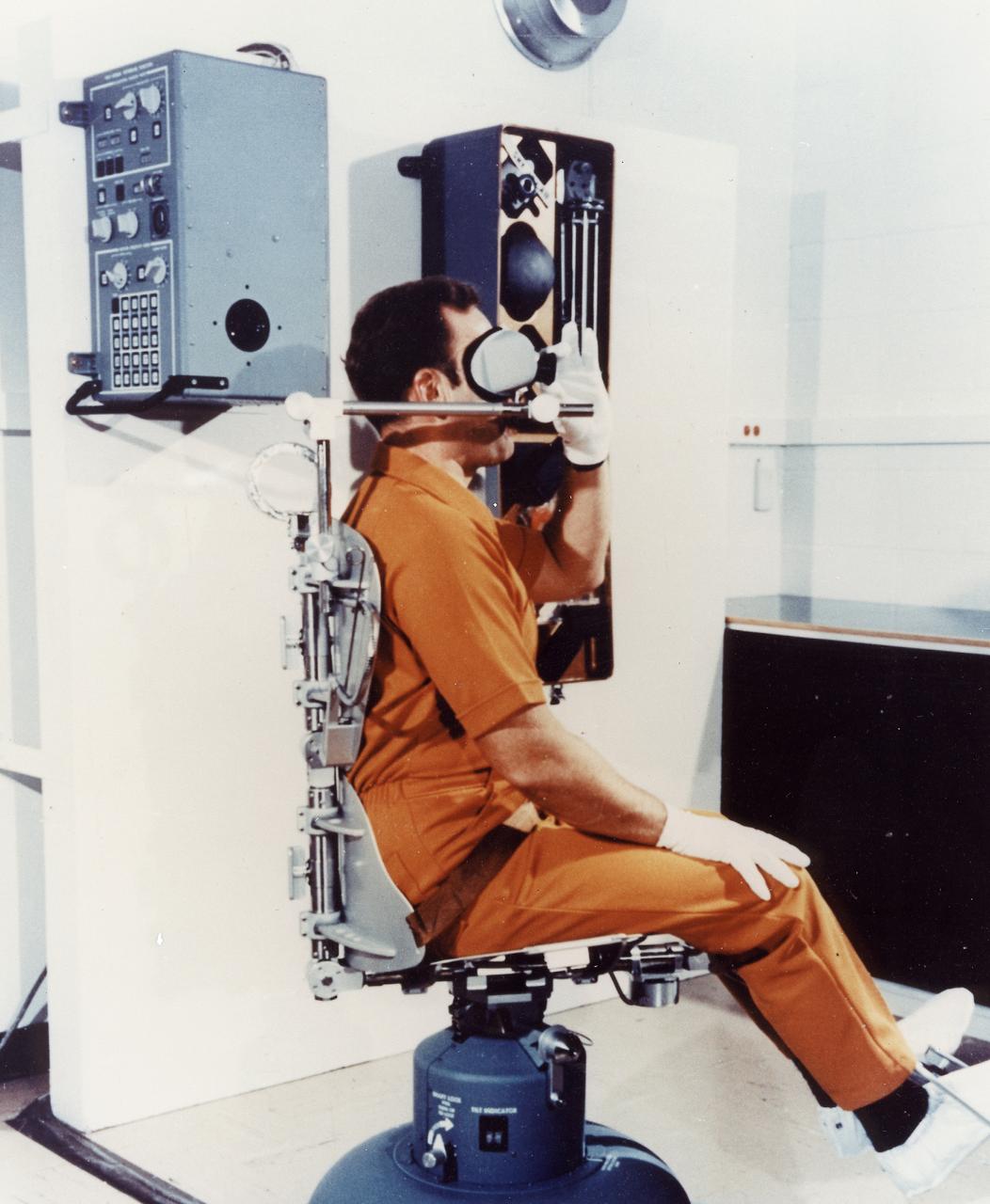
This 1970 photograph shows the Rotating Litter Chair, a major component of Skylab's Human Vestibular Function experiment (M131). The experiment was a set of medical studies designed to determine the effect of long-duration space missions on astronauts' coordination abilities. The M131 experiment tested the astronauts susceptibility to motion sickness in the Skylab environment, acquired data fundamental to an understanding of the functions of human gravity reception under prolonged absence of gravity, and tested for changes in the sensitivity of the semicircular canals. Data from this experiment was collected before, during, and after flight. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
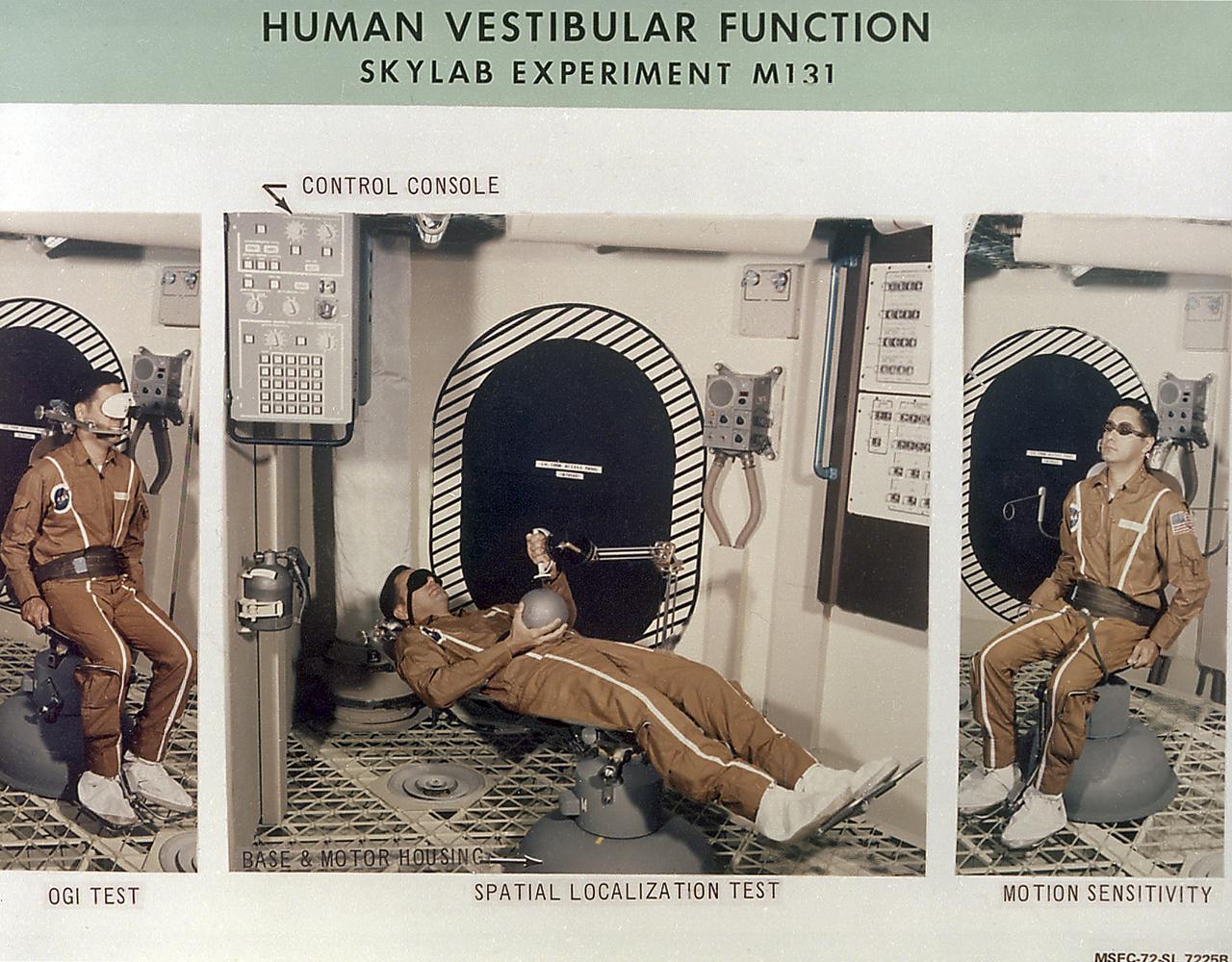
