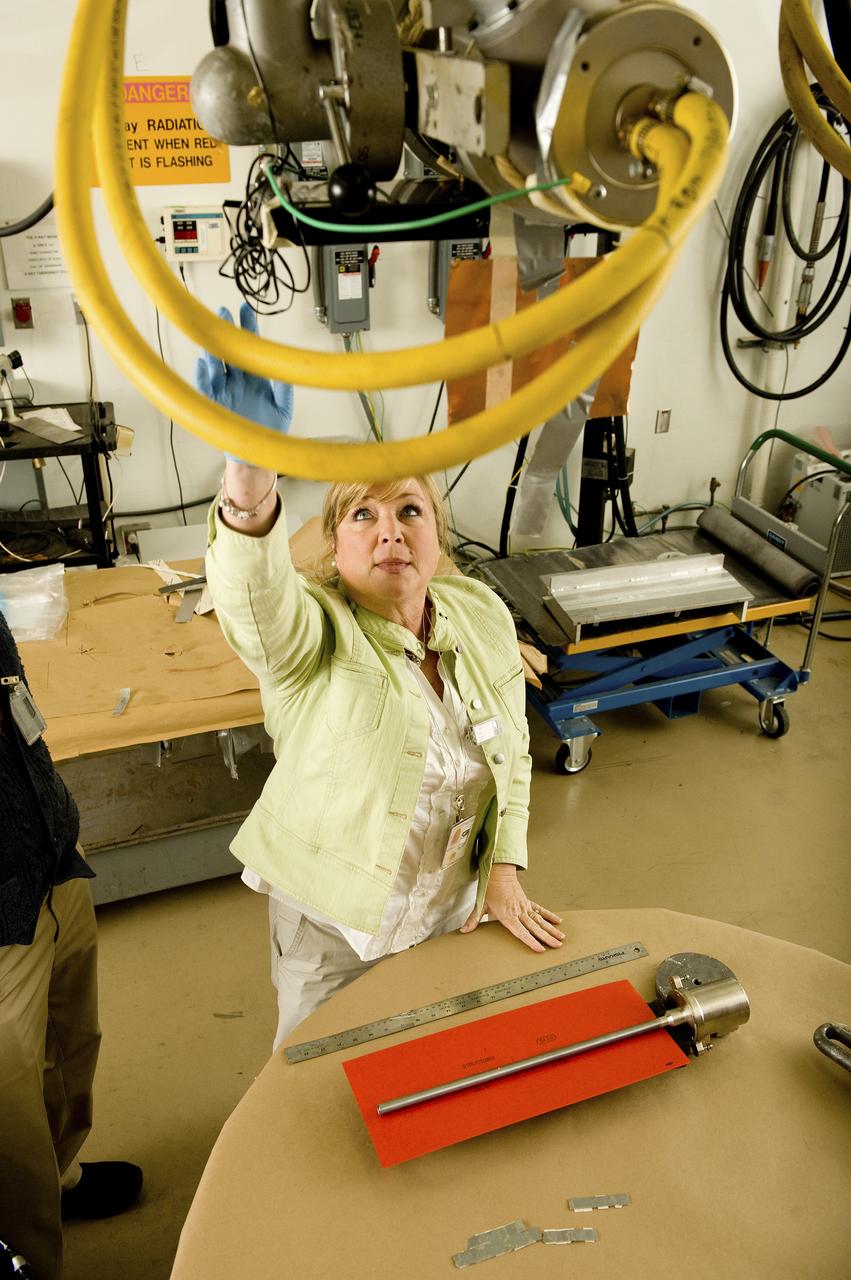

RHONDA LASH, A MATERIALS ENGINEER, PREPARES A SAMPLE CARTRIDGE FOR X-RAY. THE CARTRIDGE WAS TESTED ON THE MATERIAL SCIENCE RESEARCH RACK
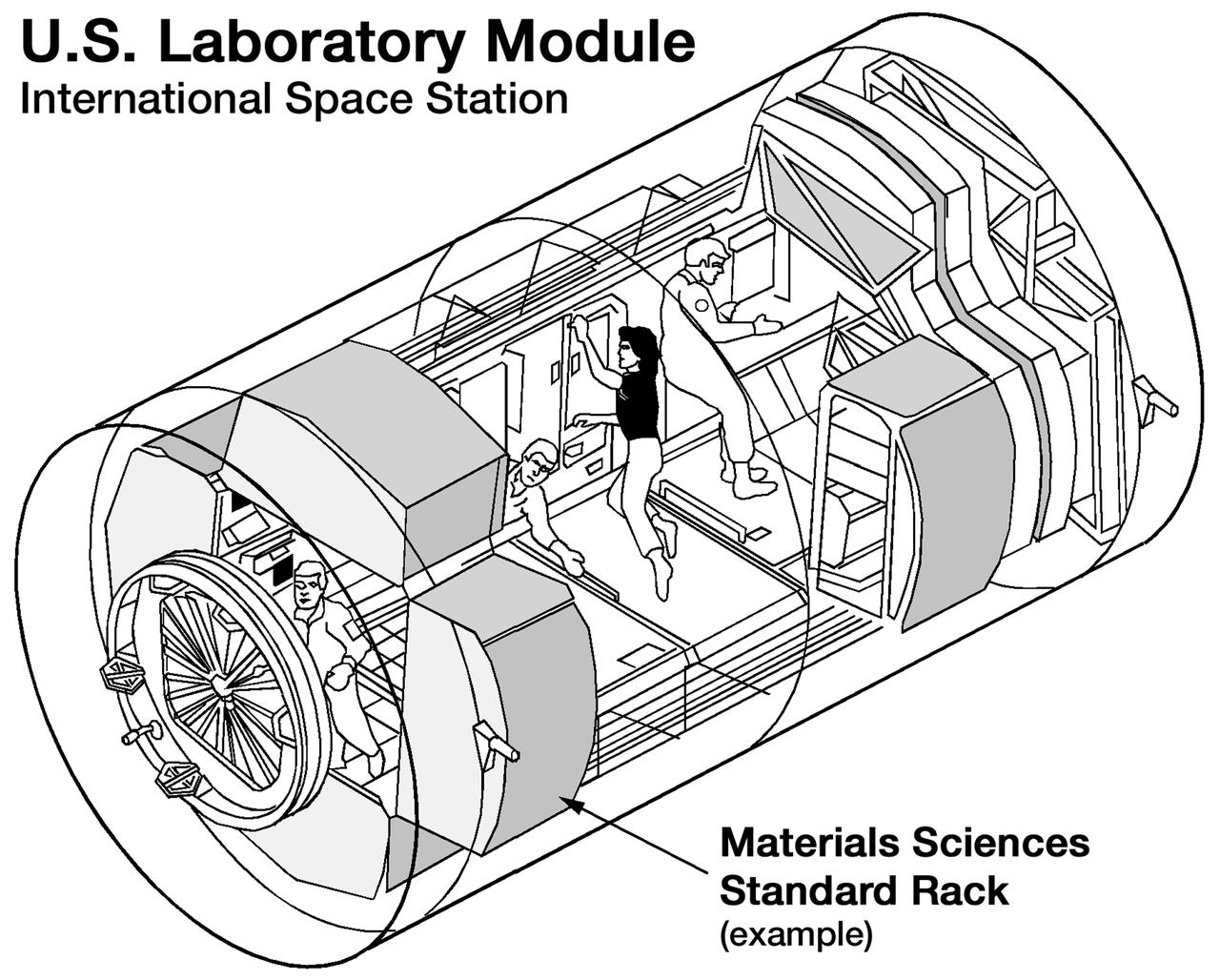
Line drawing depicts the location of one of three racks that will make up the Materials Science Research Facility in the U.S. Destiny laboratory module to be attached to the International Space Station (ISS). Other positions will be occupied by a variety of racks supporting research in combustion, fluids, biotechnology, and human physiology, and racks to support lab and station opertions. The Materials Science Research Facility is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center

NASA's first Sample Cartridge Assembly (SCA) project designed and validated a payload containing a materials research sample in a sealed environment. The SCA was heated in the European Space Agency's (ESA) Low Gradient Furnace (LGF) that is housed inside the Material Science Research Rack (MSRR) located on the International Space Station (ISS). Sintered metals and crystal growth experiments in microgravity are examples of some of the types of materials research that may be performed with a SCA.
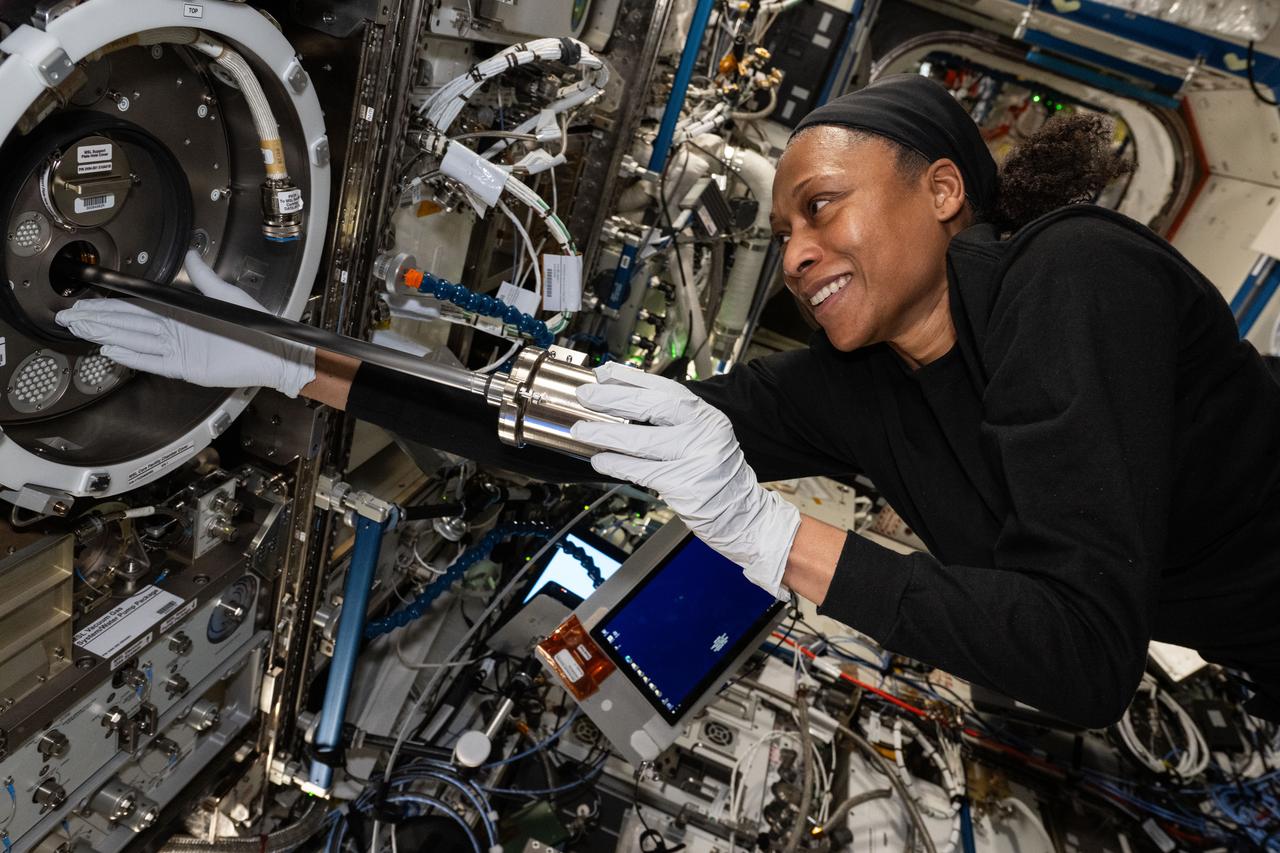

iss071e195867 (June 17, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 71 Flight Engineer Jeanette Epps works on the Materials Science Laboratory (MSL), a component of the Destiny laboratory module's Materials Science Research Rack. The MSL is a research facility used to discover new applications for existing materials and new or improved materials.

iss071e195867 (June 17, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 71 Flight Engineer Jeanette Epps works on the Materials Science Laboratory (MSL), a component of the Destiny laboratory module's Materials Science Research Rack. The MSL is a research facility used to discover new applications for existing materials and new or improved materials.
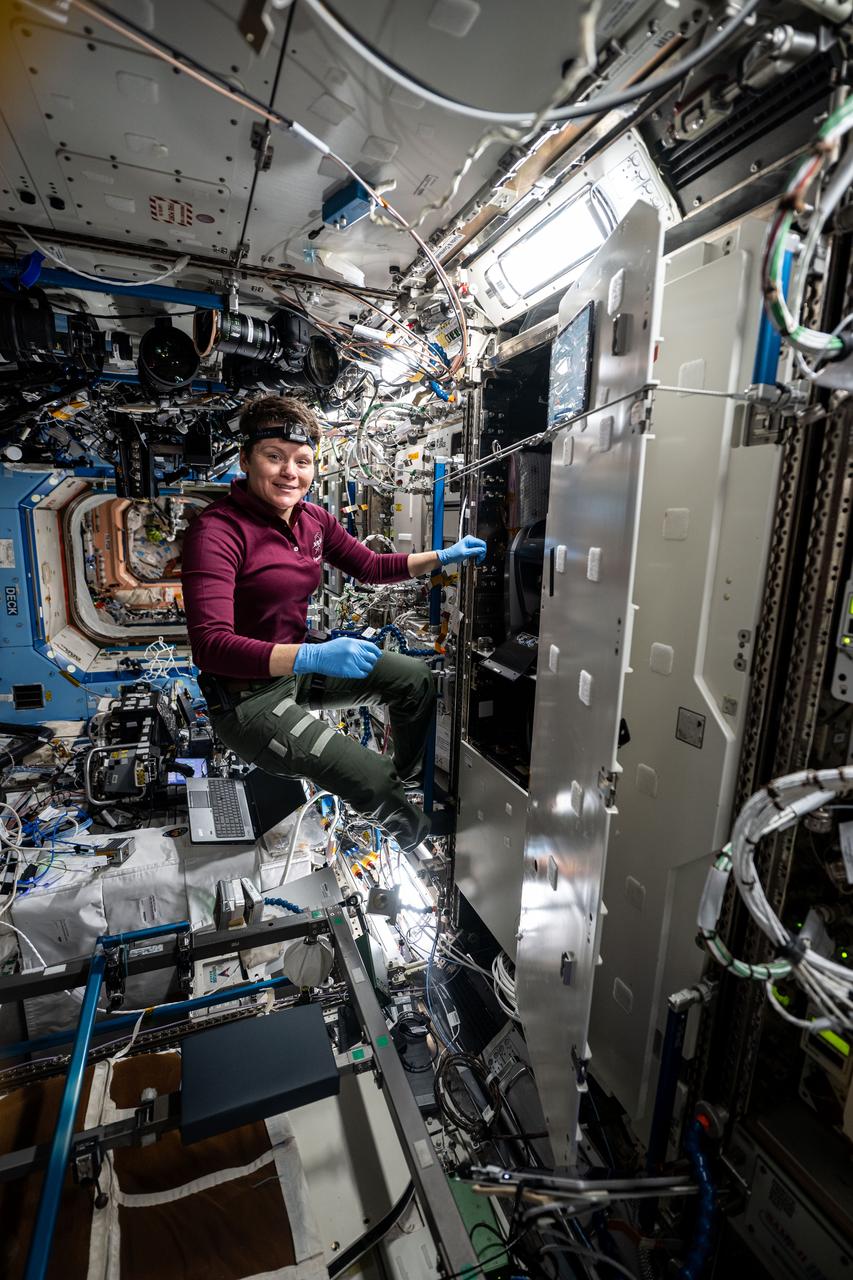

iss073e0118086 (May 29, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Anne McClain works inside the Destiny laboratory module's Materials Science Research Rack and swaps filters inside the Kermit microscope. Kermit is an all-in-one fluorescence microscope system used to conduct biological, physical, and materials science research.
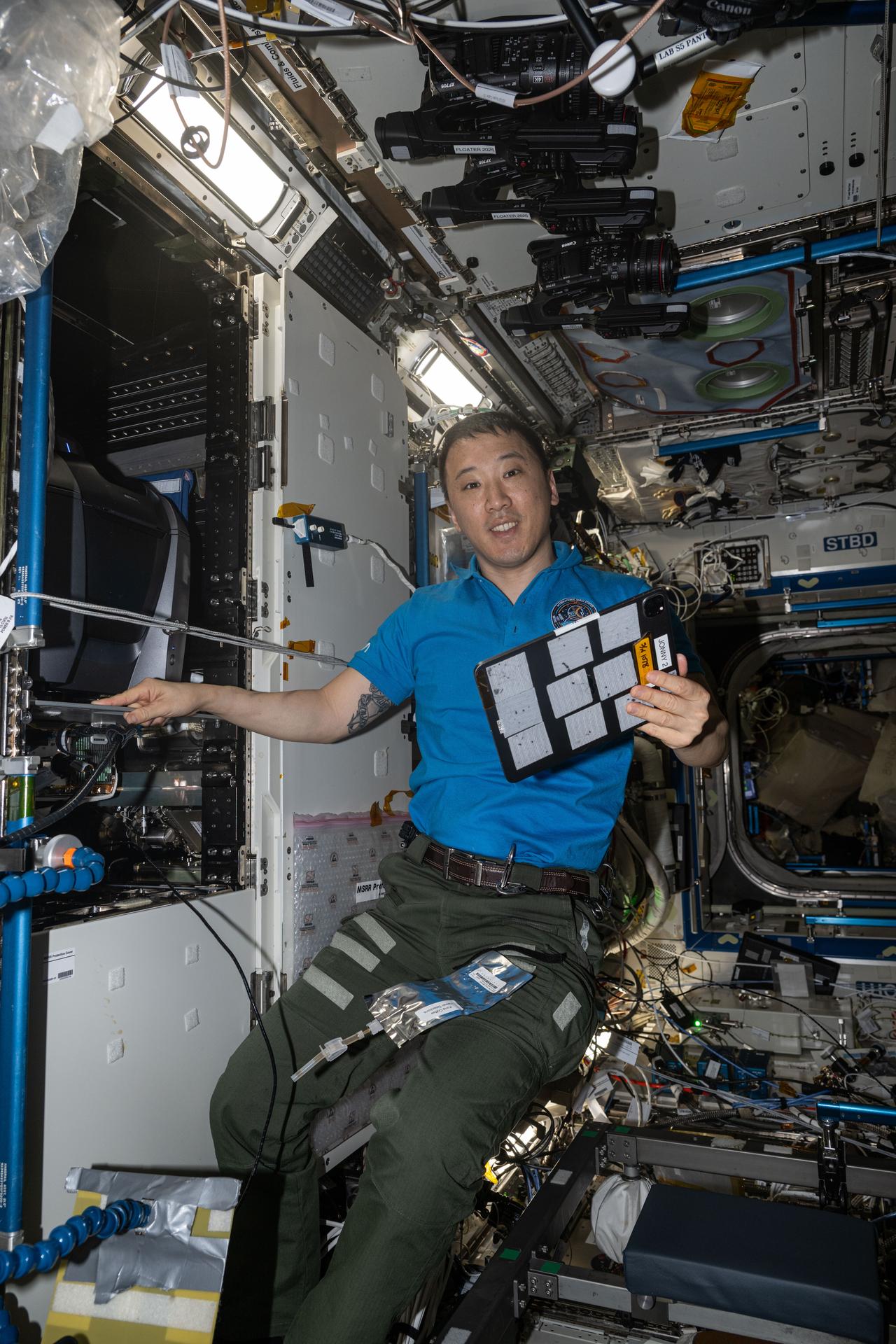

iss073e1049692 (Nov. 6, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Jonny Kim poses for a portrait while servicing the KERMIT (Keyence Research Microscope Testbed) fluorescence microscope inside the Materials Science Research Rack aboard the International Space Station’s Destiny laboratory module. KERMIT is a commercial off-the-shelf microscope that provides researchers with essential imaging capabilities for biological, physical, and materials science research in microgravity.
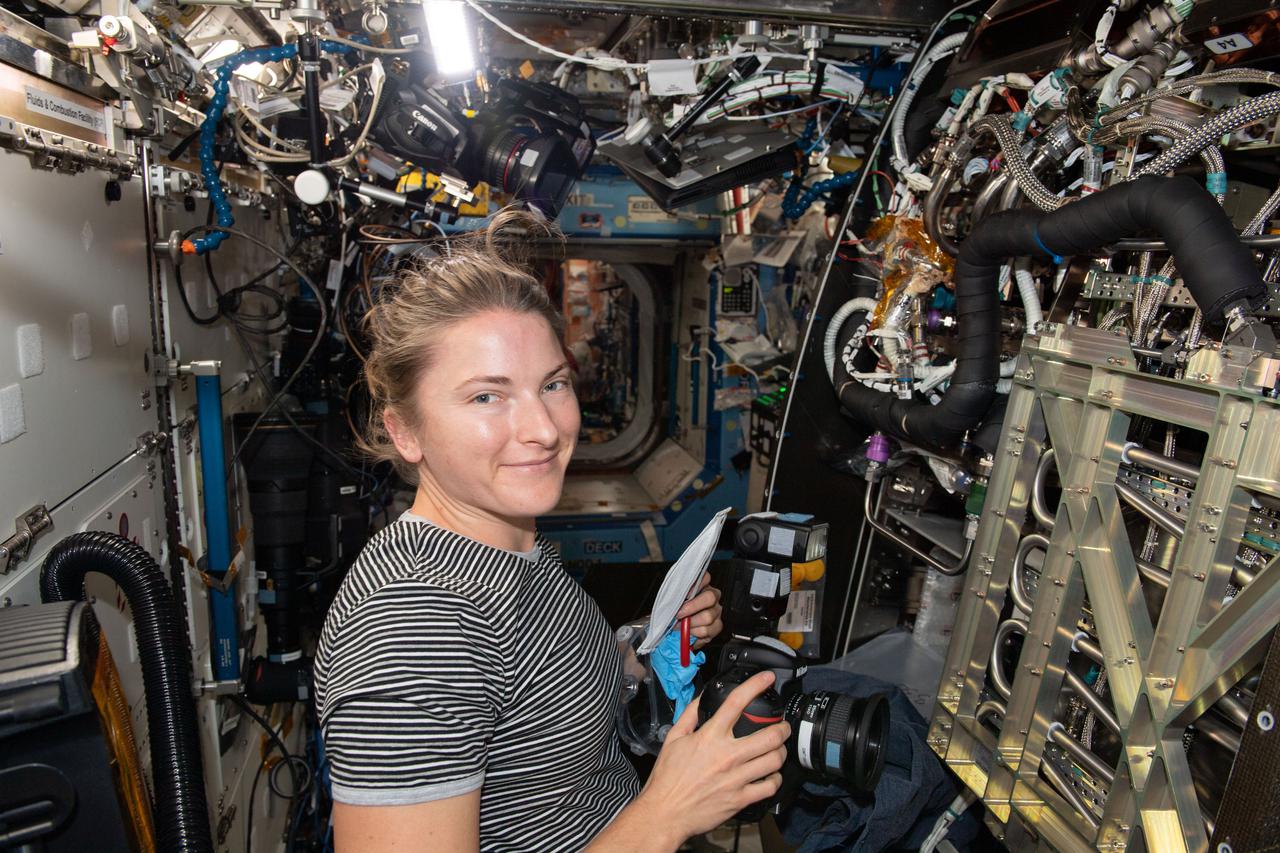

iss066e086562 (Dec. 4, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 Flight Engineer Kayla Barron is pictured inspecting and photographing components inside the Materials Science Research Rack that enables the observation of chemical and thermal properties of materials free from the effects of gravity.
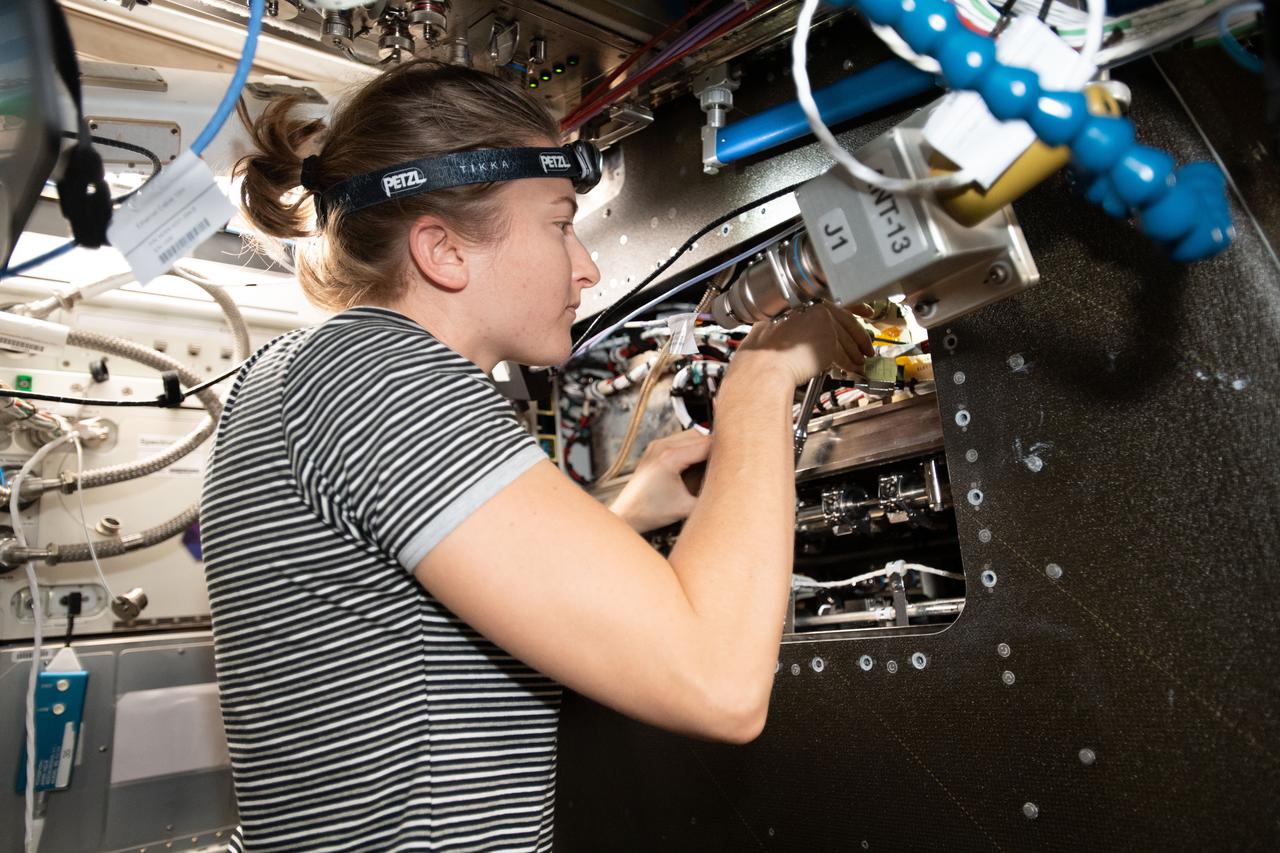

iss066e086417 (Dec. 4, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 Flight Engineer Kayla Barron inspects cables inside the Materials Science Research Rack. The space physics research device enables the observation of many material types, such as metals, alloys, polymers, semiconductors, ceramics, crystals, and glasses, to study and discover new applications for existing materials and new or improved materials.
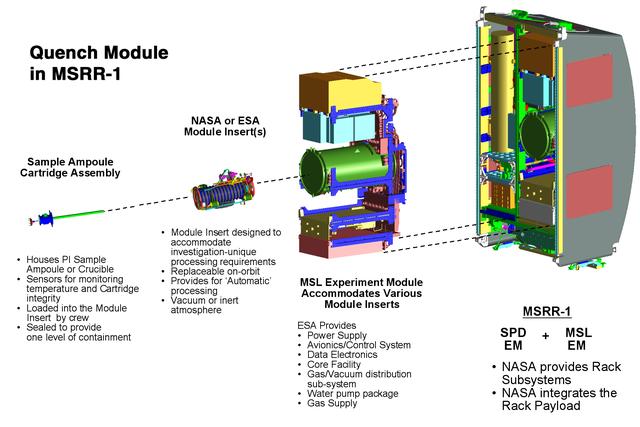
This computer-generated image depicts the Materials Science Research Rack-1 (MSRR-1) being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center and the European Space Agency (ESA) for placement in the Destiny laboratory module aboard the International Space Station. The rack is part of the plarned Materials Science Research Facility (MSRF) and is expected to include two furnace module inserts, a Quench Module Insert (being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center) to study directional solidification in rapidly cooled alloys and a Diffusion Module Insert (being developed by the European Space Agency) to study crystal growth, and a transparent furnace (being developed by NASA's Space Product Development program). Multi-user equipment in the rack is being developed under the auspices of NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research (OBPR) and ESA. Key elements are labeled in other images (0101754, 0101829, 0101830).
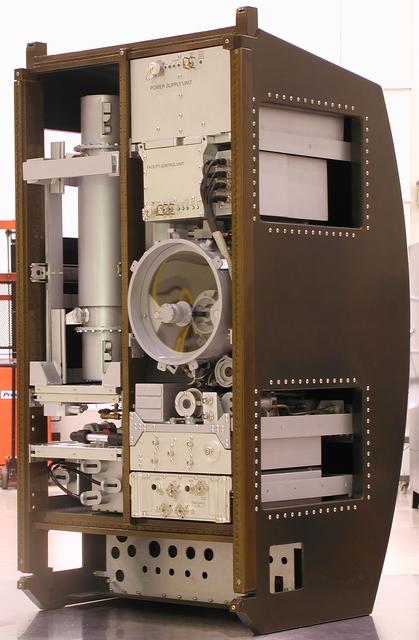
This scale model depicts the Materials Science Research Rack-1 (MSRR-1) being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center and the European Space Agency (ESA) for placement in the Destiny laboratory module aboard the International Space Station. The rack is part of the plarned Materials Science Research Facility (MSRF) and is expected to include two furnace module inserts, a Quench Module Insert (being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center) to study directional solidification in rapidly cooled alloys and a Diffusion Module Insert (being developed by the European Space Agency) to study crystal growth, and a transparent furnace (being developed by NASA's Space Product Development program). Multi-user equipment in the rack is being developed under the auspices of NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research (OBPR) and ESA. Key elements are labeled in other images (0101754, 0101829, 0101830, and TBD). This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

