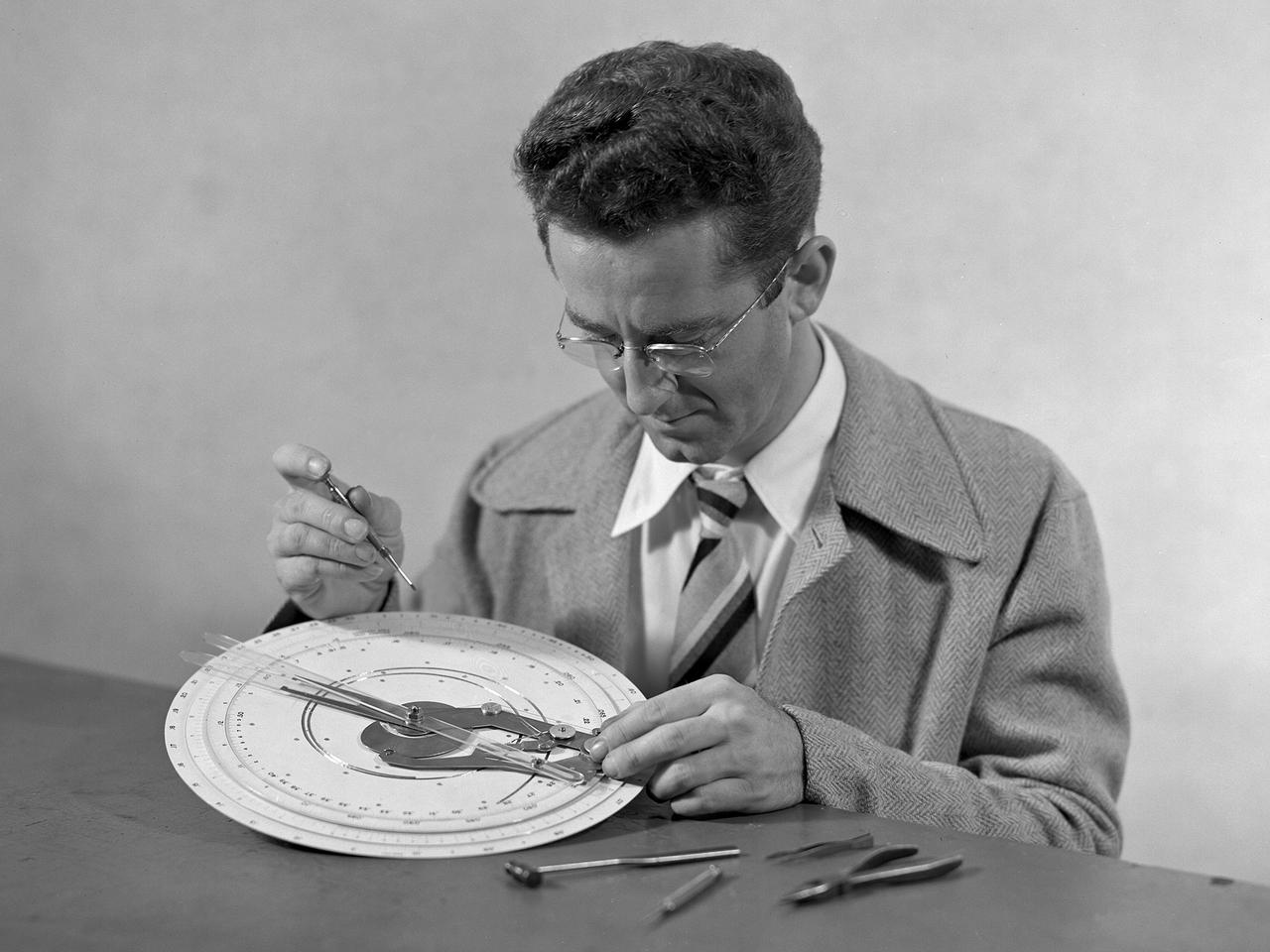

Technician at work adjusting an unidentified mechanical computing device.

A device with six mechanical legs, the hexapod is a critical part of the Planetary Instrument for X-ray Lithochemistry (PIXL), one of the instruments aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. The hexapod allows PIXL to make slow, precise movements to get closer to and point at specific parts of a rock's surface in order for the instrument to use its X-ray to discover where — and in what quantity — chemicals are distributed there. This GIF has been considerably sped up to show how the hexapod moves. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24094
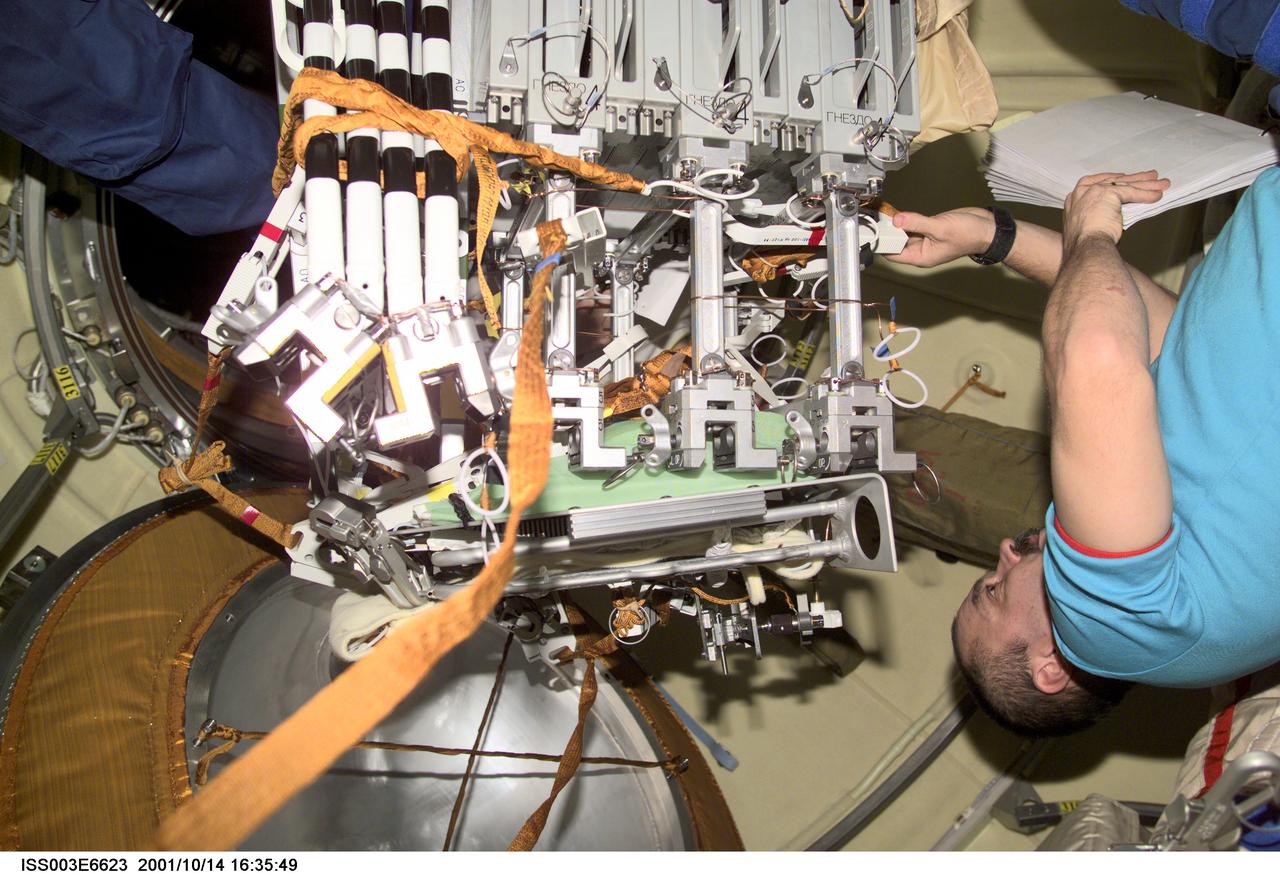

ISS003-E-6623 (14 October 2001) --- Cosmonaut Mikhail Tyurin, Expedition Three flight engineer representing Rosaviakosmos, works with hardware for the Micro-Particles Capturer (MPAC) and Space Environment Exposure Device (SEED) experiment and fixture mechanism in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). MPAC and SEED were developed by Japan’s National Space Development Agency (NASDA), and Russia developed the Fixture Mechanism. This image was taken with a digital still camera.
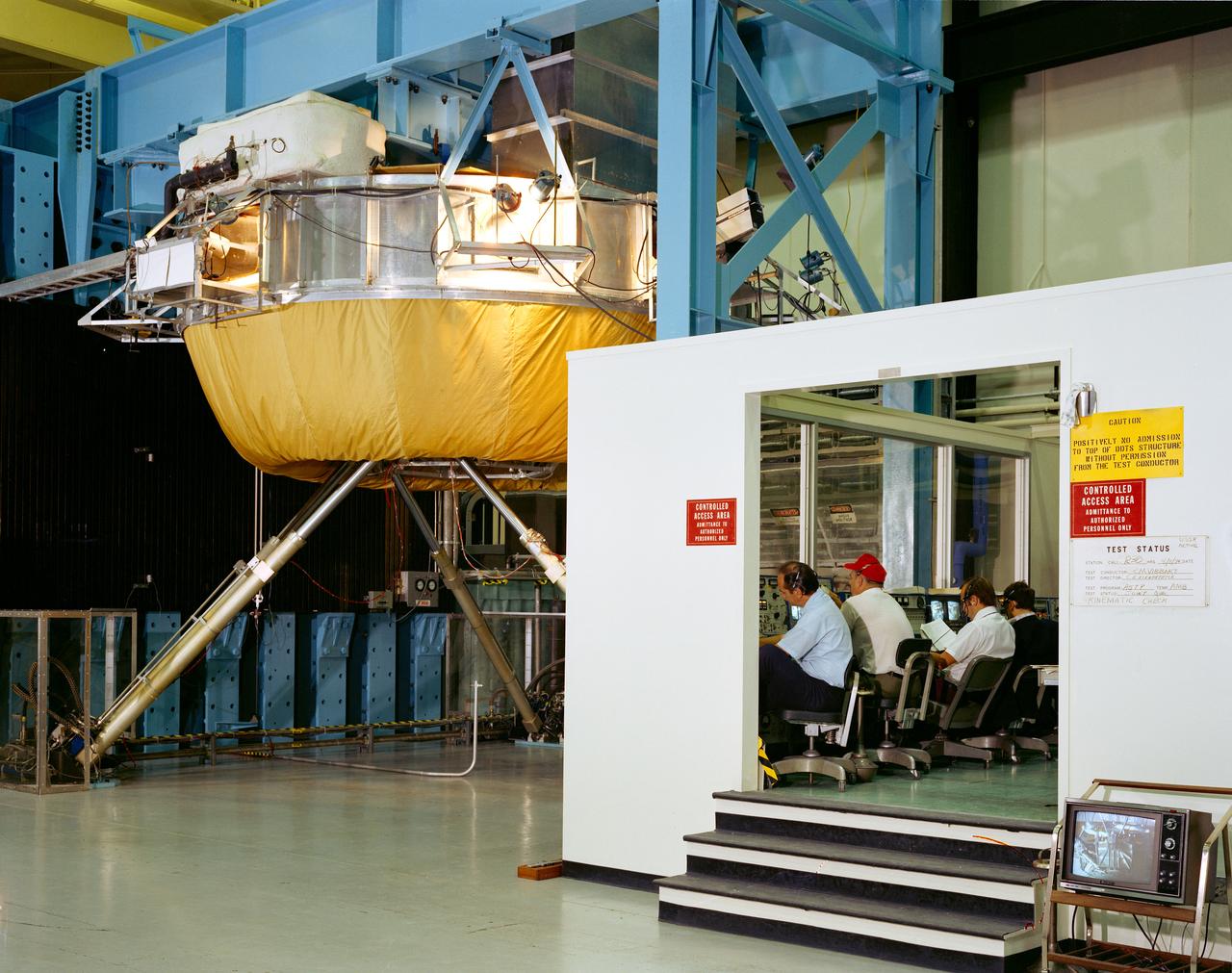

S74-27049 (4 Aug. 1974) --- Overall view of test set-up in Building 23 at the Johnson Space Center during testing of the docking mechanisms for the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The cinematic check was being made when this picture was taken. The test control room is on the right. The Soviet-developed docking system is atop the USA-NASA developed docking system. Both American and Soviet engineers can be seen taking part in the docking testing. The ASTP docking mission in Earth orbit is scheduled for July 1975.
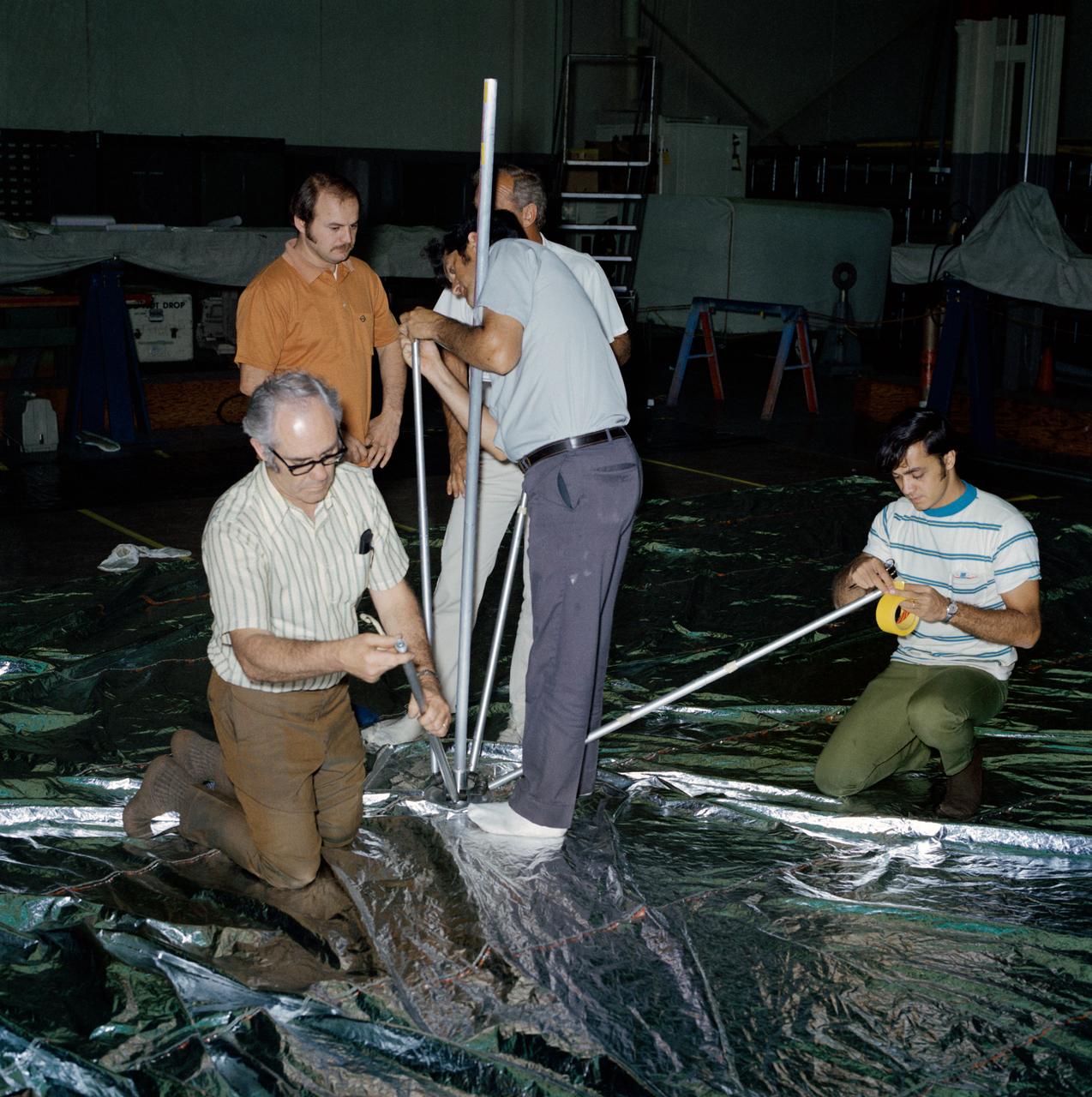

S73-26380 (23 May 1973) --- Technicians in the Technical Services shop in Building 10 work on the fabrication of the umbrella-like mechanical device called the “parasol” during Skylab 2 preflight preparations at NASA's Johnson Space Center. Here, they are attaching the telescoping extension rods to the canopy. The “parasol” is designed to fit into the TO27 experiment photometer canister. The canopy is 24 feet by 22 feet. The sunshade device will be deployed through the solar scientific airlock in the side of the OWS. The “parasol” solar shield is considered the prime possibility for use as the OWS sunshade because it will not require EVA by the Skylab 2 crewmen, because of the operational ease of using it, and because of the simplicity of the device which minimizes crew training. Photo credit: NASA
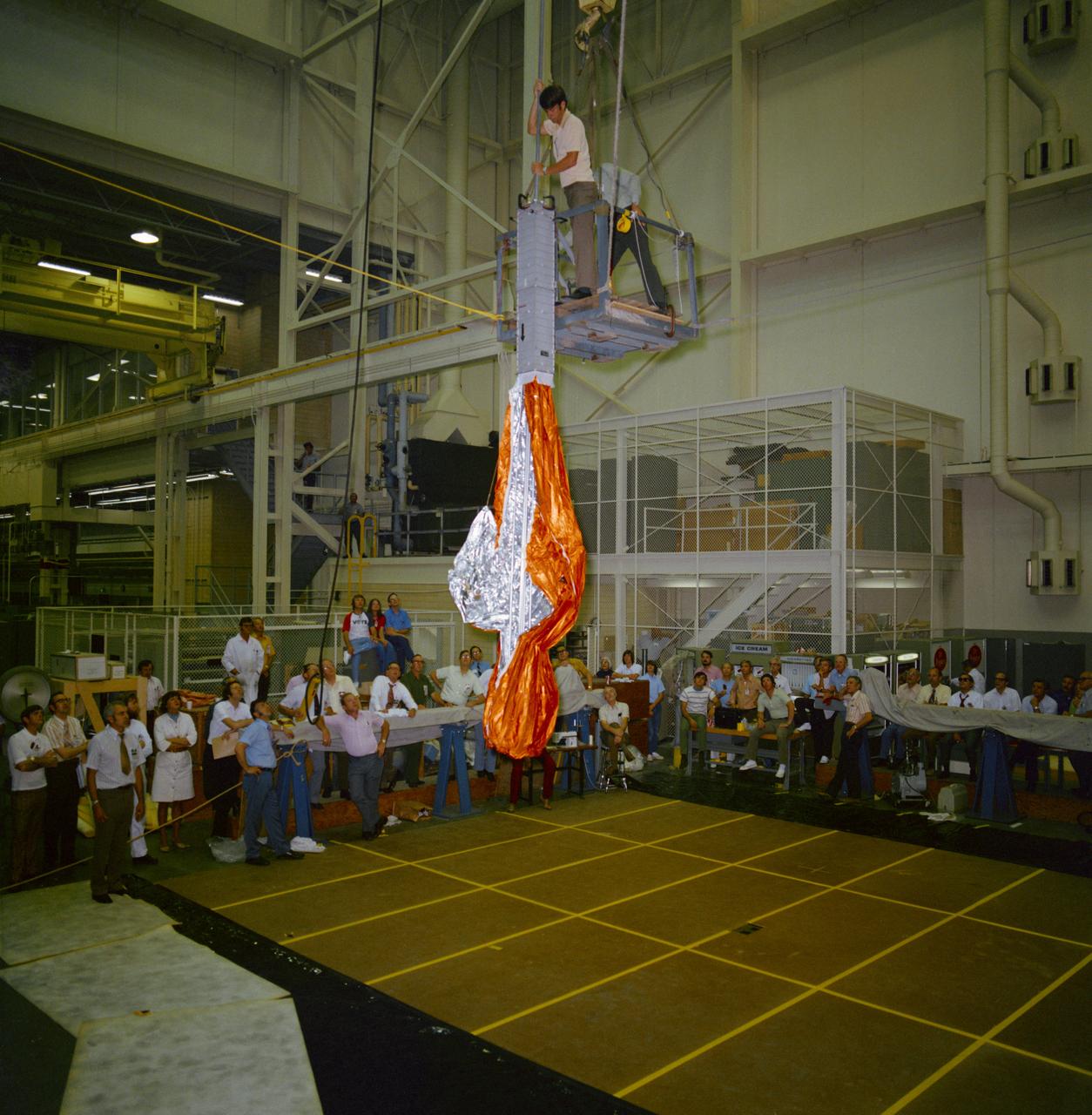

S73-26401 (23 May 1973) --- An umbrella-like mechanical device called the "parasol", one of the several sunscreen possibilities being considered for use in shading the overheated Skylab 1 Orbital Workshop (OWS), receives a checkout in the Technical Services shop in Bldg. 10 at Johnson Space Center. Here, a technician starts to deploy the "parasol" sunshade. The "parasol" is designed to fit into the T027 experiment photometer canister. The canopy portion of the "parasol" measures 24 feet by 22 feet. Photo credit: NASA
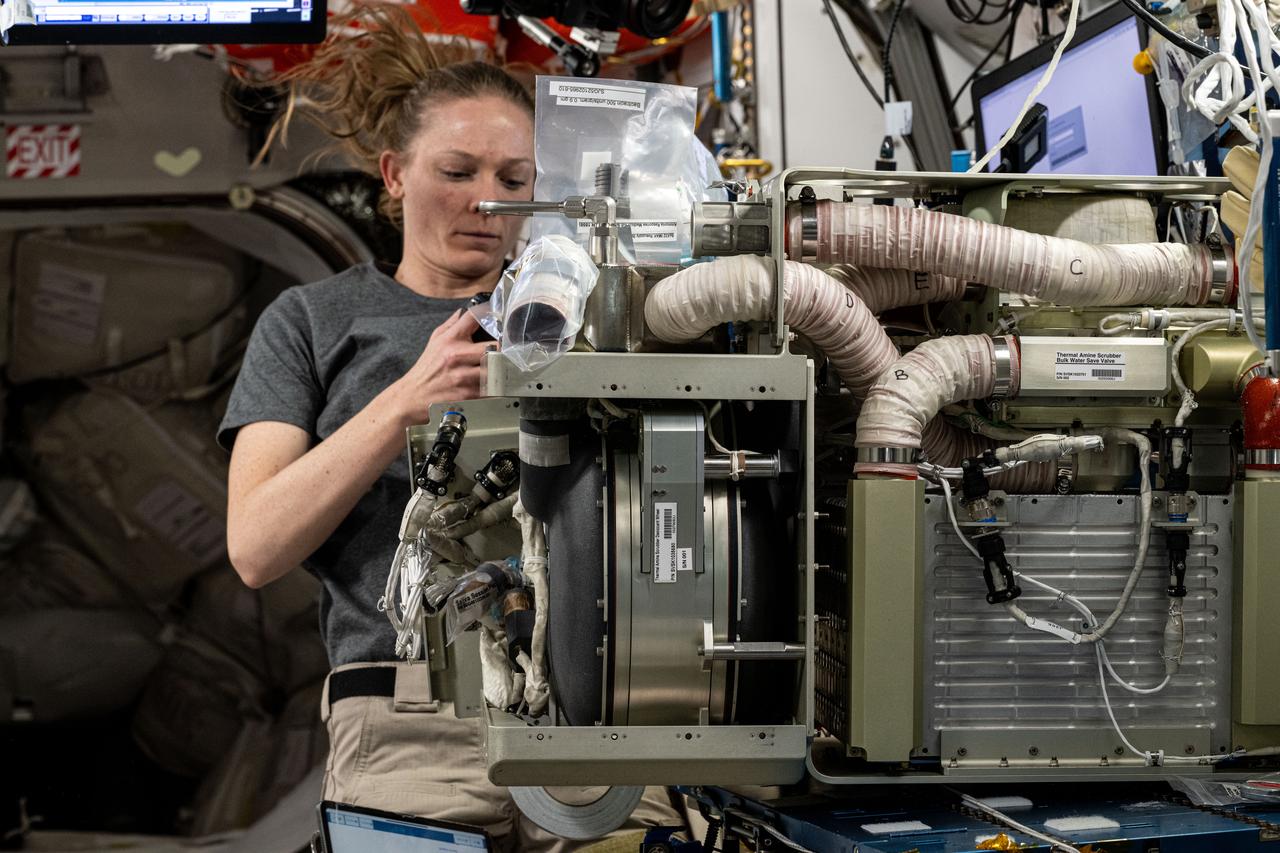

iss073e0118580 (May 27, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers replaces components on an experimental carbon dioxide removal device aboard the International Space Station. Also called the Thermal Amine Scrubber, the advanced life support mechanism is testing a new method that removes carbon dioxide from the station’s atmosphere and recovers water for oxygen generation.
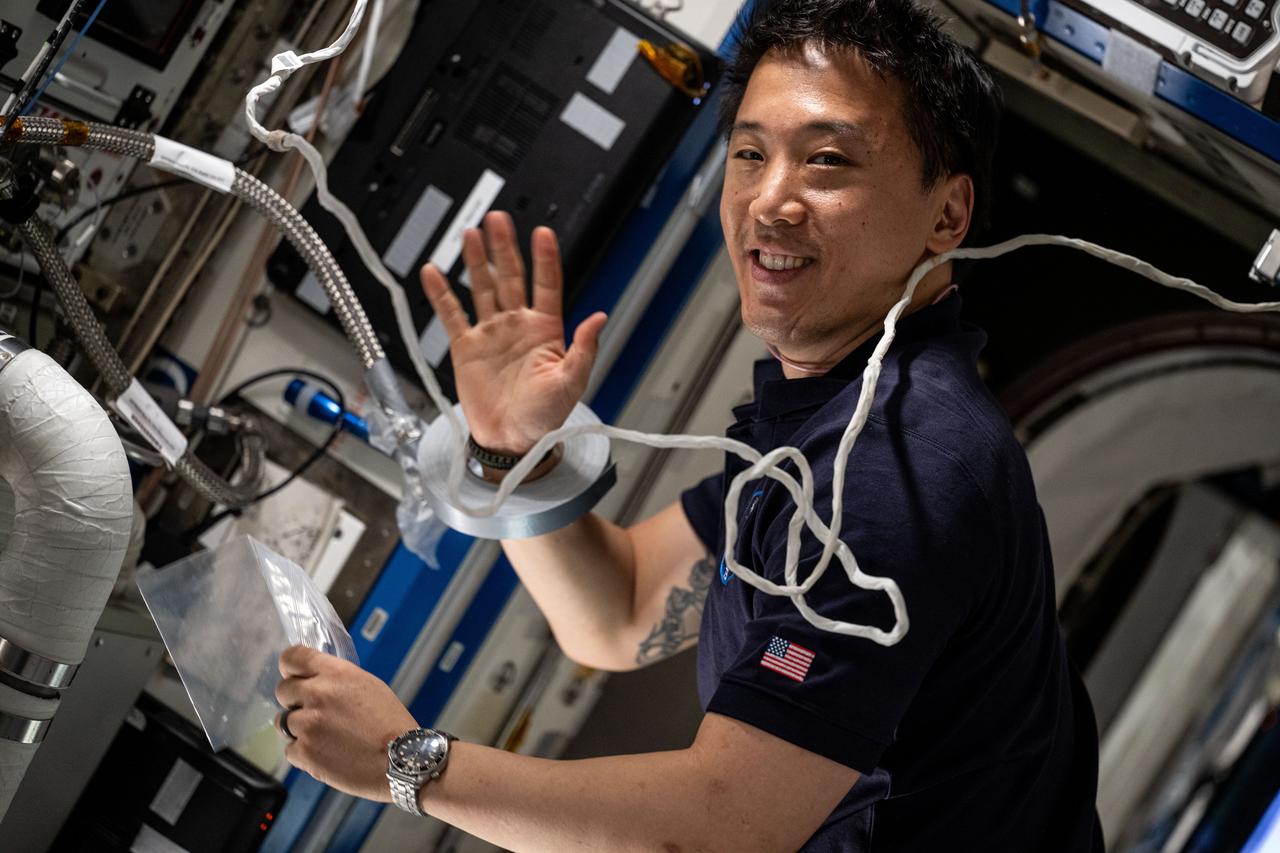

iss073e0118580 (May 27, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Jonny Kim services an experimental carbon dioxide removal device aboard the International Space Station. Also called the Thermal Amine Scrubber, the advanced life support mechanism is testing a new method that removes carbon dioxide from the station’s atmosphere and recovers water for oxygen generation.
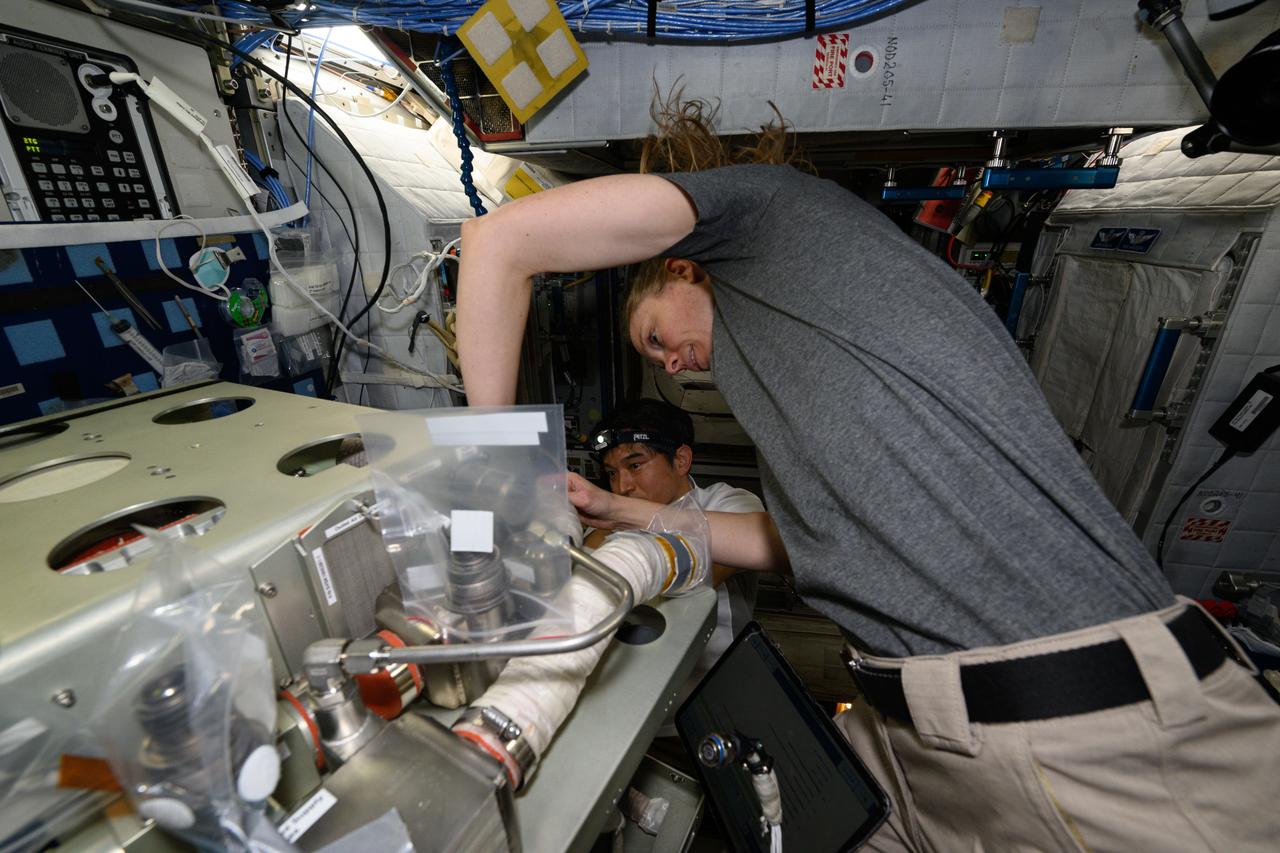

iss073e0118793 (May 27, 2025) --- Astronauts Takuya Onishi of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) and Nichole Ayers of NASA, Expedition 73 Commander and Flight Engineer respectively, replace components on an experimental carbon dioxide removal device aboard the International Space Station. Also called the Thermal Amine Scrubber, the advanced life support mechanism is testing a new method that removes carbon dioxide from the station’s atmosphere and recovers water for oxygen generation.
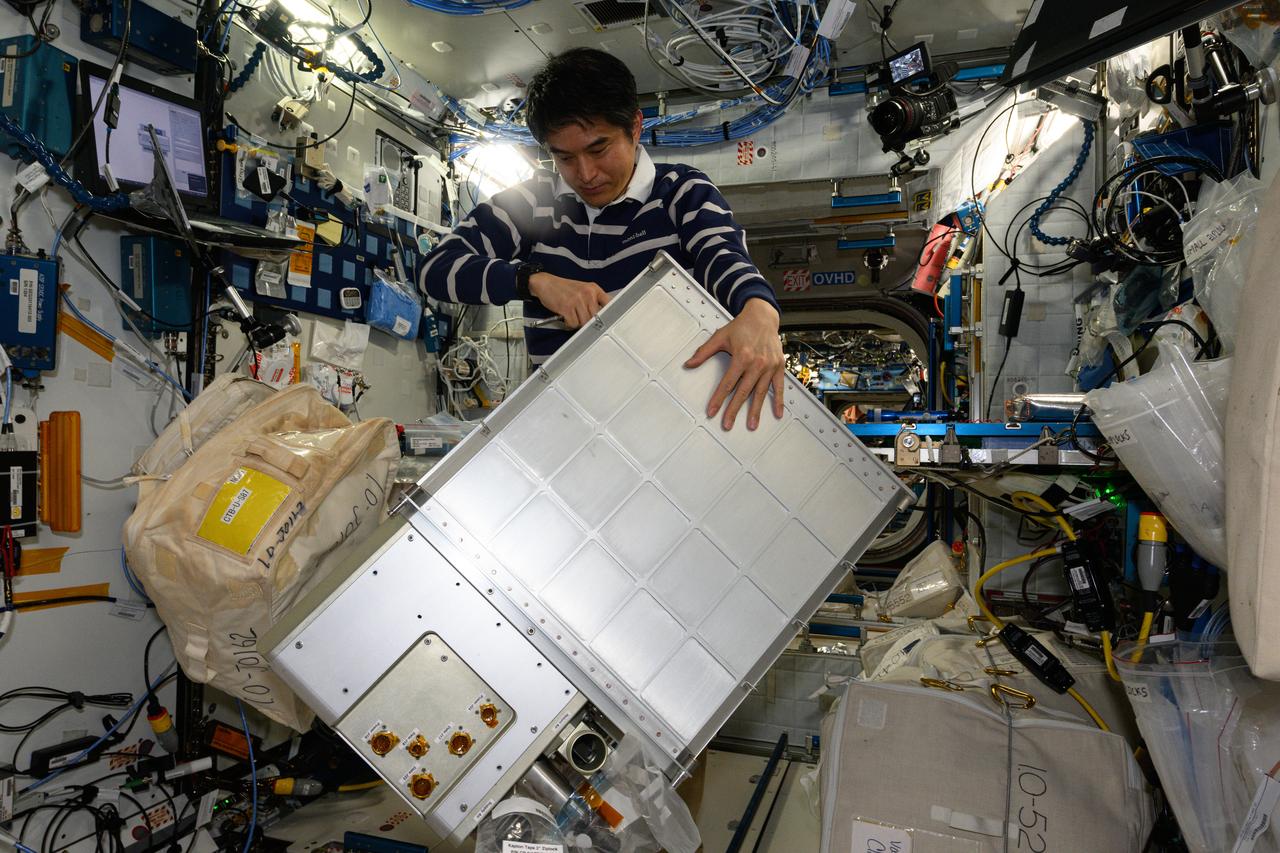

iss073e0118813 (May 28, 2025) --- JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut and Expedition 73 Commander Takuya Onishi replaces components on an experimental carbon dioxide removal device aboard the International Space Station. Also called the Thermal Amine Scrubber, the advanced life support mechanism is testing a new method that removes carbon dioxide from the station’s atmosphere and recovers water for oxygen generation.
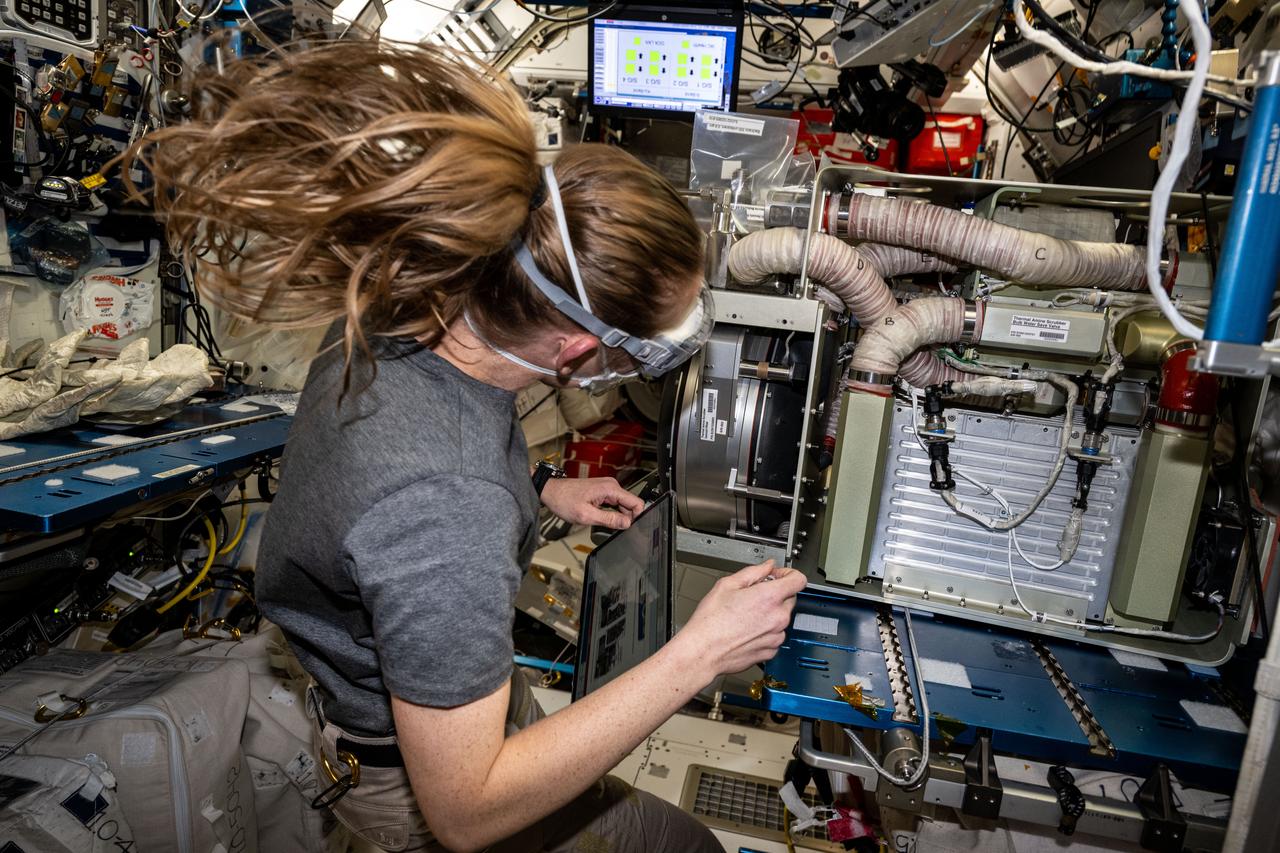

iss073e0078896 (May 27, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers replaces components on an experimental carbon dioxide removal device. Also called the Thermal Amine Scrubber, the advanced life support mechanism is testing a new method that removes carbon dioxide from the station’s atmosphere and recovers water for oxygen generation.

