
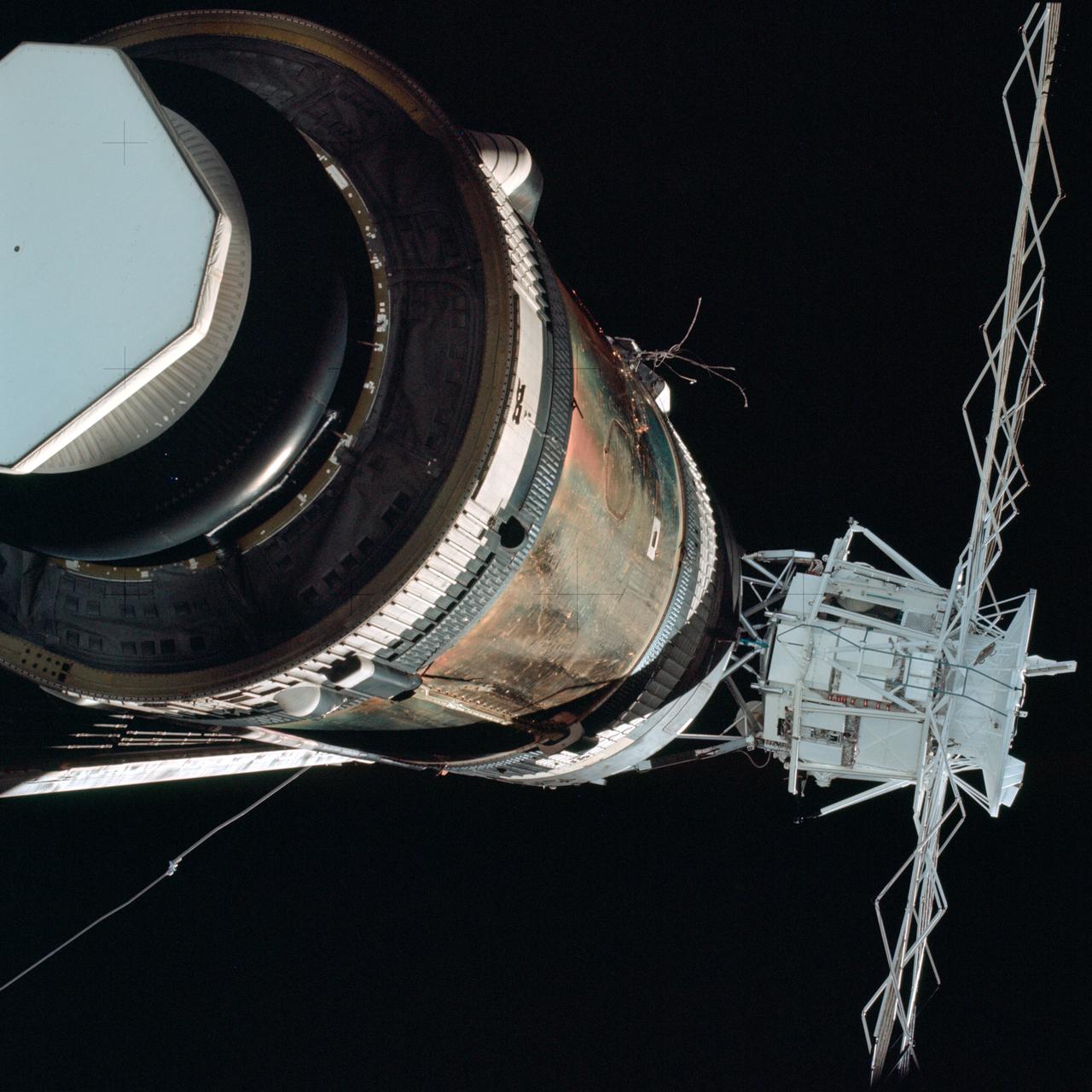
The Saturn V vehicle, carrying the unmarned orbital workshop for the Skylab-1 mission, lifted off successfully and all systems performed normally. Sixty-three seconds into flight, engineers in the operation support and control center saw an unexpected telemetry indication that signalled that damages occurred on one solar array and the micrometeoroid shield during the launch. The micrometeoroid shield, a thin protective cylinder surrounding the workshop protecting it from tiny space particles and the sun's scorching heat, ripped loose from its position around the workshop. This caused the loss of one solar wing and jammed the other. Still unoccupied, the Skylab was stricken with the loss of the heat shield and sunlight beat mercilessly on the lab's sensitive skin. Internal temperatures soared, rendering the station uninhabitable, threatening foods, medicines, films, and experiments. This image, taken during a fly-around inspection by the Skylab-2 crew, shows the damaged meteoroid shield being held by a thin aluminum strap entangled with green-hued remnants of the lost heat shield. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed, tested, rehearsed, and approved three repair options. These options included a parasol sunshade and a twin-pole sunshade to restore the temperature inside the workshop, and a set of metal cutting tools to free the jammed solar panel.
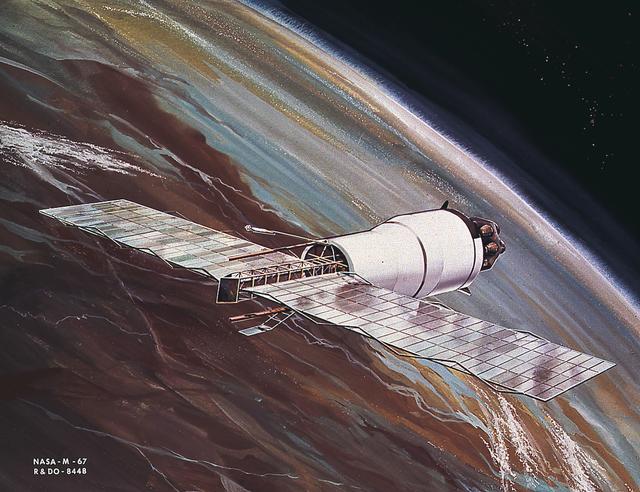

This image is an artist's conception of the Pegasus, meteoroid detection satellite, in orbit with meteoroid detector extended. The satellite, a payload for Saturn I SA-8, SA-9, and SA-10 missions, was used to obtain data on frequency and penetration of the potentially hazardous micrometeoroids in low Earth orbits and to relay the information back to Earth.
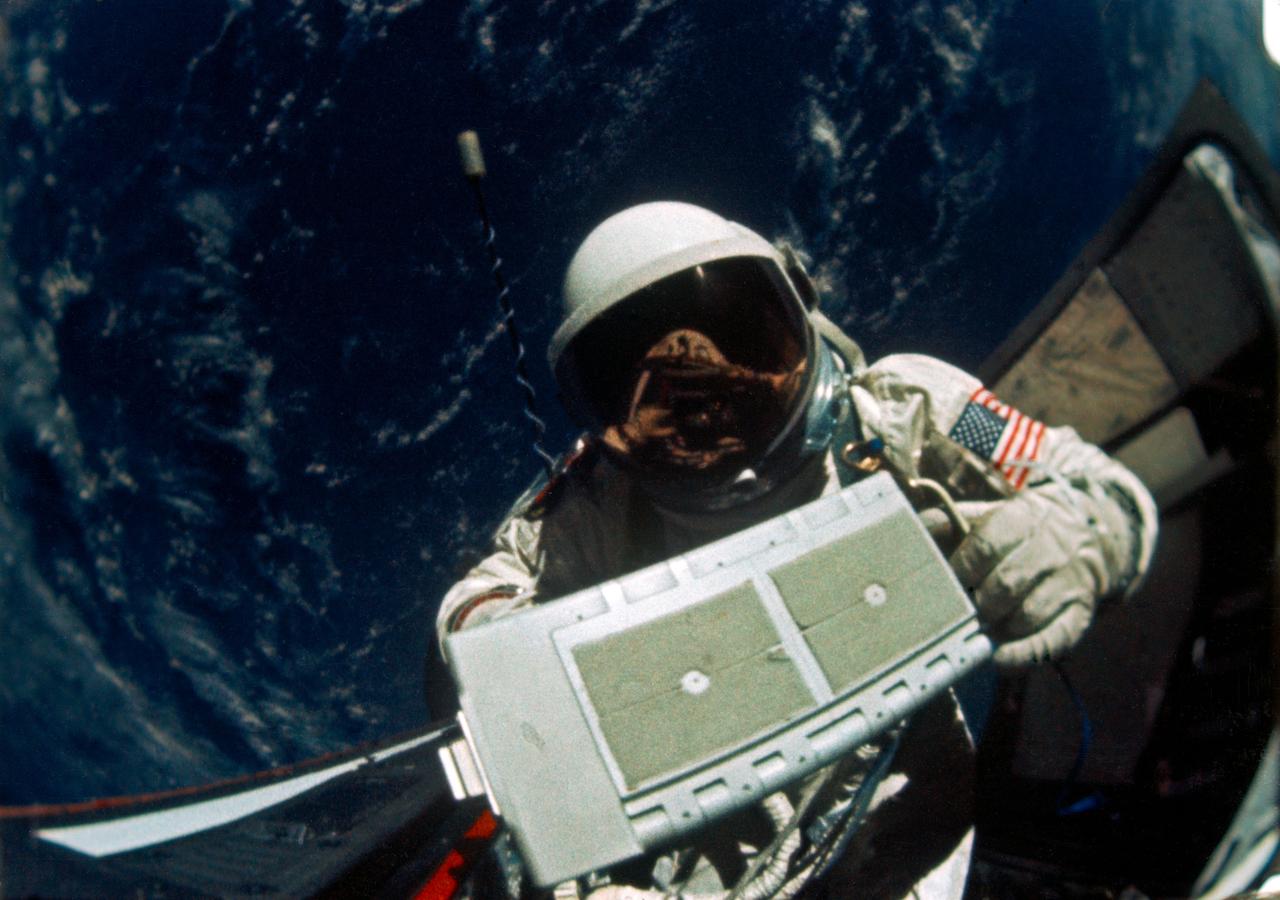

S66-63538 (11 Nov. 1966) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., pilot for the Gemini-12 spaceflight, removes micrometeoroid package for return to the spacecraft during extravehicular activity (EVA) on the first day of the four-day mission. Command pilot for the Gemini-12 mission, the last in the Gemini series, was astronaut James A. Lovell Jr. Photo credit: NASA

S73-26738 (25 May 1973) --- A close-up view of the Skylab 1 space station cluster can be seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the Skylab 2 Command Module during its ?fly-around? inspection of the cluster. The numbers across the top of the picture indicate the Skylab 1 ground lapse time. Note the missing portion of the micrometeoroid shield on the Orbital Workshop. The shield area was reported to be solid gold by the Skylab 2 crewmen. A cable appears to be wrapped around the damaged OWS solar array system wing. The crewmen reported that the other OWS solar panel was completely gone, with only tubes and wiring sticking out. One of the discone antennas extends out form the Airlock Module. The Multiple Docking Adapter is in the lower left corner of the picture. A portion of a solar panel on the Apollo Telescope Mount is visible at the bottom and at the left edge. In their ?fly around? inspection the crewmen noted that portions of the micrometeoroid shield had slid back underneath the OWS solar wing. Photo credit: NASA
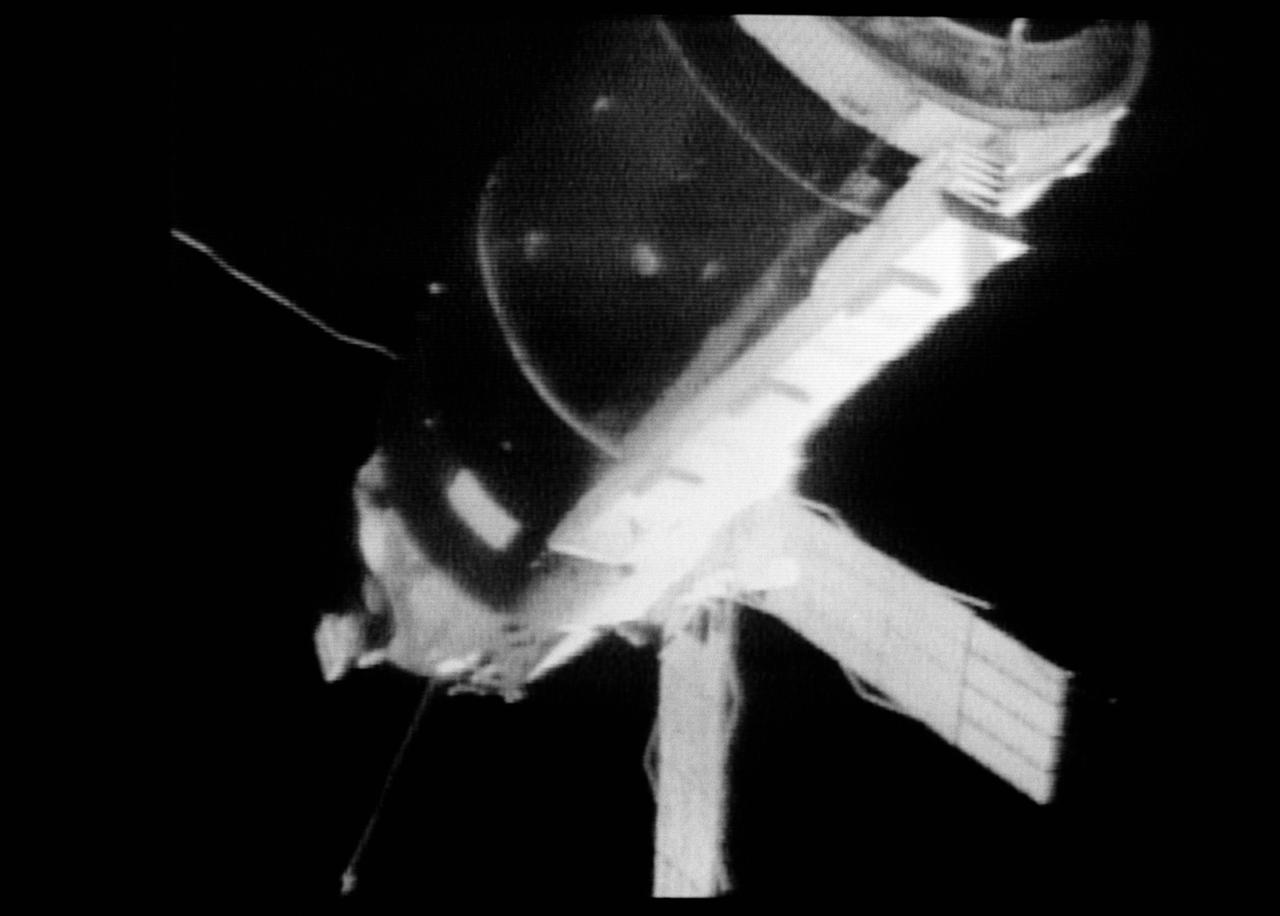
S73-27182 (25 May 1973) --- A close-up view of the Skylab 1 space station cluster can be seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the Skylab 2 Command Module during its "fly around" inspection of the cluster. This view has been enhanced. At left center the damaged solar array system wing on the Orbital Workshop (OWS) appears to be partly folded. In their preliminary inspection the crewmen noted that portions of the micrometeoroid shield had slid back underneath the OWS solar wing. Solar panels on the Apollo Telescope Mount extend out at the top center. Photo credit: NASA
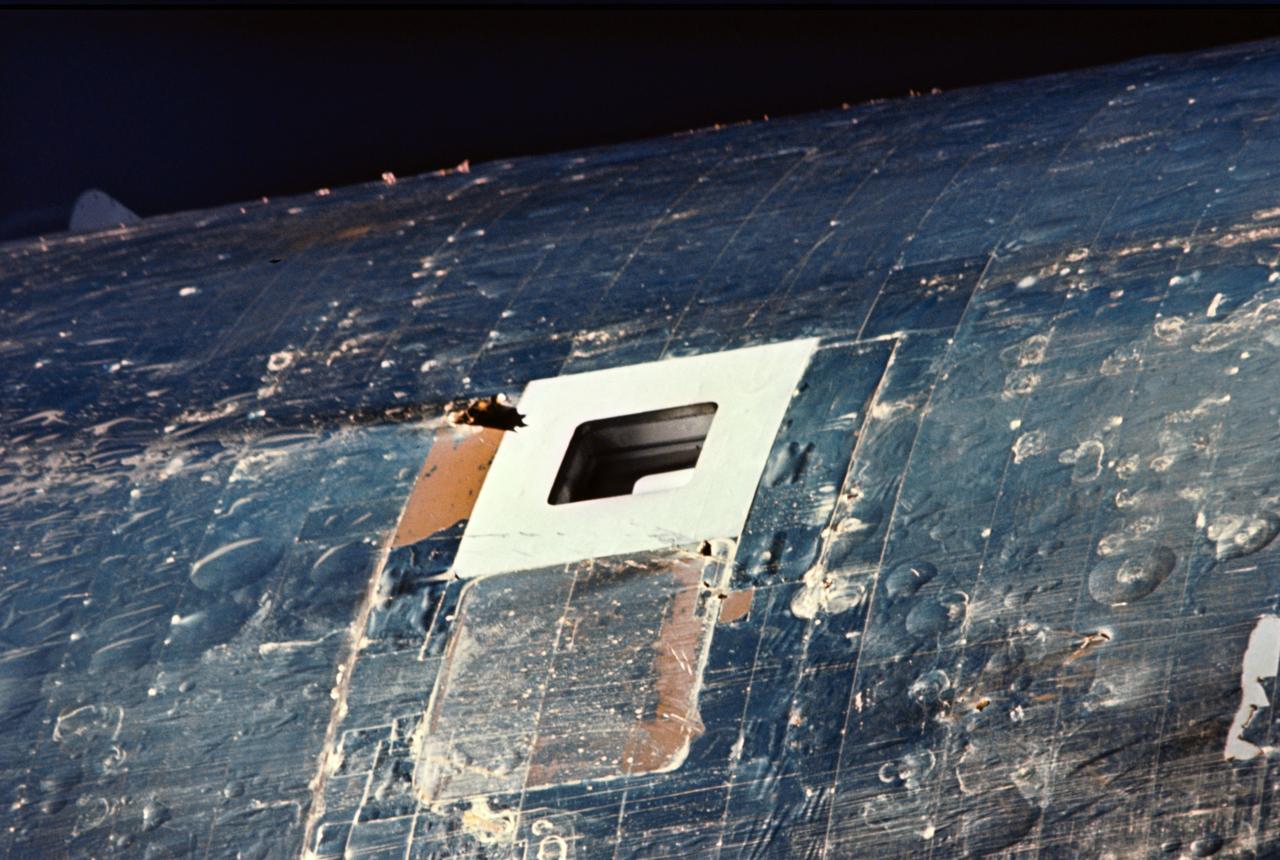

This close up view of one of the two scientific airlocks on the Skylab Orbital Workshop Section was taken from the Skylab 2 Command/Service Module during its initial fly around inspection. The micrometeoroid shield can be seen to be missing from this section of the orbital workshop. A parasol solar shield was later devised and put in place over this damaged area through this very same airlock opening.

SL2-07-667 (22 June 1973) --- This overhead view of the Skylab Space Station was taken from the Departing Skylab Command/Service Module during the Skylab 2's final fly-around inspection. The single solar panel is quite evident as well as the parasol solar shield, rigged to replace the missing micrometeoroid shield. Both the second solar panel and the micrometeoroid shield were torn away during a mishap in the original Skylab 1 liftoff and orbital insertion. Photo credit: NASA

SL2-07-651 (22 June 1973) --- This overhead view of the Skylab Space Station was taken from the Departing Skylab Command/Service Module during the Skylab 2's final fly-around inspection. The single solar panel is quite evident as well as the parasol solar shield, rigged to replace the missing micrometeoroid shield. Both the second solar panel and the micrometeoroid shield were torn away during a mishap in the original Skylab 1 liftoff and orbital insertion. Photo credit: NASA

Labeled cutaway line drawing of the Shuttle extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) identifies its various components and equipment. The portable life support system (PLSS) and protective layers of fabric (thermal micrometeoroid garment (TMG)) incorporated in this extravehicular activity (EVA) space suit are shown.
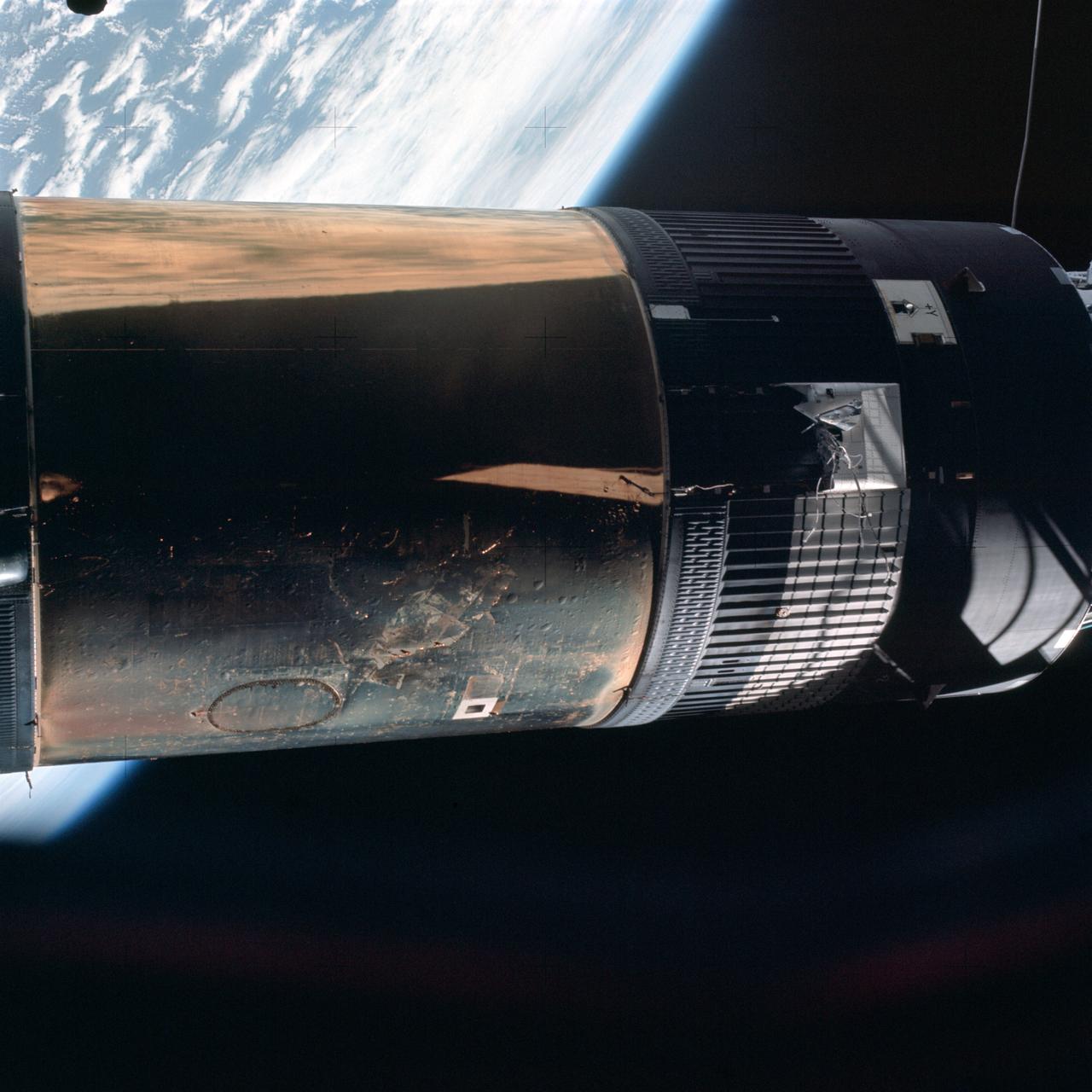
SL2-X4-256 (25 May 1973) --- This photo, made at long range from the command module during Skylab 2's approach to the Skylab complex during fly-around inspection, features the orbital workshop with the area of the missing micrometeoroid shield visible. Photo credit: NASA

SL2-4-265 (25 May 1973) --- Skylab 2, approach to Skylab at long range, fly-around inspection. Orbital Workshop with area of missing micrometeoroid shield visible and partially deployed solar array visible. Photo credit: NASA

jsc2024e065169 (5/29/2024) --- Outside view of the Nanolab Astrobeat module. This investigation tests cold welding in a space environment. Cold welding is a method in which metallic materials fuse or weld at ambient temperature provided that there is sufficient high contact force. This technology has applications for repairing spacecraft hulls that may be perforated as a result of micrometeoroids. Image courtesy of Dr. Leonardo Barilaro, The Malta College of Arts, Science & Technology..
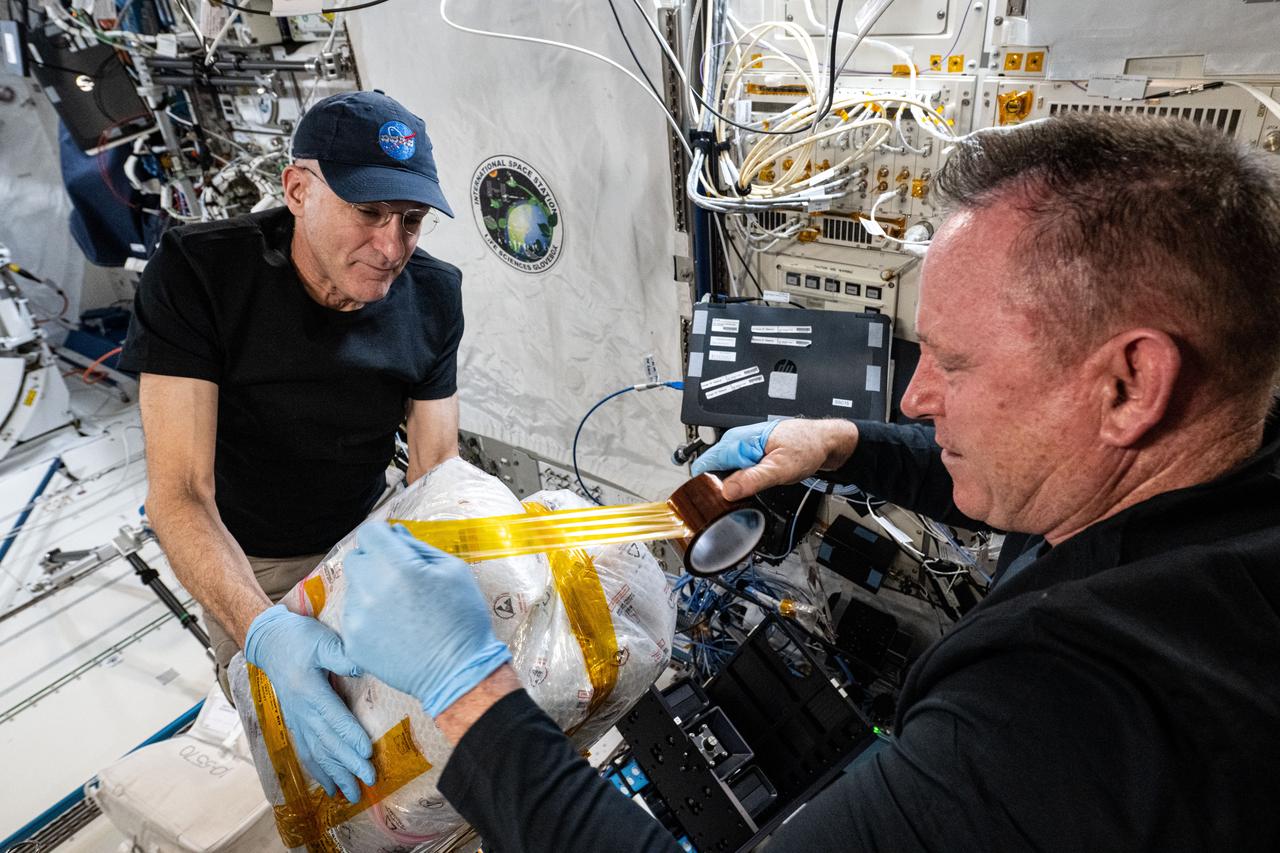

iss072e280736 (Nov. 26, 2024) --- NASA astronauts (from left) Don Pettit and Butch Wilmore, both Expedition 72 flight engineers, pack external research hardware removed from the Kibo laboratory module's airlock. The hardware housed a variety of samples exposed to the vacuum of space such as polymers, photovoltaic devices, and more. The samples will be returned to Earth and examined to understand how space radiation, the extreme thermal environment, micrometeoroids, and more affect materials possibly benefitting the space industry.

JSC2006-E-43515 (October 2006) --- Computer-generated artist's rendering of the International Space Station after flight ULF4. U.S. Orbiter delivers EXPRESS Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) and EXPRESS Logistics Carrier-4 (ELC-4). Micrometeoroid Debris panels are installed on Zvezda Service Module and the Zvezda solar arrays are feathered.
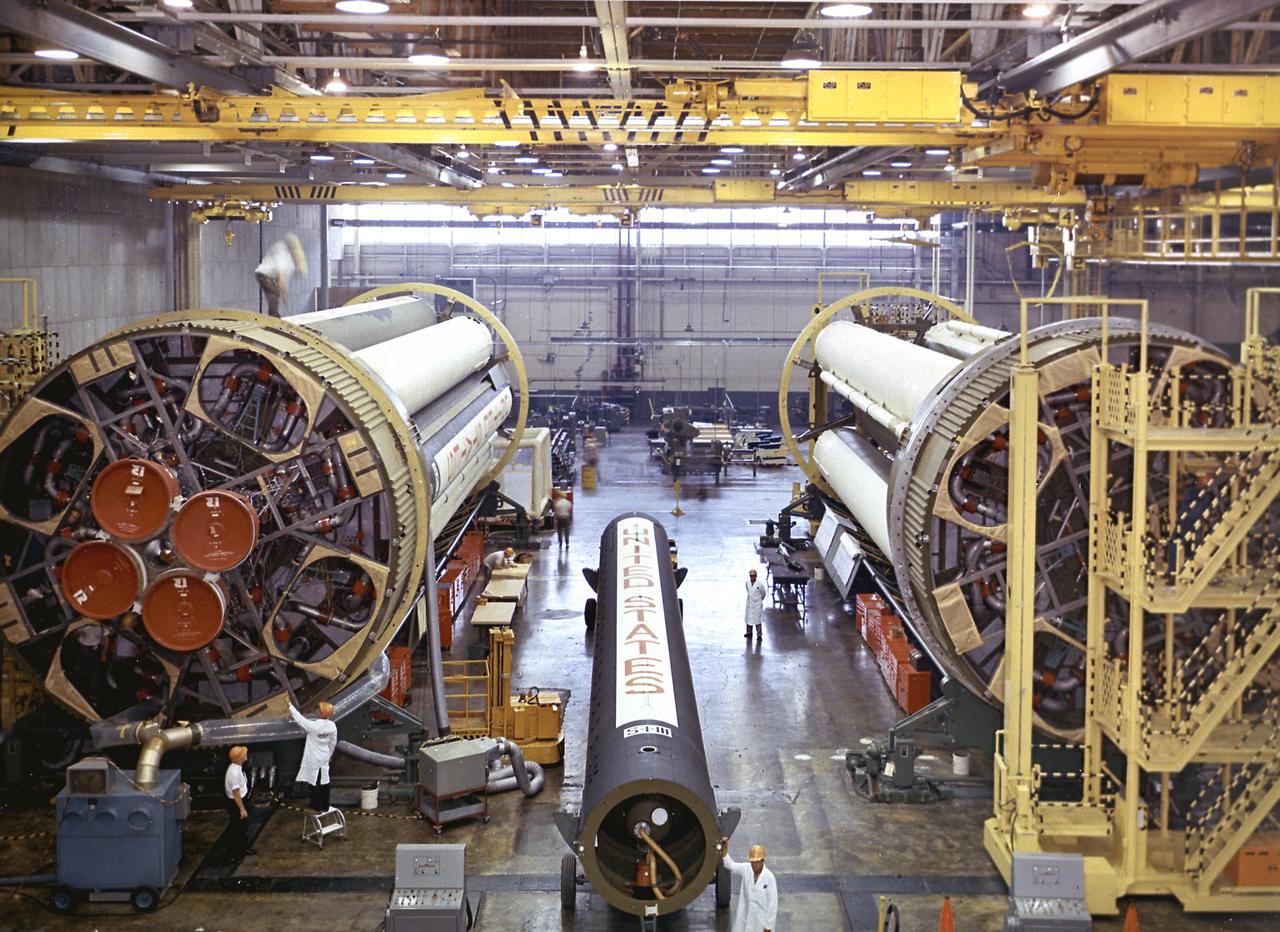

The Saturn I S-I stages for the SA-8 and SA-10 mission in final assembly phase in a manufacturing building at the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana. The SA-8 mission was launched on May 25, 1965 with the first industry-built booster, and deployed the Pegasus II Micrometeoroid Detection satellite. The SA-10 mission was the last Saturn I mission, launched on July 30, 1965, and carried the Pegasus III Meteoroid Detection satellite.
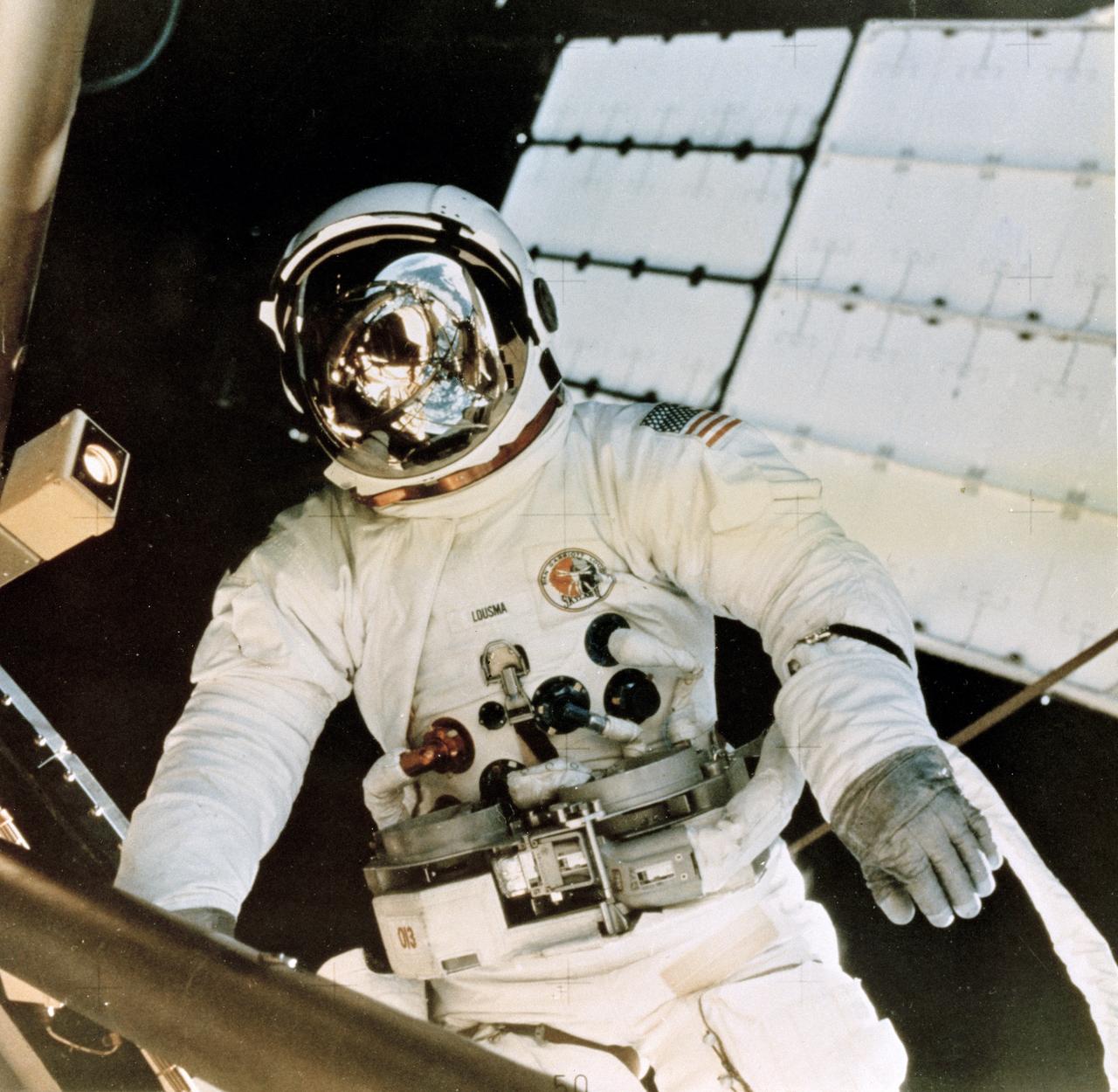

Skylab-3 was the second marned mission in the skylab project. The crew spent 59 days in orbit. In this photo, Astronaut Jack Lousma deploys the Twin Pole Sun Shield created by Marshall Space Flight Center team members to replace the micrometeoroid shield, a thin protective cylinder surrounding the workshop protecting it from tiny space particles and the sun's scorching heat. The shield was damaged during the Skylab-2 mission.
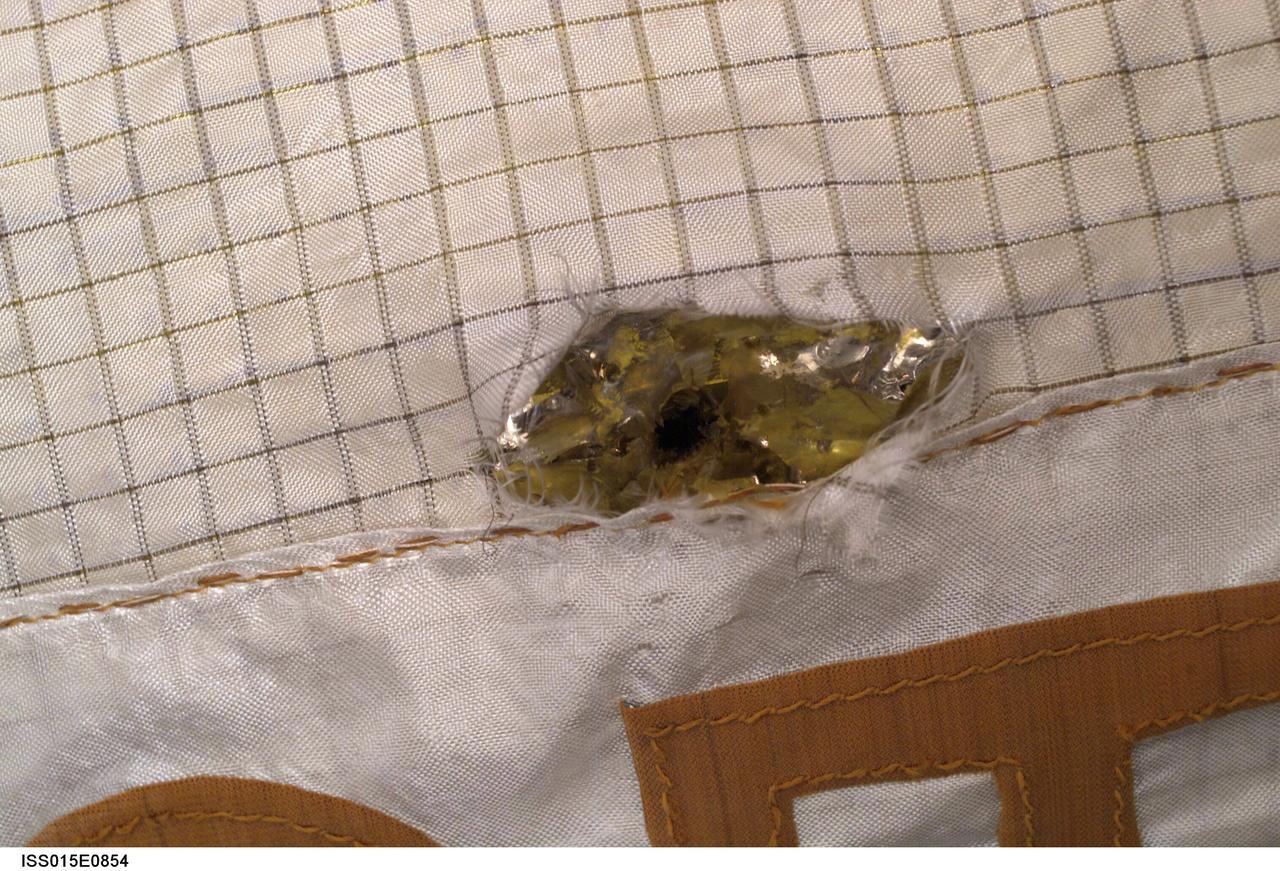
ISS015-E-10854 (6 June 2007) --- During the Russian spacewalk conducted by cosmonauts Fyodor Yurchikhin, Expedition 15 commander, and Oleg Kotov, flight engineer, on June 6, 2007, Yurchikhin commented on damage to a multi-layer insulation (MLI) protective blanket on the Zarya module. The damage, he noted, was apparently from a micrometeoroid impact. The date the damage occurred is unknown but has had no impact to vehicle operations.
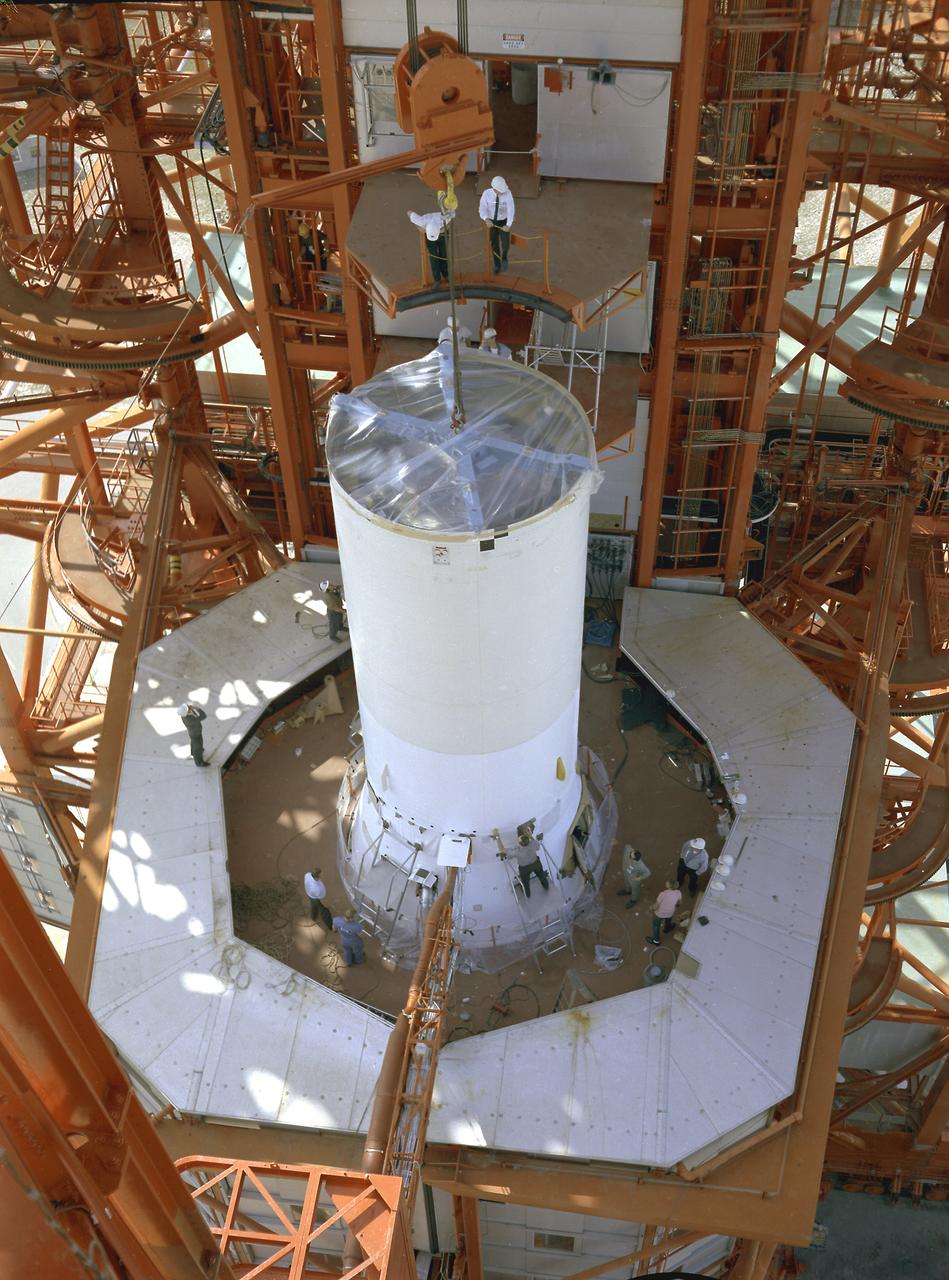

Pegasus-1, meteoroid detection satellite, installed on Saturn I (SA-9 mission) S-IV stage, January 13, 1965. The satellite was used to obtain data on frequency and penetration of the potentially hazardous micrometeoroids in low Earth orbits and to relay the information back to Earth. SA-9 was launched on February 16, 1965 and the Pegasus-1 satellite was the first operational payload for Saturn I.
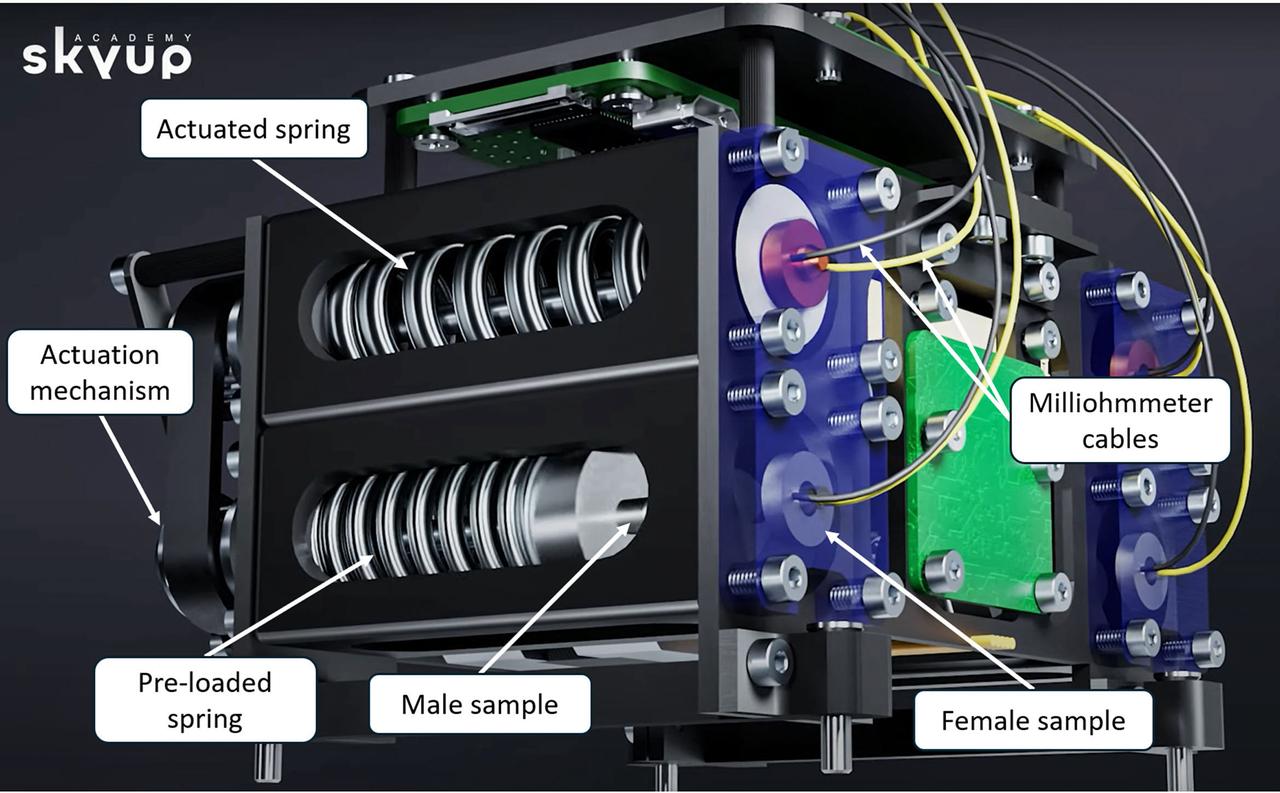
jsc2024e065165 (10/3/2024) --- Render of the Nanolab Astrobeat module core with labels. This investigation tests cold welding in a space environment. Cold welding is a method in which metallic materials fuse or weld at ambient temperature provided that there is sufficient high contact force. This technology has applications for repairing spacecraft hulls that may be perforated as a result of micrometeoroids. Image courtesy of Dr. Leonardo Barilaro, The Malta College of Arts, Science & Technology..
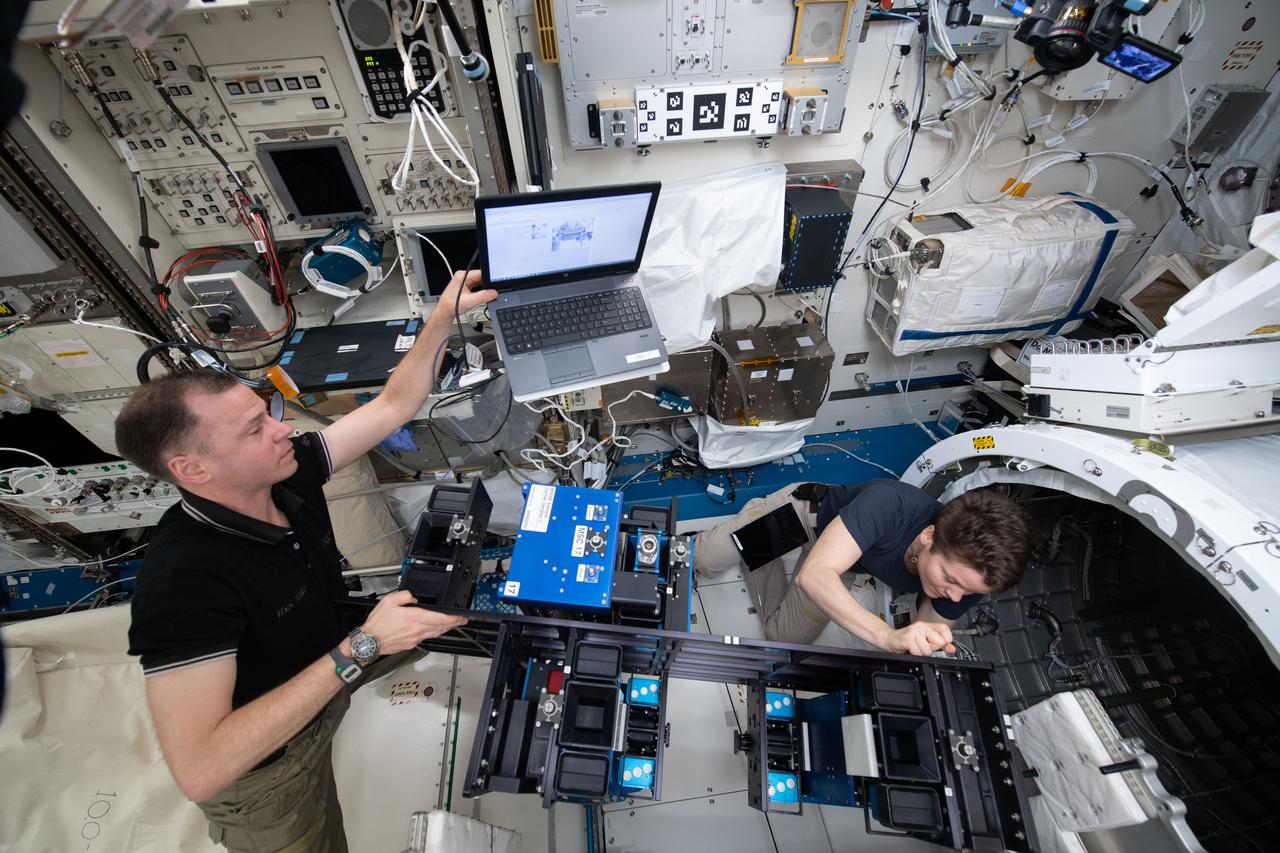

iss059e034507 (April 23, 2019) --- NASA astronauts Nick Hague and Anne McClain install the Materials ISS Experiment-Flight Facility (MISSE-FF) gear inside the Japanese Kibo laboratory module’s airlock before depressurizing the unit. MISSE-FF contains new materials exposure experiments ready for deployment outside Kibo. The study will help scientists understand how radiation, the vacuum of space and micrometeoroids affect a variety of materials.

iss072e188539 (Nov. 15, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Don Pettit unpacks and gathers research hardware to be placed outside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module. The scientific gear known as MISSE, or Materials International Space Station Experiment, places a variety of materials in the vacuum of space exposing them to the extreme thermal environment, different types of radiation, micrometeoroids, and more to promote the space industry.
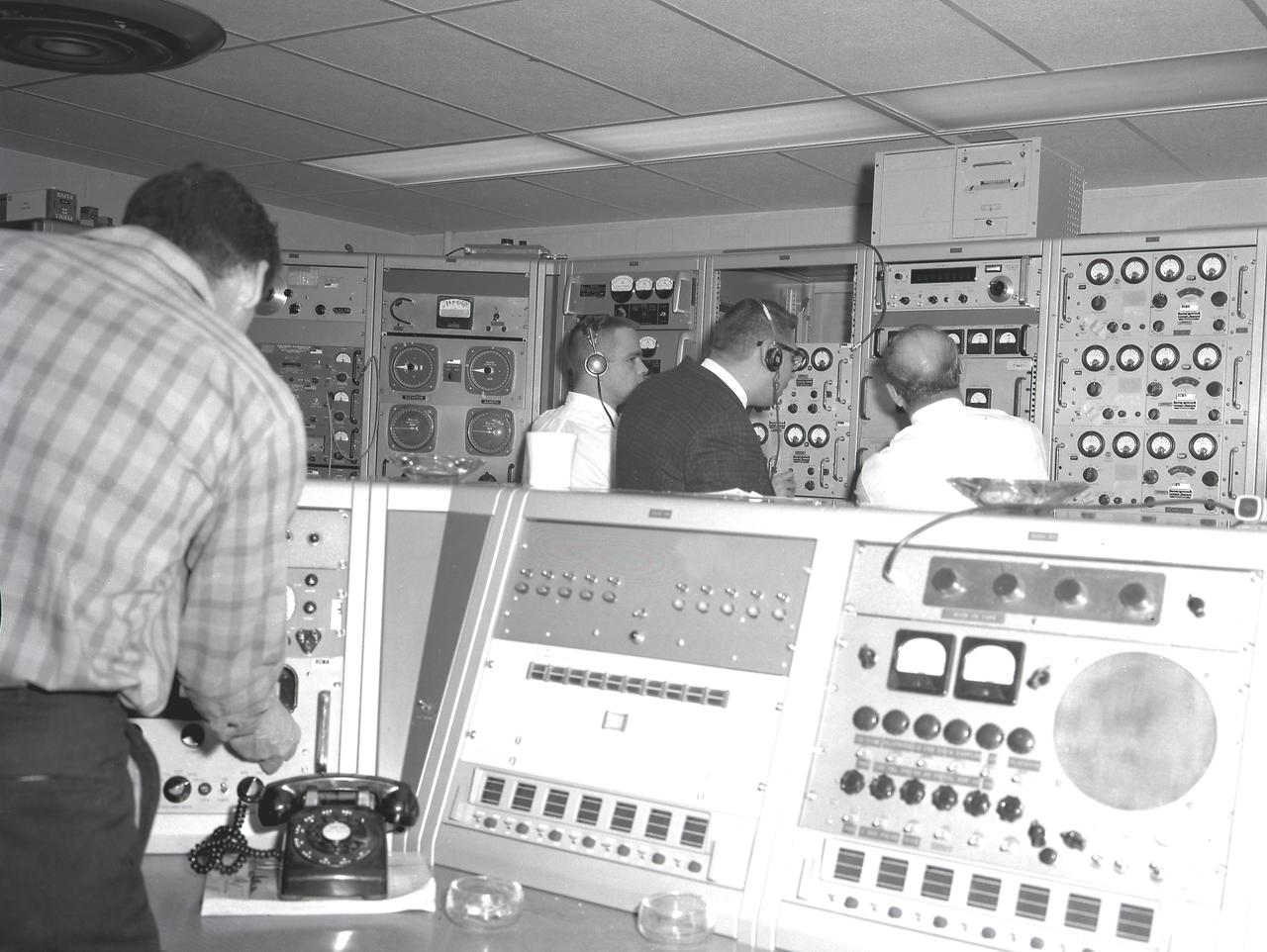

Activities at Green Mountain Tracking Station, Alabama, during lift-off of the Saturn I, SA-9 mission, showing the overall view of instrument panels used in tracking the Pegasus, meteoroid-detection satellite. The satellite was used to obtain data on frequency and penetration of the potentially hazardous micrometeoroids in low Earth orbits and to relay the information back to Earth.
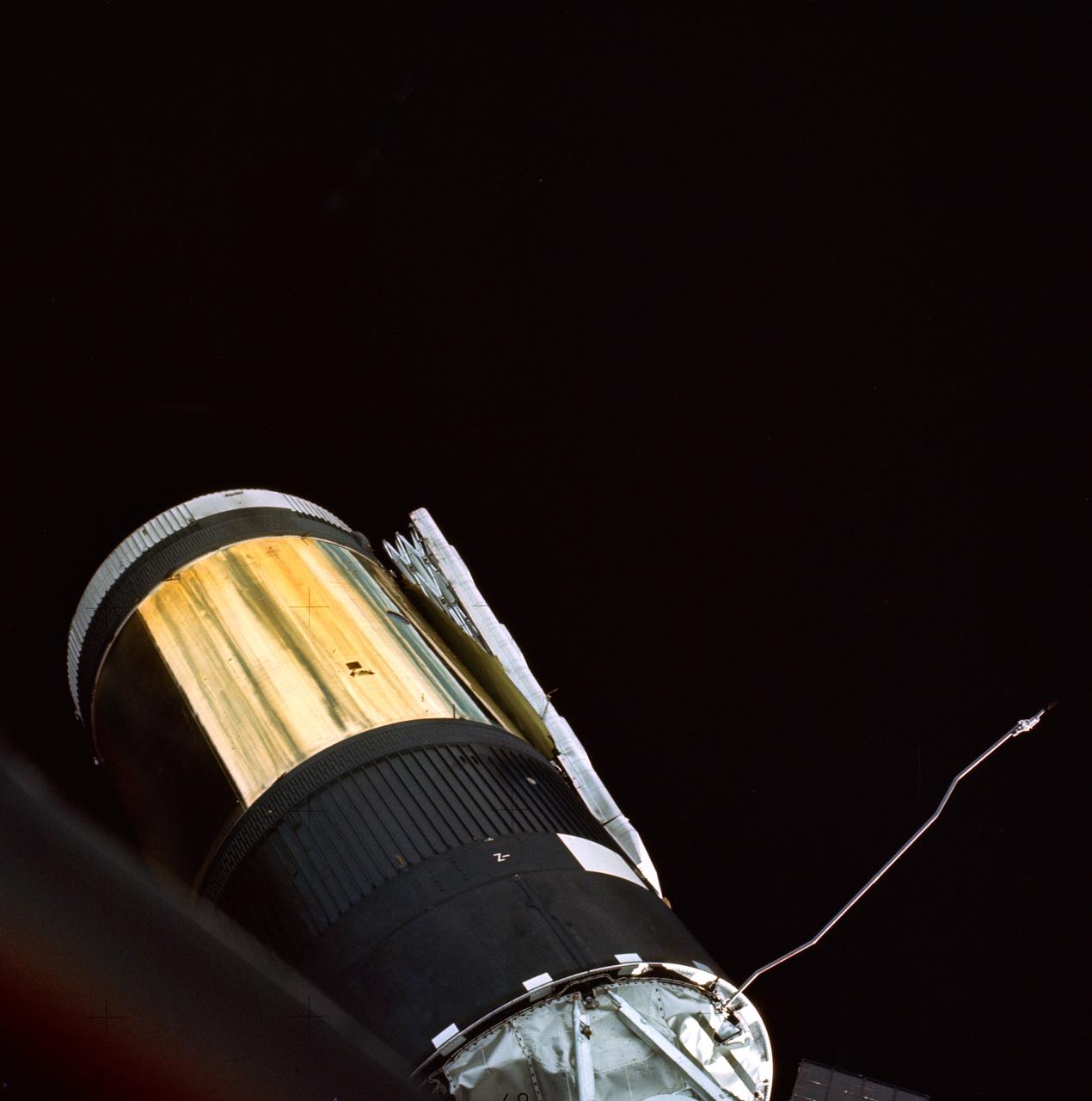

This view of the Skylab Orbital Space Station was taken from the Skylab 2 Command/Service Module during it's initial fly around inspection. The micrometeoroid shield can be seen to be missing and a parasol solar shield was later fitted in its place. The damaged and partially deployed solar array, in the center of the scene, can be seen to be restrained by a strap that was later cut during an early EVA, allowing the panel to fully deploy.
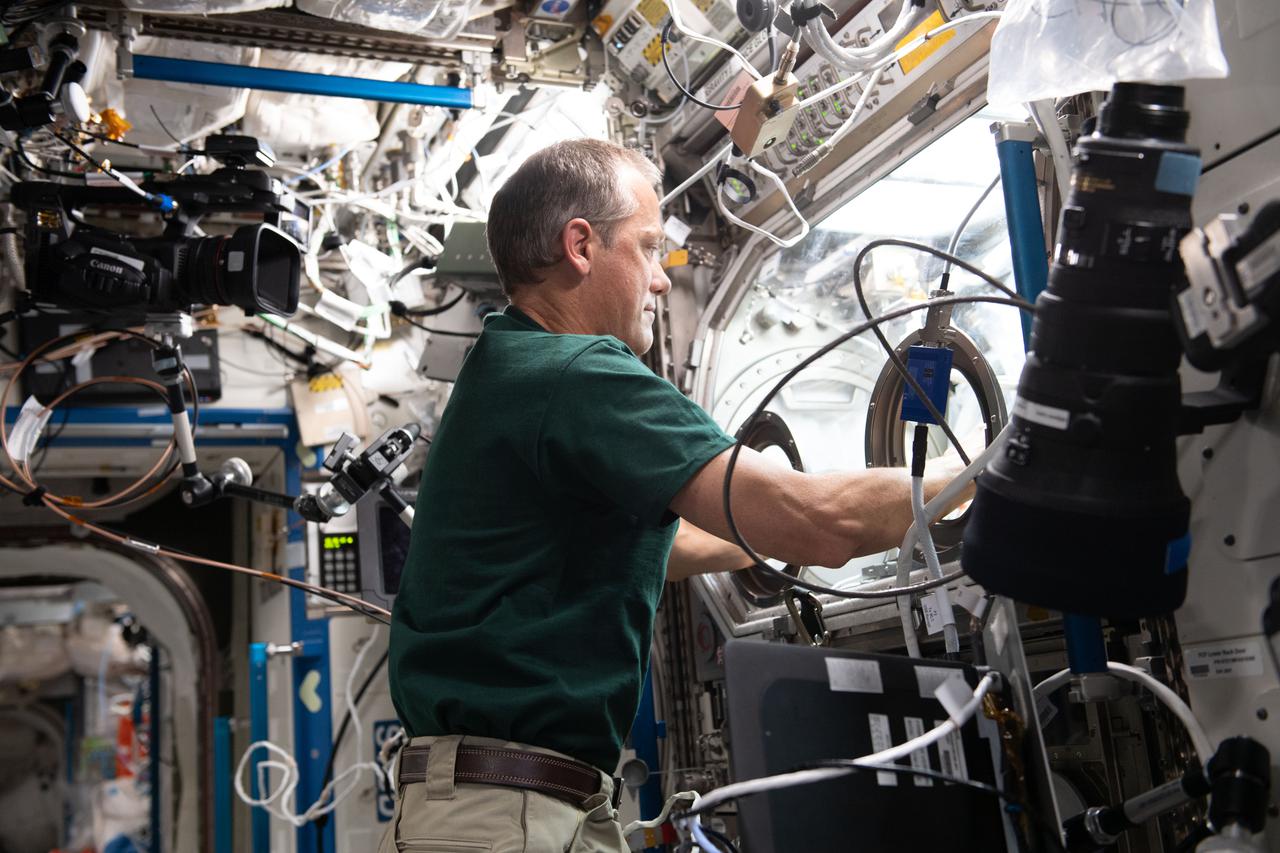

iss066e078282 (November 17, 2021) --- NASA astronaut Tom Marshburn works on the SUBSA-BRAINS space physics experiment, which examines differences in capillary flow, interface reactions, and bubble formation during solidification of brazing alloys in microgravity. Brazing technology bonds similar materials (such as an aluminum alloy to aluminum) or dissimilar ones (such as aluminum alloy to ceramics) at temperatures above 450°C. It is a potential tool for construction of human space habitats and manufactured systems as well as to repair damage from micrometeoroids or space debris.
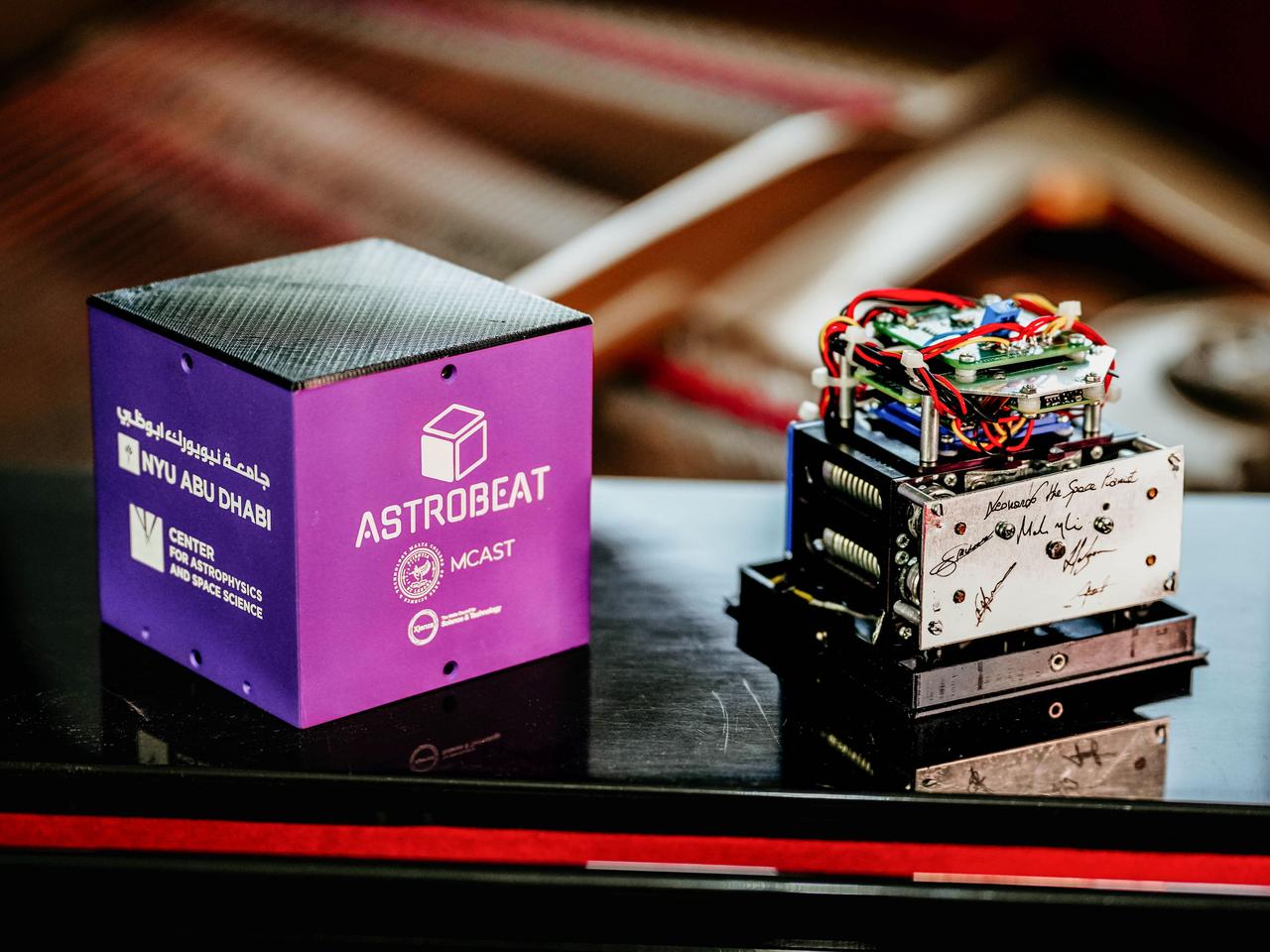

jsc2024e065168 (10/3/2024) --- Nanolab Astrobeat module hull and core side by side. This investigation tests cold welding in a space environment. Cold welding is a method in which metallic materials fuse or weld at ambient temperature provided that there is sufficient high contact force. This technology has applications for repairing spacecraft hulls that may be perforated as a result of micrometeoroids. Image courtesy of Dr. Leonardo Barilaro, The Malta College of Arts, Science & Technology..

The Saturn V vehicle, carrying the unmarned orbital workshop for the Skylab-1 mission, lifted off successfully and all systems performed normally. Sixty-three seconds into flight, engineers in the operation support and control center saw an unexpected telemetry indication that signalled that damages occurred on one solar array and the micrometeoroid shield during the launch. The micrometeoroid shield, a thin protective cylinder surrounding the workshop protecting it from tiny space particles and the sun's scorching heat, ripped loose from its position around the workshop. This caused the loss of one solar wing and jammed the other. Still unoccupied, the Skylab was stricken with the loss of the heat shield and sunlight beat mercilessly on the lab's sensitive skin. Internal temperatures soared, rendering the the station uninhabitable, threatening foods, medicines, films, and experiments. This image shows the sun-ravaged skin of the Orbital Workshop, bared by the missing heat shield, with blister scars and tarnish from temperatures that reached 300 degrees F. The rectangular opening at the upper center is the scientific airlock through which the parasol to protect the workshop from sun's rays was later deployed. This view was taken during a fly-around inspection by the Skylab-2 crew. The Marshall Space Flight Center had a major role in developing the procedures to repair the damaged Skylab.
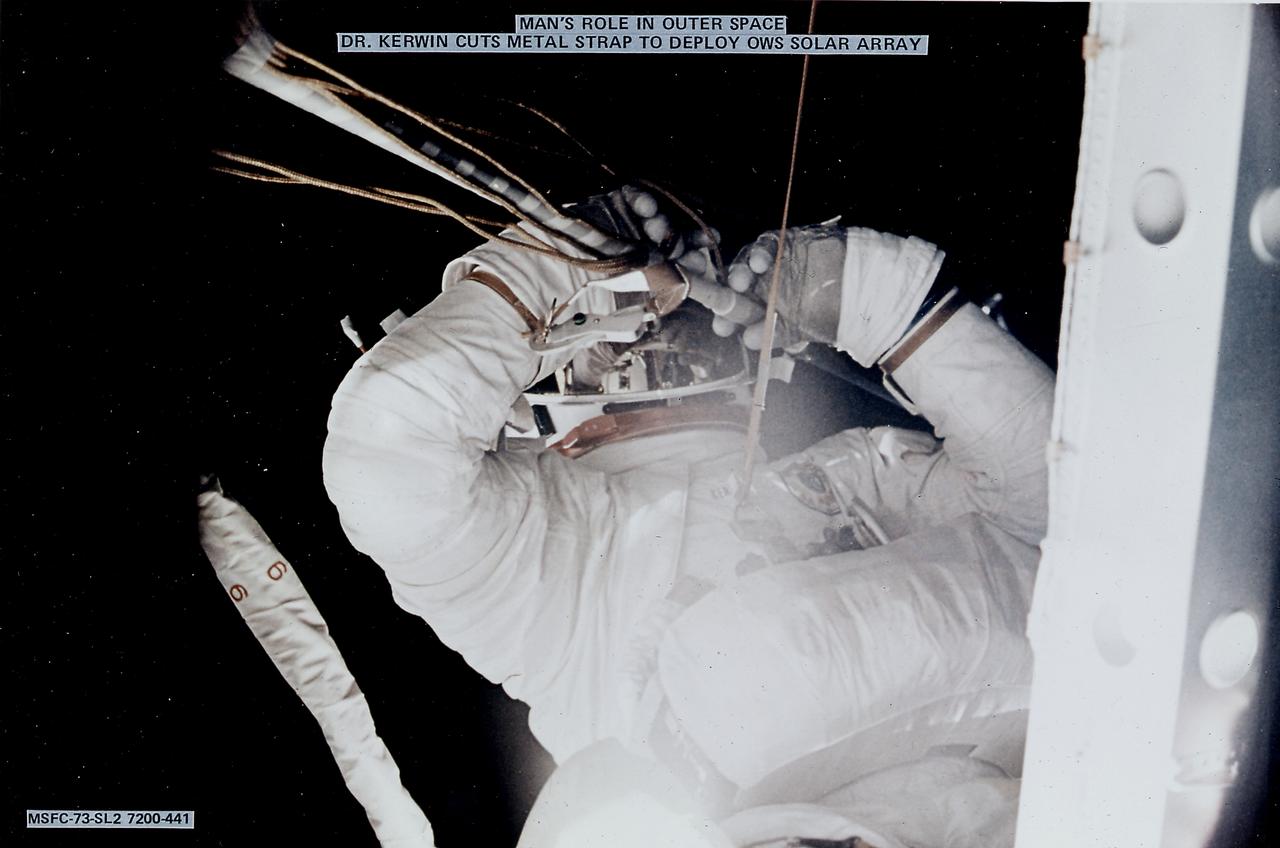

The Saturn V vehicle, carrying the unmarned orbital workshop for the Skylab-1 mission, lifted off successfully and all systems performed normally. Sixty-three seconds into the flight, engineers in the operation support and control center saw an unexpected telemetry indication that signalled that damages occurred on one solar array and the micrometeoroid shield during the launch. The micrometeoroid shield, a thin protective cylinder surrounding the workshop protecting it from tiny space particles and the sun's scorching heat, ripped loose from its position around the workshop. This caused the loss of one solar wing and jammed the other. Still unoccupied, the Skylab was stricken with the loss of the heat shield and sunlight beat mercilessly on the lab's sensitive skin. Intrnal temperatures soared, rendering the station uninhabitable, threatening foods, medicines, films, and experiments. This image shows astronaut Kerwin cutting the metal strap to free and deploy the Orbital Workshop solar array. Kerwin used special cutting tools developed by engineers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The MSFC had a major role in developing the procedures to repair the damaged Skylab.

The Saturn V vehicle, carrying the unmarned orbital workshop for the Skylab-1 mission, lifted off successfully and all systems performed normally. Sixty-three seconds into the flight, engineers in the operation support and control center saw an unexpected telemetry indication that signalled that damages occurred on one solar array and the micrometeoroid shield during the launch. The micrometeoroid shield, a thin protective cylinder surrounding the workshop protecting it from tiny space particles and the sun's scorching heat, ripped loose from its position around the workshop. This caused the loss of one solar wing and jammed the other. Still unoccupied, the Skylab was stricken with the loss of the heat shield and sunlight beat mercilessly on the lab's sensitive skin. Internal temperatures soared, rendering the station uninhabitable, threatening foods, medicines, films, and experiments. This image, taken during a fly-around inspection by the Skylab-2 crew, shows the station's remaining solar panel jammed against its side. The Marshall Space Flight Center had a major role in developing the procedures to repair the damaged Skylab.
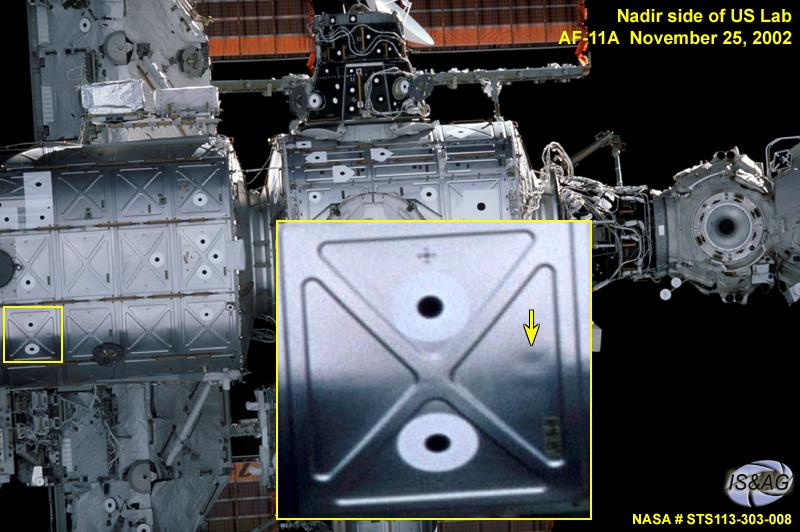
JSC2004-E-50470 (25 November 2002) --- The original photograph in this image was taken during the Space Shuttle Endeavour’s approach to the International Space Station for docking during the STS-113/11A assembly mission. An indentation in a micrometeoroid debris panel on the exterior of the Destiny Laboratory module is indicated by an arrow in an enhanced section of the image provided by the Image Science and Analysis Group at the Johnson Space Center. Analysis of this image and additional video indicates that the indentation is not from a debris strike, but is consistent with flat spots seen on other areas that are likely the result of significant temperature changes. The protective shield’s function is not affected by the indentations.
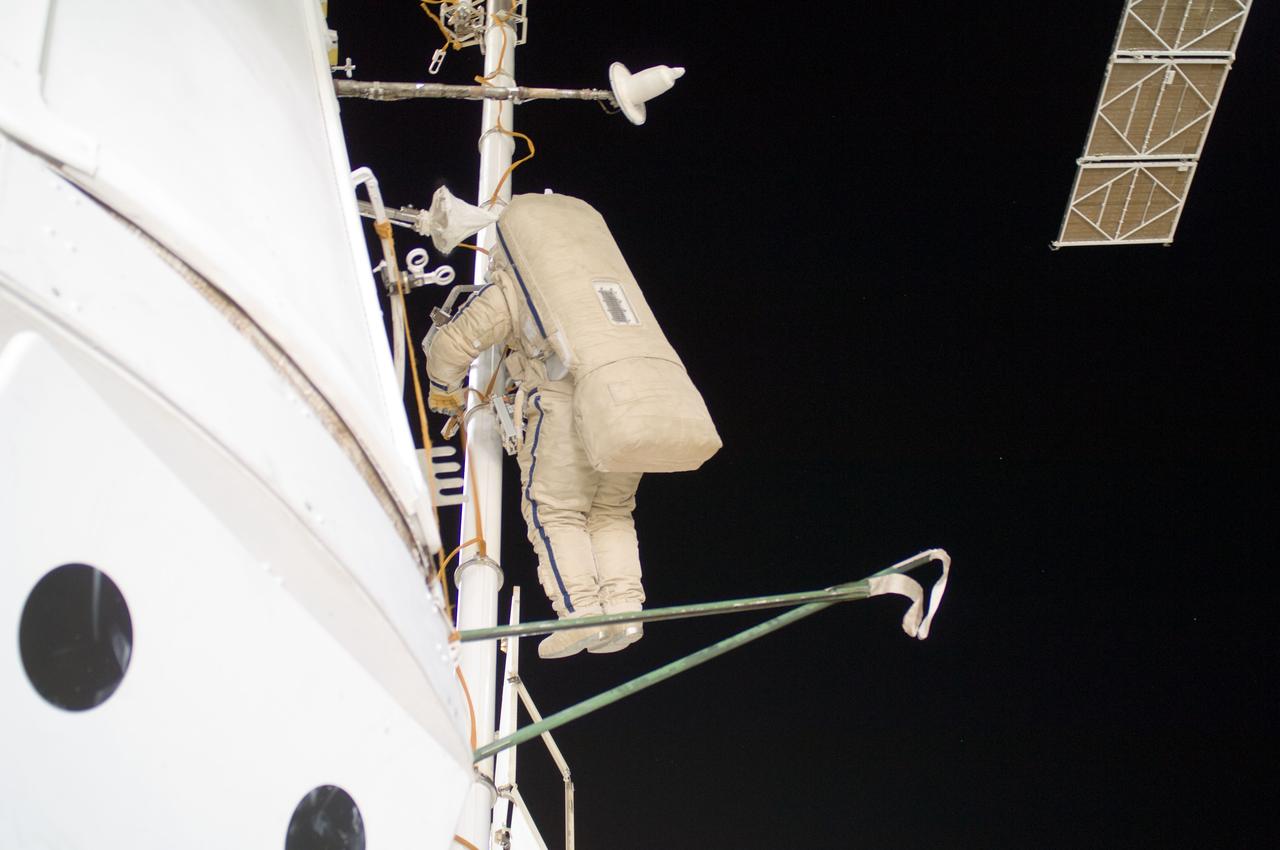

ISS032-E-020884 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko, Expedition 32 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Malenchenko and Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka (out of frame), commander, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
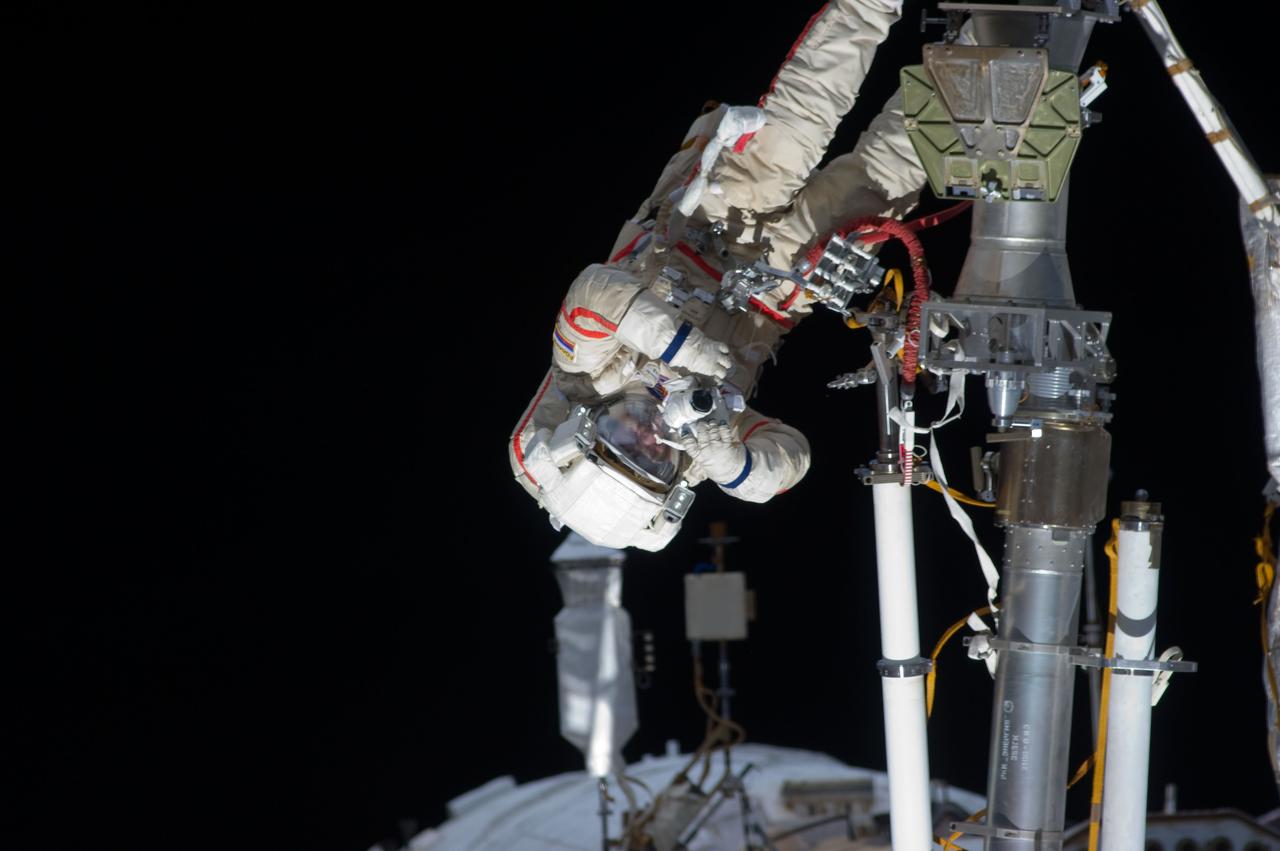

ISS032-E-021078 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, uses a still camera during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.

ISS032-E-021054 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko, Expedition 32 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Malenchenko and Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka (out of frame), commander, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
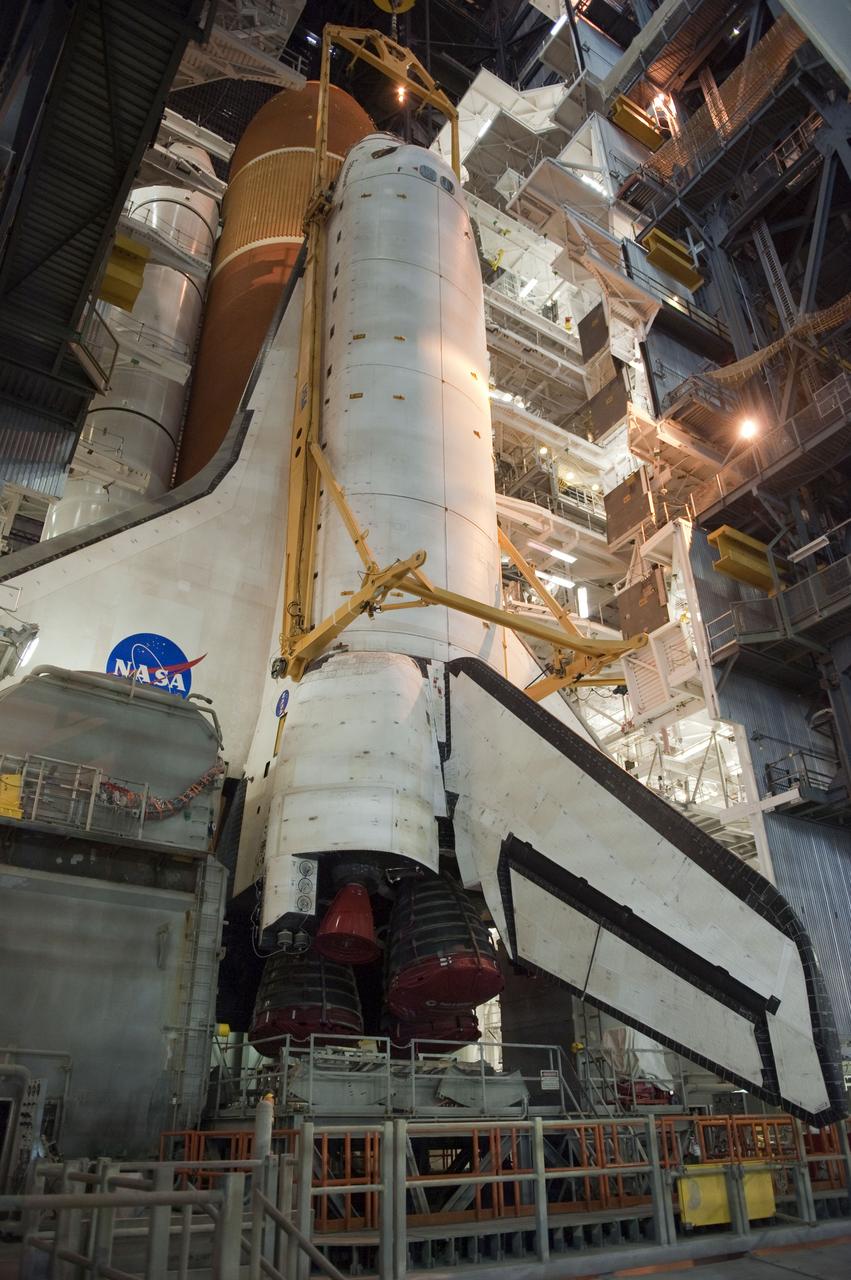

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shuttle Endeavour is lowered into place where it is being attached to its external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters, already positioned on the mobile launcher platform. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Endeavour's final launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
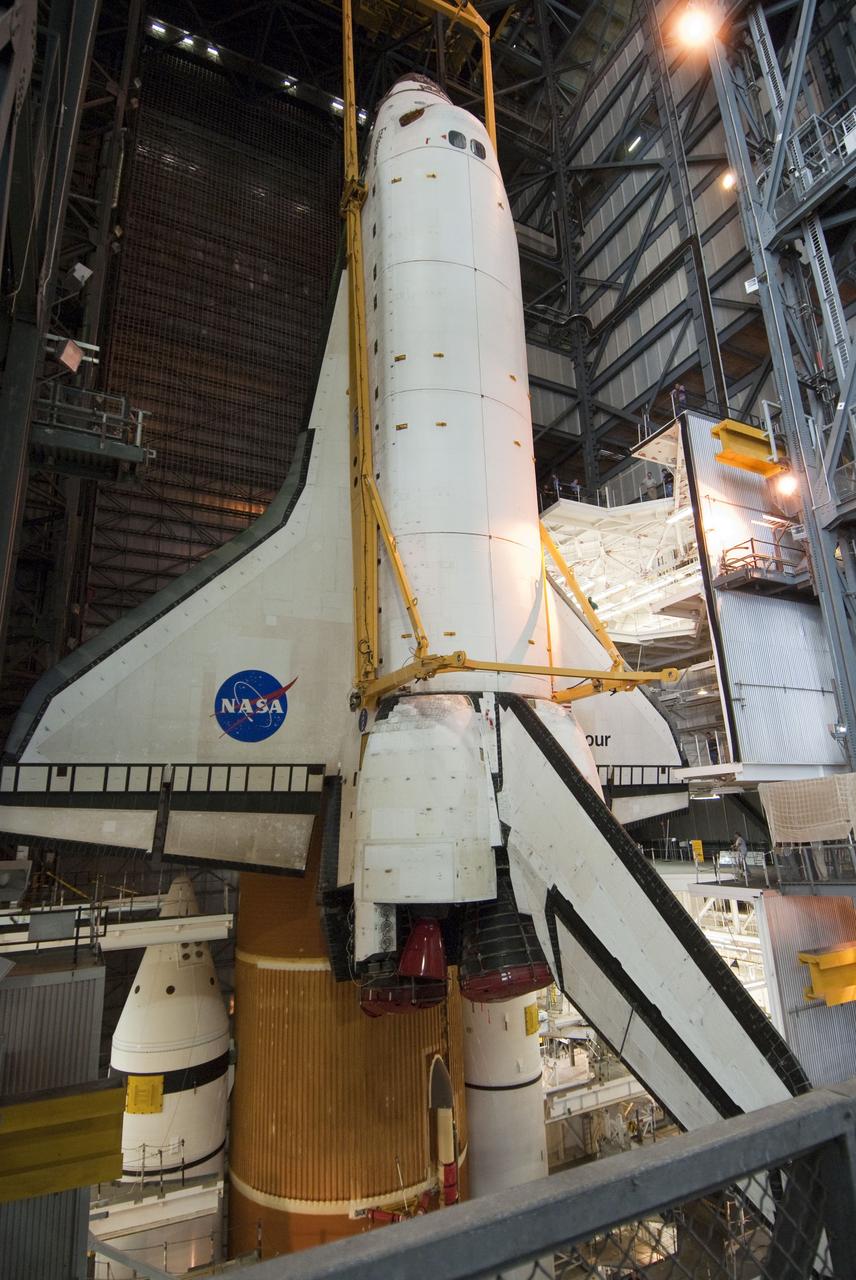

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shuttle Endeavour is lowered into place where it will be attached to its external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters, already positioned on the mobile launcher platform. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Endeavour's final launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
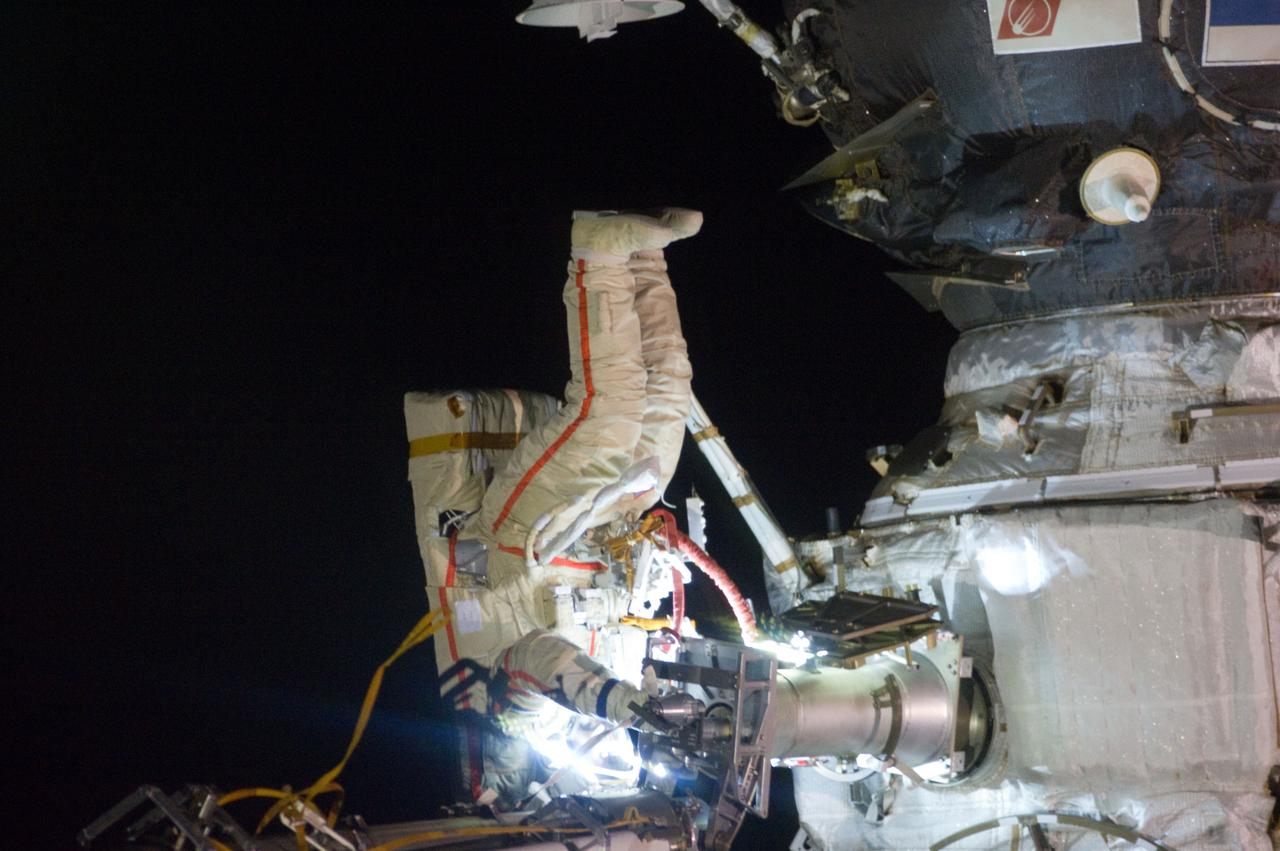

ISS032-E-021037 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
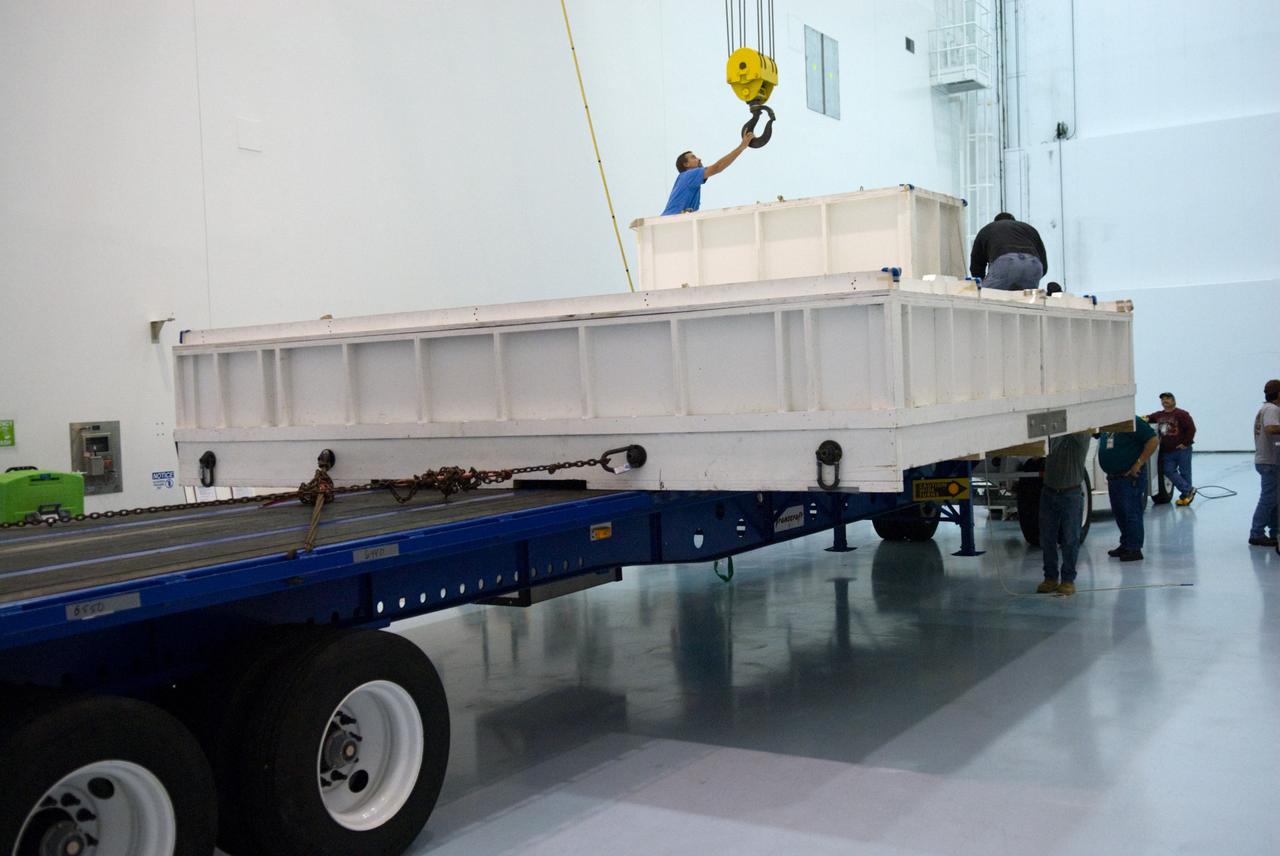

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are under way to uncrate the ExPRESS Logistics Carrier 3, or ELC-3. ELC-3 and the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer are the primary payloads for space shuttle Endeavour's STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The STS-134 crew will also deliver spare parts including two S-band communications antennas, a high pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields. Endeavour's launch is targeted for July 29, 2010. For information on the STS-134 mission objectives and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
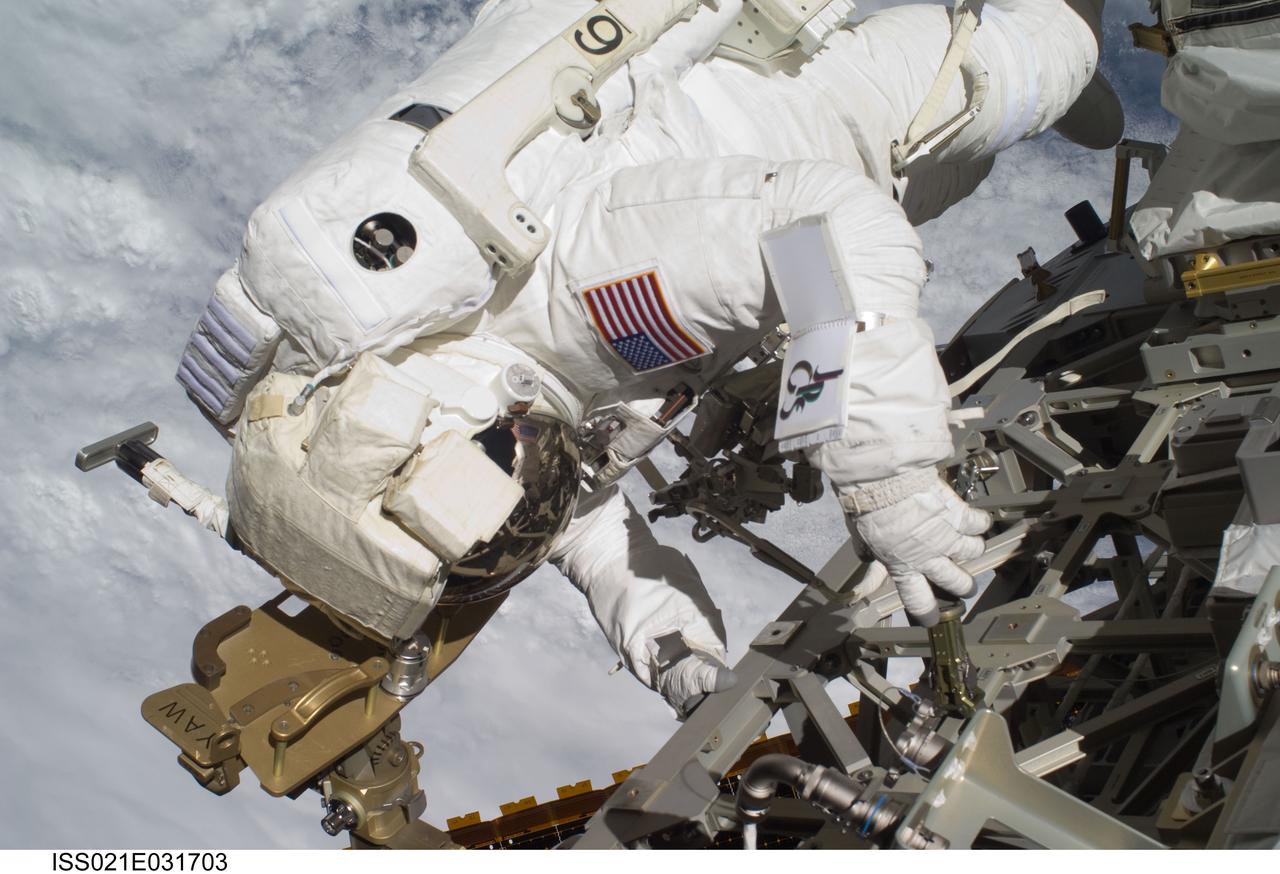

ISS021-E-031703 (23 Nov. 2009) --- Astronaut Robert L. Satcher Jr., STS-129 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third and final session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 42-minute spacewalk, Satcher and astronaut Randy Bresnik (out of frame), mission specialist, removed a pair of micrometeoroid and orbital debris shields from the Quest airlock and strapped them to the External Stowage Platform #2, then moved an articulating foot restraint to the airlock, and released a bolt on a starboard truss ammonia tank assembly (ATA) in preparation for an STS-131 spacewalk that will replace the ATA.
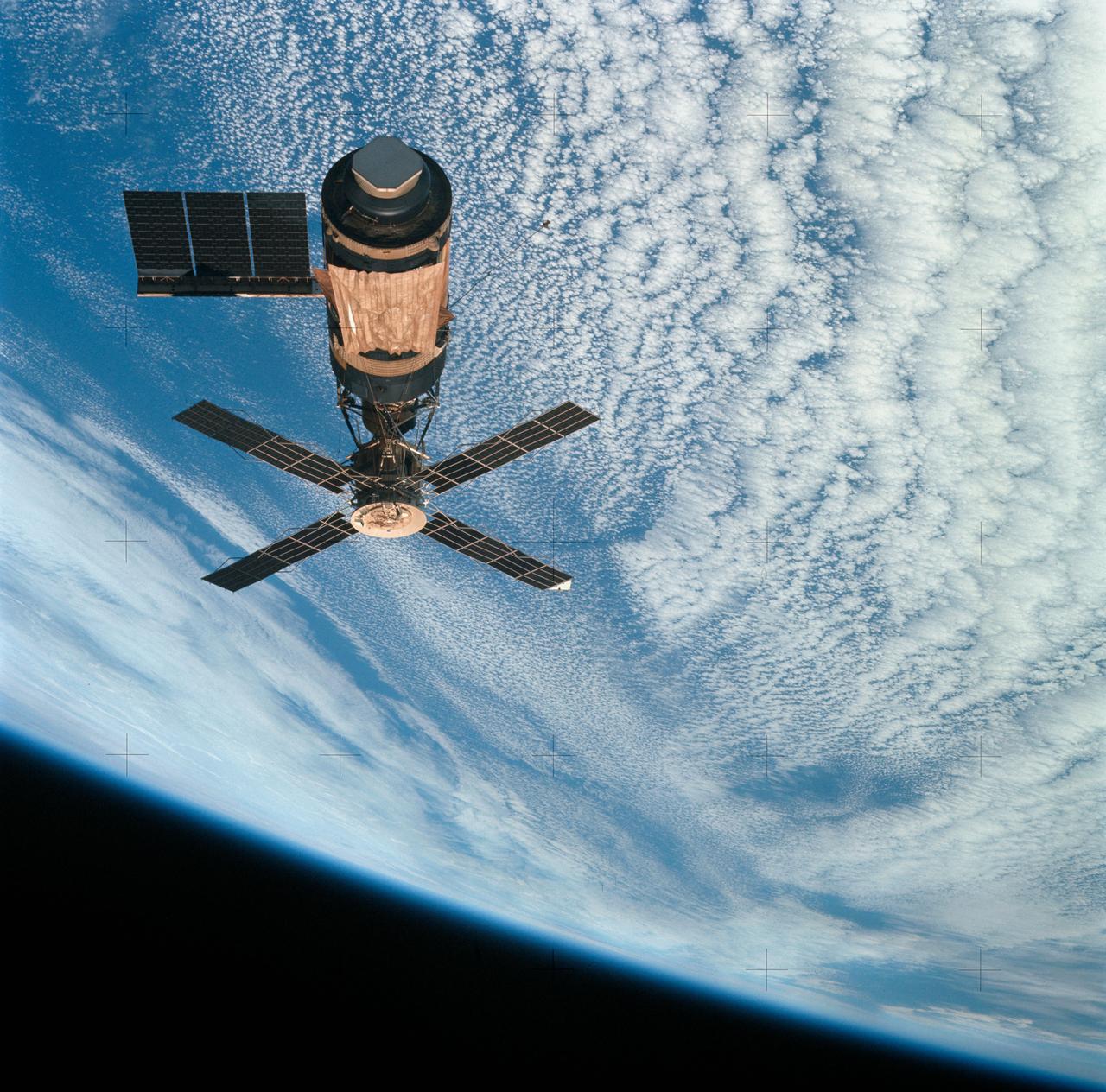

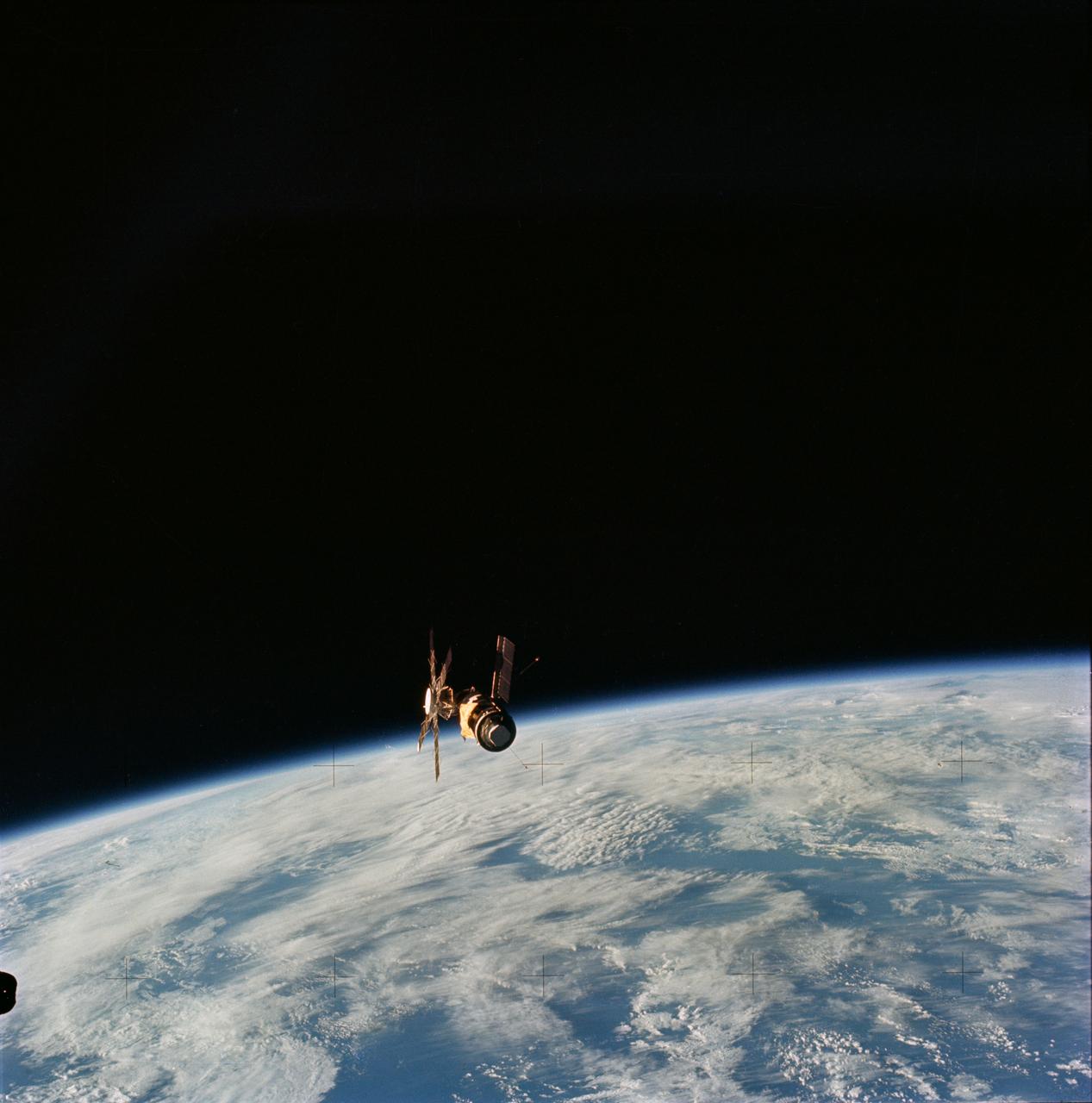
SL4-143-4707 (8 Feb. 1974) --- An overhead view of the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit as photographed from the Skylab 4 Command and Service Modules (CSM) during the final fly-around by the CSM before returning home. The space station is contrasted against a cloud-covered Earth. Note the solar shield which was deployed by the second crew of Skylab and from which a micrometeoroid shield has been missing since the cluster was launched on May 14, 1973. The OWS solar panel on the left side was also lost on workshop launch day. Photo credit: NASA
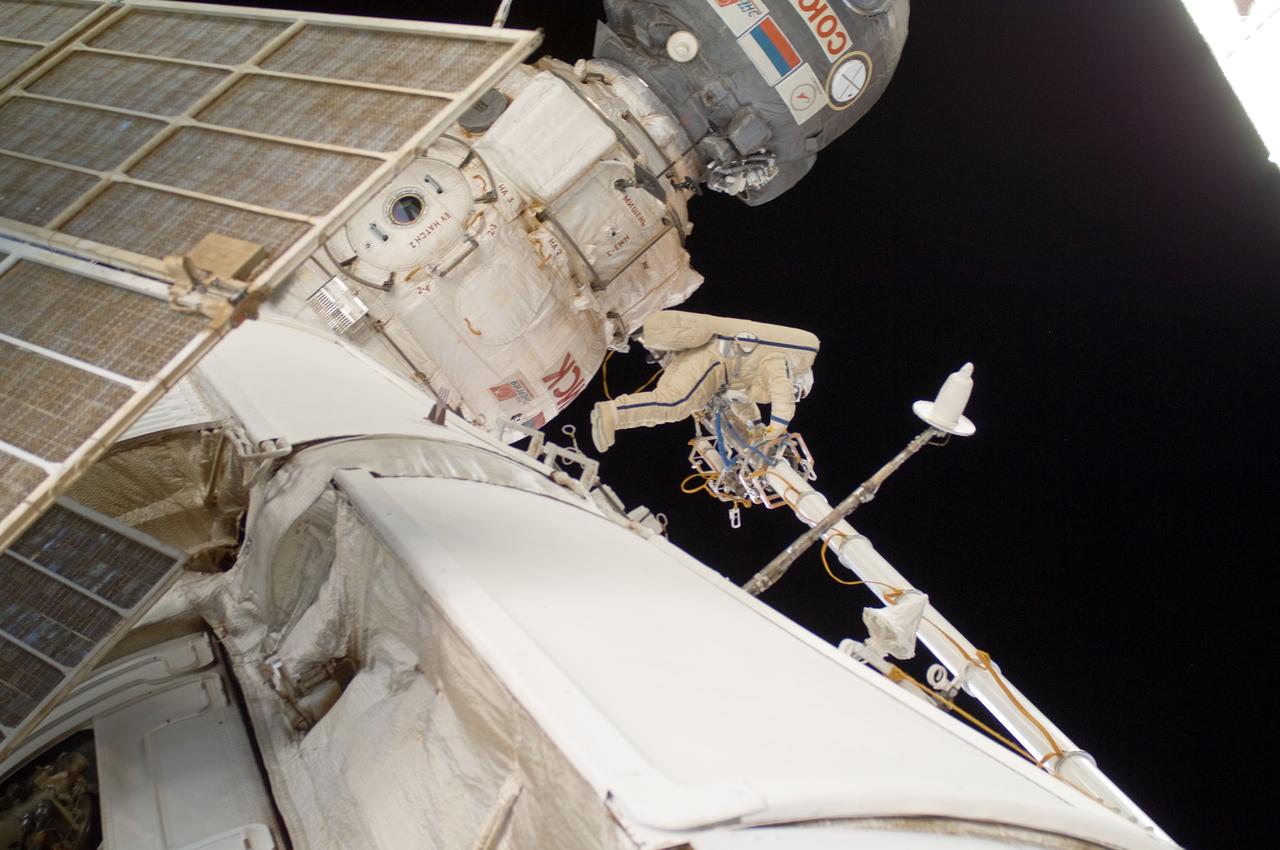

ISS032-E-020892 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko, Expedition 32 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Malenchenko and Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka (out of frame), commander, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
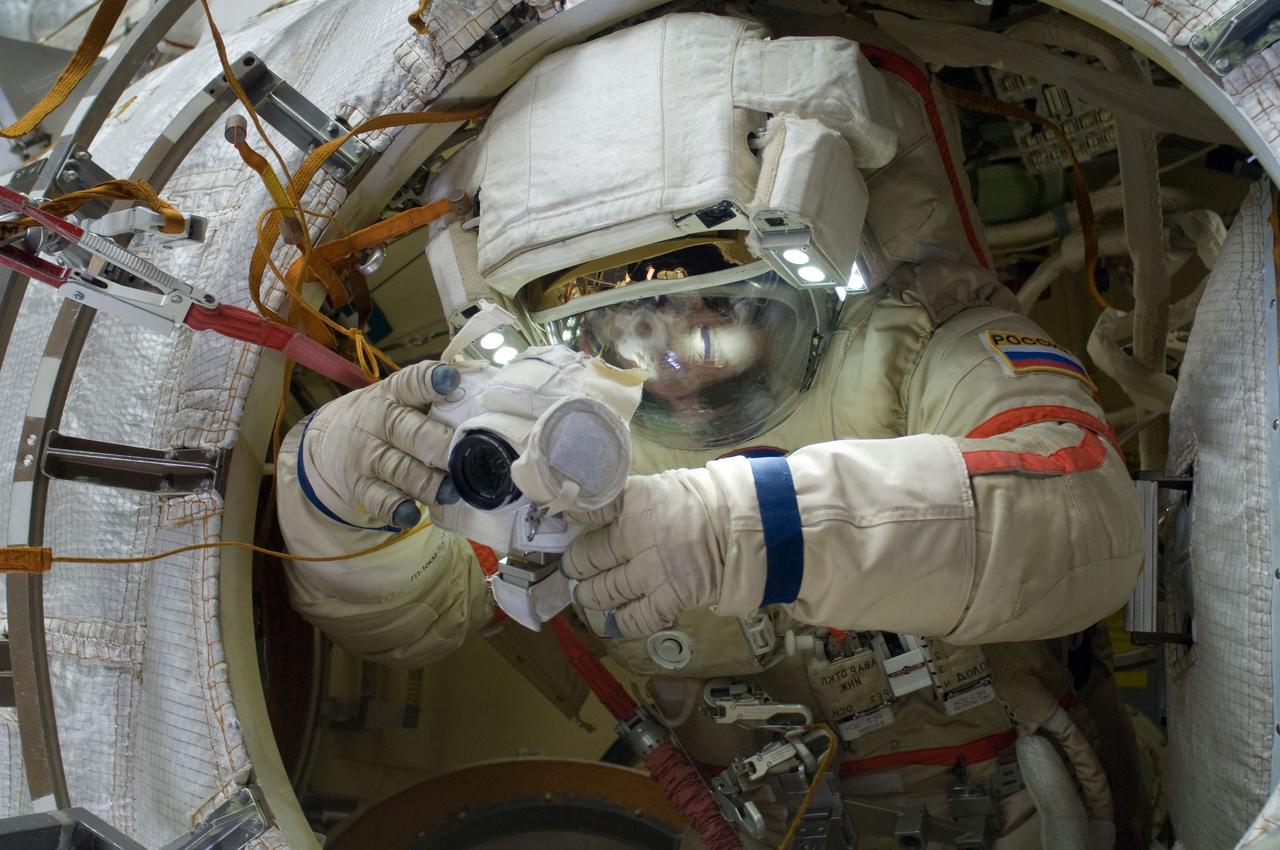

ISS032-E-020619 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, uses a still camera during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
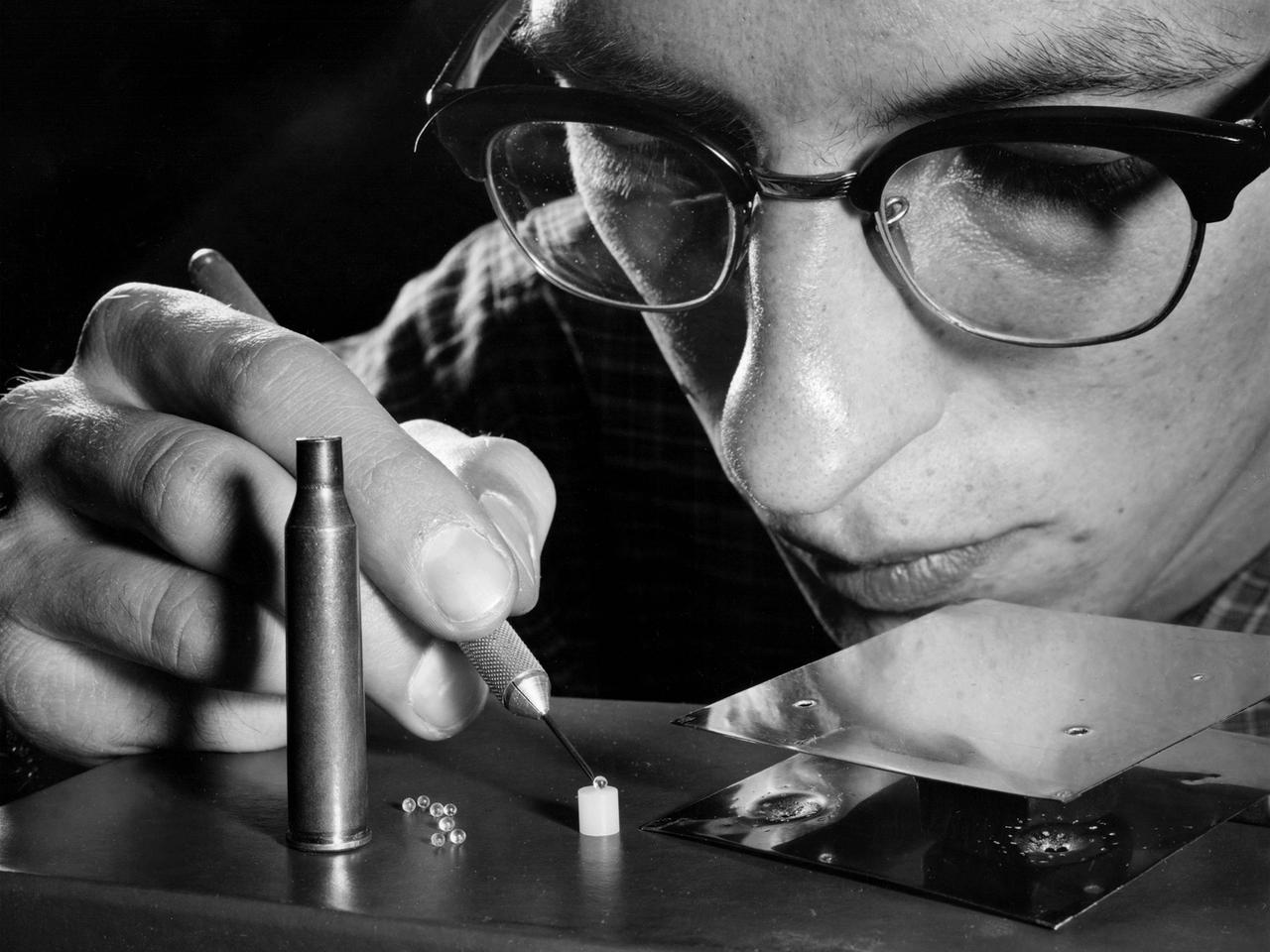

A researcher at the NASA Lewis Research Center manipulates cartridge pellets and a strain gauge target as part of a study on the impact of micrometeorites striking space vehicles. Early in the space program NASA researchers were concerned that small micrometeorites would penetrate spacecraft, injure engines, or damage solar arrays. In response, researchers worked to develop stronger materials to withstand meteorite strikes and screens to block the objects. NASA launched a series of experimental spacecraft into orbit with foil shields that were used to determine the number of meteorite strikes. By the early 1960s the experiments and computer modelling efforts revealed that the micrometeoroid threat was lower than previously anticipated.
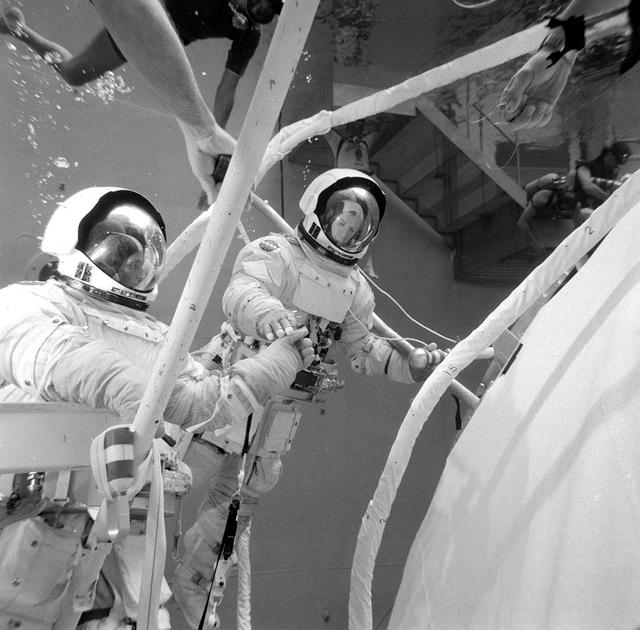

This photograph was taken during testing of an emergency procedure to free jammed solar array panels on the Skylab workshop. A metal strap became tangled over one of the folded solar array panels when Skylab lost its micrometeoroid shield during the launch. This photograph shows astronauts Schweickart and Gibson in the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) using various cutting tools and methods developed by the MSFC to free the jammed solar wing. Extensive testing and many hours of practice in simulators such as the NBS tank helped prepare the Skylab crewmen for extravehicular performance in the weightless environment. This huge water tank simulated the weightless environment that the astronauts would encounter in space.
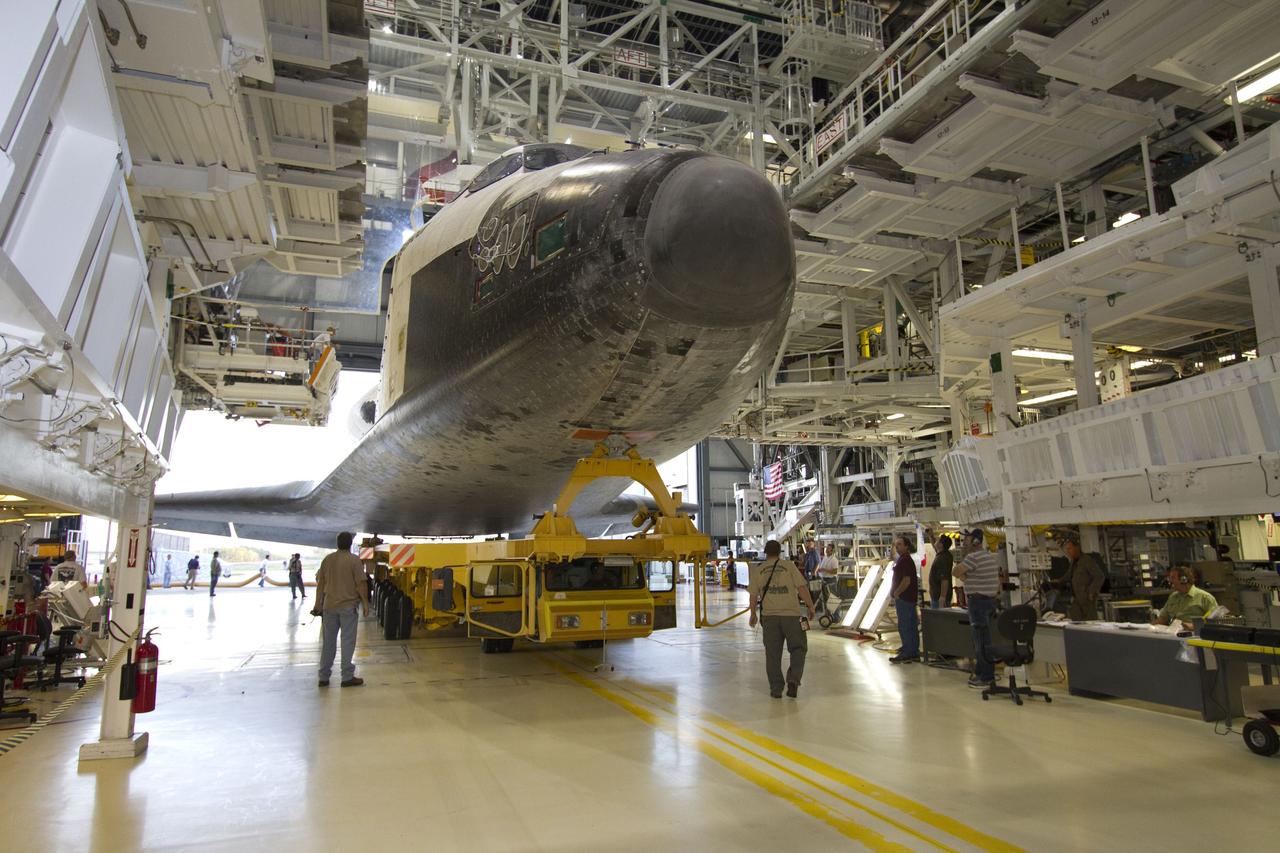

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers prepare space shuttle Endeavour for its move, or "rollover," from its hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, spare parts, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
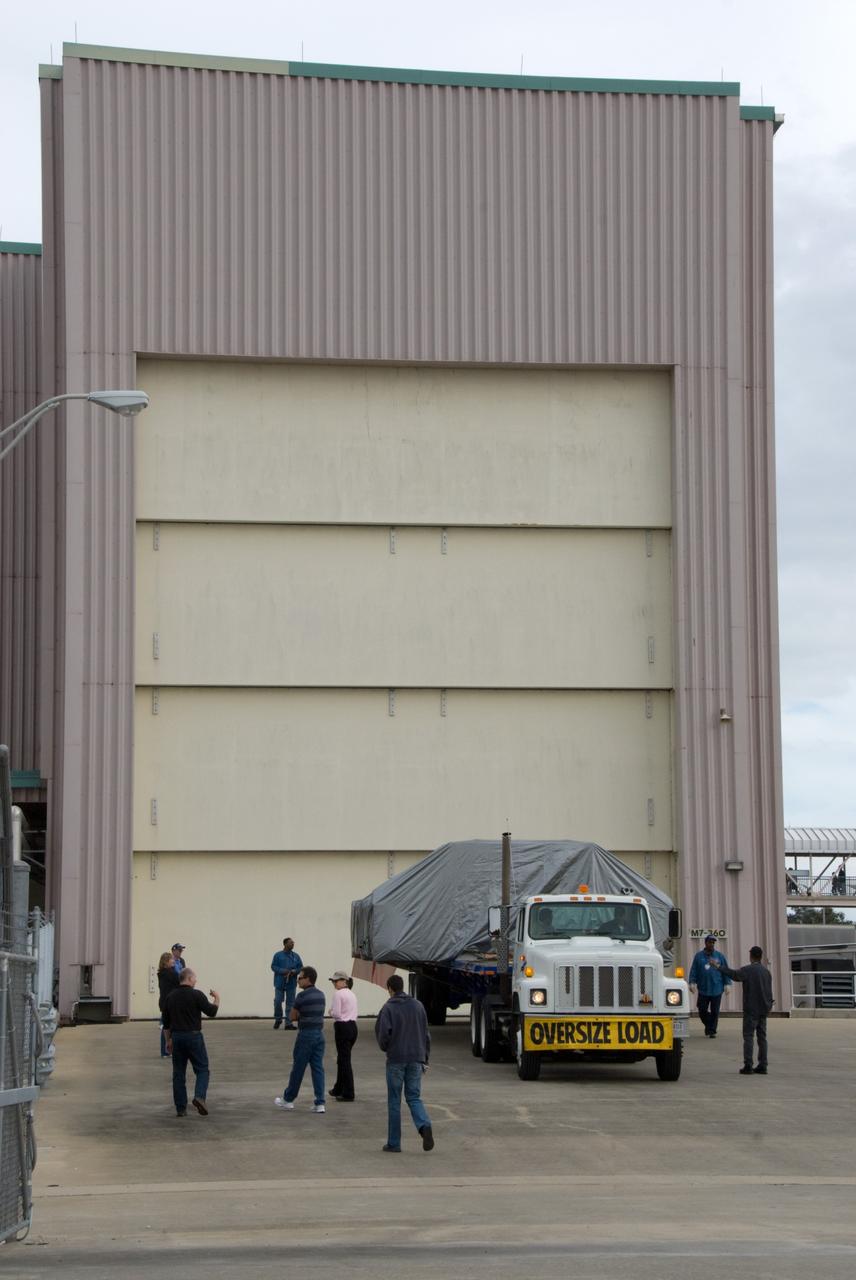

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the ExPRESS Logistics Carrier 3, or ELC-3, arrives at the Space Station Processing Facility. ELC-3 and the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer are the primary payloads for space shuttle Endeavour's STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The STS-134 crew will also deliver spare parts including two S-band communications antennas, a high pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields. Endeavour's launch is targeted for July 29, 2010. For information on the STS-134 mission objectives and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, employees hold up a banner to commemorate space shuttle Endeavour's STS-134 mission as it is transported from Orbiter Processing Facility-2 to the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, spare parts, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
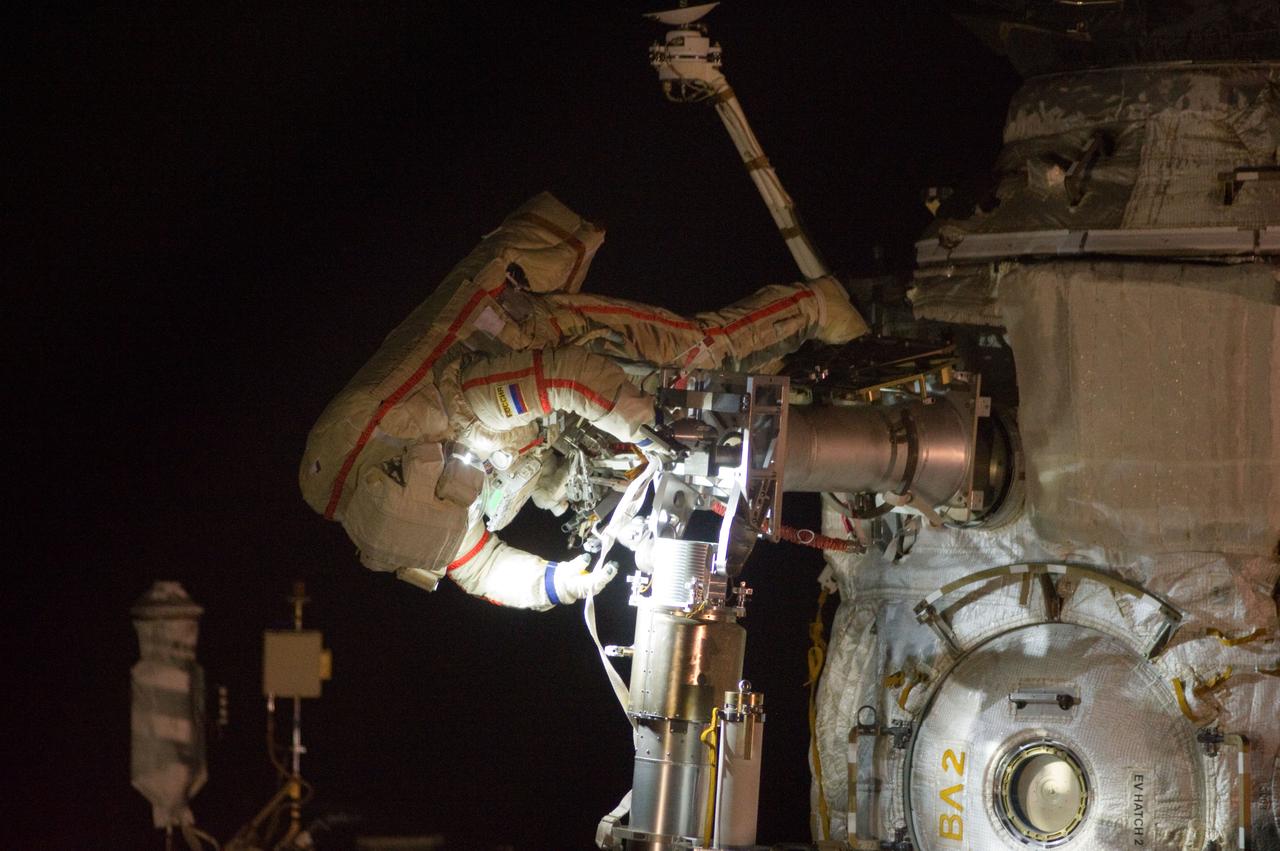

ISS032-E-021024 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
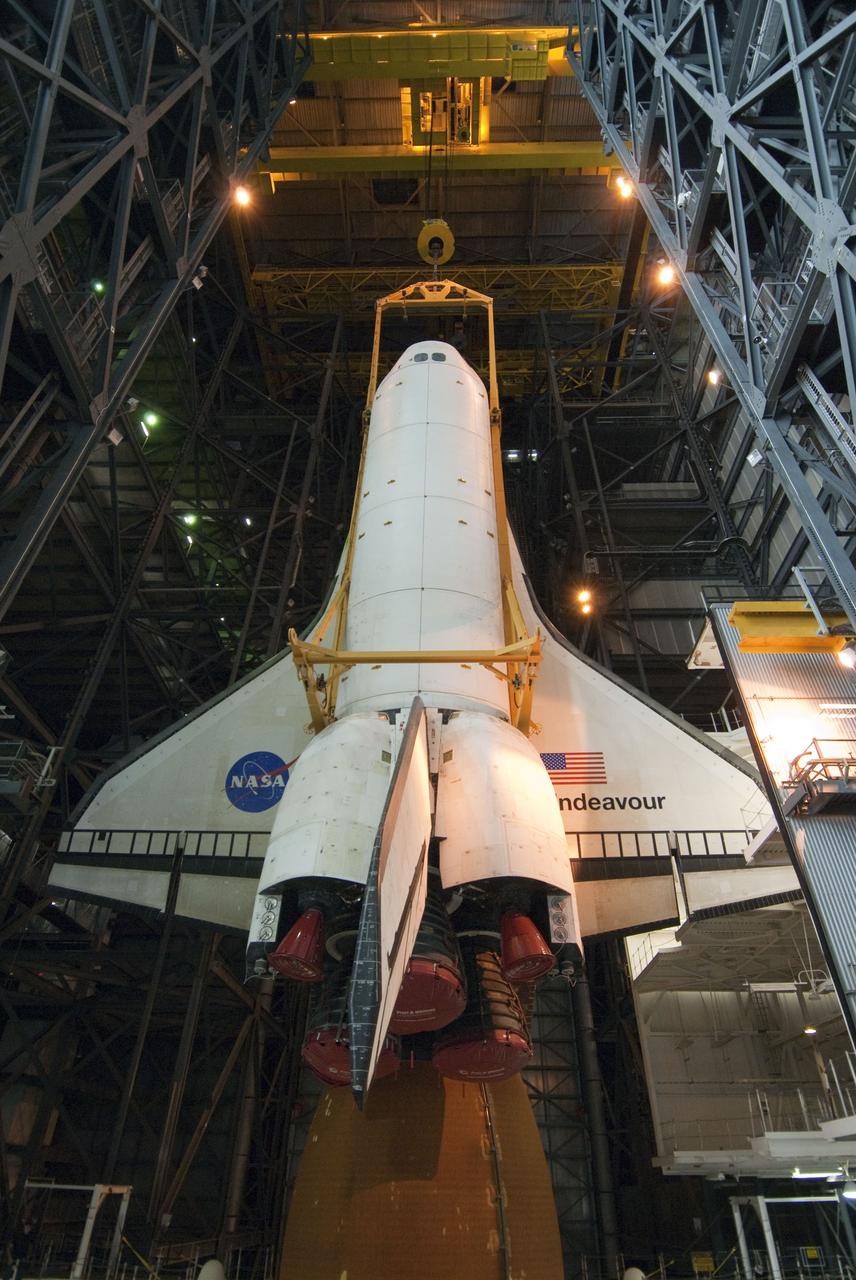

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shuttle Endeavour is being lowered into place where it will be attached to its external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters, already positioned on the mobile launcher platform. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Endeavour's final launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
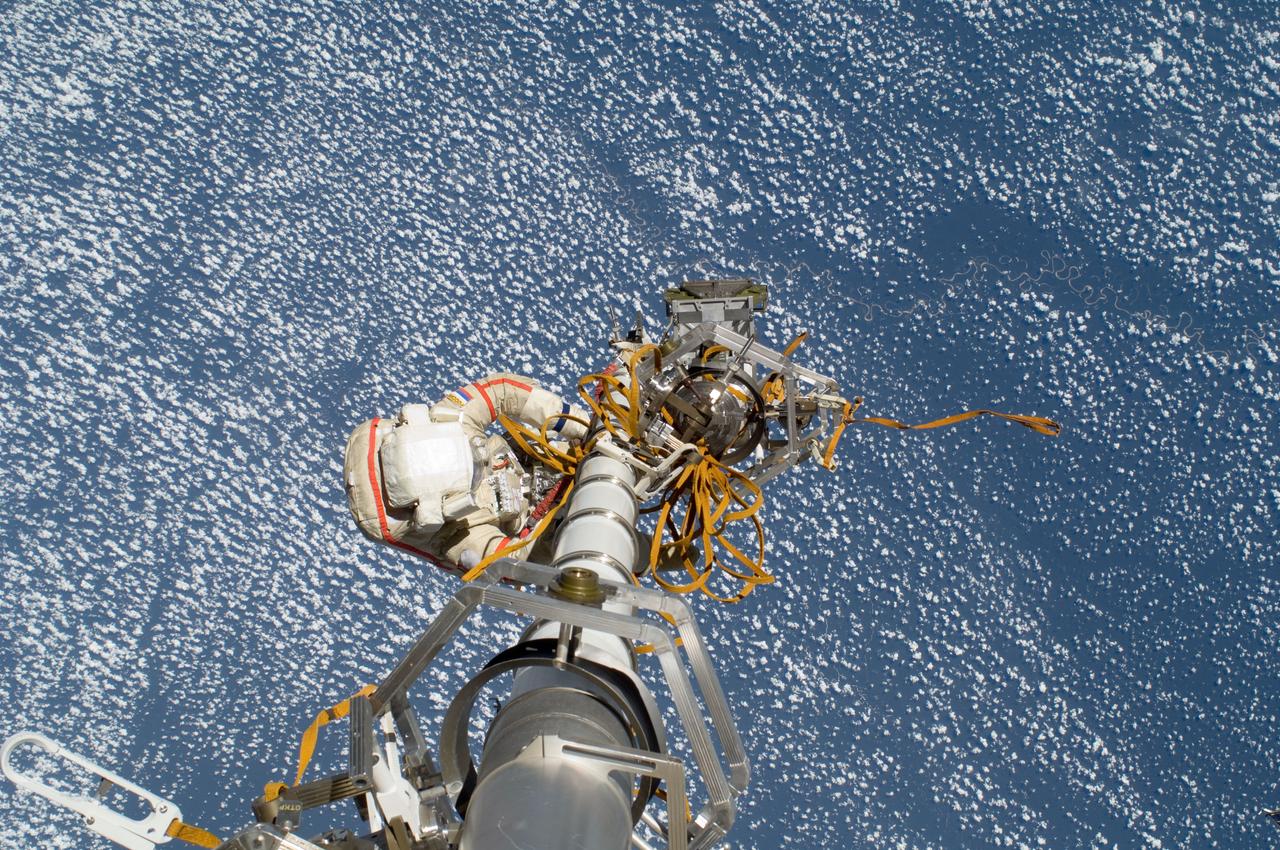

ISS032-E-020581 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
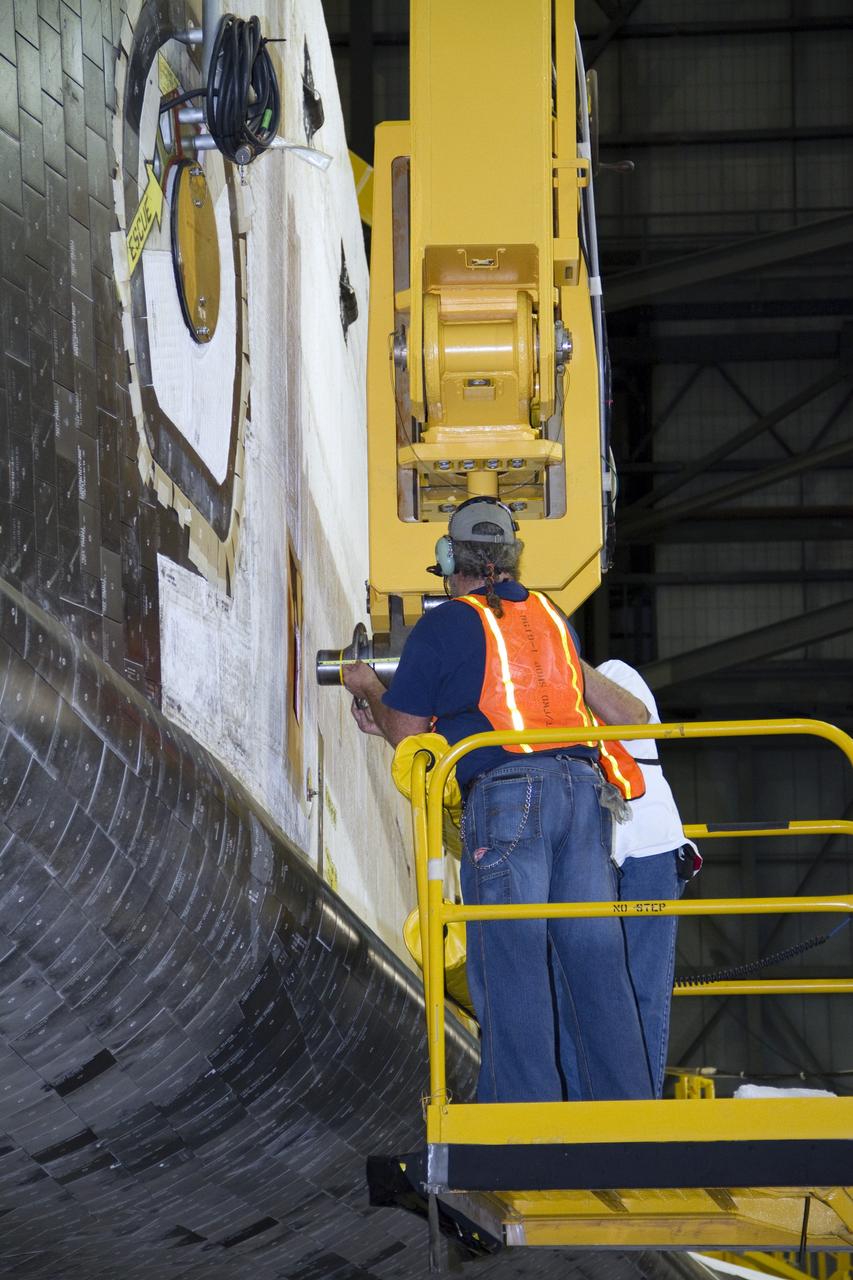

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers attach an overhead crane to shuttle Endeavour. The crane will lift the spacecraft into a high bay where it will be attached to the waiting external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Endeavour's final launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
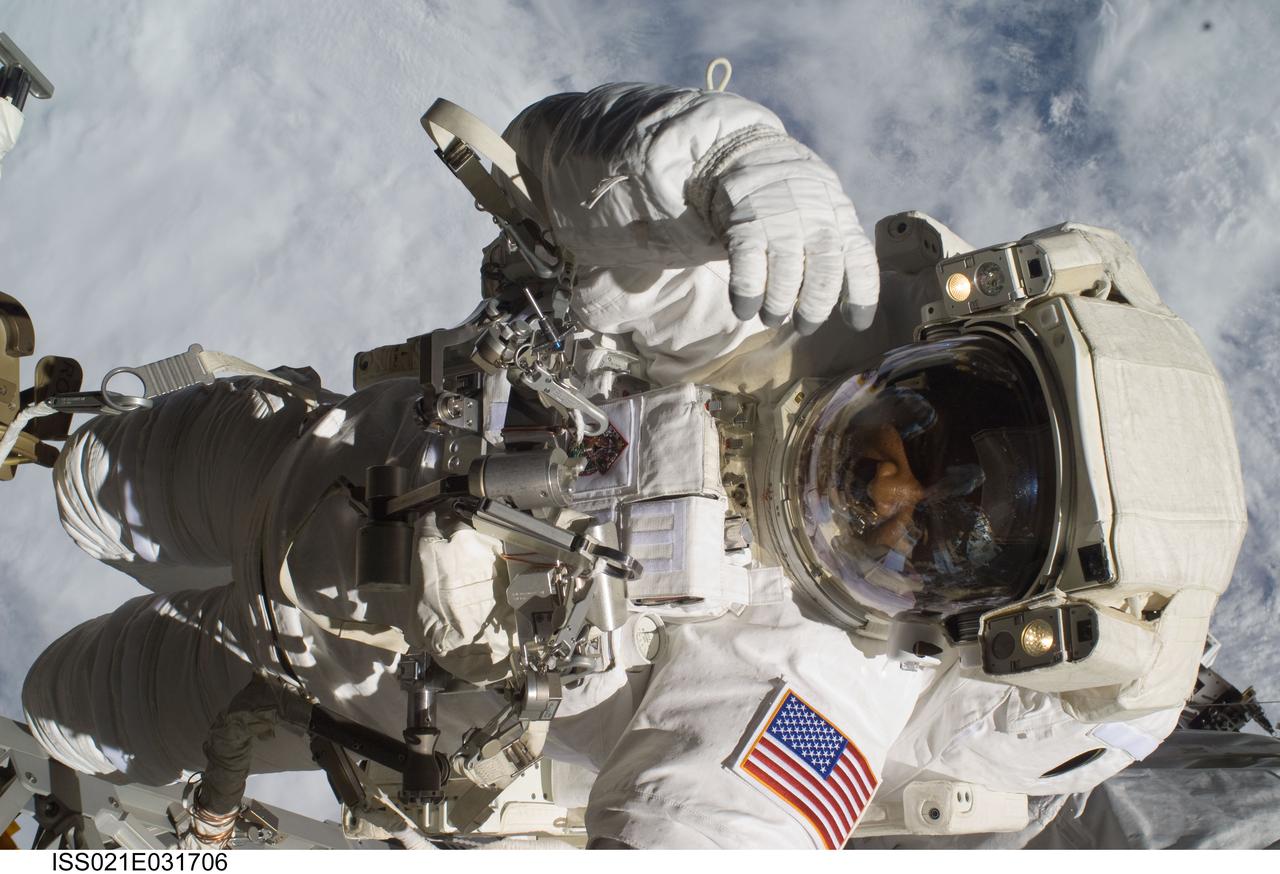

ISS021-E-031706 (23 Nov. 2009) --- Astronaut Robert L. Satcher Jr., STS-129 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third and final session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 42-minute spacewalk, Satcher and astronaut Randy Bresnik (out of frame), mission specialist, removed a pair of micrometeoroid and orbital debris shields from the Quest airlock and strapped them to the External Stowage Platform #2, then moved an articulating foot restraint to the airlock, and released a bolt on a starboard truss ammonia tank assembly (ATA) in preparation for an STS-131 spacewalk that will replace the ATA.
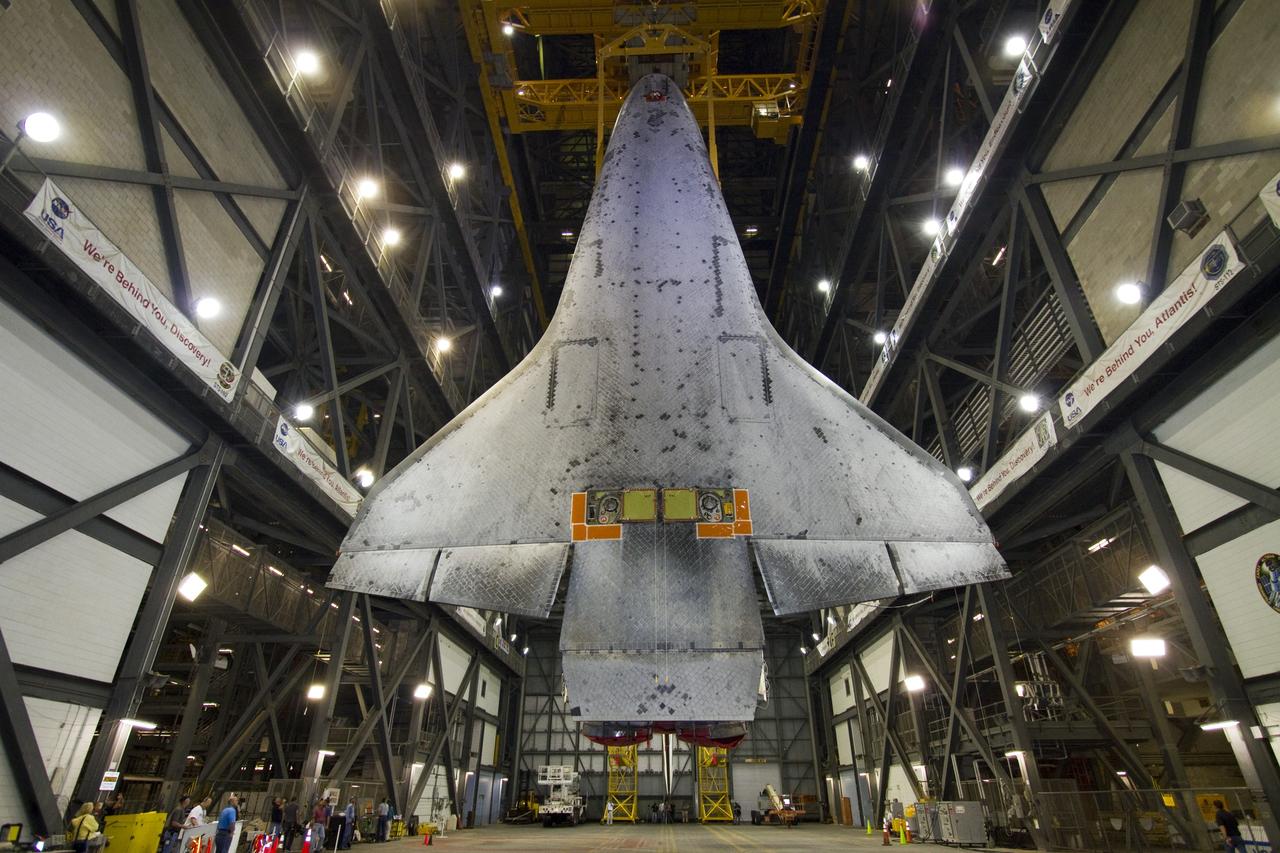

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shuttle Endeavour is suspended vertically over the transfer aisle. The spacecraft will be moved into a high bay where it will be installed to the waiting external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Endeavour's final launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
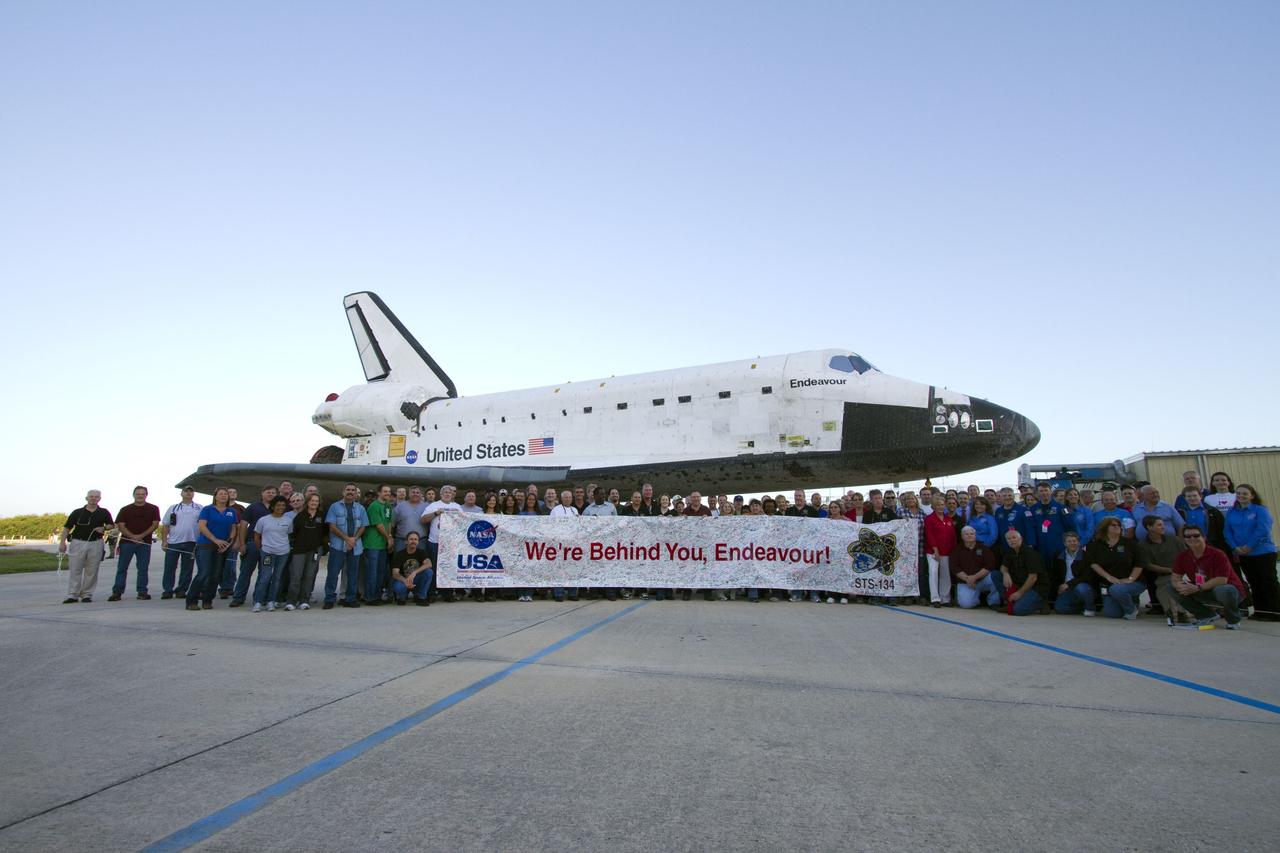

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, employees gather to hold up a banner to commemorate space shuttle Endeavour's STS-134 mission, as it is moved from Orbiter Processing Facility-2 to the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, spare parts, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
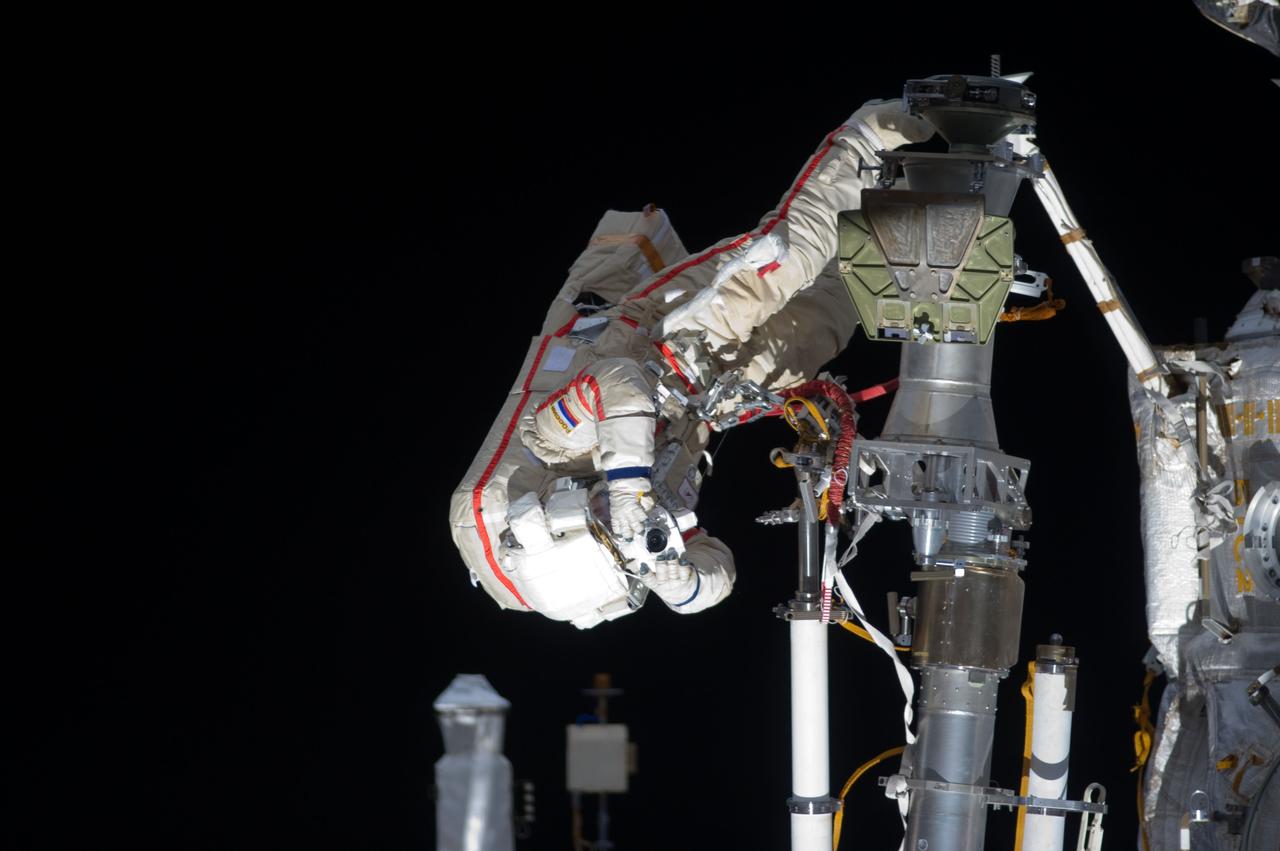
ISS032-E-021072 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, uses a still camera during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
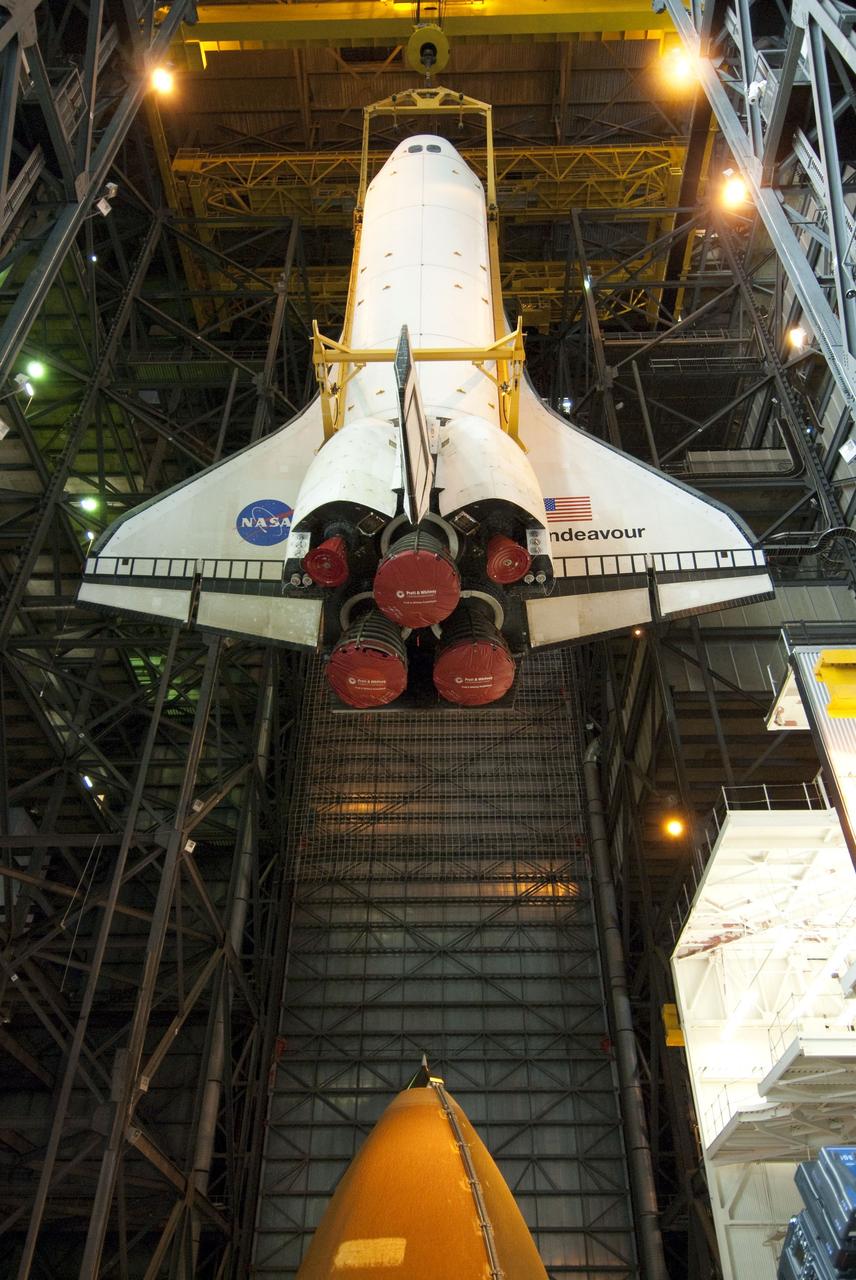

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shuttle Endeavour is being lowered into a high bay to be attached to its external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters, already positioned on the mobile launcher platform. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Endeavour's final launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

This image depicts the tension in the Launch Control Center of the Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral, Florida, during the SA-8 on May 25, 1965. Pointing, center is Dr. Kurt Debus, Director, Launch Operations Directorate, MSFC. To the right is Dr. Hans Gruene, Deputy Director, Launch Operations Directorate, MSFC; Dr. von Braun, Director, Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC); and leaning, Dr. Eberhard Rees, Director, Deputy Director for Research and Development, MSFC. The SA-8 mission, with a Saturn I launch vehicle, made the first night launch and deployed Pegasus II, micrometeoroid detection satellite.
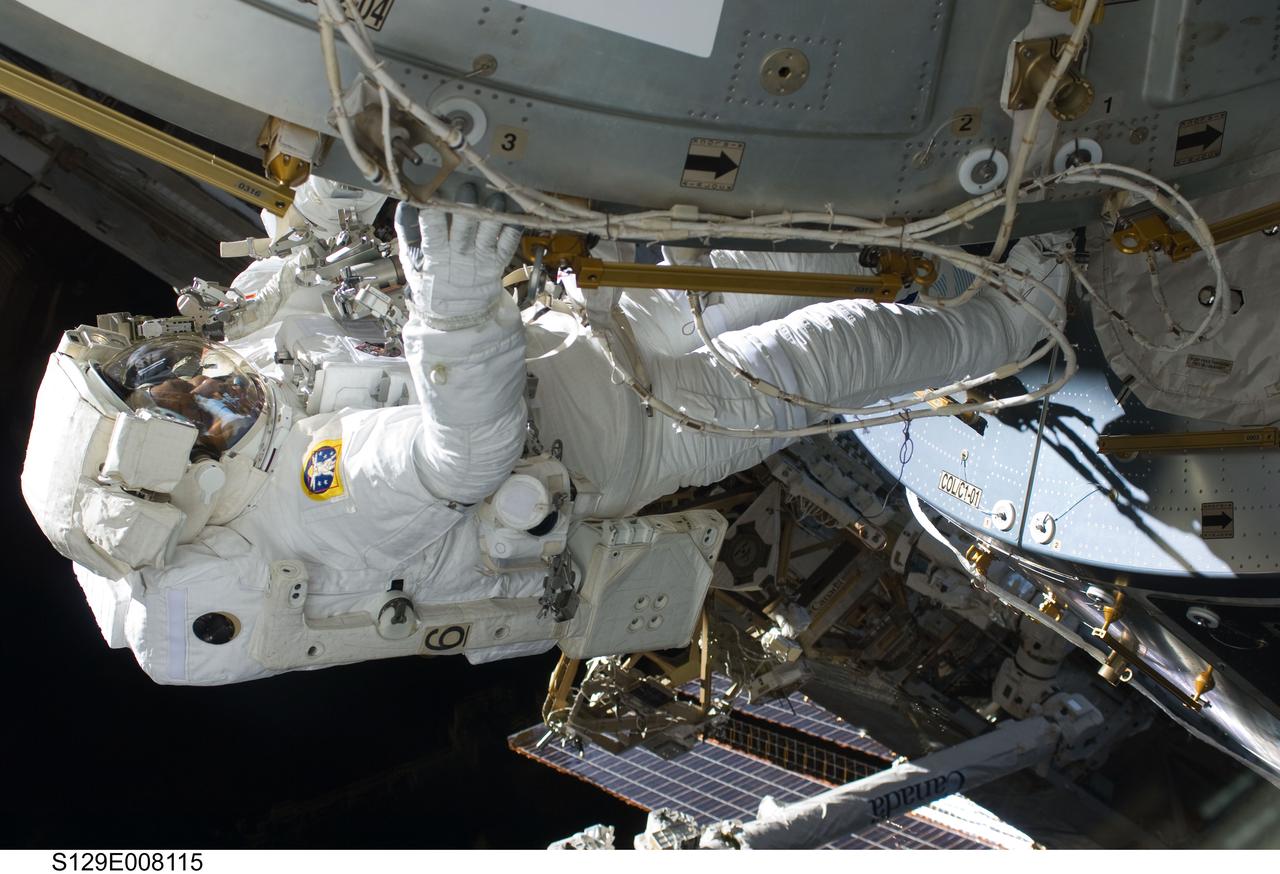

S129-E-008115 (23 Nov. 2009) --- Astronaut Robert L. Satcher Jr., STS-129 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third and final session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 42-minute spacewalk, Satcher and astronaut Randy Bresnik (out of frame), mission specialist, removed a pair of micrometeoroid and orbital debris shields from the Quest airlock and strapped them to the External Stowage Platform #2, then moved an articulating foot restraint to the airlock, and released a bolt on a starboard truss ammonia tank assembly (ATA) in preparation for an STS-131 spacewalk that will replace the ATA.
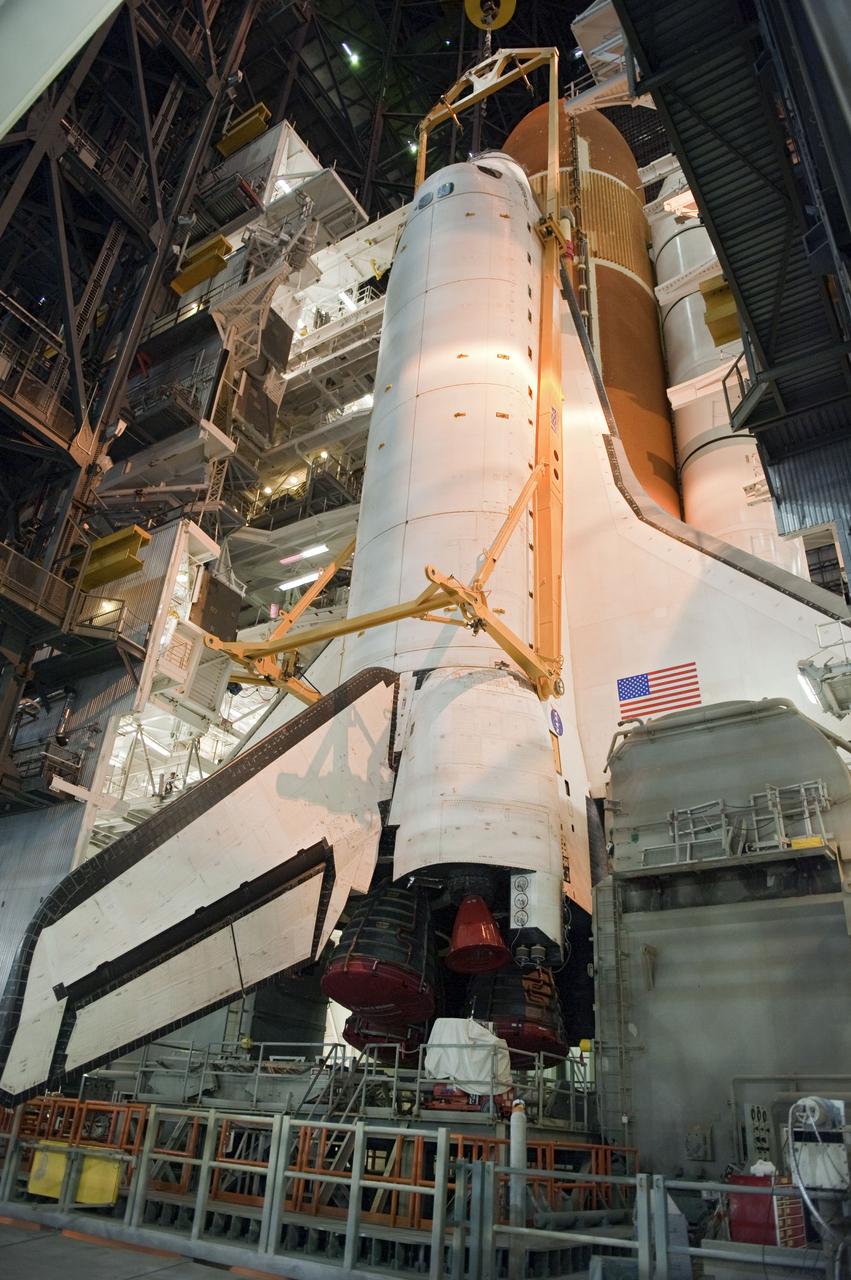

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shuttle Endeavour is lowered into place where it is being attached to its external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters, already positioned on the mobile launcher platform. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Endeavour's final launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
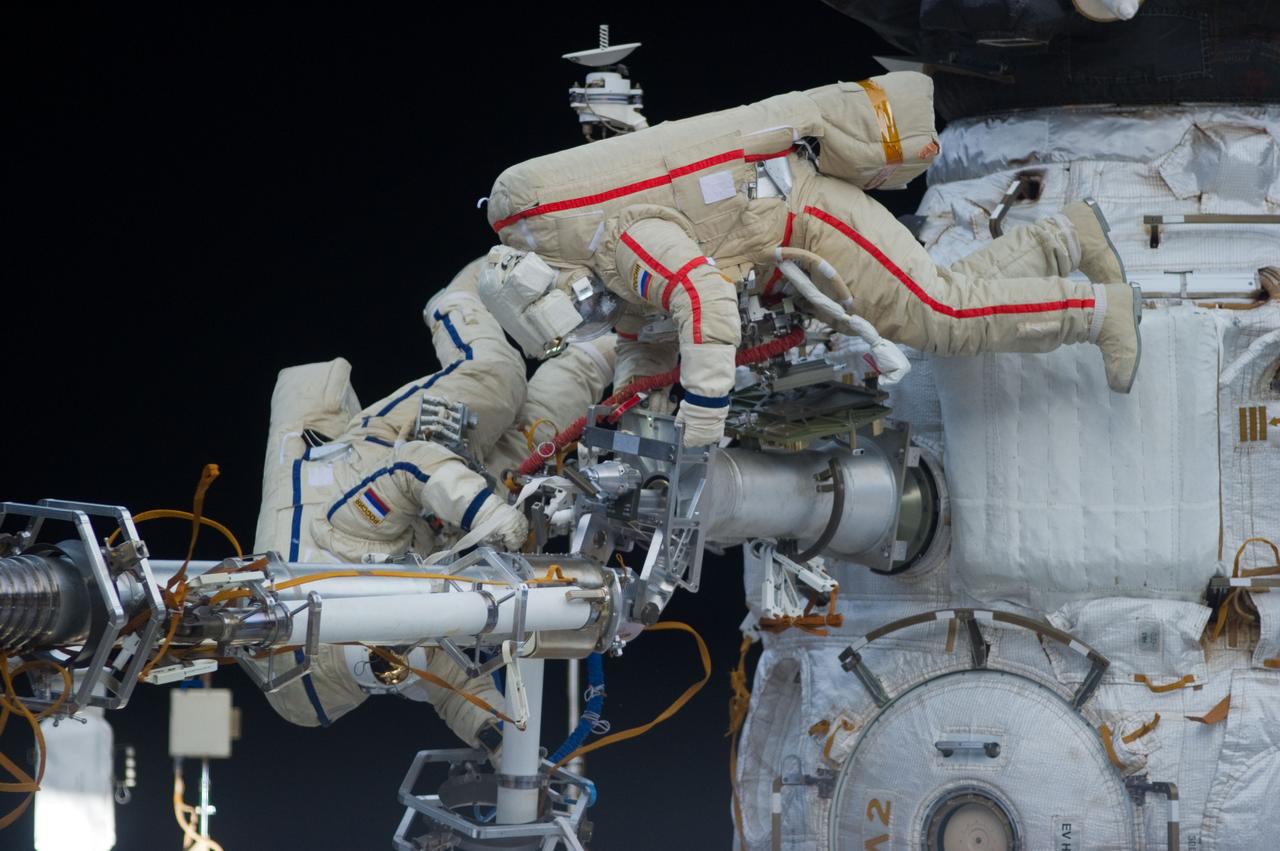

ISS032-E-021061 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Gennady Padalka (top), Expedition 32 commander; and Yuri Malenchenko, flight engineer, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Malenchenko moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
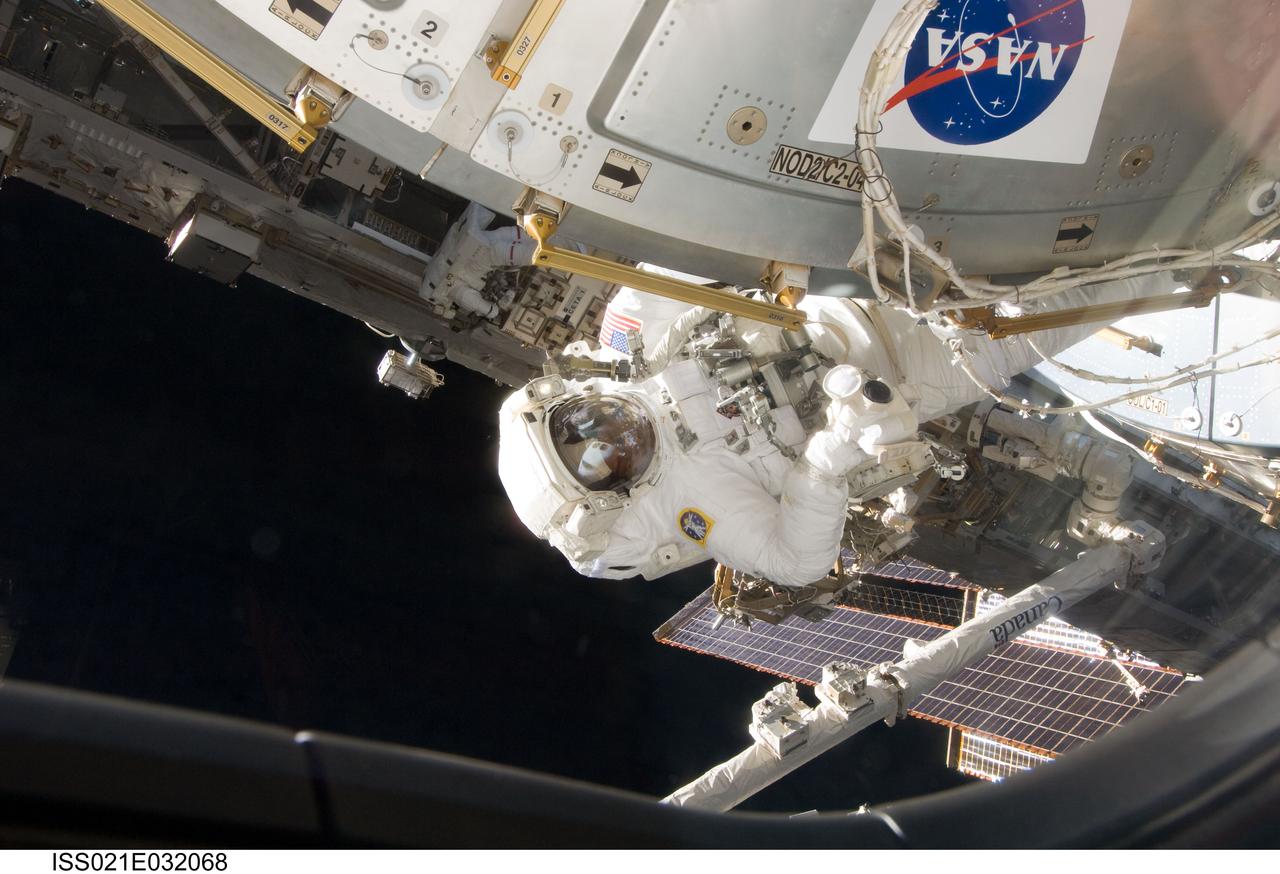

ISS021-E-032068 (23 Nov. 2009) --- Astronaut Robert L. Satcher Jr., STS-129 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third and final session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 42-minute spacewalk, Satcher and astronaut Randy Bresnik (out of frame), mission specialist, removed a pair of micrometeoroid and orbital debris shields from the Quest airlock and strapped them to the External Stowage Platform #2, then moved an articulating foot restraint to the airlock, and released a bolt on a starboard truss ammonia tank assembly (ATA) in preparation for an STS-131 spacewalk that will replace the ATA.
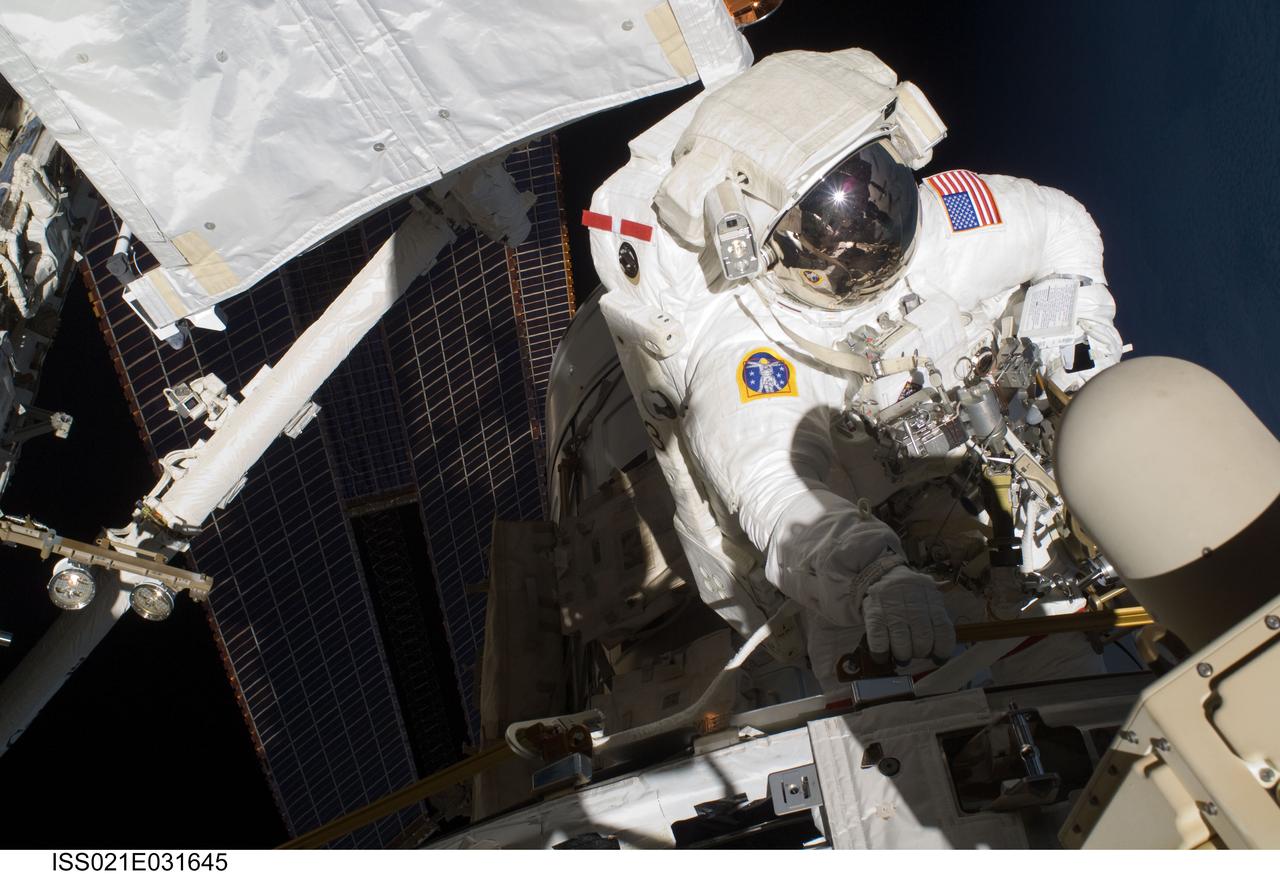

ISS021-E-031645 (23 Nov. 2009) --- Astronaut Randy Bresnik, STS-129 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third and final session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 42-minute spacewalk, Bresnik and Robert L. Satcher Jr. (out of frame), mission specialist, removed a pair of micrometeoroid and orbital debris shields from the Quest airlock and strapped them to the External Stowage Platform #2, then moved an articulating foot restraint to the airlock, and released a bolt on a starboard truss ammonia tank assembly (ATA) in preparation for an STS-131 spacewalk that will replace the ATA.
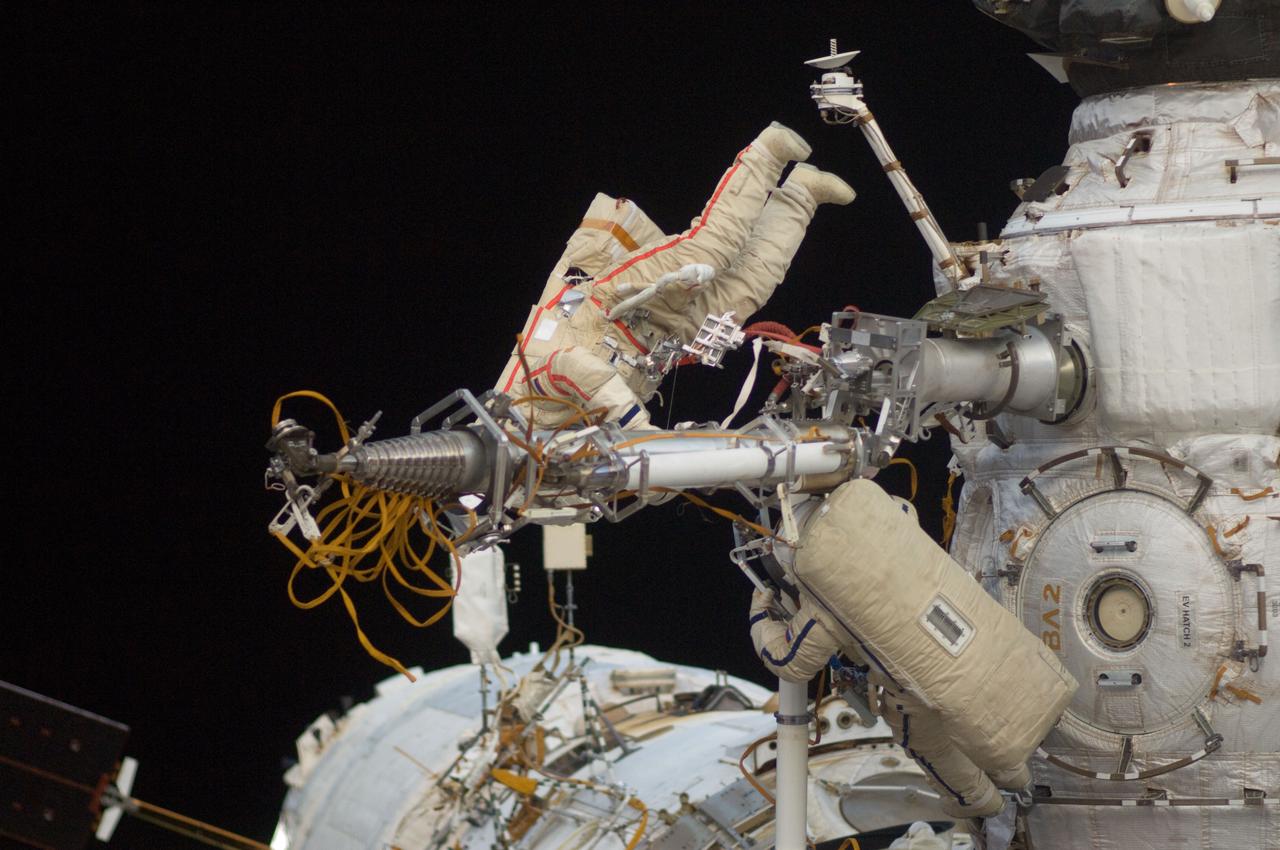

ISS032-E-021286 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Gennady Padalka (top), Expedition 32 commander; and Yuri Malenchenko, flight engineer, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Malenchenko moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
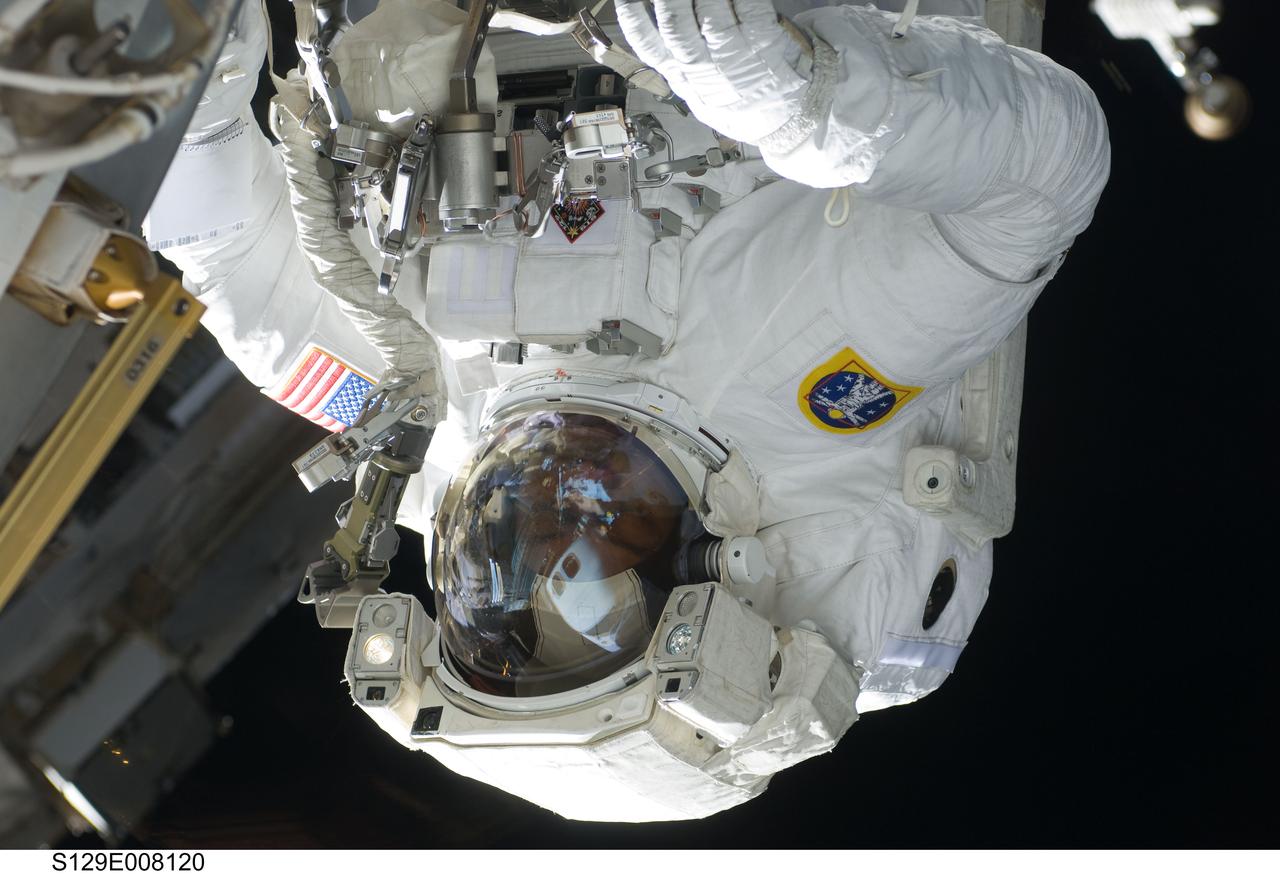

S129-E-008120 (23 Nov. 2009) --- Astronaut Robert L. Satcher Jr., STS-129 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third and final session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 42-minute spacewalk, Satcher and astronaut Randy Bresnik (out of frame), mission specialist, removed a pair of micrometeoroid and orbital debris shields from the Quest airlock and strapped them to the External Stowage Platform #2, then moved an articulating foot restraint to the airlock, and released a bolt on a starboard truss ammonia tank assembly (ATA) in preparation for an STS-131 spacewalk that will replace the ATA.
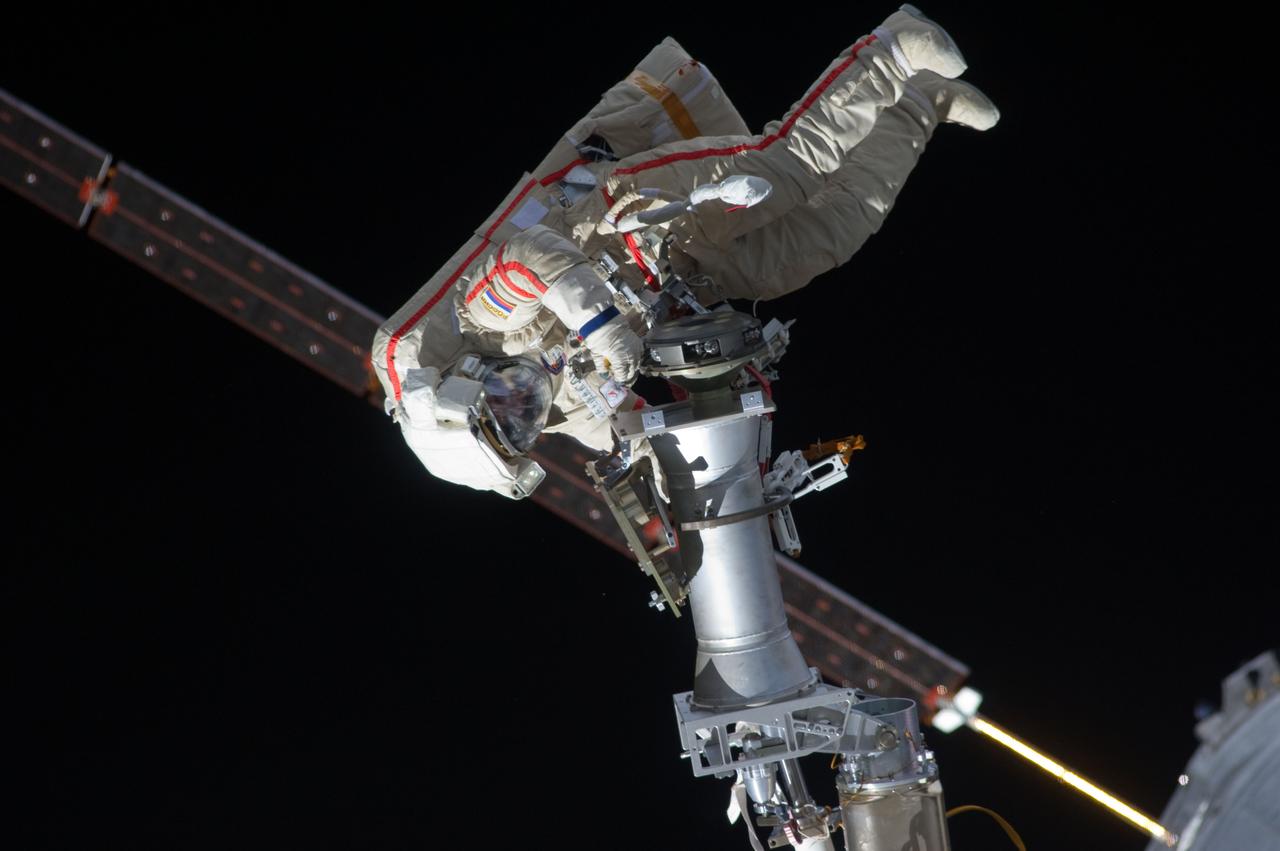

ISS032-E-021085 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
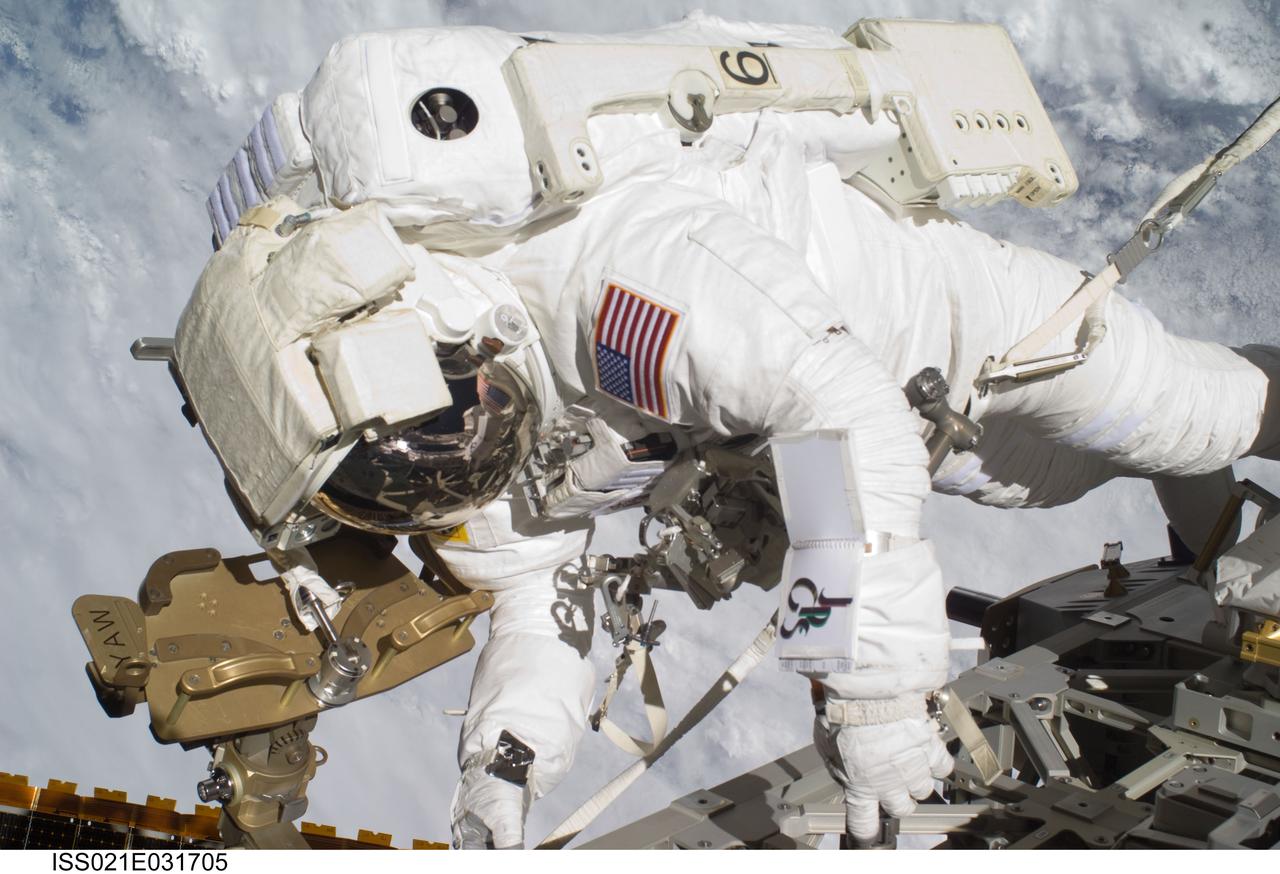

ISS021-E-031705 (23 Nov. 2009) --- Astronaut Robert L. Satcher Jr., STS-129 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third and final session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 42-minute spacewalk, Satcher and astronaut Randy Bresnik (out of frame), mission specialist, removed a pair of micrometeoroid and orbital debris shields from the Quest airlock and strapped them to the External Stowage Platform #2, then moved an articulating foot restraint to the airlock, and released a bolt on a starboard truss ammonia tank assembly (ATA) in preparation for an STS-131 spacewalk that will replace the ATA.
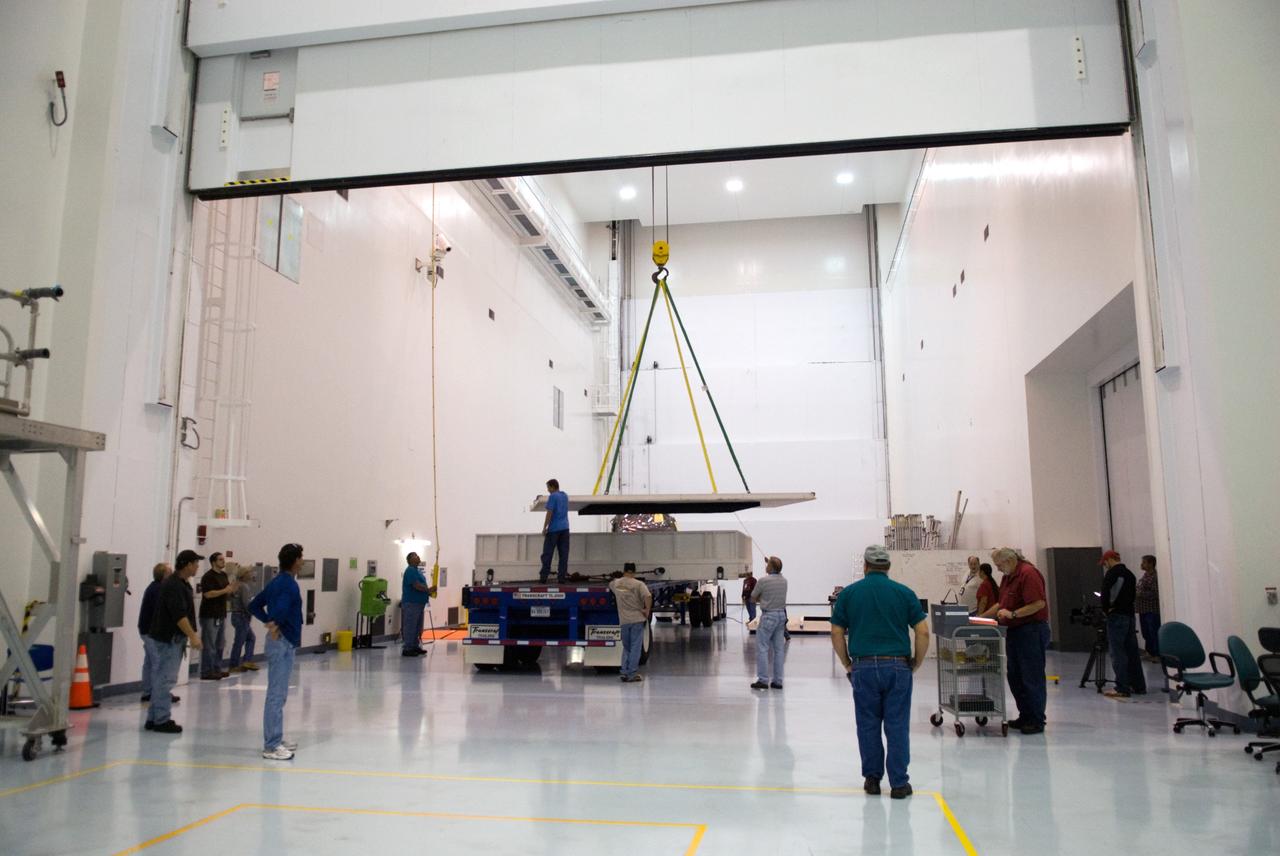

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers supervise the uncrating of the ExPRESS Logistics Carrier 3, or ELC-3. ELC-3 and the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer are the primary payloads for space shuttle Endeavour's STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. The STS-134 crew will also deliver spare parts including two S-band communications antennas, a high pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields. Endeavour's launch is targeted for July 29, 2010. For information on the STS-134 mission objectives and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
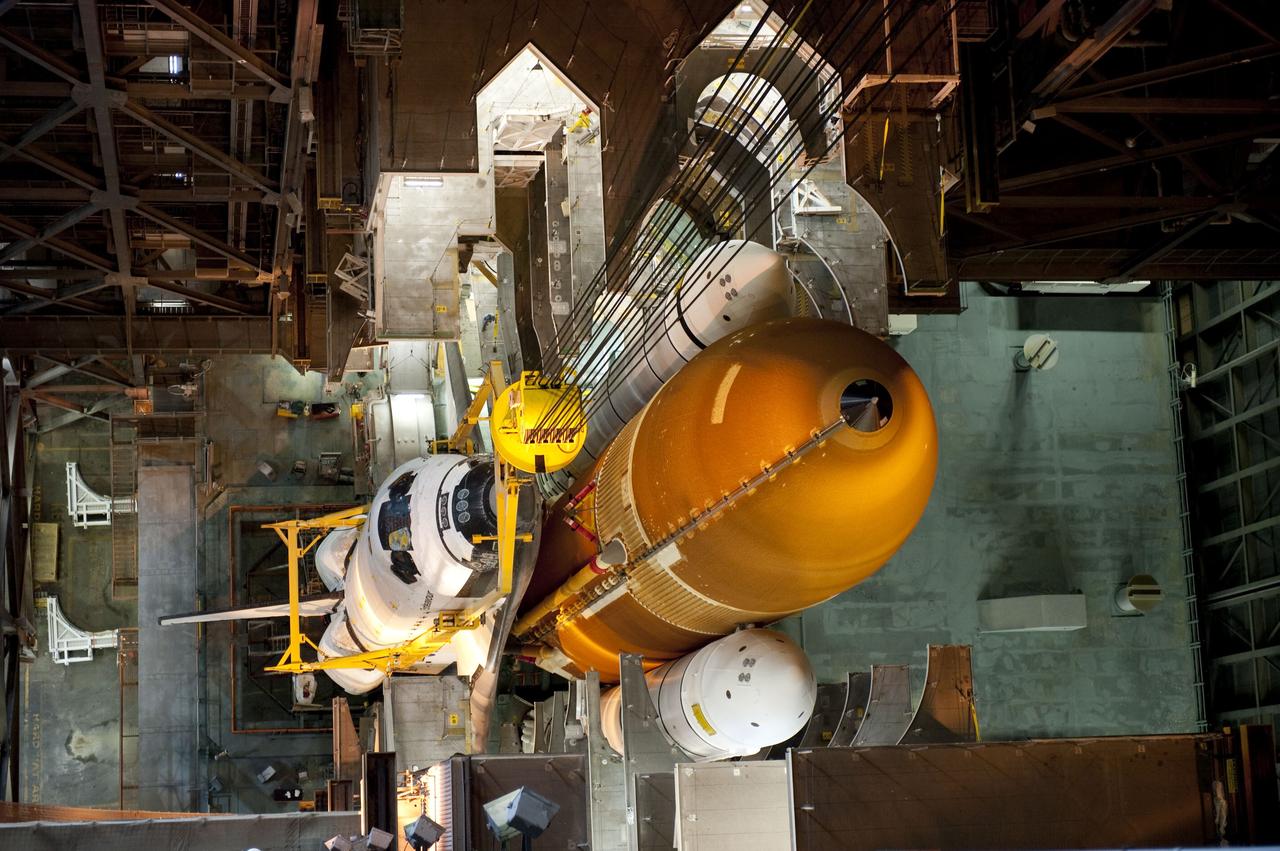

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shuttle Endeavour is lowered into place where it is being attached to its external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters, already positioned on the mobile launcher platform. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Endeavour's final launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
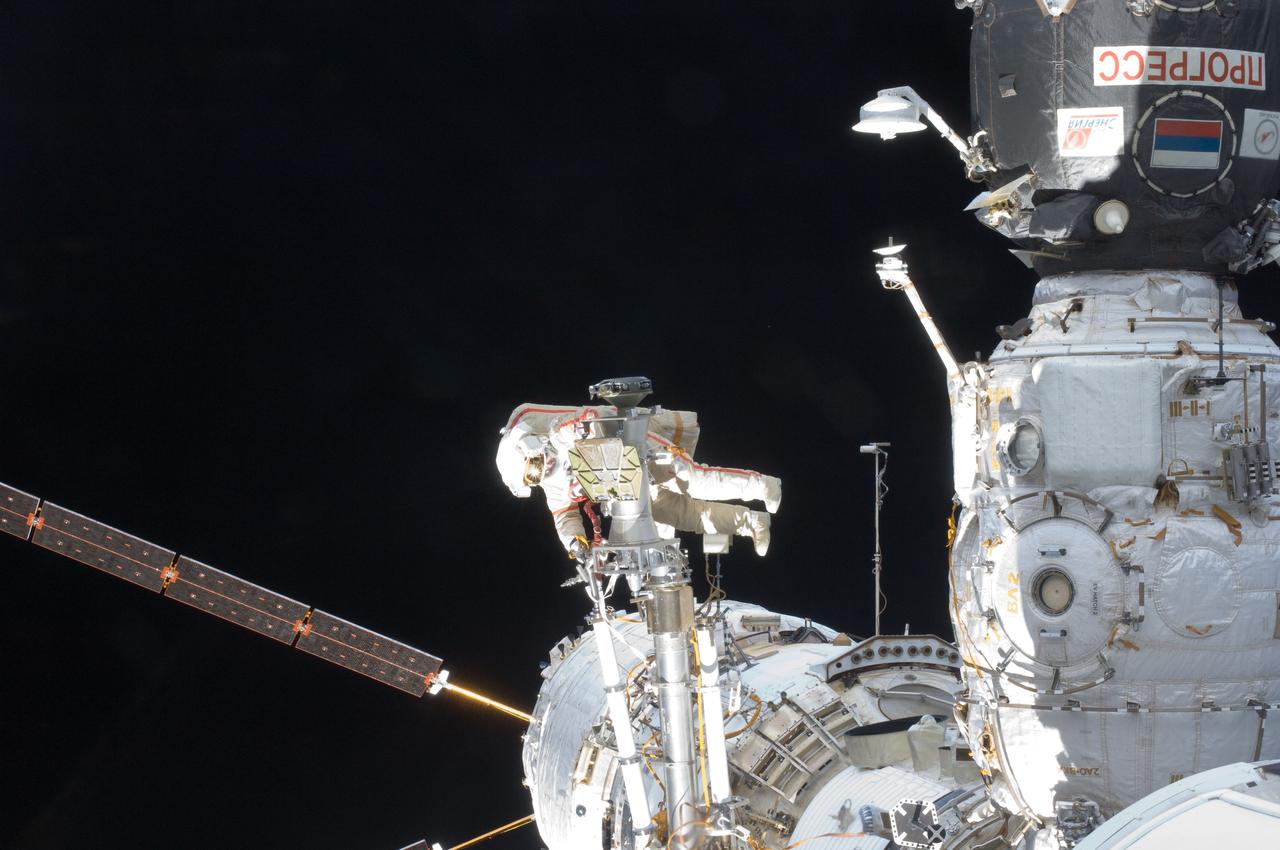

ISS032-E-020683 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
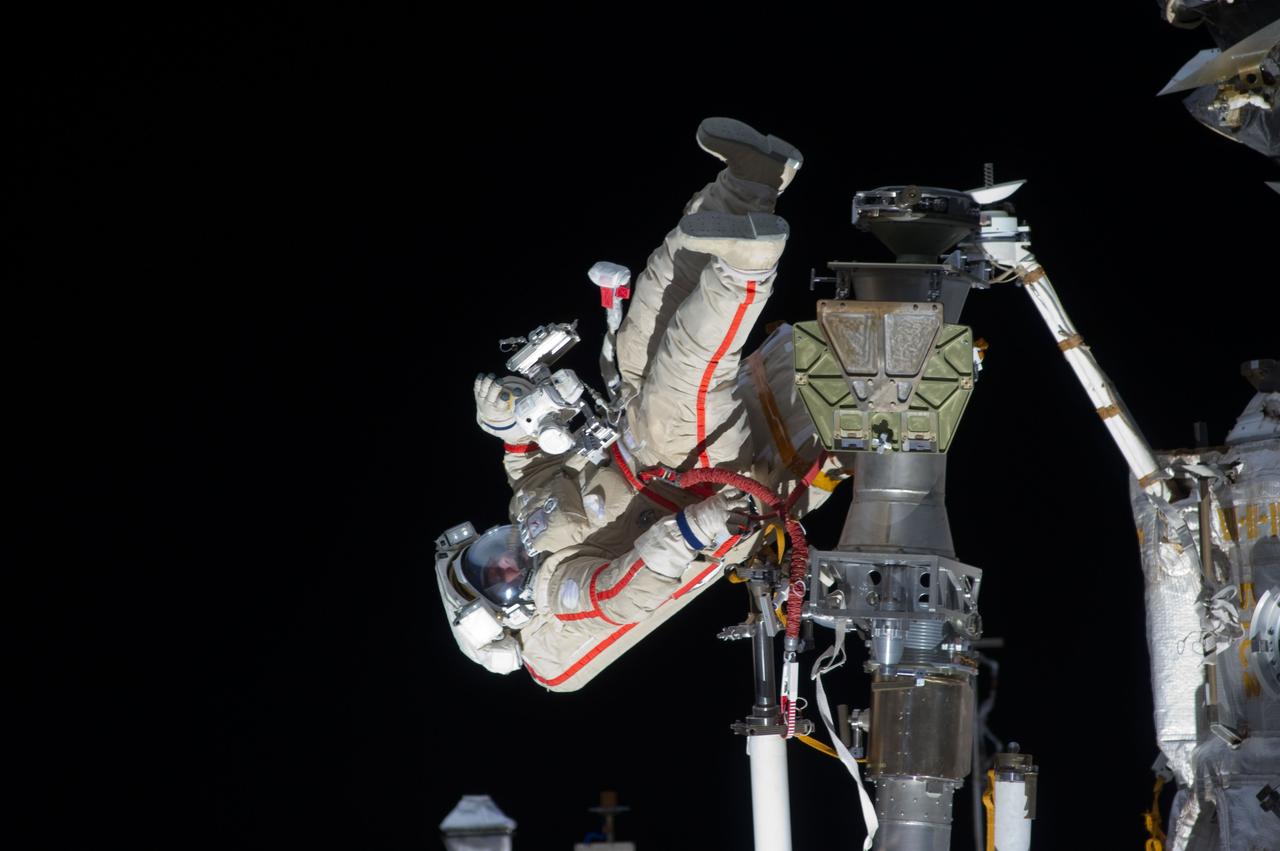
ISS032-E-021080 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
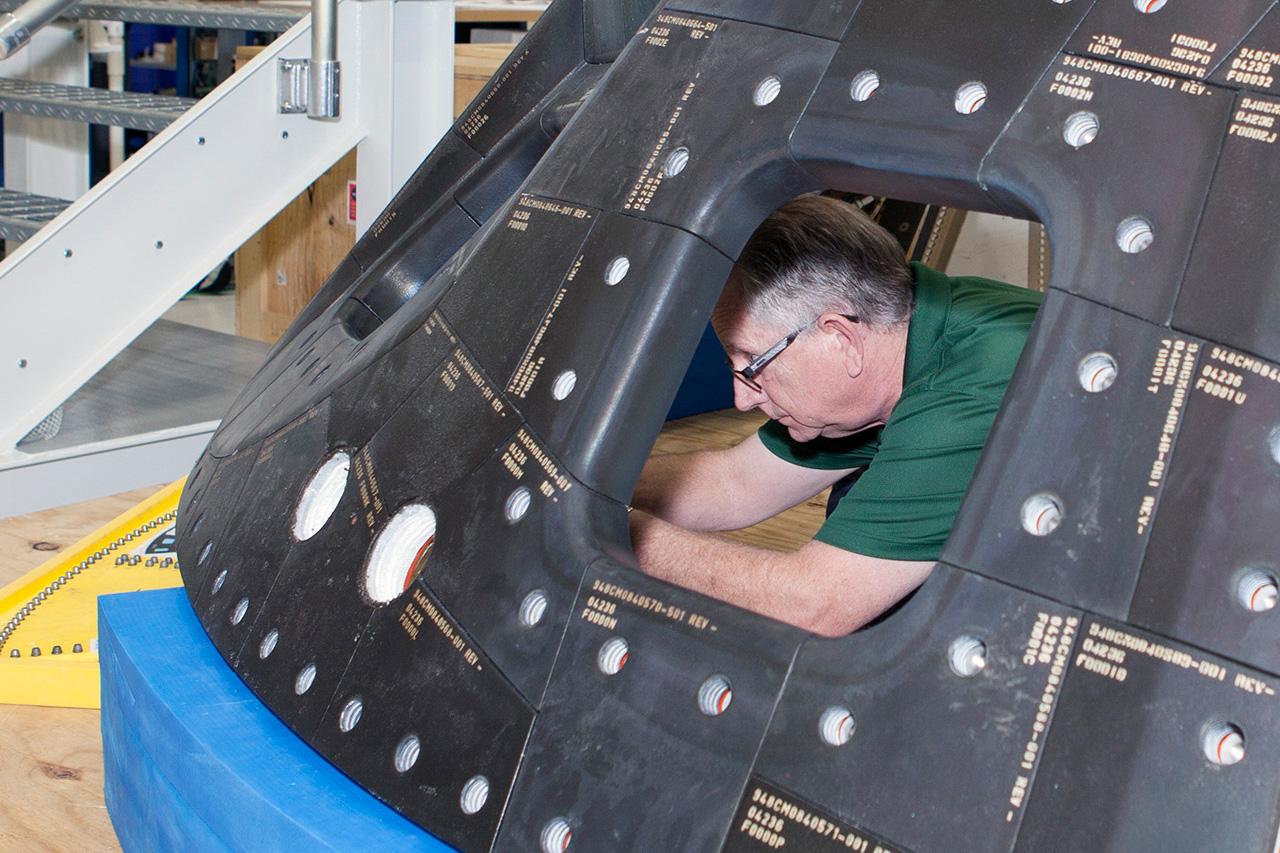

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians remove a side thermal window from one of Orion's tile panels on May 15, 2015. The tile panels with thermal windows intact were removed from Orion in the Launch Abort System Facility after the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) spacecraft returned to Kennedy in late December. All of the windows are being removed and disassembled for post-flight inspection for any signs of micrometeoroid or orbital debris impacts or other potential glass damage. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
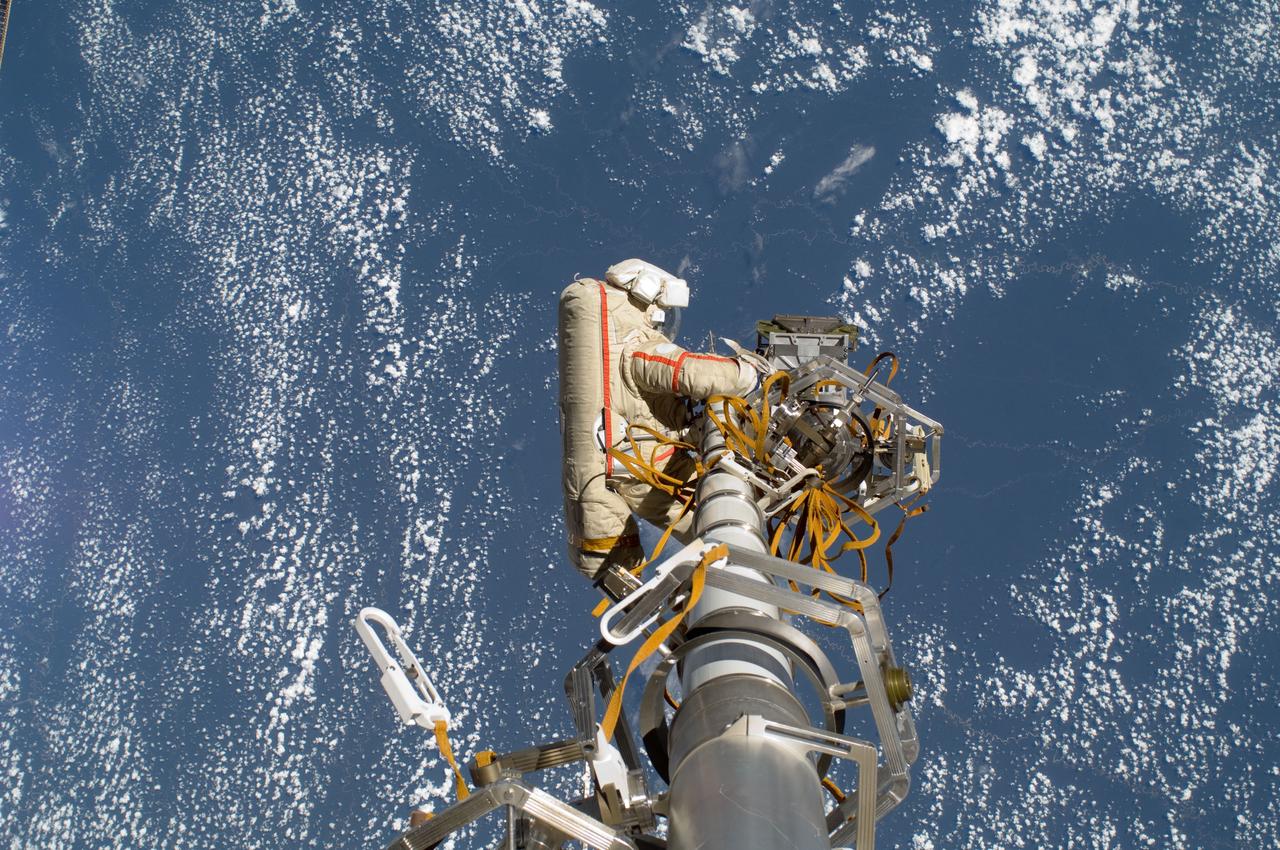

ISS032-E-020576 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
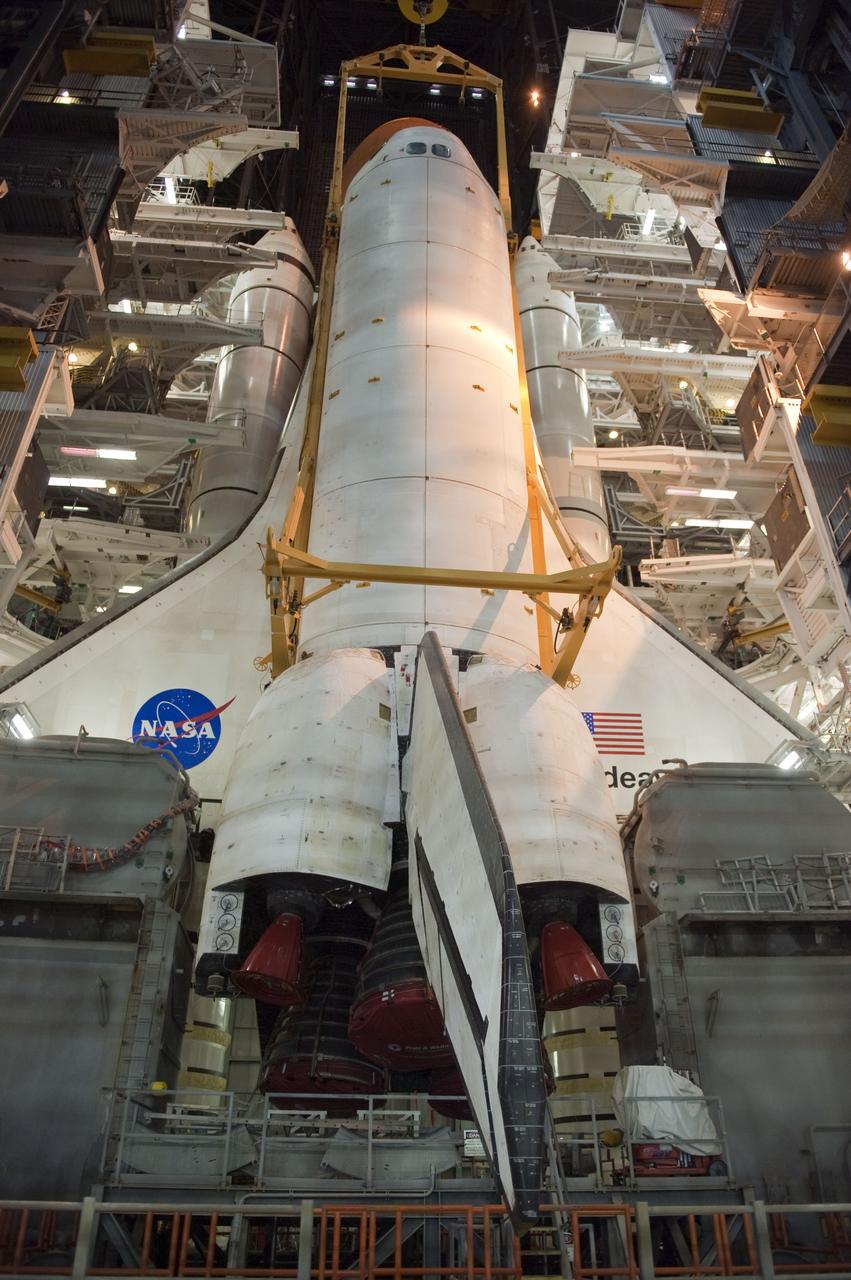

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shuttle Endeavour is lowered into place where it is being attached to its external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters, already positioned on the mobile launcher platform. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Endeavour's final launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
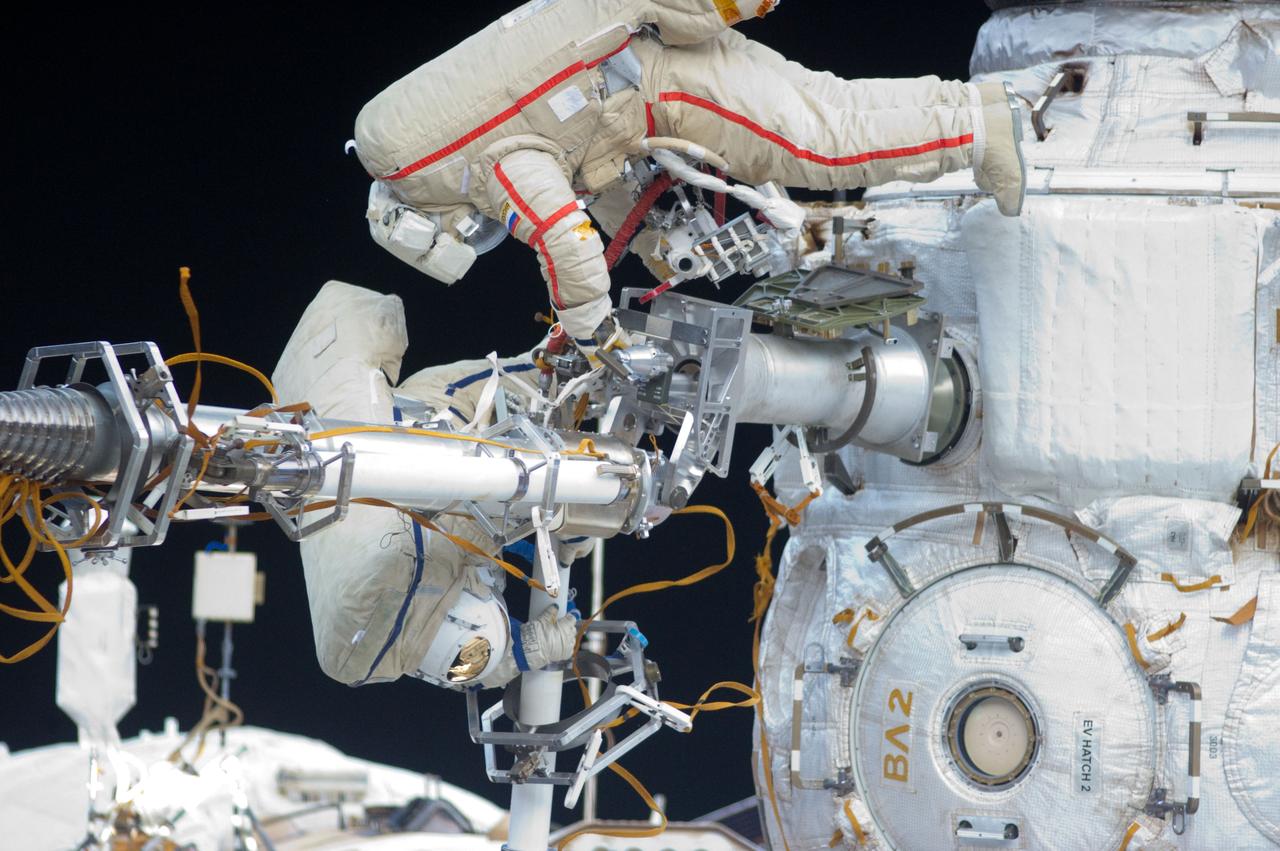
ISS032-E-021060 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Gennady Padalka (top), Expedition 32 commander; and Yuri Malenchenko, flight engineer, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Malenchenko moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
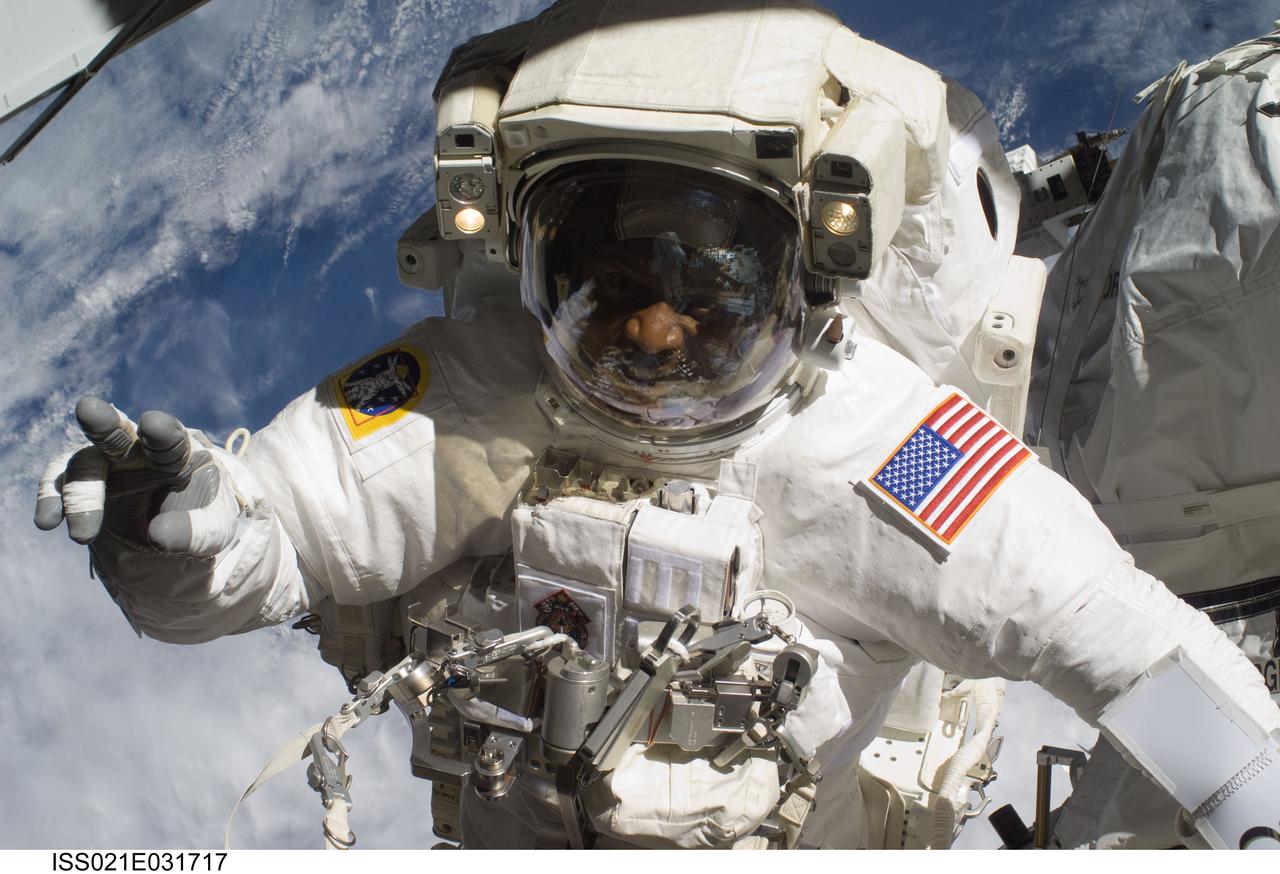

ISS021-E-031717 (23 Nov. 2009) --- Astronaut Robert L. Satcher Jr., STS-129 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third and final session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 42-minute spacewalk, Satcher and astronaut Randy Bresnik (out of frame), mission specialist, removed a pair of micrometeoroid and orbital debris shields from the Quest airlock and strapped them to the External Stowage Platform #2, then moved an articulating foot restraint to the airlock, and released a bolt on a starboard truss ammonia tank assembly (ATA) in preparation for an STS-131 spacewalk that will replace the ATA.
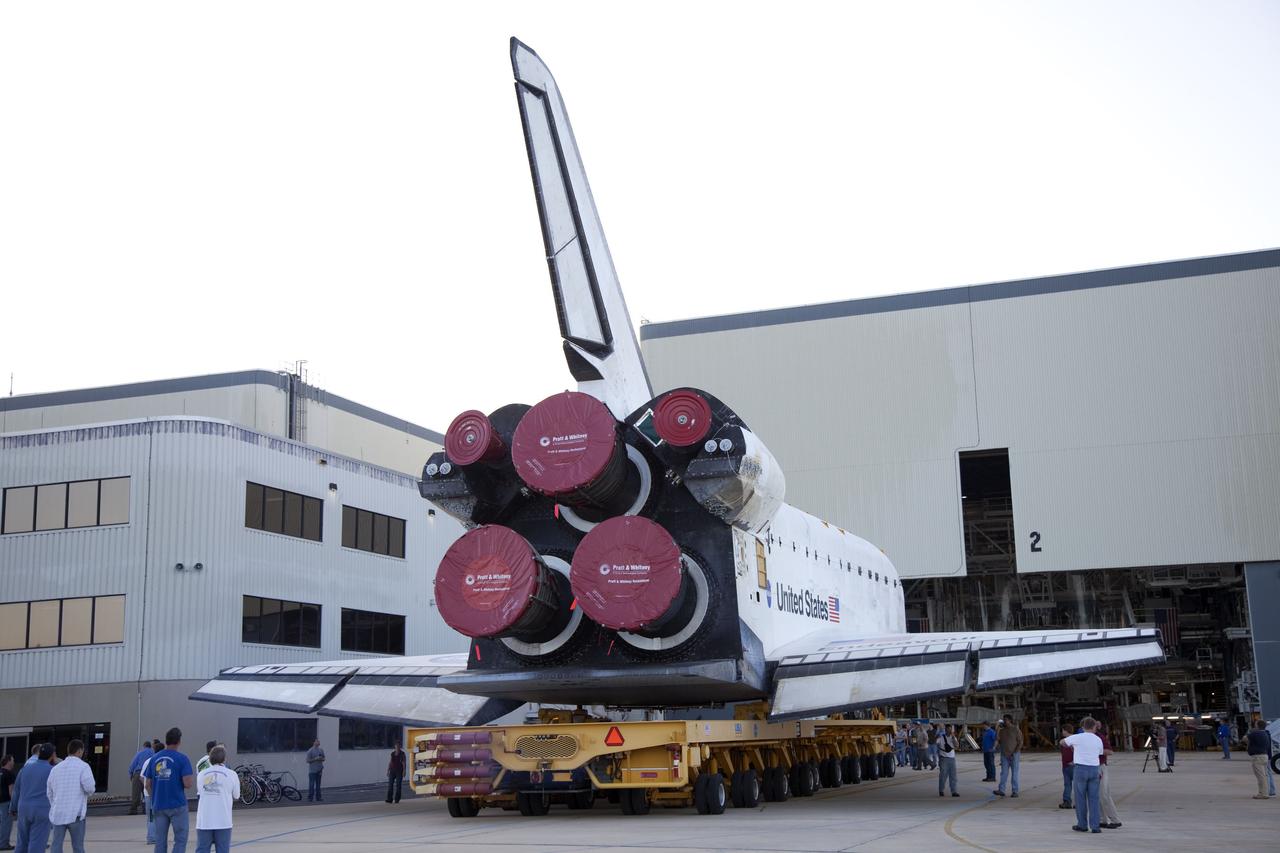

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers accompany space shuttle Endeavour as it is backed out of Orbiter Processing Facility-2 for its move, or "rollover," to the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, spare parts, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
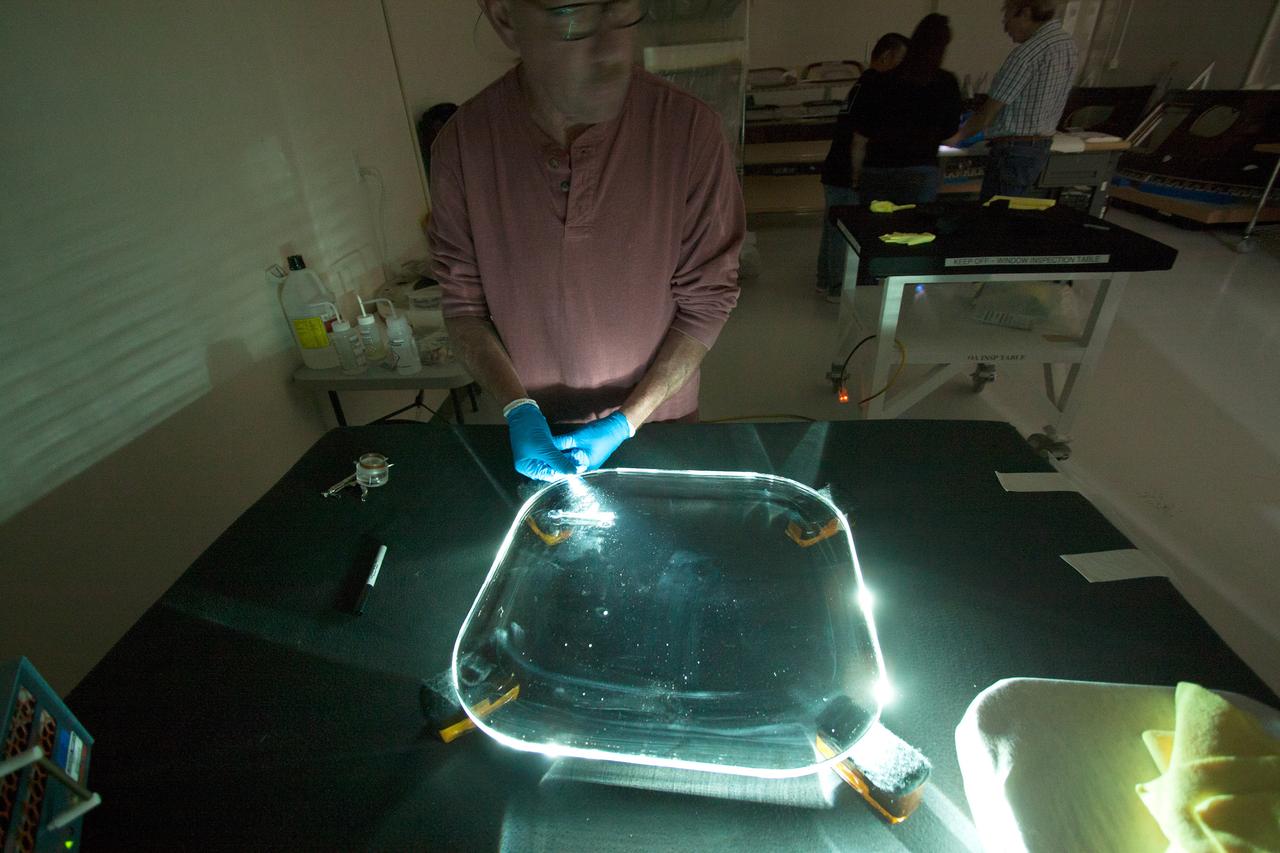

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians remove a side thermal window from one of Orion's tile panels on May 15, 2015. The tile panels with thermal windows intact were removed from Orion in the Launch Abort System Facility after the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) spacecraft returned to Kennedy in late December. All of the windows are being removed and disassembled for post-flight inspection for any signs of micrometeoroid or orbital debris impacts or other potential glass damage. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
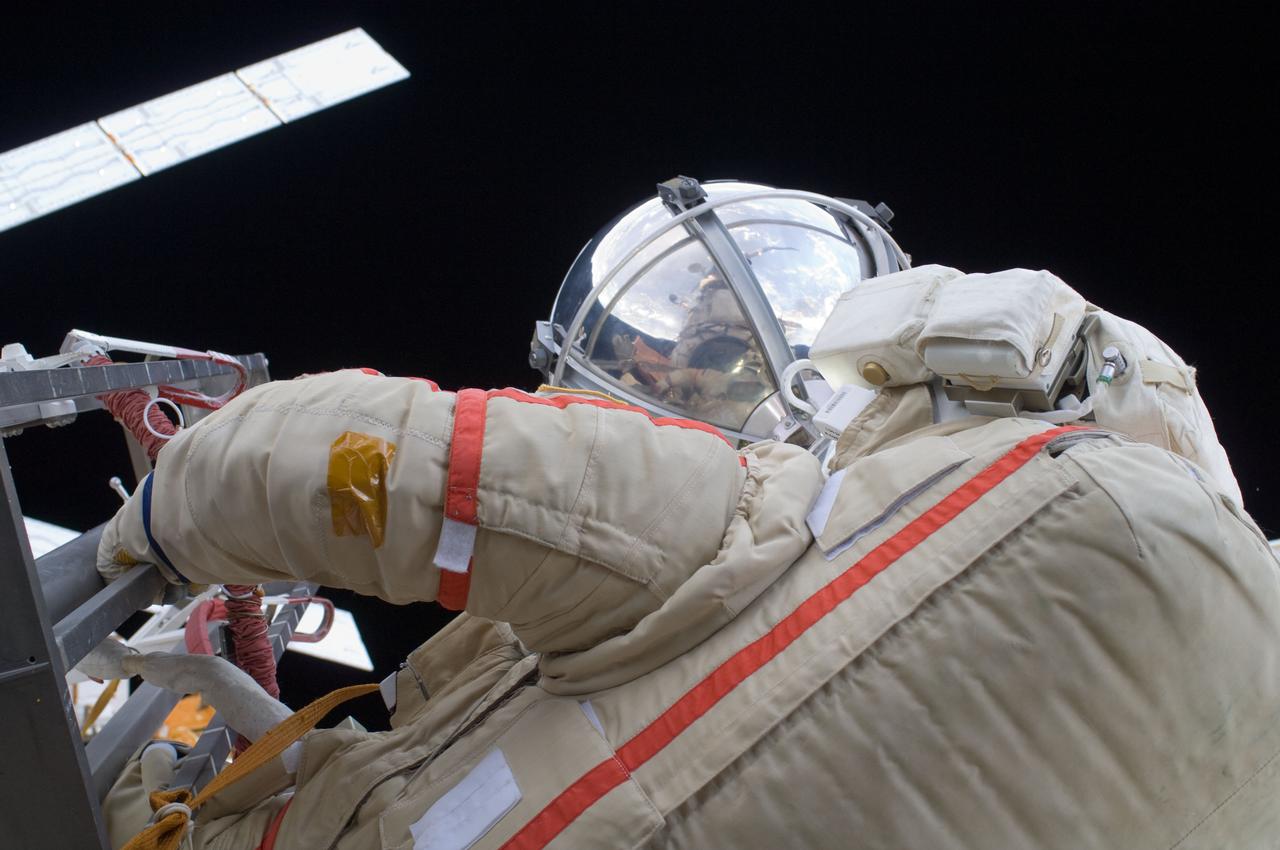

ISS032-E-020596 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, deploys a small ball-shaped science satellite during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, also moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module.
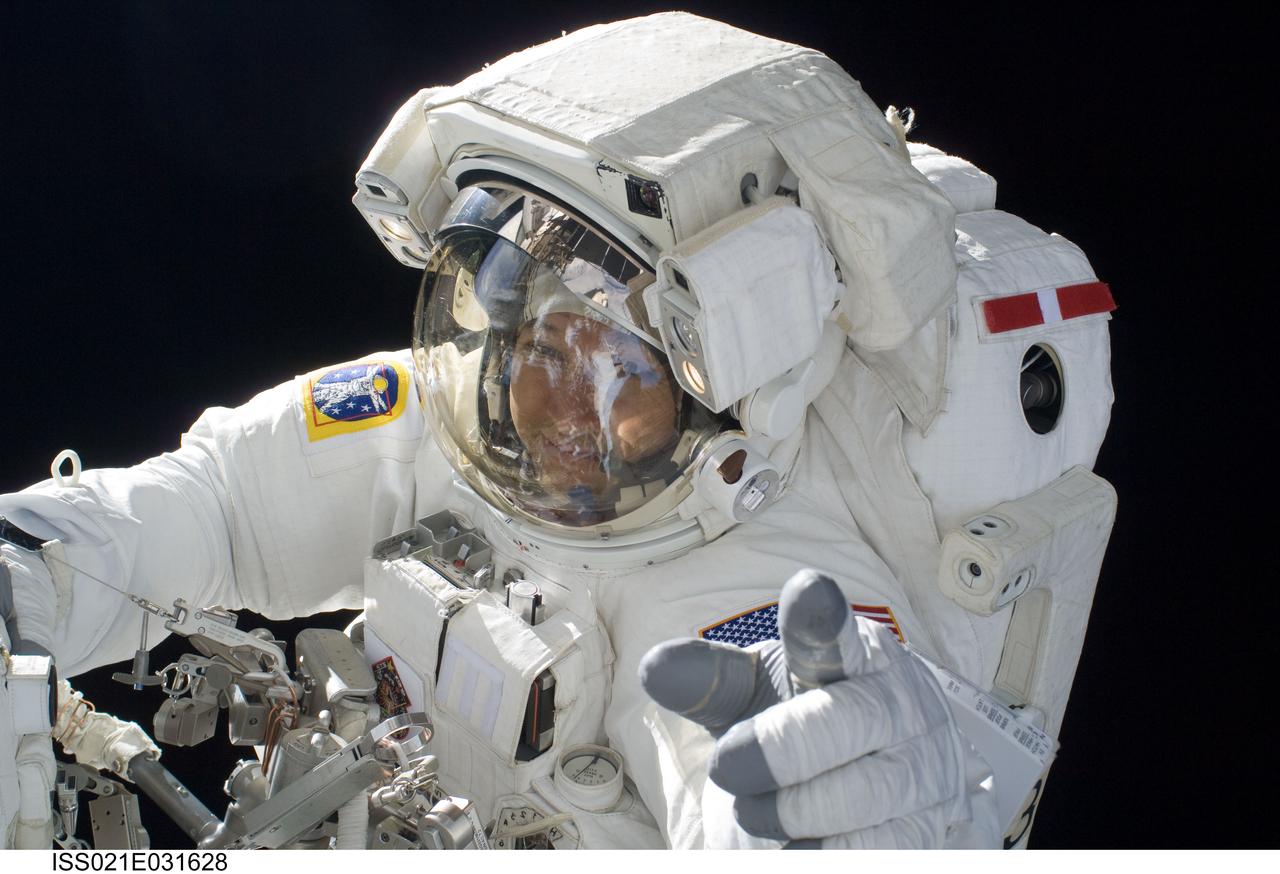

ISS021-E-031628 (23 Nov. 2009) --- Astronaut Randy Bresnik, STS-129 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third and final session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 42-minute spacewalk, Bresnik and Robert L. Satcher Jr. (out of frame), mission specialist, removed a pair of micrometeoroid and orbital debris shields from the Quest airlock and strapped them to the External Stowage Platform #2, then moved an articulating foot restraint to the airlock, and released a bolt on a starboard truss ammonia tank assembly (ATA) in preparation for an STS-131 spacewalk that will replace the ATA.
In this photograph, the Pegasus, meteoroid detection satellite is installed in its specially modified Apollo service module atop the S-IV stage (second stage) of a Saturn I vehicle for the SA-9 mission at Cape Kennedy. Personnel in the service structure moved the boilerplate Apollo command module into place to cap the vehicle. The command and service modules, visible here, were jettisoned into orbit to free the Pegasus for wing deployment. The satellite was used to obtain data on frequency and penetration of the potentially hazardous micrometeoroids in low Earth orbits and to relay the information back to Earth. The SA-9 was launched on February 16, 1965.
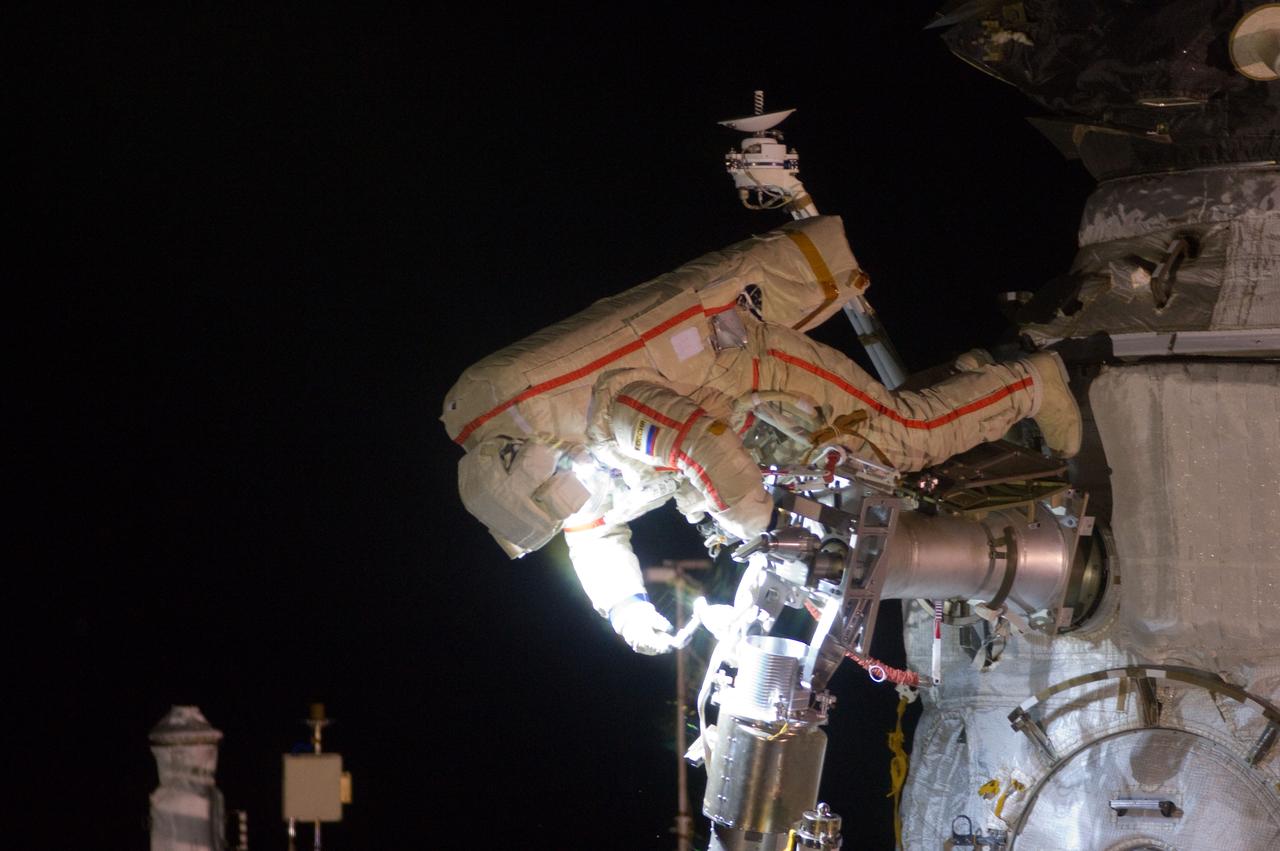

ISS032-E-021028 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
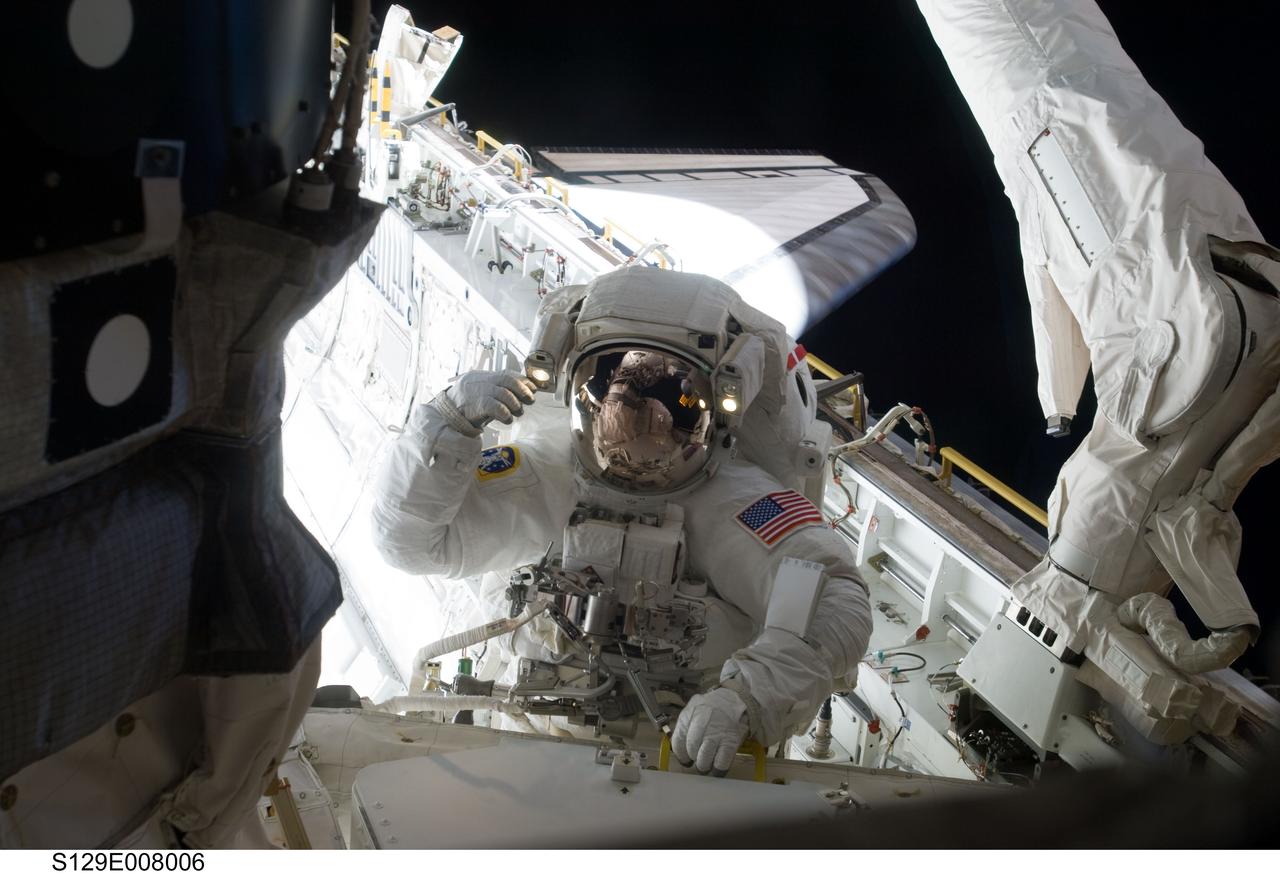

S129-E-008006 (23 Nov. 2009) --- Astronaut Randy Bresnik, STS-129 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third and final session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 42-minute spacewalk, Bresnik and astronaut Robert L. Satcher Jr. (out of frame), mission specialist, removed a pair of micrometeoroid and orbital debris shields from the Quest airlock and strapped them to the External Stowage Platform #2, then moved an articulating foot restraint to the airlock, and released a bolt on a starboard truss ammonia tank assembly (ATA) in preparation for an STS-131 spacewalk that will replace the ATA.
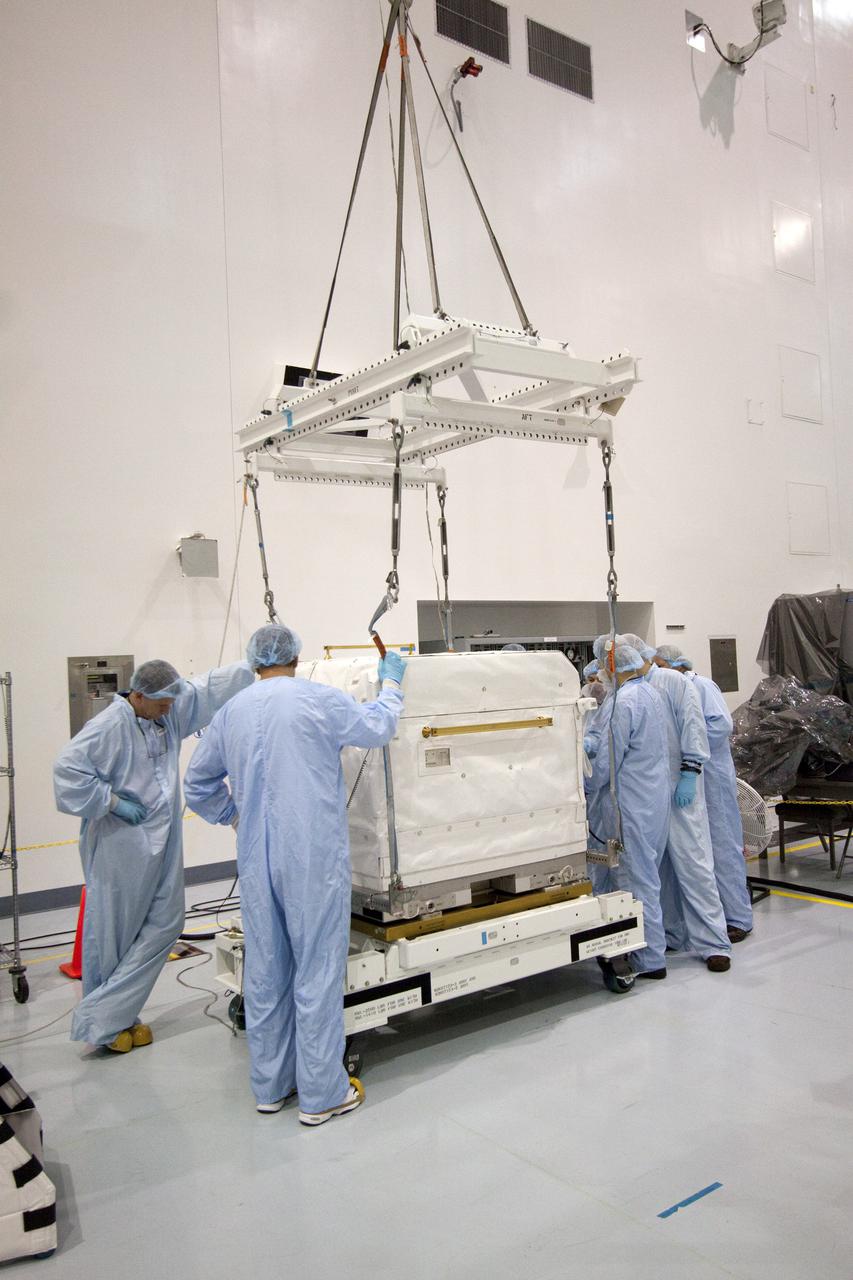

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are under way to move a cargo transport container to the ExPRESS Logistics Carrier-3, or ELC-3, on which it will be installed. The ELC-3 and the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer are the primary payloads on space shuttle Endeavour's STS-134 mission to the International Space Station. Spare parts, including two S-band communications antennas; a high pressure gas tank; replacement parts for Dextre, the robotic hand on the station; and micrometeoroid debris shields, also will be delivered to the station. Endeavour's launch is targeted for mid-November. For information on the STS-134 mission, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts134_index.html. Photo credit: NASA_Jack Pfaller
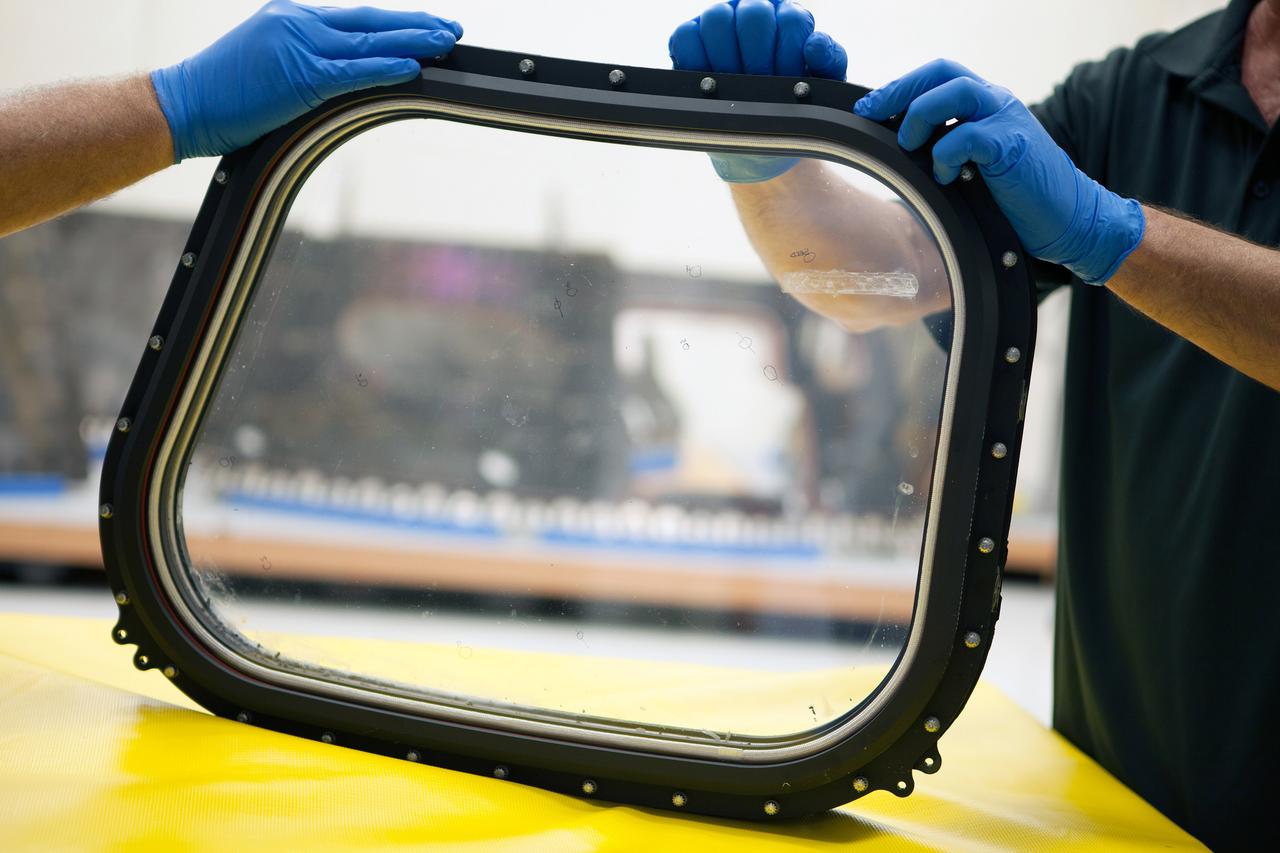

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians remove a side thermal window from one of Orion's tile panels on May 15, 2015. The tile panels with thermal windows intact were removed from Orion in the Launch Abort System Facility after the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) spacecraft returned to Kennedy in late December. All of the windows are being removed and disassembled for post-flight inspection for any signs of micrometeoroid or orbital debris impacts or other potential glass damage. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
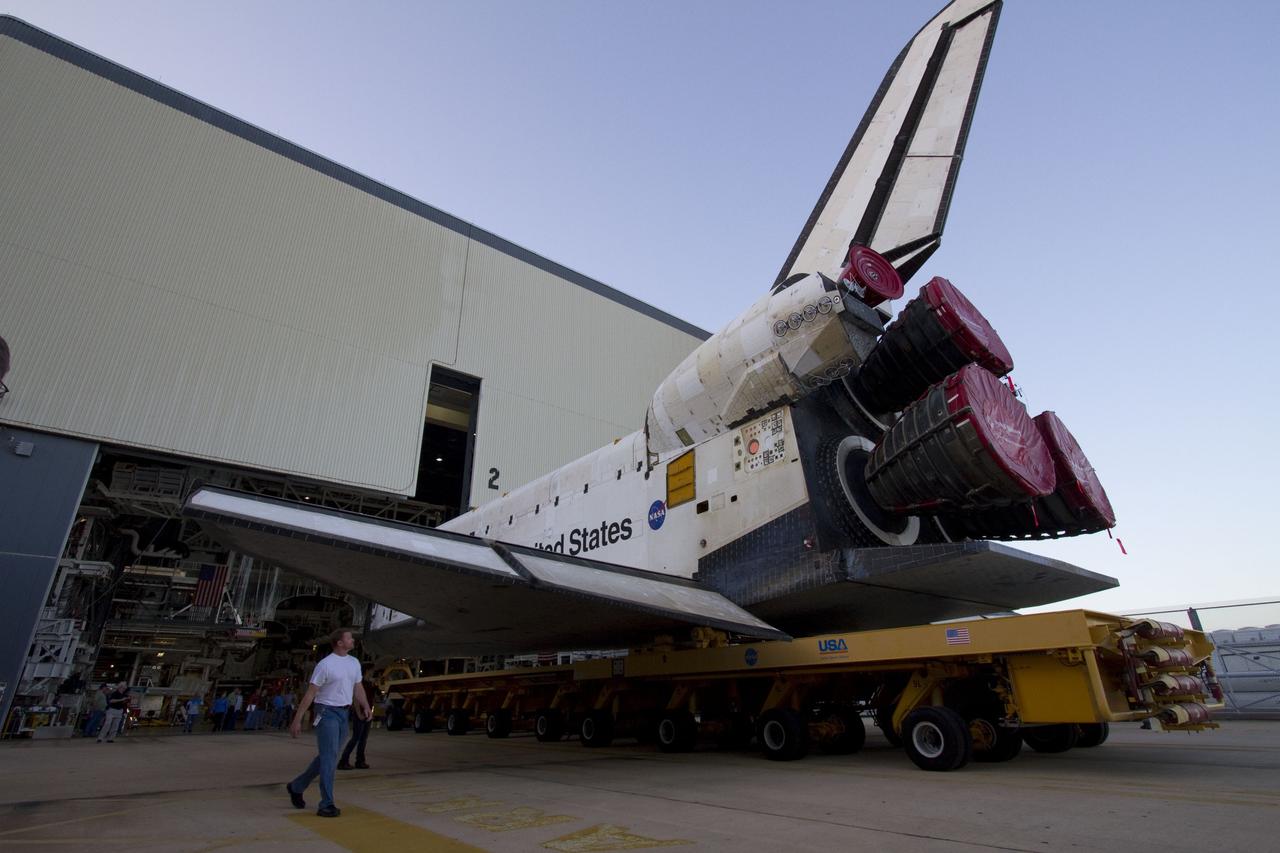

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers accompany space shuttle Endeavour as it is backed out of Orbiter Processing Facility-2 for its move, "or rollover," to the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, spare parts, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
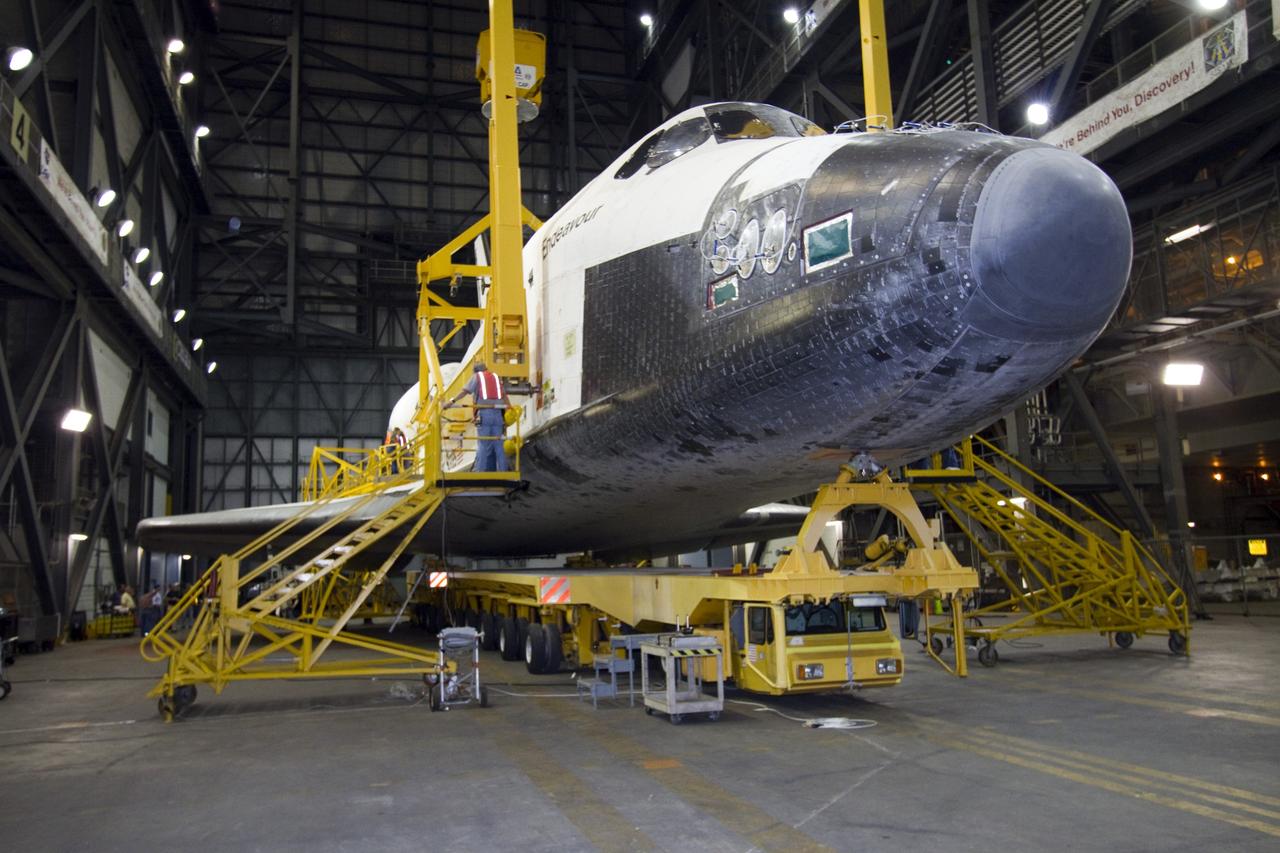

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers attach an overhead crane to shuttle Endeavour. The crane will lift the spacecraft into a high bay where it will be attached to the waiting external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Endeavour's final launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
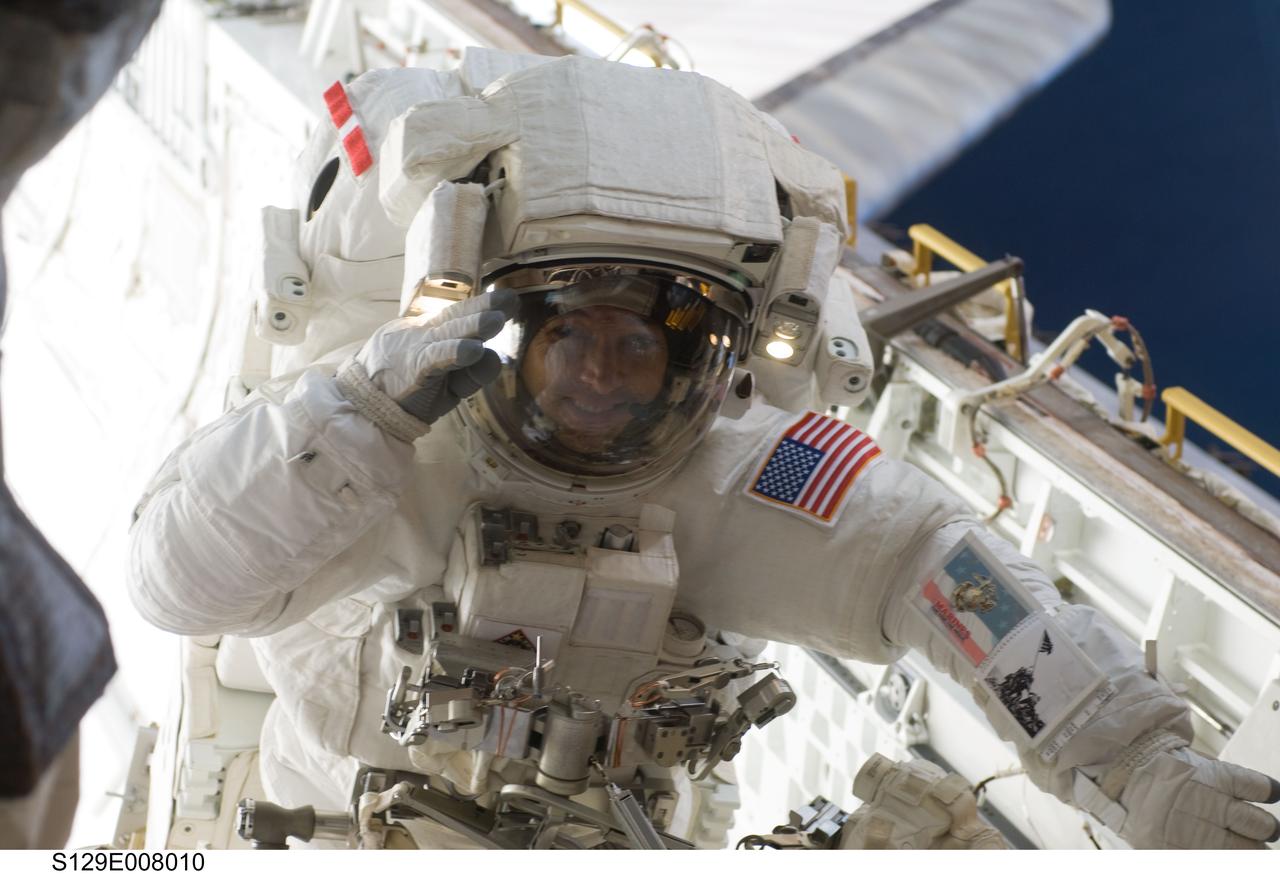

S129-E-008010 (23 Nov. 2009) --- Astronaut Randy Bresnik, STS-129 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third and final session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 42-minute spacewalk, Bresnik and astronaut Robert L. Satcher Jr. (out of frame), mission specialist, removed a pair of micrometeoroid and orbital debris shields from the Quest airlock and strapped them to the External Stowage Platform #2, then moved an articulating foot restraint to the airlock, and released a bolt on a starboard truss ammonia tank assembly (ATA) in preparation for an STS-131 spacewalk that will replace the ATA.
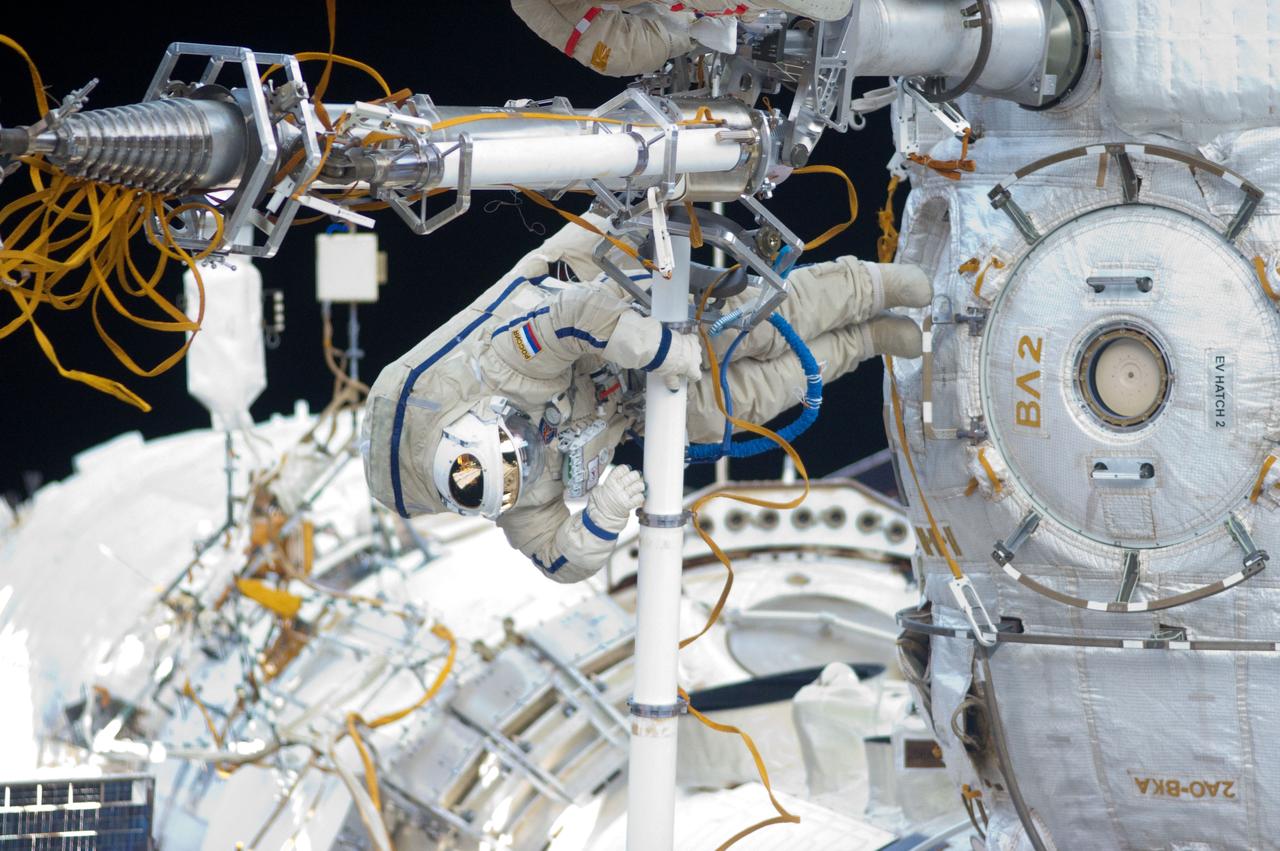

ISS032-E-021058 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko, Expedition 32 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Malenchenko and Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka (out of frame), commander, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
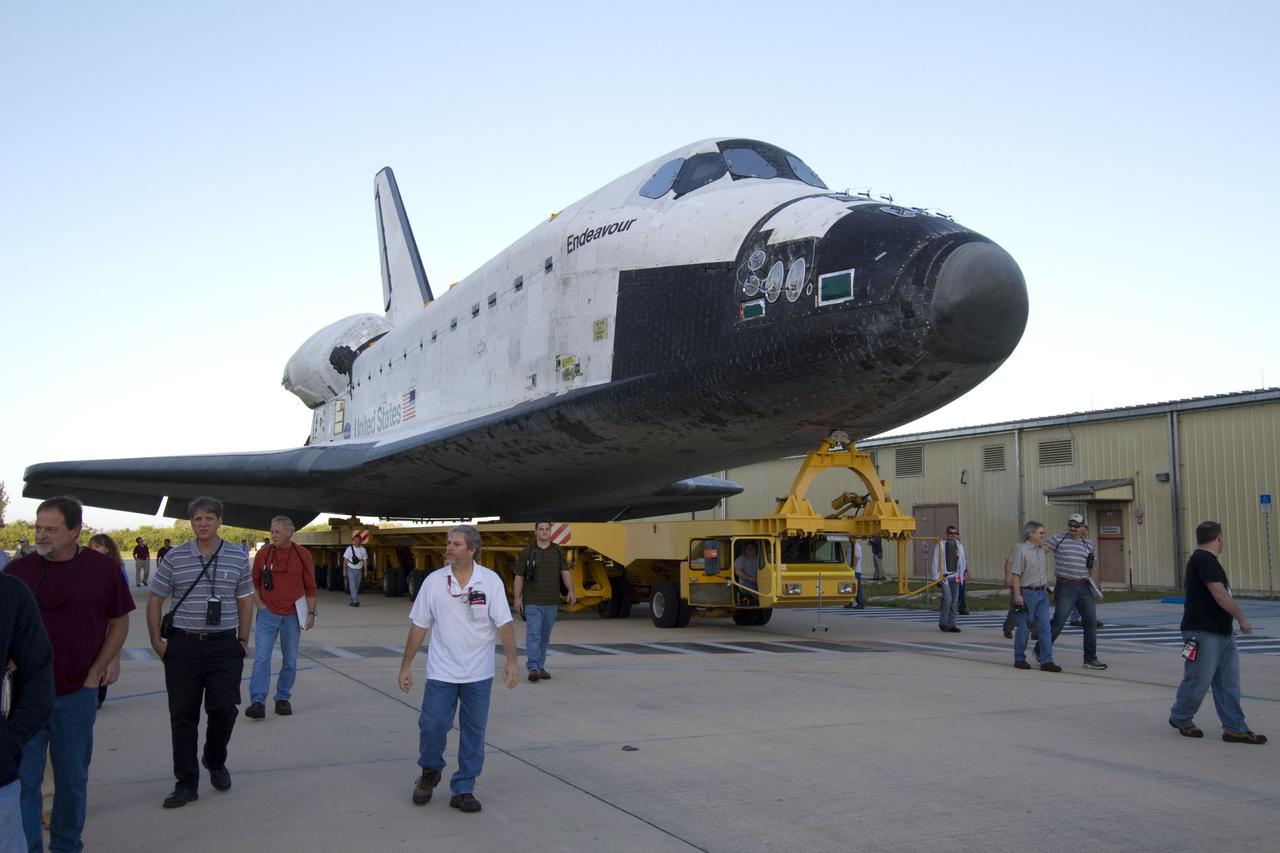

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers accompany space shuttle Endeavour as it is being transported from Orbiter Processing Facility-2 to the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, spare parts, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, employees hold up a banner to commemorate space shuttle Endeavour's STS-134 mission as it is transported from Orbiter Processing Facility-2 to the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, spare parts, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shuttle Endeavour is lowered into place where it will be attached to its external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters, already positioned on the mobile launcher platform. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Endeavour's final launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
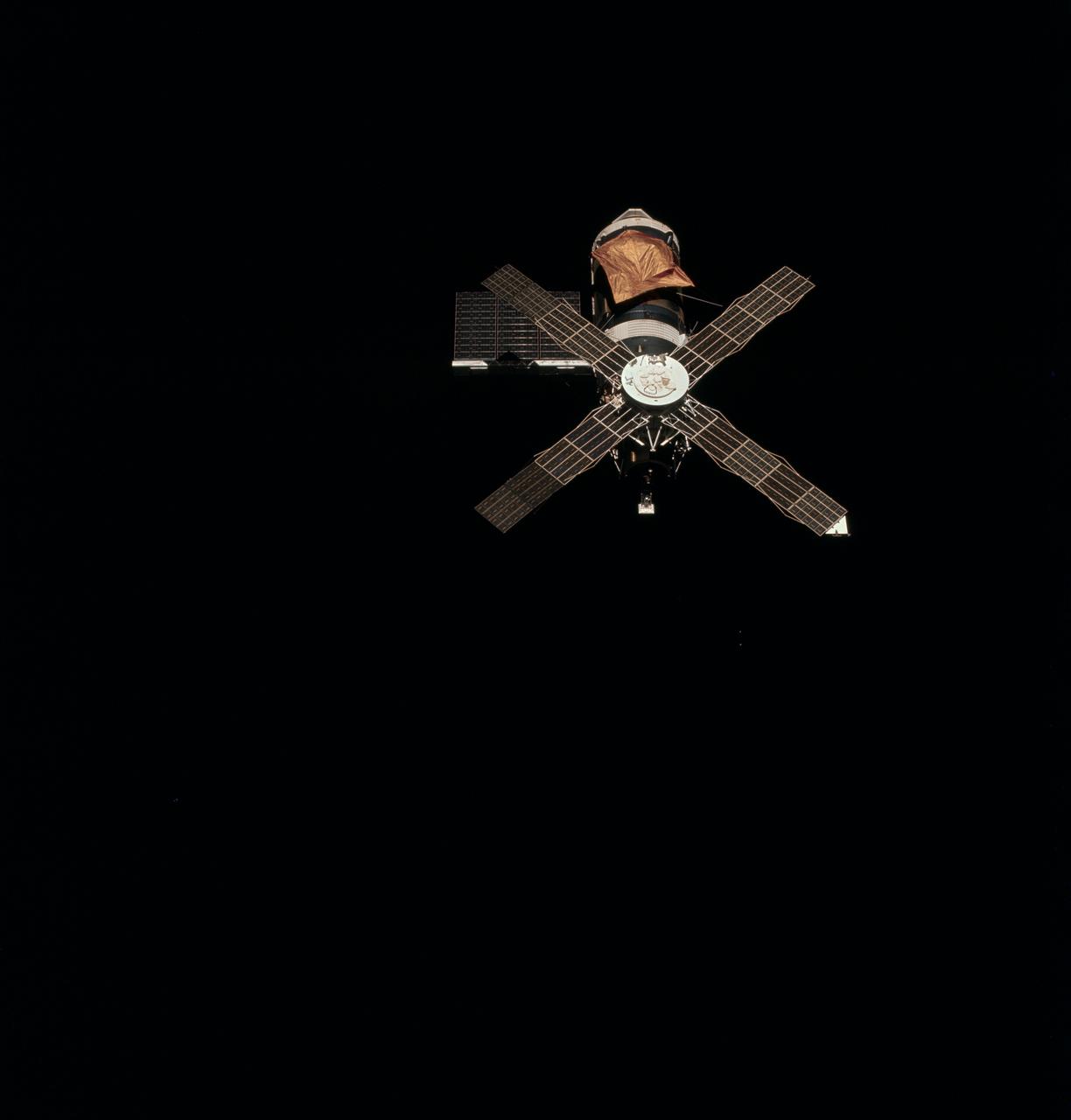

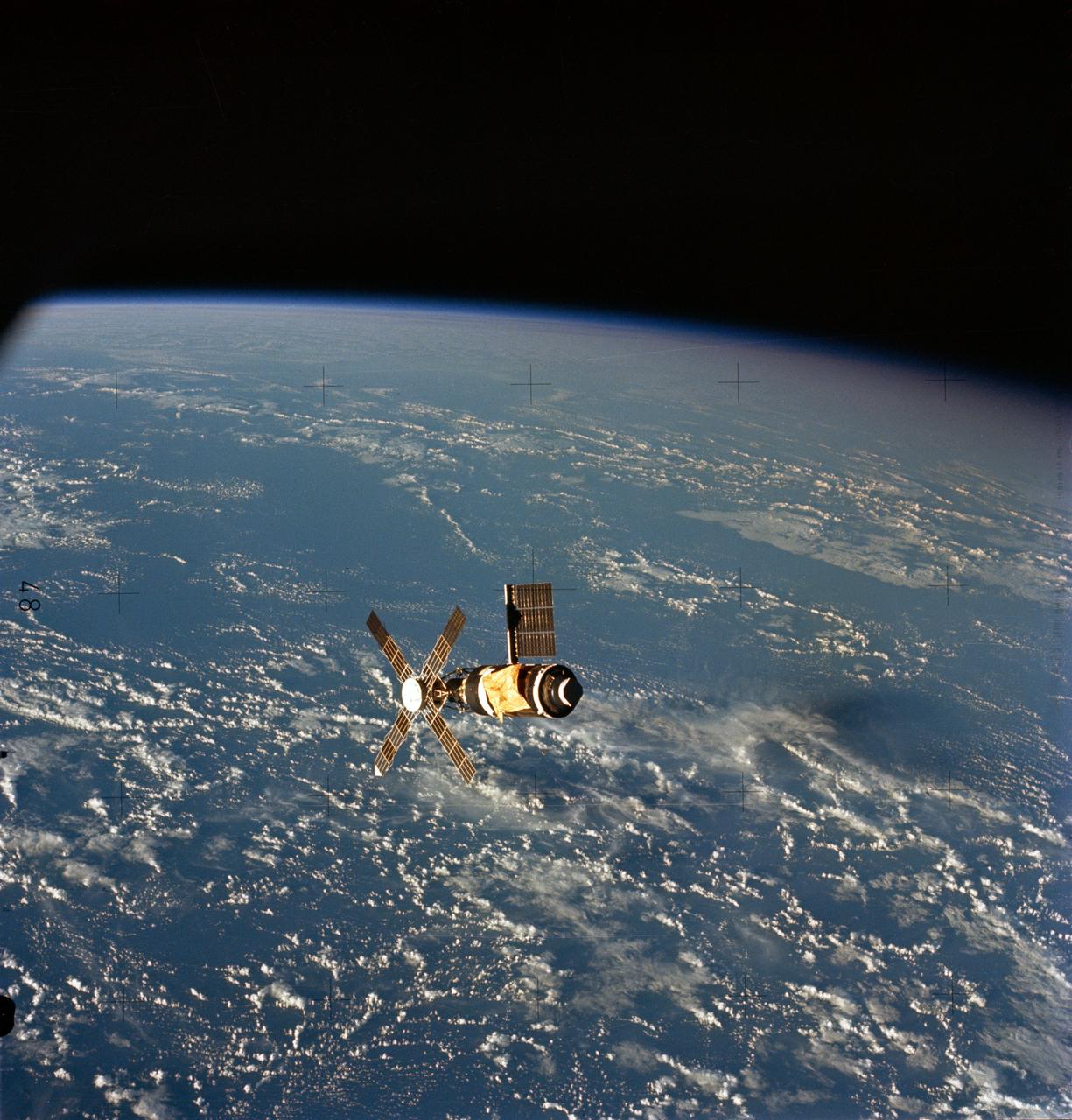
SL2-X7-615 (22 June 1973) --- An overhead view of the Skylab 1 space station cluster in Earth orbit photographed from the Skylab 2 Command/Service Module during the final ?fly around? inspection by the CSM. The space station is sharply contrasted against a black sky background. Note the deployed parasol solar shield which shades the Orbital Workshop where the micrometeoroid shield is missing. The one remaining OWS solar array system wing has been fully deployed successfully. The OWS solar panel on the opposite side is missing completely. Photo credit: NASA

ISS032-E-021044 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Gennady Padalka (top), Expedition 32 commander; and Yuri Malenchenko, flight engineer, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Malenchenko moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
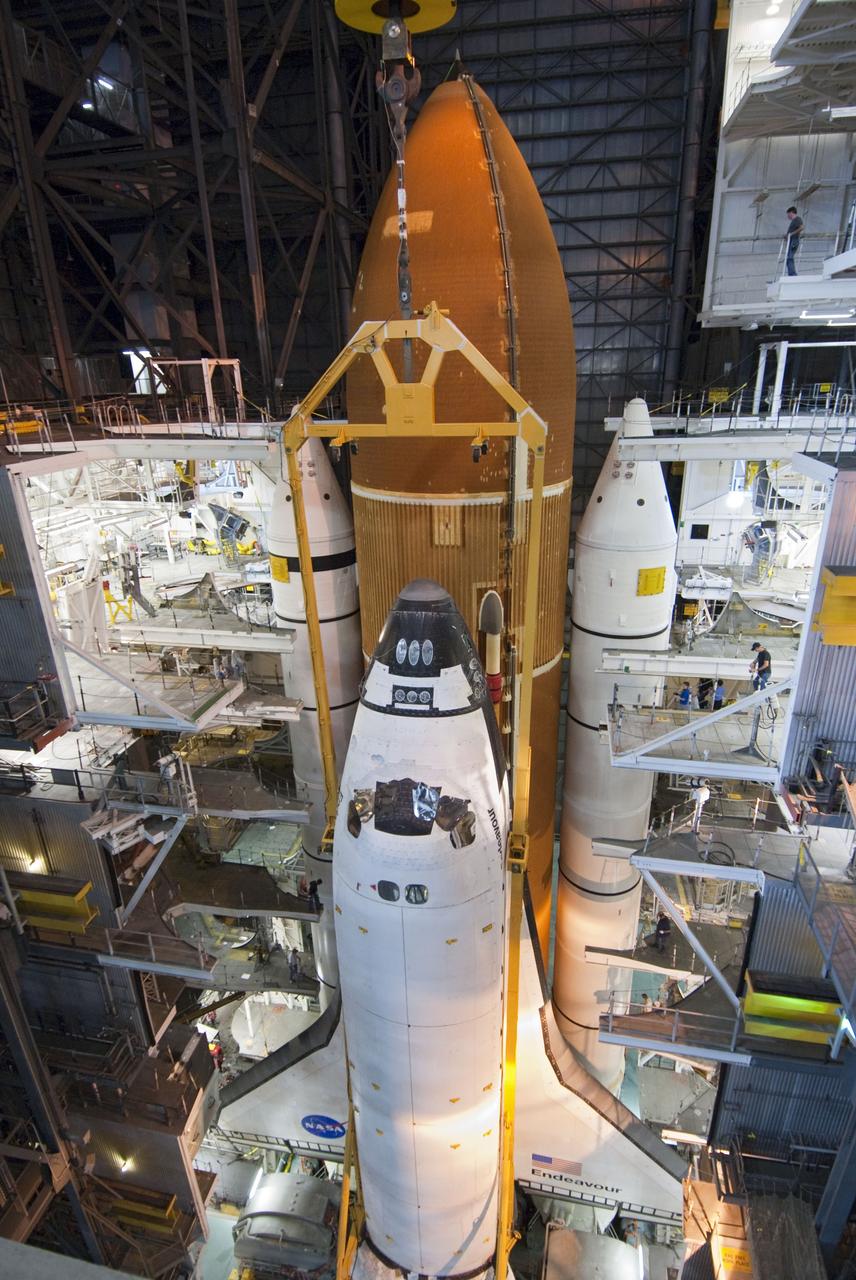

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shuttle Endeavour is lowered into place where it will be attached to its external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters, already positioned on the mobile launcher platform. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Endeavour's final launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
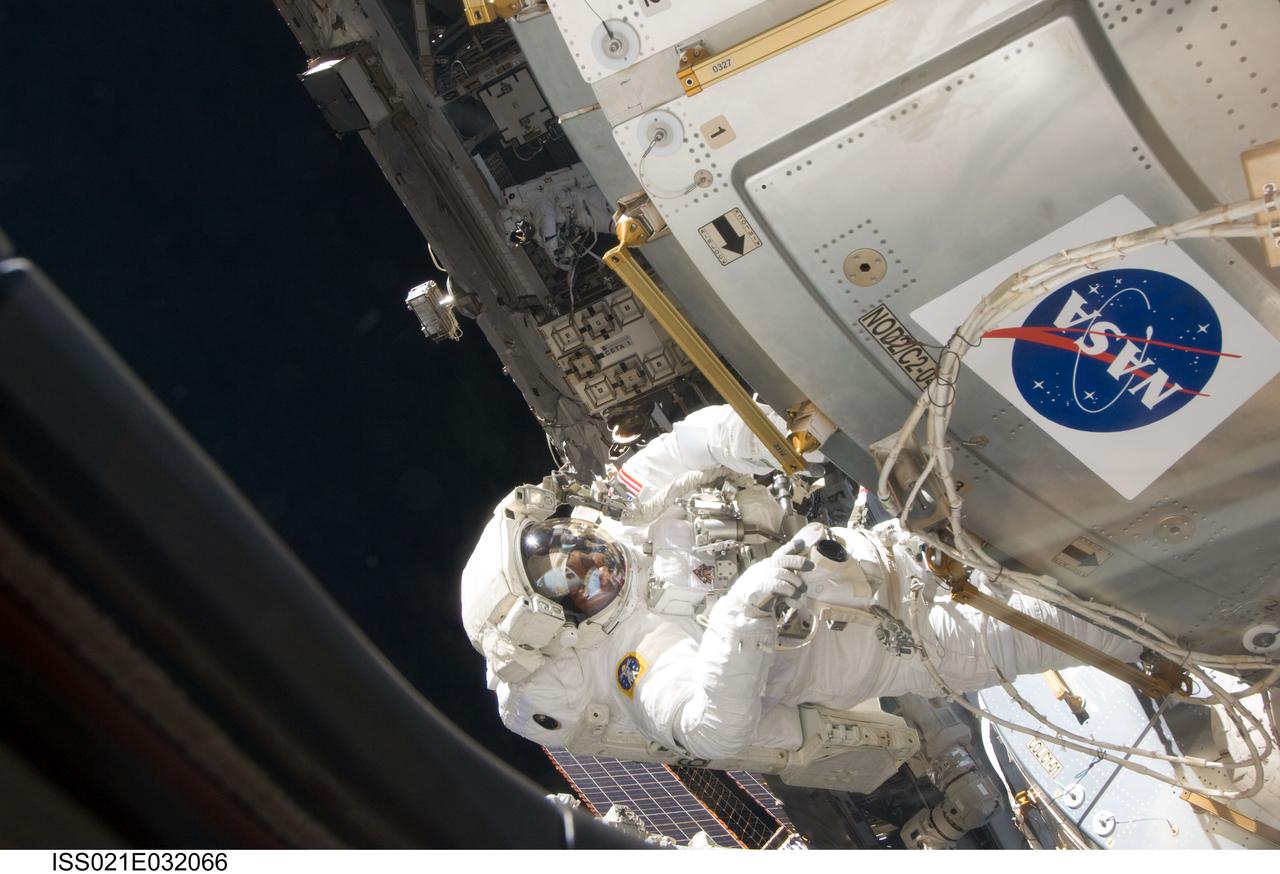

ISS021-E-032066 (23 Nov. 2009) --- Astronaut Robert L. Satcher Jr., STS-129 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third and final session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 42-minute spacewalk, Satcher and astronaut Randy Bresnik (out of frame), mission specialist, removed a pair of micrometeoroid and orbital debris shields from the Quest airlock and strapped them to the External Stowage Platform #2, then moved an articulating foot restraint to the airlock, and released a bolt on a starboard truss ammonia tank assembly (ATA) in preparation for an STS-131 spacewalk that will replace the ATA.
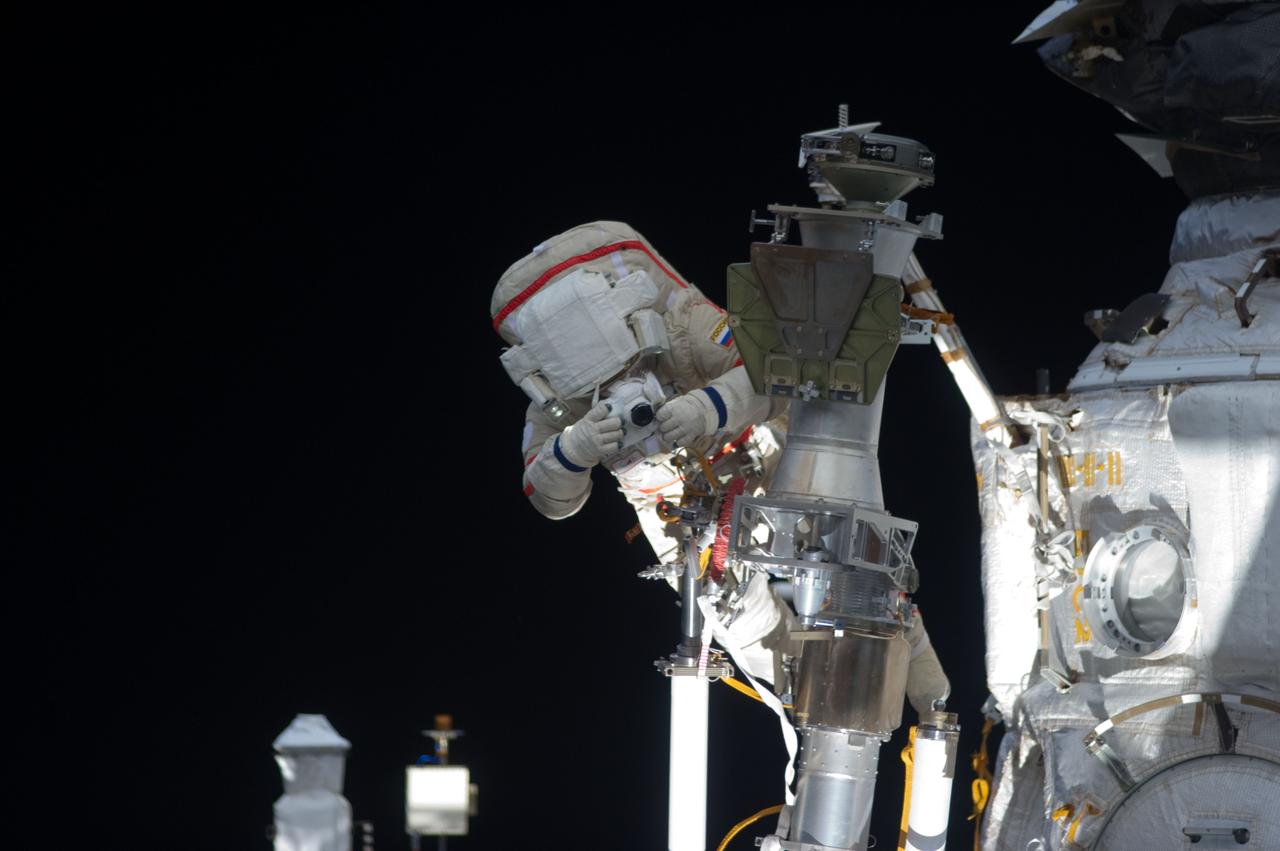

ISS032-E-021067 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, uses a still camera during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
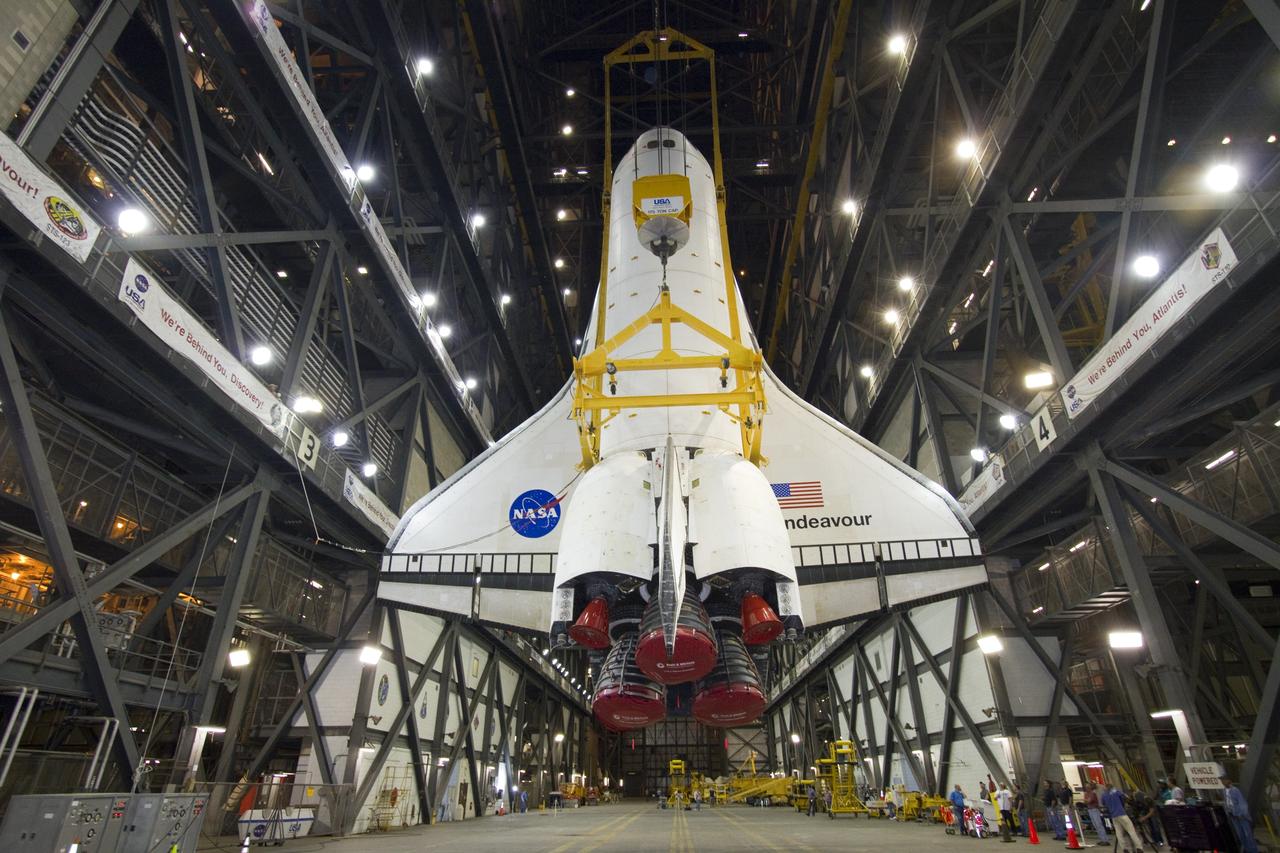

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shuttle Endeavour is suspended vertically over the transfer aisle. The spacecraft will be moved into a high bay where it will be installed to the waiting external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Endeavour's final launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
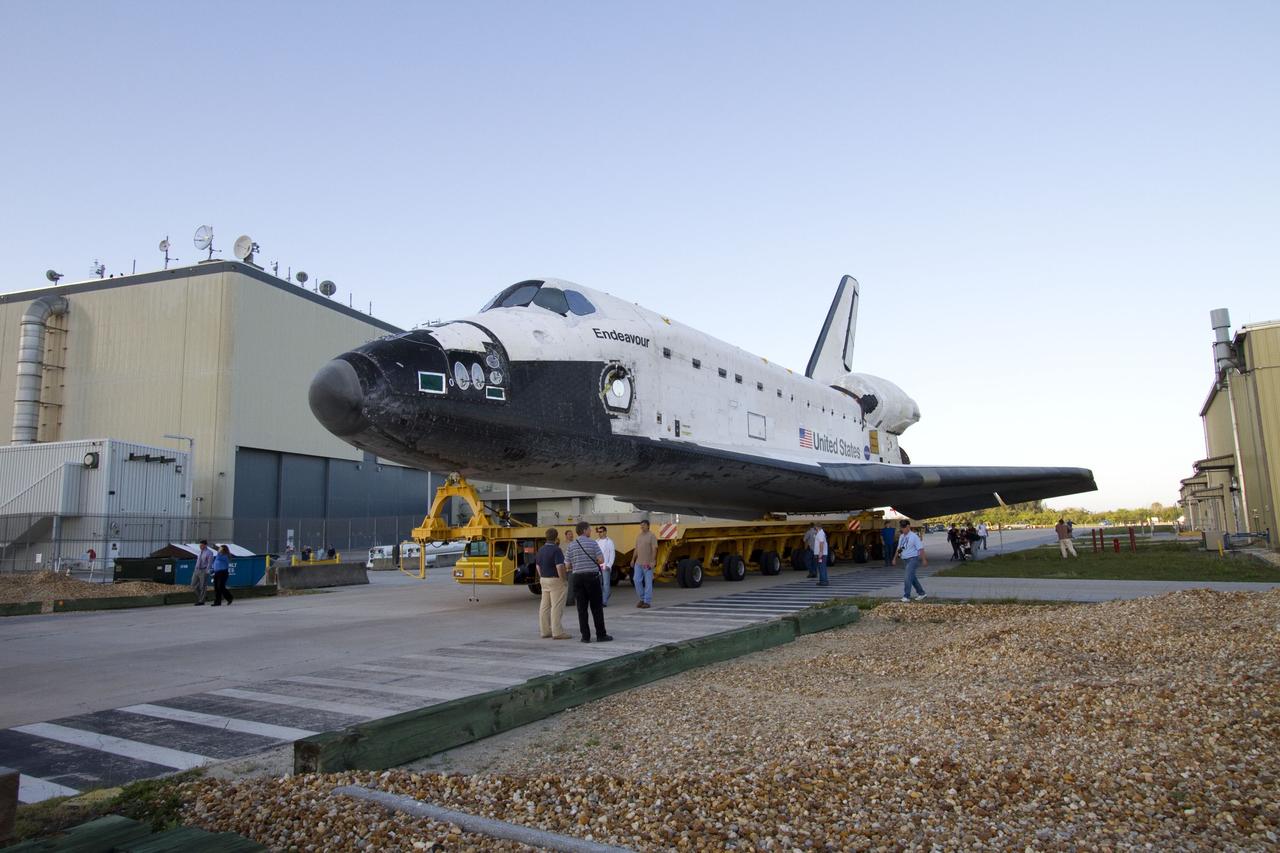

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers accompany space shuttle Endeavour as it is being transported from Orbiter Processing Facility-2 to the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour and its STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, spare parts, a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for Dextre and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
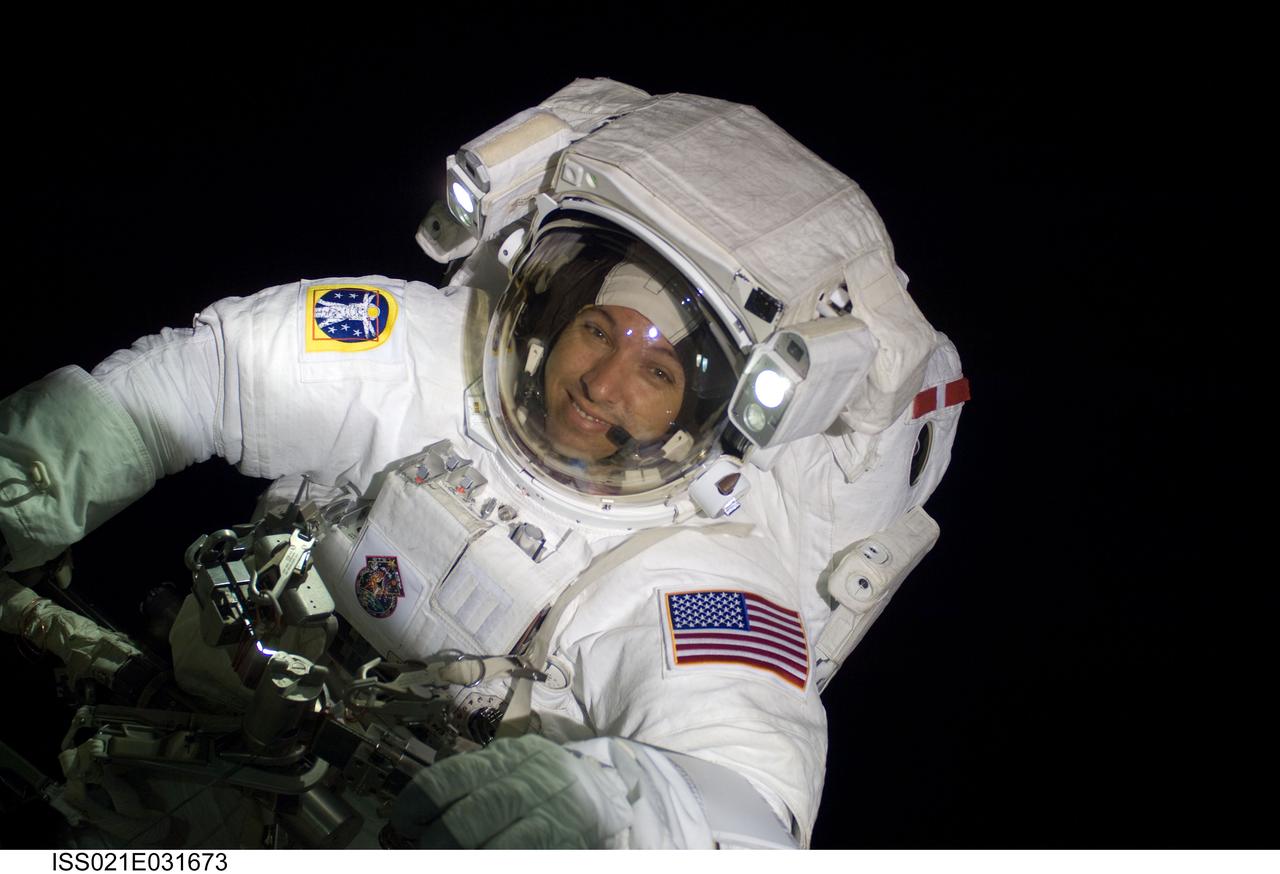

ISS021-E-031673 (23 Nov. 2009) --- Astronaut Randy Bresnik, STS-129 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third and final session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 42-minute spacewalk, Bresnik and Robert L. Satcher Jr. (out of frame), mission specialist, removed a pair of micrometeoroid and orbital debris shields from the Quest airlock and strapped them to the External Stowage Platform #2, then moved an articulating foot restraint to the airlock, and released a bolt on a starboard truss ammonia tank assembly (ATA) in preparation for an STS-131 spacewalk that will replace the ATA.
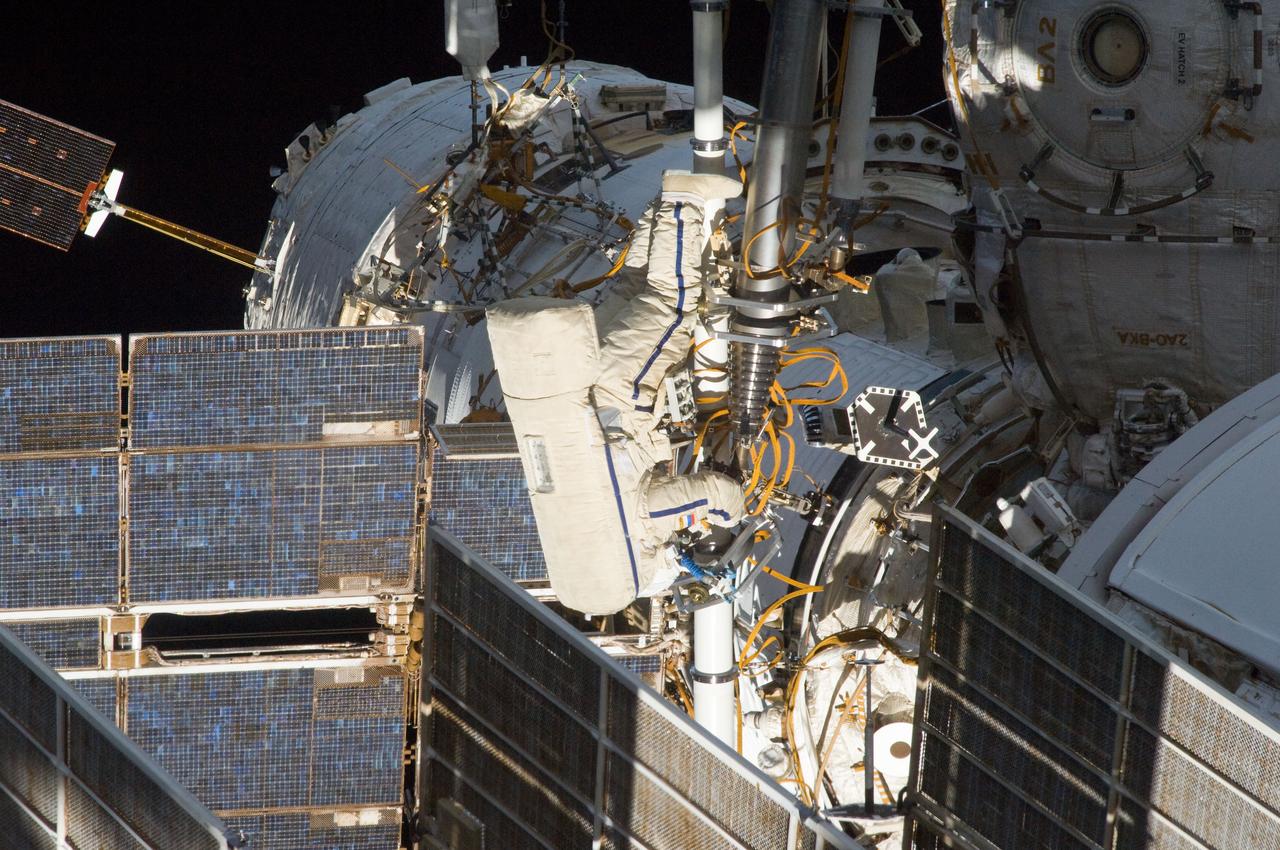

ISS032-E-021293 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko, Expedition 32 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Malenchenko and Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka (out of frame), commander, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians begin to lift the new S-band antenna support assembly for installation on ExPRESS Logistics Carrier-3 in the Space Station Processing Facility. The assembly will be used aboard the International Space Station to transmit and receive audio communications, and is being installed for the STS-134 mission. Space shuttle Endeavour will take up other spare parts, including a high-pressure gas tank, micrometeoroid debris shields and replacement parts for Dextre, the robotic arm on the station. STS-134, the last planned shuttle mission, is targeted to launch in the fall of 2010. For information on the upcoming mission and crew, visit www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts134_index.html. NASA_Jack Pfaller
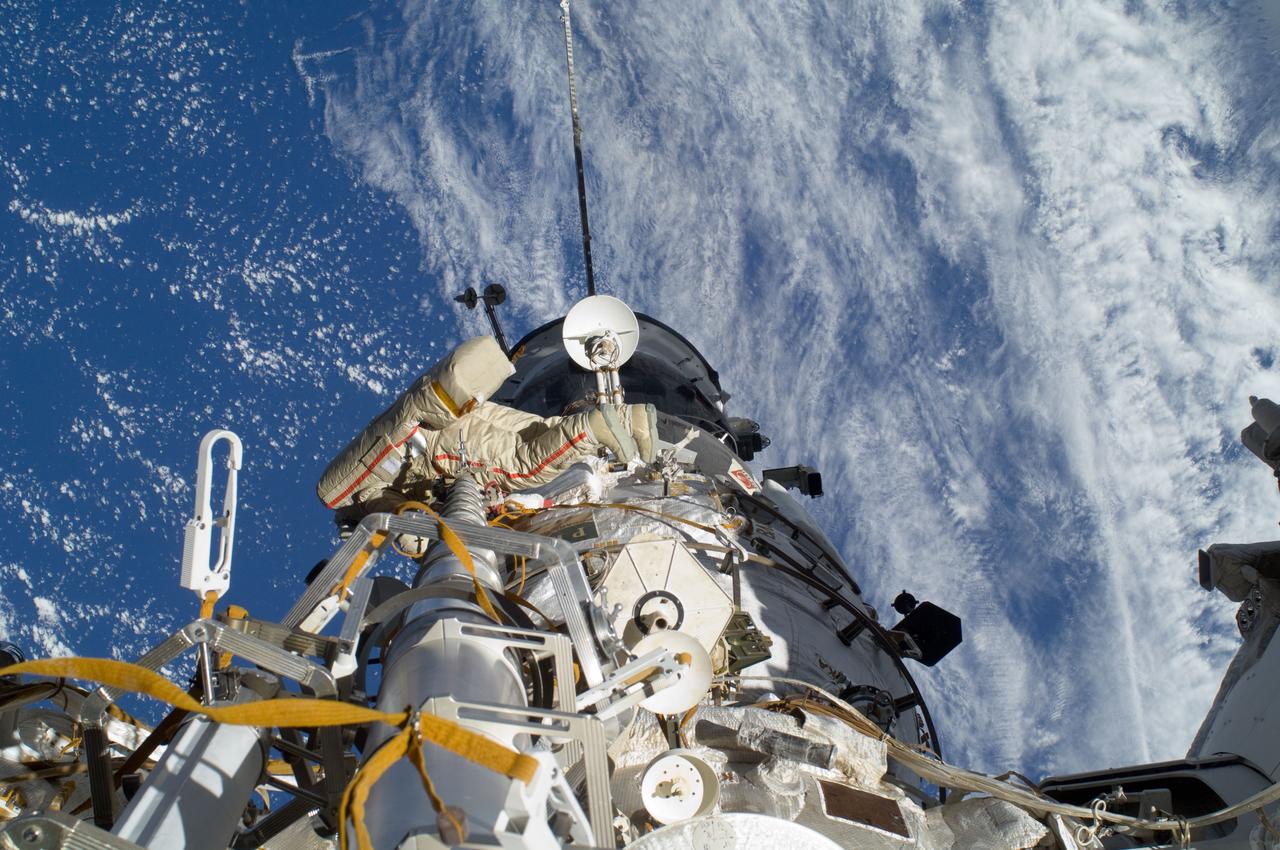

ISS032-E-020594 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.