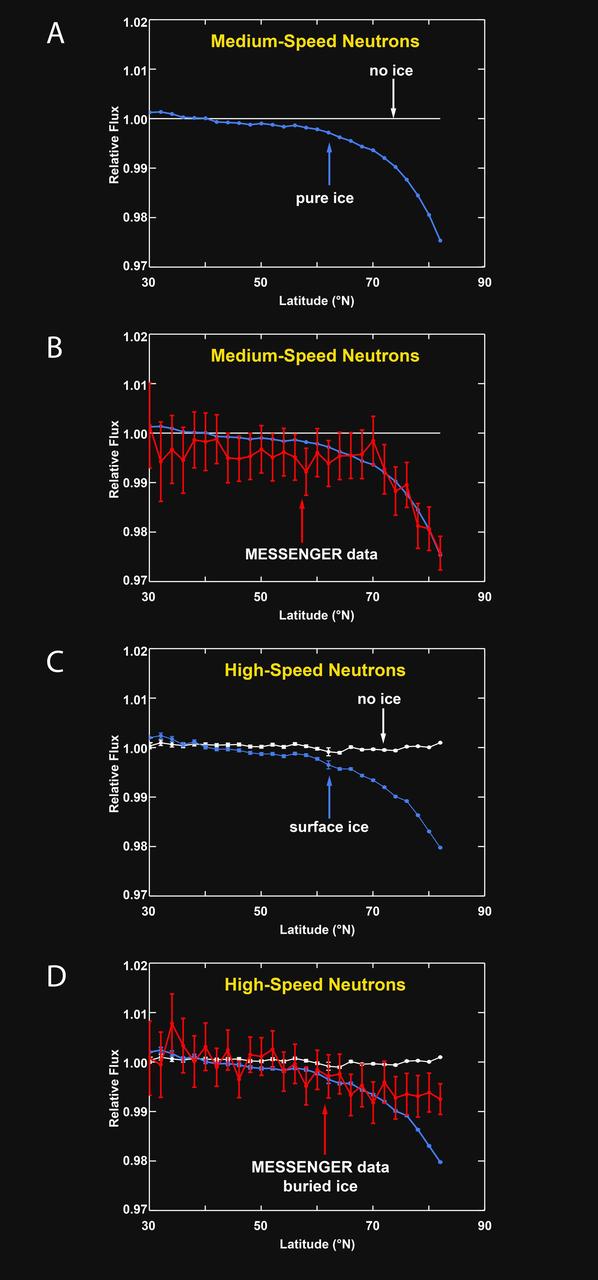
Neutron Spectrometer Measurements
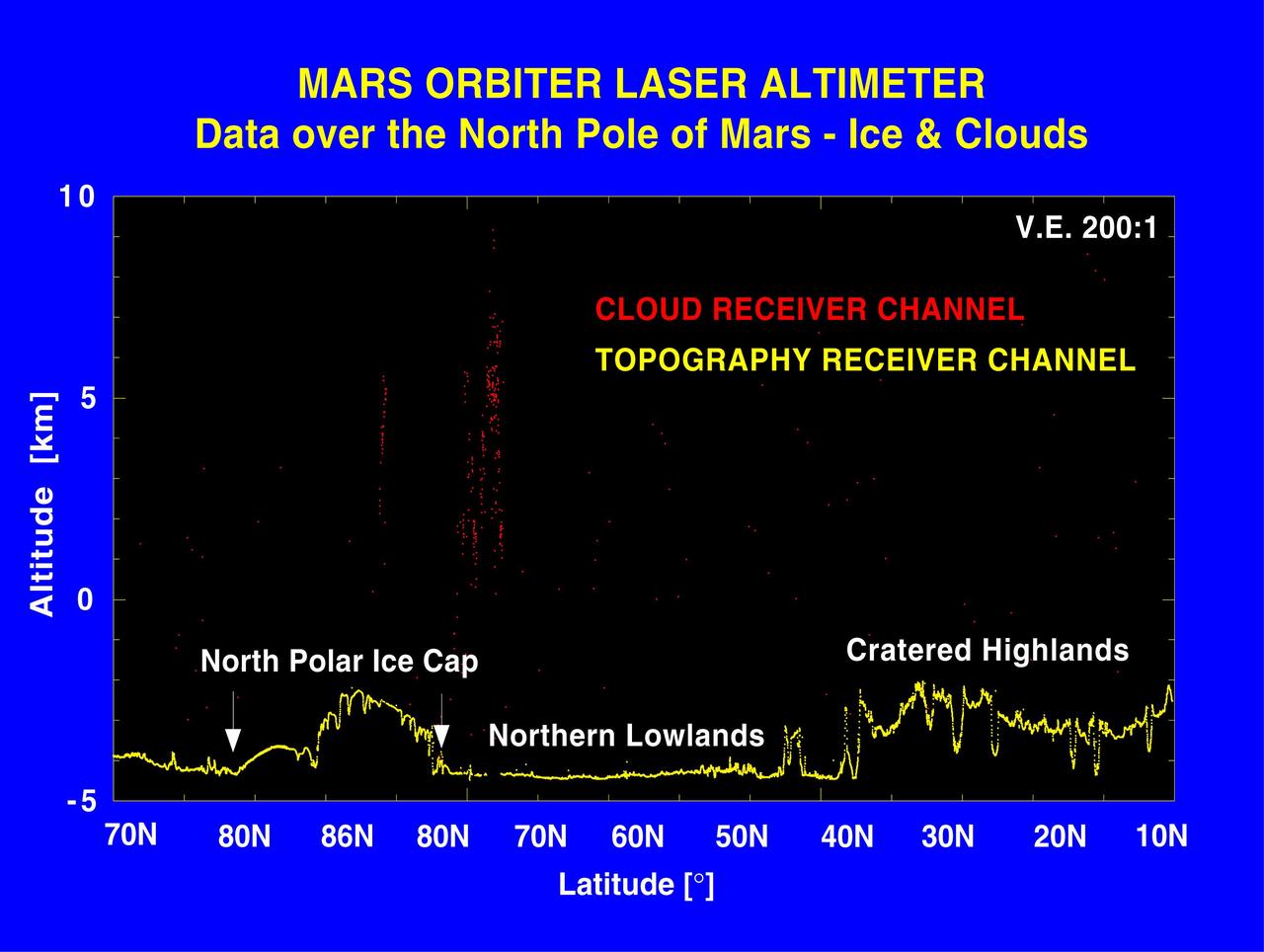
Elevation Measurement Profile of Mars

A NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission shirt is seen drying in the mid-day sun outside the Sun Pearl Hotel where many of the NASA GPM team are staying, Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
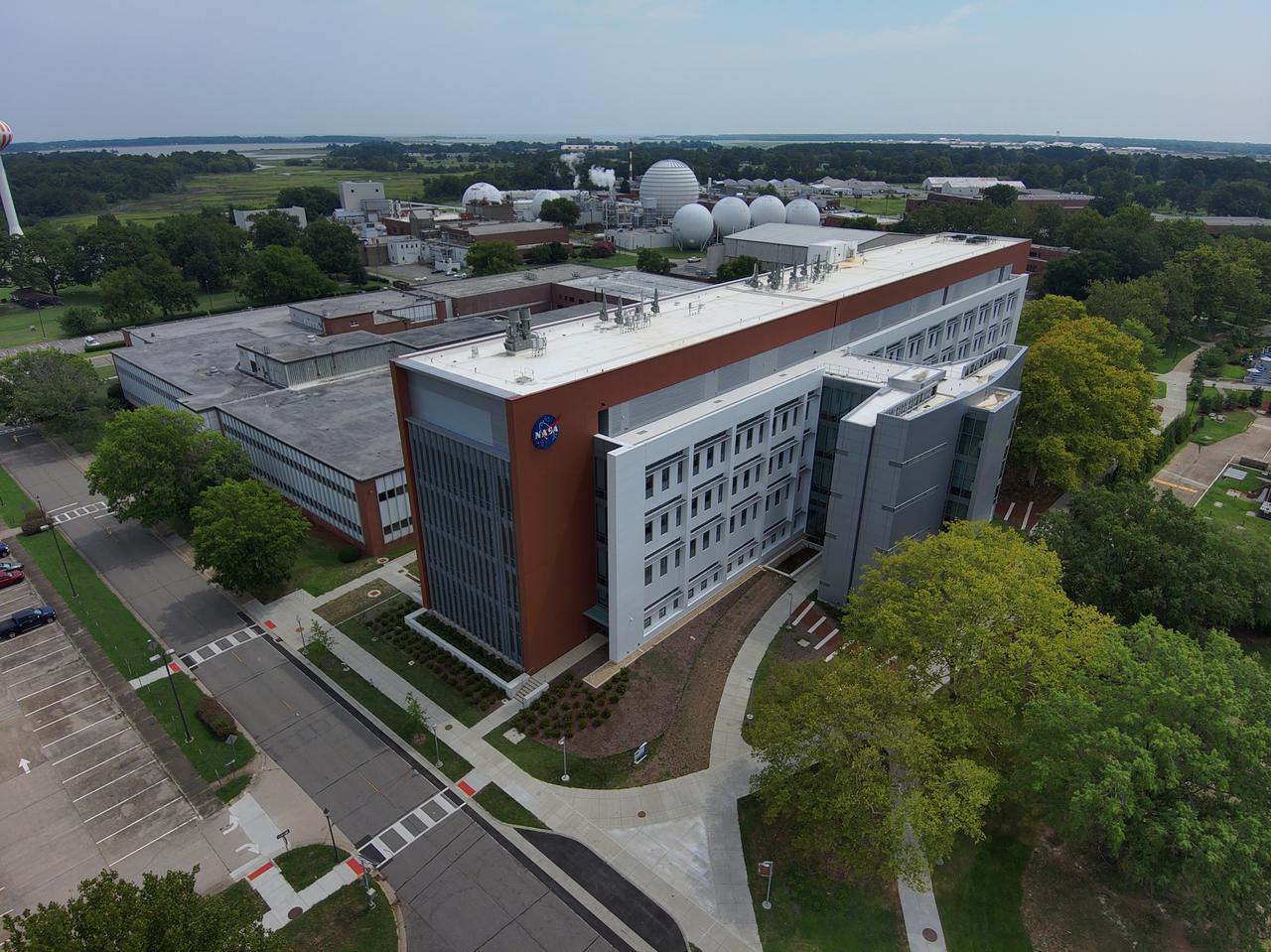

Langley’s newly built Measurement Systems Laboratory will serve as the primary research and development location for six branches within the Research and Engineering Directorates. The ribbon cutting will take place in April 2022.
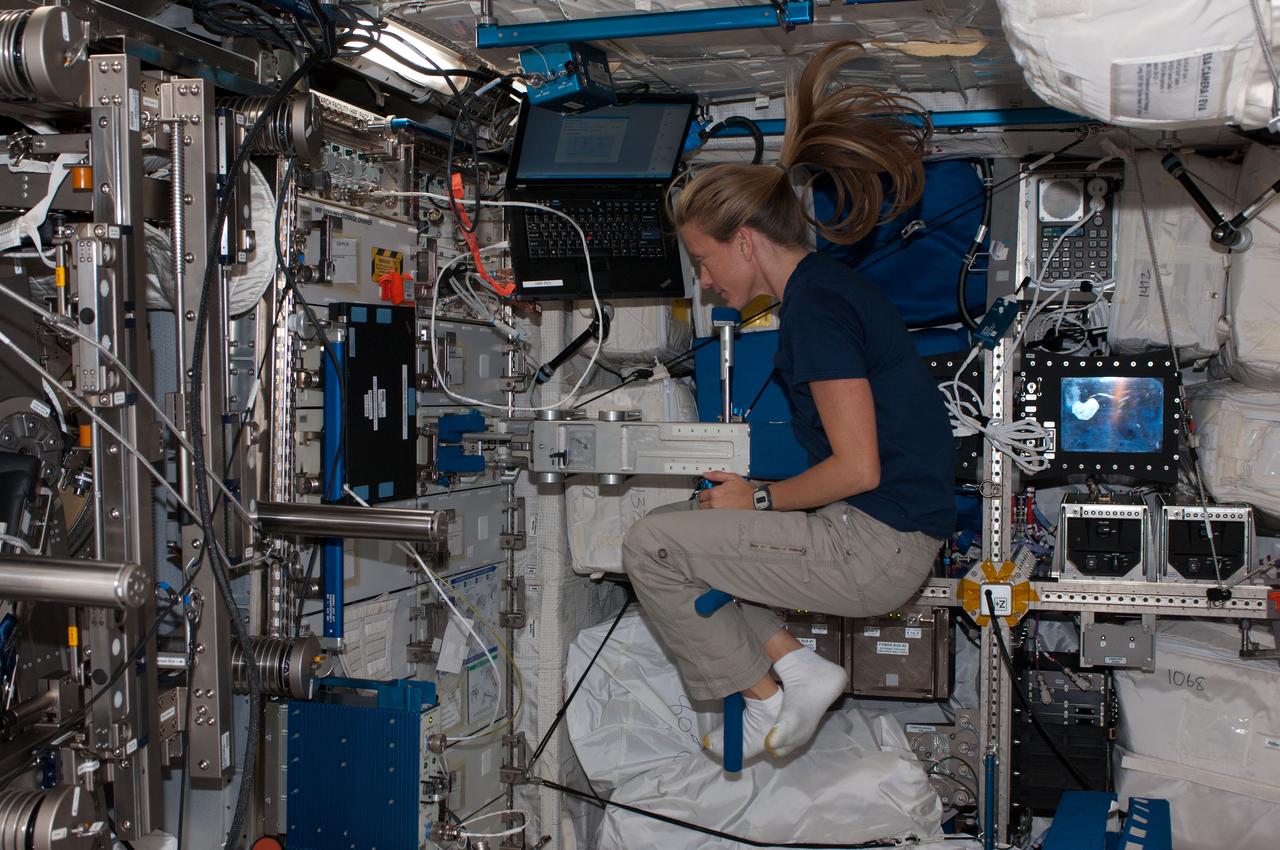

Astronaut Karen Nyberg,Expedition 36 flight engineer,performs a Space Linear Acceleration Mass Measurement Device (SLAMMD) Body Mass Measurement test in the U.S. Laboratory.

Ultrasonic Measurement System. Ultrasonic measurement system will enable simultaneous measurement of temperature, velocity and density fields through a grid of ultrasonic sensors. This method incorporates a theoretical approach and machine learning techniques to develop a physics-informed data-driven calibration and operation workflow. This allows at least ten times faster data processing times as well as potential capability of transient measurements and solid particle detection. The system can also be utilized for health monitoring. This measurement technique is in line with the “air-breathing propulsion” core competency of GRC. However it can also enables next generation space data processing with higher performance computing capable of operating in harsh deep space environments.
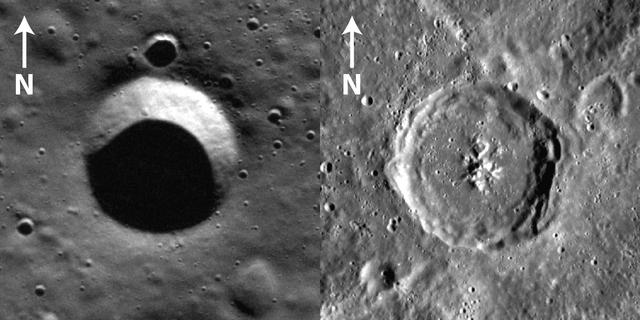
Using Shadows to Measure Crater Depths
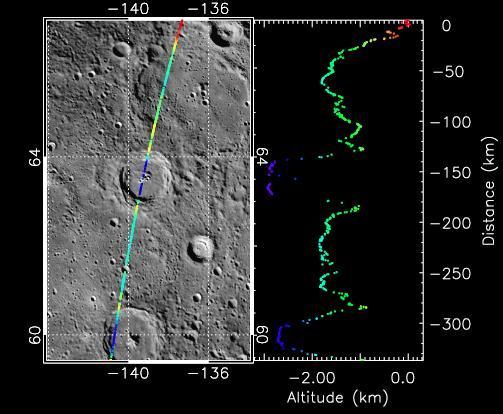
Taking the Measure of Impact Craters on Mercury
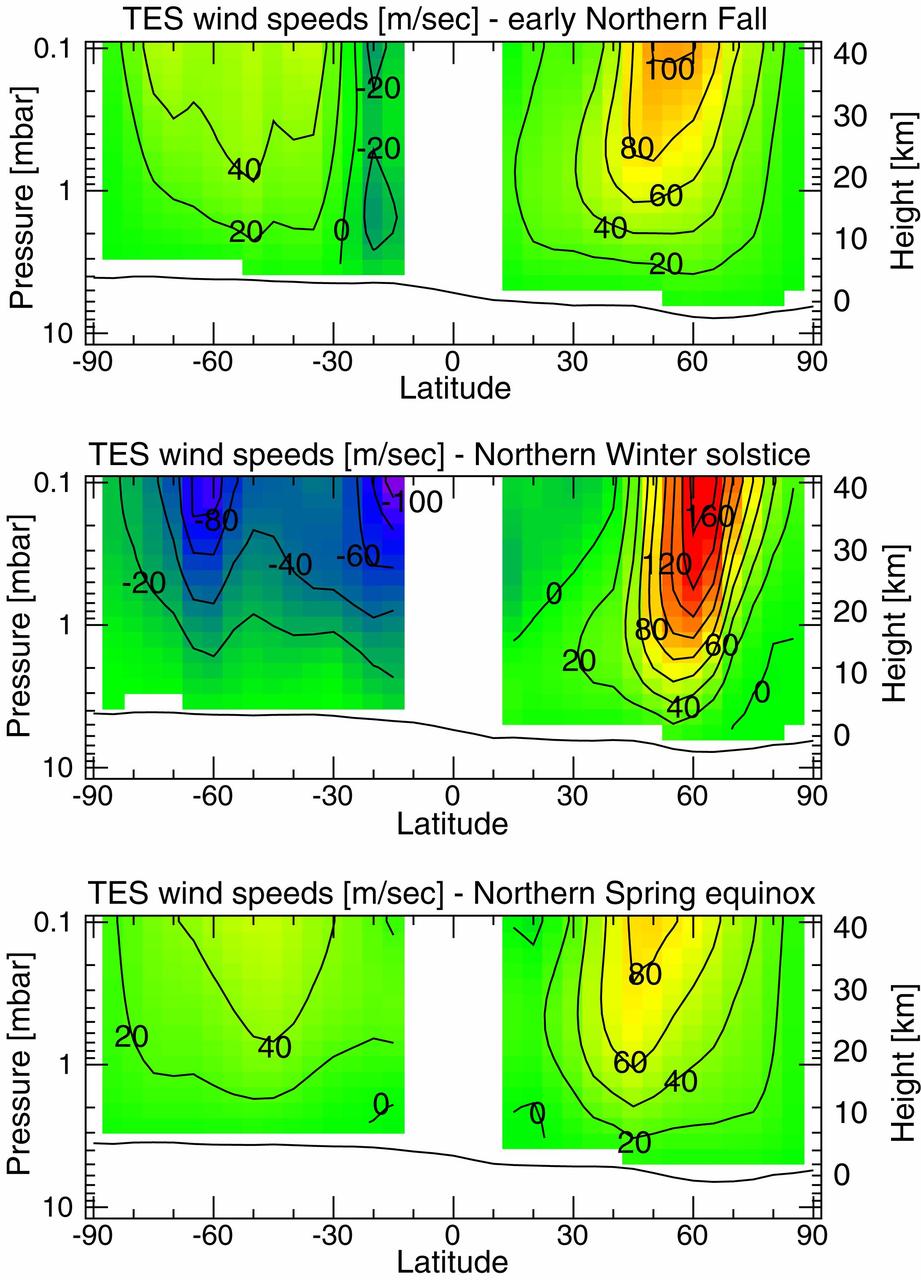
Measurements of the Martian Winds for Three Seasons
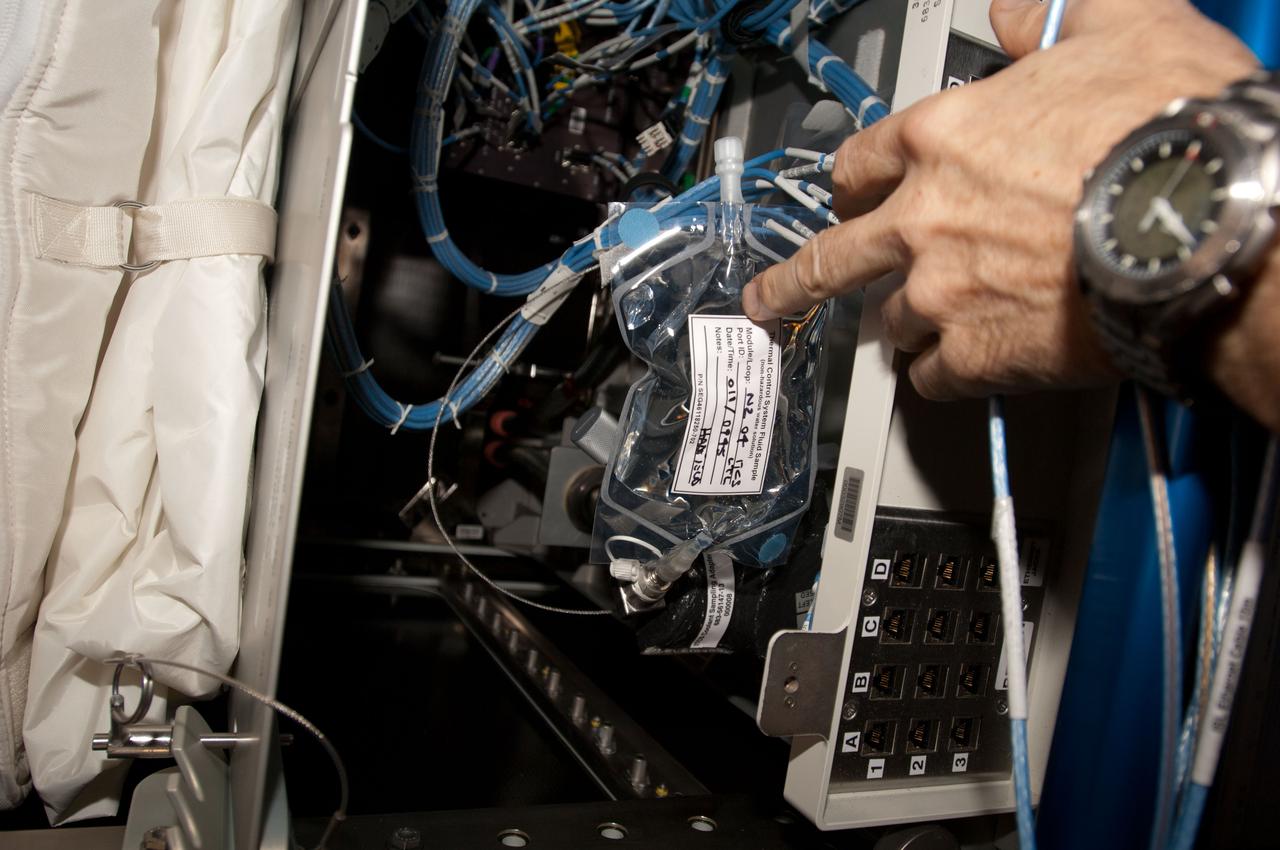
View during Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) - Measuring valve parameters in the Node 3. Photo was taken during Expedition 34.

A sign guides travelers to the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for Feb. 28, 2014 from the space center. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
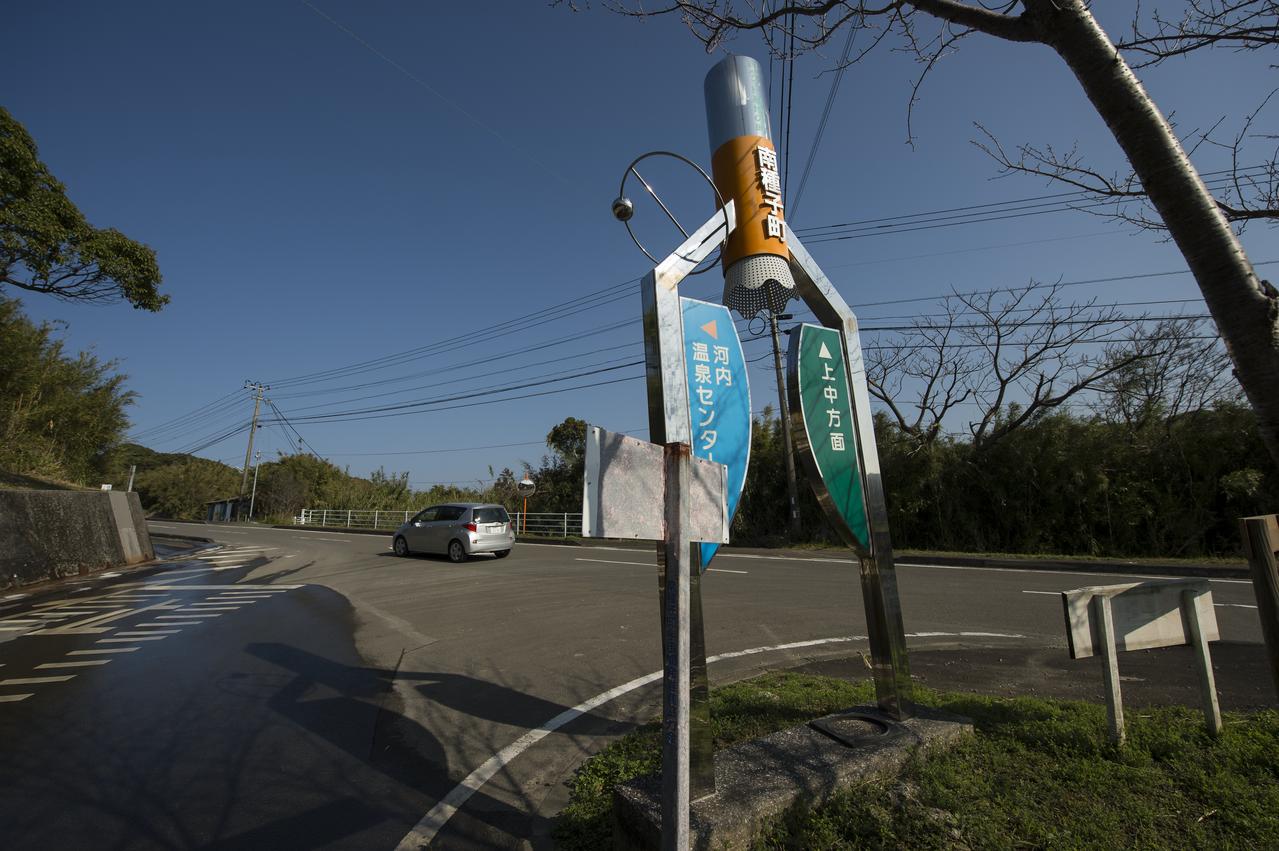

Space themed signs are seen along the roads to and from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for Feb. 28, 2014 from the space center. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
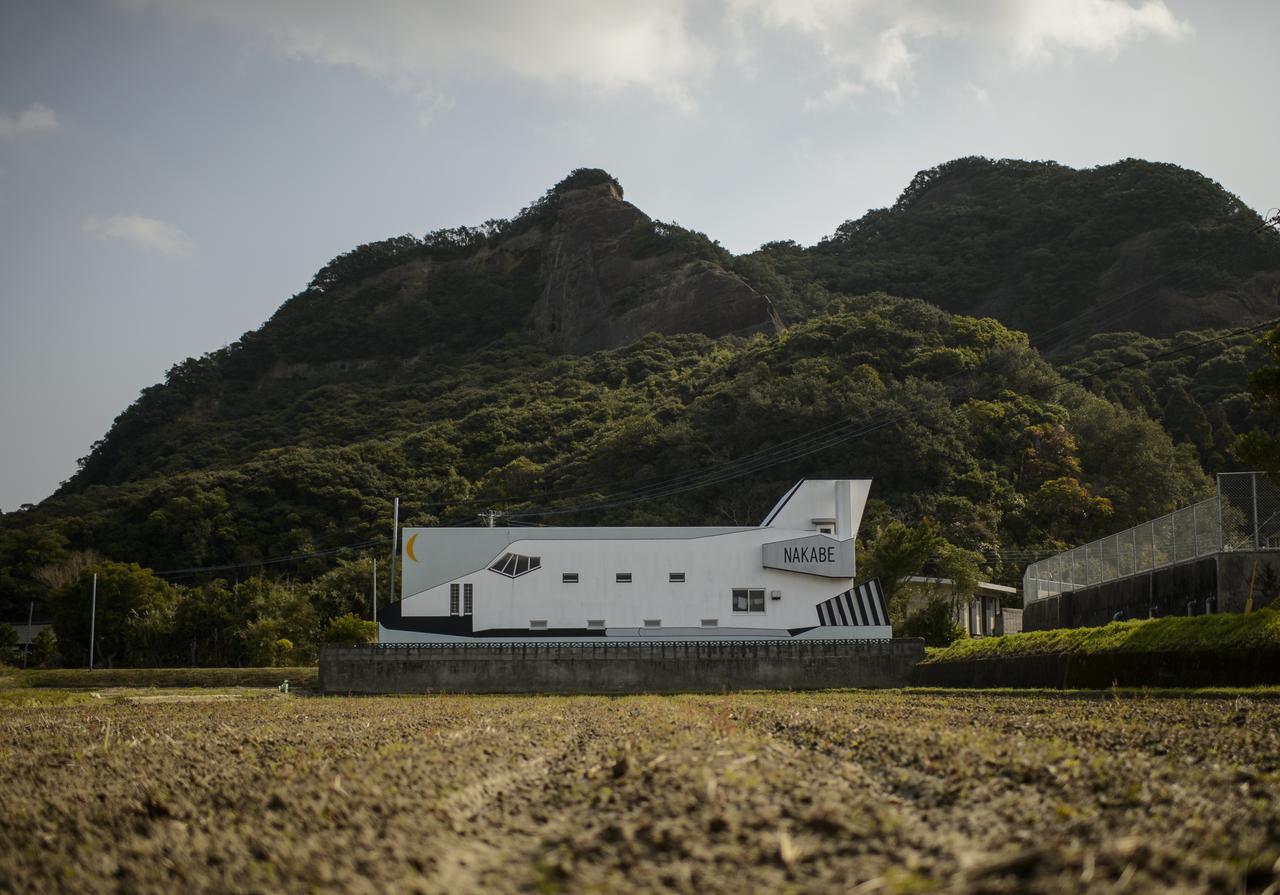

A building designed to look like a space shuttle is seen a few kilometers outside of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
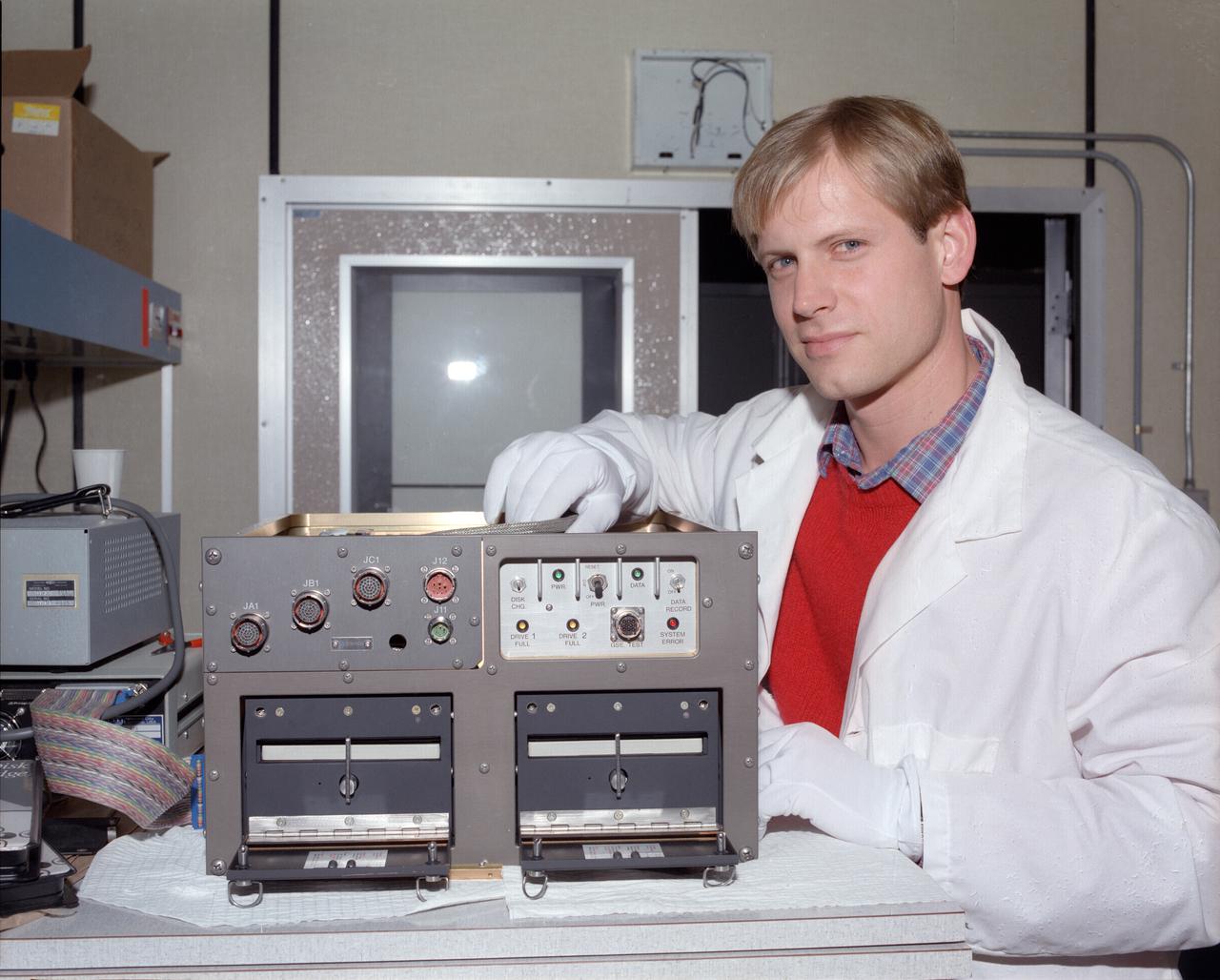

Space Acceleration Measurement System, SAMS Flight Hardware, Unit A
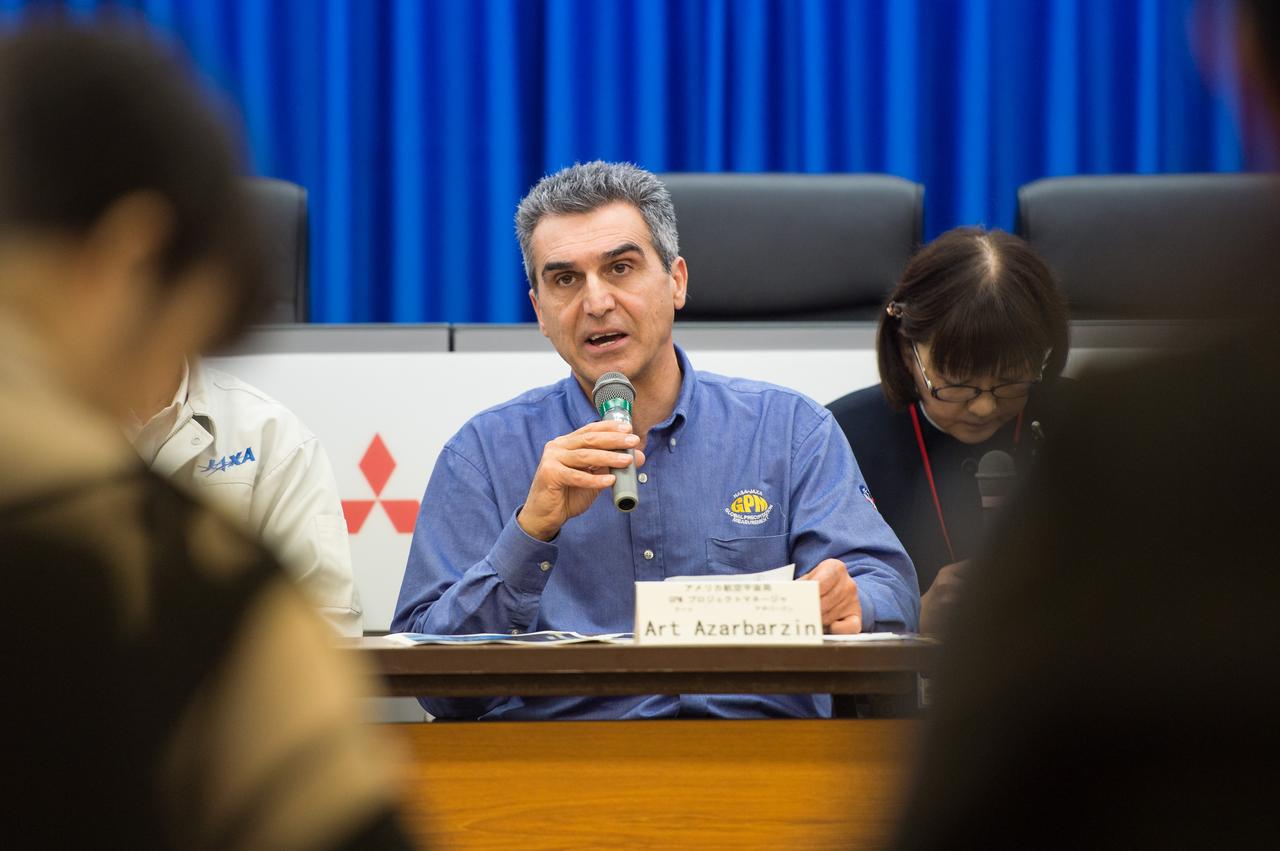

Art Azarbarzin, NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) project manager talks during a technical briefing for the launch of the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory aboard an H-IIA rocket, Wednesday, Feb. 26, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center, Japan. Launch is scheduled for early in the morning of Feb. 28 Japan time. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
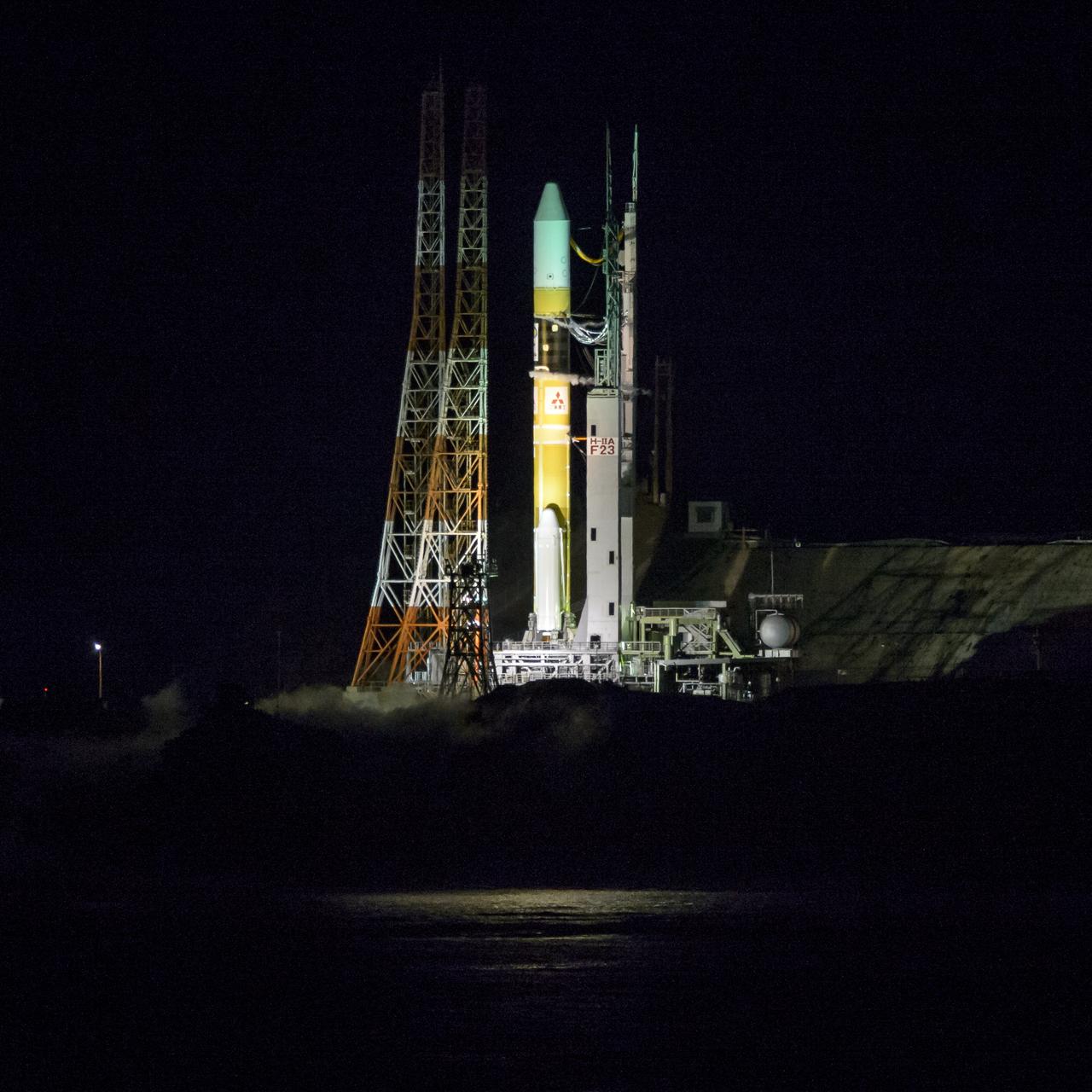

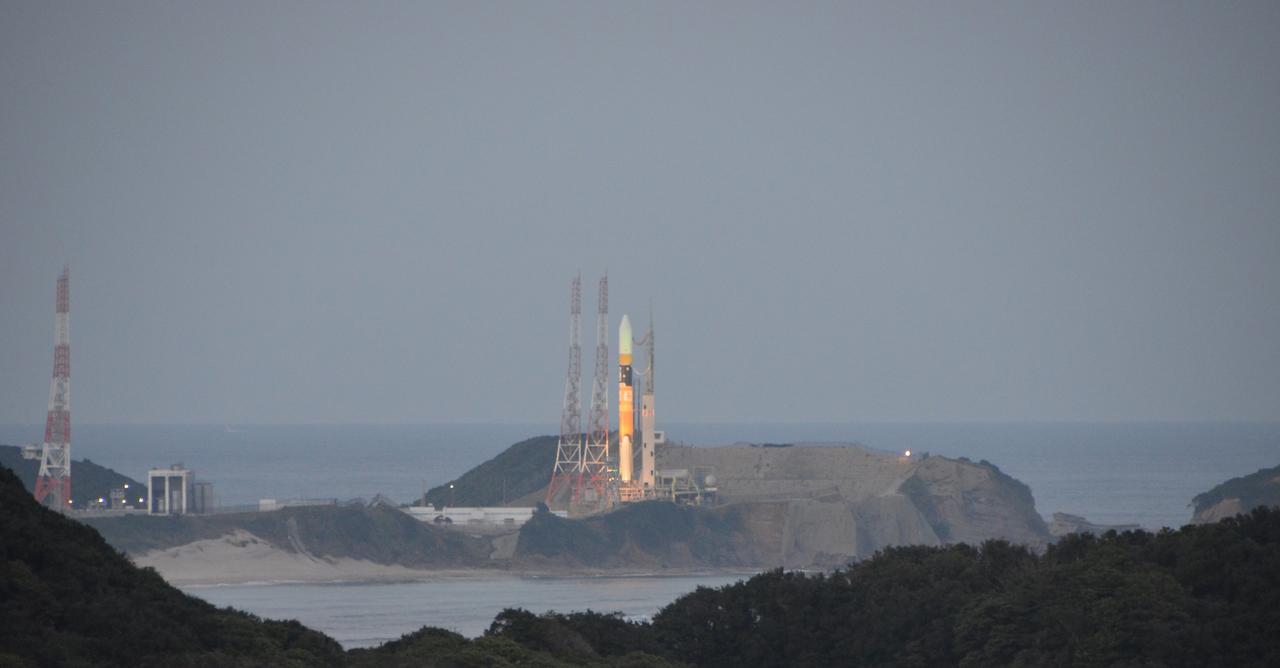
A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, is seen on launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Friday, Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
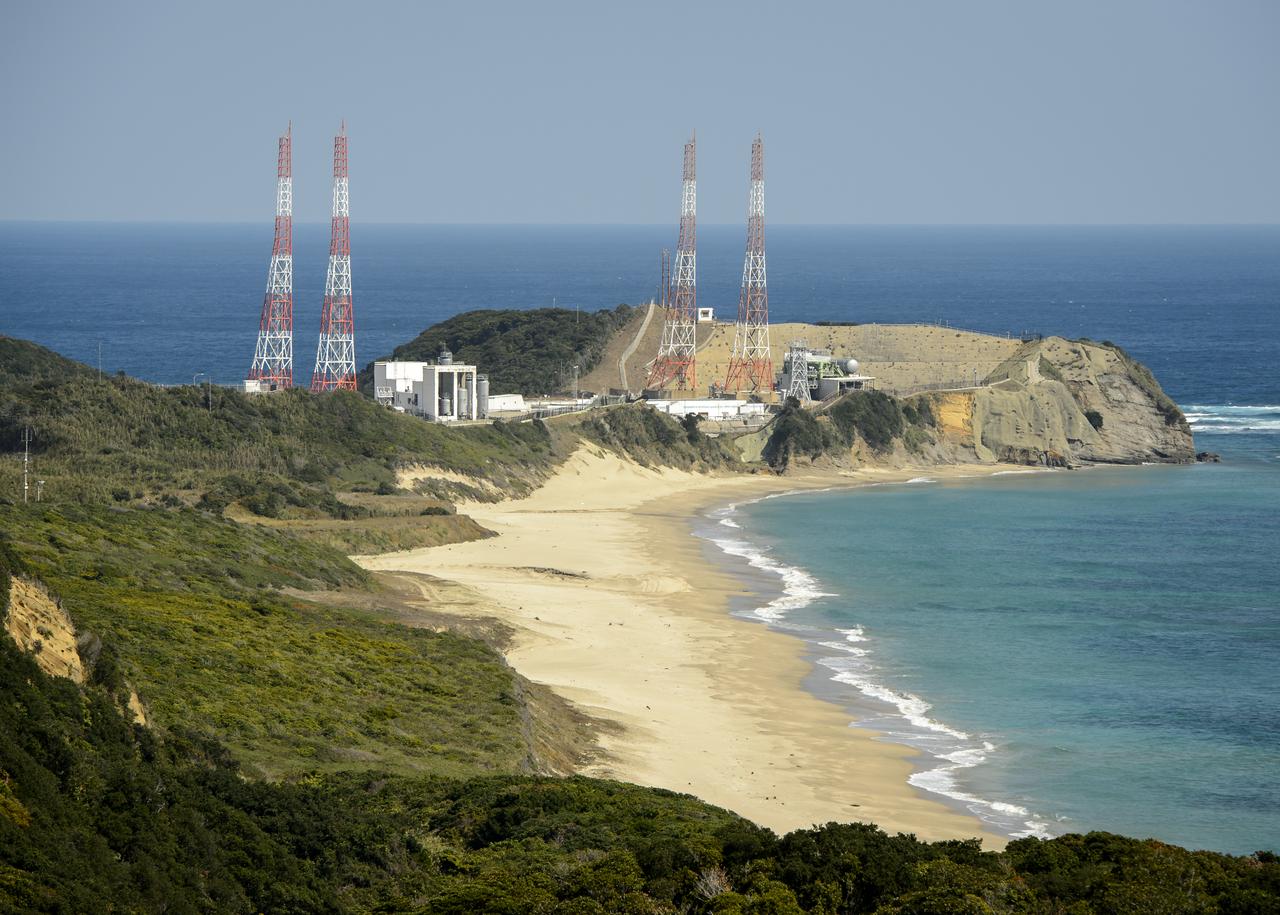

The launch pads at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center are seen a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Topiary shaped into the logo of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) is seen at the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
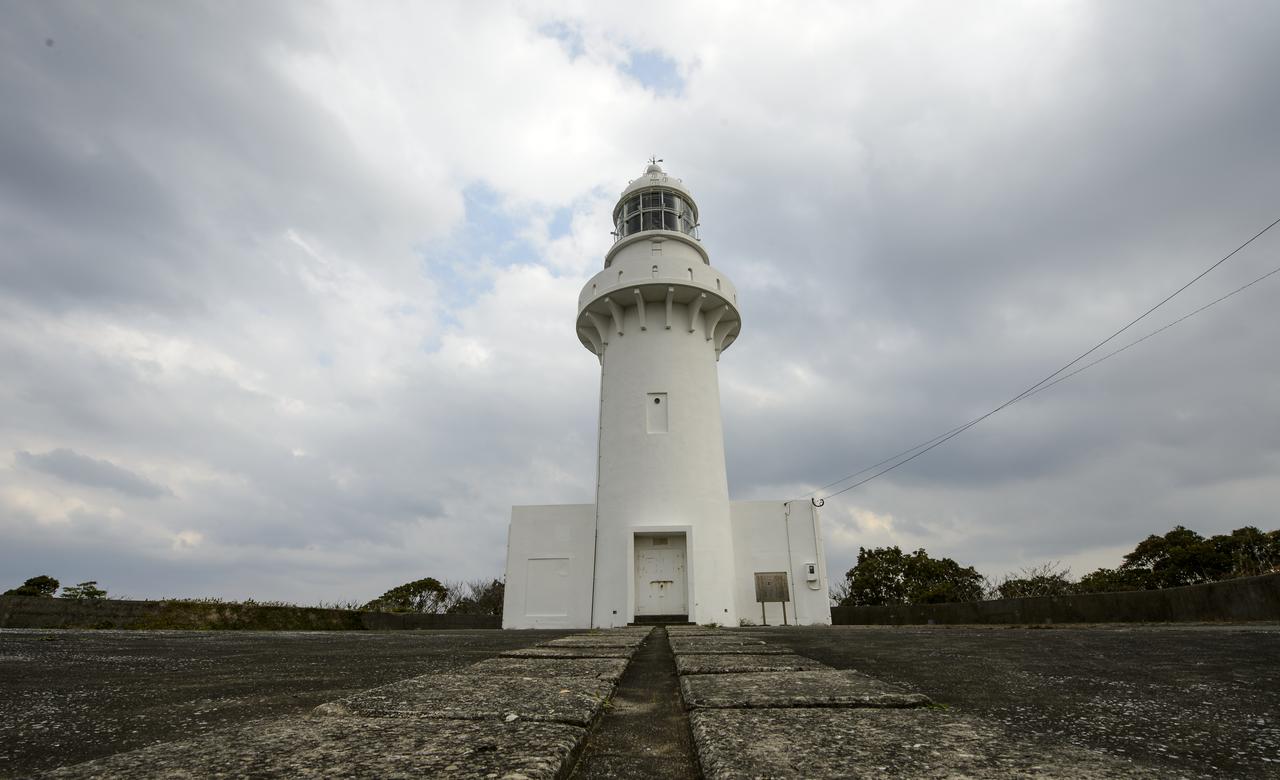

The Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) lighthouse is seen on Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
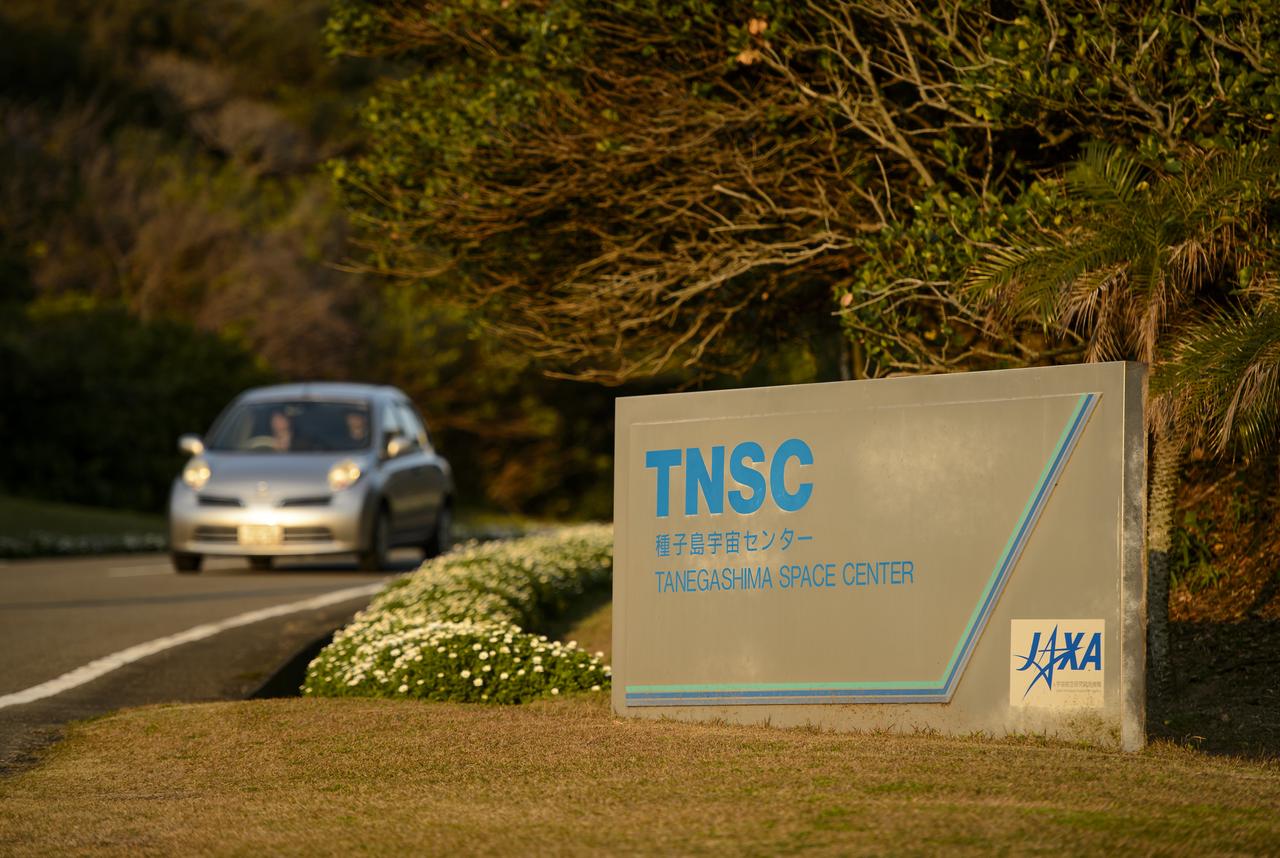

The entrance sign to the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) is seen a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
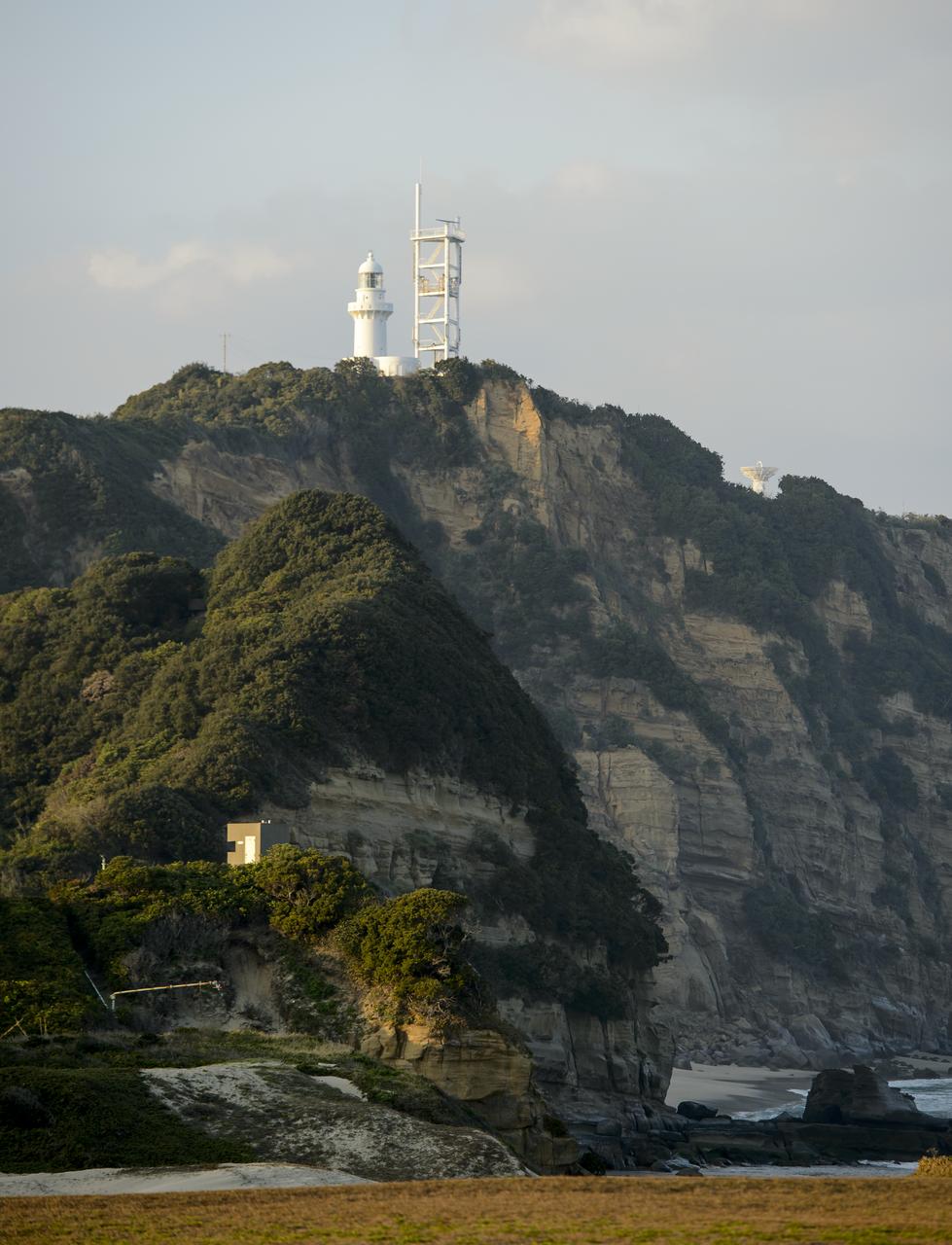

A light house and weather station is seen at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
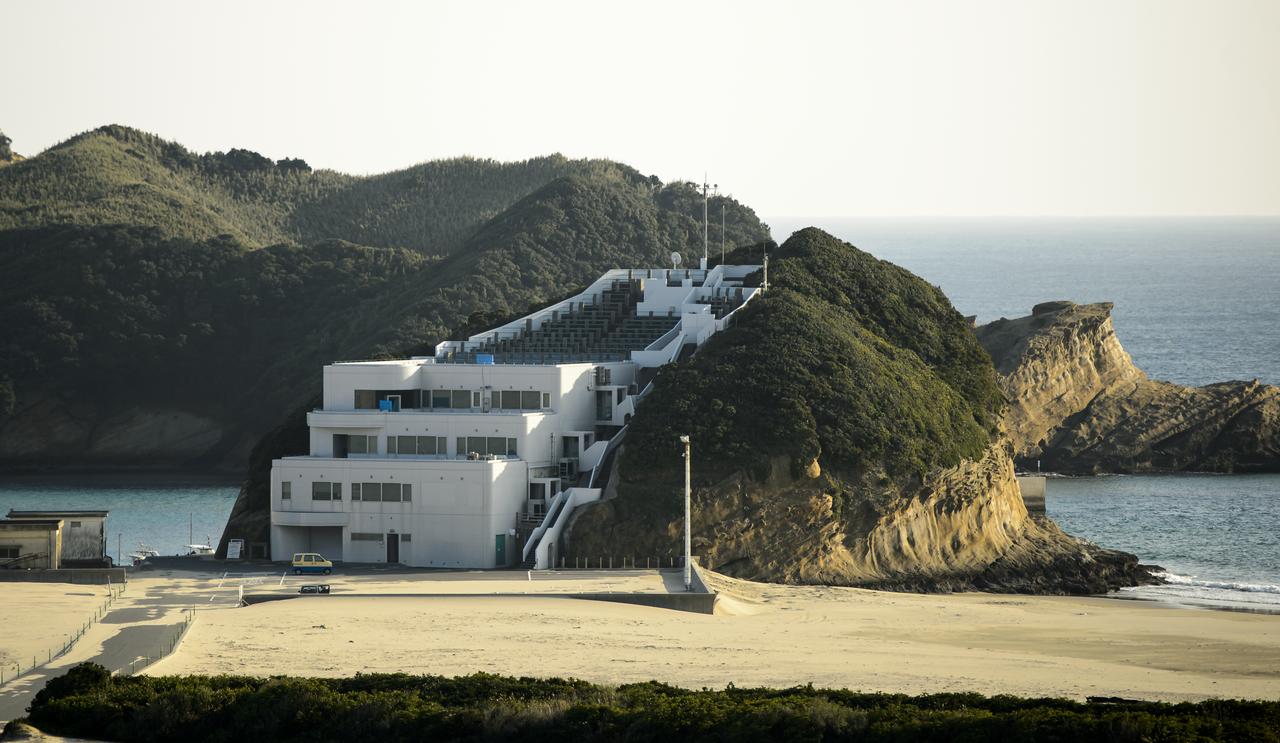

The Takesaki Observation Center is seen at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The sun sets just outside the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
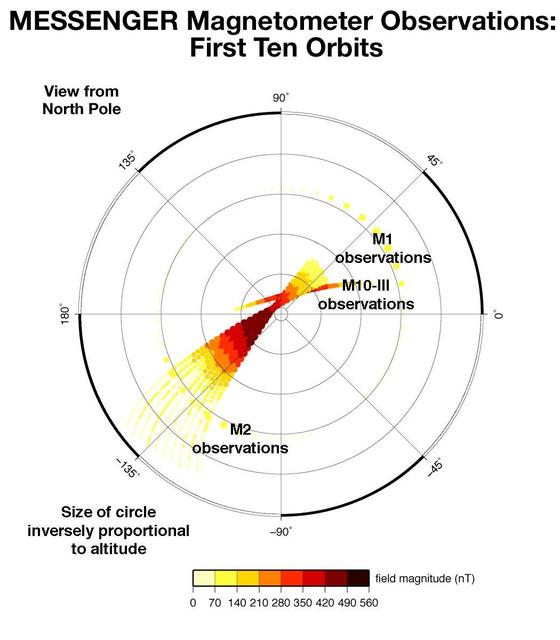
First Magnetometer Measurements from Mercury Orbit

Martian Surface after Phoenix Conductivity Measurements
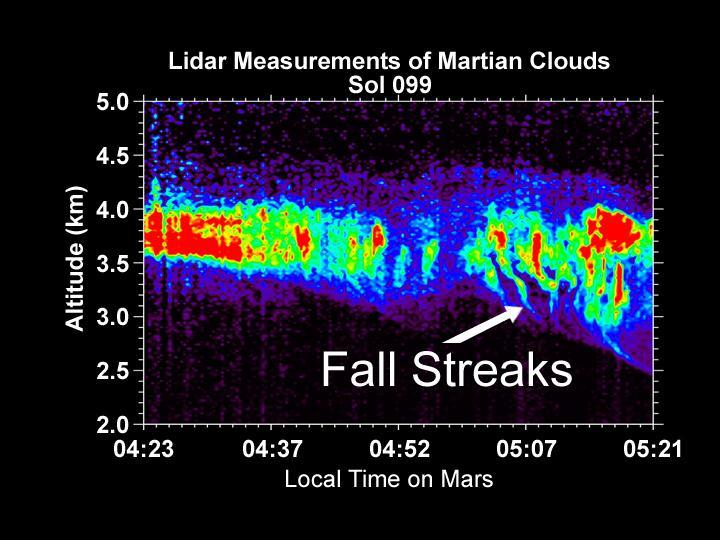
Lidar Measurements of Snow Falling from Martian Clouds
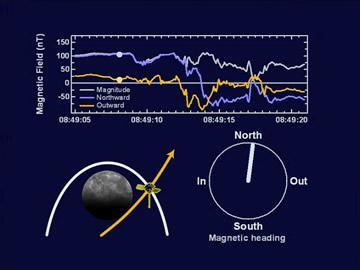
A Movie of Magnetometer Measurements from the Second Mercury Flyby
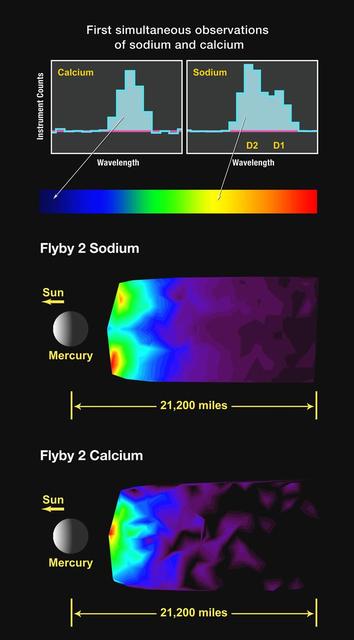
First Simultaneous Measurements of Sodium and Calcium in Mercury Exosphere
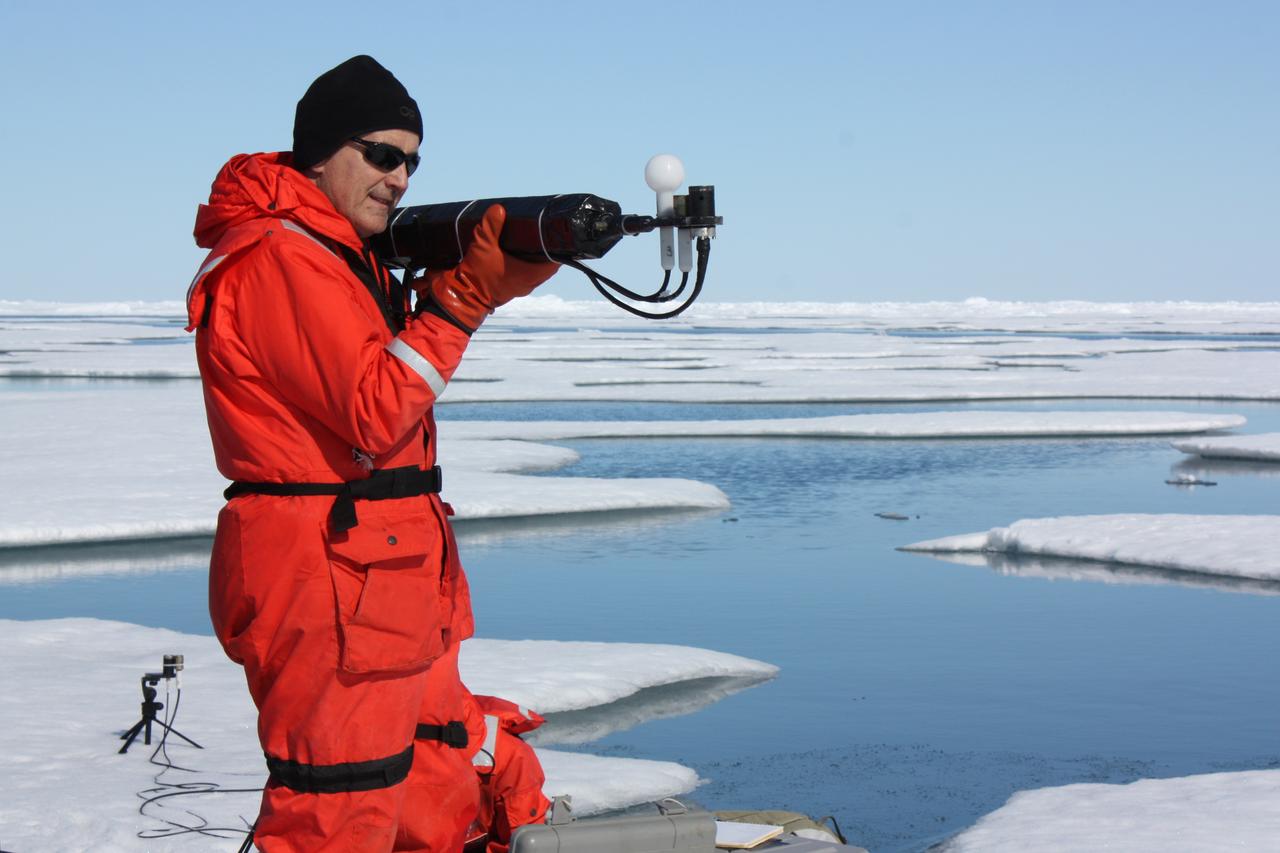

On July 13, 2011, Don Perovich, of Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, measured the light that drives photosynthesis at the sixth sea ice station of the 2011 ICESCAPE mission. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

A rocket is seen at the entrance to the visitor's center of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Tourist photograph themselves in astronaut space suites next to a cardboard cutout of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Astronaut Akihiko Hoshide at the visitor's center of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
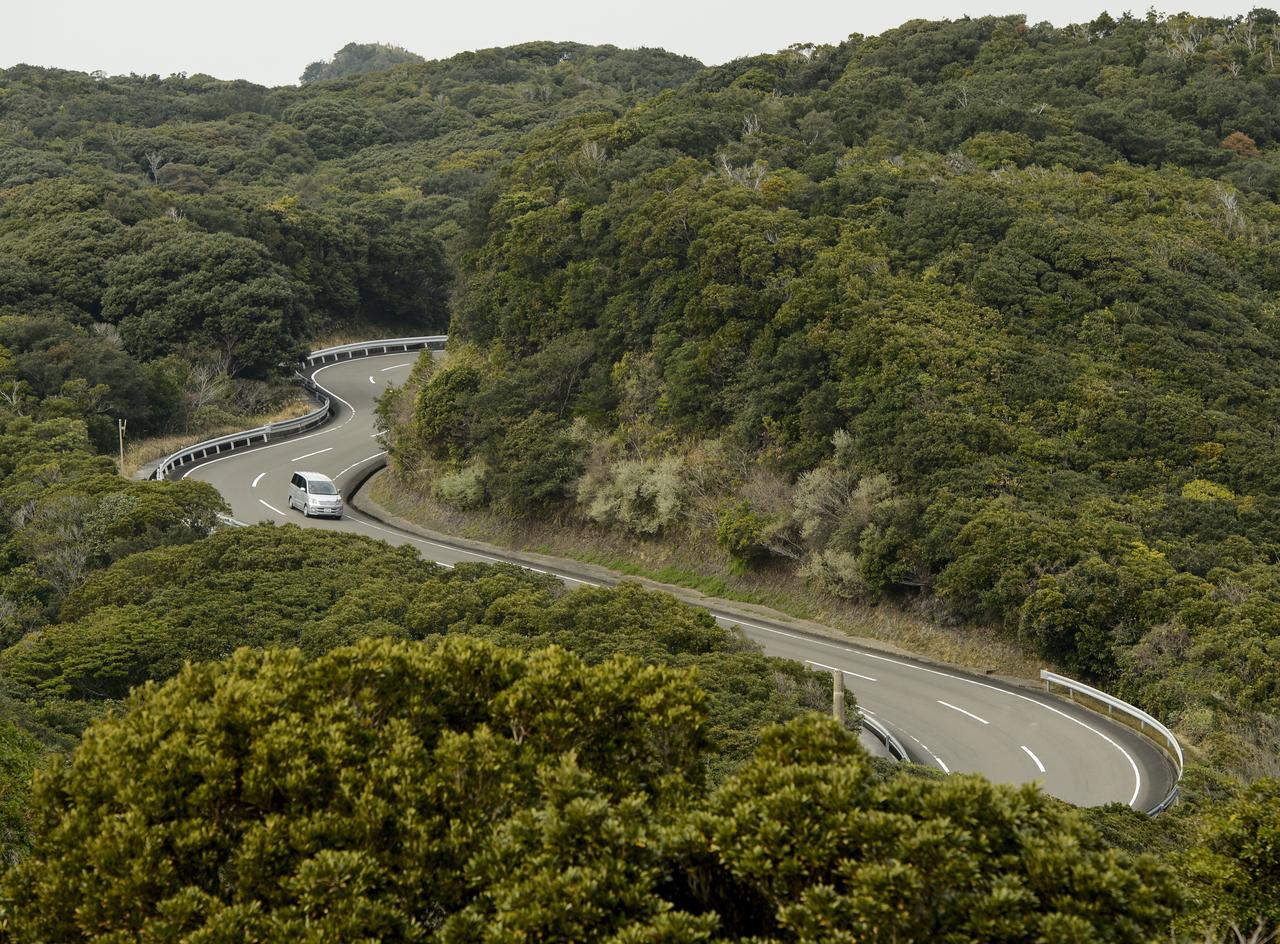

A car drives on the twisty roads that hug the coast line of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
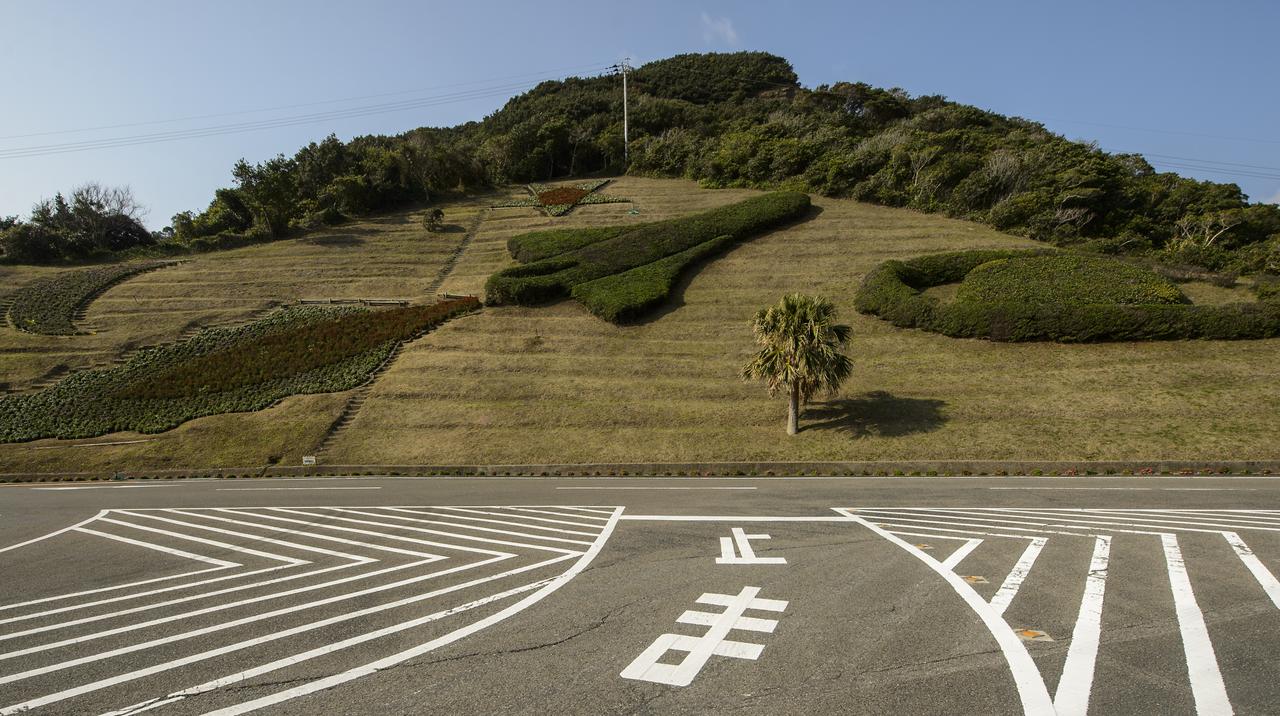

Shrubs and flowers in the shape of a space shuttle, star and planet are seen just outside the visitor's center of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
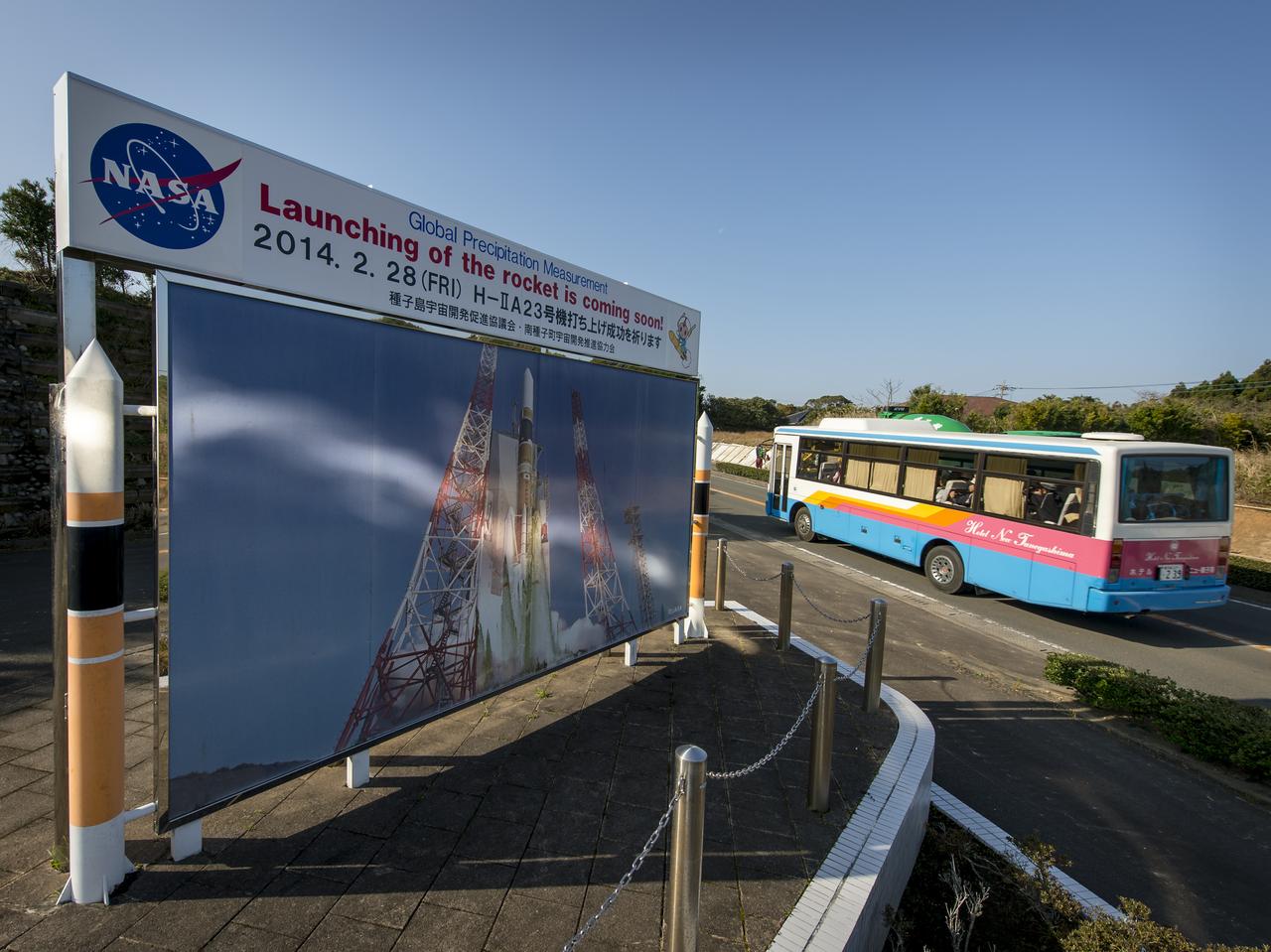

A roadside sign announces the upcoming launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Minamitane Town, Tanegashima Island, Japan. Once launched from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) the NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. The launch is planned for Feb. 28, 2014. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
A visitor looks over a Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) Facility Map, Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
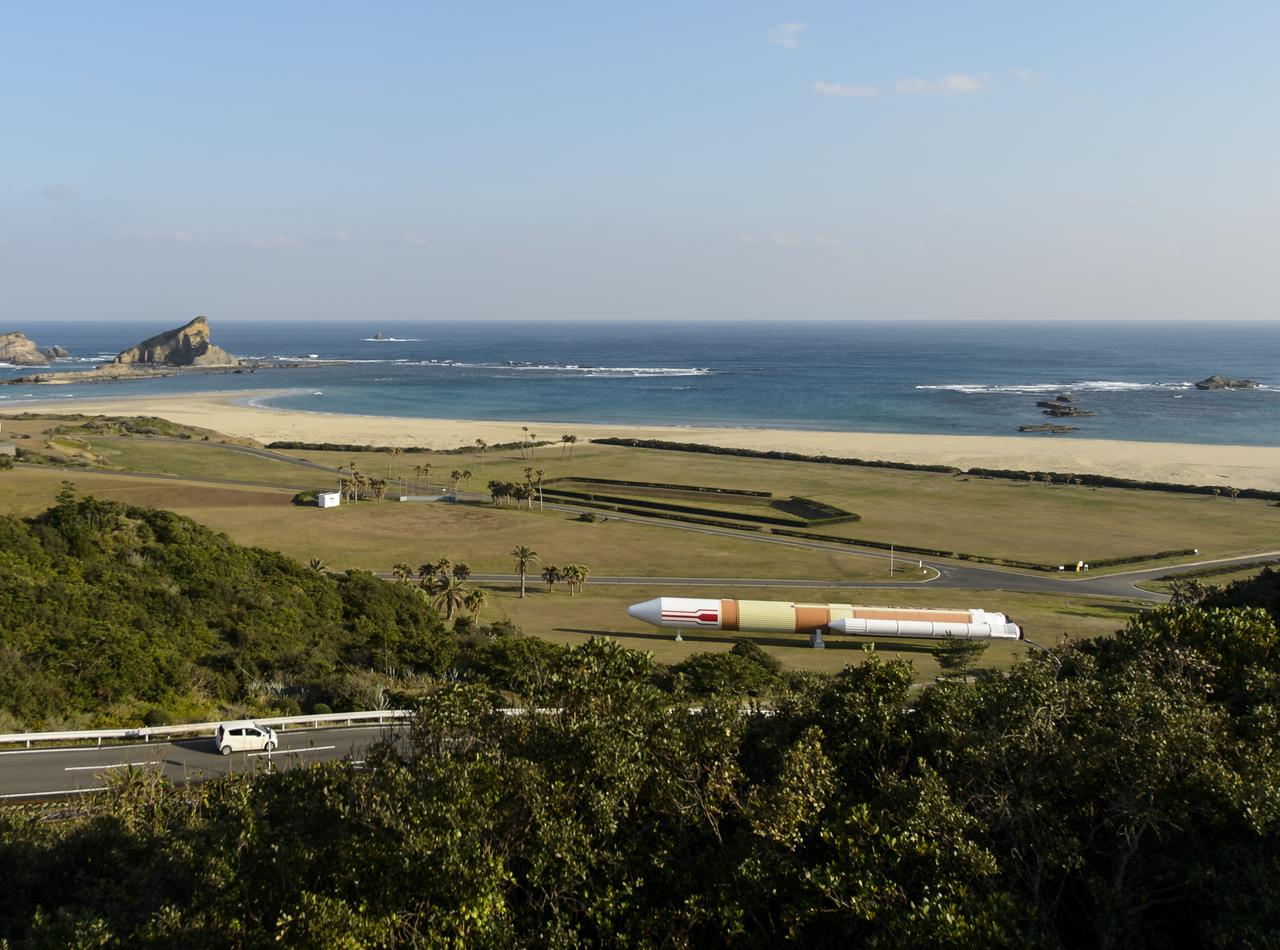
A full size model of an H-II rocket is seen at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) visitors center a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
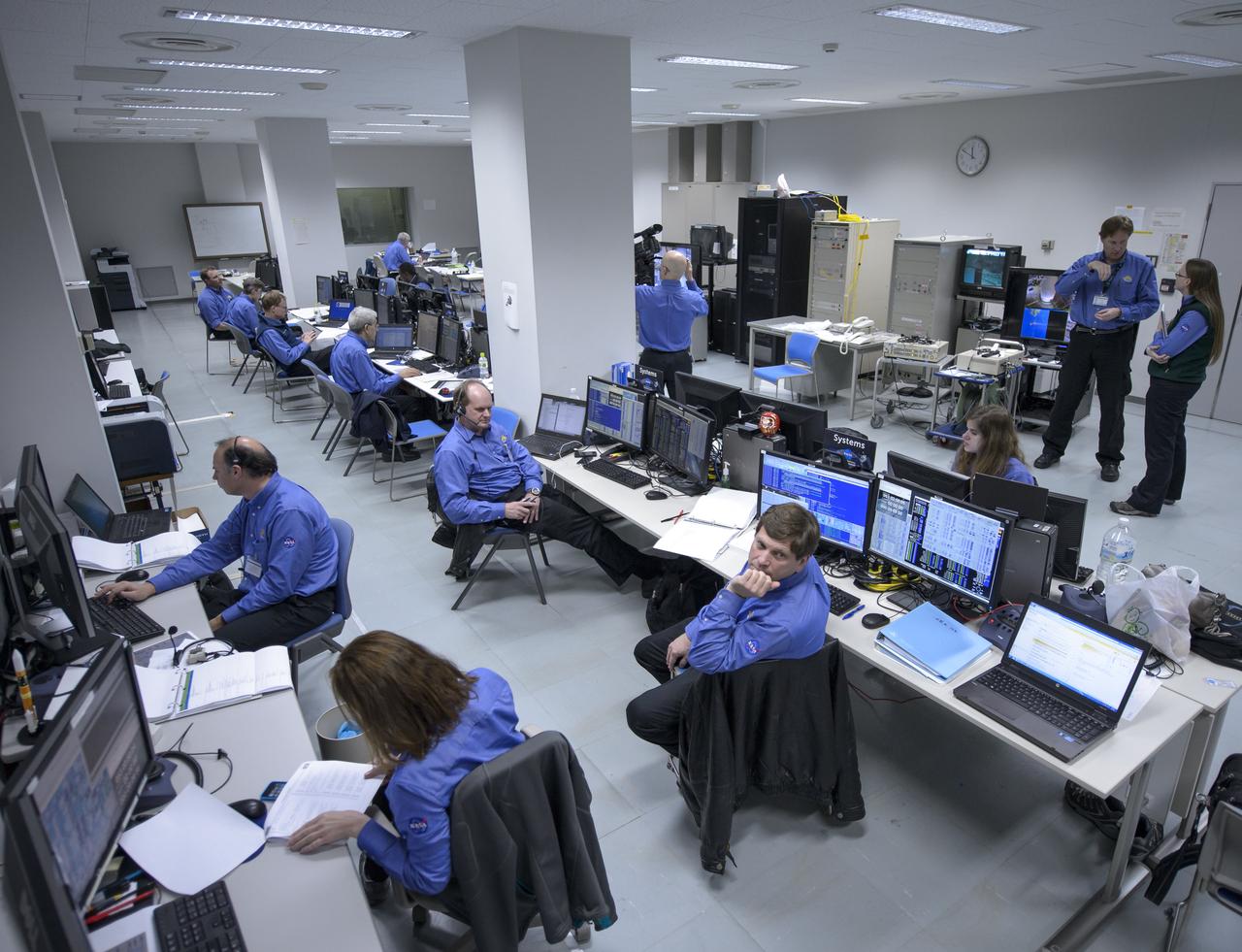

The NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory team is seen during an all-day launch simulation for GPM at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
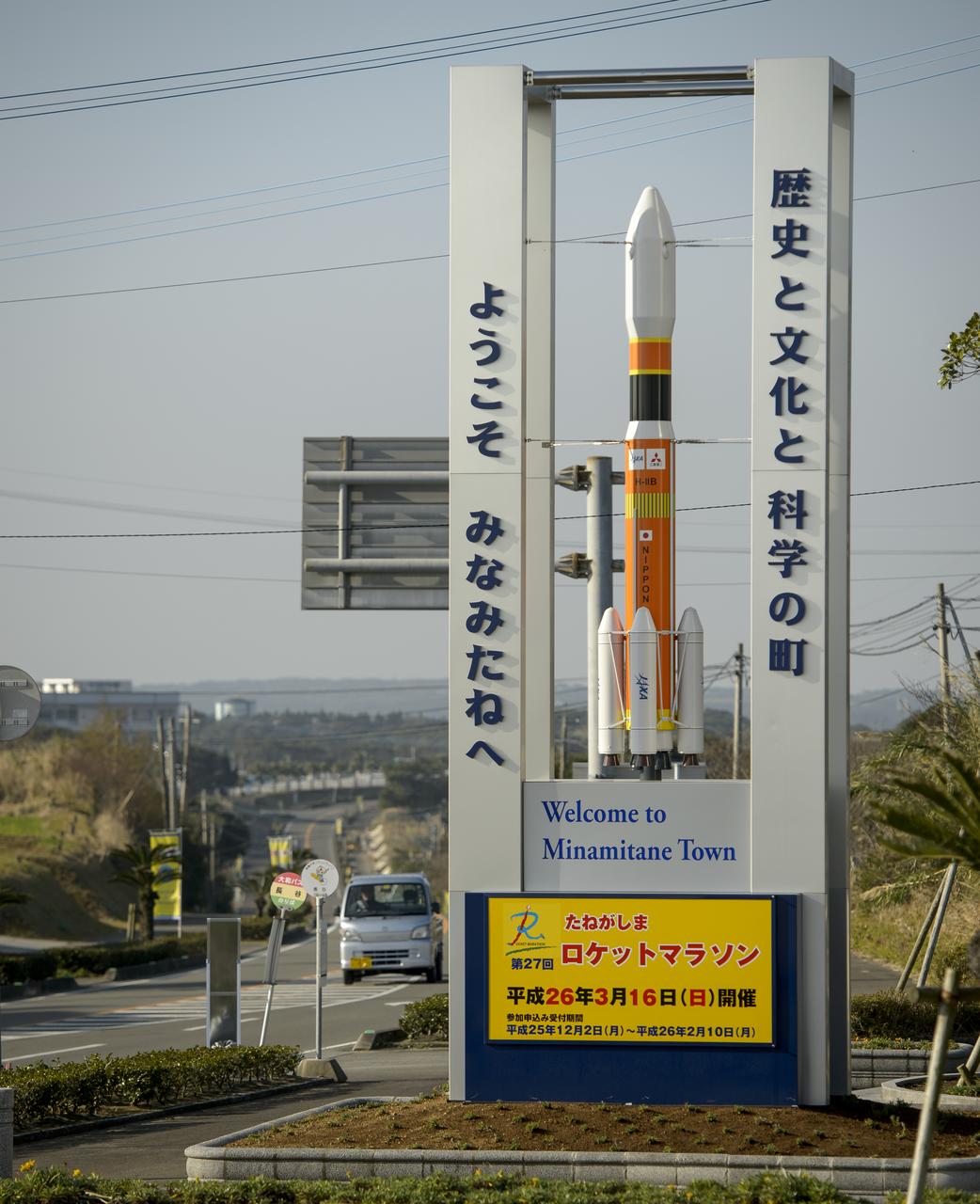

A sign with a model of the Japanese H-IIB rocket welcomes visitors to Minamitane Town, one of only a few small towns located outside of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), where the launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory will take place in the next week, Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
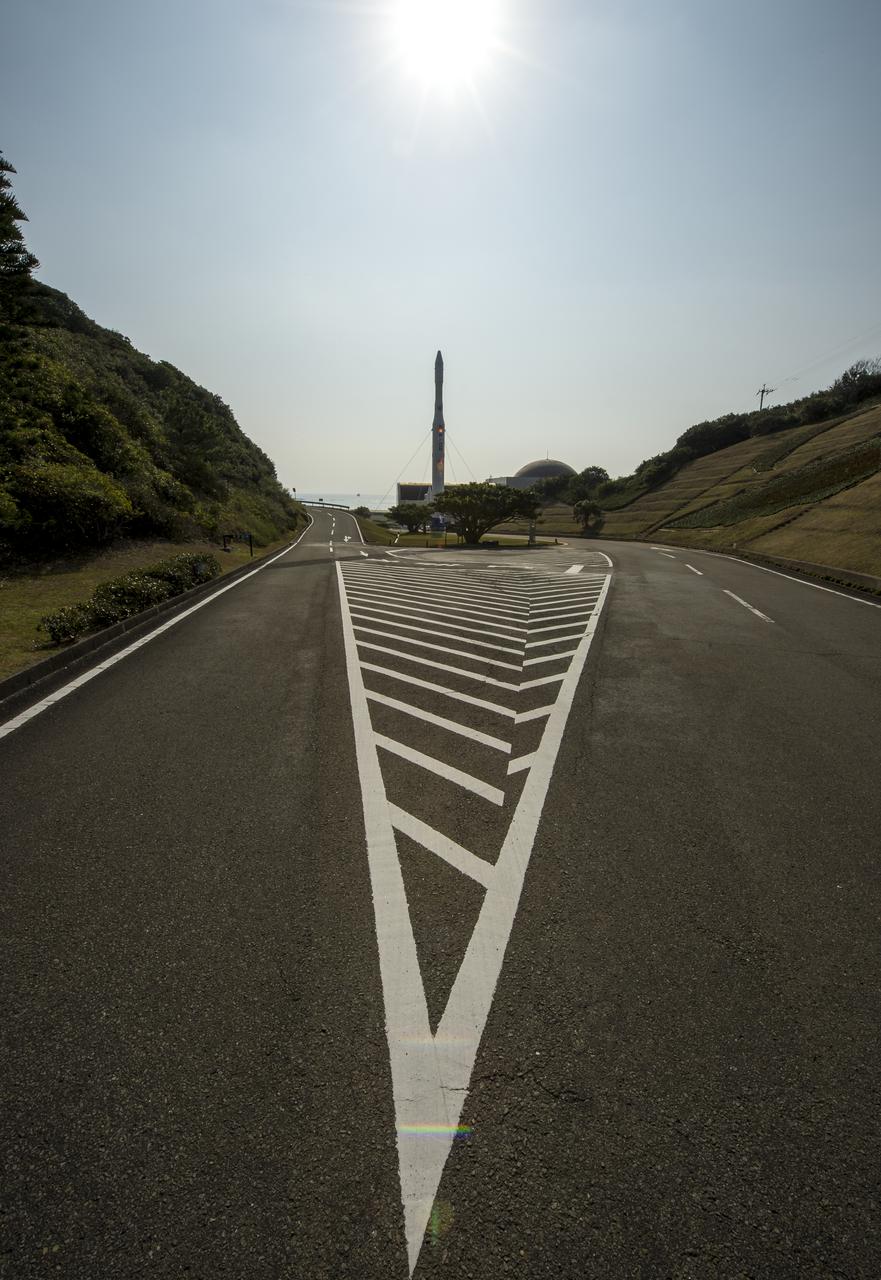

A rocket is seen at the entrance to the visitor's center of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
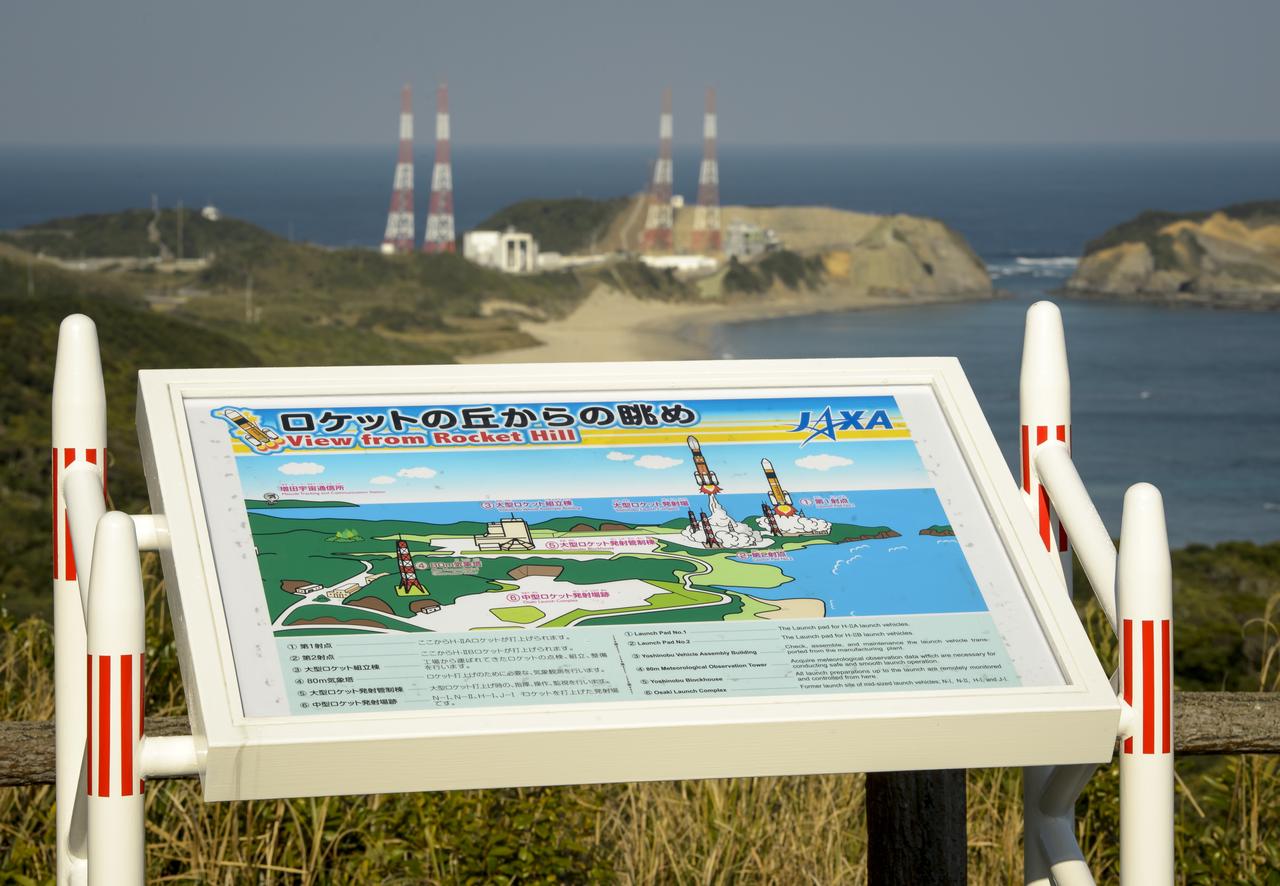

A sign at an overlook, named Rocket Hill, helps viewers identify the various facilities of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), including launch pad 1 that will be used Feb. 28, 2014 for the launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
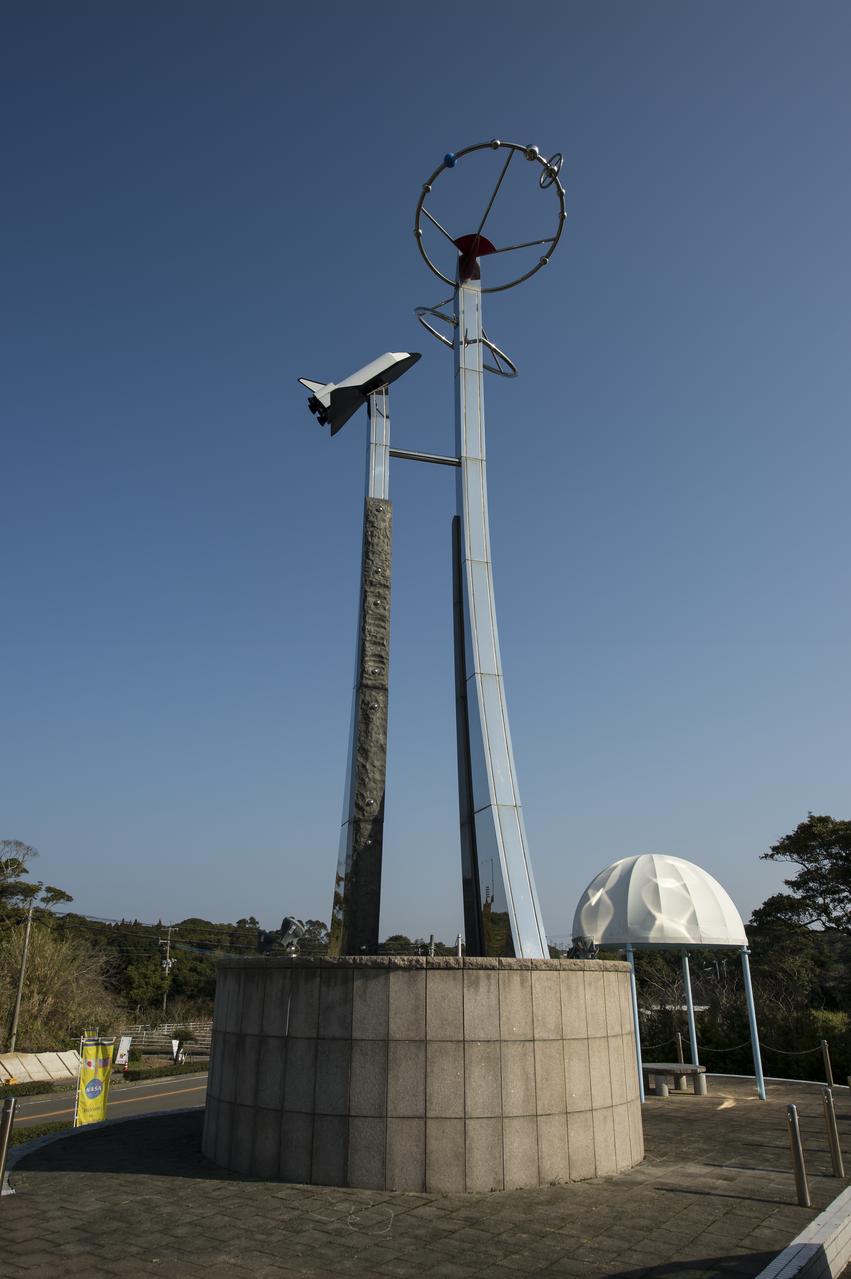

A small roadside park honoring spaceflight is seen in Minamitane Town, Saturday Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. Minamitane Town is located not far from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), where the launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
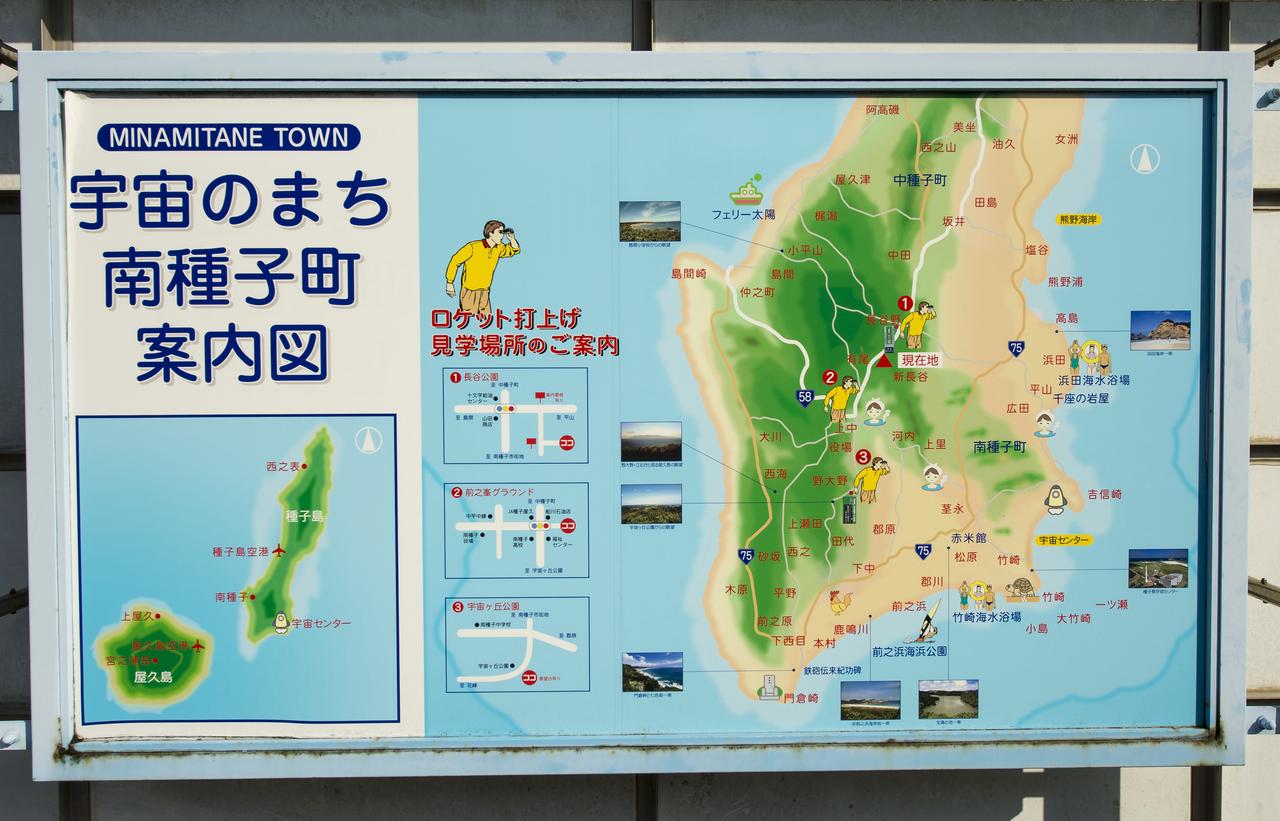
A roadside sign shows visitors of Minamitane Town various locations for activities, including the viewing of rocket launches from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), where the launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is scheduled to take place in the next week, Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Minamitane Town, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Launch is planned for Feb. 28, 2014. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A full size model of an H-II rocket is seen at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) visitors center a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
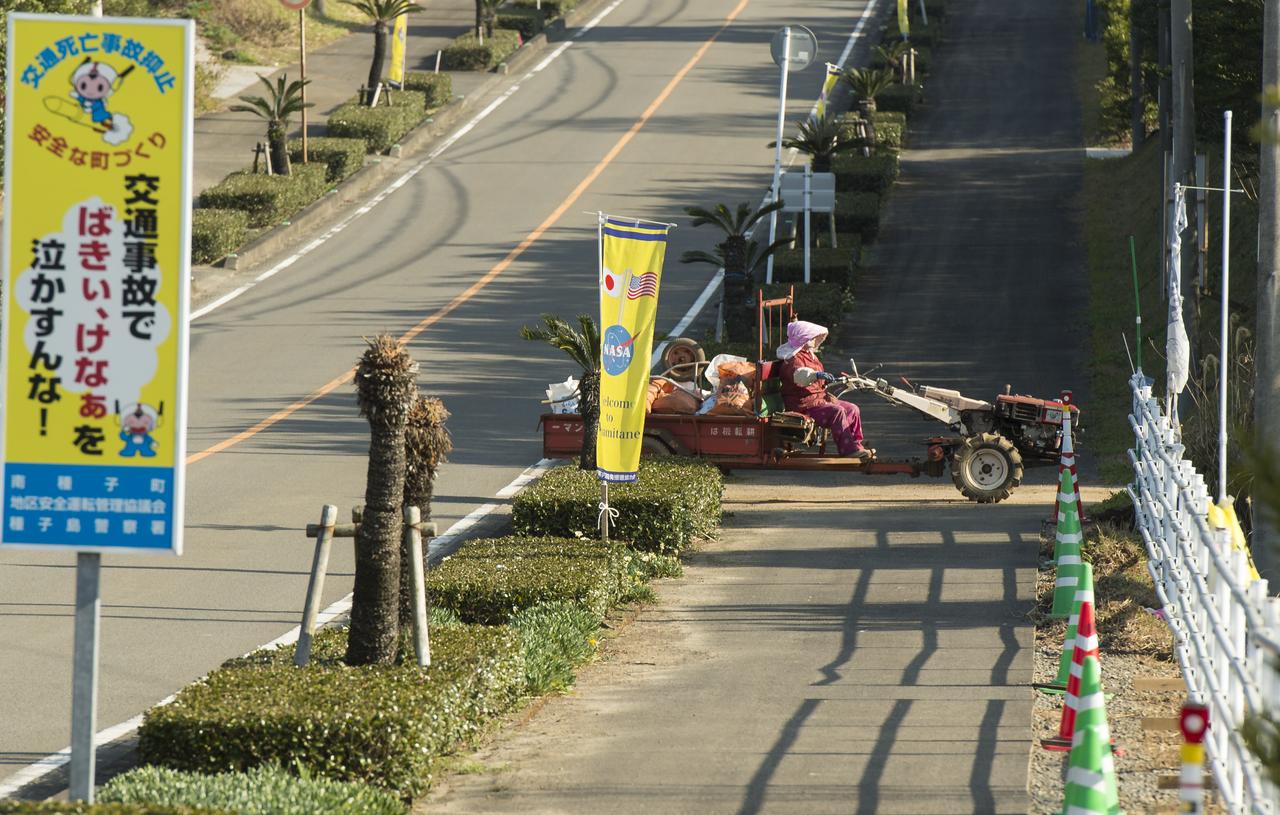

Roadside flags welcome the NASA team and visitors to Minamitame Town, one of only a few small towns located outside of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), where the launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory will take place in the next week, Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. The launch is planned for Feb. 28, 2014. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
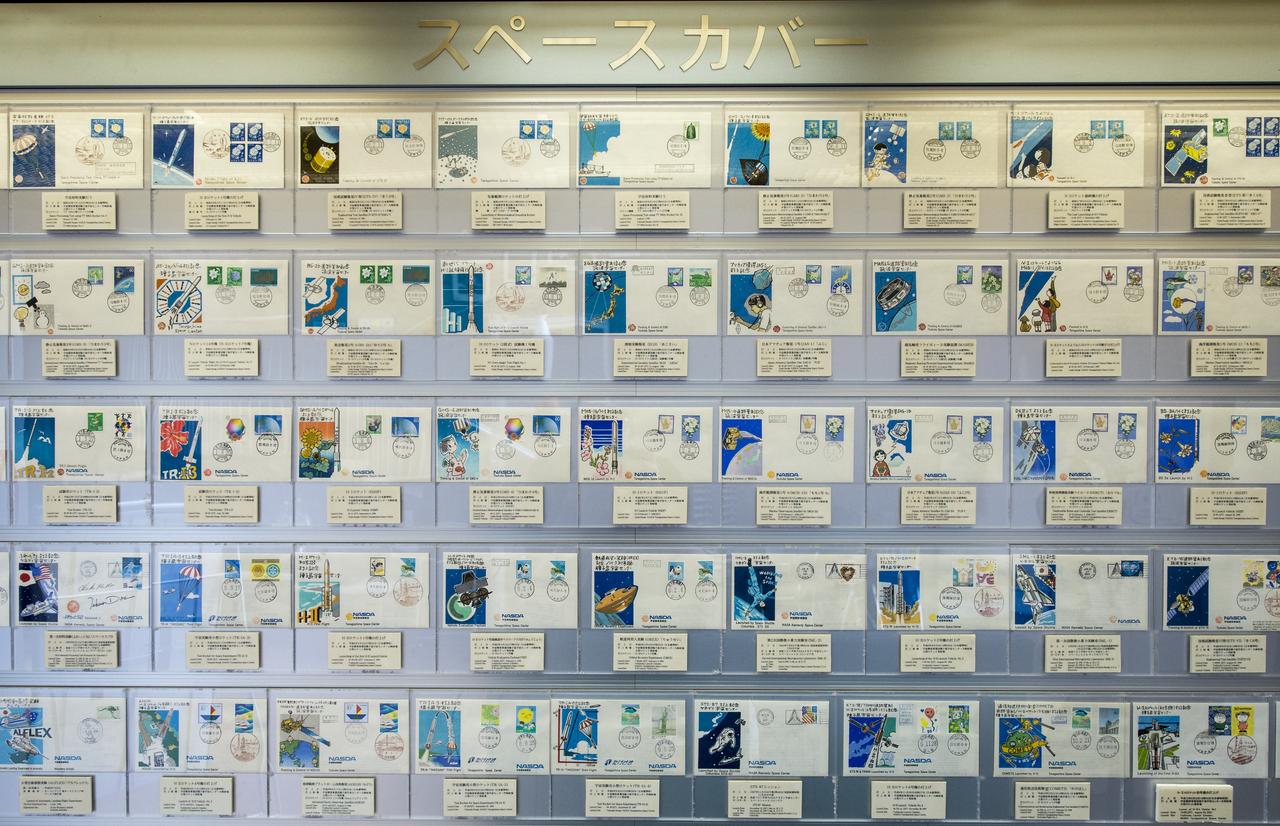

Envelopes with stamps depicting various space missions are shown at the visitor's center of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, is seen on launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Friday, Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
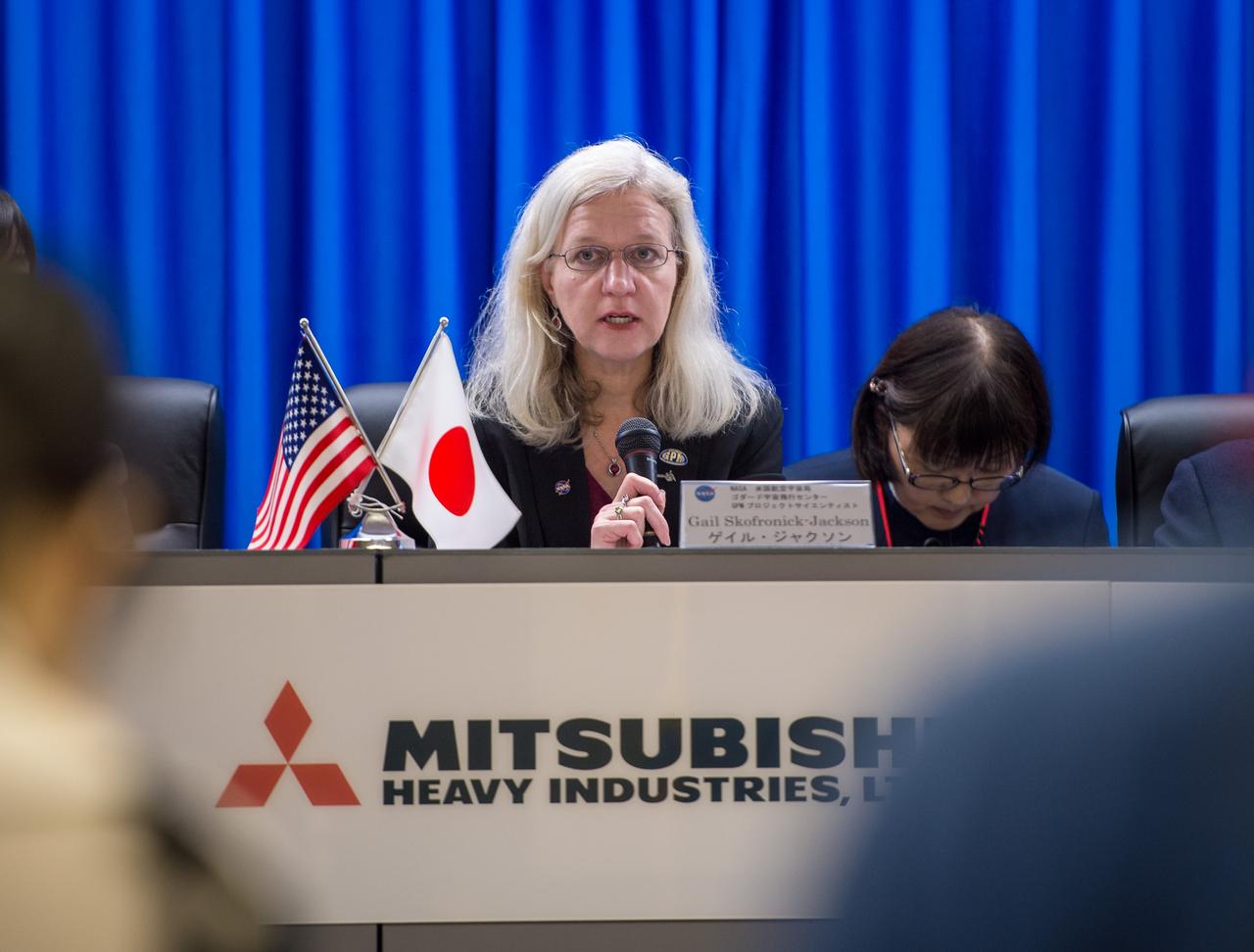

Gail Skofronick-Jackson, NASA GPM Project Scientist, talks during a science briefing for the launch of the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory aboard an H-IIA rocket, Wednesday, Feb. 26, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center, Japan. Launch is scheduled for early in the morning of Feb. 28 Japan time. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
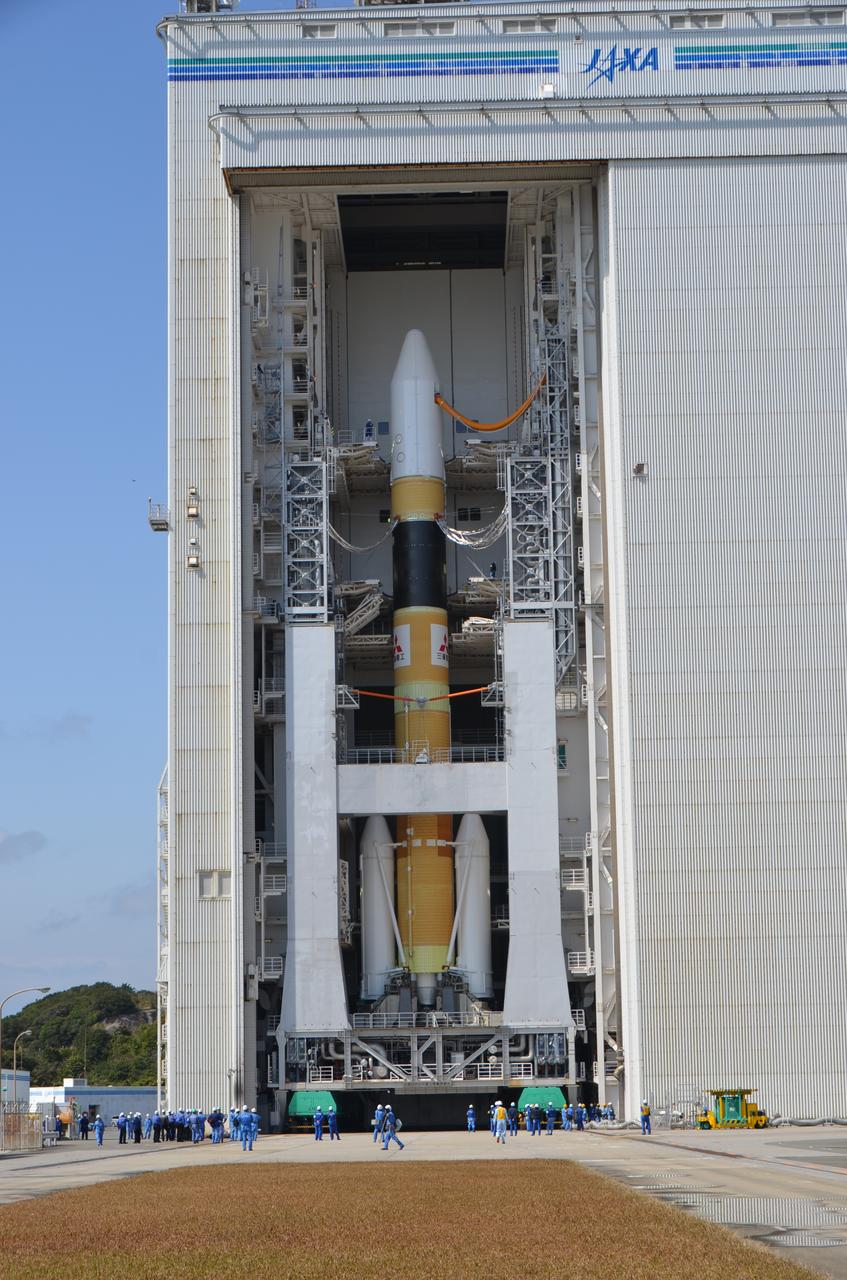
A Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (HMI) H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard is during roll out at the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Credit: Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

A Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (HMI) H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard is during roll out at the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Credit: Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
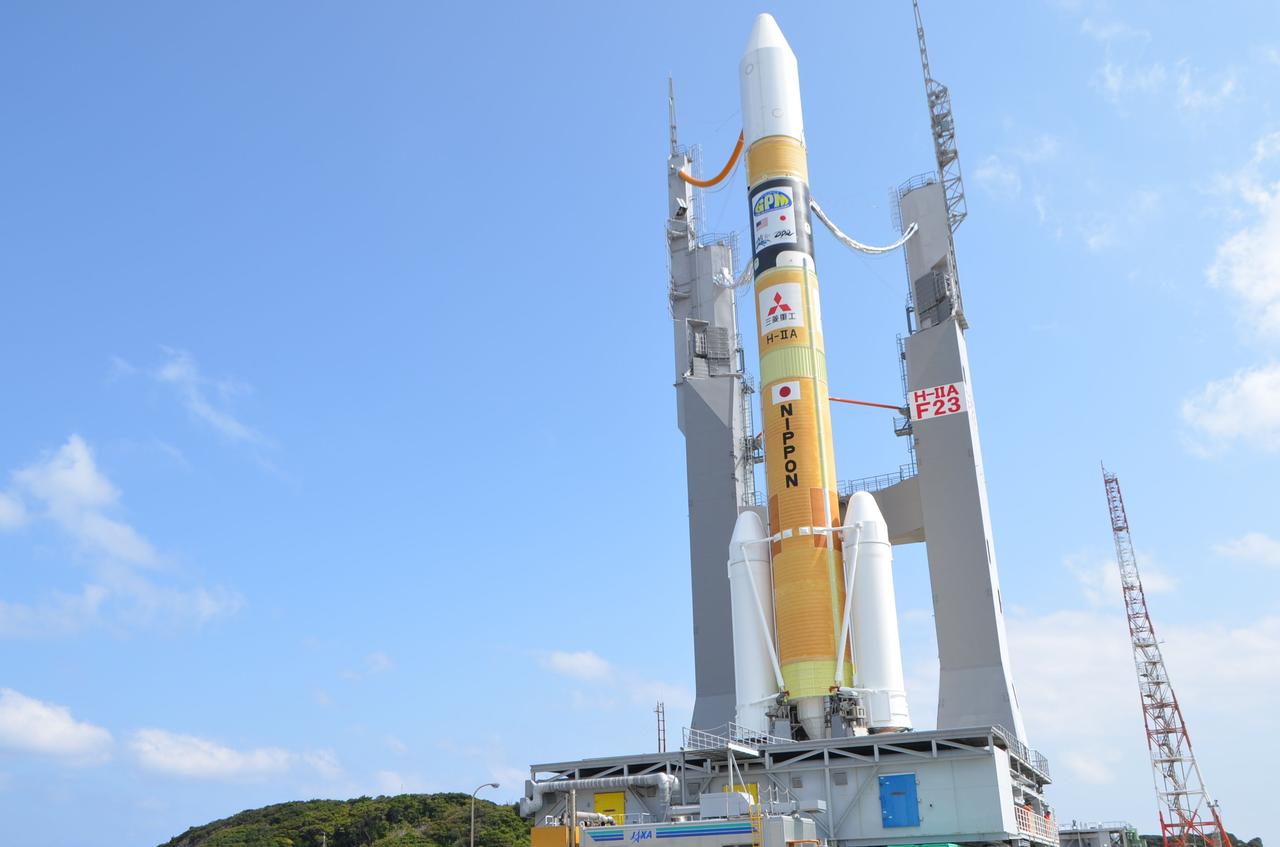

A Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (HMI) H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard is during roll out at the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Credit: Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
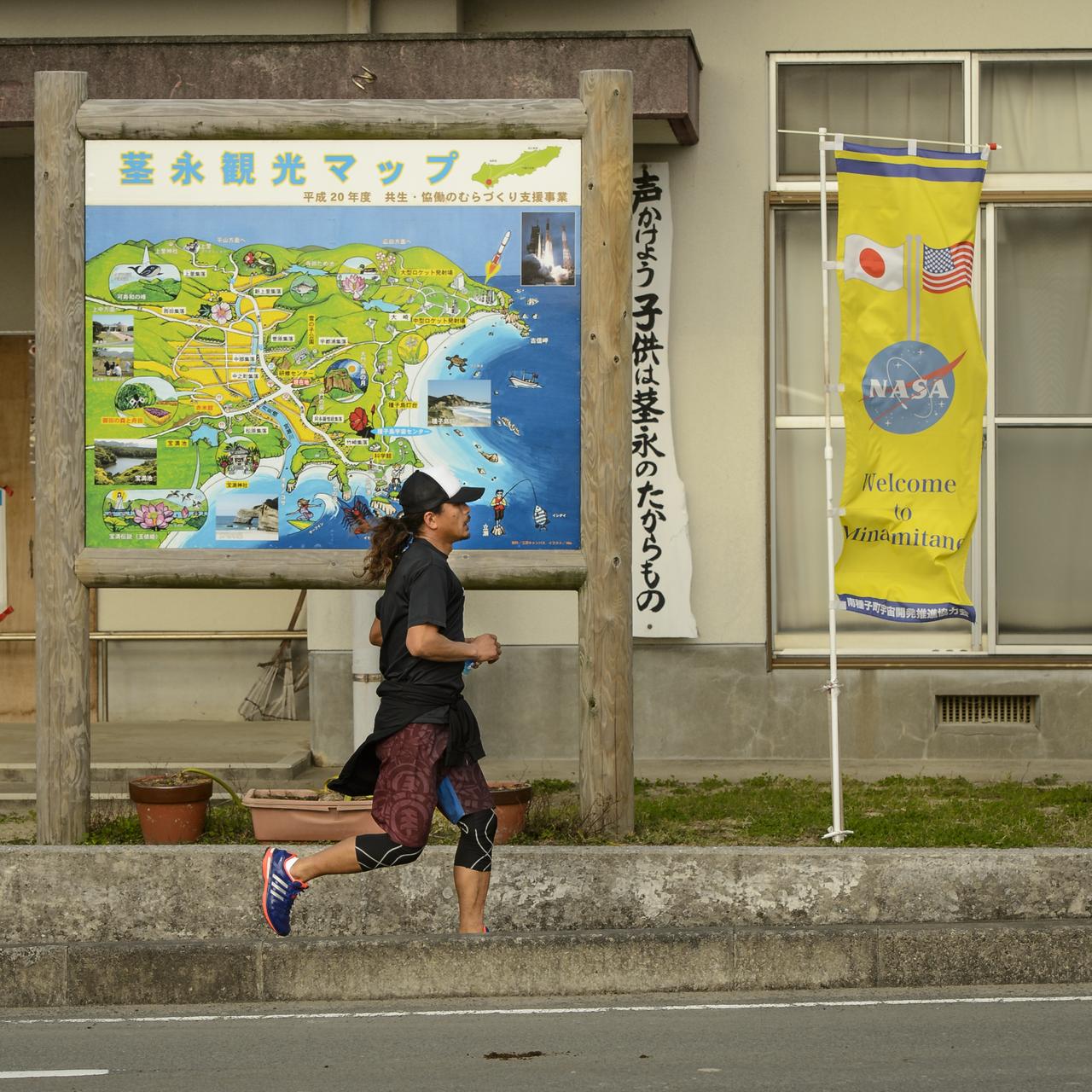

A jogger runs past a sign welcoming NASA and other visitors to Minamitane Town on Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Caroline Bouvier Kennedy, U.S. Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary to Japan, right, is welcomed by Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), President, Naoki Okumura, at the Tanegashima Space Center Visitors Center on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. The Ambassador is visiting the space center and hopes to witness the planned launch of a Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Caroline Bouvier Kennedy, U.S. Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary to Japan, center, tours the Tanegashima Space Center, Visitors Center with Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), President, Naoki Okumura, right, on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. The Ambassador visiting the space center and hopes to witness the planned launch of a Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
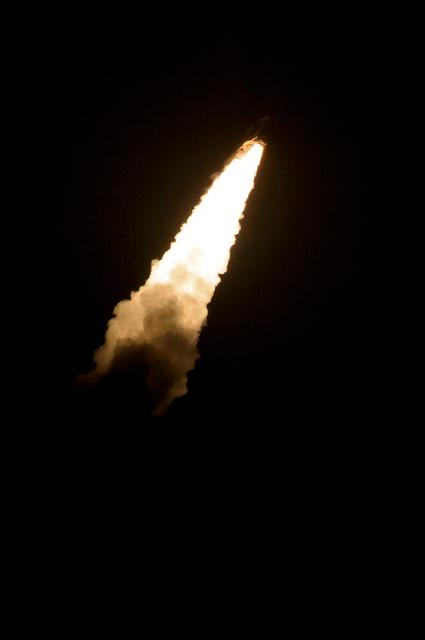

A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, fades into the dark as it launches from the Tanegashima Space Center, Friday, Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. The GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
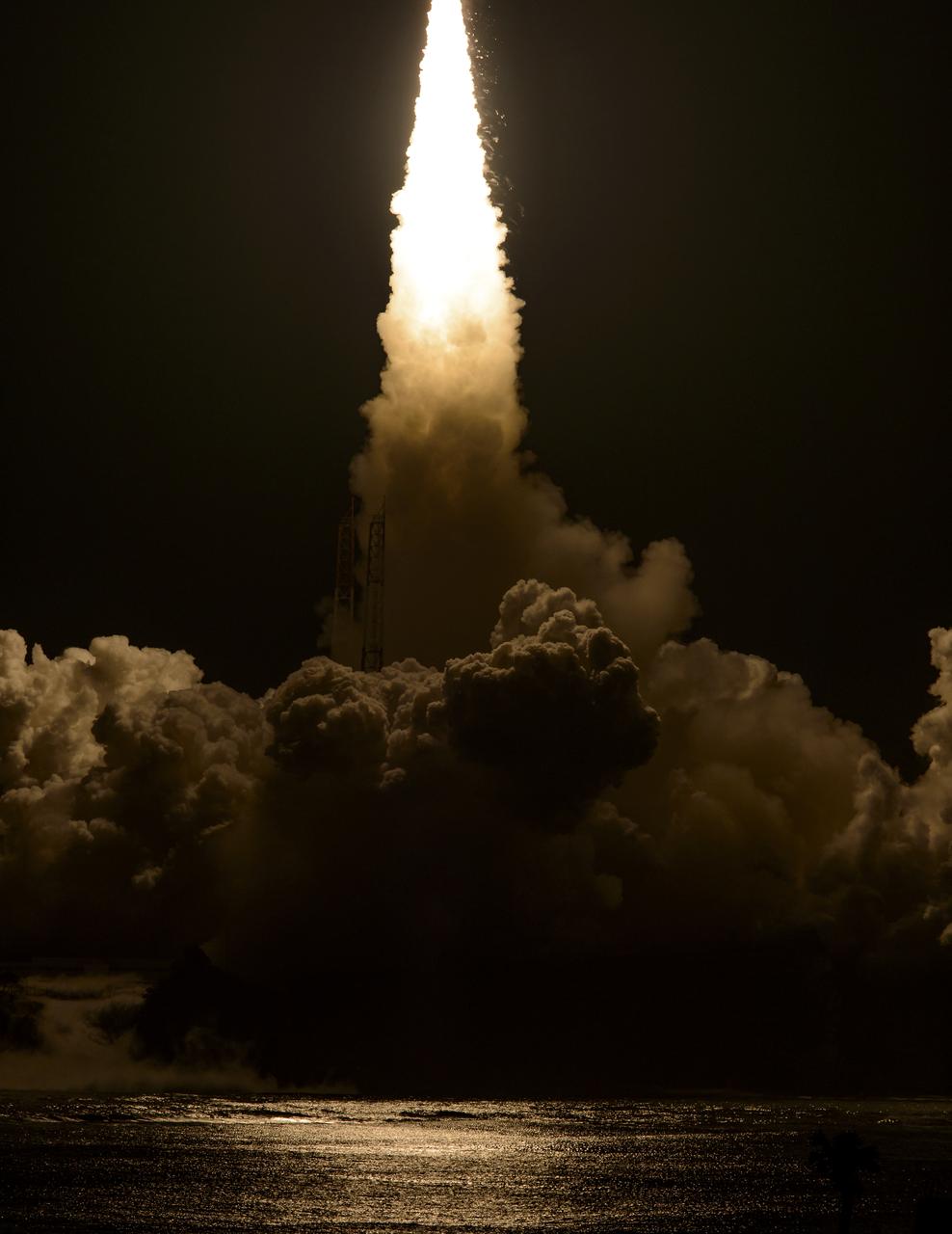

Flames and smoke from a Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, are seen during the launch from the Tanegashima Space Center, Friday, Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. The GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
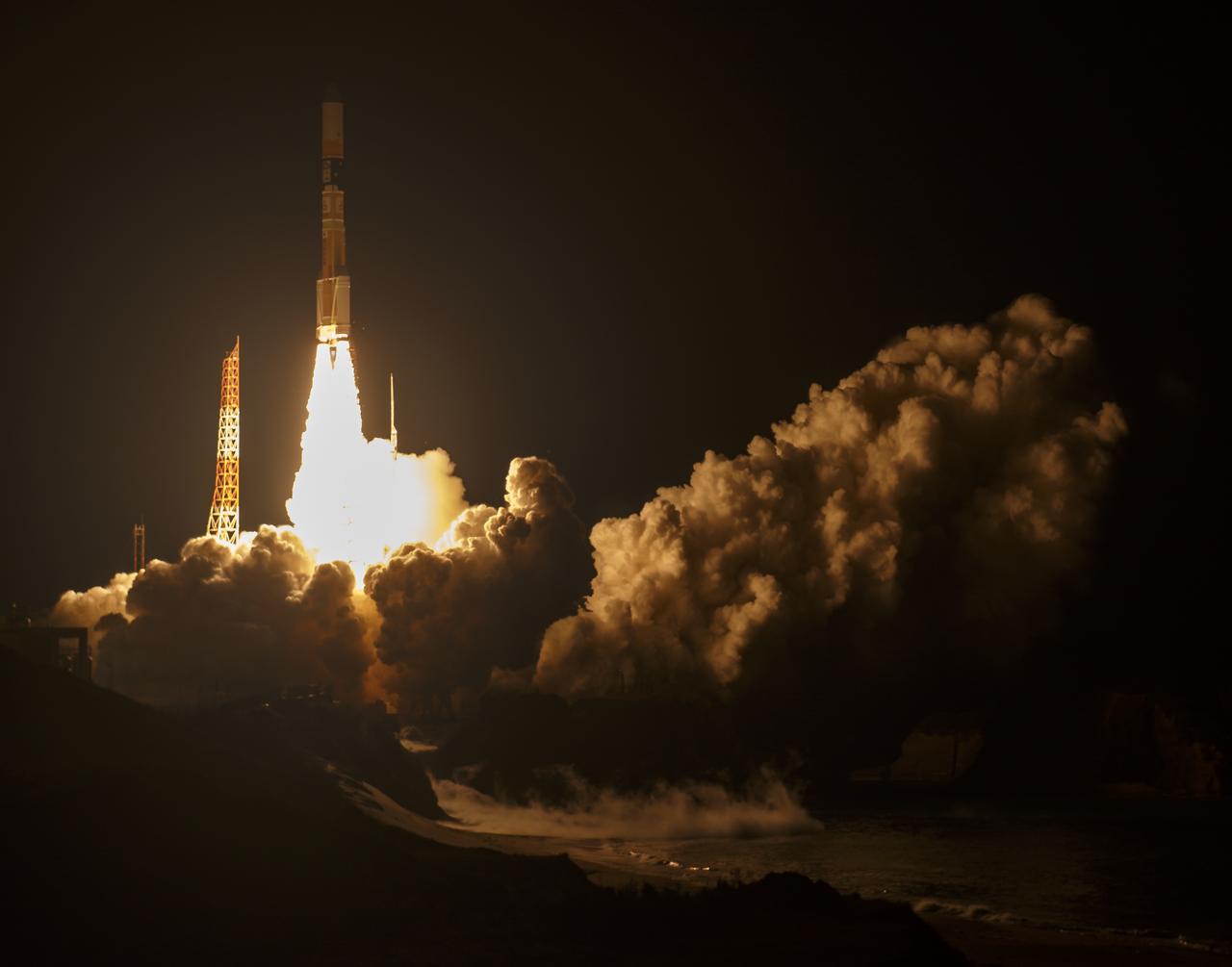

A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, is seen launching from the Tanegashima Space Center, Friday, Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. The GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
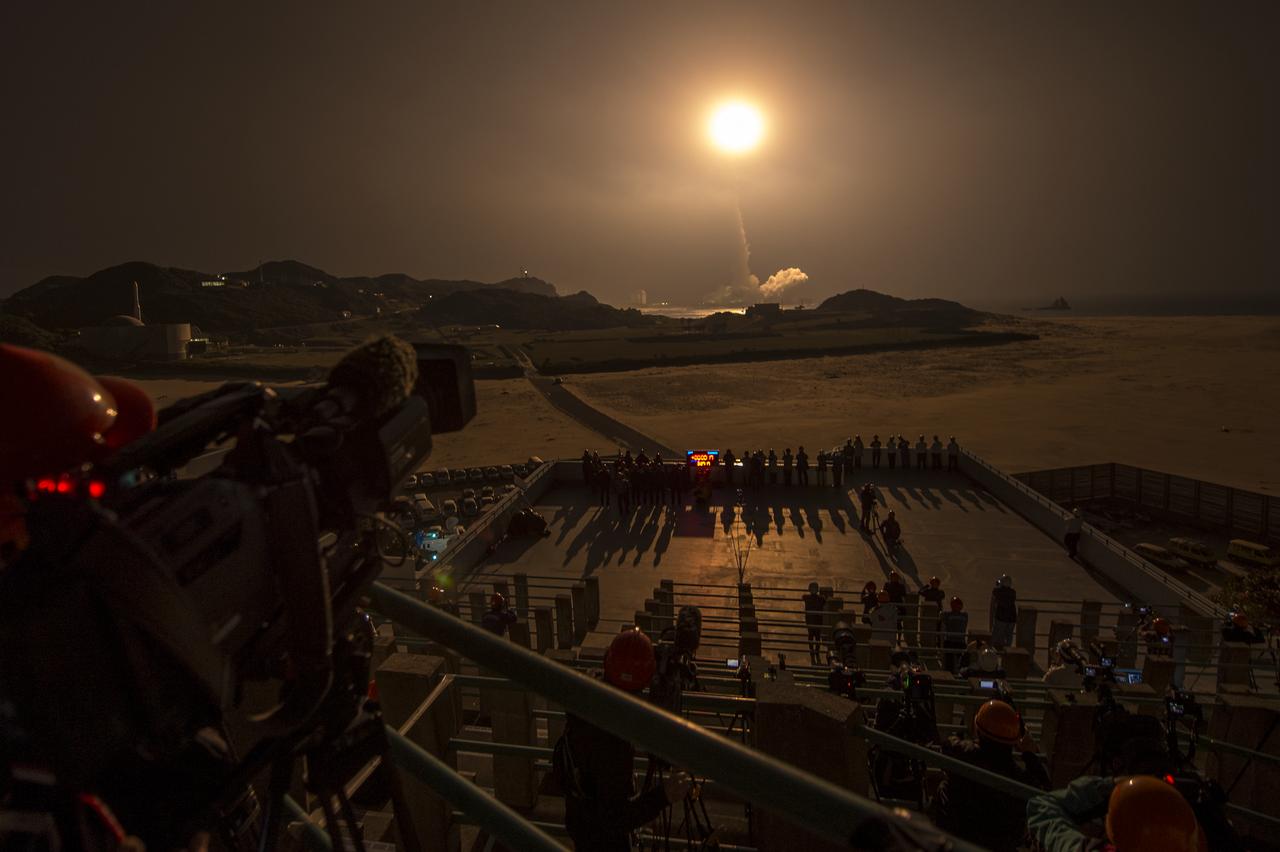

A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, is seen launching from the Tanegashima Space Center, Friday, Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. The GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
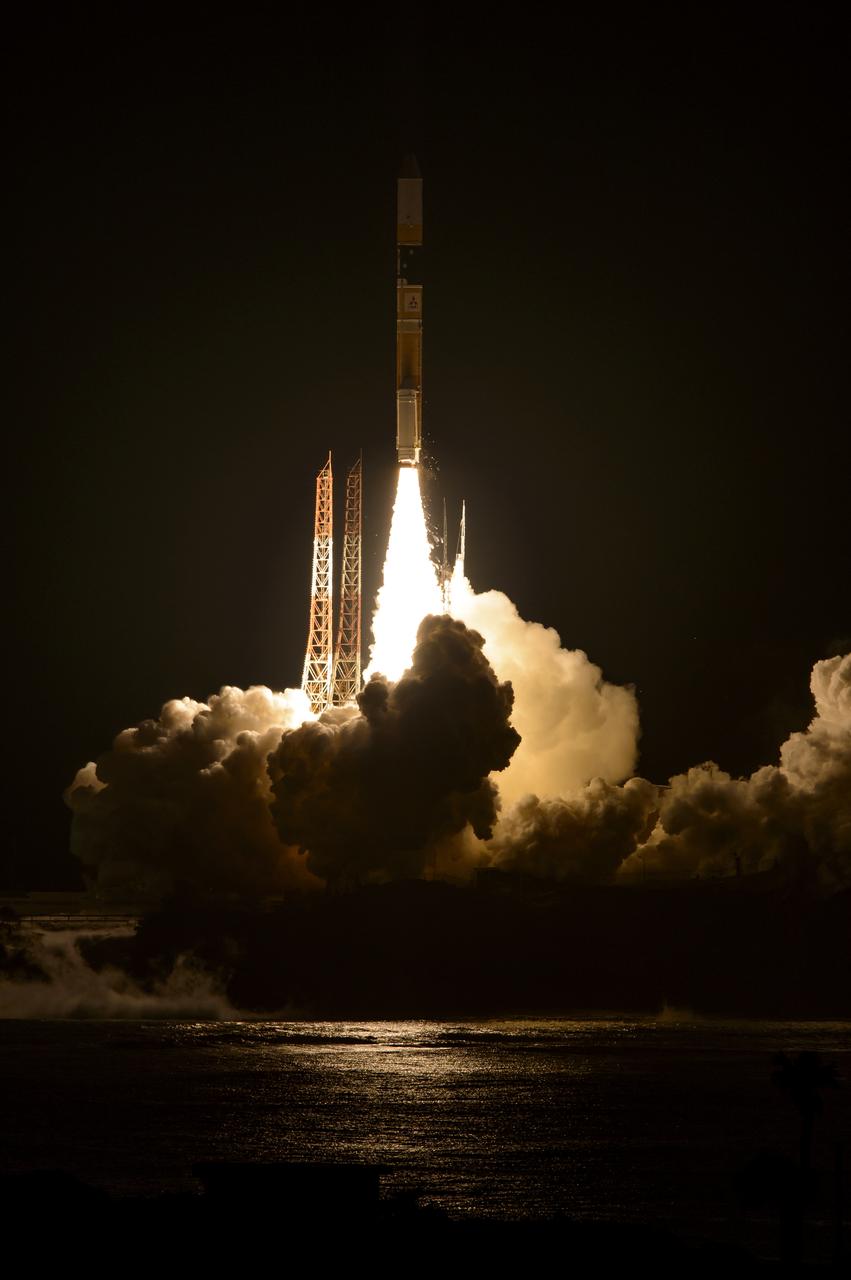

A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, is seen launching from the Tanegashima Space Center, Friday, Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. The GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
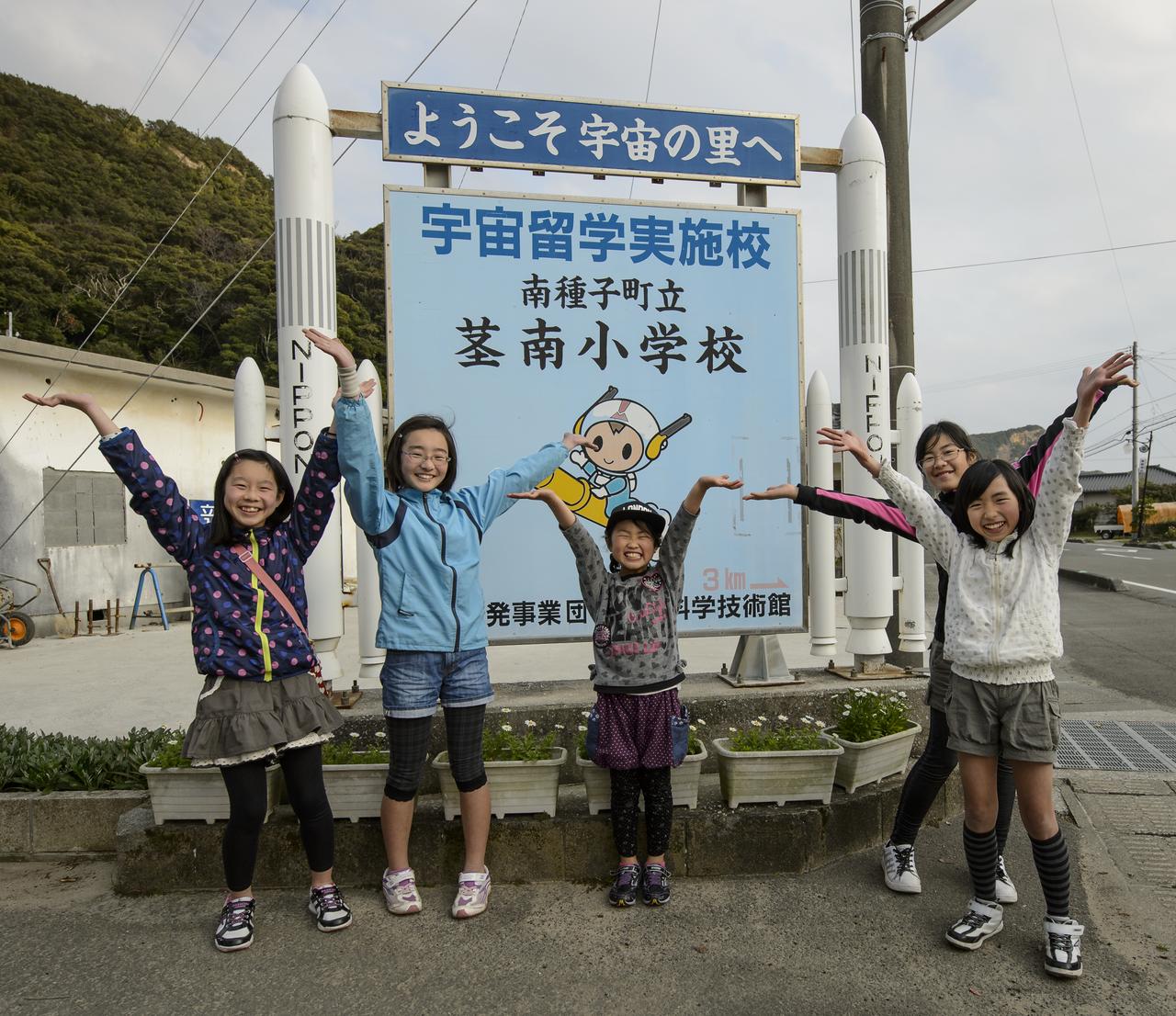

Minamitane elementary school girls pose for a photo in front of a sign featuring the town's mascot "Chuta-kun", Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The Chuta-kun mascot rides a rocket and has guns on the side of his helmet to show the areas history as the site of the first known contact of Europe and the Japanese, in 1543 and the introduction of the gun. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
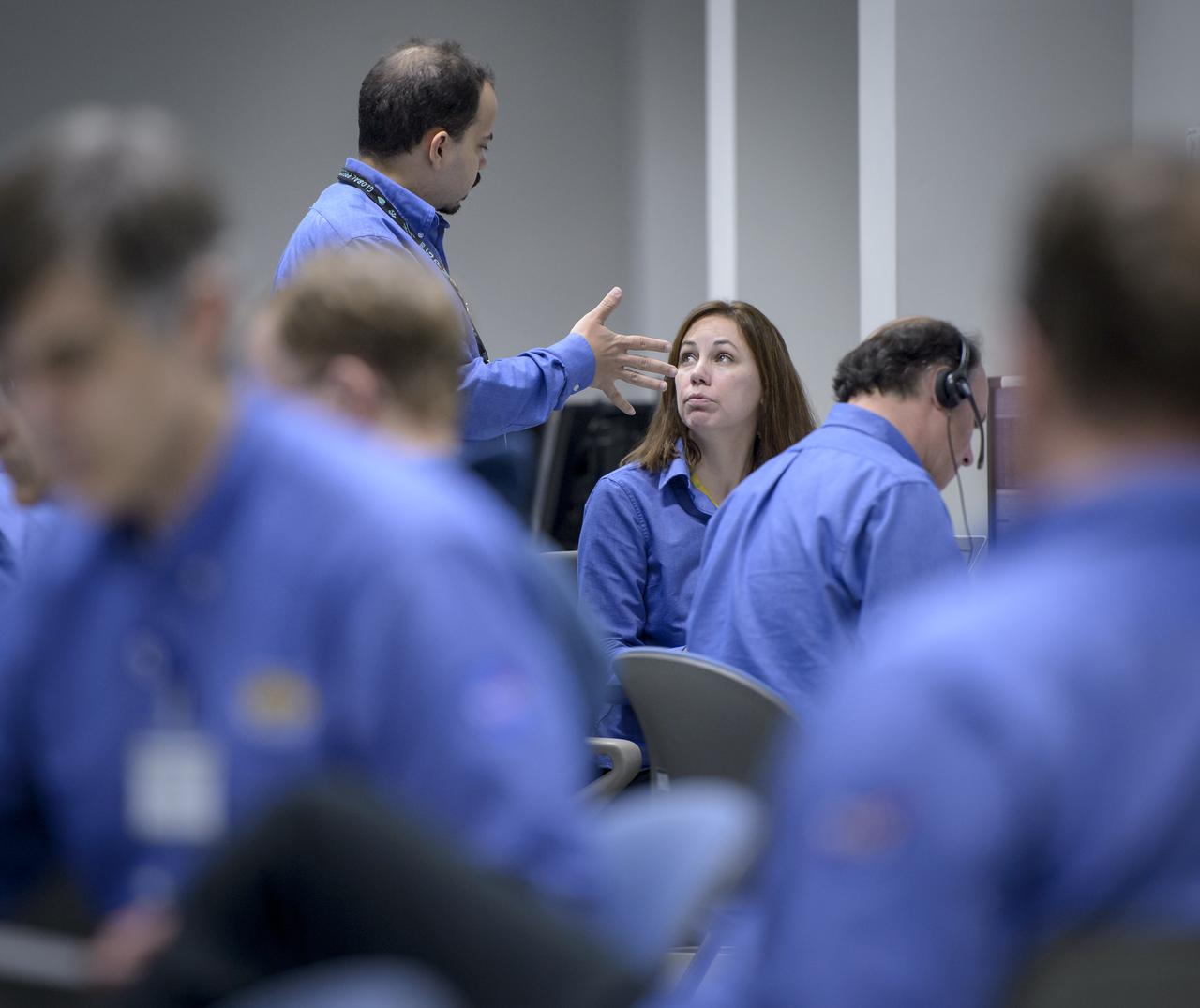

NASA GPM Test Conductors John Pope, and, Michelle Lacombe talk during the all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
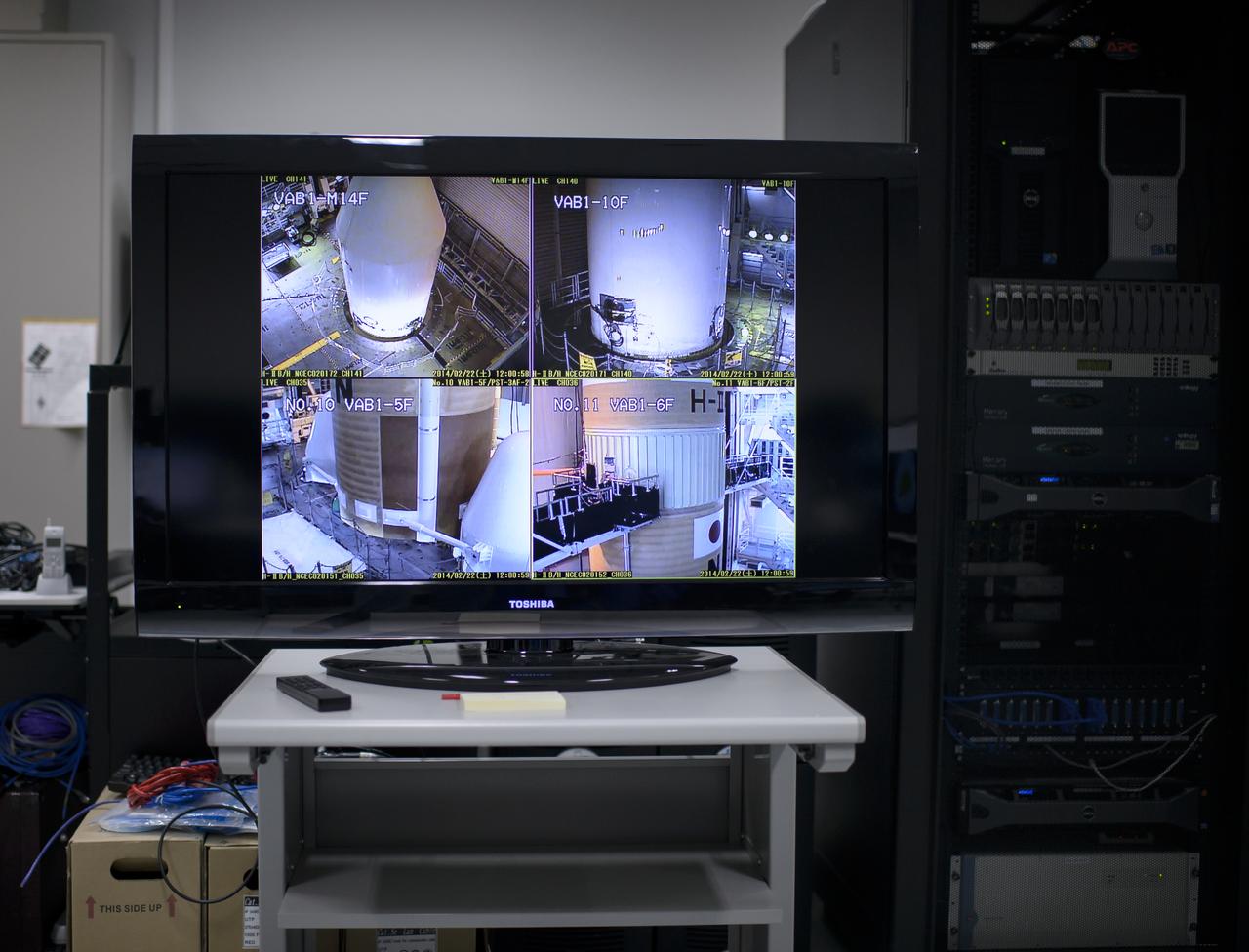

A live television view of the H-IIA rocket, with the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, is seen inside the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2) during an all-day launch simulation, Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
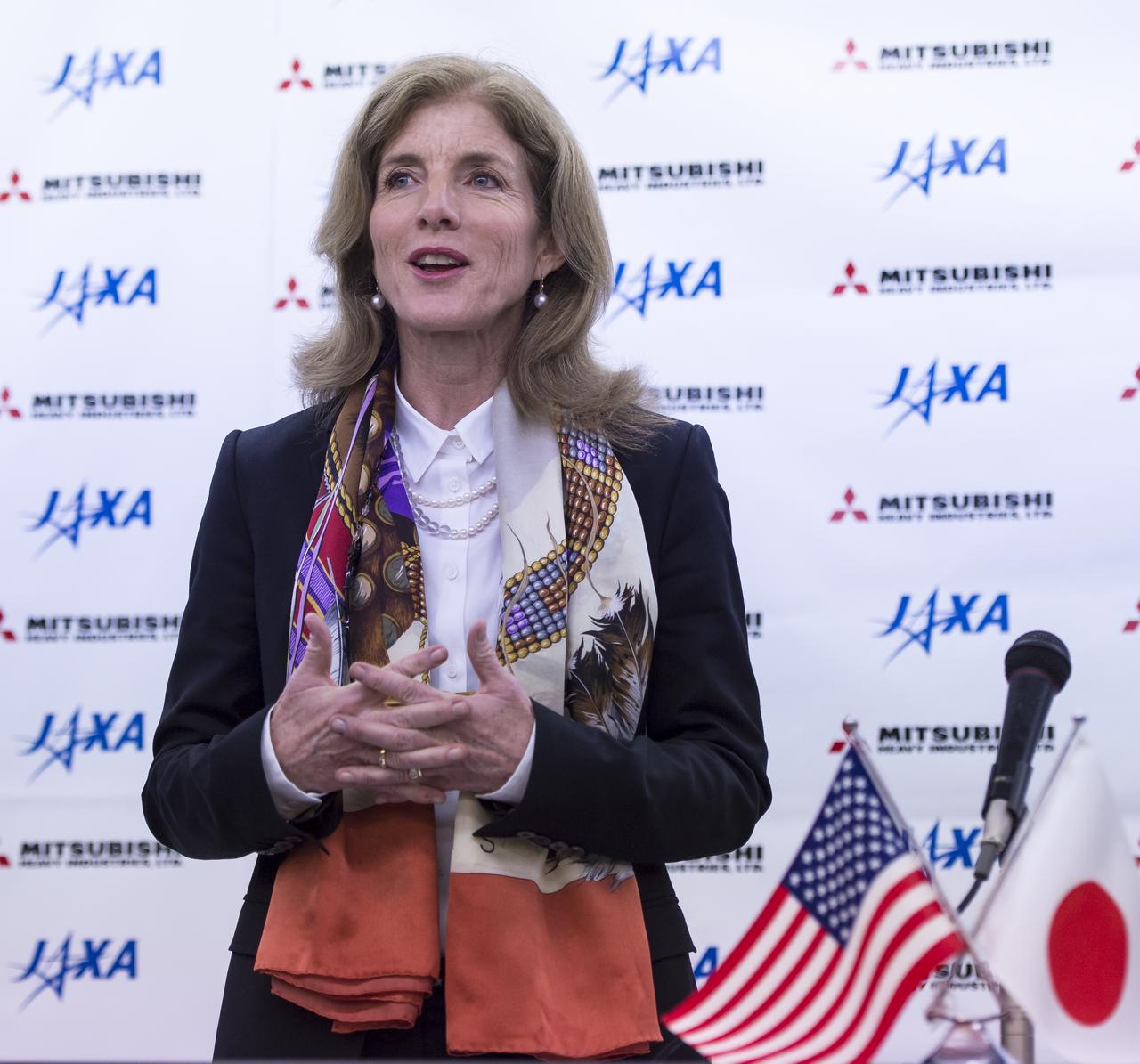

Caroline Kennedy, U.S. Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary to Japan, congratulated both NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory teams and noted it was an example of over 40 years of strong U.S. and Japan relations, Friday Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) Tanegashima, Japan. The Ambassador witnessed the launch of a Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-JAXA, GPM Core Observatory. The GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
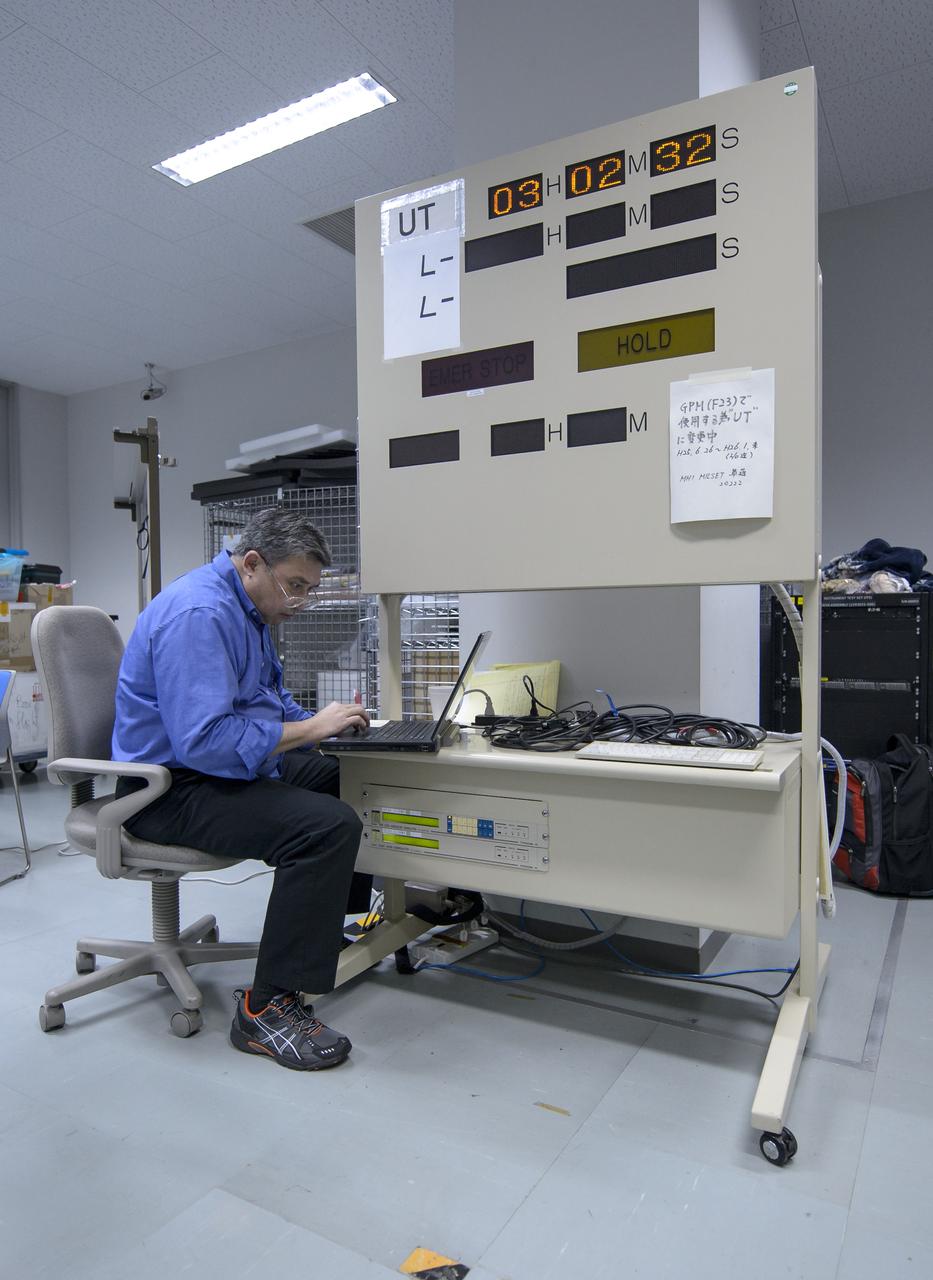

Clyde Woodall, NASA GPM launch services, is seen during the all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

George Dakermanji, NASA GPM Power, monitors the progress of an all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA GPM Radio Frequency Engineer David Lassiter monitors the progress of an all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Andy Aylward, GPM EGSE, monitors the progress of an all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
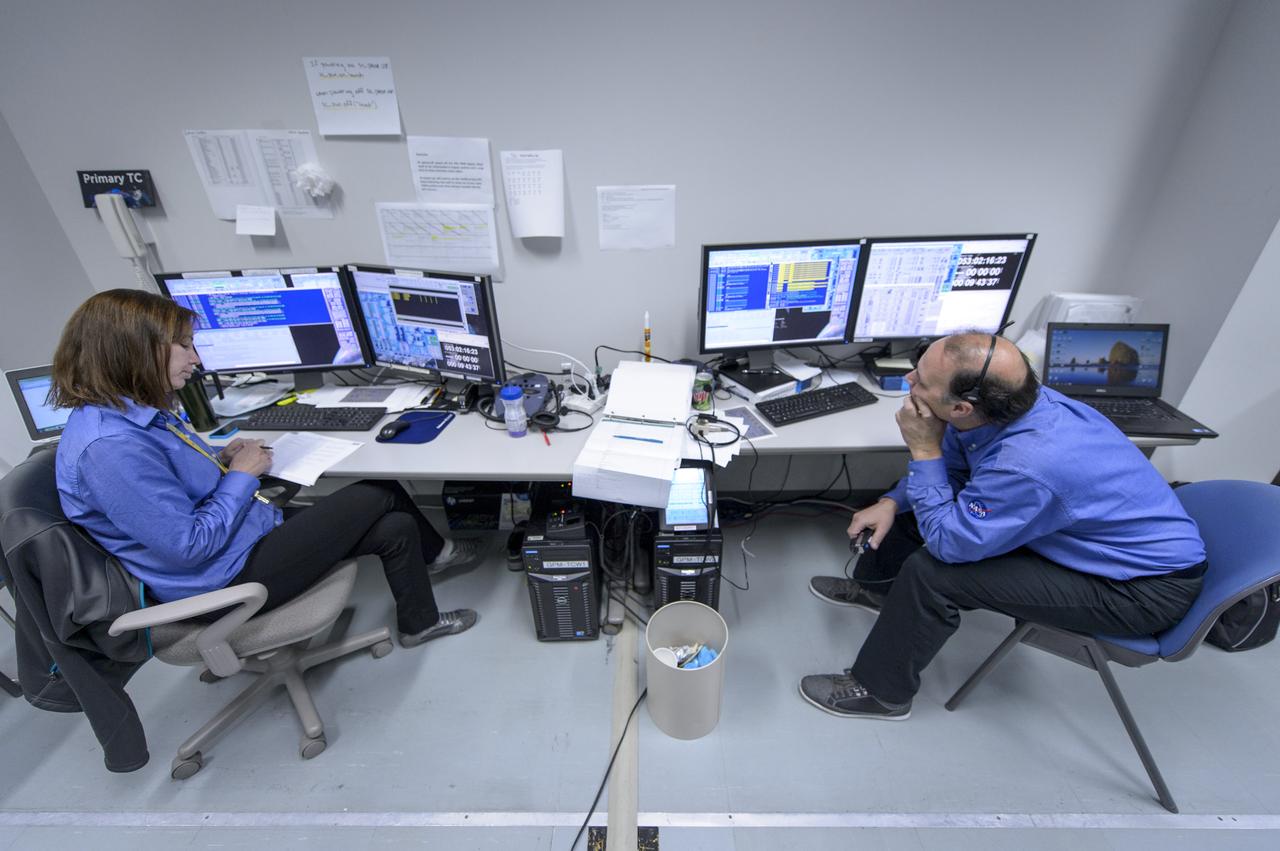

NASA GPM Test Conductors, Michelle Lacombe, left, and Bill Dehaven participate in an all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

This diagram based on results from NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer and the Anglo-Australian Telescope illustrates two ways to measure how fast the universe is expanding.
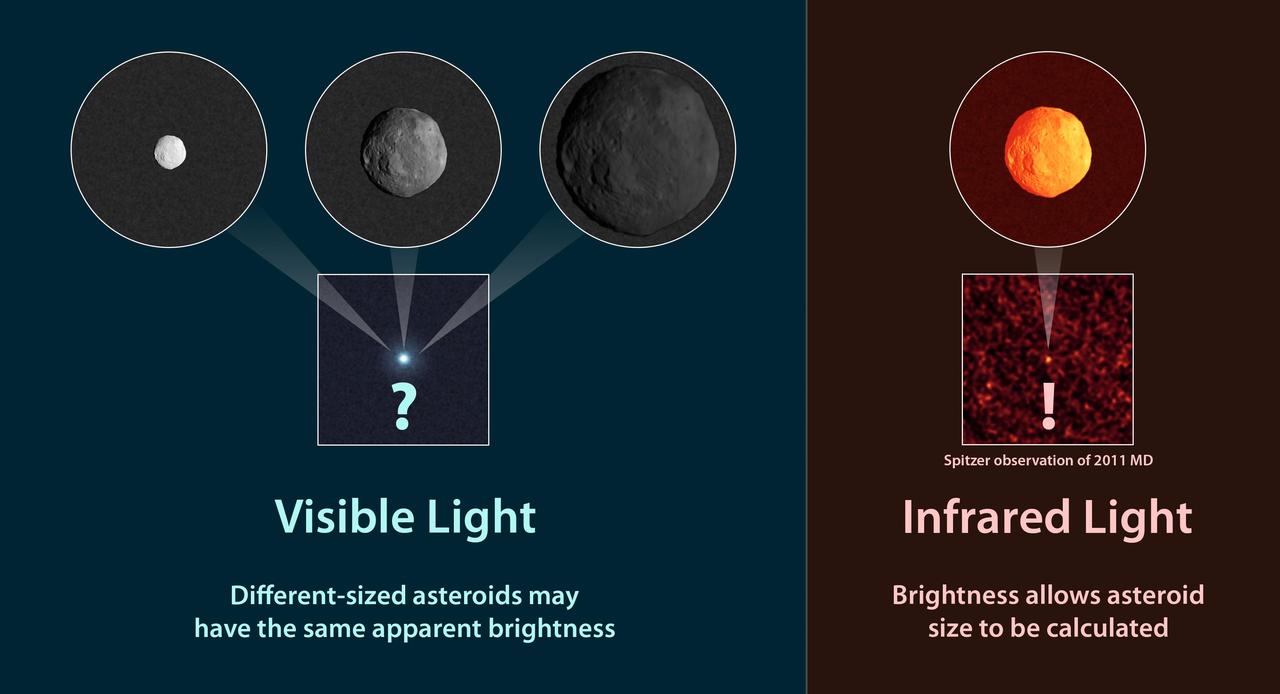
Observations of infrared light from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope coming from asteroids provide a better estimate of their true sizes than visible-light measurements.
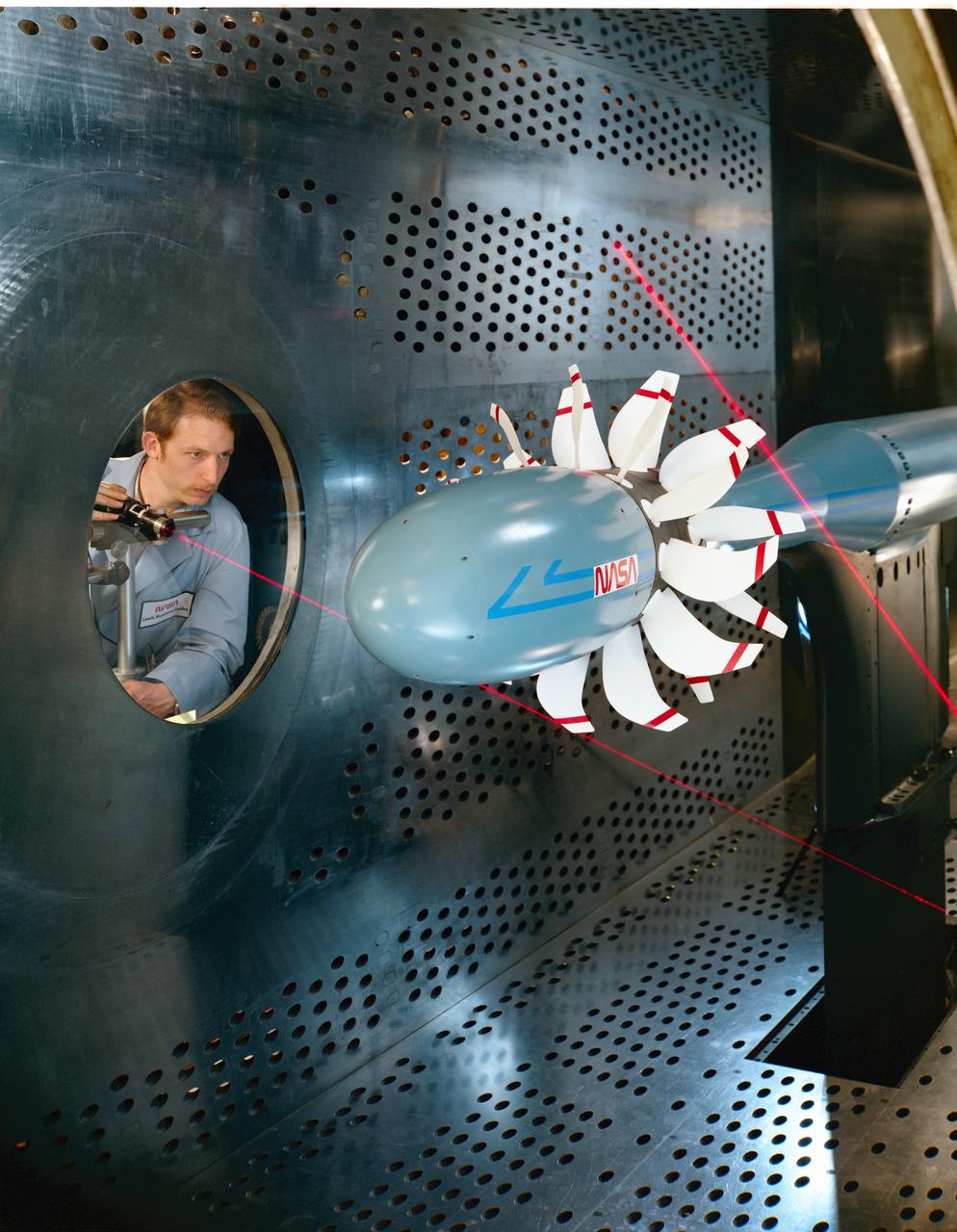
Laser based blade deflection measurement system on Counter Rotation Pusher Propeller model in 8x6 SWT (Supersonic Wind Tunnel)
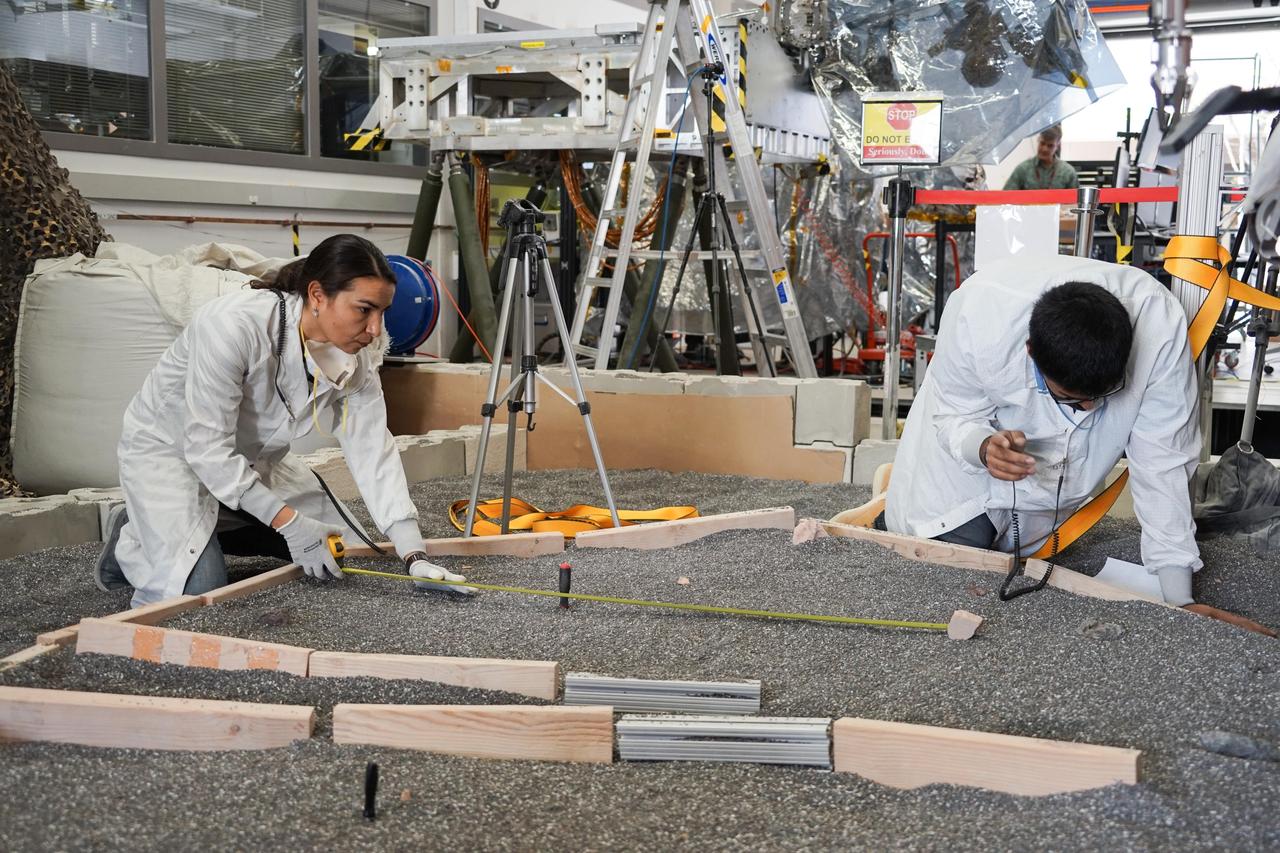

Engineers Marleen Sundgaard (left) and Pranay Mishra measure their test lander's "workspace" -- the terrain where scientists want to set InSight's instruments -- at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Making sure each feature of the workspace on Mars is mimicked here on Earth allows for more reliable tests to be performed before actually setting down InSight's instruments. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22880
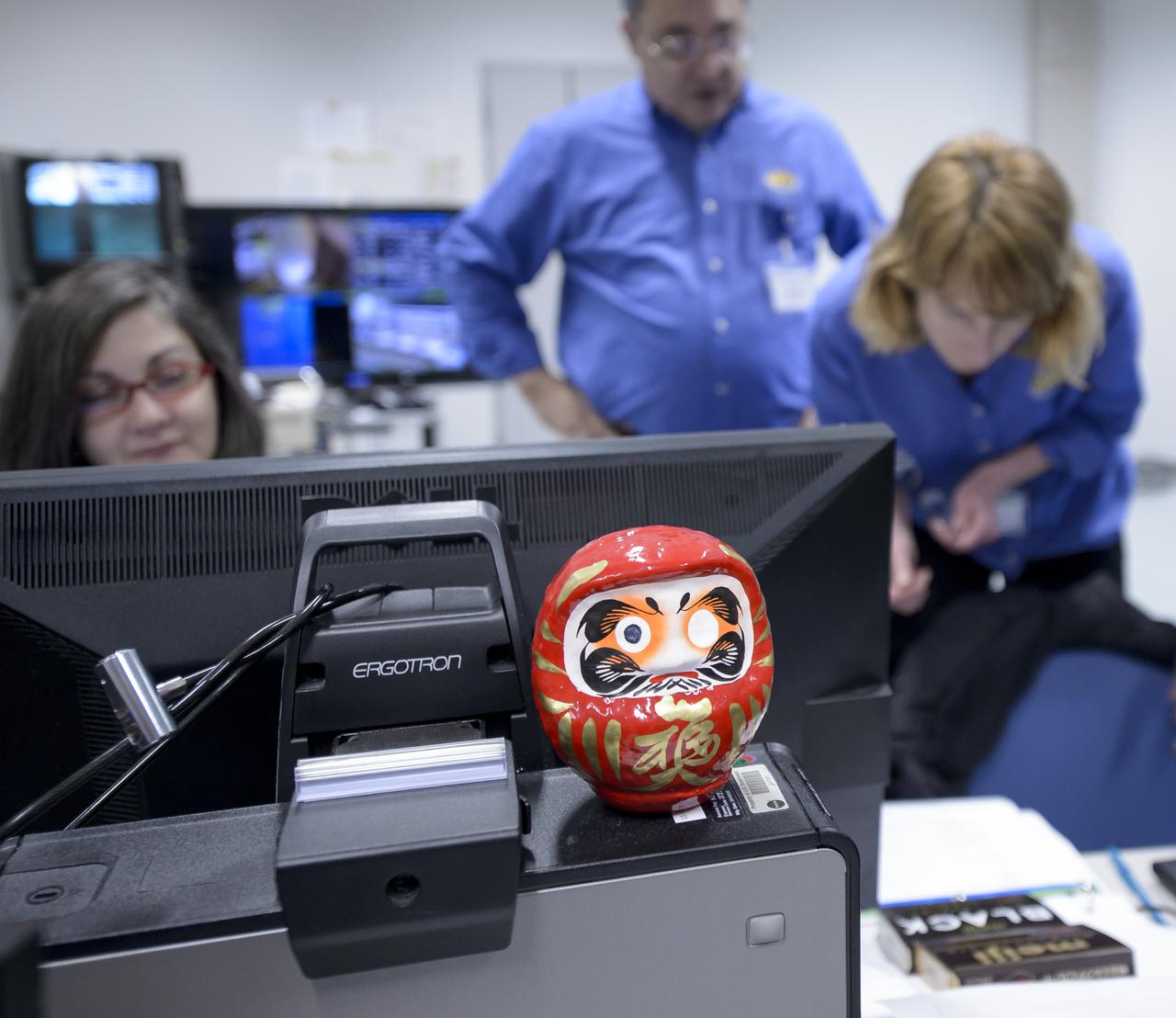

A daruma doll is seen amongst the NASA GPM Mission launch team in the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2) during the all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. One eye of the daruma doll is colored in when a goal is set, in this case a successful launch of GPM, and the second eye is colored in at the completion of the goal. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
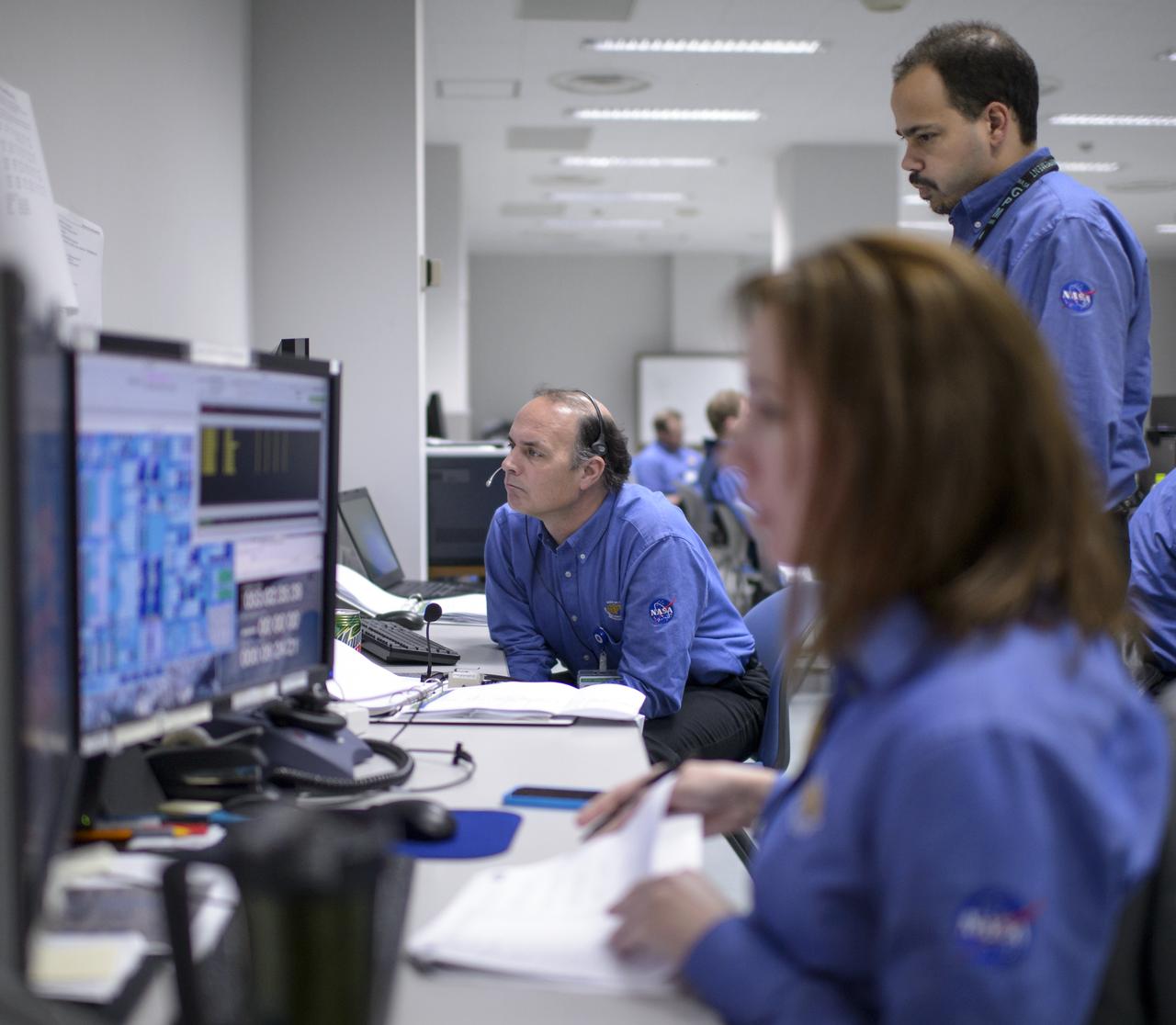

NASA GPM Test Conductors, Bill Dehaven, left, and John Pope, standing, and other GPM team members, participate in an all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
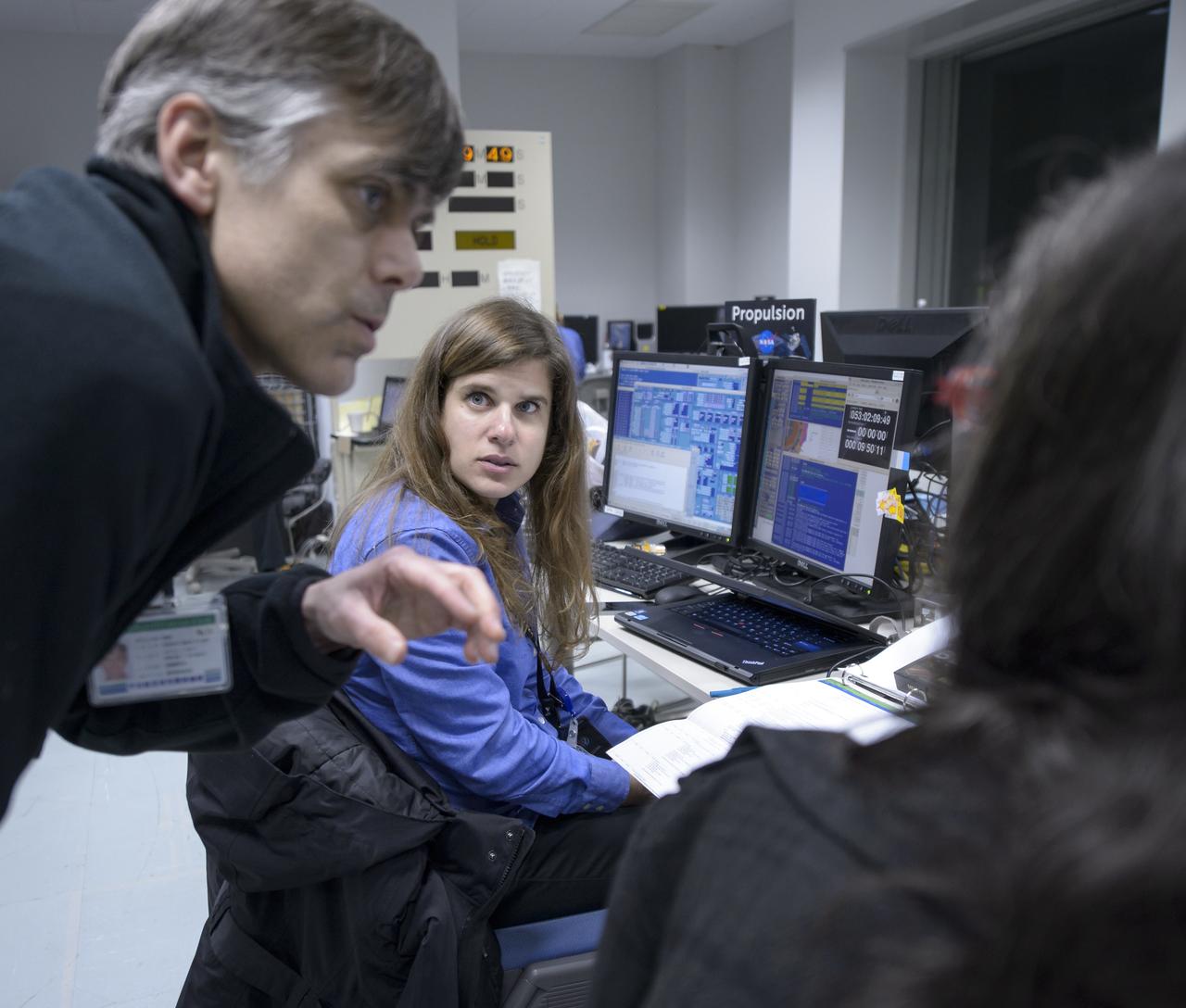

Andy Aylward, NASA GPM EGSE, left, Beth Weinsteen, NASA GPM Integration and Testing Team, center, and another GPM team member, talk during the all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
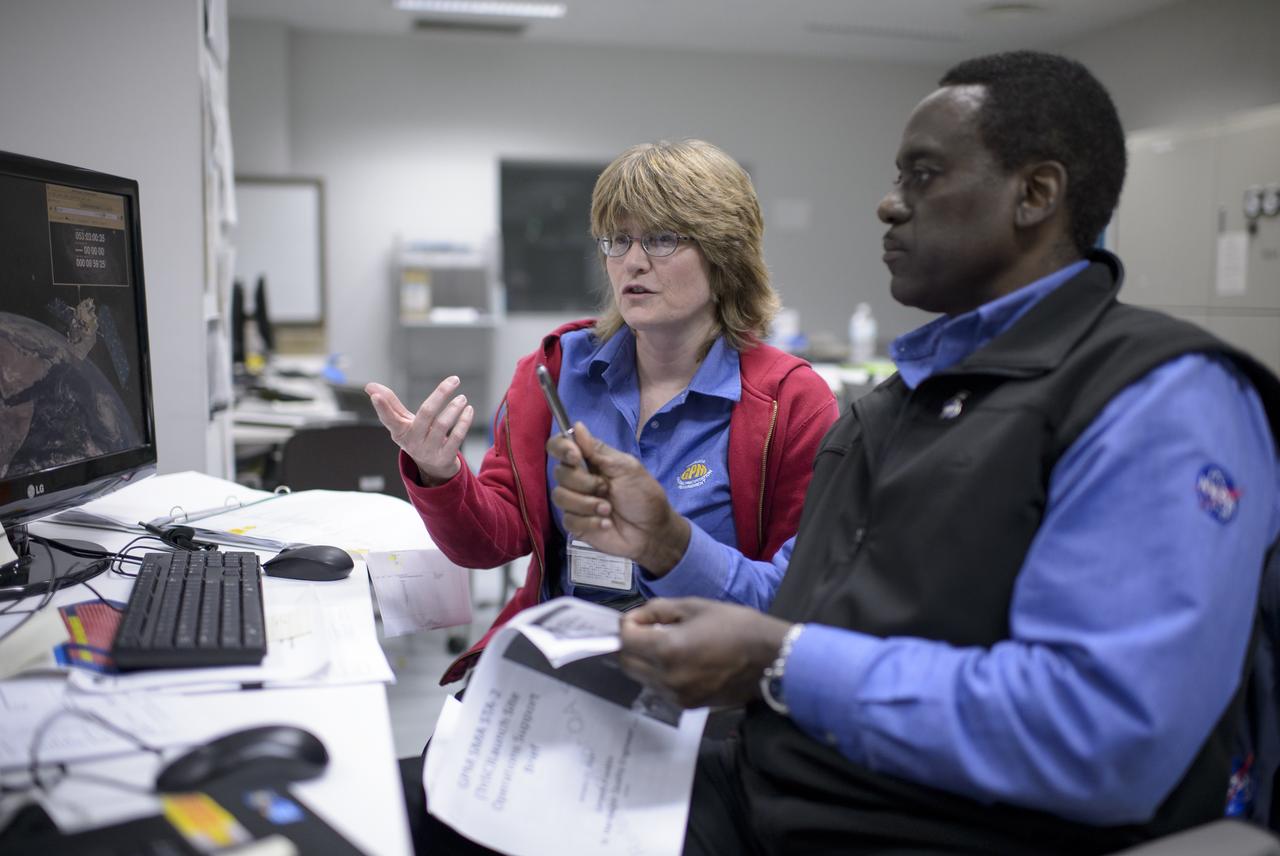

NASA GPM Safety Quality and Assurance, Shirley Dion, and, NASA GPM Quality and Assurance, Larry Morgan, monitor the all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
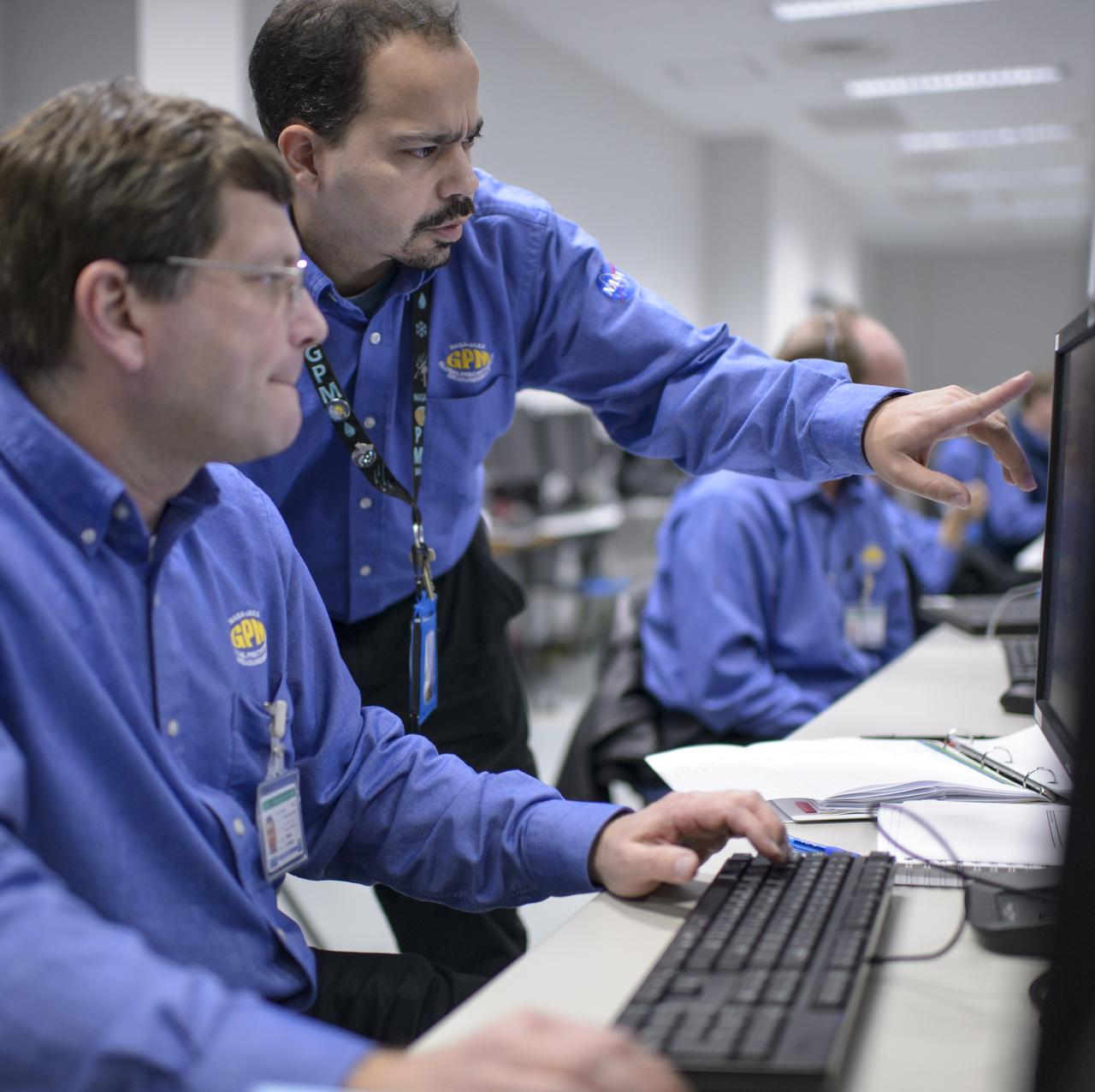

NASA GPM Systems team member Tim Grunner, left, and NASA GPM Test Conductor John Pope talk during an all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
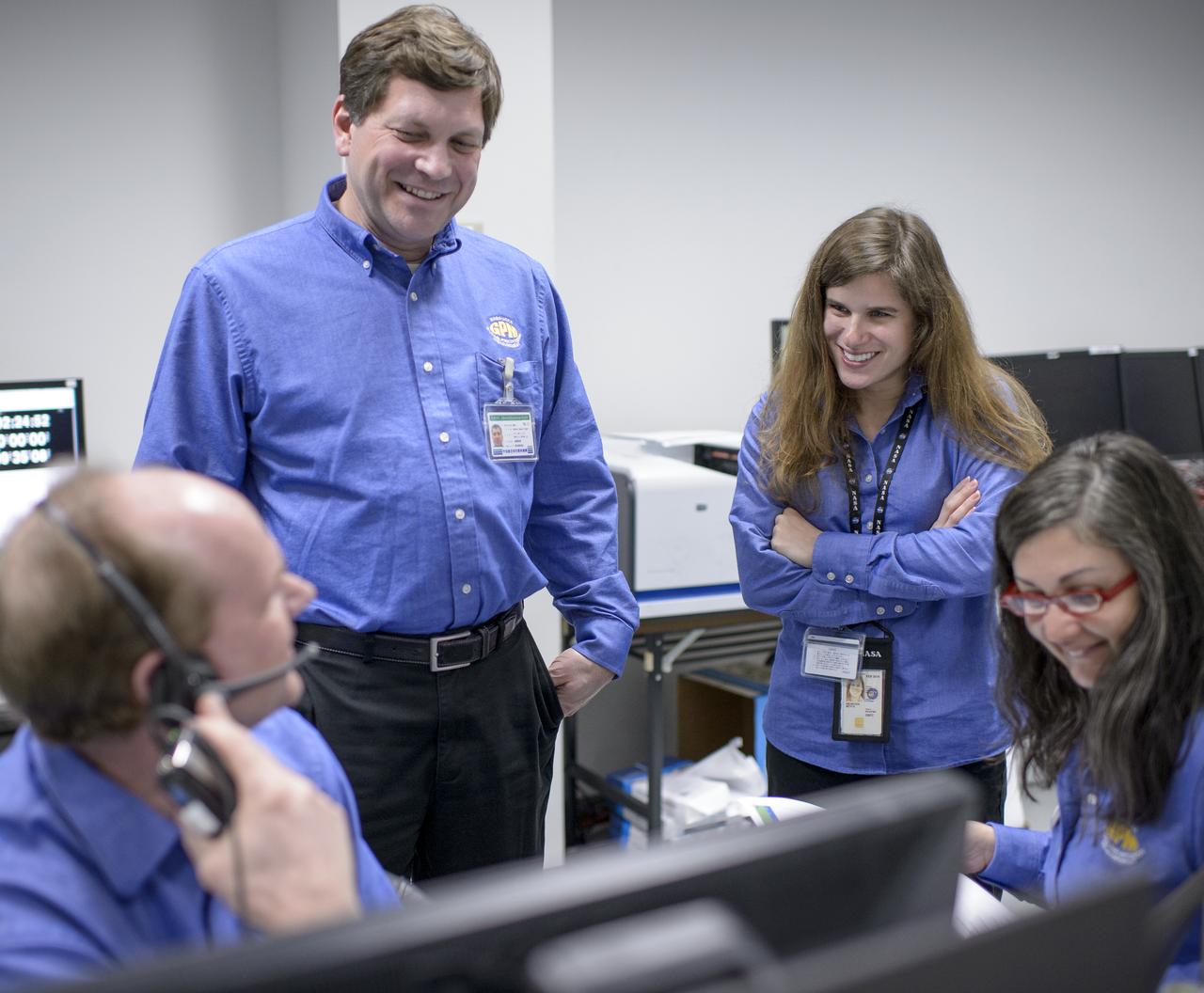

NASA GPM Systems team members, Tim Grunner, left, Harry Culver, 2nd from left, and, Liza Bartusek, right, talk, along with with GPM Testing team member Beth Weinsteen, during an all-day launch simulation for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory at the Spacecraft Test and Assembly Building 2 (STA2), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Tanegashima Island, Japan. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) plans to launch an H-IIA rocket carrying the GPM Core Observatory on Feb. 28, 2014. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
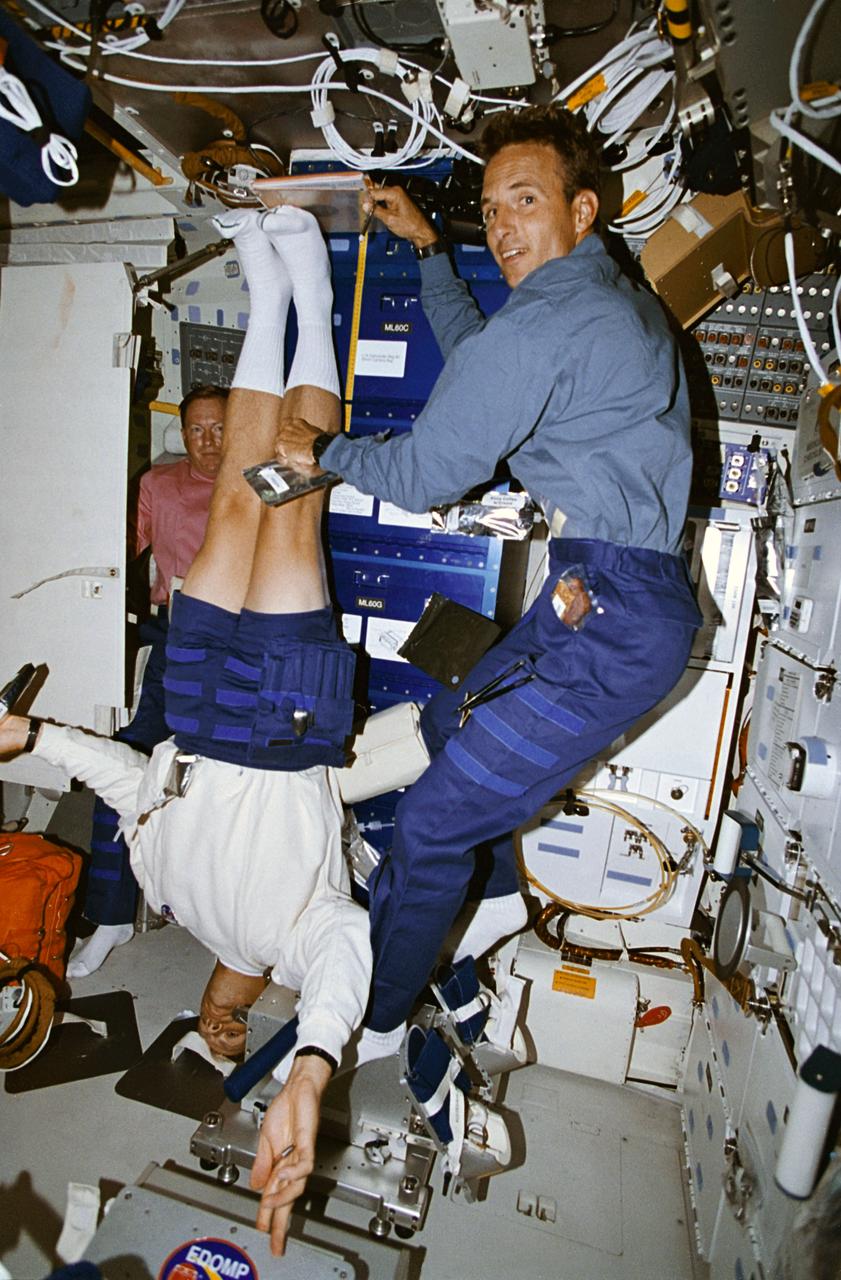

STS064-05-020 (9-20 Sept. 1994) --- Astronaut Mark C. Lee gets his height measured by astronaut Jerry M. Linenger as part of a daily in-flight routine supporting a medical Detailed Supplementary Objective (DSO). Astronaut Richard N. Richards, STS-64 mission commander, looks on in the background. This study was designed to collect information about back pain and height changes experienced by astronauts during flight. Crew members participating in this DSO are required to record height measurements and long back-pain symptoms daily. As an ongoing program, this DSO will gather data from 30 astronauts who spend more than eight consecutive days in space. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
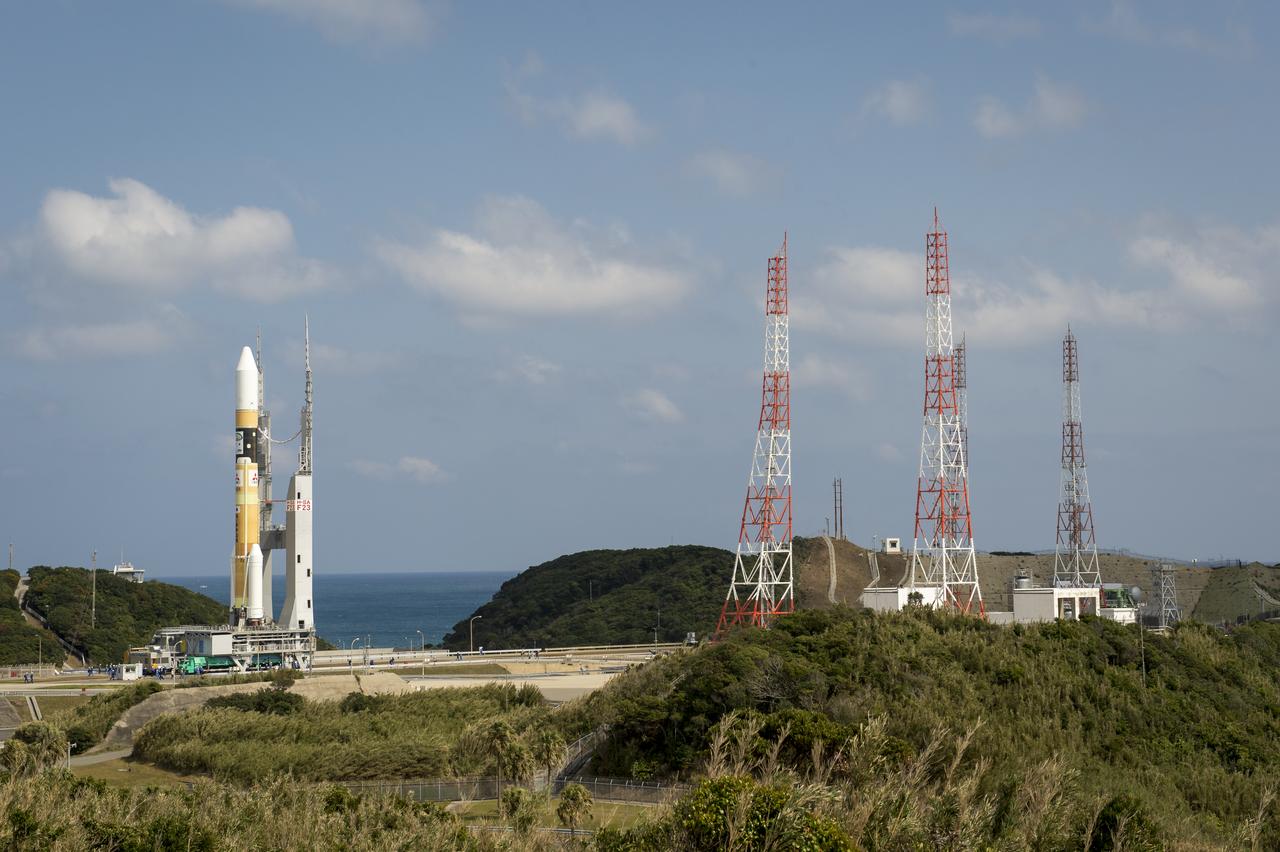

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
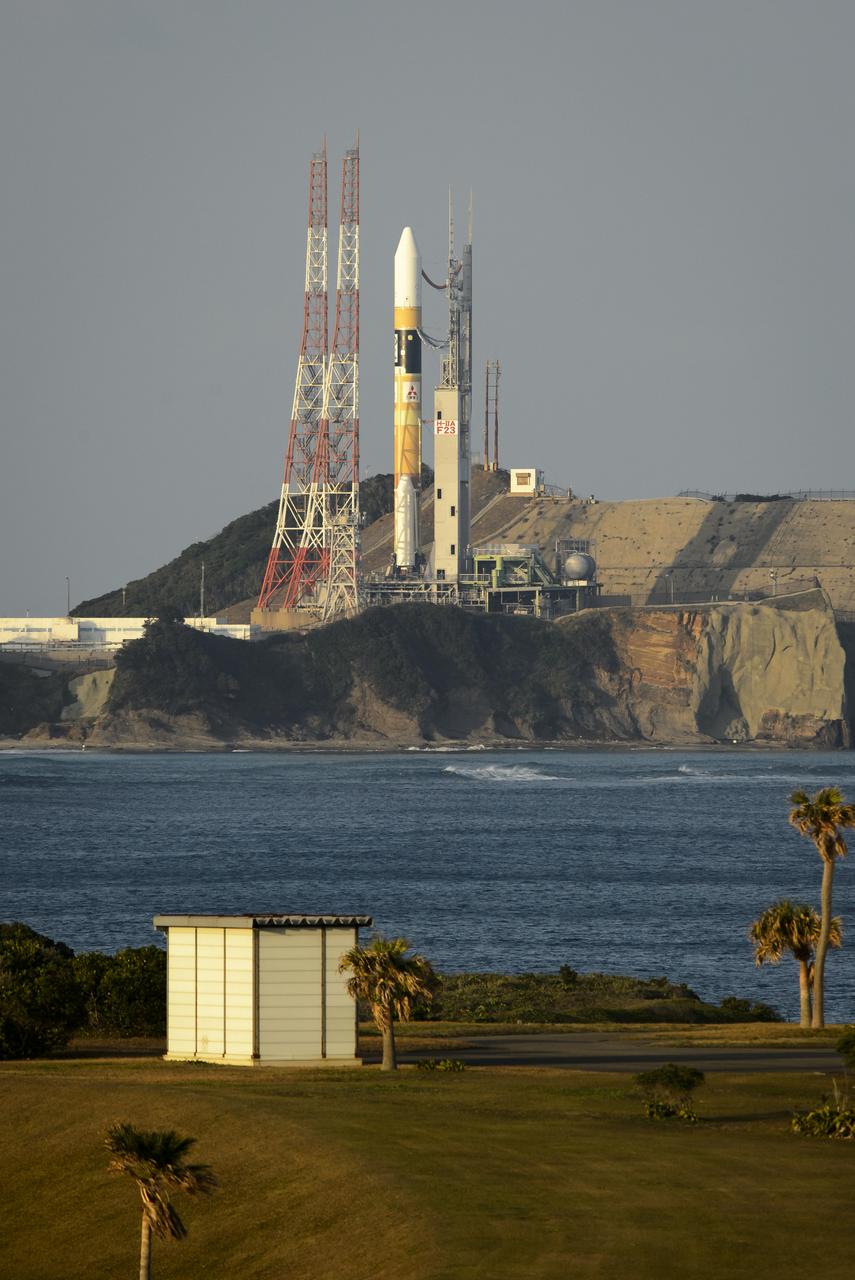

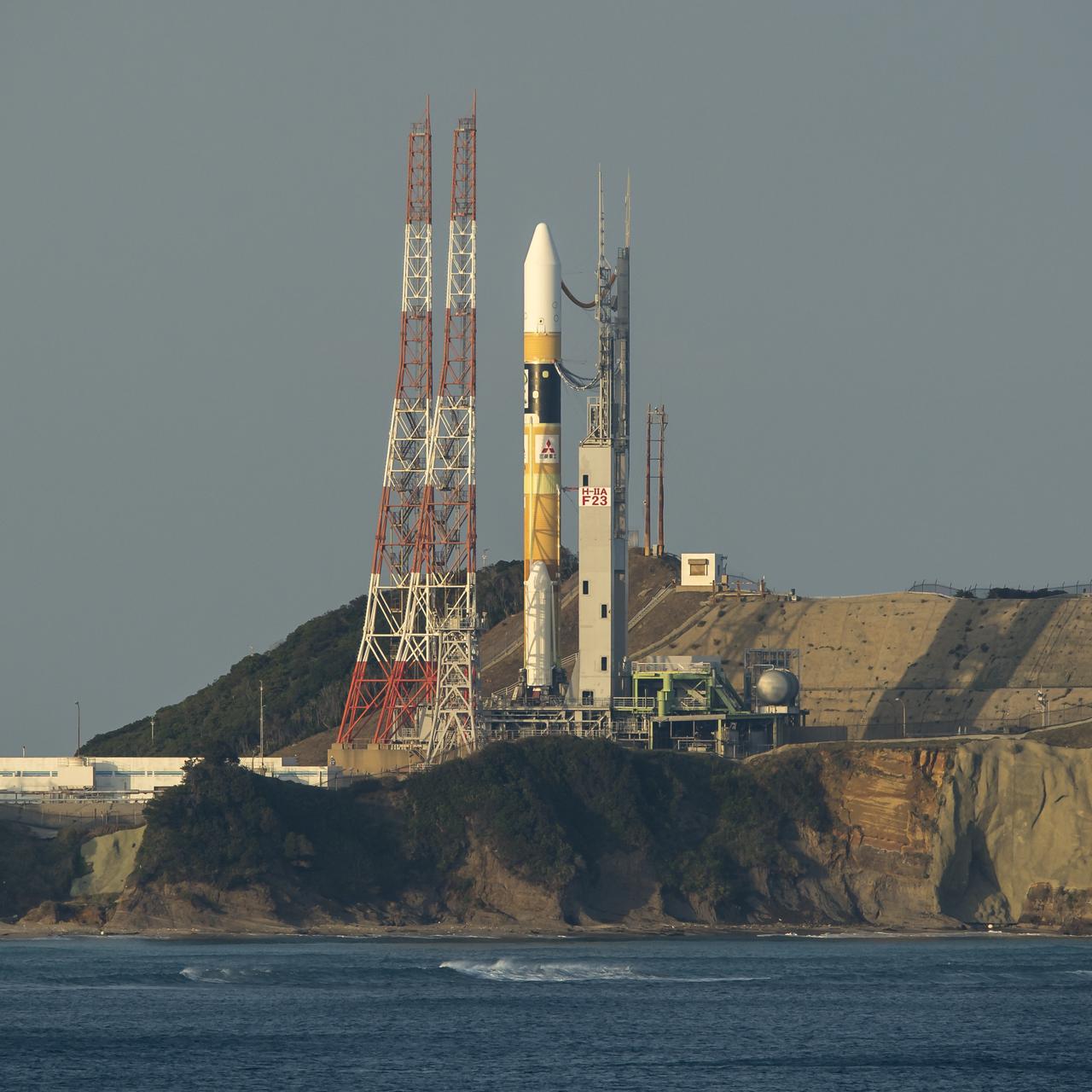
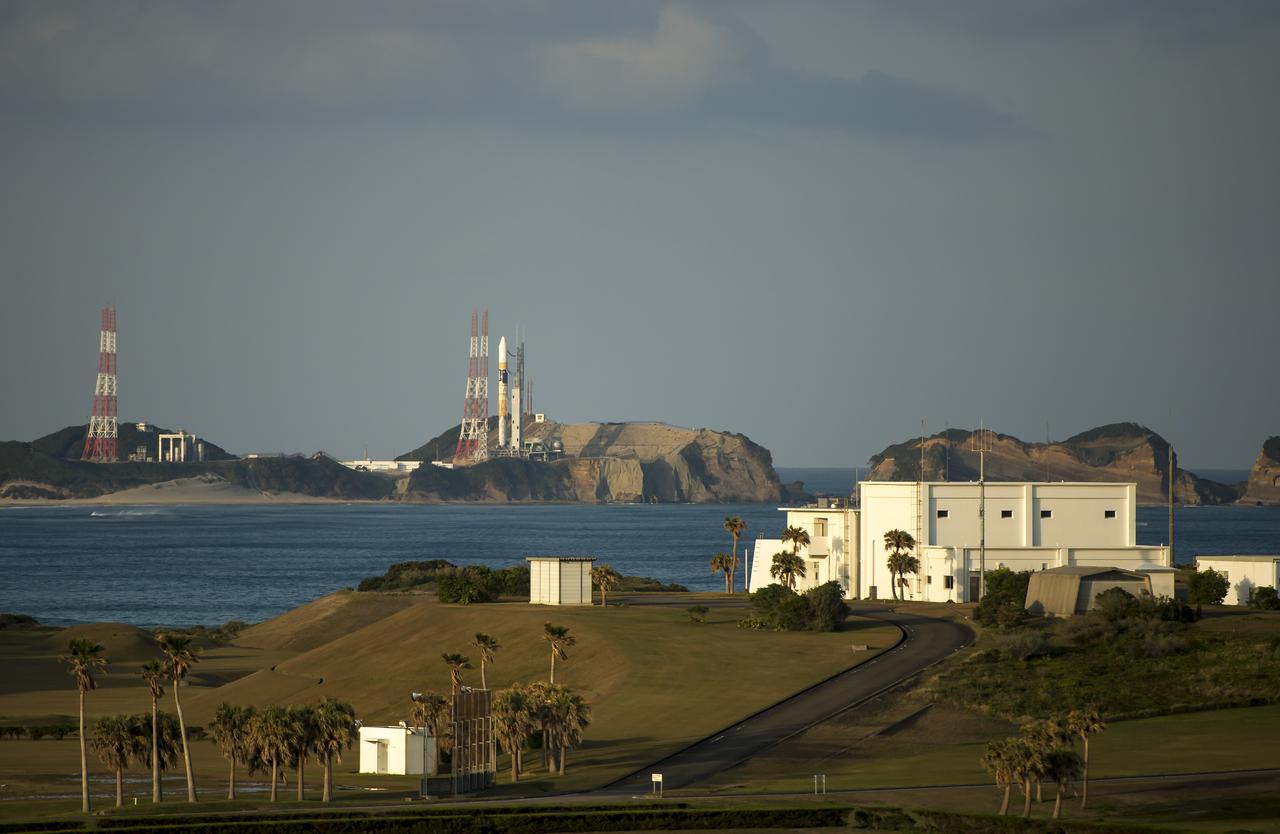
A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard is seen on launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

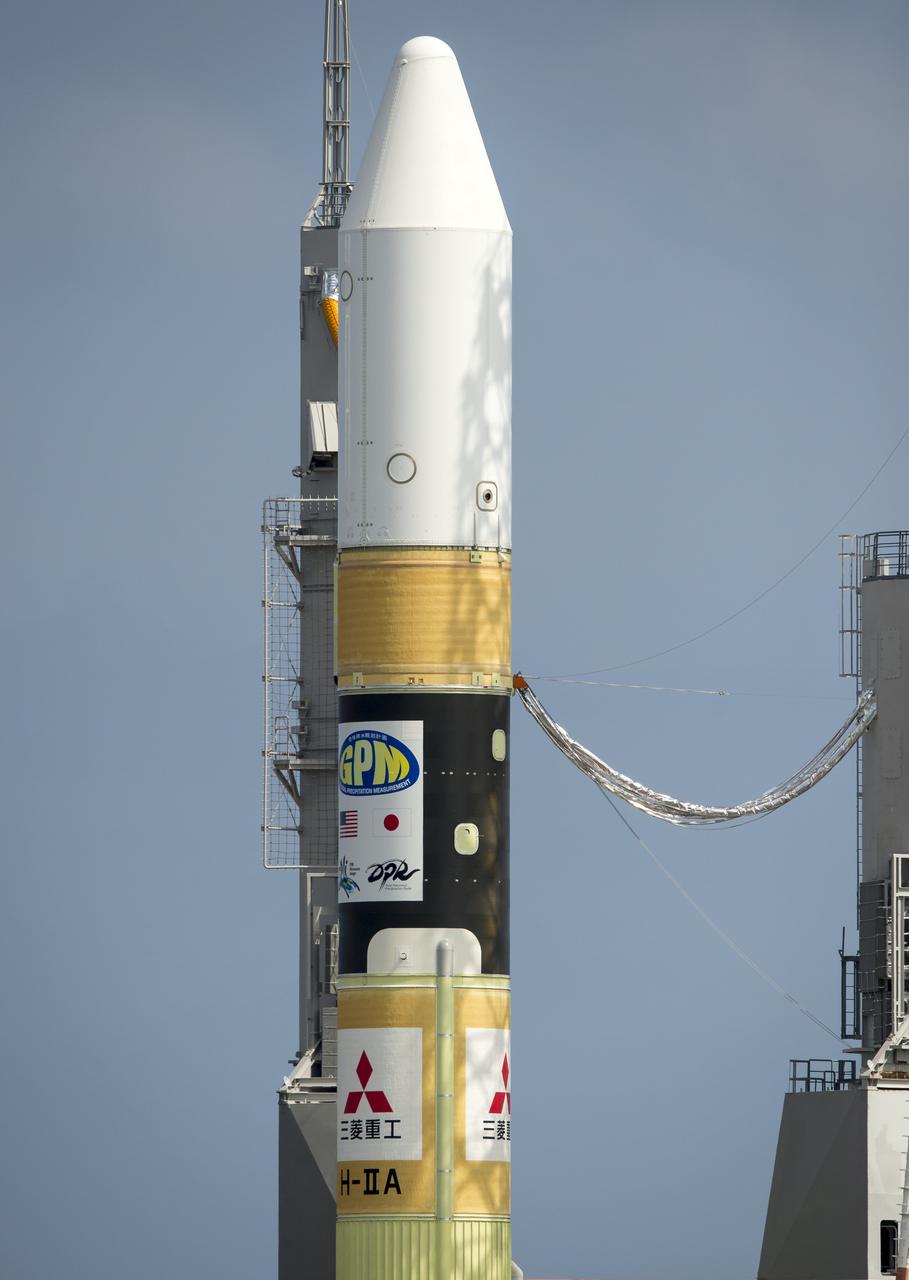
A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard is seen on launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
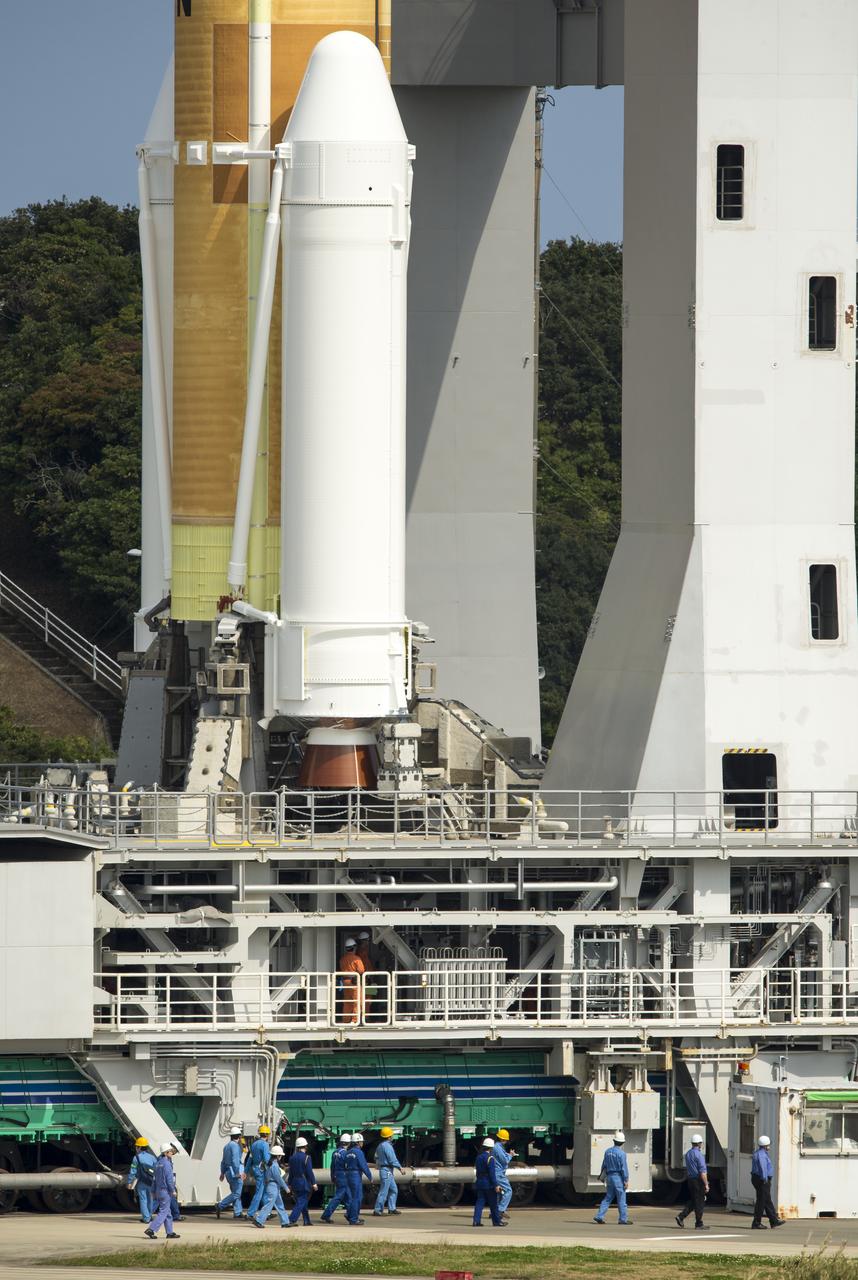

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
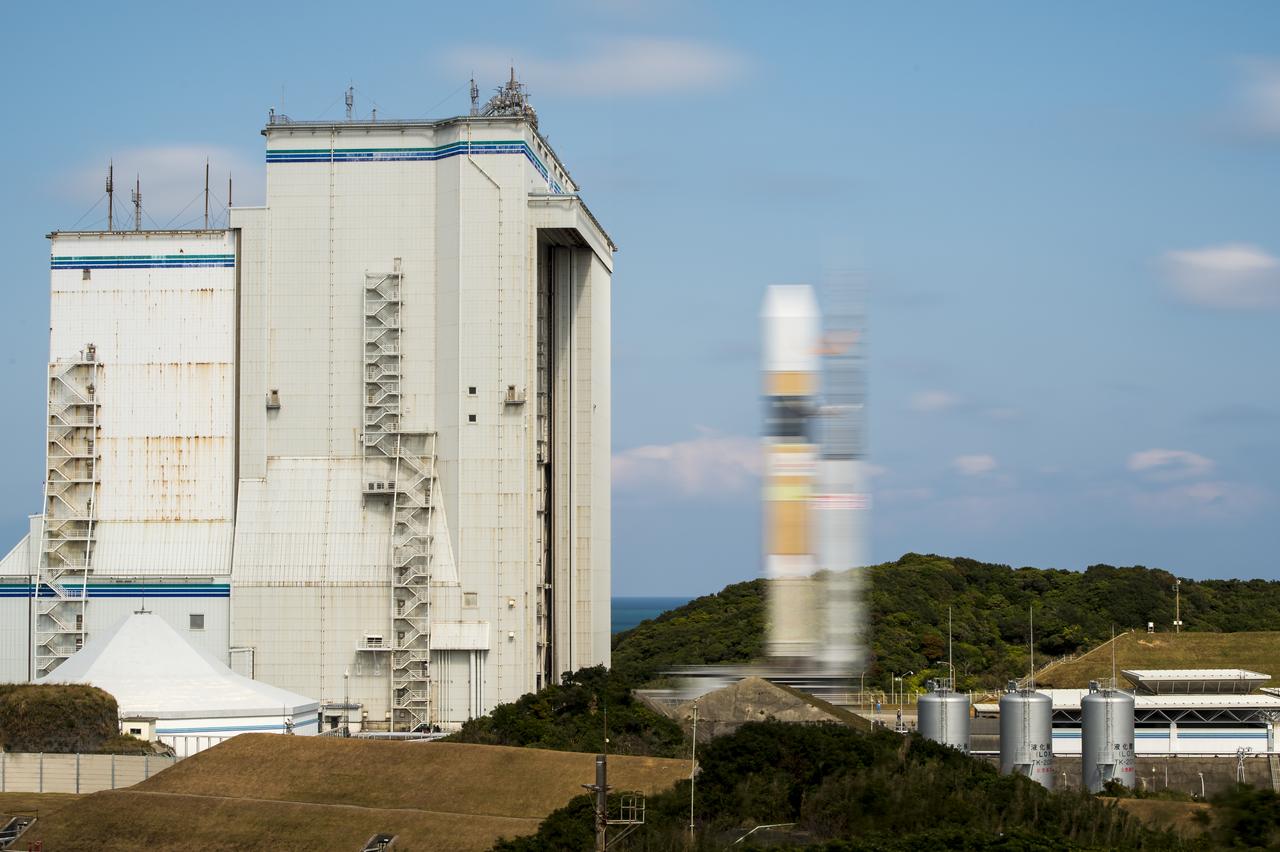

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen in this 10 second exposure as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
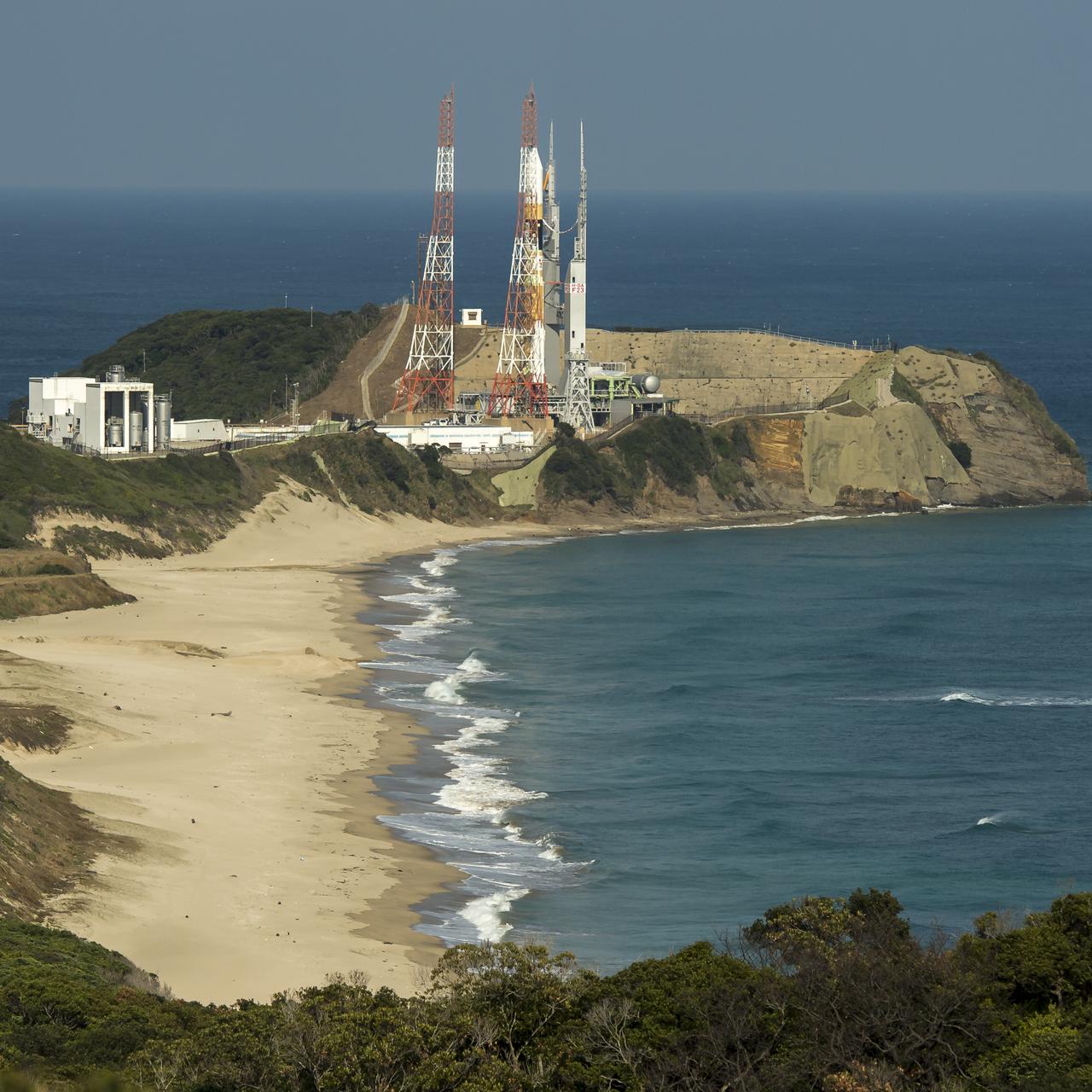

A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard is seen on launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
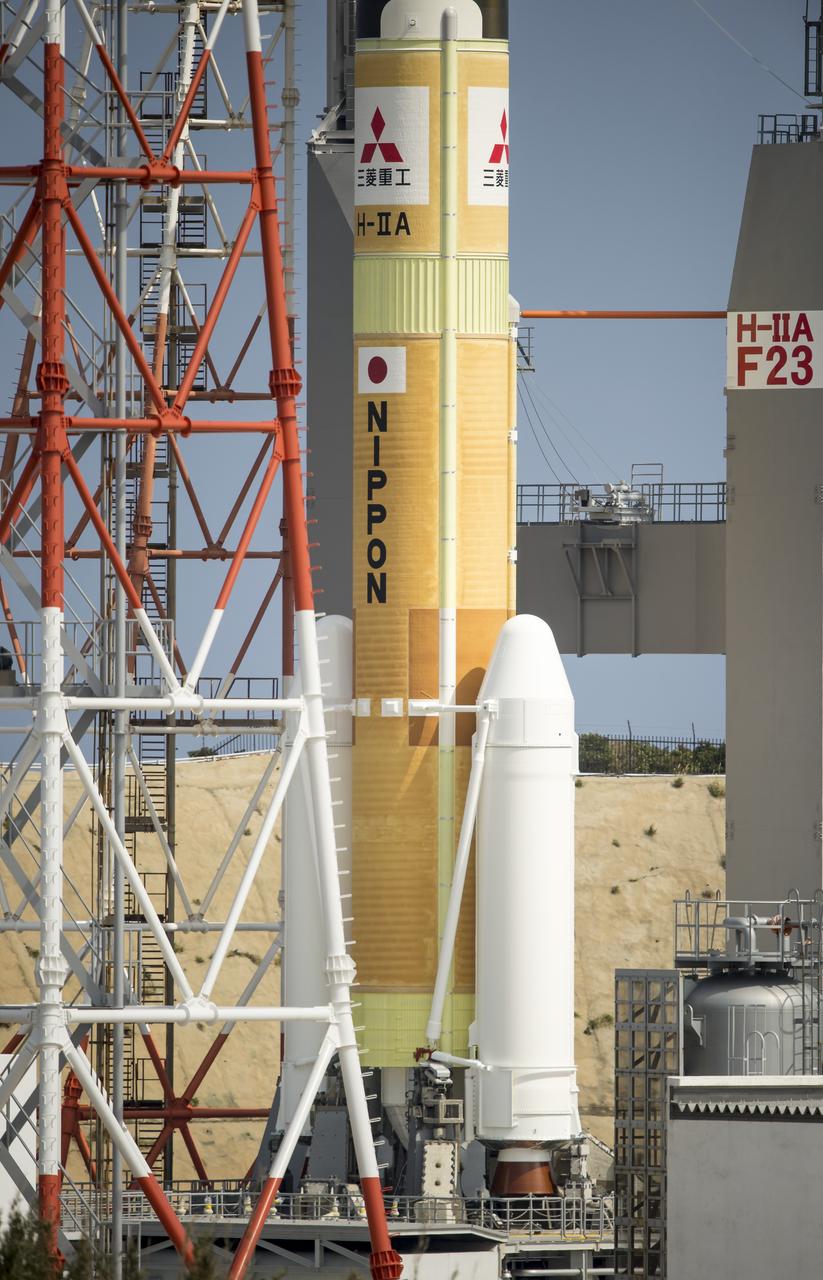

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

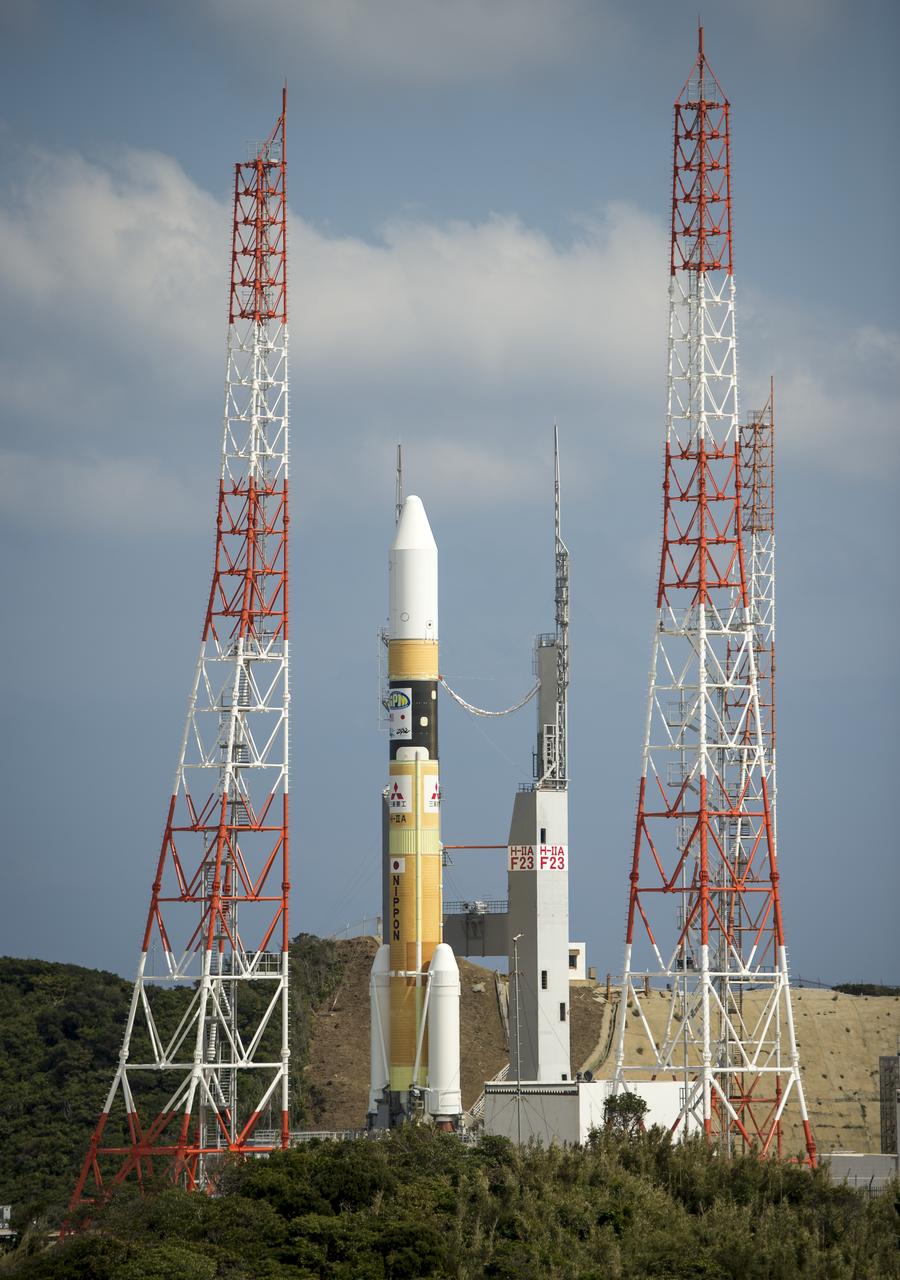
A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard is seen on launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
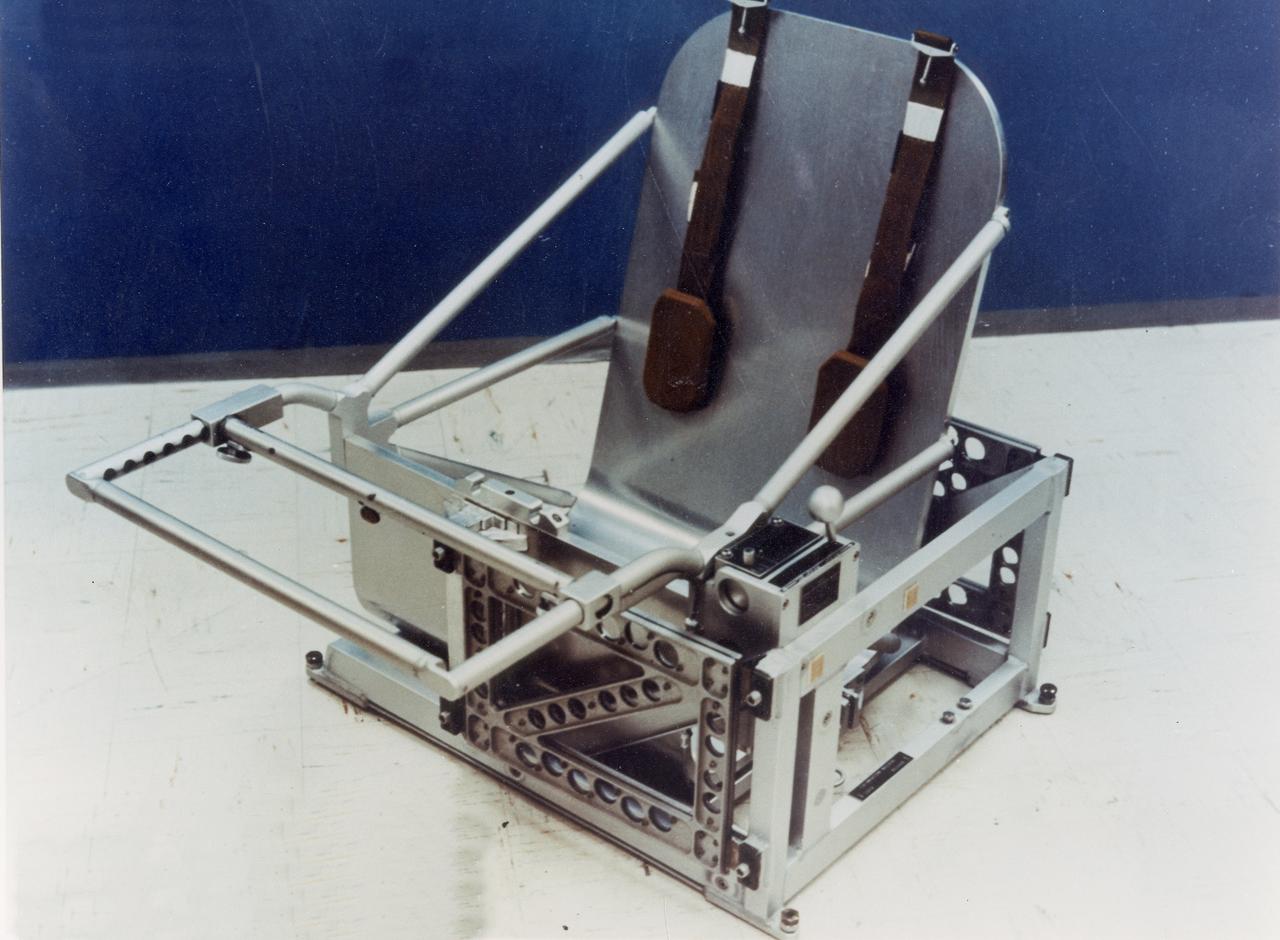
Skylab's Body Mass Measurement chair, the facility of the Body Mass Measurement experiment (M172), is shown here in this 1970 photograph. The M172 experiment determined the body mass of each crew member and observed changes in body masses during flight. Knowledge of exact body mass variations throughout the flight in significantly aided in the correlation of other medical data obtained during the flight. Mass measurements under zero-gravity conditions were achieved by the application of Newton's second law (force equals mass times acceleration). The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
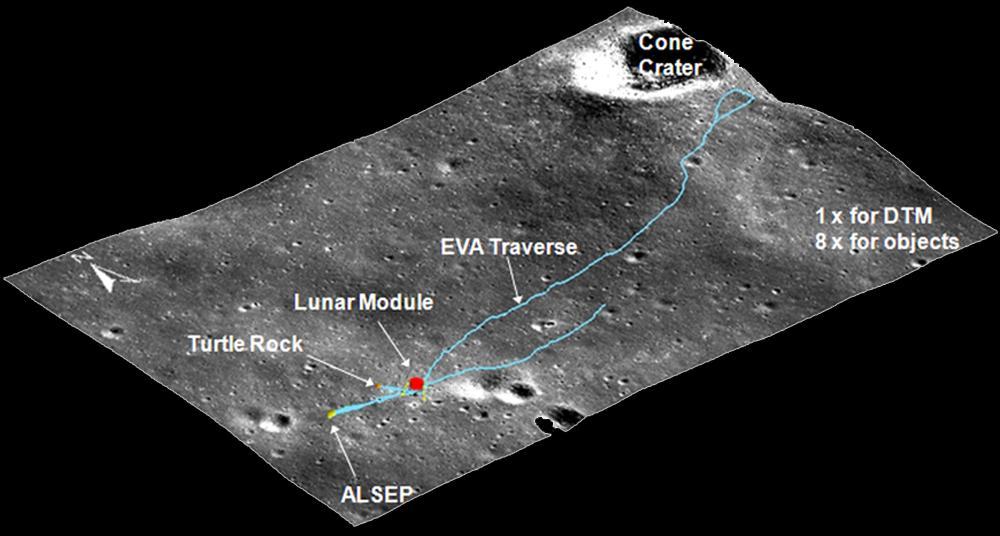
Precise 3D Measurements of Objects at Apollo 14 Landing Site
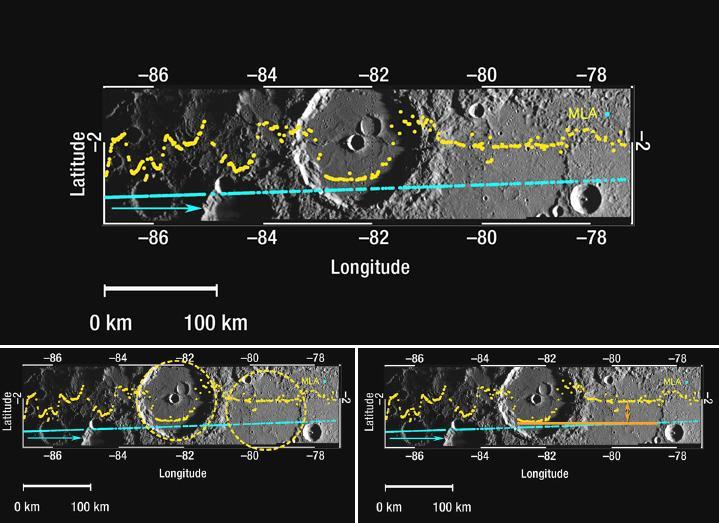
Mercury Laser Altimeter MLA Measures the Depths of Mercury Craters
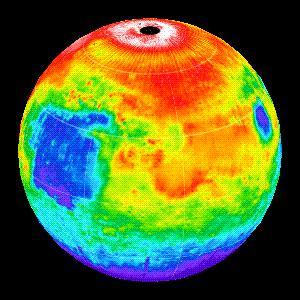
Martian Temperatures Measured by the Thermal Emission Spectrometer TES. Isidis Planitia View