iss073e0078897 (May 27, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers replaces components on an experimental carbon dioxide removal device. Also called the Thermal Amine Scrubber, the advanced life support mechanism is testing a new method that removes carbon dioxide from the station’s atmosphere and recovers water for oxygen generation.
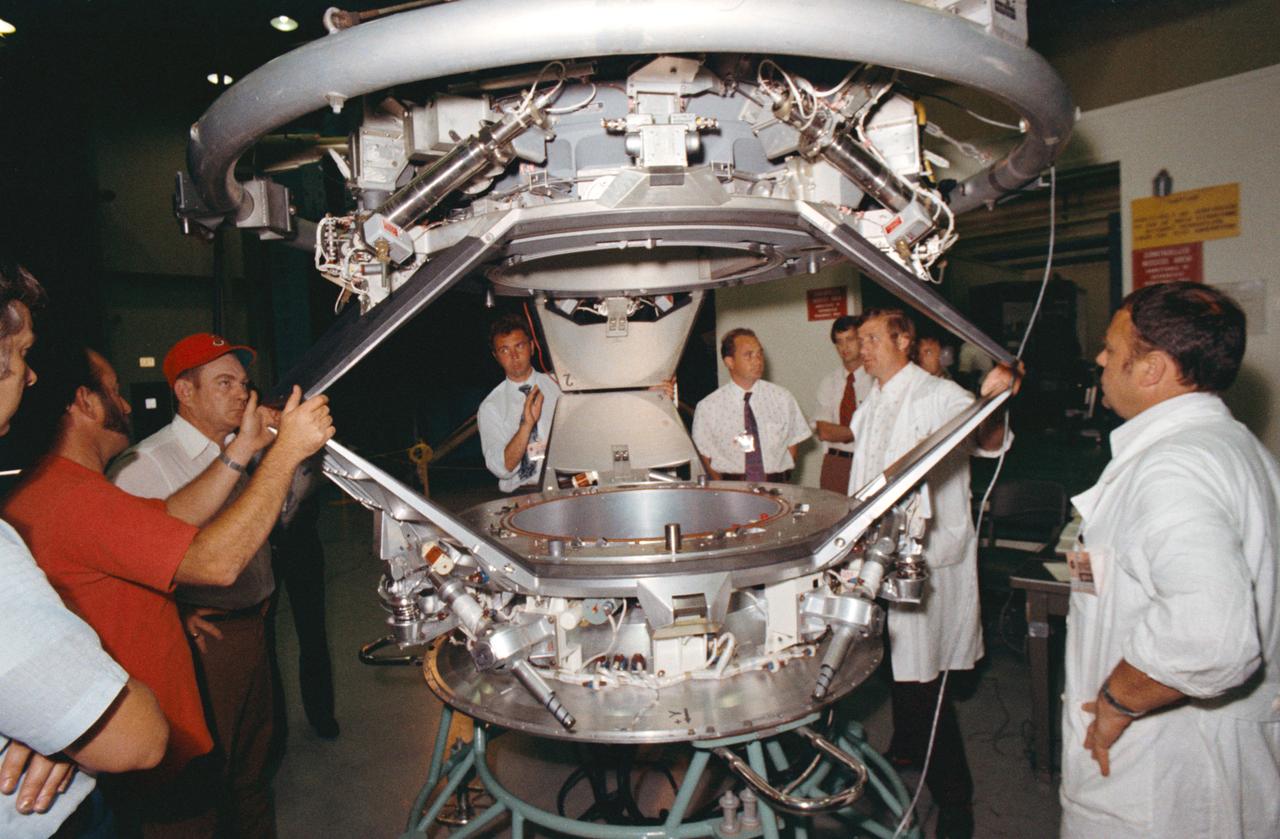

S74-25394 (10 July 1974) --- A group of American and Soviet engineers of the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project working group three examines an ASTP docking set-up following a docking mechanism fitness test conducted in Building 13 at the Johnson Space Center. Working Group No. 3 is concerned with ASTP docking problems and techniques. The joint U.S.-USSR ASTP docking mission in Earth orbit is scheduled for the summer of 1975. The Apollo docking mechanism is atop the Soyuz docking mechanism.
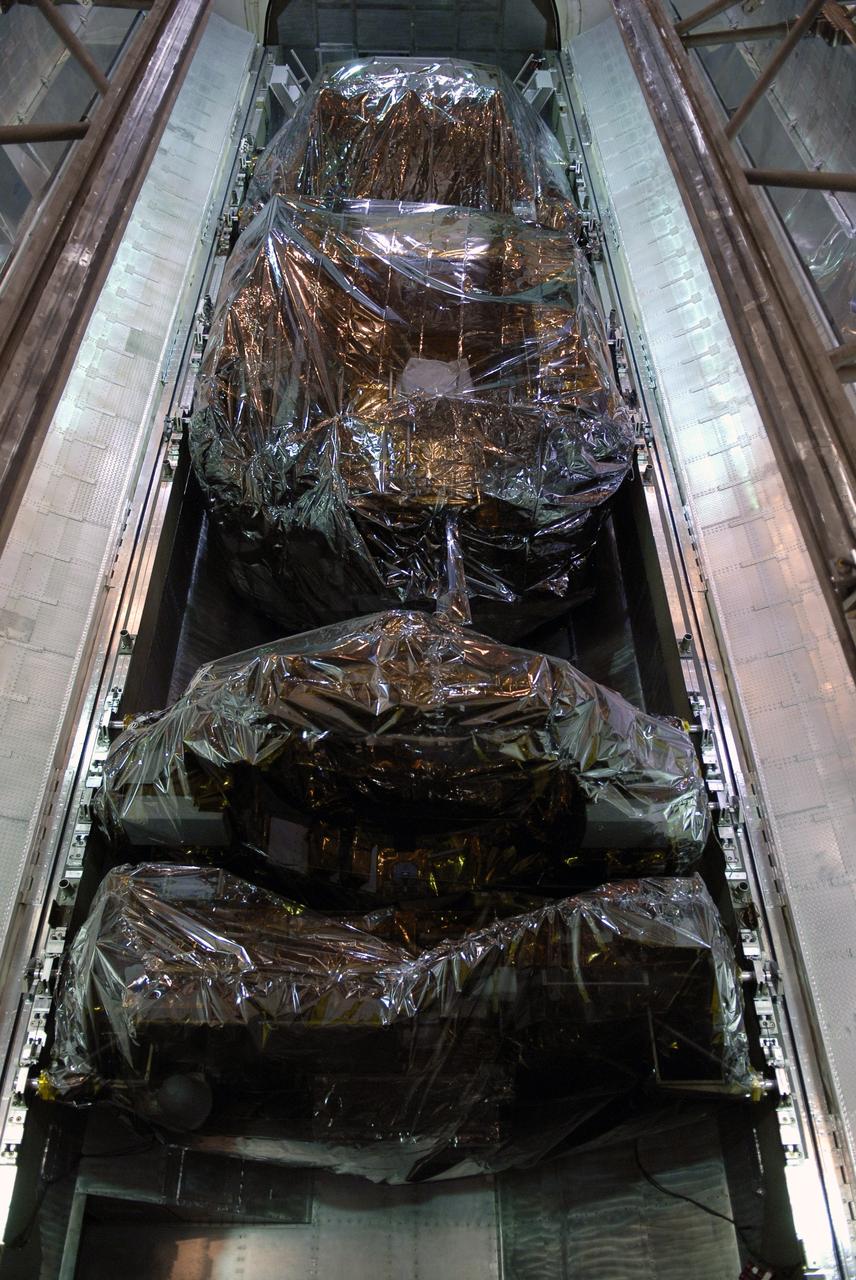

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A on NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Atlantis’ HST payload for the STS-125 mission has been moved into the payload canister via the payload ground handling mechanism. The payload comprises four carriers holding various equipment for the mission. The hardware will be transported back to Kennedy’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be stored until a new target launch date can be set for Atlantis’ STS-125 mission in 2009. Atlantis’ October target launch date was delayed after a device on board Hubble used in the storage and transmission of science data to Earth shut down on Sept. 27. Replacing the broken device will be added to Atlantis’ servicing mission to the telescope. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A on NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a worker supervises the movement of space shuttle Atlantis’ HST payload for the STS-125 mission that was installed into the payload canister via the payload ground handling mechanism. The payload comprises four carriers holding various equipment for the mission. The hardware will be transported back to Kennedy’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be stored until a new target launch date can be set for Atlantis’ STS-125 mission in 2009. Atlantis’ October target launch date was delayed after a device on board Hubble used in the storage and transmission of science data to Earth shut down on Sept. 27. Replacing the broken device will be added to Atlantis’ servicing mission to the telescope. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
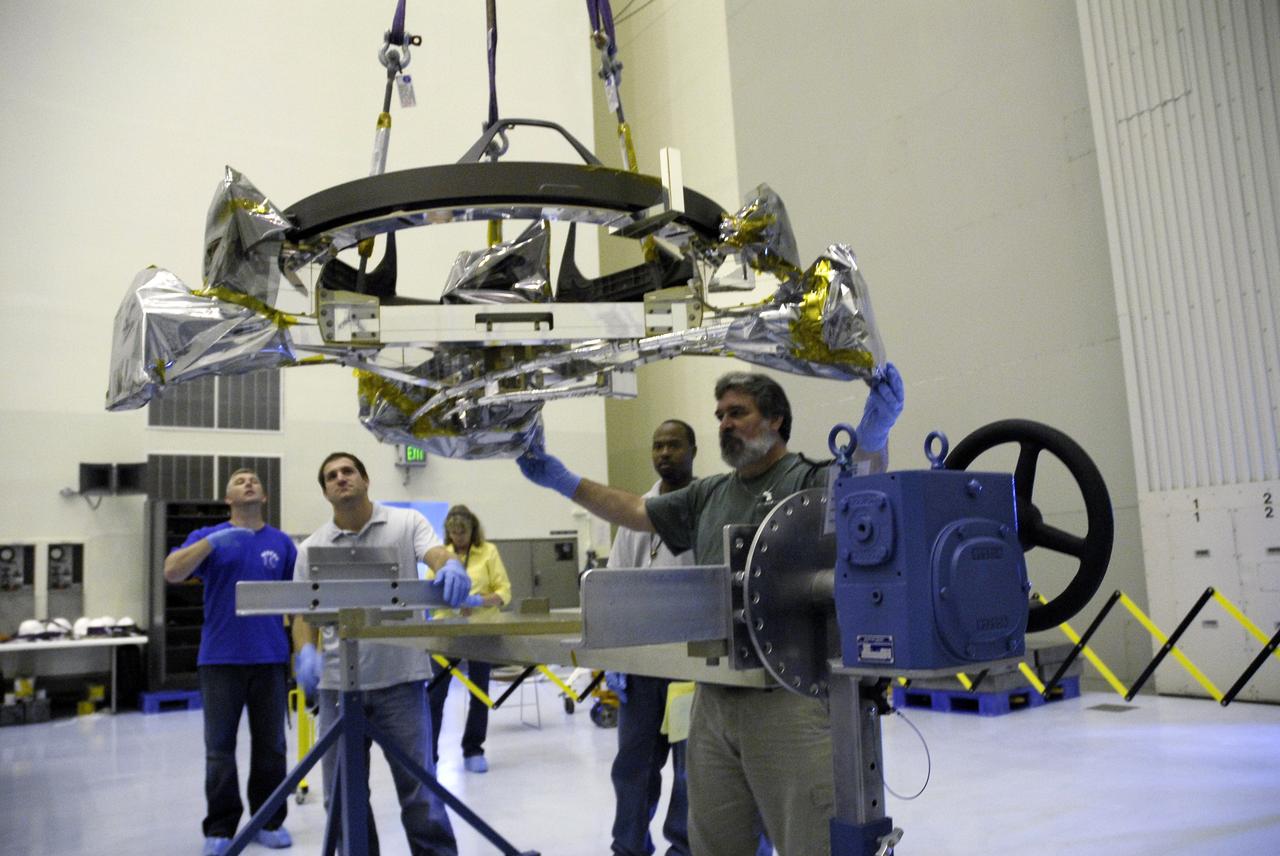

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technician stabilizes the Soft Capture Mechanism (SCM), part of the Soft Capture and Rendezvous System, or SCRS, as it is lowered onto a stand. The SCRS will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of Hubble by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The SCRS greatly increases the current shuttle capture interfaces on Hubble, therefore significantly reducing the rendezvous and capture design complexities associated with the disposal mission. The SCRS comprises the Soft Capture Mechanism system and the Relative Navigation System and is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, crew members with the STS-125 mission get a close look at some of the equipment associated with their mission to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. Mission Specialist Michael Good points out part of the Flight Support Structure to Mission Specialist Andrew Feustel, right. The Soft Capture Mechanism is above him. The mechanism will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The STS-125 crew is taking part in a crew equipment interface test, which provides experience handling tools, equipment and hardware they will use on their mission. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted to launch on the STS-125 mission Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, crew members with the STS-125 mission get a close look at some of the equipment associated with their mission to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. A technician, at left, provides information about the Soft Capture Mechanism on the Flight Support Structure to Mission Specialists Michael Good, Andrew Feustel and Mike Massimino. The mechanism will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The STS-125 crew is taking part in a crew equipment interface test, which provides experience handling tools, equipment and hardware they will use on their mission. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted to launch on the STS-125 mission Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians make a final check of the Soft Capture Mechanism (SCM), part of the Soft Capture and Rendezvous System, or SCRS, after its placement on a stand. The SCRS will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of Hubble by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The SCRS greatly increases the current shuttle capture interfaces on Hubble, therefore significantly reducing the rendezvous and capture design complexities associated with the disposal mission. The SCRS comprises the Soft Capture Mechanism system and the Relative Navigation System and is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
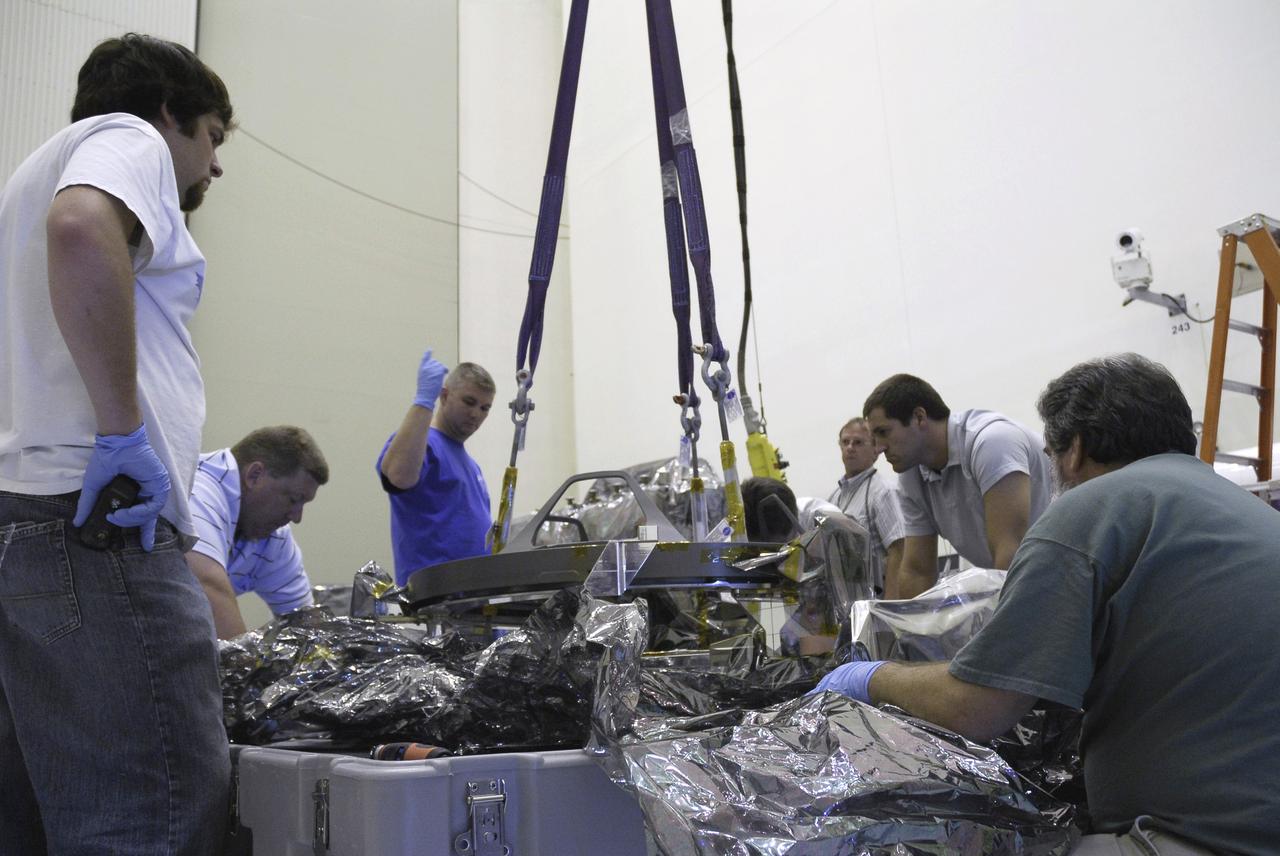

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians monitor the lifting of the Soft Capture Mechanism (SCM), part of the Soft Capture and Rendezvous System, or SCRS, from its shipping container. The SCRS will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of Hubble by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The SCRS greatly increases the current shuttle capture interfaces on Hubble, therefore significantly reducing the rendezvous and capture design complexities associated with the disposal mission. The SCRS comprises the Soft Capture Mechanism system and the Relative Navigation System and is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
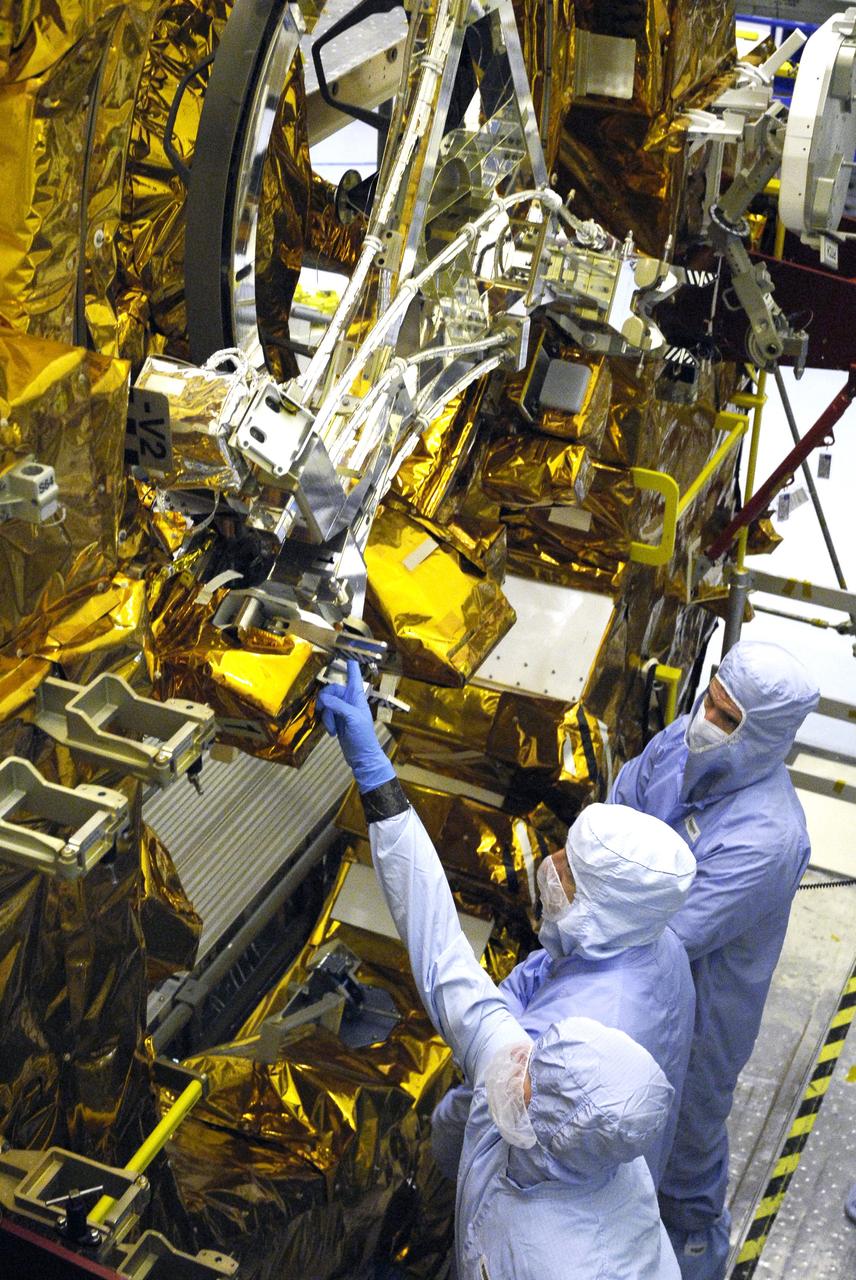

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, crew members with the STS-125 mission get a close look at some of the equipment associated with their mission to service NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. Looking at the Soft Capture Mechanism on the Flight Support Structure are a technician (pointing) and Mission Specialists Mike Massimino and Michael Good. The mechanism will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The STS-125 crew is taking part in a crew equipment interface test, which provides experience handling tools, equipment and hardware they will use on their mission. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted to launch on the STS-125 mission Oct. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
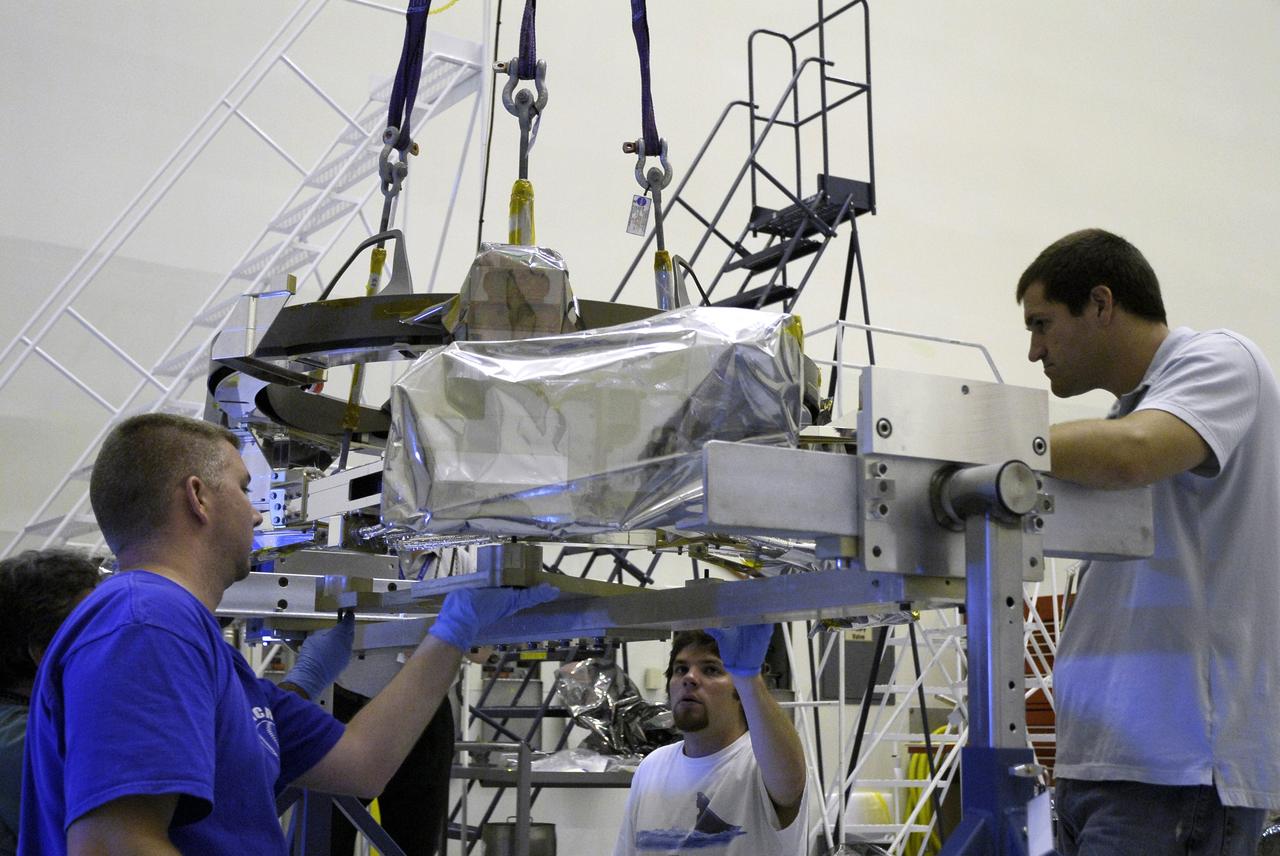

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians monitor the placement of the Soft Capture Mechanism (SCM), part of the Soft Capture and Rendezvous System, or SCRS, as it is lowered onto a stand. The SCRS will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of Hubble by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The SCRS greatly increases the current shuttle capture interfaces on Hubble, therefore significantly reducing the rendezvous and capture design complexities associated with the disposal mission. The SCRS comprises the Soft Capture Mechanism system and the Relative Navigation System and is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
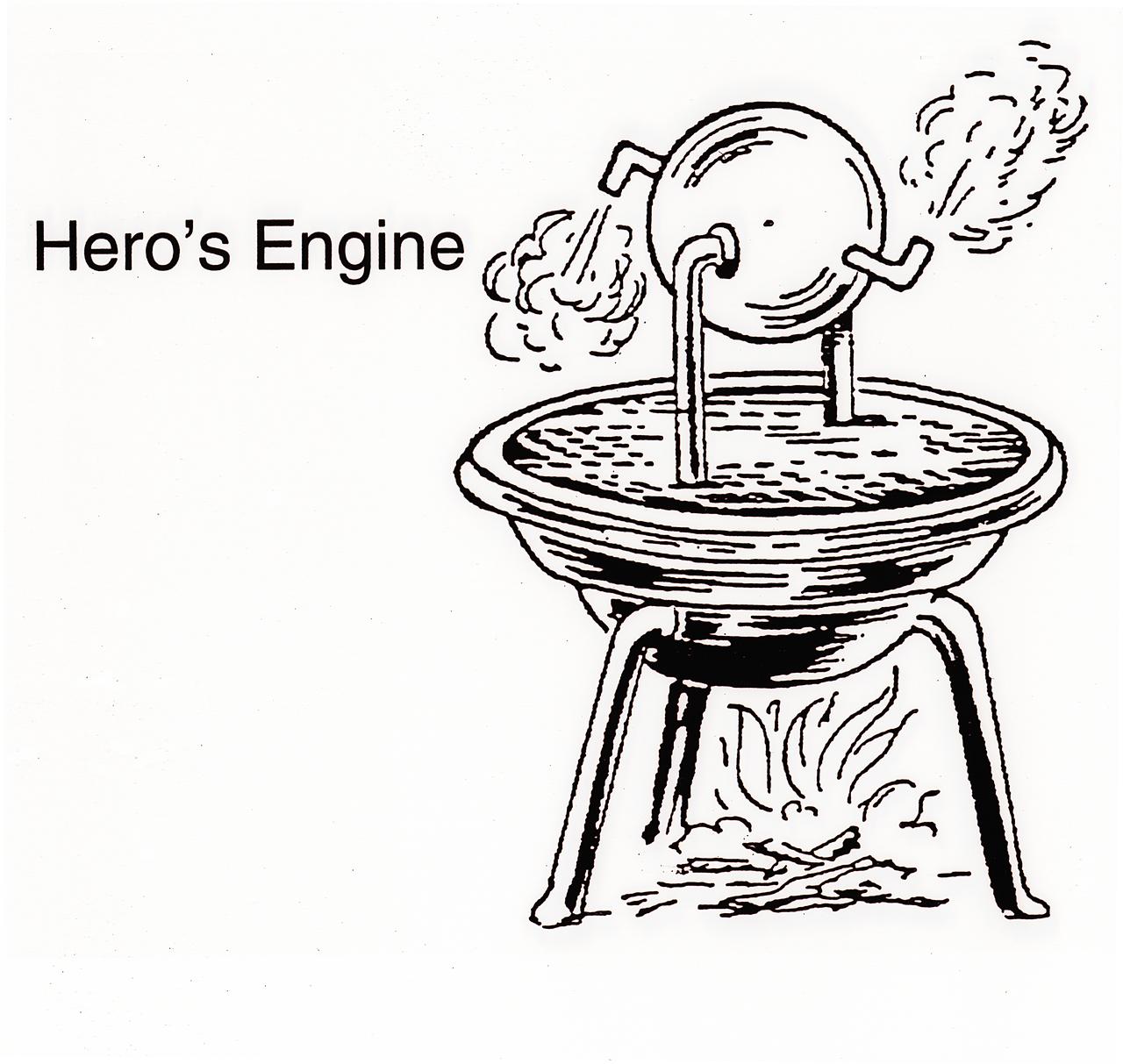
Legendary characters used the power of mythology to fly through the heavens. About 200 BC, a Greek inventor known as Hero of Alexandria came up with a new invention that depended on the mechanical interaction of heat and water. He invented a rocket-like device called an aeolipile. It used steam for propulsion. Hero mounted a sphere on top of a water kettle. A fire below the kettle turned the water into steam, and the gas traveled through the pipes to the sphere. Two L-shaped tubes on opposite sides of the sphere allowed the gas to escape, and in doing so gave a thrust to the sphere that caused it to rotate.

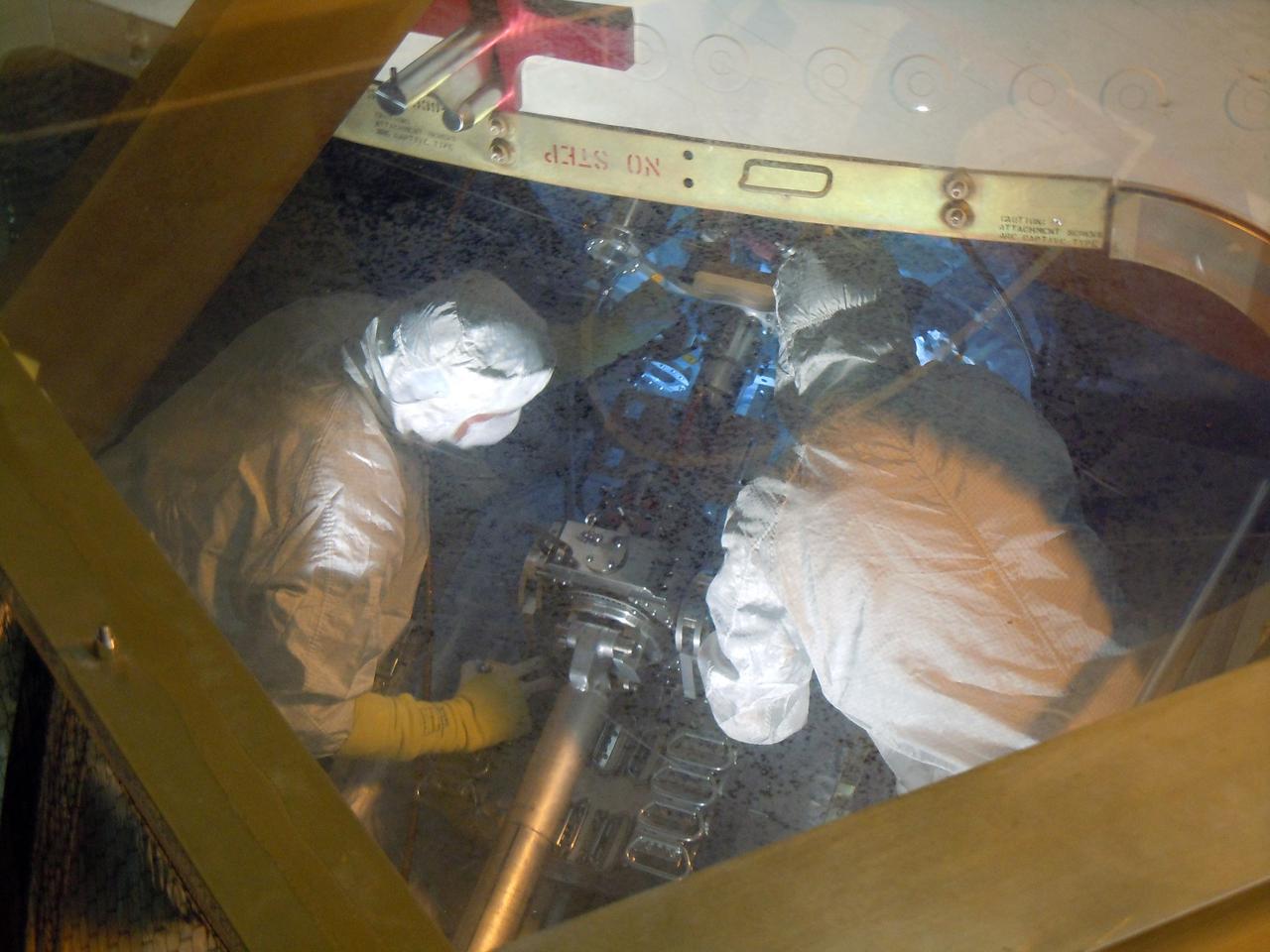
Jet Propulsion Research Lab (JPL) workers use a borescope to verify the pressure relief device bellow's integrity on a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) that has been installed on the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The activity is part of the mechanical and electrical verification testing of RTGs during prelaunch processing. RTGs use heat from the natural decay of plutonium to generate electrical power. The three RTGs on Cassini will enable the spacecraft to operate far from the Sun where solar power systems are not feasible. They will provide electrical power to Cassini on it seven year trip to the Saturnian system and during its four year mission at Saturn.

Jet Propulsion Research Lab (JPL) workers use a borescope to verify the pressure relief device bellow's integrity on a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) that has been installed on the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The activity is part of the mechanical and electrical verification testing of RTGs during prelaunch processing. RTGs use heat from the natural decay of plutonium to generate electrical power. The three RTGs on Cassini will enable the spacecraft to operate far from the Sun where solar power systems are not feasible. They will provide electrical power to Cassini on it seven year trip to the Saturnian system and during its four year mission at Saturn.
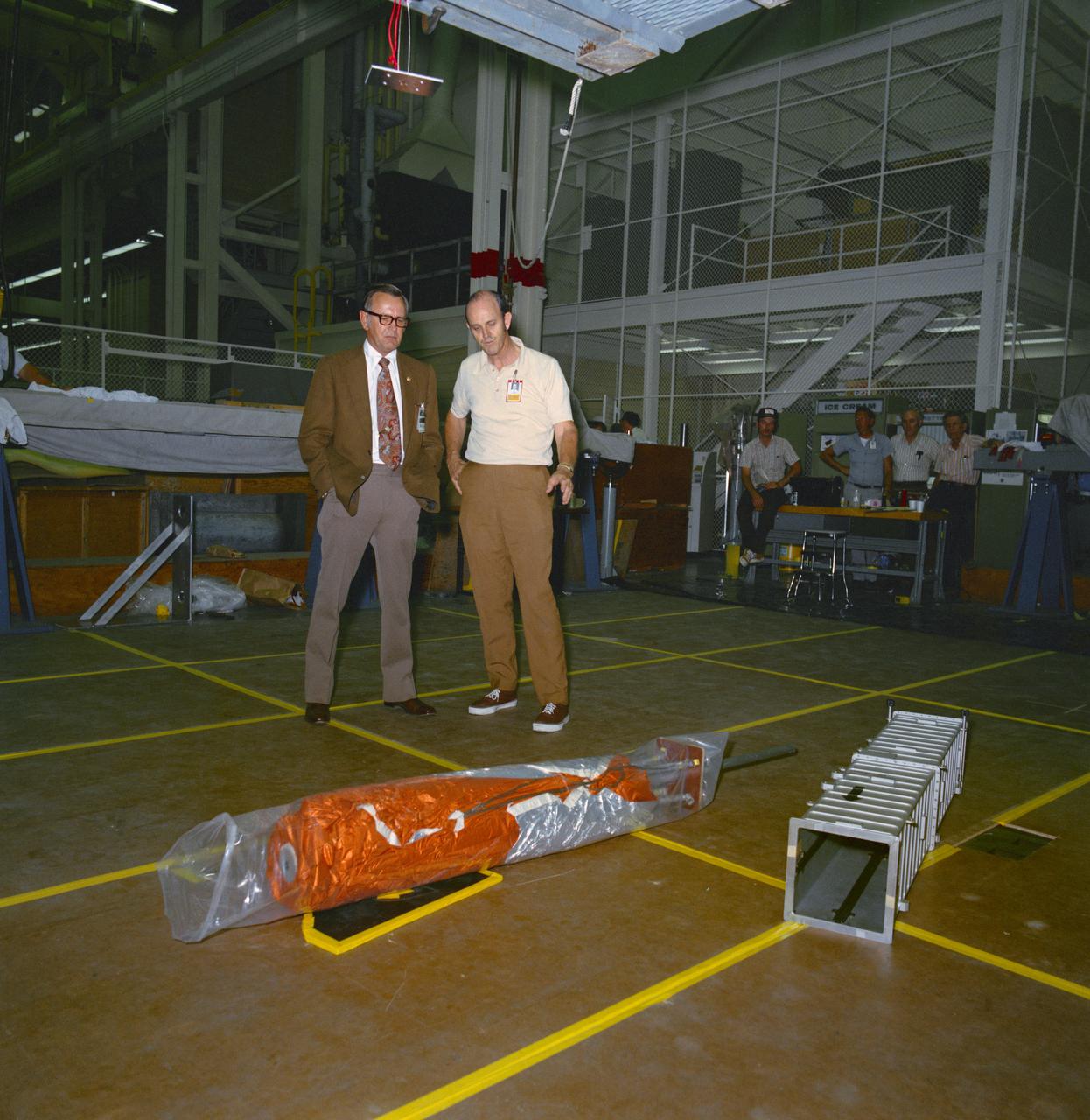

S73-26394 (23 May 1973) --- Dr. Christopher C. Kraft Jr. (left), JSC Director, and George A. Post, JSC Crew Systems Division, look over the packaged "parasol" during fabrication and checkout of the umbrella-like mechanical device in the Technical Services shop in building 10 at Johnson Space Center. The "parasol" is designed to fit into the T027 experiment photometer canister. The canopy portion of the "parasol" measures 24 feet by 22 feet. The "parasol" is one of several sunscreen possibilities being considered for use in shading the overheated Skylab 1 Orbital Workshop. Photo credit: NASA
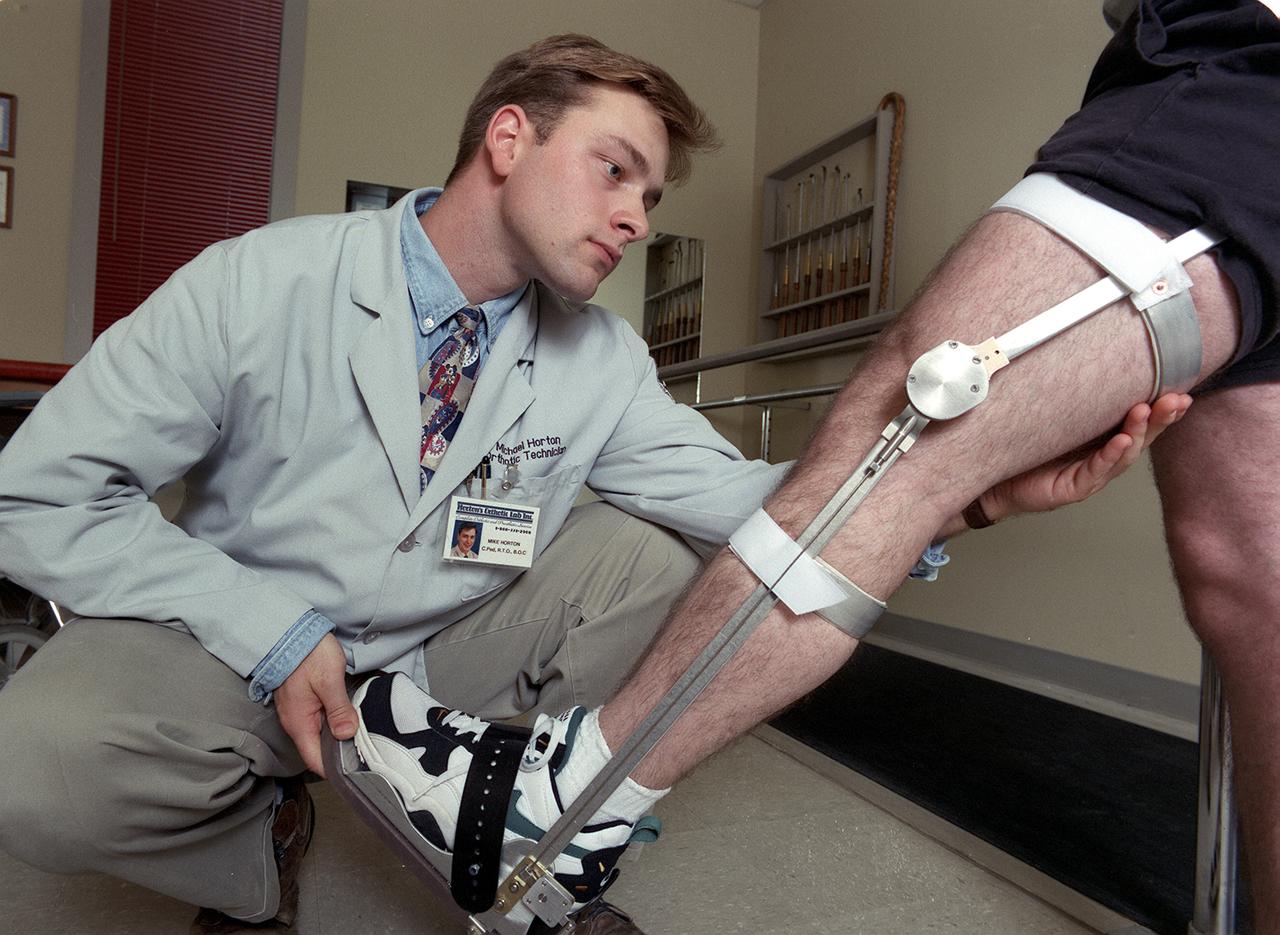
A knee brace that uses Space Shuttle propulsion technology has moved a step closer to being available to help knee injury and stroke patients and may possibly benefit patients with birth defects, spinal cord injuries, and post-polio conditions. After years of hard work, inventors at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Huntsville, Alabama, have turned over the final design and prototype to industry partners at Horton's Orthotic Lab in Little Rock, Arkansas for further clinical testing. The device, called the Selectively Lockable Knee Brace, may mean faster, less painful rehabilitation for patients by allowing the knee to move when weight is not on the heel. Devices currently on the market lock the knee in a rigid, straight-leg position, or allow continuous free motion. Pictured here is a knee brace prototype being tested and fitted at Horton's Orthotic Lab. The knee brace is just one example of how space technology is being used to improve the lives of people on Earth. NASA's MSFC inventors Michael Shadoan and Neill Myers are space propulsion engineers who use the same mechanisms and materials to build systems for rockets that they used to design and develop the knee brace.

