/jsc2024e041788 (1)~medium.jpg)
The Gateway lunar space station configuration and major international and commercial partners.
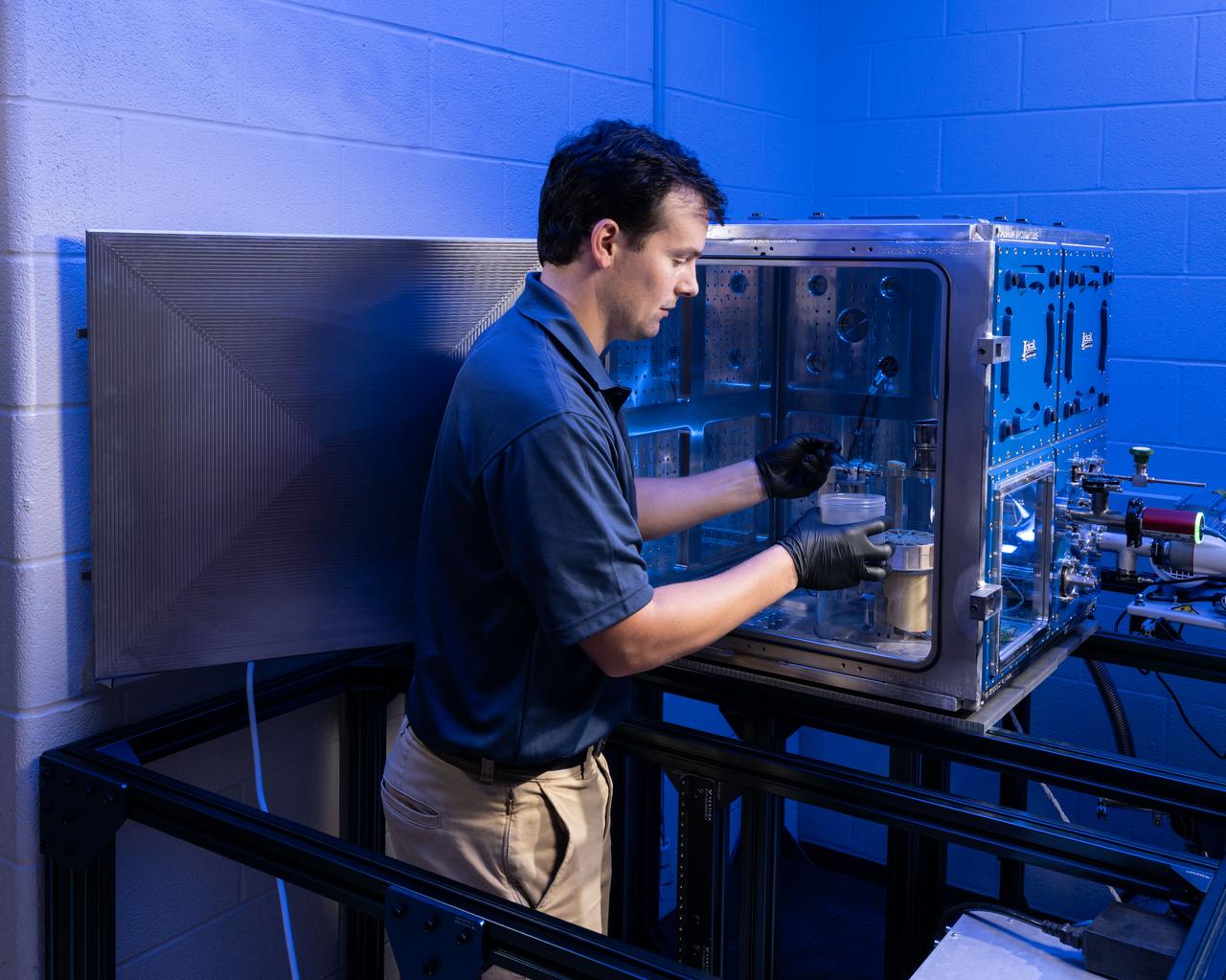

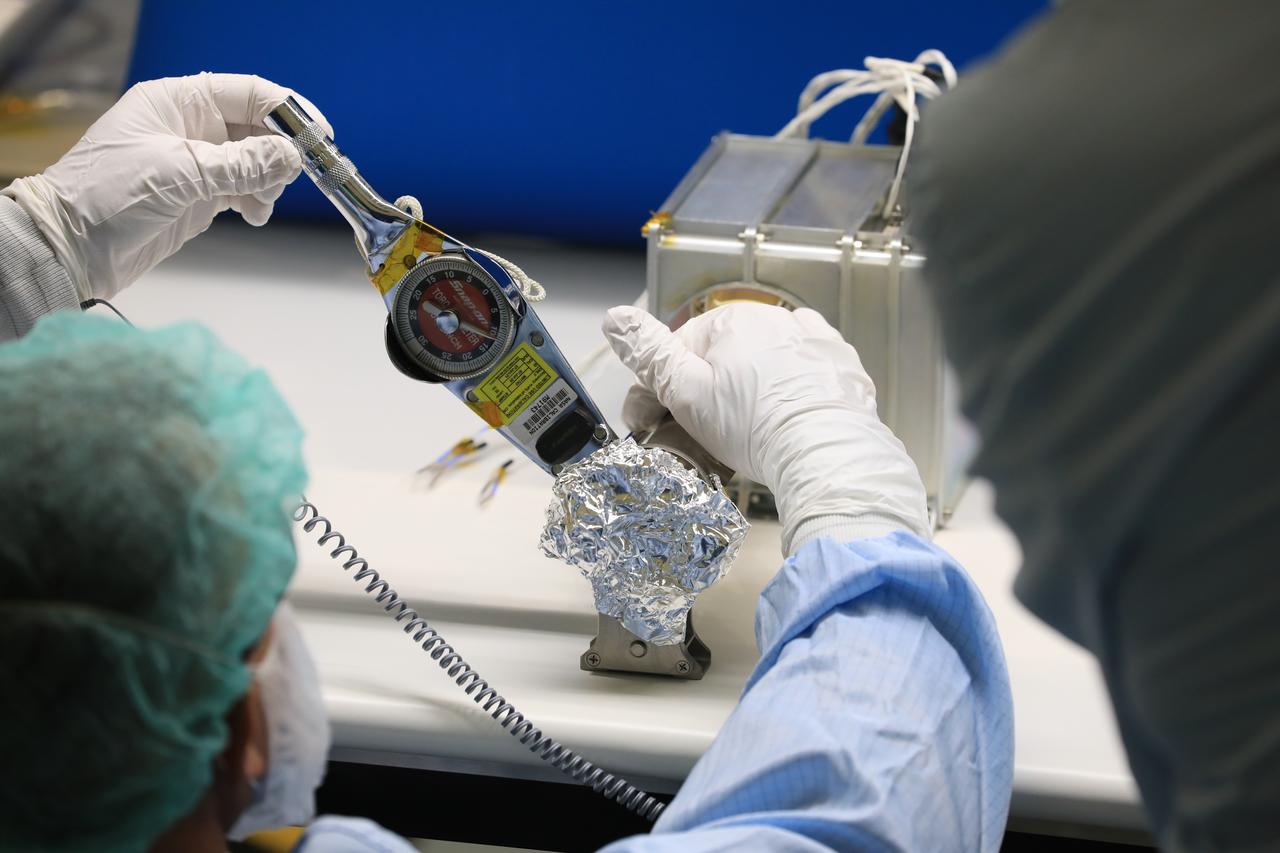
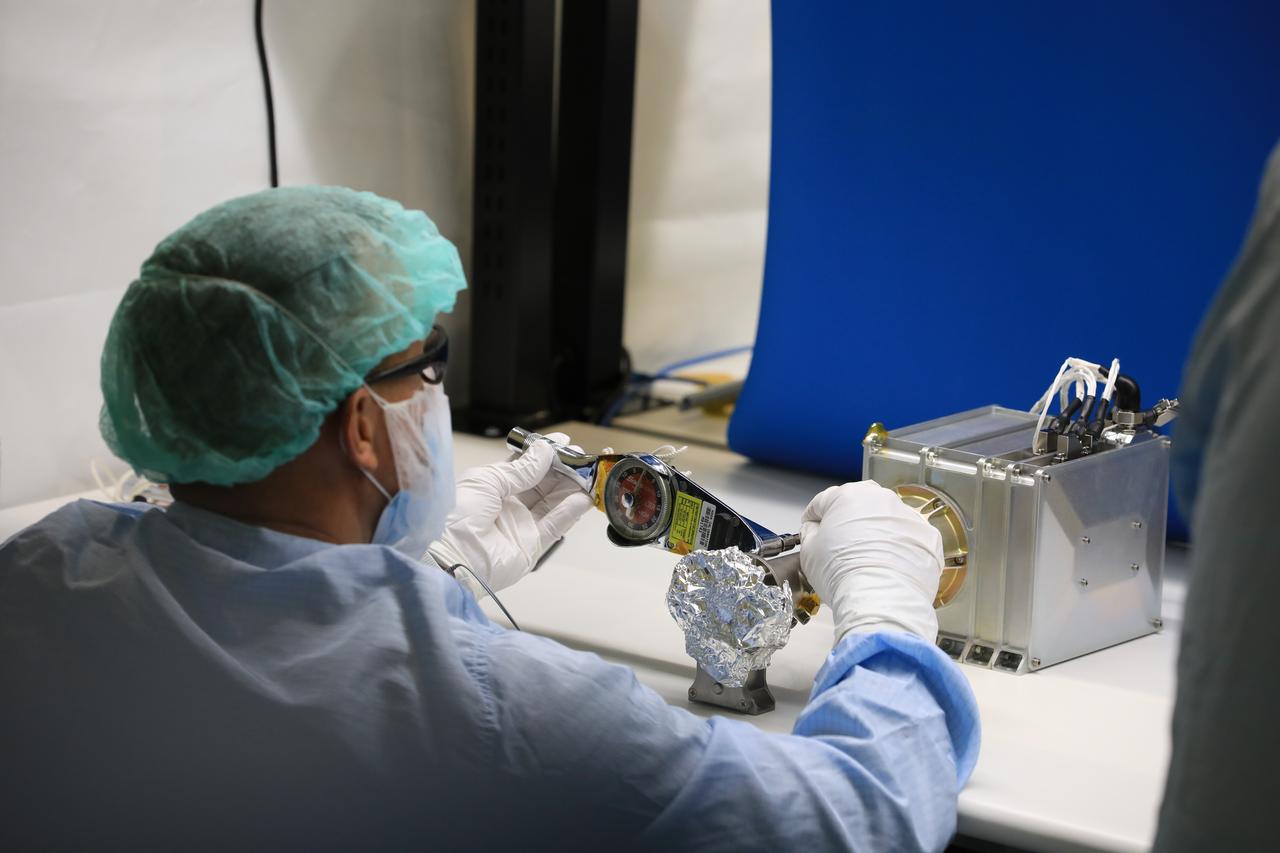
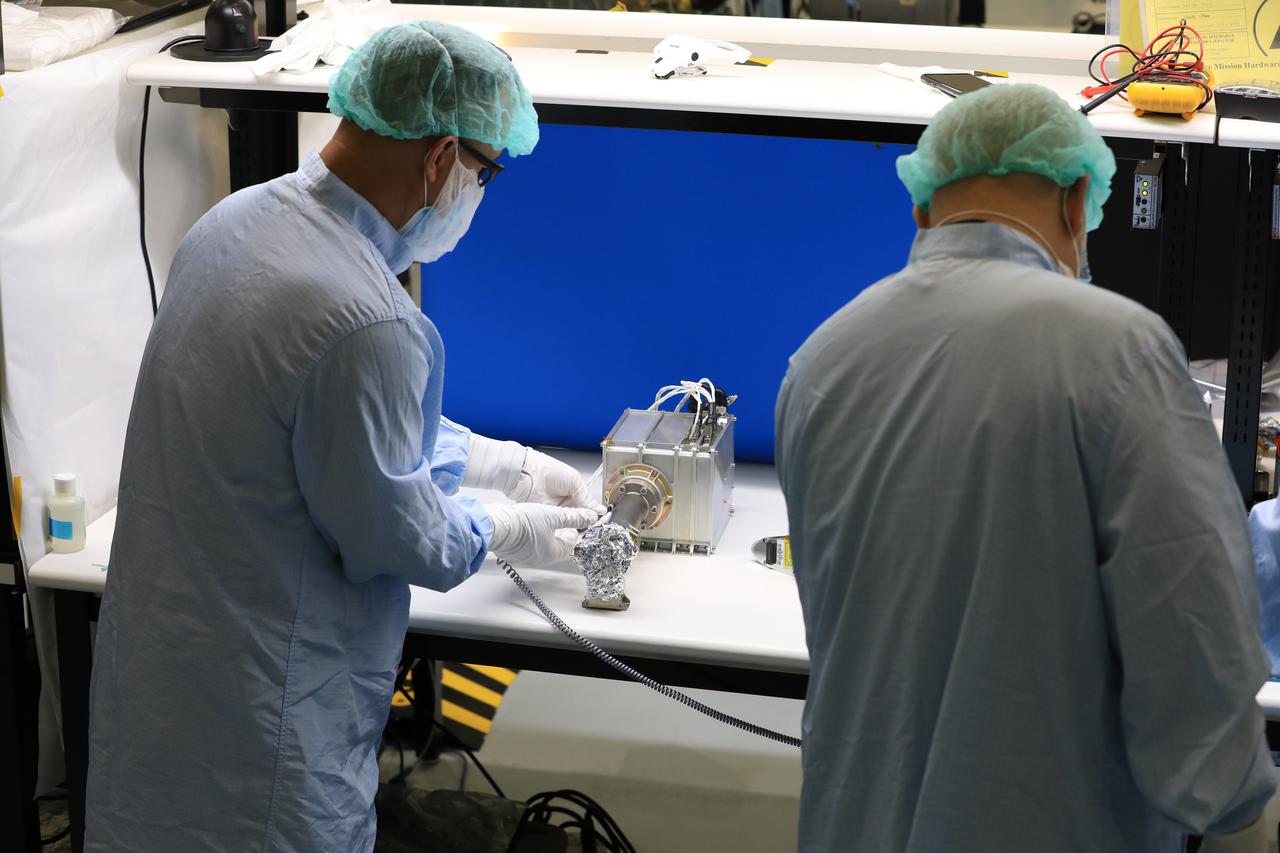
Josh Litofsky leads a Gateway lunar dust adhesion testing campaign at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. His team studies how lunar dust interacts with materials chosen for Gateway's construction. Here, Litofsky scoops lunar stimulant into a sample holder. Litofksy’s work seeks to validate the Gateway On-orbit Lunar Dust Modeling and Analysis Program (GOLDMAP), developed by Ronald Lee, also of Johnson Space Center. By considering factors such as the design and configuration of the space station, the materials used, and the unique conditions in lunar orbit, GOLDMAP helps predict how dust may move and settle on Gateway’s external surfaces.
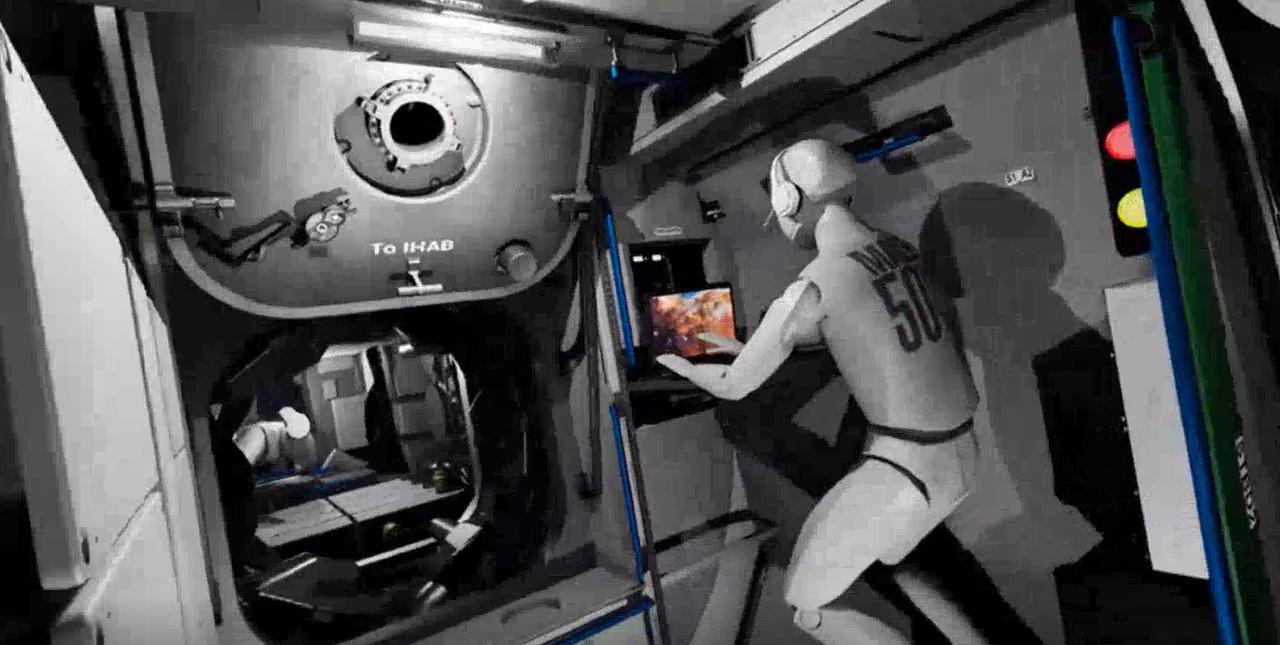

What astronauts see as they tour the Gateway lunar space station in virtual reality.
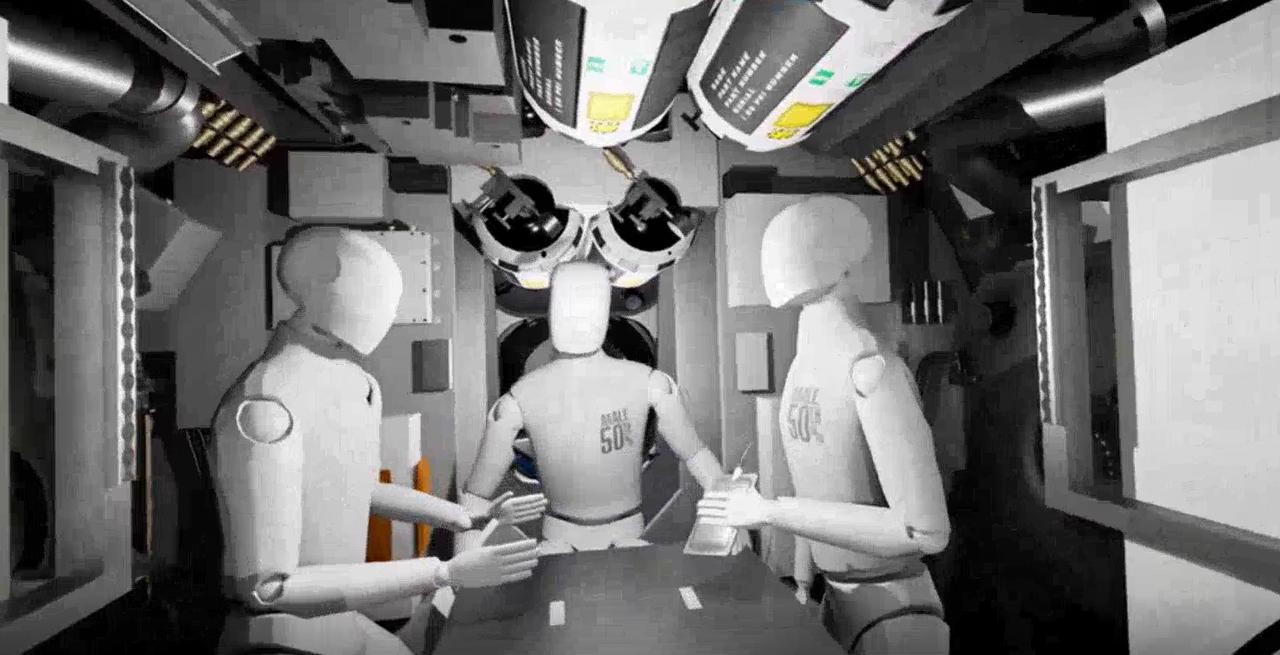

What astronauts see as they tour the Gateway lunar space station in virtual reality.
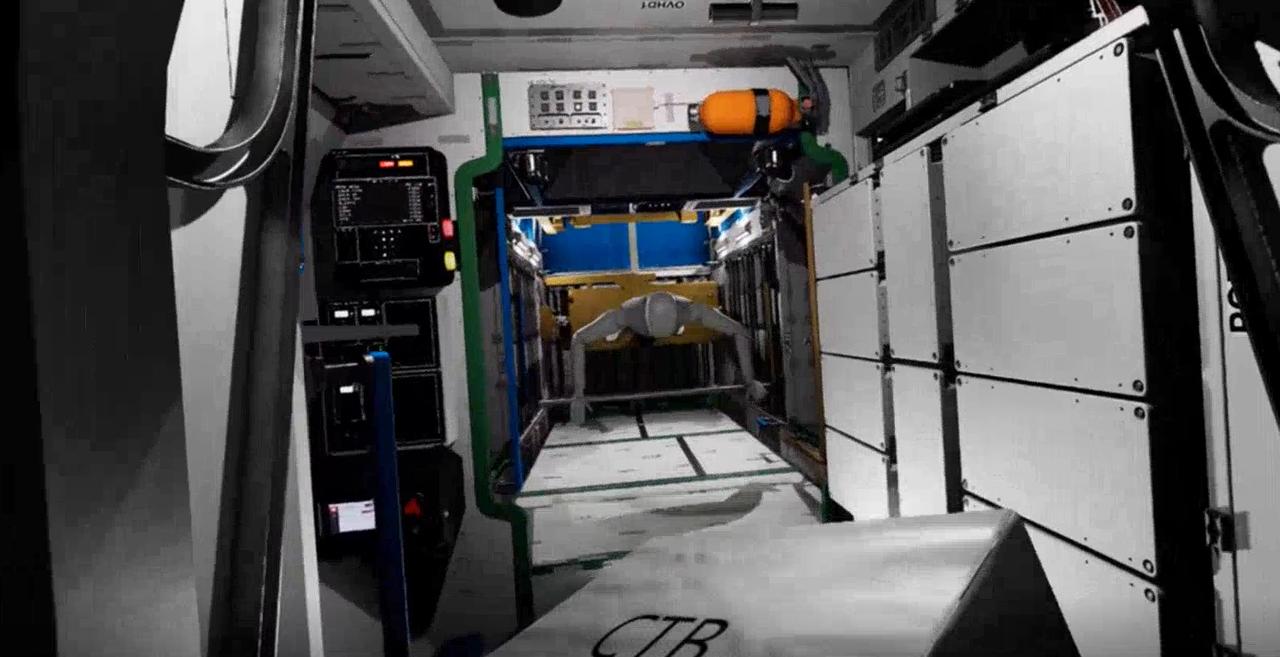

What astronauts see as they tour the Gateway lunar space station in virtual reality.
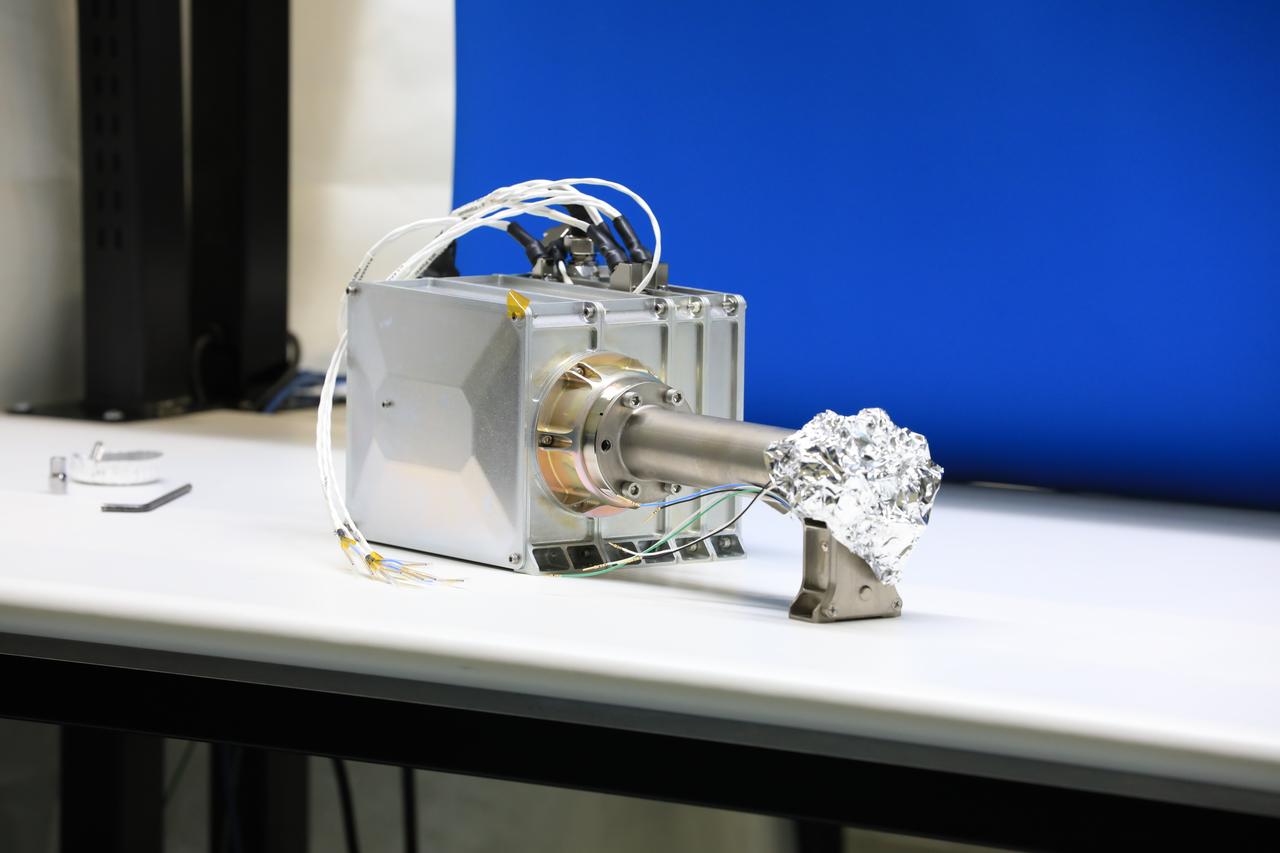
Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida are preparing the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) for launch inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo hardware is a payload for a robotic mission to the Moon as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).
Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida are preparing the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) for launch inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo hardware is a payload for a robotic mission to the Moon as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).

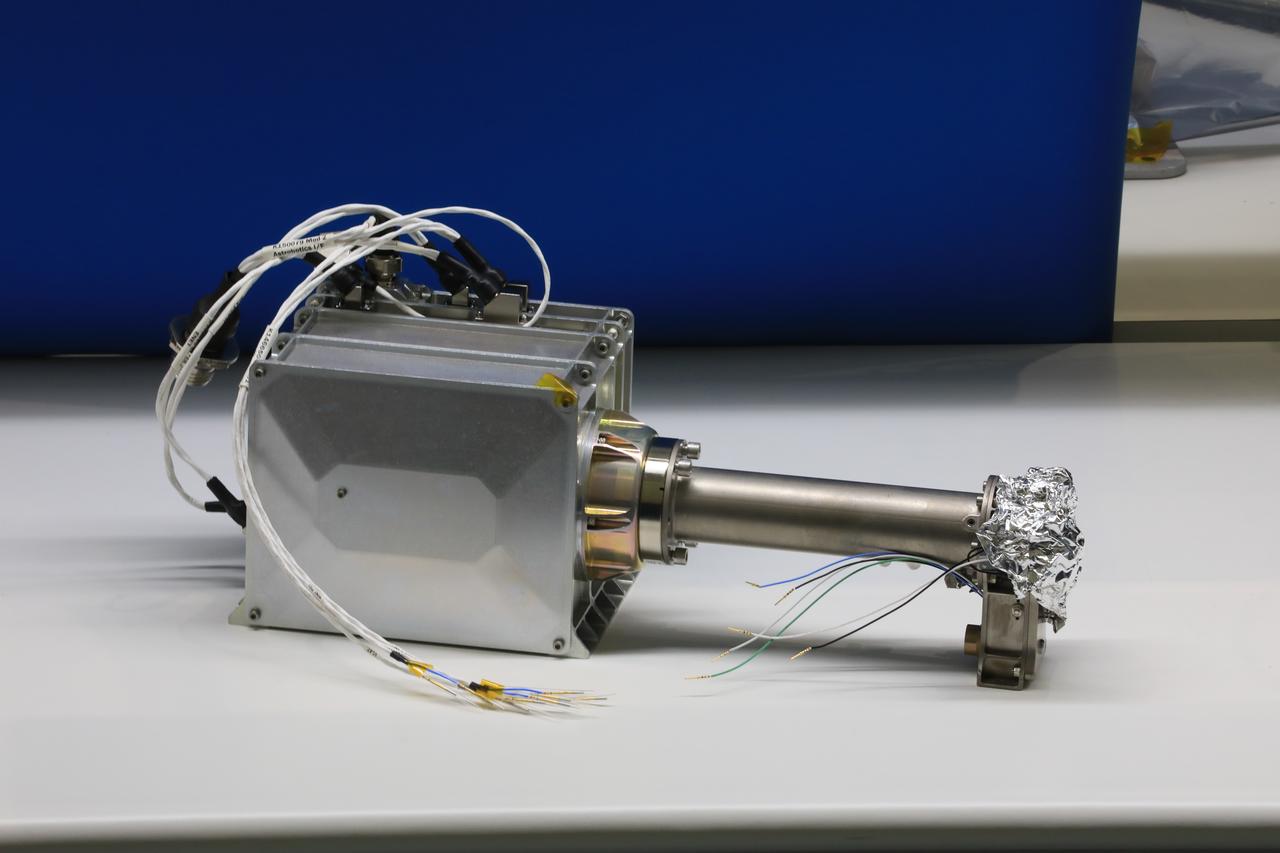
Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work with instruments for Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) inside the Space Station Processing on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This work is preparing MSolo hardware for a robotic mission as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).

Team members working inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Sept. 23, 2021, meticulously assemble ground support equipment that will protect shipment of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) flight hardware for preparations before it launches in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo, scheduled to first launch in 2022, is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will include science experiments, testing of technologies and demonstrations of capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work with instruments for Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) inside the Space Station Processing on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This work is preparing MSolo hardware for a robotic mission as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work with instruments for Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) inside the Space Station Processing on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This work is preparing MSolo hardware for a robotic mission as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).
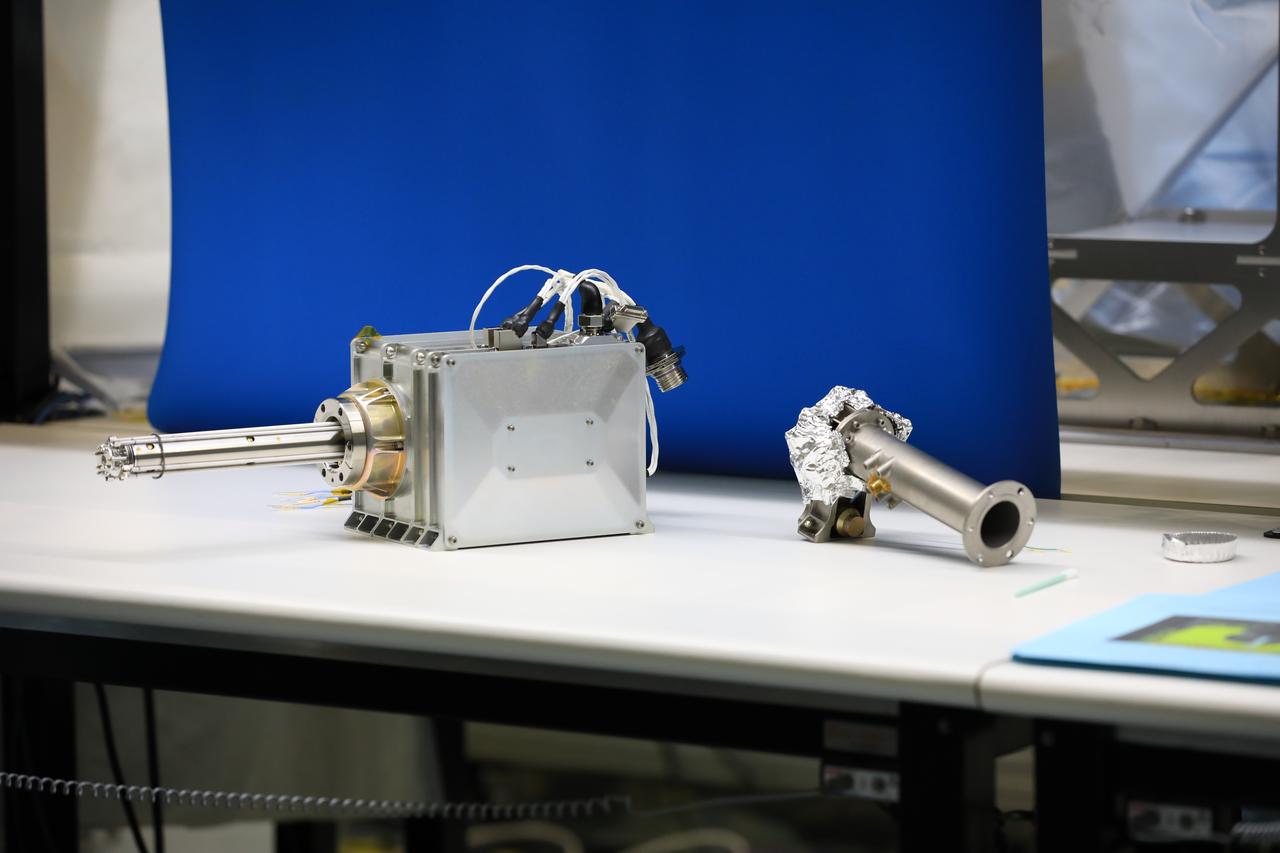
Instruments for the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) are in view inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This work is preparing MSolo hardware for a robotic mission as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work with instruments for Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) inside the Space Station Processing on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This work is preparing MSolo hardware for a robotic mission as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).

Team members working inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Sept. 23, 2021, meticulously assemble ground support equipment that will protect shipment of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) flight hardware for preparations before it launches in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo, scheduled to first launch in 2022, is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will include science experiments, testing of technologies and demonstrations of capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.

Team members working inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Sept. 23, 2021, meticulously assemble ground support equipment that will protect shipment of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) flight hardware for preparations before it launches in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo, scheduled to first launch in 2022, is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will include science experiments, testing of technologies and demonstrations of capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work with instruments for Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) inside the Space Station Processing on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This work is preparing MSolo hardware for a robotic mission as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).
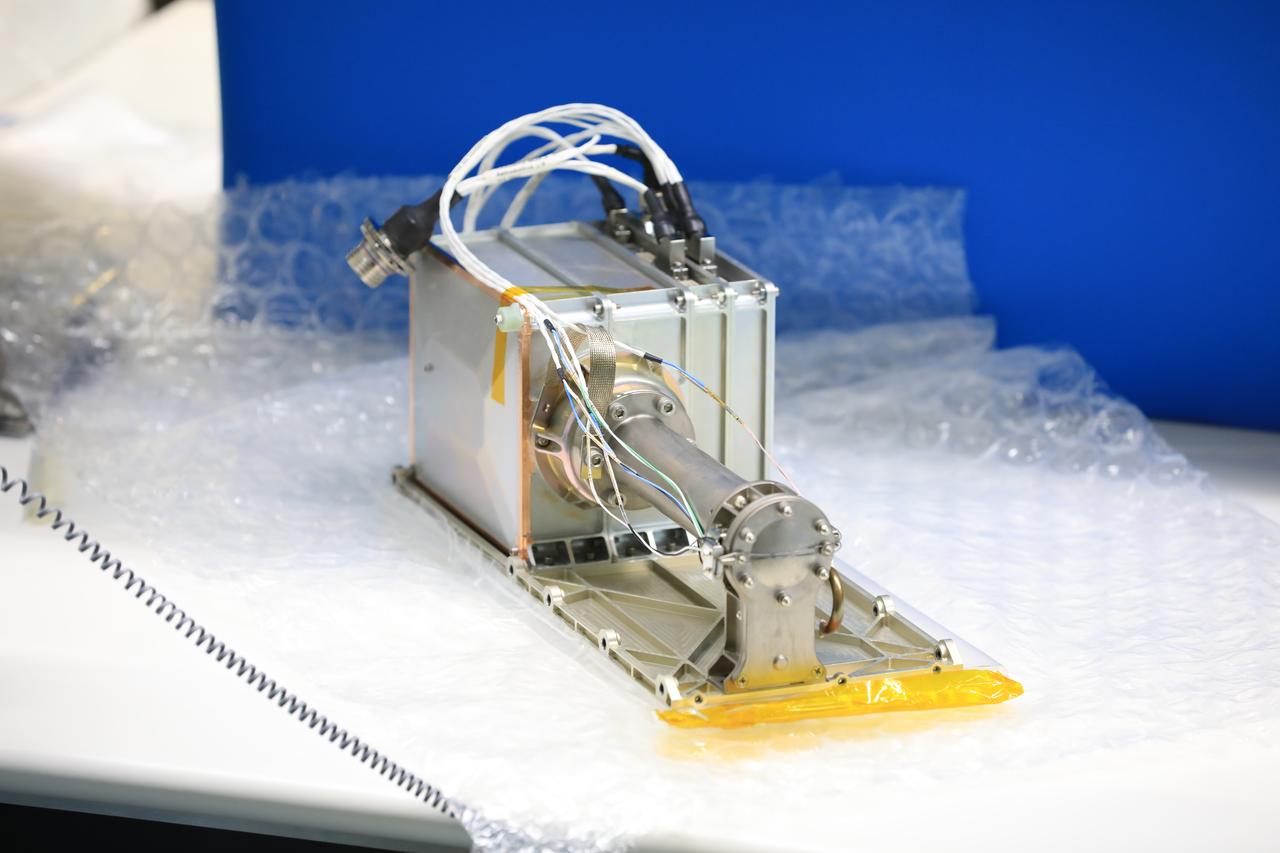

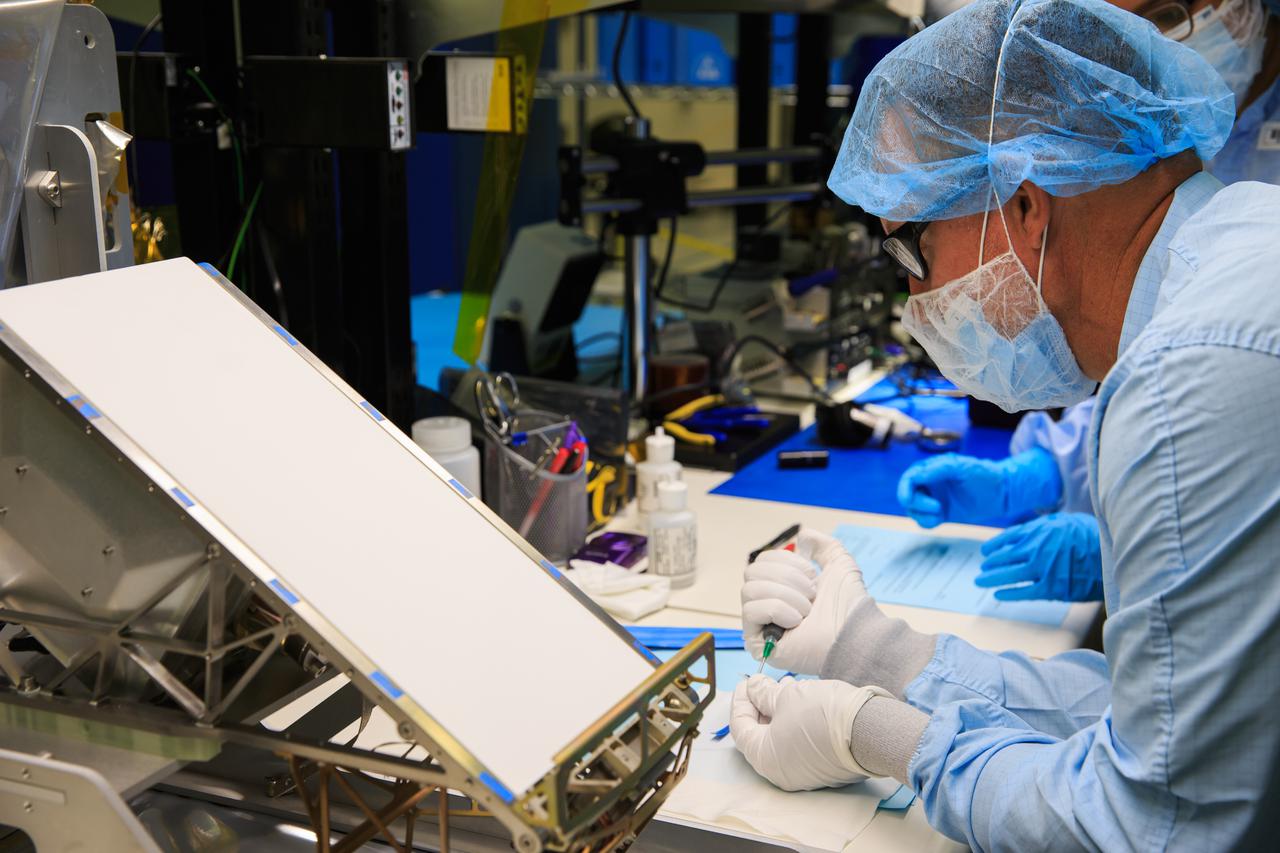
The Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument is photographed inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida following installation of its radiator on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.

