
Satellite Control Simulator Emphasizing Flywheel Magnet Control
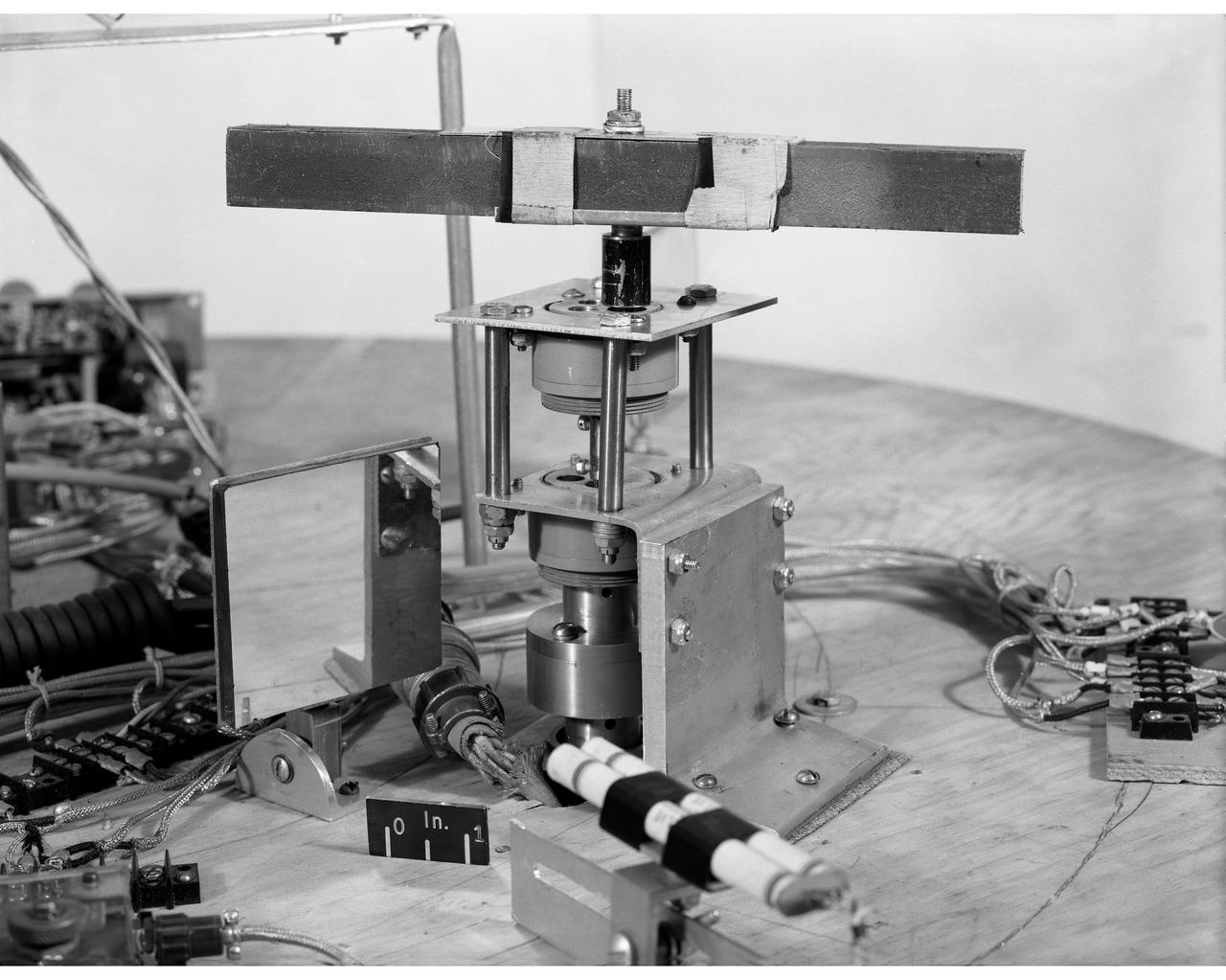
Satellite Control Simulator Emphasizing Flywheel Magnet Control

Control utilizing inertia wheel and bar magnet.

Control utilizing inertia wheel and bar magnet.

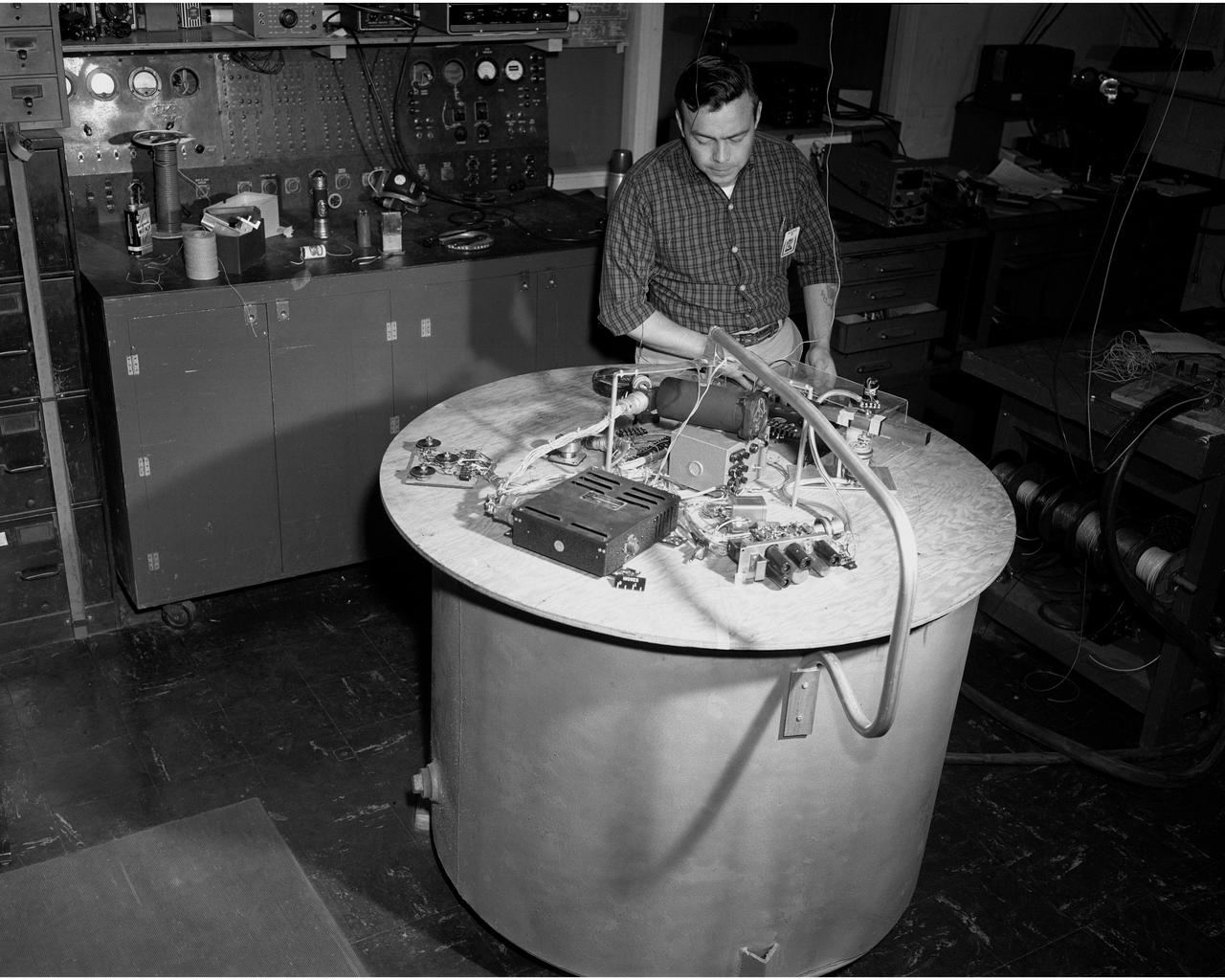
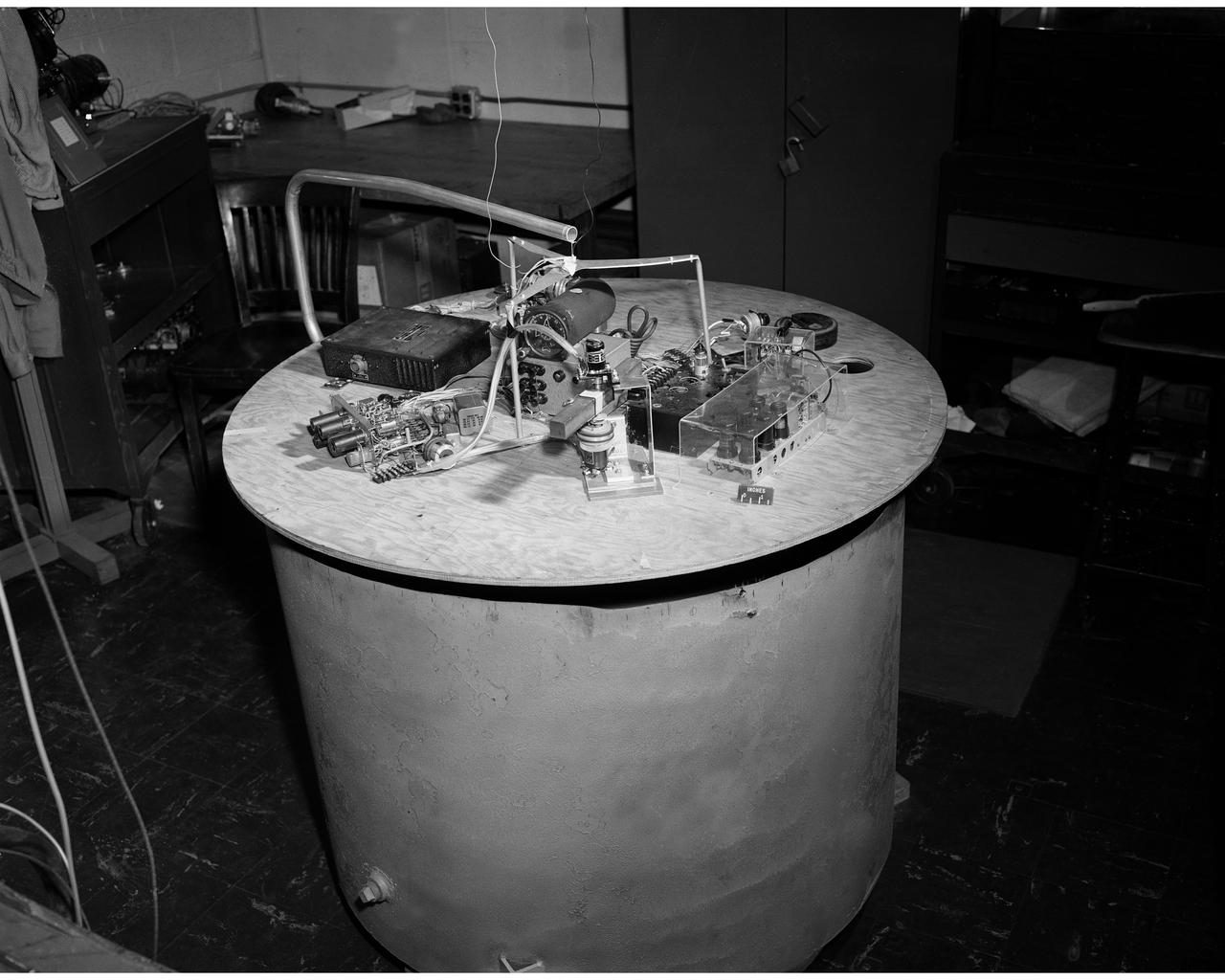
ELECTRO MAGNETIC RADIATION CONTROL EXPERIMENT IN TANK 6

Control utilizing inertia wheel and bar magnet.

ELECTRO MAGNETIC RADIATION CONTROL EXPERIMENT IN TANK 6

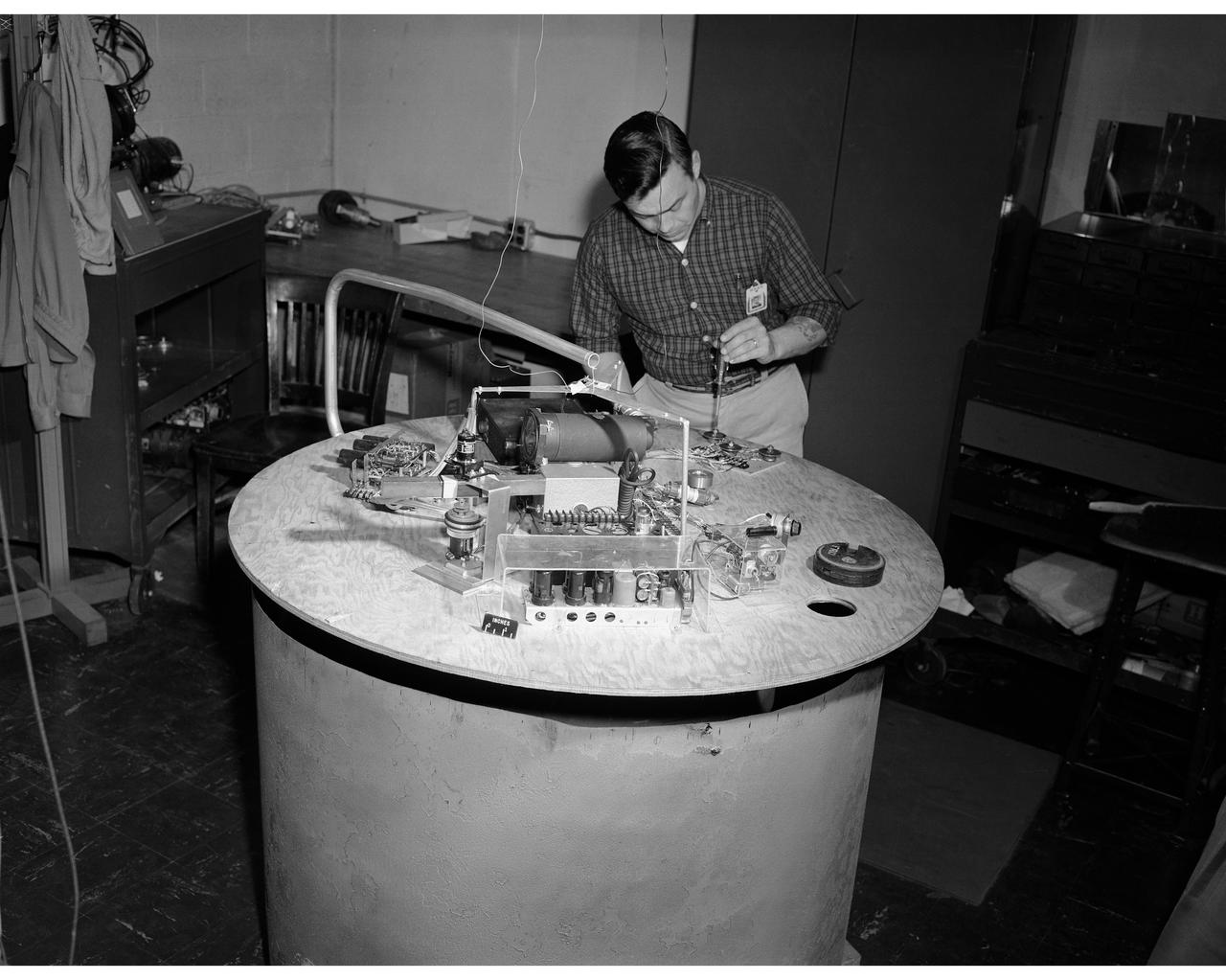
Control utilizing inertia wheel and bar magnet.
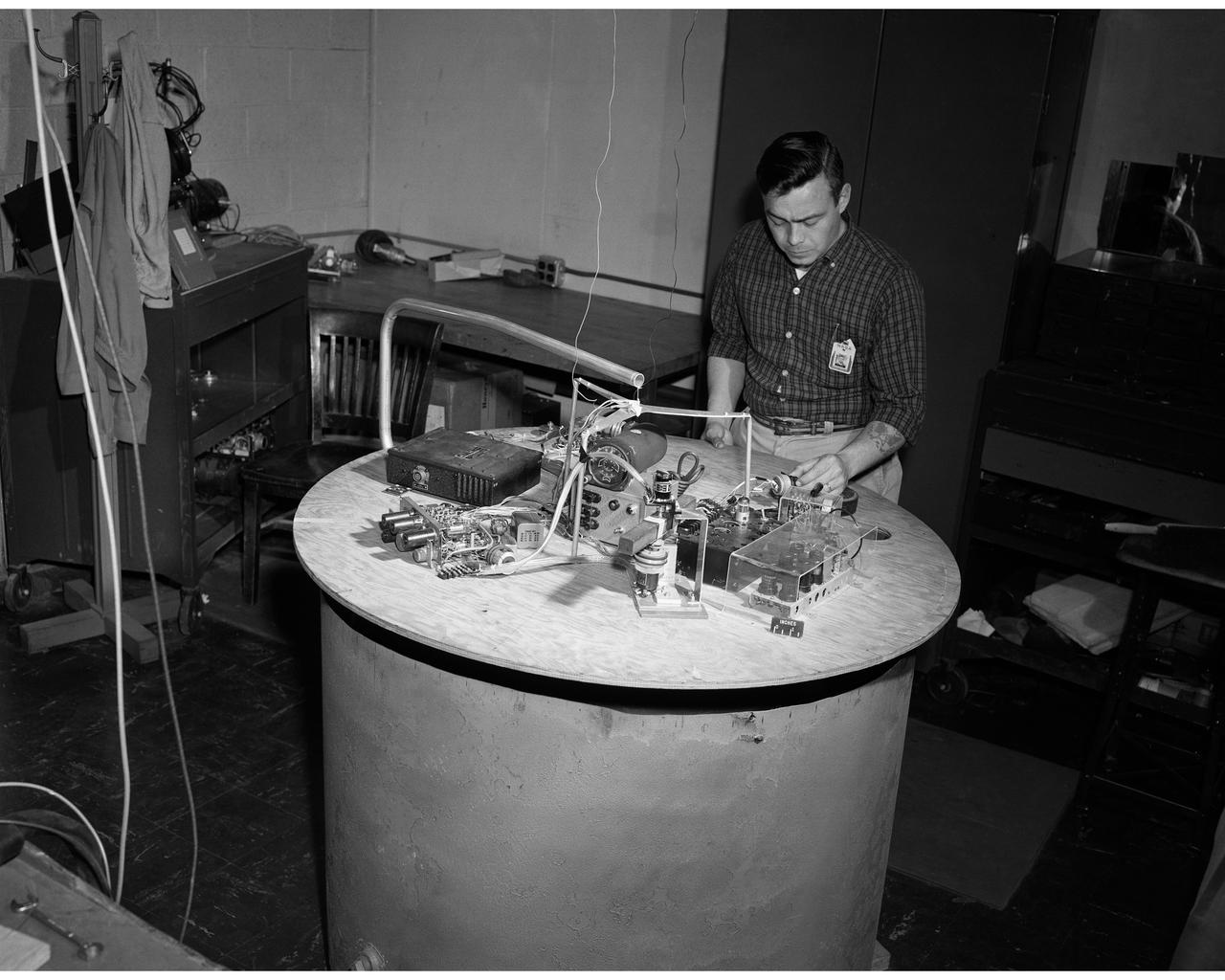

Control utilizing inertia wheel and bar magnet.
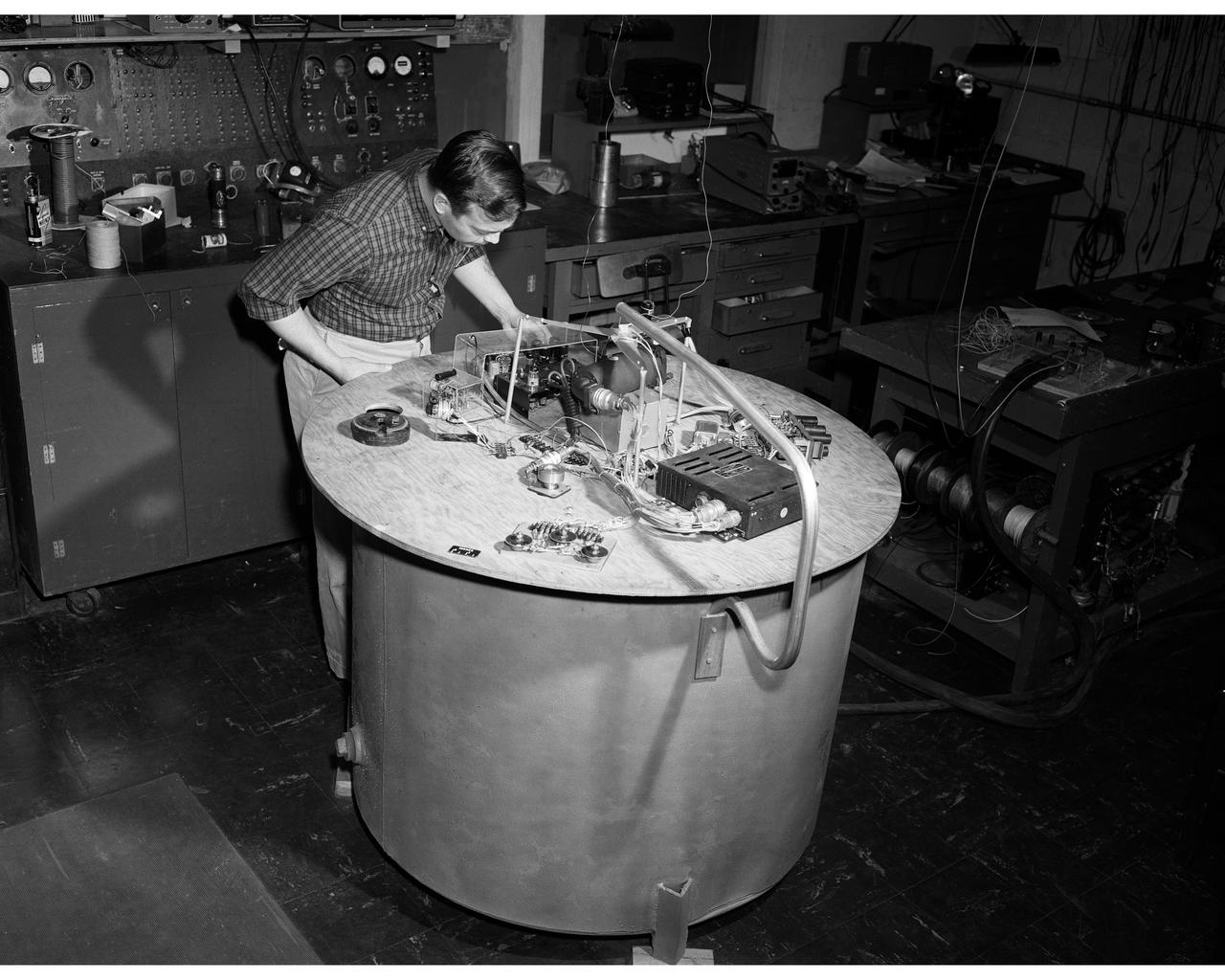
Control utilizing inertia wheel and bar magnet.
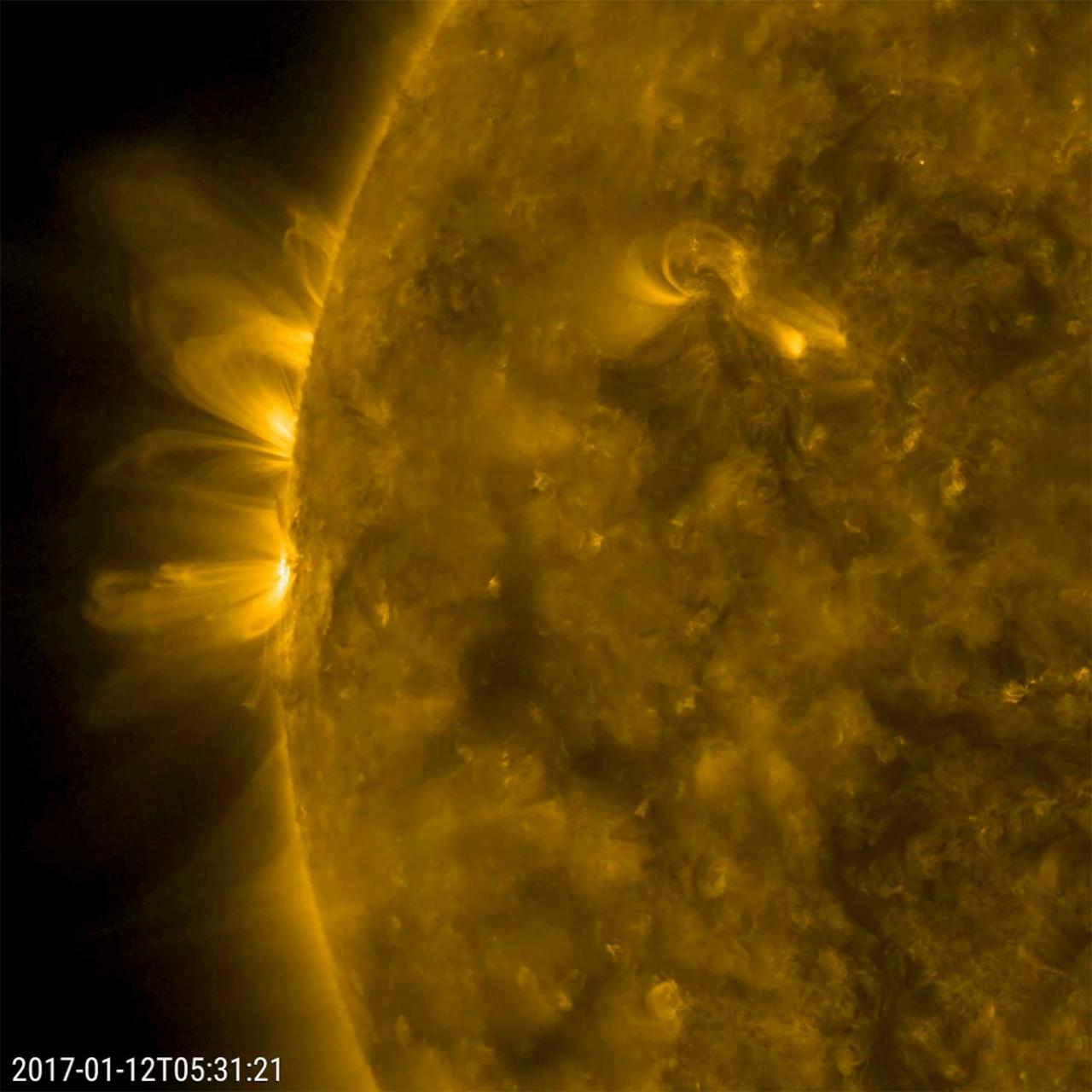

Magnetic arcs of plasma that spiraled above two active regions held their shape fairly well over 18 hours (Jan. 11-12, 2017). The charged plasma is being controlled the magnetic field lines of the active regions. The field lines become clearly visible when viewed in this wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light. Often the arches bend and twist more dynamically than the relatively stable ones seen here. Movies are available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA12327
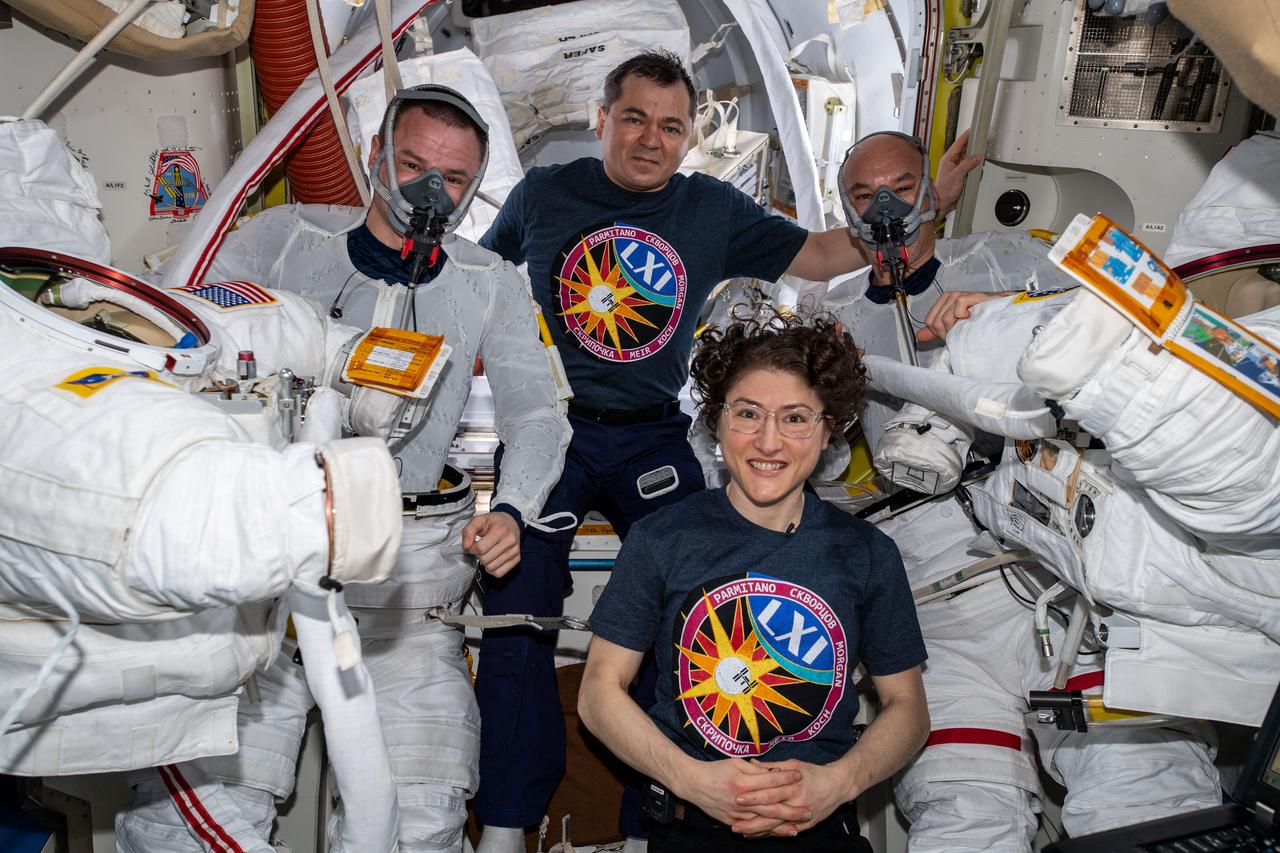

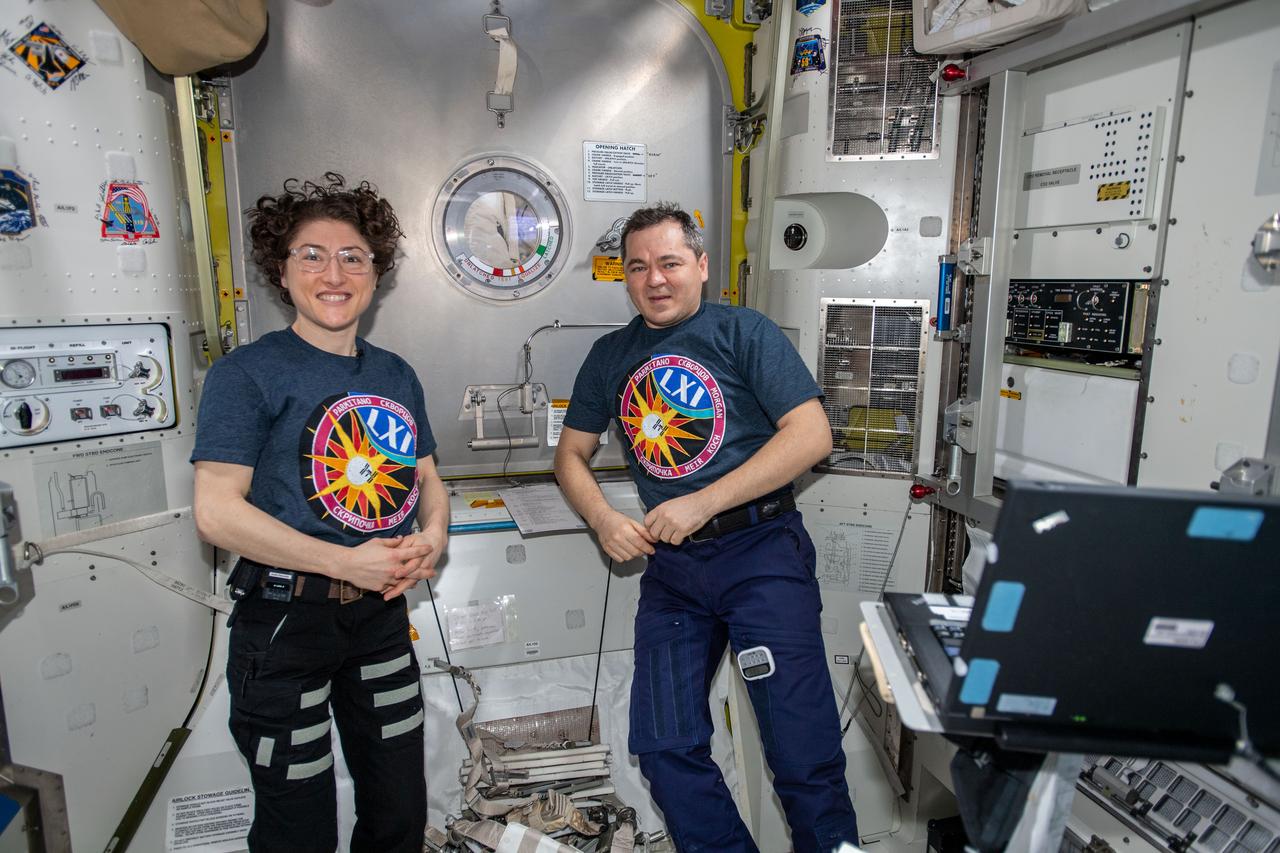
iss061e054283 (Nov. 22, 2019) --- Flight Engineers Christina Koch and Oleg Skripochka are pictured assisting spacewalkers Andrew Morgan (left) and Luca Parmitano (right) in the U.S. Quest airlock before they would begin the second spacewalk to repair the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer's thermal control system.

