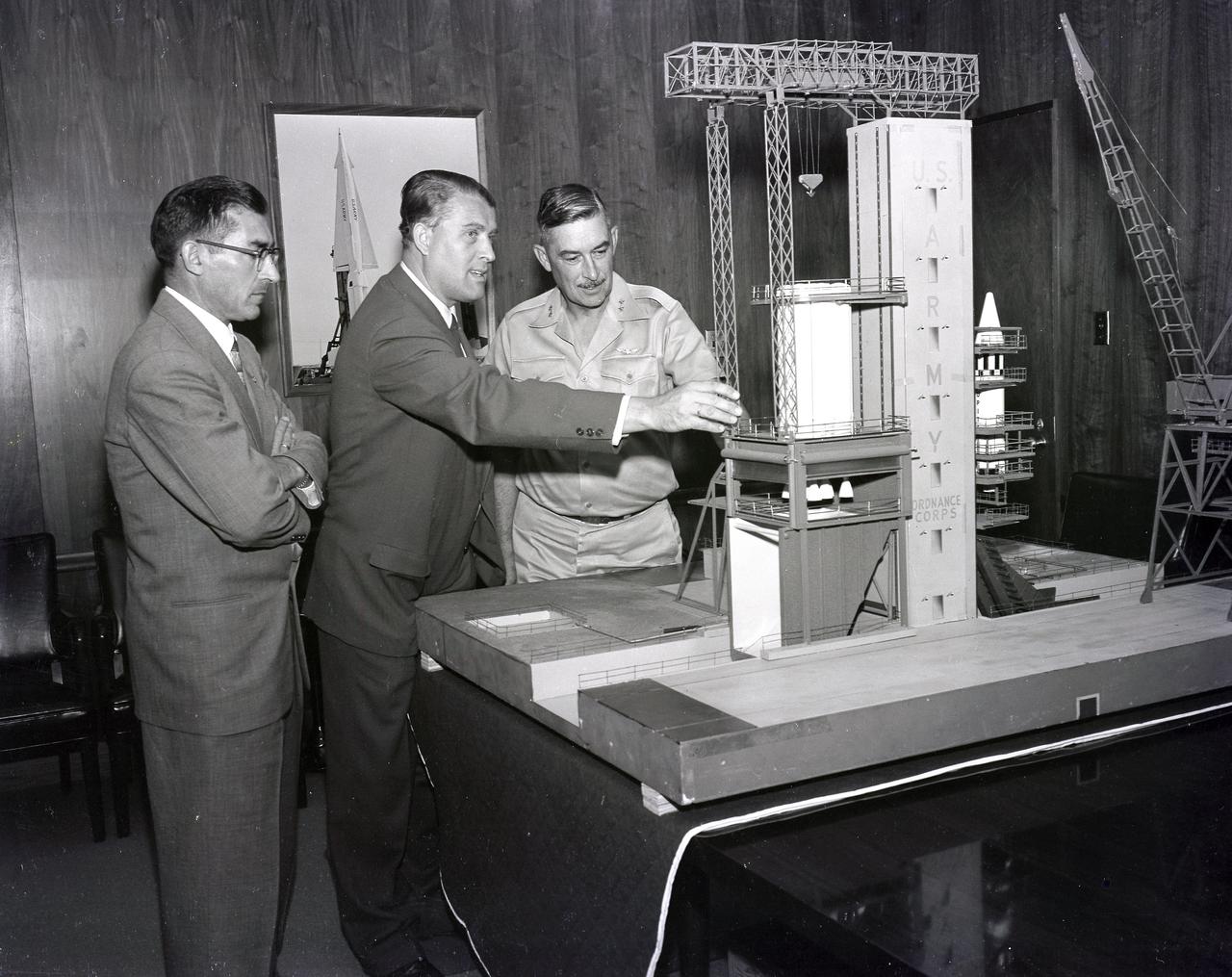

(From left to right) Karl L. Heimburg, Director of the Test Laboratory; Dr. Wernher von Braun, Director of the Development Operation Division; and Major General John B. Medaris with the model of S-1B Test Stand. Gen. Medaris was a Commander of the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) in Redstone Arsenal, Alabama, during 1955 to 1958.
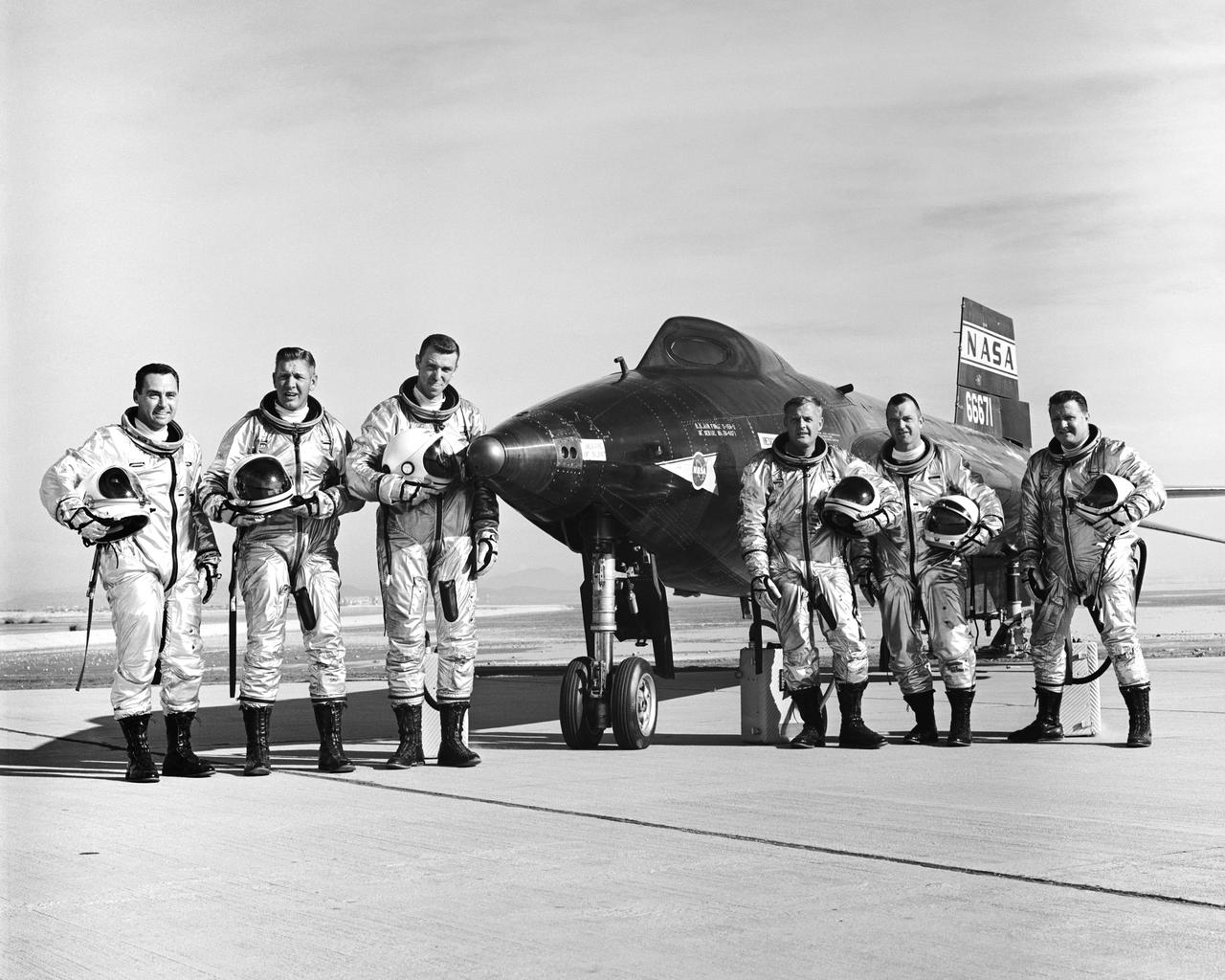

X-15 Pilots, Left to Right: Air Force pilot William J. "Pete" Knight, Air Force Major Robert A. Rushworth, Air Force Captain Joseph H. Engle, NASA pilot Milton O. Thompson, NASA pilot Bill Dana, and NASA pilot John B. "Jack" McKay.
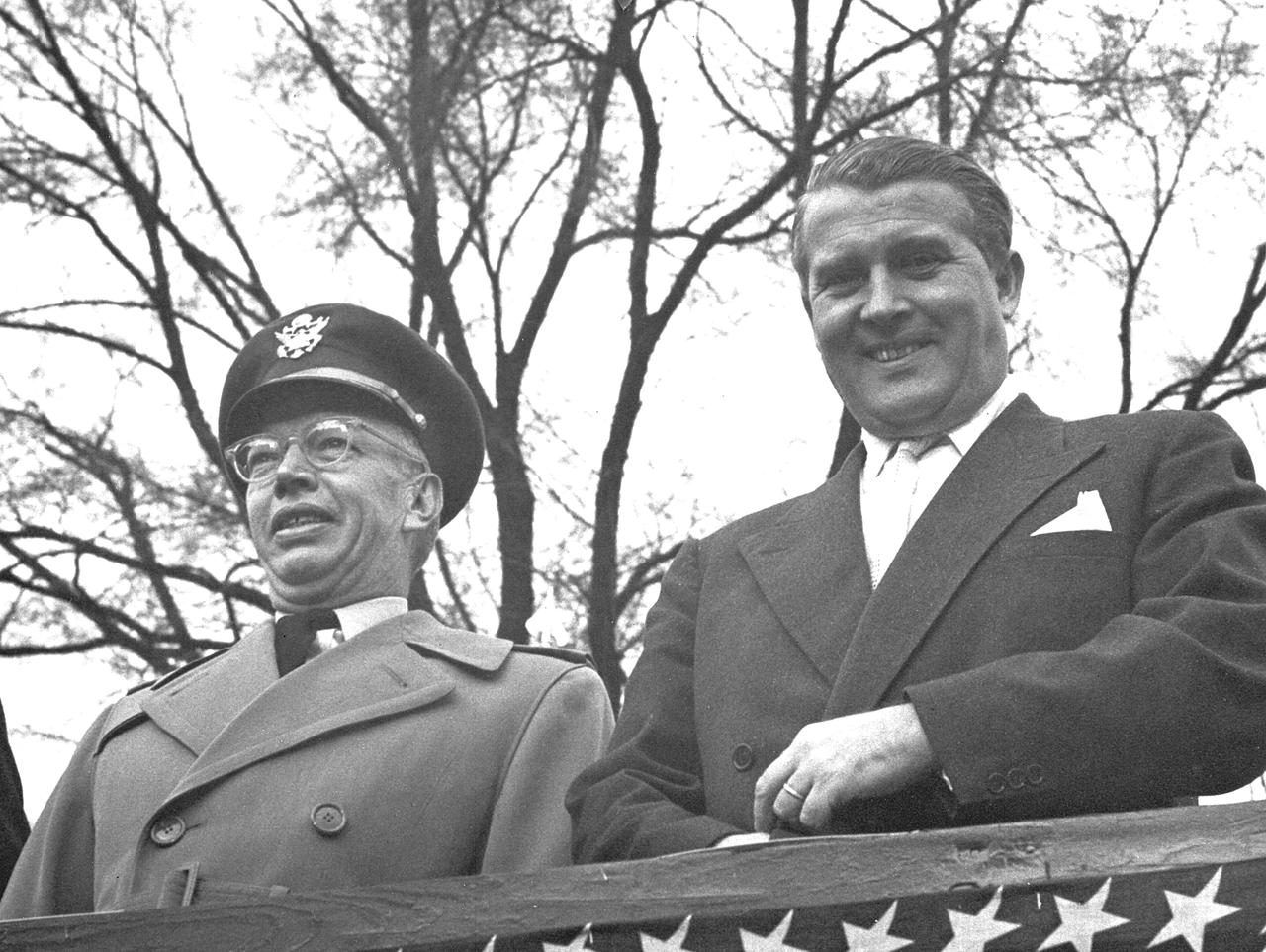

This photograph was taken about 1960 and shows Dr. von Braun viewing a parade with Major General John Barclay.
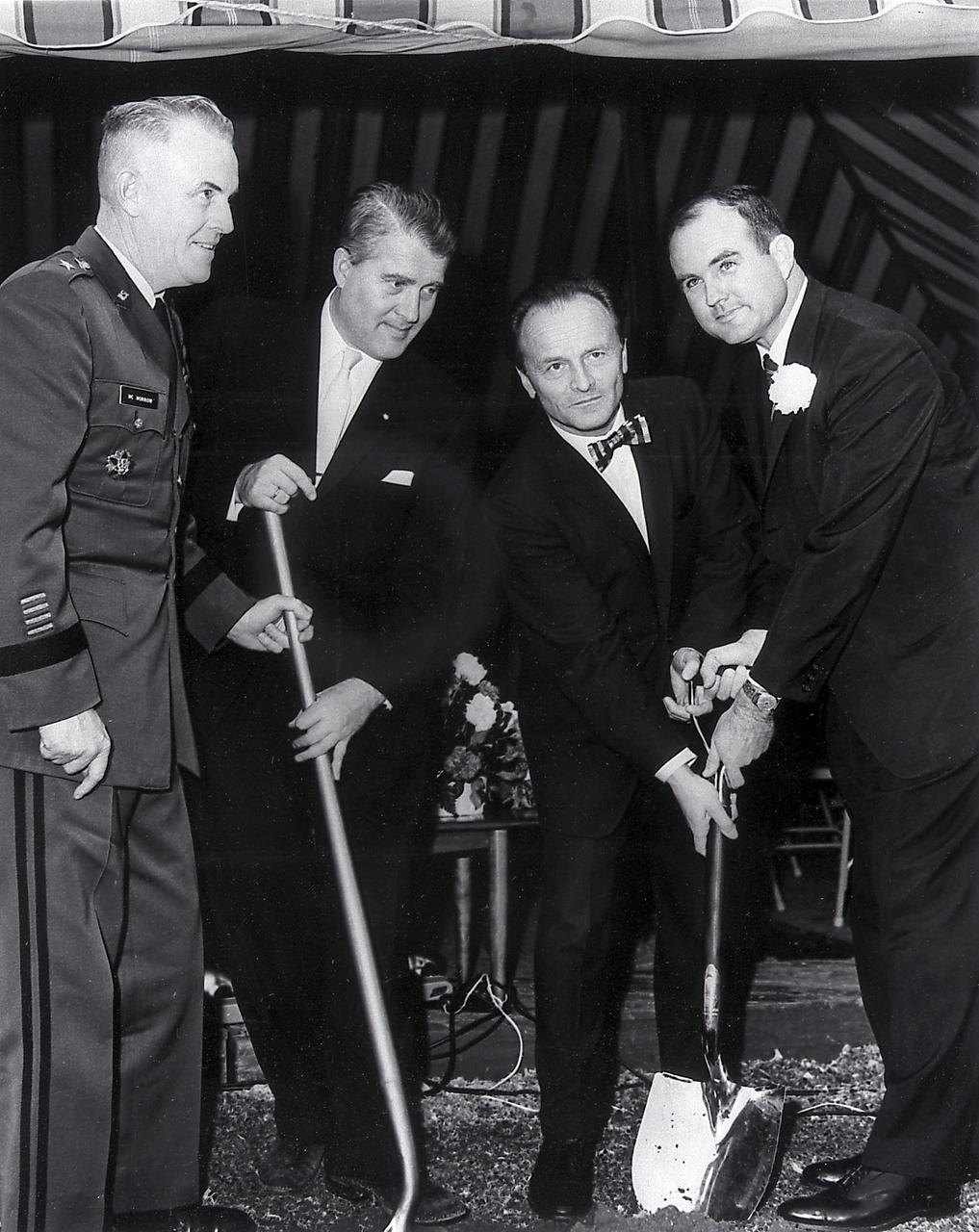

Dr. von Braun, Major General Francis McMorrow, and Alabama Governor, John Patterson (far left) participated in the ground breaking ceremony for the University of Alabama Research Institute in Huntsville, December 20, 1962.
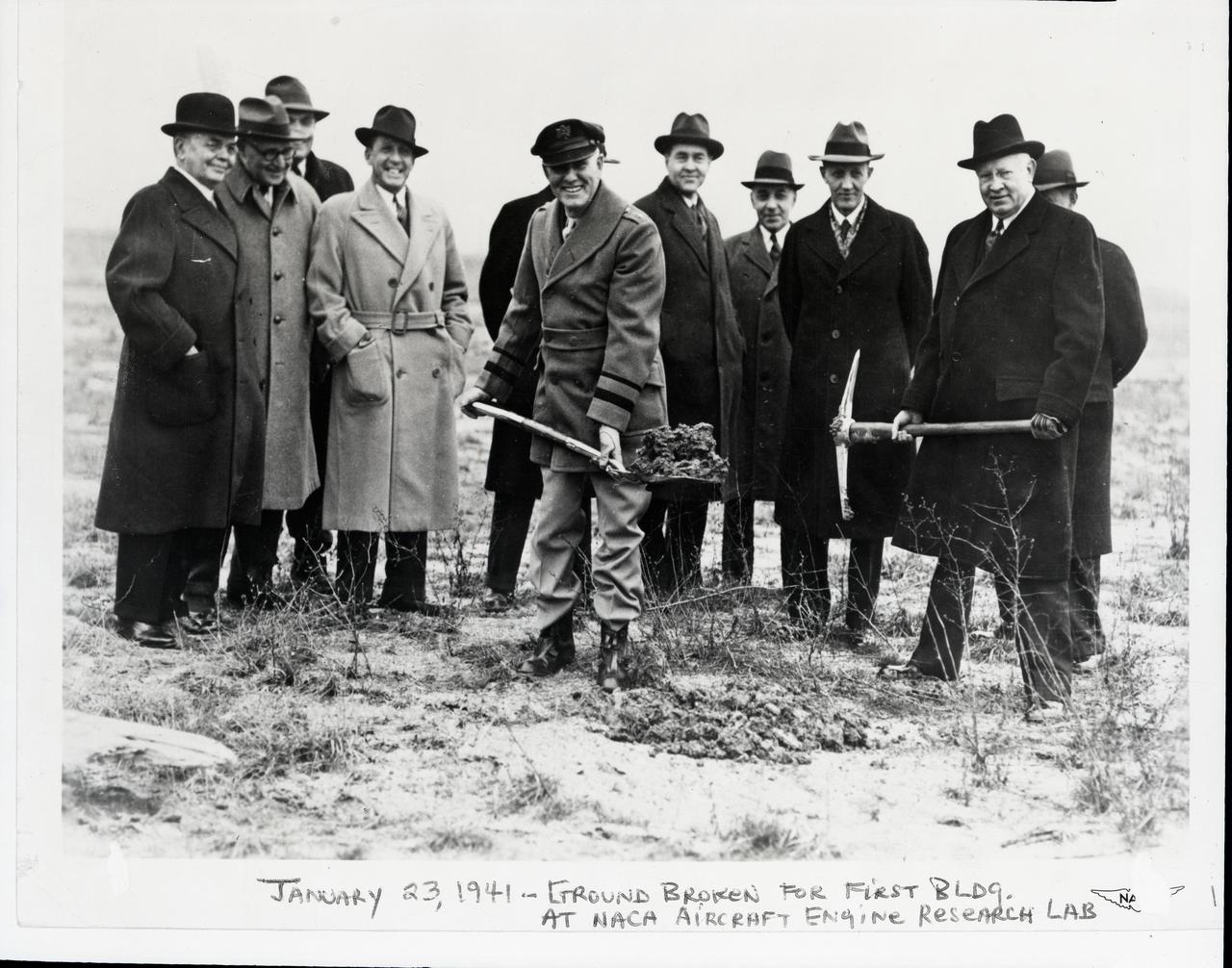

January 23, 1941 groundbreaking ceremony at the NACA Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory: left to right (does not include two individuals obscured from view behind Maj. Brett and Dr. Lewis): • William R. Hopkins – Cleveland City Manager from 1924-1930, was personally responsible for planning and acquiring the land for the Cleveland Airport. The airport’s huge capacity for handling aircraft was one factor in selecting Cleveland for the site of the research center. The Cleveland Airport was renamed Cleveland Hopkins airport in his honor in 1951. • Major John Berry – Cleveland Airport Manager • Edward R. Sharp – GRC’s first director, serving from 1942 to his retirement in 1961. He came to Cleveland in 1941 as the construction manager for the new facility. • Frederick C. Crawford – President of Thompson Products, which became the Thompson-Ramo-Woolridge Corporation (TRW) in 1958. Crawford was, at the time, also president of the Cleveland Chamber of Commerce. He began in 1939 to campaign for Cleveland as the location for the new NACA facility. • Major George H. Brett – A Cleveland native, Brett served in WWI and was commanding officer at Wright Field in Dayton, Ohio before becoming chief of the Army Air Corps. • Dr. Edward P. Warner – Acting chairman of the NACA. • Captain Sydney M. Kraus – Officer in charge of Navy procurement • Edward Blythin – Mayor of Cleveland • Dr. George Lewis – Director of Aeronautical Research for the NACA from 1924-1947, Lewis devoted his life to building a scientific basis for aeronautical engineering. The Cleveland laboratory was renamed the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in his honor in 1948. A description of the event, based on newspaper accounts and later NASA publications is as follows: On January 23, 1941, a brief groundbreaking ceremony at the site marked the start of construction. Dr. George W. Lewis, director of research for the NACA, loosened the soil with a
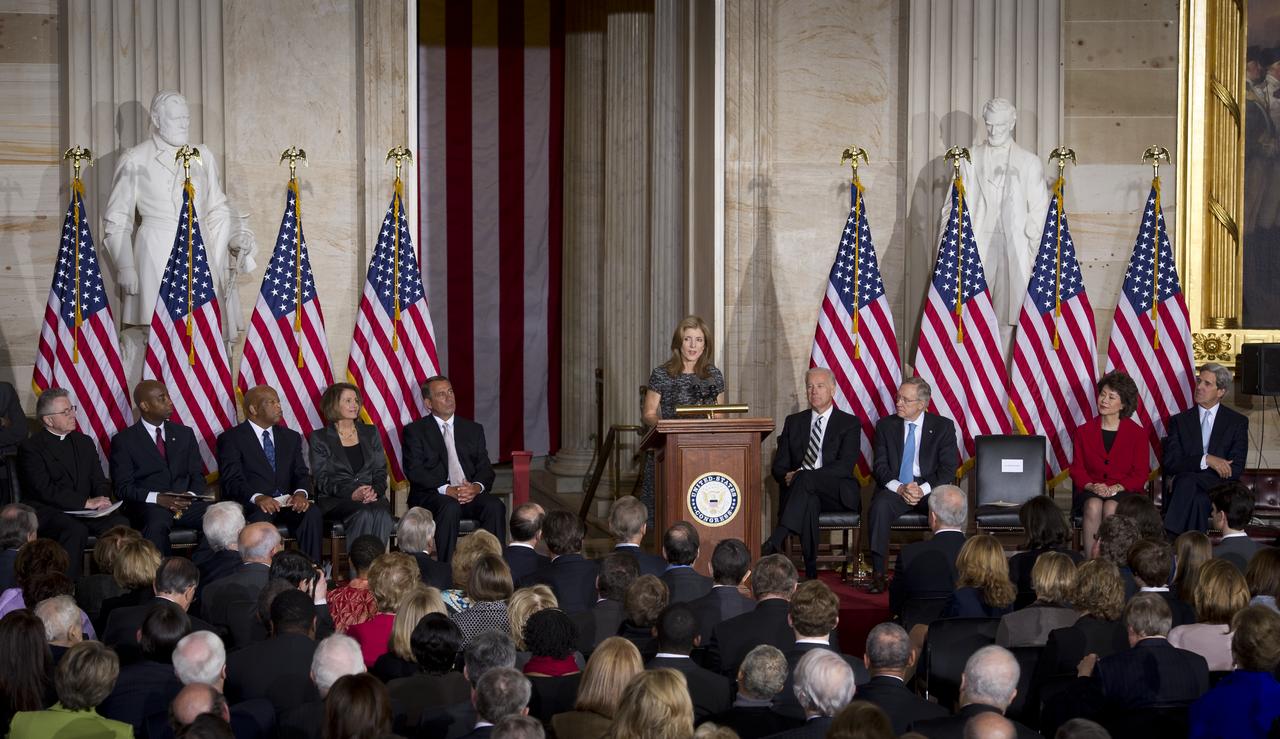

Caroline Kennedy speaks at an event recognizing the 50th anniversary of the inauguration of John F. Kennedy as President of the United States, Thursday, Jan. 20, 2011 in the rotunda at the U.S. Capitol. Also participating in the event, seated from left, Reverend Daniel P. Coughlin, Dr. Barry Black, U.S. Congressman John Lewis (D-GA), U.S. House Minority Leader Nancy Pelosi (D-CA), House Speaker John Boehner (R-OH), U.S. Vice President Joe Biden, Senate Majority Leader Harry Reid (D-NV), former U.S. Labor Secretary Elaine Chao, and U.S. Senator John Kerry (D-MA). Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Caroline Kennedy, center, is recognized by U.S. Vice President Joe Biden, left, Senate Majority Leader Harry Reid (D-NV), second from left, former U.S. Labor Secretary Elaine Chao, and U.S. Senator John Kerry (D-MA), right, at an event recognizing the 50th anniversary of the inauguration of John F. Kennedy as President of the United States, Thursday, Jan. 20, 2011 in the rotunda at the U.S. Capitol. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
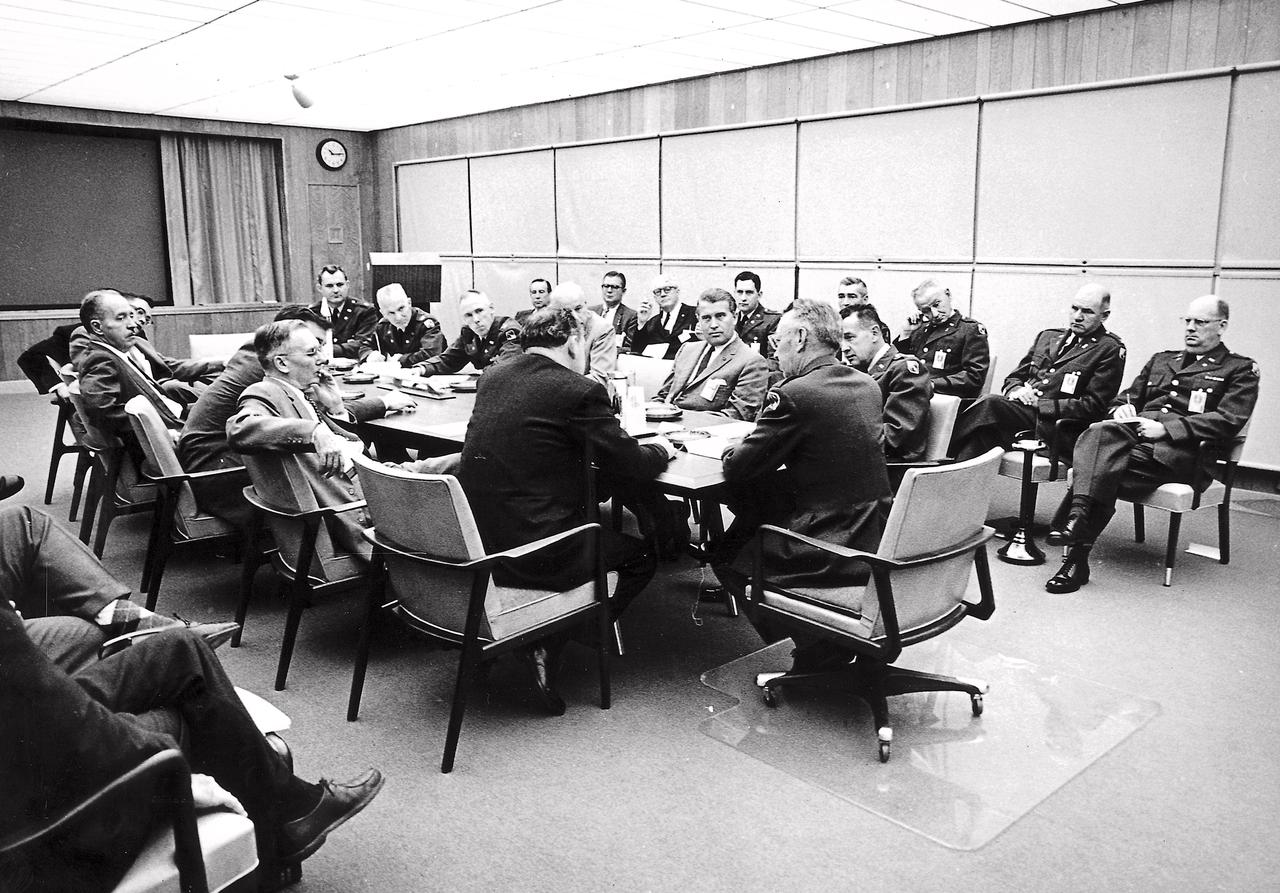

In this picture, negotiations are under way between officials of the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) on August 11, 1959. Seated at the table with his back to the camera, is Dr. T. Keith Glernan, NASA Administrator. At the head of the table is Major General John Barclay, Commander of ABMA and at the right side of the table are Colonel John G. Zierdt of ABMA and Dr. von Braun.
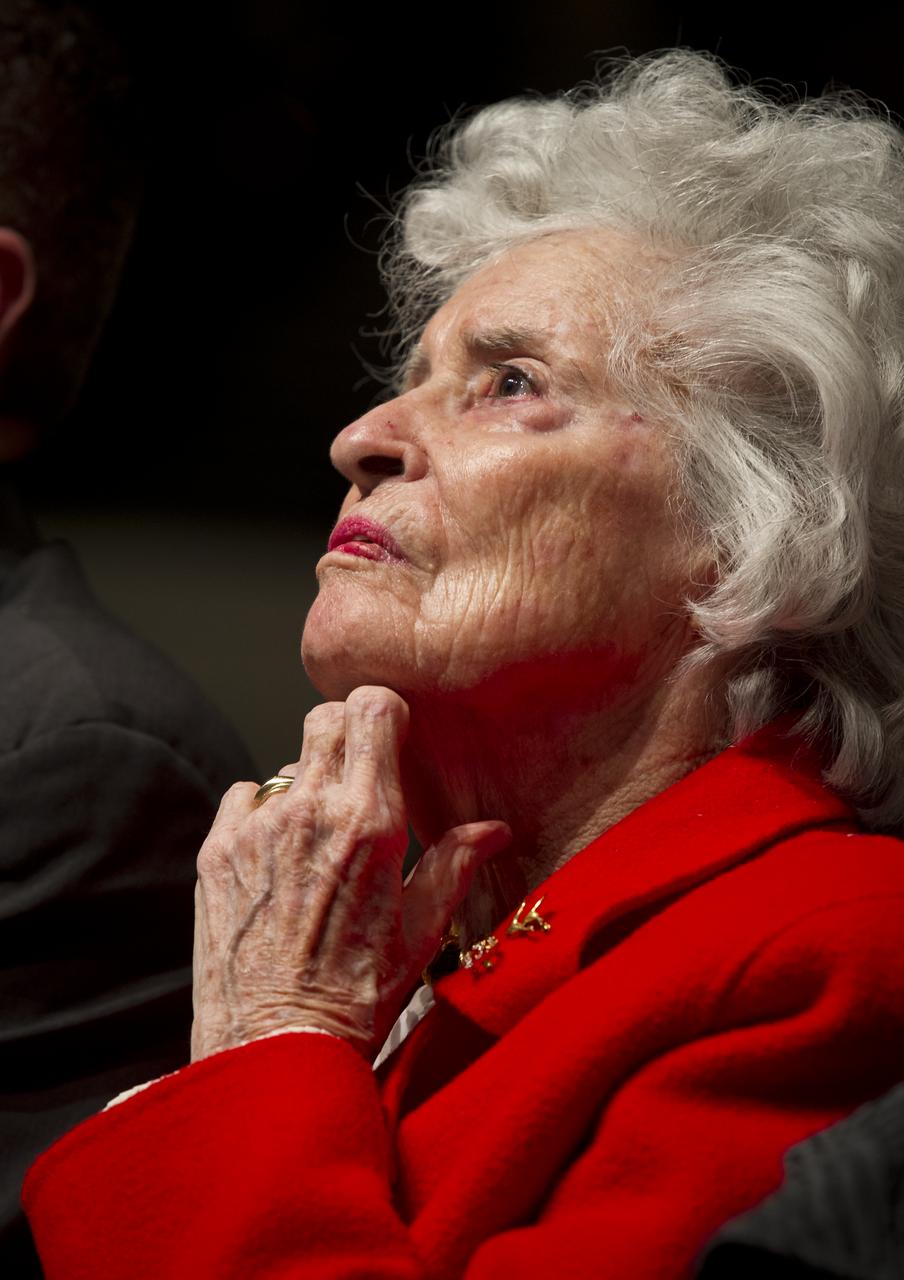

Wife of former astronaut and Senator John Glenn, Annie Glenn, listens intently to Cleveland State University Master of Music Major James Binion Jr. as he sings a musical tribute during an event celebrating John Glenn's legacy and 50 years of americans in orbit held at the university's Wolstein Center on Friday, March 3, 2012 in Cleveland, Ohio. Glenn became the first American to orbit Earth in 1962. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
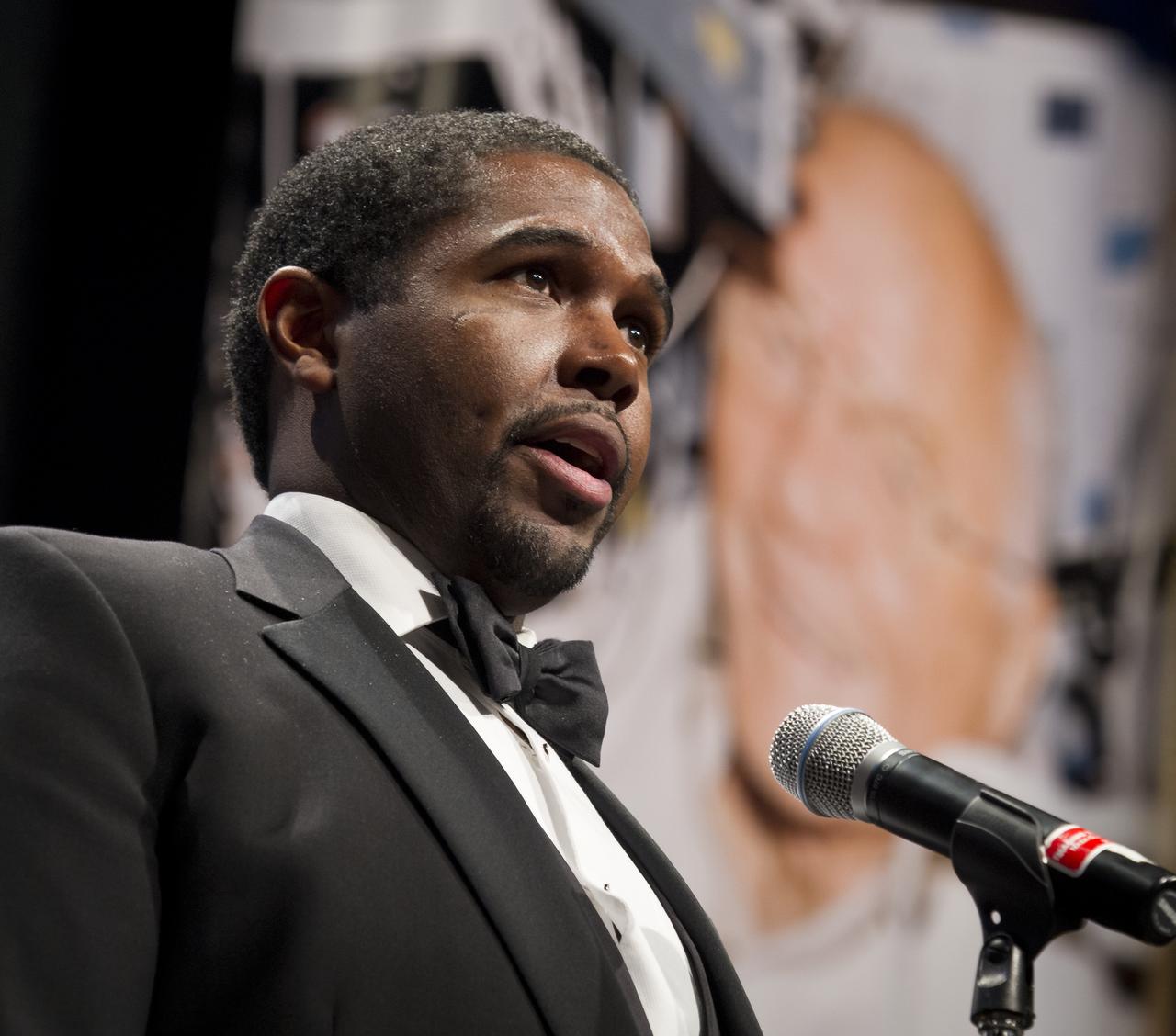