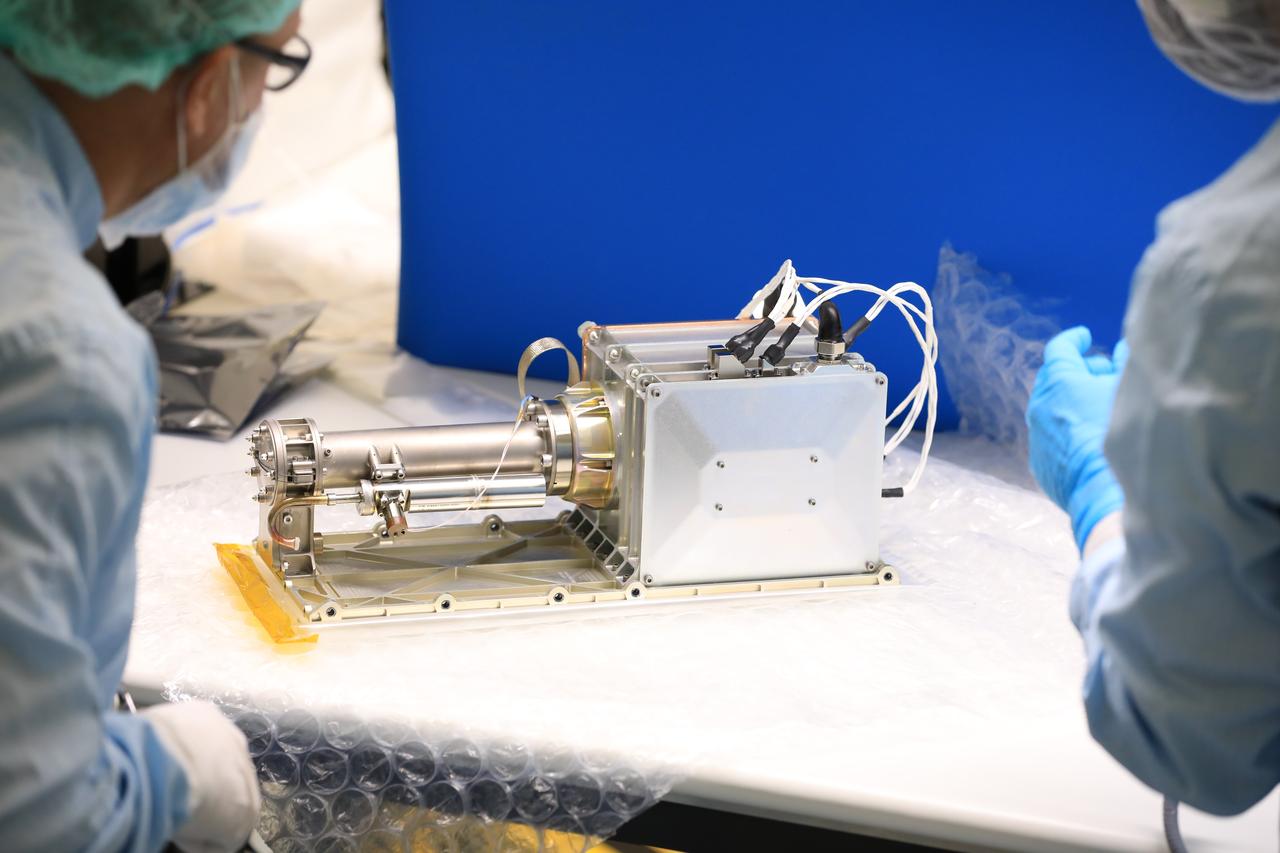
Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prepare to install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
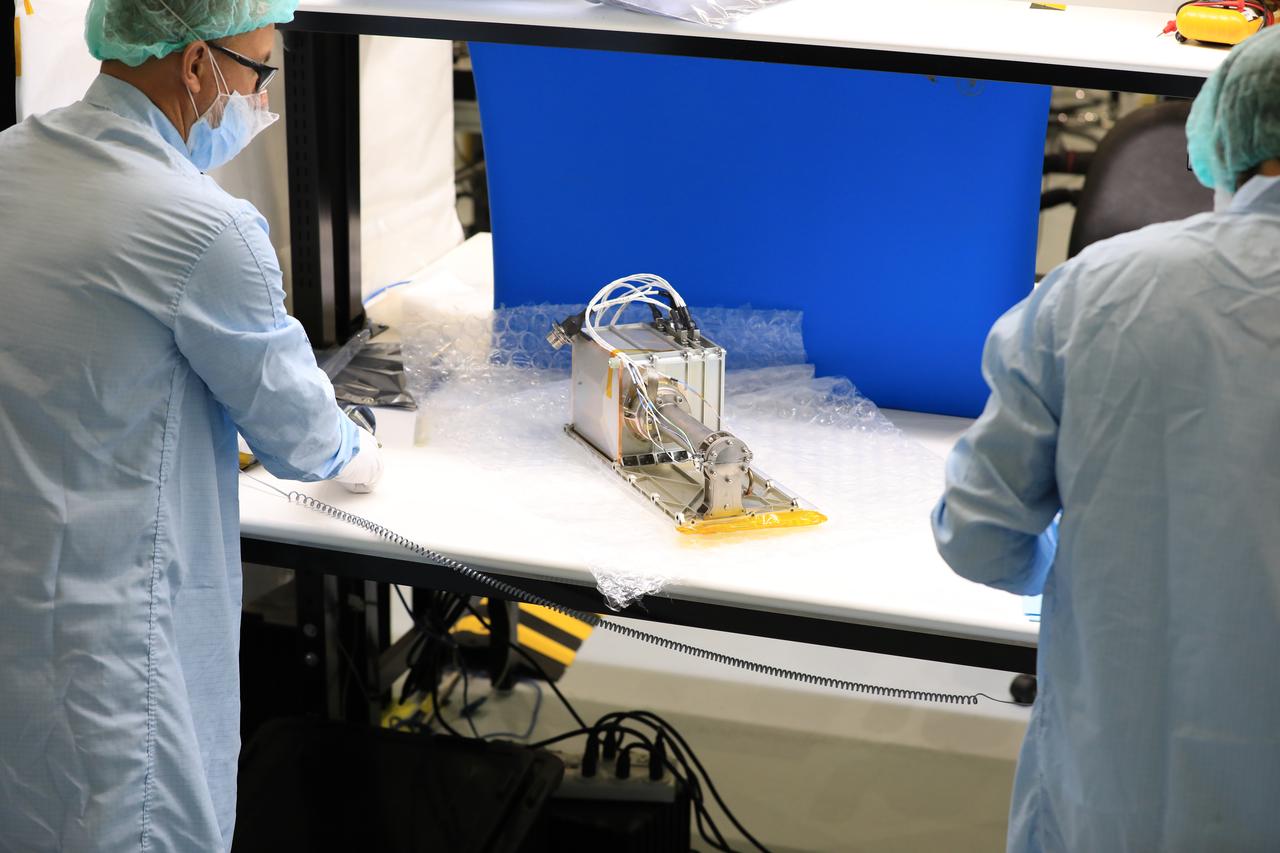
Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.

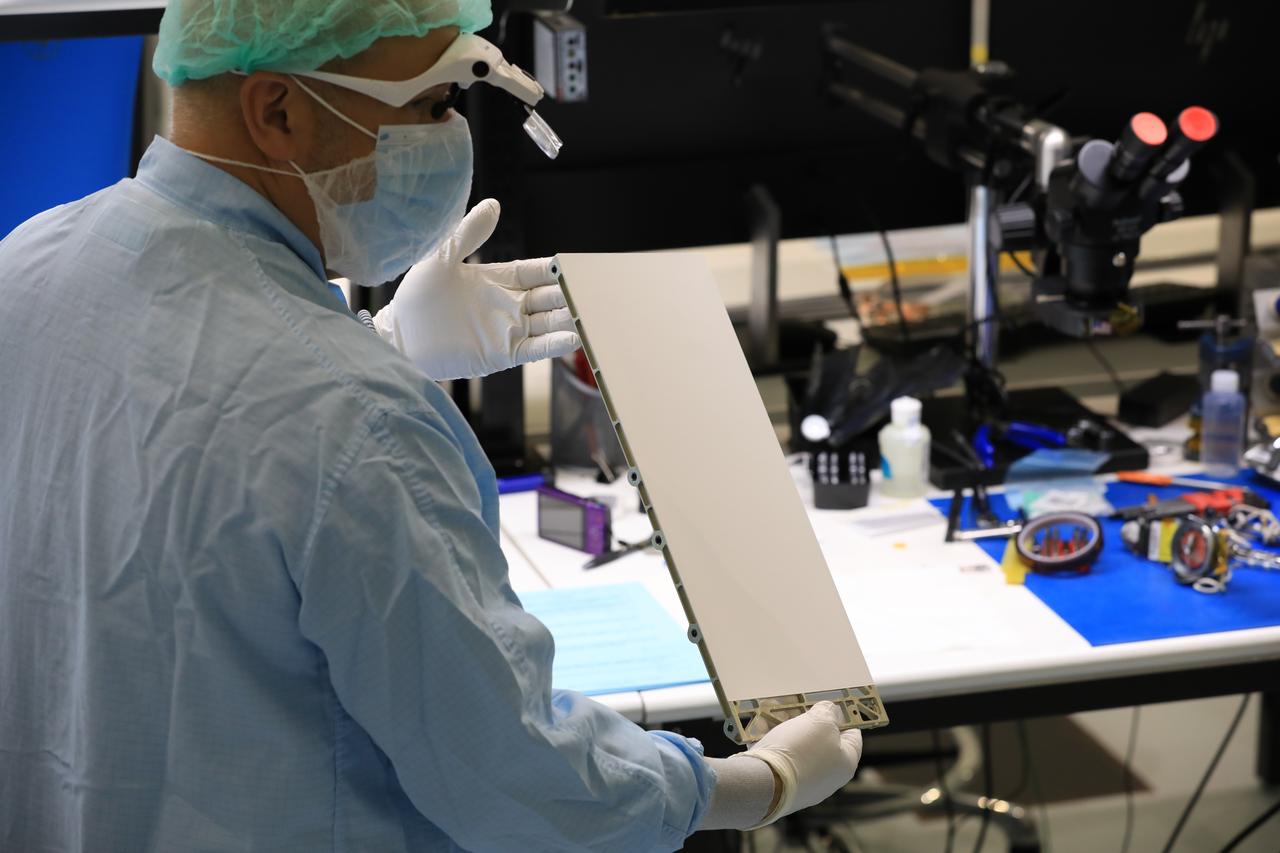
Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
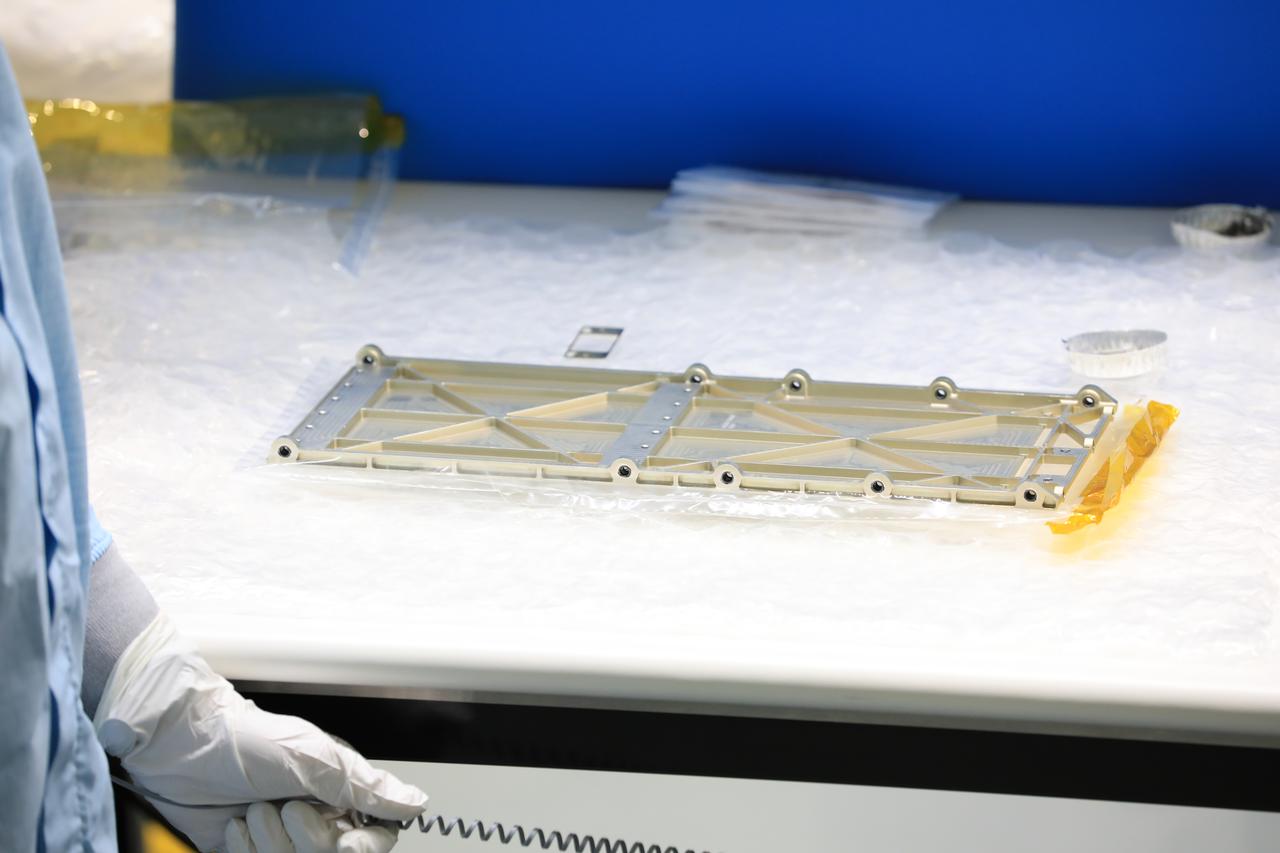
Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida have prepped the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument’s radiator for installation inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prepare to install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prepare to install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
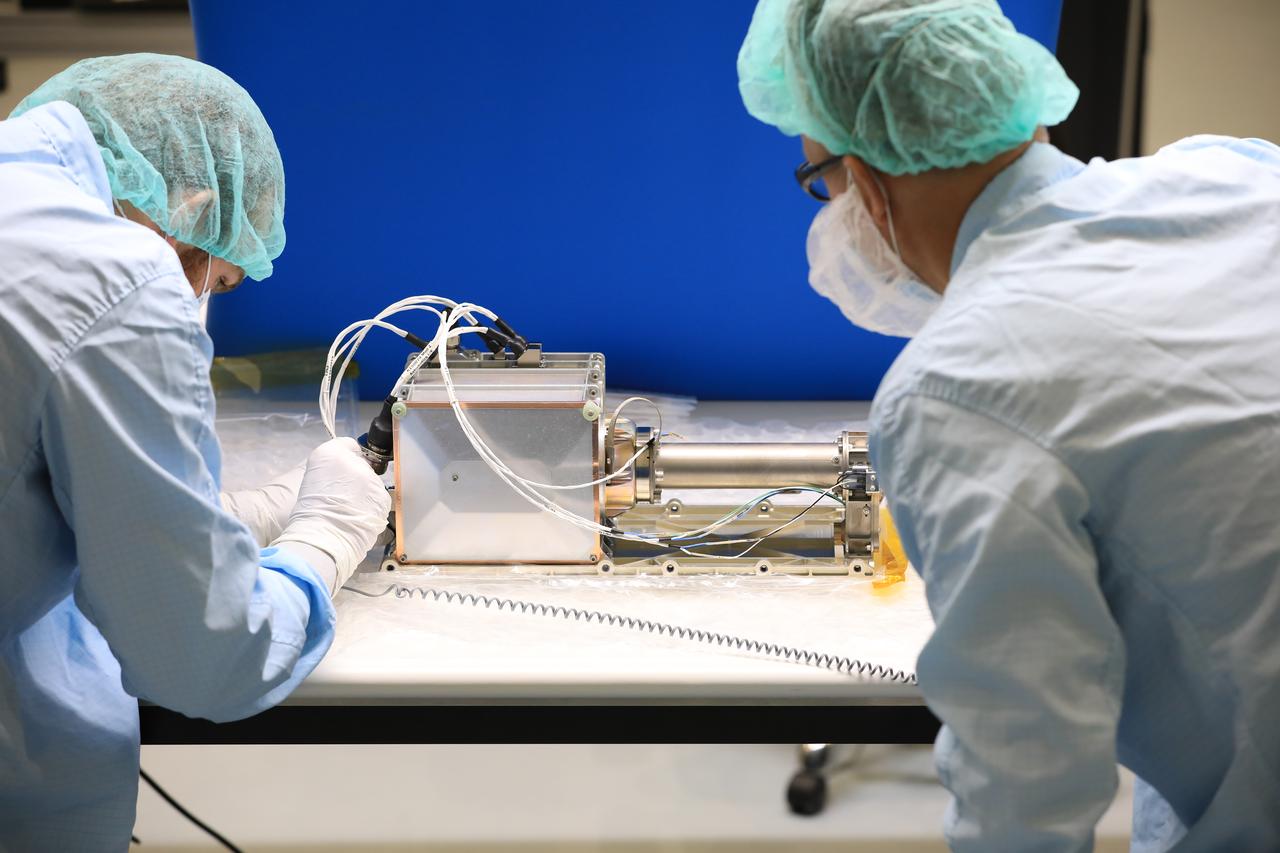

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prepare to install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
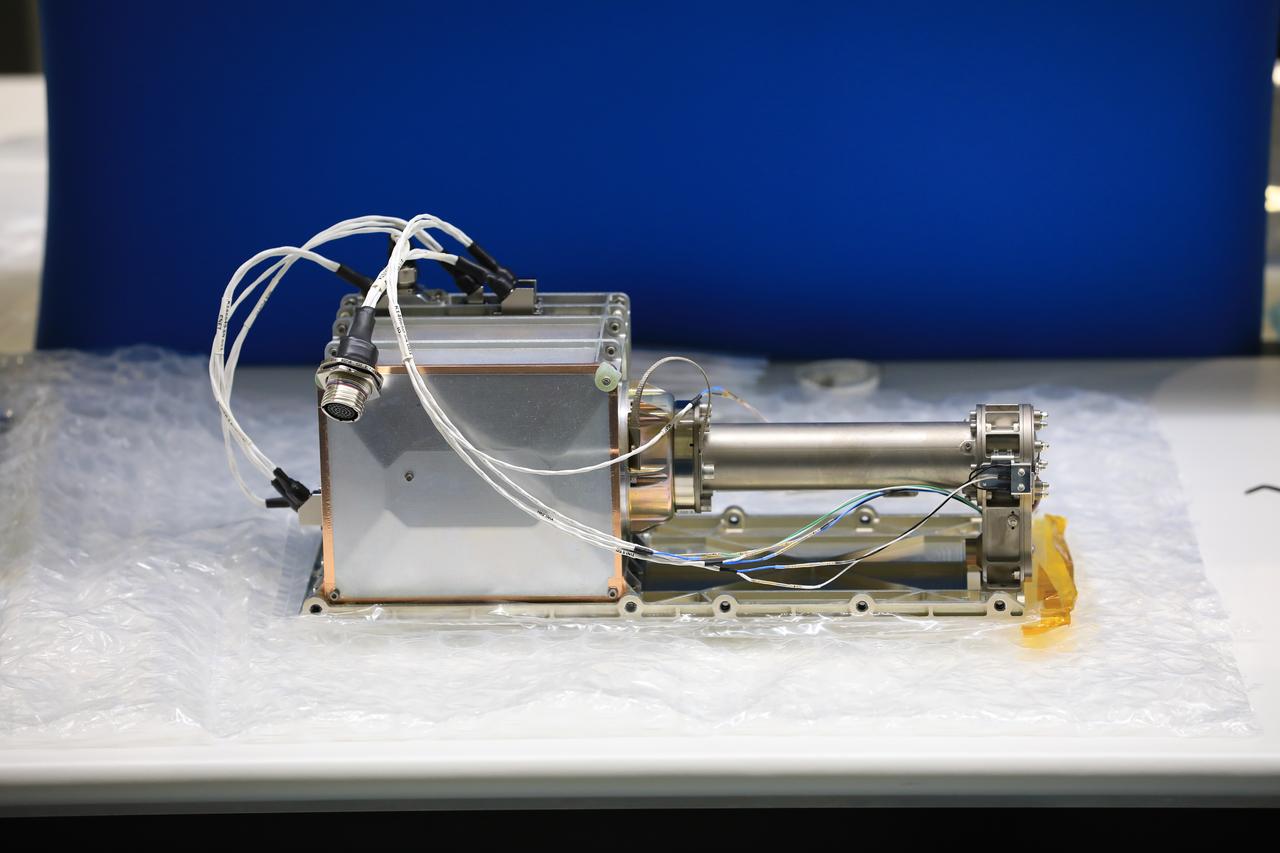
The Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument is photographed inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida following installation of its radiator on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
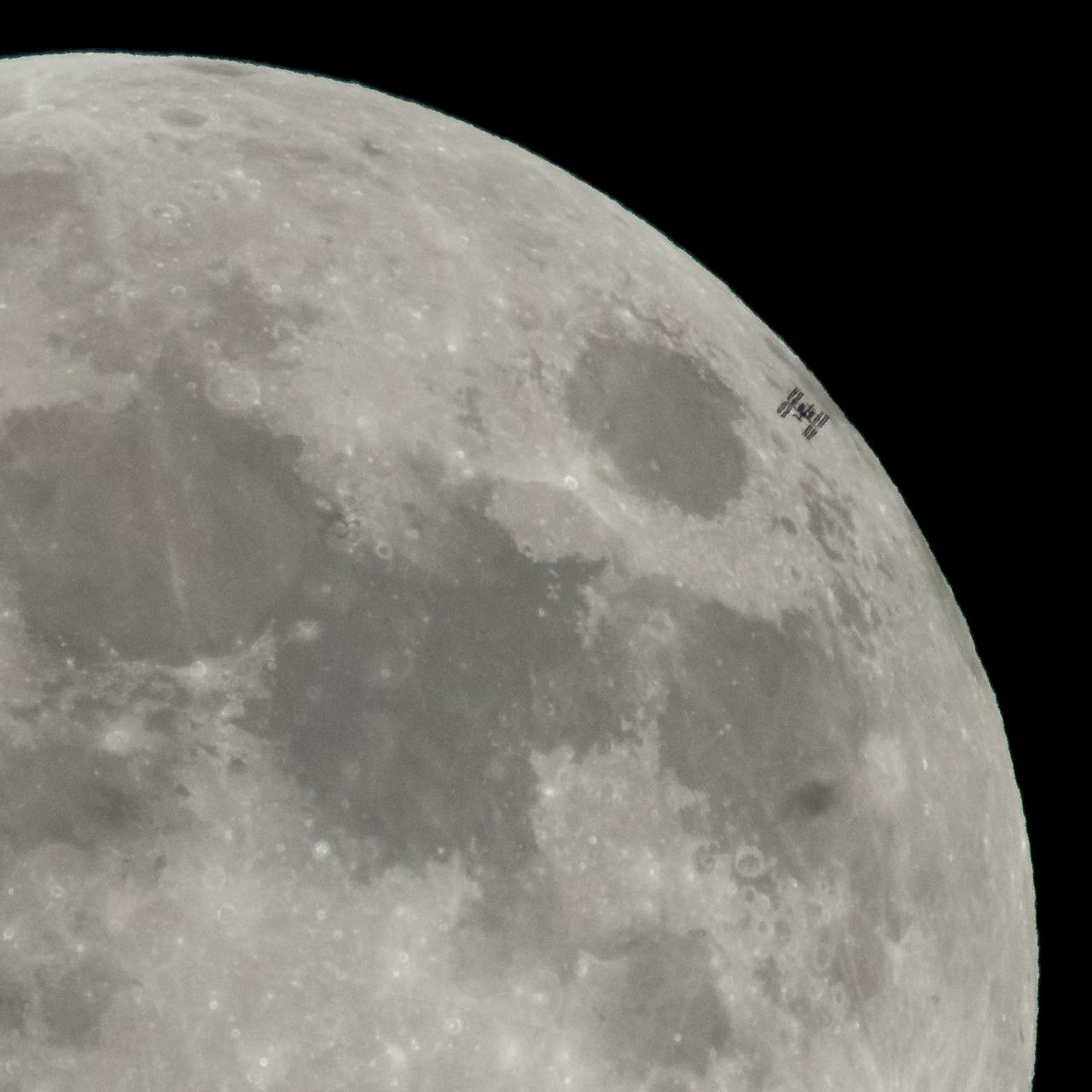

The International Space Station, with a crew of six onboard, is seen in silhouette as it transits the moon at roughly five miles per second Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2018, Alexandria, Virginia. Onboard are; NASA astronauts Joe Acaba, Mark Vande Hei, and Scott Tingle: Russian Cosmonauts Alexander Misurkin and Anton Shkaplerov, and Japanese astronaut Norishige Kanai. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
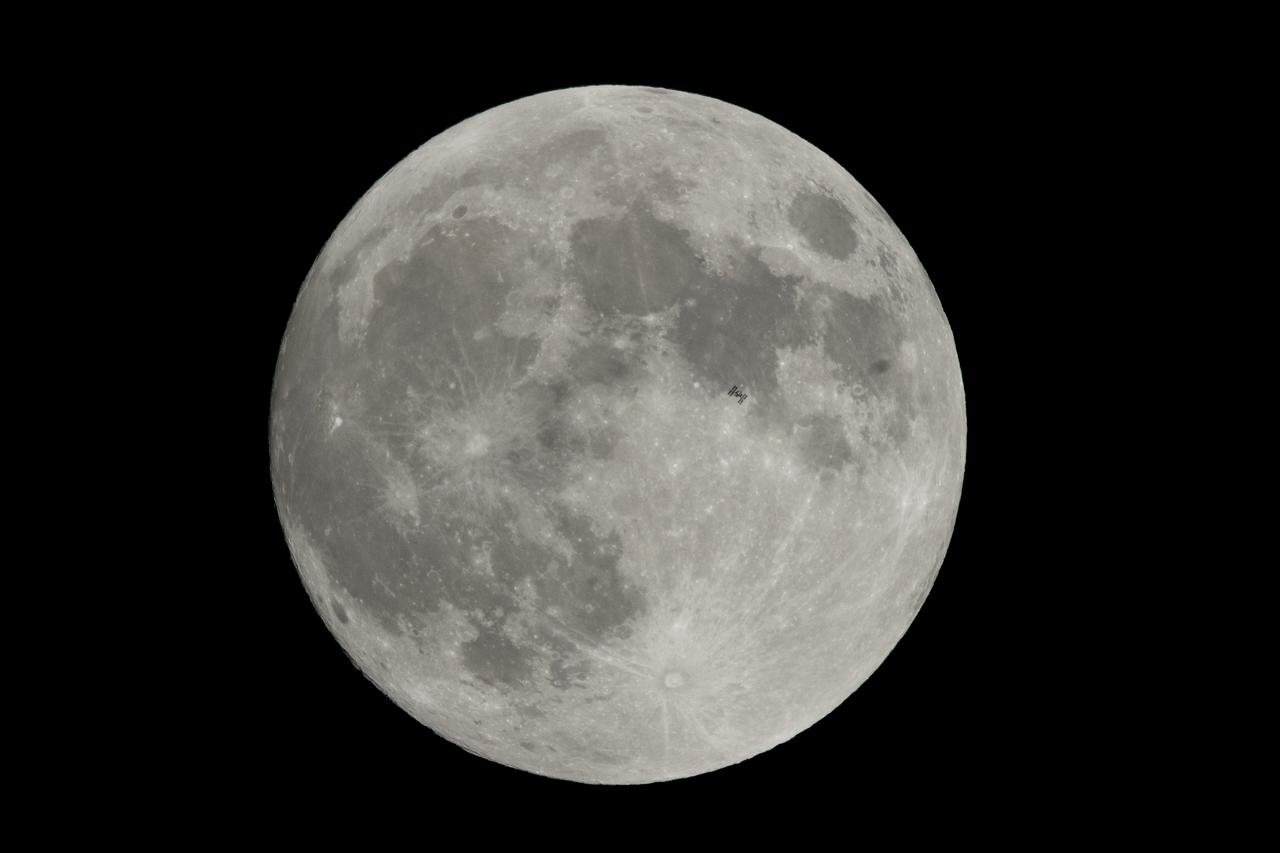

The International Space Station, with a crew of six onboard, is seen in silhouette as it transits the moon at roughly five miles per second Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2018, Alexandria, Virginia. Onboard are; NASA astronauts Joe Acaba, Mark Vande Hei, and Scott Tingle: Russian Cosmonauts Alexander Misurkin and Anton Shkaplerov, and Japanese astronaut Norishige Kanai. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
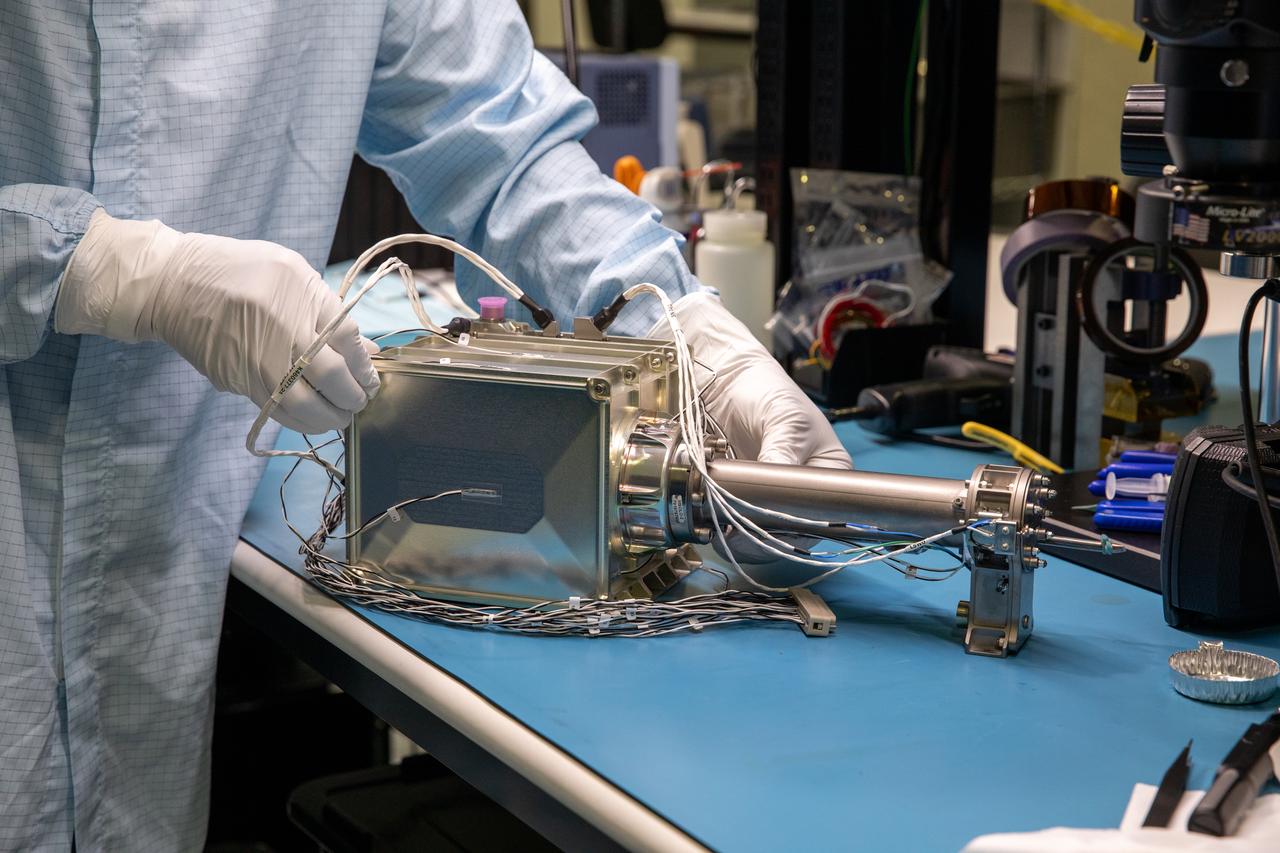

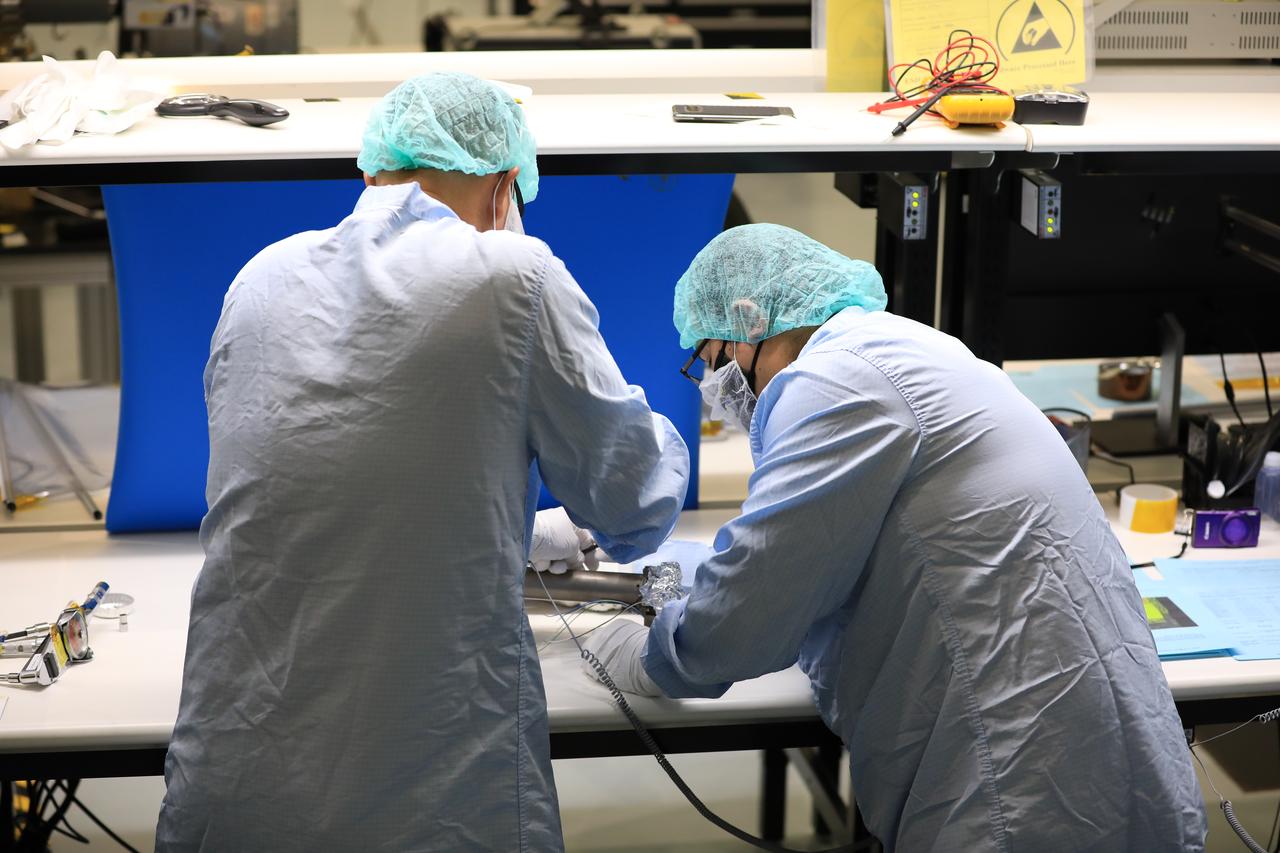
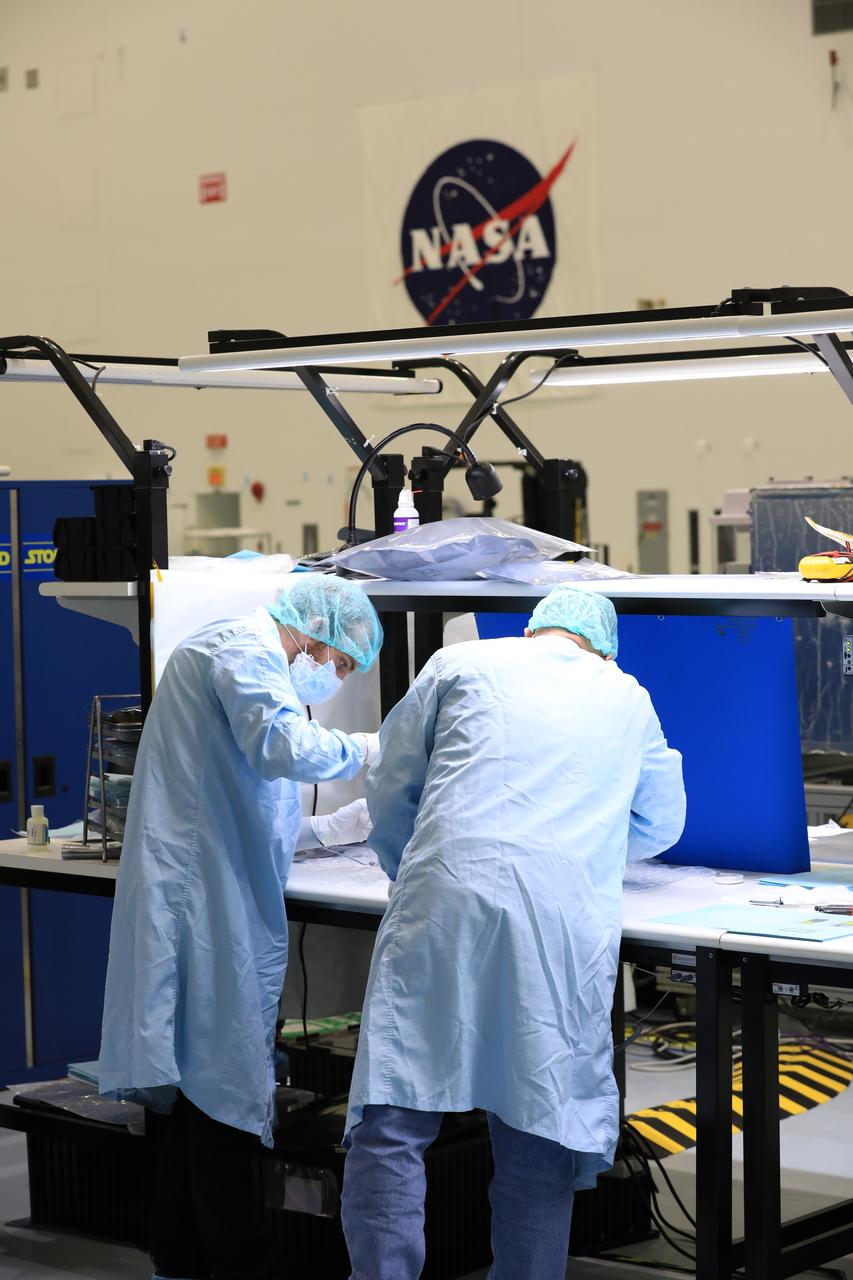
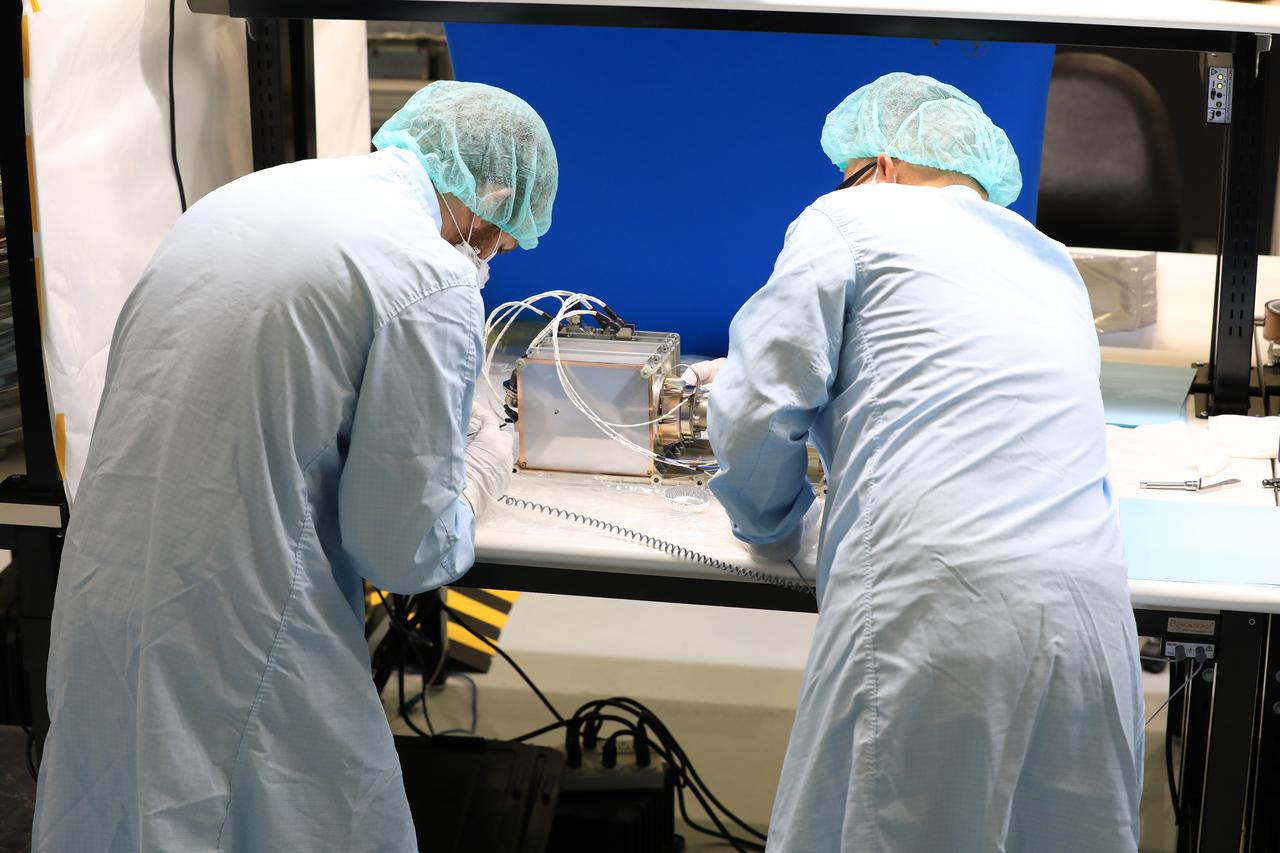
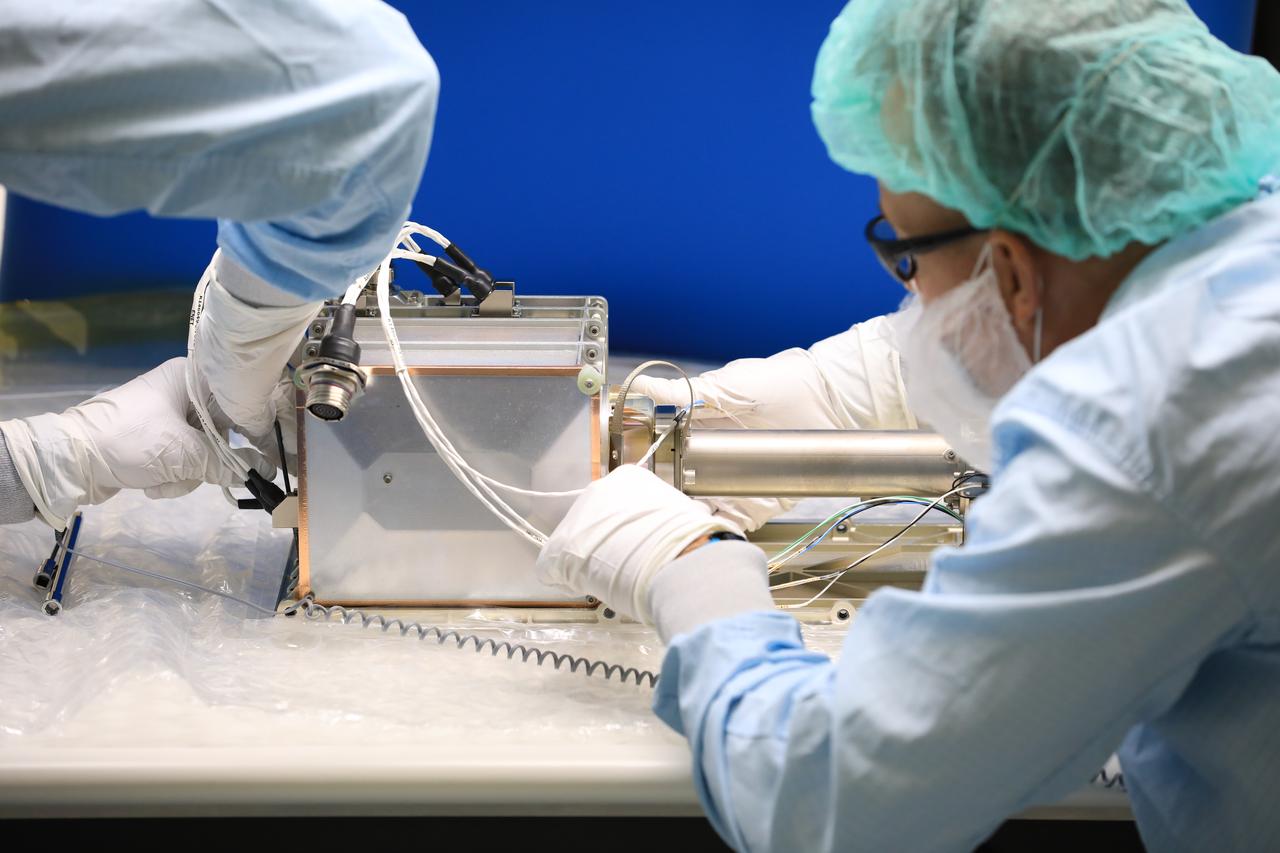
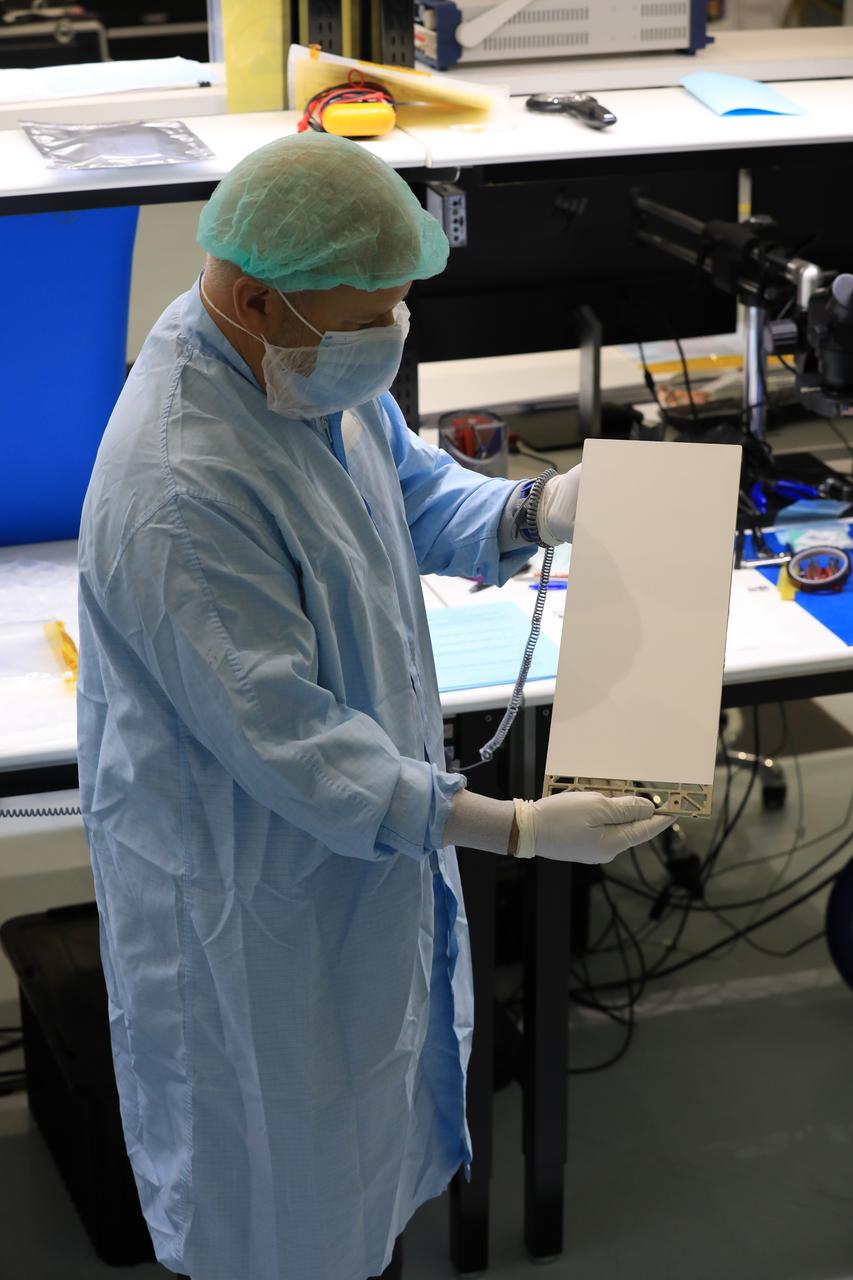
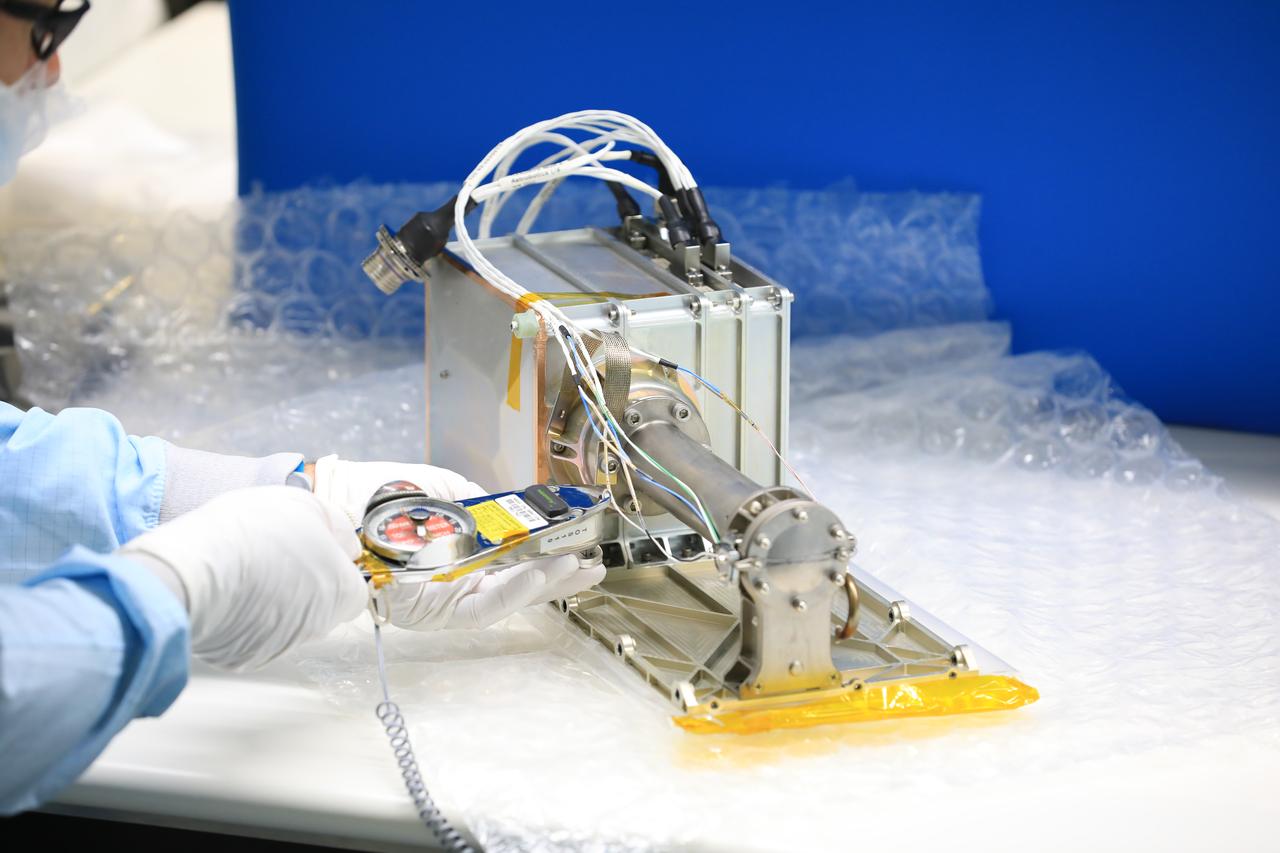
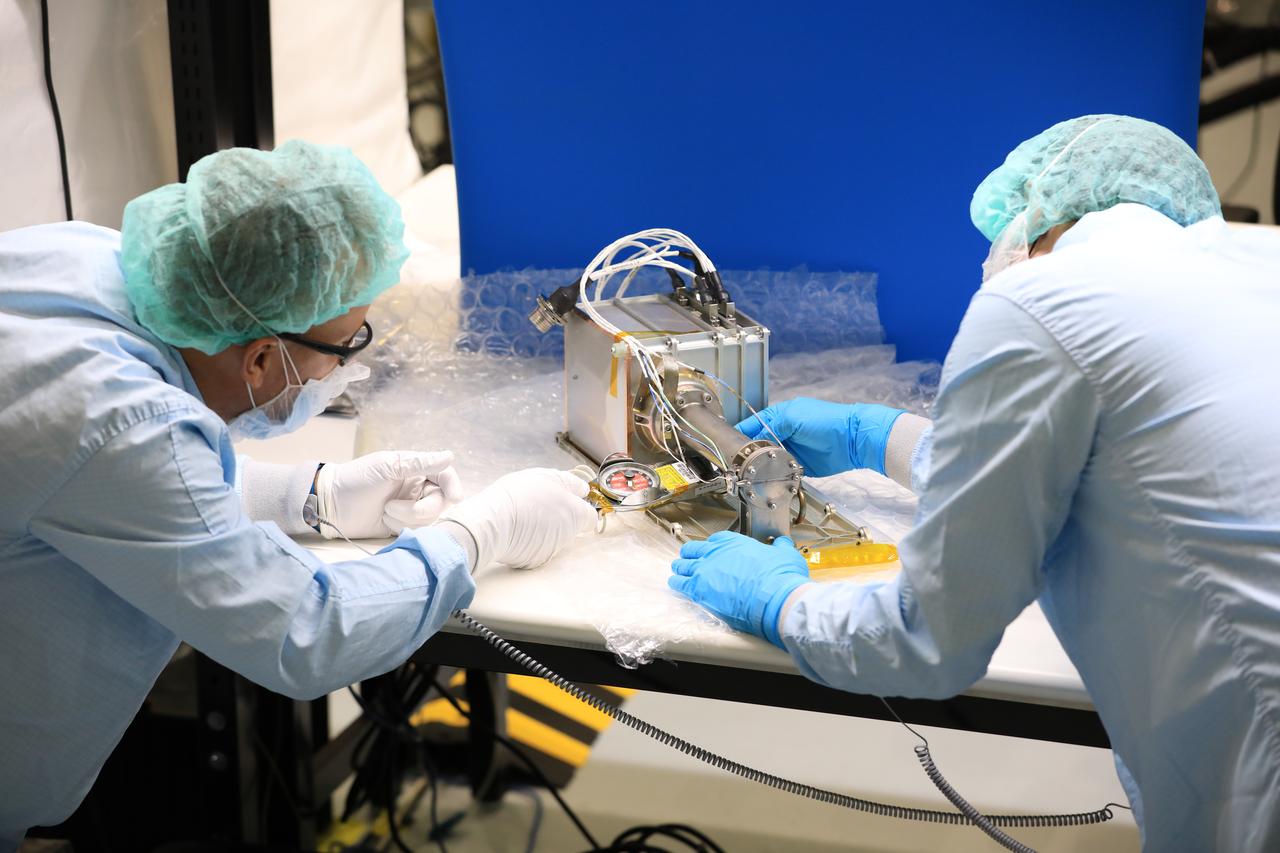
A team of engineers and technicians finished the final assembly step for the MSOLO-2 (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) flight instrument by installing the Calibration Gas System inside of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 21, 2023. MSOLO is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface.
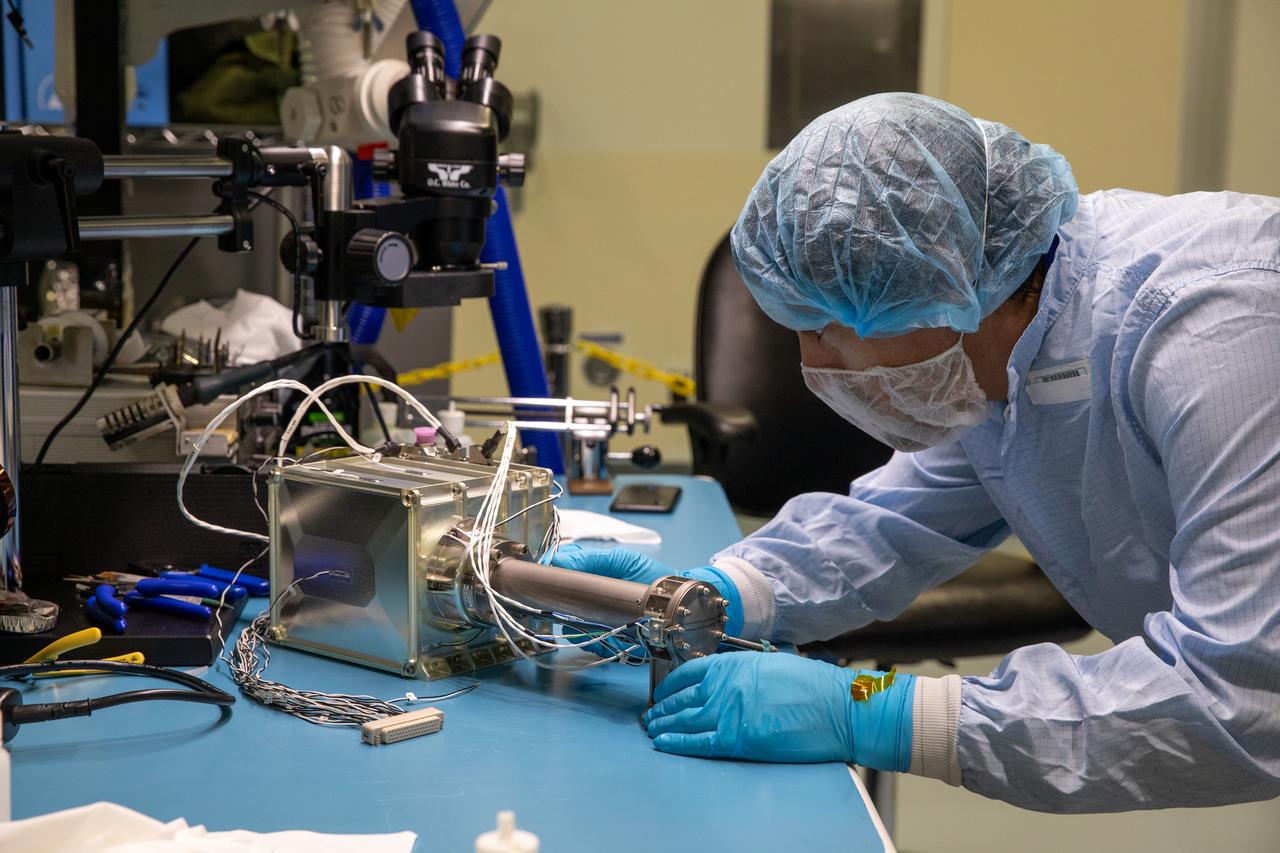

A team of engineers and technicians finished the final assembly step for the MSOLO-2 (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) flight instrument by installing the Calibration Gas System inside of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 21, 2023. MSOLO is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface.

A team of engineers and technicians finished the final assembly step for the MSOLO-2 (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) flight instrument by installing the Calibration Gas System inside of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 21, 2023. MSOLO is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface.
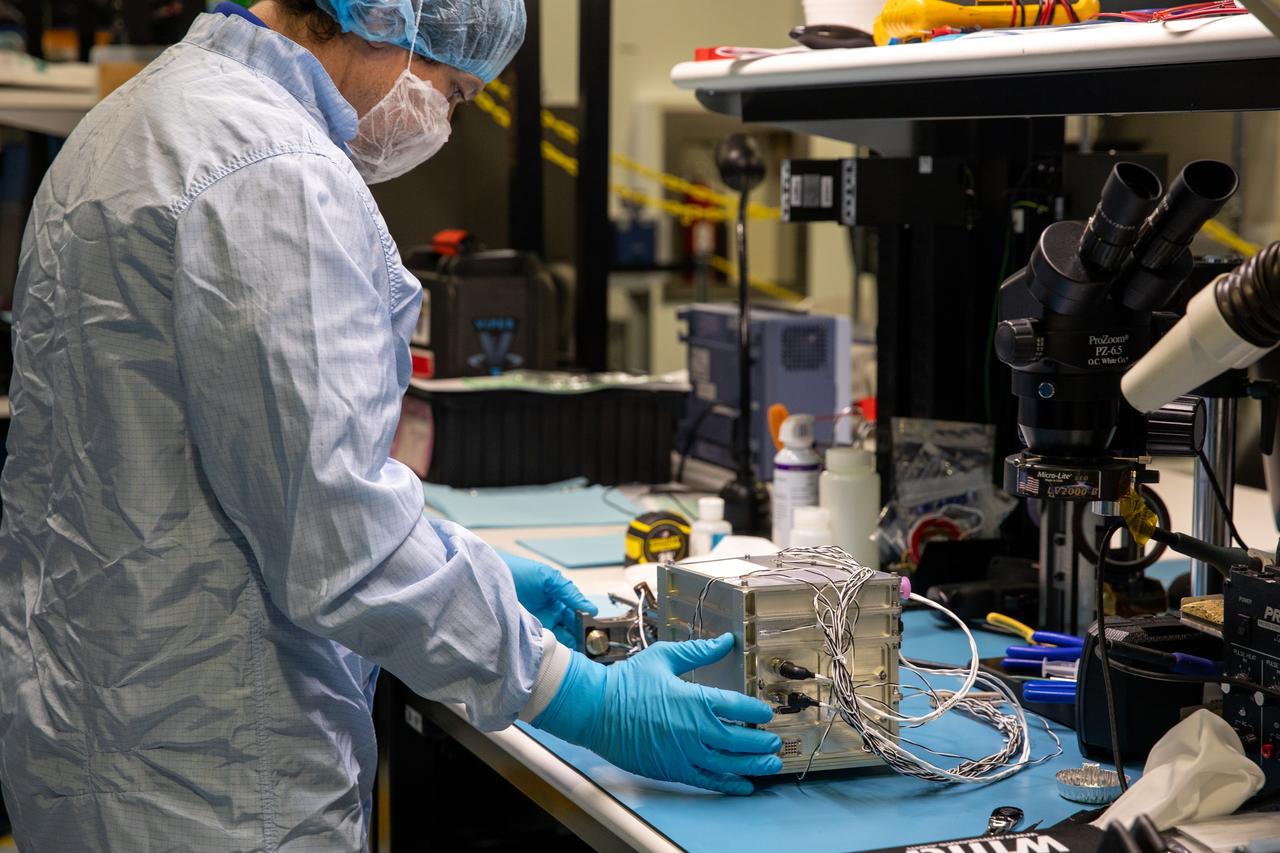

A team of engineers and technicians finished the final assembly step for the MSOLO-2 (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) flight instrument by installing the Calibration Gas System inside of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 21, 2023. MSOLO is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface.
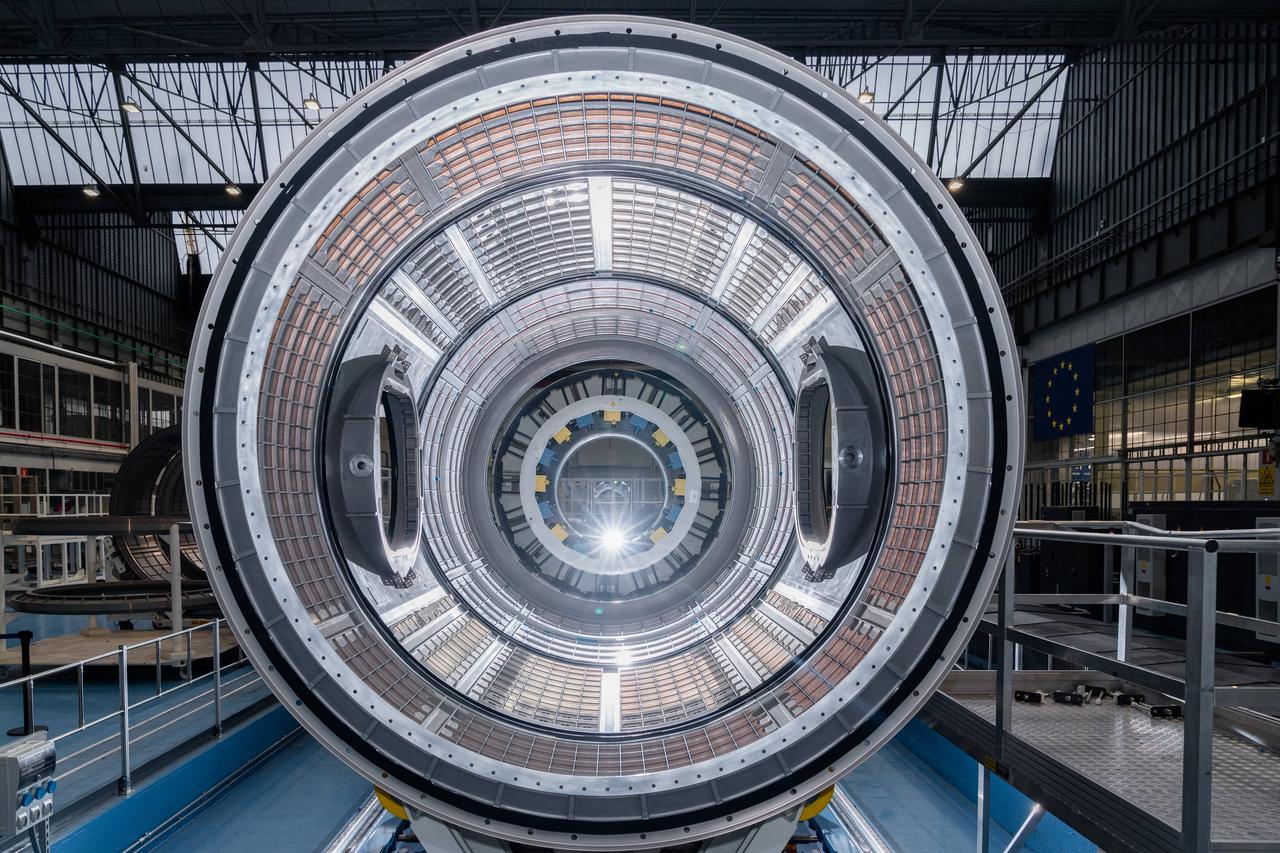

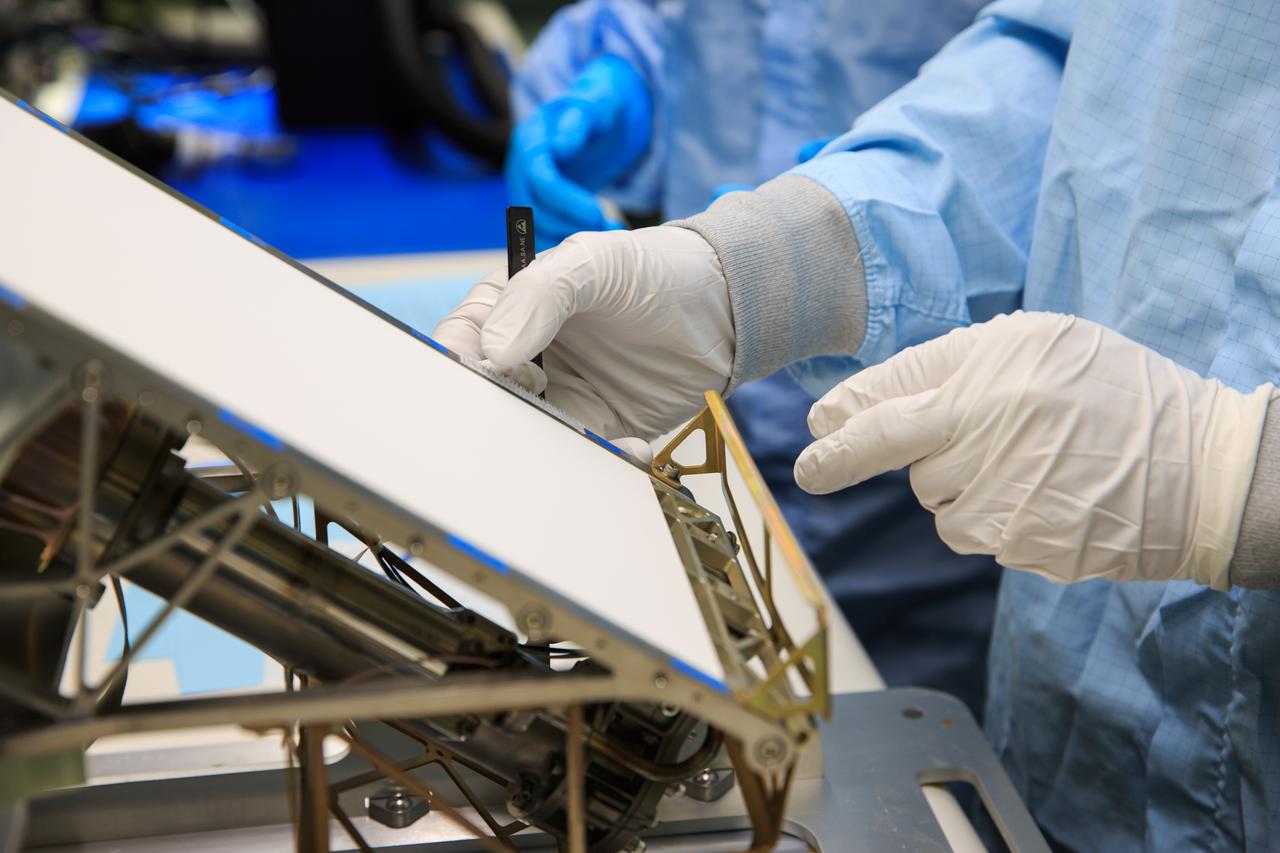
The primary structure of the Gateway space station's HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) module is one step closer to launch following welding completion in Turin, Italy. HALO is one of four Gateway modules where astronauts will live, conduct science, and prepare for lunar surface missions. NASA is partnering with Northrop Grumman and their subcontractor Thales Alenia Space to develop HALO.
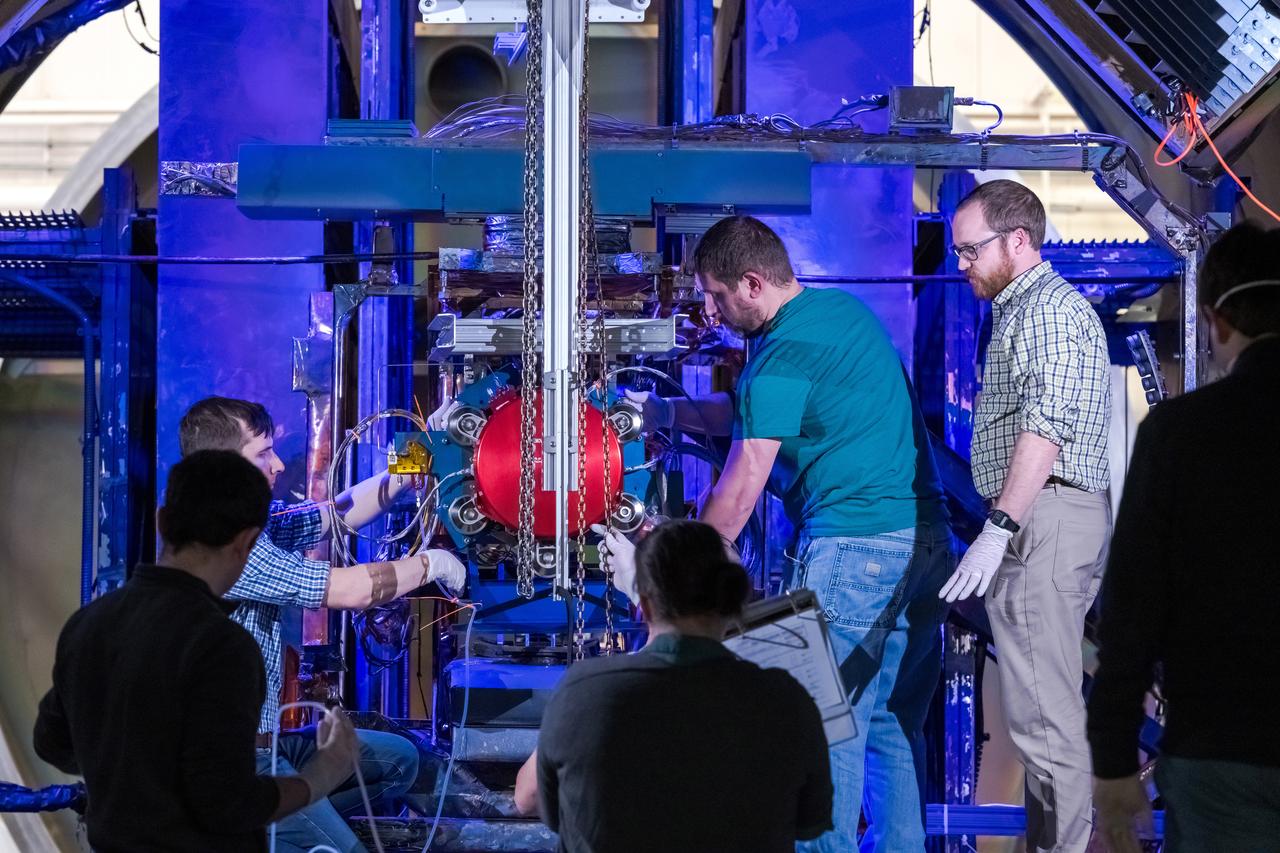
NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.
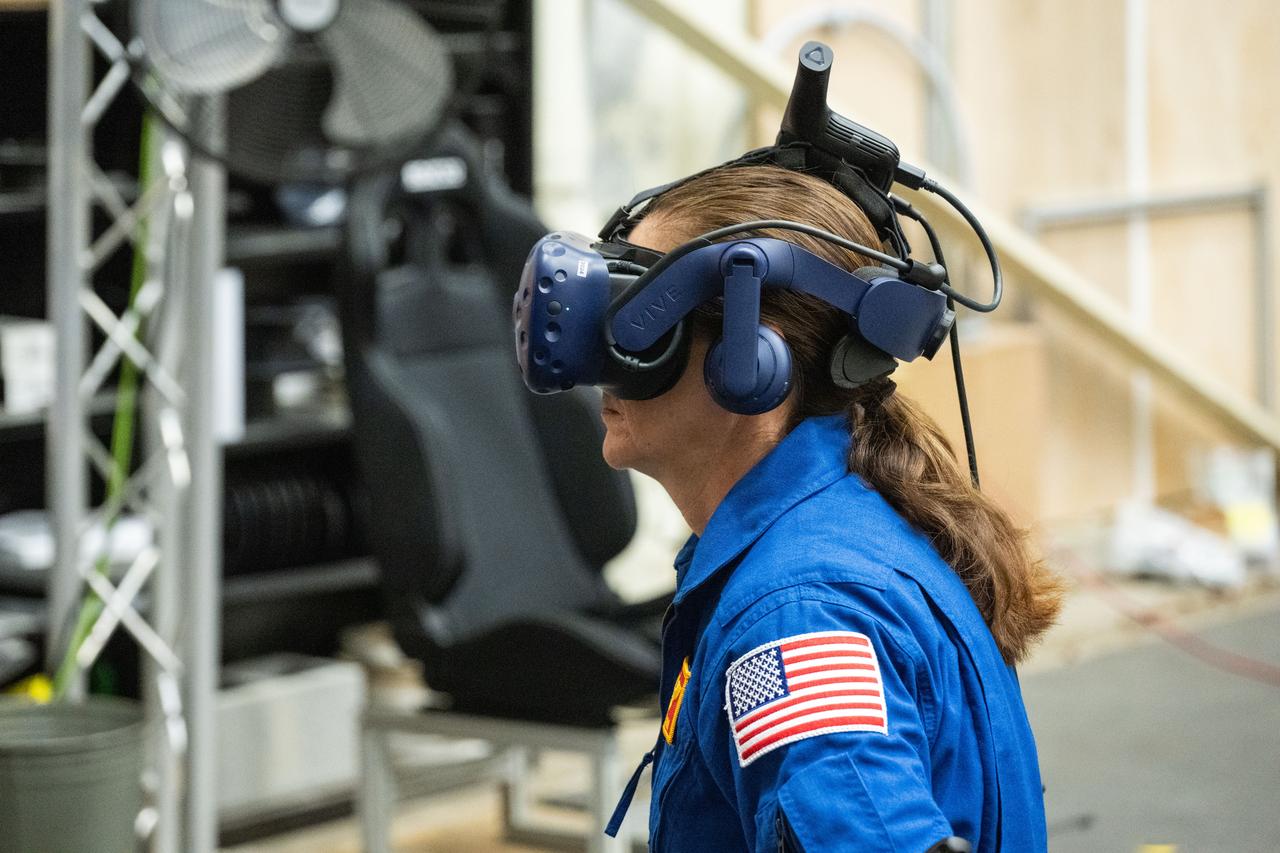

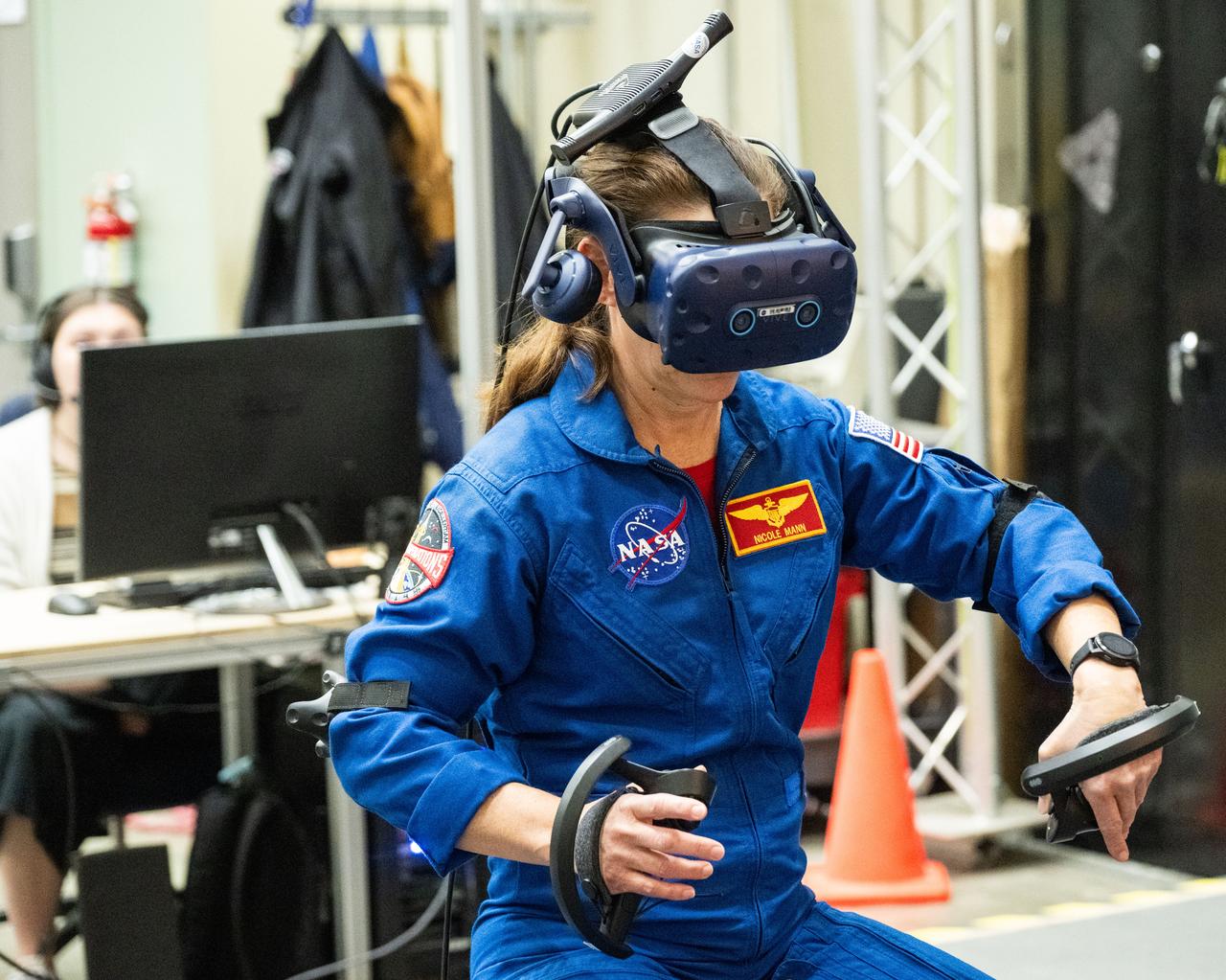
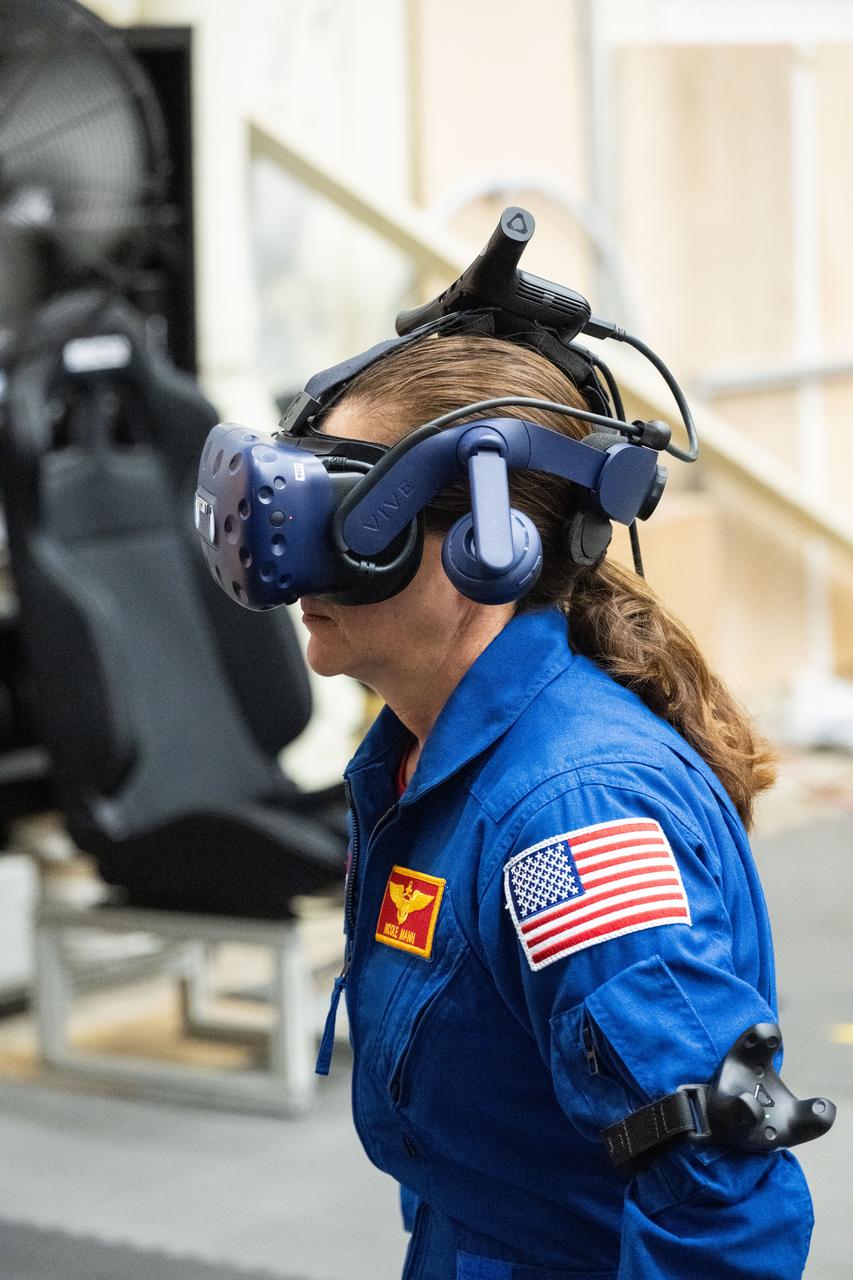
NASA astronaut Nicole Mann participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: 02-13-24 LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: Photographic support for Gateway Web Feature: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Nicole Mann PHOTOGRAPHER: Photo Credit: NASA / Bill Stafford
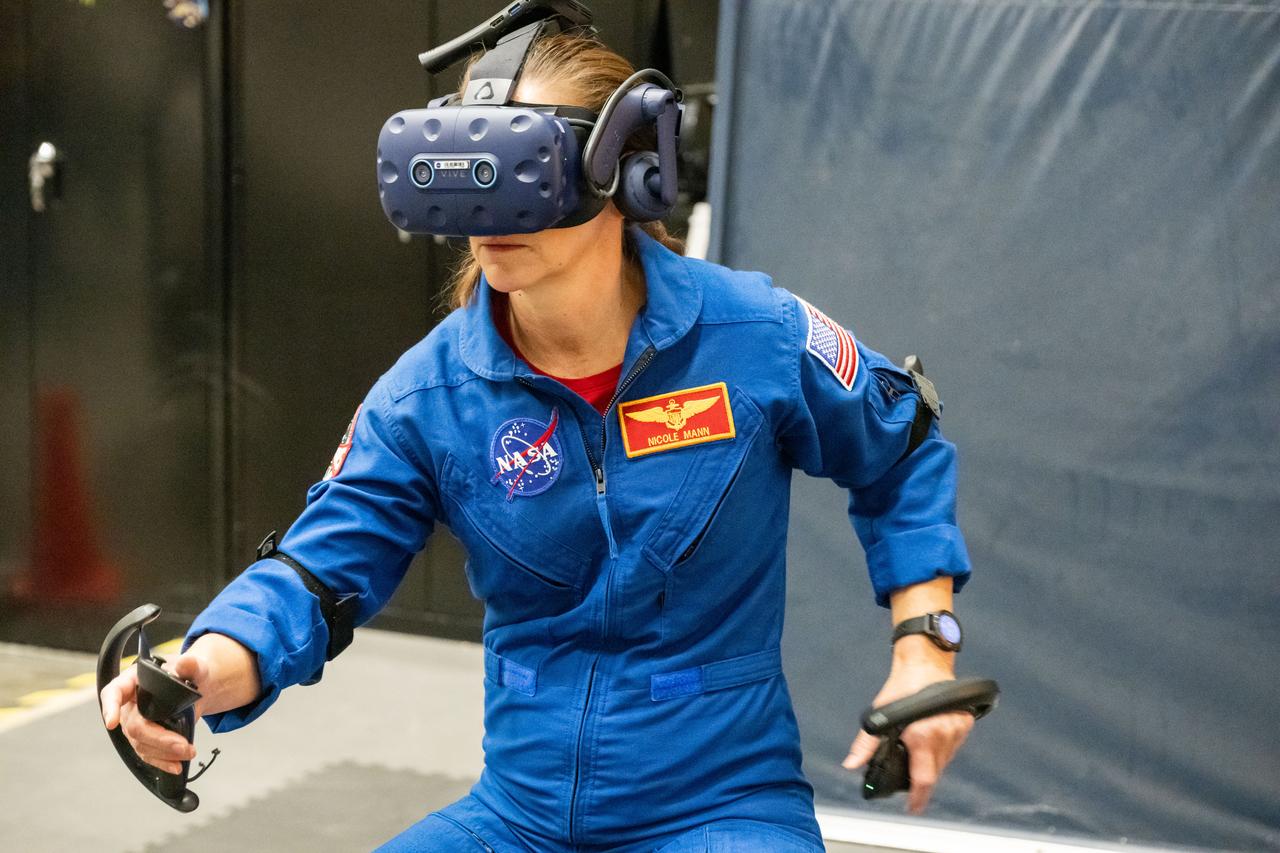

NASA astronaut Nicole Mann participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: 02-13-24 LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: Photographic support for Gateway Web Feature: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Nicole Mann PHOTOGRAPHER: Photo Credit: NASA / Bill Stafford
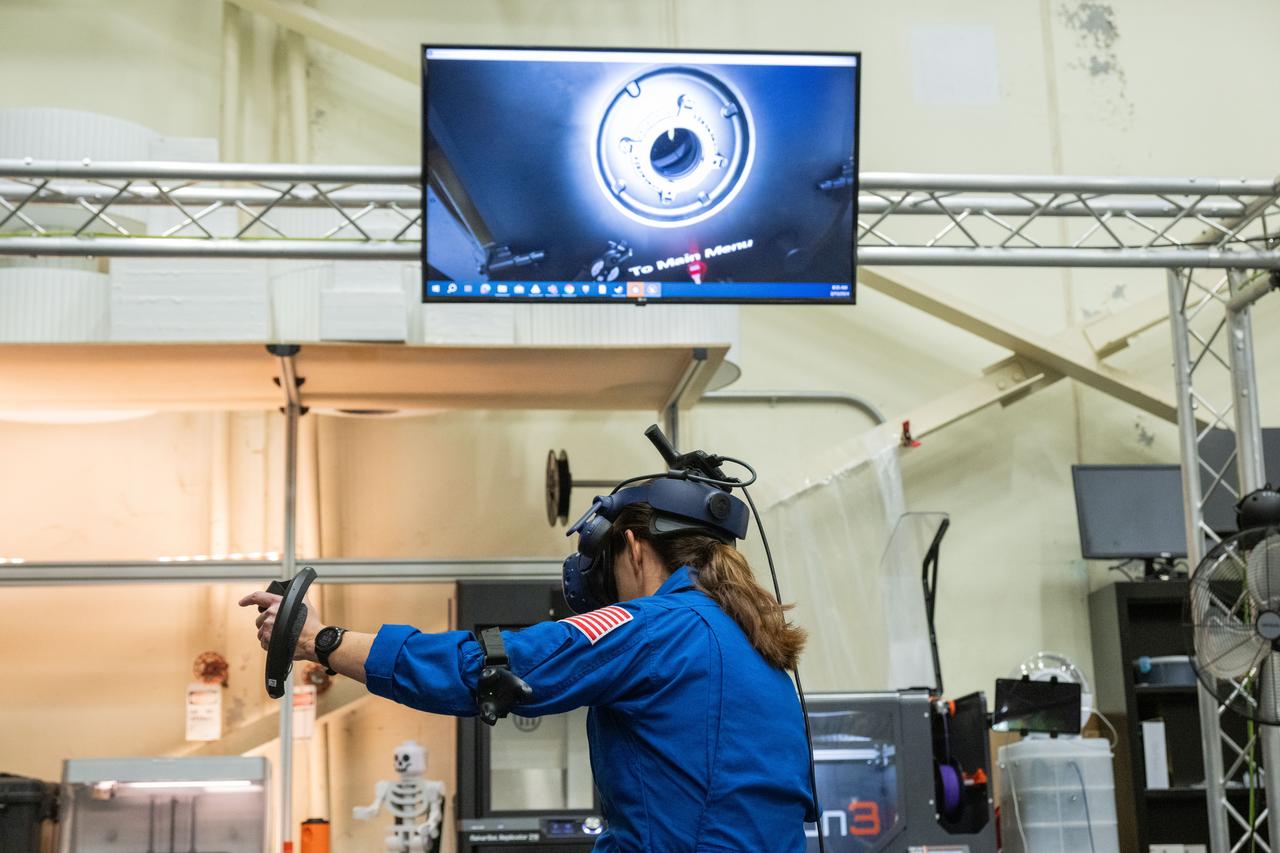

NASA astronaut Nicole Mann participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: 02-13-24 LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: Photographic support for Gateway Web Feature: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Nicole Mann PHOTOGRAPHER: Photo Credit: NASA / Bill Stafford
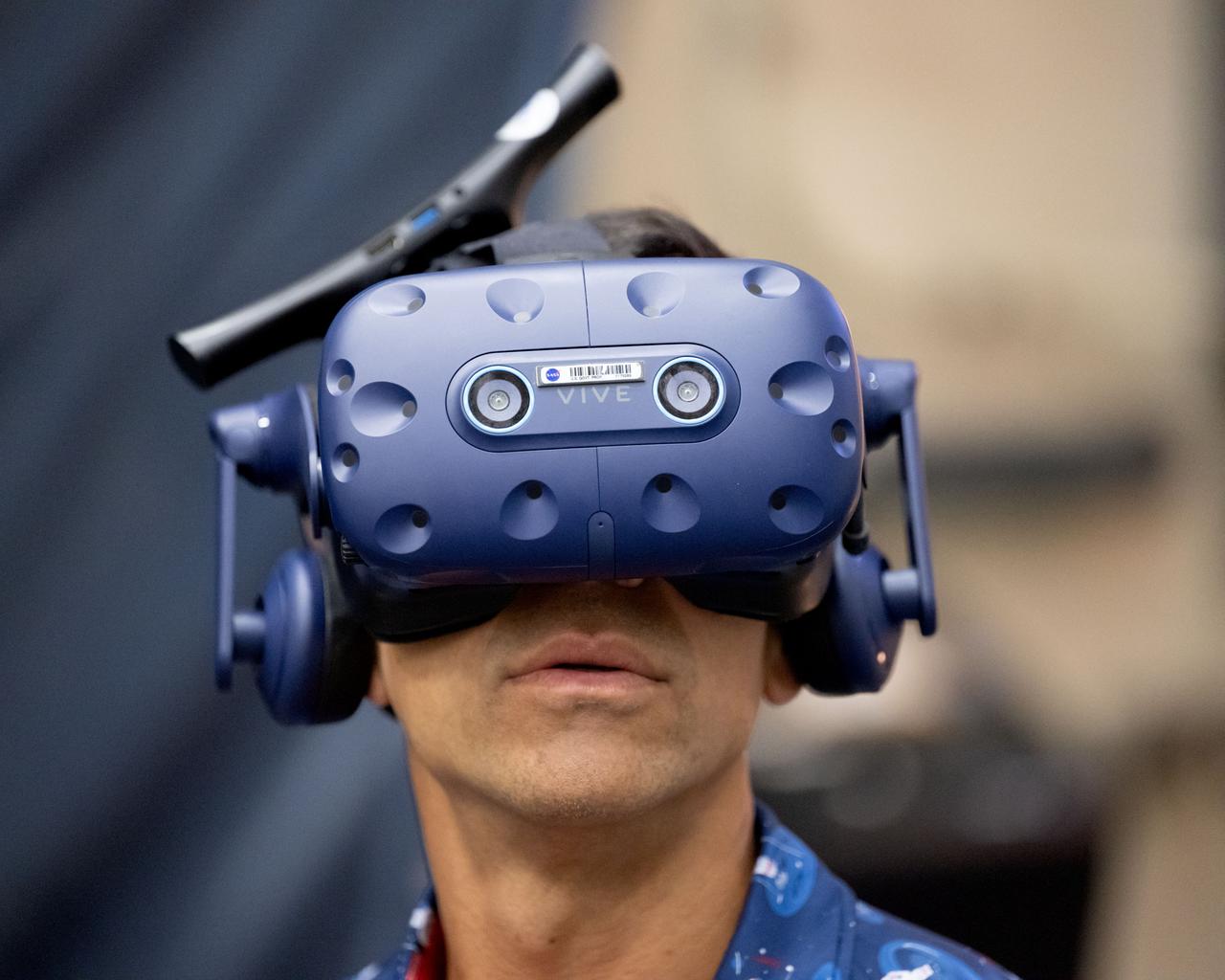

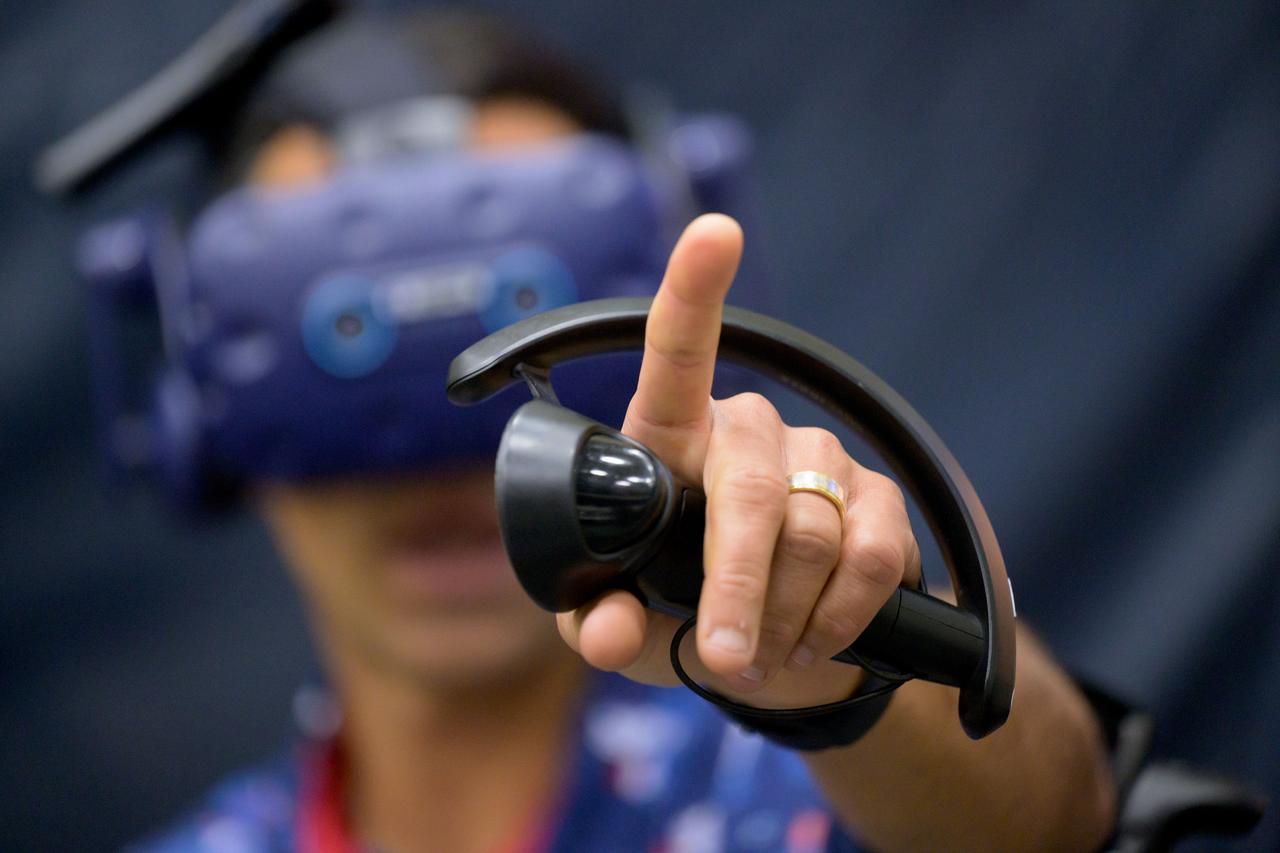
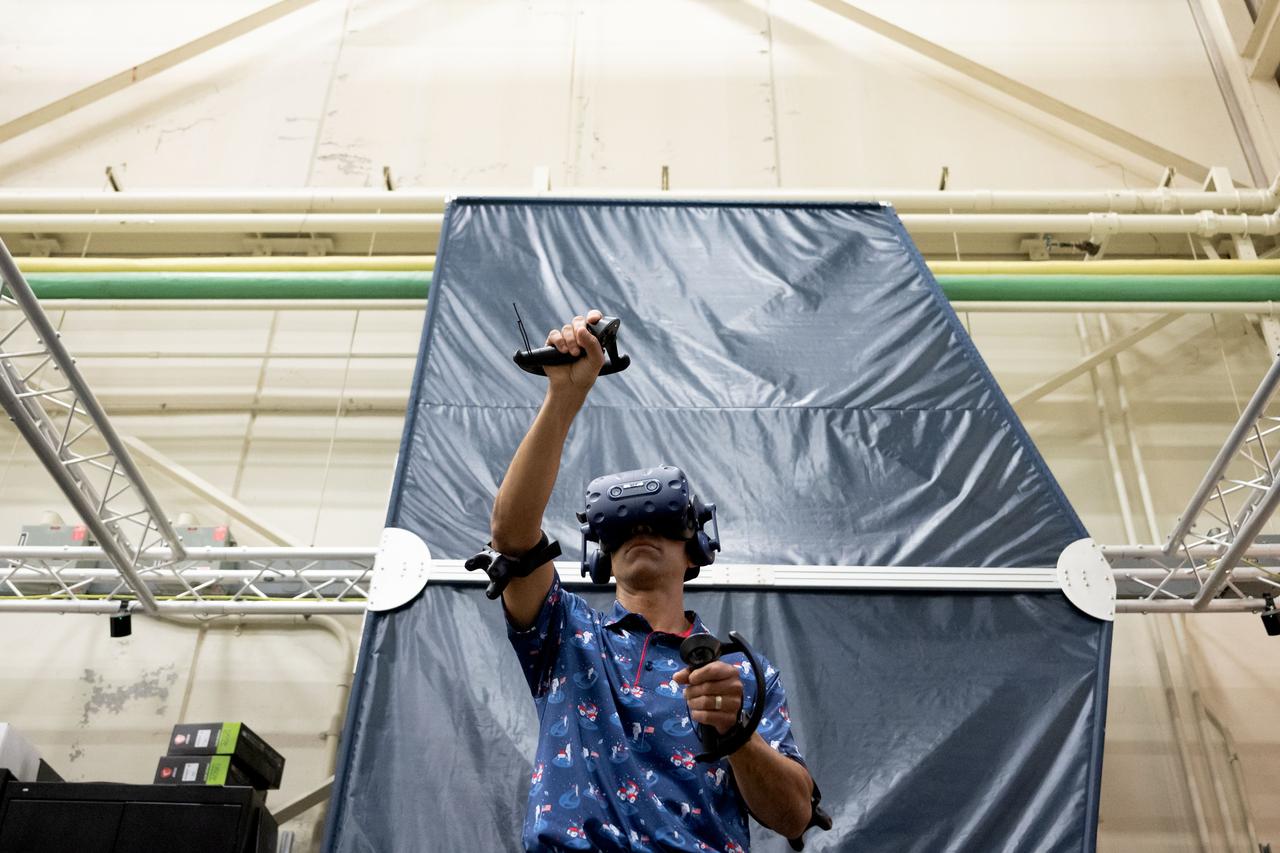
NASA astronaut Raja Chari participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: February 09, 2022. LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Raja Chari. Photo Credit: NASA / Josh Valcarcel
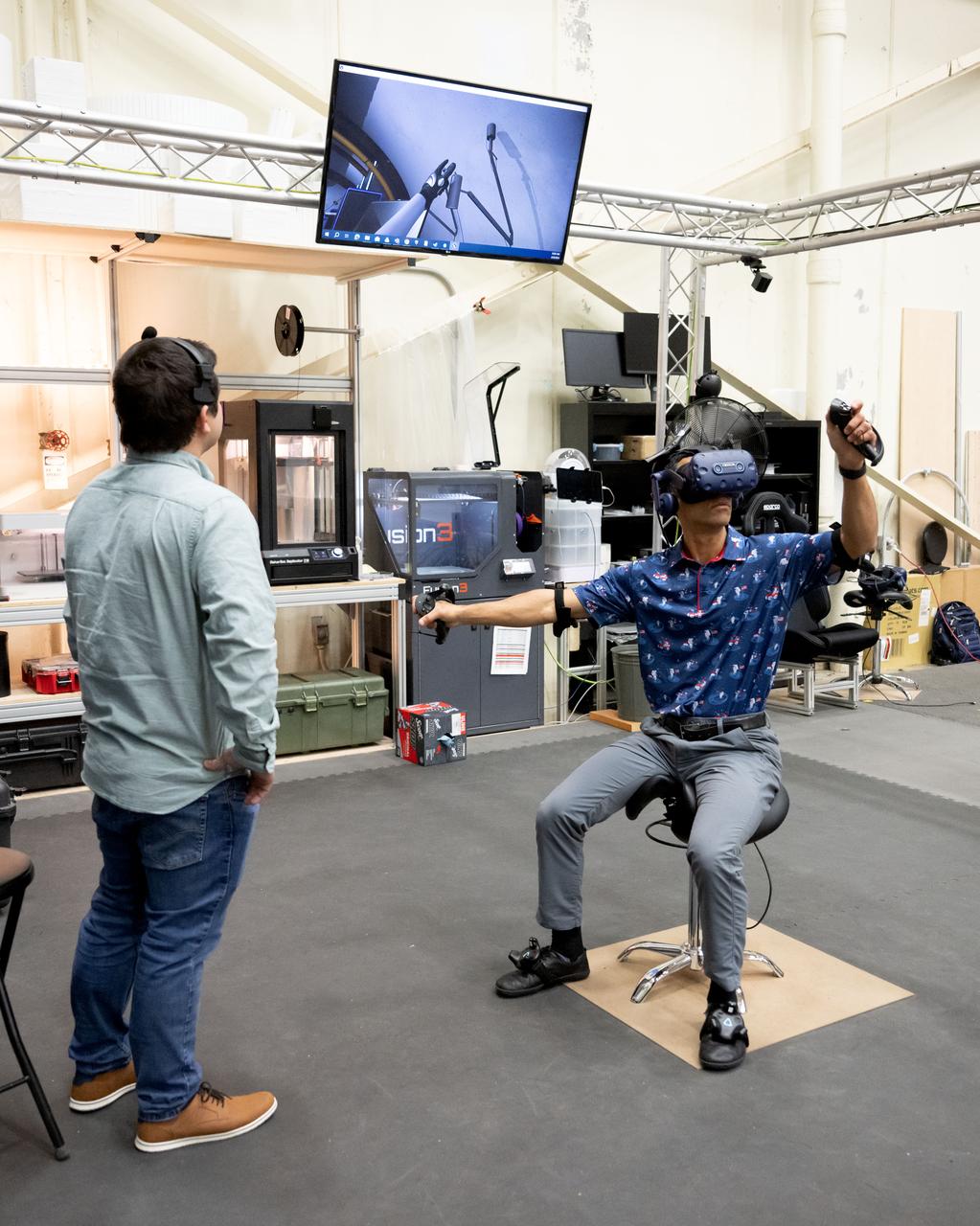

NASA astronaut Raja Chari participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: February 09, 2022. LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Raja Chari. Photo Credit: NASA / Josh Valcarcel
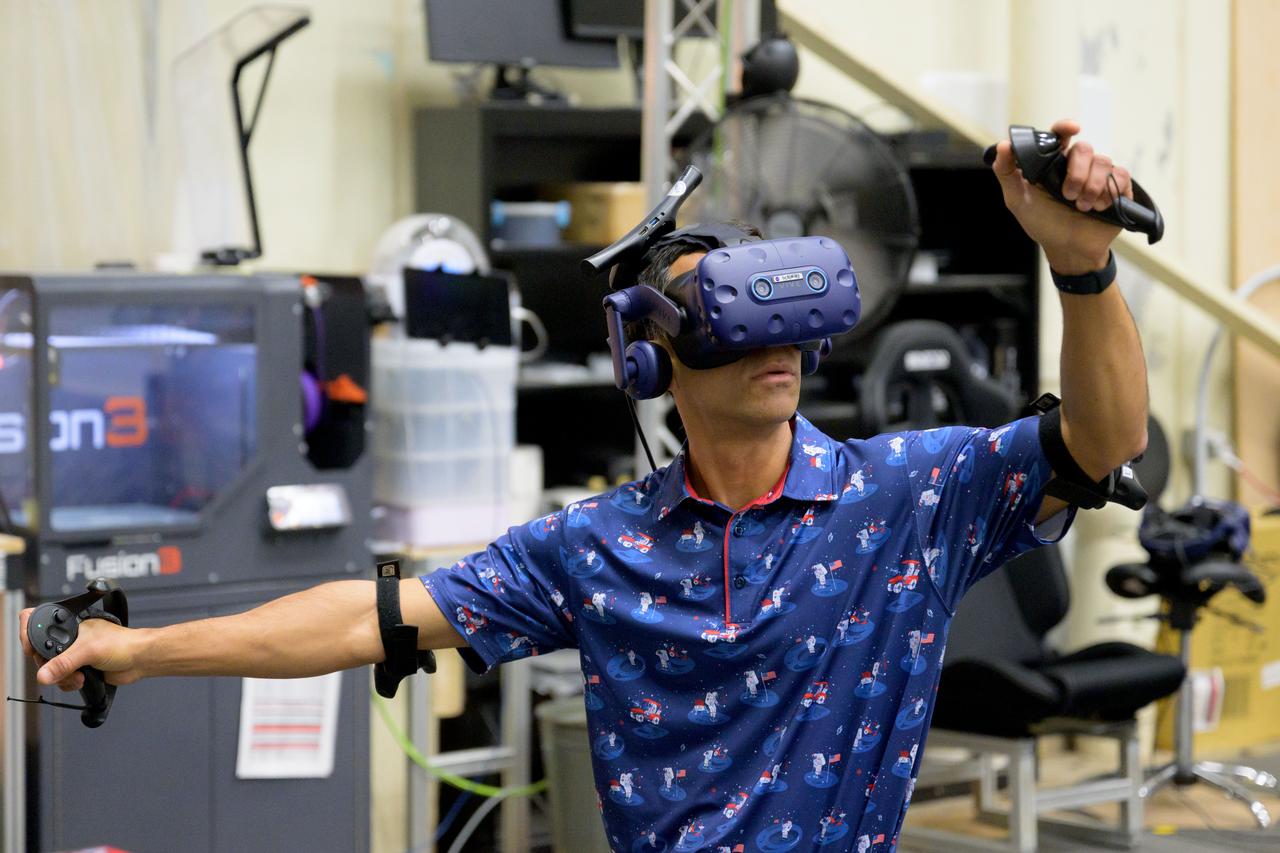

NASA astronaut Raja Chari participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: February 09, 2022. LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Raja Chari. Photo Credit: NASA / Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Raja Chari participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: February 09, 2022. LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Raja Chari. Photo Credit: NASA / Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Nicole Mann participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: 02-13-24 LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: Photographic support for Gateway Web Feature: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Nicole Mann PHOTOGRAPHER: Photo Credit: NASA / Bill Stafford

NASA astronaut Raja Chari participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: February 09, 2022. LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Raja Chari. Photo Credit: NASA / Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Nicole Mann participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: 02-13-24 LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: Photographic support for Gateway Web Feature: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Nicole Mann PHOTOGRAPHER: Photo Credit: NASA / Bill Stafford

NASA astronaut Raja Chari participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: February 09, 2022. LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Raja Chari. Photo Credit: NASA / Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Nicole Mann participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: 02-13-24 LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: Photographic support for Gateway Web Feature: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Nicole Mann PHOTOGRAPHER: Photo Credit: NASA / Bill Stafford

NASA astronaut Raja Chari participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: February 09, 2022. LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Raja Chari. Photo Credit: NASA / Josh Valcarcel
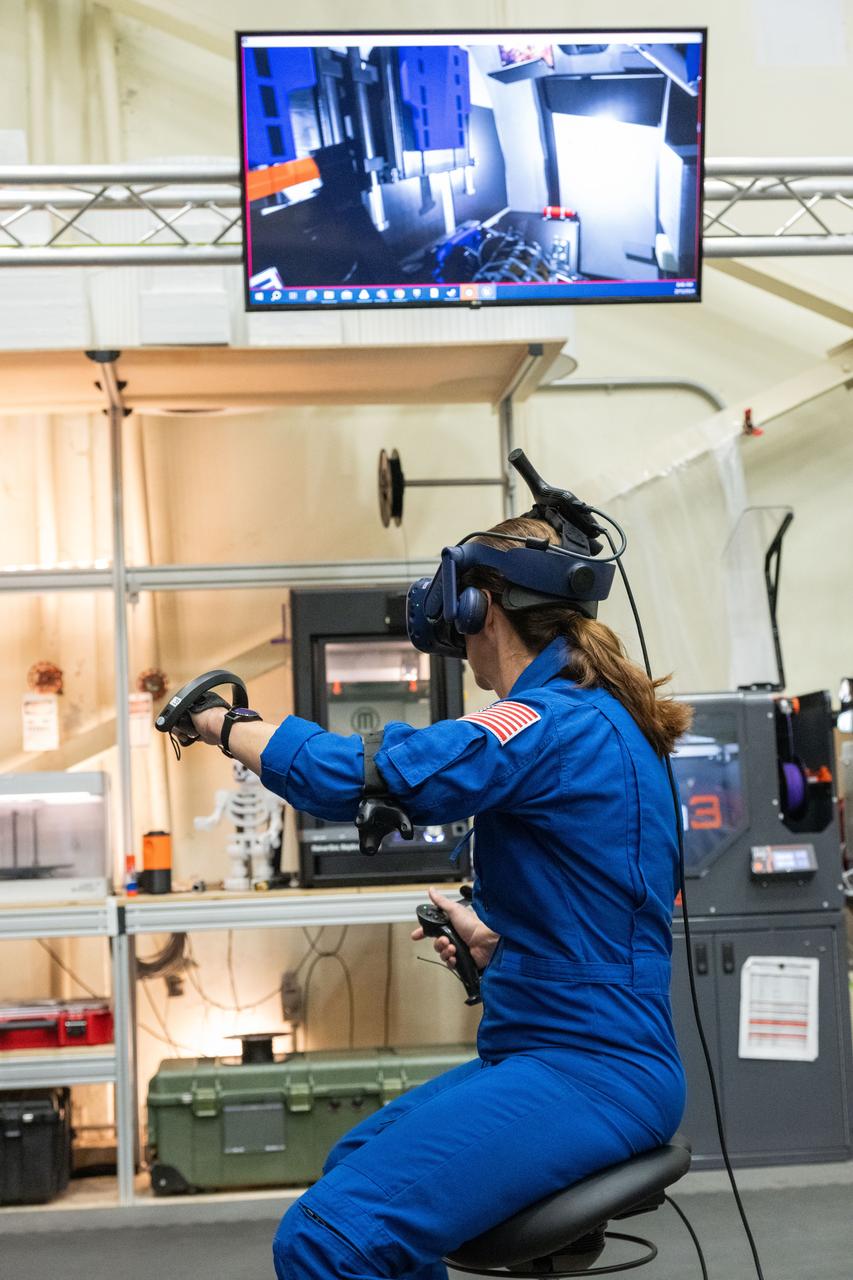

NASA astronaut Nicole Mann participates in virtual reality testing of the Gateway lunar space station to ensure its comfort and safety when astronauts live and conduct science there on future Artemis missions. PHOTO DATE: 02-13-24 LOCATION: Bldg. 15 - VR Lab SUBJECT: Photographic support for Gateway Web Feature: VR Technology for Interior Gateway Training with astronaut Nicole Mann PHOTOGRAPHER: Photo Credit: NASA / Bill Stafford
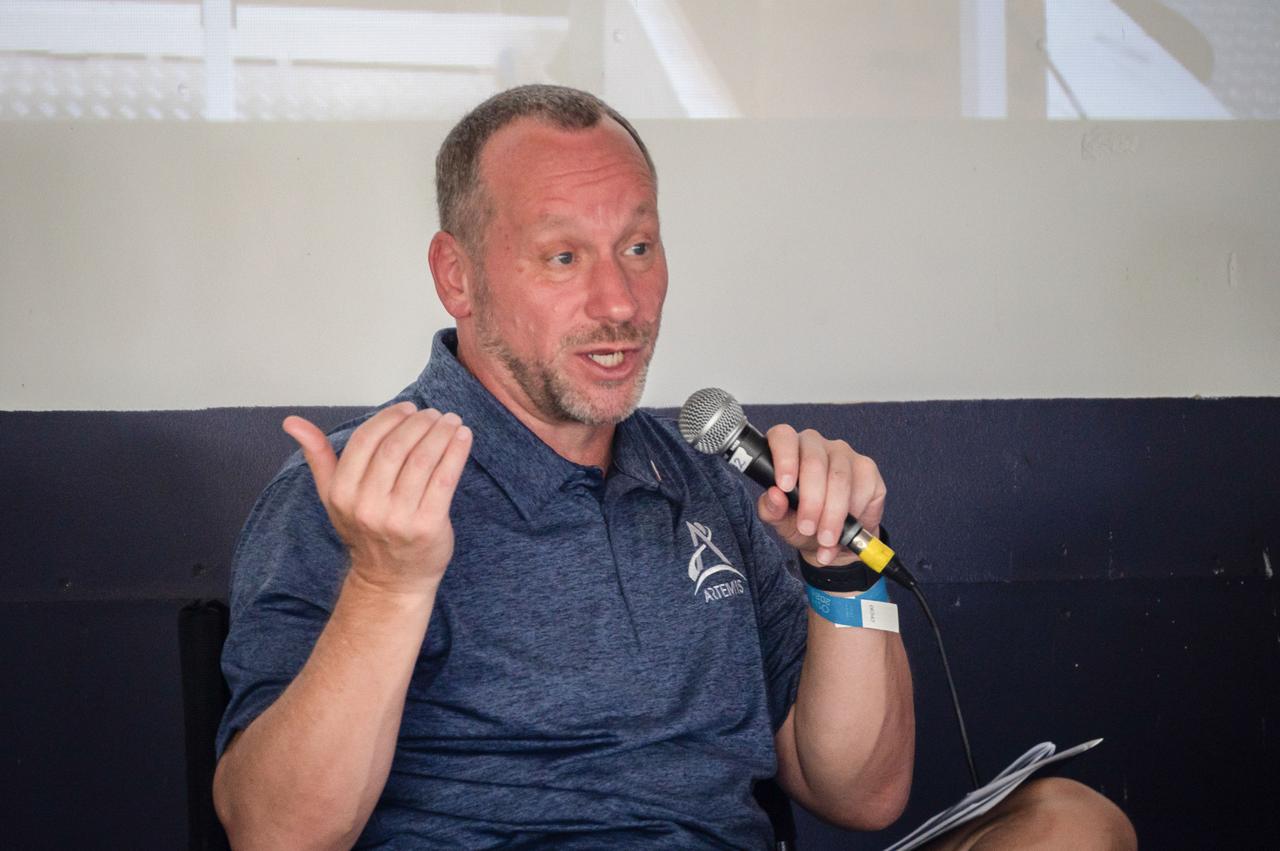

jsc2024e055764 (July 26, 2024) -- Dr. Jon Olansen discusses lunar habitation during the "Living the Lunar Life" forum at EAA AirVenture Oshkosh 2024. As Gateway Program Manager, Olansen highlights the innovative technologies and mission planning essential for living and working in the harsh environment of deep space. Photo Credit: NASA/Andrew Carlsen
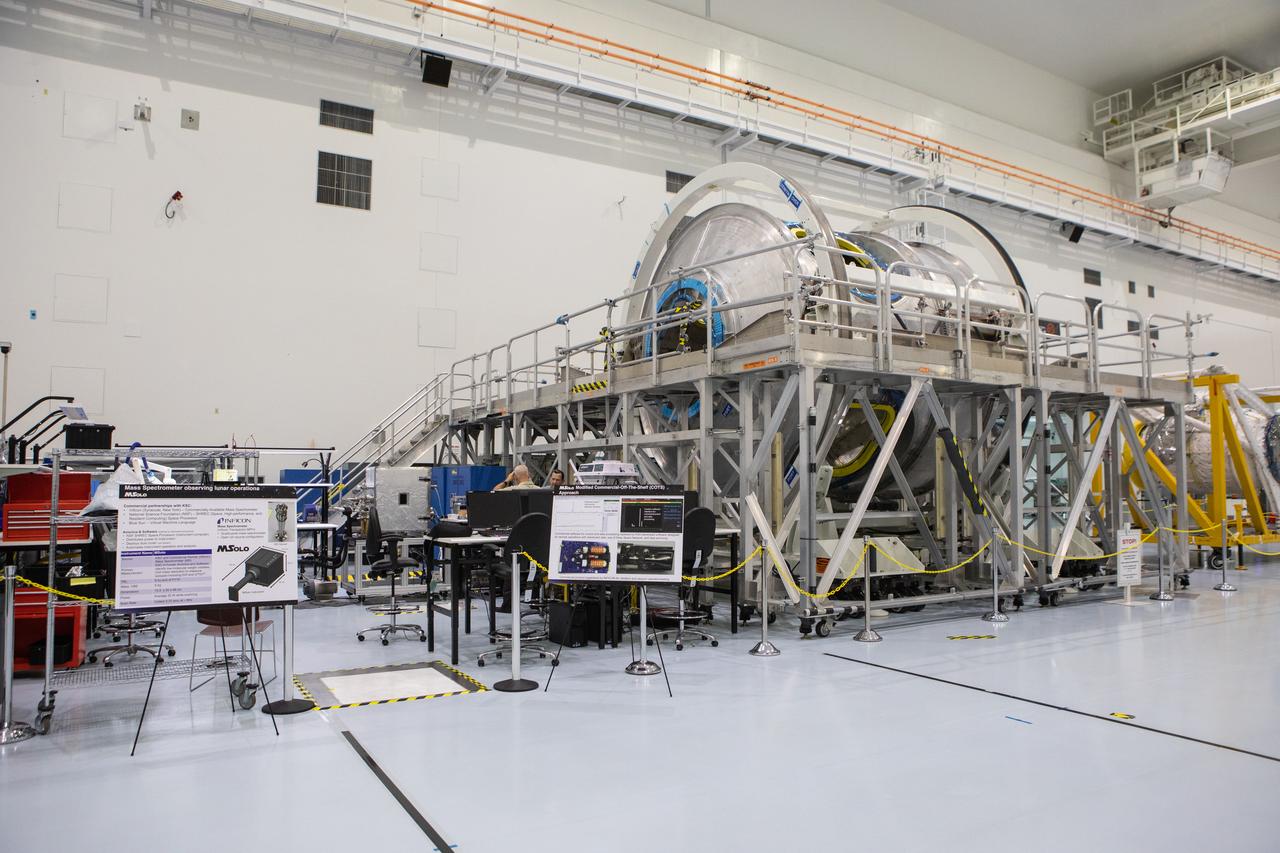

Instruments for NASA’s Mars Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) are in view at left in the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on May 16, 2019. The center is celebrating the SSPF’s 25th anniversary. The facility was built to process elements for the International Space Station. Now it is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
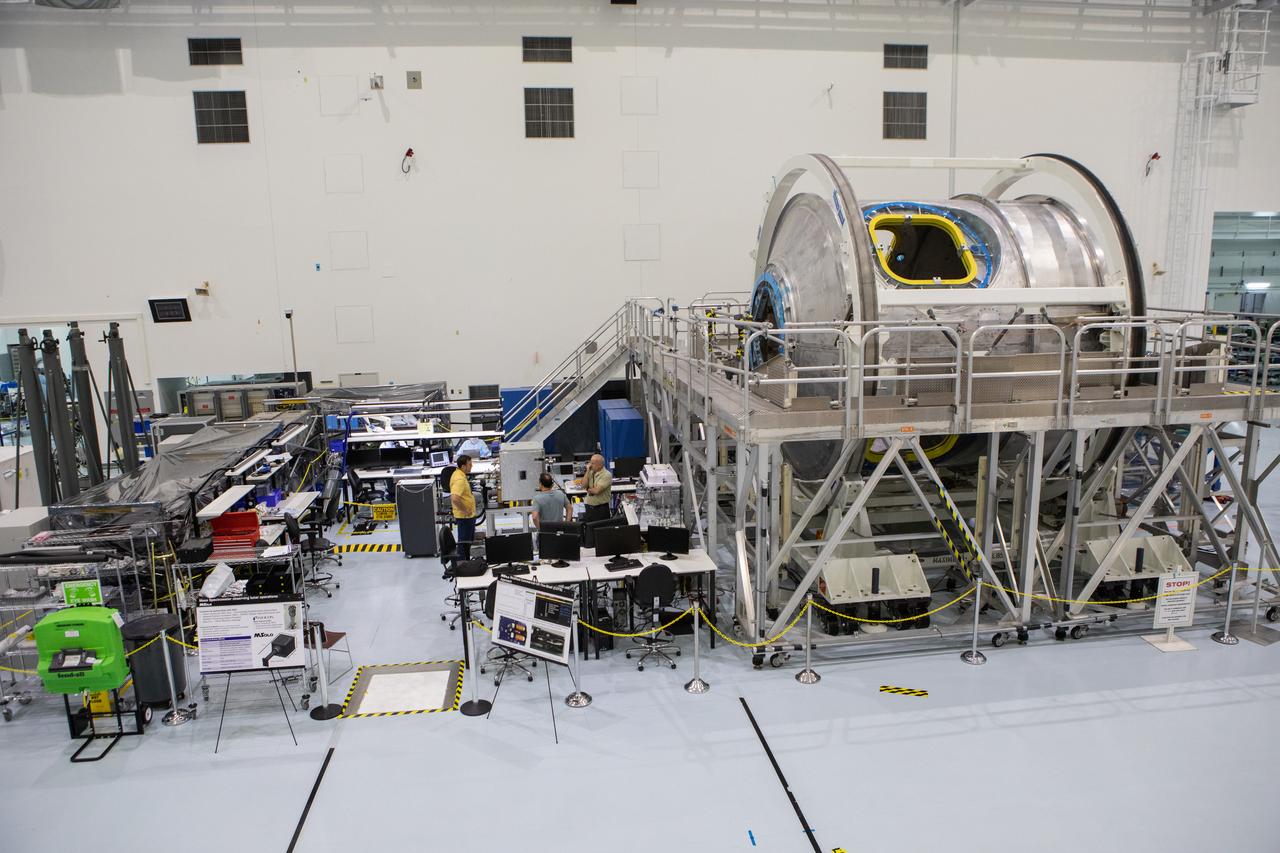

Instruments for NASA’s Mars Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) are in view at left in the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on May 16, 2019. The center is celebrating the SSPF’s 25th anniversary. The facility was built to process elements for the International Space Station. Now it is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.

Gateway - HALO Static Test Complete. Location: Turin, Italy Date: July 9, 2024 Photo Credit: Thales Alenia Space
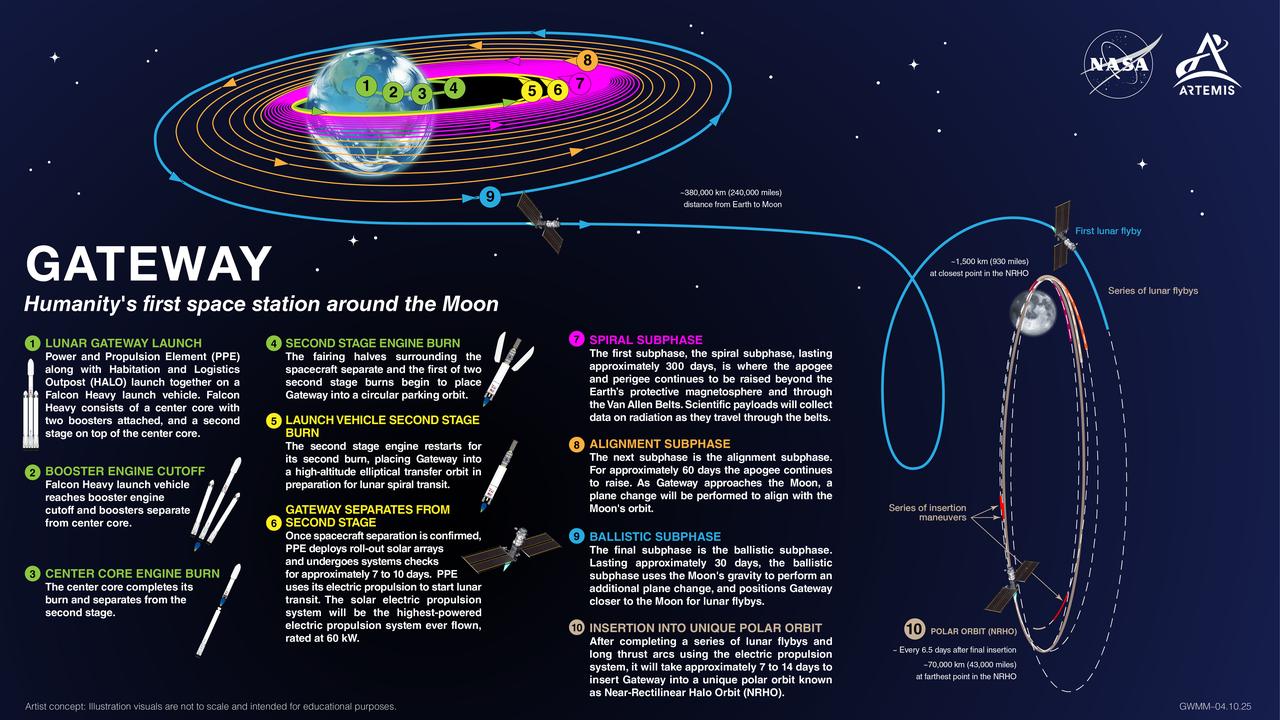
The Lunar Gateway Launch, mapped. Gateway's first elements, the Power and Propulsion Element and HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost), will launch together to lunar orbit, where they’ll set the stage for Artemis IV: the first Gateway assembly mission. During this milestone mission, the Artemis IV crew will deliver the European Space Agency's Lunar I-Hab, dock it to HALO, and enter the space station for the very first time. NASA is currently targeting a 2027 launch for HALO and the Power and Propulsion Element. This timeline allows for the roughly year-long journey to lunar orbit and ensures everything is in place ahead of Artemis IV.
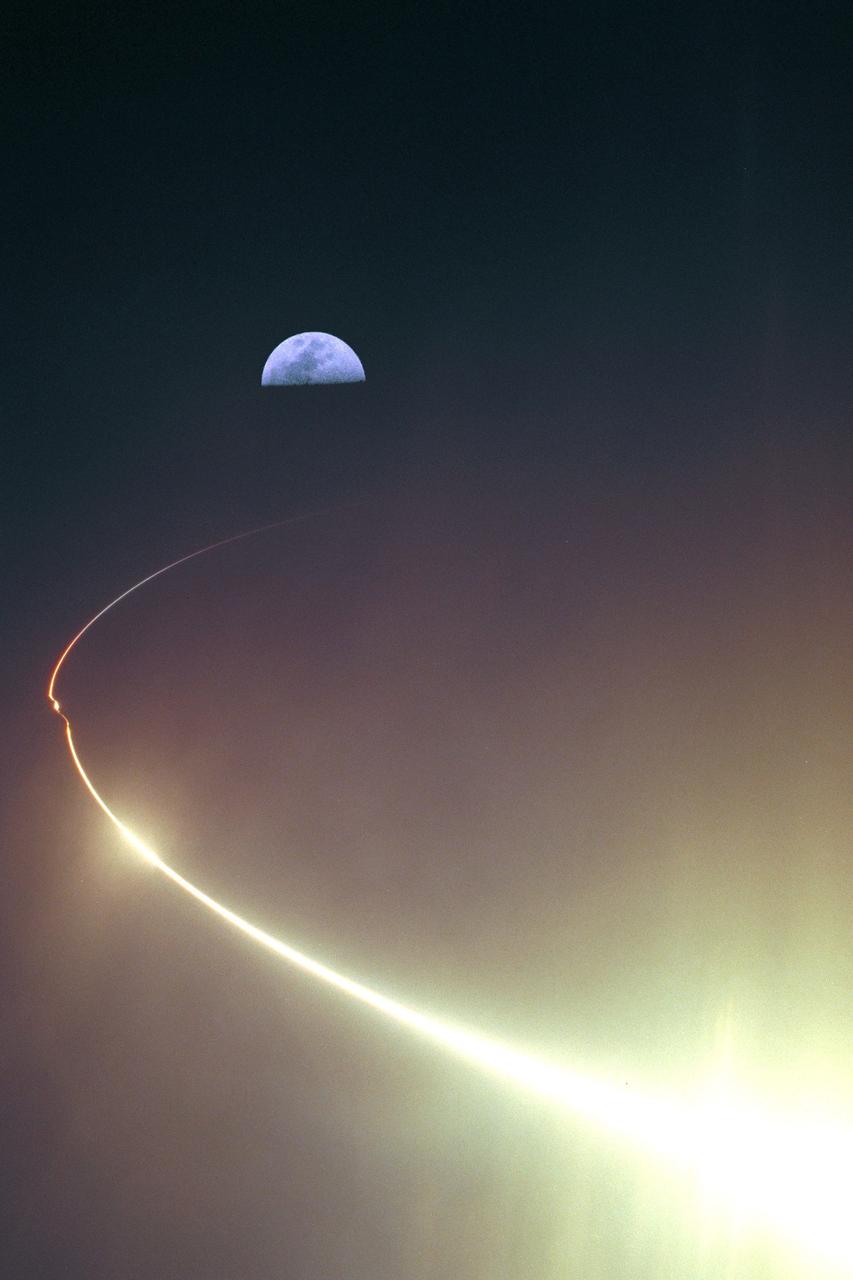

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA's Lunar Prospector spacecraft launched successfully on its way to the Moon from Launch Complex 46 (LC46) at Cape Canaveral Air Station on Jan. 6 at 9:38 p.m. EST. It was the inaugural launch of Lockheed Martin's Athena II launch vehicle and the first launch from LC46, operated by Spaceport Florida Authority. Lunar Prospector, built for the NASA Ames Research Center by Lockheed Martin, is a spin-stabilized spacecraft designed to provide NASA with the first global maps of the Moon's surface and its gravitational magnetic fields, as well as look for the possible presence of ice near the lunar poles. It will orbit the Moon at an altitude of approximately 63 miles during a one-year mission.
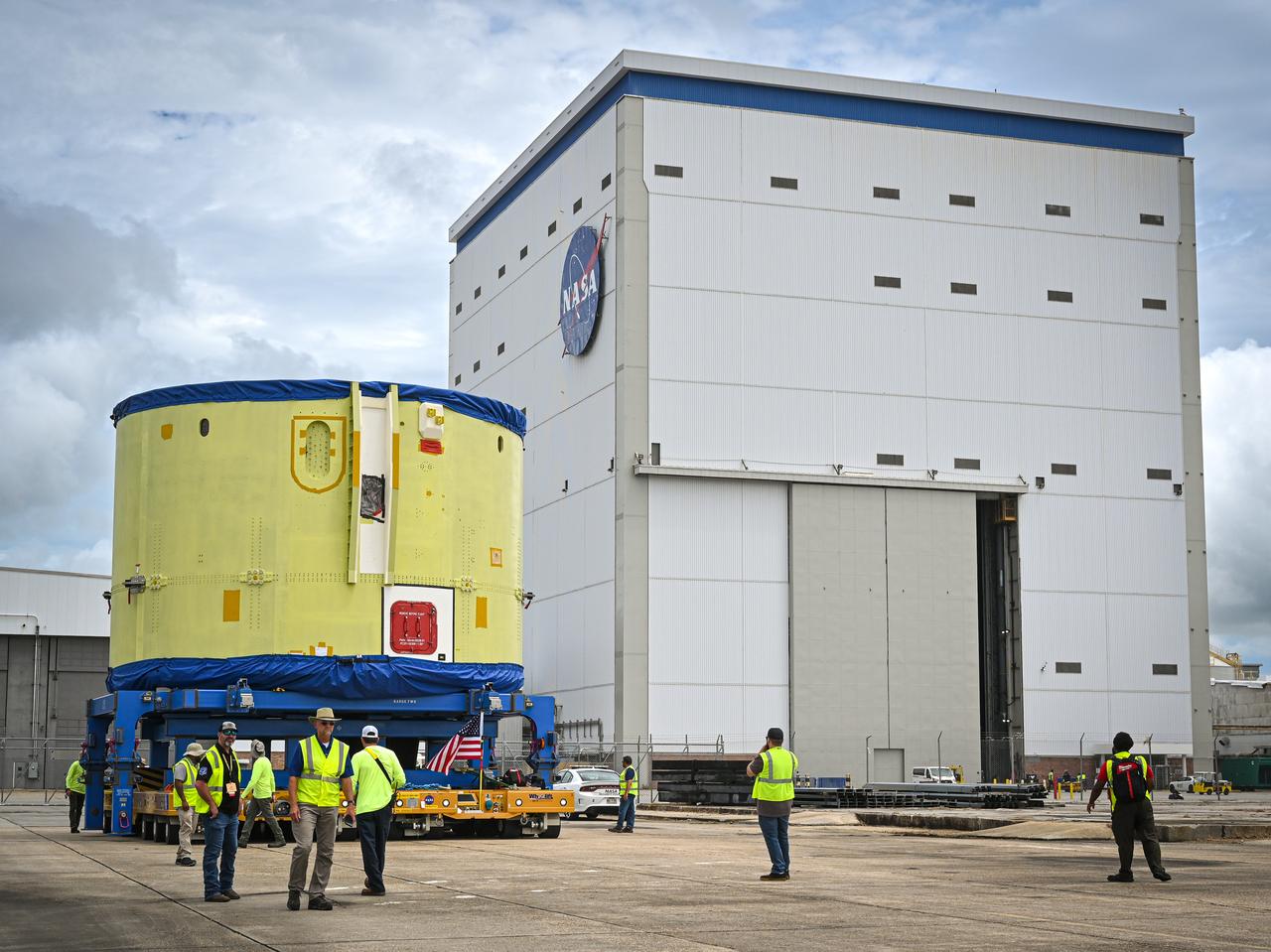

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.
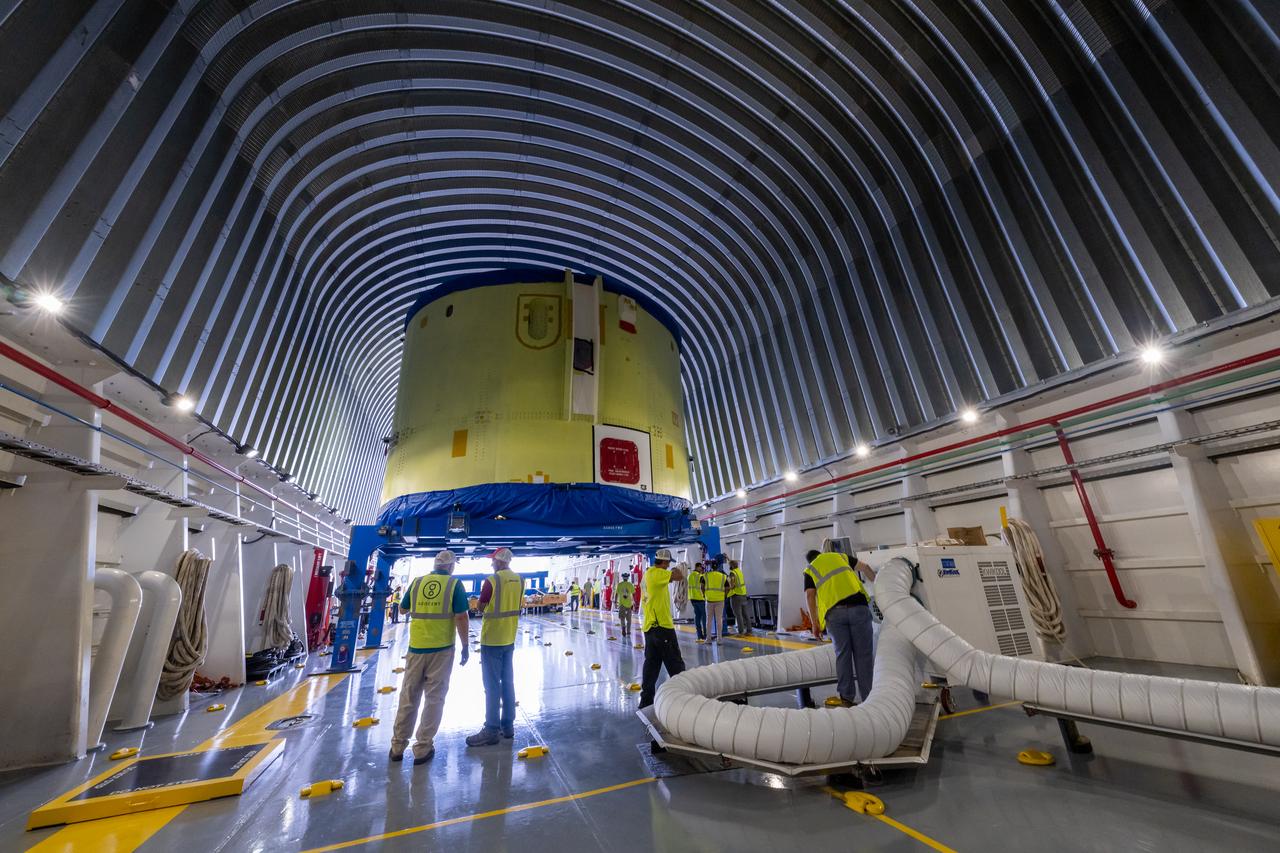

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.
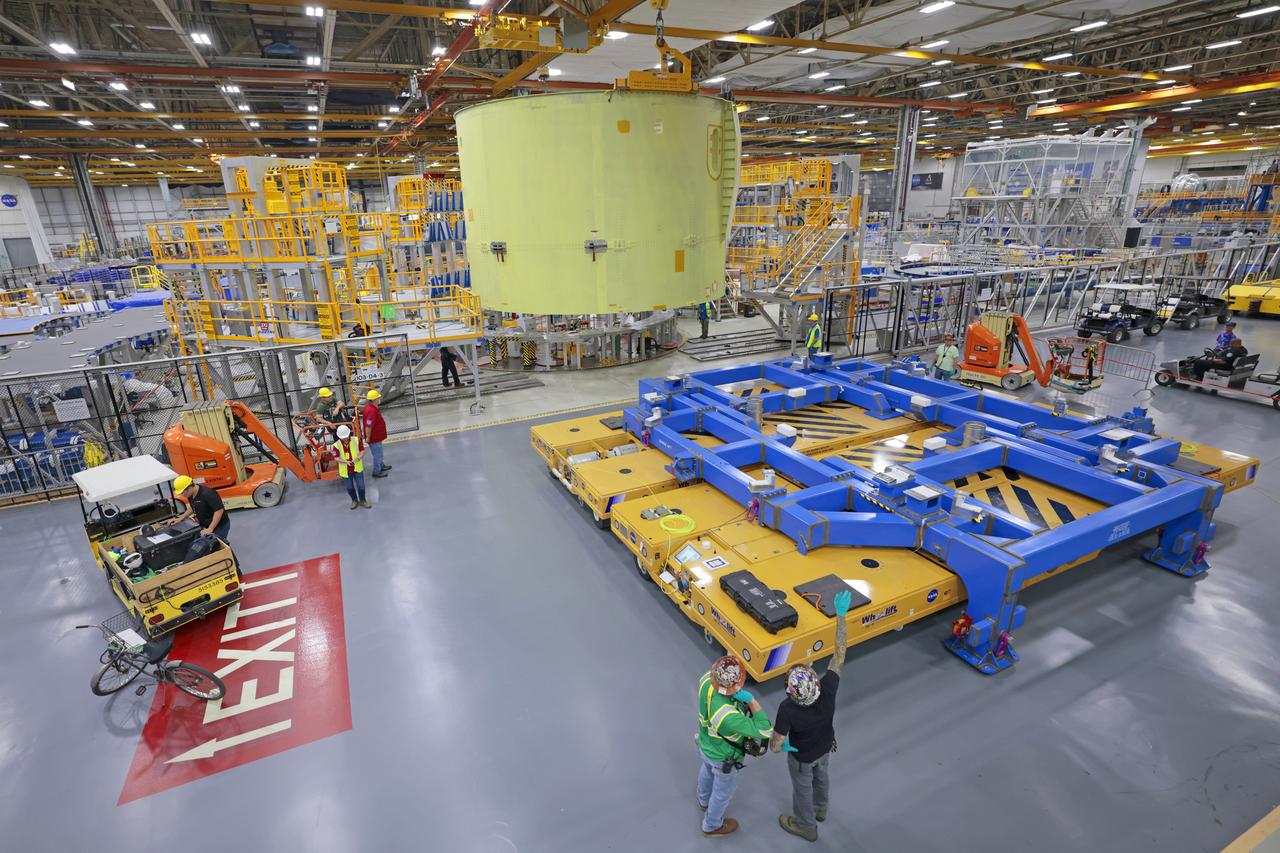

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
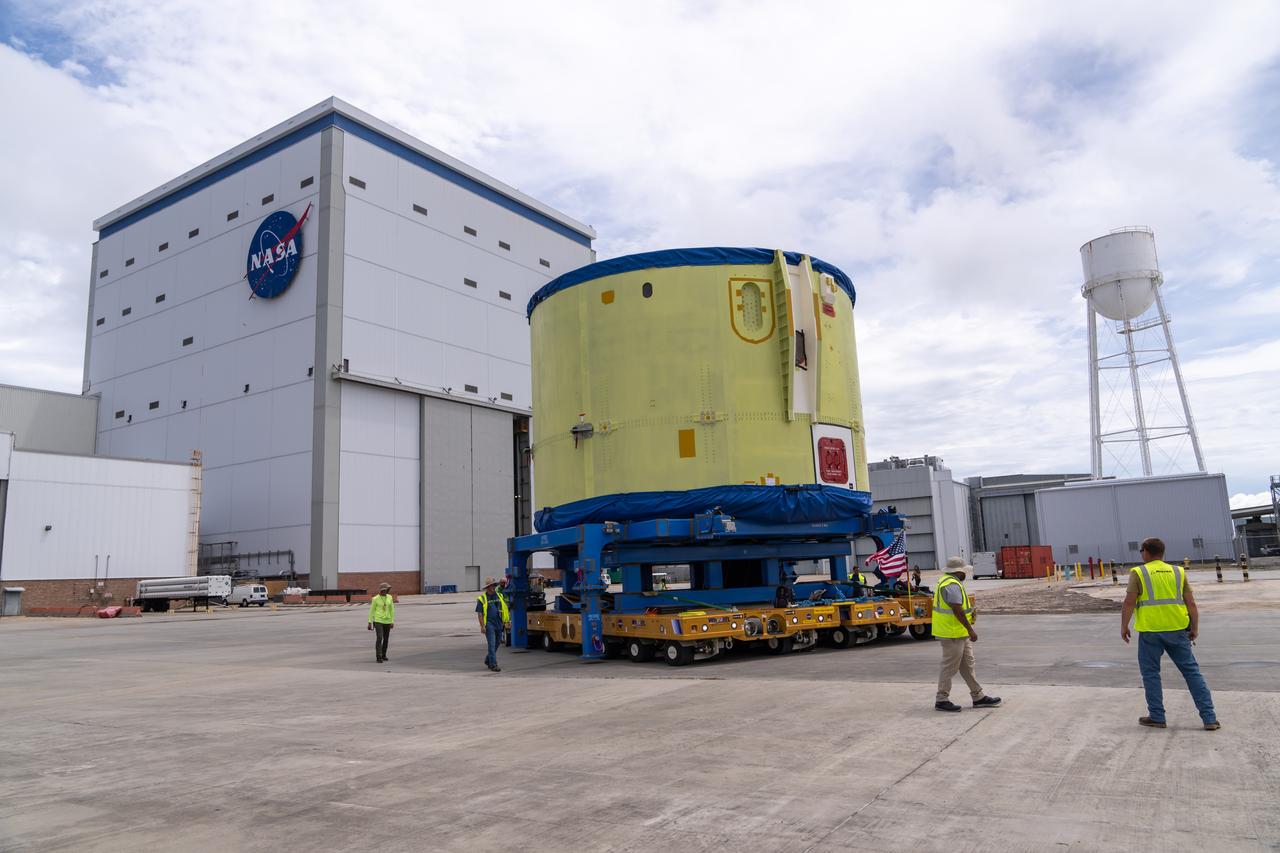

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.
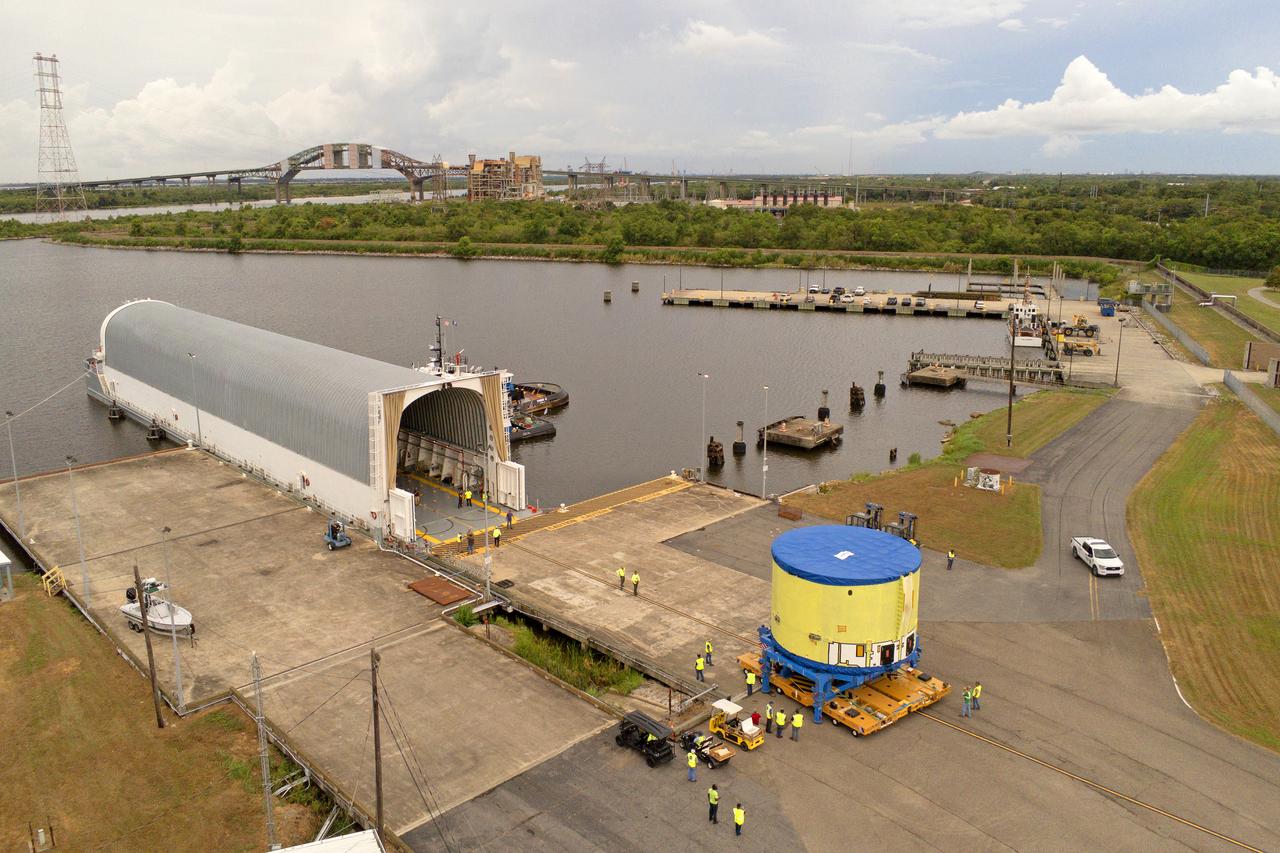