This set of photographs details Skylab's Human Vestibular Function experiment (M131). This experiment was a set of medical studies designed to determine the effect of long-duration space missions on astronauts' coordination abilities. This experiment tested the astronauts susceptibility to motion sickness in the Skylab environment, acquired data fundamental to an understanding of the functions of human gravity reception under prolonged absence of gravity, and tested for changes in the sensitivity of the semicircular canals. Data from this experiment was collected before, during, and after flight. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
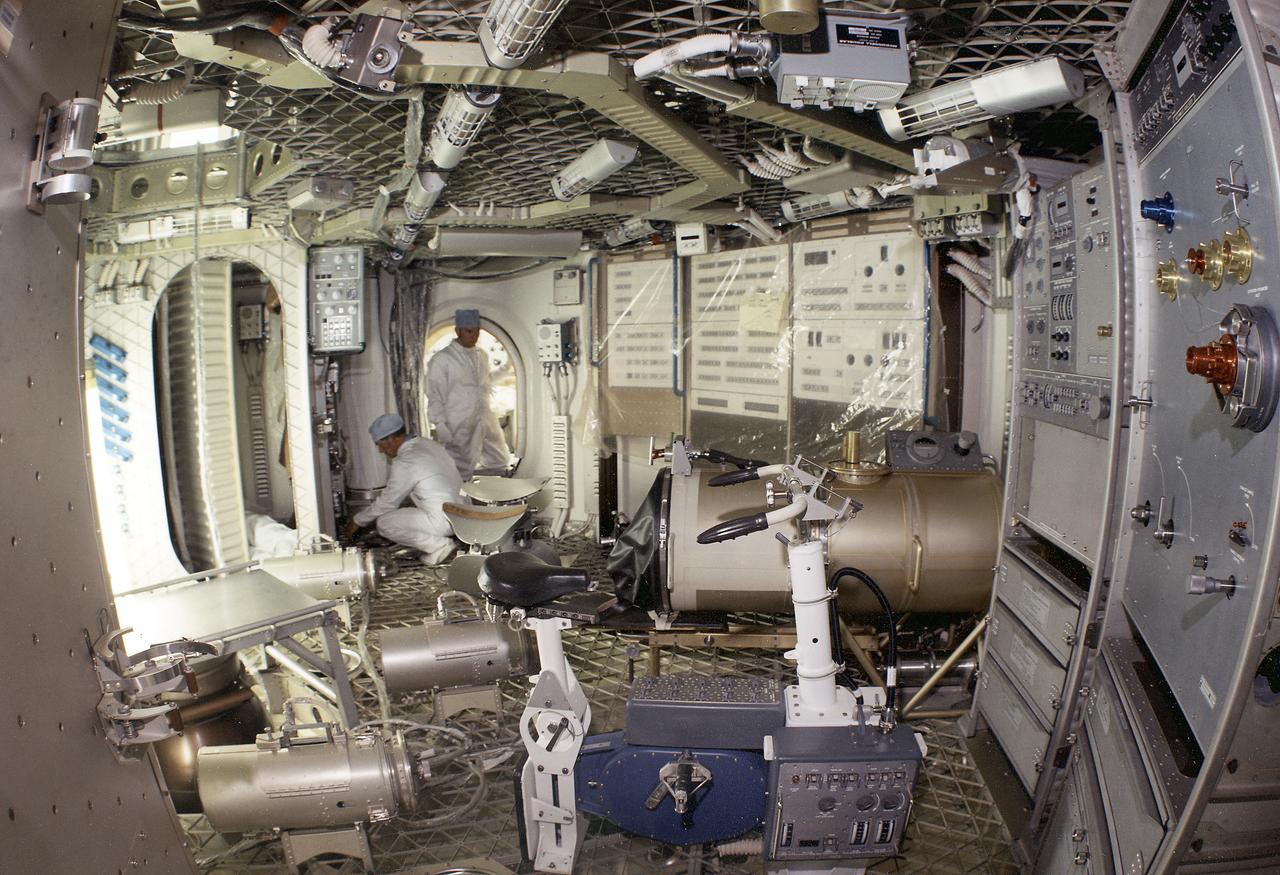
This is a wide-angle view of the Orbital Workshop lower level experiment area. In center foreground is the ergometer bicycle. In center background is a litter chair for the Human Vestibular Function experiment (Skylab Experiment M131) and in right background is the Lower Body Negative Pressure System experiment (Skylab Experiment M092). The ergometer bicycle was used for metabolic activity experiments and exercise. The purpose of the Human Vestibular (irner ear) Function experiment was to examine the effect of weightlessness on man's sensitivity and susceptibility to motion rotation, and his perception of orientation. The Lower Body Negative Pressure experiment investigated the relationship between the zero gravity environment and cardiovascular deconditioning. A characteristic of cardiovascular deconditoning is the partial failure of the blood vessels resulting in the excessive pooling of the blood in the legs when a person assumes an erect posture in a gravity field. The Marshall Space Flight Center had the program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.

S73-32113 (9 Aug. 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, Skylab 3 science pilot, serves as test subject for the Skylab ?Human Vestibular Function? M131 Experiment, as seen in this photographic reproduction taken from a television transmission made by a color TV camera aboard the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The objectives of the Skylab M131 experiment are to obtain data pertinent to establishing the validity of measurements of specific behavioral/physiological responses influenced by vestibular activity under one-g and zero-g conditions; to determine man?s adaptability to unusual vestibular conditions and predict habitability of future spacecraft conditions involving reduced gravity and Coriollis forces; and to measure the accuracy and variability in man?s judgment of spatial coordinates based on atypical gravity receptor cues and inadequate visual cues. Photo credit: NASA
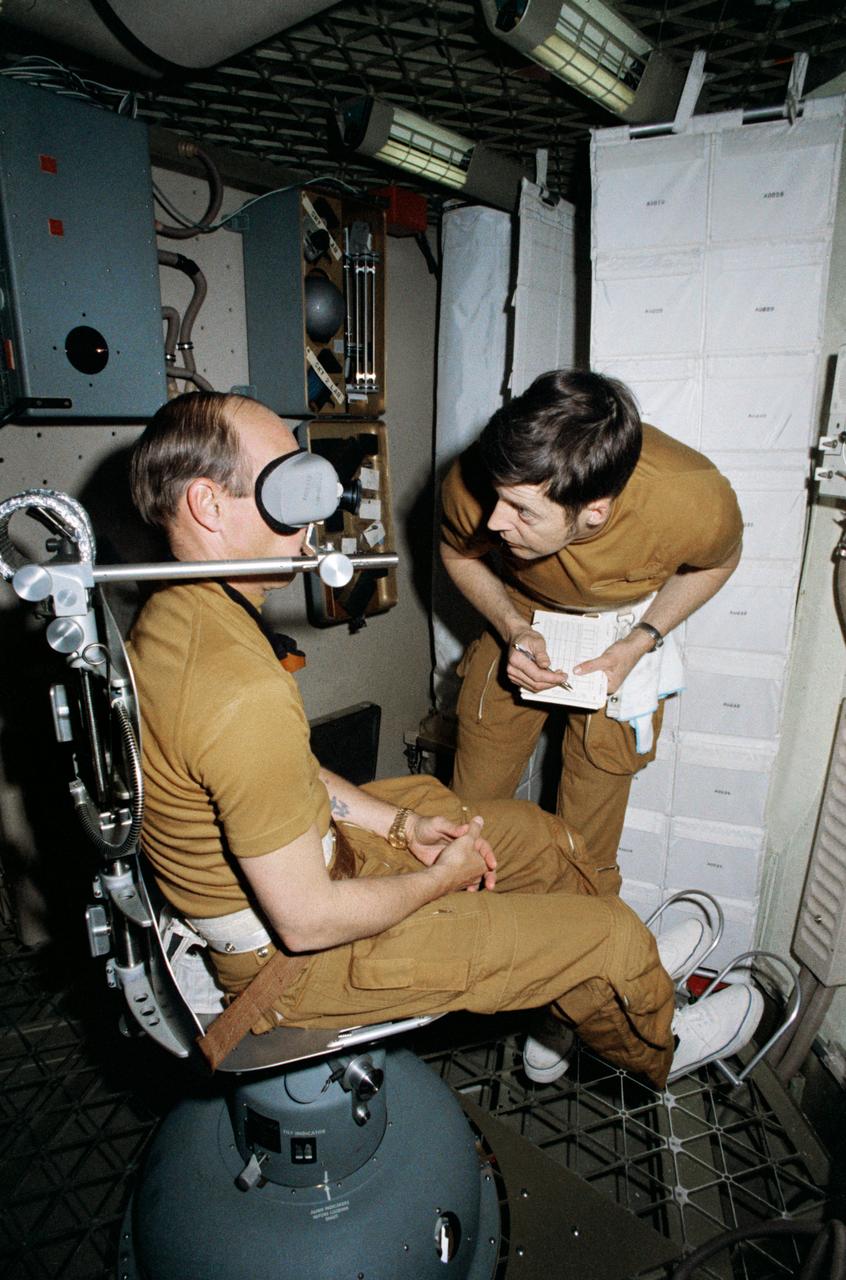
S73-20678 (1 March 1973) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander of the first manned Skylab mission, checks out the Human Vestibular Function, Experiment M131, during Skylab training at Johnson Space Center. Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot of the mission, goes over a checklist. The two men are in the work and experiments compartment of the crew quarters of the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) trainer at JSC. Photo credit: NASA