Close-up view of the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-02 (AMS-02), in the area where the Tracker Thermal Control System (TTCS) wedge will be installed. Image was taken by Extravehicular Crewmember 2 (EV2) during Extravehicular Activity 32 (EVA 32) and released on social media.
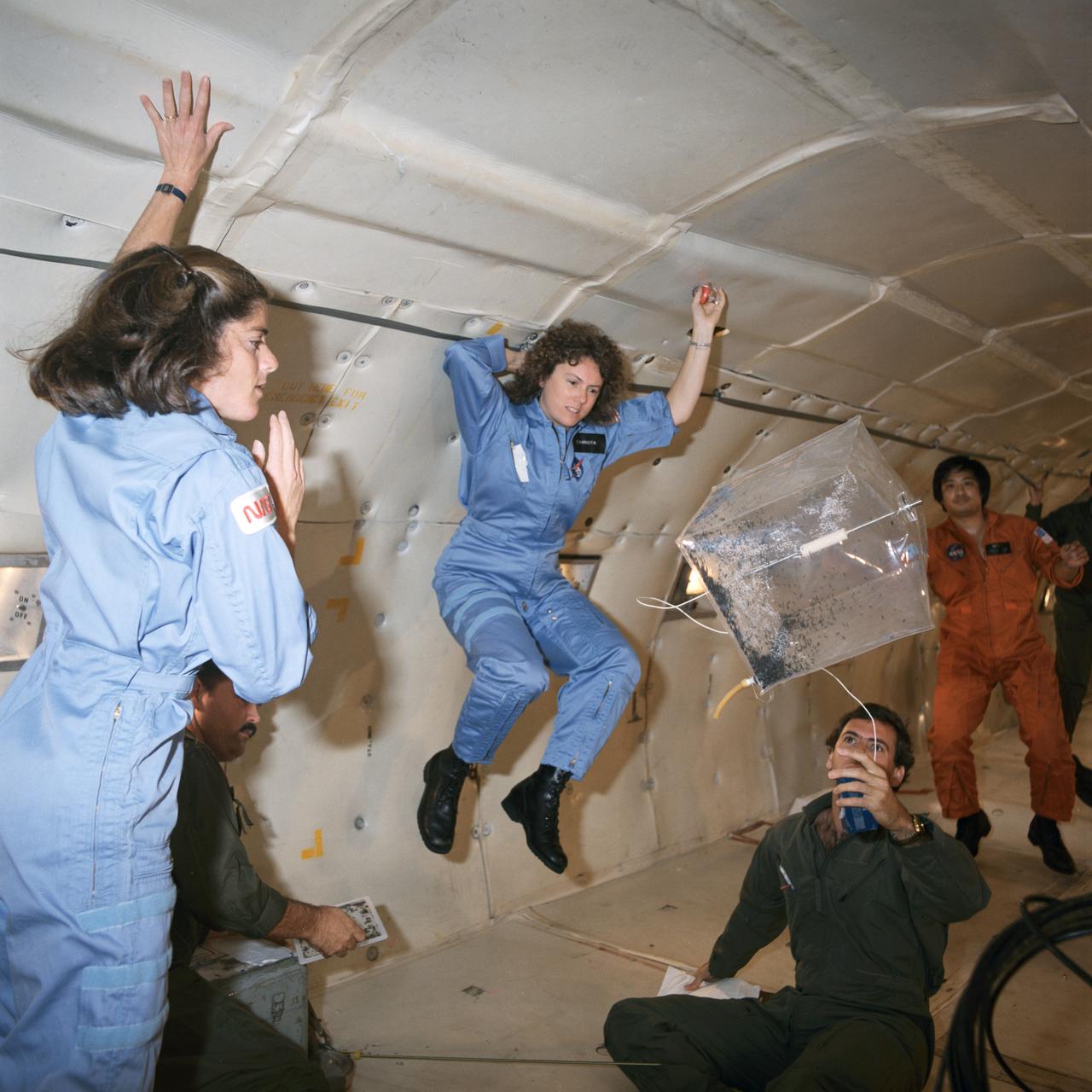

S85-42474 (16 Oct. 1985) --- A KC-135 aircraft provides a brief period of weightlessness as a preview for a teacher, in training to fly onboard a space shuttle for the Teacher-in-Space Project, and her backup. Sharon Christa McAuliffe (center frame), STS-51L prime crew member, and Barbara Morgan, her backup, monitor an experiment involving magnetic effects - one of the tests to be performed on the STS-51L flight. The experiment uses a control box, a square receptacle containing rubber tubing, stainless steel rod, a filter with desiccant, soft iron wire and a magnet. Photo credit: NASA
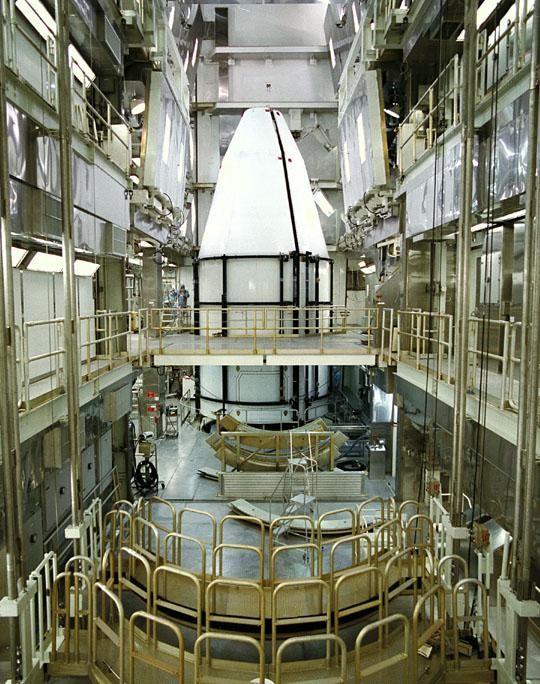

The Cassini spacecraft, protected by an environmentally controlled protective fairing, is sitting at Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station, awaiting its launch scheduled for mid-October atop a Titan IV/Centaur launch vehicle. A four-year, close-up study of the Saturnian system, the Cassini mission will take seven years for the spacecraft to reach Saturn. Scientific instruments carried aboard the spacecraft will study Saturn’s atmosphere, magnetic field, rings, and several moons. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory is managing the Cassini project

Launch of a three-stage Vanguard (SLV-7) from Cape Canaveral, Florida, September 18, 1959. Designated Vanguard III, the 100-pound satellite was used to study the magnetic field and radiation belt. In September 1955, the Department of Defense recommended and authorized the new program, known as Project Vanguard, to launch Vanguard booster to carry an upper atmosphere research satellite in orbit. The Vanguard vehicles were used in conjunction with later booster vehicle such as the Thor and Atlas, and the technique of gimbaled (movable) engines for directional control was adapted to other rockets.
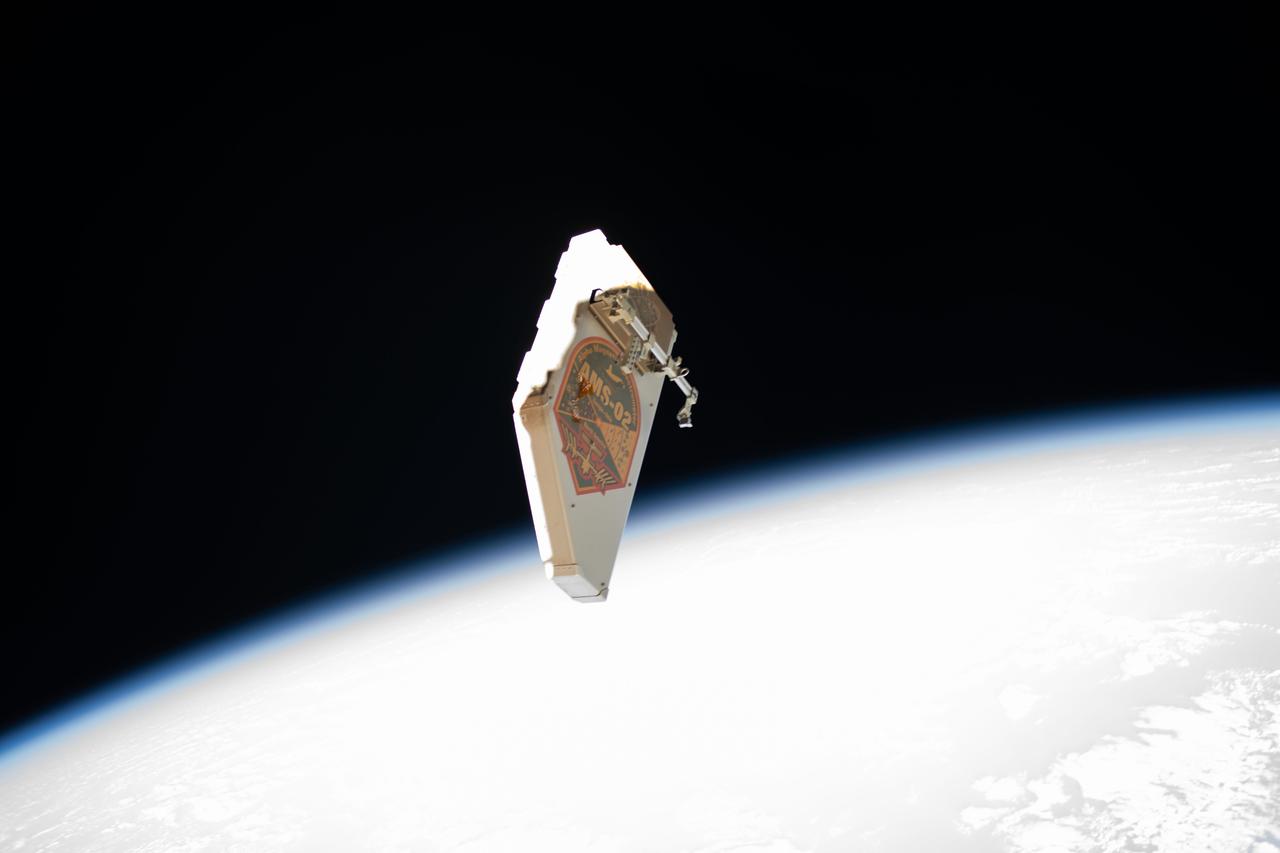

iss061e045319 (Nov. 15, 2019) --- A debris shield that was removed from the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS), the International Space Station's cosmic particle detector, is pictured drifting away from the orbiting lab after spacewalkers Andrew Morgan and Luca Parmitano jettisoned it. The debris shield was detached by the spacewalkers so they could access and begin the repairs of the AMS thermal control system.
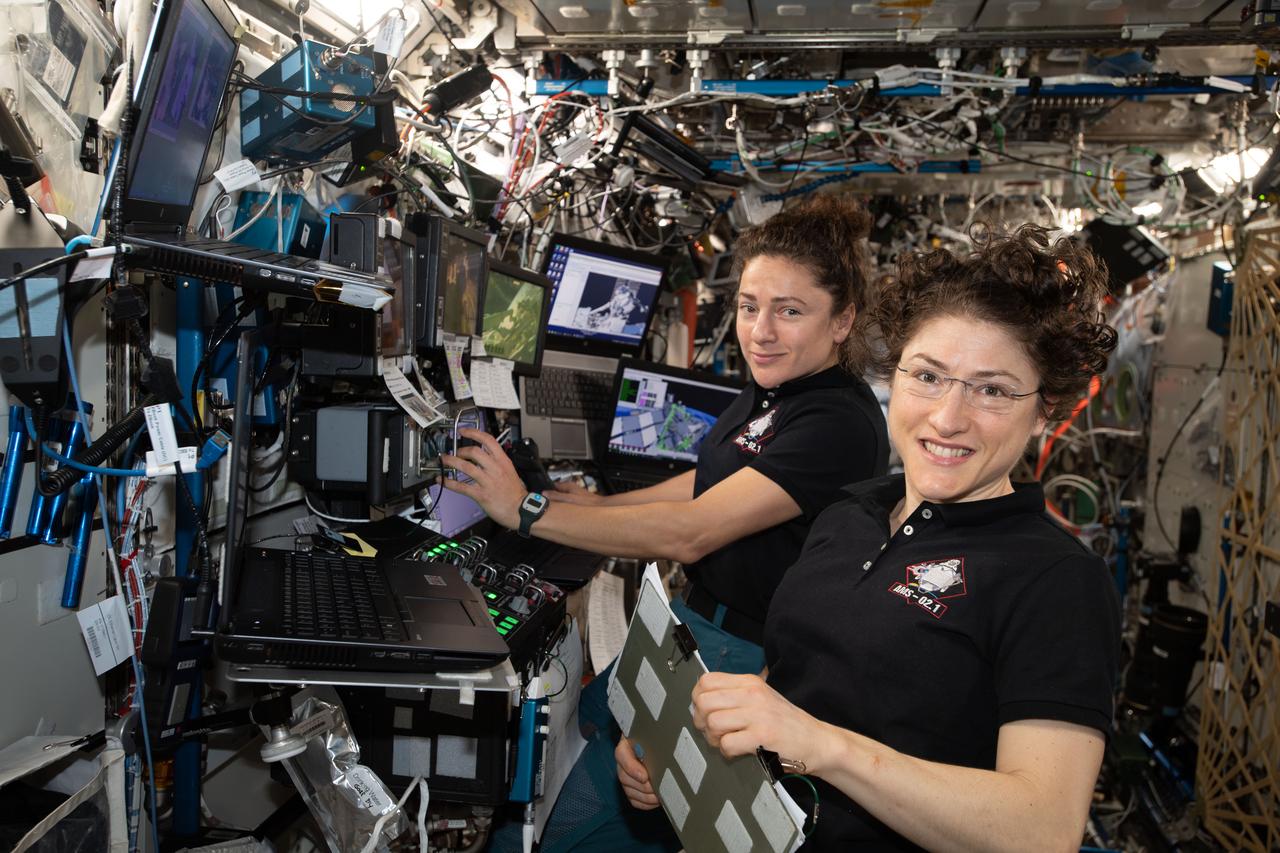

iss061e045472 (Nov. 15, 2019) --- NASA astronauts (from left ) Jessica Meir and Christina Koch are at the robotics workstation controlling the Canadarm2 robotic arm to support the first spacewalk to repair the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS), the International Space Station's cosmic particle detector. Astronauts Luca Parmitano of ESA (European Space Agency) and Andrew Morgan of NASA worked six hours and 39 minutes in the vacuum of space during the first of at least four planned AMS repair spacewalks.
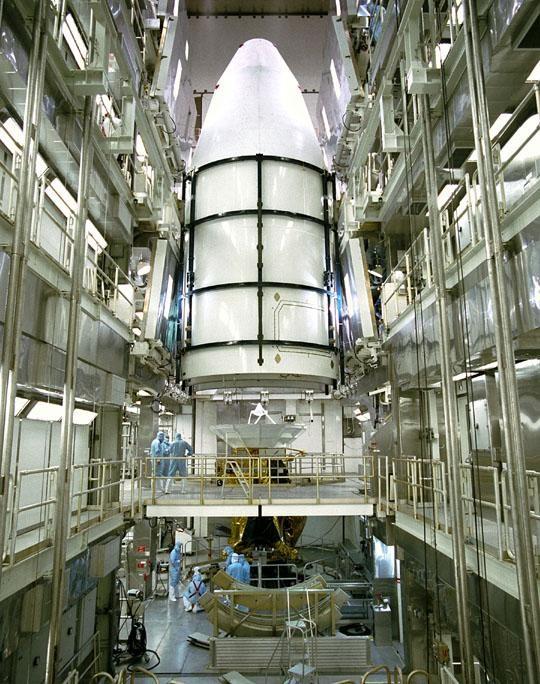

The Cassini spacecraft, protected by an environmentally controlled protective fairing, is sitting at Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station, awaiting its launch scheduled for mid-October atop a Titan IV/Centaur launch vehicle. A fouryear, close-up study of the Saturnian system, the Cassini mission will take seven years for the spacecraft to reach Saturn. Scientific instruments carried aboard the spacecraft will study Saturn’s atmosphere, magnetic field, rings, and several moons. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory is managing the Cassini project

iss061e054290 (Nov. 22, 2019) --- NASA astronaut Christina Koch and Roscosmos cosmonaut Oleg Skripochka are pictured in the equipment lock portion of the Quest joint airlock. The duo assisted astronauts Andrew Morgan and Luca Parmitano into their U.S. spacesuits and into the crew lock before the spacewalkers began the second spacewalk to repair the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer's thermal control system.
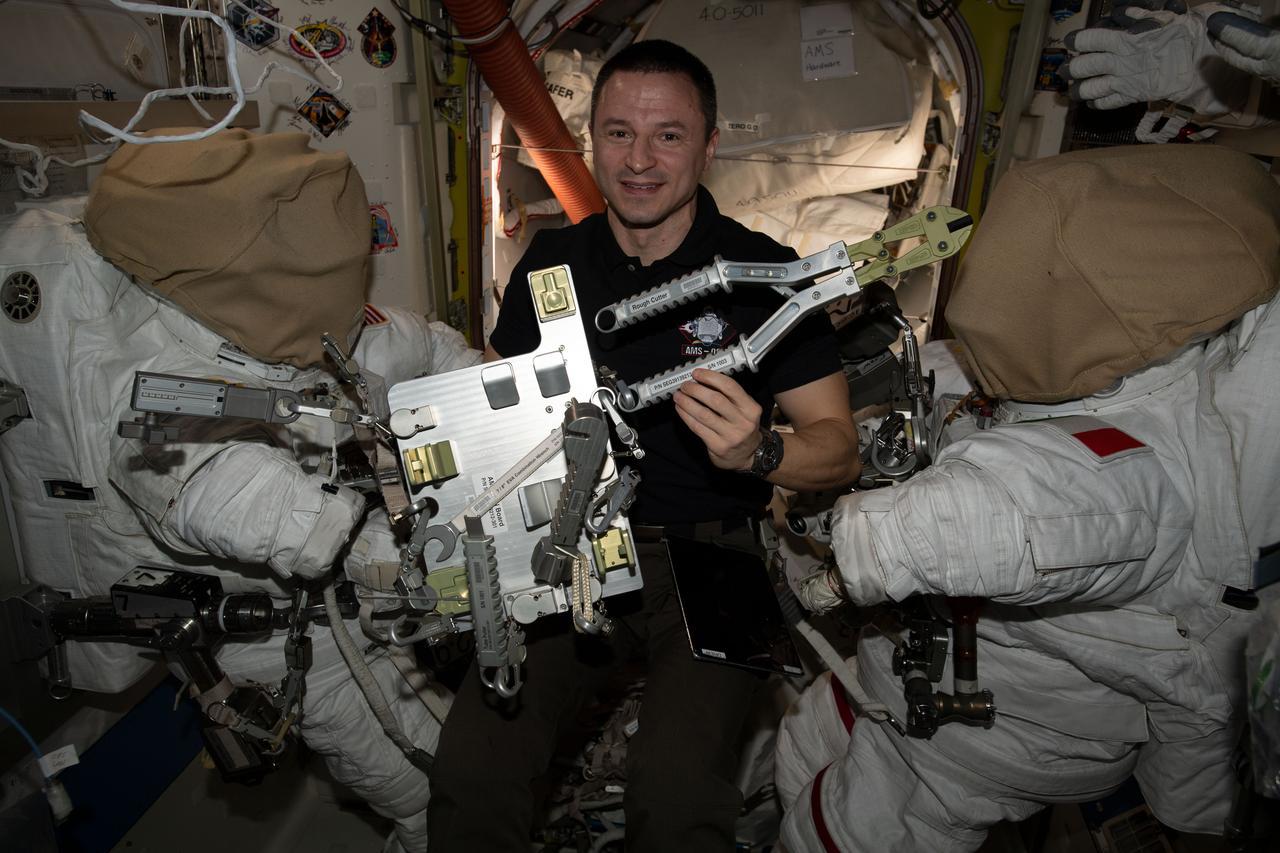

iss061e034876 (Nov. 12, 2019) --- NASA astronaut Andrew Morgan checks specialized spacewalking tools designed specifically to repair the International Space Station's cosmic particle detector, the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS). Morgan and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Luca Parmitano will conduct several spacewalks in November to upgrade the AMS thermal control system.
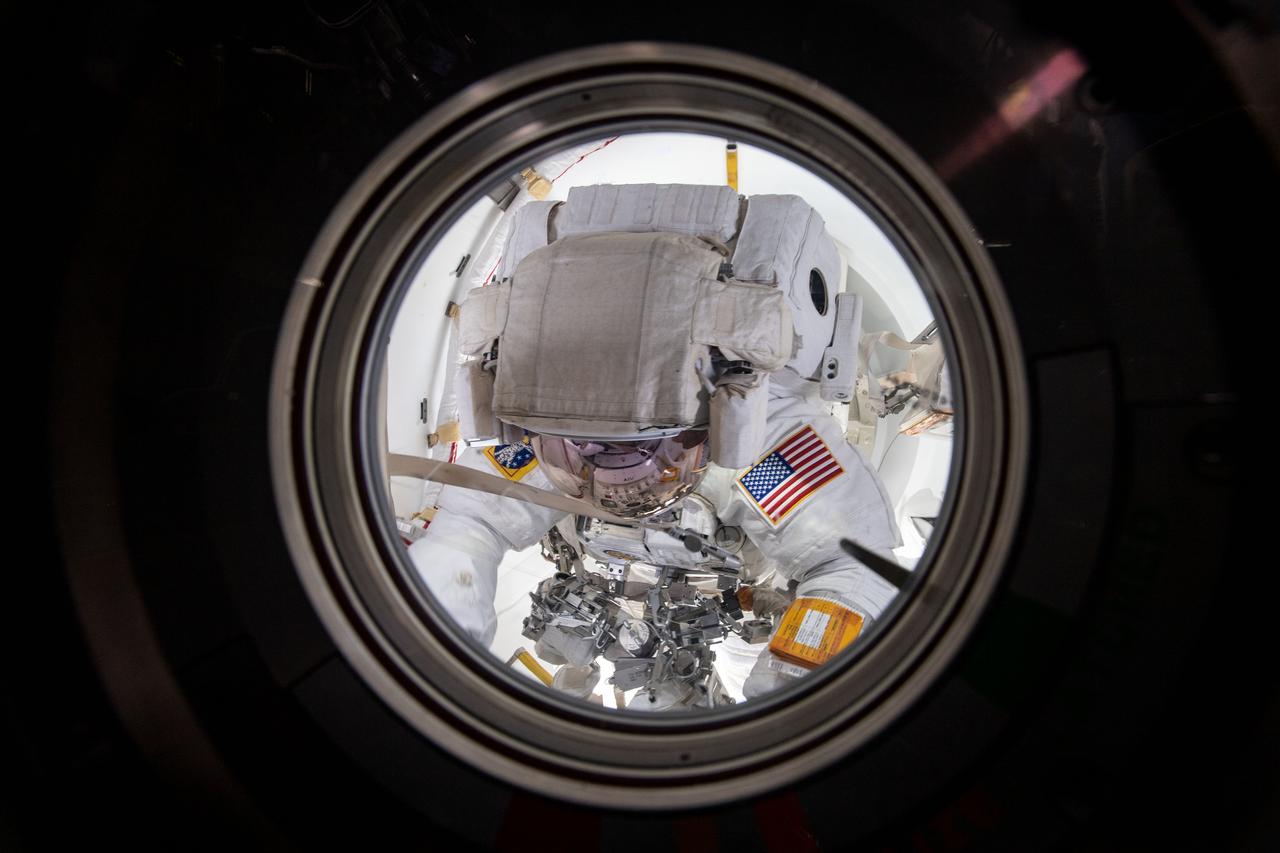

iss061e057469 (Nov. 22, 2019) --- NASA astronaut Andrew Morgan is pictured in his U.S. spacesuit inside the crew lock portion of the Quest joint airlock. He and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Luca Parmitano worked outside in the vacuum of space for six hours and 33 minutes during the second spacewalk to repair the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer's thermal control system.
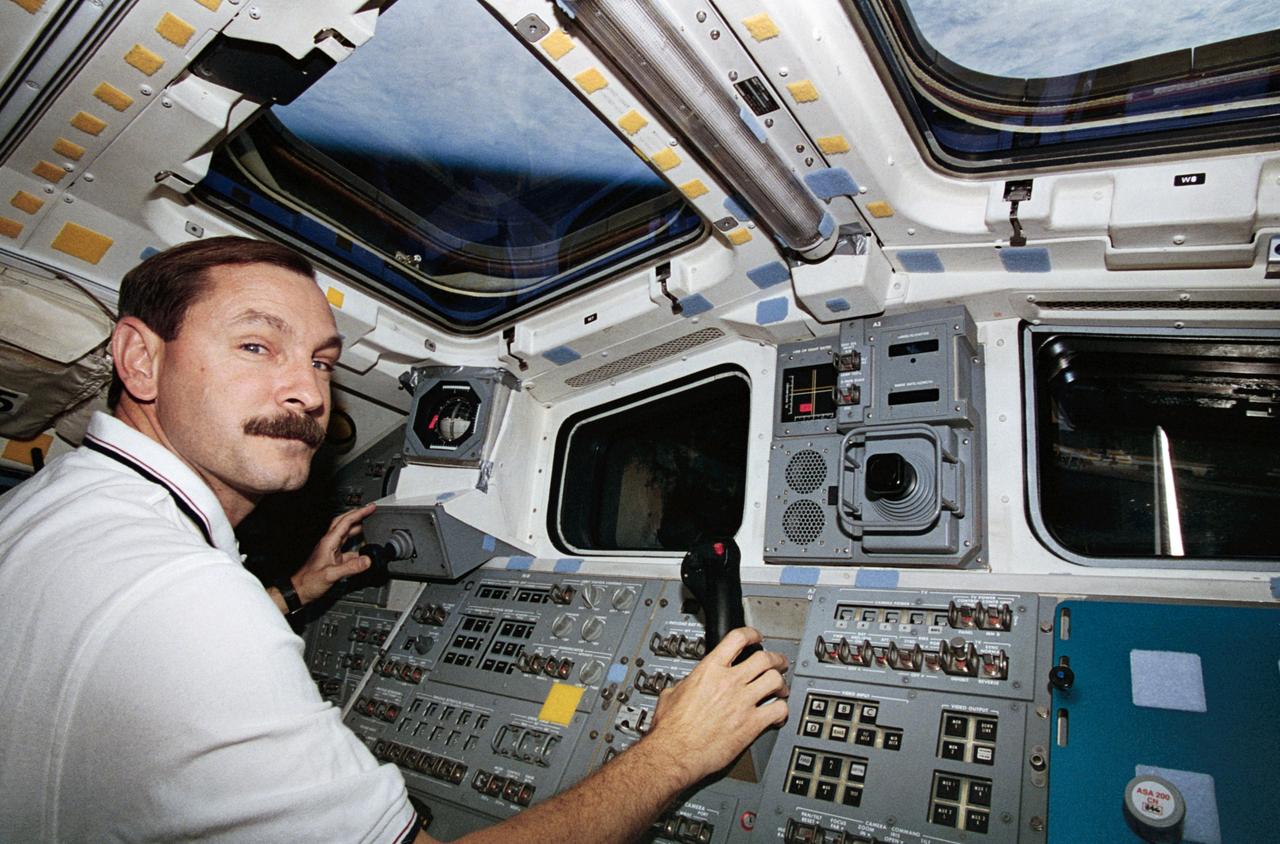

STS077-312-015 (19-29 May 1996) --- Astronaut Curtis L. Brown, Jr., pilot, mans the controls for the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) on the Space Shuttle Endeavour?s aft flight deck during rendezvous operations. During the flight, the six-member crew was involved in deployment and rendezvous operations with the Spartan 207/Inflatable Antenna Experiment (IAE) as well as the Passive Aerodynamically Stabilized Magnetically Damped Satellite (PAMS)/Satellite Test Unit (STU).
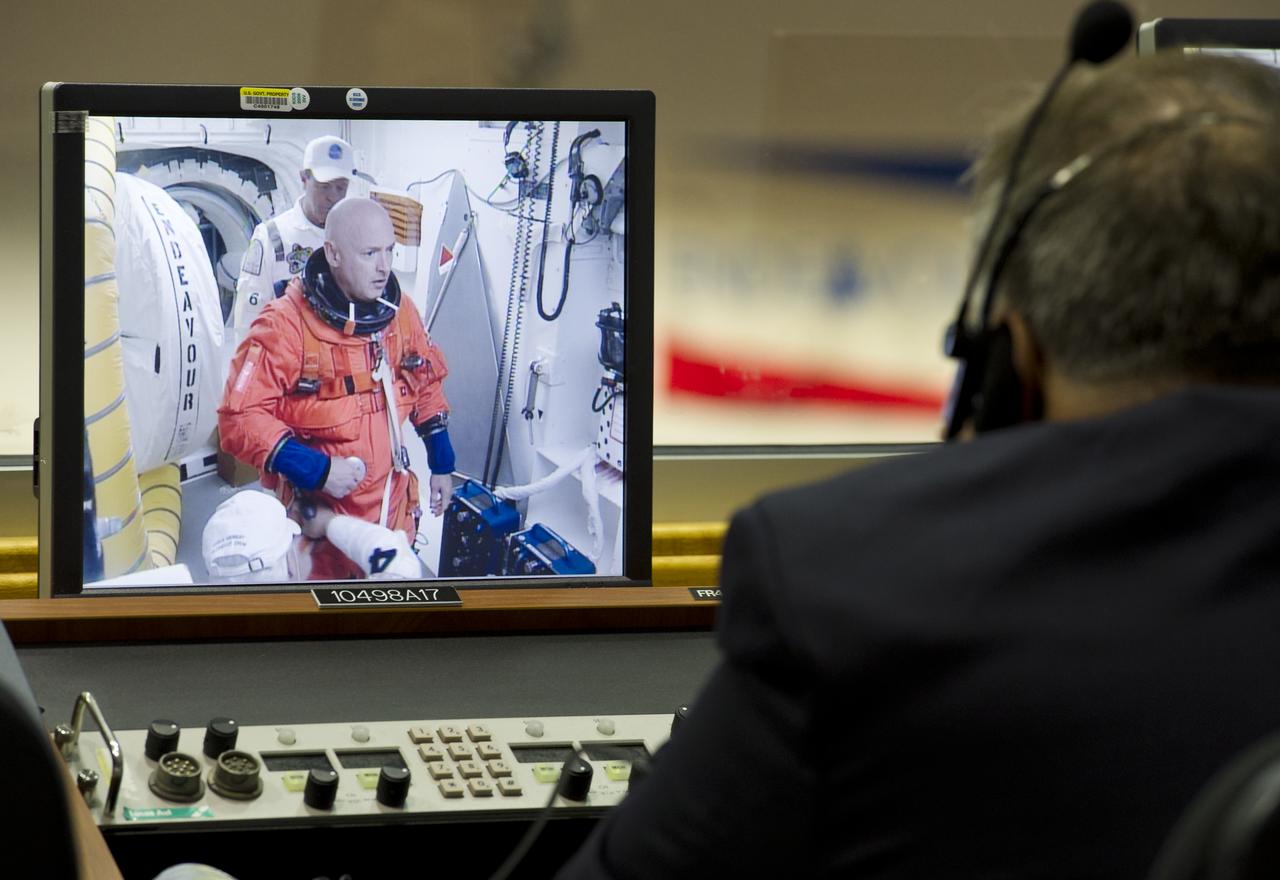

STS-134 mission Commander Mark Kelly is seen preparing to enter space shuttle Endeavour on a monitor in Firing Room Four of the Launch Control Center (LCC), Monday, May 16, 2011, at the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Fla. During the mission, Endeavour and the STS-134 crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) and spare parts including two S-band communications antennas, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for Dextre. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
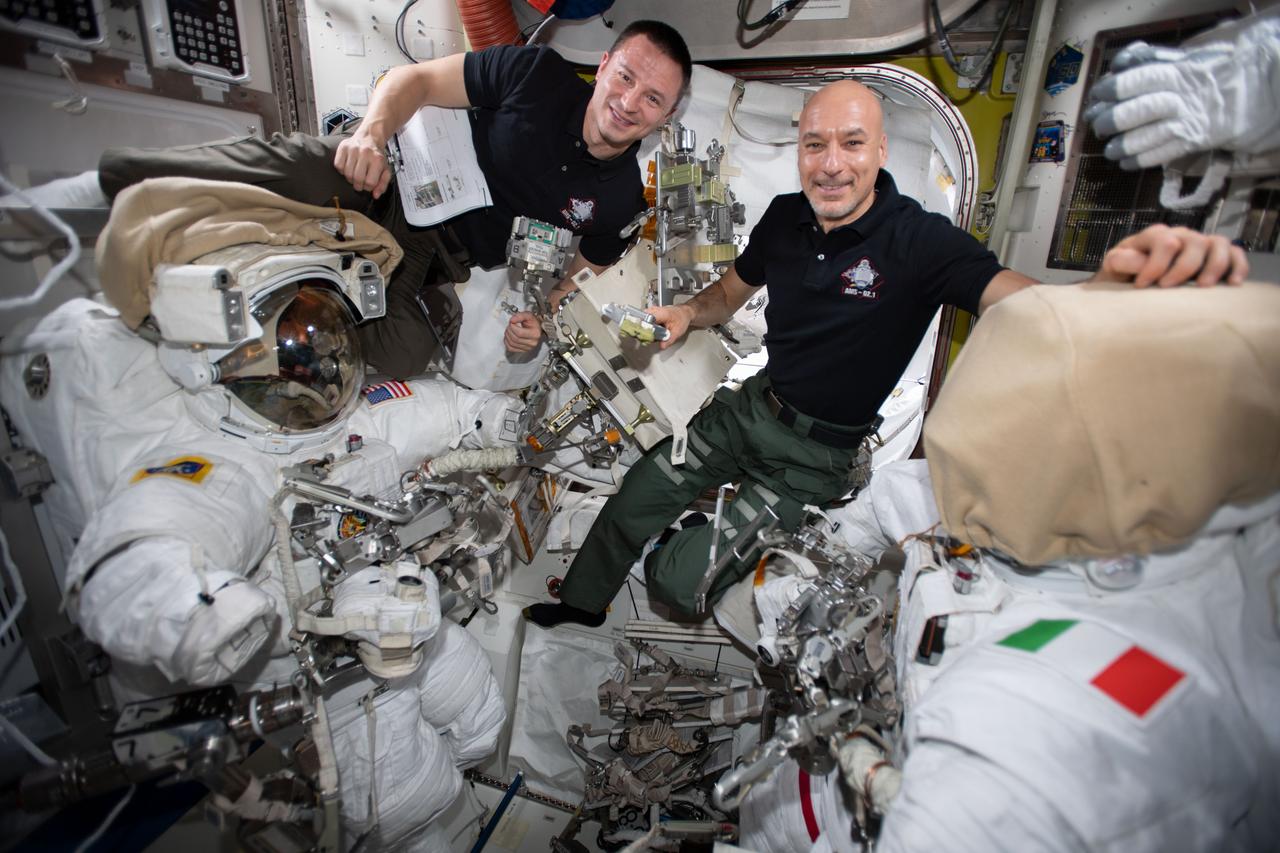

iss061e033873 (Nov. 11, 2019) --- (From left) NASA astronaut Andrew Morgan and ESA (European Space Agency) Commander Luca Parmitano work inside the Quest airlock checking U.S. spacesuits and spacewalking tools. The duo will conduct several spacewalks in November to upgrade the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer's (AMS) thermal control system. The AMS is the International Space Station's cosmic particle detector.
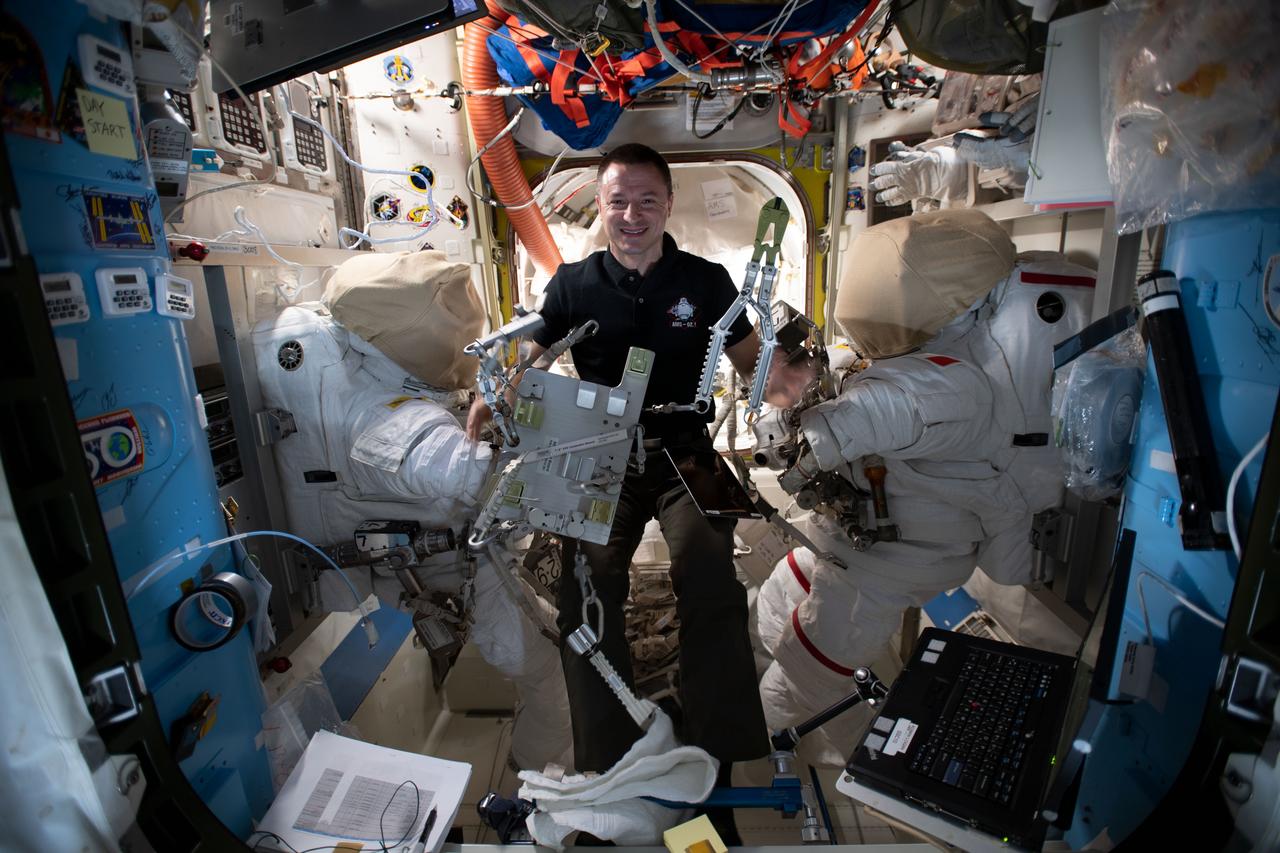

iss061e034867 (Nov. 12, 2019) --- NASA astronaut Andrew Morgan checks specialized spacewalking tools designed specifically to repair the International Space Station's cosmic particle detector, the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS). Morgan and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Luca Parmitano will conduct several spacewalks in November to upgrade the AMS thermal control system.
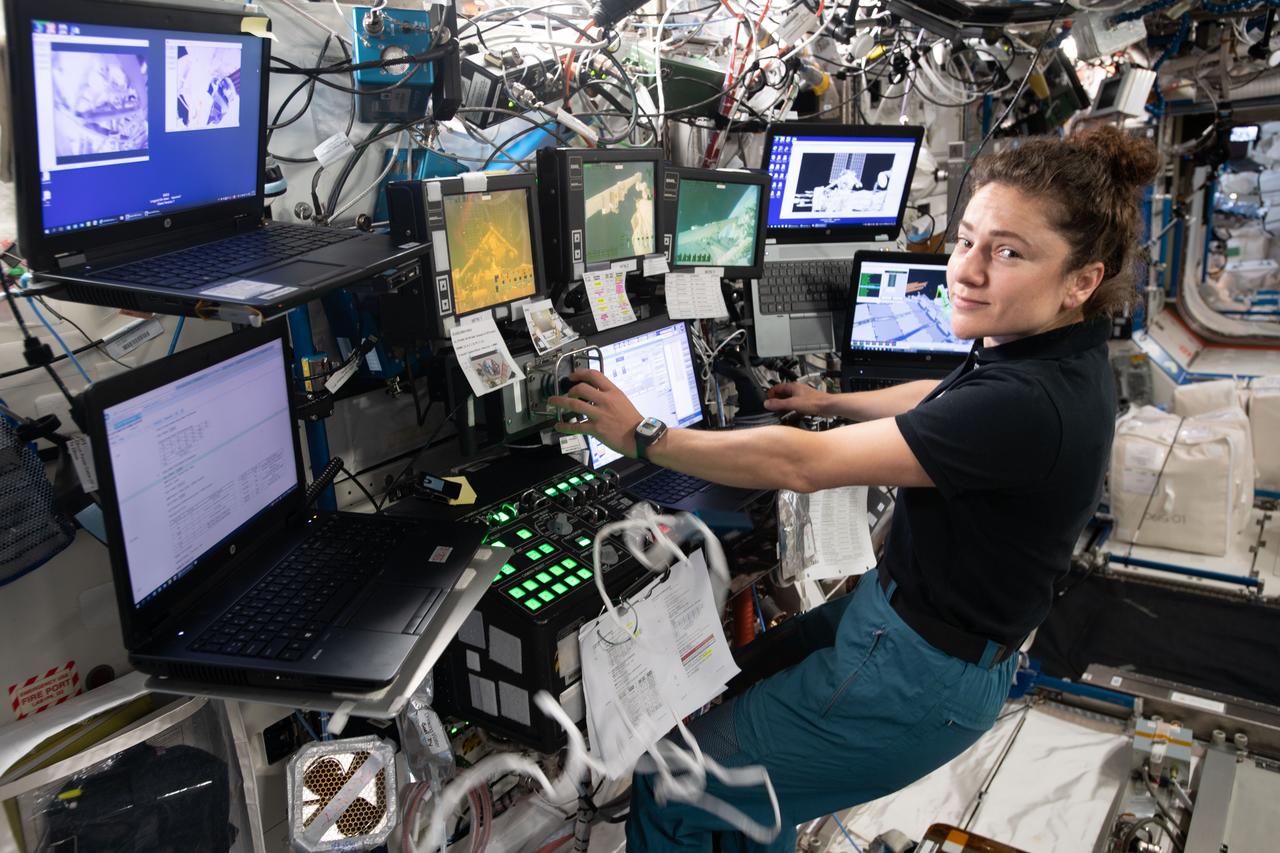

iss061e045447 (Nov. 15, 2019) --- NASA astronaut Jessica Meir is at the robotics workstation controlling the Canadarm2 robotic arm to support the first spacewalk to repair the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS), the International Space Station's cosmic particle detector. Astronauts Luca Parmitano of ESA (European Space Agency) and Andrew Morgan of NASA worked six hours and 39 minutes in the vacuum of space during the first of at least four planned AMS repair spacewalks.