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.
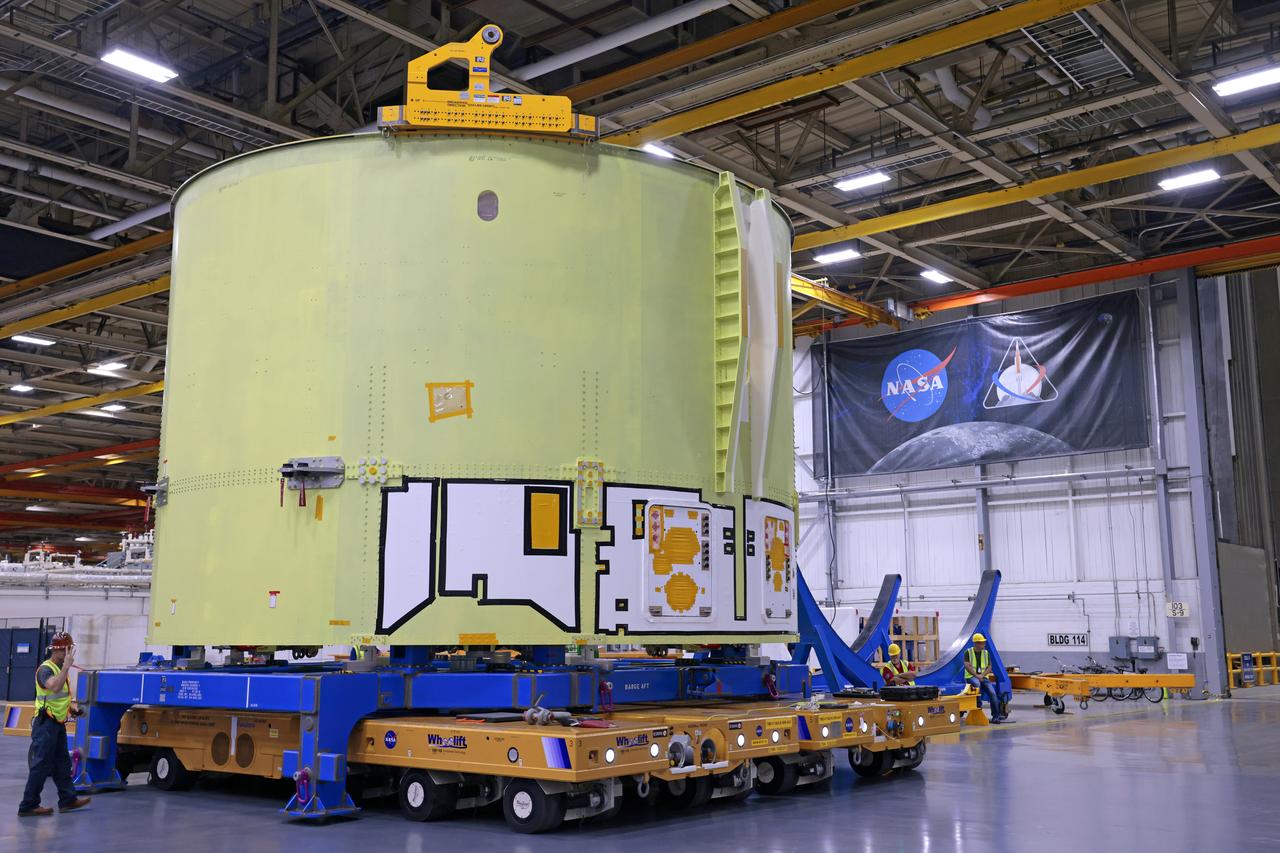

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
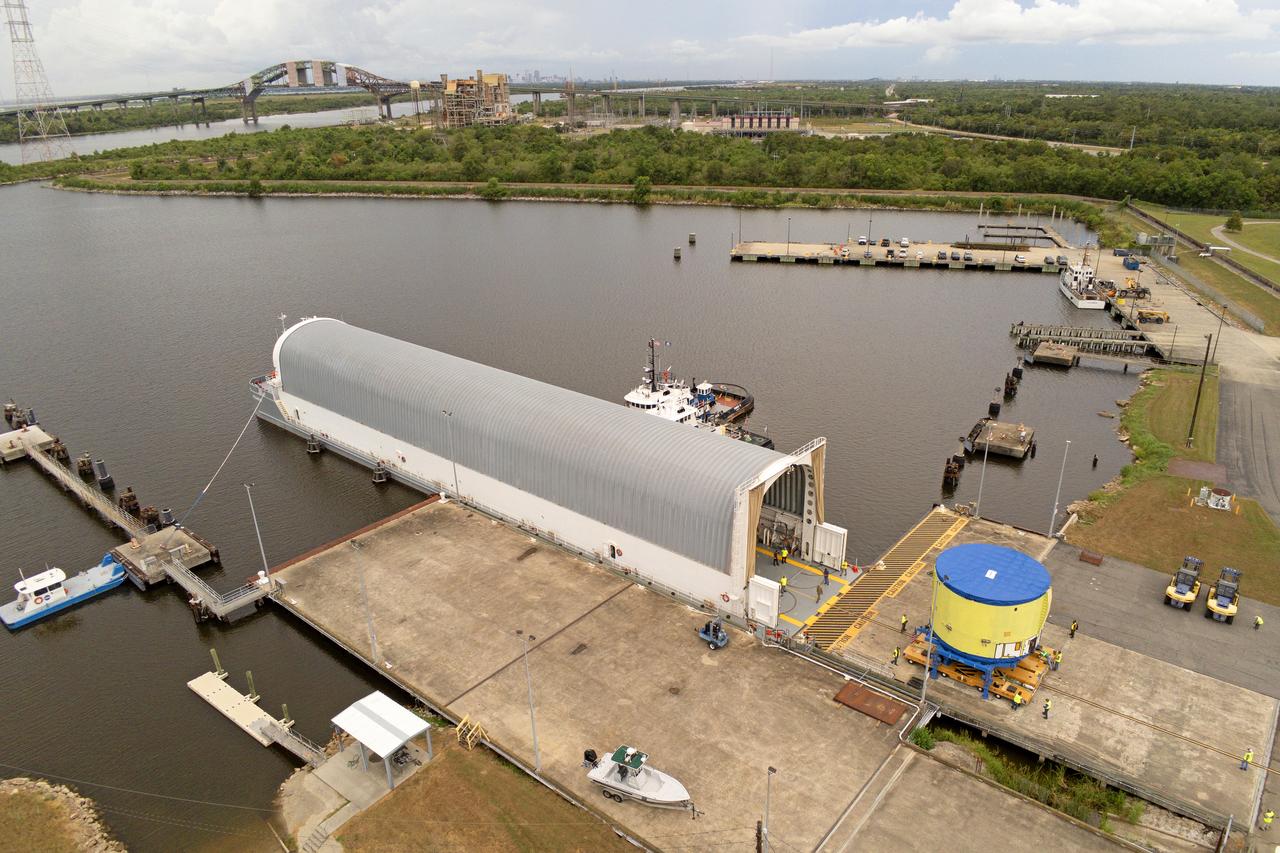

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.
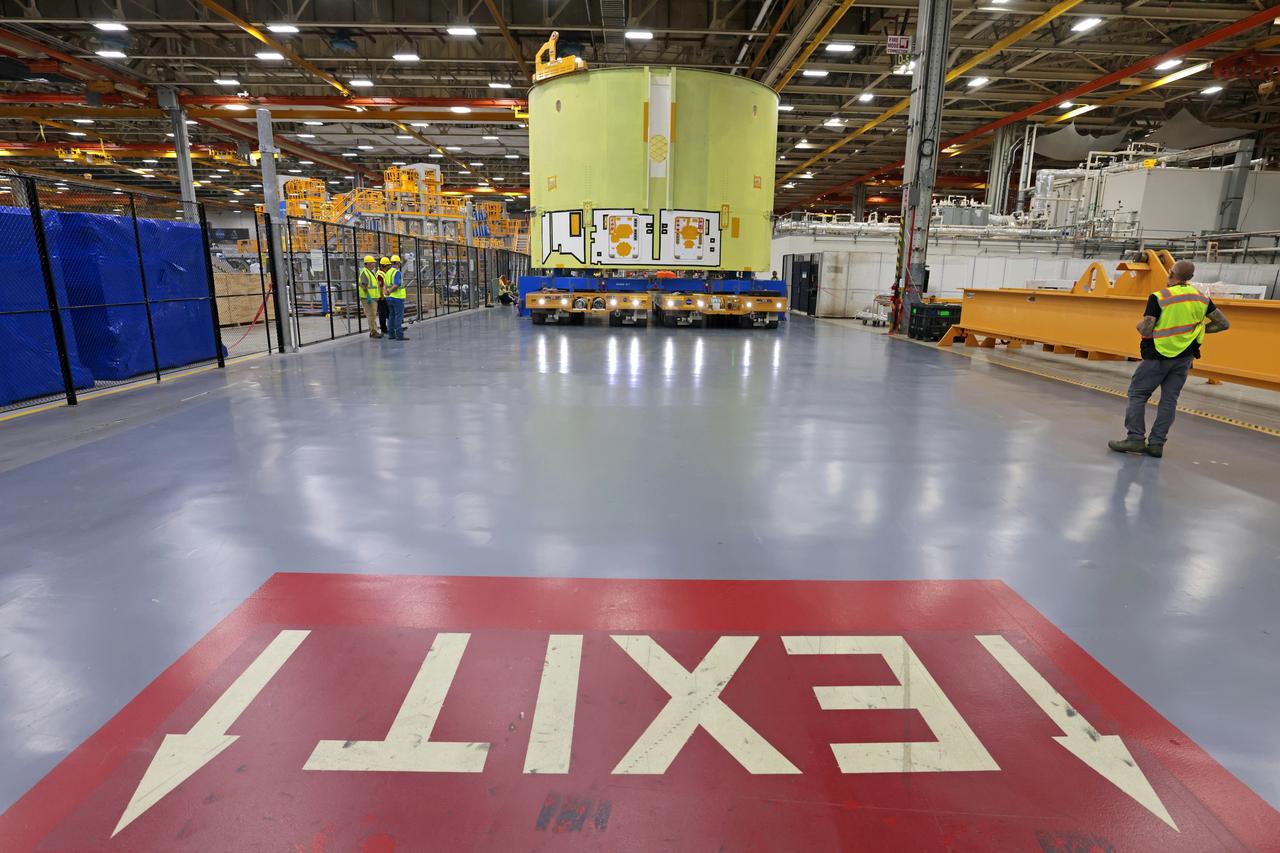

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

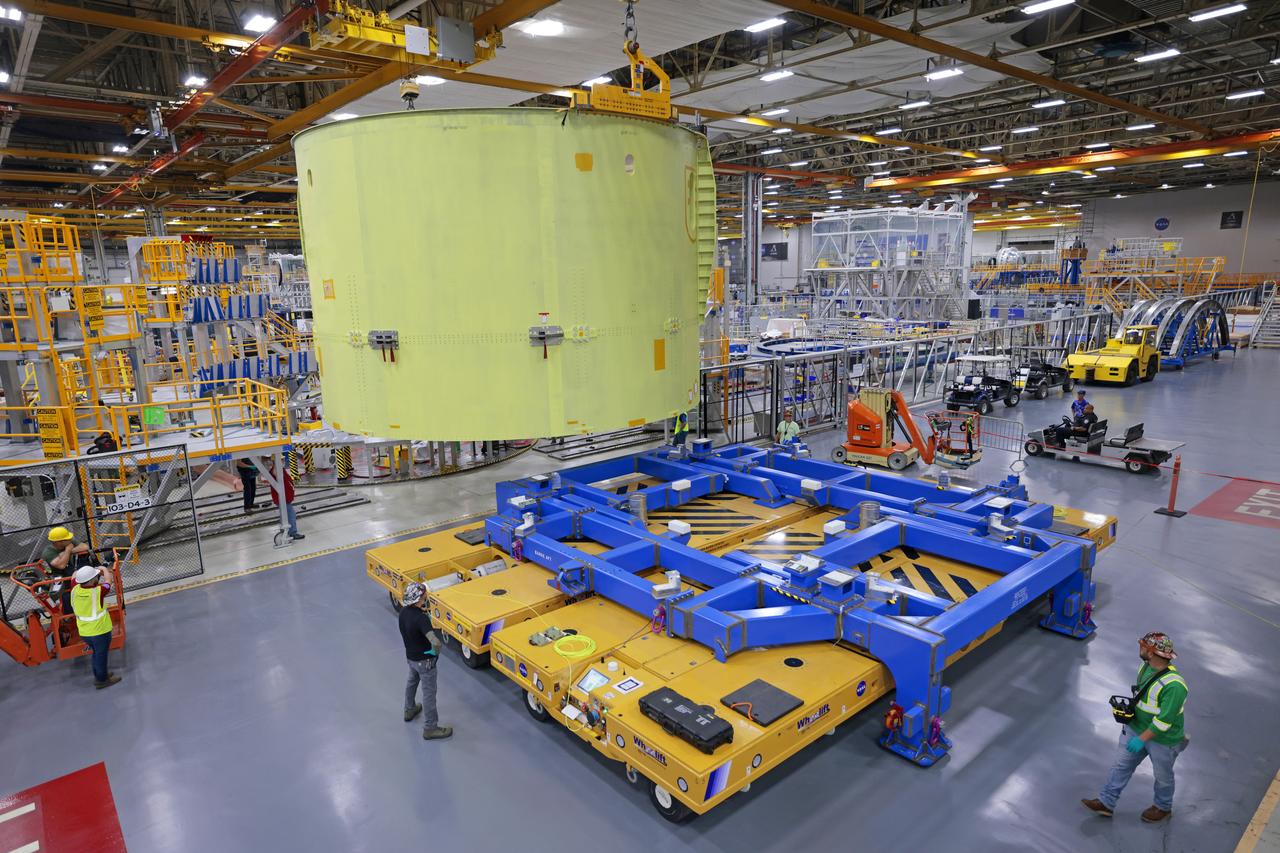
These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.
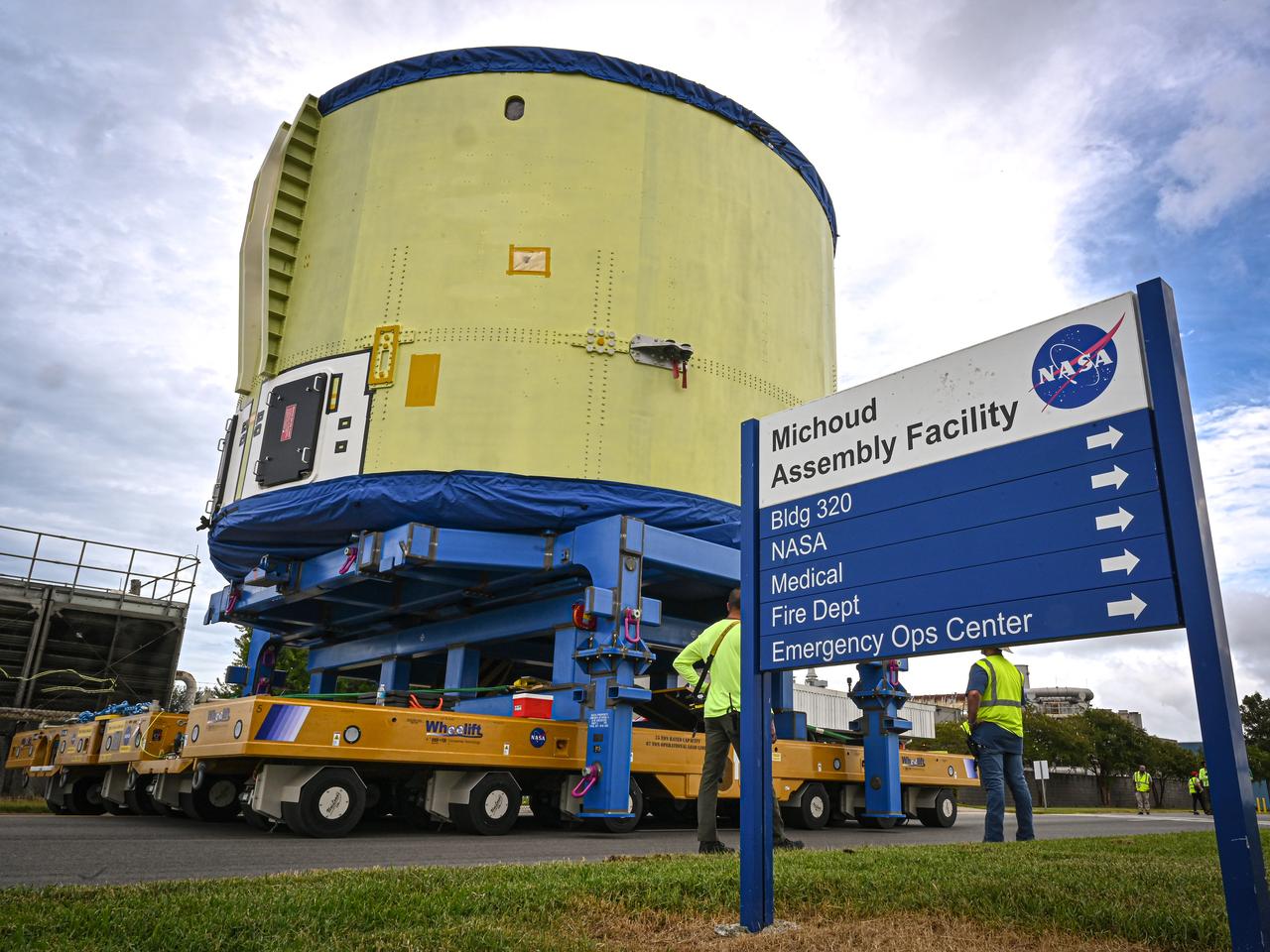

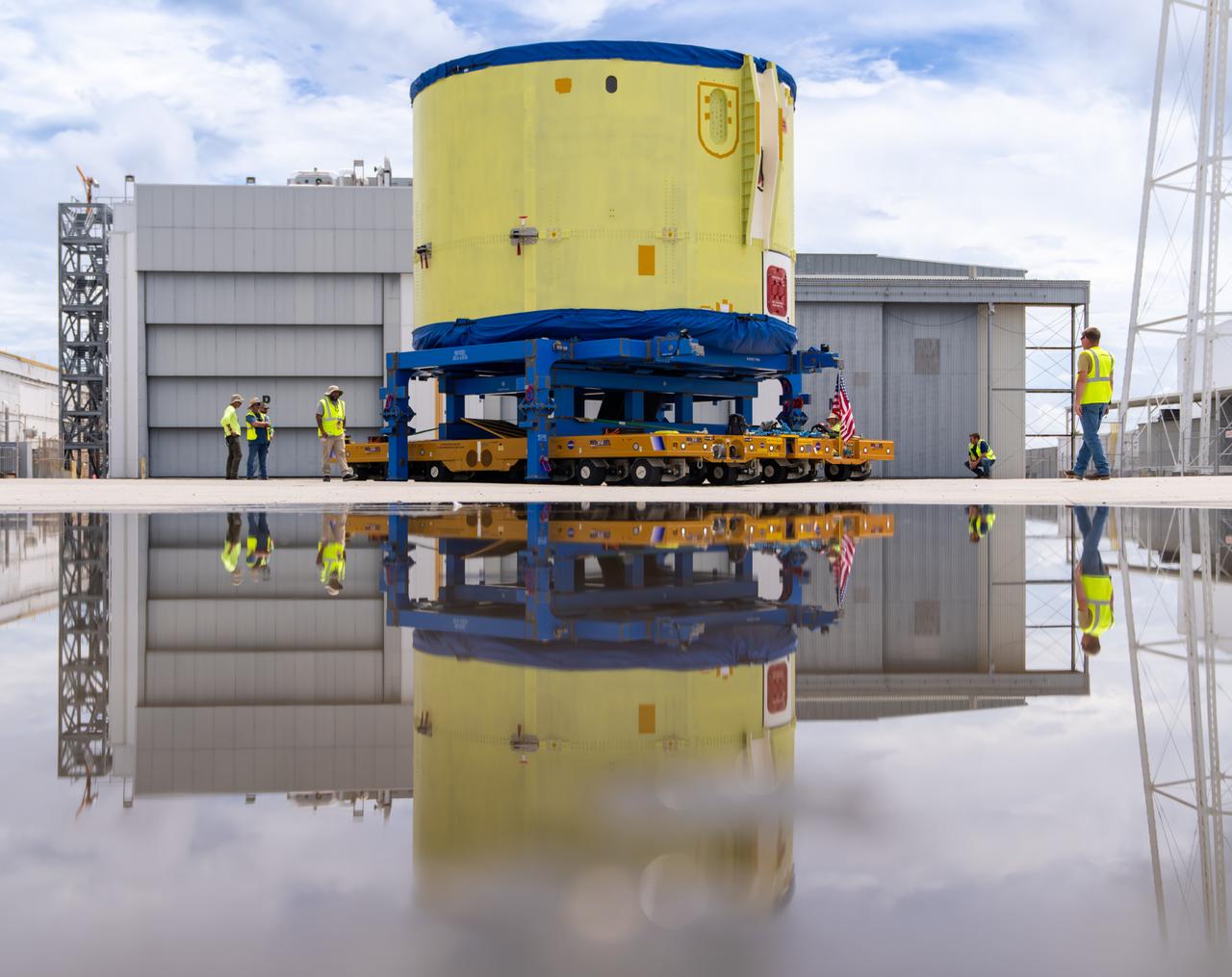
These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.
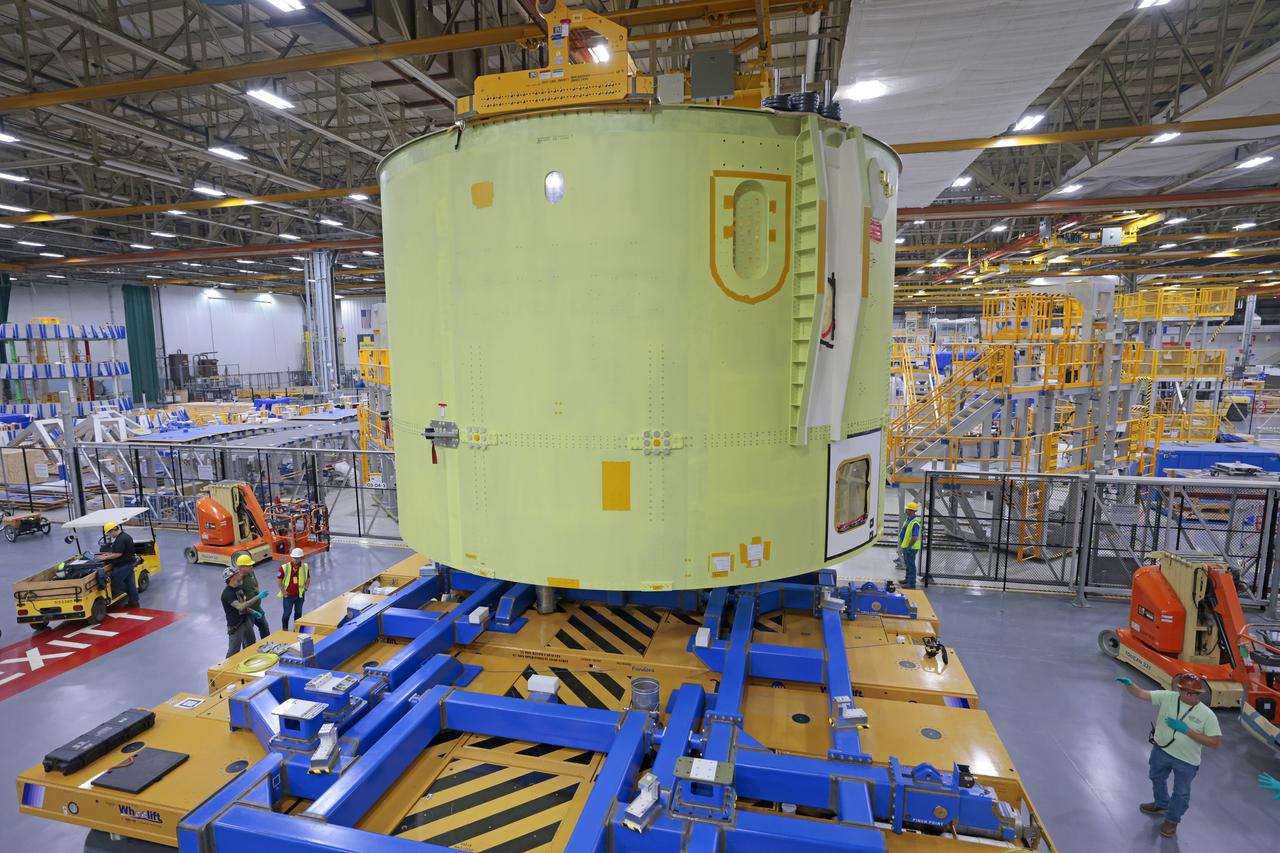

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
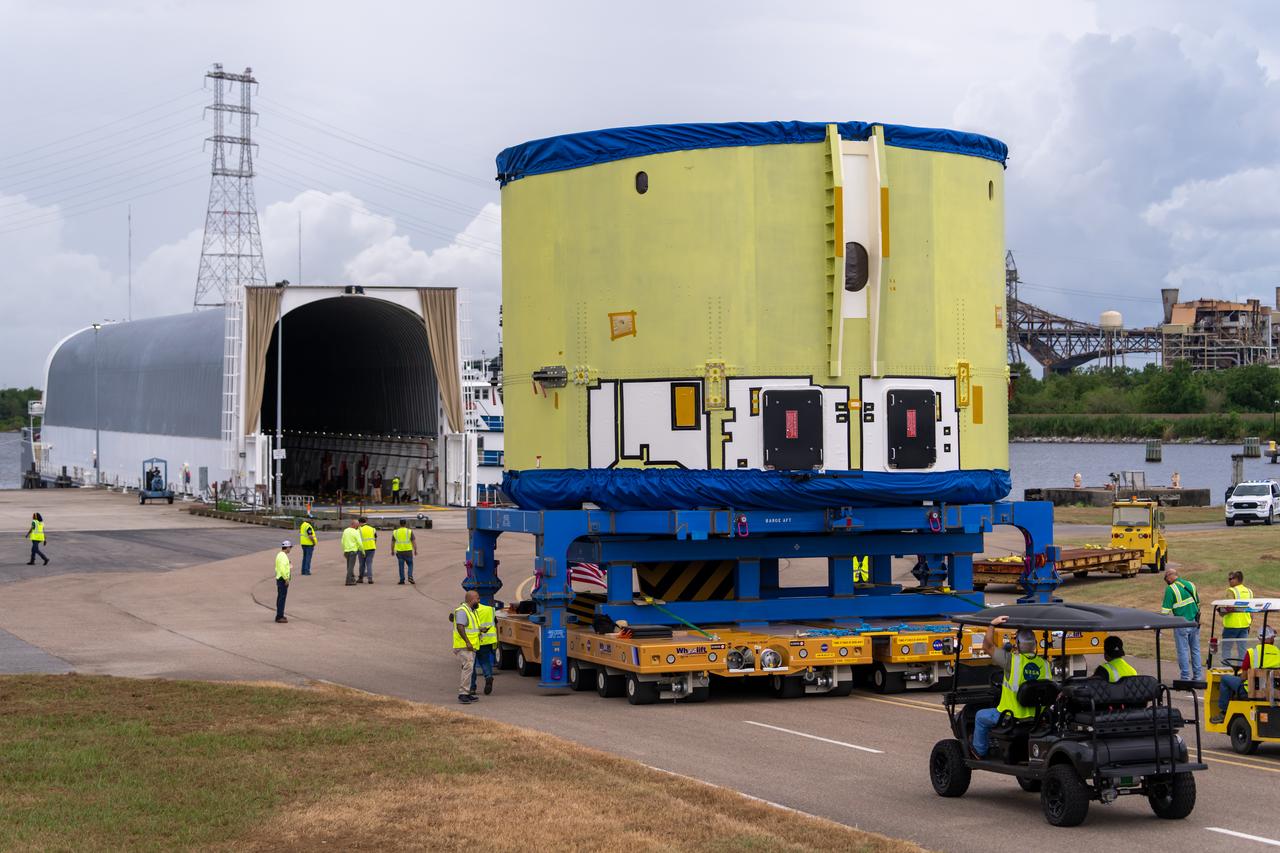

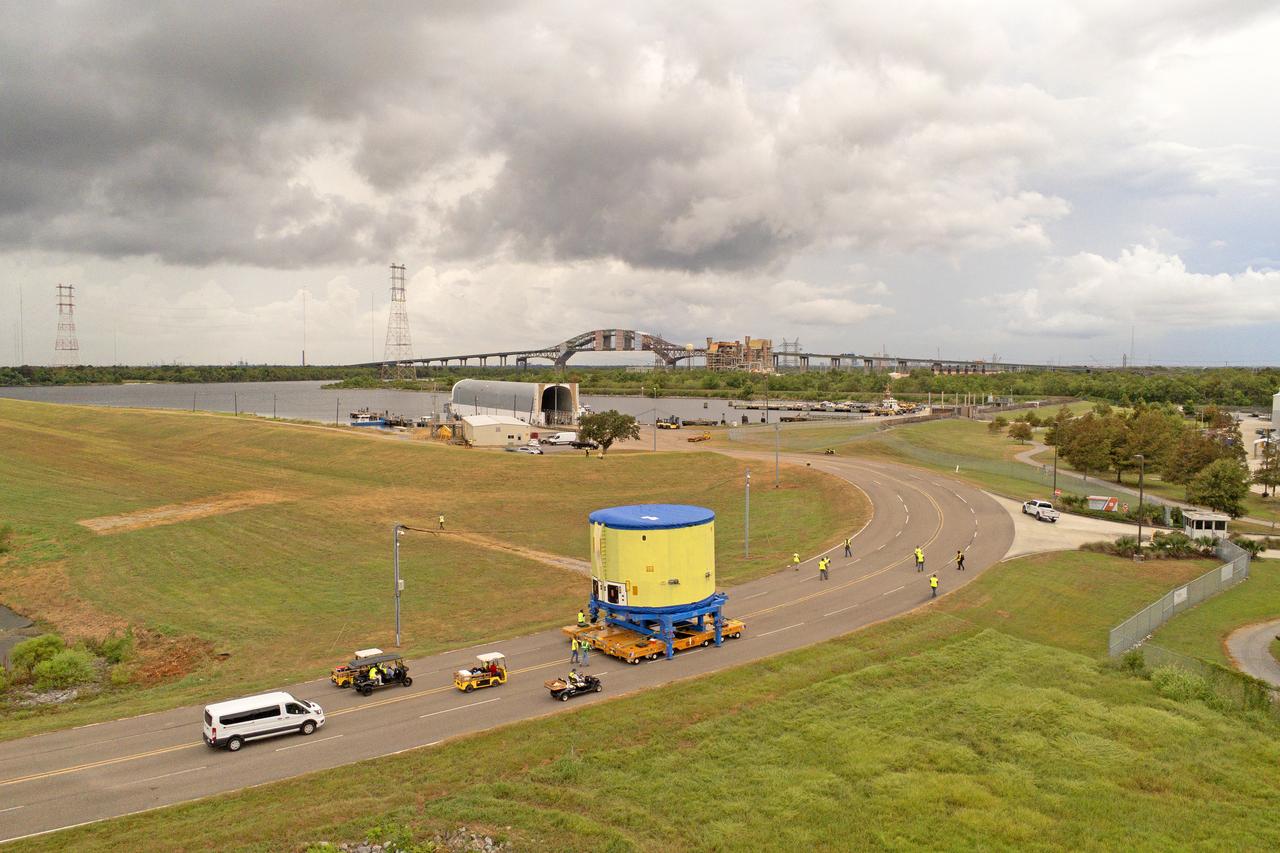
These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.
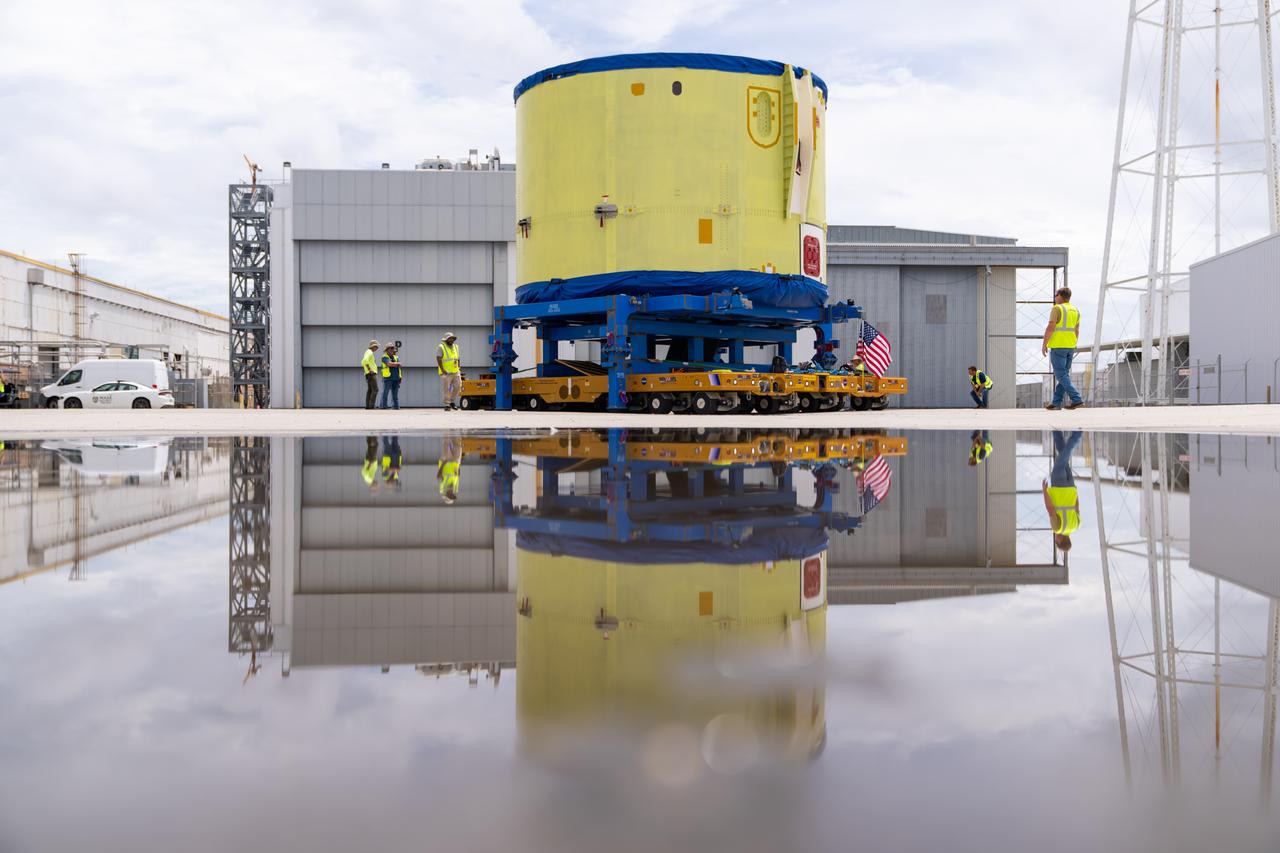

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.
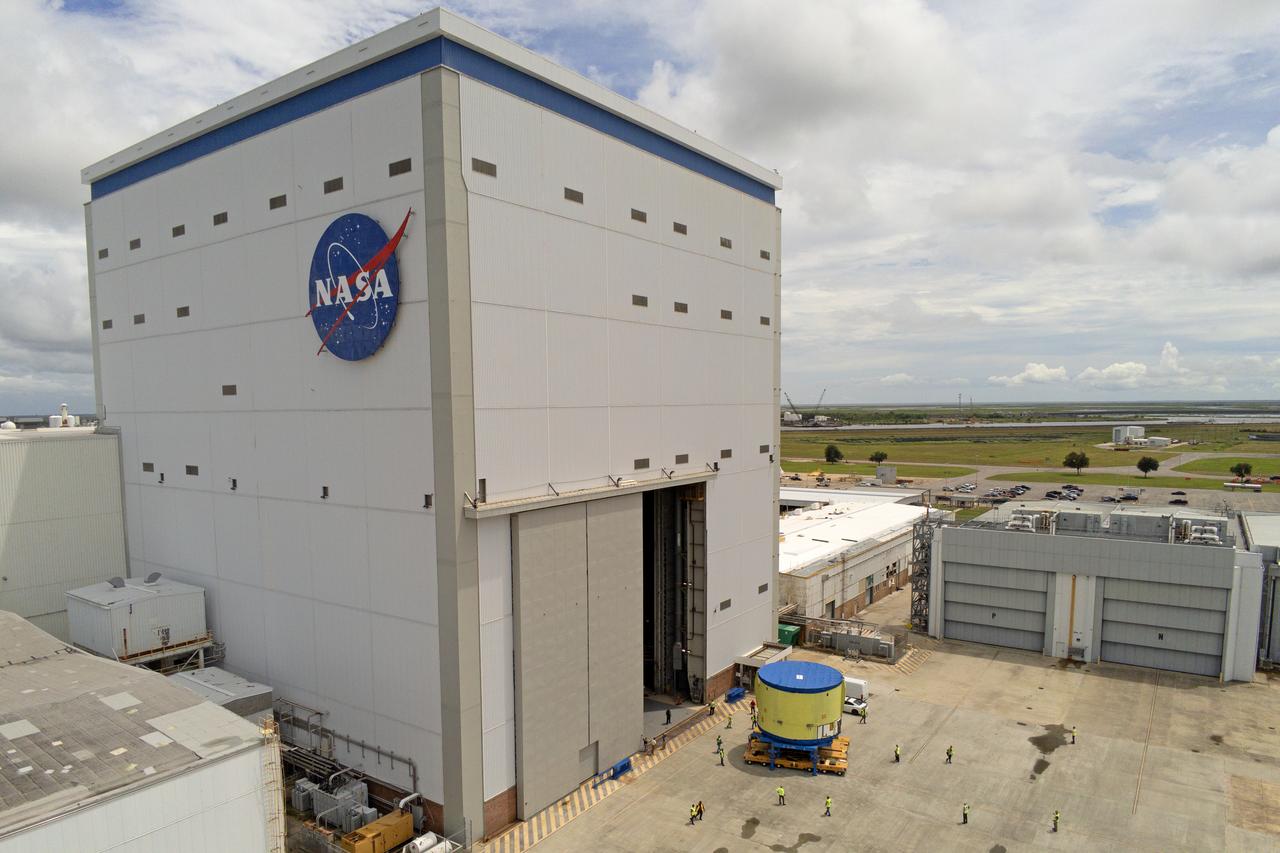