Expedition Five flight engineer Peggy Whitson is shown installing the Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules (SUBSA) experiment in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) in the Destiny laboratory aboard the International Space Station (ISS). SUBSA examines the solidification of semiconductor crystals from a melted material. Semiconductor crystals are used for many products that touch our everyday lives. They are found in computer chips, integrated circuits, and a multitude of other electronic devices, such as sensors for medical imaging equipment and detectors of nuclear radiation. Materials scientists want to make better semiconductor crystals to be able to further reduce the size of high-tech devices. In the microgravity environment, convection and sedimentation are reduced, so fluids do not remove and deform. Thus, space laboratories provide an ideal environment of studying solidification from the melt. This investigation is expected to determine the mechanism causing fluid motion during production of semiconductors in space. It will provide insight into the role of the melt motion in production of semiconductor crystals, advancing our knowledge of the crystal growth process. This could lead to a reduction of defects in semiconductor crystals produced in space and on Earth.
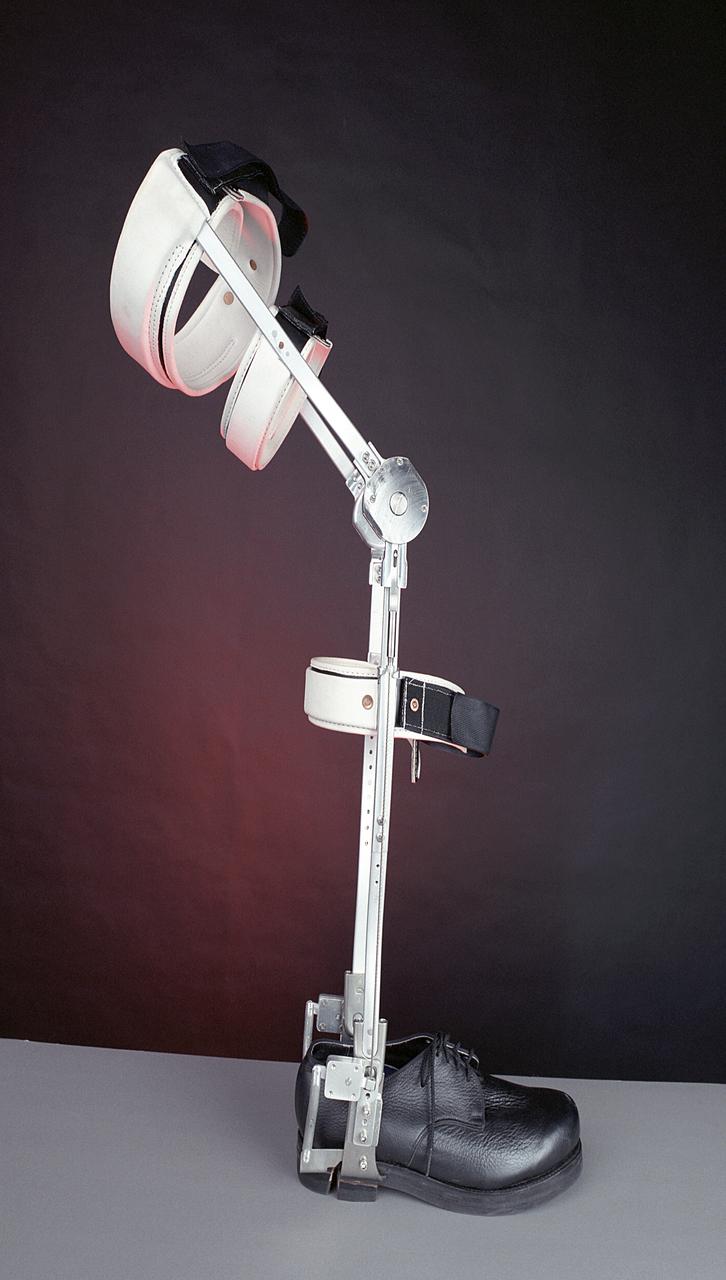

A knee brace that uses Space Shuttle propulsion technology has moved a step closer to being available to help knee injury and stroke patients and may possibly benefit patients with birth defects, spinal cord injuries, and post-polio conditions. After years of hard work, inventors at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Huntsville, Alabama, have turned over the final design and prototype to industry partners at Horton's Orthotic Lab in Little Rock, Arkansas for further clinical testing. The device, called the Selectively Lockable Knee Brace, may mean faster, less painful rehabilitation for patients by allowing the knee to move when weight is not on the heel. Devices currently on the market lock the knee in a rigid, straight-leg position, or allow continuous free motion. The knee brace is just one example of how space technology is being used to improve the lives of people on Earth. NASA's MSFC inventors Michael Shadoan and Neill Myers are space propulsion engineers who use the same mechanisms and materials to build systems for rockets that they used to design and develop the knee brace.
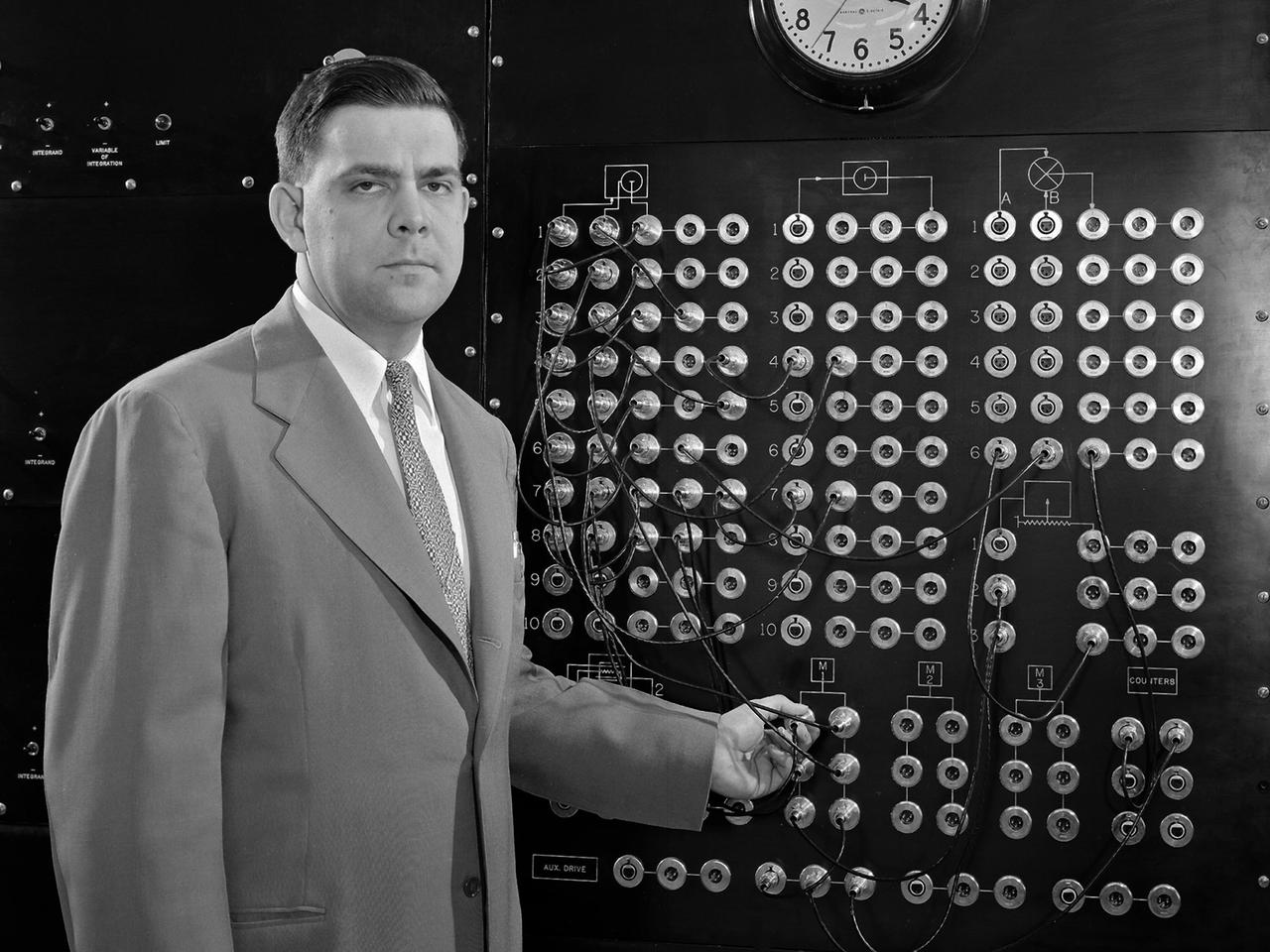

Harry Mergler stands at the control board of a differential analyzer in the new Instrument Research Laboratory at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The differential analyzer was a multi-variable analog computation machine devised in 1931 by Massachusetts Institute of Technology researcher and future NACA Committee member Vannevar Bush. The mechanical device could solve computations up to the sixth order, but had to be rewired before each new computation. Mergler modified Bush’s differential analyzer in the late 1940s to calculate droplet trajectories for Lewis’ icing research program. In four days Mergler’s machine could calculate what previously required weeks. NACA Lewis built the Instrument Research Laboratory in 1950 and 1951 to house the large analog computer equipment. The two-story structure also provided offices for the Mechanical Computational Analysis, and Flow Physics sections of the Physics Division. The division had previously operated from the lab’s hangar because of its icing research and flight operations activities. Mergler joined the Instrument Research Section of the Physics Division in 1948 after earning an undergraduate degree in Physics from the Case Institute of Technology. Mergler’s focus was on the synthesis of analog computers with the machine tools used to create compressor and turbine blades for jet engines.

The NASA Dryden 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft crew poses in an engine inlet; Standing L to R - aircraft mechanic John Goleno and SCA Team Leader Pete Seidl; Kneeling L to R - aircraft mechanics Todd Weston and Arvid Knutson, and avionics technician Jim Bedard NASA uses two modified Boeing 747 jetliners, originally manufactured for commercial use, as Space Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA). One is a 747-100 model, while the other is designated a 747-100SR (short range). The two aircraft are identical in appearance and in their performance as Shuttle Carrier Aircraft. The 747 series of aircraft are four-engine intercontinental-range swept-wing "jumbo jets" that entered commercial service in 1969. The SCAs are used to ferry space shuttle orbiters from landing sites back to the launch complex at the Kennedy Space Center, and also to and from other locations too distant for the orbiters to be delivered by ground transportation. The orbiters are placed atop the SCAs by Mate-Demate Devices, large gantry-like structures which hoist the orbiters off the ground for post-flight servicing, and then mate them with the SCAs for ferry flights.
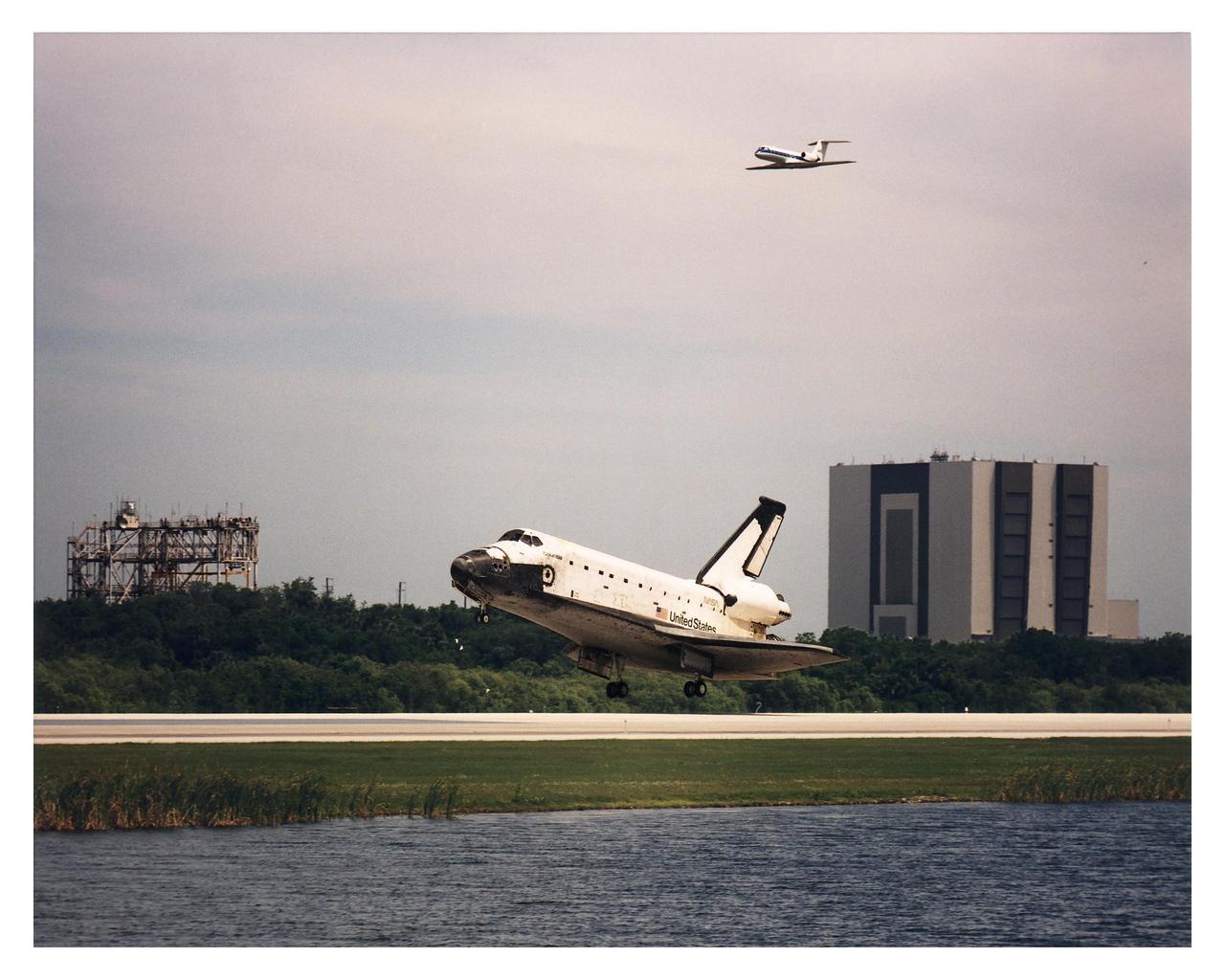

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia glides in for a touchdown on Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility that will conclude the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission. Columbia was scheduled to touch down at 2:33 p.m. EDT, April 8. The Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) is to the right, while the Mate/Demate Device (MDD) is to the left. A NASA Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA) that acts as a chase plane during landings passes by overhead. With Columbia’s on-time main gear touchdown, the STS-83 mission duration will be 3 days, 23 hours, 12 minutes. The planned 16-day mission was cut short by a faulty fuel cell. This is only the third time in Shuttle program history that an orbiter was brought home early due to mechanical problems. This was also the 36th KSC landing since the program began in 1981
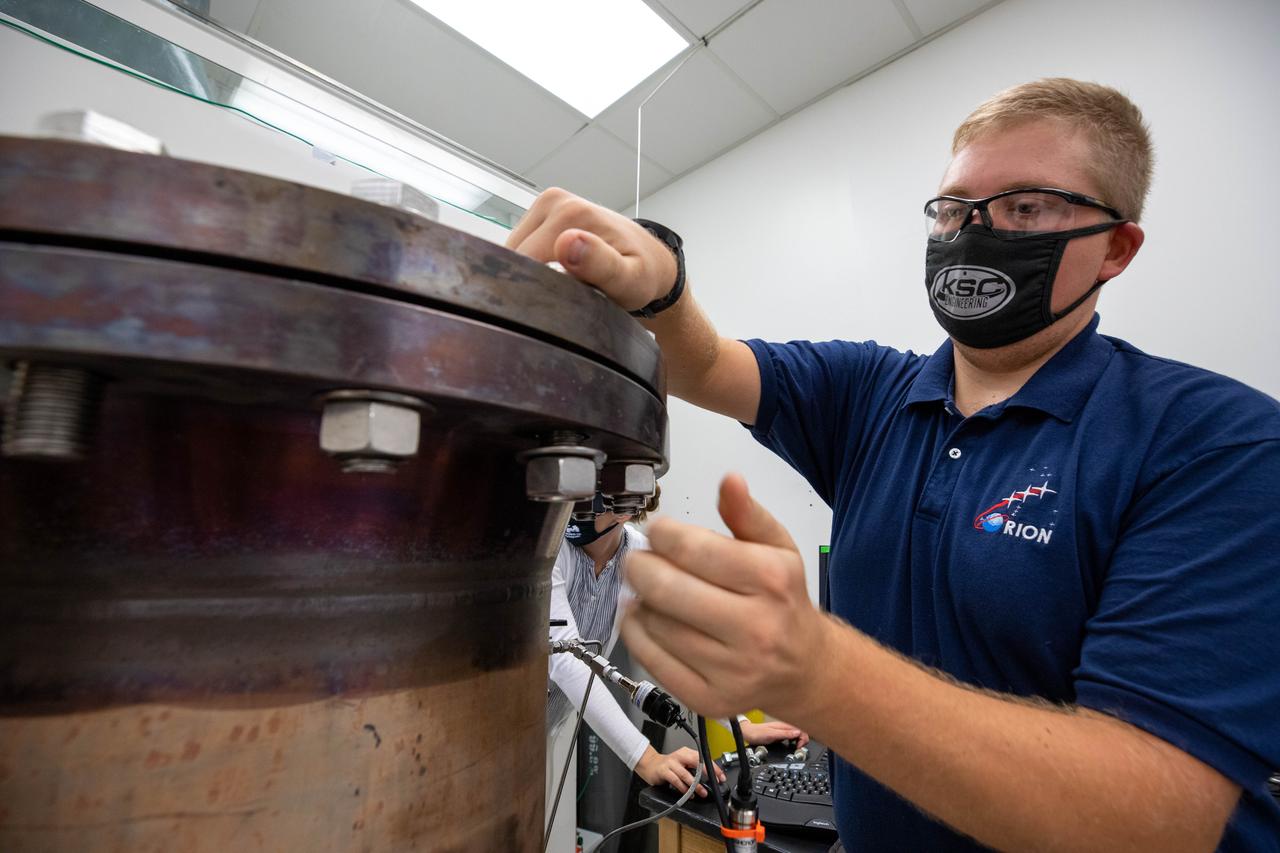

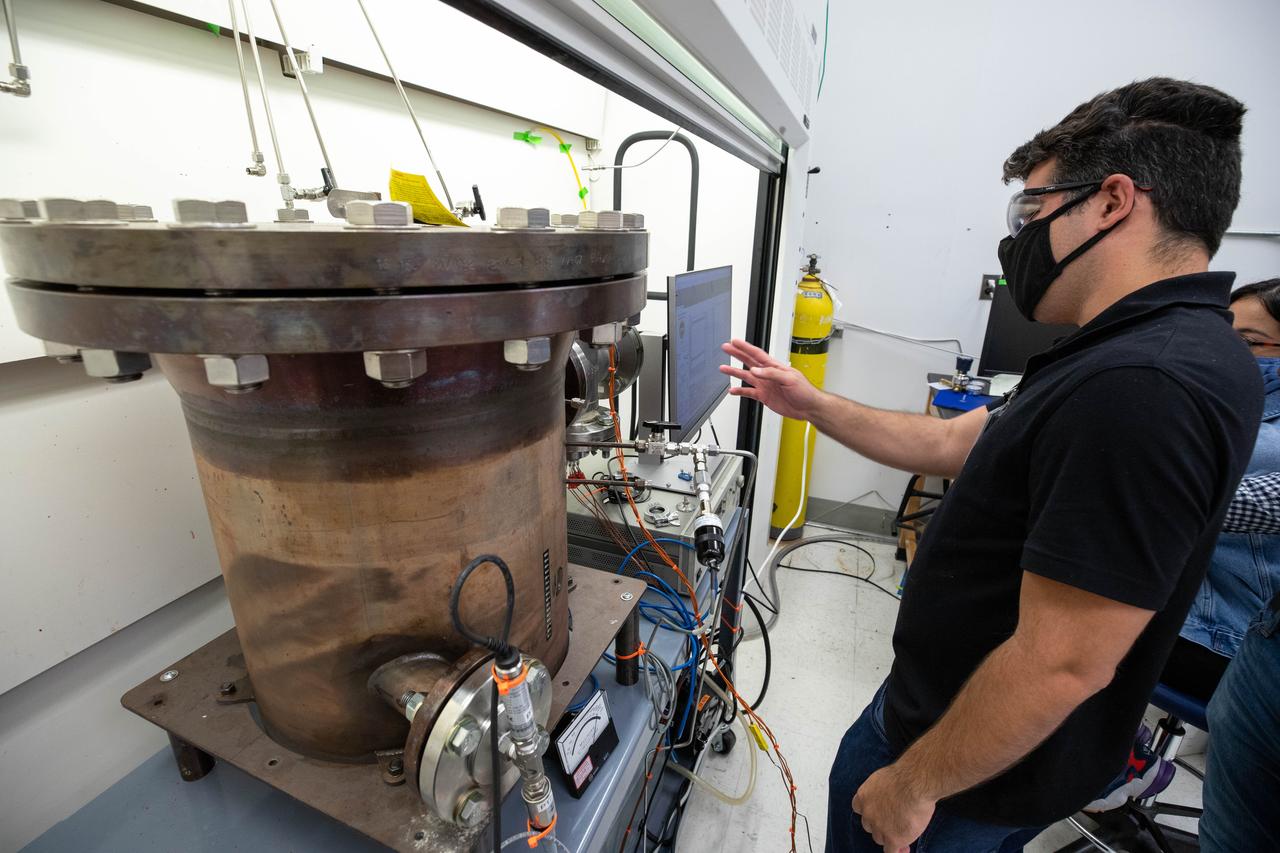
Evan Bell, a mechanical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
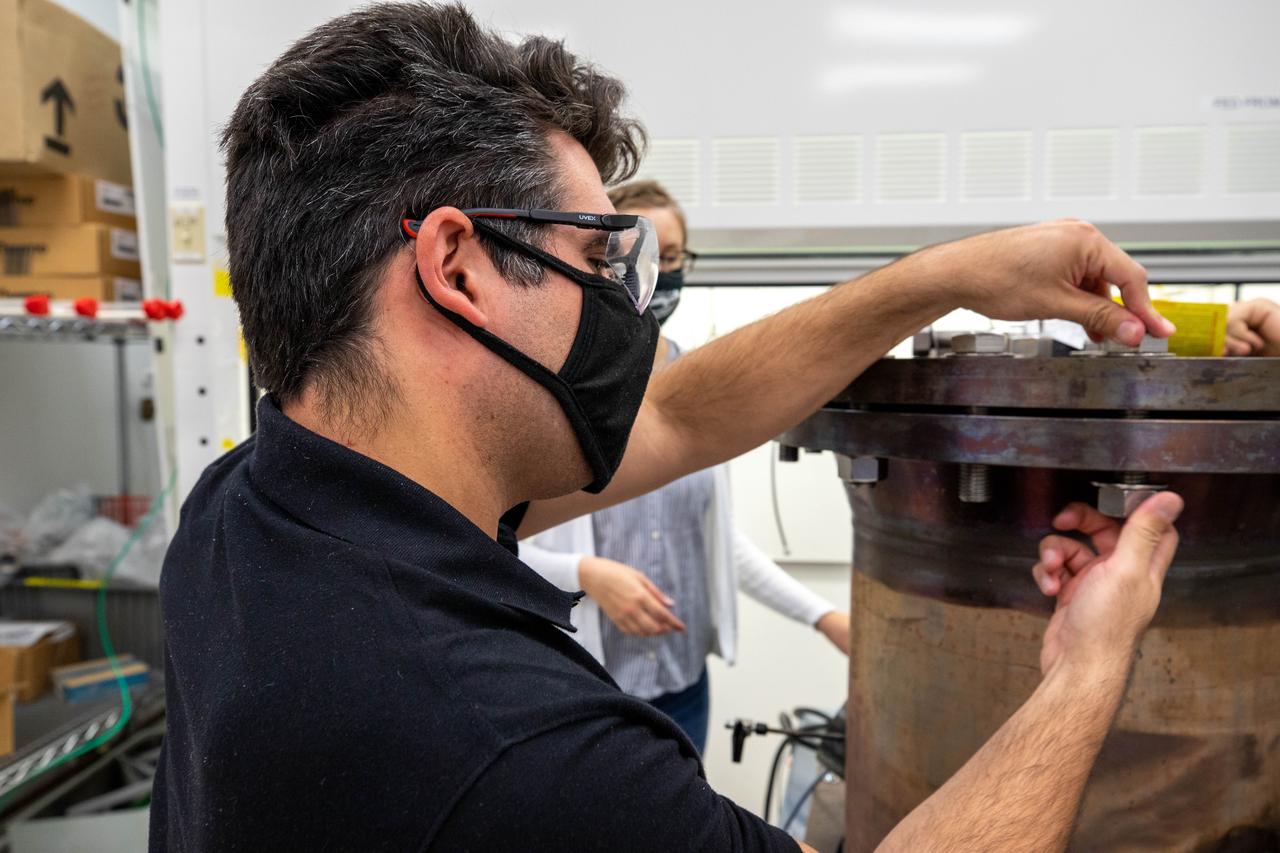

Jaime Toro, a mechanical engineer supporting the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
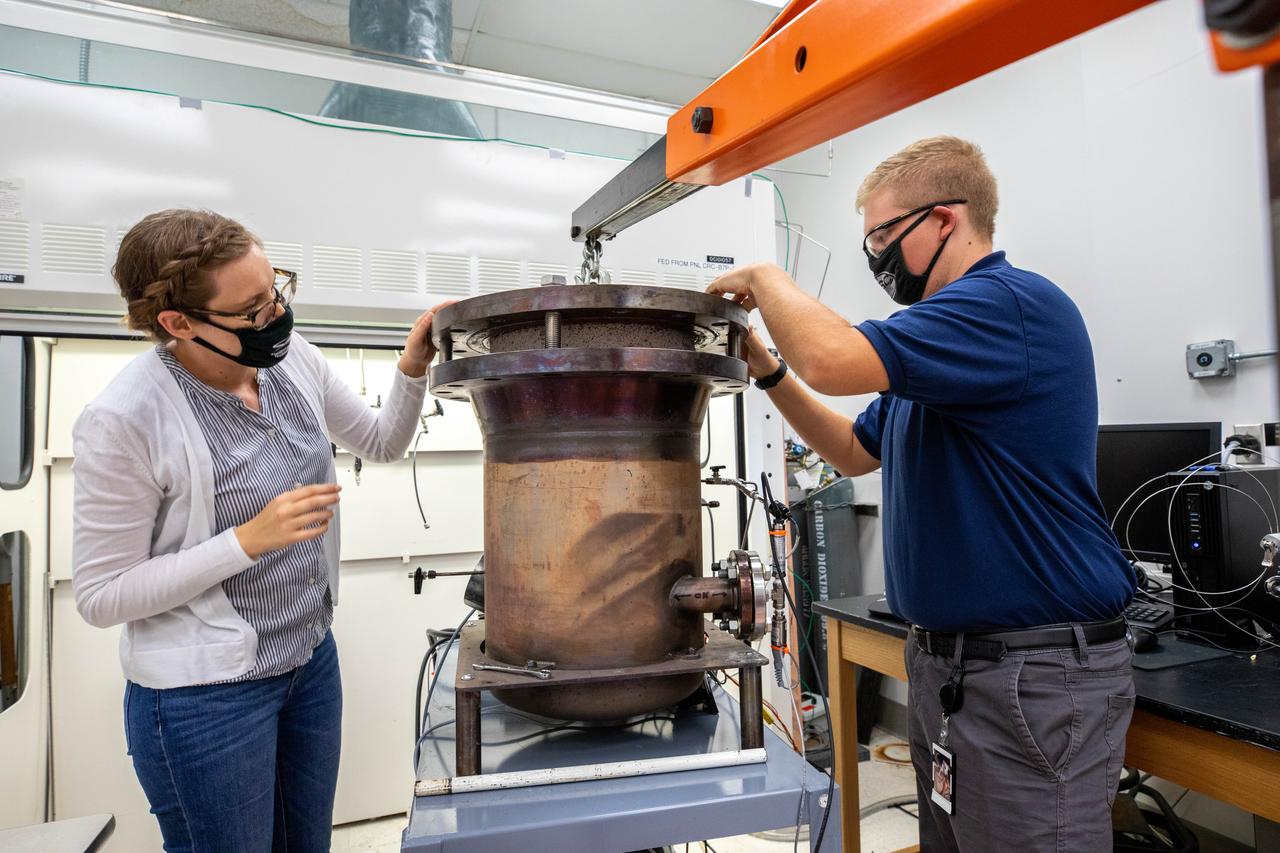

Elspeth Petersen, left, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, and Evan Bell, GaLORE mechanical engineer, inspect hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – stimulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
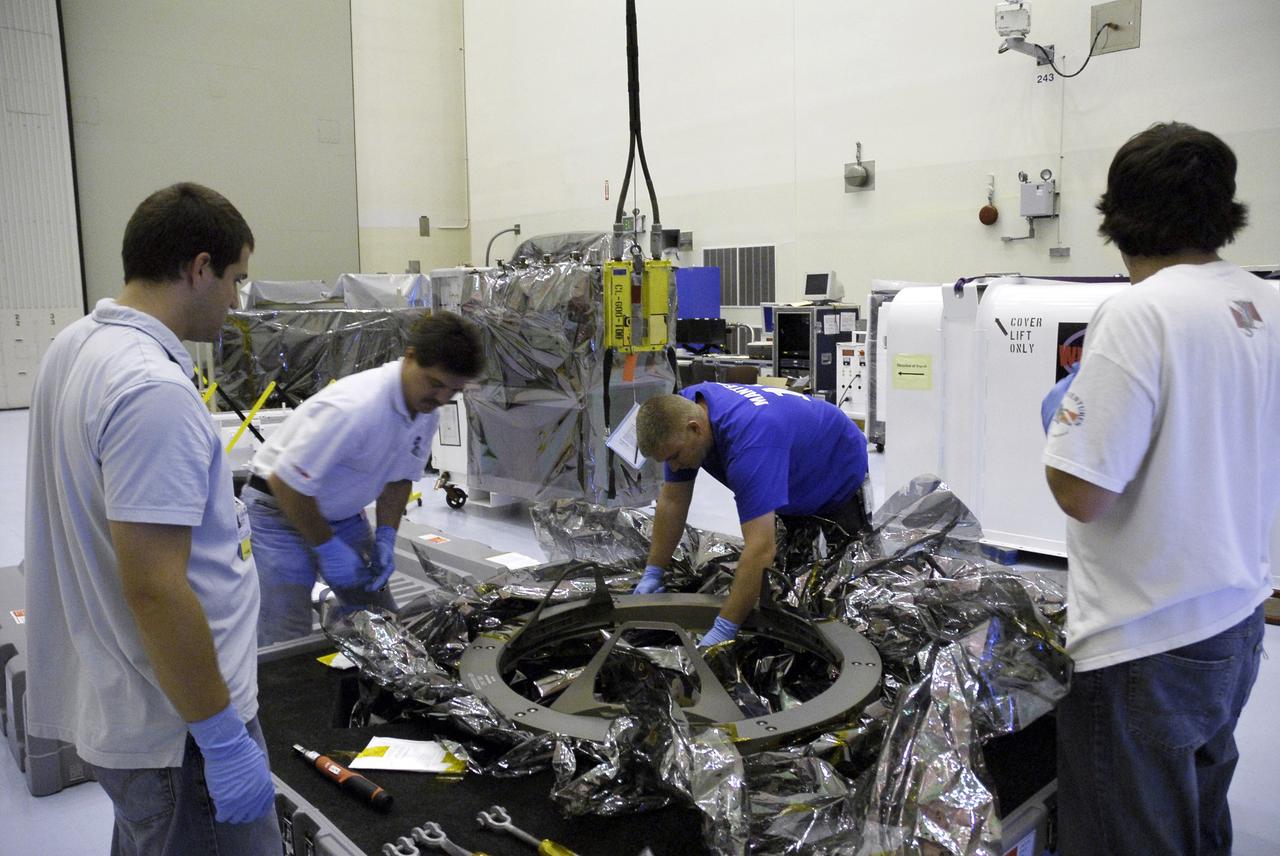

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians attach cables to lift the Soft Capture and Rendezvous System, or SCRS. The SCRS will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of Hubble by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The SCRS greatly increases the current shuttle capture interfaces on Hubble, therefore significantly reducing the rendezvous and capture design complexities associated with the disposal mission. The SCRS comprises the Soft Capture Mechanism system and the Relative Navigation System and is part of the payload on the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
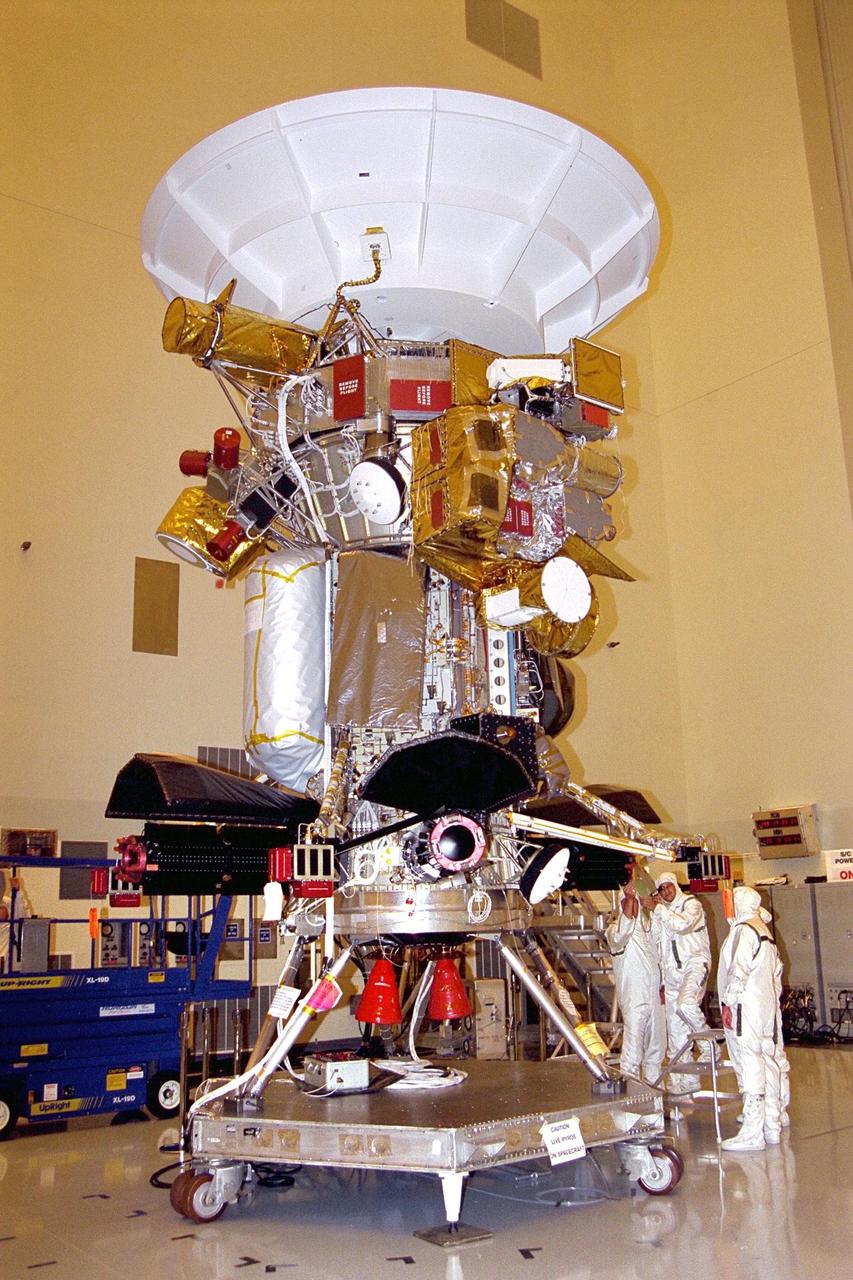
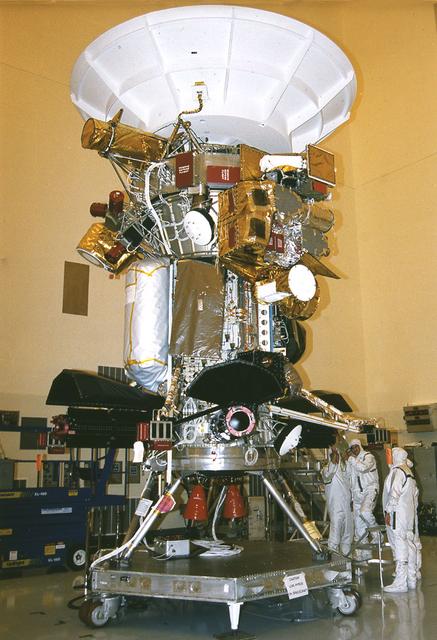
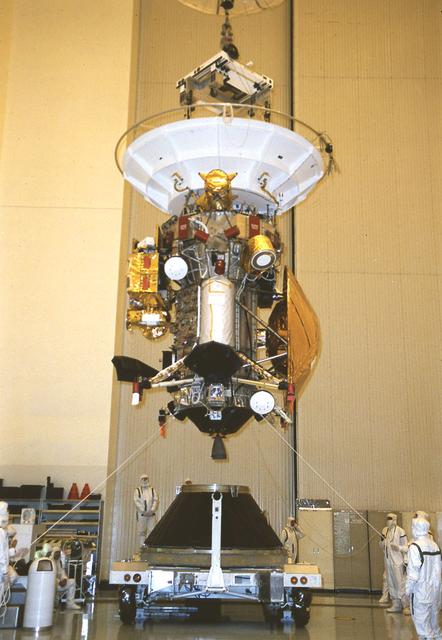
Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) workers use a borescope to verify pressure relief device bellows integrity on a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) which has been installed on the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The activity is part of the mechanical and electrical verification testing of RTGs during prelaunch processing. RTGs use heat from the natural decay of plutonium to generate electric power. The three RTGs on Cassini will enable the spacecraft to operate far from the Sun where solar power systems are not feasible. They will provide electrical power to Cassini on its 6.7-year trip to the Saturnian system and during its four-year mission at Saturn. The Cassini mission is scheduled for an Oct. 6 launch aboard a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle. Cassini is built and managed for NASA by JPL
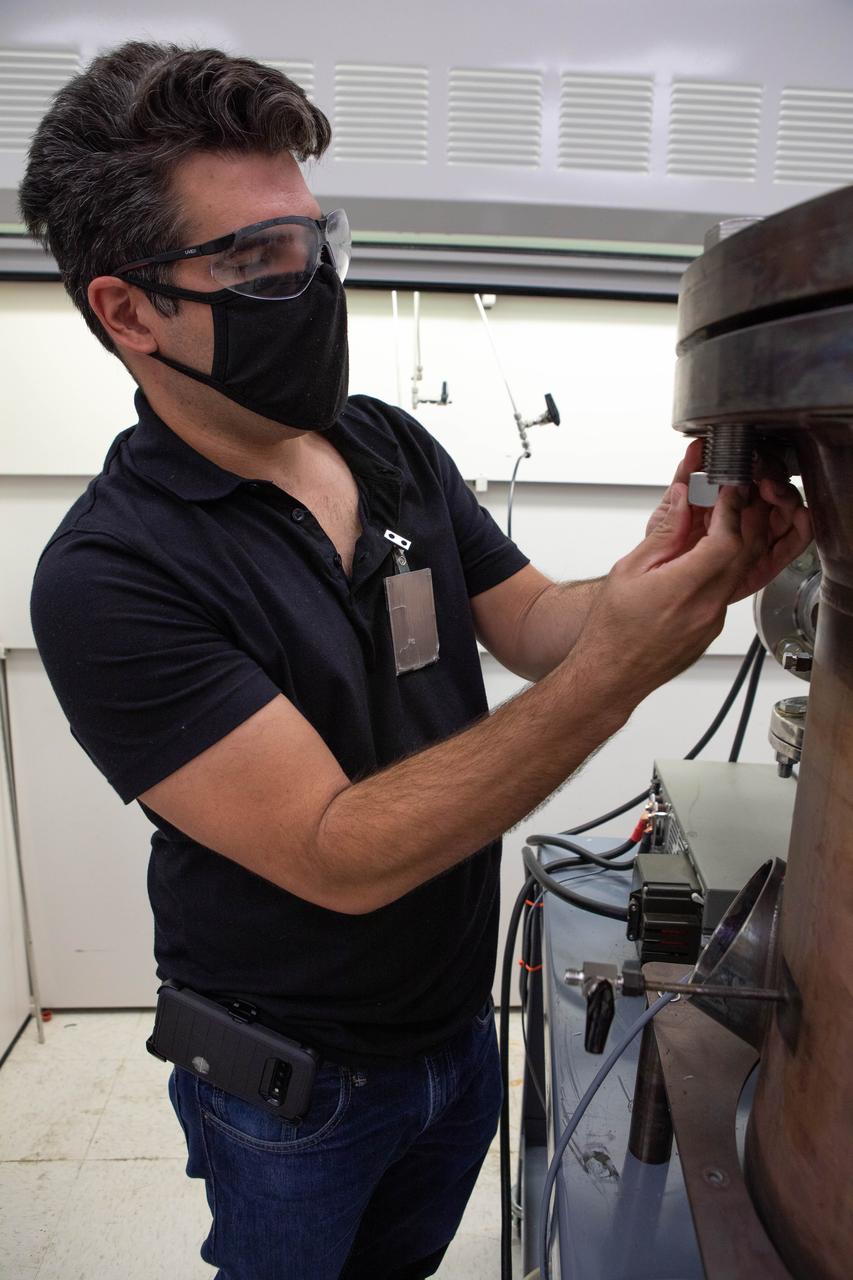

Jaime Toro, a mechanical engineer supporting the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
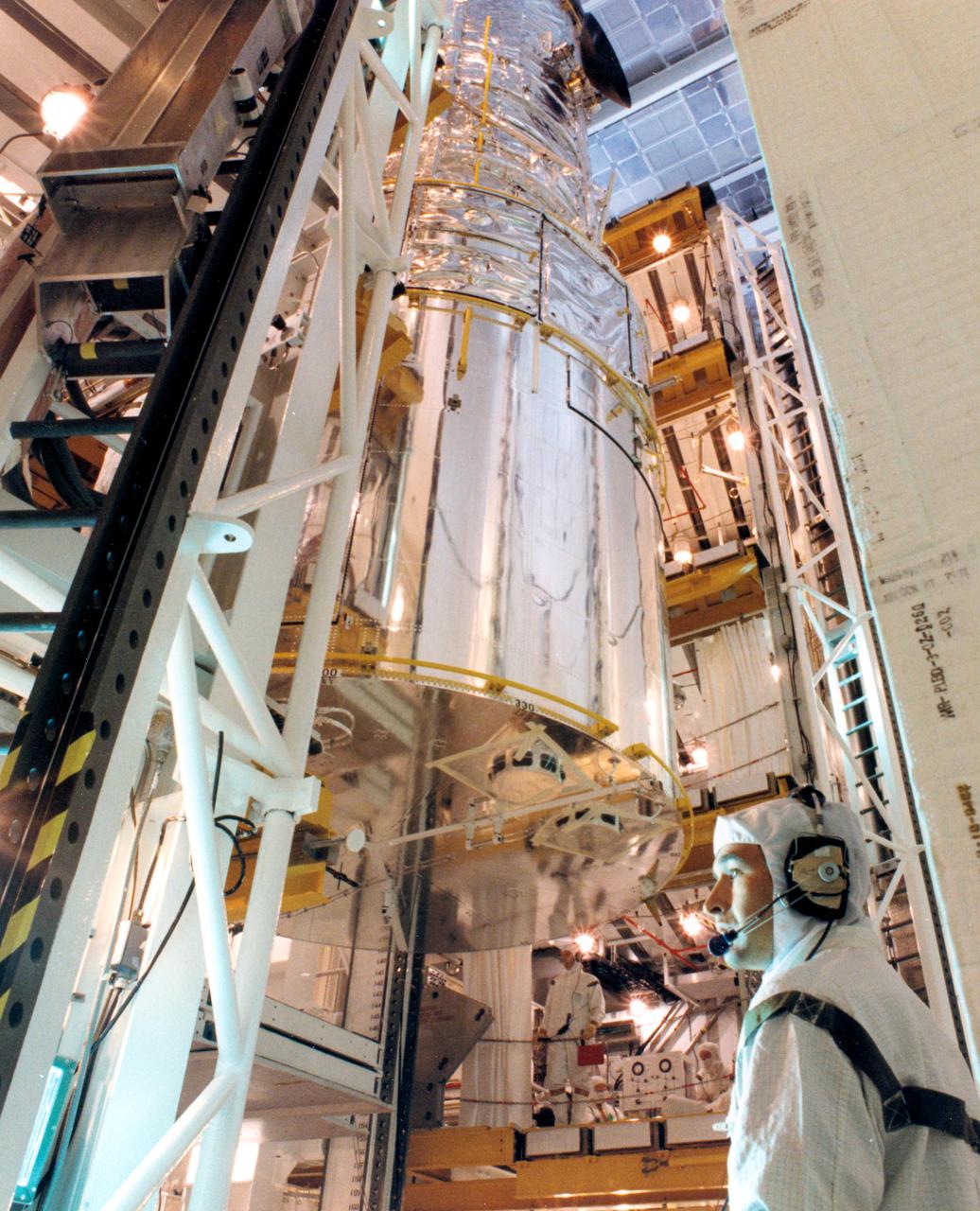
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The bus-size Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is carefully being transferred on March 29 from the surgically clean Payload Changeout Room at Launch Pad 39B into the cargo bay of the orbiter Discovery. The payload ground handling mechanism (left) is a device that extends the HST into the cargo bay (right), allowing workers to fasten it in place with four retention latches. Deployment of Hubble will occur during the five-day flight of Space Shuttle Mission STS-31, set for April 10. With HST, astronomers will be able to view 97 percent of the known universe, and will be able to get pictures unlimited and undistorted by the Earth's atmosphere. Compared with earth-based observatories, the HST will be able to view celestial objects that are 50 times fainter, provide images that are 10 times sharper, and see objects that are seven times farther away. .

Jaime Toro, a mechanical engineer supporting the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
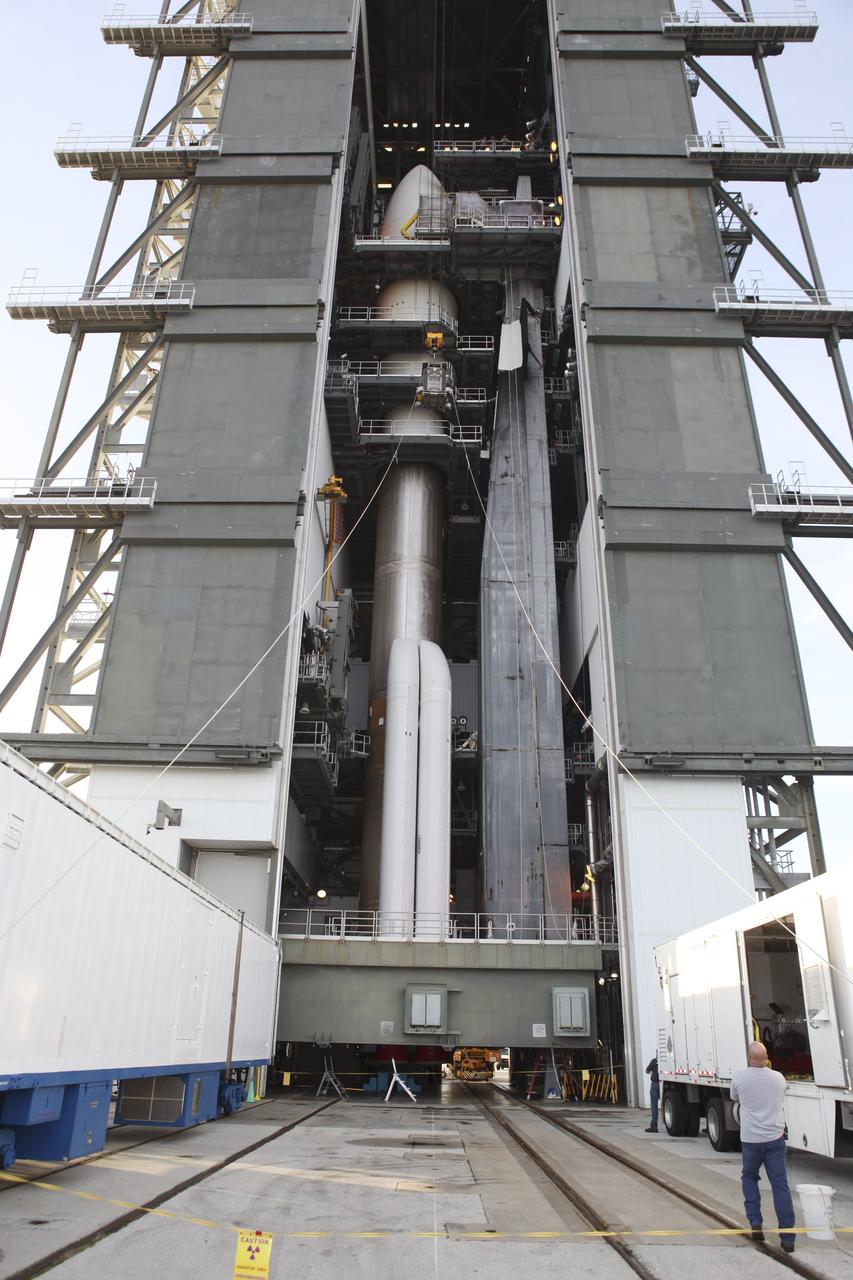

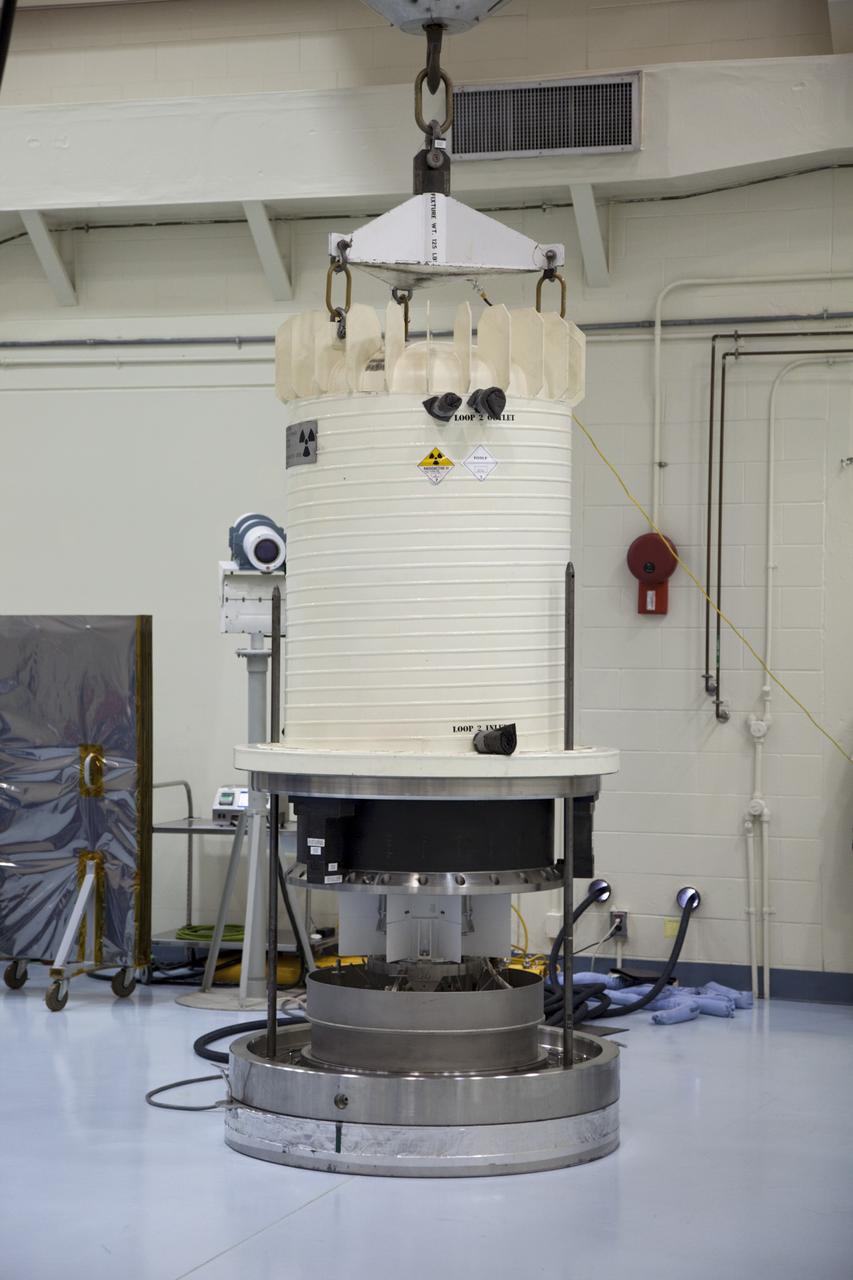
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Enclosed in the protective mesh container known as the "gorilla cage," the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is hoisted up beside the Atlas V rocket standing in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41. The generator will be installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat produced by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
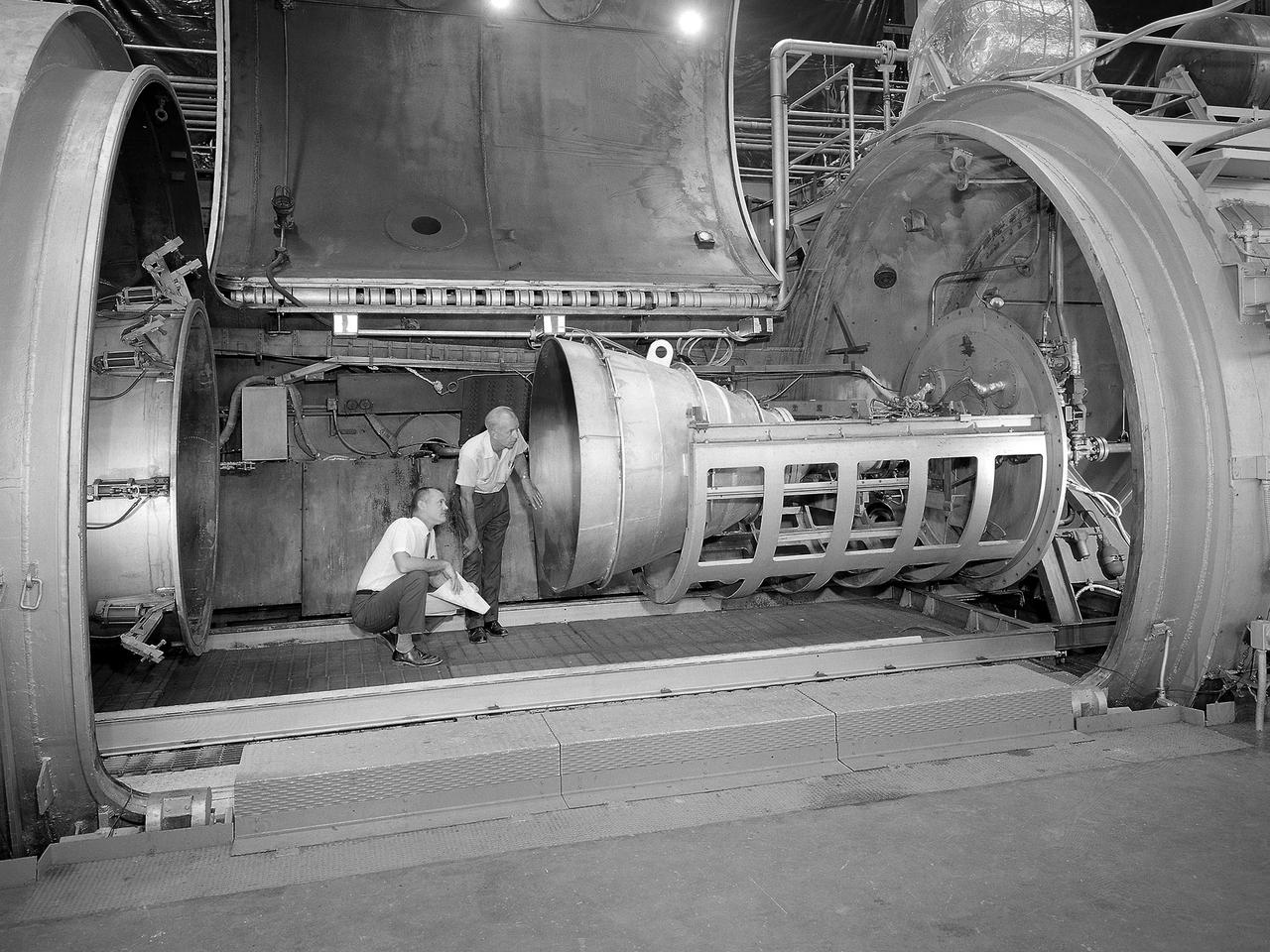

Bill Harrison and Bud Meilander check the setup of an Apollo Contour rocket nozzle in the Propulsion Systems Laboratory at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The Propulsion Systems Laboratory contained two 14-foot diameter test chambers that could simulate conditions found at very high altitudes. The facility was used in the 1960s to study complex rocket engines such as the Pratt and Whitney RL-10 and rocket components such as the Apollo Contour nozzle, seen here. Meilander oversaw the facility’s mechanics and the installation of test articles into the chambers. Harrison was head of the Supersonic Tunnels Branch in the Test Installations Division. Researchers sought to determine the impulse value of the storable propellant mix, classify and improve the internal engine performance, and compare the results with analytical tools. A special setup was installed in the chamber that included a device to measure the thrust load and a calibration stand. Both cylindrical and conical combustion chambers were examined with the conical large area ratio nozzles. In addition, two contour nozzles were tested, one based on the Apollo Service Propulsion System and the other on the Air Force’s Titan transtage engine. Three types of injectors were investigated, including a Lewis-designed model that produced 98-percent efficiency. It was determined that combustion instability did not affect the nozzle performance. Although much valuable information was obtained during the tests, attempts to improve the engine performance were not successful.
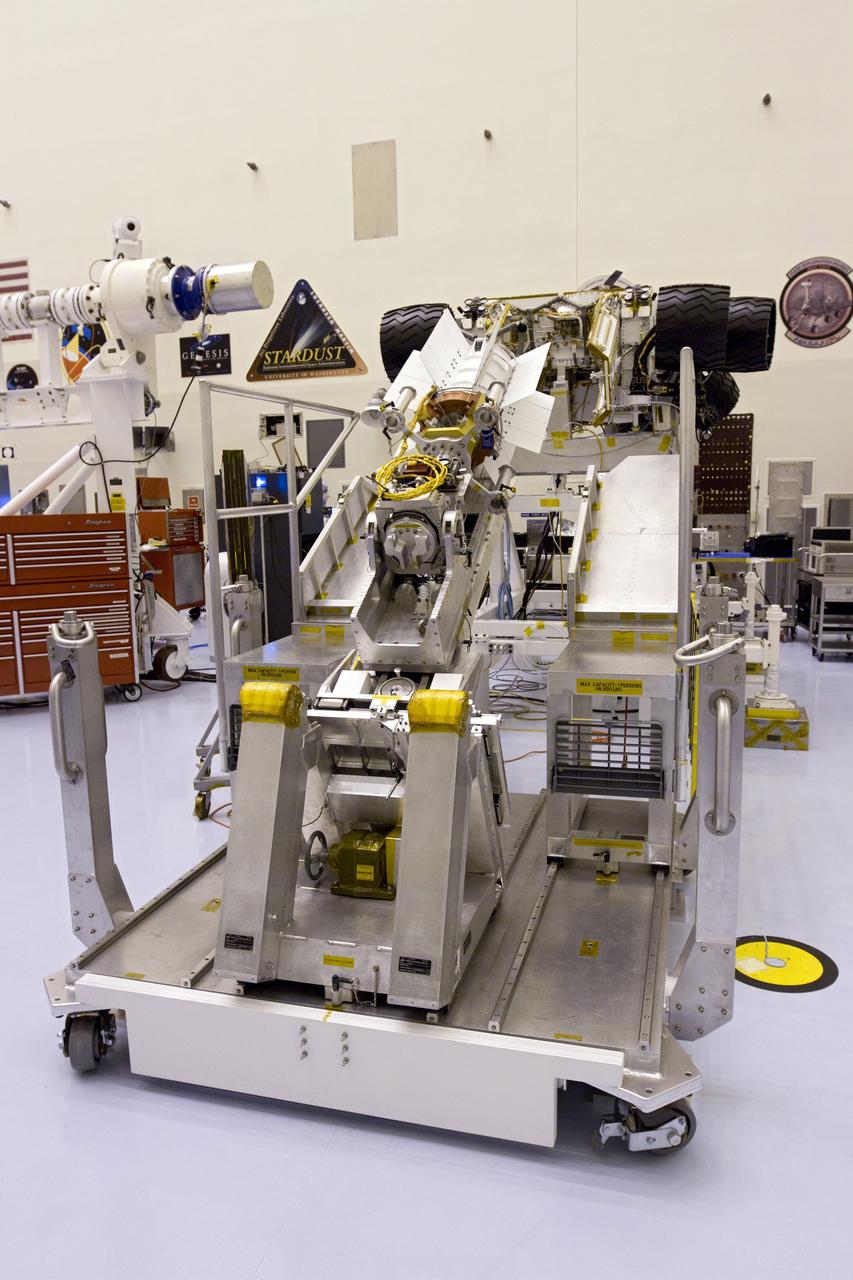

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is attached to the MMRTG integration cart. The cart will be used to install the MMRTG on the Curiosity rover for a fit check. The wheels of the rover appear to stick out on either side of the cart. The MMRTG will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
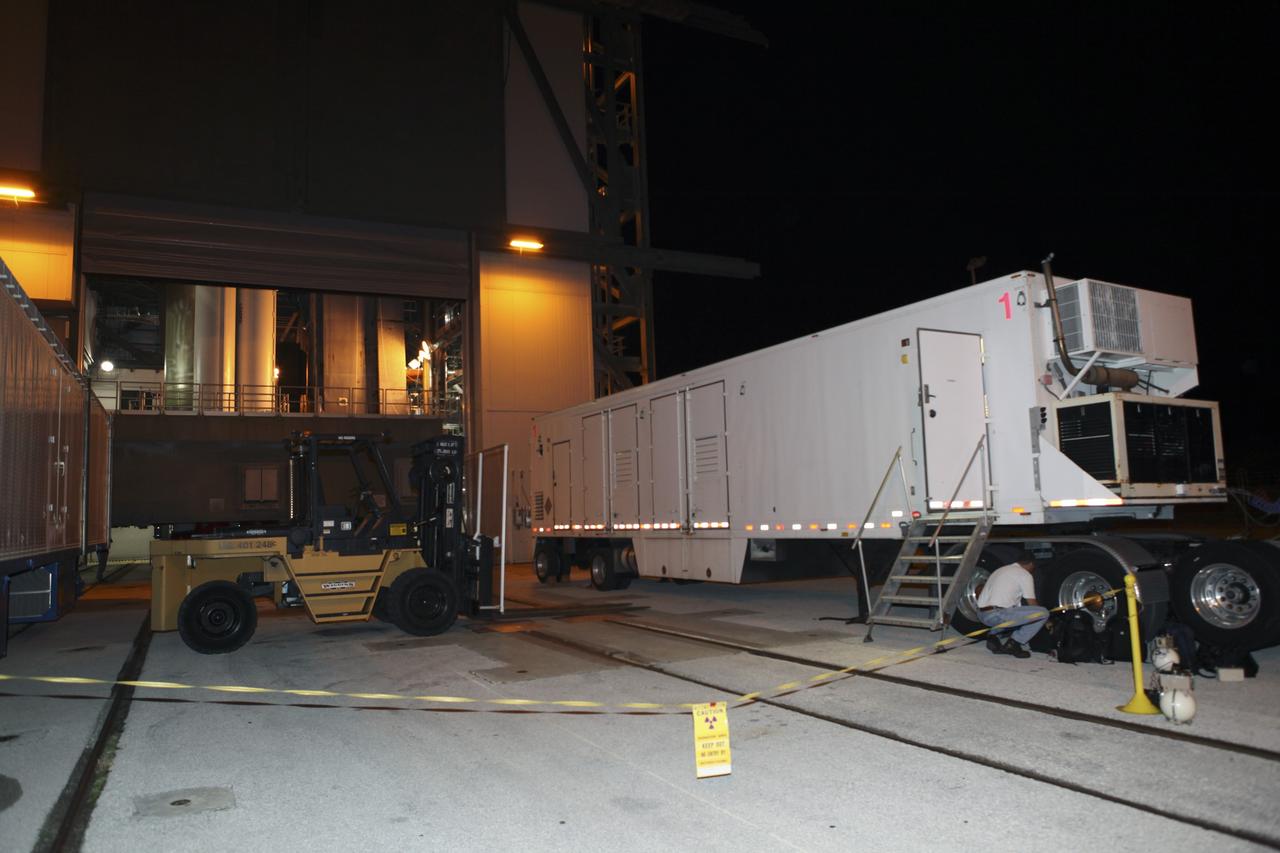

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Outside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41, an area has been cordoned off beside the trailer which has arrived at the pad carrying the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The generator will be lifted up to the top of the rocket and installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat produced by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
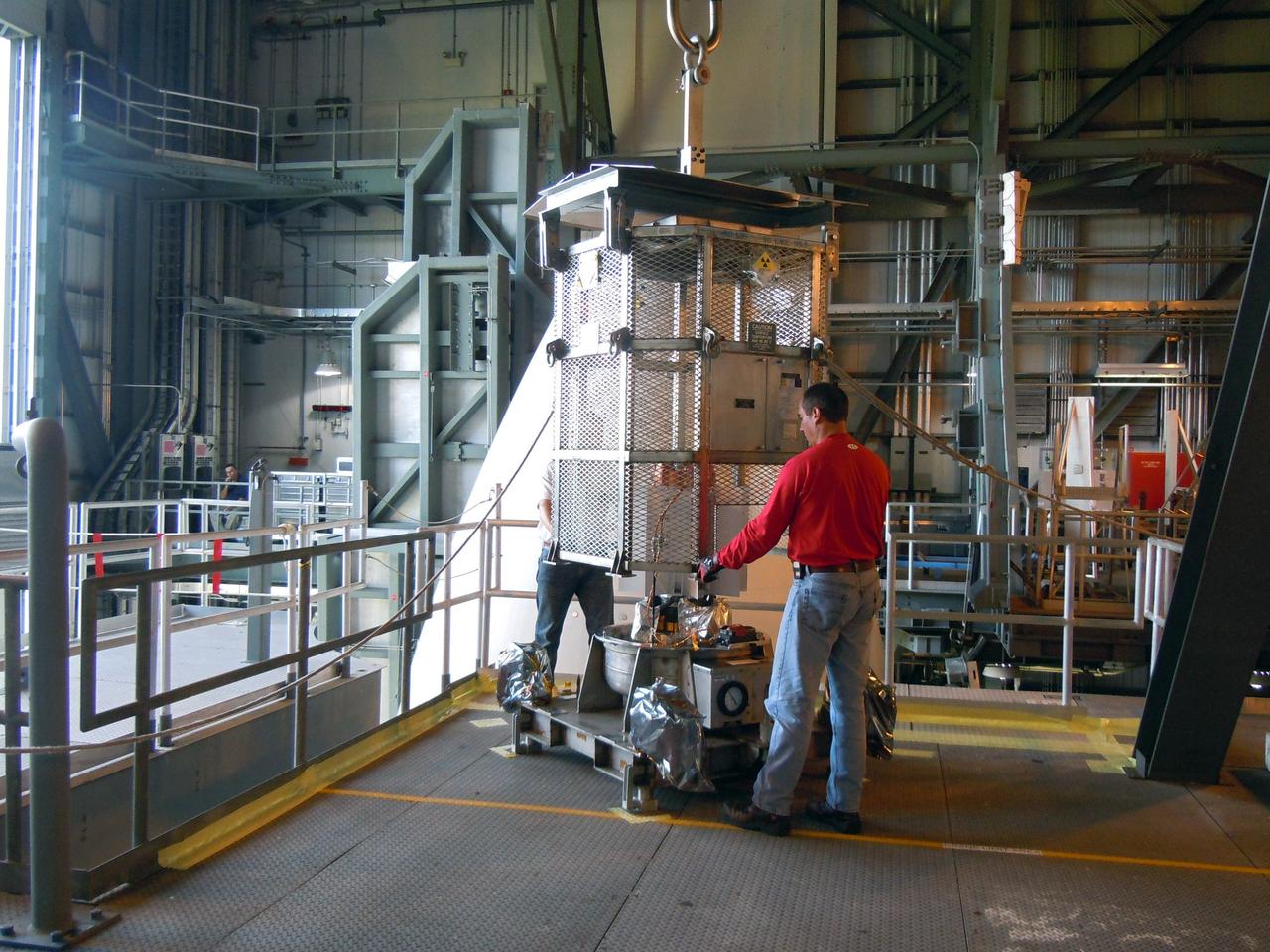

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, spacecraft technicians guide the mesh container protecting the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission as a crane lifts it from around the generator. The container, known as the "gorilla cage," protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. Next, the MMRTG will be installed on MSL's Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: Department of Energy/Idaho National Laboratory
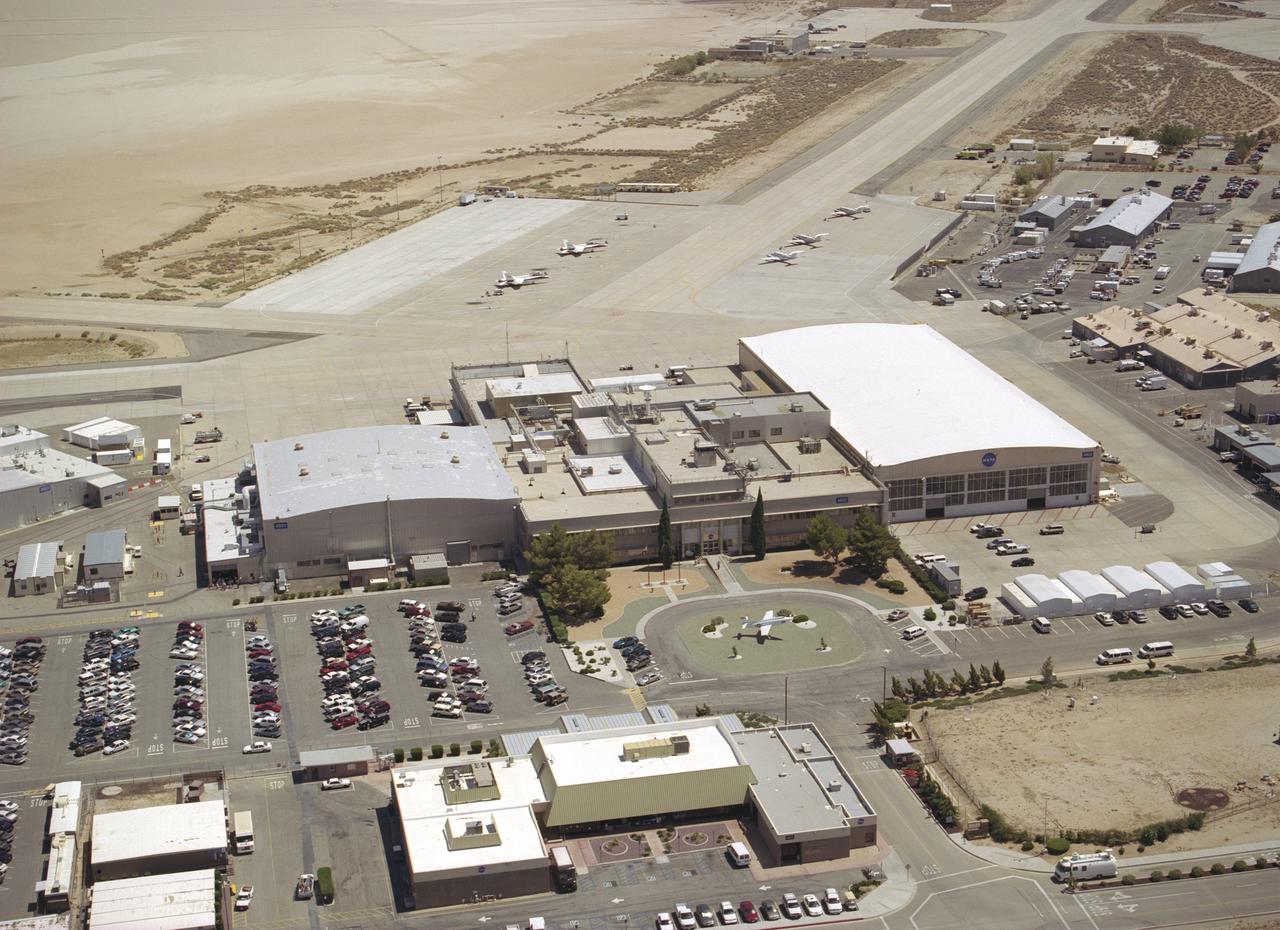

Since the 1940s the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, has developed a unique and highly specialized capability for conducting flight research programs. The organization, made up of pilots, scientists, engineers, technicians, and mechanics, has been and will continue to be leaders in the field of advanced aeronautics. Located on the northwest "shore" of Rogers Dry Lake, the complex was built around the original administrative-hangar building constructed in 1954. Since then many additional support and operational facilities have been built including a number of unique test facilities such as the Thermalstructures Research Facility, Flow Visualization Facility, and the Integrated Test Facility. One of the most prominent structures is the space shuttle program's Mate-Demate Device and hangar in Area A to the north of the main complex. On the lakebed surface is a Compass Rose that gives pilots an instant compass heading. The Dryden complex originated at Edwards Air Force Base in support of the X-1 supersonic flight program. As other high-speed aircraft entered research programs, the facility became permanent and grew from a staff of five engineers in 1947 to a population in 2006 of nearly 1100 full-time government and contractor employees.
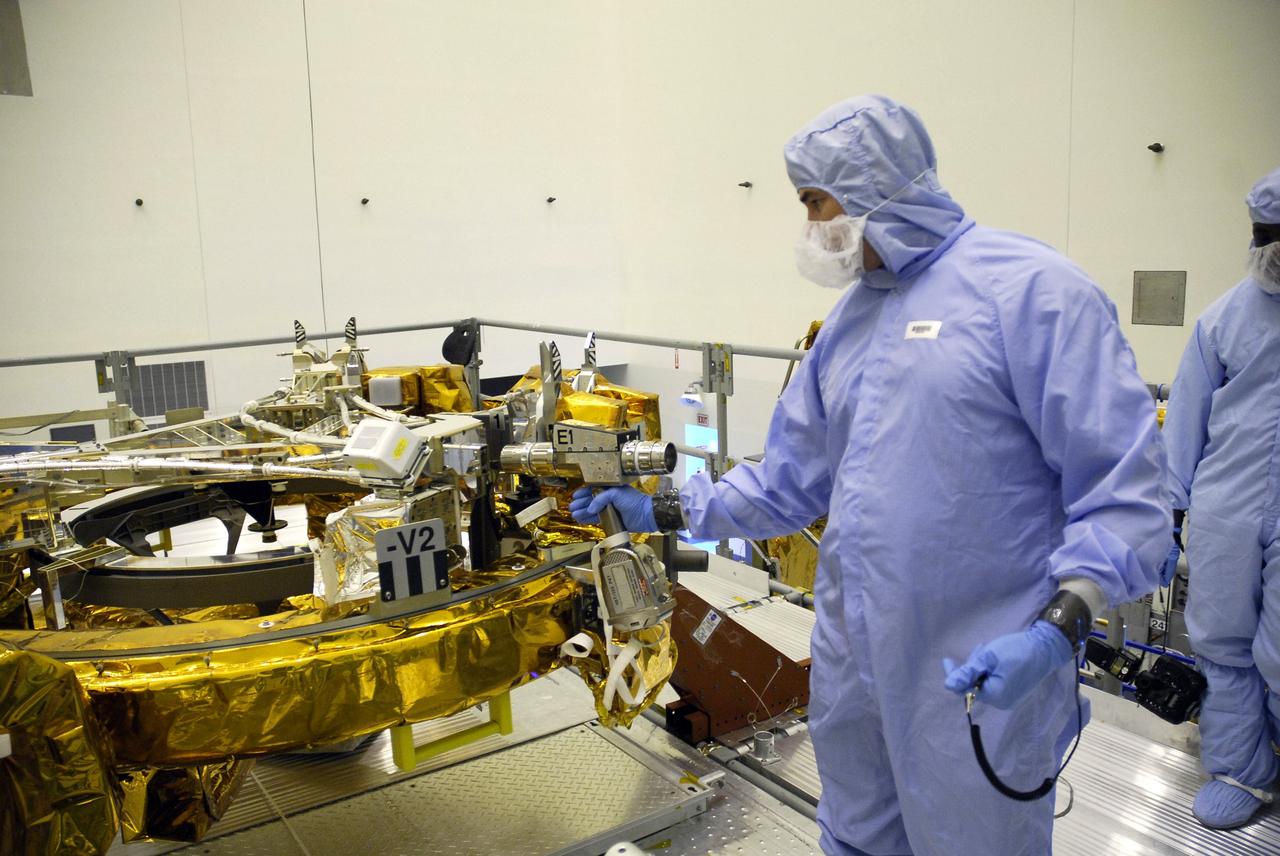

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians check the sensors on the Soft Capture Mechanism (SCM), part of the Soft Capture and Rendezvous System, or SCRS, after mating of the SCM to the Flight Support System, or FSS, carrier. The SCRS will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The SCRS greatly increases the current shuttle capture interfaces on Hubble, therefore significantly reducing the rendezvous and capture design complexities associated with the disposal mission. The FSS will join the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier as payload on space shuttle Atlantis's STS-125 mission. The payload is scheduled to go to Launch Pad 39A in mid-September to be installed into Atlantis' payload bay. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 at 1:34 a.m. EDT. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
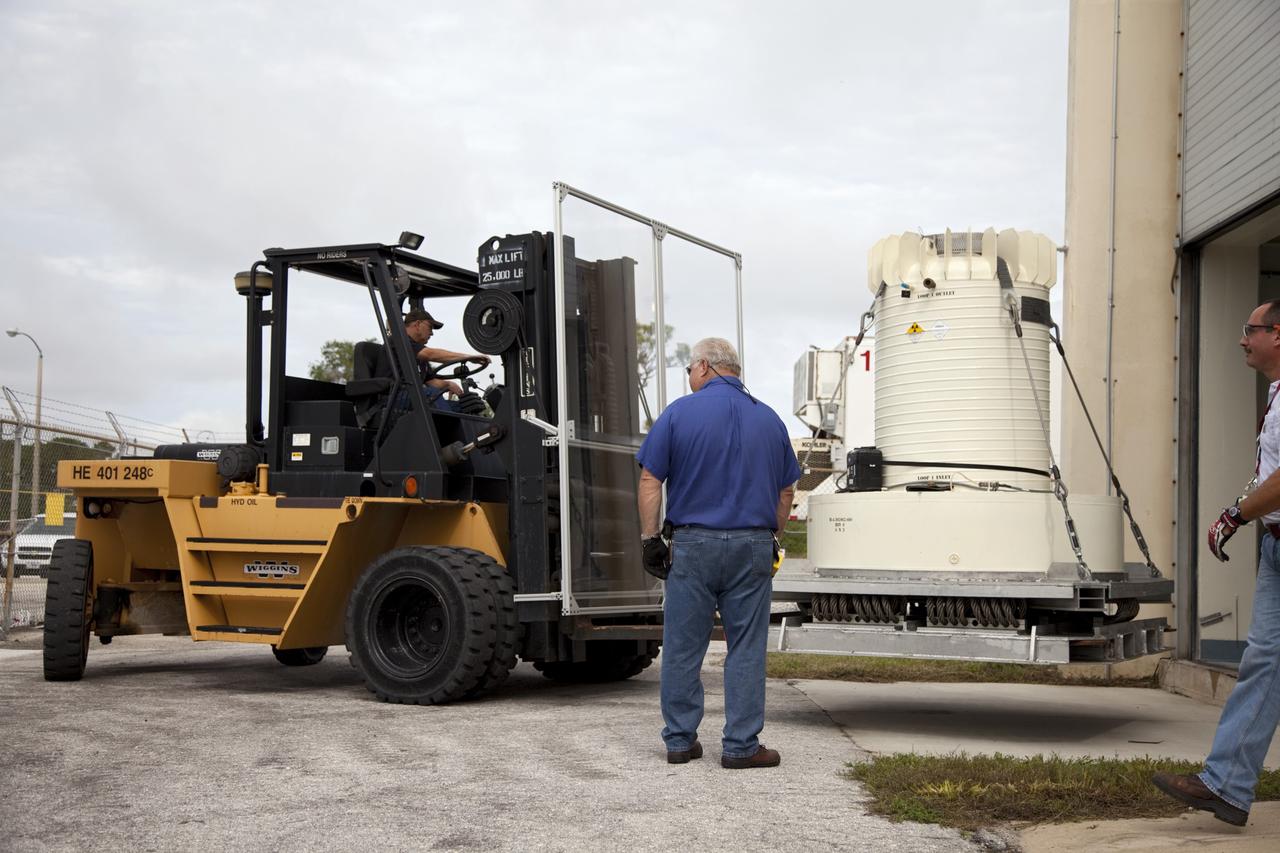

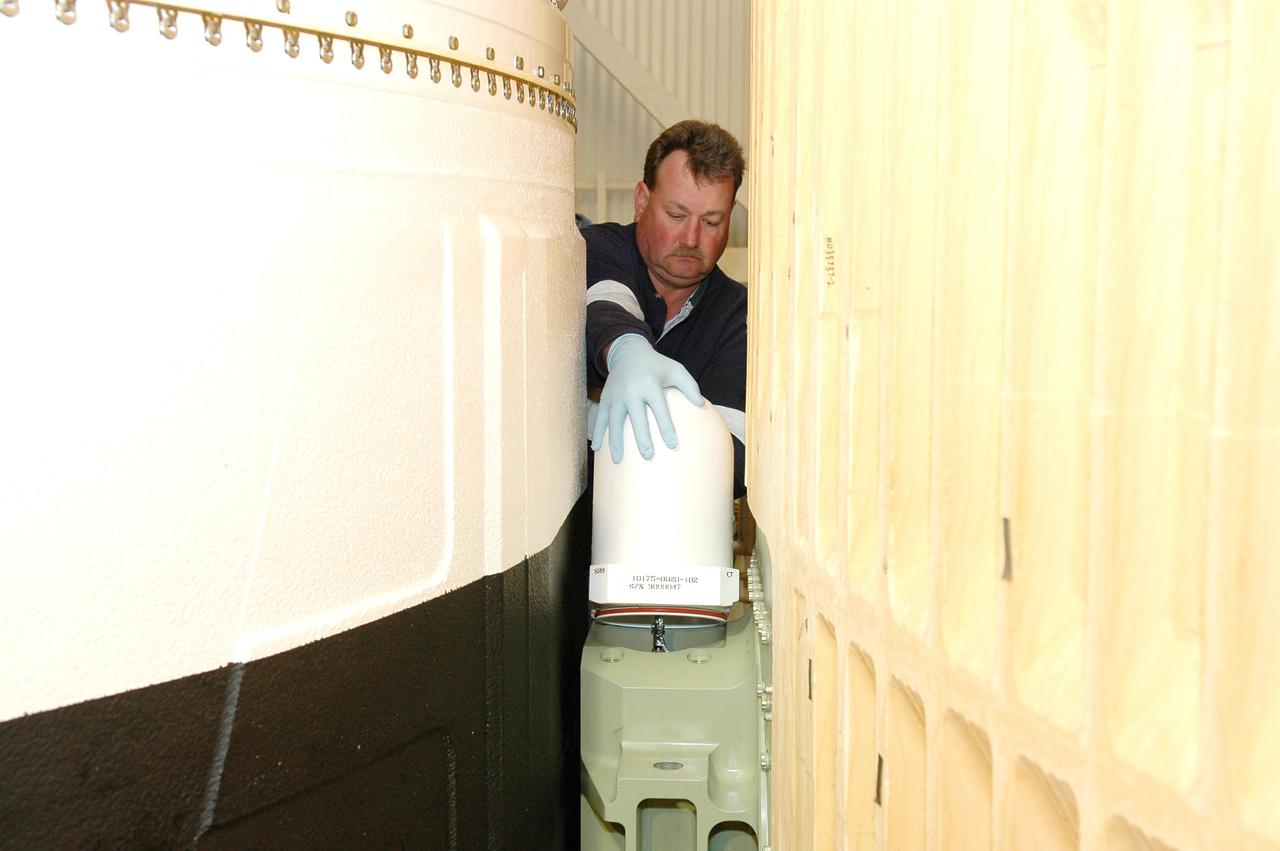
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers use a forklift to transport the shipping cask enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission to the door of the high bay of the RTG storage facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
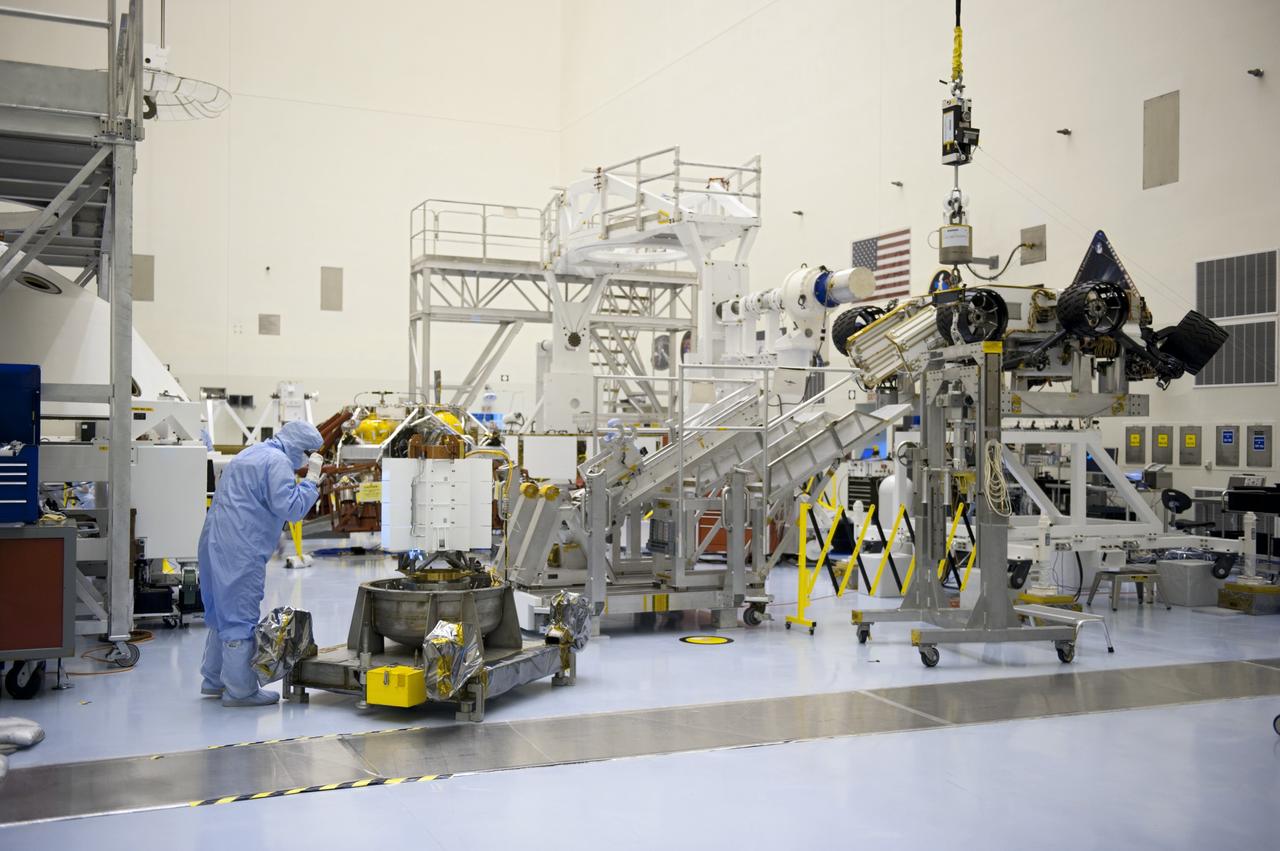

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a spacecraft technician from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory conducts a visual inspection of the cooling tubes on the exterior of the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. At right is the Curiosity rover on an elevated work stand. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
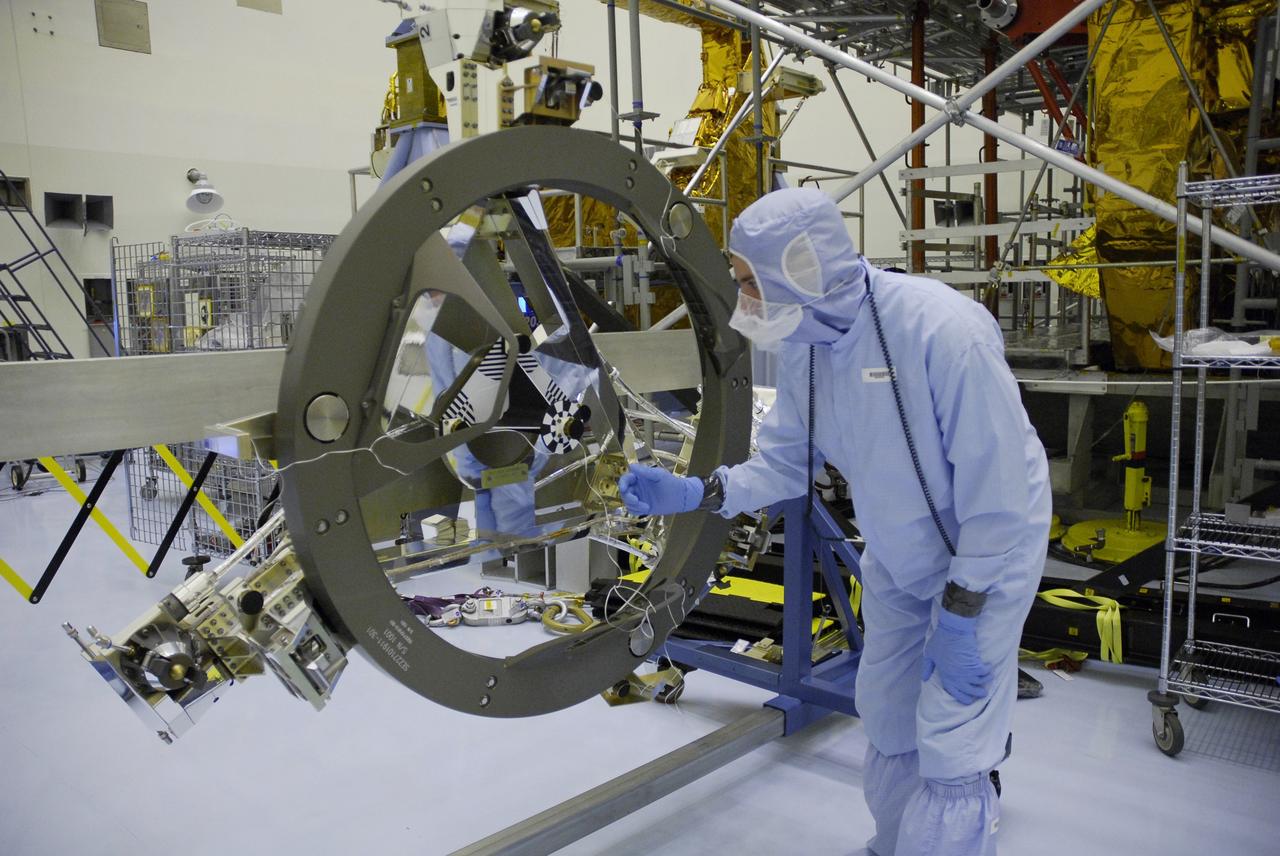

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Soft Capture Mechanism (SCM), part of the Soft Capture and Rendezvous System, or SCRS, is being prepared for transfer to the Flight Support System, or FSS, carrier. The SCRS will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The SCRS greatly increases the current shuttle capture interfaces on Hubble, therefore significantly reducing the rendezvous and capture design complexities associated with the disposal mission. The FSS will join the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier as payload on space shuttle Atlantis's STS-125 mission. The payload is scheduled to go to Launch Pad 39A in mid-September to be installed into Atlantis' payload bay. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 at 1:34 a.m. EDT. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
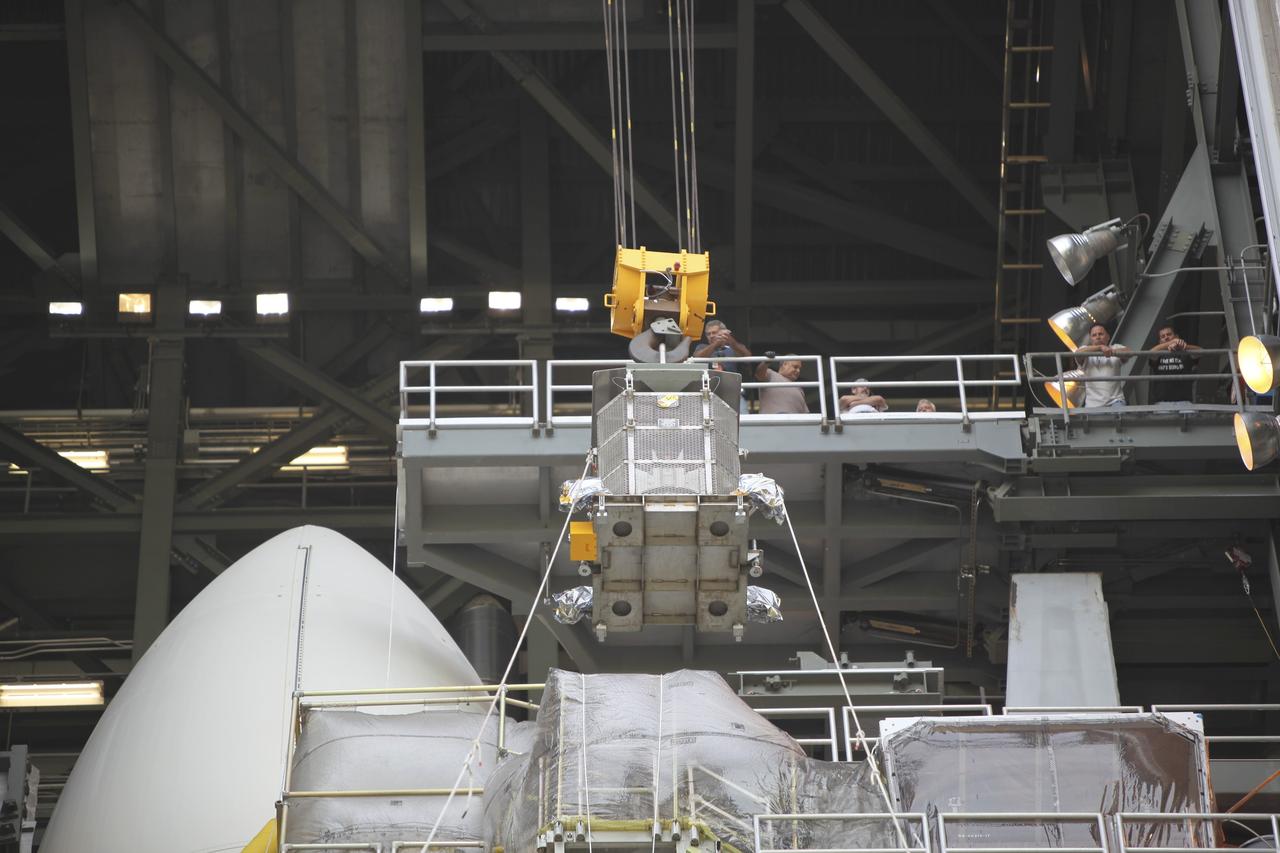

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Employees monitor the progress of the protective mesh container known as the "gorilla cage," holding the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, as it is lifted near the top of the Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41. The MMRTG will be installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat emitted by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
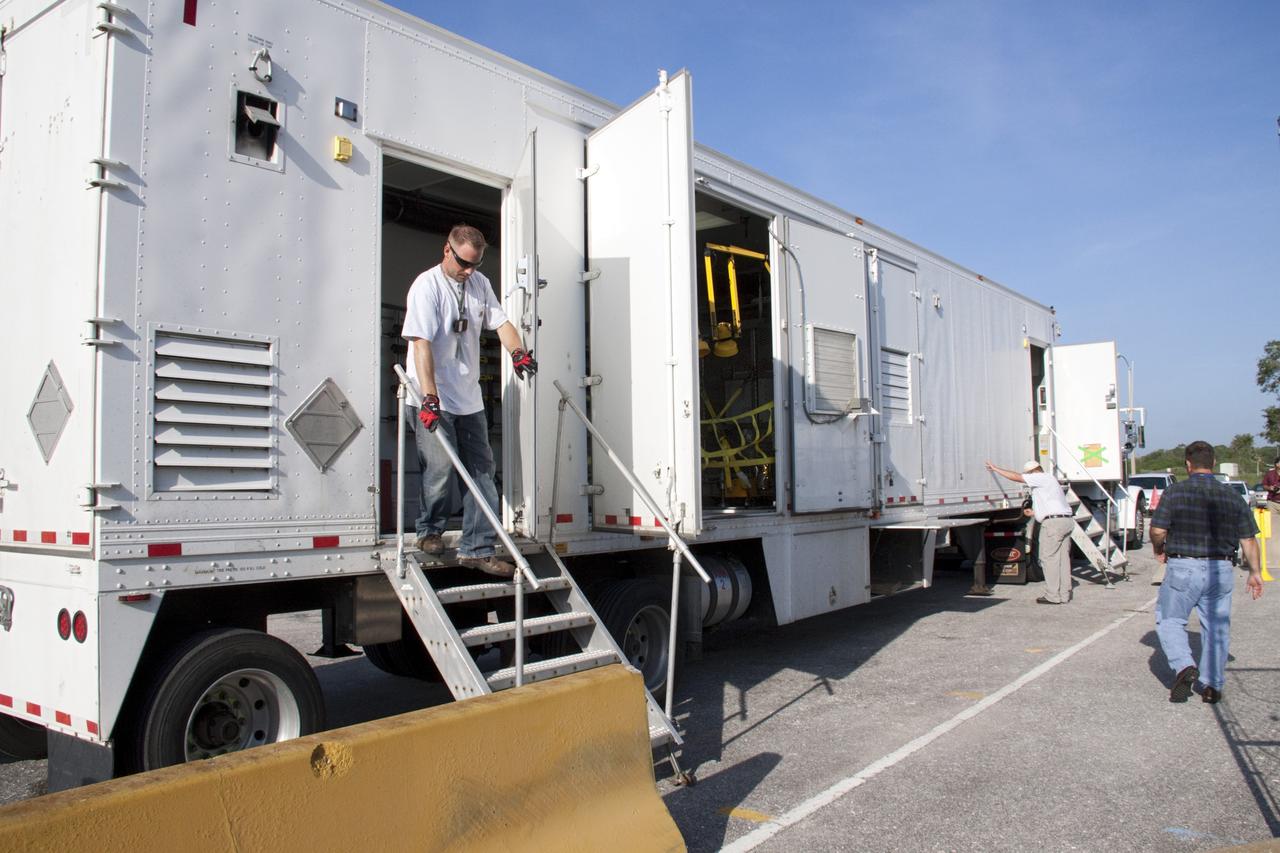

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are under way to offload the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission from the MMRTG trailer. The MMRTG is returning to the RTGF following a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians prepare to mate the Soft Capture Mechanism (SCM), part of the Soft Capture and Rendezvous System, or SCRS, onto the Flight Support System, or FSS, carrier. The SCRS will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The SCRS greatly increases the current shuttle capture interfaces on Hubble, therefore significantly reducing the rendezvous and capture design complexities associated with the disposal mission. The FSS will join the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier as payload on space shuttle Atlantis's STS-125 mission. The payload is scheduled to go to Launch Pad 39A in mid-September to be installed into Atlantis' payload bay. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 at 1:34 a.m. EDT. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
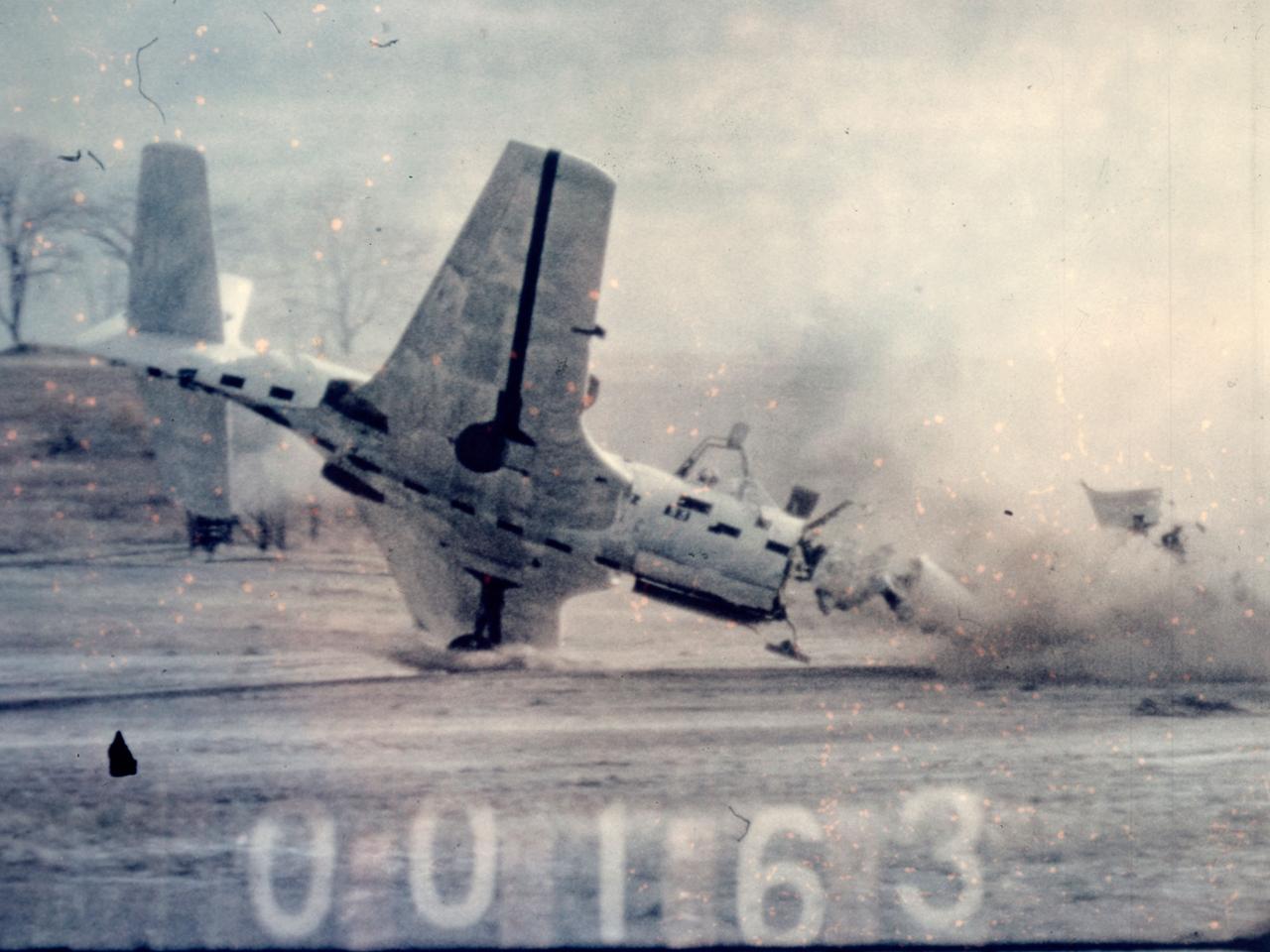

Researchers at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory purposely wreck a McDonnell FH-1 Phantom as part of the laboratory’s Crash Fire Program. NACA Lewis researchers created the program in 1949 to investigate methods for improving survival rates for take-off and landing-type crashes. In these types of crashes, the passengers often survived the impact only to perish in the ensuing fire. Previously there had been little information on the nature of post-crash fires, and it was difficult to use analytical studies in this area. Irving Pinkel, Chief of the Lewis Flight Propulsion Division, was the primary researcher. He enlisted flight safety specialist and aeronautics researchers G. Merritt Preston and Gerard Pesman, mechanical engineer Dugald Black, and others. The tests were conducted at the nearby Ravenna Arsenal using decommissioned Air Force fighter and transport aircraft. The pilotless aircraft were accelerated down a rail on a 1700-foot track at take-off speeds and run into barriers to simulate a variety of different types of crashes. The first barrier stripped off the landing gears and another briefly sent the aircraft off the ground before it crashed into a dirt mound. Telemetry and high-speed cameras were crucial elements in these studies. NACA Lewis photographer Bill Wynne developed a method for inserting timekeeping devices on test film that were able to show time to one thousandth of a second.
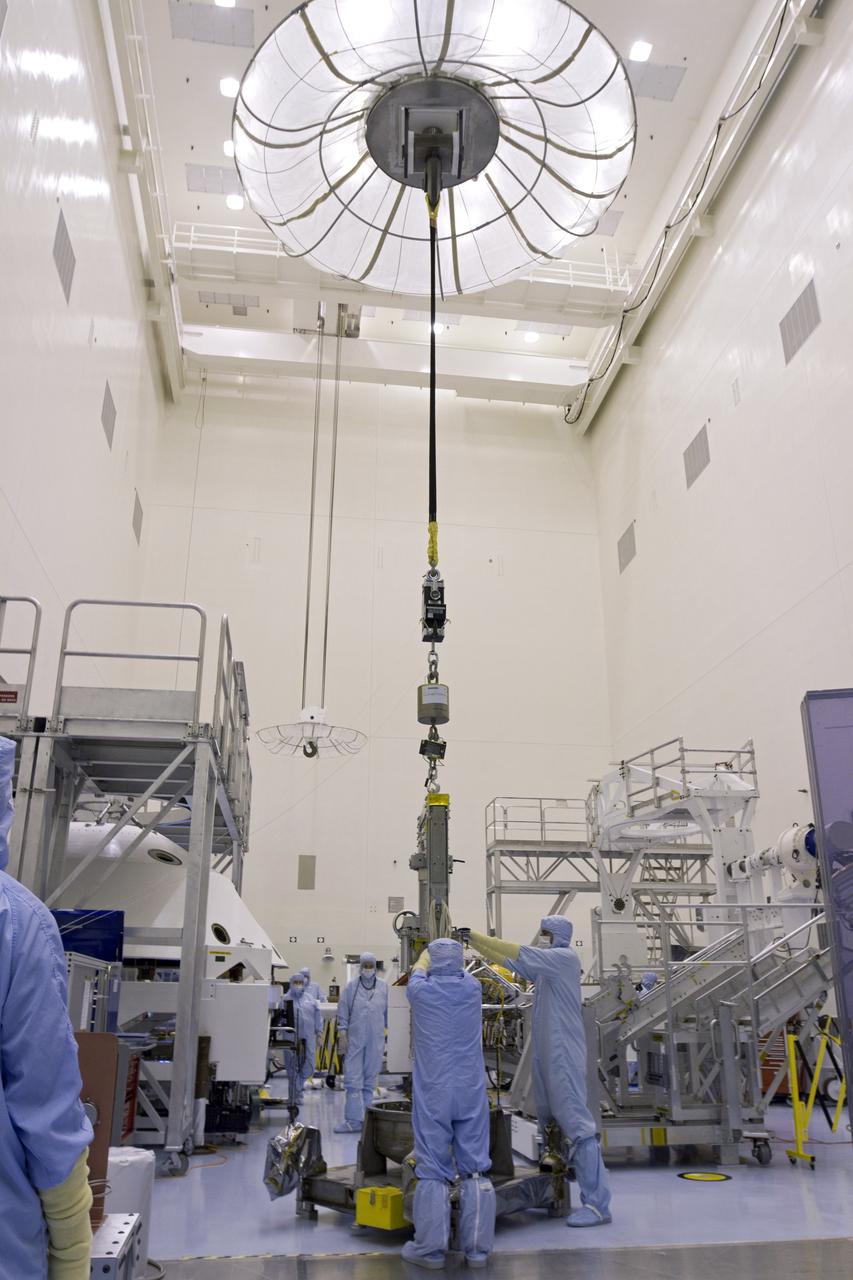

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory connect a crane to a turning fixture connected to the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The fixture will lift and lower the MMRTG onto the MMRTG integration cart. The cart will be used to install the MMRTG on Curiosity for a fit check. The MMRTG will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Vehicle Assembly Building, Lead Technician Todd Reeves, with United Space Alliance, moves a bolt catcher into place between the Solid Rocket Booster and left and the External Tank at right.A bolt catcher is a vertical bolt mechanism at the forward end of the External Tank that attaches each booster to the tank. At approximately two minutes into launch, SRB separation begins when pyrotechnic devices fire to break the 25-inch, 62-pound steel bolts. One half of the bolt is caught in canister-like 'bolt catchers' located on the tank; the other half remains with the boosters. Discovery is flying with a modified bolt catcher, which was upgraded from a two-piece welded design to a one-piece, machine-made design as part of NASA's effort to return to safe, reliable spaceflight. Eliminating the weld makes a structurally stronger bolt catcher design. Though the bolt catcher is mounted on the External Tank, it is considered part of the Solid Rocket Booster element design. It is built by Summa Technologies, Inc. in Huntsville, Ala., insulated at Lockheed Martin’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, and installed on the External Tank at KSC.
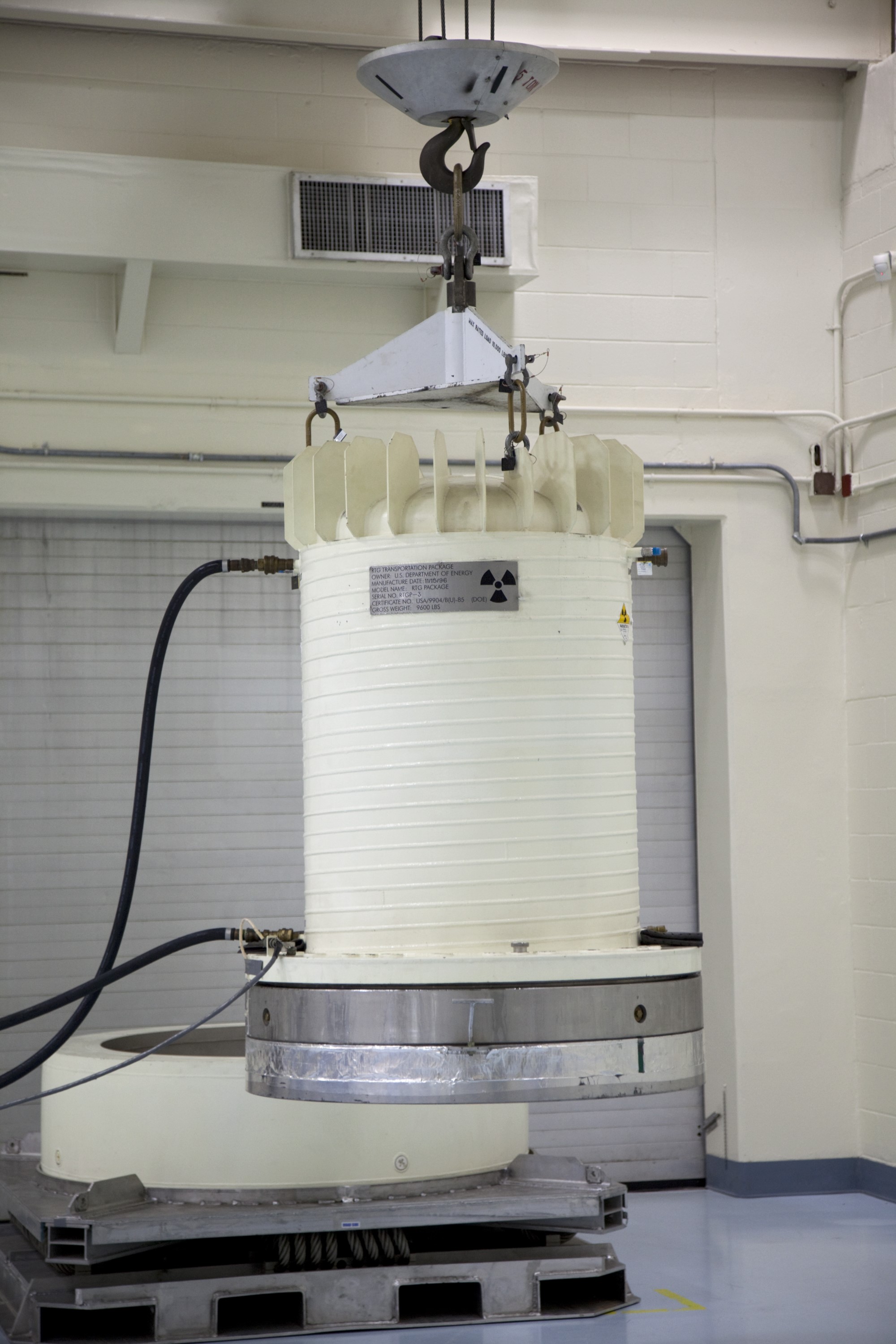

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the RTG storage facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts the shipping cask enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission from its transportation pallet. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, spacecraft technicians install the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: Department of Energy/Idaho National Laboratory
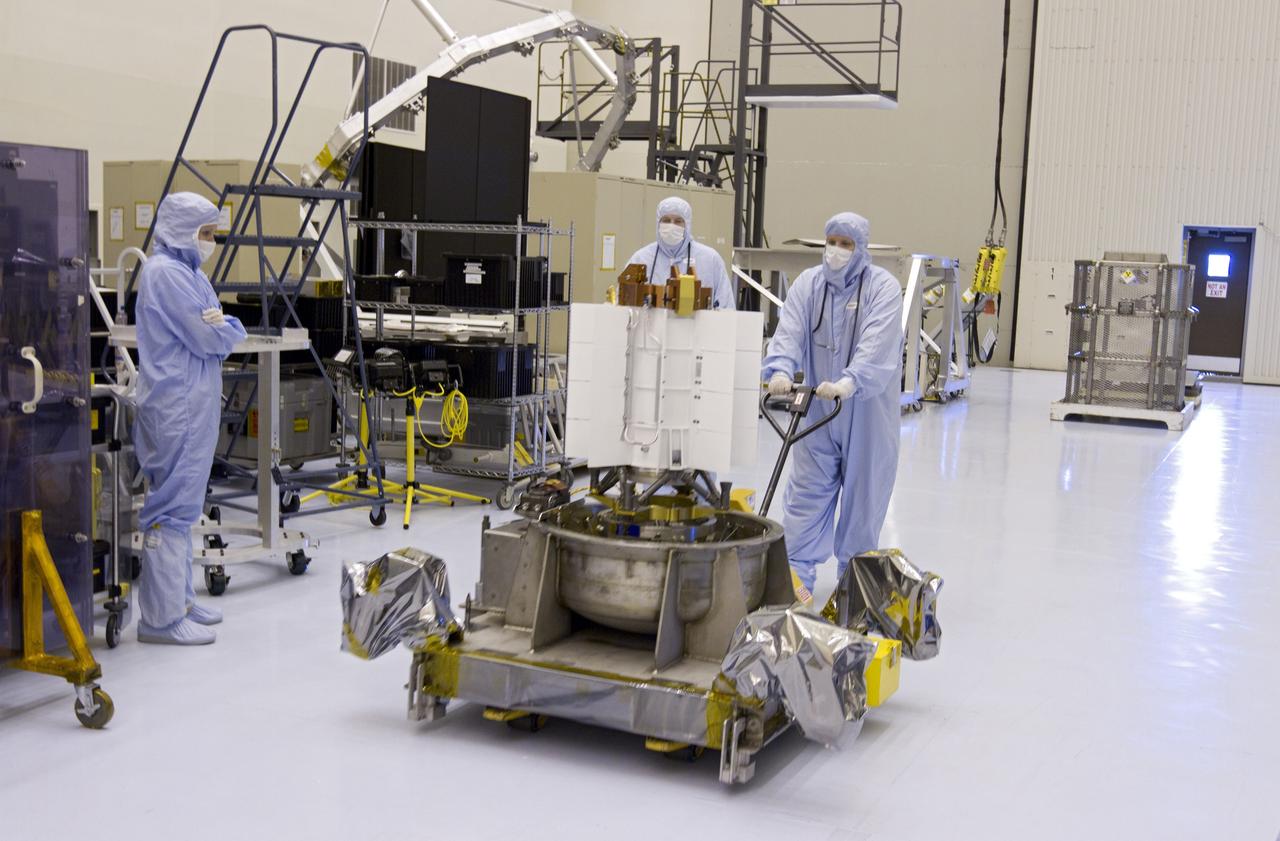

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers dressed in clean room attire, known as bunny suits, transfer the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on its holding base from the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) into the facility's high bay. In the high bay, the MMRTG temporarily will be installed on the MSL rover, Curiosity, for a fit check but will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory position the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on the turning fixture above the MMRTG integration cart. The cart will be used to install the MMRTG on the Curiosity rover for a fit check. The rover is on an elevated work stand, at right. The MMRTG will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the RTG storage facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the external and internal protective layers of the shipping cask are lifted from around the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
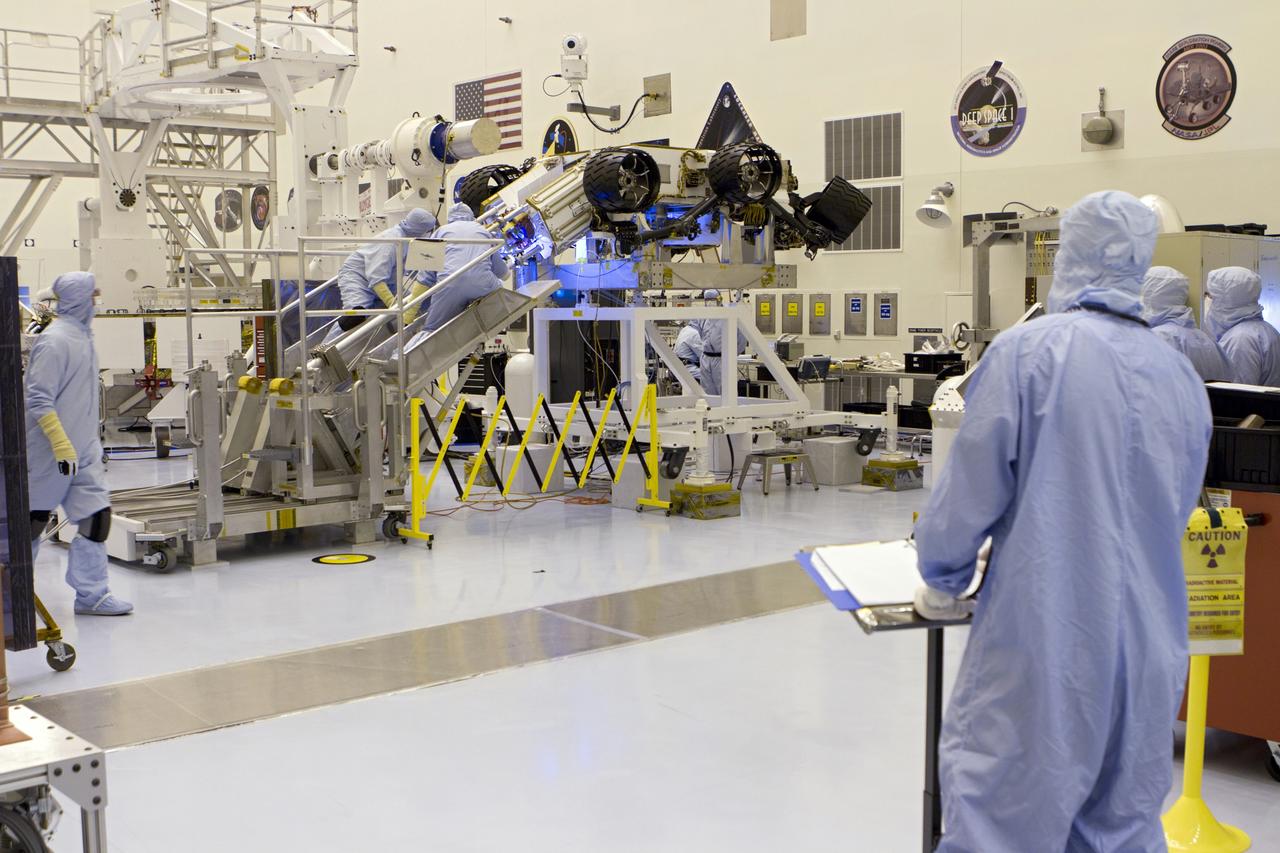

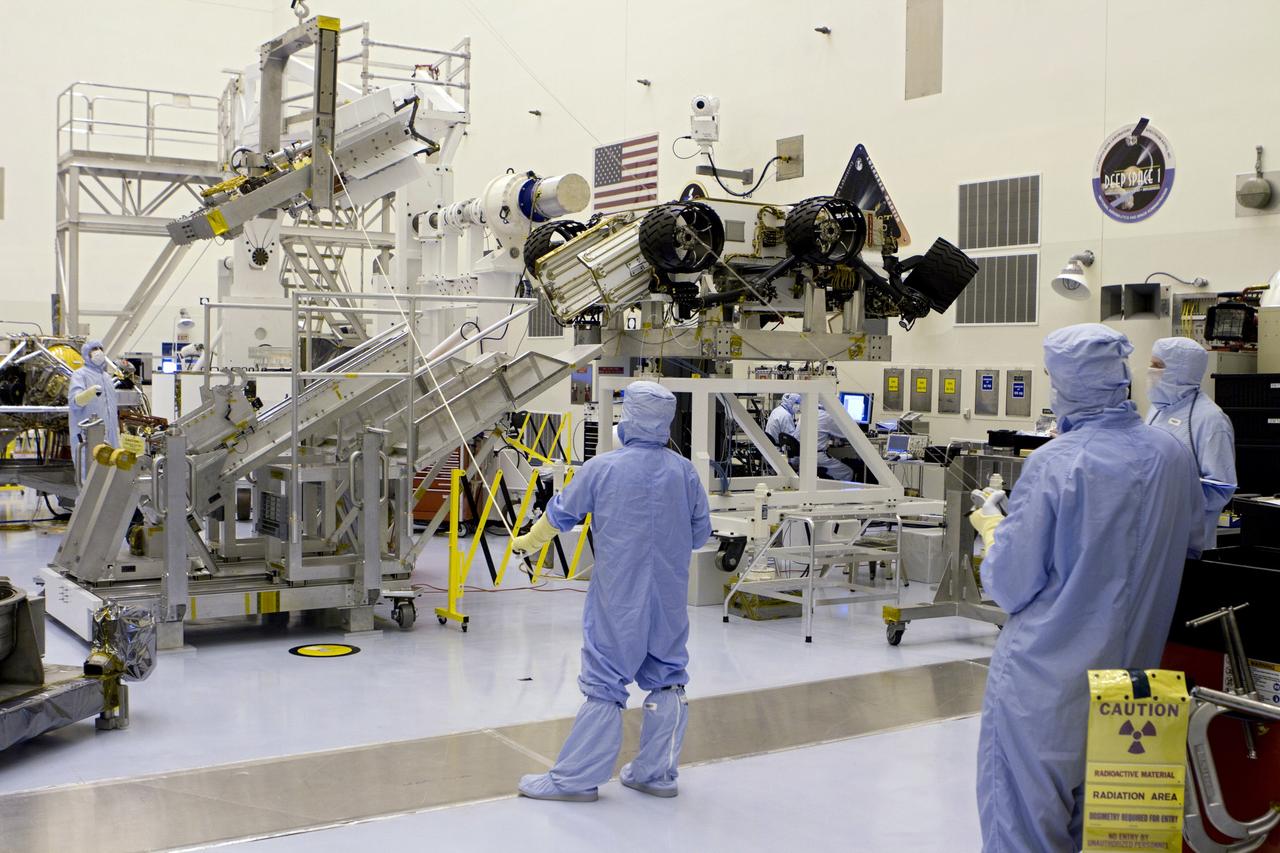
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory transfer the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission onto the aft of the Curiosity rover for a fit check with the aid of the MMRTG integration cart. The MMRTG then will be removed and installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
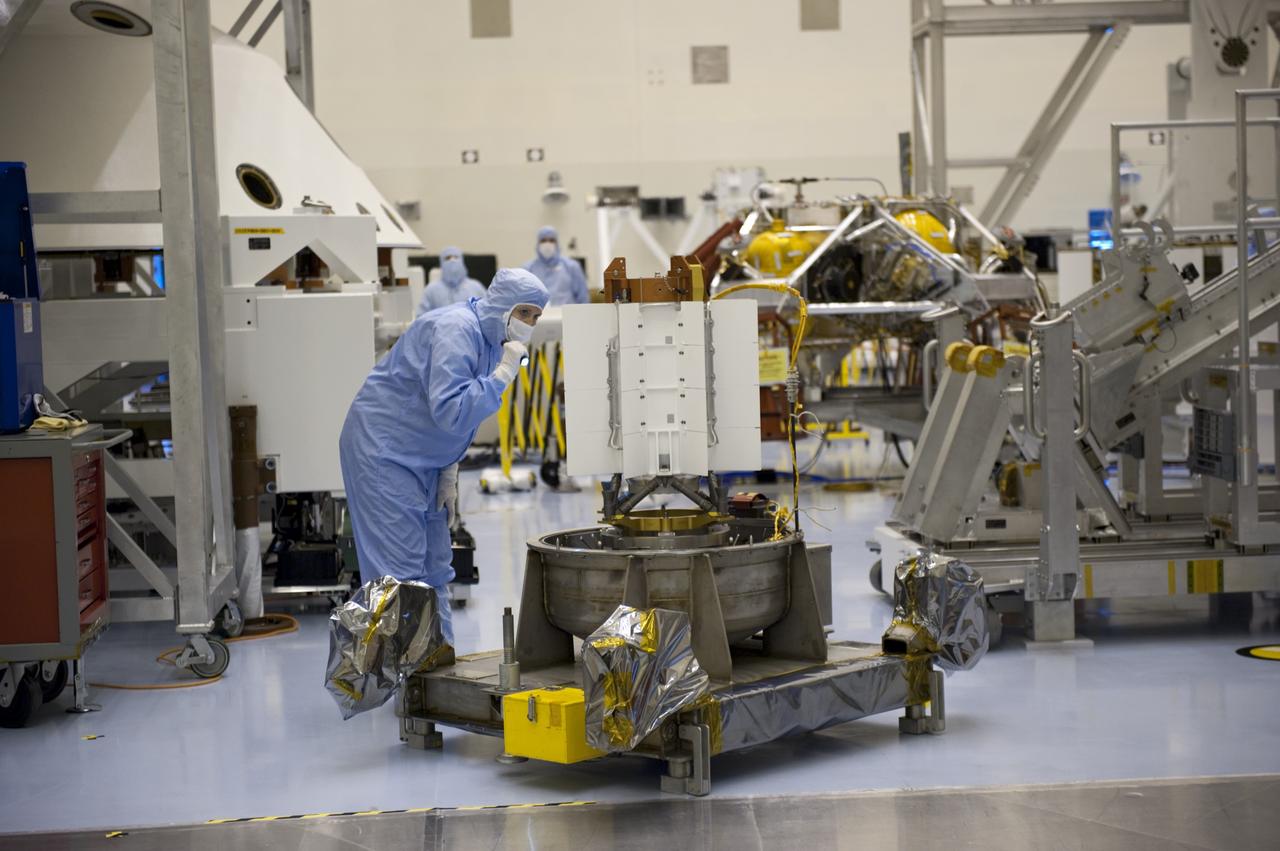

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a spacecraft technician from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory conducts a visual inspection of the cooling tubes on the exterior of the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
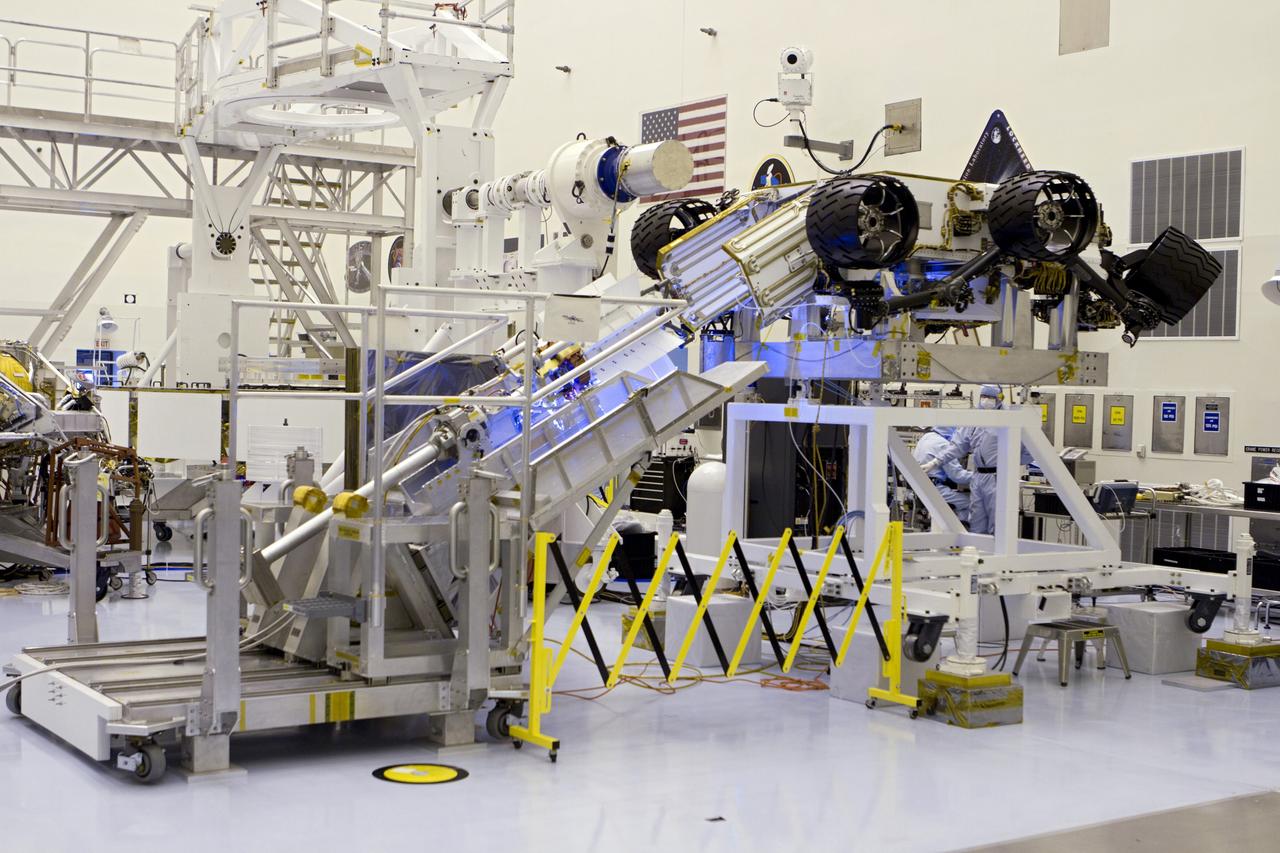

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is attached to the MMRTG integration cart. The cart will be used to install the MMRTG on the Curiosity rover for a fit check. The rover is on an elevated work stand, at right. The MMRTG then will be removed and installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
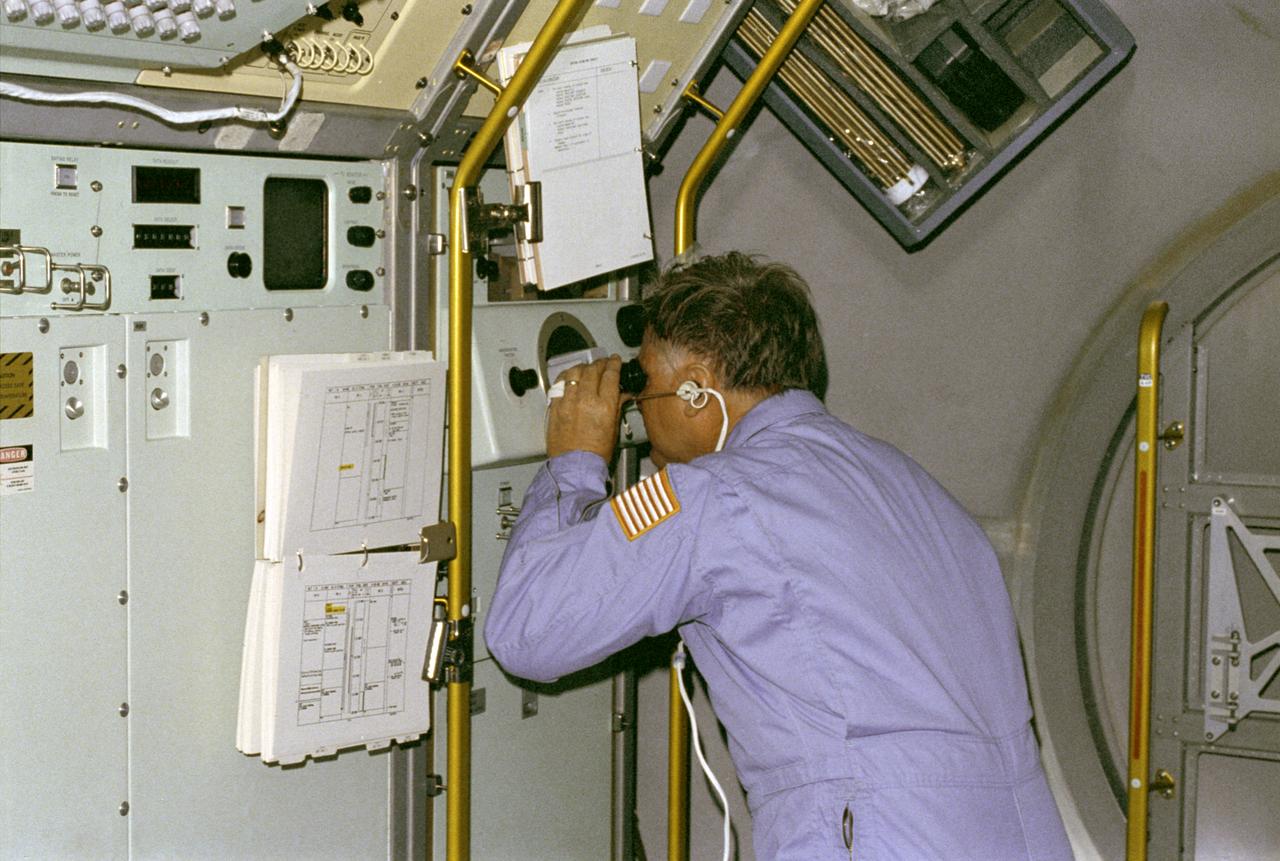

The primary purpose of the Spacelab-3 mission was to conduct materials science experiments in a stable low-gravity environment. In addition, the crew performed research in life sciences, fluid mechanics, atmospheric science, and astronomy. Spacelab-3 was equipped with several new minilabs, special facilities that would be used repeatedly on future flights. Two elaborate crystal growth furnaces, a life support and housing facility for small animals, and two types of apparatus for the study of fluids were evaluated on their inaugural flight. In this photograph, astronaut Don Lind observes the mercuric iodide growth experiment through a microscope at the vapor crystal growth furnace. The goals of this investigation were to grow near-perfect single crystals of mercuric iodide and to gain improved understanding of crystal growth by a vapor process. Mercuric iodide crystals have practical use as sensitive x-ray and gamma-ray detectors, and in portable detector devices for nuclear power plant monitoring, natural resource prospecting, biomedical applications in diagnosis and therapy, and in astronomical instruments. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, Spacelab-3 (STS-51B) was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger on April 29, 1985.
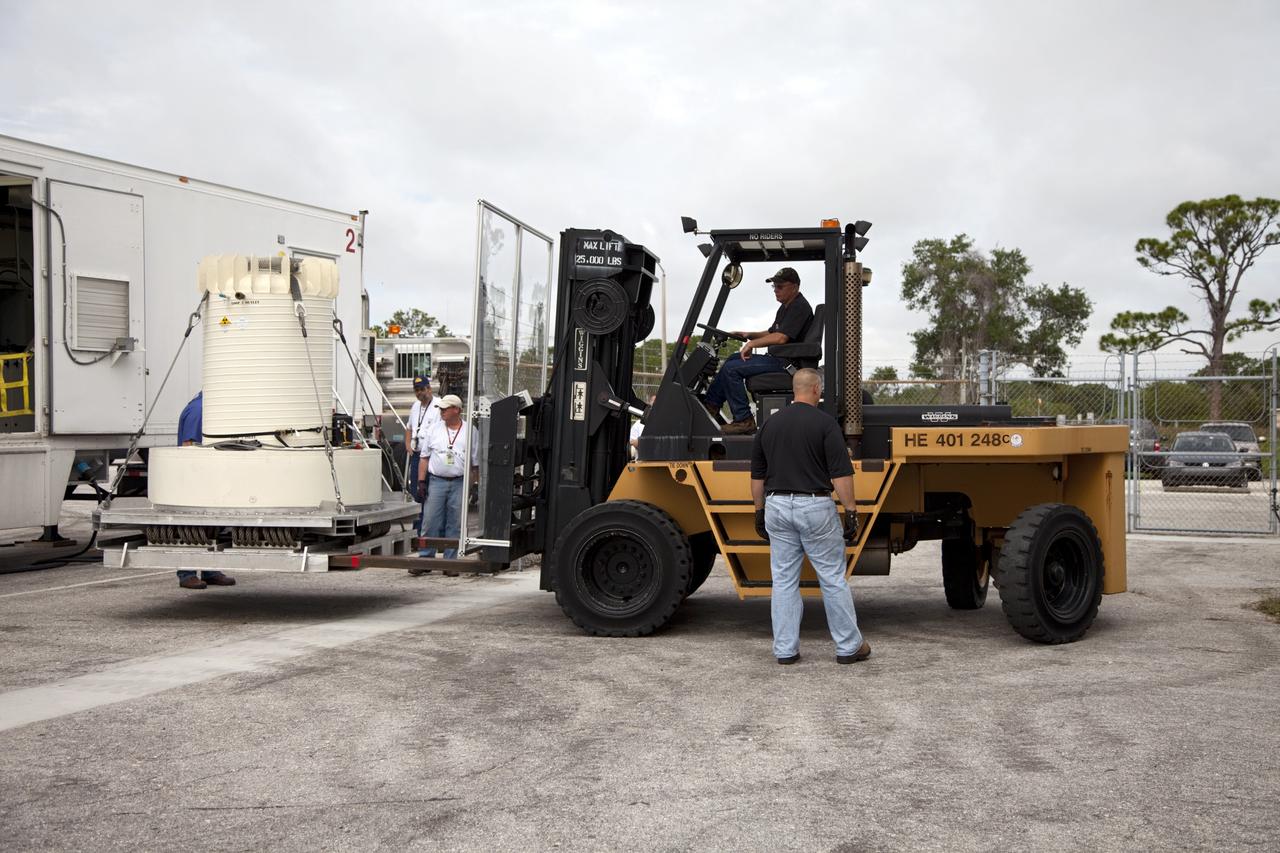

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers use a forklift to offload the shipping cask enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission from the MMRTG trailer that delivered it to the RTG storage facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
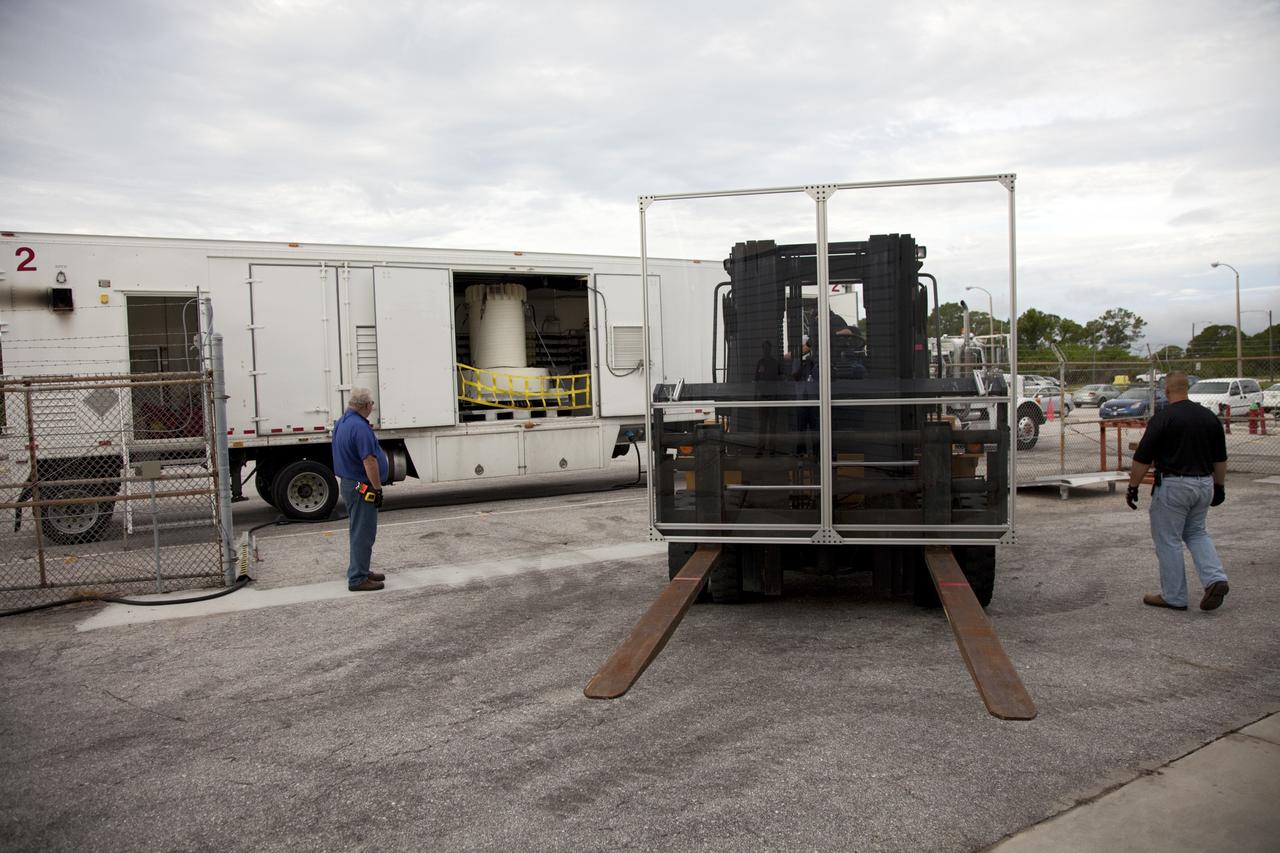

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission, enclosed in a shipping cask, is seen through the open door of the MMRTG trailer that delivered it to the RTG storage facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
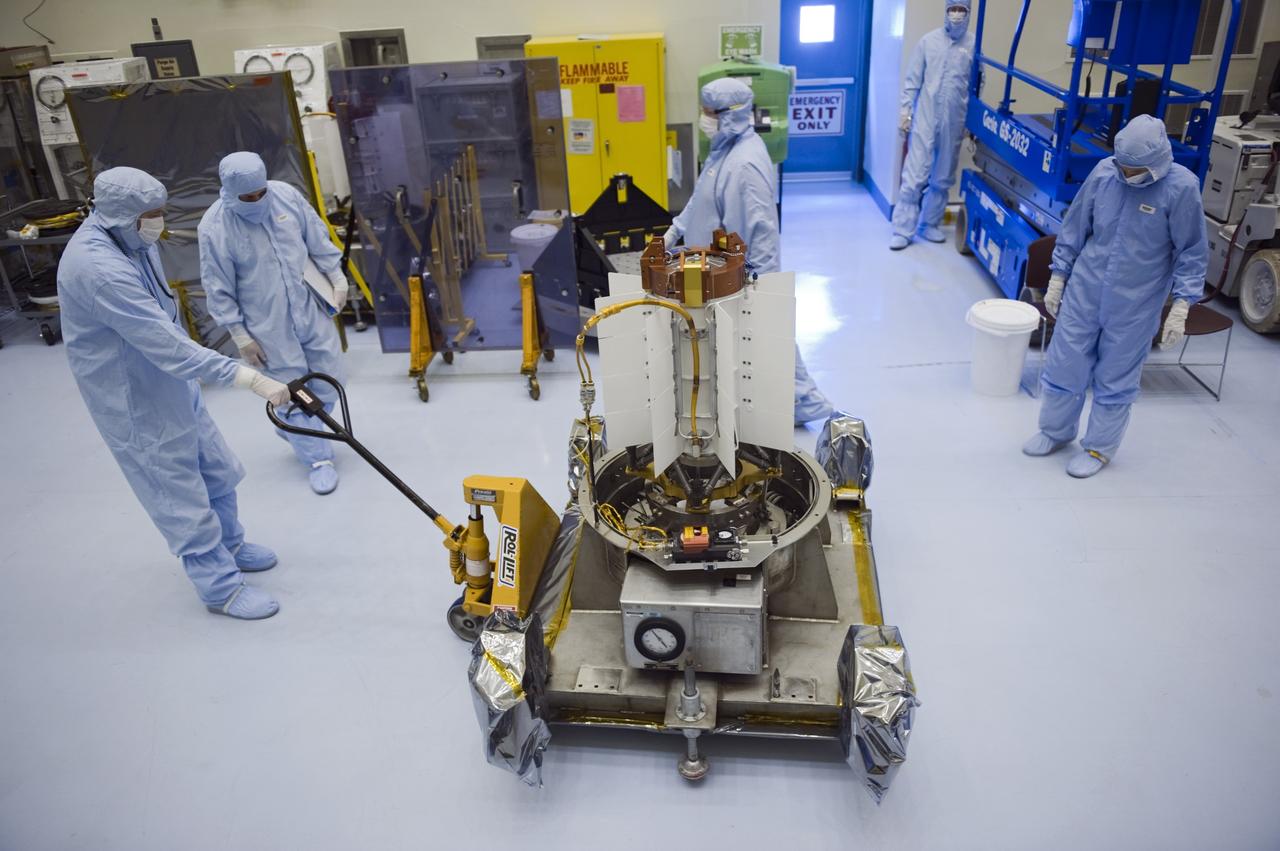

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory park the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on its support base in the airlock following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover in the high bay. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is lowered onto a support base with the aid of a turning fixture following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
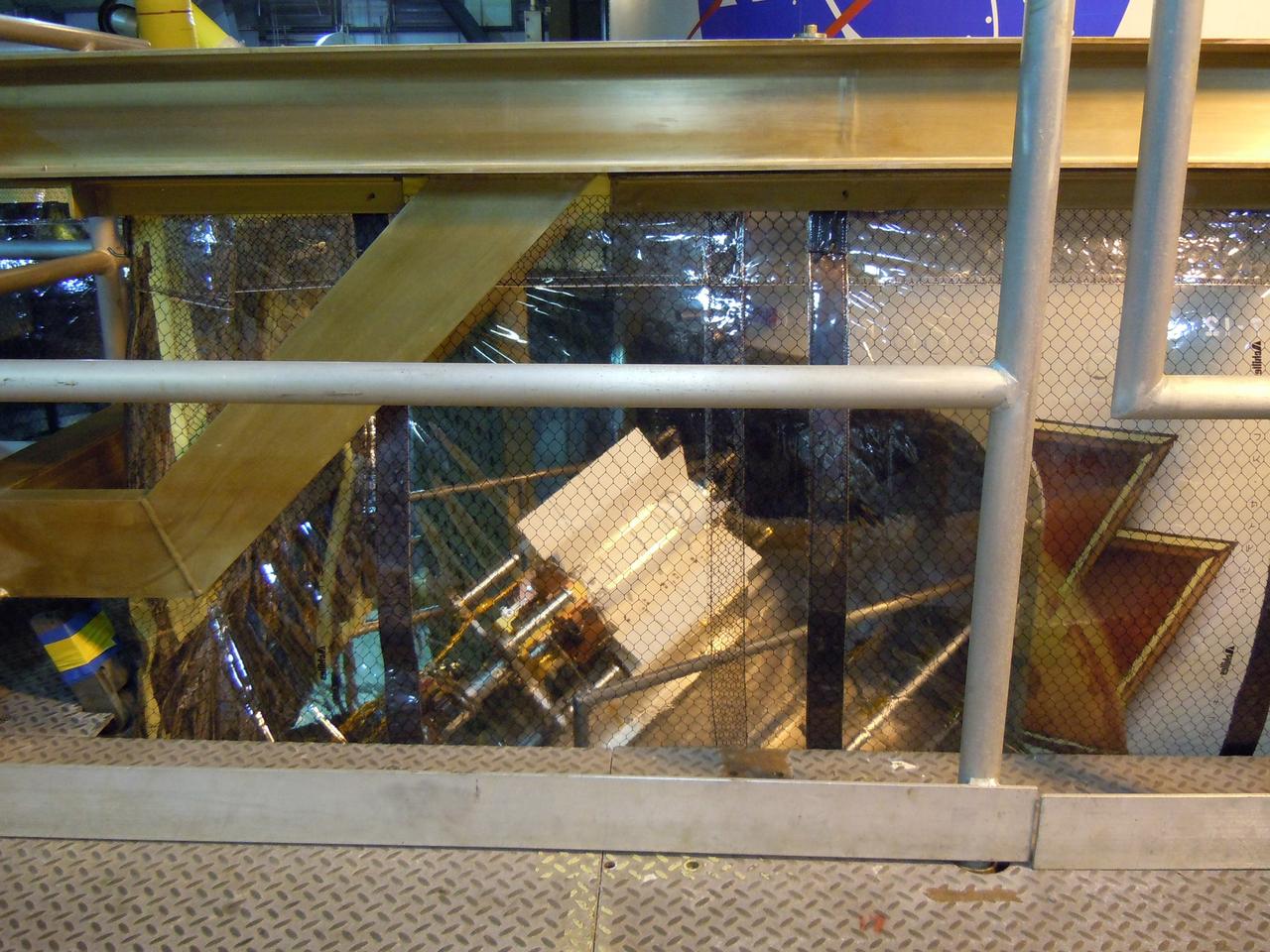

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, secured to a turning fixture, is positioned on the radioisotope power system integration cart (RIC). The MMRTG will be installed on the Curiosity rover with the aid of the RIC. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: Department of Energy/Idaho National Laboratory

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a forklift positions the protective mesh container enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission onto the floor of the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The container, known as the "gorilla cage," protects the MMRTG and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. In the PHSF, the MMRTG temporarily will be installed on the MSL rover, Curiosity, for a fit check but will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians check the sensors on the Soft Capture Mechanism (SCM), part of the Soft Capture and Rendezvous System, or SCRS, after mating of the SCM to the Flight Support System, or FSS, carrier. The SCRS will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The SCRS greatly increases the current shuttle capture interfaces on Hubble, therefore significantly reducing the rendezvous and capture design complexities associated with the disposal mission. The FSS will join the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier as payload on space shuttle Atlantis's STS-125 mission. The payload is scheduled to go to Launch Pad 39A in mid-September to be installed into Atlantis' payload bay. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 at 1:34 a.m. EDT. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
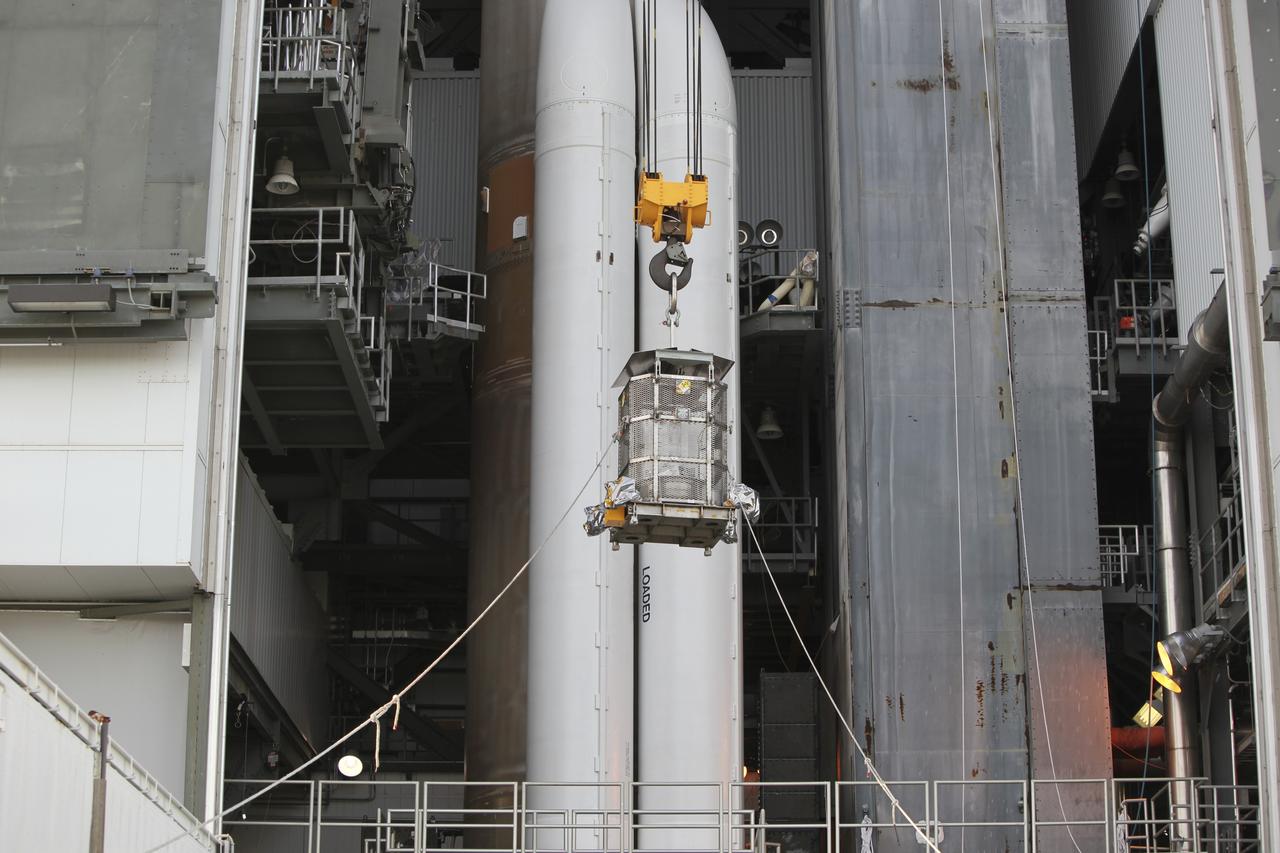

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Enclosed in the protective mesh container known as the "gorilla cage," the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is lifted up the side of the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41. The generator will be hoisted up to the top of the rocket and installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat produced by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
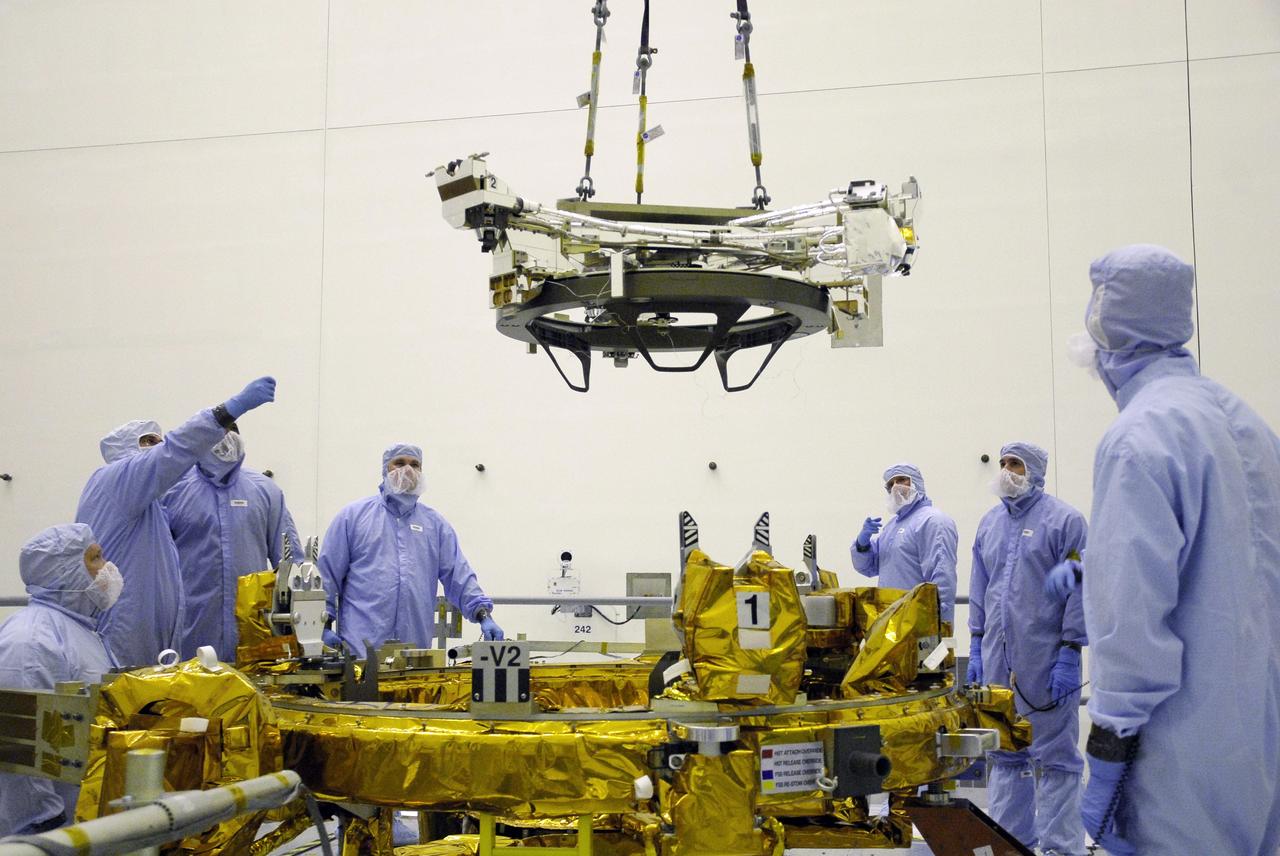

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lowers the Soft Capture Mechanism (SCM), part of the Soft Capture and Rendezvous System, or SCRS, toward the Flight Support System, or FSS, carrier. The SCRS will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The SCRS greatly increases the current shuttle capture interfaces on Hubble, therefore significantly reducing the rendezvous and capture design complexities associated with the disposal mission. The FSS will join the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier as payload on space shuttle Atlantis's STS-125 mission. The payload is scheduled to go to Launch Pad 39A in mid-September to be installed into Atlantis' payload bay. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 at 1:34 a.m. EDT. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
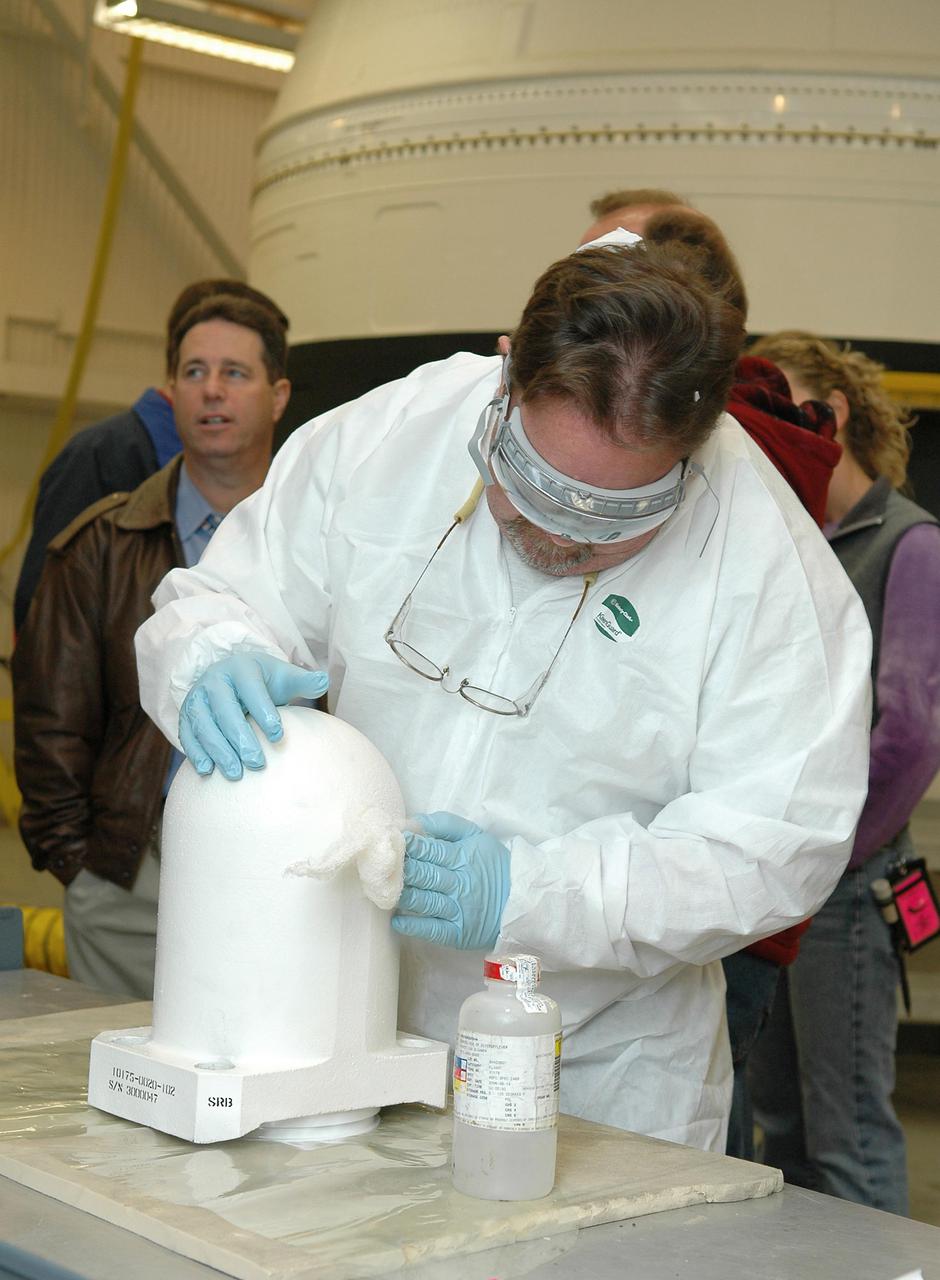

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Vehicle Assembly Building, Senior Technician Kevin Reagan, with United Space Alliance, prepares one of two bolt catchers for installation on orbiter Discovery’s External Tank. A bolt catcher is a vertical bolt mechanism at the forward end of the External Tank that attaches each booster to the tank. At approximately two minutes into launch, SRB separation begins when pyrotechnic devices fire to break the 25-inch, 62-pound steel bolts. One half of the bolt is caught in canister-like 'bolt catchers' located on the tank; the other half remains with the boosters. Discovery is flying with a modified bolt catcher, which was upgraded from a two-piece welded design to a one-piece, machine-made design as part of NASA's effort to return to safe, reliable spaceflight. Eliminating the weld makes a structurally stronger bolt catcher design. Though the bolt catcher is mounted on the External Tank, it is considered part of the Solid Rocket Booster element design. It is built by Summa Technologies, Inc. in Huntsville, Ala., insulated at Lockheed Martin’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, and installed on the External Tank at KSC.
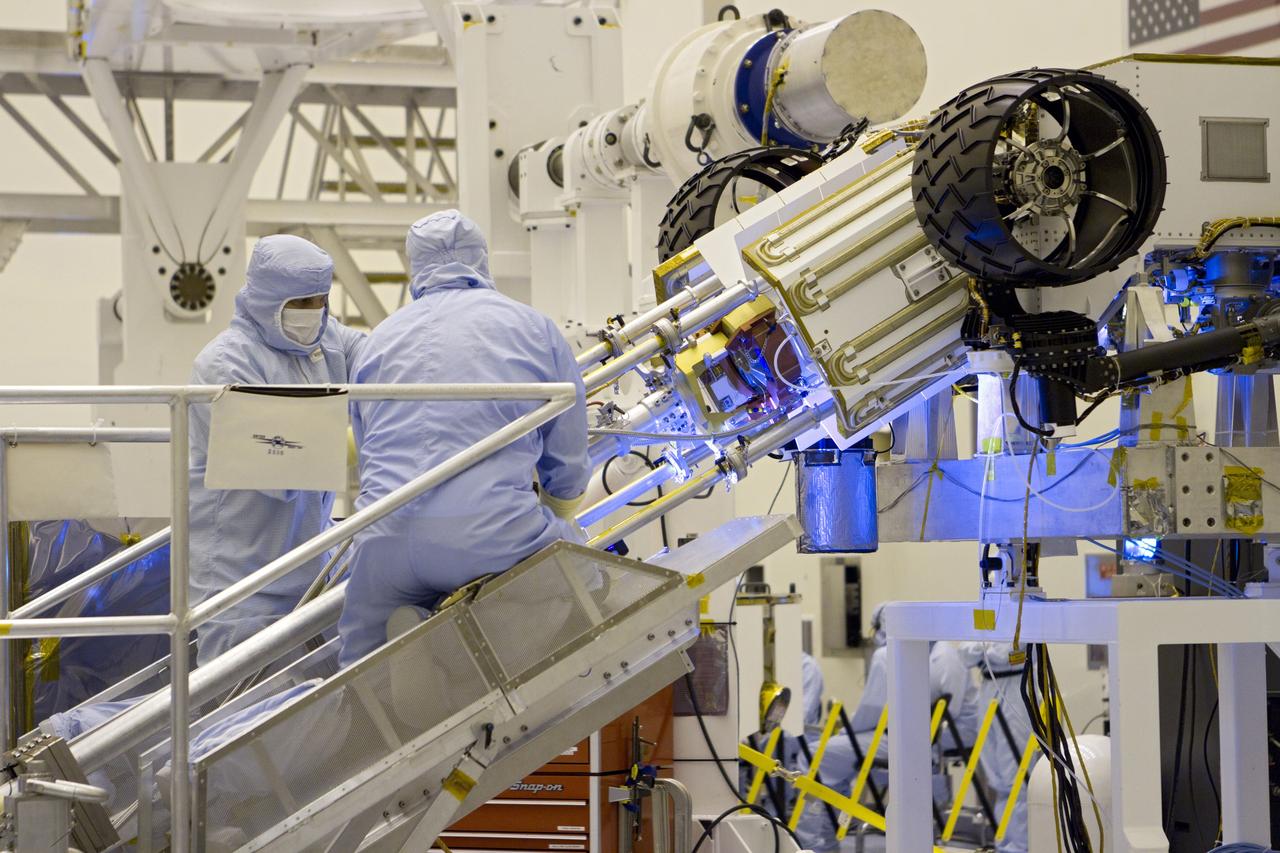

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory use extension tools to attach the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on the MMRTG integration cart onto the aft of the Curiosity rover for a fit check. The MMRTG then will be removed and installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
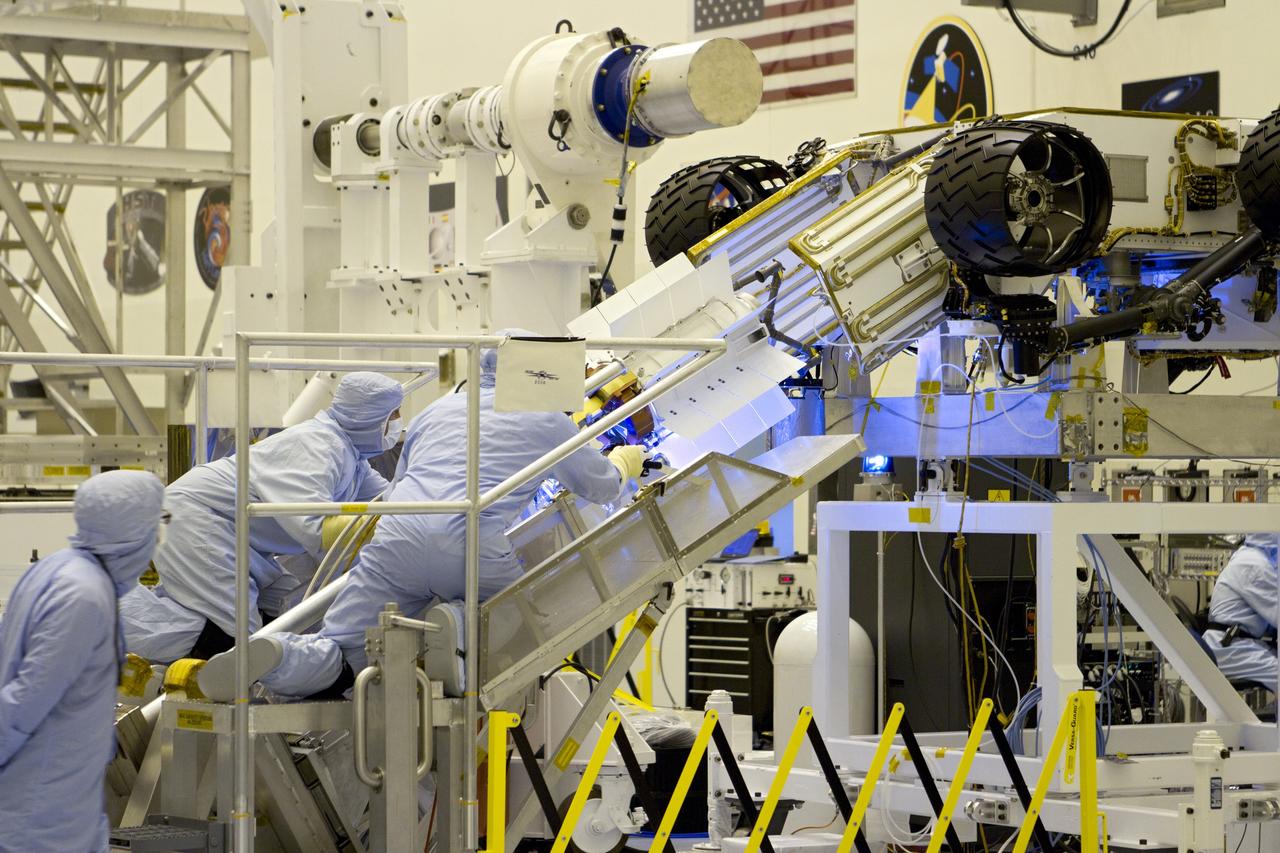

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory transfer the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission onto the aft of the Curiosity rover for a fit check with the aid of the MMRTG integration cart. The MMRTG then will be removed and installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
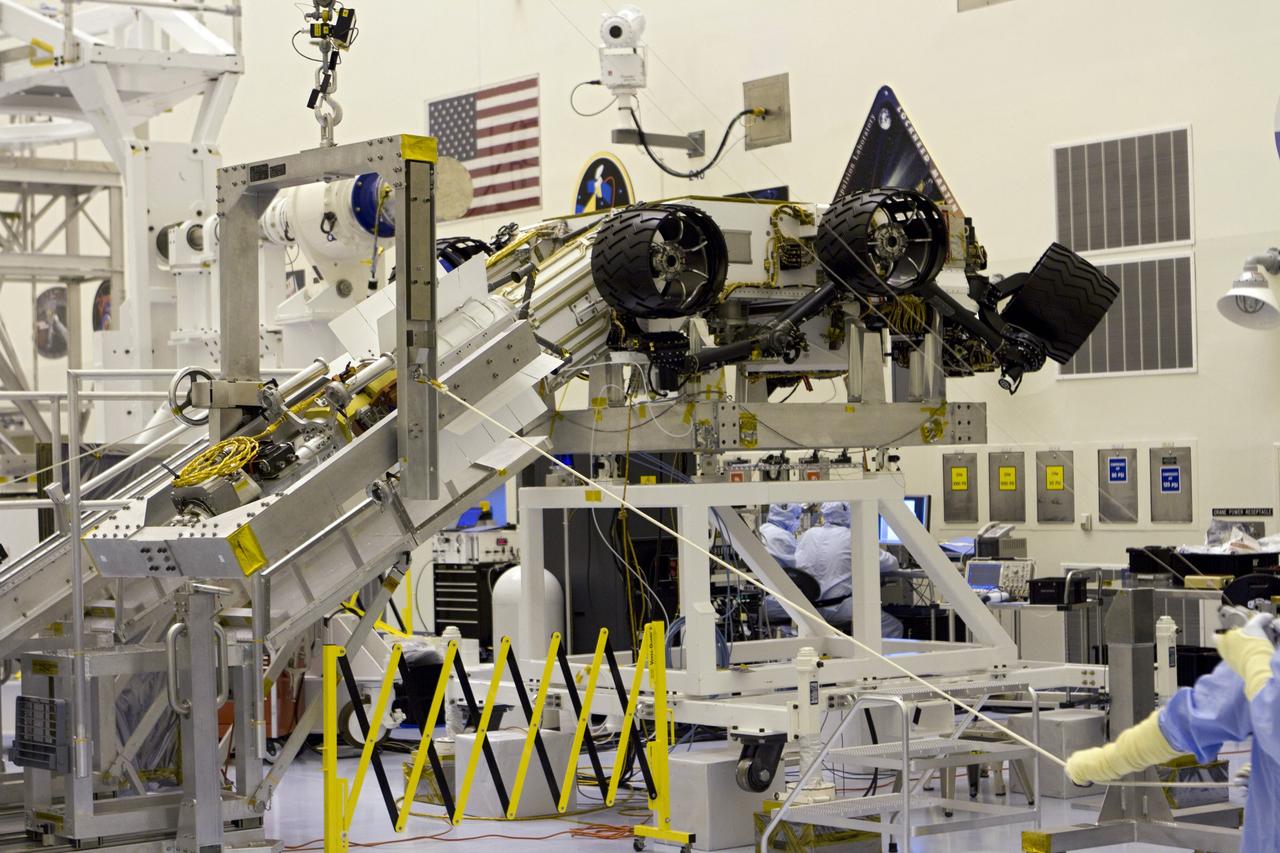

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory guide the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on the turning fixture toward the MMRTG integration cart. The cart will be used to install the MMRTG on the Curiosity rover for a fit check. The rover is on an elevated work stand, at right. The MMRTG will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

Kennedy Space Center Associate Director, Technical, Jennifer Kunz speaks at an event Sept. 27, 2021, announcing that Terran Orbital will locate its Commercial Spacecraft and Constellation Facility on NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new manufacturing facility will be built near the center’s Launch and Landing Facility, which is being managed and developed by Space Florida under a long-term agreement with NASA. Terran Orbital develops end-to-end satellite solutions as well as commercial spacecraft. The 660,000 square foot manufacturing facility will consist of ten automated and augmented hangers capable of producing thousands of different types of space vehicles and electro-mechanical devices per year. The project is expected to create about 2,100 new jobs, with a planned completion date in 2025. The announcement ceremony was held at Space Florida’s Space Life Sciences Lab in Exploration Park, Florida. Seated directly behind Kunz is Space Florida President and CEO Frank DiBello (left) and Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis (second from left).

An inlet duct lowered into the 20-foot diameter test section of the Altitude Wind Tunnel at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. Engines and hardware were prepared in the facility’s shop area. The test articles were lifted by a two-rail Shaw box crane through the high-bay and the second-story test chamber before being lowered into the test section. Technicians then spent days or weeks hooking up the supply lines and data recording telemetry. The engines were mounted on wingspans that stretched across the test section. The wingtips attached to the balance frame’s trunnions, which could adjust the angle of attack. The balance frame included six devices that recorded data and controlled the engine. The measurements were visible in banks of manometer boards next to the control room. Photographs recorded the pressure levels in the manometer tubes, and the computing staff manually converted the data into useful measurements. A mechanical pulley system was used to raise and lower the tunnel’s large clamshell lid into place. The lid was sealed into place using hand-turned locks accessible from the viewing platform. The lid had viewing windows above and below the test article, which permitted the filming and visual inspection of the tests.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the trailer transporting the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission arrives at the RTG storage facility (RTGF). The MMRTG is returning to the RTGF following a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
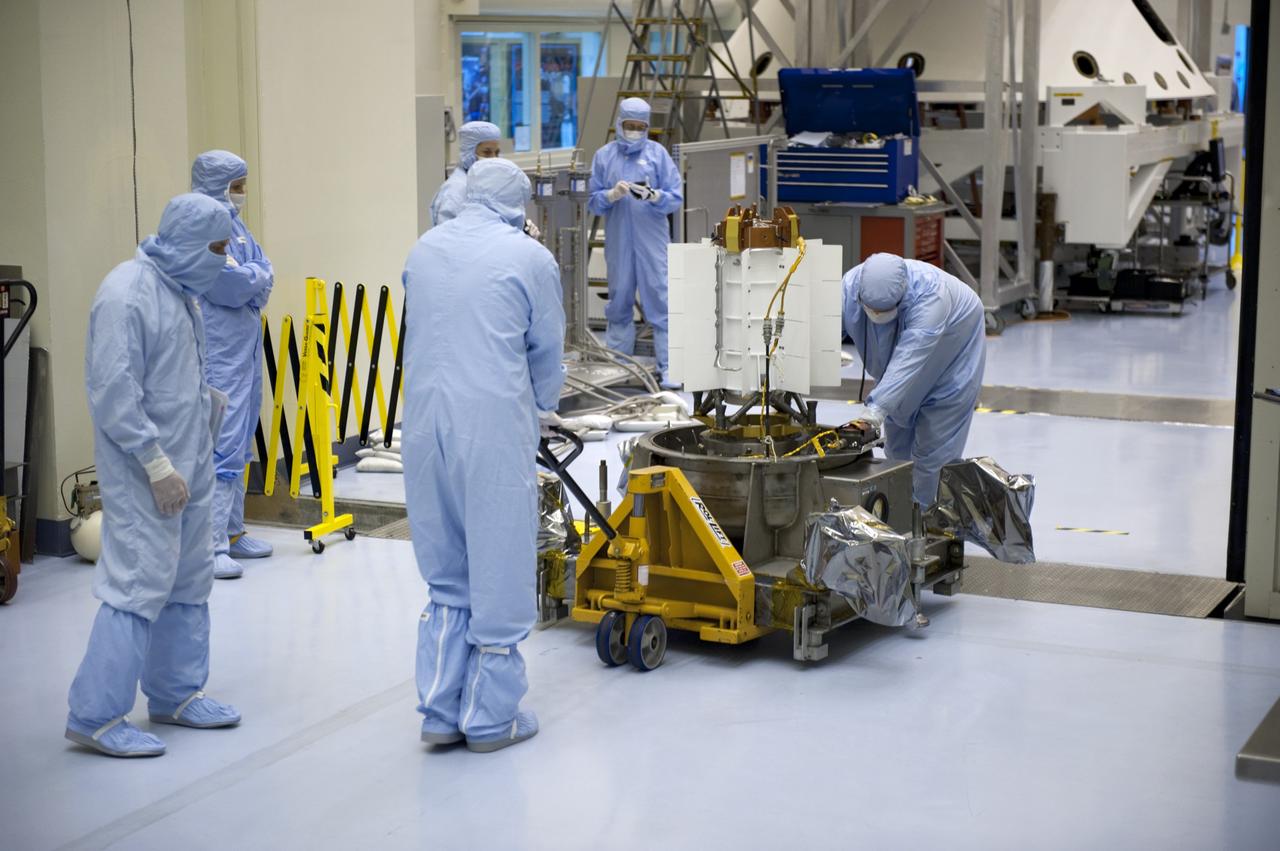

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory roll the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on its support base from the high bay into the airlock following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
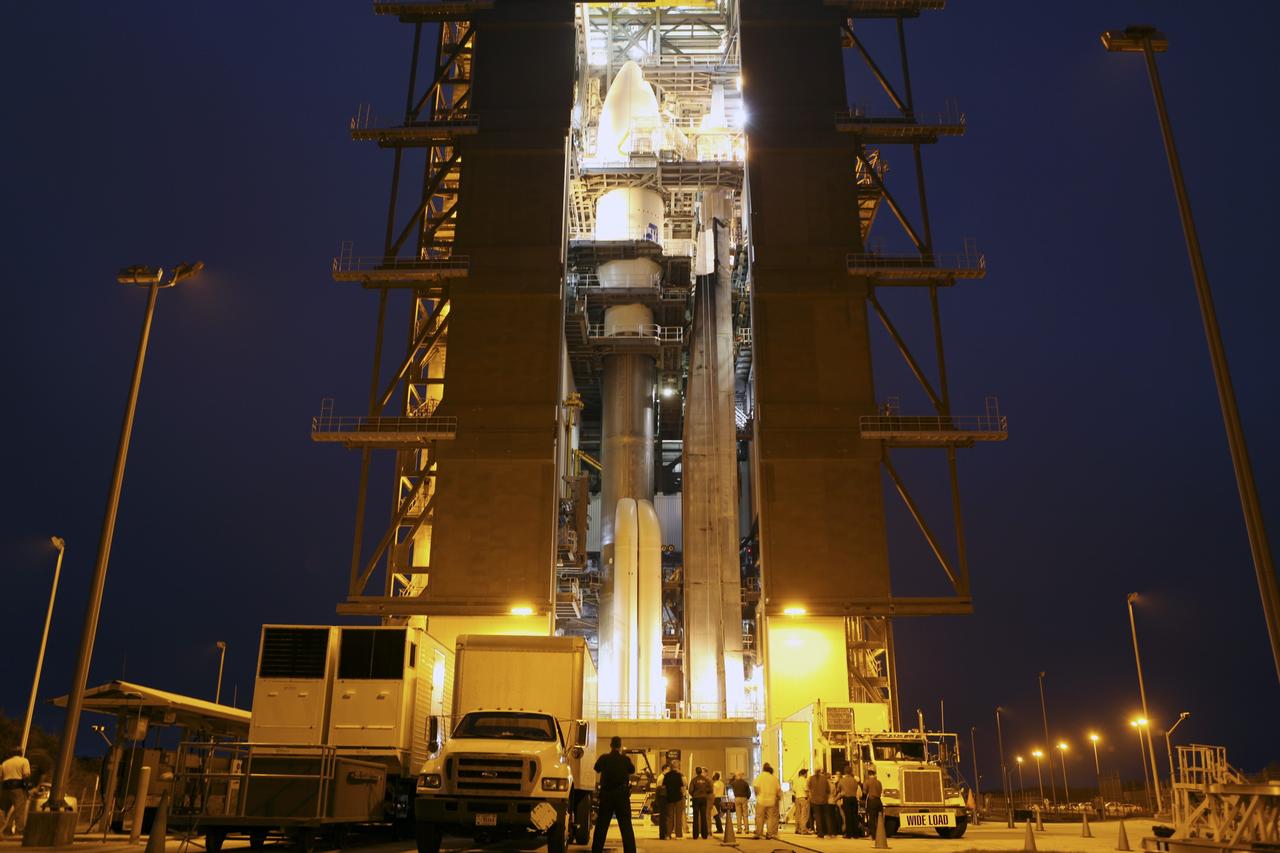

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Atlas V rocket set to launch NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is illuminated inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41, where employees have gathered to hoist the spacecraft's multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG). The MMRTG will be lifted up to the top of the rocket and installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat emitted by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
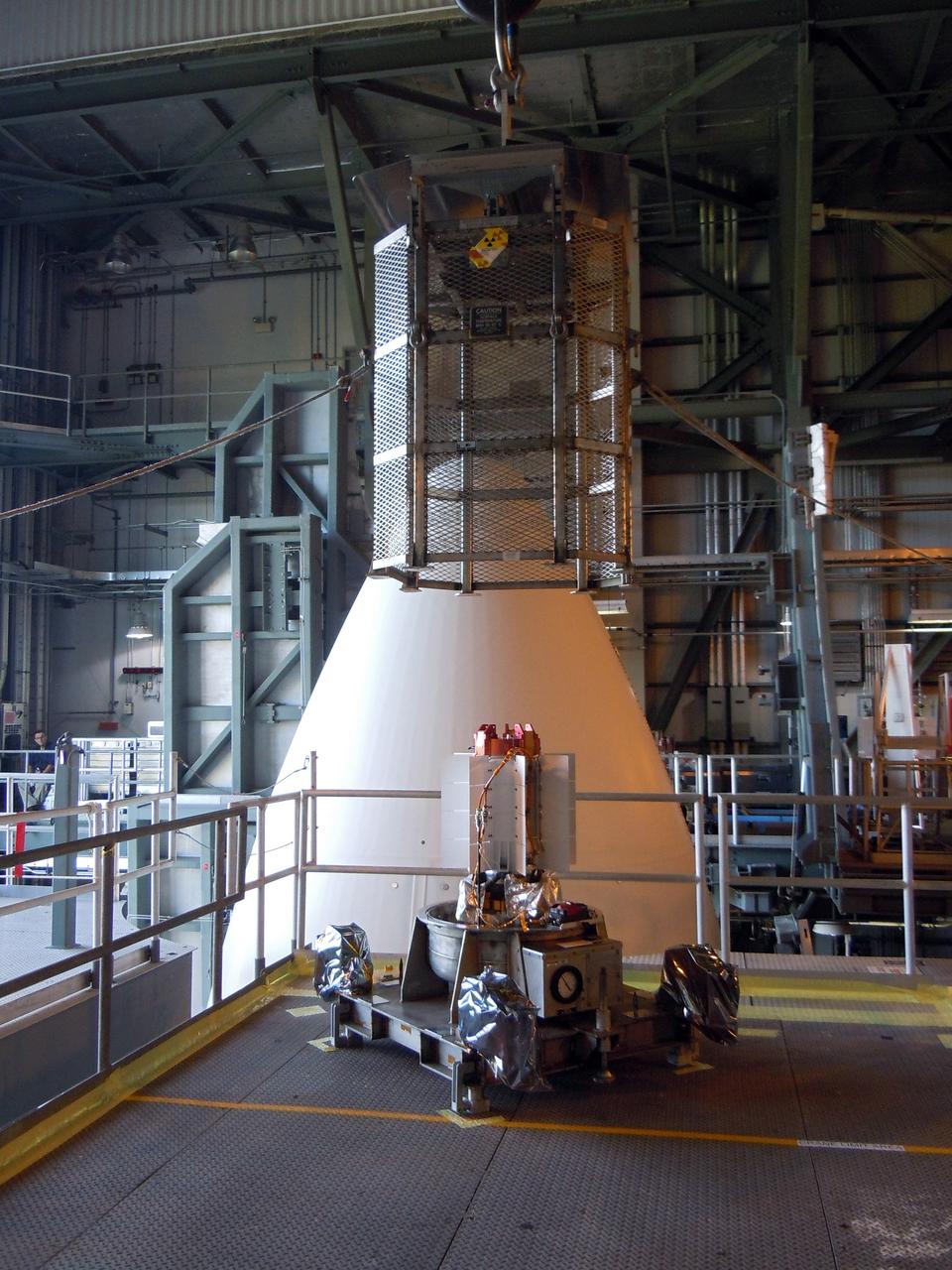

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is uncovered during preparations to install it on MSL's Curiosity rover. The mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," is suspended above the generator as it is lifted off the MMRTG's support base. The cage protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: Department of Energy/Idaho National Laboratory
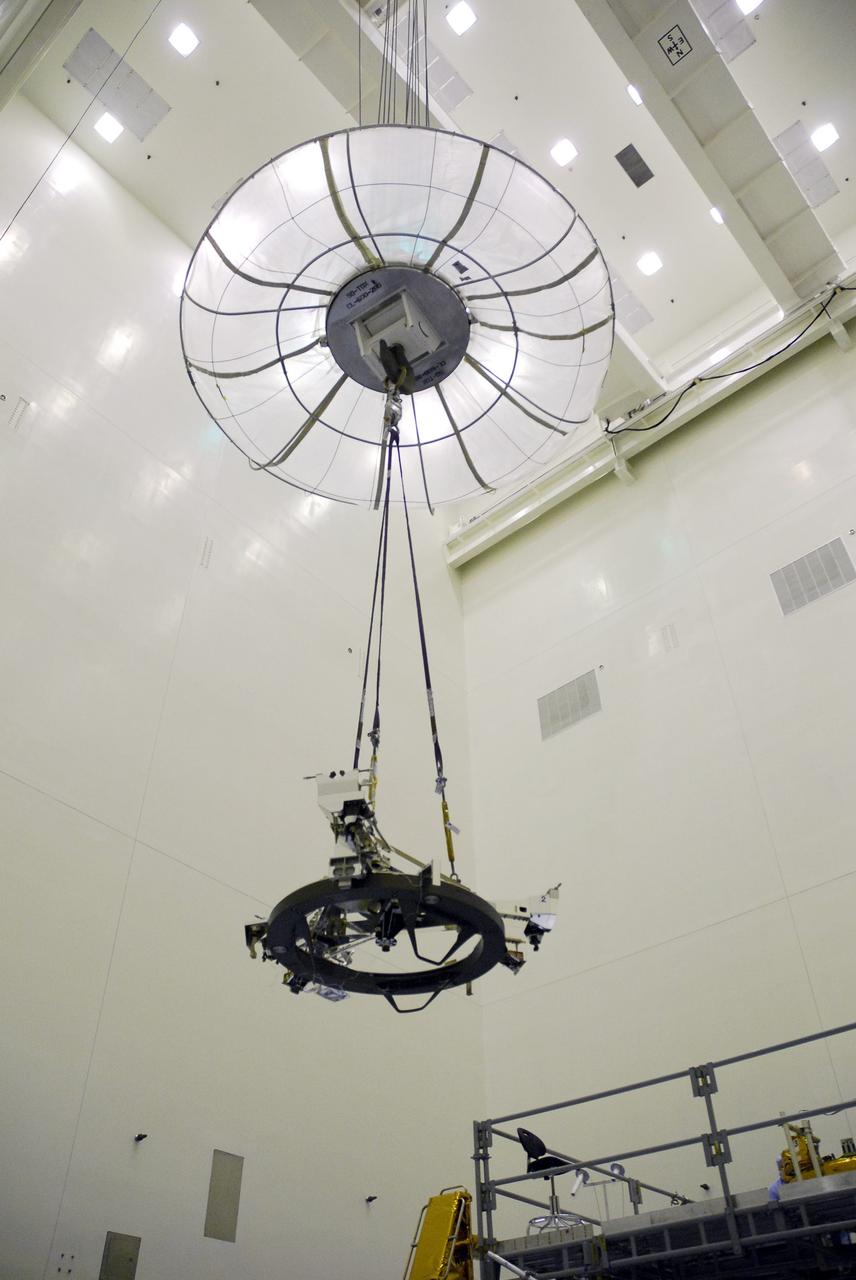

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Soft Capture Mechanism (SCM), part of the Soft Capture and Rendezvous System, or SCRS, moves above the floor via an overhead crane toward the stand holding the Flight Support System, or FSS,carrier where the SCM will be mated to the FSS. The SCRS will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The SCRS greatly increases the current shuttle capture interfaces on Hubble, therefore significantly reducing the rendezvous and capture design complexities associated with the disposal mission. The FSS will join the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier as payload on space shuttle Atlantis's STS-125 mission. The payload is scheduled to go to Launch Pad 39A in mid-September to be installed into Atlantis' payload bay. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 at 1:34 a.m. EDT. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
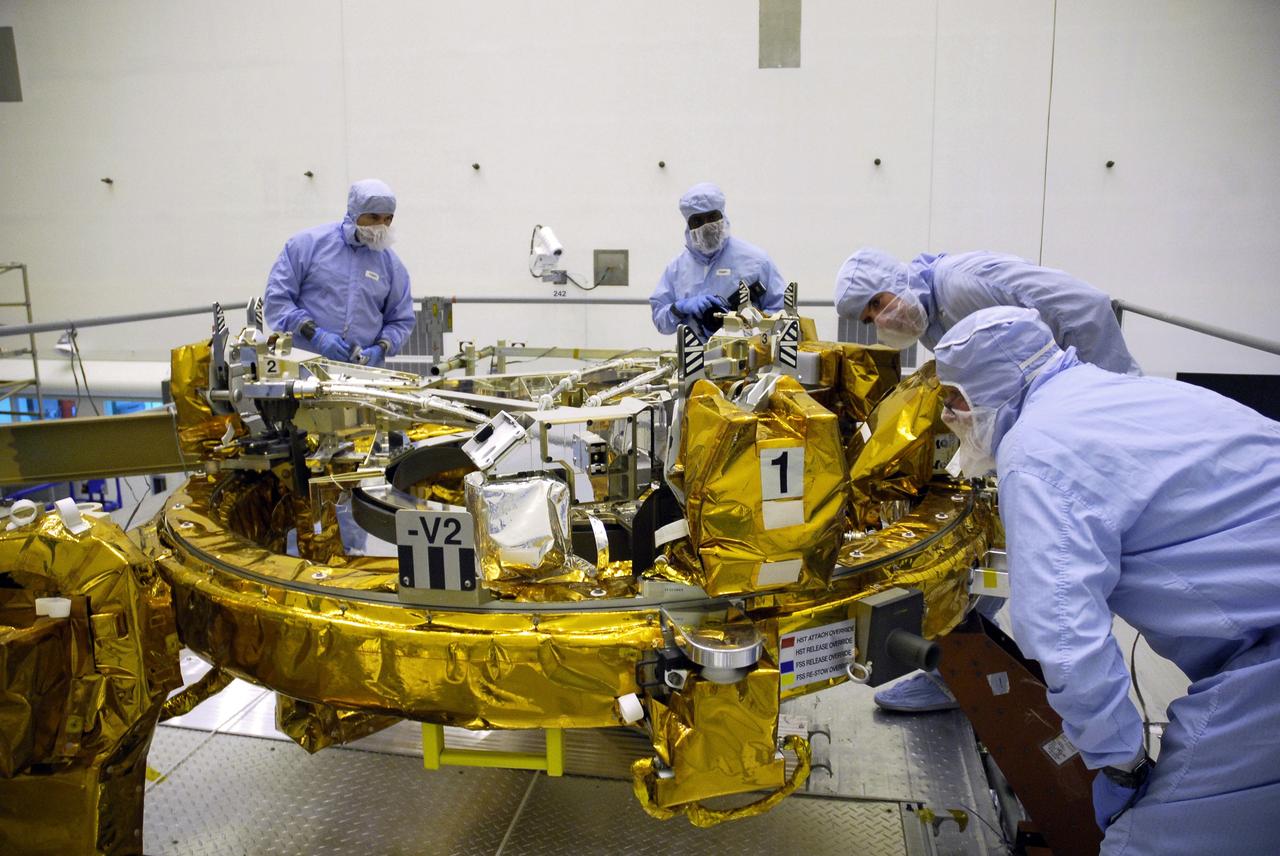

