
Caption: Composite shot of all four rockets for the M-TeX and MIST experiments is made up of 30 second exposures. The rocket salvo began at 4:13 a.m. EST, Jan. 26, 2015, from the Poker Flat Research Range, Alaska. Credit: NASA/Jamie Adkins More info: The Mesosphere-Lower Thermosphere Turbulence Experiment, or M-TeX, and the Mesospheric Inversion-layer Stratified Turbulence, or MIST, experiment were successfully conducted the morning of Jan. 26, 2015, from the Poker Flat Research Range, Alaska. The first M-Tex rocket, a NASA Terrier-Improved Malemute sounding rocket, was launched at 4:13 a.m. EST and was followed one-minute later by the first MIST experiment payload on a NASA Terrier-Improved Orion. The second M-TeX payload was launched at 4:46 a.m. EST and also was followed one minute later by the second MIST payload. Preliminary data show that all four payloads worked as planned and the trimethyl aluminum, or TMA, vapor trails were seen at the various land-based observation sites in Alaska. A fifth rocket carrying the Auroral Spatial Structures Probe remains ready on the launch pad. The launch window for this experiment runs through Jan. 27. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
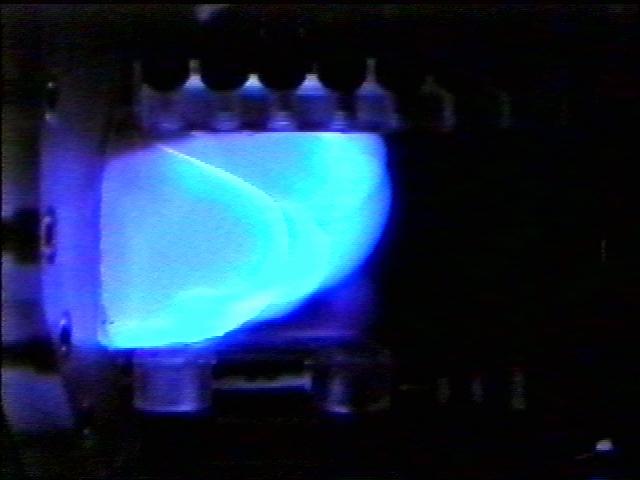
The Water Mist commercial research program is scheduled to fly an investigation on STS-107 in 2002 in the updated Combustion Module (CM-2), a sophisticated combustion chamber plus diagnostic equipment. The Center for the Commercial Applications of Combustion in Space (CCACS), a NASA Commercial Space Center located at the Colorado School of Mines, is investigating the properties of mist fire suppression in microgravity with Industry Partner Environmental Engineering Concepts. These experiments consist of varying water droplet sizes and water mist concentrations applied to flame fronts of different propane/air mixtures. Observations from these tests will provide valuable information on the change of flame speed in the presence of water mist. Shown here is a flame front propagating through the Mist flame tube during 1-g testing at NASA/Glenn Research Center.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Mars Simulation Chamber is being prepared for the Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or MIST, mission support. The chamber allows MIST scientists and engineers to simulate the stratosphere prior to high altitude flight experiments. The MIST mission will fly a small biological payload in low altitudes aboard a blimp in July to measure microbial survival and cellular responses to exposure in the upper atmosphere. Later in the year, the MIST mission will deploy samples at even high altitudes in the stratosphere using scientific balloons. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
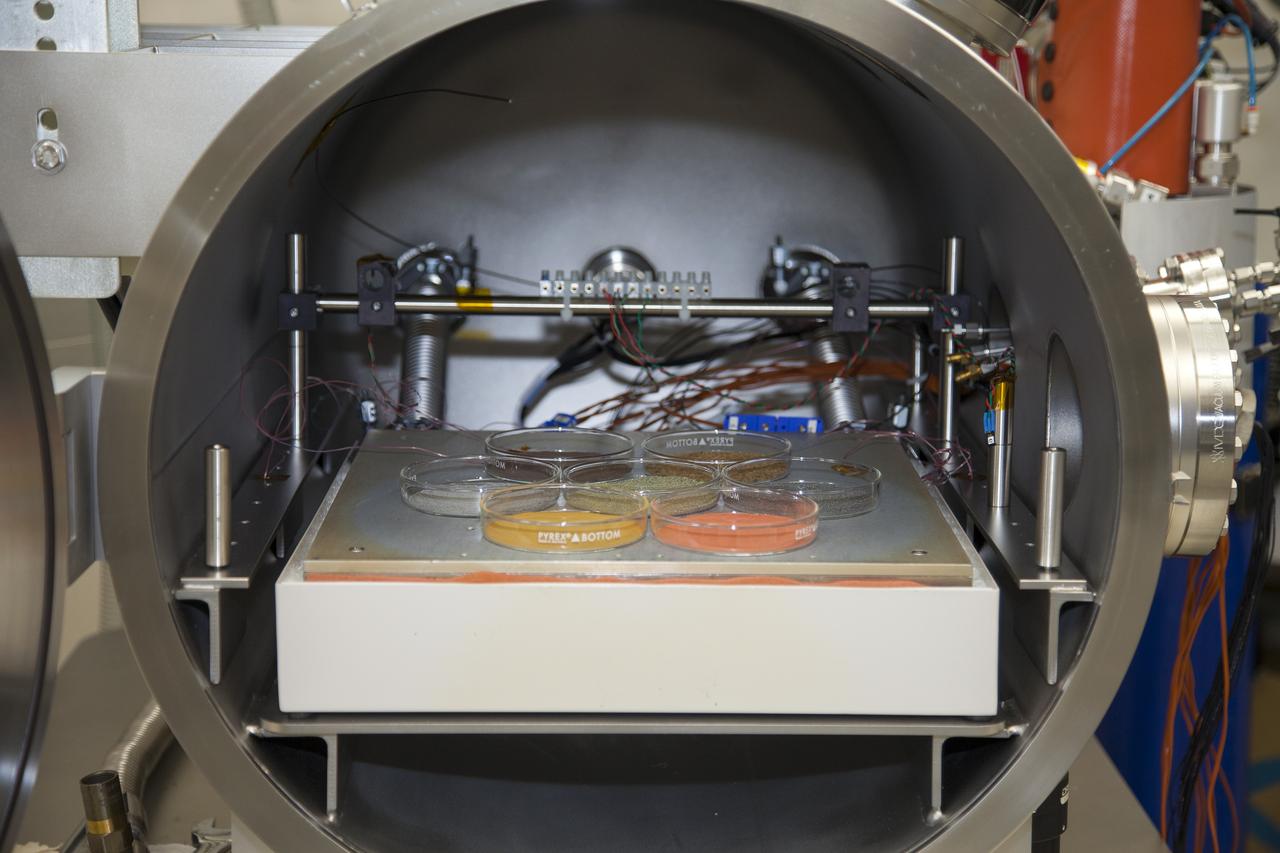

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Mars Simulation Chamber is being prepared for the Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or MIST, mission support. The chamber allows MIST scientists and engineers to simulate the stratosphere prior to high altitude flight experiments. The MIST mission will fly a small biological payload aboard a blimp in July to measure microbial survival and cellular responses to exposure in the upper atmosphere. Later in the year, the MIST mission will deploy samples at even higher altitudes in the stratosphere using scientific balloons. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
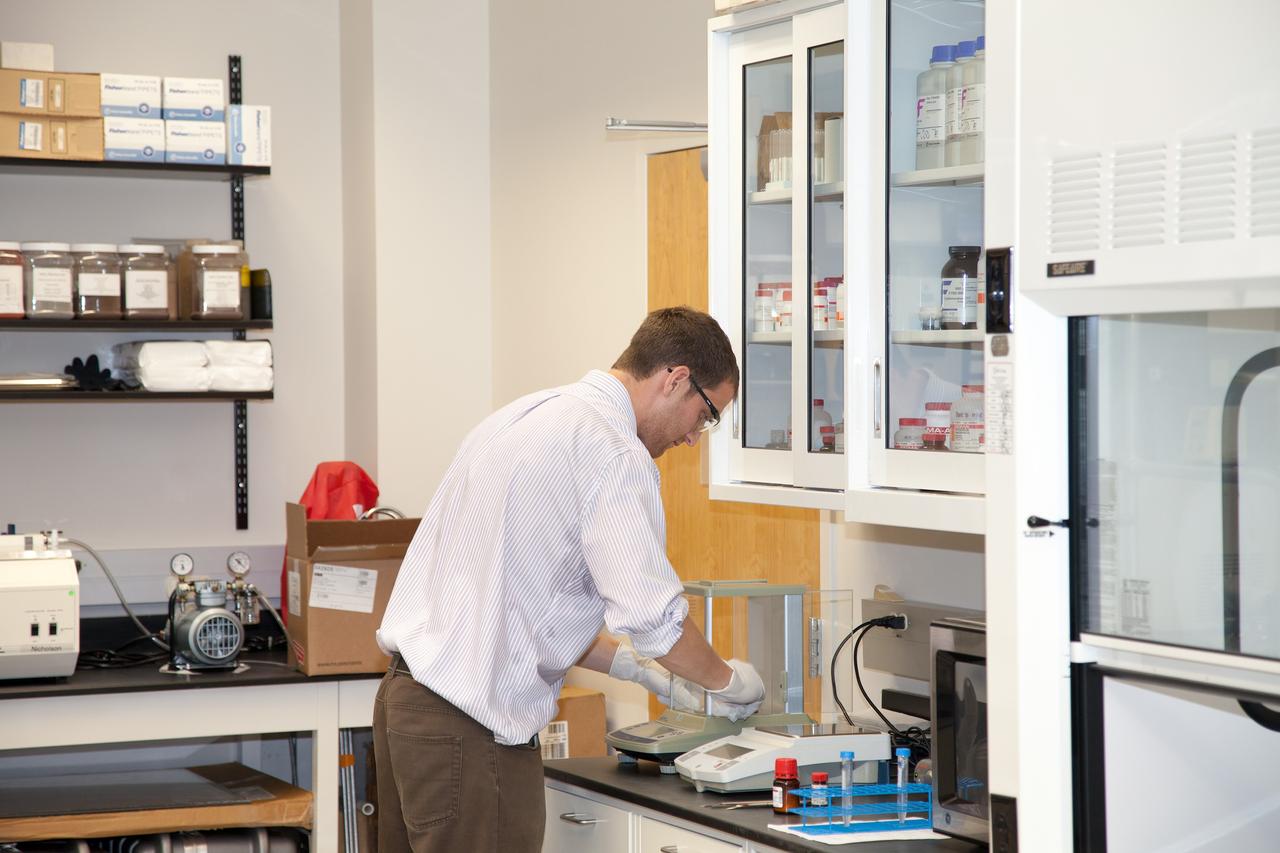

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Dr. David J. Smith, a microbiologist in the Surface Systems Office, prepares microbes that will be deployed for the Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or MIST, mission. High altitudes exert a unique combination of stresses on microbes, outside the range of conditions normally encountered on the Earth's surface. Results from MIST may improve our understanding of the physical limits and habitable environments for life. The MIST mission will fly a small biological payload aboard a blimp in July to measure microbial survival and cellular responses to exposure in the upper atmoshere. Later in the year, the MIST mission will deploy samples at even higher altitudes in the stratosphere using scientific balloons. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
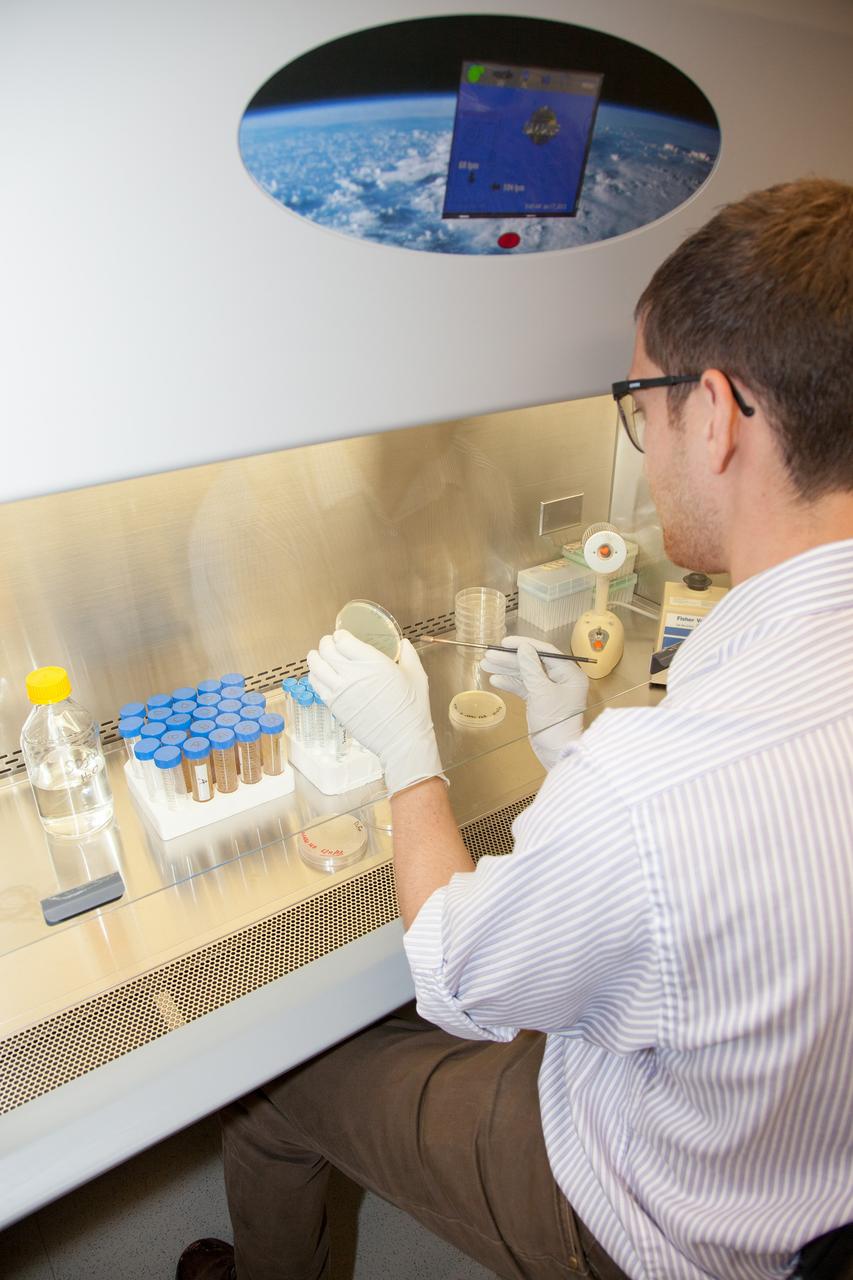

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Dr. David J. Smith, a microbiologist in the Surface Systems Office, prepares microbes that will be deployed for the Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or MIST, mission. High altitudes exert a unique combination of stresses on microbes, outside the range of conditions normally encountered on the Earth's surface. Results from MIST may improve our understanding of physical limits and habitable environments for life. The MIST mission will fly a small biological payload aboard a blimp in July to measure microbial survival and cellular responses to exposure in the upper atmosphere. Later in the year, the MIST mission will deploy samples at even higher altitudes in the stratosphere using scientific balloons. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
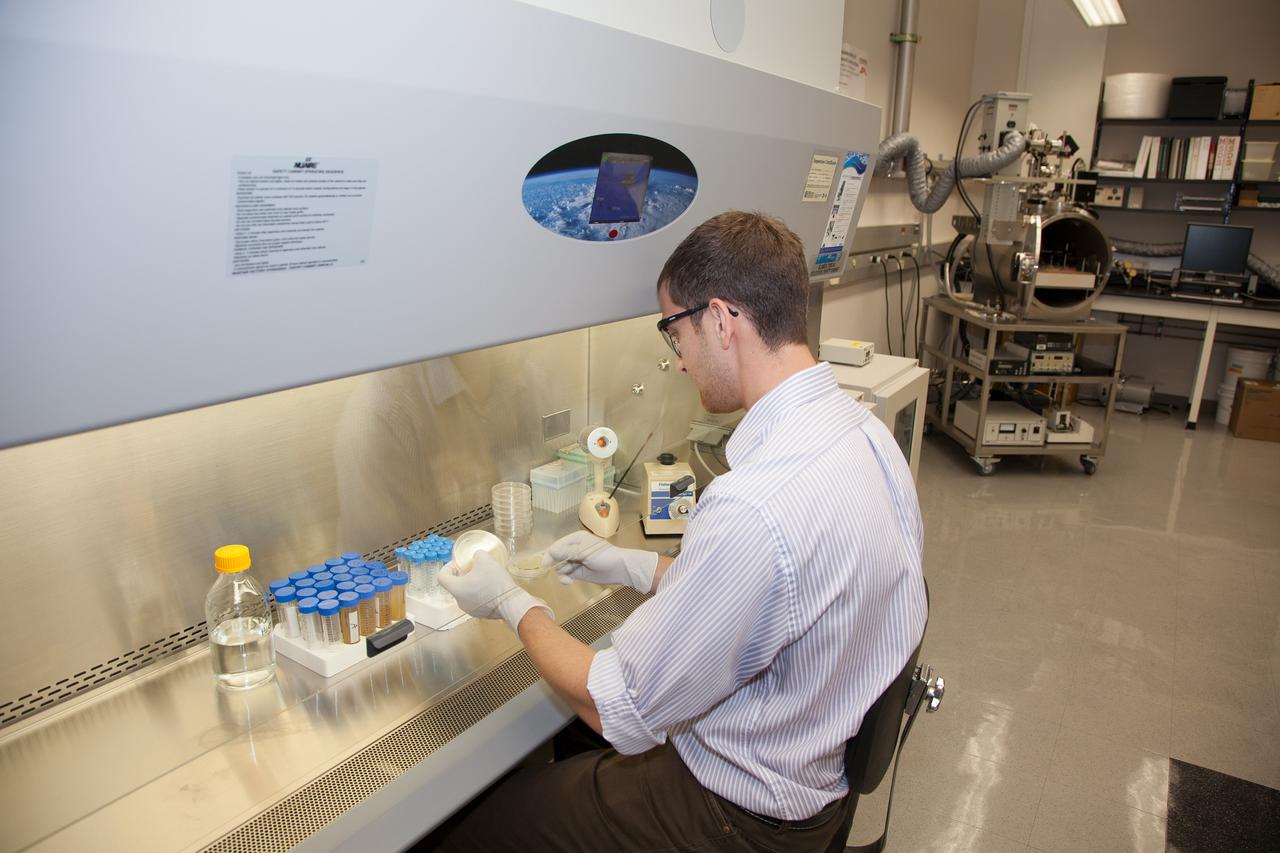

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Dr. David J. Smith, a microbiologist in the Surface Systems Office, prepares microbes that will be deployed for the Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or MIST, mission. High altitudes exert a unique combination of stresses on microbes, outside the range of conditions normally encountered on the Earth's surface. Results from MIST may improve our understanding of the physical limits and habitable environments for life. The MIST mission will fly a small biological payload aboard a blimp in July to measure the microbial survival and cellular responses to exposure in the upper atmosphere. Later in the year, the MIST mission will deploy samples at even higher altitudes in the stratosphere using scientific balloons. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
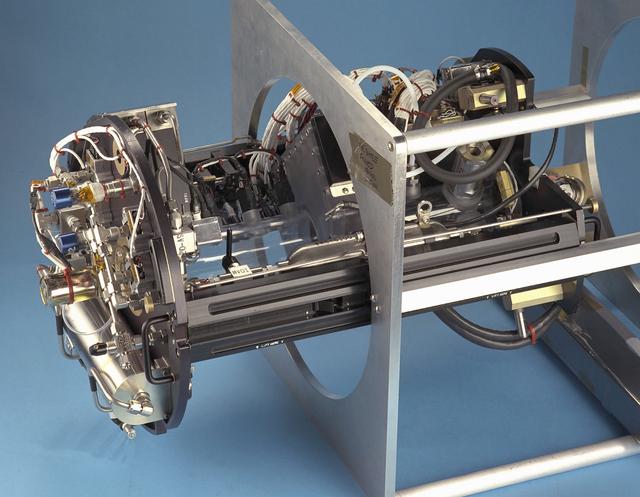
The Water Mist commercial research program is scheduled to fly an investigation on STS-107 in 2002. This investigation will be flown as an Experimental Mounting Structure (EMS) insert into the updated Combustion Module (CM-2), a sophisticated combustion chamber plus diagnostic equipment. (The investigation hardware is shown here mounted in a non-flight frame similar to the EMS.) Water Mist is a commercial research program by the Center for Commercial Applications of Combustion in Space (CCACS), a NASA Commercial Space Center located at the Colorado School of Mines, in Golden, CO and Industry Partner Environmental Engineering Concepts. The program is focused on developing water mist as a replacement for bromine-based chemical fire suppression agents (halons). By conducting the experiments in microgravity, interference from convection currents is minimized and fundamental knowledge can be gained. This knowledge is incorporated into models, which can be used to simulate a variety of physical environments. The immediate objective of the project is to study the effect of a fine water mist on a laminar propagating flame generated in a propane-air mixture at various equivalence ratios. The effects of droplet size and concentration on the speed of the flame front is used as a measure of the effectiveness of fire suppression in this highly controlled experimental environment.
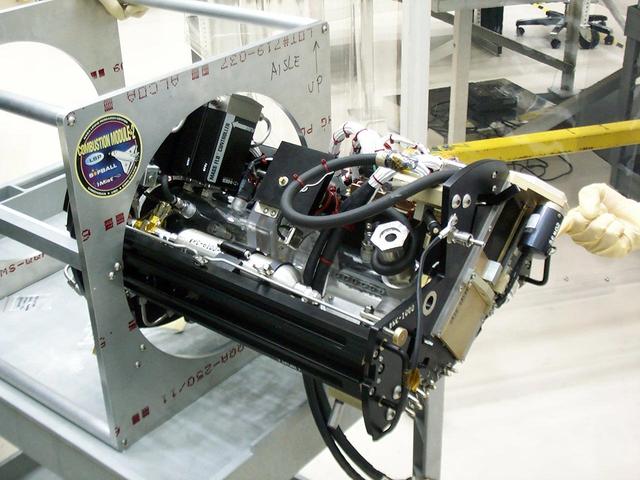

The Water Mist commercial research program is scheduled to fly an investigation on STS-107 in 2002. This investigation will be flown as an Experimental Mounting Structure (EMS) insert into the updated Combustion Module (CM-2), a sophisticated combustion chamber plus diagnostic equipment. (The investigation hardware is shown here mounted in a non-flight frame similar to the EMS.) Water Mist is a commercial research program by the Center for Commercial Applications of Combustion in Space (CCACS), a NASA Commercial Space Center located at the Colorado School of Mines, in Golden, CO and Industry Partner Environmental Engineering Concepts. The program is focused on developing water mist as a replacement for bromine-based chemical fire suppression agents (halons). By conducting the experiments in microgravity, interference from convection currents is minimized and fundamental knowledge can be gained. This knowledge is incorporated into models, which can be used to simulate a variety of physical environments. The immediate objective of the project is to study the effect of a fine water mist on a laminar propagating flame generated in a propane-air mixture at various equivalence ratios. The effects of droplet size and concentration on the speed of the flame front is used as a measure of the effectiveness of fire suppression in this highly controlled experimental environment.
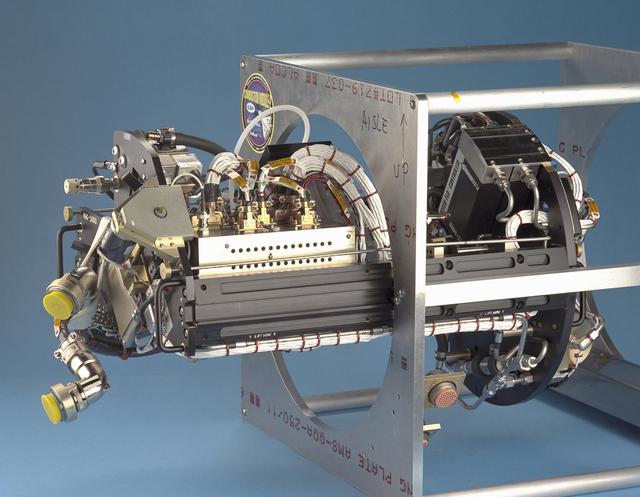
The Water Mist commercial research program is scheduled to fly an investigation on STS-107 in 2002. This investigation will be flown as an Experimental Mounting Structure (EMS) insert into the updated Combustion Module (CM-2), a sophisticated combustion chamber plus diagnostic equipment. (The investigation hardware is shown here mounted in a non-flight frame similar to the EMS.) Water Mist is a commercial research program by the Center for Commercial Applications of Combustion in Space (CCACS), a NASA Commercial Space Center located at the Colorado School of Mines, in Golden, CO and Industry Partner Environmental Engineering Concepts. The program is focused on developing water mist as a replacement for bromine-based chemical fire suppression agents (halons). By conducting the experiments in microgravity, interference from convection currents is minimized and fundamental knowledge can be gained. This knowledge is incorporated into models, which can be used to simulate a variety of physical environments. The immediate objective of the project is to study the effect of a fine water mist on a laminar propagating flame generated in a propane-air mixture at various equivalence ratios. The effects of droplet size and concentration on the speed of the flame front is used as a measure of the effectiveness of fire suppression in this highly controlled experimental environment.
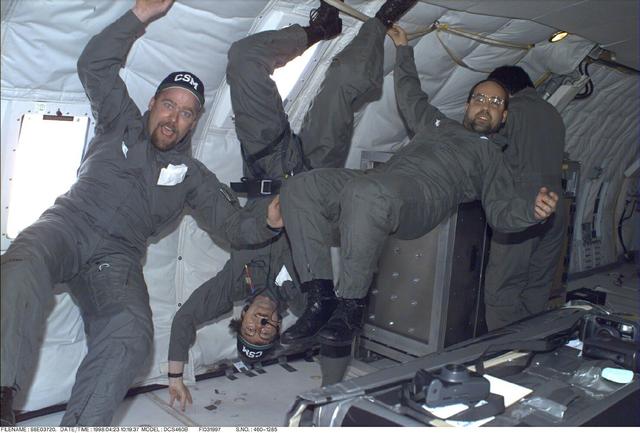

Members of the Water Mist experiment team float in the NASA KC-135 low-g aircraft during preflight tests of the experiment. At center is J. Thomas McKirnon (principal investigator); at right is Angel Abbud-Madrid (co-PI and project scientist). They are with the Center for Commercial Applications of Combustion in Space at the Colorado School of Mines. Water Mist will investigate how best to extinguish flames by using ultrafine droplets of water.

jsc2024e053517 (8/8/2024) --- A plexiglass rod burns in microgravity for the Solid Fuel Ignition and Extinction - Material Ignition and Suppression Test (SoFIE-MIST) investigation. Once each rod is ignited, the flame spreads upstream from the ignition end of the rod. As tests progress, the flame spreads along the rod, consuming oxygen. Once the oxygen concentration drops low enough, the flame extinguishes due to natural oxygen depletion. Data to measure the oxygen concentration, flow rate, and heat loss is obtained at the three test pressures. SoFIE-MIST aims to improve understanding of early fire growth behavior and validate models for material flammability, helping to inform the selection of safer materials for future space facilities and determine the best methods for extinguishing fires in space. .
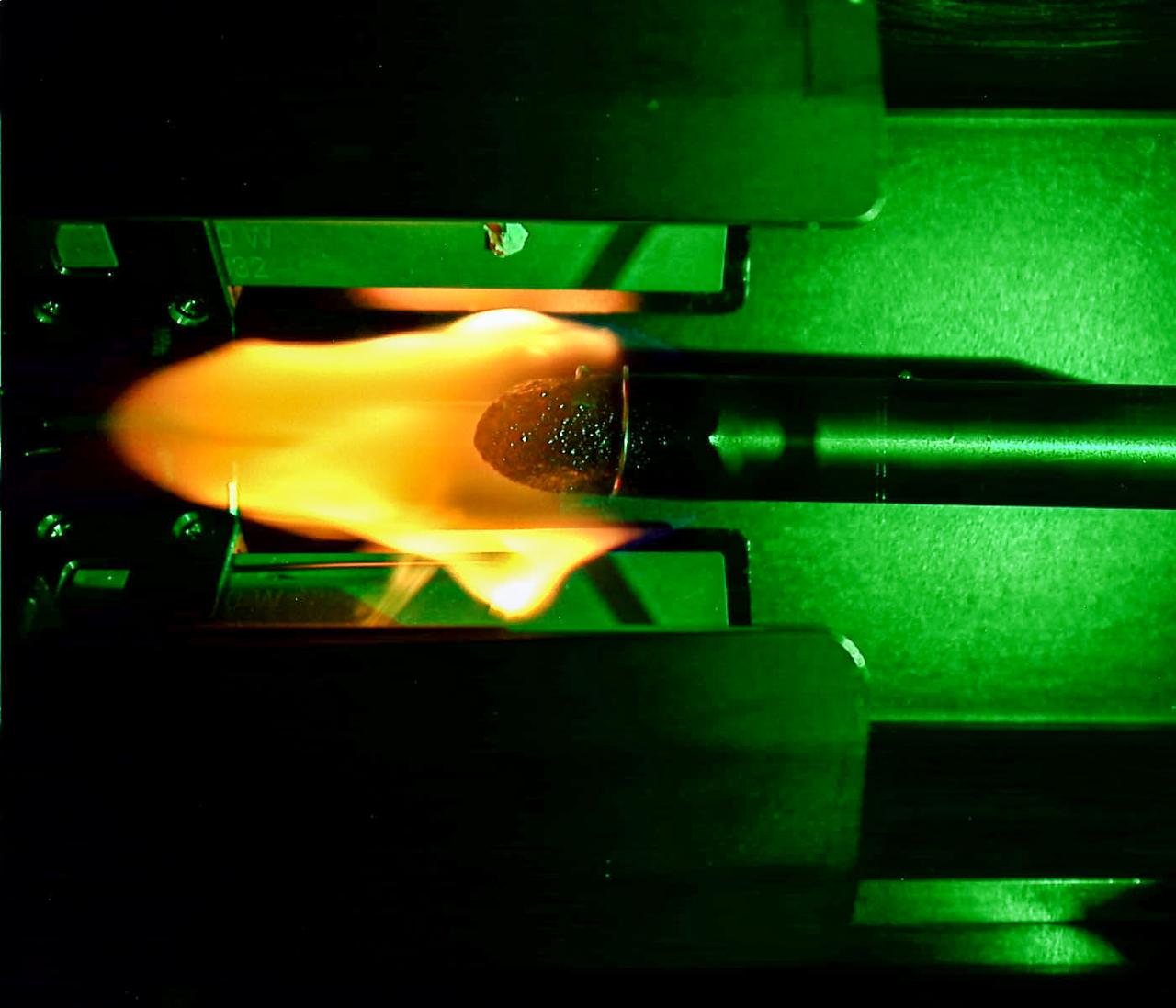

jsc2024e053516 (8/8/2024) --- A plexiglass rod burns in microgravity for the Solid Fuel Ignition and Extinction - Material Ignition and Suppression Test (SoFIE-MIST) investigation. Once each rod is ignited, the flame spreads upstream from the ignition end of the rod. As tests progress, the flame spreads along the rod, consuming oxygen. Once the oxygen concentration drops low enough, the flame extinguishes due to natural oxygen depletion. Data to measure the oxygen concentration, flow rate, and heat loss is obtained at the three test pressures. SoFIE-MIST aims to improve understanding of early fire growth behavior and validate models for material flammability, helping to inform the selection of safer materials for future space facilities and determine the best methods for extinguishing fires in space.
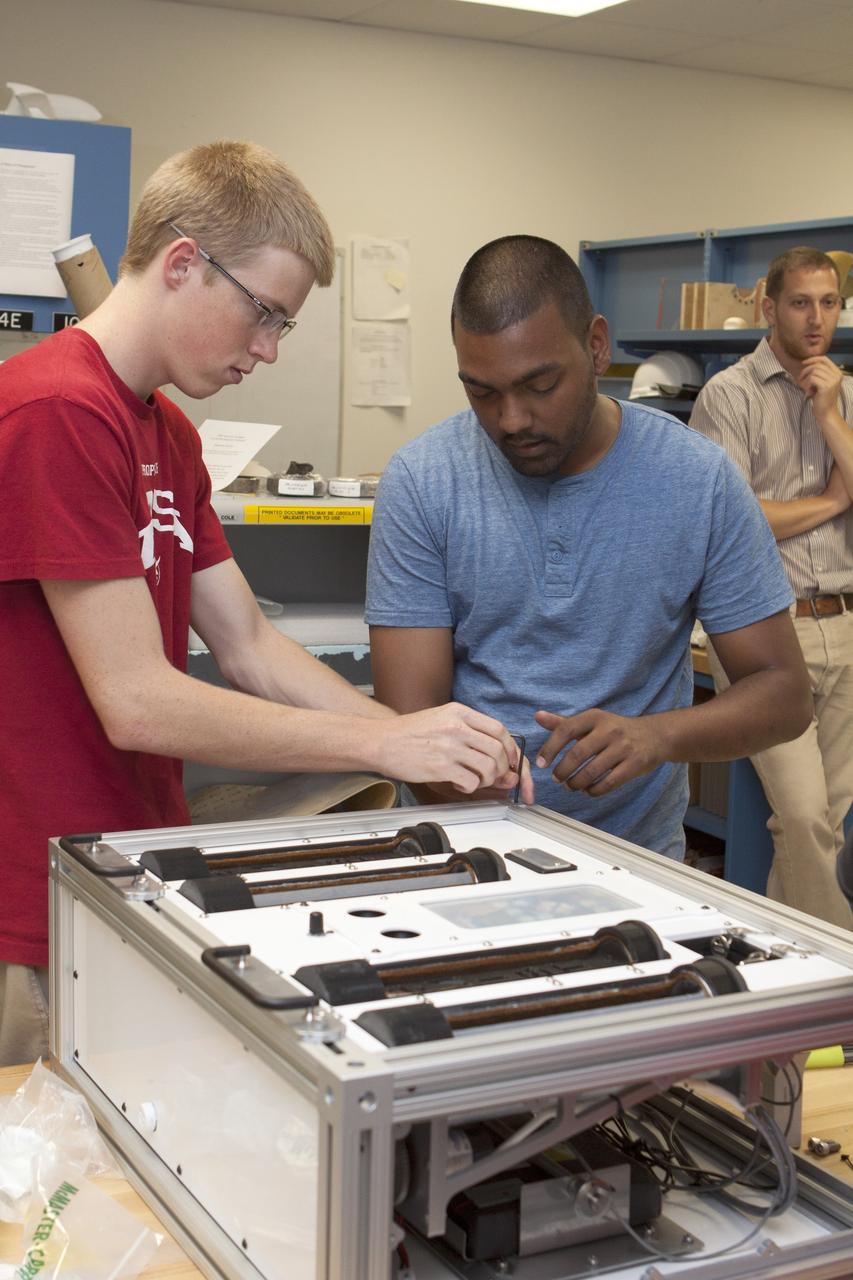

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Prototype Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Evan Williams, left, an Education intern from the University of Central Florida, and Anthony Bharrat, NASA avionics lead, prepare the experiment container for NASA's Exposing Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or E-MIST, experiment. In the background is David J. Smith, Ph.D., NASA E-MIST principal investigator. The container was designed and built at Kennedy. The 80-pound structure features four doors that rotate to expose up to 10 microbial samples each for a predetermined period of time in the Earth's stratosphere. The E-MIST experiment will launch on the exterior of a giant scientific balloon gondola at about 8 a.m. MST on Aug. 24 from Ft. Sumner, New Mexico. It will soar 125,000 feet above the Earth during a 5-hour journey over the desert to understand how spore-forming bacteria, commonly found in spacecraft assembly facilities can survive. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
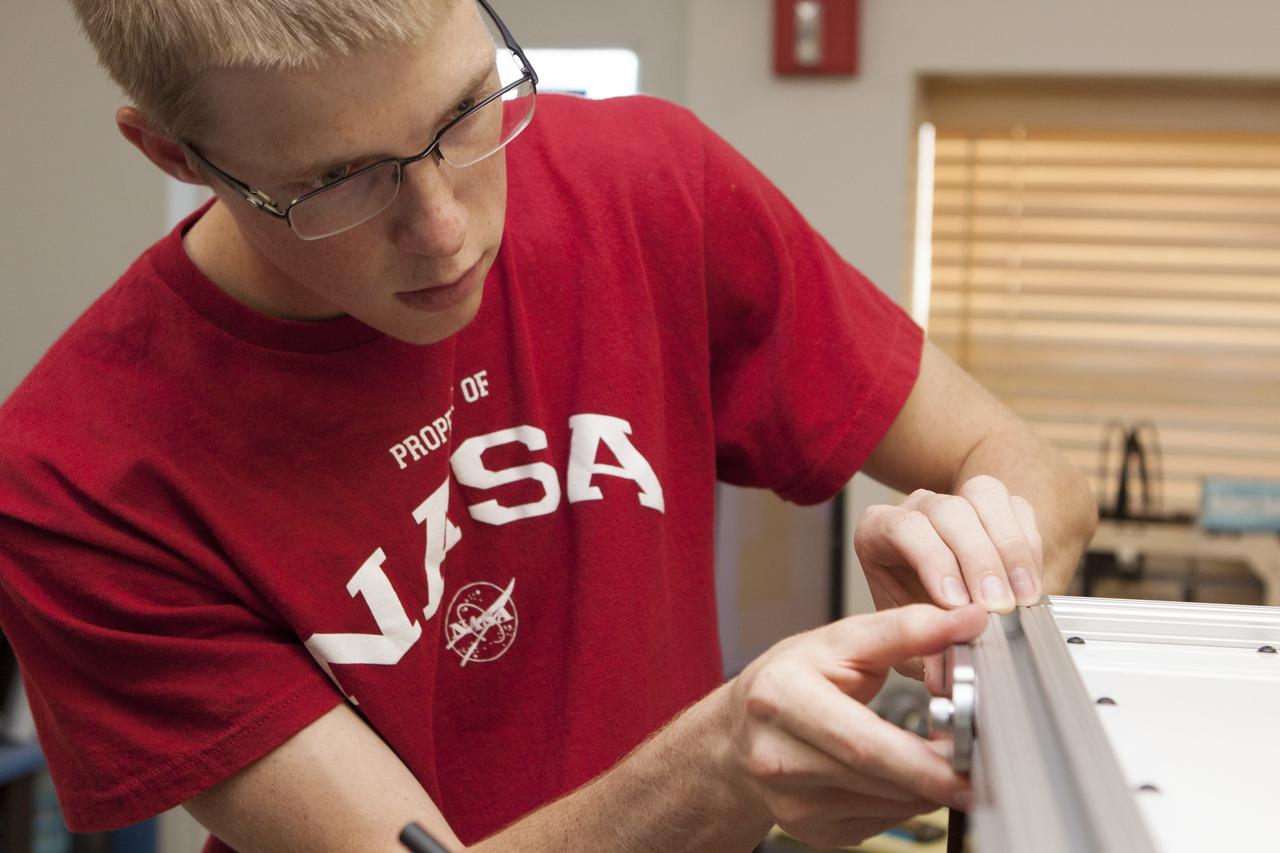

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Prototype Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Evan Williams, an Education intern from the University of Central Florida, prepares the experiment container for NASA's Exposing Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or E-MIST, experiment. The container was designed and built at Kennedy. The 80-pound structure features four doors that rotate to expose up to 10 microbial samples each for a predetermined period of time in the Earth's stratosphere. The E-MIST experiment will launch on the exterior of a giant scientific balloon gondola at about 8 a.m. MST on Aug. 24 from Ft. Sumner, New Mexico. It will soar 125,000 feet above the Earth during a 5-hour journey over the desert to understand how spore-forming bacteria, commonly found in spacecraft assembly facilities can survive. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
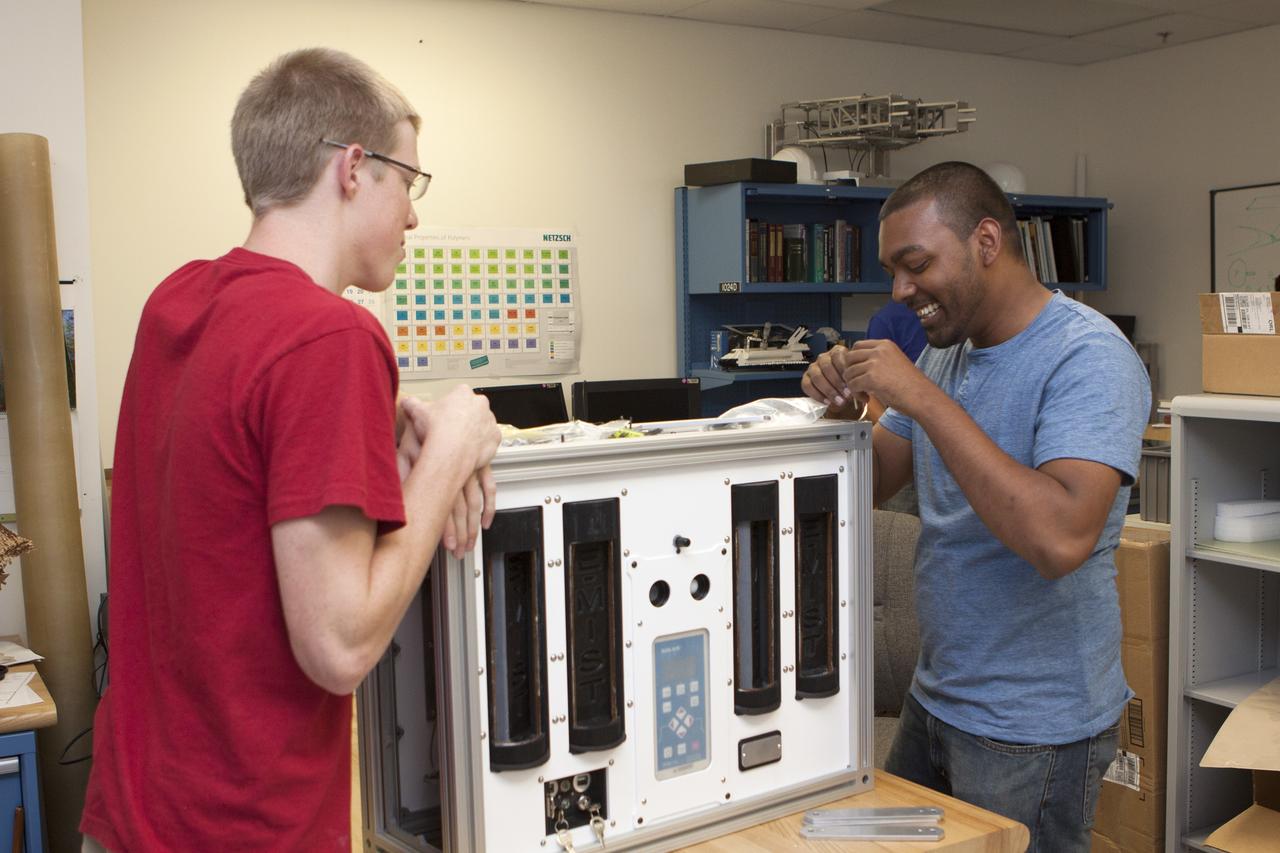

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Prototype Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Evan Williams, left, an Education intern from the University of Central Florida, and Anthony Bharrat, NASA avionics lead, prepare the experiment container for NASA's Exposing Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or E-MIST, experiment. The container was designed and built at Kennedy. The 80-pound structure features four doors that rotate to expose up to 10 microbial samples each for a predetermined period of time in the Earth's stratosphere. The E-MIST experiment will launch on the exterior of a giant scientific balloon gondola at about 8 a.m. MST on Aug. 24 from Ft. Sumner, New Mexico. It will soar 125,000 feet above the Earth during a 5-hour journey over the desert to understand how spore-forming bacteria, commonly found in spacecraft assembly facilities can survive. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
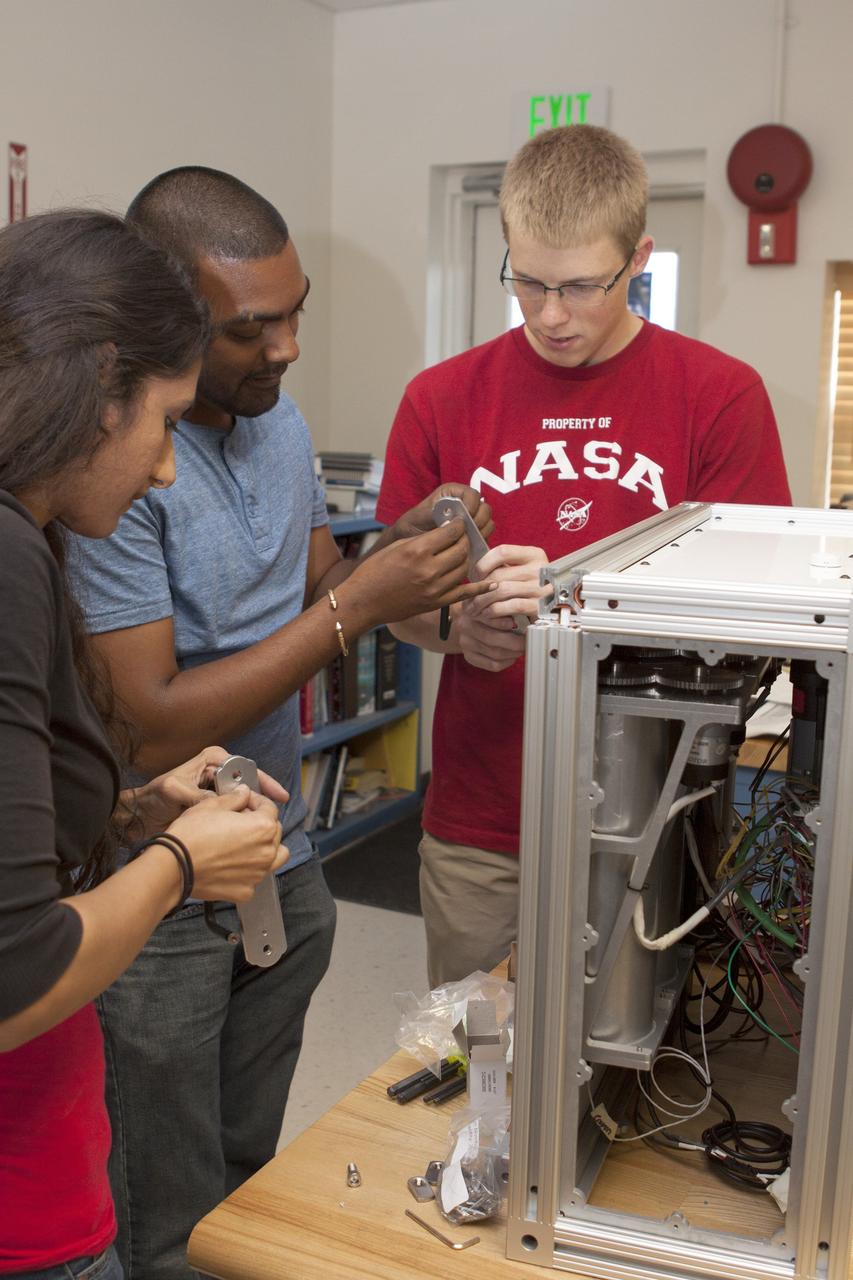

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Prototype Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Prital Thakrar, left, design lead and student engineer trainee from the University of Florida in Gainesville, Anthony Bharrat, NASA avionics lead, and Evan Williams, an Education intern from the University of Central Florida, prepare the experiment container for NASA's Exposing Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or E-MIST, experiment. The container was designed and built at Kennedy. The 80-pound structure features four doors that rotate to expose up to 10 microbial samples each for a predetermined period of time in the Earth's stratosphere. The E-MIST experiment will launch on the exterior of a giant scientific balloon gondola at about 8 a.m. MST on Aug. 24 from Ft. Sumner, New Mexico. It will soar 125,000 feet above the Earth during a 5-hour journey over the desert to understand how spore-forming bacteria, commonly found in spacecraft assembly facilities can survive. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
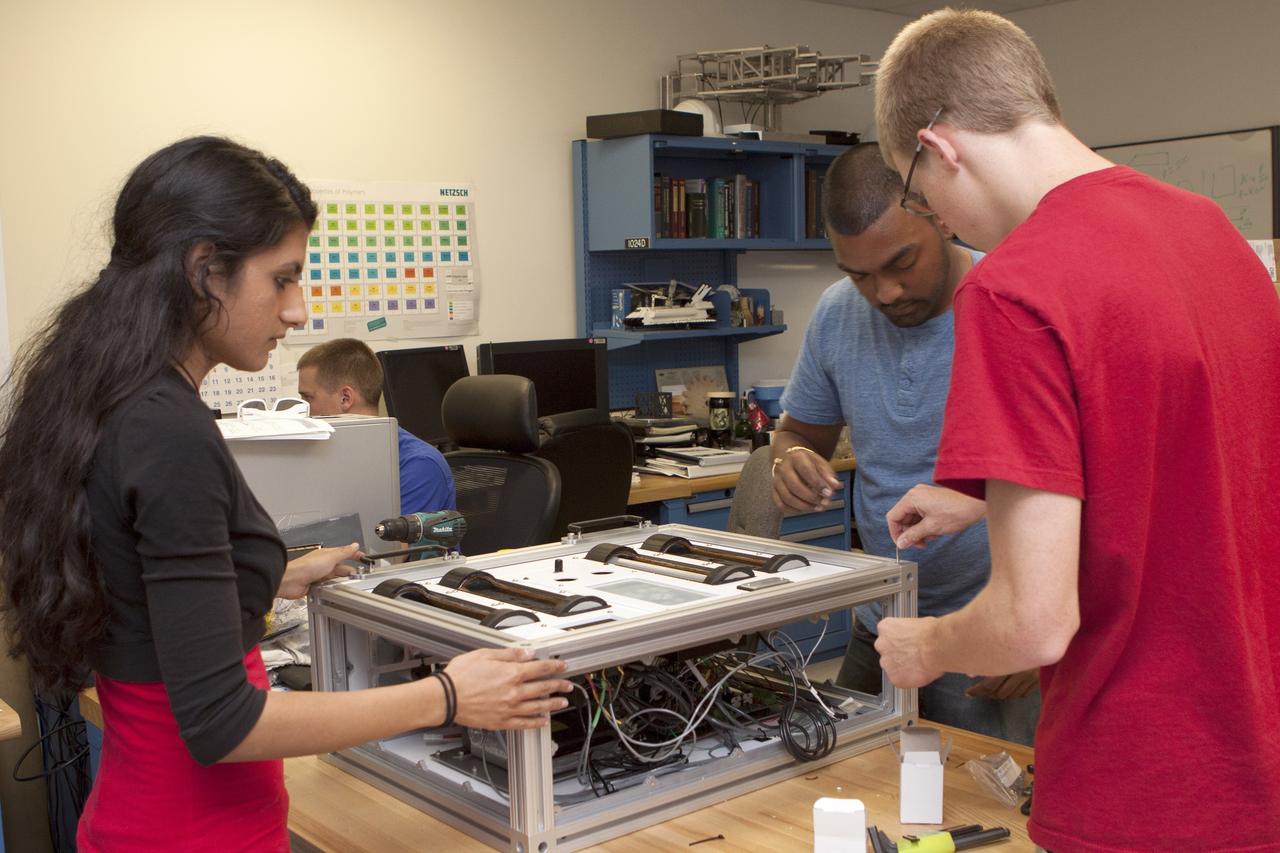

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Prototype Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Prital Thakrar, left, design lead and student engineer trainee from the University of Florida in Gainesville, Anthony Bharrat, NASA avionics lead, and Evan Williams, an Education intern from the University of Central Florida, prepare the experiment container for NASA's Exposing Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or E-MIST, experiment. The container was designed and built at Kennedy. The 80-pound structure features four doors that rotate to expose up to 10 microbial samples each for a predetermined period of time in the Earth's stratosphere. The E-MIST experiment will launch on the exterior of a giant scientific balloon gondola at about 8 a.m. MST on Aug. 24 from Ft. Sumner, New Mexico. It will soar 125,000 feet above the Earth during a 5-hour journey over the desert to understand how spore-forming bacteria, commonly found in spacecraft assembly facilities can survive. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
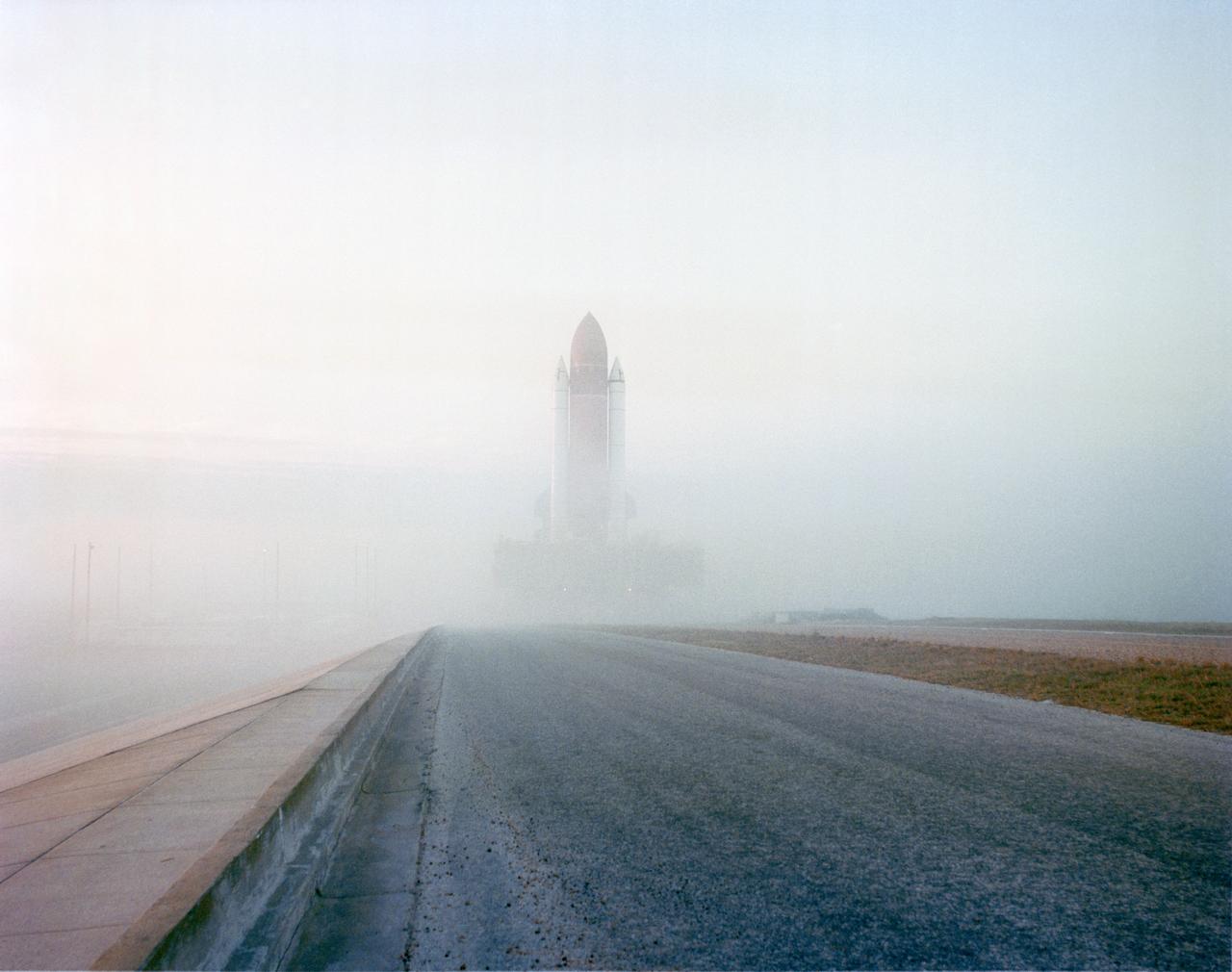

STS-32 Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, rolls through the morning's foggy mist atop the mobile launcher platform and crawler transporter to Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39A. OV-102's wings appear on either side of the two solid rocket boosters (SRBs) and external tank (ET). Rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) began at 2:32 am Eastern Standard Time (EST), and OV-102 was on the pad pedestals about 8 hours later. This marks the first time a Space Shuttle has been at LC Pad 39A since 01-12-85 when OV-102 was launched on mission 61C. View provided by KSC with alternate number KSC-89PC-1259.
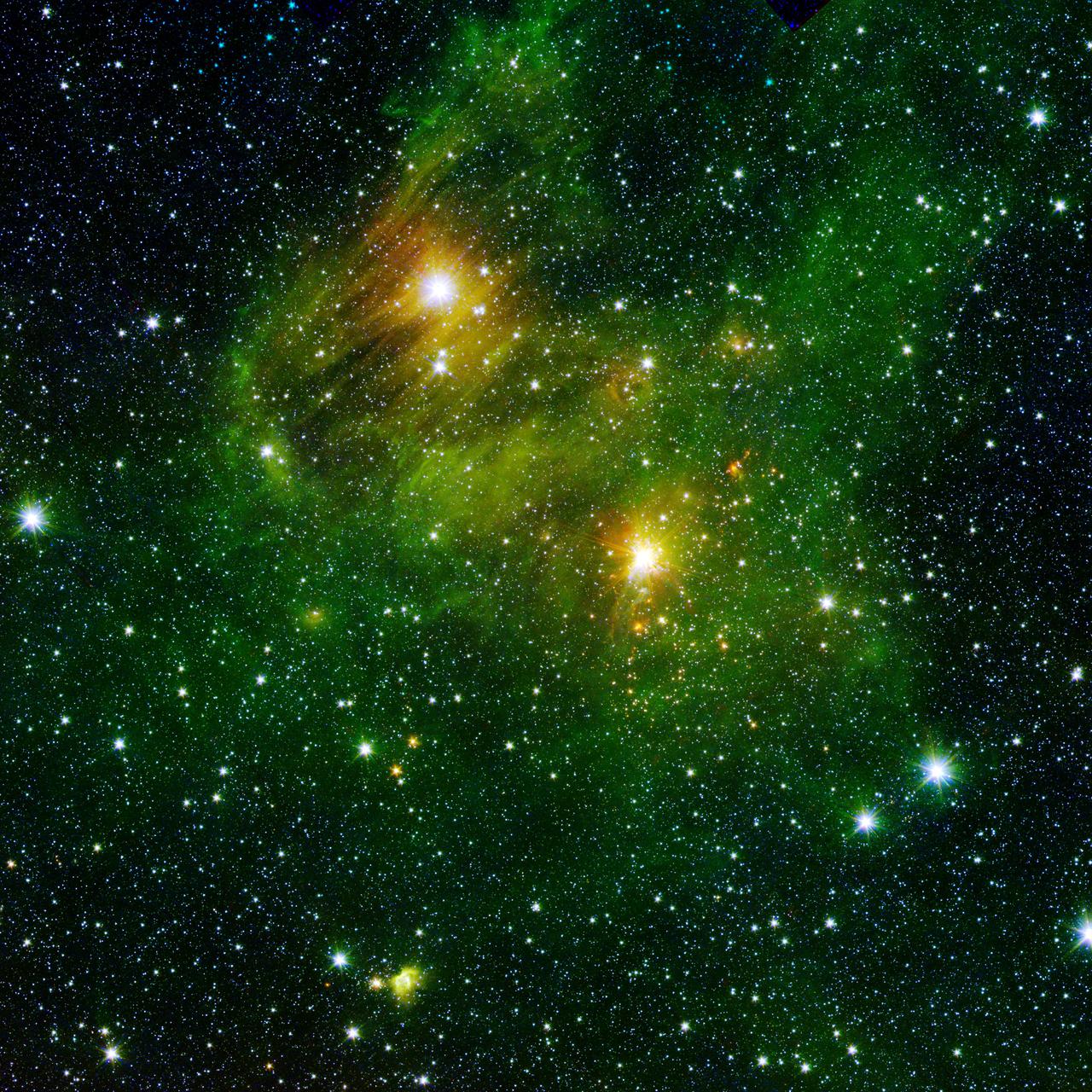

Two extremely bright stars illuminate a greenish mist in this image from the new GLIMPSE360 survey from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. The fog is comprised of hydrogen and carbon compounds called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.

An enhanced close-up view shows at least two distinct jets spraying a mist of fine particles from the south polar region of Enceladus. This image shows the night side of Saturn and the active moon against dark sky
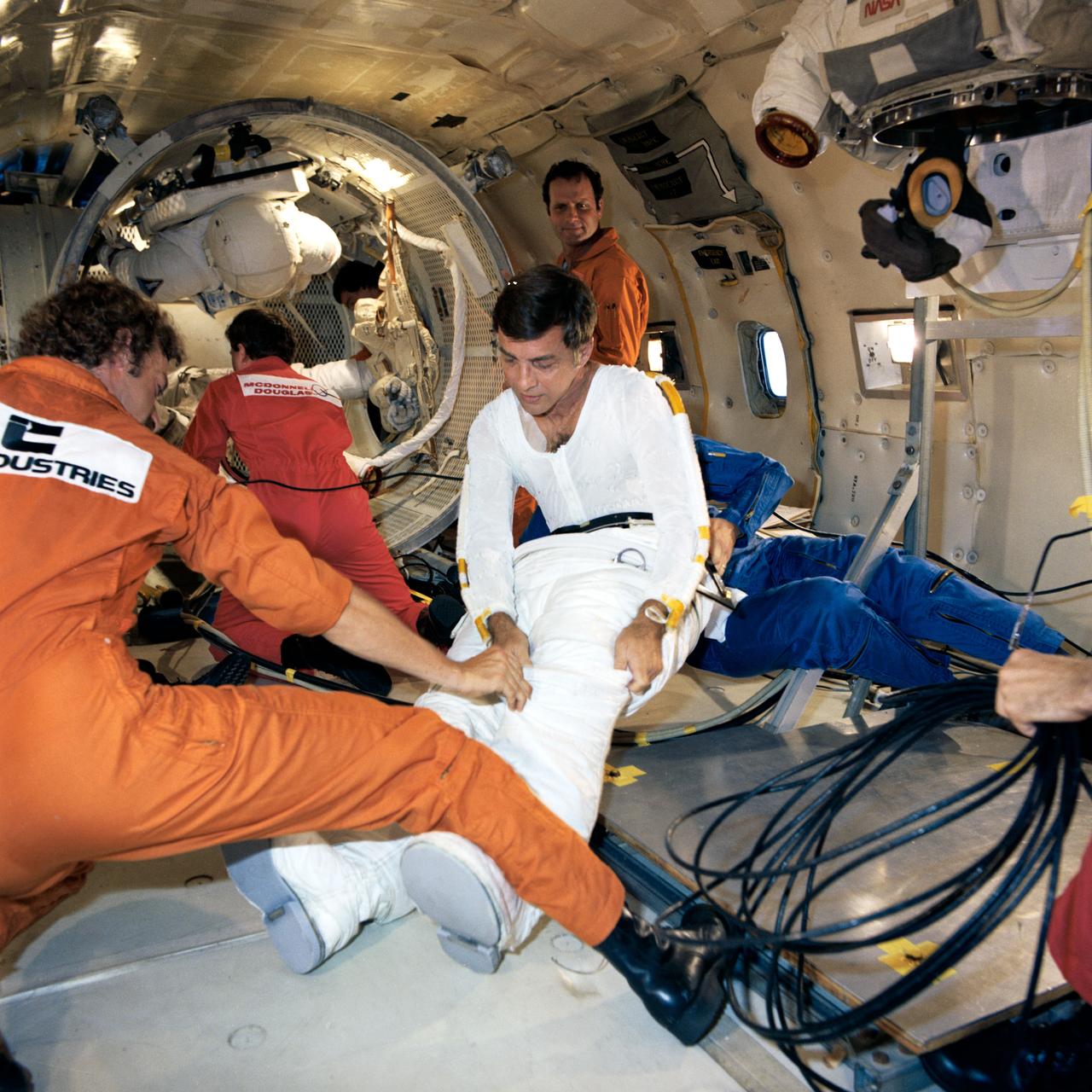

Spacesuit Donning and Doffing in Zero-G Training for Don Peterson of the STS-6 Crew with Astronaut Jerry Ross assisting; and, apparatus for testing the JSC Mechanically-Induced Settling Technology (MIST) Experiment. The training is being held aboard the KC-135 to simulate weightlessness. He is being assisted to don the lower torso of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) by an ILC Technician. 1. ASTRONAUT ROSS, JERRY L. - ZERO-G SUITING 2. SHUTTLE - EXPERIMENTS (MIST)

This false-color image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope shows a distant galaxy yellow that houses a quasar, a super-massive black hole circled by a ring, or torus, of gas and dust.
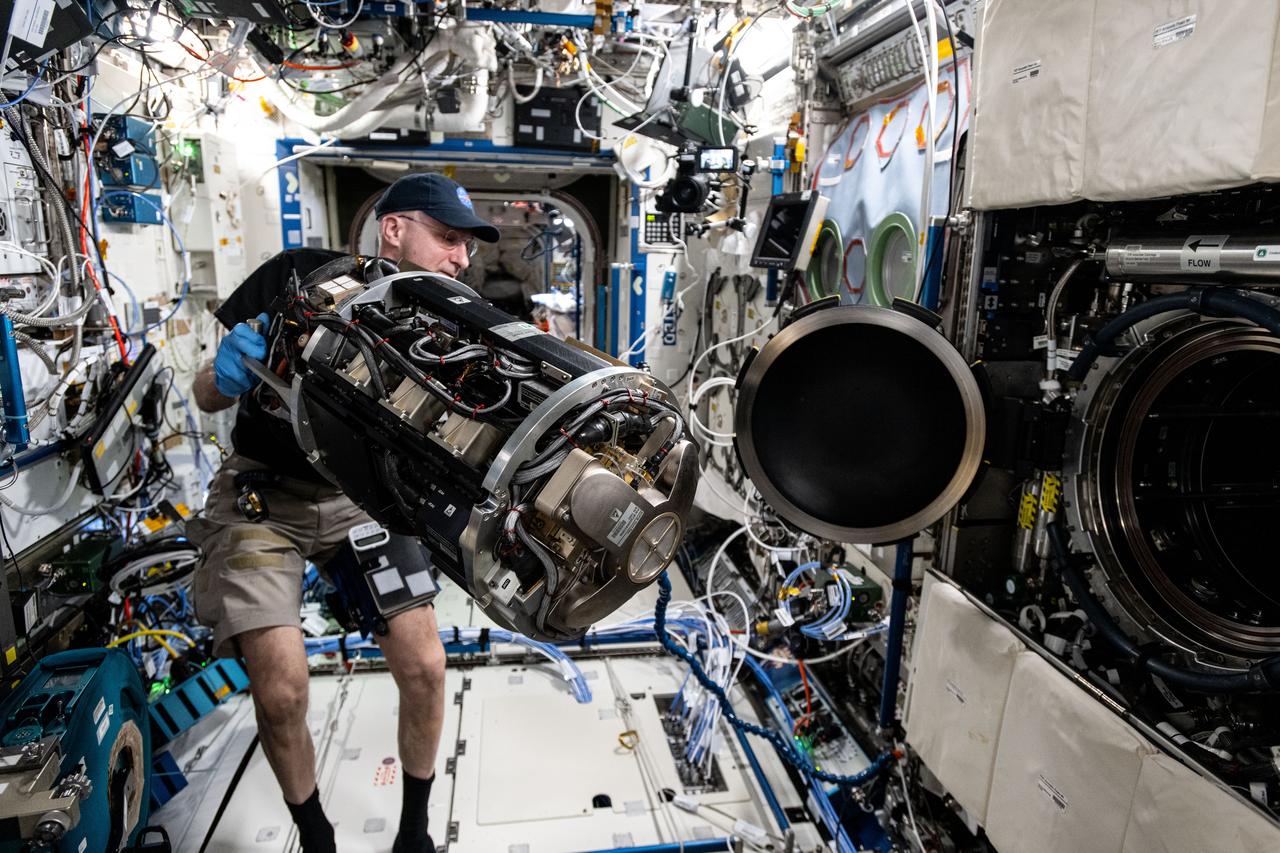

iss072e747148 (March 18, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Don Pettit inserts research hardware into the Combustion Integrated Rack located inside the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module. Pettit was configuring the SoFIE-MIST, or the Solid Fuel Ignition and Extinction - Material Ignition and Suppression Test, investigation that is exploring the flammability of materials in microgravity to improve spacecraft fire safety.
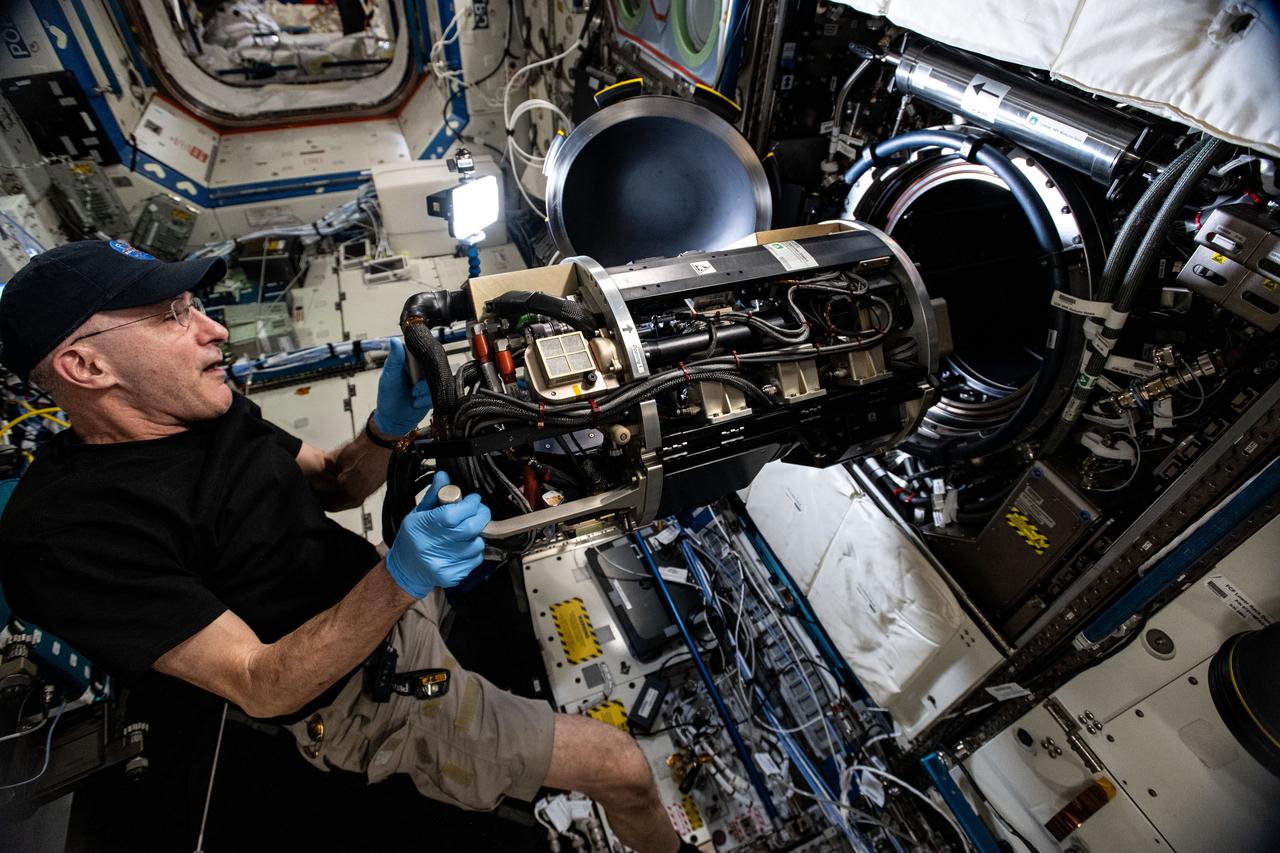

iss072e747154 (March 18, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Don Pettit inserts research hardware into the Combustion Integrated Rack located inside the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module. Pettit was configuring the SoFIE-MIST, or the Solid Fuel Ignition and Extinction - Material Ignition and Suppression Test, investigation that is exploring the flammability of materials in microgravity to improve spacecraft fire safety.
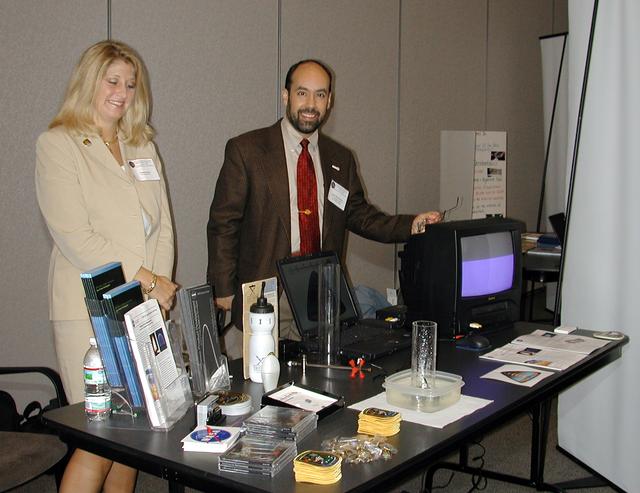

Christi Parker of CST Inc. of Huntsville, AL, and Angel Abbud-Madrid, of the Center for Commercial Applications of Combustion in Space (CCACS) at the Colorado school of Mines, prepare a demonstration of the CCACS Water Mist experiment scheduled to fly on the STS-107 space research mission in 2003. The activity was part of the Space Research and You education event held by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research on June 25, 2002, in Arlington, VA, to highlight the research that will be conducted on STS-107. (Digital camera image; no film original.
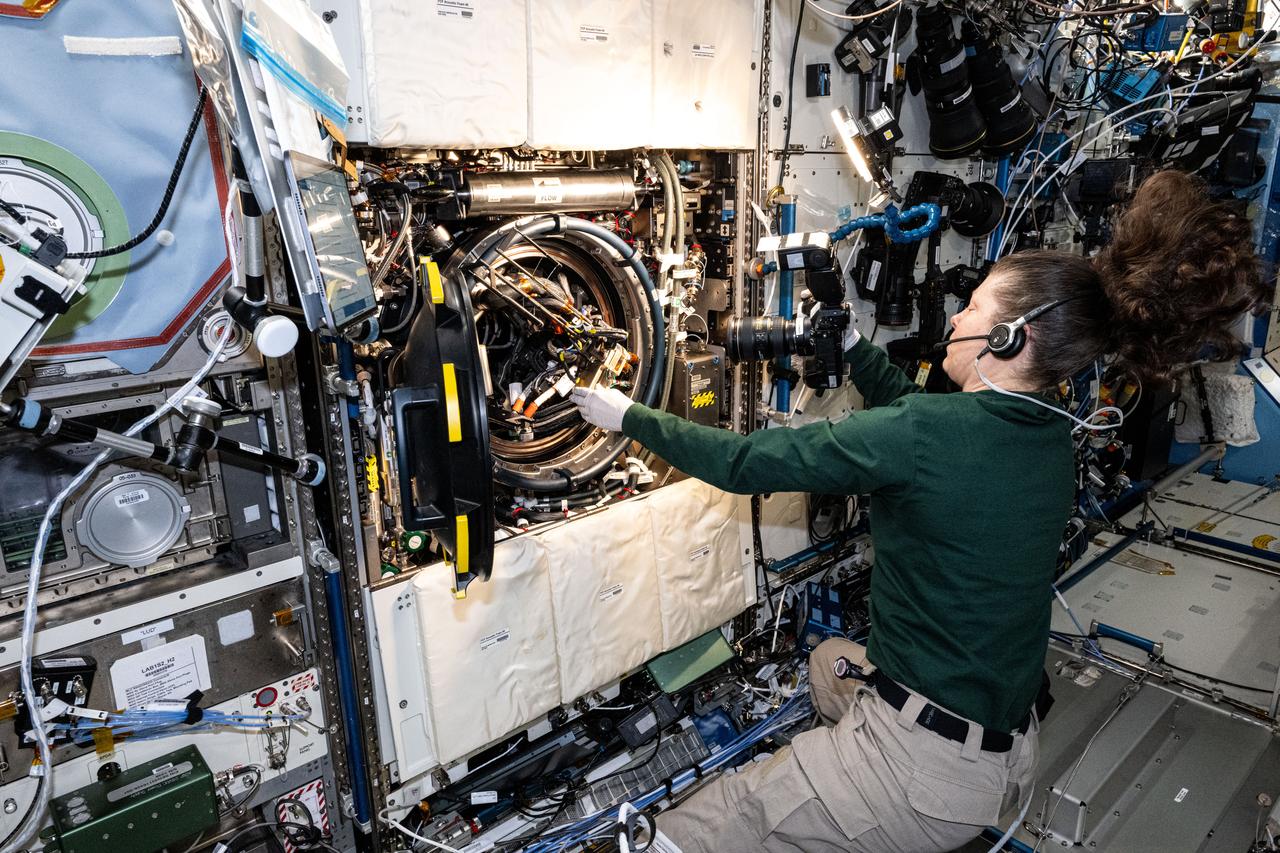

iss071e549501 (Aug. 26, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 71 Flight Engineer Tracy C. Dyson replaces experiment hardware in the Combustion Integrated Rack located aboard the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module. The hardware replacement work was for the SoFIE-MIST investigation that is exploring ways to design safer materials for future space facilities and determine the best methods for extinguishing fires in space.
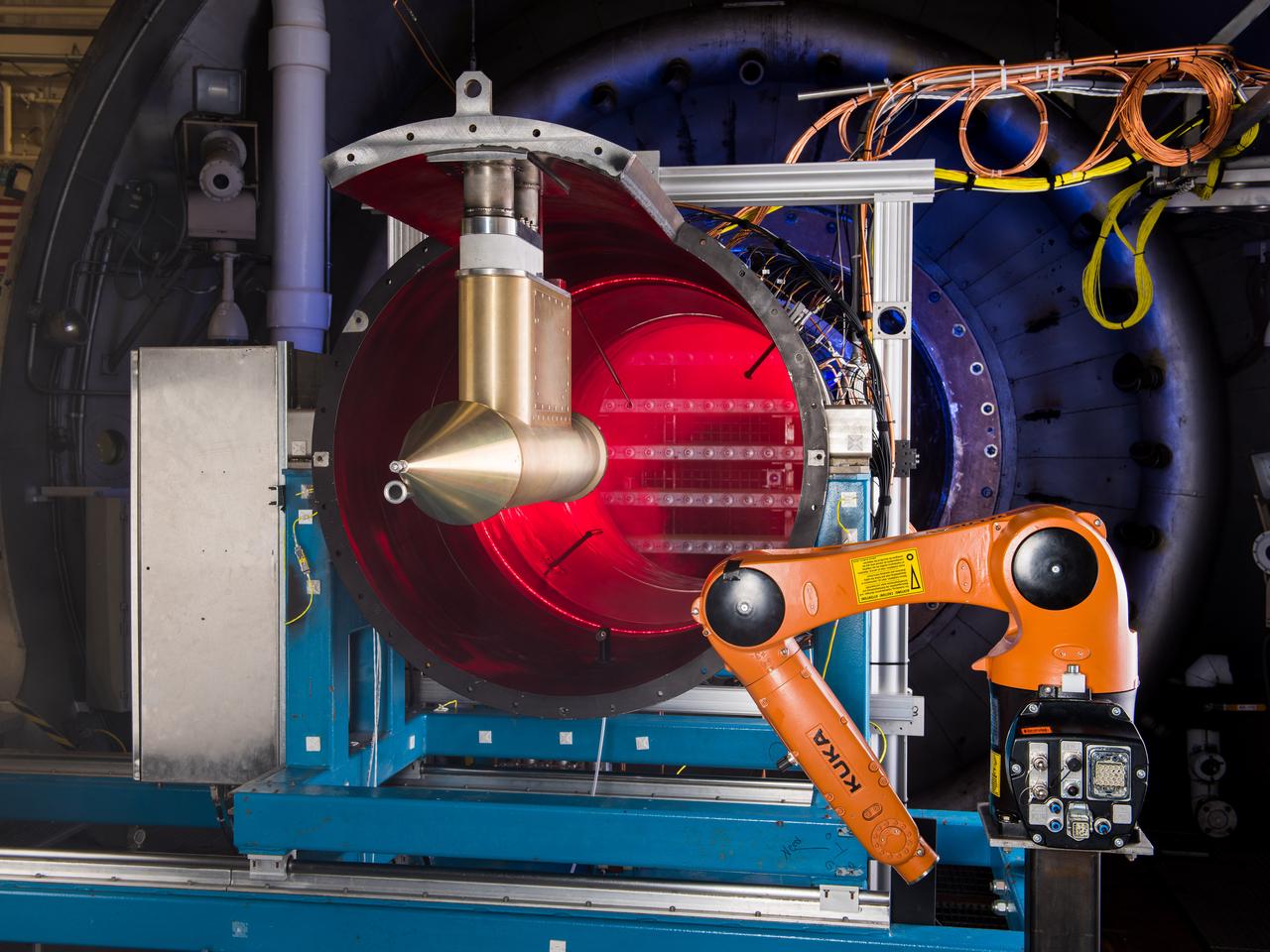
NASA Glenn’s Propulsion Systems Lab (PSL) is conducting research to characterize ice crystal clouds that can create a hazard to aircraft engines in certain conditions. With specialized equipment, scientists can create a simulated ice crystal cloud with the set of bars in the back spraying out a mist. The red area includes lasers, which measure the intensity of the cloud and a series of probes to measure everything from humidity to air pressure. The isokinetic probe (in gold) samples particles and the robotic arm (in orange) has a test tube on the end that catches ice particles for further measuring. NASA Glenn’s PSL is the only place in the world which can create these kind of ice crystal cloud conditions.
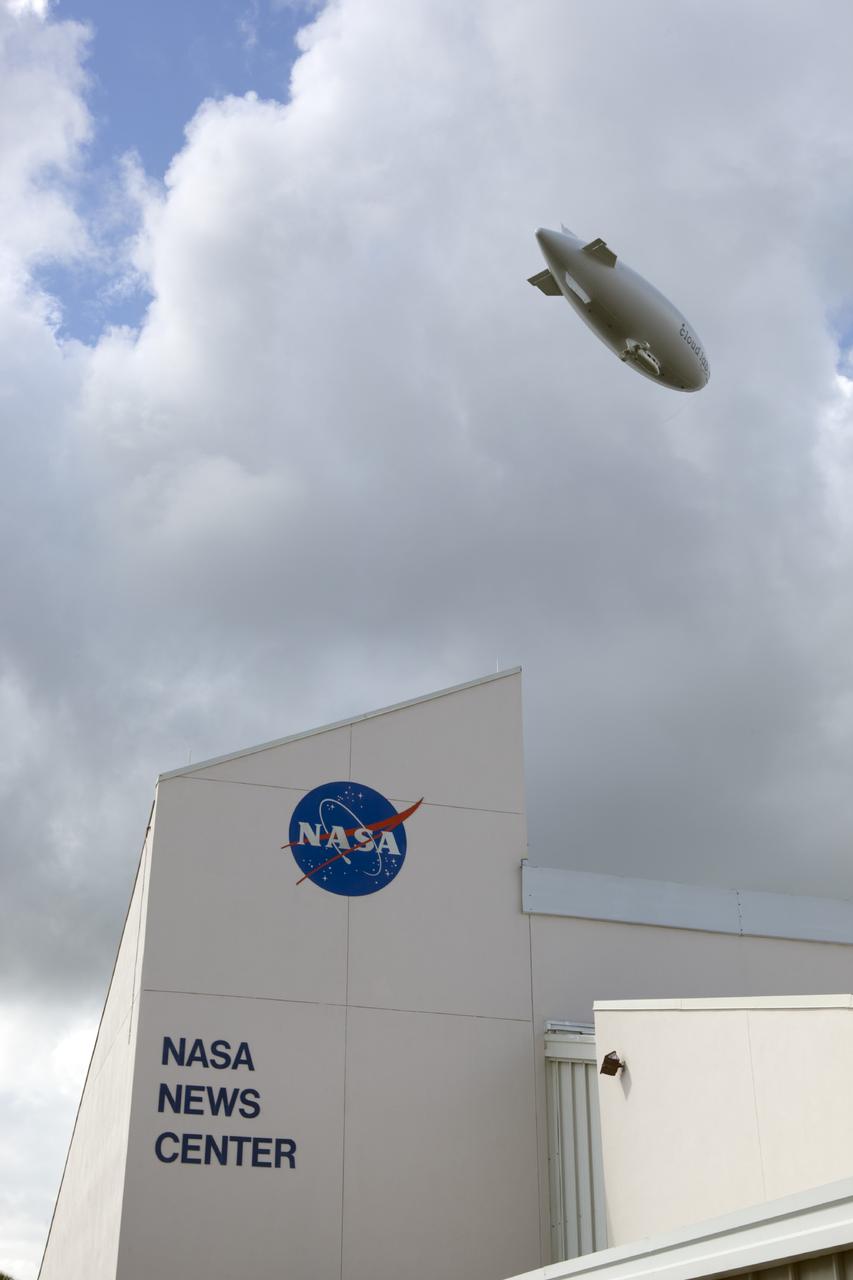

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- An airship from the British Broadcasting Corp., or BBC, flies over Launch Complex 39 past the NASA News Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A team of scientists from the BBC's television project "Cloud Lab" are conducting a number of experiments aboard the airship as it flies across the U.S., exploring all aspects of the Earth's atmosphere. One of the experiments is NASA's Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or MIST, which is designed to measure the microbial survival and cellular responses to exposure in the upper atmosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
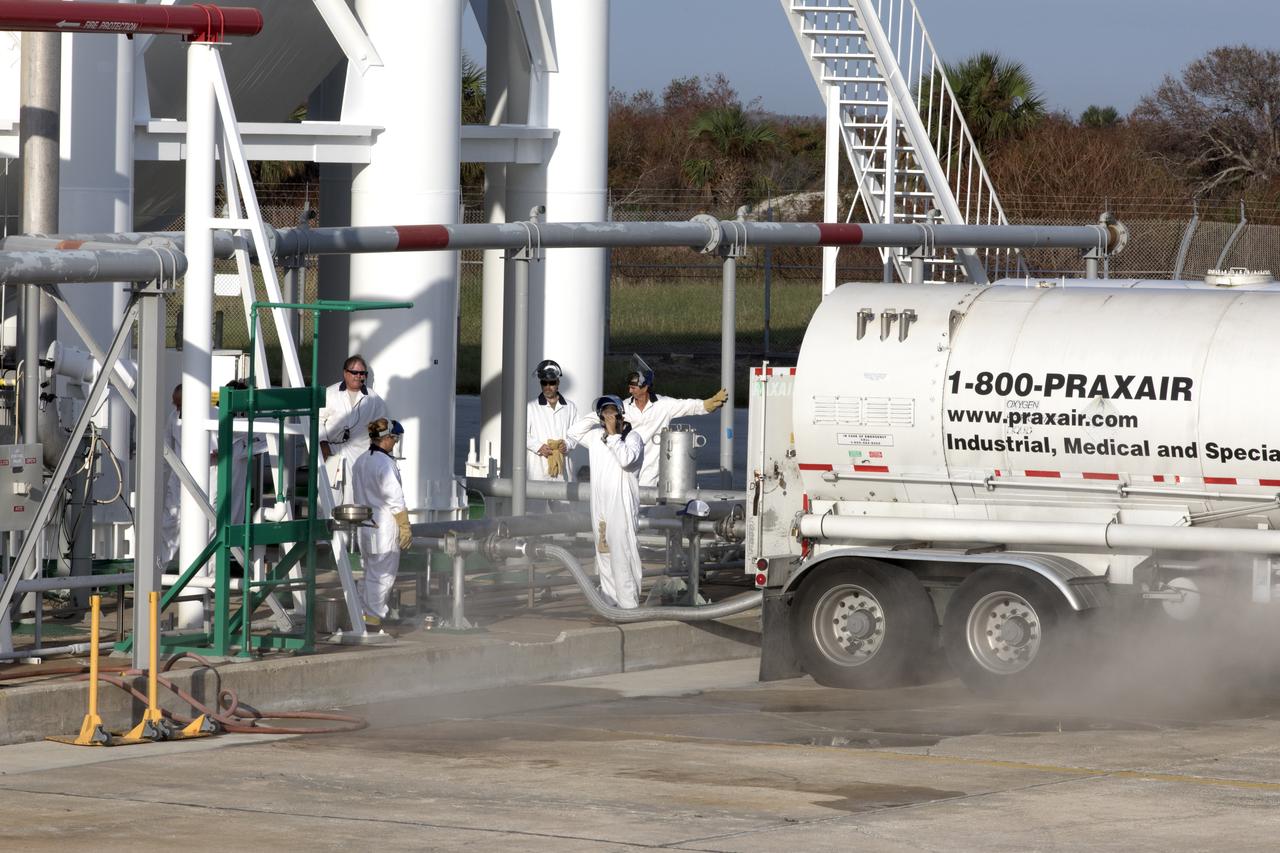

Mist or vapor is visible as a Praxair truck slowly transfers its load of liquid oxygen, or LO2, into a giant storage sphere at the northwest corner of Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The sphere will gradually be chilled down from normal temperature to about negative 298 degrees Fahrenheit, during the first major integrated operation to prepare for the launch of the agency's Orion spacecraft atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to pad B to support the launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1, deep space missions and NASA’s journey to Mars.
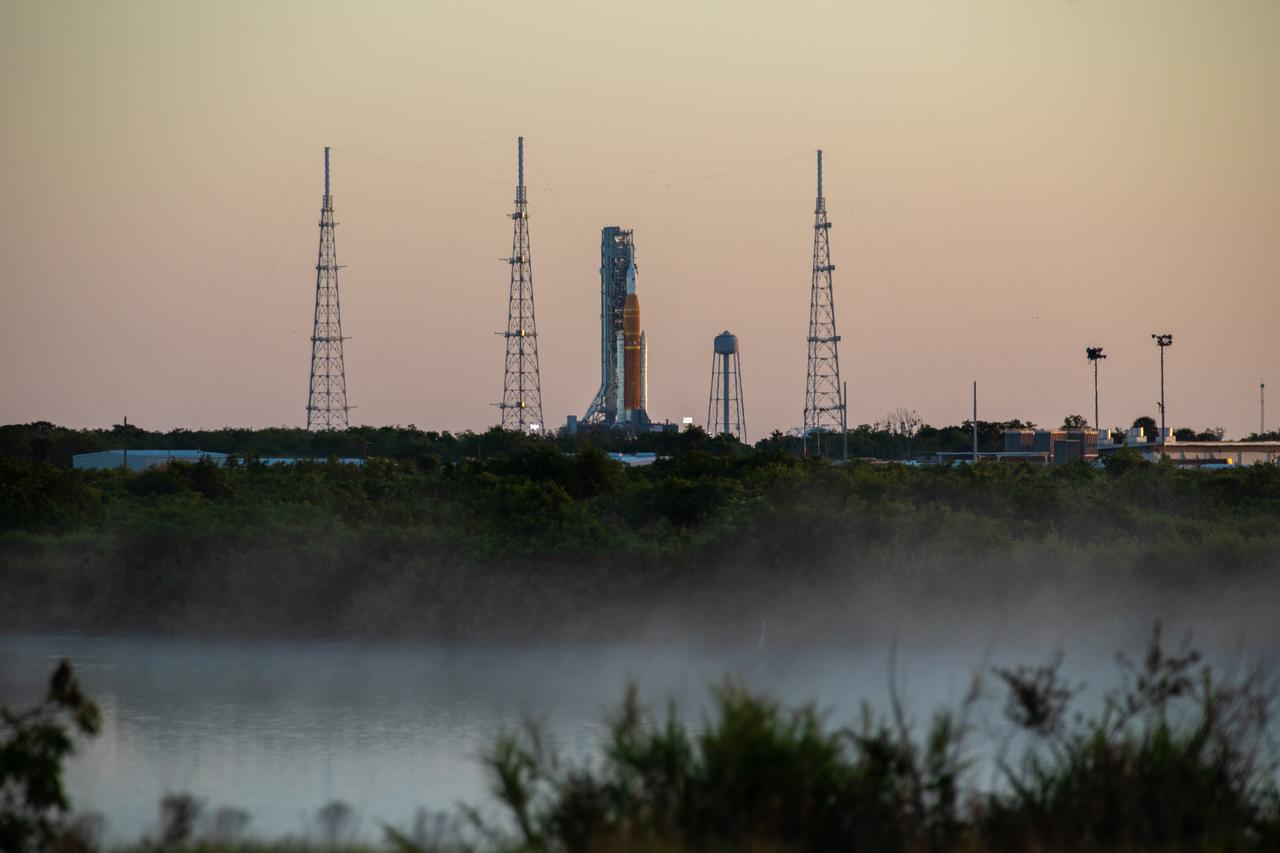

A sunrise view of the Artemis I Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 11, 2022. Mist rises from a nearby waterway. The SLS and Orion atop the mobile launcher were transported to the pad on crawler-transporter 2 for a prelaunch test called a wet dress rehearsal. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In later missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
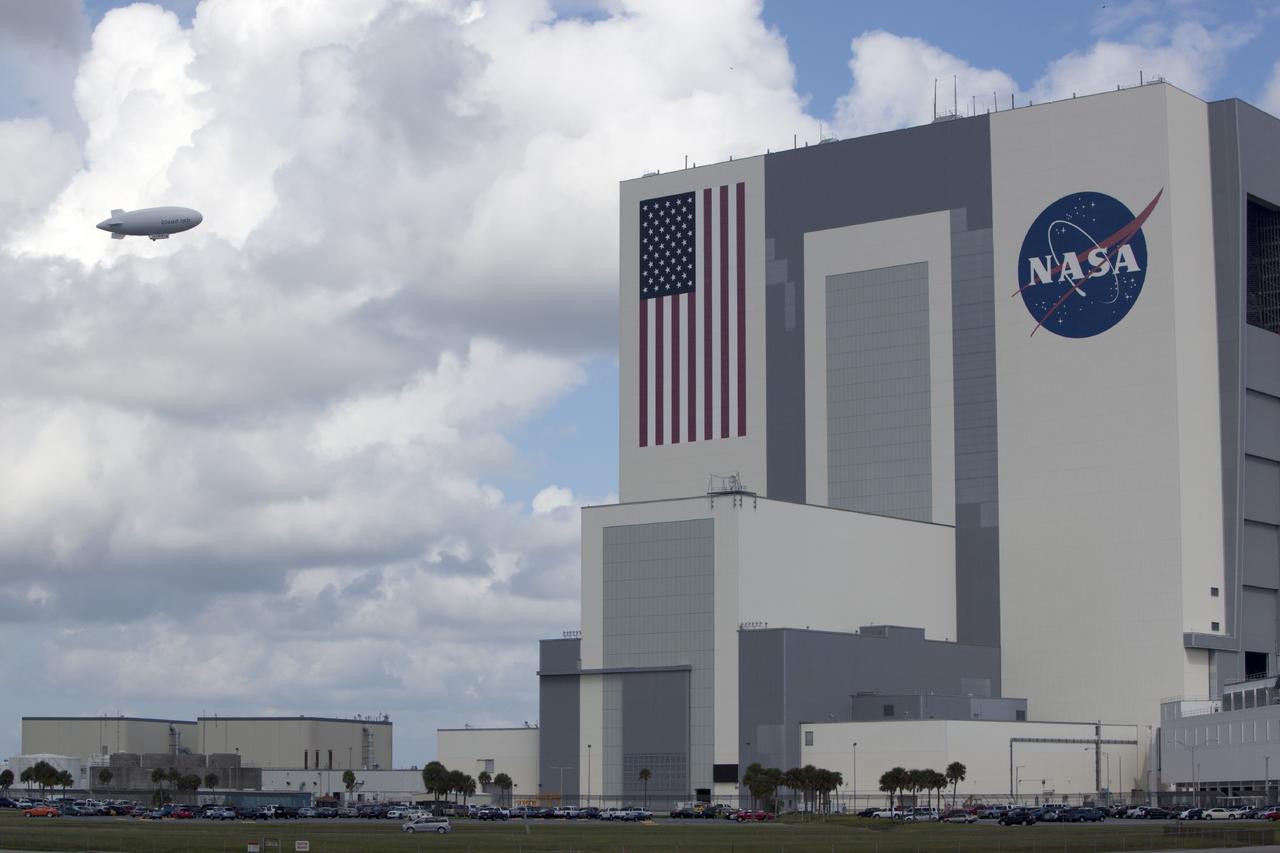

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- An airship from the British Broadcasting Corp., or BBC, flies over the processing facilities in Launch Complex 39 toward the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A team of scientists from the BBC's television project "Cloud Lab" are conducting a number of experiments aboard the airship as it flies across the U.S., exploring all aspects of the Earth's atmosphere. One of the experiments is NASA's Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or MIST, which is designed to measure the microbial survival and cellular responses to exposure in the upper atmosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
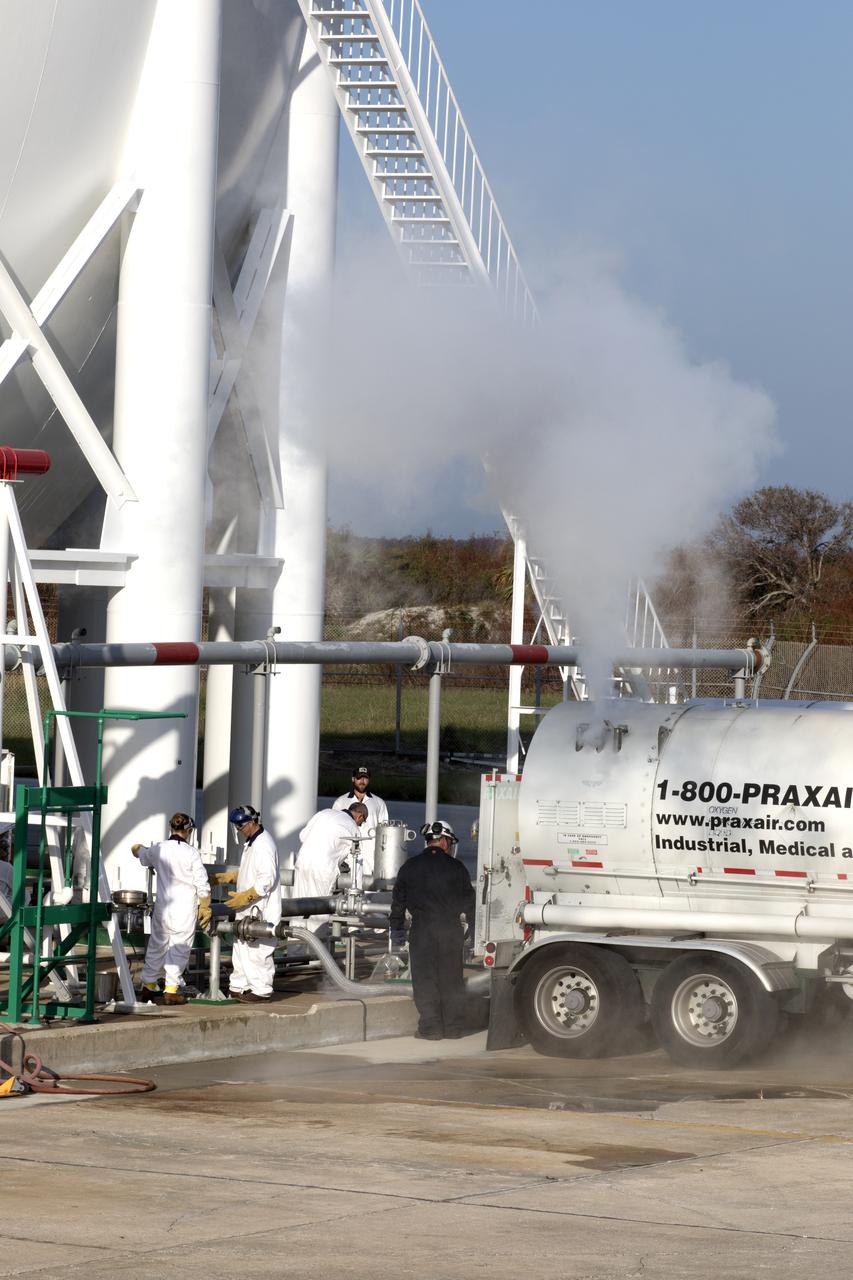

A large plume of mist or vapor is visible as a Praxair truck slowly transfers its load of liquid oxygen, or LO2, into a giant storage sphere at the northwest corner of Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The sphere will gradually be chilled down from normal temperature to about negative 298 degrees Fahrenheit, during the first major integrated operation to prepare for the launch of the agency's Orion spacecraft atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to pad B to support the launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1, deep space missions and NASA’s journey to Mars.
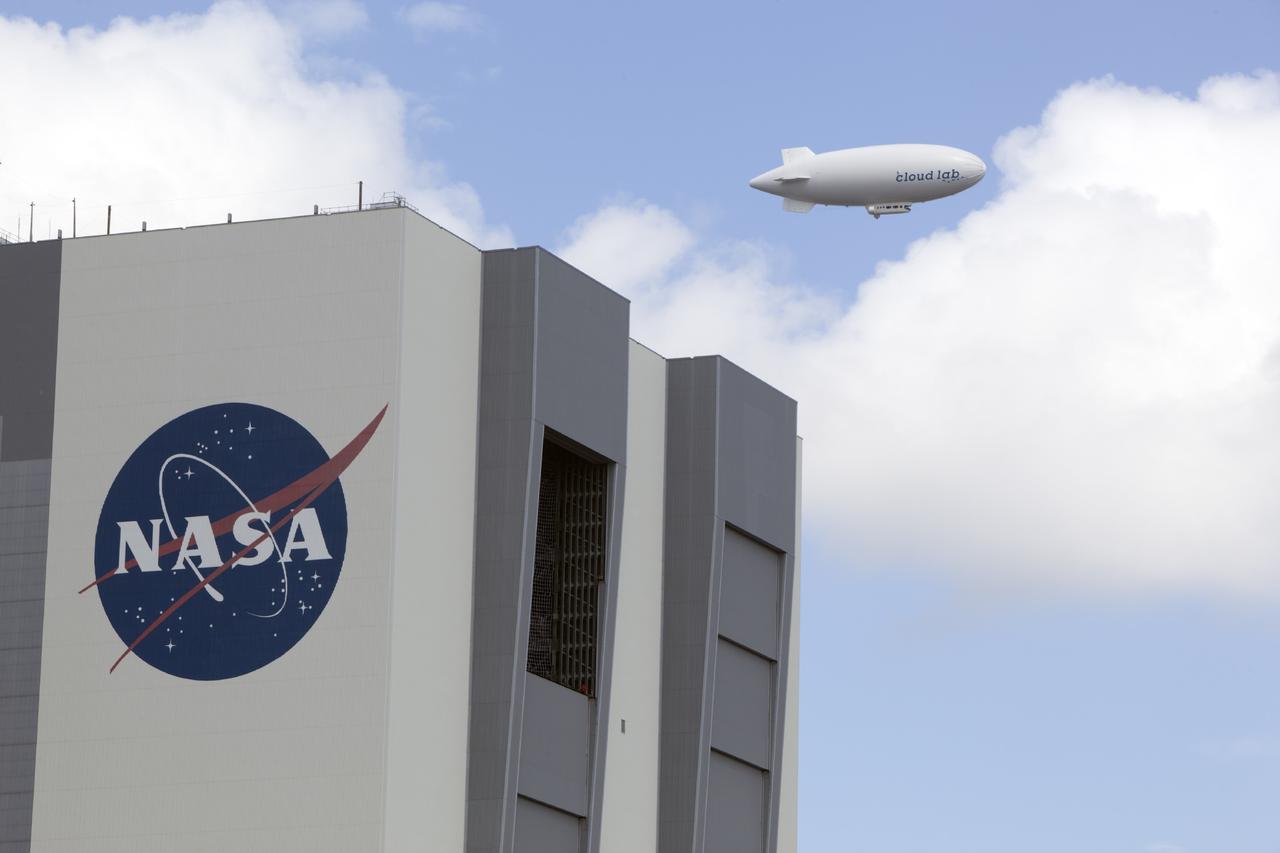

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- An airship from the British Broadcasting Corp., or BBC, flies over Launch Complex 39 past the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A team of scientists from the BBC's television project "Cloud Lab" are conducting a number of experiments aboard the airship as it flies across the U.S., exploring all aspects of the Earth's atmosphere. One of the experiments is NASA's Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or MIST, which is designed to measure the microbial survival and cellular responses to exposure in the upper atmosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
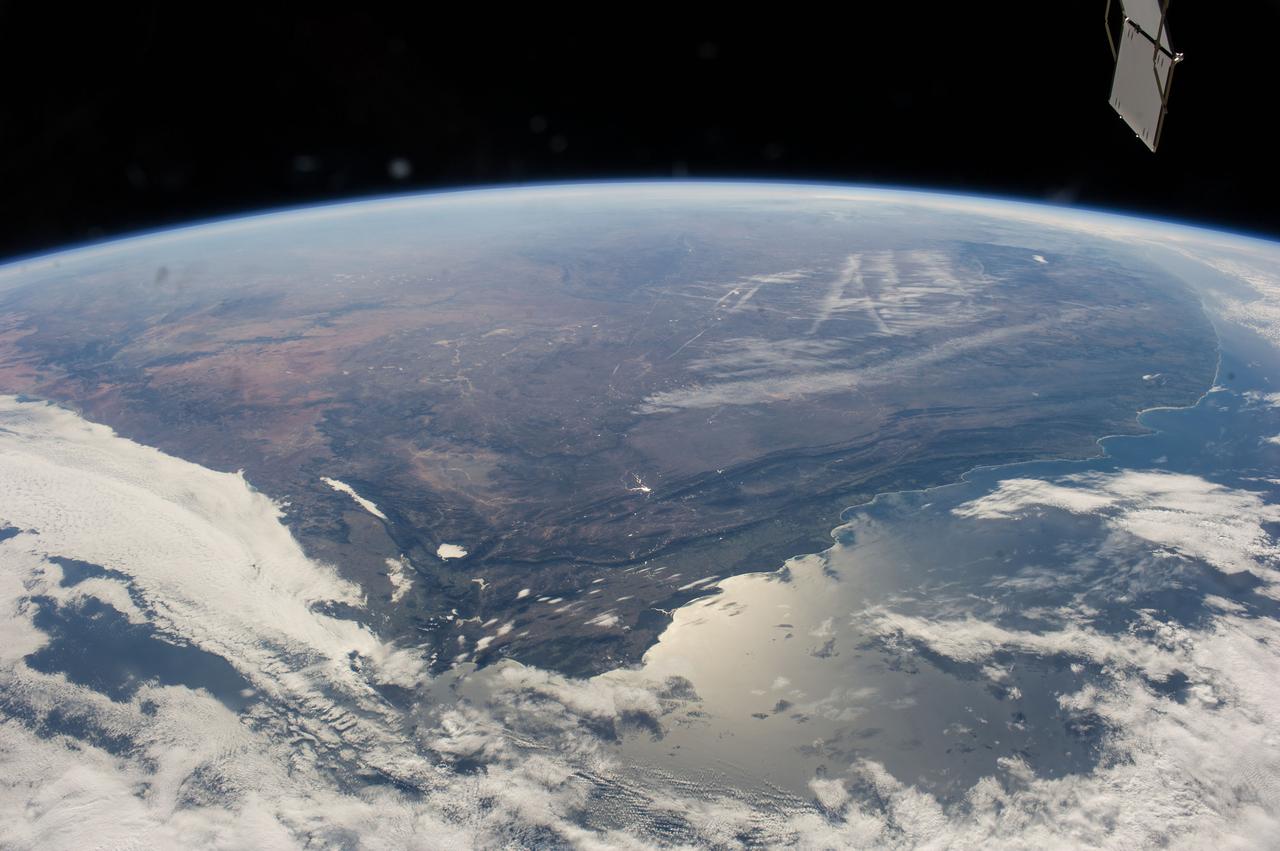

ISS040-E-006271 (31 May 2014) --- One of the Expedition 40 crew members aboard the Earth-orbiting International Space Station captured this panoramic image of South Africa on May 31, 2014. A combination of contrails and a bit of winter mist appears to have formed alphabetic and/or numeric characters in the upper right near the horizon. Sun glint off the south coast is slightly confusing as it is similar in brightness to the west-coast cloud cover, where an Atlantic storm rolls in. The Cape Fold Mountains cross the center of the view, going east from the Cape Town region (clouds obscure the Cape peninsula which normally serves as an icon for this part of Africa). A popular winegrowing region attributable to the Mediterranean climate is the area around Cape Town near lower left. Witwatersrand lies at the top of the picture obscured by the seemingly ever-present winter smoke and smog. The Orange River valley appears as a dark, nearly horizontal line at left.
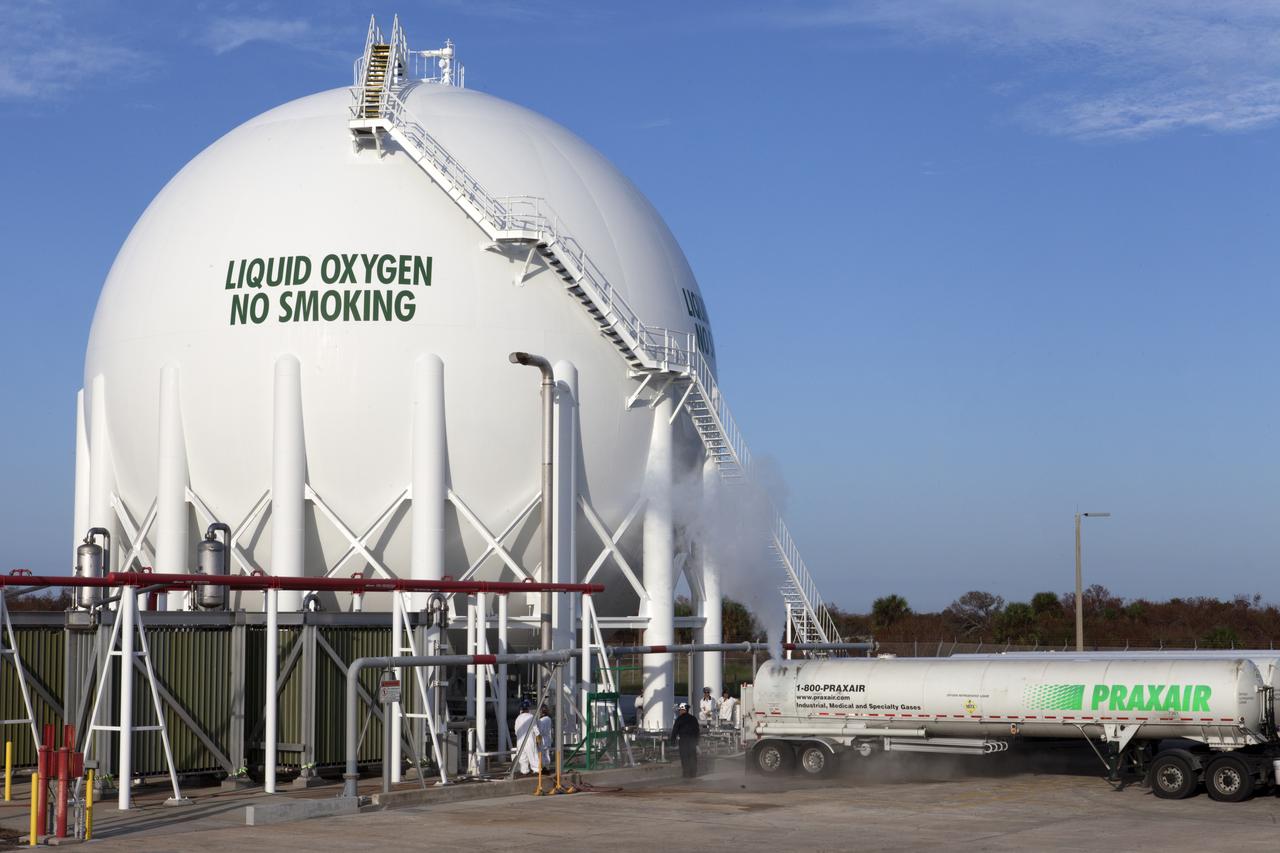

Several Praxair trucks carrying their loads of liquid oxygen, or LO2, have arrived at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mist is visible as LO2 is offloaded from one of the trucks into the giant storage sphere located at the northwest corner of the pad has begun. The sphere will gradually be chilled down from normal temperature to about negative 298 degrees Fahrenheit, during the first major integrated operation to prepare for the launch of the agency's Orion spacecraft atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to pad B to support the launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1, deep space missions and NASA’s journey to Mars.
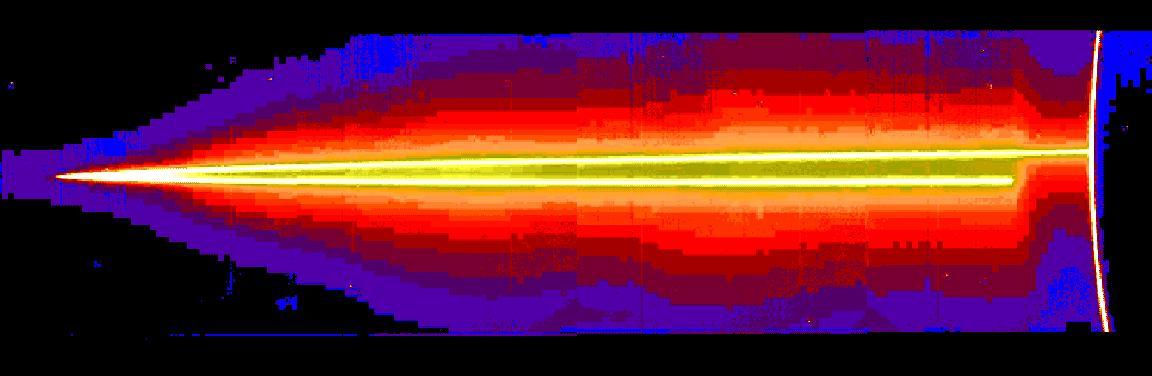
A mosaic of four images taken through the clear filter (610 nanometers) of the solid state imaging (CCD) system aboard NASA's Galileo spacecraft on November 8, 1996, at a resolution of approximately 46 kilometers (km) per picture element (pixel) along the rings; however, because the spacecraft was only about 0.5 degrees above the ring plane, the image is highly foreshortened in the vertical direction. The images were obtained when Galileo was in Jupiter's shadow peering back toward the Sun; the ring was approximately 2,300,000 kilometers (km) away. The arc on the far right of the image is produced by sunlight scattered by small particles comprising Jupiter's upper atmospheric haze. The ring also efficiently scatters light, indicating that much of its brightness is due to particles that are microns or less in diameter. Such small particles are believed to have human-scale lifetimes, i.e., very brief compared to the solar system's age. Jupiter's ring system is composed of three parts -- a flat main ring, a lenticular halo interior to the main ring, and the gossamer ring, which lies exterior to the main ring. The near and far arms of Jupiter's main ring extend horizontally across the mosaic, joining together at the ring's ansa, on the far left side of the figure. The near arm of the ring appears to be abruptly truncated close to the planet, at the point where it passes into Jupiter's shadow. A faint mist of particles can be seen above and below the main rings; this vertically extended, toroidal "halo" is unusual in planetary rings, and is probably caused by electromagnetic forces which can push small grains out of the ring plane. Halo material is present across this entire image, implying that it reaches more than 27,000 km above the ring plane. Because of shadowing, the halo is not visible close to Jupiter in the lower right part of the mosaic. In order to accentuate faint features in the image, different brightnesses are shown through color, with the brightest being white or yellow and the faintest purple. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00658