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.
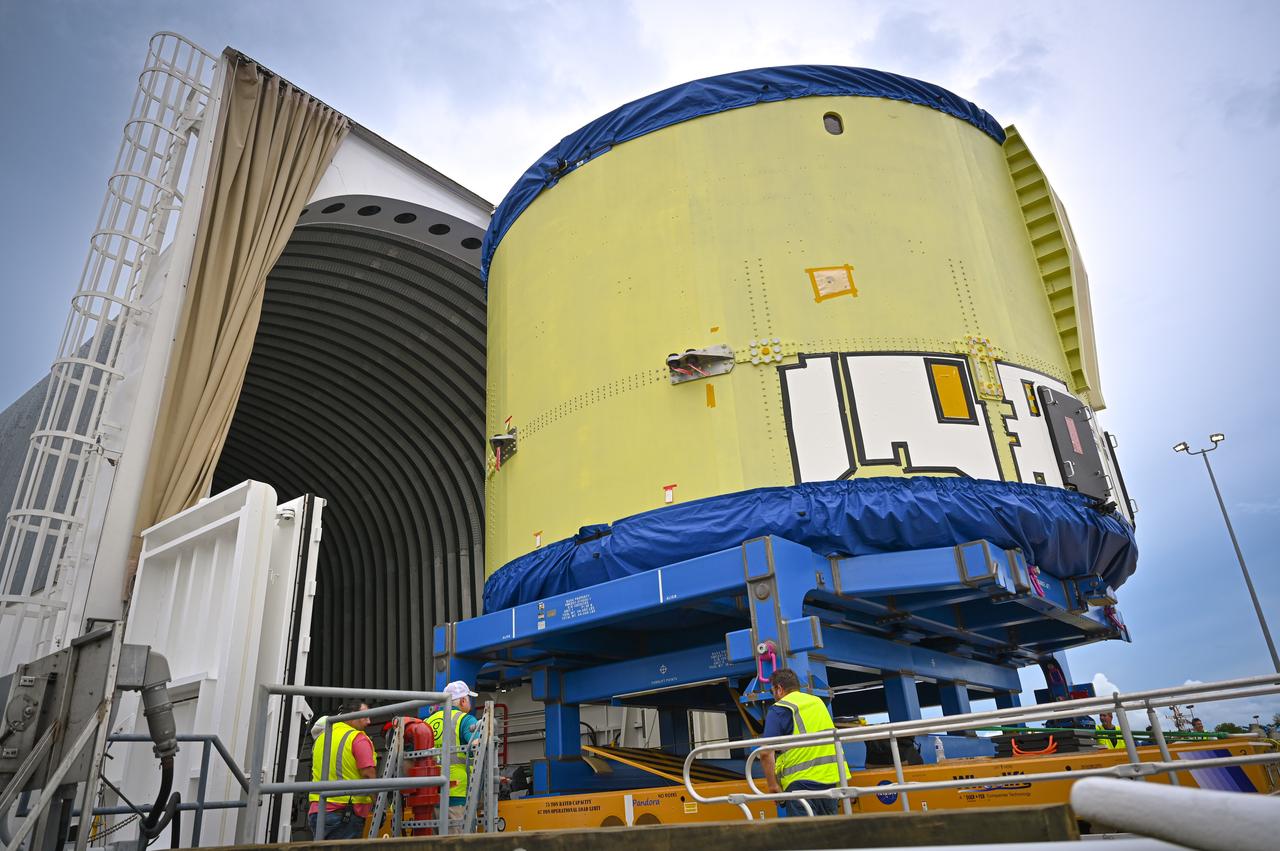

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.
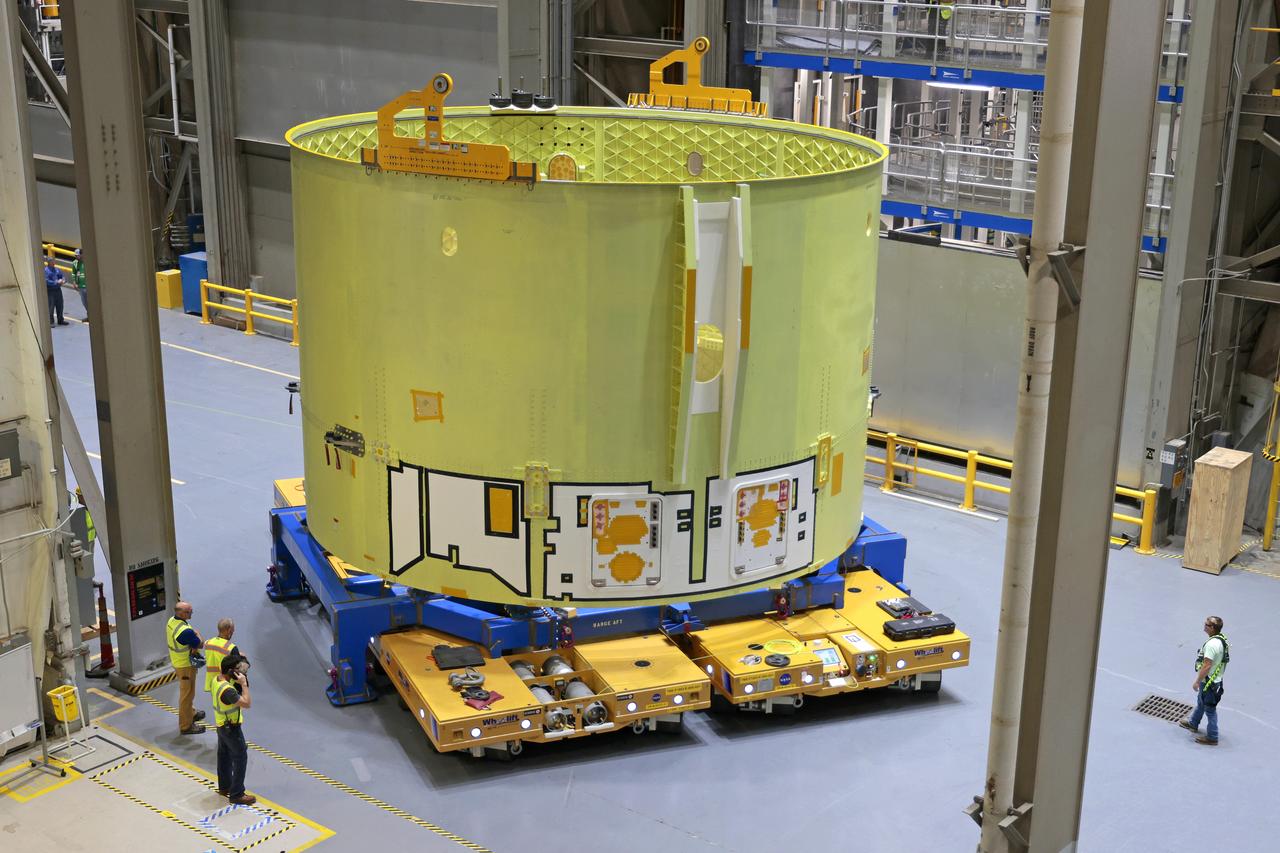

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
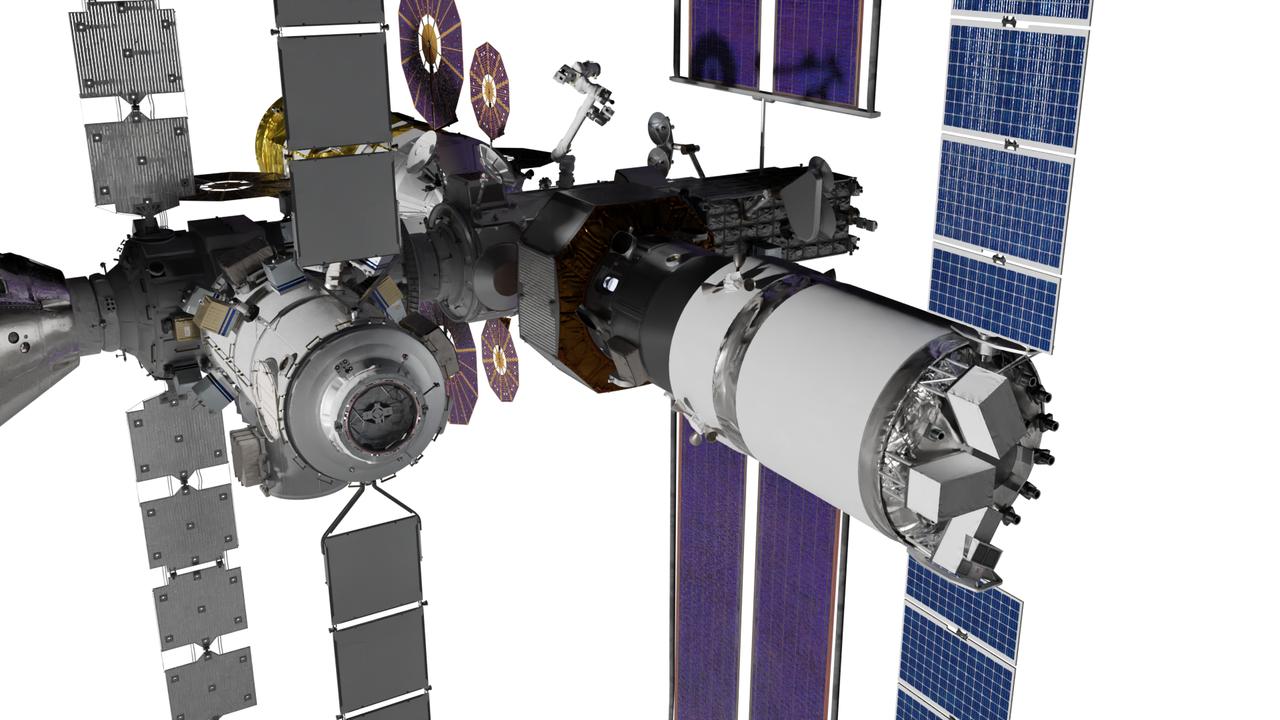
An artist’s rendering displays a configuration of the lunar-orbiting Gateway space station’s modules and visiting spacecraft. The core elements of Gateway consist of the Habitation and Logistics Outpost (HALO) element, the Power and Propulsion Element (PPE), and Lunar I-Hab. Visiting vehicles include the Orion spacecraft, the Logistics Module, and the Human Landing System. Gateway is built in collaboration with NASA’s commercial and international partners to serve as a multiuse space port for lunar science as humanity’s first place to live and work in lunar orbit.
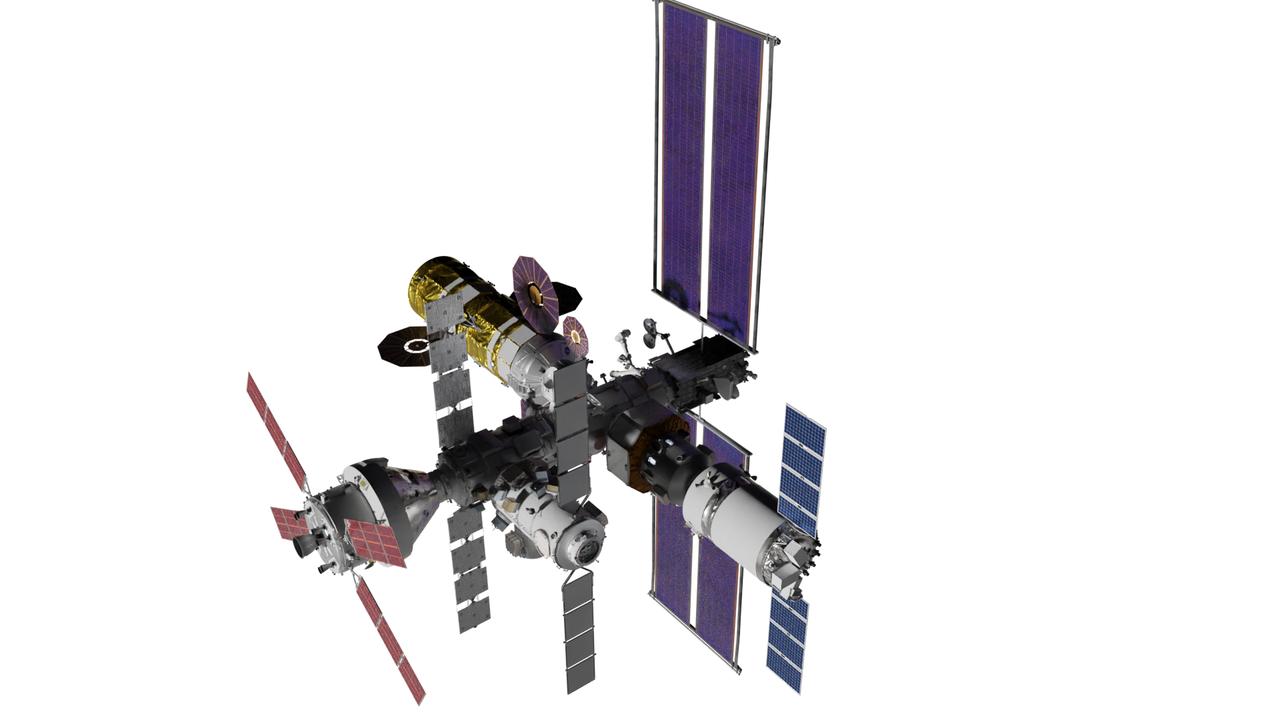

An artist’s rendering displays a configuration of the lunar-orbiting Gateway space station’s modules and visiting spacecraft. The core elements of Gateway consist of the Habitation and Logistics Outpost (HALO) element, the Power and Propulsion Element (PPE), and Lunar I-Hab. Visiting vehicles include the Orion spacecraft, the Logistics Module, and the Human Landing System. Gateway is built in collaboration with NASA’s commercial and international partners to serve as a multiuse space port for lunar science as humanity’s first place to live and work in lunar orbit.
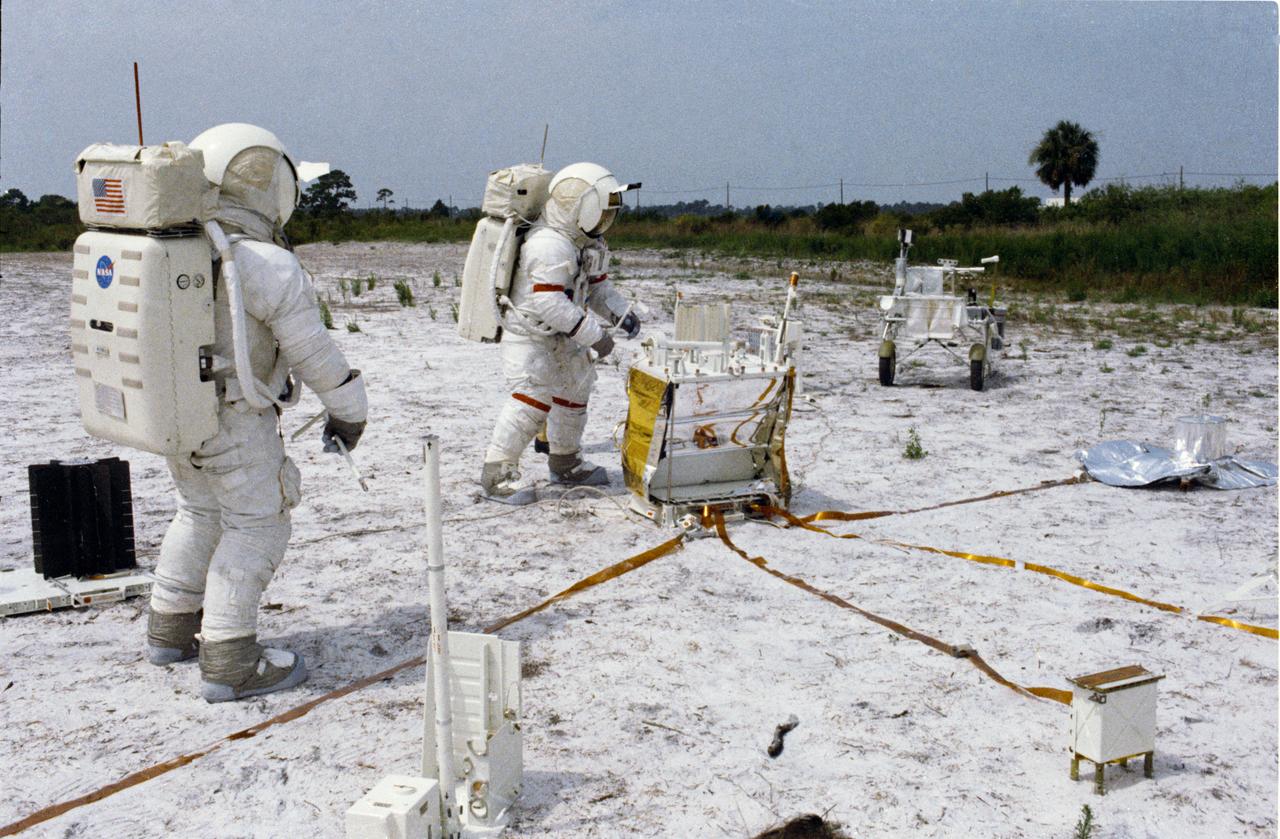

S70-46152 (July 1970) --- Two crew men of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission participate in lunar surface simulation training at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). They are deploying components of the Apollo lunar surface experiments package (ALSEP). Standing in the center next to the ALSEP central station is astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr. (wearing red stripe on space suit), commander. Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, is in the left foreground. Both crew men are wearing the Extravehicular Mobility Units (EMU).
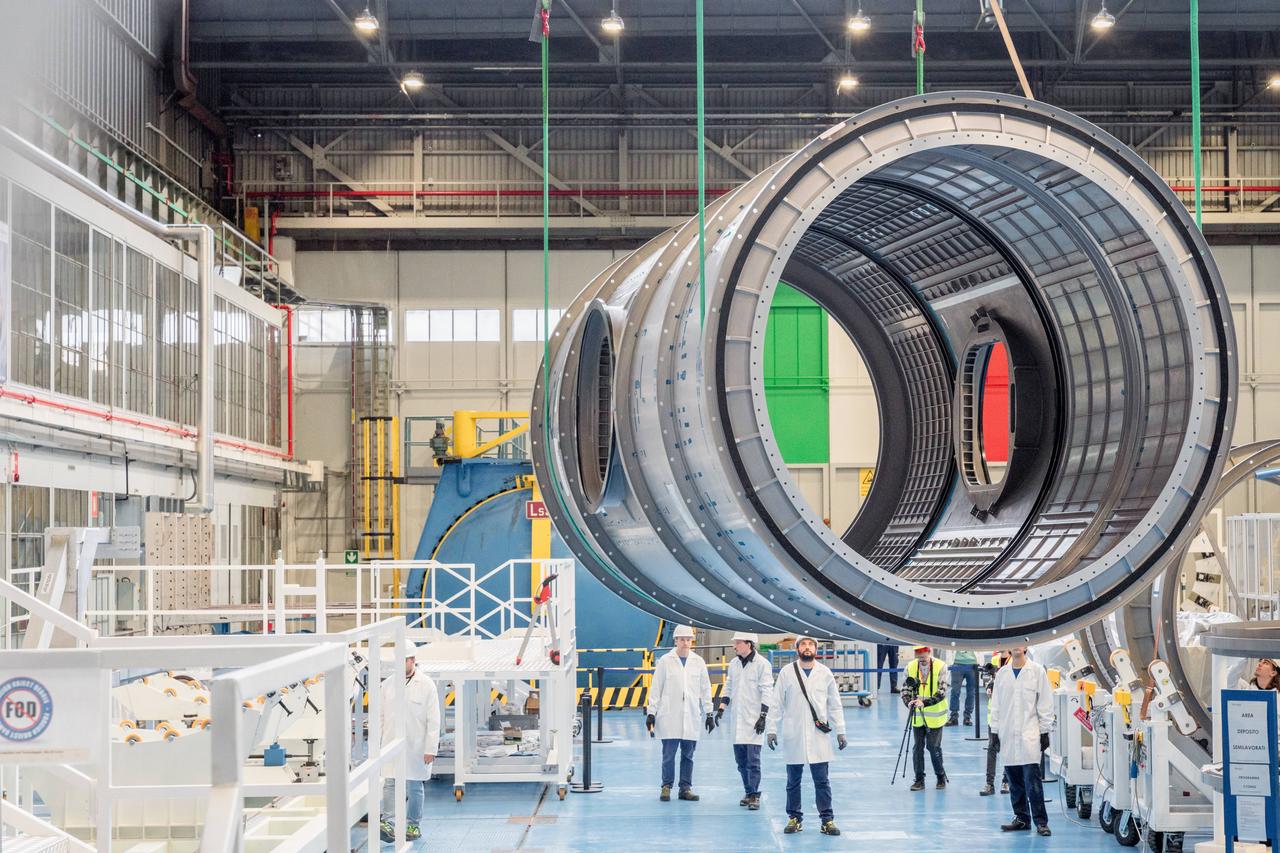

Gateway's HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) floats through the Thales Alenia Space industrial facility in Turin, Italy for stress testing to ensure its safety.
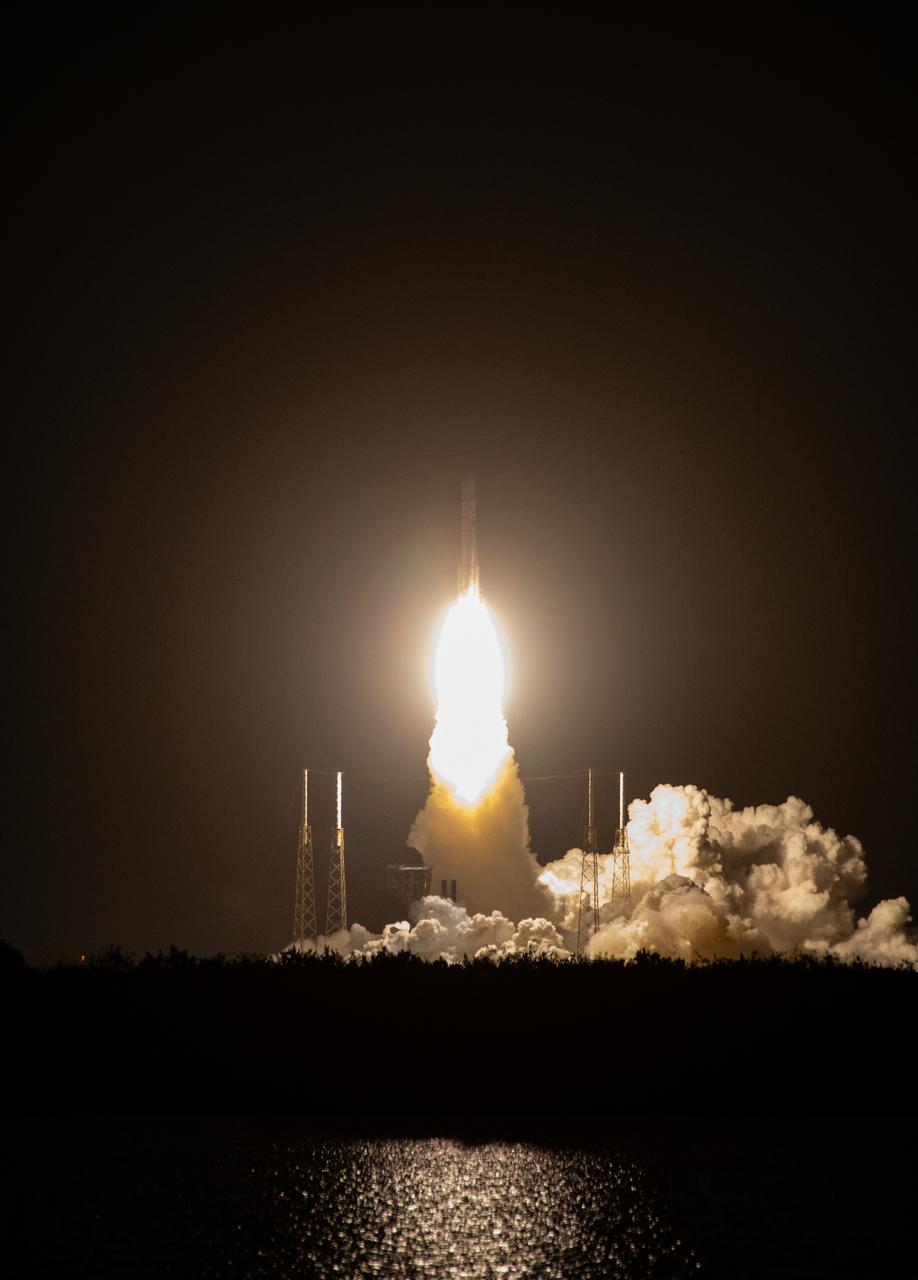

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
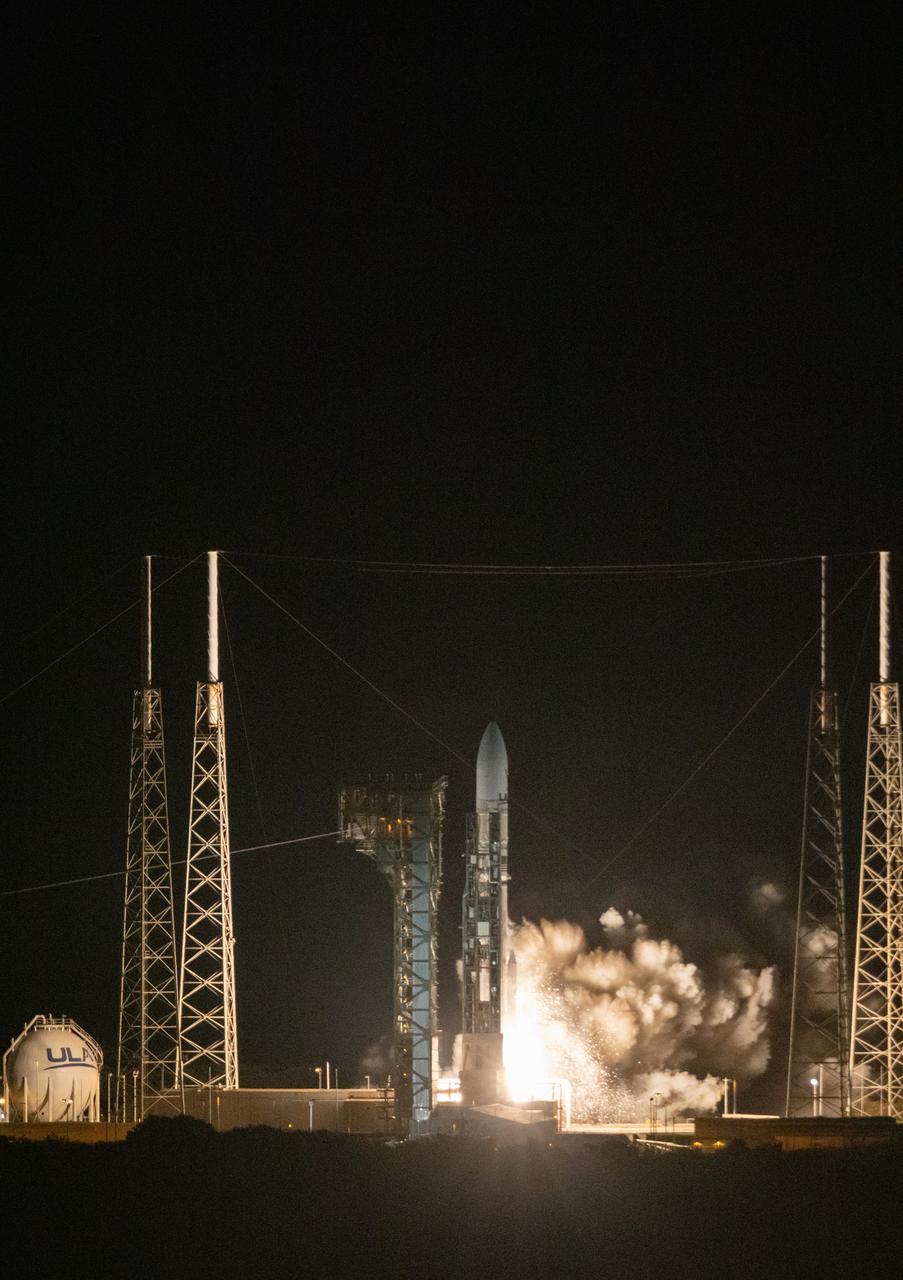

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
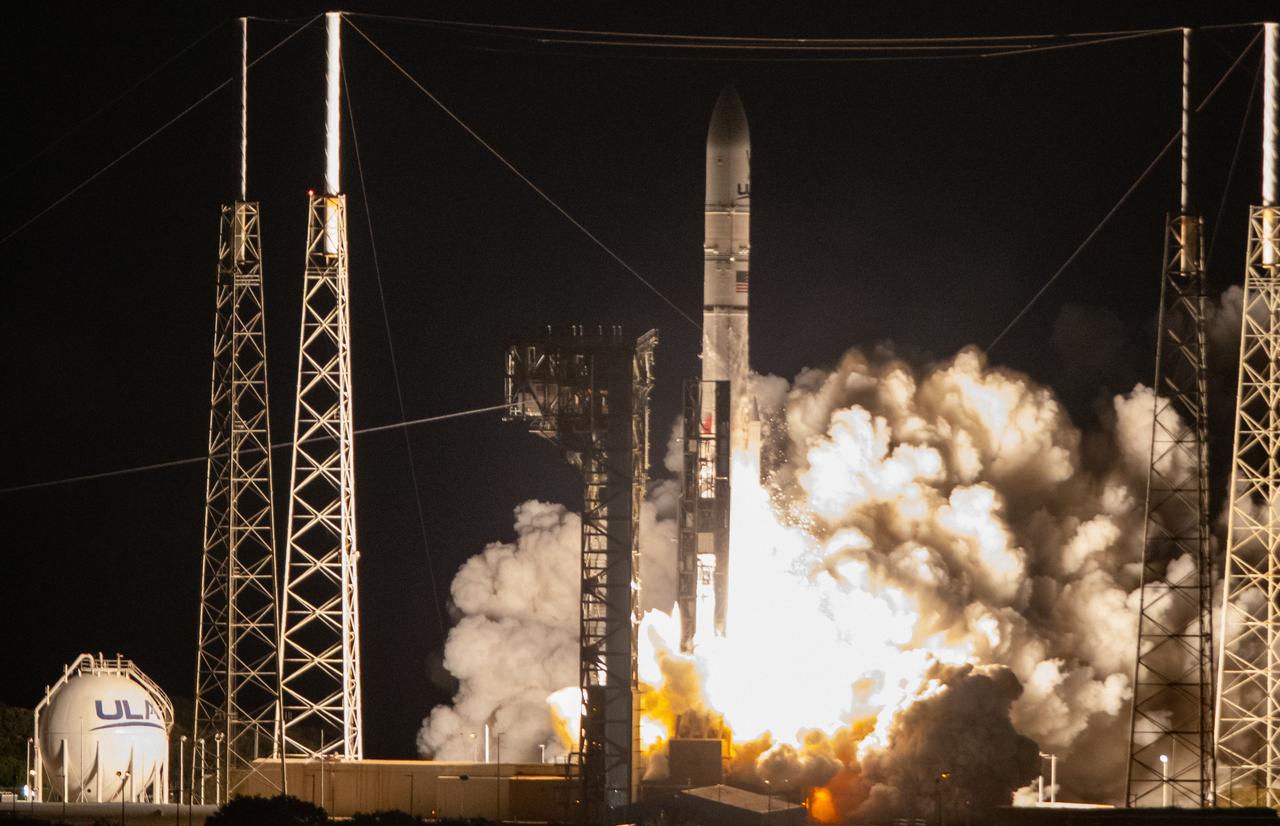

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
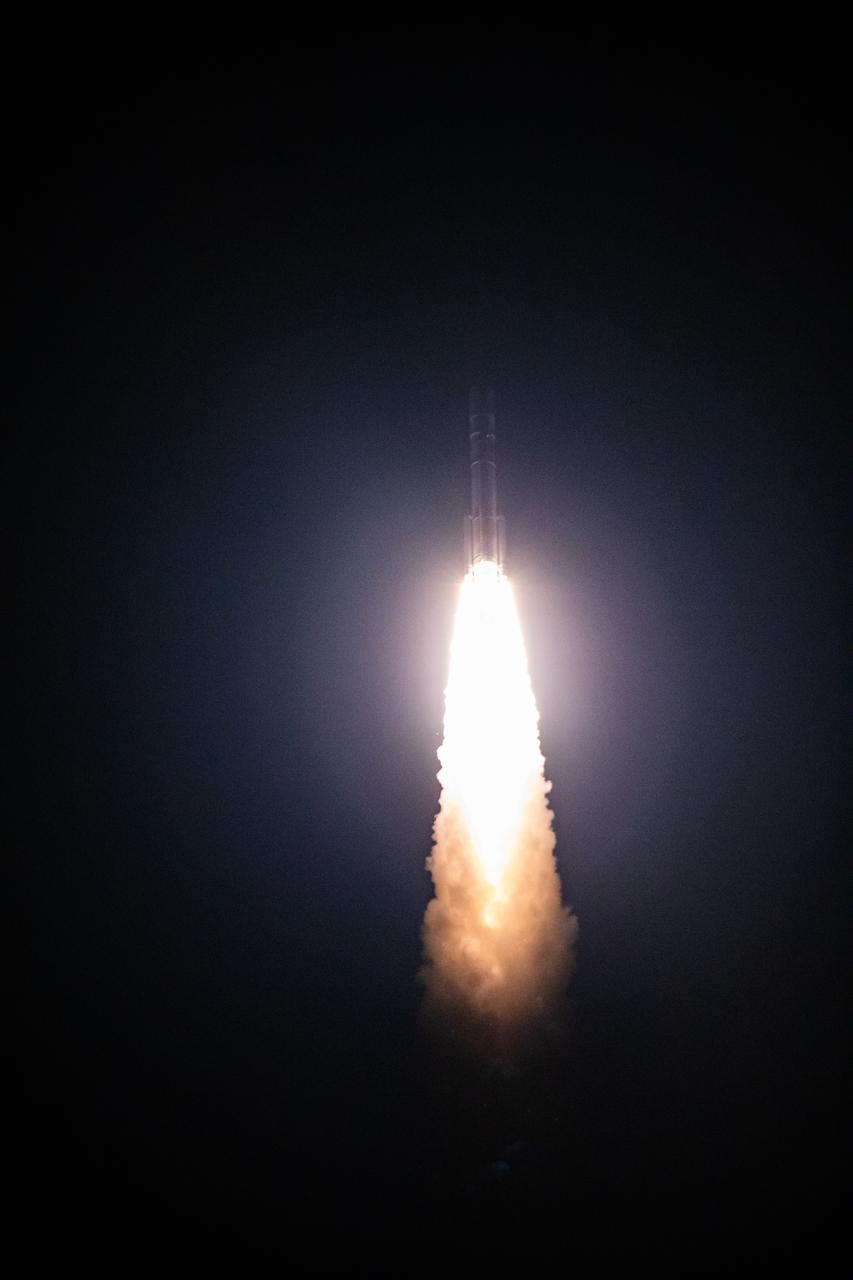

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

On the first flight of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis program, a United Launch Alliance Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander lifts off at 2:18 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
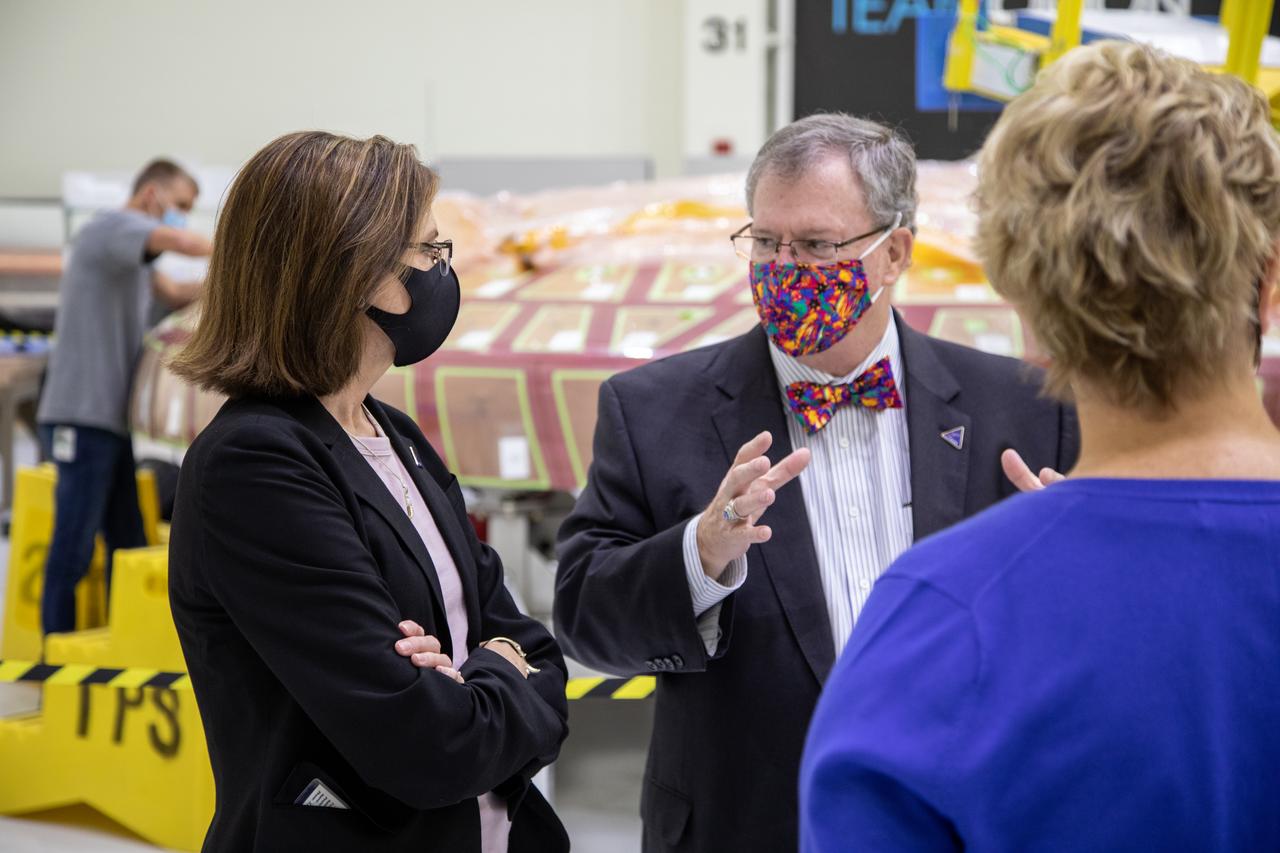

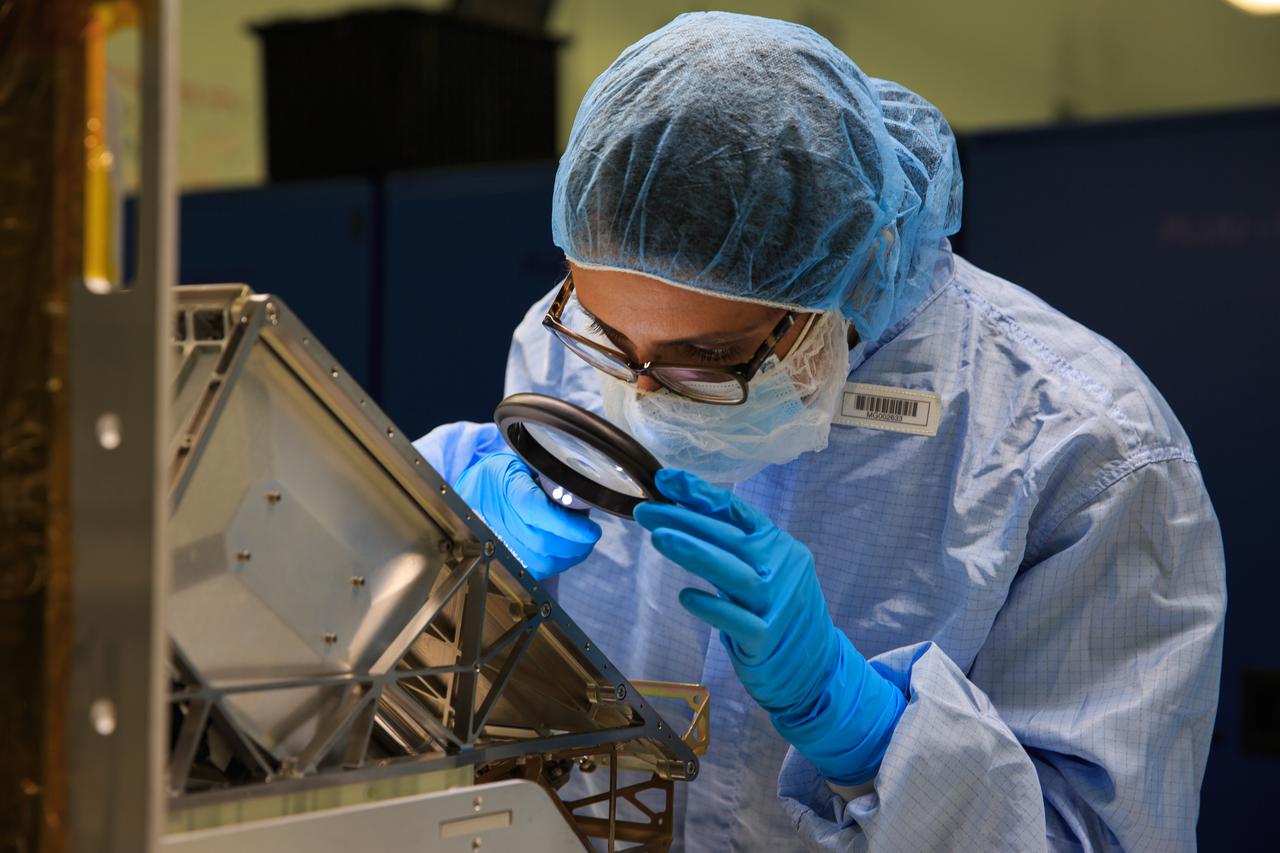
Engineers and technicians are completing assembly work inside the Space Station Processing Facility, on flight hardware for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations. MSolo, is a commercial off-the shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will be an instrument on the agency’s first mission as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services.