Cleveland State University Master of Music Major James Binion Jr. sings a musical tribute during an event celebrating John Glenn's legacy and 50 years of americans in orbit held at the university's Wolstein Center on Friday, March 3, 2012 in Cleveland, Ohio. In 1998 Lindsey flew onboard the space shuttle Discovery along with then 77 year-old Sen. John Glenn for the STS-95 mission. Glenn became the first American to orbit Earth in 1962. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
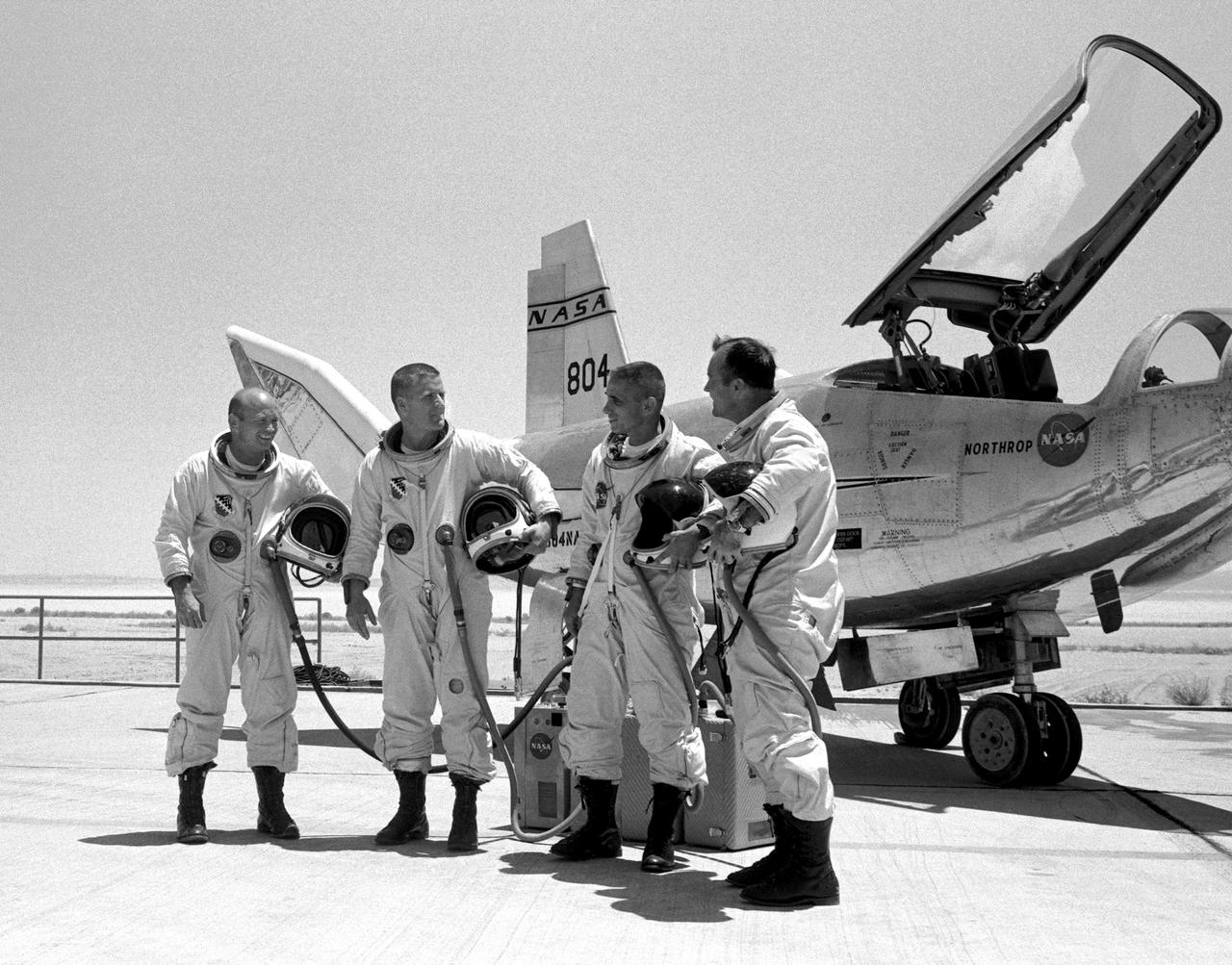

The four principal HL-10 pilots are seen here with the lifting body aircraft. They are, left to right; Air Force Major Jerauld R. Gentry, Air Force test pilot Peter Hoag, and NASA pilots John A. Manke and Bill Dana. All are wearing the pressure suits needed for flying above 50,000 feet.
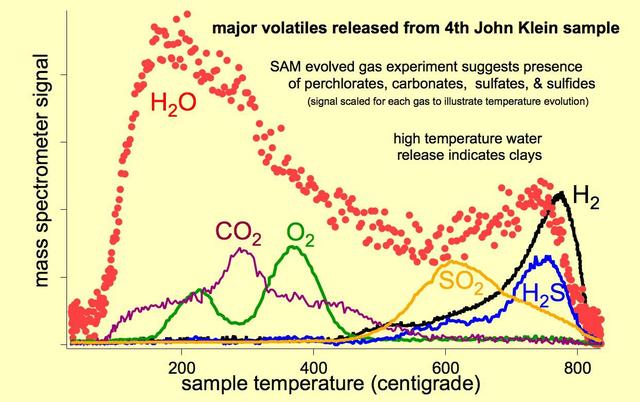
As the Sample Analysis at Mars SAM suite of instruments on NASA Curiosity Mars rover heats a sample, gases are released or evolved from the sample and can be identified using SAM quadrupole mass spectrometer.
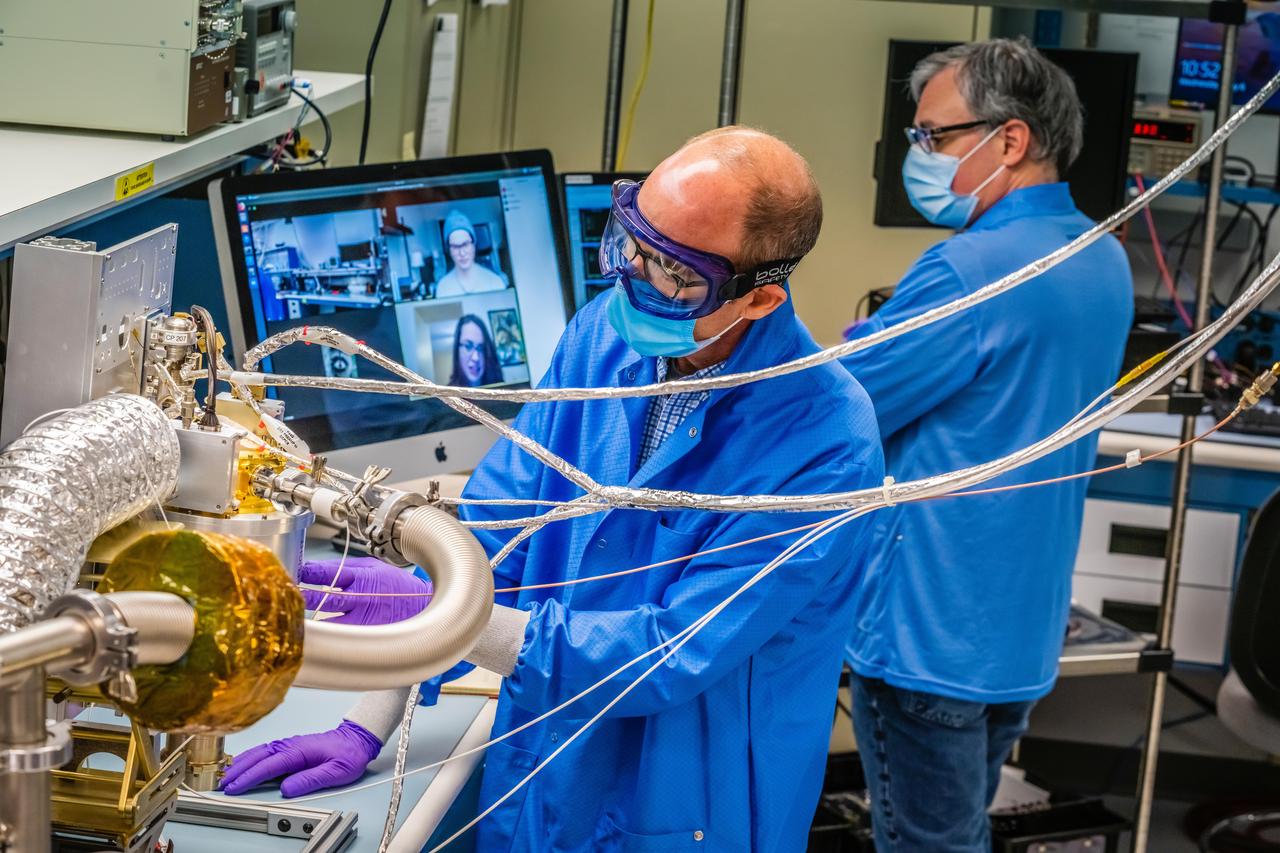

Engineers at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, continue to make progress on Psyche's spectrometer while observing COVID-19 safety procedures. Engineers John Goldsten (left) and Sam Fix work on the Gamma Ray/Neutron Spectrometer (GRNS) instrument that will launch aboard the Psyche spacecraft in 2022 to detect, measure and map the asteroid Psyche's elemental composition. The instrument's team at APL moved the majority of its work to video conferencing, which has enabled the team to whittle operations down to requiring just one or two staff members on campus once or twice a week. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23880
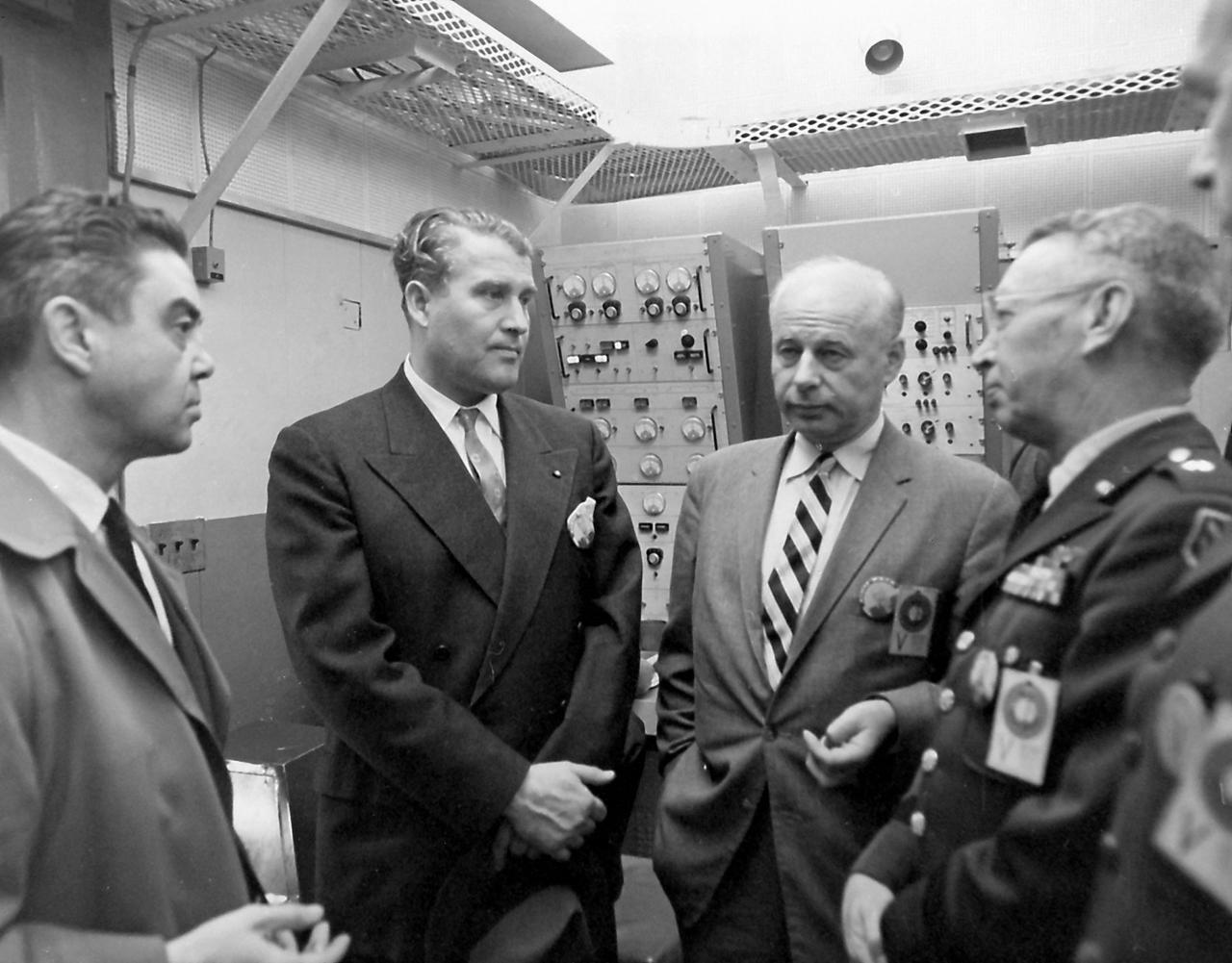

In this 1959 photo, taken at Cape Canaveral, Florida, Dr. von Braun (2nd from left) Director of the U.S. Army Ballistic Missile Agency's (ABMA) Development Operations Division, is shown conferring with Air Force Major General Donald R. Ostrander (left), on assignment at NASA as launch vehicle director; Dr. Eberhard Rees, deputy to Dr. von Braun, and Army Brigadier General John Barclay, commander of the ABMA.
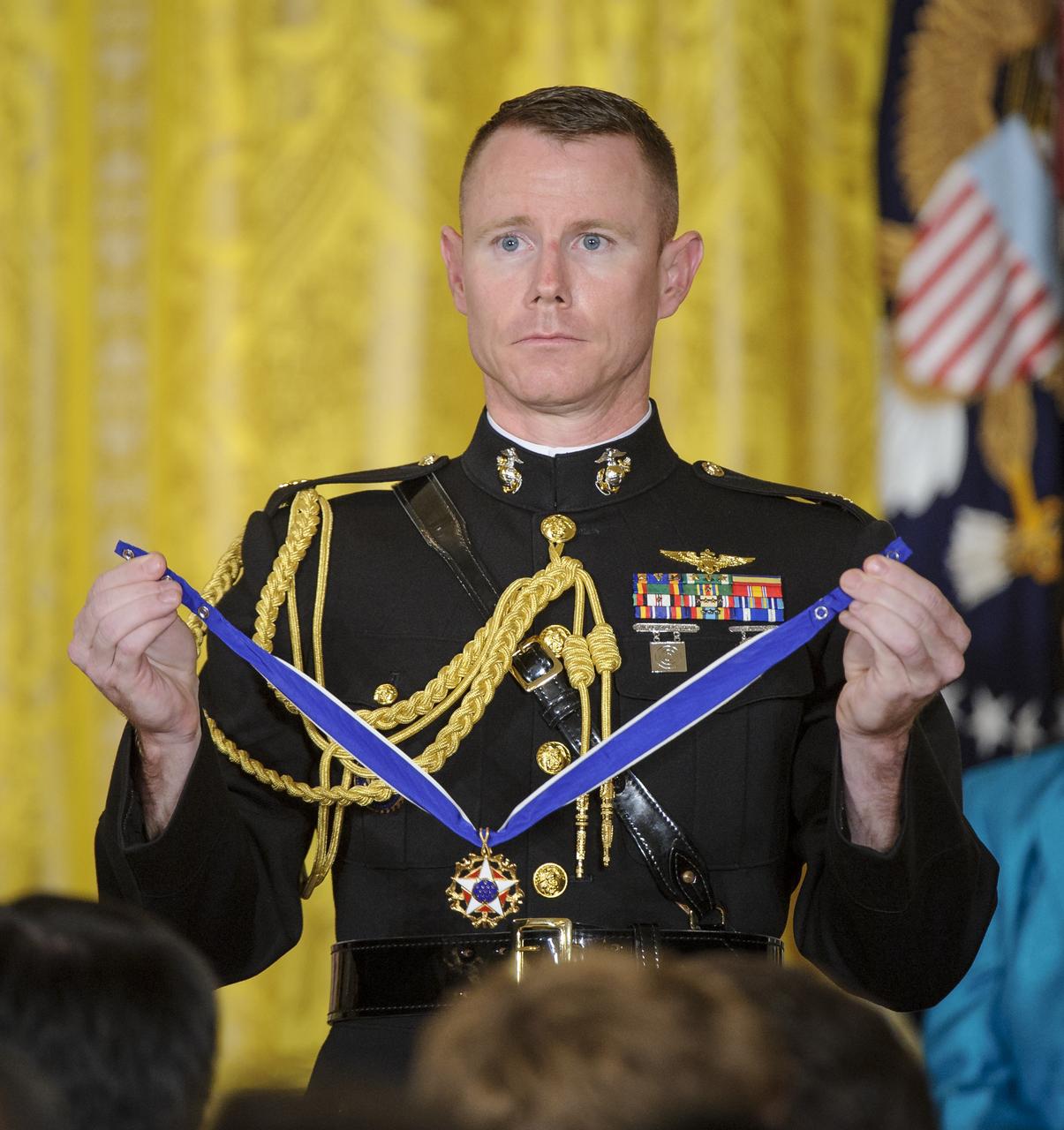

Major S. Lee Meyer, USMC, Military Aide to the President, holds the Presidential Medal of Freedom that is to be presented by President Barack Obama to former United States Marine Corps pilot, astronaut, and United States Senator John Glenn, Tuesday, May 29, 2012, during a ceremony at the White House in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
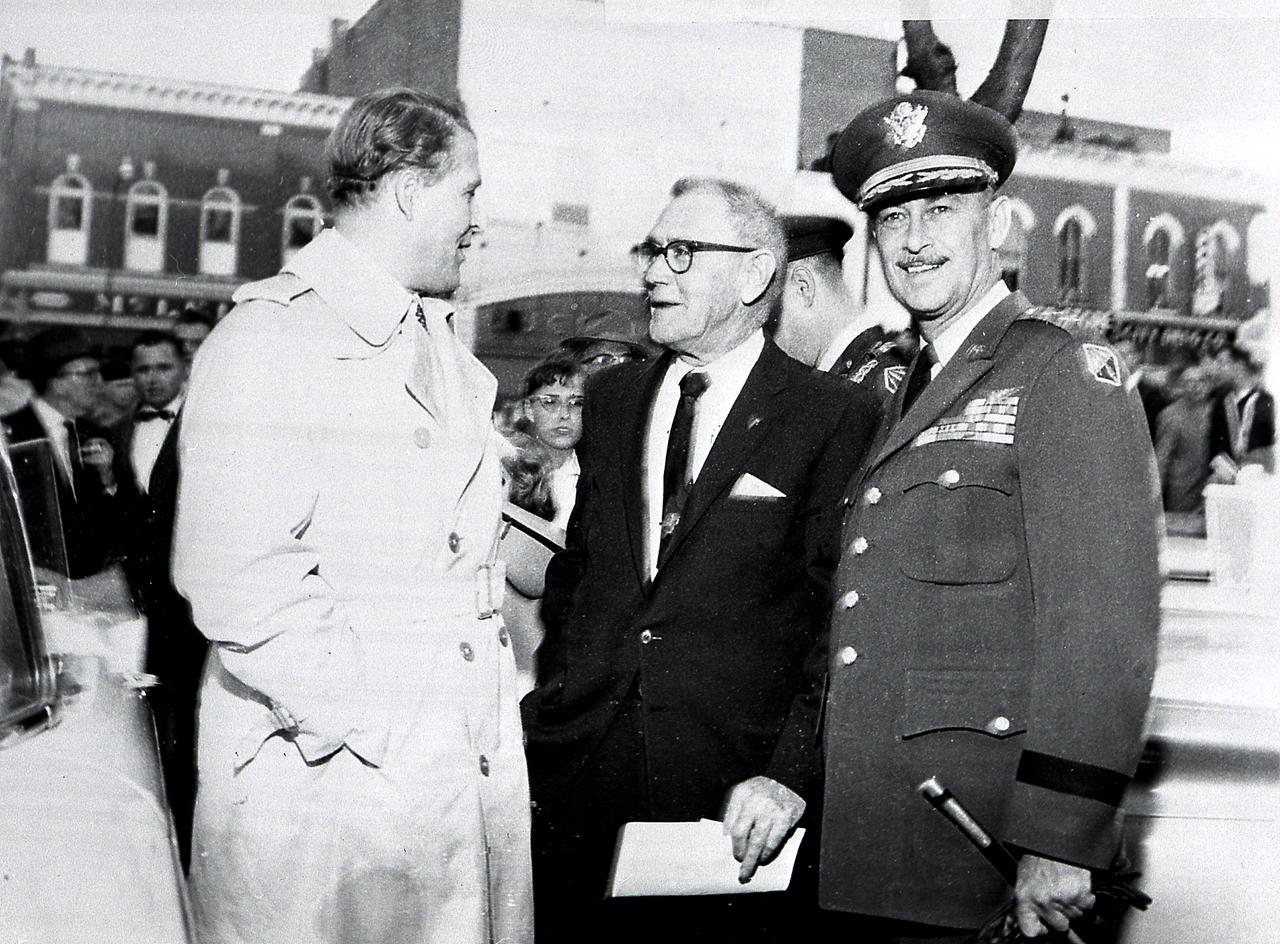

Dr. Wernher von Braun, Director of the U.S. Army Ballistic Missile Agency's (ABMA) Development Operations Division, talks to Huntsville Mayor R. B. "Speck" Searcy, center, and Army Ordnance Missile Command (ARMC) Major General John B. Medaris, right, during "Moon Day" celebrations in downtown Huntsville, Alabama. (Courtesy of Huntsville/Madison County Public Library)

StenniSphere, the John C. Stennis Space Center's visitor center in Hancock County, Miss., features a 14,000-square-foot museum and outdoor exhibits about Stennis Space Center. Designed to entertain while educating, StenniSphere includes informative displays and exhibits from NASA, the Naval Meteorology and Oceanography Command, and other resident agencies. Recently named Mississippi's Travel Attraction of the Year, StenniSphere hosted a quarter of a million visitors in its first year and is a major school field trip destination.
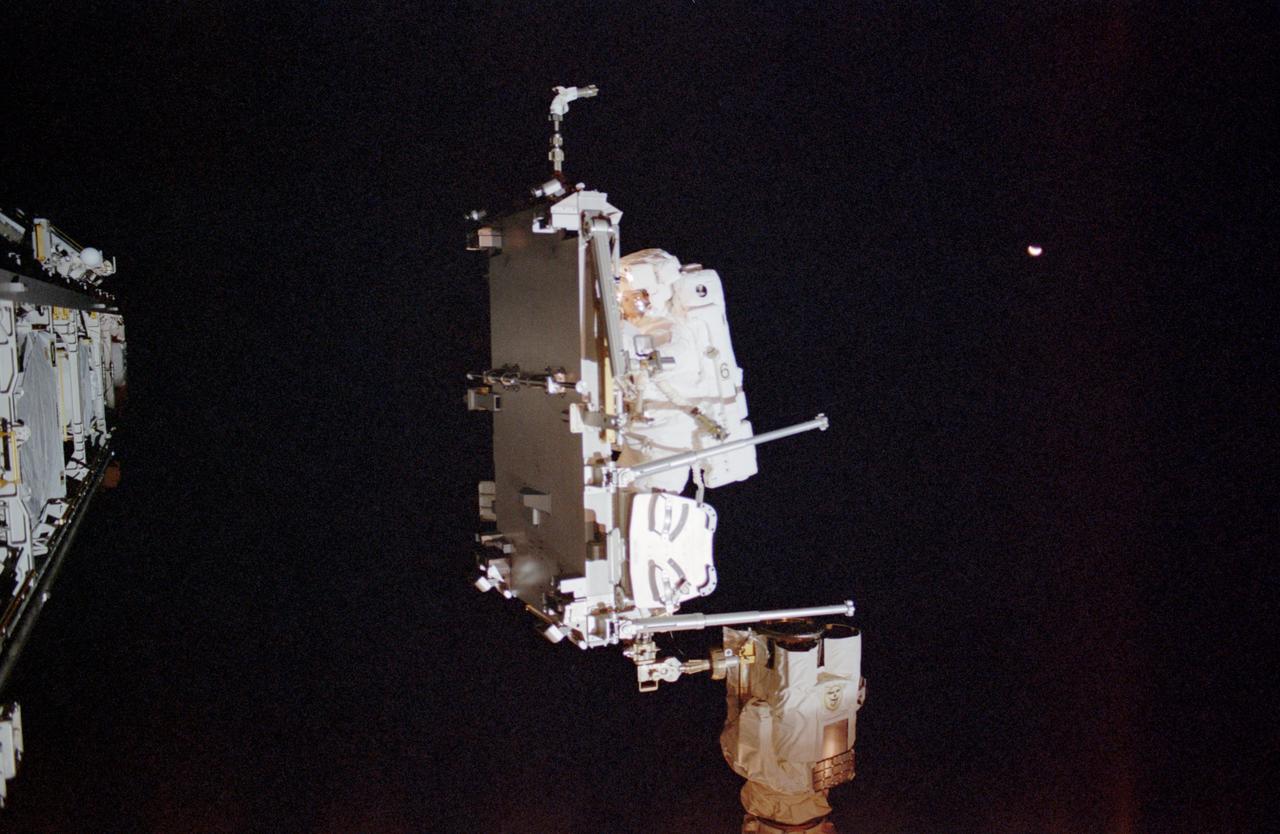
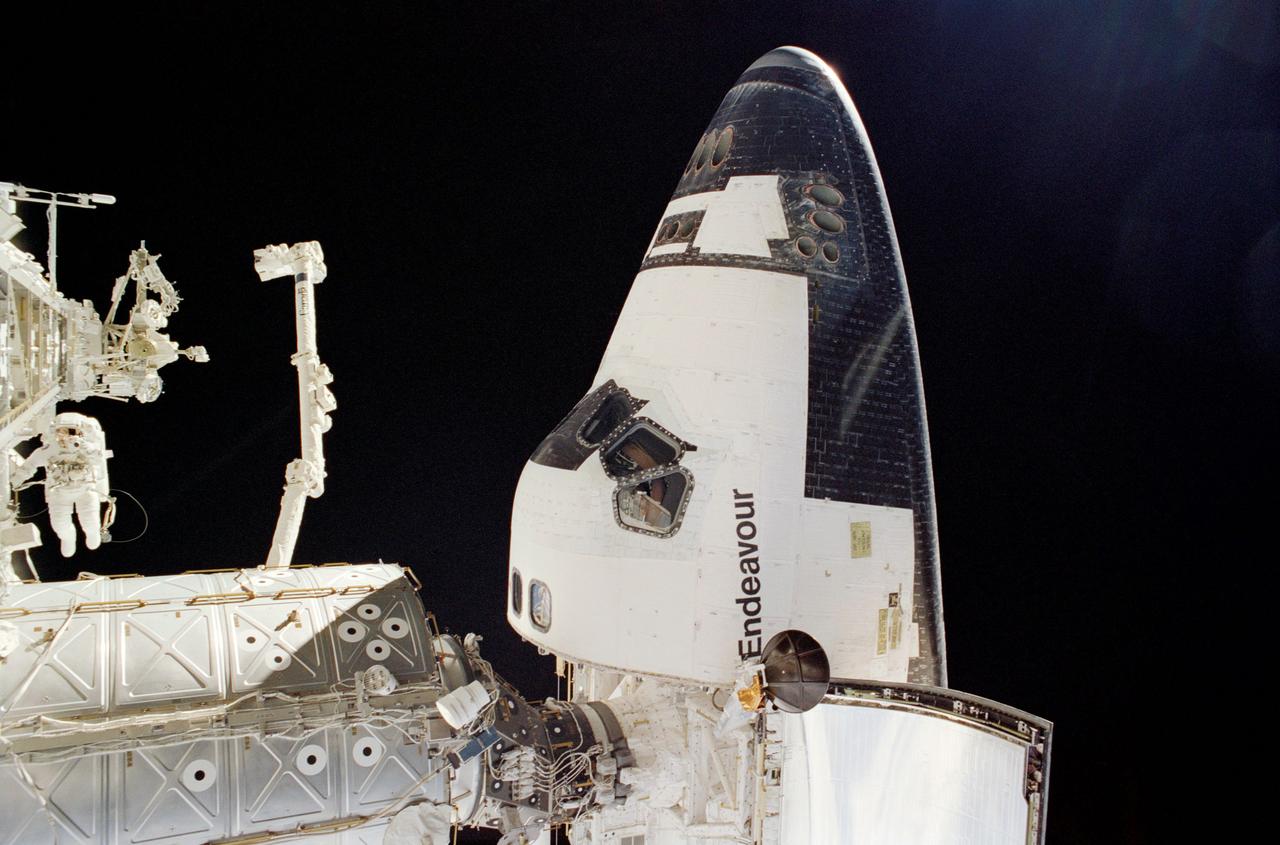
STS113-310-023 (28 November 2002) --- Astronaut John B. Herrington, STS-113 mission specialist, anchored on the mobile foot restraint on the International Space Station’s (ISS) Canadarm2, moves the Crew and Equipment Translation Aid (CETA) during the mission’s second scheduled spacewalk. The final major task of the spacewalk was the relocation of the CETA cart from the Port One (P1) to the Starboard One (S1) Truss, which will allow the Mobile Transporter to move along the P1 to assist in upcoming assembly missions.
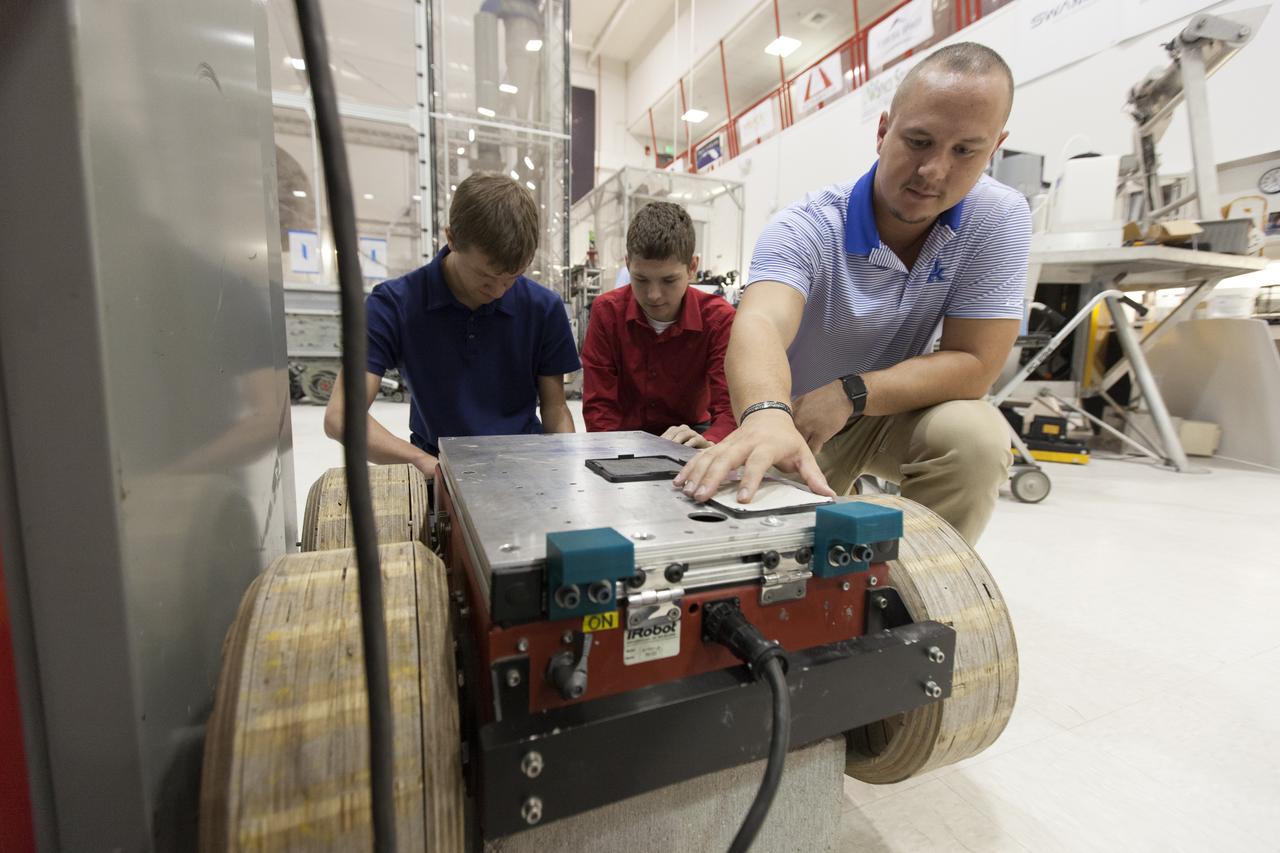

In the Swamp Works laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, student interns, from the left, Jeremiah House, Thomas Muller and Austin Langdon are joining agency scientists, contributing in the area of Exploration Research and Technology. House is studying computer/electrical engineering at John Brown University in Siloam Springs, Arkansas. Muller is pursuing a degree in computer engineering and control systems and Florida Tech. Langdon is an electrical engineering major at the University of Kentucky. The agency attracts its future workforce through the NASA Internship, Fellowships and Scholarships, or NIFS, Program.
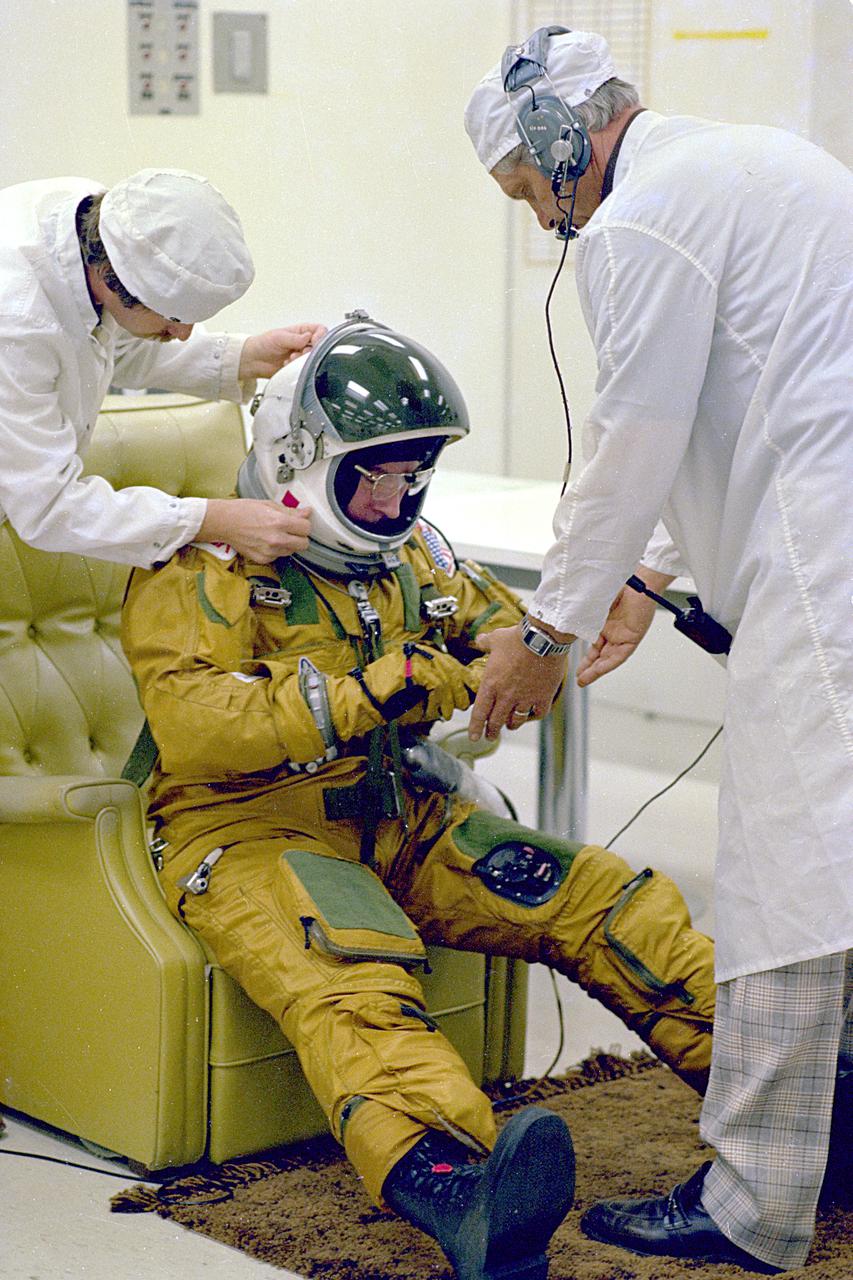
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Astronaut John Young, in the 'white room' at Launch Pad 39A, suits up for the dry Countdown Demonstration Test, the last major simulated countdown and launch for spaceraft and crew before the launch of America's first Space Shuttle. Young, commander, and Robert Crippen, pilot, are scheduled as the total crew for the maiden flight of the pioneer reusable space transportation system (STS-1).

Lockheed Martin Skunk Works Vice President and General Manager John Clark speaks on stage prior to the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
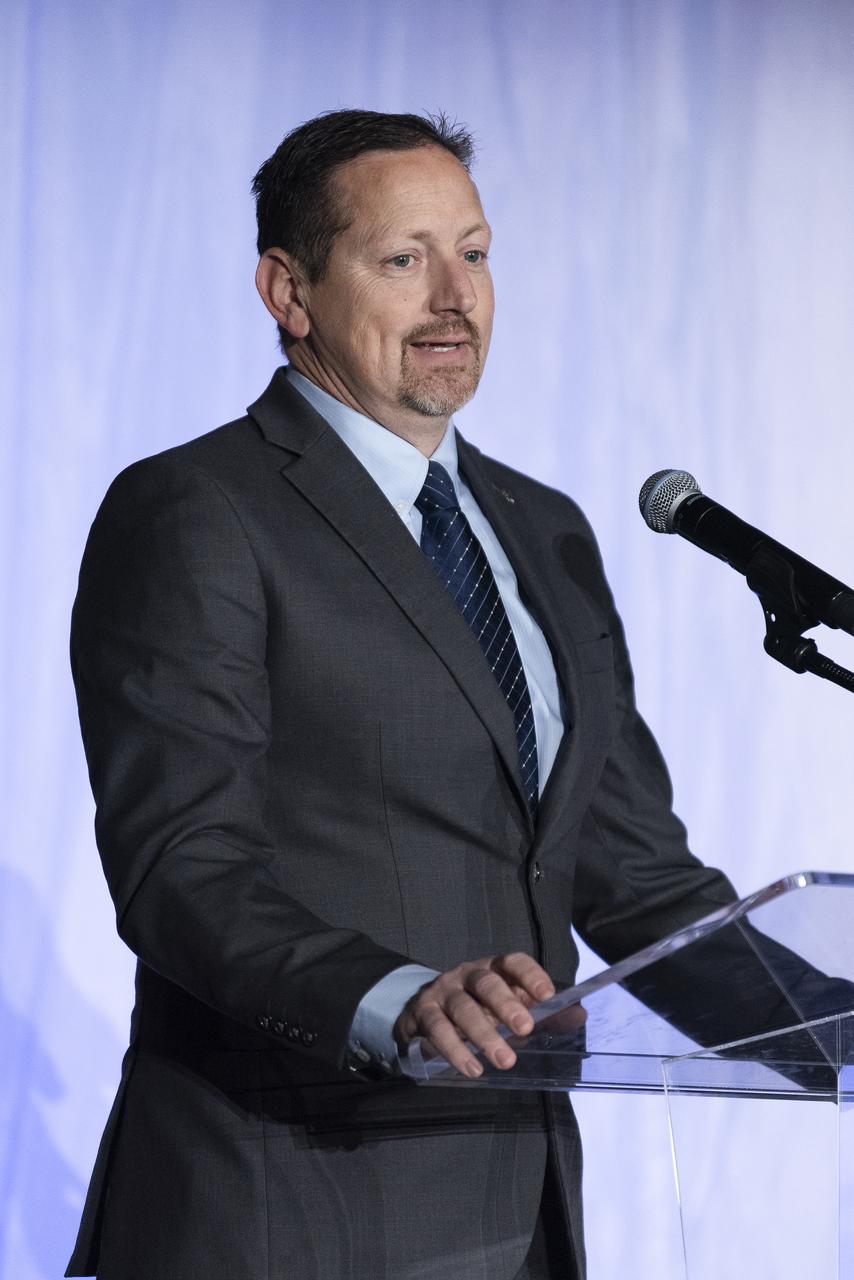

Lockheed Martin Skunk Works Vice President and General Manager John Clark speaks on stage prior to the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
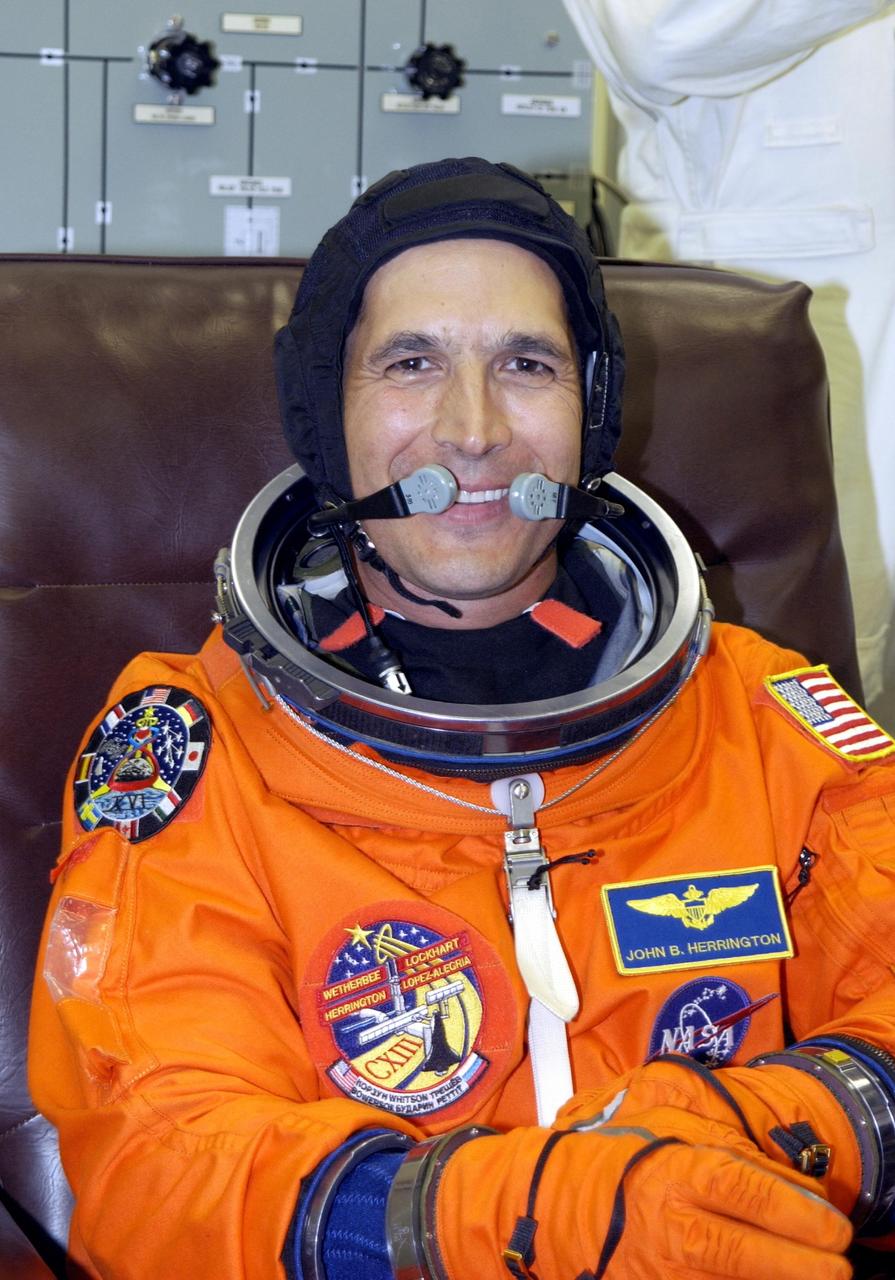

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-113 Mission Specialist John Herrington suits up for launch. Herrington will be making his first Shuttle flight. This is also the first launch of the first tribally enrolled Native American astronaut -- John B. Herrington -- on Space Transportation System. The primary mission for the crew is bringing the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and returning the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is scheduled for 8:15 p.m. EST.
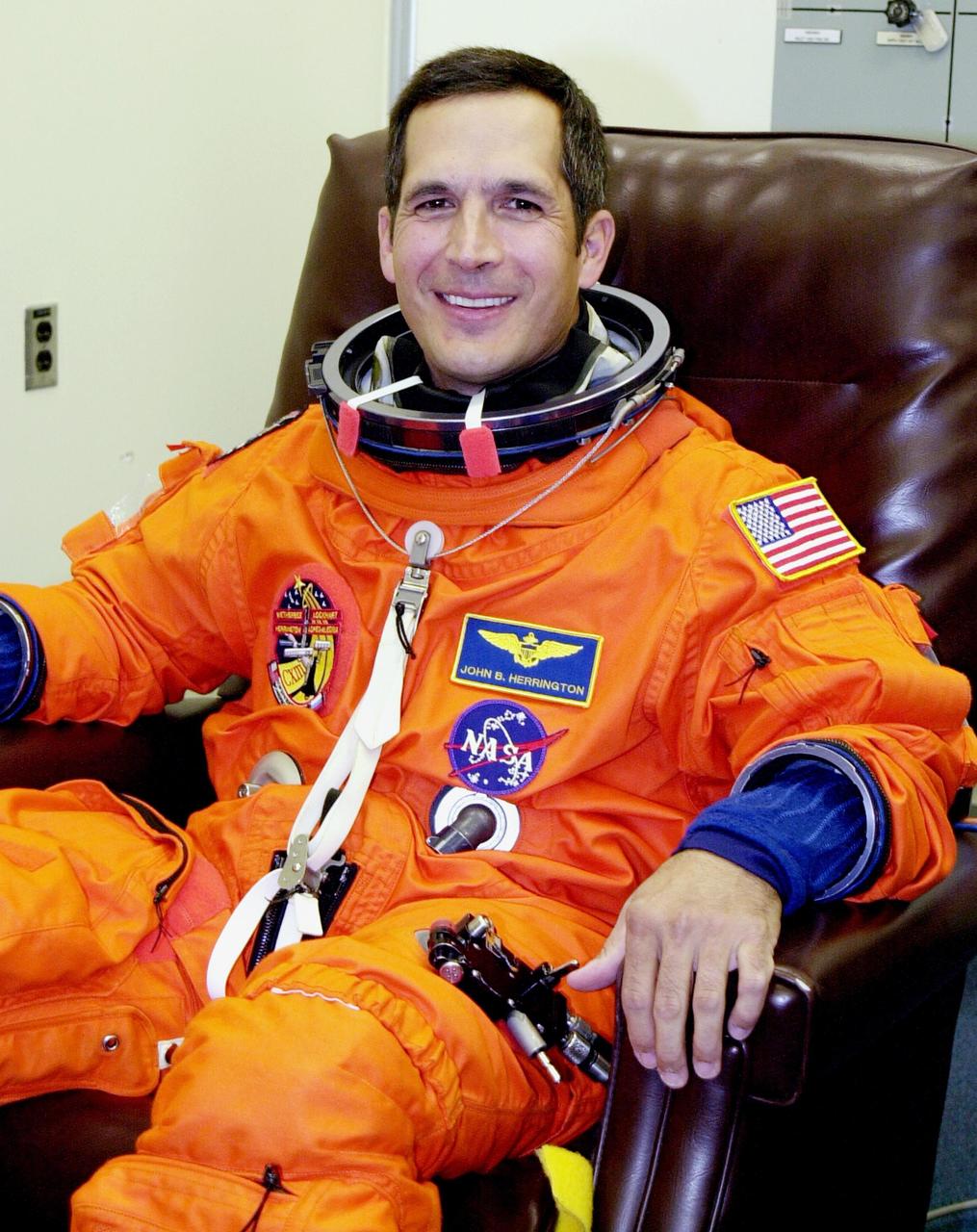

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-113 Mission Specialist John Herrington suits up before launch. This will be his first Shuttle flight. The primary mission is bringing the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and returning the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is scheduled for Nov. 11 at 12:58 p.m. EST.
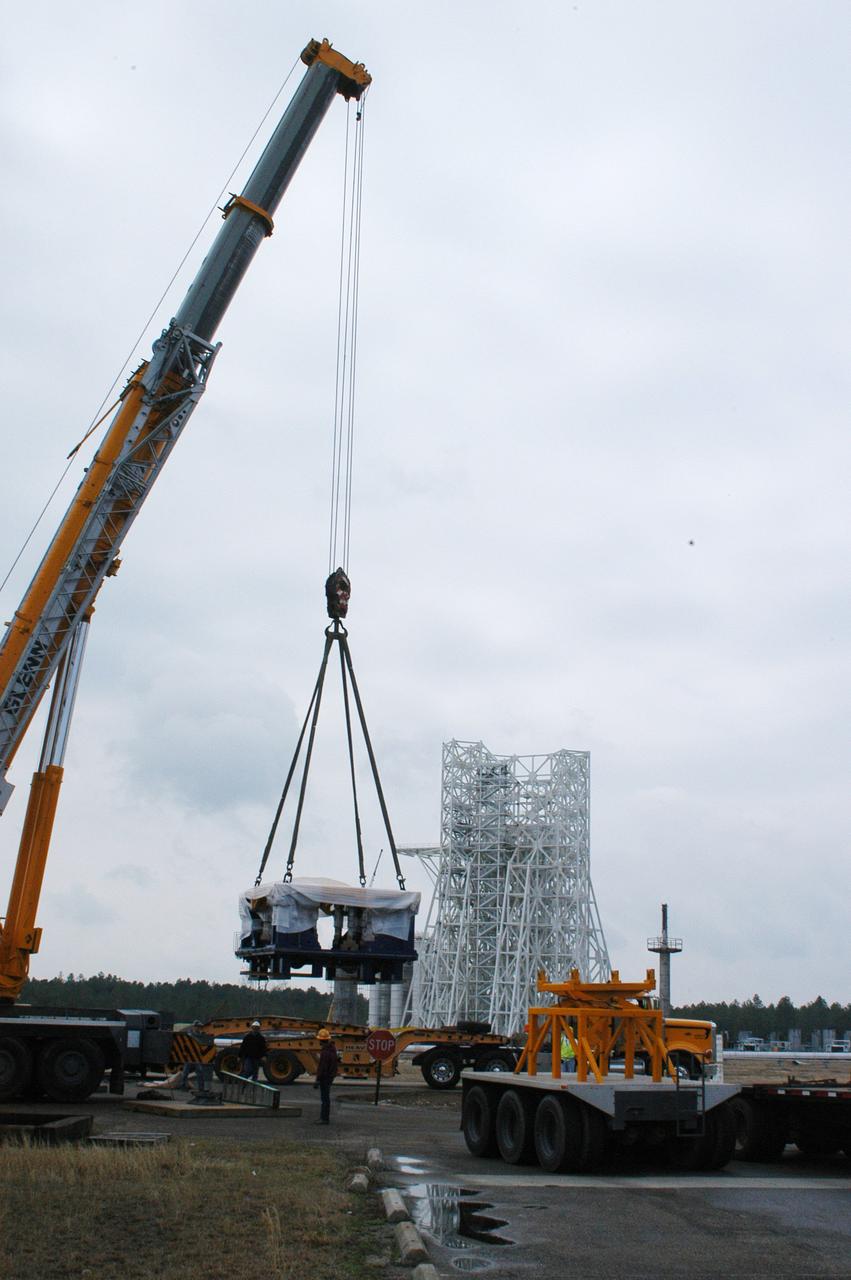

A state-of-the-art thrust measurement system for the A-3 Test Stand under construction at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center was delivered March 17. Once completed, the A-3 stand (seen in background) will allow simulated high-altitude testing on the next generation of rocket engines for America's space program. Work on the stand began in 2007, with activation scheduled for 2012. The stand is the first major test structure to be built at Stennis since the 1960s. The recently delivered TMS was fabricated by Thrust Measurement Systems in Illinois. It is an advanced calibration system capable of measuring vertical and horizontal thrust loads with an accuracy within 0.15 percent at 225,000 pounds.

The STS-95 patch, designed by the crew, is intended to reflect the scientific, engineering, and historic elements of the mission. The Space Shuttle Discovery is shown rising over the sunlit Earth limb, representing the global benefits of the mission science and the solar science objectives of the Spartan Satellite. The bold number '7' signifies the seven members of Discovery's crew and also represents a historical link to the original seven Mercury astronauts. The STS-95 crew member John Glenn's first orbital flight is represented by the Friendship 7 capsule. The rocket plumes symbolize the three major fields of science represented by the mission payloads: microgravity material science, medical research for humans on Earth and in space, and astronomy.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-113 Mission Specialist John Herrington arrives at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility to get ready for launch. STS-113 is the 16th American assembly flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is bringing the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and returning the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is scheduled for Nov. 11 between midnight and 4 a.m. EST.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the White Room on Launch Pad 39A, STS-113 Mission Specialist John Herrington is helped with his launch and entry suit by Rick Welty, United Space Alliance Vehicle Closeout chief. The launch will carry the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and return the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is scheduled for Nov. 23 at 7:50 p.m. EST.
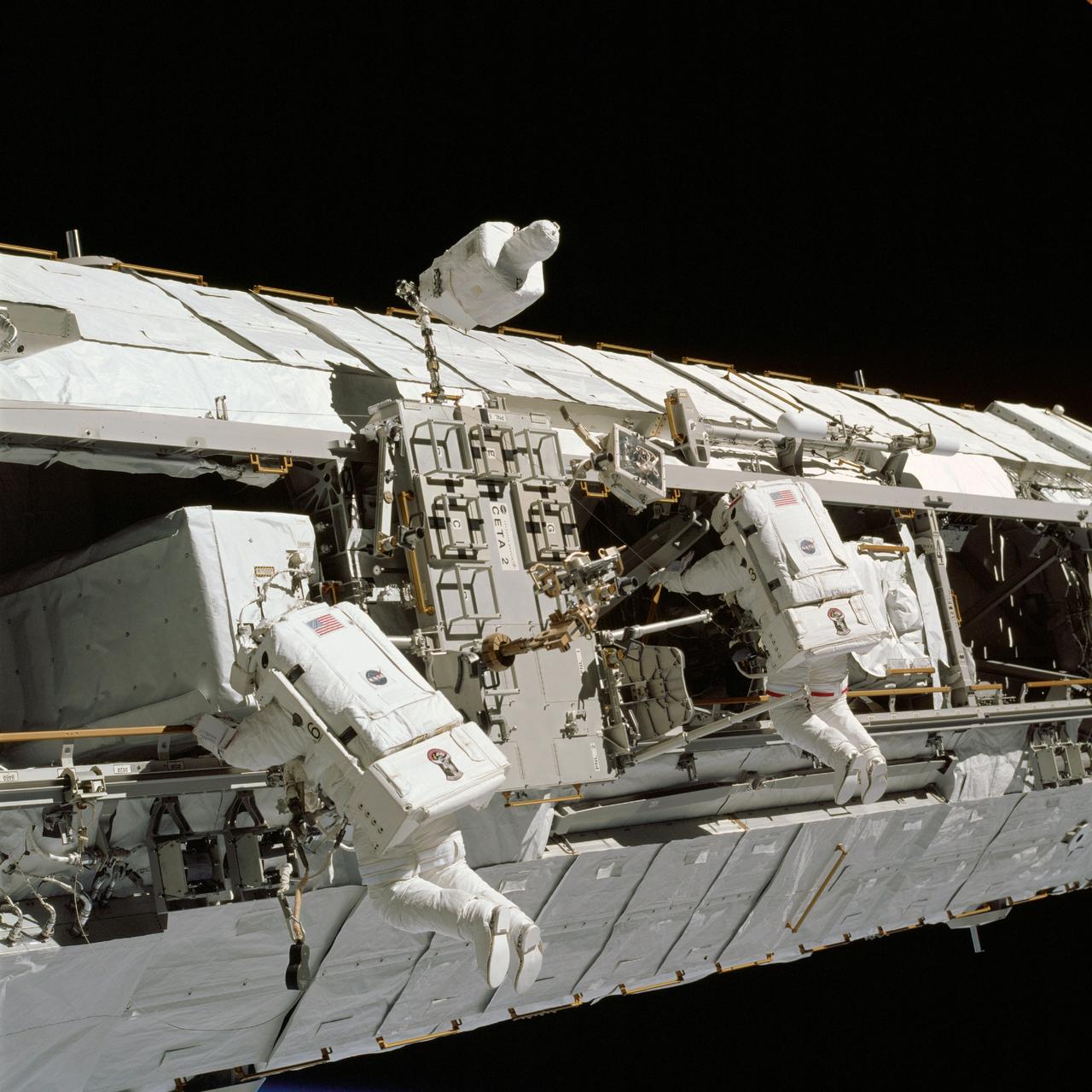

The 16th American assembly flight and 112th overall American flight to the International Space Station (ISS) launched on November 23, 2002 from Kennedy's launch pad 39A aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour STS-113. Mission objectives included the delivery of the Expedition Six Crew to the ISS, the return of Expedition Five crew back to Earth, the delivery of the Crew and Equipment Translation Aid (CETA) cart, and the installation and activation of the Port 1 Integrated Truss Assembly (P1). The first major component installed on the left side of the Station, the P1 truss provides an additional three External Thermal Control System radiators. Weighing in at 27,506 pounds, the P1 truss is 45 feet (13.7 meters) long, 15 feet (4.6 meters) wide, and 13 feet (4 meters) high. Three space walks, aided by the use of the Robotic Manipulator Systems of both the Shuttle and the Station, were performed in the installation of P1. In this photograph, astronauts and mission specialists John B. Herrington (left) and Michael E. Lopez-Alegria (right) work near the CETA cart on a truss on the ISS during a scheduled space walk for the mission. The final major task of the space walk was the relocation of the CETA cart from the Port One (P1) to the Starboard One (S1) Truss, which will allow the Mobile Transporter to move along the P1 to assist in upcoming assembly missions.
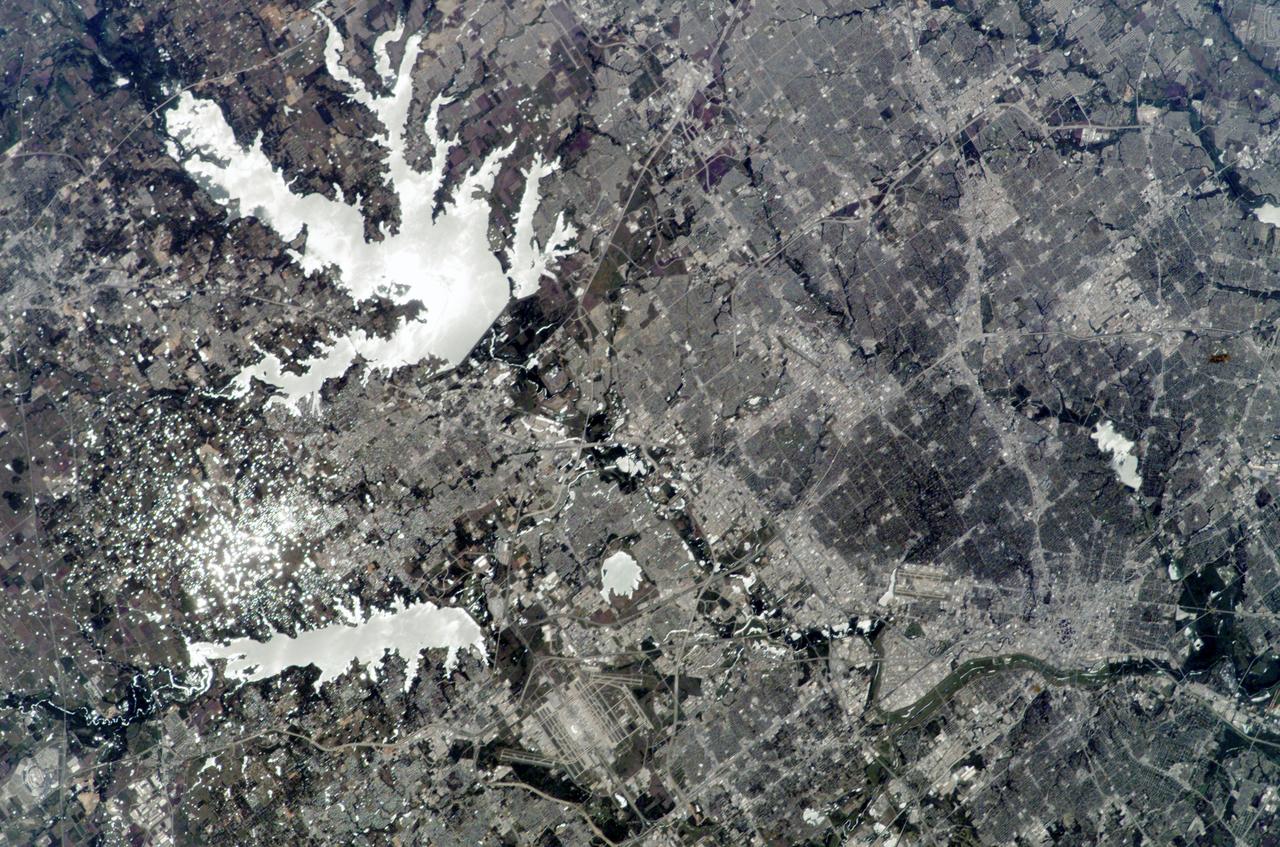

ISS010-E-24596 (14 April 2005) --- Dallas, Texas is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 10 crew member on the International Space Station. The Dallas-Fort Worth metropolitan area is the largest in Texas with an approximate population of 6 million people in 2005. Founded by John Neely Bryan in 1841, the city became the center for the United States oil economy with the discovery of oilfields to the east of the city in 1930. The Dallas-Forth Worth region today is a major corporate, banking, and technological center. This image captures the northwestern portion of the metropolitan area. Standing water bodies such as Lake Lewisville and Grapevine Lake are highlighted by sunglint, where the surface of the water acts as a mirror reflecting sunlight back towards the astronauts on the Station. Using the sunglint to define edges of water helps when mapping water bodies and stream courses on a landscape ? note the region of small ponds to the north of Grapevine Lake highlighted by sunglint. Photo credit: NASA

STS-113, the 16th American assembly flight and 112th overall American flight to the International Space Station (ISS), launched on November 23, 2002 from Kennedy's launch pad 39A aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour. The main mission objective was the the installation and activation of the Port 1 Integrated Truss Assembly (P1). The first major component installed on the left side of the Station, the P1 truss provides an additional three External Thermal Control System radiators. Weighing in at 27,506 pounds, the P1 truss is 45 feet (13.7 meters) long, 15 feet (4.6 meters) wide, and 13 feet (4 meters) high. Three space walks, aided by the use of the Robotic Manipulator Systems of both the Shuttle and the Station, were performed in the installation of P1. In this photograph astronaut and mission specialist John B. Herrington, (center frame), participates in the mission's third space walk. The forward section of the Space Shuttle Endeavour is in right frame.
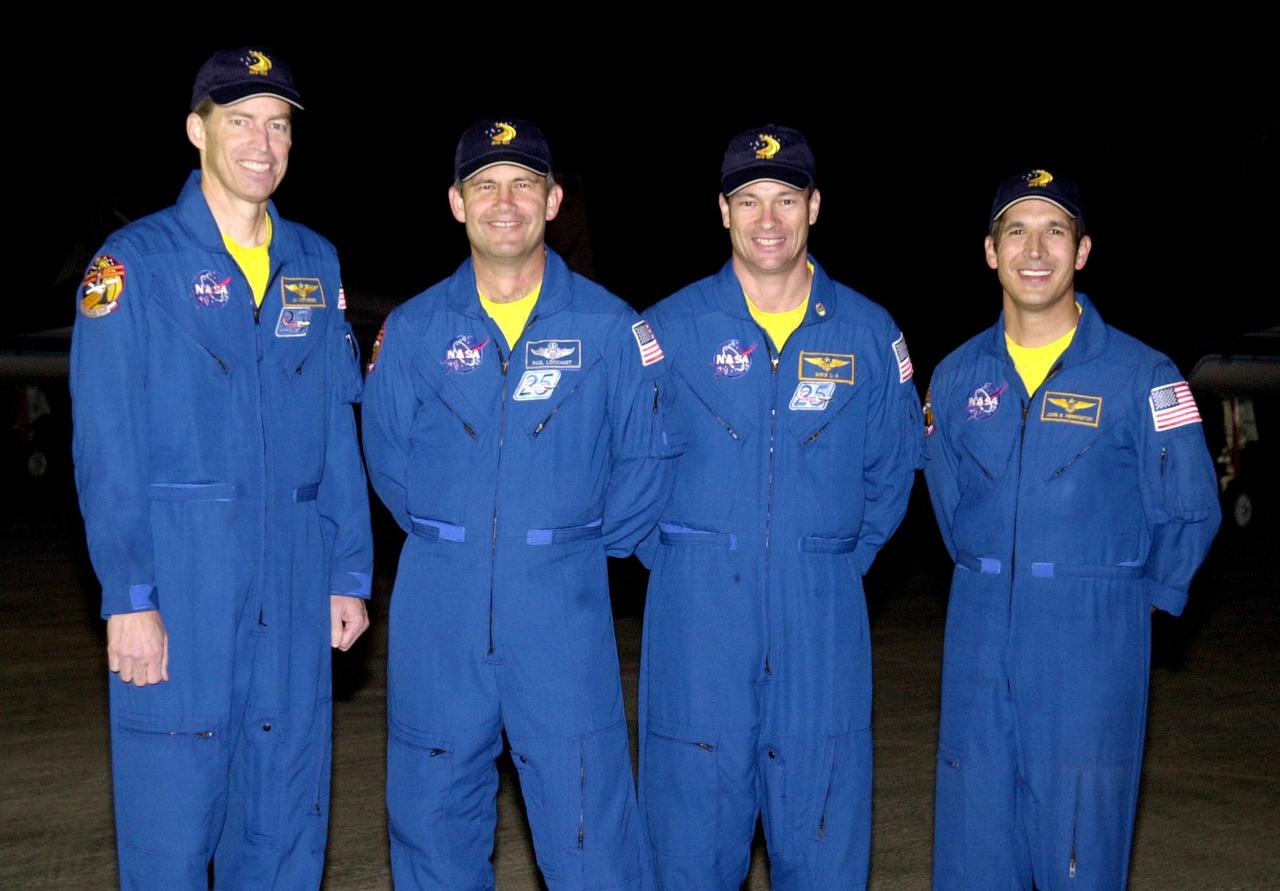

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The STS-113 crew poses for a photo after their arrival at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility to prepare for launch. From left are Commander James Wetherbee, Pilot Paul Lockhart, and Mission Specialists Michael Lopez-Alegria and John Herrington. The primary mission of STS-113 is bringing the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and returning the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. In addition, the major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is scheduled for Nov. 11 between midnight and 4 a.m. EST.
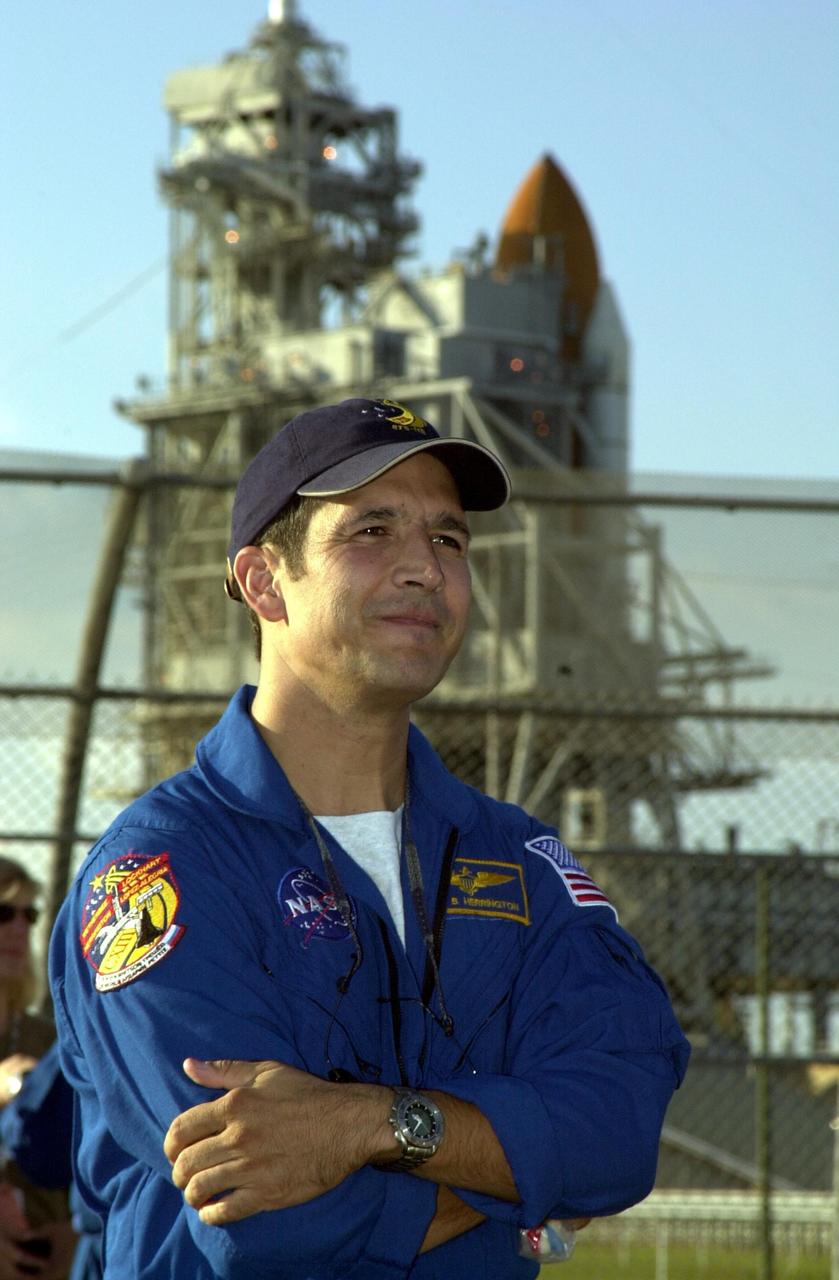

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-113 Mission Specialist John Herrington pauses in front of Space Shuttle Endeavour at Launch Pad 39A during a tour of Kennedy Space Center prior to his launch. Upon launch, Herrington will become the first Native American in space. The primary mission of STS-113 is bringing the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and returning the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. Another major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is scheduled for Nov. 11 between midnight and 4 a.m. EST.
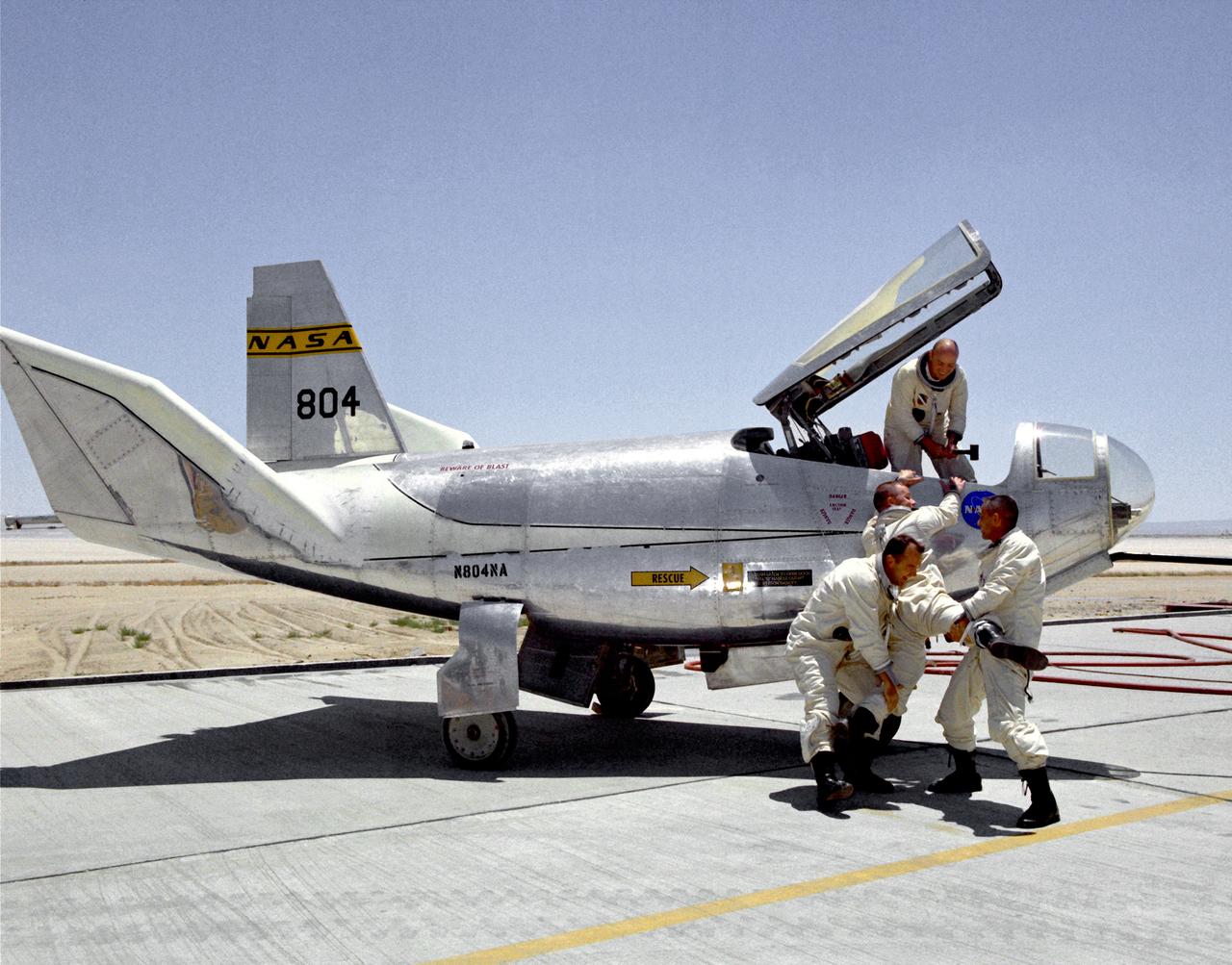

Not every moment of a test pilot's day is serious business. In a moment of levity, NASA pilots Bill Dana (left) and John A. Manke try to drag Air Force test pilot Peter Hoag away from the HL-10 lifting body while Air Force Major Jerauld R. Gentry helps from the cockpit. These four men were the principal pilots for the HL-10 program. This was not the only prank involving the HL-10 and its pilots. Once "Captain Midnight" (Gentry) and the "Midnight Skulkers" sneaked into the NASA hangar and put "U.S. Air Force" on the aircraft using stick-on letters. Later, while Gentry was making a lifting-body flight, his 1954 Ford was "borrowed" from the parking lot, painted with yellow-green zinc-chromate primer, and decorated with large stick-on flowers about one foot in diameter. After Gentry returned from the flight, he was surprised to see what had happened to his car.
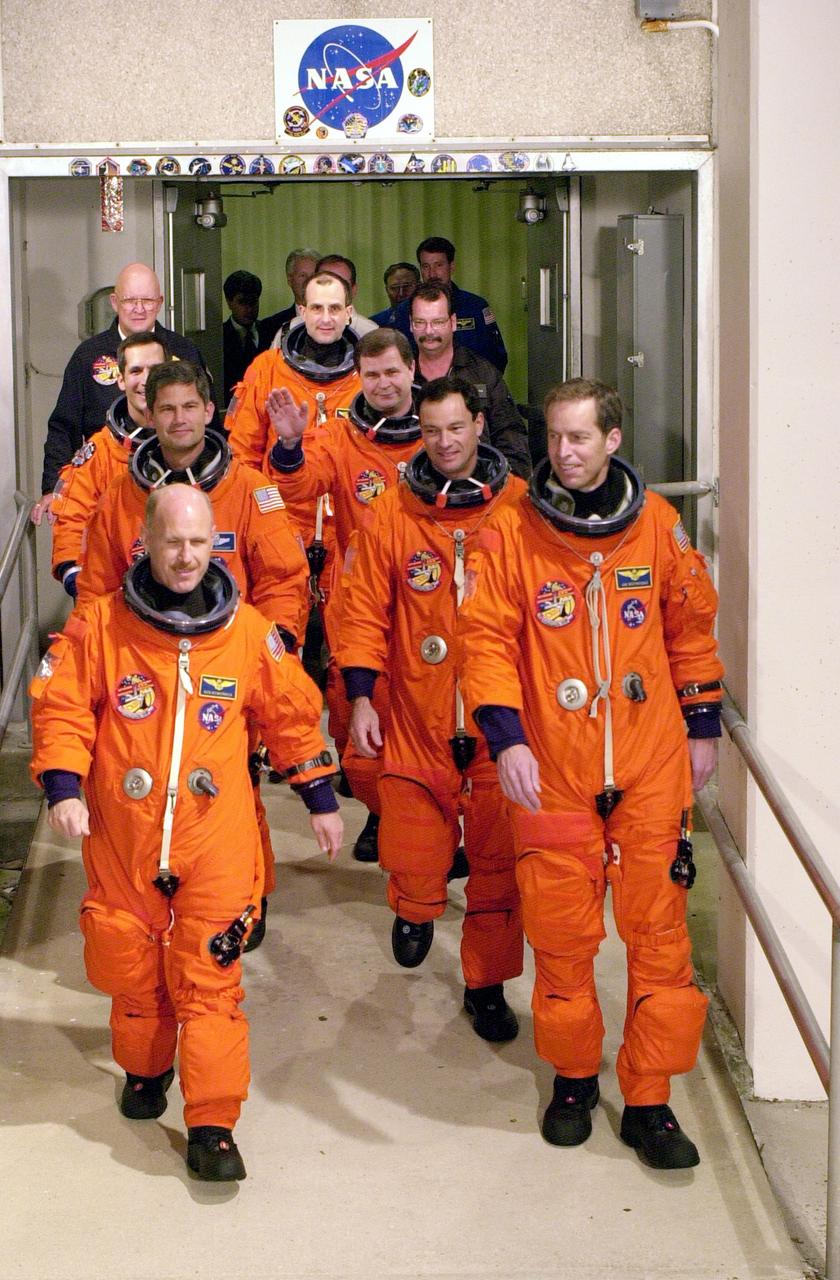

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The STS-113 and Expedition 6 crews exit the Operations and Checkout Building on their way to Launch Pad 39A and liftoff of Space Shuttle Endeavour. From front to back are Expedition 6 Commander Ken Bowersox and Mission Commander James Wetherbee; Pilot Paul Lockhart and Mission Specialist Michael Lopez-Alegria; Mission Specialist John Herrington and Expedition 6 flight engineer Nikolai Budarin; and flight engineer Donald Pettit. The primary mission is bringing the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and returning the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is scheduled for Nov. 11 at 12:58 a.m. EST.

Engineers at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, inspect the propulsion module of NASA's Europa Clipper spacecraft. In 2022, this major piece of hardware, designed and built at APL, will ship to NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California for assembly, test, and launch operations (ATLO). With an internal global ocean under a thick layer of ice, Jupiter's moon Europa may have the potential to harbor existing life. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will swoop around Jupiter on an elliptical path, dipping close to the moon on each flyby to collect data. Understanding Europa's habitability will help scientists better understand how life developed on Earth and the potential for finding life beyond our planet. Europa Clipper is set to launch in 2024. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24783
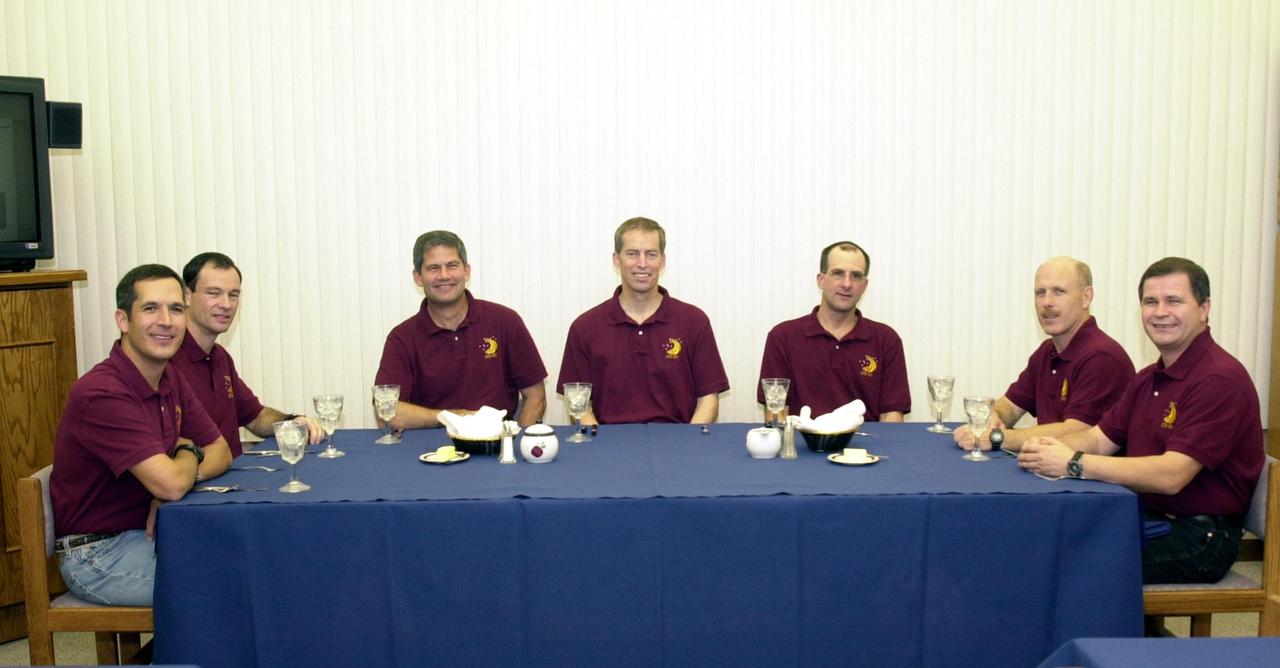

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-113 crew enjoys a snack before suiting up for launch. Seated left to right are Mission Specialists John Herrington and Michael Lopez-Alegria, Pilot Paul Lockhart and Commander James Wetherbee; Expedition 6 flight engineer Donald Pettit, Commander Ken Bowersox and flight engineer Nikolai Budarin. STS-113 is the 16th American assembly flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is bringing the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and returning the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is scheduled for Nov. 11 at 12:58 a.m. EST.
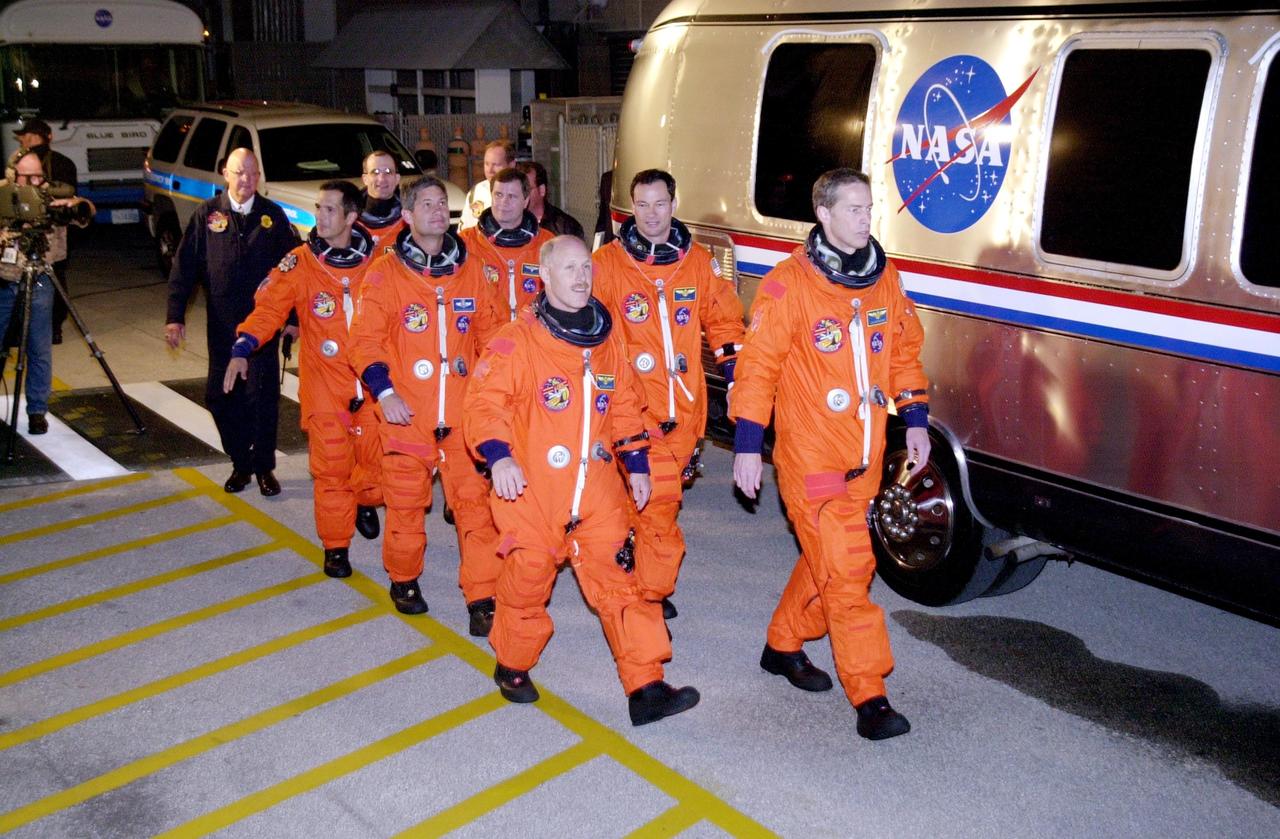

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-113 and Expedition 6 crews head for the Astrovan that will take them to Launch Pad 39A and Space Shuttle Endeavour. In the foreground, from left to right, are Mission Specialist John Herrington, Pilot Paul Lockhart and Expedition 6 Commander Ken Bowersox. In the back, from left to right, are Expedition 6 flight engineers Donald Pettit and Nikolai Budarin, Mission Specialist Michael Lopez-Alegria and Commander James Wetherbee. The primary mission is bringing the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and returning the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is scheduled for Nov. 11 at 12:58 a.m. EST.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-113 and Expedition 6 crews head for the Astrovan to transport them to Launch Pad 39A and Space Shuttle Endeavour. In the foreground, from left, are Mission Specialist Michael Lopez-Alegria and John Herrington, and Expedition 6 Commander Ken Bowersox. In the background, from left, are Expedition 6 flight engineers Donald Pettit and Nikolai Budarin, Pilot Paul Lockhart and Commander James Wetherbee. The primary mission for the crew is bringing the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and returning the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is scheduled for Nov. 22, 2002, at 8:15 p.m. EST.
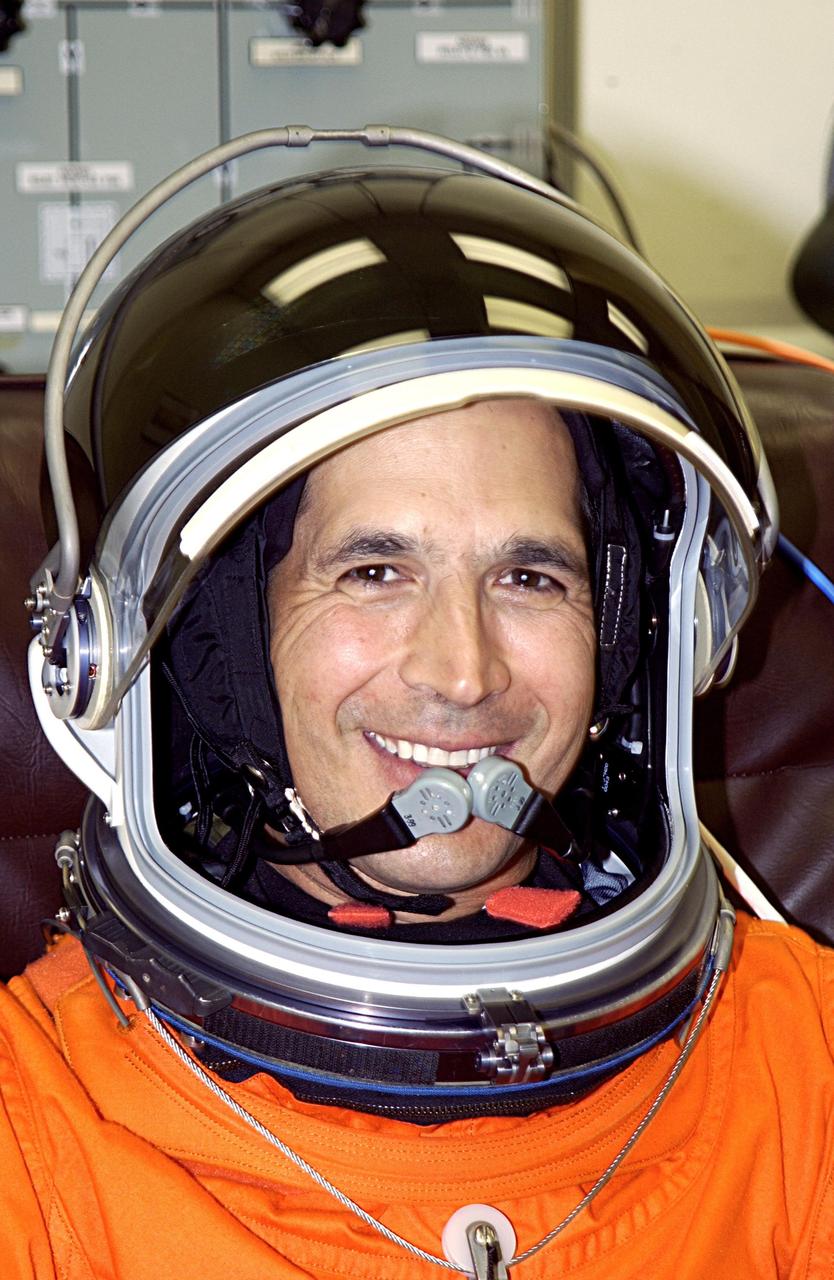

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- - STS-113 Mission Specialist John Herrington smiles as he finishes suiting up for a second launch attempt on mission STS-113. The launch on Nov. 22 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at the Transoceanic Abort Landing sites. Herrington will be making his first Shuttle flight. The launch will carry the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and return the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is now scheduled for Nov. 23 at 7:50 p.m. EST.
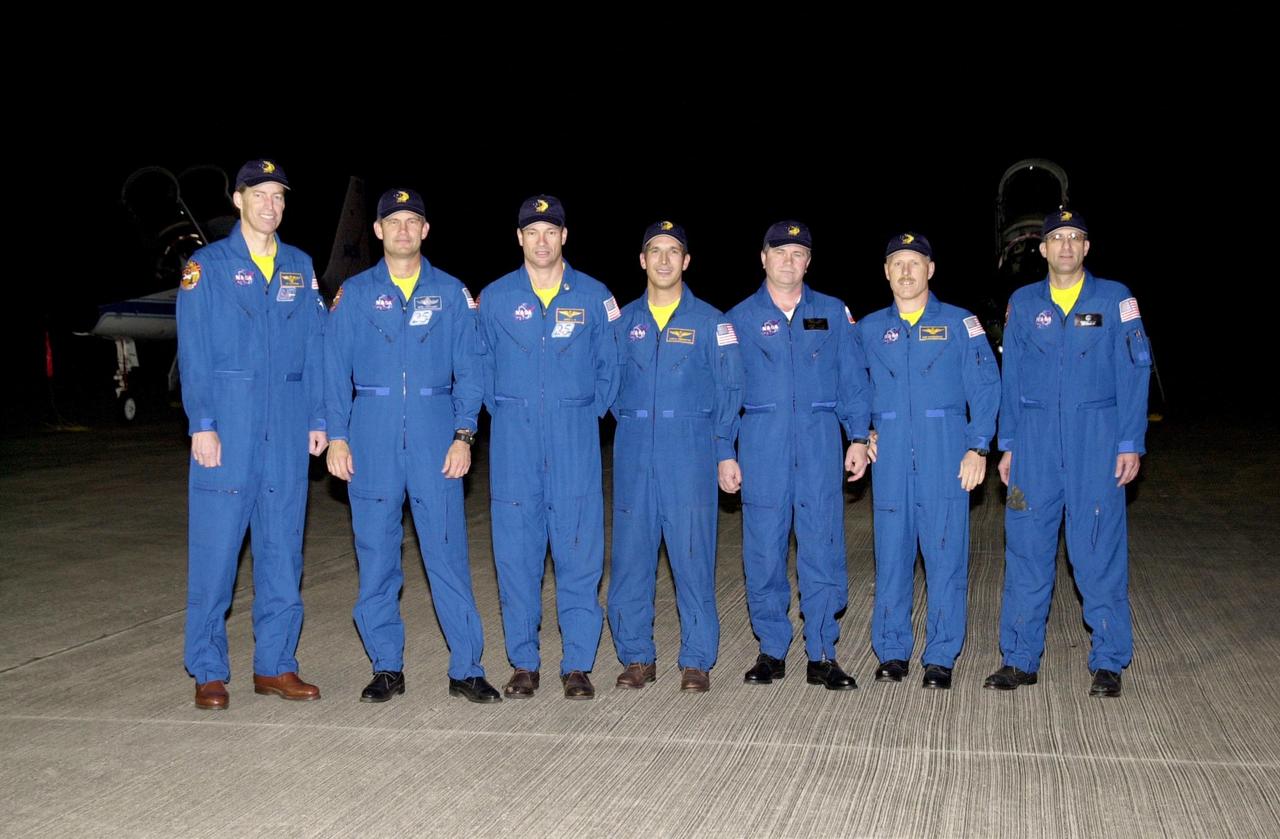

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After their arrival at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility, the crews of mission STS-113 pause for a group photo. From left are STS-113 Commander James Wetherbee, Pilot Paul Lockhart, and Mission Specialists Michael Lopez-Alegria and John Herrington; and the Expedition 6 crew, Flight Engineer Nikolai Budarin, Commander Ken Bowersox and Flight Engineer Donald Pettit. Budarin represents the Russian Space Agency. The primary mission of STS-113 is bringing the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and returning the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. In addition, the major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is scheduled for Nov. 11 between midnight and 4 a.m. EST.
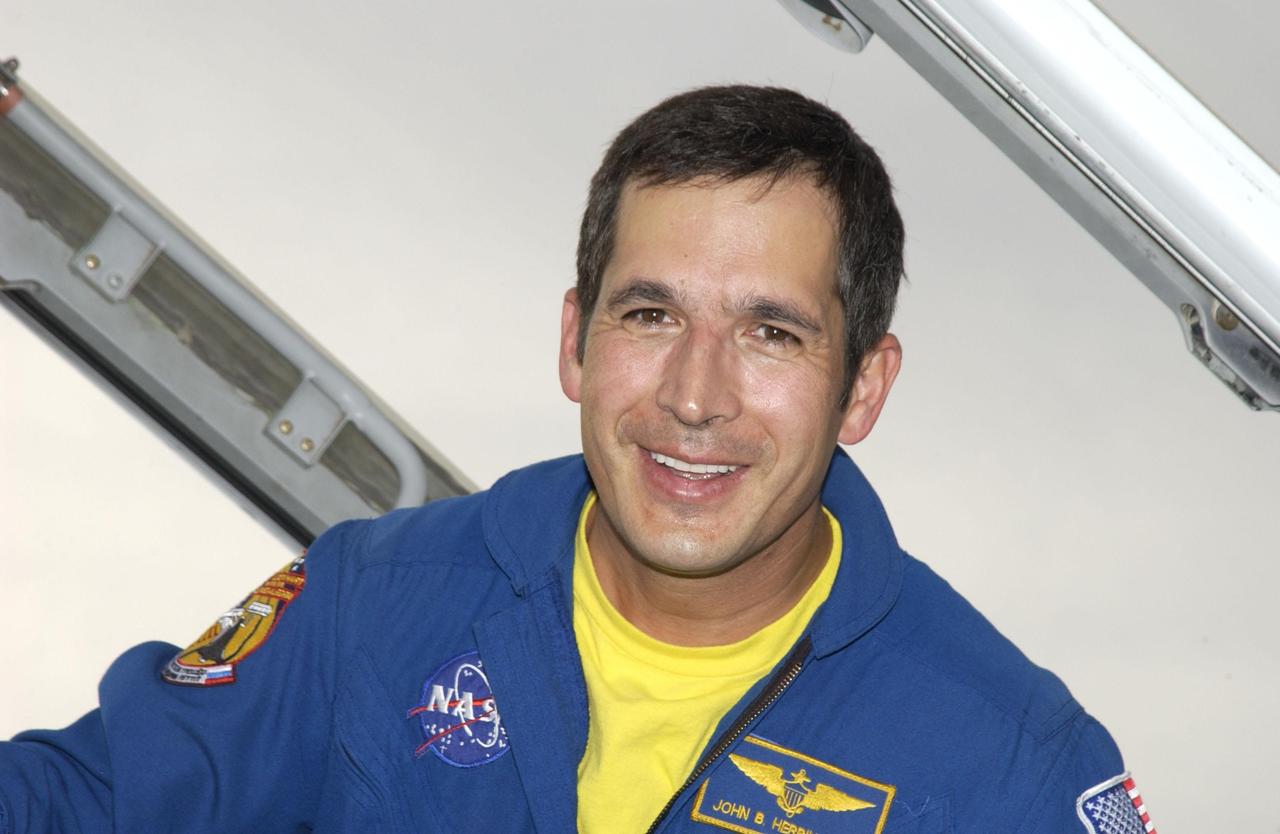

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-113 Mission Specialist John B. Herrington smiles for the camera upon his arrival at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility to prepare for launch. STS-113 is the 16th American assembly flight to the International Space Station. The primary objective of the mission is bringing the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and returning the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major task of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is targeted for no earlier than Nov. 22 between 7 and 11 p.m. EST.
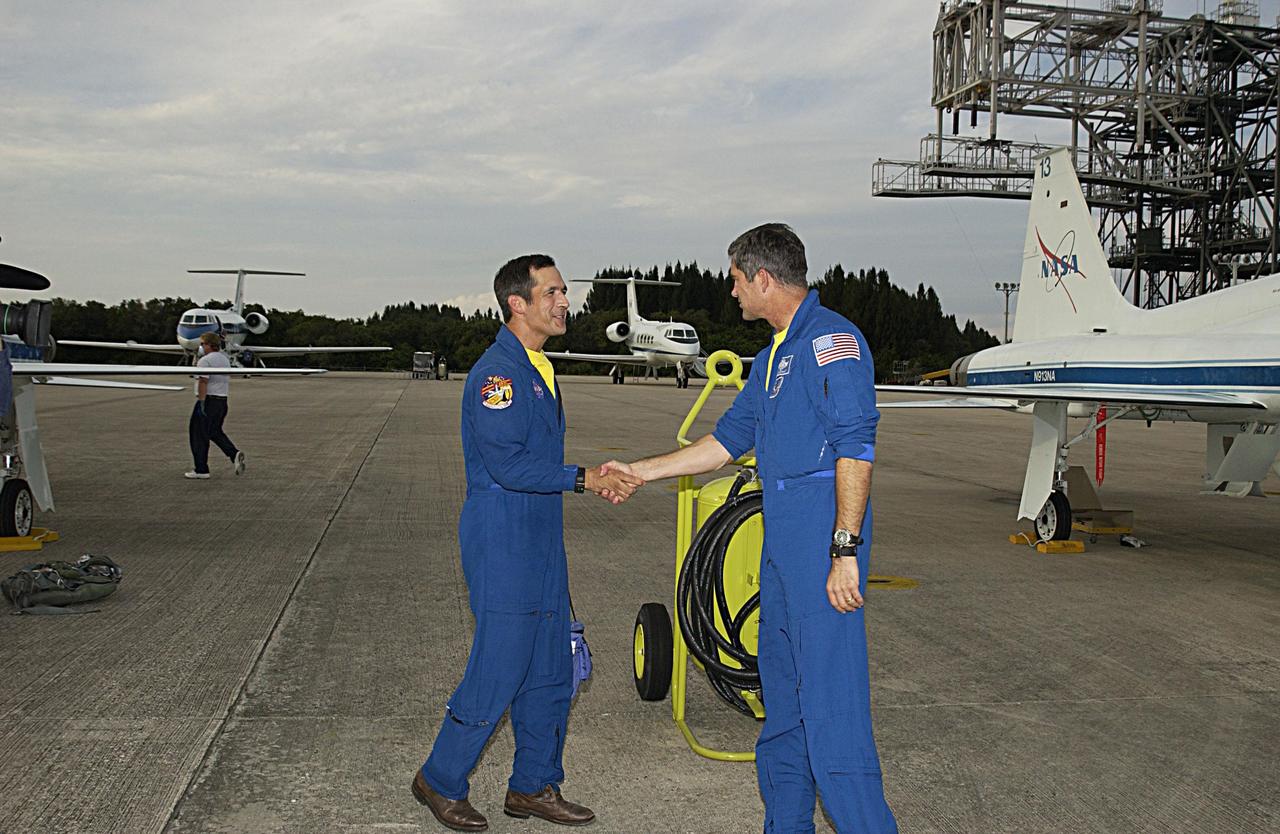

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-113 Mission Specialist John B. Herrington (left) and Pilot Paul Lockhart shake hands following their arrival at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility to prepare for launch. STS-113 is the 16th American assembly flight to the International Space Station. The primary objective of the mission is bringing the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and returning the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major task of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is targeted for no earlier than Nov. 22 between 7 and 11 p.m. EST.
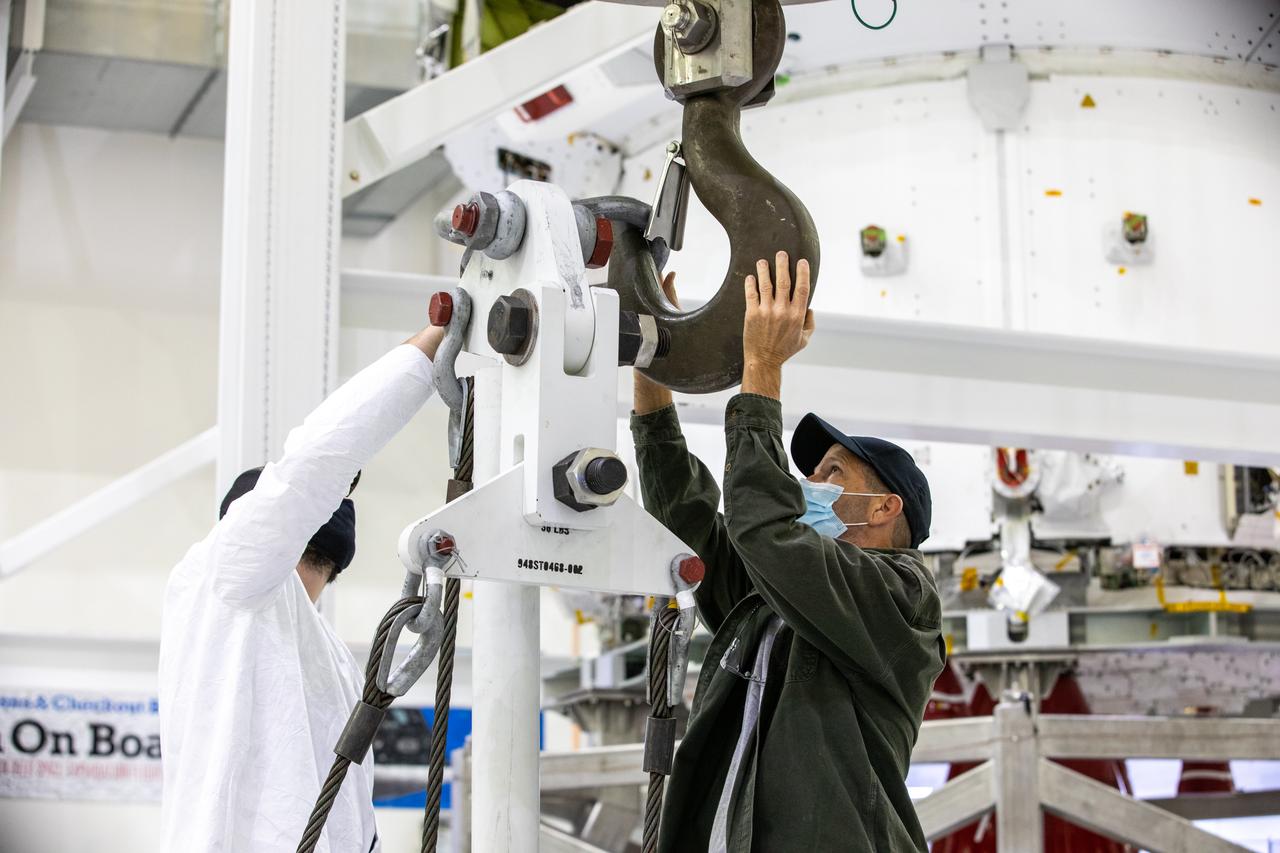

ASRC technicians Dustin Swickert, to the left. and John Nesbitt, to the right, work to attach the crane that lifts the Artemis I Orion spacecraft in preparation for installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
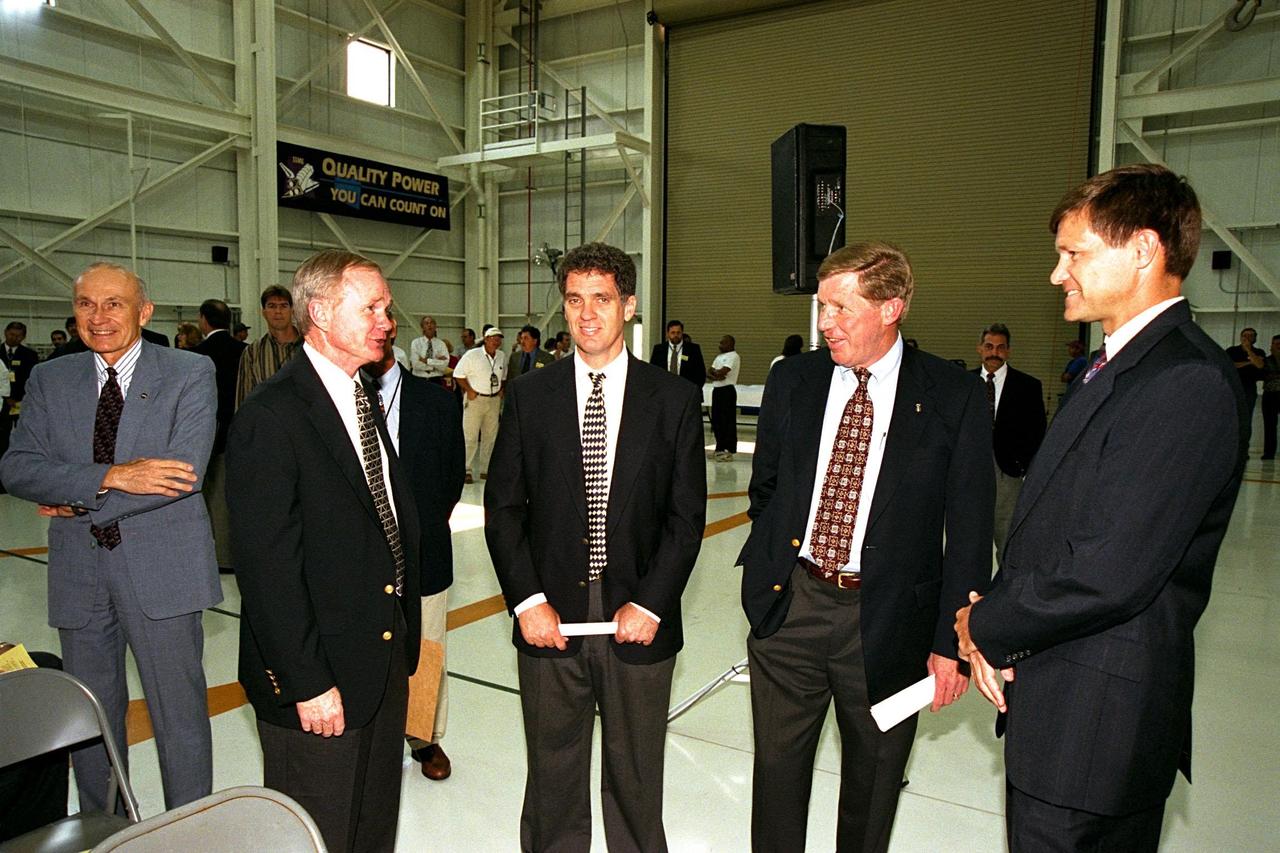

Participants in the ribbon cutting for KSC's new 34,600-square-foot Space Shuttle Main Engine Processing Facility (SSMEPF) gather to talk inside the facility following the ceremony. From left, they are Robert B. Sieck, director of Shuttle Processing; KSC Center Director Roy D. Bridges Jr.; U.S. Congressman Dave Weldon; John Plowden, vice president of Rocketdyne; and Donald R. McMonagle, manager of Launch Integration. A major addition to the existing Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3, the SSMEPF replaces the Shuttle Main Engine Shop located in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The decision to move the shop out of the VAB was prompted by safety considerations and recent engine processing improvements. The first three main engines to be processed in the new facility will fly on Shuttle Endeavour's STS-88 mission in December 1998
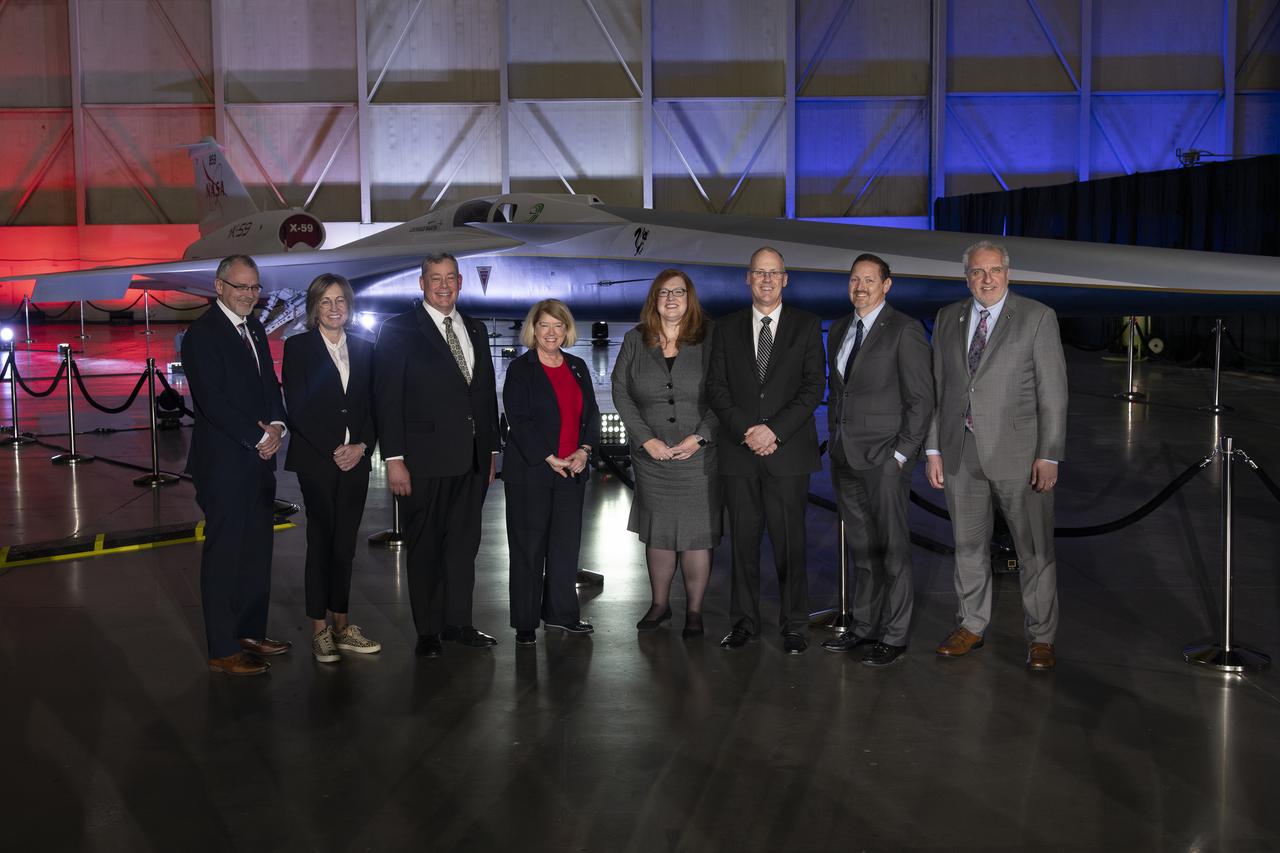

(from left to right) NASA Associate Administrator Jim Free, California Senior Economic Advisor to the Governor Dee Dee Myers, Lockheed Martin Executive Vice President of Aeronautics Greg Ulmer, NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, Low Boom Flight Demonstrator Project Manager Cathy Bahm, Lockheed Martin X-59 Project Manager David Richardson, Lockheed Martin Skunk Works Vice President and General Manager John Clark, and NASA Associate Administrator for the Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate Bob Pearce pose in front of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
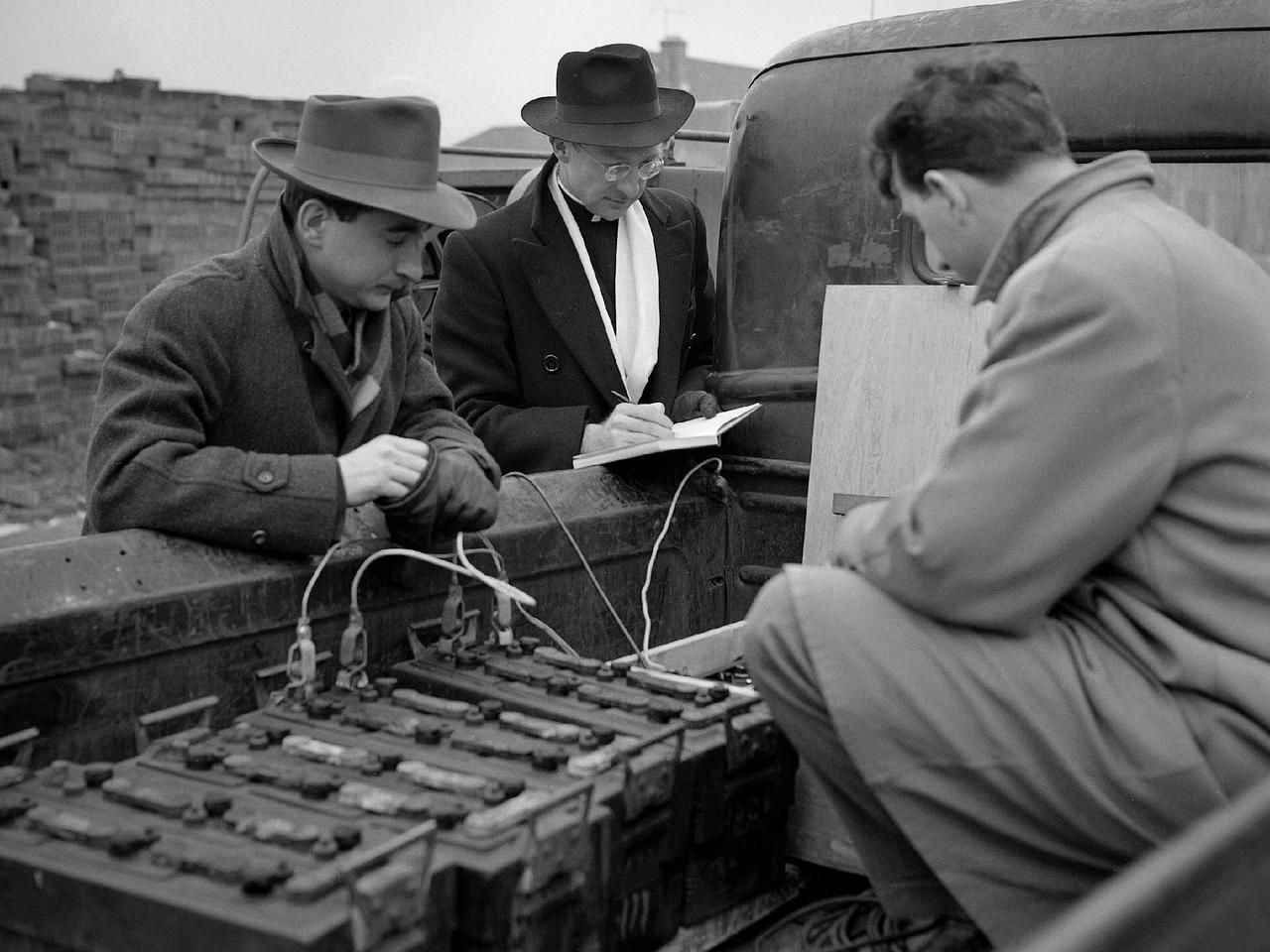

Reverend Henry Birkenhauer and E.F. Carome measure ground vibrations on West 220th Street caused by the operation of the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The 8- by 6 was the laboratory’s first large supersonic wind tunnel. It was also the NACA’s most powerful supersonic tunnel, and the NACA’s first facility capable of running an engine at supersonic speeds. The 8- by 6 was originally an open-throat and non-return tunnel. This meant that the supersonic air flow was blown through the test section and out the other end into the atmosphere. Complaints from the local community led to the installation of a muffler at the tunnel exit and the eventual addition of a return leg. Reverend Brikenhauer, a seismologist, and Carome, an electrical technician were brought in from John Carroll University to take vibration measurements during the 8- by 6 tunnel’s first run with a supersonic engine. They found that the majority of the vibrations came from the air and not the ground. The tunnel’s original muffler offered some relief during the facility checkout runs, but it proved inadequate during the operation of an engine in the test section. Tunnel operation was suspended until a new muffler was designed and installed. The NACA researchers, however, were pleased with the tunnel’s operation. They claimed it was the first time a jet engine was operated in an airflow faster than Mach 2.
![KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-113 and Expedition 6 crews leave the Operations and Checkout Building, heading for Launch Pad 39A and Space Shuttle Endeavour for a second launch attempt. The launch on Nov. 22 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at the Transoceanic Abort Landing sites. In front, left to right, are Expedition 6 Commander Ken Bowersox and Mission Commander James Wetherbee; next row, Mission Specialist Michael Lopez-Alegria and Pilot Paul Lockhart; third row, Mission Specialist John Herrington and Expedition 6 flight engineer Nikolai Budarin; and finally, Expedition 6 flight engineer Donald Pettit. The launch will carry the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and return the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is now scheduled for Nov. 23 at 7:50 p.m. EST. [Photo by Scott Andrews]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC-02pd1800/KSC-02pd1800~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-113 and Expedition 6 crews leave the Operations and Checkout Building, heading for Launch Pad 39A and Space Shuttle Endeavour for a second launch attempt. The launch on Nov. 22 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at the Transoceanic Abort Landing sites. In front, left to right, are Expedition 6 Commander Ken Bowersox and Mission Commander James Wetherbee; next row, Mission Specialist Michael Lopez-Alegria and Pilot Paul Lockhart; third row, Mission Specialist John Herrington and Expedition 6 flight engineer Nikolai Budarin; and finally, Expedition 6 flight engineer Donald Pettit. The launch will carry the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and return the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is now scheduled for Nov. 23 at 7:50 p.m. EST. [Photo by Scott Andrews]

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, two STS-93 crew members, (center) Mission Specialist Michel Tognini of France and Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, get a close look at something seldom seen, the tip of an external tank. With them are Roland Nedelkovich (far left), with the Vertical Integration Test Team, and John Hlavacka (far right). STS-93 is scheduled to launch July 9 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia and has the primary mission of the deployment of the Chandra X-ray Observatory. Formerly called the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility, Chandra comprises three major elements: the spacecraft, the science instrument module (SIM), and the world's most powerful X-ray telescope. Chandra will allow scientists from around the world to see previously invisible black holes and high-temperature gas clouds, giving the observatory the potential to rewrite the books on the structure and evolution of our universe. Other STS-93 crew members are Commander Eileen M. Collins and Mission Specialists Catherine G. Coleman and Steven A. Hawley

S83-32900 (25 May 1983) --- This is the official insignia for STS-9, the major payload of which is Spacelab-1, depicted in the cargo bay of the space shuttle Columbia. The nine stars and the path of the orbiter tell the flight's numerical designation in the Space Transportation System's mission sequence. Astronaut John W. Young is crew commander; Brewster H. Shaw Jr., pilot. NASA astronauts Owen K. Garriott and Robert A.R. Parker are mission specialists. Byron K. Lichtenberg of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Ulf Merbold of the Republic of West Germany are the Spacelab-1 payload specialists. Launch has been set for late 1983. Merbold is a physicist representing the European Space Agency (ESA). The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
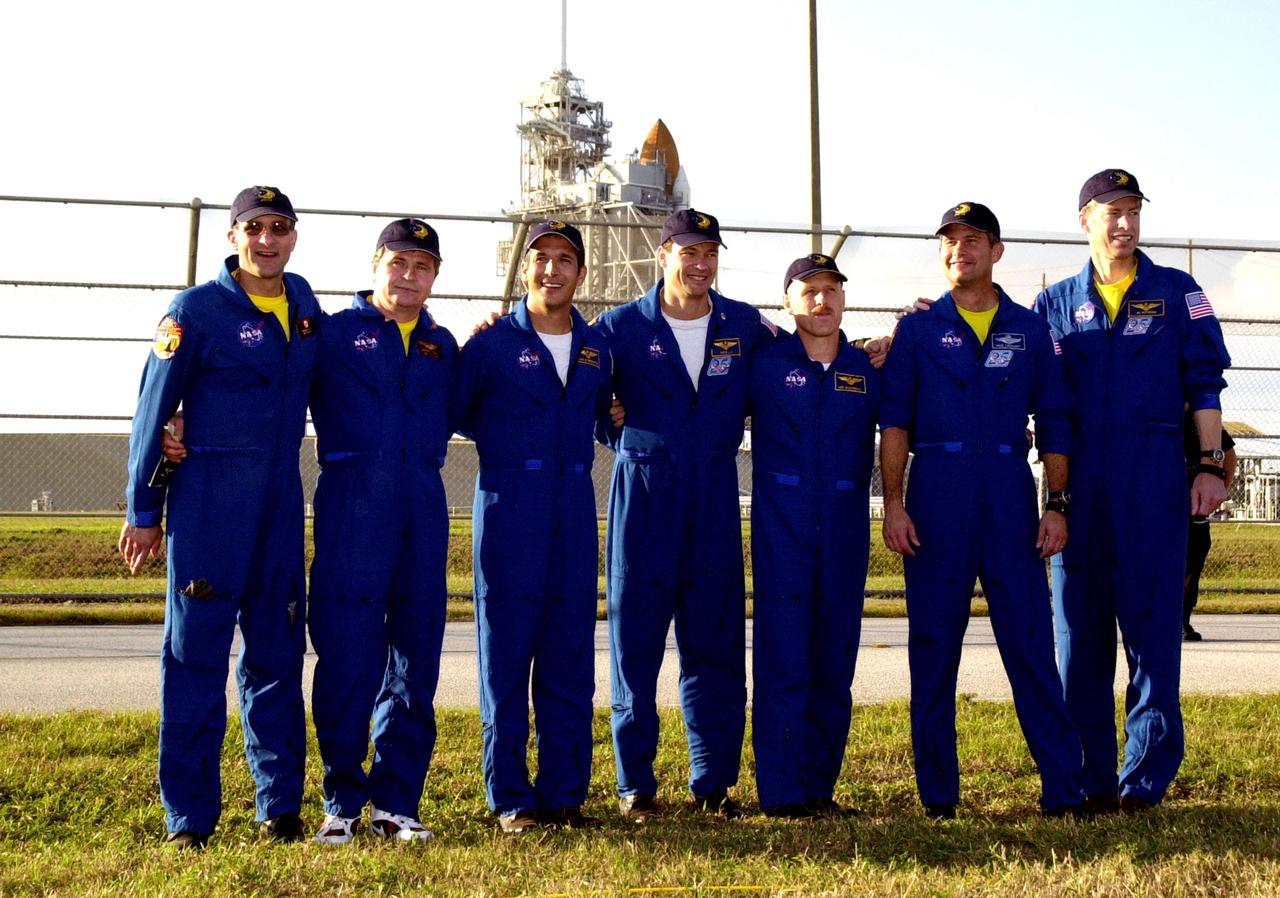

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The STS-113 and Expedition Six crews pose for a group photo at Launch Pad 39A with Space Shuttle Endeavour in the background during a tour of Kennedy Space Center prior to their launch. From left are Expedition Six crew members Donald Pettit and Nikolai Budarin of the Russian Space Agency, STS-113 Mission Specialists John Herrington and Michael Lopez-Alegria, Expedition Six Commander Ken Bowersox, STS-113 Pilot Paul Lockhart, and STS-113 Commander James Wetherbee. The primary mission of STS-113 is bringing the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and returning the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. Another major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is scheduled for Nov. 11 between midnight and 4 a.m. EST.
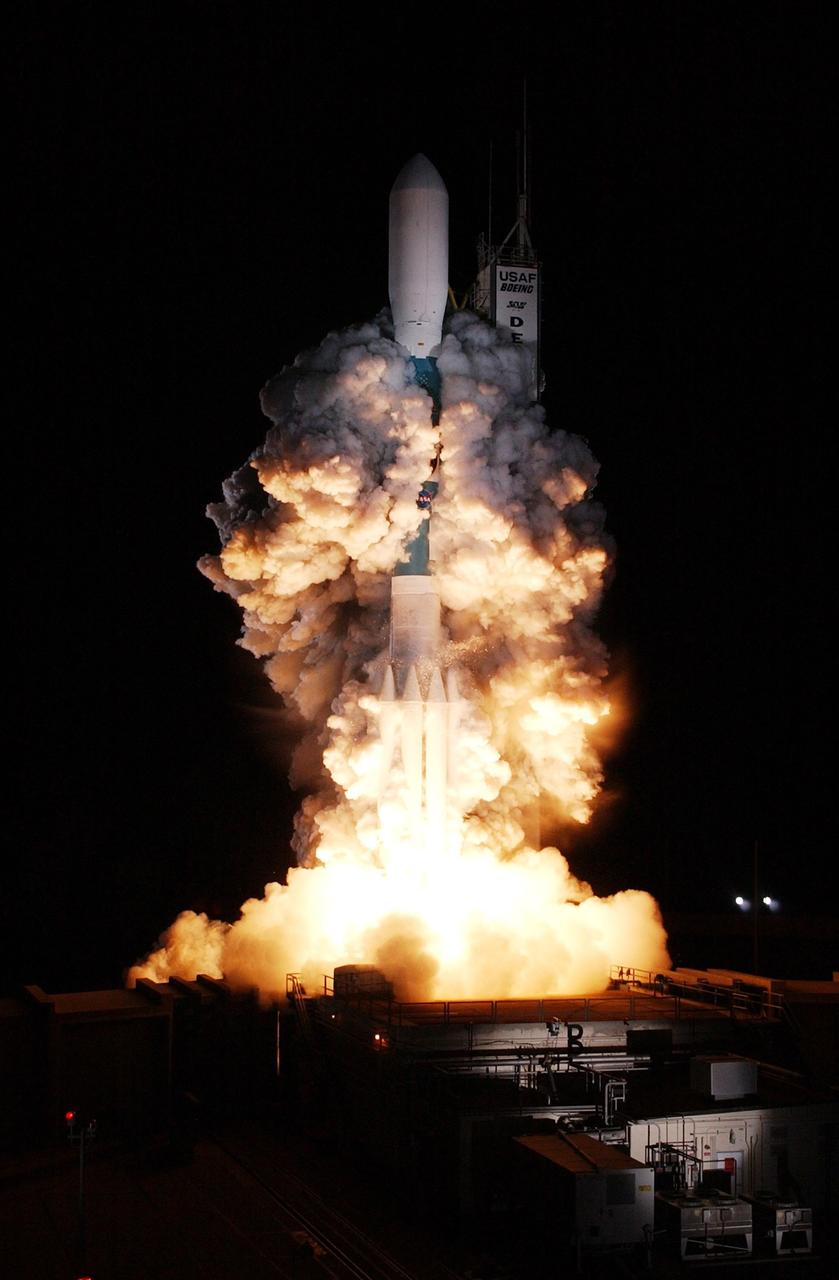

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Just after liftoff, clouds of smoke billow up and around the Delta II rocket carrying the STEREO spacecraft on top. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was at 8:52 p.m. EDT. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results.
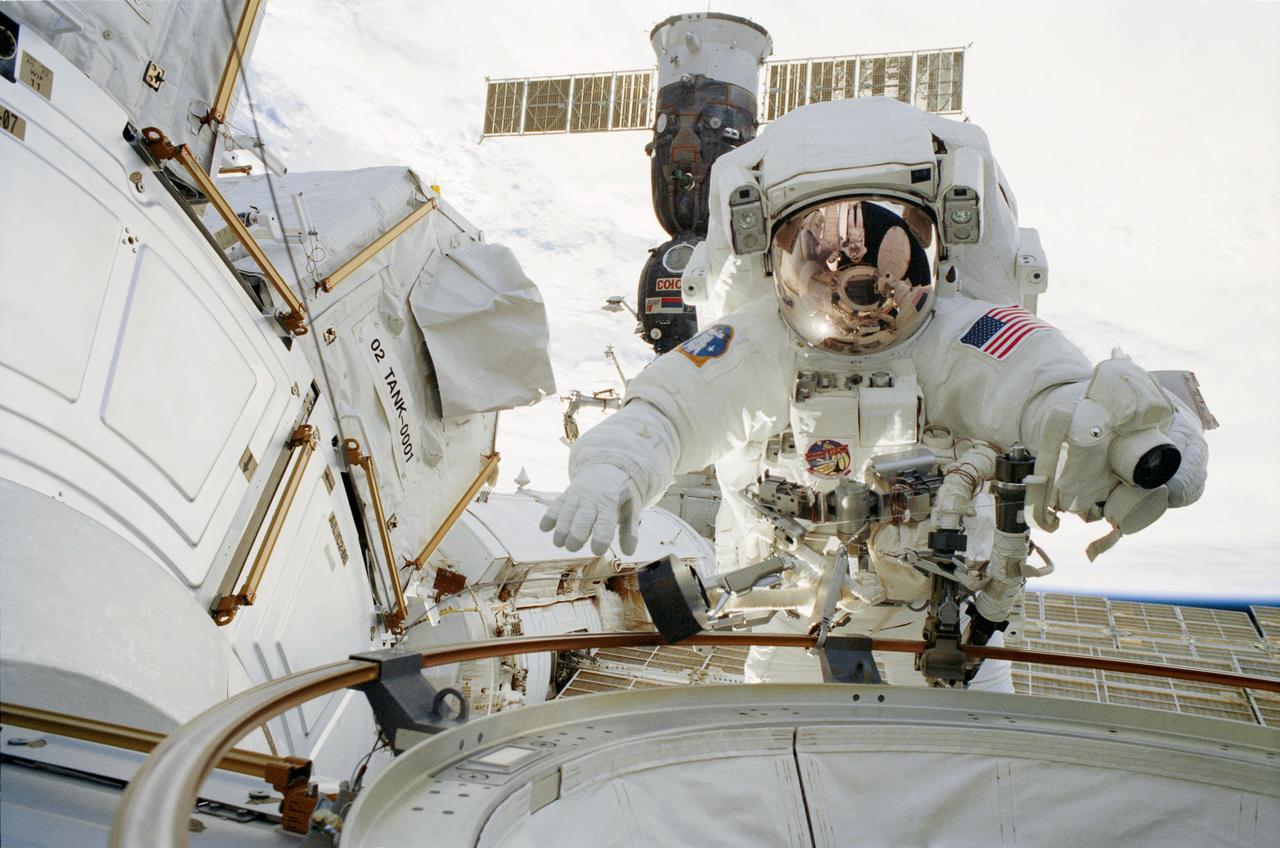

In this photograph, STS-113 astronaut and mission specialist John B. Herrington participates in the mission's first space walk. The opened hatch of the Quest Airlock can be seen reflected in Herrington's helmet visor. The airlock, located on the starboard side of the Unity Node I on the International Space Station (ISS), makes it easier to perform space walks, and allows both Russian and American space suits to be worn when the Shuttle is not docked with the ISS. American suits will not fit through Russian airlocks at the Station. STS-113, the 16th American assembly flight and 112th overall American flight to the ISS, launched on November 23, 2002 from Kennedy's launch pad 39A aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour. The main mission objective was the installation and activation of the Port 1 Integrated Truss Assembly (P1). The first major component installed on the left side of the Station, the P1 truss provides an additional three External Thermal Control System radiators. Weighing in at 27,506 pounds, the P1 truss is 45 feet (13.7 meters) long, 15 feet (4.6 meters) wide, and 13 feet (4 meters) high. Three space walks, aided by the use of the Robotic Manipulator Systems of both the Shuttle and the Station, were performed in the installation of P1.
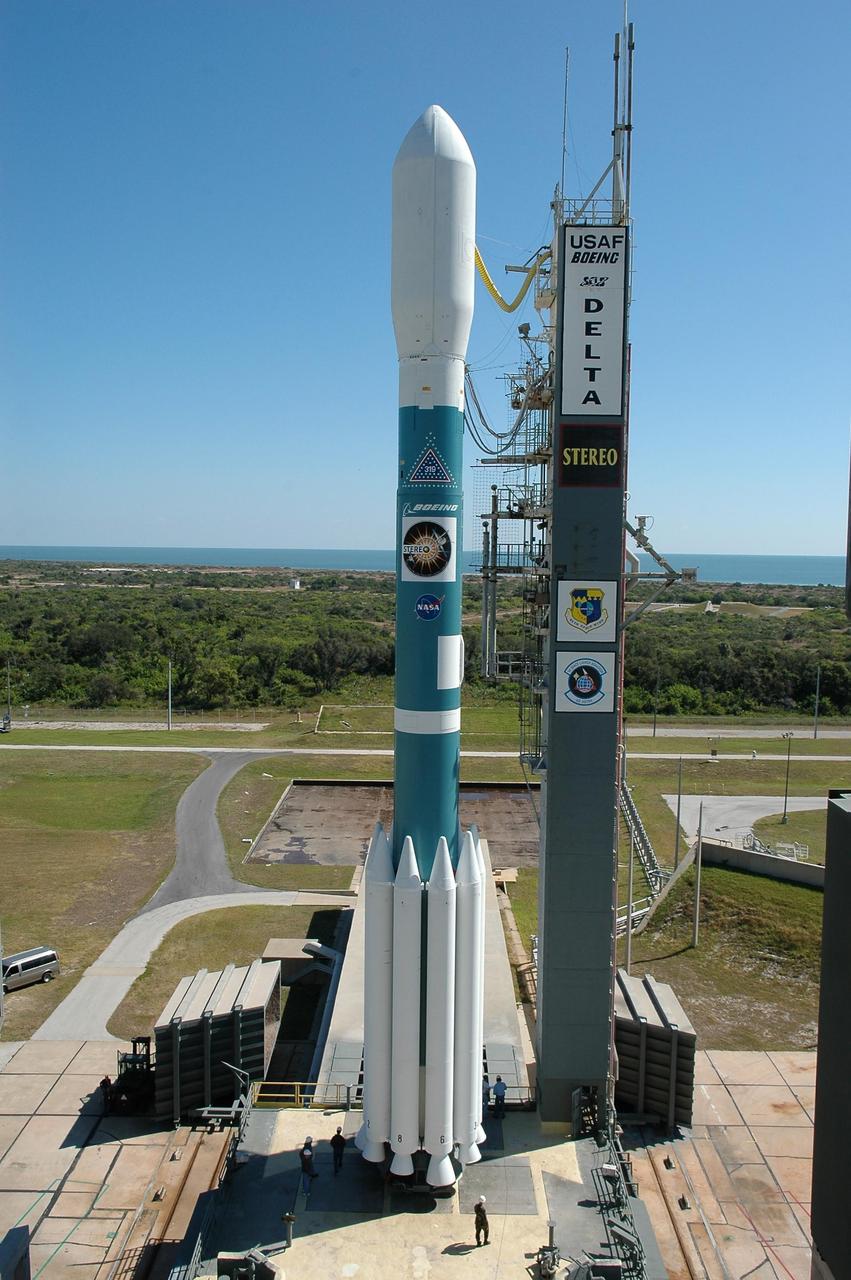

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After the mobile service tower has rolled away, the Delta II rocket with the STEREO spacecraft at top stands alone next to the launch gantry. Liftoff is scheduled in a window between 8:38 and 8:53 p.m. on Oct. 25. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
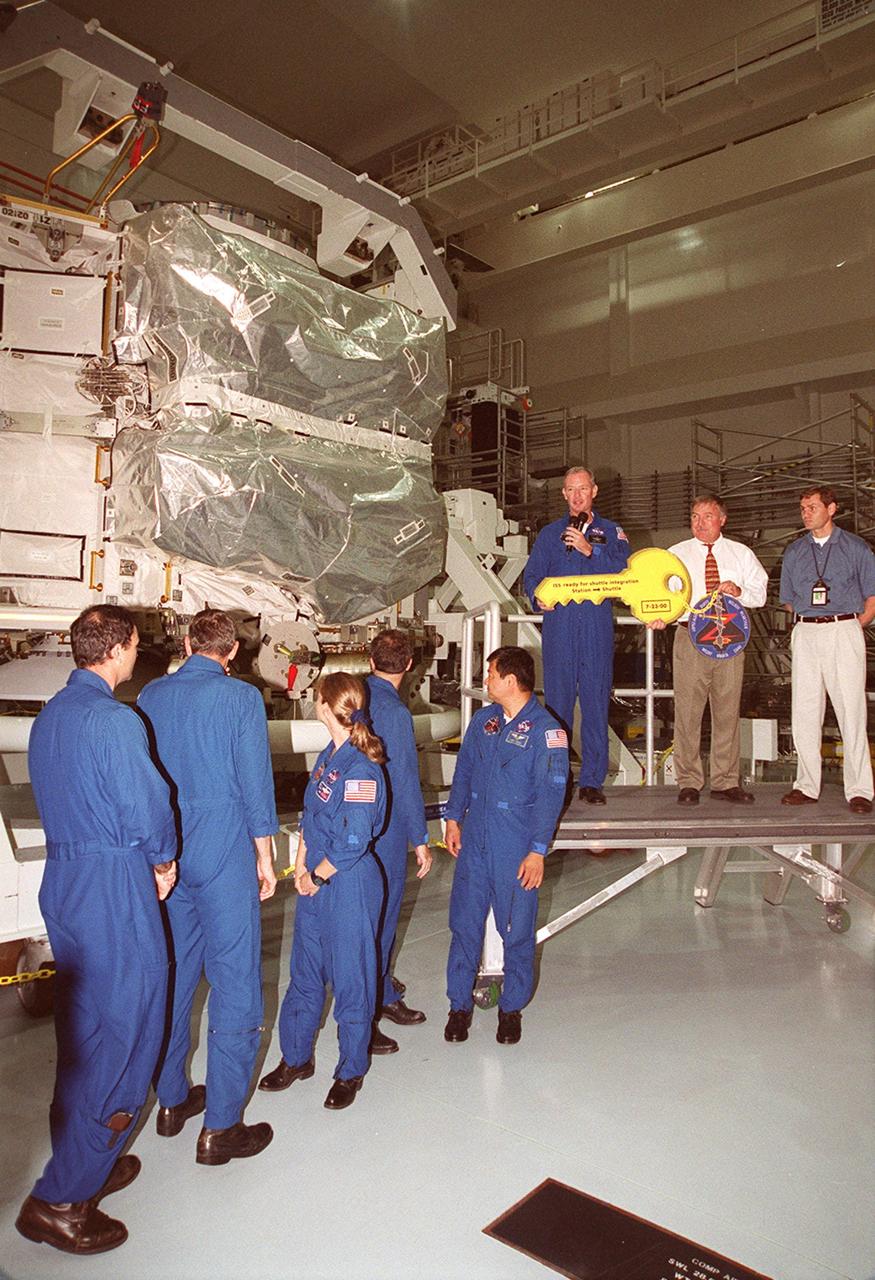
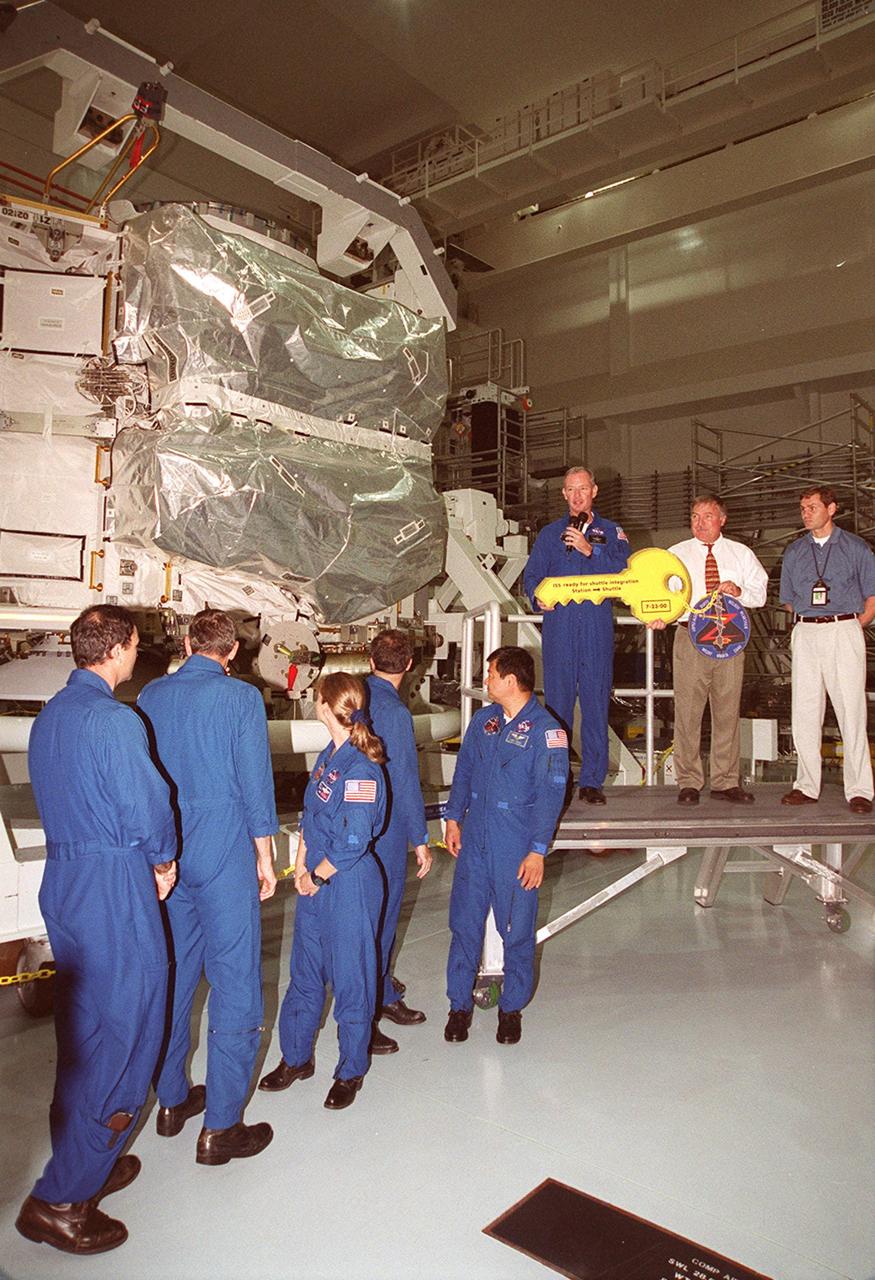
The Zenith-1 (Z-1) Truss is officially presented to NASA by The Boeing Co. on the Space Station Processing Facility floor on July 31. STS-92 Commander Col. Brian Duffy, comments on the presentation. At his side is Tip Talone, NASA director of International Space Station and Payload Processing at KSC. Talone and Col. Duffy received a symbolic key for the truss from John Elbon, Boeing director of ISS ground operations. The Z-1 Truss is the cornerstone truss of the International Space Station and is scheduled to fly in Space Shuttle Discovery's payload pay on STS-92 targeted for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The Z-1 is considered a cornerstone truss because it carries critical components of the Station's attitude, communications, thermal and power control systems as well as four control moment gyros, high and low gain antenna systems, and two plasma contactor units used to disperse electrical charge build-ups. The Z-1 truss and a Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3), also flying to the Station on the same mission, will be the first major U.S. elements flown to the ISS aboard the Shuttle since the launch of the Unity element in December 1998
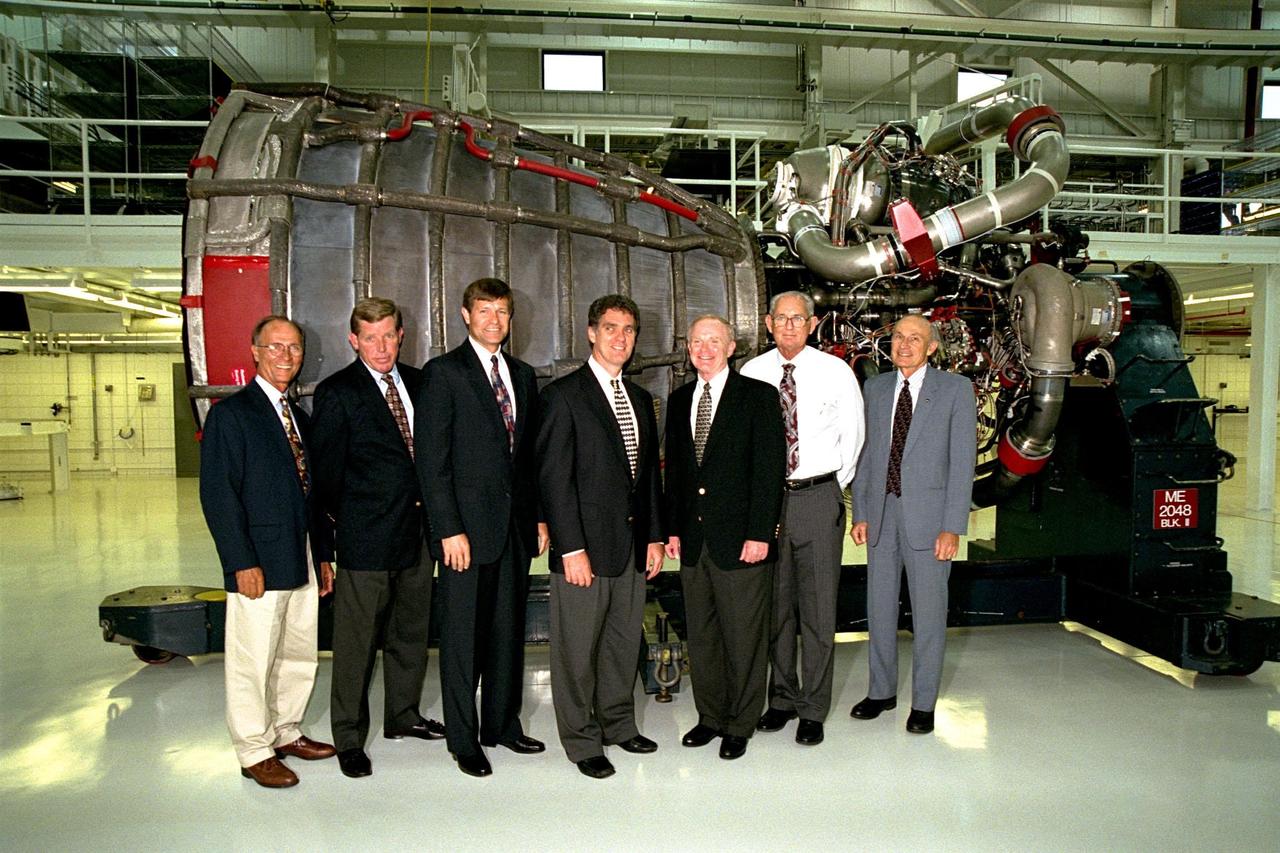

Participants in the ribbon cutting for KSC's new 34,600-square-foot Space Shuttle Main Engine Processing Facility (SSMEPF) pose in front of a Space Shuttle Main Engine on display for the ceremony. From left, they are Ed Adamek, vice president and associate program manager for Ground Operations of United Space Alliance; John Plowden, vice president of Rocketdyne; Donald R. McMonagle, manager of Launch Integration; U.S. Congressman Dave Weldon; KSC Center Director Roy D. Bridges Jr.; Wade Ivey of Ivey Construction, Inc.; and Robert B. Sieck, director of Shuttle Processing. A major addition to the existing Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3, the SSMEPF replaces the Shuttle Main Engine Shop located in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The decision to move the shop out of the VAB was prompted by safety considerations and recent engine processing improvements. The first three main engines to be processed in the new facility will fly on Shuttle Endeavour's STS-88 mission in December 1998
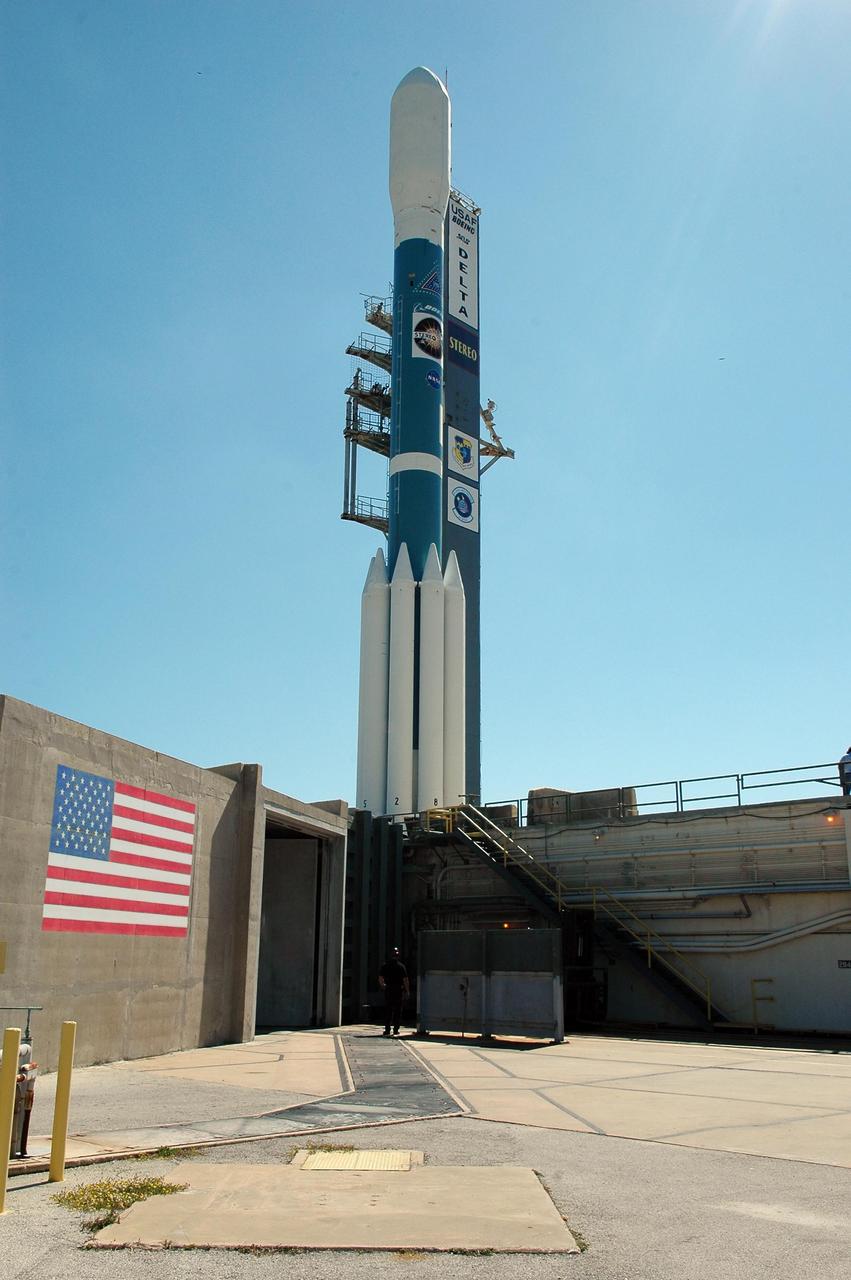

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Delta II rocket with the STEREO spacecraft at top stands next to the launch gantry, ready for liftoff. Launch is scheduled in a window between 8:38 and 8:53 p.m. on Oct. 25.STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
![KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-113 and Expedition 6 crews head for the Astrovan that will transport them to Launch Pad 39A and Space Shuttle Endeavour for a second launch attempt. The launch on Nov. 22 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at the Transoceanic Abort Landing sites. From left are Expedition 6 flight engineer Donald Pettit; a security guard; Expedition 6 flight engineer Nikolai Budarin; Mission Specialists John Herrington and Michael Lopez-Alegria, Pilot Paul Lockhart and Commander James Wetherbee (background); and Expedition 6 Commander Ken Bowersox. The launch will carry the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and return the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is now scheduled for Nov. 23 at 7:50 p.m. EST. [Photo by Scott Andrews]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC-02pd1802/KSC-02pd1802~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-113 and Expedition 6 crews head for the Astrovan that will transport them to Launch Pad 39A and Space Shuttle Endeavour for a second launch attempt. The launch on Nov. 22 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at the Transoceanic Abort Landing sites. From left are Expedition 6 flight engineer Donald Pettit; a security guard; Expedition 6 flight engineer Nikolai Budarin; Mission Specialists John Herrington and Michael Lopez-Alegria, Pilot Paul Lockhart and Commander James Wetherbee (background); and Expedition 6 Commander Ken Bowersox. The launch will carry the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and return the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is now scheduled for Nov. 23 at 7:50 p.m. EST. [Photo by Scott Andrews]
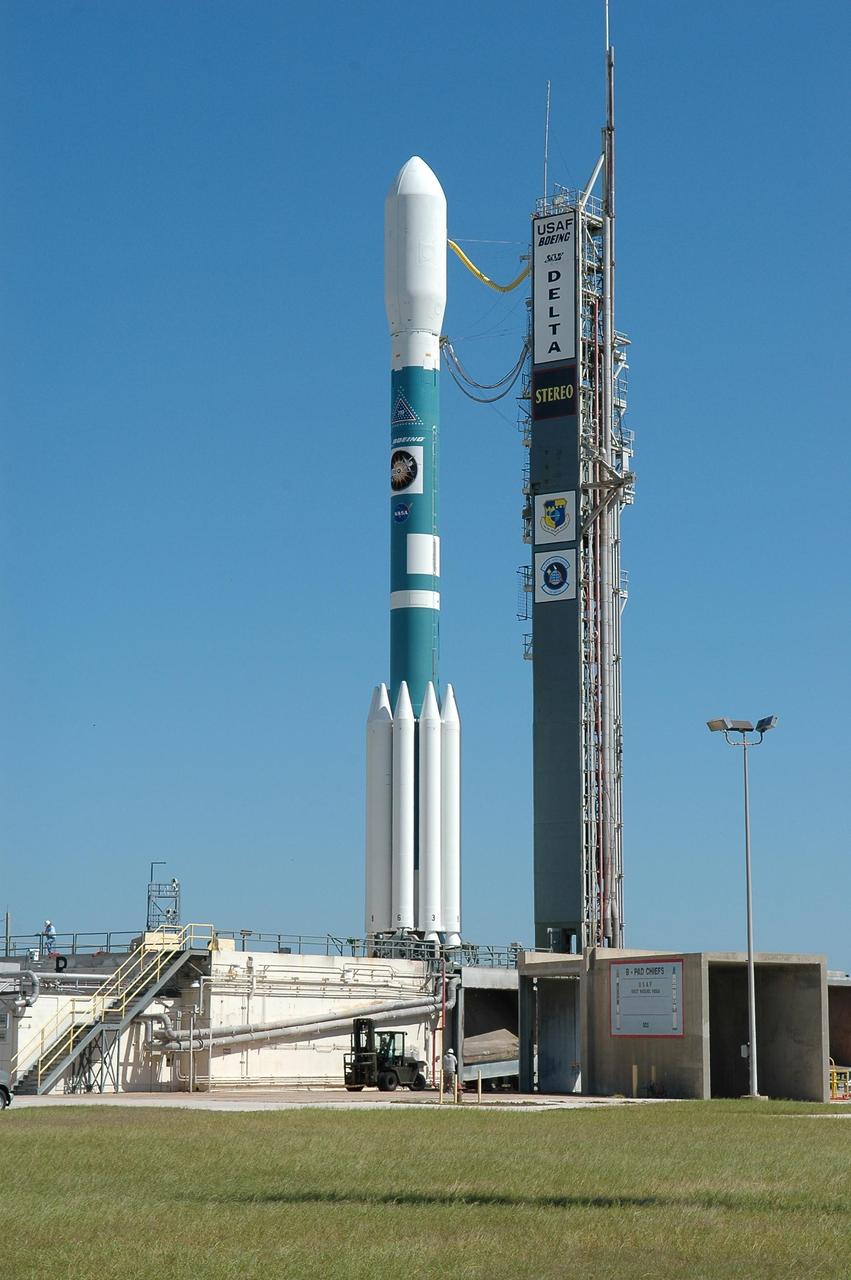

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Delta II rocket with the STEREO spacecraft at top stands next to the launch gantry, ready for liftoff. Launch is scheduled in a window between 8:38 and 8:53 p.m. on Oct. 25. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On the second launch attempt, the STS-113 crew enjoys a snack before suiting up for launch. The launch was scrubbed on Nov. 22 because of poor weather in the Transoceanic Abort Landing sites. Seated left to right are Mission Specialists Michael Lopez-Alegria and John Herrington, Pilot Paul Lockhart and Commander James Wetherbee; Expedition 6 flight engineer Nikolai Budarin, Commander Ken Bowersox and flight engineer Donald Pettit. STS-113 is the 16th American assembly flight to the International Space Station. The launch will carry the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and return the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is now scheduled for Nov. 23 at 7:50 p.m. EST.
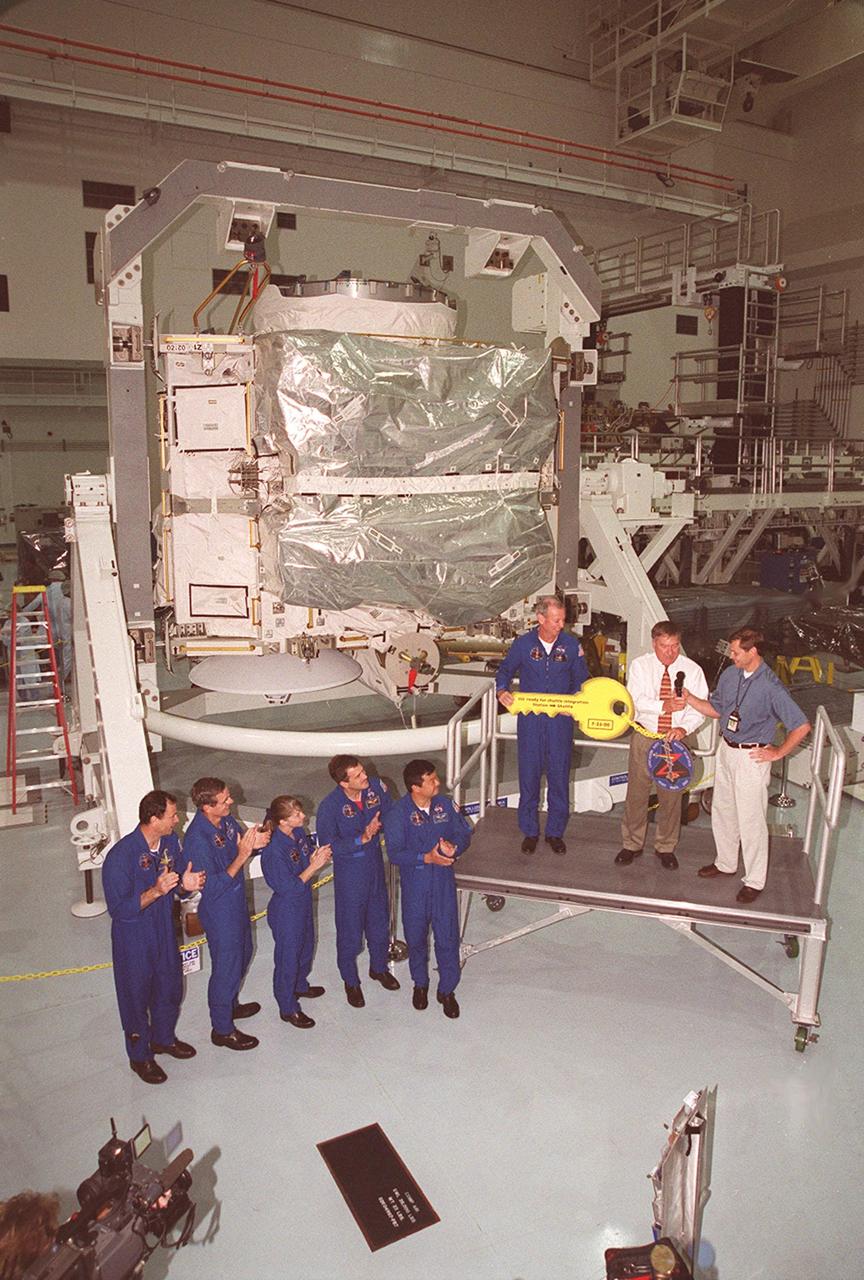
The Zenith-1 (Z-1) Truss is officially presented to NASA by The Boeing Co. on the Space Station Processing Facility floor on July 31. Astronauts from the STS-92 crew look on while their commander, Col. Brian Duffy, and Tip Talone, NASA director of International Space Station and Payload Processing at KSC, receive a symbolic key from John Elbon, Boeing director of ISS ground operations. The Z-1 Truss is the cornerstone truss of the International Space Station and is scheduled to fly in Space Shuttle Discovery's payload pay on STS-92 targeted for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The Z-1 is considered a cornerstone truss because it carries critical components of the Station's attitude, communications, thermal and power control systems as well as four control moment gyros, high and low gain antenna systems, and two plasma contactor units used to disperse electrical charge build-ups. The Z-1 truss and a Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3), also flying to the Station on the same mission, will be the first major U.S. elements flown to the ISS aboard the Shuttle since the launch of the Unity element in December 1998

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-113 and Expedition 6 crews leave the Operations and Checkout Building, heading for Launch Pad 39A and Space Shuttle Endeavour. In front, left to right, are Expedition 6 Commander Ken Bowersox and Mission Commander James Wetherbee; next row, Mission Specialist John Herrington and Pilot Paul Lockhart; third row, Mission Specialist Michael Lopez-Alegria and Expedition 6 flight engineer Nikolai Budarin; and finally, Expedition 6 flight engineer Donald Pettit. The primary mission for the crew is bringing the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and returning the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is scheduled for Nov. 22, 2002, at 8:15 p.m. EST.
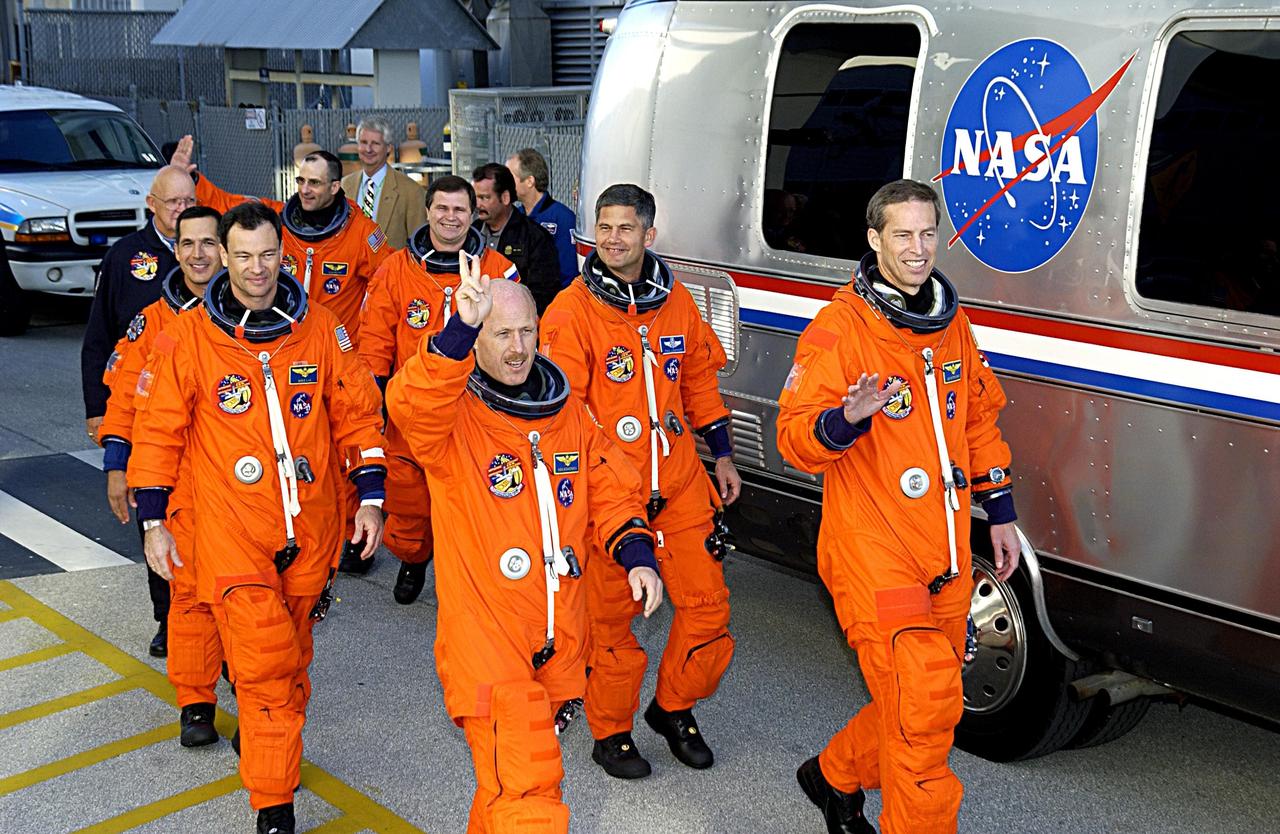

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Waving at spectators, the STS-113 and Expedition 6 crews head for the Astrovan that will transport them to Launch Pad 39A and Space Shuttle Endeavour for a second launch attempt. The launch on Nov. 22 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at the Transoceanic Abort Landing sites. In the foreground, from left, are Mission Specialists John Herrington and Michael Lopez-Alegria, and Expedition 6 Commander Ken Bowersox; in the background, from left, are Expedition 6 flight engineers Donald Pettit and Nikolai Budarin, Mission Pilot Paul Lockhart and Commander James Wetherbee. The launch will carry the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and return the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is now scheduled for Nov. 23 at 7:50 p.m. EST.
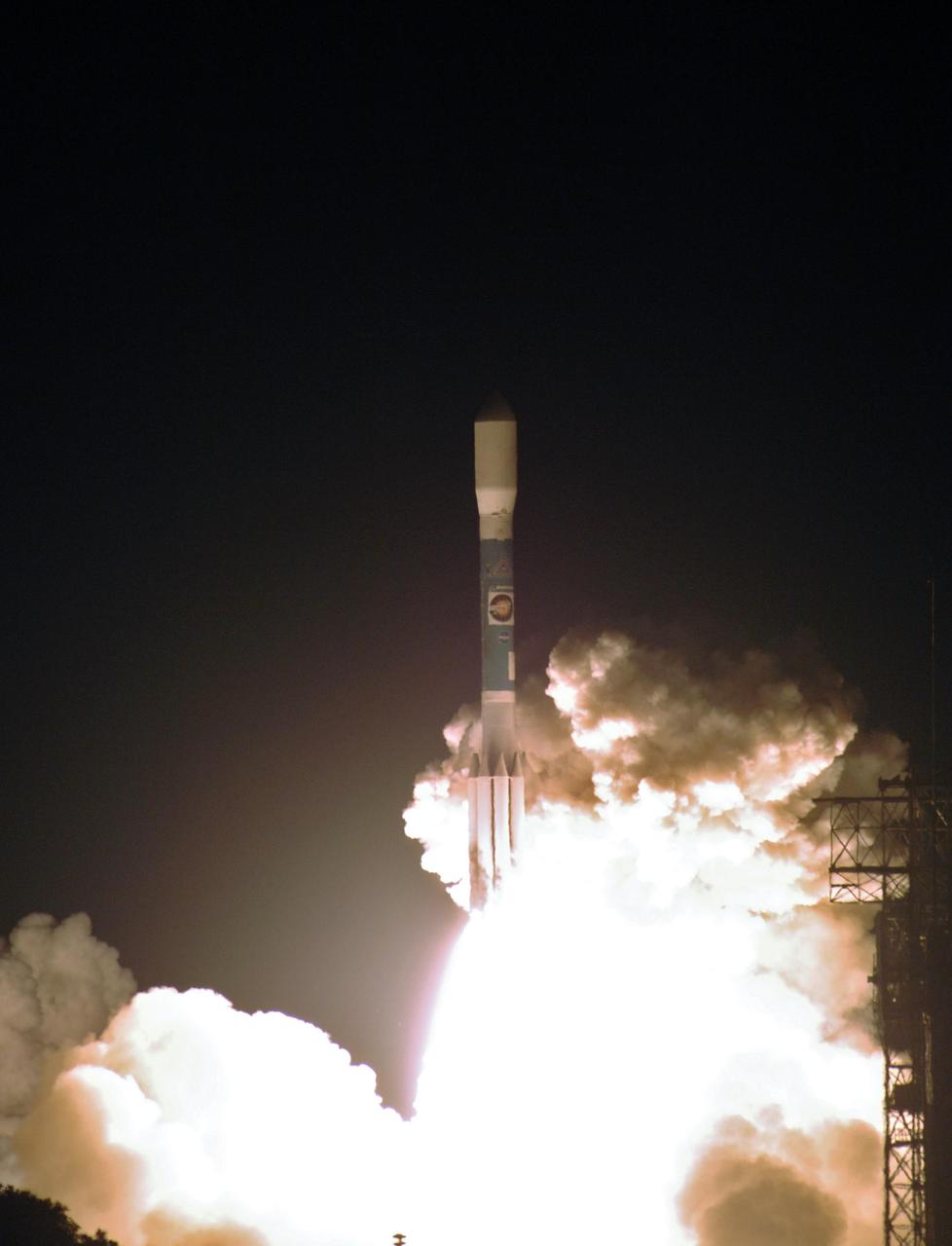

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Delta II launch vehicle carrying the STEREO spacecraft hurtles through the smoke and steam after liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Liftoff was at 8:52 p.m. EDT. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results.
![KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-113 and Expedition 6 crews stride down the ramp from the Operations and Checkout Building, eager to head for Launch Pad 39A and Space Shuttle Endeavour for a second launch attempt. The launch on Nov. 22 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at the Transoceanic Abort Landing sites. In front, left to right, are Expedition 6 Commander Ken Bowersox and Mission Commander James Wetherbee; next row, Mission Specialist Michael Lopez-Alegria and Pilot Paul Lockhart; third row, Mission Specialist John Herrington and Expedition 6 flight engineer Nikolai Budarin; and finally, Expedition 6 flight engineer Donald Pettit. The launch will carry the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and return the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is now scheduled for Nov. 23 at 7:50 p.m. EST. [Photo by Scott Andrews]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC-02pd1801/KSC-02pd1801~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-113 and Expedition 6 crews stride down the ramp from the Operations and Checkout Building, eager to head for Launch Pad 39A and Space Shuttle Endeavour for a second launch attempt. The launch on Nov. 22 was scrubbed due to poor weather conditions at the Transoceanic Abort Landing sites. In front, left to right, are Expedition 6 Commander Ken Bowersox and Mission Commander James Wetherbee; next row, Mission Specialist Michael Lopez-Alegria and Pilot Paul Lockhart; third row, Mission Specialist John Herrington and Expedition 6 flight engineer Nikolai Budarin; and finally, Expedition 6 flight engineer Donald Pettit. The launch will carry the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and return the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. The major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is now scheduled for Nov. 23 at 7:50 p.m. EST. [Photo by Scott Andrews]

STS095-S-001 (June 1998) --- The STS-95 patch, designed by the crew, is intended to reflect the scientific, engineering, and historic elements of the mission. The space shuttle Discovery is shown rising over the sunlit Earth limb, representing the global benefits of the mission science and the solar science objectives of the Spartan Satellite. The bold number "7" signifies the seven members of Discovery's crew and also represents a historical link to the original seven Mercury astronauts. The STS-95 crew member John Glenn's first orbital flight is represnted by the Friendship 7 capsule. The rocket plumes symbolize the three major fields of science represented by the mission payloads: microgravity material science, medical research for humans on Earth and in space, and astronomy. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
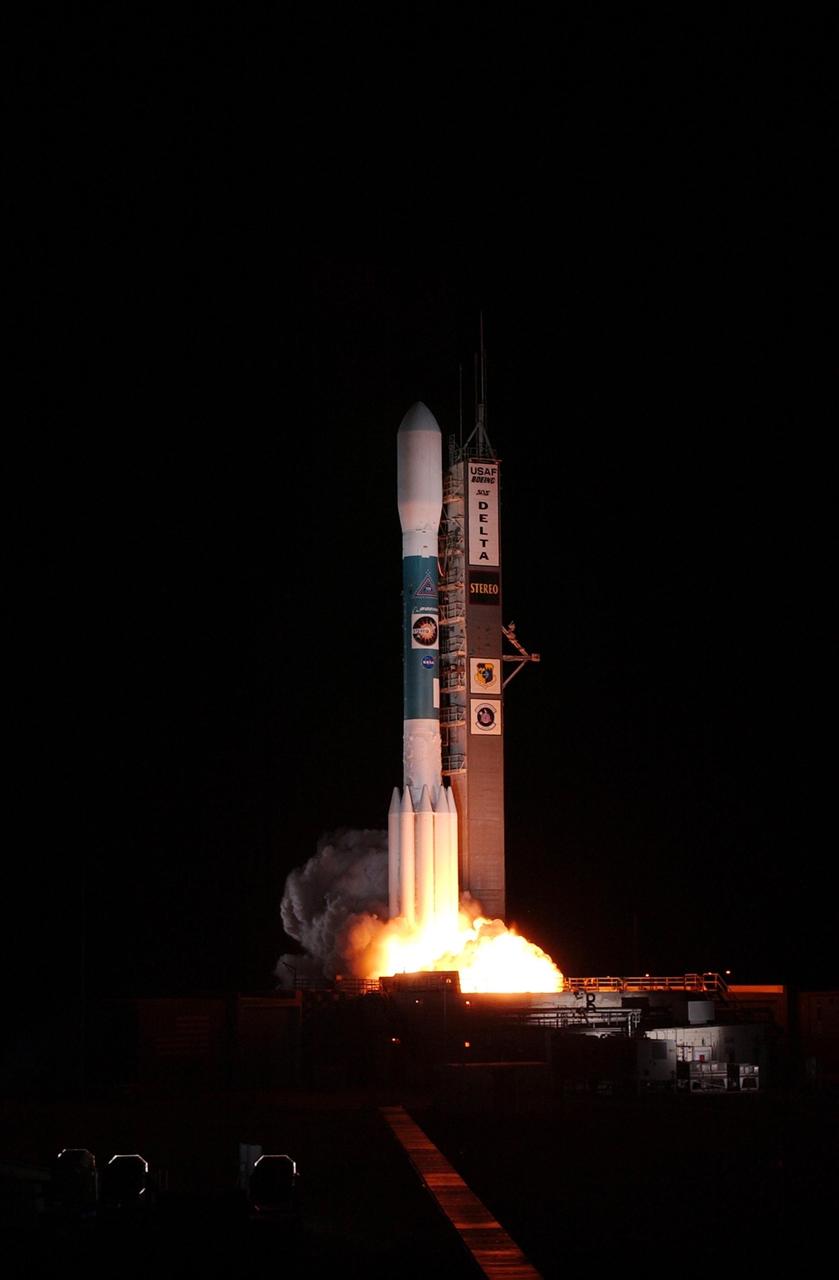

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At liftoff, clouds of smoke spread beneath the Delta II rocket carrying the STEREO spacecraft on top. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was at 8:52 p.m. EDT. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results.
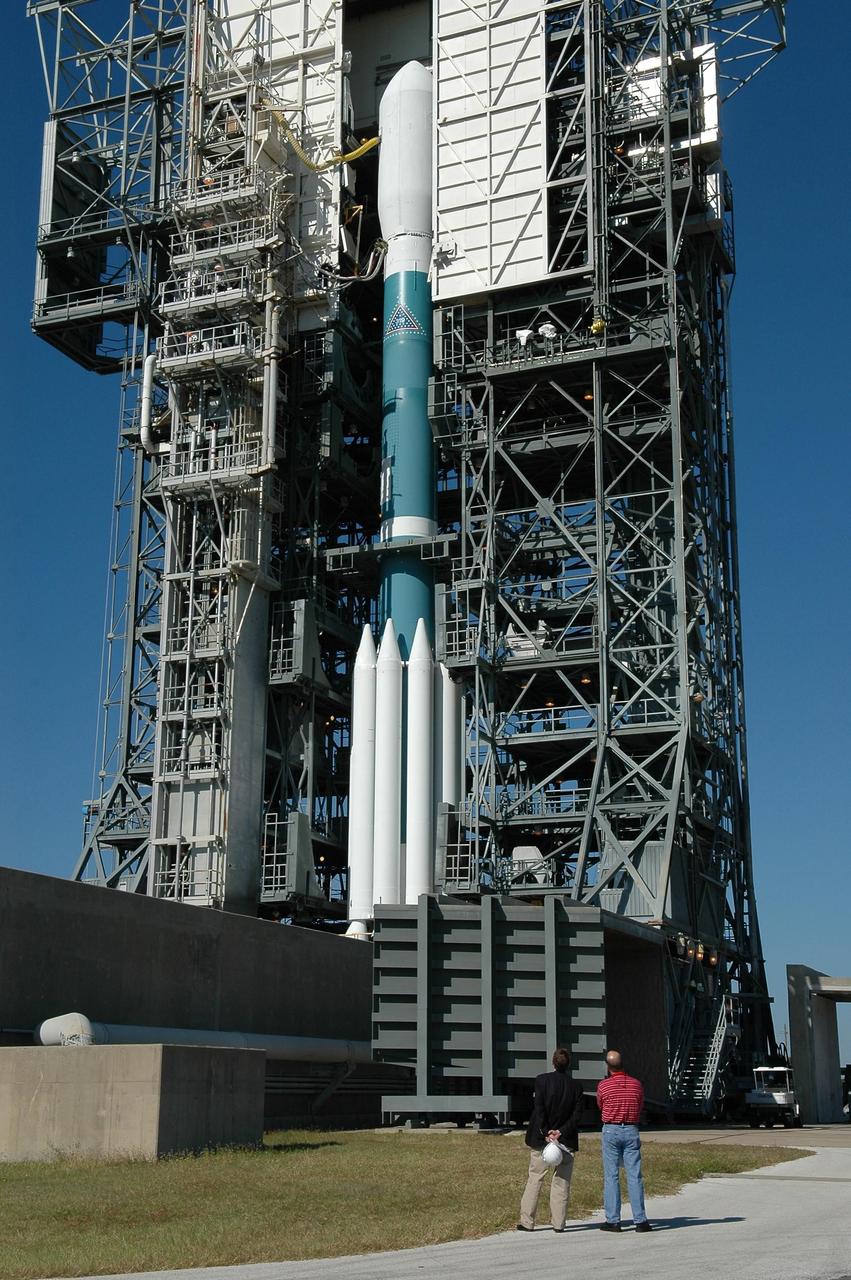

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The mobile service tower begins to roll away from the STEREO spacecraft aboard the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for launch. Liftoff is scheduled in a window between 8:38 and 8:53 p.m. on Oct. 25. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
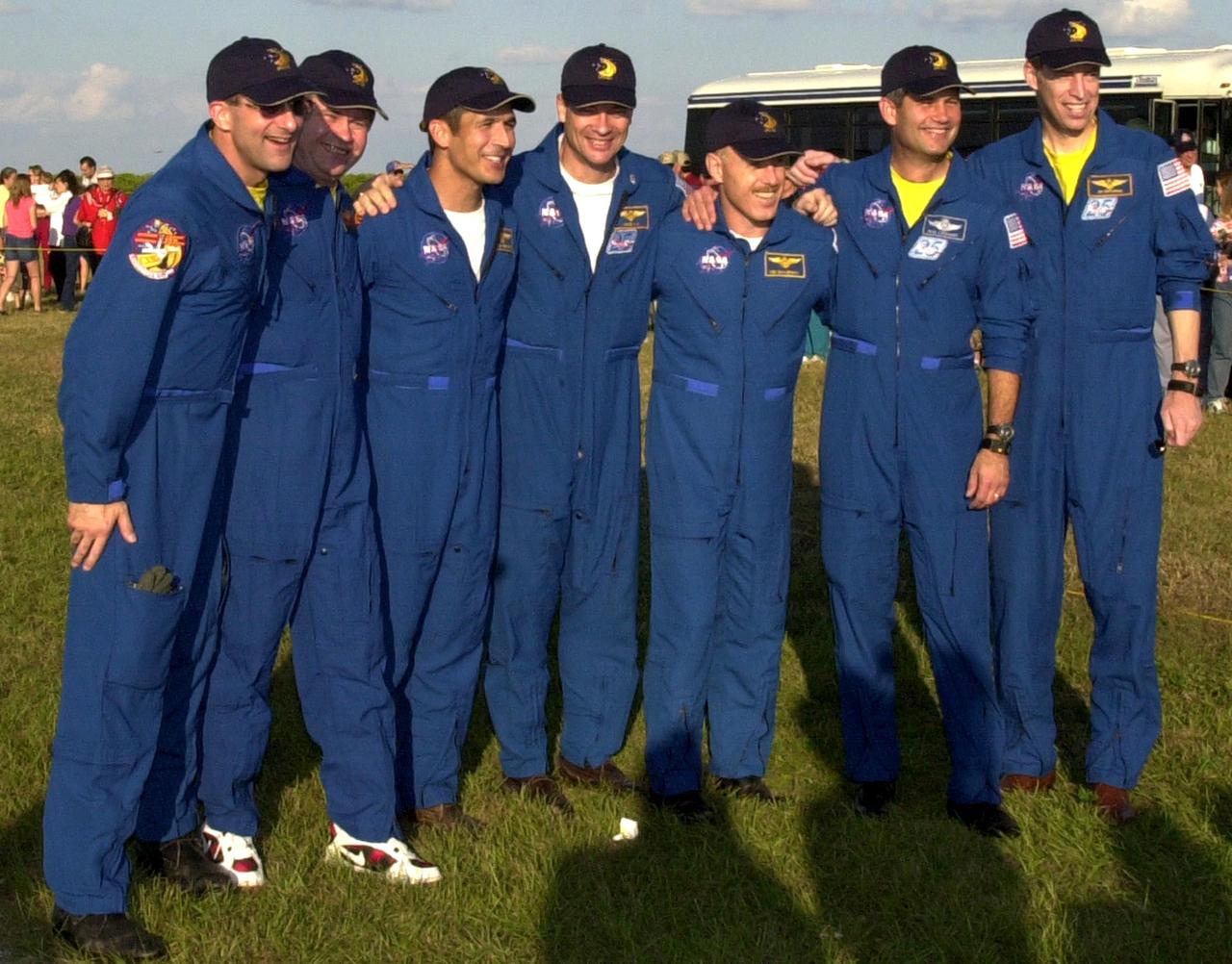

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The STS-113 and Expedition Six crews pose for a group photo at Launch Pad 39A with Space Shuttle Endeavour in the background during a tour of Kennedy Space Center prior to their launch. From left are Expedition Six crew members Donald Pettit and Nikolai Budarin of the Russian Space Agency, STS-113 Mission Specialists John Herrington and Michael Lopez-Alegria, Expedition Six Commander Ken Bowersox, STS-113 Pilot Paul Lockhart, and STS-113 Commander James Wetherbee. The primary mission of STS-113 is bringing the Expedition 6 crew to the Station and returning the Expedition 5 crew to Earth. Another major objective of the mission is delivery of the Port 1 (P1) Integrated Truss Assembly, which will be attached to the port side of the S0 truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install and activate the truss and its associated equipment. Launch of Space Shuttle Endeavour on mission STS-113 is scheduled for Nov. 11 between midnight and 4 a.m. EST.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Captured in the water of the Banana River, the brilliant light from the Delta II carrying the STEREO spacecraft lights up the night sky. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was at 8:52 p.m. EDT. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
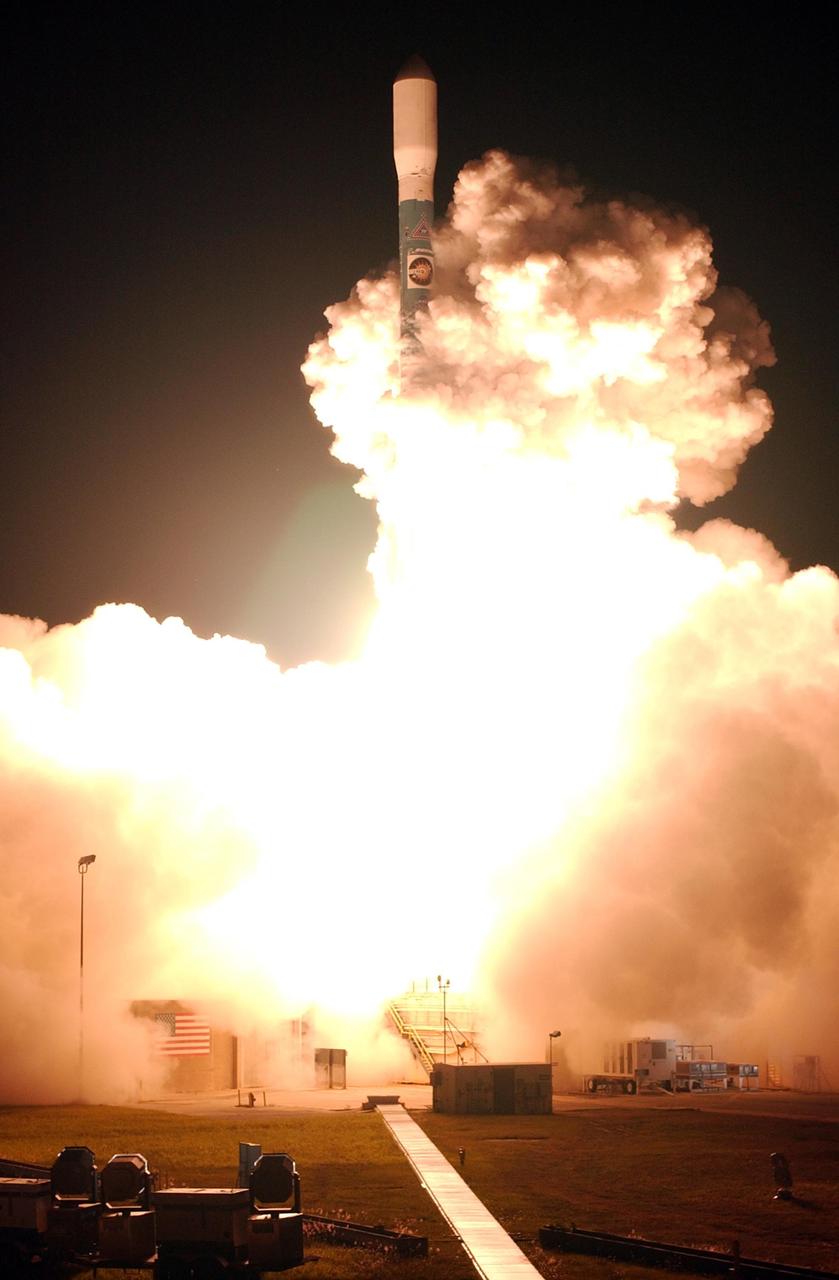

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Delta II rocket carrying the STEREO spacecraft on top streaks through the smoke as it climbs to orbit. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was at 8:52 p.m. EDT. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results.
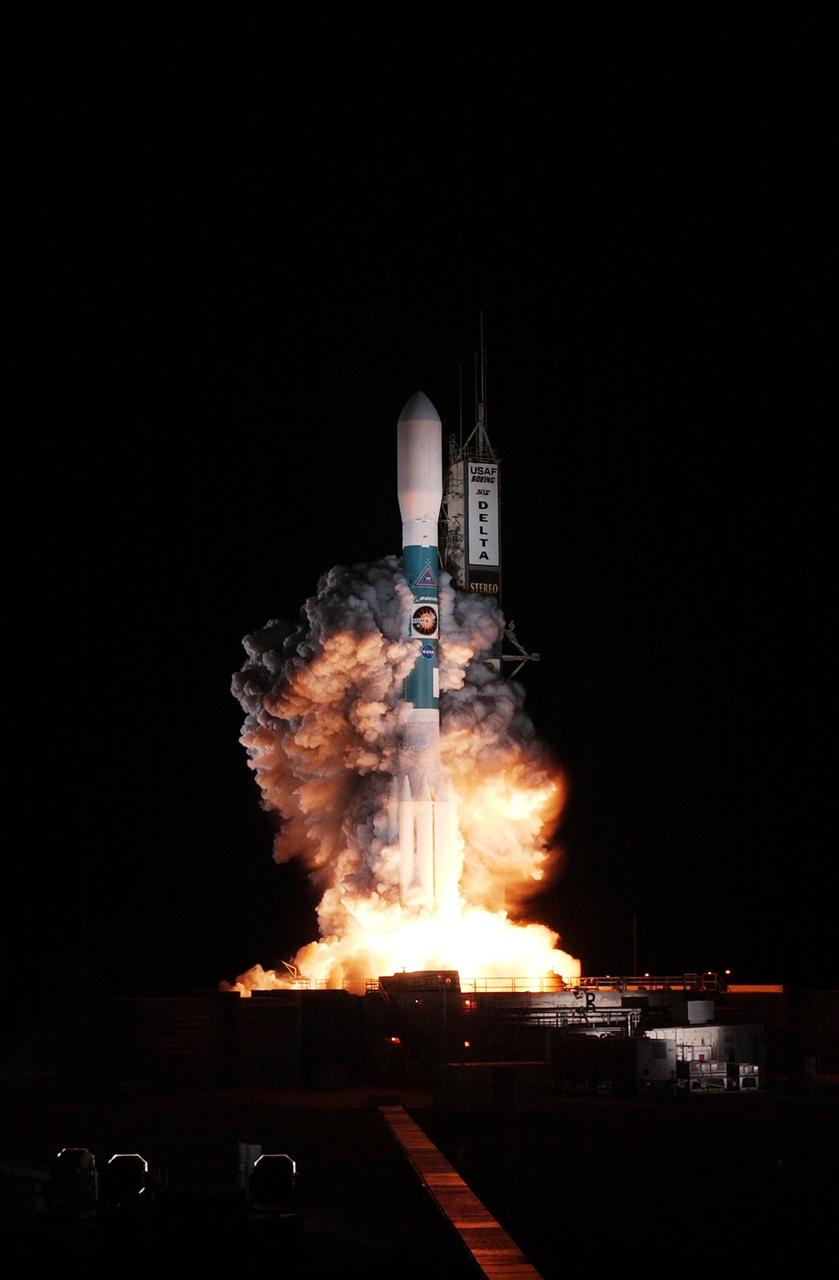

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Just after liftoff, clouds of smoke billow up and around the Delta II rocket carrying the STEREO spacecraft on top. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was at 8:52 p.m. EDT. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Banana River reflects the brilliant launch of the Delta II carrying the STEREO spacecraft. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was at 8:52 p.m. EDT. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
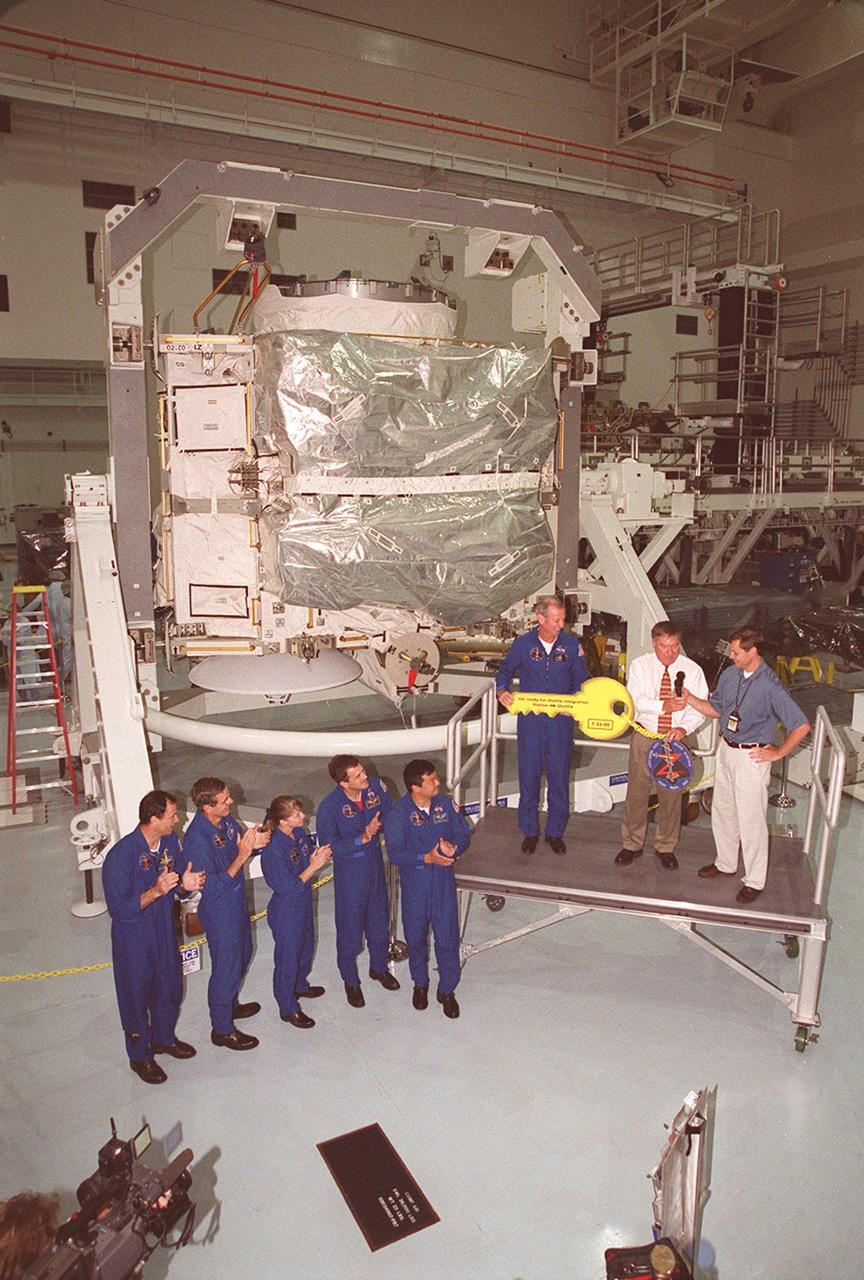
The Zenith-1 (Z-1) Truss is officially presented to NASA by The Boeing Co. on the Space Station Processing Facility floor on July 31. Astronauts from the STS-92 crew look on while their commander, Col. Brian Duffy, and Tip Talone, NASA director of International Space Station and Payload Processing at KSC, receive a symbolic key from John Elbon, Boeing director of ISS ground operations. The Z-1 Truss is the cornerstone truss of the International Space Station and is scheduled to fly in Space Shuttle Discovery's payload pay on STS-92 targeted for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The Z-1 is considered a cornerstone truss because it carries critical components of the Station's attitude, communications, thermal and power control systems as well as four control moment gyros, high and low gain antenna systems, and two plasma contactor units used to disperse electrical charge build-ups. The Z-1 truss and a Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3), also flying to the Station on the same mission, will be the first major U.S. elements flown to the ISS aboard the Shuttle since the launch of the Unity element in December 1998
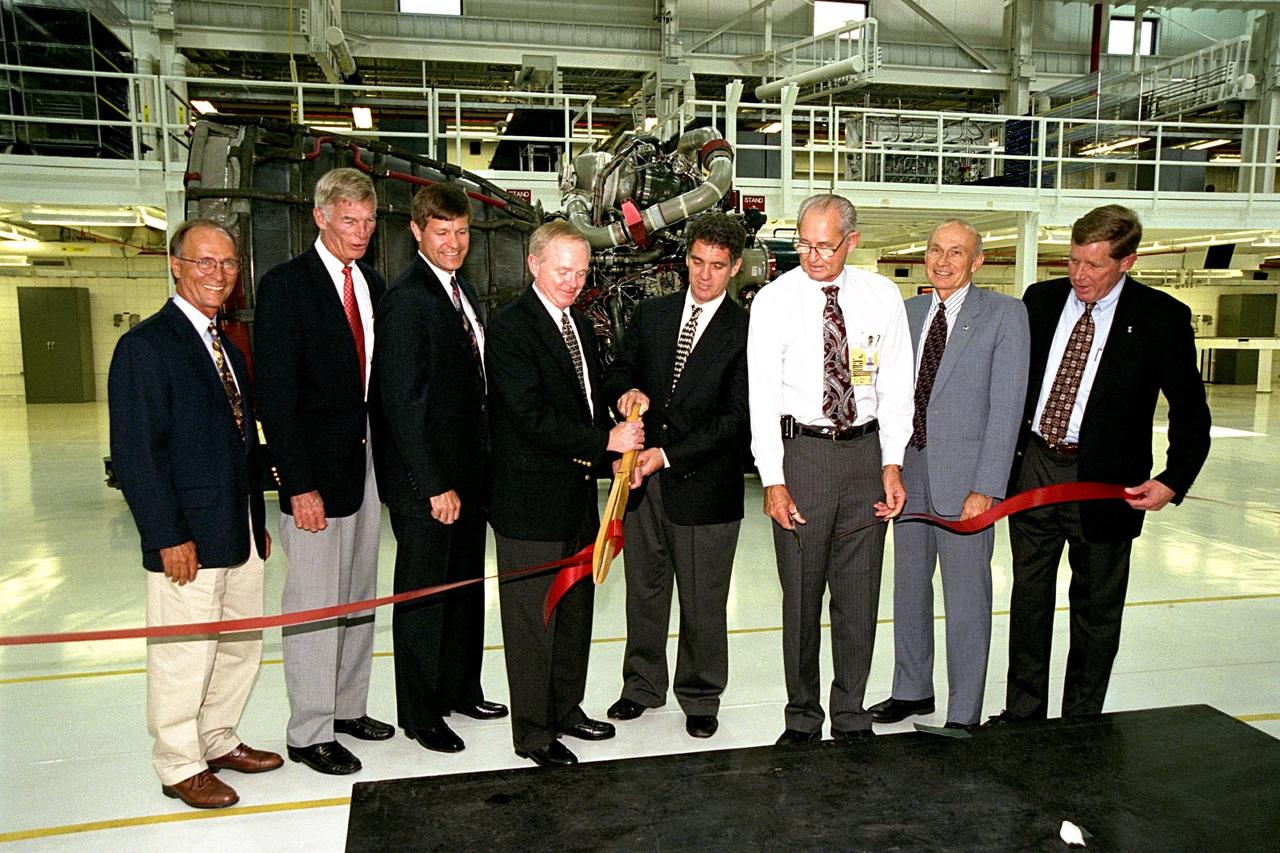

KSC Center Director Roy D. Bridges Jr. and U.S. Congressman Dave Weldon (holding scissors) cut the ribbon at a ceremony on July 6 to open KSC's new 34,600-square-foot Space Shuttle Main Engine Processing Facility (SSMEPF). Joining in the ribbon cutting are (left) Ed Adamek, vice president and associate program manager for Ground Operations of United Space Alliance; Marvin L. Jones, director of Installation Operations; Donald R. McMonagle, manager of Launch Integration; (right) Wade Ivey of Ivey Construction, Inc.; Robert B. Sieck, director of Shuttle Processing; and John Plowden, vice president of Rocketdyne. A major addition to the existing Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3, the SSMEPF replaces the Shuttle Main Engine Shop located in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The decision to move the shop out of the VAB was prompted by safety considerations and recent engine processing improvements. The first three main engines to be processed in the new facility will fly on Shuttle Endeavour's STS-88 mission in December 1998
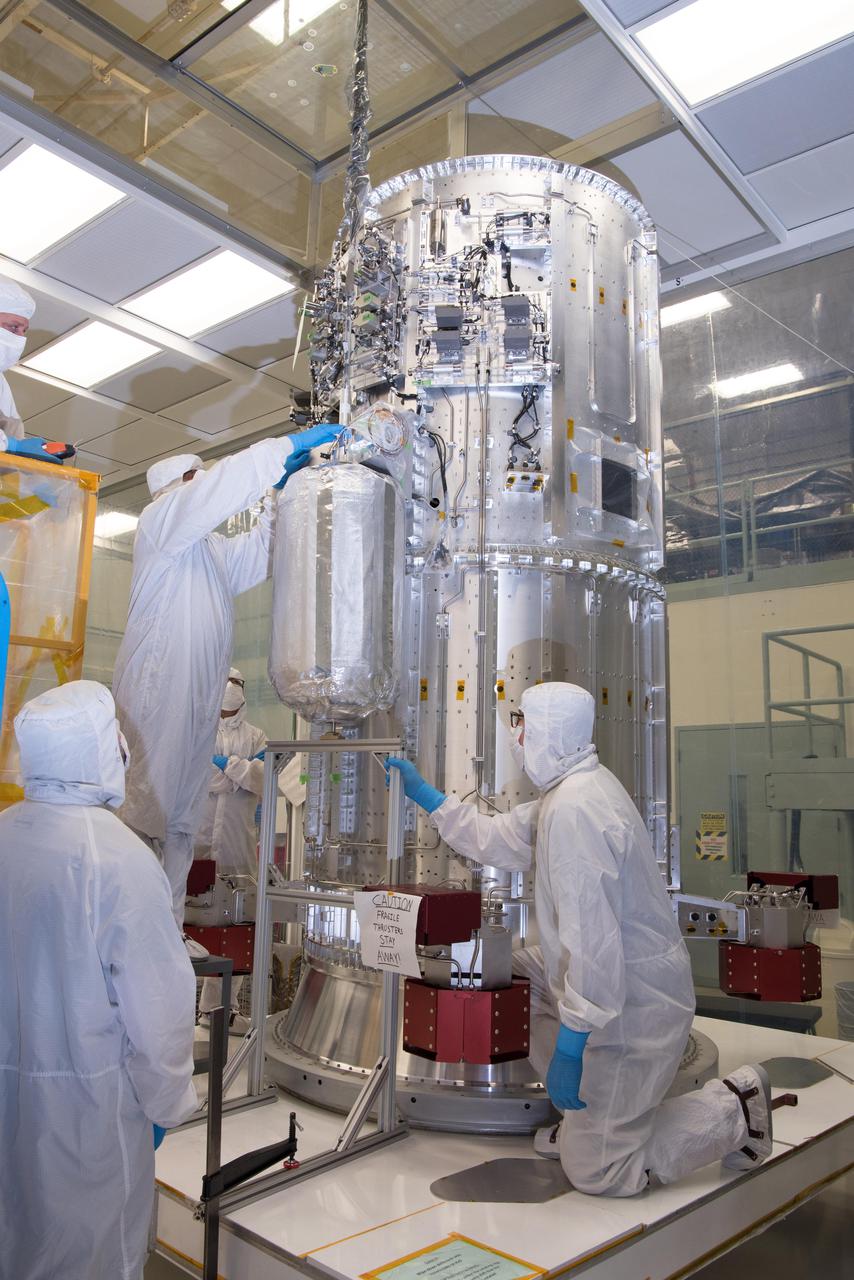

Engineers and technicians in a clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, integrate the tanks that will contain helium onto the propulsion module of NASA's Europa Clipper spacecraft. The 10-foot-tall (3-meter-tall) propulsion module was also integrated with 16 rocket engines at Goddard. The module then was shipped to the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, where engineers will install electronics, radios, antennas, and cabling. In 2022, this major piece of hardware will ship to NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California for assembly, test, and launch operations. With an internal global ocean under a thick layer of ice, Jupiter's moon Europa may have the potential to harbor existing life. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will swoop around Jupiter on an elliptical path, dipping close to the moon on each flyby to collect data. Understanding Europa's habitability will help scientists better understand how life developed on Earth and the potential for finding life beyond our planet. Europa Clipper is set to launch in 2024. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24782
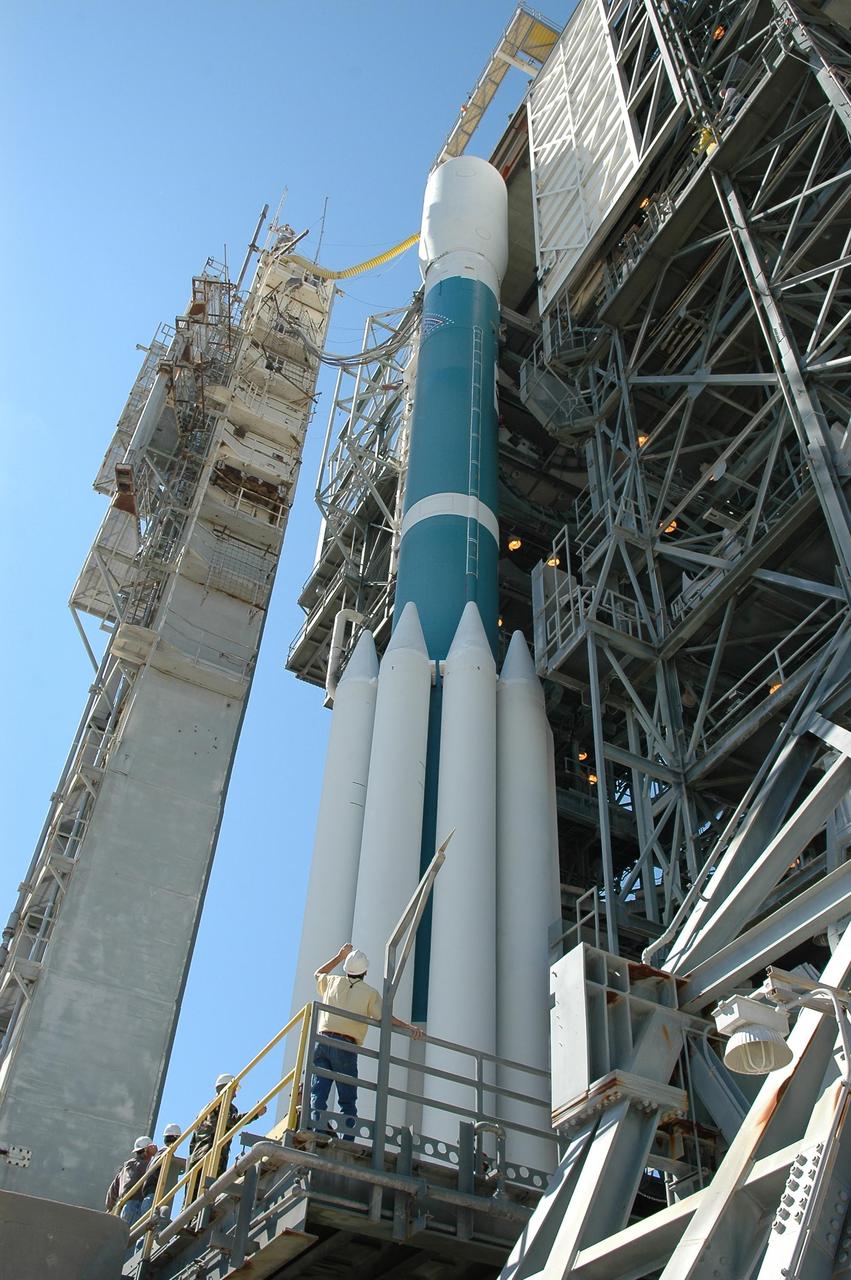

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The mobile service tower (right) begins to roll away from the STEREO spacecraft aboard the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for launch. Liftoff is scheduled in a window between 8:38 and 8:53 p.m. on Oct. 25. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
STS-113, the 16th American assembly flight and 112th overall American flight to the International Space Station (ISS), launched on November 23, 2002 from Kennedy's launch pad 39A aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour. The main mission objective was the the installation and activation of the Port 1 Integrated Truss Assembly (P1). The first major component installed on the left side of the Station, the P1 truss provides an additional three External Thermal Control System radiators. Weighing in at 27,506 pounds, the P1 truss is 45 feet (13.7 meters) long, 15 feet (4.6 meters) wide, and 13 feet (4 meters) high. Three space walks, aided by the use of the Robotic Manipulator Systems of both the Shuttle and the Station, were performed in the installation of P1. In this photograph astronaut and mission specialist John B. Herrington, (center left frame), participates in the mission's third space walk. The forward section of the Space Shuttle Endeavour, docked to the Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-2) on the ISS, is visible center frame. The station's Canadarm2 appears to stand in between the shuttle and Herrington.
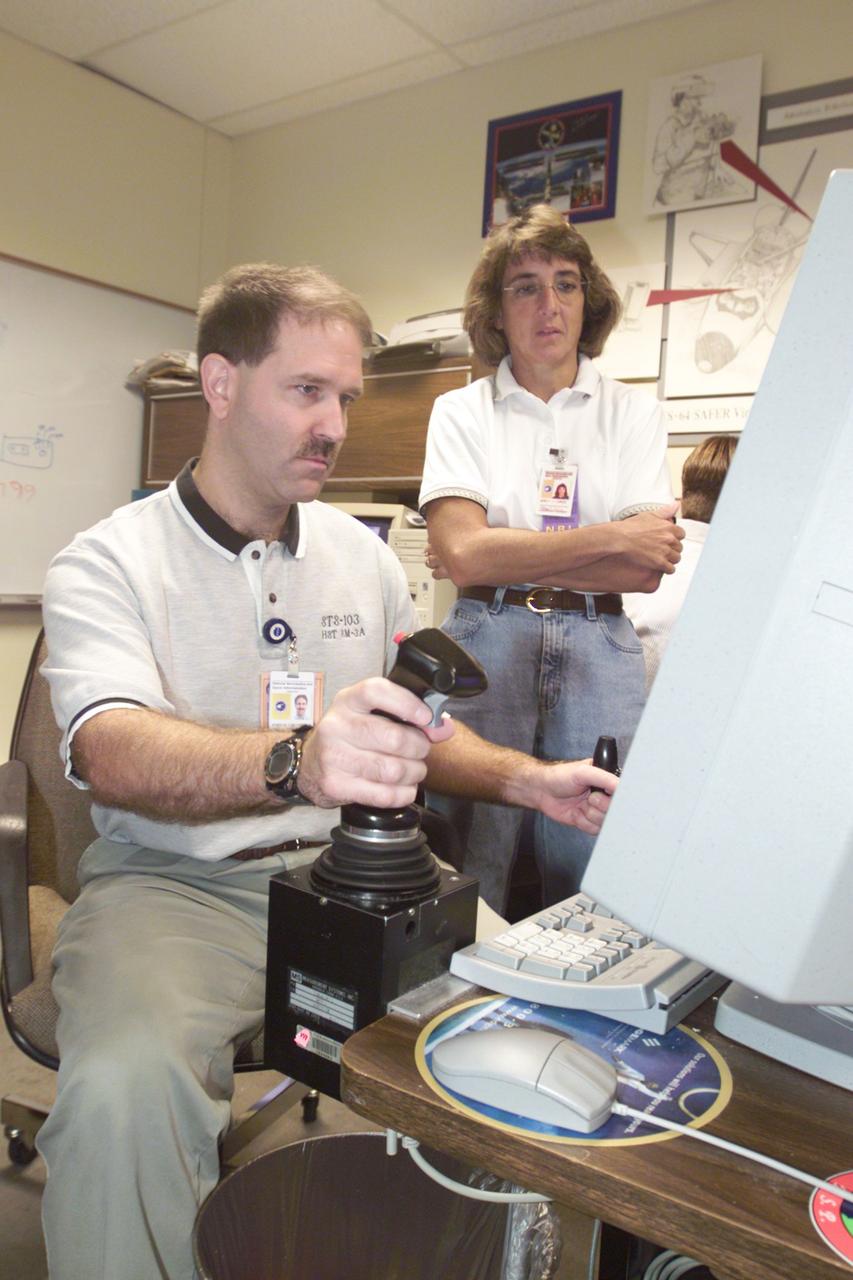

Astronauts John M. Grunsfeld (left), STS-109 payload commander, and Nancy J. Currie, mission specialist, use the virtual reality lab at Johnson Space Center to train for upcoming duties aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. This type of computer interface paired with virtual reality training hardware and software helps to prepare the entire team to perform its duties for the fourth Hubble Space Telescope Servicing mission. The most familiar form of virtual reality technology is some form of headpiece, which fits over your eyes and displays a three dimensional computerized image of another place. Turn your head left and right, and you see what would be to your sides; turn around, and you see what might be sneaking up on you. An important part of the technology is some type of data glove that you use to propel yourself through the virtual world. Currently, the medical community is using the new technologies in four major ways: To see parts of the body more accurately, for study, to make better diagnosis of disease and to plan surgery in more detail; to obtain a more accurate picture of a procedure during surgery; to perform more types of surgery with the most noninvasive, accurate methods possible; and to model interactions among molecules at a molecular level.
The Zenith-1 (Z-1) Truss is officially presented to NASA by The Boeing Co. on the Space Station Processing Facility floor on July 31. STS-92 Commander Col. Brian Duffy, comments on the presentation. At his side is Tip Talone, NASA director of International Space Station and Payload Processing at KSC. Talone and Col. Duffy received a symbolic key for the truss from John Elbon, Boeing director of ISS ground operations. The Z-1 Truss is the cornerstone truss of the International Space Station and is scheduled to fly in Space Shuttle Discovery's payload pay on STS-92 targeted for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The Z-1 is considered a cornerstone truss because it carries critical components of the Station's attitude, communications, thermal and power control systems as well as four control moment gyros, high and low gain antenna systems, and two plasma contactor units used to disperse electrical charge build-ups. The Z-1 truss and a Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3), also flying to the Station on the same mission, will be the first major U.S. elements flown to the ISS aboard the Shuttle since the launch of the Unity element in December 1998

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Just at liftoff, clouds of smoke and steam rise around the Delta II rocket carrying the STEREO spacecraft on top. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was at 8:52 p.m. EDT. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results.
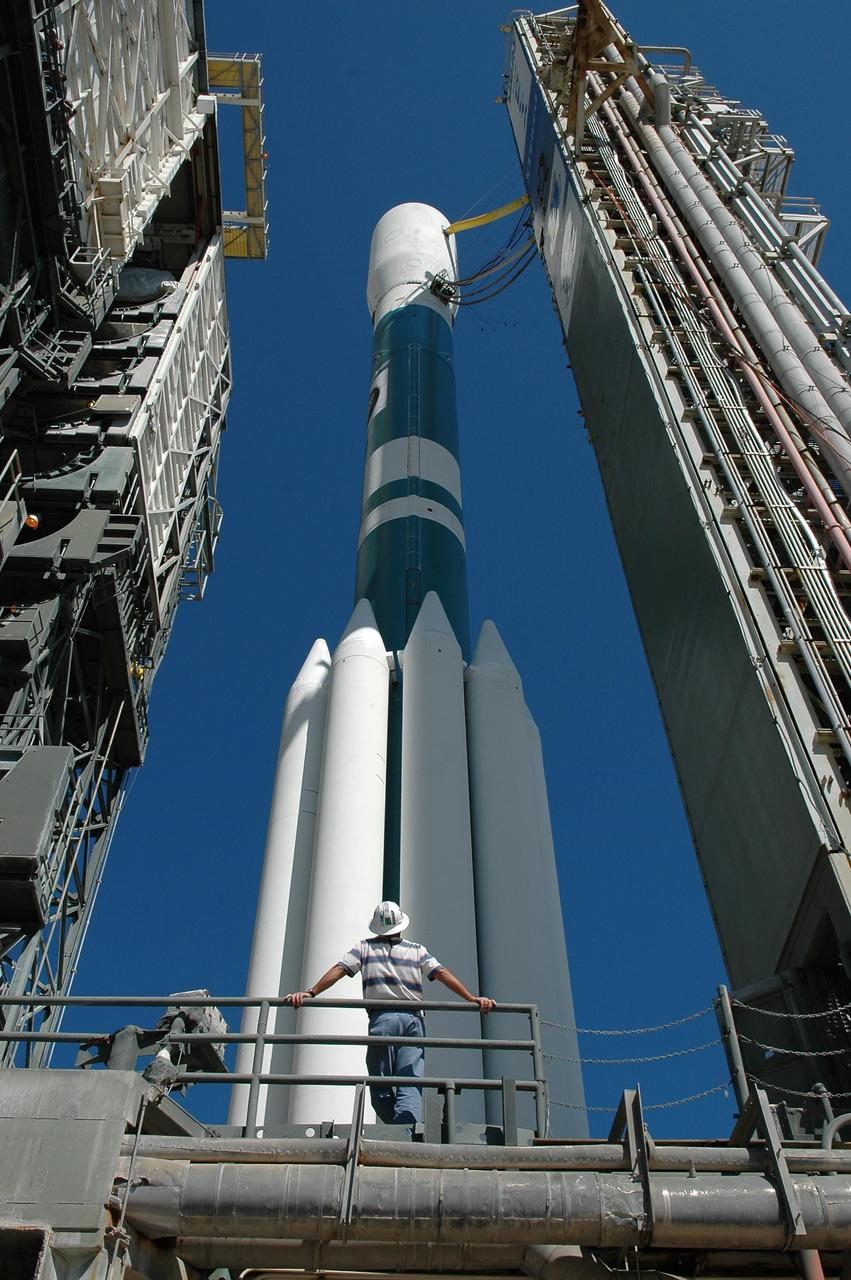

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The mobile service tower (left) rolls away from the STEREO spacecraft aboard the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for launch. Liftoff is scheduled in a window between 8:38 and 8:53 p.m. on Oct. 25. STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) is a two-year mission using two nearly identical observatories, one ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The duo will provide 3-D measurements of the sun and its flow of energy, enabling scientists to study the nature of coronal mass ejections and why they happen. The ejections are a major source of the magnetic disruptions on Earth and are a key component of space weather. The disruptions can greatly effect satellite operations, communications, power systems, humans in space and global climate. Designed and built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) , the STEREO mission is being managed by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. APL will maintain command and control of the observatories throughout the mission, while NASA tracks and receives the data, determines the orbit of the satellites, and coordinates the science results. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
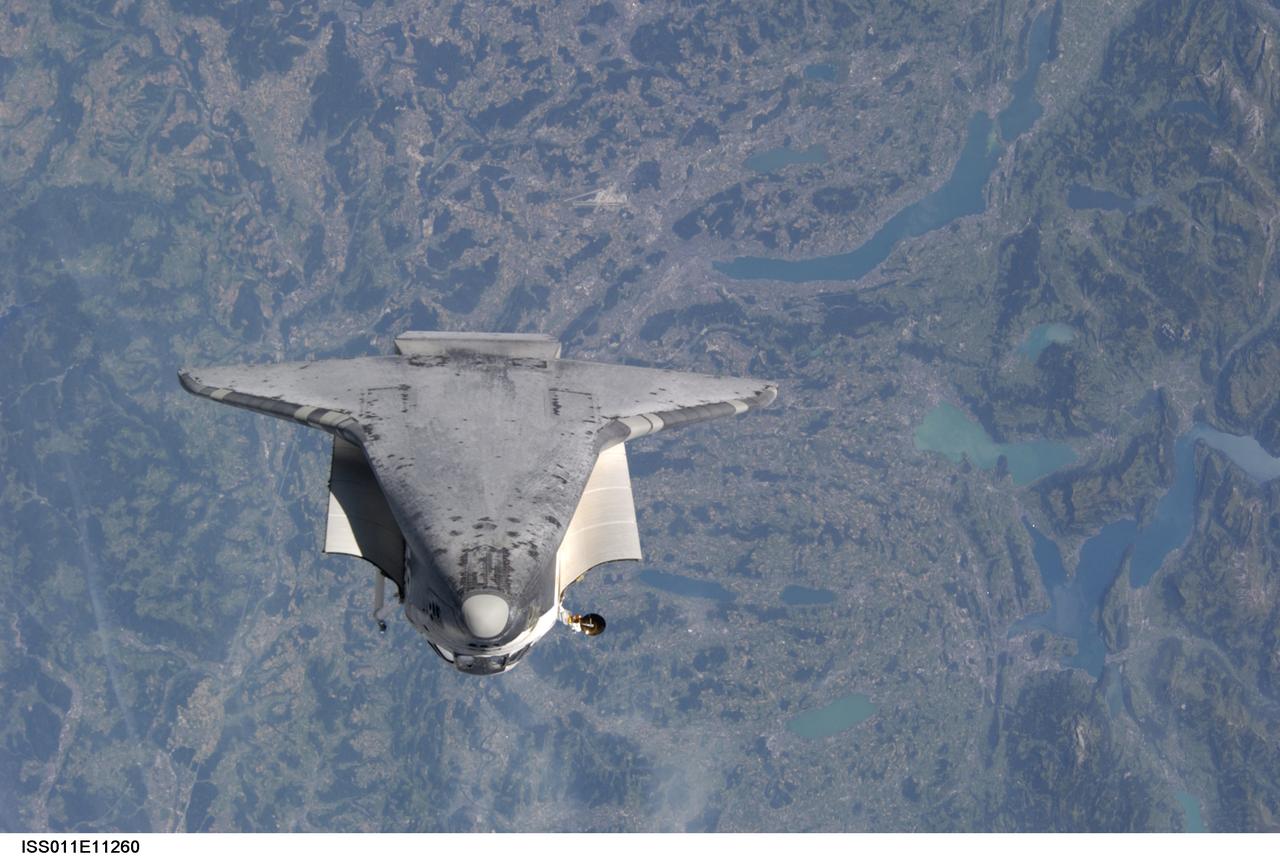

Launched on July 26, 2005, from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-114 was classified as Logistics Flight 1. Among the Station-related activities of the mission were the delivery of new supplies and the replacement of one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 also carried the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. A major focus of the mission was the testing and evaluation of new Space Shuttle flight safety, which included new inspection and repair techniques. Upon its approach to the International Space Station (ISS), the Space Shuttle Discovery underwent a photography session in order to assess any damages that may have occurred during its launch and/or journey through Space. Discovery was over Switzerland, about 600 feet from the ISS, when Cosmonaut Sergei K. Kriklev, Expedition 11 Commander, and John L. Phillips, NASA Space Station officer and flight engineer photographed the under side of the spacecraft as it performed a back flip to allow photography of its heat shield. Astronaut Eileen M. Collins, STS-114 Commander, guided the shuttle through the flip. The photographs were analyzed by engineers on the ground to evaluate the condition of Discovery’s heat shield. The crew safely returned to Earth on August 9, 2005. The mission historically marked the Return to Flight after nearly a two and one half year delay in flight after the Space Shuttle Columbia tragedy in February 2003.
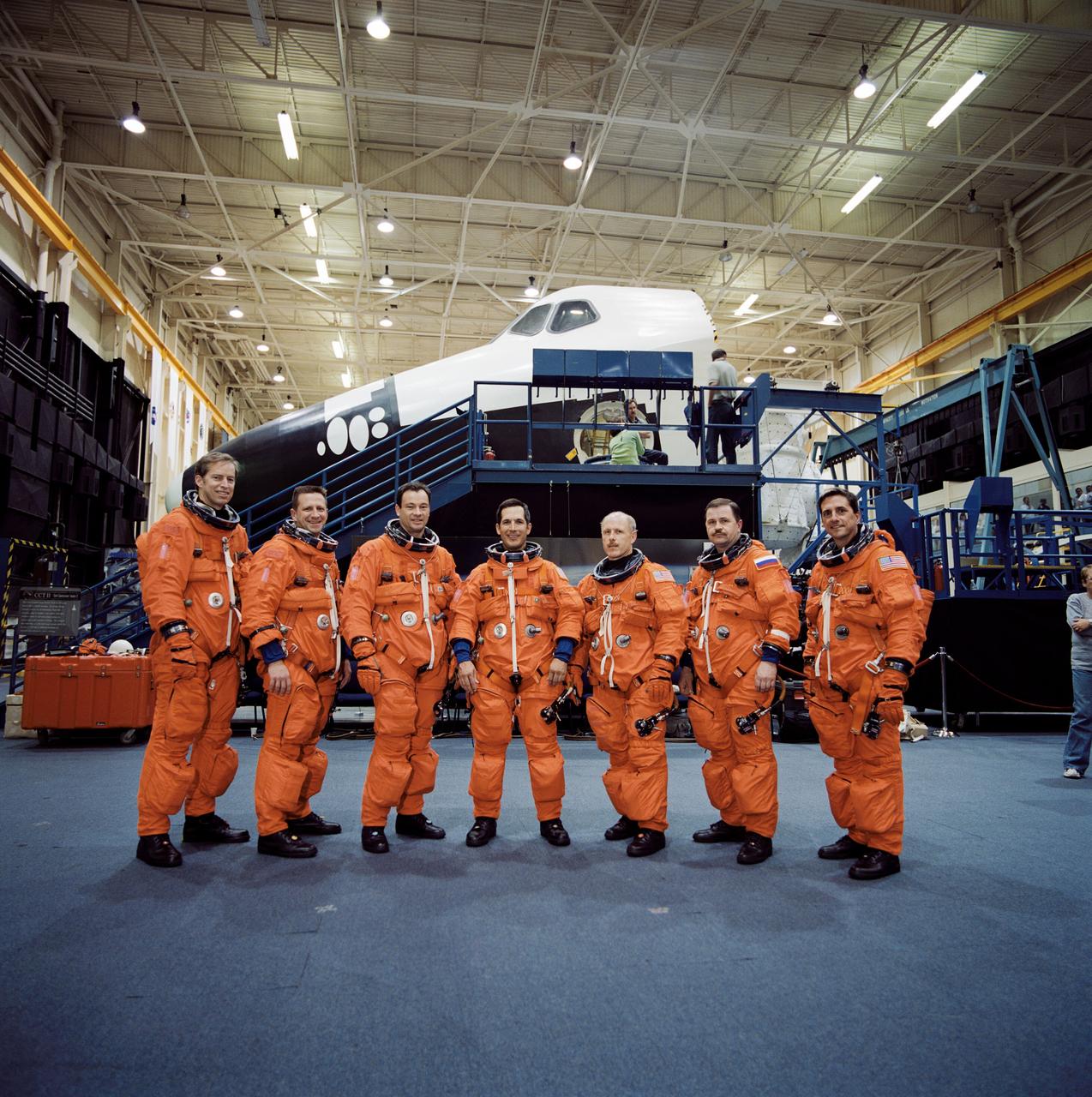

Pictured is the crew for the Shuttle Endeavor STS-113 mission snapped during a training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center. From the left are Astronauts James D. Wetherbee, STS-113 mission commander; Christopher J. (Gus) Loria, pilot; Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and John B. Herrington, mission specialists; Kerneth D. Bowersox, Expedition Six mission commander; Cosmonaut Nikloai M. Budarin and astronaut Donald A. Thomas, Expedition Six Flight Engineers. The 16th American assembly flight and 112th overall American flight to the International Space Station (ISS), STS-113 mission objectives included the delivery of the Expedition Six Crew to the ISS, the return of Expedition Five back to Earth, and the installation and activation of the Port 1 Integrated Truss Assembly (P1). The first major component installed on the left side of the Station, the P1 truss provides an additional three External Thermal Control System radiators. Weighing in at 27,506 pounds, the P1 truss is 45 feet (13.7 meters) long, 15 feet (4.6 meters) wide, and 13 feet (4 meters) high. Three space walks, aided by the use of the Robotic Manipulator Systems of both the Shuttle and the Station, were performed in the installation of P1. Also, more than 2,500 pounds (1,134 kilograms) of cargo were transferred between the Shuttle and Station. The Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavor launched on November 23, 2002 from Kennedy's launch pad 39A and returned 11 days later on December 4, 2002.
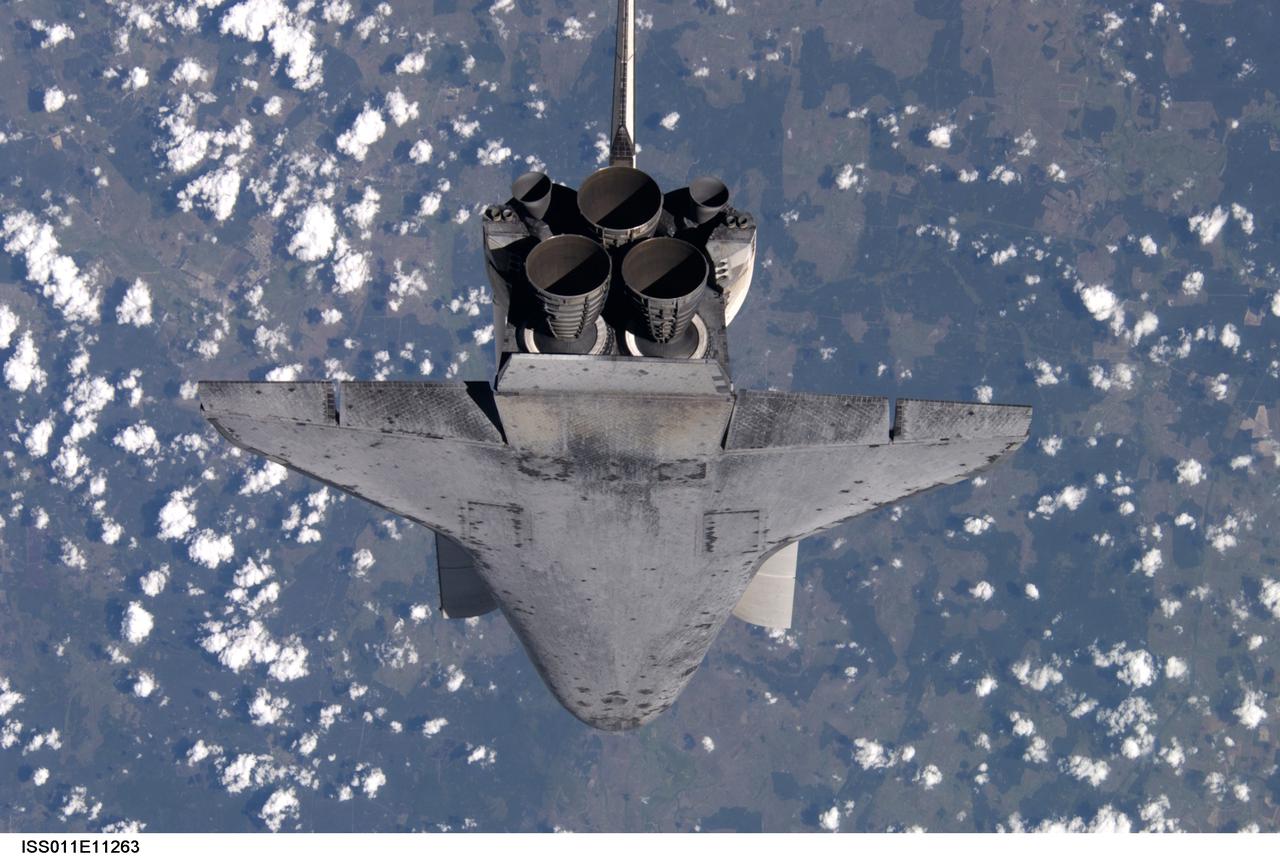

Launched on July 26, 2005 from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-114 was classified as Logistics Flight 1. Among the Station-related activities of the mission were the delivery of new supplies and the replacement of one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 also carried the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. A major focus of the mission was the testing and evaluation of new Space Shuttle flight safety, which included new inspection and repair techniques. Upon its approach to the International Space Station (ISS), the Space Shuttle Discovery underwent a photography session in order to assess any damages that may have occurred during its launch and/or journey through Space. Discovery was over Switzerland, about 600 feet from the ISS, when Cosmonaut Sergei K. Kriklev, Expedition 11 Commander, and John L. Phillips, NASA Space Station officer and flight engineer photographed the under side of the spacecraft as it performed a back flip to allow photography of its heat shield. Astronaut Eileen M. Collins, STS-114 Commander, guided the shuttle through the flip. The photographs were analyzed by engineers on the ground to evaluate the condition of Discovery’s heat shield. The crew safely returned to Earth on August 9, 2005. The mission historically marked the Return to Flight after nearly a two and one half year delay in flight after the Space Shuttle Columbia tragedy in February 2003.
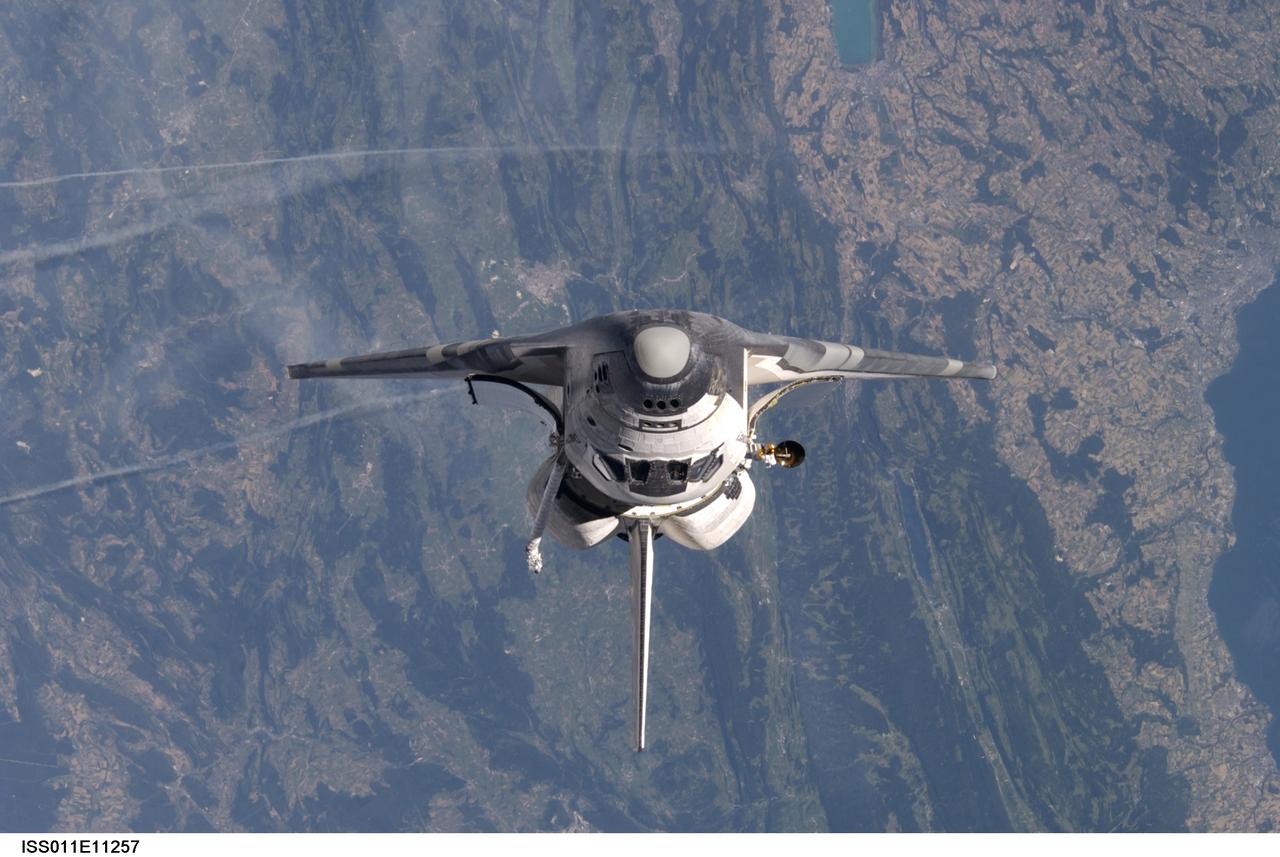

Launched on July 26, 2005 from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-114 was classified as Logistics Flight 1. Among the Station-related activities of the mission were the delivery of new supplies and the replacement of one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 also carried the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. A major focus of the mission was the testing and evaluation of new Space Shuttle flight safety, which included new inspection and repair techniques. Upon its approach to the International Space Station (ISS), the Space Shuttle Discovery underwent a photography session in order to assess any damages that may have occurred during its launch and/or journey through Space. Discovery was over Switzerland, about 600 feet from the ISS, when Cosmonaut Sergei K. Kriklev, Expedition 11 Commander, and John L. Phillips, NASA Space Station officer and flight engineer photographed the spacecraft as it performed a back flip to allow photography of its heat shield. Astronaut Eileen M. Collins, STS-114 Commander, guided the shuttle through the flip. The photographs were analyzed by engineers on the ground to evaluate the condition of Discovery’s heat shield. The crew safely returned to Earth on August 9, 2005. The mission historically marked the Return to Flight after nearly a two and one half year delay in flight after the Space Shuttle Columbia tragedy in February 2003.
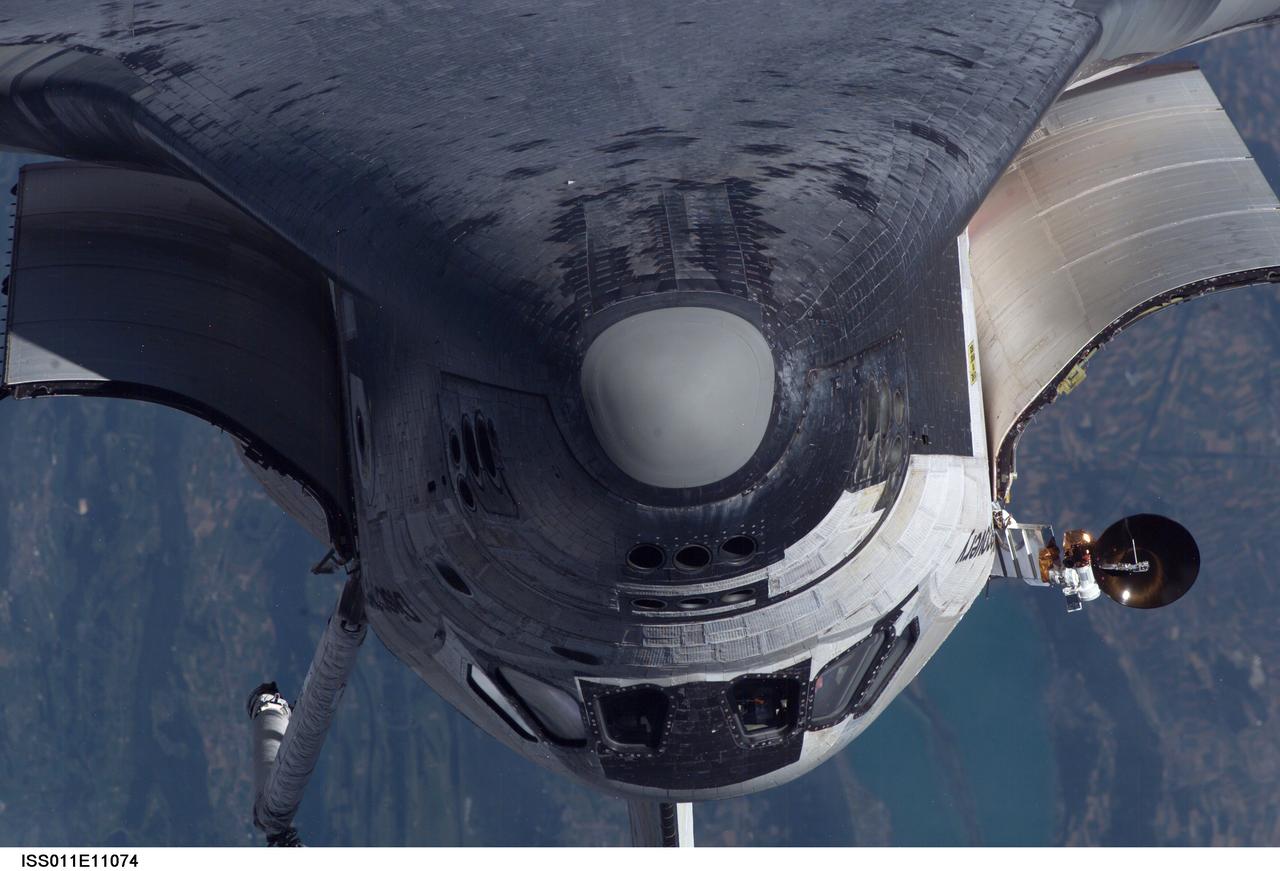

Launched on July 26, 2005 from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-114 was classified as Logistics Flight 1. Among the Station-related activities of the mission were the delivery of new supplies and the replacement of one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 also carried the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. A major focus of the mission was the testing and evaluation of new Space Shuttle flight safety, which included new inspection and repair techniques. Upon its approach to the International Space Station (ISS), the Space Shuttle Discovery underwent a photography session in order to assess any damages that may have occurred during its launch and/or journey through Space. Discovery was over Switzerland, about 600 feet from the ISS, when Cosmonaut Sergei K. Kriklev, Expedition 11 Commander, and John L. Phillips, NASA Space Station officer and flight engineer photographed the spacecraft as it performed a back flip to allow photography of its heat shield. Astronaut Eileen M. Collins, STS-114 Commander, guided the shuttle through the flip. The photographs were analyzed by engineers on the ground to evaluate the condition of Discovery’s heat shield. The crew safely returned to Earth on August 9, 2005. The mission historically marked the Return to Flight after nearly a two and one half year delay in flight after the Space Shuttle Columbia tragedy in February 2003.
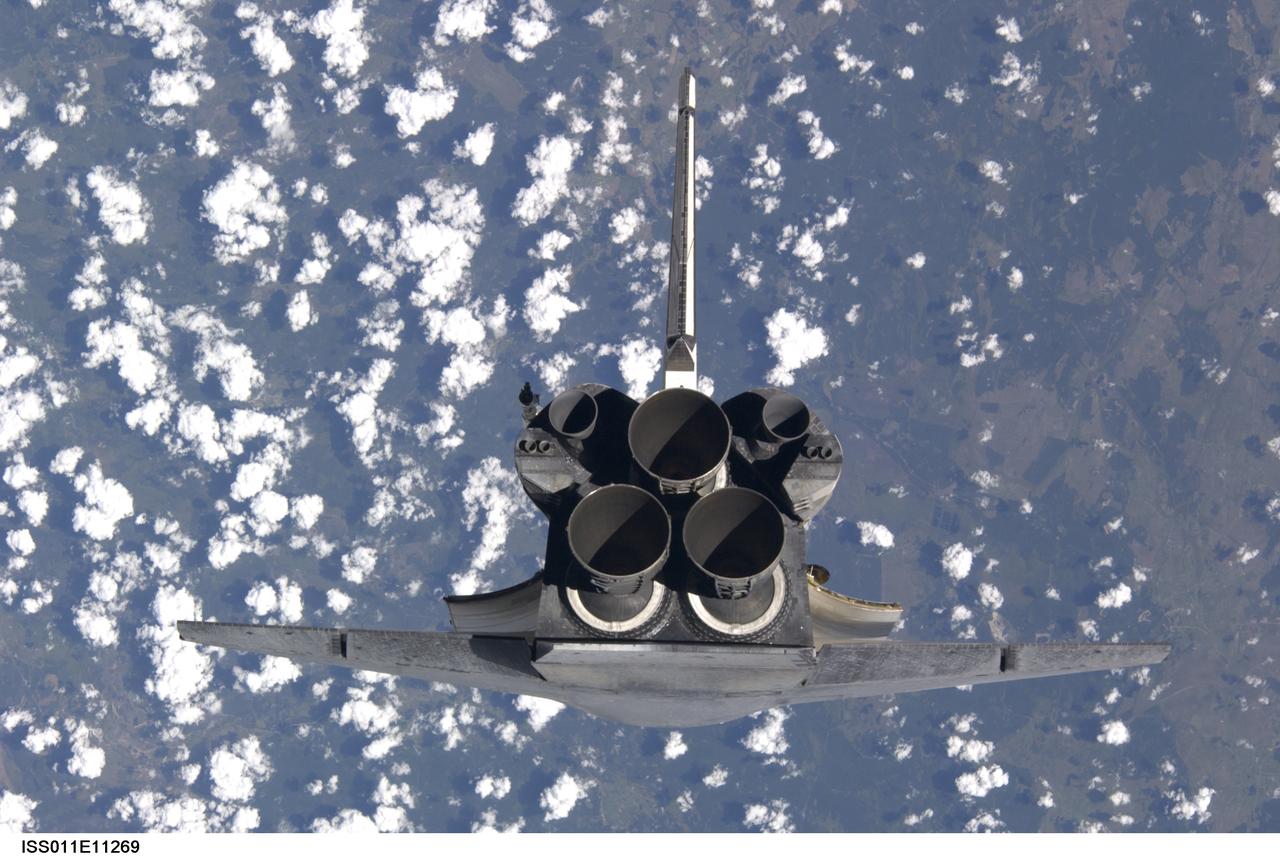

Launched on July 26, 2005 from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-114 was classified as Logistics Flight 1. Among the Station-related activities of the mission were the delivery of new supplies and the replacement of one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 also carried the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. A major focus of the mission was the testing and evaluation of new Space Shuttle flight safety, which included new inspection and repair techniques. Upon its approach to the International Space Station (ISS), the Space Shuttle Discovery underwent a photography session in order to assess any damages that may have occurred during its launch and/or journey through Space. Discovery was over Switzerland, about 600 feet from the ISS, when Cosmonaut Sergei K. Kriklev, Expedition 11 Commander, and John L. Phillips, NASA Space Station officer and flight engineer photographed the spacecraft as it performed a back flip to allow photography of its heat shield. Astronaut Eileen M. Collins, STS-114 Commander, guided the shuttle through the flip. The photographs were analyzed by engineers on the ground to evaluate the condition of Discovery’s heat shield. The crew safely returned to Earth on August 9, 2005. The mission historically marked the Return to Flight after nearly a two and one half year delay in flight after the Space Shuttle Columbia tragedy in February 2003.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Looking from the Press Site across the Turn Basin at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, the American flag is at half-mast in remembrance of Pope John Paul II. In the background is Space Shuttle Discovery in a more uplifting moment as she marks a major milestone for Return to Flight, rolling out to Launch Pad 39B. First motion out of the Vehicle Assembly Building was at 2:04 p.m. EDT. The Shuttle sits atop the Mobile Launcher Platform, which is moved by the Crawler-Transporter underneath. The Crawler is 20 feet high, 131 feet long and 114 feet wide. It moves on eight tracks, each containing 57 shoes, or cleats, weighing one ton each. Loaded with the Space Shuttle, the Crawler can move at a maximum speed of approximately 1 mile an hour. A leveling system in the Crawler keeps the Shuttle vertical while negotiating the 5 percent grade leading to the top of the launch pad. Launch of Discovery on its Return to Flight mission, STS-114, is targeted for May 15 with a launch window that extends to June 3. During its 12-day mission, Discovery’s seven-person crew will test new hardware and techniques to improve Shuttle safety, as well as deliver supplies to the International Space Station. Discovery was moved on March 29 from the Orbiter Processing Facility to the VAB and attached to its propulsion elements, a redesigned ET and twin SRBs.

The M2-F3 Lifting Body is seen here on the lakebed next to the NASA Flight Research Center (later the Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California. Redesigned and rebuilt from the M2-F2, the M2-F3 featured as its most visible change a center fin for greater stability. While the M2-F3 was still demanding to fly, the center fin eliminated the high risk of pilot induced oscillation (PIO) that was characteristic of the M2-F2.
This pair of images of the Long Island, New York region is a comparison of an optical photograph (top) and a radar image (bottom), both taken in darkness in April 1994. The photograph at the top was taken by the Endeavour astronauts at about 3 a.m. Eastern time on April 20, 1994. The image at the bottom was acquired at about the same time four days earlier on April 16,1994 by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) system aboard the space shuttle Endeavour. Both images show an area approximately 100 kilometers by 40 kilometers (62 miles by 25 miles) that is centered at 40.7 degrees North latitude and 73.5 degrees West longitude. North is toward the upper right. The optical image is dominated by city lights, which are particularly bright in the densely developed urban areas of New York City located on the left half of the photo. The brightest white zones appear on the island of Manhattan in the left center, and Central Park can be seen as a darker area in the middle of Manhattan. To the northeast (right) of the city, suburban Long Island appears as a less densely illuminated area, with the brightest zones occurring along major transportation and development corridors. Since radar is an active sensing system that provides its own illumination, the radar image shows a great amount of surface detail, despite the night-time acquisition. The colors in the radar image were obtained using the following radar channels: red represents the L-band (horizontally transmitted and received); green represents the L-band (horizontally transmitted and vertically received); blue represents the C-band (horizontally transmitted and vertically received). In this image, the water surface - the Atlantic Ocean along the bottom edge and Long Island Sound shown at the top edge - appears red because small waves at the surface strongly reflect the horizontally transmitted and received L-band radar signal. Networks of highways and railroad lines are clearly visible in the radar image; many of them can also be seen as bright lines i the optical image. The runways of John F. Kennedy International Airport appear as a dark rectangle in Jamaica Bay on the left side of the image. Developed areas appear generally as bright green and orange, while agricultural, protected and undeveloped areas appear darker blue or purple. This contrast can be seen on the barrier islands along the south coast of Long Island, which are heavily developed in the Rockaway and Long Beach areas south and east of Jamaica Bay, but further to the east, the islands are protected and undeveloped. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01785

At first glance a dry lake bed in the southern California desert seems like the last place to prepare to study ice. But on Oct. 2, 2014, NASA’s Operation IceBridge carried out a ground-based GPS survey of the El Mirage lake bed in California’s Mojave Desert. Members of the IceBridge team are currently at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center, preparing instruments aboard the DC-8 research aircraft for flights over Antarctica. Part of this preparation involves test flights over the desert, where researchers verify their instruments are working properly. El Mirage serves as a prime location for testing the mission’s laser altimeter, the Airborne Topographic Mapper, because the lake bed has a flat surface and reflects light similarly to snow and ice. This photo, taken shortly after the survey, shows the GPS-equipped survey vehicle and a stationary GPS station (left of the vehicle) on the lake bed with the constellation Ursa Major in the background. By driving the vehicle in parallel back and forth lines over a predefined area and comparing those GPS elevation readings with measurements from the stationary GPS, researchers are able to build an elevation map that will be used to precisely calibrate the laser altimeter for ice measurements. Credit: NASA/John Sonntag Operation IceBridge is scheduled to begin research flights over Antarctica on Oct. 15, 2014. The mission will be based out of Punta Arenas, Chile, until Nov. 23. For more information about IceBridge, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/icebridge" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/icebridge</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA image acquired: June 03, 2012 This scene is to the northwest of the recently named crater Magritte, in Mercury's south. The image is not map projected; the larger crater actually sits to the north of the two smaller ones. The shadowing helps define the striking "Mickey Mouse" resemblance, created by the accumulation of craters over Mercury's long geologic history. This image was acquired as part of MDIS's high-incidence-angle base map. The high-incidence-angle base map is a major mapping activity in MESSENGER's extended mission and complements the surface morphology base map of MESSENGER's primary mission that was acquired under generally more moderate incidence angles. High incidence angles, achieved when the Sun is near the horizon, result in long shadows that accentuate the small-scale topography of geologic features. The high-incidence-angle base map is being acquired with an average resolution of 200 meters/pixel. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. Visit the Why Mercury? section of this website to learn more about the key science questions that the MESSENGER mission is addressing. During the one-year primary mission, MESSENGER acquired 88,746 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER is now in a yearlong extended mission, during which plans call for the acquisition of more than 80,000 additional images to support MESSENGER's science goals. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>