S73-34171 (9 Aug. 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, Skylab 3 science pilot, serves as test subject for the Skylab ?Human Vestibular Function? M131 Experiment, as seen in this photographic reproduction taken from a television transmission made by a color TV camera aboard the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The objectives of the Skylab M131 experiment are to obtain data pertinent to establishing the validity of measurements of specific behavioral/physiological responses influenced by vestibular activity under one-g and zero-g conditions; to determine man?s adaptability to unusual vestibular conditions and predict habitability of future spacecraft conditions involving reduced gravity and Coriollis forces; and to measure the accuracy and variability in man?s judgment of spatial coordinates based on atypical gravity receptor cues and inadequate visual cures. Dr. Garriott is seated in the experiment?s litter chair which can rotate the test subject at predetermined rotational velocity or programmed acceleration/decelerational profile. Photo credit: NASA
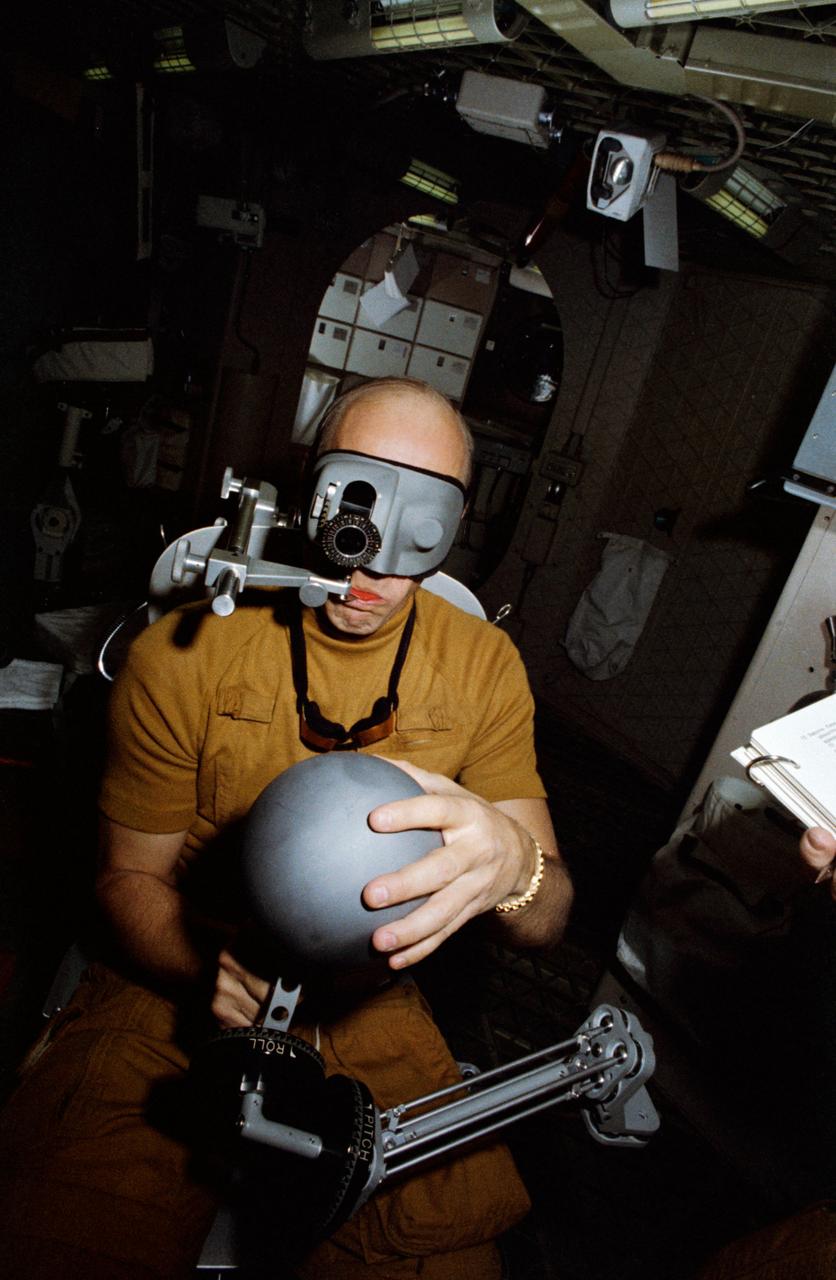

S73-20695 (1 March 1973) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander of the first manned Skylab mission, checks out the Human Vestibular Function, Experiment M131, during Skylab training at Johnson Space Center. Conrad is in the work and experiments compartment of the crew quarters of the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) trainer at JSC. The reference sphere with a magnetic rod is used by the astronaut to indicate body orientation non-visually. The litter chair in which he is seated can be rotated by a motor at its base or, when not being rotated, can tilt forward, backward or to either side. Photo credit: NASA