Principal investigator, Dr. Janine Captain, attaches a mass spectrometer sensor to electronics inside a vacuum chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Dec. 12, 2018. The Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument is a commercial off-the-shelf mass instrument modified to work in space, and can identify molecules at lunar landing sites. These MSolo instruments are part of NASA’s efforts to return to the Moon with the Commercial Lunar Payload Services Landers Program.
/jsc2024e063104 (2)~medium.jpg)
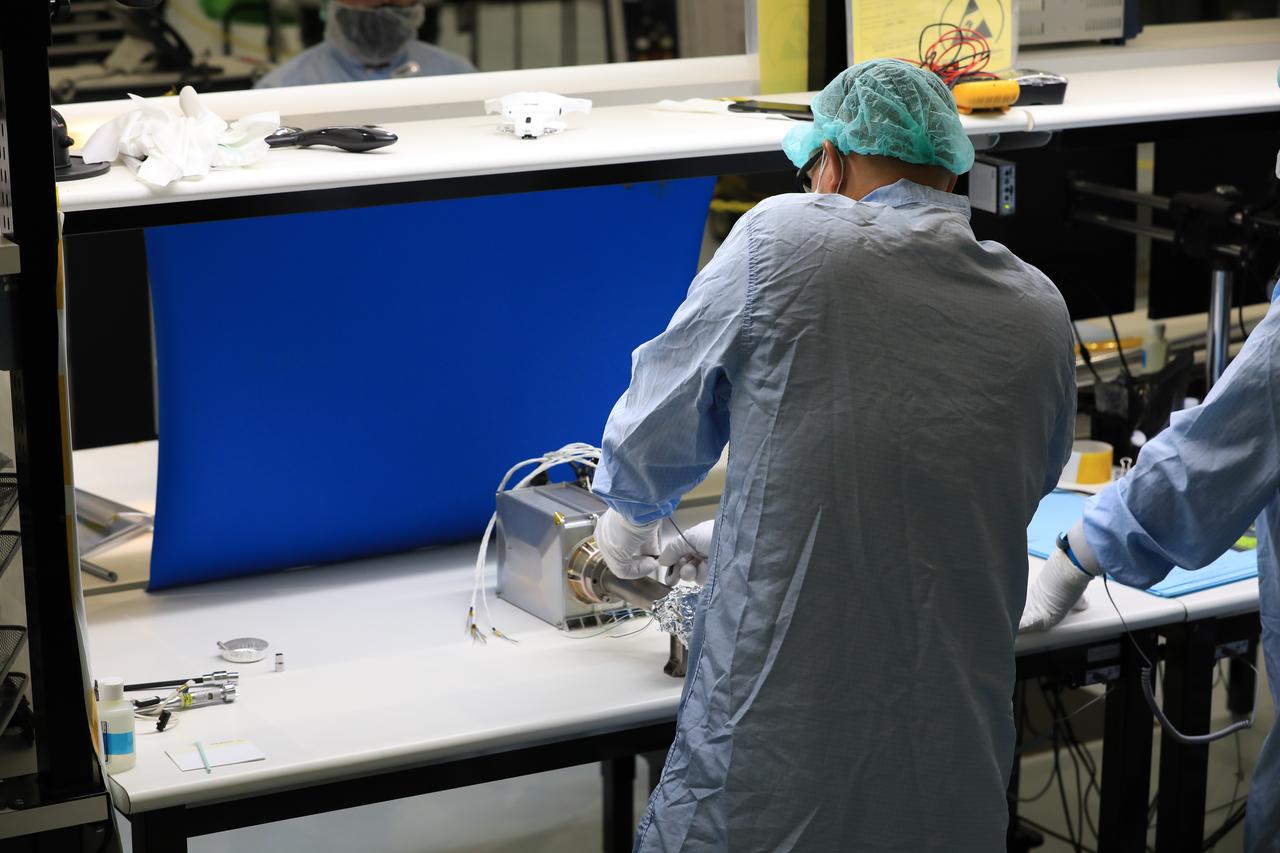
Josh Litofsky leads a Gateway lunar dust adhesion testing campaign at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. His team studies how lunar dust interacts with materials chosen for Gateway's construction. Here, Litofsky carefully positions a sample holder inside a vacuum chamber. Litofksy’s work seeks to validate the Gateway On-orbit Lunar Dust Modeling and Analysis Program (GOLDMAP), developed by Ronald Lee, also of Johnson Space Center. By considering factors such as the design and configuration of the space station, the materials used, and the unique conditions in lunar orbit, GOLDMAP helps predict how dust may move and settle on Gateway’s external surfaces.
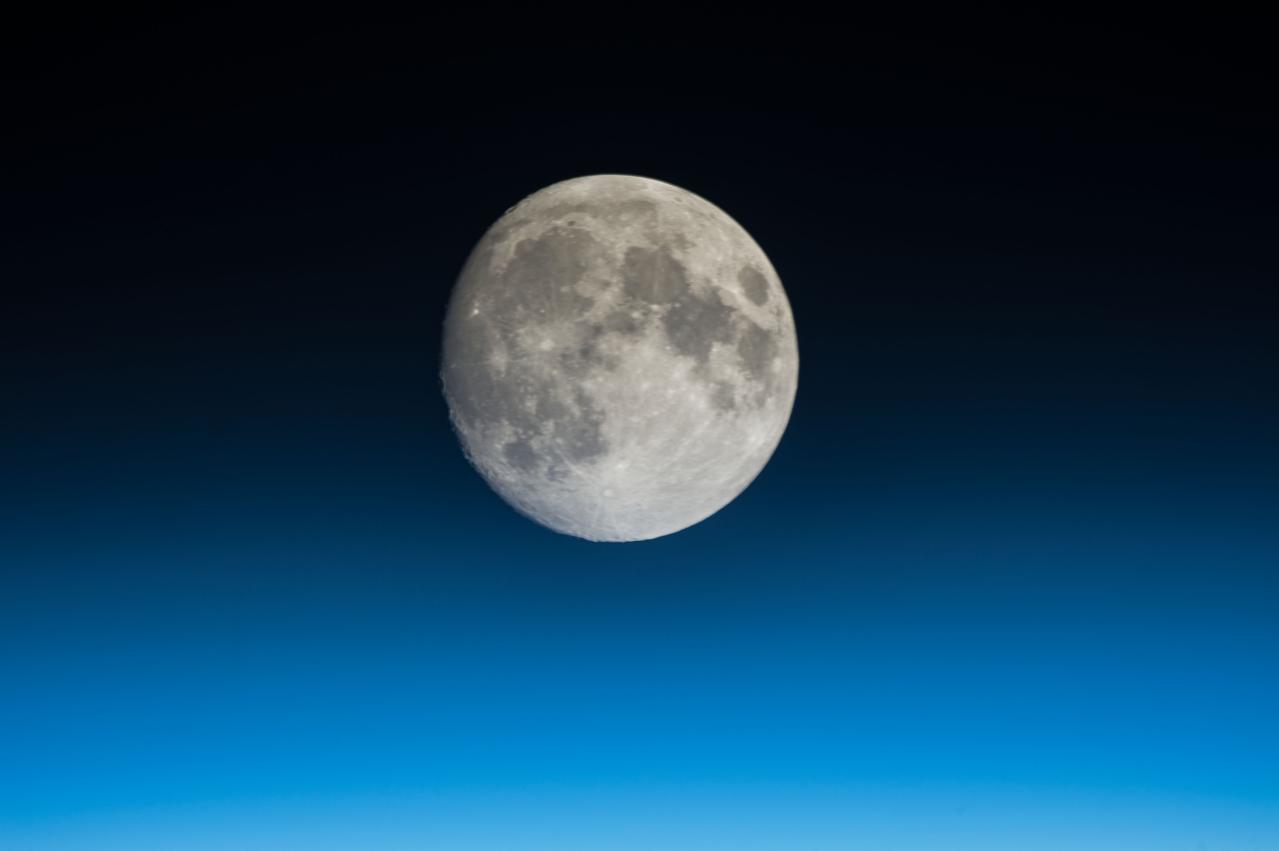

ISS045E079114 (10/25/2015) -------- This image of the lunar landscape was taken by a crewmember aboard the International Space Station on Oct. 25, 2015
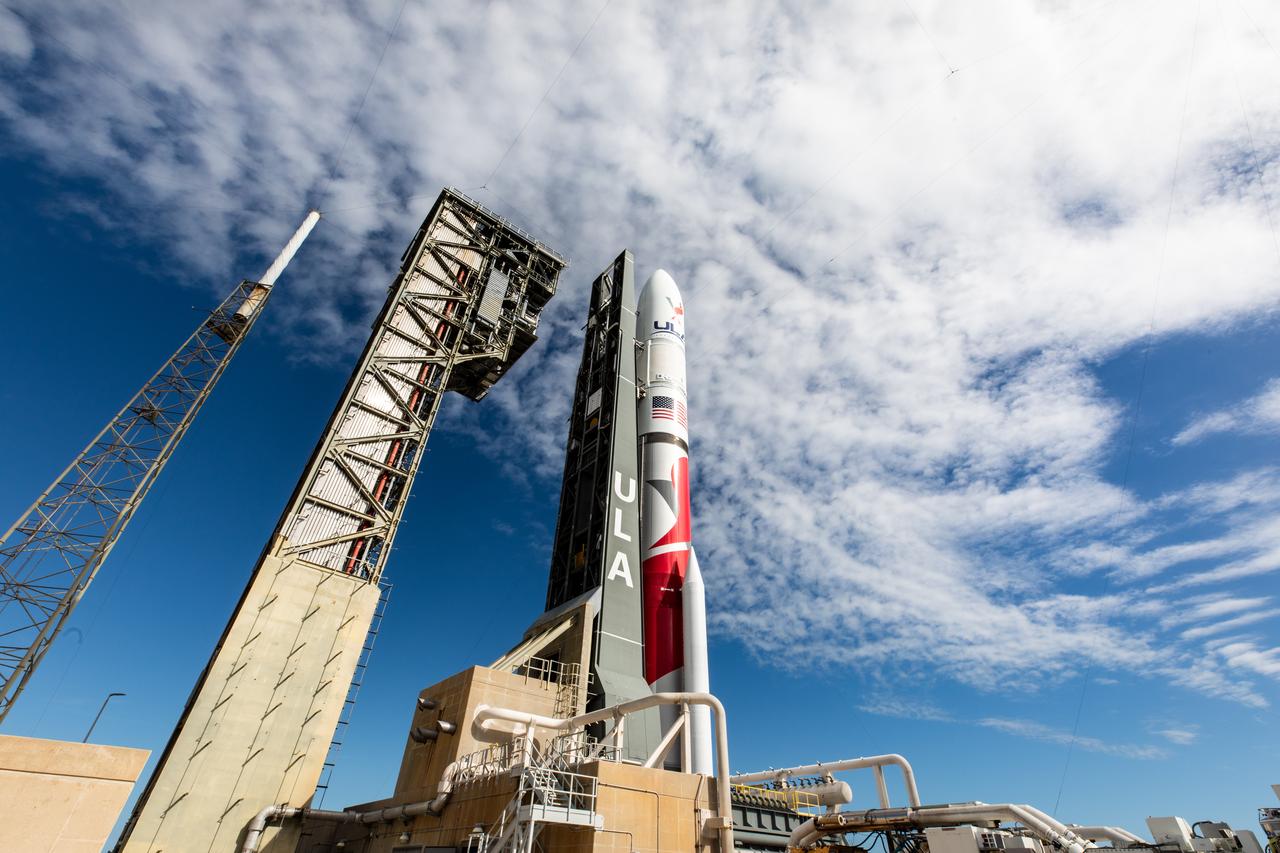

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
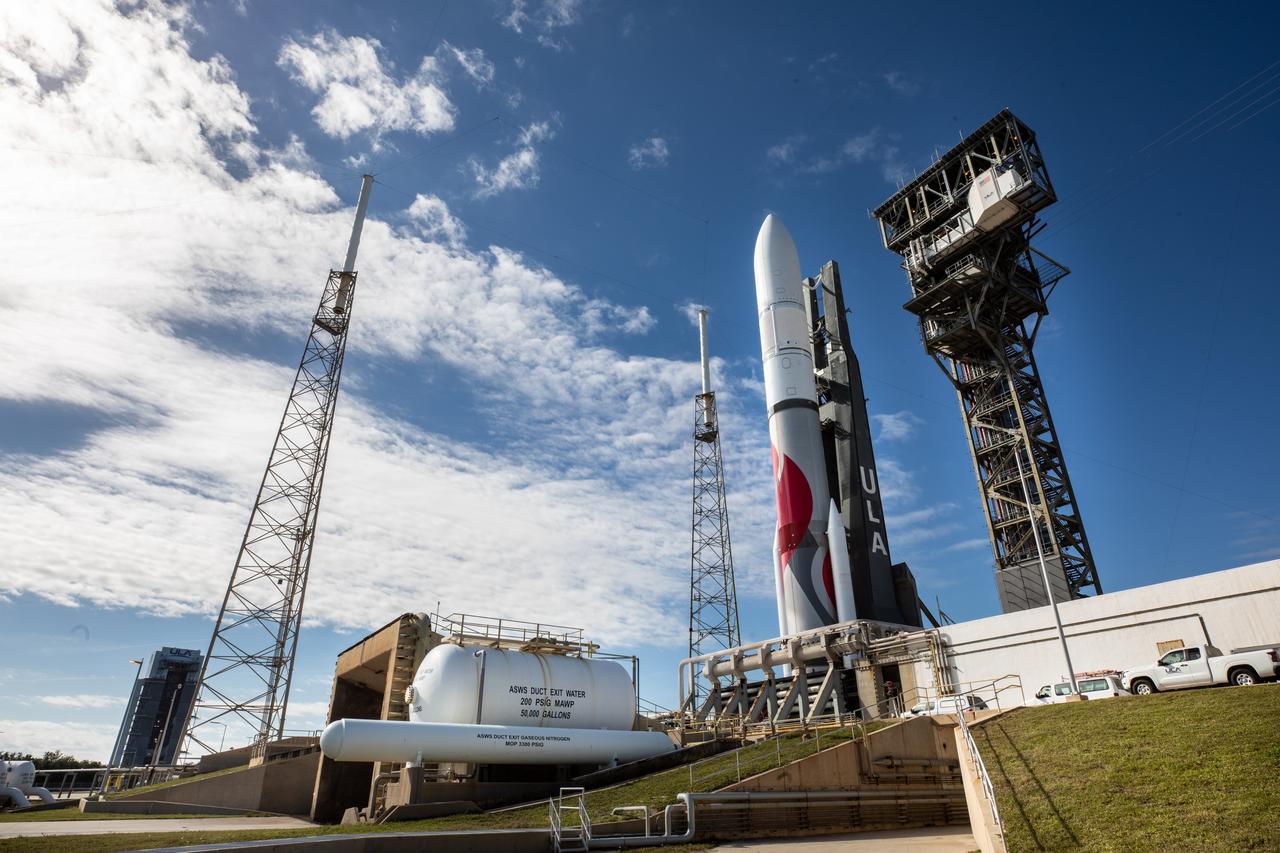

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
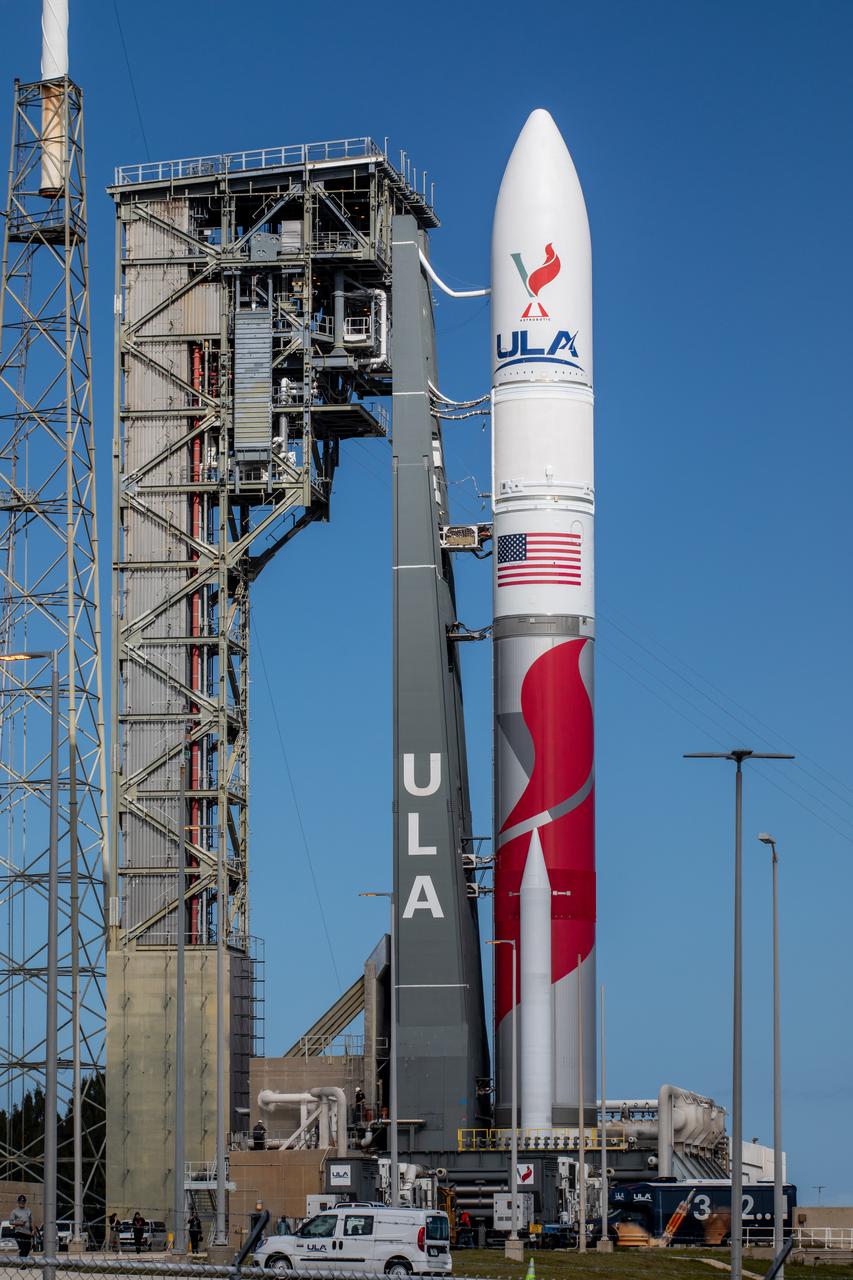

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
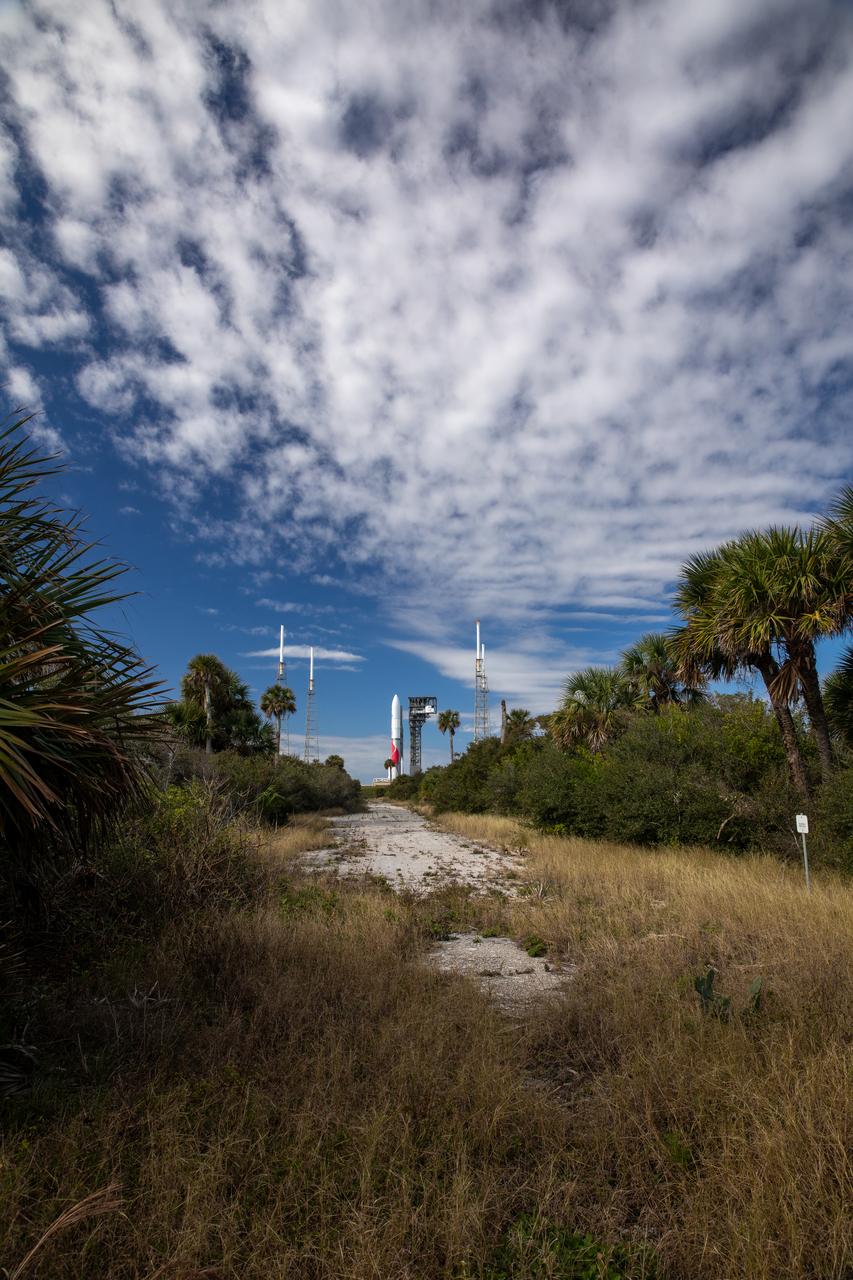

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
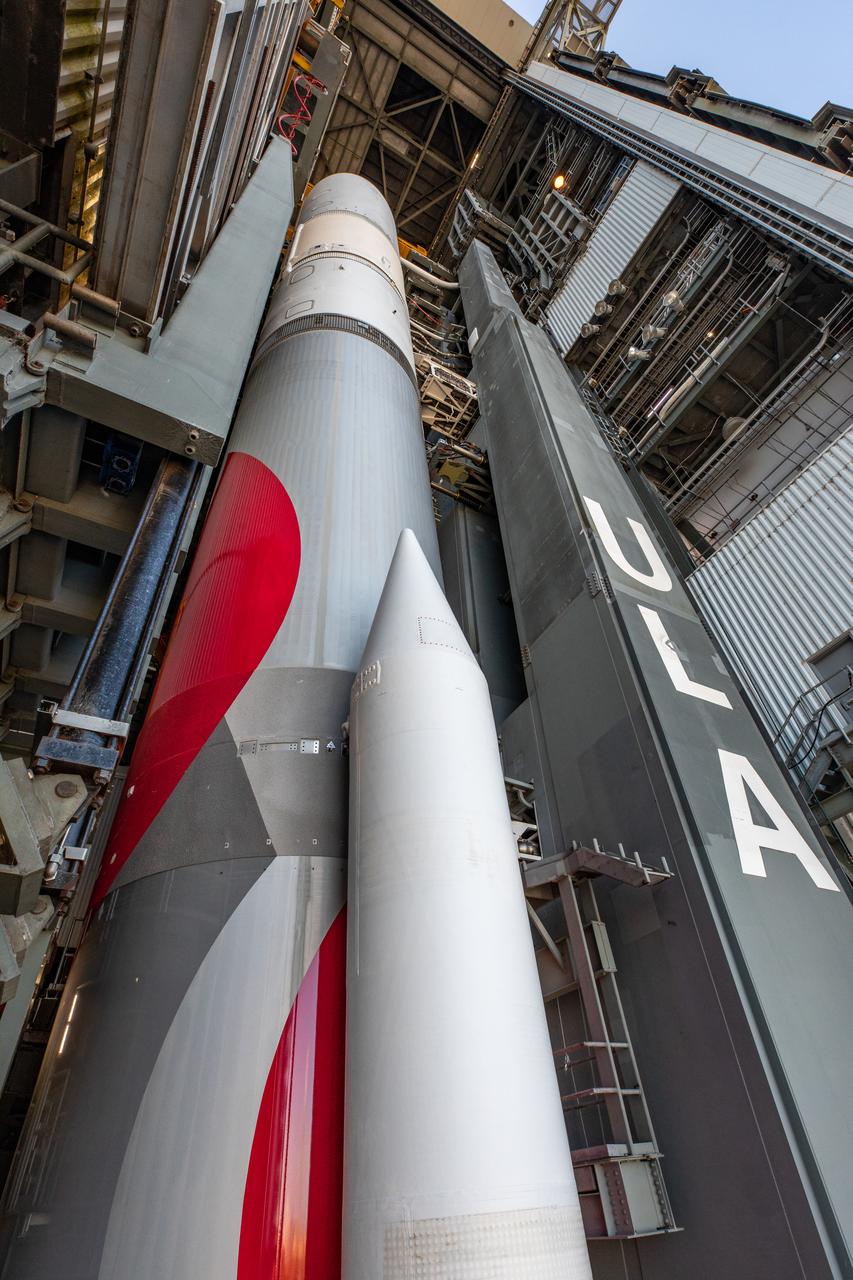

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
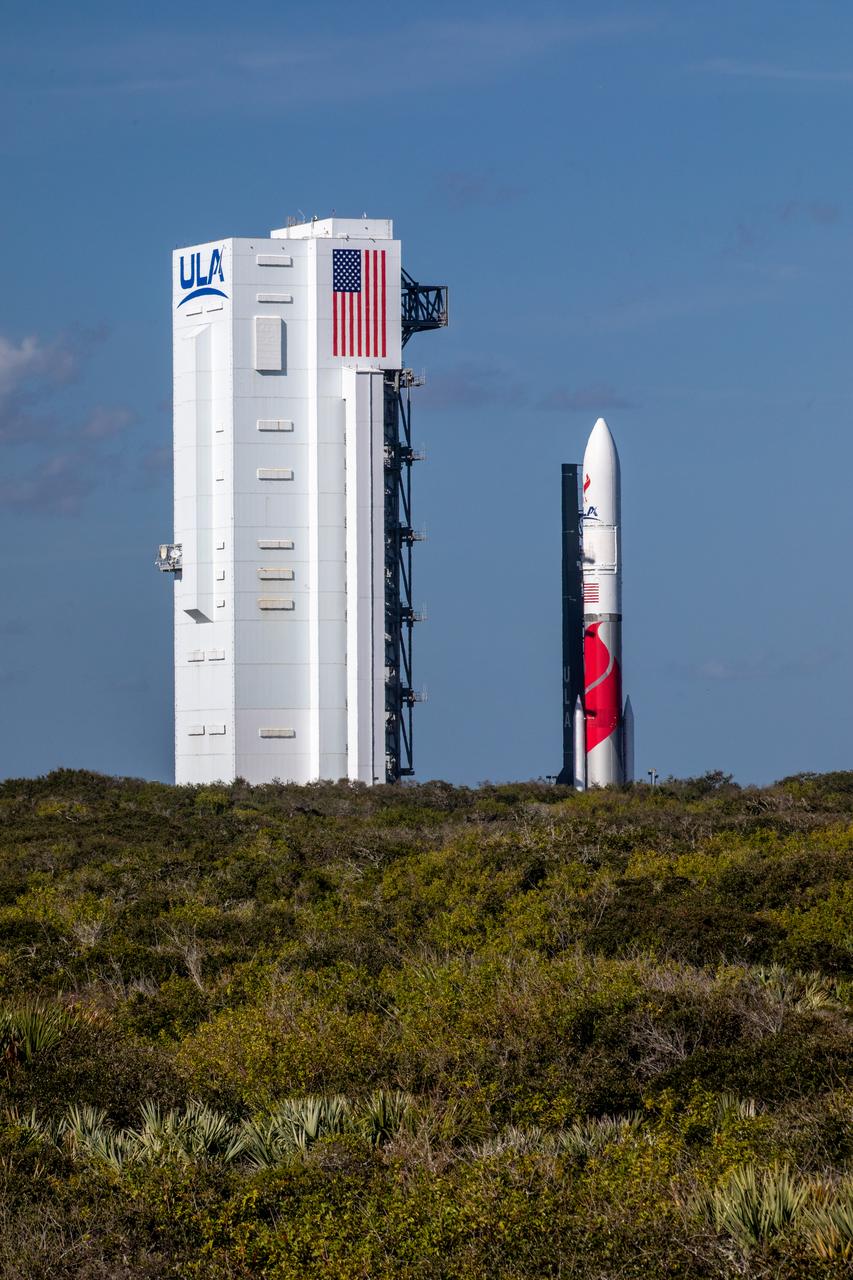

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
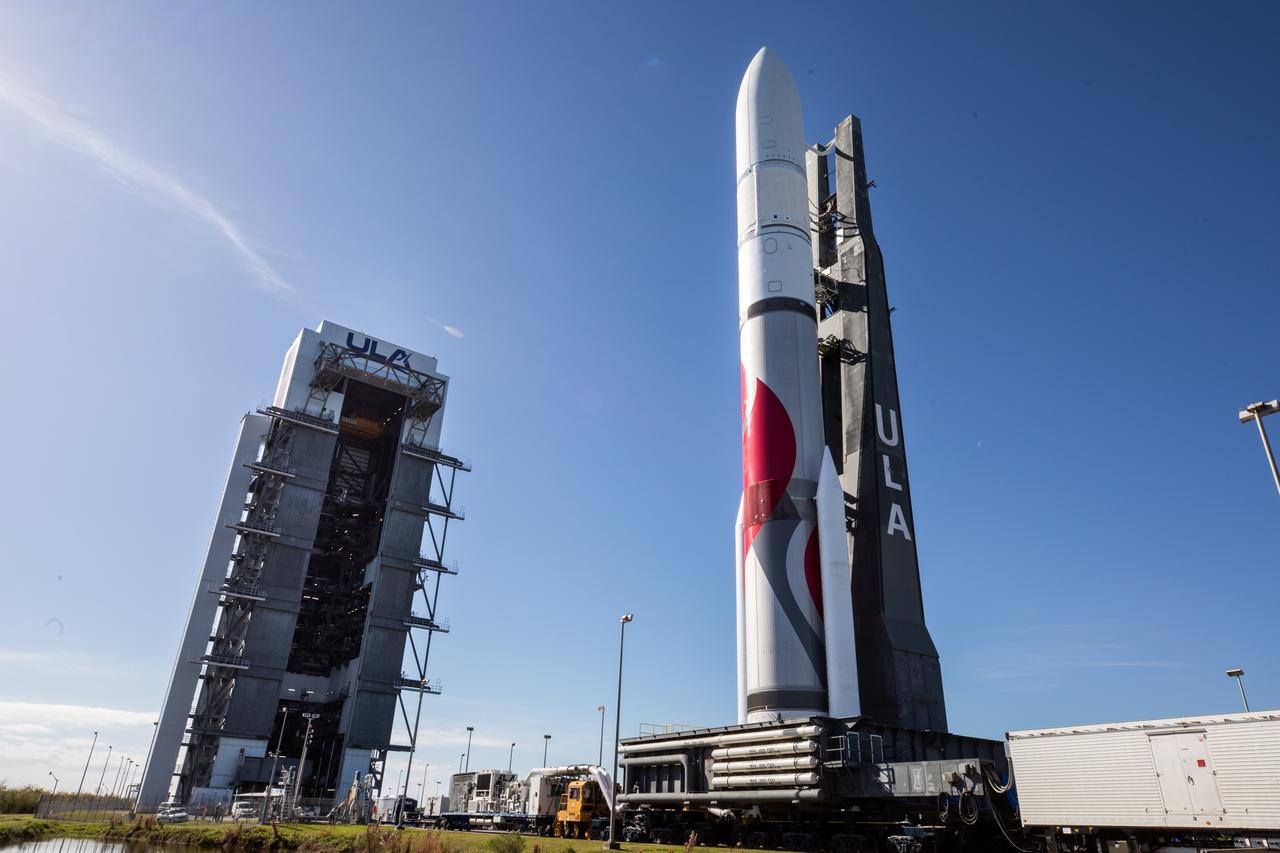

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)
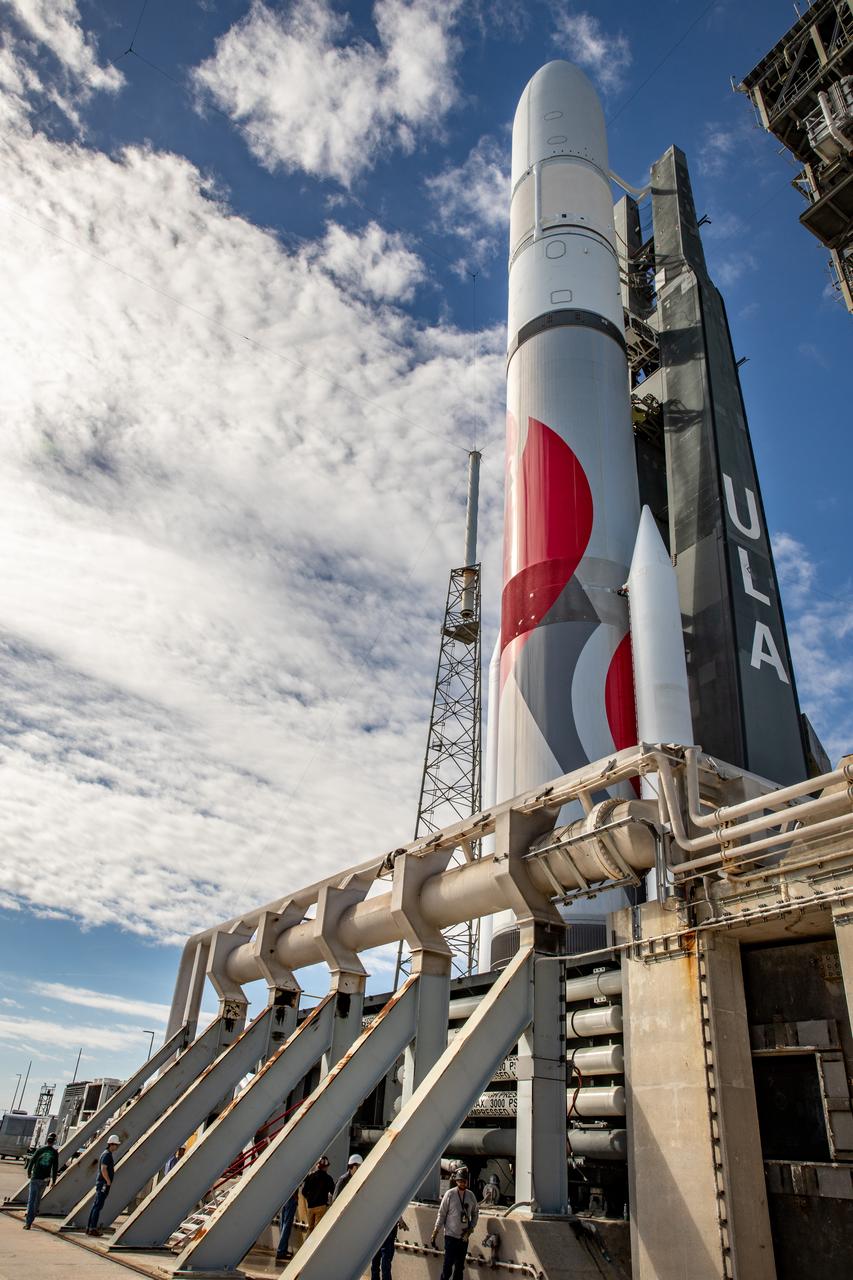

On Friday, Jan. 5, 2024, United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket carrying Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is rolled out of the Vertical Integration Facility to the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida in advance of a planned lift off at 2:18 a.m. EST Monday, Jan. 8, 2024. Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.(Multiple values)