This scale model depicts the Materials Science Research Rack-1 (MSRR-1) being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center and the European Space Agency (ESA) for placement in the Destiny laboratory module aboard the International Space Station. The rack is part of the plarned Materials Science Research Facility (MSRF) and is expected to include two furnace module inserts, a Quench Module Insert (being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center) to study directional solidification in rapidly cooled alloys and a Diffusion Module Insert (being developed by the European Space Agency) to study crystal growth, and a transparent furnace (being developed by NASA's Space Product Development program). Multi-user equipment in the rack is being developed under the auspices of NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research (OBPR) and ESA. Key elements are labeled in other images (0101754, 0101829, 0101830, and TBD).
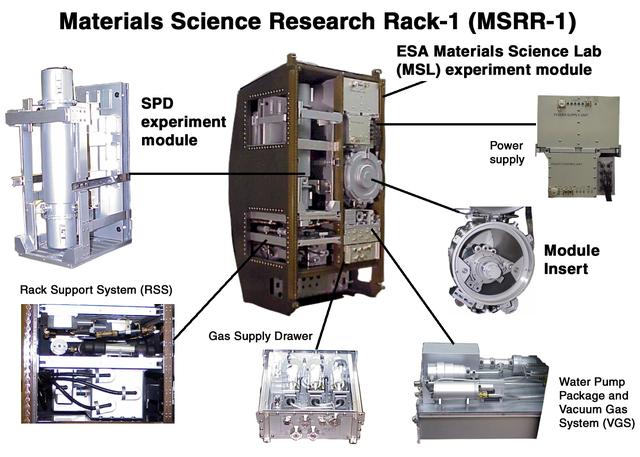
This scale model depicts the Materials Science Research Rack-1 (MSRR-1) being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center and the European Space Agency (ESA) for placement in the Destiny laboratory module aboard the International Space Station. The rack is part of the plarned Materials Science Research Facility (MSRF) and is expected to include two furnace module inserts, a Quench Module Insert (being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center) to study directional solidification in rapidly cooled alloys and a Diffusion Module Insert (being developed by the European Space Agency) to study crystal growth, and a transparent furnace (being developed by NASA's Space Product Development program). Multi-user equipment in the rack is being developed under the auspices of NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research (OBPR) and ESA. Key elements are labeled in other images (0101754, 0101829, and TBD). This composite is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.
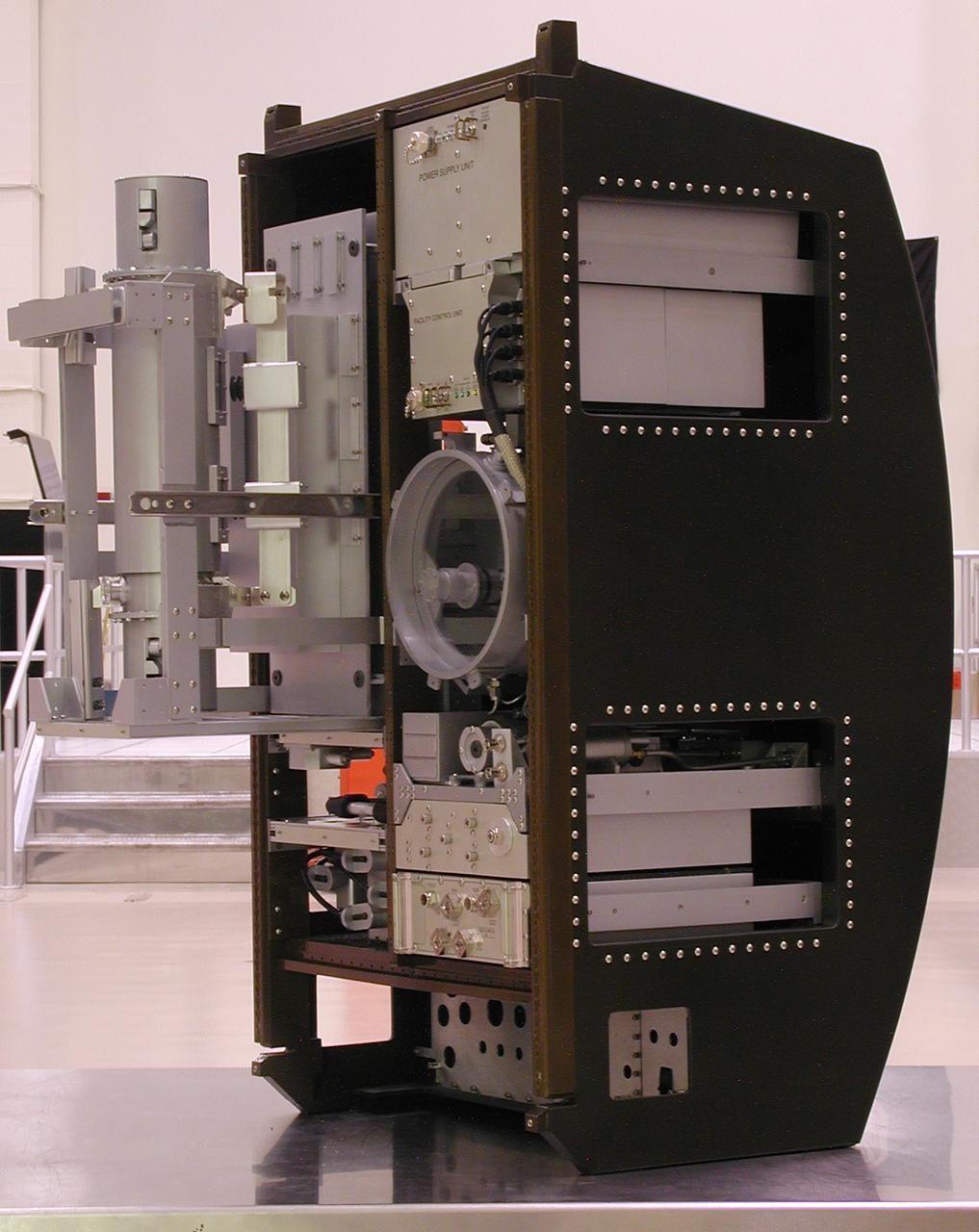
This scale model depicts the Materials Science Research Rack-1 (MSRR-1) being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center and the European Space Agency (ESA) for placement in the Destiny laboratory module aboard the International Space Station. The rack is part of the plarned Materials Science Research Facility (MSRF) and is expected to include two furnace module inserts, a Quench Module Insert (being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center) to study directional solidification in rapidly cooled alloys and a Diffusion Module Insert (being developed by the European Space Agency) to study crystal growth, and a transparent furnace (being developed by NASA's Space Product Development program). Multi-user equipment in the rack is being developed under the auspices of NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research (OBPR) and ESA. Here the transparent furnace is extracted for servicing. Key elements are labeled in other images (0101754, 0101829, 0101830, and TBD).
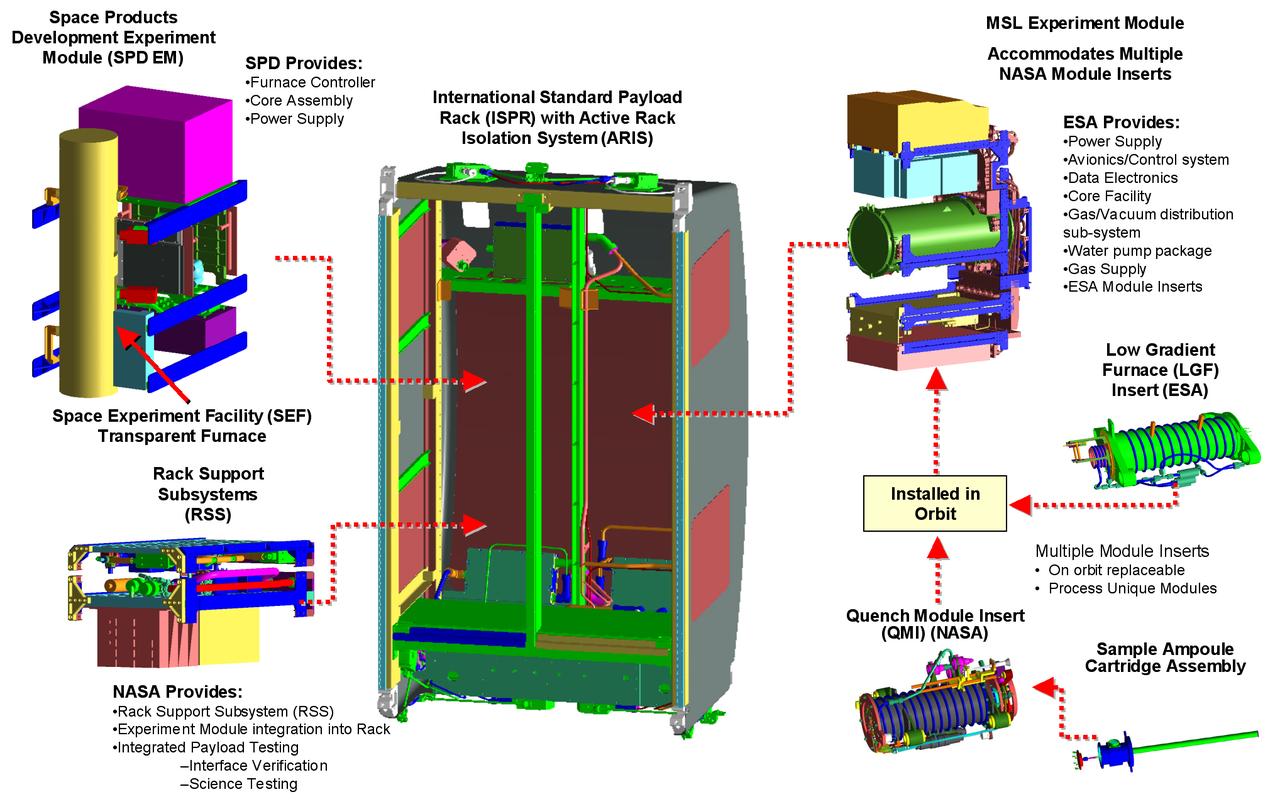
This computer-generated image depicts the Materials Science Research Rack-1 (MSRR-1) being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center and the European Space Agency (ESA) for placement in the Destiny laboratory module aboard the International Space Station. The rack is part of the plarned Materials Science Research Facility (MSRF) and is expected to include two furnace module inserts, a Quench Module Insert (being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center) to study directional solidification in rapidly cooled alloys and a Diffusion Module Insert (being developed by the European Space Agency) to study crystal growth, and a transparent furnace (being developed by NASA's Space Product Development program). Multi-user equipment in the rack is being developed under the auspices of NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research (OBPR) and ESA. Key elements are labeled in other images (0101754, 0101830, and TBD).
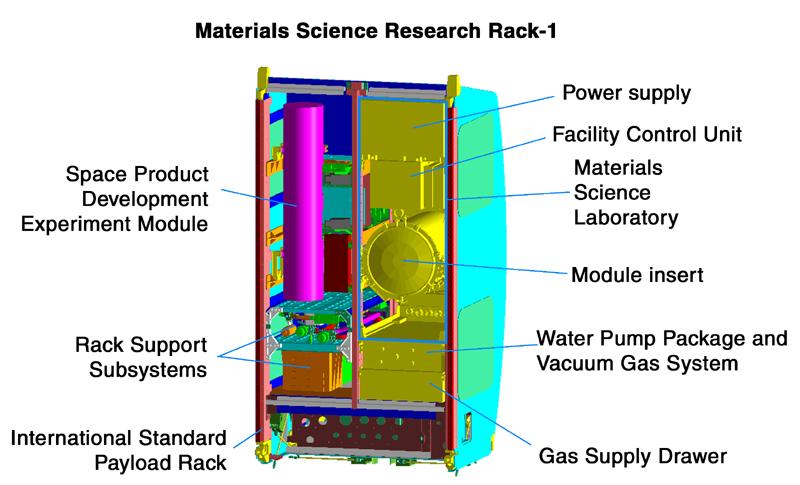
This computer-generated image depicts the Materials Science Research Rack-1 (MSRR-1) being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center and the European Space Agency (ESA) for placement in the Destiny laboratory module aboard the International Space Station. The rack is part of the plarned Materials Science Research Facility (MSRF) and is expected to include two furnace module inserts, a Quench Module Insert (being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center) to study directional solidification in rapidly cooled alloys and a Diffusion Module Insert (being developed by the European Space Agency) to study crystal growth, and a transparent furnace (being developed by NASA's Space Product Development program). Multi-user equipment in the rack is being developed under the auspices of NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research (OBPR) and ESA. A larger image is available without labels (No. 0101755).
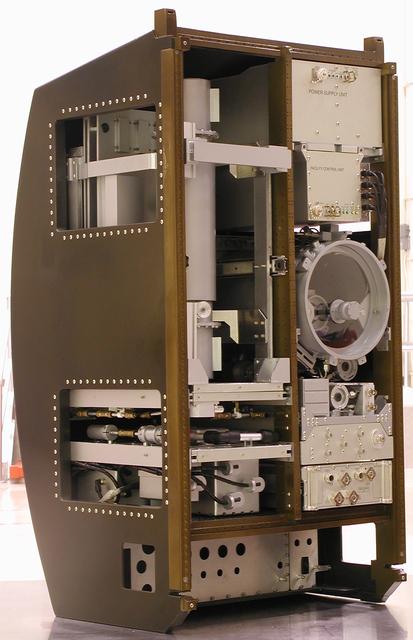

This scale model depicts the Materials Science Research Rack-1 (MSRR-1) being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center and the European Space Agency (ESA) for placement in the Destiny laboratory module aboard the International Space Station. The rack is part of the plarned Materials Science Research Facility (MSRF) and is expected to include two furnace module inserts, a Quench Module Insert (being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center) to study directional solidification in rapidly cooled alloys and a Diffusion Module Insert (being developed by the European Space Agency) to study crystal growth, and a transparent furnace (being developed by NASA's Space Product Development program). Multi-user equipment in the rack is being developed under the auspices of NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research (OBPR) and ESA. Key elements are labeled in other images (0101754, 0101829, 0101830, and TBD). This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.
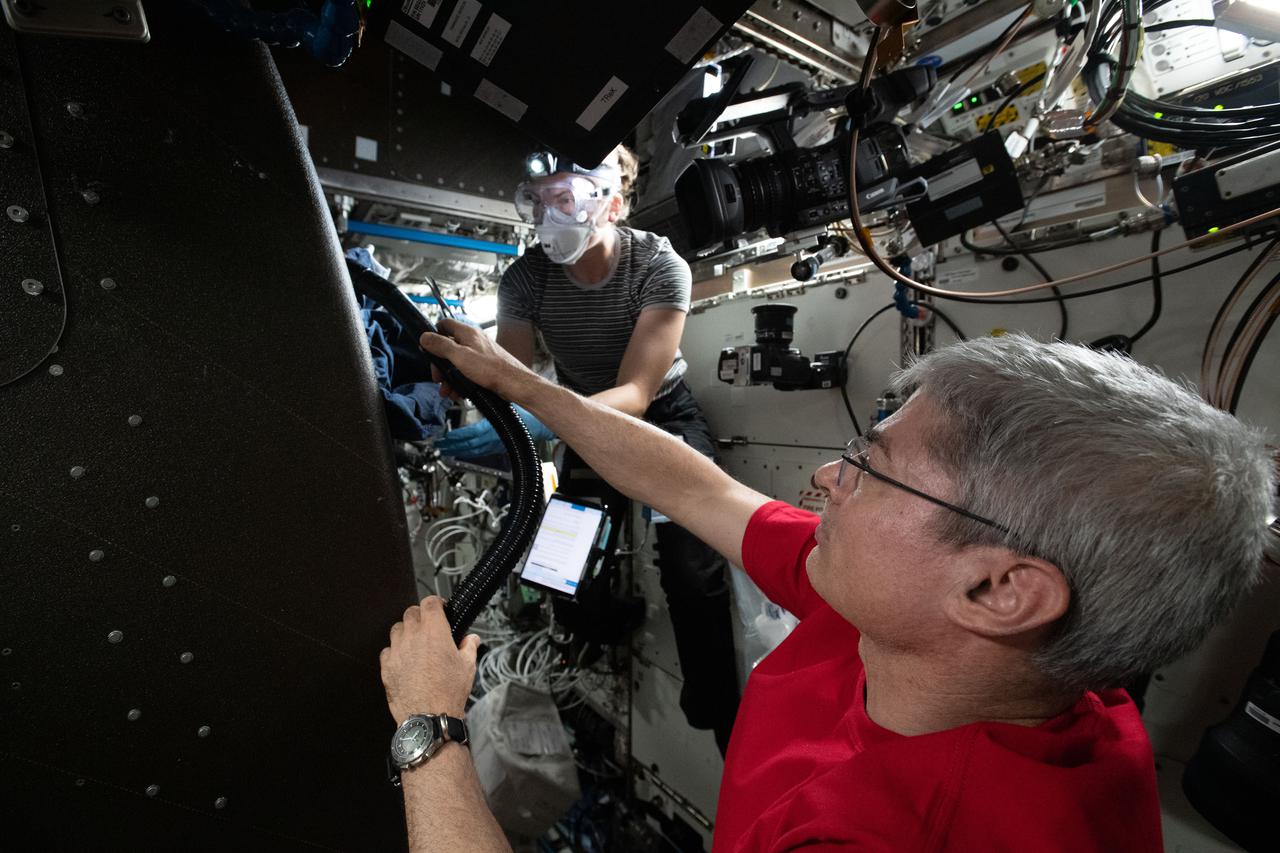

iss066e086431 (Dec. 4, 2021) --- NASA astronauts and Expedition 66 Flight Engineers Mark Vande Hei and Kayla Barron inspect cables inside the Materials Science Research Rack. The space physics device enables the observation of many material types, such as metals, alloys, polymers, semiconductors, ceramics, crystals, and glasses, to study and discover new applications for existing materials and new or improved materials.
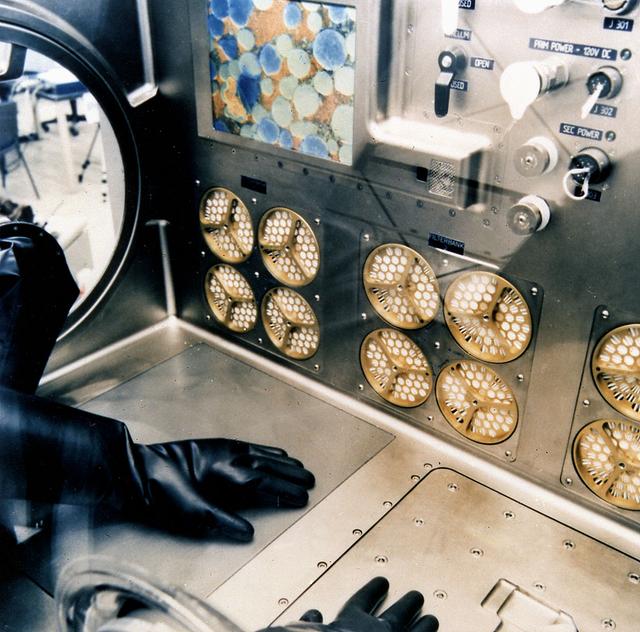

The Microgravity Science Glovebox is a facility for performing microgravity research in the areas of materials, combustion, fluids and biotechnology science. The facility occupies a full ISPR, consisting of: the ISPR rack and infrastructure for the rack, the glovebox core facility, data handling, rack stowage, outfitting equipment, and a video subsystem. MSG core facility provides the experiment developers a chamber with air filtering and recycling, up to two levels of containment, an airlock for transfer of payload equipment to/from the main volume, interface resources for the payload inside the core facility, resources inside the airlock, and storage drawers for MSG support equipment and consumables.
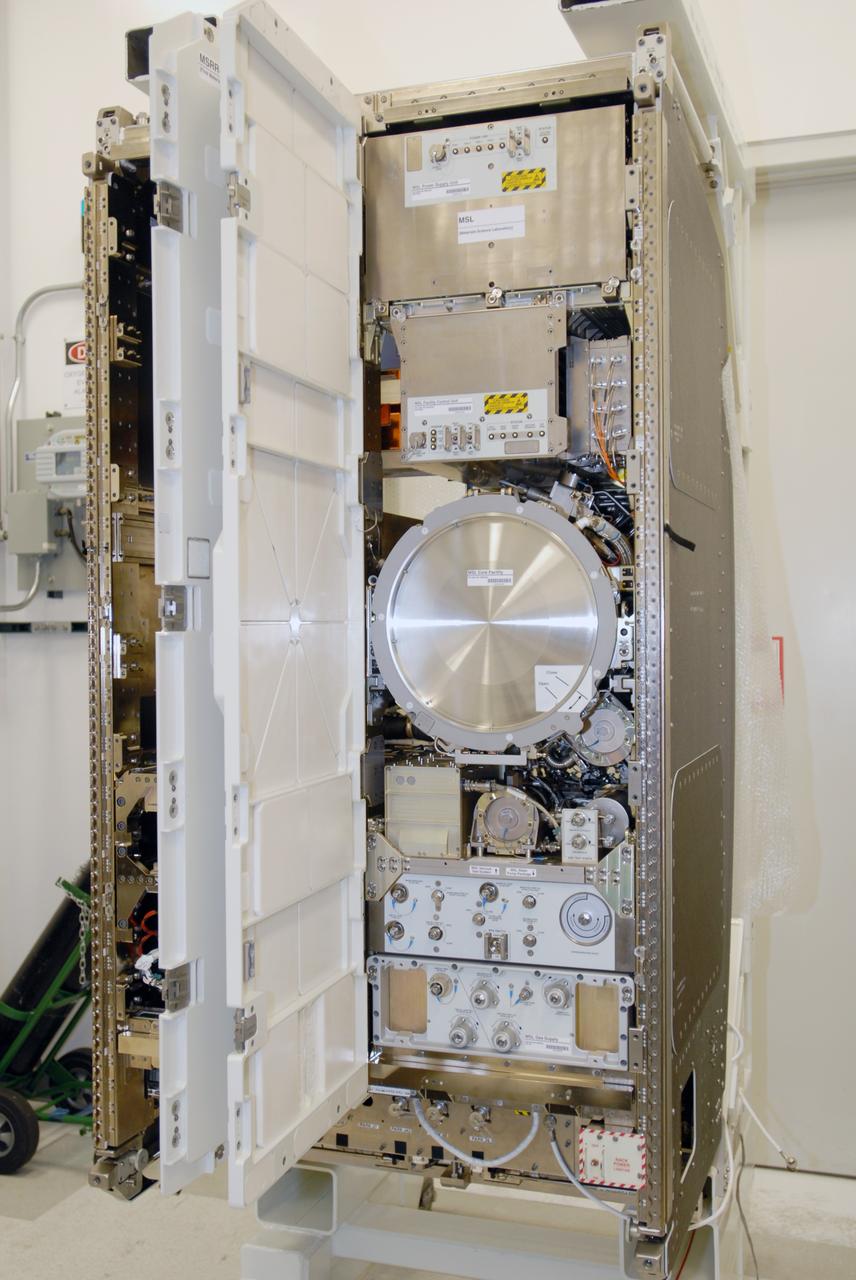

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This close-up shows some of the components of the Materials Science Research Rack-1, or MSRR-1, which arrived at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for final flight preparations. The size of a large refrigerator, MSRR-1 is 6 feet high, 3.5 feet wide and 40 inches deep and weighs about 1 ton. MSRR-1 is the payload for the STS-128 mission targeted to launch in August. The rack will be installed in the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module for transport to the International Space Station . After arriving at the station, the rack will be housed in the U.S. Destiny laboratory. MSRR-1 will allow for study of a variety of materials including metals, ceramics, semiconductor crystals and glasses onboard the orbiting laboratory. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
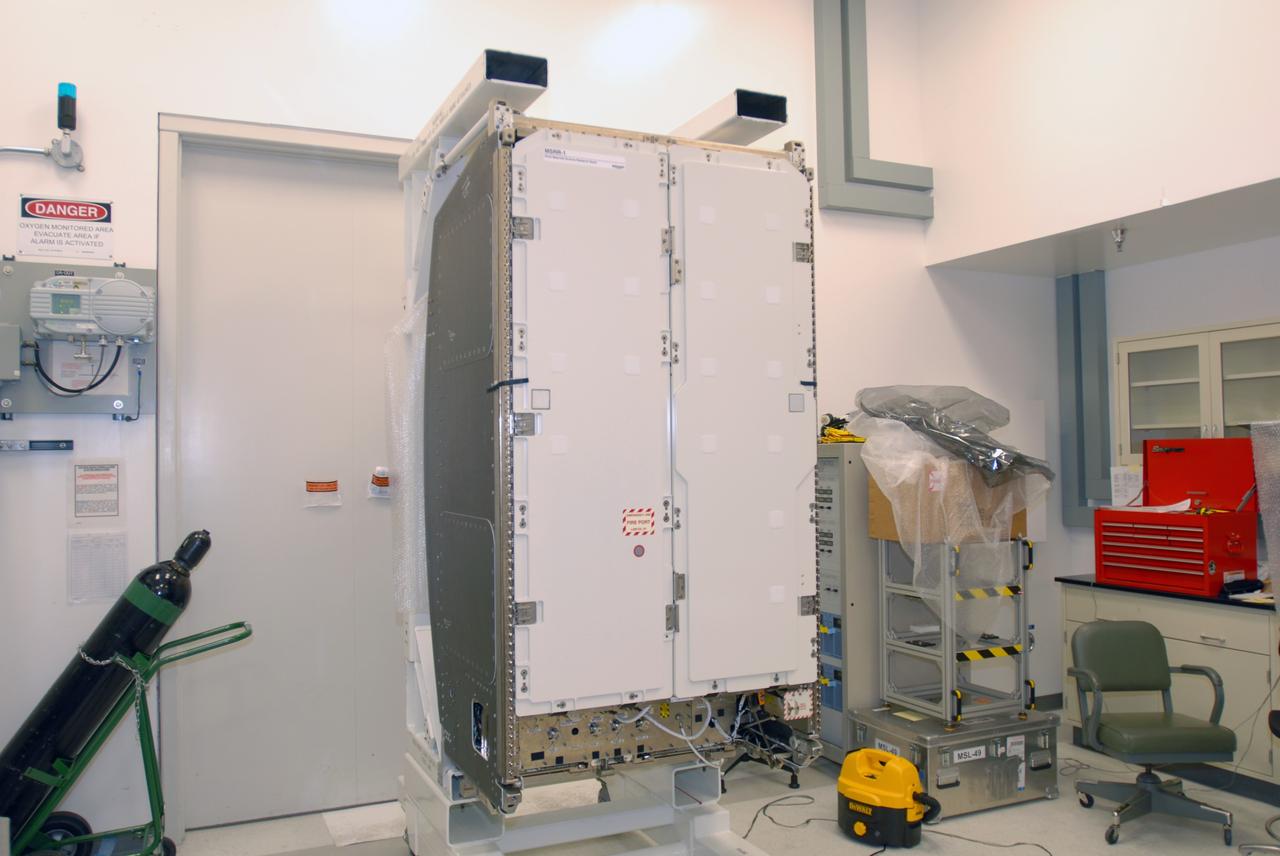

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Materials Science Research Rack-1, or MSRR-1, arrived at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for final flight preparations. The size of a large refrigerator, MSRR-1 is 6 feet high, 3.5 feet wide and 40 inches deep and weighs about 1 ton. MSRR-1 is the payload for the STS-128 mission targeted to launch in August. The rack will be installed in the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module for transport to the International Space Station . After arriving at the station, the rack will be housed in the U.S. Destiny laboratory. MSRR-1 will allow for study of a variety of materials including metals, ceramics, semiconductor crystals and glasses onboard the orbiting laboratory. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
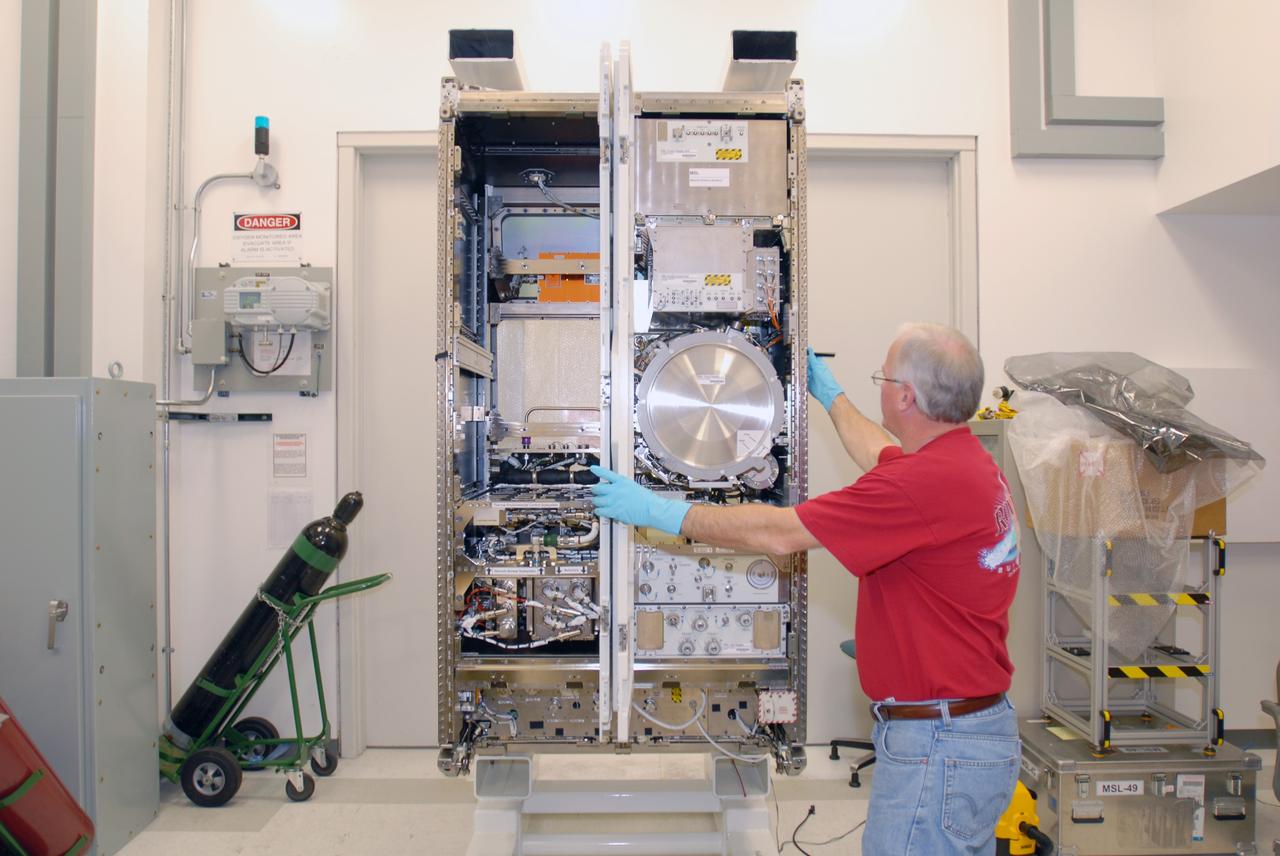

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician checks out the Materials Science Research Rack-1, or MSRR-1, which will undergo final flight preparations. The size of a large refrigerator, MSRR-1 is 6 feet high, 3.5 feet wide and 40 inches deep and weighs about 1 ton. MSRR-1 is the payload for the STS-128 mission targeted to launch in August. The rack will be installed in the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module for transport to the International Space Station . After arriving at the station, the rack will be housed in the U.S. Destiny laboratory. MSRR-1 will allow for study of a variety of materials including metals, ceramics, semiconductor crystals and glasses onboard the orbiting laboratory. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
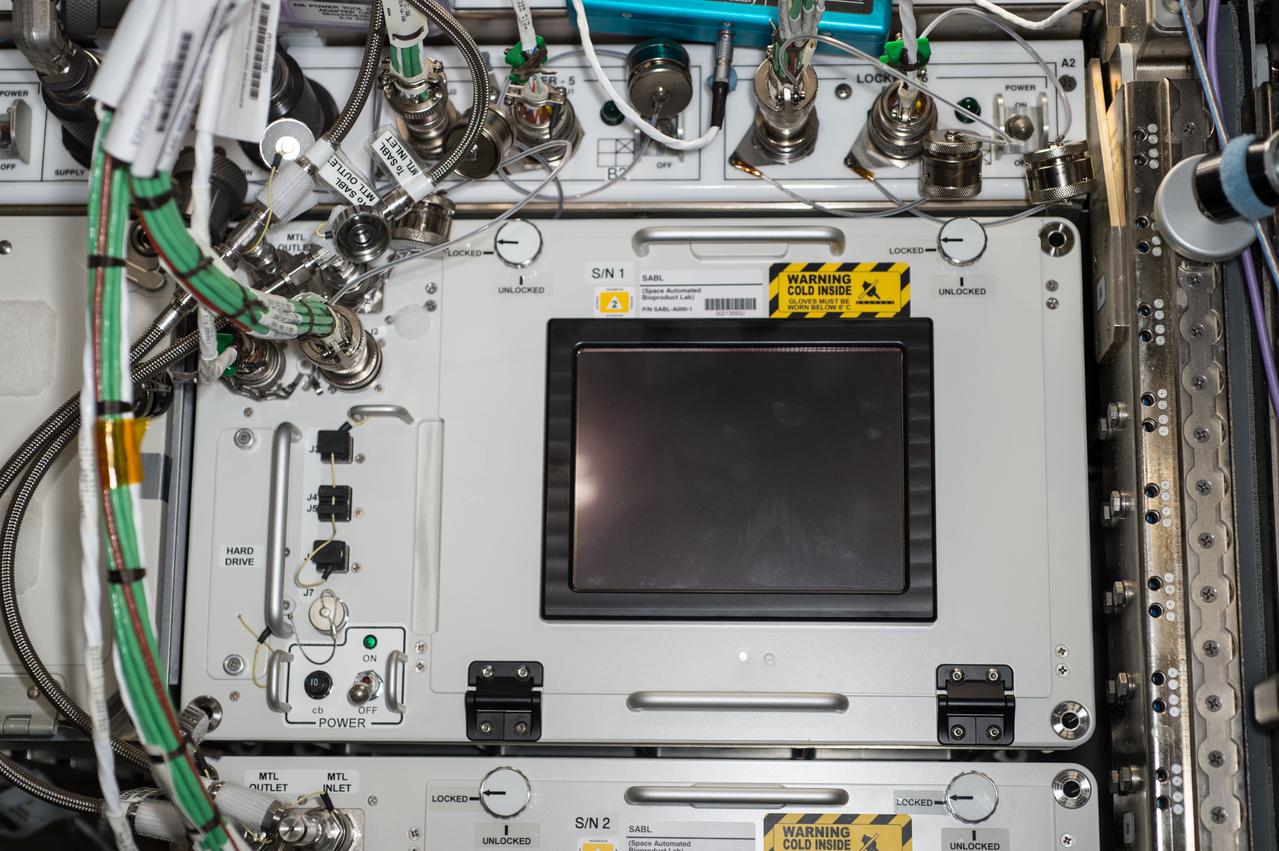

iss046e046607 (2/23/2016) --- A view of the newly installed Space Automated Bioproduct Laboratory (SABL) power, data, and thermal connections in the rack located in the U.S Lab. SABL is an upgrade to the long standing ISS incubator, Commercial Generic Bioprocessing Apparatus (CGBA). The Space Automated Bioproduct Laboratory (SABL) supports a wide variety of experiments in the life, physical and material sciences with a focus on supporting research of biological systems and processes.
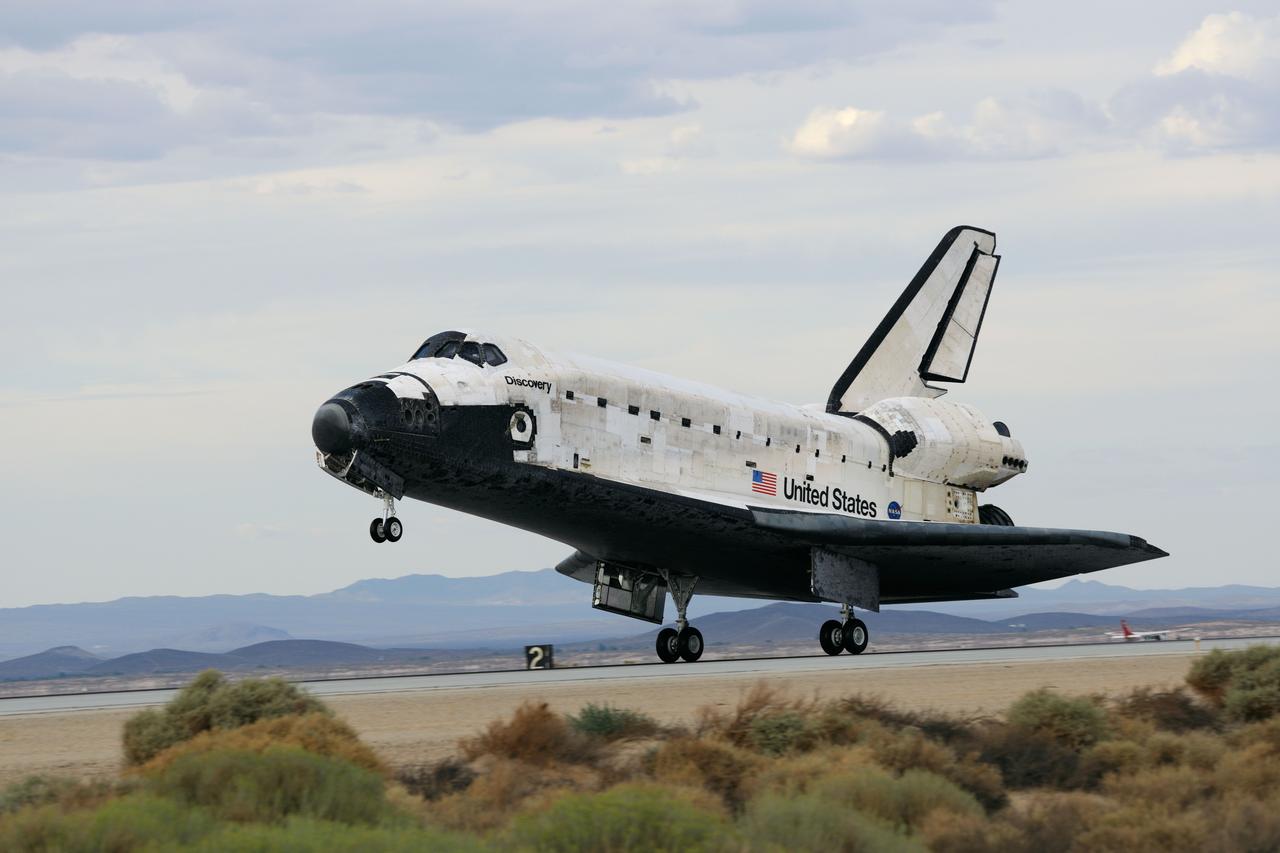

STS128-S-046 (11 Sept. 2009) --- Space Shuttle Discovery?s main landing gear touches down at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California, concluding a successful mission to the International Space Station. Onboard are NASA astronauts Rick Sturckow, commander; Kevin Ford, pilot; John ?Danny? Olivas, Patrick Forrester, Jose Hernandez and Tim Kopra, all mission specialists; along with European Space Agency astronaut Christer Fuglesang, mission specialist. Discovery landed at 5:53 p.m. (PDT) on Sept. 11, 2009 to end the STS-128 mission, completing its almost 14-day journey of more than 5.7 million miles in space. The landing was diverted to California due to marginal weather at the Kennedy Space Center. Discovery?s mission featured three spacewalks and the delivery of two refrigerator-sized science racks to the space station. One rack will be used to conduct experiments on materials such as metals, glasses and ceramics. The results from these experiments could lead to the development of better materials on Earth. The other rack will be used for fluid physics research. Understanding how fluids react in microgravity could lead to improved designs for fuel tanks, water systems and other fluid-based systems.
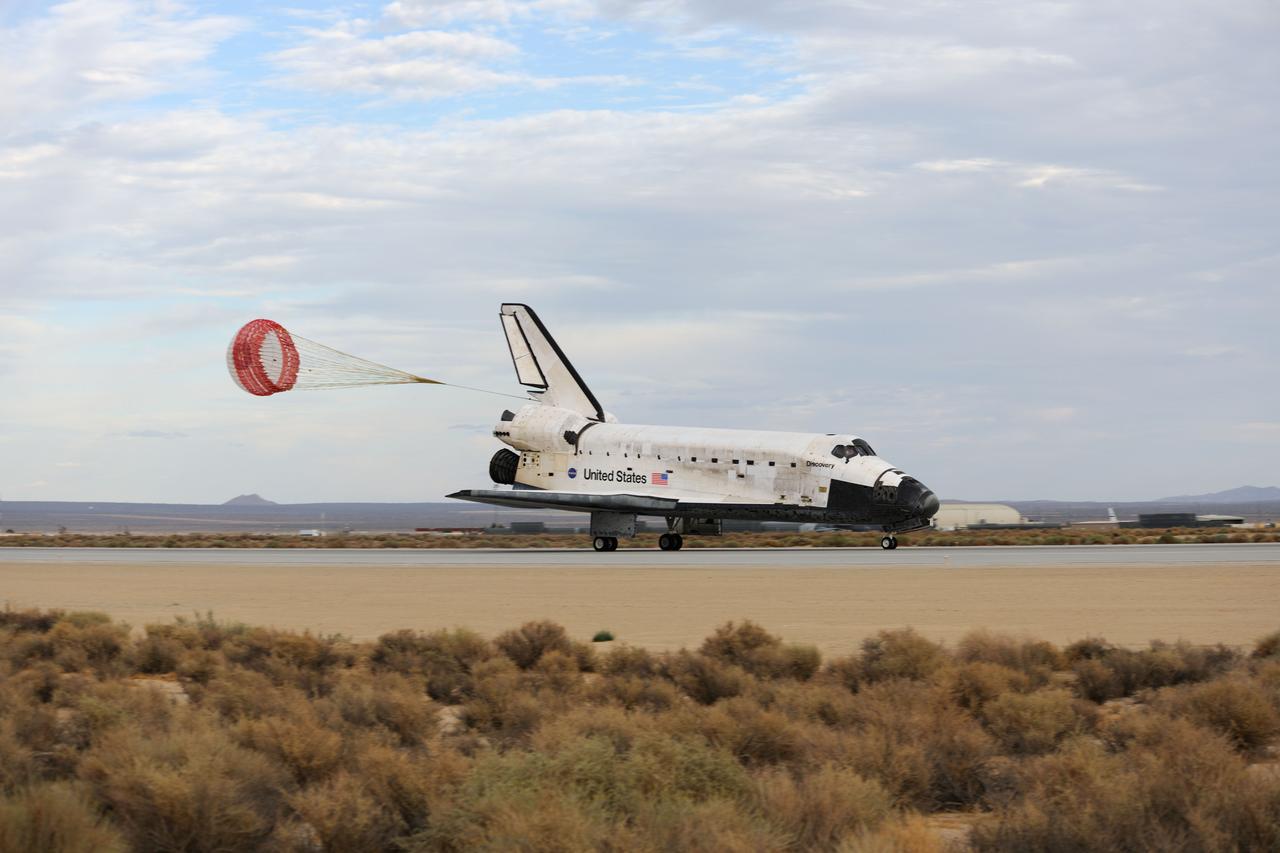

STS128-S-048 (11 Sept. 2009) --- With its drag chute deployed, Space Shuttle Discovery slows to a stop after landing at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California, concluding a successful mission to the International Space Station. Onboard are NASA astronauts Rick Sturckow, commander; Kevin Ford, pilot; John ?Danny? Olivas, Patrick Forrester, Jose Hernandez and Tim Kopra, all mission specialists; along with European Space Agency astronaut Christer Fuglesang, mission specialist. Discovery landed at 5:53 p.m. (PDT) on Sept. 11, 2009 to end the STS-128 mission, completing its almost 14-day journey of more than 5.7 million miles in space. The landing was diverted to California due to marginal weather at the Kennedy Space Center. Discovery?s mission featured three spacewalks and the delivery of two refrigerator-sized science racks to the space station. One rack will be used to conduct experiments on materials such as metals, glasses and ceramics. The results from these experiments could lead to the development of better materials on Earth. The other rack will be used for fluid physics research. Understanding how fluids react in microgravity could lead to improved designs for fuel tanks, water systems and other fluid-based systems.
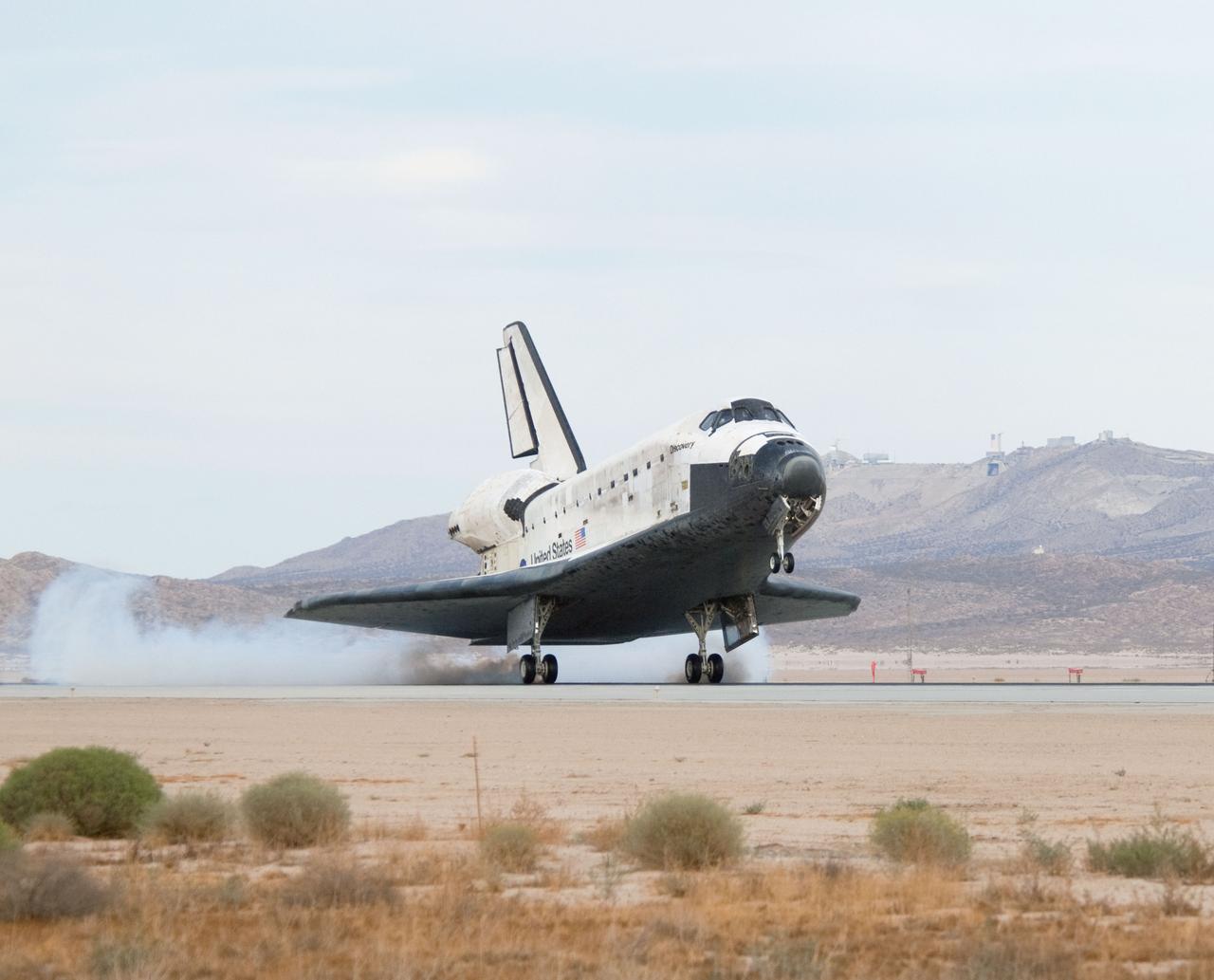

STS128-S-045 (11 Sept. 2009) --- Space Shuttle Discovery?s main landing gear touches down at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California, concluding a successful mission to the International Space Station. Onboard are NASA astronauts Rick Sturckow, commander; Kevin Ford, pilot; John ?Danny? Olivas, Patrick Forrester, Jose Hernandez and Tim Kopra, all mission specialists; along with European Space Agency astronaut Christer Fuglesang, mission specialist. Discovery landed at 5:53 p.m. (PDT) on Sept. 11, 2009 to end the STS-128 mission, completing its almost 14-day journey of more than 5.7 million miles in space. The landing was diverted to California due to marginal weather at the Kennedy Space Center. Discovery?s mission featured three spacewalks and the delivery of two refrigerator-sized science racks to the space station. One rack will be used to conduct experiments on materials such as metals, glasses and ceramics. The results from these experiments could lead to the development of better materials on Earth. The other rack will be used for fluid physics research. Understanding how fluids react in microgravity could lead to improved designs for fuel tanks, water systems and other fluid-based systems.
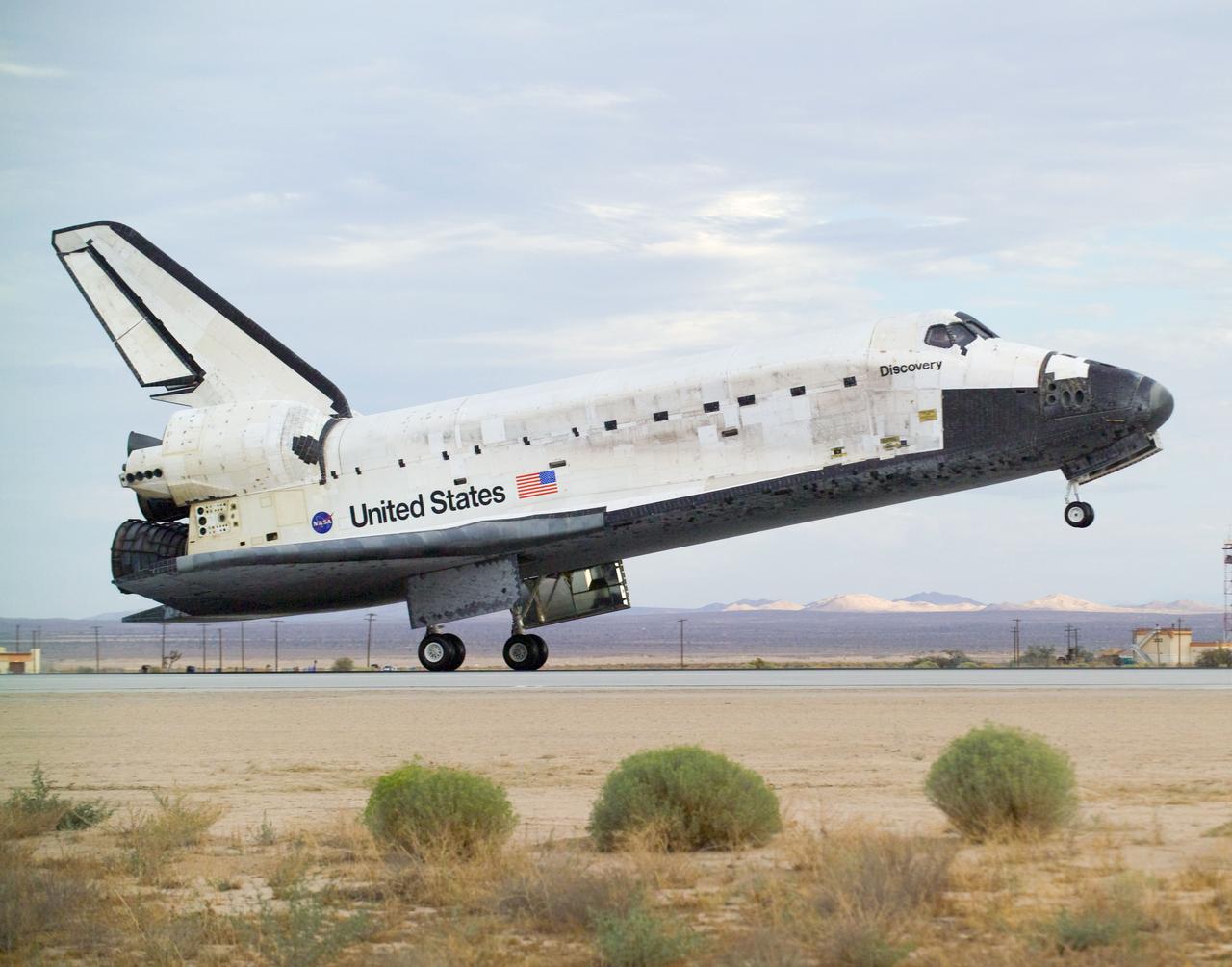

STS128-S-047 (11 Sept. 2009) --- Space Shuttle Discovery?s main landing gear touches down at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California, concluding a successful mission to the International Space Station. Onboard are NASA astronauts Rick Sturckow, commander; Kevin Ford, pilot; John ?Danny? Olivas, Patrick Forrester, Jose Hernandez and Tim Kopra, all mission specialists; along with European Space Agency astronaut Christer Fuglesang, mission specialist. Discovery landed at 5:53 p.m. (PDT) on Sept. 11, 2009 to end the STS-128 mission, completing its almost 14-day journey of more than 5.7 million miles in space. The landing was diverted to California due to marginal weather at the Kennedy Space Center. Discovery?s mission featured three spacewalks and the delivery of two refrigerator-sized science racks to the space station. One rack will be used to conduct experiments on materials such as metals, glasses and ceramics. The results from these experiments could lead to the development of better materials on Earth. The other rack will be used for fluid physics research. Understanding how fluids react in microgravity could lead to improved designs for fuel tanks, water systems and other fluid-based systems.
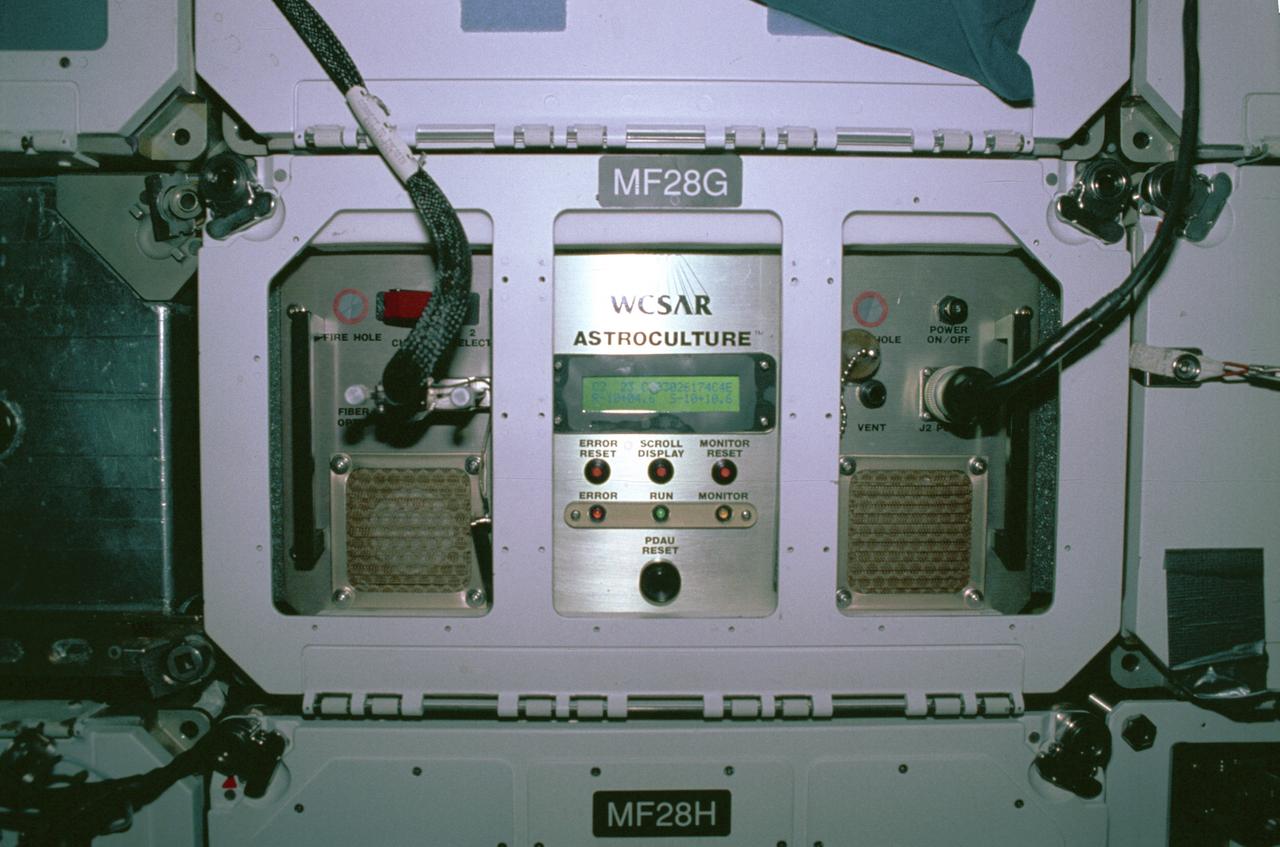

The first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) was one of NASA's science and technology programs that provided scientists an opportunity to research various scientific investigations in a weightless environment inside the Spacelab module. It also provided demonstrations of new equipment to help prepare for advanced microgravity research and processing aboard the Space Station. The USML-1 flew in orbit for extended periods, providing greater opportunities for research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology (crystal growth), and combustion science. This is a close-up view of the Astroculture experiment rack in the middeck of the orbiter. The Astroculture experiment was to evaluate and find effective ways to supply nutrient solutions for optimizing plant growth and avoid releasing solutions into the crew quarters in microgravity. Since fluids behave differently in microgravity, plant watering systems that operate well on Earth do not function effectively in space. Plants can reduce the costs of providing food, oxygen, and pure water, as well as lower the costs of removing carbon dioxide in human space habitats. The USML-1 flew aboard the STS-50 mission on June 1992 and was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center.
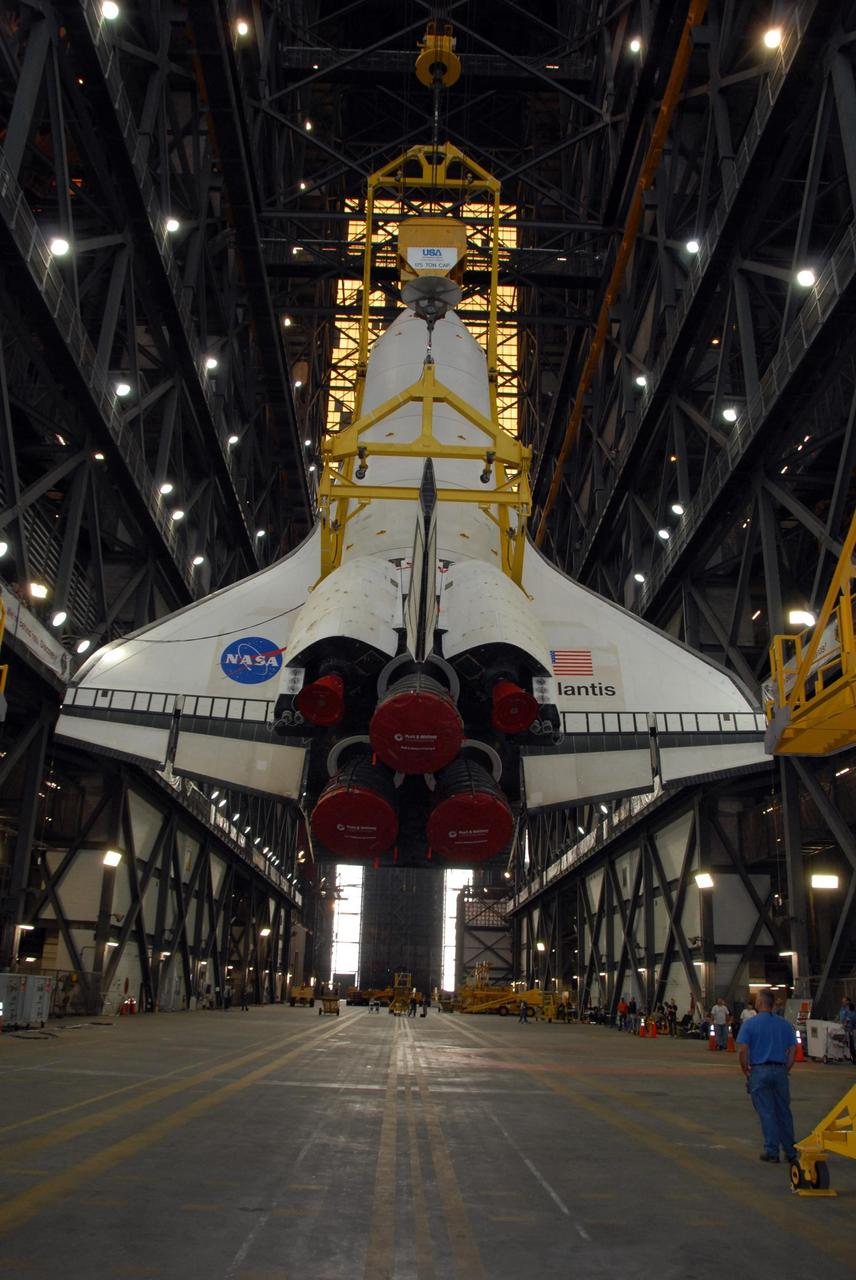

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Atlantis is raised into a vertical position. Atlantis will next be lifted into high bay 3 and mated with the external tank and solid rocket boosters designated for mission STS-122, already secured atop a mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Columbus Laboratory is positioned on a stand where it will be displayed to the media at a special showing. Columbus is the European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station. The laboratory module will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. Columbus is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
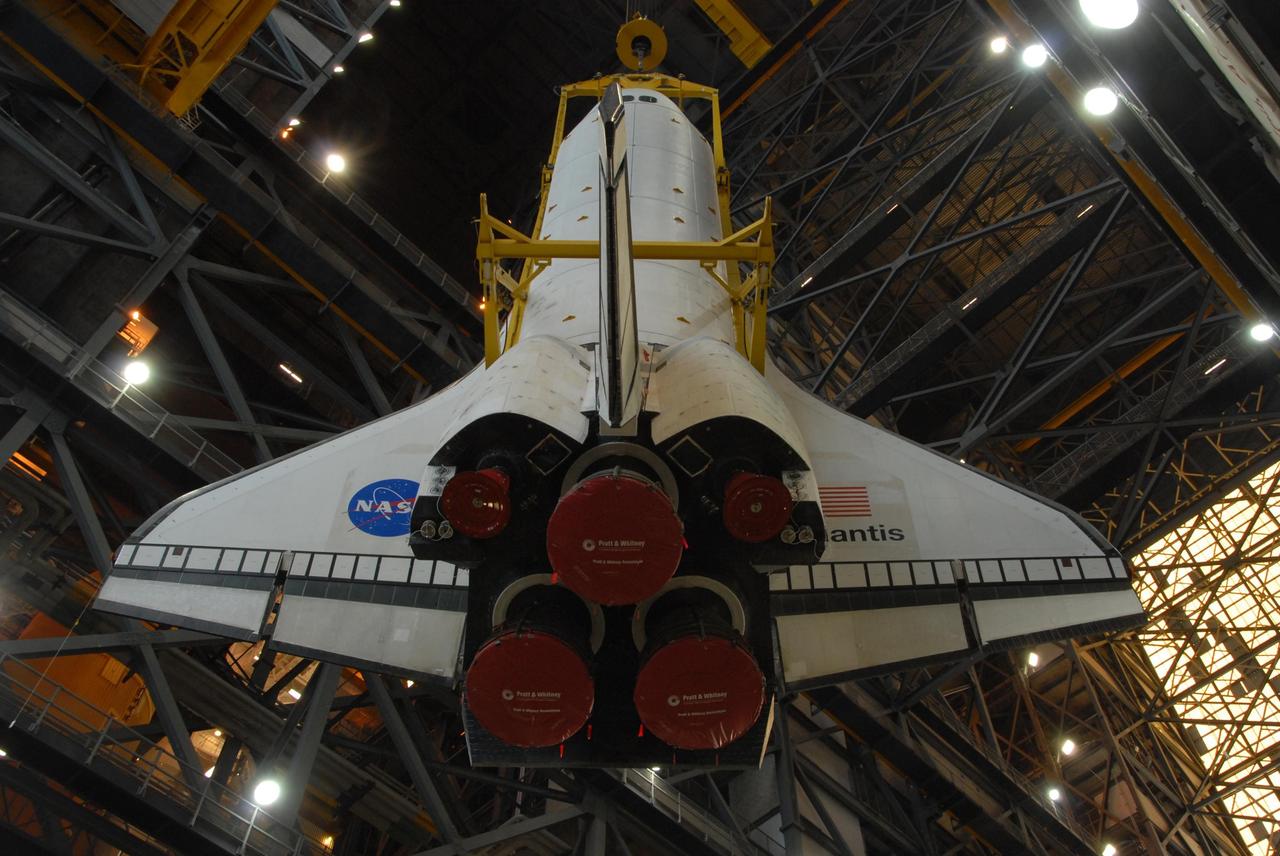

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space shuttle Atlantis is lifted into the upper levels of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Atlantis will be lowered into high bay 3 and mated with the external tank and solid rocket boosters designated for mission STS-122, already secured atop a mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
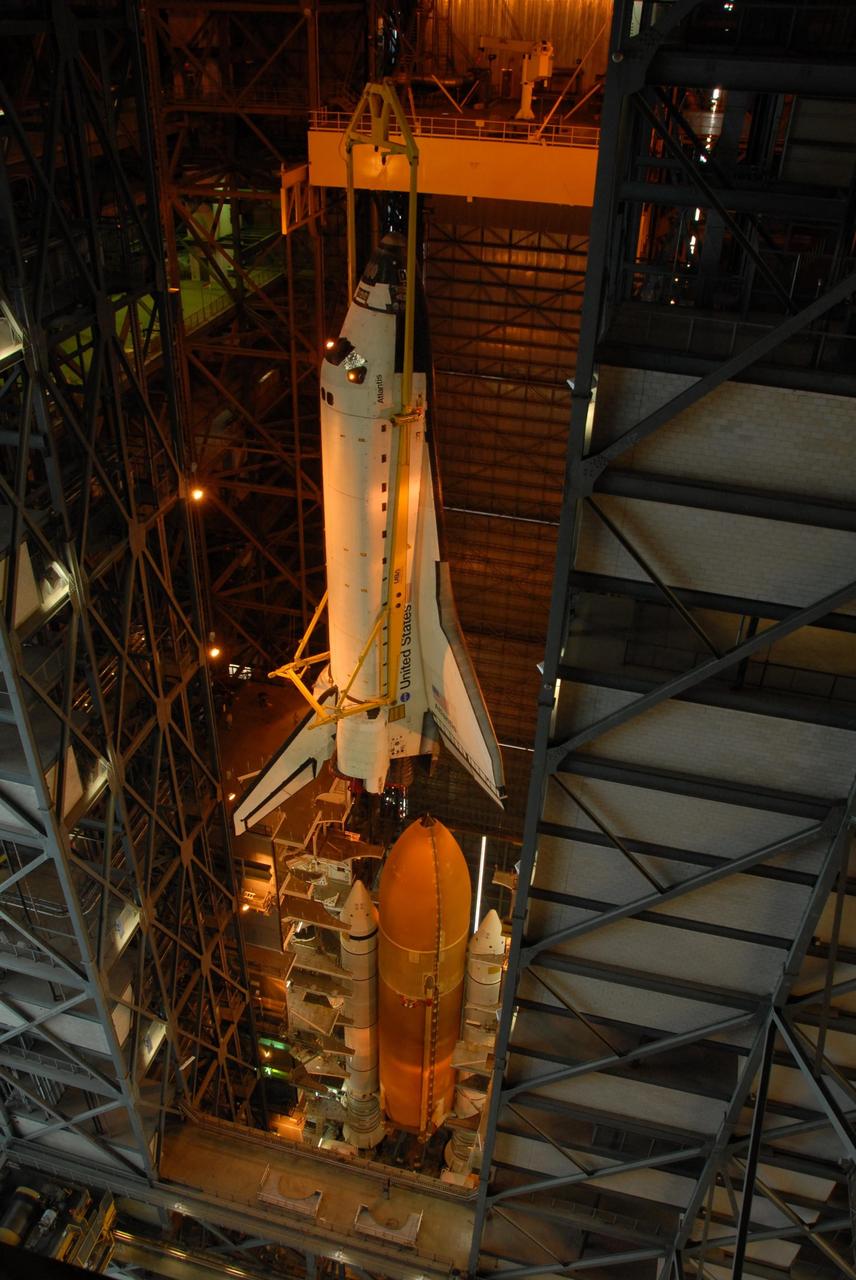

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In high bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Atlantis is lowered toward the external tank and solid rocket boosters waiting below, already secured atop the mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
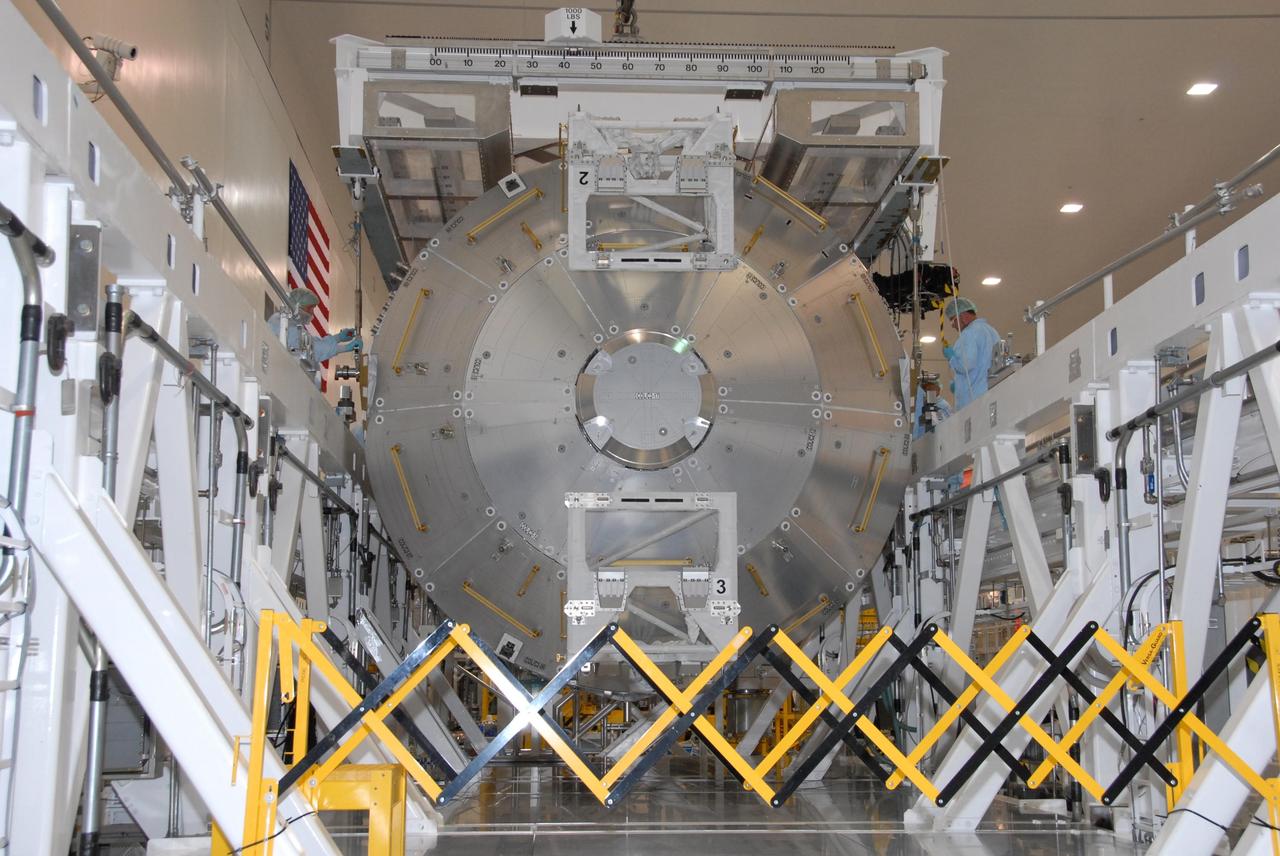
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Columbus Laboratory module is lowered onto a weigh station. After being weighed, the module will be transferred to the payload canister. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis, secured atop the mobile launch platform below, arrives at Launch Pad 39A. First motion out of the Vehicle Assembly Building was at 4:43 a.m. EST, and the shuttle was hard down on the pad at 11:51 a.m. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
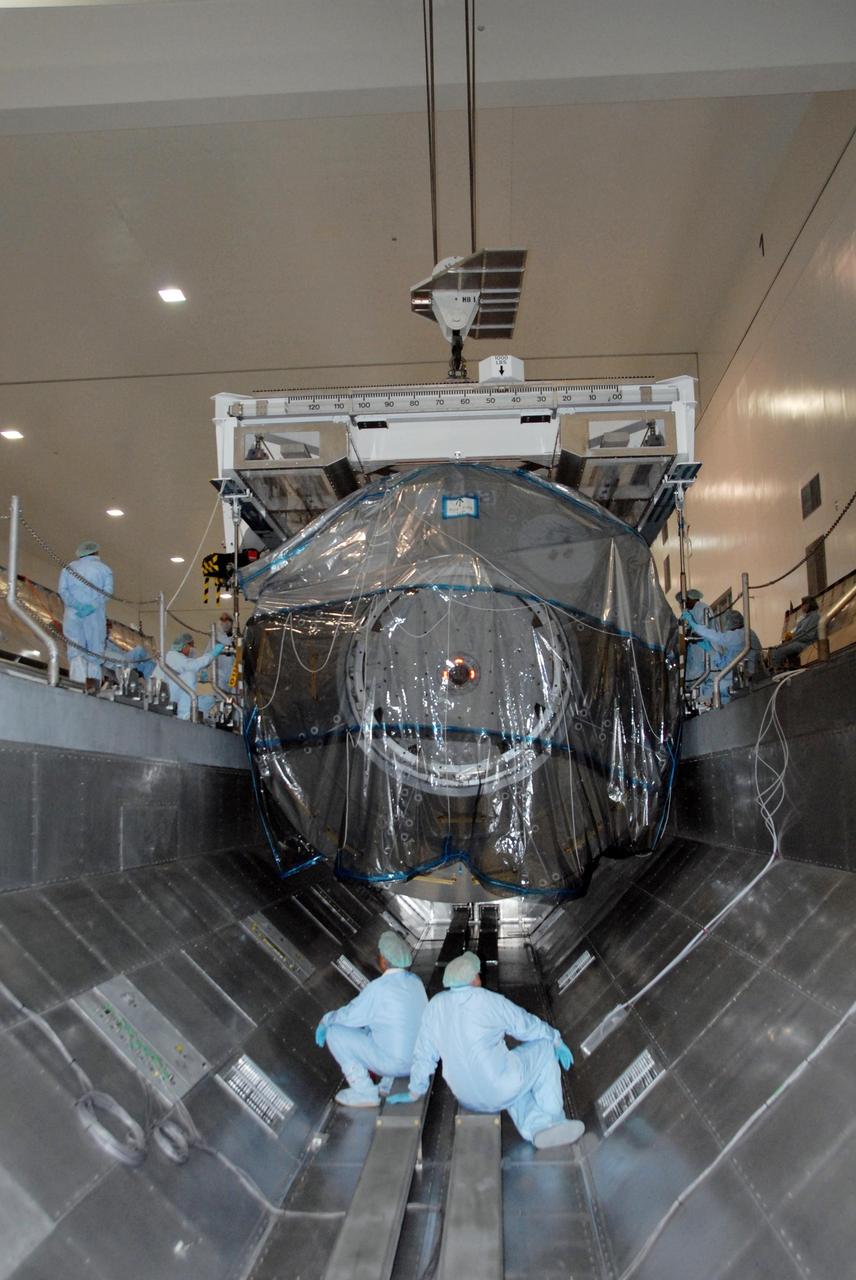

