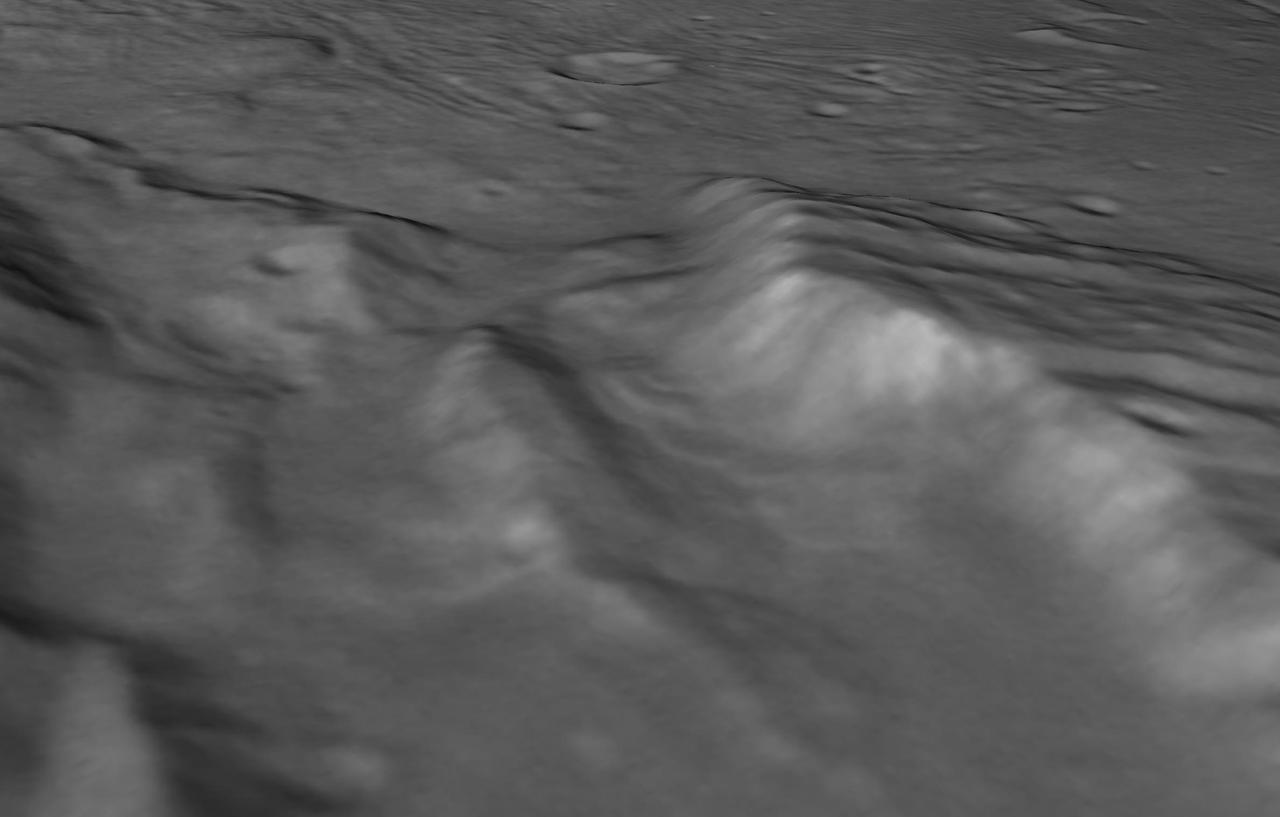
perspective view of Charon's informally named "Serenity Chasm" consists of topography generated from stereo reconstruction of images taken by New Horizons' Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) and Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC), supplemented by a "shape-from-shading" algorithm. The topography is then overlain with the PIA21128 image mosaic and the perspective view is rendered. The MVIC image was taken from a distance of 45,458 miles (73,159 kilometers) while the LORRI picture was taken from 19,511 miles (31,401 kilometers) away, both on July 14, 2015. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21129
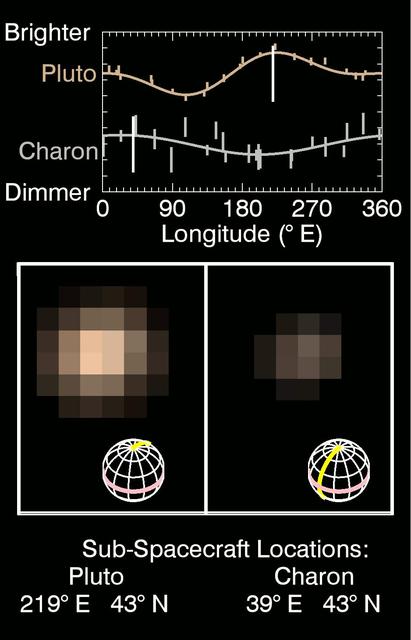
This series of images taken by NASA's New Horizons' Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) shows how Pluto and Charon change in brightness as they rotate over 6.4 Earth days.The central panel shows the true color of Pluto (left) and Charon (right) during nine epochs between May 29 May and June 3 2015, as the spacecraft approached the Pluto system from a range of 55 to 48 million km.The grids beneath the images show the orientations of Pluto and Charon, with 0° E longitude and the equator highlighted by the yellow and pink lines respectively.Sub-spacecraft locations on Pluto and Charon are listed at the bottom.The spatial resolution, at around 1000 km/pixel, is not yet sufficient in these images to reveal distinct surface features on either body. The top panel shows in graphical form how the brightness in MVIC's red channel (540-700 nm) varies with the sub-spacecraft longitude, including data from more distant images dating back to May 1.The moving white vertical lines indicate the observed central longitudes on Pluto and Charon as the images below rotate.These results are consistent with earlier Hubble Space Telescope observations of the lightcurves of Pluto and Charon.Pluto appears dimmest when the dark region on its trailing hemisphere (around 90° E) is oriented toward the observer and brighter when the dark area has rotated off the visible hemisphere and a bright region on the anti-Charon hemisphere is seen.A different, lower amplitude lightcurve variation is seen on Charon, where the Pluto-facing hemisphere (around 0° E) appears brighter than the anti-Pluto hemisphere. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19692
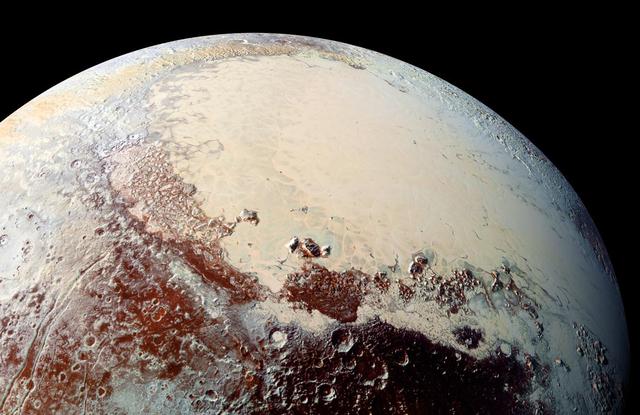

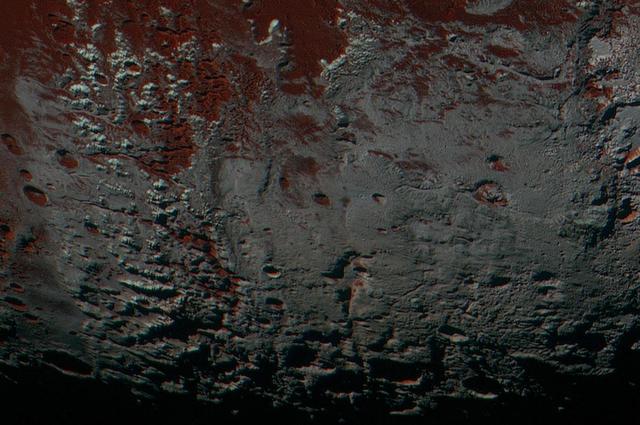
This high-resolution image captured by NASA's New Horizons spacecraft combines blue, red and infrared images taken by the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC). The bright expanse is the western lobe of the "heart," informally called Sputnik Planum, which has been found to be rich in nitrogen, carbon monoxide and methane ices. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20007

NASA's New Horizons spacecraft captured this high-resolution enhanced color view of Pluto on July 14, 2015. The image combines blue, red and infrared images taken by the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC). Pluto's surface sports a remarkable range of subtle colors, enhanced in this view to a rainbow of pale blues, yellows, oranges, and deep reds. Many landforms have their own distinct colors, telling a complex geological and climatological story that scientists have only just begun to decode. The image resolves details and colors on scales as small as 0.8 miles (1.3 kilometers). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19952
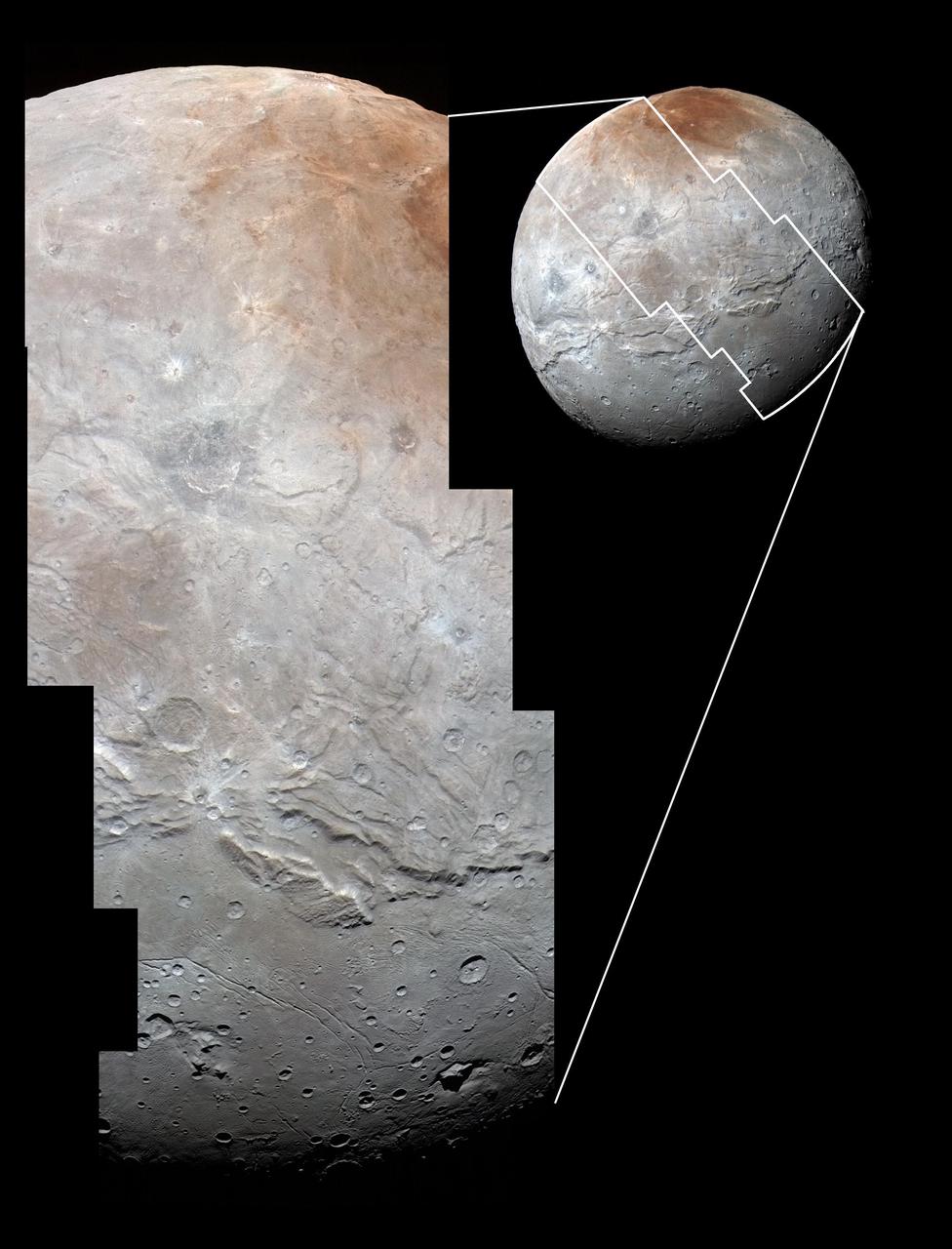

High-resolution images of Charon were taken by the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) on NASA's New Horizons spacecraft, shortly before closest approach on July 14, 2015, and overlaid with enhanced color from the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC). Charon's cratered uplands at the top are broken by series of canyons, and replaced on the bottom by the rolling plains of the informally named Vulcan Planum. The scene covers Charon's width of 754 miles (1,214 kilometers) and resolves details as small as 0.5 miles (0.8 kilometers). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19967
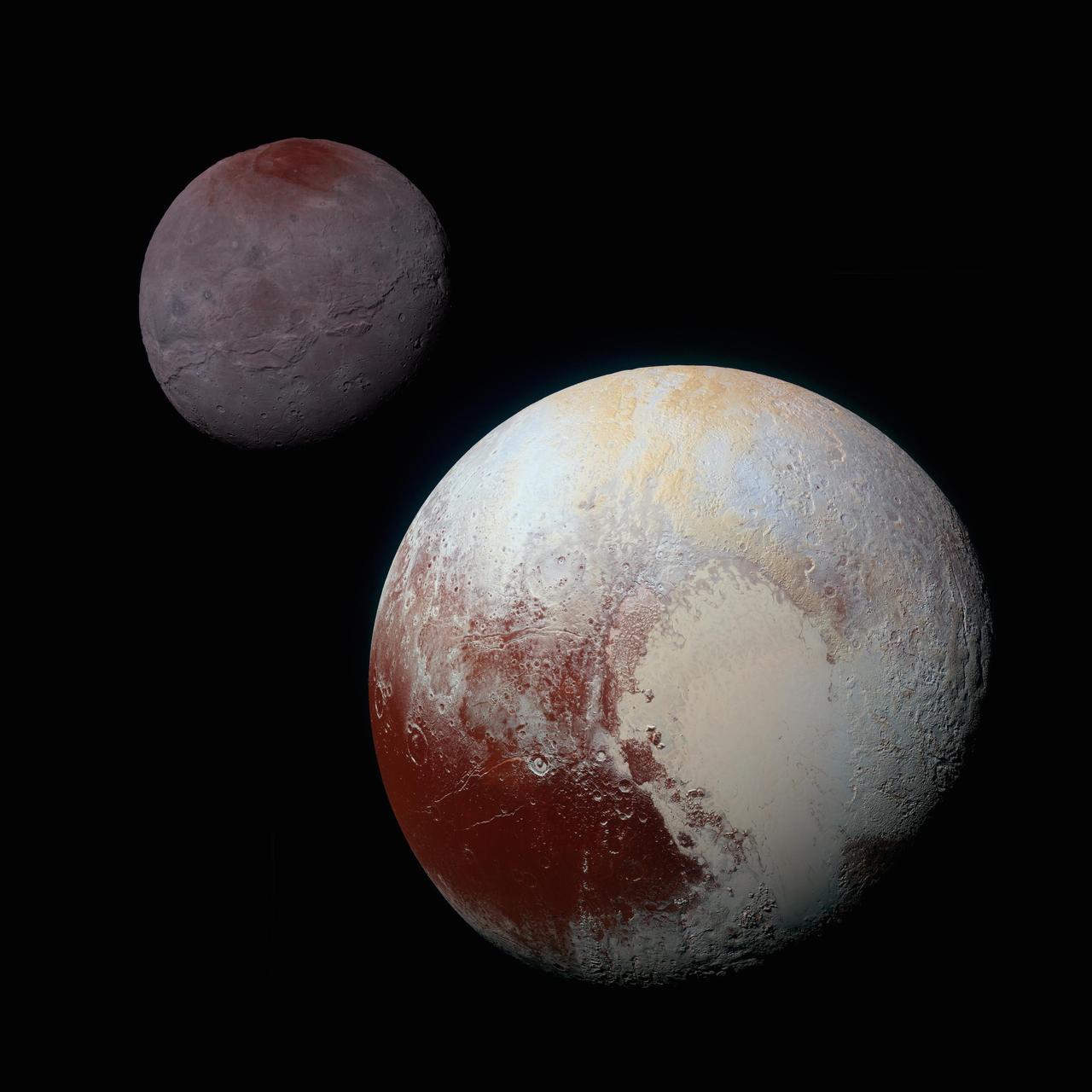

A composite of enhanced color images of Pluto (lower right) and Charon (upper left), taken by NASA's New Horizons spacecraft as it passed through the Pluto system on July 14, 2015. This image highlights the striking differences between Pluto and Charon. The color and brightness of both Pluto and Charon have been processed identically to allow direct comparison of their surface properties, and to highlight the similarity between Charon's polar red terrain and Pluto's equatorial red terrain. Pluto and Charon are shown with approximately correct relative sizes, but their true separation is not to scale. The image combines blue, red and infrared images taken by the spacecraft's Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19966

Regions with exposed water ice are highlighted in blue in this composite image from New Horizons' Ralph instrument, combining visible imagery from the Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) with infrared spectroscopy from the Linear Etalon Imaging Spectral Array (LEISA). The strongest signatures of water ice occur along Virgil Fossa, just west of Elliot crater on the left side of the inset image, and also in Viking Terra near the top of the frame. A major outcrop also occurs in Baré Montes towards the right of the image, along with numerous much smaller outcrops, mostly associated with impact craters and valleys between mountains. The scene is approximately 280 miles (450 kilometers) across. Note that all surface feature names are informal. http://ppj2:8080/catalog/PIA19963

This is a composite of several images taken in several colors by the New Horizons Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera, or MVIC.

This processed image is the highest-resolution color look yet at the haze layers in Pluto's atmosphere. Shown in approximate true color, the picture was constructed from a mosaic of four panchromatic images from the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) splashed with Ralph/Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) four-color filter data, all acquired by NASA's New Horizons spacecraft on July 14, 2015. The resolution is 1 kilometer (0.6 miles) per pixel; the sun illuminates the scene from the right. Scientists believe the haze is a photochemical smog resulting from the action of sunlight on methane and other molecules in Pluto's atmosphere, producing a complex mixture of hydrocarbons such as acetylene and ethylene. These hydrocarbons accumulate into small particles, a fraction of a micrometer in size, and scatter sunlight to make the bright blue haze seen in this image. As they settle down through the atmosphere, the haze particles form numerous intricate, horizontal layers, some extending for hundreds of miles around Pluto. The haze layers extend to altitudes of over 200 kilometers (120 miles). Adding to the stark beauty of this image are mountains on Pluto's limb (on the right, near the 4 o'clock position), surface features just within the limb to the right, and crepuscular rays (dark finger-like shadows to the left) extending from Pluto's topographic features. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20362
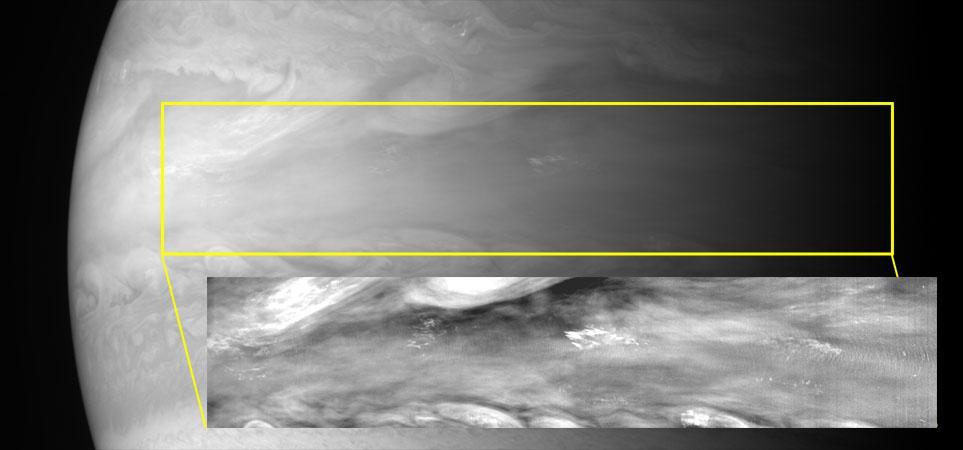
With its Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera MVIC, half of the Ralph instrument, New Horizons captured several pictures of mesoscale gravity waves in Jupiter equatorial atmosphere.

In September, NASA's New Horizons team released a stunning but incomplete image of Pluto's crescent. Thanks to new processing work by the science team, New Horizons is releasing the entire, breathtaking image of Pluto. This image was made just 15 minutes after New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015, as the spacecraft looked back at Pluto toward the sun. The wide-angle perspective of this view shows the deep haze layers of Pluto's atmosphere extending all the way around Pluto, revealing the silhouetted profiles of rugged plateaus on the night (left) side. The shadow of Pluto cast on its atmospheric hazes can also be seen at the uppermost part of the disk. On the sunlit side of Pluto (right), the smooth expanse of the informally named icy plain Sputnik Planum is flanked to the west (above, in this orientation) by rugged mountains up to 11,000 feet (3,500 meters) high, including the informally named Norgay Montes in the foreground and Hillary Montes on the skyline. Below (east) of Sputnik, rougher terrain is cut by apparent glaciers. The backlighting highlights more than a dozen high-altitude layers of haze in Pluto's tenuous atmosphere. The horizontal streaks in the sky beyond Pluto are stars, smeared out by the motion of the camera as it tracked Pluto. The image was taken with New Horizons' Multi-spectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) from a distance of 11,000 miles (18,000 kilometers) to Pluto. The resolution is 700 meters (0.4 miles).
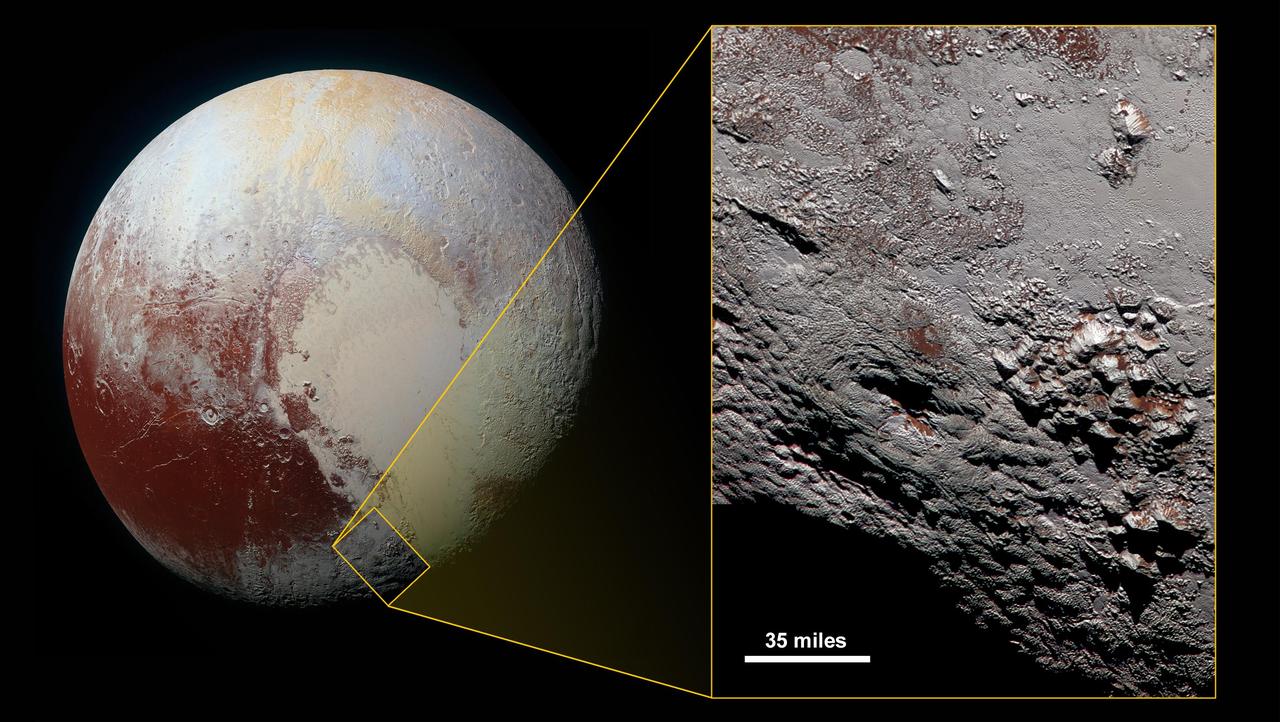
Scientists with NASA New Horizons mission have assembled the highest-resolution color view of one of two potential cryovolcanoes spotted on the surface of the distant planet by the passing New Horizons spacecraft in July 2015. At about 90 miles (150 kilometers) across and 2.5 miles (4 kilometers) high, the feature -- informally named Wright Mons -- is enormous. If it is in fact a volcano, as suspected, it would be the largest such feature discovered in the outer solar system. Mission scientists are intrigued by the sparse distribution of red material in the image and wonder why it is not more widespread. Also perplexing is that there is only one identified impact crater on Wright Mons itself, telling scientists that the surface (as well as some of the crust underneath) was created relatively recently. This is turn may indicate that Wright Mons was volcanically active late in Pluto's history. This composite image includes pictures taken by the New Horizons spacecraft's Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) on July 14, 2015, from a range of about 30,000 miles (48,000 kilometers), showing features as small as 1,500 feet (450 meters) across. Sprinkled across the LORRI mosaic is enhanced color data from the Ralph/Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) gathered about 20 minutes after the LORRI snapshots were taken, from a range of 21,000 miles (34,000 kilometers) and at a resolution of about 2,100 feet (650 meters) per pixel. The entire scene is 140 miles (230 kilometers) across. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20361

The first color movies from NASA's New Horizons mission show Pluto and its largest moon, Charon, and the complex orbital dance of the two bodies, known as a double planet. A near-true color movie was assembled from images made in three colors -- blue, red and near-infrared -- by the Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera on the instrument known as Ralph. The images were taken on nine different occasions from May 29-June 3, 2015. The movie is barycentric, meaning that both Pluto and Charon are shown in motion around the binary's barycenter -- the shared center of gravity between the two bodies as they do a planetary jig. Because Pluto is much more massive than Charon, the barycenter (marked by a small "x" in the movie) is much closer to Pluto than to Charon. Looking closely at the images in this movie, one can detect a regular shift in Pluto's brightness-due to the brighter and darker terrains on its differing faces. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19688
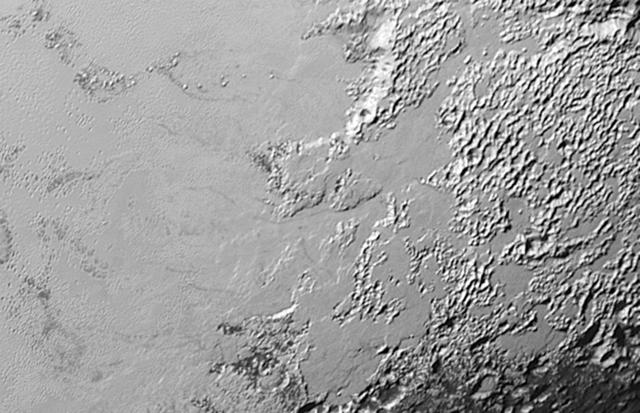

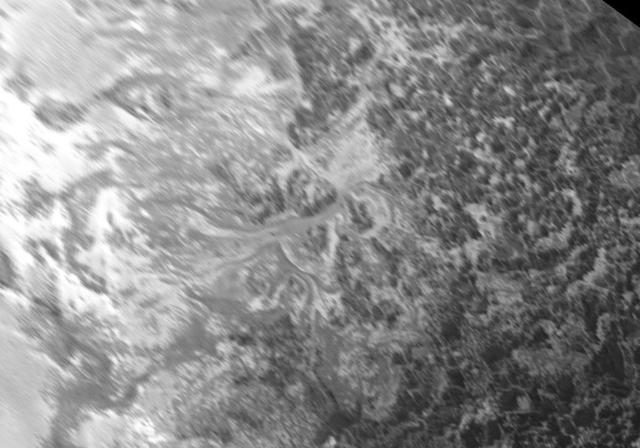
Ice (probably frozen nitrogen) that appears to have accumulated on the uplands on the right side of this 390-mile (630-kilometer) wide image is draining from Pluto's mountains onto the informally named Sputnik Planum through the 2- to 5-mile (3- to 8- kilometer) wide valleys. The flow front of the ice moving into Sputnik Planum is outlined by the blue arrows. The origin of the ridges and pits on the right side of the image remains uncertain. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19944

The first color movies from NASA's New Horizons mission show Pluto and its largest moon, Charon, and the complex orbital dance of the two bodies, known as a double planet. A near-true color movie were assembled from images made in three colors -- blue, red and near-infrared -- by the Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera on the instrument known as Ralph. The images were taken on nine different occasions from May 29-June 3, 2015. The movie is "Pluto-centric," meaning that Charon is shown as it moves in relation to Pluto, which is digitally centered in the movie. (The North Pole of Pluto is at the top.) Pluto makes one turn around its axis every 6 days, 9 hours and 17.6 minutes-the same amount of time that Charon rotates in its orbit. Looking closely at the images in this movie, one can detect a regular shift in Pluto's brightness-due to the brighter and darker terrains on its differing faces. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19689

The backlighting highlights the intricate flow lines on the glaciers. The flow front of the ice is moving into the informally named Sputnik Planum. The origin of the ridges and pits on the right side of the image remains uncertain. This image is 390 miles (630 kilometers) across. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19943
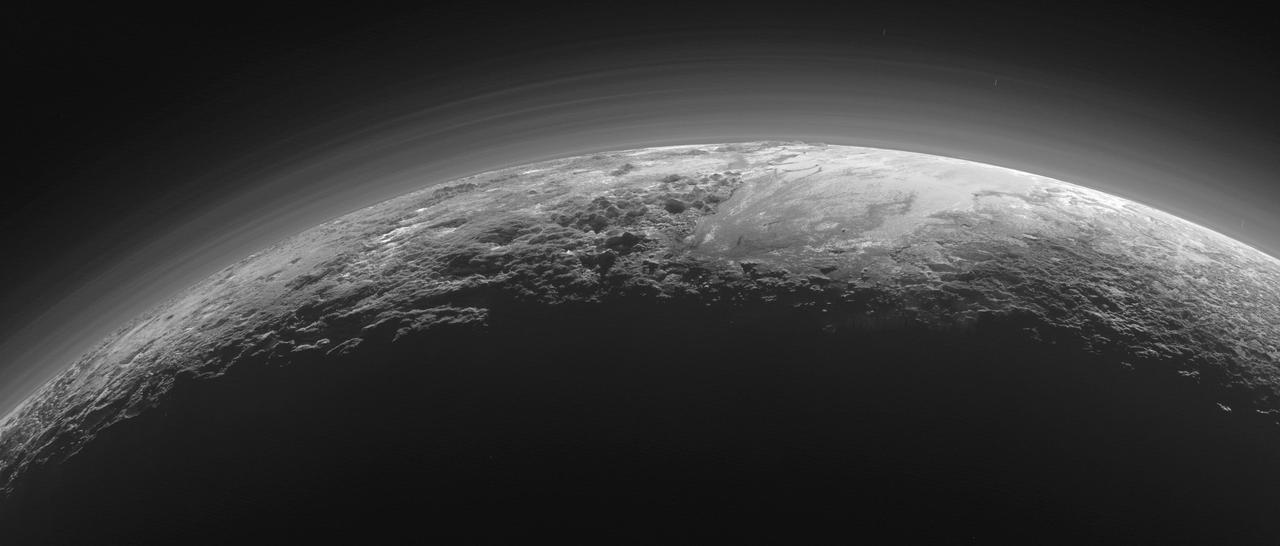

Just 15 minutes after its closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015, NASA's New Horizons spacecraft looked back toward the sun and captured this near-sunset view of the rugged, icy mountains and flat ice plains extending to Pluto's horizon. The smooth expanse of the informally named icy plain Sputnik Planum (right) is flanked to the west (left) by rugged mountains up to 11,000 feet (3,500 meters) high, including the informally named Norgay Montes in the foreground and Hillary Montes on the skyline. To the right, east of Sputnik, rougher terrain is cut by apparent glaciers. The backlighting highlights more than a dozen layers of haze in Pluto's tenuous but distended atmosphere. The image was taken from a distance of 11,000 miles (18,000 kilometers) to Pluto; the scene is 780 miles (1,250 kilometers) wide. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19948
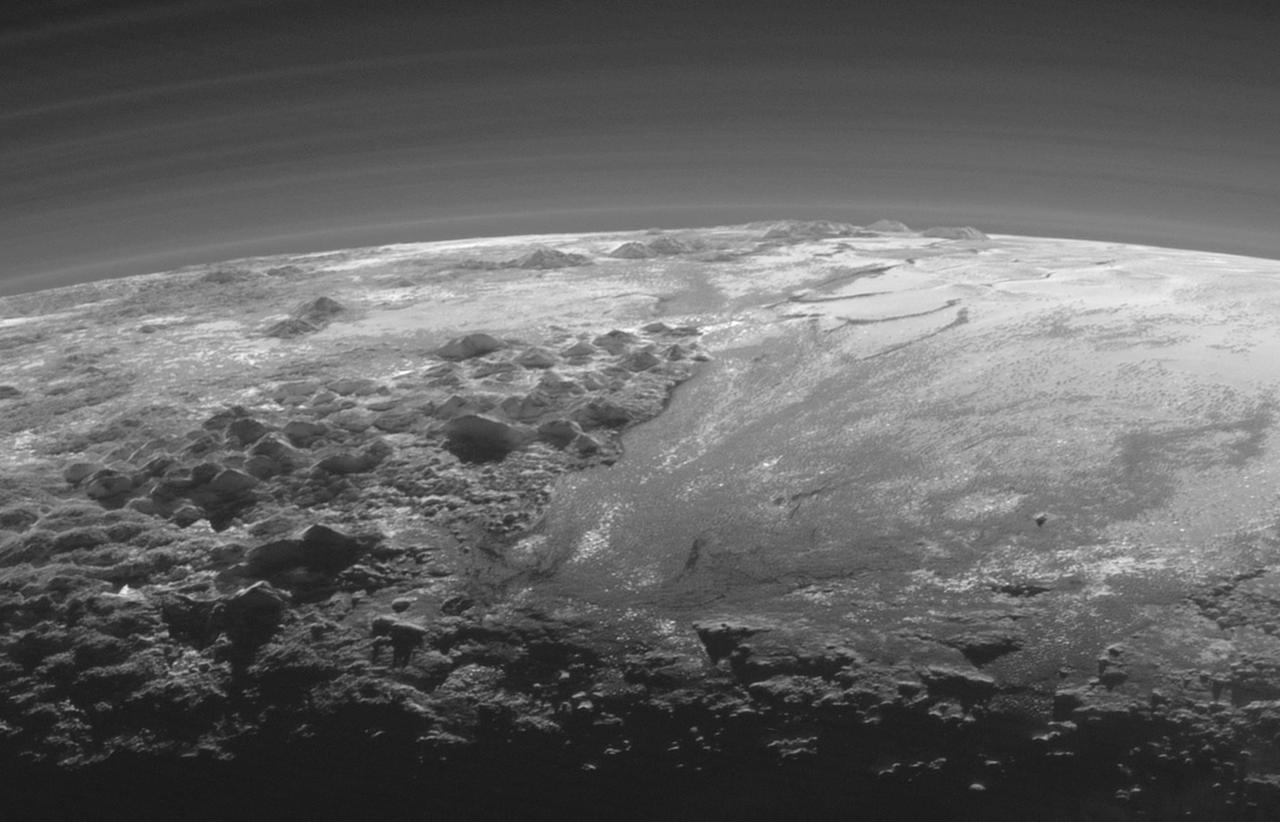

Just 15 minutes after its closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015, NASA's New Horizons spacecraft looked back toward the sun and captured a near-sunset view of the rugged, icy mountains and flat ice plains extending to Pluto's horizon. The smooth expanse of the informally named Sputnik Planum (right) is flanked to the west (left) by rugged mountains up to 11,000 feet (3,500 meters) high, including the informally named Norgay Montes in the foreground and Hillary Montes on the skyline. The backlighting highlights more than a dozen layers of haze in Pluto's tenuous but distended atmosphere. The image was taken from a distance of 11,000 miles (18,000 kilometers) to Pluto; the scene is 230 miles (380 kilometers) across. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19947
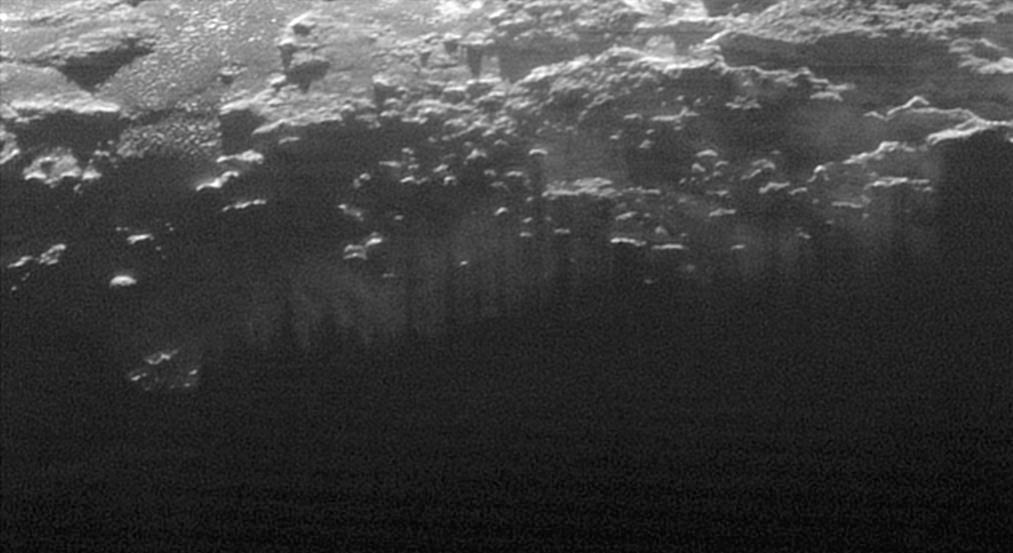

In this small section of the larger crescent image of Pluto, taken by NASA's New Horizons just 15 minutes after the spacecraft's closest approach on July 14, 2015, the setting sun illuminates a fog or near-surface haze, which is cut by the parallel shadows of many local hills and small mountains. The image was taken from a distance of 11,000 miles (18,000 kilometers), and the width of the image is 115 miles (185 kilometers). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19946

What would it be like to actually land on Pluto? This image is one of more than 100 images taken by NASA's New Horizons spacecraft over six weeks of approach and close flyby in the summer of 2015. A video offers a trip down onto the surface of Pluto -- starting with a distant view of Pluto and its largest moon, Charon -- and leading up to an eventual ride in for a "landing" on the shoreline of Pluto's informally named Sputnik Planitia. After a 9.5-year voyage covering more than three billion miles, New Horizons flew through the Pluto system on July 14, 2015, coming within 7,800 miles (12,500 kilometers) of Pluto. Carrying powerful telescopic cameras that could spot features smaller than a football field, New Horizons sent back hundreds of images of Pluto and its moons that show how dynamic and fascinating their surfaces are. Movies are available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11709

Pluto's present, hazy atmosphere is almost entirely free of clouds, though scientists from NASA's New Horizons mission have identified some cloud candidates after examining images taken by the New Horizons Long Range Reconnaissance Imager and Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera, during the spacecraft's July 2015 flight through the Pluto system. All are low-lying, isolated small features -- no broad cloud decks or fields -- and while none of the features can be confirmed with stereo imaging, scientists say they are suggestive of possible, rare condensation clouds. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21127

This pair of approximately true color images of Pluto and its big moon Charon, taken by NASA's New Horizons spacecraft, highlight the dramatically different appearance of different sides of the dwarf planet, and reveal never-before-seen details on Pluto's varied surface. The views were made by combining high-resolution black-and-white images from the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) with color information from the lower-resolution color camera that is part of the Ralph instrument. The left-hand image shows the side of Pluto that always faces away from Charon -- this is the side that will be seen at highest resolution by New Horizons when it makes its close approach to Pluto on July 14th. This hemisphere is dominated by a very dark region that extends along the equator and is redder than its surroundings, alongside a strikingly bright, paler-colored region which straddles the equator on the right-hand side of the disk. The opposite hemisphere, the side that faces Charon, is seen in the right-hand image. The most dramatic feature on this side of Pluto is a row of dark dots arranged along the equator. The origin of all these features is still mysterious, but may be revealed in the much more detailed images that will be obtained as the spacecraft continues its approach to Pluto. In both images, Charon shows a darker and grayer color than Pluto, and a conspicuous dark polar region. The left-hand image was obtained at 5:37 UT on June 25th 2015, at a distance from Pluto of 22.9 million kilometers (14.3 million miles) and has a central longitude of 152 degrees. The right-hand image was obtained at 23:15 UT on June 27th 2015, at a distance from Pluto of 19.7 million kilometers (12.2 million miles) with a central longitude of 358 degrees. Insets show the orientation of Pluto in each image -- the solid lines mark the equator and the prime meridian, which is defined to be the longitude that always faces Charon. The smallest visible features are about 200 km (120 miles) across. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19693
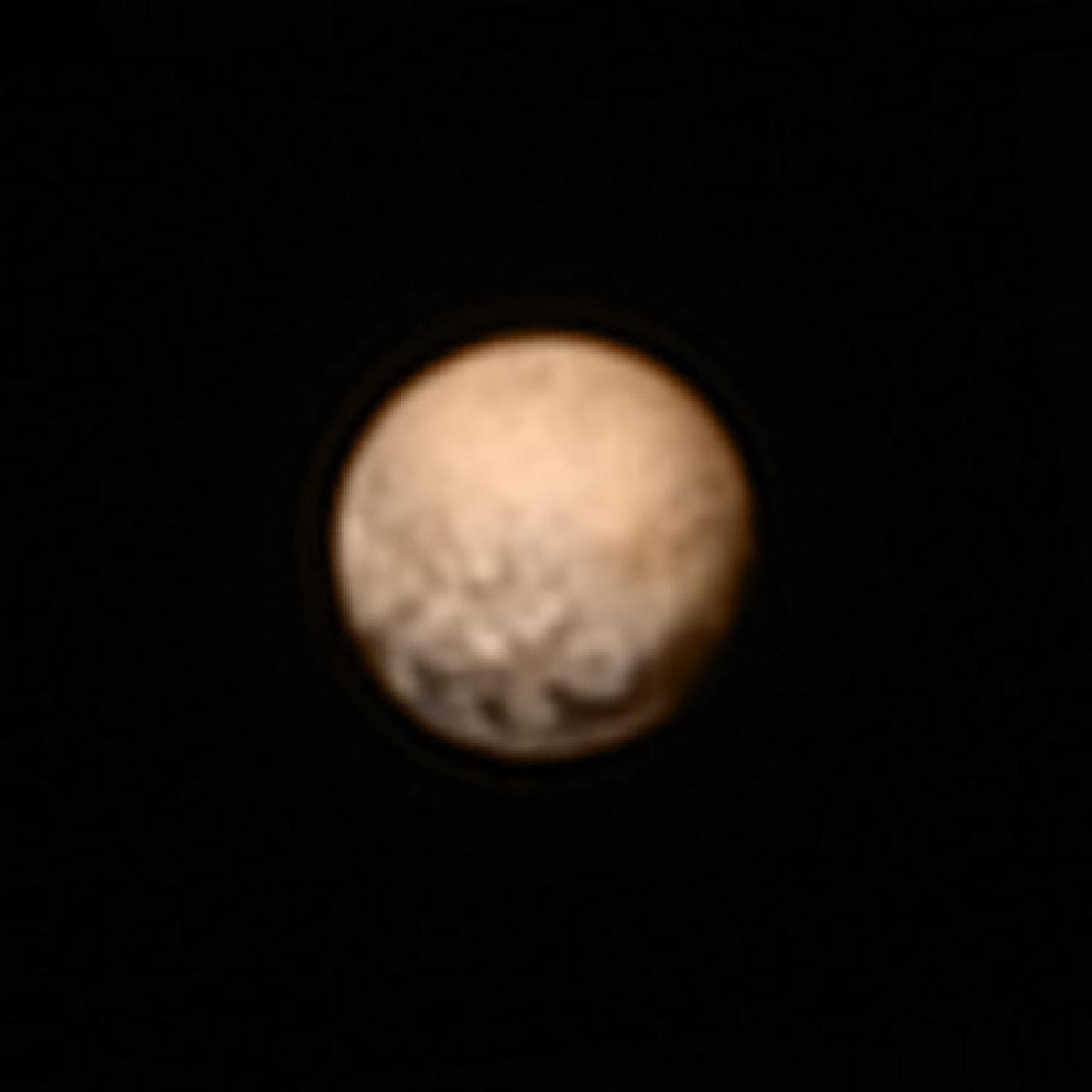

This color version of NASA's New Horizons Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) picture of Pluto taken July 3, 2015, was created by adding color data from the Ralph instrument gathered earlier in the mission. The LORRI image was taken from a range of 7.8 million miles (12.5 million km), with a central longitude of 19°. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19699

Images from NASA New Horizons spacecraft were used to create a flyover video (PIA19965) of Pluto largest moon, Charon. The flight starts with the informally named Mordor dark region near Charon north pole. In the video, the camera then moves south to a vast chasm, descending from 1,100 miles (1,800 kilometers) to just 40 miles (60 kilometers) above the surface to fly through the canyon system. From there it's a turn to the south to view the plains and "moat mountain," informally named Kubrick Mons, a prominent peak surrounded by a topographic depression. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19965
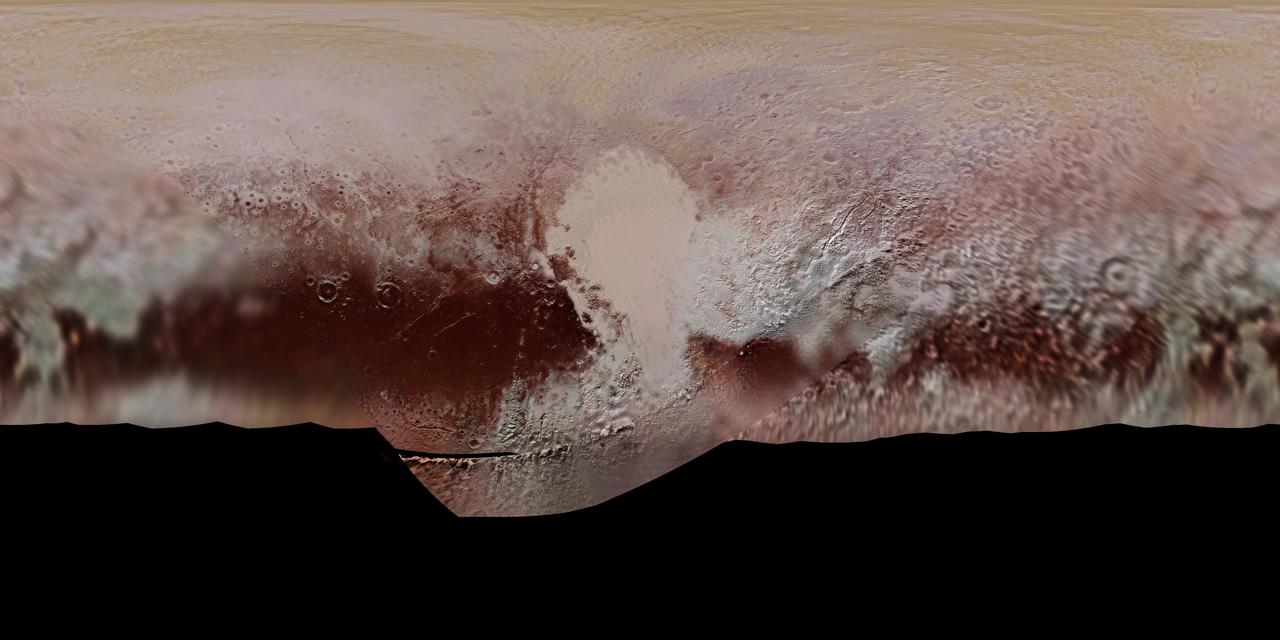
This new, detailed global mosaic color map of Pluto is based on a series of three color filter images obtained by the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera aboard New Horizons during the NASA spacecraft's close flyby of Pluto in July 2015. The mosaic shows how Pluto's large-scale color patterns extend beyond the hemisphere facing New Horizons at closest approach- which were imaged at the highest resolution. North is up; Pluto's equator roughly bisects the band of dark red terrains running across the lower third of the map. Pluto's giant, informally named Sputnik Planitia glacier - the left half of Pluto's signature "heart" feature -- is at the center of this map. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11707
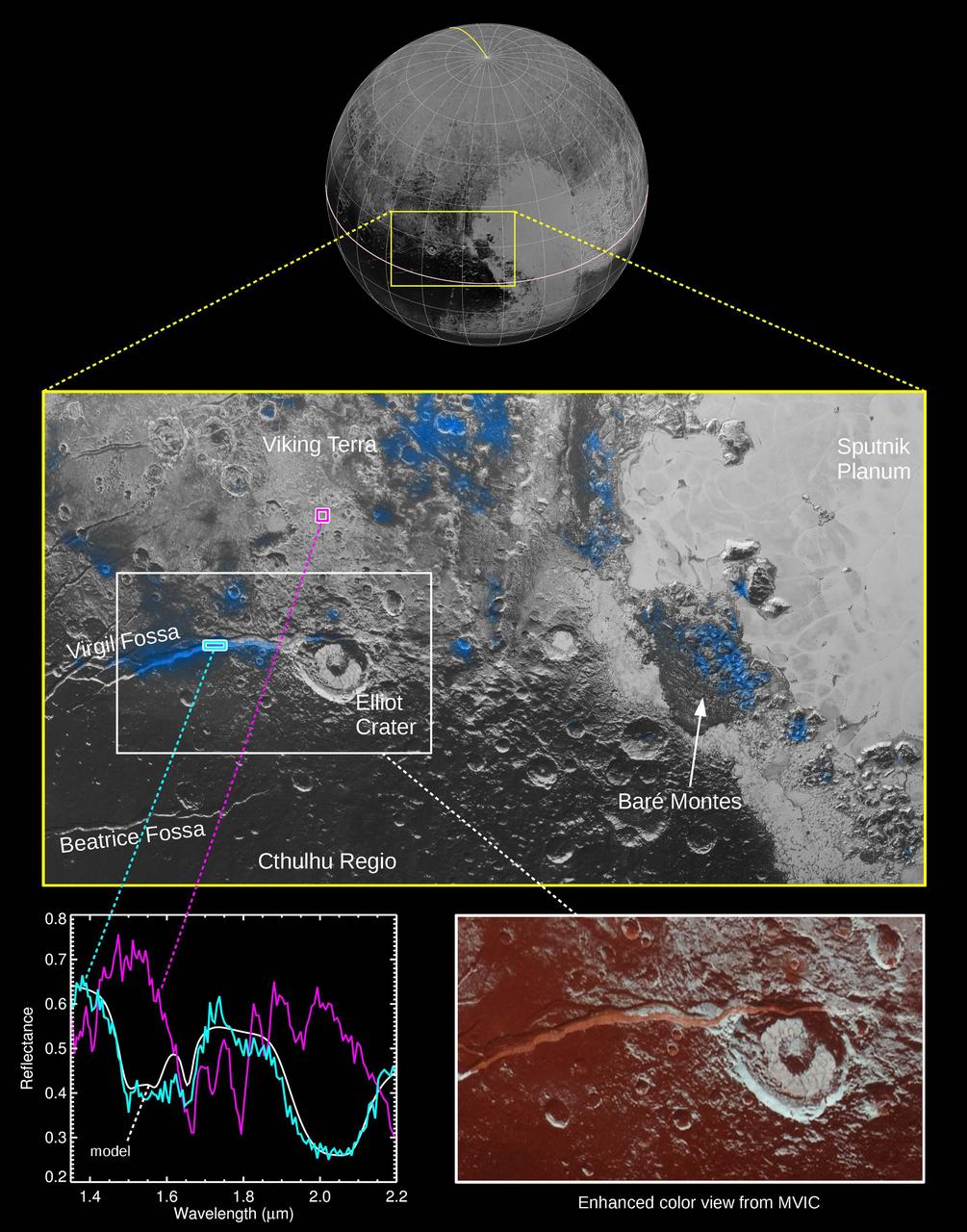
The Ralph instrument on NASA's New Horizons spacecraft detected water ice on Pluto's surface, picking up on the ice's near-infrared spectral characteristics. (See featured image from Oct. 8, 2015.) The middle panel shows a region west of Pluto's "heart" feature -- which the mission team calls Tombaugh Regio -- about 280 miles (450 kilometers) across. It combines visible imagery from Ralph's Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) with infrared spectroscopy from the Linear Etalon Imaging Spectral Array (LEISA). Areas with the strongest water ice spectral signature are highlighted in blue. Major outcrops of water ice occur in regions informally called Viking Terra, along Virgil Fossa west of Elliot crater, and in Baré Montes. Numerous smaller outcrops are associated with impact craters and valleys between mountains. In the lower left panel, LEISA spectra are shown for two regions indicated by cyan and magenta boxes. The white curve is a water ice model spectrum, showing similar features to the cyan spectrum. The magenta spectrum is dominated by methane ice absorptions. The lower right panel shows an MVIC enhanced color view of the region in the white box, with MVIC's blue, red and near-infrared filters displayed in blue, green and red channels, respectively. The regions showing the strongest water ice signature are associated with terrains that are actually a lighter shade of red. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20030
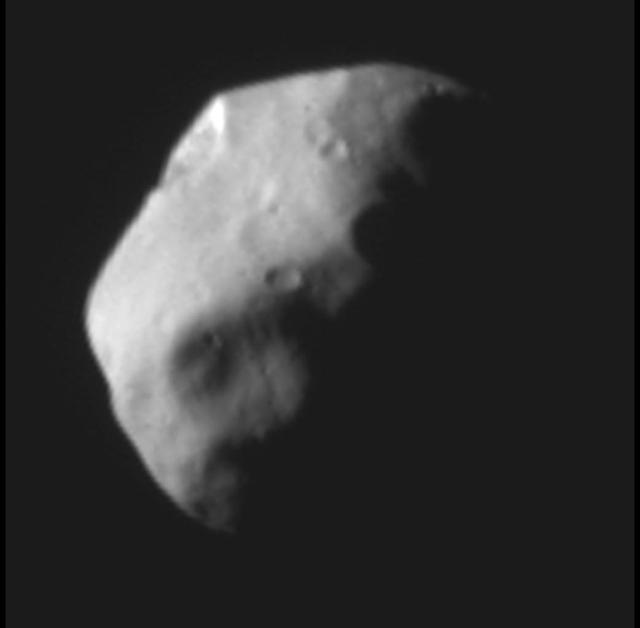

This recently received panchromatic image of Pluto's small satellite Nix taken by the Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) aboard New Horizons is one of the best images of Pluto's third-largest moon generated by the NASA mission. Taken on July 14, 2015, at a range of about 14,000 miles (23,000 kilometers) from Nix, the illuminated surface is about 12 miles (19 kilometers) by 29 miles (47 kilometers). The unique perspective of this image provides new details about Nix's geologic history and impact record. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20287
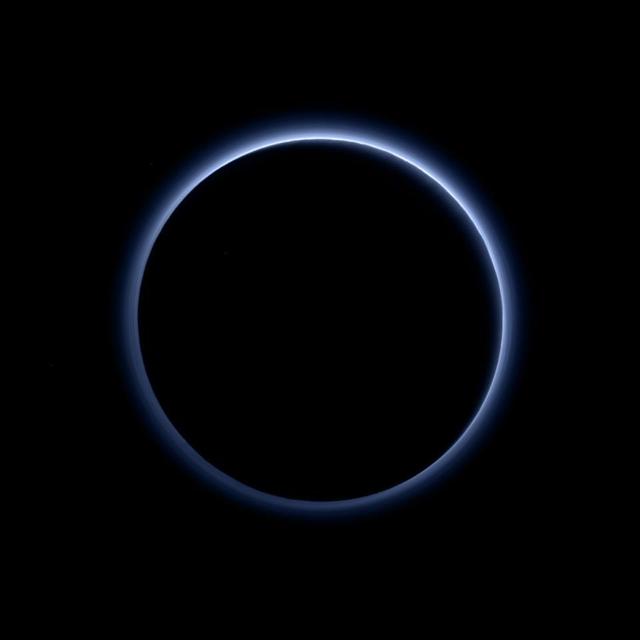

Pluto's haze layer shows its blue color in this picture taken by the New Horizons Ralph/Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC). The high-altitude haze is thought to be similar in nature to that seen at Saturn's moon Titan. The source of both hazes likely involves sunlight-initiated chemical reactions of nitrogen and methane, leading to relatively small, soot-like particles (called tholins) that grow as they settle toward the surface. This image was generated by software that combines information from blue, red and near-infrared images to replicate the color a human eye would perceive as closely as possible. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19964

In this extended color image of Pluto taken by NASA New Horizons spacecraft, rounded and bizarrely textured mountains, informally named the Tartarus Dorsa, rise up along Pluto's day-night terminator and show intricate but puzzling patterns of blue-gray ridges and reddish material in between. This view, roughly 330 miles (530 kilometers) across, combines blue, red and infrared images taken by the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC) on July 14, 2015, and resolves details and colors on scales as small as 0.8 miles (1.3 kilometers). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19957
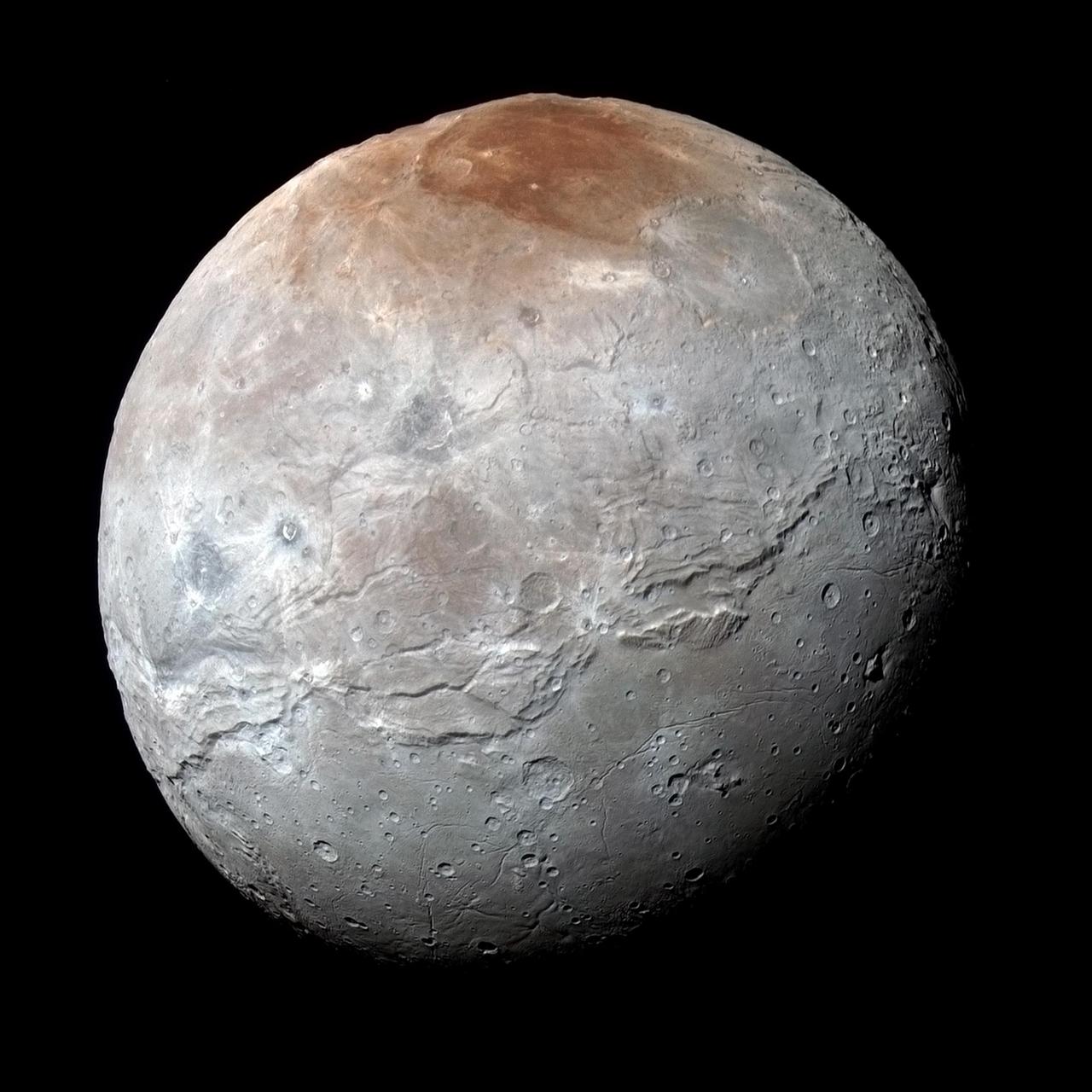

NASA's New Horizons captured this high-resolution enhanced color view of Charon just before closest approach on July 14, 2015. The image combines blue, red and infrared images taken by the spacecraft's Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC); the colors are processed to best highlight the variation of surface properties across Charon. Charon's color palette is not as diverse as Pluto's; most striking is the reddish north (top) polar region, informally named Mordor Macula. Charon is 754 miles (1,214 kilometers) across; this image resolves details as small as 1.8 miles (2.9 kilometers). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19968

This enhanced color view of Pluto's surface diversity was created by merging Ralph/Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) color imagery (650 meters per pixel) with Long Range Reconnaissance Imager panchromatic imagery (230 meters per pixel). At lower right, ancient, heavily cratered terrain is coated with dark, reddish tholins. At upper right, volatile ices filling the informally named Sputnik Planum have modified the surface, creating a chaos-like array of blocky mountains. Volatile ice also occupies a few nearby deep craters, and in some areas the volatile ice is pocked with arrays of small sublimation pits. At left, and across the bottom of the scene, gray-white CH4 ice deposits modify tectonic ridges, the rims of craters, and north-facing slopes. The scene in this image is 260 miles (420 kilometers) wide and 140 miles (225 kilometers) from top to bottom; north is to the upper left. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20534
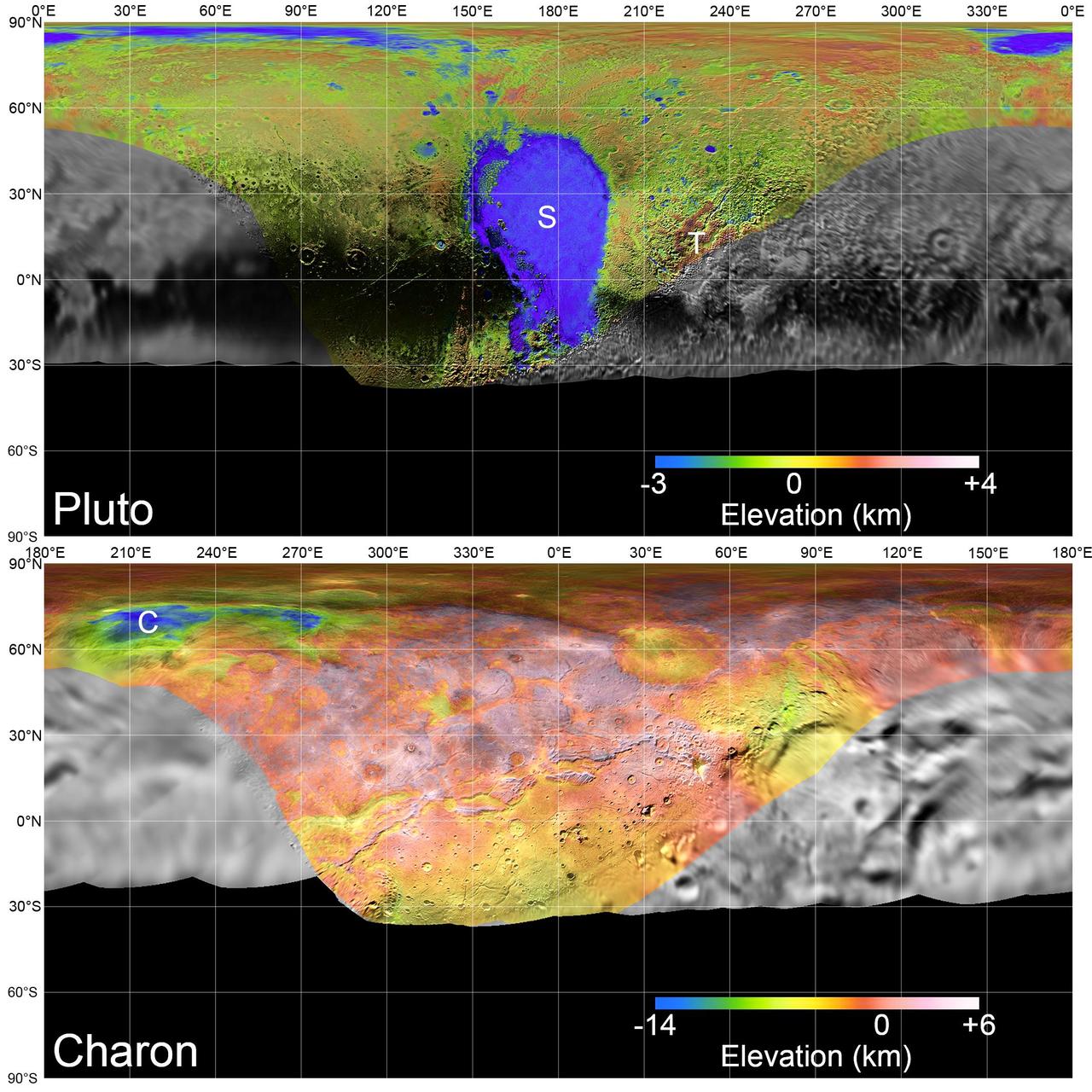
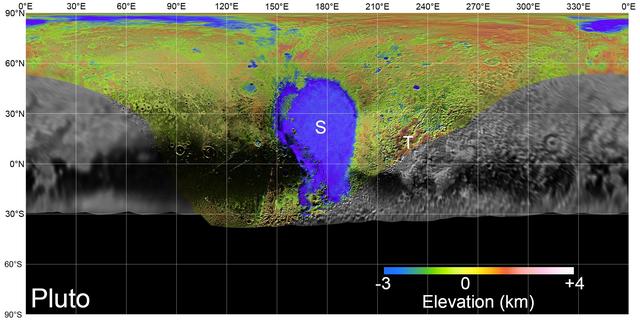
Global mosaics of Pluto and Charon projected at 300 meters (985 feet) per pixel that have been assembled from most of the highest resolution images obtained by the Long-Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) and the Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) onboard New Horizons. Transparent, colorized stereo topography data generated for the encounter hemispheres of Pluto and Charon have been overlain on the mosaics. Terrain south of about 30°S on Pluto and Charon was in darkness leading up to and during the flyby, so is shown in black. "S" and "T" respectively indicate Sputnik Planitia and Tartarus Dorsa on Pluto, and "C" indicates Caleuche Chasma on Charon. All feature names on Pluto and Charon are informal. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21862
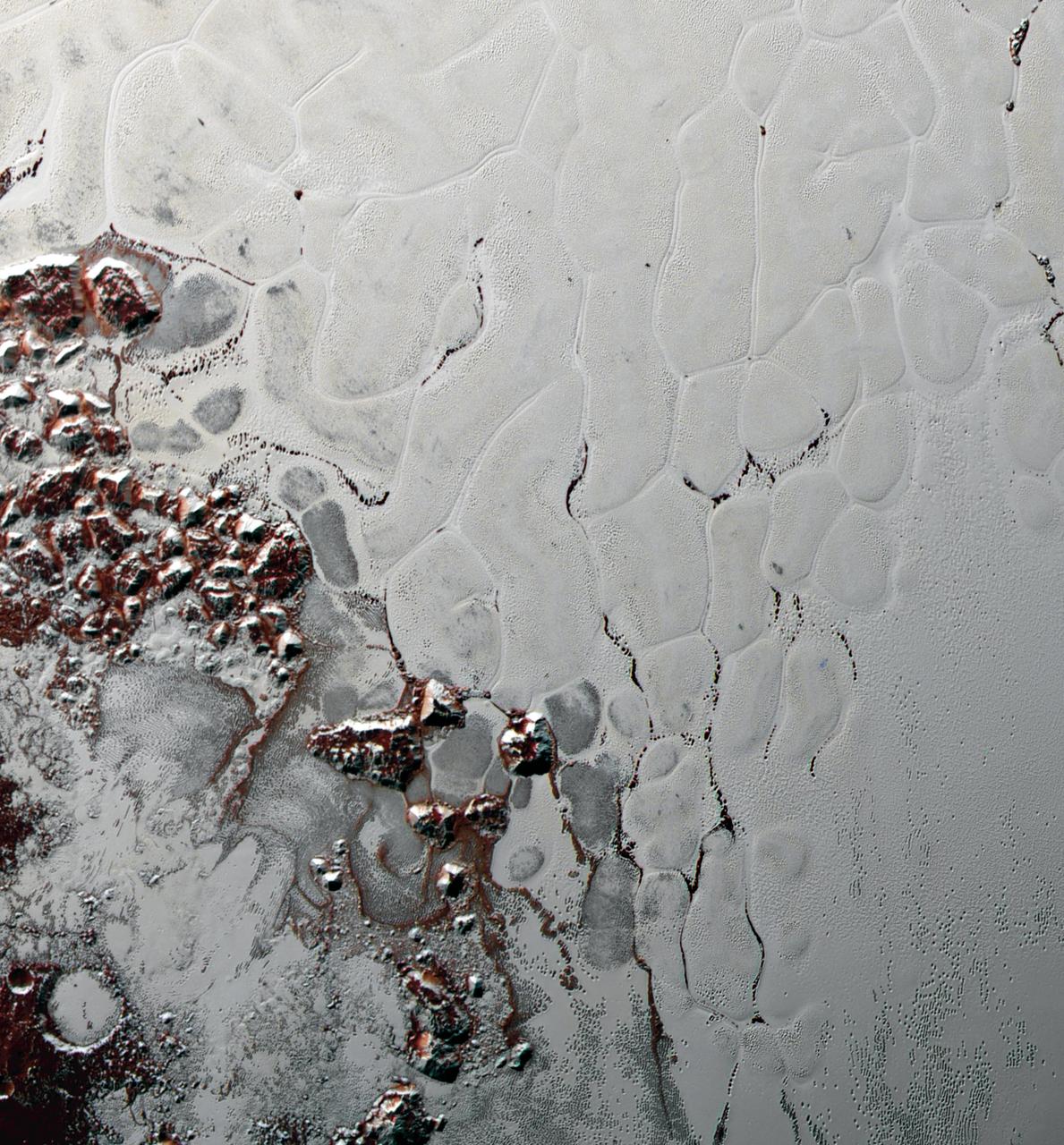

Like a cosmic lava lamp, a large section of Pluto's icy surface is being constantly renewed by a process called convection that replaces older surface ices with fresher material. Scientists from NASA's New Horizons mission used state-of-the-art computer simulations to show that the surface of Pluto's informally named Sputnik Planum is covered with churning ice "cells" that are geologically young and turning over due to a process called convection. The scene above, which is about 250 miles (400 kilometers) across, uses data from the New Horizons Ralph/Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC), gathered July 14, 2015. Their findings are published in the June 2, 2016, issue of the journal Nature. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20726
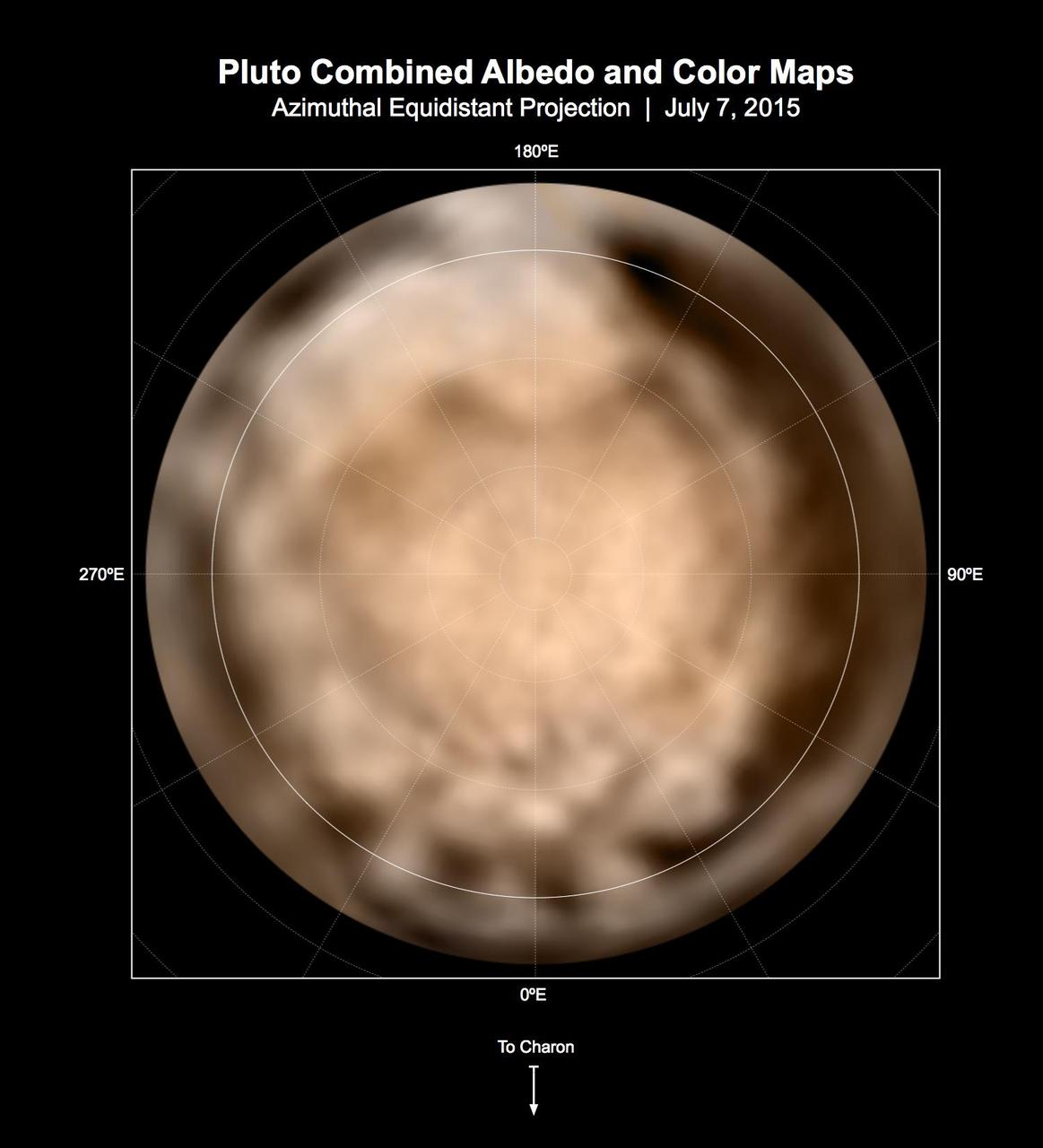
These circular maps shows the distribution of Pluto's dark and bright terrains as revealed by NASA's New Horizons mission prior to July 4, 2015. Each map is an azimuthal equidistant projection centered on the north pole, with latitude and longitude indicated. Both a gray-scale and color version are shown. The gray-scale version is based on 7 days of panchromatic imaging from the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI), whereas the color version uses the gray-scale base and incorporates lower-resolution color information from the Multi-spectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC), part of the Ralph instrument. The color version is also shown in a simple cylindrical projection in PIA19700. In these maps, the polar bright terrain is surrounded by a somewhat darker polar fringe, one whose latitudinal position varies strongly with longitude. Especially striking are the much darker regions along the equator. A broad dark swath ("the whale") stretches along the equator from approximately 20 to 160 degrees of longitude. Several dark patches appear in a regular sequence centered near 345 degrees of longitude. A spectacular bright region occupies Pluto's mid-latitudes near 180 degrees of longitude, and stretches southward over the equator. New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto will occur near this longitude, which will permit high-resolution visible imaging and compositional mapping of these various regions. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19706
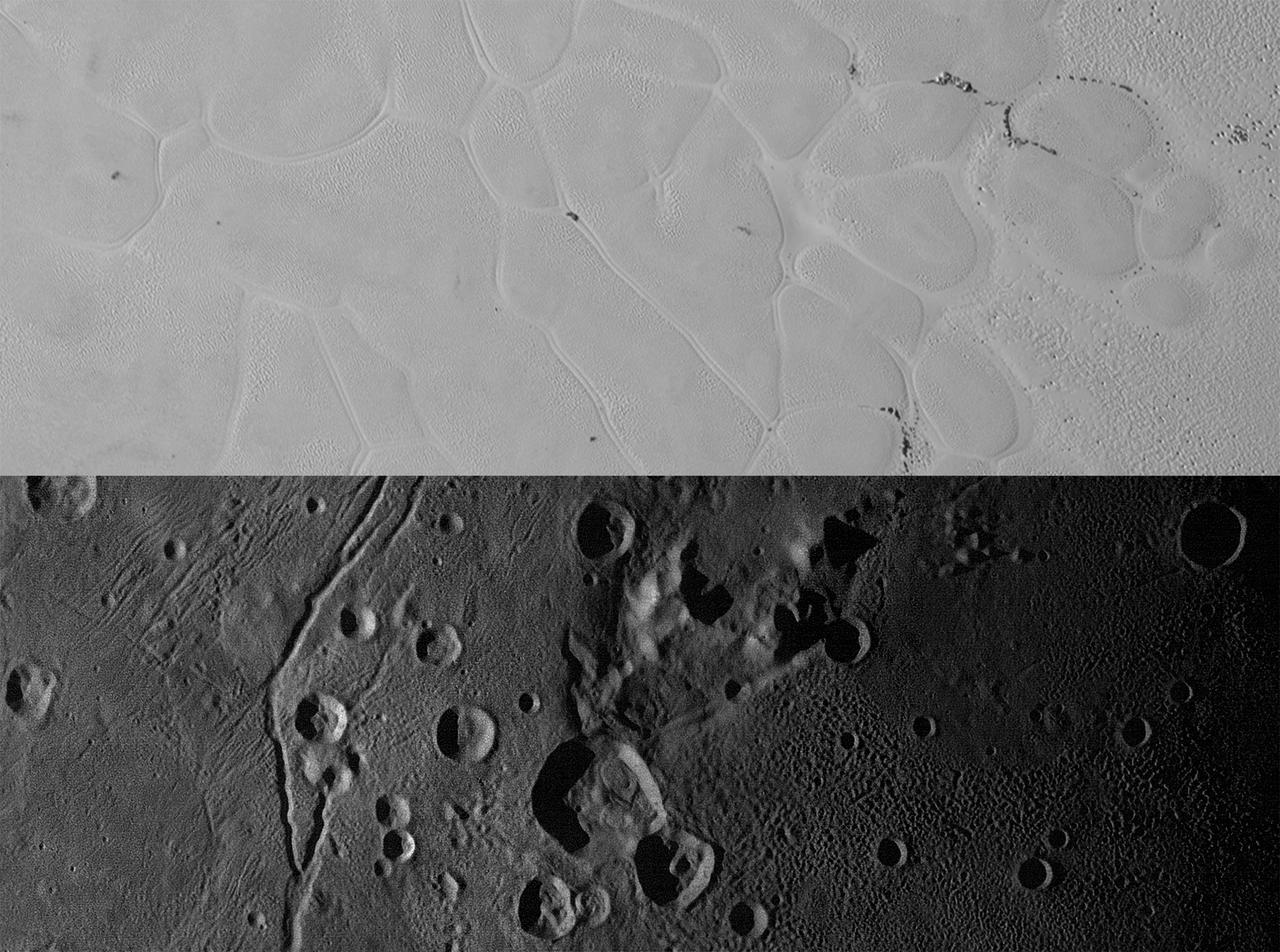
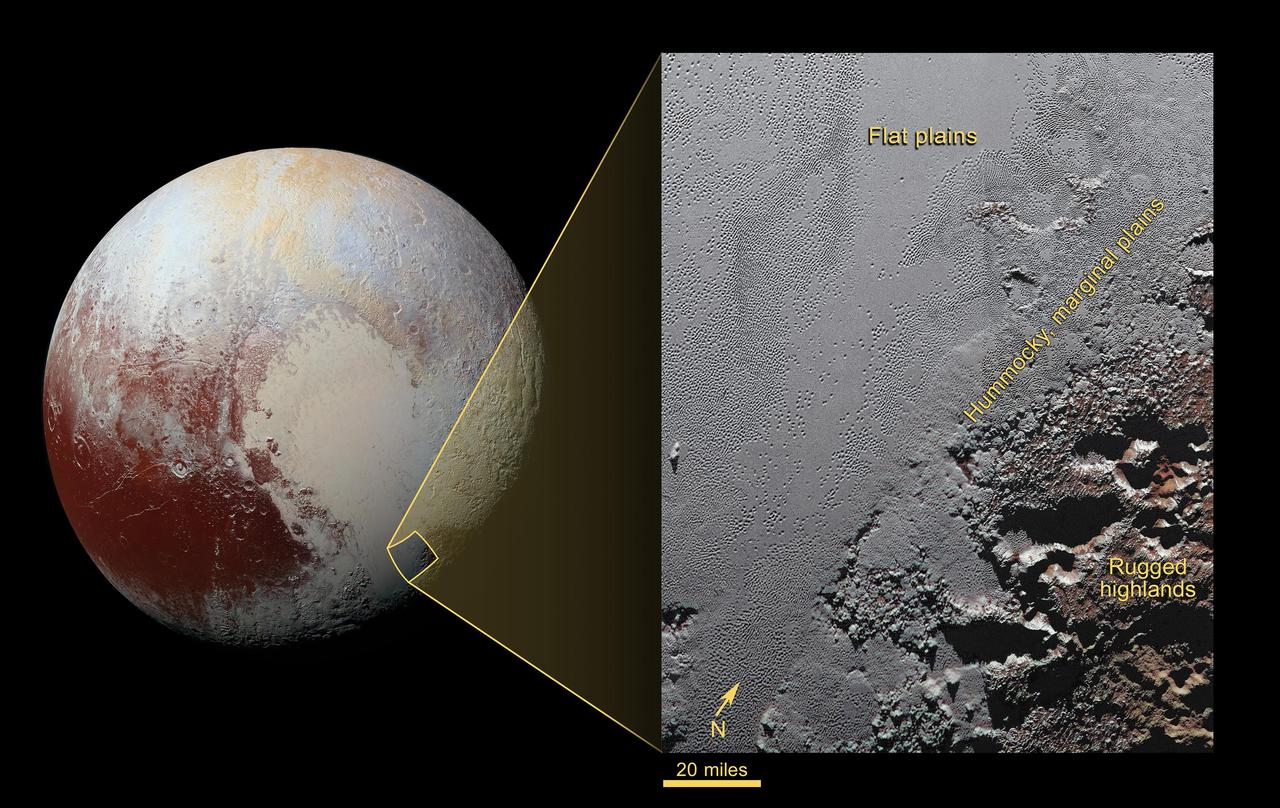
New Horizons views of the informally named Sputnik Planum on Pluto (top) and the informally named Vulcan Planum on Charon (bottom). Both scale bars measure 20 miles (32 kilometers) long; illumination is from the left in both instances. The Sputnik Planum view is centered at 11°N, 180°E, and covers the bright, icy, geologically cellular plains. Here, the cells are defined by a network of interconnected troughs that crisscross these nitrogen-ice plains. At right, in the upper image, the cellular plains yield to pitted plains of southern Sputnik Planum. This observation was obtained by the Ralph/Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) at a resolution of 1,050 feet (320 meters) per pixel. The Vulcan Planum view in the bottom panel is centered at 4°S, 4°E, and includes the "moated mountain" Clarke Mons just above the center of the image. As well as featuring impact craters and sinuous troughs, the water ice-rich plains display a range of surface textures, from smooth and grooved at left, to pitted and hummocky at right. This observation was obtained by the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) at a resolution of 525 feet (160 meters) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20535

This enhanced color mosaic combines some of the sharpest views of Pluto that NASA's New Horizons spacecraft obtained during its July 14 flyby. The pictures are part of a sequence taken near New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto, with resolutions of about 250-280 feet (77-85 meters) per pixel -- revealing features smaller than half a city block on Pluto's surface. Lower resolution color data (at about 2,066 feet, or 630 meters, per pixel) were added to create this new image. The images form a strip 50 miles (80 kilometers) wide, trending (top to bottom) from the edge of "badlands" northwest of the informally named Sputnik Planum, across the al-Idrisi mountains, onto the shoreline of Pluto's "heart" feature, and just into its icy plains. They combine pictures from the telescopic Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) taken approximately 15 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto, with -- from a range of only 10,000 miles (17,000 kilometers) -- with color data (in near-infrared, red and blue) gathered by the Ralph/Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) 25 minutes before the LORRI pictures. The wide variety of cratered, mountainous and glacial terrains seen here gives scientists and the public alike a breathtaking, super-high-resolution color window into Pluto's geology. e border between the relatively smooth Sputnik Planum ice sheet and the pitted area, with a series of hills forming slightly inside this unusual "shoreline." http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20213
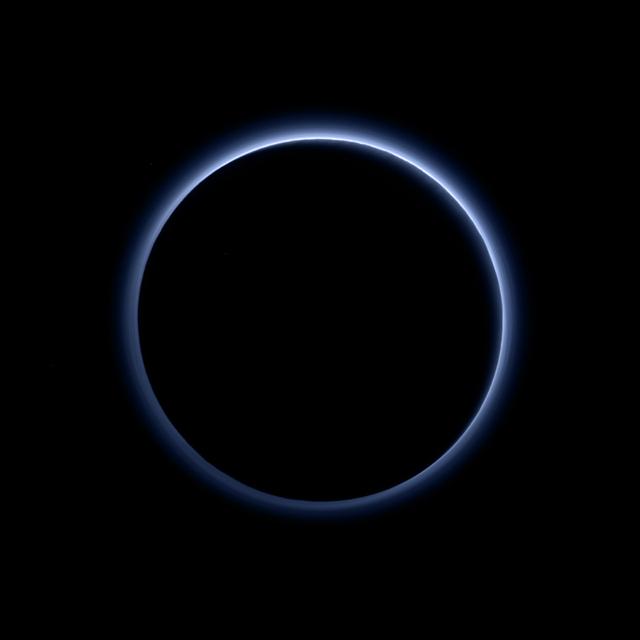

Pluto’s Blue Sky: Pluto’s haze layer shows its blue color in this picture taken by the New Horizons Ralph/Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC). The high-altitude haze is thought to be similar in nature to that seen at Saturn’s moon Titan. The source of both hazes likely involves sunlight-initiated chemical reactions of nitrogen and methane, leading to relatively small, soot-like particles (called tholins) that grow as they settle toward the surface. This image was generated by software that combines information from blue, red and near-infrared images to replicate the color a human eye would perceive as closely as possible. Credits: NASA/JHUAPL/SwRI Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/nh/nh-finds-blue-skies-and-water-ice-on-pluto" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/nh/nh-finds-blue-skies-and-water-ice-on-pluto</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
On July 14, 2015, NASA's New Horizons spacecraft made its historic flight through the Pluto system. This detailed, high-quality global mosaic of Pluto was assembled from nearly all of the highest-resolution images obtained by the Long-Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) and the Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) on New Horizons. The mosaic is the most detailed and comprehensive global view yet of Pluto's surface using New Horizons data. It includes topography data of the hemisphere visible to New Horizons during the spacecraft's closest approach. The topography is derived from digital stereo-image mapping tools that measure the parallax -- or the difference in the apparent relative positions -- of features on the surface obtained at different viewing angles during the encounter. Scientists use these parallax displacements of high and low terrain to estimate landform heights. The global mosaic has been overlain with transparent, colorized topography data wherever on the surface stereo data is available. Terrain south of about 30°S was in darkness leading up to and during the flyby, so is shown in black. Examples of large-scale topographic features on Pluto include the vast expanse of very flat, low-elevation nitrogen ice plains of Sputnik Planitia ("P") -- note that all feature names in the Pluto system are informal -- and, on the eastern edge of the encounter hemisphere, the aligned, high-elevation ridges of Tartarus Dorsa ("T") that host the enigmatic bladed terrain, mountains, possible cryovolcanos, canyons, craters and more. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21861
This area is south of Pluto's dark equatorial band informally named Cthulhu Regio, and southwest of the vast nitrogen ice plains informally named Sputnik Planitia. North is at the top; in the western portion of the image, a chain of bright mountains extends north into Cthulhu Regio. New Horizons compositional data indicate the bright snowcap material covering these mountains isn't water, but atmospheric methane that has condensed as frost onto these surfaces at high elevation. Between some mountains are sharply cut valleysindicated by the white arrows. These valleys are each a few miles across and tens of miles long. A similar valley system in the expansive plains to the east (blue arrows) appears to be branched, with smaller valleys leading into it. New Horizons scientists think flowing nitrogen ice that once covered this area -- perhaps when the ice in Sputnik was at a higher elevation -- may have formed these valleys. The area is also marked by irregularly shaped, flat-floored depressions (green arrows) that can reach more than 50 miles (80 kilometers) across and almost 2 miles (3 kilometers) deep. The great widths and depths of these depressions suggest that they may have formed when the surface collapsed, rather than through the sublimation of ice into the atmosphere. This enhanced color image was obtained by New Horizons' Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC). The image resolution is approximately 2,230 feet (680 meters) per pixel. It was obtained at a range of approximately 21,100 miles (33,900 kilometers) from Pluto, about 45 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21026
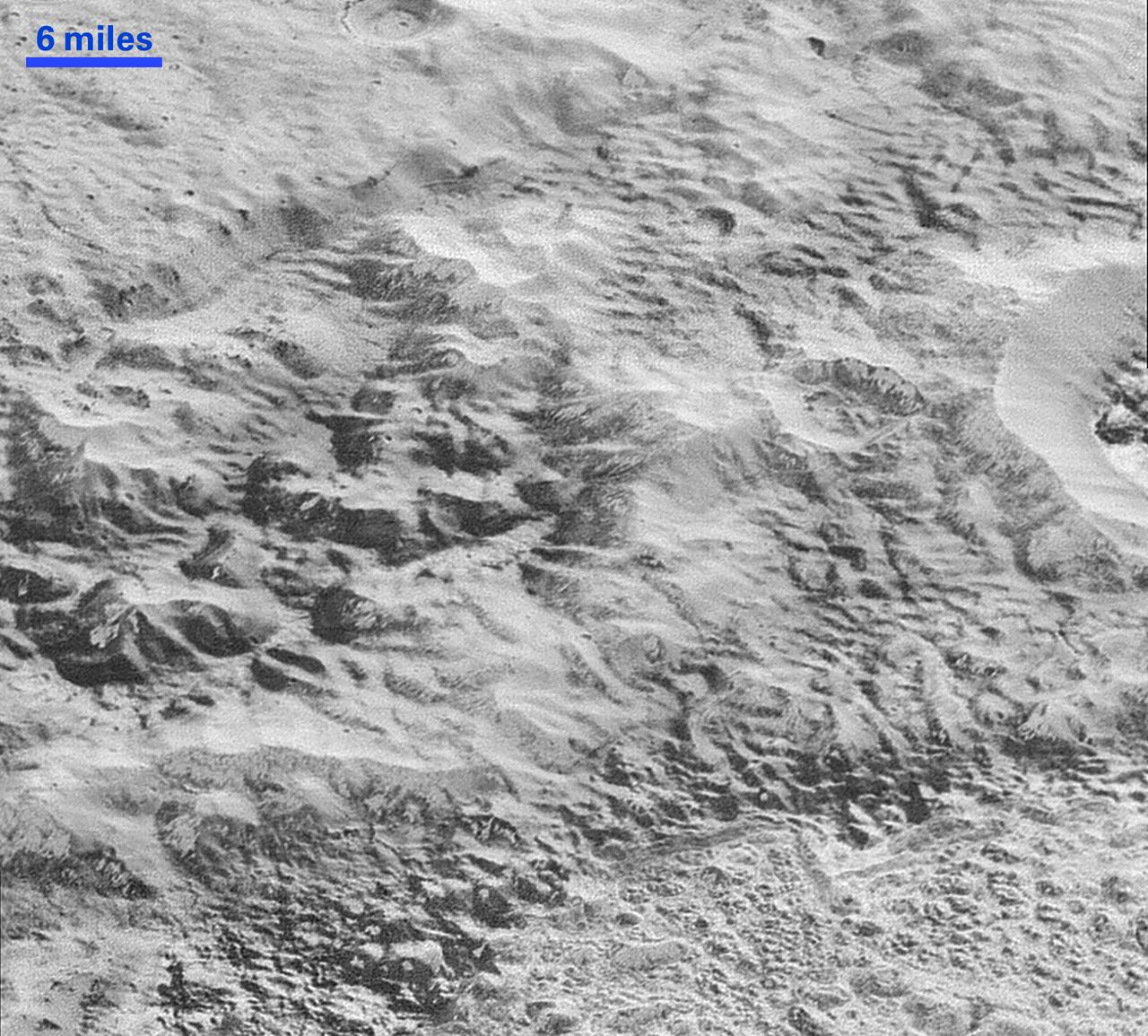

This highest-resolution image from NASA's New Horizons spacecraft shows how erosion and faulting has sculpted this portion of Pluto's icy crust into rugged badlands. The prominent 1.2-mile-high cliff at the top, running from left to upper right, is part of a great canyon system that stretches for hundreds of miles across Pluto's northern hemisphere. New Horizons team members think that the mountains in the middle are made of water ice, but have been modified by the movement of nitrogen or other exotic ice glaciers over long periods of time, resulting in a muted landscape of rounded peaks and intervening sets of short ridges. At the bottom of this 50-mile-wide image, the terrain transforms dramatically into a fractured and finely broken up floor at the northwest margin of the giant ice plain informally called Sputnik Planum. The top of the image is to Pluto's northwest. These images were made with the telescopic Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) aboard New Horizons, in a timespan of about a minute centered on 11:36 UT on July 14 -- just about 15 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto -- from a range of just 10,000 miles (17,000 kilometers). They were obtained with an unusual observing mode; instead of working in the usual "point and shoot," LORRI snapped pictures every three seconds while the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC) aboard New Horizons was scanning the surface. This mode requires unusually short exposures to avoid blurring the images. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20199
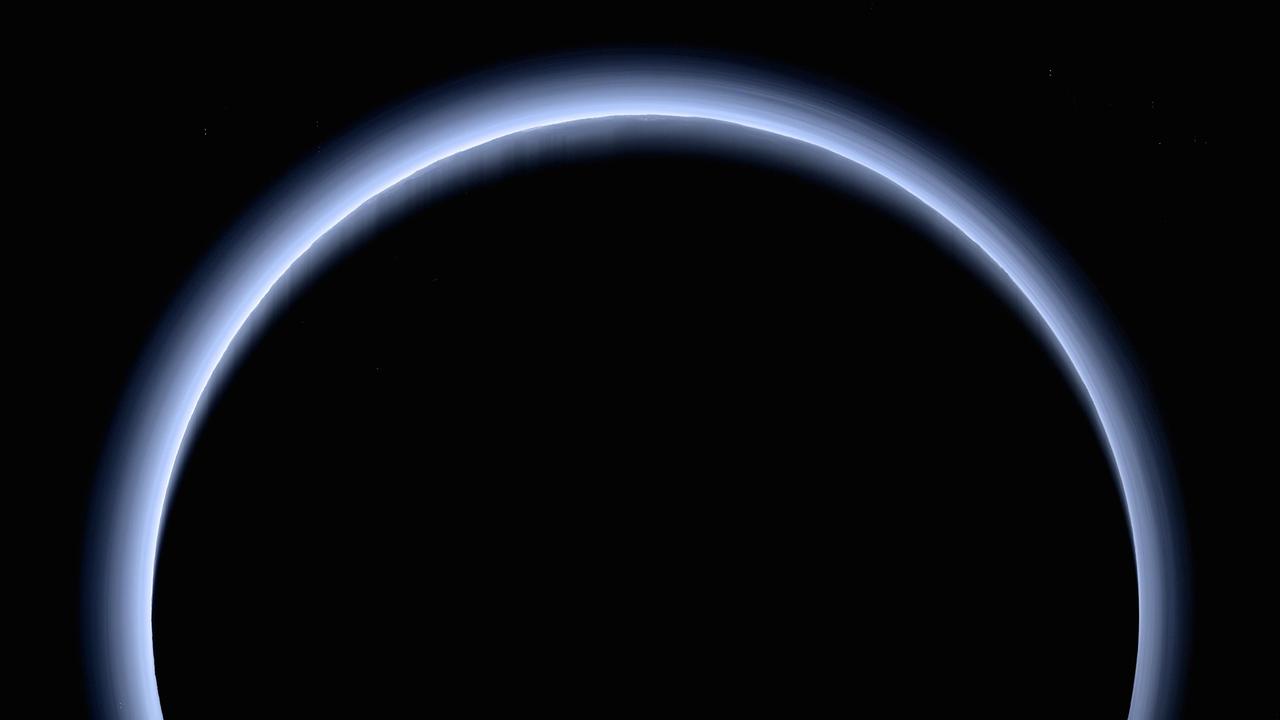

This is the highest-resolution color departure shot of Pluto's receding crescent from NASA's New Horizons spacecraft, taken when the spacecraft was 120,000 miles (200,000 kilometers) away from Pluto. Shown in approximate true color, the picture was constructed from a mosaic of six black-and-white images from the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI), with color added from a lower resolution Ralph/Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) color image, all acquired between 15:20 and 15:45 UT -- about 3.5 hours after closest approach to Pluto -- on July 14, 2015. The resolution of the LORRI images is about 0.6 miles (1 kilometer) per pixel; the sun illuminates the scene from the other side of Pluto and somewhat toward the top of this image. The image is dominated by spectacular layers of blue haze in Pluto's atmosphere. Scientists believe the haze is a photochemical smog resulting from the action of sunlight on methane and other molecules in Pluto's atmosphere, producing a complex mixture of hydrocarbons such as acetylene and ethylene. These hydrocarbons accumulate into small haze particles, a fraction of a micrometer in size, which preferentially scatter blue sunlight -- the same process that can make haze appear bluish on Earth. As they settle down through the atmosphere, the haze particles form numerous intricate, horizontal layers, some extending for hundreds of miles around large portions of the limb of Pluto. The haze layers extend to altitudes of over 120 miles (200 kilometers). Pluto's circumference is 4,667 miles (7,466 kilometers). Adding to the beauty of this picture are mountains and other topographic features on Pluto's surface that are silhouetted against the haze near the top of the image. Sunlight casts dramatic and beautiful finger-like shadows from many of these features onto the haze (especially on the left, near the 11 o'clock position), forming crepuscular rays like those often seen in Earth's atmosphere near sunrise or sunset. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21590

This frame from a movie is composed of the sharpest views of Pluto that NASA's New Horizons spacecraft obtained during its flyby of the distant planet on July 14, 2015. The pictures are part of a sequence taken near New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto, with resolutions of about 250-280 feet (77-85 meters) per pixel -- revealing features smaller than half a city block on Pluto's diverse surface. The images include a wide variety of spectacular, cratered, mountainous and glacial terrains -- giving scientists and the public alike a breathtaking, super-high resolution window on Pluto's geology. The images form a strip 50 miles (80 kilometers) wide trending from Pluto's jagged horizon about 500 miles (800 kilometers) northwest of the informally named Sputnik Planum, across the al-Idrisi mountains, onto the shoreline of Sputnik Planum and then across its icy plains. They were made with the telescopic Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) aboard New Horizons, over a timespan of about a minute centered on 11:36 UT on July 14 -- just about 15 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto -- from a range of just 10,000 miles (17,000 kilometers). They were obtained with an unusual observing mode; instead of working in the usual "point and shoot," LORRI snapped pictures every three seconds while the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC) aboard New Horizons was scanning the surface. This mode requires unusually short exposures to avoid blurring the images. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20202
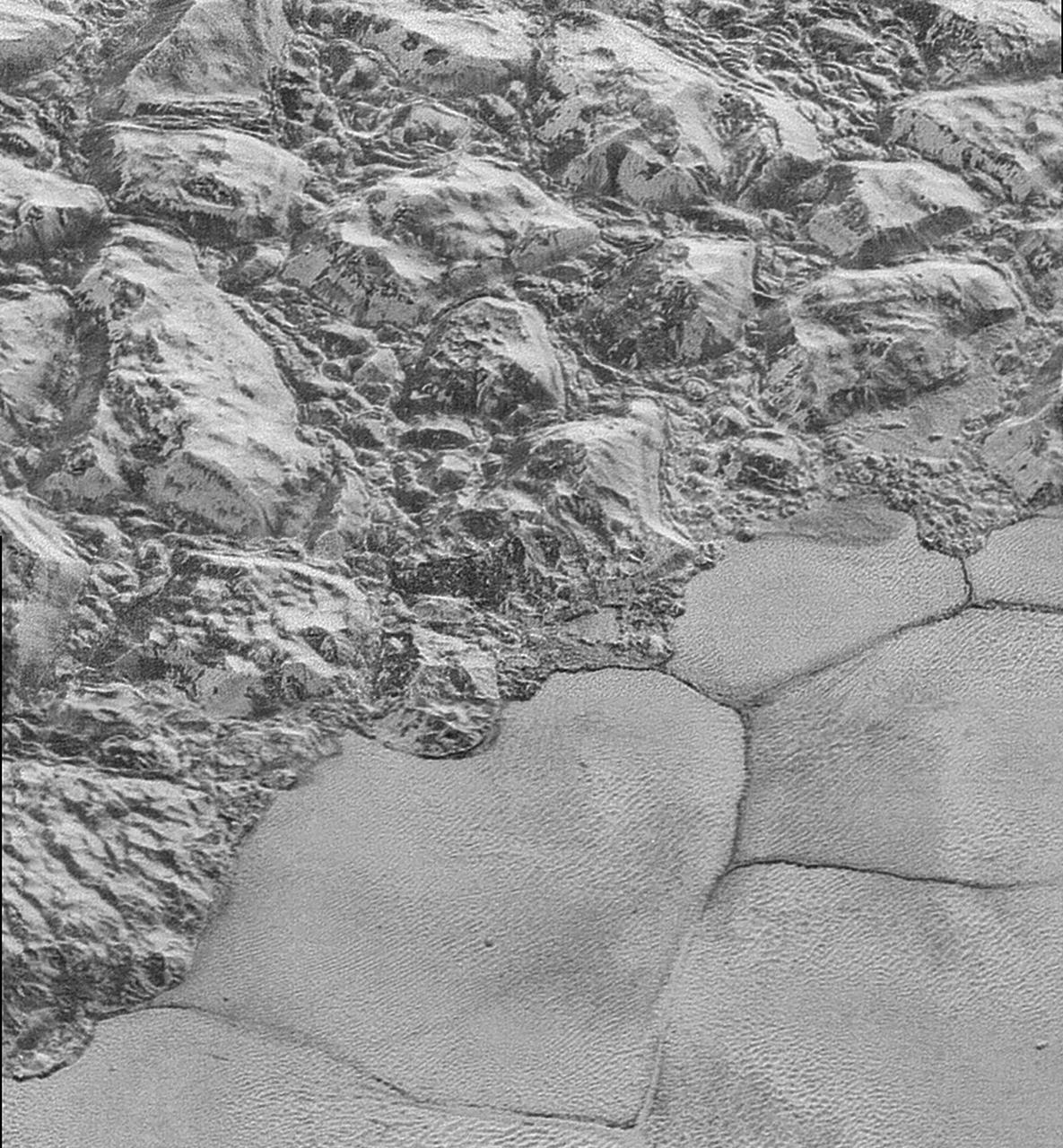

In this highest-resolution image from NASA's New Horizons spacecraft, great blocks of Pluto's water-ice crust appear jammed together in the informally named al-Idrisi mountains. Some mountain sides appear coated in dark material, while other sides are bright. Several sheer faces appear to show crustal layering, perhaps related to the layers seen in some of Pluto's crater walls. Other materials appear crushed between the mountains, as if these great blocks of water ice, some standing as much as 1.5 miles high, were jostled back and forth. The mountains end abruptly at the shoreline of the informally named Sputnik Planum, where the soft, nitrogen-rich ices of the plain form a nearly level surface, broken only by the fine trace work of striking, cellular boundaries and the textured surface of the plain's ices (which is possibly related to sunlight-driven ice sublimation). This view is about 50 miles wide. The top of the image is to Pluto's northwest. These images were made with the telescopic Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) aboard New Horizons, in a timespan of about a minute centered on 11:36 UT on July 14 -- just about 15 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto -- from a range of just 10,000 miles (17,000 kilometers). They were obtained with an unusual observing mode; instead of working in the usual "point and shoot," LORRI snapped pictures every three seconds while the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC) aboard New Horizons was scanning the surface. This mode requires unusually short exposures to avoid blurring the images. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20198
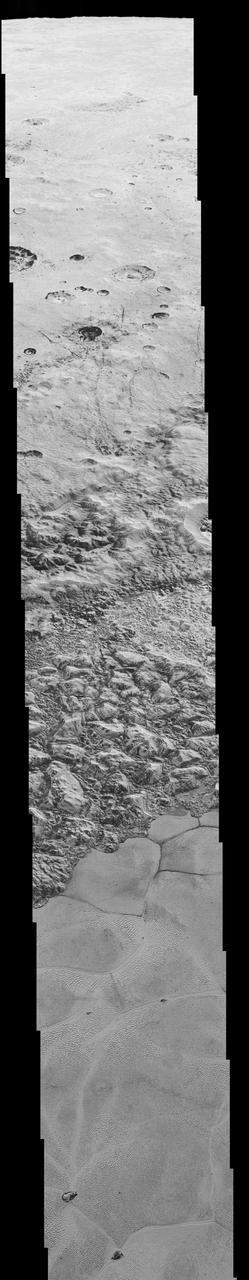
This mosaic is composed of the sharpest views of Pluto that NASA's New Horizons spacecraft obtained during its flyby of the distant planet on July 14, 2015. The pictures are part of a sequence taken near New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto, with resolutions of about 250-280 feet (77-85 meters) per pixel -- revealing features smaller than half a city block on Pluto's diverse surface. The images include a wide variety of spectacular, cratered, mountainous and glacial terrains -- giving scientists and the public alike a breathtaking, super-high resolution window on Pluto's geology. The images form a strip 50 miles (80 kilometers) wide trending from Pluto's jagged horizon about 500 miles (800 kilometers) northwest of the informally named Sputnik Planum, across the al-Idrisi mountains, onto the shoreline of Sputnik Planum and then across its icy plains. They were made with the telescopic Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) aboard New Horizons, over a timespan of about a minute centered on 11:36 UT on July 14 -- just about 15 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto -- from a range of just 10,000 miles (17,000 kilometers). They were obtained with an unusual observing mode; instead of working in the usual "point and shoot," LORRI snapped pictures every three seconds while the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC) aboard New Horizons was scanning the surface. This mode requires unusually short exposures to avoid blurring the images. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20201
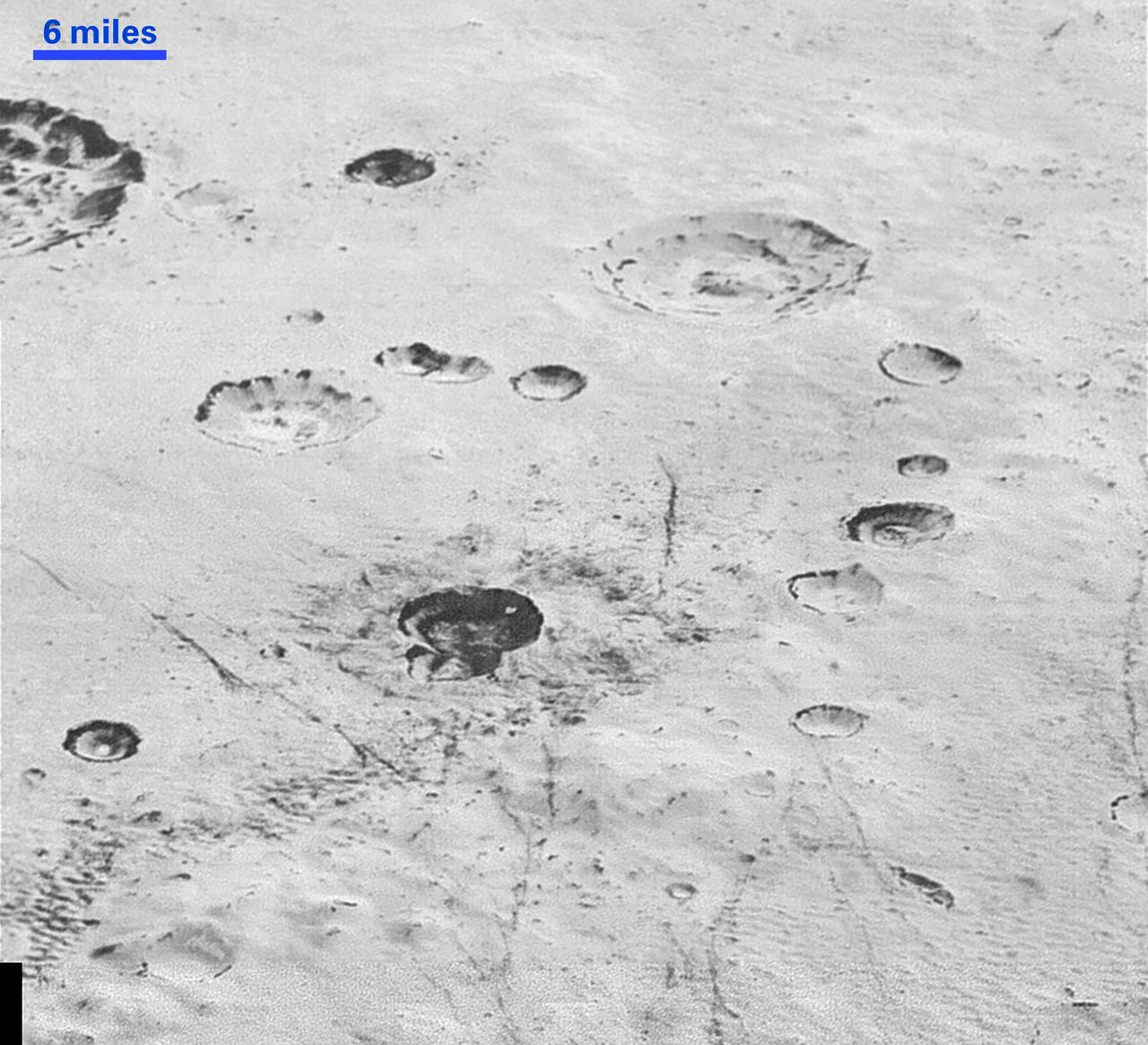

This highest-resolution image from NASA's New Horizons spacecraft reveals new details of Pluto's rugged, icy cratered plains. Notice the layering in the interior walls of many craters (the large crater at upper right is a good example) -- layers in geology usually mean an important change in composition or event but at the moment New Horizons team members do not know if they are seeing local, regional or global layering. The darker crater in the lower center is apparently younger than the others, because dark material ejected from within -- its "ejecta blanket" -- have not been erased and can still be made out. The origin of the many dark linear features trending roughly vertically in the bottom half of the image is under debate, but may be tectonic. Most of the craters seen here lie within the 155-mile (250-kilometer)-wide Burney Basin, whose outer rim or ring forms the line of hills or low mountains at bottom. The basin is informally named after Venetia Burney, the English schoolgirl who first proposed the name "Pluto" for the newly discovered planet in 1930. The top of the image is to Pluto's northwest. These images were made with the telescopic Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) aboard New Horizons, in a timespan of about a minute centered on 11:36 UT on July 14 -- just about 15 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto-- from a range of just 10,000 miles (17,000 kilometers). They were obtained with an unusual observing mode; instead of working in the usual "point and shoot," LORRI snapped pictures every three seconds while the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC) aboard New Horizons was scanning the surface. This mode requires unusually short exposures to avoid blurring the images. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20200
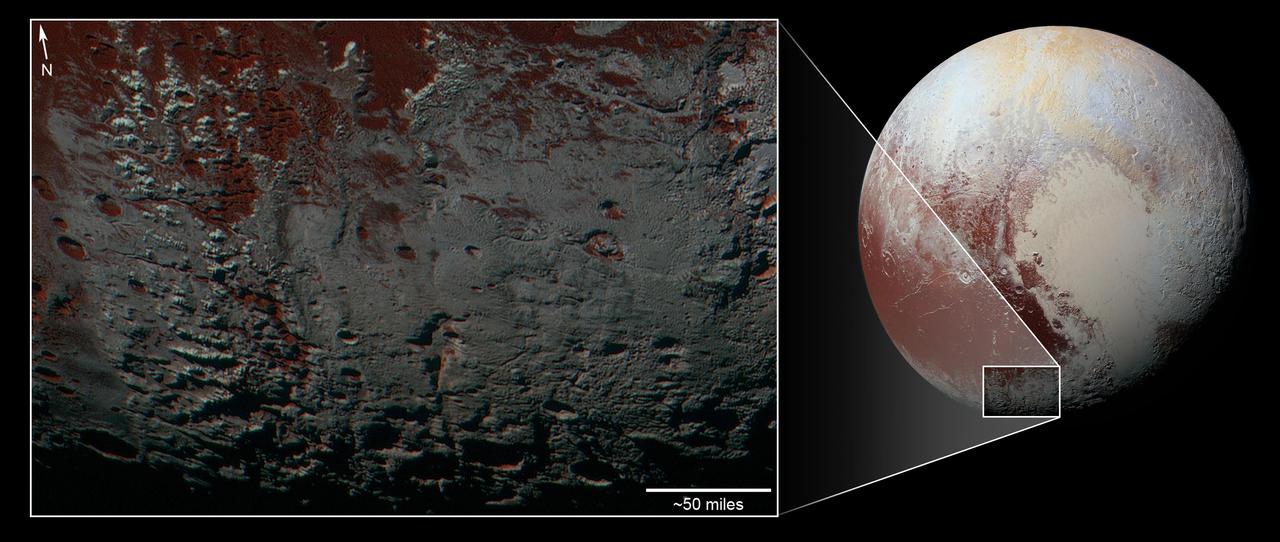

This area is south of Pluto's dark equatorial band informally named Cthulhu Regio, and southwest of the vast nitrogen ice plains informally named Sputnik Planitia. North is at the top; in the western portion of the image, a chain of bright mountains extends north into Cthulhu Regio. New Horizons compositional data indicate the bright snowcap material covering these mountains isn't water, but atmospheric methane that has condensed as frost onto these surfaces at high elevation. Between some mountains are sharply cut valleys -- indicated by the white arrows. These valleys are each a few miles across and tens of miles long. A similar valley system in the expansive plains to the east (blue arrows) appears to be branched, with smaller valleys leading into it. New Horizons scientists think flowing nitrogen ice that once covered this area -- perhaps when the ice in Sputnik was at a higher elevation -- may have formed these valleys. The area is also marked by irregularly shaped, flat-floored depressions (green arrows) that can reach more than 50 miles (80 kilometers) across and almost 2 miles (3 kilometers) deep. The great widths and depths of these depressions suggest that they may have formed when the surface collapsed, rather than through the sublimation of ice into the atmosphere. This enhanced color image was obtained by New Horizons' Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC). The image resolution is approximately 2,230 feet (680 meters) per pixel. It was obtained at a range of approximately 21,100 miles (33,900 kilometers) from Pluto, about 45 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21025
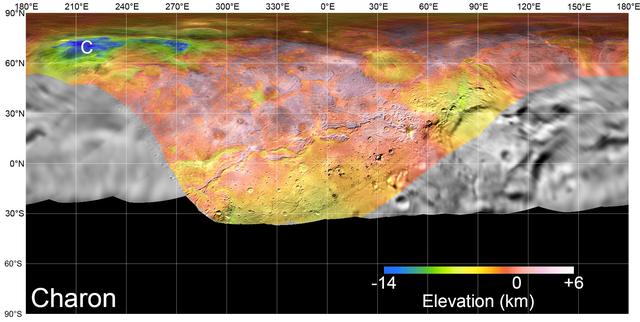
On July 14, 2015, NASA's New Horizons spacecraft made its historic flight through the Pluto system. This detailed, high-quality global mosaic of Pluto's largest moon, Charon, was assembled from nearly all of the highest-resolution images obtained by the Long-Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) and the Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) on New Horizons. The mosaic is the most detailed and comprehensive global view yet of Charon's surface using New Horizons data. It includes topography data of the hemisphere visible to New Horizons during the spacecraft's closest approach. The topography is derived from digital stereo-image mapping tools that measure the parallax -- or the difference in the apparent relative positions -- of features on the surface obtained at different viewing angles during the encounter. Scientists use these parallax displacements of high and low terrain to estimate landform heights. The global mosaic has been overlain with transparent, colorized topography data wherever on the surface stereo data is available. Terrain south of about 30°S was in darkness leading up to and during the flyby, so is shown in black. All feature names on Pluto and Charon are informal. The global mosaic has been overlain with transparent, colorized topography data wherever on their surfaces stereo data is available. Standing out on Charon is the Caleuche Chasma ("C") in the far north, an enormous trough at least 350 kilometers (nearly 220 miles) long, and reaching 14 kilometers (8.5 miles) deep -- more than seven times as deep as the Grand Canyon. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21860

This enhanced color view from NASA's New Horizons spacecraft zooms in on the southeastern portion of Pluto's great ice plains, where at lower right the plains border rugged, dark highlands informally named Krun Macula. Krun Macula -- Krun is the lord of the underworld in the Mandaean religion, and a macula is a dark feature on a planetary surface -- is believed to get its dark red color from tholins, complex molecules found across Pluto. Krun Macula rises 1.5 miles (2.5 kilometers) above the surrounding plain -- informally named Sputnik Planum -- and is scarred by clusters of connected, roughly circular pits that typically reach between 5 and 8 miles (8 and 13 kilometers) across, and up to 1.5 miles (2.5 kilometers) deep. At the boundary with Sputnik Planum, these pits form deep valleys reaching more than 25 miles (40 kilometers) long, 12.5 miles (20 kilometers) wide and almost 2 miles (3 kilometers) deep (almost twice as deep as the Grand Canyon in Arizona), and have floors covered with nitrogen ice. New Horizons scientists think these pits may have formed through surface collapse, although what may have prompted such a collapse is a mystery. This scene was created using three separate observations made by New Horizons in July 2015. The right half of the image is composed of 260 feet- (80 meter-) per-pixel data from the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI), obtained at 9,850 miles (15,850 kilometers) from Pluto, about 23 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach. The left half is composed of 410 feet- (125 meter-) per-pixel LORRI data, obtained about six minutes earlier, with New Horizons 15,470 miles (24,900 kilometers) from Pluto. These data respectively represent portions of the highest- and second-highest-resolution observations obtained by New Horizons in the Pluto system. The entire scene was then colorized using 2230 feet- (680 meter-) per-pixel data from New Horizons' Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC), obtained at 21,100 miles (33,900 kilometers) from Pluto, about 45 minutes before closest approach. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20733

This enhanced color view from NASA's New Horizons spacecraft zooms in on the southeastern portion of Pluto's great ice plains, where at lower right the plains border rugged, dark highlands informally named Krun Macula. Krun Macula -- Krun is the lord of the underworld in the Mandaean religion, and a macula is a dark feature on a planetary surface -- is believed to get its dark red color from tholins, complex molecules found across Pluto. Krun Macula rises 1.5 miles (2.5 kilometers) above the surrounding plain -- informally named Sputnik Planum -- and is scarred by clusters of connected, roughly circular pits that typically reach between 5 and 8 miles (8 and 13 kilometers) across, and up to 1.5 miles (2.5 kilometers) deep. At the boundary with Sputnik Planum, these pits form deep valleys reaching more than 25 miles (40 kilometers) long, 12.5 miles (20 kilometers) wide and almost 2 miles (3 kilometers) deep (almost twice as deep as the Grand Canyon in Arizona), and have floors covered with nitrogen ice. New Horizons scientists think these pits may have formed through surface collapse, although what may have prompted such a collapse is a mystery. This scene was created using three separate observations made by New Horizons in July 2015. The right half of the image is composed of 260 feet- (80 meter-) per-pixel data from the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI), obtained at 9,850 miles (15,850 kilometers) from Pluto, about 23 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach. The left half is composed of 410 feet- (125 meter-) per-pixel LORRI data, obtained about six minutes earlier, with New Horizons 15,470 miles (24,900 kilometers) from Pluto. These data respectively represent portions of the highest- and second-highest-resolution observations obtained by New Horizons in the Pluto system. The entire scene was then colorized using 2230 feet- (680 meter-) per-pixel data from New Horizons' Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC), obtained at 21,100 miles (33,900 kilometers) from Pluto, about 45 minutes before closest approach. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20732

NASA's New Horizons spacecraft took this stunning image of Pluto only a few minutes after closest approach on July 14, 2015. The image was obtained at a high phase angle -- that is, with the sun on the other side of Pluto, as viewed by New Horizons. Seen here, sunlight filters through and illuminates Pluto's complex atmospheric haze layers. The southern portions of the nitrogen ice plains informally named Sputnik Planum, as well as mountains of the informally named Norgay Montes, can also be seen across Pluto's crescent at the top of the image. Looking back at Pluto with images like this gives New Horizons scientists information about Pluto's hazes and surface properties that they can't get from images taken on approach. The image was obtained by New Horizons' Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC) approximately 13,400 miles (21,550 kilometers) from Pluto, about 19 minutes after New Horizons' closest approach. The image has a resolution of 1,400 feet (430 meters) per pixel. Pluto's diameter is 1,475 miles (2,374 kilometers). The inset at top right in the annotated version shows a detail of Pluto's crescent, including an intriguing bright wisp (near the center) measuring tens of miles across that may be a discreet, low-lying cloud in Pluto's atmosphere; if so, it would be the only one yet identified in New Horizons imagery. This cloud -- if that's what it is -- is visible for the same reason the haze layers are so bright: illumination from the sunlight grazing Pluto's surface at a low angle. Atmospheric models suggest that methane clouds can occasionally form in Pluto's atmosphere. The scene in this inset is 140 miles (230 kilometers) across. The inset at bottom right shows more detail on the night side of Pluto. This terrain can be seen because it is illuminated from behind by hazes that silhouette the of the annotated version limb. The topography here appears quite rugged, and broad valleys and sharp peaks with relief totaling 3 miles (5 kilometers) are apparent. This image, made from closer range, is much better than the lower-resolution images of this same terrain taken several days before closest approach. These silhouetted terrains therefore act as a useful "anchor point," giving New Horizons scientists a rare, detailed glimpse at the lay of the land in this mysterious part of Pluto seen at high resolution only in twilight. The scene in this inset is 460 miles (750 kilometers) wide. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20727