Workers at Launch Complex 17 Pad A, Kennedy Space Center (KSC) encapsulate the Geomagnetic Tail (GEOTAIL) spacecraft (upper) and attached payload Assist Module-D upper stage (lower) in the protective payload fairing. GEOTAIL project was designed to study the effects of Earth's magnetic field. The solar wind draws the Earth's magnetic field into a long tail on the night side of the Earth and stores energy in the stretched field lines of the magnetotail. During active periods, the tail couples with the near-Earth magnetosphere, sometimes releasing energy stored in the tail and activating auroras in the polar ionosphere. GEOTAIL measures the flow of energy and its transformation in the magnetotail and will help clarify the mechanisms that control the imput, transport, storage, release, and conversion of mass, momentum, and energy in the magnetotail.
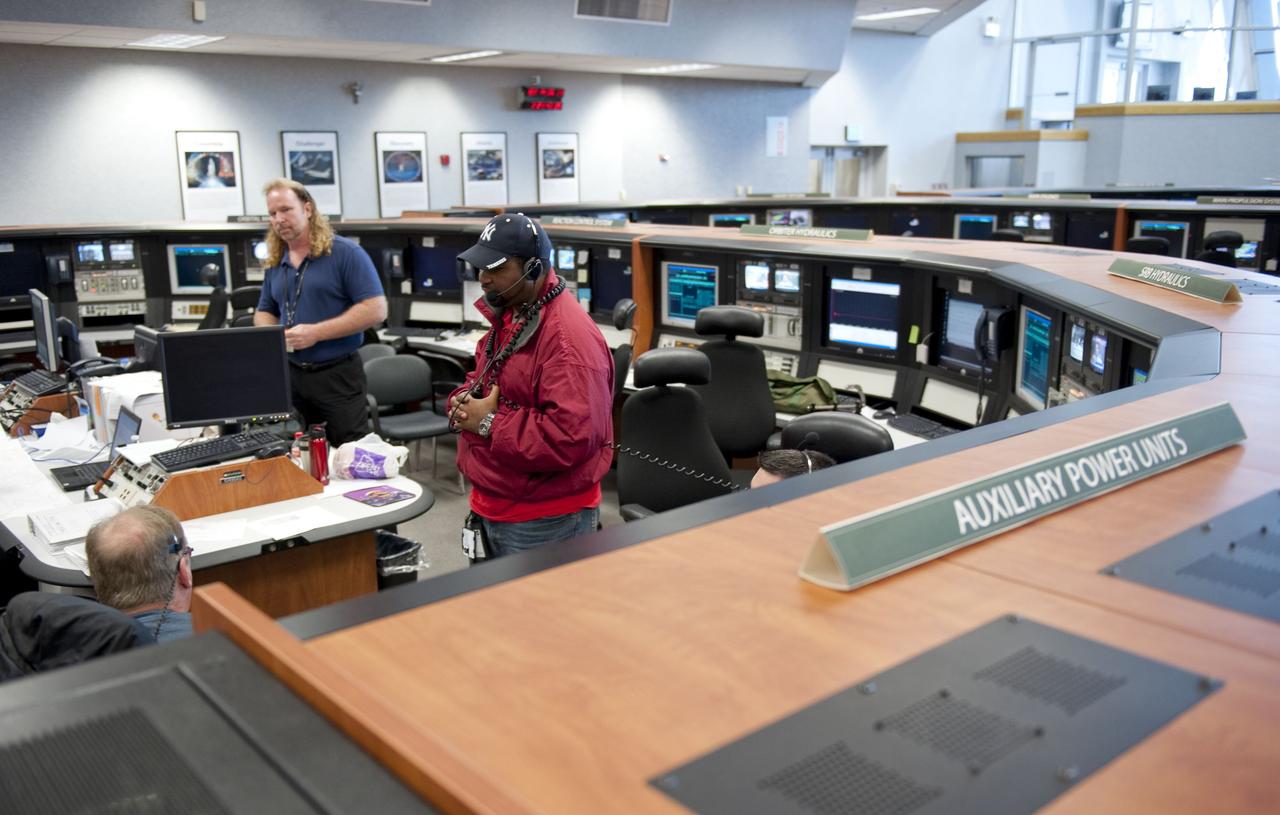

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Control Center, teams monitor the testing of the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) located in space shuttle Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
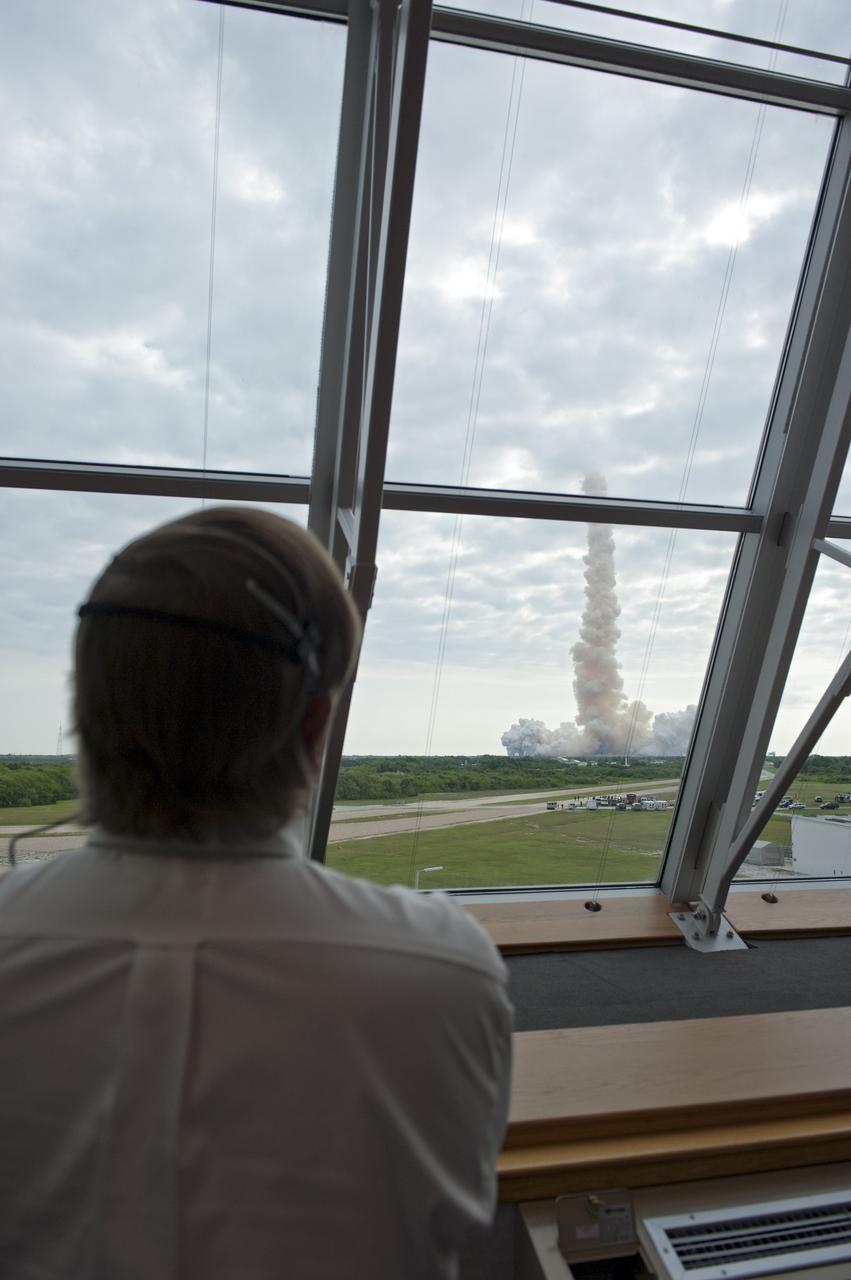

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach watches space shuttle Endeavour soar into space from Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
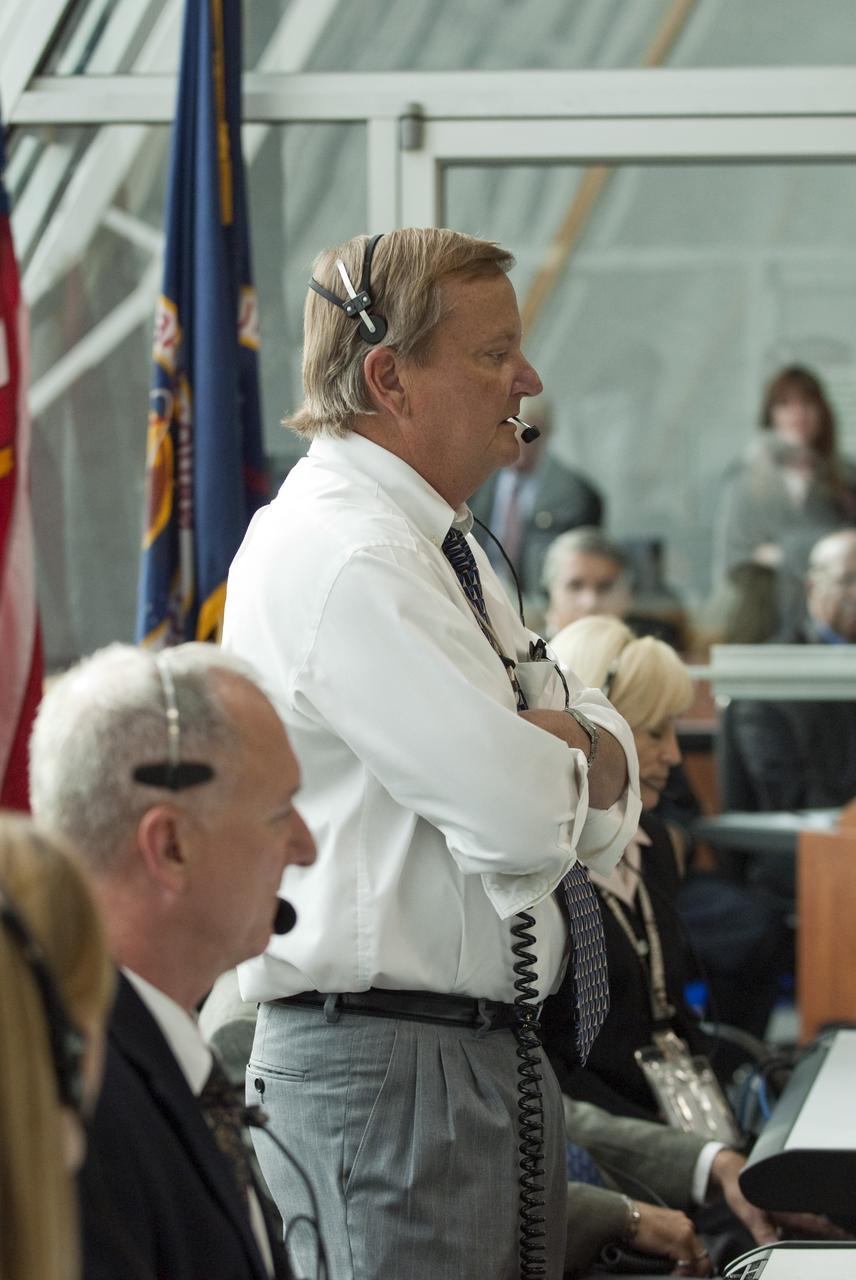

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach, standing, and his launch team monitor the countdown to liftoff of space shuttle Endeavour in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
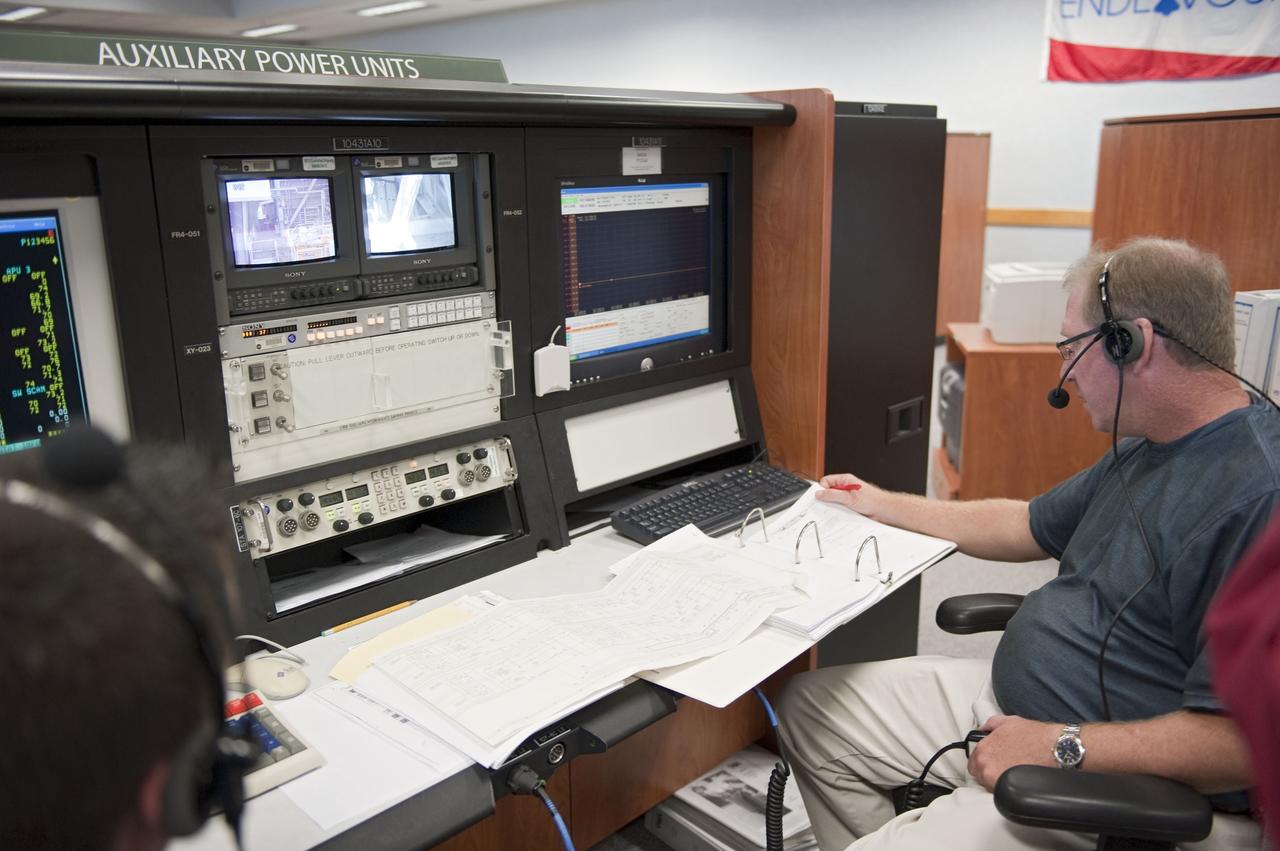

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Control Center, teams monitor the testing of the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) located in space shuttle Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
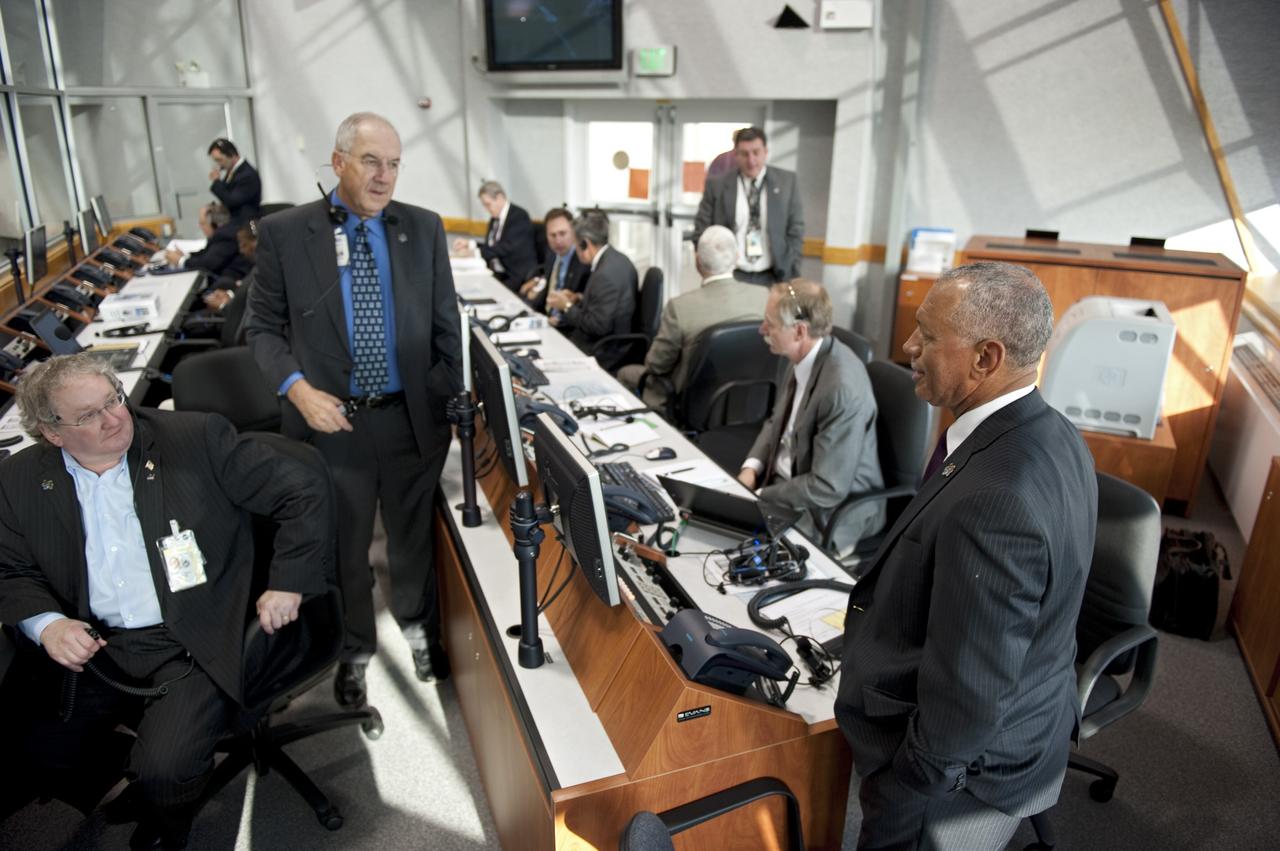

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden, right, monitors the countdown to liftoff of space shuttle Endeavour in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
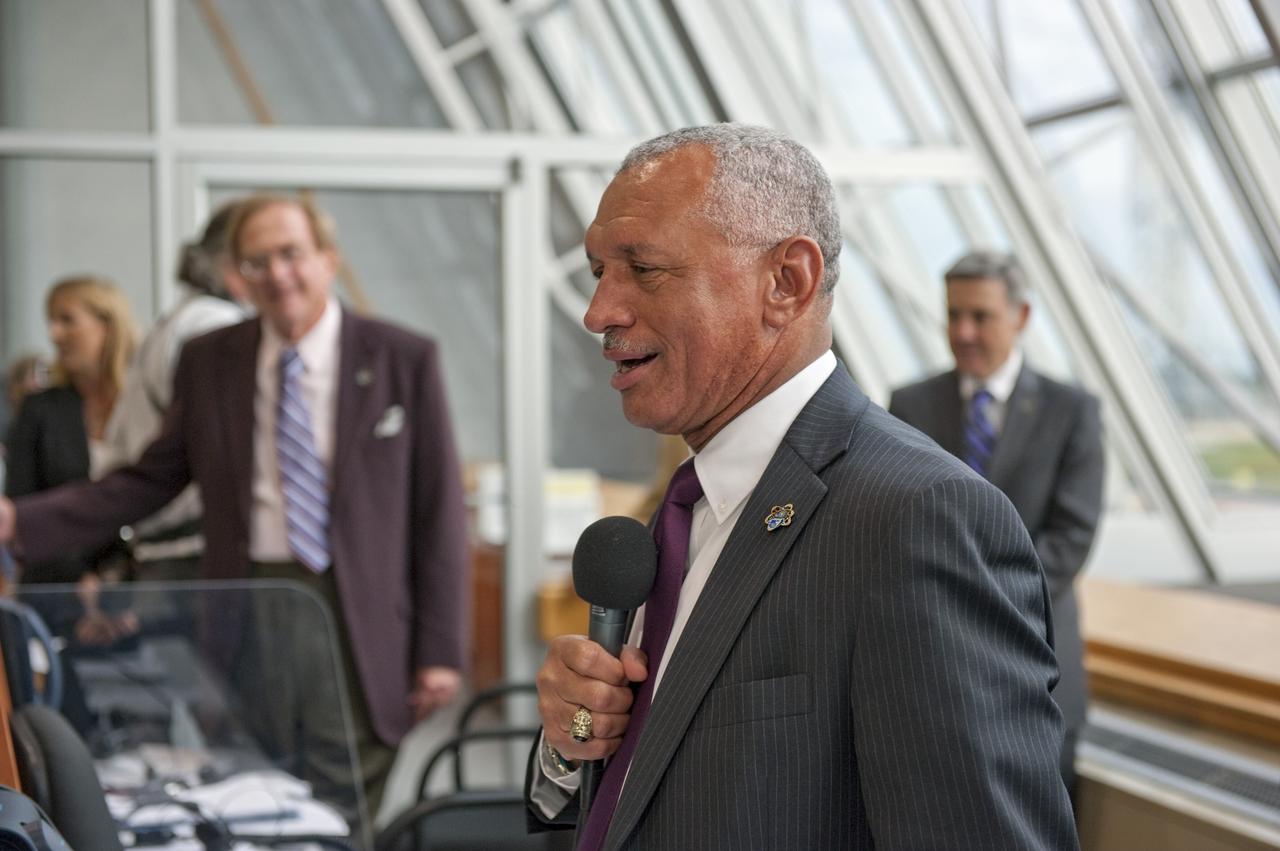

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden congratulates the launch team in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the successful launch of space shuttle Endeavour. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
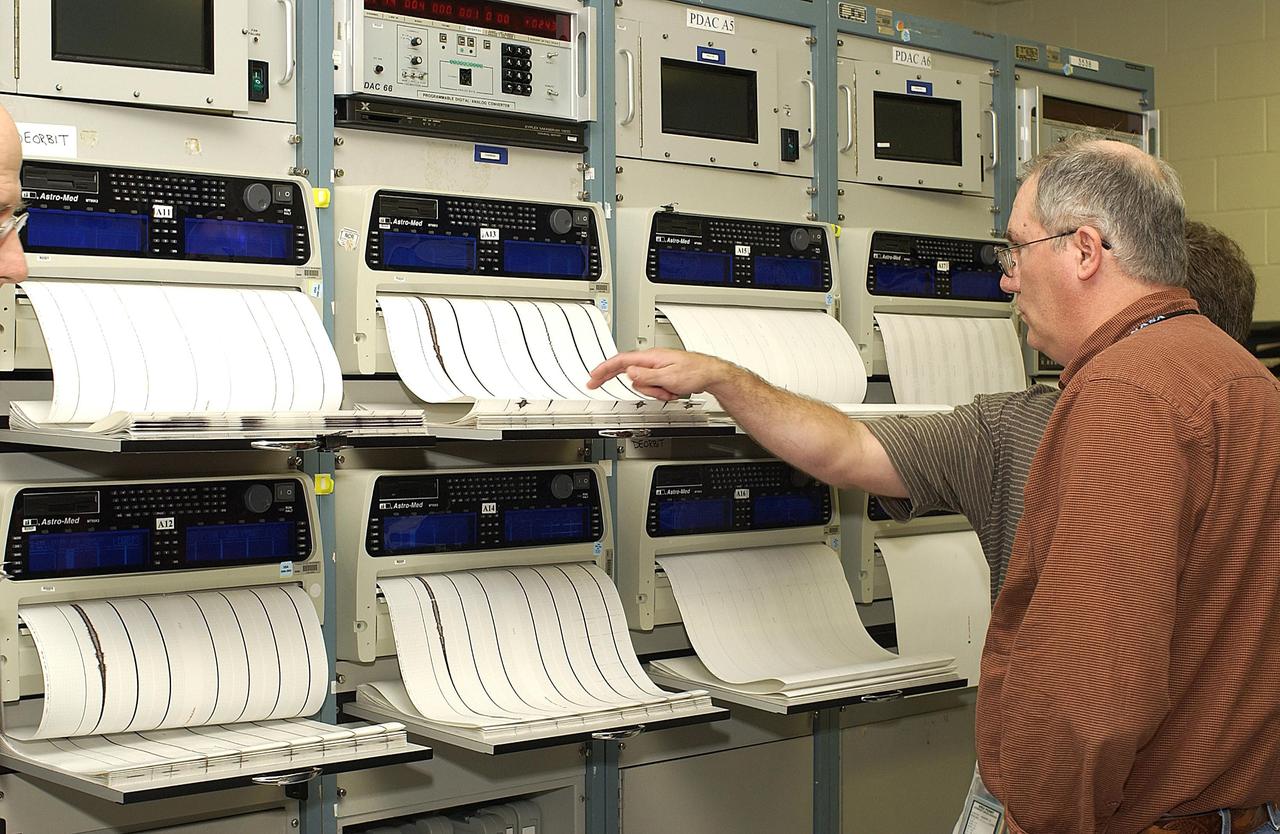

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the KSC Launch Control Center look at the printout from Columbia's Orbiter Experiment Support System (OEX) recorder. After duplication the tape will be reviewed at the Johnson Space Center in Houston and other facilities. No actual sensor data on that tape has been reviewed at this time. Search teams near Hemphill, Texas recovered the recorder, which stores sensor information about temperature, aerodynamic pressure, vibrations and other data from dozens of sensor locations on the orbiter, operating only during launch and re-entry. The OEX uses magnetic tape to record data that is not sent to the ground by telemetry.
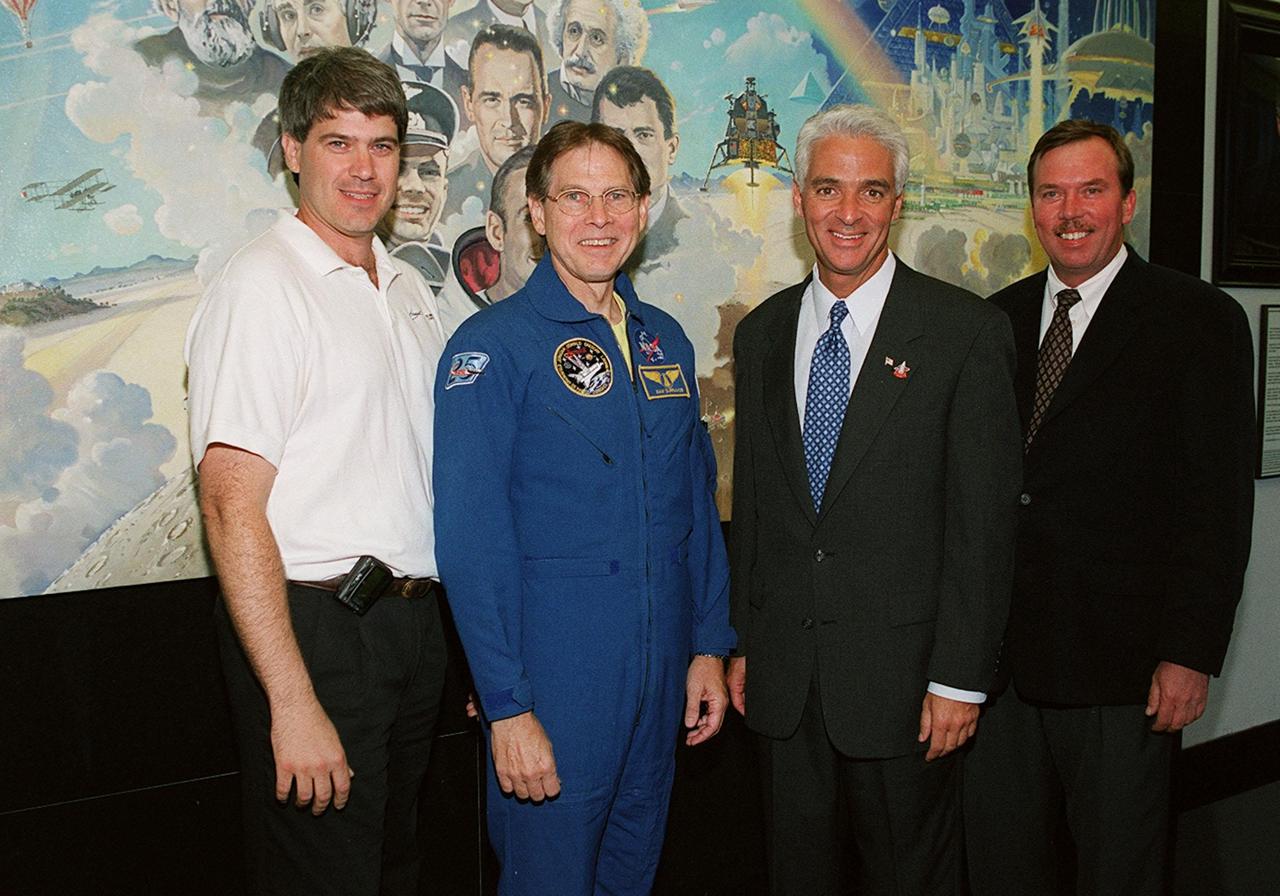

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Astronaut Sam Durrance (second from left) and State Education Commissioner Charlie Crist (third from left) pose with Kevin Brown (left), vice president of Command and Control Technologies, Inc., and Jerry Moyer, of Dynamac (Bionetics) at the Center for Space Education in the KSC Visitor Complex. Crist commemorated the 20th anniversary of the Shuttle program with his visit to watch the launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-100. He and Durrance accompanied students from Ronald McNair Magnet School, Cocoa, Fla., for the launch
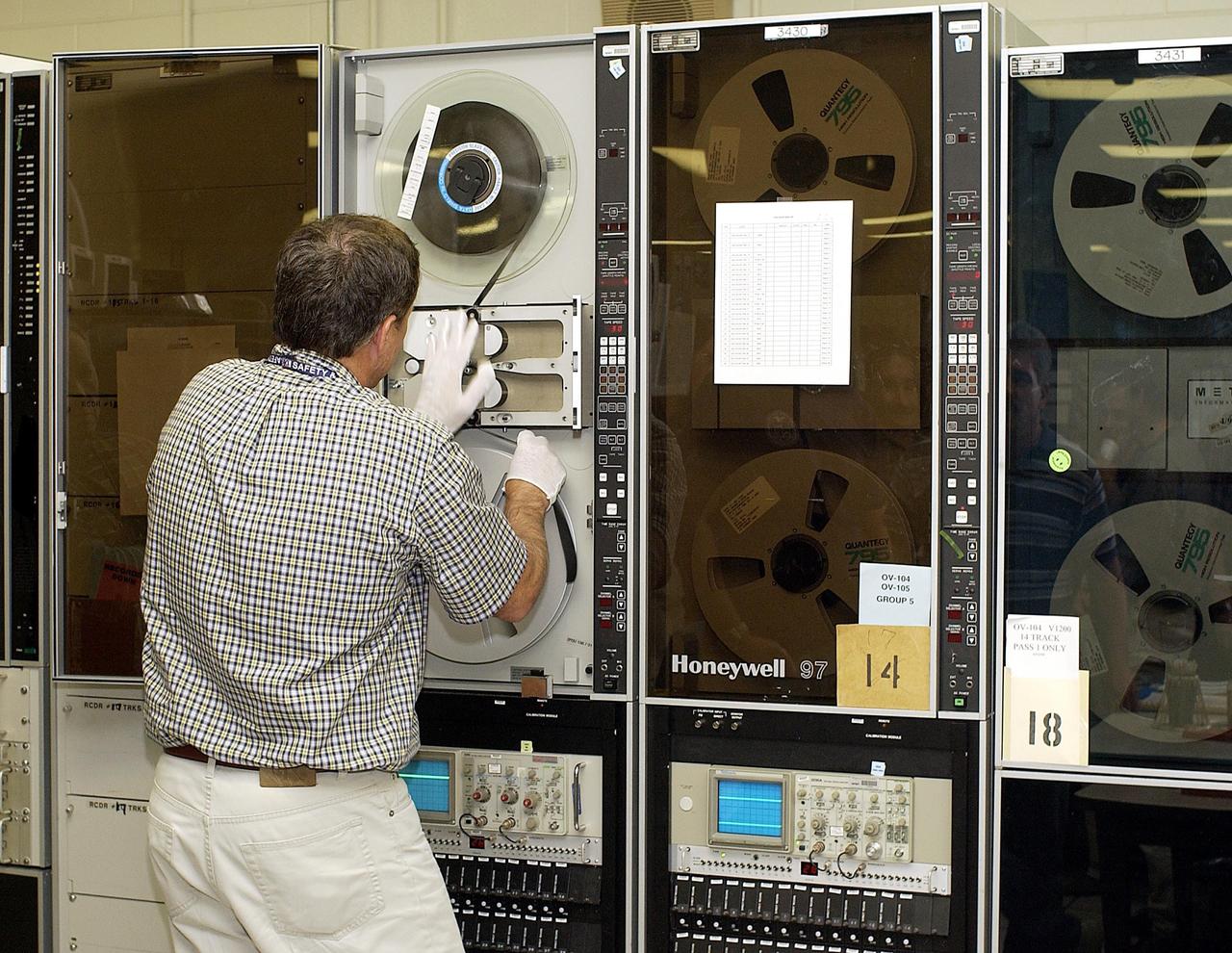

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Columbia's Orbiter Experiment Support System (OEX) recorder is put on taping equipment in the KSC Launch Control Center. The recorder tape is being duplicated and will be reviewed at the Johnson Space Center in Houston and other facilities. No actual sensor data on that tape has been reviewed at this time, Search teams near Hemphill, Texas recovered the recorder, which stores sensor information about temperature, aerodynamic pressure, vibrations and other data from dozens of sensor locations on the orbiter, operating only during launch and re-entry. The OEX uses magnetic tape to record data that is not sent to the ground by telemetry.
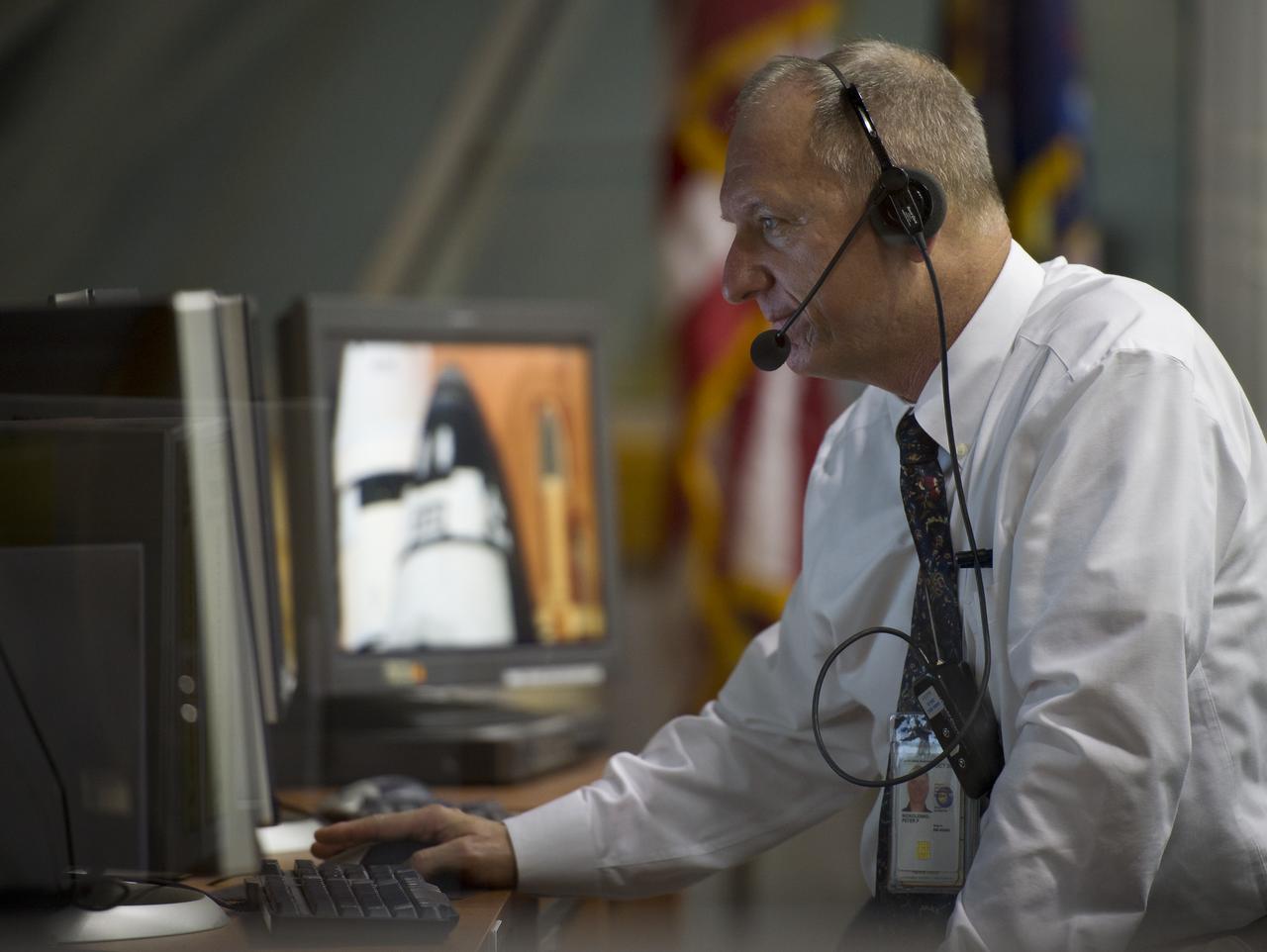

NASA Kennedy Space Center Assistant Launch Director Pete Nickolenko monitors the countdown to the launch of the space shuttle Endeavour (STS-134) from Firing Room Four of the Launch Control Center (LCC), Monday May 16, 2011, at the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Fla. During the mission, Endeavour and the STS-134 crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) and spare parts including two S-band communications antennas, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for Dextre. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
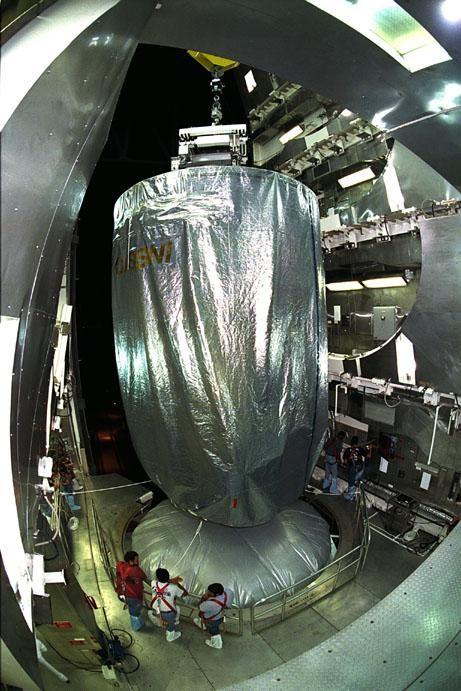

The Cassini spacecraft, covered by an environmentally controlled protective enclosure, is lifted at Launch Complex 40, Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS), in preparation to mate it to the top of its Titan IV/Centaur launch vehicle. Cassini is an international mission conducted by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). The two-story-tall spacecraft, scheduled for launch on Oct. 13, is destined to arrive at Saturn in July 2004, where it will orbit and study Saturn, its rings, moons and magnetic environment in detail over a four-year period. The Cassini mission is managed for NASA's Office of Space Science by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology
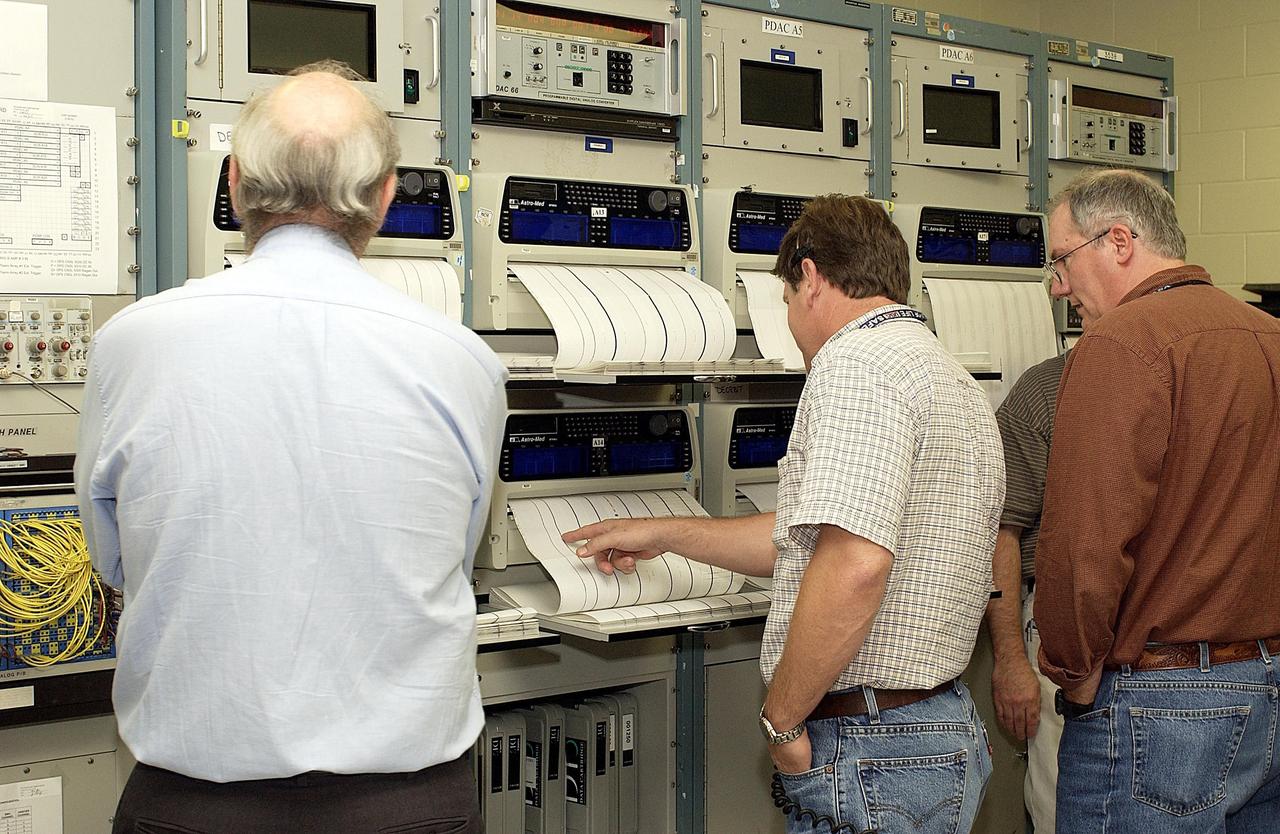

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the KSC Launch Control Center look at the printout from Columbia's Orbiter Experiment Support System (OEX) recorder. After duplication the tape will be reviewed at the Johnson Space Center in Houston and other facilities. No actual sensor data on that tape has been reviewed at this time. Search teams near Hemphill, Texas recovered the recorder, which stores sensor information about temperature, aerodynamic pressure, vibrations and other data from dozens of sensor locations on the orbiter, operating only during launch and re-entry. The OEX uses magnetic tape to record data that is not sent to the ground by telemetry.
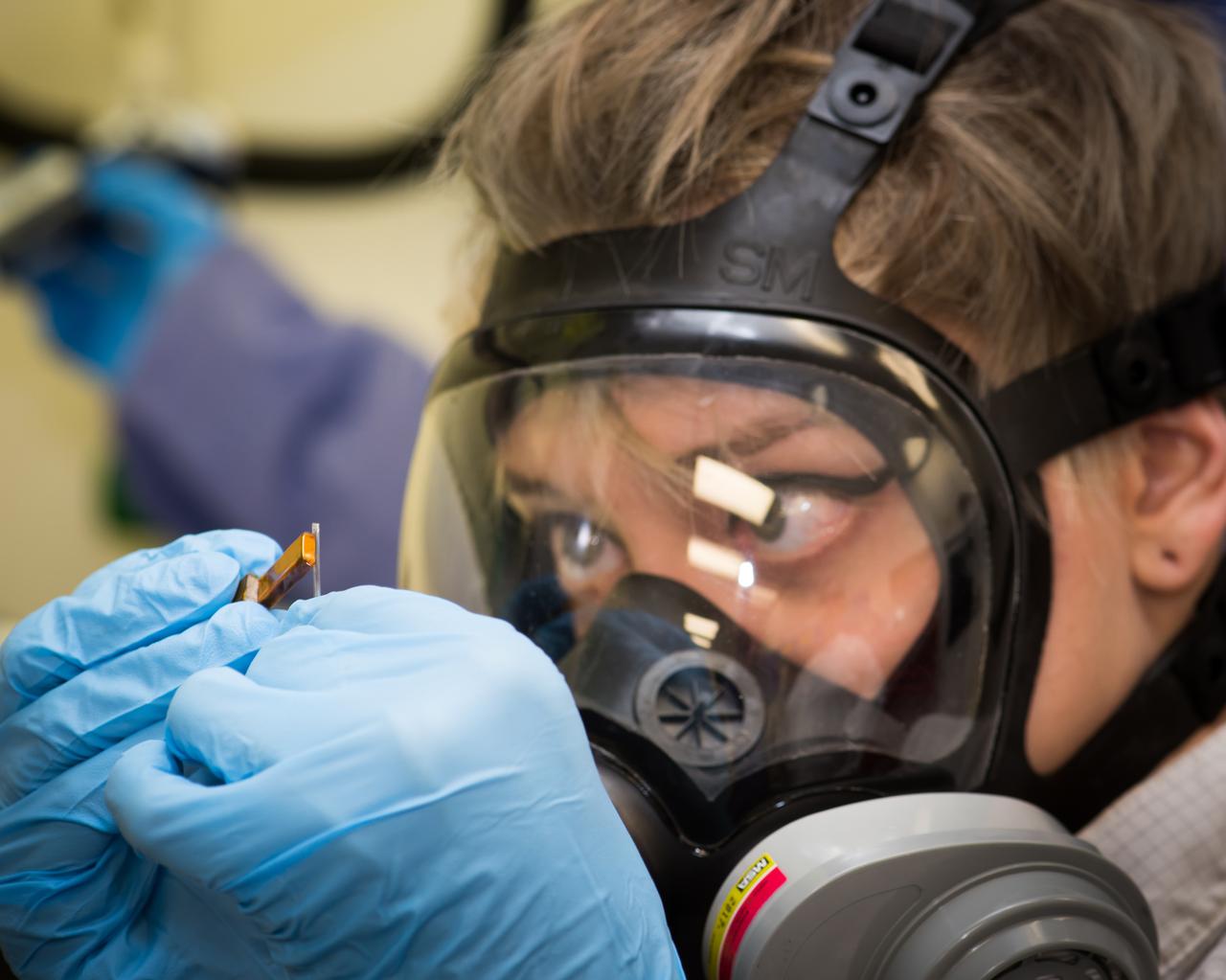

Light Microscopy Modle, LMM, Ground Unit Testing, GU. Control Systems Engineer using a small magnet to maneuver a 1mm metal stir-bar into a colloid sample fluid-filled capillary. The capillary tubes of sample fluid will be filled and sealed. The sample fluid supplied by a Principal Investigator typically contains some hazardous/toxic chemicals that she must ensure will not leak and put the astronauts at risk. On-orbit on the LMM, ‘insitu mixing’ is used, which uses electromagnetic inductors to stimulate the metal stir-bar to mix the fluid within the sealed capillary.
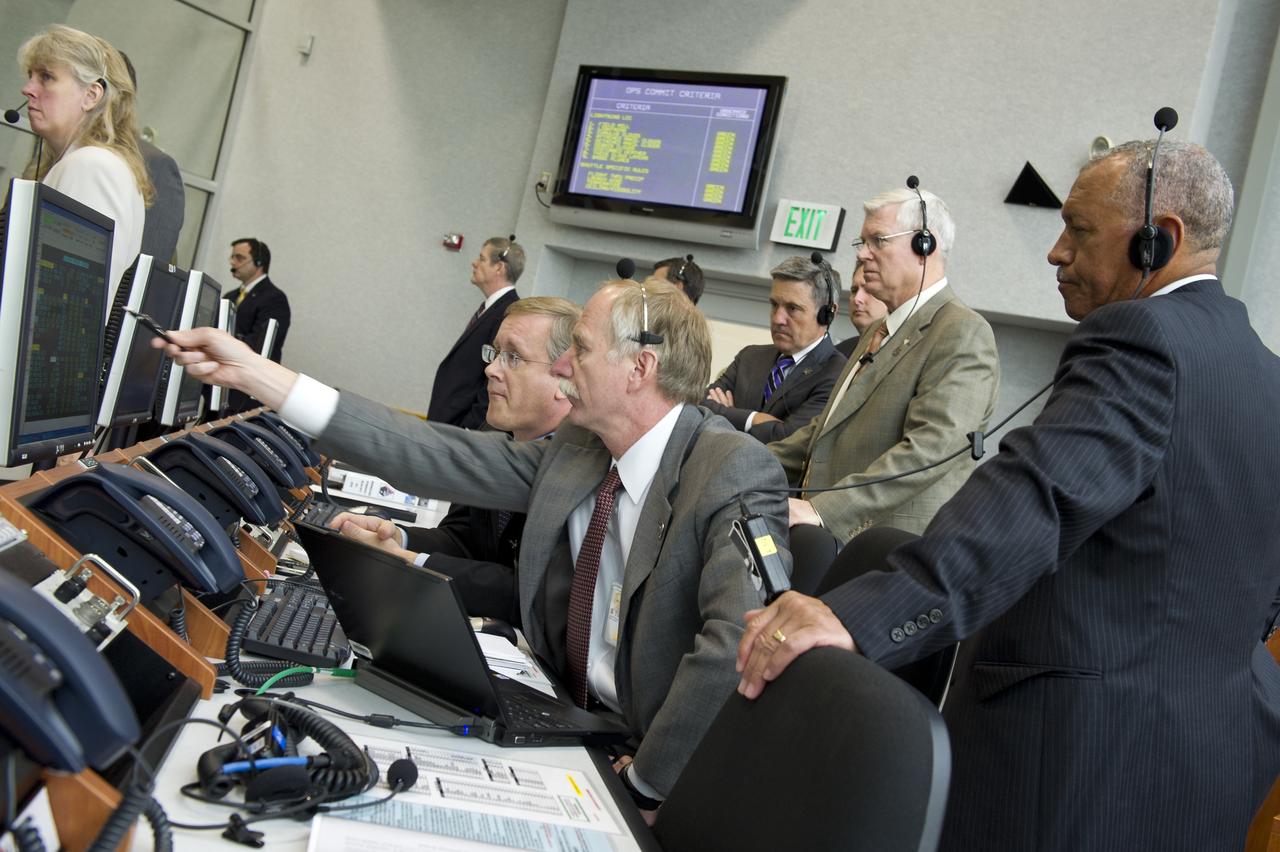

NASA Associate Administrator for Space Operations William Gerstenmaier points to one the monitors in Firing Room Four of the Launch Control Center (LCC) as NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, right, and other NASA managers look on during the launch of the space shuttle Endeavour (STS-134), Monday, May 16, 2011, at Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Fla. During the mission, Endeavour and the STS-134 crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) and spare parts including two S-band communications antennas, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for Dextre. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the KSC Launch Control Center watch the taping operation involving Columbia's Orbiter Experiment Support System (OEX) recorder. After duplication the tape will be reviewed at the Johnson Space Center in Houston and other facilities. No actual sensor data on that tape has been reviewed at this time. Search teams near Hemphill, Texas recovered the recorder, which stores sensor information about temperature, aerodynamic pressure, vibrations and other data from dozens of sensor locations on the orbiter, operating only during launch and re-entry. The OEX uses magnetic tape to record data that is not sent to the ground by telemetry.
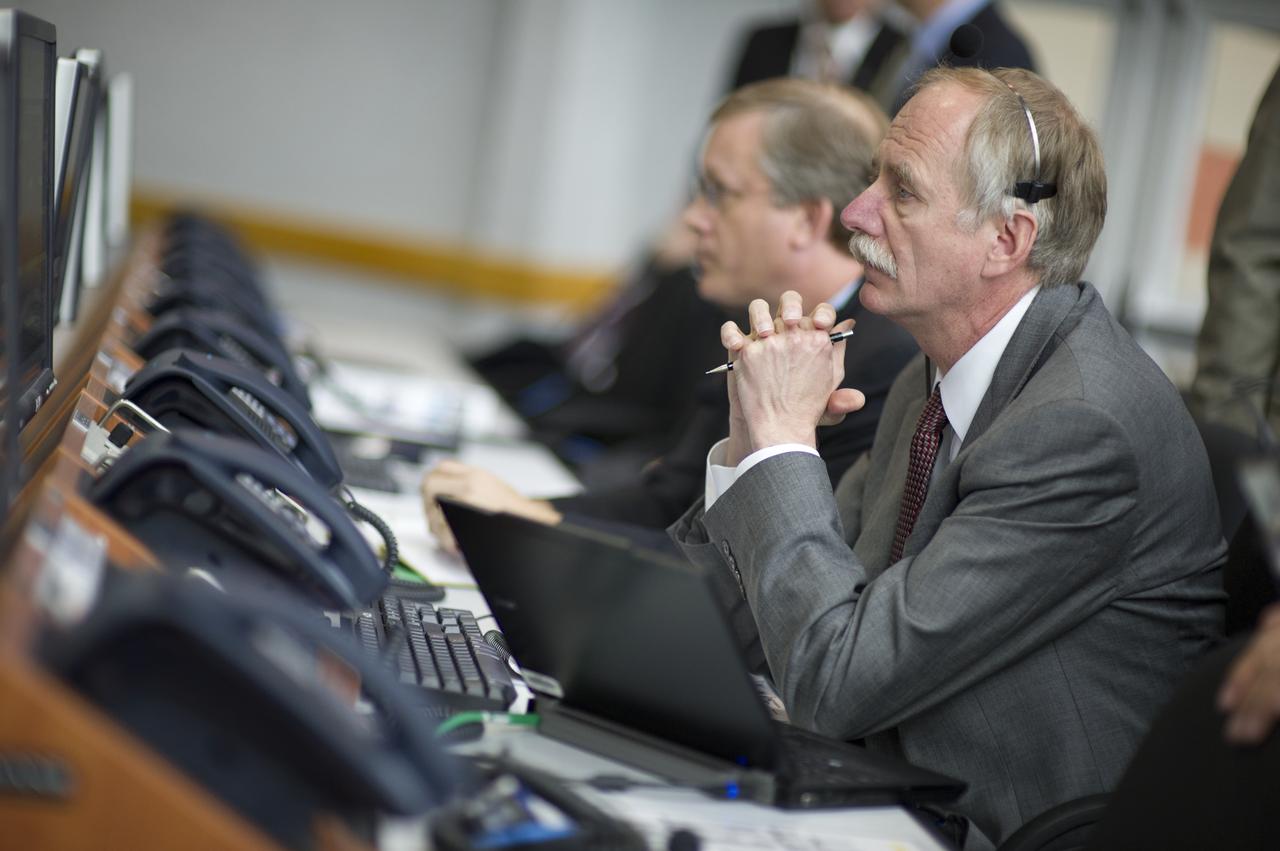

NASA Associate Administrator for Space Operations William Gerstenmaier monitors the countdown to the launch of the space shuttle Endeavour (STS-134) from Firing Room Four of the Launch Control Center (LCC), Monday, May 16, 2011, at Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Fla. During the mission, Endeavour and the STS-134 crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) and spare parts including two S-band communications antennas, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for Dextre. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
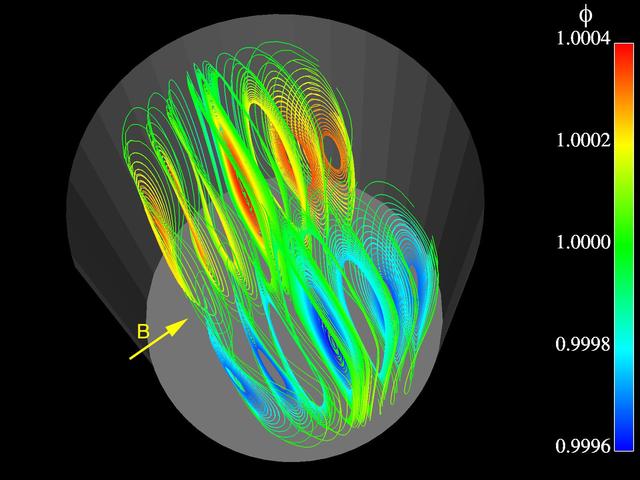
Advanced finite element models are used to study three-dimensional, time-dependent flow and segregation in crystal growth systems. In this image of a prototypical model for melt and crystal growth, pathlines at one instant in time are shown for the flow of heated liquid silicon in a cylindrical container. The container is subjected to g-jitter disturbances along the vertical axis. A transverse magnetic field is applied to control them. Such computations are extremely powerful for understanding melt growth in microgravity where g-jitter drives buoyant flows. The simulation is part of the Theoretical Analysis of 3D, Transient Convection and Segregation in Microgravity Bridgman Crystal Growth investigation by Dr. Jeffrey J. Derby of the University of Mirnesota, Minneapolis.
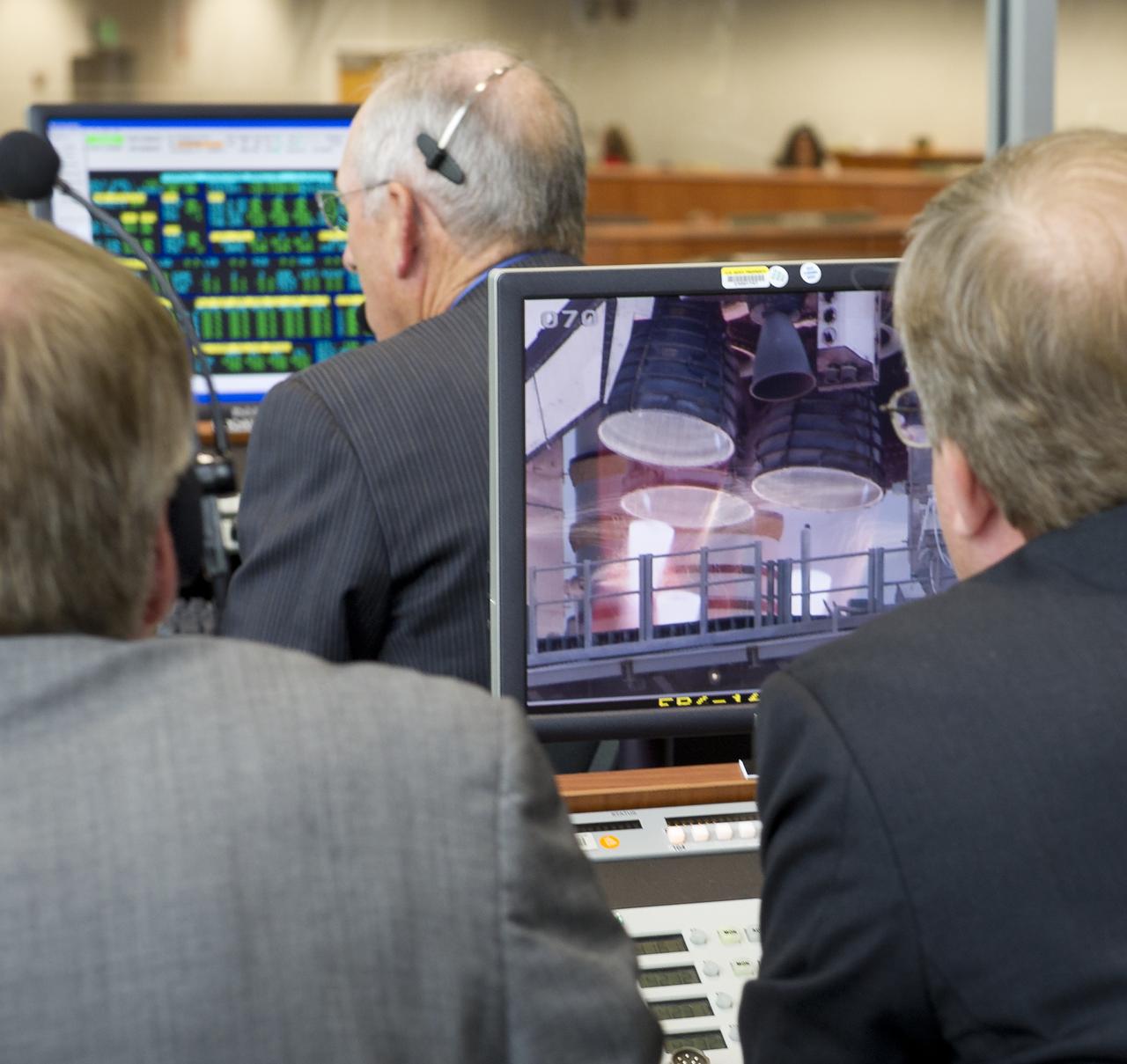

NASA officials in Firing Room Four of the NASA Kennedy Space Center Launch Control Center (LCC) monitor space shuttle Endeavour (STS-134) as it launches Monday, May 16, 2011, from Cape Canaveral, Fla. During the 16-day mission, Endeavour, with Commander Mark Kelly, Pilot Gregory H. Johnson, Mission Specialists Michael Fincke, Greg Chamitoff, Andrew Feustel and European Space Agency astronaut Robert Vittori will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) and spare parts including two S-band communications antennas, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for Dextre. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
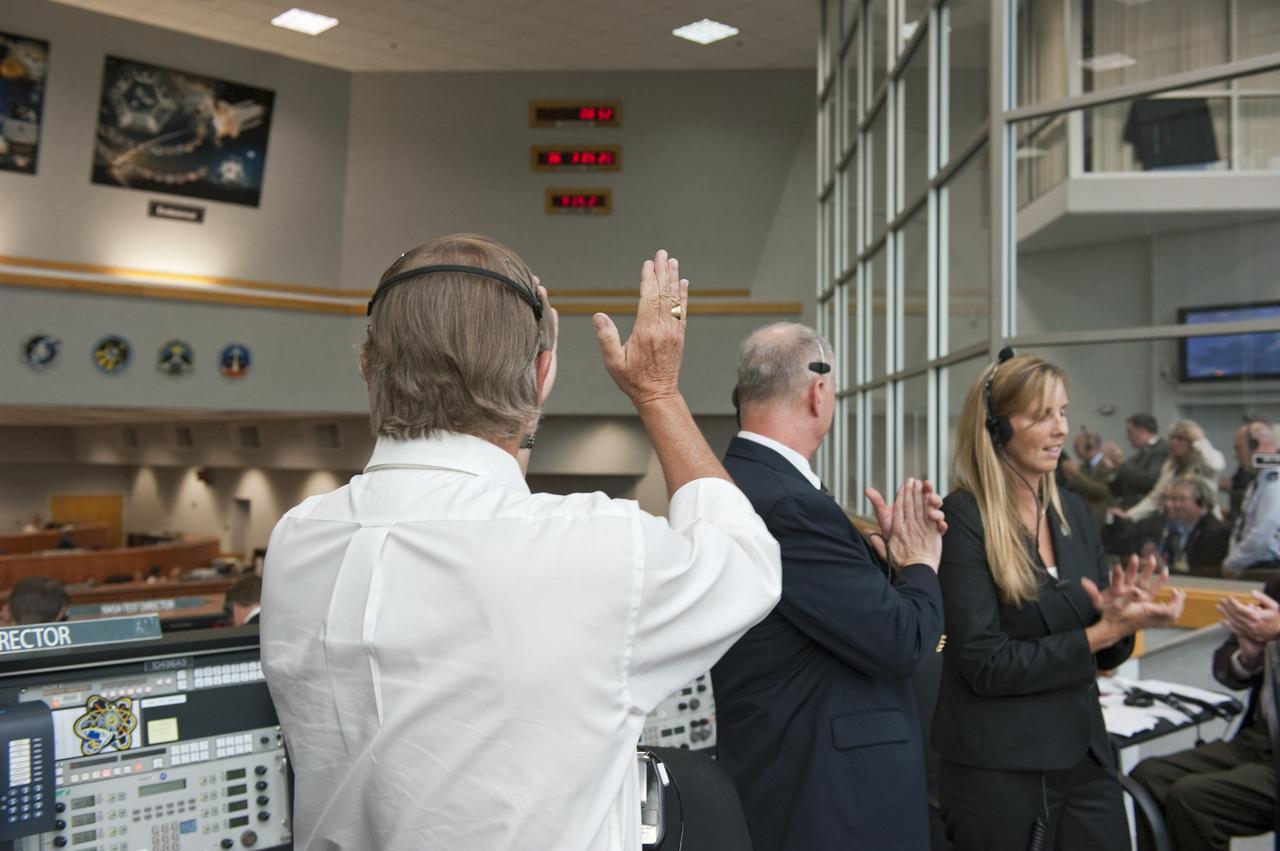

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach, left, STS-134 Assistant Launch Director Pete Nickolenko and Endeavour's NASA Flow Director Dana Hutcherson give a round of applause to the launch controllers in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
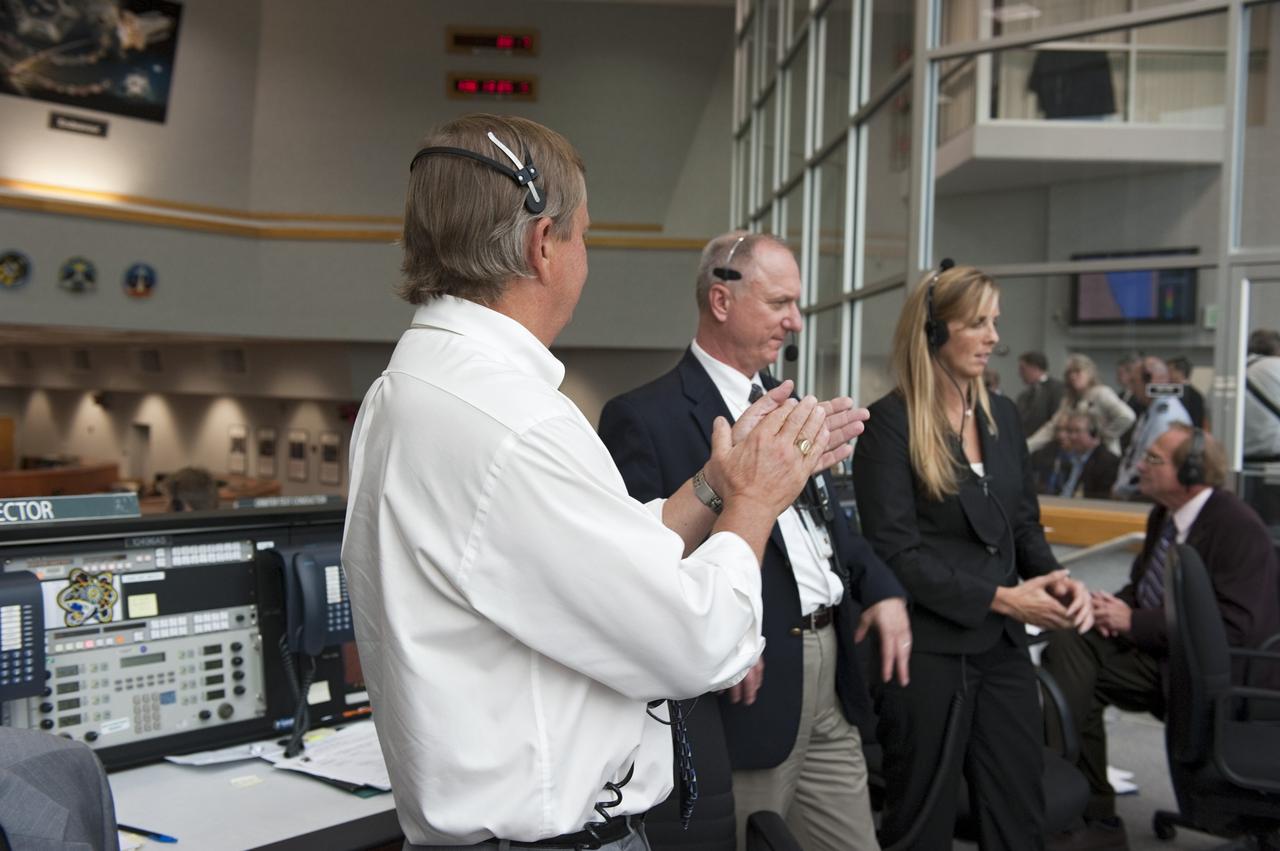

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach, left, STS-134 Assistant Launch Director Pete Nickolenko and Endeavour's NASA Flow Director Dana Hutcherson give a round of applause to the launch controllers in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
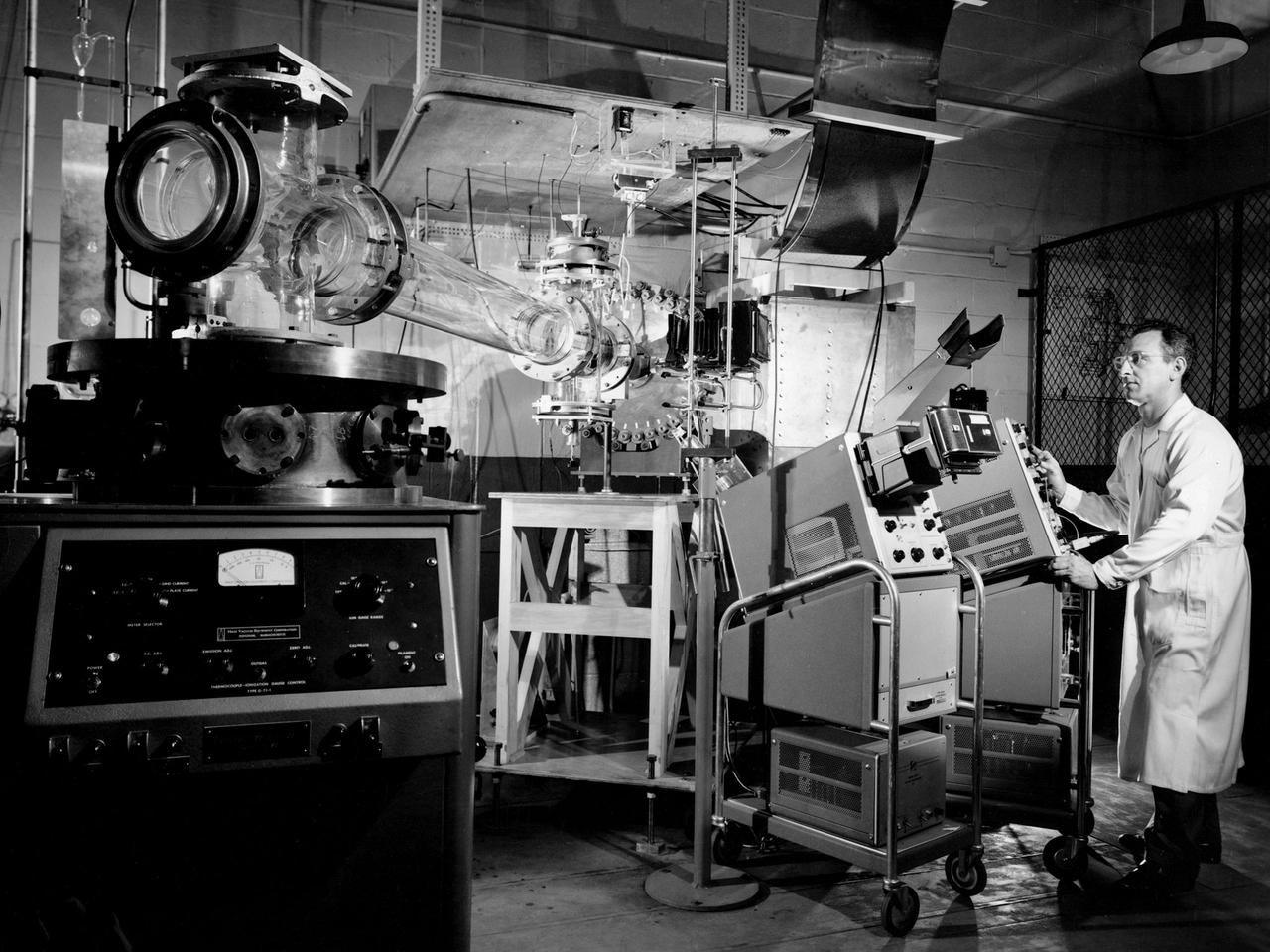

Researcher Charles Michels operates a coaxial plasma gun rig in Cell SW-13 of the Engine Research Building at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. From 1962 to 1967 NASA Lewis investigated coaxial plasma guns powered by conventional capacitor banks. The studies were part of a larger effort to identify electromagnetic accelerators for space propulsion. NASA worked with General Dynamics, General Electric, General Motors, and Republic Aviation on the project. NASA Lewis conducted a research program to determine which factors influenced the coaxial gun’s efficiency and analyze the acceleration process. The system had not previously been used for propulsion applications. The single-shot gun’s fast gas valve and capacitor banks with variable-delay ignition source permitted the evaluation of gun performance under controllable propellant quantity and distribution conditions. The coaxial plasma gun was the most basic type of electromagnetic accelerator. It included a charged capacitor in series with a pair of coaxial electrodes. An electrical breakdown occurred when gas was admitted to the inter-electrode region. The gas instantly became a good conductor and formed a conducting sheet that separated the magnetic field from the open region beyond. The highly-conducting gas was basically expelled by the force of the magnetic pressure. This type of thruster could operate at the high instantaneous power levels without decreasing its average power level.
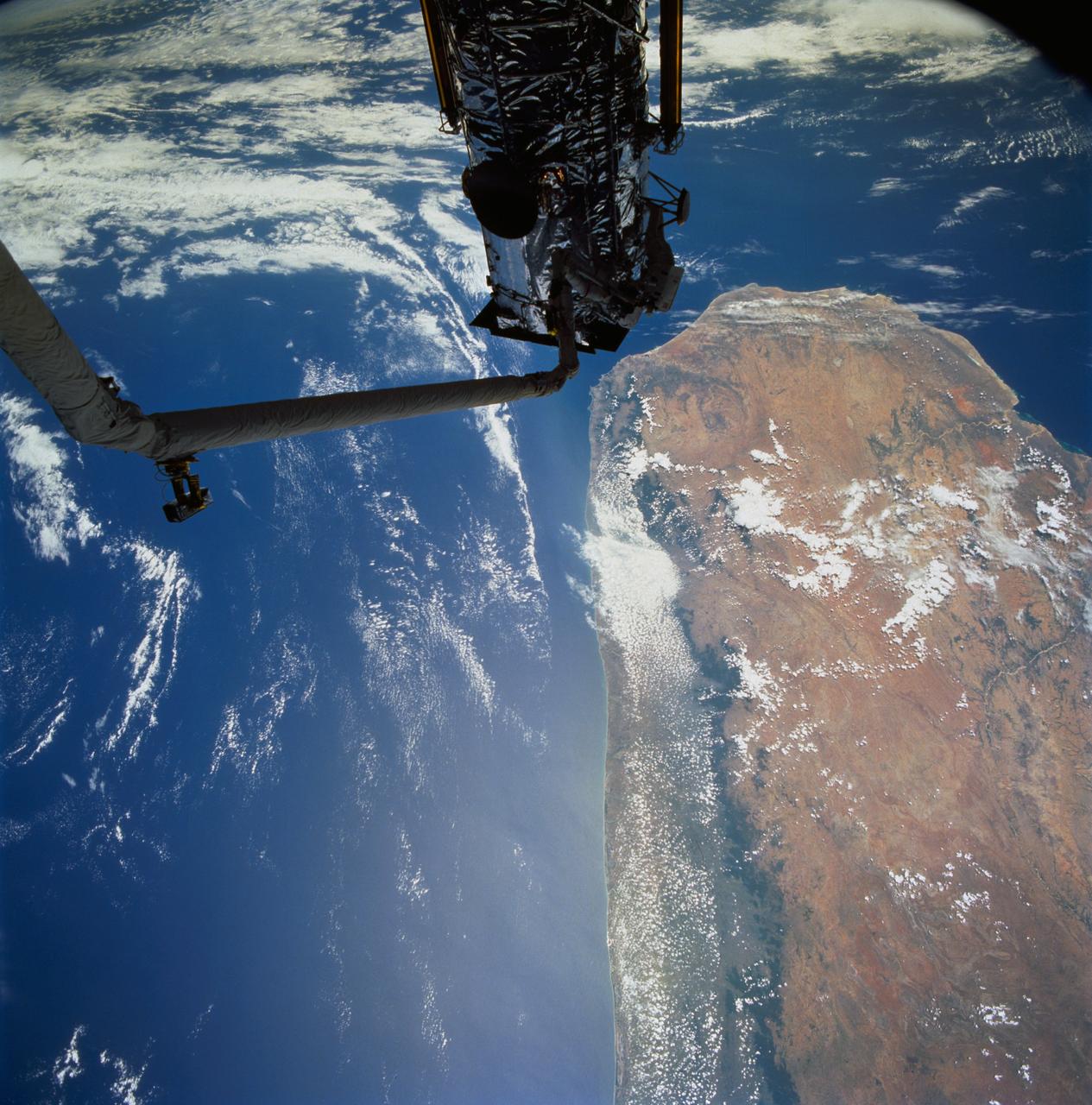

STS061-77-102 (7 Dec 1993) --- Astronauts Jeffrey A. Hoffman (left) and F. Story Musgrave are partially silhouetted against the Indian Ocean as they work to install the Magnetic Sensing System (MSS) on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Musgrave is anchored to the end of the Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm. The HST is positioned along the southern end of Madagascar, 325 nautical miles away. Visible on the western coast are the sediment laden Onilahy and Fiherenana Rivers which empty into Saint Augustin Bay. North of Fiherenana River is the Mangoky River. The circular feature on the southern end of Madagascar and to the right of HST is the L'ivakoany Mountains. The eastern coast is relatively straight compared to the western coast.
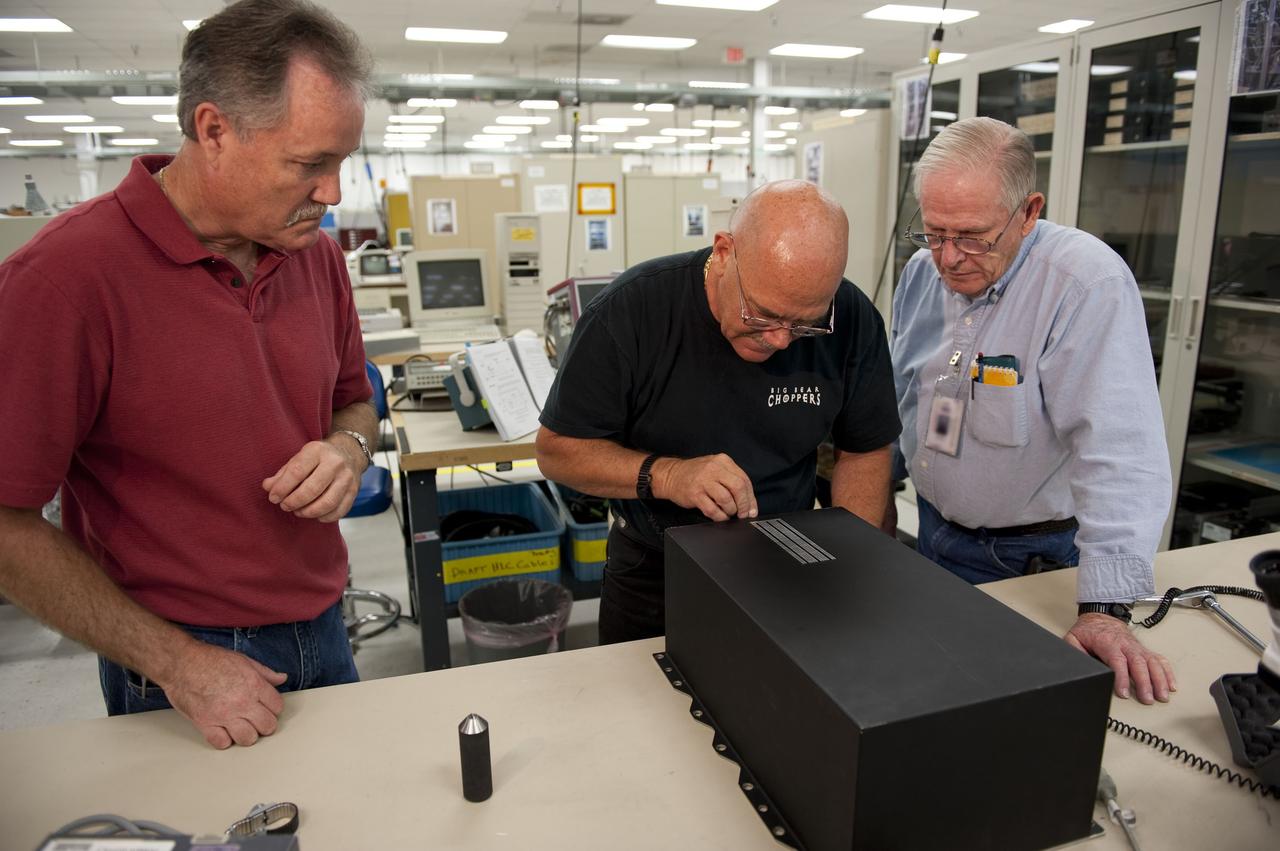

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the NASA Shuttle Logistics Depot in Cape Canaveral, Florida, technicians remove the cover on the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) to begin the testing process. Located in space shuttle Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The LCA-2 will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
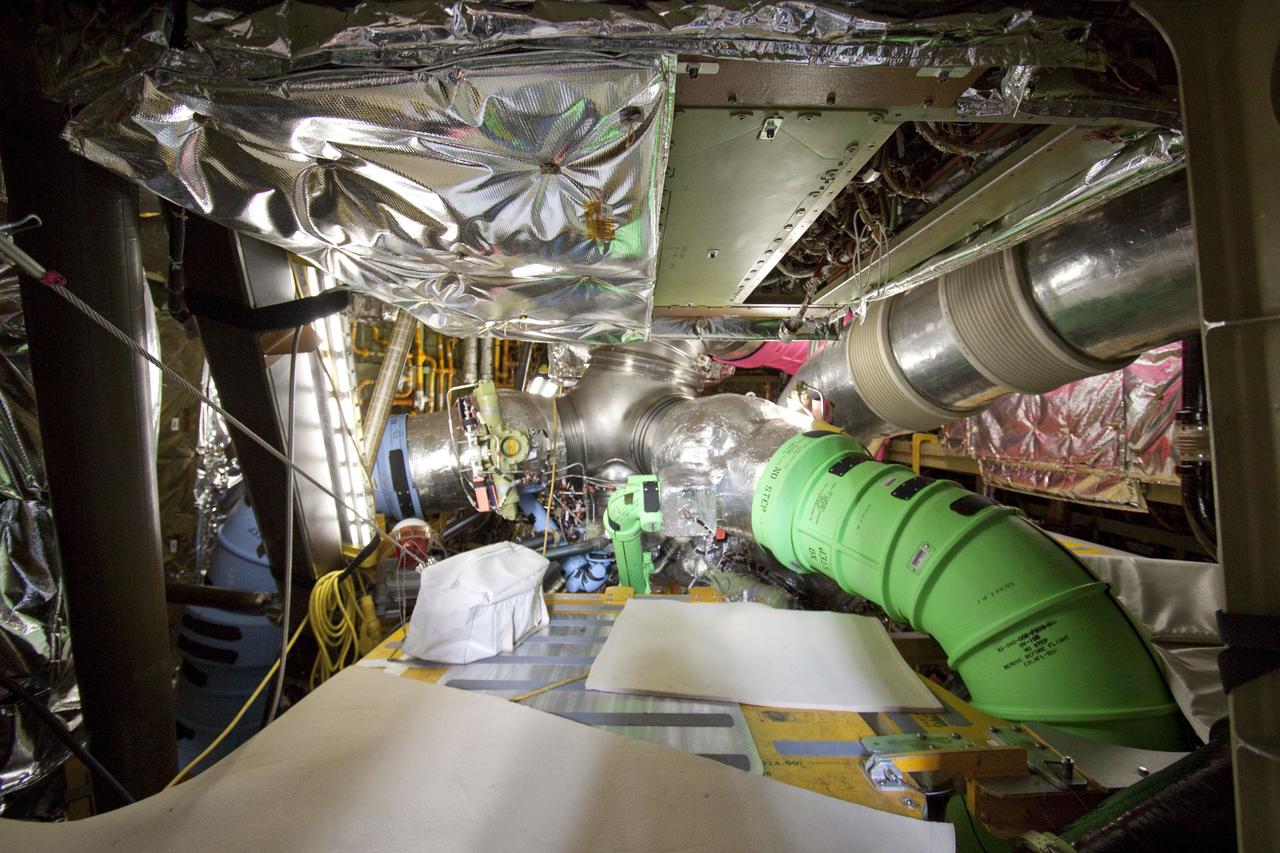

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) has been replaced inside of space shuttle Endeavour. Located in Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission and has been replaced. Systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
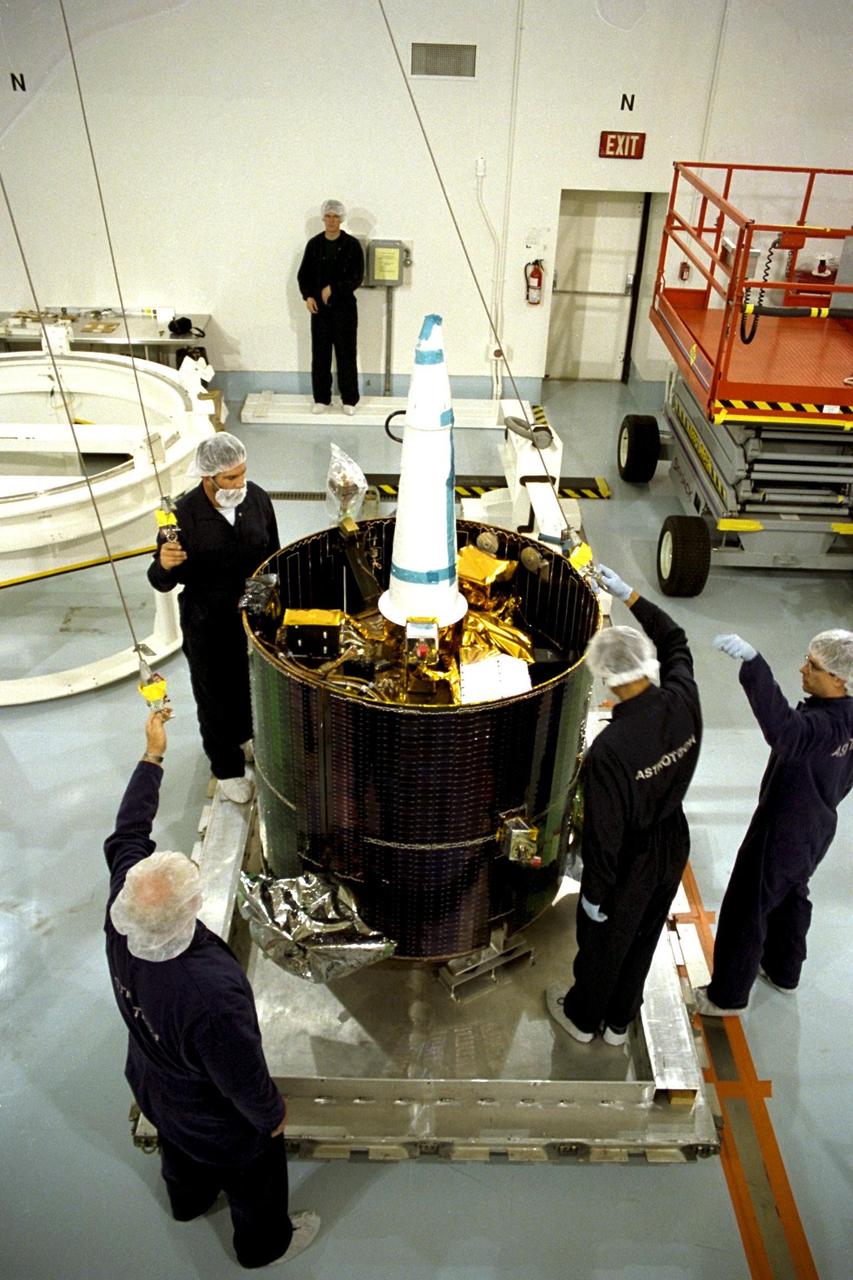

NASA's Lunar Prospector is taken out of its crate at Astrotech, a commercial payload processing facility, in Titusville, Fla. The small robotic spacecraft, to be launched for NASA on an Athena 2 rocket by Lockheed Martin, is designed to provide the first global maps of the Moon's surface compositional elements and its gravitational and magnetic fields. While at Astrotech, Lunar Prospector will be fueled with its attitude control propellant and then mated to a Trans-Lunar Injection Stage which is a solid propellant upper stage motor. The combination will next be spin tested to verify proper balance, then encapsulated into an Athena nose fairing. Then the Lunar Prospector will be transported from Astrotech to Cape Canaveral Air Station and mated to an Athena rocket. The launch of Lunar Prospector is scheduled for Jan. 5, 1998 at 8:31 p.m
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden talks to a crowd of spectators gathered at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to watch the launch of space shuttle Endeavour. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kurtis Korwan
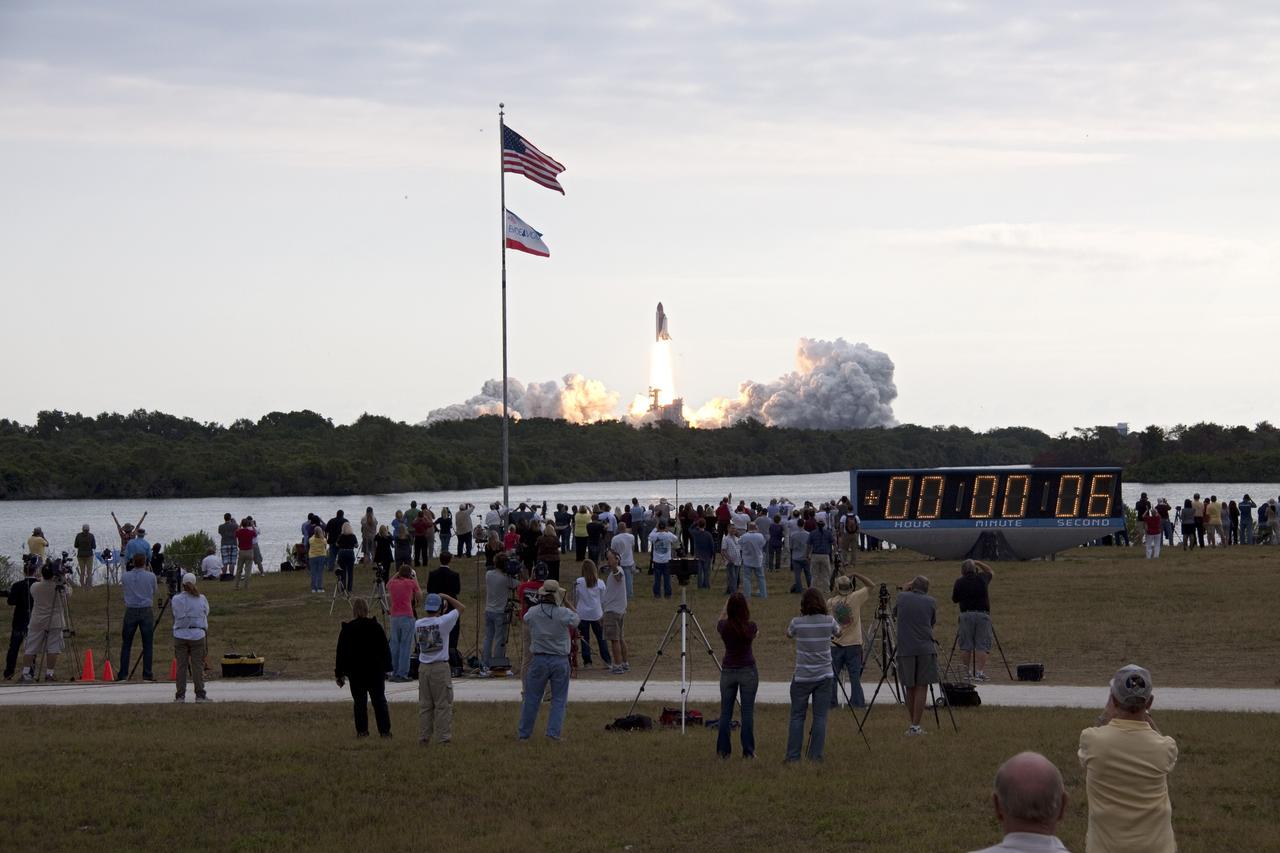

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The American flag sways in the breeze as space shuttle Endeavour launches on the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The shuttle and its six-member crew lifted off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. STS-134 will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). STS-134 will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
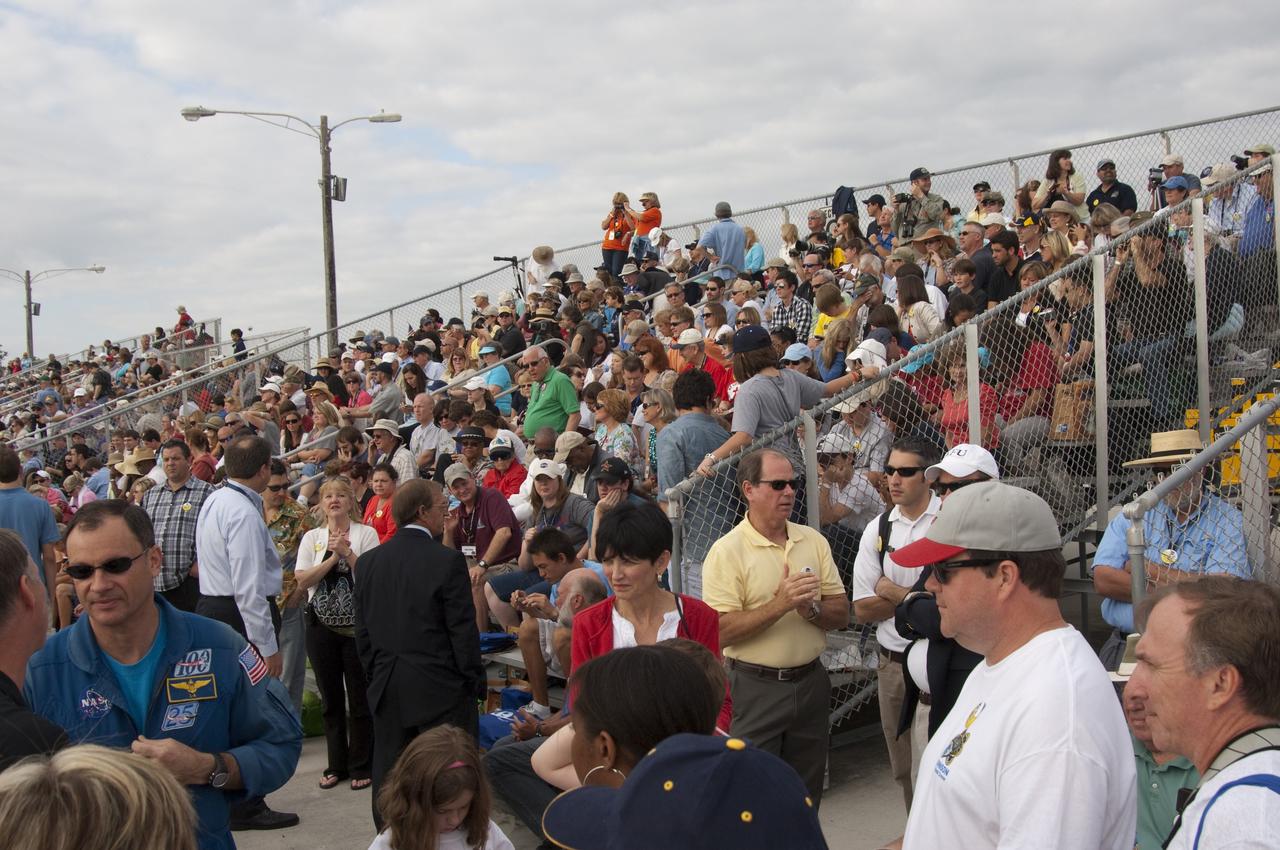

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Spectators at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida await the liftoff of space shuttle Endeavour. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the NASA Shuttle Logistics Depot in Cape Canaveral, Florida, technicians remove the cover on the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) to begin the testing process. Located in space shuttle Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The LCA-2 will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, a worker inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section removes a cover to provide access for the removal and replacement of the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.

The Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) Electro-Magnetic Interference (EMI) & Electrical Ground Support Equipment (EGSE) Team pose in the control room. From this room, they are able to analyze the data from the test remotely and send commands through electrical cables that run through the walls into the EMI lab. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
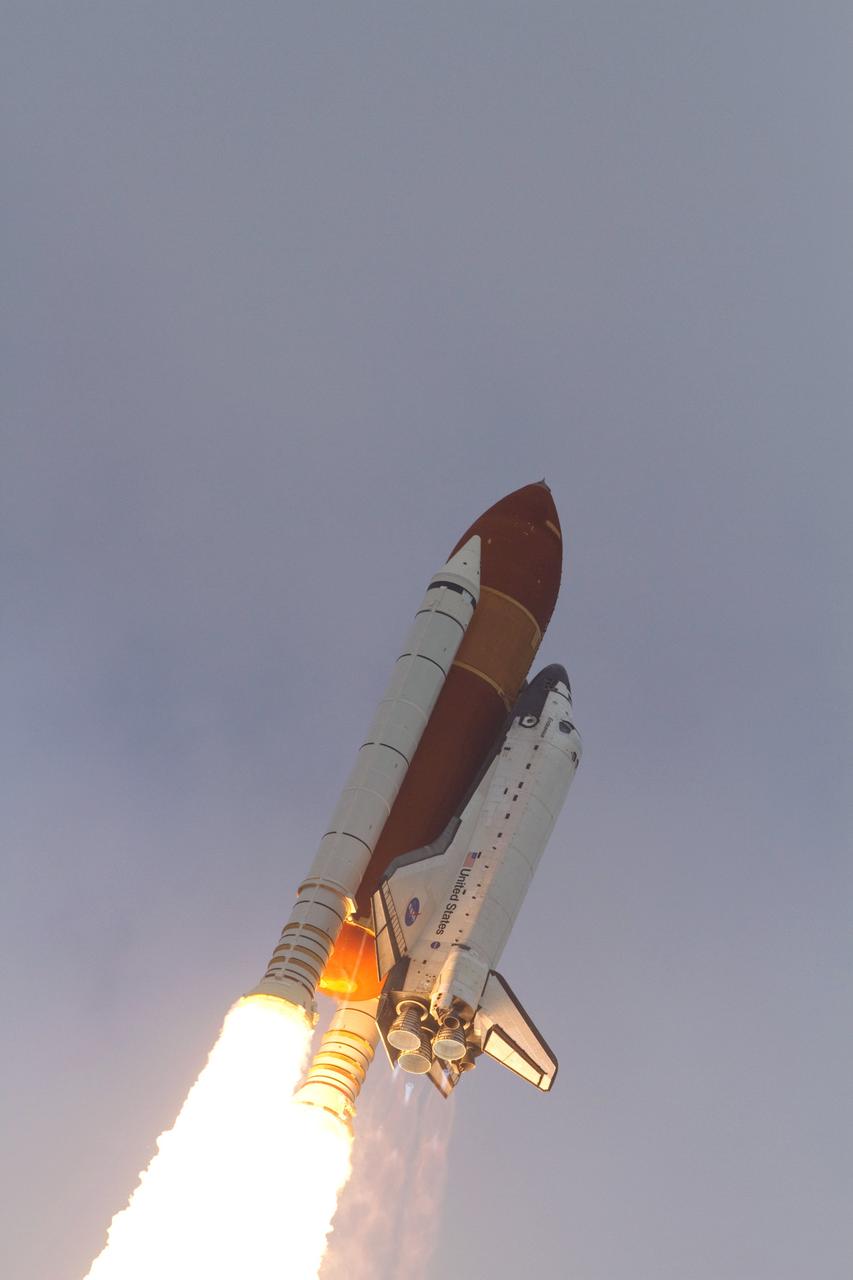

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising on twin columns of fire, space shuttle Endeavour lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida beginning its final flight, the STS-134 mission, to the International Space Station. Launch was on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. STS-134 and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) is removed from inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The assembly will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
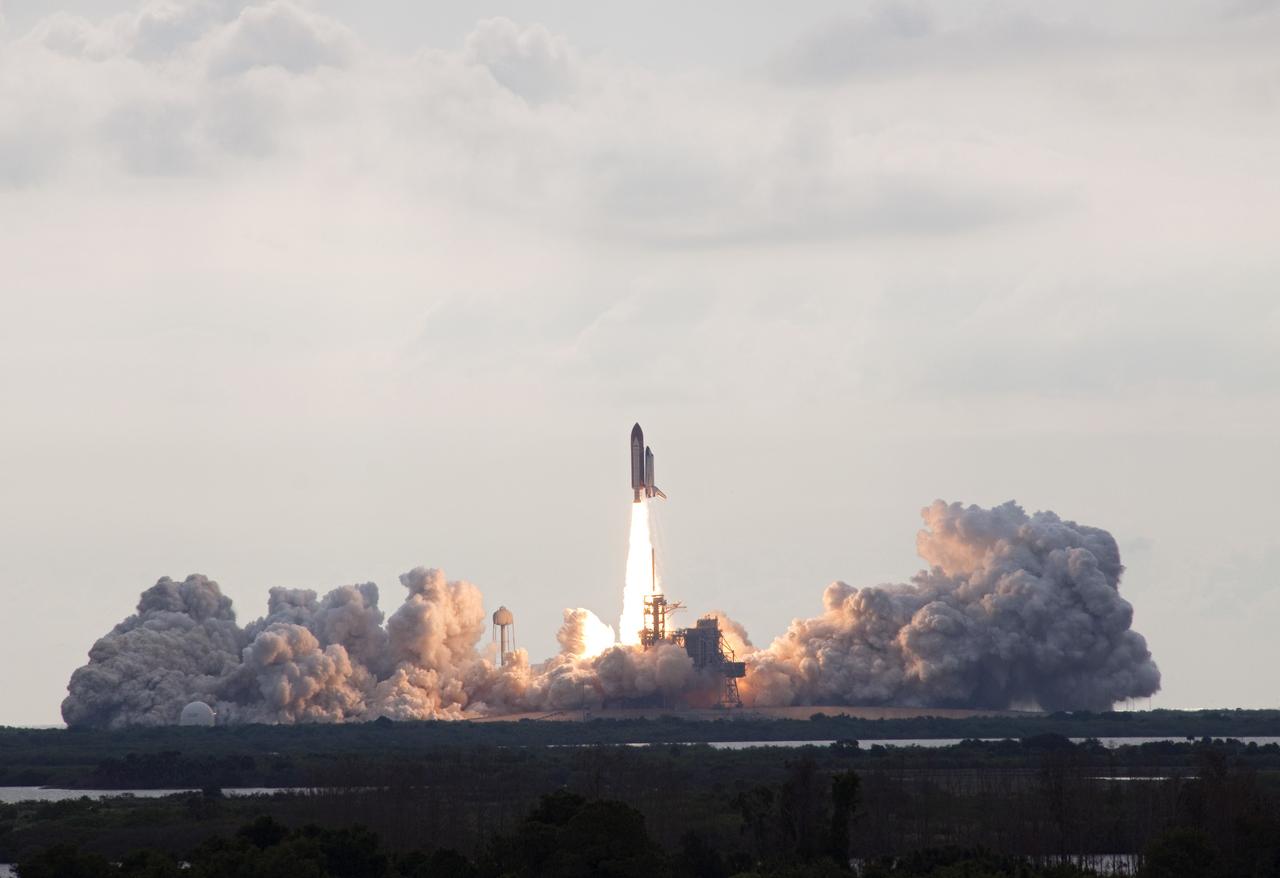

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Kicking up a trail of smoke and steam, space shuttle Endeavour lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station, on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
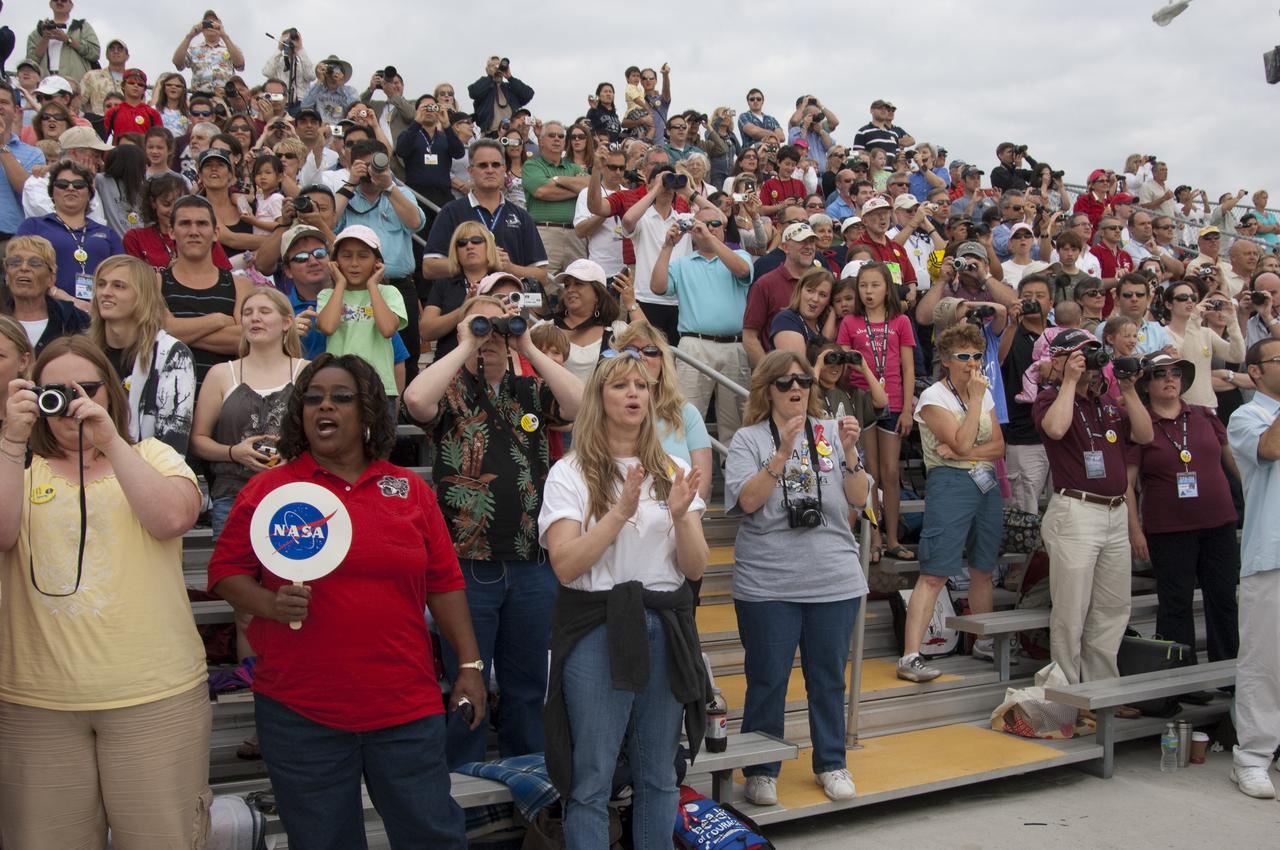

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Spectators at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as space shuttle Endeavour soars skyward. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
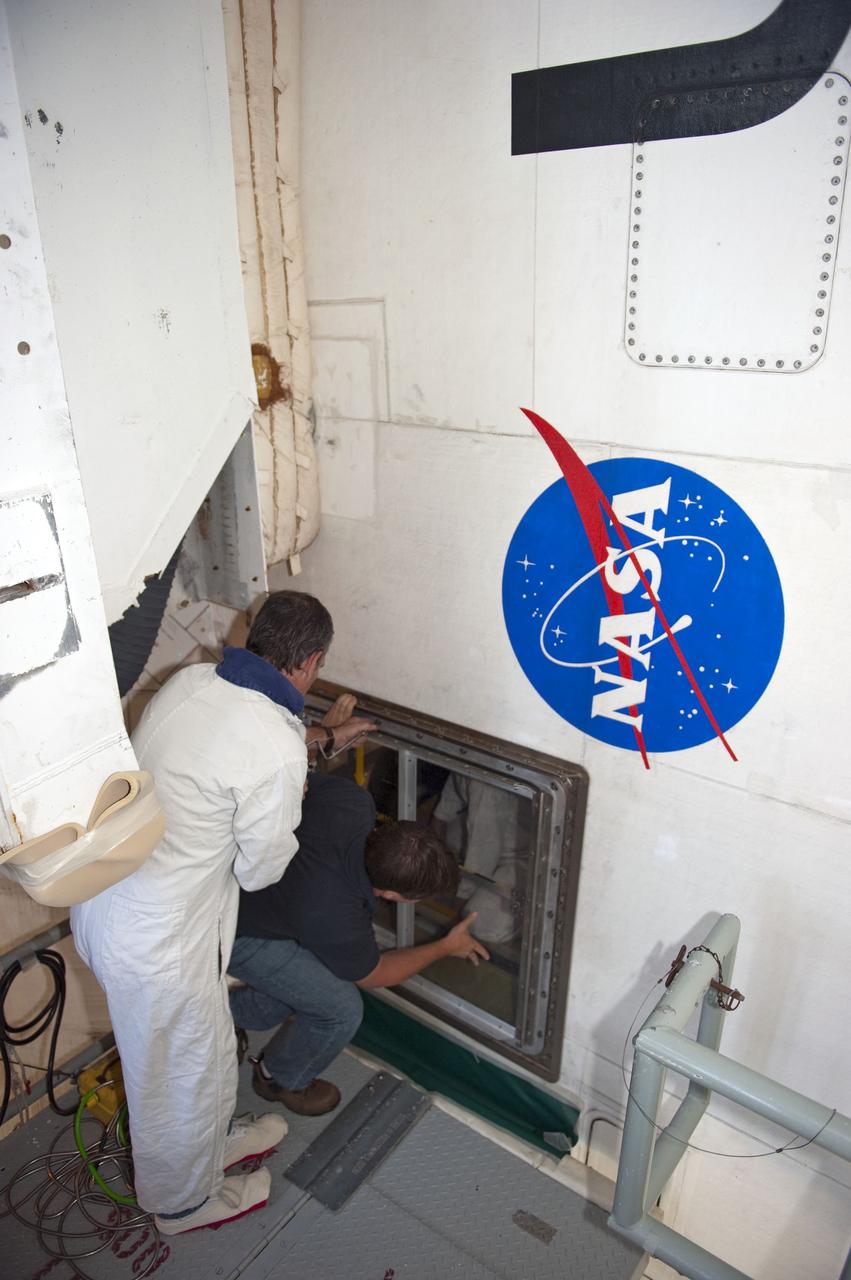

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, workers gain entrance to space shuttle Endeavour's aft section as teams prepare to remove and replace the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the assembly is believed to have caused heaters on a fuel line for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
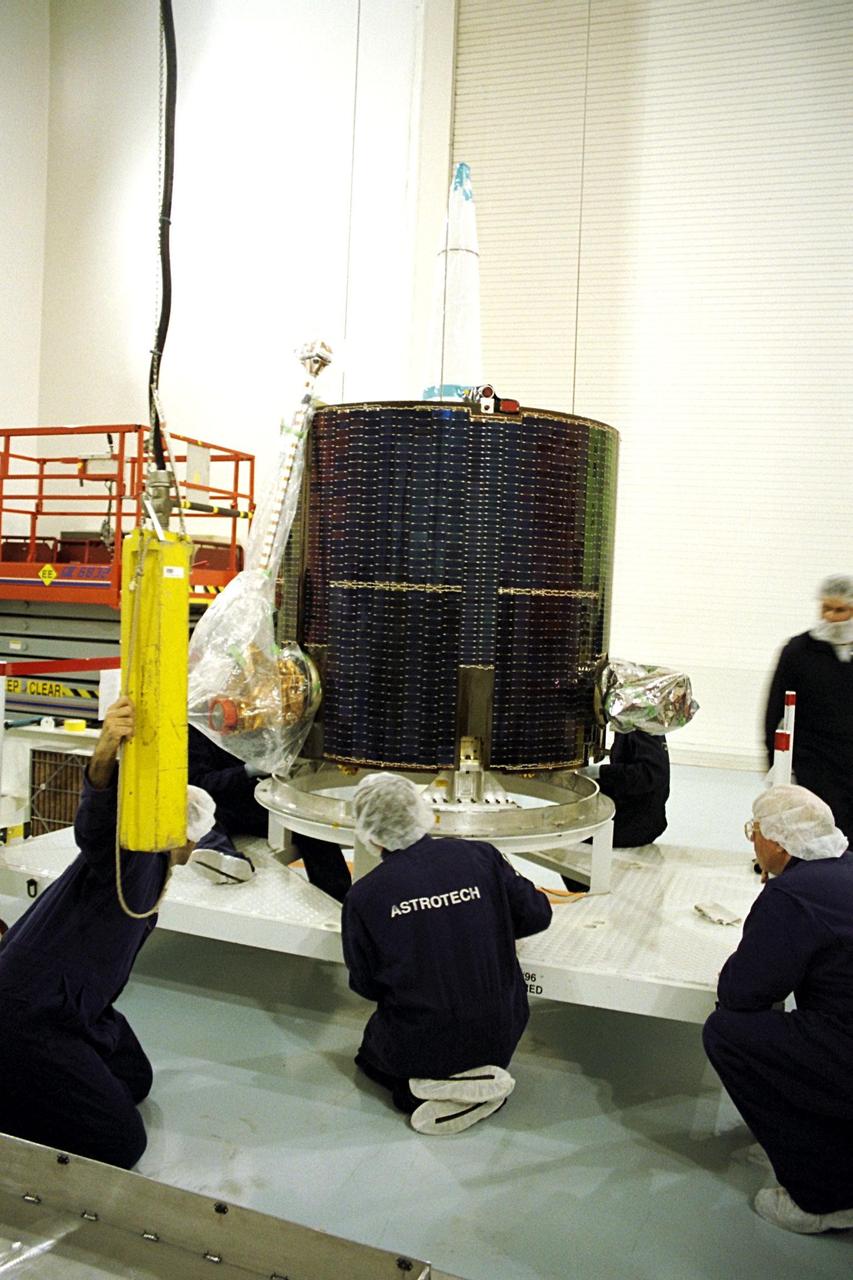

NASA's Lunar Prospector is taken out of its crate at Astrotech, a commercial payload processing facility, in Titusville, Fla. The small robotic spacecraft, to be launched for NASA on an Athena 2 rocket by Lockheed Martin, is designed to provide the first global maps of the Moon's surface compositional elements and its gravitational and magnetic fields. While at Astrotech, Lunar Prospector will be fueled with its attitude control propellant and then mated to a Trans-Lunar Injection Stage which is a solid propellant upper stage motor. The combination will next be spin tested to verify proper balance, then encapsulated into an Athena nose fairing. Then the Lunar Prospector will be transported from Astrotech to Cape Canaveral Air Station and mated to an Athena rocket. The launch of Lunar Prospector is scheduled for Jan. 5, 1998 at 8:31 p.m
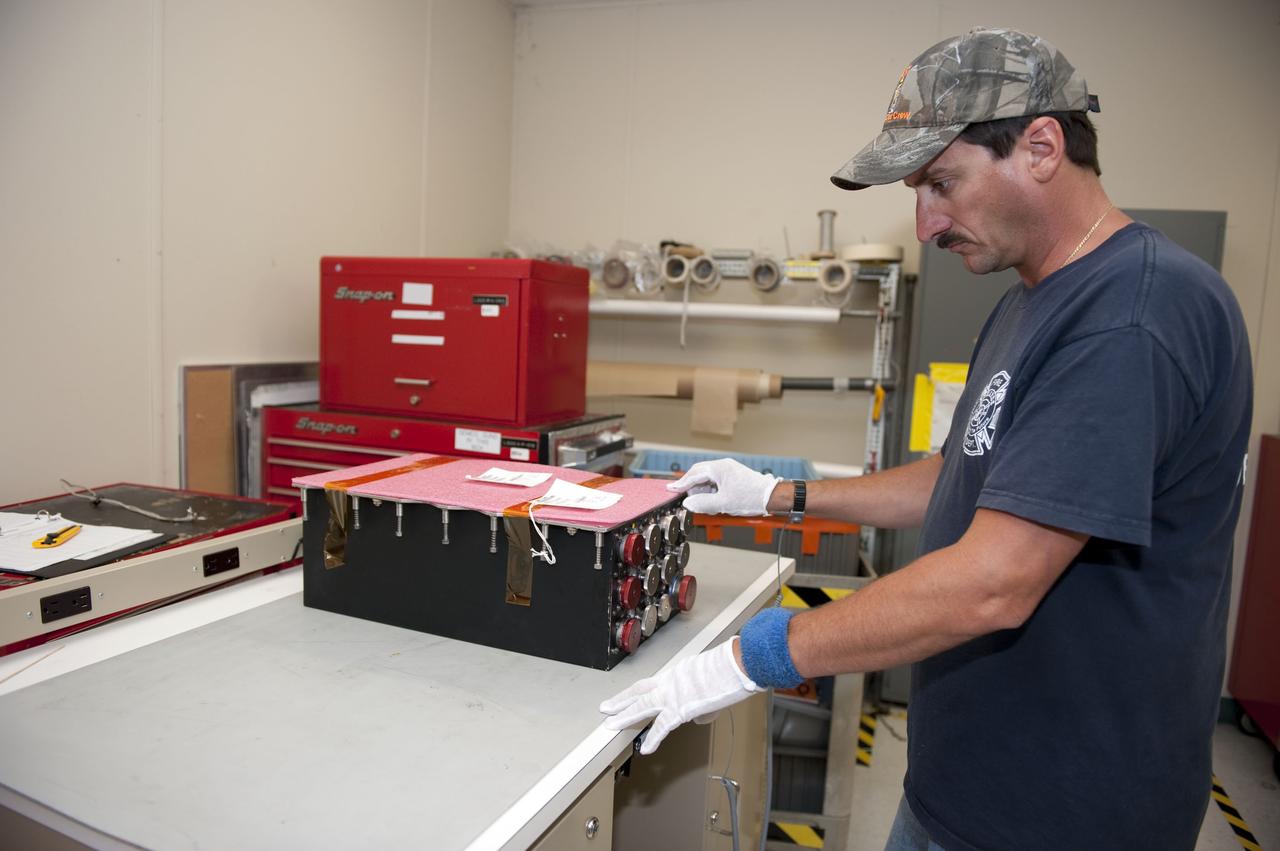

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A work station, a worker inspects the replacement Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) which is being prepared for installation into Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
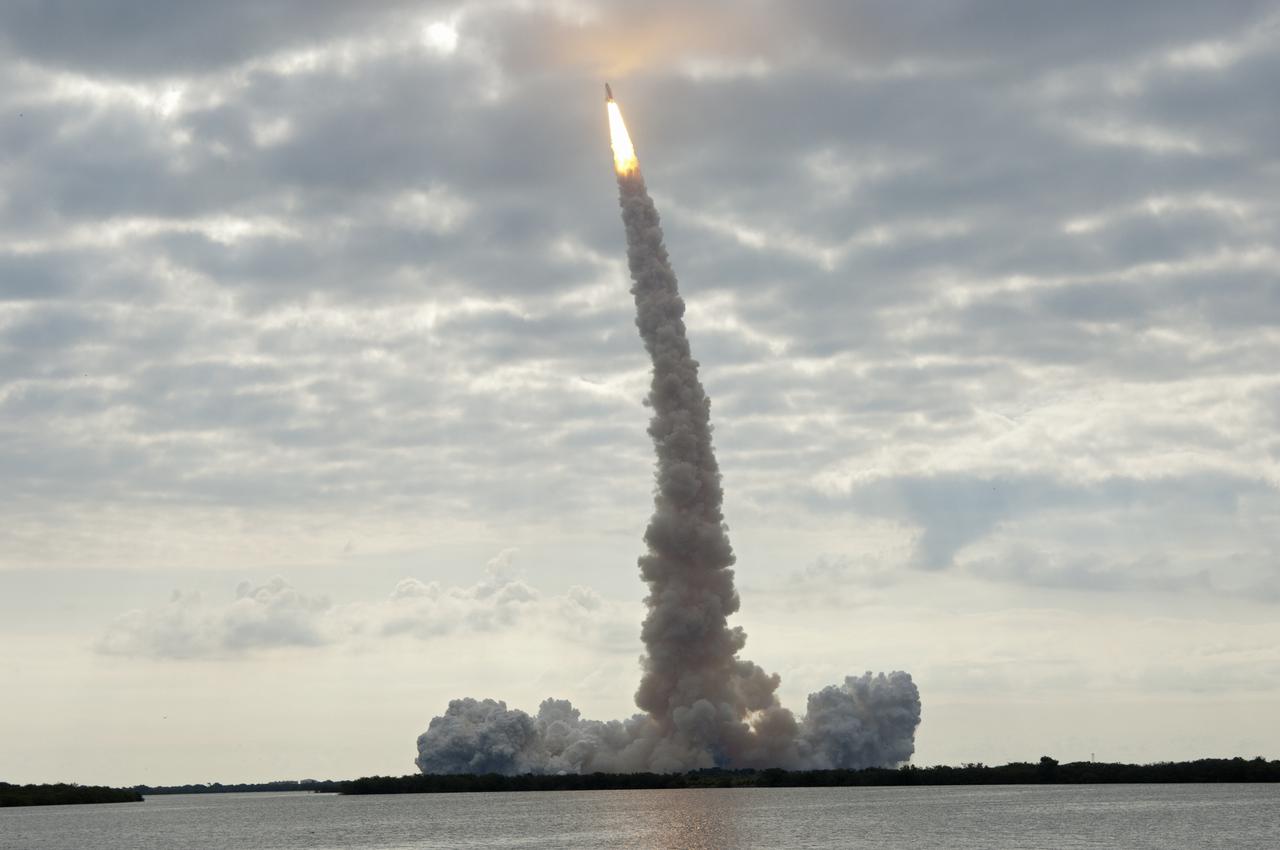

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Seen from across the Banana River Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center, space shuttle Endeavour soars skyward. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16 from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts134_index.html. Photo credit: NASA_Chad Baumer
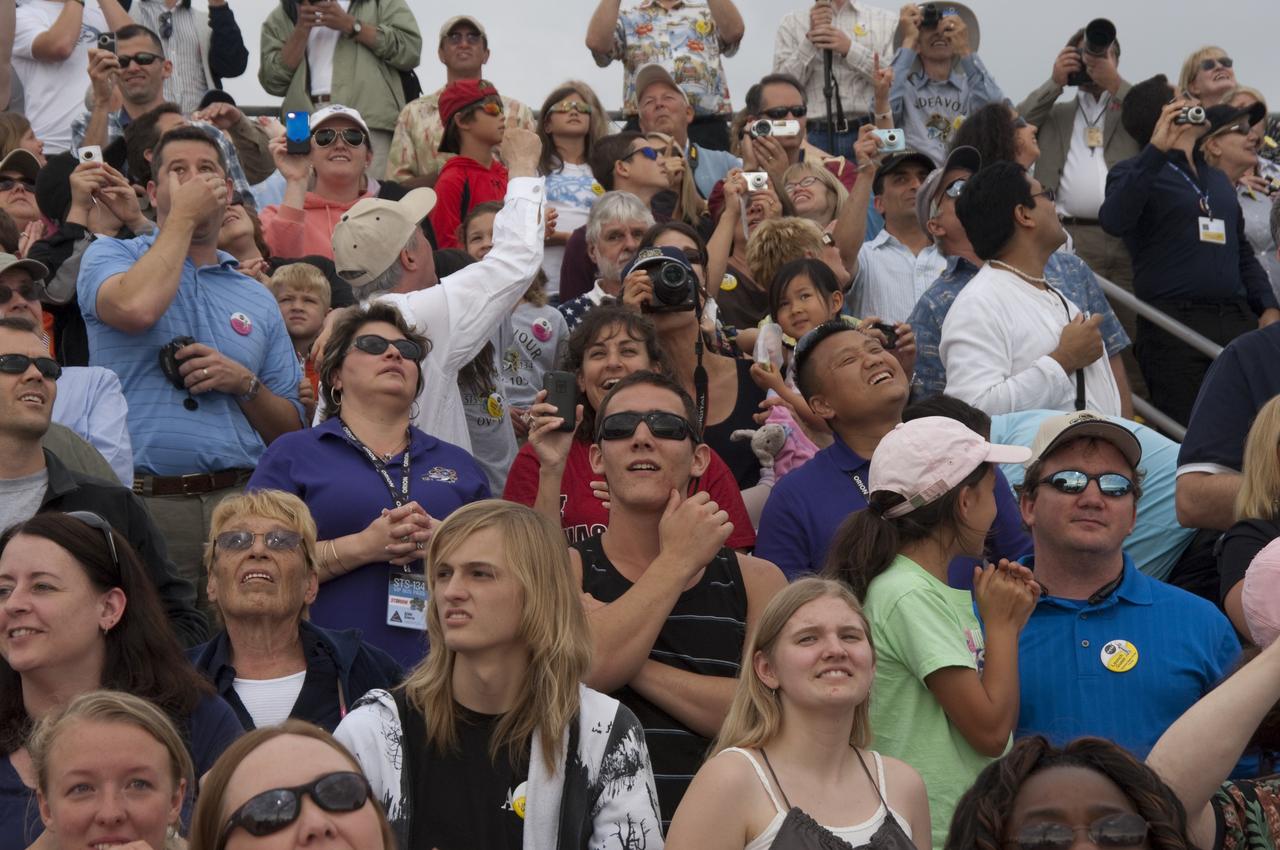

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Spectators at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as space shuttle Endeavour soars skyward. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
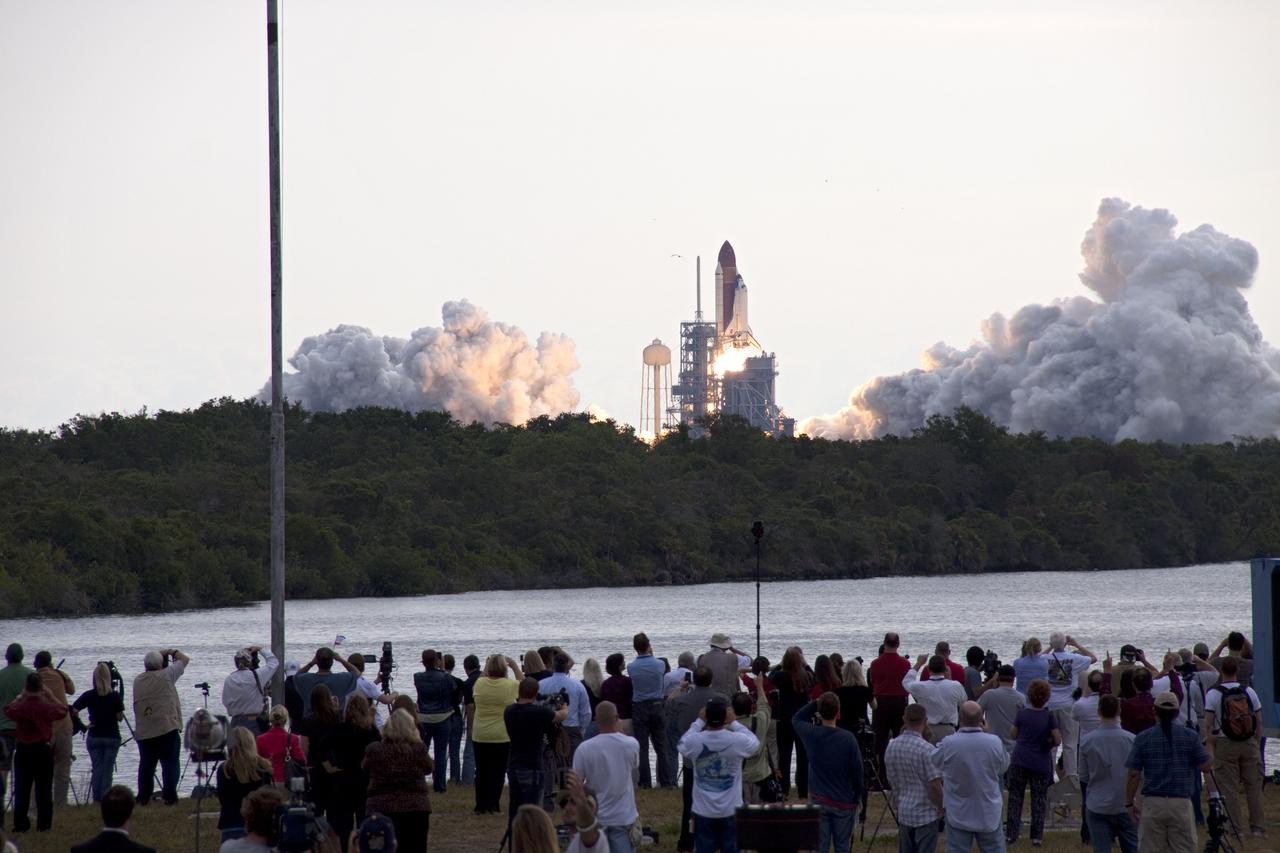

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media capture the launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-134 mission to the International Space Station from the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The shuttle and its six-member crew lifted off on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. STS-134 will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). STS-134 will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. --The Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) is outside at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A after it was removed from inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The assembly will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
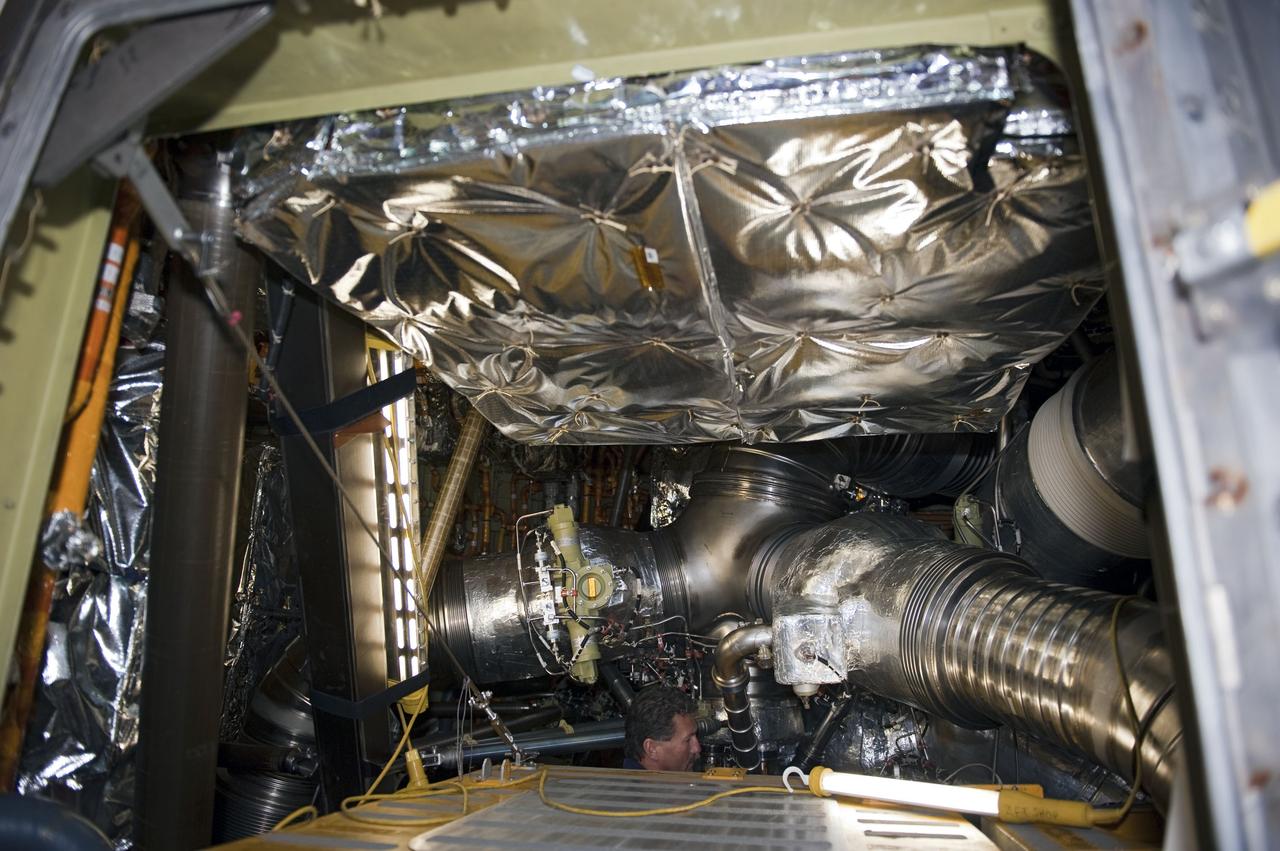

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Barely visible inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section, a technician at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A helps prepare for the upcoming removal and replacement of the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the assembly is believed to have caused heaters on a fuel line for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
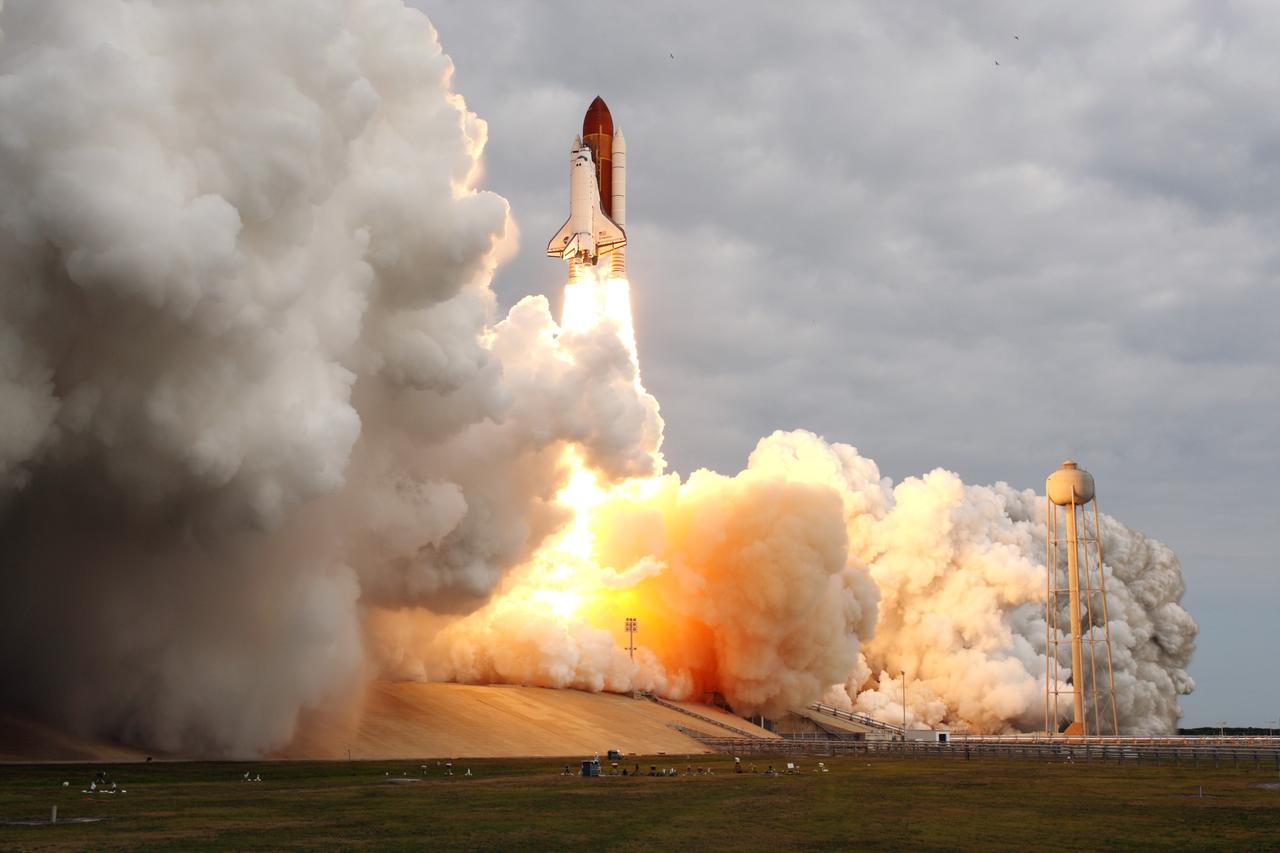

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising on twin columns of fire and kicking up a trail of smoke and steam, space shuttle Endeavour lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida beginning its final flight, the STS-134 mission, to the International Space Station. Launch was on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. STS-134 and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, a worker inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section removed a cover to provide access for the removal and replacement of the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
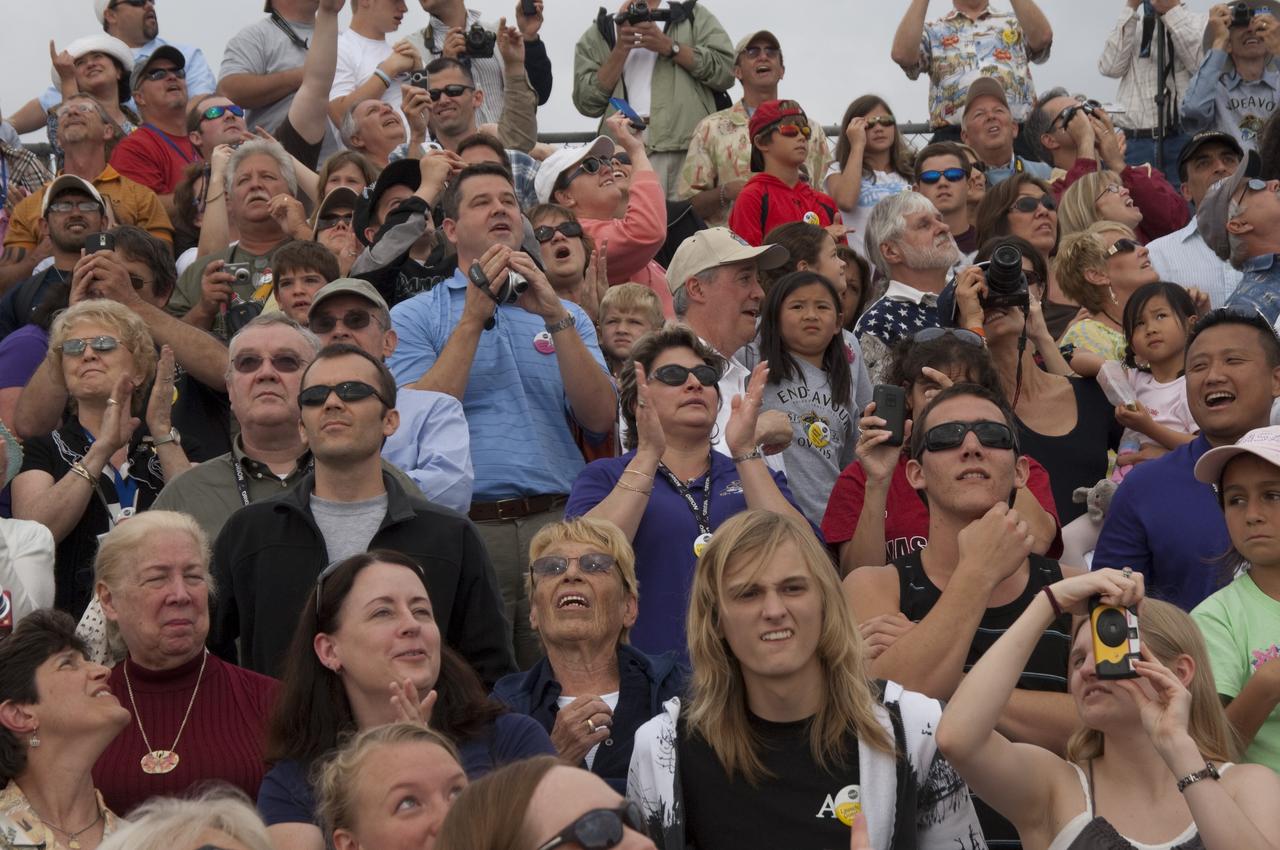

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Spectators at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as space shuttle Endeavour soars skyward. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
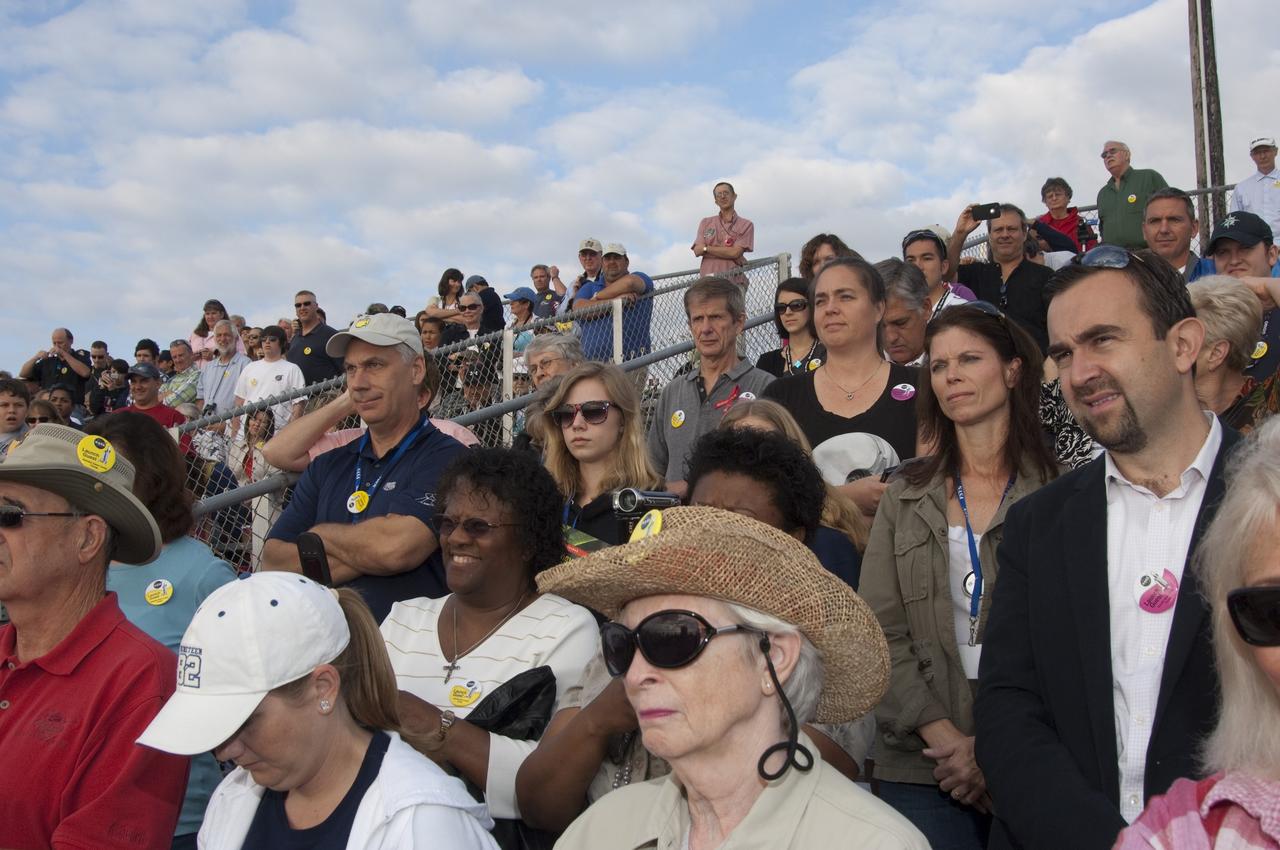

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Spectators at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida await the liftoff of space shuttle Endeavour. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Chad Baumer
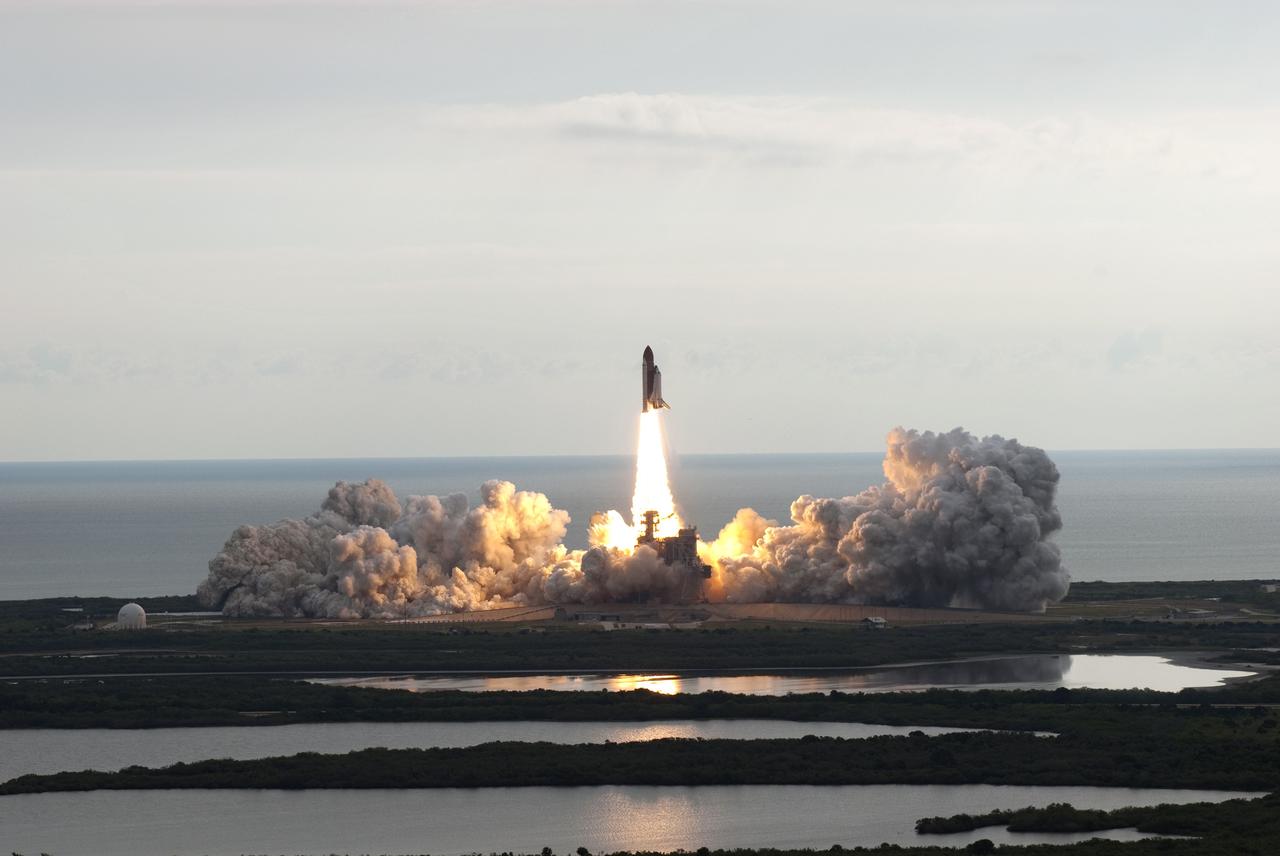

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising on twin columns of fire and kicking up a trail of smoke and steam, space shuttle Endeavour lifts off from its seaside launch pad at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission, to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
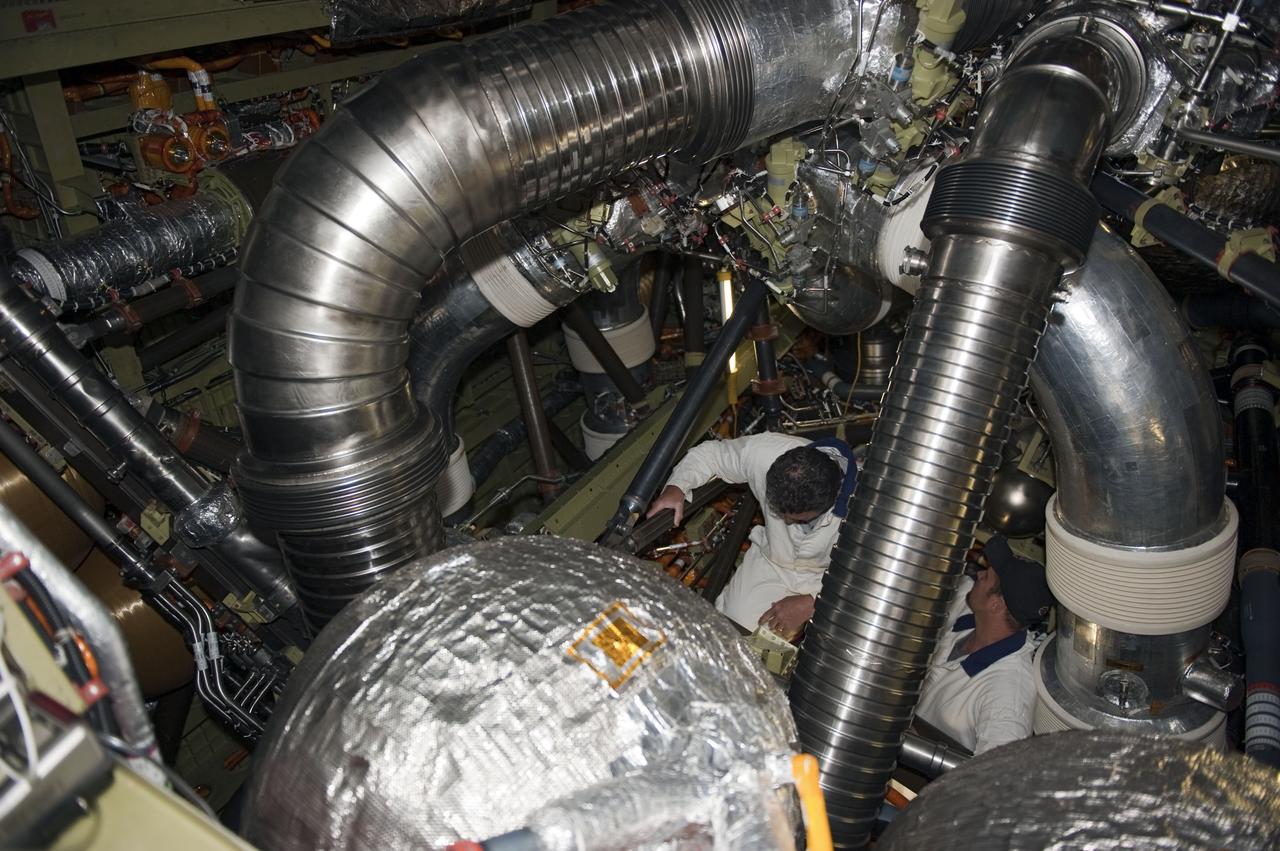

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, workers inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section help prepare for the upcoming removal and replacement of the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the assembly is believed to have caused heaters on a fuel line for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
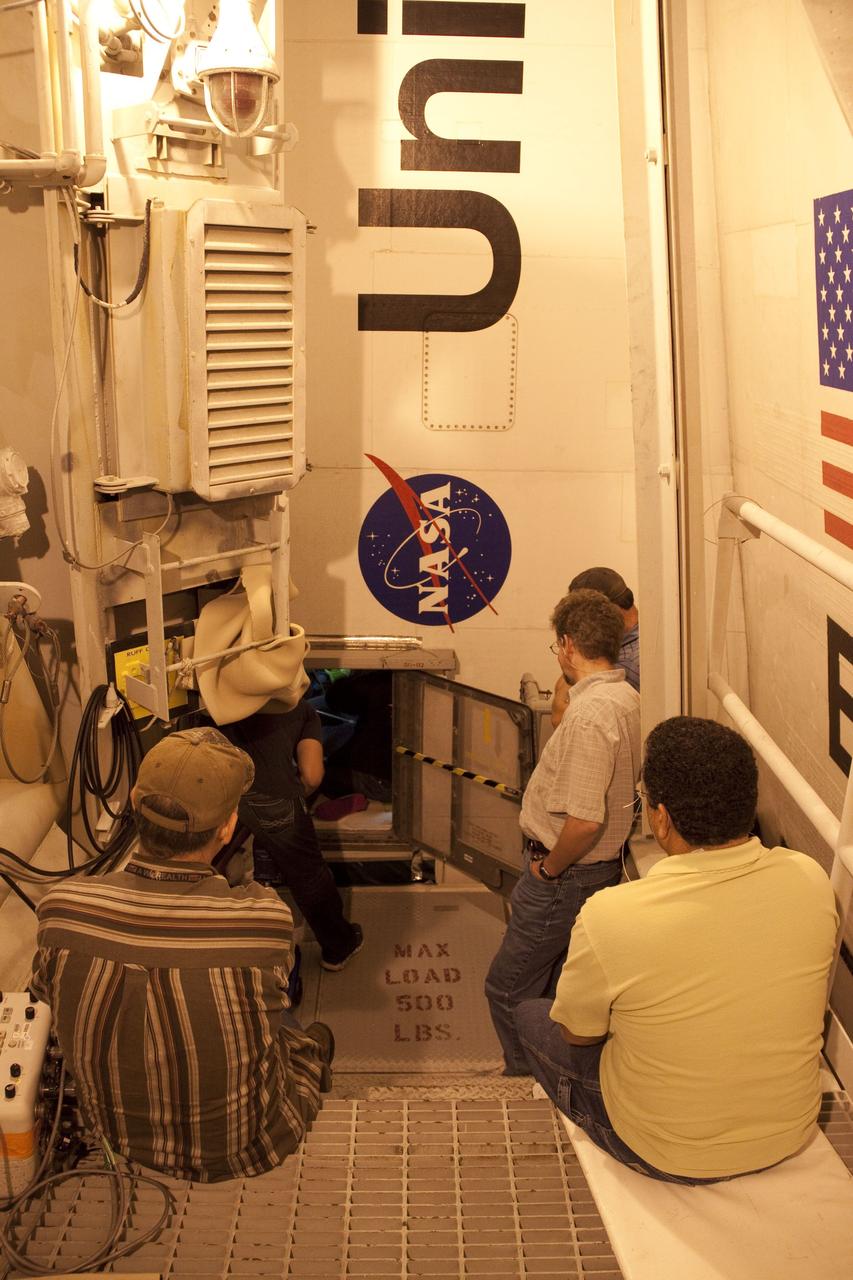