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians inside the payload canister monitor movement of the Columbus Laboratory module as it is lowered into the canister. The canister will transport the module and other payloads to Launch Pad 39A in preparation for its journey to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
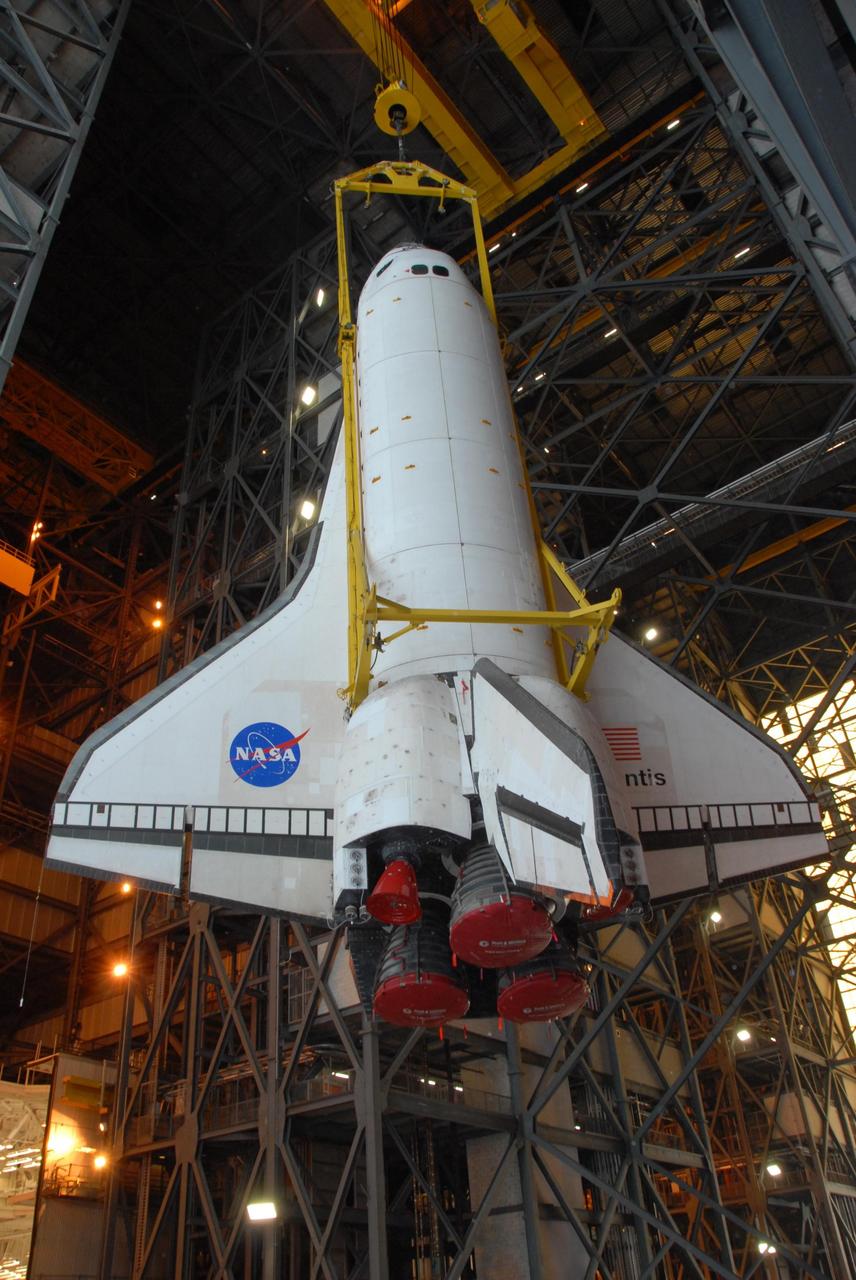

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space shuttle Atlantis is lifted into the upper levels of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Atlantis will be lifted into high bay 3 and mated with the external tank and solid rocket boosters designated for mission STS-122, already secured atop a mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
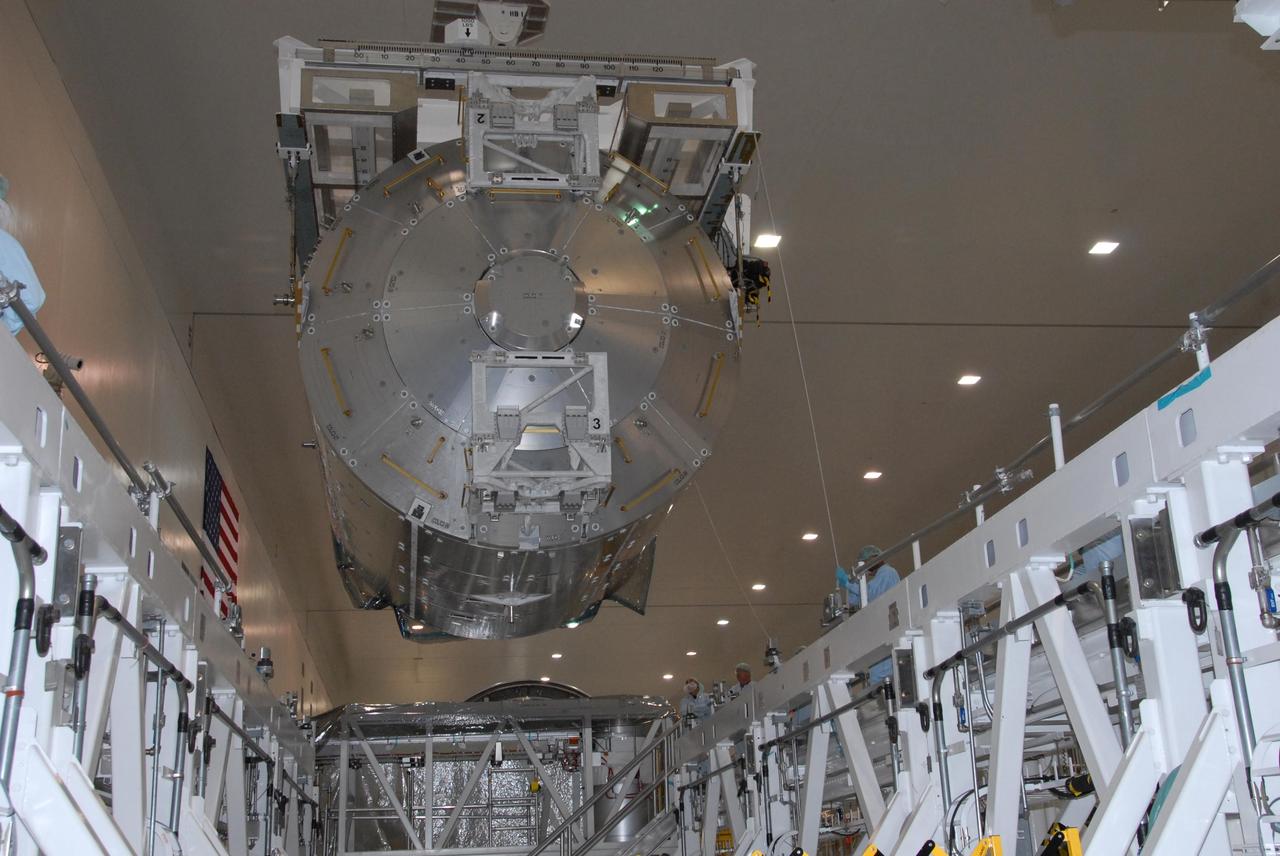

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Columbus Laboratory module is lowered toward a weigh station. After being weighed, the module will be transferred to the payload canister. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
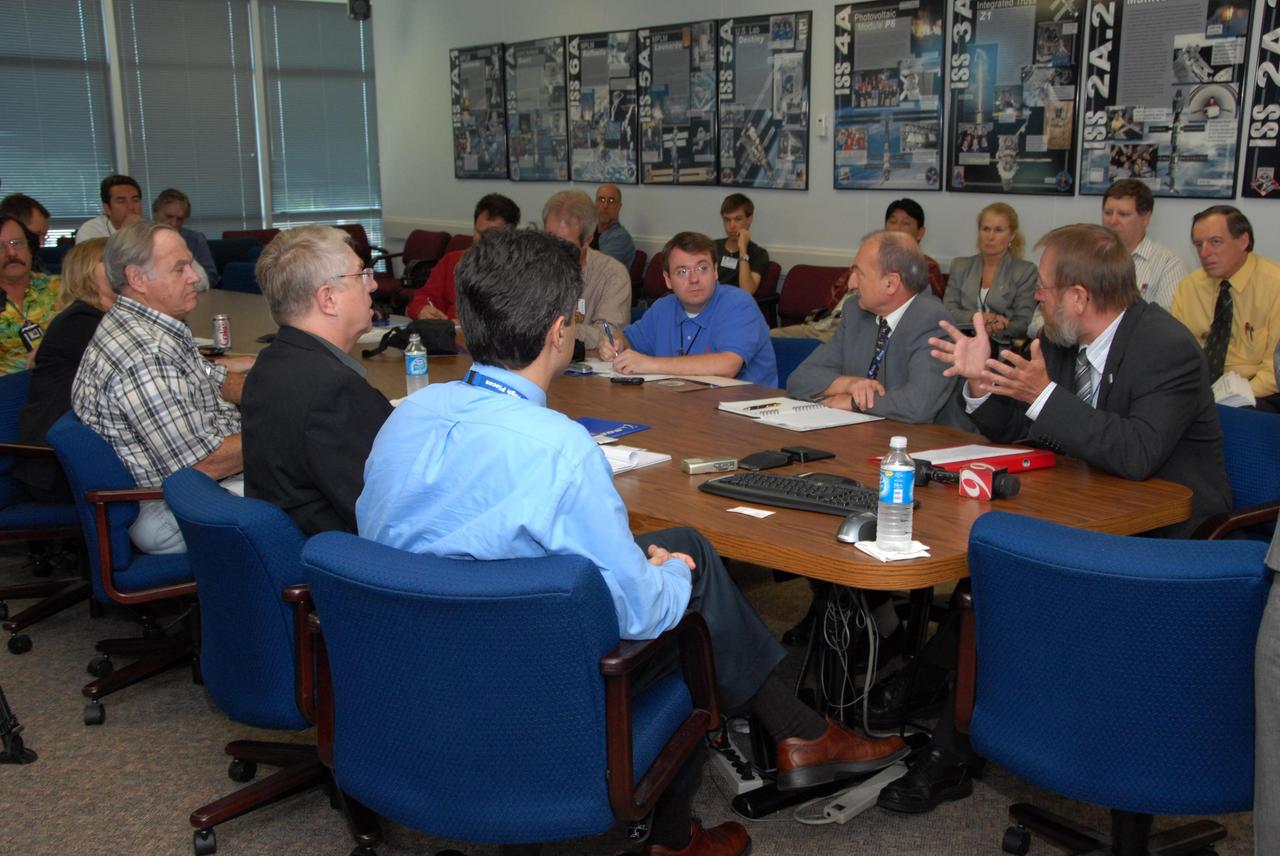

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Prior to a showing of the European Space Agency's Columbus Laboratory module, Gregor Woop (seated at right) talks to the media about the module. Woop is the European Space Agency's product assurance and safety manager. Columbus is the European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station. The laboratory module will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. Columbus is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
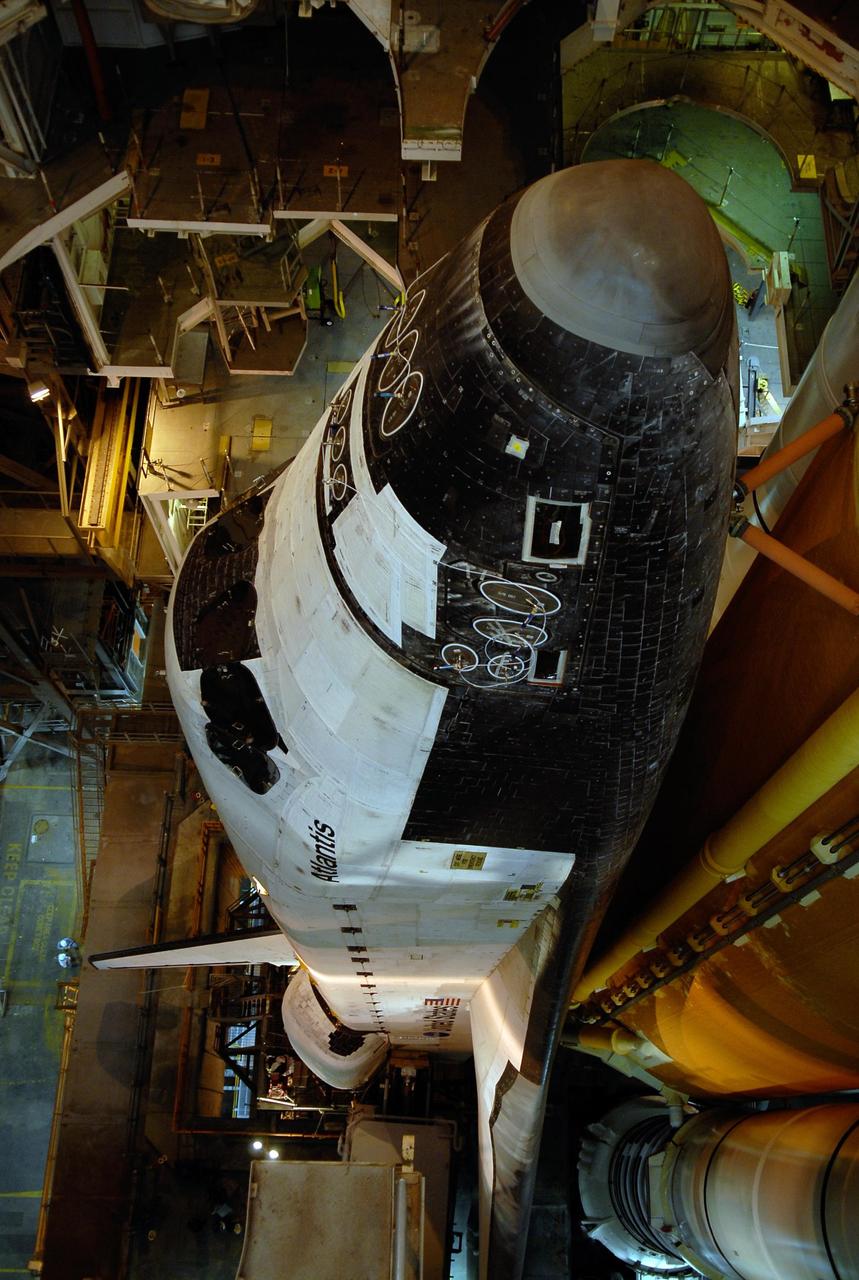

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Seen from above, Space Shuttle Atlantis is ready to move through the doors of the Vehicle Assembly Building toward Launch Pad 39A. First motion out of the VAB was at 4:43 a.m. EST. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
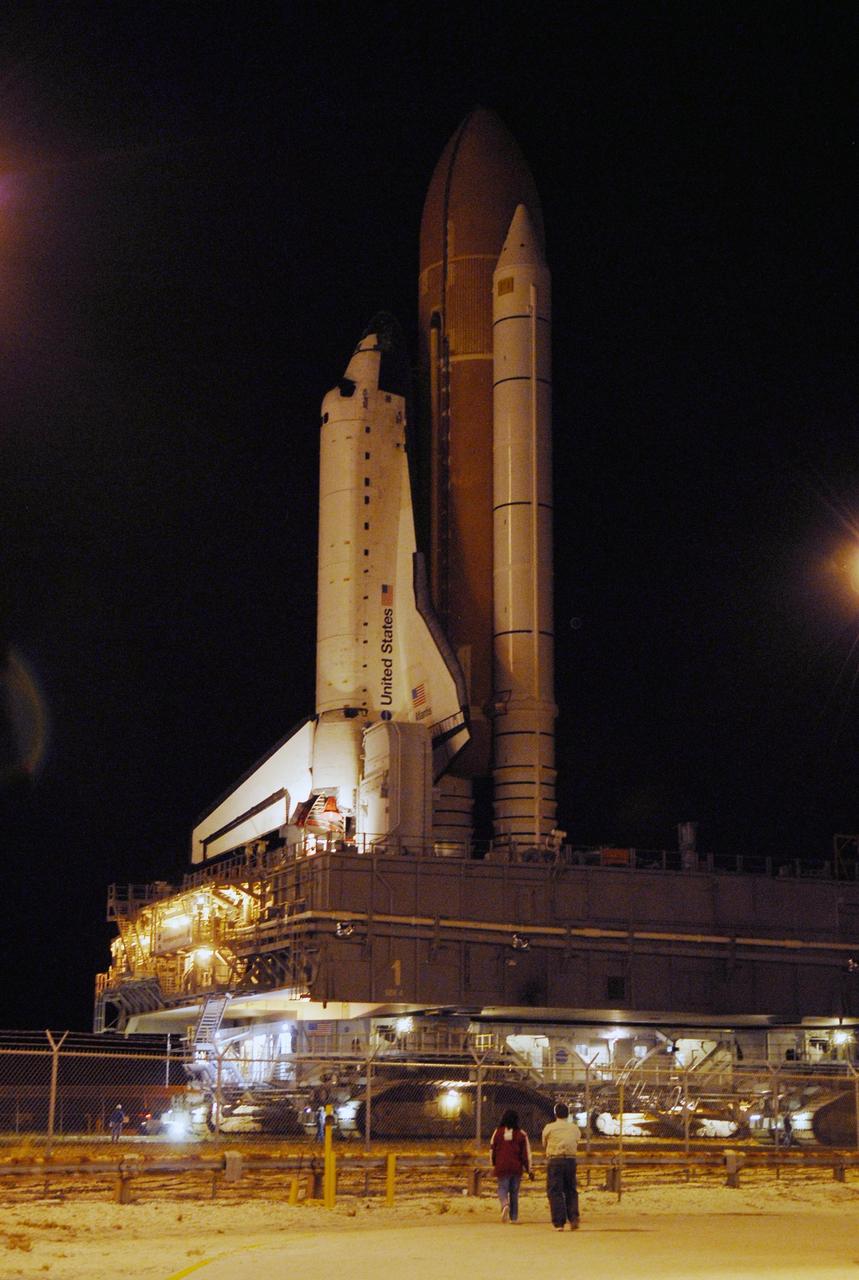

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers monitor the progress of Space Shuttle Atlantis as it moves through the doors of the Vehicle Assembly Building along the crawlerway toward Launch Pad 39A. First motion out of the VAB was at 4:43 a.m. EST. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
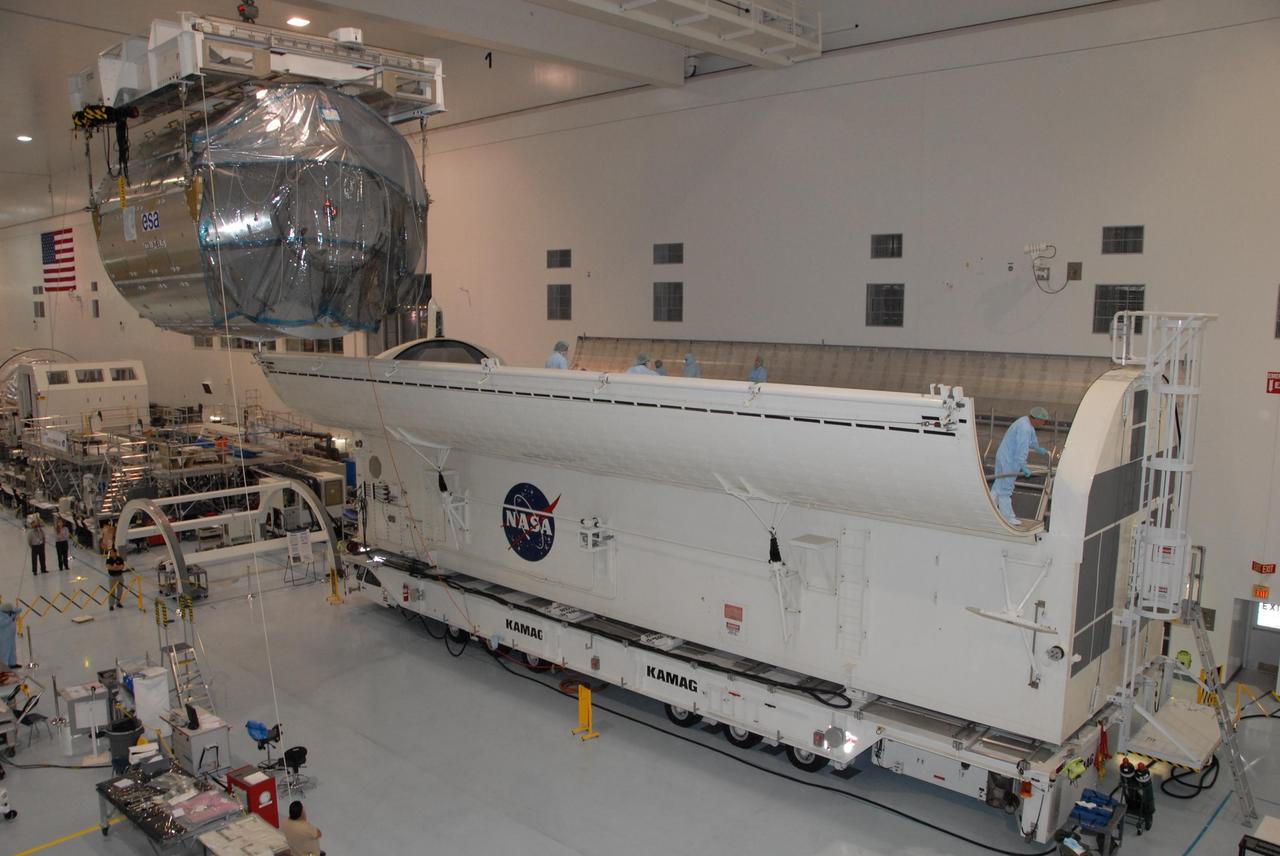

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Columbus Laboratory module moves toward the waiting payload canister at right. The canister will transport the module and other payloads to Launch Pad 39A in preparation for its journey to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space shuttle Atlantis is lifted into the upper levels of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Atlantis will be lifted into high bay 3 and mated with the external tank and solid rocket boosters designated for mission STS-122, already secured atop a mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
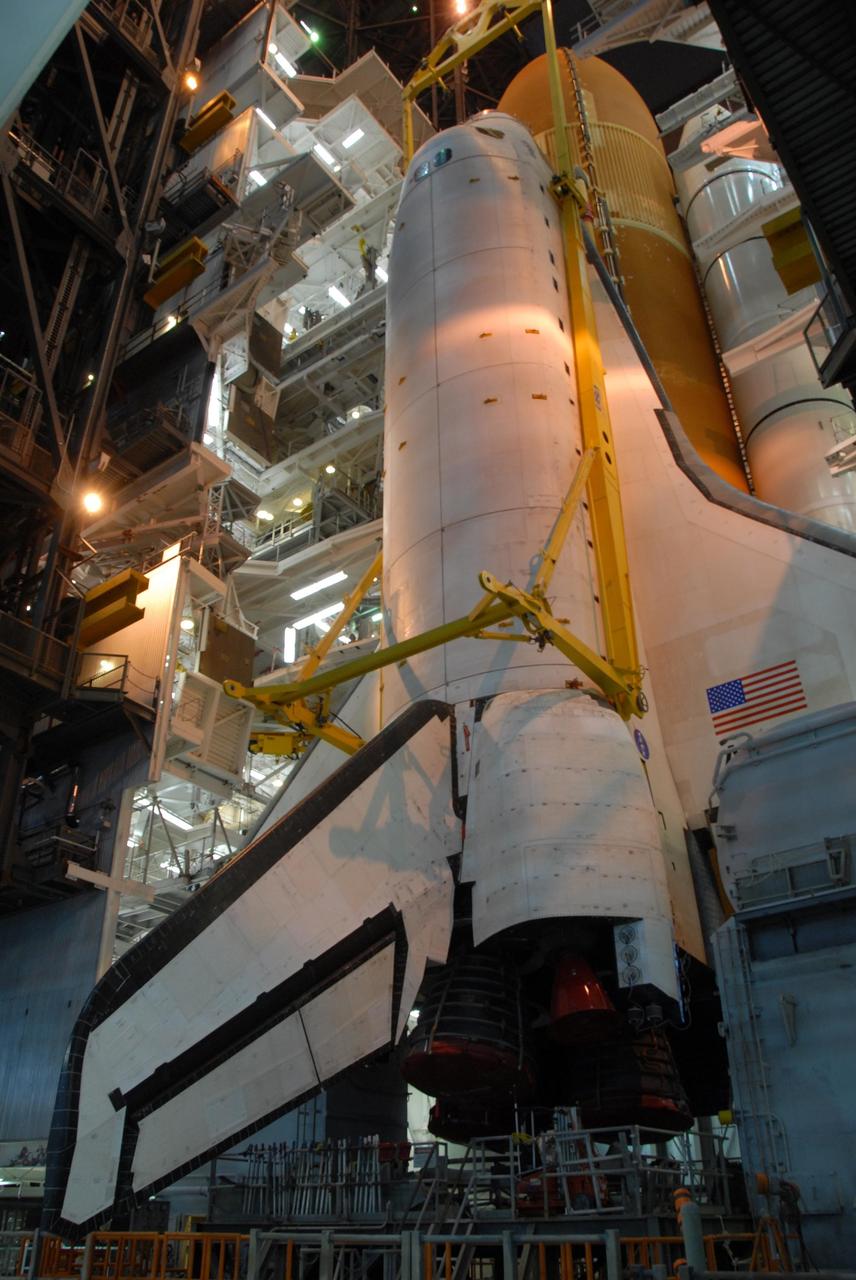

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In high bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Atlantis is lowered onto the mobile launcher platform alongside the external tank and solid rocket boosters already secured there. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Columbus Laboratory module is lowered into the waiting payload canister. The canister will transport the module and other payloads to Launch Pad 39A in preparation for its journey to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
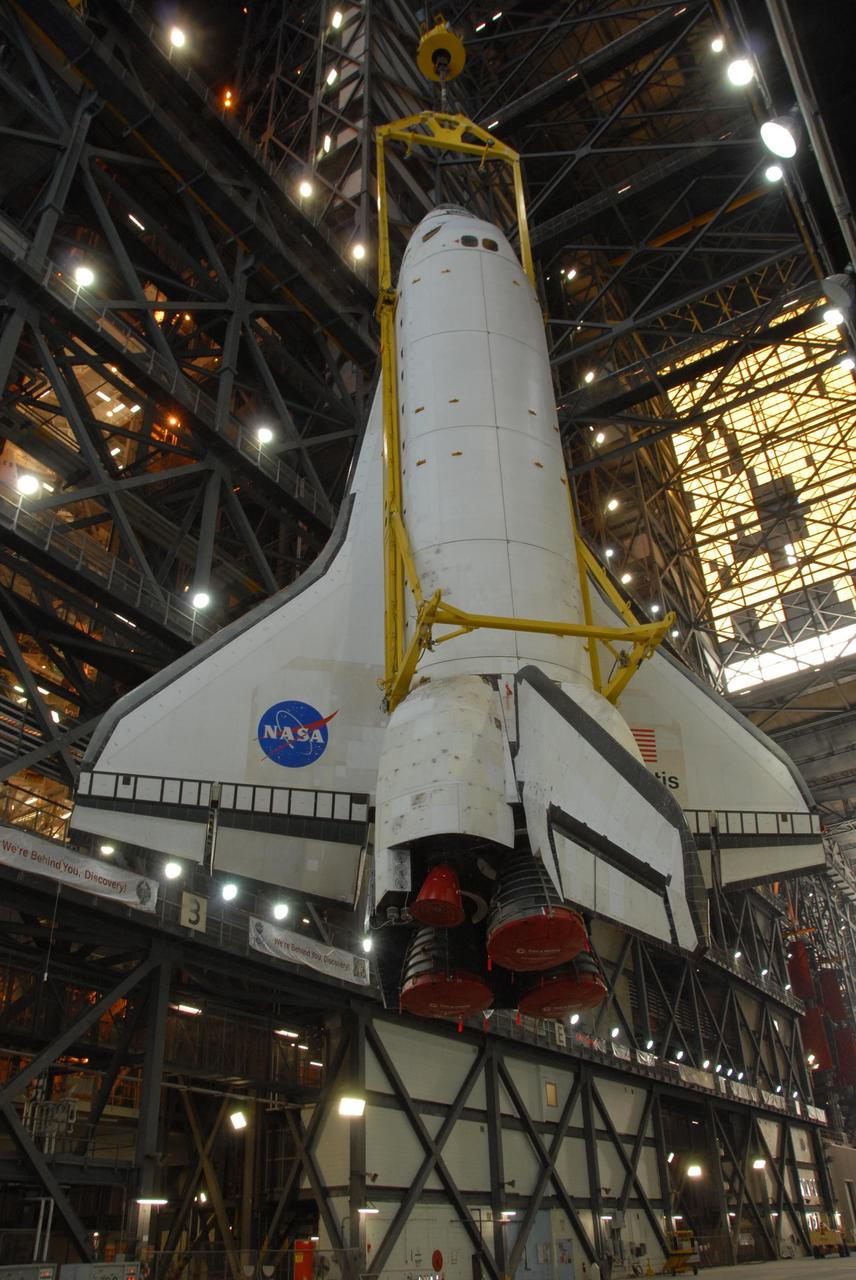

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space shuttle Atlantis is lifted into the upper levels of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Atlantis will be lowered into high bay 3 and mated with the external tank and solid rocket boosters designated for mission STS-122, already secured atop a mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Columbus Laboratory module is moved across the facility to a weigh station before transfer to the payload canister. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
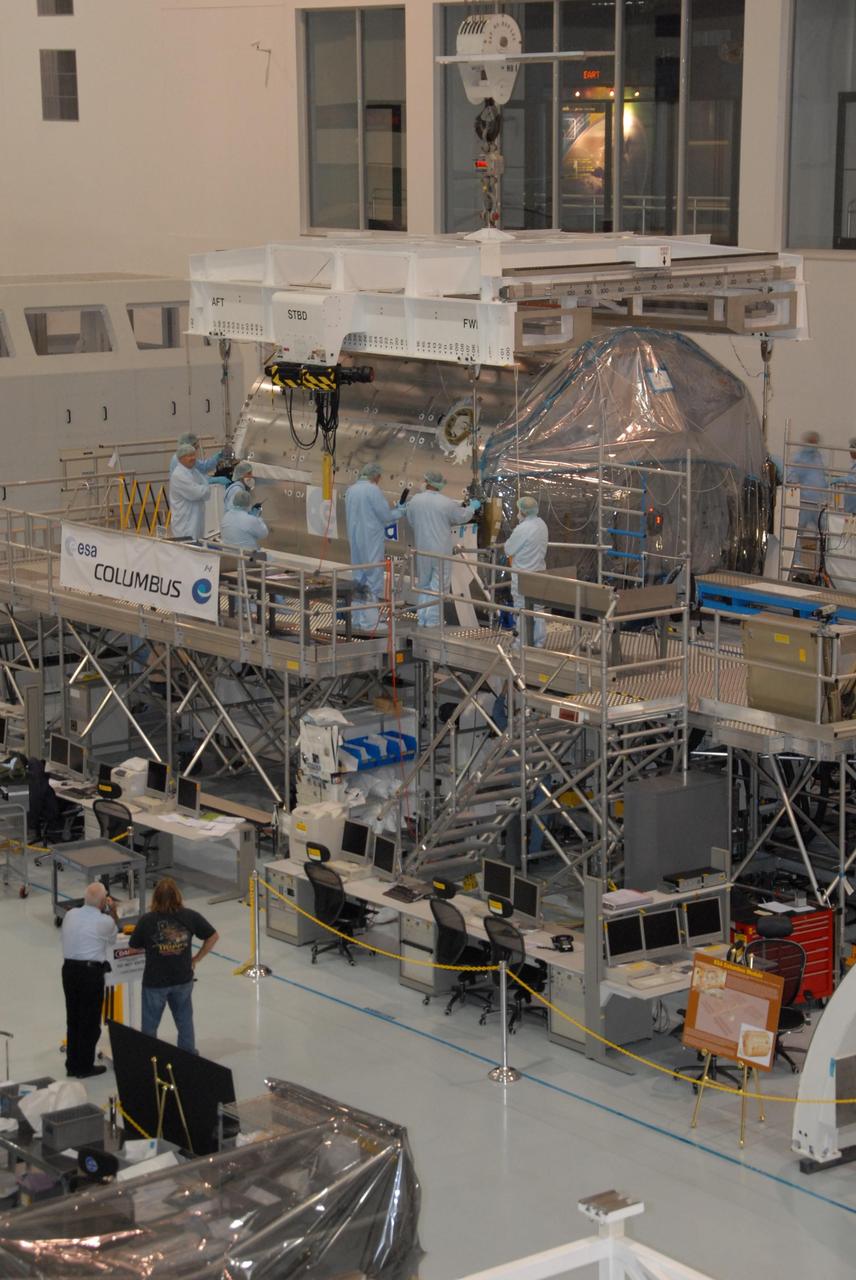

