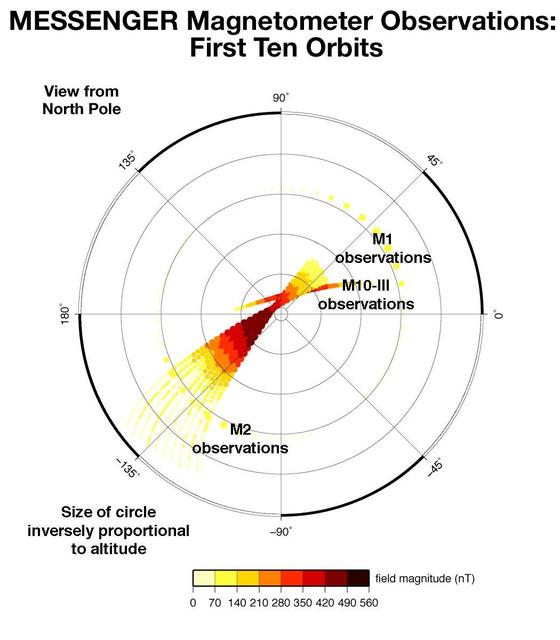
First Magnetometer Measurements from Mercury Orbit
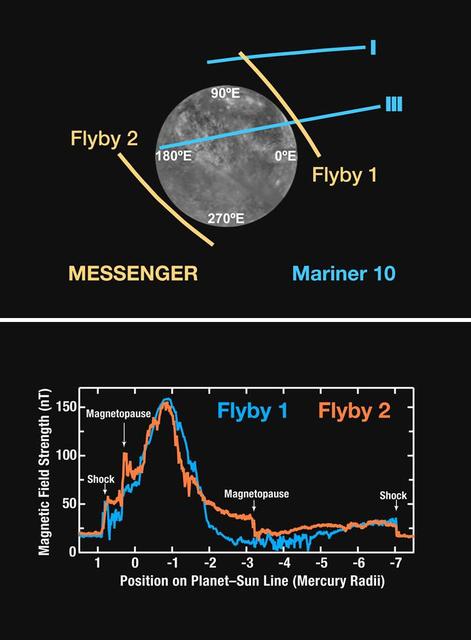
Magnetometer Results from MESSENGER Second Mercury Encounter
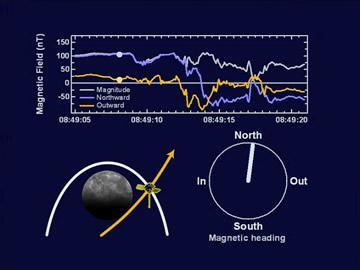
A Movie of Magnetometer Measurements from the Second Mercury Flyby
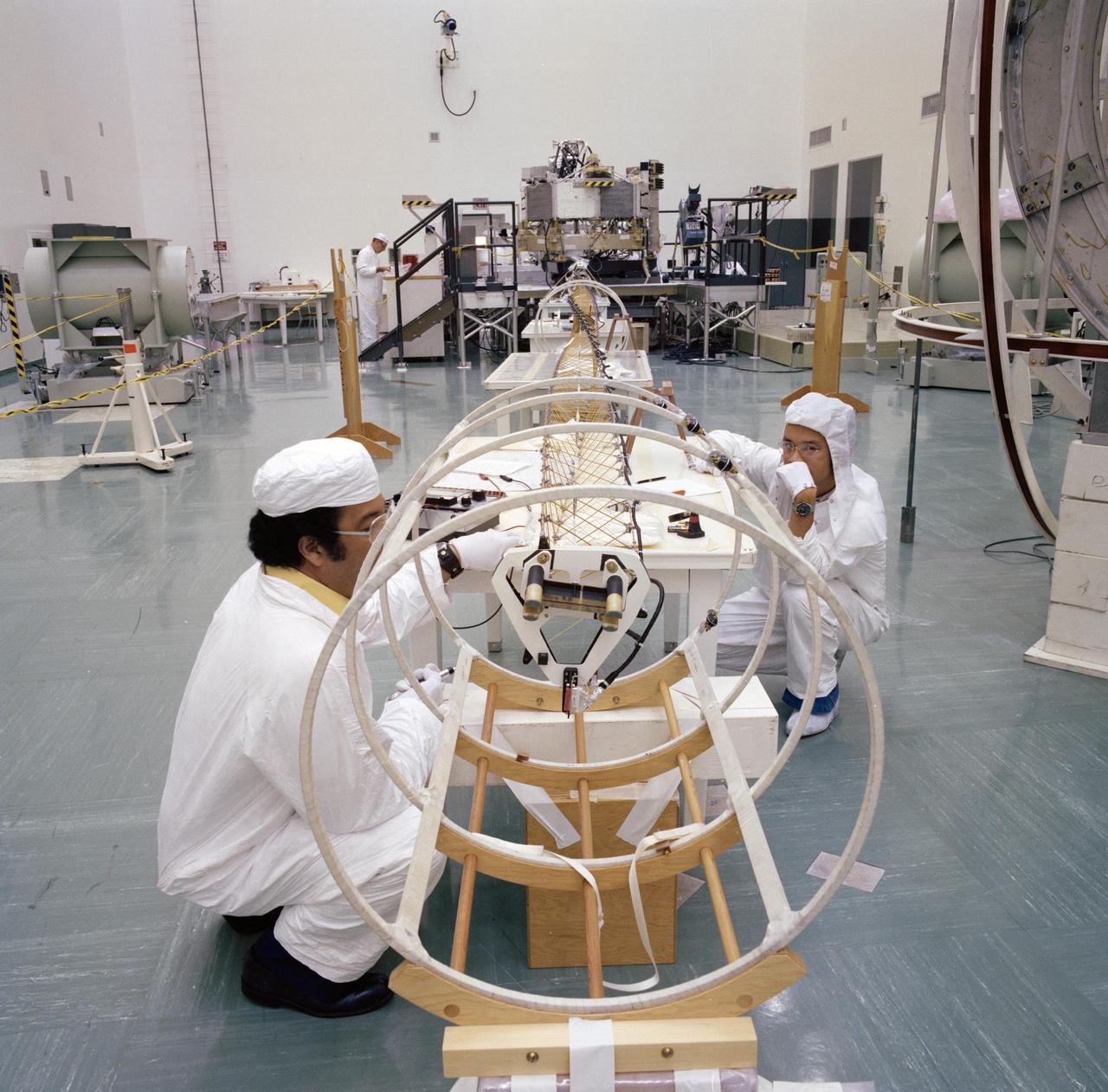

This archival photo shows engineers working with the deployed magnetometer boom of one of NASA's Voyager spacecraft in Florida on June 17, 1977. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21738
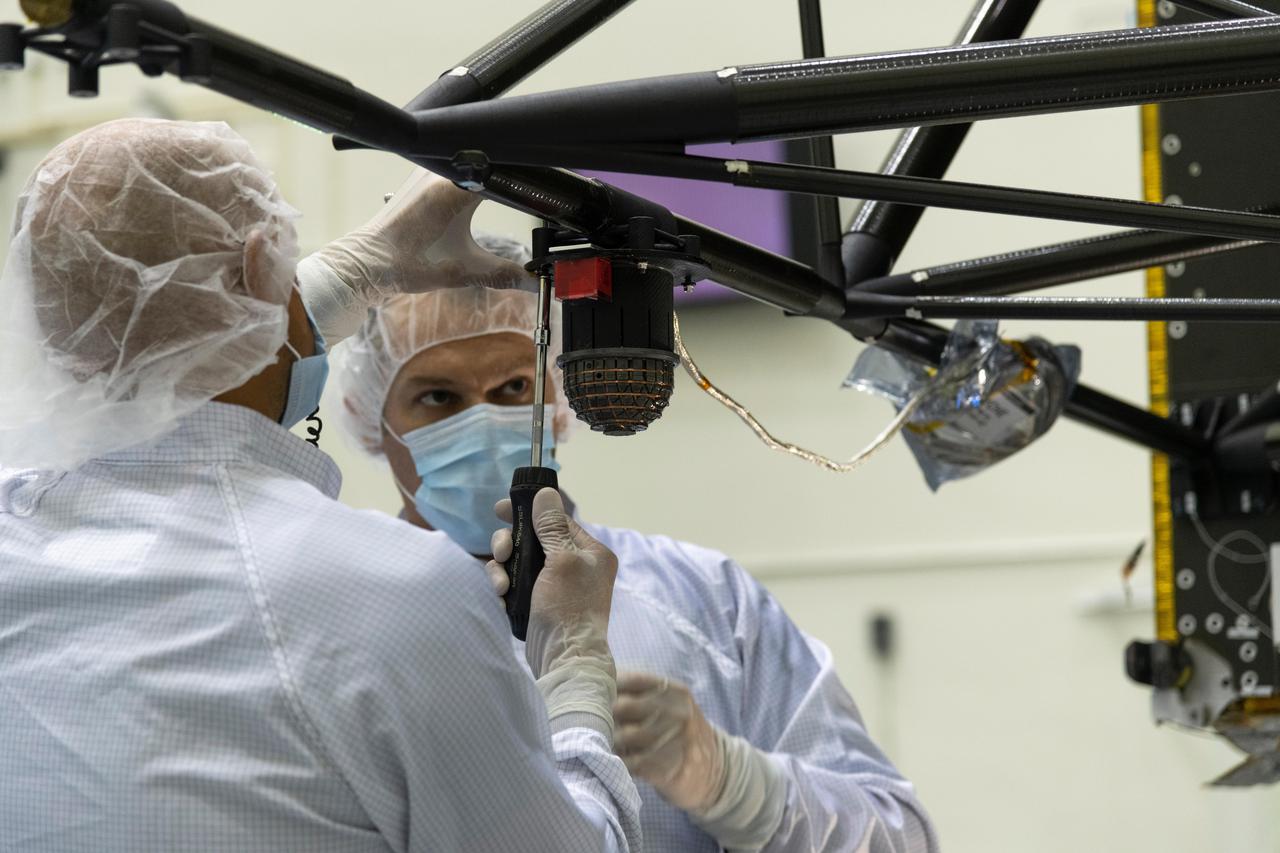

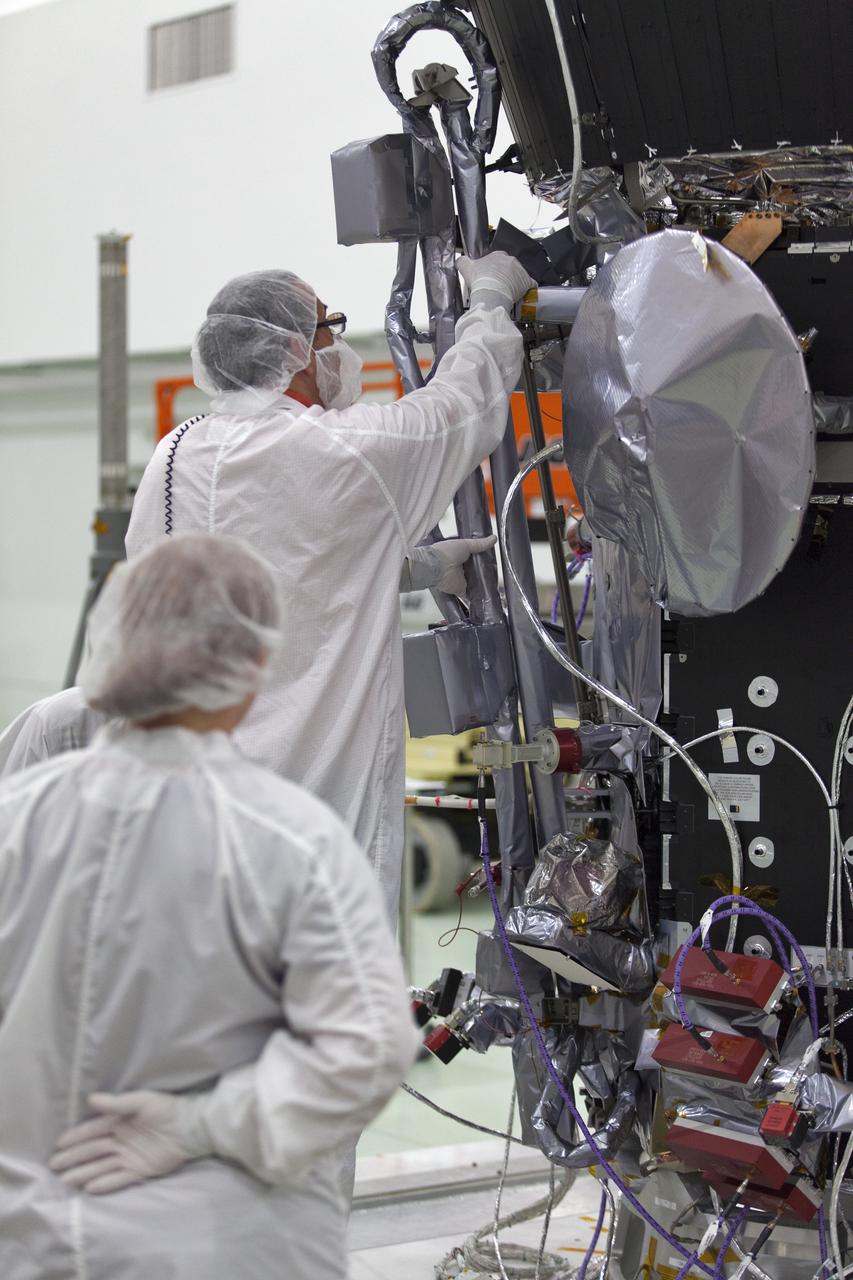
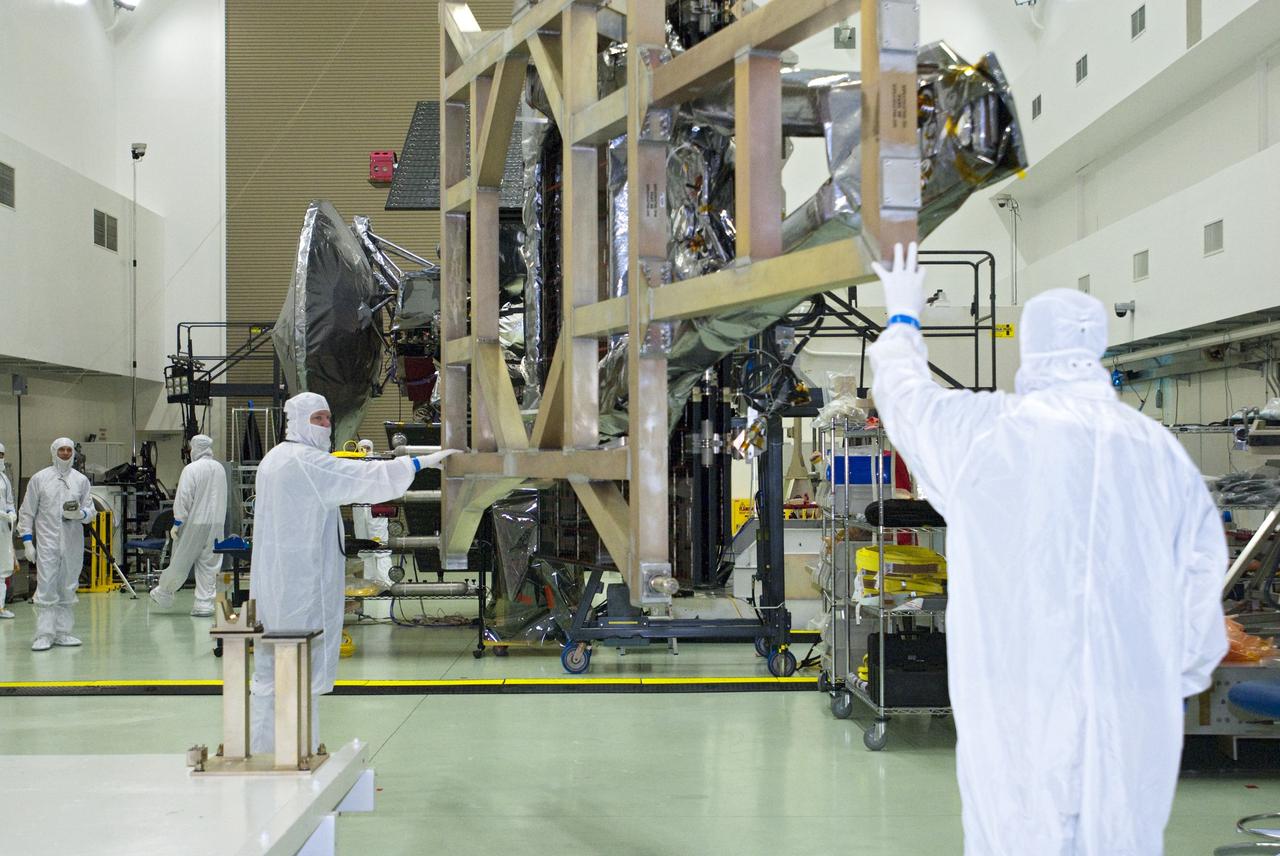
Engineers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California integrate the magnetometer instrument into the agency's Psyche spacecraft on June 28, 2021. Psyche, set to launch in August 2022, will investigate a metal-rich asteroid of the same name, which lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Scientists believe the asteroid could be part or all of the iron-rich interior of an early planetary building block that was stripped of its outer rocky shell as it repeatedly collided with other large bodies during the early formation of the solar system. Scientists know that the asteroid doesn't generate a magnetic field the way Earth does; but if Psyche had a magnetic field in the past, that magnetic field could still be recorded in Psyche's material today. With sensors mounted onto a 6-foot (2-meter) boom, the magnetometer can determine if Psyche is still magnetized. If so, that would confirm that the asteroid is part of the core of a planetesimal, the building block of an early planet. This photo shows one of the magnetometer's sensors. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24893
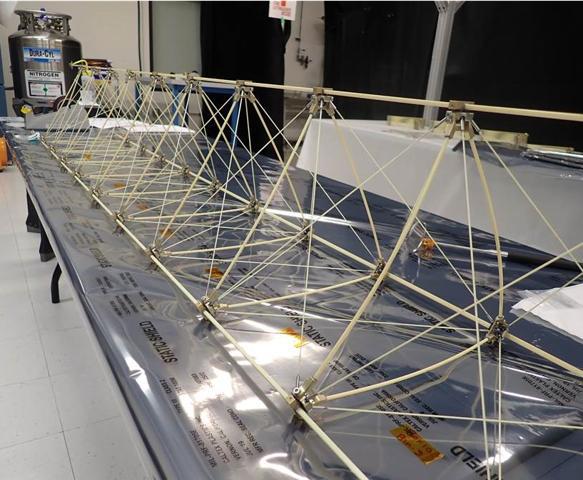

A test model of the boom that will be used for the magnetometer aboard NASA's Europa Clipper spacecraft is readied in NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. Called a dynamic test model, it is an exact duplicate of the Europa Clipper Magnetometer (ECM) boom that will fly on Europa Clipper. To fit aboard the rocket, the boom will be stowed in a canister and will deploy to its full length of 25 feet (8.5 meters) in the days after launch. The ECM will allow scientists to measure Europa's magnetic field and to measure the salinity and depth of Europa's internal global ocean. NASA scientists believe Jupiter's moon Europa may have the potential to harbor existing life, because of the internal ocean. Europa Clipper will swoop around Jupiter on an elliptical path, dipping close to the moon on each flyby. Understanding Europa's habitability will help scientists better understand how life developed on Earth and the potential for finding life beyond our planet. Europa Clipper is set to launch in 2024. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24786
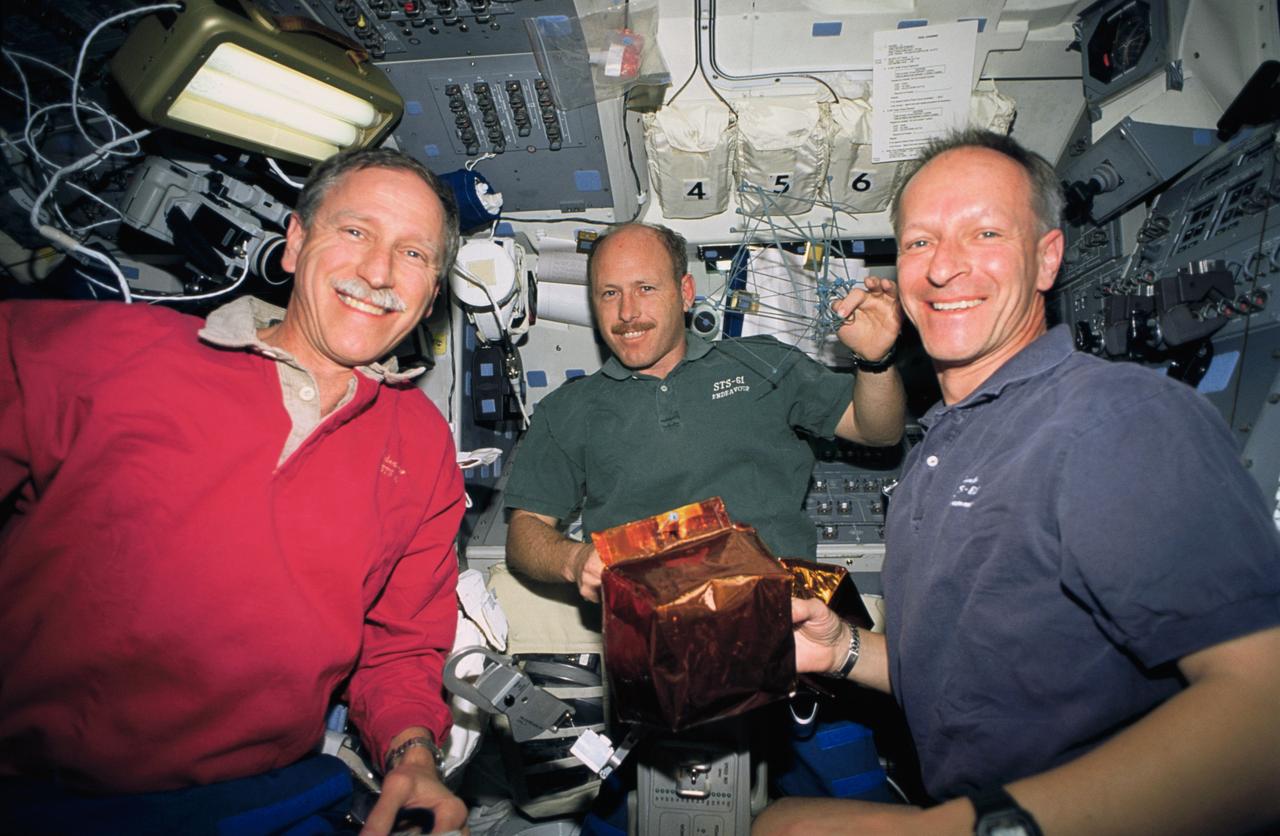

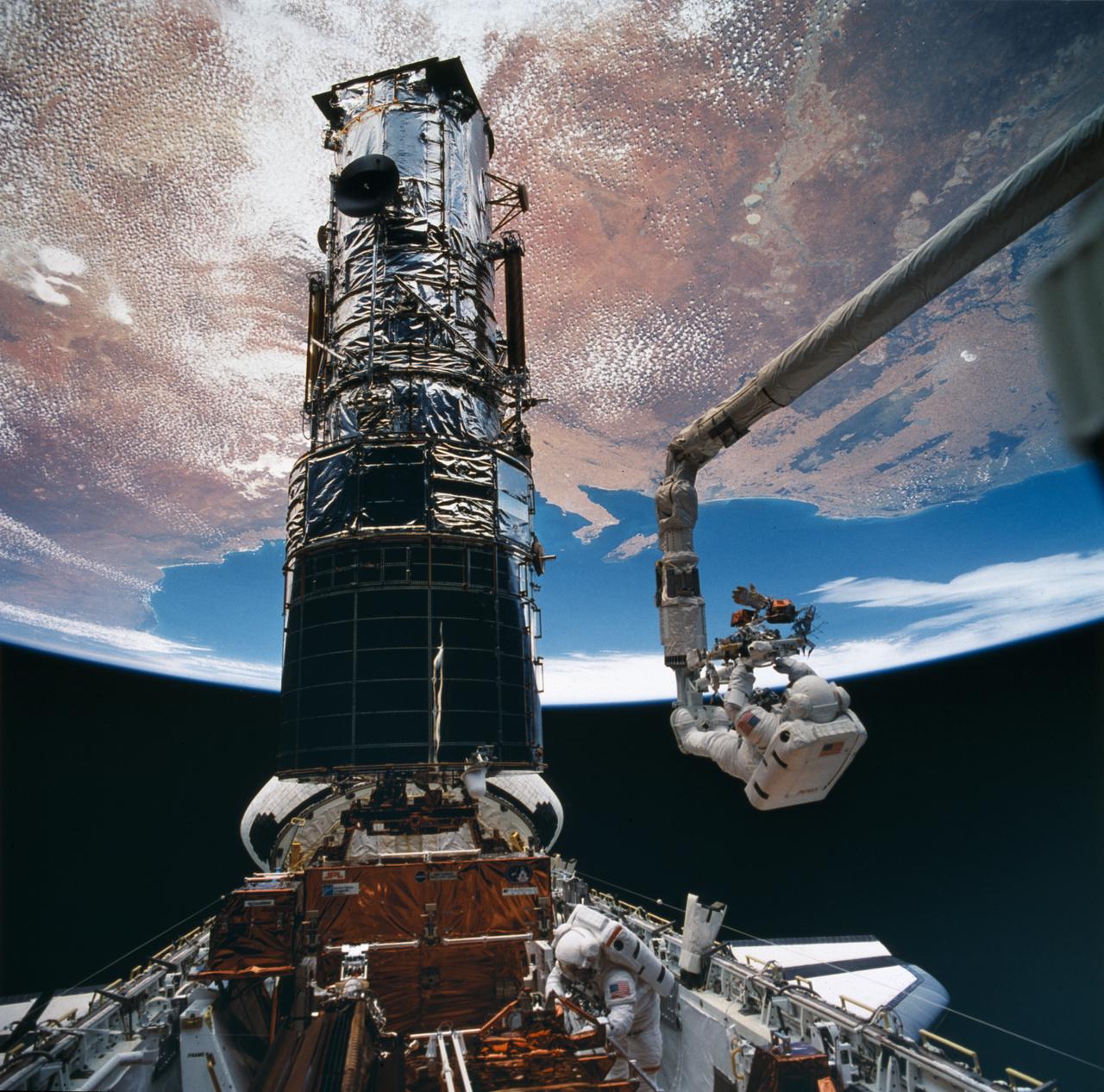
STS061-23-005 (8 Dec 1993) --- Three members of the STS-61 crew prepare covers to be placed on magnetometers near the top of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Left to right are Richard O. Covey, mission commander; Kenneth D. Bowersox, pilot and Claude Nicollier, mission specialist. On the following day, astronauts Jeffrey A. Hoffman and F. Story Musgrave placed the covers on the magnetometers as they wrapped up five days of servicing on HST.
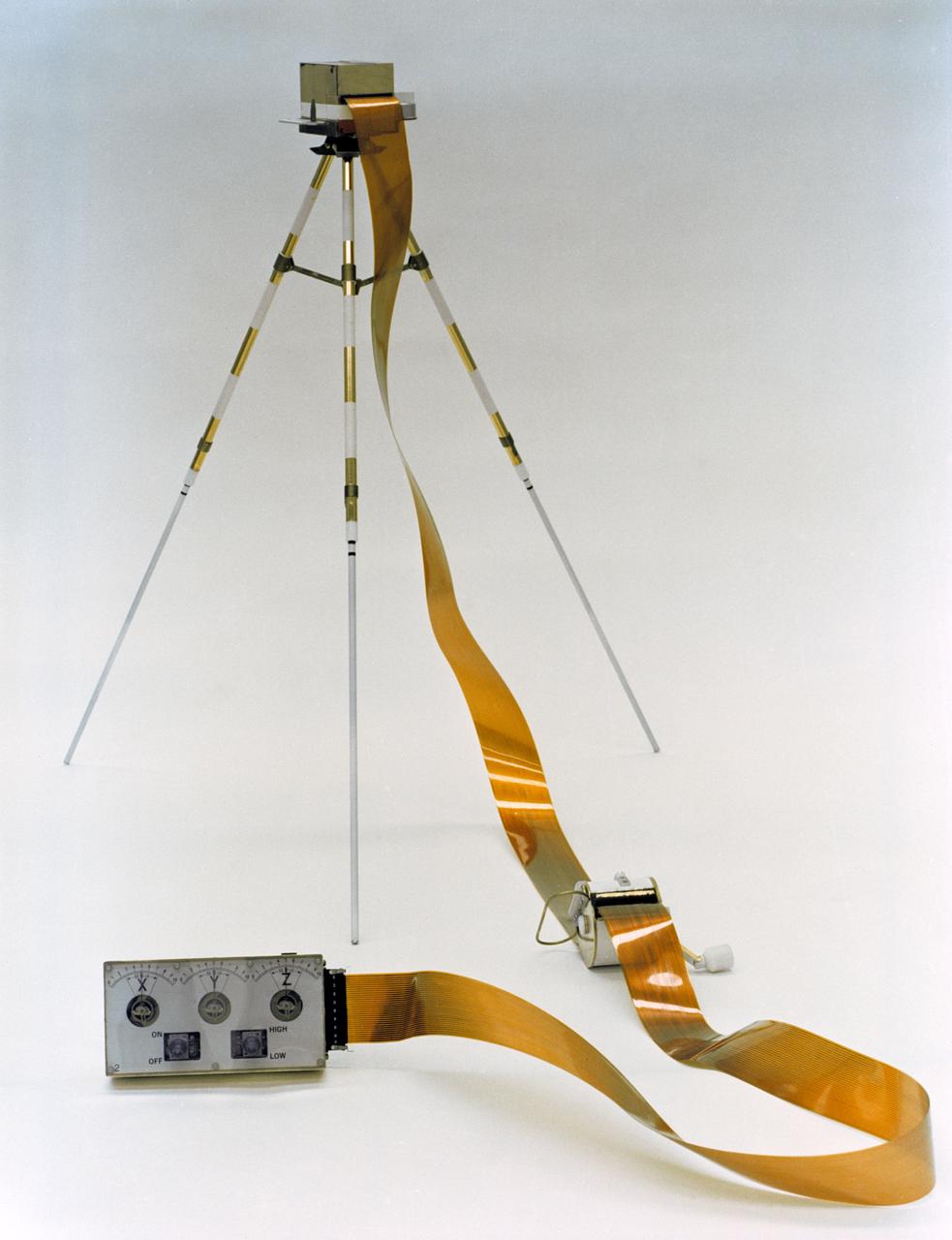

S70-56721 (December 1970) --- A close-up view of the Lunar Portable Magnetometer (LPM), which will be used by the crew of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission during the second extravehicular activity (EVA). The LPM's components, a tripod-mounted flux-gate magnetometer sensor head and an electronics data package, connected by a 50-feet flat cable, function together to measure variations in the lunar magnetic field at several points on the geological traverse. Data gathered will be used to determine the location, strength and dimensions of magnetic sources, as well as knowledge of the local and total selenological structure. The LPM will be carried on the Modular Equipment Transporter (MET), and deployed by the lunar module pilot, who will align the sensor head at least 35 feet from the data package. The LM pilot will then return to the MET and verbally relay the LPM readouts to Earth. Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell is the lunar module pilot for the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission.

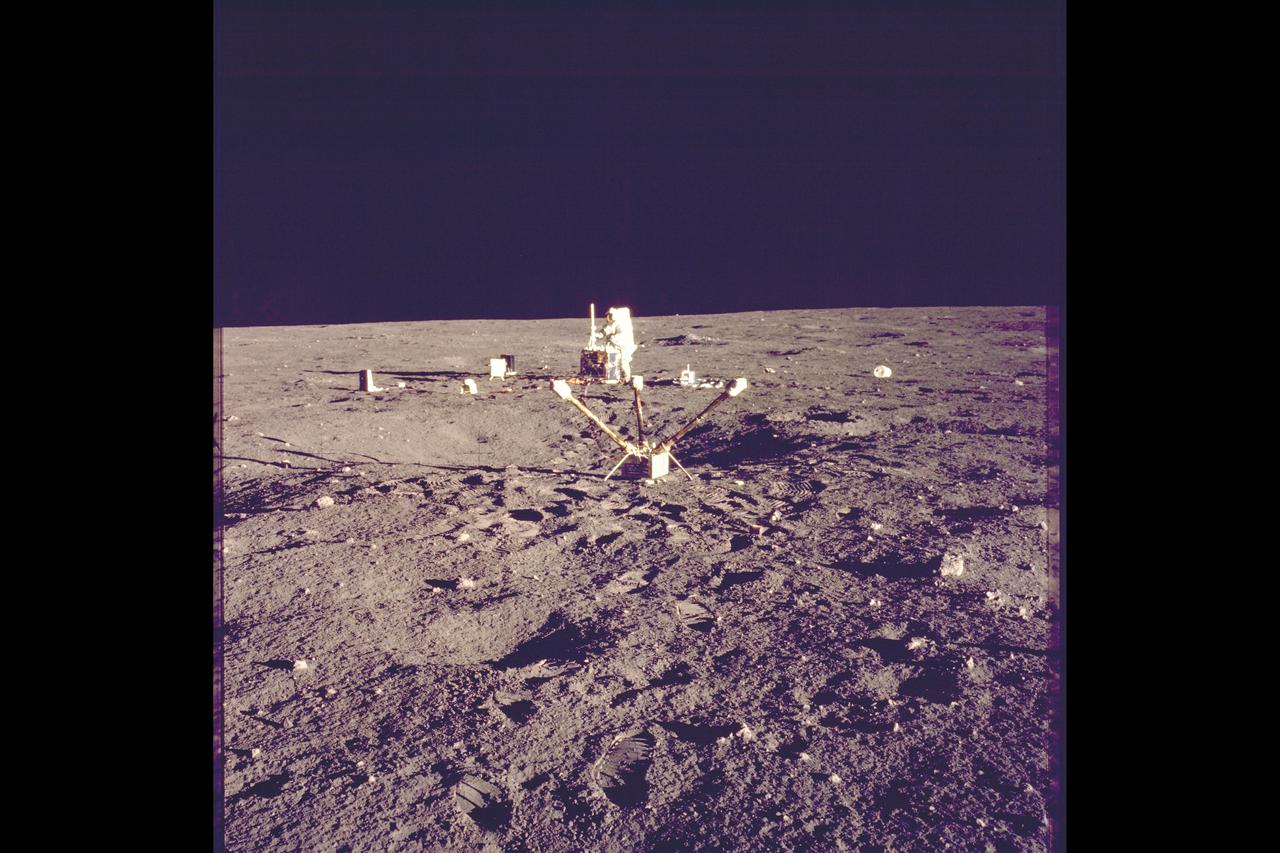
Astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, deploys the Lunar Surface Magnetometer (LSM) during the first Apollo 12 extravehicular activity on the Moon. The LSM is a component of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP). The Lunar Module can be seen in the left background.

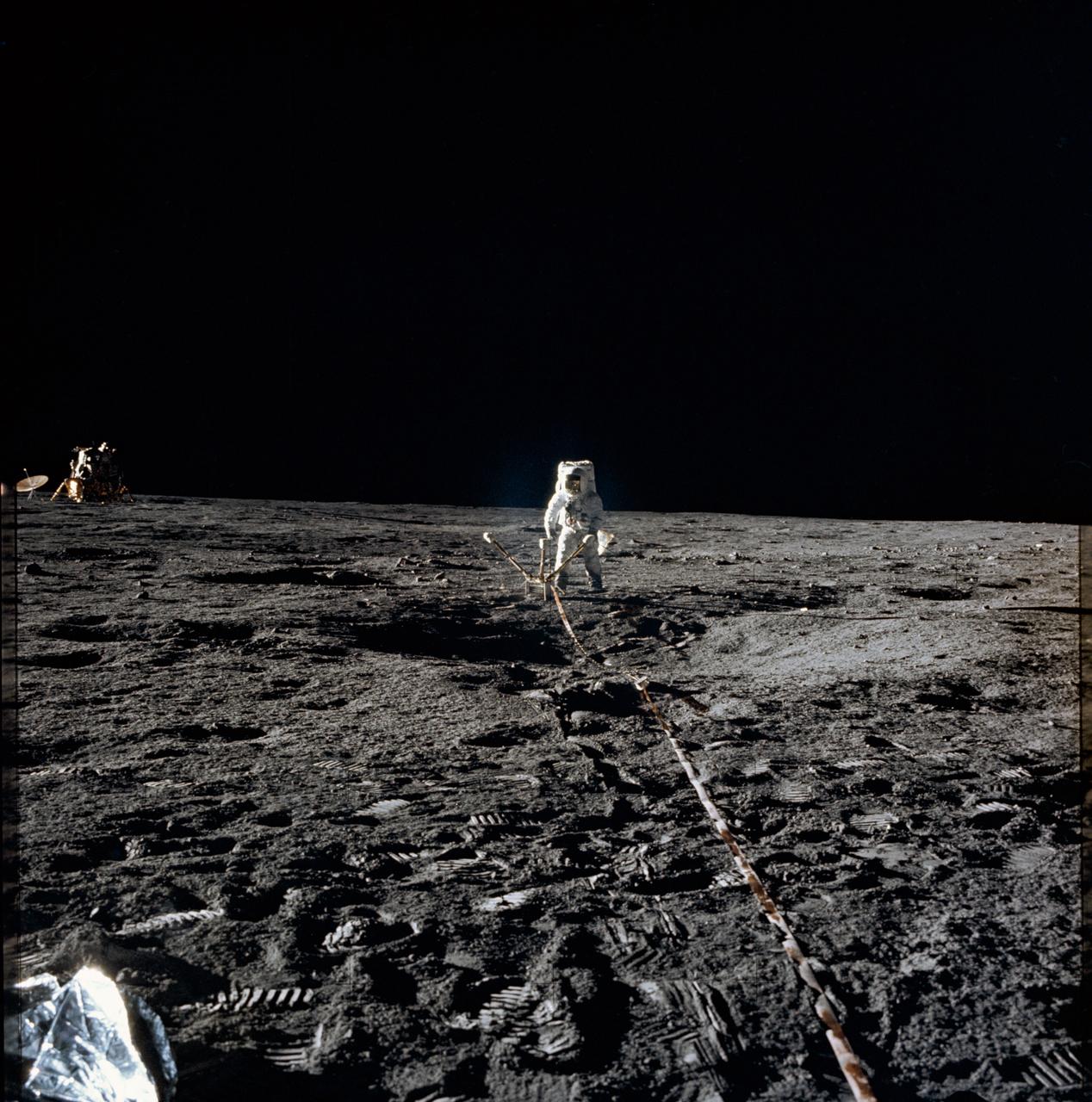
AS16-114-18433 (22 April 1972) --- View of the Lunar Portable Magnetometer mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) which was parked at Station No. 2 on the Descartes lunar landing site. The Apollo 16 crew photographed it during their second extravehicular activity (EVA). Note the shadow of the astronaut taking the photograph in the left foreground.

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, May 23, 2018, technicians and engineers deploy the magnetometer boom on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
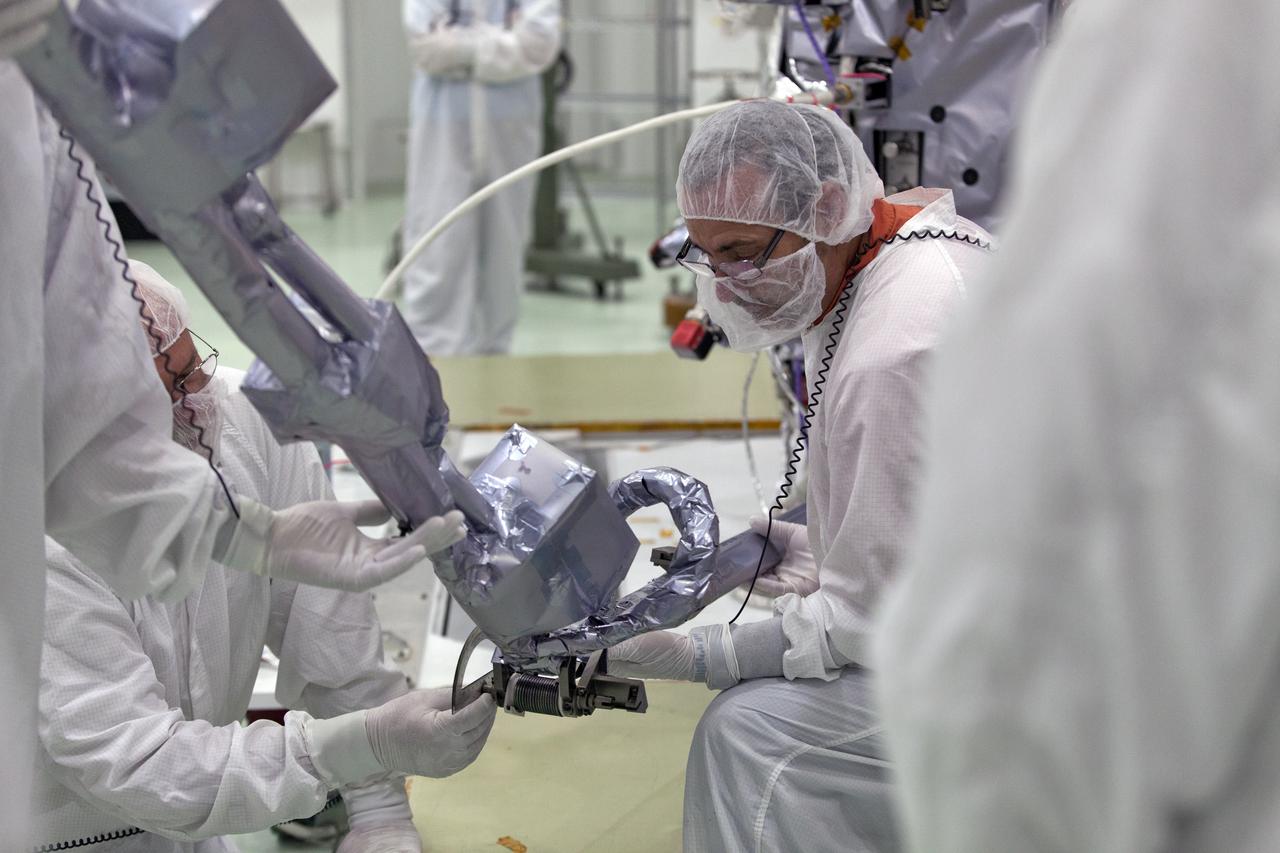

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, May 23, 2018, technicians and engineers deploy the magnetometer boom on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
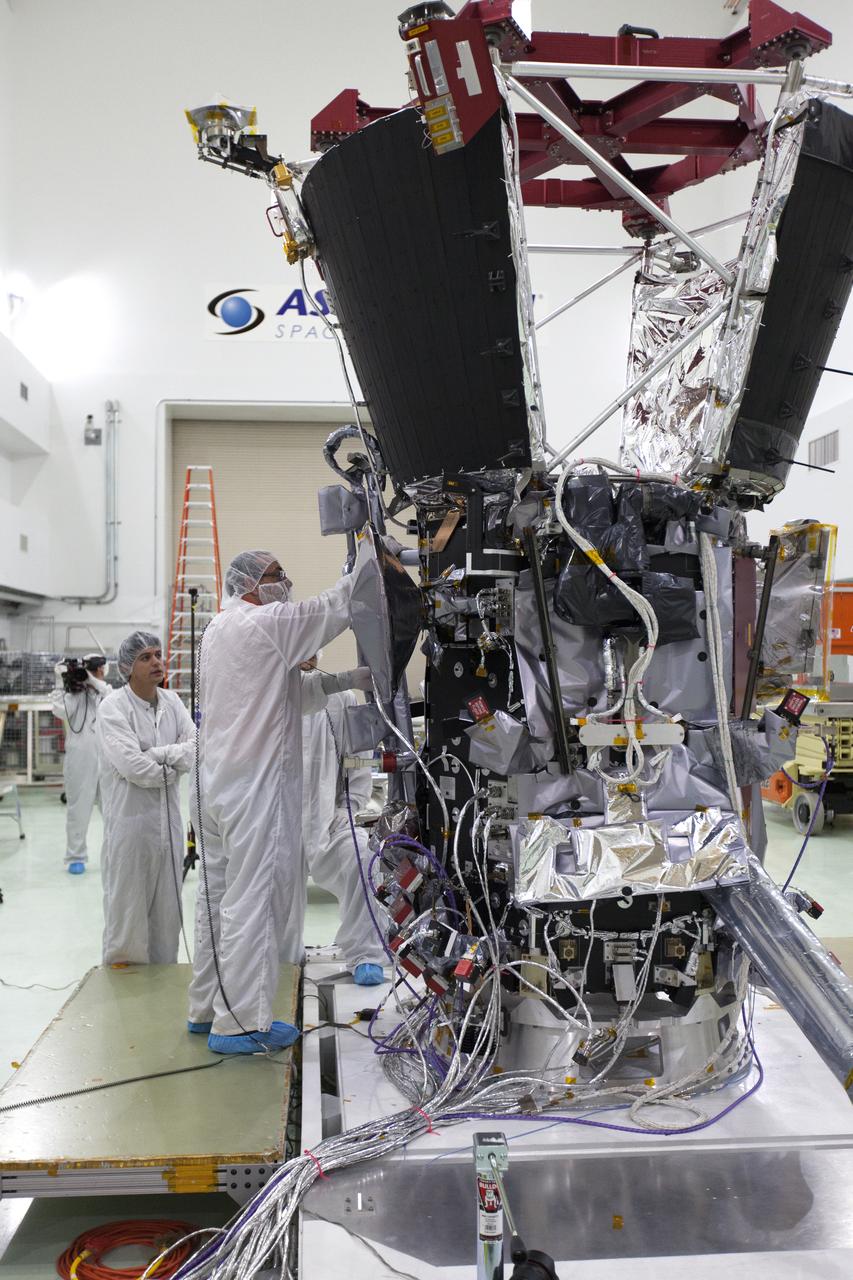

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, May 23, 2018, technicians and engineers deploy the magnetometer boom on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
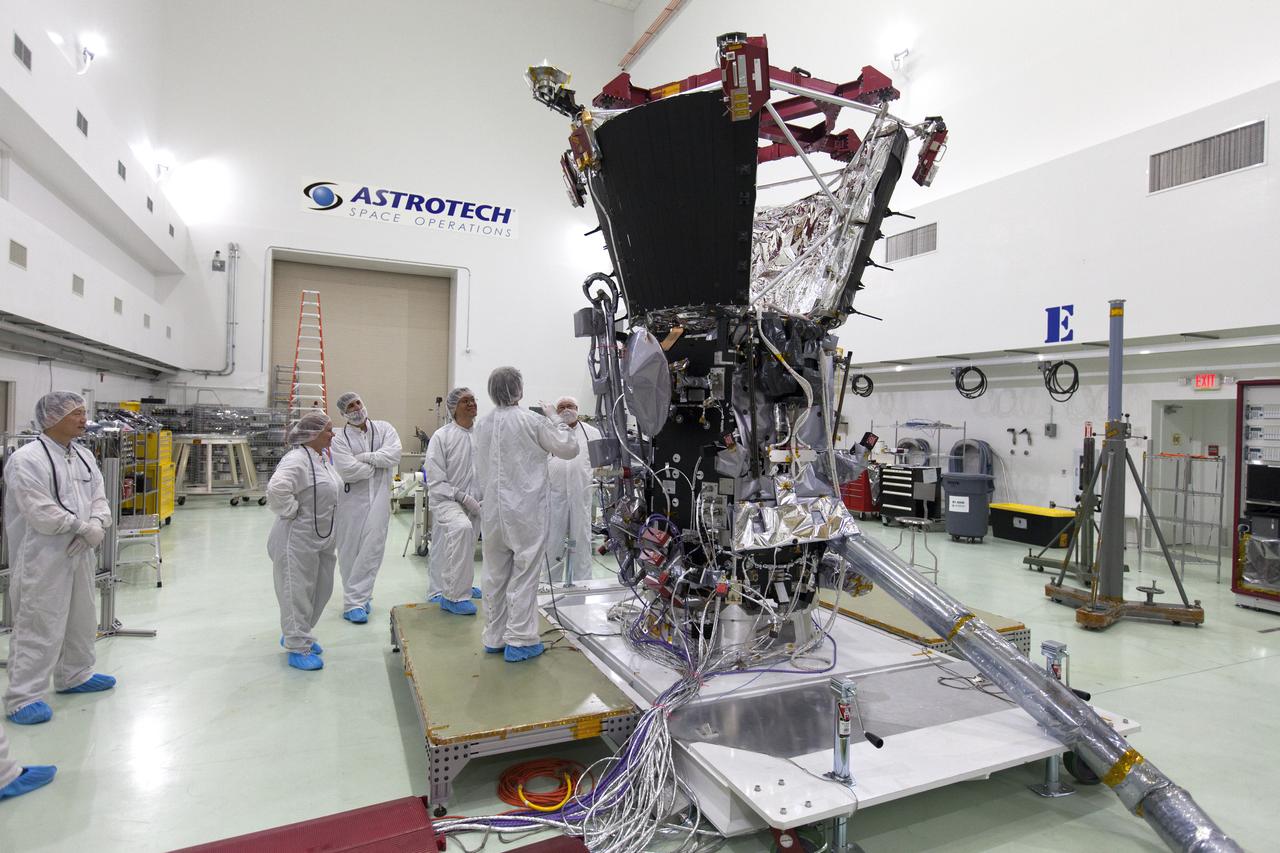

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, May 23, 2018, technicians and engineers deploy the magnetometer boom on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
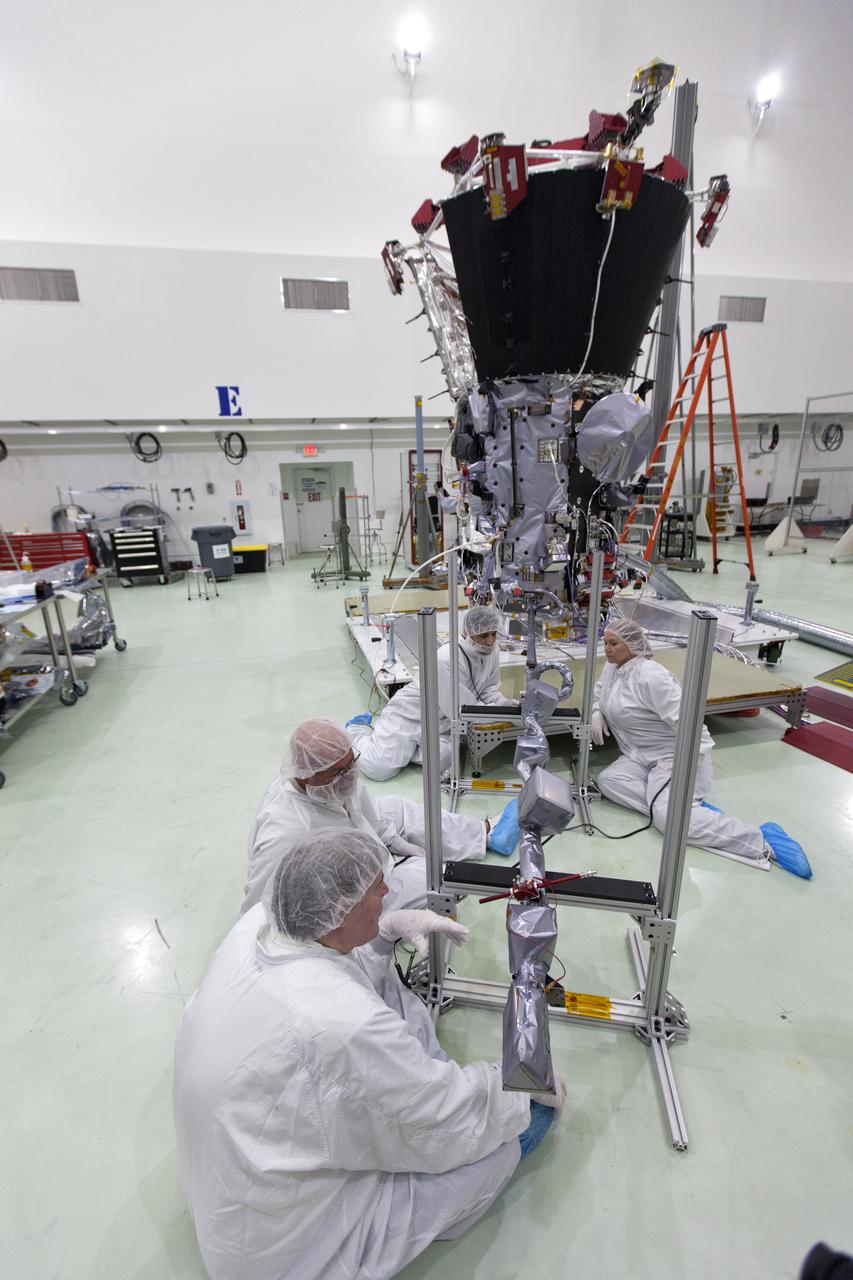

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, May 23, 2018, technicians and engineers deploy the magnetometer boom on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
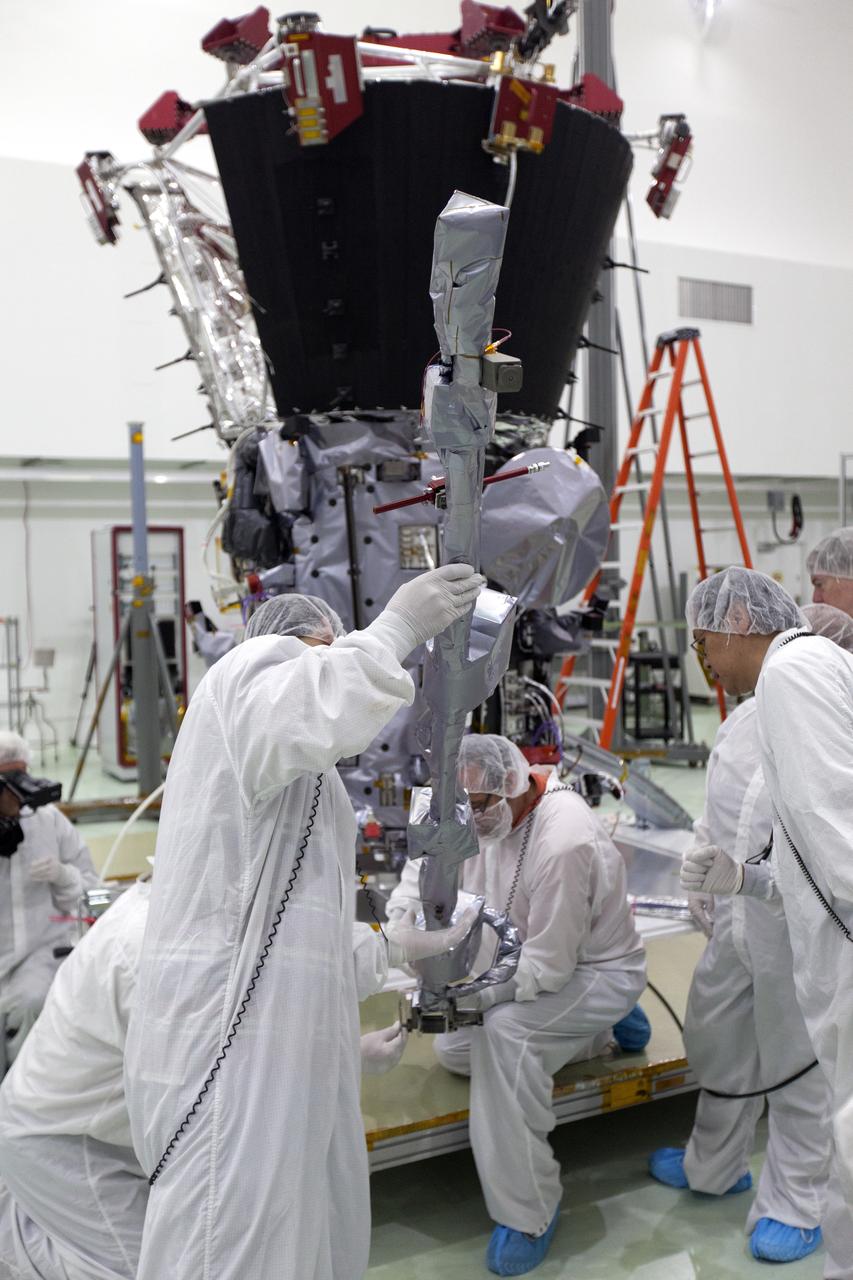

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, May 23, 2018, technicians and engineers deploy the magnetometer boom on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
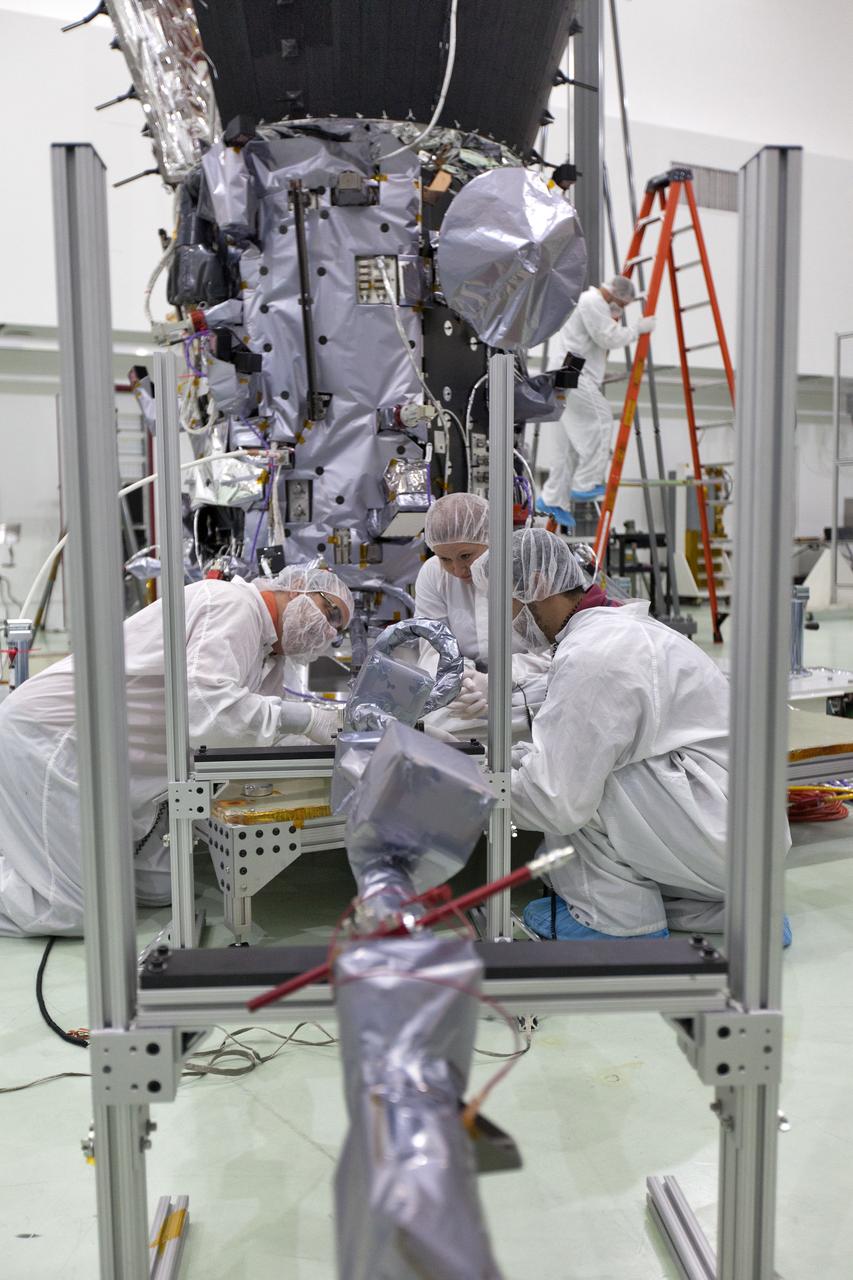

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, May 23, 2018, technicians and engineers deploy the magnetometer boom on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
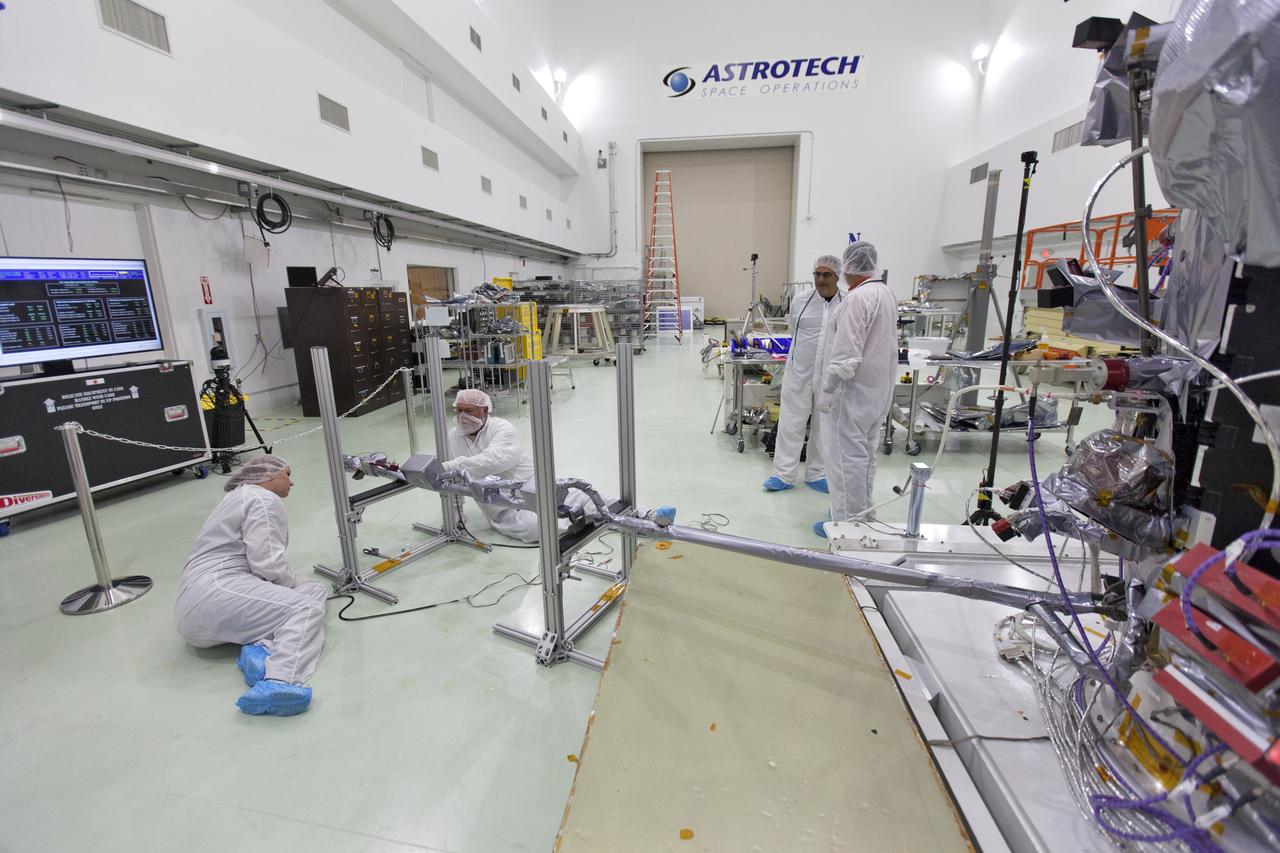

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, May 23, 2018, technicians and engineers deploy the magnetometer boom on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
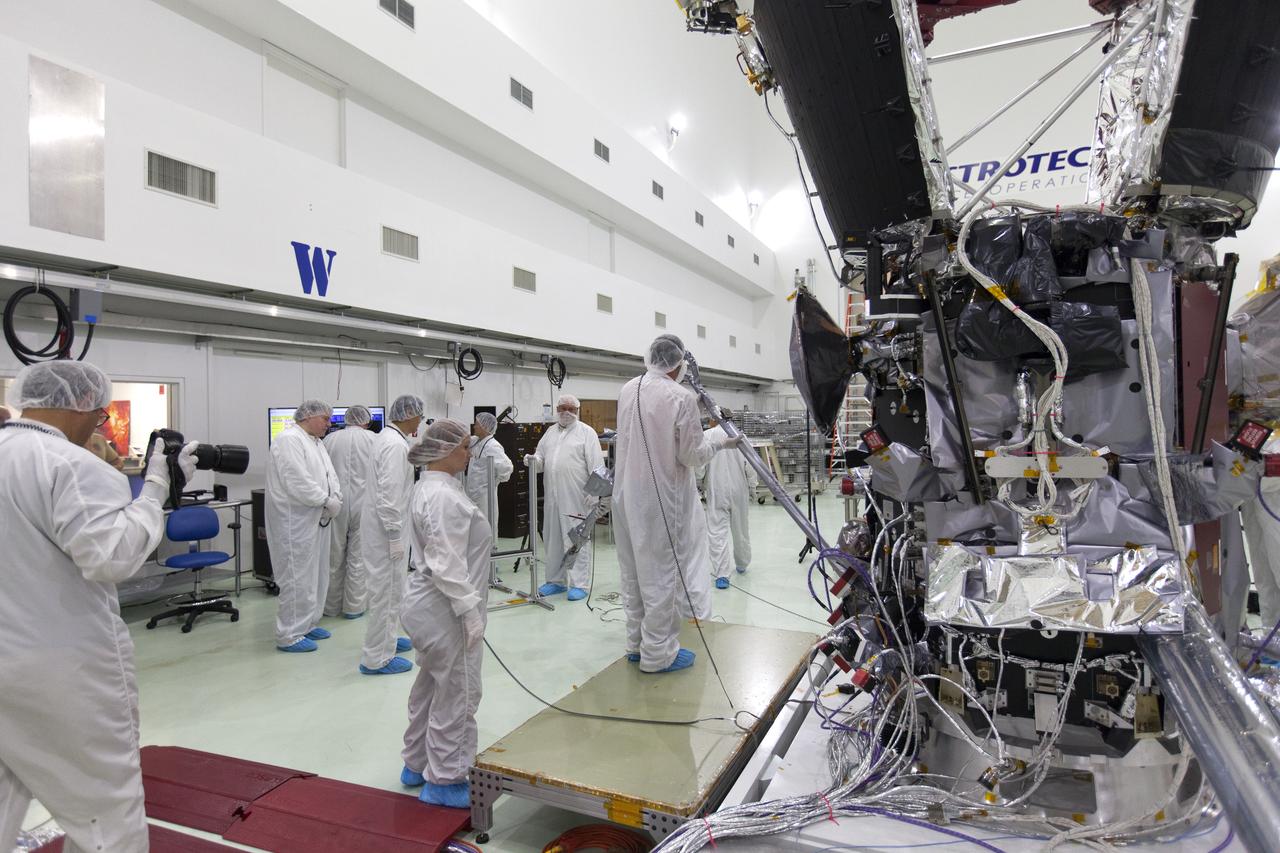

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, May 23, 2018, technicians and engineers deploy the magnetometer boom on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, May 23, 2018, technicians and engineers deploy the magnetometer boom on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
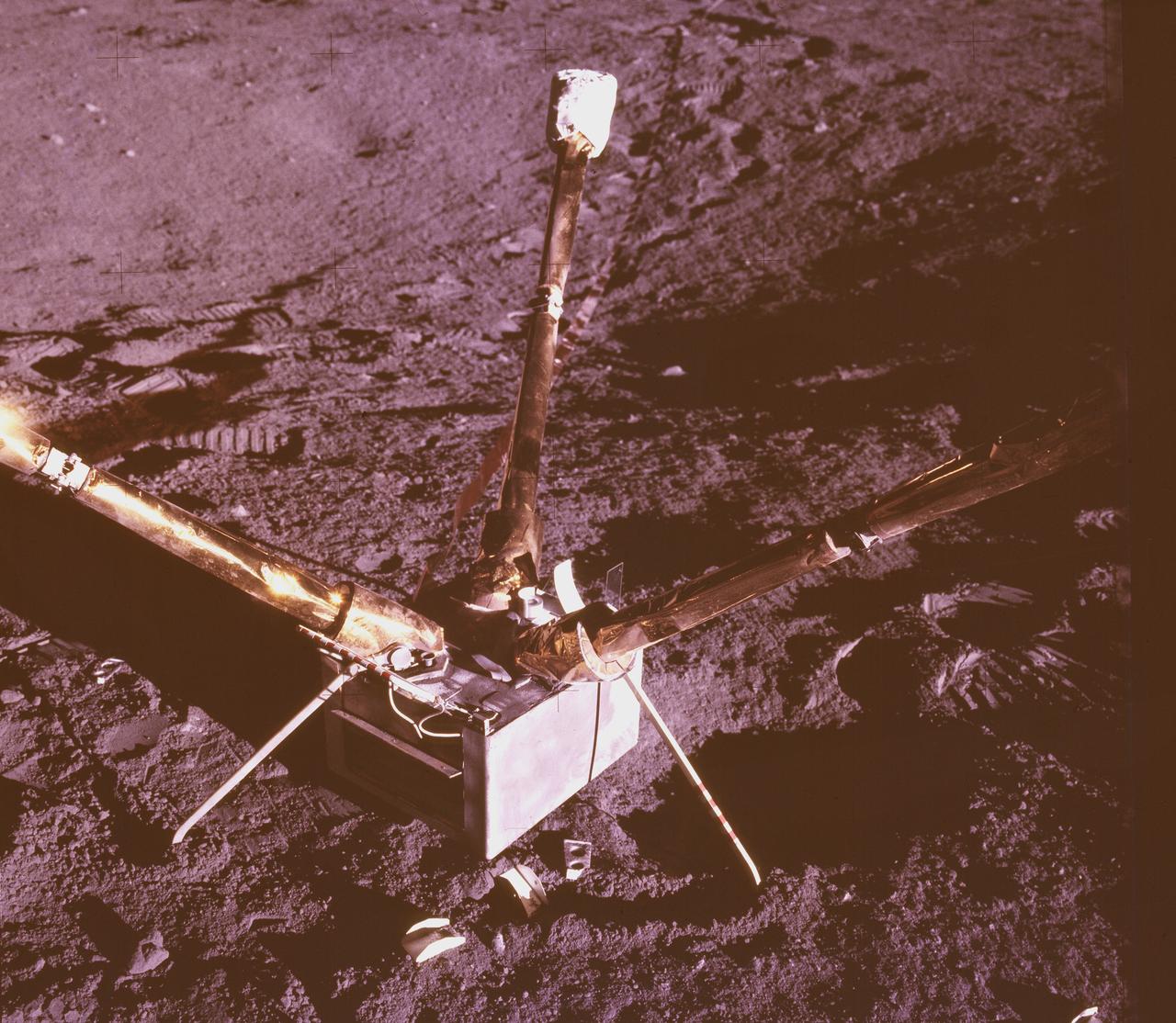
Sitting on the lunar surface, this magnetometer provided new data on the Moon’s magnetic field. This was one of the instruments used during the Apollo 12 mission. The second manned lunar landing mission, Apollo 12 launched from launch pad 39-A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on November 14, 1969 via a Saturn V launch vehicle. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard Apollo 12 was a crew of three astronauts: Alan L. Bean, pilot of the Lunar Module (LM), Intrepid; Richard Gordon, pilot of the Command Module (CM), Yankee Clipper; and Spacecraft Commander Charles Conrad. The LM, Intrepid, landed astronauts Conrad and Bean on the lunar surface in what’s known as the Ocean of Storms while astronaut Richard Gordon piloted the CM, Yankee Clipper, in a parking orbit around the Moon. Lunar soil activities included the deployment of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP), finding the unmanned Surveyor 3 that landed on the Moon on April 19, 1967, and collecting 75 pounds (34 kilograms) of rock samples. Apollo 12 safely returned to Earth on November 24, 1969.

S66-09379 (1 Oct. 1966) --- Tri-Axis Magnetometer-Sensor Unit mounted on telescoping boom. Cable connects Sensor Unit with Electronics Unit mounted on retrograde beam in retrograde adapter section. Objective of experiment is to monitor the direction and amplitude of Earth's magnetic field (Gemini-12). Photo credit: NASA

Apollo 12 mission deploys Ames developed special Lunar surface Magnetometer to measure magnetic fields on the moon (Tri-axis magnetometer)

Astronaut Story Musgrave, anchored to the end of the remote manipulator arm, prepares to be elevated to the top of the towering Hubble Space Telescope (HST) to install protective covers on magnetometers. Astornaut Jeffrey Hoffman assisted Musgrave with the final servicing tasks.
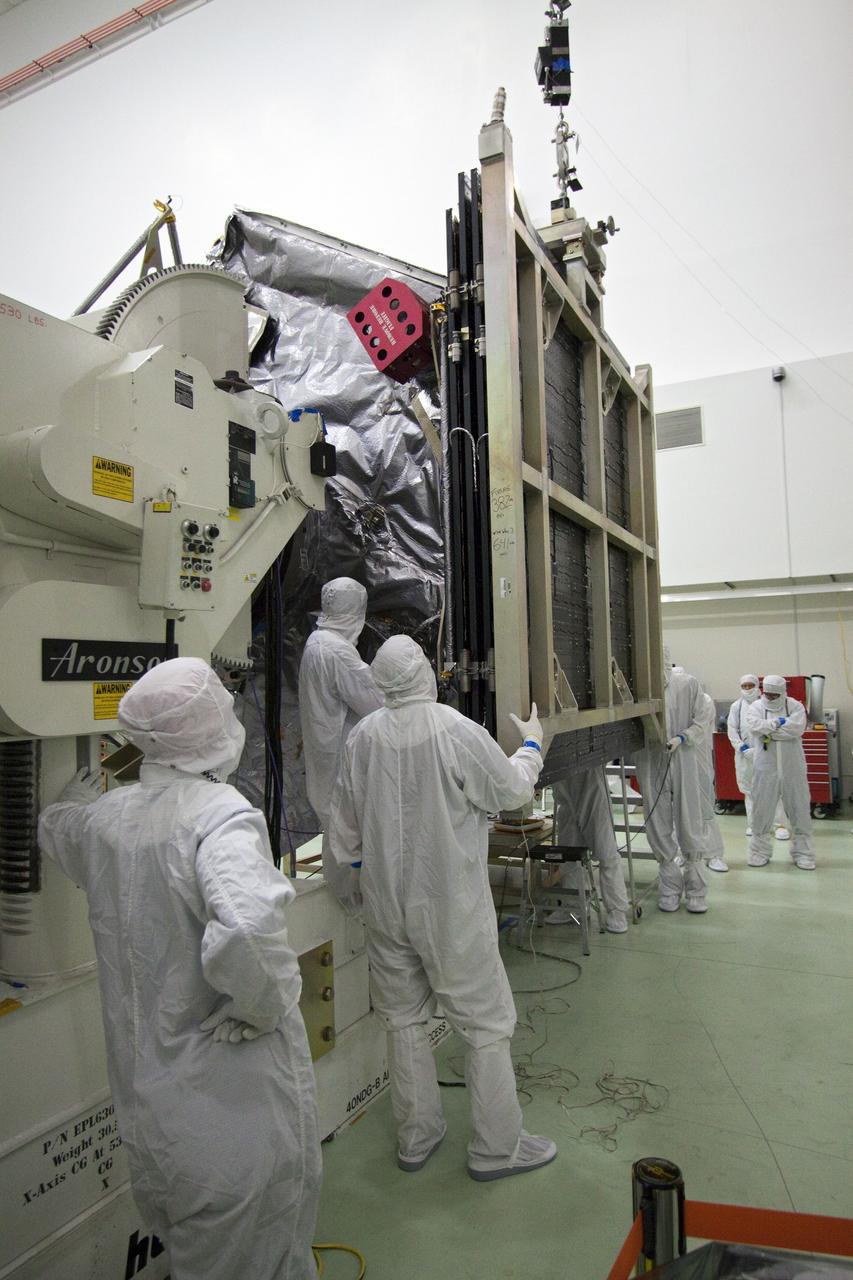

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians at Astrotech's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. guide the solar arrays into position on NASA's Juno spacecraft for installation. Later in processing, the magnetometer will be installed; a solar array illumination and magnetometer boom deployment test also are planned. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians at Astrotech's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. have positioned the solar arrays onto NASA's Juno spacecraft for installation. Later in processing, the magnetometer will be installed; a solar array illumination and magnetometer boom deployment test also are planned. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians at Astrotech's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. have secured solar array #2 to NASA's Juno spacecraft. Later in processing, the magnetometer will be installed; a solar array illumination and magnetometer boom deployment test also are planned. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
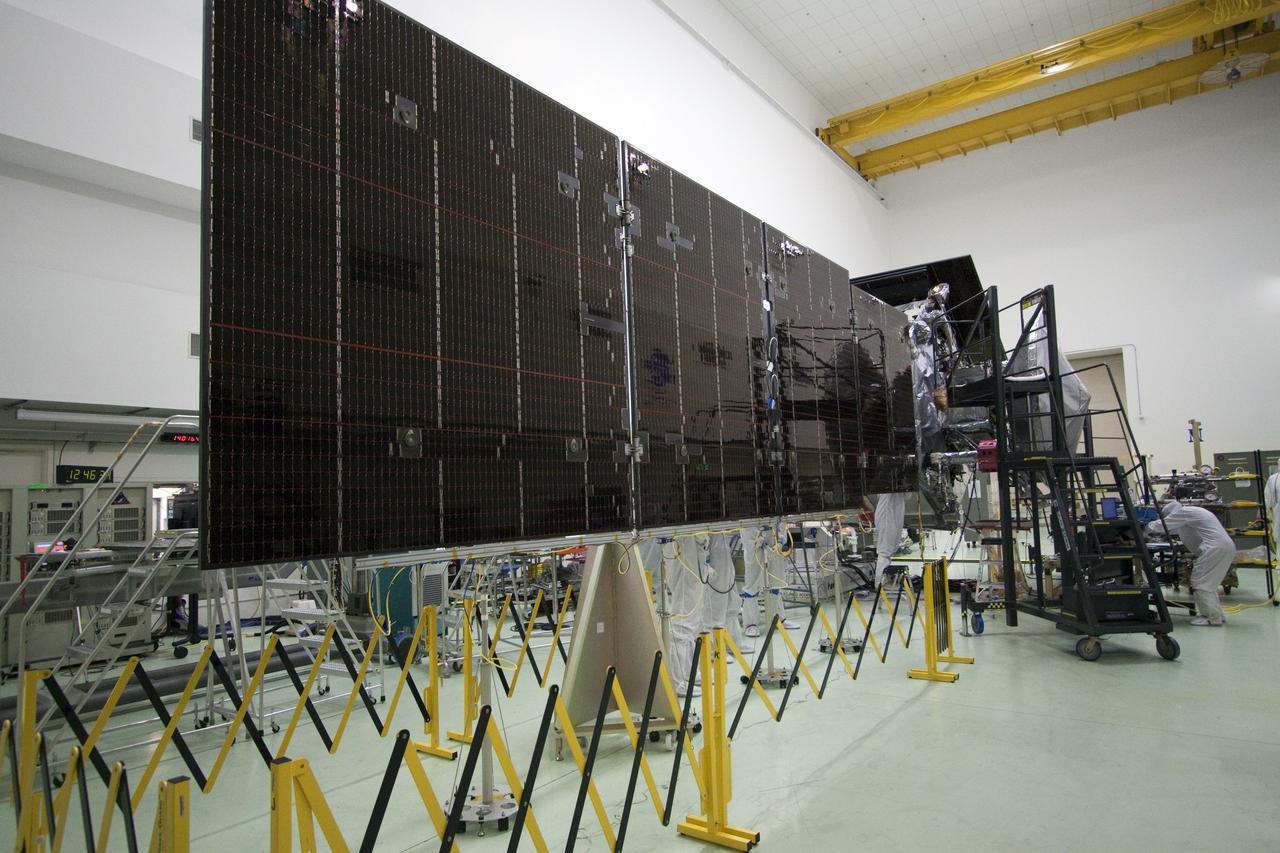

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians at Astrotech's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. are preparing to stow unfurled solar array #2 for NASA's Juno spacecraft. Later in processing, the magnetometer will be installed; a solar array illumination and magnetometer boom deployment test also are planned. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians at Astrotech's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. guide the solar arrays toward NASA's Juno spacecraft for installation. Later in processing, the magnetometer will be installed; a solar array illumination and magnetometer boom deployment test also are planned. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians at Astrotech's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. are stowing solar array #2 for NASA's Juno spacecraft. Later in processing, the magnetometer will be installed; a solar array illumination and magnetometer boom deployment test also are planned. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians at Astrotech's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. are stowing solar array #2 for NASA's Juno spacecraft. Later in processing, the magnetometer will be installed; a solar array illumination and magnetometer boom deployment test also are planned. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians at Astrotech's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. guide the solar arrays toward NASA's Juno spacecraft for installation. Later in processing, the magnetometer will be installed; a solar array illumination and magnetometer boom deployment test also are planned. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
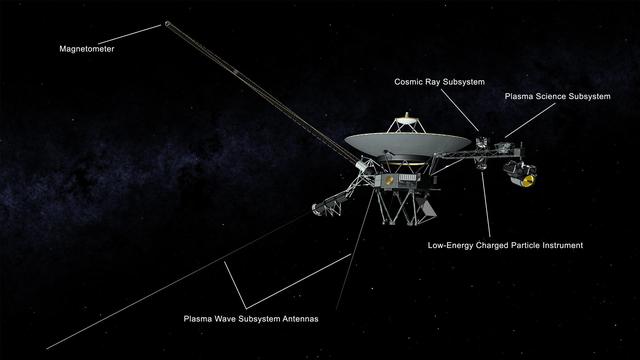
This illustration of NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft shows the location of the onboard science instruments that are still operating: the magnetometer, the cosmic ray subsystem, the plasma science experiment, the low-energy charged particle instrument and the antennas used by the plasma wave subsystem. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22915
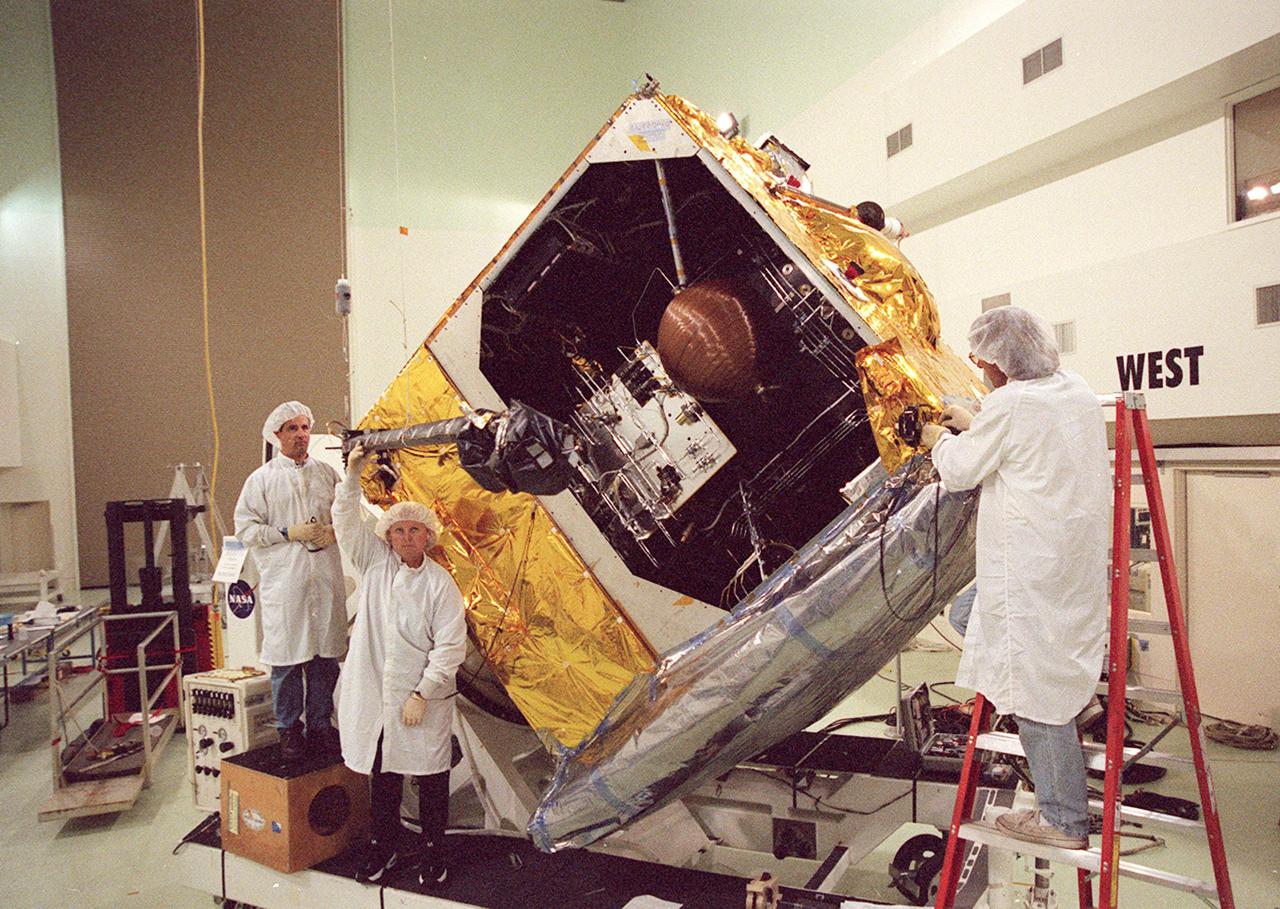

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., begin deploying the magnetometer boom on the GOES-M satellite. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
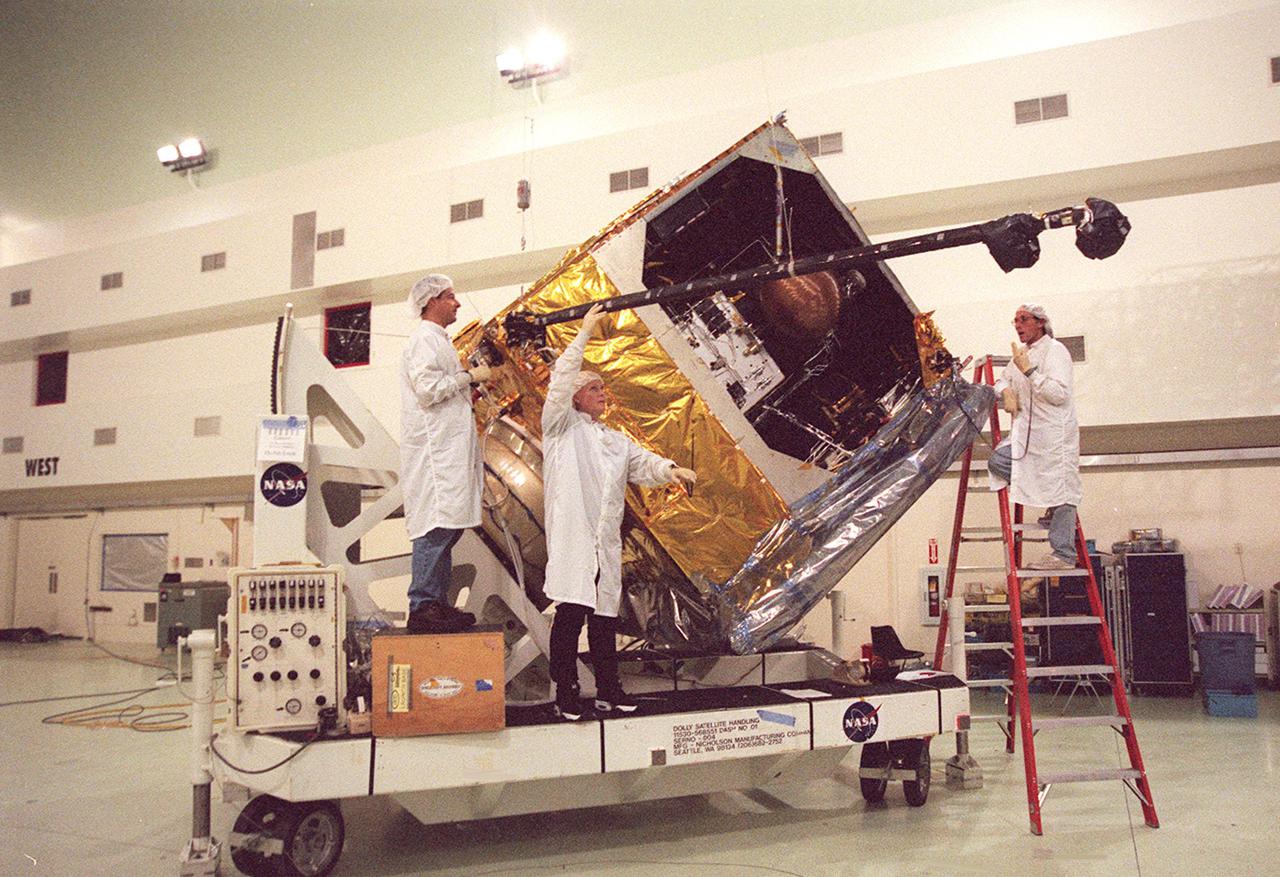

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., deploy the magnetometer boom on the GOES-M satellite. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
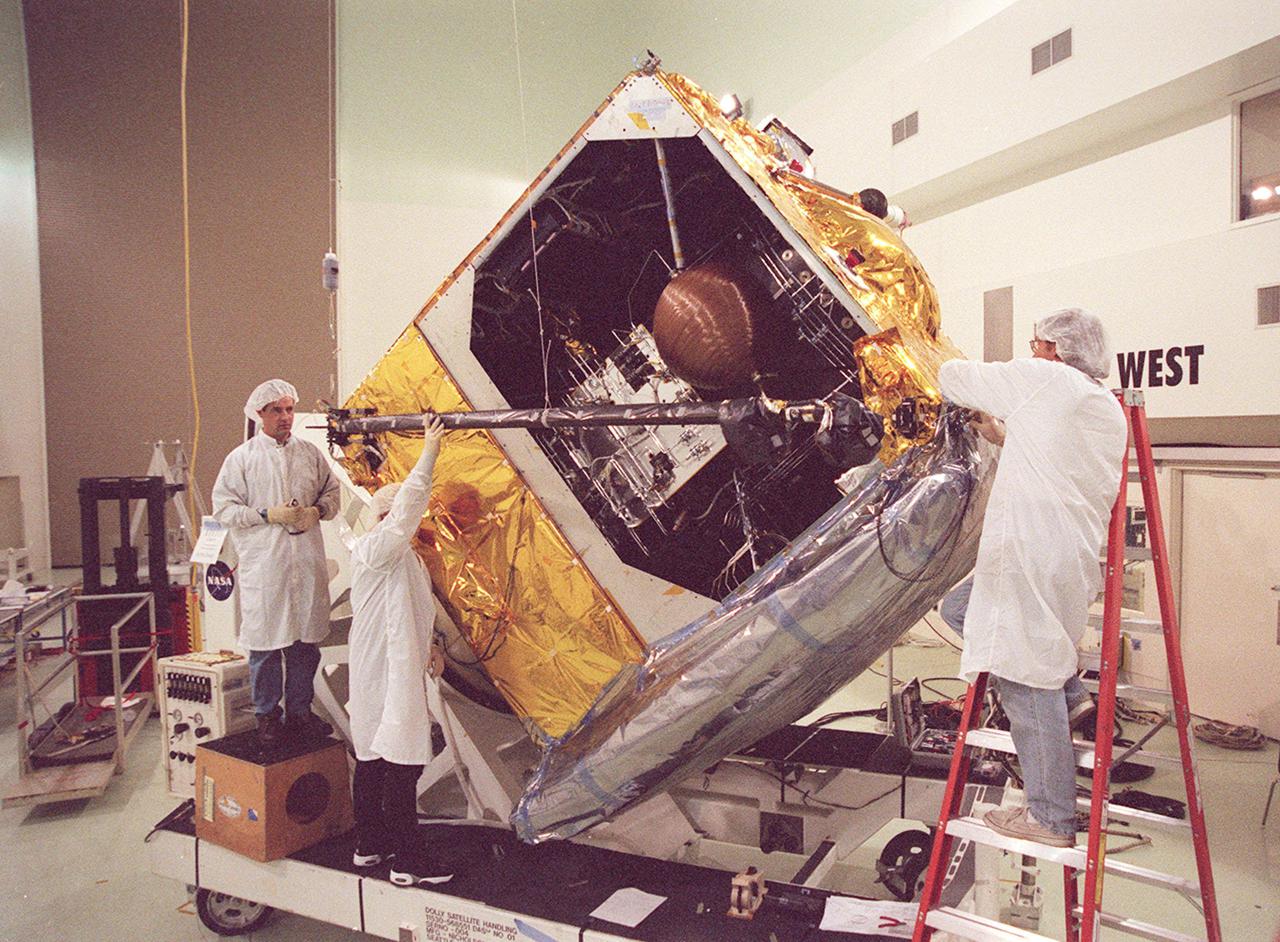

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., begin deploying the magnetometer boom on the GOES-M satellite. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - Inside Orbital Sciences Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a worker installs one of the fins on the aft skirt of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Space Technology 5 spacecraft later this month. ST5 contains three micro-satellites that will be positioned in a "string of pearls" constellation to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the Earth's magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The scheduled launch date is Feb. 28.

This archival photo shows the Voyager Proof Test Model undergoing a mechanical preparation and weight center of gravity test at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, on January 12, 1977. The stack of three white cylinders seen near center is a stand-in for the spacecraft's power generators (called RTGs). Above that, a silvery canister holds the spacecraft's magnetometer in its stowed configuration. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21477
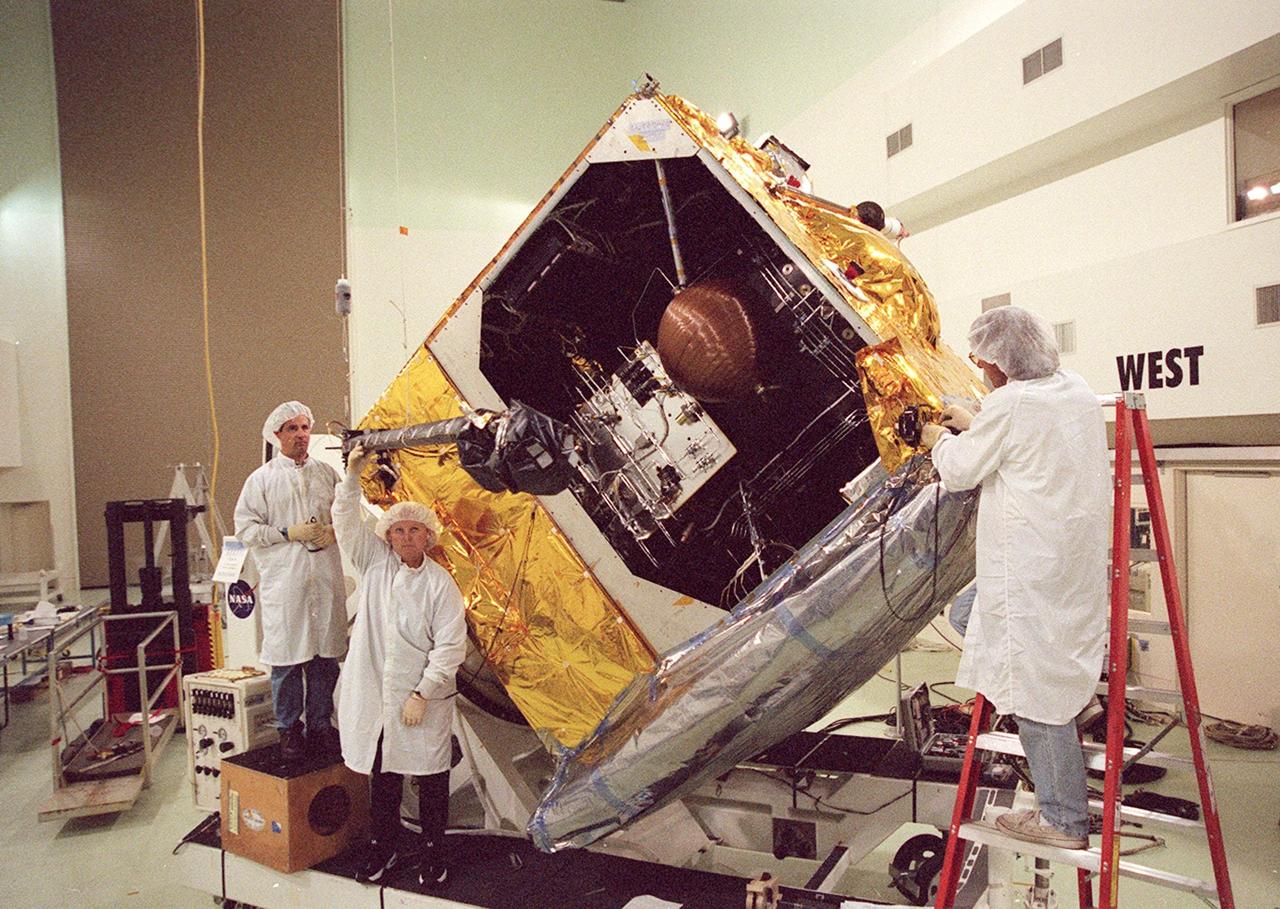

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., begin deploying the magnetometer boom on the GOES-M satellite. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
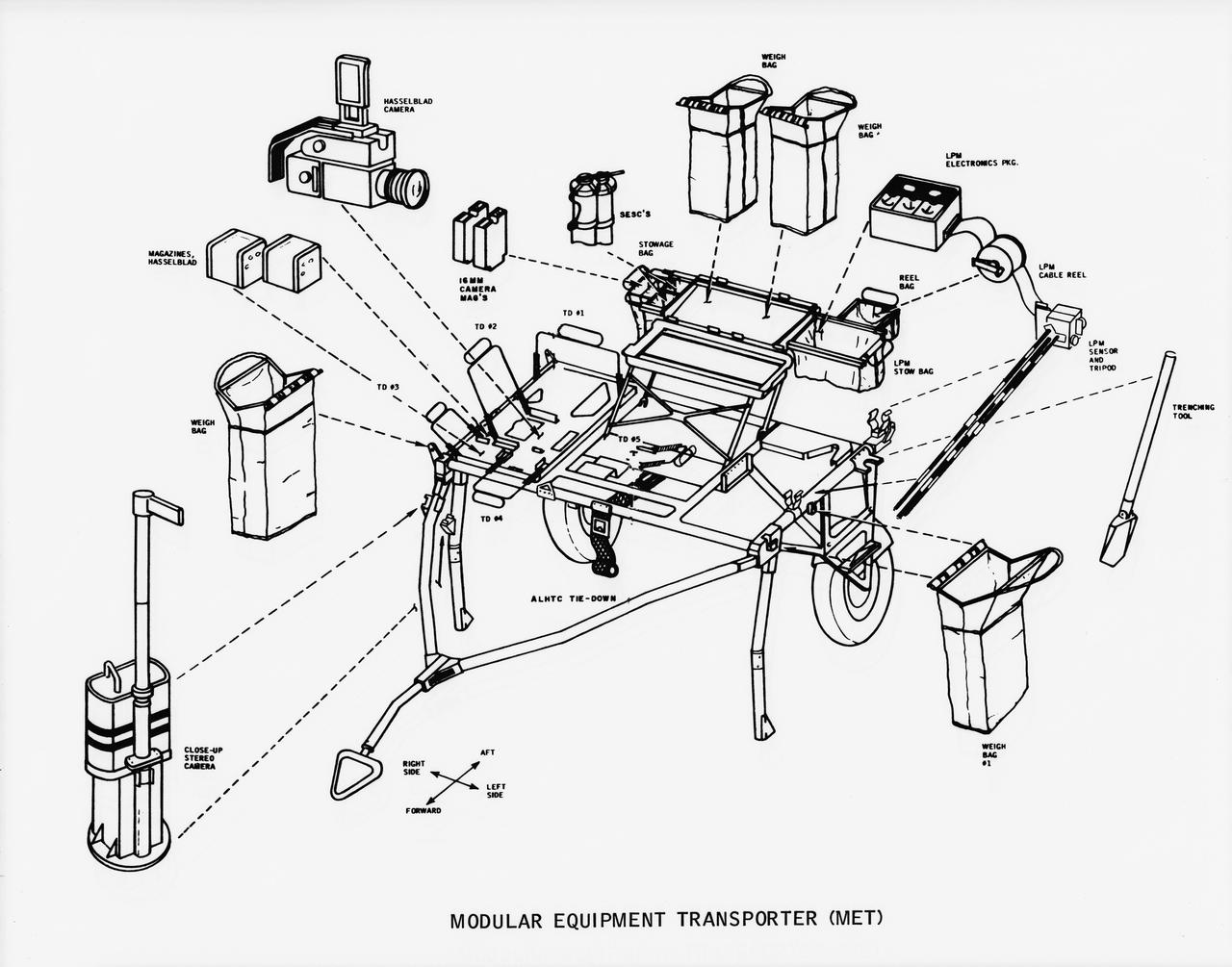
S70-50762 (November 1970) --- A line drawing illustrating layout view of the modular equipment transporter (MET) and its equipment. A MET (or Rickshaw, as it has been nicknamed) will be used on the lunar surface for the first time during the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission. The Rickshaw will serve as a portable workbench with a place for the Apollo lunar hand tools (ALHT) and their carrier, three cameras, two sample container bags, a special environment sample container (SESC), a lunar portable magnetometer (LPM) and spare film magazines.

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - Inside Orbital Sciences Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a worker underneath the tail of the Pegasus XL rocket completes installation of the fin. The Pegasus will launch the Space Technology 5 spacecraft later this month. ST5 contains three micro-satellites that will be positioned in a "string of pearls" constellation to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the Earth's magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The scheduled launch date is Feb. 28.

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - Inside Orbital Sciences Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers get ready to install one of the fins on the aft skirt of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Space Technology 5 spacecraft later this month. ST5 contains three micro-satellites that will be positioned in a "string of pearls" constellation to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the Earth's magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The scheduled launch date is Feb. 28.
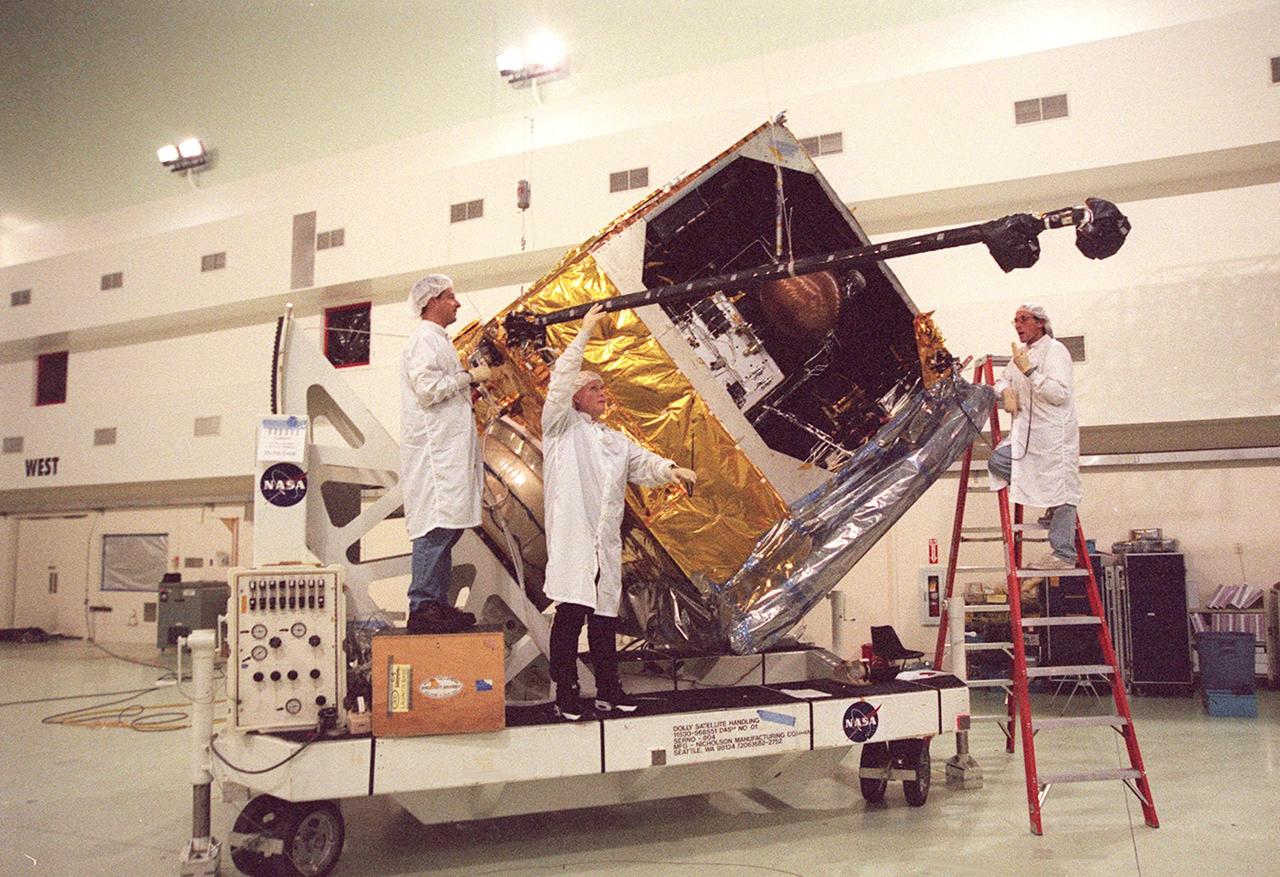

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., deploy the magnetometer boom on the GOES-M satellite. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - Inside Orbital Sciences Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers attach segments of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Space Technology 5 spacecraft later this month. ST5 contains three micro-satellites that will be positioned in a "string of pearls" constellation to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the Earth's magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The scheduled launch date is Feb. 28.
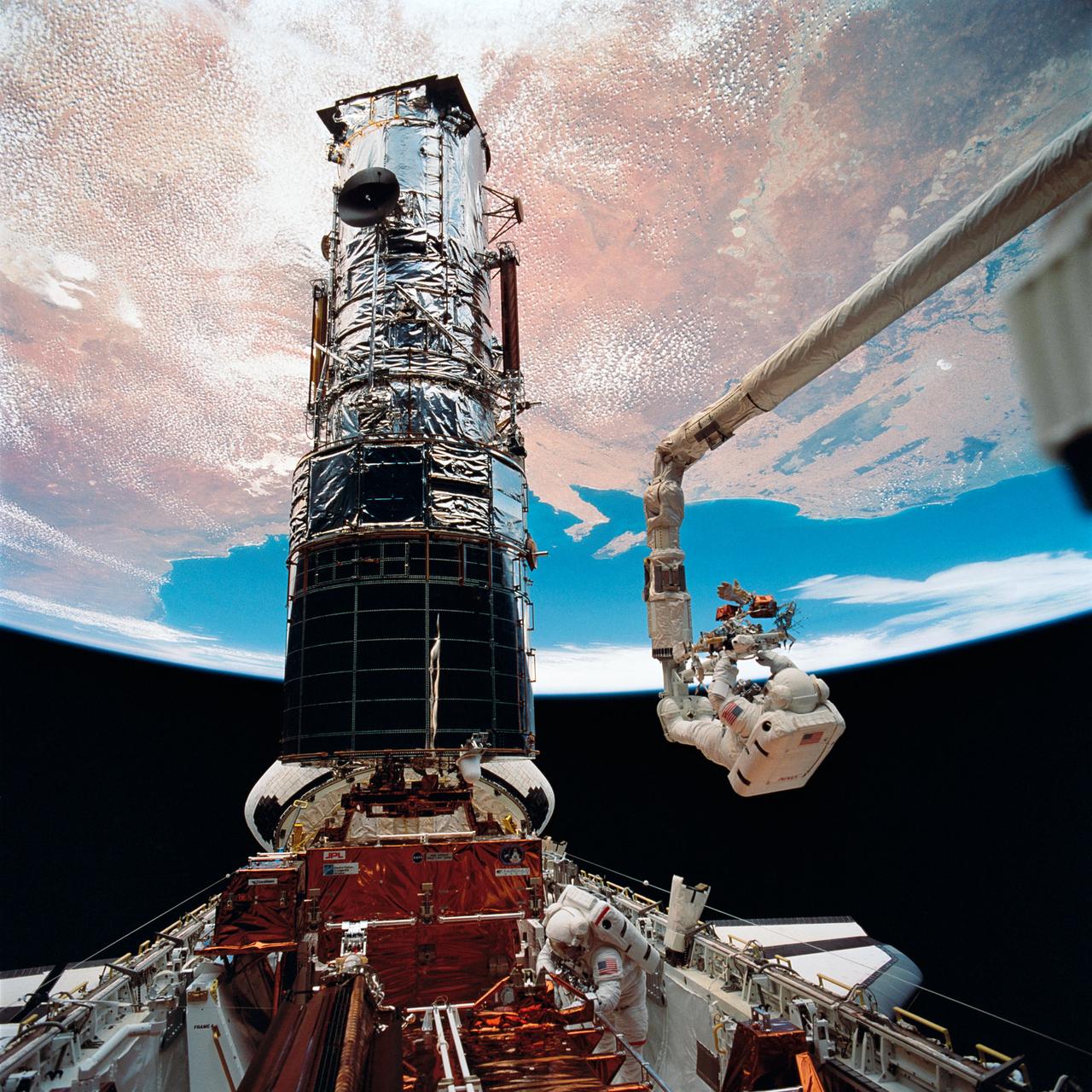

STS061-98-050 (9 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut F. Story Musgrave, anchored on the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, prepares to be elevated to the top of the towering Hubble Space Telescope (HST) to install protective covers on magnetometers. Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman (bottom of frame) assisted Musgrave with final servicing tasks on the telescope, wrapping up five days of extravehicular activities (EVA).

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - Inside Orbital Sciences Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers move the aft skirt toward the Pegasus XL launch vehicle for mating. The Pegasus will launch the Space Technology 5 spacecraft later this month. ST5 contains three micro-satellites that will be positioned in a "string of pearls" constellation to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the Earth's magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The scheduled launch date is Feb. 28.
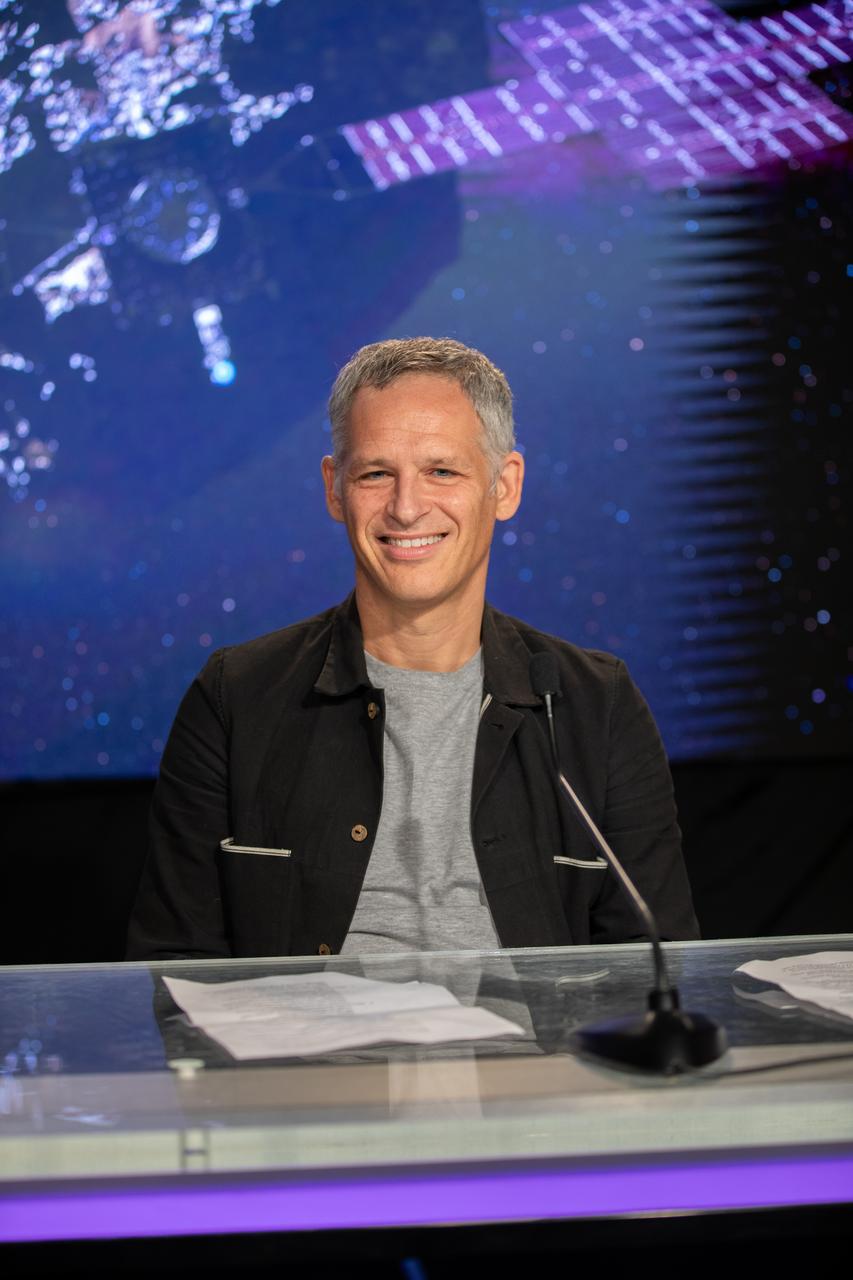

Ben Weiss, Psyche deputy principal investigator and magnetometer lead, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, participates in a Psyche mission and science briefing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Oct. 10, 2023. Psyche is the first mission to explore an asteroid with a surface that likely contains substantial amounts of metal rather than rock or ice. Liftoff of NASA’s Psyche spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket, is targeted for 10:16 a.m. EDT Thursday, Oct. 12, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
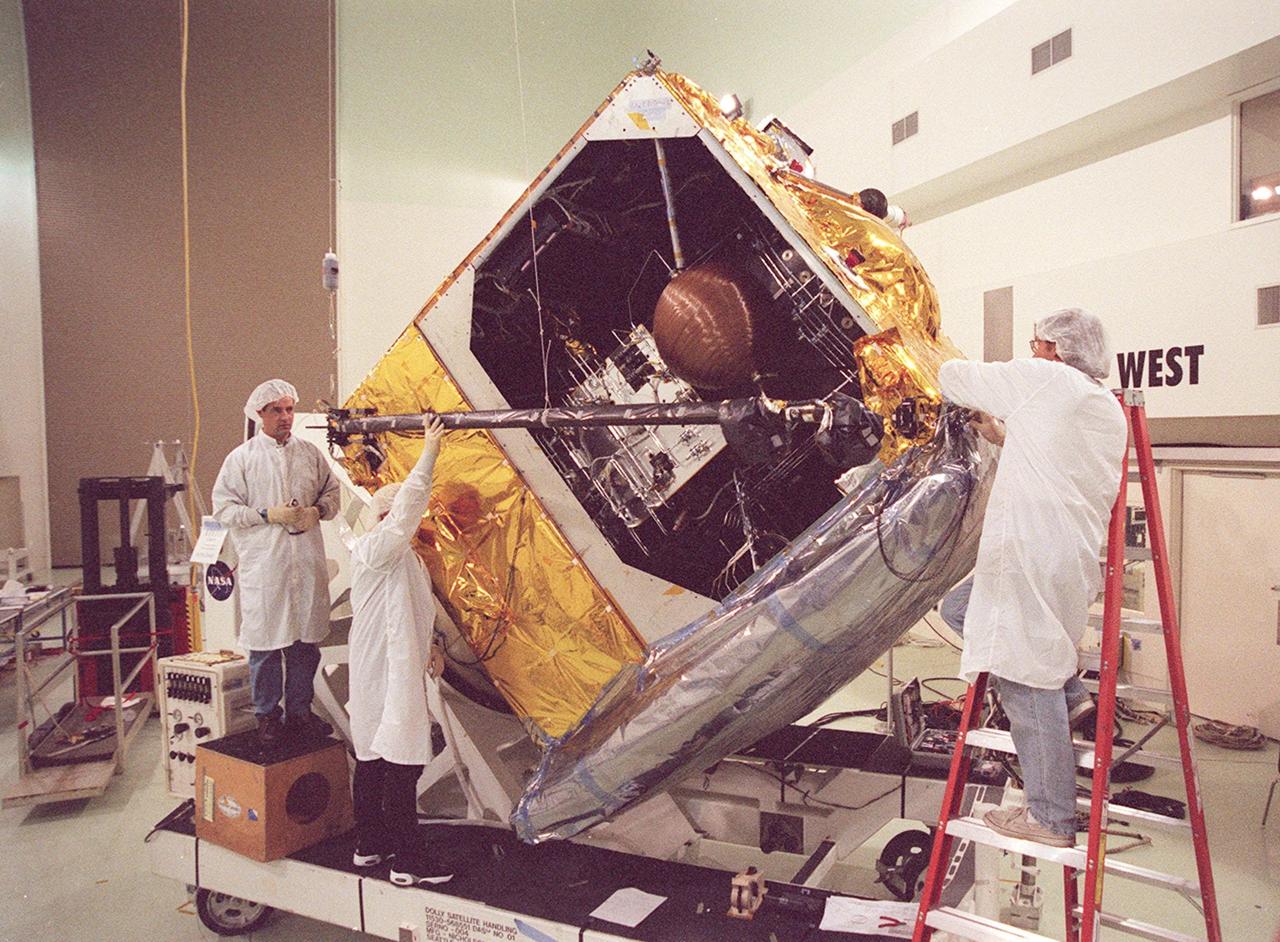

Workers at Astrotech, Titusville, Fla., begin deploying the magnetometer boom on the GOES-M satellite. The satellite is undergoing testing at Astrotech. The GOES-M provides weather imagery and quantitative sounding data used to support weather forecasting, severe storm tracking and meteorological research. The satellite is scheduled to launch July 12 on an Atlas-IIA booster, Centaur upper stage from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
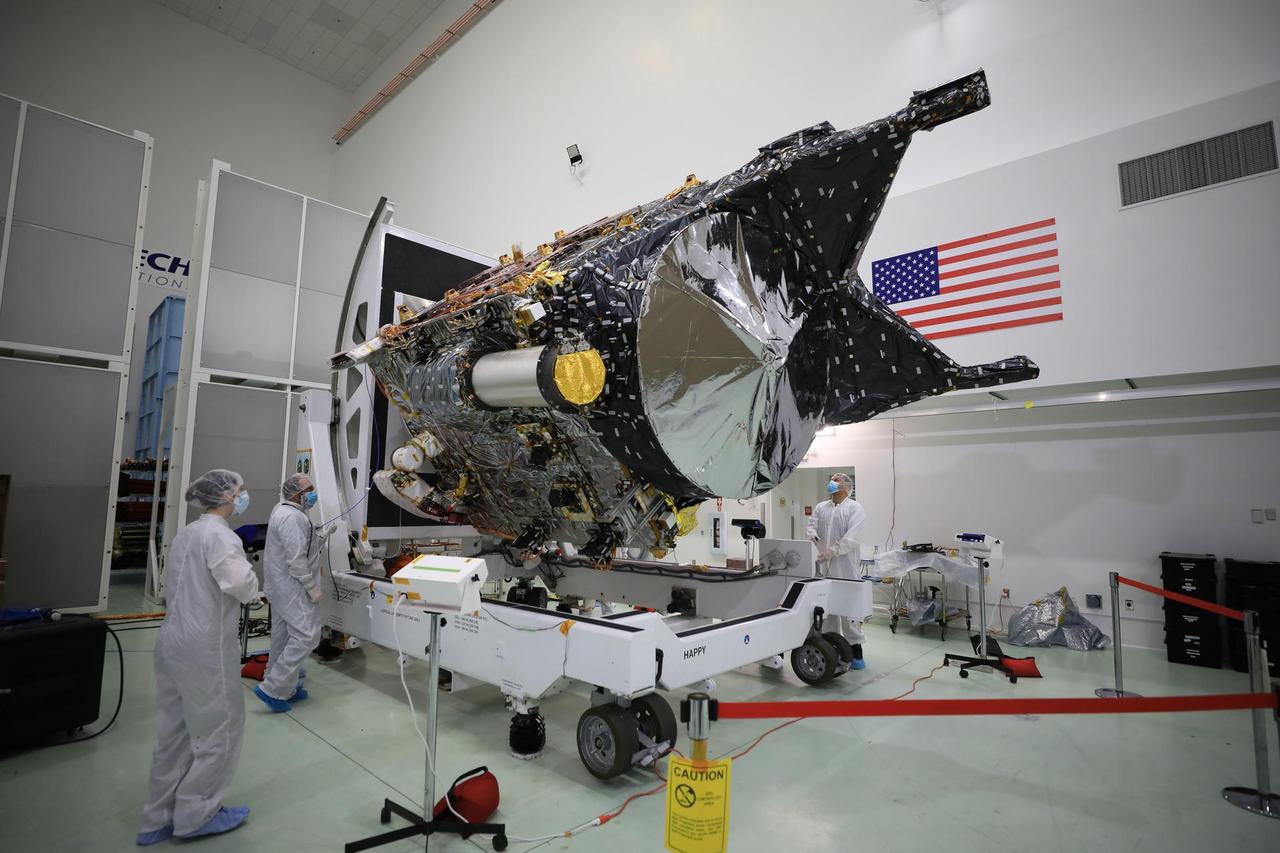

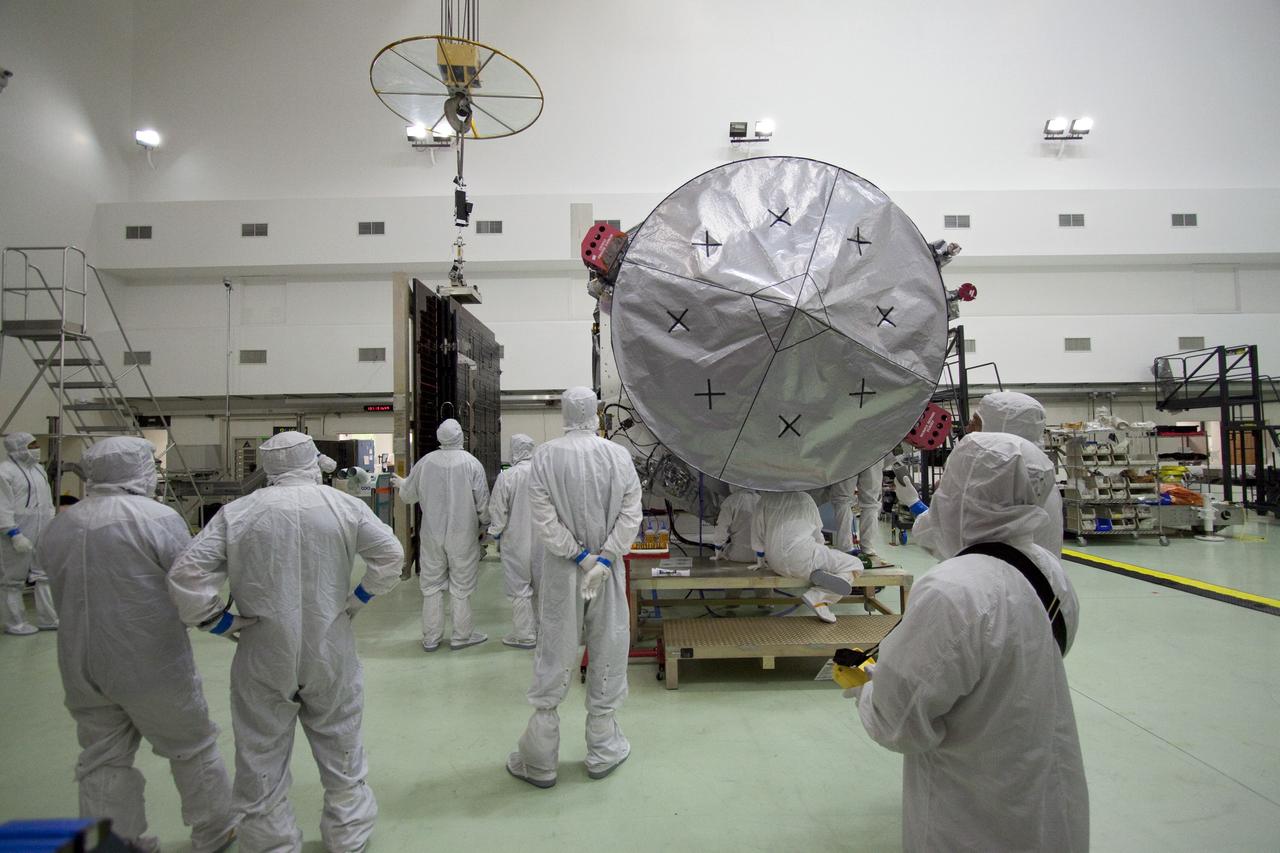
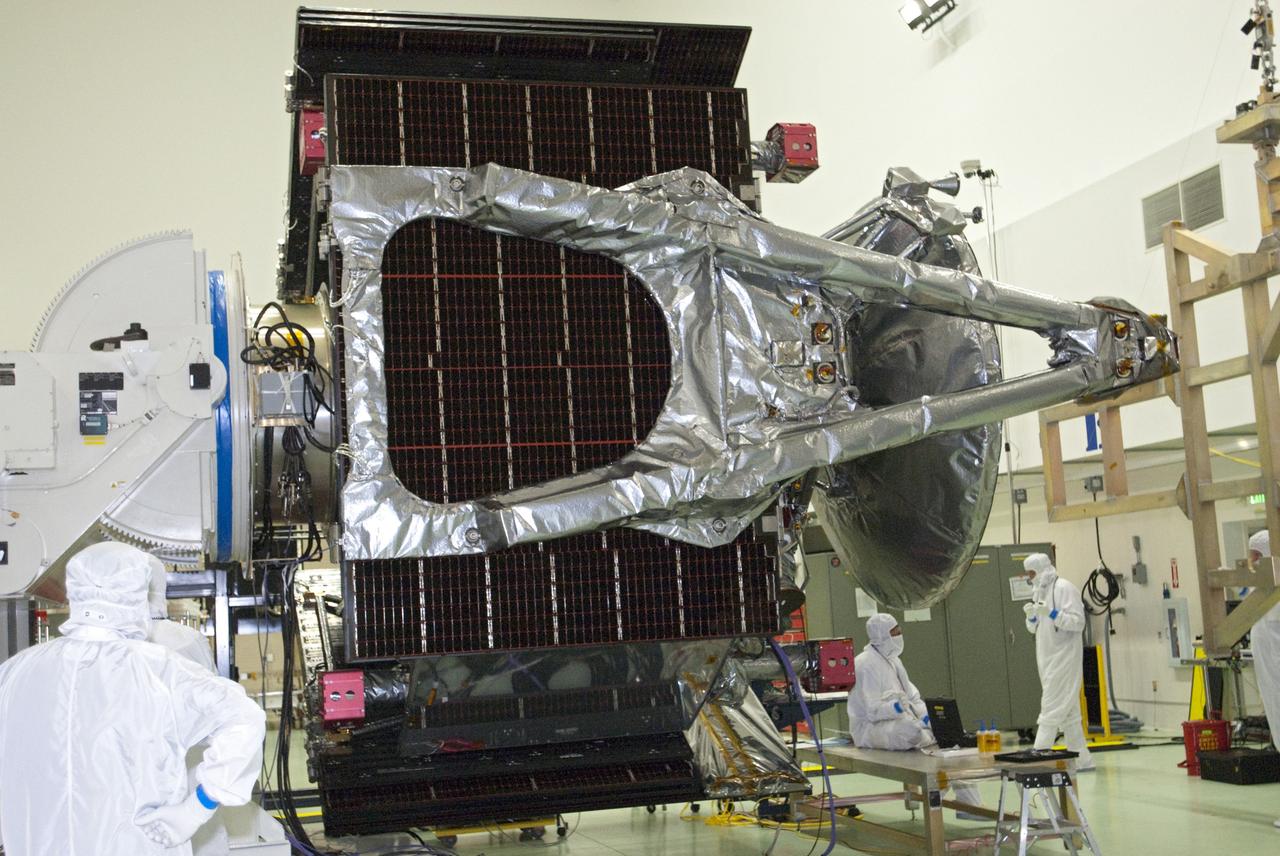
NASA's Psyche spacecraft is shown in a clean room on Dec. 8, 2022, at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft was powered on and connected to ground support equipment, enabling engineers and technicians to prepare it for launch in 2023. Teams working at Astrotech and at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California continue to monitor the health of its systems. After a one-year delay to complete critical testing, the Psyche project is targeting an October 2023 launch on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket. NASA's Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) technology demonstration, testing high-data-rate laser communications, is integrated into Psyche and will travel with it when it launches to its target, a metal-rich asteroid, also named Psyche, that lies in the main asteroid belt. The silver-colored cylinder shown in the photo is the sunshade for DSOC, and the gold blanketing is the aperture cover for the DSOC payload. The spacecraft's target may be the partial core of a planetesimal, a building block of rocky planets in our solar system. Researchers will study Psyche using a suite of instruments including multispectral cameras, a Gamma Ray and Neutron Spectrometer (GRNS) and a magnetometer. The GRNS and magnetometer sensors are visible in the photo as the tips of the two black protrusions at the far end of the spacecraft. Also visible is the large, disc-shaped high-gain antenna, which will enable the spacecraft to communicate with Earth. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25664
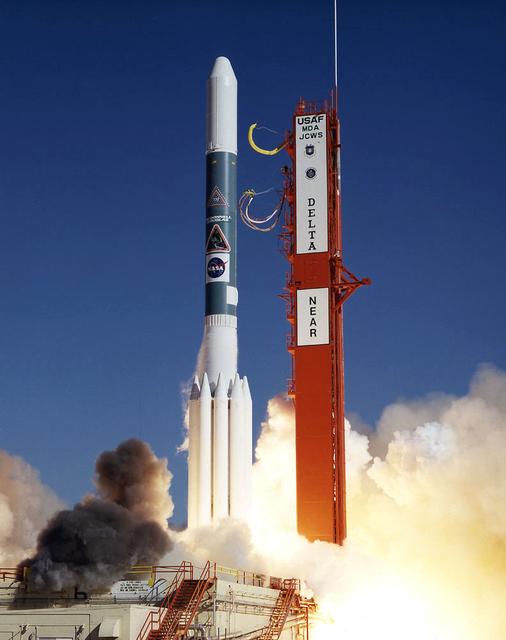

The Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous (NEAR) spacecraft embarks on a journey that will culminate in a close encounter with an asteroid. The launch of NEAR inaugurates NASA's irnovative Discovery program of small-scale planetary missions with rapid, lower-cost development cycles and focused science objectives. NEAR will rendezvous in 1999 with the asteroid 433 Eros to begin the first long-term, close-up look at an asteroid's surface composition and physical properties. NEAR's science payload includes an x-ray/gamma ray spectrometer, an near-infrared spectrograph, a laser rangefinder, a magnetometer, a radio science experiment and a multi-spectral imager.
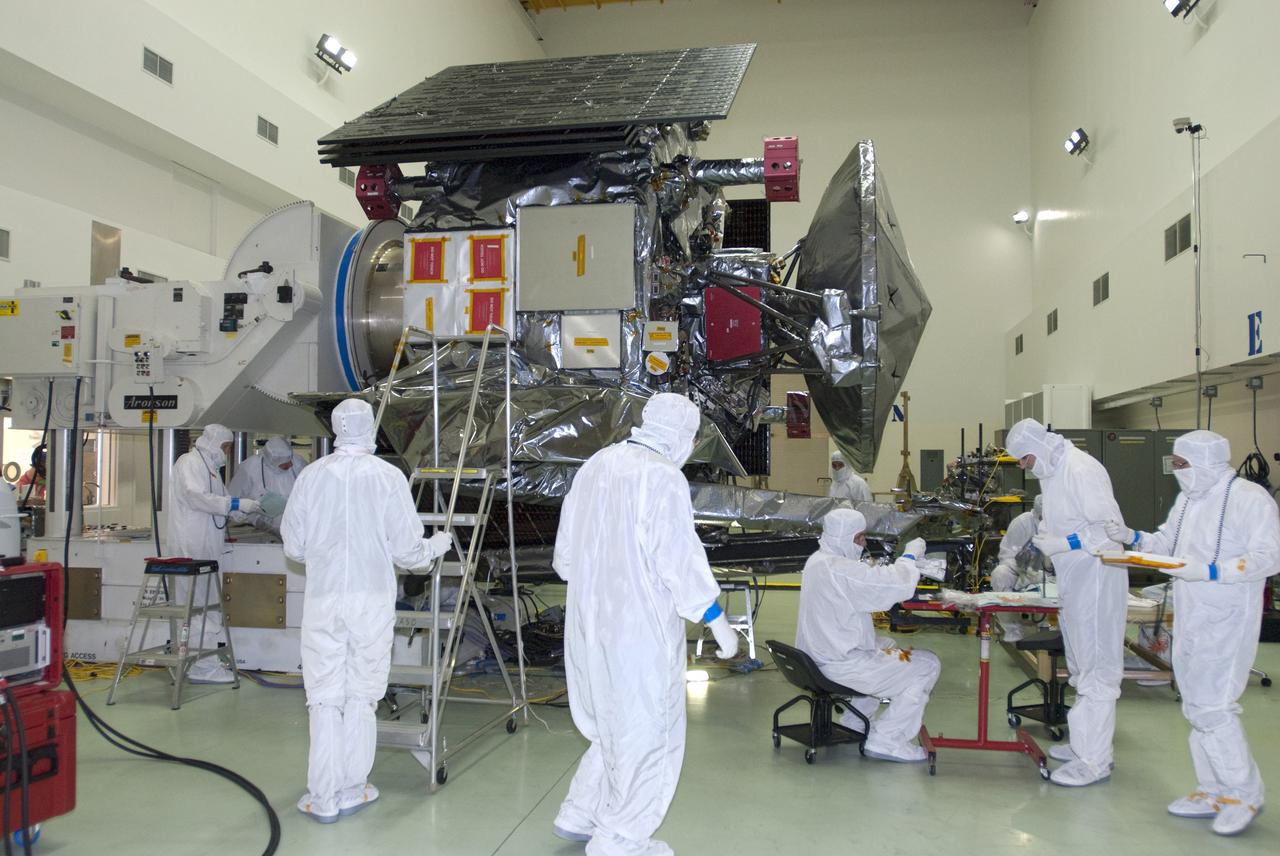

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians test the connections of solar array #1 with its magnetometer boom to NASA's Juno spacecraft after installation. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians conduct illumination tests on solar array panel #1 with its magnetometer boom for NASA's Juno spacecraft. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
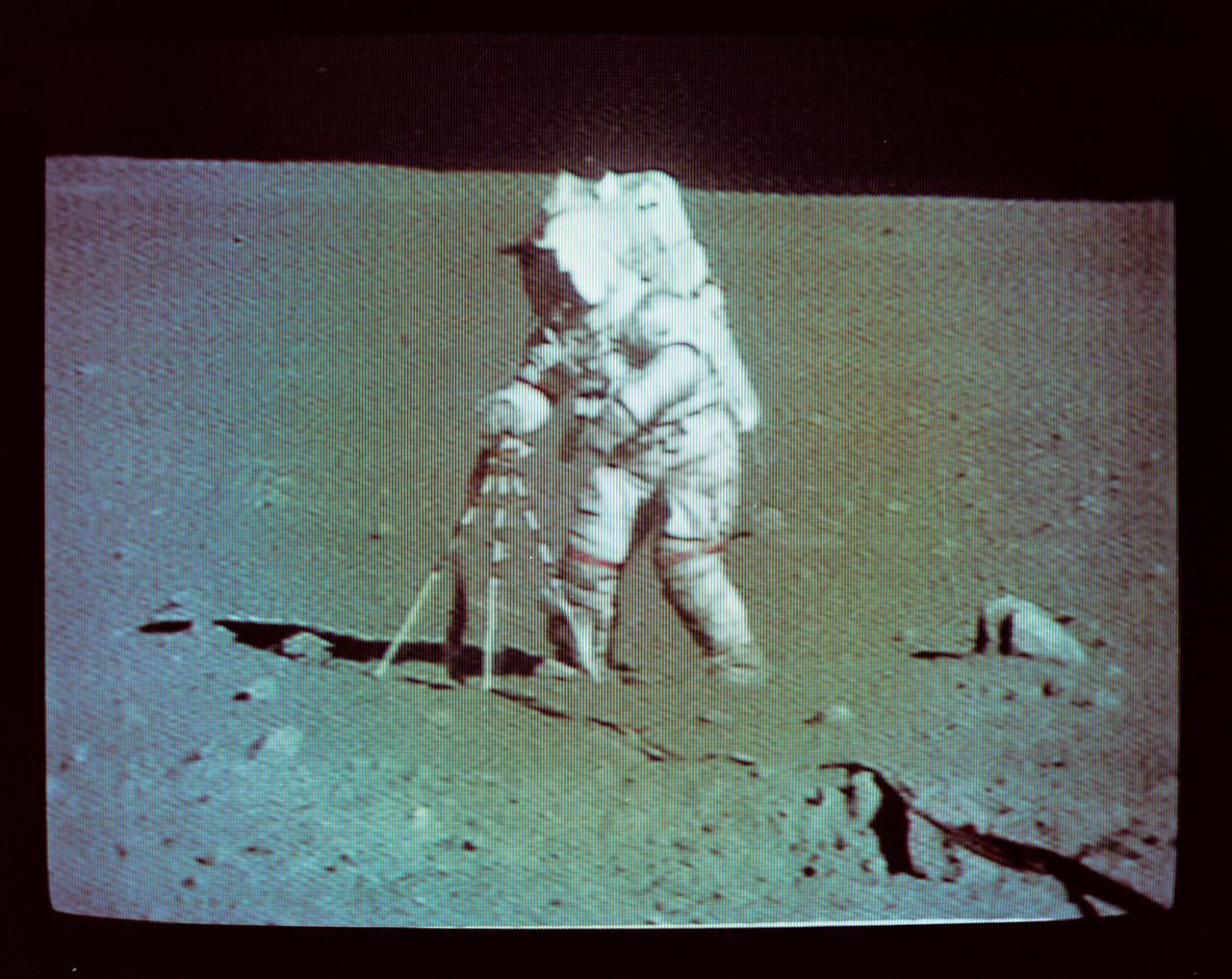

S72-35610 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, deploys the lunar Portable Magnetometer during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color television camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). While astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit, astronauts Young and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the Descartes landing site.
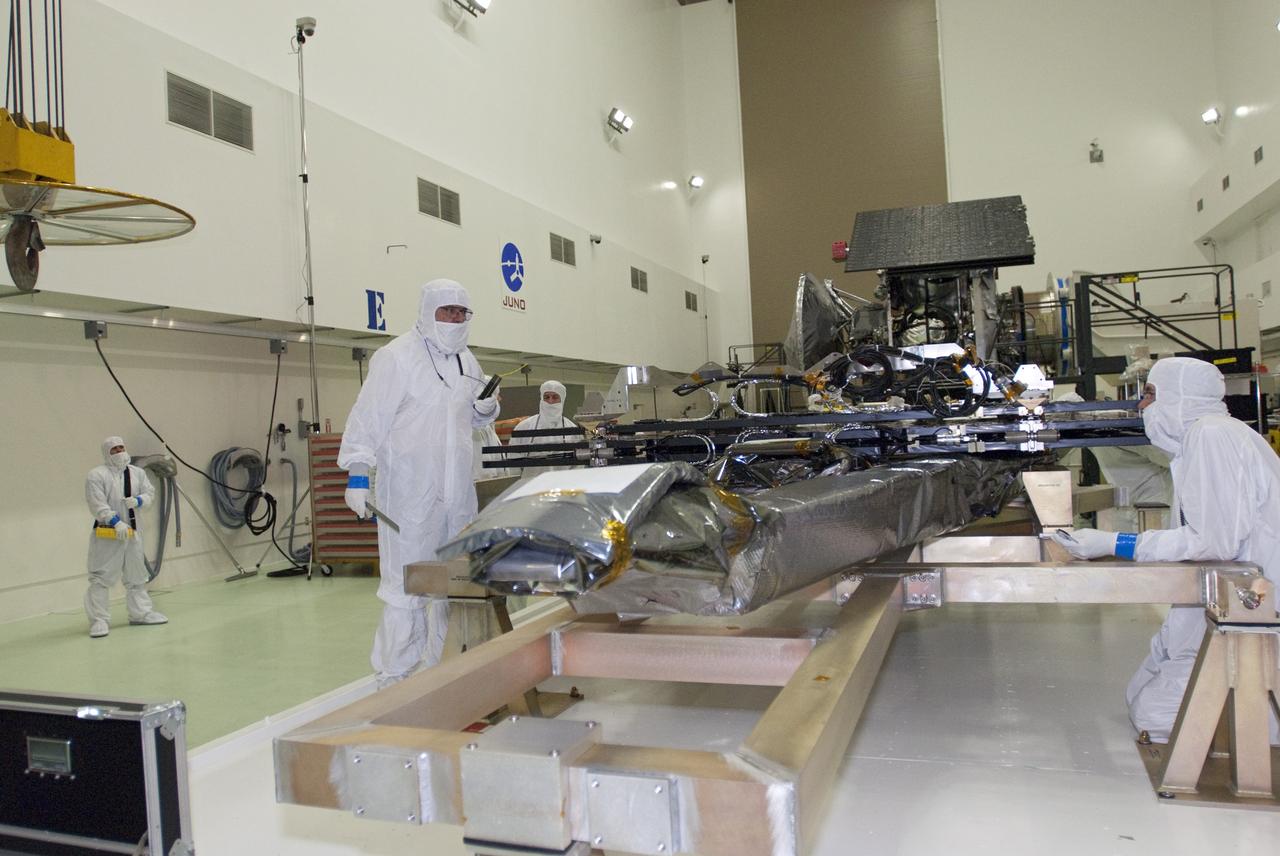

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians prepare solar array #1 with its magnetometer boom for installation to NASA's Juno spacecraft. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
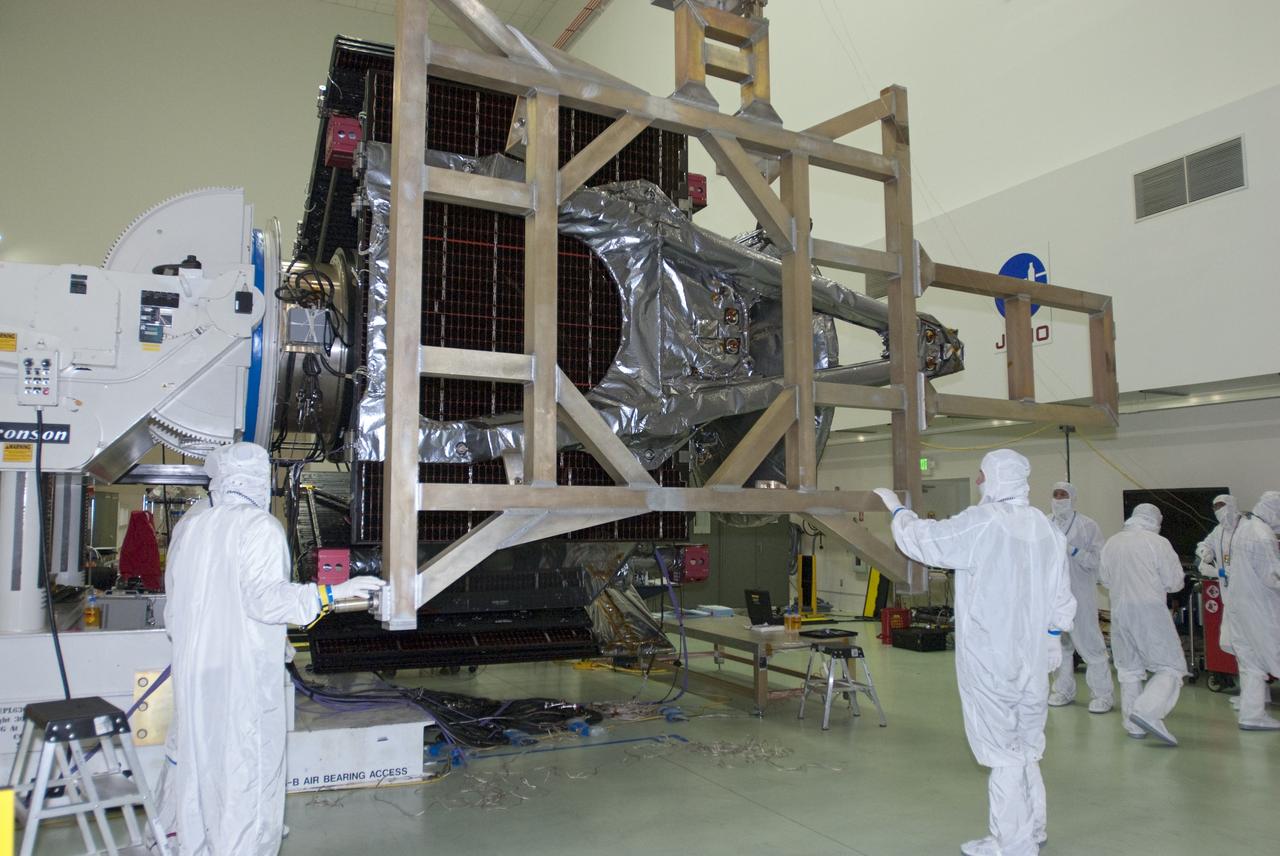

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians have installed a solar array #1 with its magnetometer boom to NASA's Juno spacecraft. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
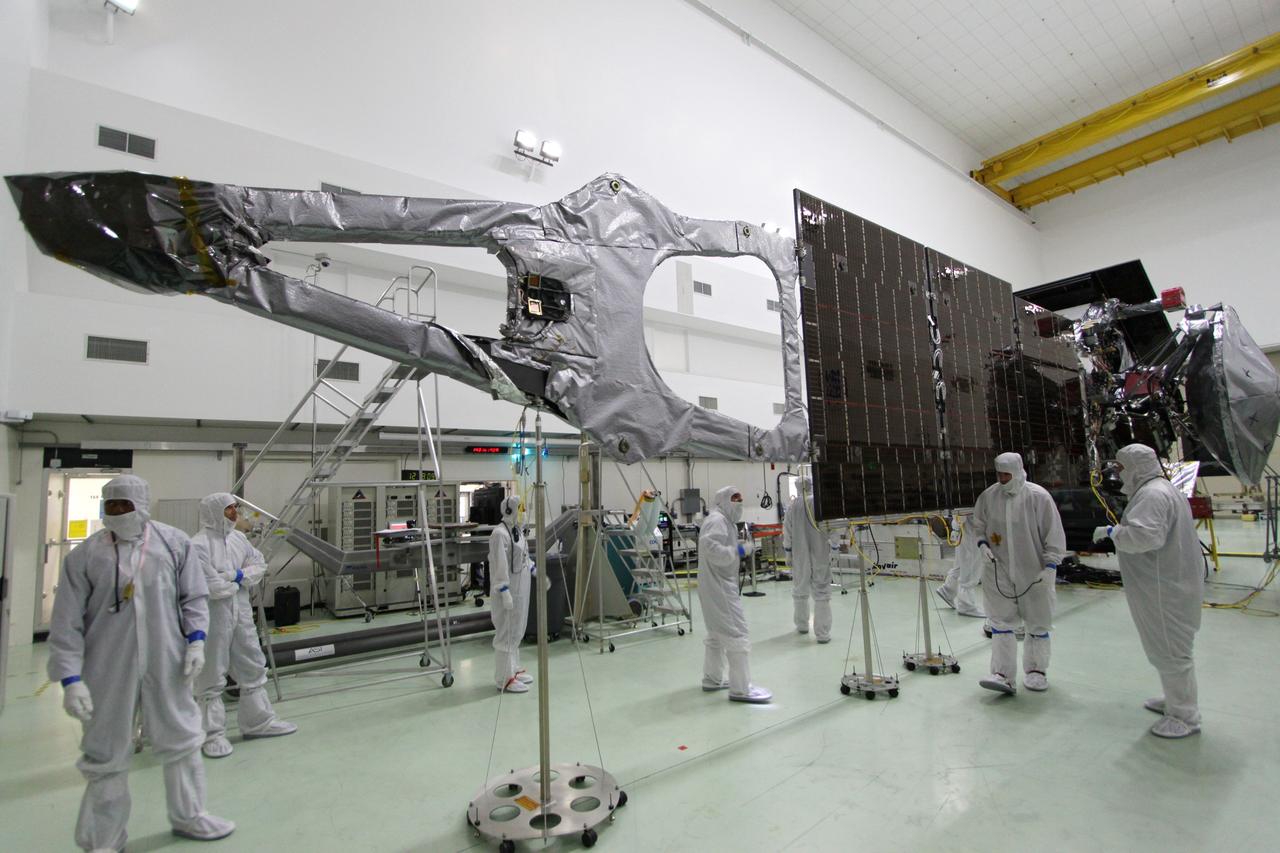

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians conduct deployment tests on solar array panel #1 with its magnetometer boom for NASA's Juno spacecraft prior to illumination testing. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
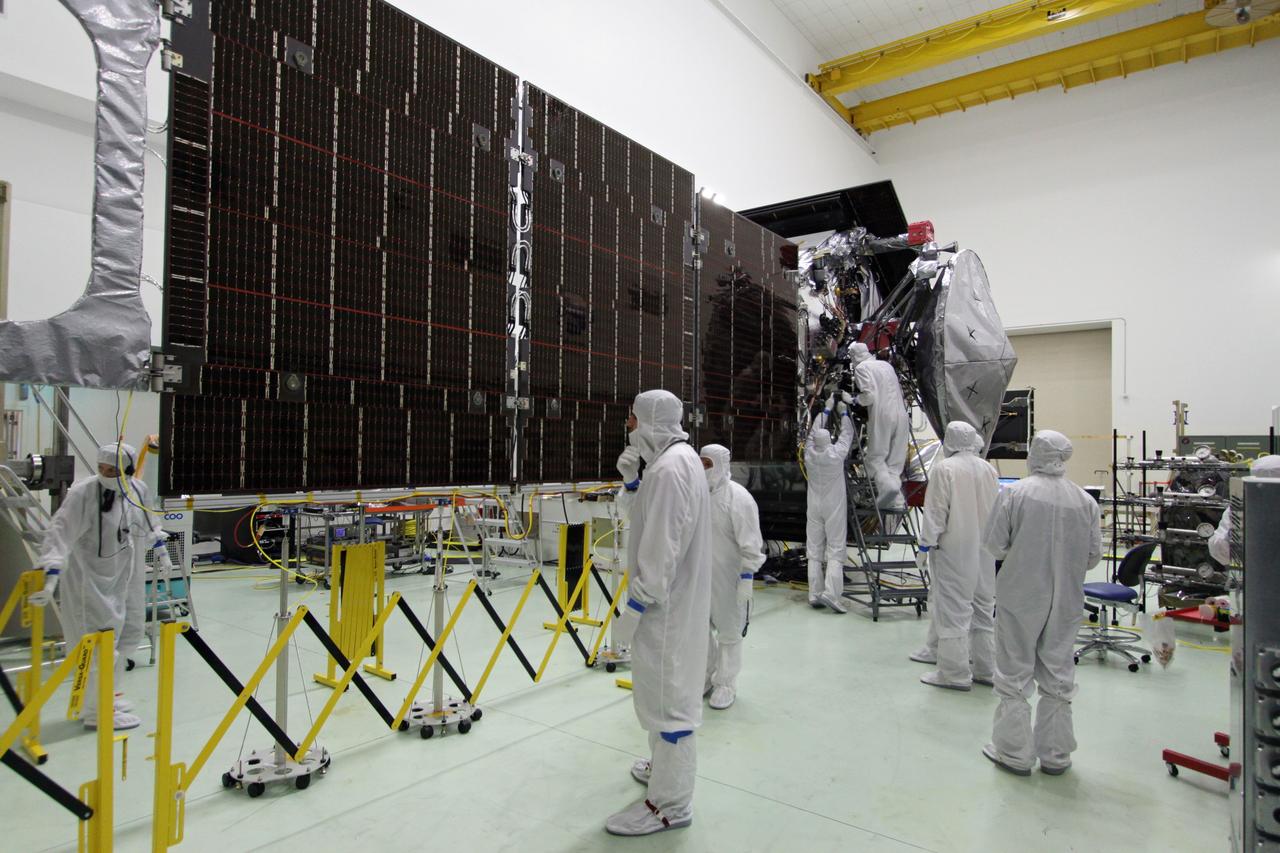

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians conduct deployment tests on solar array panel #1 with its magnetometer boom for NASA's Juno spacecraft prior to illumination testing. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
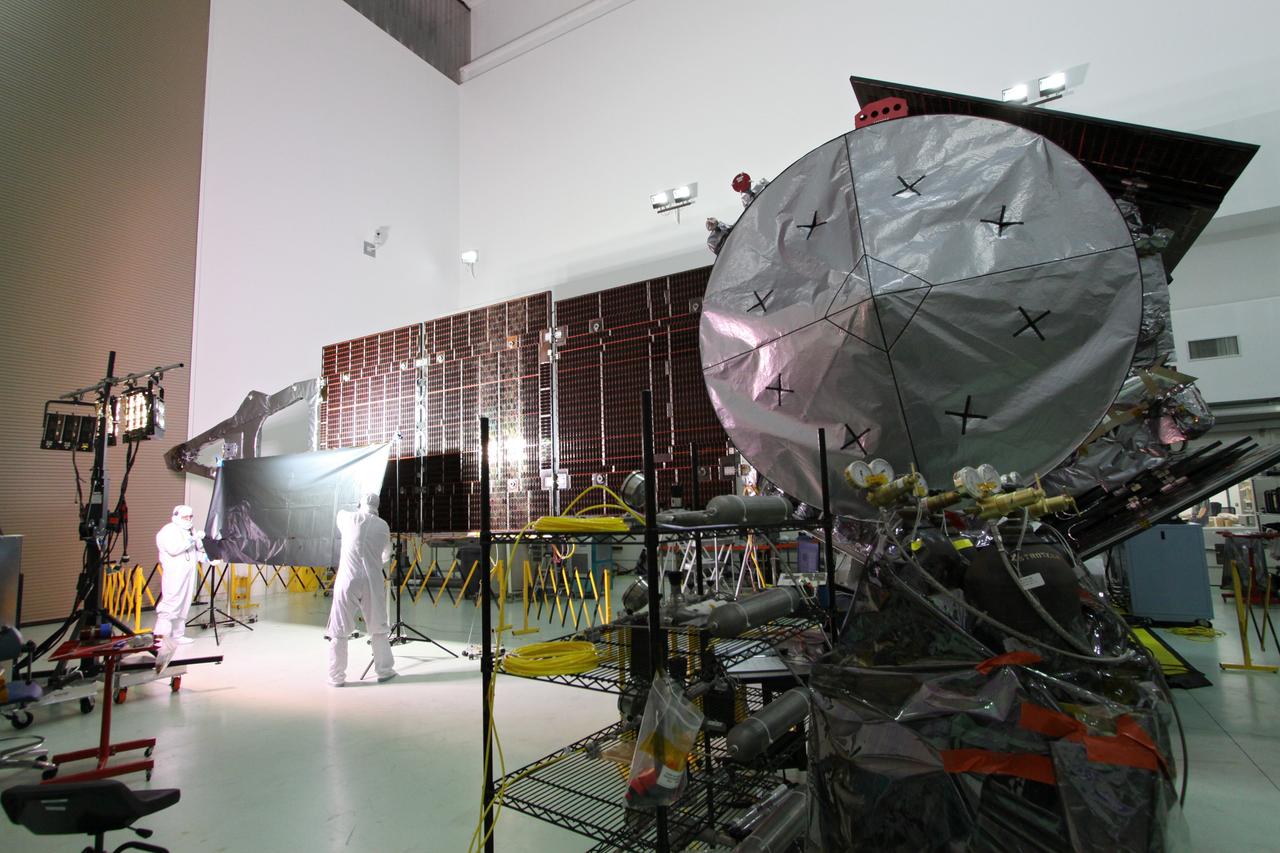

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians conduct illumination tests on solar array panel #1 with its magnetometer boom for NASA's Juno spacecraft. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
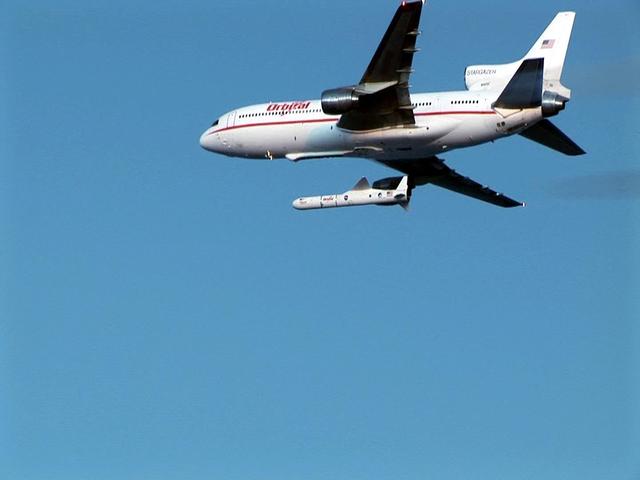

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - Orbital Sciences' L-1011 jet aircraft releases the Pegasus rocket carrying the Space Technology 5 spacecraft with its trio of micro-satellites. The Pegasus will launch the trio of satellites in a "string of pearls" sequence on a near-Earth polar elliptical orbit that will take them from approximately 190 miles (300 kilometers) to 2,800 miles (4,500 kilometers) from the planet. The three spacecraft will conduct science validation using measurements of the Earth's magnetic field collected by the miniature boom-mounted magnetometers on each.
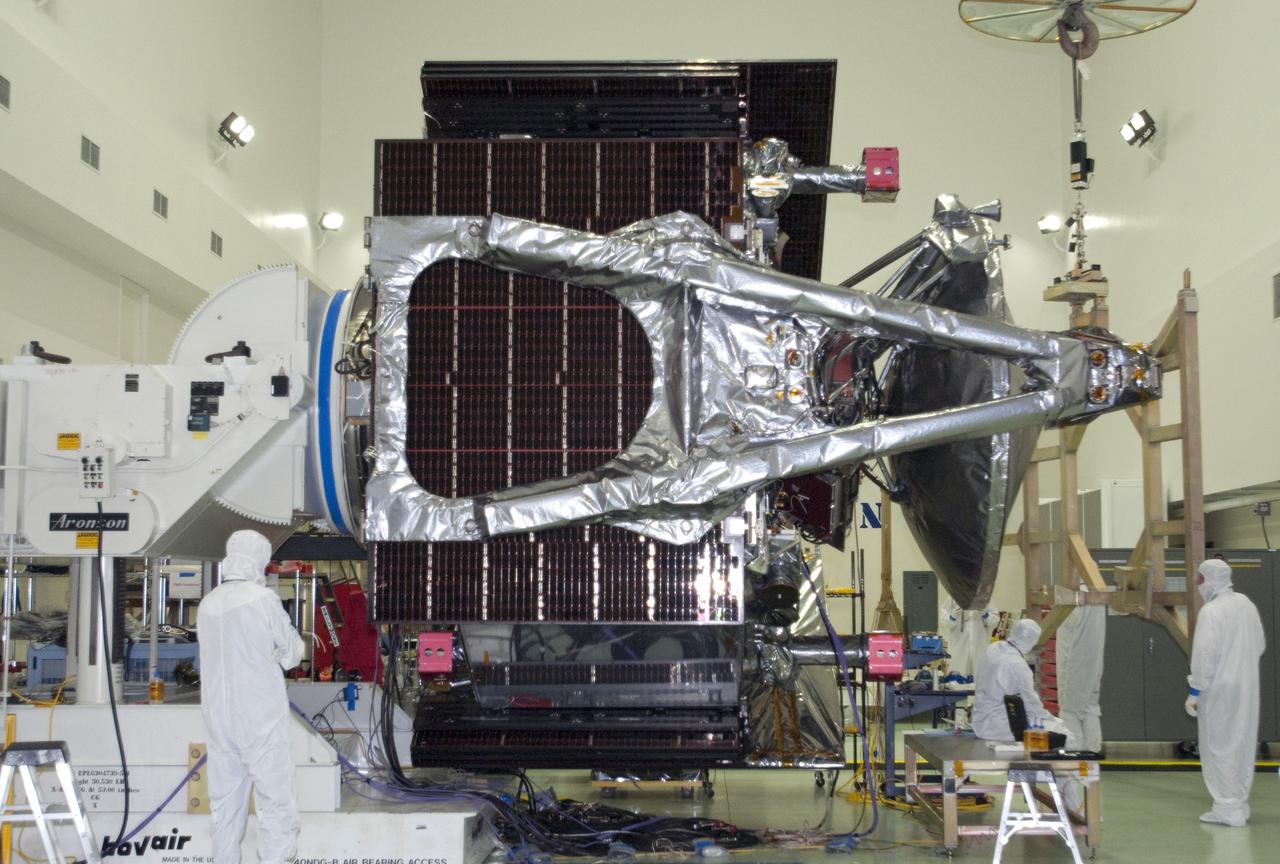

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians have installed solar array #1 with its magnetometer boom to NASA's Juno spacecraft. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
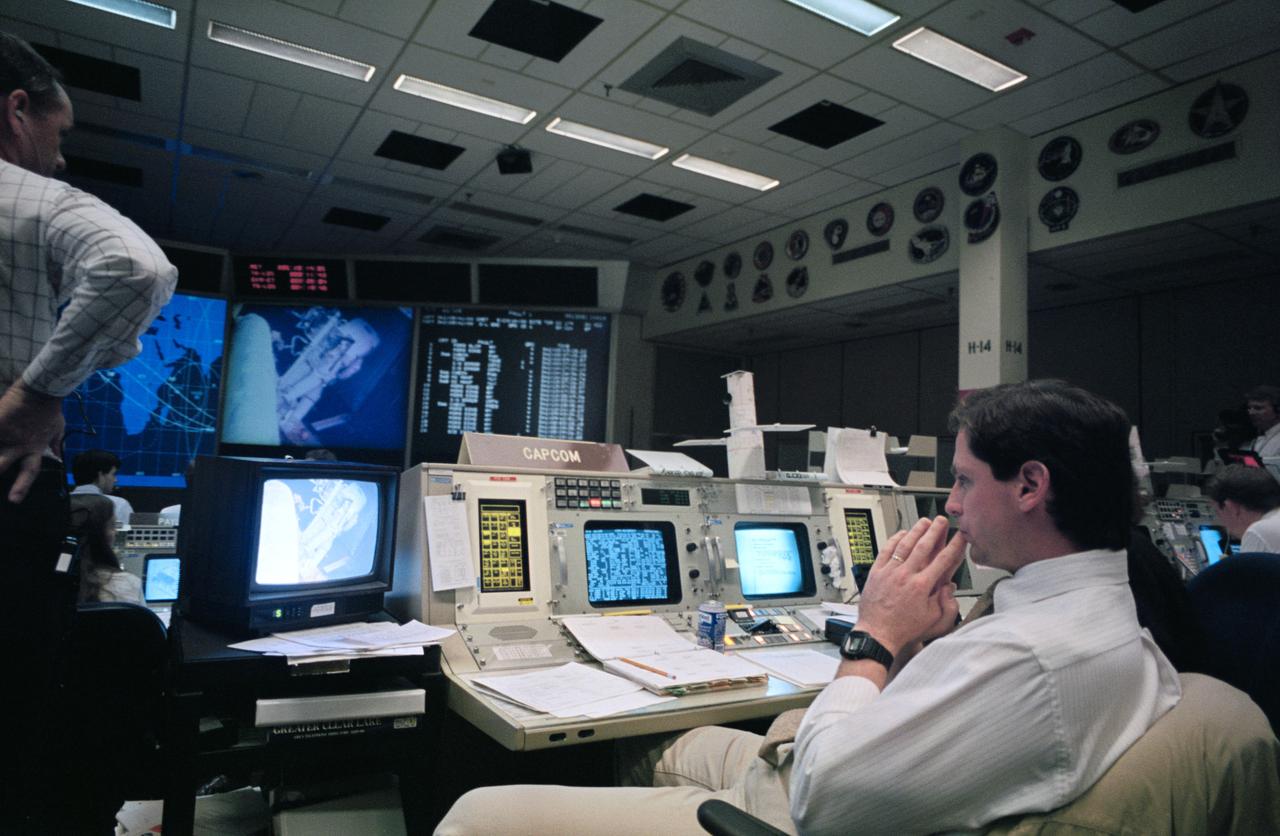

STS61-S-101 (8 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut Gregory J. Harbaugh, spacecraft communicator (CAPCOM), observes as two astronauts work through a lengthy period of extravehicular activity (EVA) in the cargo bay of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour. Seen on the screen in the front of the flight control room, preparing to work with the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST) magnetometers, are astronauts F. Story Musgrave and Jeffrey A. Hoffman. Harbaugh stayed busy passing up flight controllers suggestions and directions during the record-breaking battery of in-space servicing sessions. Lead flight director Milt Heflin is partially visible at left edge of frame.
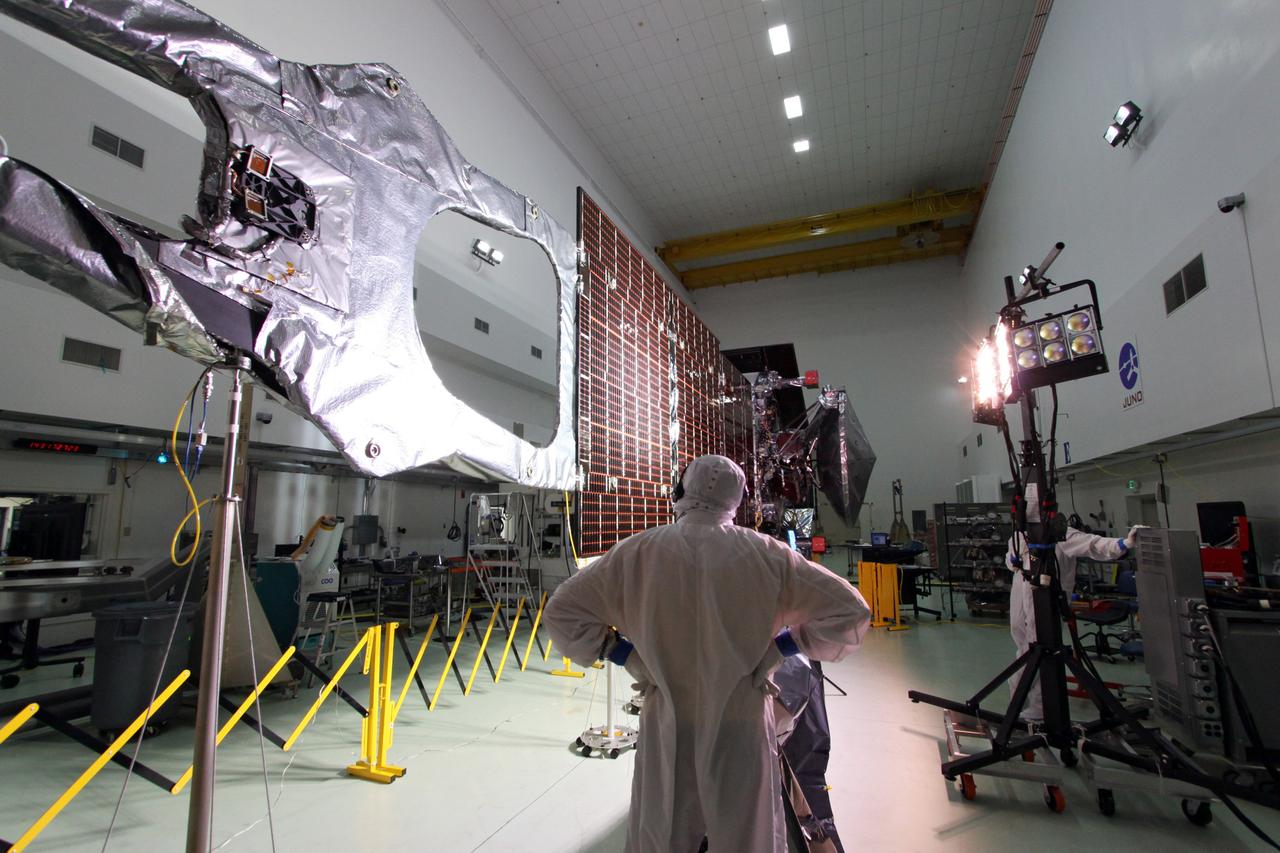

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians conduct illumination tests on solar array panel #1 with its magnetometer boom for NASA's Juno spacecraft. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
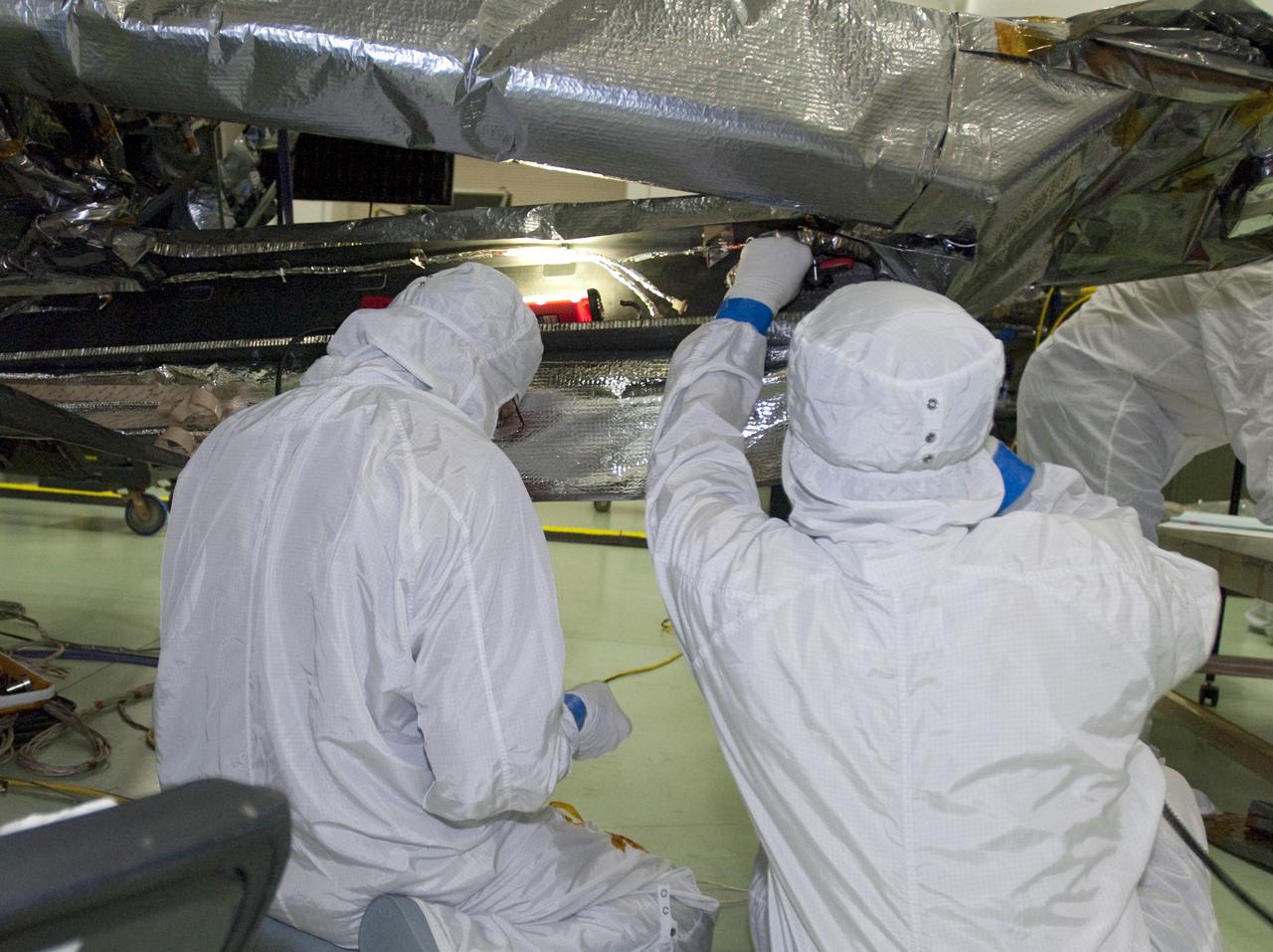

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians test the connections of solar array #1 with its magnetometer boom to NASA's Juno spacecraft after installation. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
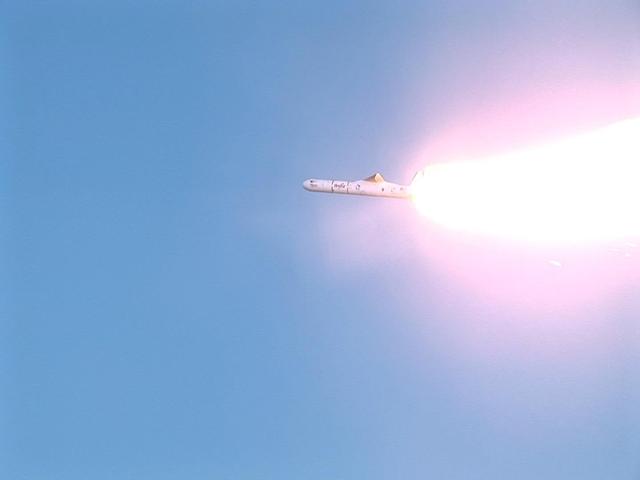

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - Orbital Sciences' Pegasus launch vehicle rockets away from the L-1011 jet aircraft after being released. Pegasus carries the Space Technology 5 spacecraft with its trio of micro-satellites that will be launched in a "string of pearls" sequence on a near-Earth polar elliptical orbit that will take them from approximately 190 miles (300 kilometers) to 2,800 miles (4,500 kilometers) from the planet. The three spacecraft will conduct science validation using measurements of the Earth's magnetic field collected by the miniature boom-mounted magnetometers on each.
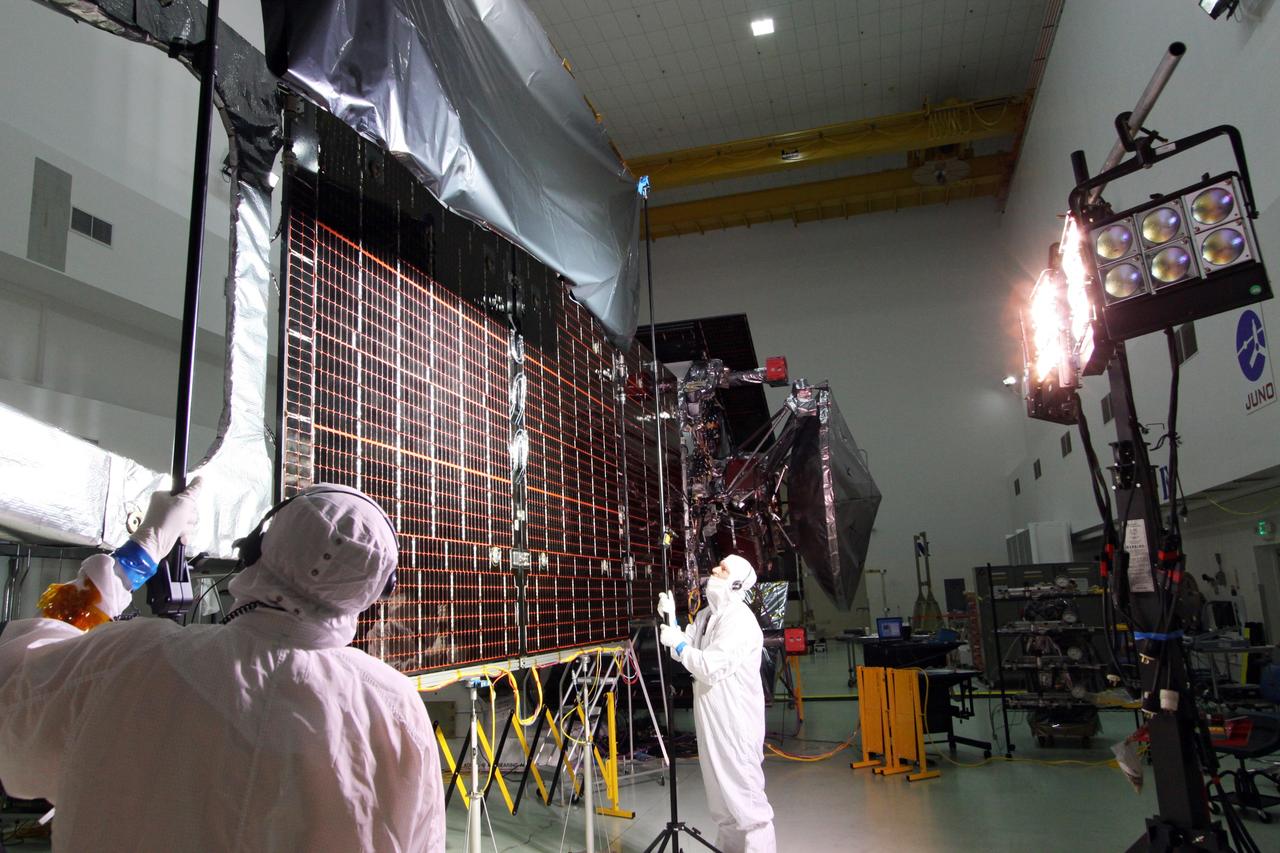

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians conduct illumination tests on solar array panel #1 with its magnetometer boom for NASA's Juno spacecraft. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians conduct illumination tests on solar array panel #1 with its magnetometer boom for NASA's Juno spacecraft. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
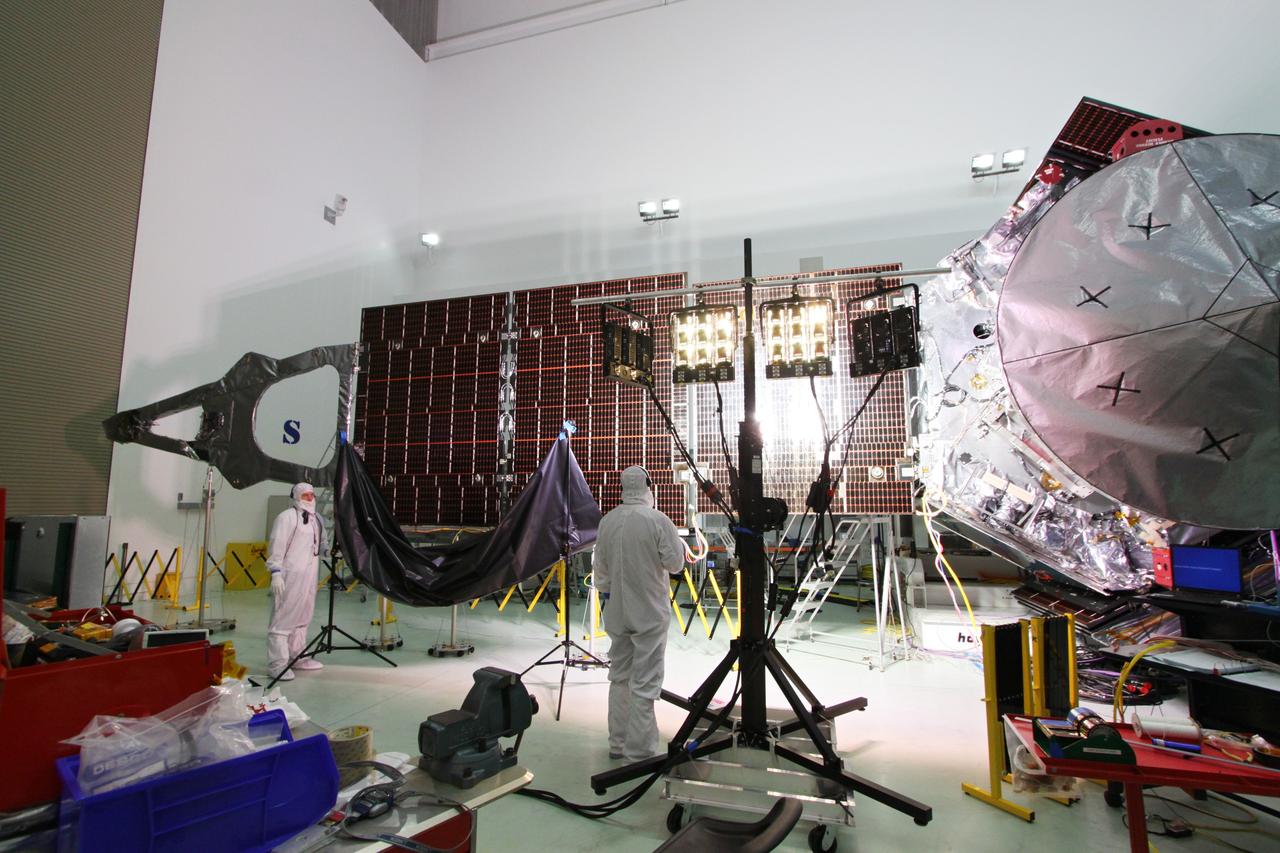

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians conduct illumination tests on solar array panel #1 with its magnetometer boom for NASA's Juno spacecraft. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
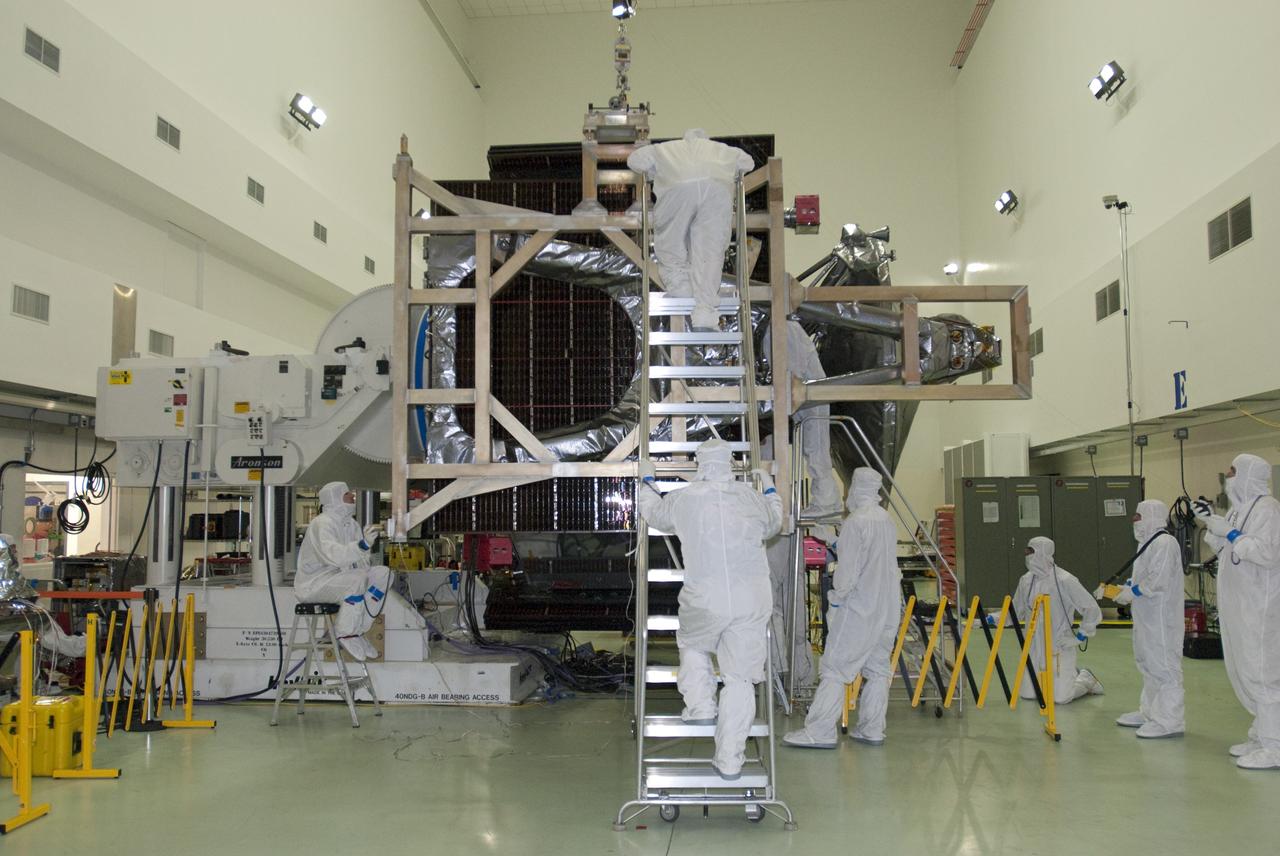

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians install solar array #1 with its magnetometer boom to NASA's Juno spacecraft. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
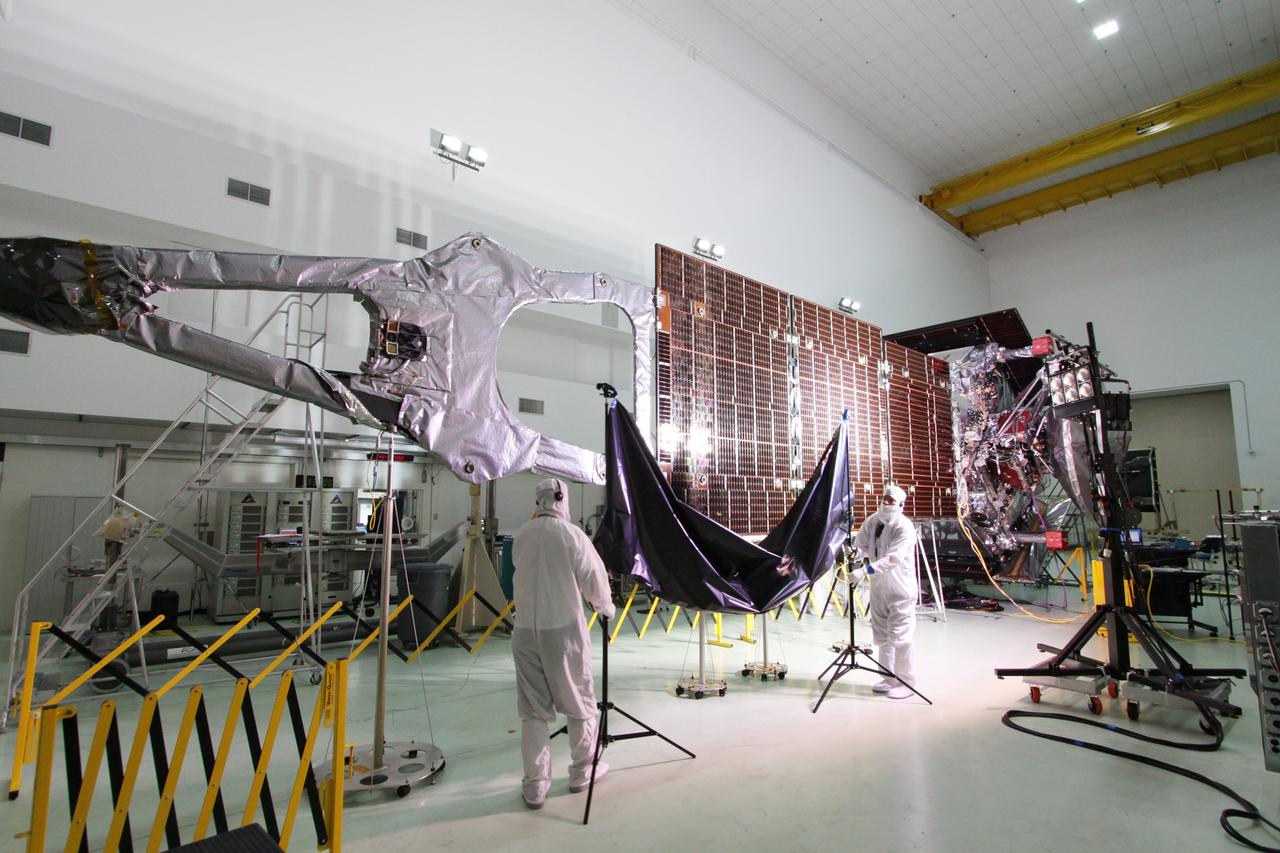

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians conduct illumination tests on solar array panel #1 with its magnetometer boom for NASA's Juno spacecraft. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians conduct illumination tests on solar array panel #1 with its magnetometer boom for NASA's Juno spacecraft. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
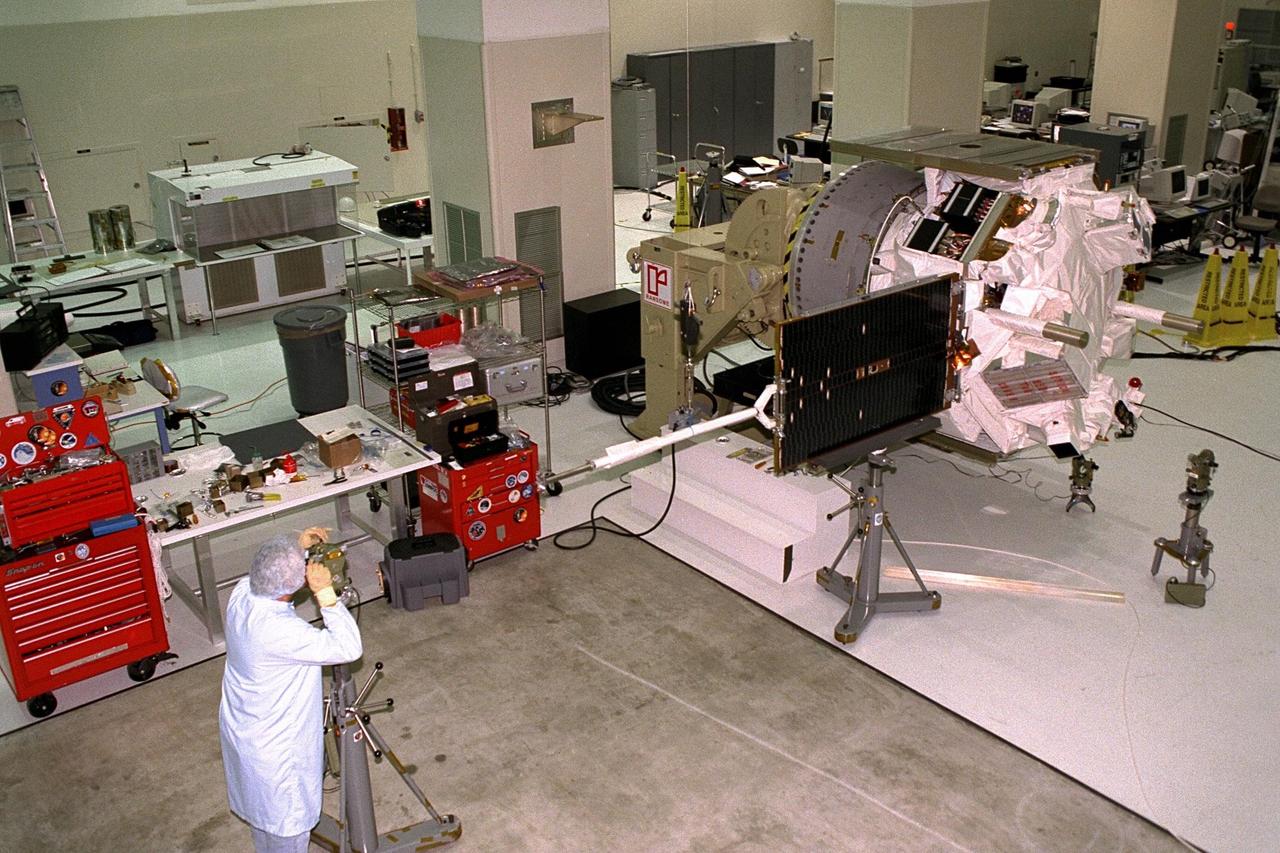

An Applied Physics Laboratory engineer from Johns Hopkins University tests for true perpendicular solar array deployment of the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-II (SAEF-II). The white magnetometer boom seen across the solar array panel will deploy the panel once in space. Scheduled for launch on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Station on Aug. 25, ACE will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles. The ACE observatory will be placed into an orbit almost a million miles (1.5 million kilometers) away from the Earth, about 1/100 the distance from the Earth to the Sun

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians conduct illumination tests on solar array panel #1 with its magnetometer boom for NASA's Juno spacecraft. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
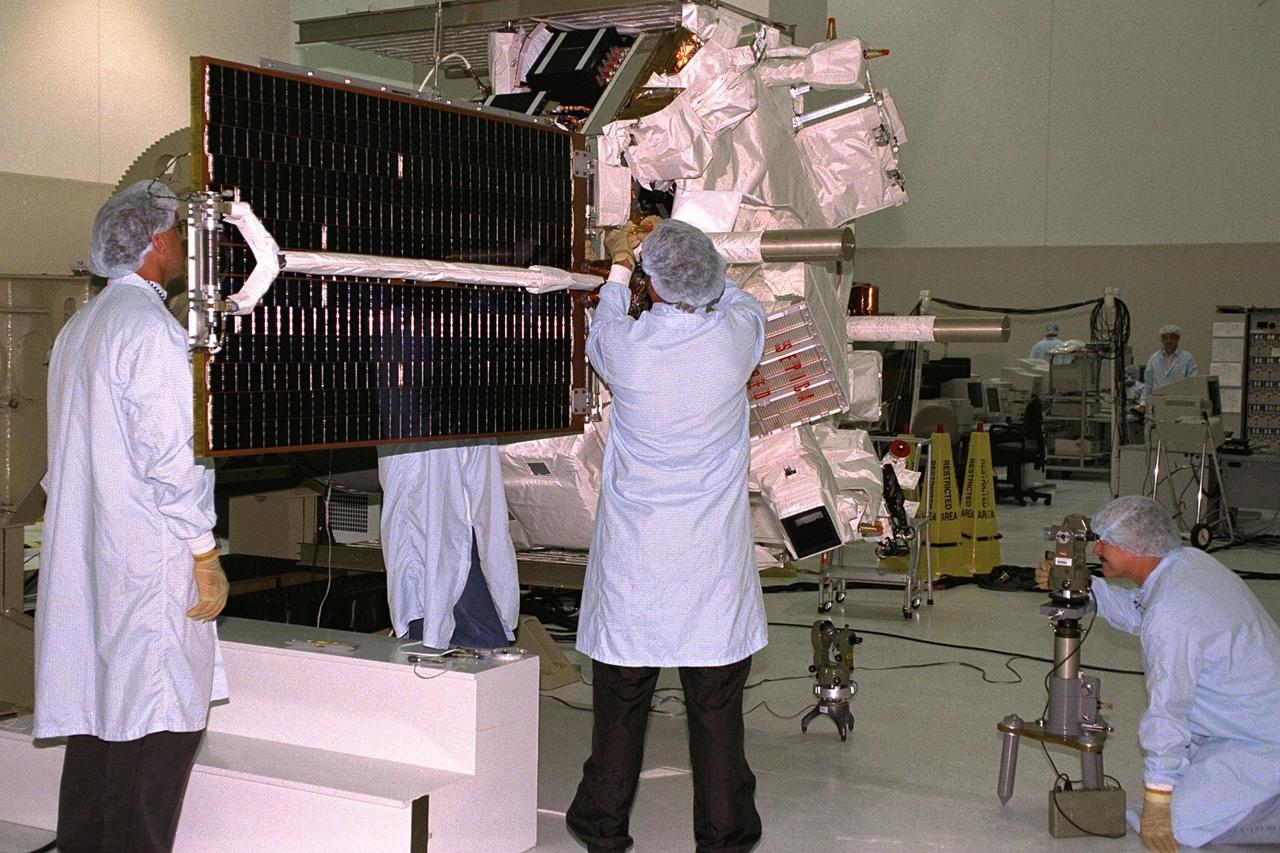

Applied Physics Laboratory engineers and technicians from Johns Hopkins University test for true perpendicular solar array deployment of the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-II (SAEF-II). The white magnetometer boom seen across the solar array panel will deploy the panel once in space. Scheduled for launch on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Station on Aug. 25, ACE will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles. The ACE observatory will be placed into an orbit almost a million miles (1.5 million kilometers) away from the Earth, about 1/100 the distance from the Earth to the Sun

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians prepare solar array #1 with its magnetometer boom for installation to NASA's Juno spacecraft. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians conduct deployment tests on solar array panel #1 with its magnetometer boom for NASA's Juno spacecraft prior to illumination testing. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians have installed solar array #1 with its magnetometer boom to NASA's Juno spacecraft. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla. Aug. 5.The solar-powered spacecraft will orbit Jupiter's poles 33 times to find out more about the gas giant's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core. For more information visit: www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
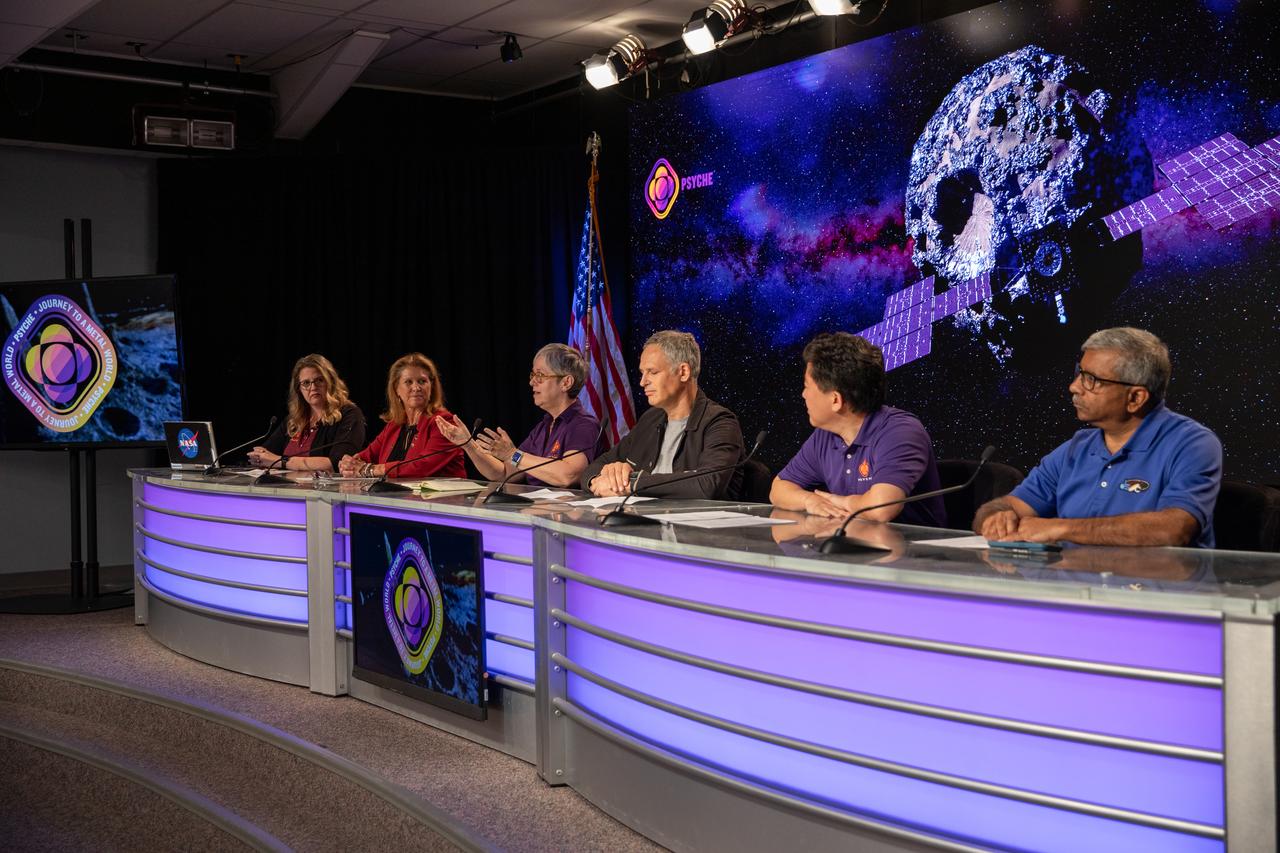

A Psyche mission and science briefing takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Oct. 10, 2023. Participants, from left, are: Alana Johnson, NASA Communications; Lori Glaze, Planetary Science division director, NASA Headquarters; Lindy Elkins-Tanton, Psyche principal investigator, Arizona State University; Ben Weiss, Psyche deputy principal investigator and magnetometer lead, Massachusetts Institute of Technology; David Oh, Psyche chief engineer for operations, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL); and Abi Biswas, Deep Space Optical Communications project technologist, JPL. Psyche is the first mission to explore an asteroid with a surface that likely contains substantial amounts of metal rather than rock or ice. Liftoff of NASA’s Psyche spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket, is targeted for 10:16 a.m. EDT Thursday, Oct. 12, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
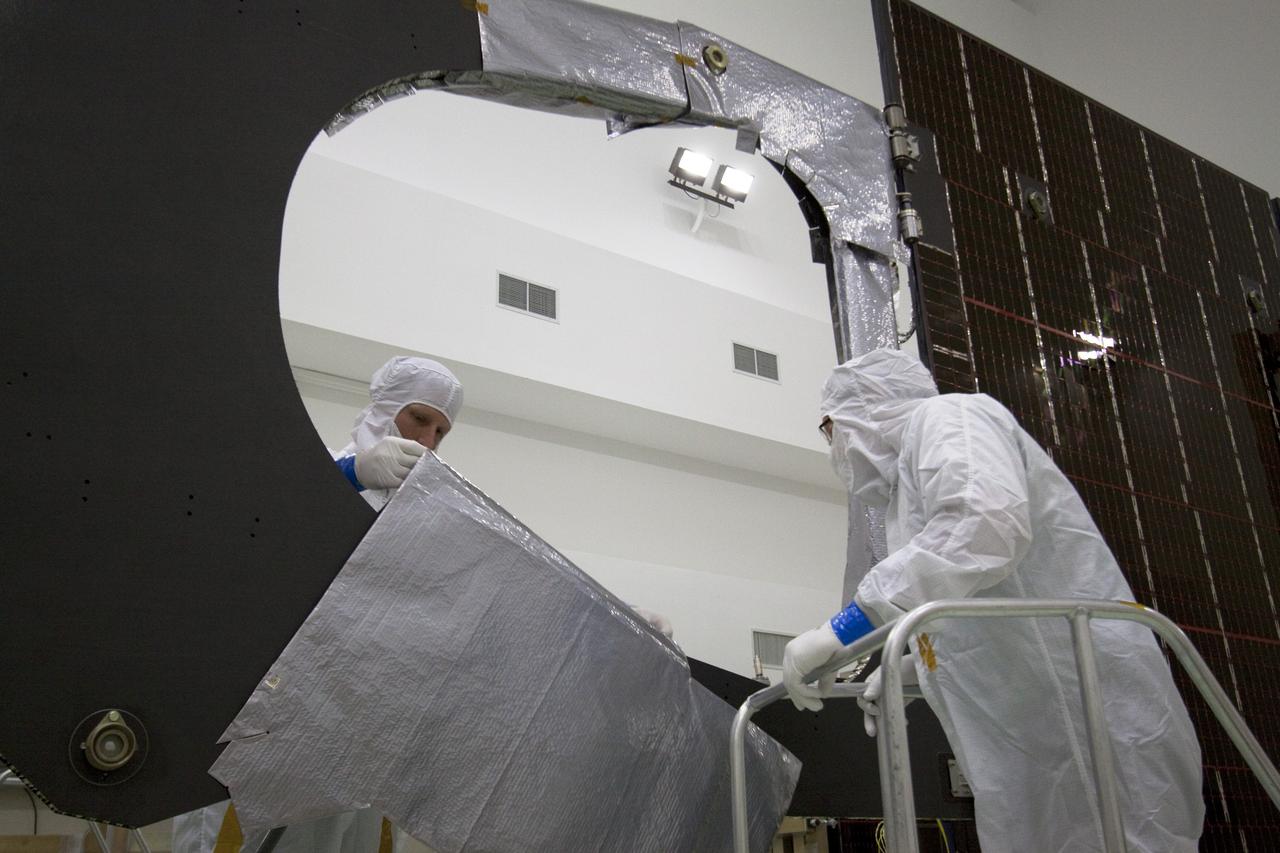

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., begin installing insulating blankets around the magnetometer boom. The boom structure is attached to Juno's solar array #1 that will help power the NASA spacecraft on its mission to Jupiter. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
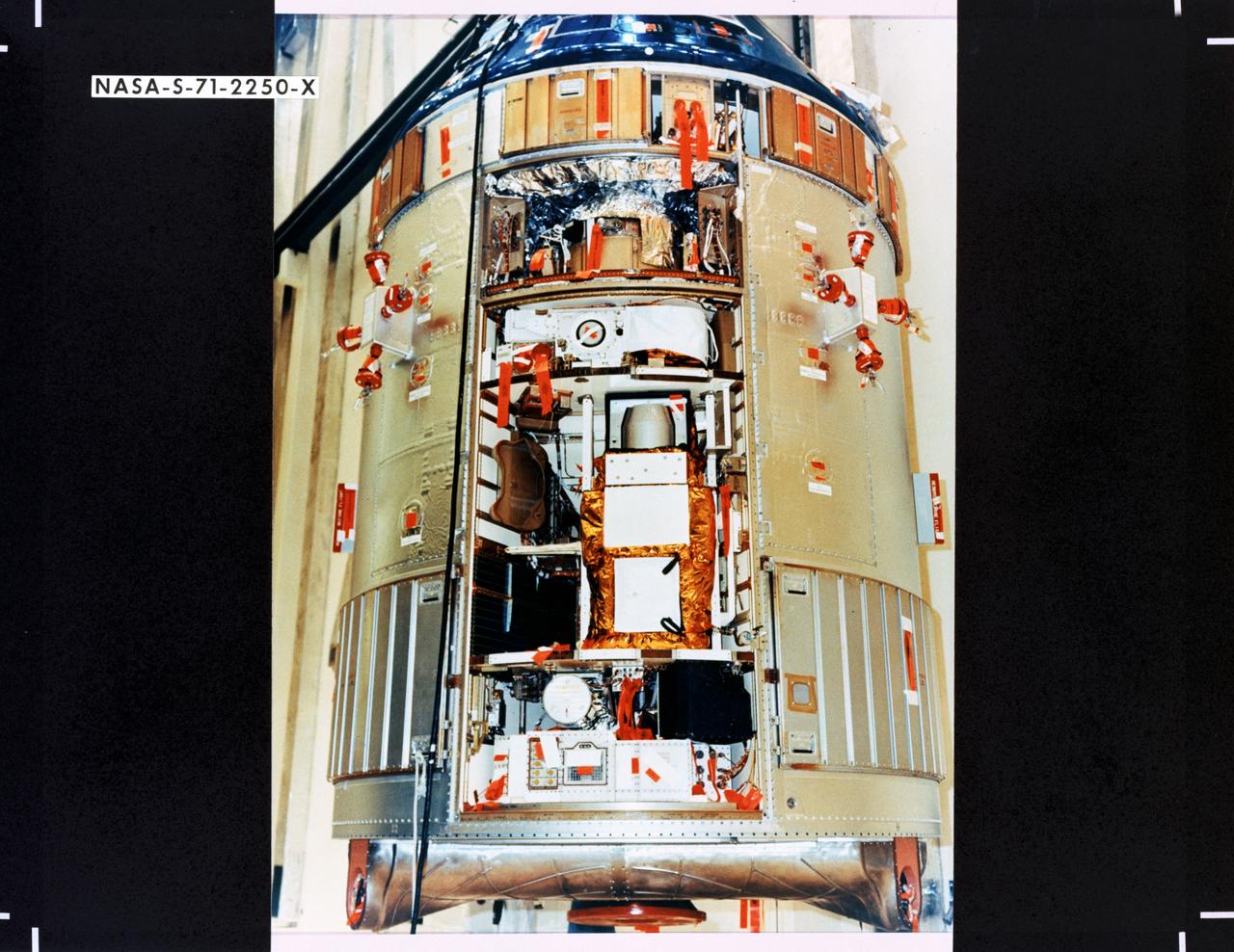
S71-2250X (June 1971) --- A close-up view of the Scientific Instrument Module (SIM) to be flown for the first time on the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission. Mounted in a previously vacant sector of the Apollo Service Module (SM), the SIM carries specialized cameras and instrumentation for gathering lunar orbit scientific data. SIM equipment includes a laser altimeter for accurate measurement of height above the lunar surface; a large-format panoramic camera for mapping, correlated with a metric camera and the laser altimeter for surface mapping; a gamma ray spectrometer on a 25-feet extendible boom; a mass spectrometer on a 21-feet extendible boom; X-ray and alpha particle spectrometers; and a subsatellite which will be injected into lunar orbit carrying a particle and magnetometer, and the S-Band transponder.

This artist's concept depicts the 140-mile-wide (226-kilometer-wide) asteroid Psyche, which lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Psyche is the focal point of NASA's mission of the same name. The Psyche spacecraft is set to launch in August 2022 and arrive at the asteroid in 2026, where it will orbit for 21 months and investigate its composition. Scientists think that Psyche, unlike most other asteroids that are rocky or icy bodies, is made up of mostly iron and nickel — similar to the Earth's core. Exploring the asteroid could give valuable insight into how our own planet and others formed. The Psyche team will use a magnetometer to measure the asteroid's magnetic field. A multispectral imager will capture images of the surface, as well as data about the Psyche's composition and topography. Spectrometers will analyze the neutrons and gamma rays coming from the surface to reveal the elements that make up the asteroid itself. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23876

S61-E-017 (6 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut F. Story Musgrave uses one of the handrails on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) during the second of his three sessions of STS-61 extravehicular activity (EVA-3). Astronauts Musgrave and Jeffrey A. Hoffman used this particular EVA to change out the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC) and two magnetometers (also known as magnetic sensing systems). The photo was recorded with the Electronic Still Camera (ESC) inside Endeavour's cabin. Electronic still photography is a relatively new technology which provides the means for a handheld camera to electronically capture and digitize an image with resolution approaching film quality. The electronic still camera has flown as an experiment on several other shuttle missions.
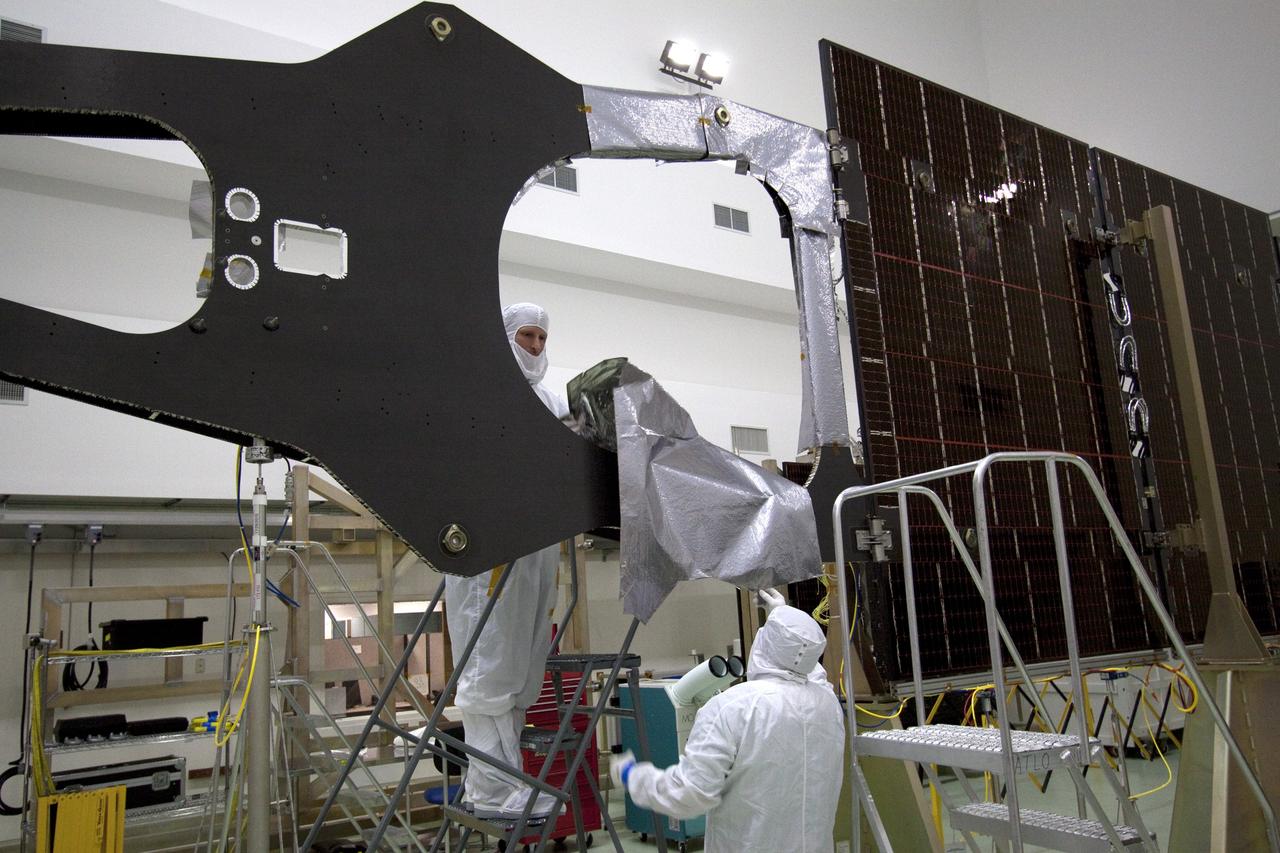

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., begin installing insulating blankets around the magnetometer boom. The boom structure is attached to Juno's solar array #1 that will help power the NASA spacecraft on its mission to Jupiter. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
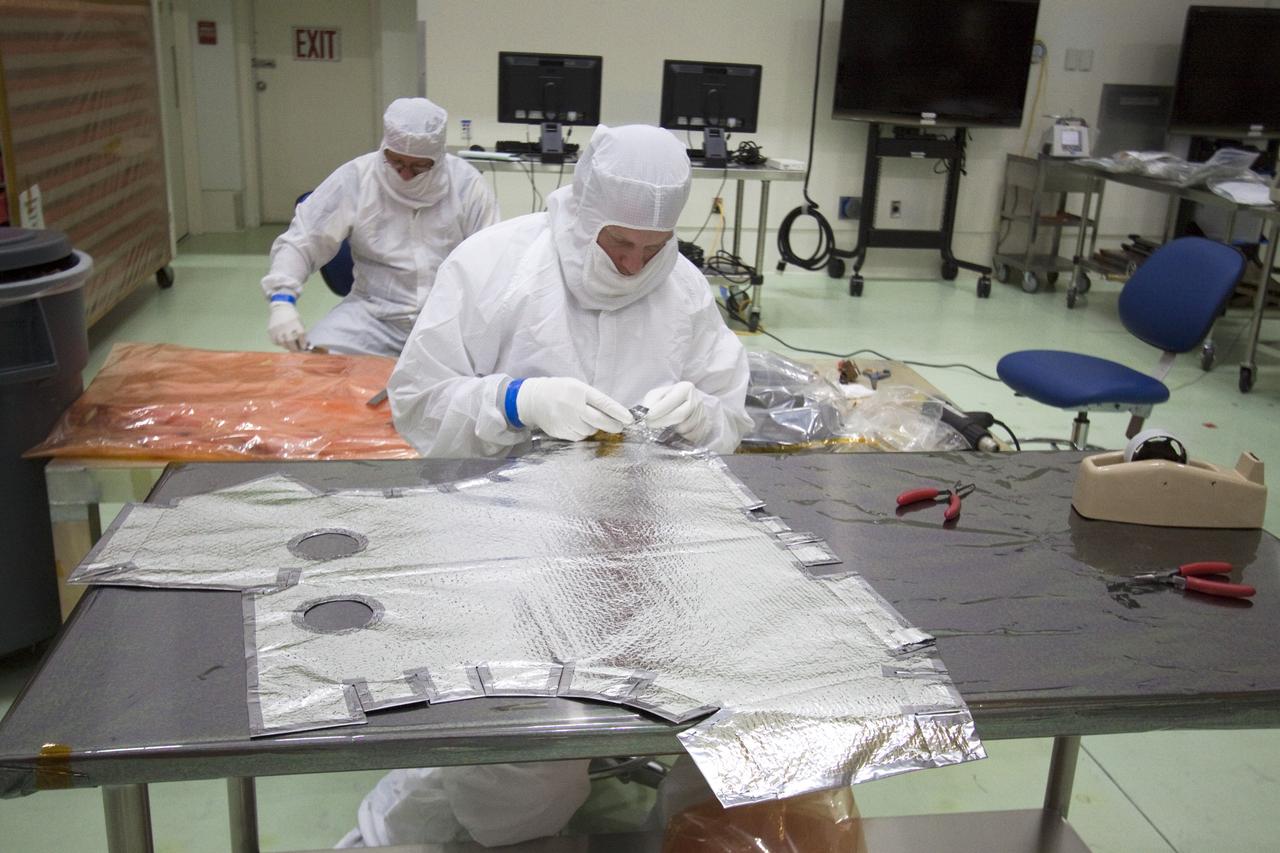

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A technician in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., inspects one of the insulating blanket sections that will be installed on the magnetometer boom. The boom structure is attached to Juno's solar array #1 that will help power the NASA spacecraft on its mission to Jupiter. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
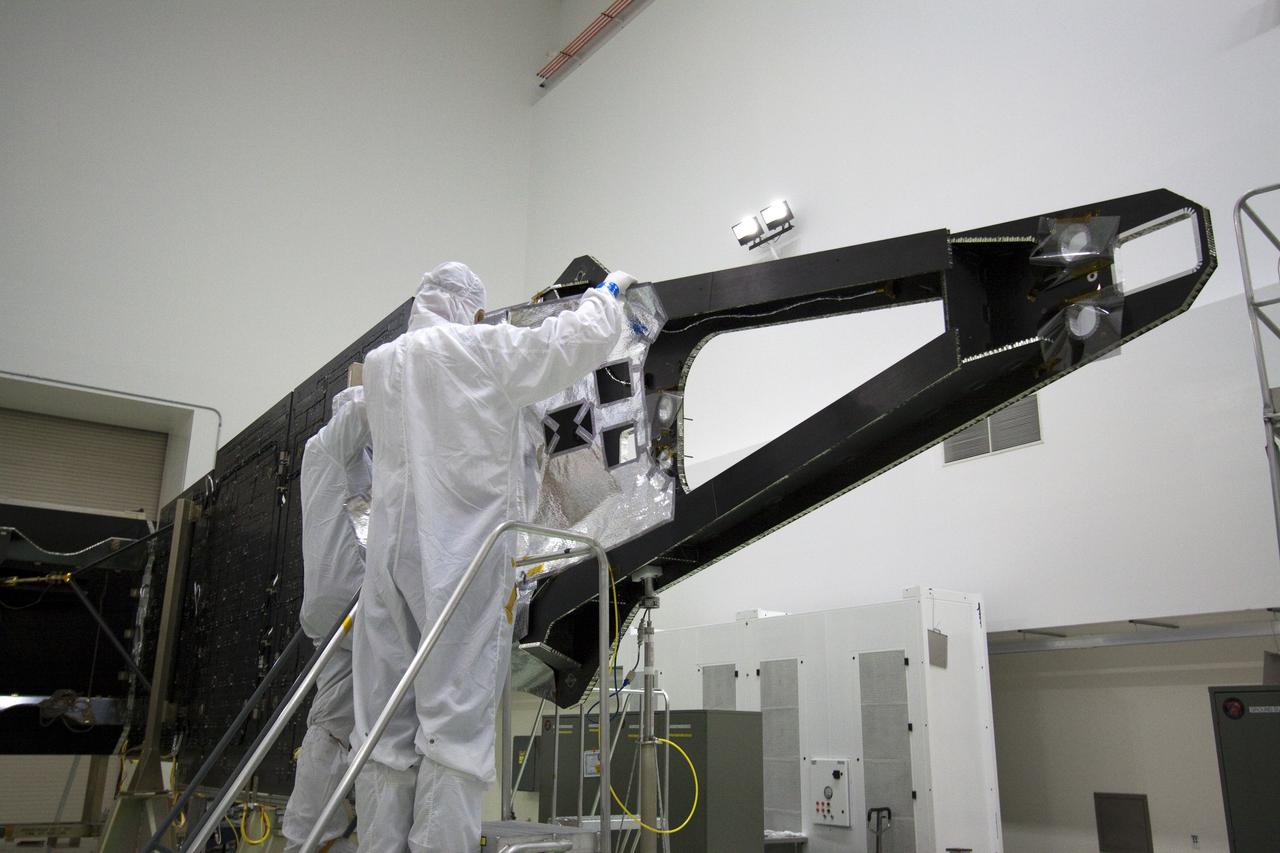

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., install insulating blankets around a magnetometer boom. The boom structure is attached to Juno's solar array #1 that will help power the NASA spacecraft on its mission to Jupiter. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
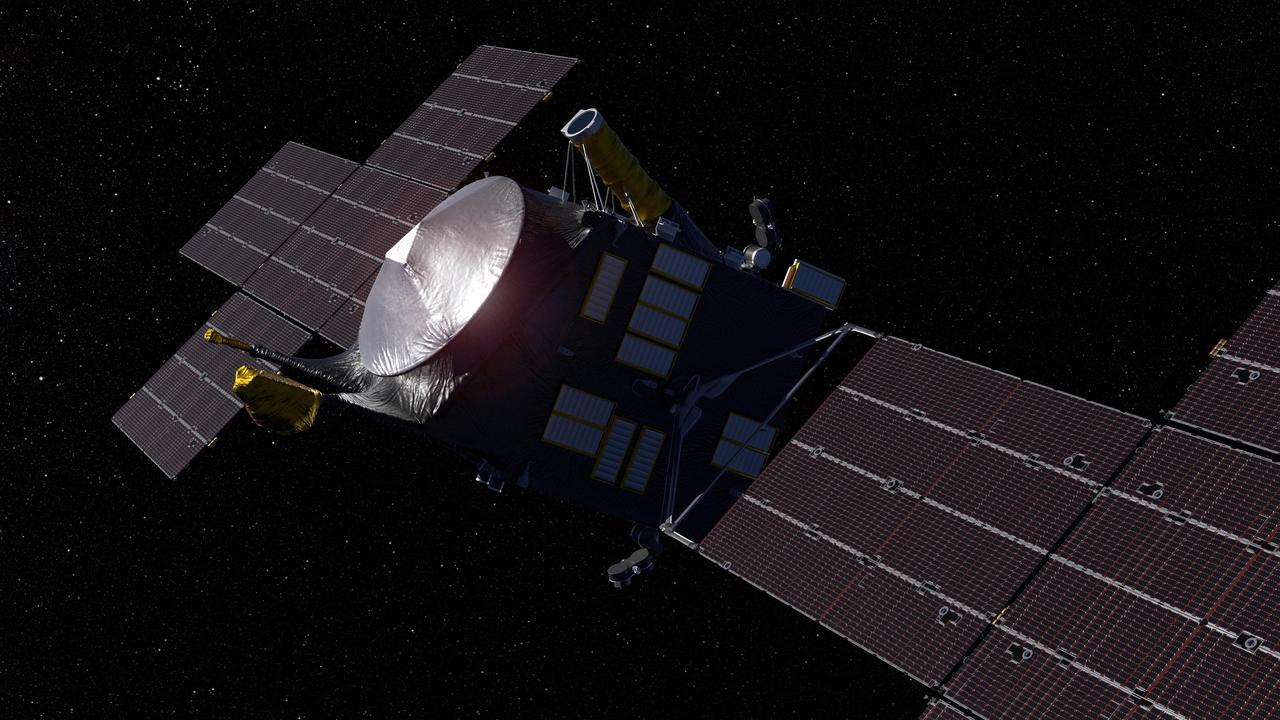

This artist's concept, updated as of June 2020, depicts NASA's Psyche spacecraft. Set to launch in August 2022, the Psyche mission will explore a metal-rich asteroid of the same name that lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. The spacecraft will arrive in early 2026 and orbit the asteroid for nearly two years to investigate its composition. Scientists think that Psyche, unlike most other asteroids that are rocky or icy bodies, is made up of mostly iron and nickel — similar to the Earth's core. The Psyche team will use a magnetometer to measure the asteroid's magnetic field. A multispectral imager will capture images of the surface, as well as data about the Psyche's composition and topography. Spectrometers will analyze the neutrons and gamma rays coming from the surface to reveal the elements that make up the asteroid itself. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23875

This artist's concept shows NASA's InSight lander with its instruments deployed on the Martian surface. InSight's package of weather sensors, called the Auxiliary Payload Subsystem (APSS), includes an air pressure sensor inside the lander -- its inlet is visible on InSight's deck -- and two air temperature and wind sensors on the deck. Under the deck's edge is a magnetometer, provided by UCLA, to measure changes in the local magnetic field that could also influence SEIS. InSight's air temperature and wind sensors are actually refurbished spares built for Curiosity's Rover Environmental Monitoring Station (REMS). Called Temperature and Wind for InSight, or TWINS, these two east- and west-facing booms sit on the lander's deck and were provided by Spain's Centro de Astrobiología (CAB). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22957
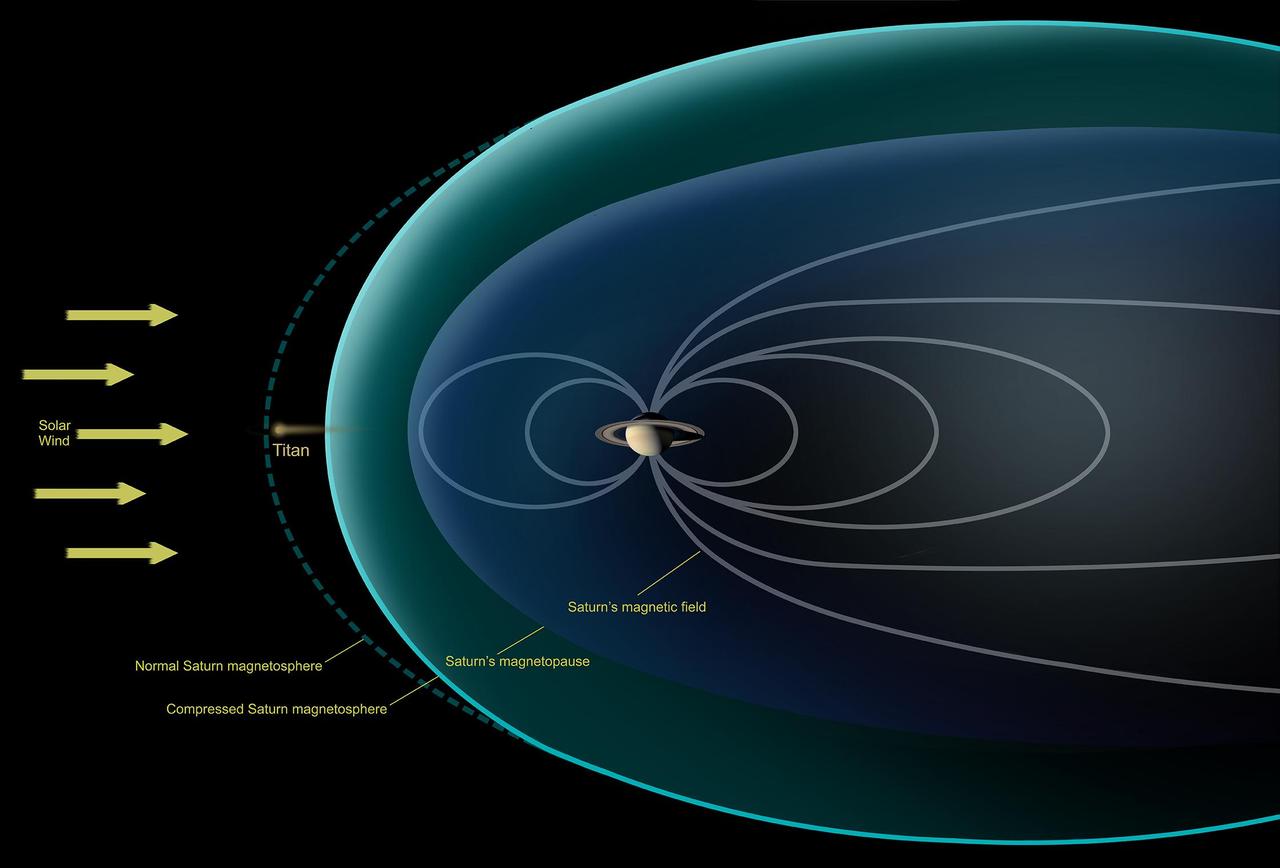
This diagram depicts conditions observed by NASA's Cassini spacecraft during a flyby in Dec. 2013, when Saturn's magnetosphere was highly compressed, exposing Titan to the full force of the solar wind. In analyzing data from the encounter, scientists with Cassini's magnetometer team observed that the giant moon interacted with the solar wind much like the planets Mars and Venus, or a comet -- none of which possess their own internal magnetic field. Specifically, they saw that the solar wind draped itself around Titan, creating a shockwave that formed around Titan where the full-force solar wind rammed into the moon's atmosphere. Previously, researchers had thought Titan would have a different sort of interaction with the solar wind because of the moon's complex atmospheric chemistry. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19055

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., prepare an insulating a blanket for installation onto the magnetometer boom. The boom structure is attached to Juno's solar array #1 that will help power the NASA spacecraft on its mission to Jupiter. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
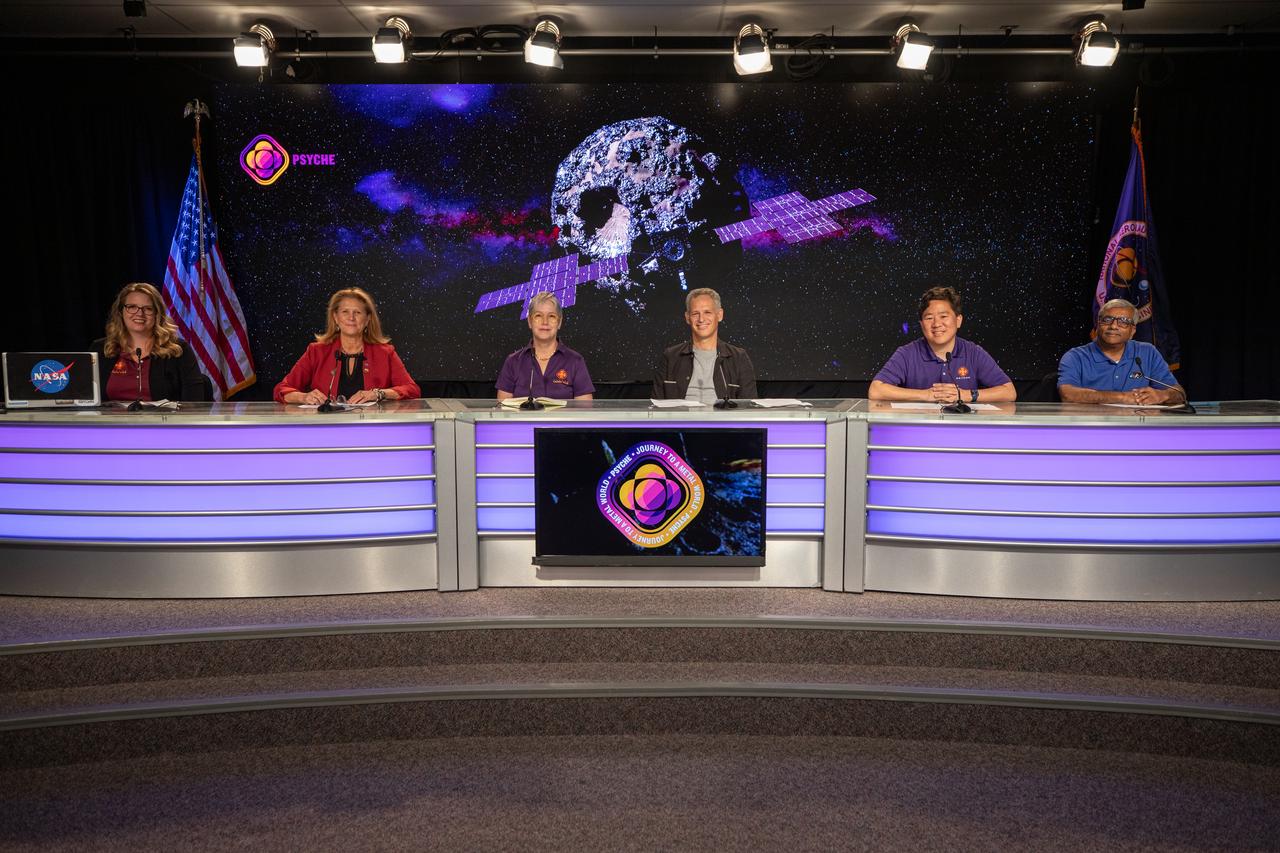

A Psyche mission and science briefing takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Oct. 10, 2023. Participants, from left, are: Alana Johnson, NASA Communications; Lori Glaze, Planetary Science division director, NASA Headquarters; Lindy Elkins-Tanton, Psyche principal investigator, Arizona State University; Ben Weiss, Psyche deputy principal investigator and magnetometer lead, Massachusetts Institute of Technology; David Oh, Psyche chief engineer for operations, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL); and Abi Biswas, Deep Space Optical Communications project technologist, JPL. Psyche is the first mission to explore an asteroid with a surface that likely contains substantial amounts of metal rather than rock or ice. Liftoff of NASA’s Psyche spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket, is targeted for 10:16 a.m. EDT Thursday, Oct. 12, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
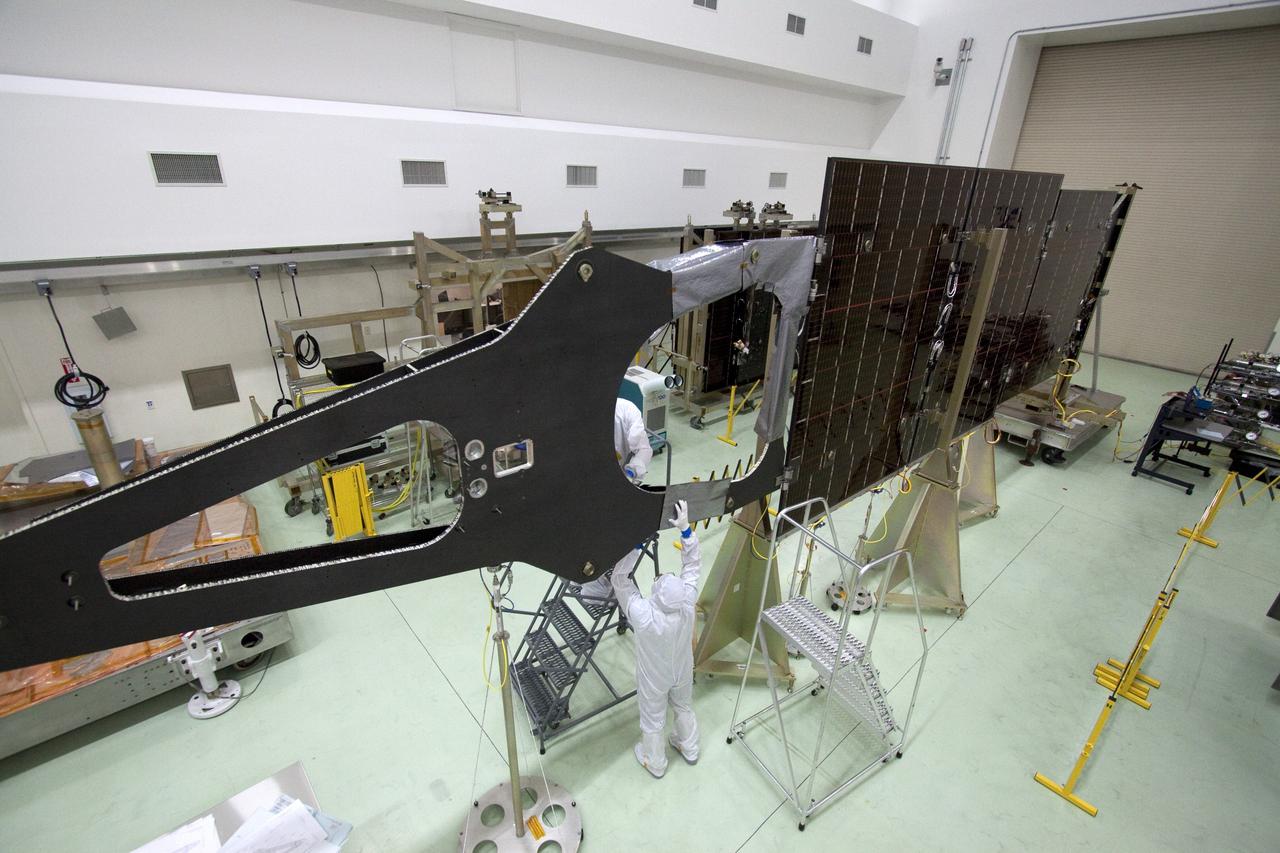

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., install insulating blankets around the magnetometer boom. The boom structure is attached to Juno's solar array #1 that will help power the NASA spacecraft on its mission to Jupiter. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., install insulating blankets around the magnetometer boom. The boom structure is attached to Juno's solar array #1 that will help power the NASA spacecraft on its mission to Jupiter. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
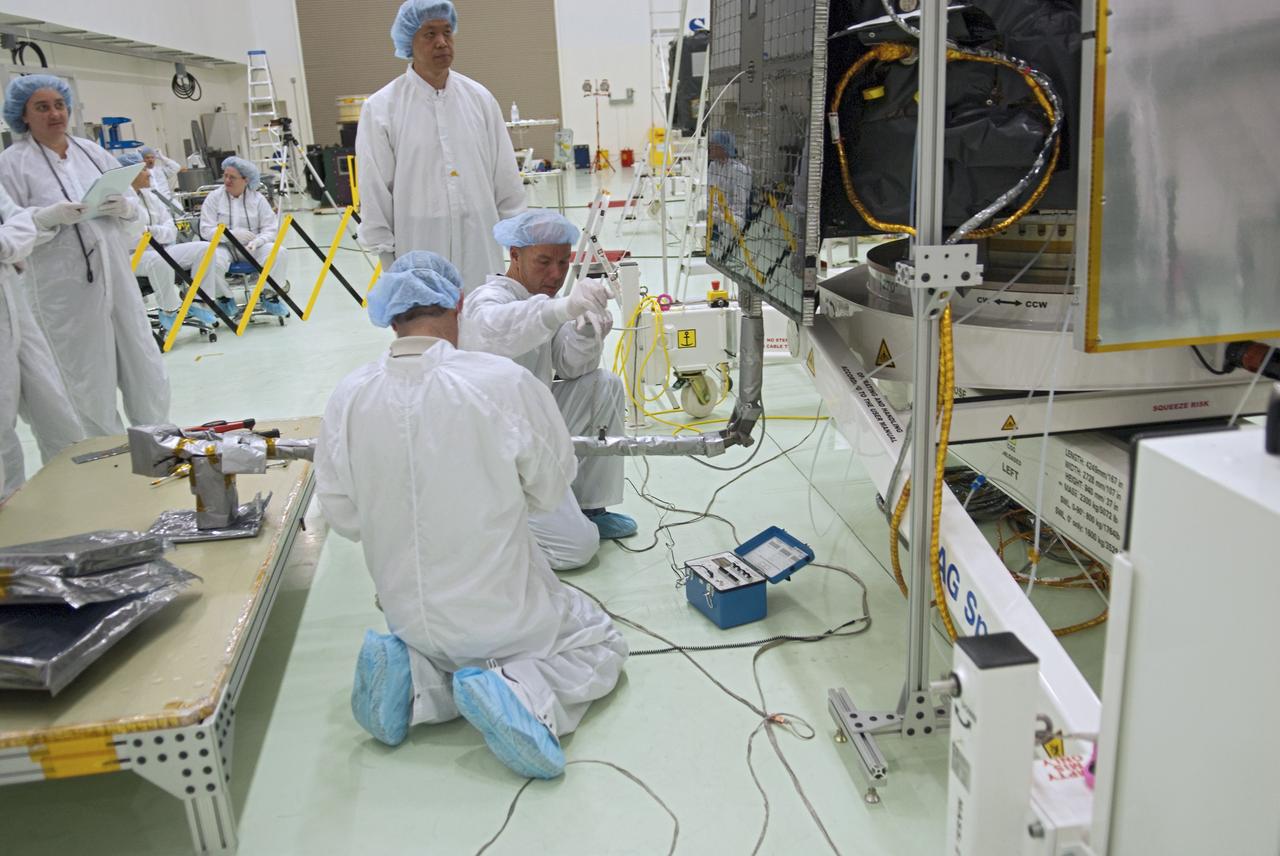

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians deploy the magnetometer boom of the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A. Deploying this instrument is standard procedure to ensure it will work properly on Earth before it heads into space. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. The boom will provide data of the electric fields that energize radiation particles and modify the structure of the inner magnetosphere. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
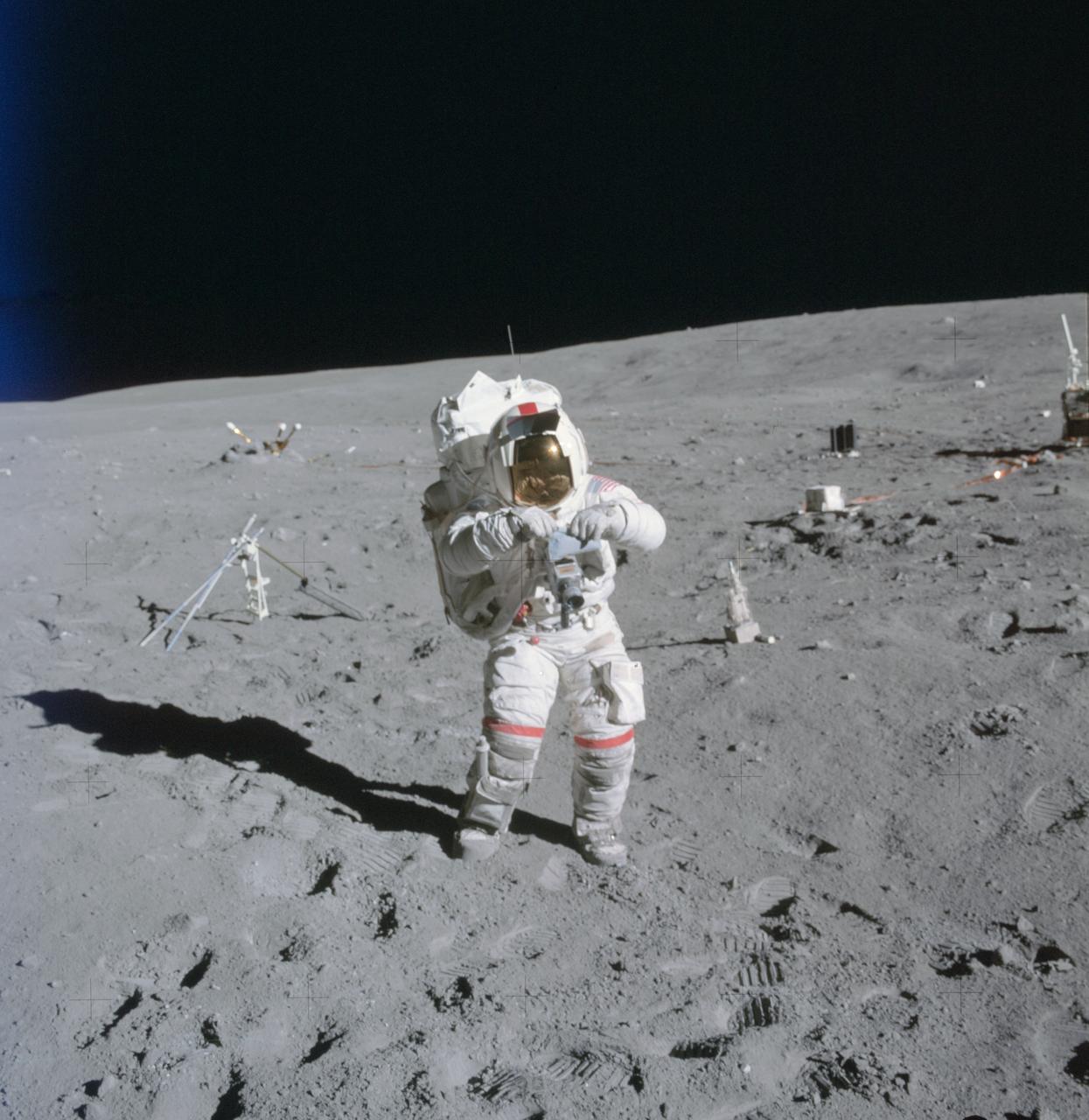

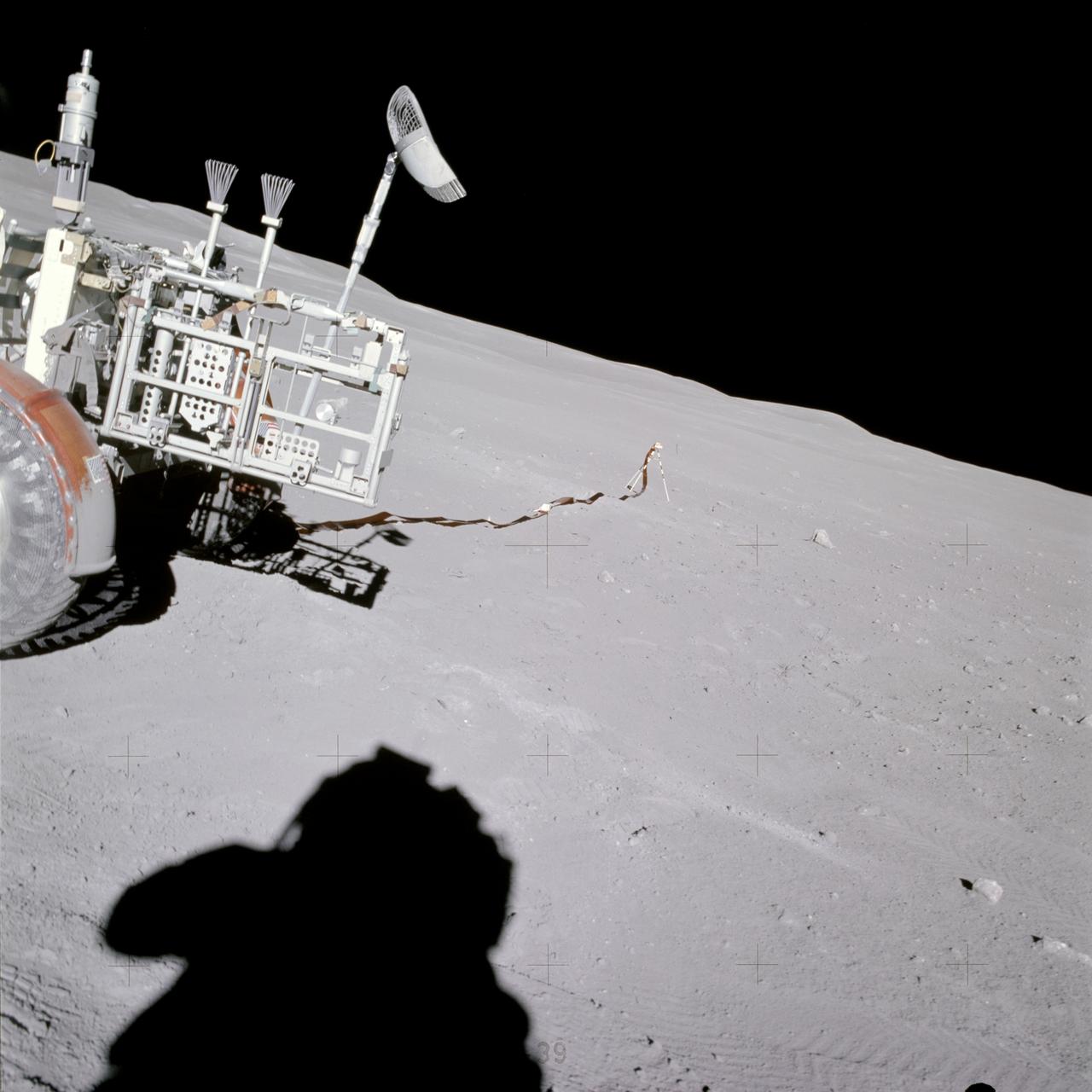
AS16-114-18388 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, stands at the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) deployment site during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. The components of the ALSEP are in the background. The lunar surface drill is just behind and to the right of astronaut Young. The drill's rack and bore stems are to the left. The three-sensor Lunar Surface Magnetometer is beyond the rack. The dark object in the right background is the Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (RTG). Between the RTG and the drill is the Heat Flow Experiment. A part of the Central Station is at the right center edge of the picture. This photograph was taken by astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot.
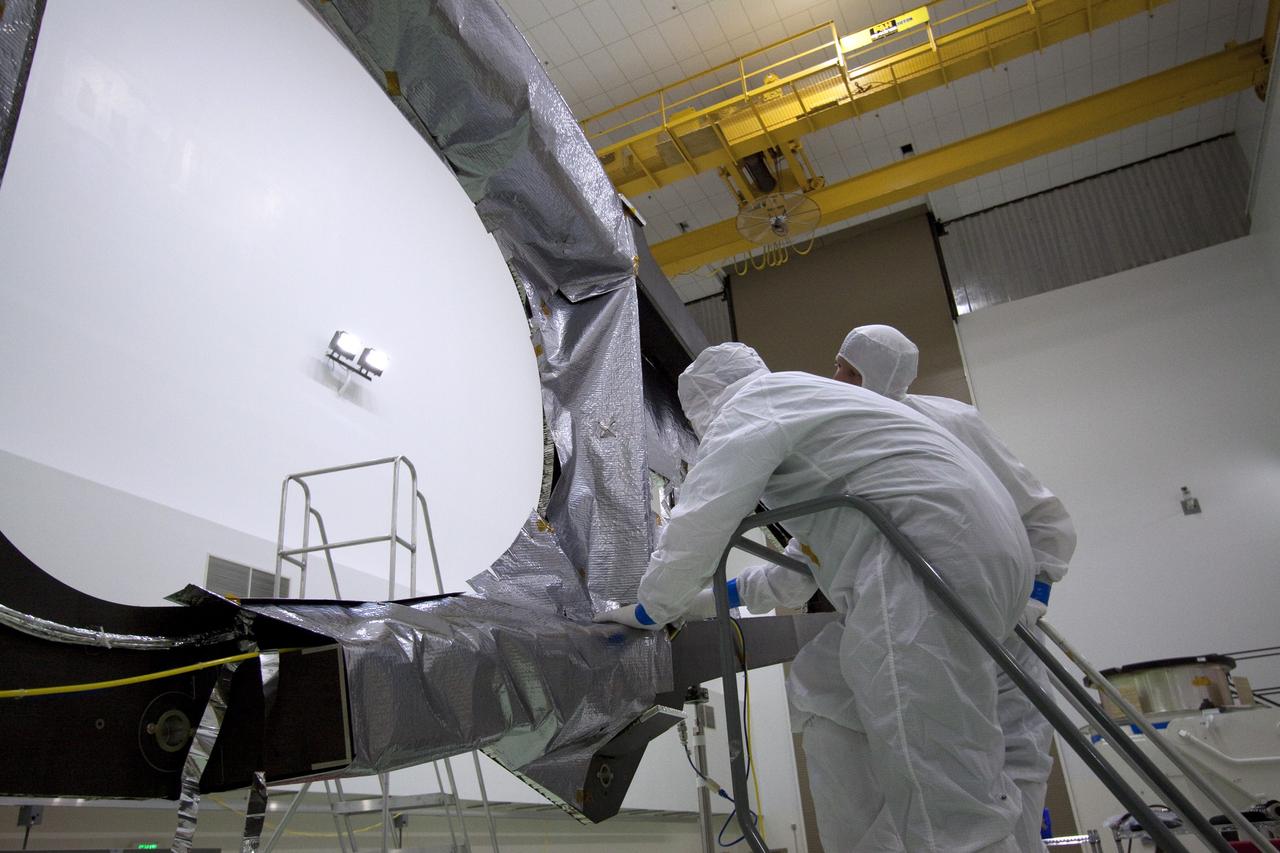

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., install insulating blankets around a magnetometer boom. The boom structure is attached to Juno's solar array #1 that will help power the NASA spacecraft on its mission to Jupiter. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
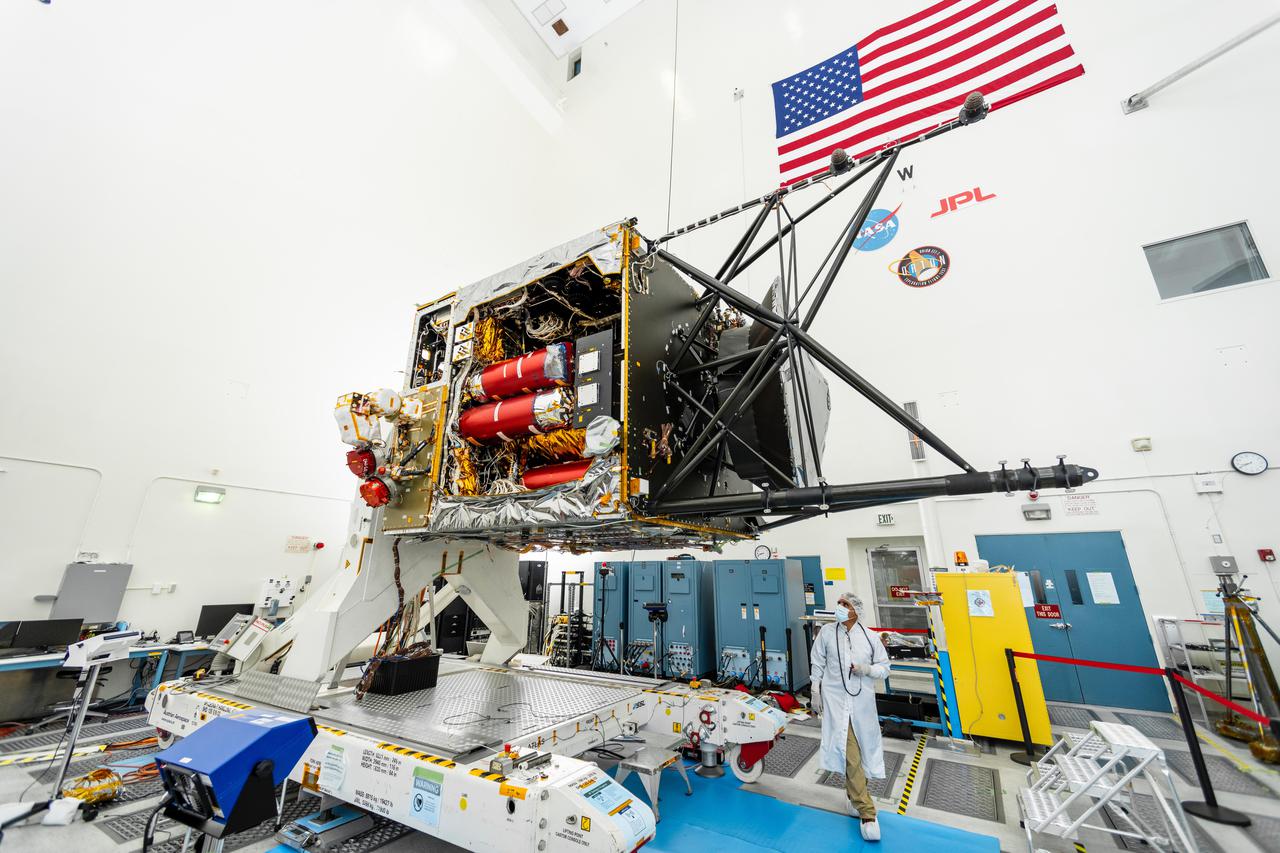
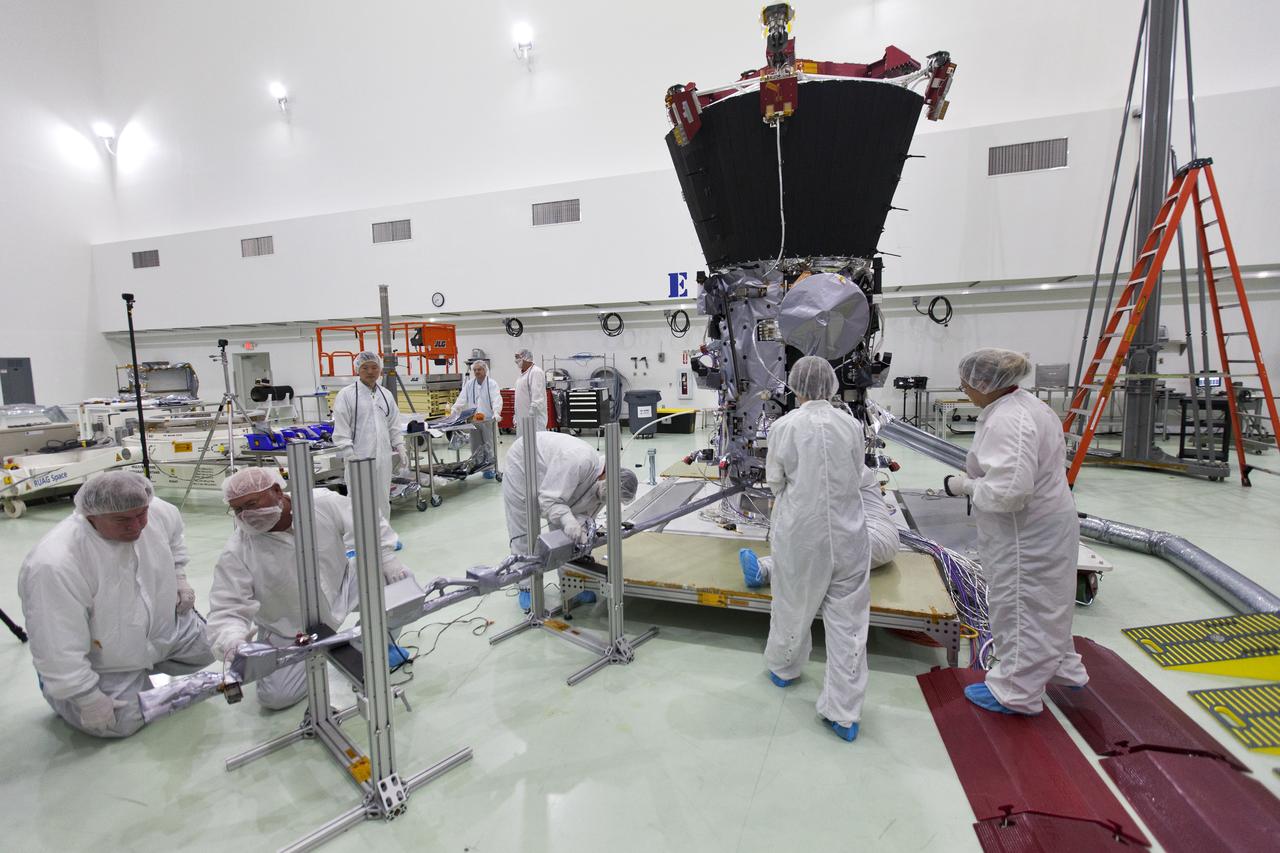
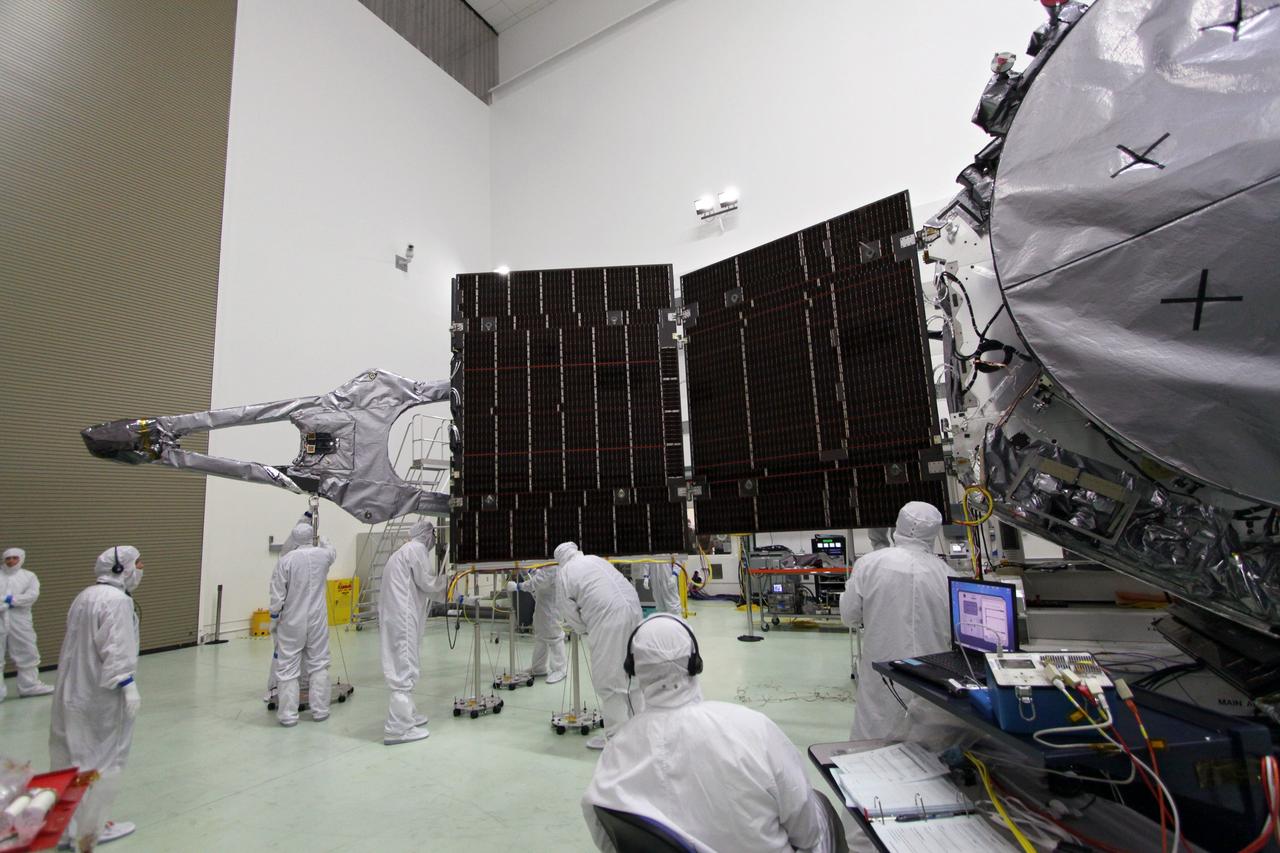
NASA's Psyche spacecraft is captured here on August 18, 2021, in a clean room at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California – in the midst of system integration and test. The mission's launch period opens August 1, 2022. The nitrogen tanks are visible in the center of the spacecraft chassis, encased in red protective "remove before flight" covers. Mounted on the right is the strut tower, which will host the sensors for two of the science instruments – the magnetometer and the Gamma Ray and Neutron Spectrometer (GRNS). By spring of 2022, the fully assembled Psyche spacecraft will ship from JPL to NASA's Kennedy Space Center for launch. In early 2026, the spacecraft will arrive at its target, an asteroid of the same name in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Scientists believe asteroid Psyche, which is about 140 miles (226 kilometers) wide, is made largely of iron and nickel and could be the core of an early planet. The spacecraft will spend 21 months orbiting the asteroid and gathering science data. Besides the magnetometer and the GRNS, Psyche will carry a multispectral imager. The mission also will test a sophisticated new laser communications technology, recently completed by JPL, called Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC). The technology demonstration will focus on using lasers to enhance communications speeds and prepare for data-intensive transmissions, which could potentially include livestream videos for future missions. Arizona State University leads the mission. JPL is responsible for the mission's overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies is providing a high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. Psyche is the 14th mission selected as part of NASA's Discovery Program. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24787
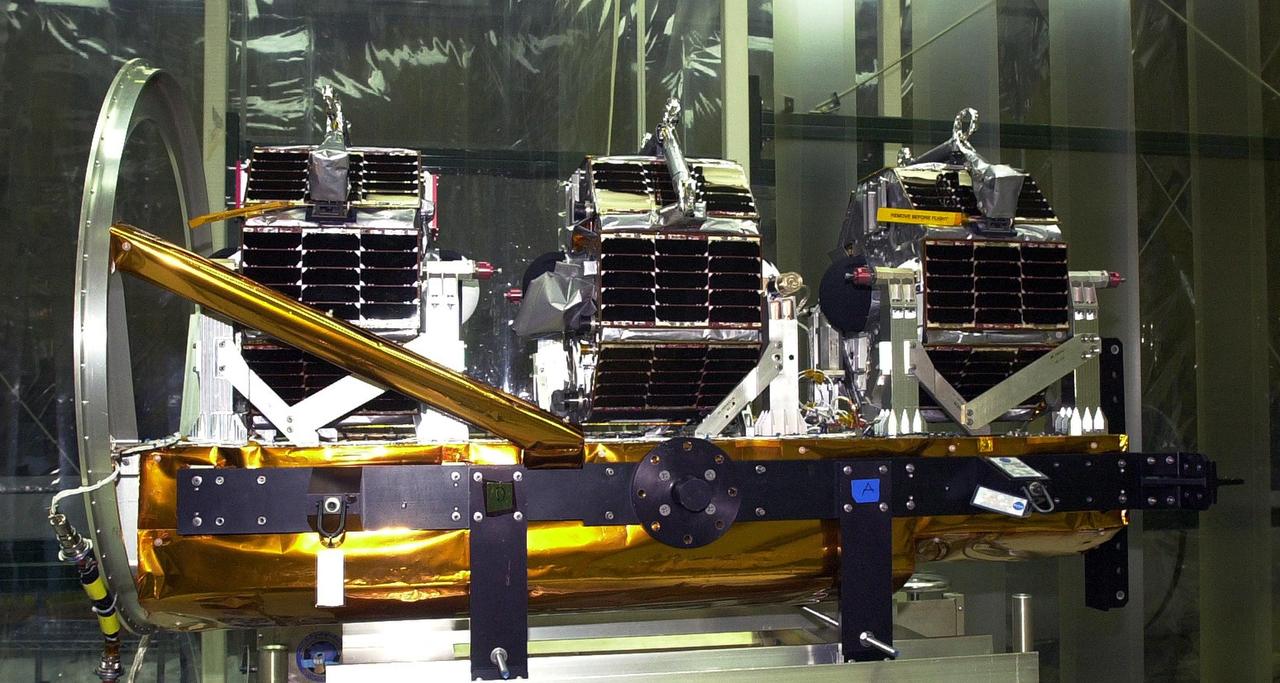

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside Orbital Sciences’ Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft is ready for mating to the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. Seen in the photo are the three satellites that make up the ST5, containing miniaturized redundant components and technologies. Each will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. With such missions, NASA hopes to improve scientists’ ability to accurately forecast space weather and minimize its harmful effects on space- and ground-based systems. Launch of ST5 is scheduled no earlier than March 6 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
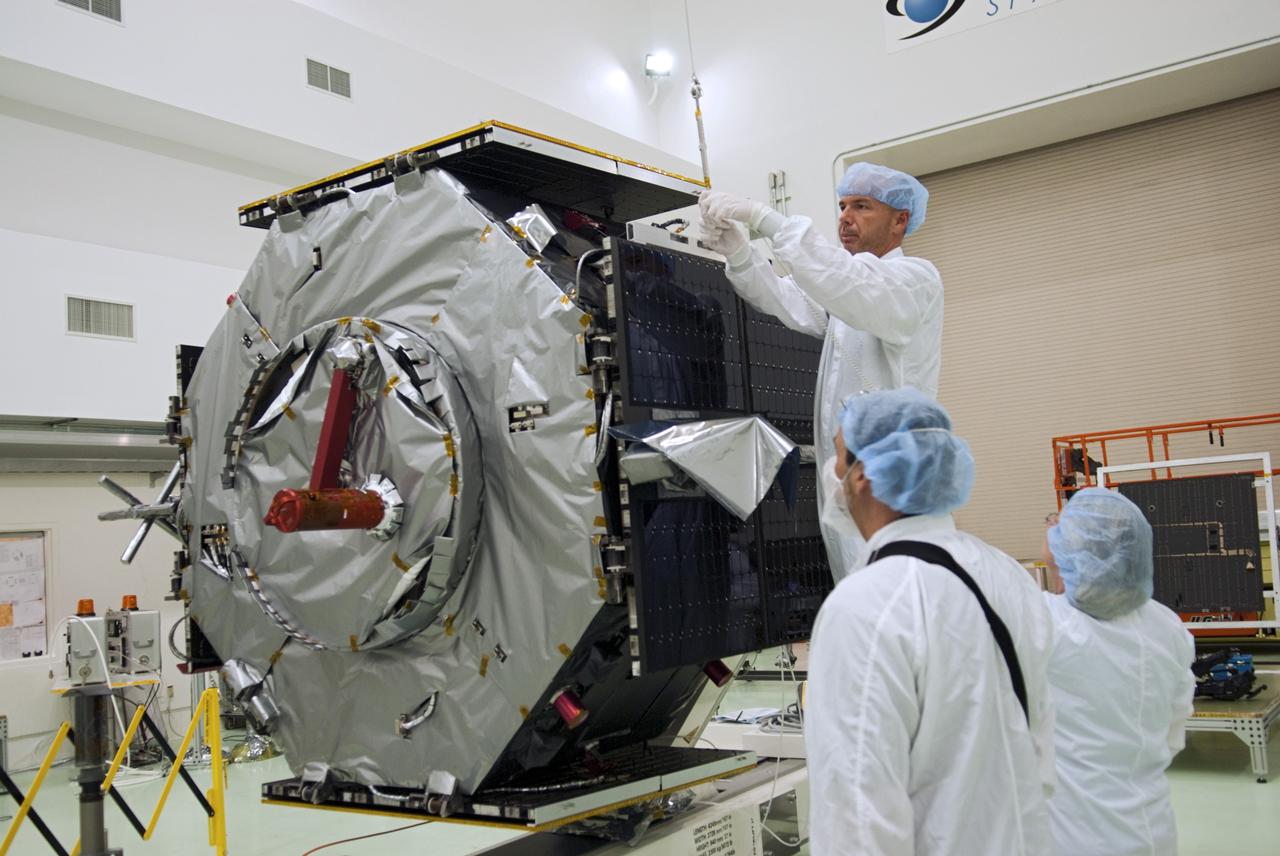

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to deploy the solar arrays and magnetometer boom of the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, spacecraft A. Deploying these components are standard procedure to ensure they work properly on Earth before they head into space. NASA’s RBSP mission will help us understand the sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the Earth’s radiation belts on various scales of space and time. As the spacecraft orbits Earth, the four solar panels will continuously face the sun to provide constant power to its instruments. The boom will provide data of the electric fields that energize radiation particles and modify the structure of the inner magnetosphere. RBSP will begin its mission of exploration of Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts and the extremes of space weather after its launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Launch is targeted for Aug. 23. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/rbsp. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
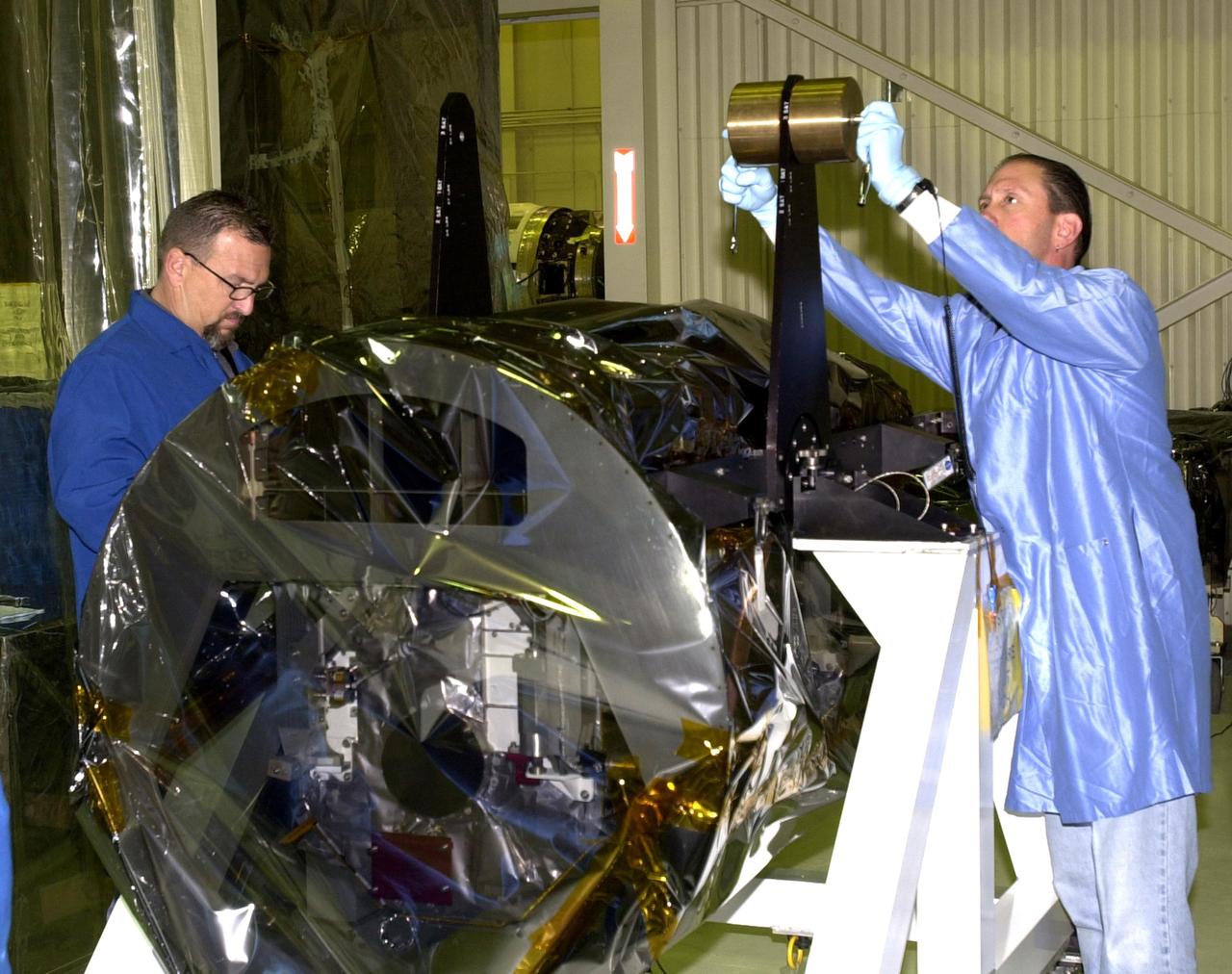

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. — Inside Orbital Sciences’ Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the wrapped Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft is being prepared for mating to the Pegasus XL launch vehicle. The satellites contain miniaturized redundant components and technologies. Each will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. With such missions, NASA hopes to improve scientists’ ability to accurately forecast space weather and minimize its harmful effects on space- and ground-based systems. Launch of ST5 is scheduled for Feb. 28 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
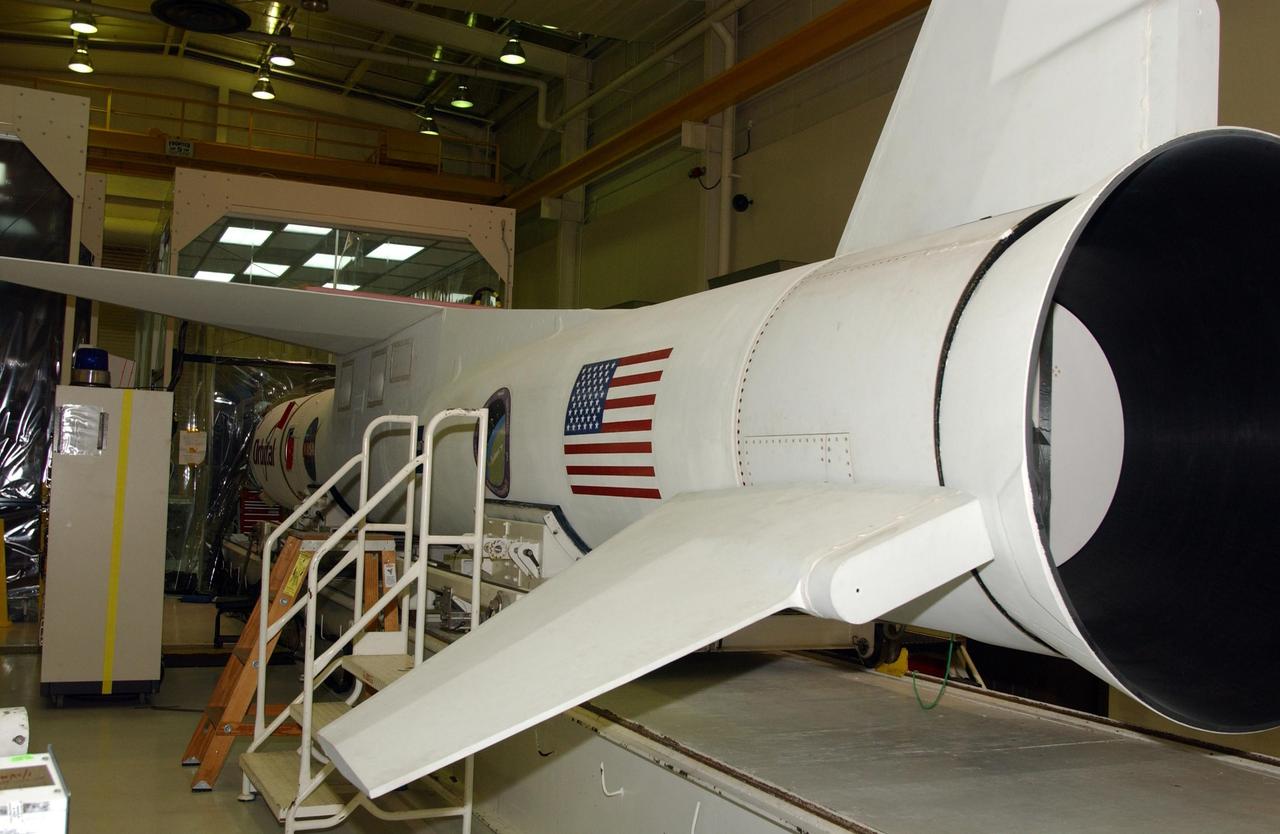

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. -Inside Orbital Sciences’ Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California is the Pegasus XL launch vehicle and the Space Technology 5 (ST5) spacecraft being prepared for encapsulation before launch. The ST5, mated to Orbital Sciences' Pegasus XL launch vehicle, contains three microsatellites with miniaturized redundant components and technologies. Each will validate New Millennium Program selected technologies, such as the Cold Gas Micro-Thruster and X-Band Transponder Communication System. After deployment from the Pegasus, the micro-satellites will be positioned in a “string of pearls” constellation that demonstrates the ability to position them to perform simultaneous multi-point measurements of the magnetic field using highly sensitive magnetometers. The data will help scientists understand and map the intensity and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field, its relation to space weather events, and affects on our planet. With such missions, NASA hopes to improve scientists’ ability to accurately forecast space weather and minimize its harmful effects on space- and ground-based systems. Launch of ST5 is scheduled from the belly of an L-1011 carrier aircraft no earlier than March 14 from Vandenberg Air Force Base.
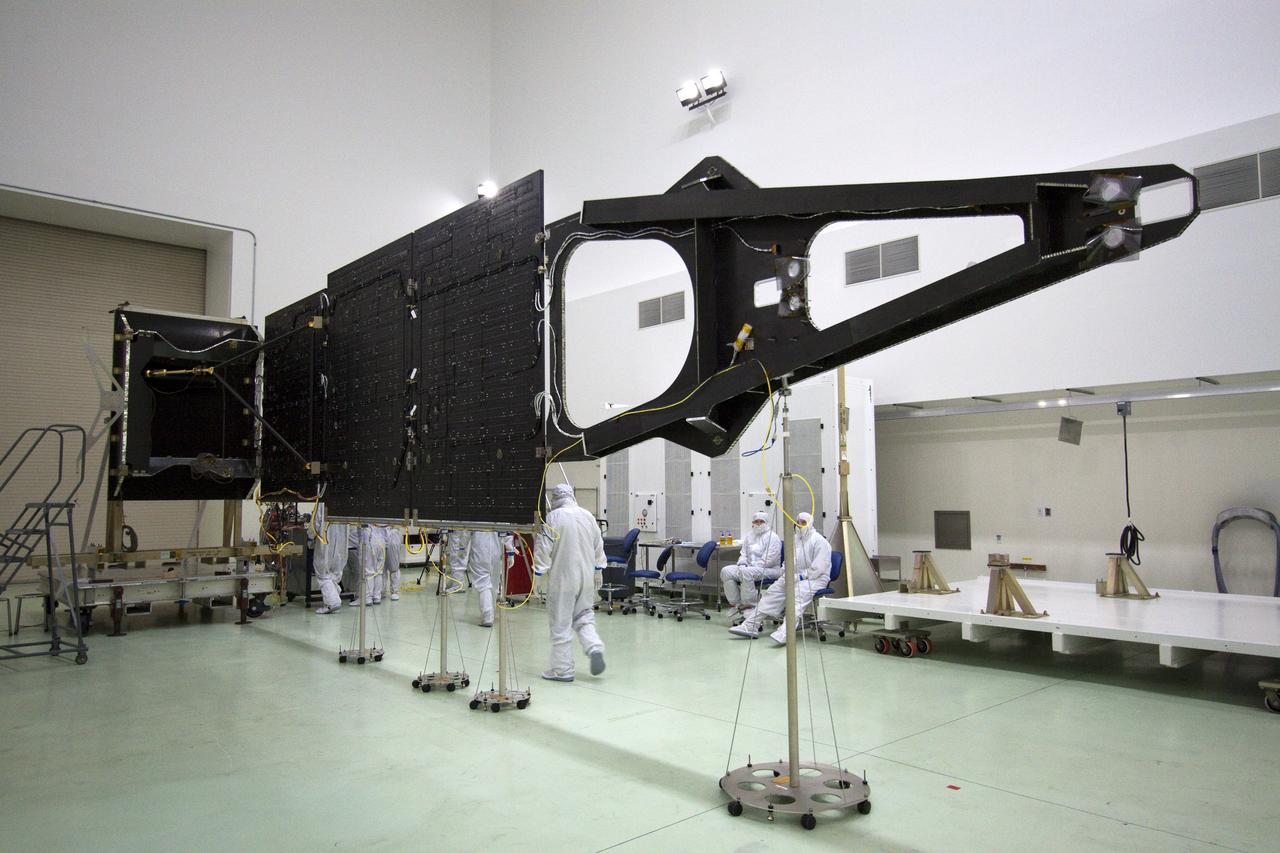

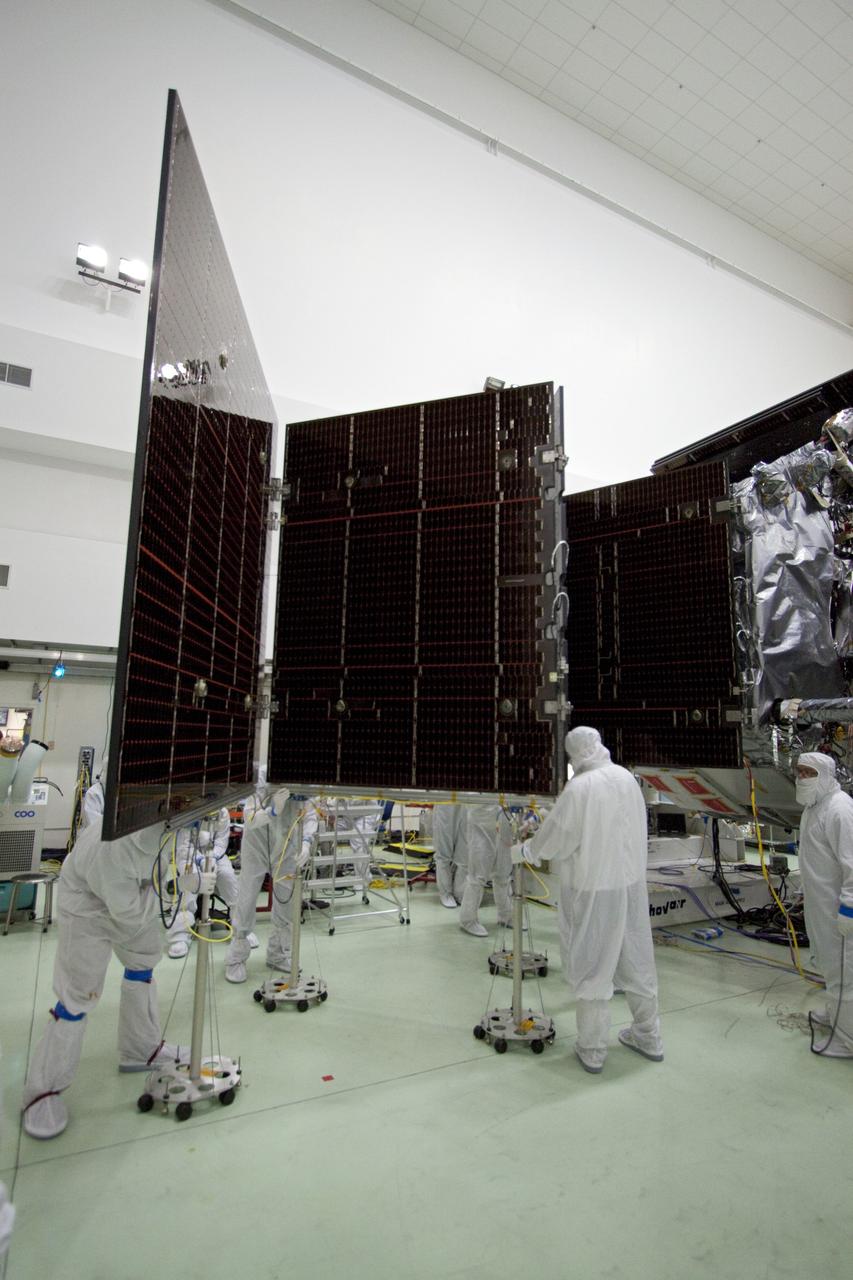
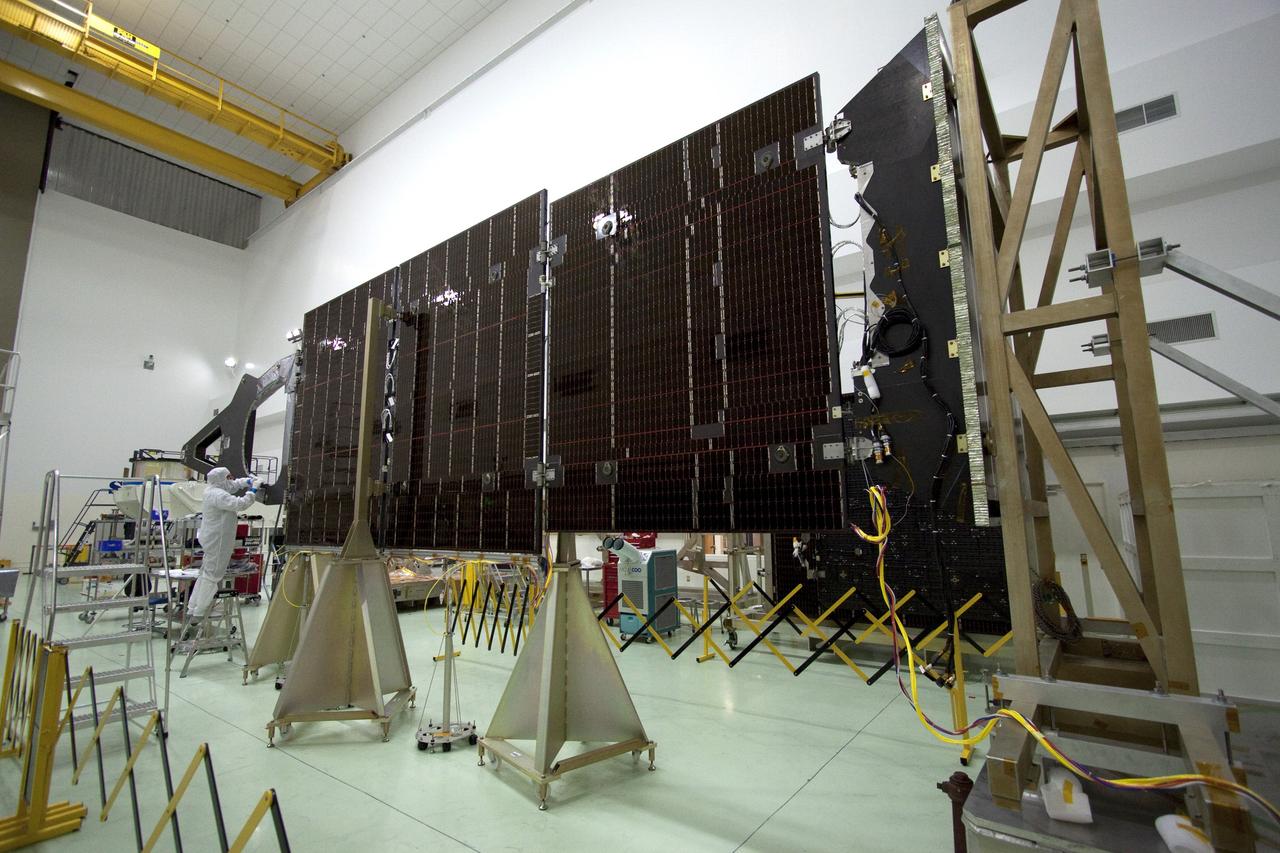
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., unfurl solar array No. 1 with a magnetometer boom that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller