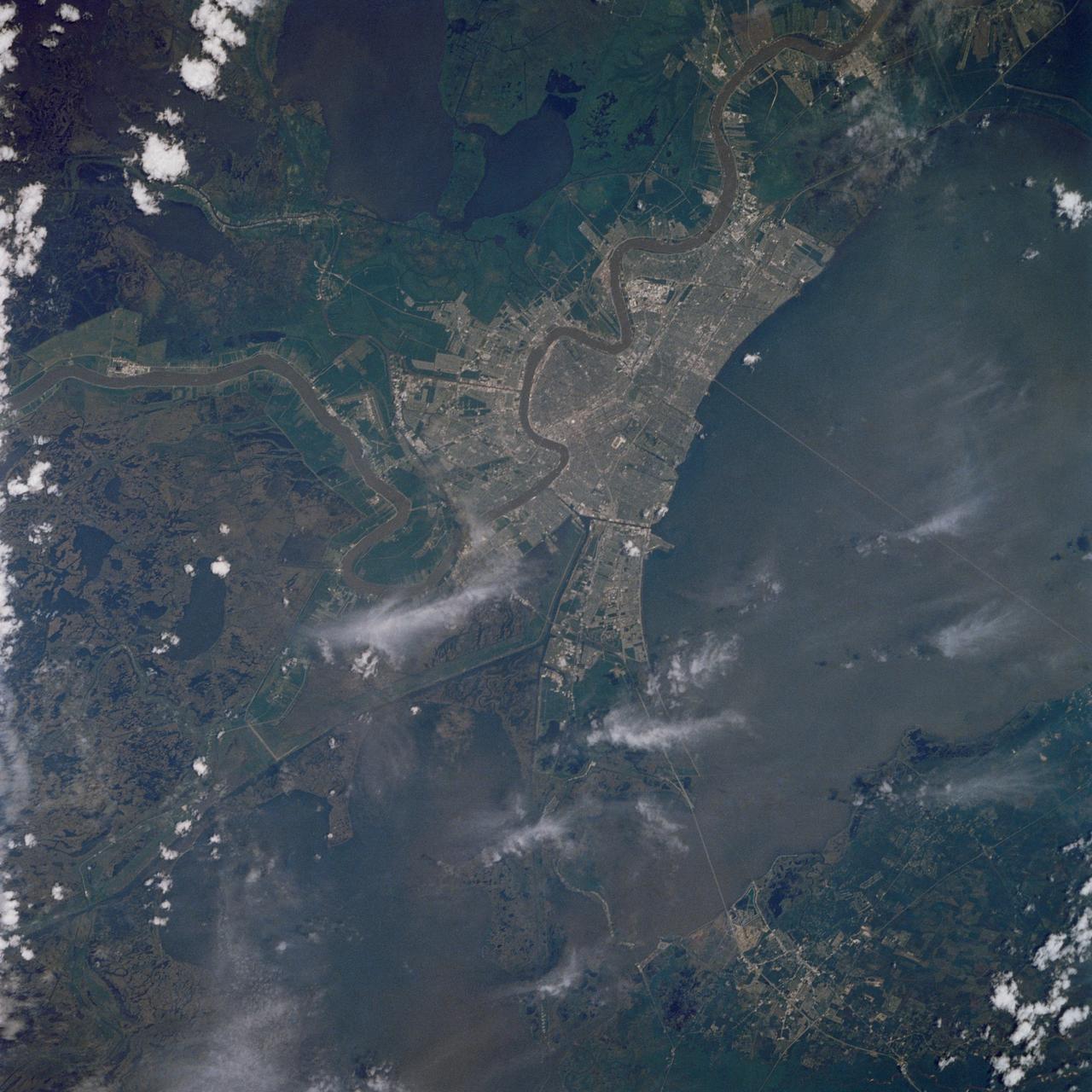

As one of the best ever views of the city of New Orleans, LA (30.0N, 90.0W) from space, this image allows the study of the city and the region in minute detail. Major city street and highway patterns can easily be traced. Even the Superdome near the old French Quarter can be seen as a large round white circle near the middle of the photo. The French Napoleonic Code land distribution system of long narrow fields fronting the river is also evident.

Earth Observation taken during a day pass by the Expedition 40 crew aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Folder lists this as: Eastern half of US, sun glint, Texas, Maryland, Mississippi river, Great Lakes.

Meandering Mississippi - May 28th, 2003 Description: Small, blocky shapes of towns, fields, and pastures surround the graceful swirls and whorls of the Mississippi River. Countless oxbow lakes and cutoffs accompany the meandering river south of Memphis, Tennessee, on the border between Arkansas and Mississippi, USA. The "mighty Mississippi" is the largest river system in North America. Credit: USGS/NASA/Landsat 7 To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
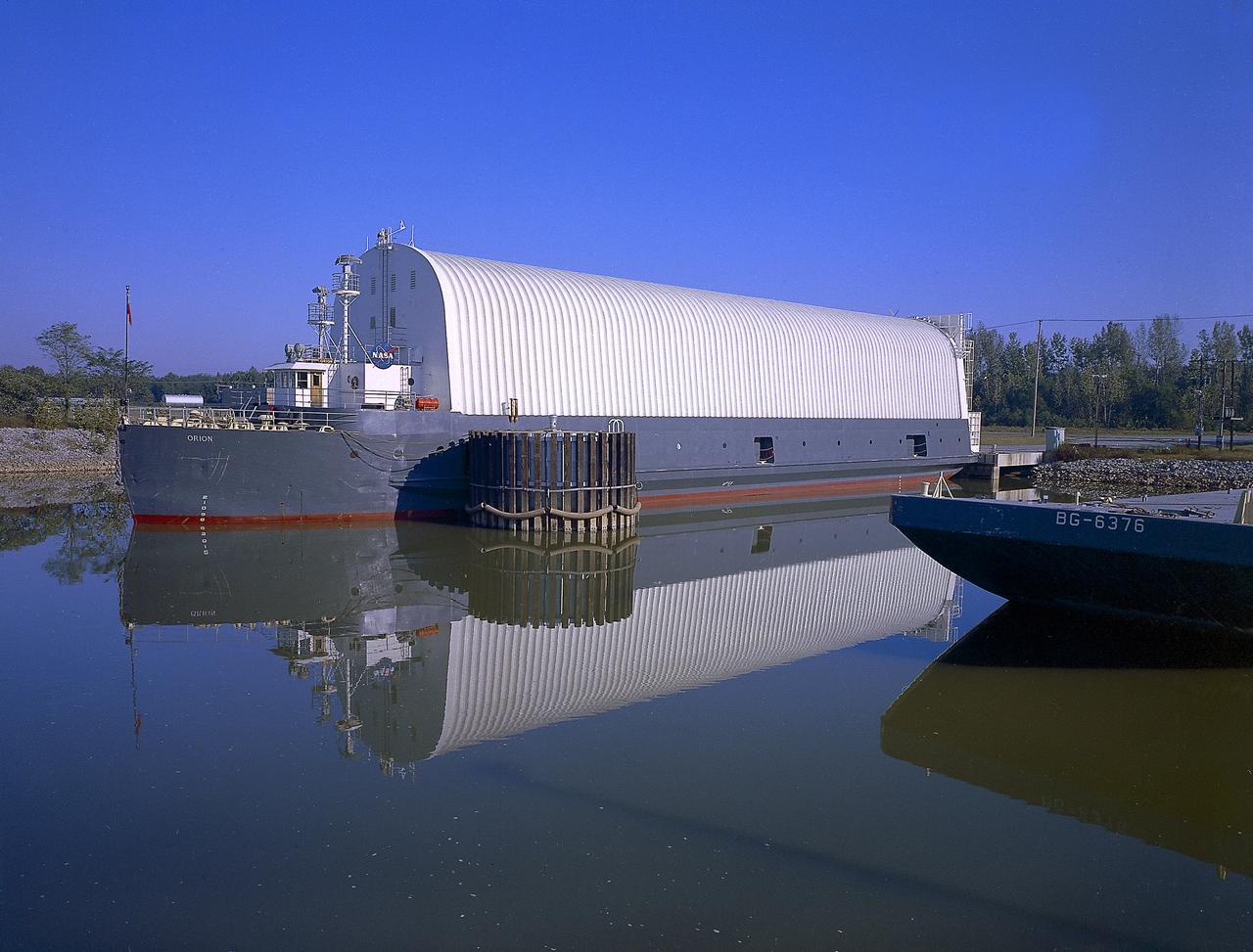

NASA used barges for transporting full-sized stages for the Saturn I, Saturn IB, and Saturn V vehicles between the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the manufacturing plant at the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF), the Mississippi Test Facility for testing, and the Kennedy Space Center. The barges traveled from the MSFC dock to the MAF, a total of 1,086.7 miles up the Tennessee River and down the Mississippi River. The barges also transported the assembled stages of the Saturn vehicle from the MAF to the Kennedy Space Center, a total of 932.4 miles along the Gulf of Mexico and up along the Atlantic Ocean, for the final assembly and the launch. This photograph shows the barge Orion at the MSFC dock.
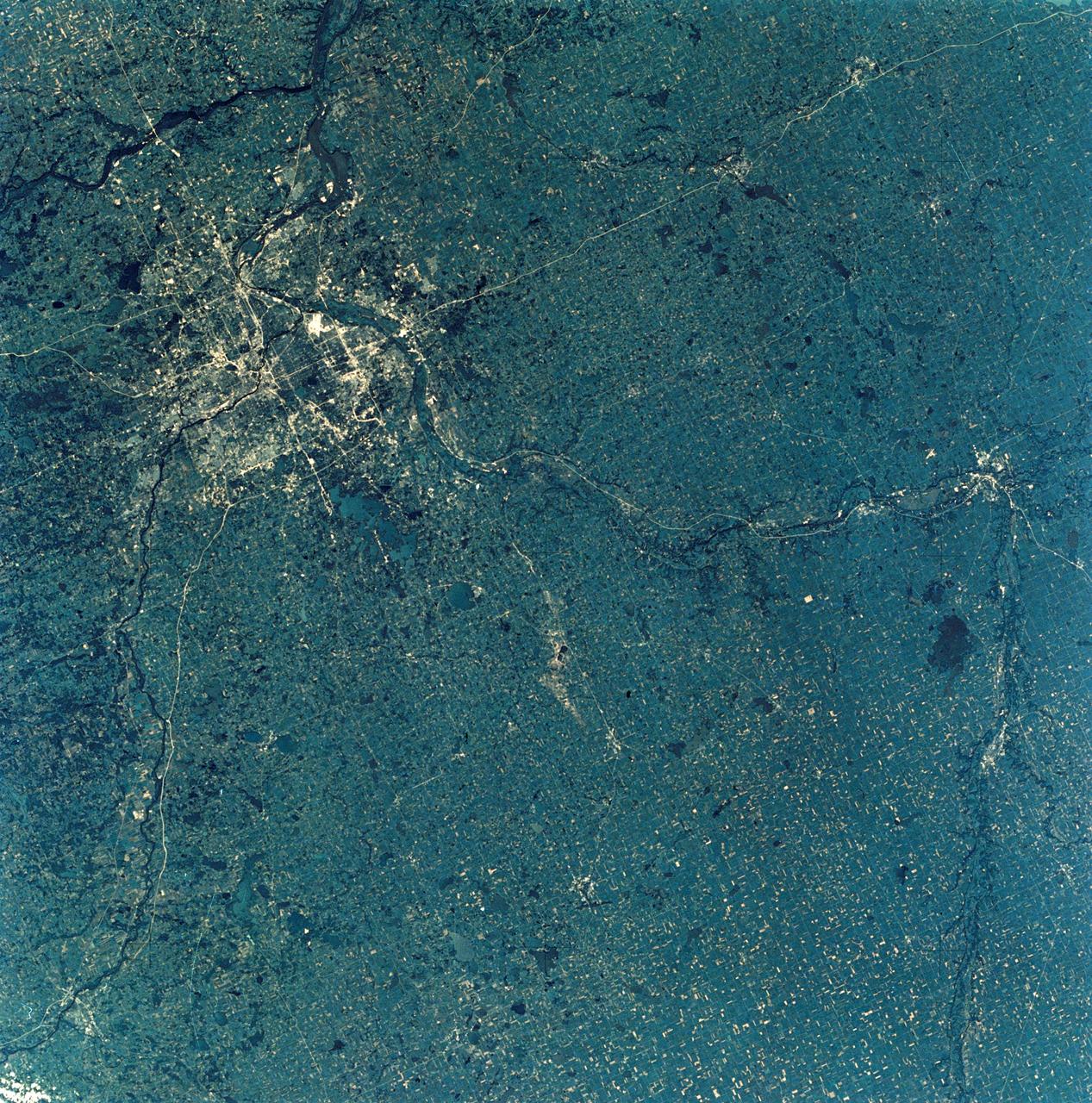
SL3-28-009 (July-September 1973) --- A near vertical view of the Minneapolis-St. Paul, Minnesota area, as photographed from Earth orbit by one of the six lenses of the Itek-furnished S190-A Multispectral Photographic Facility Experiment in the Multiple Docking Adapter of the Skylab space station. A 150mm lens, with SO-356 high definition Ektachrome film, was used to take this picture. The Mississippi River flows southeasterly through this large metropolitan area. Minneapolis is on the west bank of the Mississippi. The Minnesota River makes a large bend at the southern edge of the picture then flows northeasterly to empty into the Mississippi at Minneapolis-St. Paul. The St. Croix River, which serves as a portion of the boundary between Minnesota and Wisconsin, flows into the Mississippi downstream from the twin cities. A long, nearly straight, stretch of Interstate 35 leads southward from Minneapolis-St. Paul. Interstate 94 parallels the Mississippi toward the northwest. The highway and road network in the area is clearly visible. Note the numerous small lakes in the photograph. This view includes the smaller cities of Hastings, Faribault, Owatonna, Mankato, St. Peter, New Ulm and St. Cloud. The S190-A experiment is part of the Skylab Earth Resources Experiments Package. Photo credit: NASA
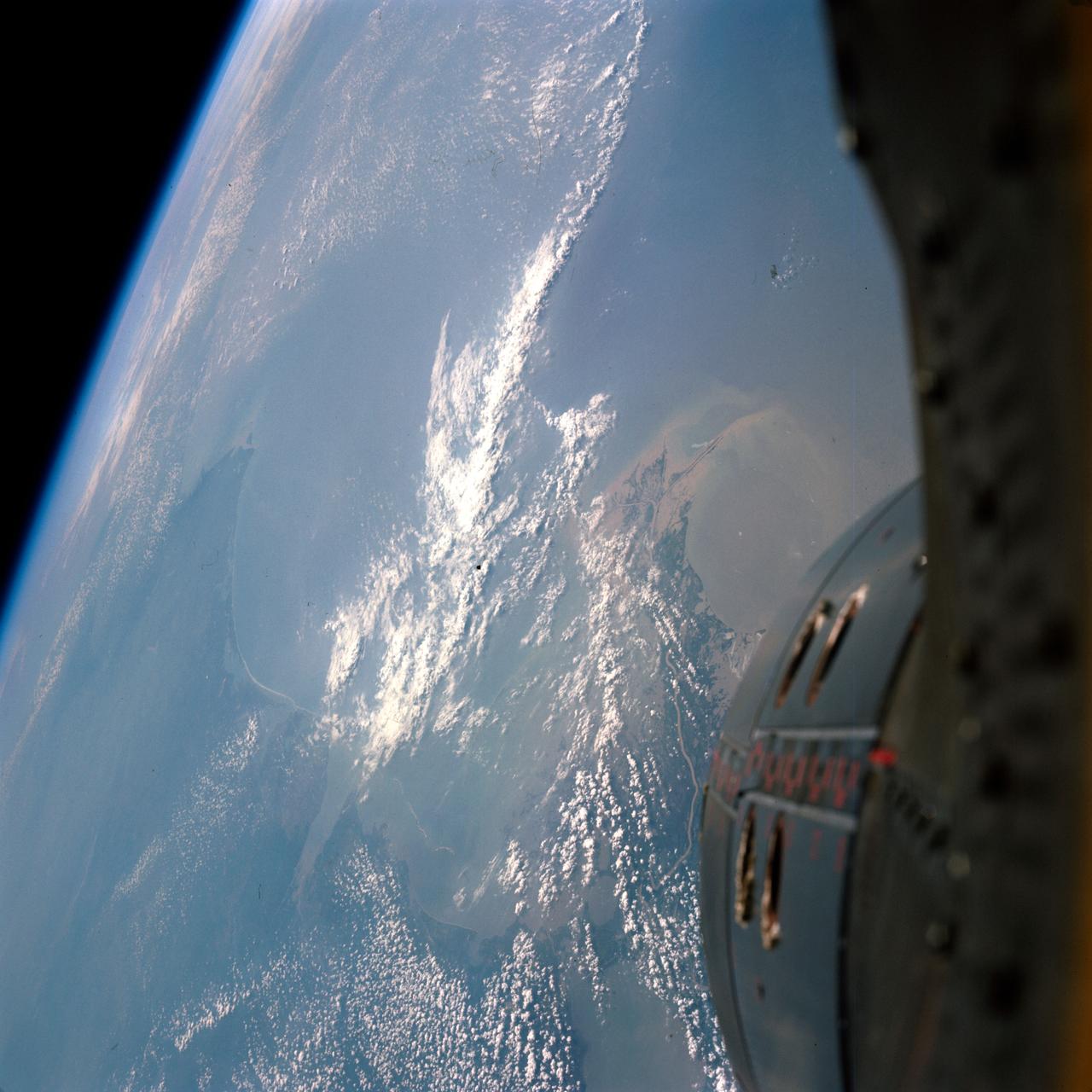

S66-37910 (3 June 1966) --- The Mississippi River delta, and Gulf coasts of Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama and Florida as seen from the Gemini-9 spacecraft during its first revolution of Earth. The Florida peninsula is seen at upper right corner of the picture. Lake Pontchartrain is a lower left. New Orleans is located between the lake and the U-shaped bend in the river. Large bay at top left center is Mobile Bay. The next bay to the east is Pensacola Bay. Cape San Blas near Apalachicola, Florida, is the point of land at top center of the picture. Note alluvial deposit at the mouths of the Mississippi. The image was taken with a modified 70mm Hasselblad camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome MS (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA
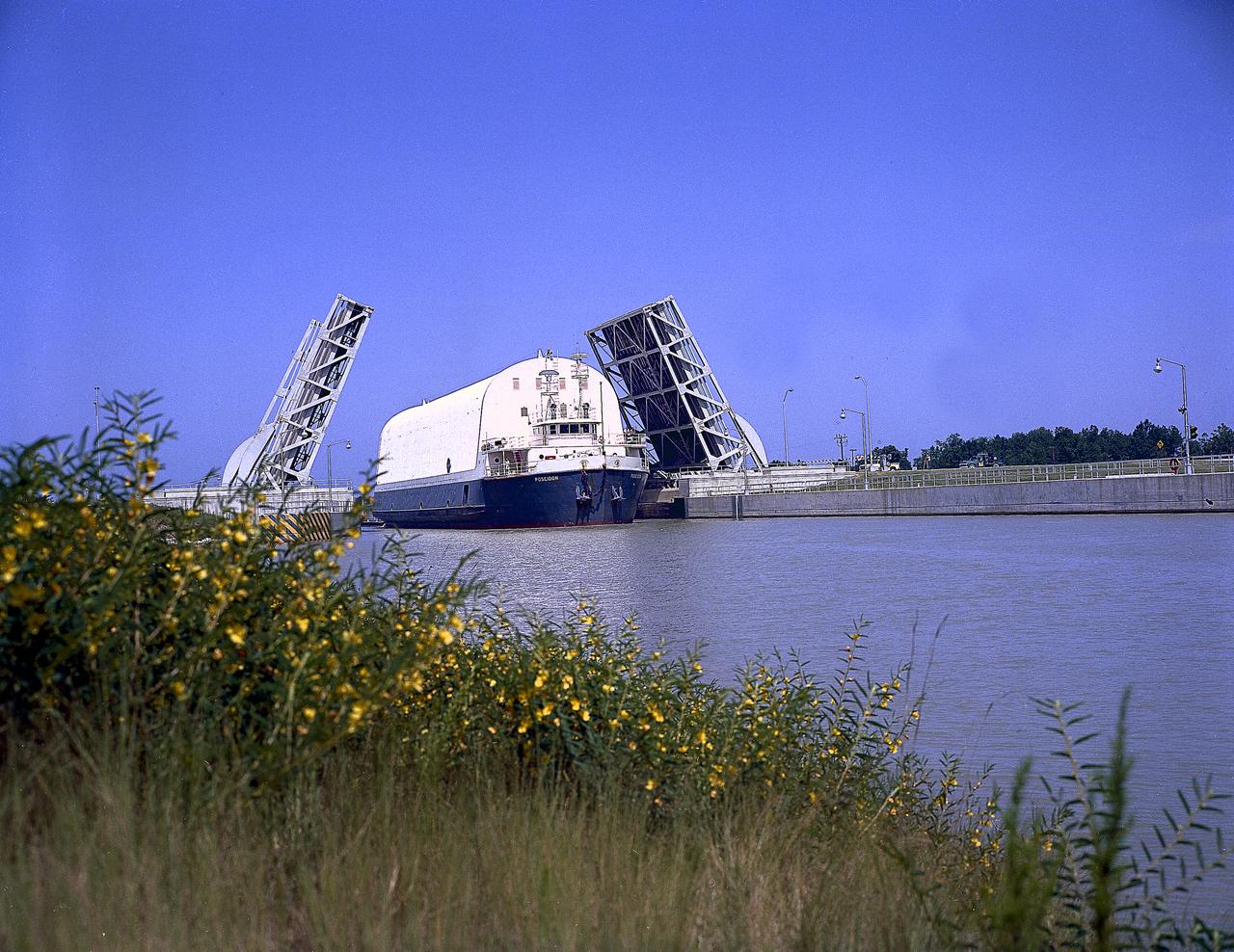

NASA used barges for transporting full-sized stages for the Saturn I, Saturn IB, and Saturn V vehicles between the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the manufacturing plant at the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF), the Mississippi Test Facility for testing, and the Kennedy Space Center. The barges traveled from the MSFC dock to the MAF, a total of 1,086.7 miles up the Tennessee River and down the Mississippi River. The barges also transported the assembled stages of the Saturn vehicle from the MAF to the Kennedy Space Center, a total of 932.4 miles along the Gulf of Mexico and up along the Atlantic Ocean, for the final assembly and the launch. This photograph shows the barge Poseidon loaded with the Saturn V S-II (second) stage passing through a bascule bridge.
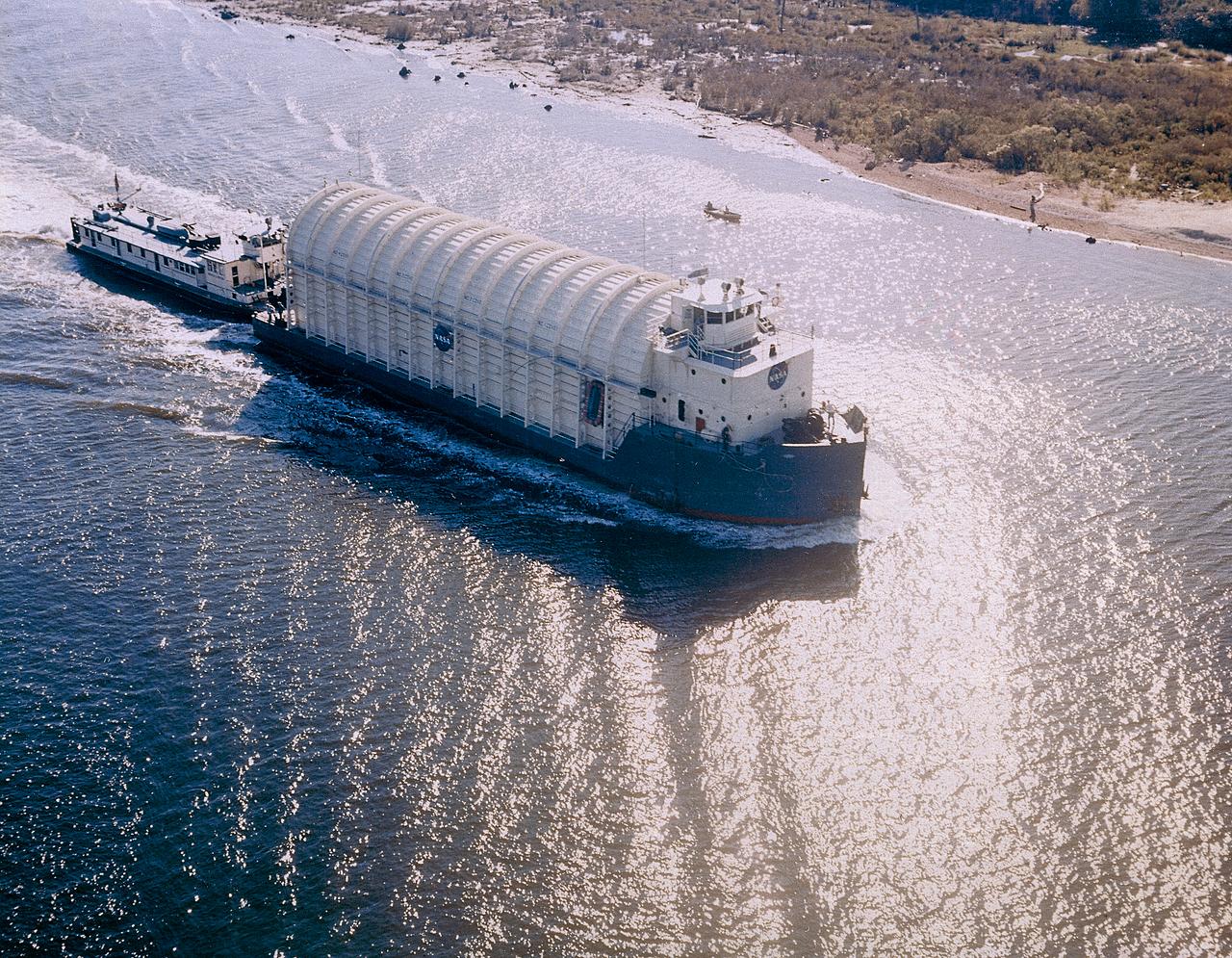

NASA used barges for transporting full-sized stages for the Saturn I, Saturn IB, and Saturn V vehicles between the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the manufacturing plant at the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF), the Mississippi Test Facility for testing, and the Kennedy Space Center. The barges traveled from the MSFC dock to the MAF, a total of 1,086.7 miles up the Tennessee River and down the Mississippi River. The barges also transported the assembled stages of the Saturn vehicle from the MAF to the Kennedy Space Center, a total of 932.4 miles along the Gulf of Mexico and up along the Atlantic Ocean, for the final assembly and the launch. Pictured is the barge Palaemon carrying Saturn IV S-IB flight stage enroute to MSFC.
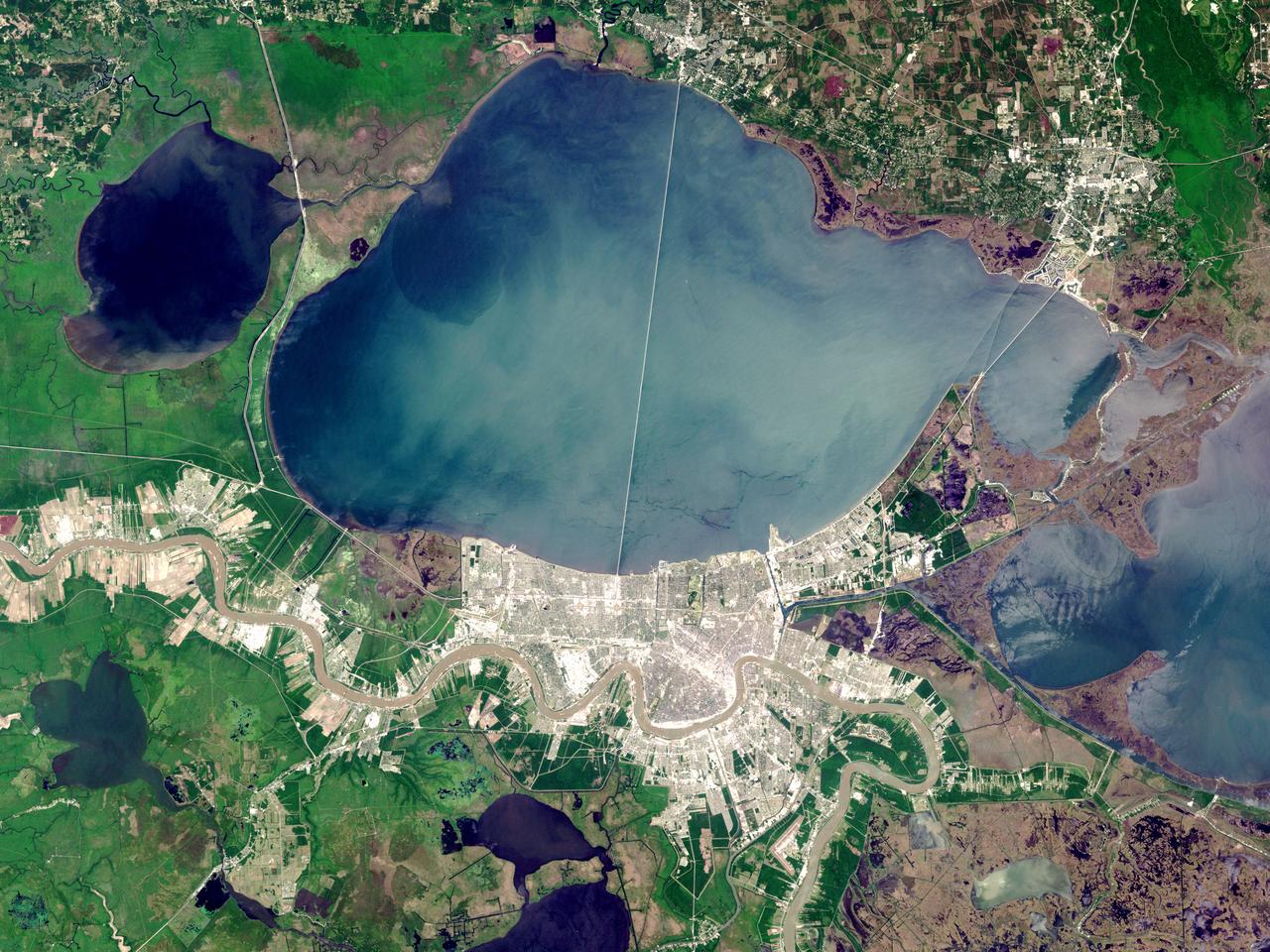

On Sunday, February 3, roughly 800 million eyes from all over the world focused on the Louisiana Superdome in New Orleans as the New England Patriots battled the St. Louis Rams for the NFL Championship in Super Bowl XXXVI. This true color image of New Orleans was acquired on April 26, 2000, by the Enhanced Thematic Mapper plus (ETM+), flying aboard the Landsat 7 satellite. Lake Pontchartrain borders the city to the north. The big river winding its way east to west through the image is the Mississippi. The Louisiana Superdome, built in 1975, sits just inside the rightmost portion of the big river bend that cradles downtown New Orleans. The city, however, may not be around to hold a Super Bowl in 2102. New Orleans is slowly sinking into the Gulf of Mexico. The construction of flood walls and dams north of New Orleans over the past century have prevented sediments carried by the Mississippi River from reaching New Orleans and the Mississippi River Delta. Before the dams were built, river sediments would empty out onto the delta adding layer upon layer of new soil each year. The additional soil prevented the Gulf from subsuming the delta. Unless drastic measures are taken, the city and the delta could be awash in seawater by the end of this century. Image by Robert Simmon, based on data provided by the Landsat 7 Science Team Credit: NASA/GSFC/Landsat <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
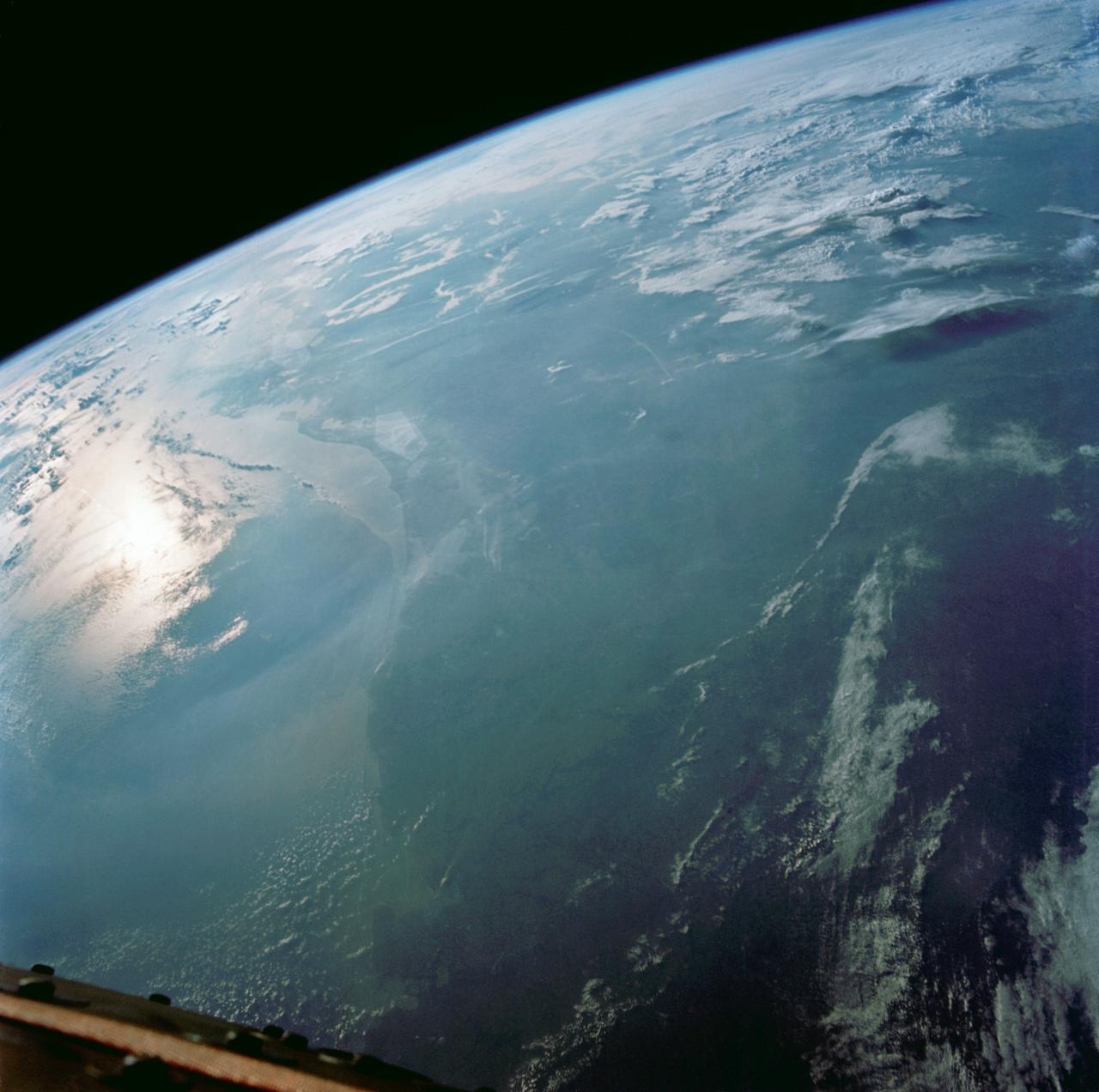

S66-54560 (14 Sept. 1966) --- U.S. Gulf coast area from Aransas Bay, Texas, to Mobile Bay, Alabama, as seen from the Gemini-11 spacecraft during its 29th revolution of Earth. The Galveston Bay and Houston area is in center of photograph. Further eastward along the coast can be seen the Mississippi River delta and New Orleans area. Taken with a modified 70mm Hasselblad camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome, MS (S.O. 368) color film. Photo credit: NASA

ISS026-E-028375 (22 Feb. 2011) --- Having enjoyed a clear sky nocturnal photo opportunity over New Orleans earlier (Jan. 26) in their mission, Expedition 26 crew members aboard the International Space Station had another window on Feb. 22 to capture images of the Crescent City or Big Easy from 220 miles above Earth. The Mississippi River is visible winding its way through the city. A 200-mm lens was used to take the picture.

AS09-26A-3743A (9 March 1969) --- Color infrared photograph of the Yazoo River Valley, Pearl River, Pearl River Reservoir, and Jackson, Mississippi, area, taken on March 9, 1969, by one of the four synchronized cameras of the Apollo 9 Earth Resources Survey SO65 Experiment. At 1:08 p.m. (EST) when this photograph was made the Apollo 9 spacecraft was at an altitude of 105 nautical miles, and the sun elevation was at 55 degrees above the horizon. The location of the point on Earth's surface at which the four-camera combination was aimed was 32 degrees 34 minutes north latitude, and 89 degrees 57 minutes west longitude. The other three cameras used: (B) black and white film with a red filter; (C) black and white infrared film; and (D) black and white film with a green filter.
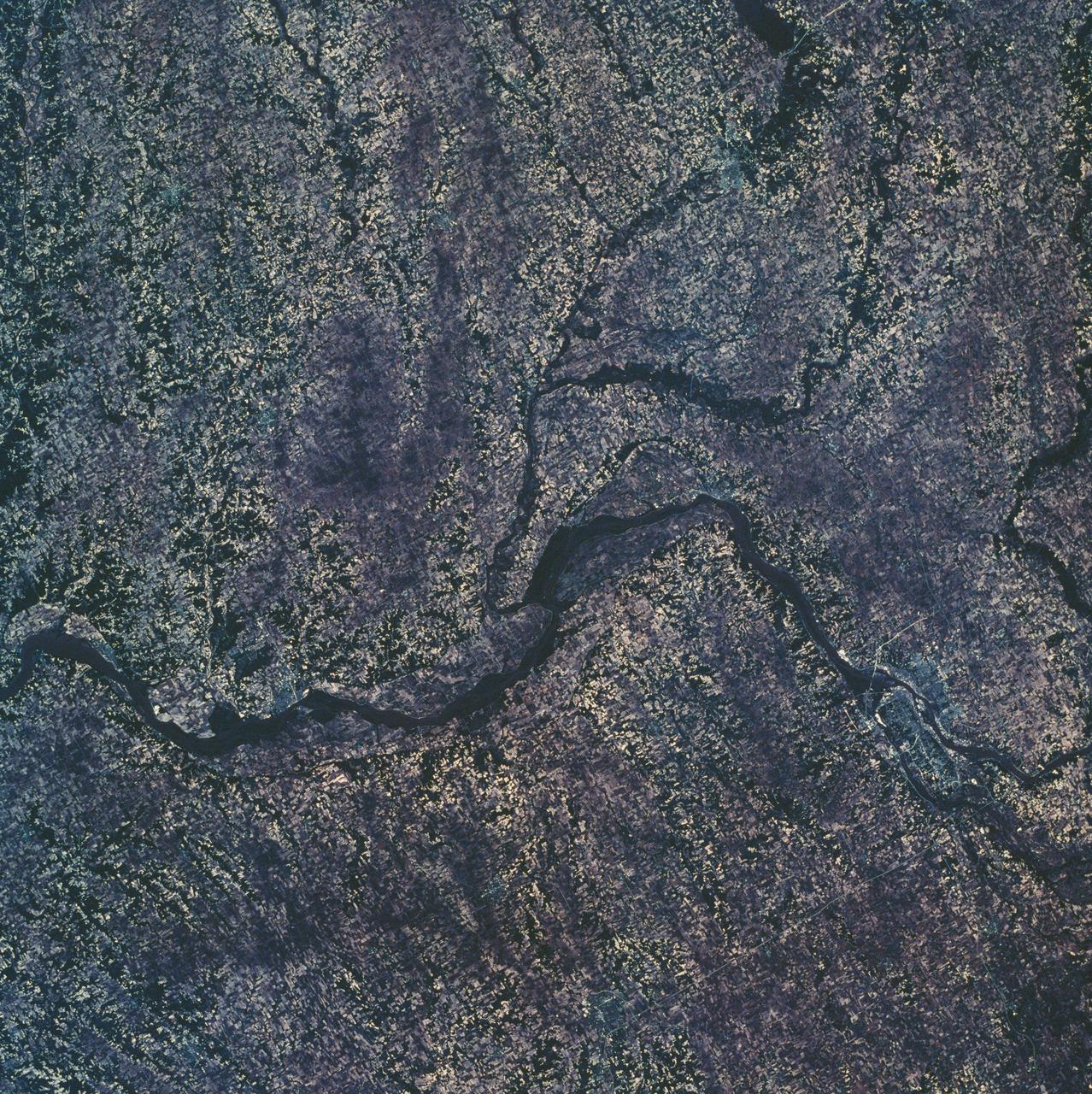

SL2-10-250 (May-June 1973) --- A vertical view of eastern Iowa and northwestern Illinois, as photographed from Skylab space station in Earth orbit. Davenport, Burlington and Muscatine, Iowa; and Rock Island and Moline, Illinois can be delineated on opposite sides of the Mississippi River. The Iowa River and tributaries of it can also be delineated. This photograph was taken with one of six lenses of the Itek-furnished Multispectral Photographic Facility Experiment S190-A mounted in the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) of the space station. A six-inch lens, using 70mm medium speed Ektachrome (SO-356) film, was used. Agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce and Interior; the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior's Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA

ISS038-E-023651 (26 Dec. 2013) --- Lake Sharpe near Lower Brule, South Dakota is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 38 crew member on the International Space Station. The Missouri River rises in the Rocky Mountains of western Montana, and flows generally to the southeast for approximately 3,767 kilometers (2,341 miles) to its confluence with the Mississippi River north of St. Louis, Missouri -- making it the longest river in North America. The river does not follow a straight southeasterly course along this distance, but includes may meander bends such as illustrated in this photograph. This particular bend is occupied by Lake Sharpe, an approximately 130-kilometer (80 miles) long reservoir formed behind the Big Bend Dam on the Missouri River. The lake surface is frozen and covered with snow, presenting a uniform white appearance in the image. As meander bends develop, they tend to assume a distinctive U-shape when viewed from above. Over time, the river channel can continue to cut into the ends of the "U", eventually bringing them so close together that the river then cuts across the gap to achieve a shorter flow path, essentially short-circuiting or cutting off the meander bend. When this happens and the meander ceases to be part of the active river channel, it may become an oxbow lake. The distance across the narrow neck of land (lower right) associated with this meander near Lower Brule, South Dakota is approximately one kilometer (0.62 miles); however, as the river flow is controlled by the Big Bend Dam downstream, the natural process of meander cutoff has been significantly slowed. The snow cover also highlights circular agricultural fields on the small peninsula within the meander bend. This type of field indicates center-pivot irrigation, where water is distributed from a central point radially outwards using sprinklers to cover the field area. Crops grown here include corn and soybeans according to data from the US Department of Agriculture's CropScape database.
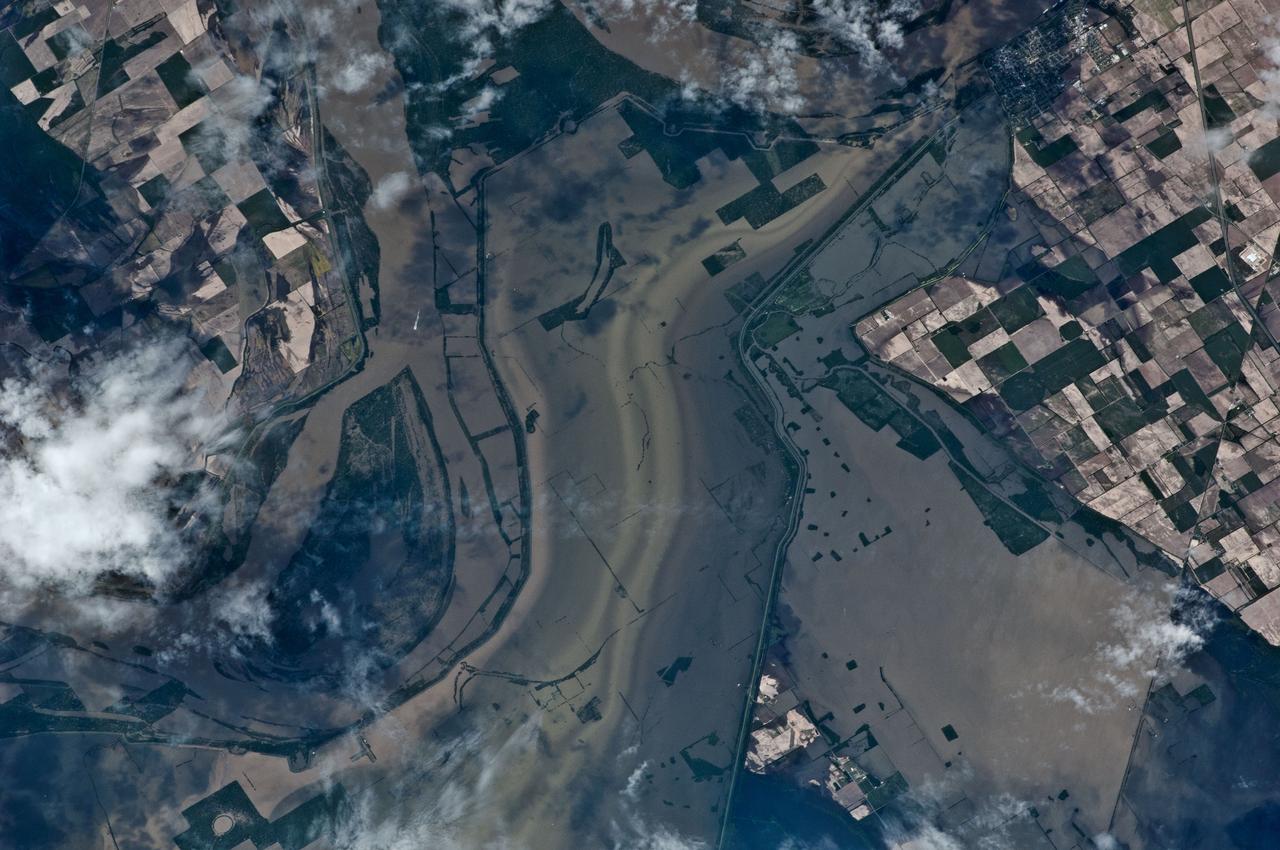

ISS027-E-027026 (12 May 2011) --- An Expedition 27 crew member recorded this image aboard the International Space Station as the orbital outpost was passing over the Mississippi River flood waters from 220 miles above. North is toward the bottom of the image, which was captured using a 400-mm lens. This highly impacted area, centered near 36.6 degrees north latitude and 89.5 degrees west longitude, is just east of New Madrid, Mo. (visible in upper right). Levees appear to be intact here, but there is extensive lowland crop flooding.
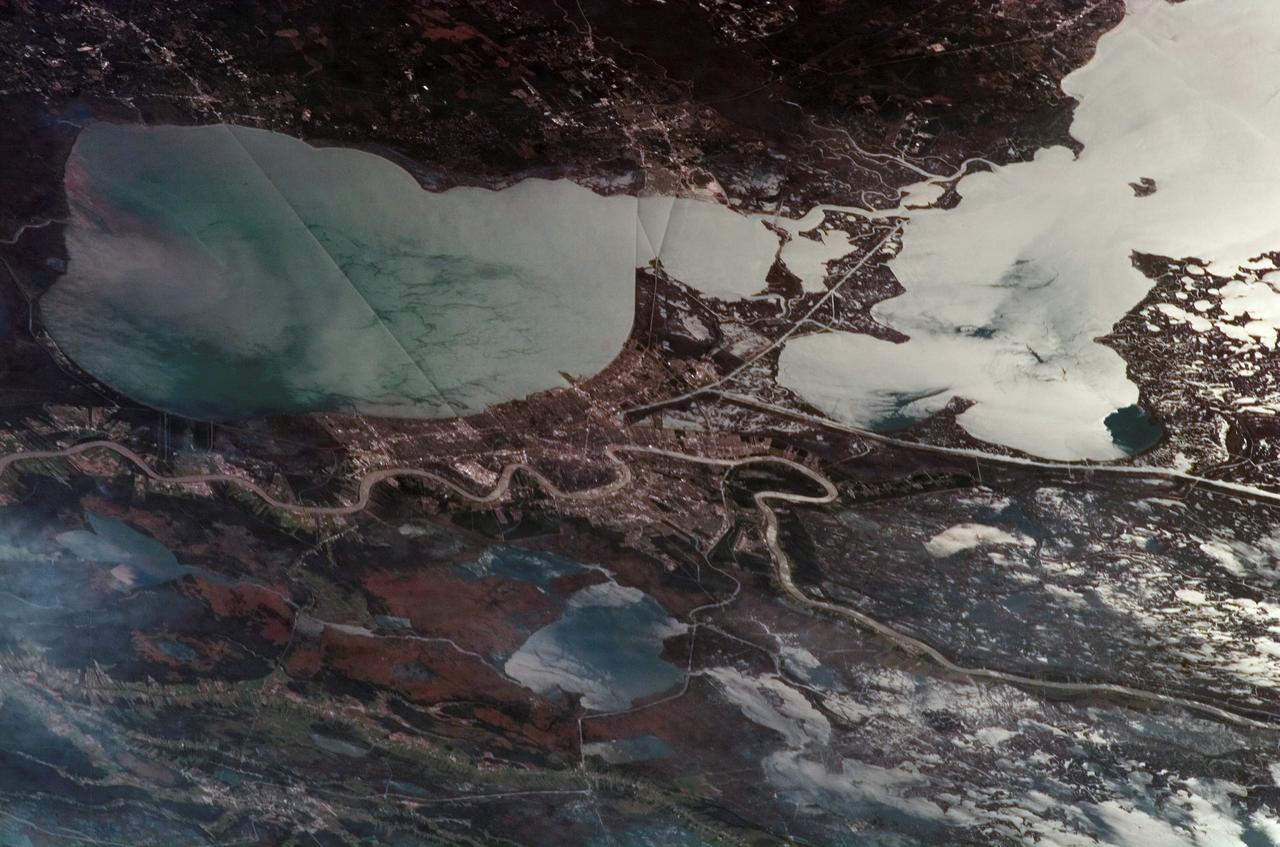

ISS014-E-08179 (18 Nov. 2006) --- New Orleans, Louisiana is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 14 crewmember on the International Space Station. The location of New Orleans, in a shallow depression within unconsolidated deltaic sediments, makes it particularly vulnerable to subsidence and increased likelihood of flooding. The average elevation of metropolitan New Orleans is 1.8 meters below sea level, and a complicated system of levees, pumps, and upstream control structures on the Mississippi River is necessary to maintain dry conditions in the city. The ground subsidence occurs from groundwater withdrawal, reduction of sediment delivery by the Mississippi River, and land use changes (such as draining of wetlands) associated with continuing development. The low areas can be flooded by river floods, storm surges, or failure of levees holding back surrounding lake waters - as demonstrated catastrophically during Hurricane Katrina in 2005. Sunglint accentuates the wetland setting of New Orleans in this image by highlighting the numerous lakes, pond, and rivers (in various shades of silver-gray) surrounding the city. The view was acquired by a crewmember looking southwest from the station, which was located over north-central Alabama at the time this image was taken. Lake Pontchartrain borders New Orleans to the north, and the Lake Pontchartrain Causeway (36 kilometers in length) appears as a dark linear feature against the lake surface. Variations in surface water coloration to the east and west of the Causeway reflect the dynamics of the surface waters (including surface currents and wind-induced roughening). The patterns are made visible by the presence of surfactants on the water surface. Low cloud cover produces a blue-gray haze visible at lower left.
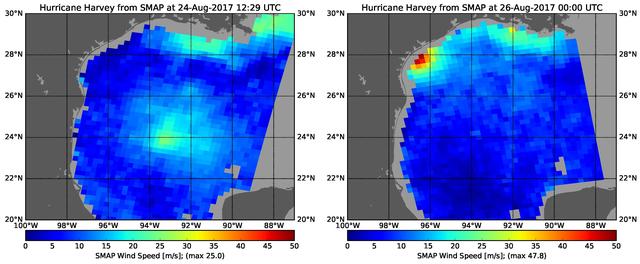
The rapid intensification of Hurricane Harvey is seen in this pair of images of ocean surface wind speeds as observed by the radiometer instrument aboard NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) satellite at 7:29 a.m. CDT Aug. 24th, 2017 (left) and at 7 p.m. CDT Aug. 26th (right). Color indicates wind speed, with red being highest and blue lowest. The images show Harvey's maximum wind speeds increased from approximately 56 miles per hour (25 meters per second) to about 107 miles per hour (47.8 meters per second) in the 36 hours just before landfall. The higher wind speeds estimated near the mouth of the Mississippi River are erroneous and are due to errors in the ancillary sea-surface-salinity data product used by SMAP to estimate extreme wind speeds. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21884
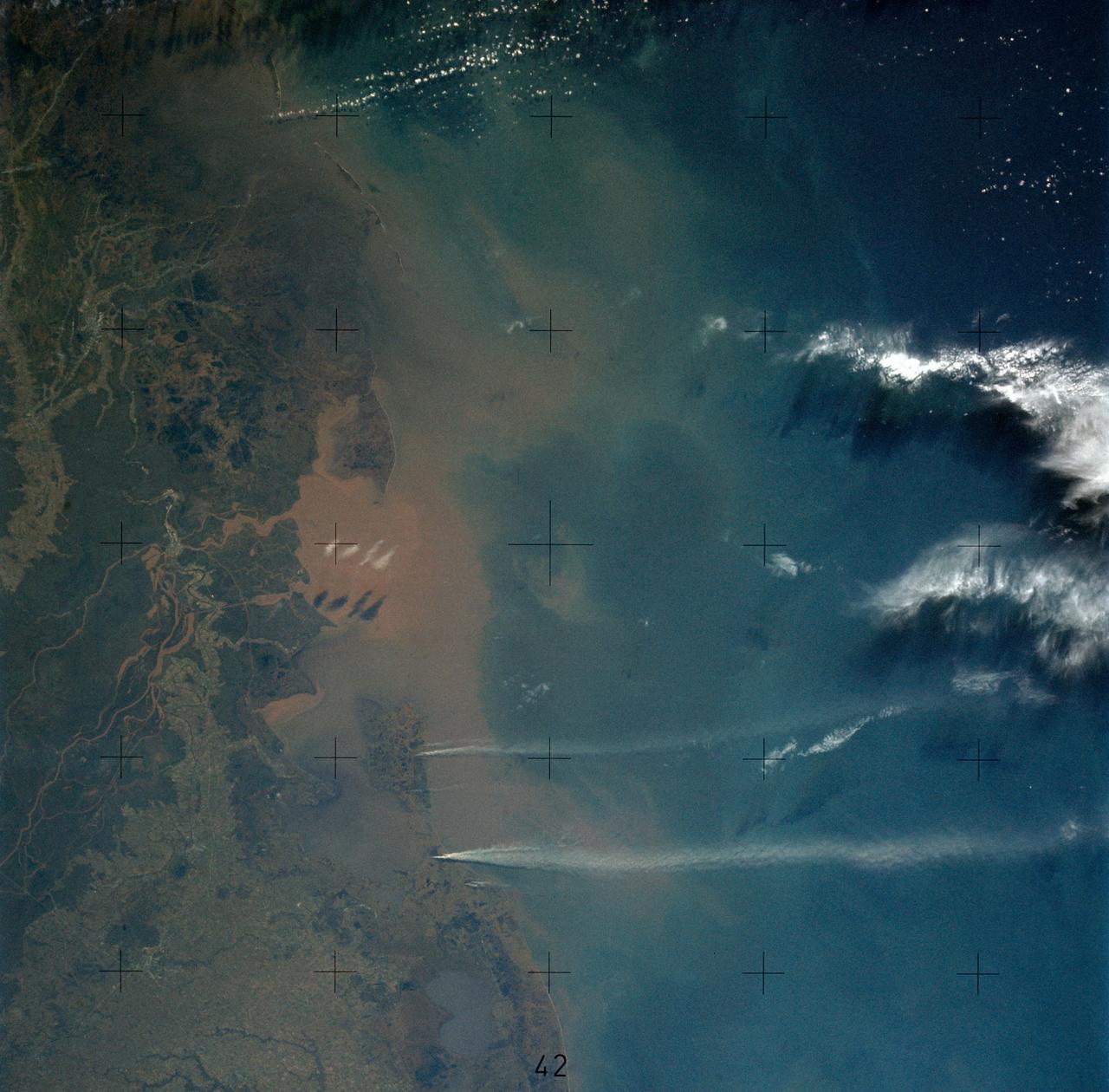

SL4-136-3475 (February 1974) --- A vertical view of the Gulf coast area of Louisiana (29.0N, 92.0W) as seen from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. A Skylab 4 crewman used a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad camera to take this picture. This view extends from White Lake and Pecan Island (bottom border) eastward to the Mississippi River delta (top left). Atchafalaya Bay (red) is in the center. The Bayou Teche area is included in this view. A prominent feature of this photograph is two large white smoke plumes extending from Louisiana south into the Gulf of Mexico. The larger smoke plume originates on the southern shore of Vermillion Bay. The other plume extends from the southern shore of Marsh Island. The prononced narrow width and length of the plumes indicate that a strong offshore wind is present. Approximately 100 miles of the plumes are visible in this photograph; but they probably extend well into the Gulf of Mexico. Photo credit: NASA
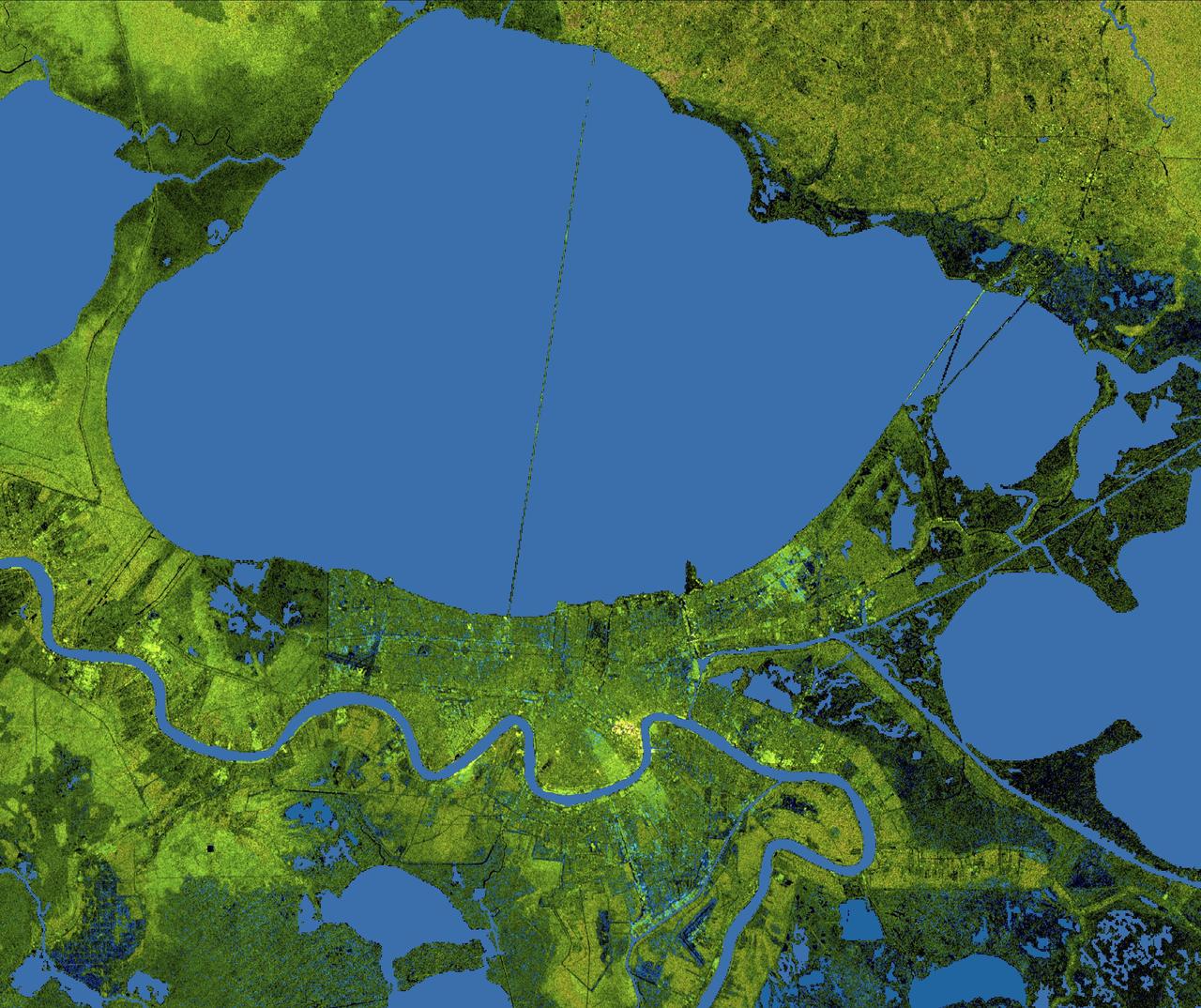
The city of New Orleans, situated on the southern shore of Lake Pontchartrain, is shown in this radar image from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM). In this image bright areas show regions of high radar reflectivity, such as from urban areas, and elevations have been coded in color using height data also from the SRTM mission. Dark green colors indicate low elevations, rising through yellow and tan, to white at the highest elevations. New Orleans is near the center of this scene, between the lake and the Mississippi River. The line spanning the lake is the Lake Pontchartrain Causeway, the world’s longest overwater highway bridge. Major portions of the city of New Orleans are actually below sea level, and although it is protected by levees and sea walls that are designed to protect against storm surges of 18 to 20 feet, flooding during storm surges associated with major hurricanes is a significant concern. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04174
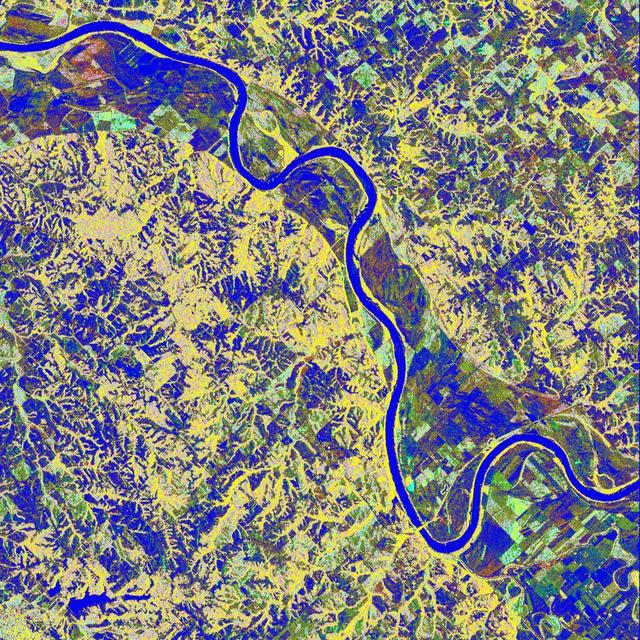

This is a false-color L-band image of an area near Glasgow, Missouri, centered at about 39.2 degrees north latitude and 92.8 degrees west longitude. The image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the space shuttle Endeavour on its 50th orbit on October 3, 1994. The false-color composite was made by displaying the L-band (horizontally transmitted and received) return in red; the L-band (horizontally transmitted and vertically received) return in green; and the sum of the two channels in blue. The area shown is approximately 37 kilometers by 25 kilometers (23 miles by 16 miles). The radar data, coupled with pre-flood aerial photography and satellite data and post-flood topographic and field data, are being used to evaluate changes associated with levee breaks in landforms, where deposits formed during the widespread flooding in 1993 along the Missouri and Mississippi Rivers. The distinct radar scattering properties of farmland, sand fields and scoured areas will be used to inventory floodplains along the Missouri River and determine the processes by which these areas return to preflood conditions. The image shows one such levee break near Glasgow, Missouri. In the upper center of the radar image is a region covered by several meters of sand, shown as blue regions below the bend in the river. West (left) of this dark area, a blue gap in the levee tree canopy can be seen, showing the area where the levee failed. Radar data such as these can help scientists more accurately assess the potential for future flooding in this region and how that might impact surrounding communities. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01744
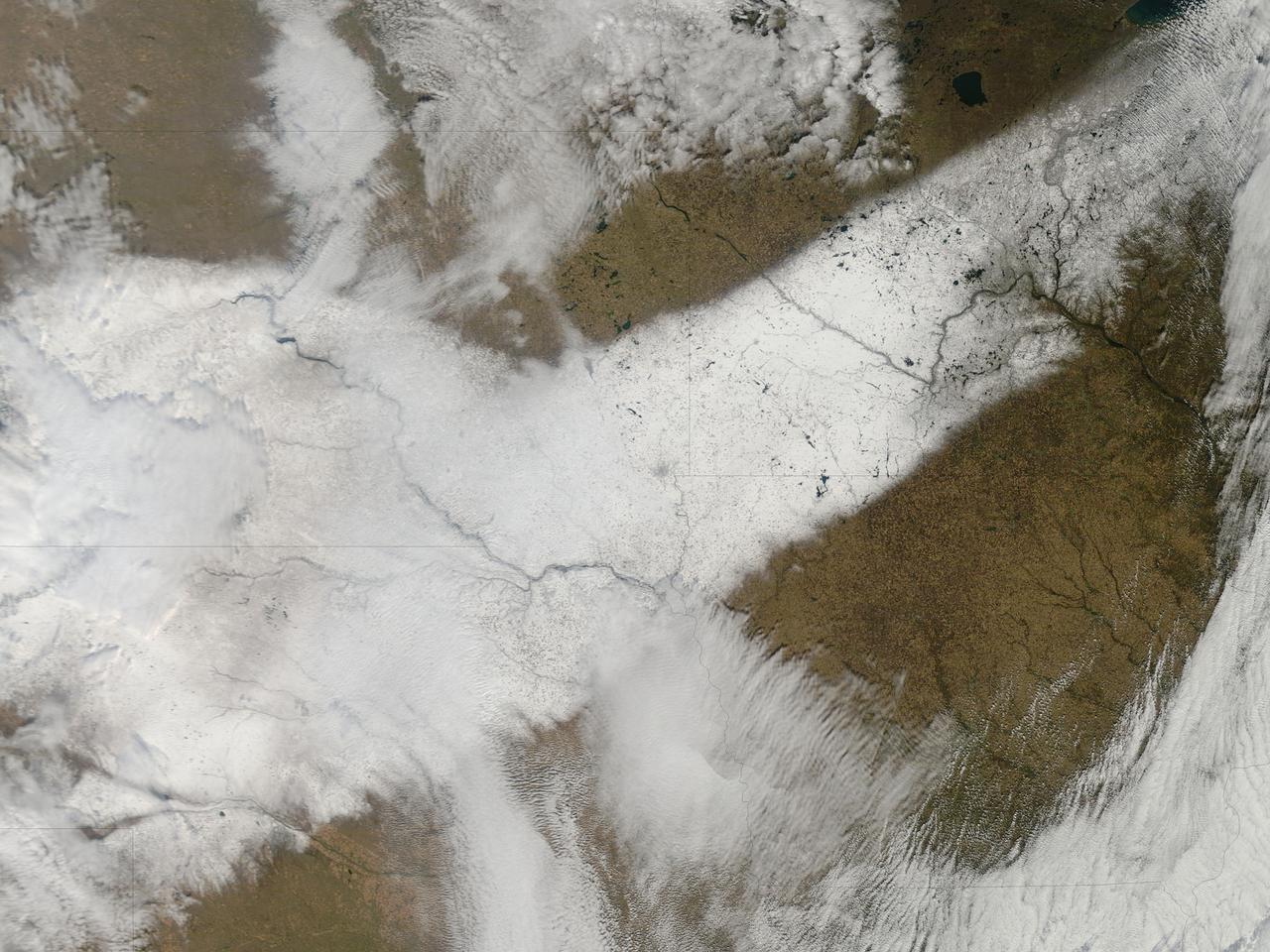

An autumn storm brought the first snow of the season to the Upper Mississippi River Valley and the Midwestern United States in early November, 2013. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard NASA’s Terra satellite captured this true color image on November 6 just as the storm was clearing. A long band of snow stretching from Colorado in the southwest to Wisconsin in the northeast marked the path of the blowing storm. According to WeatherBug, up to 10 inches blanketed Gordon, Nebraska and Pipestone, Minnesota. Most snow totals in the Central and Northern Plains and Upper Mississippi Valley ranged from 2-5 inches, while Minneapolis-St. Paul metro area picked up 1-2 inches of new snow from the event. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

FIRST LEGO League participants listen to Aerospace Education Specialist Chris Copelan explain the playing field for 'Nano Quest' during a recent FLL kickoff event at StenniSphere, the visitor center at NASA Stennis Space Center. The kickoff began the 2006 FLL competition season. Eighty-five teachers, mentors, parents and 9- to 14-year-old students from southern and central Mississippi came to SSC to hear the rules for Nano Quest. The challenge requires teams to spend eight weeks building and programming robots from LEGO Mindstorms kits. They'll battle their creations in local and regional competitions. The Dec. 2 competition at Mississippi Gulf Coast Community College will involve about 200 students. FIRST LEGO League, considered the 'little league' of the FIRST (For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology) Robotics Competition, partners FIRST and the LEGO Group. Competitions aim to inspire and celebrate science and technology using real-world context and hands-on experimentation, and to promote the principles of team play and gracious professionalism. Because NASA advocates robotics and science-technology education, the agency and SSC support FIRST by providing team coaches, mentors and training, as well as competition event judges, referees, audio-visual and other volunteer staff personnel. Two of Mississippi's NASA Explorer Schools, Bay-Waveland Middle and Hattiesburg's Lillie Burney Elementary, were in attendance. The following schools were also represented: Ocean Springs Middle, Pearl Upper Elementary, Long Beach Middle, Jackson Preparatory Academy, North Woolmarket Middle, D'Iberville Middle, West Wortham Middle, Picayune's Roseland Park Baptist Academy and Nicholson Elementary, as well as two home-school groups from McComb and Brandon. Gulfport and Picayune Memorial-Pearl River high schools' FIRST Robotics teams conducted robotics demonstrations for the FLL crowd.
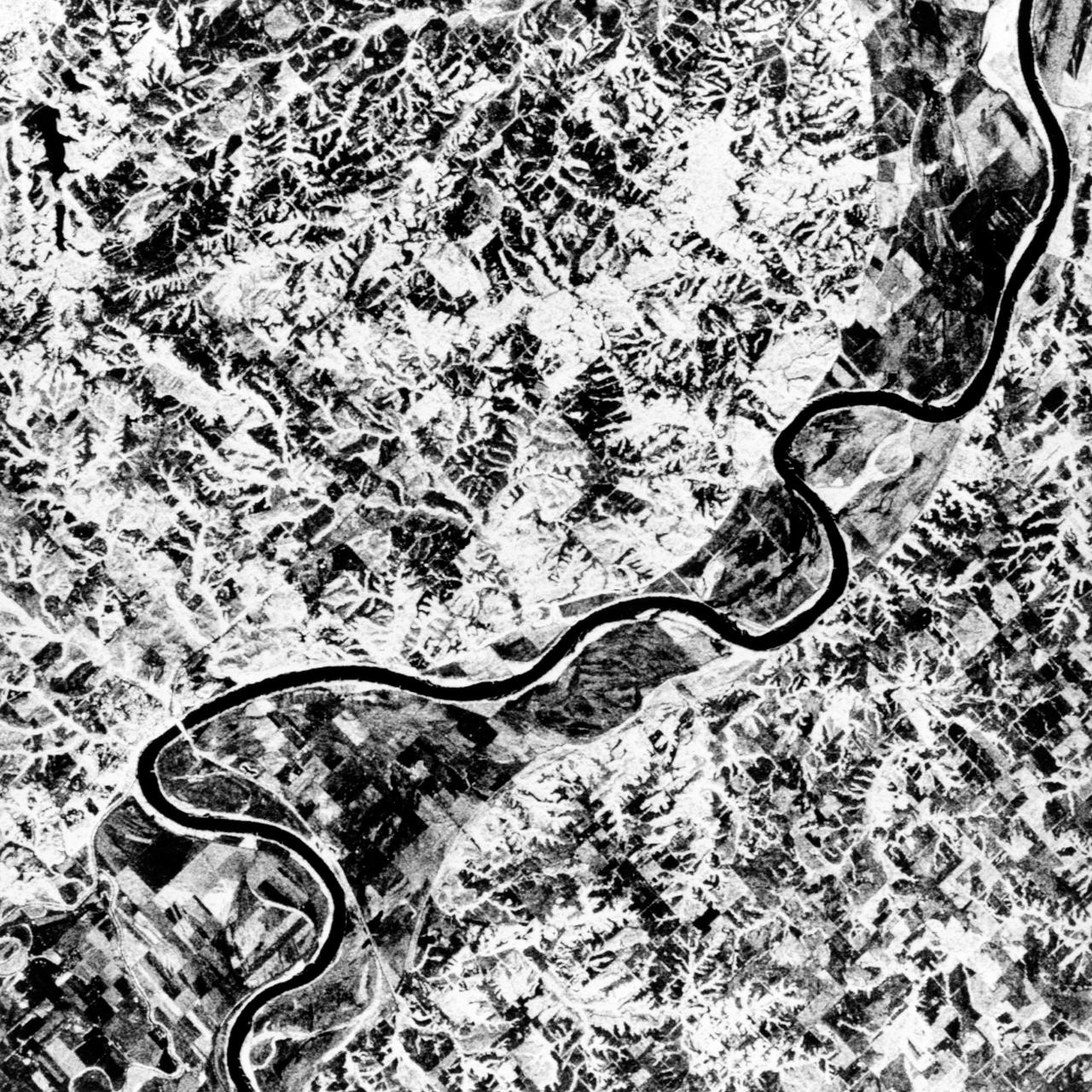
STS068-S-055 (7 October 1994) --- This is a false-color L-Band image of an area near Glasgow, Missouri, centered at about 39.2 degrees north latitude and 92.8 degrees west longitude. The image was acquired using the L-Band radar channel (horizontally transmitted and received and horizontally transmitted and vertically received) polarization's combined. The data were acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on orbit 50 on October 3, 1994. The area shown is approximately 37 by 25 kilometers (23 by 16 miles). The radar data, coupled with pre-flood aerial photography and satellite data and post-flood topographic and field data, are being used to evaluate changes associated with levee breaks in land forms, where deposits formed during the widespread flooding in 1993 along the Missouri and Mississippi Rivers. The distinct radar scattering properties of farmland, sand fields and scoured areas will be used to inventory flood plains along the Missouri River and determine the processes by which these areas return to preflood conditions. The image shows one such levee break near Glasgow, Missouri. In the upper center of the radar image, below the bend of the river, is a region covered by several meters of sand, shown as dark regions. West (left) of the dark areas, a gap in the levee tree canopy shows the area where the levee failed. Radar data such as these can help scientists more accurately assess the potential for future flooding in this region and how that might impact surrounding communities. Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth. The radars illuminate Earth with microwaves, allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses the three microwave wavelengths: the L-Band (24 centimeters), C-Band (6 centimeters) and X-Band (3 centimeters). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornier and Alenia Spazio companies for the German space agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian space agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI), with the Deutsche Forschungsanstalt fuer Luft und Raumfahrt e.v. (DLR), the major partner in science, operations and data processing of X-SAR. (P-44734)
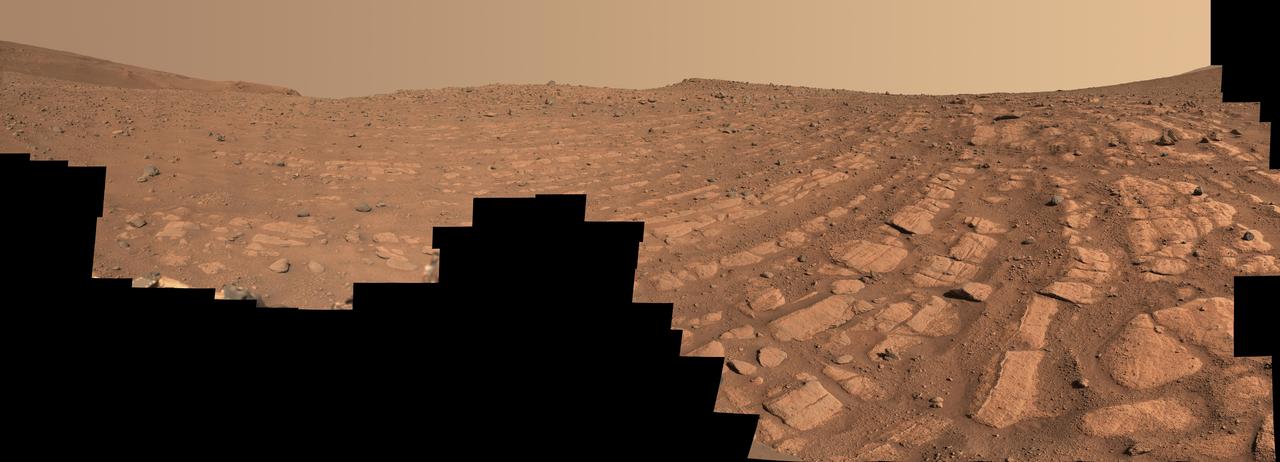

Scientists think that the bands of rocks seen in this image may have been formed by a very fast, deep river – the first of its kind evidence has been found for on Mars. NASA's Perseverance Mars rover captured this mosaic at a location nicknamed "Skrinkle Haven" using its Mastcam-Z camera between Feb. 28 and March 9, 2023 (between the 721st and 729th Martian days, or sols, of the mission). The mosaic is made up of 203 individual images that were stitched together after being sent back from Mars. This natural color view is approximately how the scene would appear to an average person if they were on Mars. "Skrinkle Haven" offers the clearest example of these curved rock layers – called "the curvilinear unit" – that had previously only been seen from space. Scientists are now debating what kind of powerfully flowing water formed those curves: a river like the Mississippi, which winds snakelike across the landscape, or a braided river like Nebraska's Platte, which forms small islands of sediment called sandbars. When viewed from the ground, the curved layers are arranged in rows, and appear to ripple out across the landscape. They could be the remnants of a river's banks that shifted over time – or the remnants of sandbars that formed in the river. The layers were likely much taller in the past; scientists suspect that after these piles of sediment turned to rock, they were sand-blasted by wind over the course of eons and carved down to their present size. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25829
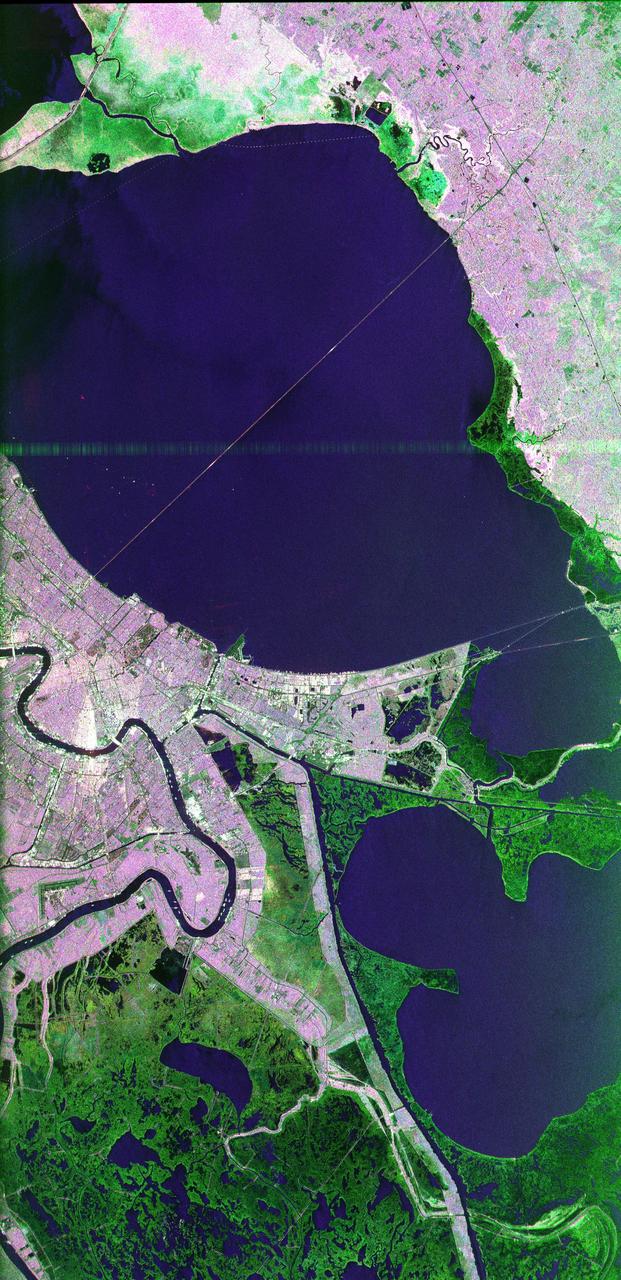

This image of the area surrounding the city of New Orleans, Louisiana in the southeastern United States demonstrates the ability of multi-frequency imaging radar to distinguish different types of land cover. The dark area in the center is Lake Pontchartrain. The thin line running across the lake is a causeway connecting New Orleans to the city of Mandeville. Lake Borgne is the dark area in the lower right of the image. The Mississippi River appears as a dark, wavy line in the lower left. The white dots on the Mississippi are ships. The French Quarter is the brownish square near the left center of the image. Lakefront Airport, a field used mostly for general aviation, is the bright spot near the center, jutting out into Lake Pontchartrain. The image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar C/X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) during orbit 39 of space shuttle Endeavour on October 2, 1994. The area is located at 30.10 degrees north latitude and 89.1 degrees west longitude. The area shown is approximately 100 kilometers (60 miles) by 50 kilometers (30 miles). The colors in this image were obtained using the following radar channels: red represents the L-band (horizontally transmitted and received); green represents the C-band (horizontally transmitted and received); blue represents the L-band (vertically transmitted and received). The green areas are primarily vegetation consisting of swamp land and swamp forest (bayou) growing on sandy soil, while the pink areas are associated with reflections from buildings in urban and suburban areas. Different tones and colors in the vegetation areas will be studied by scientists to see how effective imaging radar data is in discriminating between different types of wetlands. Accurate maps of coastal wetland areas are important to ecologists studying wild fowl and the coastal environment. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01300
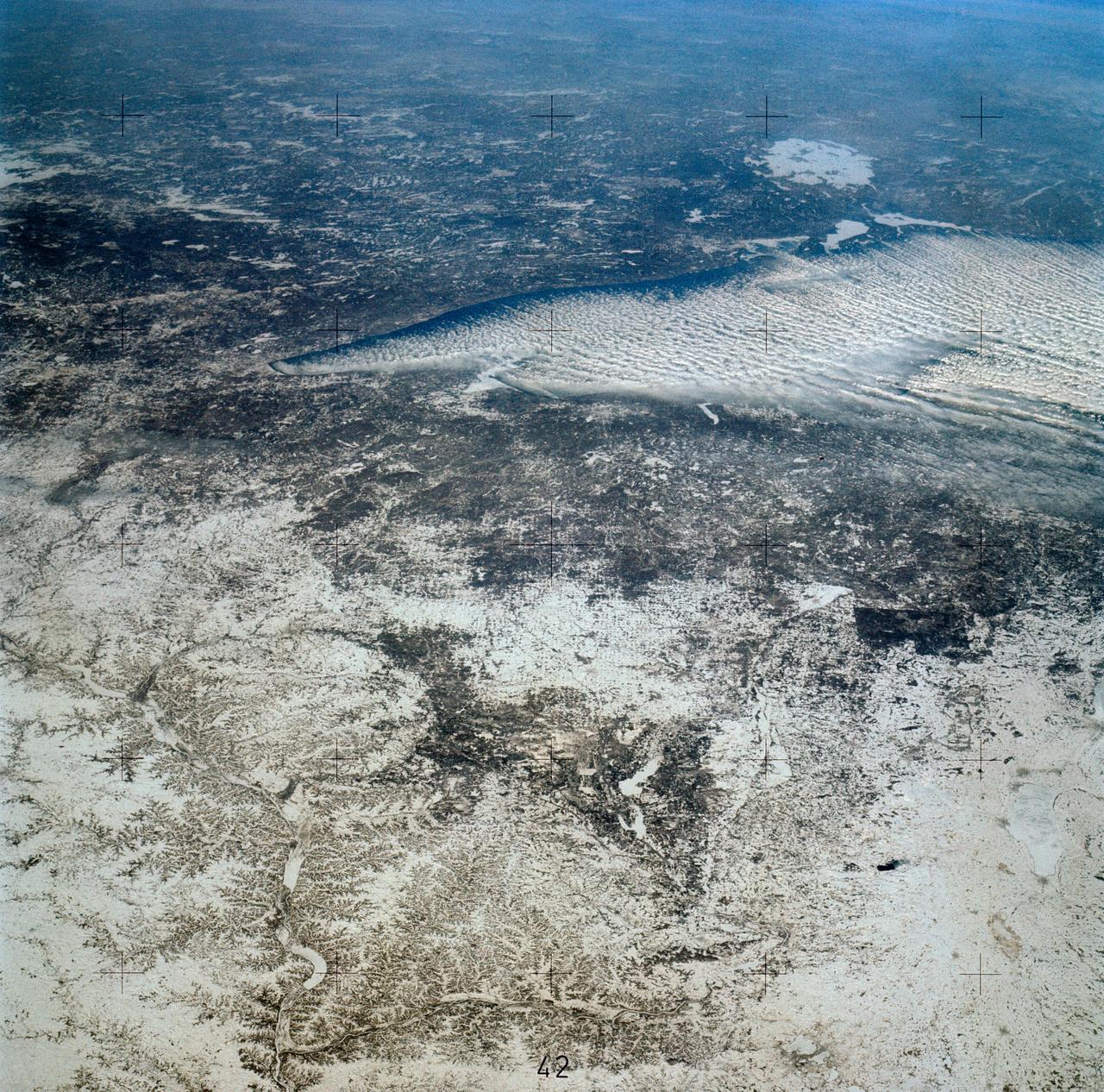

SL4-139-3953 (7 Jan. 1974) --- An oblique view of a portion of the Middle West looking northeastward toward Lake Superior and Ontario, Canada, as seen from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. This picture was taken by one of the Skylab 4 crewmen with a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad camera using a 100mm lens. Most of the land mass in the foreground is Wisconsin. Iowa is in the lower left corner. Minnesota is at left and upper left. Ontario is in the far right background. Michigan is at right center. Note the circular-shaped feature at center left which was first observed by the Skylab 4 crewmen. The feature is 85 kilometers (55 miles) in diameter, and it is centered near 91.5 degrees west longitude and 44.5 degrees north latitude. The Mississippi River Valley forms the southwest side of the circular feature. The City of La Crosse, Wisconsin, is just south of the near side of the circle, and the Black River completes the southern and eastern part. The City of Eau Claire is at the north edge of the circle. The most likely origin of circular features of this magnitude are (1) volcanic, (2) structural, or (3) meteorite impact. The feature is not volcanic -- the rocks are the wrong type. Possibly it is structural, formed by slight warping of layered rocks into a basin or dome, followed by erosion of all but the most subtle trace of the structure. The feature could be a severely eroded meteorite impact crater. If so, a thorough study of the area may yield evidence of the extreme pressure and temperature the rocks were subjected to by the shock of an impacting meteorite. Photo credit: NASA
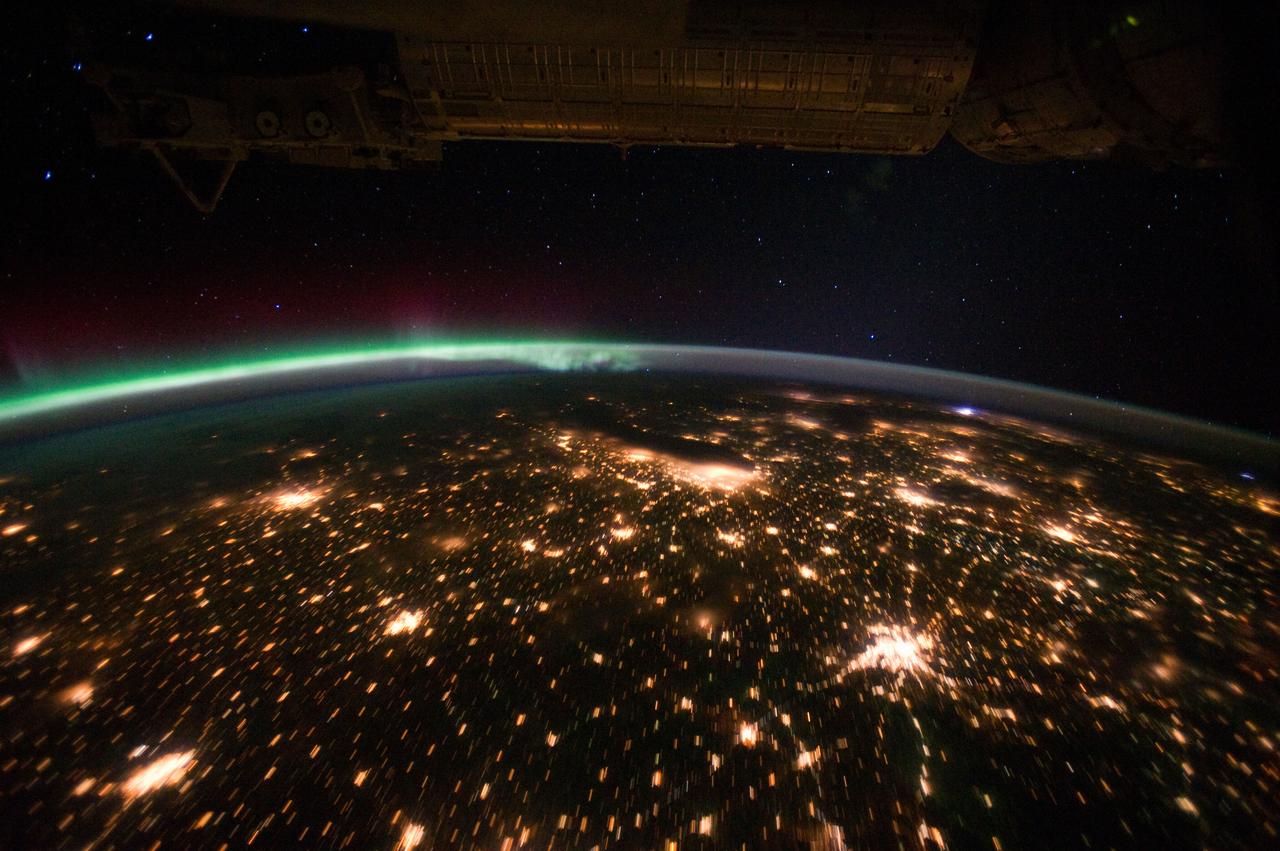

ISS029-E-012564 (29 Sept. 2011) --- The Midwestern United States at night with Aurora Borealis is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 29 crew member on the International Space Station. The night skies viewed from the space station are illuminated with light from many sources. For example, the Midwestern United States presents a night-time appearance not unlike a patchwork quilt when viewed from orbit. The artificial light from human settlements appears everywhere with a characteristic yellow tinge in this photograph. But green light of the Aurora Borealis also appears strongly in this view (top left)—even seeming to be reflected off Earth’s surface—in Canada—beneath the aurora. A small white patch of light is almost certainly lightning from a storm on the East coast (top right). Part of the International Space Station appears across the top of the image. This photograph highlights the Chicago, IL, metropolitan area as the largest cluster of lights at center, next to the dark patch of Lake Michigan. The other largest metropolitan areas include St. Louis, MO (lower right), Minneapolis–St. Paul, MN (left) and the Omaha–Council Bluffs region on the Nebraska–Iowa border (lower left). City light clusters give an immediate sense of relative city size; demographers have used night time satellite imagery to make estimates of city populations, especially in the developing world where city growth can be very rapid. The U.S. northeast seaboard lies in the most oblique (meaning viewed at an angle) part of the image at top right, just beyond the Appalachian Mts., a dark winding zone without major cities. Scales change significantly in oblique views: Omaha is only 200 kilometers from Des Moines, but appears roughly the same distance from Minneapolis—which is actually 375 kilometers to the north of Des Moines. In addition to the major metropolitan areas, the rectangular NS/EW-oriented pattern of townships is clearly visible in the rural, lower left part of the image. This pattern instantly gives the sense of north orientation (toward the top left corner) and is a distinctive characteristic of the United States, so that ISS crew members can quickly know which continent they are flying over even at night. In contrast to the regular township pattern, interstate highways converge on St. Louis (e.g. Hwy 44), Chicago and other large cities, much like wheel spokes around a central hub. Rivers—major visual features in daylight—become almost invisible at night. The course of the Mississippi River appears as a slightly meandering zone from Minneapolis through St. Louis (dashed line)—the river course continues out of the lower right corner of the image.
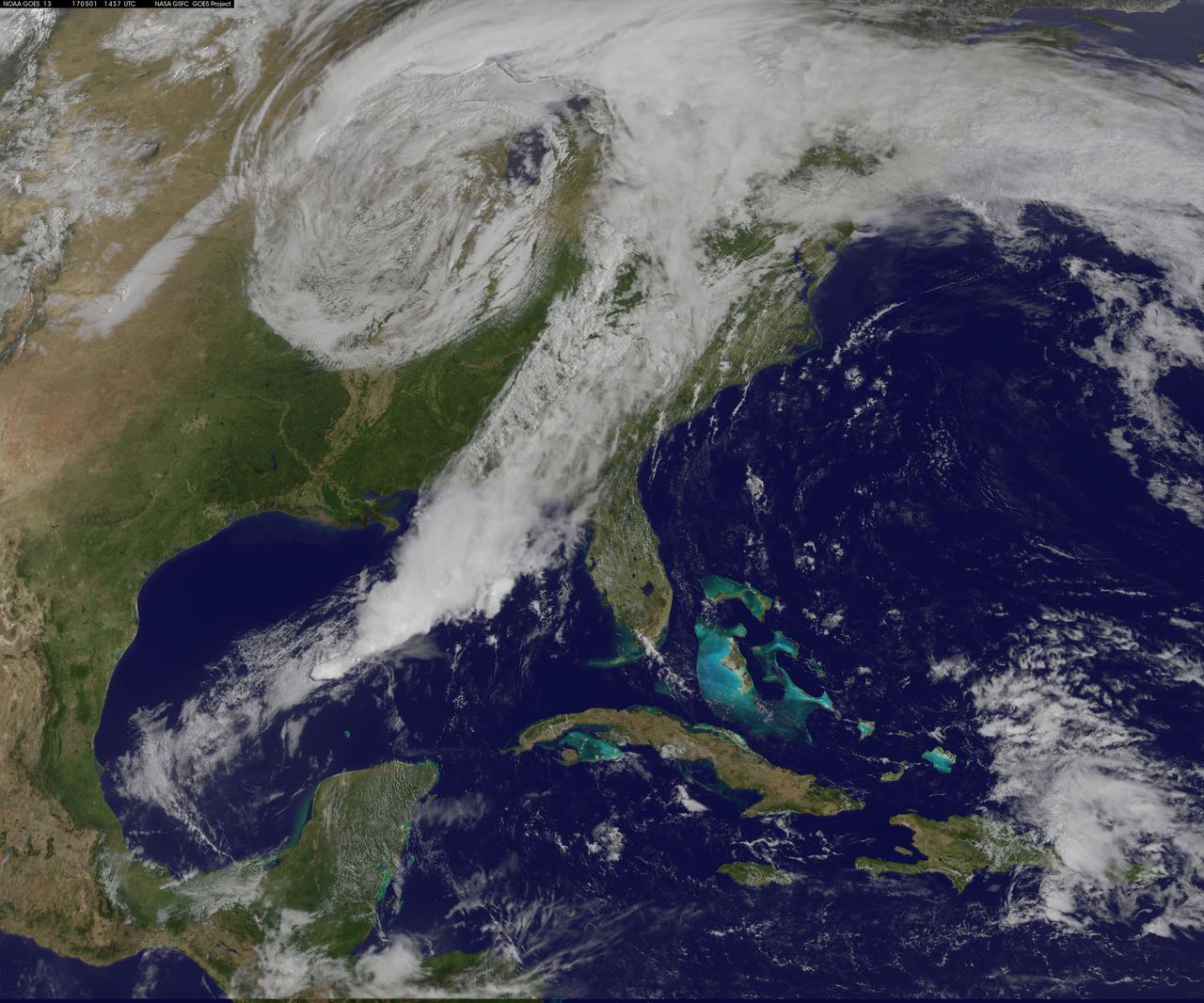
NASA Sees Severe Weather from Central to Eastern US A vigorous weather system has generated severe weather over the mid-section of the U.S. and satellites are providing a look at it as it is moving toward the East Coast. NASA and NOAA satellites have been tracking a storm system that has generated flooding and tornadic thunderstorms in the central U.S. and is expected bring severe weather to the U.S. Mid-Atlantic region. At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, data from NOAA's GOES-East satellite were used to create images and an animation of the movement of the powerful storm. On April 30, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS, instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of the storms moving over eastern Texas and Louisiana. Tornadoes in eastern Texas killed four people. The system generated heavy rainfall and caused additional fatalities and damages in Arkansas, Missouri, Mississippi, Alabama and Tennessee. On Monday, May 1, NOAA's National Weather Service noted, "Major to record flooding continues over portions of the central U.S. Severe thunderstorms are possible from the Mid-Atlantic to the northeastern U.S. "Major to record flooding will continue over portions of eastern Oklahoma, northern Arkansas, Missouri, Illinois and Indiana. Rivers will gradually recede over the next several days. Additional strong to severe thunderstorms will be possible Monday afternoon and evening over portions of the Mid-Atlantic and Northeast U.S. Damaging winds, large hail, and isolated tornadoes will be possible." Image caption: On May 1, 2017, at 10:37 a.m. EDT (1437 UTC) NOAA's GOES-East satellite captured this visible image of the storm system centered over Iowa with an associated cold front that stretches into the Gulf of Mexico. Credits: NASA/NOAA GOES Project <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

An oil slick in the Gulf of Mexico following Hurricane Ida – a high-end Category 4 when it made landfall near Port Fourchon, Louisiana, on Aug. 29, 2021 – appears as a green trail in the inset false-color graphic provided by NASA's Delta-X project, while the surrounding seawater appears orange. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) regularly monitors U.S. coastal waters for potential spills and noticed slicks that appeared just off the coast after the hurricane. They were able to use this information from Delta-X to corroborate other data they had about oil slicks in the area (satellite image in the second inset picture). The blue-green swath crossing from the Gulf of Mexico over the Louisiana coast denotes the flight path of the Delta-X radar instrument on Sept. 1, just before 11:30 a.m. CDT. Charged with studying the Mississippi River Delta, Delta-X was gearing up to collect data on Louisiana's coastal wetlands when Hurricane Ida barreled ashore in late August. The storm damaged buildings and infrastructure alike, resulting in power outages, flooding, and oil slicks in the Gulf of Mexico. Oil tends to smooth out the bumps on the ocean's surface, which results in a distinct radar signal that the Delta-X mission was able to pick out of their data. Delta-X added flight paths to their planned schedule – with the support of NASA's Applied Science Disaster Program – in order to collect information over the gulf in areas of interest to NOAA. Delta-X is studying two wetlands – the Atchafalaya and Terrebonne Basins – by land, boat, and air to quantify water and sediment flow as well as vegetation growth. While the Atchafalaya Basin has been gaining land through sediment accumulation, Terrebonne Basin, which is right next to the Atchafalaya, has been rapidly losing land. The data collected by the project will be applied to models used to forecast which areas of the delta are likely to gain or lose land under various sea level rise, river flow, and watershed management scenarios. The mission uses several instruments to collect its data. Affixed to the bottom of a Gulfstream-III airplane, one of those instruments, the all-weather Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar (UAVSAR), bounces radar signals off of Earth's surface, forming a kind of image of a particular area. Repeated images of the same regions, captured at different times, enable researchers to detect changes in those areas, such as fluctuating water levels beneath the vegetation as the tides move in and out of these wetlands. In addition to radar measurements, teams from Caltech, Louisiana State University, Florida International University, and other collaborating institutions gather water and vegetation samples – among other data – by boat, other airborne sensors, and from instruments on the ground. Funded by NASA's Earth Venture Suborbital (EVS-3) program, Delta-X is managed by the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages JPL for NASA. Fall 2021 was Delta-X's last scheduled field campaign, although the five-year mission will run through the end of 2023. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24540