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers attach an overhead crane to the Columbus Laboratory module. The module will be moved to a weigh station before transfer to the payload canister. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
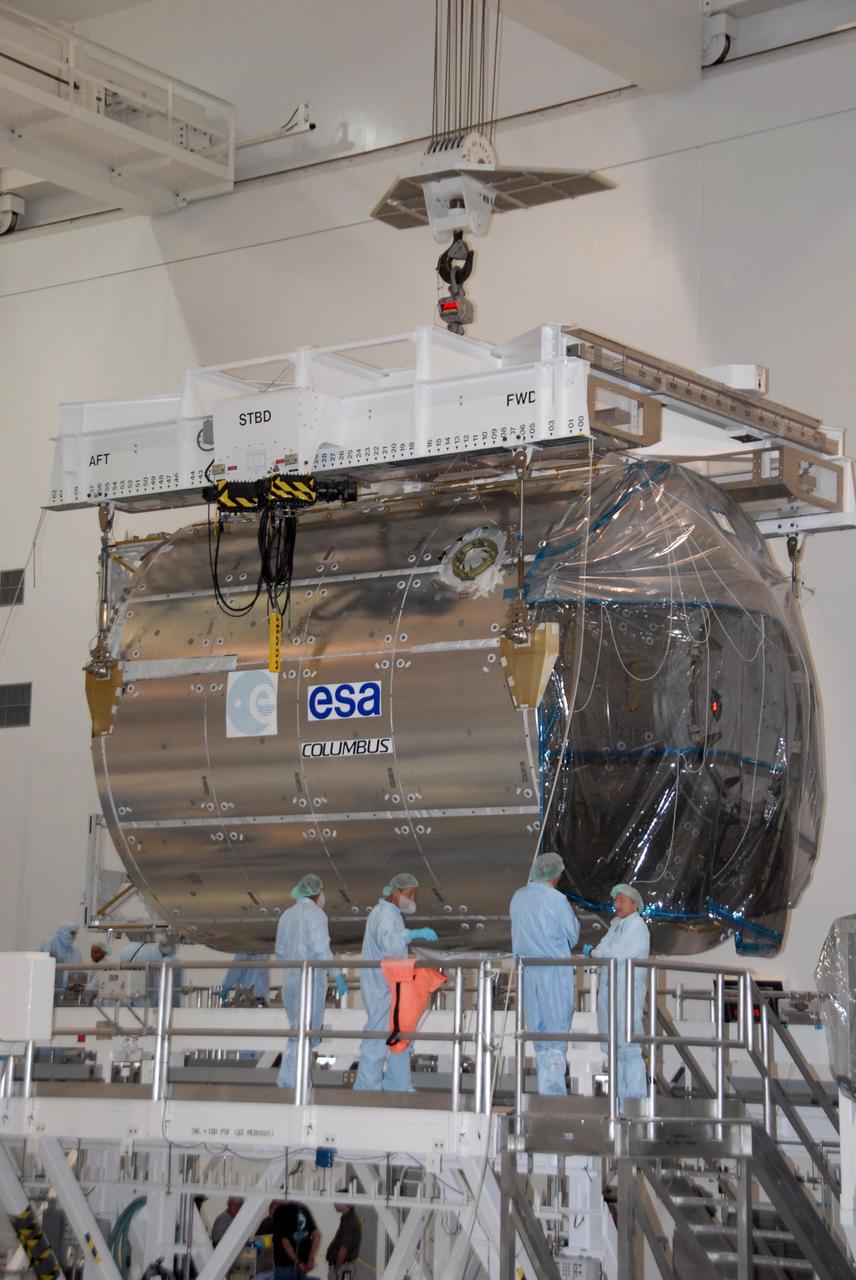

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Columbus Laboratory module is lifted for its transfer to a payload canister. The canister will transport the module and other payloads to Launch Pad 39A in preparation for its journey to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers attach an overhead crane to the Columbus Laboratory module, situated underneath the windows at right. The module will be moved to a weigh station before transfer to the payload canister. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
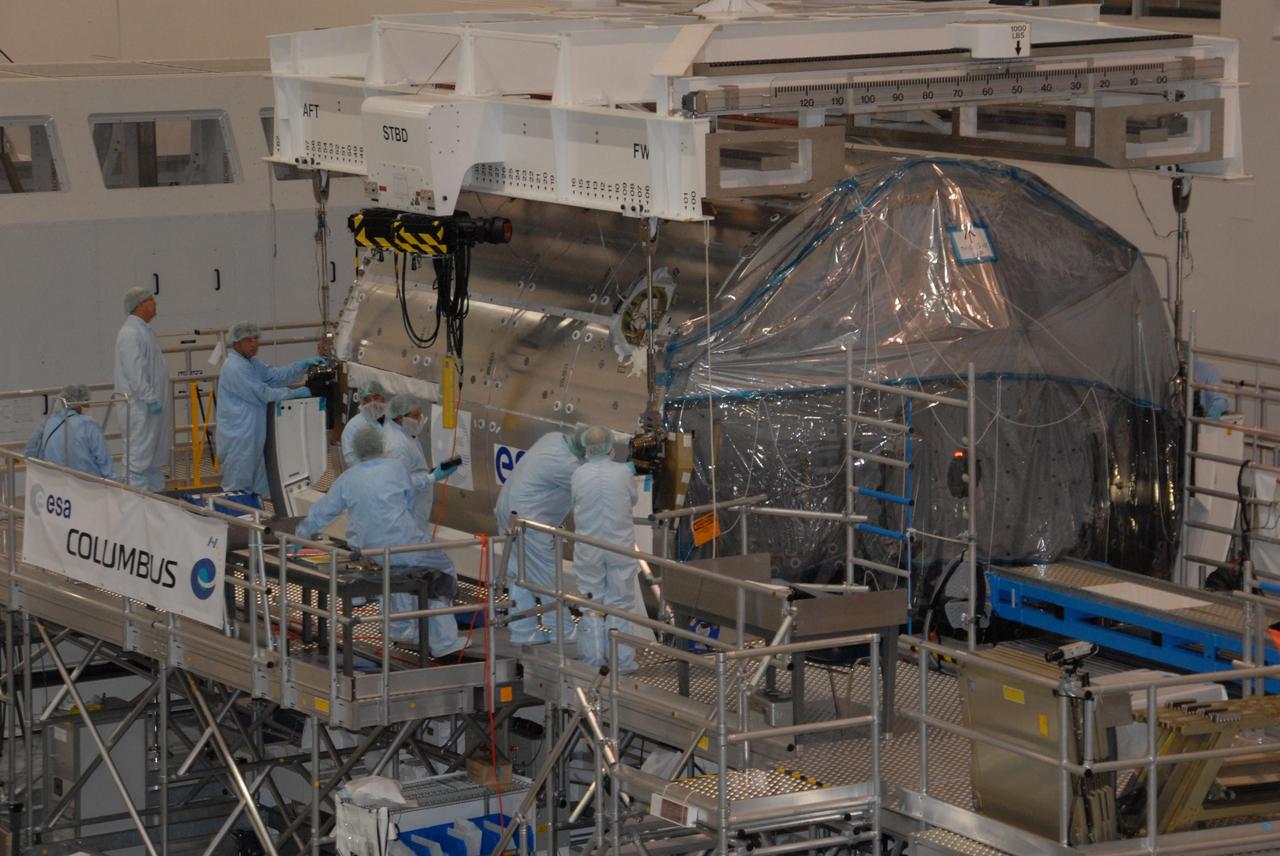

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers attach an overhead crane to the Columbus Laboratory module. The module will be moved to a weigh station before transfer to the payload canister. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
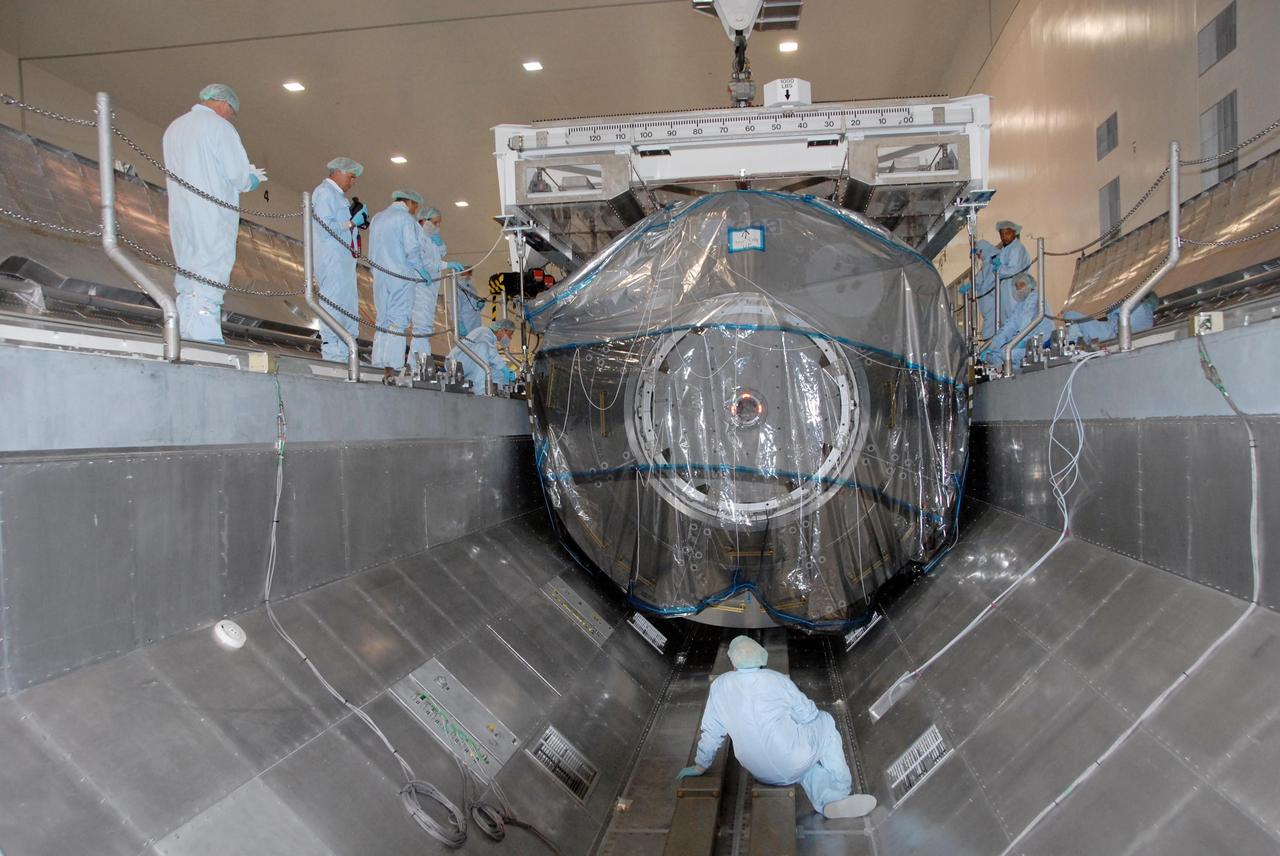

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians inside and around the payload canister monitor movement of the Columbus Laboratory module as it is lowered into the canister. The canister will transport the module and other payloads to Launch Pad 39A in preparation for its journey to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
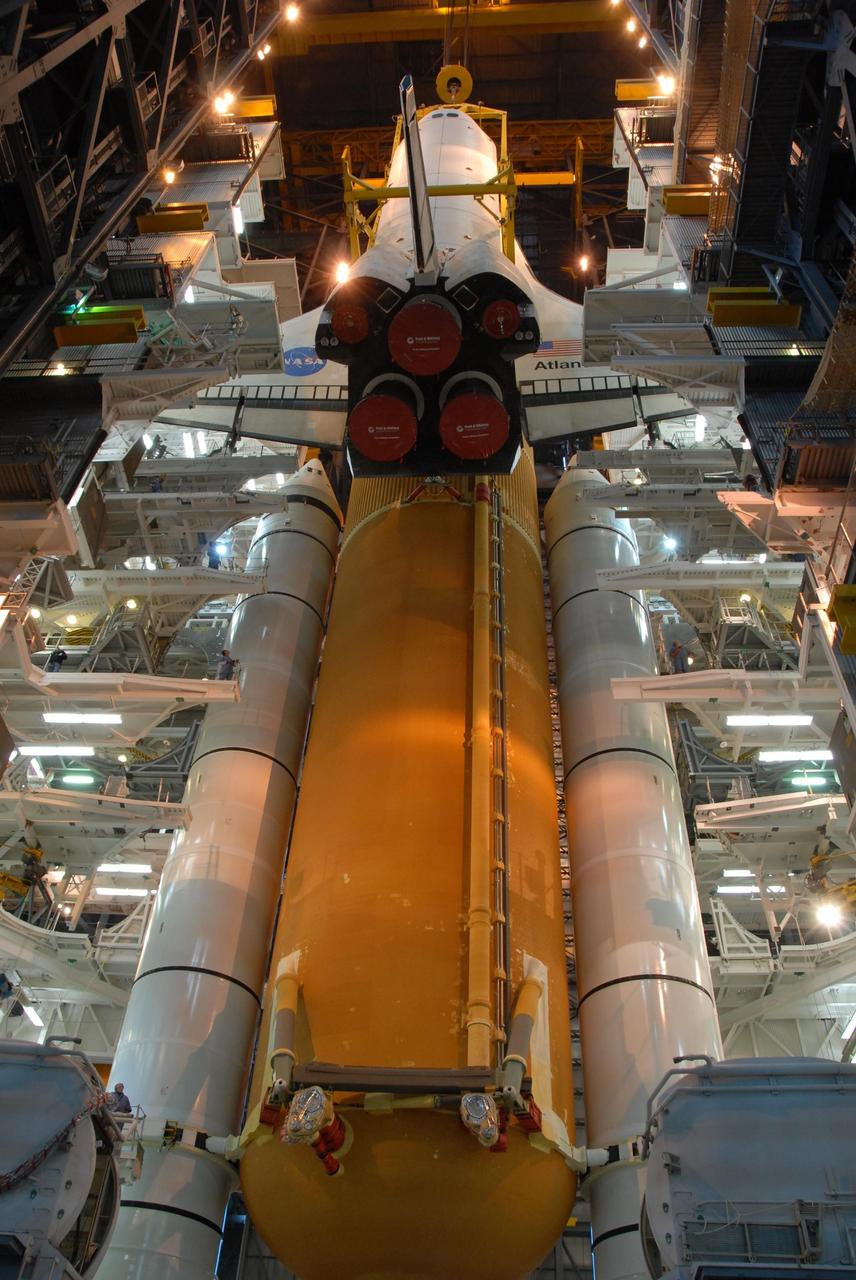

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In high bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Atlantis is lowered alongside the external tank and solid rocket boosters waiting below, already secured atop the mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
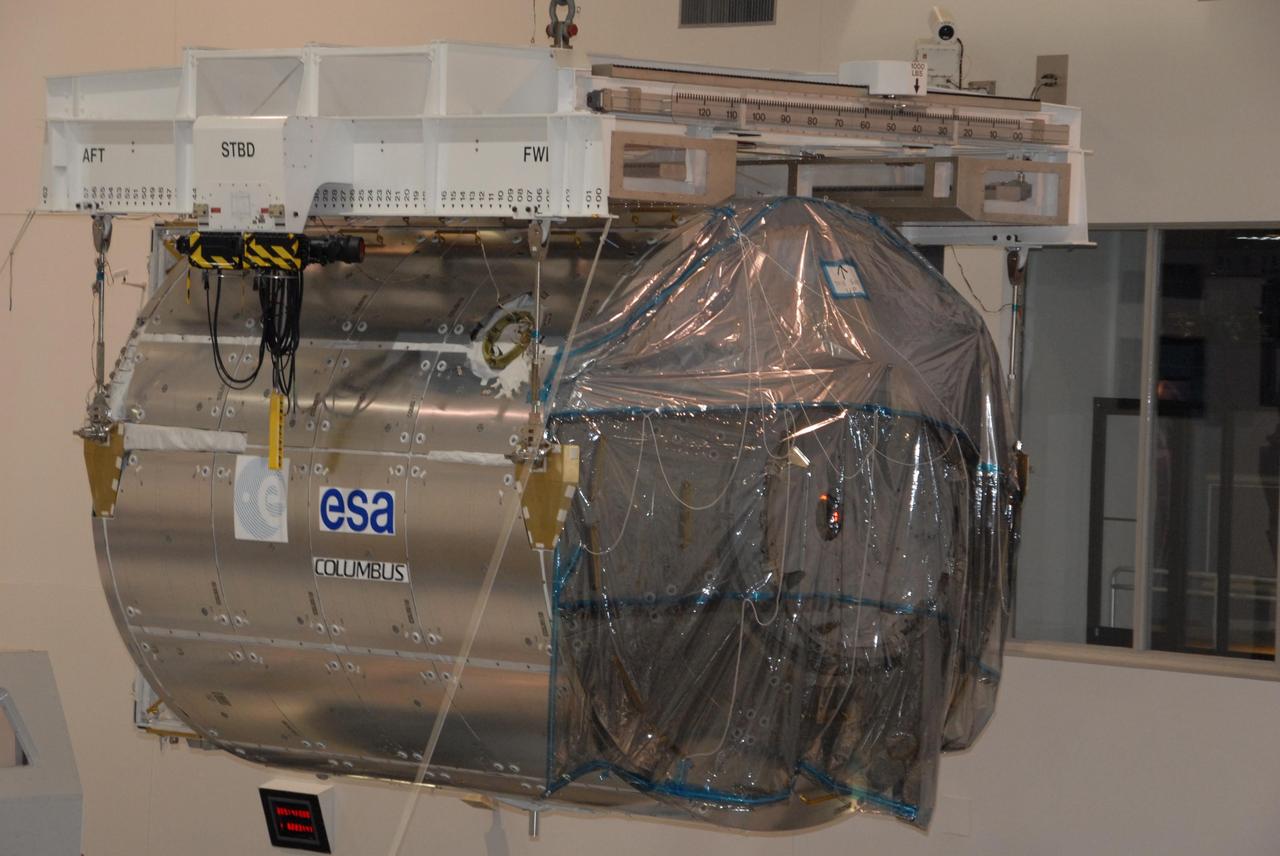

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lifts the Columbus Laboratory module from its stand. The module is being moved to a weigh station before transfer to the payload canister. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
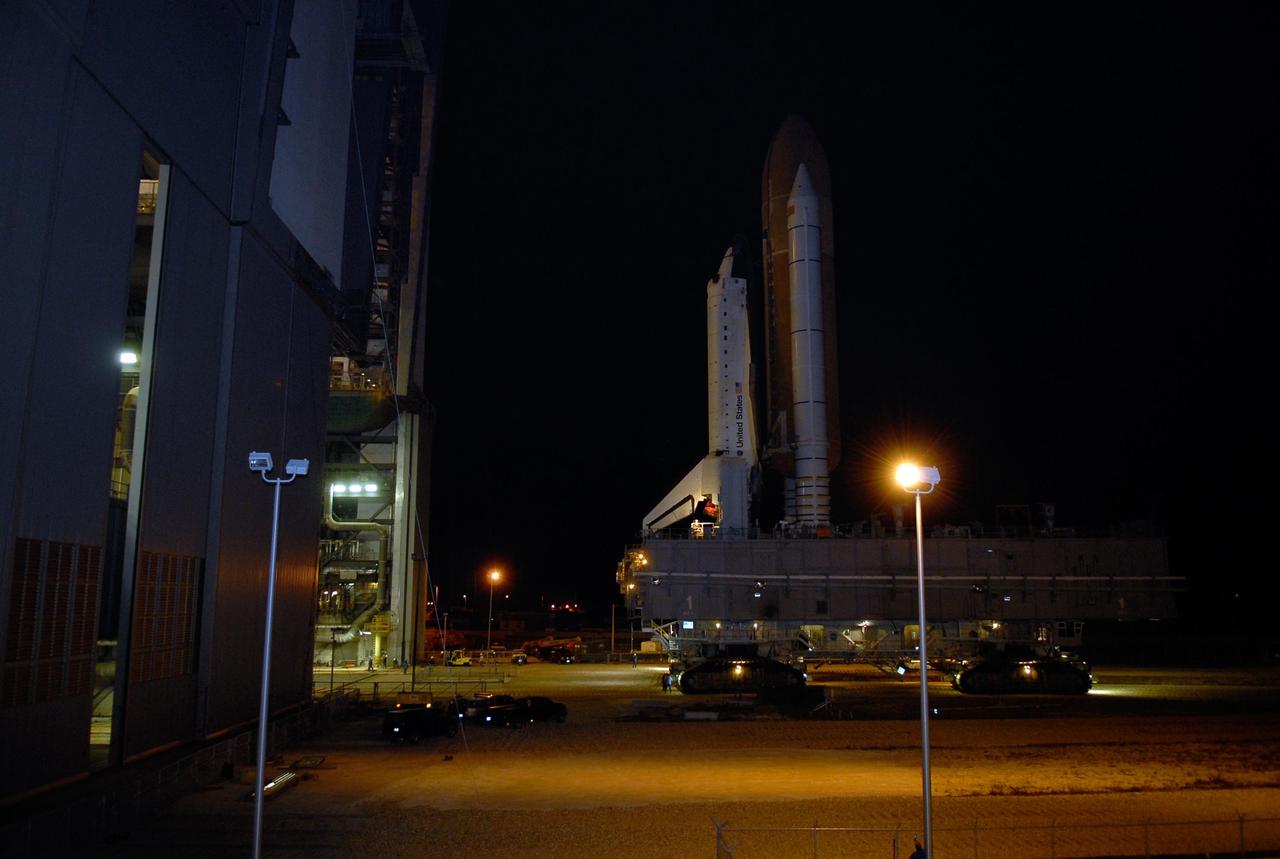

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis has cleared the doors of the high bay of the Vehicle Assembly Building and begins its trek along the crawlerway to Launch Pad 39A. First motion out of the VAB was at 4:43 a.m. EST. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
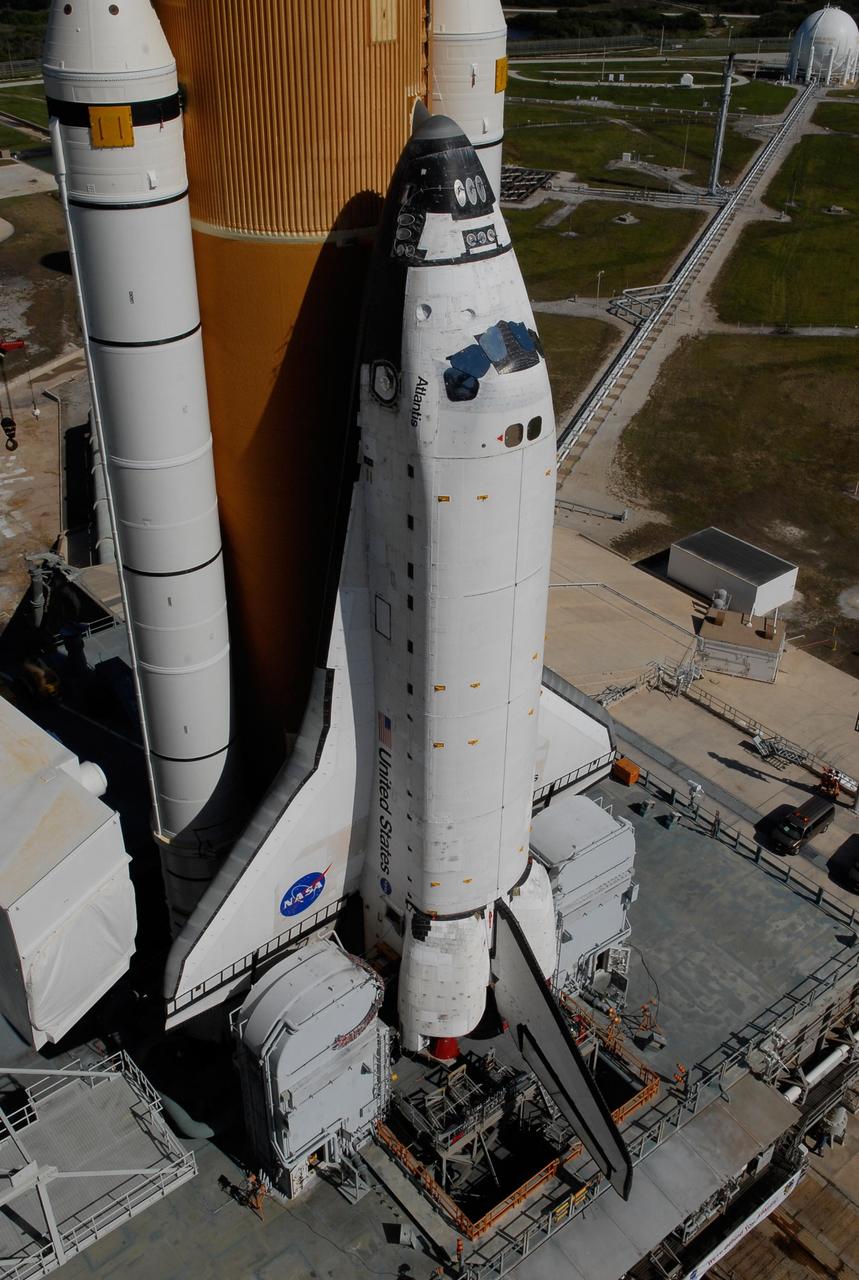

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Processing begins on Space Shuttle Atlantis upon its arrival at Launch Pad 39A. First motion out of the Vehicle Assembly Building was at 4:43 a.m. EST, and the shuttle was hard down on the pad at 11:51 a.m. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In high bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Atlantis is lowered alongside the external tank and solid rocket boosters waiting below, already secured atop the mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
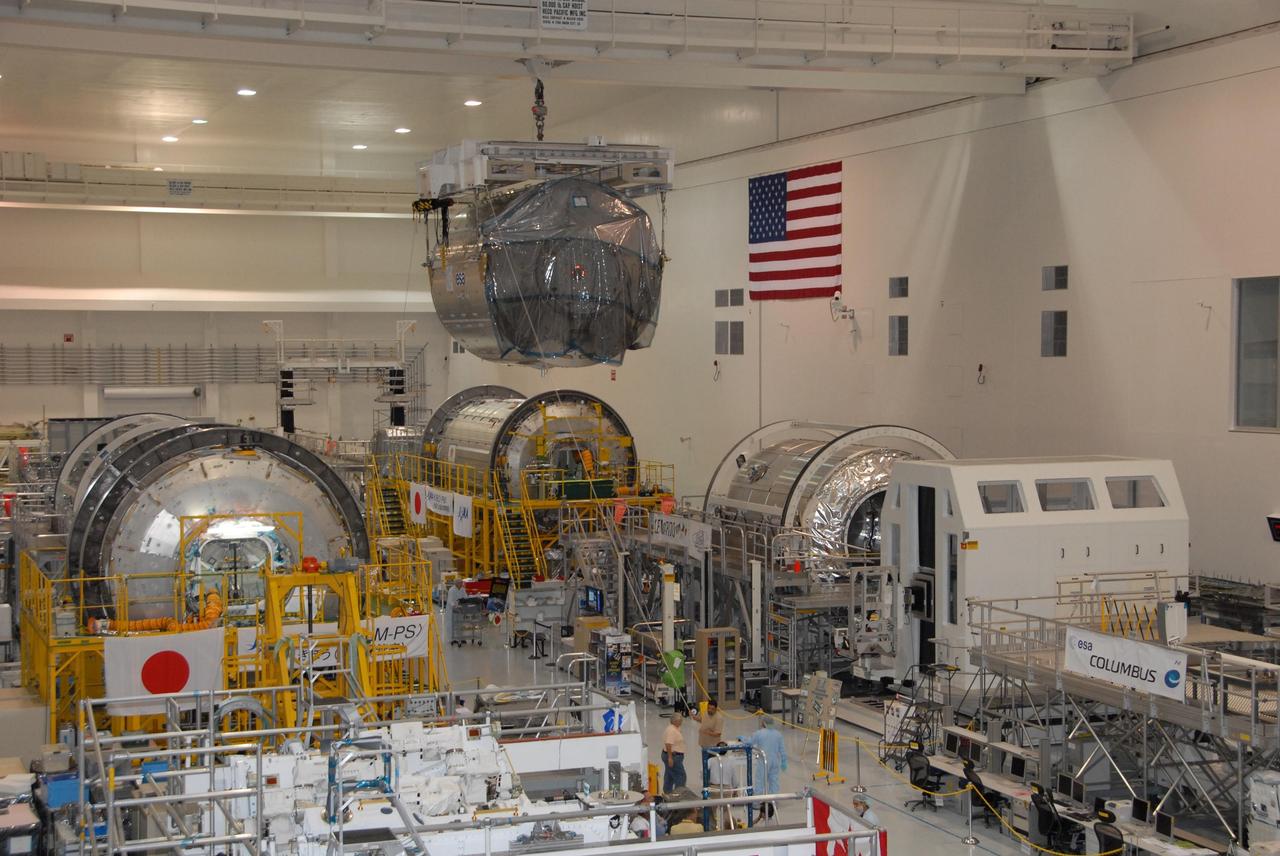

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Columbus Laboratory module moves across the facility to a payload canister. The canister will transport the module and other payloads to Launch Pad 39A in preparation for its journey to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
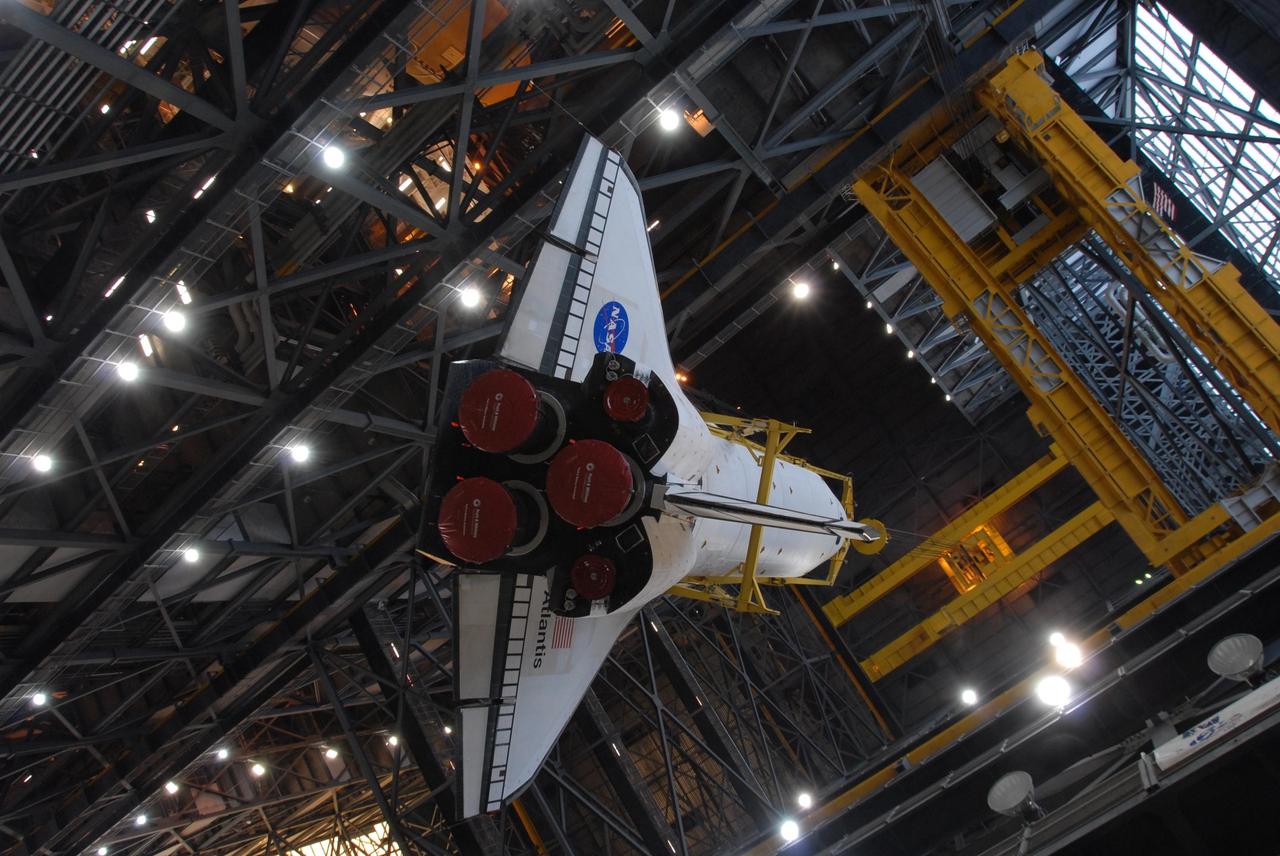

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space shuttle Atlantis is lifted into the upper levels of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Atlantis will be lifted into high bay 3 and mated with the external tank and solid rocket boosters designated for mission STS-122, already secured atop a mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Jose Nunez (center), NASA mission project engineer, points to the Columbus Laboratory above, being displayed to the media at a special showing. Columbus is the European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station. The laboratory module will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. Columbus is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
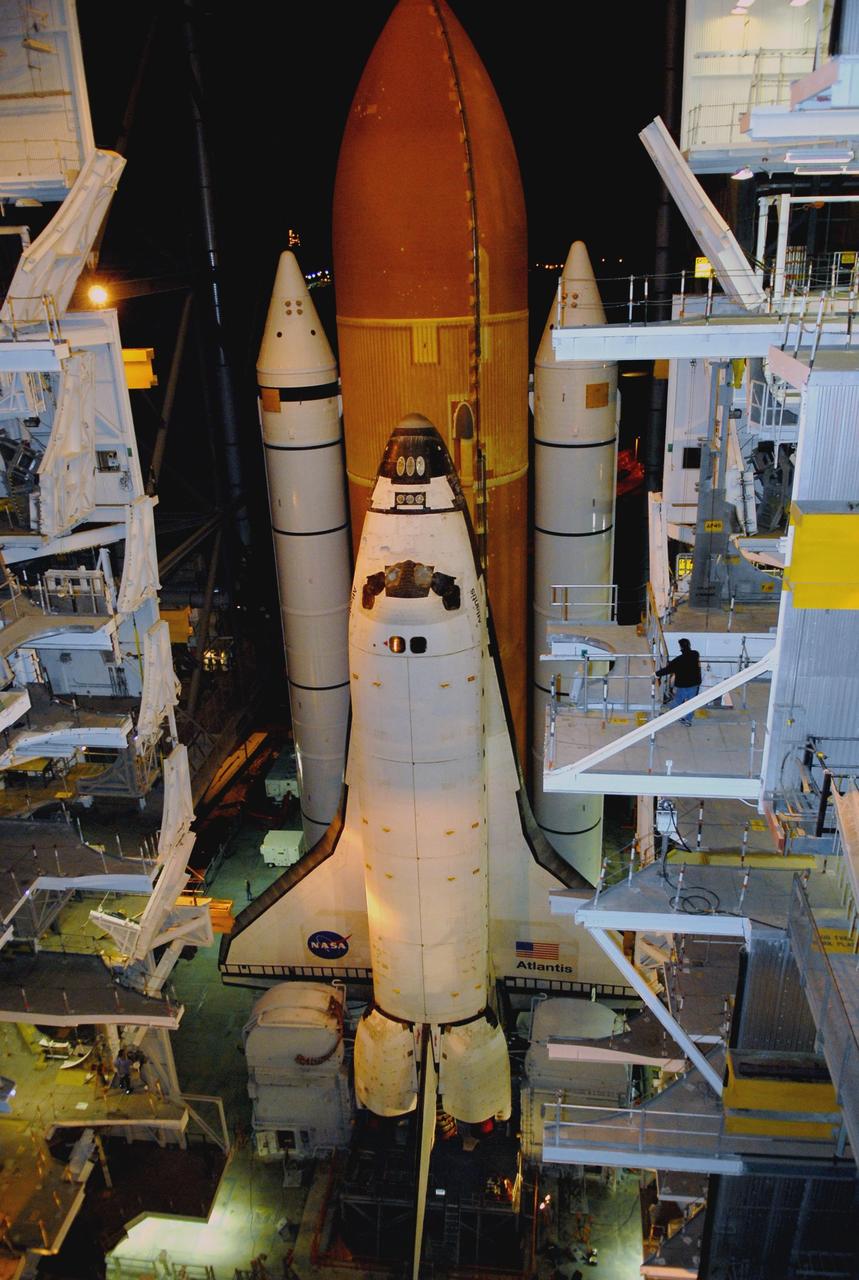

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis begins moving through the doors of the Vehicle Assembly Building toward Launch Pad 39A before sunrise. First motion out of the VAB was at 4:43 a.m. EST. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
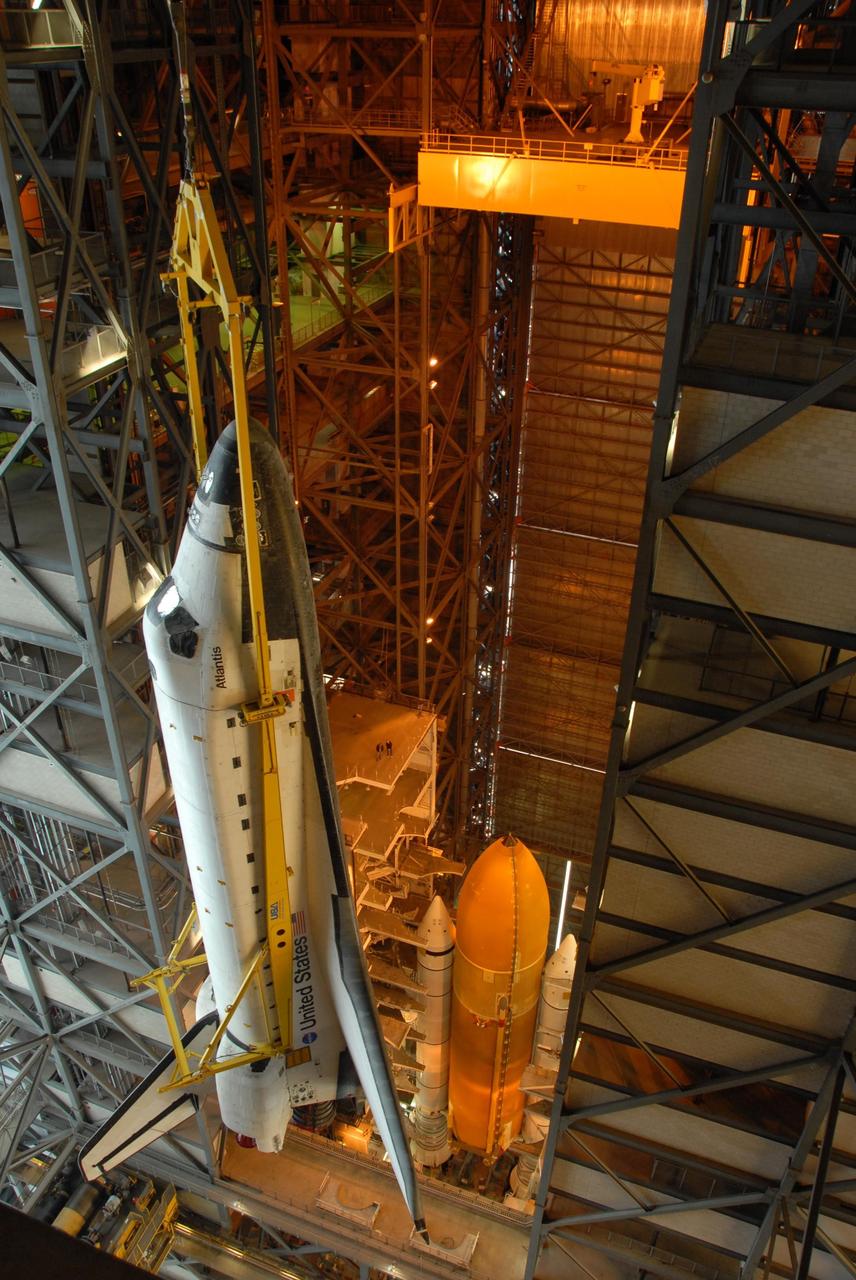

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the upper levels of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Space shuttle Atlantis is moved laterally into high bay 3. The external tank and solid rocket boosters can be seen below where they are already secured atop the mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Columbus Laboratory module is moved toward a weigh station. After being weighed, the module will be transferred to the payload canister. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
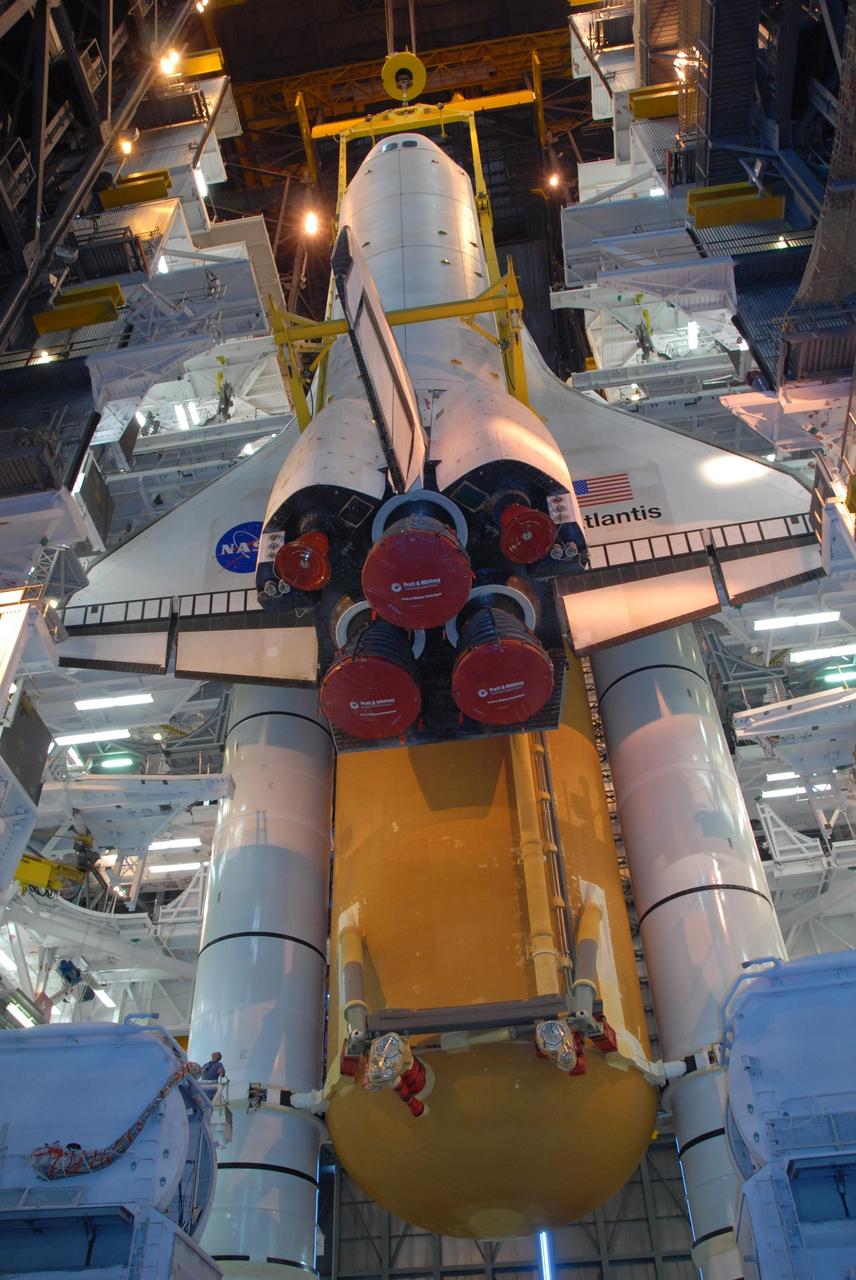

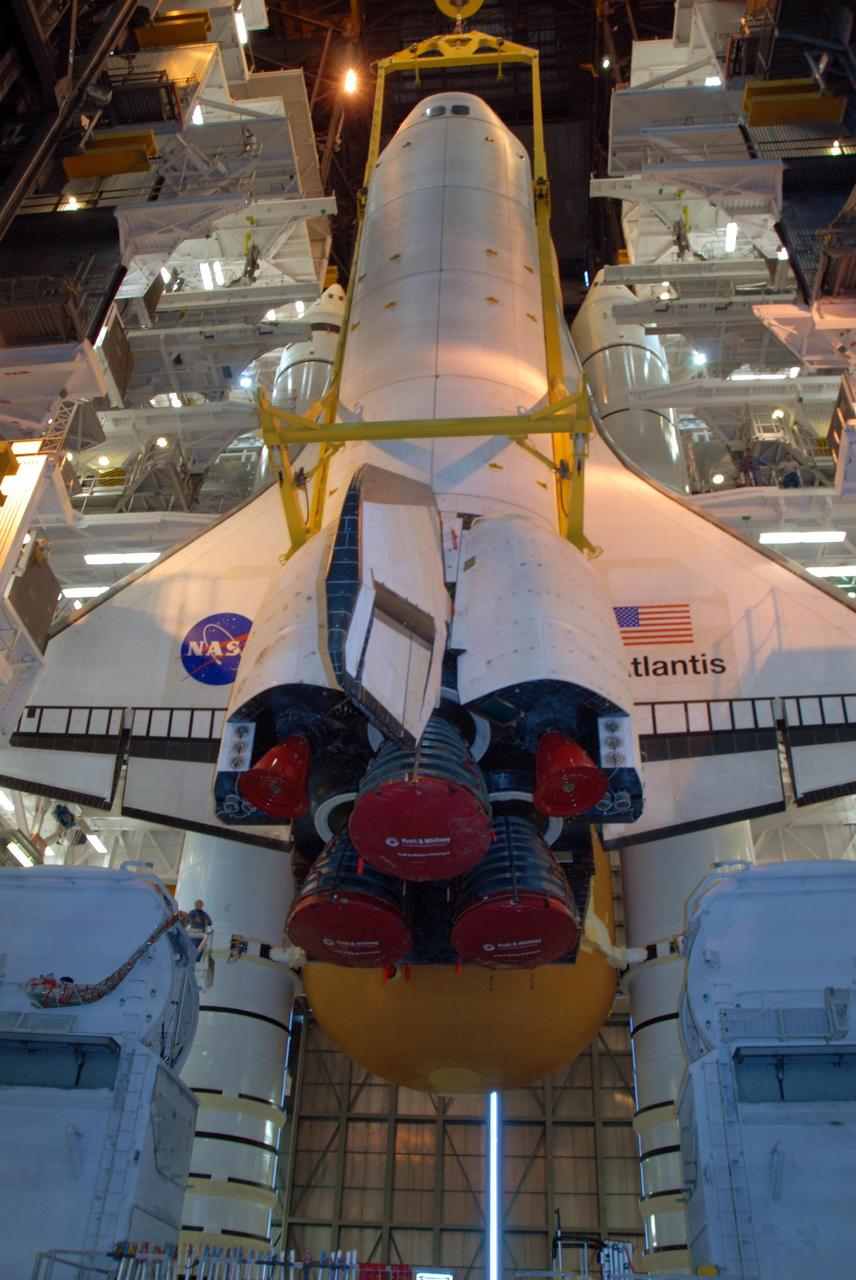
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In high bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Atlantis is lowered alongside the external tank and solid rocket boosters waiting below, already secured atop the mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
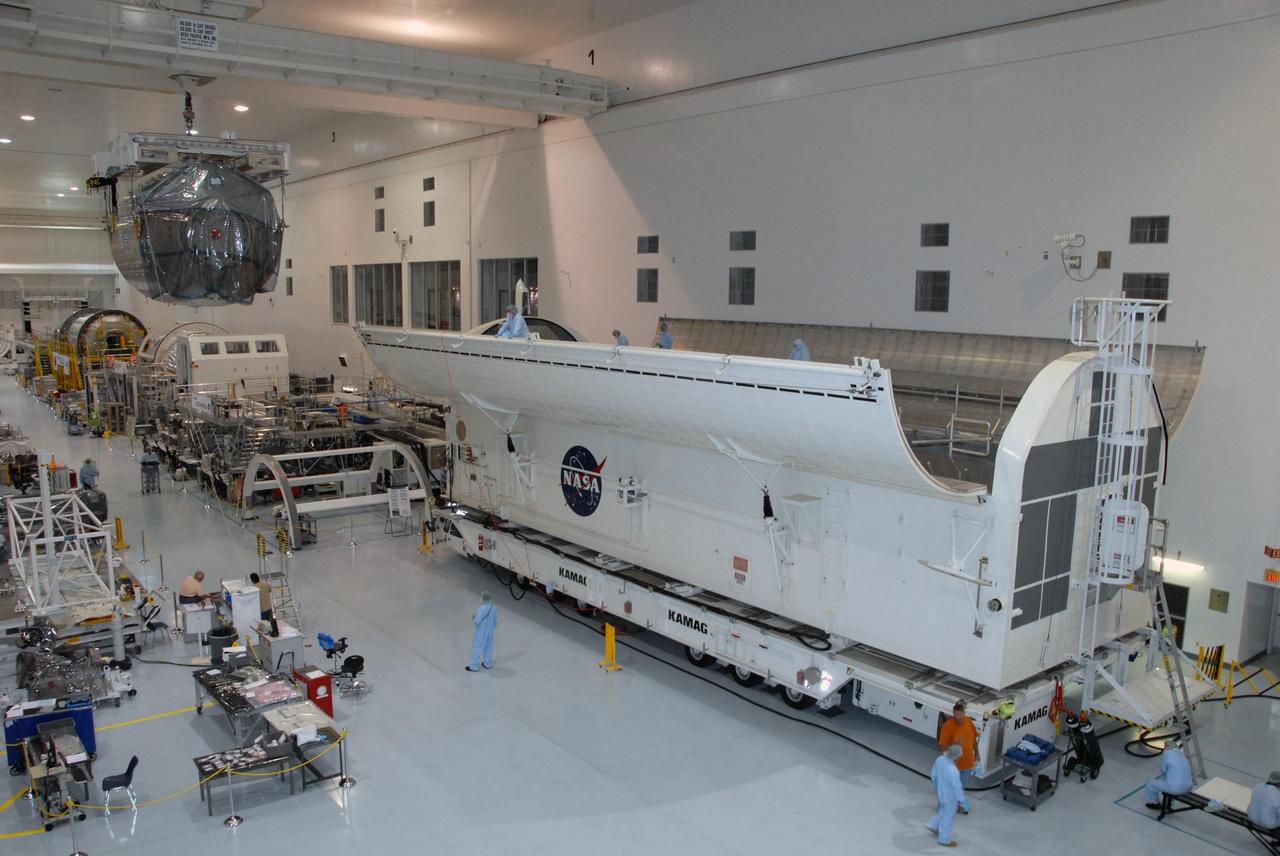

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Columbus Laboratory module moves across the facility to the waiting payload canister at right. The canister will transport the module and other payloads to Launch Pad 39A in preparation for its journey to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
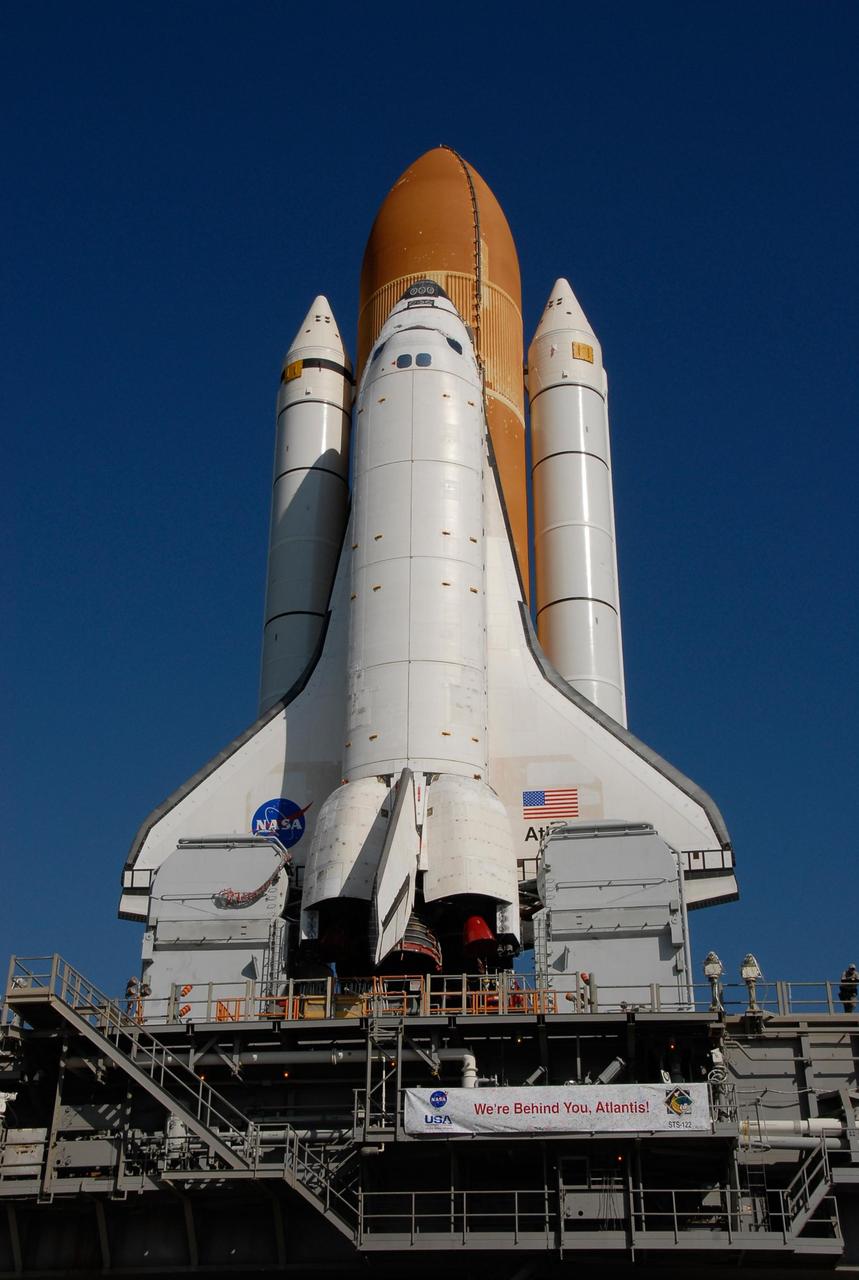

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A banner affixed to the mobile launch platform proclaims the sentiments of the work force at Kennedy Space Center as Space Shuttle Atlantis makes its way to Launch Pad 39A. First motion out of the Vehicle Assembly Building was at 4:43 a.m. EST. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lifts the Columbus Laboratory module away from its stand. The module is being moved to a weigh station before transfer to the payload canister. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
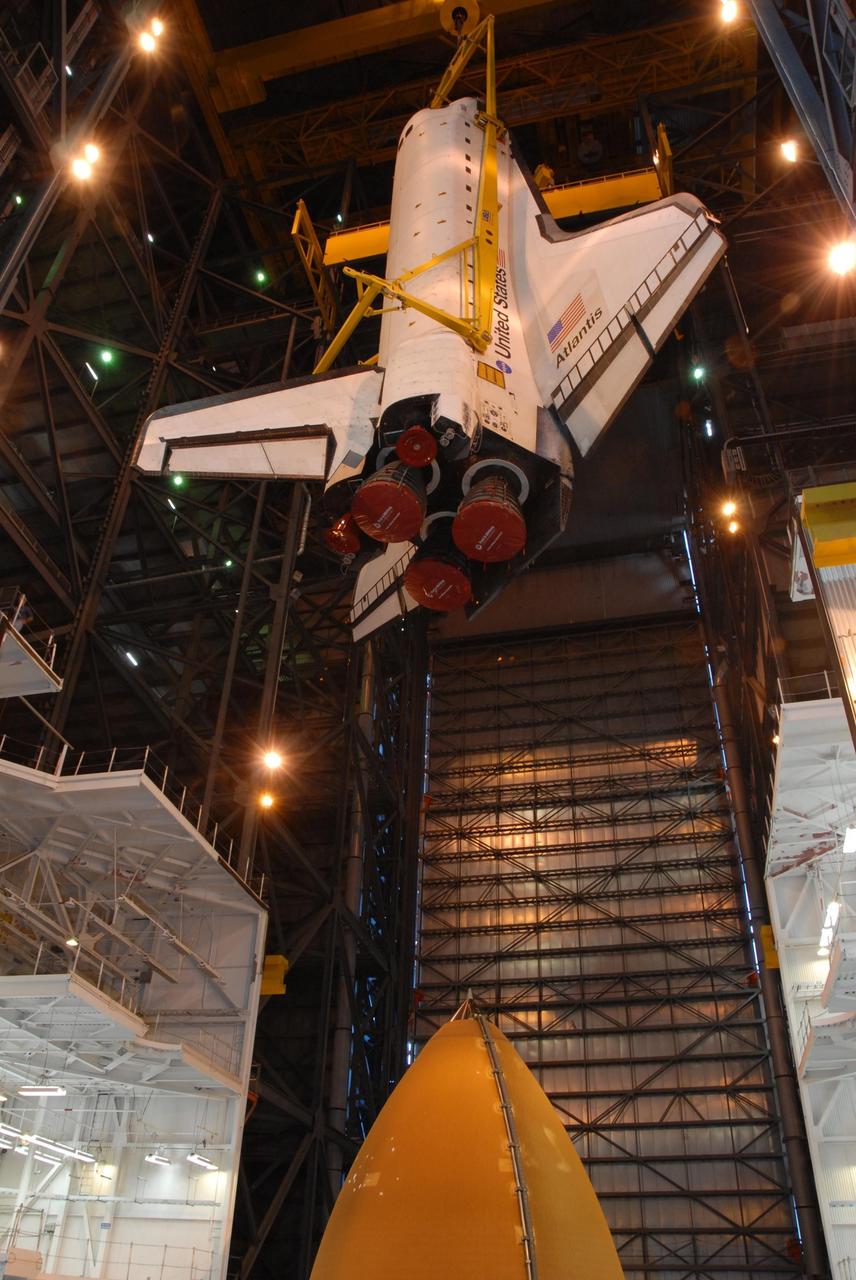

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In high bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Atlantis is lowered toward the external tank (seen at the bottom) and solid rocket boosters waiting below, already secured atop the mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
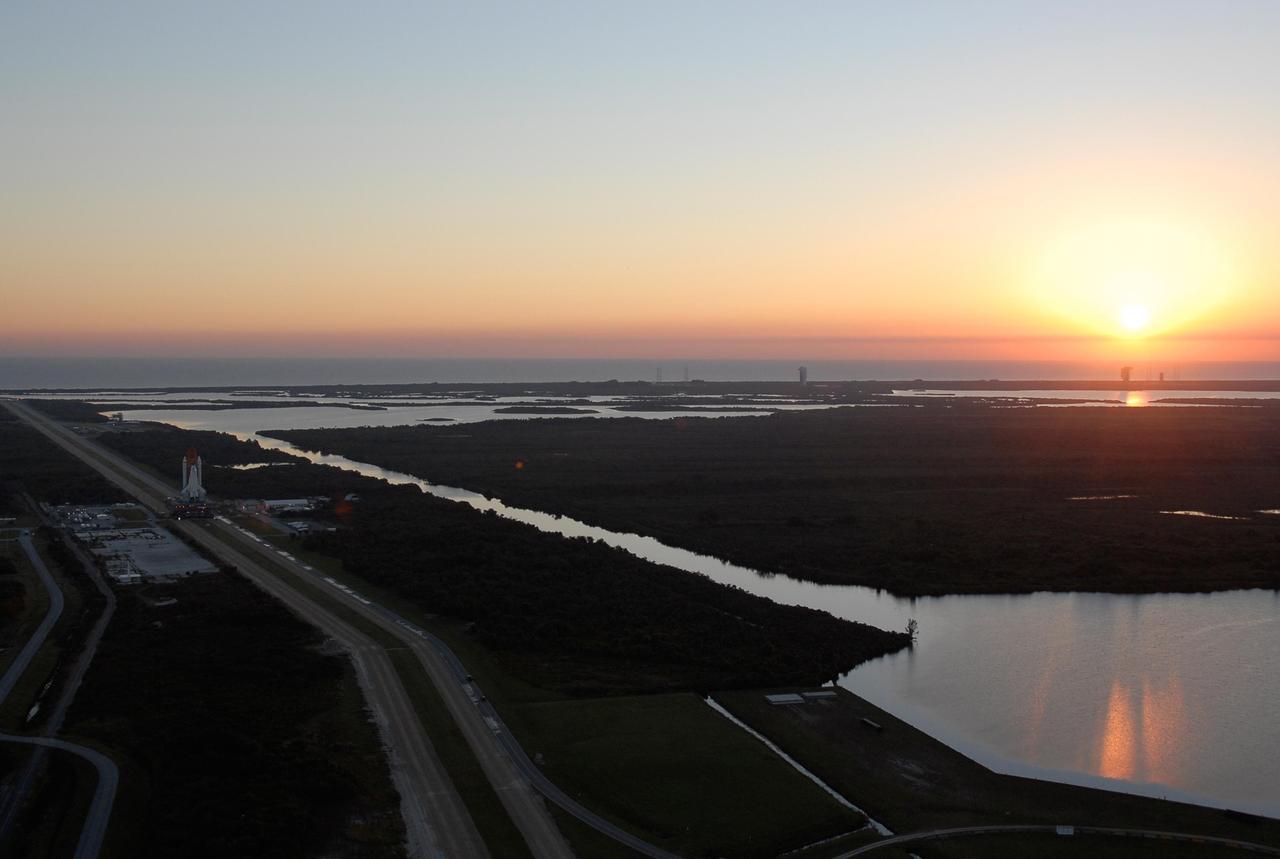

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis, atop a mobile launch platform, passes by the turn basin in Launch Complex 39 toward Pad A as the sun rises on a balmy Florida morning. First motion out of the VAB was at 4:43 a.m. EST. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
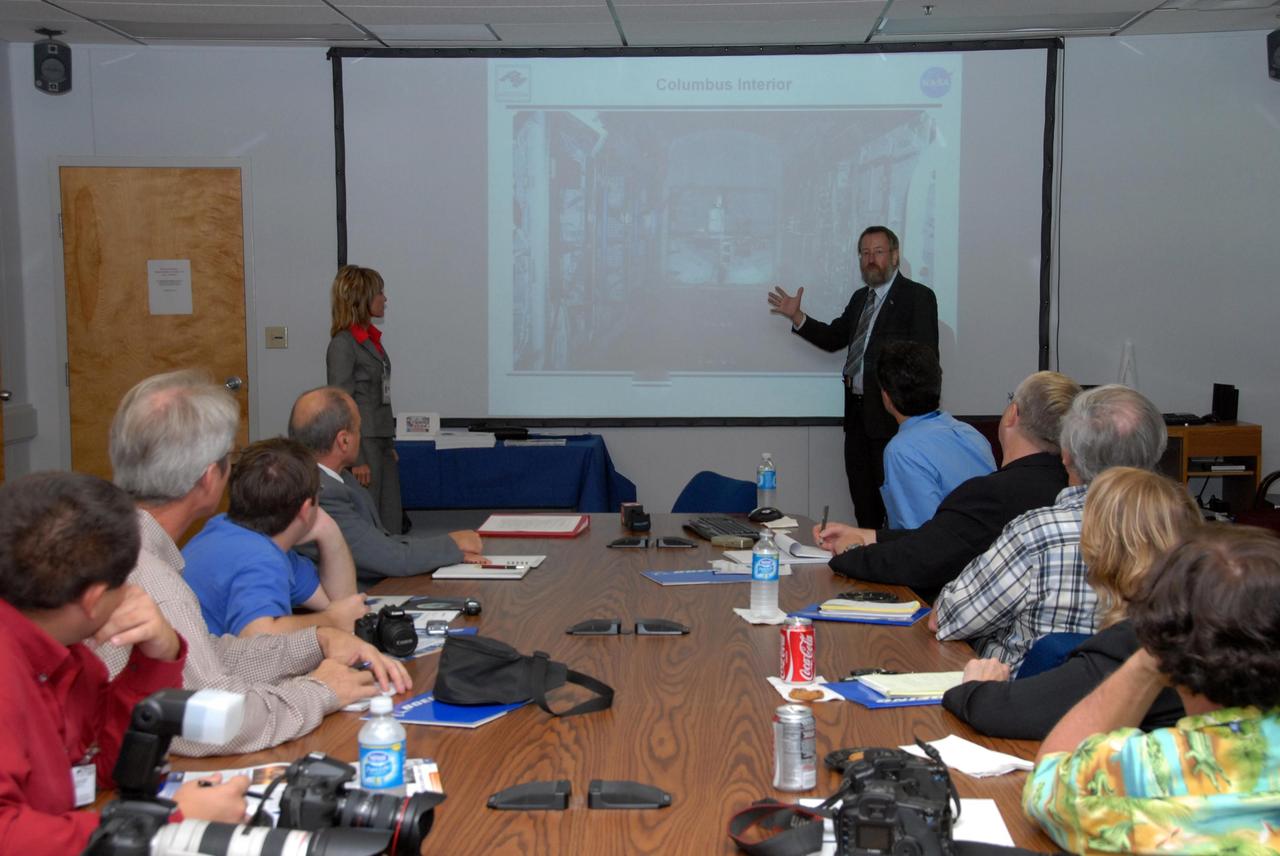

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Prior to a showing of the European Space Agency's Columbus Laboratory module, Gregor Woop, in front of the screen, provides information about the module for the media gathered at the table. Woop is the European Space Agency's product assurance and safety manager. Standing at left is Debbie Hahn, NASA mission manager. Columbus is the European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station. The laboratory module will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. Columbus is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
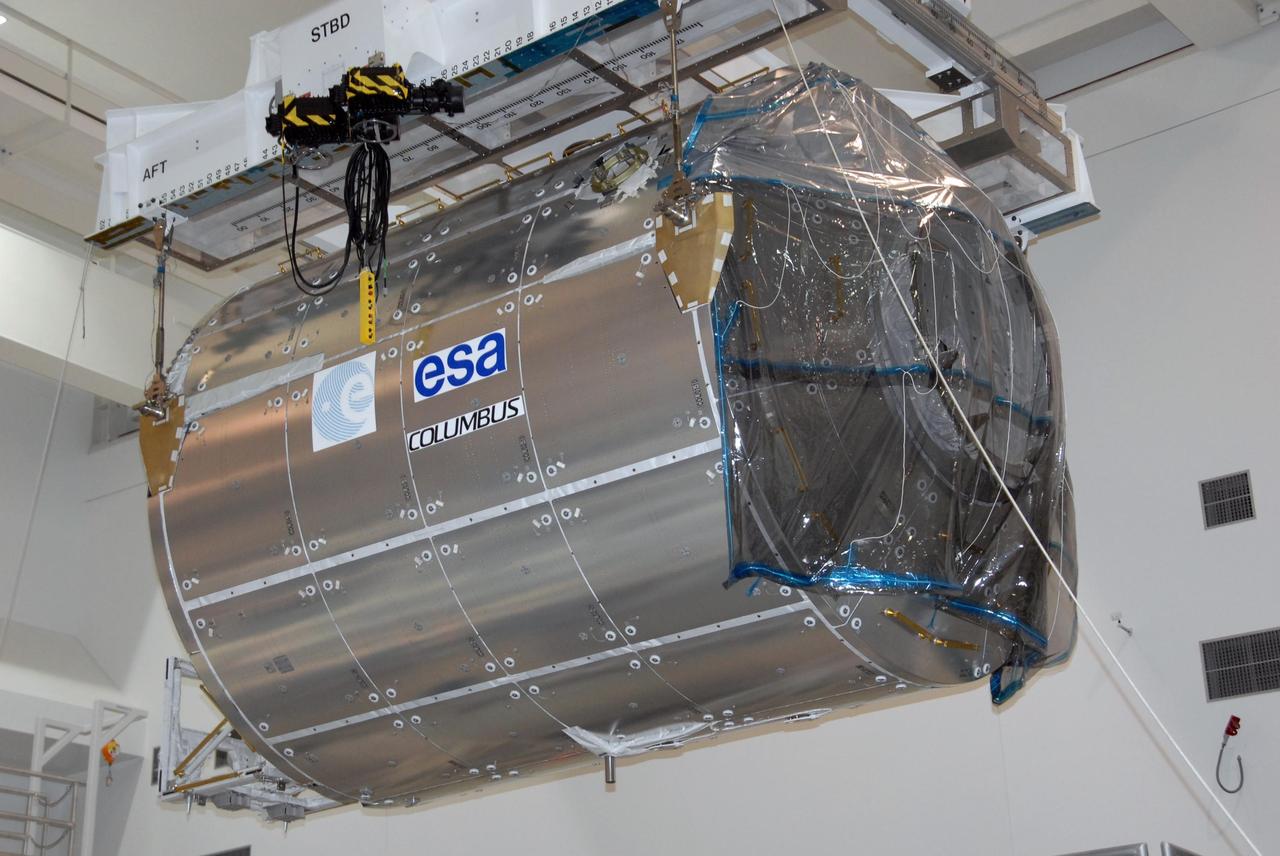

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Columbus Laboratory module is being moved across the facility for its transfer to a payload canister. The canister will transport the module and other payloads to Launch Pad 39A in preparation for its journey to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Atlantis is raised into a vertical position. Atlantis will next be lifted into high bay 3 and mated with the external tank and solid rocket boosters designated for mission STS-122, already secured atop a mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Columbus Laboratory is positioned on a stand where it is being displayed to the media at a special showing. Columbus is the European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station. The laboratory module will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. Columbus is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
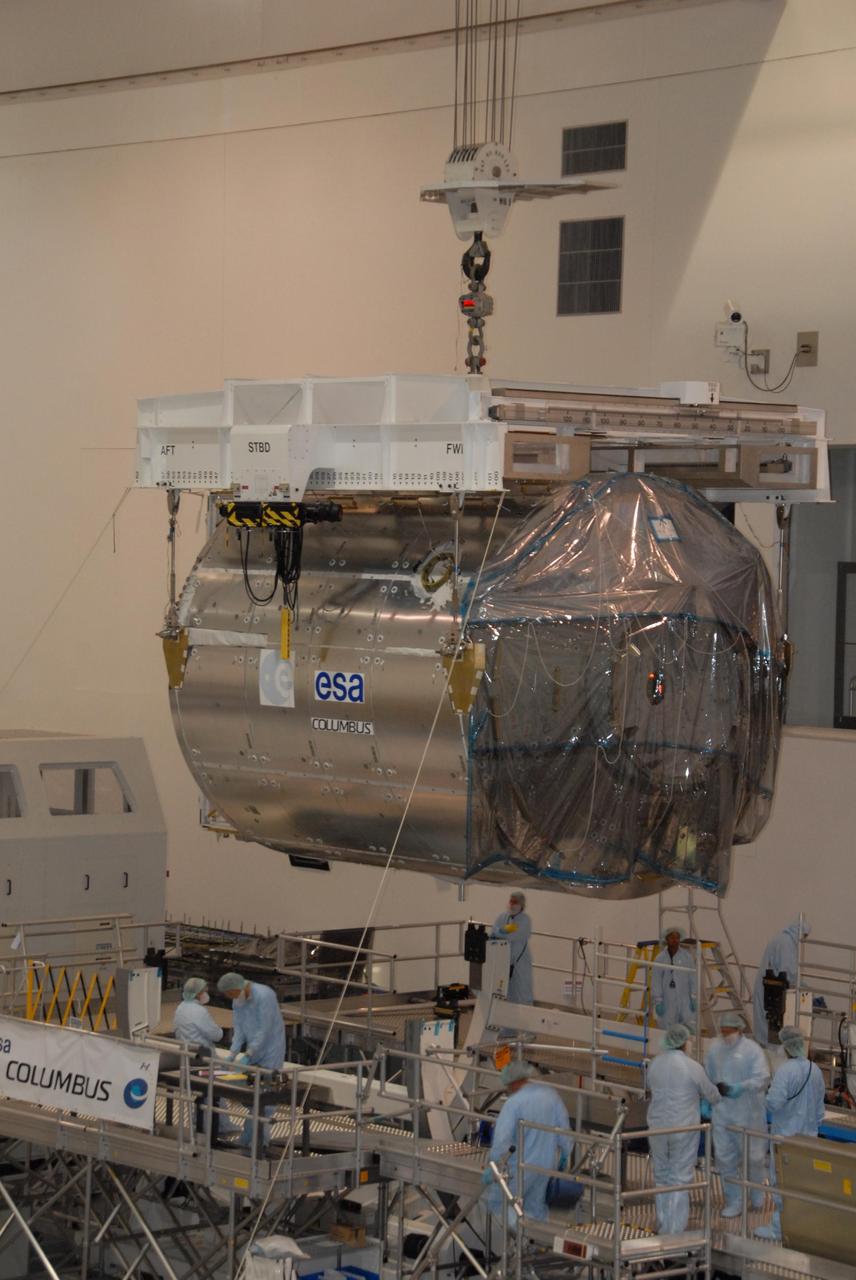

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lifts the Columbus Laboratory module from its stand. The module is being moved to a weigh station before transfer to the payload canister. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis, atop a mobile launch platform, moves through the doors of the Vehicle Assembly Building toward Launch Pad 39A before sunrise. First motion out of the VAB was at 4:43 a.m. EST. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
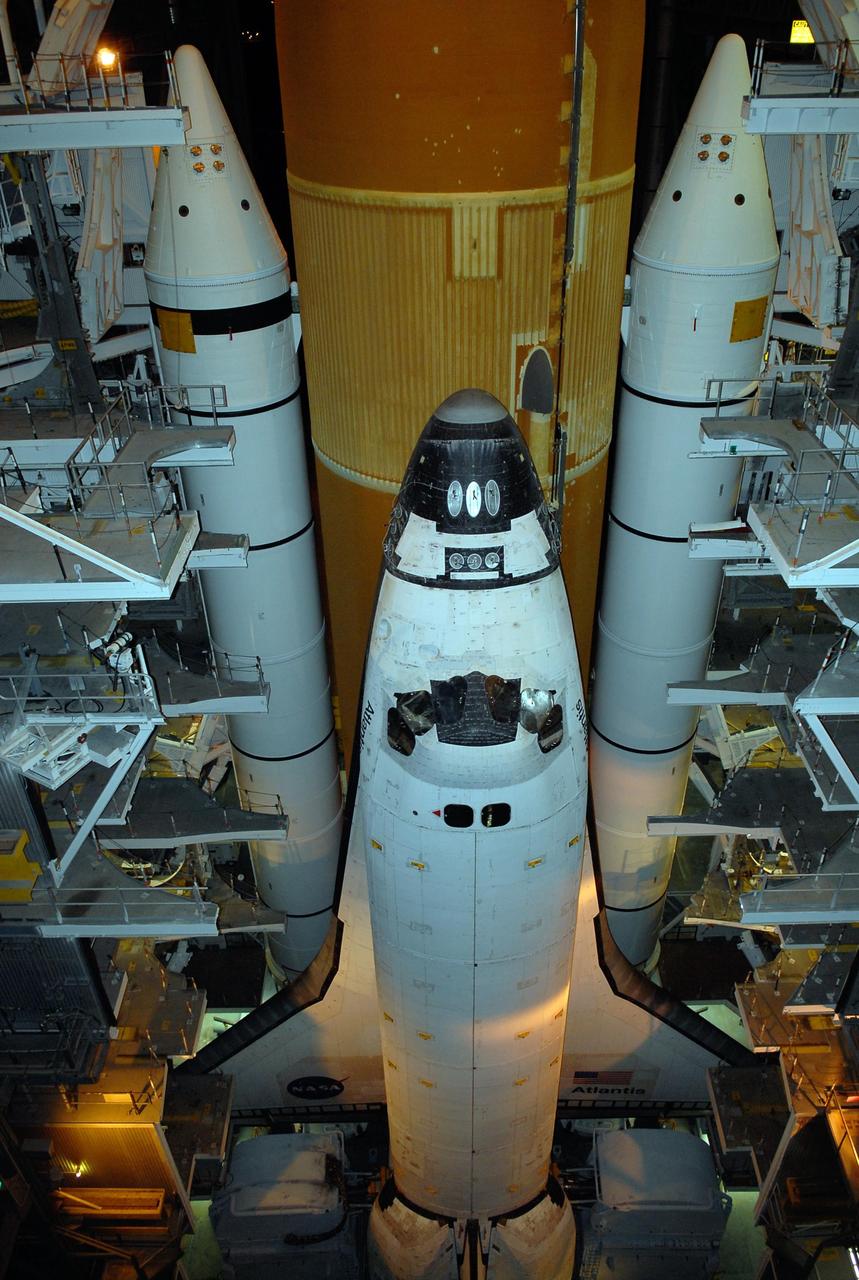

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis is ready to move through the doors of the Vehicle Assembly Building toward Launch Pad 39A. First motion out of the VAB was at 4:43 a.m. EST. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
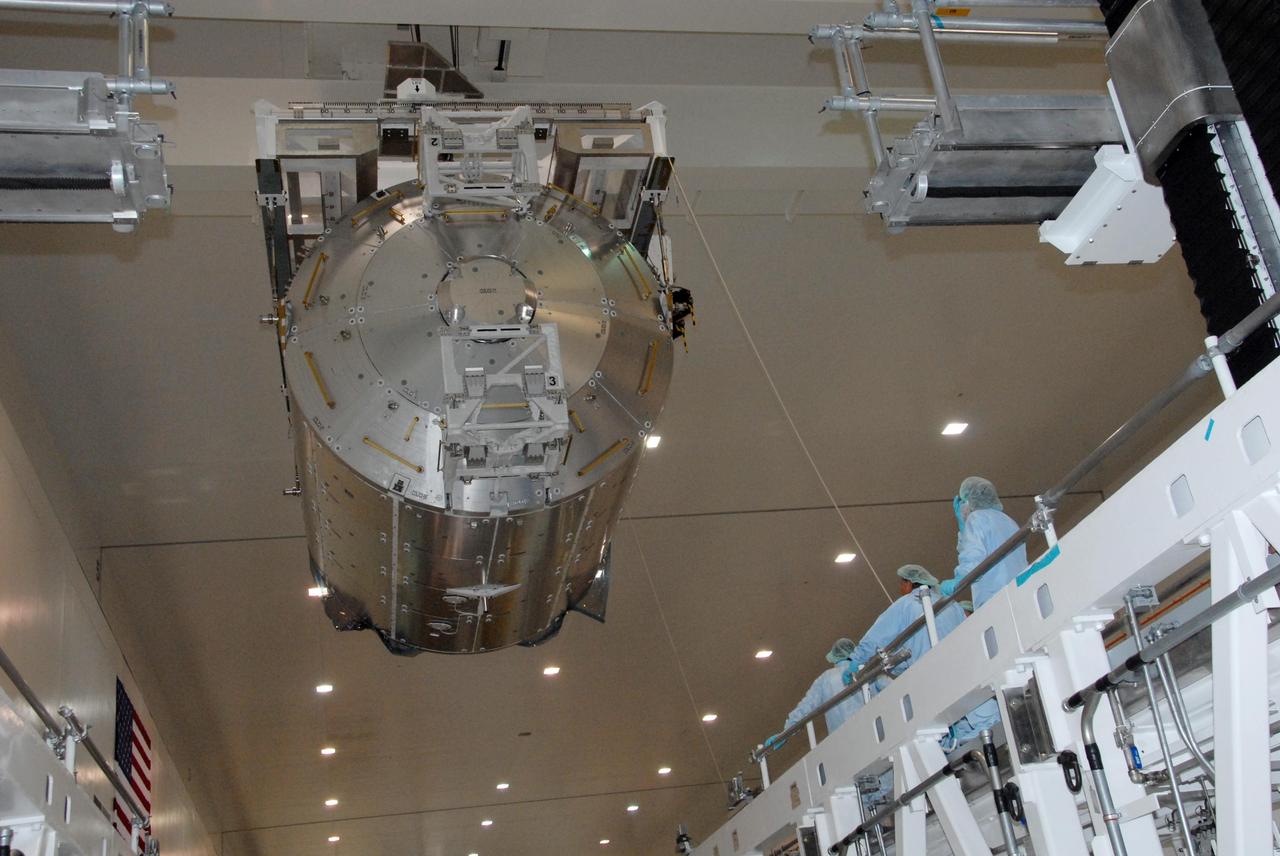

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Columbus Laboratory module is lowered toward a weigh station. After being weighed, the module will be transferred to the payload canister. The European Space Agency 's largest single contribution to the International Space Station, Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station, providing crew members and scientists around the world the ability to conduct a variety of life, physical and materials science experiments. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The module is scheduled to be transferred to Launch Pad 39A in early November, in preparation for its journey to the station. Columbus will fly aboard space shuttle Atlantis on the STS-122 mission, targeted for launch Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
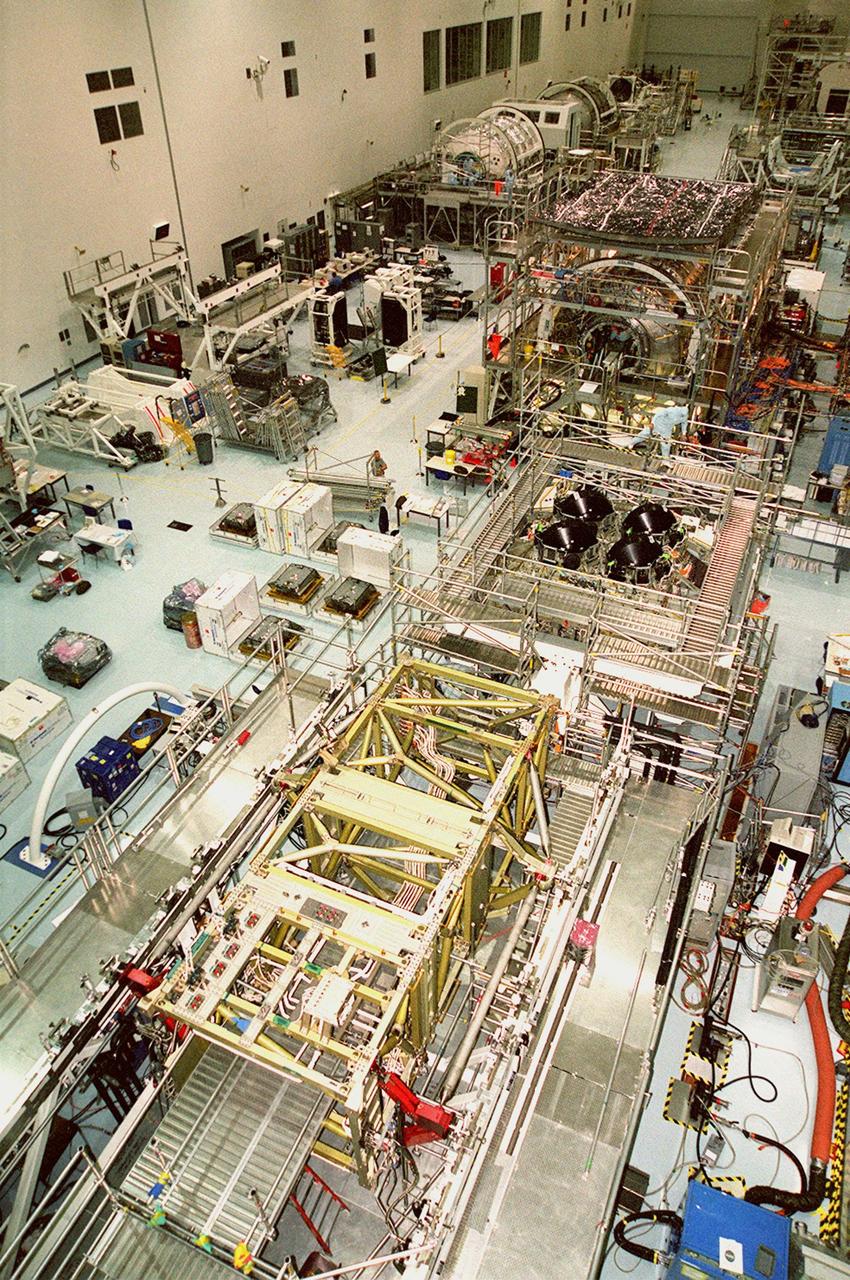
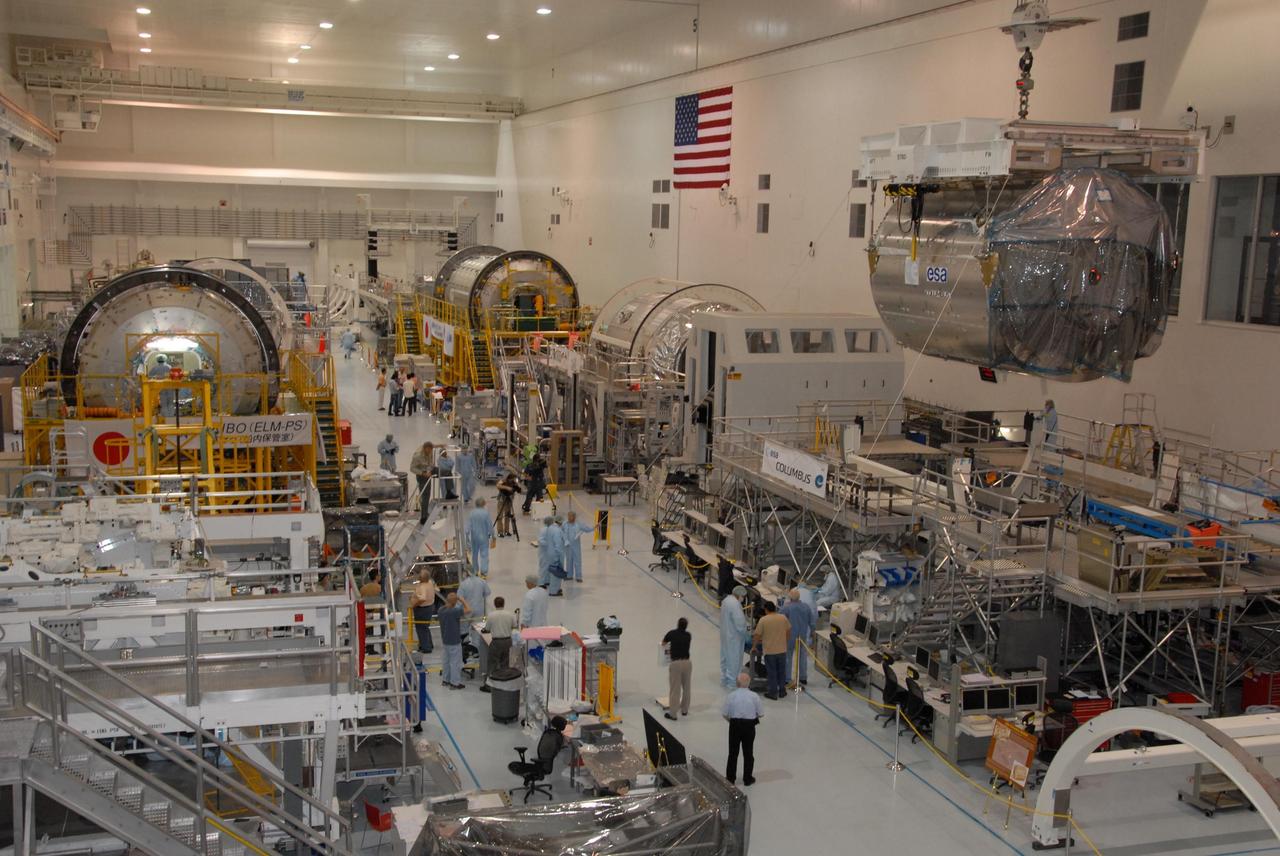
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The floor of the Space Station Processing Facility is filled with racks and hardware for testing the various components of the International Space Station (ISS). The large module in the center of the floor (top) is the U.S. Lab, Destiny. The U.S. Laboratory module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research. It is scheduled to be launched on mission STS-98 (no date determined yet for launch). At top left are the Multi-Purpose Logistics Modules Raffaello and Leonardo and the Pressurized Mating Adapter-3 (PMA-3). Italy's major contributions to the ISS program, Raffaello and Leonardo are reusable logistics carriers to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment. They are slated as payloads on missions STS-102 and STS-100, respectively. Dates have not yet been determined for the two missions. The PMA-3, once launched, will be mated to Node 1, a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the Space Station. The primary purpose of PMA-3 is to serve as a Shuttle docking port through which crew members and equipment will transfer to the Space Station during later assembly missions. PMA-3 is scheduled as payload on mission STS-92, whose date for launch is not yet determined
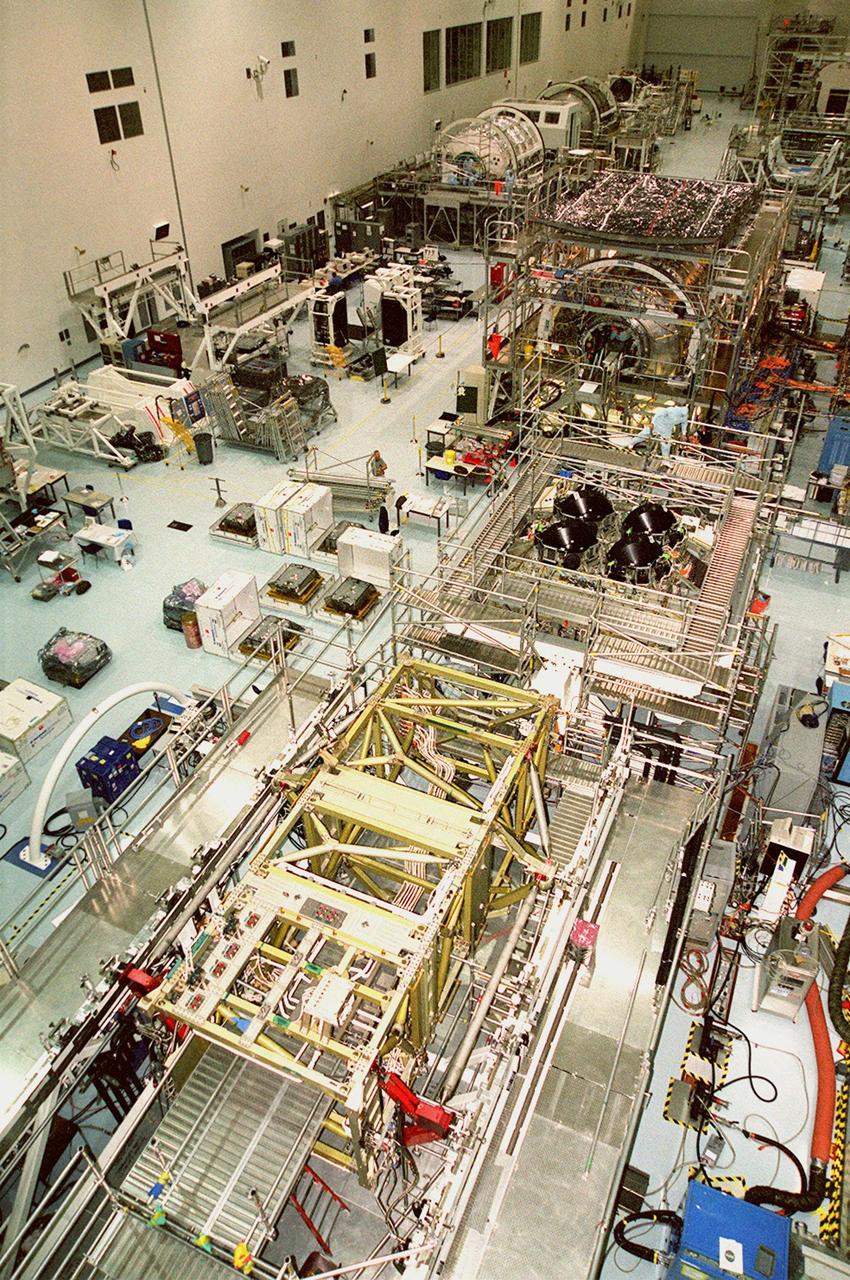
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The floor of the Space Station Processing Facility is filled with racks and hardware for testing the various components of the International Space Station (ISS). The large module in the center of the floor (top) is the U.S. Lab, Destiny. The U.S. Laboratory module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research. It is scheduled to be launched on mission STS-98 (no date determined yet for launch). At top left are the Multi-Purpose Logistics Modules Raffaello and Leonardo and the Pressurized Mating Adapter-3 (PMA-3). Italy's major contributions to the ISS program, Raffaello and Leonardo are reusable logistics carriers to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment. They are slated as payloads on missions STS-102 and STS-100, respectively. Dates have not yet been determined for the two missions. The PMA-3, once launched, will be mated to Node 1, a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of the Space Station. The primary purpose of PMA-3 is to serve as a Shuttle docking port through which crew members and equipment will transfer to the Space Station during later assembly missions. PMA-3 is scheduled as payload on mission STS-92, whose date for launch is not yet determined
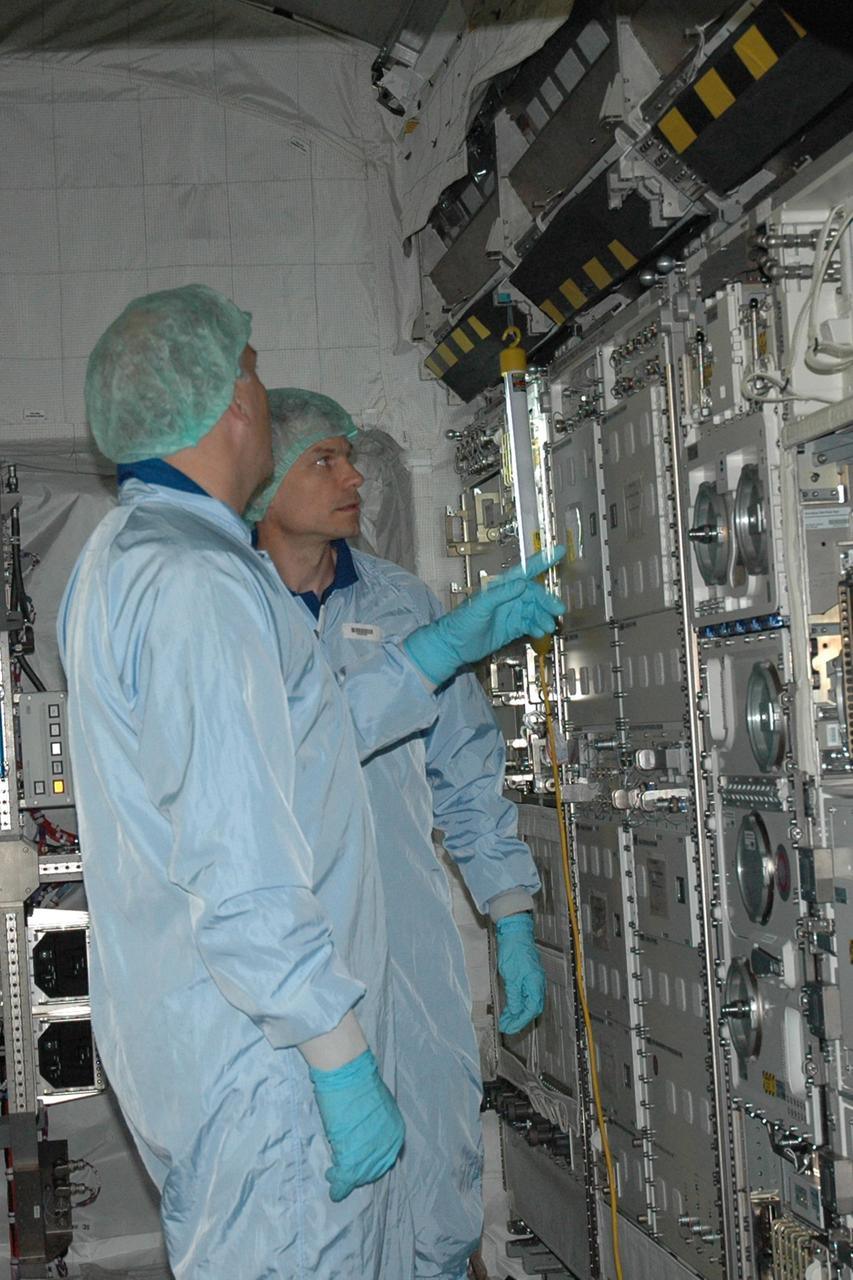

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-122 Mission Specialist Stanley Love looks at the experiment racks inside the Columbus Research Laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility. He and other crew members are at Kennedy to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The crew comprises Commander Stephen Frick, Pilot Alan Poindexter, and Mission Specialists Rex Walheim, Stanley Love, Leland Melvin and Hans Schlegel, who represents the European Space Agency. The Columbus Lab is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station. It will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. Columbus, a program of ESA, is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
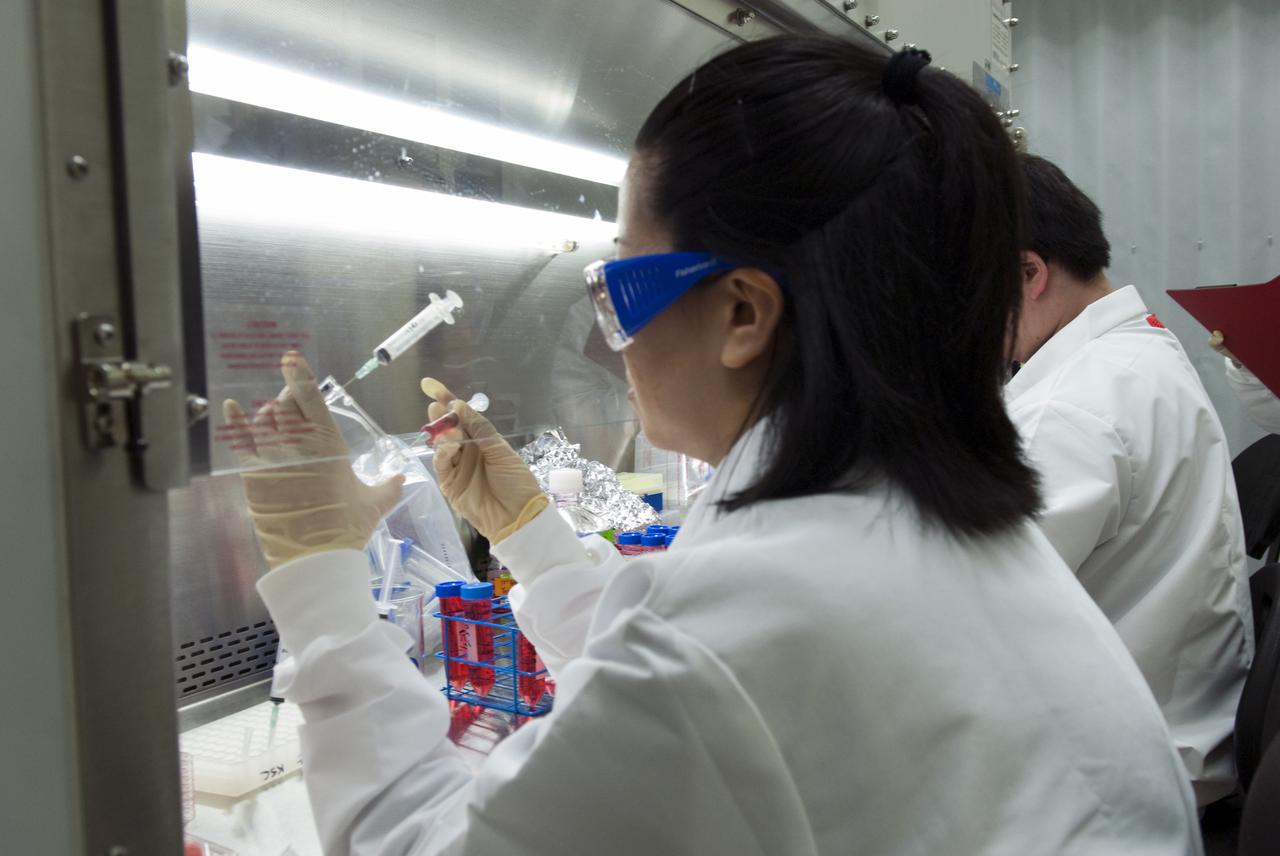

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency scientist prepares samples for the Molecular Mechanism of Microgravity-Induced Skeletal Muscle Atrophy – Physiological Relevance of Cbl-b Ubiquitin Ligase, or MyoLab, experiment. MyoLab will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard Discovery on the STS-131 mission. MyoLab will study a rat muscle gene modified cell line to determine the effects of microgravity. The MyoLab experiment is one of several biology and biotechnology, human research, physical, materials science and technology experiments that will be delivered to the space station aboard Discovery. The STS-131 mission also will deliver the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo, filled with resupply stowage platforms and science racks. STS-131, scheduled to launch at 6:21 a.m. on April 5, will be the 33rd shuttle mission to the station and the 131st shuttle mission overall. For more information on the mission and crew, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts131_index.htm. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
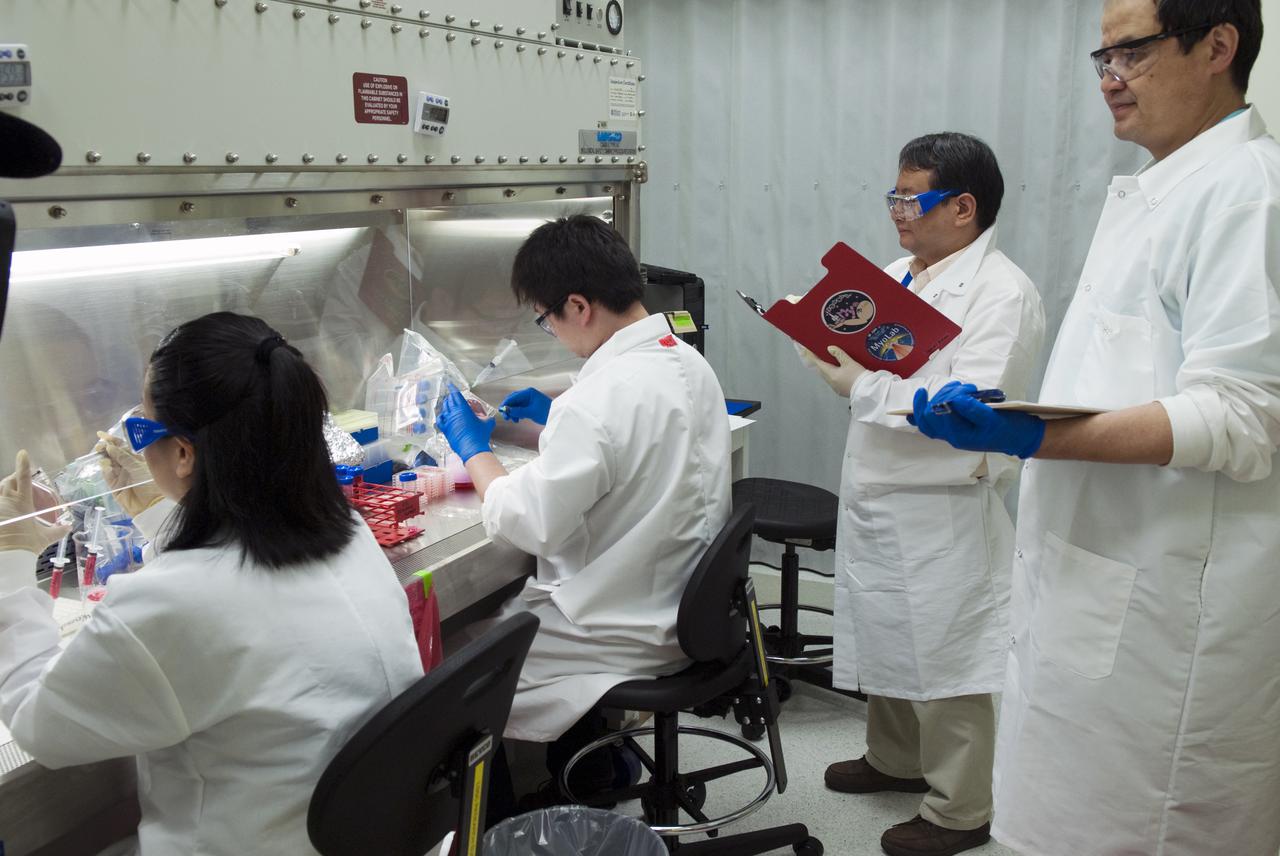

