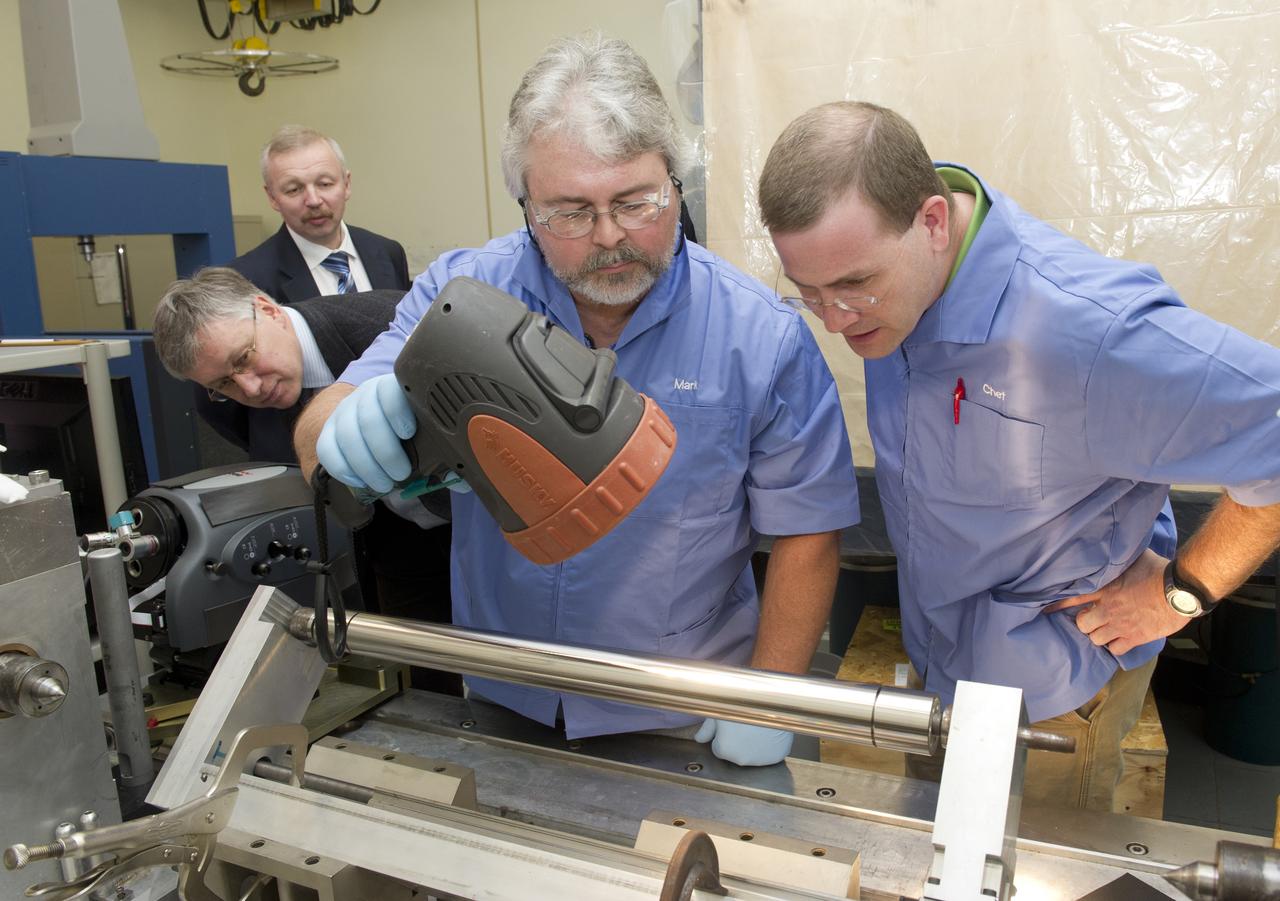

(L TO R) DR. VIKTOR VORON AND DR. MIKHAIL PAVLINSKIY WATCH AS MARK YOUNG AND CHET SPEEGLE CONDUCT BRIGHT LIGHT INSPECTION OF MIRROR MANDREL IN MARSHALL'S OPTICAL INSPECTION LAB.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Astronaut John Young speaks to veterans of the space program in front of the U.S. Space Walk of Fame’s Gemini Monument in Space View Park in Titusville, Fla. More than 50 former Gemini workers attended the event marking the 40th anniversary of Project Gemini. Young, himself a veteran of Project Gemini, told members of the group they should be pleased with their accomplishments, which ultimately helped to land a man on the moon and will lead to future Mars exploration. Following the ceremony, the former workers and their families enjoyed a guided tour of the Kennedy Space Center.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Astronaut John Young speaks to veterans of the space program in front of the U.S. Space Walk of Fame’s Gemini Monument in Space View Park in Titusville, Fla. More than 50 former Gemini workers attended the event marking the 40th anniversary of Project Gemini. Young, himself a veteran of Project Gemini, told members of the group they should be pleased with their accomplishments, which ultimately helped to land a man on the moon and will lead to future Mars exploration. Following the ceremony, the former workers and their families enjoyed a guided tour of the Kennedy Space Center. Photo credit:NASA/George Shelton
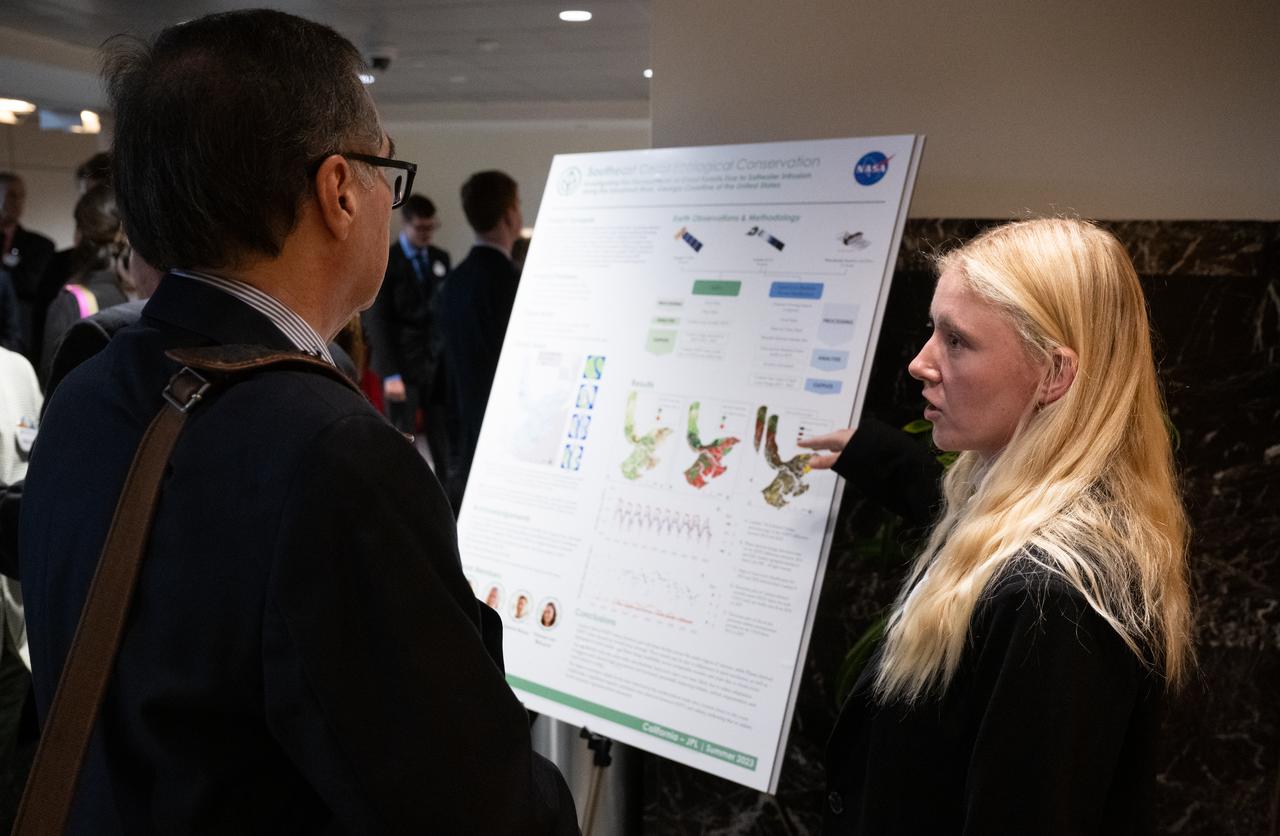

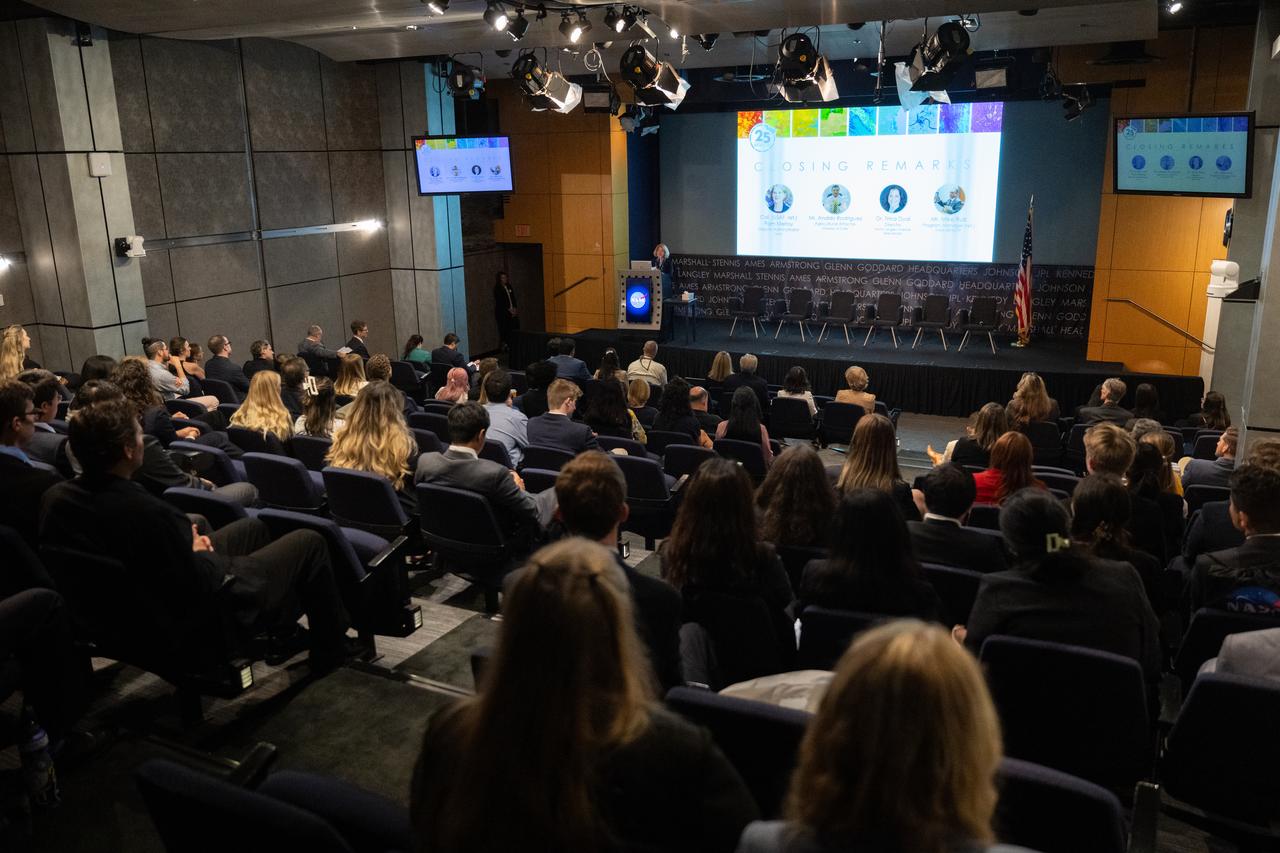
Students and young professionals discuss their projects during the 2023 DEVELOP Day, Wednesday, Aug. 9, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters to present their research. This year marks the 25th year of DEVELOP, a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisors from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In tribute to the 25th anniversary of the first space shuttle flight, NASA's Kennedy Space Center has honored the crew of STS-1, Commander John Young and Pilot Robert Crippen, by dedicating the firing room that launched the historic flight as the "Young · Crippen Firing Room." Making the dedication were (from left) Center Director Jim Kennedy; the NASA test director for STS-1, Norm Carlson; and the project flight engineer for Space Shuttle Columbia, Bob Sieck. On the wall behind them is the plaque marking the dedication. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
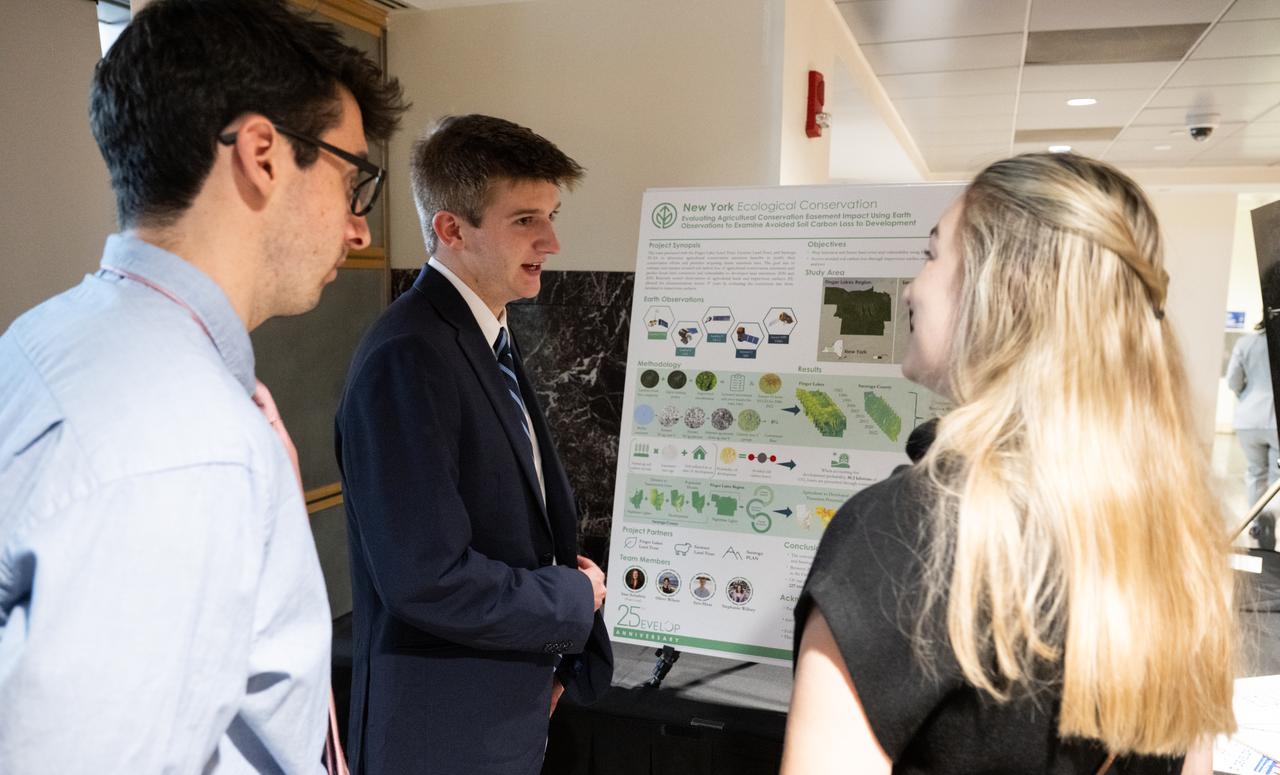

Students and young professionals discuss their projects during the 2023 DEVELOP Day, Wednesday, Aug. 9, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters to present their research. This year marks the 25th year of DEVELOP, a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisors from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
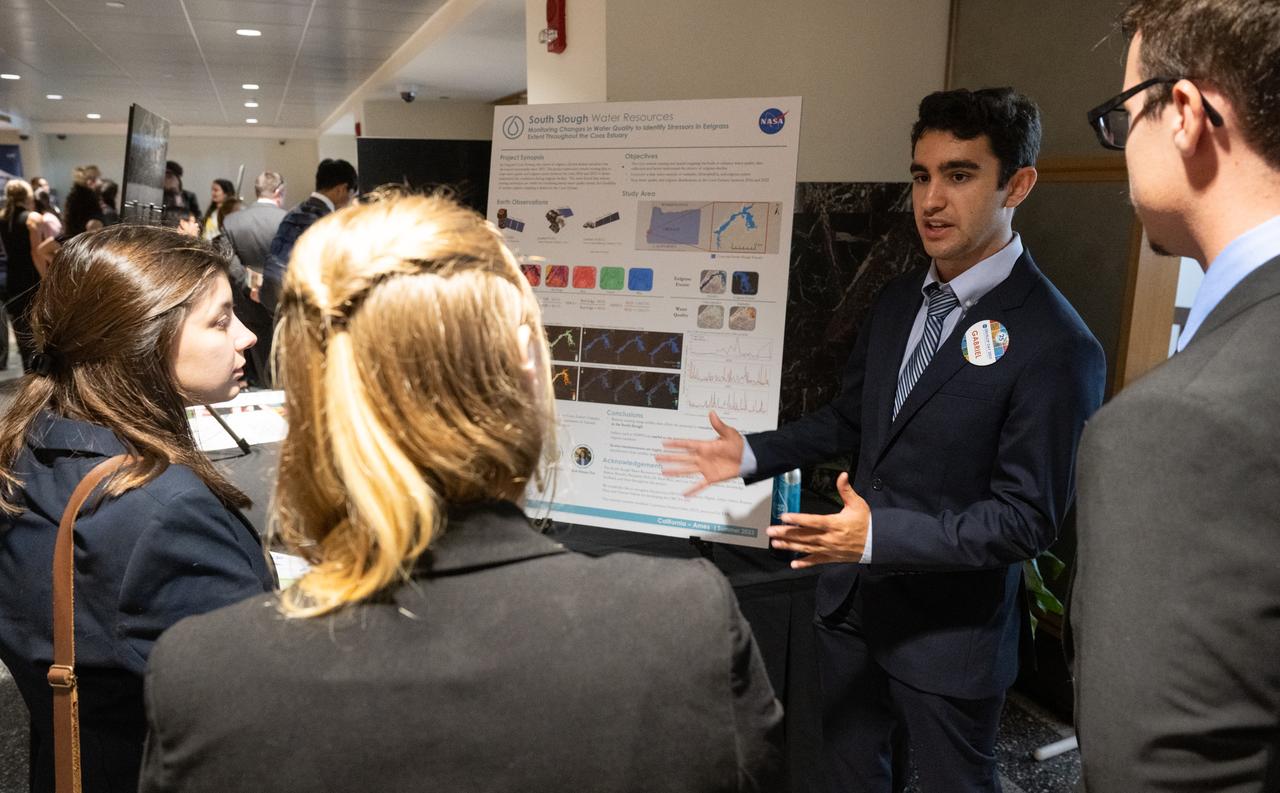

Students and young professionals discuss their projects during the 2023 DEVELOP Day, Wednesday, Aug. 9, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters to present their research. This year marks the 25th year of DEVELOP, a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisors from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
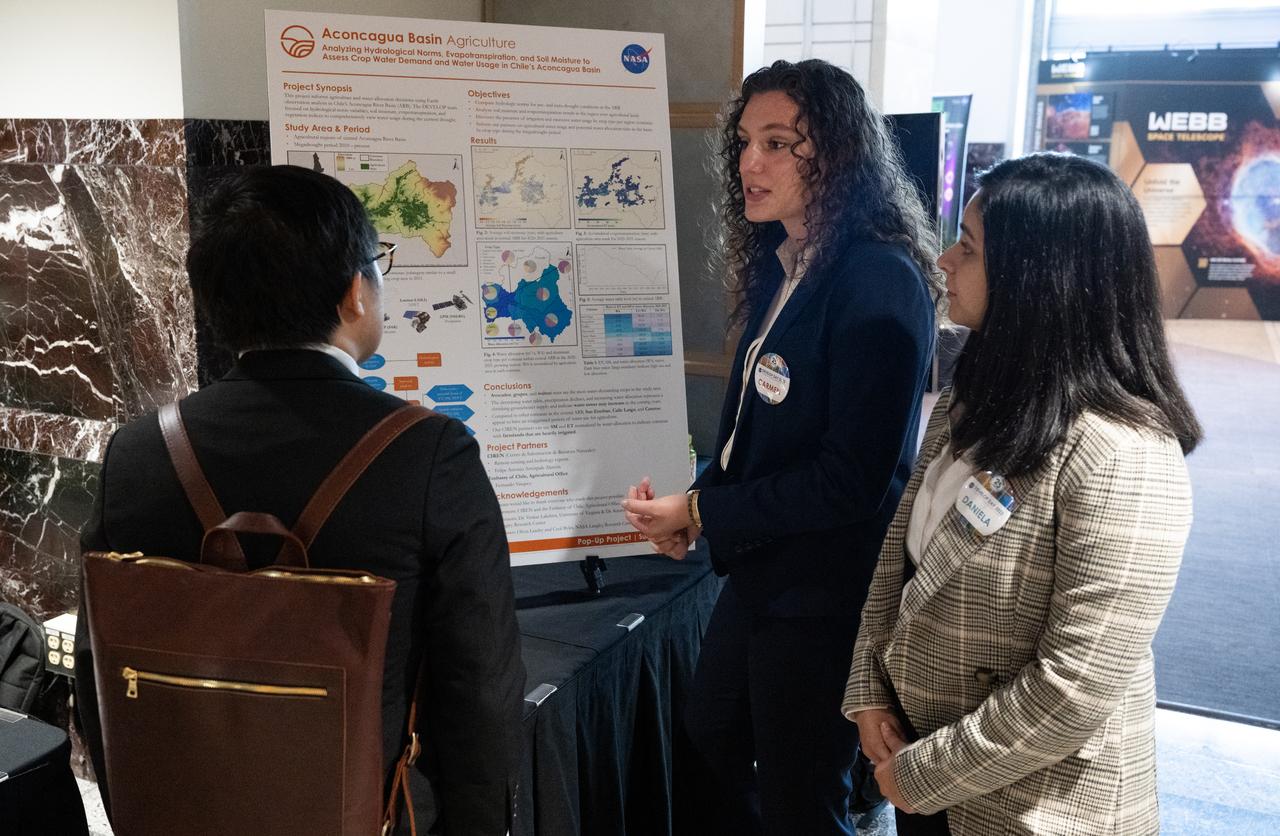
Students and young professionals discuss their projects during the 2023 DEVELOP Day, Wednesday, Aug. 9, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters to present their research. This year marks the 25th year of DEVELOP, a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisors from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
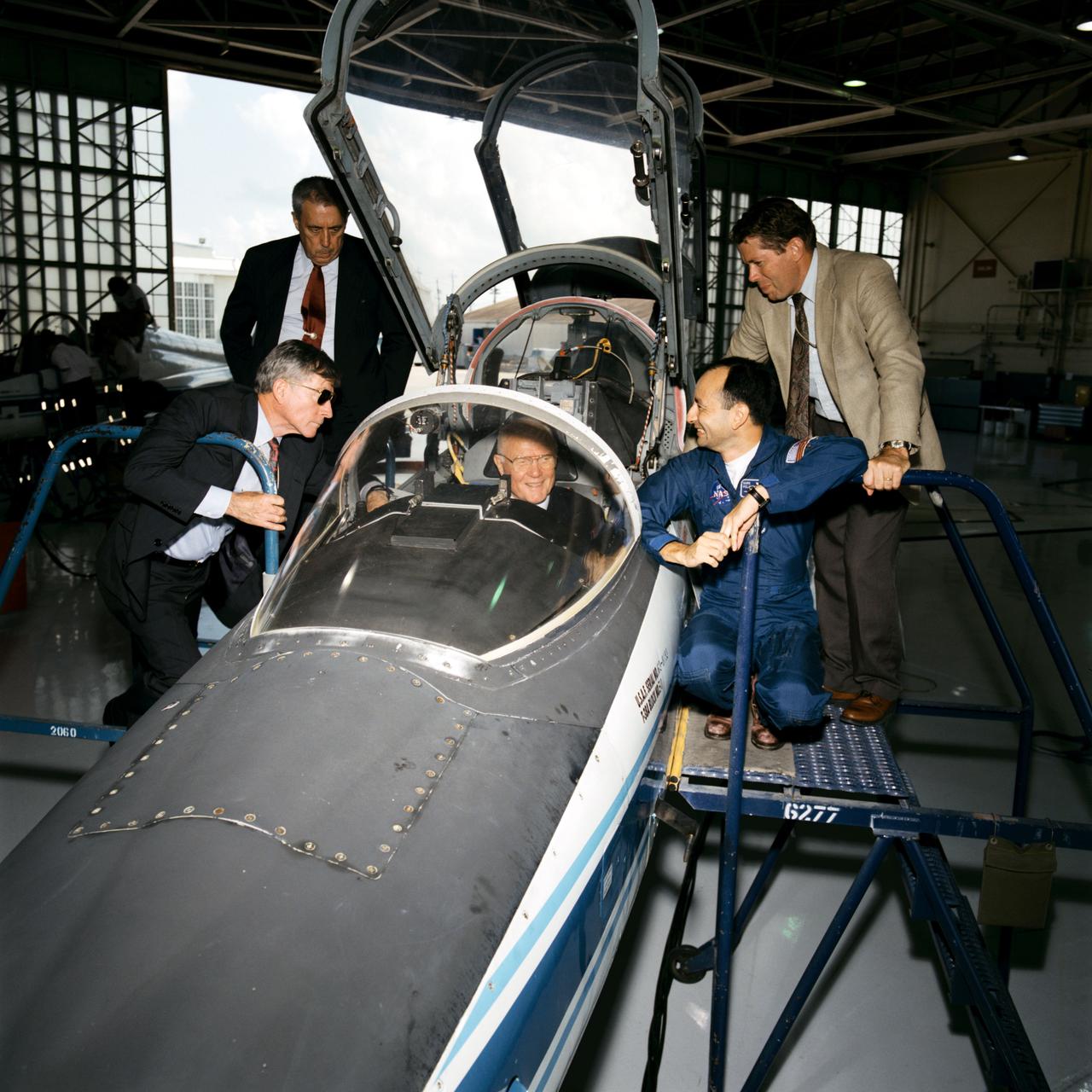

Senator John Glenn visit to Johnson Space Center (JSC). Views of Glenn sitting in cockpit of T-38 in Hangar 276 with John Young, George Abbey, David Leestma and Mark Polansky observing (11150). An engineer explains SPIFEX experiment hardware to Abby, Young and Glenn in Bldg 13 (11151, 11153). Glenn talks with astronaut Terrence T. Henricks and employees in Bldg 9C, Virtual reality lab (11152). Lunch in Bldg 17 Flight Crew support division with Dr. Ellen Baker, Robert "Hoot" Gibson and John Glenn (11154). Linda Godwin, Robert Cabana, Abbey, Young, Baker, Gibson and Glenn at lunch (11155). Astronaut Mark Lee shows Glenn and his aide how to use the virtural reality helmets (11156-7). Glenn shakes the hand of Franklin Chang-Diaz with his plasma rocket in the background in the Sonny Carter Training Facility (SCTF) (11158). Glenn in the Manipulator Development Facility (MDF) Remote Manipulator System (RMS) station mock-up in Bldg 9A with Abbey, Young and aide (11159, 11186). Glenn signs a book for Thomas D. Jones as Frederick Sturckow and Linda Godwin look on (11160). Glenn inside visual-vestibular trainer in Bldg 9B (11161). In conference room meeting with astronaut corps in Bldg 4S, Glenn shakes Robert Cabana's hand (11162). John Glenn and John Young pose for a group shot with Bldg 17 Food lab personnel (11163). Glenn thanks the food lab personnel (11164). Glenn visits Bldg 5 Fixed Base (FB) middeck simulator with astronauts Terrence Henricks and Mary Ellen Weber (11165). Glenn with Charles T. Bourland (11166). STS-70 crew Donald Thomas, Terrence Henricks, Mary Ellen Weber, Nancy Currie and Kevin Kregel with Glenn's advisor (11167). STS-70 crew Thomas, Henricks, Weber, Currie and Kregel with John Glenn (11175). Glenn with Thomas, Kregel, Weber, Henricks and trainer (11176-7). David J. Homan assists Glenn's aide with virtual reality goggles (11168) and Glenn (11174). John Young in Bldg 9C equilibrium trainer (11169). Glenn with Carl Walz in flight deck mock-up of MDF in Bldg 9NE (11170, 11187). Young, Abbey, aides, Glenn and Walz examine helium balloon in MDF (11171-2). Chang-Diaz shows Glenn's tour group the plasma rocket (11173). Glenn's presentation to astronaut corps (11178-81, 11184-5). Glenn is presented with framed picture of Sonny Carter Training Facility (SCTF) (11182) and framed picture of space station (11183).
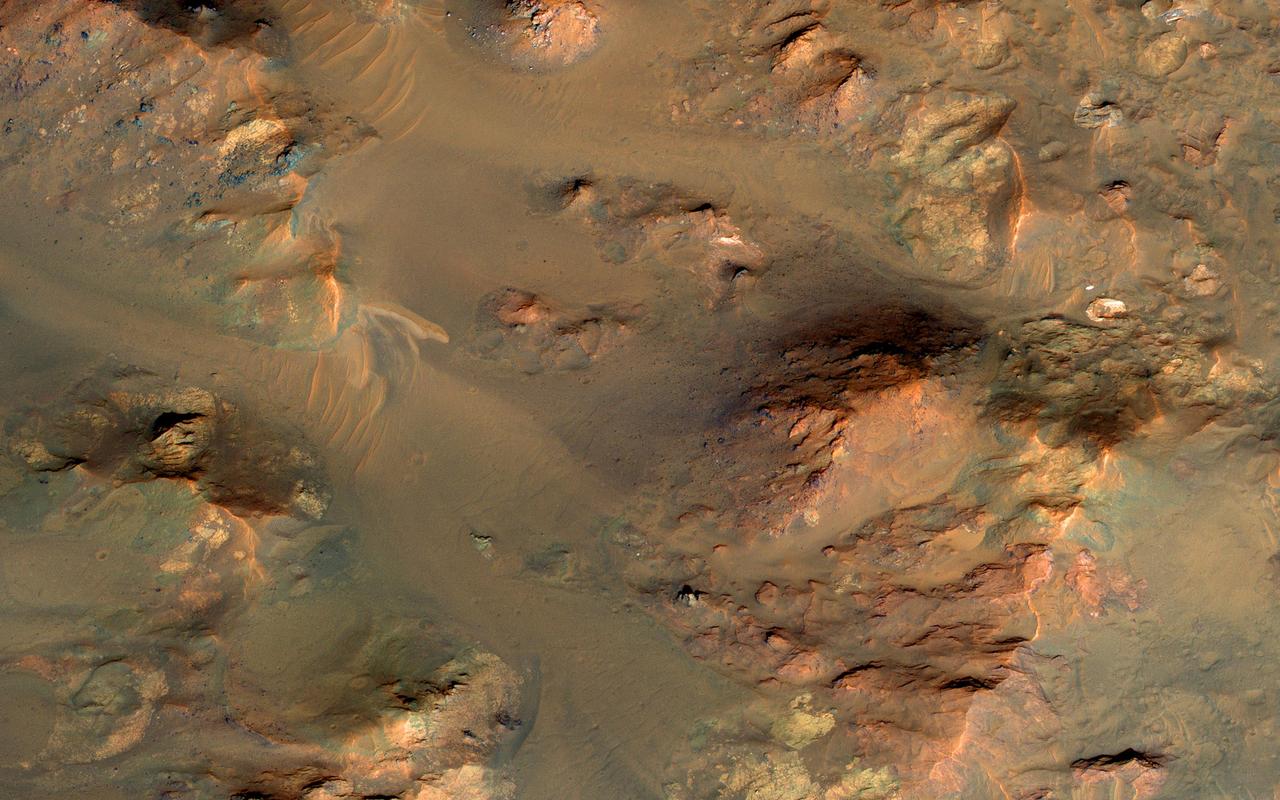

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows part of the central uplifted region of an impact crater more than 50 kilometers wide. That means that the bedrock has been raised from a depth of about 5 kilometers, exposing ancient materials. The warm (yellowish-reddish) colors mark the presence of minerals altered by water, whereas the bluish and greenish rocks have escaped alteration. Sharp-crested ridges and smooth areas are young windblown materials. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21640

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mark Geyer, Orion program manager, takes part in a briefing inside the Young-Crippen Firing Room at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA officials discussed the goals and expectations for a September 2014 flight test called Exploration Flight Test-1 or EFT-1 as part of the agency's goal of launching astronauts into deep space. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
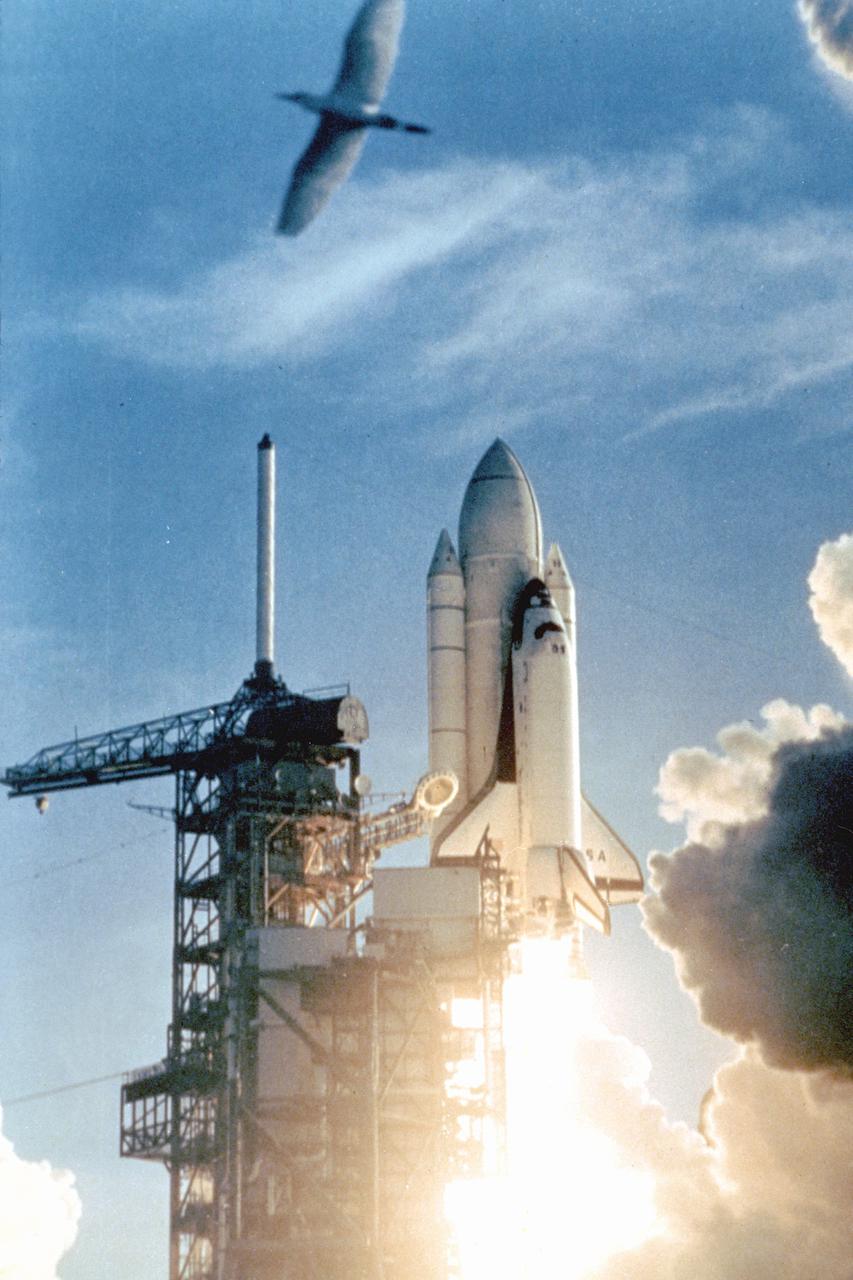

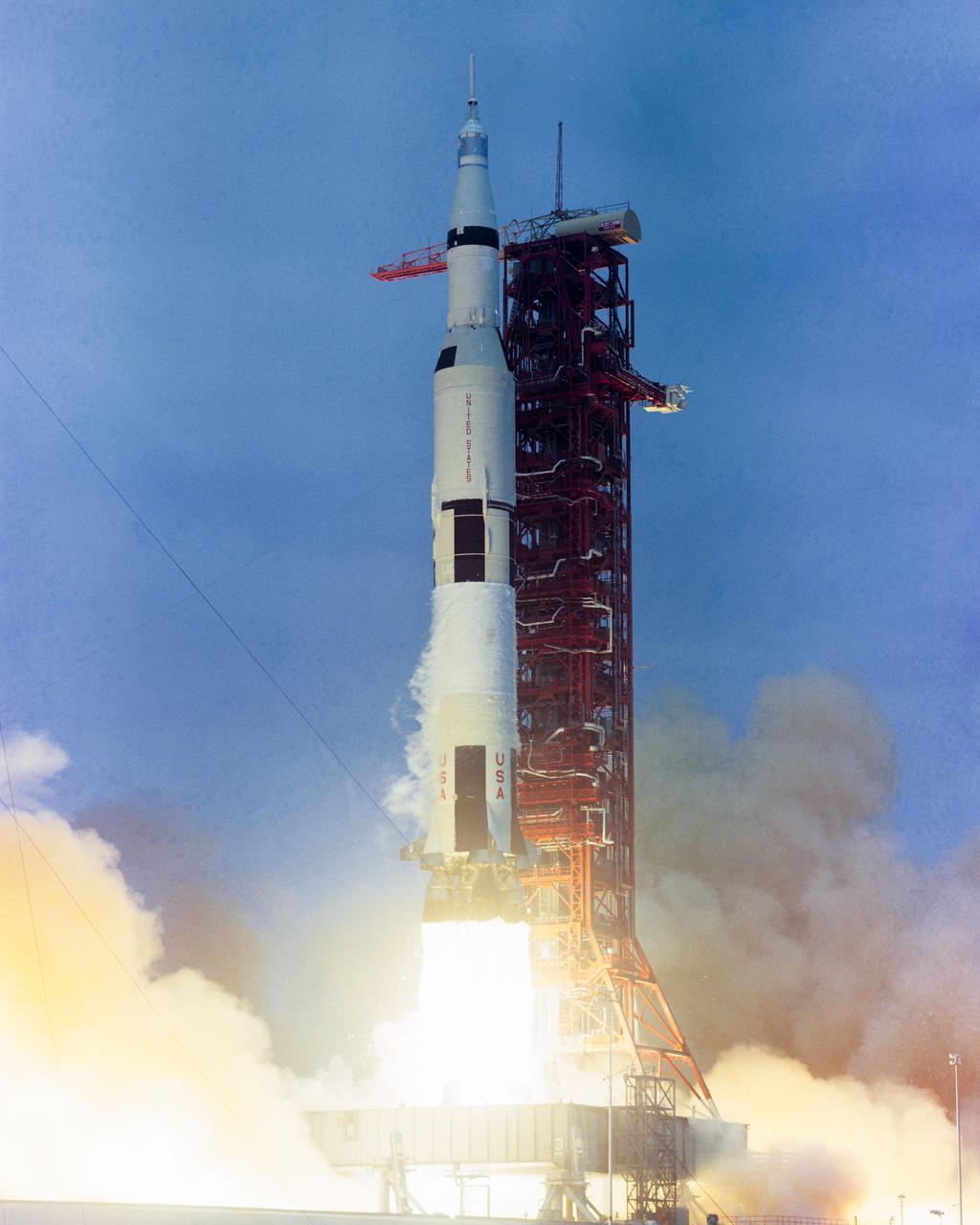
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Space Shuttle rises majestically above Launch Complex 39's Pad A on the first leg of its maiden journey into space. On board for the historic flight are astronauts John Young and Bob Crippen, scheduled to spend nearly 54 hours in space on this first shakedown test of America’s new reusable Space Transportation System (STS). The Sunday morning liftoff came a few seconds after 7 a.m. and marked the dawn of a new era in spaceflight.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Veterans of the space program enjoy a guided tour of the Kennedy Space Center following a ceremony marking the 40th anniversary of Project Gemini. More than 50 former Gemini workers attended the event. Astronaut John Young, himself a veteran of Project Gemini, was the key speaker, telling members of the group they should be pleased with their accomplishments, which ultimately helped to land a man on the moon and will lead to future Mars exploration. Photo credit:NASA/George Shelton
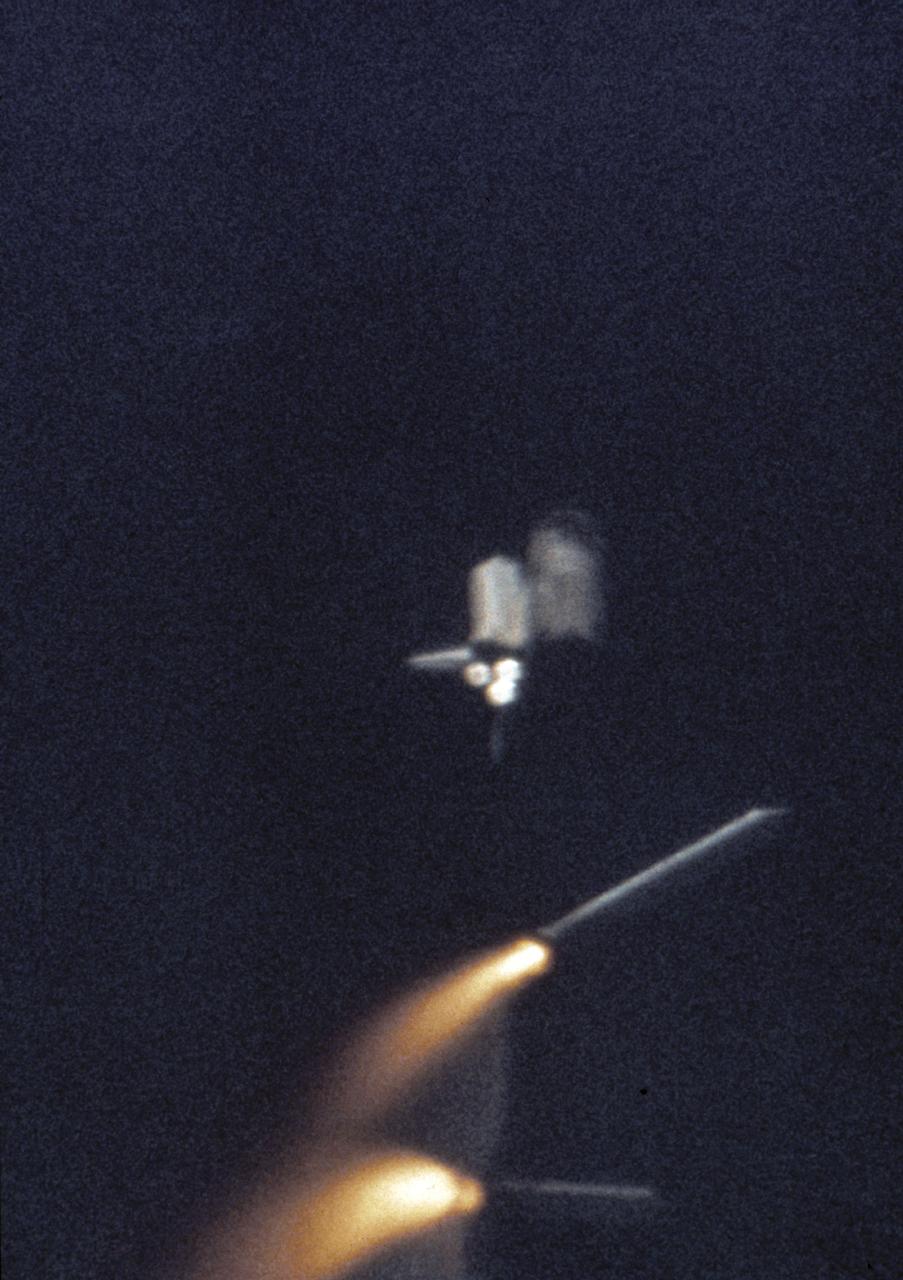
S81-33179 (12 April 1981) --- Though their STS-1 task has been performed, the two solid rocket boosters (SRB) still glow following their jettisoning from the space shuttle Columbia on its way to many firsts. Among the history recorded by the spacecraft is the marking of a mission in a reusable spacecraft. STS-1 is NASA's first manned mission since the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project in 1975. Inside the cabin of the climbing spacecraft are astronauts John W. Young and Robert L. Crippen. Photo credit: NASA
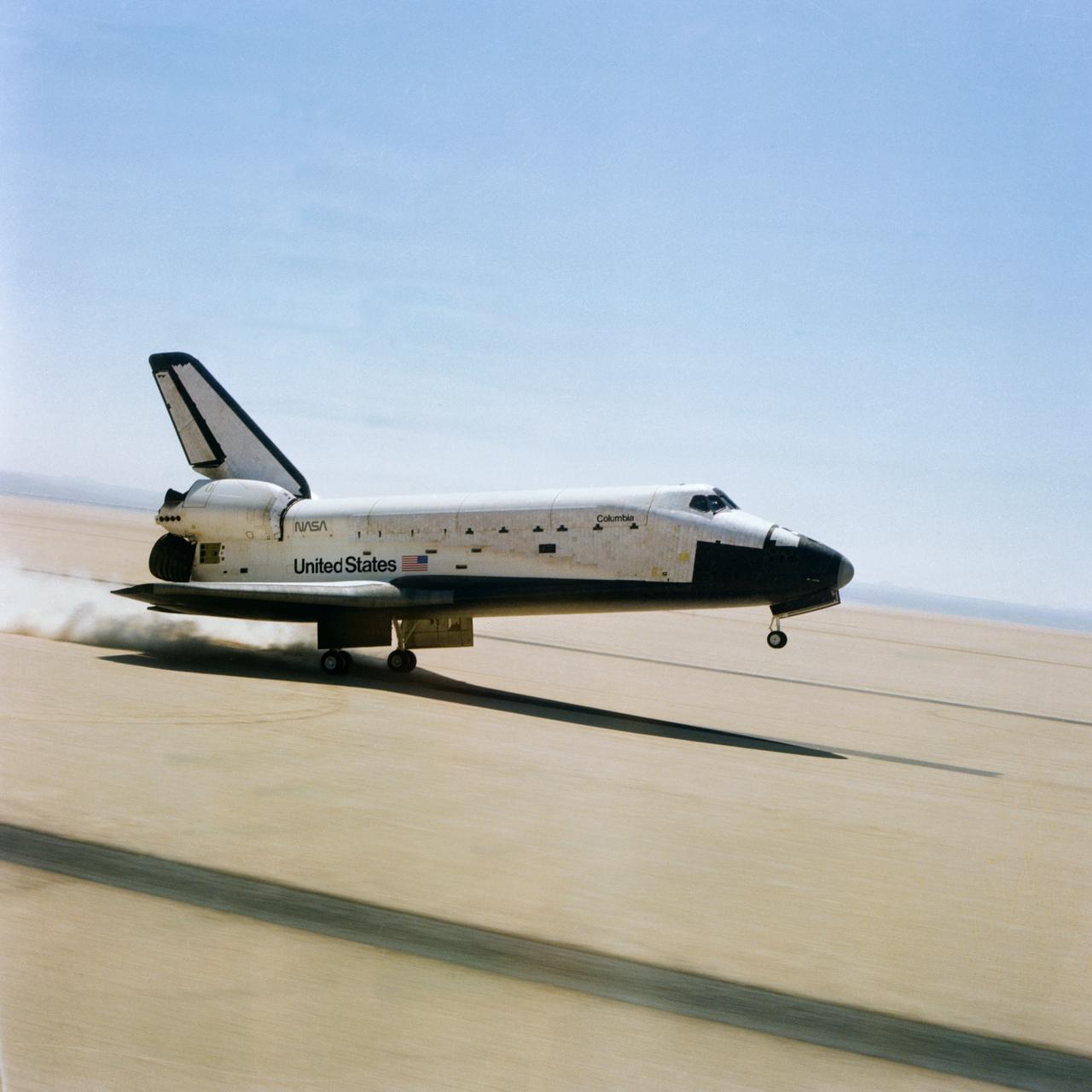

S81-30734 (14 April 1981) --- The rear wheels of the space shuttle orbiter Columbia (STS-1) touch down on Rogers dry lake at Edwards Air Force Base in southern California to successfully complete a stay in space of more than two days. Astronauts John W. Young, commander, and Robert L. Crippen, pilot, are aboard the vehicle. The mission marked the first NASA flight to end with a wheeled landing and represents the beginning of a new age of spaceflight that will employ the same hardware repeatedly. Photo credit: NASA
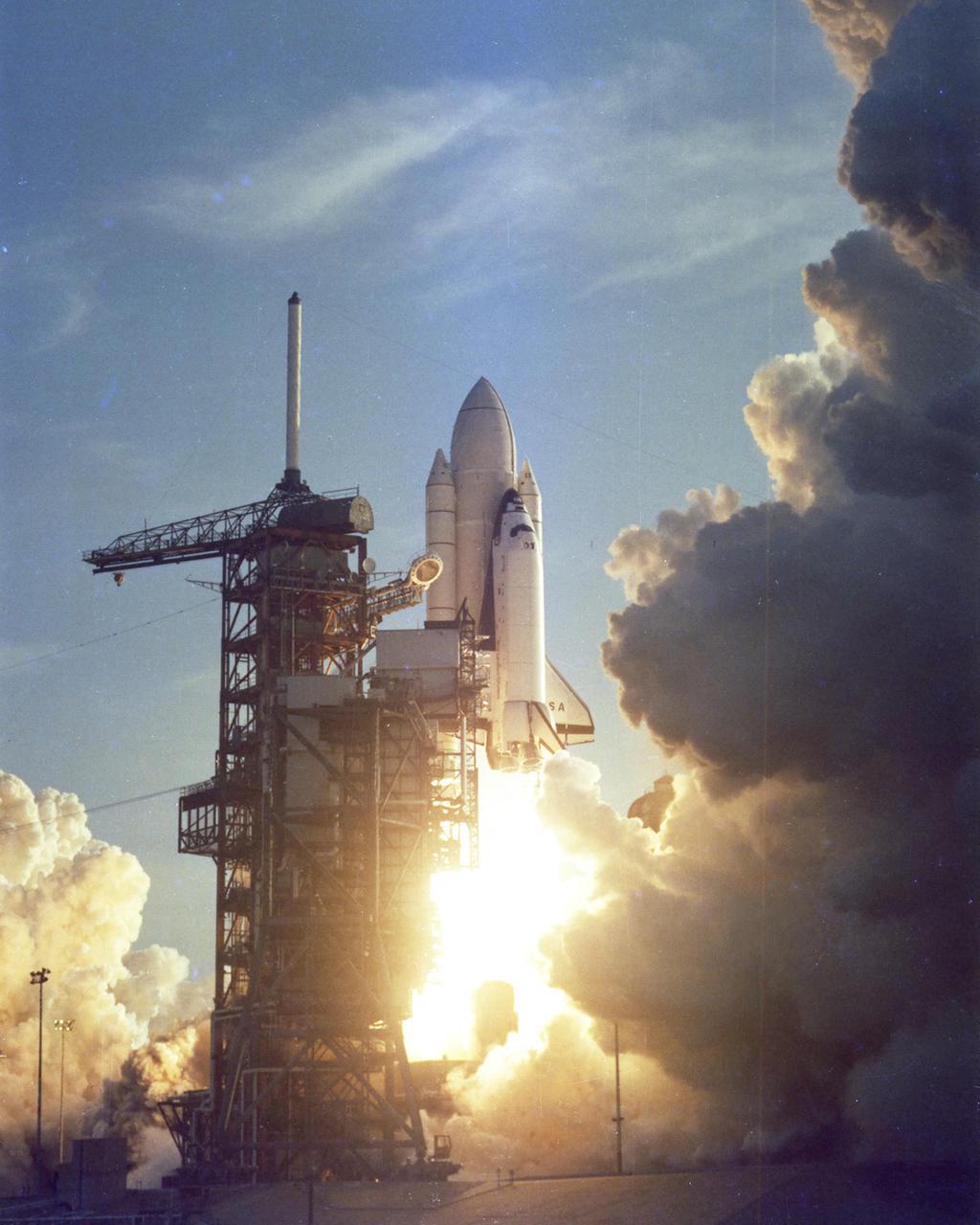

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle Columbia rises majestically above Launch Complex 39's Pad A on the first leg of its maiden journey into space. On board for the historic flight are Astronauts John Young and Bob Crippen, scheduled to spend nearly 54 hours in space on this first shakedown test of America's new reusable Space Transportation System (STS-1). The Sunday morning liftoff came a few seconds after 7:00 a.m. and marked the dawn of a new era in spaceflight.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-1: Columbia. The Space Shuttle rises majestically above Launch Complex 39’s Pad A on the first leg of its maiden journey into space. On board for the historic flight are Astronauts John Young and Bob Crippen, scheduled to spend nearly 54 hours in space on this first shakedown test of America’s new reusable Space Transportation System (STS). The Sunday morning liftoff came a few seconds after 7 a.m. and marked the dawn of a new era in spaceflight.
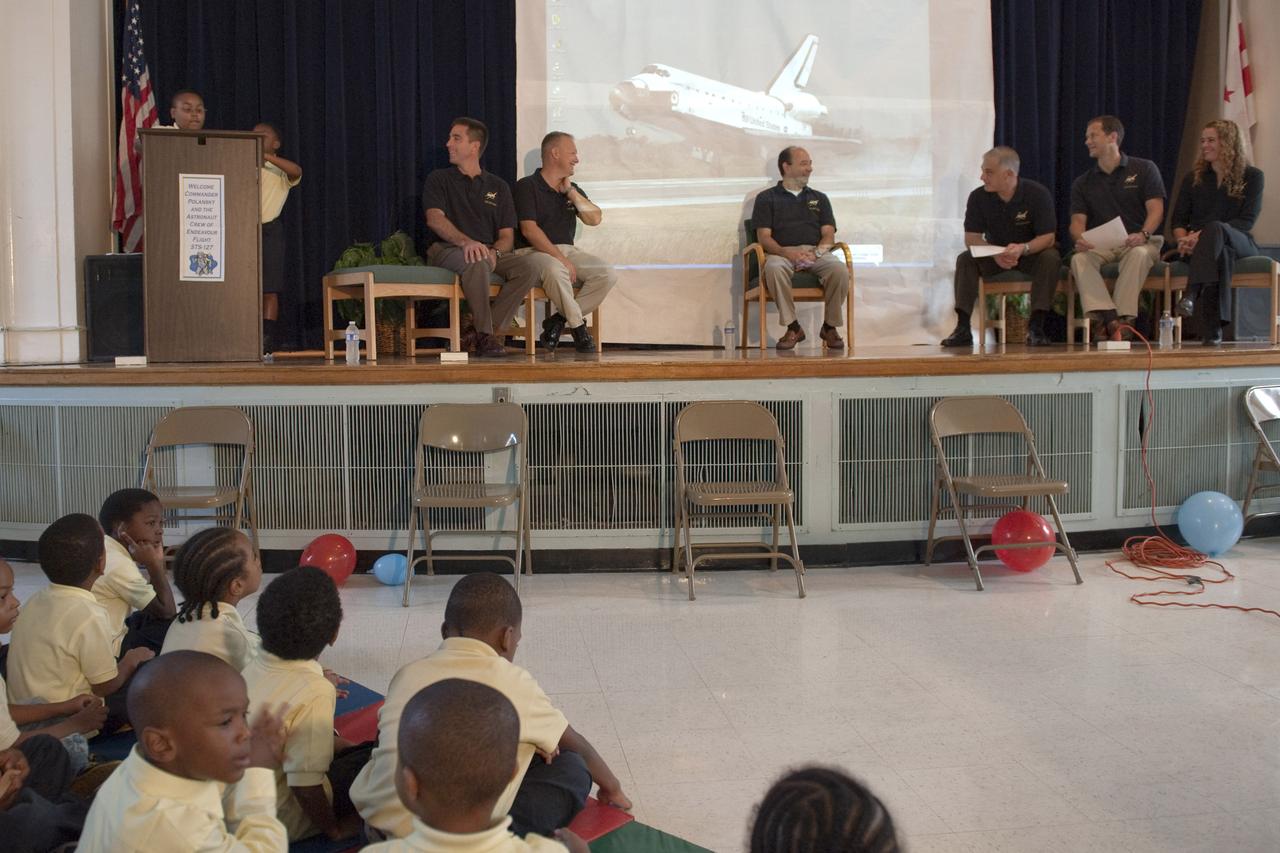

Ajani Young, a fourth grade student at Anne Beers Elementary school, at podium, introduces the crew of STS-127 during their visit, Thursday, Sept. 24, 2009, in Washington. Seated from left are crew members, Chris Cassidy, Doug Hurley, Commander Mark Polansky, David Wolf, Tom Marshburn and Canadian Space Agency astronaut Julie Payette. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

Young people prepare model rockets during an Astro Camp activity at Keesler Air Force Base in Biloxi. Stennis hosted the camp June 28 - July 1 in support of the White House Military Families Initiative. The camp also marked the beginning of a partnership between Stennis and Keesler to provide NASA education experiences to military children and to train children and youth care-providers. It is hoped that this activity can be expanded to other military bases next summer.
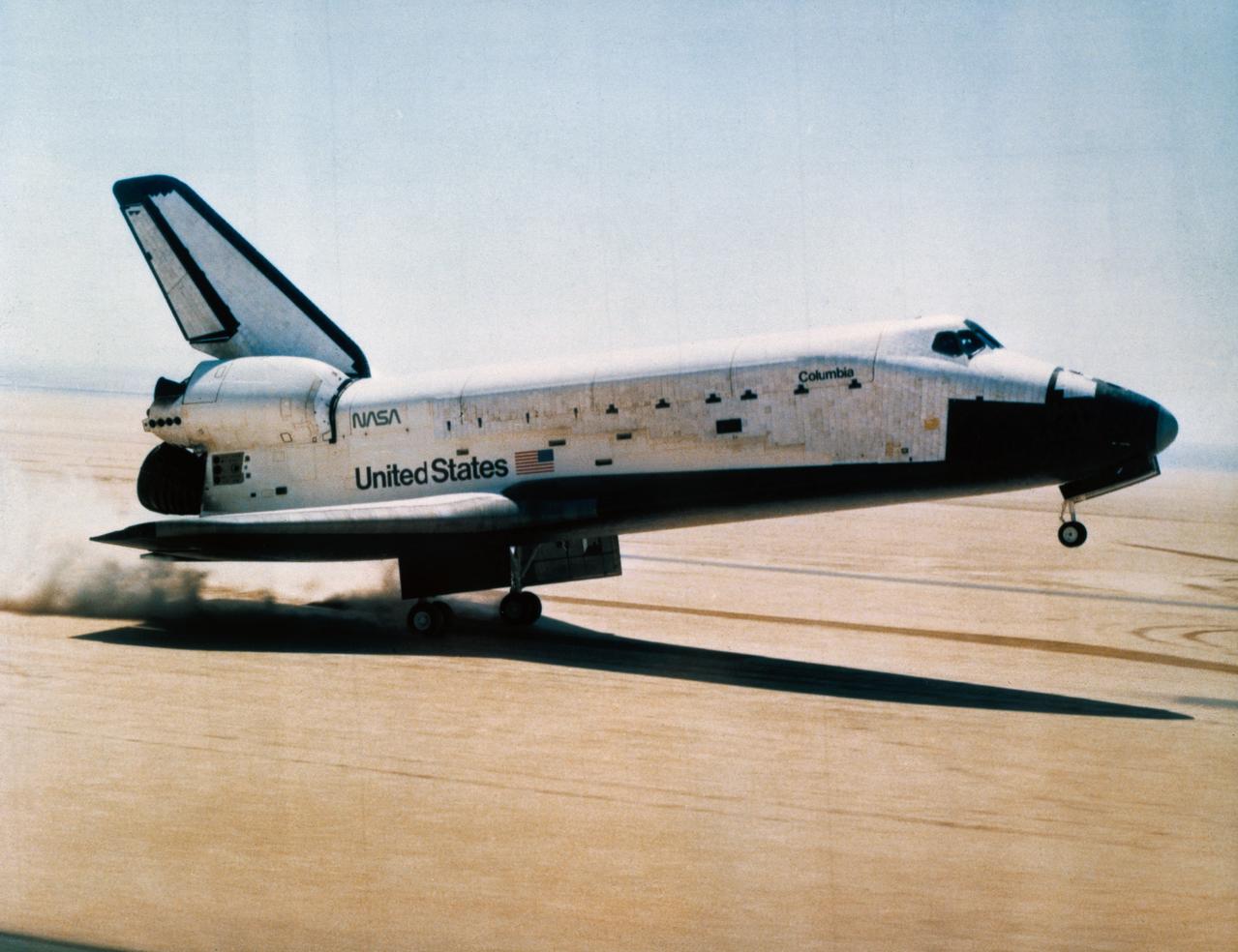
S81-30746 (14 April 1981) --- The rear wheels of the space shuttle orbiter Columbia touch down on Rogers dry lake at Edwards Air Force Base in southern California to successfully complete a stay in space of more than two days. Astronauts John W. Young, STS-1 commander, and Robert L. Crippen, pilot, are aboard the vehicle. The mission marked the first NASA flight to end with a wheeled landing and represents the beginning of a new age of spaceflight that will employ the same hardware repeatedly. Photo credit: NASA
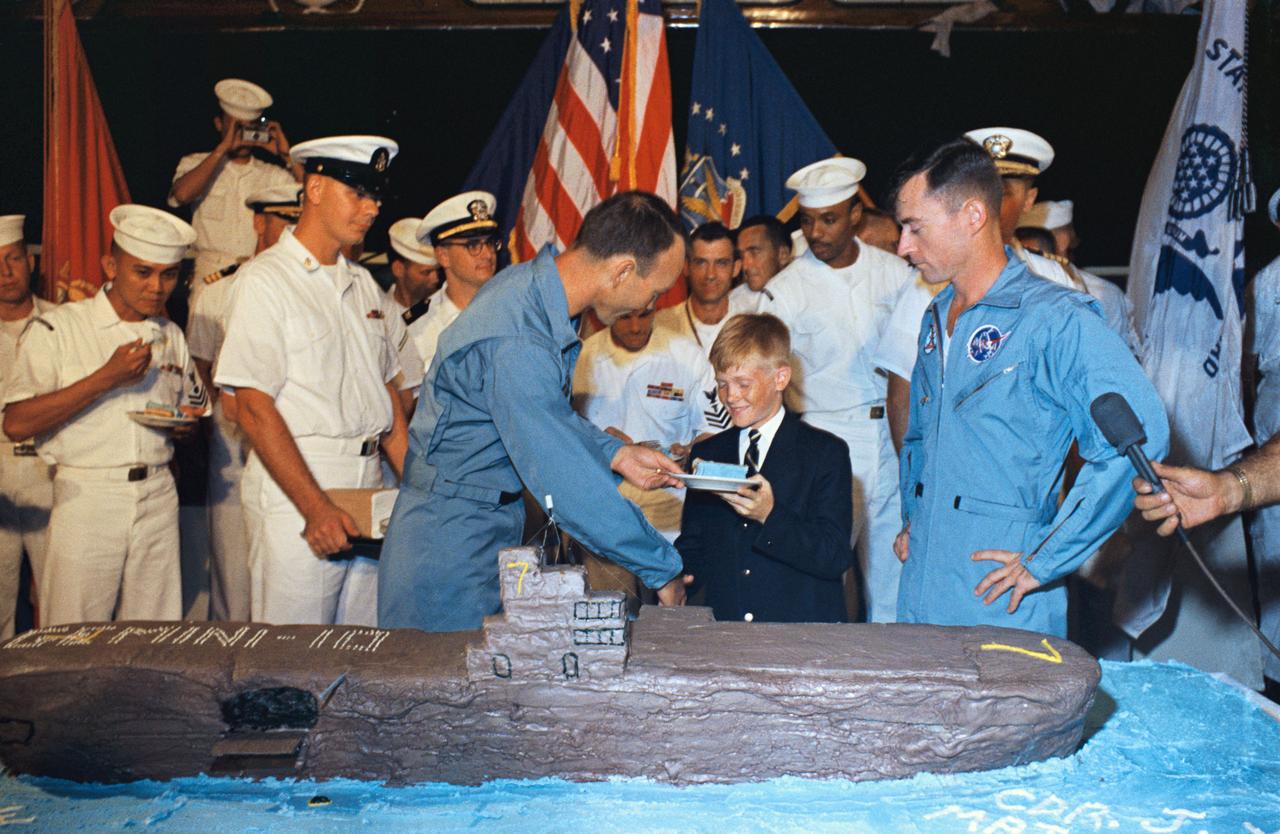

S66-42787 (21 July 1966) --- Twelve-year -old Billy Doyle of Virginia Beach, VA., shakes hands with astronaut Michael Collins, Gemini-10 pilot, aboard the recovery ship USS Guadalcanal. At right is John W. Young, command pilot of the Gemini-10 spaceflight. Billy represented 41 youngsters permitted aboard the Guadalcanal to witness the recovery with their Naval fathers or close relatives, marking the first time dependents have been permitted aboard a ship during a Gemini recovery operation. Photo credit: NASA
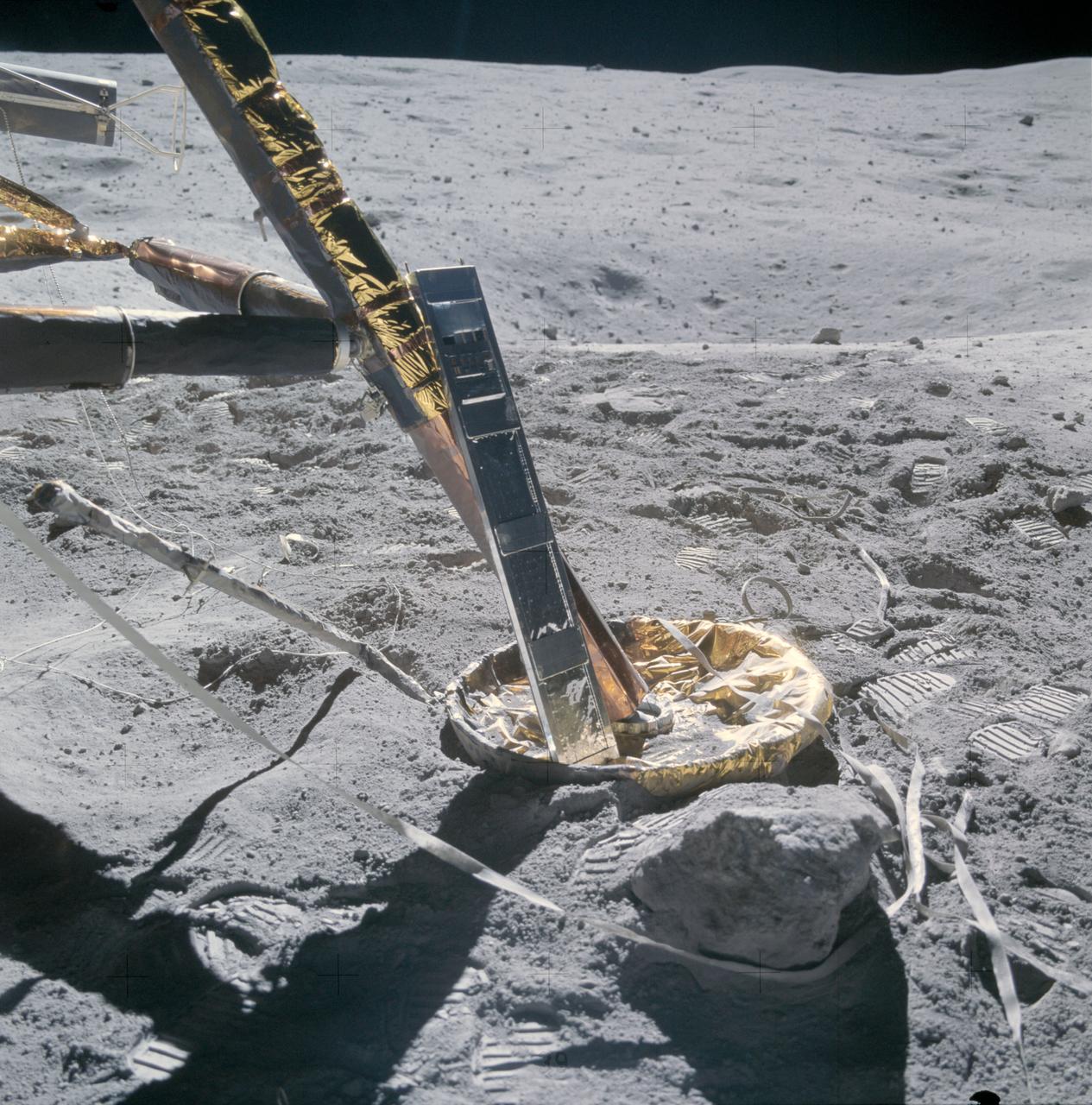

AS16-107-17442 (22 April 1972) --- A close-up view of the Apollo 16 Cosmic Ray Detector (CRD) experiment deployed at the +Y strut of the Lunar Module (LM). The crewmembers moved it to this position from near the deployment site of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) because, in the words of astronaut John W. Young, commander, "The panels were getting a little warm." Note that the LM did not skid upon landing, as evidenced by the landing contact probe's folded back (neatly) position and the lack of skid marks. While astronauts Young, and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
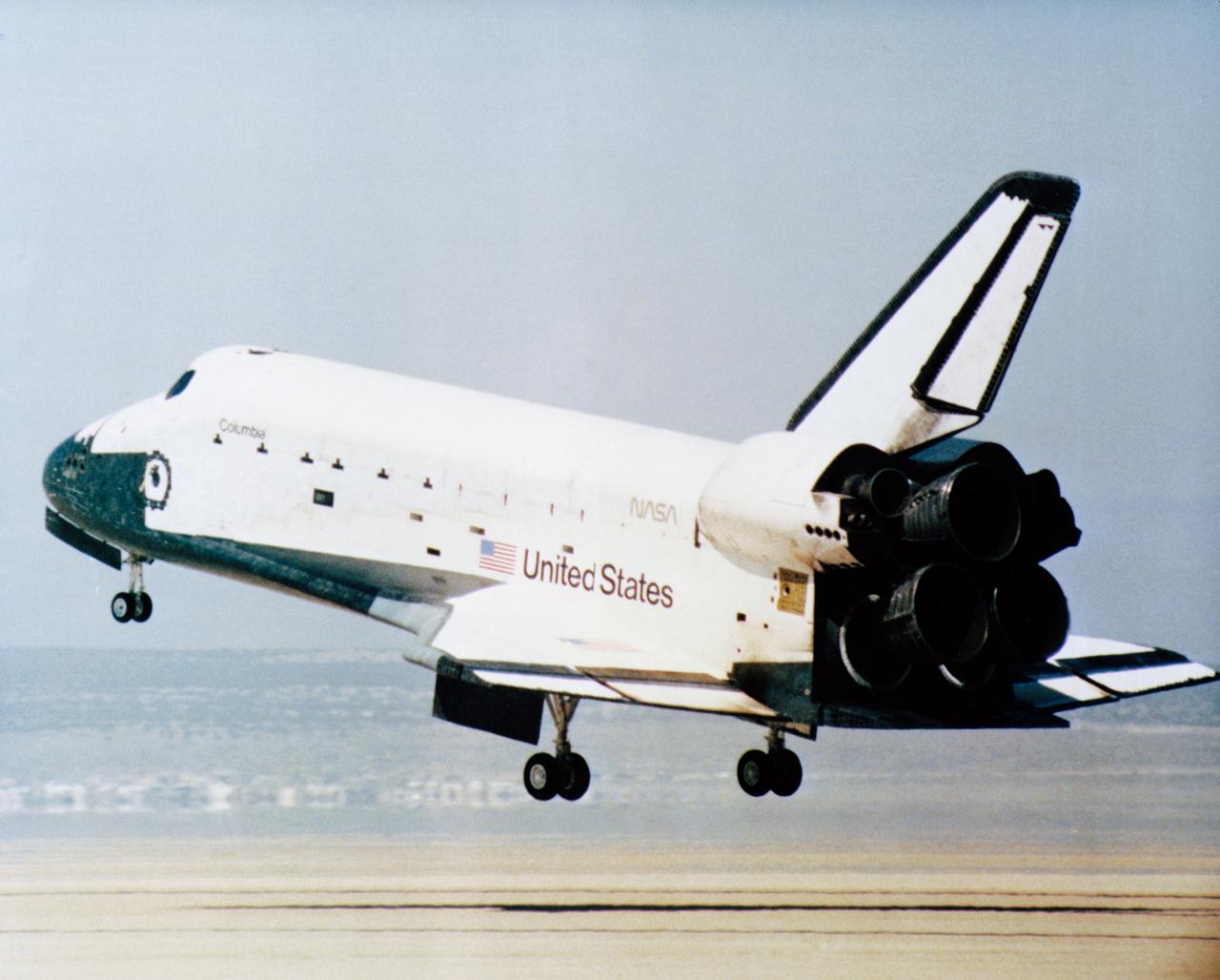

S81-30744 (14 April 1981) --- The rear wheels of the space shuttle orbiter Columbia are about to touch down on Rogers Lake (a dry bed) at Edwards Air Force Base in southern California to successfully complete a stay in space of more than two days. Astronauts John W. Young, STS-1 commander, and Robert L. Crippen, pilot, are aboard the vehicle. The mission marked the first NASA flight to end with a wheeled landing and represents the beginning of a new age of spaceflight that will employ the same hardware repeatedly. Photo credit: NASA
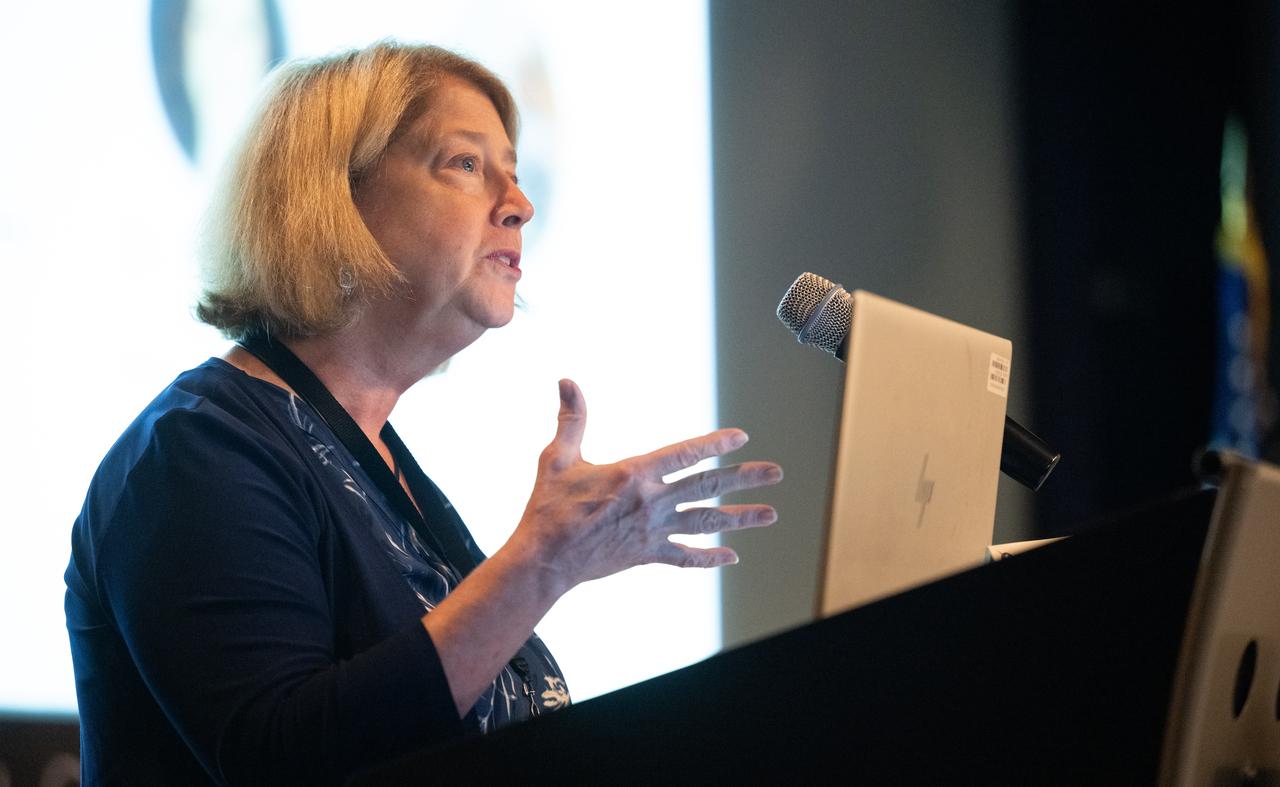

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy delivers closing remarks during the 2023 DEVELOP Day, Wednesday, Aug. 9, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters to present their research. This year marks the 25th year of DEVELOP, a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisors from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
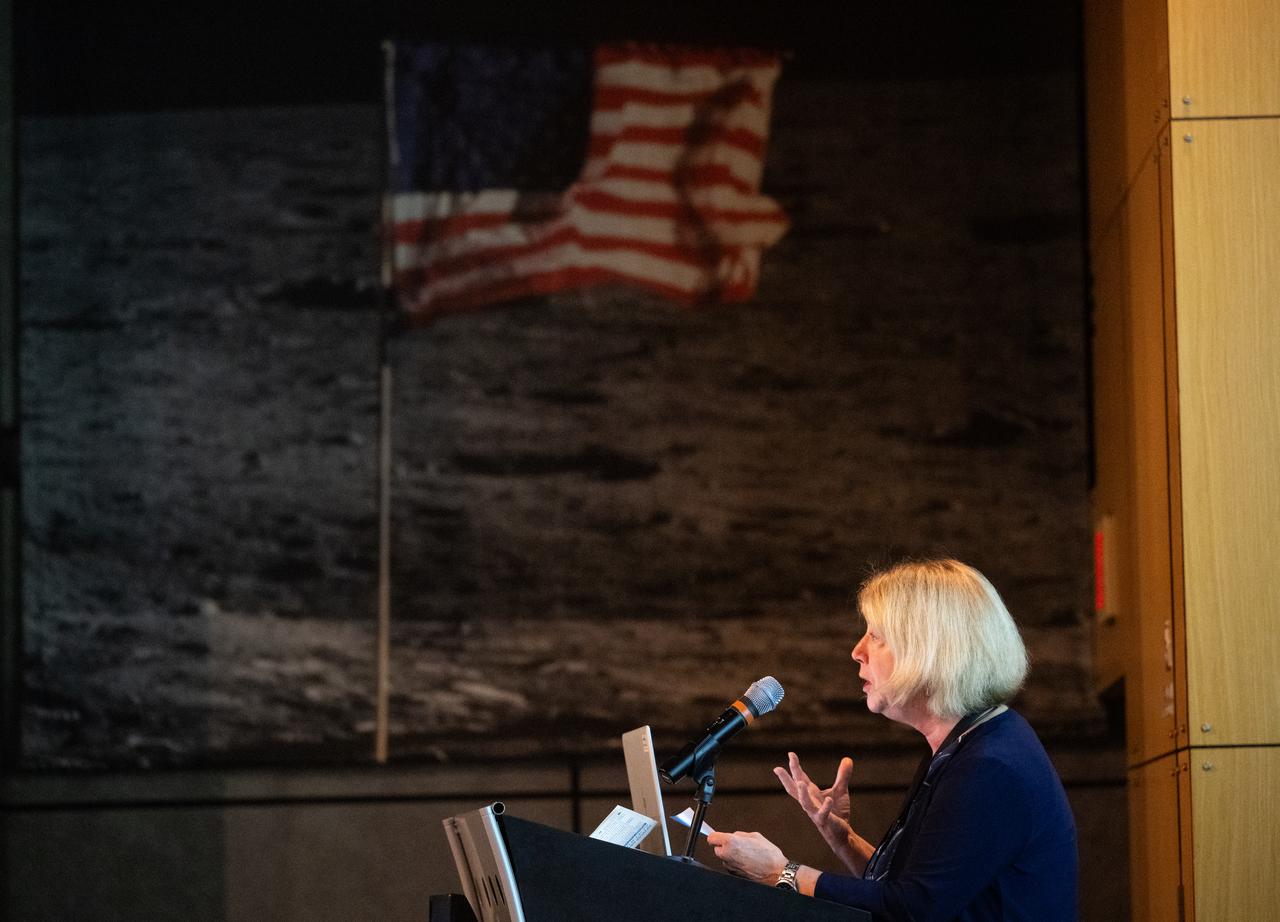

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy delivers closing remarks during the 2023 DEVELOP Day, Wednesday, Aug. 9, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters to present their research. This year marks the 25th year of DEVELOP, a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisors from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
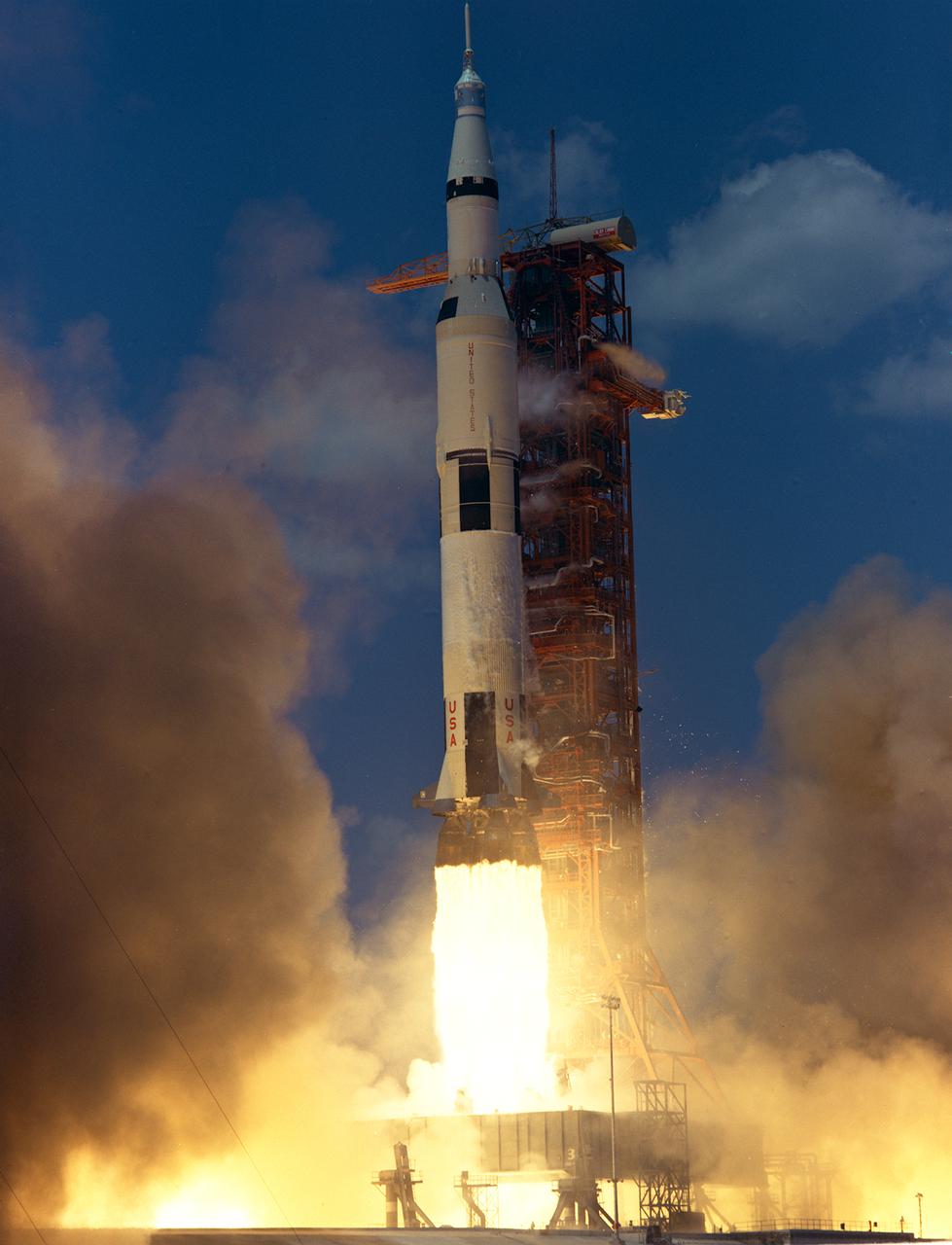

The sixth marned lunar landing mission, the Apollo 16 (SA-511), carrying three astronauts: Mission commander John W. Young, Command Module pilot Thomas K. Mattingly II, and Lunar Module pilot Charles M. Duke, lifted off on April 16, 1972. The Apollo 16 continued the broad-scale geological, geochemical, and geophysical mapping of the Moon's crust, begun by the Apollo 15, from lunar orbit. This mission marked the first use of the Moon as an astronomical observatory by using the ultraviolet camera/spectrograph. It photographed ultraviolet light emitted by Earth and other celestial objects. The Lunar Roving Vehicle was also used. The mission ended on April 27, 1972.
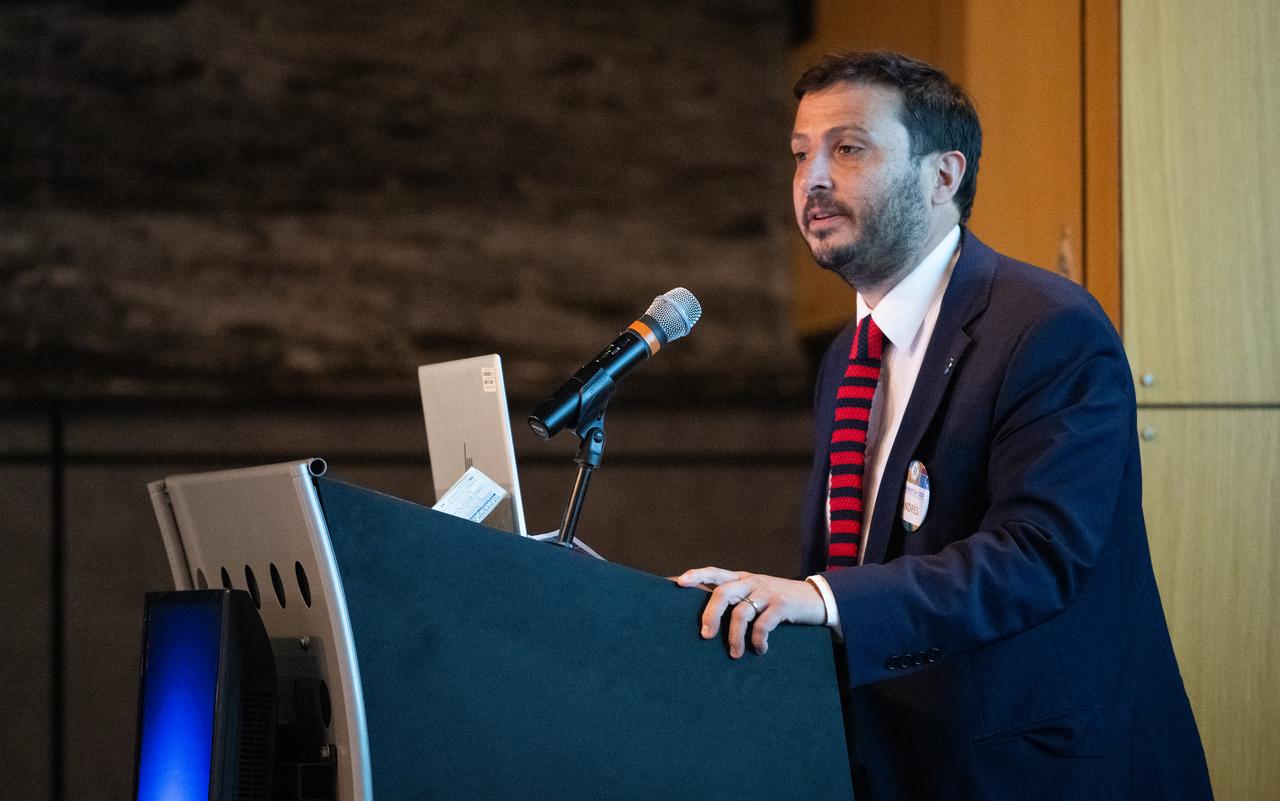

Andrés Rodriguez, Agricultural Attaché at the Embassy of Chile, delivers closing remarks during the 2023 DEVELOP Day, Wednesday, Aug. 9, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters to present their research. This year marks the 25th year of DEVELOP, a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisors from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
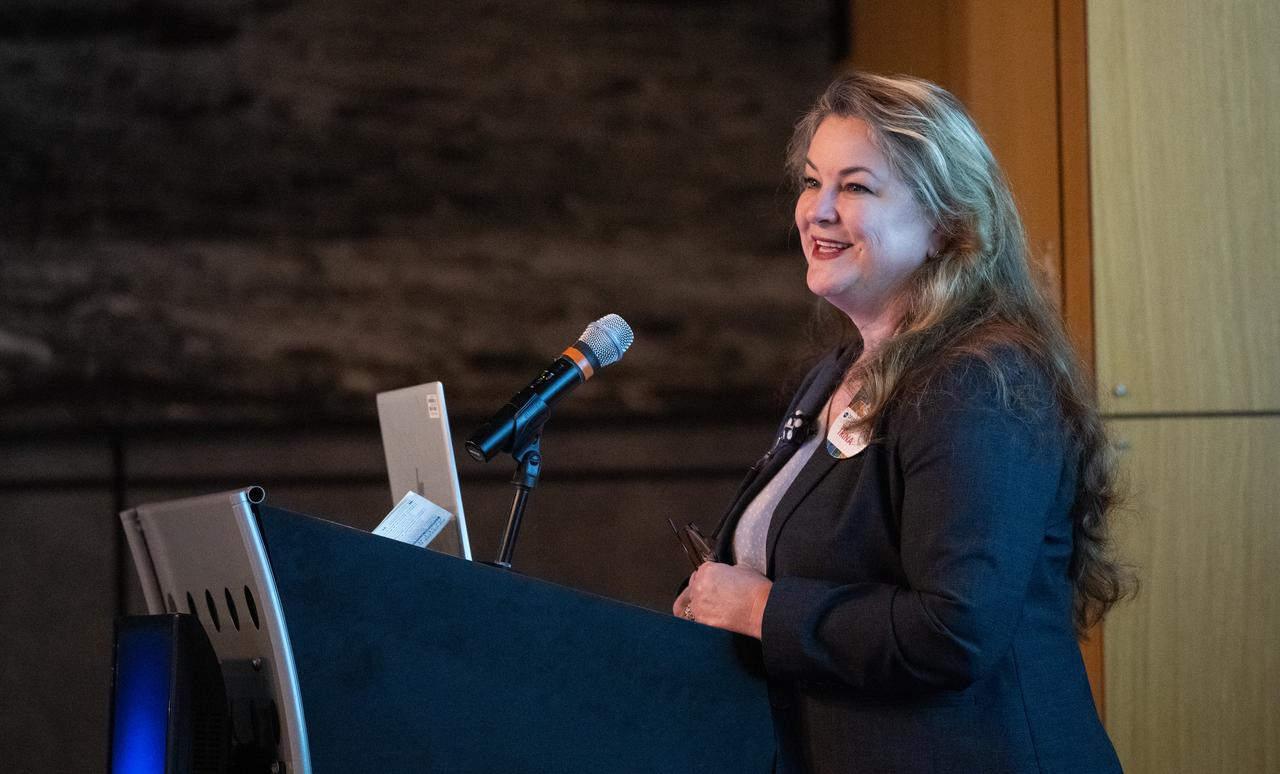

Trina Dyal, Director of the Science Directorate at NASA’s Langley Research Center, delivers closing remarks during the 2023 DEVELOP Day, Wednesday, Aug. 9, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters to present their research. This year marks the 25th year of DEVELOP, a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisors from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
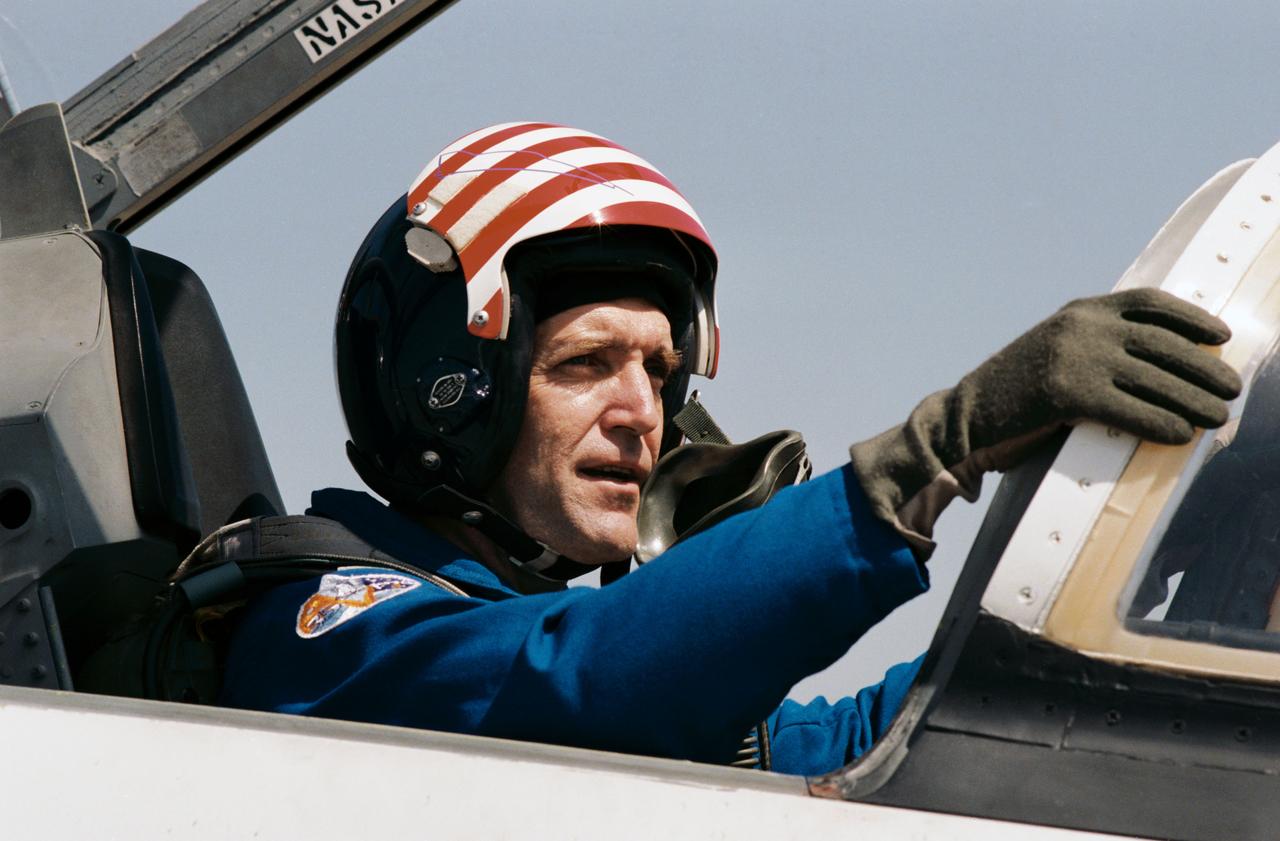

41C-3002 (3 April 1984) --- Astronaut Francis R. (Dick) Scobee, 41-C pilot, is only minutes away from leaving Ellington Air Base in a T-38. Scobee and four other 41-C crewmembers, along with Astronaut John W. Young, are headed for Florida, site of a launch in three days of the Space Shuttle Challenger. Scobee, an experienced pilot, is responsible for helping a number of other NASA astronauts learn to fly. The eleventh Space Shuttle mission will mark his first experience in space. This photograph was taken by Otis Imboden.
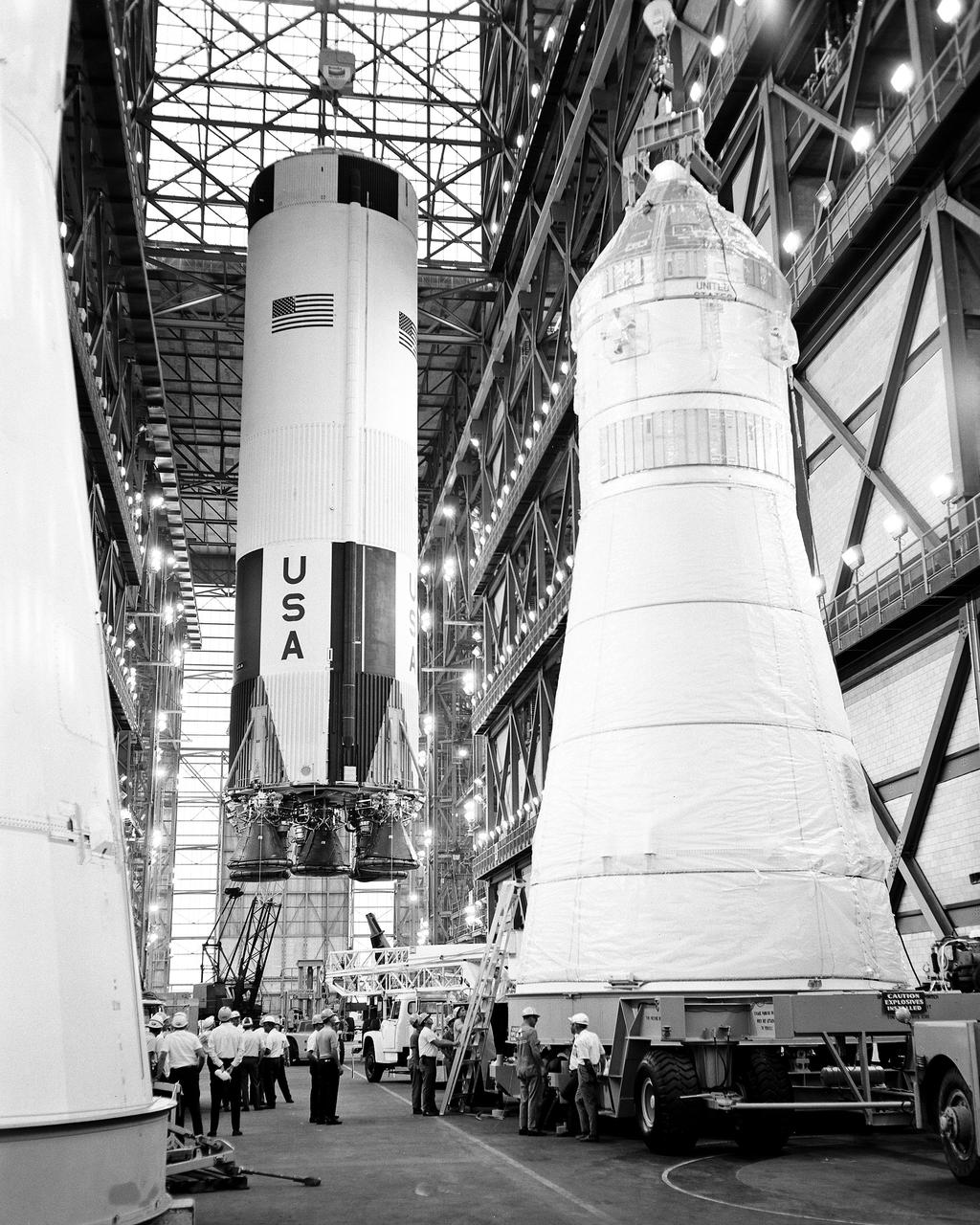

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The first stage of the Apollo 10 Saturn V space vehicle is hoisted above the transfer aisle in preparation for erection on a mobile launcher within High Bay 2 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. The erection of the 138-foot-long stage marked the first use of mobile launcher 3 and high bay 2. Apollo 10 will be piloted by astronauts Thomas Stafford, John Young and Eugene Cernan. In the foreground are the mated command, service and lunar modules the latter enclosed within the adapter for the Apollo 9 flight of James McDivitt, David Scott and Russel Schweickart. Photo credit: NASA
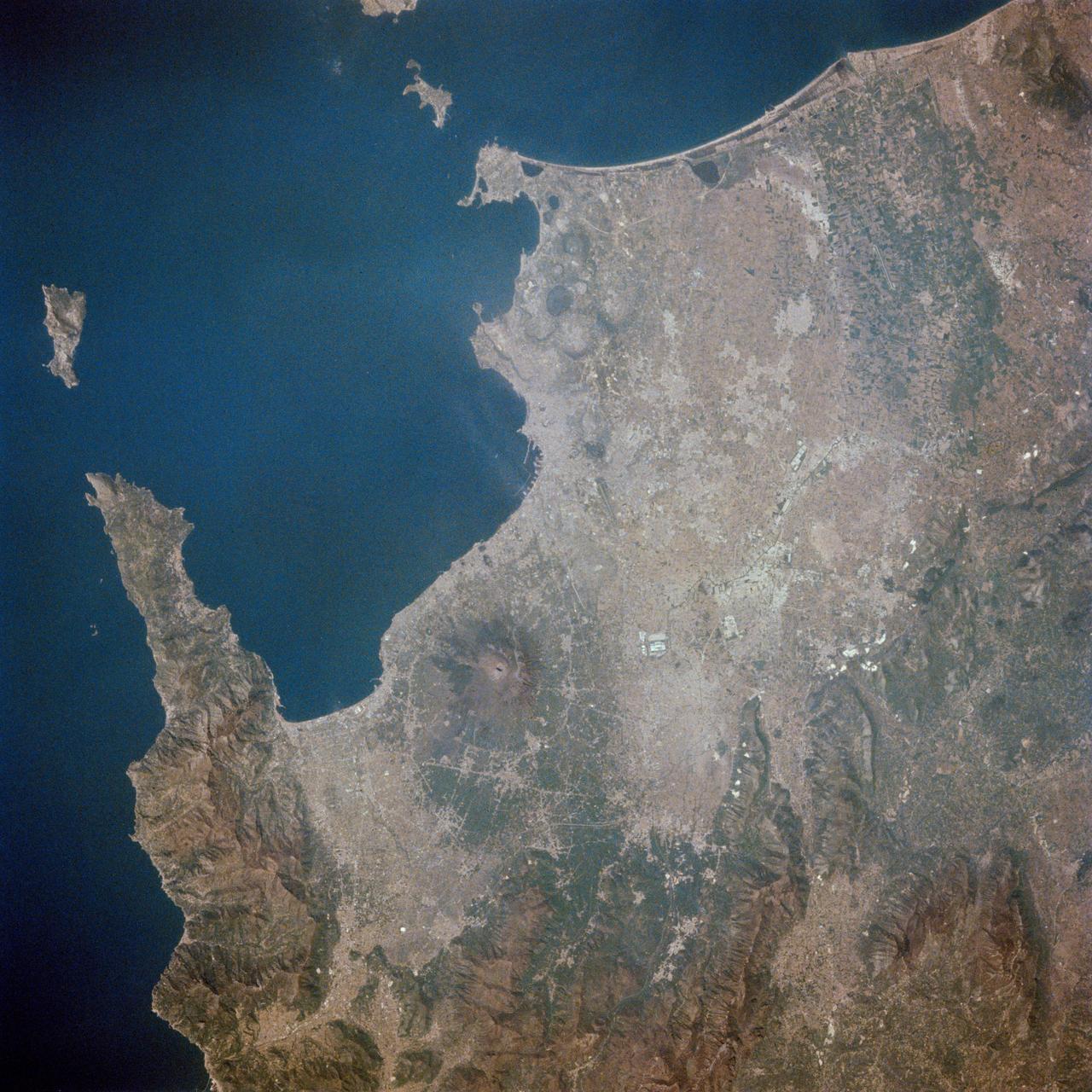

STS001-13-443 (12-14 April 1981) --- This photograph showing much of Italy was taken with a hand-held 70mm camera from 276 kilometers above Earth as the NASA space shuttle Columbia and its crew were marking their last few hours in space on the historic first space mission utilizing a reusable vehicle. Included in the area of the frame are Golfo de Napoli, Napoli (Naples), Castellammare, Amalfi, Capri, Sorrento, Mt. Vesuvius and the ruins of Pompei. Astronauts John W. Young and Robert L. Crippen exposed eight magazines of color 70mm film during their two-and-one-third days in Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy delivers closing remarks during the 2023 DEVELOP Day, Wednesday, Aug. 9, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters to present their research. This year marks the 25th year of DEVELOP, a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisors from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Mike Ruiz, former program manager for DEVELOP, delivers closing remarks during the 2023 DEVELOP Day, Wednesday, Aug. 9, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters to present their research. This year marks the 25th year of DEVELOP, a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisors from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
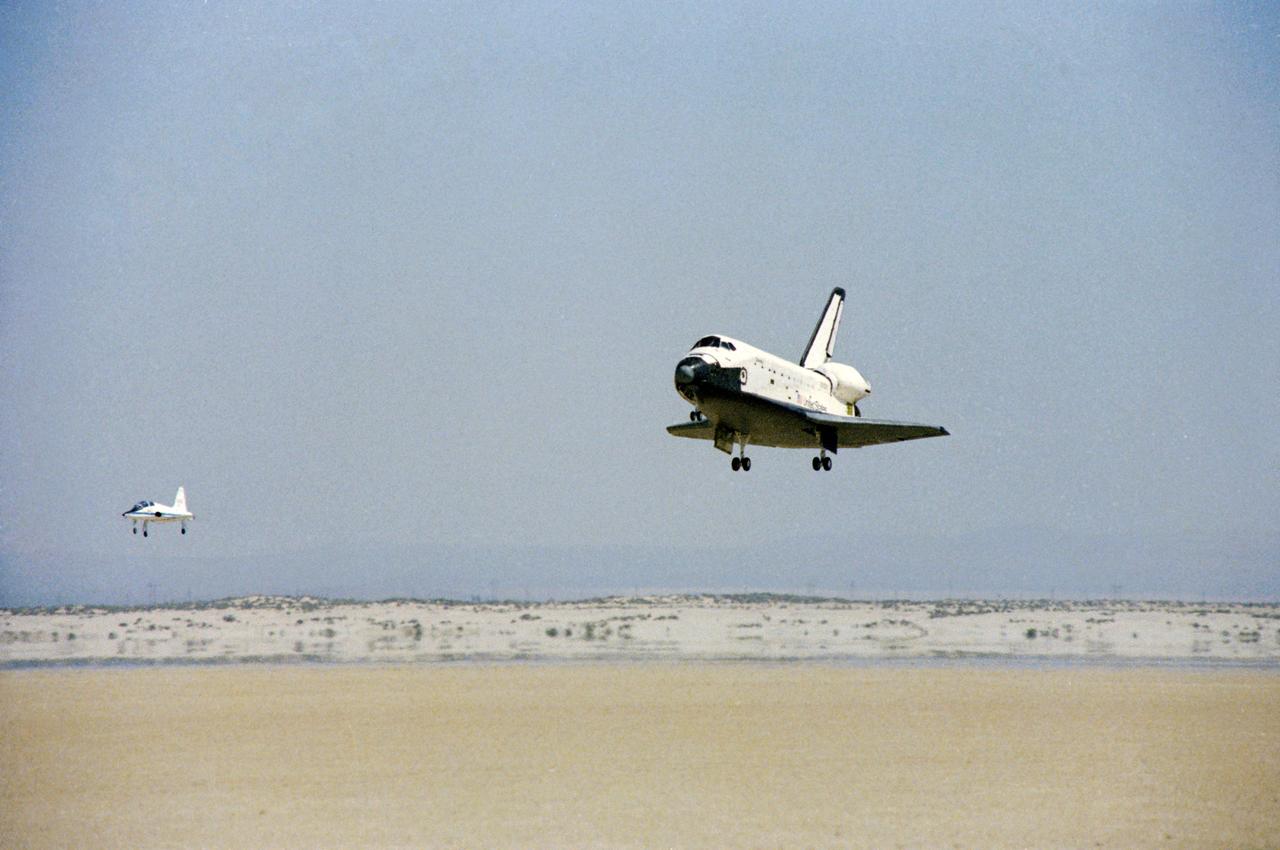

S81-30425 (14 April 1981) --- The space shuttle orbiter Columbia is seen from the front as it heads for a touchdown atop a dry lake bed at Edwards Air Force Base in southern California. A T-38 chase plane follows it in at left. Aboard Columbia were astronauts John W. Young, STS-1 commander, and Robert L. Crippen, pilot. Their landing marked the completion of a successful two-and-a-third day flight in space and the beginning of a new era of space transportation. A series of additional test flights will follow before the Space Shuttle Program becomes fully operational later in this decade. Photo credit: NASA

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy delivers closing remarks during the 2023 DEVELOP Day, Wednesday, Aug. 9, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters to present their research. This year marks the 25th year of DEVELOP, a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisors from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
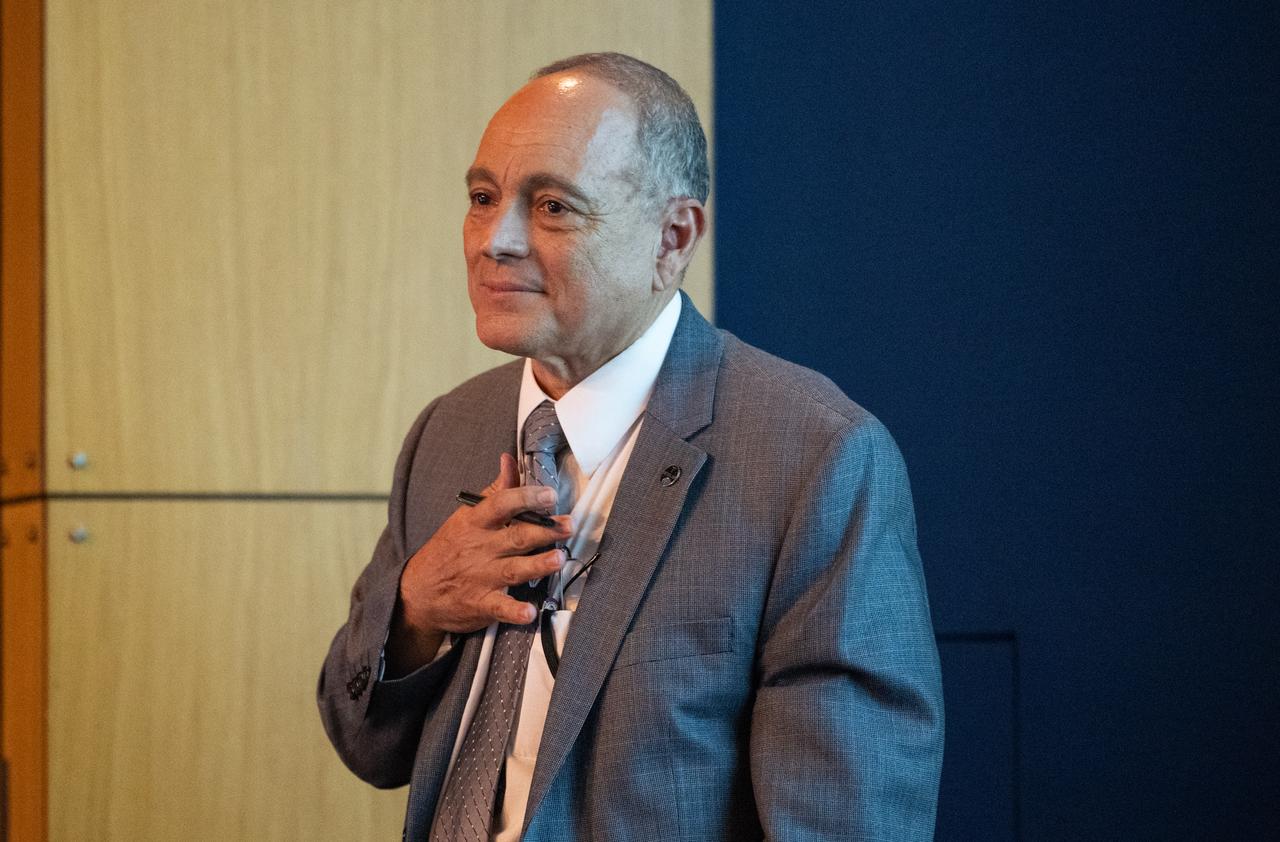

Mike Ruiz, former program manager for DEVELOP, delivers closing remarks during the 2023 DEVELOP Day, Wednesday, Aug. 9, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters to present their research. This year marks the 25th year of DEVELOP, a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisors from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
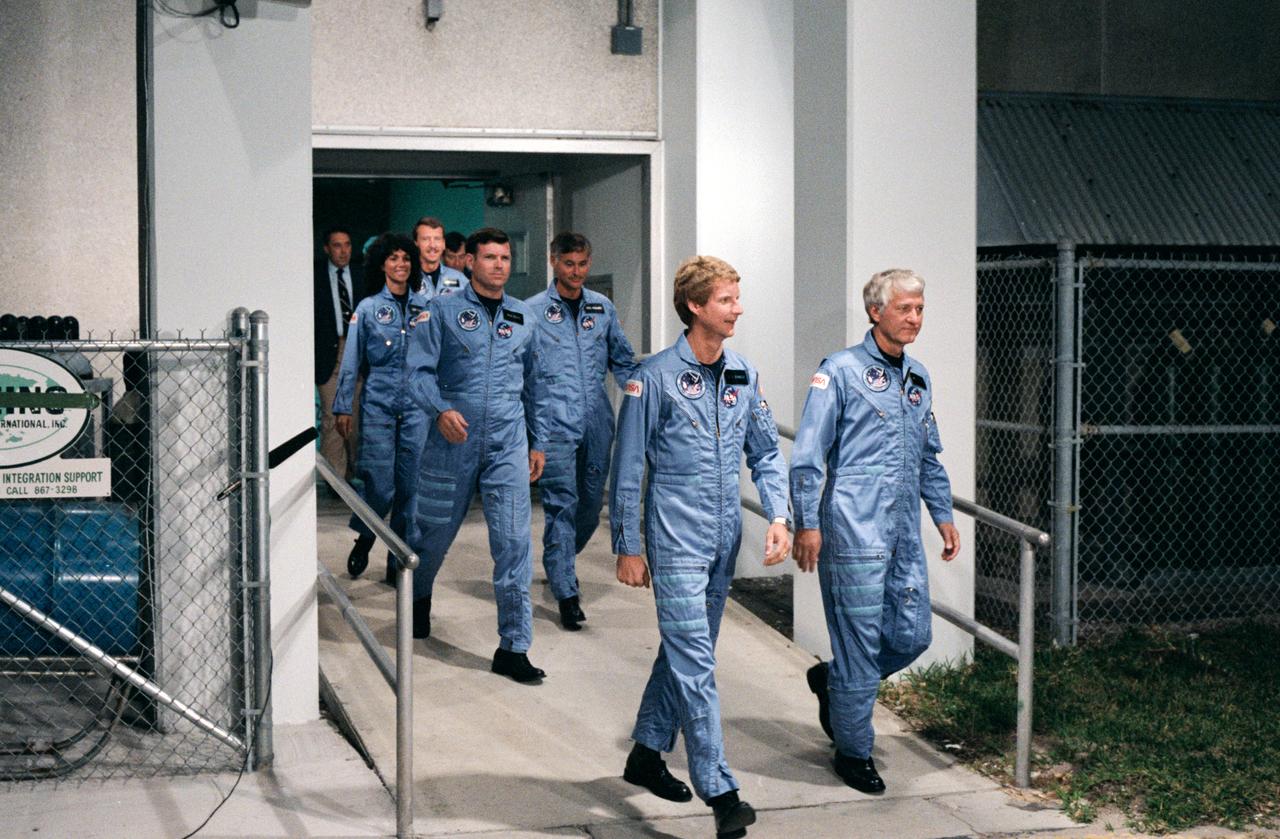

41D-3194 (30 Aug 1984)--- The six members of the 41-D Discovery crew leave the operations and checkout building at Kennedy Space to marke their way to Launch Pad 39A and a date with space. Leading the group is Henry W. hartsfield Jr., commander. Michael L. Coats, pilot, is left center. The mission specialists are Steven A. Hawley, second right, Richard M. (Mike) Mullane, right center, and Judith A. Resnik. Charles D. Walker, payload specialist, follows Resnik. Behind the blue-suited crewmembers are George W.S. Abbey, left, director of flight crew operations and John W. Young, chief of the astronaut office.
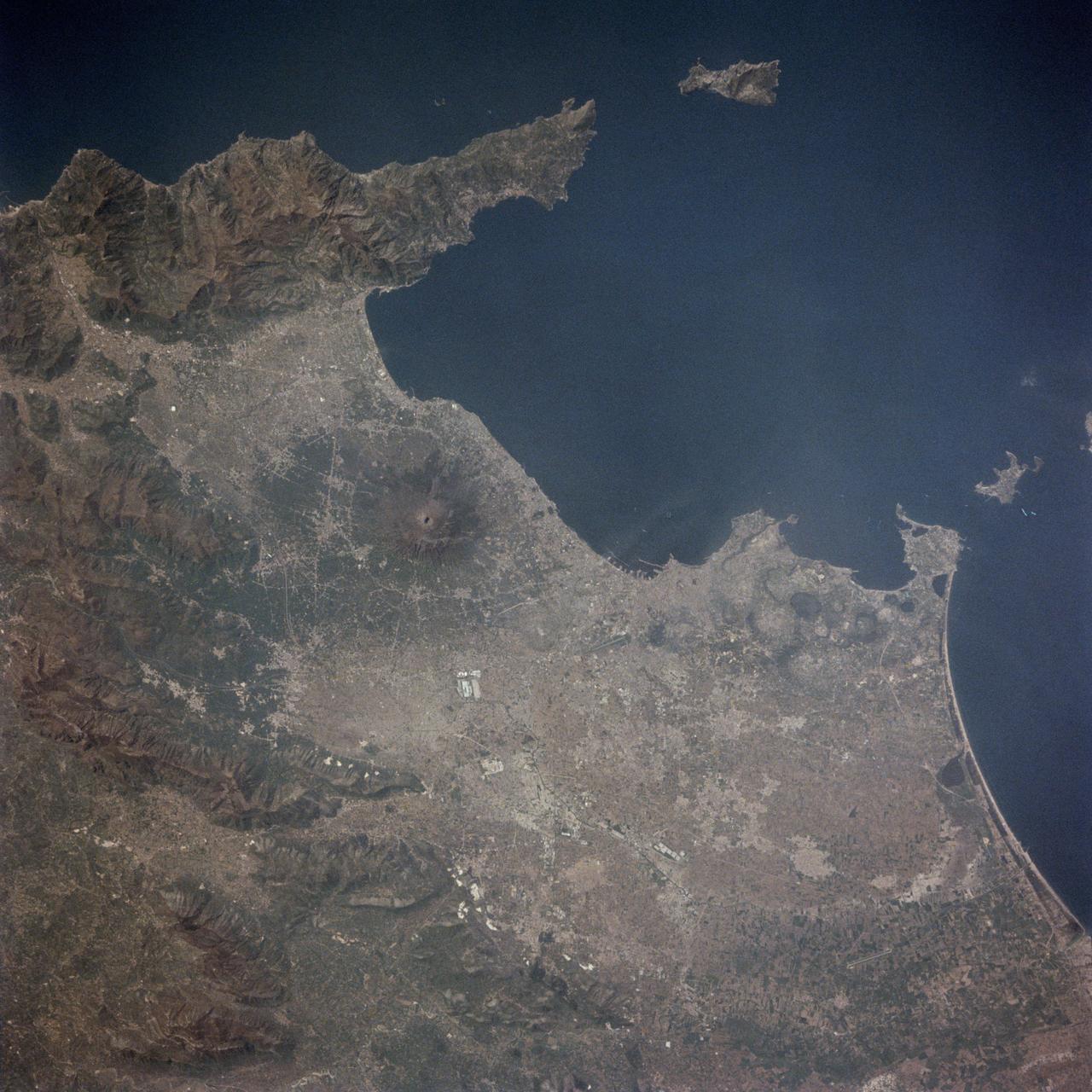

STS001-13-442 (14 April 1981) --- This photograph showing much of Italy was taken with a handheld 70mm camera from 276 kilometers above Earth as the NASA space shuttle Columbia and its crew were marking their last few hours in space on the historic first space mission utilizing a reusable vehicle. Included in the area of the frame are Golfo de Napoli, Napoli (Naples), Castellammare, Amalfi, Capri, Sorrento, Mt. Vesuvius and the ruins of Pompei. Astronauts John W. Young and Robert L. Crippen exposed eight magazines of color 70mm film during their two and one-third days in Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA
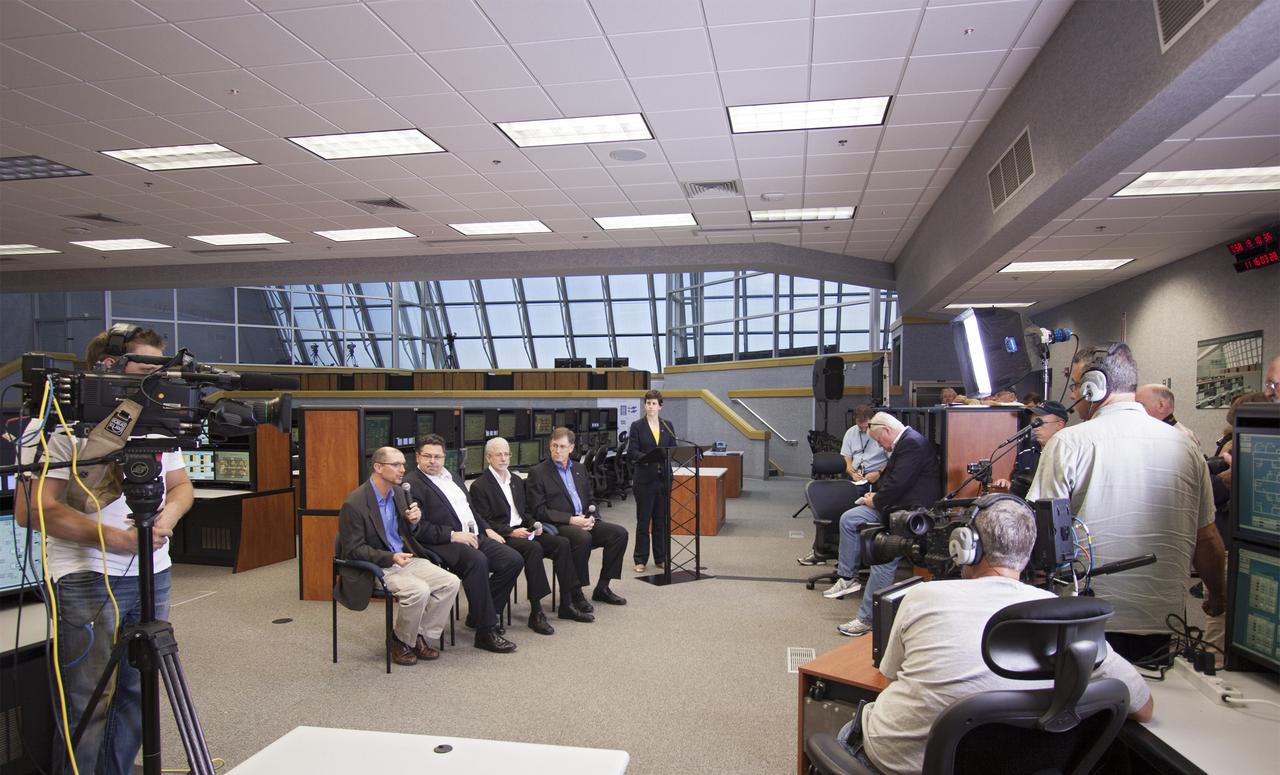

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA officials detail progress toward a September 2014 flight test called Exploration Flight Test-1 or EFT-1 as part of the agency's goal of launching astronauts into deep space. Speaking inside the Young-Crippen Firing Room at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the officials discussed the goals and expectations for EFT-1 with news media. Seated, facing the camera from left to right are Pepper Phillips, Ground Systems Development and Operations program manager, Todd May, Space Launch System program manager, Mark Geyer, Orion program manager and Dan Dumbacher, deputy associate administrator for the Exploration Systems Development Division. Standing is Rachel Kraft, a public affairs officer from NASA Headquarters in Washington D.C. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

The sixth manned lunar landing mission, the Apollo 16 (SA-511), carrying three astronauts: Mission Commander John W. Young, Command Module pilot Thomas K. Mattingly II, and Lunar Module pilot Charles M. Duke, lifted off on April 16, 1972. The Apollo 16 mission continued the broad-scale geological, geochemical, and geophysical mapping of the Moon’s crust, begun by the Apollo 15, from lunar orbit. This mission marked the first use of the Moon as an astronomical observatory by using the ultraviolet camera/spectrograph which photographed ultraviolet light emitted by Earth and other celestial objects. The Lunar Roving Vehicle, developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, was also used. The mission ended on April 27, 1972.

The Apollo 16 Command Module splashed down in the Pacific Ocean on April 27, 1972 after an 11-day moon exploration mission. The sixth manned lunar landing mission, the Apollo 16 (SA-511), carrying three astronauts: Mission Commander John W. Young, Command Module pilot Thomas K. Mattingly II, and Lunar Module pilot Charles M. Duke, lifted off on April 16, 1972. The Apollo 16 continued the broad-scale geological, geochemical, and geophysical mapping of the Moon’s crust, begun by the Apollo 15, from lunar orbit. This mission marked the first use of the Moon as an astronomical observatory by using the ultraviolet camera/spectrograph which photographed ultraviolet light emitted by Earth and other celestial objects. The Lunar Roving Vehicle, developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, was also used.

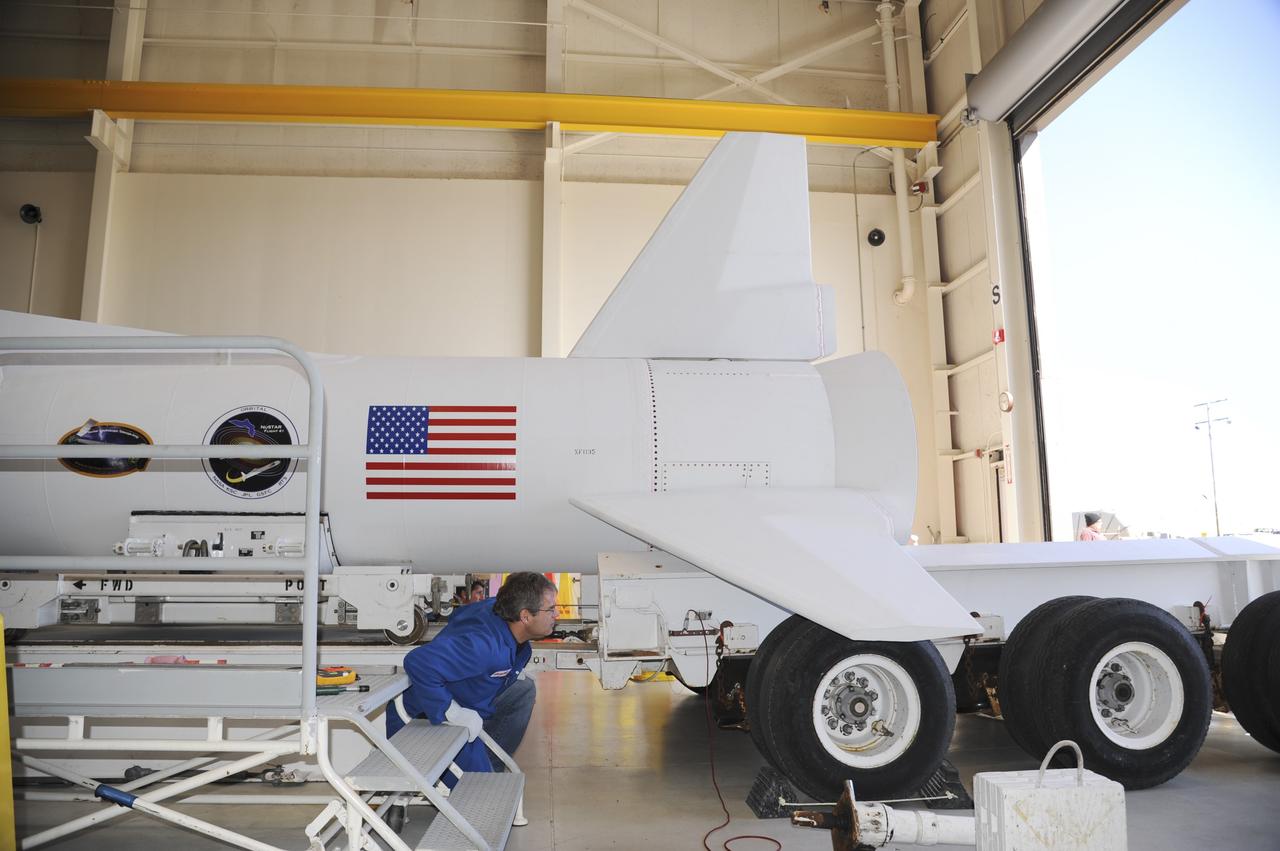
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a transporter is moved toward the Orbital Science’s Pegasus XL inside Orbital’s hangar. The rocket is mated to NASA’s encapsulated Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, out of sight inside the hangar. The transporter will move them to the runway ramp where they will be attached to the underside of Orbital’s L-1011 carrier aircraft. The aircraft will fly the pair from Vandenberg to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site on the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. A revised launch date is expected to be set at the Flight Readiness Review. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census of black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackiey
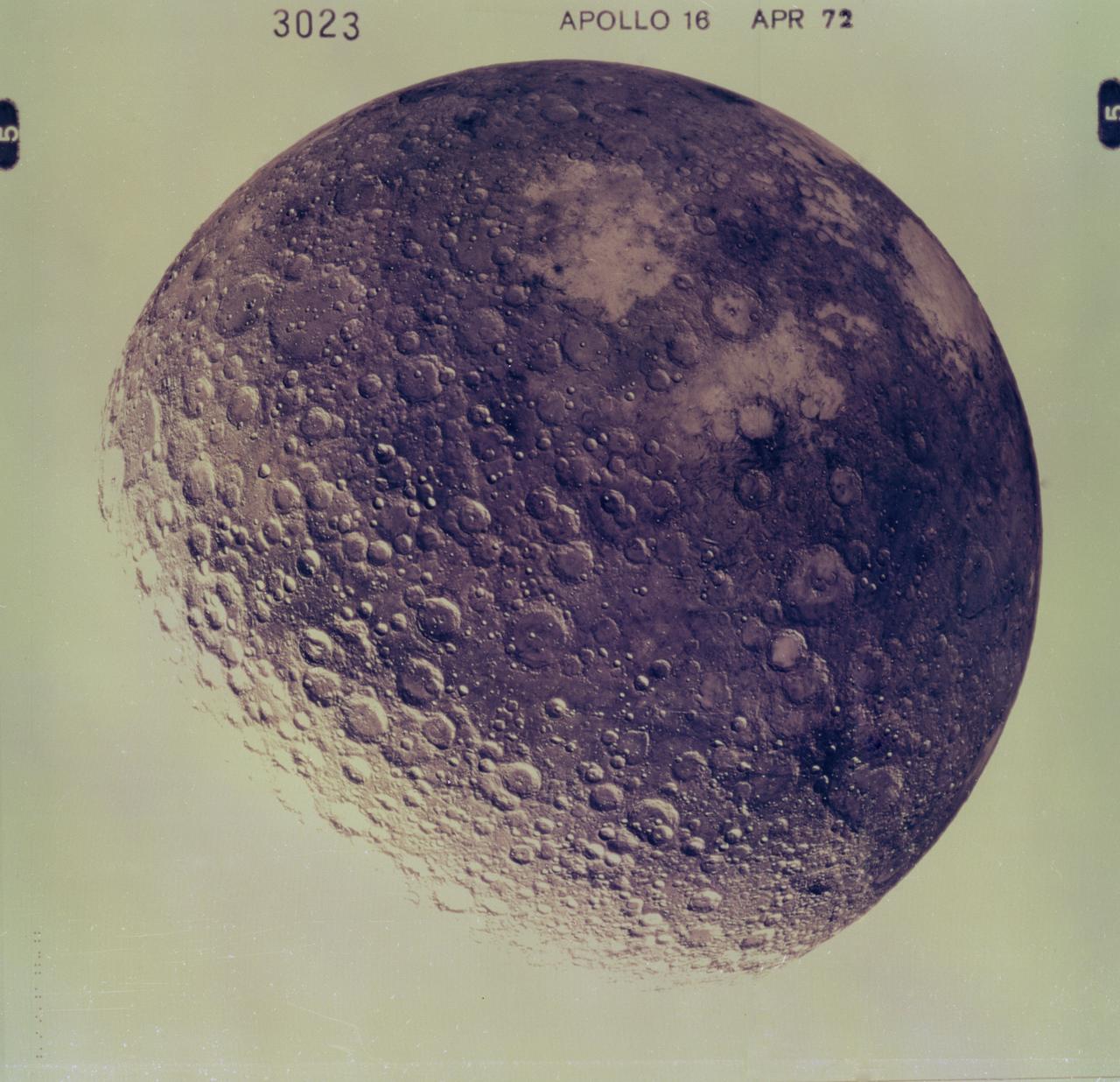

This view of the back side of the Moon was captured by the Apollo 16 mission crew. The sixth manned lunar landing mission, the Apollo 16 (SA-511), carrying three astronauts: Mission Commander John W. Young, Command Module pilot Thomas K. Mattingly II, and Lunar Module pilot Charles M. Duke, lifted off on April 16, 1972. The Apollo 16 continued the broad-scale geological, geochemical, and geophysical mapping of the Moon’s crust, begun by the Apollo 15, from lunar orbit. This mission marked the first use of the Moon as an astronomical observatory by using the ultraviolet camera/spectrograph which photographed ultraviolet light emitted by Earth and other celestial objects. The Lunar Roving Vehicle, developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, was also used. The mission ended on April 27, 1972.
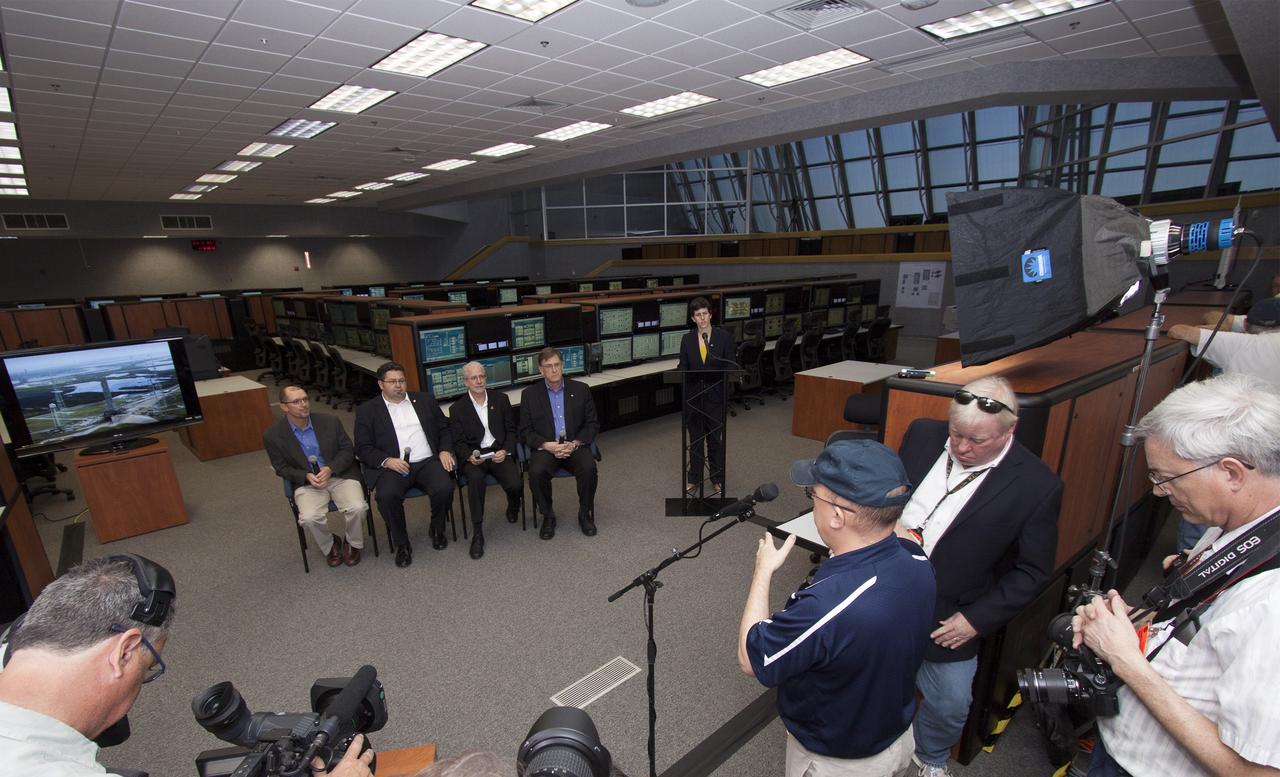

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA officials detail progress toward a September 2014 flight test called Exploration Flight Test-1 or EFT-1 as part of the agency's goal of launching astronauts into deep space. Speaking inside the Young-Crippen Firing Room at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the officials discussed the goals and expectations for EFT-1 with news media. Seated, facing the camera from left to right are Pepper Phillips, Ground Systems and Development program manager, Todd May, Space Launch System program manager, Mark Geyer, Orion program manager and Dan Dumbacher, deputy associate administrator for the Exploration Systems Development Division. Standing is Rachel Kraft, a public affairs officer from NASA Headquarters in Washington D.C. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
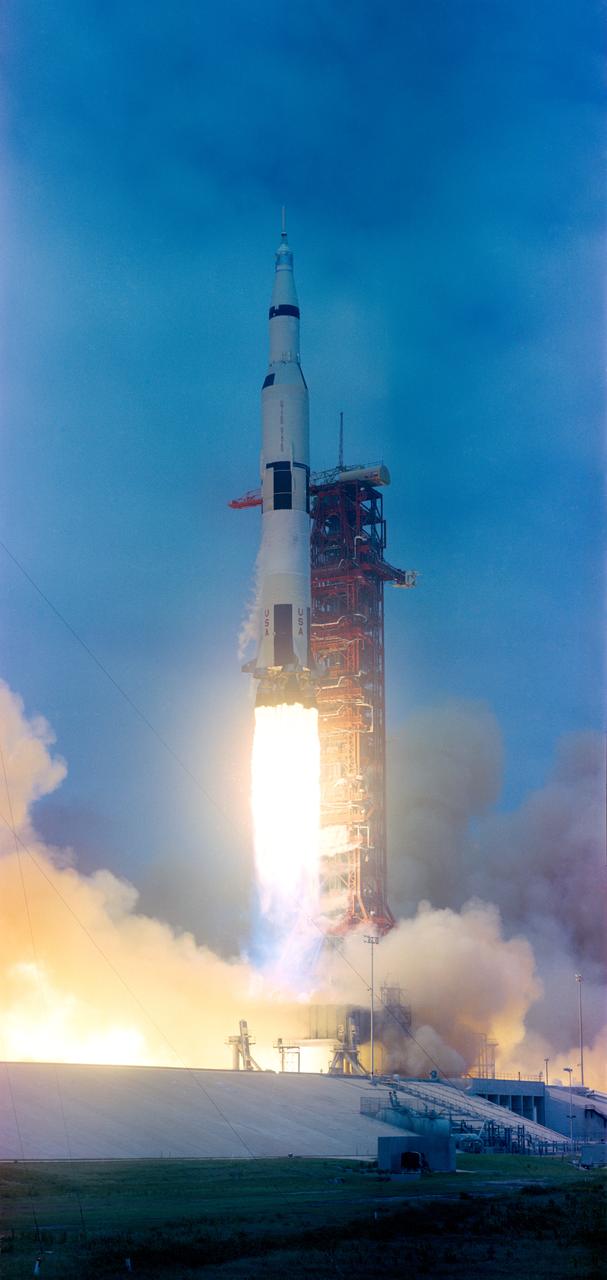

S69-34145 (18 May 1969) --- The Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space vehicle is launched from Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center at 12:49 p.m. (EDT), May 18, 1969. Aboard the spacecraft are astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot. The eight-day, lunar orbit mission will mark the first time the complete Apollo spacecraft has operated around the moon and the second manned flight for the Lunar Module (LM). Two Apollo 10 astronauts, Stafford and Cernan, are scheduled to descend to within eight nautical miles of the moon's surface in the LM.

S69-34144 (18 May 1969) --- The Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space vehicle is launched from Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida at 12:49 p.m., May 18, 1969. Aboard the spacecraft are astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot. The eight-day, lunar orbit mission will mark the first time the complete Apollo spacecraft has operated around the moon and the second manned flight for the Lunar Module (LM). Two Apollo 10 astronauts, Stafford and Cernan, are scheduled to descend to within eight nautical miles of the moon's surface in the LM.

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician monitors the progress as a transporter is moved underneath the Orbital Science’s Pegasus XL inside Orbital’s hangar. The rocket is mated to NASA’s encapsulated Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, out of sight inside the hangar. The transporter will move them to the runway ramp where they will be attached to the underside of Orbital’s L-1011 carrier aircraft. The aircraft will fly the pair from Vandenberg to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site on the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. A revised launch date is expected to be set at the Flight Readiness Review. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census of black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackiey
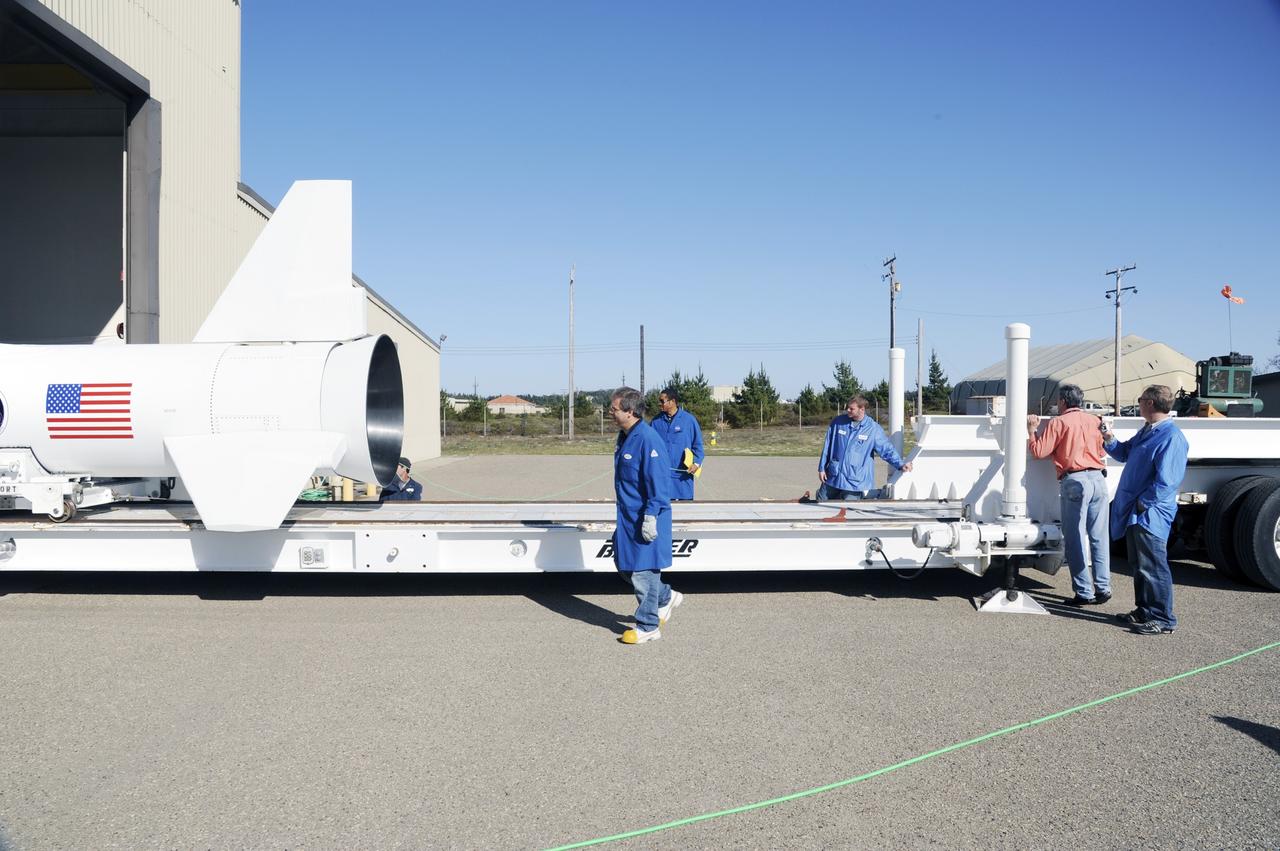

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians monitor the progress as the Orbital Science’s Pegasus XL is moved onto a transporter inside Orbital’s hangar. The rocket is mated to NASA’s encapsulated Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, out of sight inside the hangar. The transporter will move them to the runway ramp where they will be attached to the underside of Orbital’s L-1011 carrier aircraft. The aircraft will fly the pair from Vandenberg to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site on the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. A revised launch date is expected to be set at the Flight Readiness Review. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census of black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackiey

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians monitor the progress as a transporter is moved underneath the Orbital Science’s Pegasus XL inside Orbital’s hangar. The rocket is mated to NASA’s encapsulated Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, out of sight inside the hangar. The transporter will move them to the runway ramp where they will be attached to the underside of Orbital’s L-1011 carrier aircraft. The aircraft will fly the pair from Vandenberg to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site on the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. A revised launch date is expected to be set at the Flight Readiness Review. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census of black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackiey
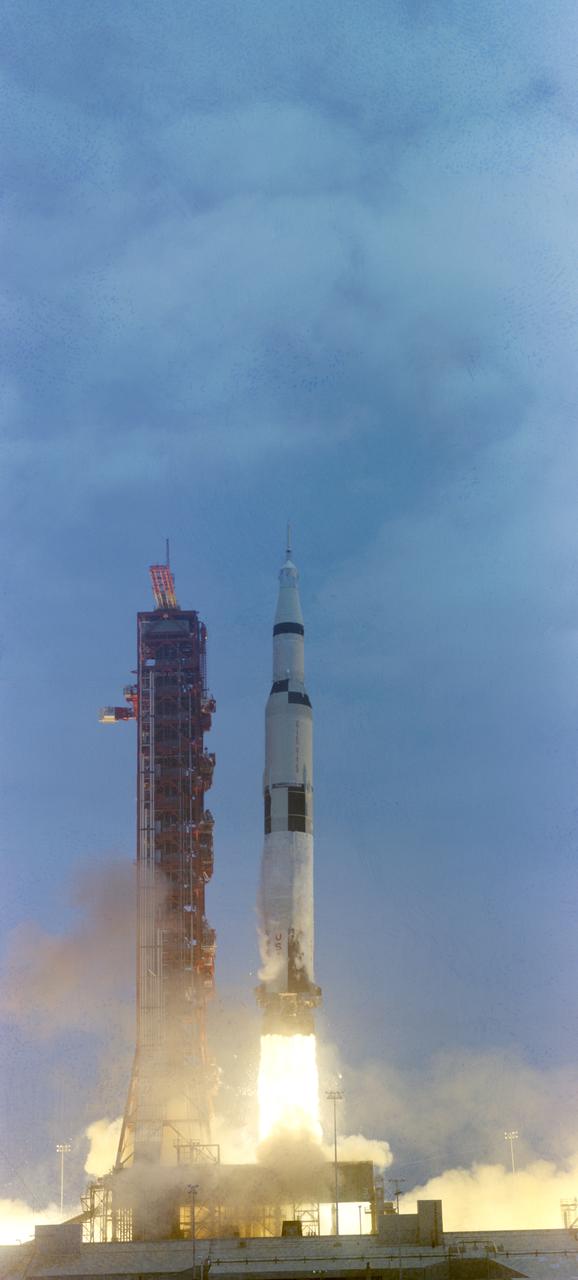

S69-34143 (18 May 1969) --- The Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space vehicle is launched from Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center at 12:49 p.m. (EDT), May 18, 1969. Aboard the spacecraft are astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot. The eight-day, lunar orbit mission will mark the first time the complete Apollo spacecraft has operated around the moon and the second manned flight for the Lunar Module. Two Apollo 10 astronauts, Stafford and Cernan, are scheduled to descend within eight nautical miles of the moon's surface in the LM.
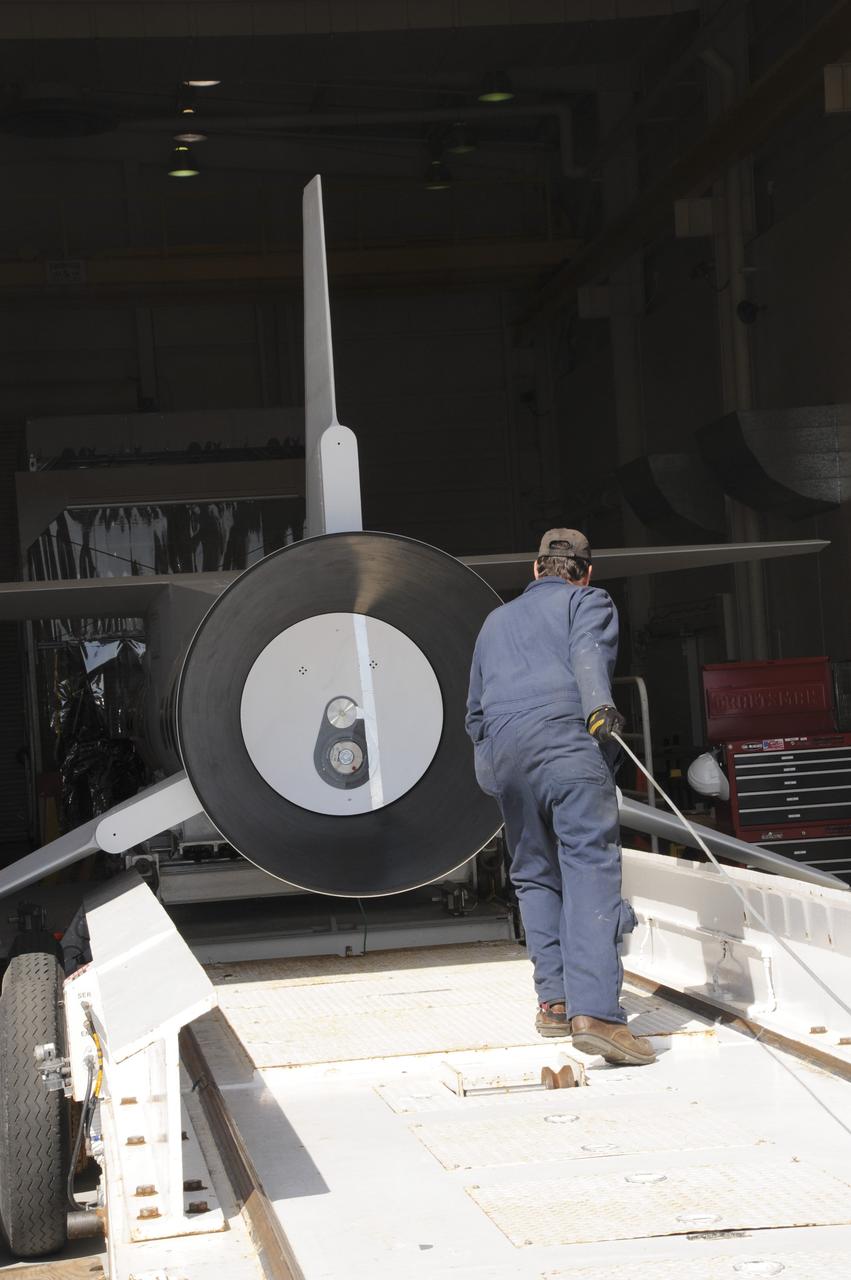

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician monitors the progress as a transporter is moved underneath the Orbital Science’s Pegasus XL inside Orbital’s hangar. The rocket is mated to NASA’s encapsulated Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, out of sight inside the hangar. The transporter will move them to the runway ramp where they will be attached to the underside of Orbital’s L-1011 carrier aircraft. The aircraft will fly the pair from Vandenberg to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site on the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. A revised launch date is expected to be set at the Flight Readiness Review. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census of black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackiey

The Apollo 16 Command Module splashed down in the Pacific Ocean on April 27, 1972 after an 11-day moon exploration mission. The 3-man crew is shown here aboard the rescue ship, USS Horton. From left to right are: Mission Commander John W. Young, Lunar Module pilot Charles M. Duke, and Command Module pilot Thomas K. Mattingly II. The sixth manned lunar landing mission, the Apollo 16 (SA-511) lifted off on April 16, 1972. The Apollo 16 mission continued the broad-scale geological, geochemical, and geophysical mapping of the Moon’s crust, begun by the Apollo 15, from lunar orbit. This mission marked the first use of the Moon as an astronomical observatory by using the ultraviolet camera/spectrograph which photographed ultraviolet light emitted by Earth and other celestial objects. The Lunar Roving Vehicle, developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, was also used.
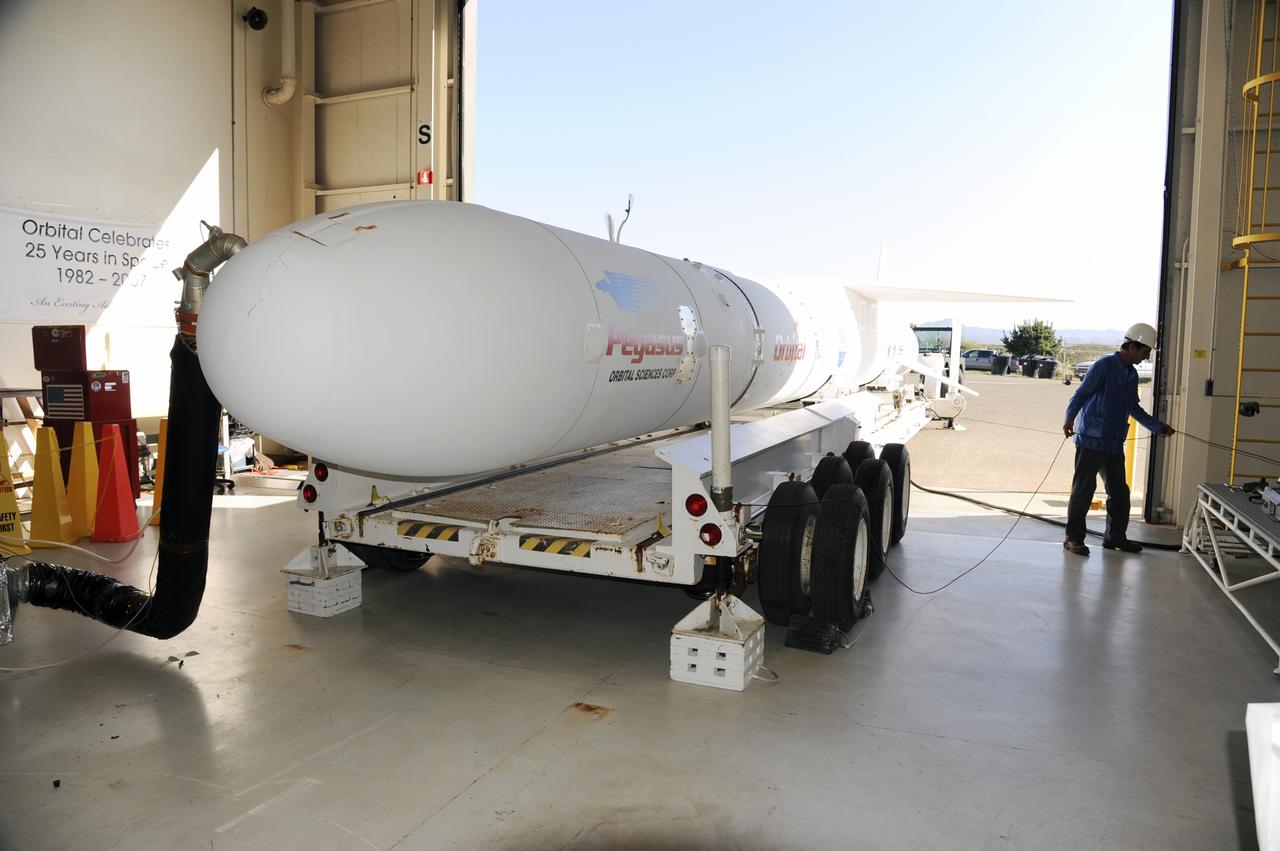

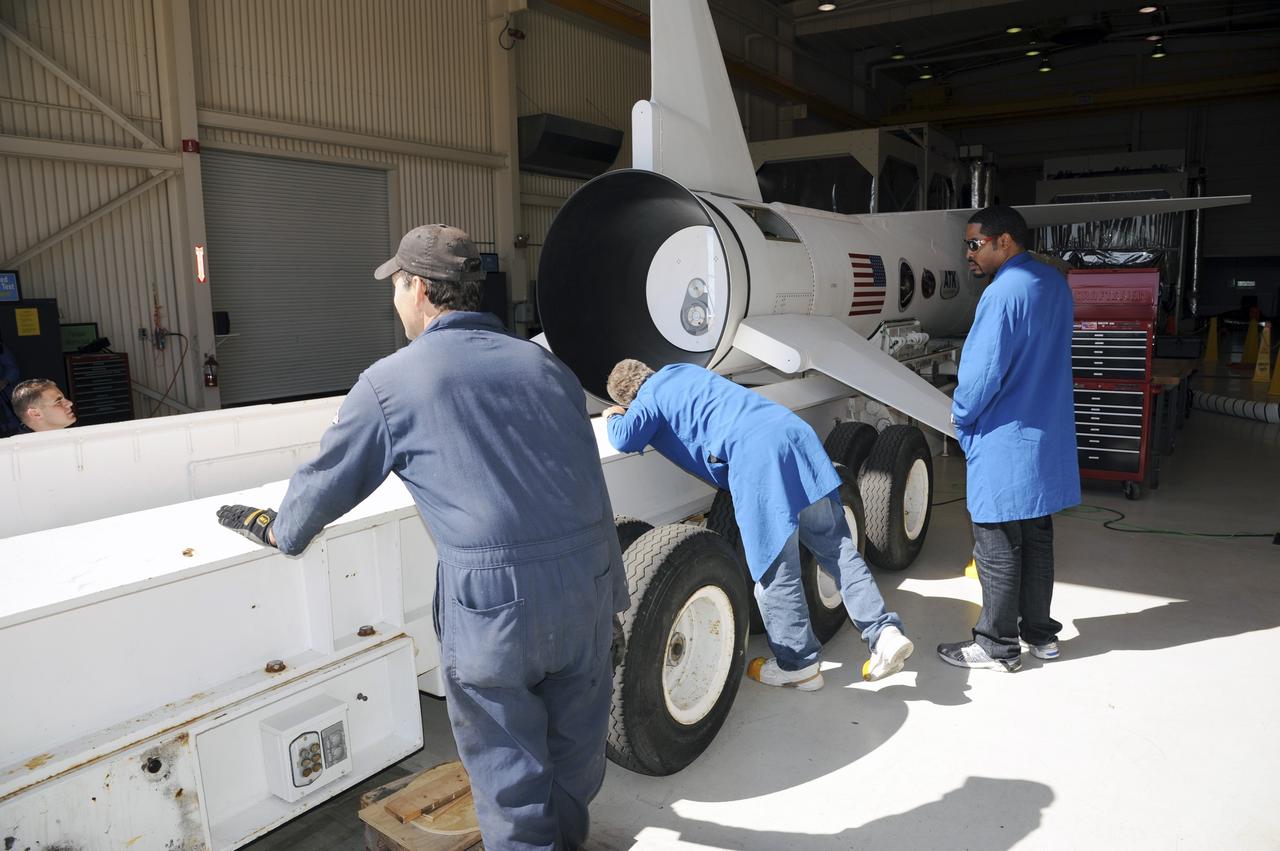
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbital Science’s Pegasus LX has been moved onto a transporter inside Orbital’s hangar. The rocket is mated to NASA’s encapsulated Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, spacecraft. The transporter will move them to the runway ramp where they will be attached to the underside of Orbital’s L-1011 carrier aircraft. The aircraft will fly the pair from Vandenberg to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site on the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. A revised launch date is expected to be set at the Flight Readiness Review. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census of black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackiey
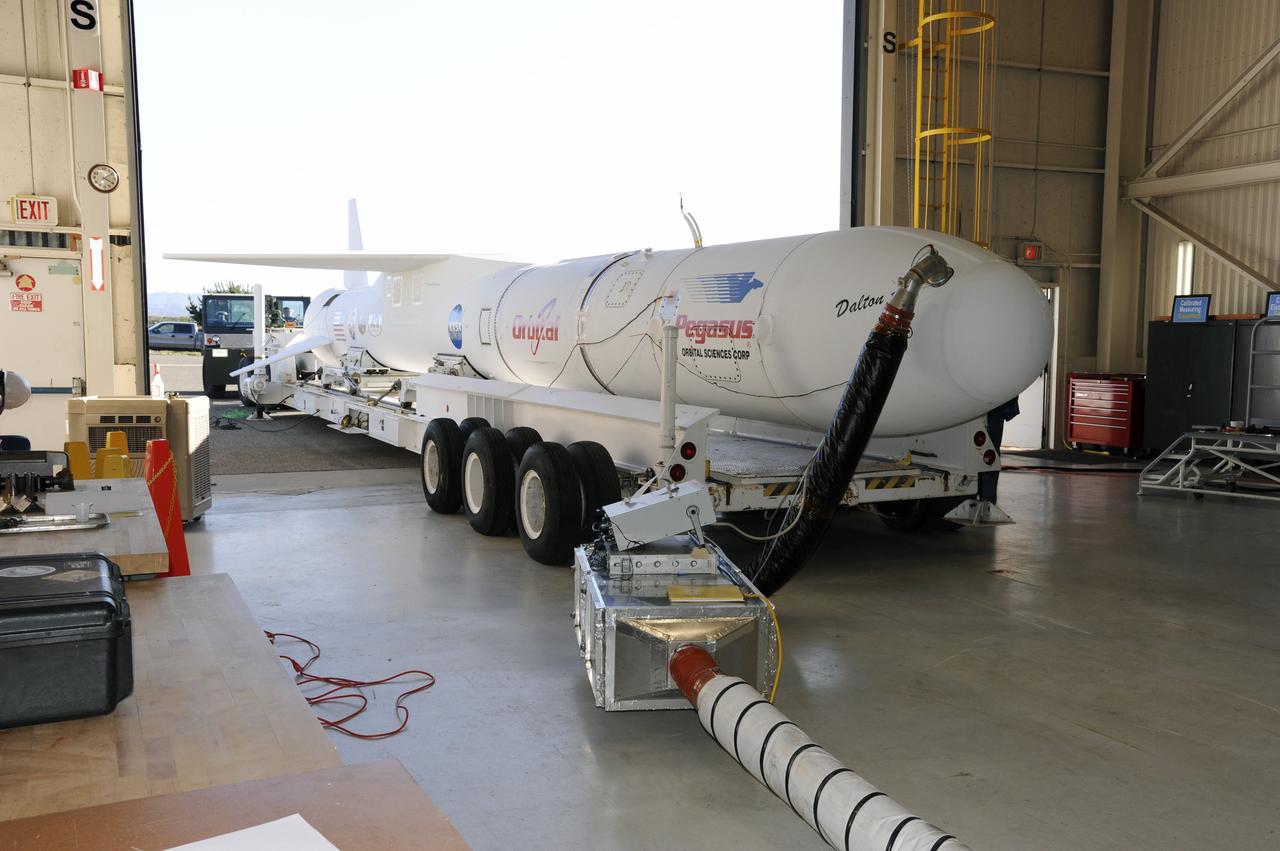

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbital Science’s Pegasus LX has been moved onto a transporter inside Orbital’s hangar. The rocket is mated to NASA’s encapsulated Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, spacecraft. The transporter will move them to the runway ramp where they will be attached to the underside of Orbital’s L-1011 carrier aircraft. The aircraft will fly the pair from Vandenberg to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site on the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. A revised launch date is expected to be set at the Flight Readiness Review. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census of black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackiey
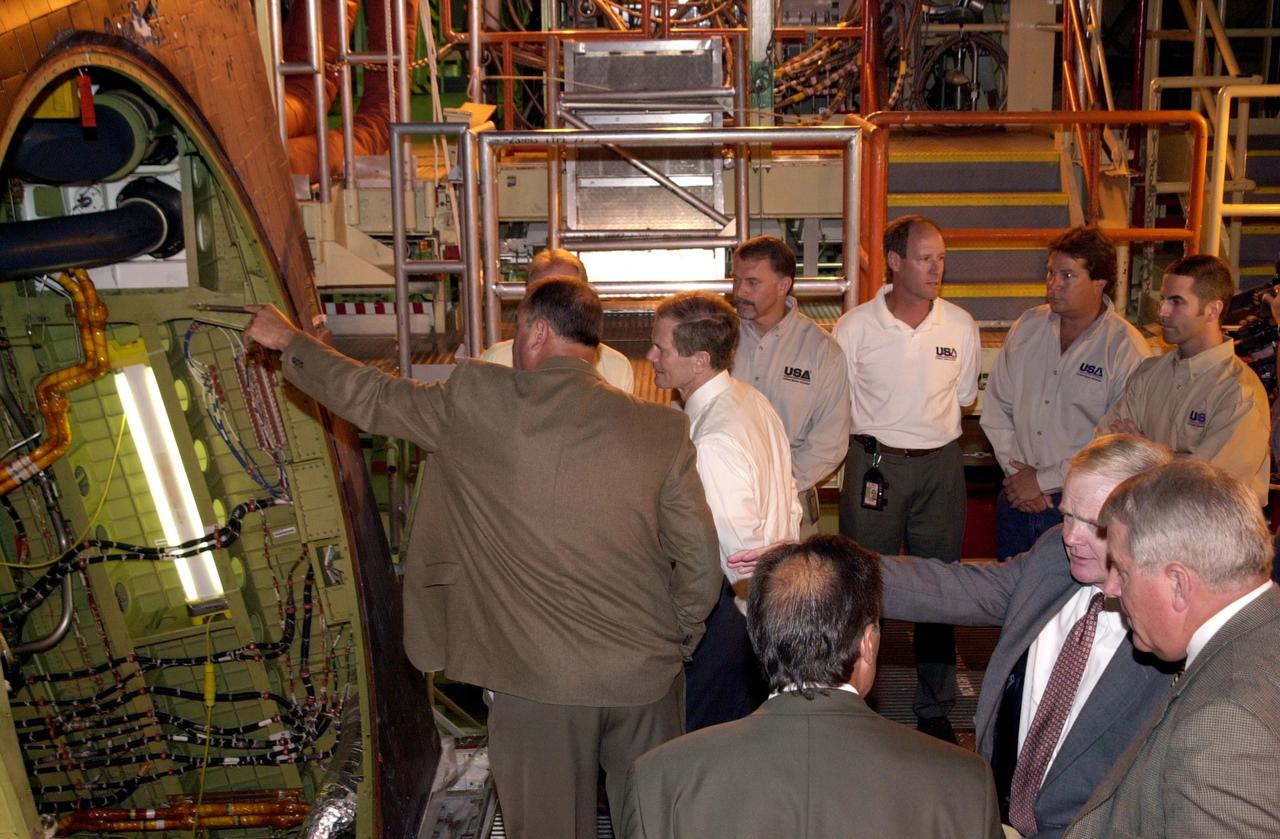

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Bob Herman,chief engineer, Ground Operations for United Space Alliance (USA), shows U.S. Sen. Bill Nelson (center) part of orbiter Atlantis. Nelson was at KSC to present gold seal Senate certificates to the Flow Liner Inspection & Repair team for their part in finding the cracks in orbiter flow liners and repairing them. Team members are (behind Herman and Nelson, left to right) Mike Young, Jerry Goudy, Rick Beckwith, Tony Nesotas and David Strait. Goudy performed arc welding on one of Atlantis' flow liners; Strait found the original crack. In the foreground are Shuttle Engineering Director, USA, Mark Nappi; Center Director Roy Bridges; and vice president and deputy program manager, Florida Operations, USA, Bill Pickavance.
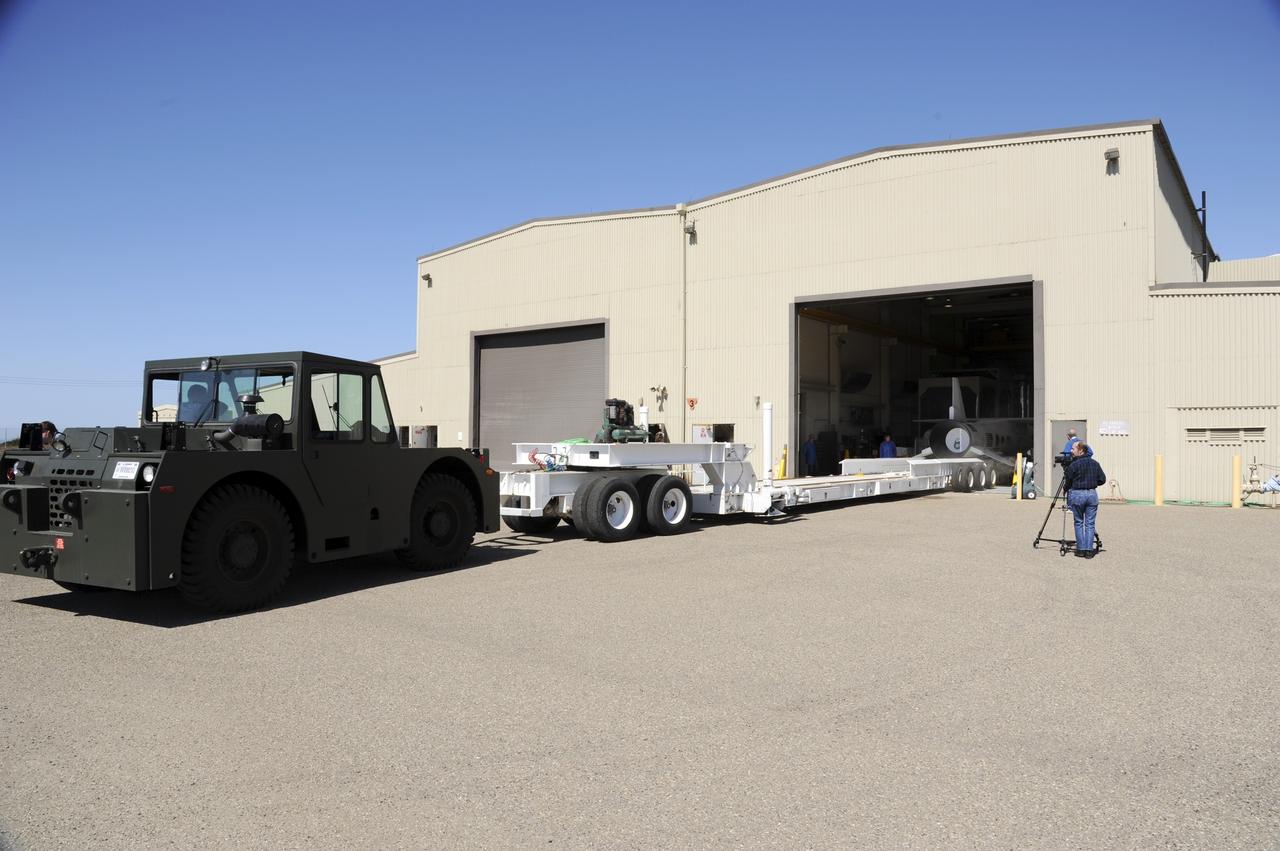

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a transporter is moved toward the Orbital Science’s Pegasus XL inside Orbital’s hangar. The rocket is mated to NASA’s encapsulated Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, out of sight inside the hangar. The transporter will move them to the runway ramp where they will be attached to the underside of Orbital’s L-1011 carrier aircraft. The aircraft will fly the pair from Vandenberg to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site on the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. A revised launch date is expected to be set at the Flight Readiness Review. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census of black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackiey
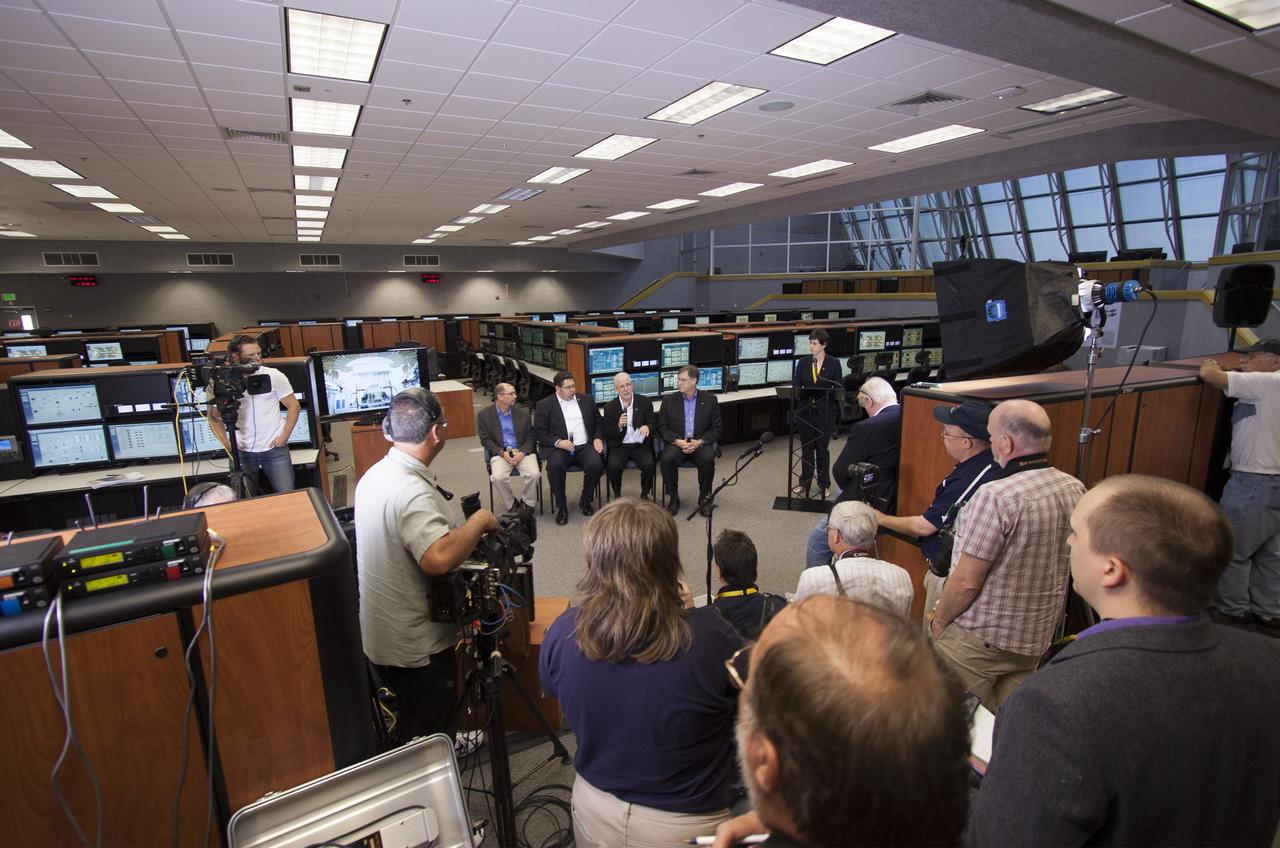

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA officials detail progress toward a September 2014 flight test called Exploration Flight Test-1 or EFT-1 as part of the agency's goal of launching astronauts into deep space. Speaking inside the Young-Crippen Firing Room at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the officials discussed the goals and expectations for EFT-1 with news media. Seated, facing the camera from left to right are Pepper Phillips, Ground Systems Development and Operations program manager, Todd May, Space Launch System program manager, Mark Geyer, Orion program manager and Dan Dumbacher, deputy associate administrator for the Exploration Systems Development Division. Standing is Rachel Kraft, a public affairs officer from NASA Headquarters in Washington D.C. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
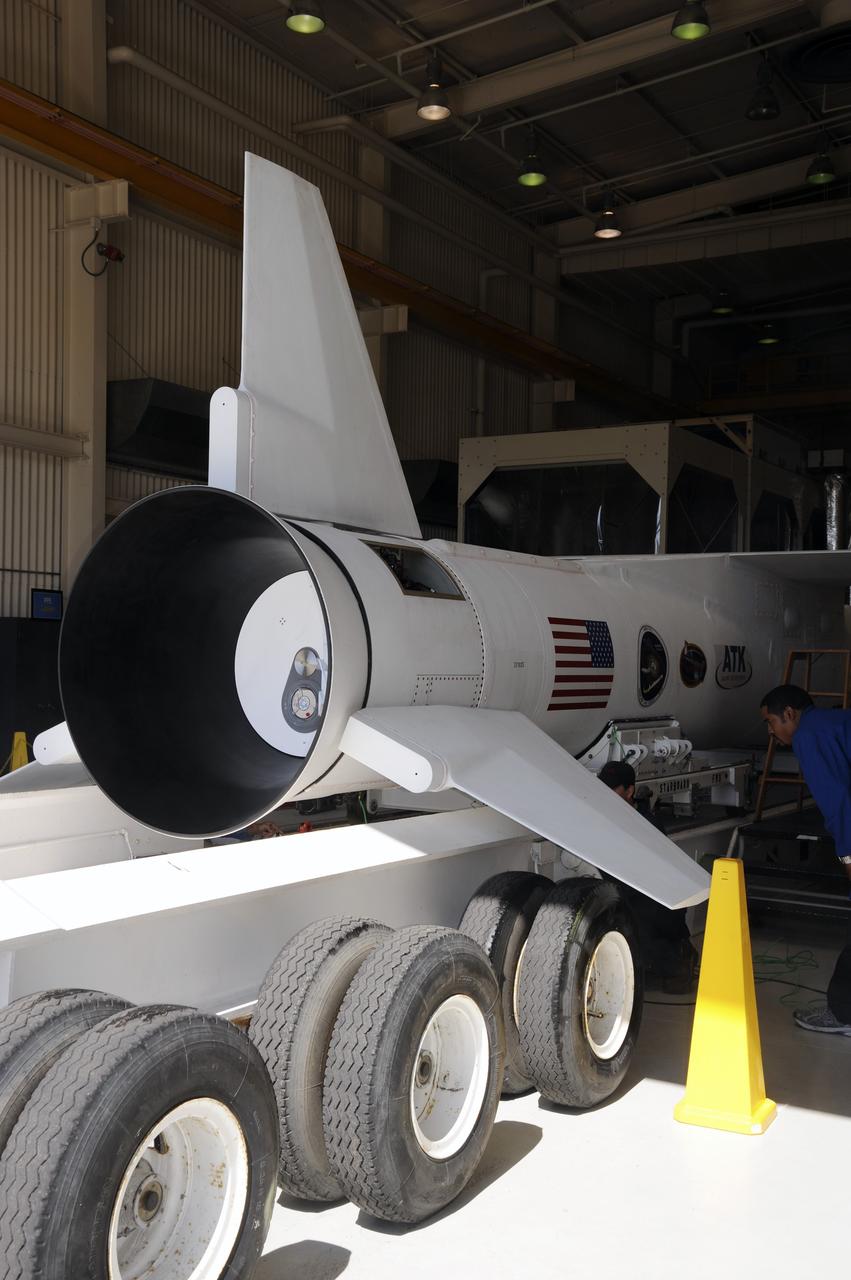

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a transporter is moved underneath the Orbital Science’s Pegasus XL inside Orbital’s hangar. The rocket is mated to NASA’s encapsulated Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, out of sight inside the hangar. The transporter will move them to the runway ramp where they will be attached to the underside of Orbital’s L-1011 carrier aircraft. The aircraft will fly the pair from Vandenberg to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site on the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. A revised launch date is expected to be set at the Flight Readiness Review. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census of black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/nustar. Photo credit: NASA/Mark Mackiey
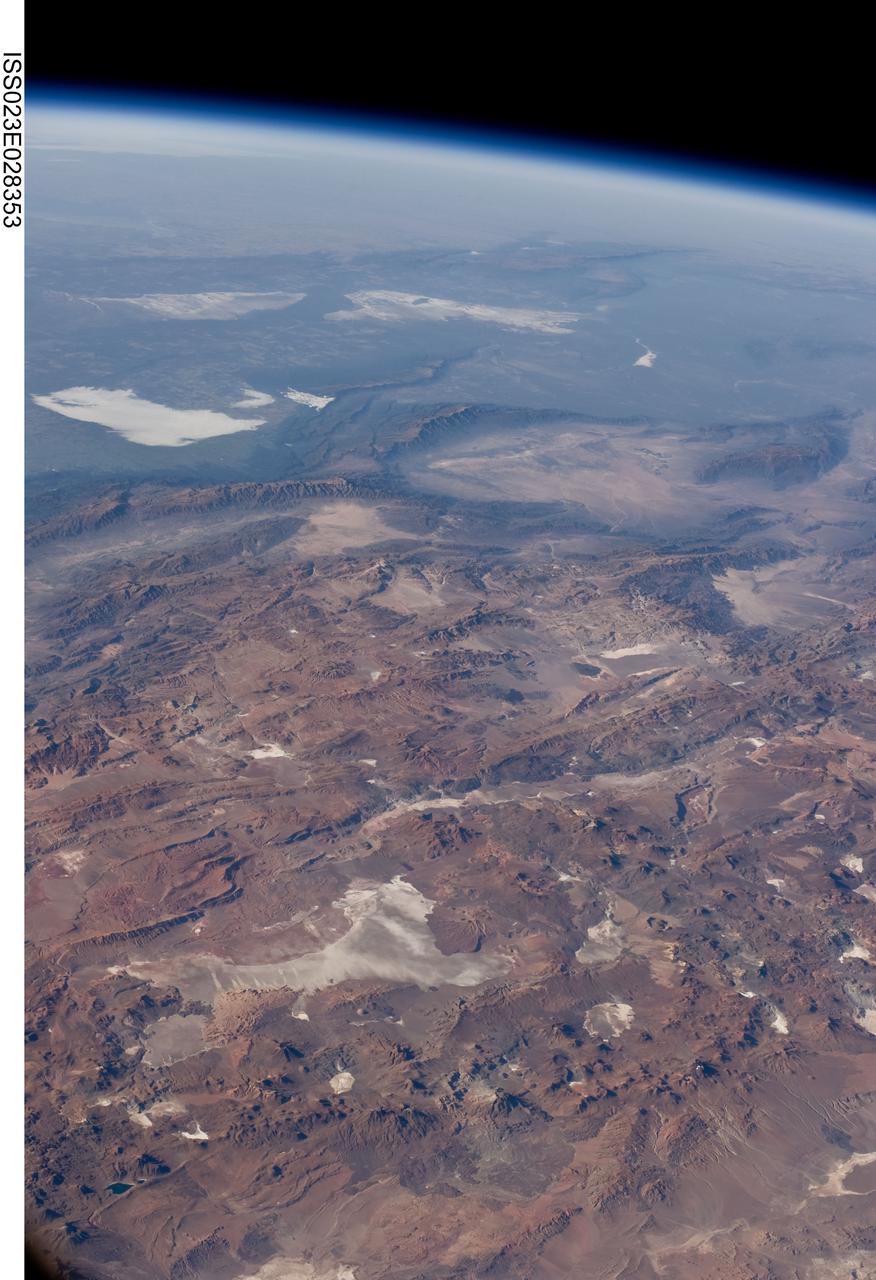

ISS023-E-028353 (26 April 2010) --- Central Andes Mountains, Salar de Arizaro, Argentina are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 23 crew member on the International Space Station. The high plains (3,000 to greater than 5,000 meters elevation, 13,000 to 19,000 feet) of the Andes Mountains, also known as the Puna, appear in the foreground of this photograph, with a line of young volcanoes facing the much lower Atacama Desert (1,000–2,000 meters elevation). Several large dry lakes, marked by light-toned salt crusts, occupy the basins between major thrust faults in the Puna. Salar de Arizaro (foreground) is the largest of the dry lakes in this view (salar means waterless salt flat in Spanish). This panorama was taken by a station crew member looking southeast across the South American continent when the ISS was almost directly over the Atacama Desert near Chile’s Pacific coast. The Atlantic Ocean coastline (River Plate where Argentina’s capital city of Buenos Aires is located) is dimly visible at top left. A striking geological and landscape contrast is visible at center which separates two distinct geological zones, namely the Puna and the Sierras Pampeanas. The Sierras Pampeanas Mountains are lower in elevation and have few young volcanoes, in contrast to the Puna. Sharp-crested ranges are separated by wide, low valleys in this region. The Salinas Grandes—ephemeral shallow salt lakes at top left (salina means salt lake in Spanish) — occupies one of these valleys. The general color change from reds and browns in the foreground to blues and greens in the upper part of the image reflects the major climatic regions, namely the deserts of the Atacama and Puna, versus the low grassy plains of central Argentina where rainfall is sufficient to promote lush prairie grass growth—known famously as the pampas in Argentina. The Salinas Grandes mark an intermediate semiarid region. What accounts for the changes in landscape? The geology of this part of the Andes is a result of the eastward subduction of the Nazca tectonic plate underneath South America. Investigations using seismic data suggest that the Puna is underlain by a steeply dipping sector of the subducting Nazca plate. The Sierras Pampeanas zone however, is underlain by a sector of the Nazca plate that is almost horizontal, possibly due to the subduction of a submarine mountain range known as the Juan Fernandez Ridge. In the simplest terms, ridges are topographic highs that are difficult to stuff down subduction zones, with profound effects on the volcanism and structures of the upper plate.

The Kunlun fault is one of the gigantic strike-slip faults that bound the north side of Tibet. Left-lateral motion along the 1,500-kilometer (932-mile) length of the Kunlun has occurred uniformly for the last 40,000 years at a rate of 1.1 centimeter per year, creating a cumulative offset of more than 400 meters (1300 feet). In this image, two splays of the fault are clearly seen crossing from east to west. The northern fault juxtaposes sedimentary rocks of the mountains against alluvial fans. Its trace is also marked by lines of vegetation, which appear red in the image. The southern, younger fault cuts through the alluvium. A dark linear area in the center of the image is wet ground where groundwater has pounded against the fault. Measurements from the image of displacements of young streams that cross the fault show 15 to 75 meters (16 to 82 yards) of left-lateral offset. This image of Tibet covers an area 40 kilometers (25 miles) wide and 15 kilometers (10 miles) long in three bands of the reflected visible and infrared wavelength region. ASTER acquired the scene on July 20, 2000. The image is located at 35.8 degrees north latitude and 93.6 degrees east longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02658
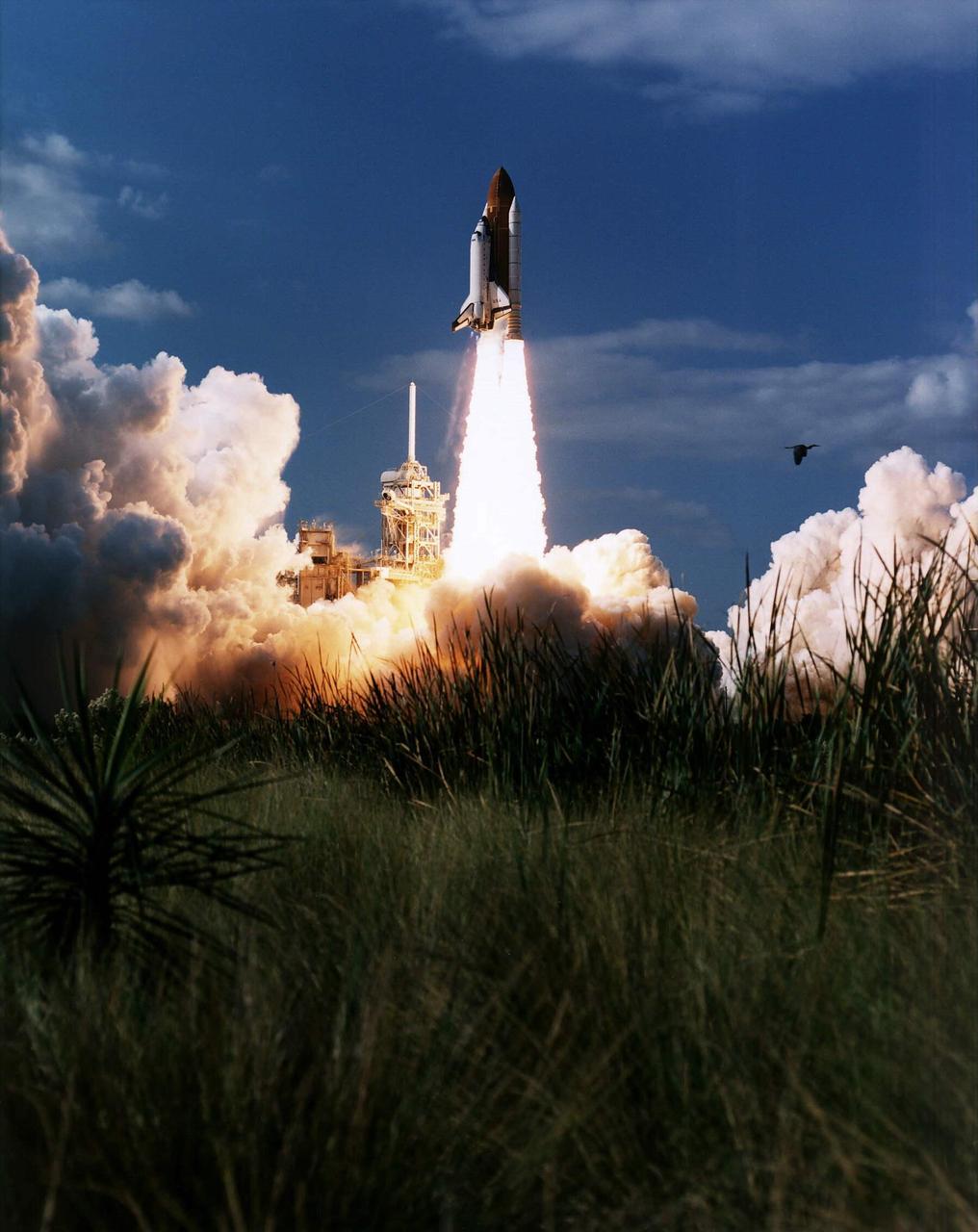

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Vividly framed by a tranquil Florida landscape, the Space Shuttle Columbia lifts off from Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. EST, Nov. 19, 1996. Leading the veteran crew of Mission STS-80 is Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell; Kent V. Rominger is the pilot and the three mission specialists are Tamara E. Jernigan, Story Musgrave and Thomas D. Jones. At age 61, Musgrave becomes the oldest person ever to fly in space; he also ties astronaut John Young’s record for most number of spaceflights by a human being, and in embarking on his sixth Shuttle flight Musgrave has logged the most flights ever aboard NASA’s reusable space vehicle. The two primary payloads for STS-80 are the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II). Two spacewalks also will be performed during the nearly 16-day mission. Mission STS-80 closes out the Shuttle flight schedule for 1996; it marks the 21st flight for Columbia and the 80th in Shuttle program history.
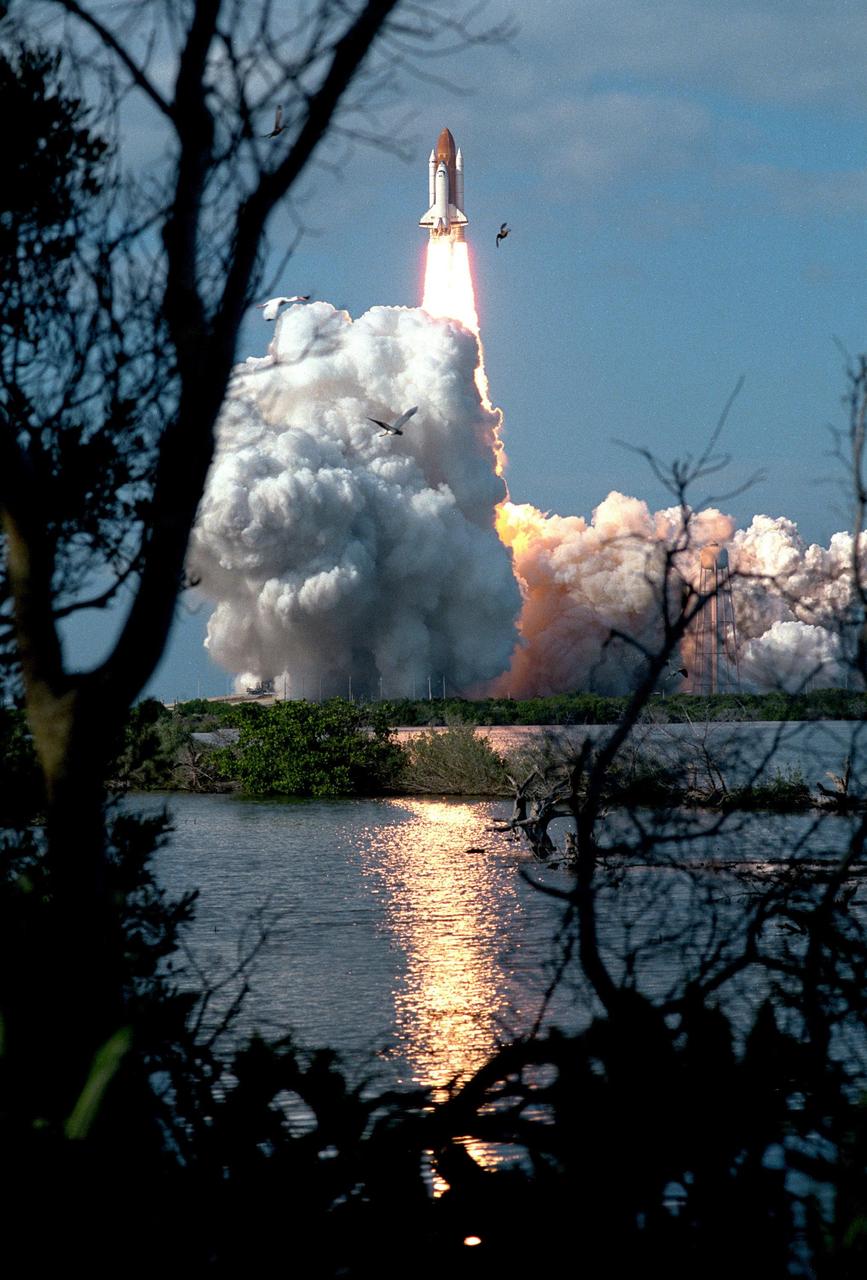

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A diversified mission of astronomy, commercial space research and International Space Station preparation gets under way as the Space Shuttle Columbia climbs skyward from Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. EST, Nov. 19, 1996. Leading the veteran crew of Mission STS-80 is Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell; Kent V. Rominger is the pilot and the three mission specialists are Tamara E. Jernigan, Story Musgrave and Thomas D. Jones. At age 61, Musgrave becomes the oldest person ever to fly in space; he also ties astronaut John Young’s record for most number of spaceflights by a human being, and in embarking on his sixth Shuttle flight Musgrave has logged the most flights ever aboard NASA’s reusable space vehicle. The two primary payloads for STS-80 are the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II). Two spacewalks also will be performed during the nearly 16-day mission. Mission STS-80 closes out the Shuttle flight schedule for 1996; it marks the 21st flight for Columbia and the 80th in Shuttle program history.
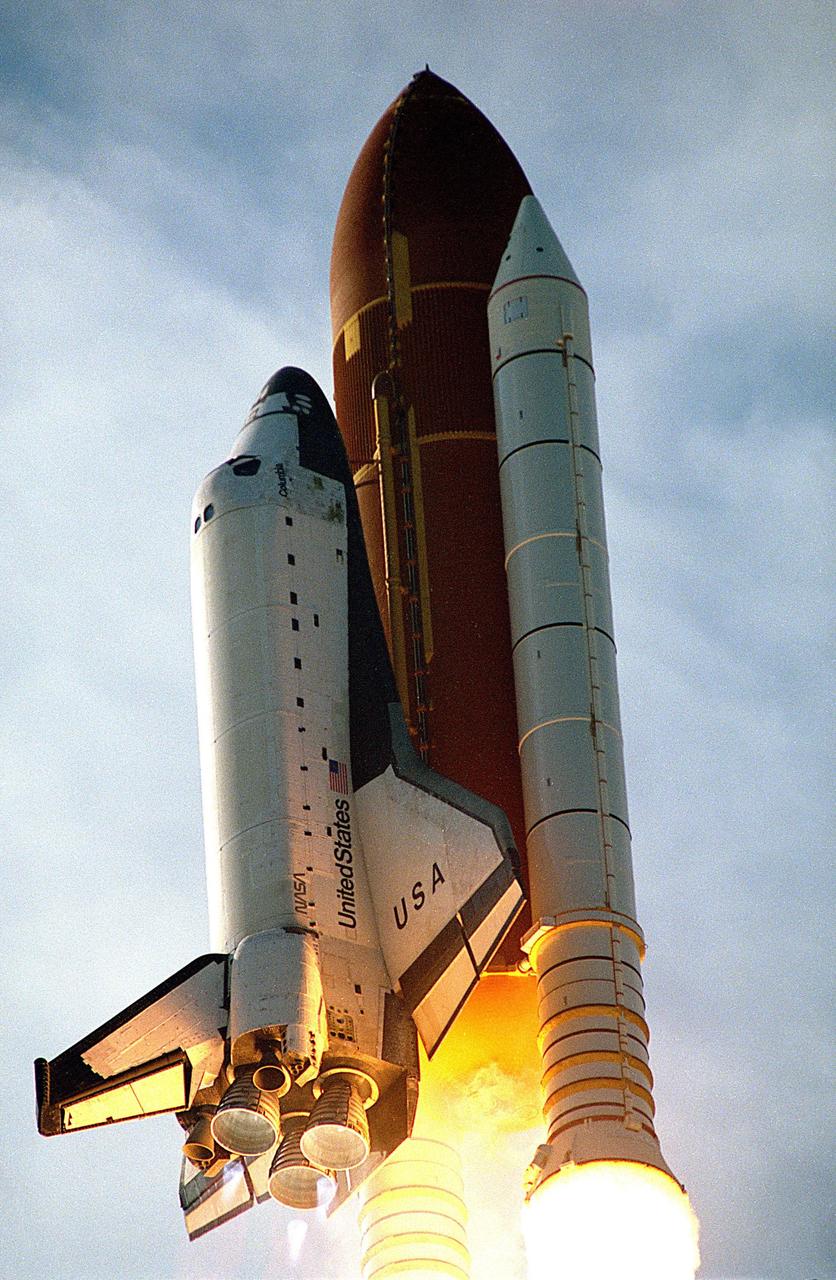

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A diversified mission of astronomy, commercial space research and International Space Station preparation gets under way as the Space Shuttle Columbia climbs skyward from Launch Pad 39B at 2:55:47 p.m. EST, Nov. 19, 1996. Leading the veteran crew of Mission STS-80 is Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell; Kent V. Rominger is the pilot and the three mission specialists are Tamara E. Jernigan, Story Musgrave and Thomas D. Jones. At age 61, Musgrave becomes the oldest person ever to fly in space; he also ties astronaut John Young’s record for most number of spaceflights by a human being, and in embarking on his sixth Shuttle flight Musgrave has logged the most flights ever aboard NASA’s reusable space vehicle. The two primary payloads for STS-80 are the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3) and the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II). Two spacewalks also will be performed during the nearly 16-day mission. Mission STS-80 closes out the Shuttle flight schedule for 1996; it marks the 21st flight for Columbia and the 80th in Shuttle program history.

On February 4, 2014 the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) flying aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite captured a true-color image of sea ice off of western Alaska. In this true-color image, the snow and ice covered land appears bright white while the floating sea ice appears a duller grayish-white. Snow over the land is drier, and reflects more light back to the instrument, accounting for the very bright color. Ice overlying oceans contains more water, and increasing water decreases reflectivity of ice, resulting in duller colors. Thinner ice is also duller. The ocean waters are tinted with green, likely due to a combination of sediment and phytoplankton. Alaska lies to the east in this image, and Russia to the west. The Bering Strait, covered with ice, lies between to two. South of the Bering Strait, the waters are known as the Bering Sea. To the north lies the Chukchi Sea. The bright white island south of the Bering Strait is St. Lawrence Island. Home to just over 1200 people, the windswept island belongs to the United States, but sits closer to Russia than to Alaska. To the southeast of the island a dark area, loosely covered with floating sea ice, marks a persistent polynya – an area of open water surrounded by more frozen sea ice. Due to the prevailing winds, which blow the sea ice away from the coast in this location, the area rarely completely freezes. The ice-covered areas in this image, as well as the Beaufort Sea, to the north, are critical areas for the survival of the ringed seal, a threatened species. The seals use the sea ice, including ice caves, to rear their young, and use the free-floating sea ice for molting, raising the young and breeding. In December 2014, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) proposed that much of this region be set aside as critical, protected habitat for the ringed seal. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
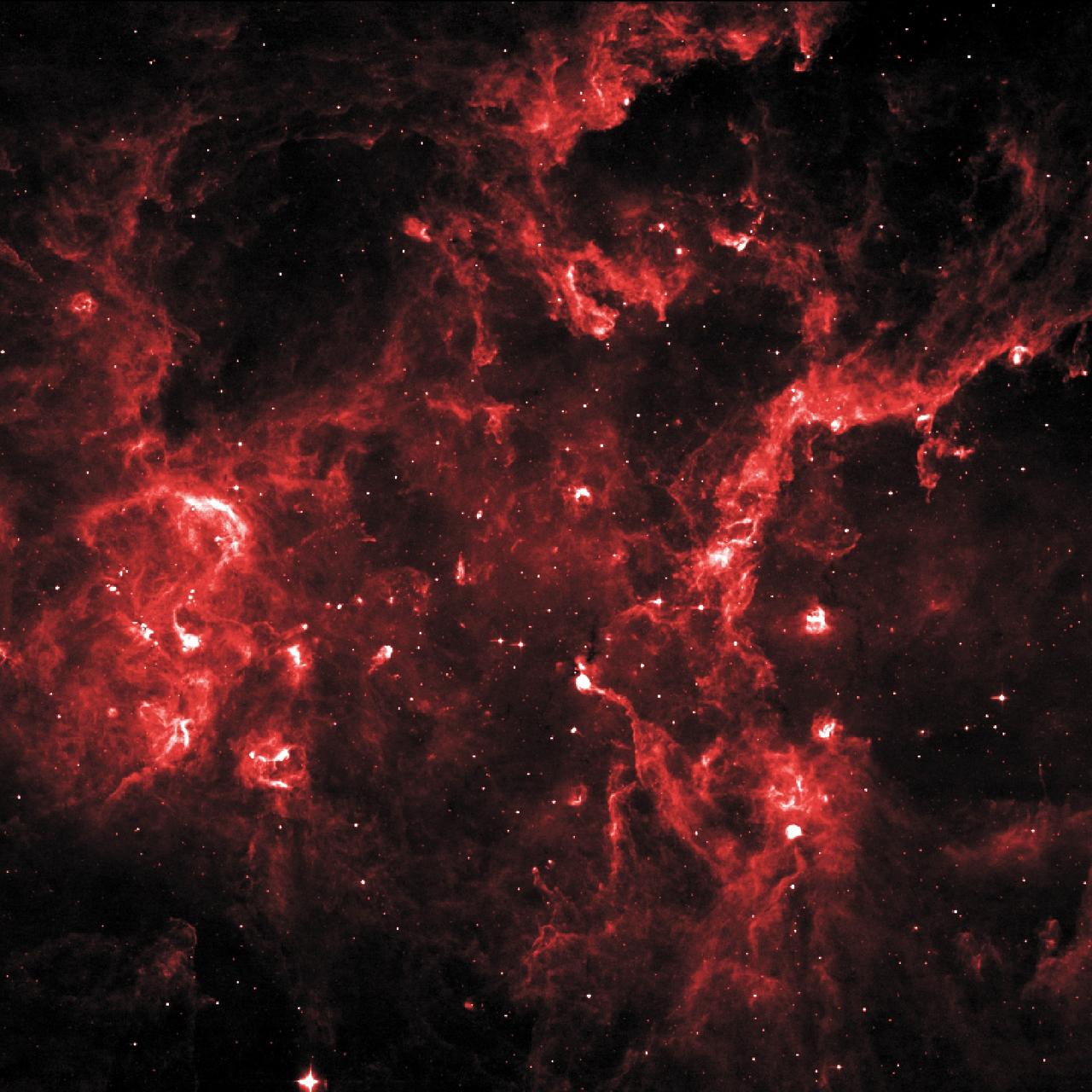

Cygnus X hosts many young stellar groupings. The combined outflows and ultraviolet radiation from the region's numerous massive stars have heated and pushed gas away from the clusters, producing cavities of hot, lower-density gas. In this 8-micron infrared image, ridges of denser gas mark the boundaries of the cavities. Bright spots within these ridges show where stars are forming today. Credit: NASA/IPAC/MSX To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/cygnus-cocoon.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/cygnus-cocoon.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
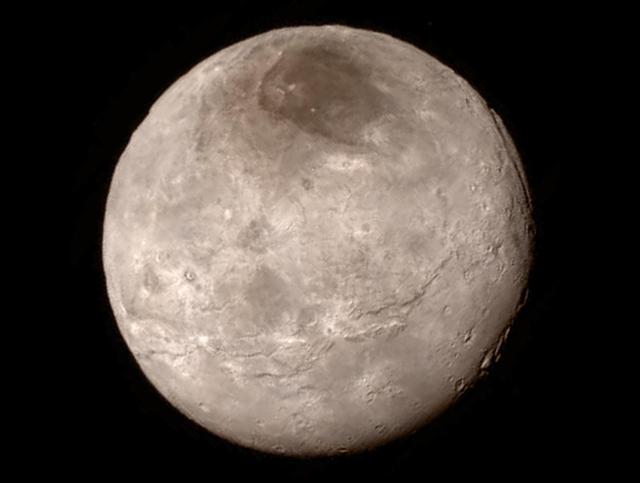

Remarkable new details of Pluto's largest moon Charon are revealed in this image from New Horizons' Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI), taken late on July 13, 2015 from a distance of 289,000 miles (466,000 kilometers). A swath of cliffs and troughs stretches about 600 miles (1,000 kilometers) from left to right, suggesting widespread fracturing of Charon's crust, likely a result of internal processes. At upper right, along the moon's curving edge, is a canyon estimated to be 4 to 6 miles (7 to 9 kilometers) deep. Mission scientists are surprised by the apparent lack of craters on Charon. South of the moon's equator, at the bottom of this image, terrain is lit by the slanting rays of the sun, creating shadows that make it easier to distinguish topography. Even here, however, relatively few craters are visible, indicating a relatively young surface that has been reshaped by geologic activity. In Charon's north polar region, a dark marking prominent in New Horizons' approach images is now seen to have a diffuse boundary, suggesting it is a thin deposit of dark material. Underlying it is a distinct, sharply bounded, angular feature; higher resolution images still to come are expected to shed more light on this enigmatic region. The image has been compressed to reduce its file size for transmission to Earth. In high-contrast areas of the image, features as small as 3 miles (5 kilometers) across can be seen. Some lower-contrast detail is obscured by the compression of the image, which may make some areas appear smoother than they really are. The uncompressed version still resides in New Horizons' computer memory and is scheduled to be transmitted at a later date. The image has been combined with color information obtained by New Horizons' Ralph instrument on July 13. New Horizons traveled more than three billion miles over nine-and-a-half years to reach the Pluto system. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19709
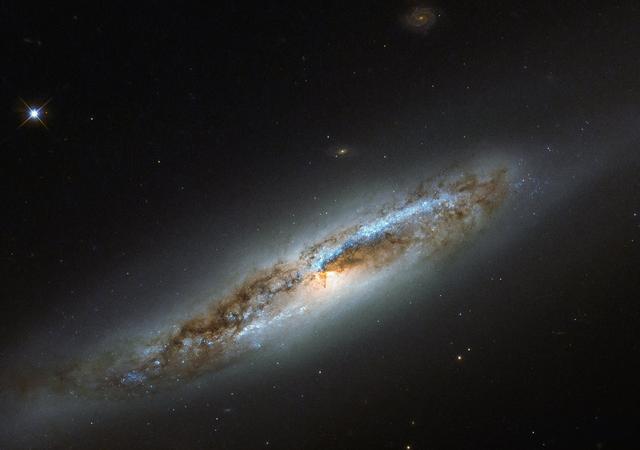

The constellation of Virgo (The Virgin) is especially rich in galaxies, due in part to the presence of a massive and gravitationally-bound collection of more than 1300 galaxies called the Virgo Cluster. One particular member of this cosmic community, NGC 4388, is captured in this image, as seen by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope’s Wide Field Camera 3. Located some 60 million light-years away, NGC 4388 is experiencing some of the less desirable effects that come with belonging to such a massive galaxy cluster. It is undergoing a transformation and has taken on a somewhat confused identity. While the galaxy’s outskirts appear smooth and featureless, a classic feature of an elliptical galaxy, its center displays remarkable dust lanes constrained within two symmetric spiral arms, which emerge from the galaxy’s glowing core — one of the obvious features of a spiral galaxy. Within the arms, speckles of bright blue mark the locations of young stars, indicating that NGC 4388 has hosted recent bursts of star formation. Despite the mixed messages, NGC 4388 is classified as a spiral galaxy. Its unusual combination of features are thought to have been caused by interactions between NGC 4388 and other galaxies in the Virgo Cluster. Gravitational interactions — from glancing blows to head-on collisions, tidal influencing, mergers, and galactic cannibalism — can be devastating to galaxies. While some may be lucky enough to simply suffer a distorted spiral arm or newly-triggered wave of star formation, others see their structure and contents completely and irrevocably altered. Image credits: ESA/NASA
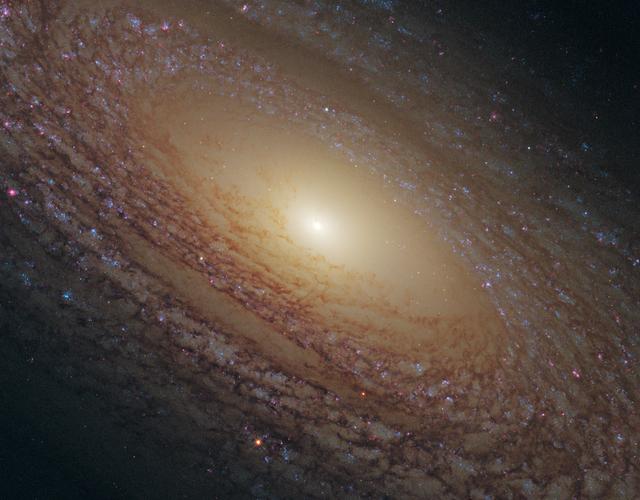

NASA image release Feb. 17, 2011 <b>To see a hd vidoe of this sprial galaxy go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5453173577/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5453173577/</a></b> The Hubble Space Telescope revealed this majestic disk of stars and dust lanes in this view of the spiral galaxy NGC 2841. A bright cusp of starlight marks the galaxy's center. Spiraling outward are dust lanes that are silhouetted against the population of whitish middle-aged stars. Much younger blue stars trace the spiral arms. Notably missing are pinkish emission nebulae indicative of new star birth. It is likely that the radiation and supersonic winds from fiery, super-hot, young blue stars cleared out the remaining gas (which glows pink), and hence shut down further star formation in the regions in which they were born. NGC 2841 currently has a relatively low star formation rate compared to other spirals that are ablaze with emission nebulae. NGC 2841 lies 46 million light-years away in the constellation of Ursa Major (The Great Bear). This image was taken in 2010 through four different filters on Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3. Wavelengths range from ultraviolet light through visible light to near-infrared light. NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage (STScI/AURA)-ESA/Hubble Collaboration; Acknowledgment: M. Crockett and S. Kaviraj (Oxford University, UK), R. O’Connell (University of Virginia), B. Whitmore (STScI), and the WFC3 Scientific Oversight Committee <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

Scientists on NASA's New Horizons mission have discovered what looks like a giant bite-mark on the planet's surface. In this image, north is up. The southern portion of the left inset above shows the cratered plateau uplands informally named Vega Terra (note that all feature names are informal). This terrain is separated from the young, nearly uncratered, mottled plains of Piri Planitia in the center of the image by a generally north-facing jagged scarp called Piri Rupes. The scarp breaks up into isolated mesas in several places. Cutting diagonally across Piri Planitia is the long extensional fault of Inanna Fossa, which stretches eastward 370 miles (600 kilometers) from here to the western edge of the great nitrogen ice plains of Sputnik Planum. Compositional data from the New Horizons spacecraft's Ralph/Linear Etalon Imaging Spectral Array (LEISA) instrument, shown in the right inset, indicate that the plateau uplands south of Piri Rupes are rich in methane ice (shown in false color as purple). Scientists speculate that sublimation of methane may be causing the plateau material to erode along the face of the scarp cliffs, causing them to retreat south and leave the plains of Piri Planitia in their wake. Compositional data also show that the surface of Piri Planitia is more enriched in water ice (shown in false color as blue) than the plateau uplands, which may indicate that Piri Planitia's surface is made of water ice bedrock, on top of which the layer of retreating methane ice had been sitting. Because the surface of Pluto is so cold, the water ice behaves like rock and is immobile. The light/dark mottled pattern of Piri Planitia in the left inset is reflected in the composition map, with the lighter areas corresponding to areas richer in methane – these may be remnants of methane that have not yet sublimated away entirely. The inset at left shows about 650 feet (200 meters) per pixel; the image measures approximately 280 miles (450 kilometers) long by 255 miles (410 kilometers) wide. It was obtained by New Horizons at a range of approximately 21,100 miles (33,900 kilometers) from Pluto, about 45 minutes before the spacecraft's closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015.The LEISA data at right was gathered when the spacecraft was about 29,000 miles (47,000 kilometers) from Pluto; best resolution is 1.7 miles (2.7 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20531

For the 26th birthday of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers are highlighting a Hubble image of an enormous bubble being blown into space by a super-hot, massive star. The Hubble image of the Bubble Nebula, or NGC 7635, was chosen to mark the 26th anniversary of the launch of Hubble into Earth orbit by the STS-31 space shuttle crew on April 24, 1990 “As Hubble makes its 26th revolution around our home star, the sun, we celebrate the event with a spectacular image of a dynamic and exciting interaction of a young star with its environment. The view of the Bubble Nebula, crafted from WFC-3 images, reminds us that Hubble gives us a front row seat to the awe inspiring universe we live in,” said John Grunsfeld, Hubble astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, in Washington, D.C. The Bubble Nebula is seven light-years across—about one-and-a-half times the distance from our sun to its nearest stellar neighbor, Alpha Centauri, and resides 7,100 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cassiopeia. The seething star forming this nebula is 45 times more massive than our sun. Gas on the star gets so hot that it escapes away into space as a “stellar wind” moving at over four million miles per hour. This outflow sweeps up the cold, interstellar gas in front of it, forming the outer edge of the bubble much like a snowplow piles up snow in front of it as it moves forward. As the surface of the bubble's shell expands outward, it slams into dense regions of cold gas on one side of the bubble. This asymmetry makes the star appear dramatically off-center from the bubble, with its location in the 10 o’clock position in the Hubble view. Dense pillars of cool hydrogen gas laced with dust appear at the upper left of the picture, and more “fingers” can be seen nearly face-on, behind the translucent bubble. The gases heated to varying temperatures emit different colors: oxygen is hot enough to emit blue light in the bubble near the star, while the cooler pillars are yellow from the combined light of hydrogen and nitrogen. The pillars are similar to the iconic columns in the “Pillars of Creation” Eagle Nebula. As seen with the structures in the Eagle Nebula, the Bubble Nebula pillars are being illuminated by the strong ultraviolet radiation from the brilliant star inside the bubble. The Bubble Nebula was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, a prominent British astronomer. It is being formed by a proto-typical Wolf-Rayet star, BD +60º2522, an extremely bright, massive, and short-lived star that has lost most of its outer hydrogen and is now fusing helium into heavier elements. The star is about four million years old, and in 10 million to 20 million years, it will likely detonate as a supernova. Hubble’s Wide Field Camera-3 imaged the nebula in visible light with unprecedented clarity in February 2016. The colors correspond to blue for oxygen, green for hydrogen, and red for nitrogen. This information will help astronomers understand the geometry and dynamics of this complex system. The Bubble Nebula is one of only a handful of astronomical objects that have been observed with several different instruments onboard Hubble. Hubble also imaged it with the Wide Field Planetary Camera (WFPC) in September 1992, and with Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (WFPC2) in April 1999. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)

For the 26th birthday of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers are highlighting a Hubble image of an enormous bubble being blown into space by a super-hot, massive star. The Hubble image of the Bubble Nebula, or NGC 7635, was chosen to mark the 26th anniversary of the launch of Hubble into Earth orbit by the STS-31 space shuttle crew on April 24, 1990 “As Hubble makes its 26th revolution around our home star, the sun, we celebrate the event with a spectacular image of a dynamic and exciting interaction of a young star with its environment. The view of the Bubble Nebula, crafted from WFC-3 images, reminds us that Hubble gives us a front row seat to the awe inspiring universe we live in,” said John Grunsfeld, Hubble astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, in Washington, D.C. The Bubble Nebula is seven light-years across—about one-and-a-half times the distance from our sun to its nearest stellar neighbor, Alpha Centauri, and resides 7,100 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cassiopeia. The seething star forming this nebula is 45 times more massive than our sun. Gas on the star gets so hot that it escapes away into space as a “stellar wind” moving at over four million miles per hour. This outflow sweeps up the cold, interstellar gas in front of it, forming the outer edge of the bubble much like a snowplow piles up snow in front of it as it moves forward. As the surface of the bubble's shell expands outward, it slams into dense regions of cold gas on one side of the bubble. This asymmetry makes the star appear dramatically off-center from the bubble, with its location in the 10 o’clock position in the Hubble view. Dense pillars of cool hydrogen gas laced with dust appear at the upper left of the picture, and more “fingers” can be seen nearly face-on, behind the translucent bubble. The gases heated to varying temperatures emit different colors: oxygen is hot enough to emit blue light in the bubble near the star, while the cooler pillars are yellow from the combined light of hydrogen and nitrogen. The pillars are similar to the iconic columns in the “Pillars of Creation” Eagle Nebula. As seen with the structures in the Eagle Nebula, the Bubble Nebula pillars are being illuminated by the strong ultraviolet radiation from the brilliant star inside the bubble. The Bubble Nebula was discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, a prominent British astronomer. It is being formed by a proto-typical Wolf-Rayet star, BD +60º2522, an extremely bright, massive, and short-lived star that has lost most of its outer hydrogen and is now fusing helium into heavier elements. The star is about four million years old, and in 10 million to 20 million years, it will likely detonate as a supernova. Hubble’s Wide Field Camera-3 imaged the nebula in visible light with unprecedented clarity in February 2016. The colors correspond to blue for oxygen, green for hydrogen, and red for nitrogen. This information will help astronomers understand the geometry and dynamics of this complex system. The Bubble Nebula is one of only a handful of astronomical objects that have been observed with several different instruments onboard Hubble. Hubble also imaged it with the Wide Field Planetary Camera (WFPC) in September 1992, and with Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (WFPC2) in April 1999. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)

NASA image release July 3, 2012 Caption: Resembling a Fourth of July skyrocket, Herbig-Haro 110 is a geyser of hot gas from a newborn star that splashes up against and ricochets off the dense core of a cloud of molecular hydrogen. Although the plumes of gas look like whiffs of smoke, they are actually billions of times less dense than the smoke from a July 4 firework. This Hubble Space Telescope photo shows the integrated light from plumes, which are light-years across. -- Herbig-Haro (HH) objects come in a wide array of shapes, but the basic configuration stays the same. Twin jets of heated gas, ejected in opposite directions away from a forming star, stream through interstellar space. Astronomers suspect that these outflows are fueled by gas accreting onto a young star surrounded by a disk of dust and gas. The disk is the "fuel tank," the star is the gravitational engine, and the jets are the exhaust. When these energetic jets slam into colder gas, the collision plays out like a traffic jam on the interstate. Gas within the shock front slows to a crawl, but more gas continues to pile up as the jet keeps slamming into the shock from behind. Temperatures climb sharply, and this curving, flared region starts to glow. These "bow shocks" are so named because they resemble the waves that form at the front of a boat. In the case of the single HH 110 jet, astronomers observe a spectacular and unusual permutation on this basic model. Careful study has repeatedly failed to find the source star driving HH 110, and there may be good reason for this: perhaps the HH 110 outflow is itself generated by another jet. Astronomers now believe that the nearby HH 270 jet grazes an immovable obstacle - a much denser, colder cloud core - and gets diverted off at about a 60-degree angle. The jet goes dark and then reemerges, having reinvented itself as HH 110. The jet shows that these energetic flows are like the erratic outbursts from a Roman candle. As fast-moving blobs of gas catch up and collide with slower blobs, new shocks arise along the jet's interior. The light emitted from excited gas in these hot blue ridges marks the boundaries of these interior collisions. By measuring the current velocity and positions of different blobs and hot ridges along the chain within the jet, astronomers can effectively "rewind" the outflow, extrapolating the blobs back to the moment when they were emitted. This technique can be used to gain insight into the source star's history of mass accretion. This image is a composite of data taken with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys in 2004 and 2005 and the Wide Field Camera 3 in April 2011. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>