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, technicians work to remove the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) from inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The assembly will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
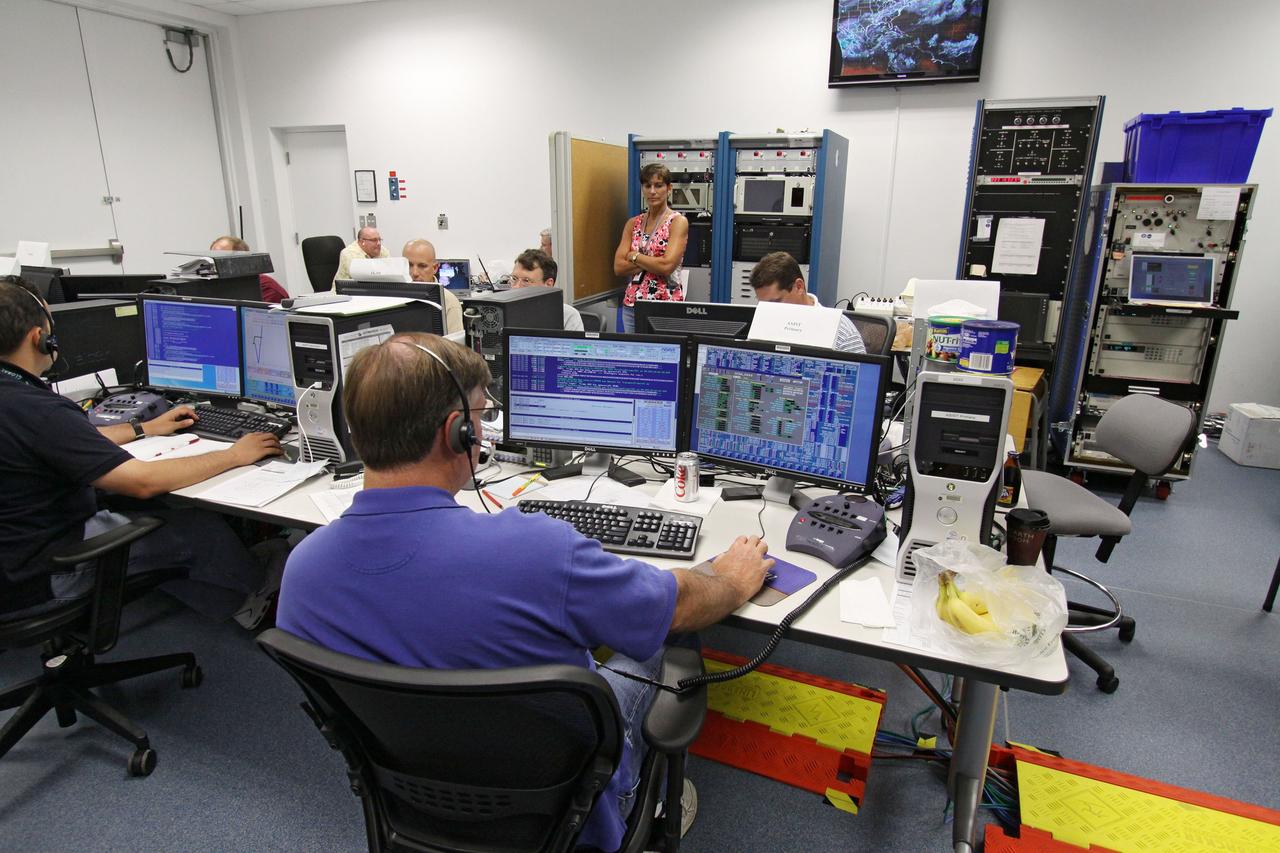

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., workers in the control room monitor the data on computer screens from the movement of the high-gain antenna on the Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO. The SDO is undergoing performance testing. All of the spacecraft science instruments are being tested in their last major evaluation before launch. SDO is the first space weather research network mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information about changes in the sun's magnetic field and insight into how they affect Earth. In preparation for launch, engineers will perform a battery of comprehensive tests to ensure SDO can withstand the stresses and vibrations of the launch itself, as well as what it will encounter in the space environment after launch. Liftoff on an Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Dec. 4. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
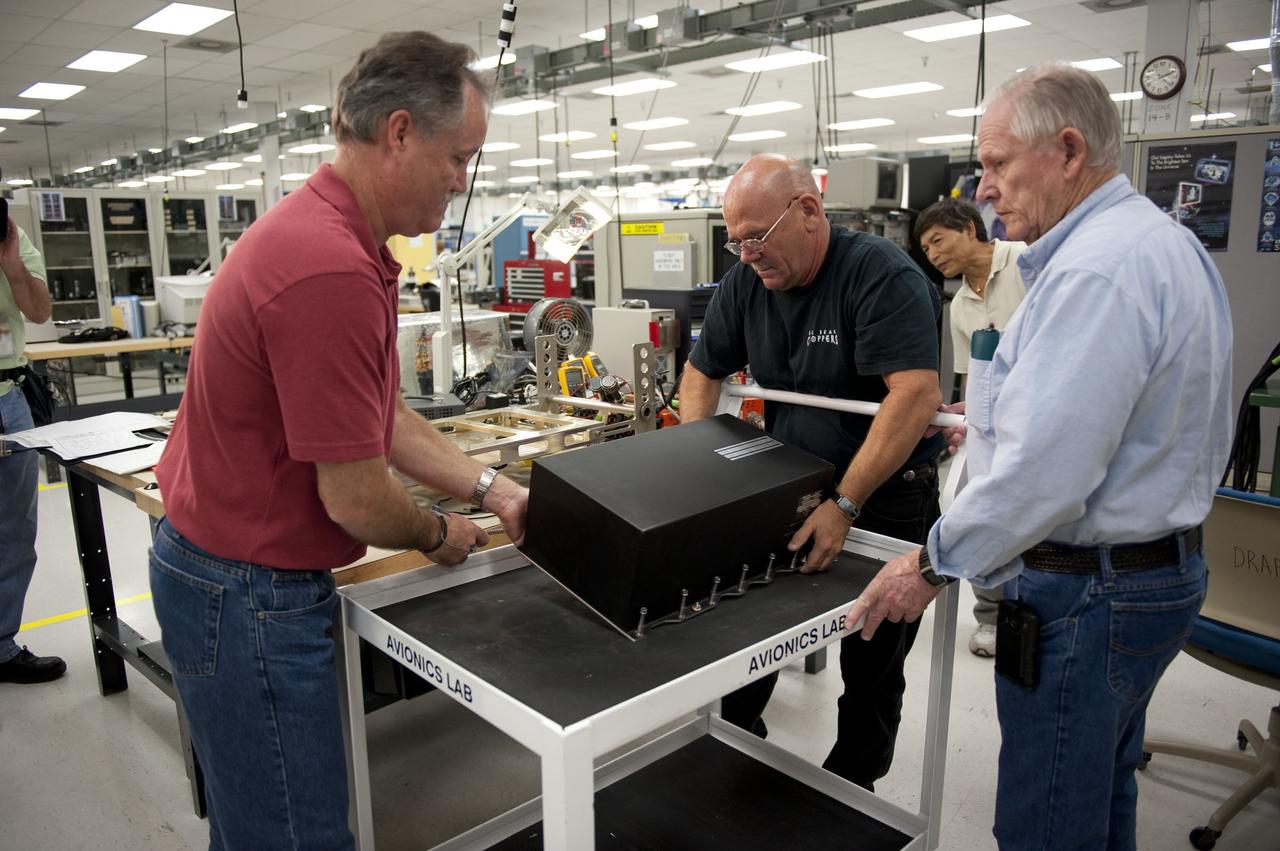

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the NASA Shuttle Logistics Depot in Cape Canaveral, Florida, technicians carefully remove the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) from a cart for testing. Located in space shuttle Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The LCA-2 will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) has been replaced inside of space shuttle Endeavour. Located in Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission and has been replaced. Systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
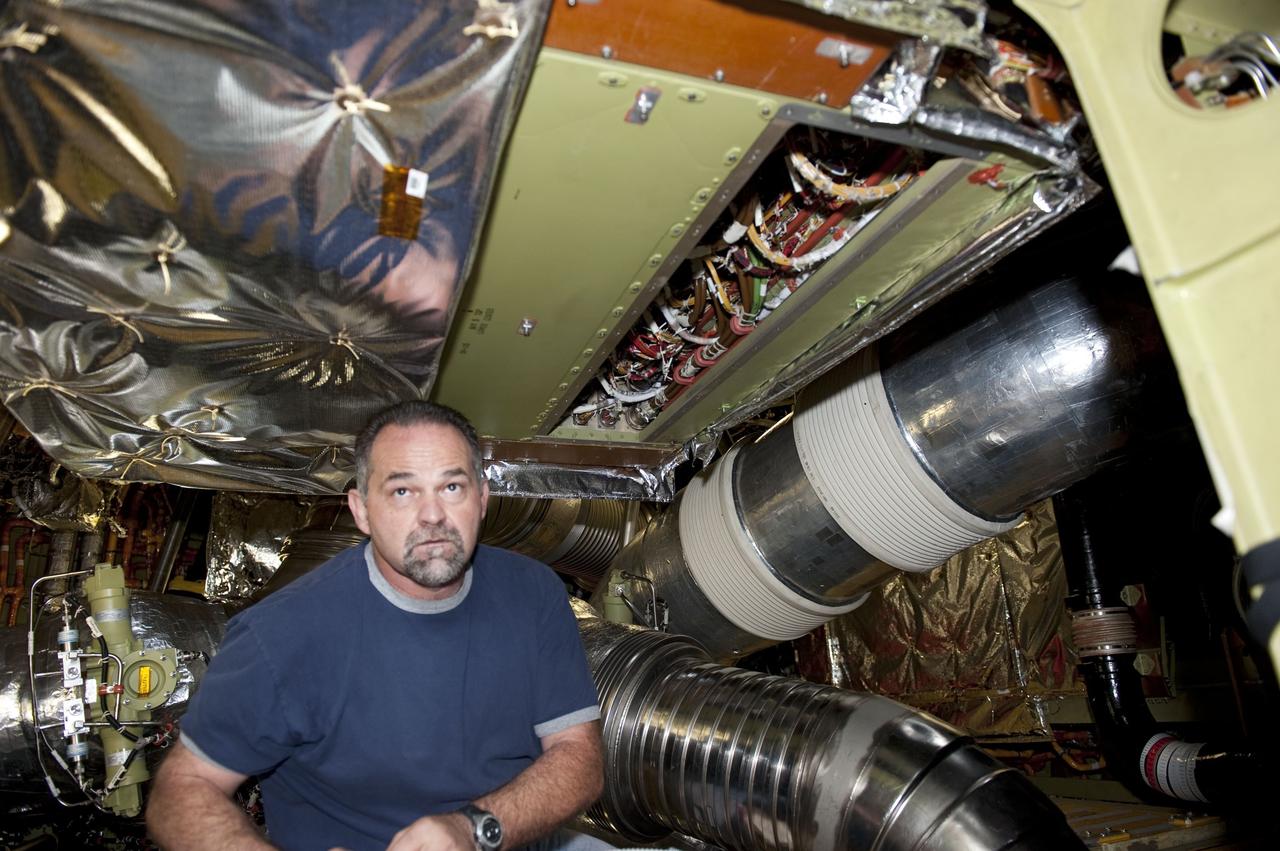

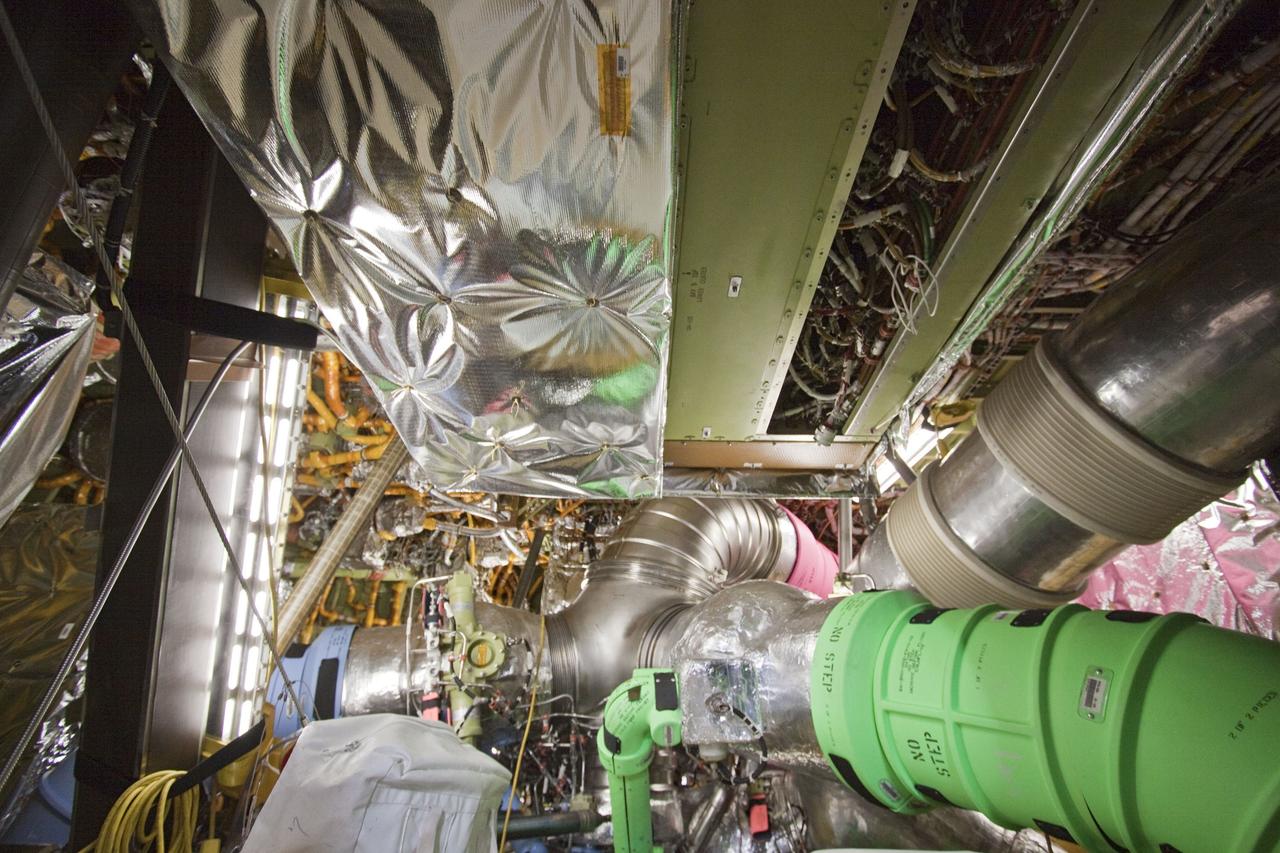
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, a worker inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section removes a cover to provide access for the removal and replacement of the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
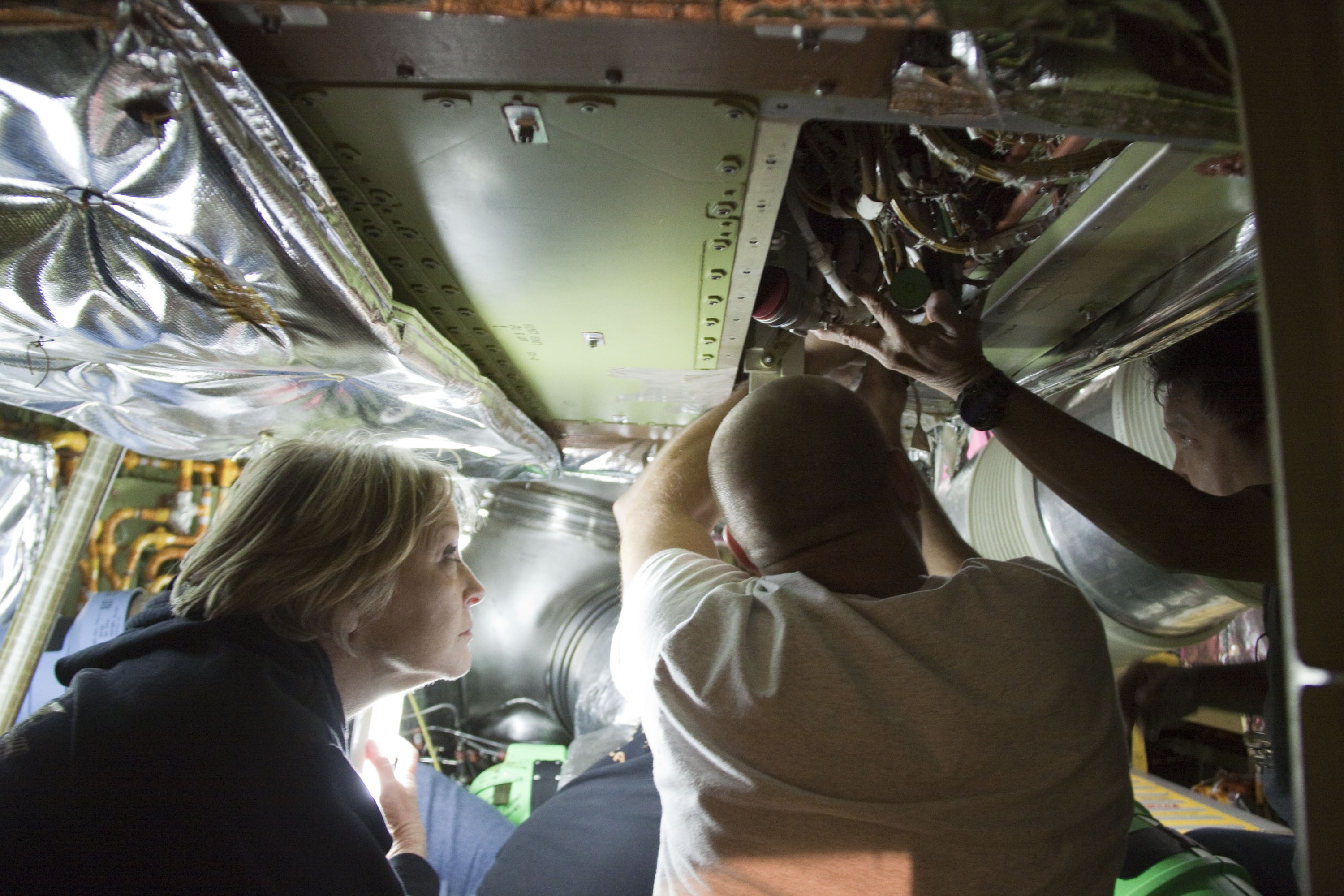

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, technicians begin to remove the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) from inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The assembly will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
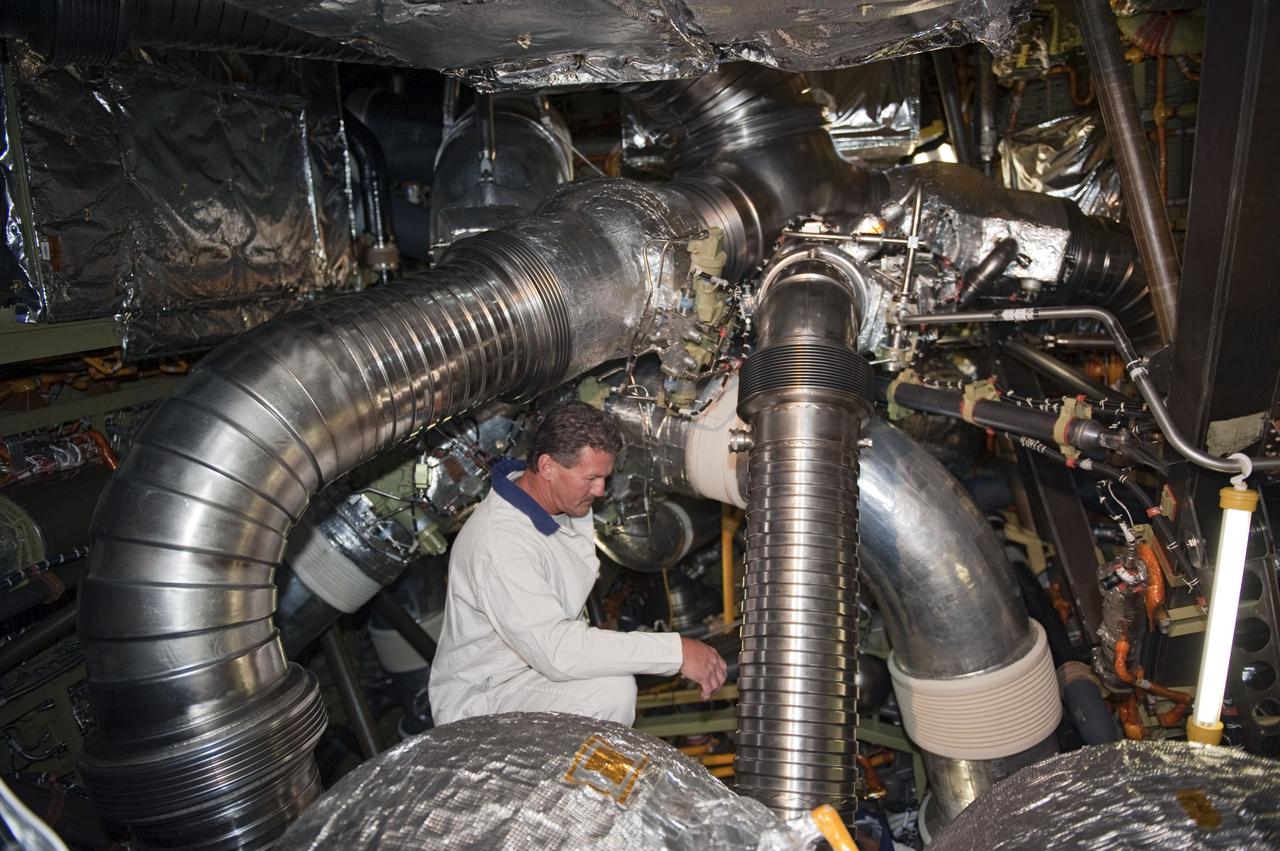

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A technician at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A crouches in space shuttle Endeavour's aft section, where teams are preparing to remove and replace the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the assembly is believed to have caused heaters on a fuel line for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
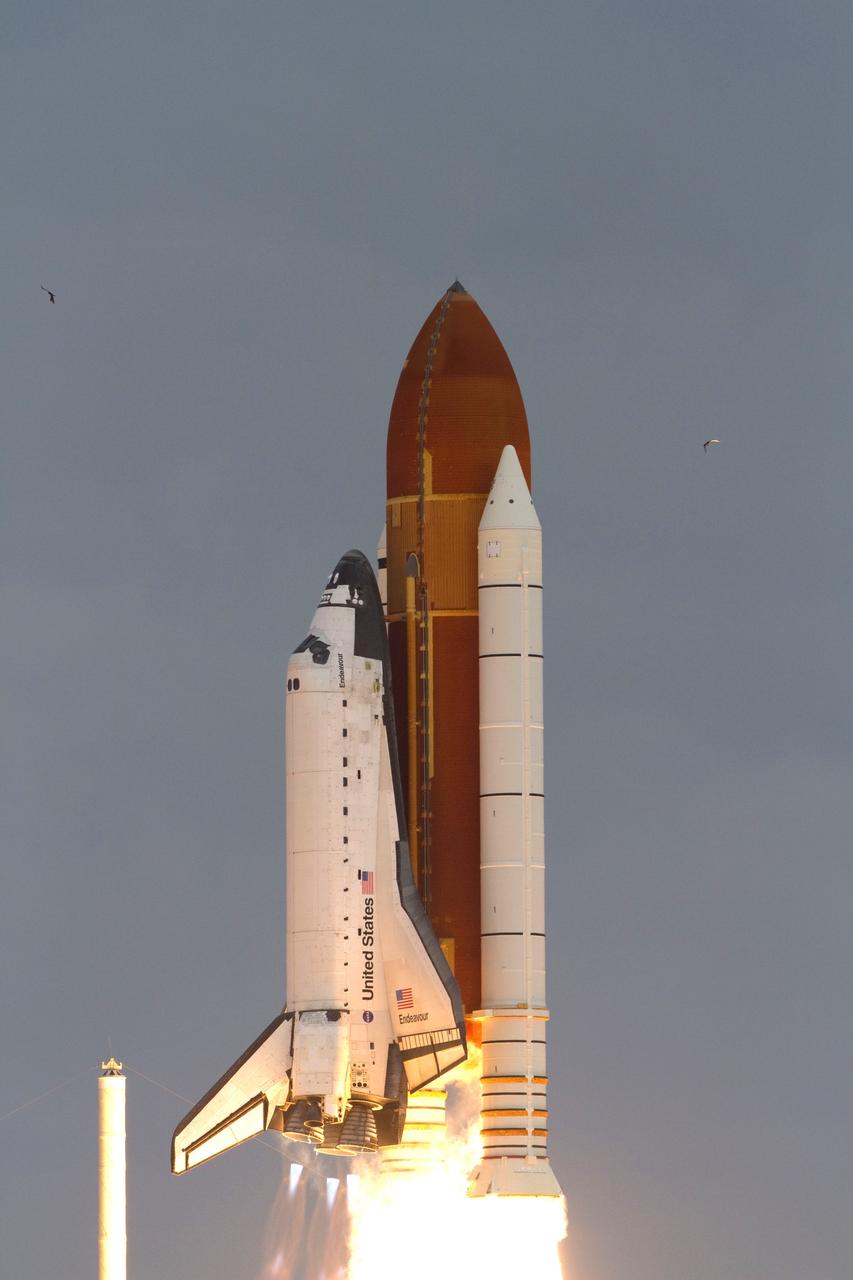

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising on twin columns of fire, space shuttle Endeavour lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida beginning its final flight, the STS-134 mission, to the International Space Station. Launch was on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. STS-134 and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA
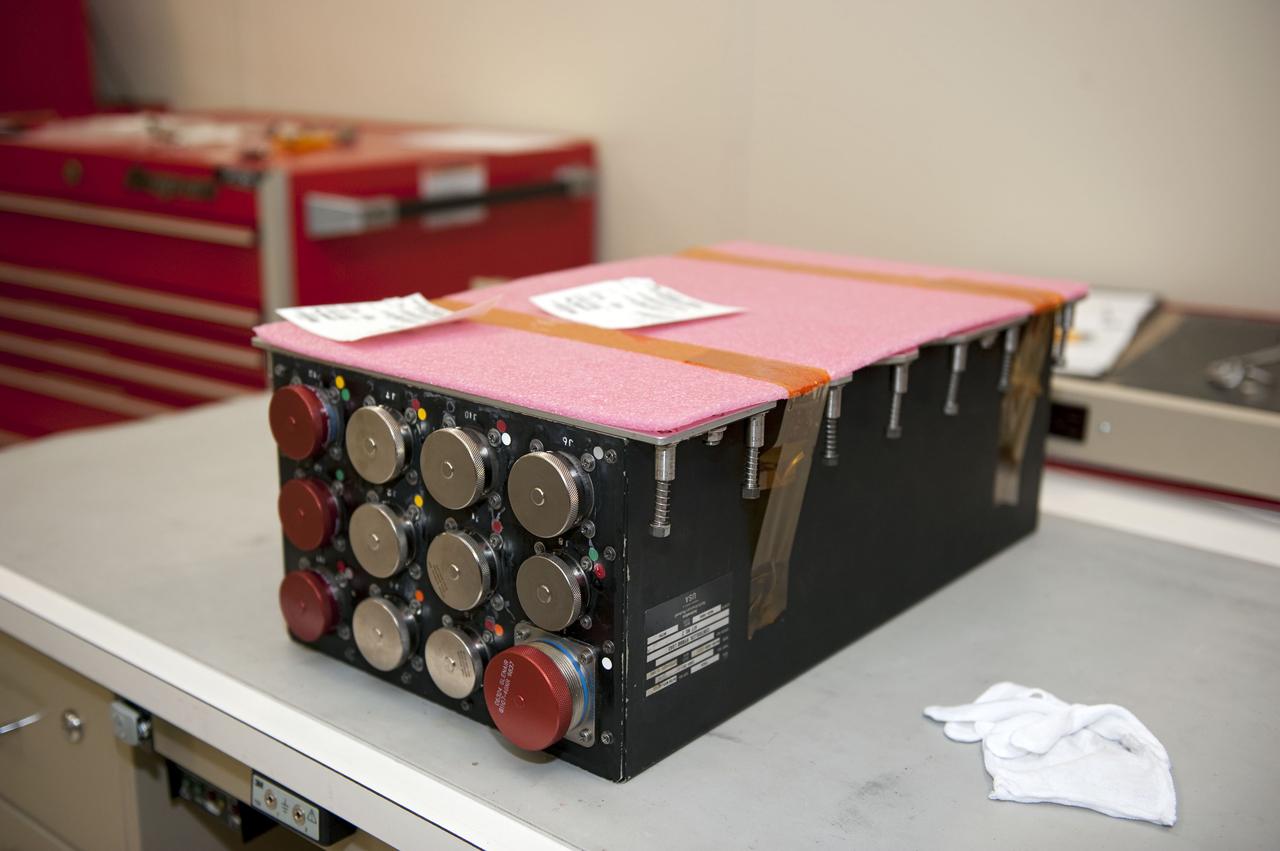

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A work station, a replacement Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) is being prepared for installation into Endeavour's aft section. Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
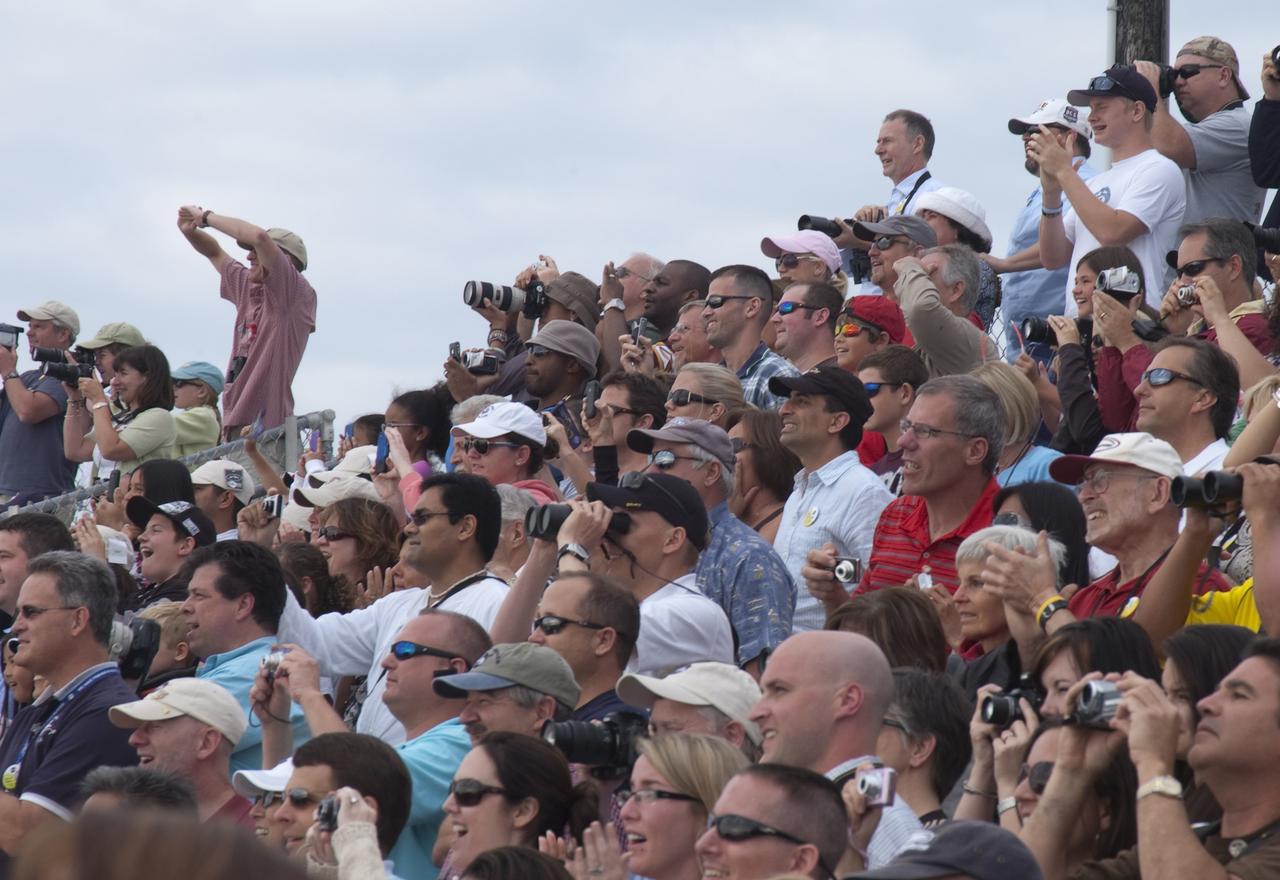

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Spectators at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida watch as space shuttle Endeavour soars skyward. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kurtis Korwan
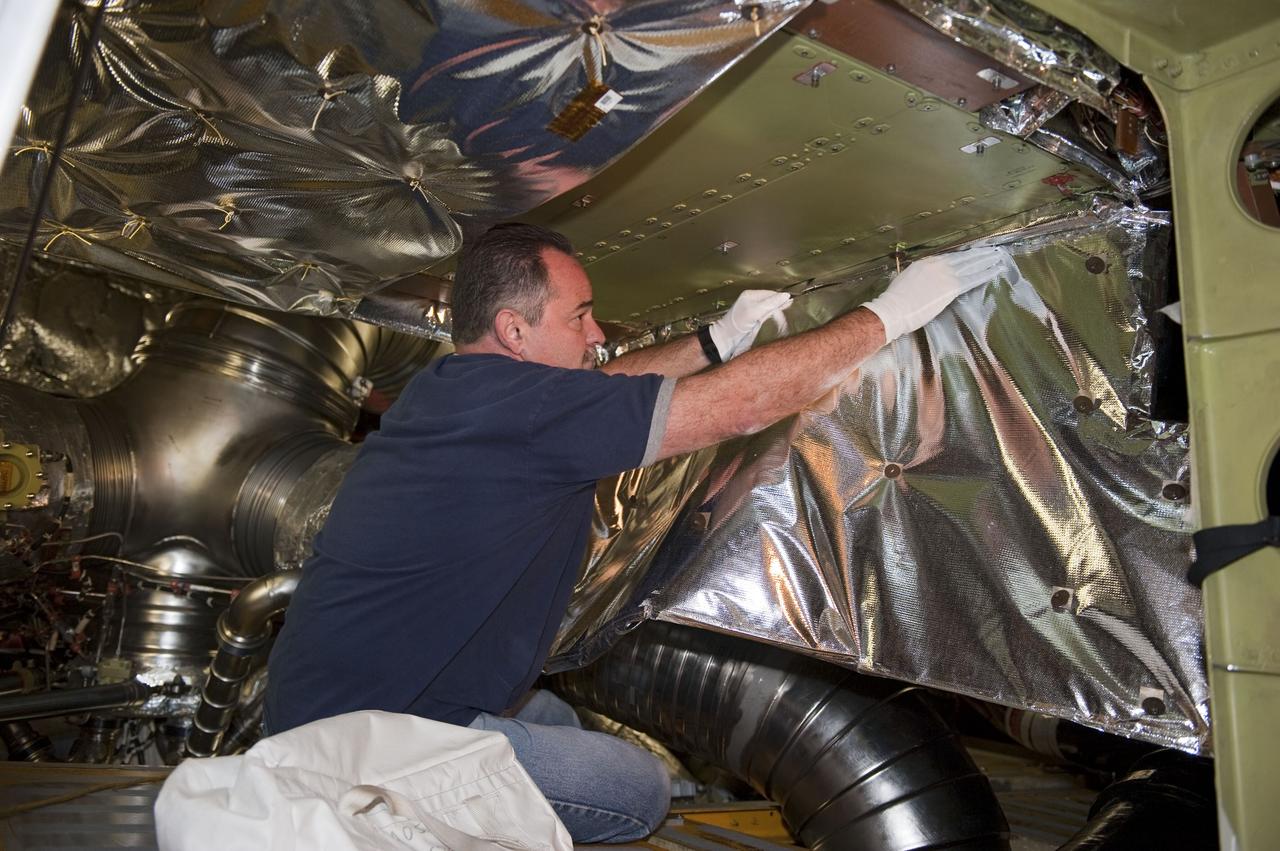

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, a worker inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section removes an insulating blanket and cover to provide access for the removal and replacement of the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
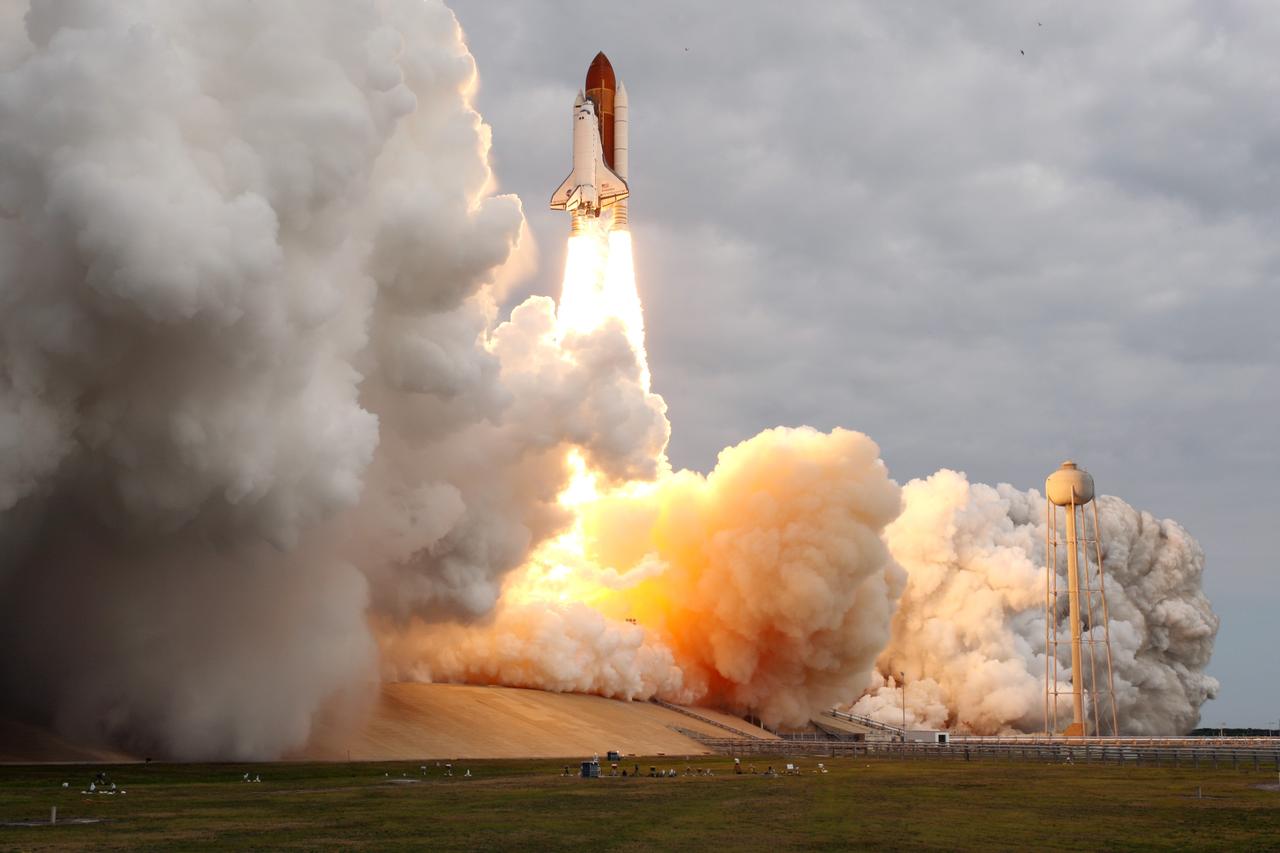

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising on twin columns of fire and kicking up a trail of smoke and steam, space shuttle Endeavour lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida beginning its final flight, the STS-134 mission, to the International Space Station. Launch was on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. STS-134 and its six-member crew will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA
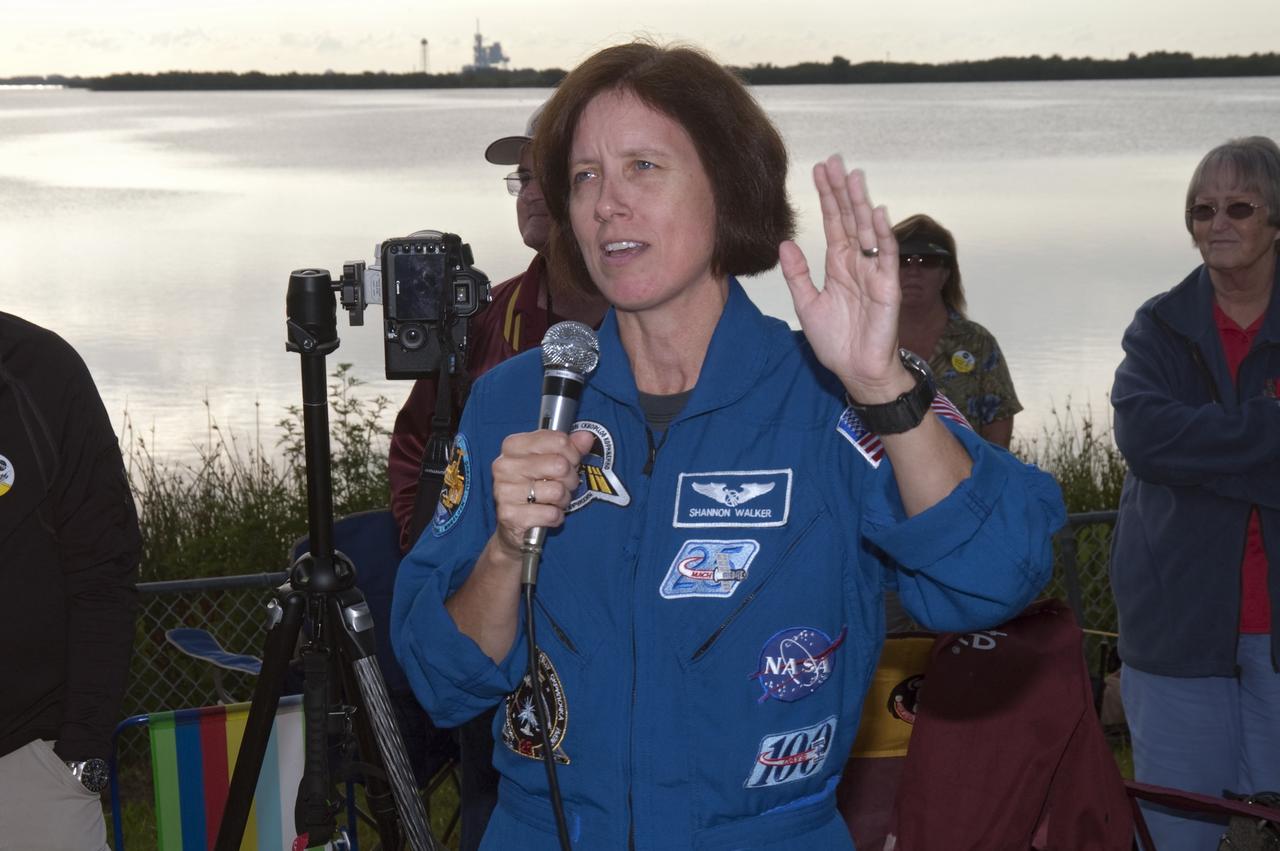

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA astronaut Shannon Walker talks to a crowd of spectators gathered at the Banana Creek Viewing Site near the Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to watch the launch of space shuttle Endeavour. The shuttle lifted off on its STS-134 mission to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. The shuttle and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kurtis Korwan
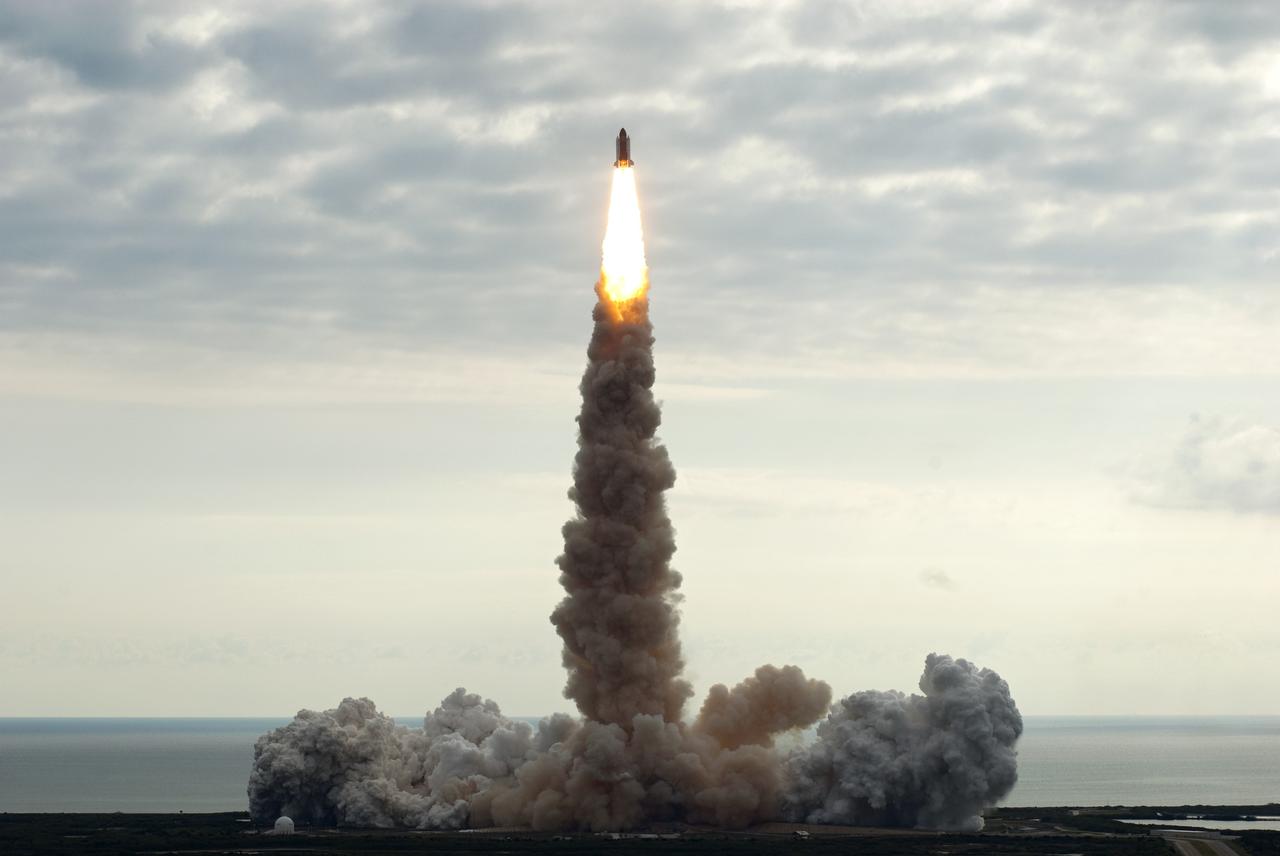

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Rising on twin columns of fire and kicking up a trail of smoke and steam, space shuttle Endeavour lifts off from its seaside launch pad at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission, to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
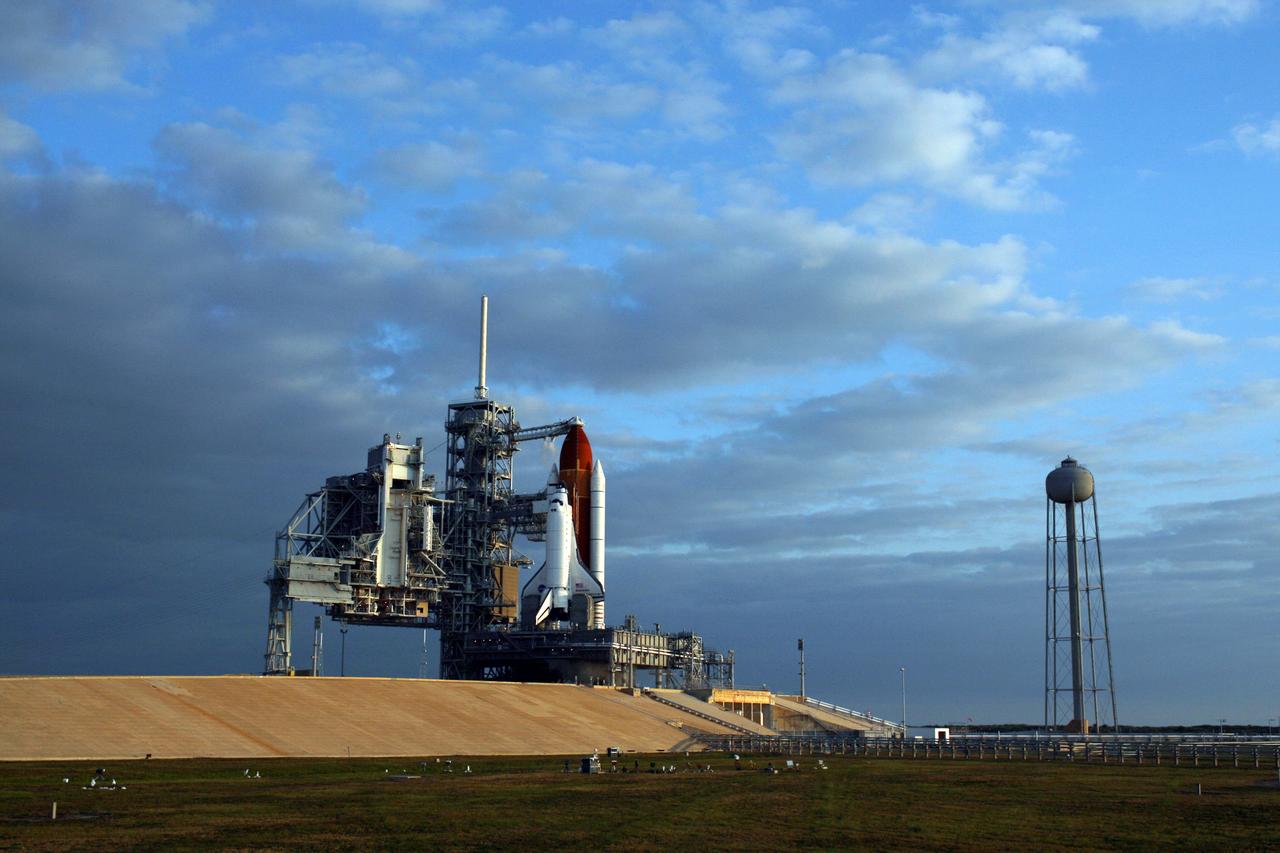

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Under a vividly painted blue sky, space shuttle Endeavour awaits liftoff on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. STS-134 will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. May 16 at 8:56 a.m. will be the second launch attempt for Endeavour. The first attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). STS-134 will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA
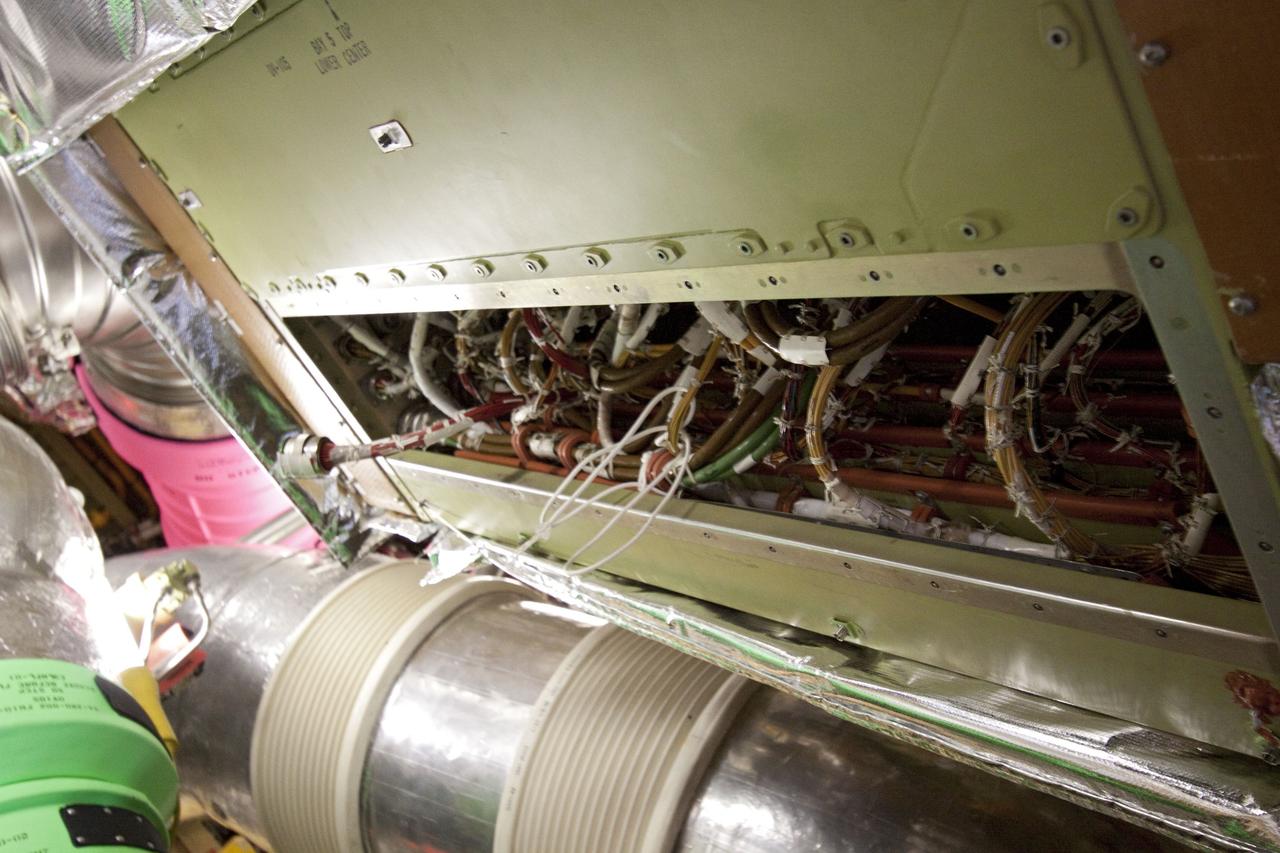

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) has been replaced inside of space shuttle Endeavour. Located in Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission and has been replaced. Systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the NASA Shuttle Logistics Depot in Cape Canaveral, Florida, the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) is uncovered for testing. Located in space shuttle Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The LCA-2 will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
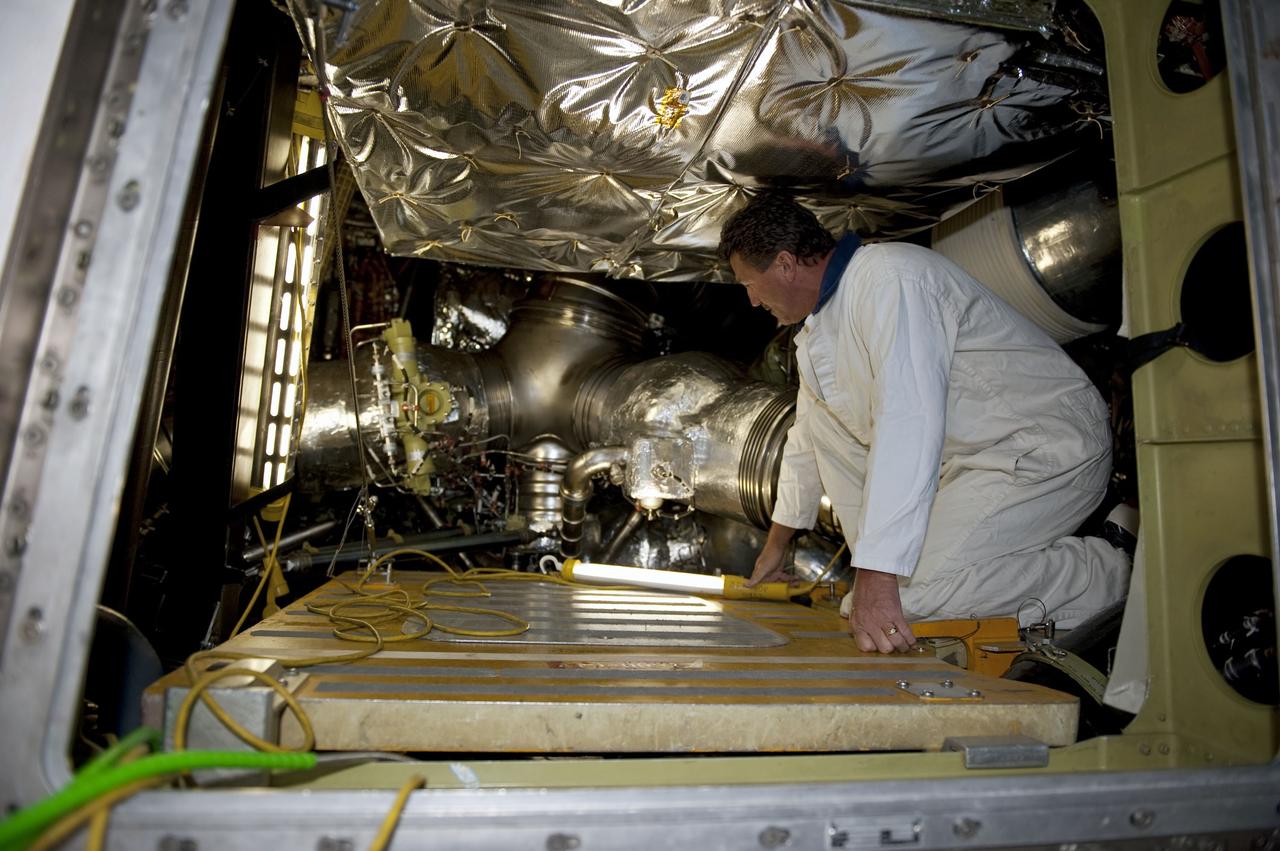

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, a technician makes his way across a platform in space shuttle Endeavour's aft section as work begins to remove and replace the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the assembly is believed to have caused heaters on a fuel line for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
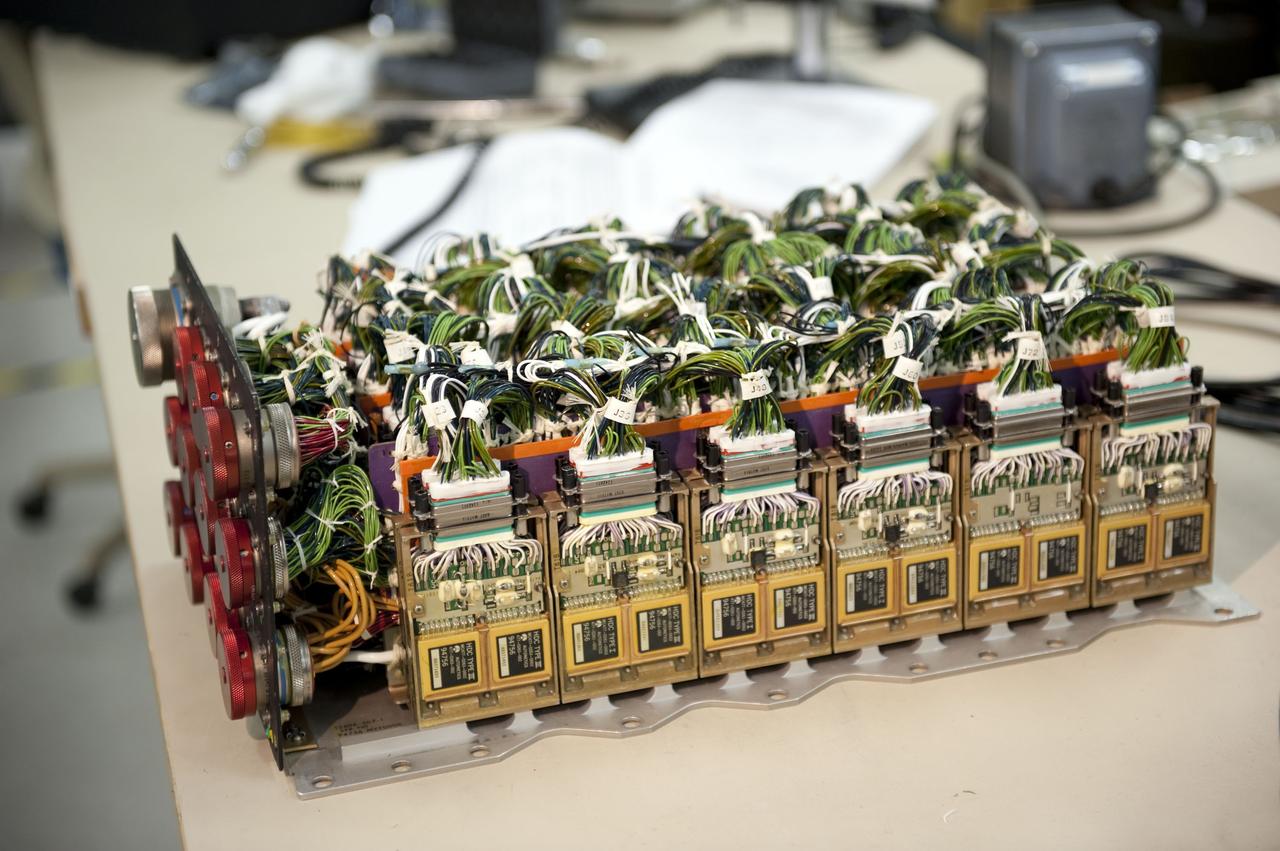
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the NASA Shuttle Logistics Depot in Cape Canaveral, Florida, the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2) is uncovered for testing. Located in space shuttle Endeavour's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2, which distributes power to nine shuttle systems, is believed to have caused fuel line heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. The LCA-2 will be replaced and systems will be retested before the launch is rescheduled. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
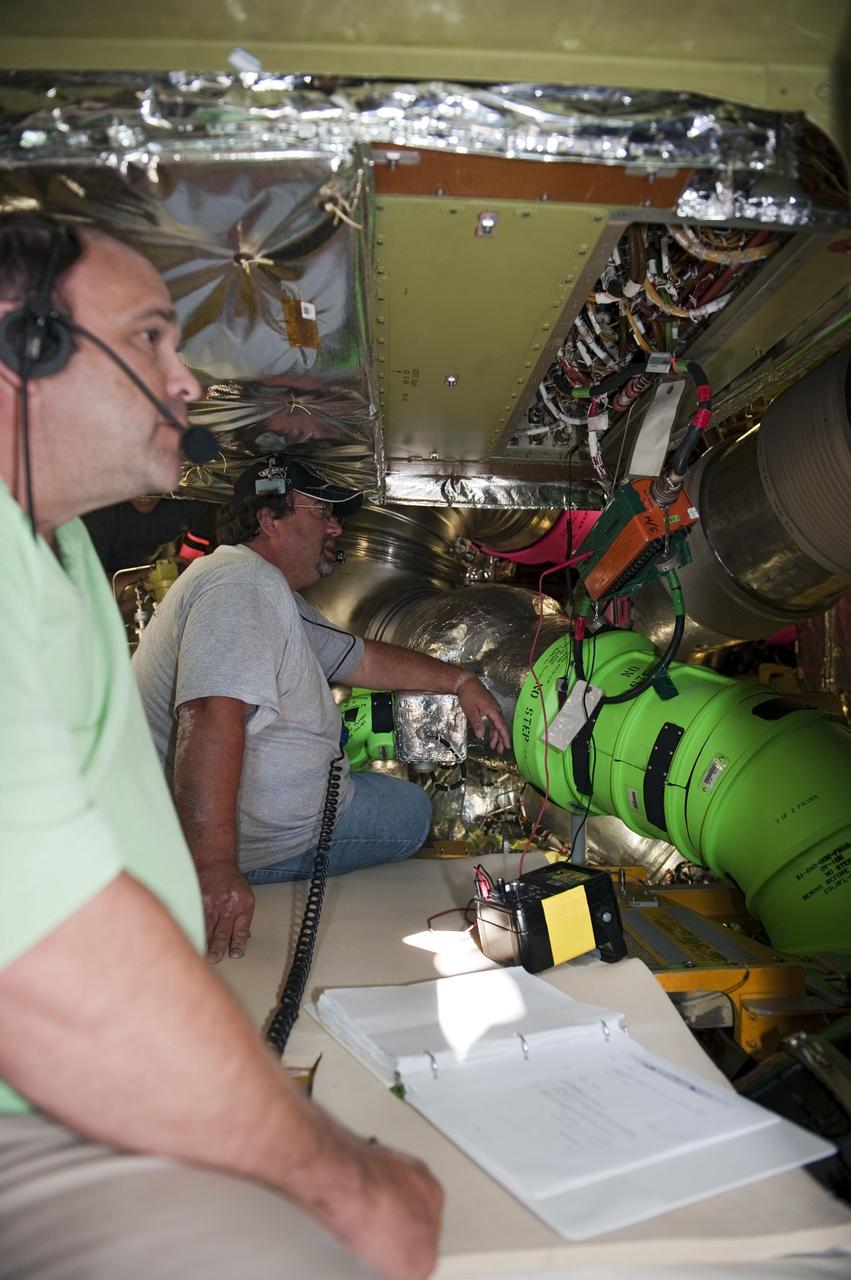

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, technicians inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section test the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
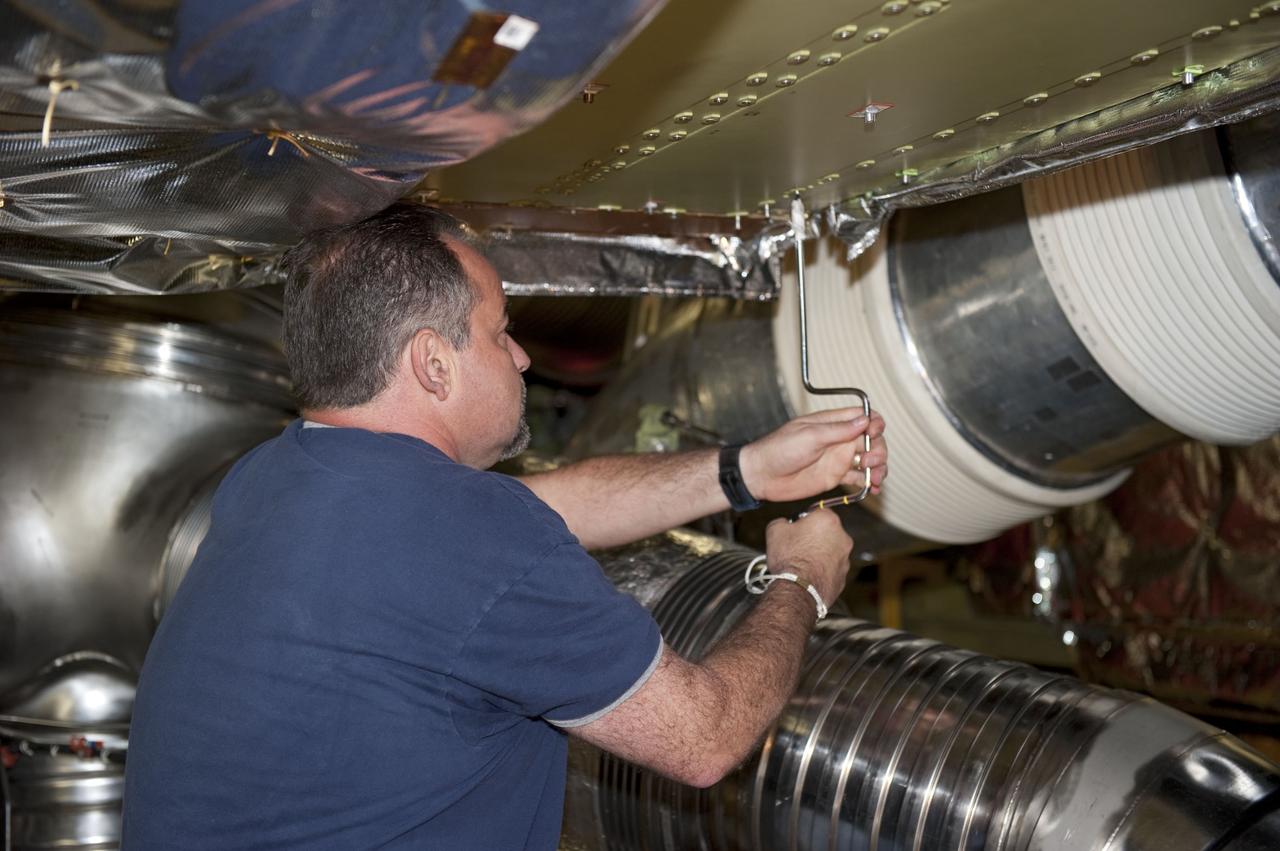

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, a worker inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section removes a cover to provide access for the removal and replacement of the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
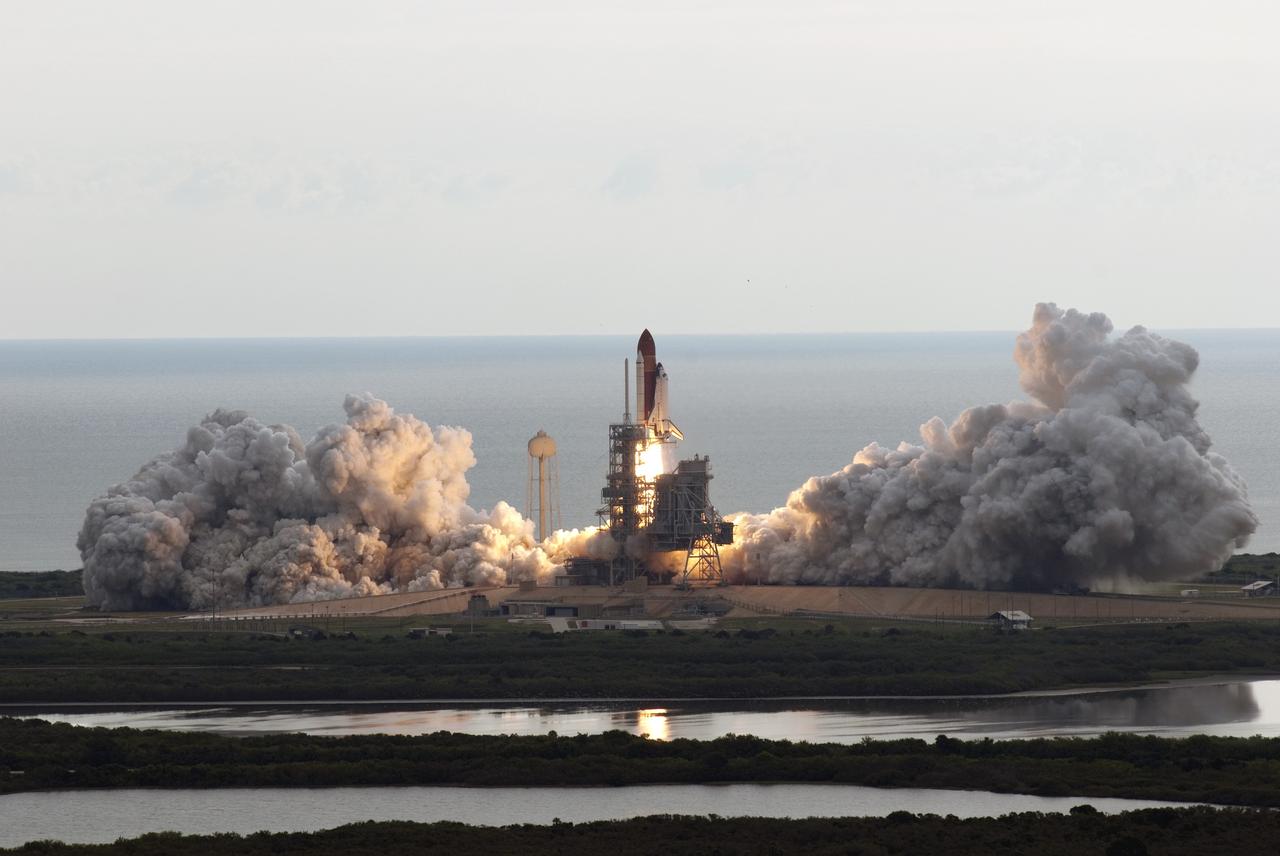

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Kicking up a trail of smoke and steam, space shuttle Endeavour lifts off from its seaside launch pad at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour began its final flight, the STS-134 mission, to the International Space Station on time at 8:56 a.m. EDT on May 16. Endeavour and its six-member crew are embarking on a mission to deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour's first launch attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
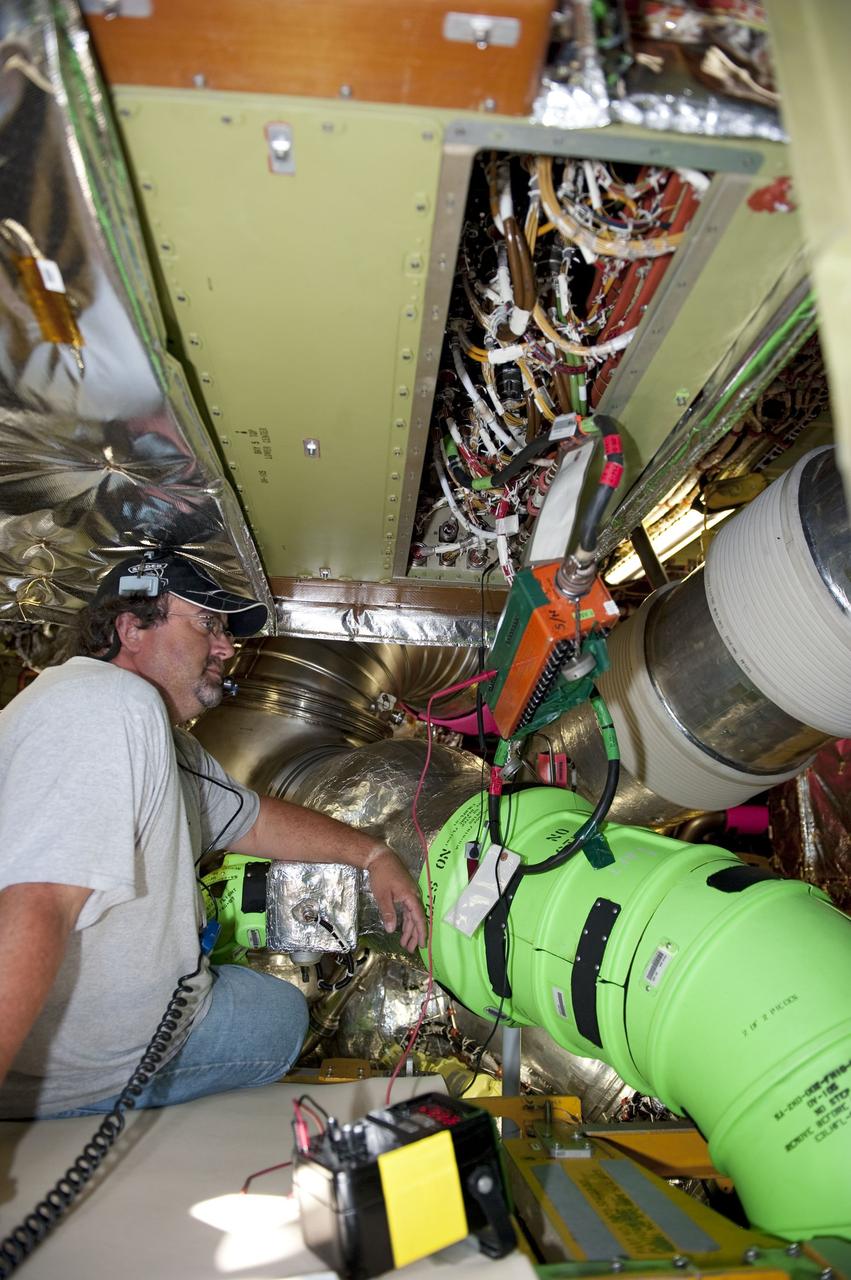

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A, technicians inside space shuttle Endeavour's aft section test the Load Control Assembly-2 (LCA-2). Located in the orbiter's aft avionics bay 5, the LCA-2 assembly, which feeds power to the fuel line heaters, is believed to have caused the heaters for Endeavour's auxiliary power unit-1 (APU-1) to fail April 29 during the first launch attempt for the STS-134 mission. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. The mission also will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.