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency scientists prepare samples for the Molecular Mechanism of Microgravity-Induced Skeletal Muscle Atrophy – Physiological Relevance of Cbl-b Ubiquitin Ligase, or MyoLab, experiment. MyoLab will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard Discovery on the STS-131 mission. MyoLab will study a rat muscle gene modified cell line to determine the effects of microgravity. The MyoLab experiment is one of several biology and biotechnology, human research, physical, materials science and technology experiments that will be delivered to the space station aboard Discovery. The STS-131 mission also will deliver the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo, filled with resupply stowage platforms and science racks. STS-131, scheduled to launch at 6:21 a.m. on April 5, will be the 33rd shuttle mission to the station and the 131st shuttle mission overall. For more information on the mission and crew, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts131_index.htm. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
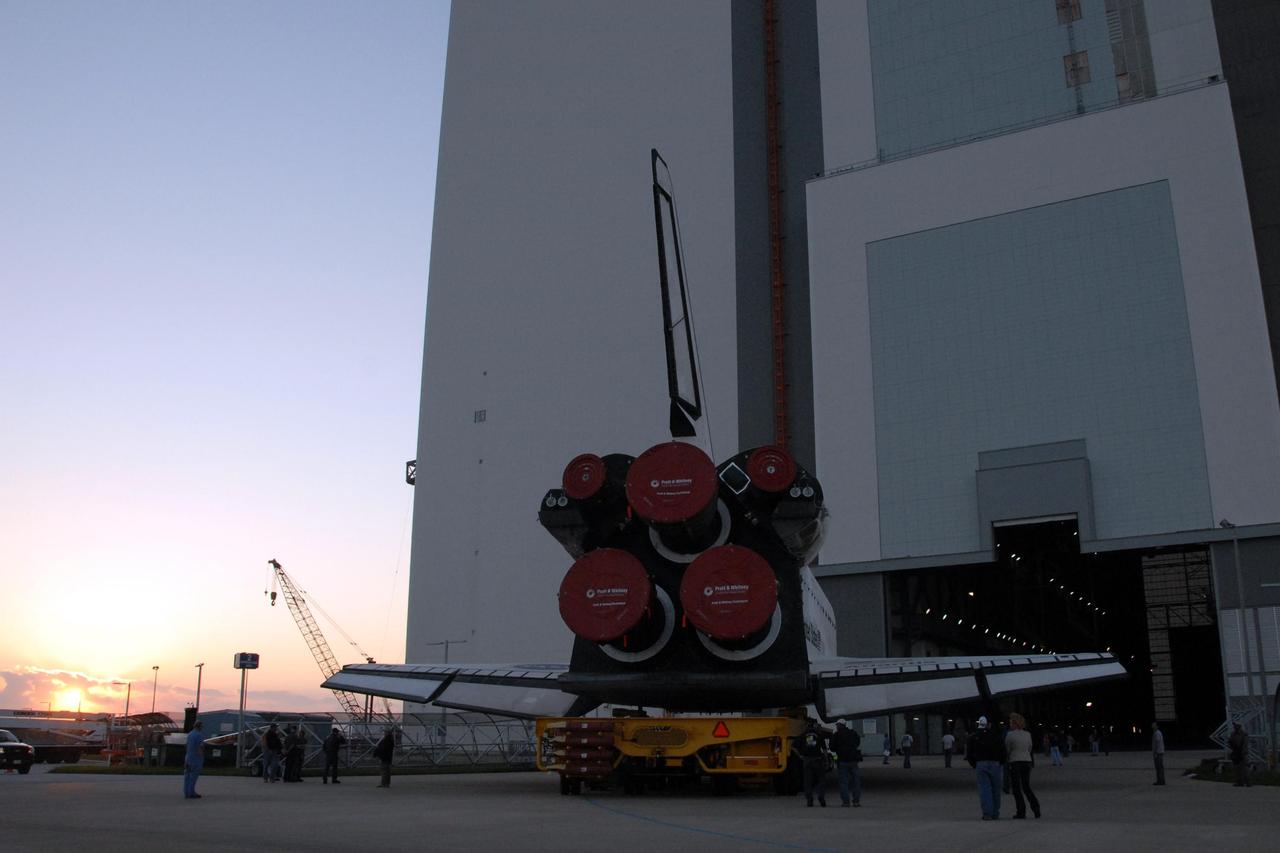

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- As the sun rises, space shuttle Atlantis turns toward the door of the Vehicle Assembly Building after rolling out of Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1. Rollover from its processing bay began at 7:05 a.m. EDT. Atlantis arrived in the VAB's transfer aisle at 8:03 a.m. In the VAB, the shuttle will be lifted and mated with the external tank and solid rocket boosters designated for mission STS-122, already secured atop a mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
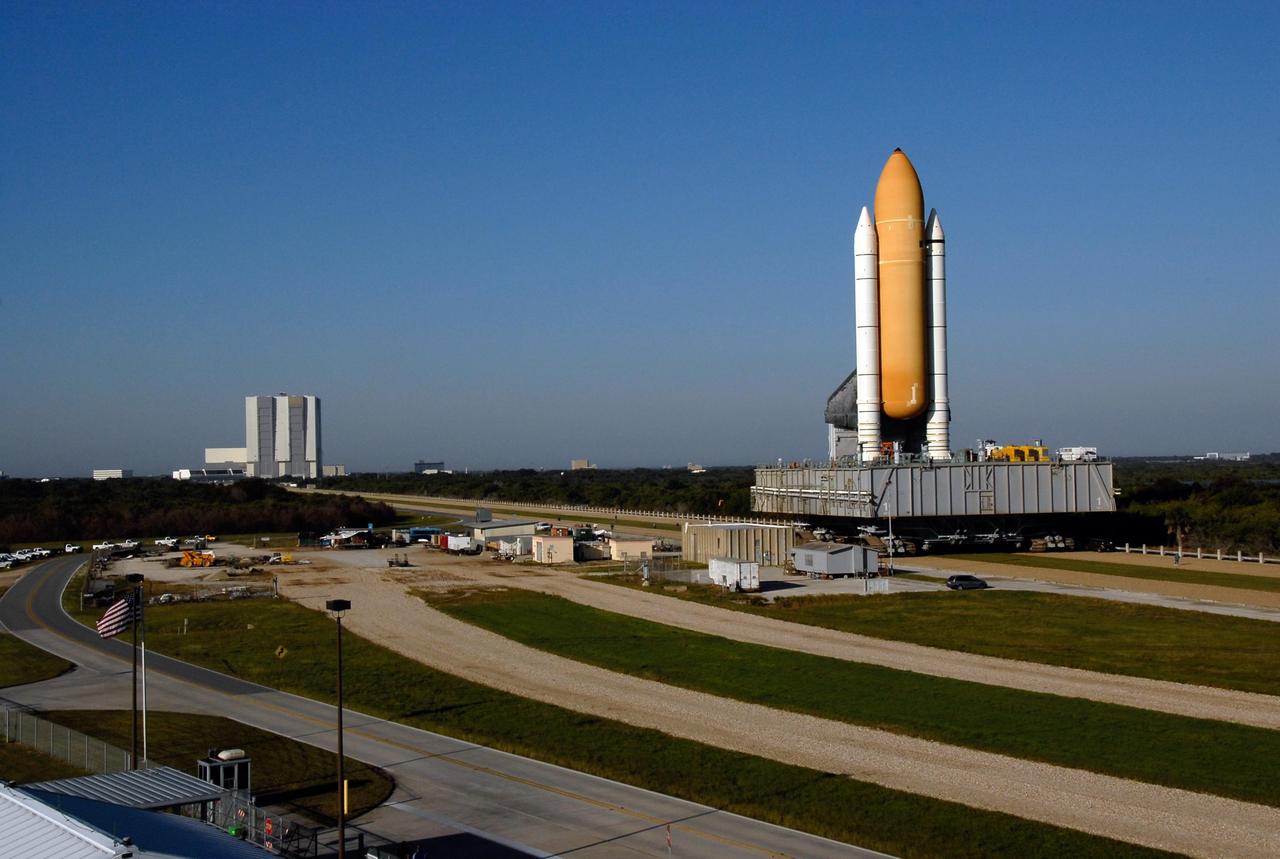

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis, secured atop a mobile launch platform, passes by the crawler kraal in Launch Complex 39 on its way to Pad A. This area is used to perform maintenance on the crawler transporter. First motion out of the Vehicle Assembly Building was at 4:43 a.m. EST. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
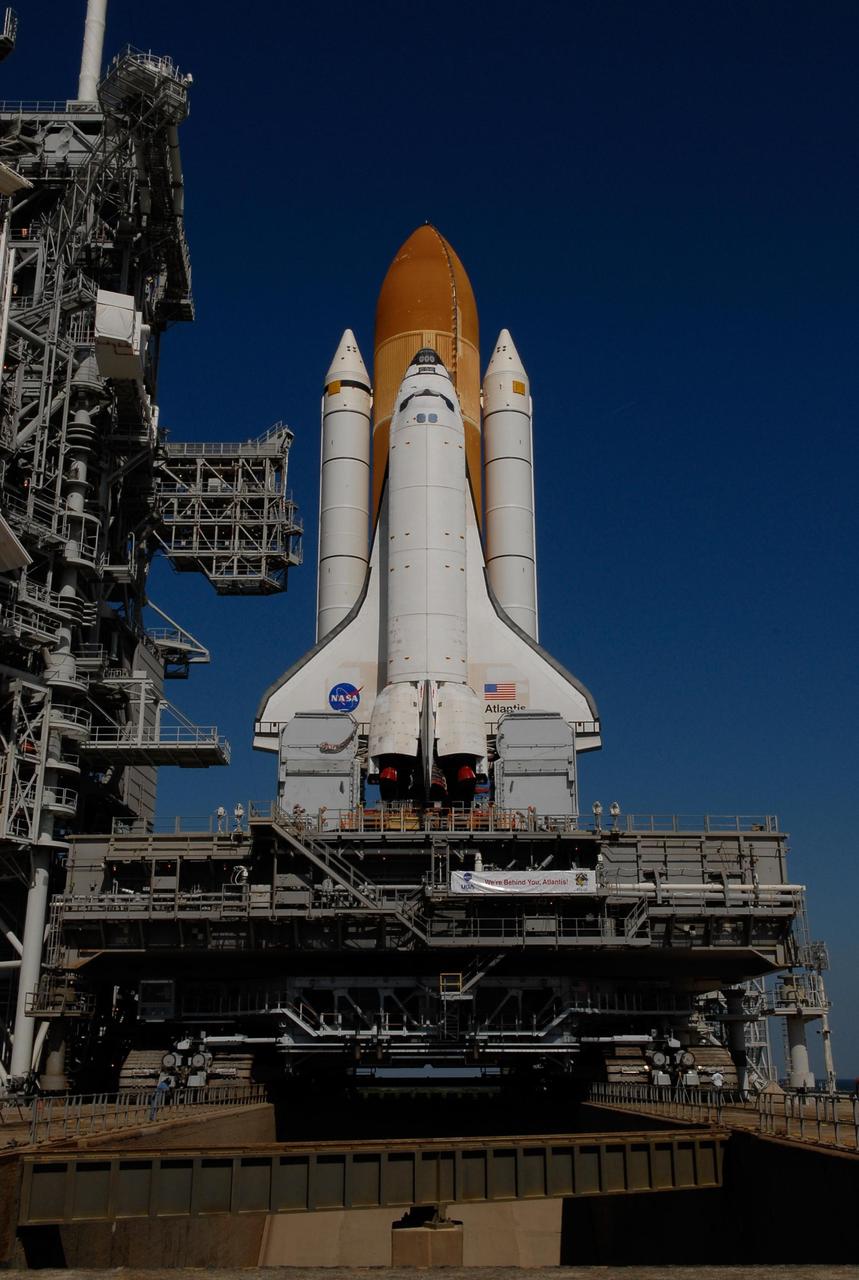

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis and the mobile launch platform on which it is secured are positioned over the flame trench at Launch Pad 39A. First motion out of the Vehicle Assembly Building was at 4:43 a.m. EST, and the shuttle was hard down on the pad at 11:51 a.m. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
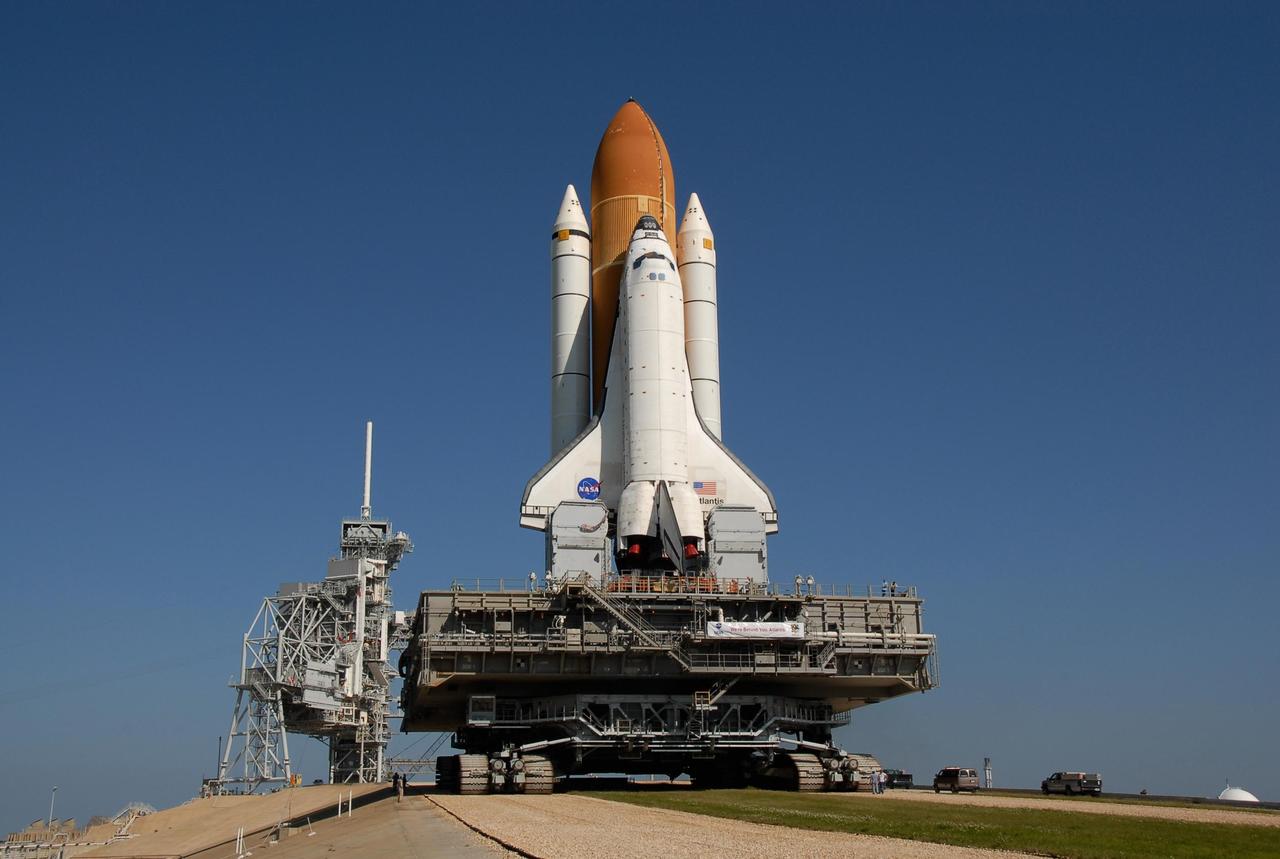

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis, secured atop a mobile launch platform, is nearing the top of the five percent grade to the top of the hardstand on its final approach to Launch Pad 39A. The rotating service structure, adjoined to the fixed service structure at left, has been rolled back in preparation for the shuttle's arrival. First motion out of the Vehicle Assembly Building was at 4:43 a.m. EST, and the shuttle was hard down on the pad at 11:51 a.m. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, members of the space shuttle Atlantis STS-122 crew view the Columbus module during terminal countdown demonstration test, or TCDT, activities. Columbus was installed in the orbiter's payload bay on Nov. 11. From left, in clean room attire, are former astronaut Jerry Ross, chief of the Vehicle Integration Test Office at NASA Johnson Space Center, Pilot Alan Poindexter and Commander Steve Frick. The TCDT provides astronauts and ground crews with equipment familiarization, emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. On mission STS-122, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest single contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Launch is targeted for Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- As the sun rises, workers accompany space shuttle Atlantis as it rolls from Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1 on a transporter to the Vehicle Assembly Building, at left. Rollover from its processing bay began at 7:05 a.m. EDT. Atlantis arrived in the VAB's transfer aisle at 8:03 a.m. In the VAB, the shuttle will be lifted and mated with the external tank and solid rocket boosters designated for mission STS-122, already secured atop a mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
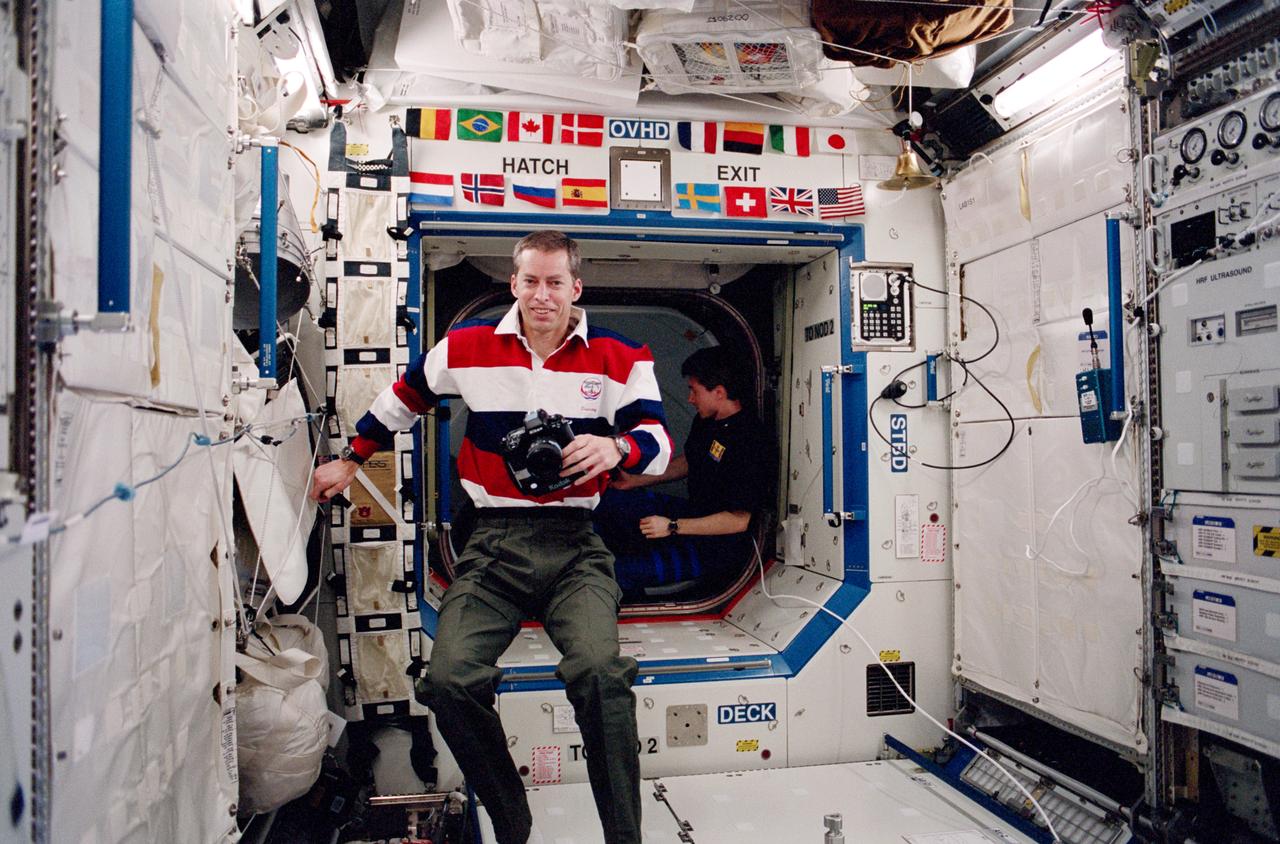

In this Space Shuttle STS-102 mission image, the Payload Equipment Restraint System H-Strap is shown at the left side of the U.S. Laboratory hatch and behind Astronaut James D. Weatherbee, mission specialist. PERS is an integrated modular system of components designed to assist the crew of the International Space Station (ISS) in restraining and carrying necessary payload equipment and tools in a microgravity environment. The Operations Development Group, Flight Projects Directorate at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), while providing operation support to the ISS Materials Science Research Facility (MSRF), recognized the need for an on-orbit restraint system to facilitate control of lose objects, payloads, and tools. The PERS is the offspring of that need and it helps the ISS crew manage tools and rack components that would otherwise float away in the near-zero gravity environment aboard the Space Station. The system combines Kevlar straps, mesh pockets, Velcro and a variety of cornecting devices into a portable, adjustable system. The system includes the Single Strap, the H-Strap, the Belly Pack, the Laptop Restraint Belt, and the Tool Page Case. The Single Strap and the H-Strap were flown on this mission. The PERS concept was developed by industrial design students at Auburn University and the MSFC Flight Projects Directorate.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Atlantis is fitted with a sling to raise it off its transporter into a vertical position. Atlantis will be lifted into high bay 3 and mated with the external tank and solid rocket boosters designated for mission STS-122, already secured atop a mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, members of the space shuttle Atlantis STS-122 crew view the Columbus module during terminal countdown demonstration test, or TCDT, activities. Columbus was installed in the orbiter's payload bay on Nov. 11. From left, in clean room attire, are Pilot Alan Poindexter and Mission Specialists Stanley Love, Hans Schlegel of the European Space Agency and Rex Walheim. The TCDT provides astronauts and ground crews with equipment familiarization, emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. On mission STS-122, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest single contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Launch is targeted for Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space shuttle Atlantis rolls out of Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1 on a transporter just before sunrise for the short trip to the Vehicle Assembly Building. Rollover from its processing bay began at 7:05 a.m. EDT. Atlantis arrived in the VAB's transfer aisle at 8:03 a.m. In the VAB, the shuttle will be lifted and mated with the external tank and solid rocket boosters designated for mission STS-122, already secured atop a mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, members of the space shuttle Atlantis STS-122 crew pose for a photo in front of the Columbus module during terminal countdown demonstration test, or TCDT, activities. Columbus was installed in the orbiter's payload bay on Nov. 11. From left, in clean room attire, are Commander Steve Frick; Mission Specialist Leland Melvin; former astronaut Jerry Ross, kneeling, chief of the Vehicle Integration Test Office at NASA Johnson Space Center; Pilot Alan Poindexter; and Mission Specialist Stanley Love. The TCDT provides astronauts and ground crews with equipment familiarization, emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. On mission STS-122, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest single contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Launch is targeted for Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, members of the space shuttle Atlantis STS-122 crew get a close look at the Columbus module during terminal countdown demonstration test, or TCDT, activities. Columbus was installed in the orbiter's payload bay on Nov. 11. From left, in clean room attire, are Mission Specialists Stanley Love, Hans Schlegel of the European Space Agency and Rex Walheim. The TCDT provides astronauts and ground crews with equipment familiarization, emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. On mission STS-122, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest single contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Launch is targeted for Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Atlantis is raised off its transporter. After raised to a vertical position, Atlantis will be lifted into high bay 3 and mated with the external tank and solid rocket boosters designated for mission STS-122, already secured atop a mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- As the sun rises, workers accompany space shuttle Atlantis as it rolls out of Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1 on a transporter. The orbiter is headed for the Vehicle Assembly Building. Rollover from its processing bay began at 7:05 a.m. EDT. Atlantis arrived in the VAB's transfer aisle at 8:03 a.m. In the VAB, the shuttle will be lifted and mated with the external tank and solid rocket boosters designated for mission STS-122, already secured atop a mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
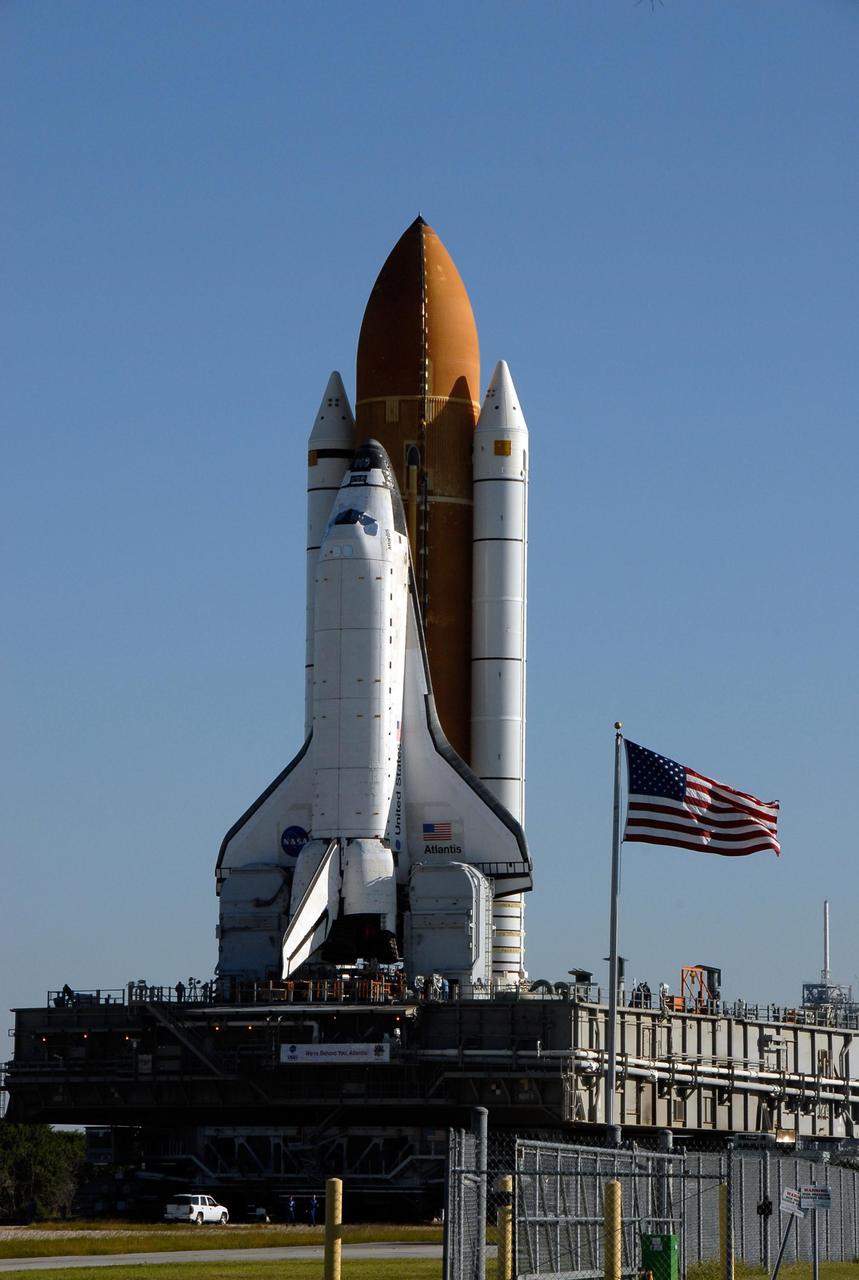

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis, secured atop a mobile launch platform, passes by a United States flag on its way to Launch Pad 39A on a breezy Florida morning. The crawler transporter has a top speed of one mile per hour while it is moving the space shuttle. First motion out of the Vehicle Assembly Building was at 4:43 a.m. EST. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis, secured atop a mobile launch platform, makes its way to Launch Pad 39A on a breezy Florida morning. The crawler transporter has a top speed of one mile per hour while it is moving the space shuttle. First motion out of the Vehicle Assembly Building was at 4:43 a.m. EST. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
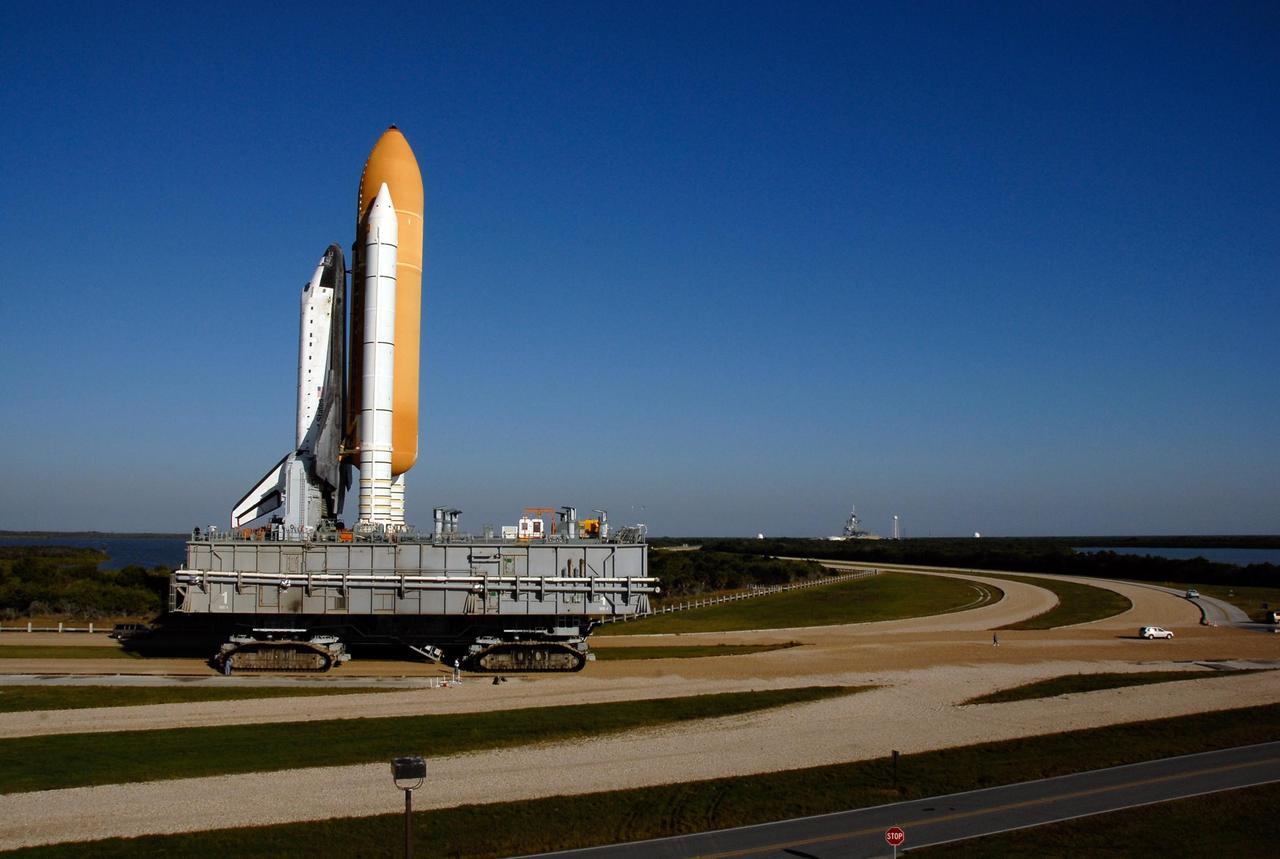

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis, secured atop a mobile launch platform, rounds a curve on the crawlerway in Launch Complex 39 on its way to Pad A. The crawler transporter has a top speed of one mile per hour while it is moving the space shuttle. First motion out of the Vehicle Assembly Building was at 4:43 a.m. EST. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
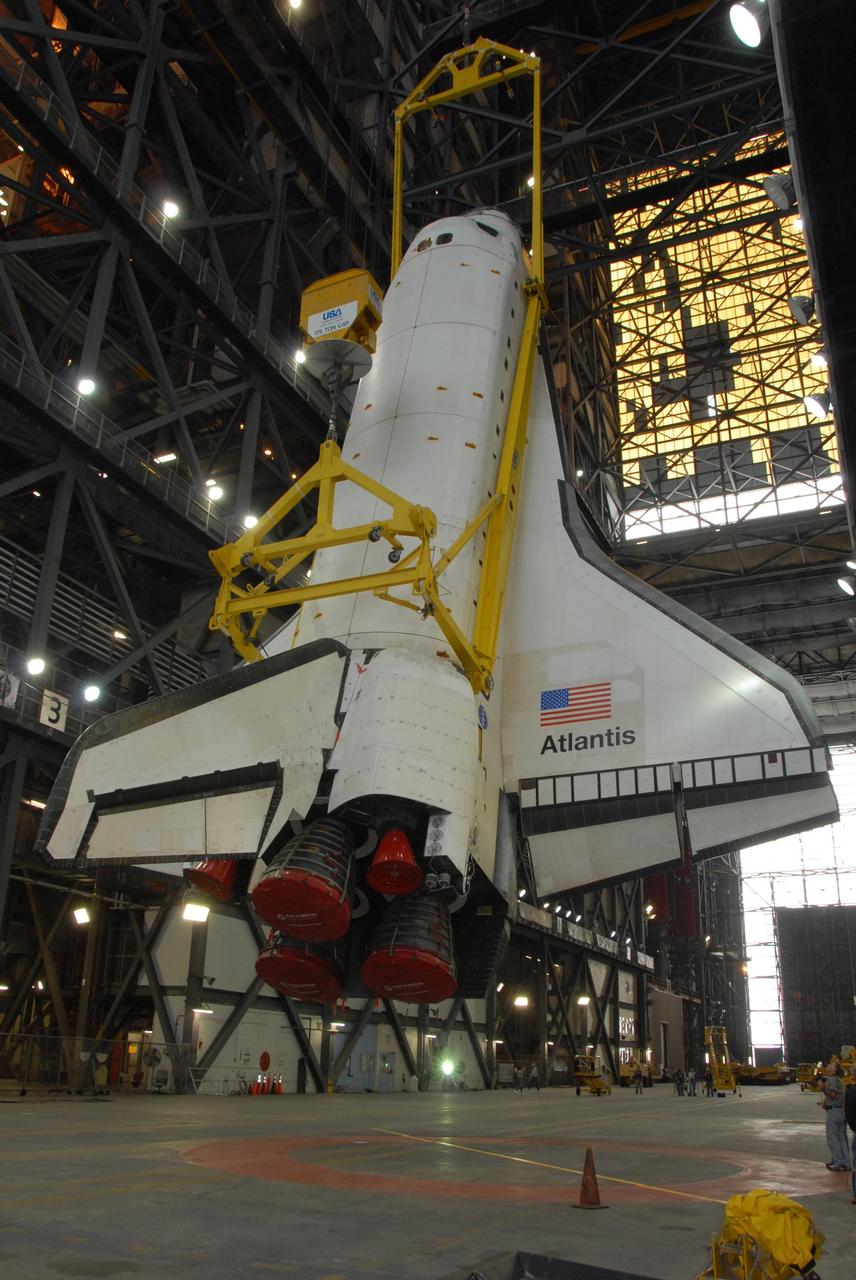

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Atlantis is raised to a nearly vertical position. Atlantis will next be lifted into high bay 3 and mated with the external tank and solid rocket boosters designated for mission STS-122, already secured atop a mobile launcher platform. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Mission STS-122 is targeted for launch on Dec. 6. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Two symbols of American pride, the Space Shuttle Atlantis and a United States flag, appear side by side as Atlantis makes its way to Launch Pad 39A on a breezy Florida morning. The crawler transporter has a top speed of one mile per hour while it is moving the space shuttle. First motion out of the Vehicle Assembly Building was at 4:43 a.m. EST. Rollout is a milestone for Atlantis' launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-122, targeted for Dec. 6. On this mission, Atlantis will deliver the Columbus module to the International Space Station. The European Space Agency's largest contribution to the station, Columbus is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. The module is approximately 23 feet long and 15 feet wide, allowing it to hold 10 large racks of experiments. The laboratory will expand the research facilities aboard the station, providing crew members and scientists from around the world the ability to conduct a variety of experiments in the physical, materials and life sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett