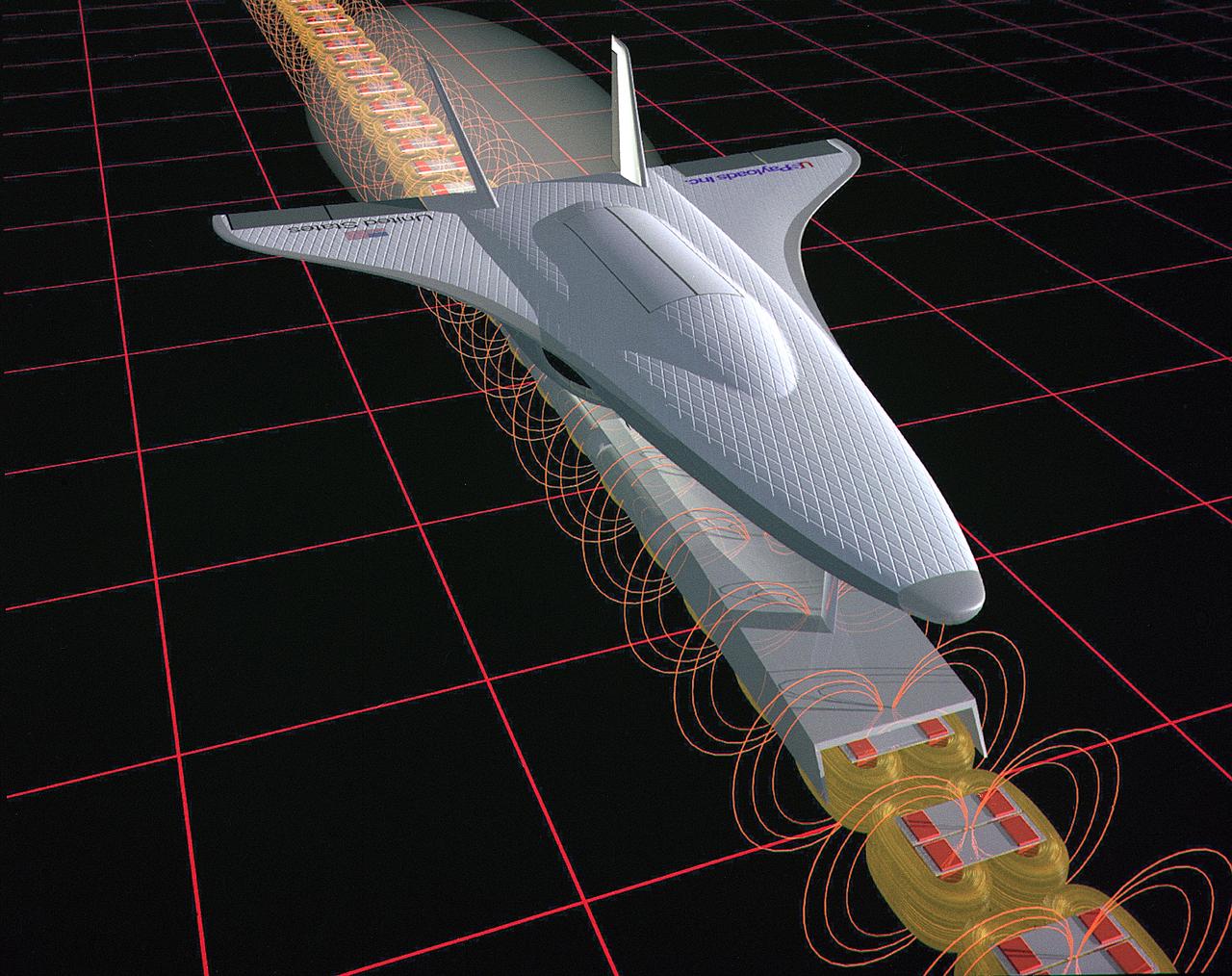
This illustration is an artist’s concept of a Magnetic Launch Assist System, formerly referred as the Magnetic Levitation (Maglev) system, for space launch. Overcoming the grip of Earth’s gravity is a supreme challenge for engineers who design rockets that leave the planet. Engineers at the Marshall Space Flight Center have developed and tested Magnetic Launch Assist System technologies that could levitate and accelerate a launch vehicle along a track at high speeds before it leaves the ground. Using electricity and magnetic fields, a Magnetic Launch Assist system would drive a spacecraft along a horizontal track until it reaches desired speeds. A full-scale, operational track would be about 1.5-miles long and capable of accelerating a vehicle to 600 mph in 9.5 seconds. The major advantages of launch assist for NASA launch vehicles is that it reduces the weight of the take-off, landing gear and the wing size, as well as the elimination of propellant weight resulting in significant cost savings. The US Navy and the British MOD (Ministry of Defense) are planning to use magnetic launch assist for their next generation aircraft carriers as the aircraft launch system. The US Army is considering using this technology for launching target drones for anti-aircraft training.
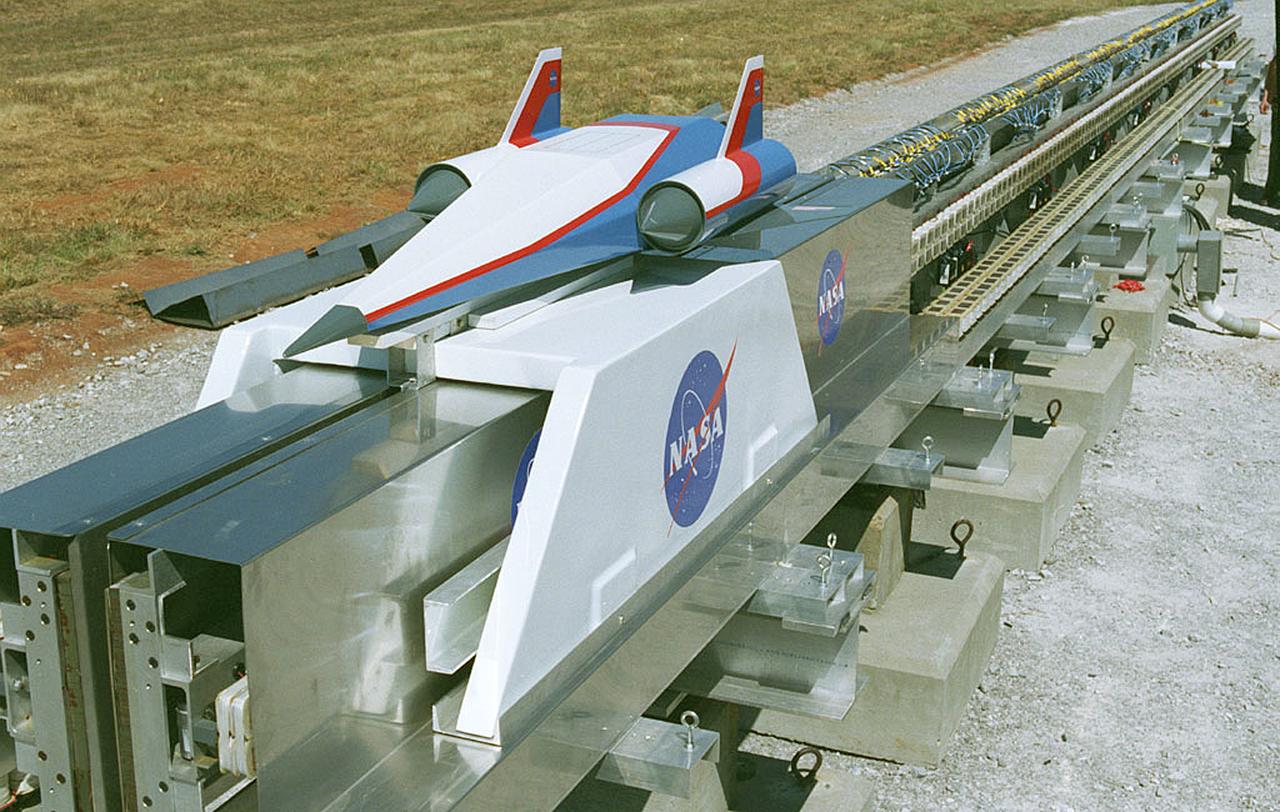

In this photograph, a futuristic spacecraft model sits atop a carrier on the Magnetic Launch Assist System, formerly known as the Magnetic Levitation (MagLev) System, experimental track at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Engineers at MSFC have developed and tested Magnetic Launch Assist technologies that would use magnetic fields to levitate and accelerate a vehicle along a track at very high speeds. Similar to high-speed trains and roller coasters that use high-strength magnets to lift and propel a vehicle a couple of inches above a guideway, a Magnetic Launch Assist system would electromagnetically drive a space vehicle along the track. A full-scale, operational track would be about 1.5-miles long and capable of accelerating a vehicle to 600 mph in 9.5 seconds. This track is an advanced linear induction motor. Induction motors are common in fans, power drills, and sewing machines. Instead of spinning in a circular motion to turn a shaft or gears, a linear induction motor produces thrust in a straight line. Mounted on concrete pedestals, the track is 100-feet long, about 2-feet wide, and about 1.5-feet high. The major advantages of launch assist for NASA launch vehicles is that it reduces the weight of the take-off, the landing gear, the wing size, and less propellant resulting in significant cost savings. The US Navy and the British MOD (Ministry of Defense) are planning to use magnetic launch assist for their next generation aircraft carriers as the aircraft launch system. The US Army is considering using this technology for launching target drones for anti-aircraft training.
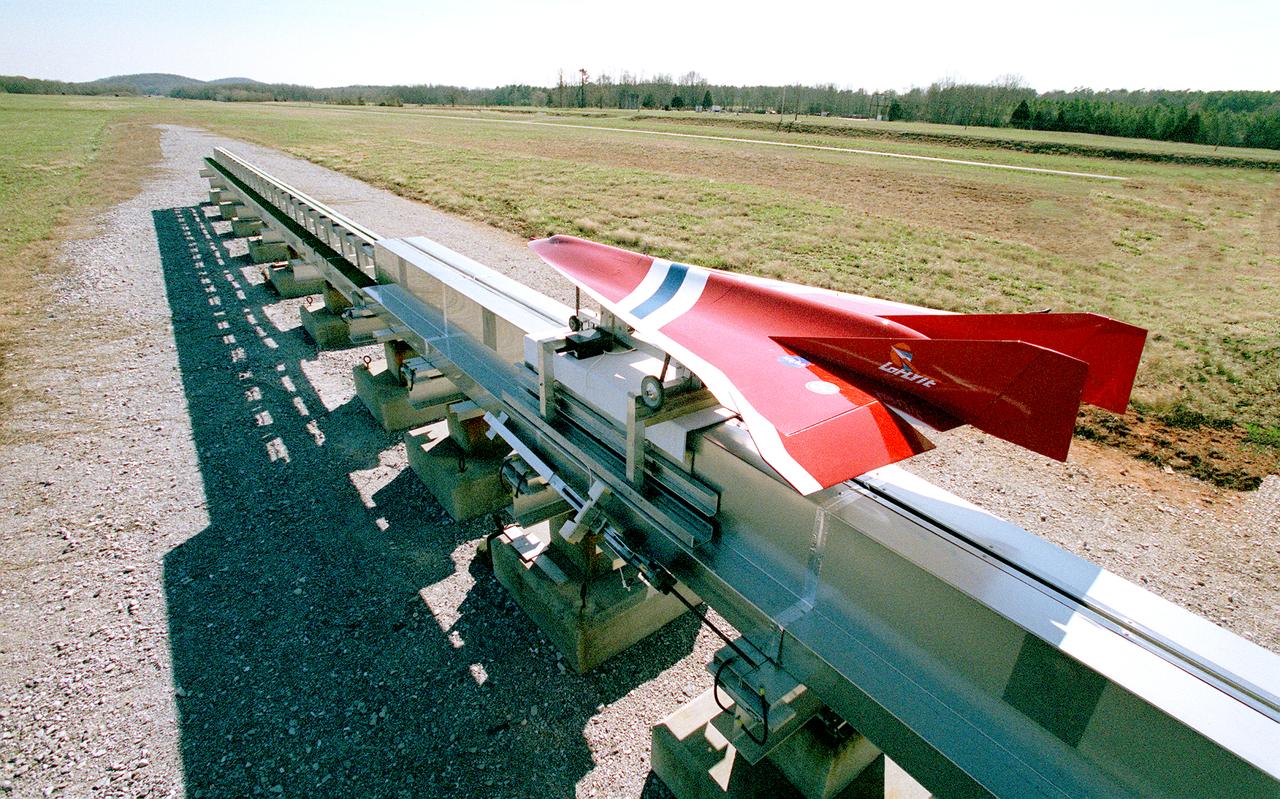

Engineers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) have been testing Magnetic Launch Assist Systems, formerly known as Magnetic Levitation (MagLev) technologies. To launch spacecraft into orbit, a Magnetic Launch Assist system would use magnetic fields to levitate and accelerate a vehicle along a track at a very high speed. Similar to high-speed trains and roller coasters that use high-strength magnets to lift and propel a vehicle a couple of inches above a guideway, the launch-assist system would electromagnetically drive a space vehicle along the track. A full-scale, operational track would be about 1.5-miles long and capable of accelerating a vehicle to 600 mph in 9.5 seconds. This photograph shows a subscale model of an airplane running on the experimental track at MSFC during the demonstration test. This track is an advanced linear induction motor. Induction motors are common in fans, power drills, and sewing machines. Instead of spinning in a circular motion to turn a shaft or gears, a linear induction motor produces thrust in a straight line. Mounted on concrete pedestals, the track is 100-feet long, about 2-feet wide, and about 1.5- feet high. The major advantages of launch assist for NASA launch vehicles is that it reduces the weight of the take-off, the landing gear, the wing size, and less propellant resulting in significant cost savings. The US Navy and the British MOD (Ministry of Defense) are planning to use magnetic launch assist for their next generation aircraft carriers as the aircraft launch system. The US Army is considering using this technology for launching target drones for anti-aircraft training.
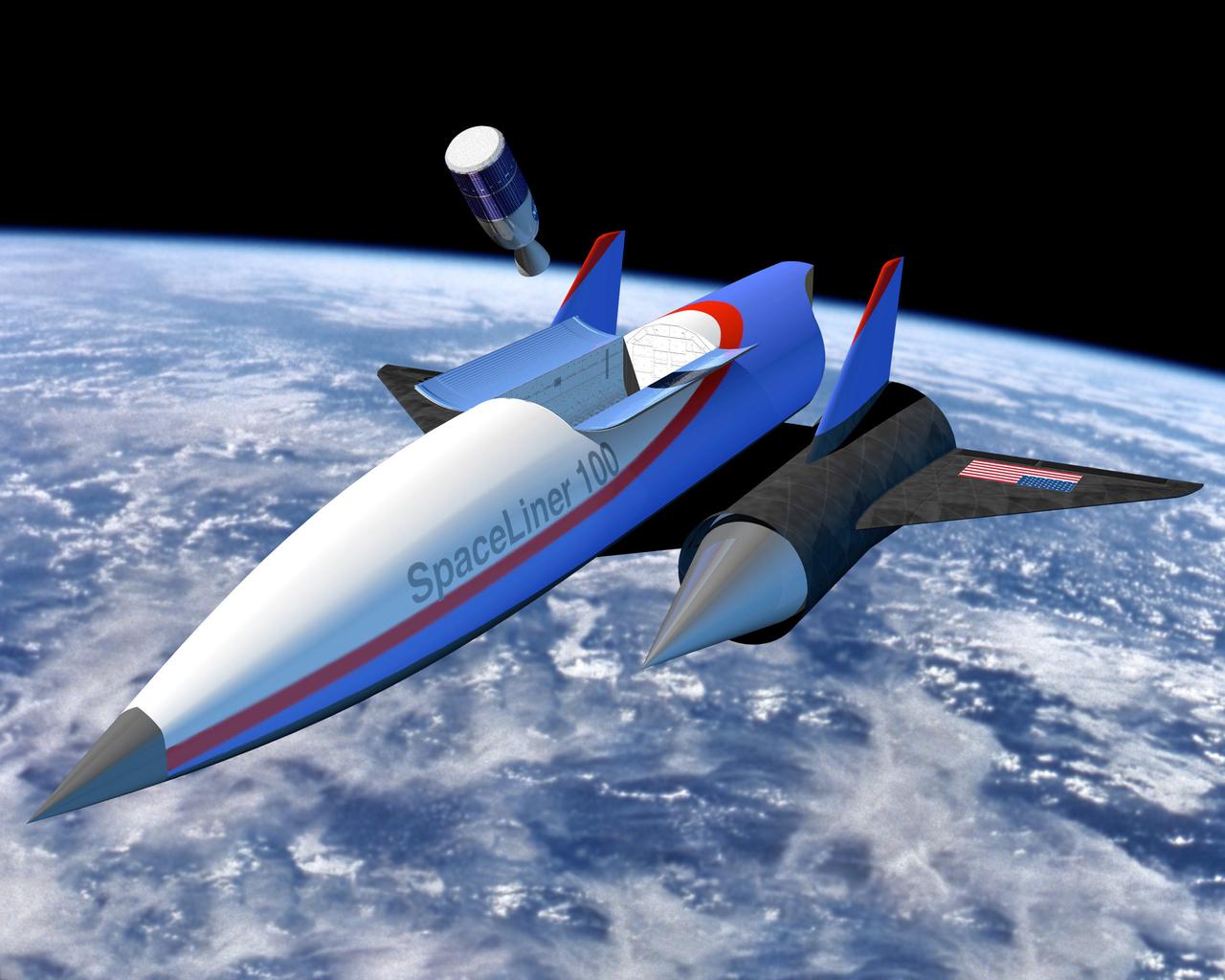

This artist’s concept depicts a Magnetic Launch Assist vehicle in orbit. Formerly referred to as the Magnetic Levitation (Maglev) system, the Magnetic Launch Assist system is a launch system developed and tested by engineers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) that could levitate and accelerate a launch vehicle along a track at high speeds before it leaves the ground. Using electricity and magnetic fields, a Magnetic Launch Assist system would drive a spacecraft along a horizontal track until it reaches desired speeds. The system is similar to high-speed trains and roller coasters that use high-strength magnets to lift and propel a vehicle a couple of inches above a guideway. A full-scale, operational track would be about 1.5-miles long, capable of accelerating a vehicle to 600 mph in 9.5 seconds, and the vehicle would then shift to rocket engines for launch into orbit. The major advantages of launch assist for NASA launch vehicles is that it reduces the weight of the take-off, the landing gear, the wing size, and less propellant resulting in significant cost savings. The US Navy and the British MOD (Ministry of Defense) are planning to use magnetic launch assist for their next generation aircraft carriers as the aircraft launch system. The US Army is considering using this technology for launching target drones for anti-aircraft training.
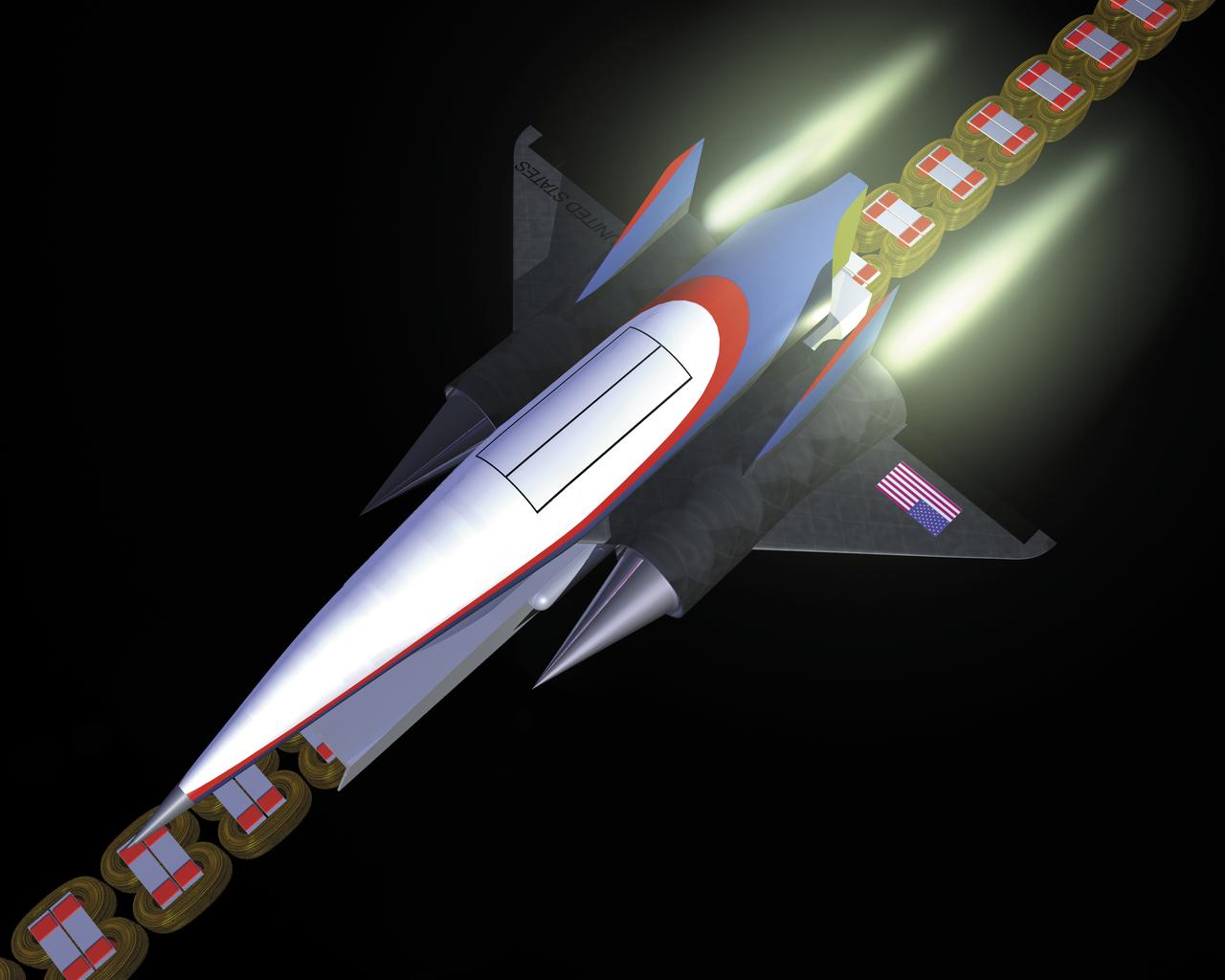

This artist’s concept depicts a Magnetic Launch Assist vehicle clearing the track and shifting to rocket engines for launch into orbit. The system, formerly referred as the Magnetic Levitation (MagLev) system, is a launch system developed and tested by Engineers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) that could levitate and accelerate a launch vehicle along a track at high speeds before it leaves the ground. Using an off-board electric energy source and magnetic fields, a Magnetic Launch Assist system would drive a spacecraft along a horizontal track until it reaches desired speeds. The system is similar to high-speed trains and roller coasters that use high-strength magnets to lift and propel a vehicle a couple of inches above a guideway. A full-scale, operational track would be about 1.5-miles long, capable of accelerating a vehicle to 600 mph in 9.5 seconds, and the vehicle would then shift to rocket engines for launch into orbit. The major advantages of launch assist for NASA launch vehicles is that it reduces the weight of the take-off, the landing gear, the wing size, and less propellant resulting in significant cost savings. The US Navy and the British MOD (Ministry of Defense) are planning to use magnetic launch assist for their next generation aircraft carriers as the aircraft launch system. The US Army is considering using this technology for launching target drones for anti-aircraft training.
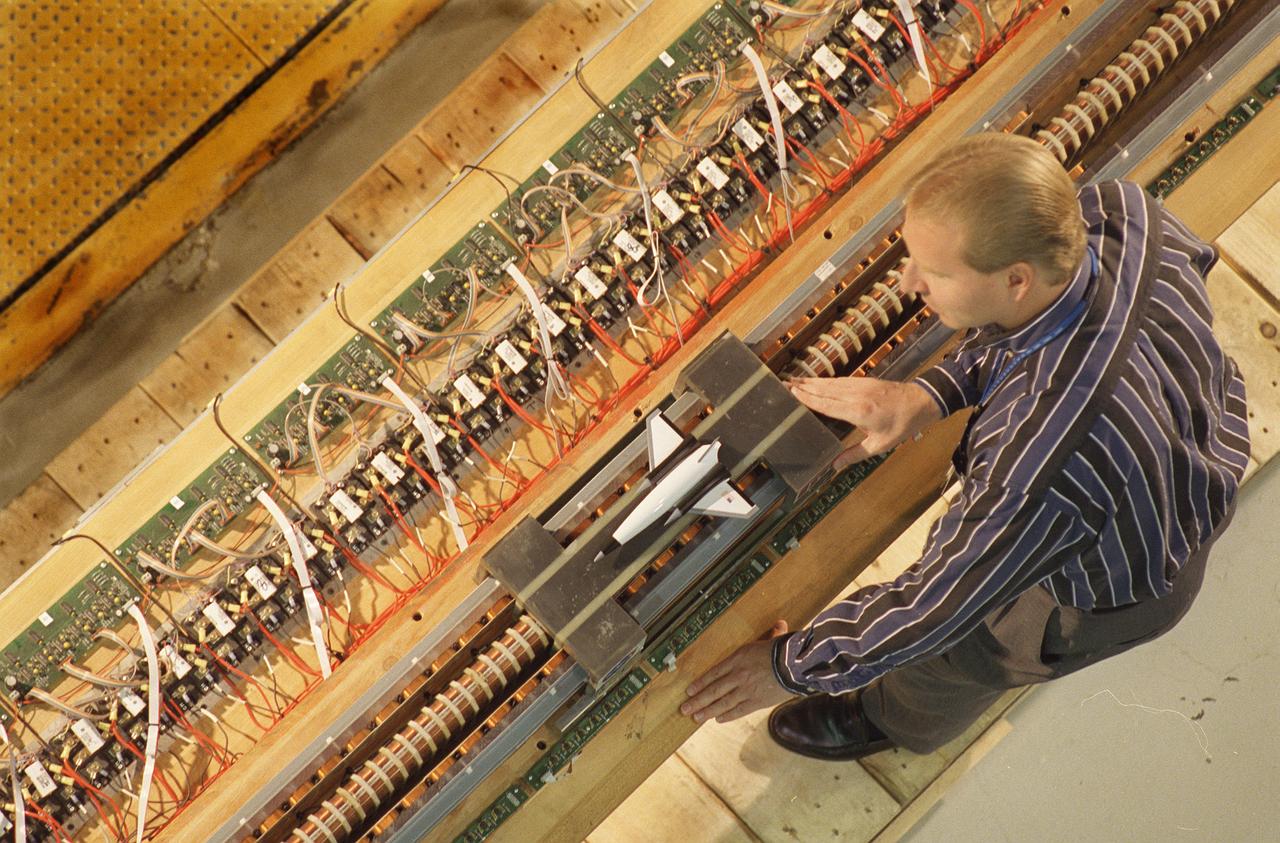

Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC’s) Advanced Space Transportation Program has developed the Magnetic Launch Assist System, formerly known as the Magnetic Levitation (MagLev) technology that could give a space vehicle a running start to break free from Earth’s gravity. A Magnetic Launch Assist system would use magnetic fields to levitate and accelerate a vehicle along a track at speeds up to 600 mph. The vehicle would shift to rocket engines for launch into orbit. Similar to high-speed trains and roller coasters that use high-strength magnets to lift and propel a vehicle a couple of inches above a guideway, a Magnetic Launch Assist system would electromagnetically propel a space vehicle along the track. The tabletop experimental track for the system shown in this photograph is 44-feet long, with 22-feet of powered acceleration and 22-feet of passive braking. A 10-pound carrier with permanent magnets on its sides swiftly glides by copper coils, producing a levitation force. The track uses a linear synchronous motor, which means the track is synchronized to turn the coils on just before the carrier comes in contact with them, and off once the carrier passes. Sensors are positioned on the side of the track to determine the carrier’s position so the appropriate drive coils can be energized. MSFC engineers have conducted tests on the indoor track and a 50-foot outdoor track. The major advantages of launch assist for NASA launch vehicles is that it reduces the weight of the take-off, the landing gear, the wing size, and less propellant resulting in significant cost savings. The US Navy and the British MOD (Ministry of Defense) are planning to use magnetic launch assist for their next generation aircraft carriers as the aircraft launch system. The US Army is considering using this technology for launching target drones for anti-aircraft training.
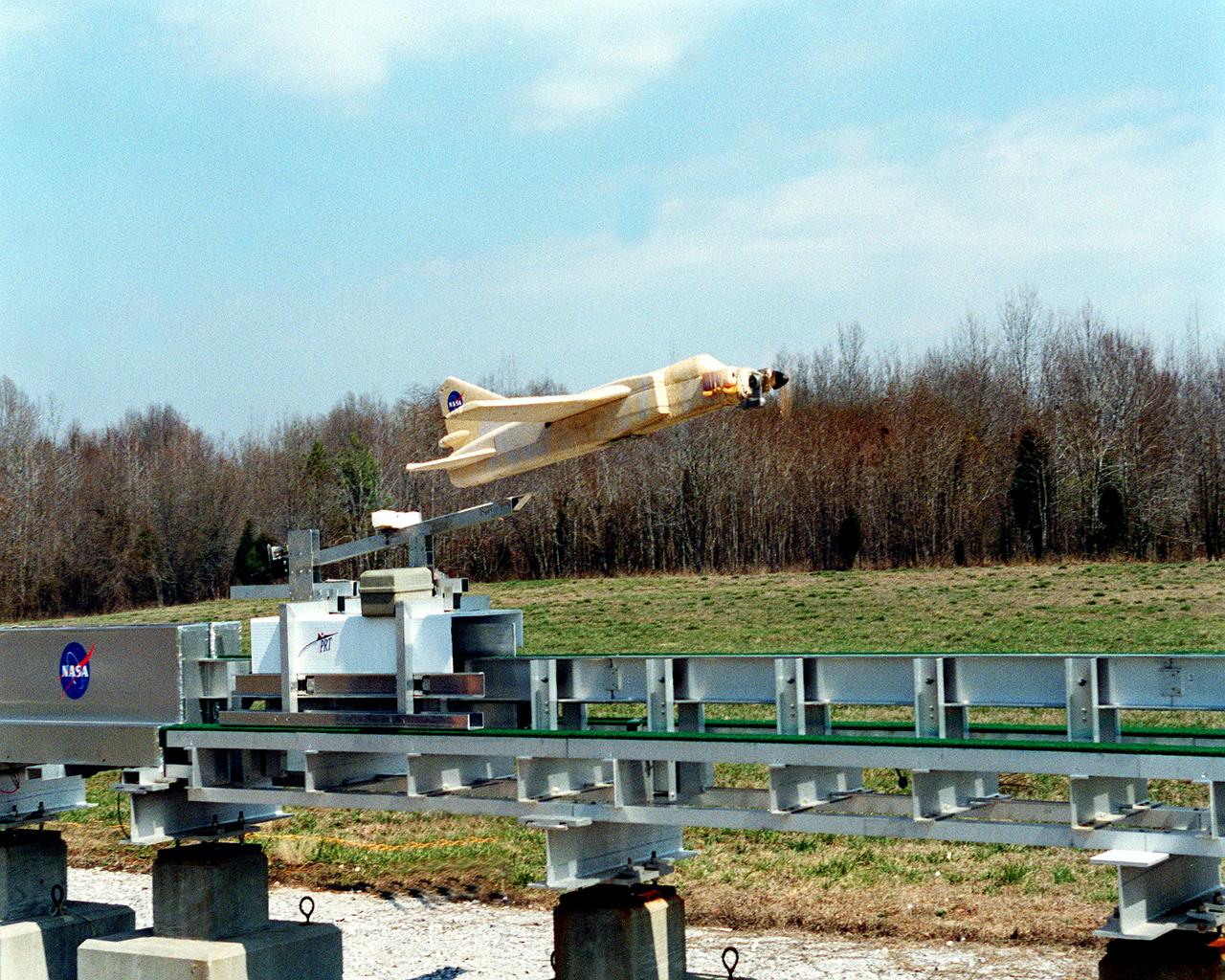

This image shows a 1/9 subscale model vehicle clearing the Magnetic Launch Assist System, formerly referred to as the Magnetic Levitation (MagLev), test track during a demonstration test conducted at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Engineers at MSFC have developed and tested Magnetic Launch Assist technologies. To launch spacecraft into orbit, a Magnetic Launch Assist System would use magnetic fields to levitate and accelerate a vehicle along a track at very high speeds. Similar to high-speed trains and roller coasters that use high-strength magnets to lift and propel a vehicle a couple of inches above a guideway, a launch-assist system would electromagnetically drive a space vehicle along the track. A full-scale, operational track would be about 1.5-miles long and capable of accelerating a vehicle to 600 mph in 9.5 seconds. This track is an advanced linear induction motor. Induction motors are common in fans, power drills, and sewing machines. Instead of spinning in a circular motion to turn a shaft or gears, a linear induction motor produces thrust in a straight line. Mounted on concrete pedestals, the track is 100-feet long, about 2-feet wide and about 1.5-feet high. The major advantages of launch assist for NASA launch vehicles is that it reduces the weight of the take-off, the landing gear, the wing size, and less propellant resulting in significant cost savings. The US Navy and the British MOD (Ministry of Defense) are planning to use magnetic launch assist for their next generation aircraft carriers as the aircraft launch system. The US Army is considering using this technology for launching target drones for anti-aircraft training.
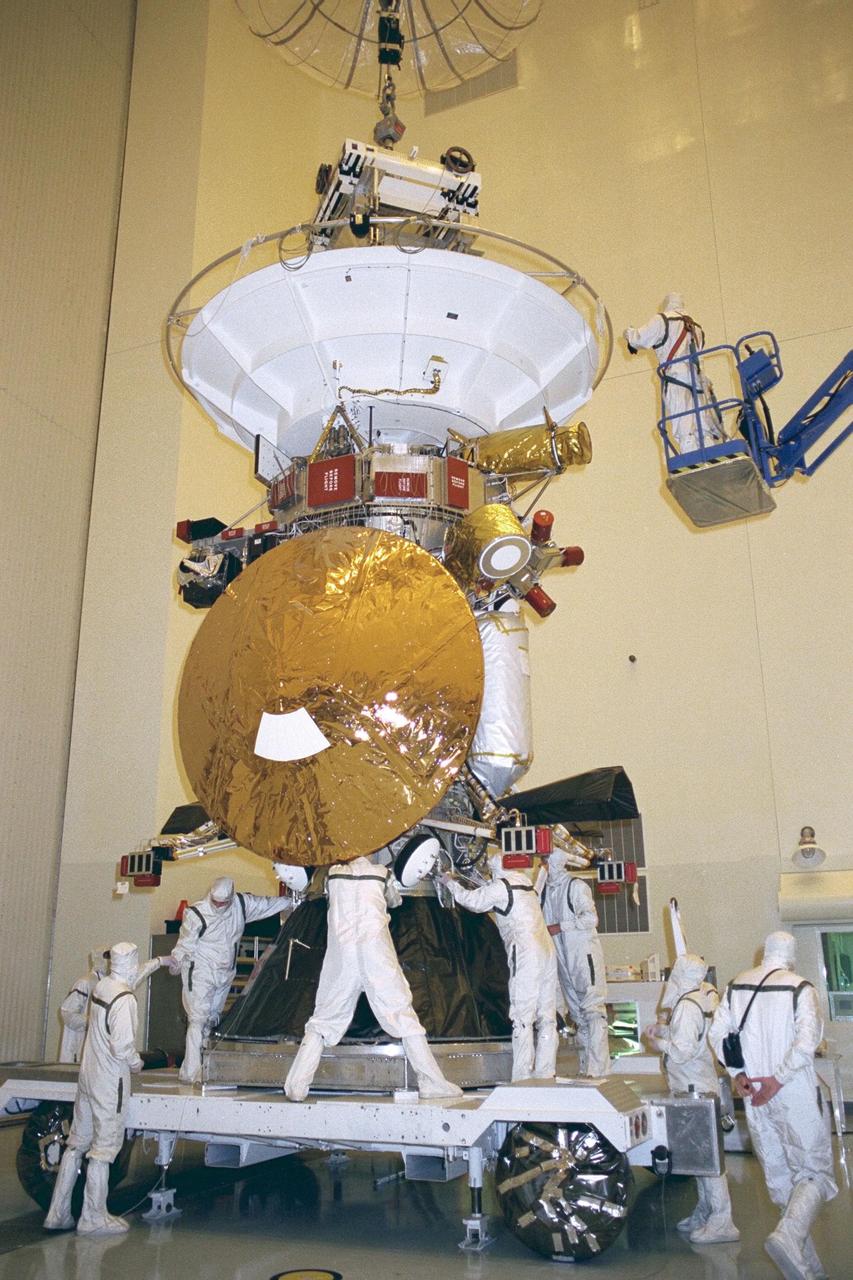

Flight mechanics from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, Calif., secure the Cassini spacecraft to its launch vehicle adapter in KSC’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The adapter will later be mated to a Titan IV/Centaur expendable launch vehicle that will lift Cassini into space. The mechanic in the crane lift at right is assisting in exact positioning of the spacecraft for precise fitting. Scheduled for launch in October, the Cassini mission seeks insight into the origins and evolution of the early solar system. Scientific instruments carried aboard the spacecraft will study Saturn’s atmosphere, magnetic field, rings, and several moons. JPL is managing the Cassini project for NASA
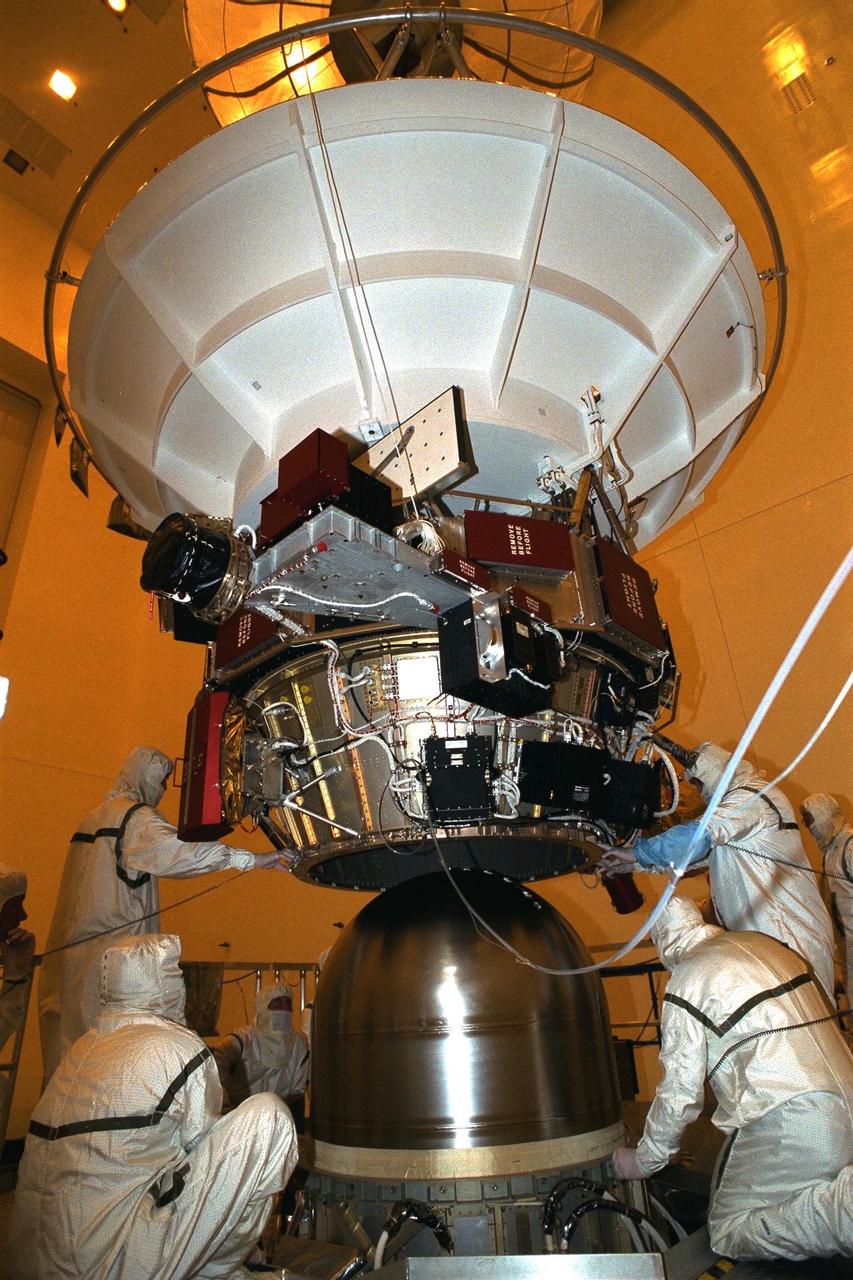

Technicians from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) lower the upper equipment module over a propellant tank in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at KSC in July prior to installation on the Cassini orbiter. A four-year, close-up study of the Saturnian system, the Cassini mission is scheduled for launch from Cape Canaveral Air Station in October 1997. The propellant tank will assist with guidance of the orbiter and power during the spacecraft’s voyage and in-orbit periods. It will take seven years for the spacecraft to reach Saturn. Scientific instruments carried aboard the spacecraft will study Saturn’s atmosphere, magnetic field, rings, and several moons. JPL is managing the Cassini project for NASA
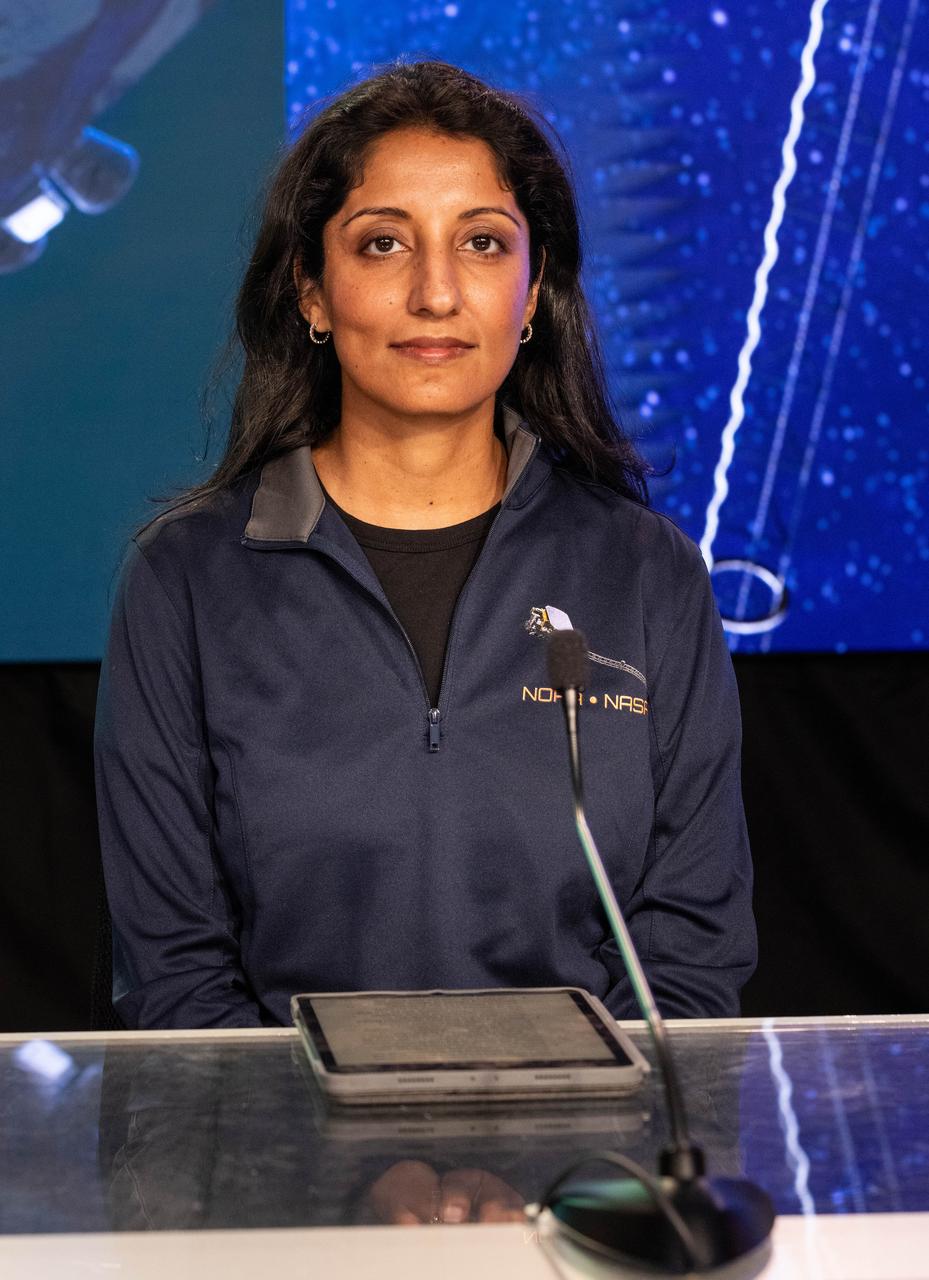

Irene Parker, deputy assistant administrator for Systems for NOAA’s National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service, participates in a prelaunch news conference on Sunday, Sept. 21, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for NASA's IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. This mission and its two rideshares – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth. Launch is targeting 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
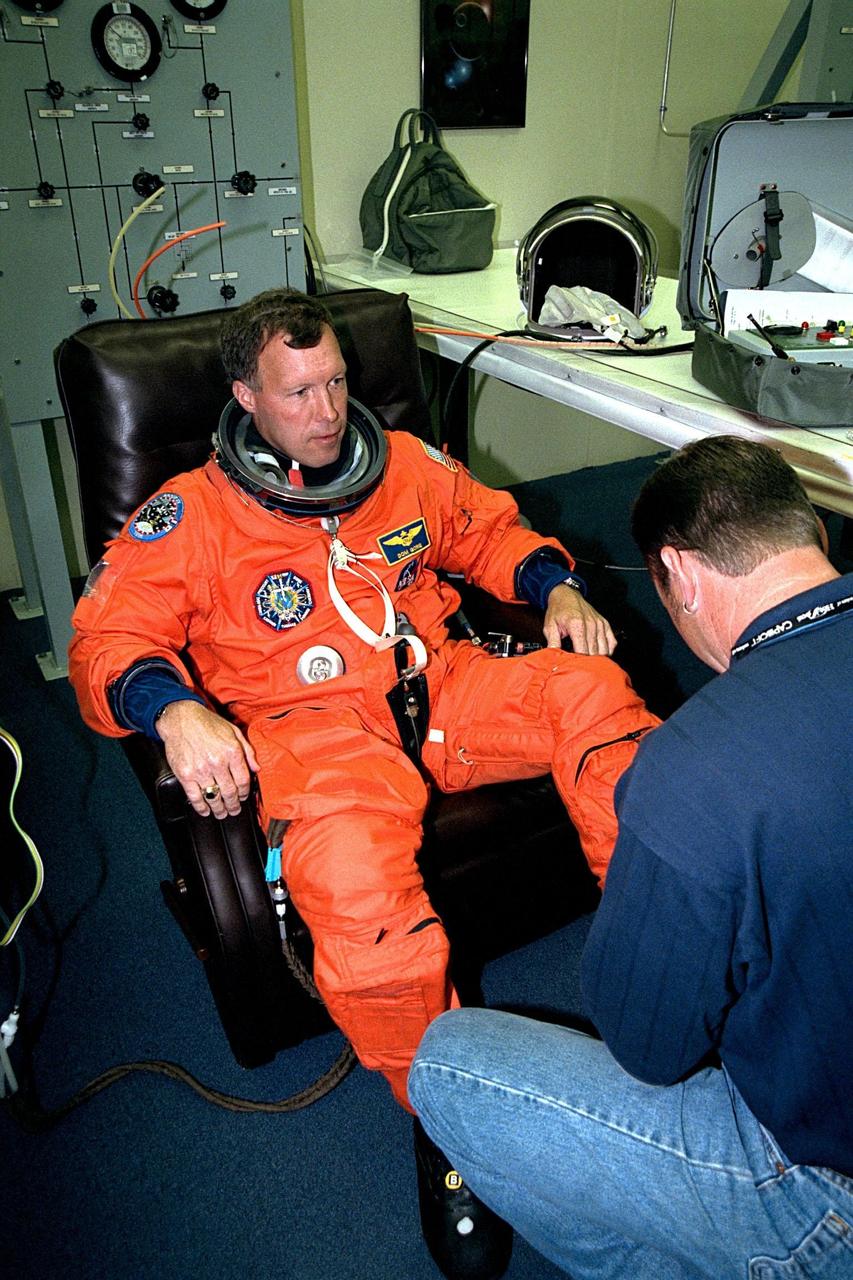

With the help of a suit technician, STS-91 Pilot Dominic L. Gorie dons his flight suit in the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building prior to the crew walkout and transport to Launch Pad 39A. Gorie is on his first Shuttle mission. As a commander in the Navy, he flew combat missions in Operation Desert Storm and has earned a Distinguished Flying Cross as well as a master’s degree in aviation systems. Along with backing up Precourt on the flight deck, Gorie will perform the final Shuttle-Mir undocking and flyaround. He will also assist with the transfer of materials to and from Mir and the photographic documentation of the space station. STS91 is scheduled to be launched on June 2 with a launch window opening around 6:10 p.m. EDT. The mission will feature the ninth and final Shuttle docking with the Russian space station Mir, the first Mir docking for Discovery, the first on-orbit test of the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS), and the first flight of the new Space Shuttle super lightweight external tank. Astronaut Andrew S. W. Thomas will be returning to Earth as a STS-91 crew member after living more than four months aboard Mir
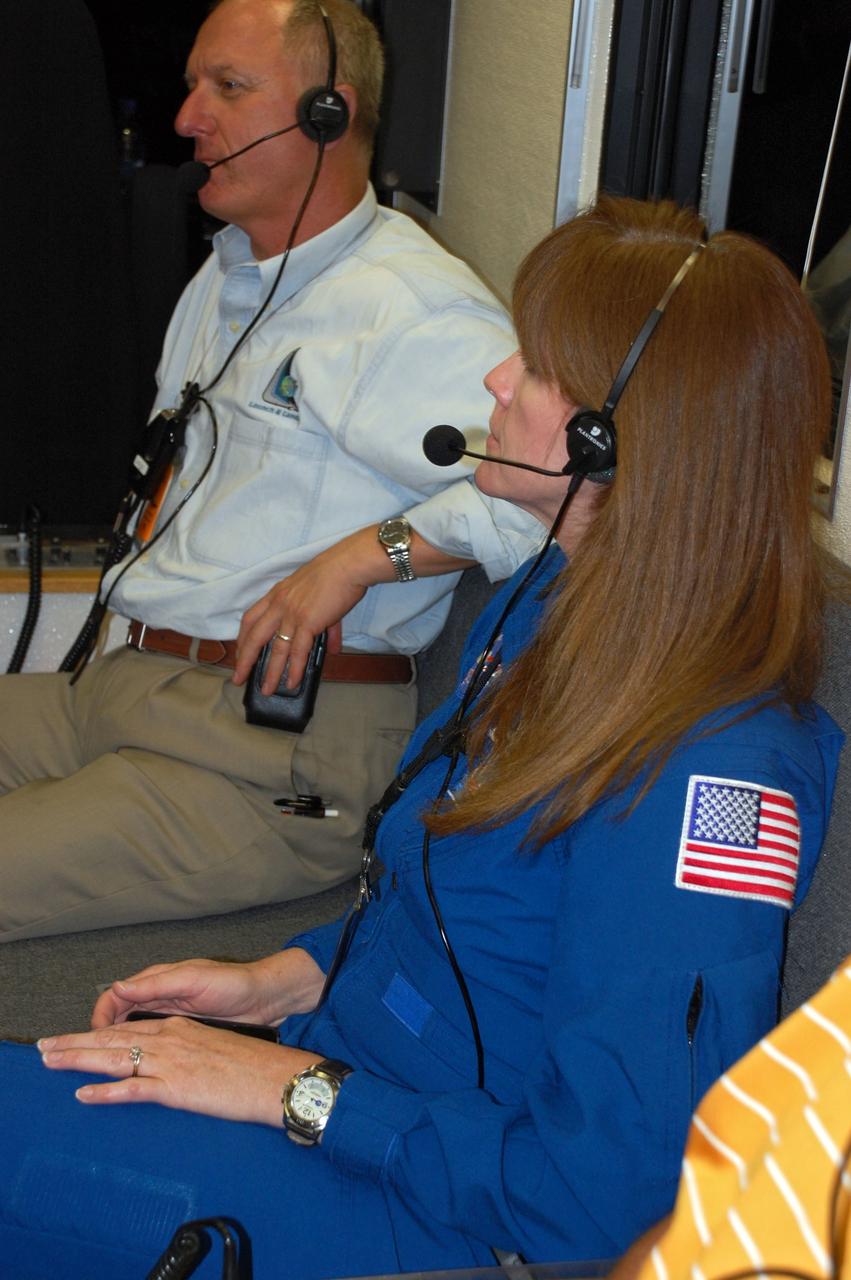

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a team of highly trained personnel inside the Convoy Command Vehicle is ready to "safe" shuttle Endeavour. The command vehicle is equipped to control critical communications between the crew still aboard Endeavour and the Launch Control Center. The team will monitor the health of the orbiter systems and direct convoy operations made up of about 40 vehicles, including 25 specially designed vehicles to assist the crew in leaving the shuttle, and prepare the vehicle for towing from the Shuttle Landing Facility to Orbiter Processing Facility-1. Accompanying the command convoy team are STS-134 assistant launch director Pete Nickolenko and NASA astronaut Janet Kavandi. Endeavour's final return from space completed the 16-day, 6.5-million-mile STS-134 mission. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. EDT, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
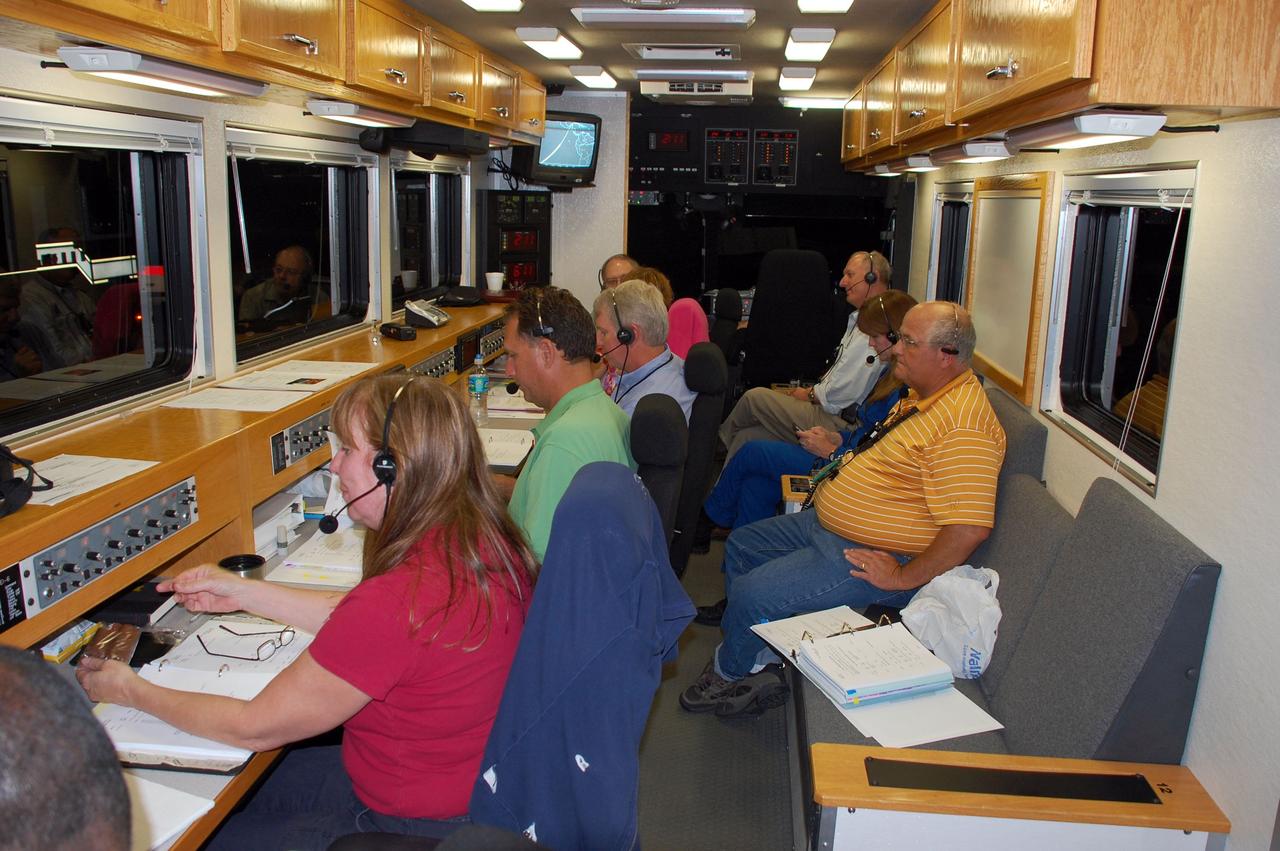

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a team of highly trained personnel inside the Convoy Command Vehicle is ready to "safe" shuttle Endeavour. The command vehicle is equipped to control critical communications between the crew still aboard Endeavour and the Launch Control Center. The team will monitor the health of the orbiter systems and direct convoy operations made up of about 40 vehicles, including 25 specially designed vehicles to assist the crew in leaving the shuttle, and prepare the vehicle for towing from the Shuttle Landing Facility to Orbiter Processing Facility-1. Endeavour's final return from space completed the 16-day, 6.5-million-mile STS-134 mission. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. EDT, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Convoy Command Center vehicle is positioned near shuttle Endeavour on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The command vehicle is equipped to control critical communications between the crew still aboard Endeavour and the Launch Control Center. The team will monitor the health of the orbiter systems and direct convoy operations made up of about 40 vehicles, including 25 specially designed vehicles to assist the crew in leaving the shuttle, and prepare the vehicle for towing from the Shuttle Landing Facility to Orbiter Processing Facility-1. Endeavour's final return from space completed the 16-day, 6.5-million-mile STS-134 mission. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. EDT, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
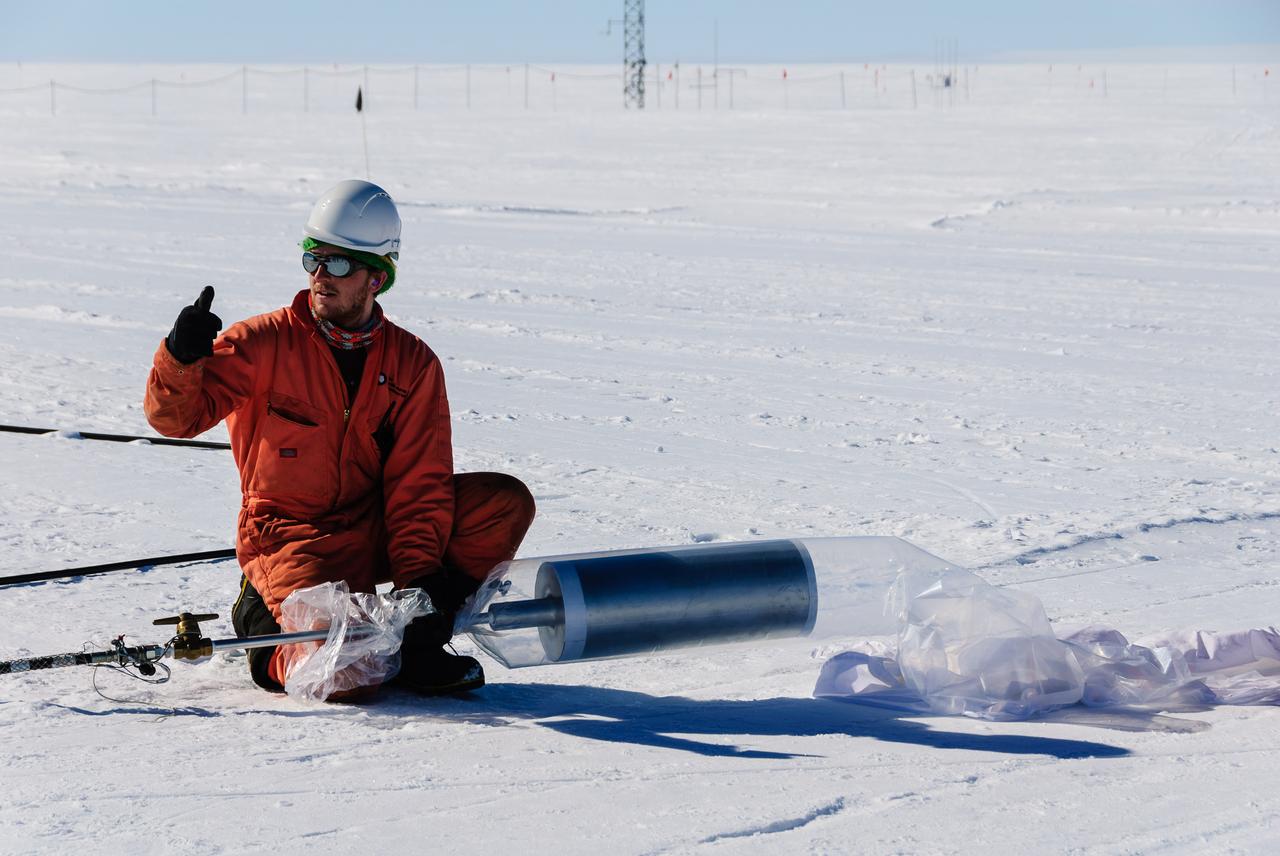

The Halley station team members assisted the BARREL team with the launches. Here, one gives the thumbs up to start inflating a BARREL balloon. Credit: NASA/Goddard/BARREL/M. Krzysztofowicz Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/nasas-barrel-returns-successful-from-antarctica/" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/nasas-barrel-returns-successful-from...</a> -- Three months, 20 balloons, and one very successful campaign. The team for NASA's BARREL – short for Balloon Array for Radiation belt Relativistic Electron Losses -- mission returned from Antarctica in March 2014. BARREL's job is to help unravel the mysterious Van Allen belts, two gigantic donuts of radiation that surround Earth, which can shrink and swell in response to incoming energy and particles from the sun and sometimes expose satellites to harsh radiation. While in Antarctica, the team launched 20 balloons carrying instruments that sense charged particles that are scattered into the atmosphere from the belts, spiraling down the magnetic fields near the South Pole. Each balloon traveled around the pole for up to three weeks. The team will coordinate the BARREL data with observations from NASA's two Van Allen Probes to better understand how occurrences in the belts relate to bursts of particles funneling down toward Earth. BARREL team members will be on hand at the USA Science and Engineering Festival in DC on April 26 and 27, 2014 for the exhibit Space Balloons: Exploring the Extremes of Space Weather. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>