
Long Scarps on Mercury Tell of the Planet Unique History
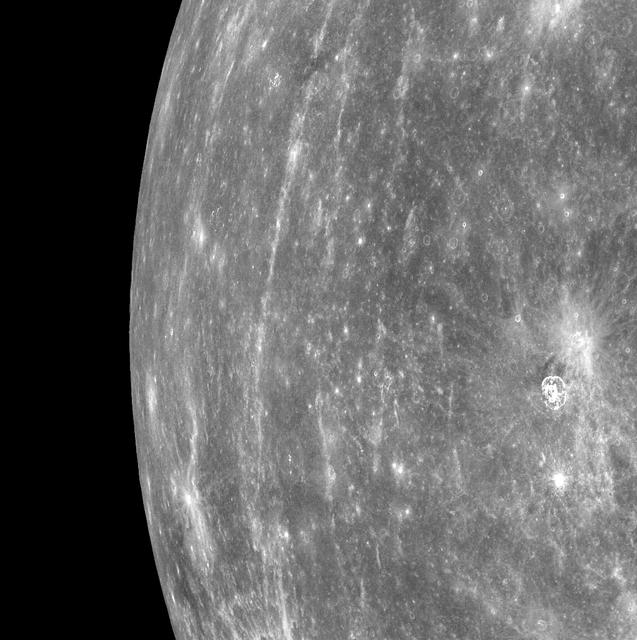
NASA image acquired: March 29, 2011 MESSENGER acquired this image of Mercury's horizon as the spacecraft was moving northward along the first orbit during which MDIS was turned on. Bright rays from Hokusai can be seen running north to south in the image. MDIS frequently acquired images that contained Mercury's horizon during the mission's three Mercury flybys. (Visit these links to see examples of horizon images from Mercury flyby 1, Mercury flyby 2, and Mercury flyby 3.) However, now that MESSENGER is in orbit about Mercury, views of Mercury's horizon in the images will be much less common. The field of view for MDIS will generally be filled with Mercury's surface as the instrument maps out the planet's geology in high resolution, stereo, and color. Occasionally, in order to obtain images of a certain portion of Mercury's surface, the horizon will also be visible. On March 17, 2011 (March 18, 2011, UTC), MESSENGER became the first spacecraft to orbit the planet Mercury. The mission is currently in its commissioning phase, during which spacecraft and instrument performance are verified through a series of specially designed checkout activities. In the course of the one-year primary mission, the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation will unravel the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. Visit the Why Mercury? section of this website to learn more about the science questions that the MESSENGER mission has set out to answer. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
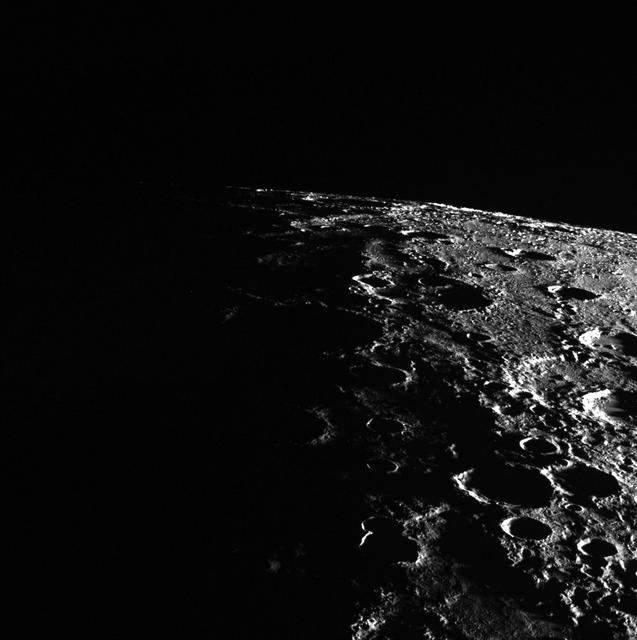

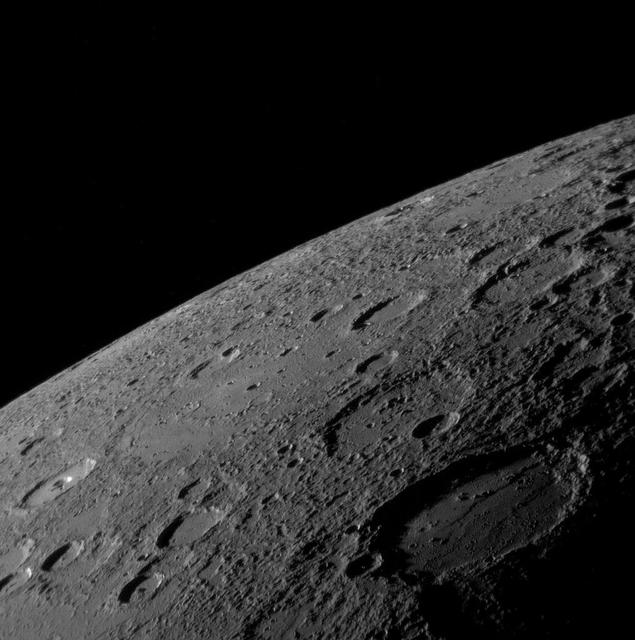
In this image, Mercury's horizon cuts a striking edge against the stark blackness of space. On the right, sunlight harshly brings the landscape into relief while on the left, the surface is shrouded in the darkness of night. This image was acquired as part of MDIS's limb imaging campaign. Once per week, MDIS captures images of Mercury's limb, with an emphasis on imaging the southern hemisphere limb. These limb images provide information about Mercury's shape and complement measurements of topography made by the Mercury Laser Altimeter (MLA) of Mercury's northern hemisphere. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. In the mission's more than three years of orbital operations, MESSENGER has acquired over 250,000 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER is capable of continuing orbital operations until early 2015. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
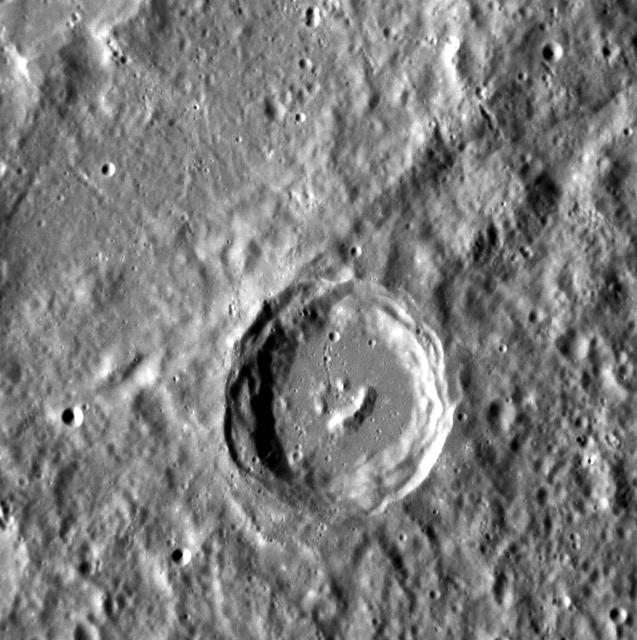

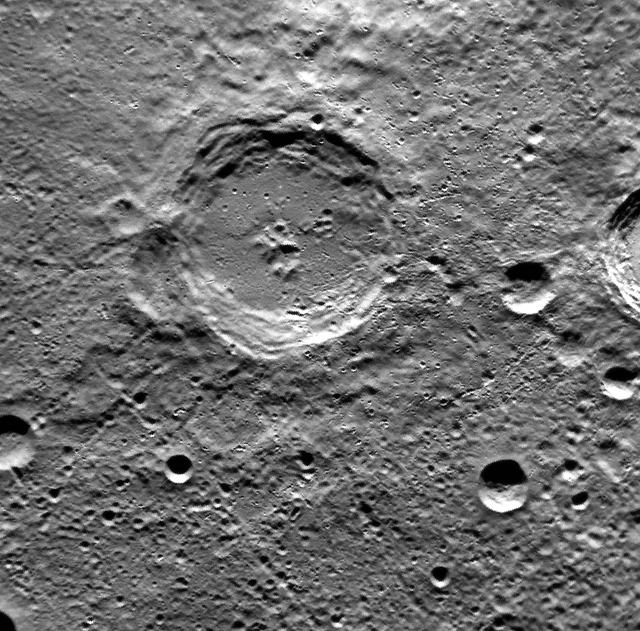
It looks like even the craters on Mercury have heard of Bob Ross! The central peaks of this complex crater have formed in such a way that it resembles a smiling face. This image is oriented so north is toward the bottom. This image was acquired as a high-resolution targeted observation. Targeted observations are images of a small area on Mercury's surface at resolutions much higher than the 200-meter/pixel morphology base map. It is not possible to cover all of Mercury's surface at this high resolution, but typically several areas of high scientific interest are imaged in this mode each week. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. Visit the Why Mercury? section of this website to learn more about the key science questions that the MESSENGER mission is addressing. During the one-year primary mission, MESSENGER acquired 88,746 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER is now in a yearlong extended mission, during which plans call for the acquisition of more than 80,000 additional images to support MESSENGER's science goals. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
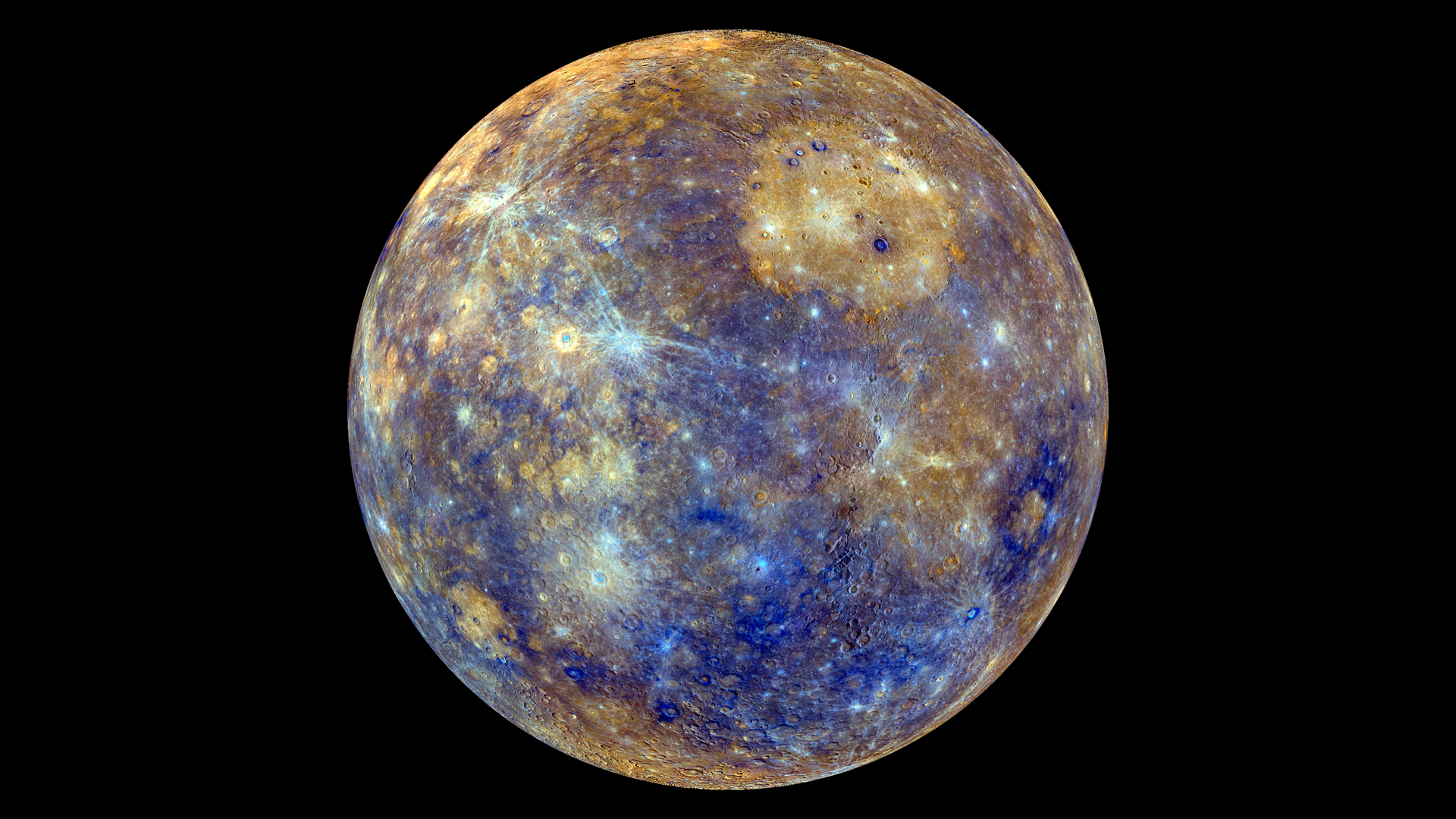
This colorful view of Mercury was produced by using images from the color base map imaging campaign during MESSENGER's primary mission. These colors are not what Mercury would look like to the human eye, but rather the colors enhance the chemical, mineralogical, and physical differences between the rocks that make up Mercury's surface. <b>To watch a movie of this colorful view of Mercury as a spinning globe go here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/8497927473">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/8497927473</a></b> Young crater rays, extending radially from fresh impact craters, appear light blue or white. Medium- and dark-blue areas are a geologic unit of Mercury's crust known as the "low-reflectance material", thought to be rich in a dark, opaque mineral. Tan areas are plains formed by eruption of highly fluid lavas. The giant Caloris basin is the large circular tan feature located just to the upper right of center of the image. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. Visit the Why Mercury? section of this website to learn more about the key science questions that the MESSENGER mission is addressing. During the one-year primary mission, MESSENGER acquired 88,746 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER is now in a yearlong extended mission, during which plans call for the acquisition of more than 80,000 additional images to support MESSENGER's science goals. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
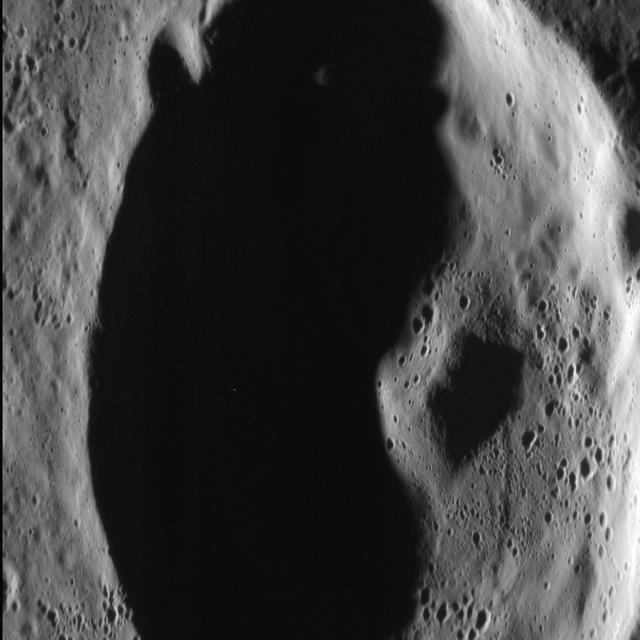

In this dramatic scene, an unnamed crater in Mercury's northern volcanic plains is bathed in darkness as the sun sits low on the horizon. Rising from the floor of the crater is its central peak, a small mountain resulting from the crater's formation. A central peak is a type of crater morphology that lies between "simple" and "peak ring" in the range of crater morphology on Mercury. This image was acquired as a high-resolution targeted observation. Targeted observations are images of a small area on Mercury's surface at resolutions much higher than the 200-meter/pixel morphology base map. It is not possible to cover all of Mercury's surface at this high resolution, but typically several areas of high scientific interest are imaged in this mode each week. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. During the first two years of orbital operations, MESSENGER acquired over 150,000 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER is capable of continuing orbital operations until early 2015. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This colorful view of Mercury was produced by using images from the color base map imaging campaign during MESSENGER's primary mission. These colors are not what Mercury would look like to the human eye, but rather the colors enhance the chemical, mineralogical, and physical differences between the rocks that make up Mercury's surface. Young crater rays, extending radially from fresh impact craters, appear light blue or white. Medium- and dark-blue areas are a geologic unit of Mercury's crust known as the "low-reflectance material", thought to be rich in a dark, opaque mineral. Tan areas are plains formed by eruption of highly fluid lavas. The crater in the upper right whose rays stretch across the planet is Hokusai. <b>To watch a movie of this colorful view of Mercury as a spinning globe go here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/8497927473">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/8497927473</a></b> Young crater rays, extending radially from fresh impact craters, appear light blue or white. Medium- and dark-blue areas are a geologic unit of Mercury's crust known as the "low-reflectance material", thought to be rich in a dark, opaque mineral. Tan areas are plains formed by eruption of highly fluid lavas. The giant Caloris basin is the large circular tan feature located just to the upper right of center of the image. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. Visit the Why Mercury? section of this website to learn more about the key science questions that the MESSENGER mission is addressing. During the one-year primary mission, MESSENGER acquired 88,746 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER is now in a yearlong extended mission, during which plans call for the acquisition of more than 80,000 additional images to support MESSENGER's science goals. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
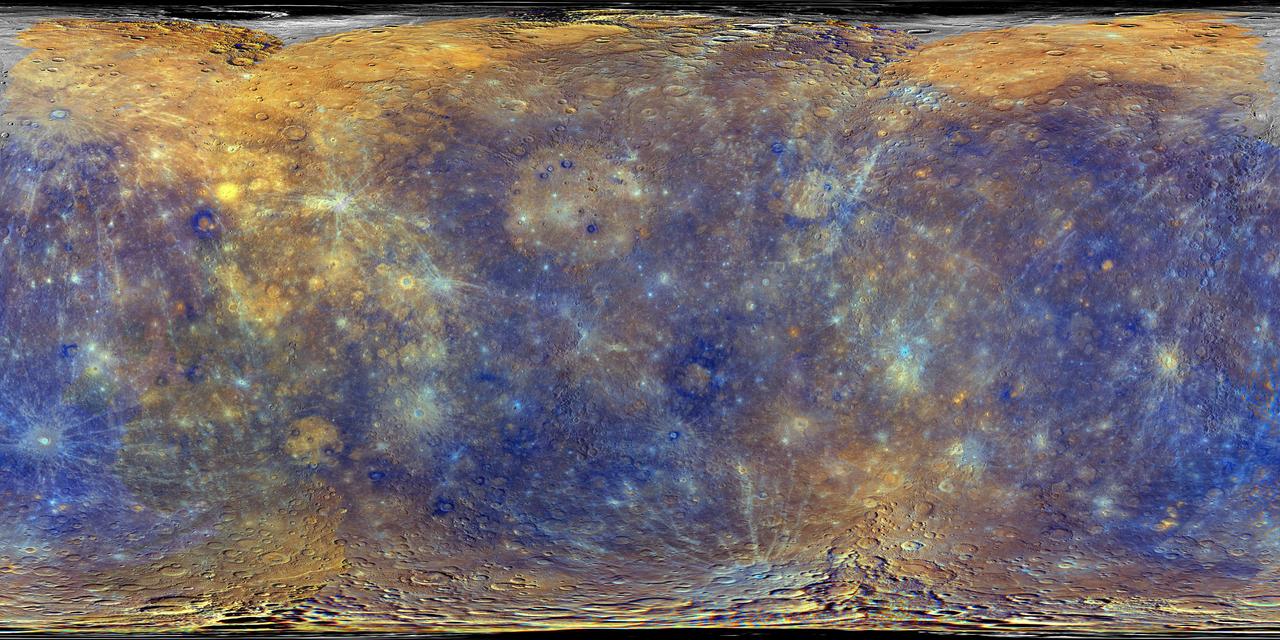
This colorful view of Mercury was produced by using images from the color base map imaging campaign during MESSENGER's primary mission. These colors are not what Mercury would look like to the human eye, but rather the colors enhance the chemical, mineralogical, and physical differences between the rocks that make up Mercury's surface. This specific color combination places the second principle component in the red channel, the first principle component in the green channel, and the ratio of the 430 nm/1000 nm filters in the blue channel. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. During the first two years of orbital operations, MESSENGER acquired over 150,000 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER is capable of continuing orbital operations until early 2015. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
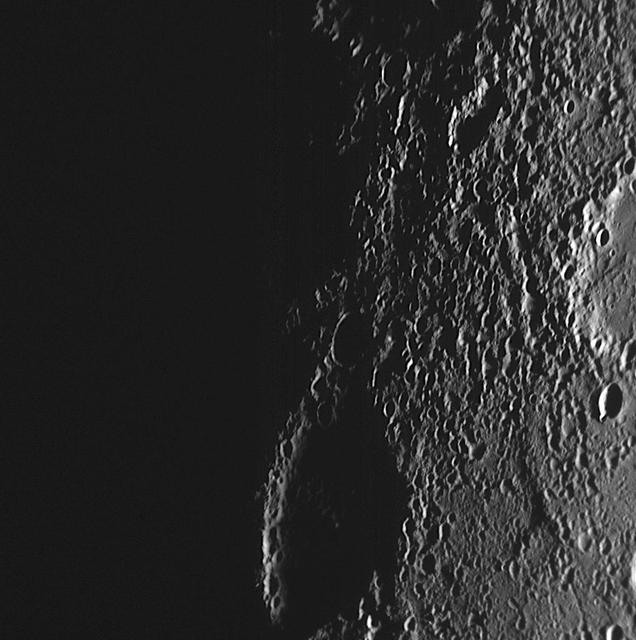

This high-resolution NAC image shows a view of Mercury dawn terminator, the division between the sunlit dayside and dark nightside of the planet, as seen as the MESSENGER spacecraft departed the planet during the mission second Mercury flyby.
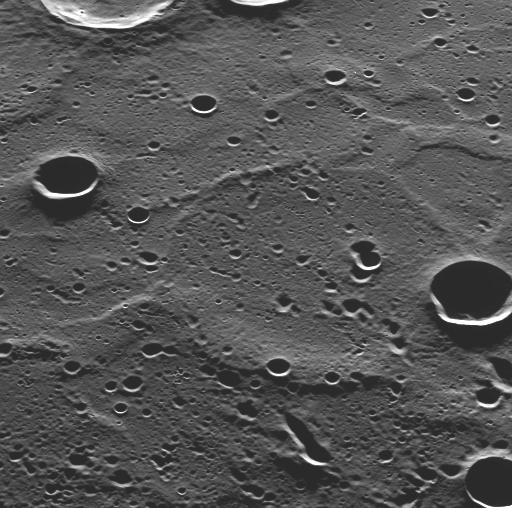

NASA acquired: March 29, 2011 As the MESSENGER spacecraft passed low over Mercury's north polar region, MDIS used its pivot to capture this image, showing terrain that had not been previously seen by spacecraft. The newly imaged surface is located in Mercury's north polar region, to the north of the bright, rayed crater Hokusai. Looking from the bottom of the image toward the top is looking southward, just as MDIS was doing when this image was acquired. This newly seen terrain shows craters with long shadows, as expected at this high northern latitude. Understanding the interiors of the craters in Mercury's polar regions and any ices they may contain is one of the main science goals of the MESSENGER mission. The long shadows also accentuate the topography of the surface, which includes a number of ridges that resemble those seen on the expansive smooth plains imaged during Mercury flyby 3. On March 17, 2011 (March 18, 2011, UTC), MESSENGER became the first spacecraft ever to orbit the planet Mercury. The mission is currently in its commissioning phase, during which spacecraft and instrument performance are verified through a series of specially designed checkout activities. In the course of the one-year primary mission, the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation will unravel the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. Visit the Why Mercury? section of this website to learn more about the science questions that the MESSENGER mission has set out to answer. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

Release Date: December 21, 2011 The crater at the center of this image is named Dickens, after Charles Dickens, the English novelist who lived from 1812 to 1870. Among Dickens' famous works is A Christmas Carol, the story of Bob Cratchit, his family, and horrible boss Mr. Scrooge. Scientists studying Mercury might consider the Mariner 10 mission to be Christmas Past, MESSENGER to be Christmas Present, and the European Bepi-Colombo mission to be Christmas Yet To Come. This image was acquired as part of MDIS's high-resolution surface morphology base map. The surface morphology base map will cover more than 90% of Mercury's surface with an average resolution of 250 meters/pixel (0.16 miles/pixel or 820 feet/pixel). Images acquired for the surface morphology base map typically have off-vertical Sun angles (i.e., high incidence angles) and visible shadows so as to reveal clearly the topographic form of geologic features. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. Visit the Why Mercury? section of this website to learn more about the key science questions that the MESSENGER mission is addressing. During the one-year primary mission, MDIS is scheduled to acquire more than 75,000 images in support of MESSENGER's science goals. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
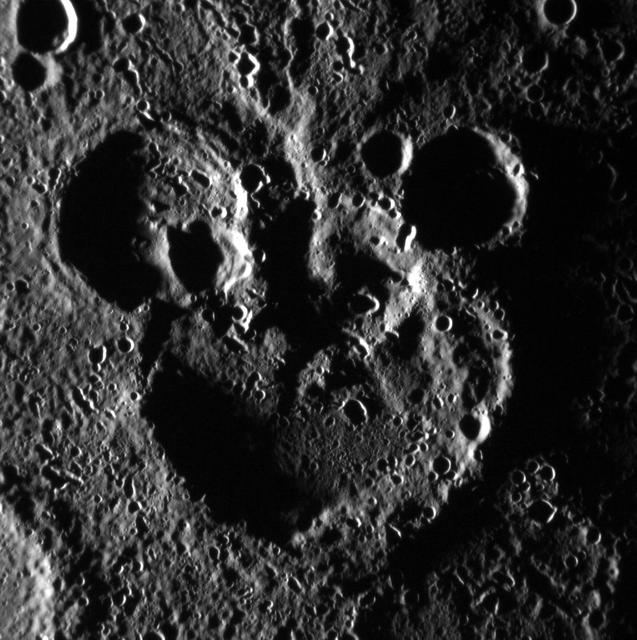

NASA image acquired: June 03, 2012 This scene is to the northwest of the recently named crater Magritte, in Mercury's south. The image is not map projected; the larger crater actually sits to the north of the two smaller ones. The shadowing helps define the striking "Mickey Mouse" resemblance, created by the accumulation of craters over Mercury's long geologic history. This image was acquired as part of MDIS's high-incidence-angle base map. The high-incidence-angle base map is a major mapping activity in MESSENGER's extended mission and complements the surface morphology base map of MESSENGER's primary mission that was acquired under generally more moderate incidence angles. High incidence angles, achieved when the Sun is near the horizon, result in long shadows that accentuate the small-scale topography of geologic features. The high-incidence-angle base map is being acquired with an average resolution of 200 meters/pixel. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. Visit the Why Mercury? section of this website to learn more about the key science questions that the MESSENGER mission is addressing. During the one-year primary mission, MESSENGER acquired 88,746 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER is now in a yearlong extended mission, during which plans call for the acquisition of more than 80,000 additional images to support MESSENGER's science goals. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This spectacular color mosaic shows the eastern limb of Mercury as seen by NASA MESSENGER as the spacecraft departed the planet following the mission first Mercury flyby in January 2008.
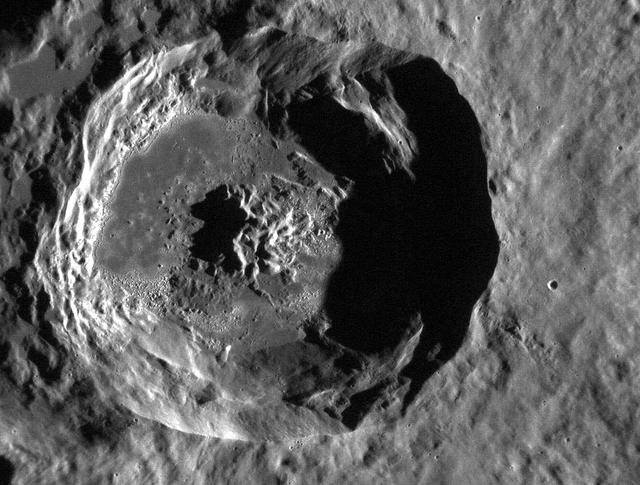
NASA image acquired October 28, 2011 This stunning, and as of yet unnamed, crater lies within the Caloris basin. Its floor provides another example of the beautiful "hollows" found on Mercury and has an etched appearance similar to that found in the crater Tyagaraja. This image was acquired as a high-resolution targeted observation. Targeted observations are images of a small area on Mercury's surface at resolutions much higher than the 250-meter/pixel (820 feet/pixel) morphology base map or the 1-kilometer/pixel (0.6 miles/pixel) color base map. It is not possible to cover all of Mercury's surface at this high resolution during MESSENGER's one-year mission, but several areas of high scientific interest are generally imaged in this mode each week. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. Visit the Why Mercury? section of this website to learn more about the key science questions that the MESSENGER mission is addressing. During the one-year primary mission, MDIS is scheduled to acquire more than 75,000 images in support of MESSENGER's science goals. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
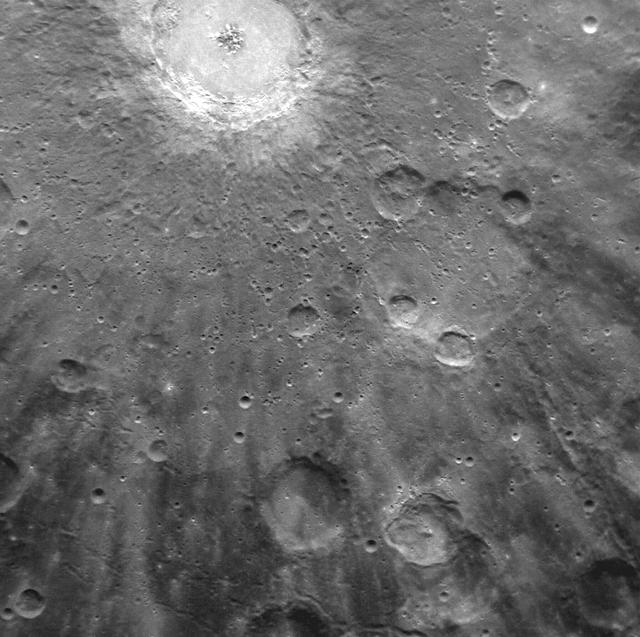

NASA image acquired: March 29, 2011 Bright rays, consisting of impact ejecta and secondary craters, spread across this NAC image and radiate from Debussy crater, located at the top. The image, acquired yesterday during the first orbit for which MDIS was imaging, shows just a small portion of Debussy's large system of rays in greater detail than ever previously seen. Images acquired during MESSENGER's second Mercury flyby showed that Debussy's rays extend for hundreds of kilometers across Mercury's surface. Debussy crater was named in March 2010, in honor of the French composer Claude Debussy (1862-1918). On March 17, 2011 (March 18, 2011, UTC), MESSENGER became the first spacecraft to orbit the planet Mercury. The mission is currently in its commissioning phase, during which spacecraft and instrument performance are verified through a series of specially designed checkout activities. In the course of the one-year primary mission, the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation will unravel the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. Visit the Why Mercury? section of this website to learn more about the science questions that the MESSENGER mission has set out to answer. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
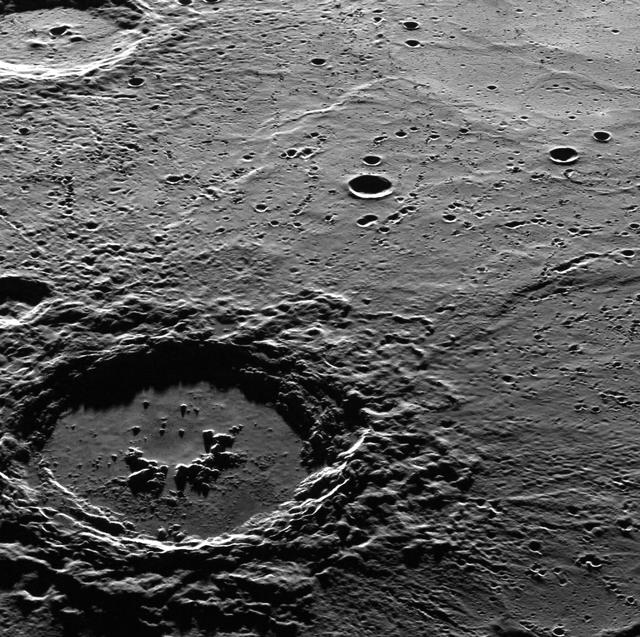
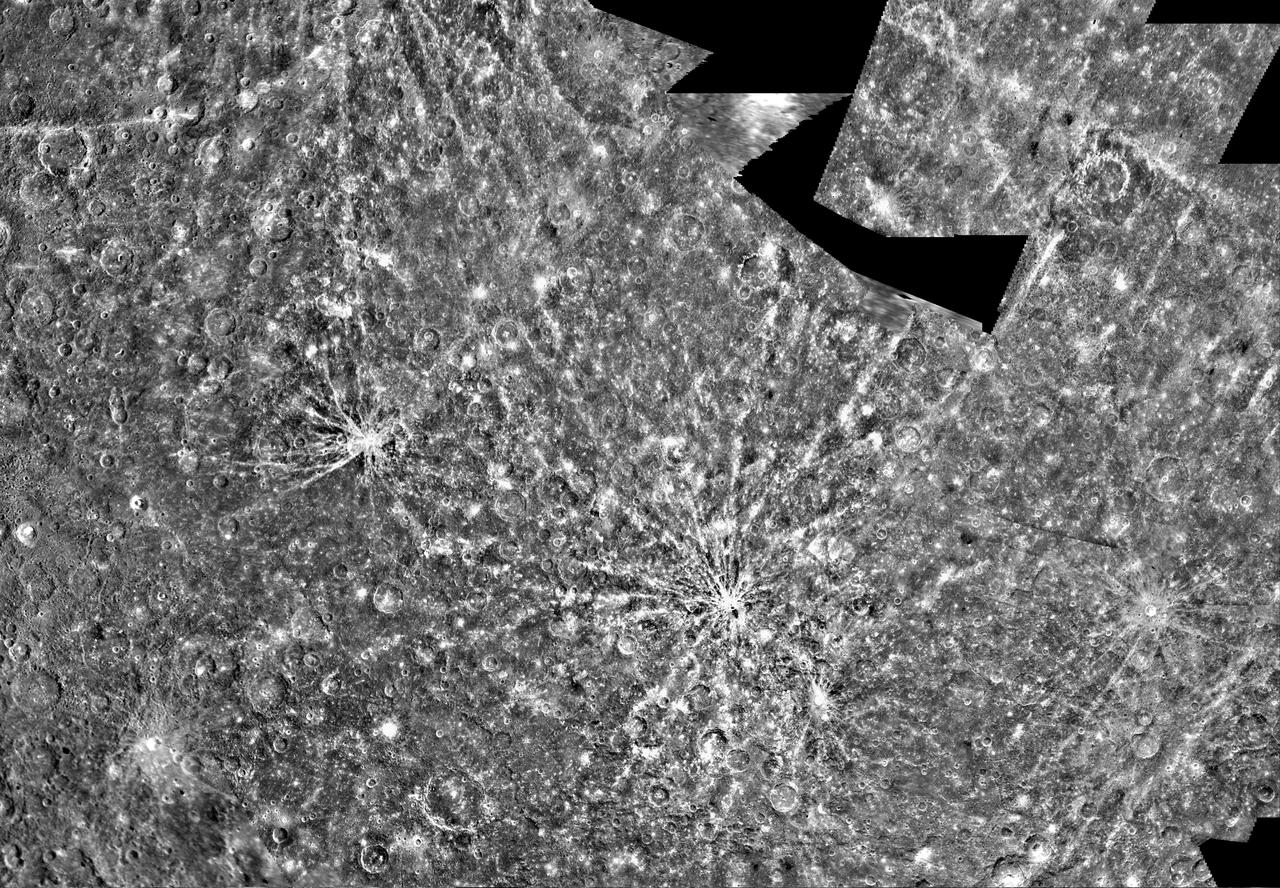
This dramatic image features Hokusai in the foreground, famous for its extensive set of rays, some of which extend for over a thousand kilometers across Mercury's surface. The extensive, bright rays indicate that Hokusai is one of the youngest large craters on Mercury. Check out previously featured images to see high-resolution details of its central peaks, rim and ejecta blanket, and impact melt on its floor. This image was acquired as part of MDIS's high-incidence-angle base map. The high-incidence-angle base map complements the surface morphology base map of MESSENGER's primary mission that was acquired under generally more moderate incidence angles. High incidence angles, achieved when the Sun is near the horizon, result in long shadows that accentuate the small-scale topography of geologic features. The high-incidence-angle base map was acquired with an average resolution of 200 meters/pixel. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. During the first two years of orbital operations, MESSENGER acquired over 150,000 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER is capable of continuing orbital operations until early 2015. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
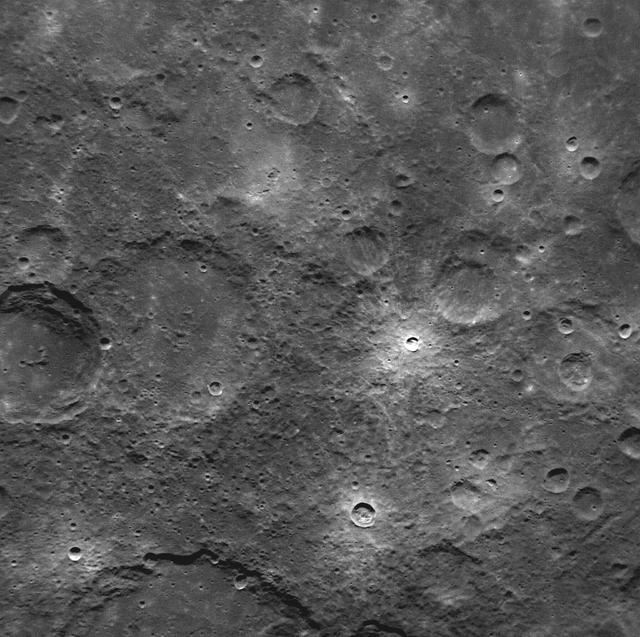

NASA image acquired: March 29, 2011 This is the first image of Mercury taken from orbit with MESSENGER’s Narrow Angle Camera (NAC). MESSENGER’s camera system, the Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS), has two cameras: the Narrow Angle Camera and the Wide Angle Camera (WAC). Comparison of this image with MESSENGER’s first WAC image of the same region shows the substantial difference between the fields of view of the two cameras. At 1.5°, the field of view of the NAC is seven times smaller than the 10.5° field of view of the WAC. This image was taken using MDIS’s pivot. MDIS is mounted on a pivoting platform and is the only instrument in MESSENGER’s payload capable of movement independent of the spacecraft. The other instruments are fixed in place, and most point down the spacecraft’s boresight at all times, relying solely on the guidance and control system for pointing. The 90° range of motion of the pivot gives MDIS a much-needed extra degree of freedom, allowing MDIS to image the planet’s surface at times when spacecraft geometry would normally prevent it from doing so. The pivot also gives MDIS additional imaging opportunities by allowing it to view more of the surface than that at which the boresight-aligned instruments are pointed at any given time. On March 17, 2011 (March 18, 2011, UTC), MESSENGER became the first spacecraft ever to orbit the planet Mercury. The mission is currently in the commissioning phase, during which spacecraft and instrument performance are verified through a series of specially designed checkout activities. In the course of the one-year primary mission, the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation will unravel the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. Visit the Why Mercury? section of this website to learn more about the science questions that the MESSENGER mission has set out to answer. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
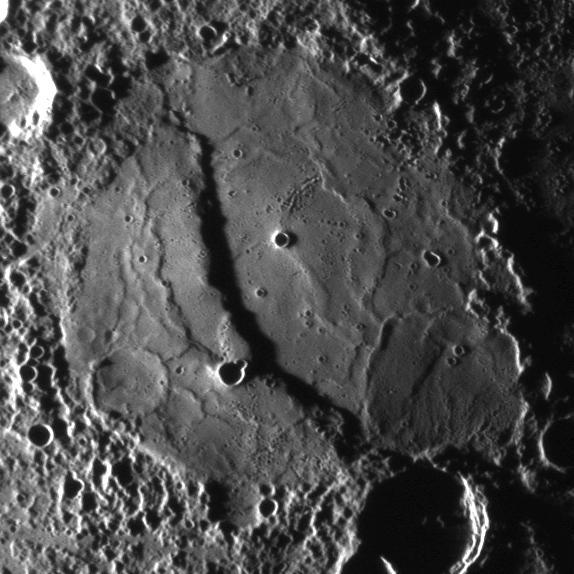
The scarp cutting through this crater was imaged as NASA MESSENGER approached the planet during the mission second Mercury flyby.
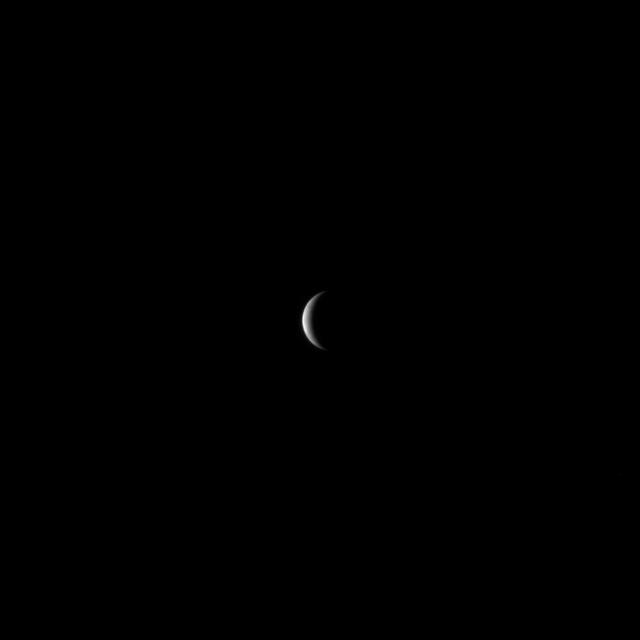

NASA MESSENGER spacecraft continued to speed toward Mercury, preparing for its closest approach to the planet on Monday, January 14, 2008.

This diagram shows the approximate distances of the terrestrial planets from the Sun; they include Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars.
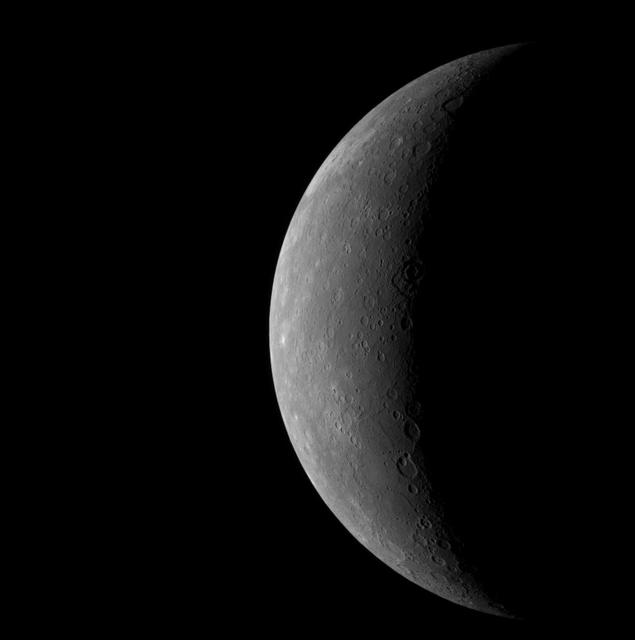

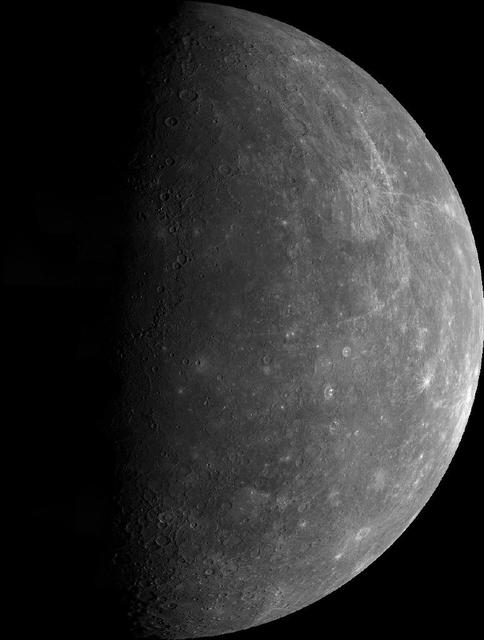
As NASA MESSENGER neared Mercury on January 14, 2008, the spacecraft Wide Angle Camera on the Mercury Dual Imaging System MDIS took this image of the planet full crescent.

As NASA MESSENGER spacecraft drew closer to Mercury for its historic first flyby, the spacecraft Narrow Angle Camera NAC on the Mercury Dual Imaging System MDIS acquired an image mosaic of the sunlit portion of the planet.

A cratered area near Mercury South Pole was photographed by NASA Mariner 10 during its second flyby of the planet of Sept. 21, 1974 the spacecraft made its first encounter with Mercury on March 19, 1974.

After NASA MESSENGER spacecraft completed its successful flyby of Mercury, the Narrow Angle Camera NAC, part of the Mercury Dual Imaging System MDIS, took these images of the receding planet. This is a frame from an animation.

As NASA MESSENGER approached Mercury on January 14, 2008, the spacecraft Narrow-Angle Camera on the Mercury Dual Imaging System MDIS instrument captured this view of the planet rugged, cratered landscape illuminated obliquely by the Sun.

On January 13, 2008, beginning 30 hours before NASA MESSENGER spacecraft closest approach to Mercury, the Wide Angle Camera, part of the Mercury Dual Imaging System MDIS, began snapping images as it approached the planet.

After NASA MESSENGER spacecraft completed its successful flyby of Mercury, the Narrow Angle Camera NAC, part of the Mercury Dual Imaging System MDIS, took these images of the receding planet.
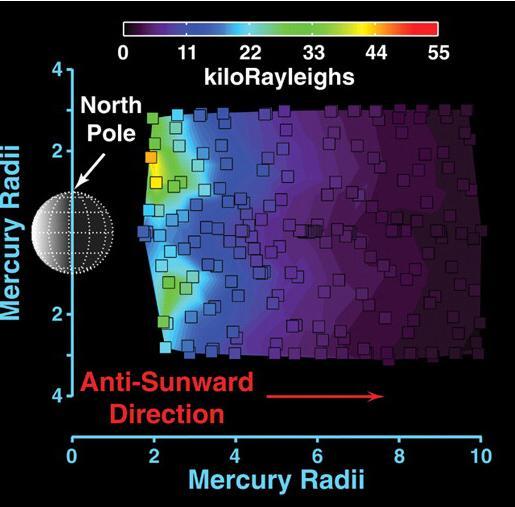
As the MESSENGER spacecraft approached Mercury, the UVVS field of view was scanned across the planet's exospheric "tail," which is produced by the solar wind pushing Mercury's exosphere (the planet's extremely thin atmosphere) outward. This figure, recently published in Science magazine, shows a map of the distribution of sodium atoms as they stream away from the planet (see PIA10396); red and yellow colors represent a higher abundance of sodium than darker shades of blue and purple, as shown in the colored scale bar, which gives the brightness intensity in units of kiloRayleighs. The escaping atoms eventually form a comet-like tail that extends in the direction opposite that of the Sun for many planetary radii. The small squares outlined in black correspond to individual measurements that were used to create the full map. These measurements are the highest-spatial-resolution observations ever made of Mercury's tail. In less than six weeks, on October 6, 2008, similar measurements will be made during MESSENGER's second flyby of Mercury. Comparing the measurements from the two flybys will provide an unprecedented look at how Mercury's dynamic exosphere and tail vary with time. Date Acquired: January 14, 2008. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11076

This mosaic, made from over 140 individual TV frames taken about two hours after encounter, shows the planet Mercury as seen by NASA Mariner 10 as it sped away from the planet on March 29, 1974.
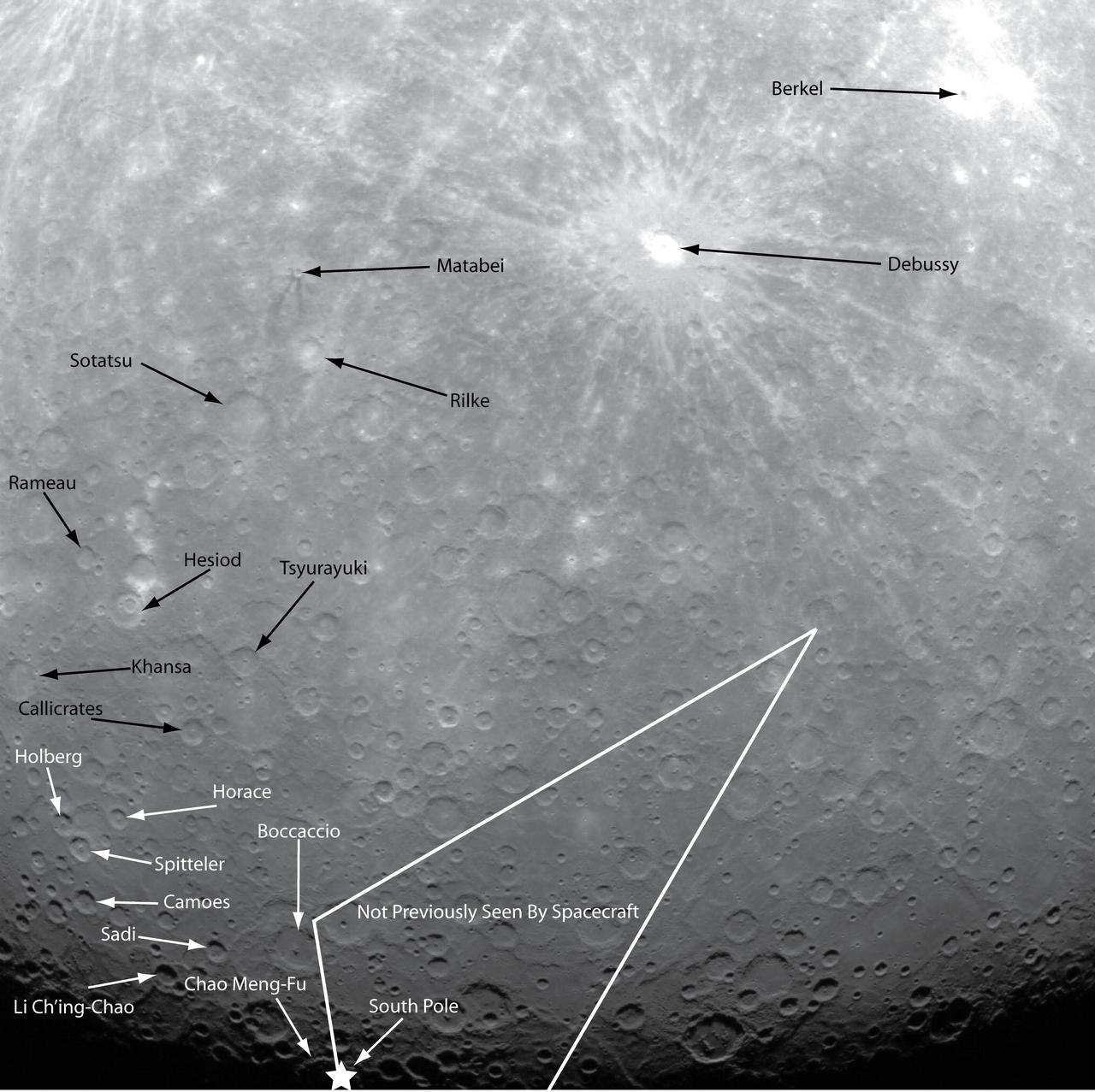
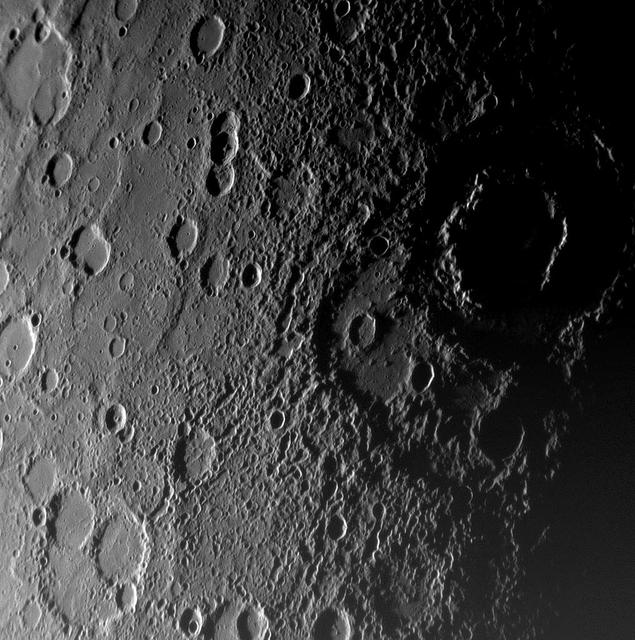
NASA image acquired: March 29, 2011 This historic first orbital image of Mercury was acquired 37 years to the day after Mariner 10’s historic first flyby of the innermost planet. Labels have been added to indicate several craters that were named based on Mariner 10 images, as well as Debussy, Matabei, and Berkel, which were named based on MESSENGER flyby images. The surface contained in the white lines is terrain previously unseen by spacecraft, and the star indicates the location of the south pole. On March 17, 2011 (March 18, 2011, UTC), MESSENGER became the first spacecraft to orbit the planet Mercury. The mission is currently in its commissioning phase, during which spacecraft and instrument performance are verified through a series of specially designed checkout activities. In the course of the one-year primary mission, the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation will unravel the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. Visit the Why Mercury? section of this website to learn more about the science questions that the MESSENGER mission has set out to answer. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
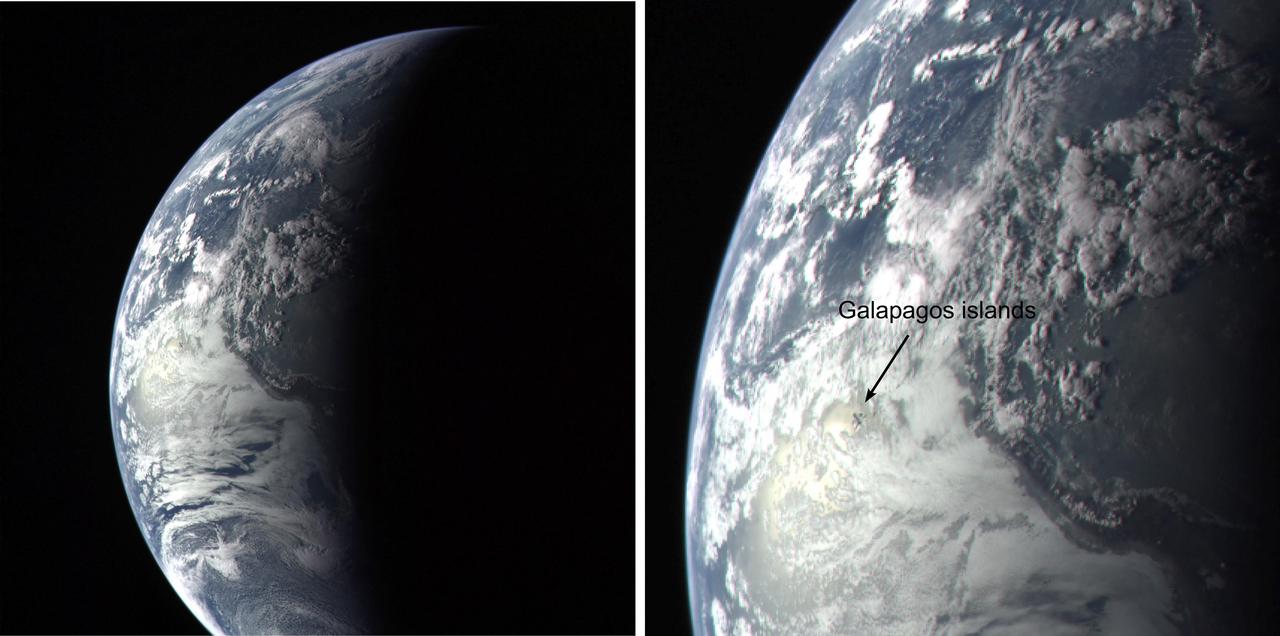

NASA Mercury-bound MESSENGER spacecraft captured several stunning images of Earth during a gravity assist swingby of its home planet on Aug. 2, 2005.

NASA Mariner 10 took this picture of the densely cratered surface of Mercury when the spacecraft was 18,200 kilometers 8085 miles from the planet on March 29, 1974.

NASA Mercury-bound MESSENGER spacecraft captured several stunning images of Earth during a gravity assist swingby of its home planet on Aug. 2, 2005.
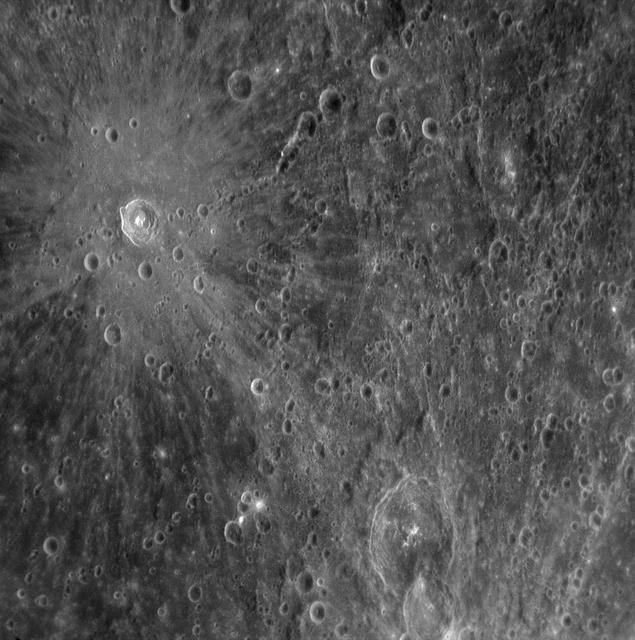
During its flyby of Mercury, NASA MESSENGER spacecraft acquired high-resolution images of the planet surface. This image was obtained on January 14, 2008.

Release Date: November 25, 2013 MESSENGER image of comet C/2012 S1 (ISON) during its closest approach to Mercury. At that time, ISON was approximately 22.5 million miles (36.2 million kilometers) from MESSENGER and 42.1 million miles (67.8 million kilometers) from the Sun. The image is 7° by 4.7° in size and has been slightly magnified and smoothed to enhance the faint tail of the comet. The tail was oriented at an angle to MESSENGER at the time and is foreshortened in this image; however, some faint structure can still be seen. MESSENGER's cameras have been acquiring targeted observations (watch an animation here) of Encke since October 28 and ISON since October 26, although the first faint detections didn't come until early November. During the closest approach of each comet to Mercury, the Mercury Atmospheric and Surface Composition Spectrometer (MASCS) and X-Ray Spectrometer (XRS) instruments also targeted the comets. Observations of ISON conclude on November 26, when the comet passes too close to the Sun, but MESSENGER will continue to monitor Encke with both the imagers and spectrometers through early December. Read this mission news story for more details. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. During the first two years of orbital operations, MESSENGER acquired over 150,000 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER is capable of continuing orbital operations until early 2015. Date acquired: 01:54:30 UTC on November 20, 2013 Instrument: Wide Angle Camera (WAC) of the Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS) Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington/Southwest Research Institute <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
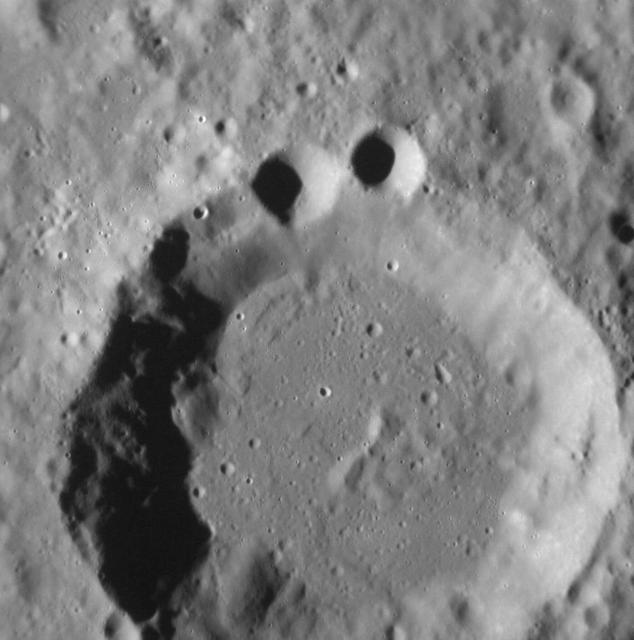

NASA image acquired August 29, 2012 Ok, so maybe it's just me. But the superposition of younger craters on older craters (in this case two smaller craters upon the rim of an older crater) can result in landforms that appear to resemble more familiar shapes to human eyes. More generally, the Law of Superposition allows scientists to determine which surface features pre- and postdate others, leading to a better understanding of the geological history of different regions of Mercury's surface. This image was acquired as a high-resolution targeted observation. Targeted observations are images of a small area on Mercury's surface at resolutions much higher than the 200-meter/pixel morphology base map. It is not possible to cover all of Mercury's surface at this high resolution, but typically several areas of high scientific interest are imaged in this mode each week. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. Visit the Why Mercury? section of this website to learn more about the key science questions that the MESSENGER mission is addressing. During the one-year primary mission, MESSENGER acquired 88,746 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER is now in a yearlong extended mission, during which plans call for the acquisition of more than 80,000 additional images to support MESSENGER's science goals. Go here to read more about the MESSENGER mission: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/messenger/main/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/messenger/main/index.html</a> Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

AS15-98-13311 (31 July 1971) --- The solar corona, as photographed from the Apollo 15 spacecraft about one minute prior to sunrise on July 31, 1971, is seen just beyond the lunar horizon. The bright object on the opposite of the frame is the planet Mercury. The bright star near the frame center is Regulus, and the lesser stars form the head of the constellation Leo. Mercury is approximately 28 degrees from the center of the sun. The solar coronal streamers, therefore, appear to extend about eight degrees from the sun's center. This solar corona photograph was the second in a series of seven. Three such series were obtained by astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, during the solo part of his lunar orbital flight. They represent man's first view of this part of the sun's light. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon, astronaut Worden remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

All seven planets discovered in orbit around the red dwarf star TRAPPIST-1 could easily fit inside the orbit of Mercury, the innermost planet of our solar system. In fact, they would have room to spare. TRAPPIST-1 also is only a fraction of the size of our Sun; it isn't much larger than Jupiter. So, the TRAPPIST-1 system's proportions look more like Jupiter and its moons than those of our solar system. The seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all Earth-sized and terrestrial. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22096

After passing on the darkside of the planet, NASA Mariner 10 photographed the other, somewhat more illuminated hemisphere of Mercury. The north pole is at the top, two-thirds down from which is the equator.
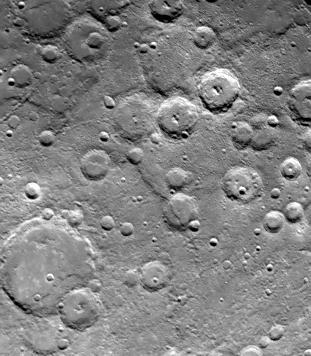
One of NASA Mariner 10 two TV cameras took this picture of a densely cratered region of Mercury on Sept. 21, 1974, 80 minutes prior to the spacecraft second close encounter with the planet.
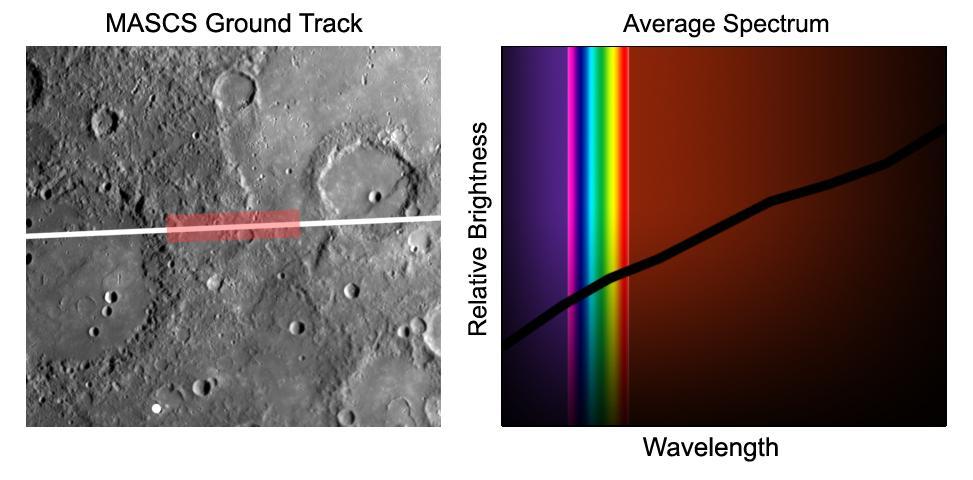
During its flyby of Mercury, on January 14, 2008 NASA MESSENGER spacecraft acquired the first high-resolution spectra of the planet surface in ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared light.
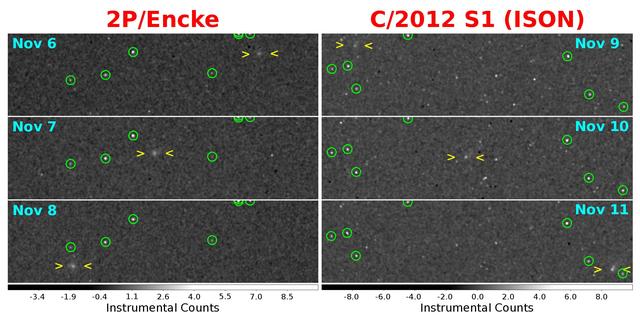
As comets C/2012 S1 ISON and the well-known short-period comet 2P/Encke both approached their closest distances to the Sun in November, 2013, they also passed close to the MESSENGER spacecraft orbiting the innermost planet Mercury.
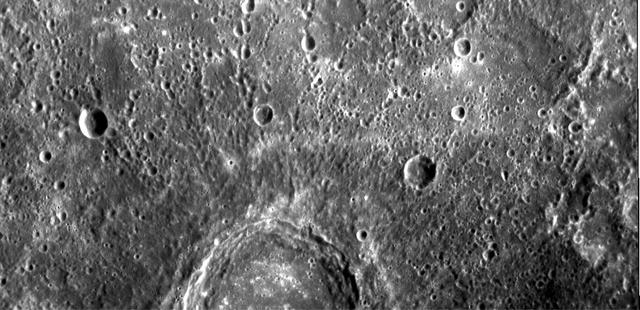
The image shows part of a large, fresh crater with secondary crater chains located near Mercury equator on the side of the planet newly imaged on January 14, 2008 by NASA MESSENGER spacecraft.

This visible-infrared image shows an incoming view of Mercury, about 80 minutes before NASA MESSENGER spacecraft closest pass of the planet on January 14, 2008, from a distance of about 27,000 kilometers 17,000 miles.

This artist concept depicts a comet-like tail of a possible disintegrating super Mercury-size planet candidate as it transits, or crosses, its parent star, named KIC 12557548. The results are based on data from NASA Kepler mission.

As NASA Mariner 10 passed by Mercury on its second encounter with the planet on Sept. 21, 1974, this picture of a large circular 350 kilometer, 220 mile diameter basin was obtained near the morning terminator.

This computer photomosaic is of the Caloris Basin, the largest basin on Mercury. NASA Mariner 10 spacecraft imaged the region during its initial flyby of the planet after its launch in 1974.
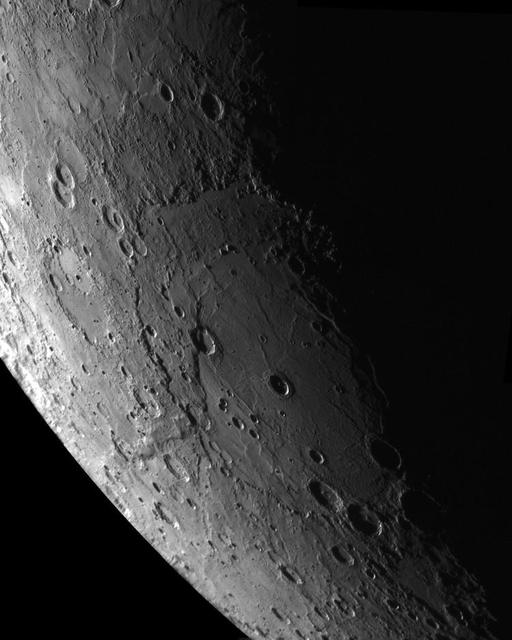

This mosaic was assembled using NAC images acquired as the MESSENGER spacecraft approached the planet during the mission second Mercury flyby The Rembrandt impact basin is seen at the center of the mosaic.
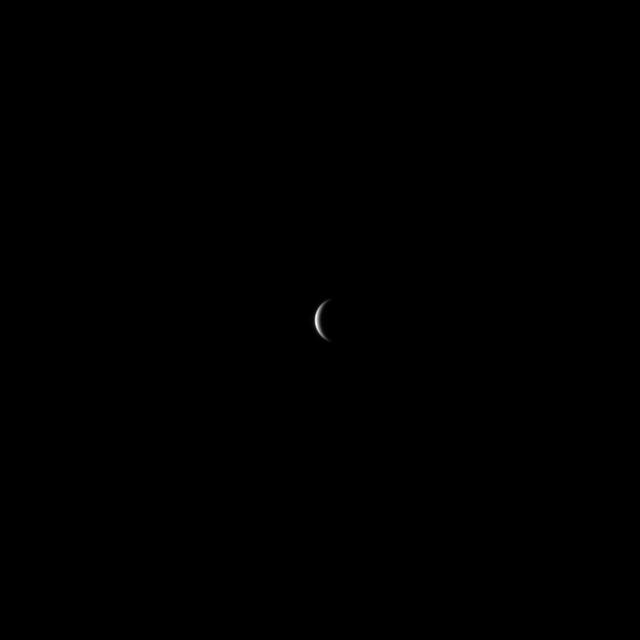

On January 9, 2008, NASA MESSENGER spacecraft snapped one of its first images of Mercury at a distance of about 2.7 million kilometers 1.7 million miles from the planet.
This image, from NASA Mariner 10 spacecraft which launched in 1974, is of the H-7 Beethoven Quadrangle, and lies in Mercury Equatorial Mercator. NASA Mariner 10 spacecraft imaged the region during its initial flyby of the planet.
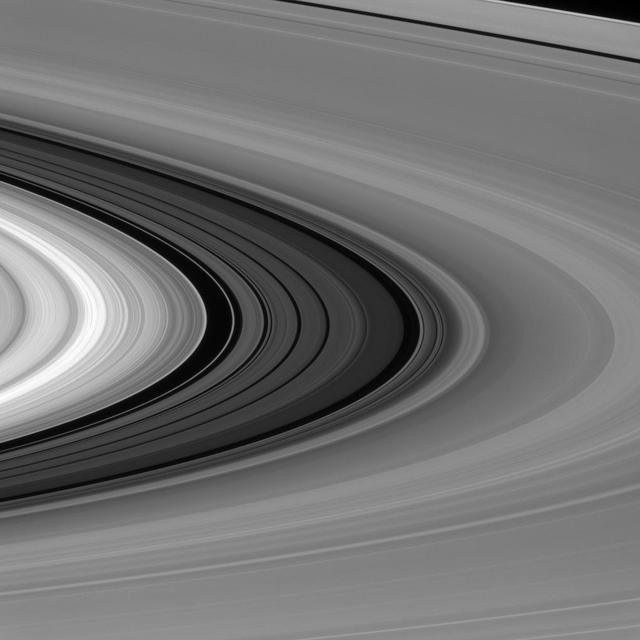

It difficult to get a sense of scale when viewing Saturn rings, but the Cassini Division seen here between the bright B ring and dimmer A ring is almost as wide as the planet Mercury as seen by NASA Cassini spacecraft.

Taken about 40 minutes before NASA Mariner 10 made its close approach to Mercury on Sept. 21,1974, this picture shows a large double-ringed basin center of picture located in the planet south polar region

A faint double ring crater is seen at upper right in this picture of Mercury taken one hour and 40 minutes before NASA Mariner 10 second rendezvous with the planet Sept. 21, 1975

A dark, smooth, relatively uncratered area on Mercury was photographed two hours after NASA Mariner 10 flew by the planet. The prominent, sharp crater with a central peak is 30 kilometers 19 miles across.

NASA MESSENGER Earth flyby on Aug. 2, 2005, not only adjusted the spacecraft path to Mercury - the gravity assist maneuver allowed the spacecraft team to test several MESSENGER science instruments by observing its home planet.

During its second encounter with Mercury on Sept. 21, 1974, NASA Mariner 10 took this picture of the planet South Polar Region. Many of the craters have denuded rims peppered by smaller craters.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - MESSENGER, a NASA Discovery mission. The MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) mission is a scientific investigation of the planet Mercury. MESSENGER will be launched in the summer of 2004 and will enter Mercury orbit in March of 2011, after one Earth flyby, two flybys of Venus, and three of Mercury along the way. The flyby and orbital phases of the mission will provide global mapping and detailed characterization of the planet's surface, interior, atmosphere and magnetosphere.
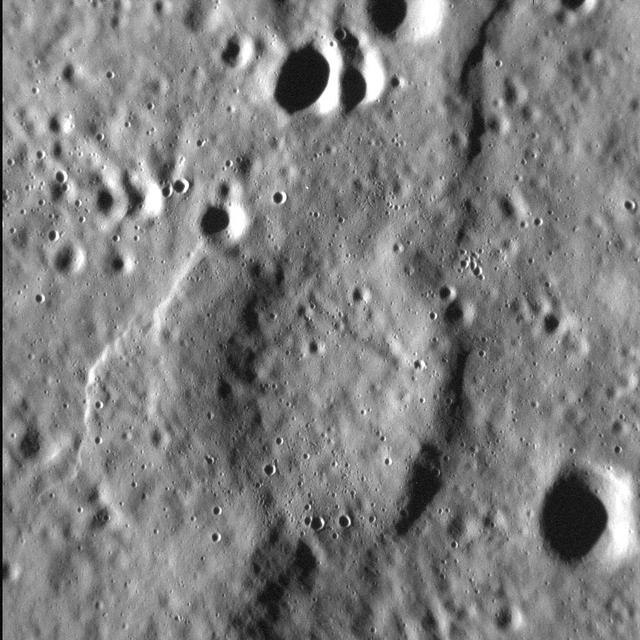
It is no secret that Mercury's surface is scarred by abundant tectonic deformation, the vast majority of which is due to the planet's history of cooling and contraction through time. Yet Mercury is also heavily cratered, and hosts widespread volcanic plains. So it's perhaps unsurprising that these three types of landform often intersect-literally-as shown in this scene. Here, an unnamed crater, about 7.5 km (4.7 mi.) in diameter was covered, and almost fully buried, by lava. At some point after, compression of the surface formed scarps and ridges in the area that, when they reached the buried crater, came to describe its curved outline. Many arcuate ridges on Mercury formed this way. In this high-resolution view, we can also see the younger, later population of smaller craters that pock-mark the surface. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19263
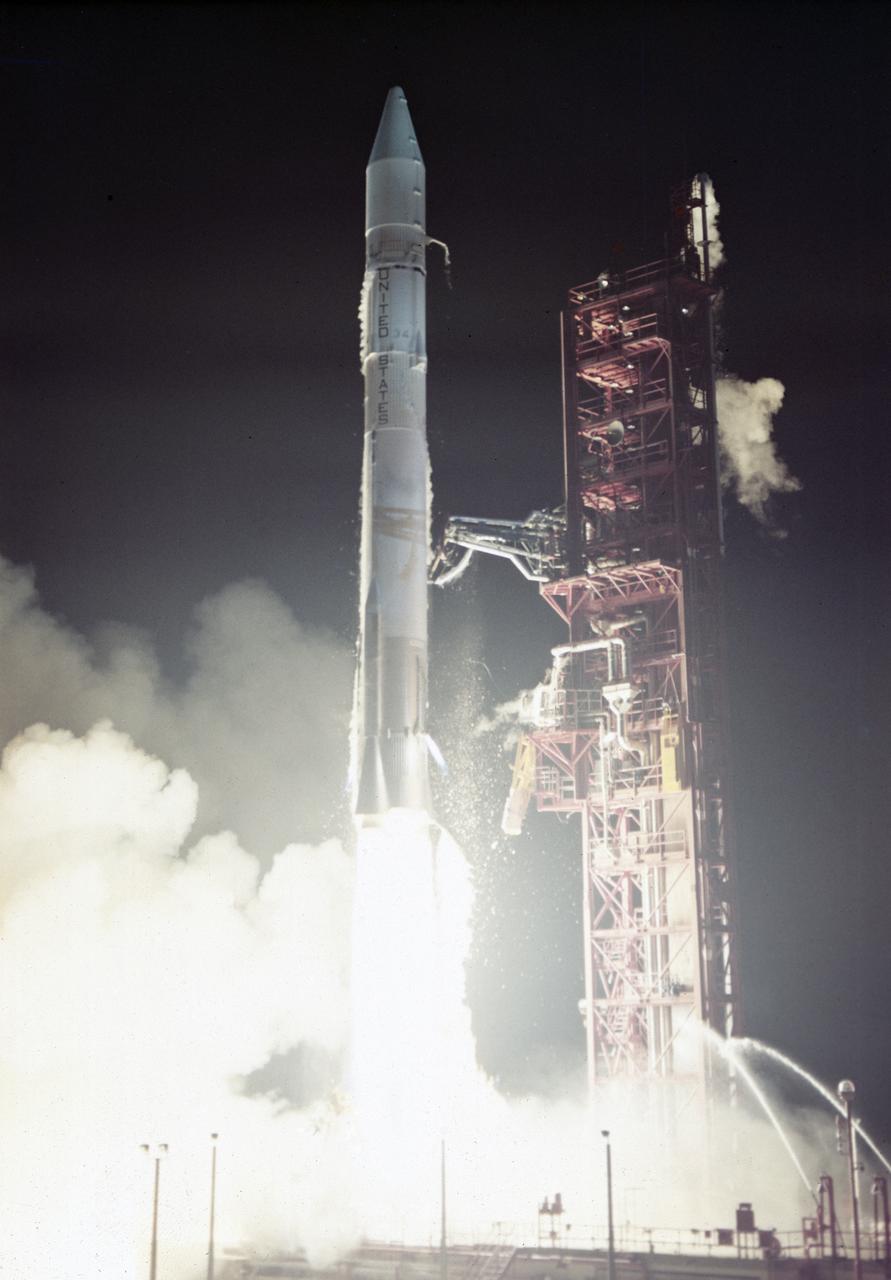

The launch of the Atlas-Centaur carrying the Mariner X spacecraft on November 3, 1973. This mission was for the exploration of the planets Venus and Mercury.
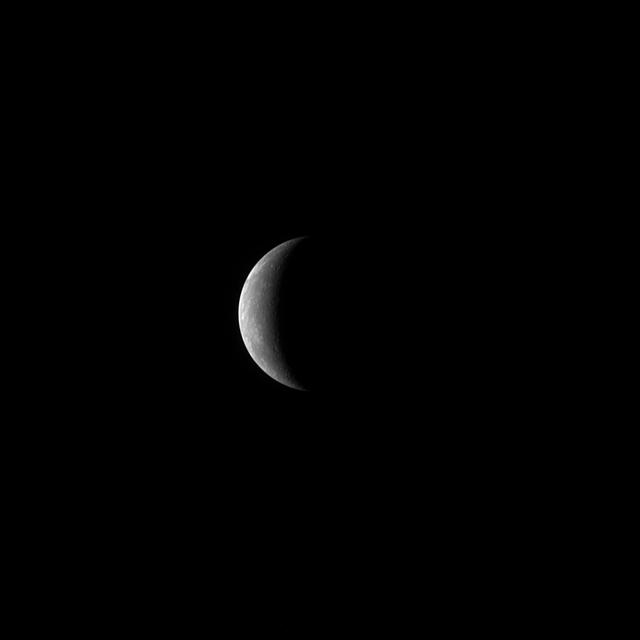

On January 14, 2008, at 19:04:39 UTC 2:04:39 pm EST, NASA MESSENGER spacecraft experienced its closest approach to Mercury, passing just 200 kilometers 124 miles above the planet surface.
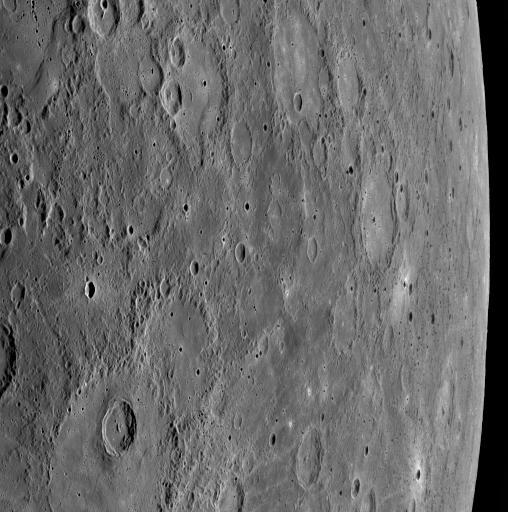

Just nine minutes after NASA MESSENGER spacecraft passed 200 kilometers 124 miles above the surface of Mercury, its closest distance to the planet during the January 14, 2008, flyby, the Wide Angle Camera WAC snapped this image.

This is the first image of Earth ever taken from another planet that actually shows our home as a planetary disk. Because Earth and the Moon are closer to the Sun than Mars, they exhibit phases, just as the Moon, Venus, & Mercury do when viewed from Earth

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers at Astrotech Space Operations facilities in Titusville, Fla., finish encapsulating the MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft for a move from its current location in the hazardous processing facility, where it has been since arrival March 10, to an adjacent nonhazardous payload processing facility. The remainder of its final assembly and testing will be completed there. The spacecraft will return to the hazardous processing facility when ready for fueling, spin balance testing and mating to the upper stage. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch no earlier than July 30 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER is a scientific investigation of the planet Mercury, the least explored terrestrial planet. Understanding Mercury and how it was formed is essential to understanding the other terrestrial planets and their evolution. The MESSENGER mission will orbit Mercury after making two flybys of the planet, using data collected during the flybys as an initial guide to perform a more focused scientific investigation of this mysterious world. The spacecraft will enter Mercury orbit in March 2011 and carry out comprehensive measurements for one full Earth year.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - - A technician at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., checks the MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft after its move to a stand inside the nonhazardous payload processing facility. Final assembly and testing will be completed at this site. The spacecraft will return to the hazardous processing facility when ready for fueling, spin balance testing and mating to the upper stage. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch no earlier than July 30 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER is a scientific investigation of the planet Mercury, the least explored terrestrial planet. Understanding Mercury and how it was formed is essential to understanding the other terrestrial planets and their evolution. The MESSENGER mission will orbit Mercury after making two flybys of the planet, using data collected during the flybys as an initial guide to perform a more focused scientific investigation of this mysterious world. The spacecraft will enter Mercury orbit in March 2011 and carry out comprehensive measurements for one full Earth year.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - - Workers at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., remove the cover from the MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft inside the nonhazardous payload processing facility. Final assembly and testing will be completed at this site. The spacecraft will return to the hazardous processing facility when ready for fueling, spin balance testing and mating to the upper stage. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch no earlier than July 30 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER is a scientific investigation of the planet Mercury, the least explored terrestrial planet. Understanding Mercury and how it was formed is essential to understanding the other terrestrial planets and their evolution. The MESSENGER mission will orbit Mercury after making two flybys of the planet, using data collected during the flybys as an initial guide to perform a more focused scientific investigation of this mysterious world. The spacecraft will enter Mercury orbit in March 2011 and carry out comprehensive measurements for one full Earth year.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - - Workers at Astrotech Space Operations facilities in Titusville, Fla., secure the cover on the MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft for a move from its current location in the hazardous processing facility, where it has been since arrival March 10, to an adjacent nonhazardous payload processing facility. The remainder of its final assembly and testing will be completed there. The spacecraft will return to the hazardous processing facility when ready for fueling, spin balance testing and mating to the upper stage. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch no earlier than July 30 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER is a scientific investigation of the planet Mercury, the least explored terrestrial planet. Understanding Mercury and how it was formed is essential to understanding the other terrestrial planets and their evolution. The MESSENGER mission will orbit Mercury after making two flybys of the planet, using data collected during the flybys as an initial guide to perform a more focused scientific investigation of this mysterious world. The spacecraft will enter Mercury orbit in March 2011 and carry out comprehensive measurements for one full Earth year.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The encapsulated MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft sits inside the nonhazardous payload processing facility at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., after leaving the hazardous processing facility, where it has been since arrival March 10. The remainder of its final assembly and testing will be completed in the new facility. The spacecraft will return to the hazardous processing facility when ready for fueling, spin balance testing and mating to the upper stage. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch no earlier than July 30 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER is a scientific investigation of the planet Mercury, the least explored terrestrial planet. Understanding Mercury and how it was formed is essential to understanding the other terrestrial planets and their evolution. The MESSENGER mission will orbit Mercury after making two flybys of the planet, using data collected during the flybys as an initial guide to perform a more focused scientific investigation of this mysterious world. The spacecraft will enter Mercury orbit in March 2011 and carry out comprehensive measurements for one full Earth year.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers at Astrotech Space Operations facilities in Titusville, Fla., finish encapsulating the MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft for a move from its current location in the hazardous processing facility, where it has been since arrival March 10, to an adjacent nonhazardous payload processing facility. The remainder of its final assembly and testing will be completed there. The spacecraft will return to the hazardous processing facility when ready for fueling, spin balance testing and mating to the upper stage. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch no earlier than July 30 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER is a scientific investigation of the planet Mercury, the least explored terrestrial planet. Understanding Mercury and how it was formed is essential to understanding the other terrestrial planets and their evolution. The MESSENGER mission will orbit Mercury after making two flybys of the planet, using data collected during the flybys as an initial guide to perform a more focused scientific investigation of this mysterious world. The spacecraft will enter Mercury orbit in March 2011 and carry out comprehensive measurements for one full Earth year.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft arrives at the nonhazardous payload processing facility at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., after leaving the hazardous processing facility, where it has been since arrival March 10. The remainder of its final assembly and testing will be completed in the new facility. The spacecraft will return to the hazardous processing facility when ready for fueling, spin balance testing and mating to the upper stage. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch no earlier than July 30 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER is a scientific investigation of the planet Mercury, the least explored terrestrial planet. Understanding Mercury and how it was formed is essential to understanding the other terrestrial planets and their evolution. The MESSENGER mission will orbit Mercury after making two flybys of the planet, using data collected during the flybys as an initial guide to perform a more focused scientific investigation of this mysterious world. The spacecraft will enter Mercury orbit in March 2011 and carry out comprehensive measurements for one full Earth year.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., prepare to remove the cover from the MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft inside the nonhazardous payload processing facility. Final assembly and testing will be completed at this site. The spacecraft will return to the hazardous processing facility when ready for fueling, spin balance testing and mating to the upper stage. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch no earlier than July 30 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER is a scientific investigation of the planet Mercury, the least explored terrestrial planet. Understanding Mercury and how it was formed is essential to understanding the other terrestrial planets and their evolution. The MESSENGER mission will orbit Mercury after making two flybys of the planet, using data collected during the flybys as an initial guide to perform a more focused scientific investigation of this mysterious world. The spacecraft will enter Mercury orbit in March 2011 and carry out comprehensive measurements for one full Earth year.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft is transported from the hazardous processing facility at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., where it has been since arrival March 10, to an adjacent nonhazardous payload processing facility. The remainder of its final assembly and testing will be completed there. The spacecraft will return to the hazardous processing facility when ready for fueling, spin balance testing and mating to the upper stage. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch no earlier than July 30 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER is a scientific investigation of the planet Mercury, the least explored terrestrial planet. Understanding Mercury and how it was formed is essential to understanding the other terrestrial planets and their evolution. The MESSENGER mission will orbit Mercury after making two flybys of the planet, using data collected during the flybys as an initial guide to perform a more focused scientific investigation of this mysterious world. The spacecraft will enter Mercury orbit in March 2011 and carry out comprehensive measurements for one full Earth year.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers at Astrotech Space Operations facilities in Titusville, Fla., encapsulate the MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft for a move from its current location in the hazardous processing facility, where it has been since arrival March 10. It is being moved to an adjacent nonhazardous payload processing facility where the remainder of its final assembly and testing will be completed. The spacecraft will return to the hazardous processing facility when ready for fueling, spin balance testing and mating to the upper stage. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch no earlier than July 30 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER is a scientific investigation of the planet Mercury, the least explored terrestrial planet. Understanding Mercury and how it was formed is essential to understanding the other terrestrial planets and their evolution. The MESSENGER mission will orbit Mercury after making two flybys of the planet, using data collected during the flybys as an initial guide to perform a more focused scientific investigation of this mysterious world. The spacecraft will enter Mercury orbit in March 2011 and carry out comprehensive measurements for one full Earth year.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations facilities in Titusville, Fla., the MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft is ready for encapsulation before being moved from its current location in the hazardous processing facility, where it has been since arrival March 10. It is being moved to an adjacent nonhazardous payload processing facility where the remainder of its final assembly and testing will be completed. The spacecraft will return to the hazardous processing facility when ready for fueling, spin balance testing and mating to the upper stage. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch no earlier than July 30 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER is a scientific investigation of the planet Mercury, the least explored terrestrial planet. Understanding Mercury and how it was formed is essential to understanding the other terrestrial planets and their evolution. The MESSENGER mission will orbit Mercury after making two flybys of the planet, using data collected during the flybys as an initial guide to perform a more focused scientific investigation of this mysterious world. The spacecraft will enter Mercury orbit in March 2011 and carry out comprehensive measurements for one full Earth year.
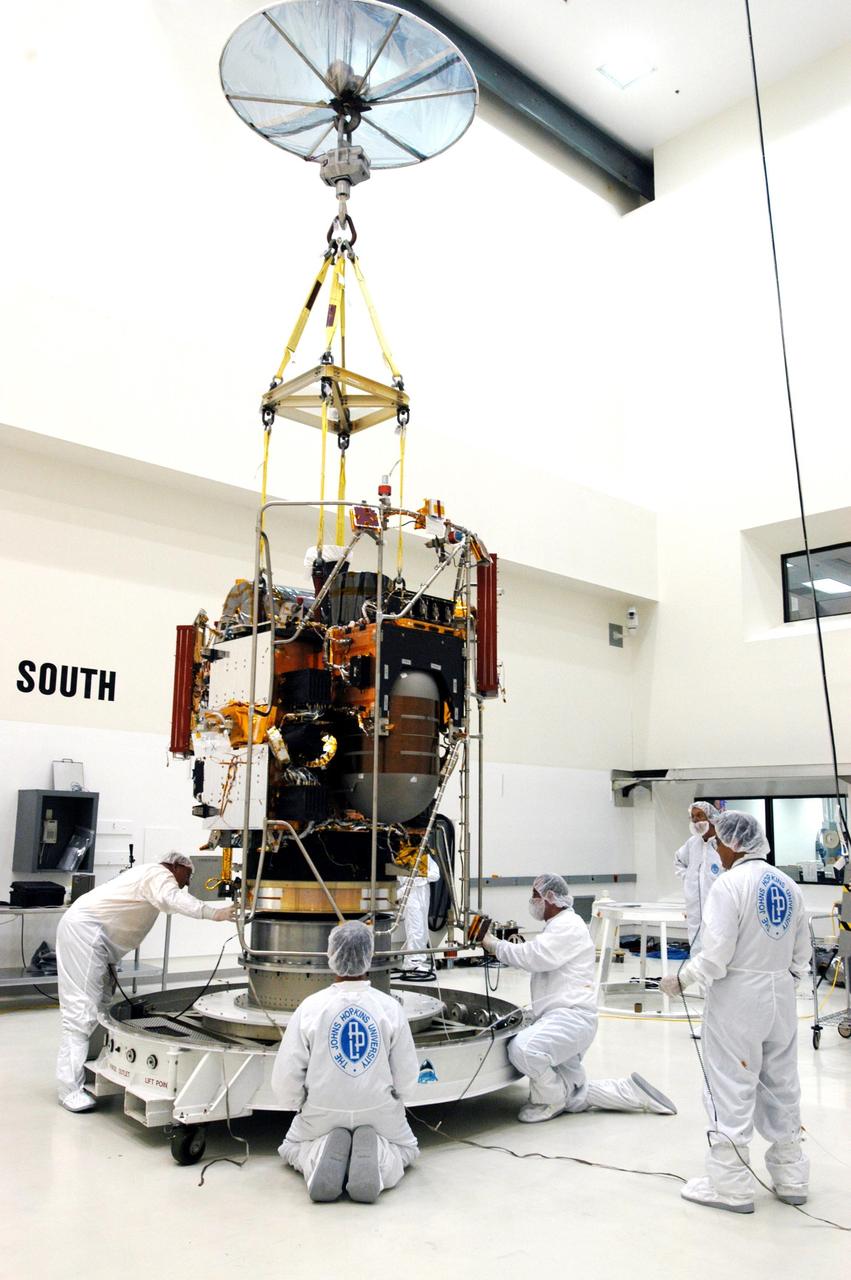

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - An overhead crane lifts the MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) spacecraft from its transporter inside the nonhazardous payload processing facility at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla. Final assembly and testing will be completed at this facility. The spacecraft will return to the hazardous processing facility when ready for fueling, spin balance testing and mating to the upper stage. MESSENGER is scheduled to launch no earlier than July 30 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER is a scientific investigation of the planet Mercury, the least explored terrestrial planet. Understanding Mercury and how it was formed is essential to understanding the other terrestrial planets and their evolution. The MESSENGER mission will orbit Mercury after making two flybys of the planet, using data collected during the flybys as an initial guide to perform a more focused scientific investigation of this mysterious world. The spacecraft will enter Mercury orbit in March 2011 and carry out comprehensive measurements for one full Earth year.

All seven planets discovered in orbit around the red dwarf star TRAPPIST-1 could easily fit inside the orbit of Mercury, the innermost planet of our solar system. In fact, they would have room to spare. TRAPPIST-1 also is only a fraction of the size of our sun; it isn't much larger than Jupiter. So the TRAPPIST-1 system's proportions look more like Jupiter and its moons than those of our solar system. The seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all Earth-sized and terrestrial, according to research published in 2017 in the journal Nature. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21428
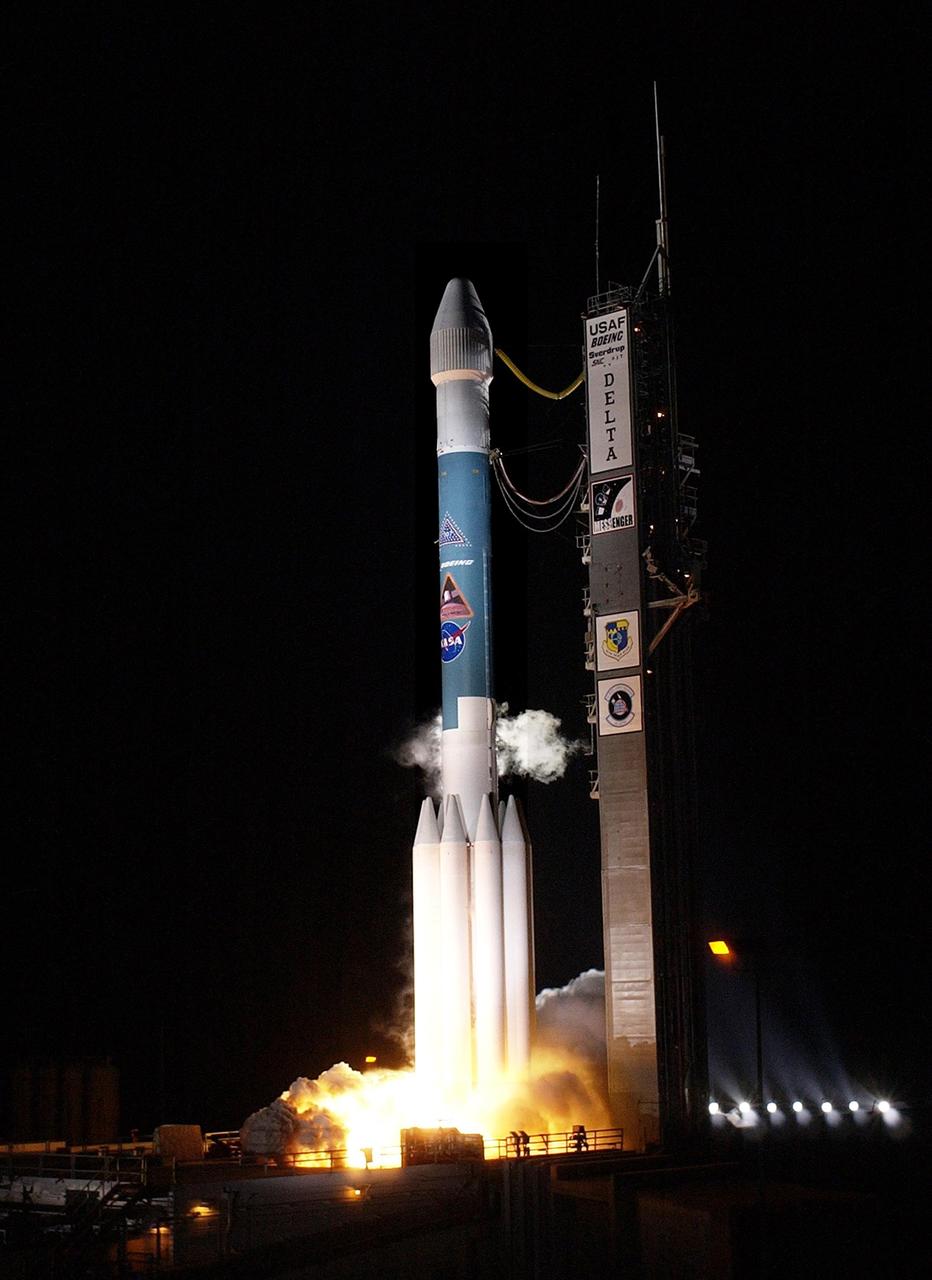

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The MESSENGER spacecraft atop a Boeing Delta II rocket lifts off on time at 2:15:56 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) is on a seven-year, 4.9-billion-mile journey to the planet Mercury. The spacecraft will fly by Earth, Venus and Mercury several times, as well as circling the sun 15 times, to burn off energy before making its final approach to the inner planet on March 18, 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The tip of the Boeing Delta II rocket with its MESSENGER spacecraft on top breaks through the billows of smoke below as it lifts off on time at 2:15:56 a.m. EDT from Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) is on a seven-year journey to the planet Mercury. The spacecraft will fly by Earth, Venus and Mercury several times to burn off energy before making its final approach to the inner planet on March 18, 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.
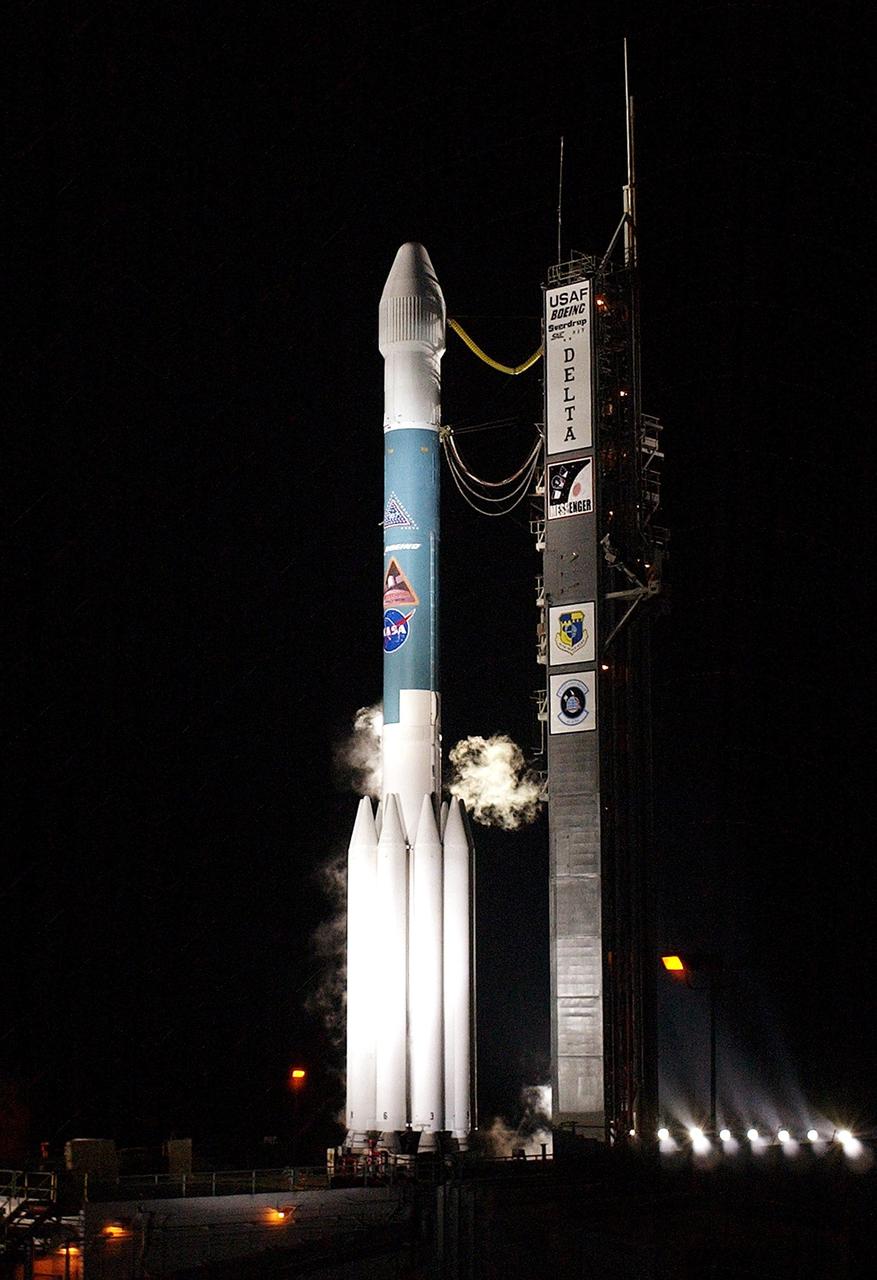

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Against the clear, black sky, spotlights flood the MESSENGER spacecraft aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket as it sits ready for liftoff, scheduled for 2:15:56 a.m. EDT, from Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) is on a seven-year journey to the planet Mercury. The spacecraft will fly by Earth, Venus and Mercury several times to burn off energy before making its final approach to the inner planet on March 18, 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.

This chart shows, on the top row, artist concepts of the seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 with their orbital periods, distances from their star, radii and masses as compared to those of Earth. On the bottom row, the same numbers are displayed for the bodies of our inner solar system: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The TRAPPIST-1 planets orbit their star extremely closely, with periods ranging from 1.5 to only about 20 days. This is much shorter than the period of Mercury, which orbits our sun in about 88 days. The artist concepts show what the TRAPPIST-1 planetary system may look like, based on available data about their diameters, masses and distances from the host star. The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. The seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all Earth-sized and terrestrial, according to research published in 2017 in the journal Nature. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21425
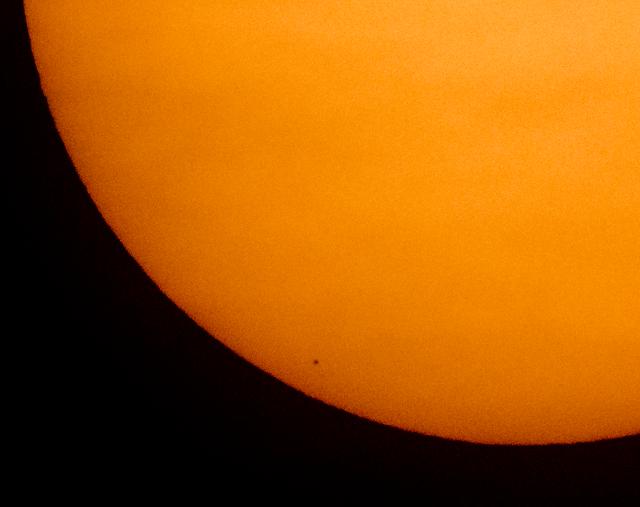

The planet Mercury is seen in silhouette, low center, as it transits across the face of the Sun Monday, Nov. 11, 2019, from Washington. Mercury’s last transit was in 2016. The next won’t happen again until 2032. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
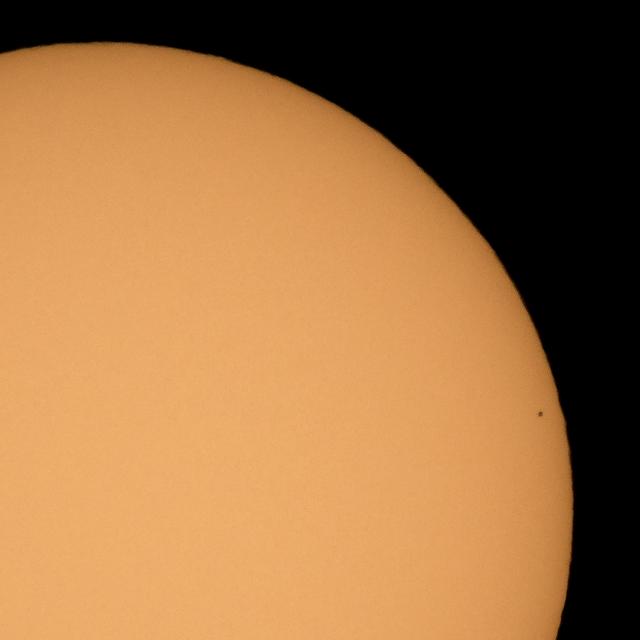

The planet Mercury is seen in silhouette as it nearly completes transiting across the face of the Sun, Monday, Nov. 11, 2019, in Arlington, Virginia. Mercury’s last transit was in 2016. the next won't happen again until 2032. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
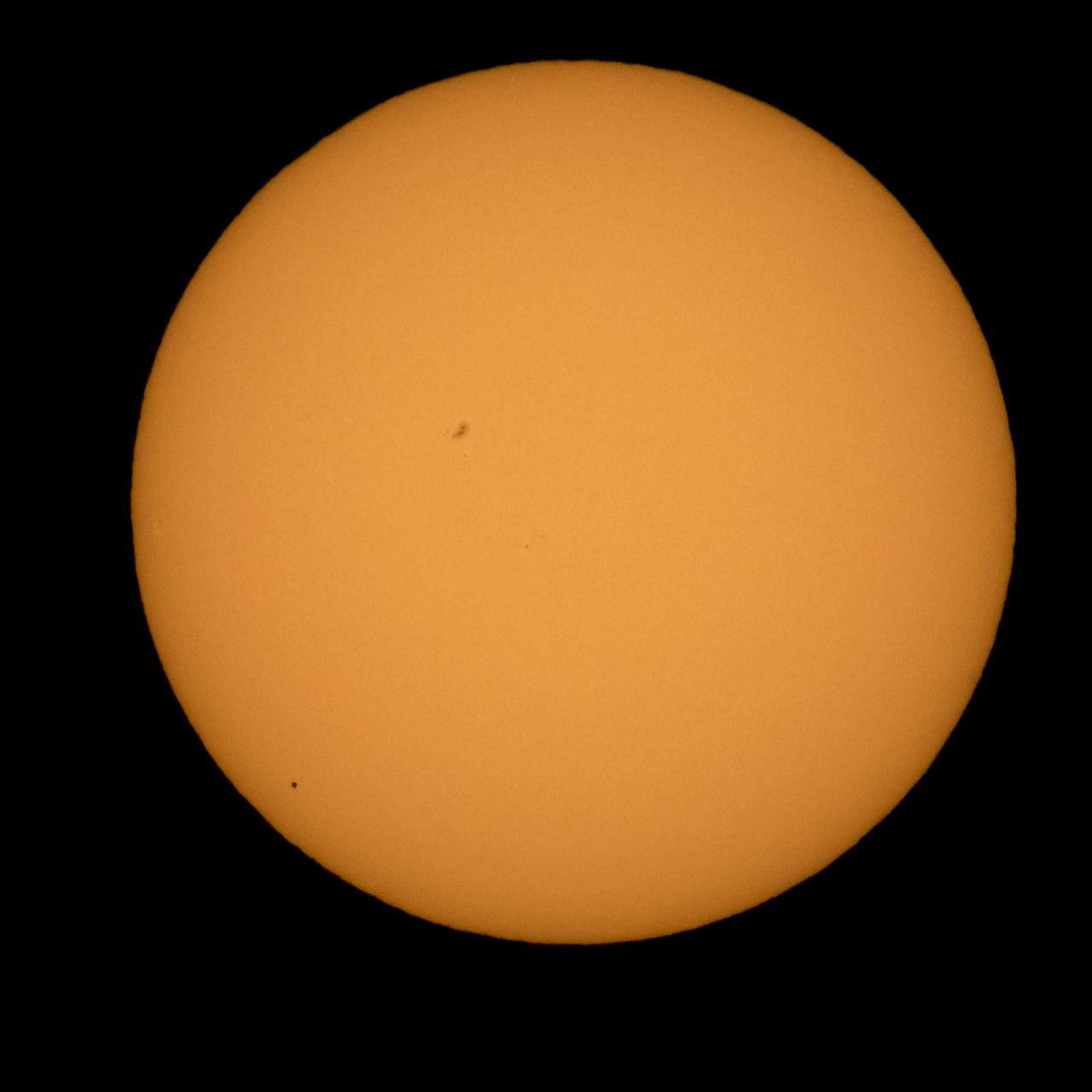

The planet Mercury is seen in silhouette, lower left, as it transits across the face of the sun Monday, May 9, 2016, as viewed from Boyertown, Pennsylvania. Mercury passes between Earth and the sun only about 13 times a century, with the previous transit taking place in 2006. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
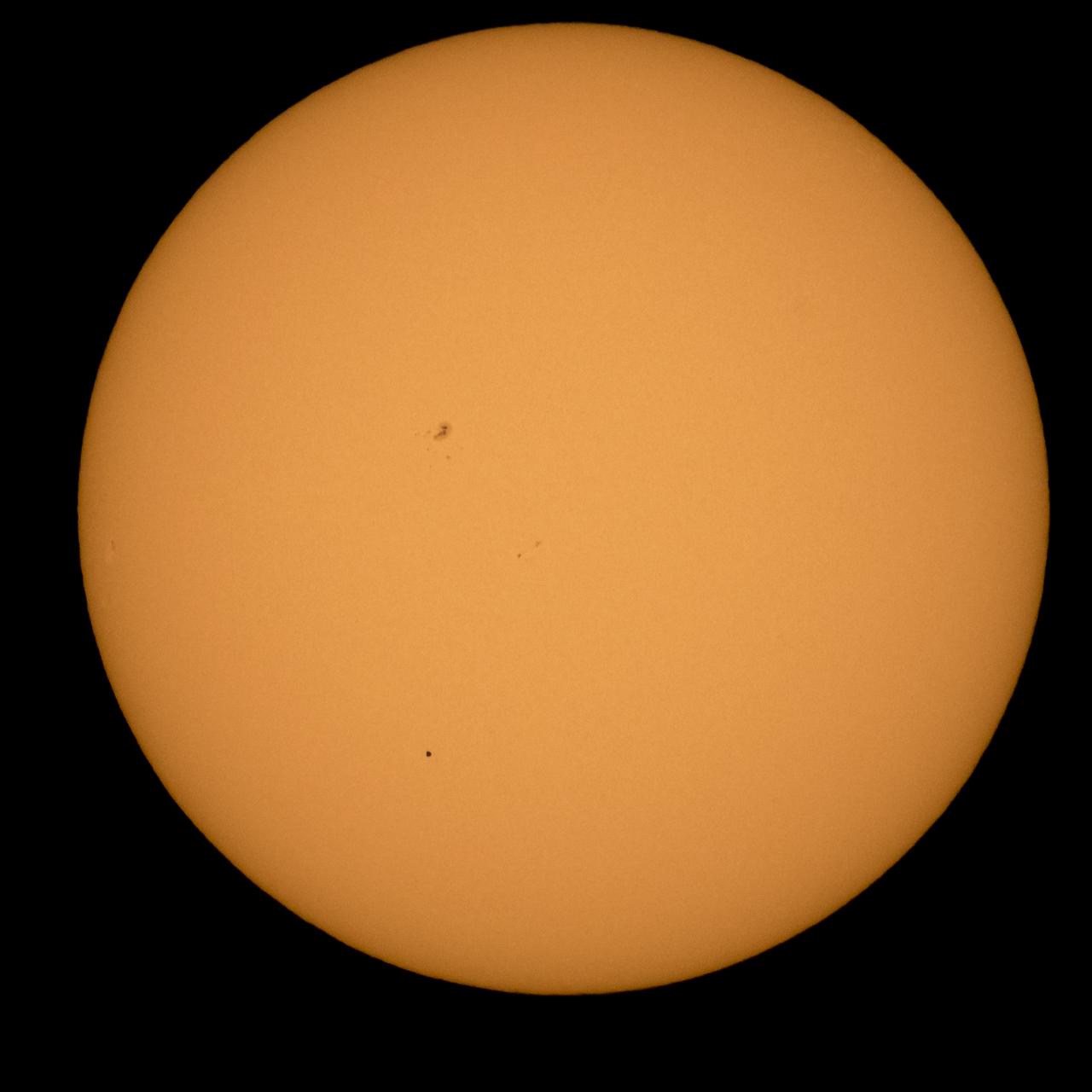

The planet Mercury is seen in silhouette, lower third of image, as it transits across the face of the sun Monday, May 9, 2016, as viewed from Boyertown, Pennsylvania. Mercury passes between Earth and the sun only about 13 times a century, with the previous transit taking place in 2006. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
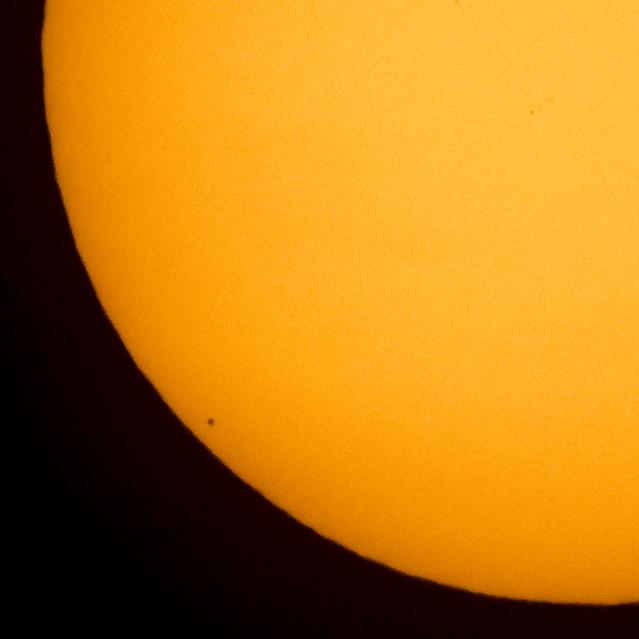

The planet Mercury is seen in silhouette, lower left of image, as it transits across the face of the sun, Monday, May 9, 2016, as viewed from Boyertown, Pennsylvania. Mercury passes between Earth and the sun only about 13 times a century, with the previous transit taking place in 2006. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
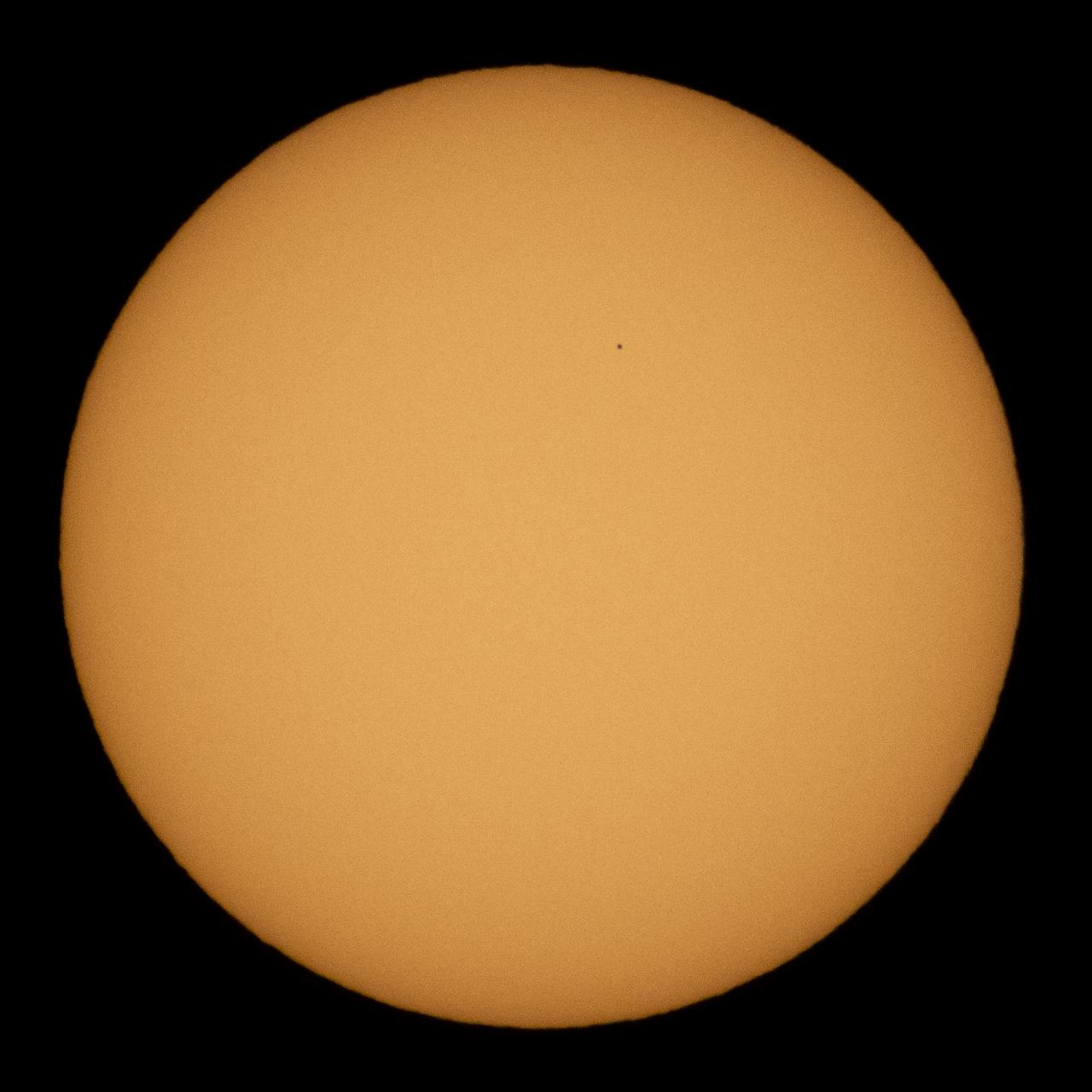

The planet Mercury is seen in silhouette as it transits across the face of the sun, Monday, Nov. 11, 2019 in Salt Lake City, Utah. Mercury’s last transit was in 2016. the next won't happen again until 2032. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
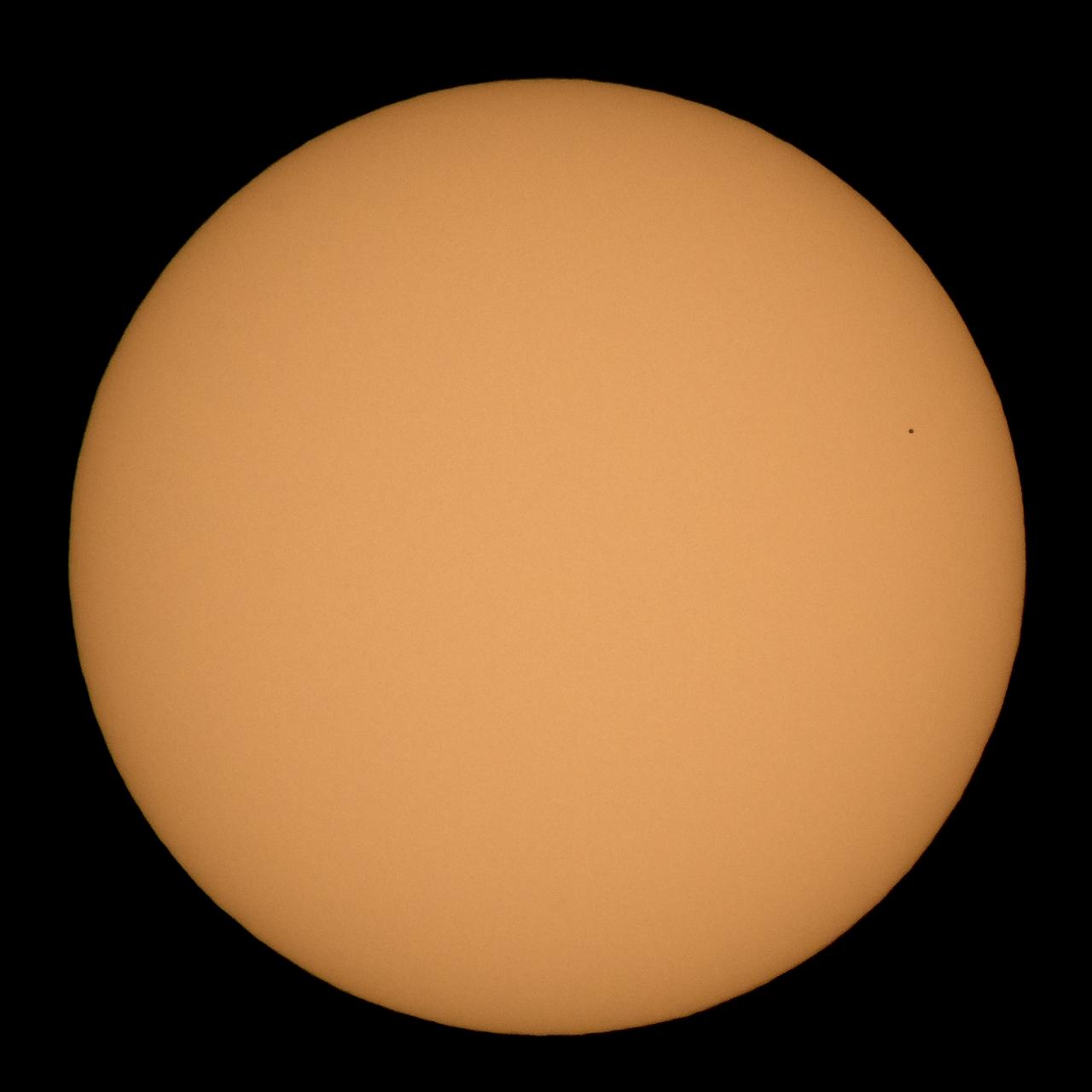

The planet Mercury is seen in silhouette as it nearly completes transiting across the face of the Sun, Monday, Nov. 11, 2019, in Arlington, Virginia. Mercury’s last transit was in 2016. the next won't happen again until 2032. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
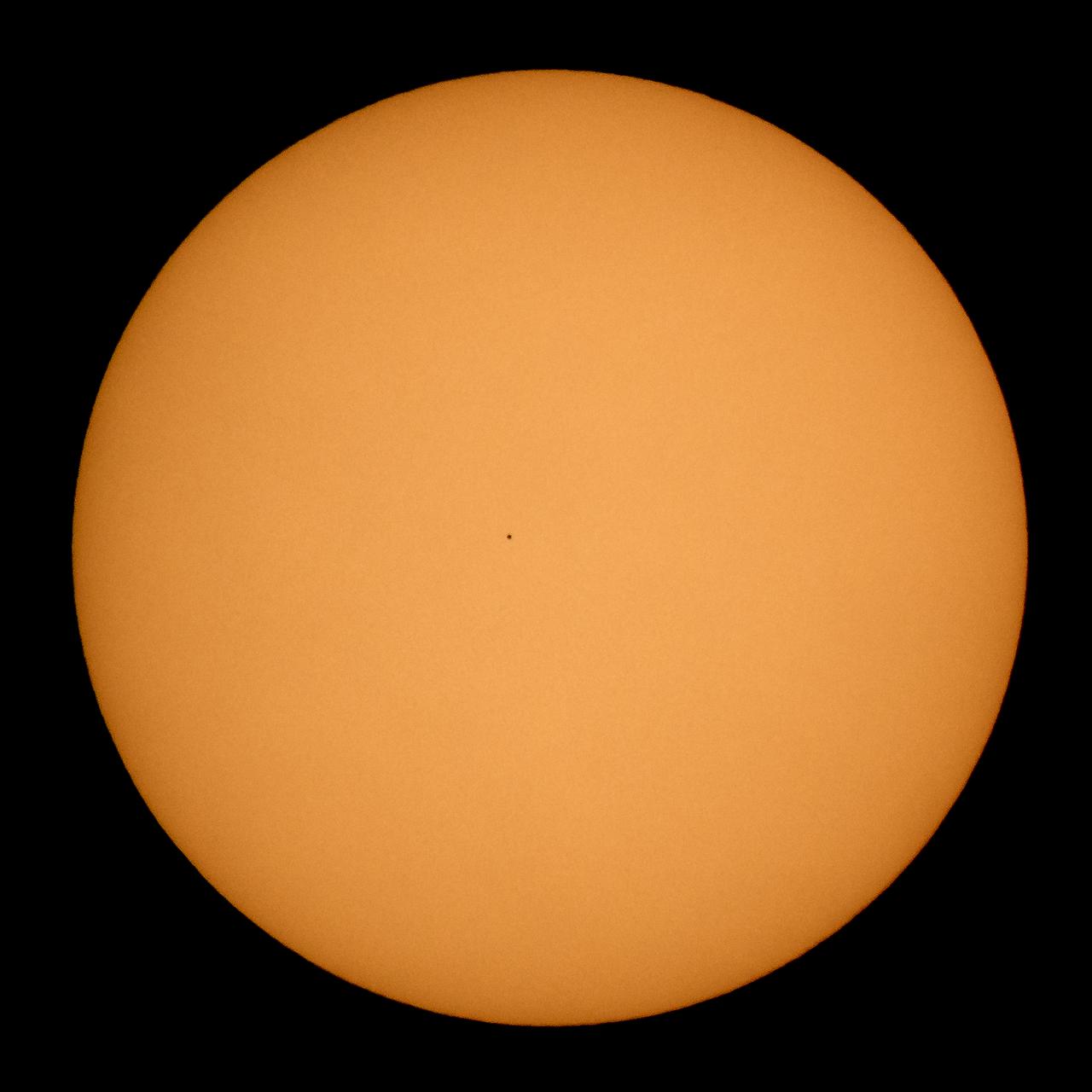

The planet Mercury is seen in silhouette, center, as it transits across the face of the Sun Monday, Nov. 11, 2019, from Washington. Mercury’s last transit was in 2016. The next won’t happen again until 2032. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
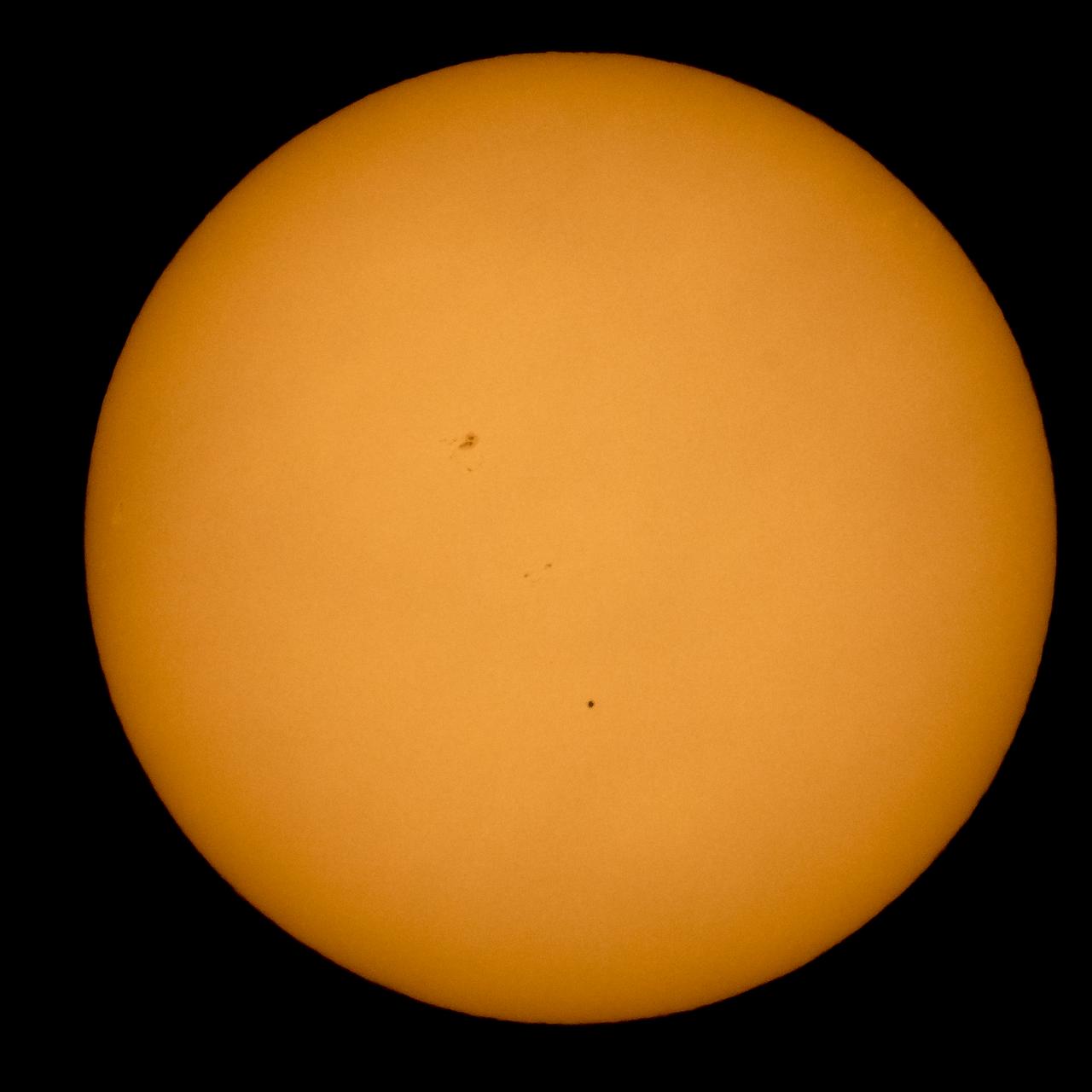

The planet Mercury is seen in silhouette, lower center of image, as it transits across the face of the sun, Monday, May 9, 2016, as viewed from Boyertown, Pennsylvania. Mercury passes between Earth and the sun only about 13 times a century, with the previous transit taking place in 2006. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
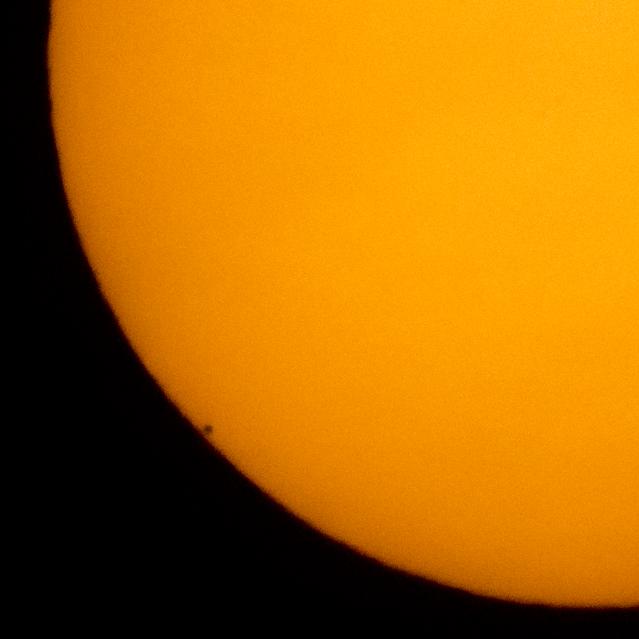

The planet Mercury is seen in silhouette, lower left of image, as it transits across the face of the sun, Monday, May 9, 2016, as viewed from Boyertown, Pennsylvania. Mercury passes between Earth and the sun only about 13 times a century, with the previous transit taking place in 2006. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
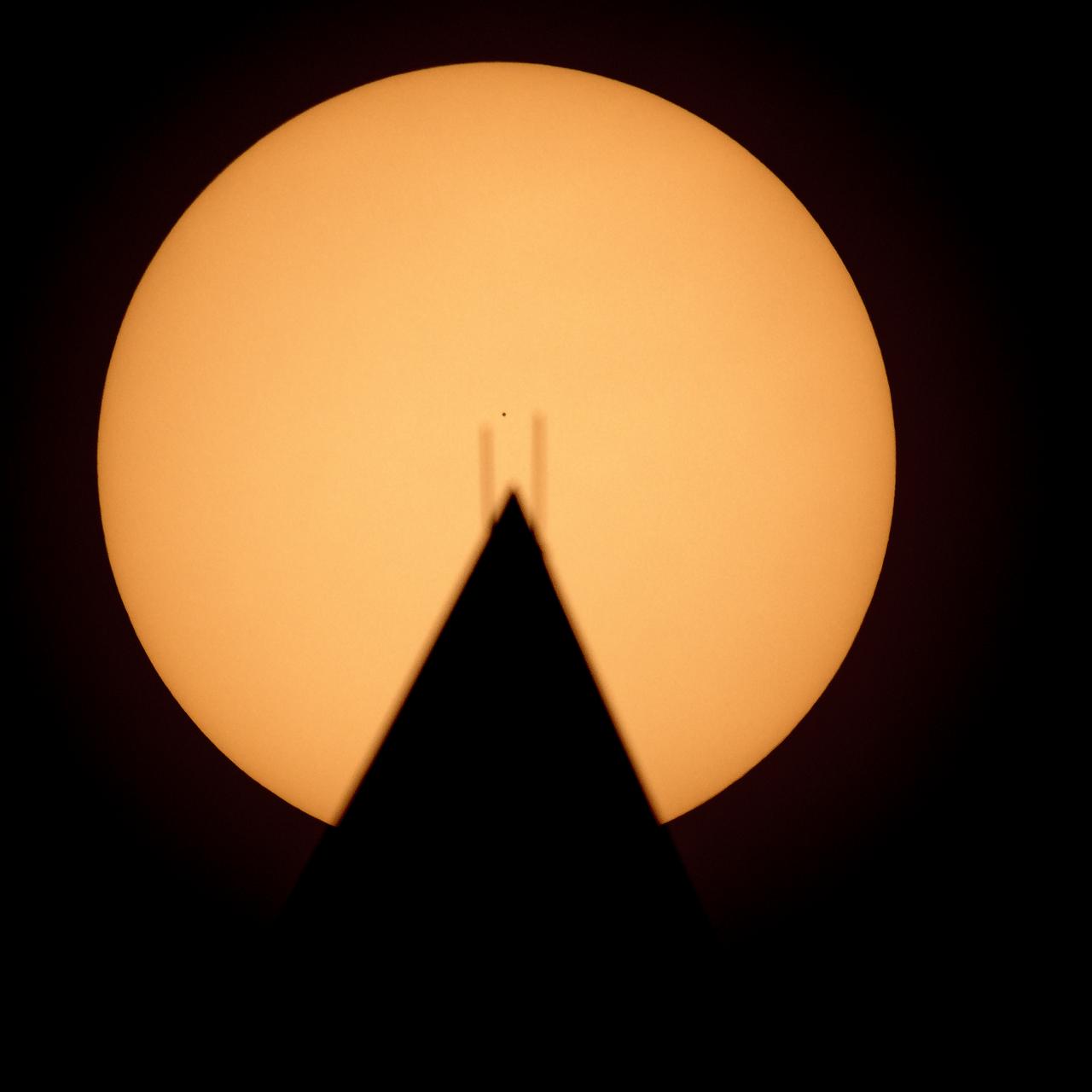

The planet Mercury is seen in silhouette, center, as it transits across the face of the Sun, behind the Washington Monument, Monday, Nov. 11, 2019, in Washington. Mercury’s last transit was in 2016. The next won’t happen again until 2032. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
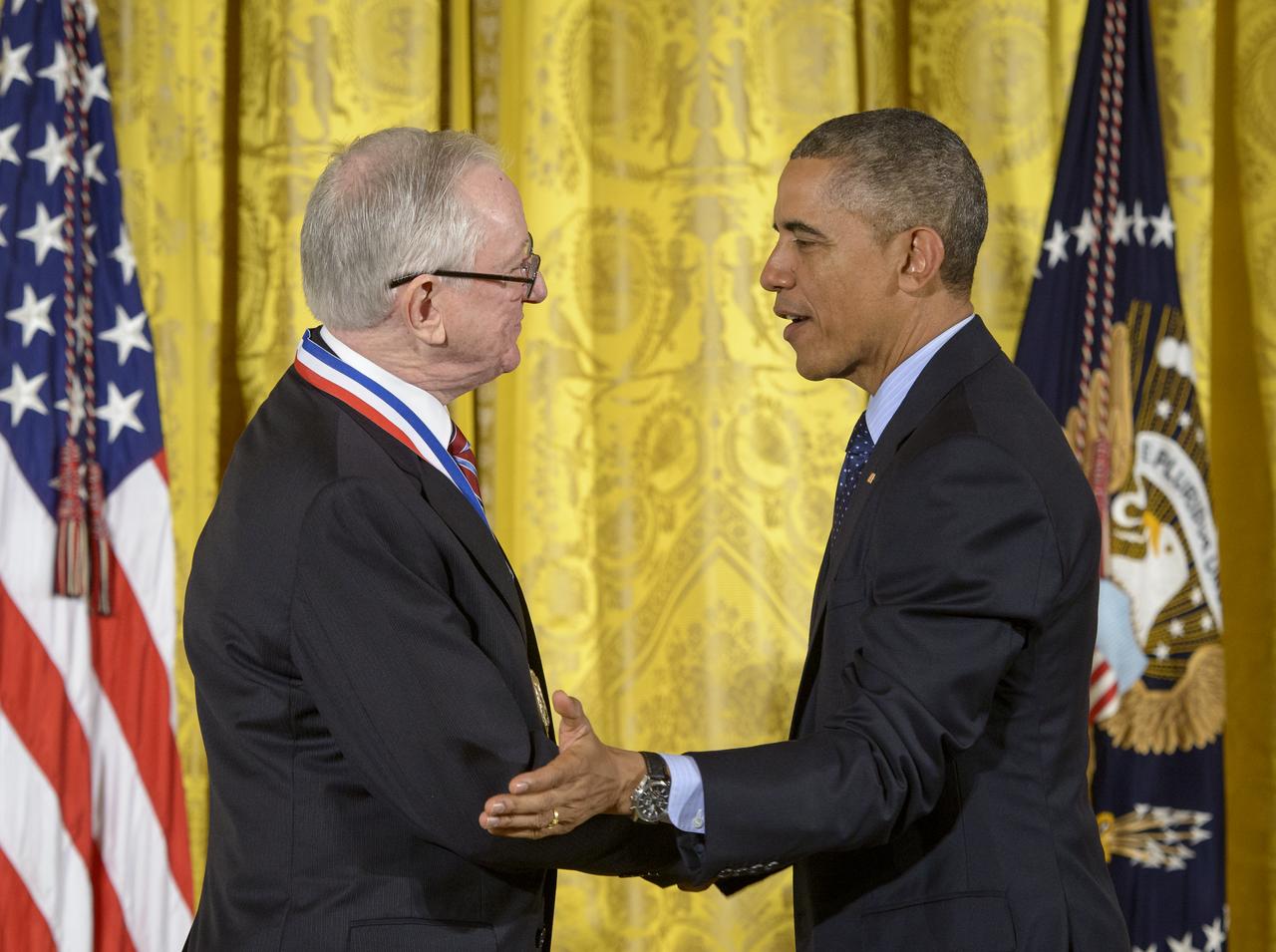

President Barack Obama congratulates MESSENGER Principal Investigator, director of Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Sean Solomon, after awarding him the National Medal of Science, the nation's top scientific honor,Thursday, Nov. 20, 2014 during a ceremony in the East Room of the White House in Washington. MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) is a NASA-sponsored scientific investigation of the planet Mercury and the first space mission designed to orbit the planet closest to the Sun. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Located in the crater Eminescu, this high-resolution image shows part of the mountainous peak ring, as well as an example of the extensive formation of hollows located within the crater. Hollows maintain an air of mystery in the realm of planetary science. Though the exact formation mechanism is unknown, most scientists agree sublimation of volatiles holds the answer. This image highlights the prevalence of these hollows on and around the peak ring, as well as captures the beauty of such enigmatic formations. This image was acquired as a high-resolution targeted observation. Targeted observations are images of a small area on Mercury's surface at resolutions much higher than the 200-meter/pixel morphology base map. It is not possible to cover all of Mercury's surface at this high resolution, but typically several areas of high scientific interest are imaged in this mode each week. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
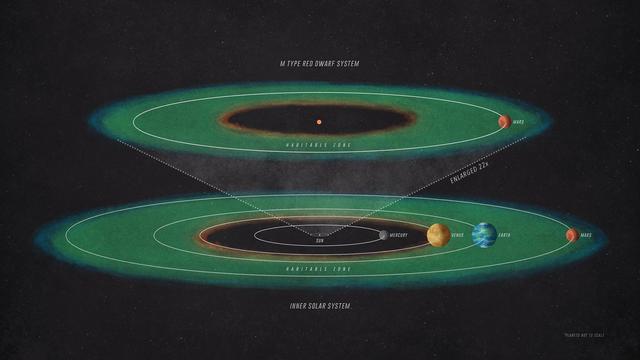
How habitable might an Exo-Mars be? It's a complex question but one that NASA's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) mission can help answer. To receive the same amount of starlight as Mars receives from our Sun, a planet orbiting an M-type red dwarf would have to be positioned much closer to its star than Mercury is to the Sun. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22075
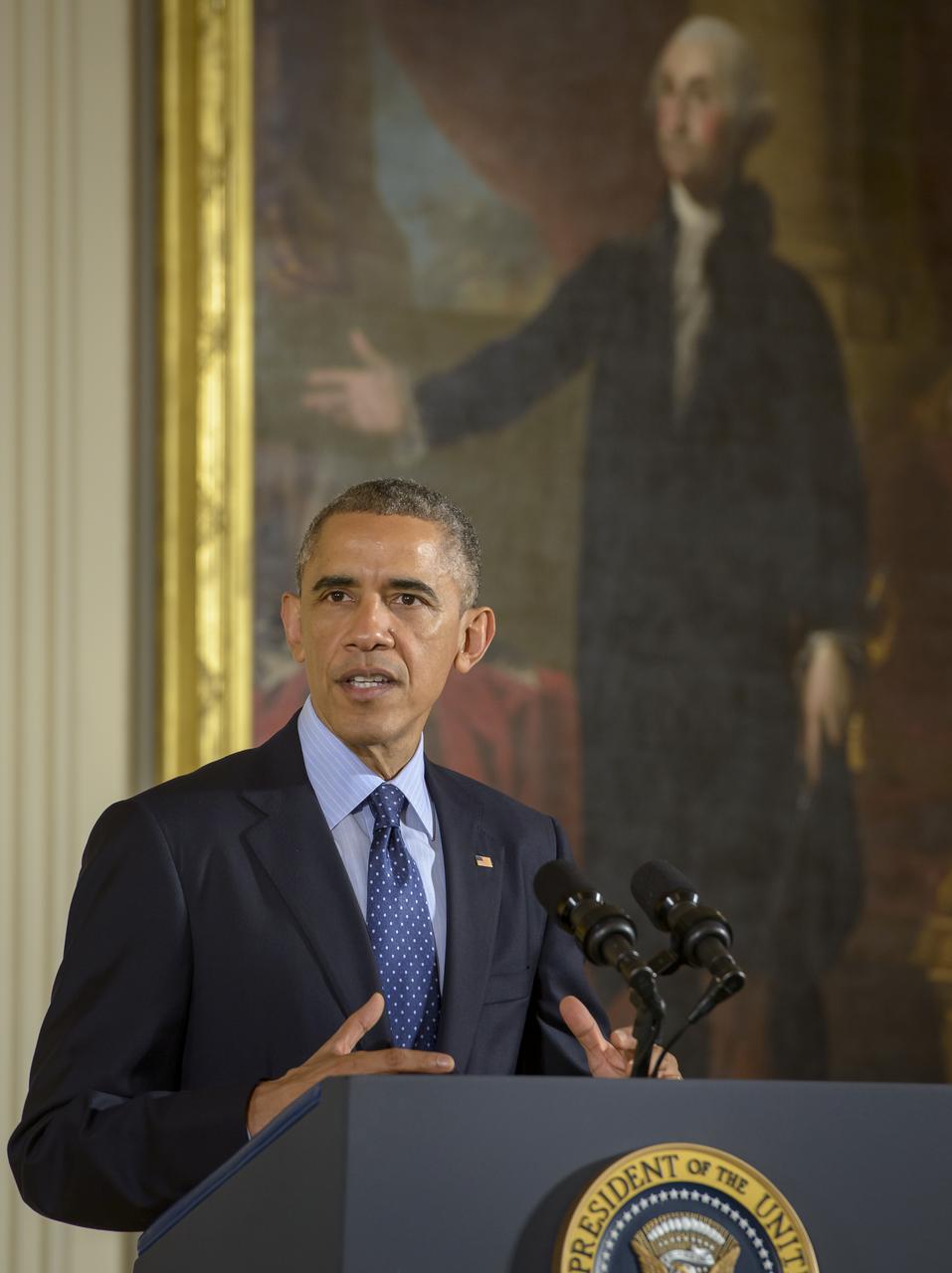

President Barack Obama delivers remarks at the National Medals of Science and National Medals of Technology and Innovation Awards Ceremony, Thursday, Nov. 20, 2014 in the East Room of the White House in Washington. MESSENGER Principal Investigator, director of Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Sean Solomon, was awarded the National Medal of Science, the nation's top scientific honor, at the ceremony. MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) is a NASA-sponsored scientific investigation of the planet Mercury and the first space mission designed to orbit the planet closest to the Sun. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
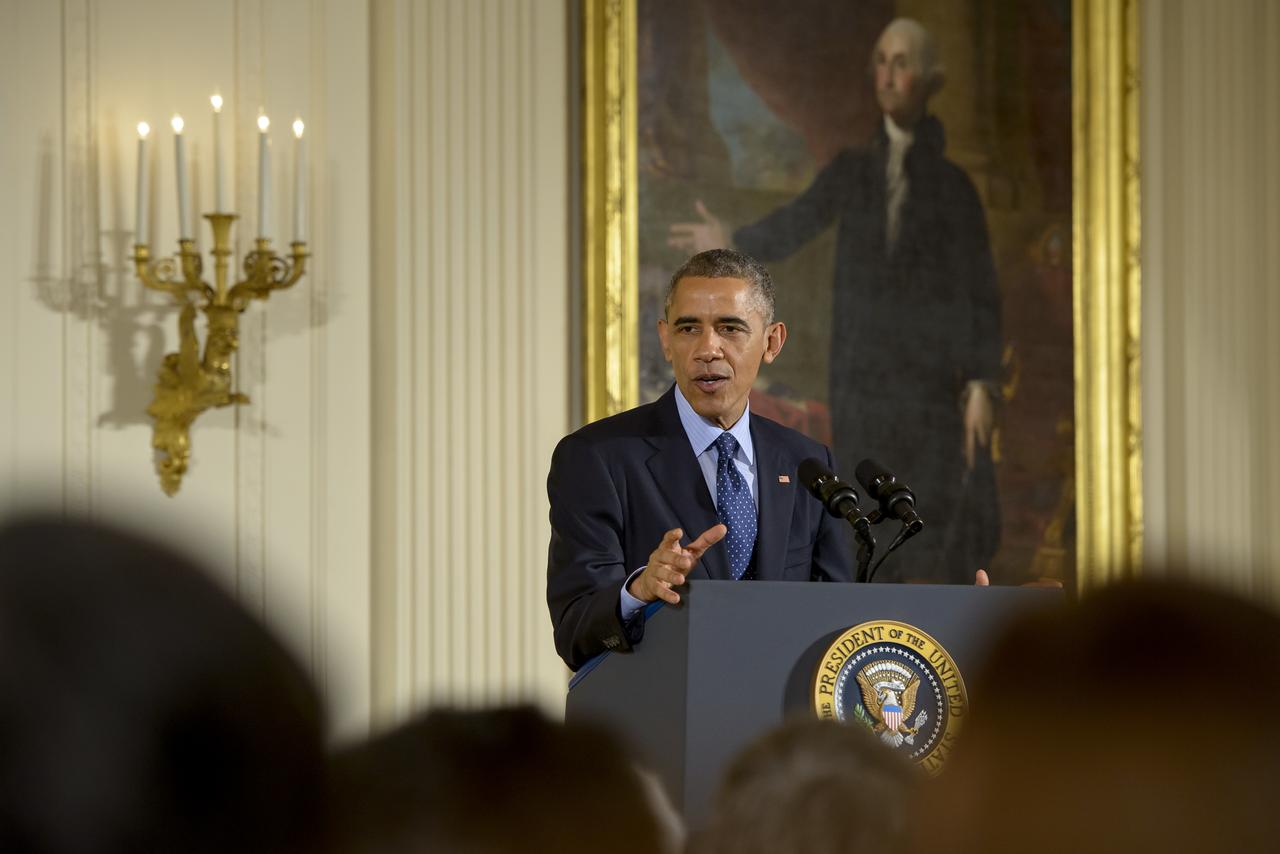

President Barack Obama delivers remarks at the National Medals of Science and National Medals of Technology and Innovation Awards Ceremony, Thursday, Nov. 20, 2014 in the East Room of the White House in Washington. MESSENGER Principal Investigator, director of Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Sean Solomon, was awarded the National Medal of Science, the nation's top scientific honor, at the ceremony. MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) is a NASA-sponsored scientific investigation of the planet Mercury and the first space mission designed to orbit the planet closest to the Sun. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
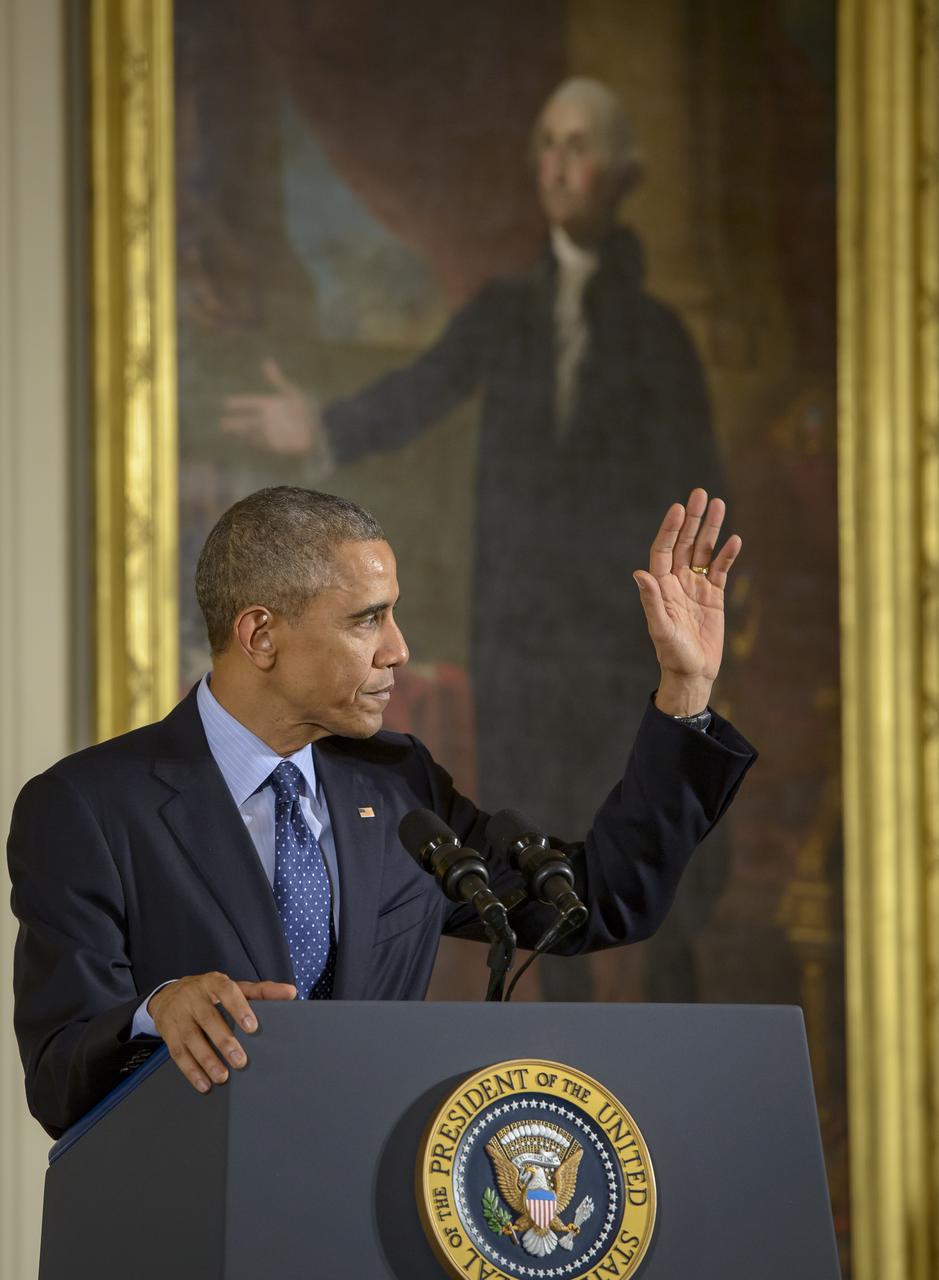

President Barack Obama delivers remarks at the National Medals of Science and National Medals of Technology and Innovation Awards Ceremony, Thursday, Nov. 20, 2014 in the East Room of the White House in Washington. MESSENGER Principal Investigator, director of Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Sean Solomon, was awarded the National Medal of Science, the nation's top scientific honor, at the ceremony. MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) is a NASA-sponsored scientific investigation of the planet Mercury and the first space mission designed to orbit the planet closest to the Sun. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

President Barack Obama, right, and MESSENGER Principal Investigator, director of Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Sean Solomon, listen as a citation is read prior to the President bestowing the National Medal of Science, the nation's top scientific honor to Solomon, Thursday, Nov. 20, 2014 during a ceremony in the East Room of the White House in Washington. MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) is a NASA-sponsored scientific investigation of the planet Mercury and the first space mission designed to orbit the planet closest to the Sun. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
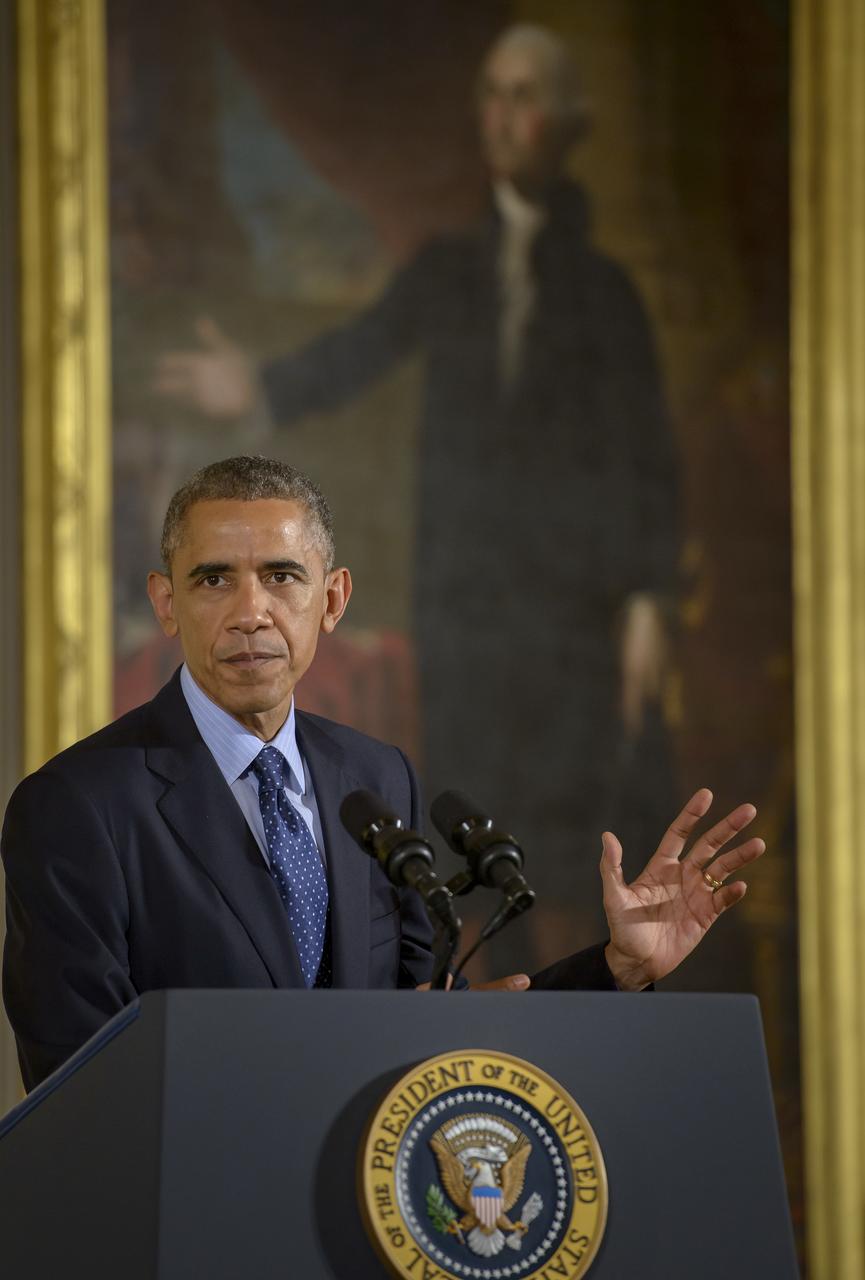

President Barack Obama delivers remarks at the National Medals of Science and National Medals of Technology and Innovation Awards Ceremony, Thursday, Nov. 20, 2014 in the East Room of the White House in Washington. MESSENGER Principal Investigator, director of Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Sean Solomon, was awarded the National Medal of Science, the nation's top scientific honor, at the ceremony. MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) is a NASA-sponsored scientific investigation of the planet Mercury and the first space mission designed to orbit the planet closest to the Sun. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
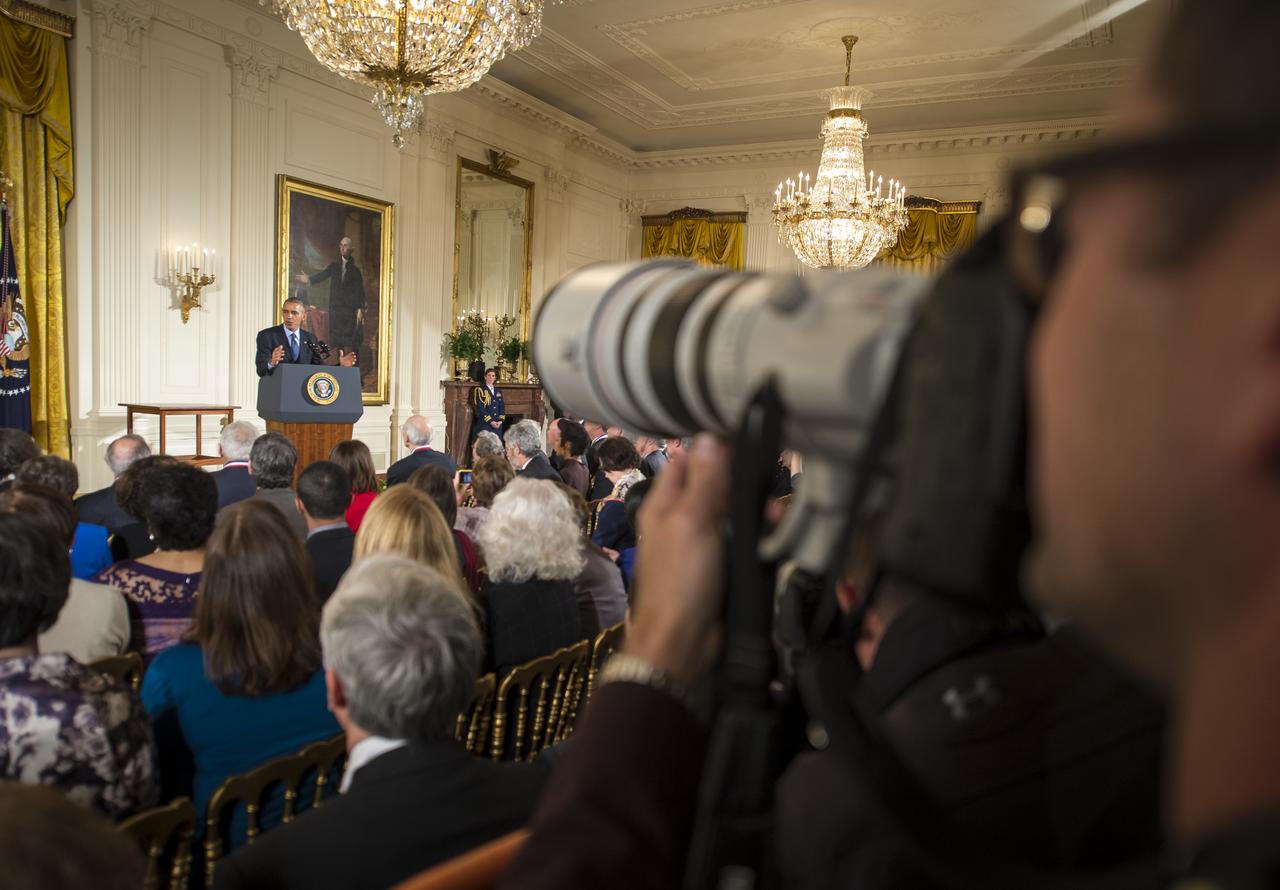
President Barack Obama delivers remarks at the National Medals of Science and National Medals of Technology and Innovation Awards Ceremony, Thursday, Nov. 20, 2014 in the East Room of the White House in Washington. MESSENGER Principal Investigator, director of Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Sean Solomon, was awarded the National Medal of Science, the nation's top scientific honor, at the ceremony. MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) is a NASA-sponsored scientific investigation of the planet Mercury and the first space mission designed to orbit the planet closest to the Sun. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Wrapped in clouds of smoke, the Boeing Delta II rocket with its MESSENGER spacecraft on top climbs free as it lifts off on time at 2:15:56 a.m. EDT from Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MESSENGER (Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry and Ranging) is on a seven-year, 4.9-billion-mile journey to the planet Mercury. The spacecraft will fly by Earth, Venus and Mercury several times, as well as circling the sun 15 times, to burn off energy before making its final approach to the inner planet on March 18, 2011. MESSENGER was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md.