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians check the connections on the Soft Capture Mechanism (SCM), part of the Soft Capture and Rendezvous System, or SCRS, being mated to the Flight Support System, or FSS, carrier. The SCRS will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The SCRS greatly increases the current shuttle capture interfaces on Hubble, therefore significantly reducing the rendezvous and capture design complexities associated with the disposal mission. The FSS will join the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier as payload on space shuttle Atlantis's STS-125 mission. The payload is scheduled to go to Launch Pad 39A in mid-September to be installed into Atlantis' payload bay. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 at 1:34 a.m. EDT. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
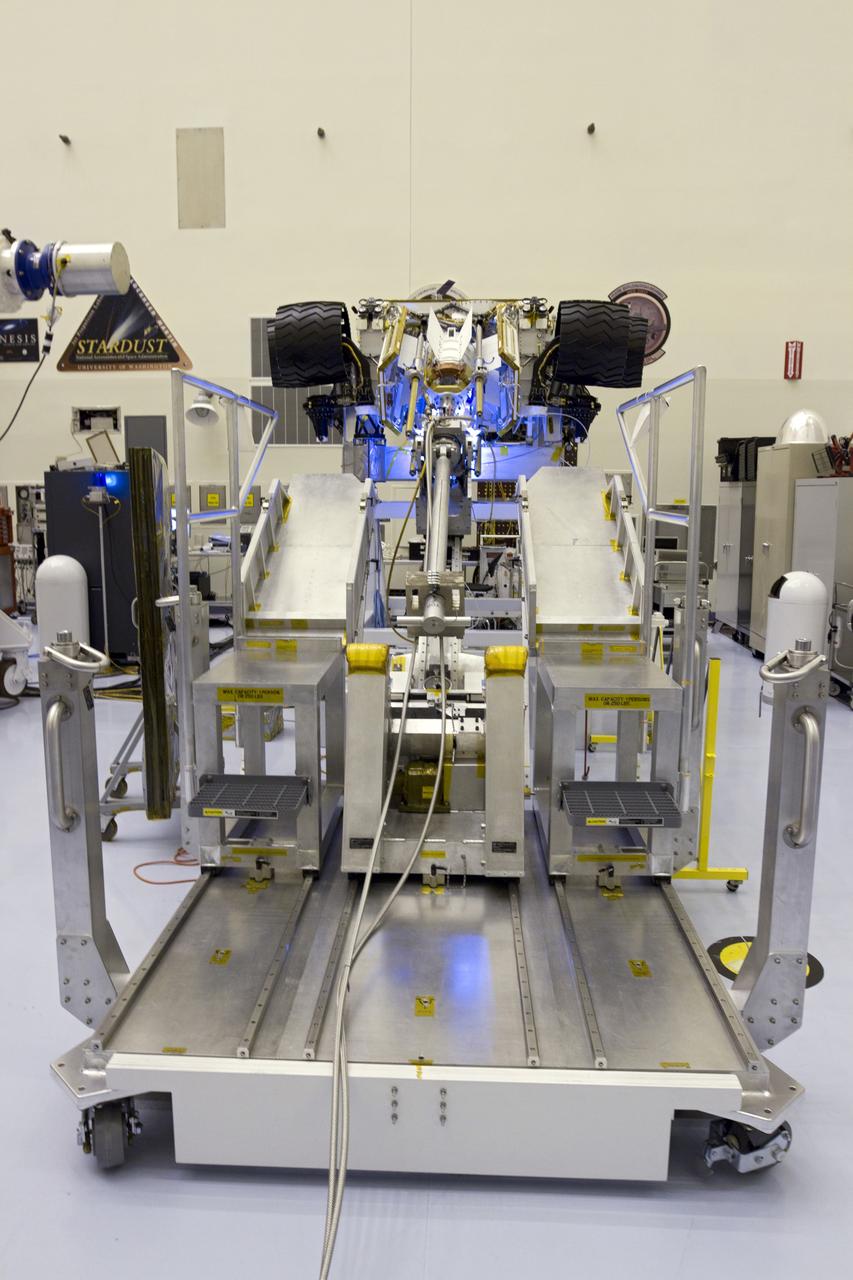

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is detached from the MMRTG integration cart and installed onto the aft of the Curiosity rover for a fit check. Next, the MMRTG will be removed and later installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
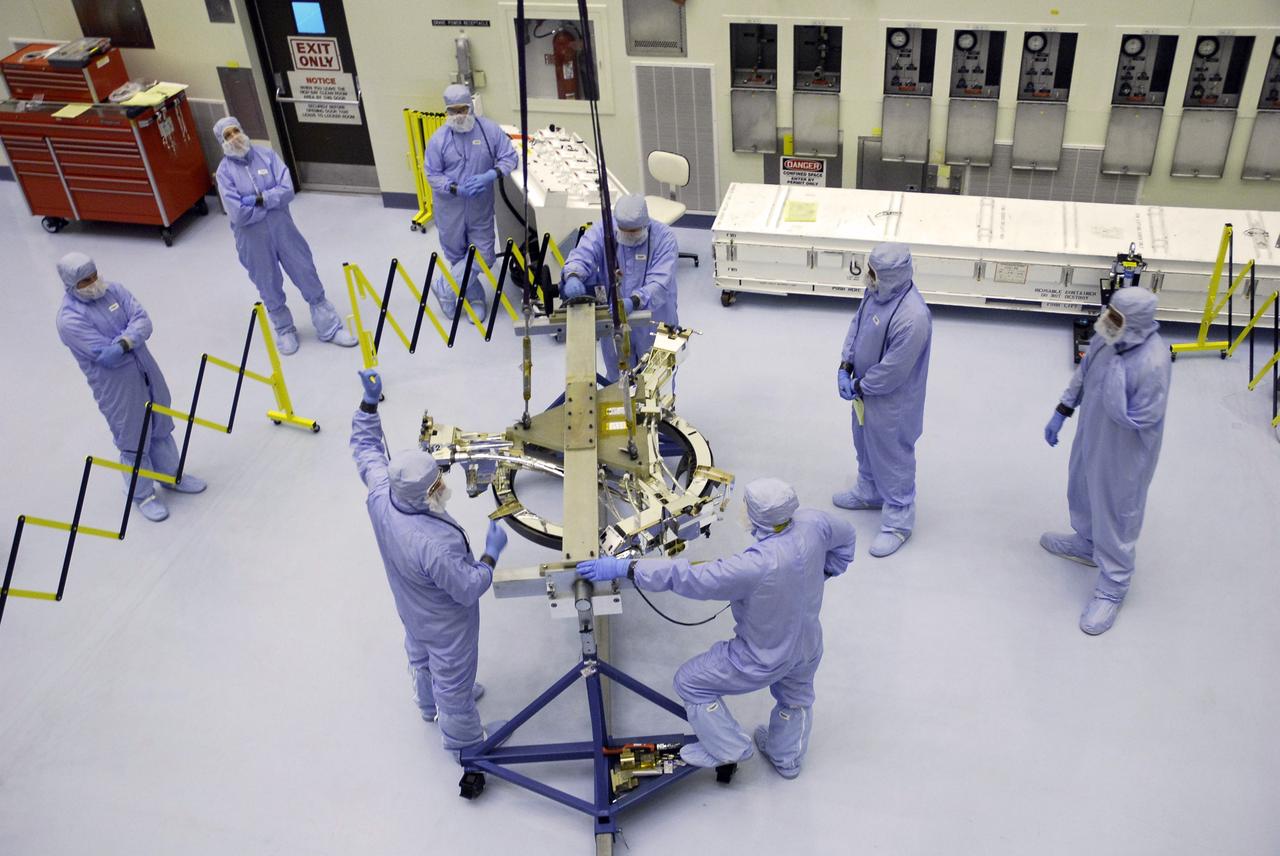

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technician signals to begin lifting the Soft Capture Mechanism (SCM), part of the Soft Capture and Rendezvous System, or SCRS. The SCM will be transferred to the stand holding the Flight Support System, or FSS, carrier where the SCM will be mated to the FSS. The SCRS will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The SCRS greatly increases the current shuttle capture interfaces on Hubble, therefore significantly reducing the rendezvous and capture design complexities associated with the disposal mission. The FSS will join the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier as payload on space shuttle Atlantis's STS-125 mission. The payload is scheduled to go to Launch Pad 39A in mid-September to be installed into Atlantis' payload bay. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 at 1:34 a.m. EDT. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Shuttle Atlantis is parked in the transfer aisle in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A large yellow sling device (foreground) will be used to lift Atlantis into a high bay for joining to the solid rocket boosters and external tank already installed on a mobile launcher platform. The move called "rollover" is a major milestone in processing for the STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are expected to launch mid July, taking with them the Raffaello multipurpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
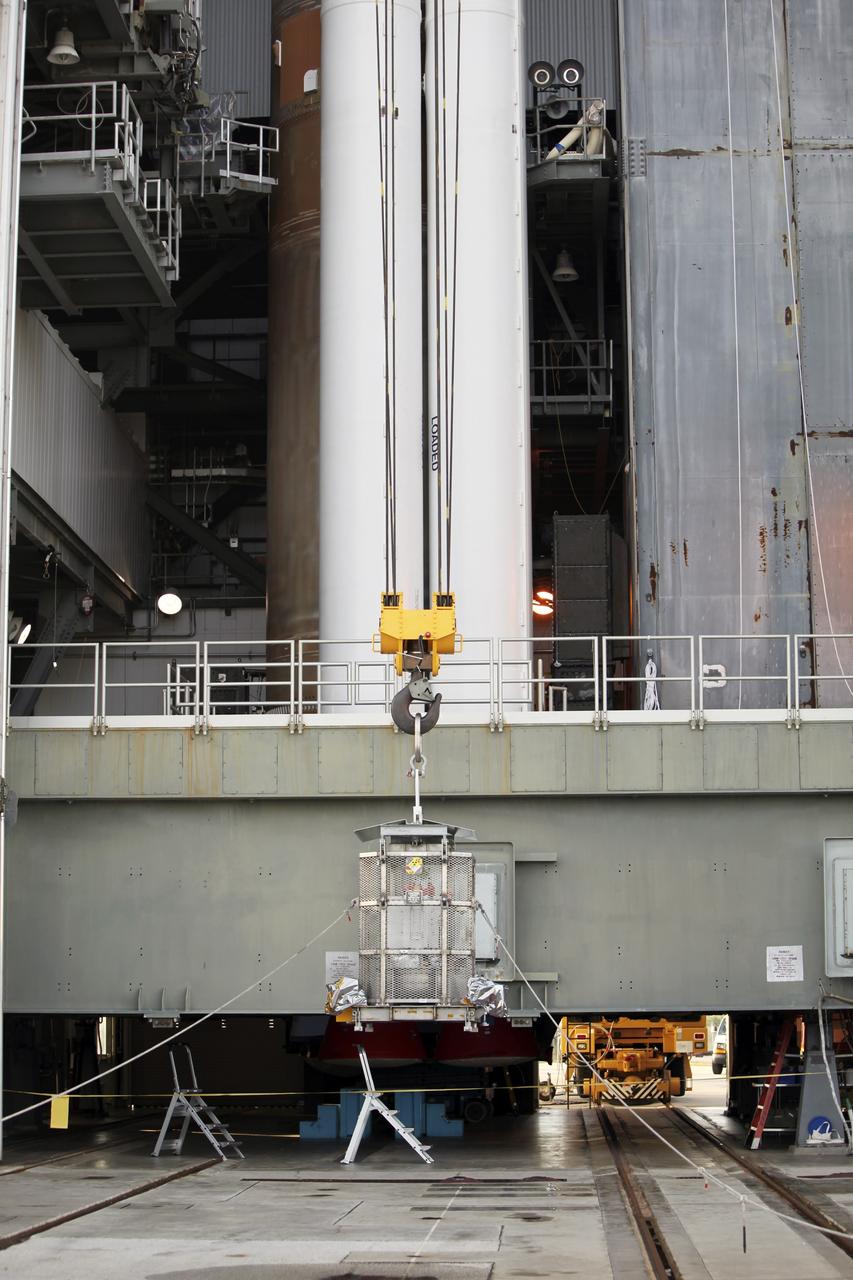

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Enclosed in the protective mesh container known as the "gorilla cage," the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is lifted off the ground at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41. The generator will be hoisted up to the top of the rocket and installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat produced by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
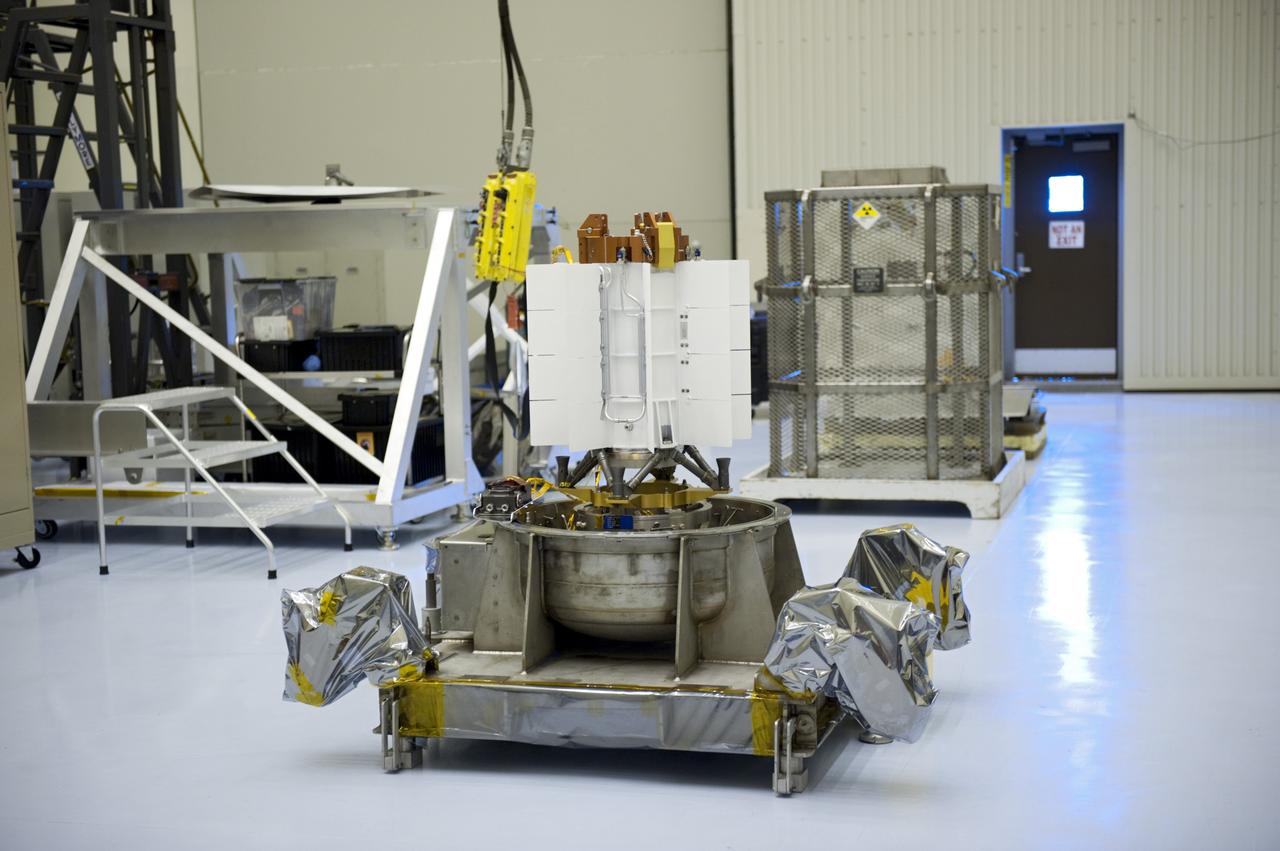
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission rests on its support base in the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover in the high bay. In the background, at right, is the mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," which protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The "gorilla cage," holding the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, is settled on one of the upper levels above the Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41. The MMRTG will be installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat emitted by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
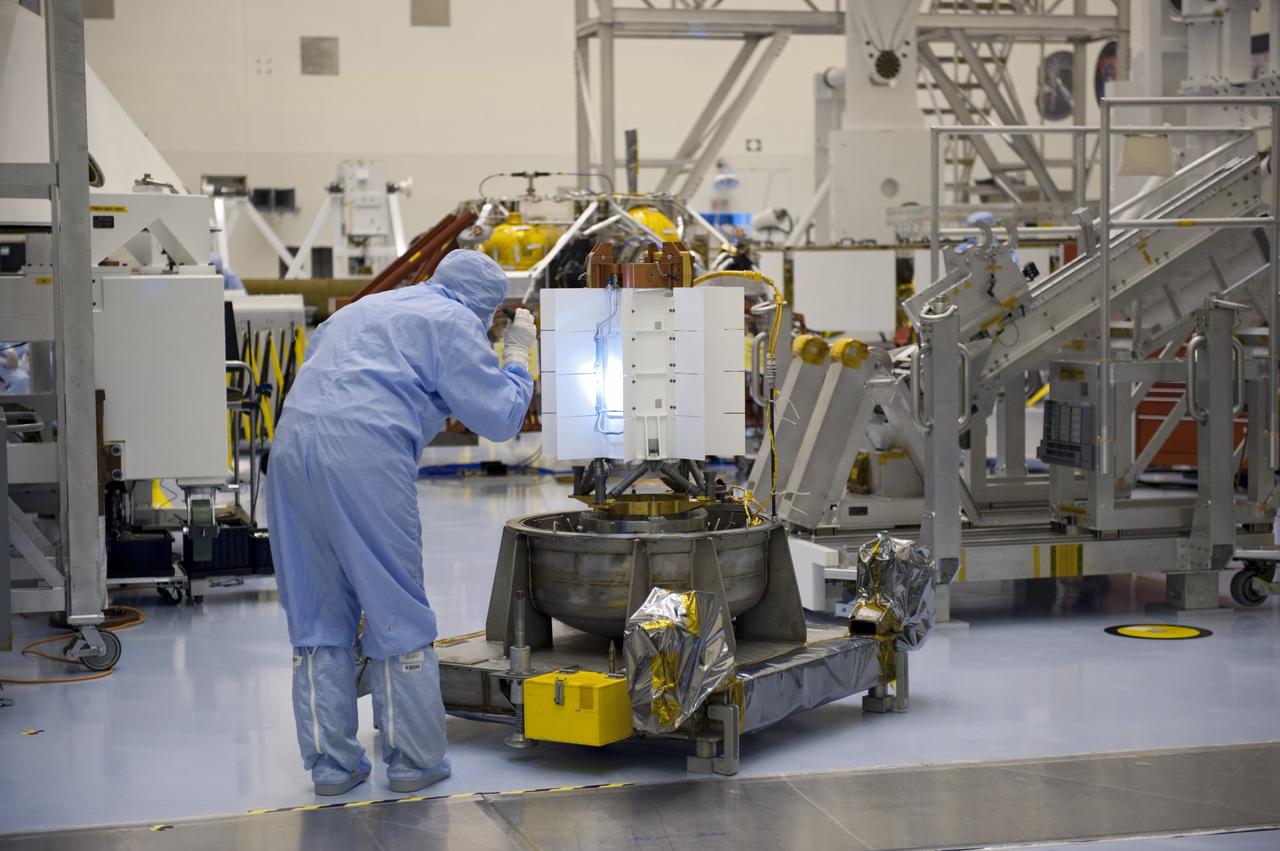

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a spacecraft technician from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory conducts a visual inspection of the cooling tubes on the exterior of the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
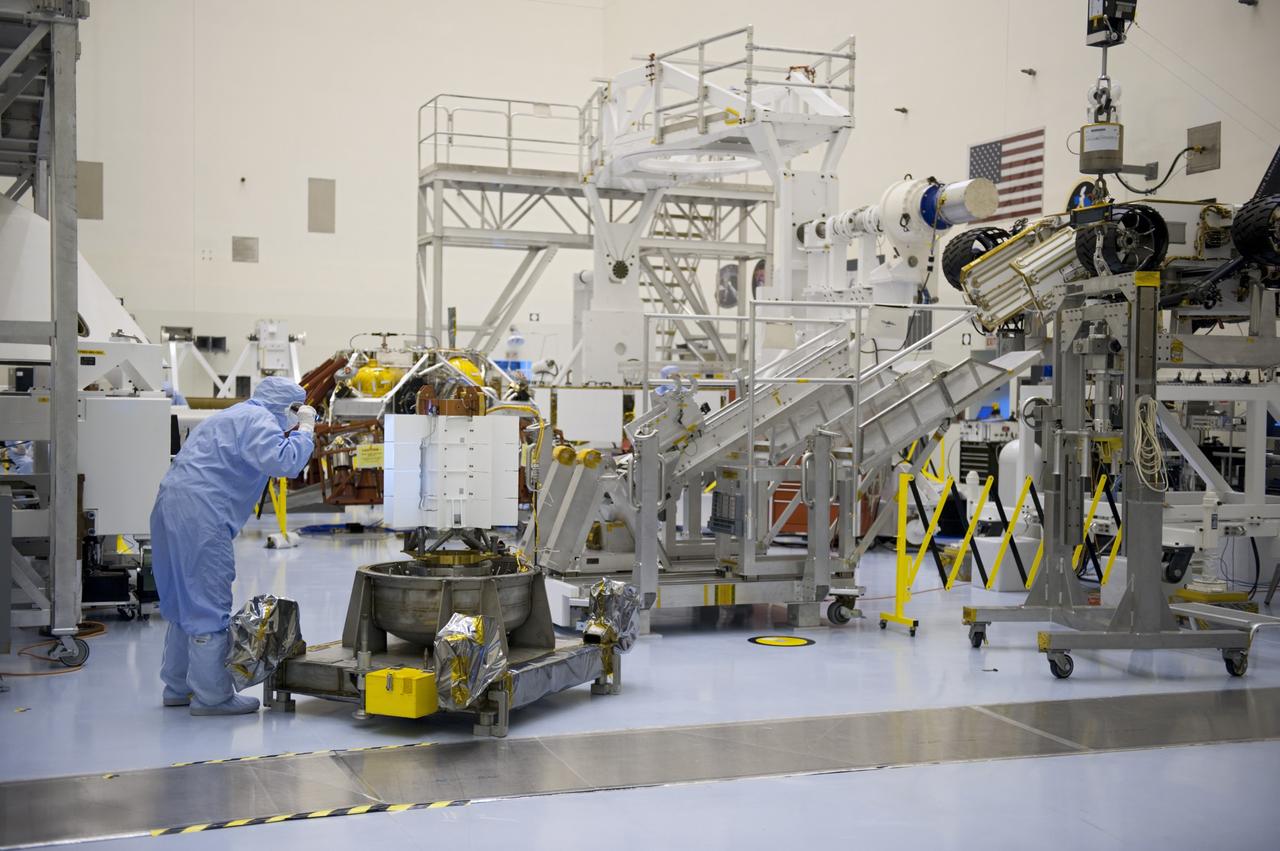

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a spacecraft technician from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory conducts a visual inspection of the cooling tubes on the exterior of the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. At right is the Curiosity rover on an elevated work stand. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
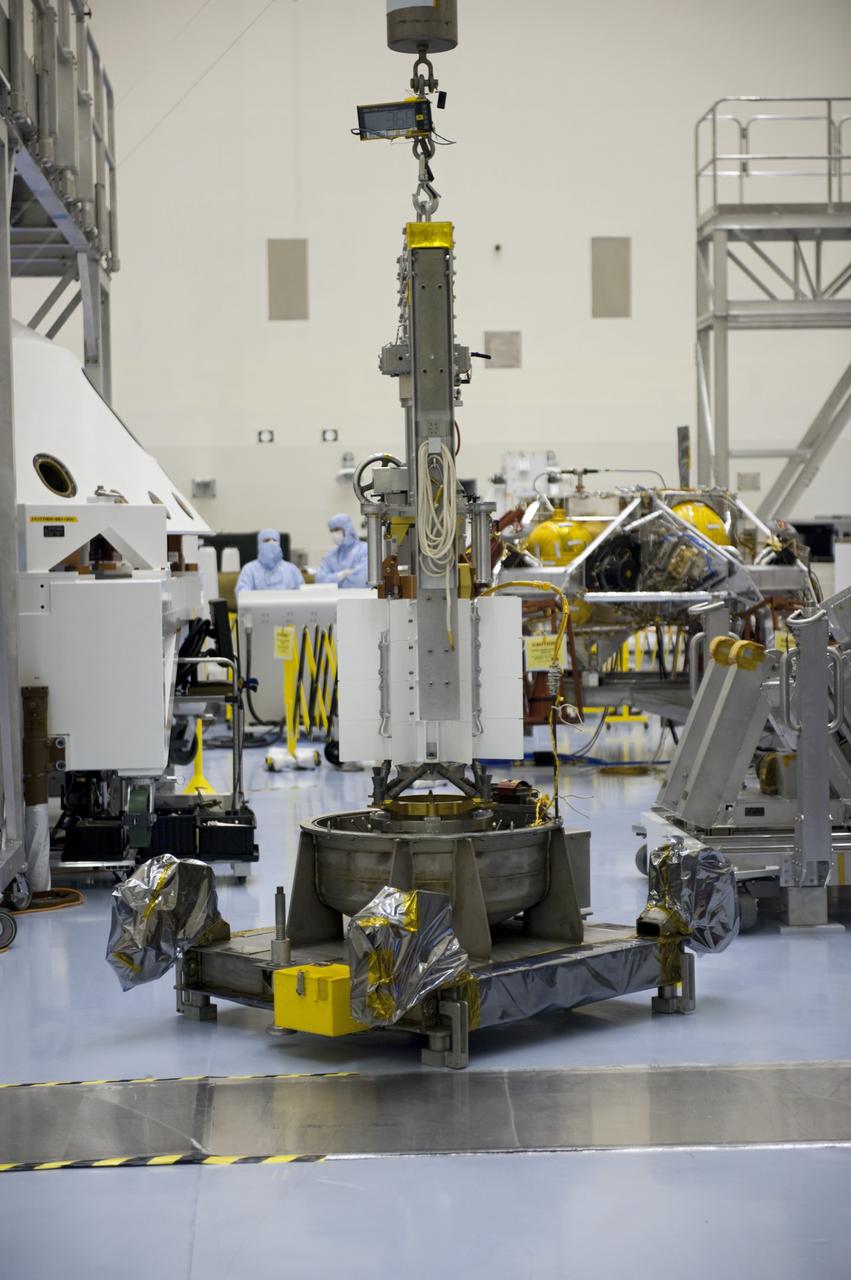

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is positioned on a support base with the aid of a turning fixture following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the descent stage for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission awaits installation on the Curiosity rover, in the background at right. MSL's multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator has been installed onto the aft of the rover for a fit check. The descent stage will cradle the rover and its MMRTG during their approach to the surface of Mars. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Soft Capture Mechanism (SCM), part of the Soft Capture and Rendezvous System, or SCRS, is being prepared for transfer to the Flight Support System, or FSS, carrier. The SCRS will enable the future rendezvous, capture and safe disposal of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope by either a crewed or robotic mission. The ring-like device attaches to Hubble’s aft bulkhead. The SCRS greatly increases the current shuttle capture interfaces on Hubble, therefore significantly reducing the rendezvous and capture design complexities associated with the disposal mission. The FSS will join the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment, or MULE, carrier, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier as payload on space shuttle Atlantis's STS-125 mission. The payload is scheduled to go to Launch Pad 39A in mid-September to be installed into Atlantis' payload bay. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 at 1:34 a.m. EDT. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
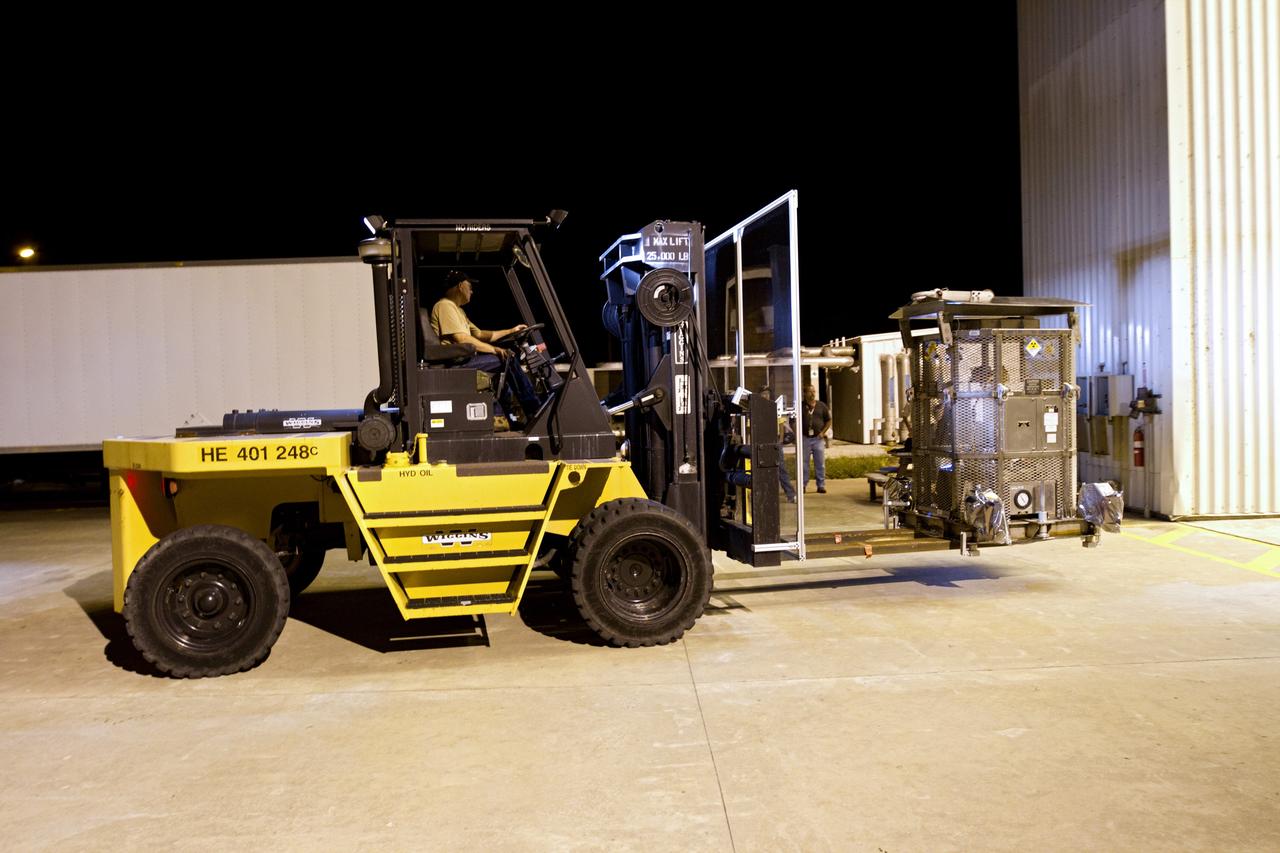

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a forklift carries the protective mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission into the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The cage protects the MMRTG and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. In the PHSF, the MMRTG temporarily will be installed on the MSL rover, Curiosity, for a fit check but will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
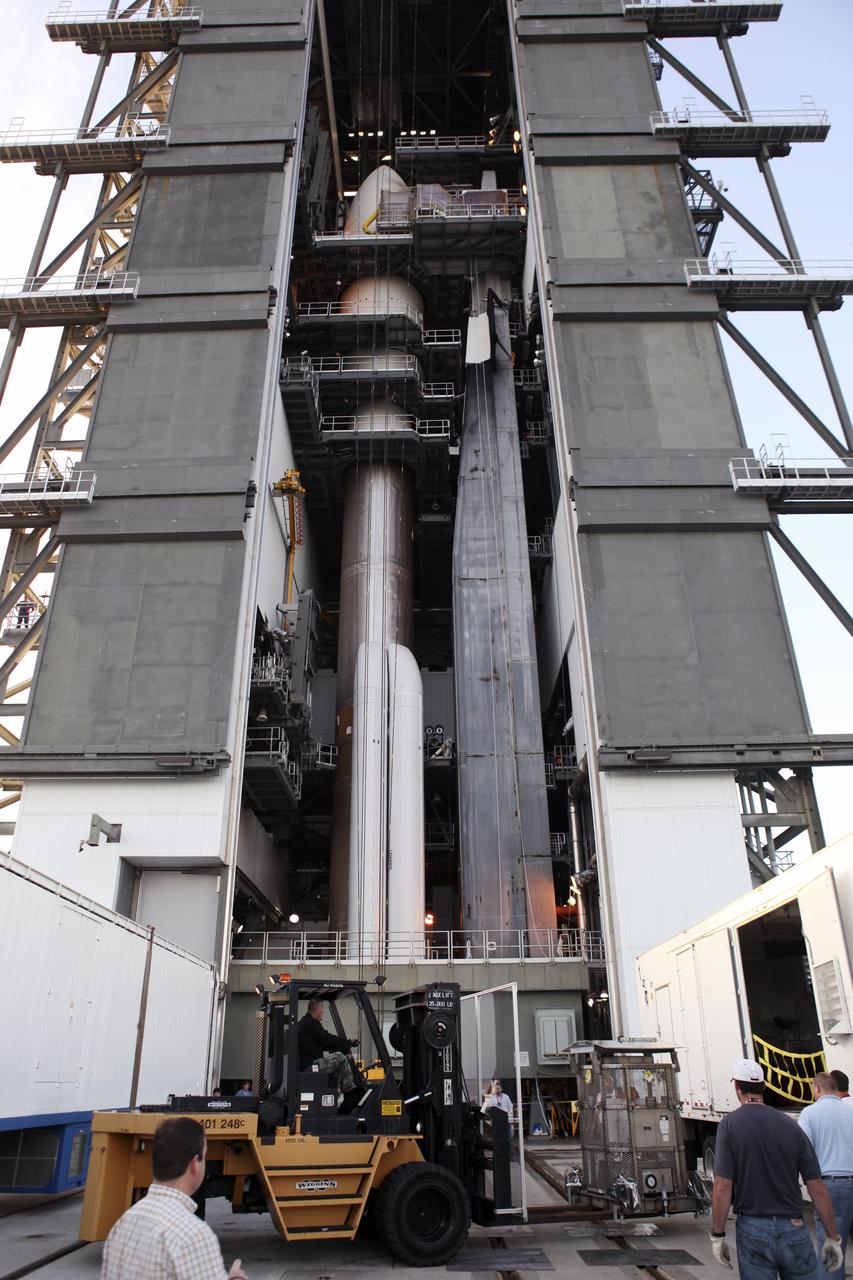

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Backdropped by the Atlas V rocket standing inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, enclosed in the mesh container known as the "gorilla cage," is removed from its trailer. The generator will be lifted up to the top of the rocket and installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat produced by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
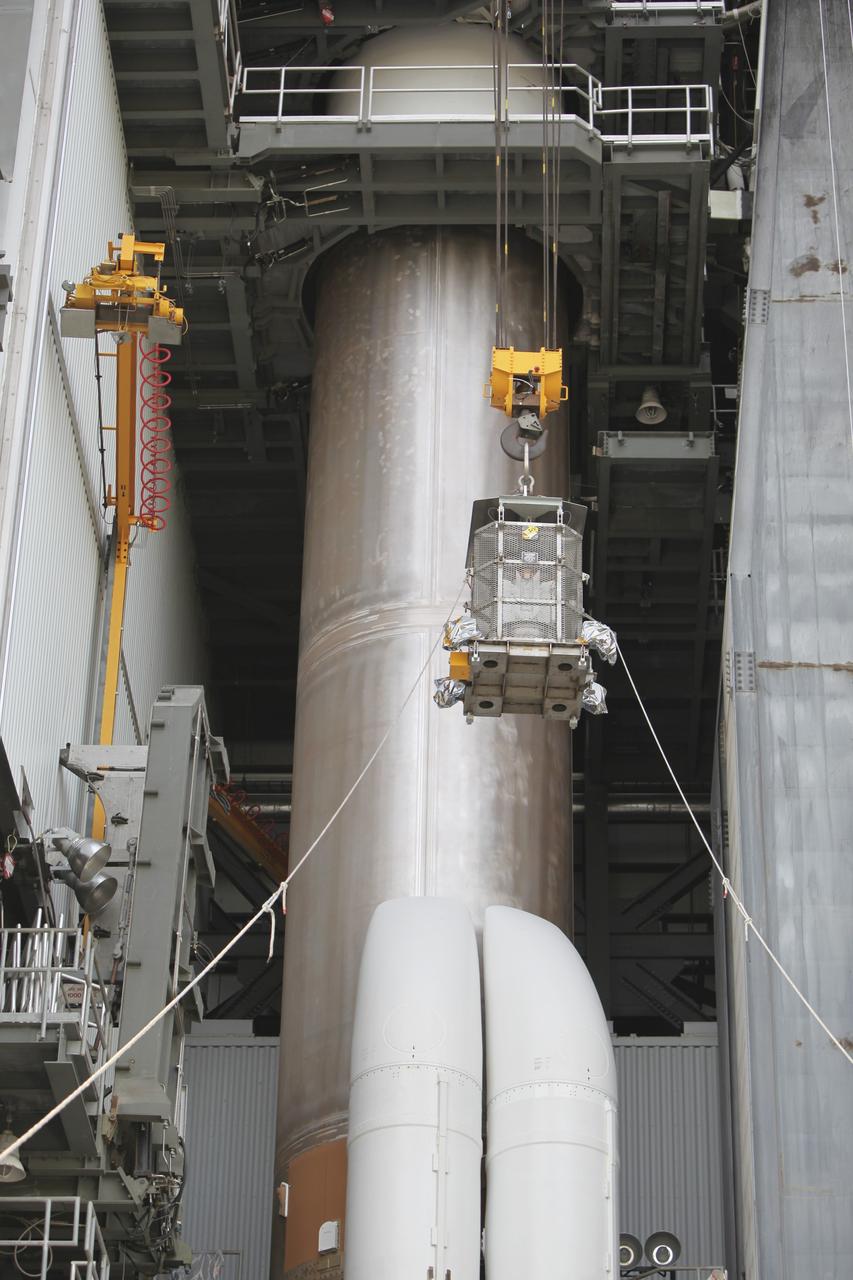

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Enclosed in the protective mesh container known as the "gorilla cage," the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is lifted up the side of the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41. The generator will be installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat produced by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis