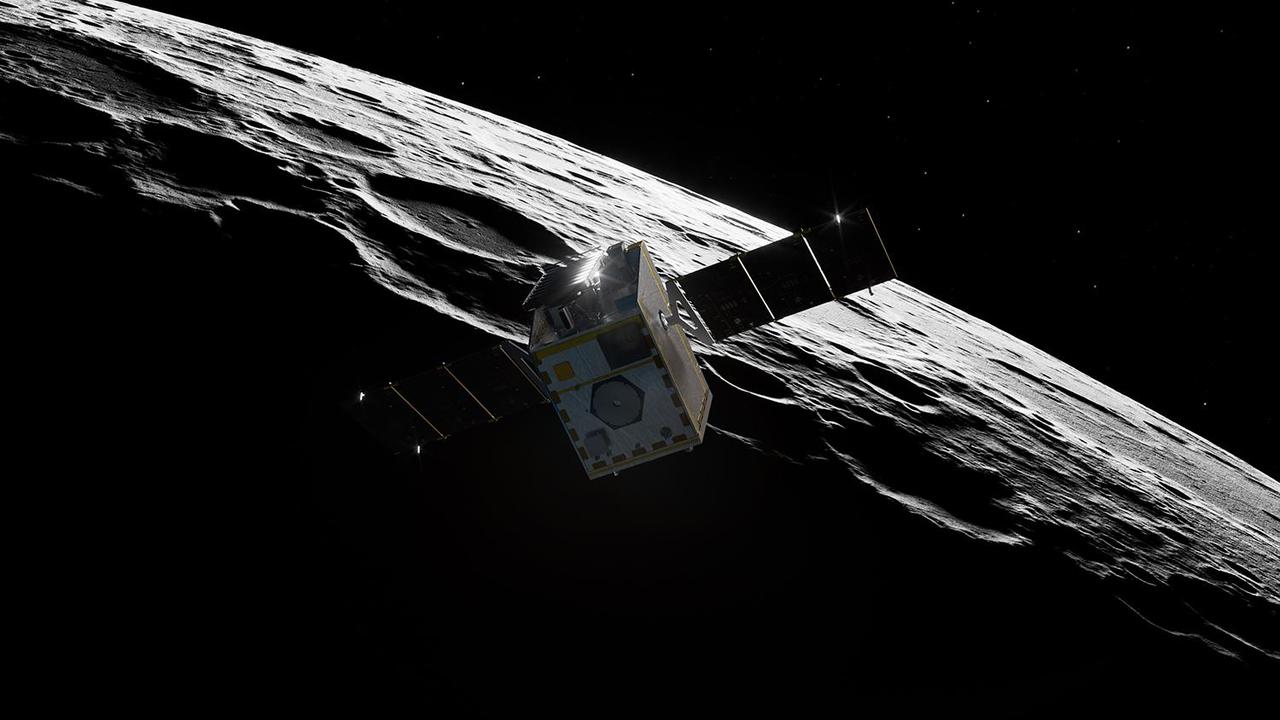

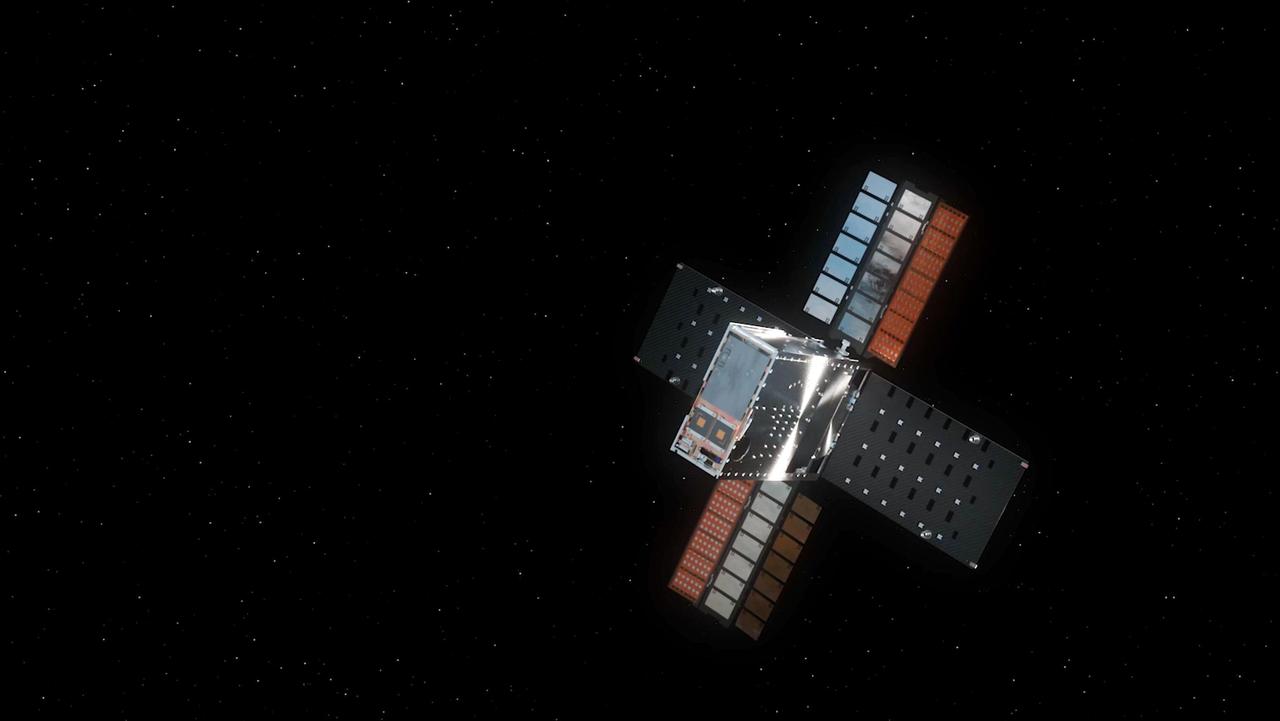
NASA's Lunar Trailblazer mission approaches the Moon as it enters its science orbit in this artist's concept. The small satellite will orbit about 60 miles (100 kilometers) above the lunar surface, producing the best-yet maps of water on the Moon. Lunar Trailblazer will discover where the Moon's water is, what form it is in, and how it changes over time. Observations gathered during the spacecraft's two-year prime mission will contribute to the understanding of water cycles on airless bodies throughout the solar system while also supporting future human and robotic missions to the Moon by identifying where water is located. Lunar Trailblazer was a selection of NASA's SIMPLEx (Small Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration), which provides opportunities for low-cost science spacecraft to ride-share with selected primary missions. To maintain the lower overall cost, SIMPLEx missions have a higher risk posture and lighter requirements for oversight and management. This higher risk acceptance allows NASA to test pioneering technologies, and the definition of success for these missions includes the lessons learned from more experimental endeavors. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26457
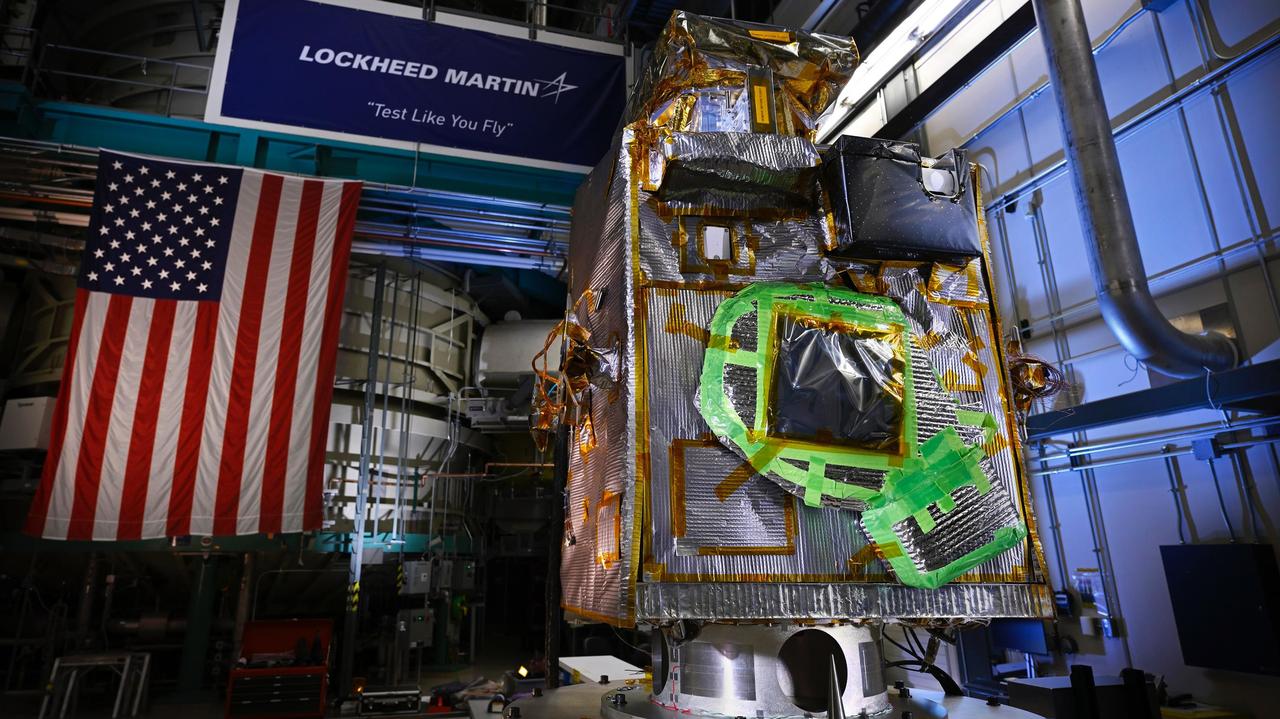

NASA's Lunar Trailblazer sits in a clean room at Lockheed Martin Space in Littleton, Colorado, shortly after being integrated with its second and final science instrument in June 2023. Called the Lunar Thermal Mapper (LTM), the instrument is visible as a black rectangular box in the upper right of the spacecraft's body. Green tape on the spacecraft will be removed before launch. Built by the University of Oxford in England and contributed by the UK Space Agency, LTM joins the High-resolution Volatiles and Minerals Moon Mapper (HVM³) that was integrated with the spacecraft late last year. Together, the instruments will enable scientists to determine the abundance, location, and form of the Moon's water. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25837
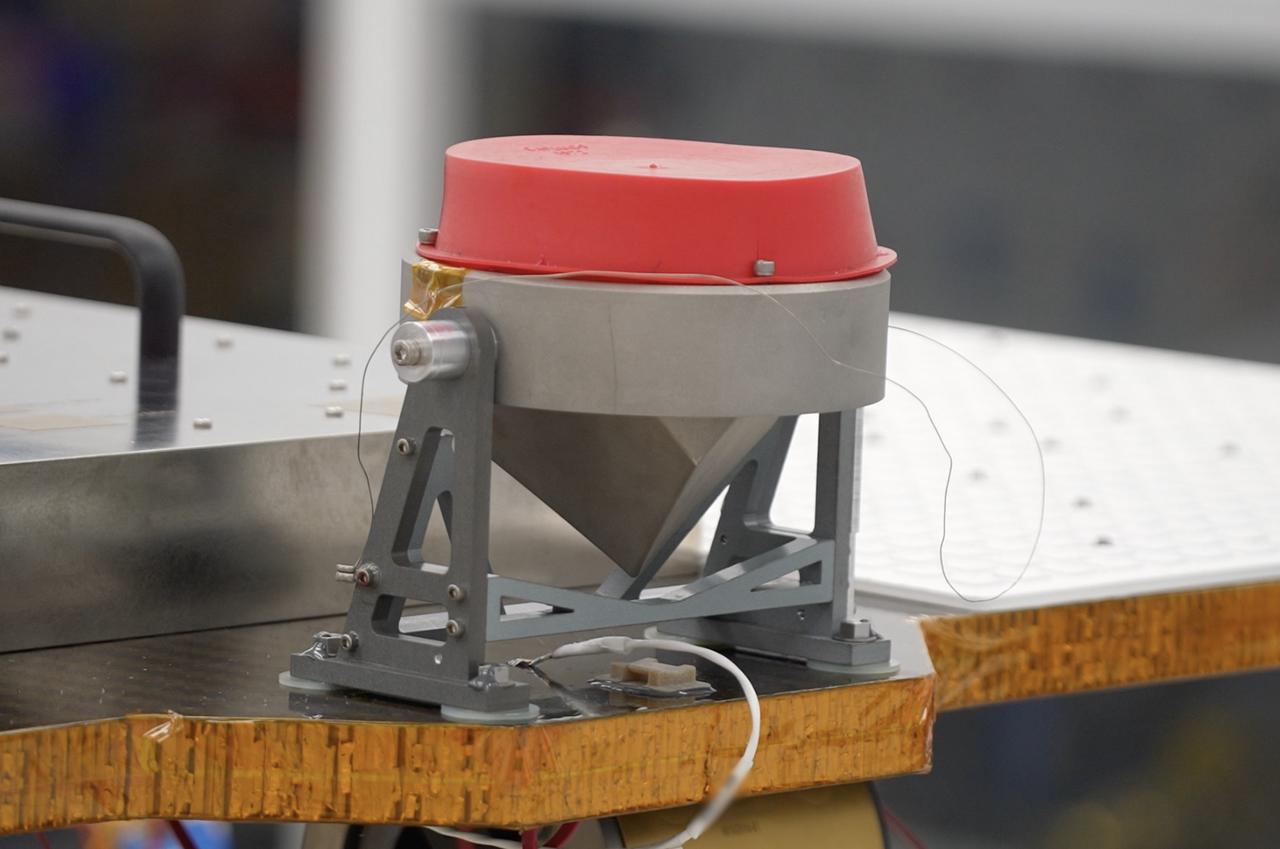

A science instrument flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative is expected to significantly expand our knowledge of the Moon. Next Generation Lunar Retroreflector, or NGLR-1, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by the University of Maryland in College Park, NGLR-1 is designed to reflect very short laser pulses from Earth-based lunar laser ranging observatories using a retroreflector, or a mirror designed to reflect the incoming light back in the same incoming direction. Investigations and demonstrations, such as NGLR-1, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
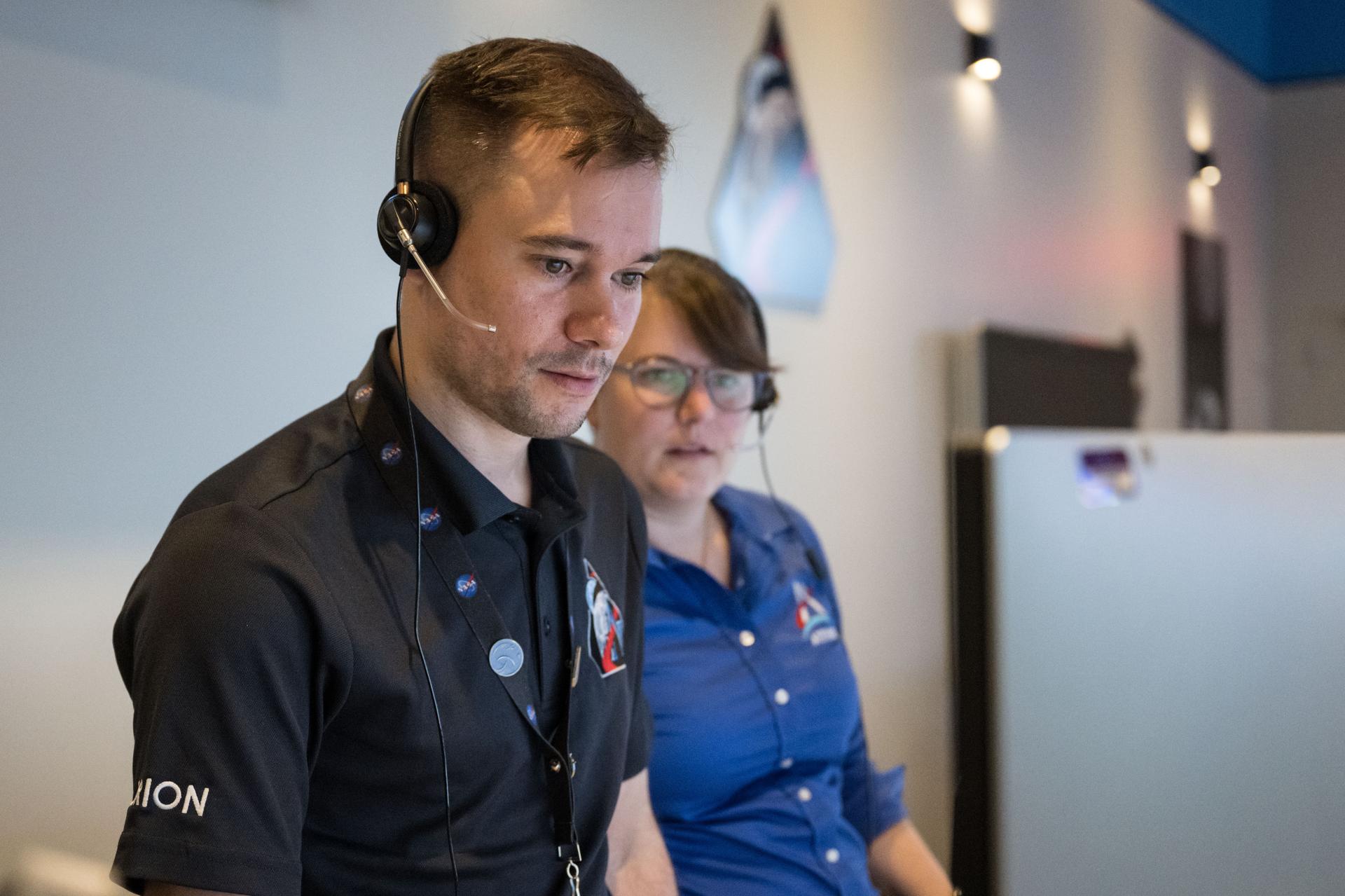

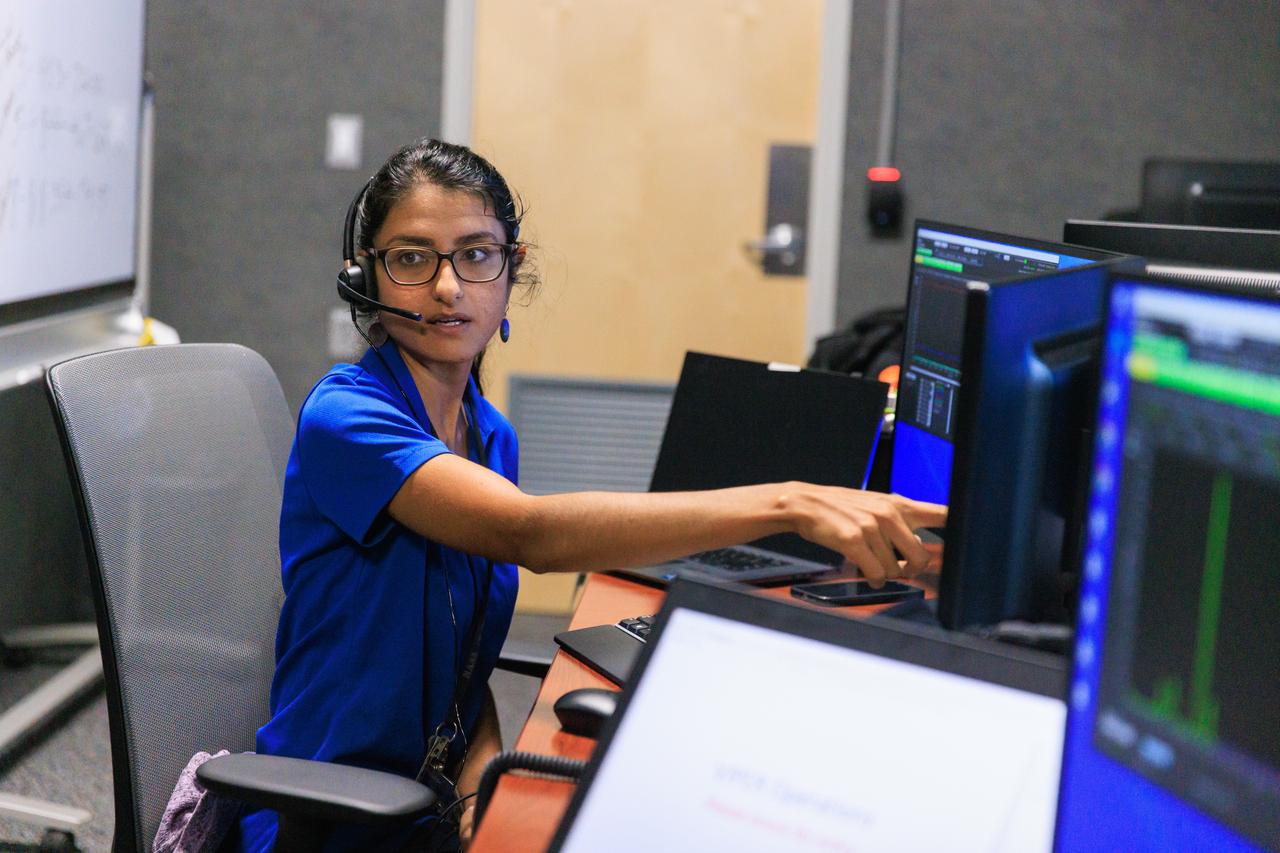
jsc2025e087854 --- Artemis lunar science team members Jacob Richardson, left, and Marie Henderson monitor an Artemis II lunar flyby simulation from the Science Evaluation Room (SER) in Mission Control at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. A team of experts will staff the SER, providing lunar scientific expertise, data analysis, and strategic guidance in real-time to the science officer sitting in the front flight control room of Mission Control.
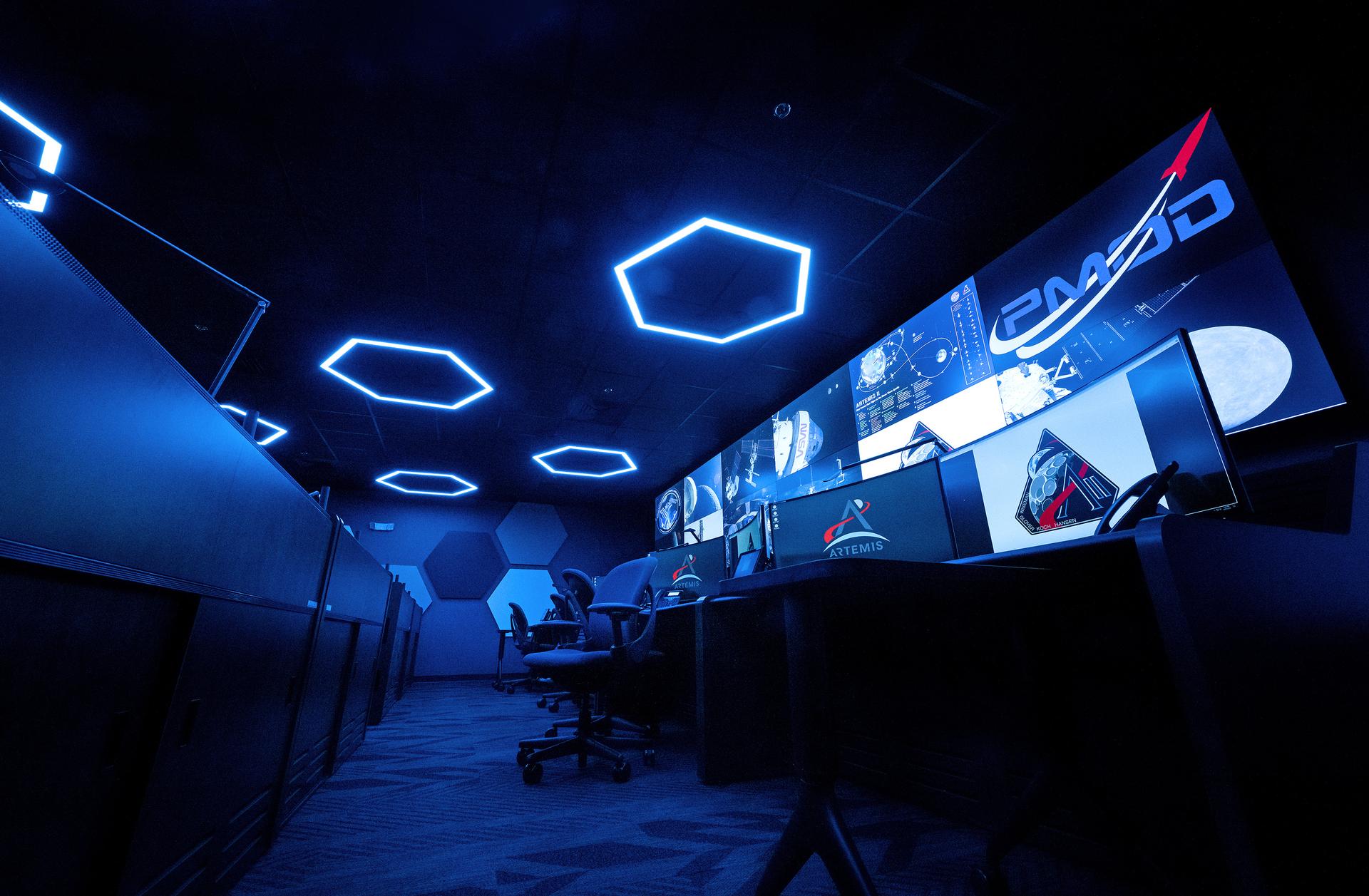

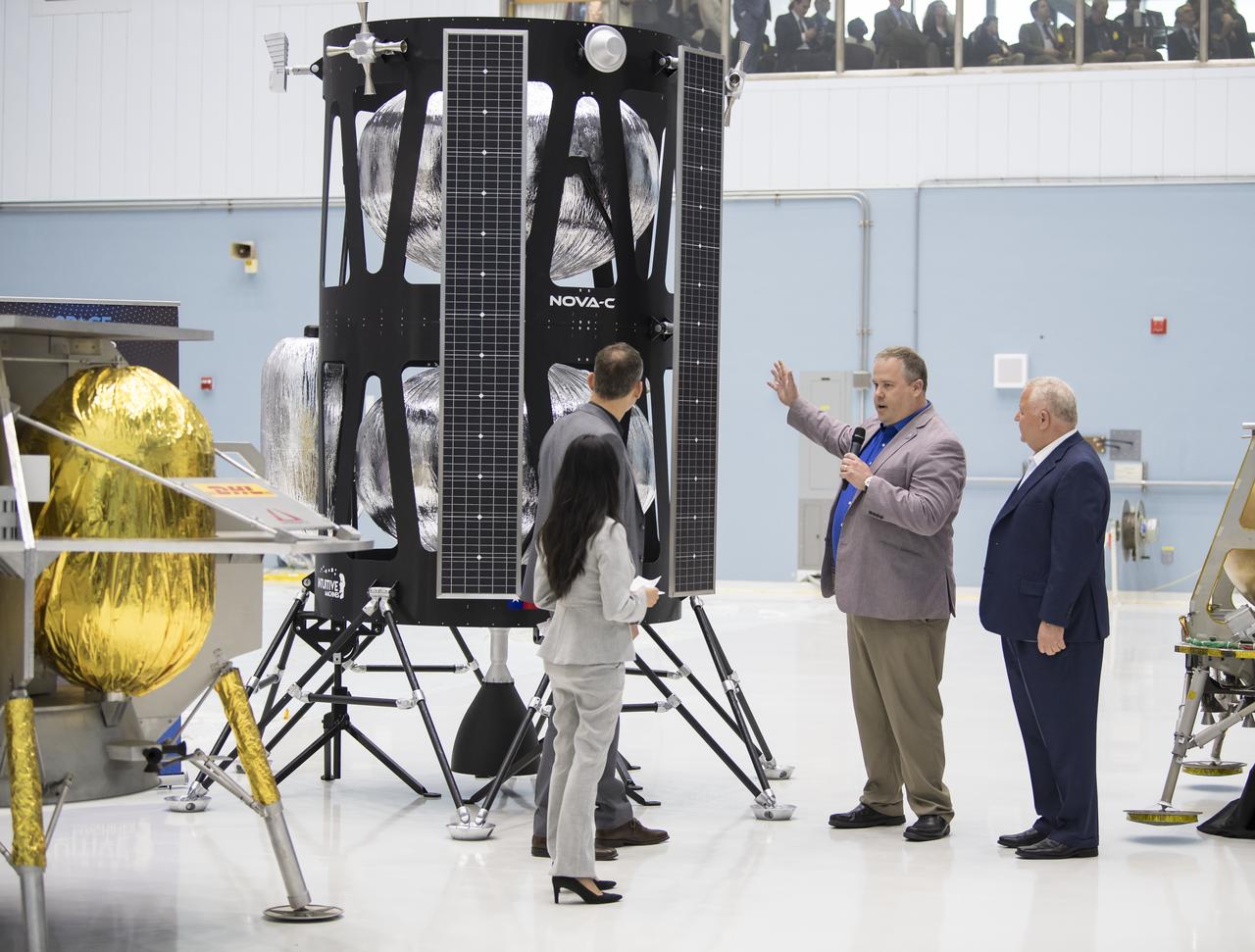
These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
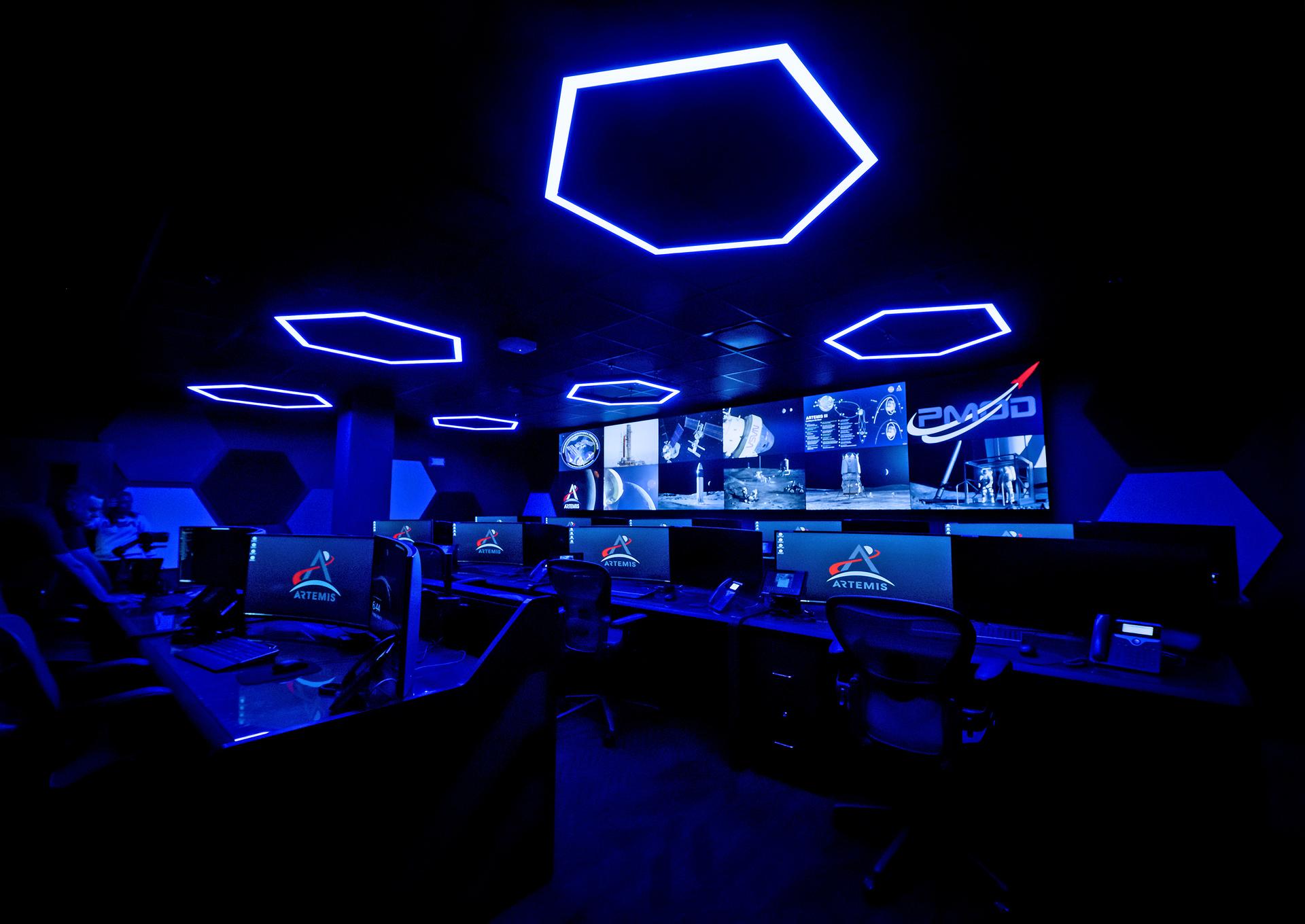

These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
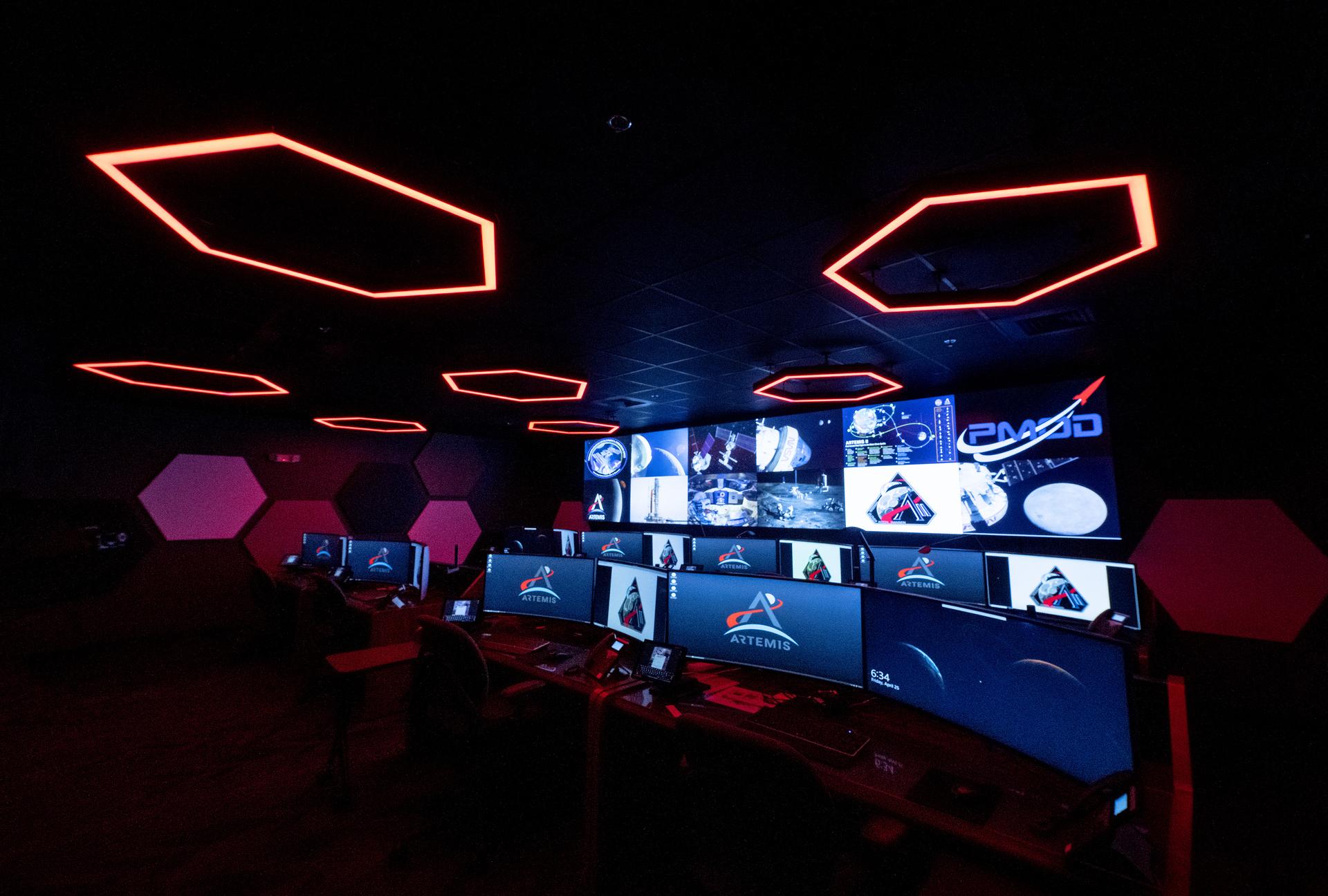

These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
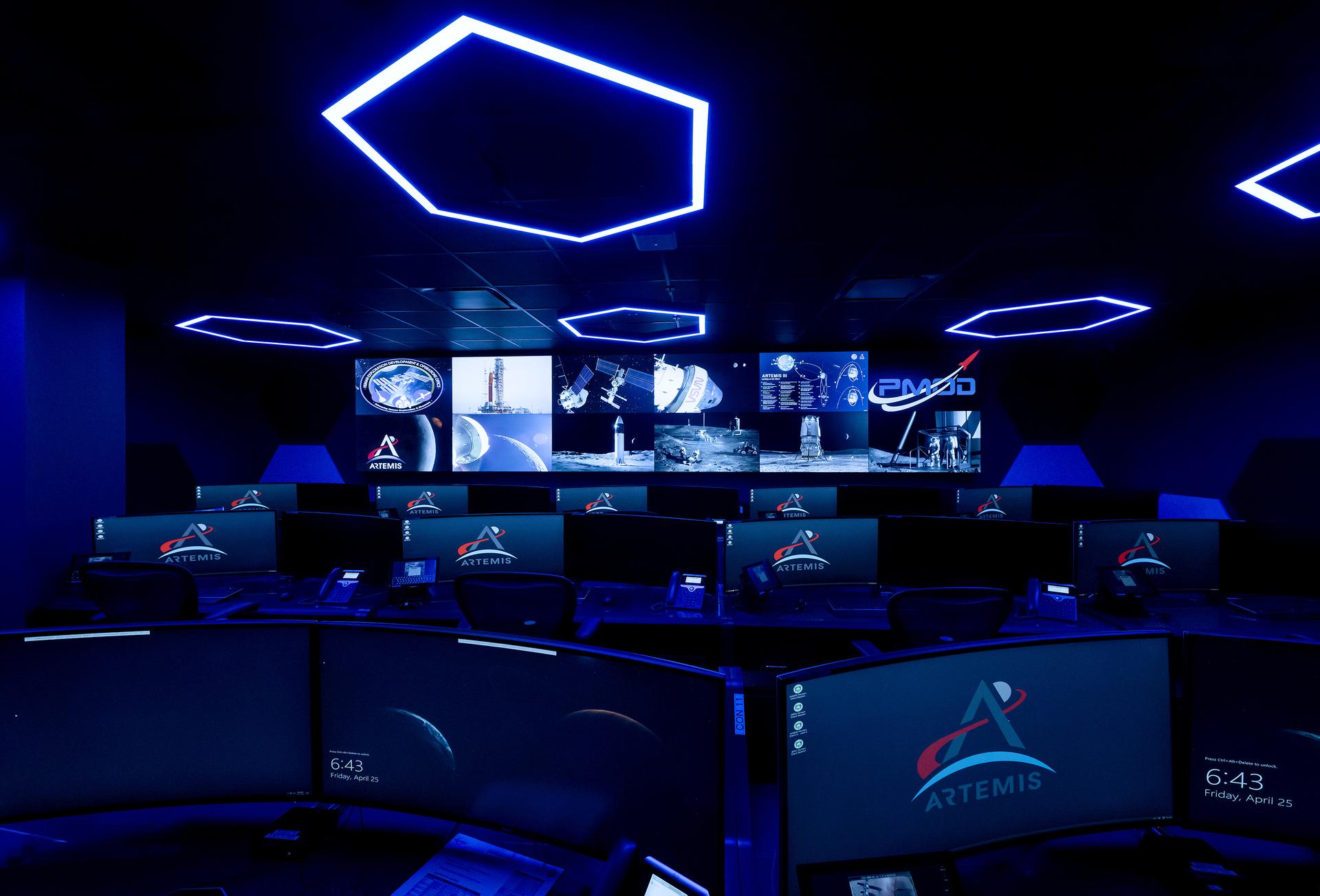

These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.

These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
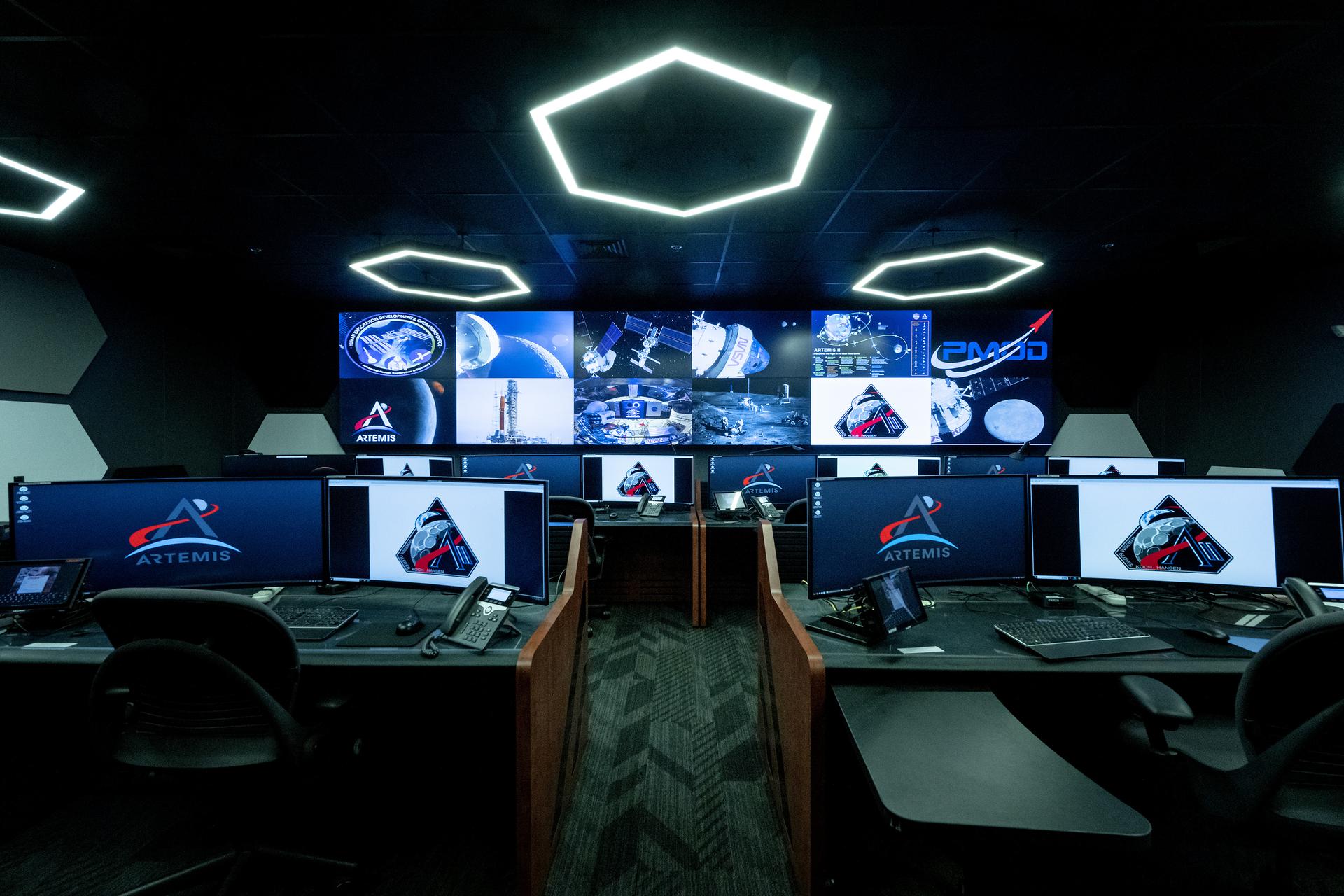

These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
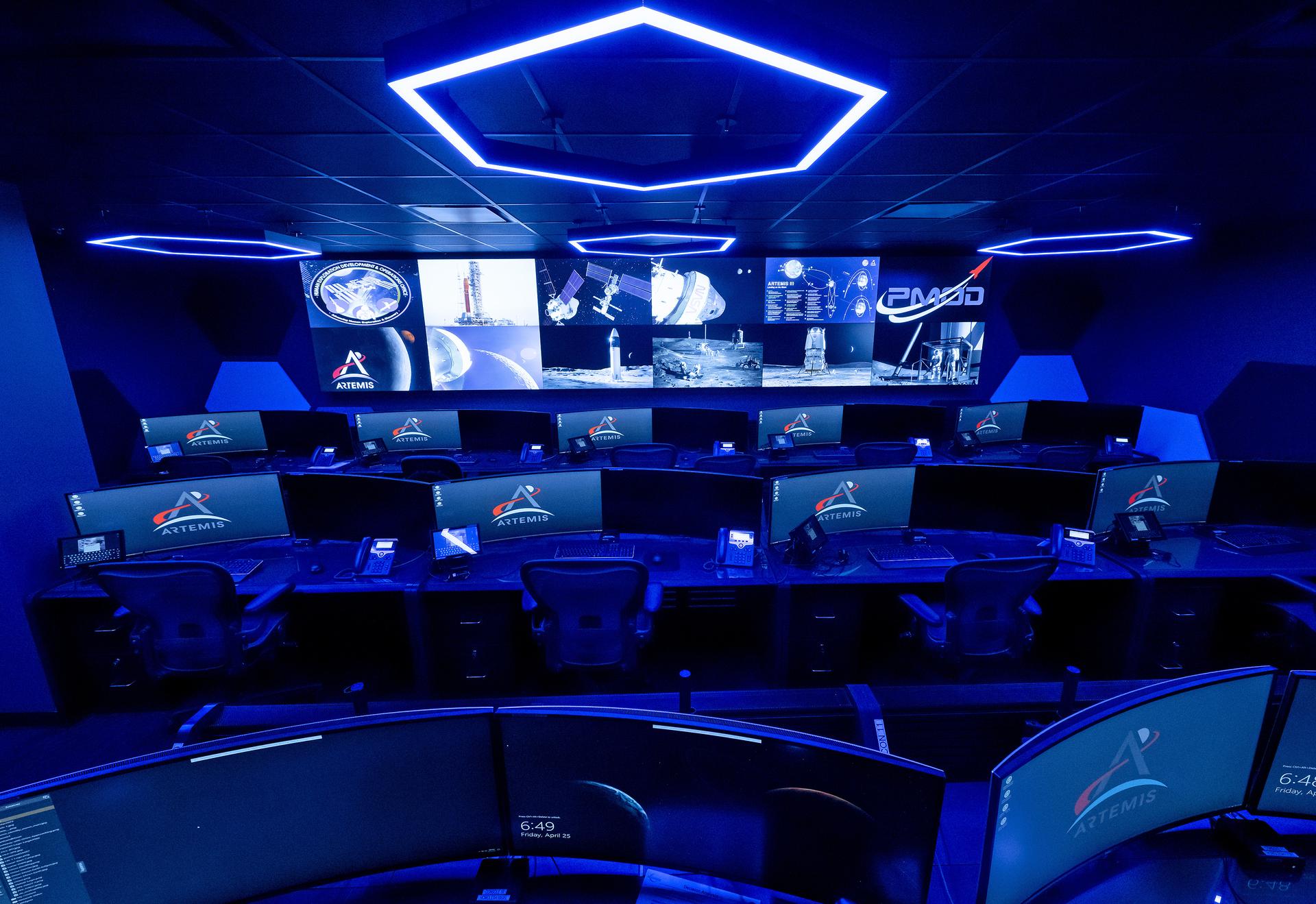

These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.

This illustration shows NASA's Lunar Flashlight, with its four solar arrays deployed, shortly after launch. The small satellite, or SmallSat, launched Nov. 30, 2022, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket as a rideshare with ispace's HAKUTO-R Mission 1. It will take about three months to reach its science orbit to seek out surface water ice in the darkest craters of the Moon's South Pole. A technology demonstration, Lunar Flashlight will use a reflectometer equipped with four lasers that emit near-infrared light in wavelengths readily absorbed by surface water ice. This is the first time that multiple colored lasers will be used to seek out ice inside these dark regions on the Moon, which haven't seen sunlight in billions of years. Should the lasers hit bare rock or regolith (broken rock and dust), the light will reflect back to the spacecraft. But if the target absorbs the light, that would indicate the presence of water ice. The greater the absorption, the more ice there may be. The science data collected by the mission will be compared with observations made by other lunar missions to help reveal the distribution of surface water ice on the Moon for potential use by future astronauts. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25626

jsc2026e000849 --- The Artemis II Lunar Science Team works in the Science Evaluation Room (SER) at the NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Located in the Christopher C. Kraft Jr. Mission Control Center, the SER supports the mission’s main flight control room for lunar science and planetary observations. Built specifically for Artemis missions with these science priorities in mind, the SER is equipped to support rapid data interpretation, collaborative analysis, real-time decision making, and seamless coordination between the science and operations teams. Credit: James Blair

jsc2026e000861 --- The Artemis II Lunar Science Team works in the Science Evaluation Room (SER) in the Mission Control Center at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. The SER supports the mission’s main flight control room for lunar science and planetary observations. Built specifically for Artemis missions with these science priorities in mind, the SER is equipped to support rapid data interpretation, collaborative analysis, real-time decision making, and seamless coordination between the science and operations teams. Credit: James Blair
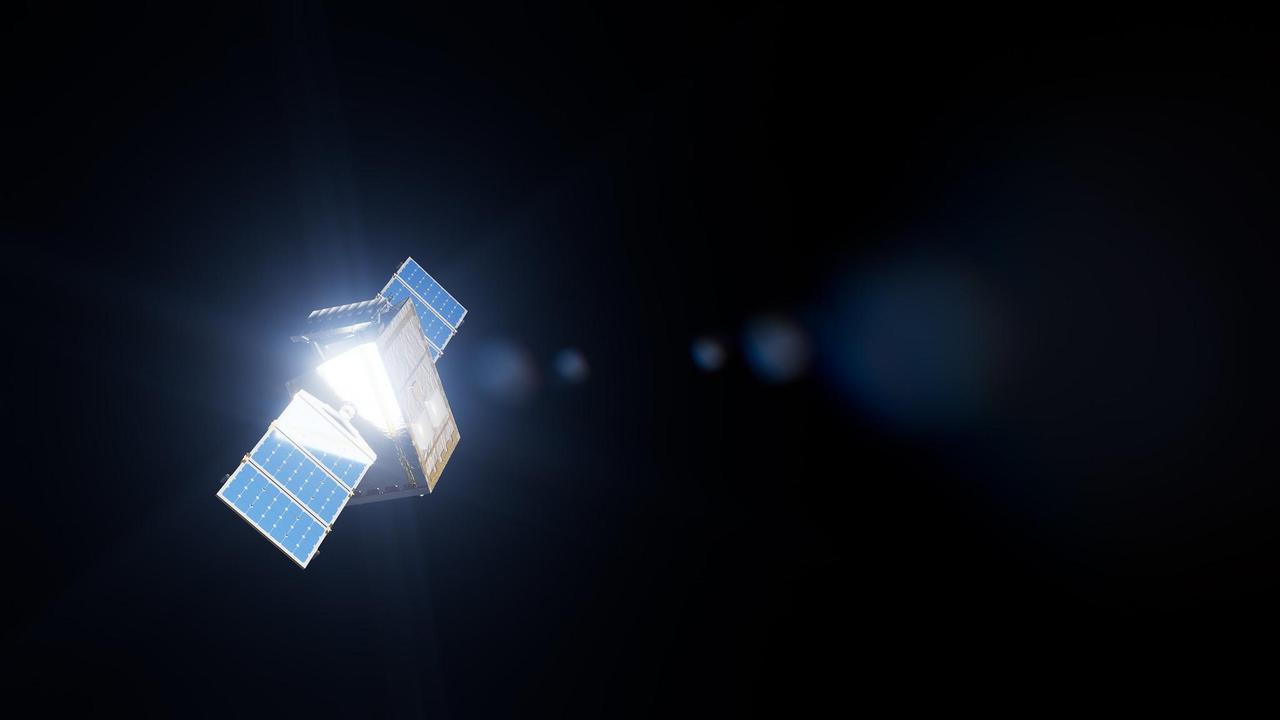
Sunlight gleams off NASA's Lunar Trailblazer in this artist's concept depicting the small satellite in lunar orbit. The spacecraft weighs only 440 pounds (200 kilograms) and measures 11.5 feet (3.5 meters) wide when its solar panels are fully deployed. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26429
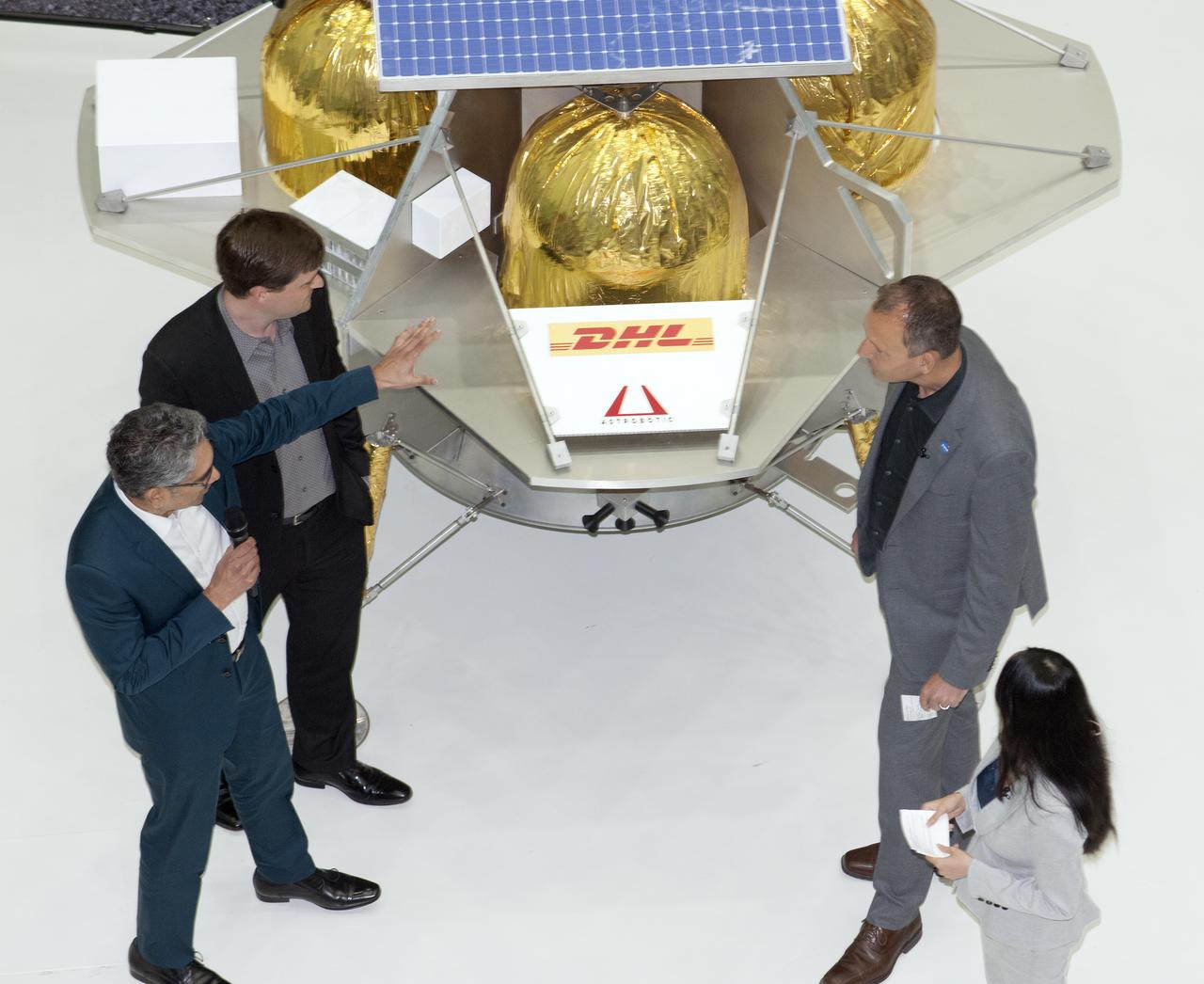

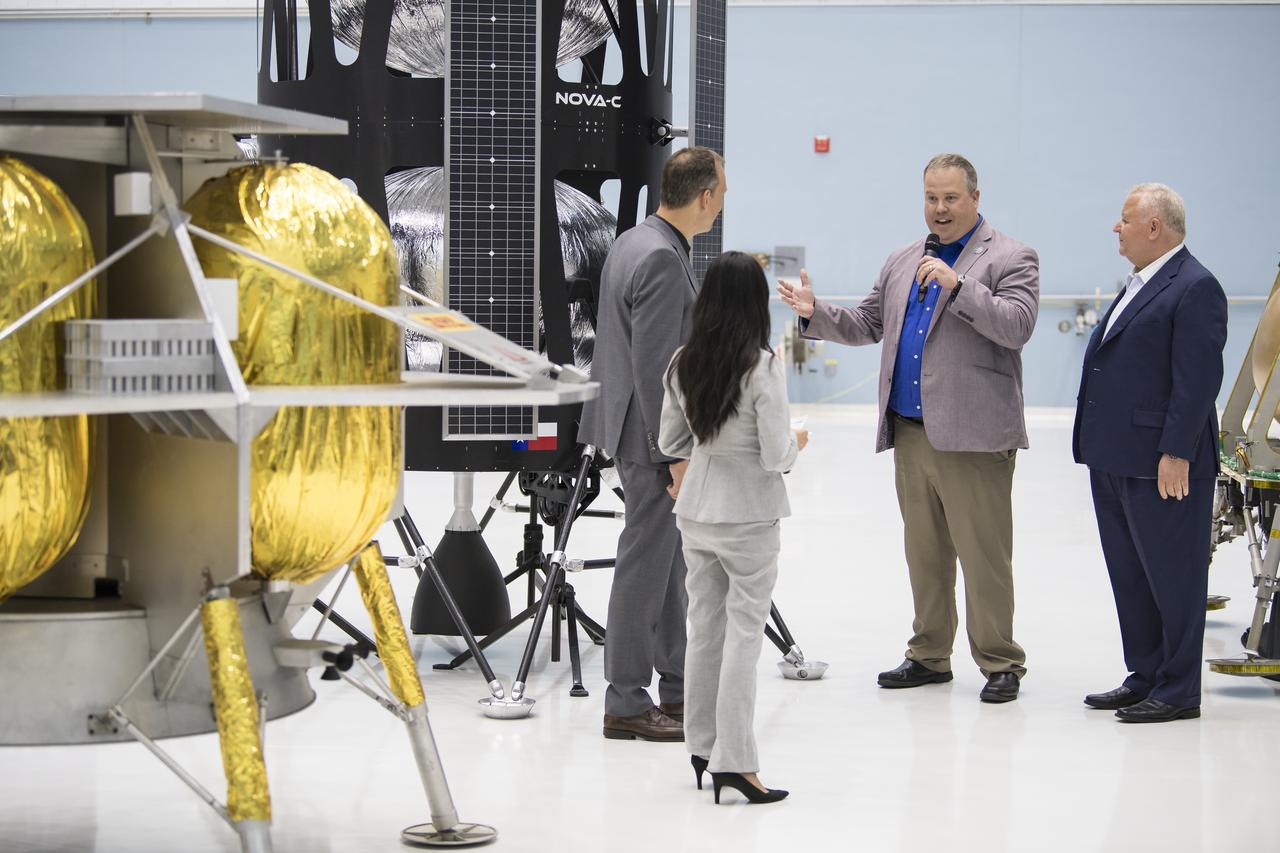
Commercial Lunar Payload Services Announcement was made at Goddard May 31, 2019. Tom Zurbuchen, AA Science Mission Directorate, congratulated three companies for providing lunar landers for Artermis: Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond
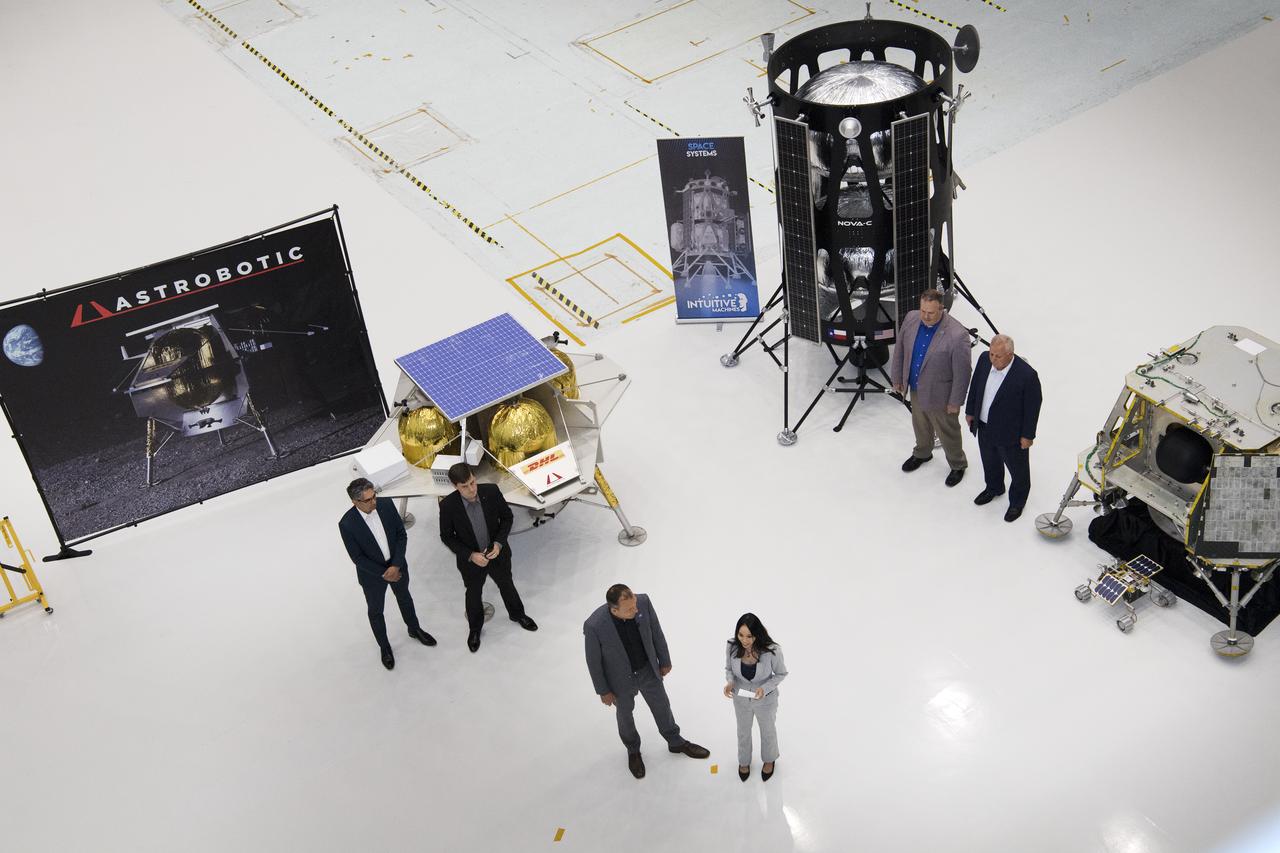

Commercial Lunar Payload Services Announcemnt was made at Goddard May 31, 2019. Tom Zurbuchen- AA Science Mission Directorate, congratulated three companies for providing lunar landers for Artemis: Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines and OrbitBeyond.

Lunar Commericial Payload Services Announcement was made at Godddard May 31, 2019. Tom Zurbuchen, AA Science Mission Directorate congratulated three companies for providing first lunar landers for Artemis: Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines and OrbitBeyond
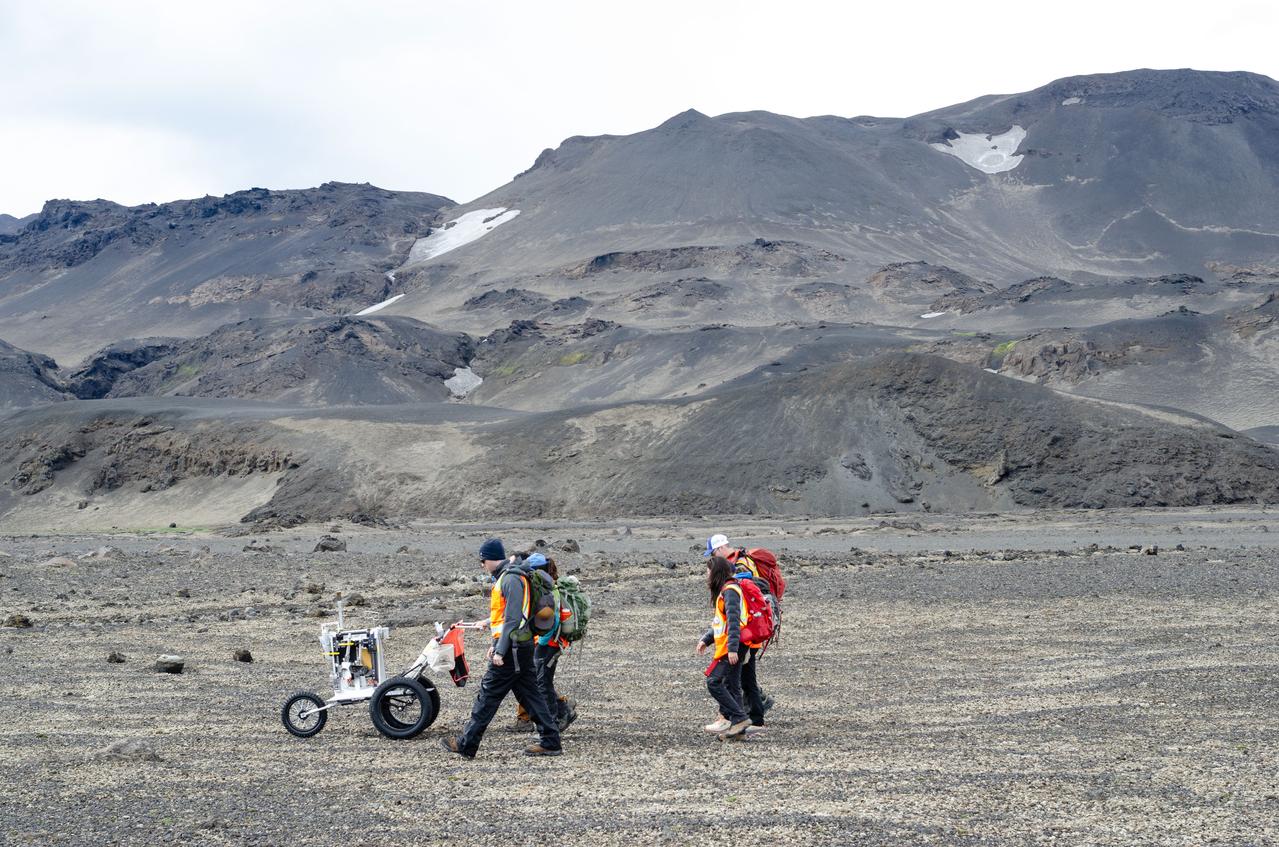

jsc2023e041422 --- Artemis II science trainers push a lunar tool cart across the lunar-like landscape of Iceland during an Artemis II crew geology field training.
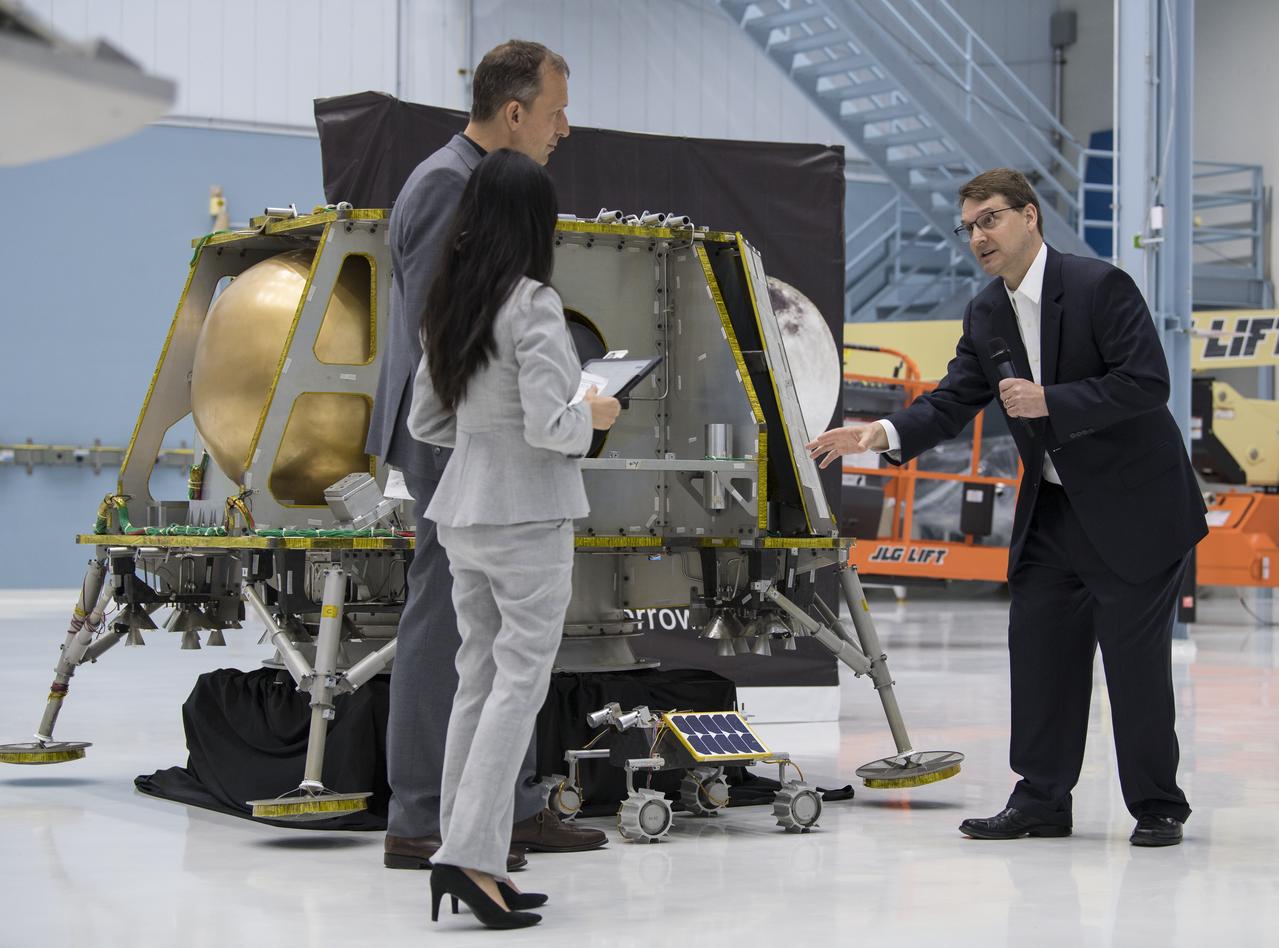

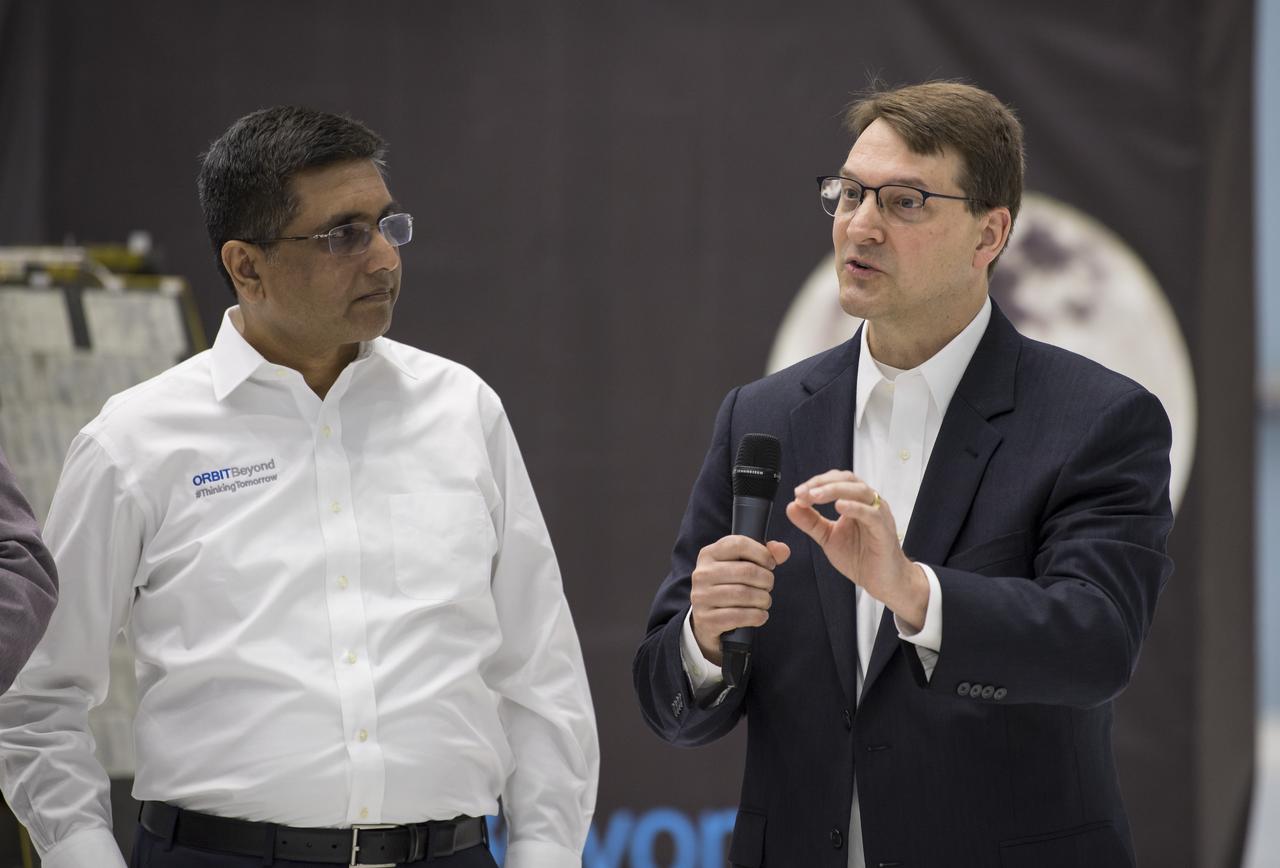
NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, second left, listens as Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse, speaks about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, left, speaks to, President and CEO of OrbitBeyond, Siba Padhi, right, and Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse, about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
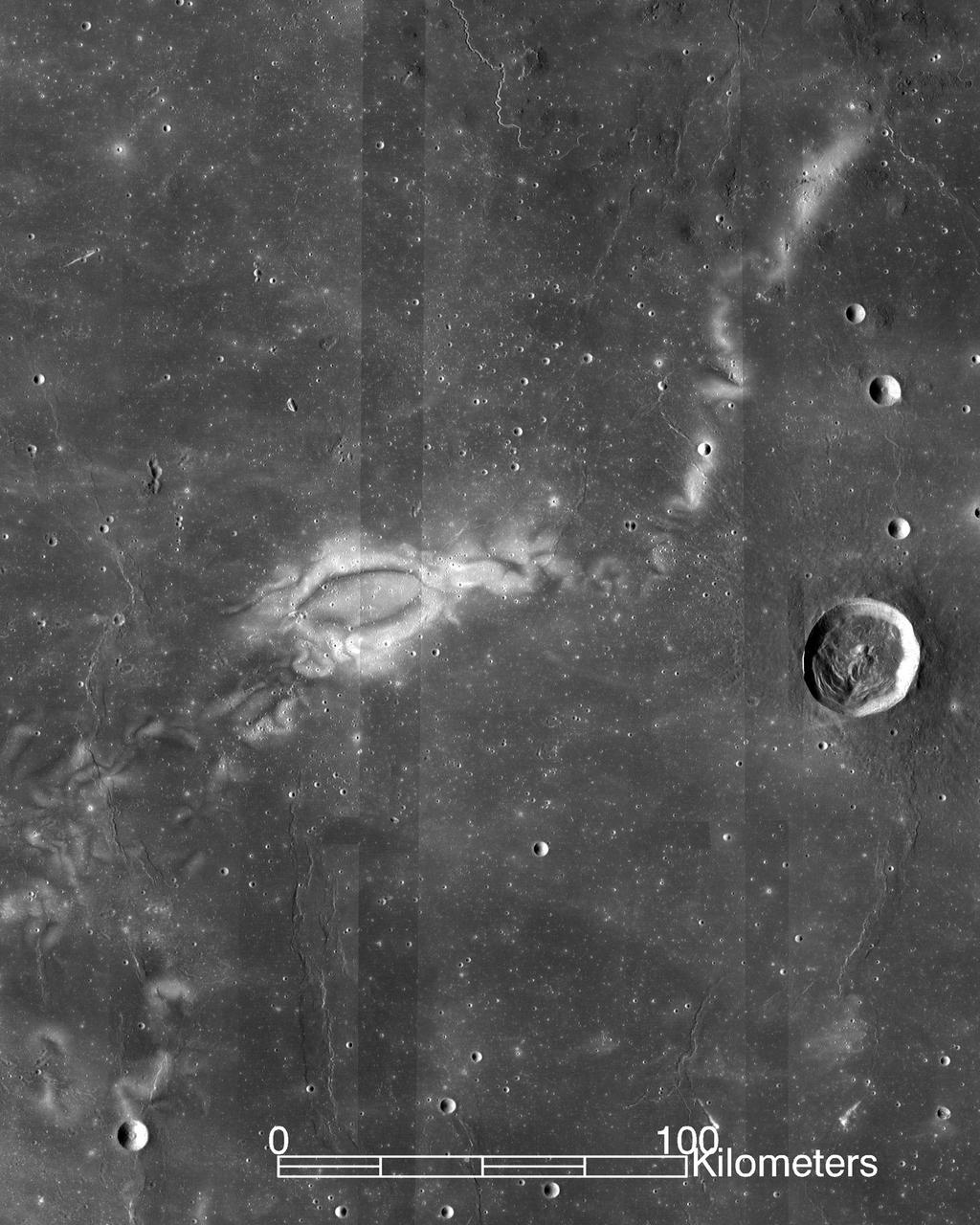
Research using data from NASA's ARTEMIS mission suggests that lunar swirls, like the Reiner Gamma lunar swirl imaged here by NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, could be the result of solar wind interactions with the Moon's isolated pockets of magnetic field. Credits: NASA LRO WAC science team

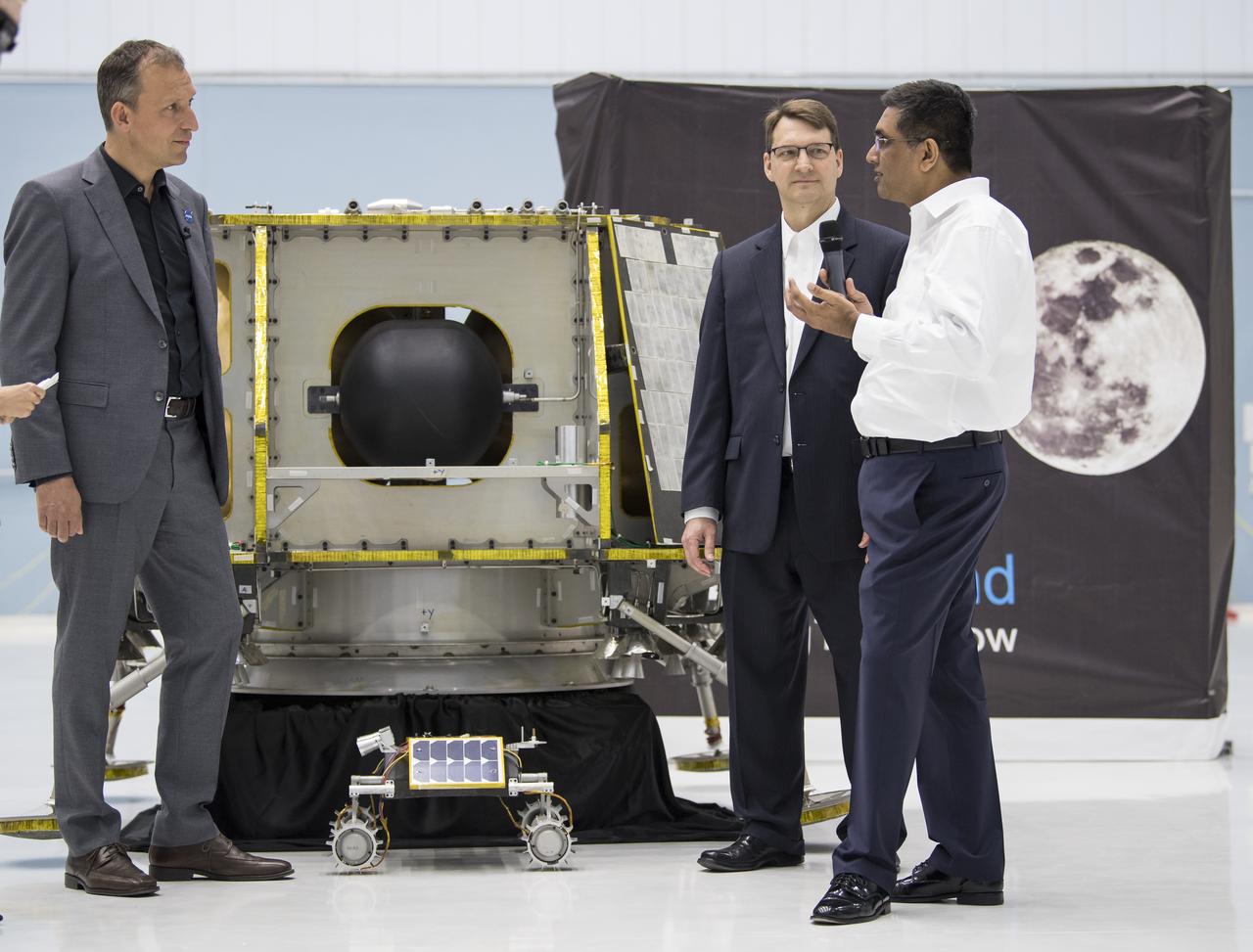
A science instrument flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative could help improve our understanding of the Moon. The Lunar Instrumentation for Subsurface Thermal Exploration with Rapidity, or LISTER, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed jointly by Texas Tech University and Honeybee Robotics, LISTER’s planned mission is to measure the flow of heat from the Moon’s interior using a specialized drill. Investigations and demonstrations, such as LISTER, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development and operations for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.

jsc2025e067512 --- Artemis II science officers Kelsey Young, left, and Angela Garcia sit at the Science console in the White Flight Control Room of the Mission Control Center at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. Artemis II will test mission science operations and integration into flight control. Lessons learned during Artemis II science operations will pave the way for lunar science operations for future Artemis missions. A team of experts will staff the Science Evaluation Room (SER) at Johnson, providing lunar scientific expertise, data analysis, and strategic guidance in real-time to the science officer and the rest of Mission Control.

NASA Ames Robotics Academy Interns at the Lunar Science Institute (LSI) building 17

LCROSS Family night at Ames. Dr. David Morrison Interim Director of the Lunar Science Institute at Ames addresses the crown.
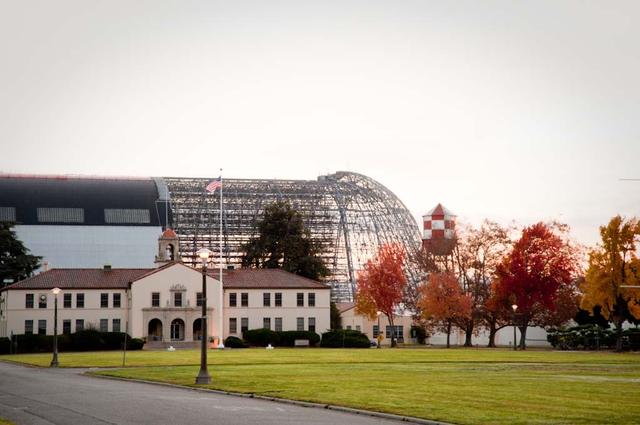

Lunar Science Institute, Bldg-17 at NASA Research Park in the fall with Hangar One deskinning project going on in backbround.

S77-22549 --- Dr. Farouk El-Baz (left), a scientist, chats with other participants of the Eighth Annual Lunar Science Conference.
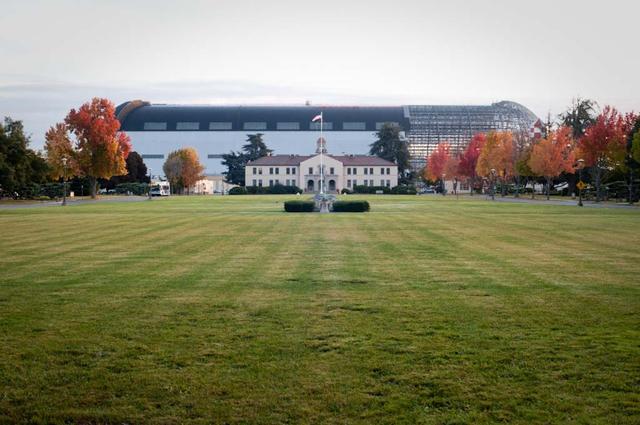

Lunar Science Institute, Bldg-17 at NASA Research Park in the fall with Hangar One deskinning project going on in backbround.
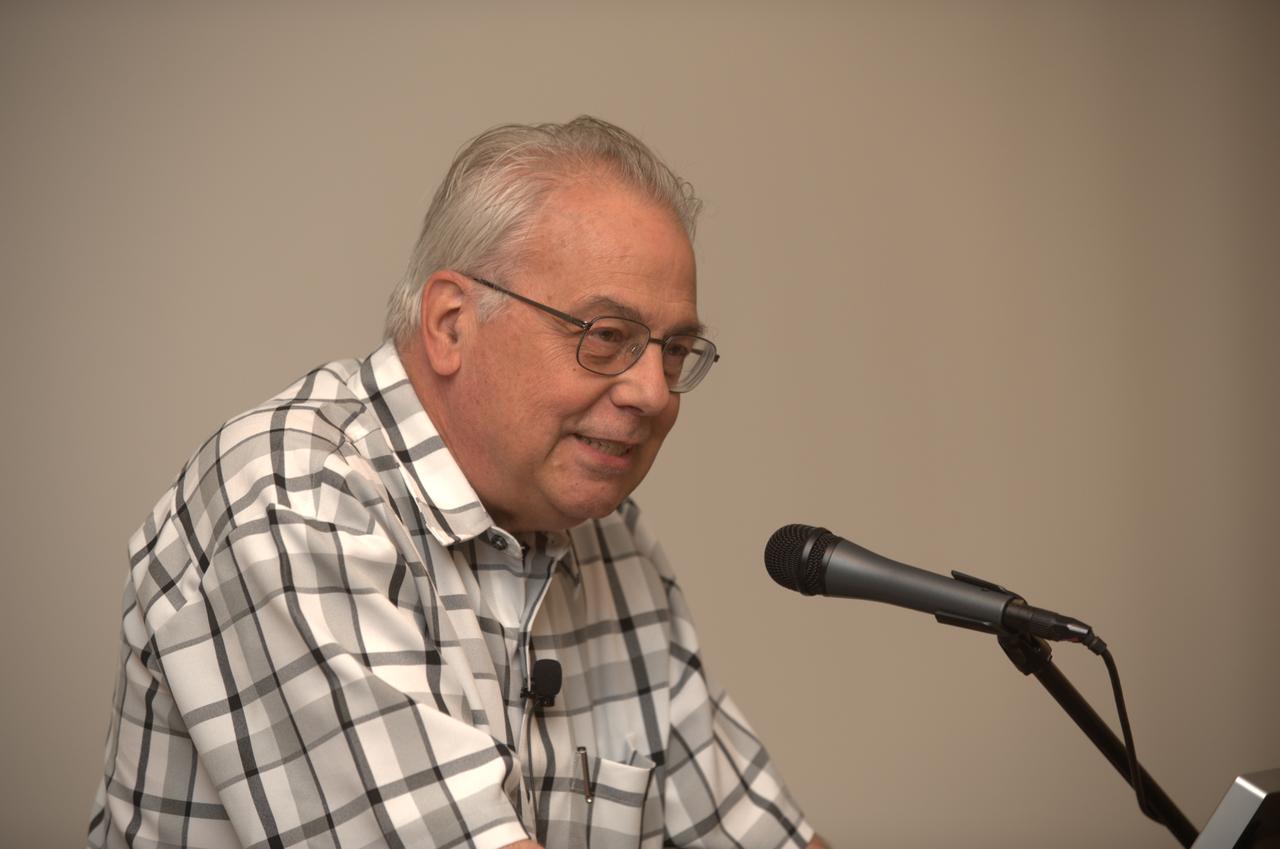

LCROSS Family night at Ames. Dr. David Morrison Interim Director of the Lunar Science Institute at Ames addresses the crown.
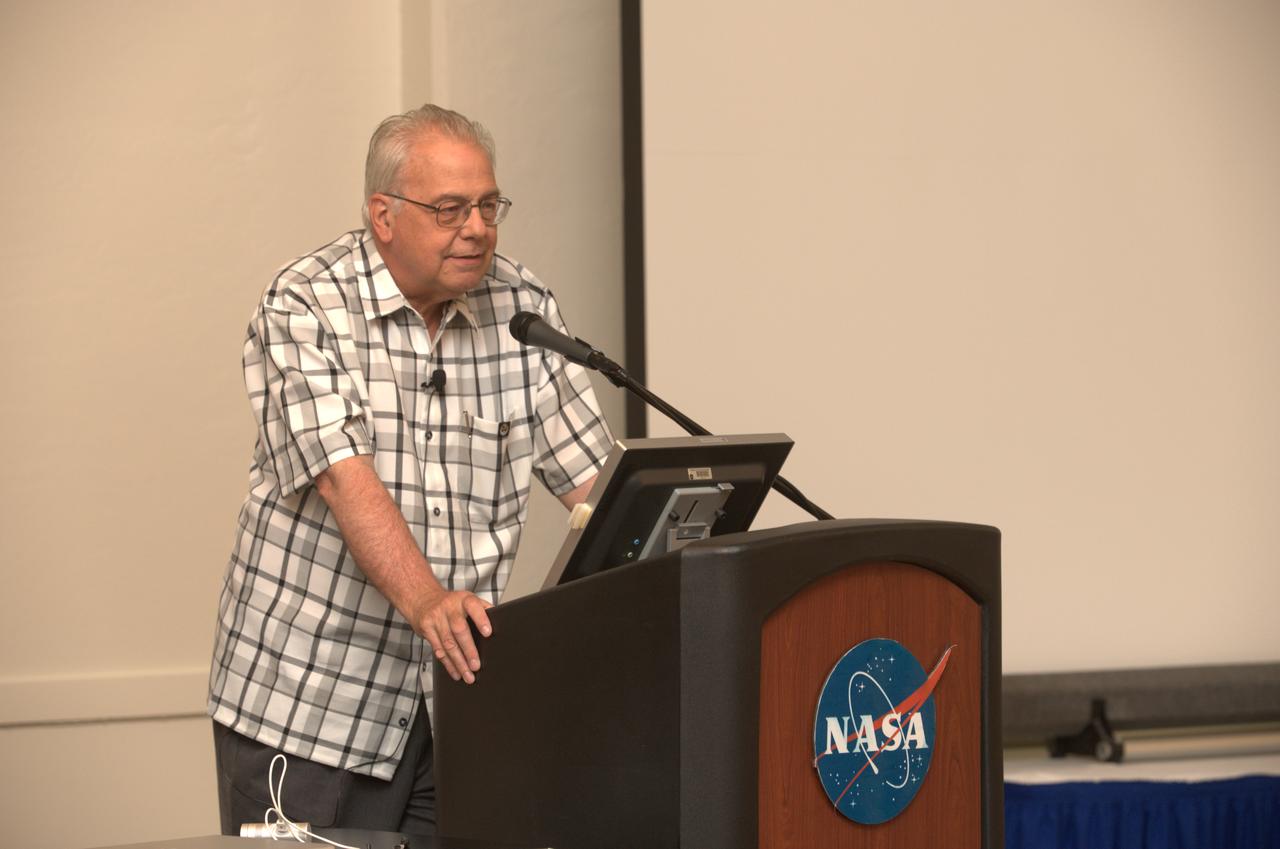

LCROSS Family night at Ames. Dr. David Morrison Interim Director of the Lunar Science Institute at Ames addresses the crown.

Dr. David Morrison being interviewed by Space News regarding the Lunar Science Institute at the NASA Research Park.
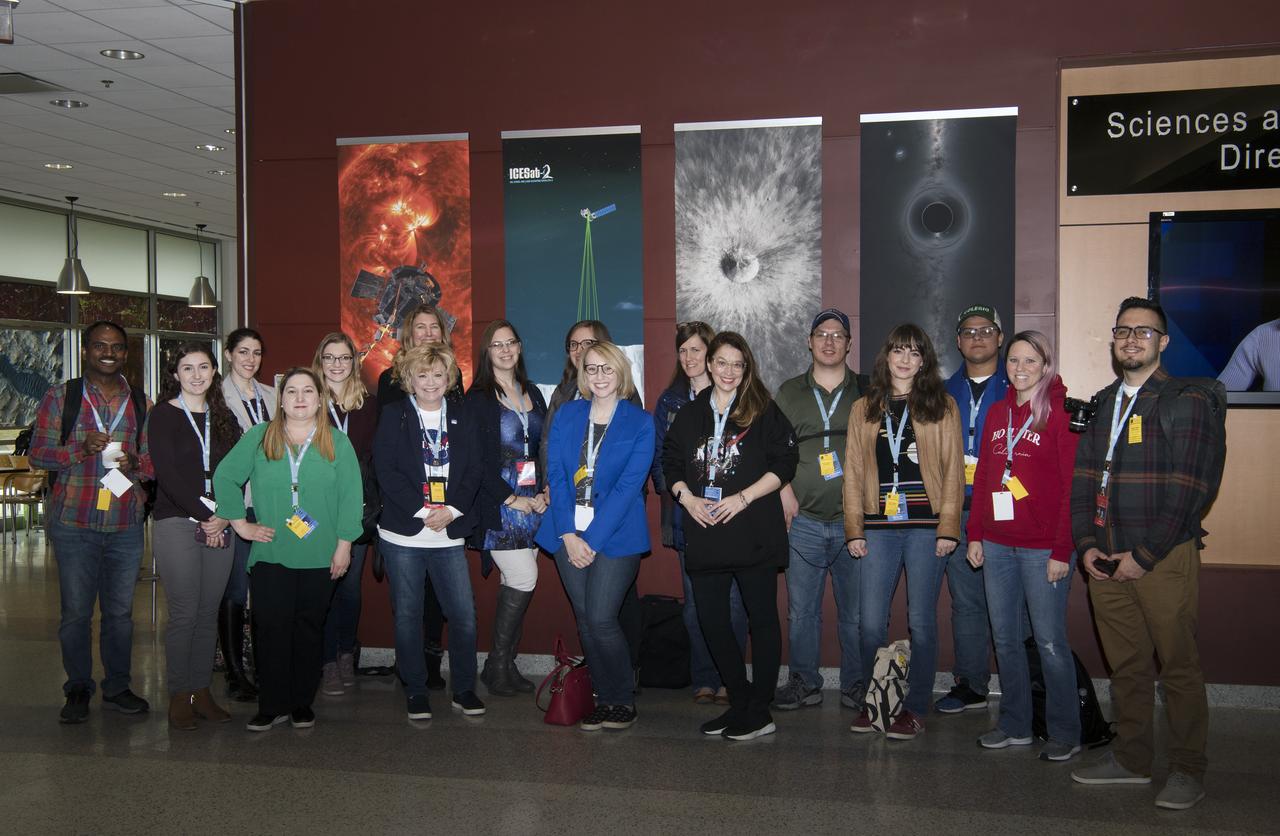

Social media followers visited GSFC Feb 10, 2020 learning role of Artemis, LRO Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, spoke with science experts while touring center Sciences B34
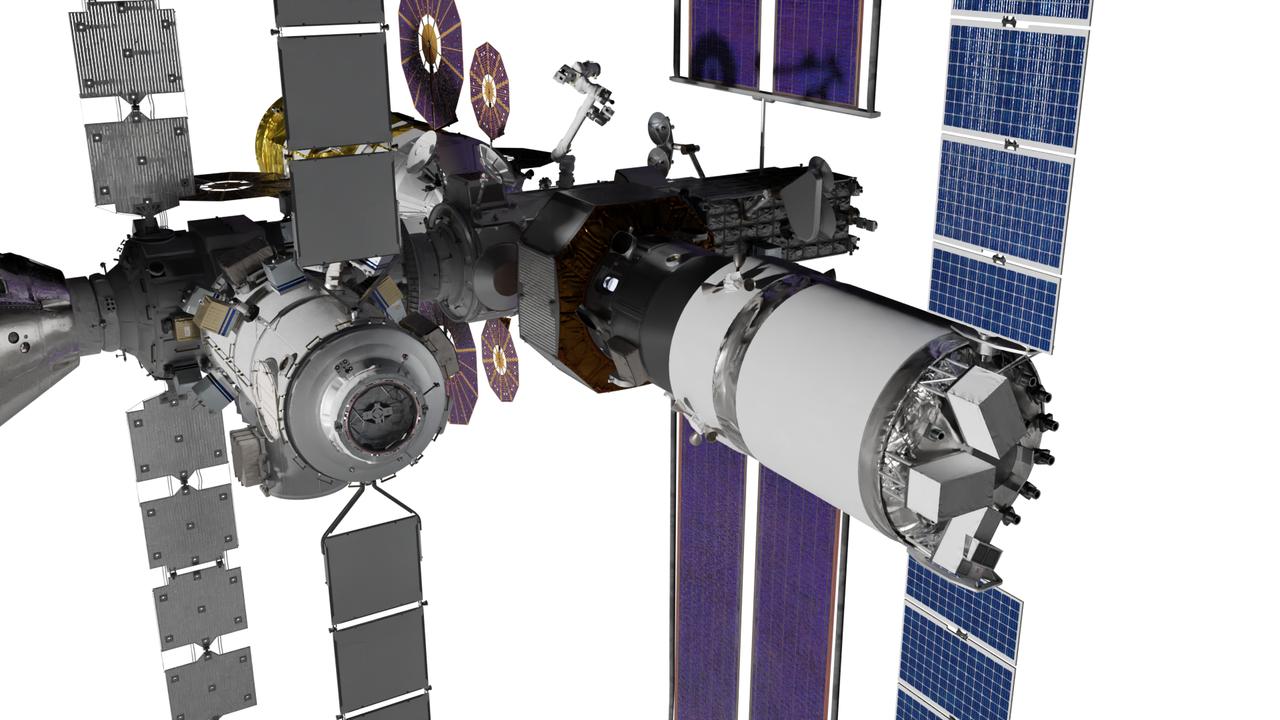
An artist’s rendering displays a configuration of the lunar-orbiting Gateway space station’s modules and visiting spacecraft. The core elements of Gateway consist of the Habitation and Logistics Outpost (HALO) element, the Power and Propulsion Element (PPE), and Lunar I-Hab. Visiting vehicles include the Orion spacecraft, the Logistics Module, and the Human Landing System. Gateway is built in collaboration with NASA’s commercial and international partners to serve as a multiuse space port for lunar science as humanity’s first place to live and work in lunar orbit.
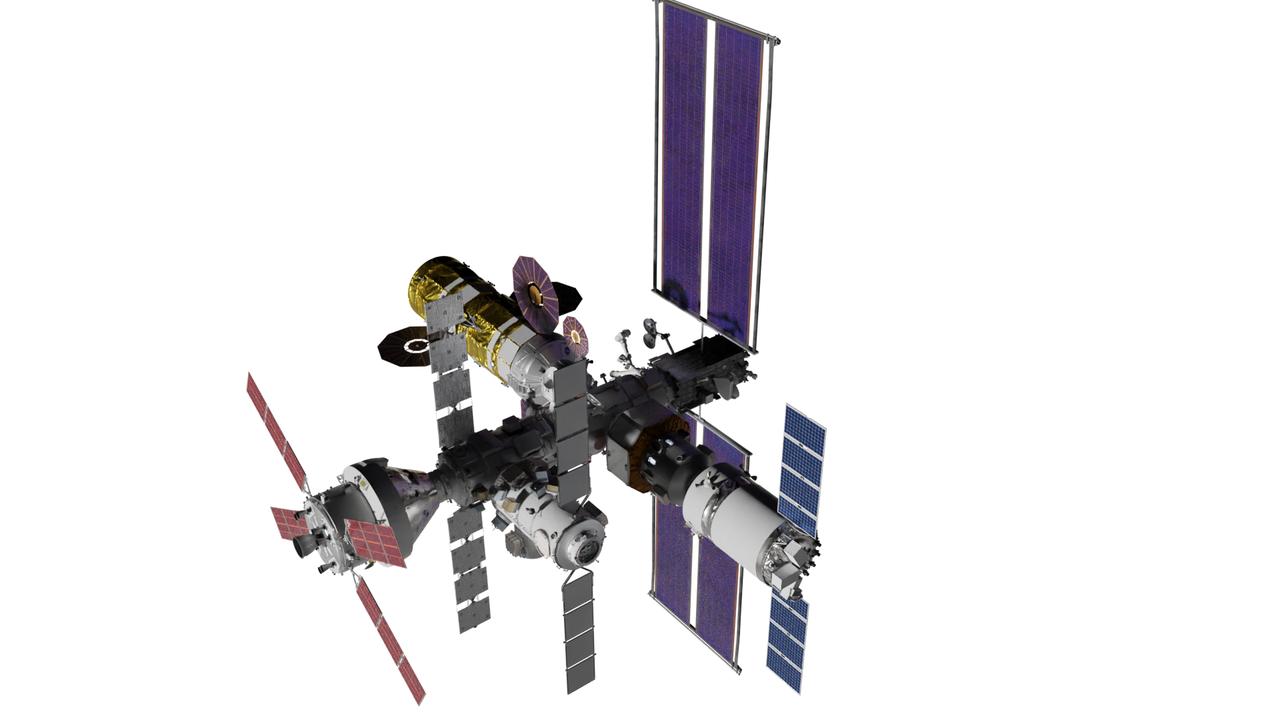

An artist’s rendering displays a configuration of the lunar-orbiting Gateway space station’s modules and visiting spacecraft. The core elements of Gateway consist of the Habitation and Logistics Outpost (HALO) element, the Power and Propulsion Element (PPE), and Lunar I-Hab. Visiting vehicles include the Orion spacecraft, the Logistics Module, and the Human Landing System. Gateway is built in collaboration with NASA’s commercial and international partners to serve as a multiuse space port for lunar science as humanity’s first place to live and work in lunar orbit.
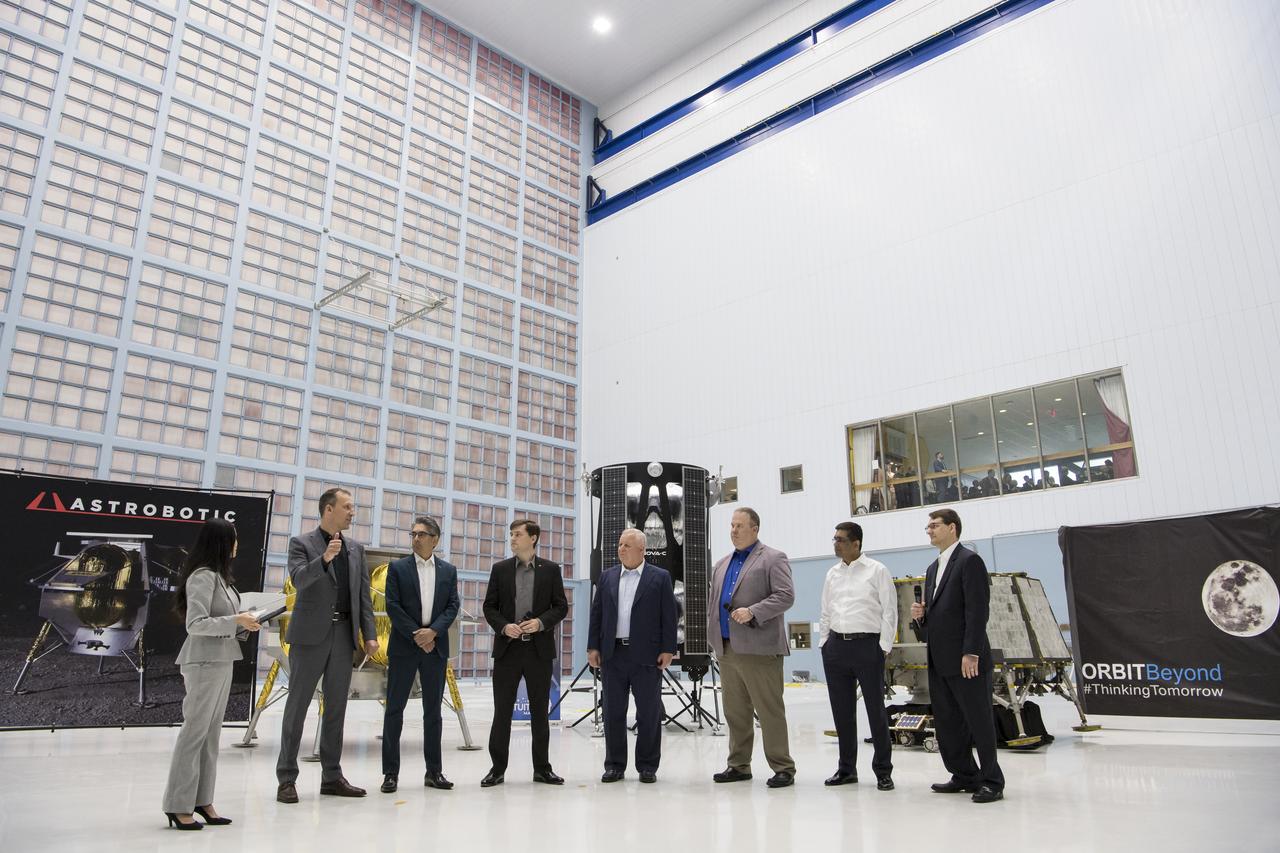

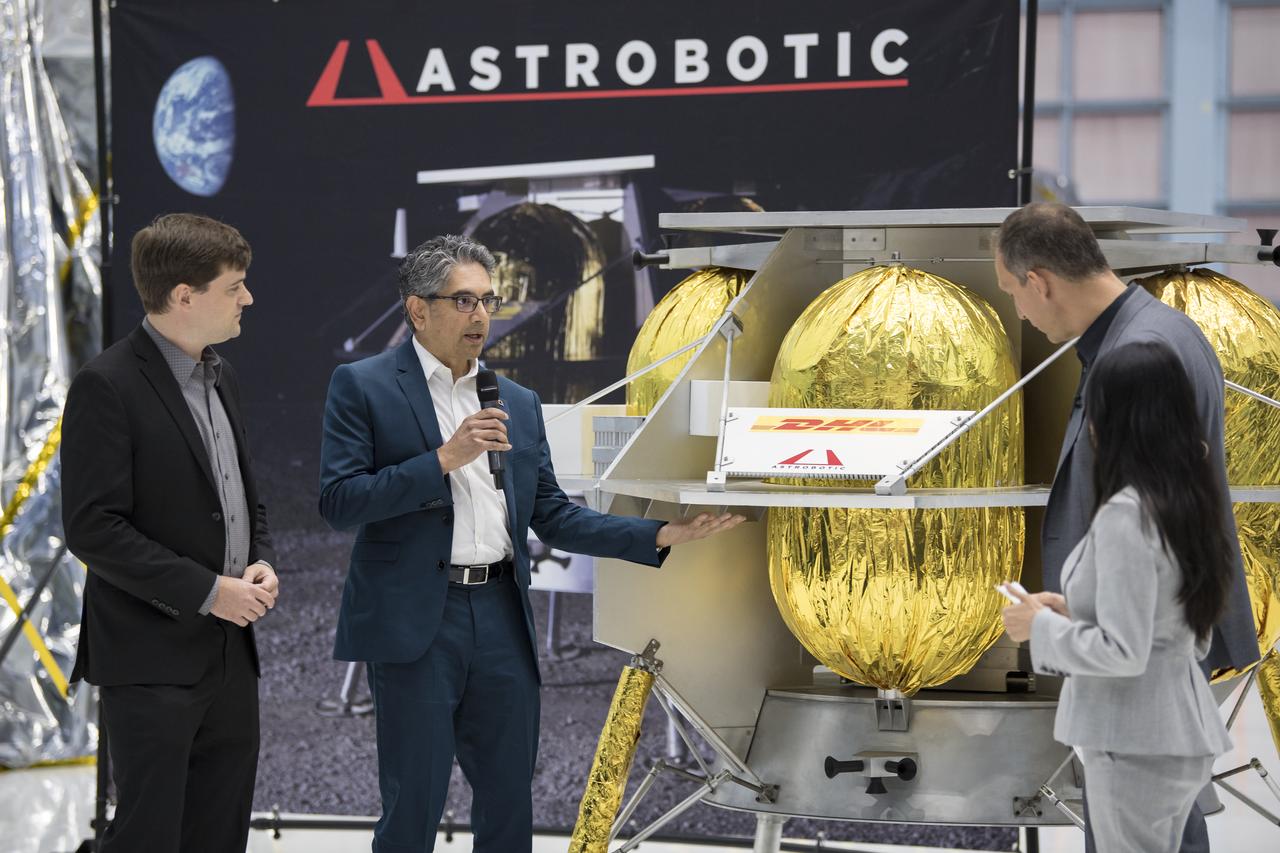
From left to right, NASA Press Officer, Felicia Chou; NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen; Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran; Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton; Chairman of the Board of Intuitive Machines, Kam Ghaffarian; VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain; President and CEO of OrbitBeyond, Siba Padhi; and Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse talk about their lunar landers, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
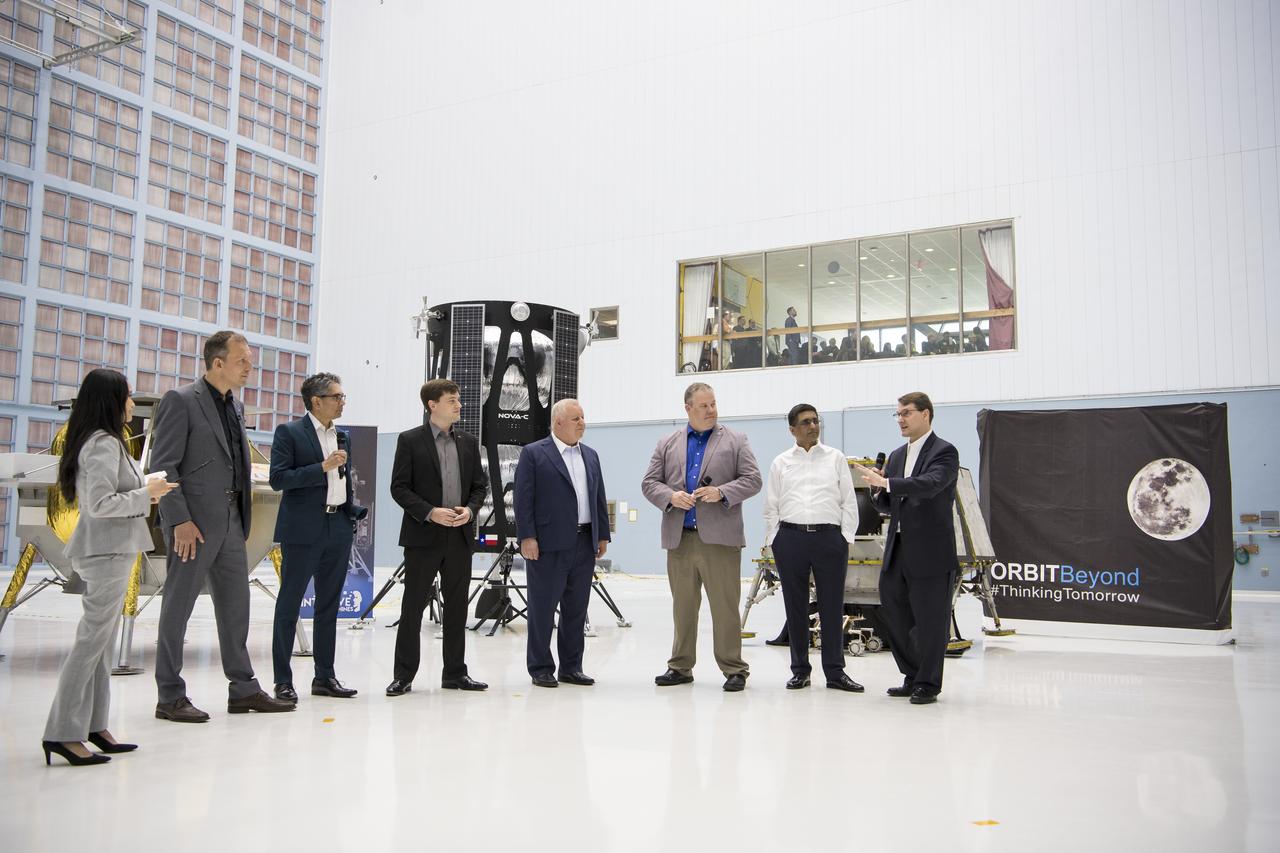

Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse speaks about their lunar lander with, from left to right, NASA Press Officer, Felicia Chou; NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen; Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran; Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton; Chairman of the Board of Intuitive Machines, Kam Ghaffarian; VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain; President and CEO of OrbitBeyond, Siba Padhi, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
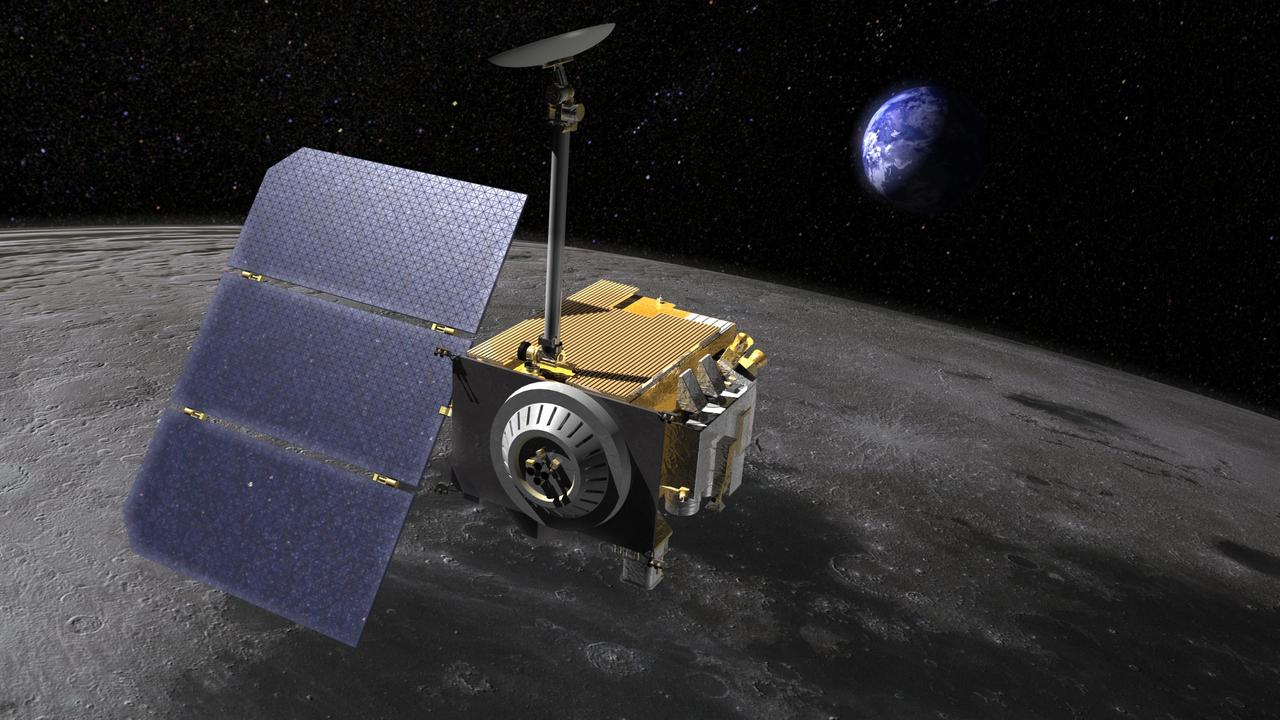

Artist rendering of the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter LRO, above the moon. LRO carries seven instruments that make comprehensive remote sensing observations of the moon and measurements of the lunar radiation environment. The LRO mission is managed by NASA Goddard for the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18163
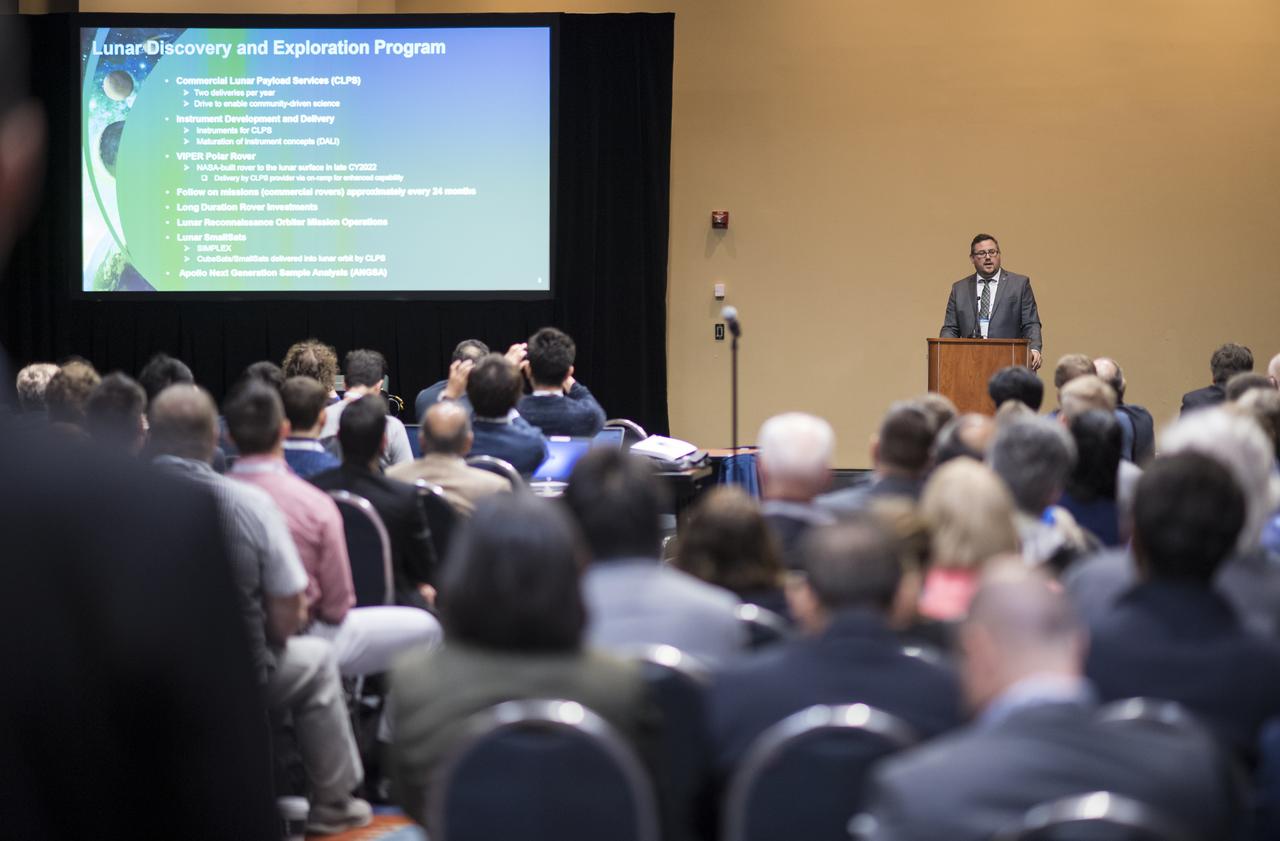

Brad Bailey, program scientist with NASA's Lunar Discovery and Exploration Program is seen during a keynote titled “An Overview of NASA’s Lunar Science Exploration Plans for Artemis” at the 70th International Astronautical Congress, Tuesday, Oct. 22, 2019 at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Brad Bailey, program scientist with NASA's Lunar Discovery and Exploration Program is seen during a keynote titled “An Overview of NASA’s Lunar Science Exploration Plans for Artemis” at the 70th International Astronautical Congress, Tuesday, Oct. 22, 2019 at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
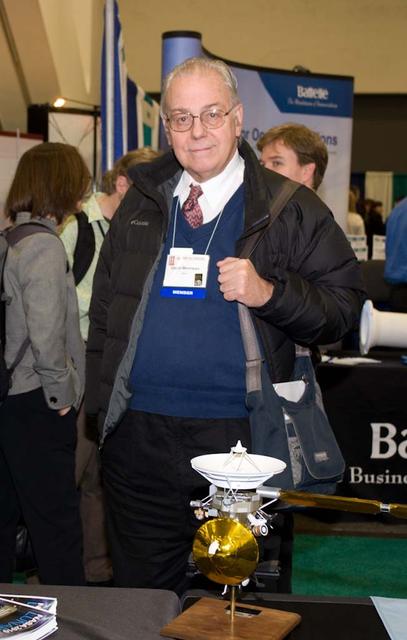

2009 American Geophysical Union (AGU) conference in San Francisco, California. Dr David Morrison, Director Lunar Science Institute and Senior Scientist, NASA Astrobiology.
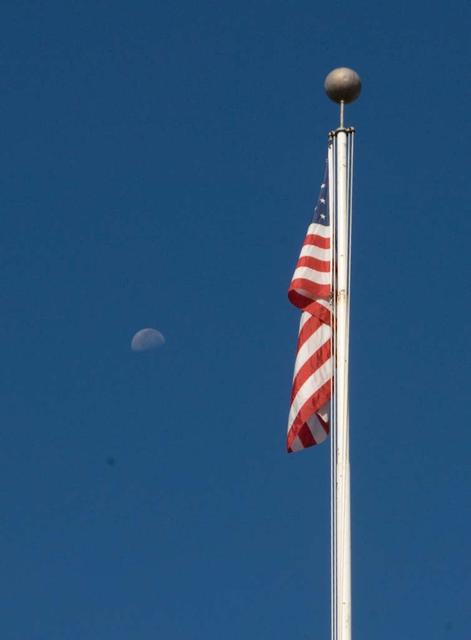

First Lunar Science Institute (LSI) collobration signing with nine (9) International partners. The Moon makes a daylight appearance over the LSI building-17.
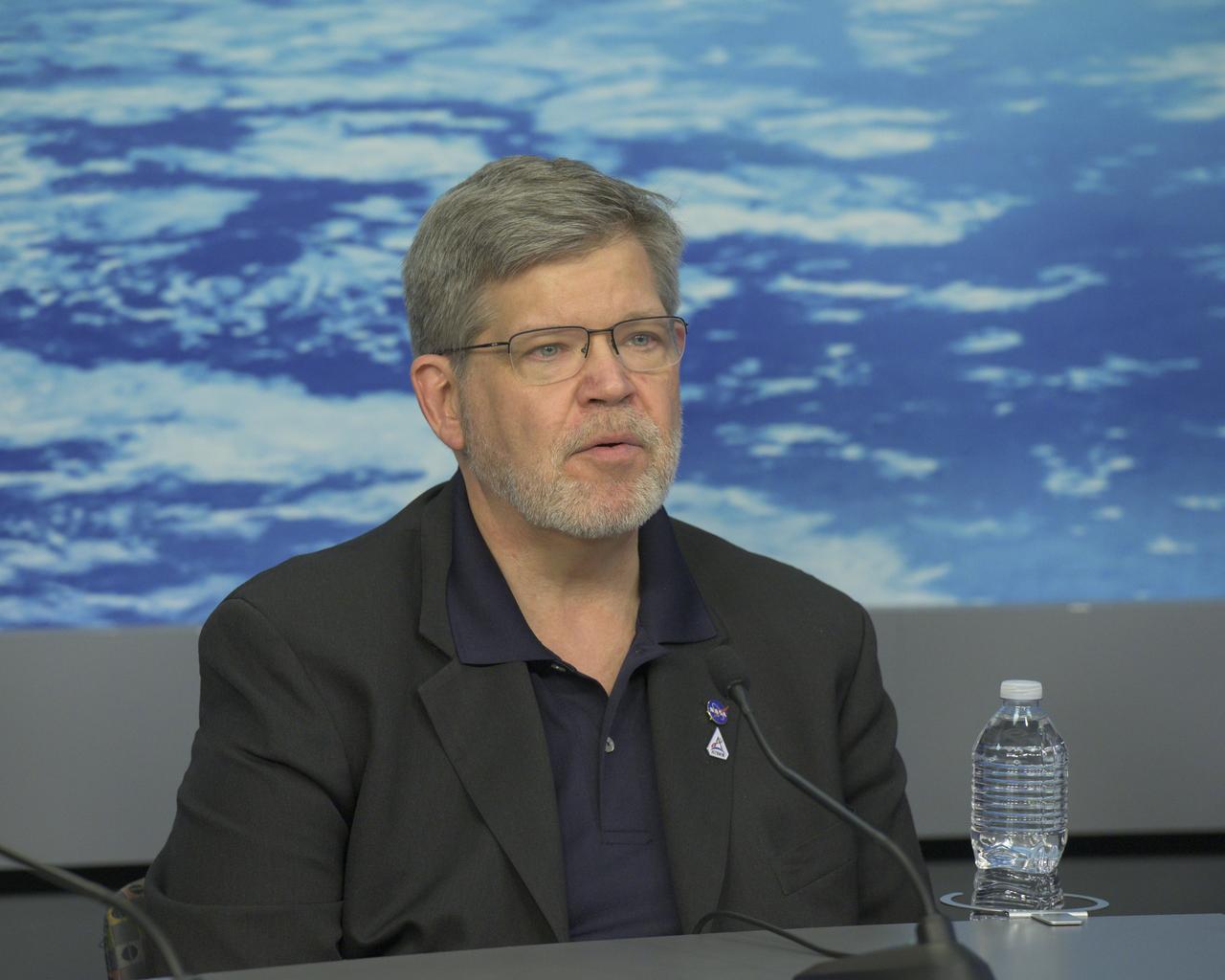

Joel Kearns, deputy associate administrator for Exploration, Science Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters, participates in a news conference Feb. 23, 2024, at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Kearns was on hand to discuss the NASA science and technology aboard Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lander, called Odysseus, and its successful soft landing on the Moon Feb. 22, 2024. The mission is the first landing under NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, and the first American lunar landing in more than 50 years.
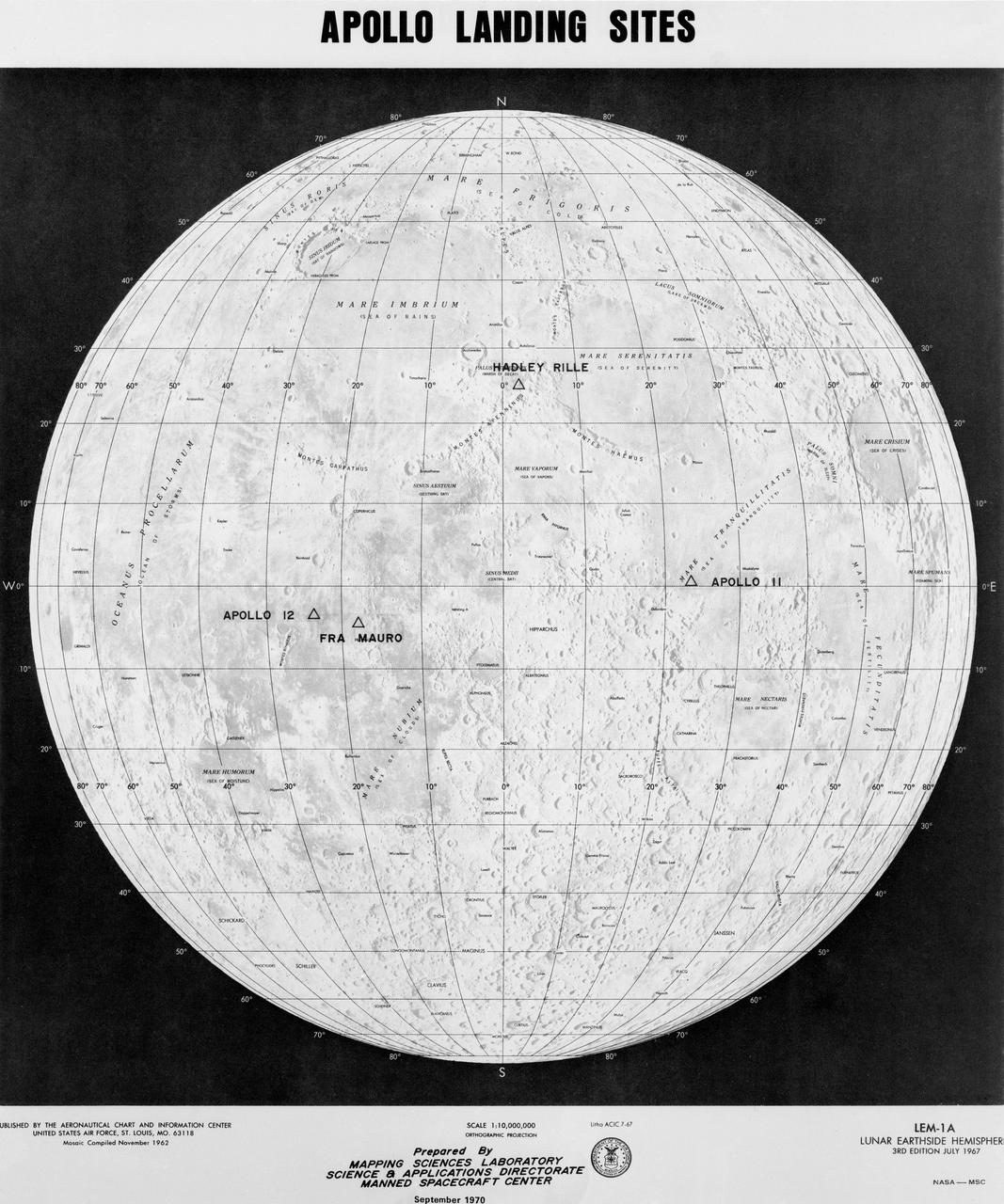
S70-50761 (September 1970) --- This map prepared by Mapping Sciences Laboratory, Science & Applications Directorate at the Manned Spacecraft Center, shows the projected Apollo landing sites. Apollo 11 completed a successful lunar landing mission in the Sea of Tranquility in July 1969. Apollo 12 completed a successful lunar landing mission in the Ocean of Storms in November 1969.
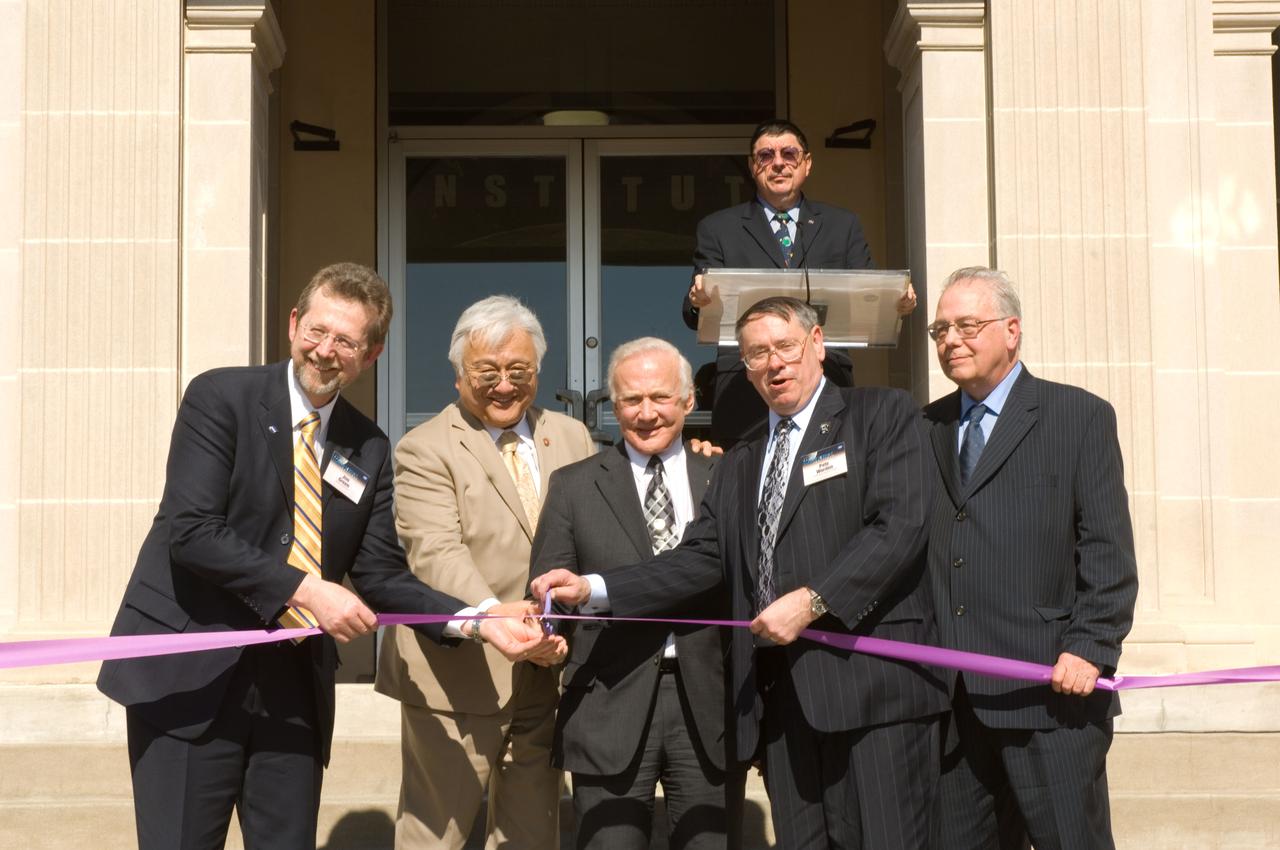

Lunar Science Institute (LSI) Grand Opening. Ribbon Cutting, L-R: James Green, Director, Planetary Programs, NASA Headquarters, Mike Honda, U.S. Congressman,15th District, Apollo Astronaut Buzz Aldrin, S. Pete Worden, Director, NASA Ames Research Center, David Morrison, Interiu Director, NASA Lunar Science Institute. David Morse at podium.
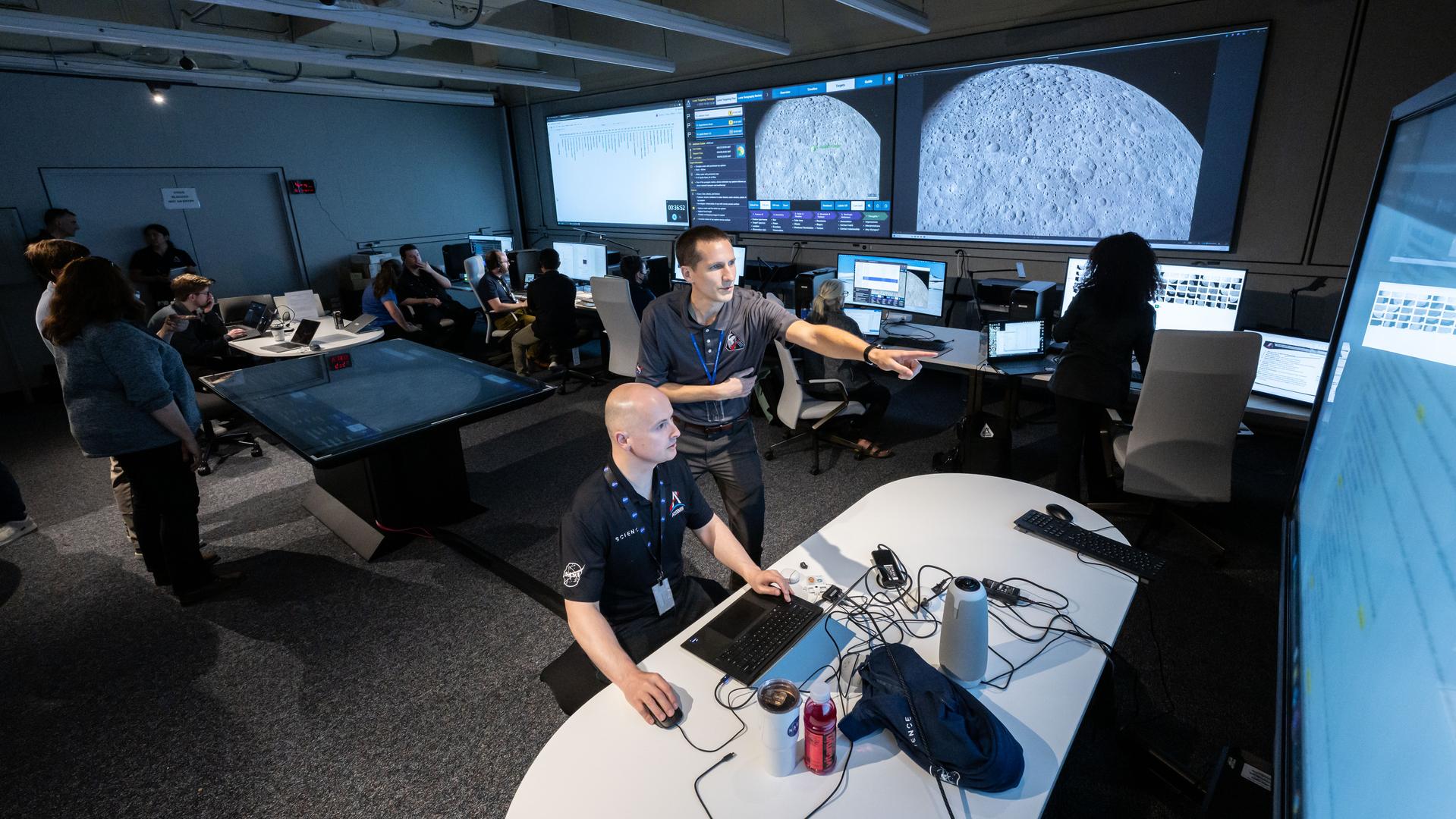

jsc2025e087237 --- Artemis lunar science team members Andrew Needham, sitting, and David Hollibaugh work in the Science Mission Operations Room (SMOR) at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston during a simulation of the Artemis II lunar flyby during which astronauts will document their observations through photographs and audio recordings to inform scientists’ understanding of the Moon. Credit: NASA/James Blair
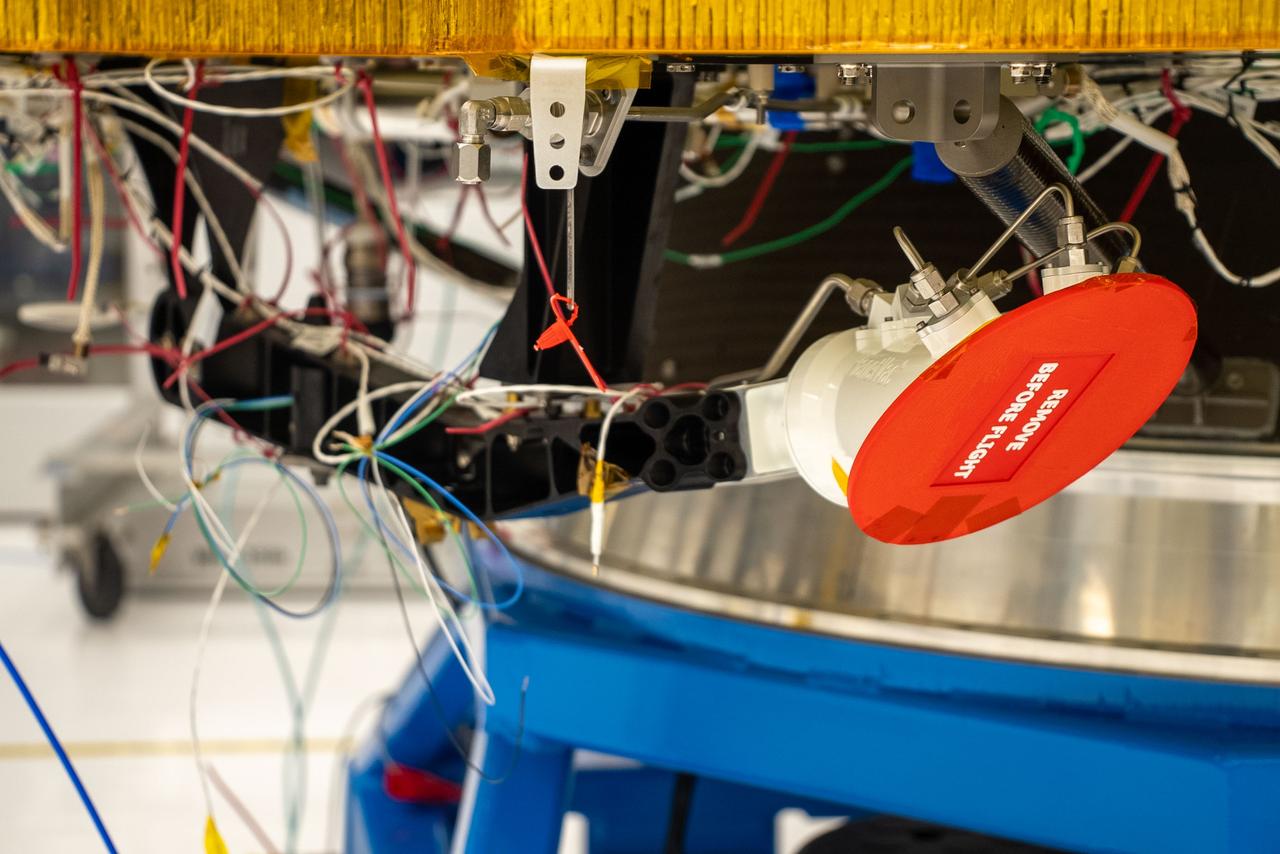
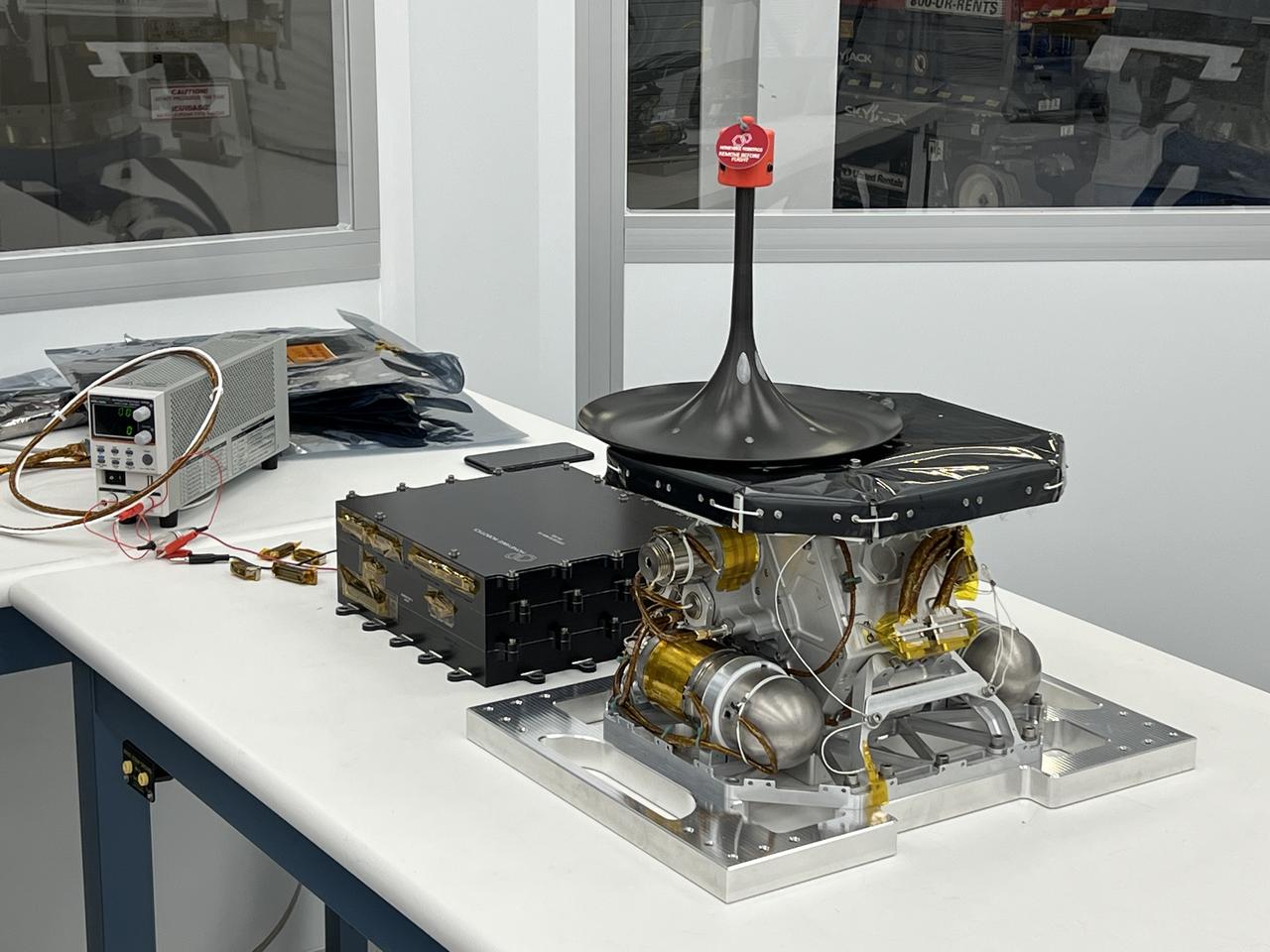
A technology demonstration flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative could change how research teams collect and study soil and rock samples on other planetary bodies. Lunar PlanetVac, or LPV, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Honeybee Robotics, a Blue Origin company of Altadena, California, LPV is designed to, essentially, operate as a vacuum cleaner with a pneumatic, compressed gas-powered sample acquisition and delivery system to efficiently collect and transfer lunar soil from the surface to other science instruments or sample return containers. Investigations and demonstrations, such as LPV, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
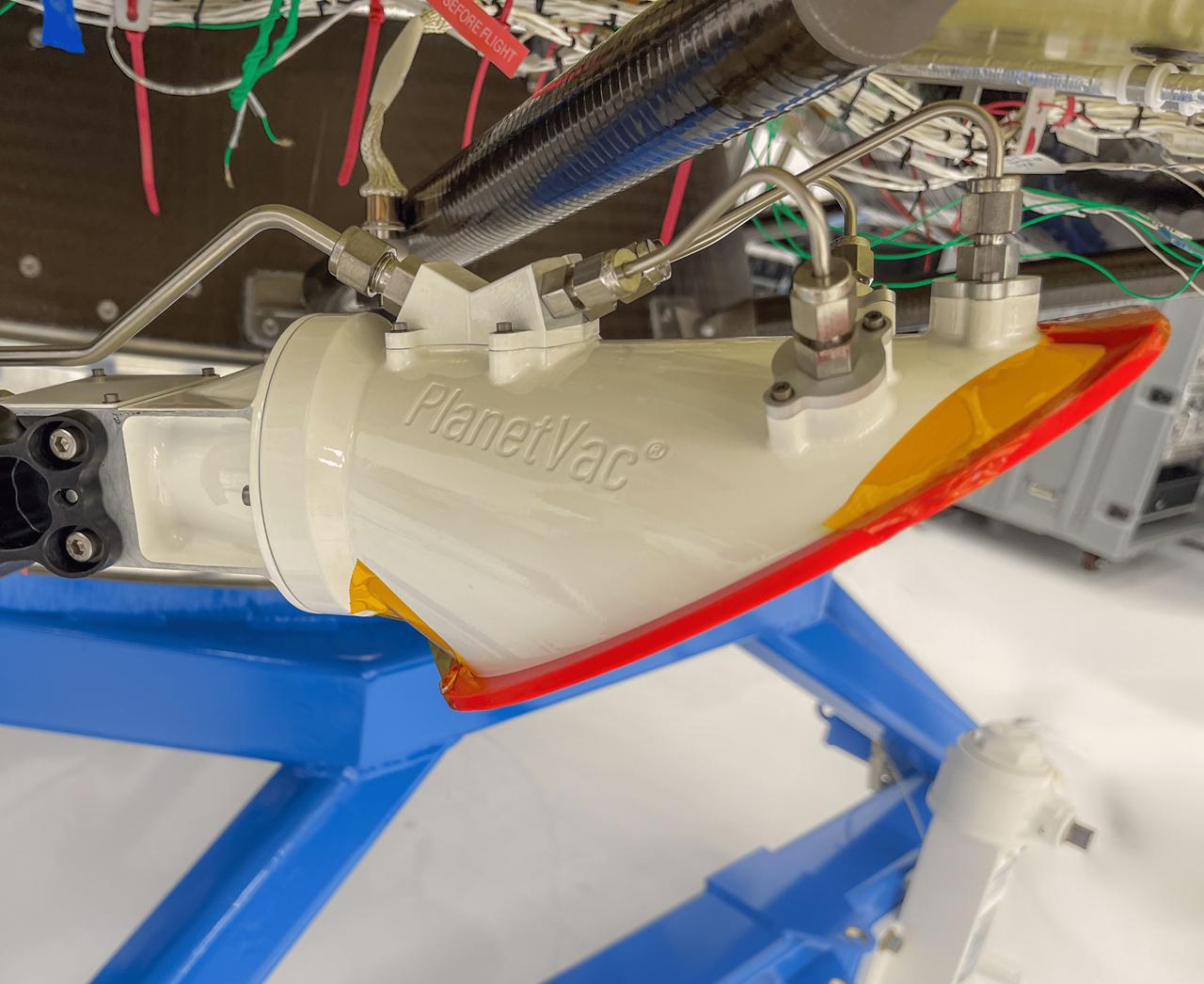

A technology demonstration flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative could change how research teams collect and study soil and rock samples on other planetary bodies. Lunar PlanetVac, or LPV, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Honeybee Robotics, a Blue Origin company of Altadena, California, LPV is designed to, essentially, operate as a vacuum cleaner with a pneumatic, compressed gas-powered sample acquisition and delivery system to efficiently collect and transfer lunar soil from the surface to other science instruments or sample return containers. Investigations and demonstrations, such as LPV, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.

A technology demonstration flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative could change how research teams collect and study soil and rock samples on other planetary bodies. Lunar PlanetVac, or LPV, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Honeybee Robotics, a Blue Origin company of Altadena, California, LPV is designed to, essentially, operate as a vacuum cleaner with a pneumatic, compressed gas-powered sample acquisition and delivery system to efficiently collect and transfer lunar soil from the surface to other science instruments or sample return containers. Investigations and demonstrations, such as LPV, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.

VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain, second from right, speaks with NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, second from left, about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
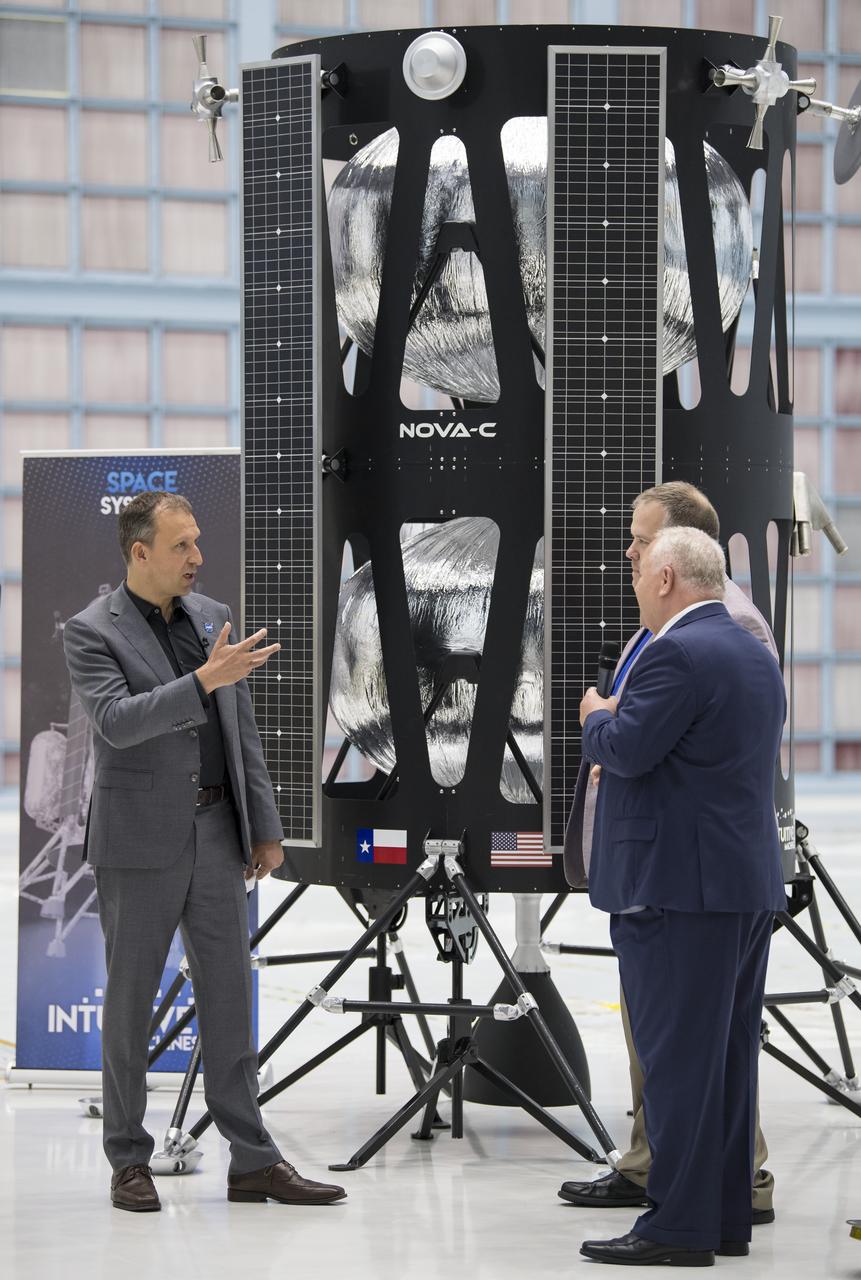

NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, left, speaks to, Chairman of the Board of Intuitive Machines, Kam Ghaffarian, right, and VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain, second from right, about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, second from right, speaks to Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton, second from left, and Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran, left, about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
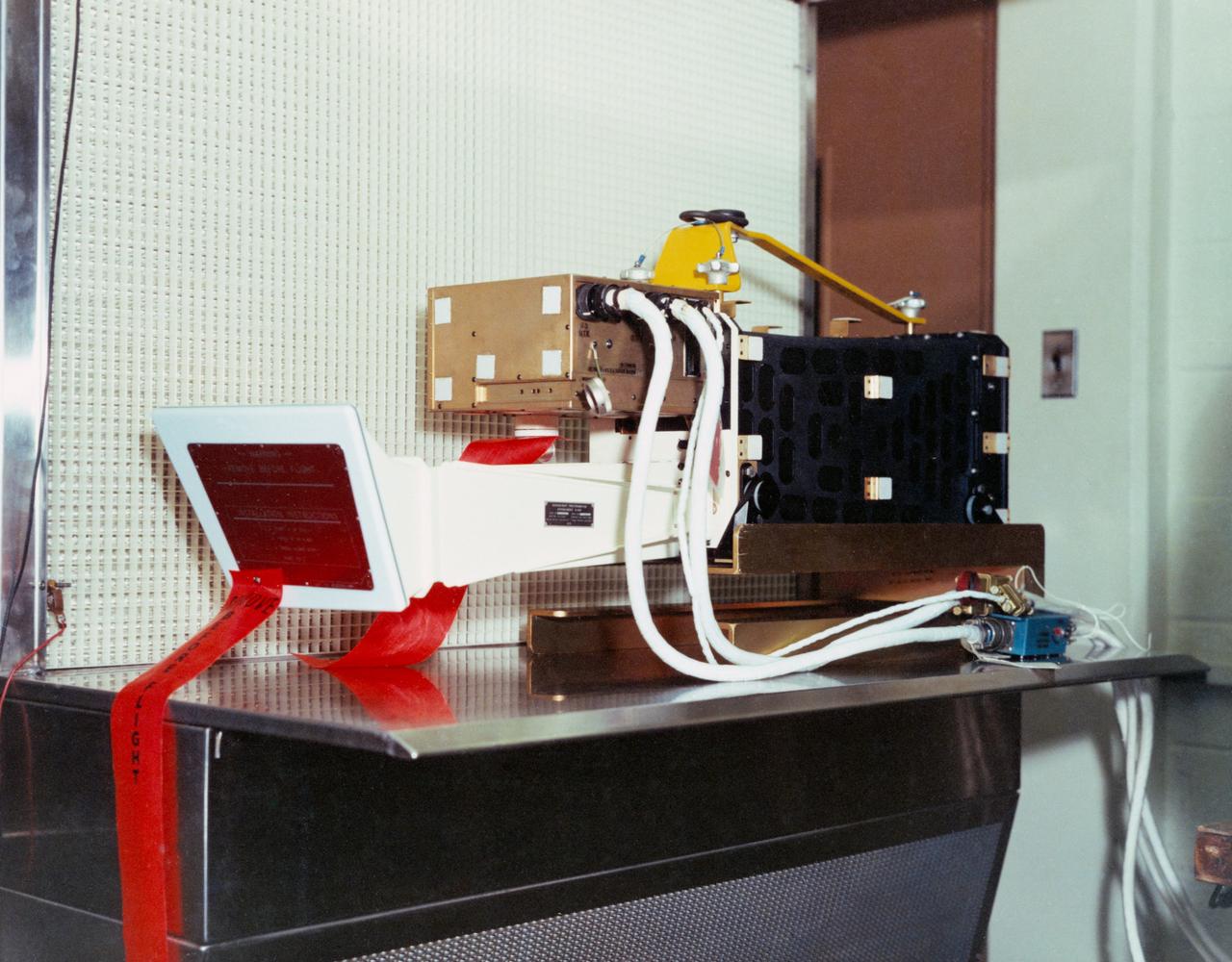

S72-53470 (November 1972) --- The Far-Ultraviolet Spectrometer, Experiment S-169, one of the lunar orbital science experiments which will be mounted in the SIM bay of the Apollo 17 Service Module. Controls for activating and deactivating the experiment and for opening and closing a protective cover are located in the Command Module. Atomic composition, density and scale height for several constituents of the lunar atmosphere will be measured by the far-ultraviolet spectrometer. Solar far-UV radiation reflected from the lunar surface as well as UV radiation emitted by galactic sources also will be detected by the instrument.

VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain, second from right, speaks with NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, second from left, about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

President and CEO of OrbitBeyond, Siba Padhi, left, and Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse, speak about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, second from right, speaks to Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton, left, and Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran, second from left, about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
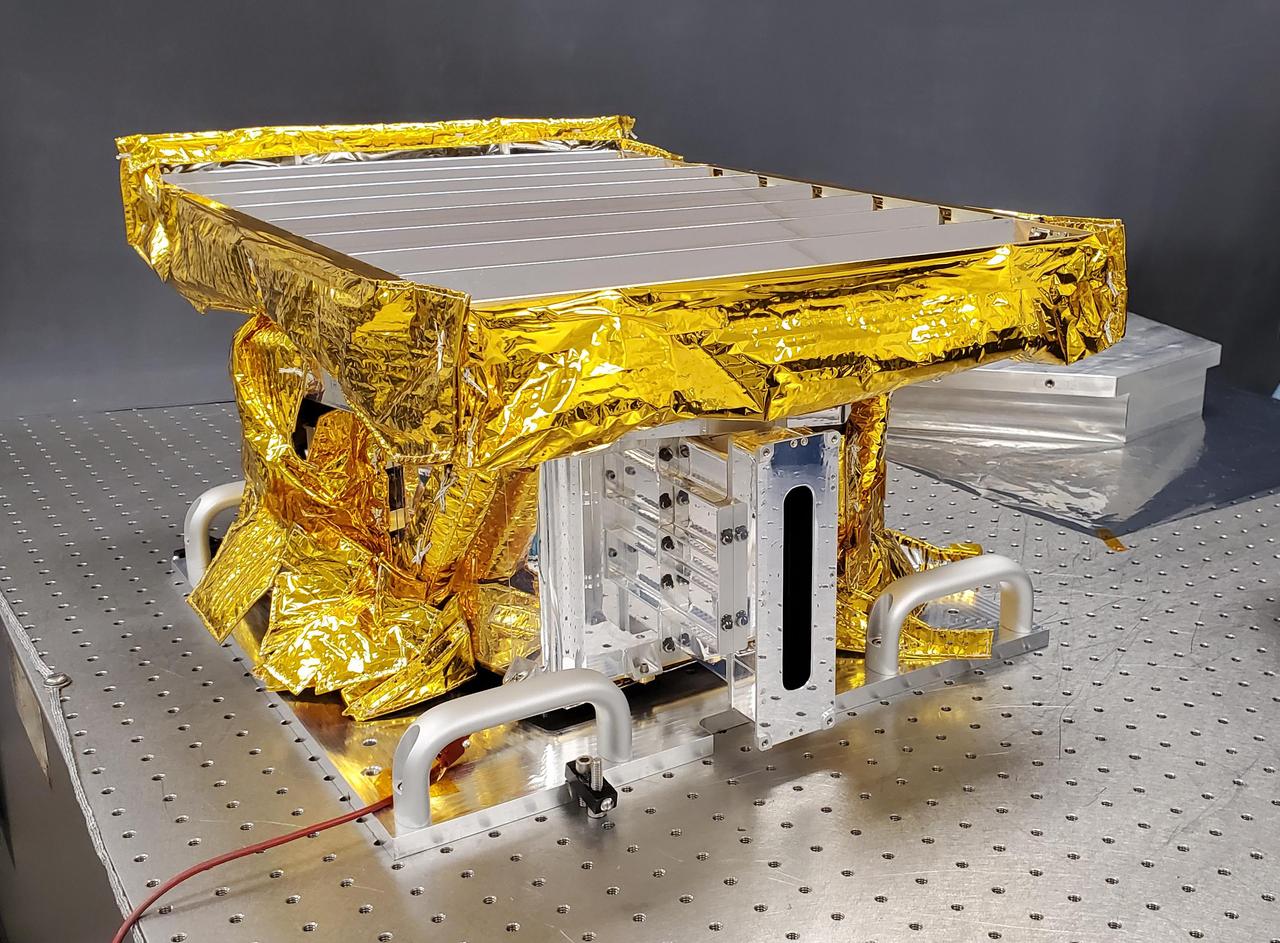

The High-resolution Volatiles and Minerals Moon Mapper (HVM³) sits in a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in early December 2022. The JPL-built instrument was later shipped to Lockheed Martin Space in Littleton, Colorado, to be integrated with NASA's Lunar Trailblazer spacecraft. HVM³ is an imaging spectrometer that will detect and map water on the Moon's surface to determine its abundance, location, form, and how it changes over time. A second instrument, the Lunar Thermal Mapper infrared multispectral imager, is being developed by the University of Oxford in the U.K. and is scheduled for delivery and integration in early 2023. Lunar Trailblazer was selected under NASA's Small Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration (SIMPLEx) program in 2019. The Lunar Trailblazer mission is managed by JPL and its science investigation is led by Caltech in Pasadena, California. Managed for NASA by Caltech, JPL also provides system engineering, mission assurance, the HVM³ instrument, as well as navigation. Lockheed Martin Space provides the spacecraft and integrates the flight system, under contract with Caltech. SIMPLEx mission investigations are managed by the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as part of the Discovery Program at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The program conducts space science investigations in the Planetary Science Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25256
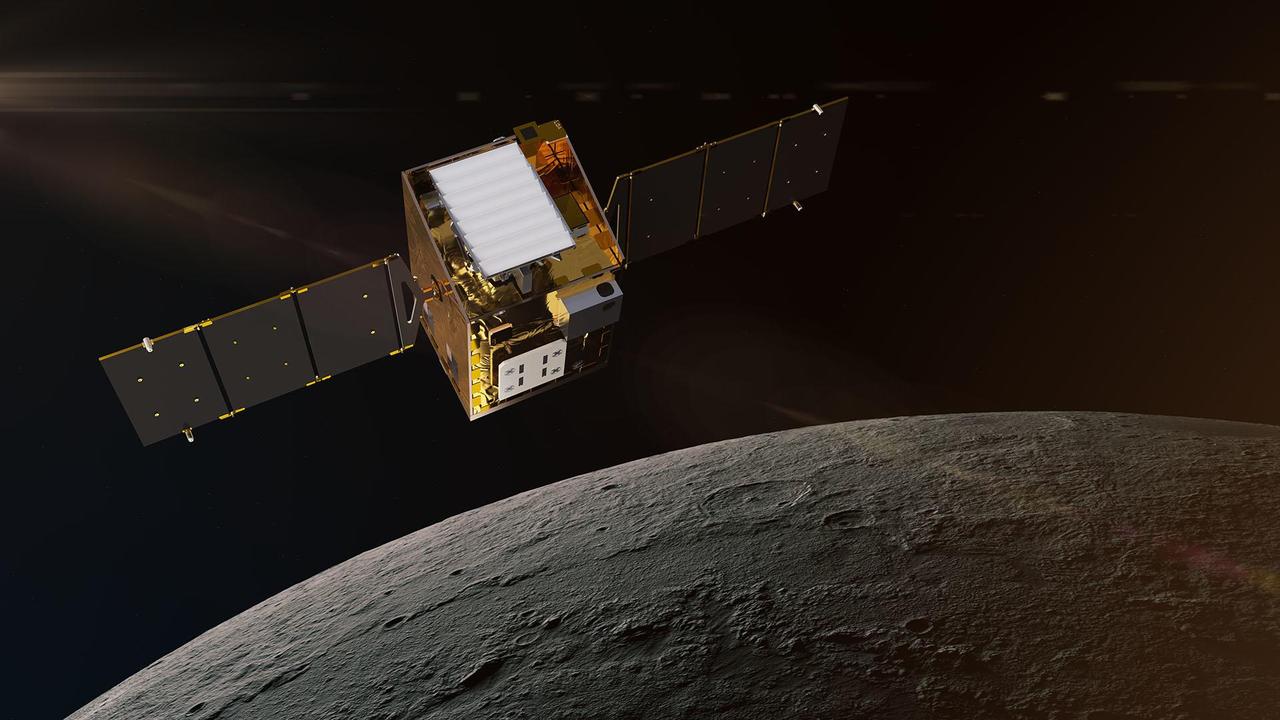

This artist's concept depicts NASA's Lunar Trailblazer in lunar orbit about 60 miles (100 kilometers) from the surface of the Moon. The spacecraft weighs only 440 pounds (200 kilograms) and measures 11.5 feet (3.5 meters) wide when its solar panels are fully deployed. Lunar Trailblazer is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and its science investigation and mission operations are led by Caltech with the mission operations center at IPAC. Managed for NASA by Caltech, JPL also provides system engineering, mission assurance, the HVM3 instrument, as well as mission design and navigation. Lockheed Martin Space provides the spacecraft, integrates the flight system, and supports operations under contract with Caltech. Lunar Trailblazer is part of NASA's Small Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration (SIMPLEx) program, which is managed by the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as part of the Discovery Program at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The program conducts space science investigations in the Planetary Science Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26453

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.
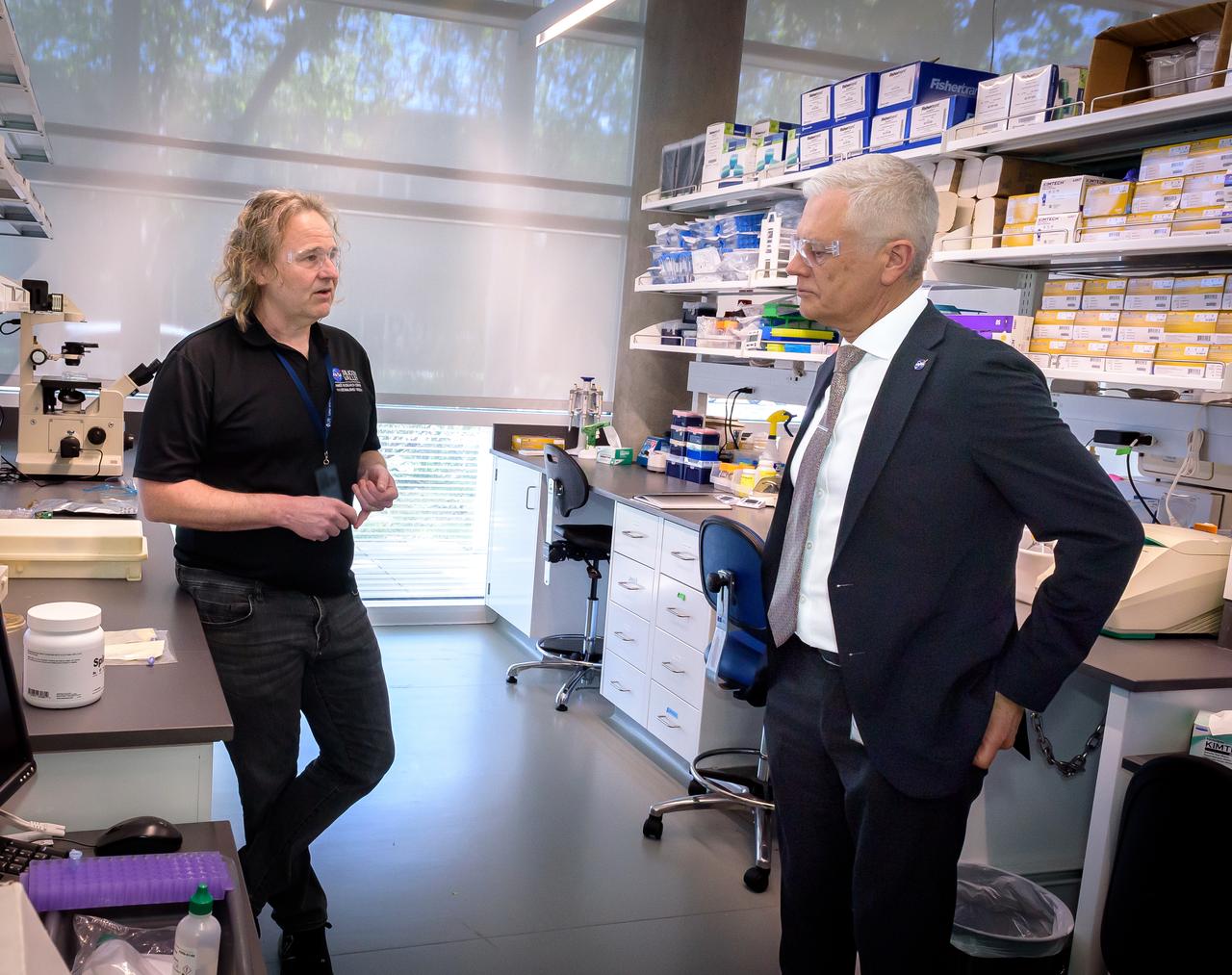

Director of Science Michael Hesse, left, presents an overview of Lunar Explorer Instrument for space biology Applications (LEIA) to Acting Deputy Associate Administrator (DAA) for the Science Mission Directorate (SMD) Mark Clampin in the Bioscience Collaborative Laboratory, N288.
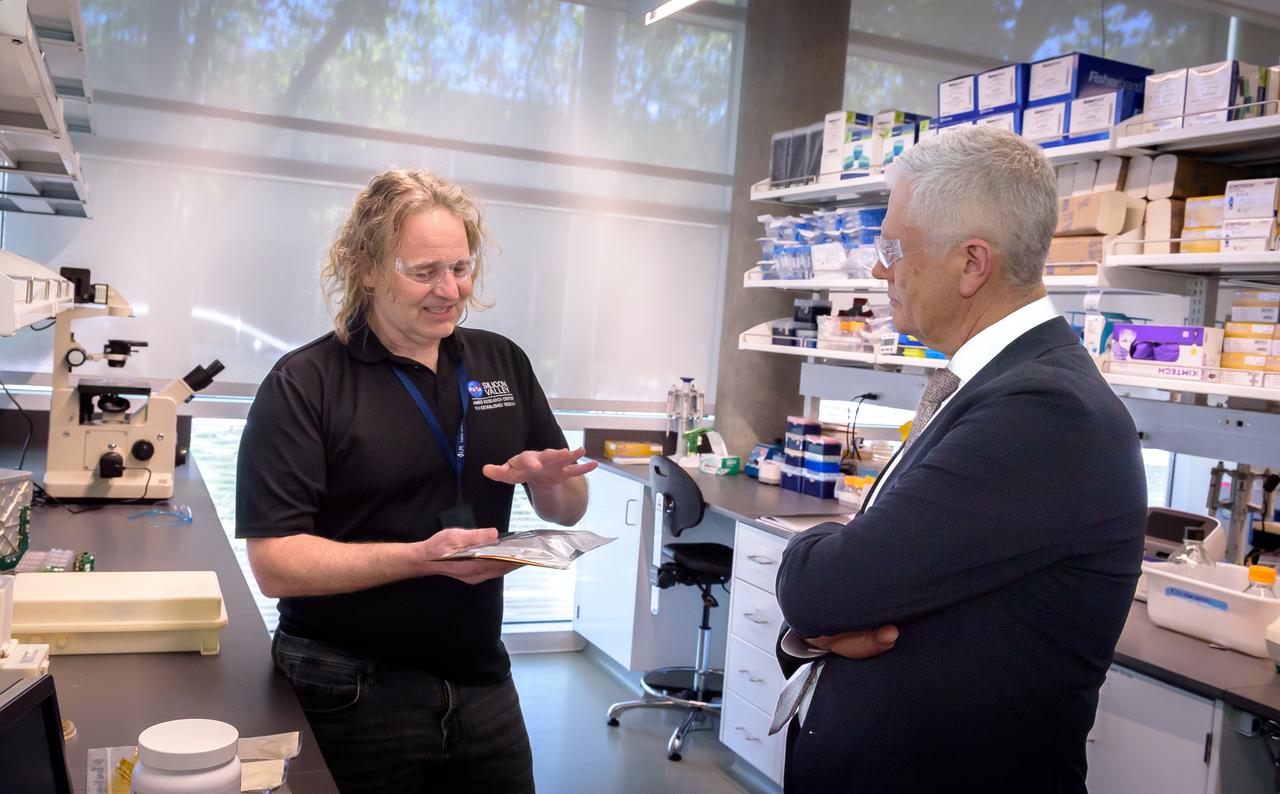

Director of Science Michael Hesse, left, presents an overview of Lunar Explorer Instrument for space biology Applications (LEIA) to Acting Deputy Associate Administrator (DAA) for the Science Mission Directorate (SMD) Mark Clampin in the Bioscience Collaborative Laboratory, N288.