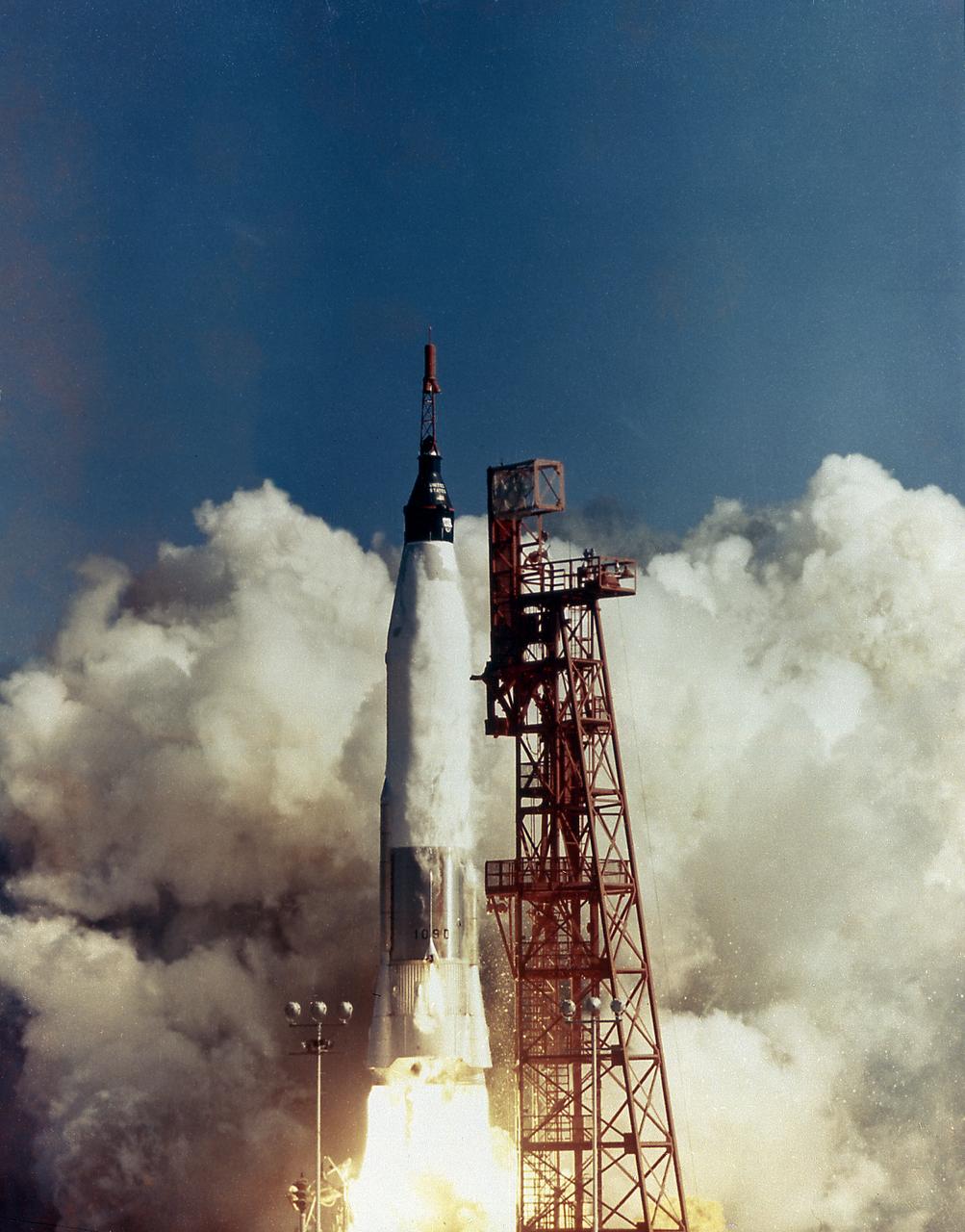

The launch of the MA-6, Friendship 7, on February 20, 1962. Boosted by the Mercury-Atlas vehicle, a modified Atlas Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM), Friendship 7 was the first U.S. marned orbital flight and carried Astronaut John H. Glenn into orbit. Astronaut Glenn became the first American to orbit the Earth.
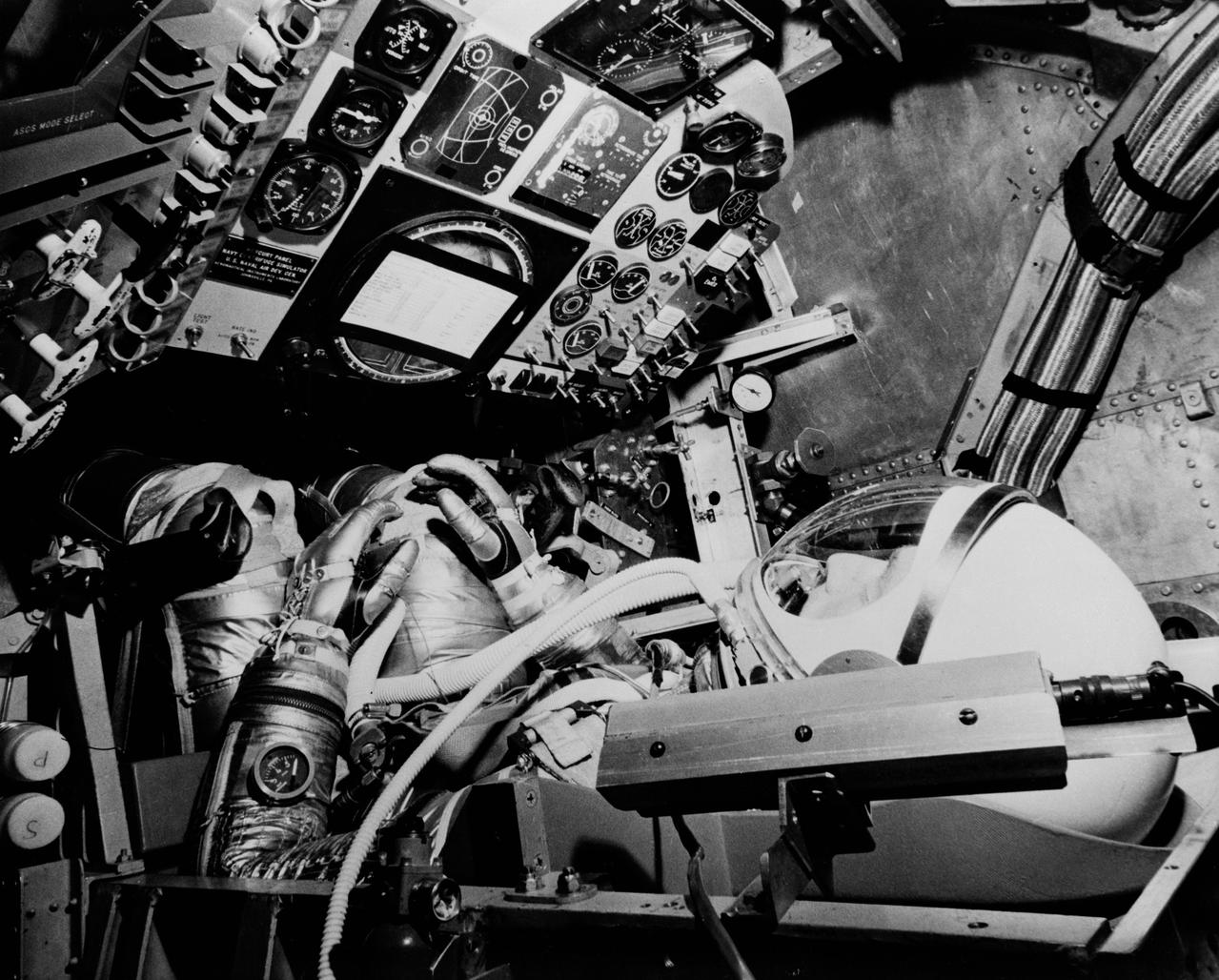
S61-03506 (1961) --- Project Mercury astronaut M. Scott Carpenter, prime pilot for the United States second manned orbital flight, undergoes a simulated mission in the procedures trainer at Langley Air Force Base, Virginia, headquarters for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration?s Manned Spacecraft Center. Photo credit: NASA
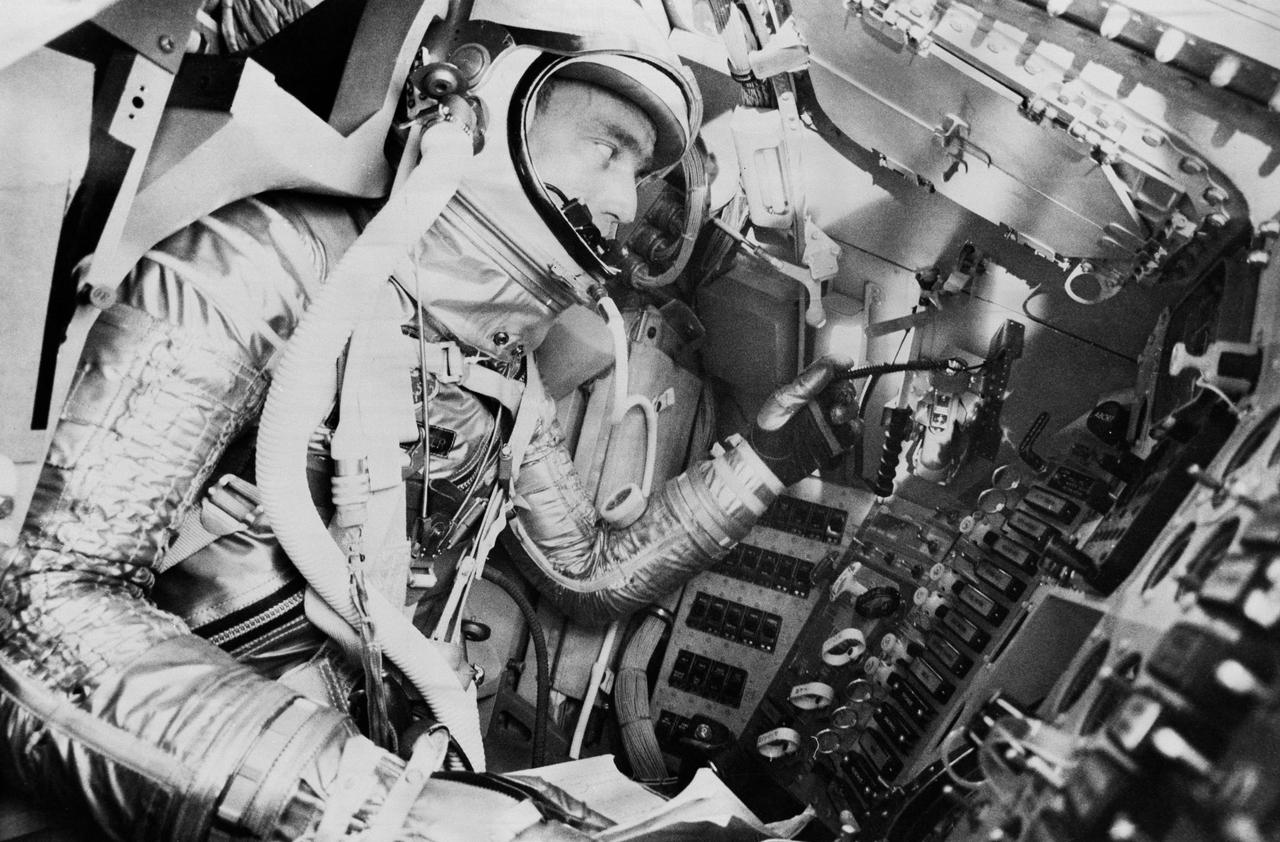

S62-01033 (1961) --- Project Mercury astronaut M. Scott Carpenter, prime pilot for the United States second manned orbital flight, undergoes a simulated mission in the procedures trainer at Langley Air Force Base, Virginia, headquarters for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration?s Manned Spacecraft Center. Photo credit: NASA
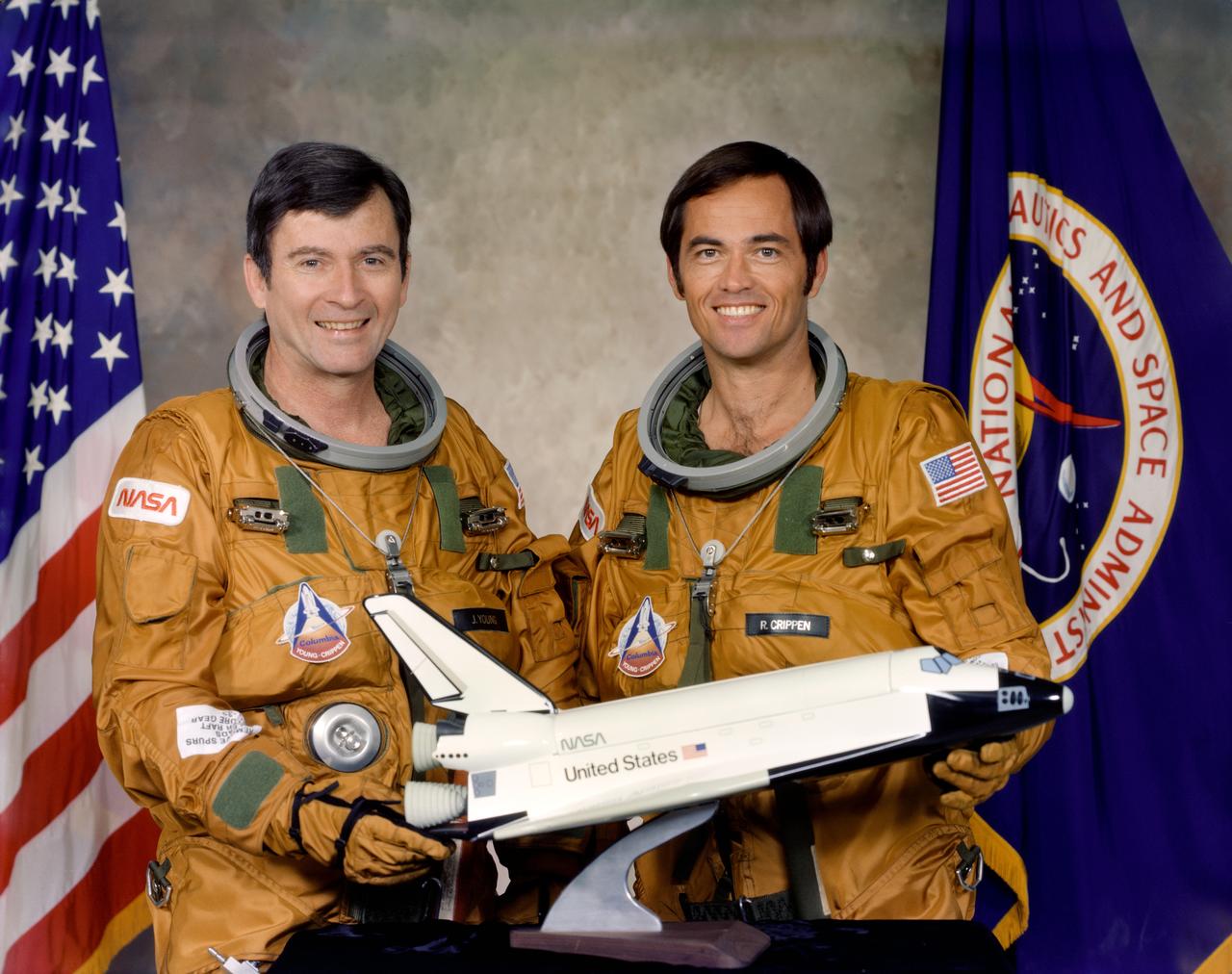

S79-31775 (29 April 1979) --- These two astronauts are the prime crewmen for the first flight in the Space Transportation System (STS-1) program. Astronauts John W. Young, left, commander, and Robert L. Crippen, pilot, will man the space shuttle orbiter 102 Columbia for the first orbital flight test. Photo credit: NASA
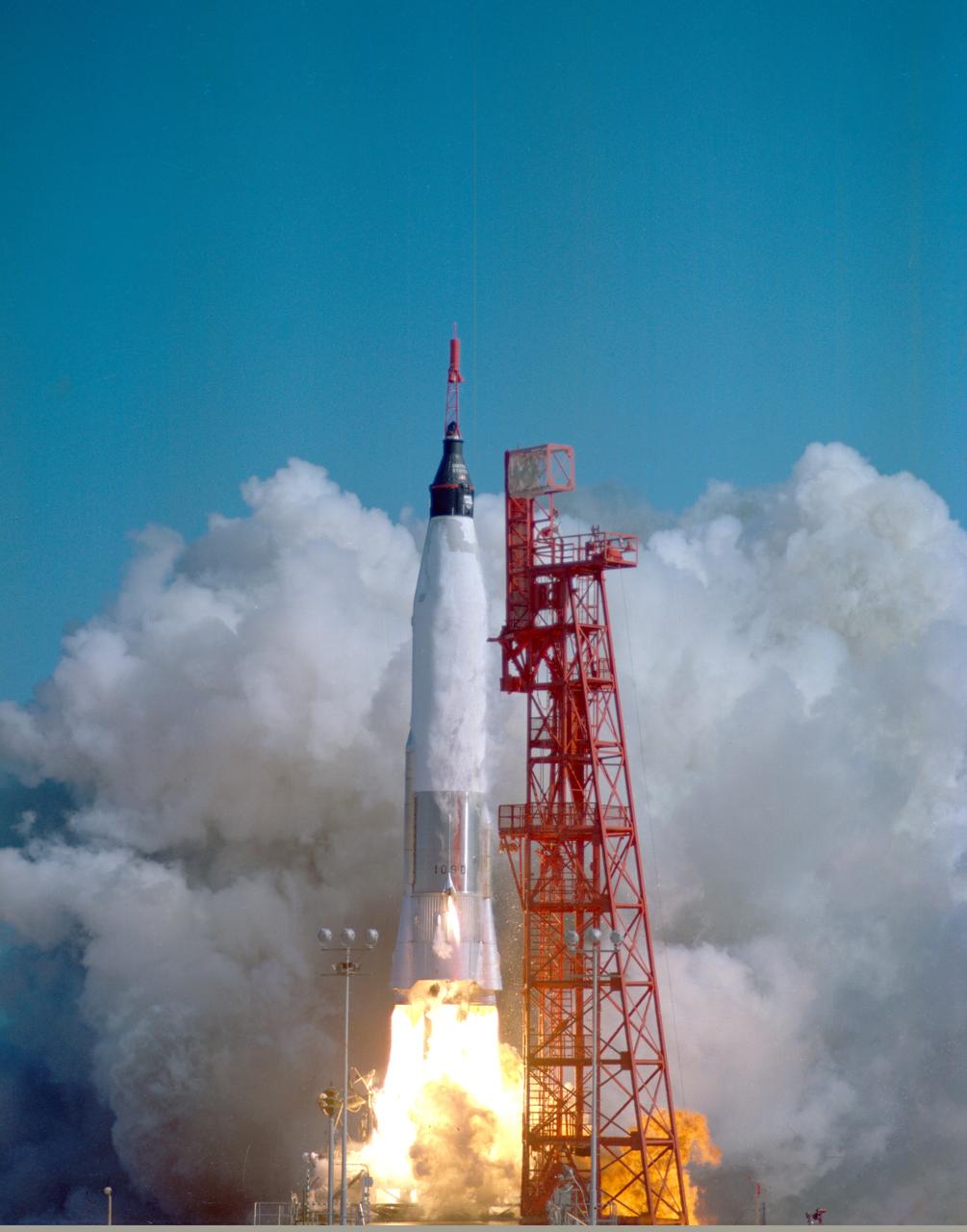

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Launch of Friendship 7, the first manned orbital space flight. Astronaut John Glenn aboard, the Mercury-Atlas rocket is launched from Pad 14. Photo credit: NASA
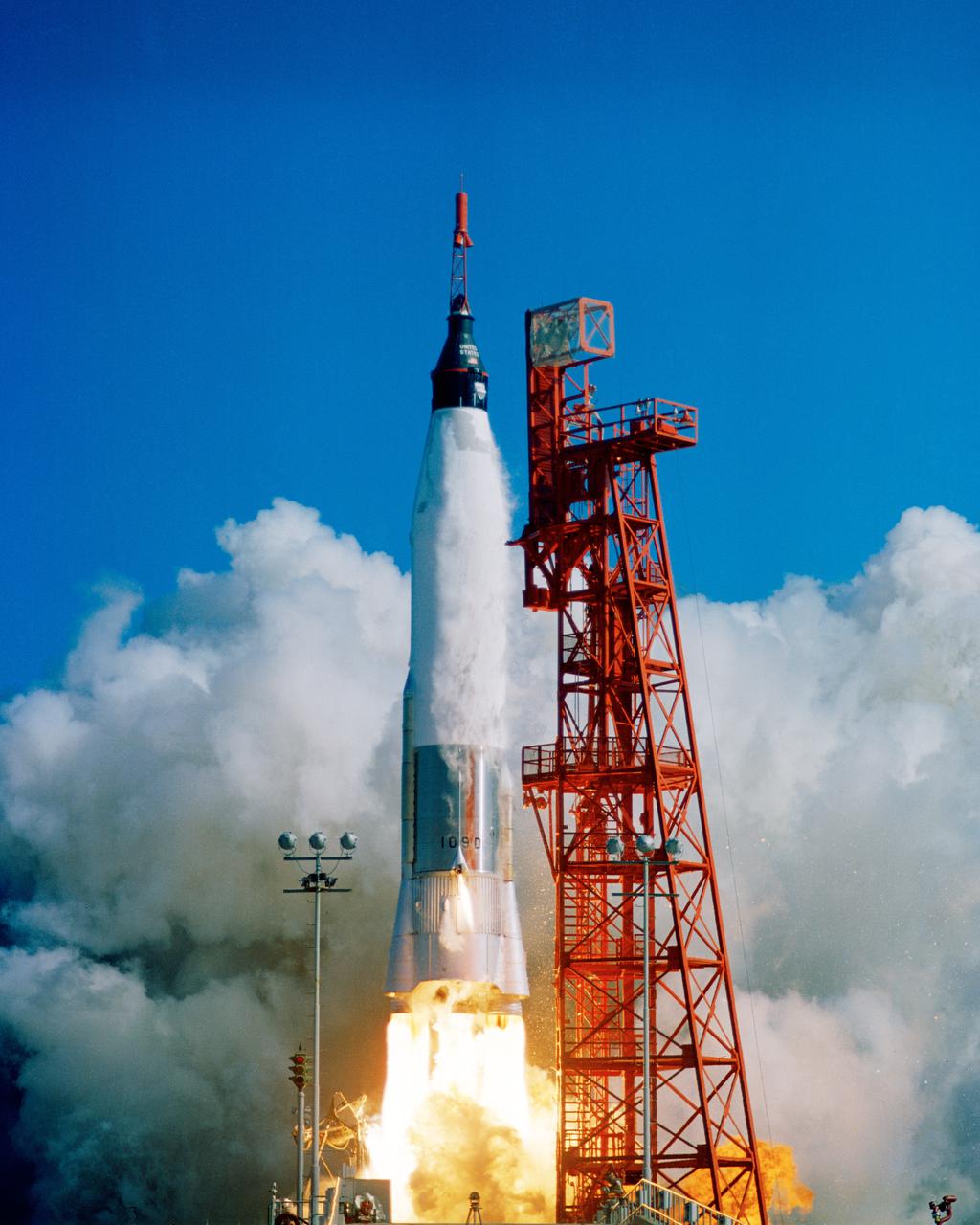

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Launch of Friendship 7, the first manned orbital space flight. Astronaut John Glenn aboard, the Mercury-Atlas rocket is launched from Pad 14. Photo credit: NASA
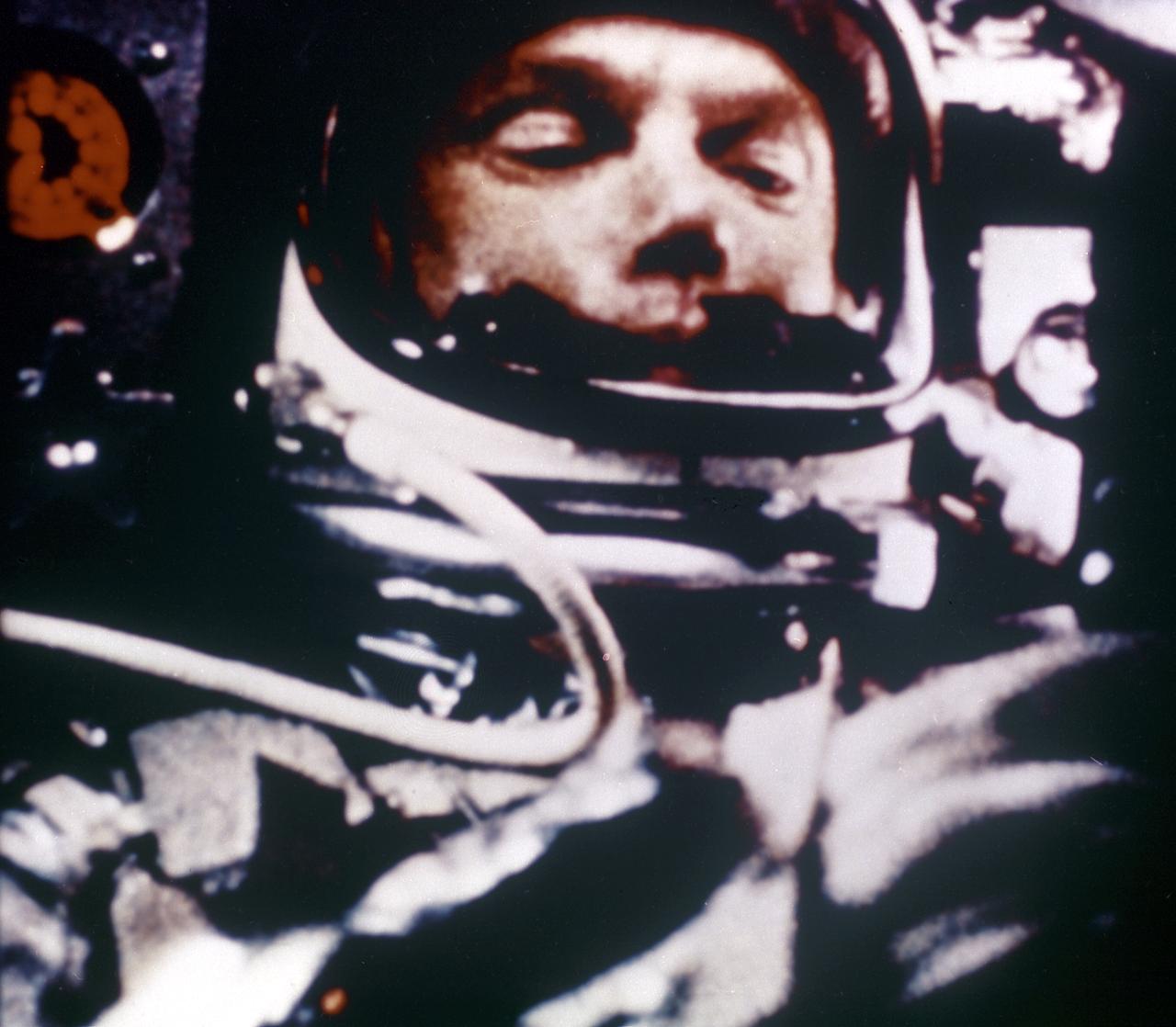

Astronaut John Glenn in the Friendship 7 capsule during the first manned orbital flight, the MA-6 mission. Boosted by the Mercury-Atlas vehicle, a modified Atlas (intercontinental ballistic missile), the MA-6 mission lasted for 5 hours and orbited the Earth three times.
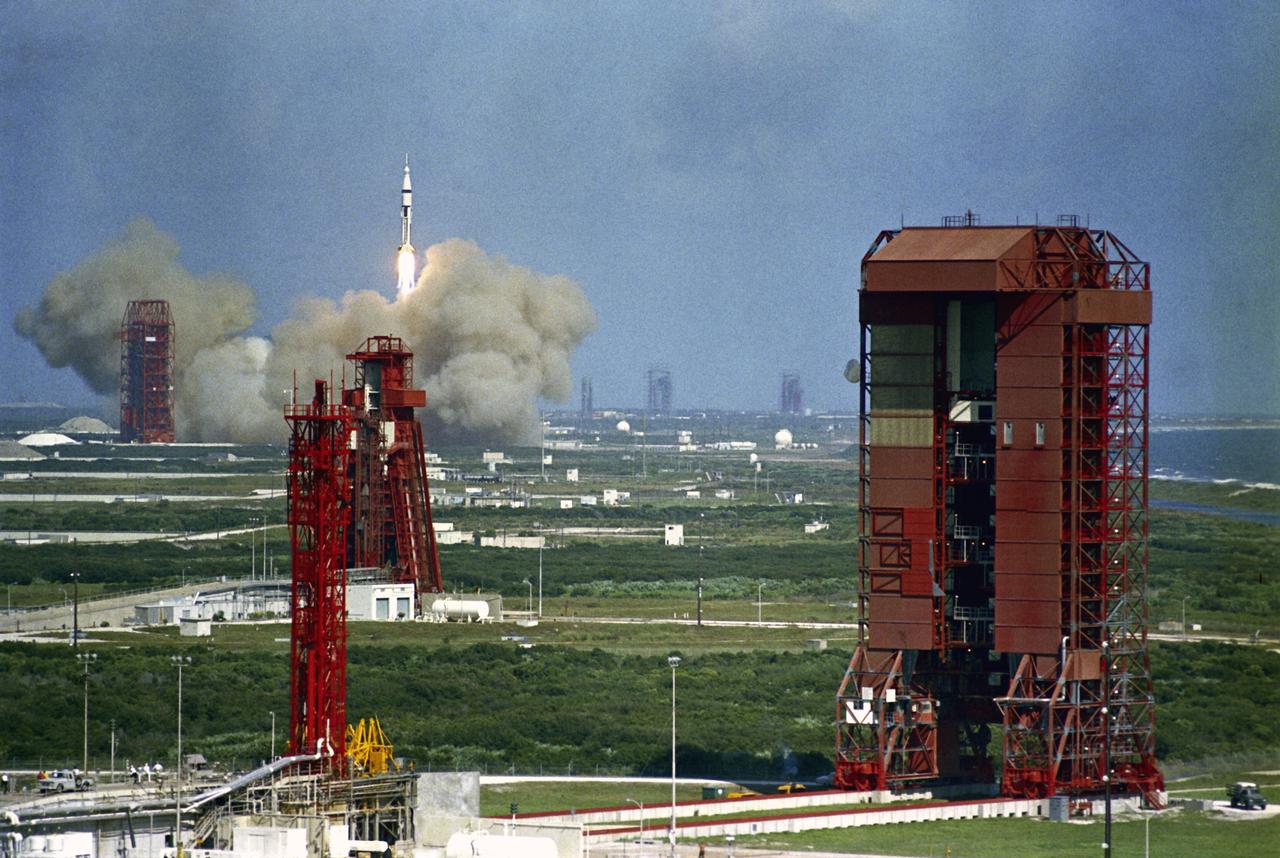

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Apollo 7 spacecraft, atop a Saturn IB rocket, lifts off from Complex 34, Cape Kennedy, at 11:03 a.m. EDT. The spacecraft achieved orbit to begin an 11-day mission. The flight is intended to qualify Apollo for a manned flight to the moon. Photo credit: NASA
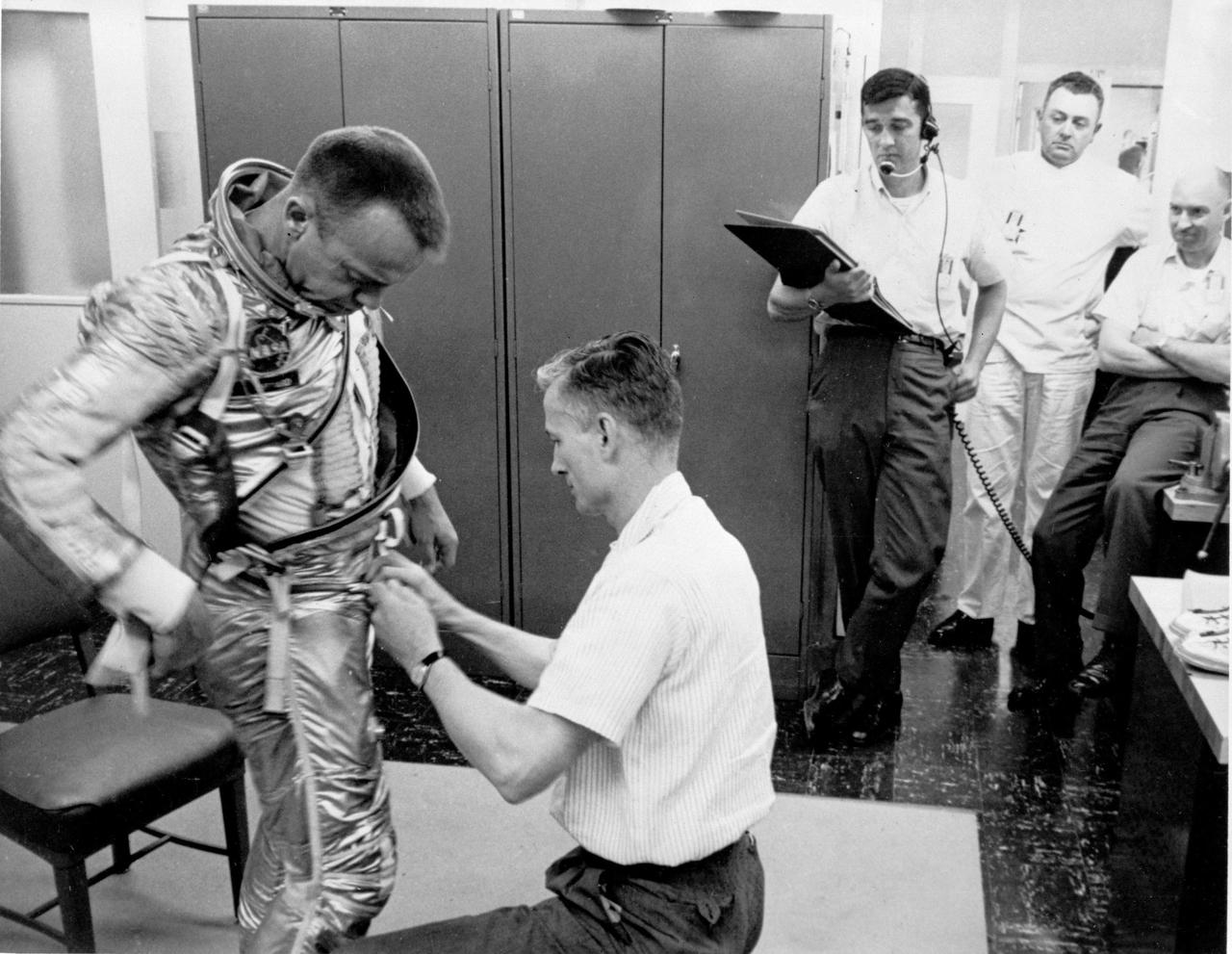

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Astronaut Alan B. Shepard is being assisted by a technician in getting into his space suit at 2:45 a.m. this morning, beginning the long countdown of the scheduled launch of the Mercury Redstone. After Astronaut Shepard is suited up, he will travel by van to the Redstone Gantry on Pad 5 and be placed into the Mercury Capsule, called Freedom 7, on top of the Redstone booster rocket. Astronaut Shepard will pilot the first U.S. manned sub-orbital space flight of the Manned Mercury Program.
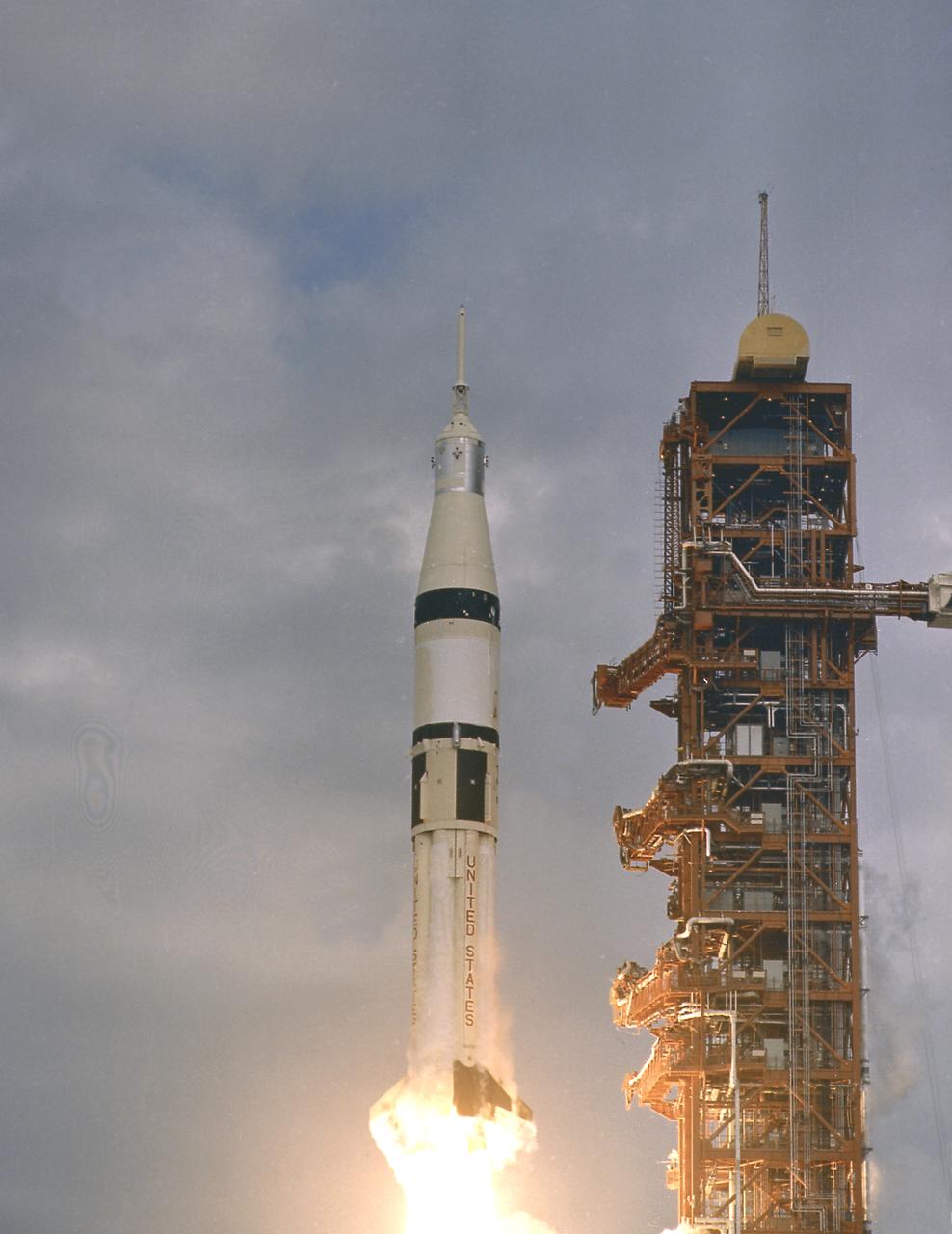
SA-206 lifts off from Kennedy Space Center's launch complex 39B, in Florida, on May 25, 1973, for the first manned Skylab mission (SL-2) with astronauts Pete Conrad, Joseph Kerwin, and Paul Weitz. The Saturn IB, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), launched five manned Earth-orbital missions between 1968 and 1975: Apollo 7, Skylab 2, Skylab 3, Skylab 4, and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP).
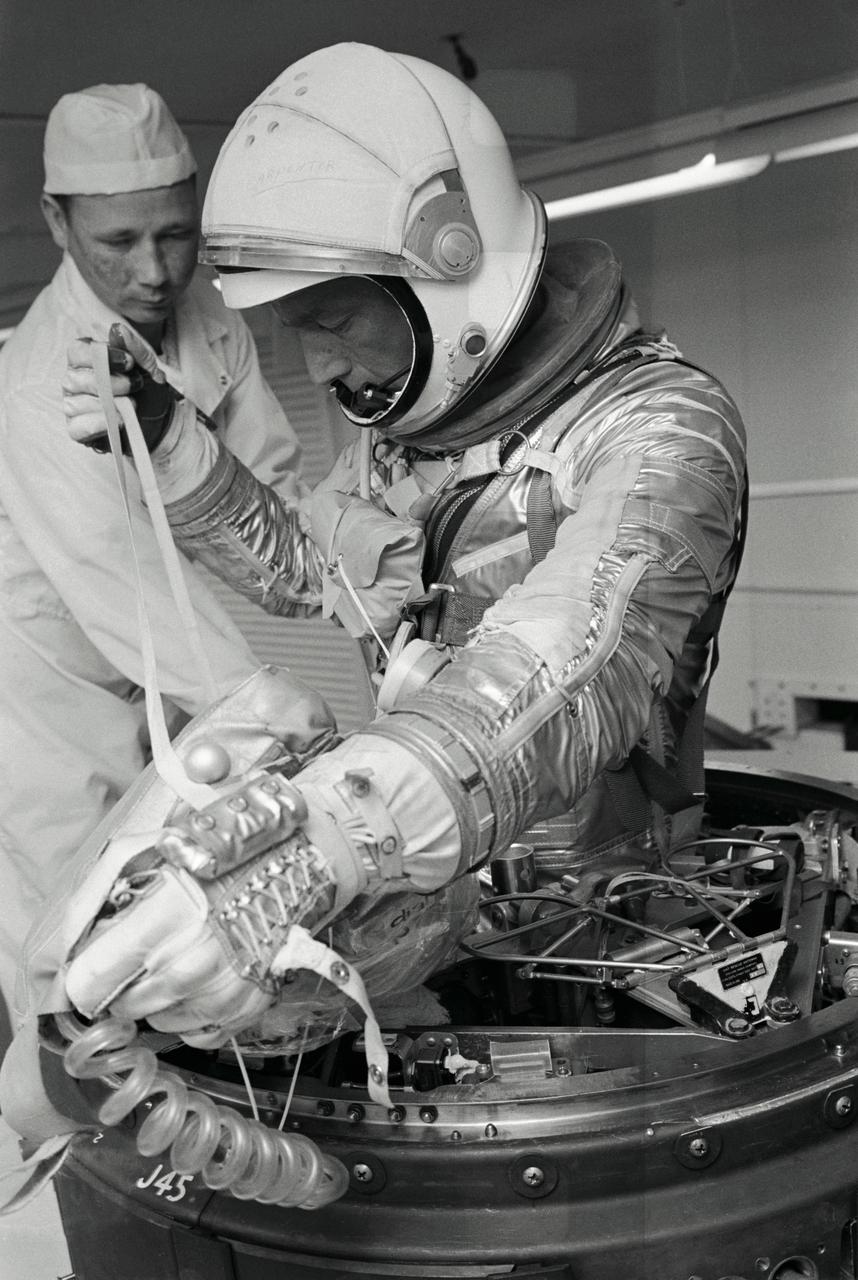

S62-01383 (1962) --- Project Mercury astronaut M. Scott Carpenter, prime pilot of the Mercury-Atlas 7 (the nation's second manned orbital flight), completes top egress training in the white room at Cape Canaveral, Florida. The line he is holding is known as the "man line" which attaches the survival kit to the astronaut. The bag is the survival kit he carries for contingency landings. Clearly visible around his neck is the bag containing the life vest. Photo credit: NASA
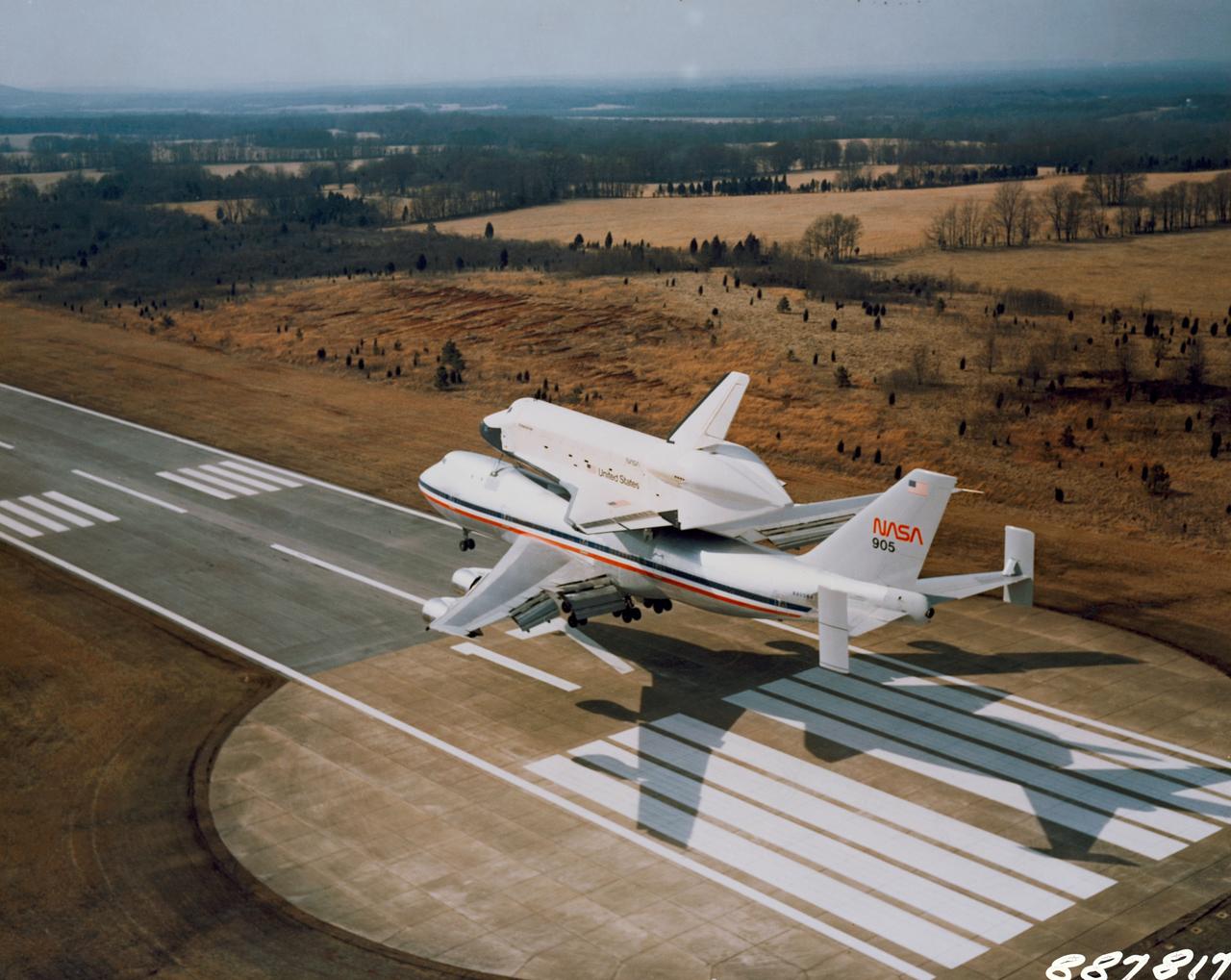

S78-27238 (13 March 1978) --- The space shuttle orbiter 101 Enterprise approaches riding atop its 747 carrier aircraft, arrives at the Redstone Arsenal airstrip near Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), Huntsville, Alabama, on March 13, 1978. It is to undergo ground vibration tests along with the external tank and solid rocket boosters, in preparation for Orbiter Flight Tests (OFT) in which its successor craft (Orbiter 102) will take several two-man crews into Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA

S69-19792 (February 1969) --- Composite of six artist's concepts illustrating key events, tasks and activities on the first day of the Apollo 9 mission, including flight crew preparation, orbital insertion, 103 nautical mile orbit, separation, docking, and docked Service Propulsion System burn. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.
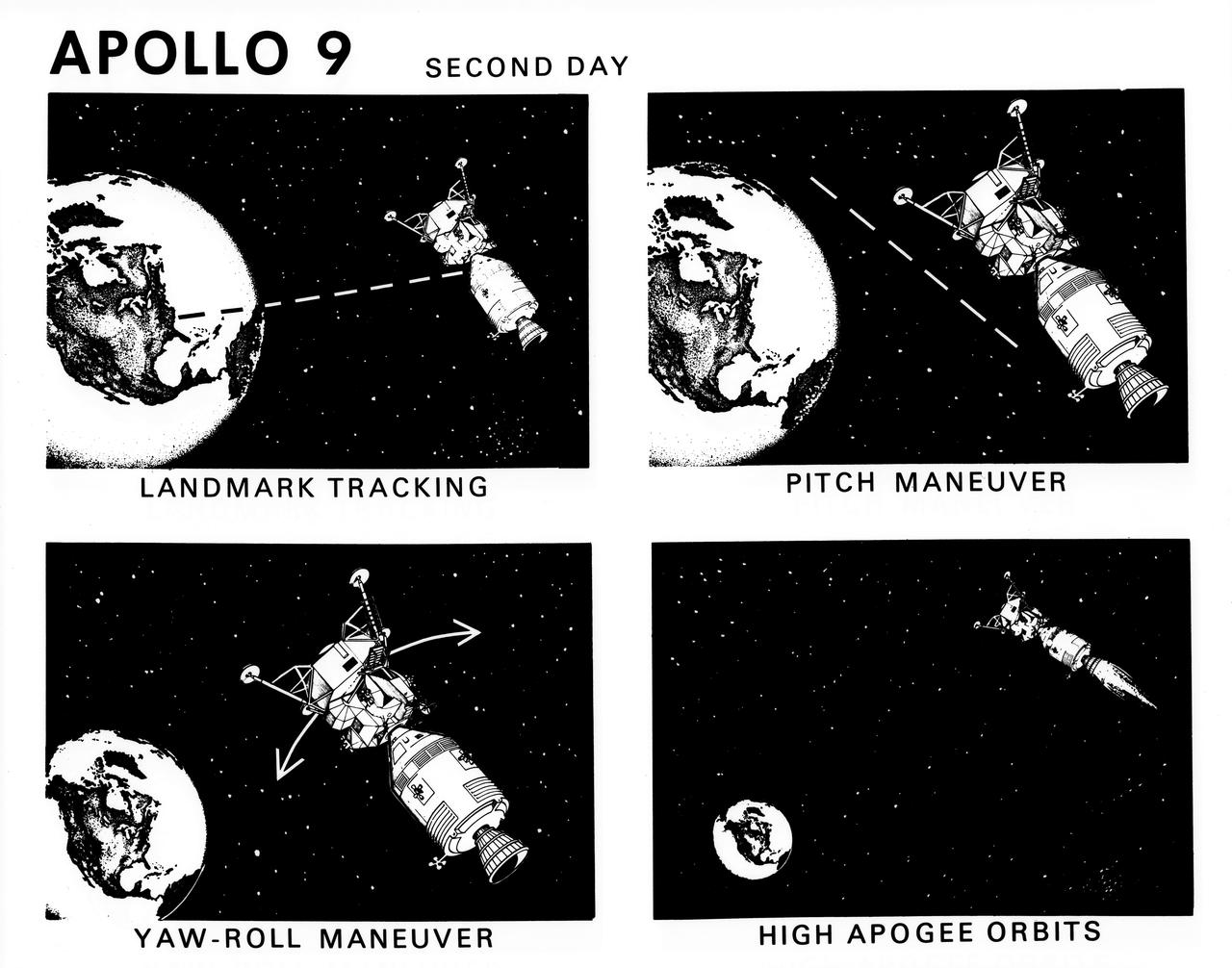
S69-19793 (February 1969) --- Composite of six artist's concepts illustrating key events, tasks and activities on the first day of the Apollo 9 mission, including flight crew preparation, orbital insertion, 103 nautical mile orbit, separation, docking, and docked Service Propulsion System burn. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.

This montage depicts the flight crew patches for the manned Apollo 7 thru Apollo 17 missions. The Apollo 7 through 10 missions were basically manned test flights that paved the way for lunar landing missions. Primary objectives met included the demonstration of the Command Service Module (CSM) crew performance; crew/space vehicle/mission support facilities performance and testing during a manned CSM mission; CSM rendezvous capability; translunar injection demonstration; the first manned Apollo docking, the first Apollo Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA), performance of the first manned flight of the lunar module (LM); the CSM-LM docking in translunar trajectory, LM undocking in lunar orbit, LM staging in lunar orbit, and manned LM-CSM docking in lunar orbit. Apollo 11 through 17 were lunar landing missions with the exception of Apollo 13 which was forced to circle the moon without landing due to an onboard explosion. The craft was,however, able to return to Earth safely. Apollo 11 was the first manned lunar landing mission and performed the first lunar surface EVA. Landing site was the Sea of Tranquility. A message for mankind was delivered, the U.S. flag was planted, experiments were set up and 47 pounds of lunar surface material was collected for analysis back on Earth. Apollo 12, the 2nd manned lunar landing mission landed in the Ocean of Storms and retrieved parts of the unmanned Surveyor 3, which had landed on the Moon in April 1967. The Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) was deployed, and 75 pounds of lunar material was gathered. Apollo 14, the 3rd lunar landing mission landed in Fra Mauro. ALSEP and other instruments were deployed, and 94 pounds of lunar materials were gathered, using a hand cart for first time to transport rocks. Apollo 15, the 4th lunar landing mission landed in the Hadley-Apennine region. With the first use of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), the crew was bale to gather 169 pounds of lunar material. Apollo 16, the 5th lunar landing mission, landed in the Descartes Highlands for the first study of highlands area. Selected surface experiments were deployed, the ultraviolet camera/spectrograph was used for first time on the Moon, and the LRV was used for second time for a collection of 213 pounds of lunar material. The Apollo program came to a close with Apollo 17, the 6th and final manned lunar landing mission that landed in the Taurus-Littrow highlands and valley area. This mission hosted the first scientist-astronaut, Schmitt, to land on the Moon. The 6th automated research station was set up, and 243 ponds of lunar material was gathered using the LRV.

Astronaut John Glenn Jr. is honored by President John F. Kennedy after Glenn's historical first manned orbital flight, Mercury-Atlas 6. The ceremony was held in front of Hangar S at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. To Glenn's left are his wife, Annie, daughter, Lyn, and his son, David.

S62-01004 (1962) --- Astronaut John H. Glenn Jr., pilot of the Mercury Atlas 6 (MA-6) mission, participates in Mercury egress training during MA-6 preflight preparations. Glenn made the free world's first manned Earth-orbital flight on Feb. 20, 1962. Photo credit: NASA
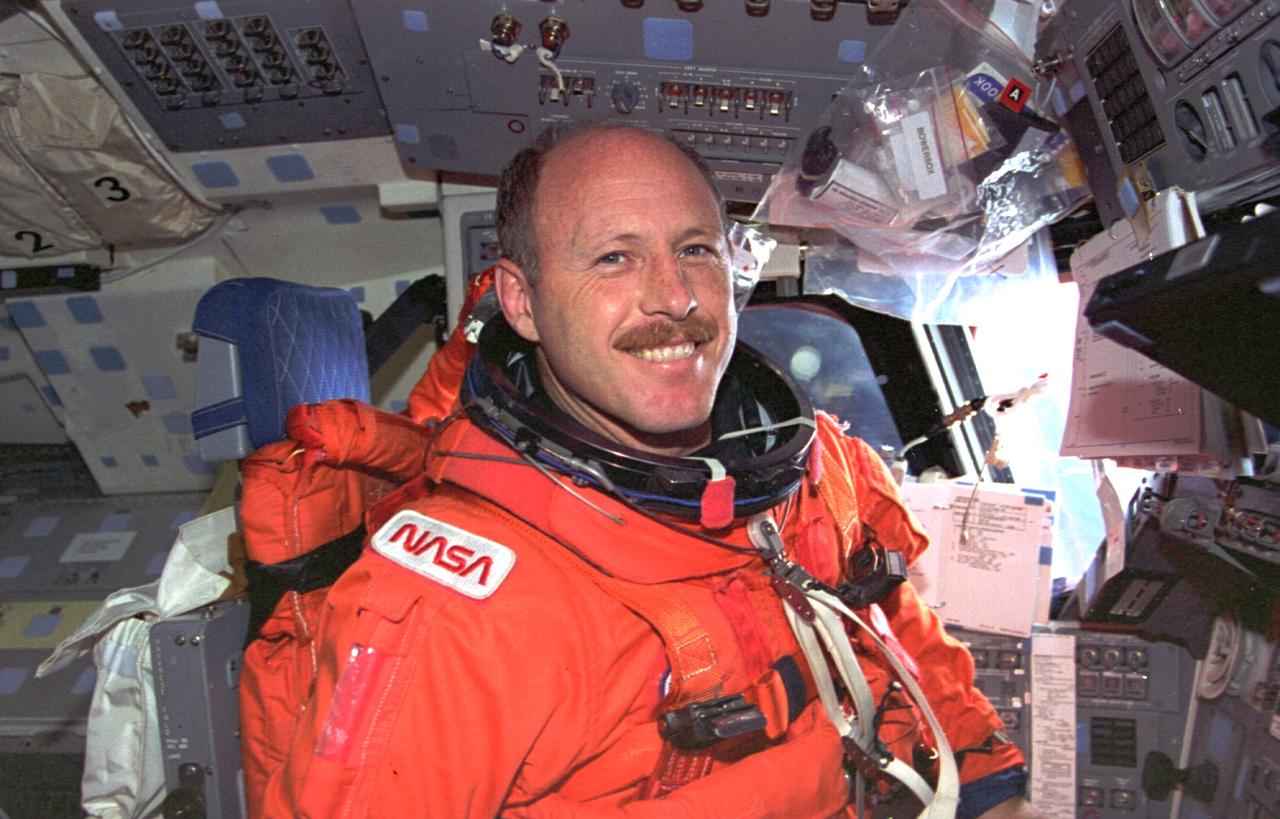

STS073-164-025 (5 November 1995) --- The countenance of astronaut Kenneth D. Bowersox signifies the near completion of a successful 16-day mission in Earth-orbit aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. Bowersox, attired in the shuttle launch and entry garment, mans the commander's station prior to the entry phase of the flight.
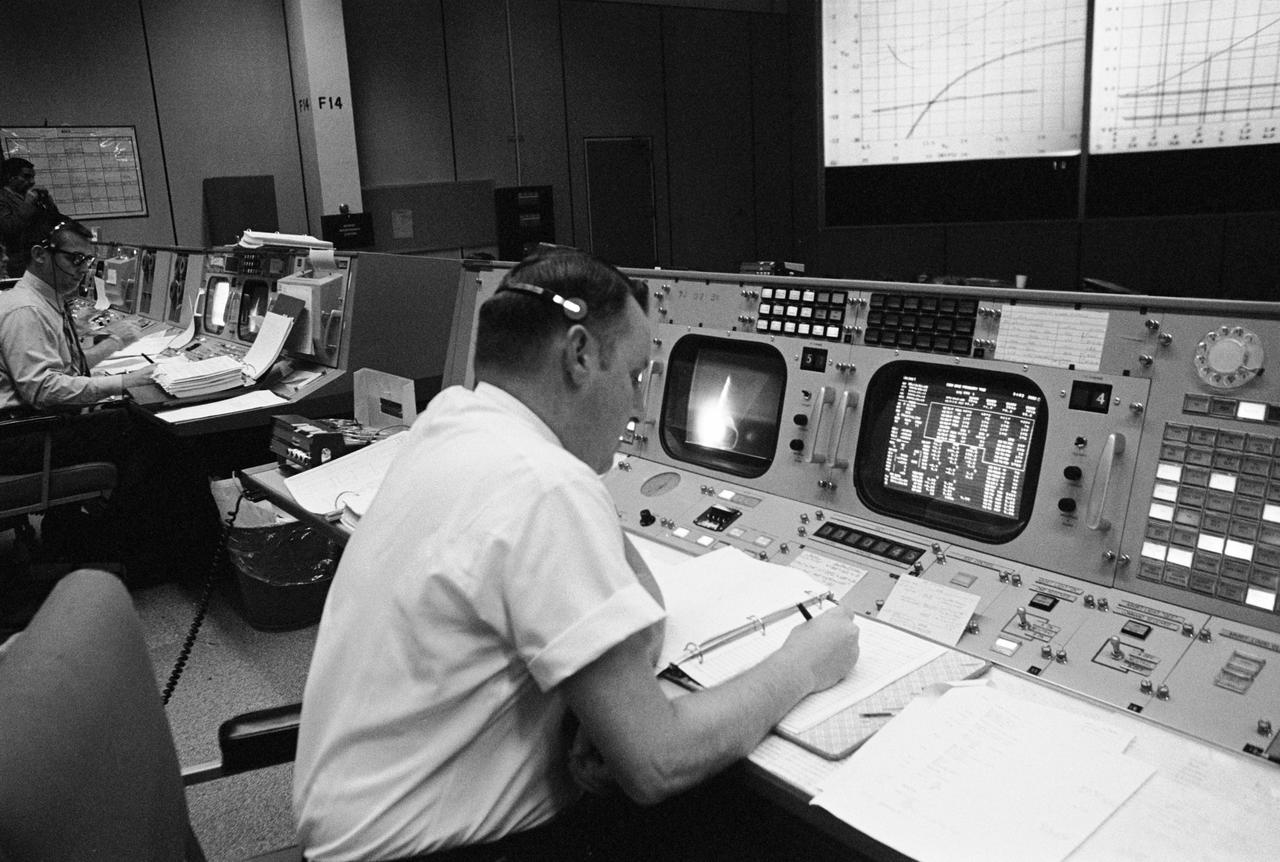

S68-55742 (21 Dec. 1968) --- Clifford E. Charlesworth, Apollo 8 "Green Team" flight director, is seated at his console in the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center, Building 30, during the launch of the Apollo 8 (Spacecraft 103/Saturn 503) manned lunar orbit space mission.

S64-14855 (23 Feb. 1962) --- Astronaut John Glenn, Jr. is honored by President John F. Kennedy after his historical first manned orbital flight, Mercury-Atlas 6. The ceremony was held at the NASA facility in Florida. Photo credit: NASA
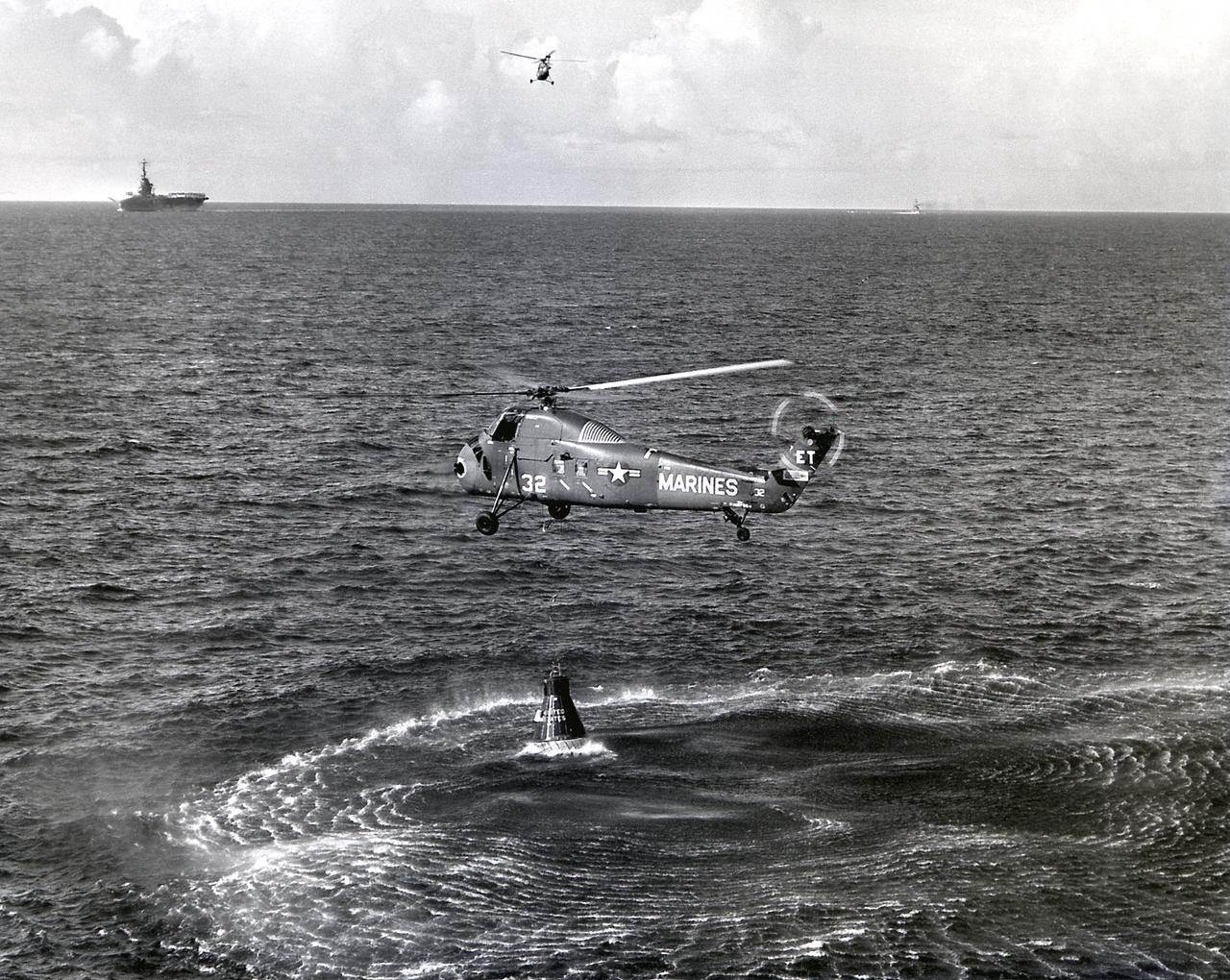

A U.S. Marine helicopter attempts to retrieve the sinking capsule, Liberty Bell 7, of the MR-4 mission. The attempt failed and the capsule sank. The MR-4 mission marned by Astronaut Virgil Grissom was the second manned orbital flight boosted by the Mercury-Redstone vehicle. The Recovery ship is in the background.

S69-19794 (February 1969) --- Composite of two artist's concepts illustrating key events, tasks and activities on the third day of the Apollo 9 mission, including crew transfer and Lunar Module system evaluation. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.

Astronaut John Glenn enters the Mercury spacecraft, Friendship 7, prior to the launch of MA-6 on February 20, 1961 and became the first American who orbited the Earth. The MA-6 mission was the first manned orbital flight boosted by the Mercury-Atlas vehicle, a modified Atlas ICBM (Intercontinental Ballistic Missile), lasted for five hours, and orbited the Earth three times.
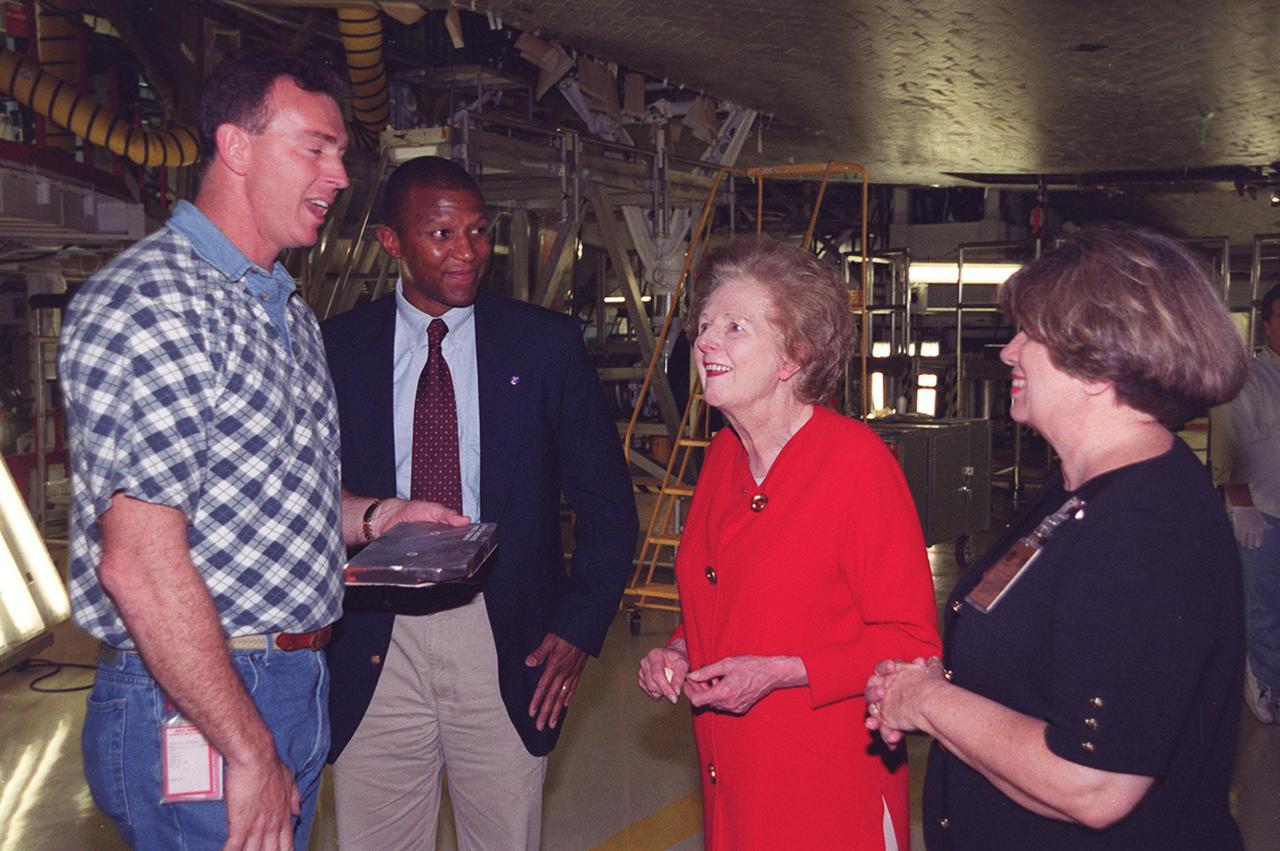

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, standing underneath the orbiter Endeavour are United Space Alliance technician Mike Parrish, NASA Test Director Kelvin Manning, Lady Margaret Thatcher, former Prime Minister of Britain, and JoAnn H. Morgan, director, External Relations and Business Development at KSC. Thatcher is on a tour of KSC. Parrish will be her guide inside the orbiter Endeavour, which is next flying on mission STS-100, the ninth construction flight to the International Space Station

Astronaut John Glenn enters the Mercury spacecraft, Friendship 7, prior to the launch of MA-6 on February 20, 1961 and became the first American who orbited the Earth. The MA-6 mission was the first manned orbital flight boosted by the Mercury-Atlas vehicle, a modified Atlas ICBM (Intercontinental Ballistic Missile), lasted for five hours, and orbited the Earth three times.
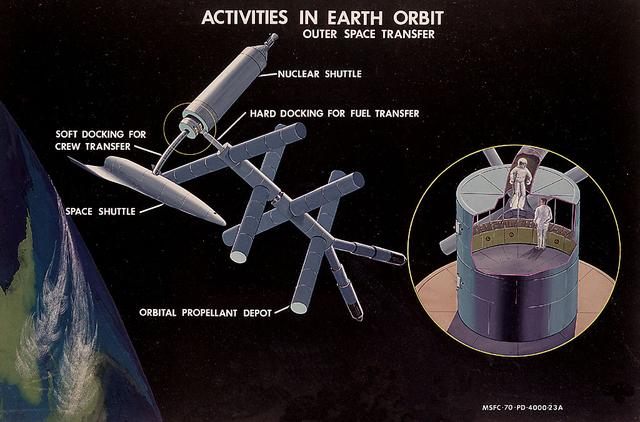
This artist's concept from 1970 shows a Nuclear Shuttle docked to an Orbital Propellant Depot and an early Space Shuttle. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center Program Development plarners, the Nuclear Shuttle, in either manned or unmanned mode, would deliver payloads to lunar orbit or other destinations then return to Earth orbit for refueling and additonal missions.

Project Mercury astronaut John H. Glenn Jr., enters the Friendship 7 spacecraft during the last part of the countdown on Feb. 20, 1962. At 9:47 a.m. EST, the Atlas launch vehicle lifted the spacecraft into orbit for a three-orbit mission lasting four hours, 55 minutes and 23 seconds. Glenn and his spacecraft were recovered by the destroyer Noa just 21 minutes after landing in the Atlantic near Grand Turk Island, to successfully complete the nation's first manned orbital flight.
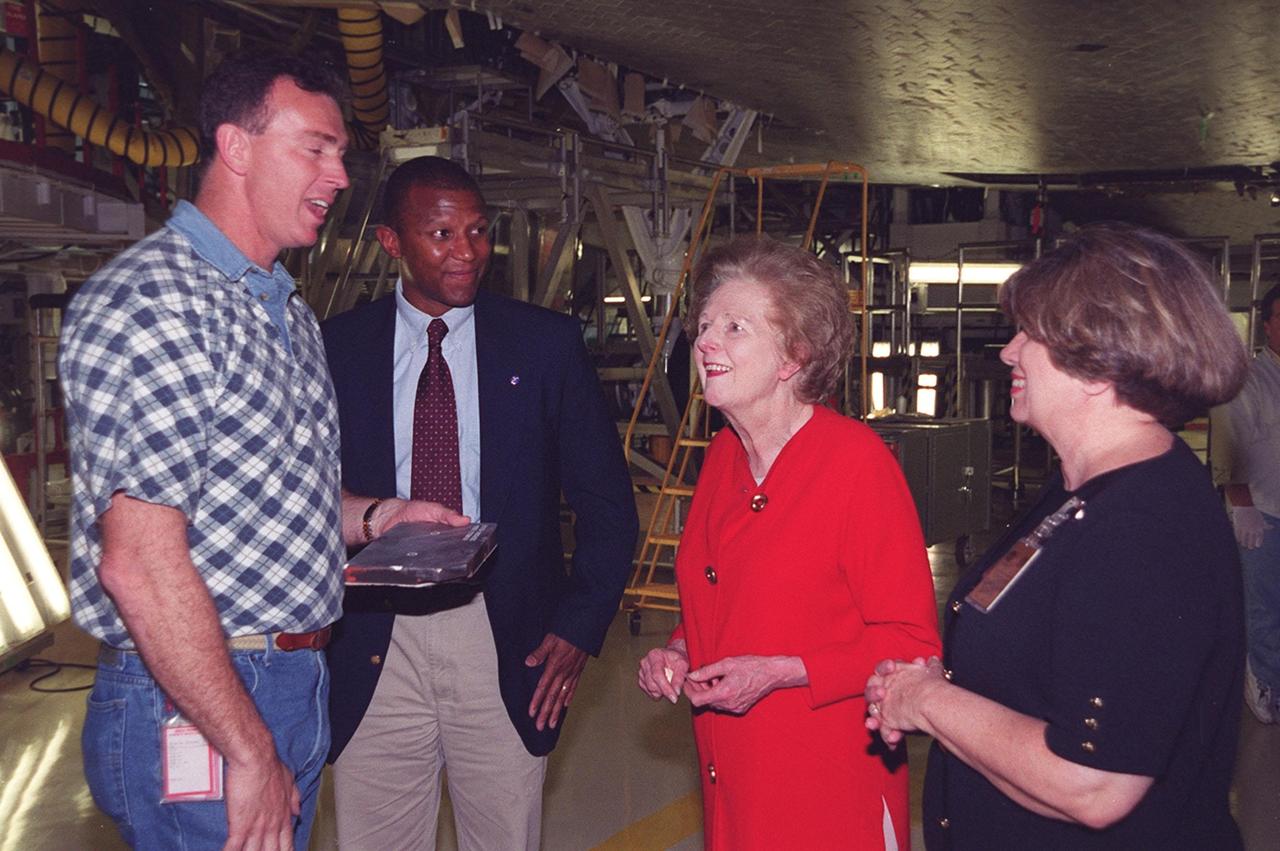

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, standing underneath the orbiter Endeavour are United Space Alliance technician Mike Parrish, NASA Test Director Kelvin Manning, Lady Margaret Thatcher, former Prime Minister of Britain, and JoAnn H. Morgan, director, External Relations and Business Development at KSC. Thatcher is on a tour of KSC. Parrish will be her guide inside the orbiter Endeavour, which is next flying on mission STS-100, the ninth construction flight to the International Space Station
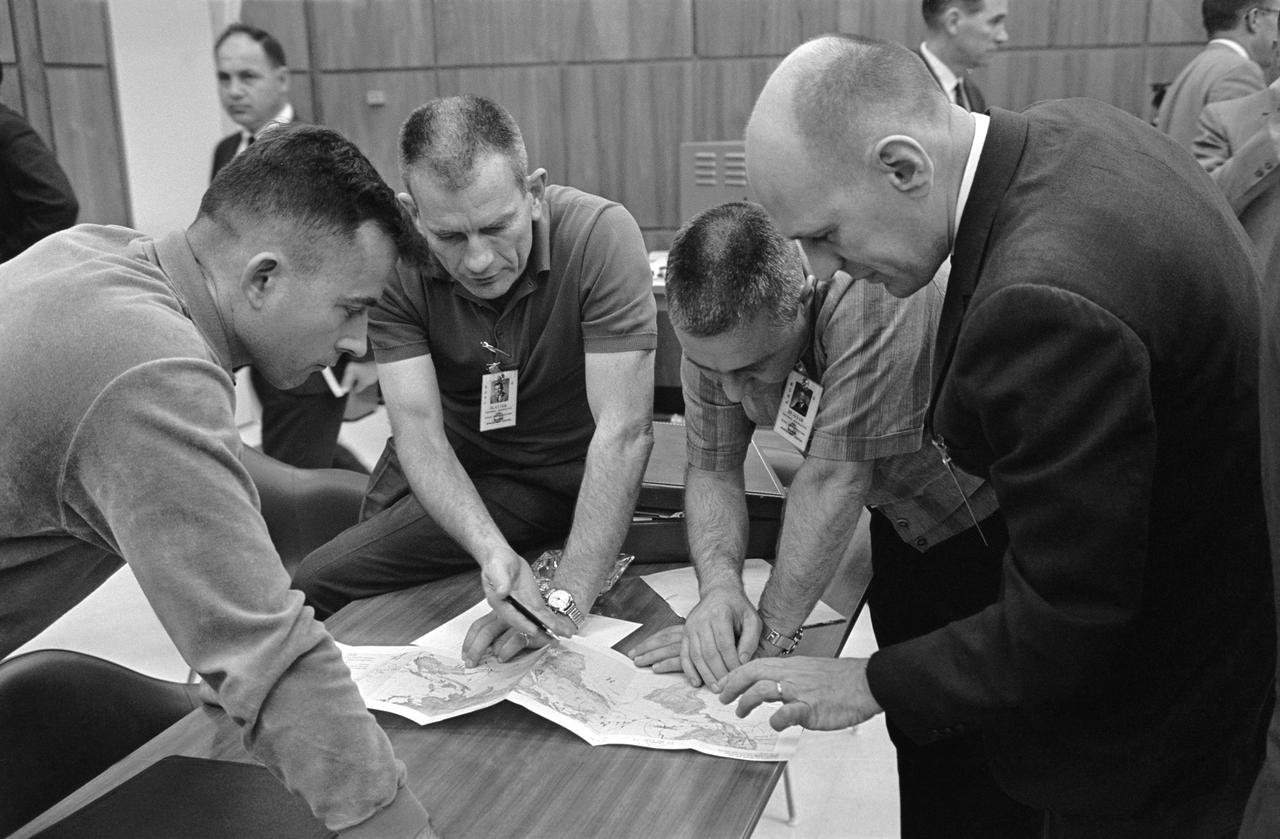

S65-20627 (20 March 1965) --- Crew members for the NASA Gemini-Titan 3 mission go over the map of the orbital track with Donald K. Slayton, assistant director for Flight Crew Operations, Manned Spacecraft Center. Shown (left to right) are astronauts John W. Young, pilot; Slayton; Virgil I. Grissom, command pilot; and Ken Nagler, U.S. Weather Bureau. The group got together at the GT-3 mission review meeting on March 20, 1965, in the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building on Merritt Island, Florida. Items covered at the review included mission description, spacecraft, launch vehicle, experiments, world-wide tracking network, recovery and weather.
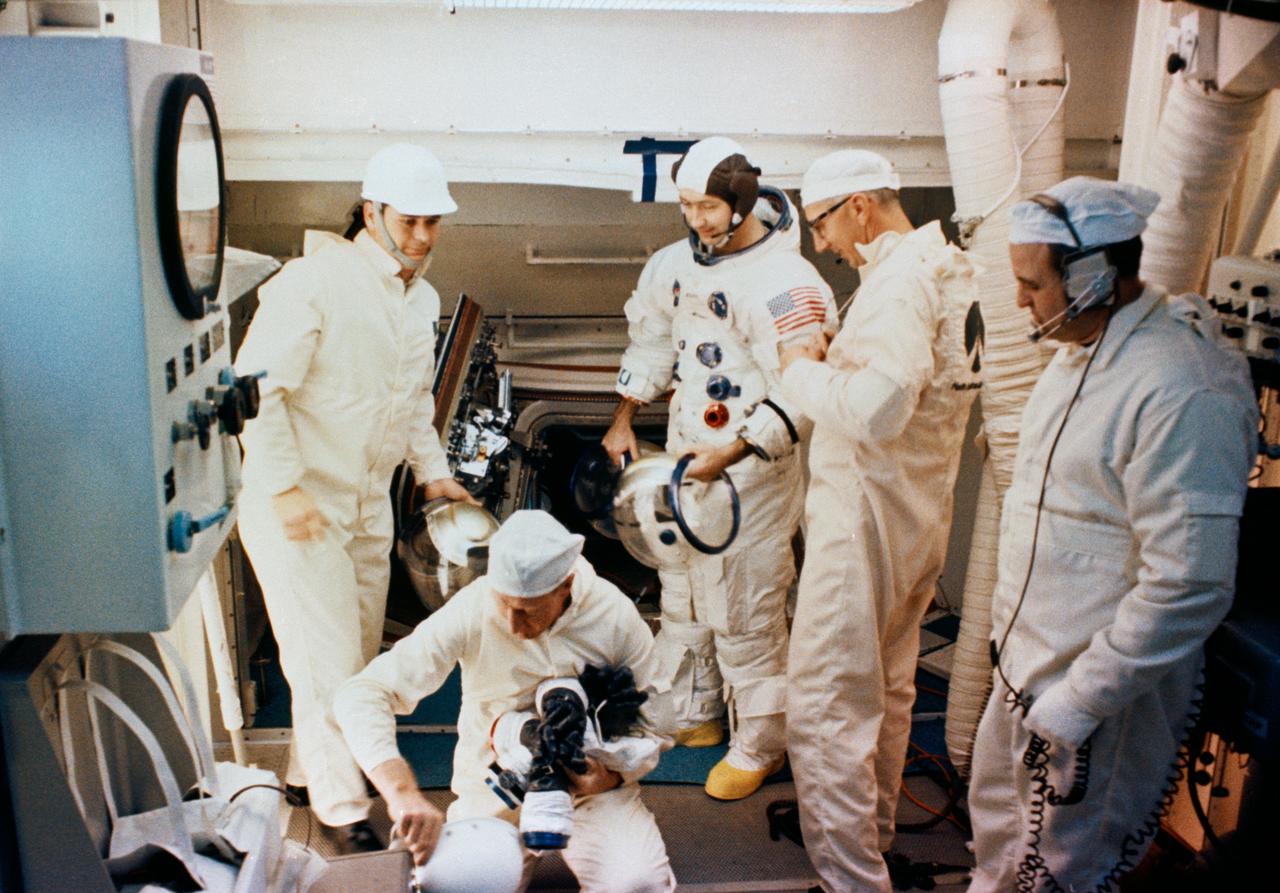

S69-25884 (23 Feb. 1969) --- Interior view of the white room atop Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, during Apollo 9 Countdown Demonstration Test activity. Standing next to spacecraft hatch is astronaut James A. McDivitt, commander. Also, taking part in the training exercise were astronauts David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight. Apollo 9 will be the second manned Saturn V mission.
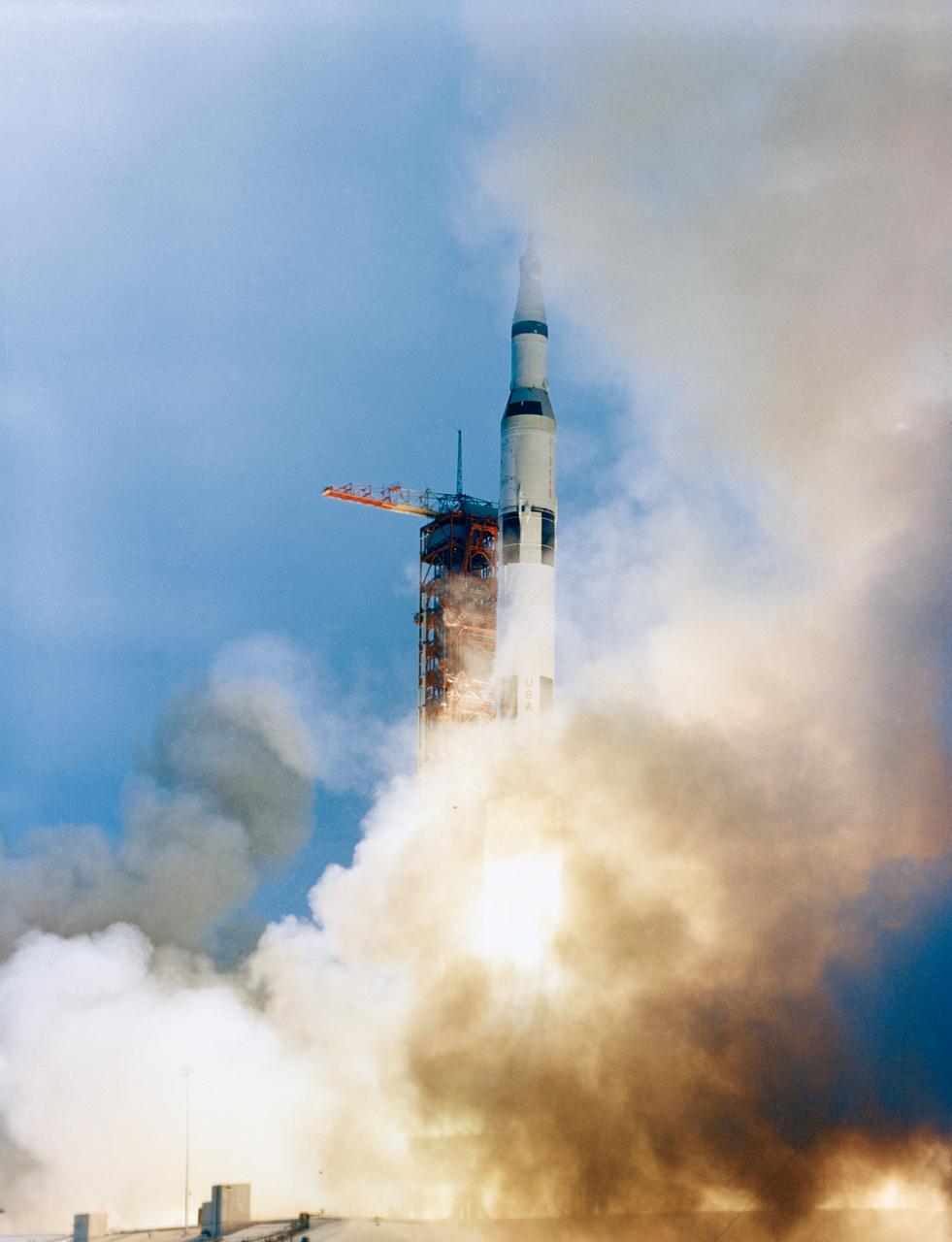

S69-25864 (3 March 1969) --- The Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/Saturn 504) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC) at 11 a.m. (EST), March 3, 1969. Aboard the spacecraft are astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight. Apollo 9 is the second manned Saturn V mission.
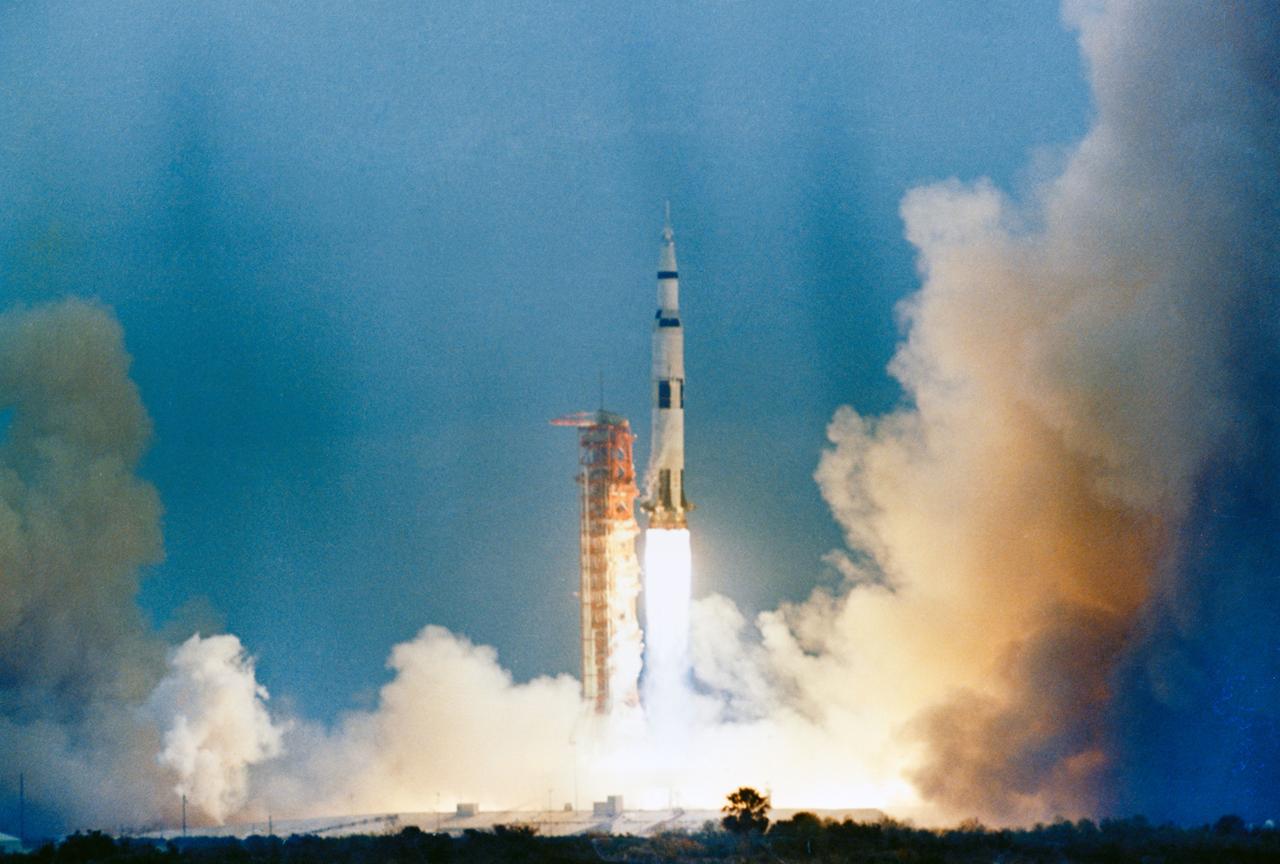

S69-25861 (3 March 1969) --- The Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/ Saturn 504) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC) at 11 a.m. (EST), March 3, 1969. Aboard the spacecraft are astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight. Apollo 9 is the second manned Saturn V mission.
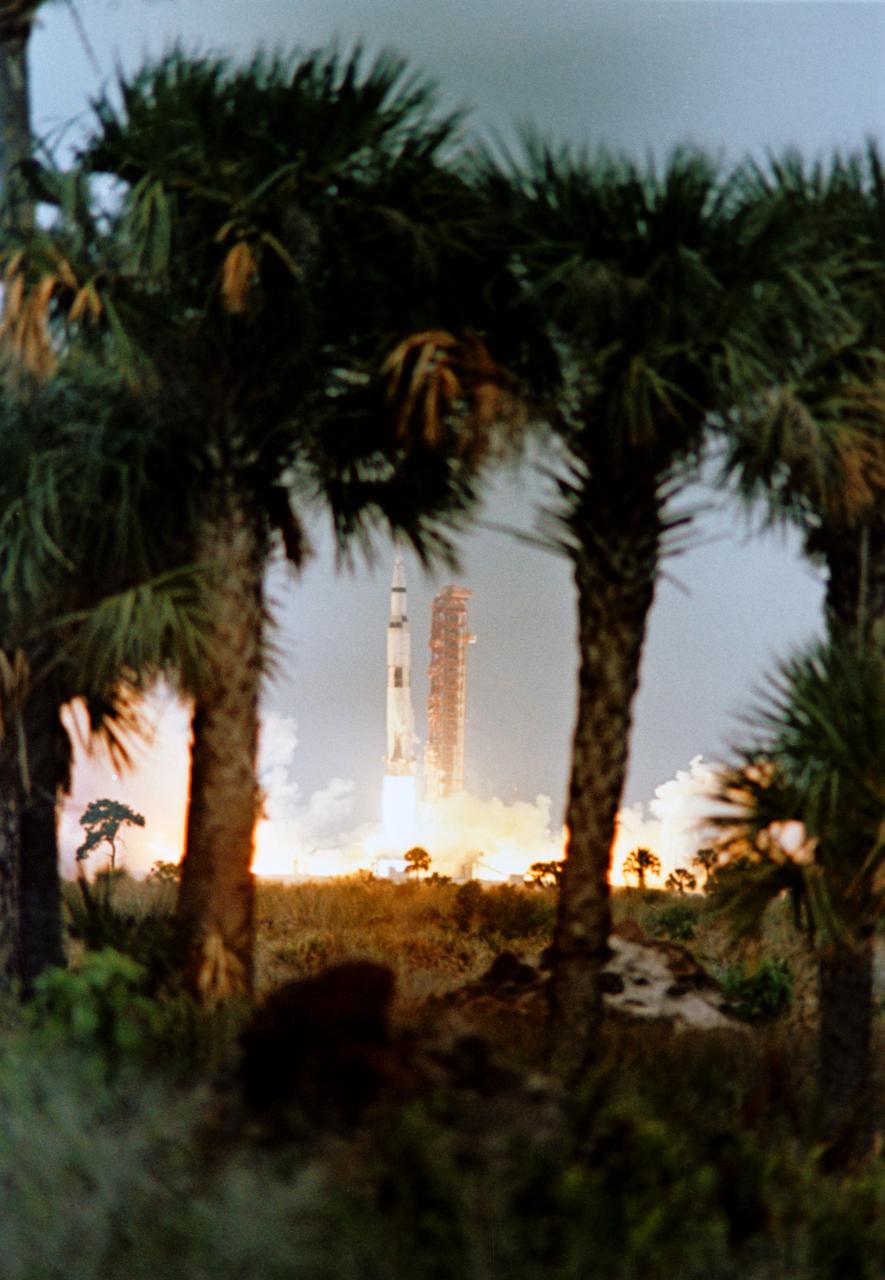

S69-25862 (3 March 1969) --- Framed by palm trees in the foreground, the Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/ Saturn 504) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC) at 11 a.m. (EST), March 3, 1969. Aboard the spacecraft are astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight. Apollo 9 is the second manned Saturn V mission.
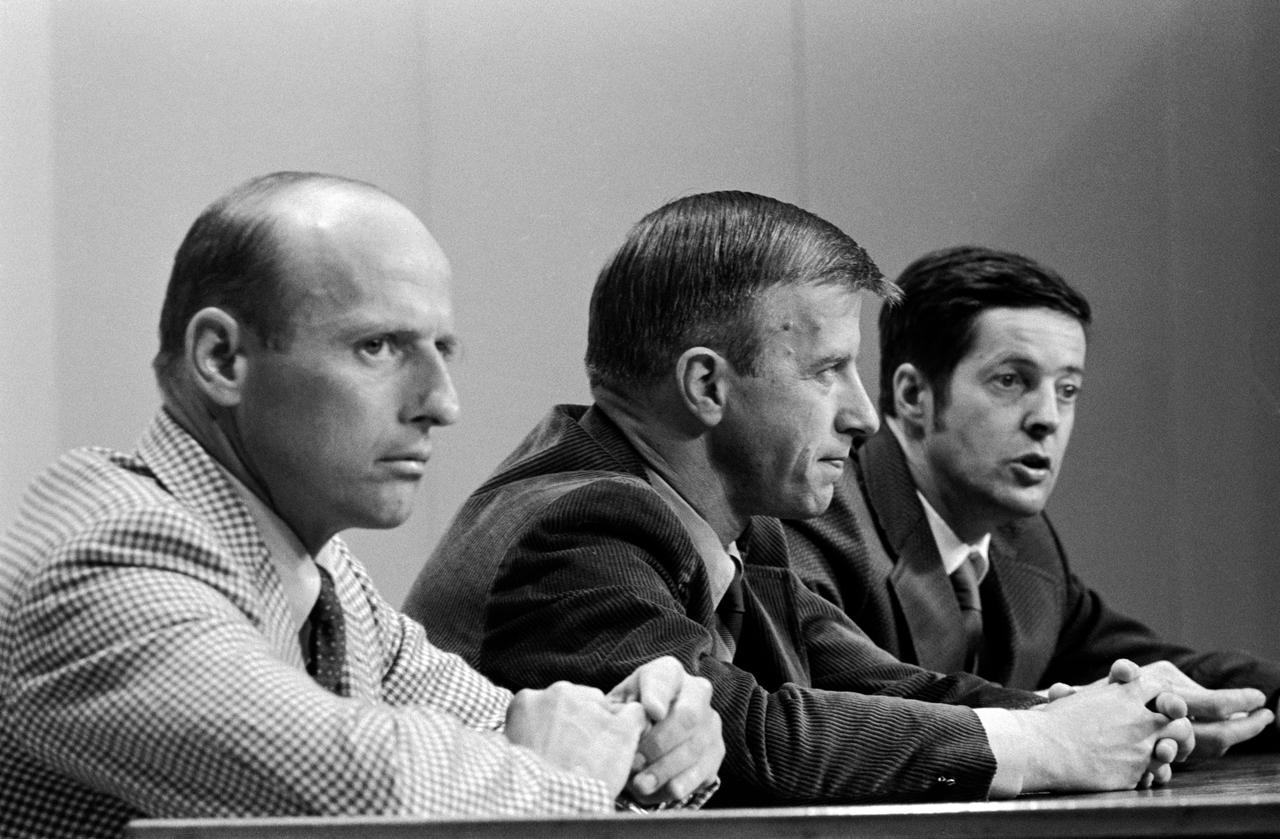

S73-24369 (17 April 1973) --- The three members of the prime crew of the first manned Skylab mission discuss their scheduled flight before a gathering of news media representatives, in building 1 auditorium, April 17, 1973. They are (left to right) astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander; Paul J. Weitz, pilot; and scientist Joseph P. Kerwin, science-pilot. Skylab is a three-part program consisting of one 28-day; and two 56-day manned visits spanning an eight-month period. One day prior to the launch of this crew, the unmanned Skylab Space Station cluster will be launched and placed in Earth orbit. The first manned mission will last up to 28 days. Photo credit: NASA
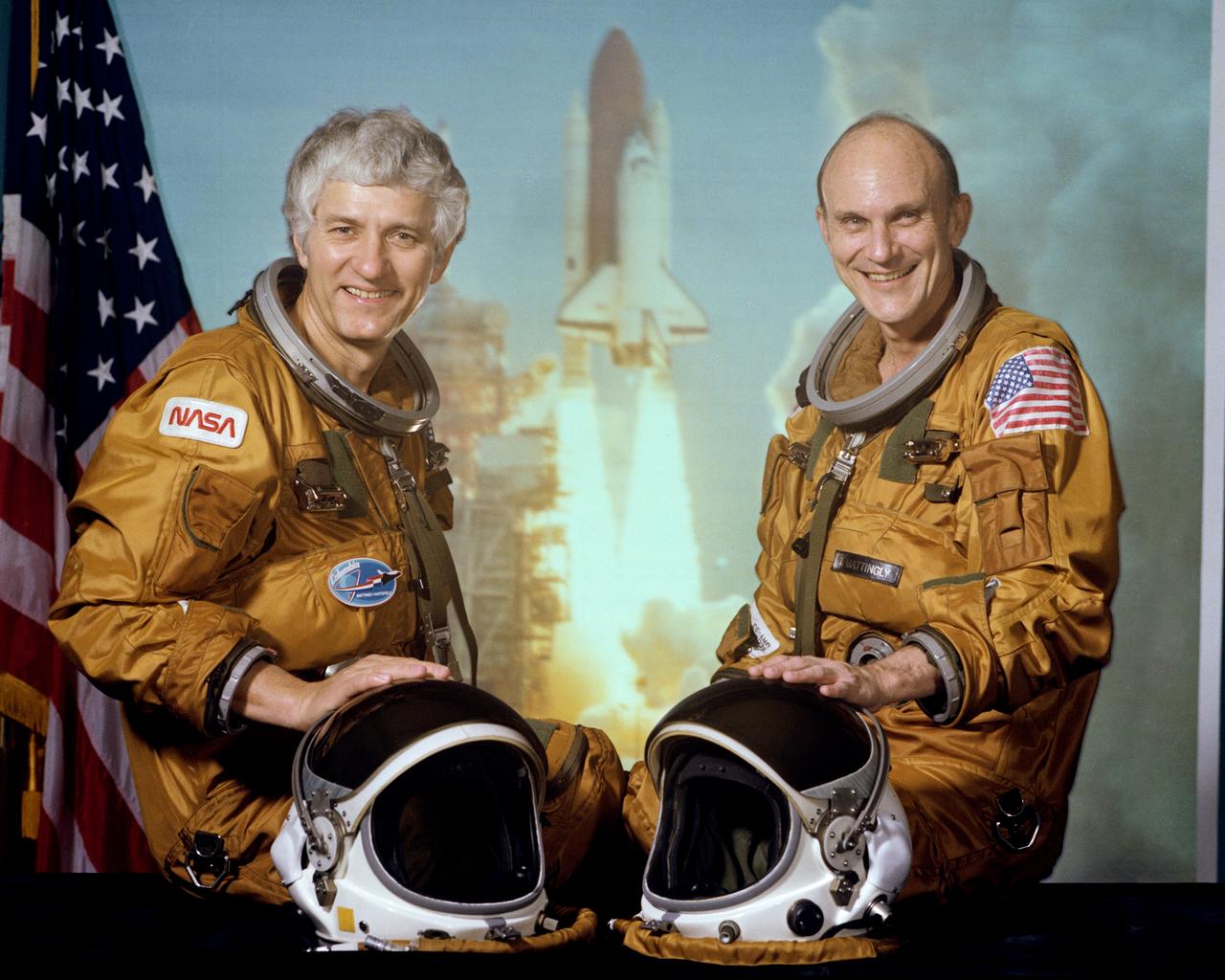

S82-31207 (1 May 1982) --- These two astronauts will man the space shuttle Columbia for NASA's fourth and final (STS-4) orbital flight test. Thomas K. (Ken) Mattingly II, right, is crew commander. Henry W. Hartsfield Jr., is pilot. Their flight is scheduled for launch in late June 1982, and is to last approximately one week, with launch to take place form KSC and landing to be on the dry lake beds of Edwards Air Force Base and Dryden Flight Research Facility (DFRC) in California. Photo credit: NASA
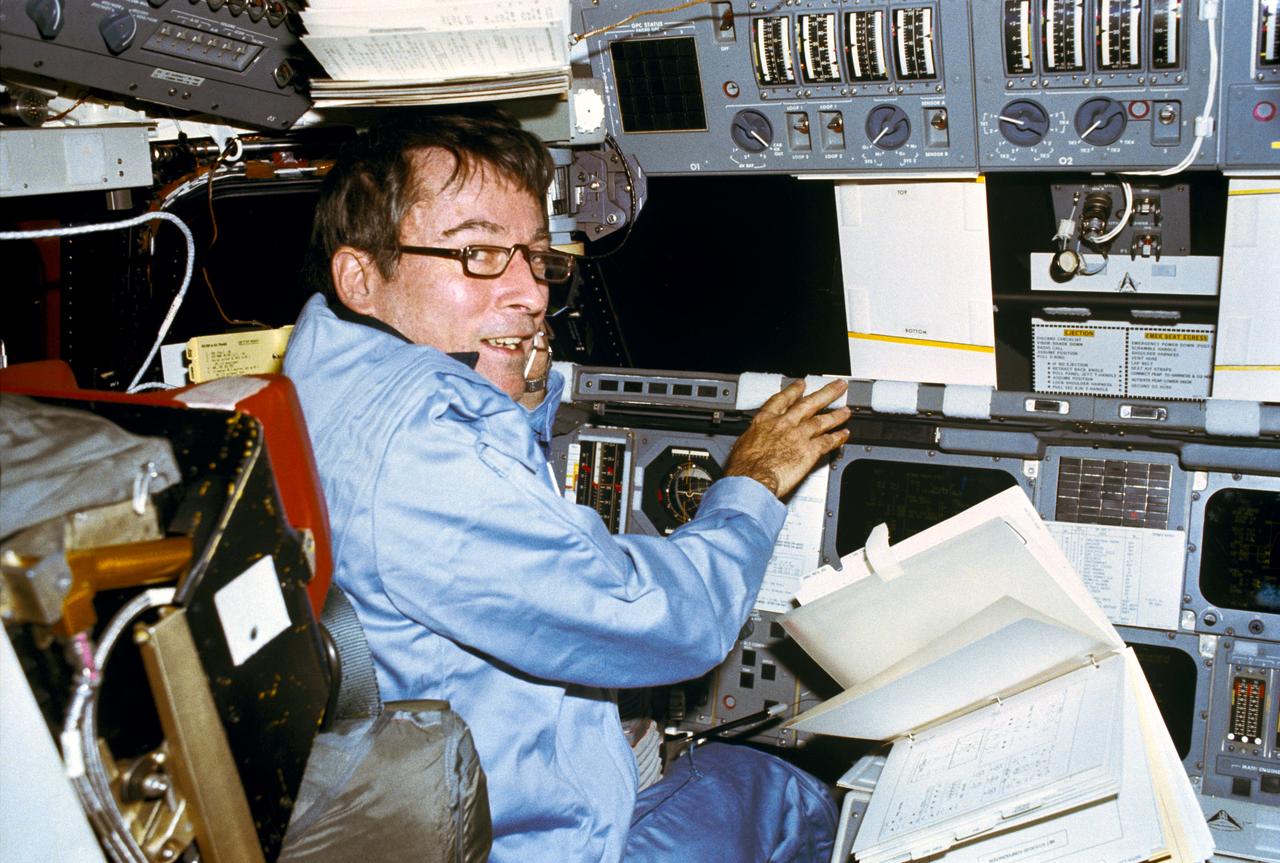

S81-30419 (12-14 April 1981) --- Astronaut John W. Young, mans the commander?s station in the Columbia during the 36-orbit STS-1 flight. A loose leaf notebook with flight activities data floats in the weightless environment. Young is wearing a three-piece constant wear flight suit. This 35mm frame was exposed by astronaut Robert L. Crippen. Photo credit: NASA
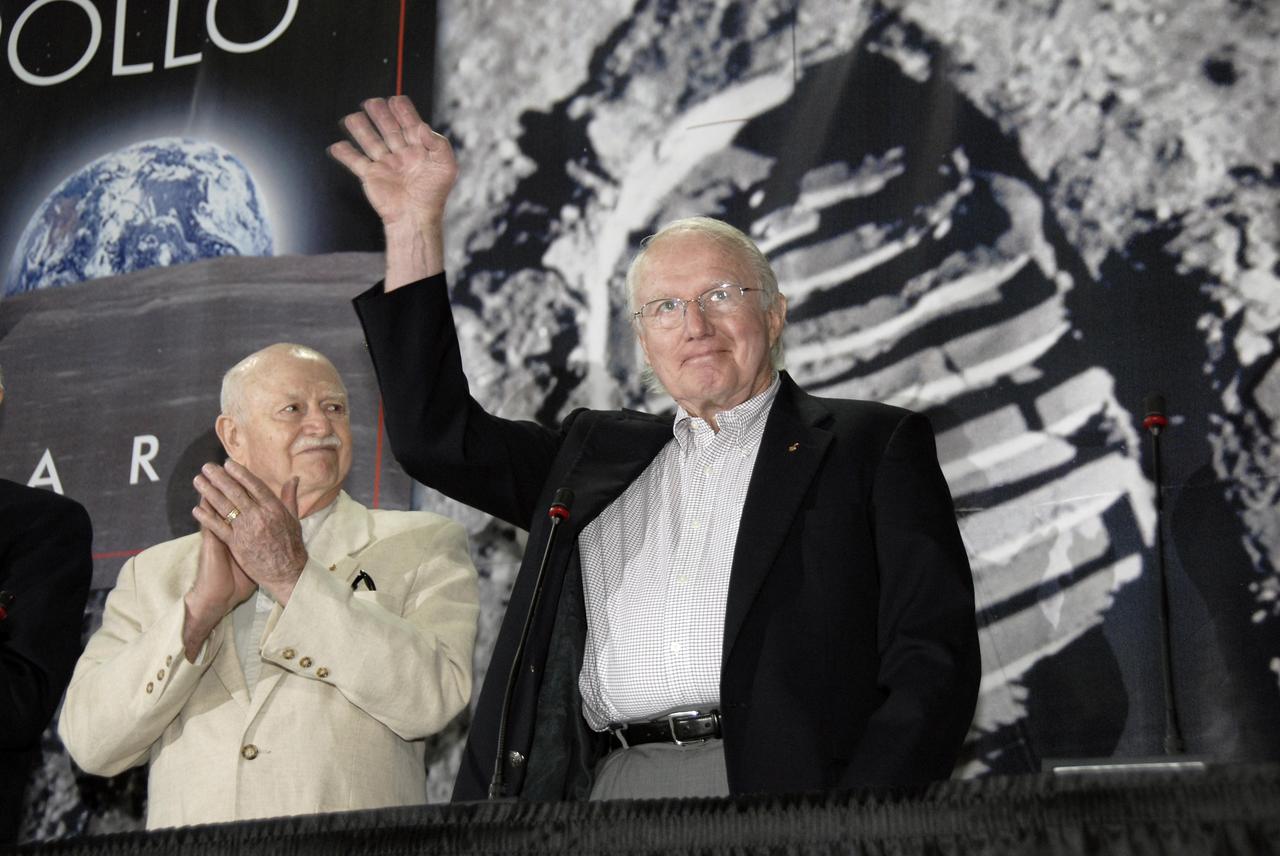

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Apollo astronaut Gerald Carr (right) joins Vance Brand (left) and six other Apollo astronauts for NASA's 40th Anniversary of Apollo Celebration of the July 1969 launch and landing on the moon. Carr served as CAPCOM for the Apollo 8 and 12 flights, and was involved in the development and testing of the lunar roving vehicle which was used on the lunar surface by Apollo flight crews. He also was commander of Skylab 4 launched in 1973 on the third and final manned visit to the Skylab Orbital Workshop. It was the longest manned flight (84 days, 1 hour, 15minutes) in history at that date. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
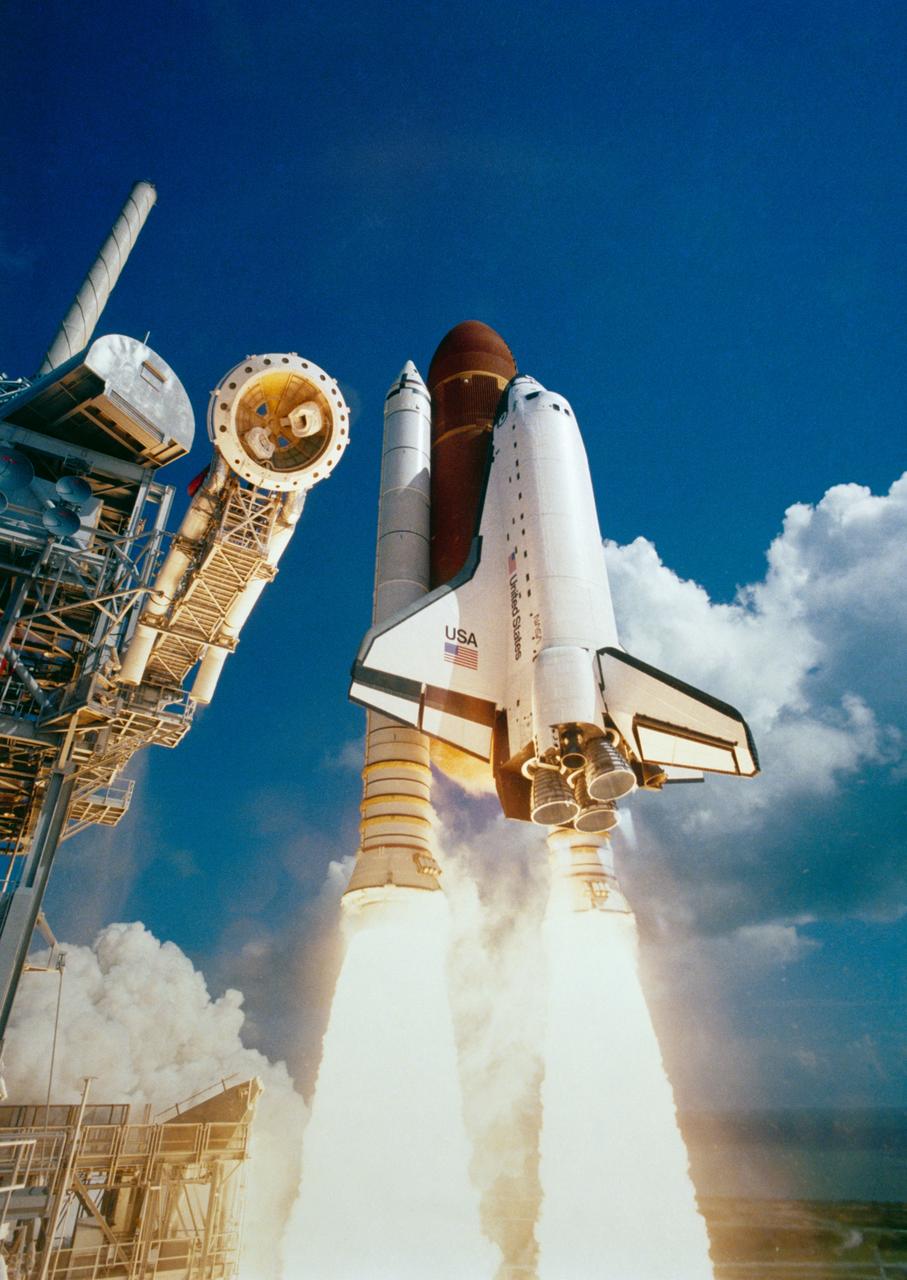

S85-44776 (3 Oct 1985) --- Space Shuttle Atlantis soars toward Florida blue skies to mark the maiden mission of NASA's fourth and newest orbiter vehicle. Launch occurred at 11:15 a.m. (EDT), October 3, 1985. A five member crew mans the orbiter for the DOD flight. They are Karol J. Bobko, Ronald J. Grabe, Robert L. Stewart, David C. Hilmers-- all of NASA-- and William A. Pailes of the USAF.
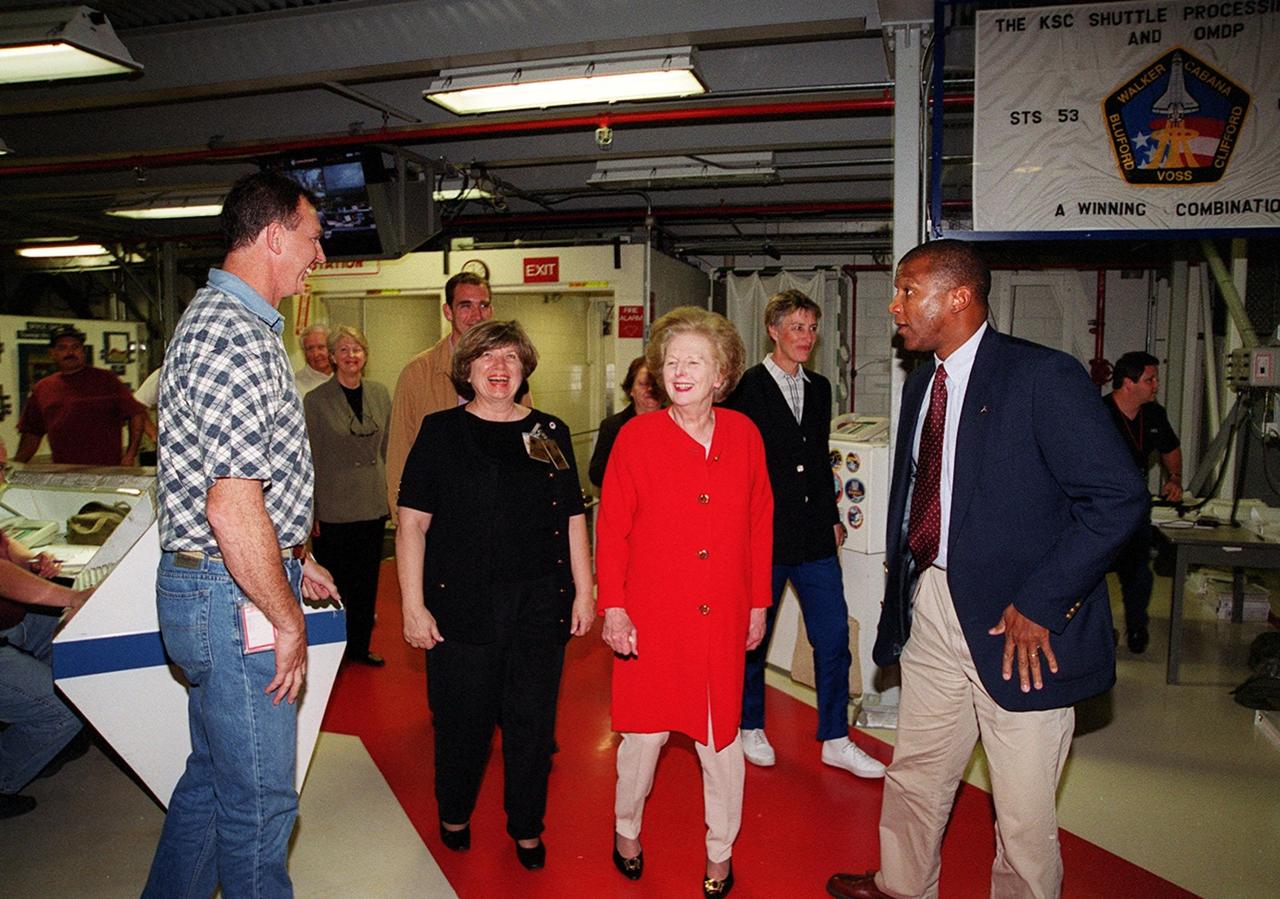

Walking into the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 while on a tour of KSC is Lady Margaret Thatcher (second from right), former Prime Minister of Britain. At far right is NASA Test Director Kelvin Manning. At left is United Space Alliance technician Mike Parrish, who will be Thatcher’s guide inside the orbiter Endeavour; second from left is JoAnn H. Morgan, director, External Relations and Business Development at KSC. Endeavour is next flying on mission STS-100, the ninth construction flight to the International Space Station
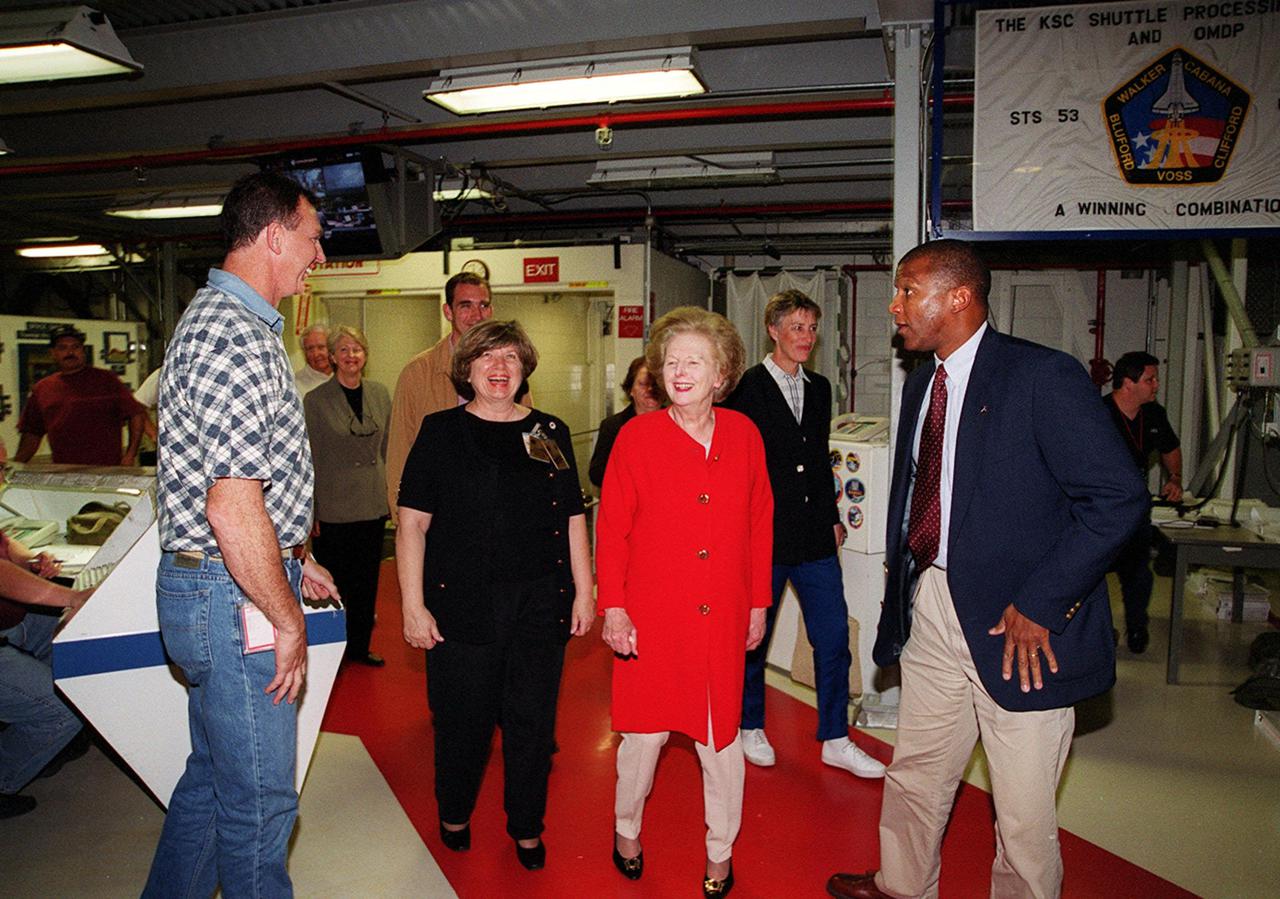

Walking into the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 while on a tour of KSC is Lady Margaret Thatcher (second from right), former Prime Minister of Britain. At far right is NASA Test Director Kelvin Manning. At left is United Space Alliance technician Mike Parrish, who will be Thatcher’s guide inside the orbiter Endeavour; second from left is JoAnn H. Morgan, director, External Relations and Business Development at KSC. Endeavour is next flying on mission STS-100, the ninth construction flight to the International Space Station

This montage illustrates the various configurations and missions of the three classes of the Saturn vehicles developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The missions for the Saturn I included atmospheric science investigations and the deployment of the Pegasus meteroid-detection satellite as well as launch vehicle development. The Saturn IB vehicle tested the Apollo spacecraft and launched the three marned Skylab missions as well as the Apollo Soyuz test project. The Saturn V vehicle launched the manned lunar orbital/landing missions, and the Skylab Orbital Workshop in 1973.
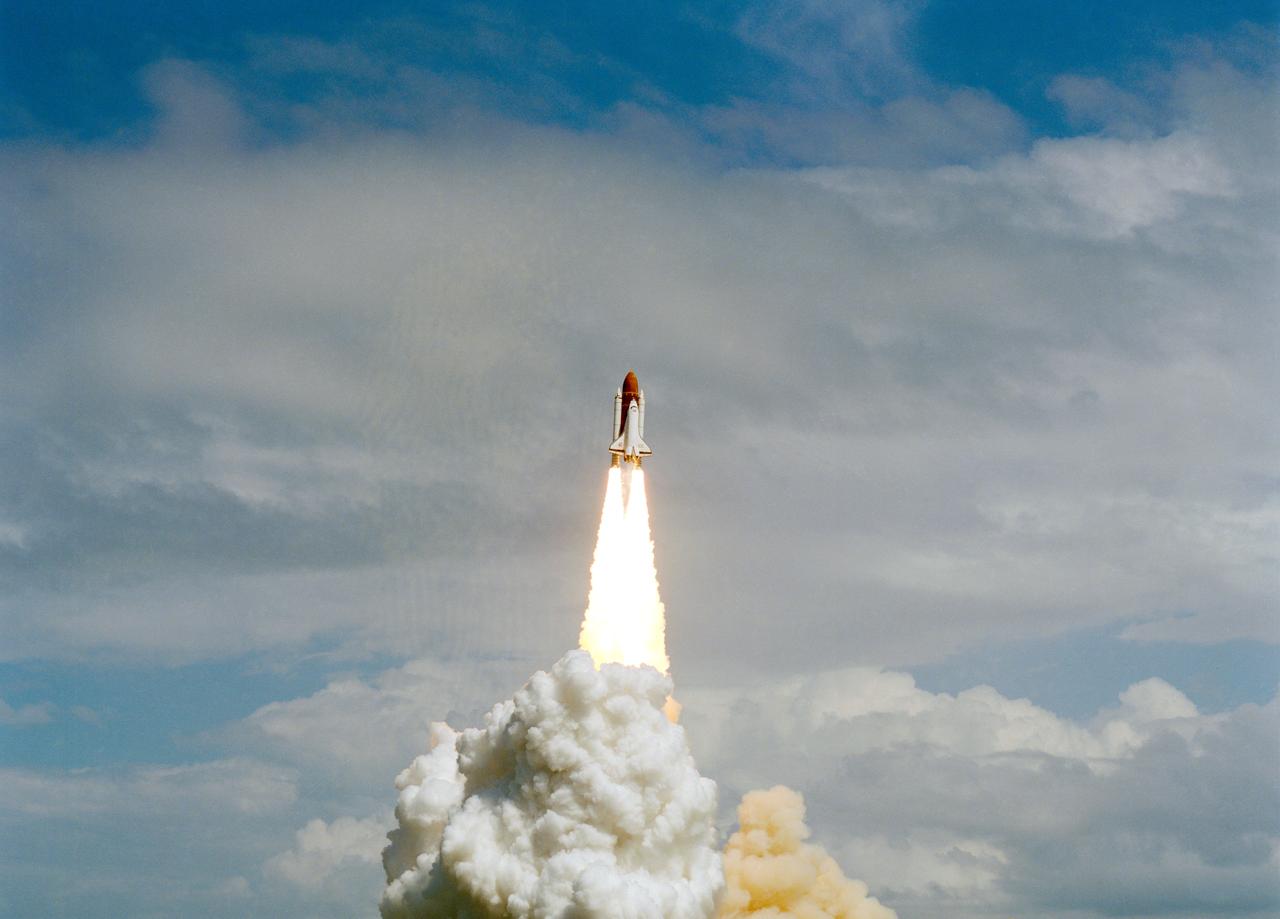

STS-26 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, rises into a cloudy sky and heads for Earth orbit atop the external tank (ET) as exhaust plumes billow from the two solid rocket boosters (SRBs) during liftoff from Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) pad 39B. STS-26 marks OV-103's first flight since September 1985 and NASA's first manned mission since 51L Challenger accident, 01-28-86.
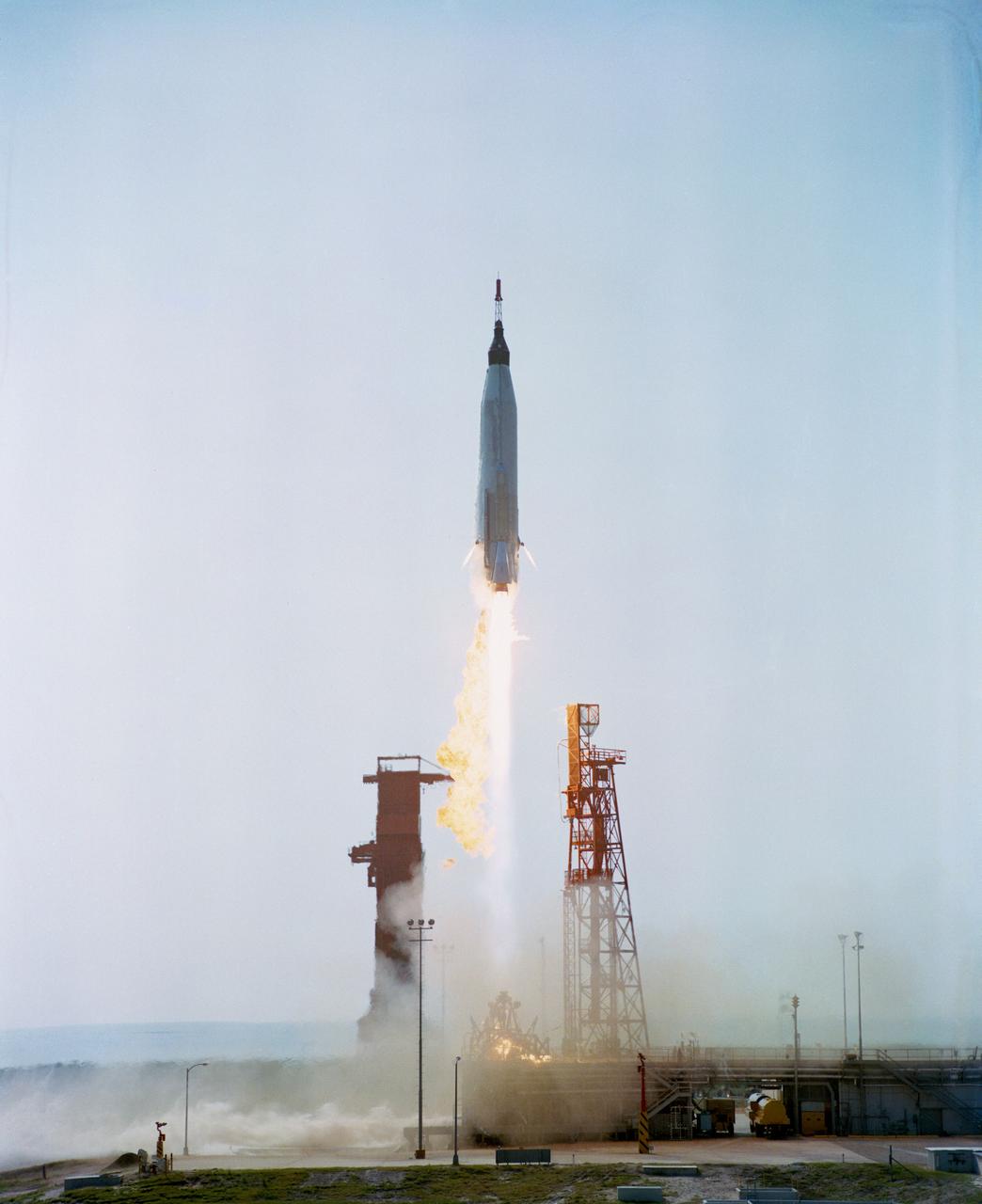

S63-07135 (16 May 1963) --- This was the Nation?s sixth manned orbital space flight, and the ?Faith 7? spacecraft was piloted by astronaut L. Gordon Cooper Jr. The launch was originally scheduled for May 14, 1963, but due to a malfunction in the radar tracking system at Bermuda. The launch was ?scrubbed? 12 minutes before countdown would have been completed. At midnight, May 15, 1963, countdown was resumed and liftoff occurred at 8:04 a.m. (EST), May 16, 1963. Astronaut L. Gordon Cooper Jr., completed a total of 22.9 orbits and spent 34 hours, 20 minutes in space flight. The launch and recovery was highly successful and was the last of the Mercury flights.
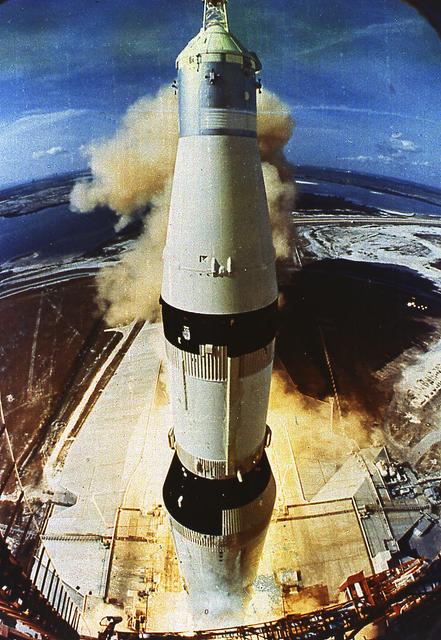

AS-506 lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at the Kennedy Space Center July 16, 1969. This sixth flight of the Saturn V launch vehicle, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, delivered astronauts Neil Armstrong, Edwin Buzz Aldrin, and Michael Collins to lunar orbit. Better known as Apollo 11, the mission marked the first manned lunar landing.
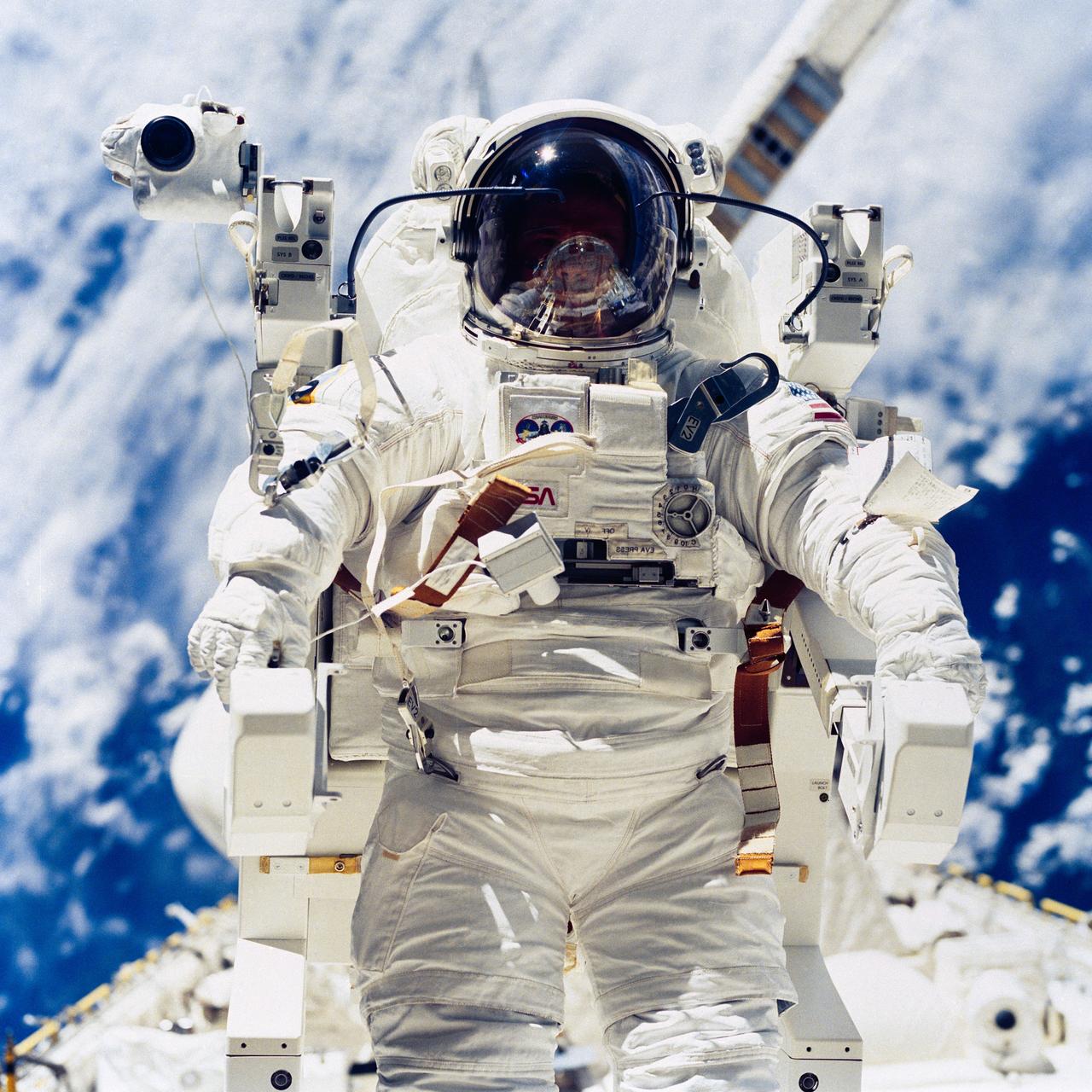

S84-27034A (9 Feb. 1984) --- Astronaut Robert L. Stewart appears to glide a few meters above the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Challenger's cargo bay during the second of two extravehicular activity (EVA) session on the Challenger's fourth flight in space. Astronauts Stewart and Bruce McCandless II, two of NASA's three mission specialists on flight STS-41B, earlier made another EVA, testing another manned maneuvering unit (MMU).
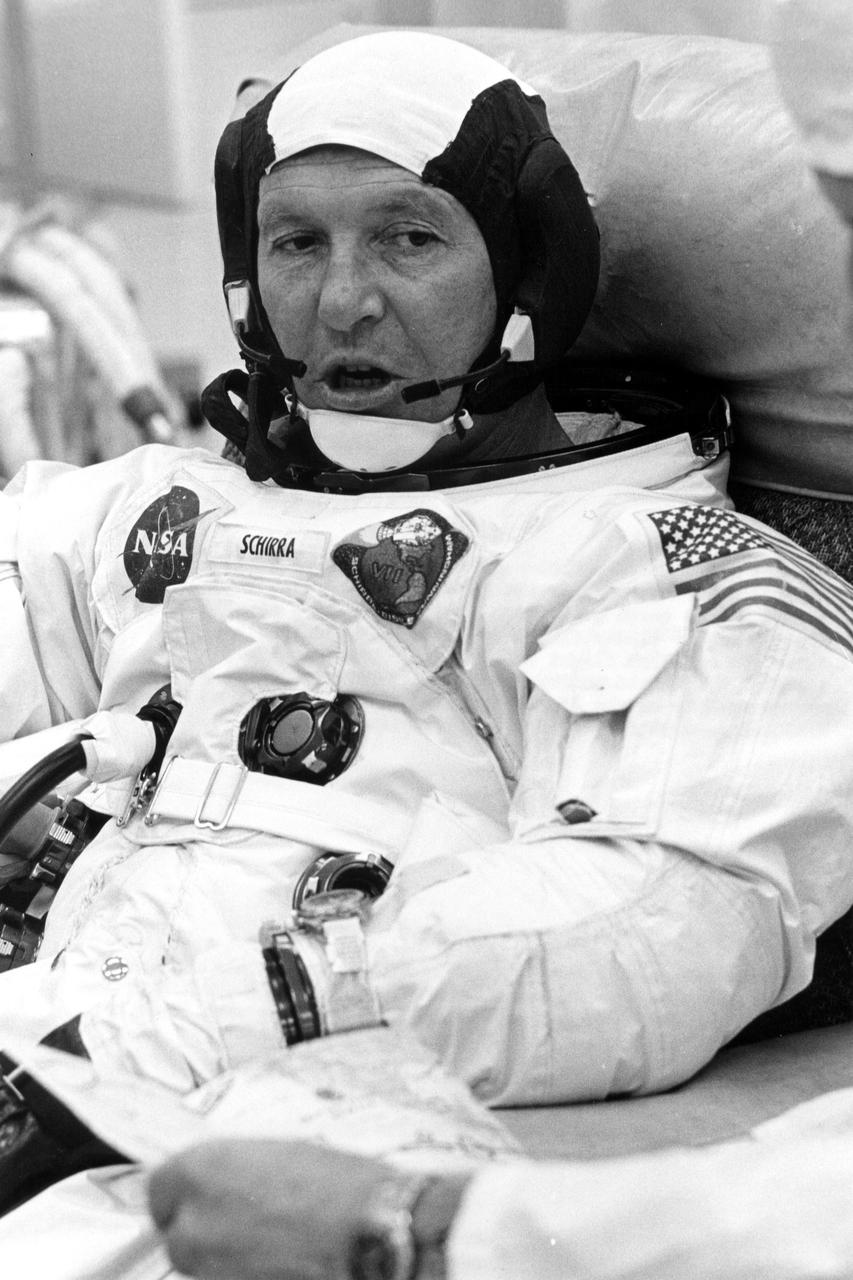

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Astsronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr. relaxes prior to boarding the Apollo 7 spacecraft, which rocketed into Earth orbit from Cape Kennedy this morning. Purpose of the 11-day flight is to qualify the Apollo spacecraft for a future flight to the moon. Other Apollo 7 pilots are Donn Eisele and Walter Cunningham. This is the first manned mission of the Apollo series. It is conducted by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
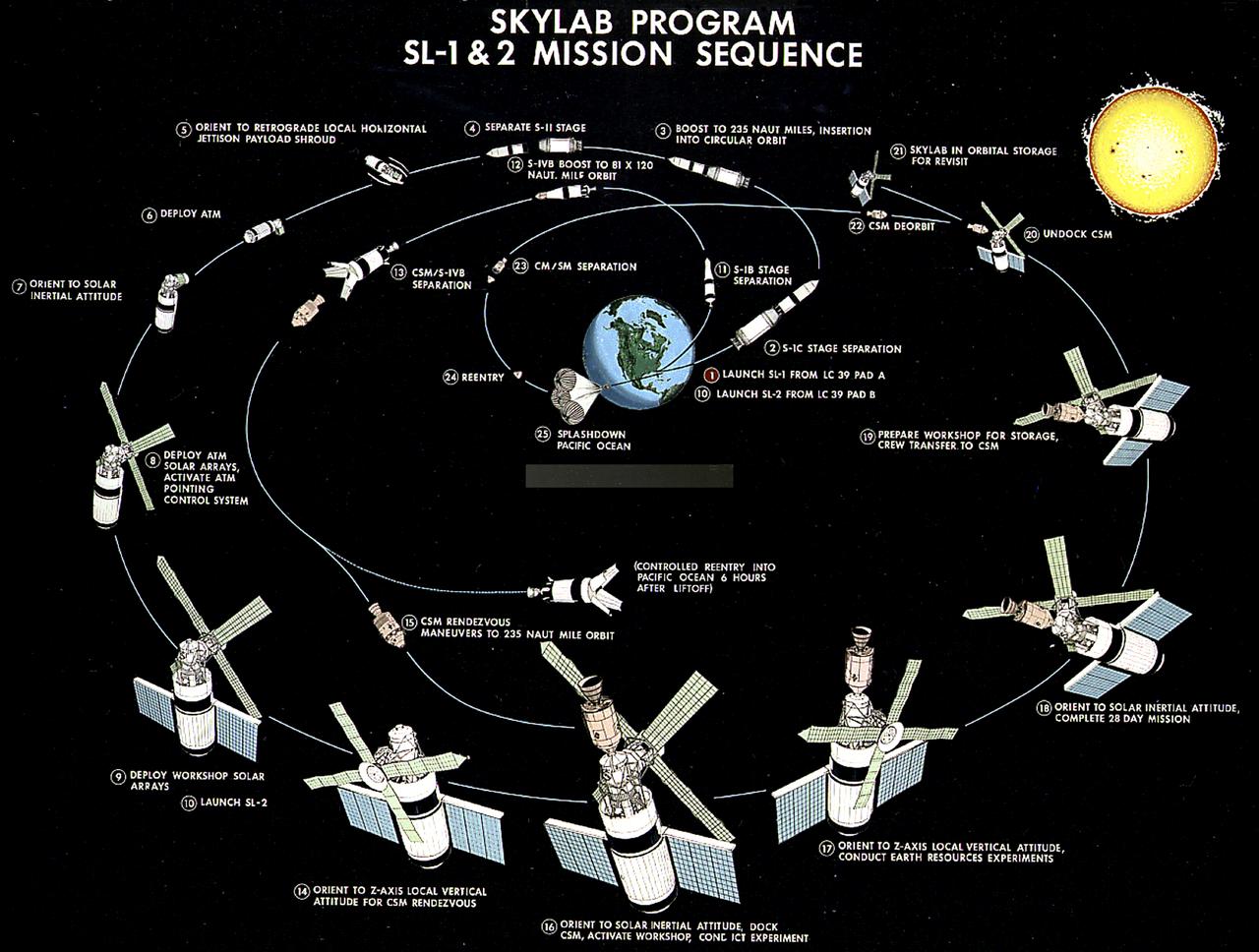
This illustration depicts the Skylab-1 and Skylab-2 mission sequence. The goals of the Skylab were to enrich our scientific knowledge of the Earth, the Sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms, including man; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials utilizing the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth resource observations. The Skylab also conducted 19 selected experiments submitted by high school students. Skylab's 3 different 3-man crews spent up to 84 days in Earth orbit. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had responsibility for developing and integrating most of the major components of the Skylab: the Orbital Workshop (OWS), Airlock Module (AM), Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Payload Shroud (PS), and most of the experiments. MSFC was also responsible for providing the Saturn IB launch vehicles for three Apollo spacecraft and crews and a Saturn V launch vehicle for the Skylab.
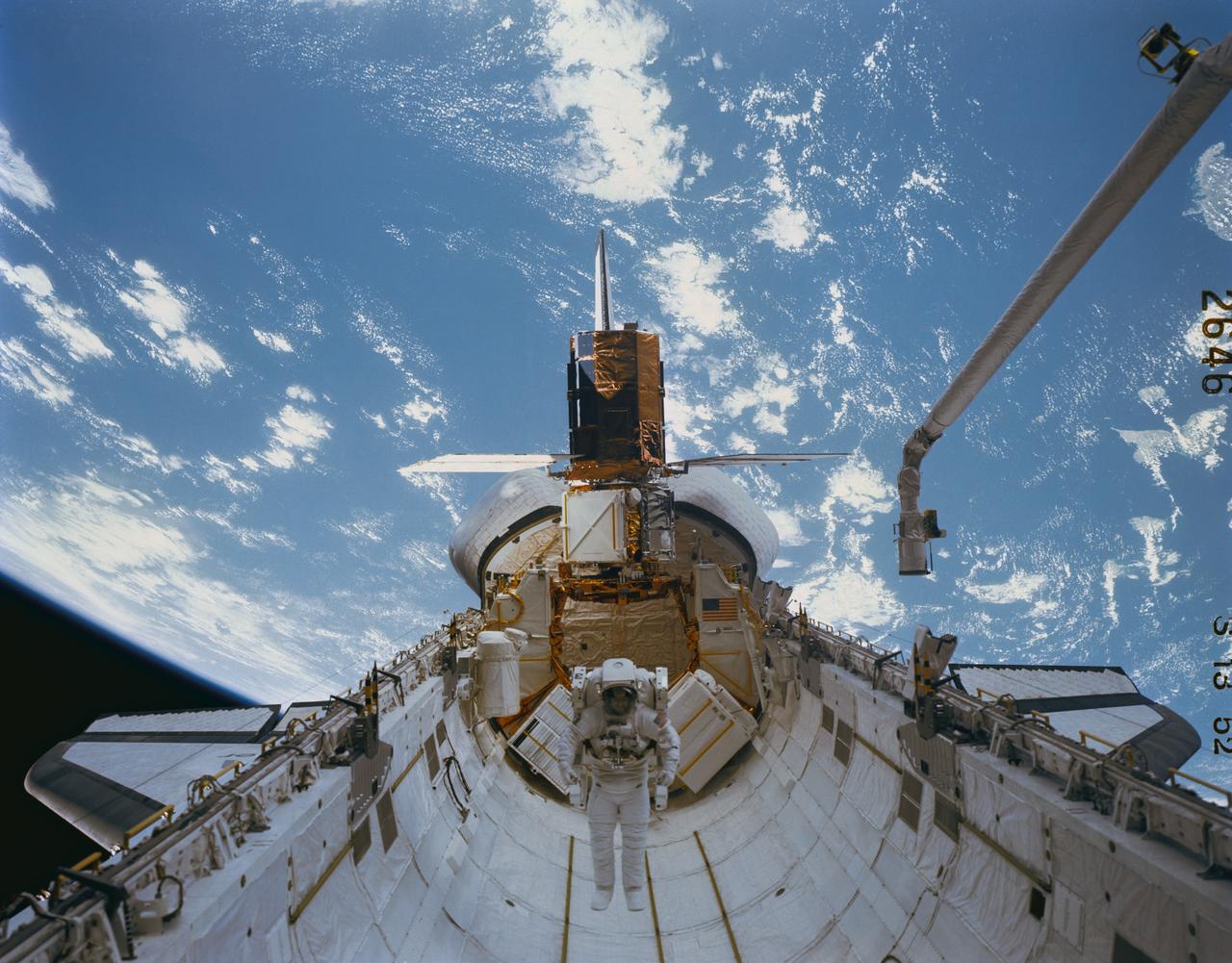

41C-52-2646 (11 April 1984) --- Astronaut James D. van Hoften and a repaired satellite are in a wide panorama recorded on film with a Linhof camera, making its initial flight aboard the Space Shuttle Challenger. Dr. van Hoften is getting in his first "field" test of the Manned Maneuvering Unit (MMU) after months of training in an underwater facility and in a simulator on Earth. The Solar Maximum Mission Satellite (SMMS), revived and almost ready for release into space once more, is docked at the Flight Support System (FSS). The Remote Manipulator System (RMS) is backdropped against the blue and white Earth at frame's edge. Outside of pictures made of the Earth from astronauts on the way to the Moon, this frame showing the planet from 285 nautical miles represents the highest orbital photography in the manned space program.
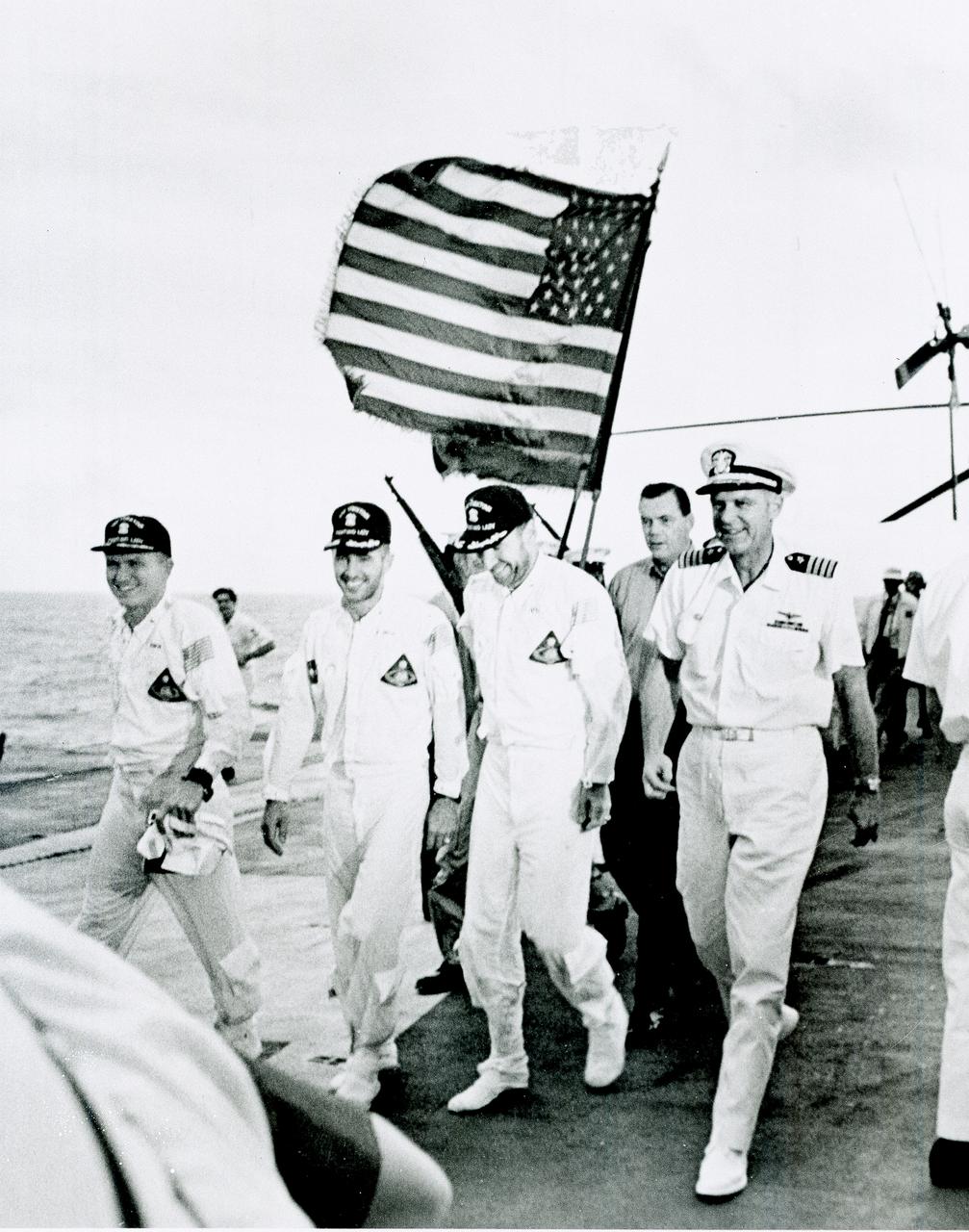

Apollo 8 astronauts and commanding officer of the recovery ship U.S.S. Yorktown walk the red carpet of the flight deck after splashdown recovery in the Pacific Ocean. Apollo 8 served as the first manned lunar orbit mission and the first manned flight of the Saturn V space vehicle, developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Liftoff occurred on December 21, 1968, carrying astronauts Frank Borman, commander; William Anders, Lunar Module (LM) Pilot; and James Lovell, Command Module (CM) pilot. The three safely returned to Earth on December 27, 1968. The mission achieved operational experience and tested the Apollo command module systems, including communications, tracking, and life-support, in cis-lunar space and lunar orbit, and allowed evaluation of crew performance on a lunar orbiting mission. The crew photographed the lunar surface, both far side and near side, obtaining information on topography and landmarks as well as other scientific information necessary for future Apollo landings. All systems operated within allowable parameters and all objectives of the mission were achieved.
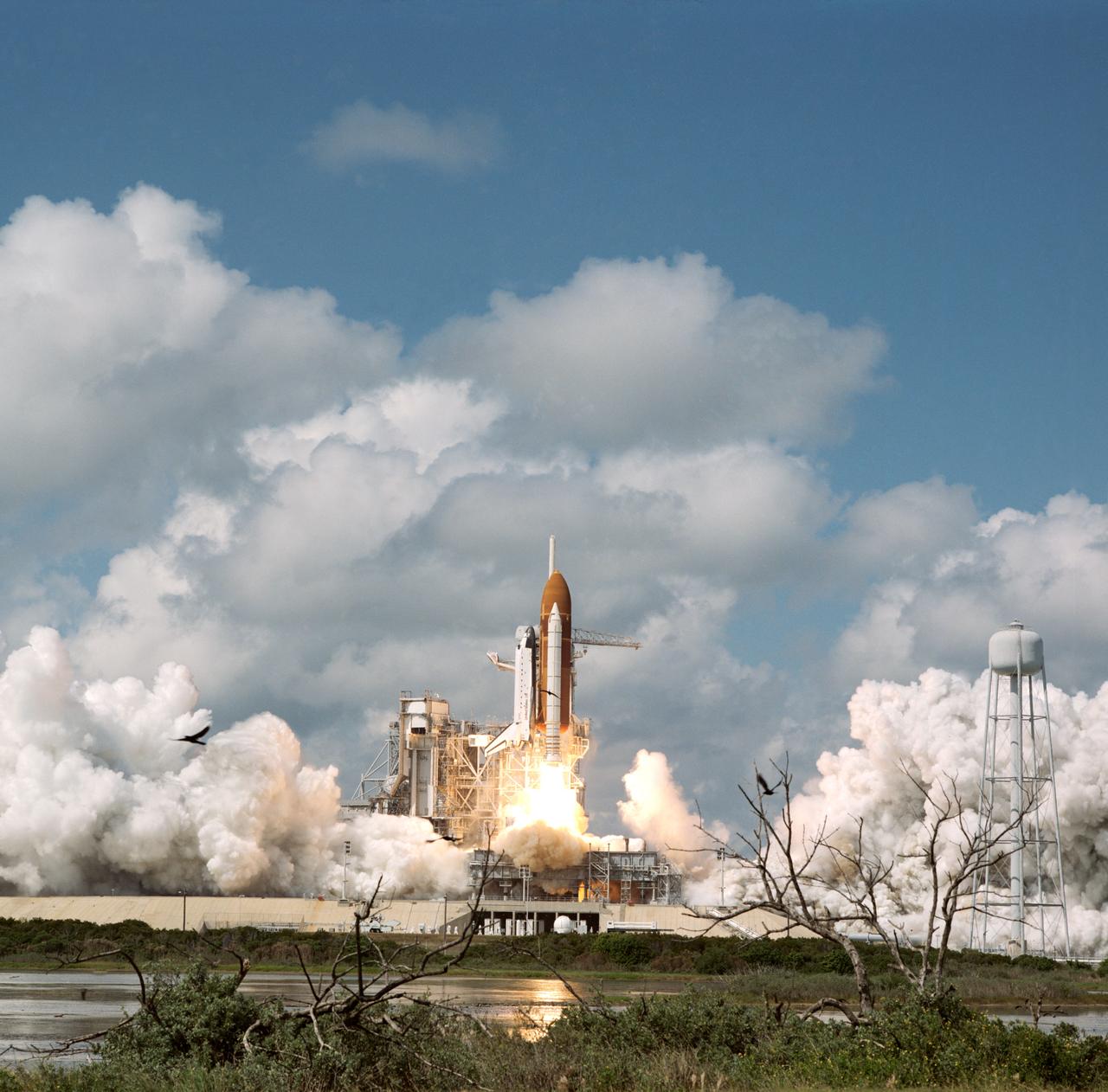

STS-26 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, lifts off from mobile launcher platform at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) pad 39B. Riding atop the orange external tank (ET), OV-103 heads for Earth orbit as the exhaust plumes from the two solid rocket boosters (SRBs) cover the mobile launcher platform and the area surrounding the launch pad. SRB firings are reflected in a nearby waterway. In the foreground are trees and several birds in flight. STS-26 marks OV-103's first flight since September 1985 and NASA's first manned mission since the 51L Challenger accident, 01-28-86.
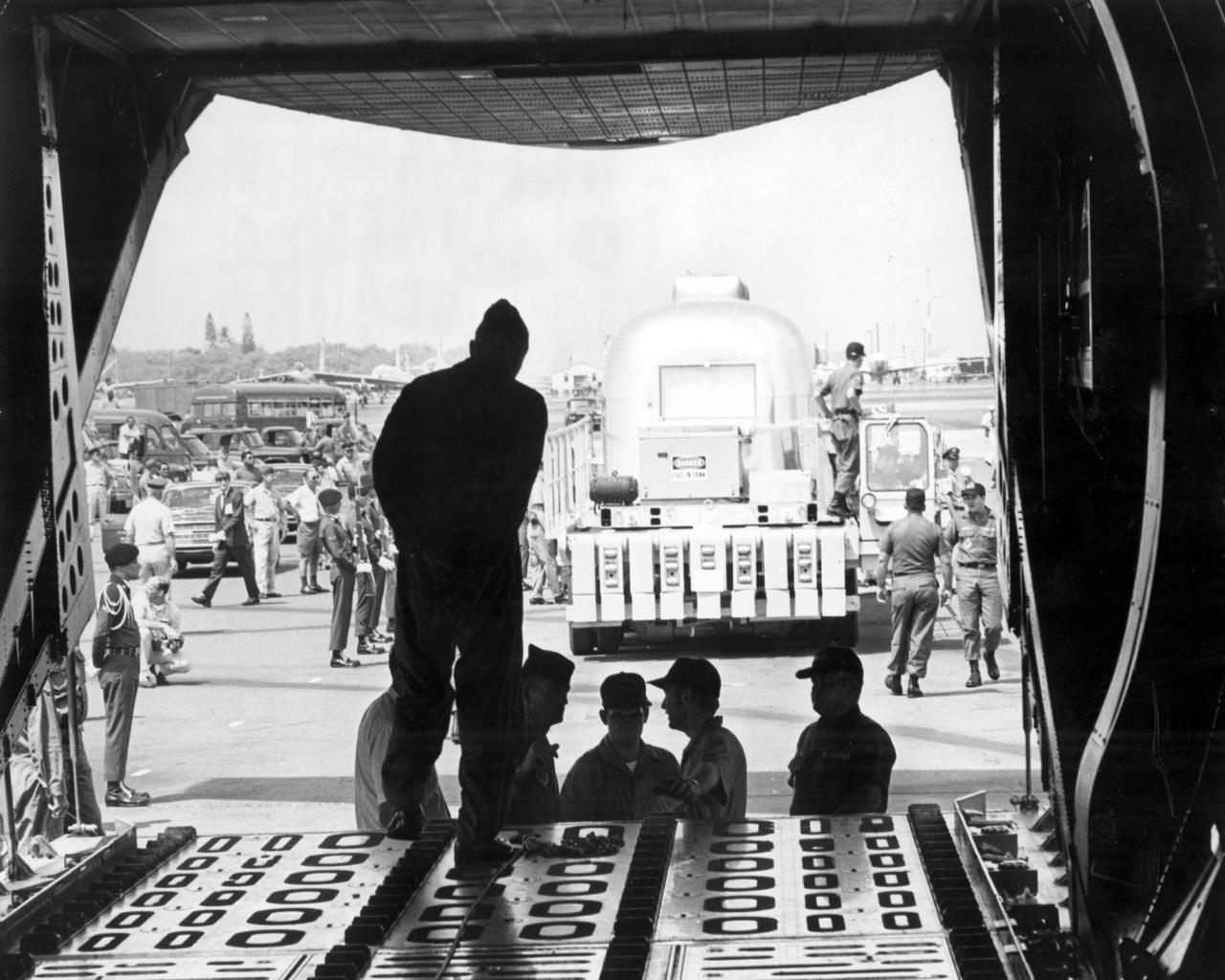

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) which served as their home until they reached the NASA Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory in Houston, Texas. In this photo taken at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, the inhabited MQF is prepared for loading into an Air Force C-141 jet transport for the flight back to Ellington Air Force Base Texas and then on to the MSC.
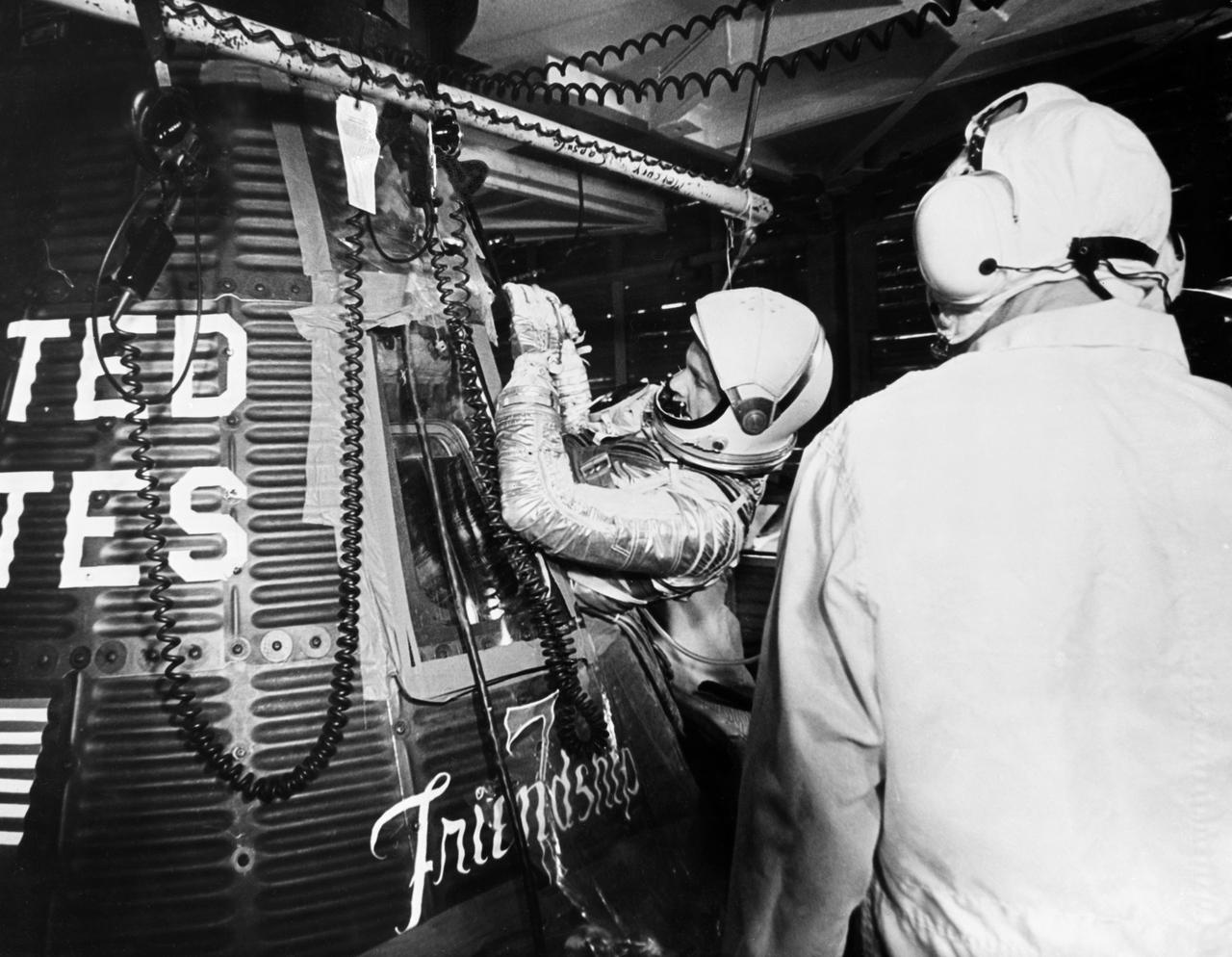

S62-00957 (20 Feb. 1962) --- Project Mercury astronaut John H. Glenn Jr., enters the Friendship 7 spacecraft during the last part of the countdown on Feb. 20, 1962. At 9:47 a.m. (EST), the Atlas launch vehicle lifted the spacecraft into orbit for a three-orbit mission lasting four hours, 55 minutes and 23 seconds. Glenn and his spacecraft were recovered by the destroyer Noa just 21 minutes after landing in the Atlantic near Grand Turk Island, to successfully complete the nation's first manned orbital flight. Photo credit: NASA

S85-26952 (20 Feb. 1962) --- Project Mercury astronaut John H. Glenn Jr., enters the Friendship 7 spacecraft during the last part of the countdown on Feb. 20, 1962. At 9:47 a.m. (EST), the Atlas launch vehicle lifted the spacecraft into orbit for a three-orbit mission lasting four hours, 55 minutes and 23 seconds. Glenn and his spacecraft were recovered by the destroyer Noa just 21 minutes after landing in the Atlantic near Grand Turk Island, to successfully complete the nation's first manned orbital flight. Photo credit: NASA

Project Mercury: With Project Mercury, the United States gained its first experience in conducting human space missions that provided scientific and engineering knowledge of astronauts in space. Alan Shepard made history May 5, 1961, as America's first man in space. Less than a year later, John Glenn made the nation’s first orbital flight on Feb. 20, 1962. After two suborbital and three orbital missions, Project Mercury ended with a 22-orbit spaceflight on May 16, 1963. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA
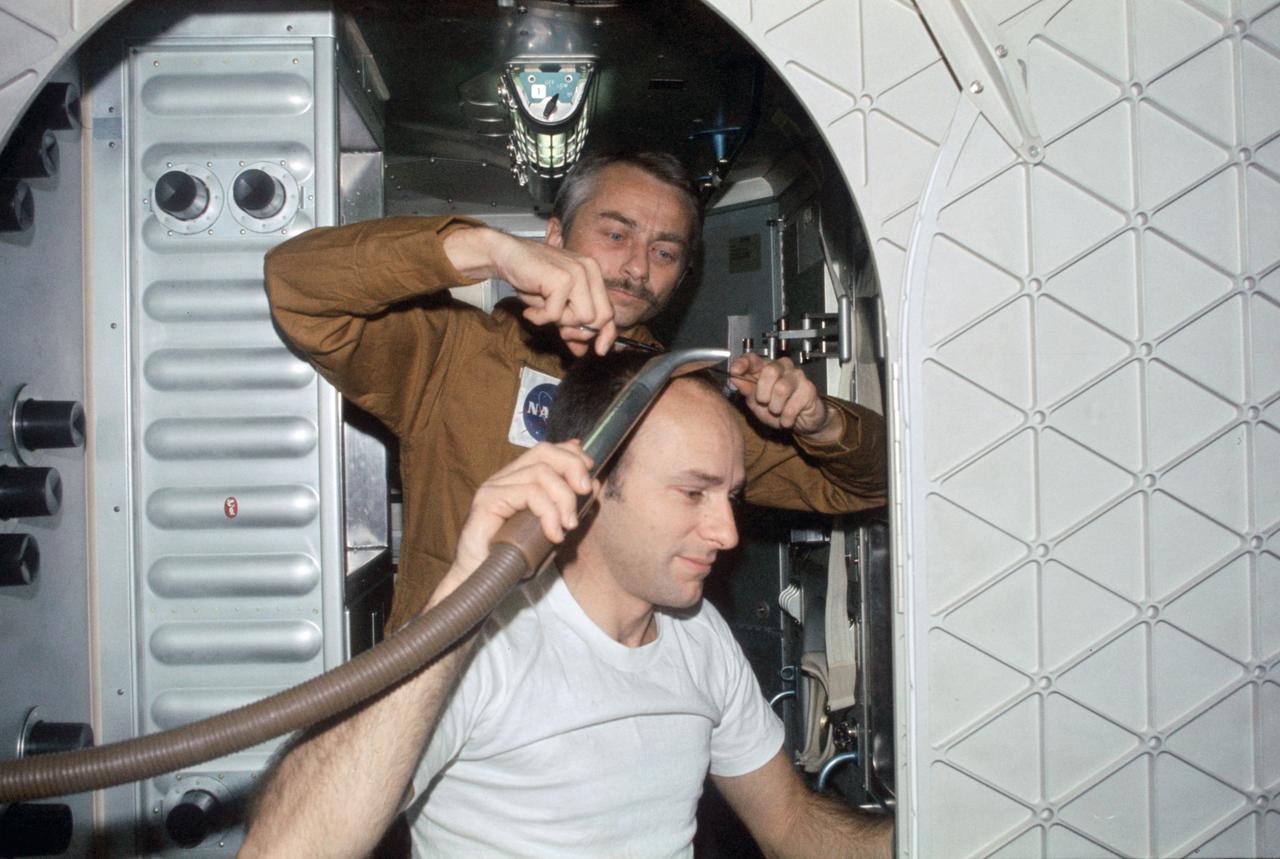
SL3-108-1292 (19 Aug. 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, Skylab 3 science pilot, trims the hair of astronaut Alan L. Bean, commander, in this onboard photograph from the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) in Earth orbit. Astronaut Jack R. Lousma, pilot, took this picture with a 35mm Nikon camera. Bean holds a vacuum hose to gather in loose hair. The crew of the second manned Skylab flight went on to successfully complete 59 days aboard the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA

Project Mercury: With Project Mercury, the United States gained its first experience in conducting human space missions that provided scientific and engineering knowledge of astronauts in space. Alan Shepard made history May 5, 1961, as America's first man in space. Less than a year later, John Glenn made the nation’s first orbital flight on Feb. 20, 1962. After two suborbital and three orbital missions, Project Mercury ended with a 22-orbit spaceflight on May 16, 1963. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA
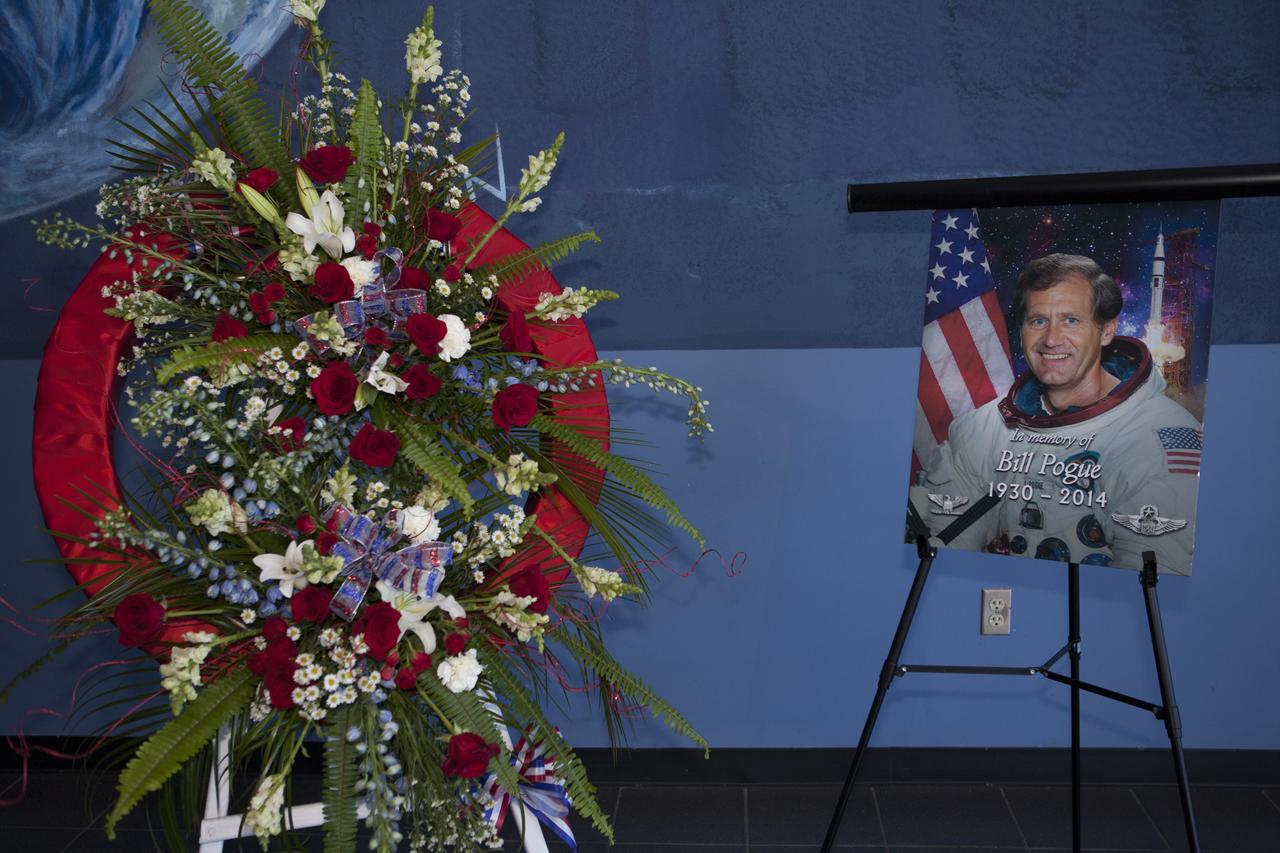

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A wreath is placed next to a photo of former NASA astronaut William R. Pogue during a ceremony to honor Pogue held at the United States Astronaut Hall of Fame at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Col. Pogue, pilot on NASA's Skylab 4 mission in 1973-74, died March 3. He was 84 years old. Skylab 4 was the third and final manned visit to the Skylab orbital workshop, launched Nov. 16, 1973, and concluded Feb. 8, 1974. At 84 days, 1 hour and 15 minutes, Skylab 4 was the longest manned space flight to that date. Pogue was accompanied on the record-setting 34.5-million-mile flight by Commander Gerald P. Carr and science-pilot Dr. Edward G. Gibson. They conducted dozens of experiments and science demonstrations during their 1,214 orbits of Earth. Pogue logged 13 hours and 31 minutes in two spacewalks outside the orbital workshop. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/content/skylab-4-pilot-william-pogue-dies. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Former NASA astronaut Edward G. Gibson, Ph.D., remarks on his friendship with former NASA astronaut William R. Pogue during a wreath laying ceremony at the United States Astronaut Hall of Fame at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Col. Pogue, pilot on NASA's Skylab 4 mission in 1973-74, died March 3. He was 84 years old. Skylab 4 was the third and final manned visit to the Skylab orbital workshop, launched Nov. 16, 1973, and concluded Feb. 8, 1974. At 84 days, 1 hour and 15 minutes, Skylab 4 was the longest manned space flight to that date. Pogue was accompanied on the record-setting 34.5-million-mile flight by Commander Gerald P. Carr and science-pilot Gibson. They conducted dozens of experiments and science demonstrations during their 1,214 orbits of Earth. Pogue logged 13 hours and 31 minutes in two spacewalks outside the orbital workshop. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/content/skylab-4-pilot-william-pogue-dies. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Former NASA astronaut Gerald P. Carr remarks on his friendship with former NASA astronaut William R. Pogue during a wreath laying ceremony at the United States Astronaut Hall of Fame at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Col. Pogue, pilot on NASA's Skylab 4 mission in 1973-74, died March 3. He was 84 years old. Skylab 4 was the third and final manned visit to the Skylab orbital workshop, launched Nov. 16, 1973, and concluded Feb. 8, 1974. At 84 days, 1 hour and 15 minutes, Skylab 4 was the longest manned space flight to that date. Pogue was accompanied on the record-setting 34.5-million-mile flight by Commander Carr and science-pilot Dr. Edward G. Gibson. They conducted dozens of experiments and science demonstrations during their 1,214 orbits of Earth. Pogue logged 13 hours and 31 minutes in two spacewalks outside the orbital workshop. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/content/skylab-4-pilot-william-pogue-dies. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Former NASA astronauts Gerald P. Carr, left, and Edward G. Gibson place a wreath on an easel during a ceremony to honor former NASA astronaut William R. Pogue at the United States Astronaut Hall of Fame at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. In the background is a painting by former NASA astronaut Alan Bean. Col. Pogue, pilot on NASA's Skylab 4 mission in 1973-74, died March 3. He was 84 years old. Skylab 4 was the third and final manned visit to the Skylab orbital workshop, launched Nov. 16, 1973, and concluded Feb. 8, 1974. At 84 days, 1 hour and 15 minutes, Skylab 4 was the longest manned space flight to that date. Pogue was accompanied on the record-setting 34.5-million-mile flight by Commander Carr and science-pilot Gibson. They conducted dozens of experiments and science demonstrations during their 1,214 orbits of Earth. Pogue logged 13 hours and 31 minutes in two spacewalks outside the orbital workshop. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/content/skylab-4-pilot-william-pogue-dies. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – From left, former NASA astronauts Robert Cabana, Gerald P. Carr and Edward G. Gibson pay their respects to former NASA astronaut William R. Pogue during a wreath laying ceremony at the United States Astronaut Hall of Fame at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Cabana now is the director of Kennedy Space Center. In the background is a painting by former NASA astronaut Alan Bean. Col. Pogue, pilot on NASA's Skylab 4 mission in 1973-74, died March 3. He was 84 years old. Skylab 4 was the third and final manned visit to the Skylab orbital workshop, launched Nov. 16, 1973, and concluded Feb. 8, 1974. At 84 days, 1 hour and 15 minutes, Skylab 4 was the longest manned space flight to that date. Pogue was accompanied on the record-setting 34.5-million-mile flight by Commander Carr and science-pilot Gibson. They conducted dozens of experiments and science demonstrations during their 1,214 orbits of Earth. Pogue logged 13 hours and 31 minutes in two spacewalks outside the orbital workshop. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/content/skylab-4-pilot-william-pogue-dies. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
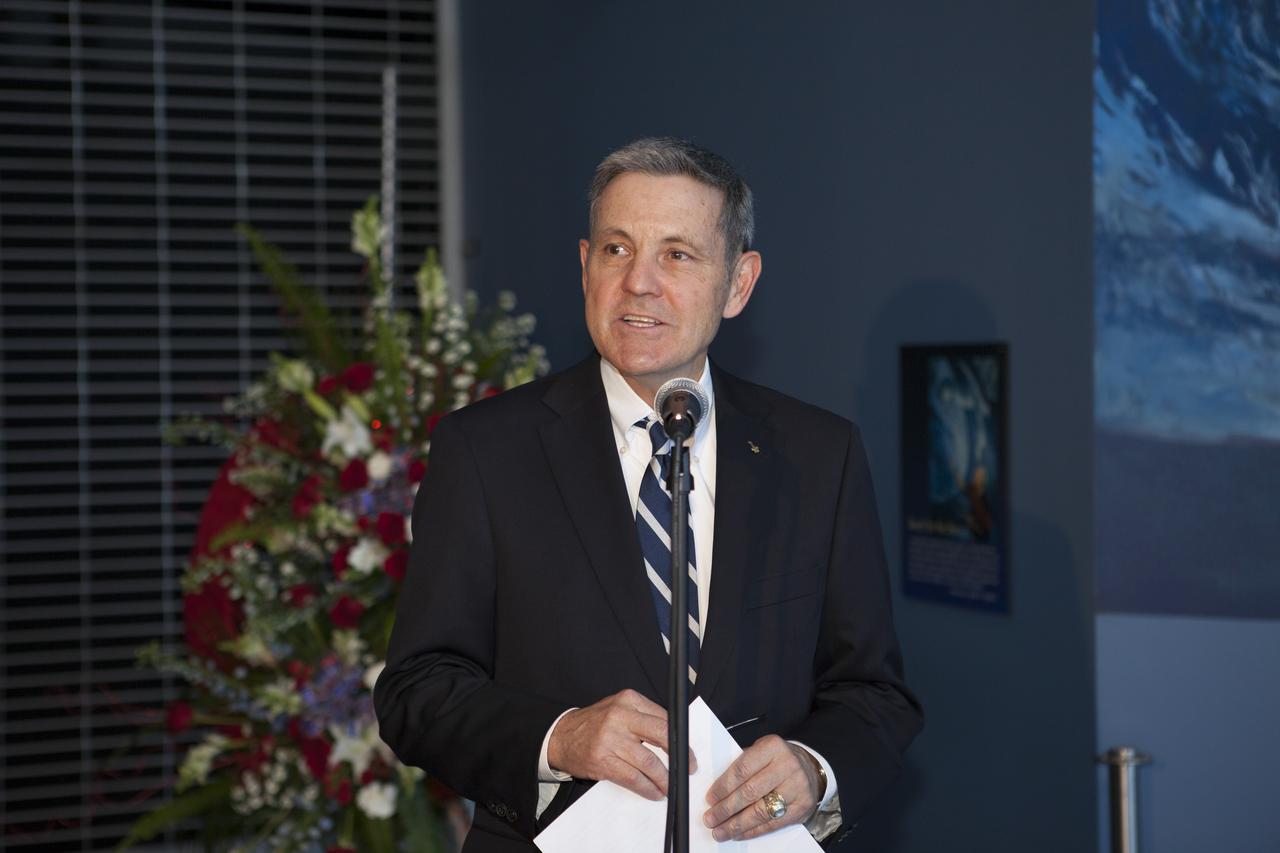

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Robert Cabana welcomes guests to the United States Astronaut Hall of Fame at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex for a wreath laying ceremony to honor former NASA astronaut William R. Pogue. Col. Pogue, pilot on NASA's Skylab 4 mission in 1973-74, died March 3. He was 84 years old. Skylab 4 was the third and final manned visit to the Skylab orbital workshop, launched Nov. 16, 1973, and concluded Feb. 8, 1974. At 84 days, 1 hour and 15 minutes, Skylab 4 was the longest manned space flight to that date. Pogue was accompanied on the record-setting 34.5-million-mile flight by Commander Gerald P. Carr and science-pilot Dr. Edward G. Gibson. They conducted dozens of experiments and science demonstrations during their 1,214 orbits of Earth. Pogue logged 13 hours and 31 minutes in two spacewalks outside the orbital workshop. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/content/skylab-4-pilot-william-pogue-dies. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
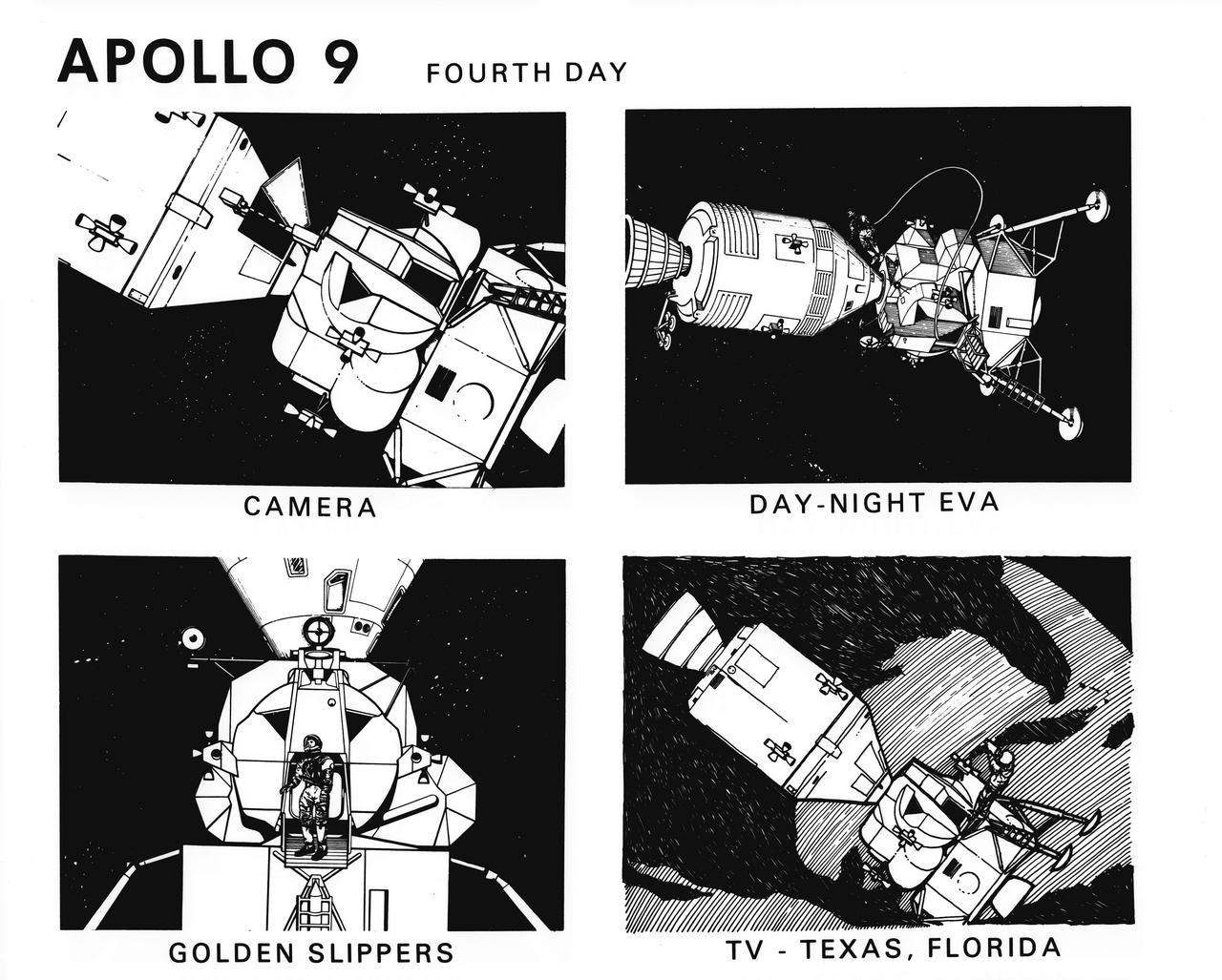
S69-19795 (February 1969) --- Composite of four artist's concepts illustrating key events, tasks and activities on the fourth day of the Apollo 9 mission, including use of camera, day-night extravehicular activity, use of golden slippers, and television over Texas and Florida. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.
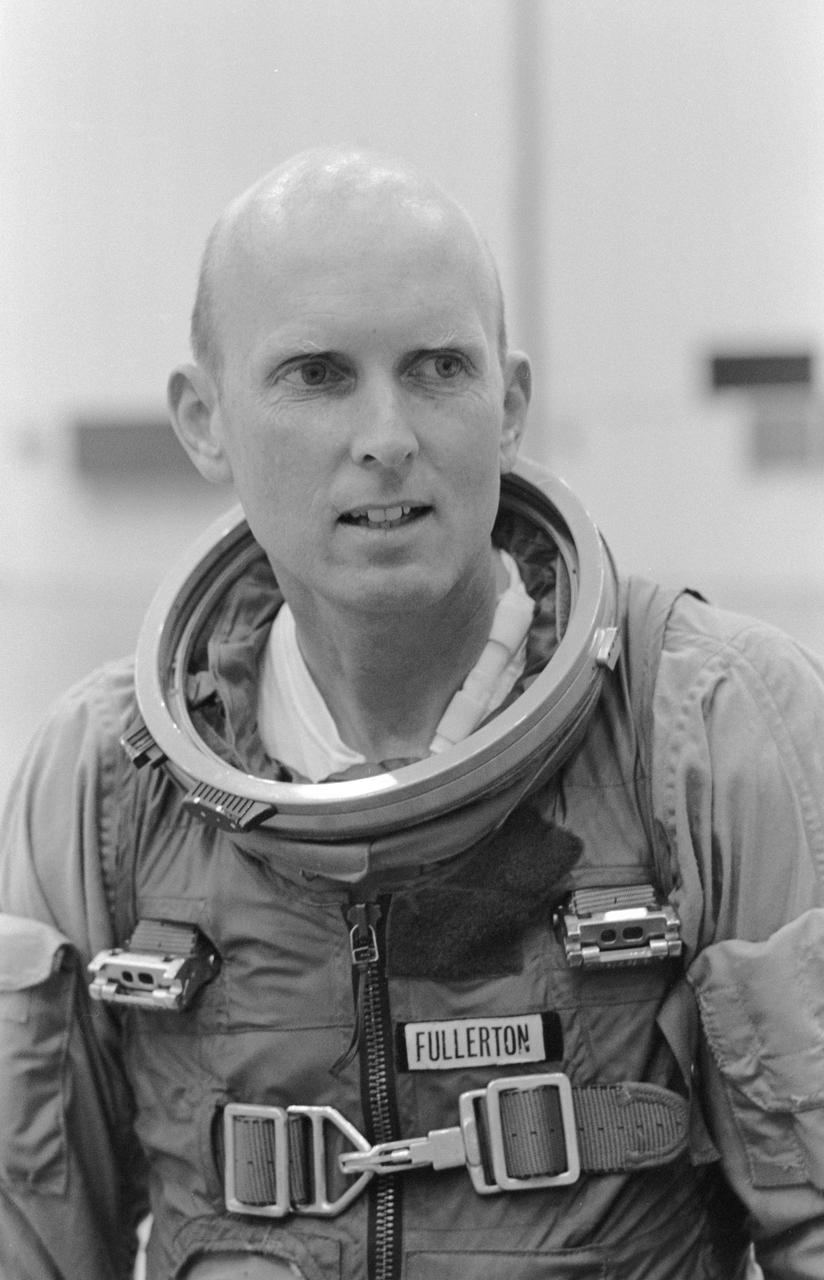

S78-34917 (31 Aug. 1978) --- Just about to don his helmet and enter JSC?s shuttle engineering mock-up/trainer is astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton, one of eight NASA astronauts recently named to man the space shuttle Columbia on a series of orbital flight tests in the early 1980s. Photo credit: NASA NOTE: Since this photograph was made, astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton was named pilot for STS-3, scheduled for launch in early spring of 1982.
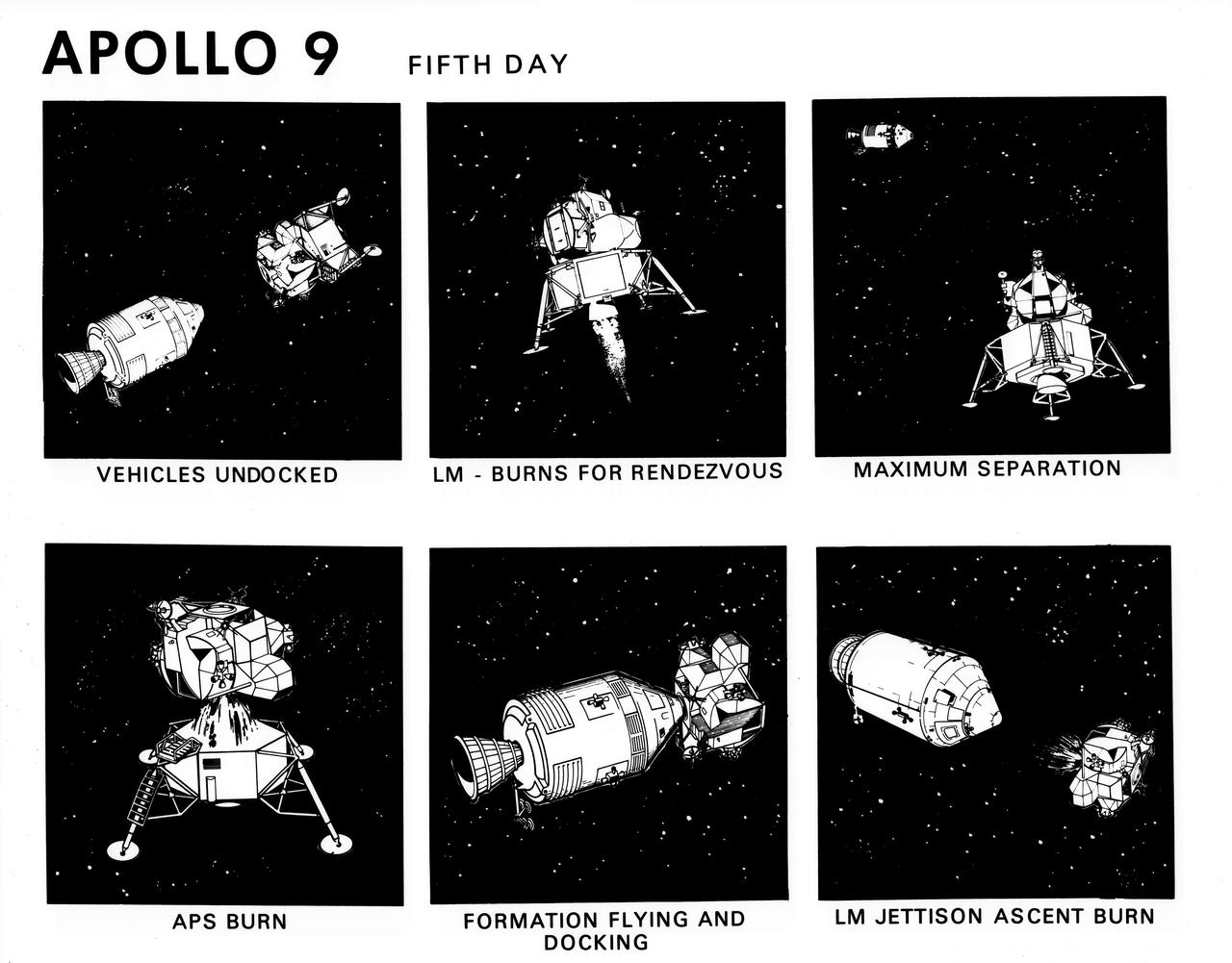
S69-19796 (February 1969) --- Composite of six artist's concepts illustrating key events, tasks and activities on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 mission, including vehicles undocked, Lunar Module burns for rendezvous, maximum separation, ascent propulsion system burn, formation flying and docking, and Lunar Module jettison ascent burn. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.

Workmen at the Kennedy Space Center position the nose cone for the 204LM-1, an unmanned Apollo mission that tested the Apollo Lunar Module (LM) in Earth orbit. Also known as Apollo 5, the spacecraft was launched on the fourth Saturn IBC launch vehicle. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IBC utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine a larger booster and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.
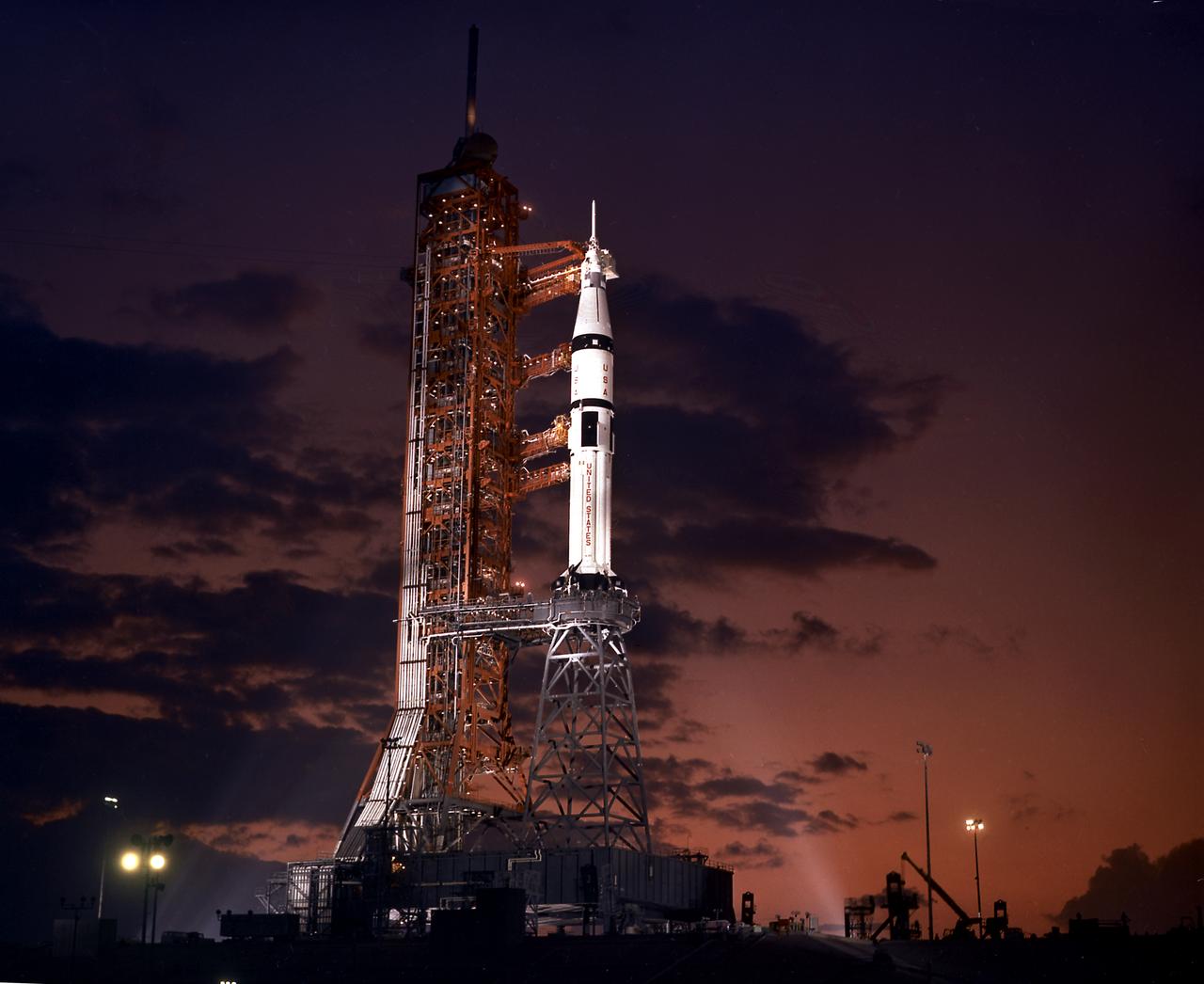

SA-210 Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) awaits the launch scheduled on July 15, 1975 on the launch pad at the Kennedy Space Center, the ASTP mission with astronauts Thomas Stafford, Vance Brand, and Donald "Deke" Slayton. The Saturn IB, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), launched five manned Earth-orbital missions between 1968 and 1975: Apollo 7, Skylab 2, Skylab 3, Skylab 4, and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project .

S73-37251 (23 November 1973) --- Astronaut Bruce McCandless II, left, shows off a mock-up of the occulting disc for the T025 Coronagraph Contamination Measurement Engineering and Technology Experiment to be used by the crewmen of the third manned Skylab mission (Skylab 4), now into their eighth day in Earth orbit. On the right is flight director Neil B. Hutchinson. The men are in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) of the Mission Control Center (MCC) at Johnson Space Center. Photo credit: NASA
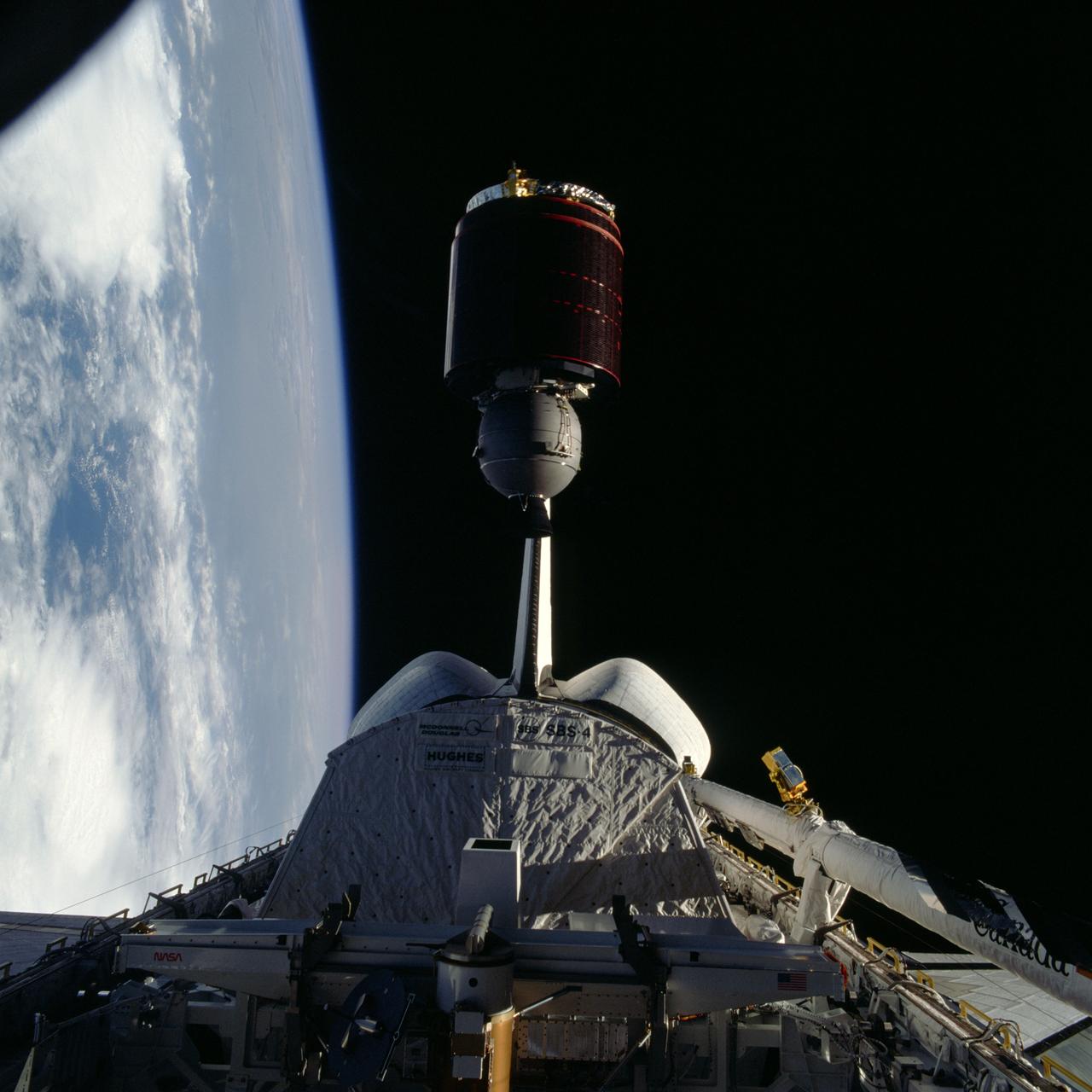

41D-37-050 (1 Sept 1984) --- Telstar, the third of three satellites to be placed into space via the Earth-orbiting Discovery, departs from the cargo bay of the manned vehicle during 41-D's third day in space. The scene was photographed at 9:35 a.m. (CDT), Sept. 1, 1984, with a 70mm handheld hasselblad camera aimed through the windows on the flight deck. Heavy clouds cover much of the water and land mass of Earth in the background.

Workmen at the Kennedy Space Center position the nose cone for the 204LM-1, an unmanned Apollo mission that tested the Apollo Lunar Module (LM) in Earth orbit. Also known as Apollo 5, the spacecraft was launched on the fourth Saturn IBC launch vehicle. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IBC utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine a larger booster and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.
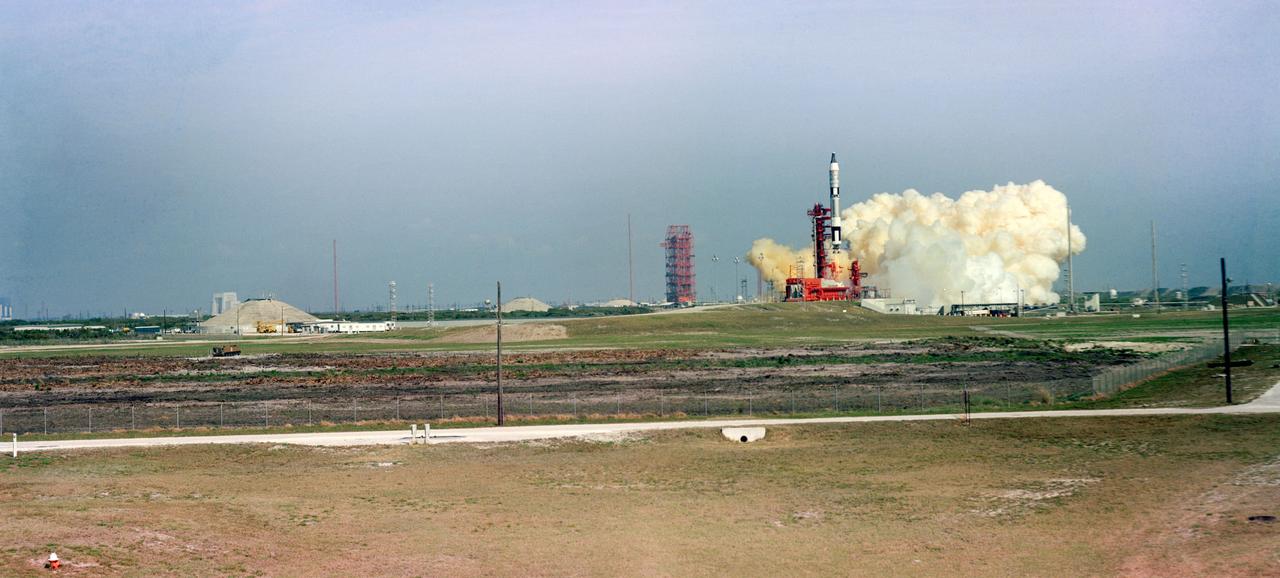

S65-21520 (23 March 1965) --- Distant view showing the successful launching of the first manned Gemini flight. The Gemini-Titan 3 (GT-3) lifted off Pad 19, at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) at 9:24 a.m. (EST), March 23, 1965. The Gemini-3 spacecraft "Molly Brown" carried astronauts Virgil I. Grissom, command pilot, and John W. Young, pilot, on three successful orbits of Earth.
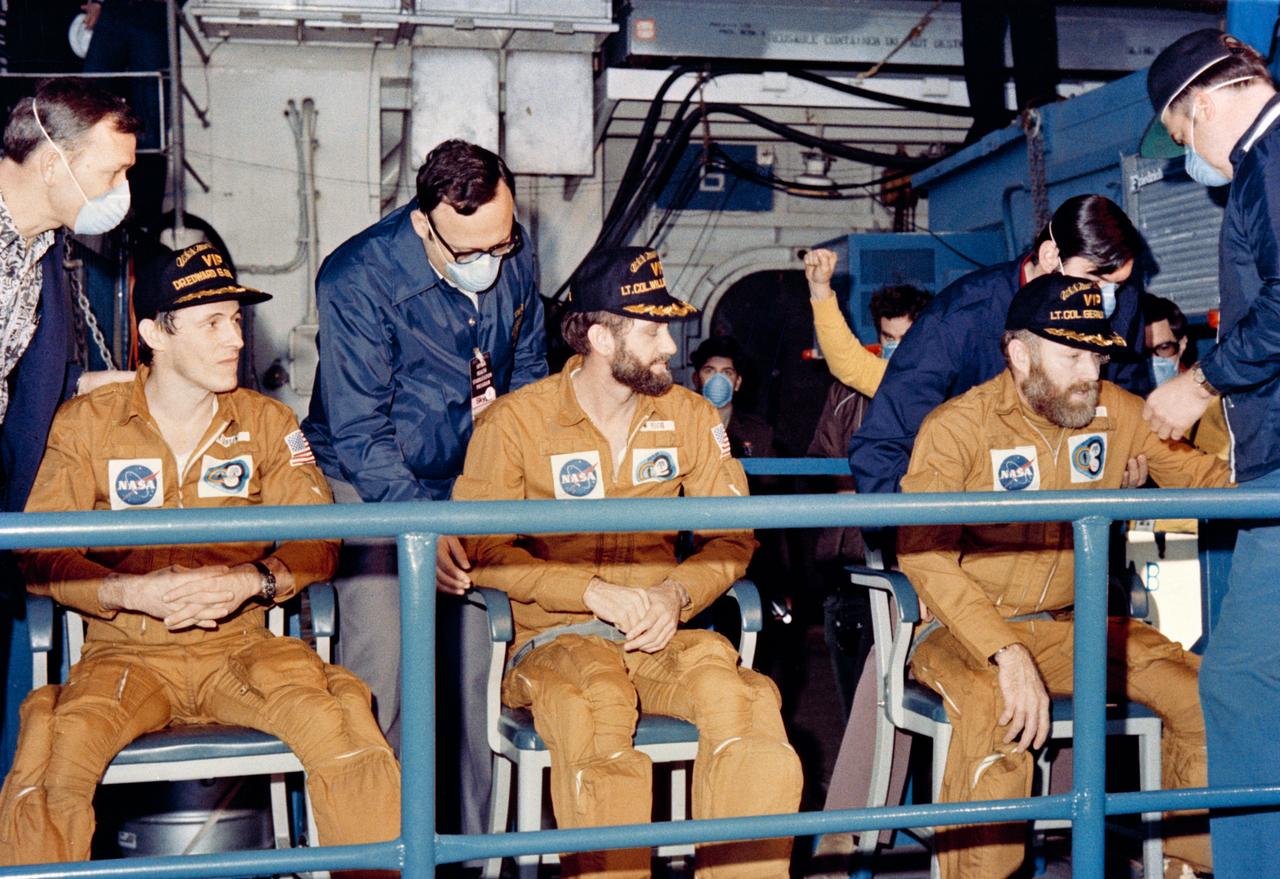

S74-17744 (8 Feb. 1974) --- The crewmen of the third and final manned Skylab mission relax on the USS New Orleans, prime recovery ship for their mission, about an hour after their Command Module splashed down at 10:17 a.m. (CDT), Feb. 8, 1974. The splashdown, which occurred 176 statute miles from San Diego, ended 84 record-setting days of flight activity aboard the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA

S62-00377 (20 Feb. 1962) --- Astronaut John H. Glenn Jr., walking out of building with Dr. William K. Douglas (to Glenn's left), and Joe W. Schmitt, NASA's suit technician (in front of Dr. Douglas). This Mercury Atlas 6 (MA-6) ?Friendship 7? flight marks America's first manned Earth-orbiting spaceflight. Photo credit: NASA
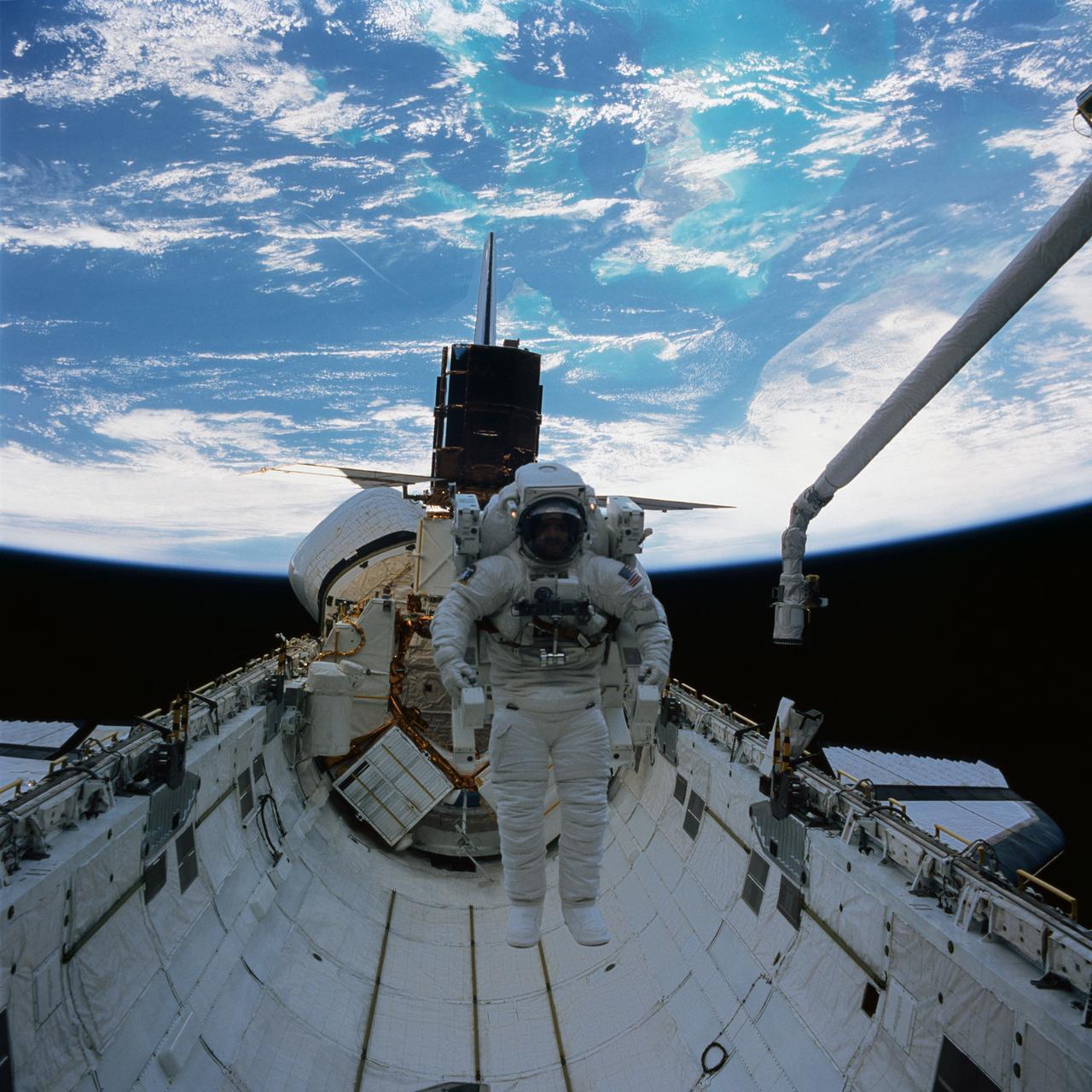

41C-37-1718 (11 April 1984) --- Astronaut James D. van Hoften and a repaired satellite are captured by a Hasselblad camera aimed through Challenger's aft cabin windows toward the cargo bay of the Earth orbiting Challenger. Dr. van Hoften is getting in his first "field" test of the manned maneuvering unit (MMU) after months of training in an underwater facility and in a simulator on Earth. The Solar Maximum Mission Satellite (SMMS), revived and almost ready for release into space once more, is docked at the flight support system (FSS).
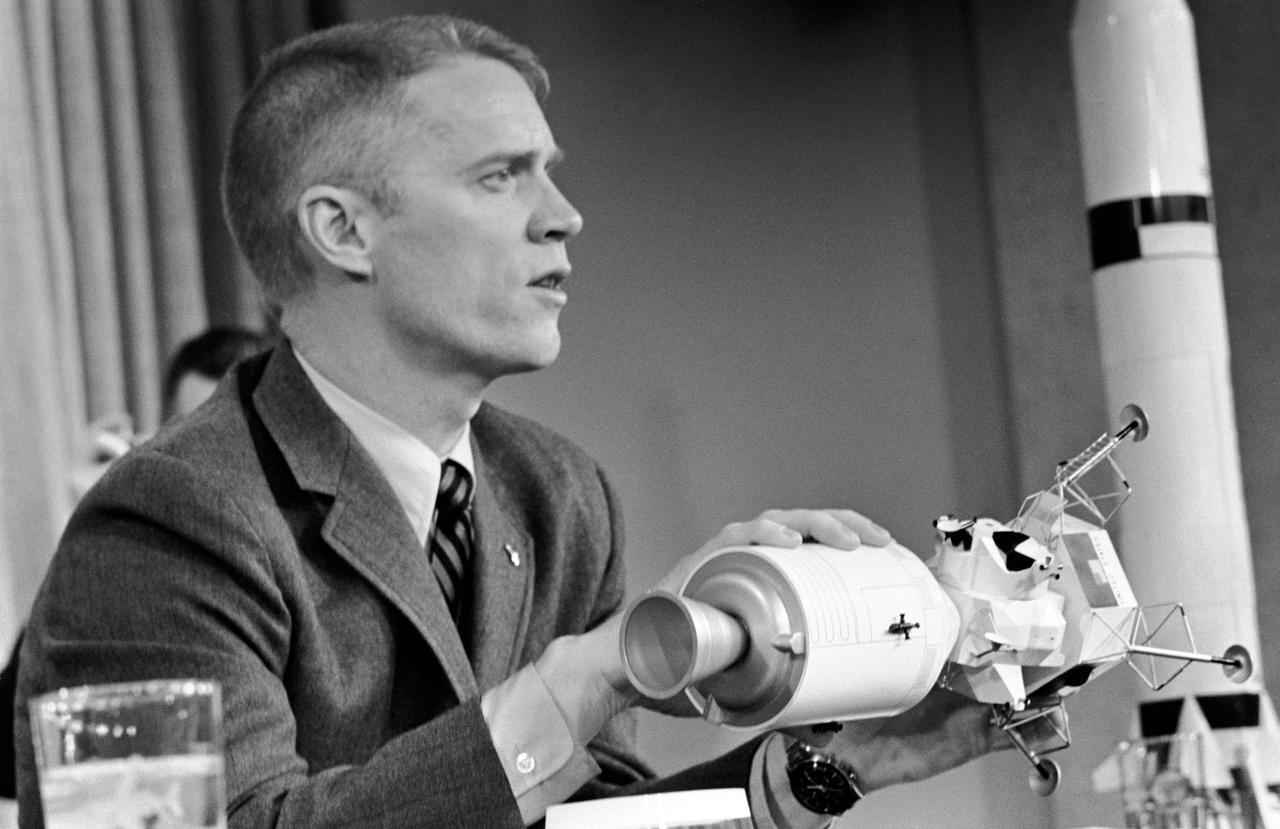

S69-17615 (25 Jan. 1969) --- Astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot of the Apollo 9 prime crew, participates in a press conference at the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation. Grumman is the contractor to NASA for the Lunar Module. Schweickart is holding a model of a docked Lunar Module/Command and Service Modules. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.
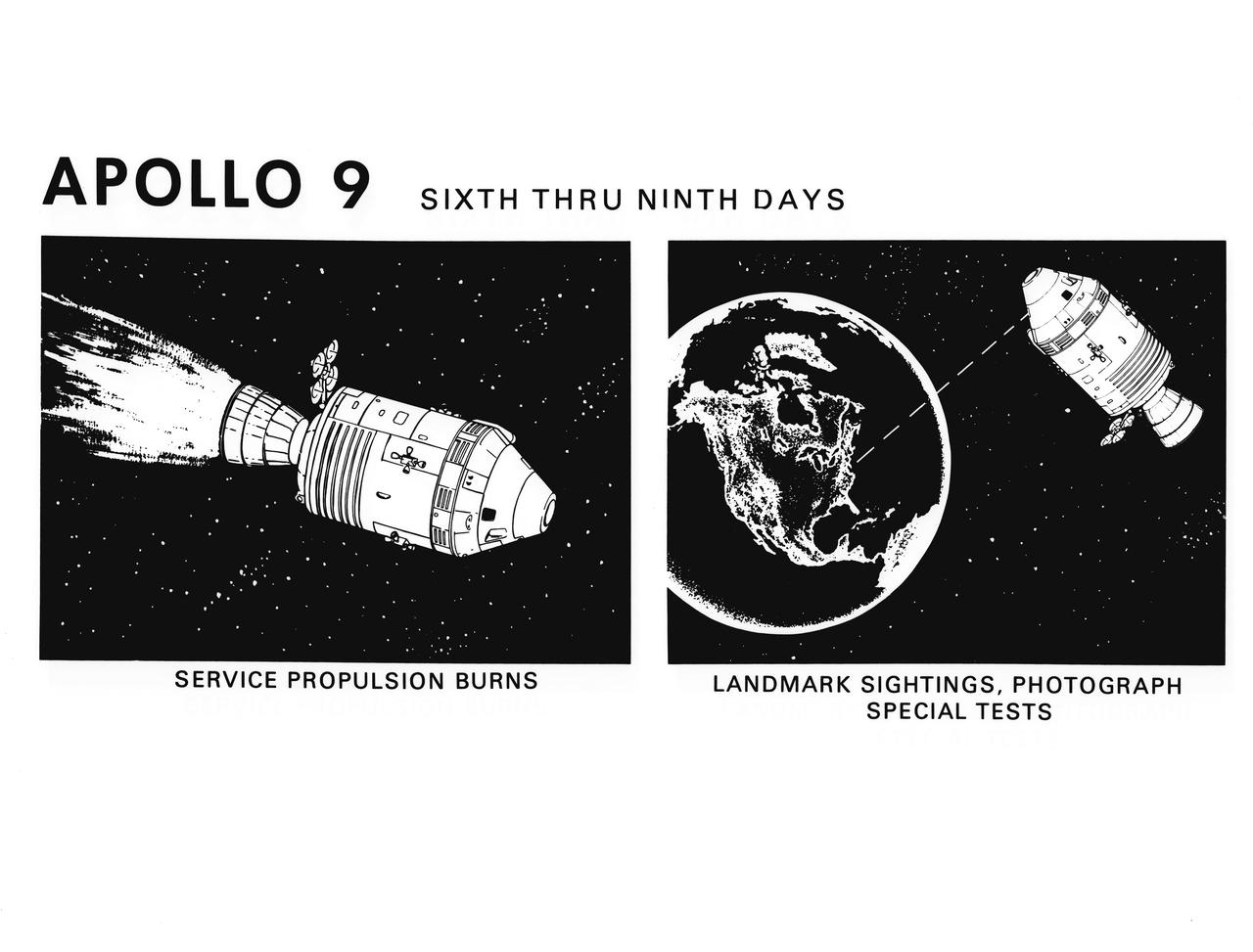
S69-19797 (February 1969) --- Composite of two artist's concepts illustrating key events, tasks and activities from the sixth through the ninth day of the Apollo 9 mission, including service propulsion system burns, and landmark sightings, photograph special tests. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.
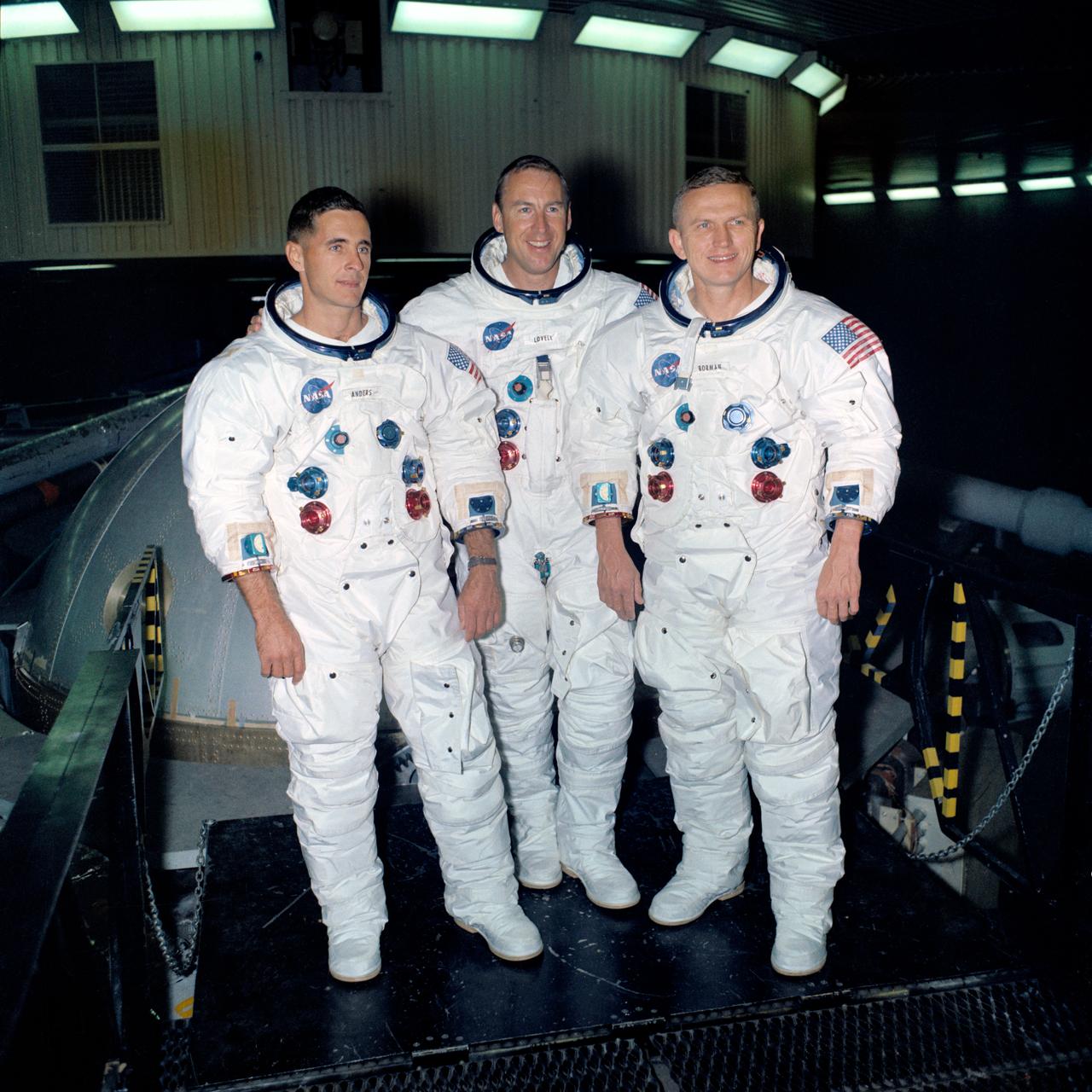

S68-53187 (1 Nov. 1968) --- The prime crew of the Apollo 8 lunar orbit mission stands beside the gondola in Building 29 after suiting up for centrifuge training in the Manned Spacecraft Center's (MSC) Flight Acceleration Facility (FAF). Left to right, are astronauts William A. Anders, lunar module pilot; James A. Lovell Jr., command module pilot; and Frank Borman, commander.
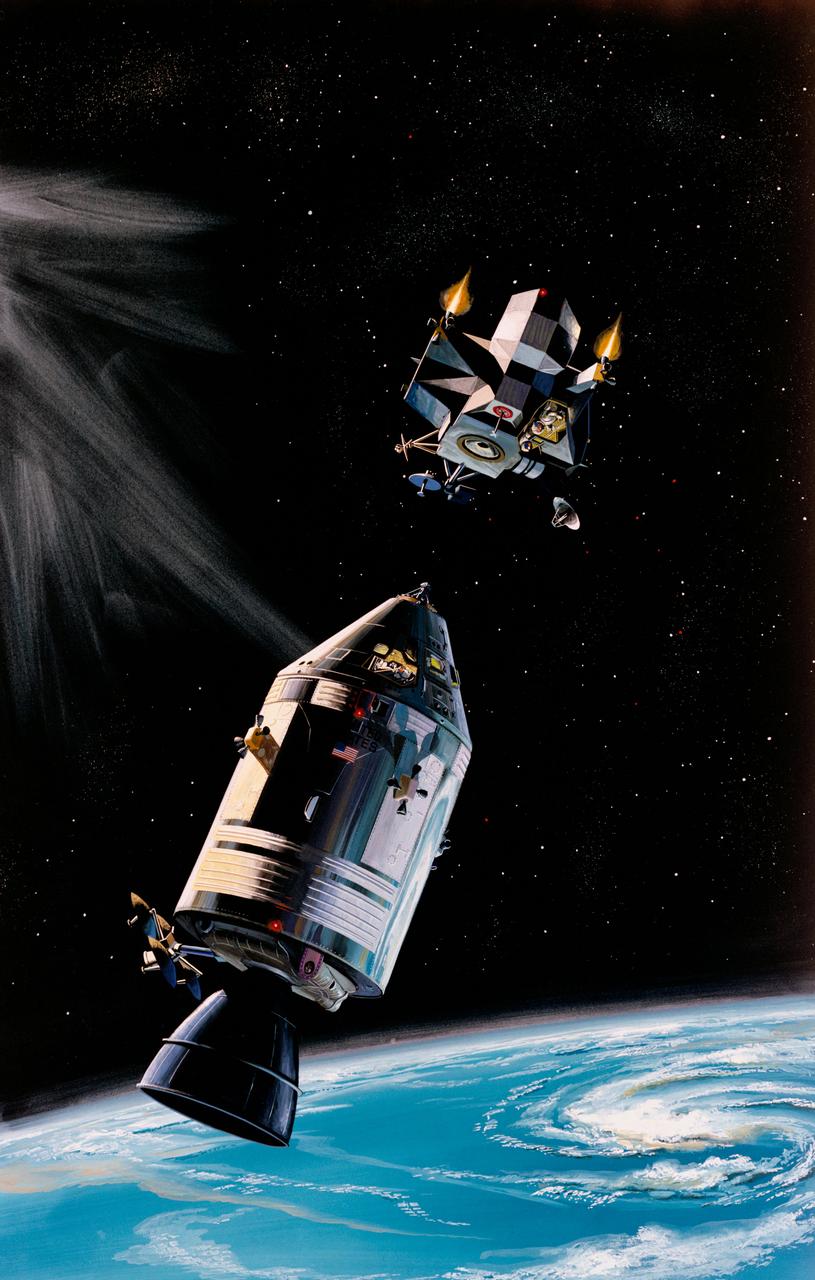

S69-18546 (February 1969) --- North American Rockwell artist's concept illustrating the docking of the Lunar Module ascent stage with the Command and Service Modules during the Apollo 9 mission. The two figures in the Lunar Module represent astronauts James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The figure in the Command Module represents astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.
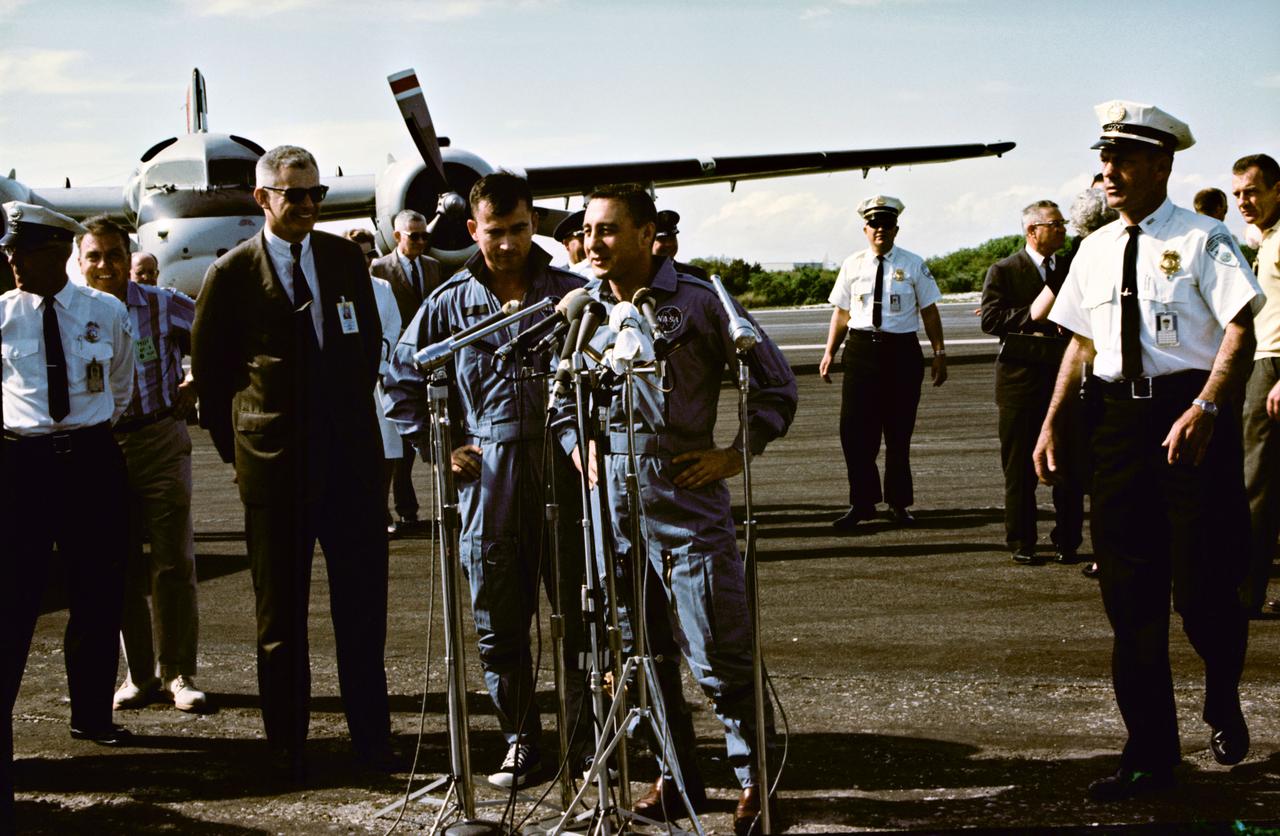

S65-20422 (24 March 1965) --- Astronauts John W. Young (left), pilot; and Virgil I. Grissom, command pilot, stand at microphones at the Cape's skid strip after being flown in from the recovery ship, USS Intrepid. The two astronauts made three orbits of Earth during the first manned Gemini flight the day before.

S69-19798 (February 1969) --- Composite of three artist's concepts illustrating key events, tasks and activities on the tenth day of the Apollo 9 mission, including Command Module and Service Modules separation, re-entry, and Atlantic splashdown. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.

Columbia, which opened the era of the Space Transportation System with four orbital flight tests, is featured in re-entry in the emblem designed by the STS-61C crew representing the seven team members who manned the vehicle for its seventh STS mission. Gold lettering against black background honors the astronaut crewmembers on the delta pattern surrounding colorful re-entry shock waves, and the payload specialists are honored similarly below the sphere

STS082-353-035 (11-21 Feb. 1997) --- Astronaut Steven A. Hawley, who spent many hours aboard Discovery controlling the shuttle's Remote Manipulator System (RMS), watches the Extravehicular Activity (EVA) of a two-man space walking team from Discovery's aft flight deck. Hawley had flown on the 1990 mission that was responsible for deploying the orbiting observatory.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A trailer hauls boxes and equipment from the 50-year-old Mission Control Center on the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Out of use for many years, and with no valid operational or other use for the facility, NASA plans to demolish the site. The facility once controlled all manned Mercury space flights and the first two unmanned Gemini flights from May 1961-1963. It provided launch, orbital, re-entry and landing control for the flights. That function was later transferred to NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Built in 1958, the Mission Control Center is located on the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Out of use for many years, and with no valid operational or other use for the facility, NASA plans to demolish the site. The facility once controlled all manned Mercury space flights and the first two unmanned Gemini flights from May 1961-1963. It provided launch, orbital, re-entry and landing control for the flights. That function was later transferred to NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
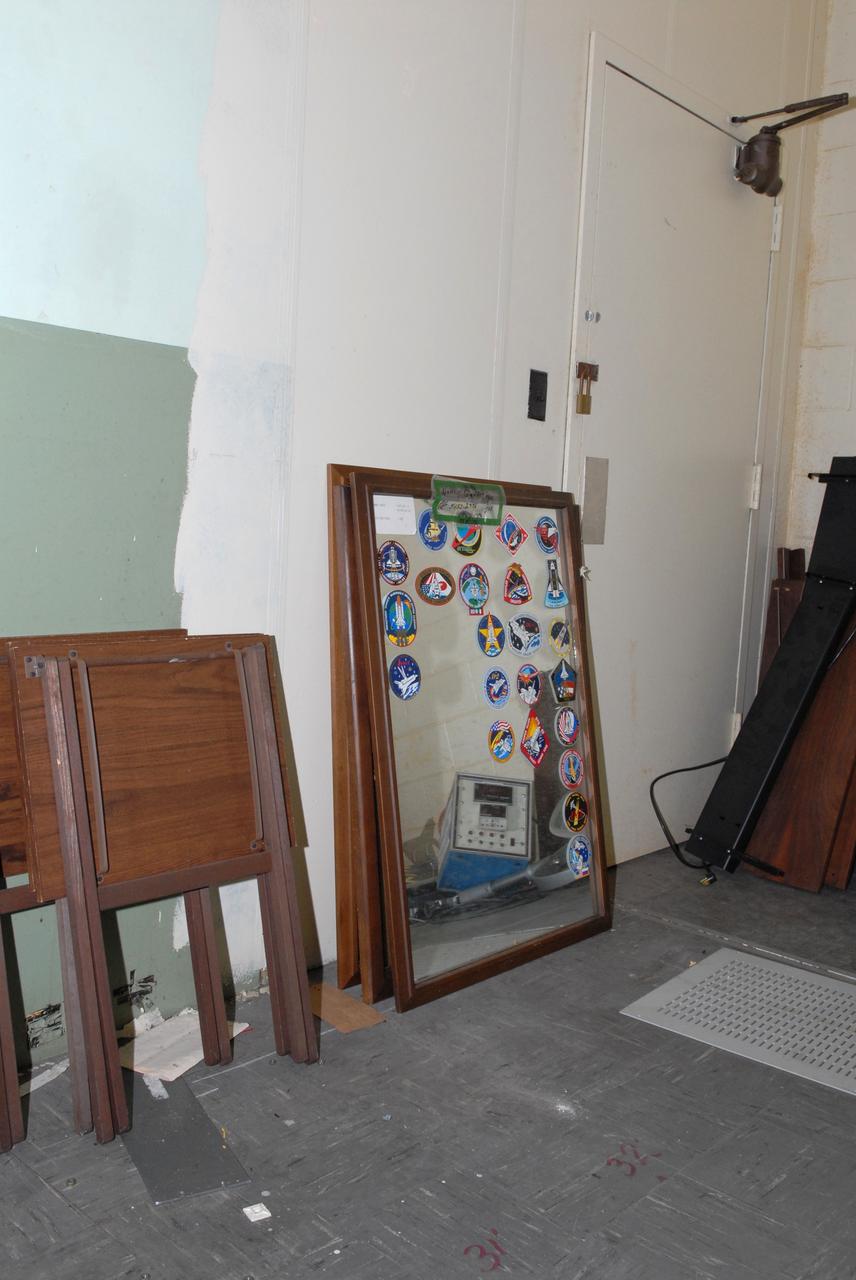

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Outdated furniture and display items are being moved out of the 50-year-old Mission Control Center on the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Out of use for many years, and with no valid operational or other use for the facility, NASA plans to demolish the site. The facility once controlled all manned Mercury space flights and the first two unmanned Gemini flights from May 1961-1963. It provided launch, orbital, re-entry and landing control for the flights. That function was later transferred to NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
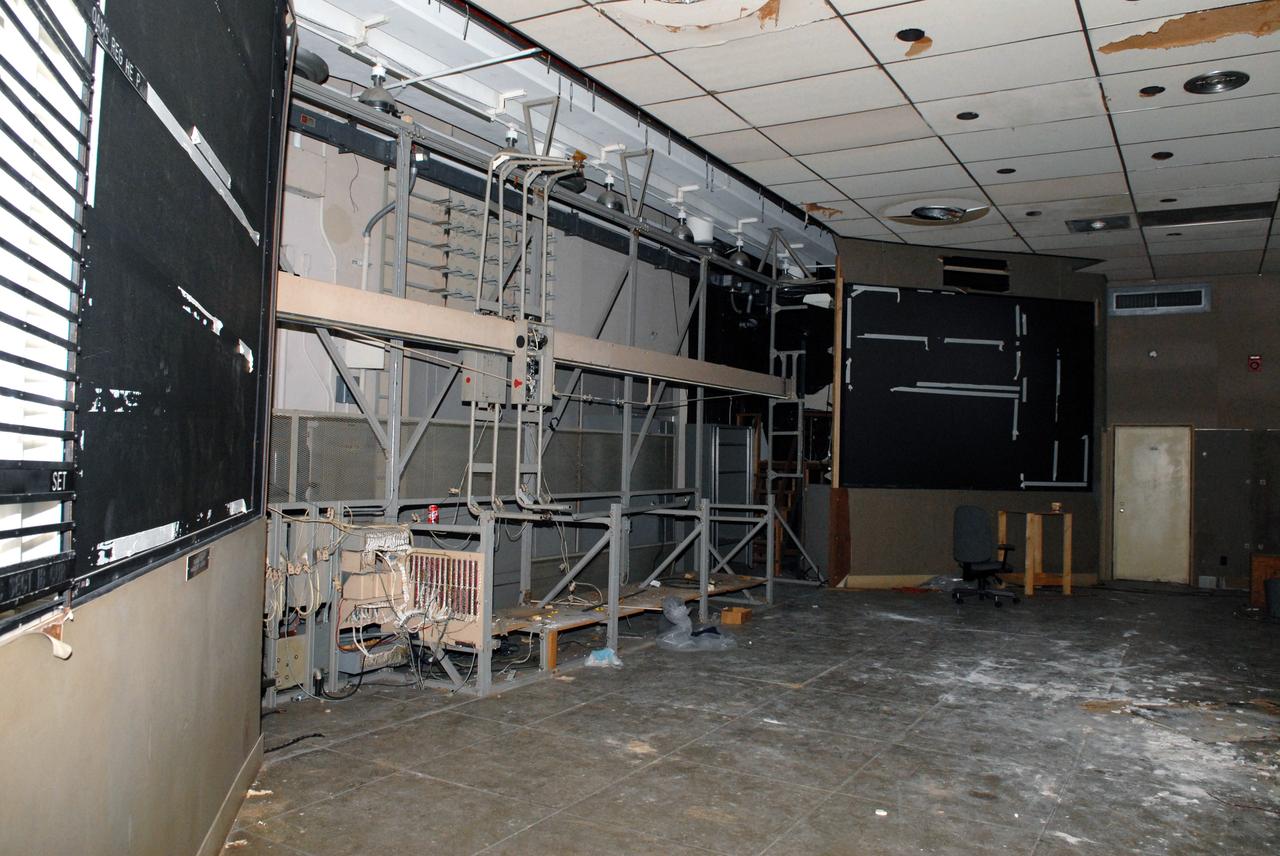

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Rooms are being dismantled in the 50-year-old Mission Control Center on the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Out of use for many years, and with no valid operational or other use for the facility, NASA plans to demolish the site. The facility once controlled all manned Mercury space flights and the first two unmanned Gemini flights from May 1961-1963. It provided launch, orbital, re-entry and landing control for the flights. That function was later transferred to NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
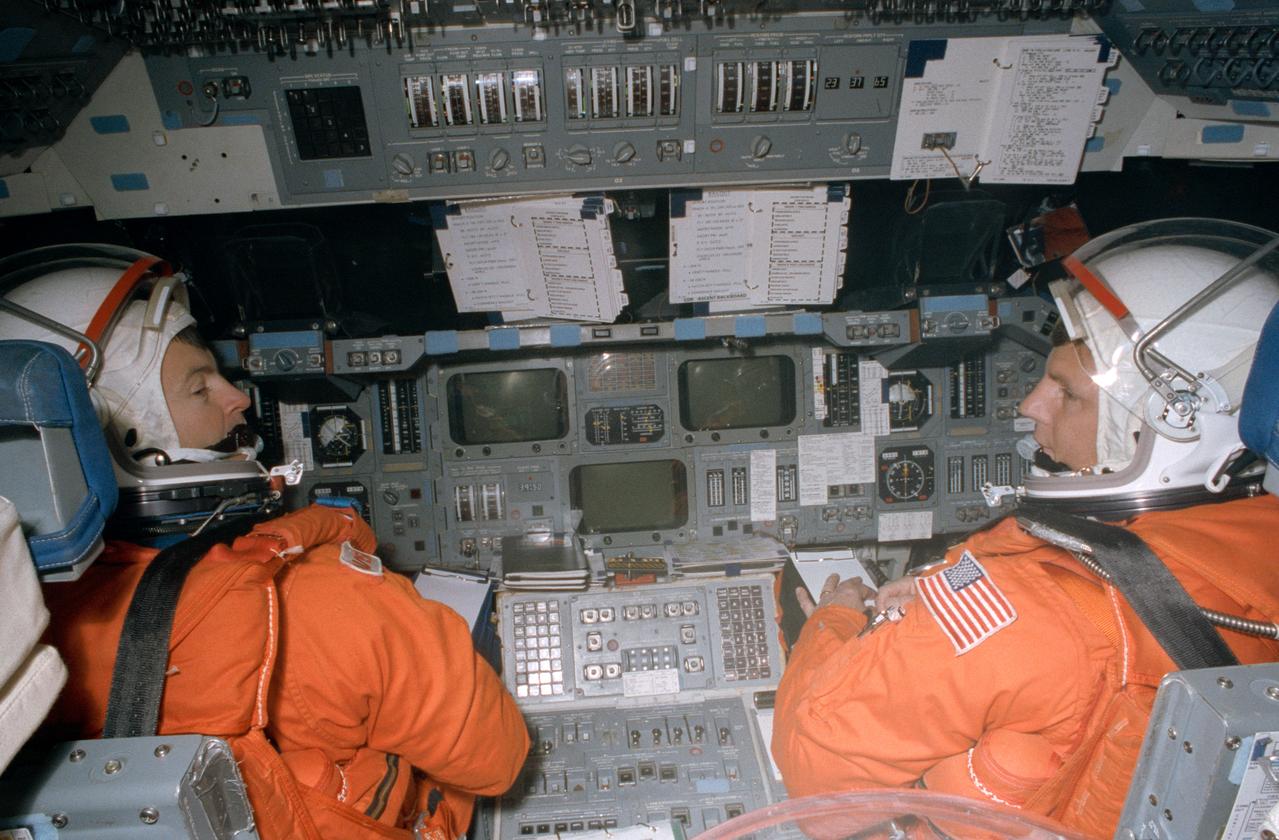

STS-56 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, Commander Kenneth Cameron, (left) and Pilot Stephen S. Oswald, wearing launch and entry suits (LESs) and launch and entry helmets (LEHs), are seated on the forward flight deck of the crew compartment trainer (CCT), a shuttle mockup. Cameron mans the commander station controls and Oswald the pilots station controls during an emergency egress (bailout) simulation. The view was taken from the aft flight deck looking forward and includes Cameron's and Oswald's profiles and the forward flight deck controls and checklists. The CCT is located in JSC's Mockup and Integration Laboratory (MAIL) Bldg 9NE.
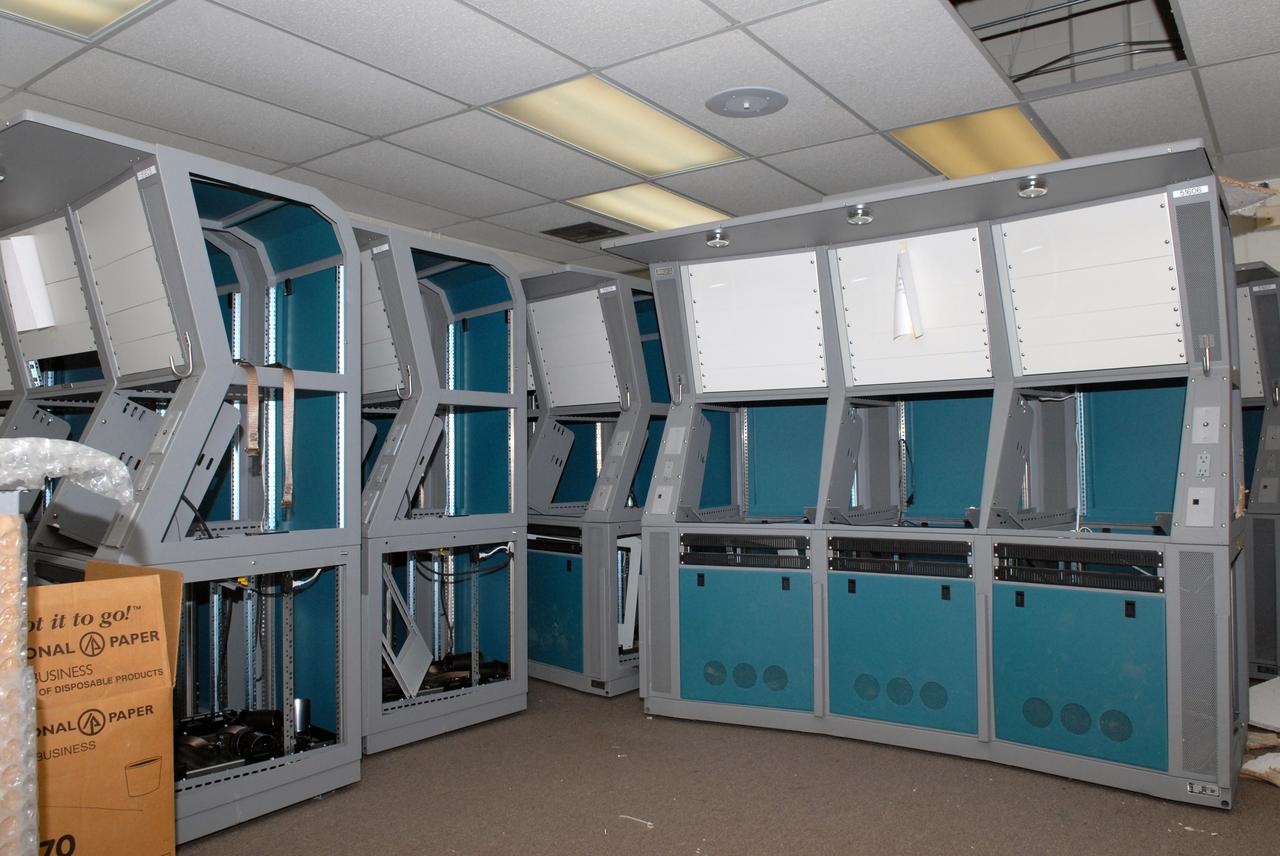

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Equipment is staged for removal from the 50-year-old Mission Control Center on the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Out of use for many years, and with no valid operational or other use for the facility, NASA plans to demolish the site. The facility once controlled all manned Mercury space flights and the first two unmanned Gemini flights from May 1961-1963. It provided launch, orbital, re-entry and landing control for the flights. That function was later transferred to NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
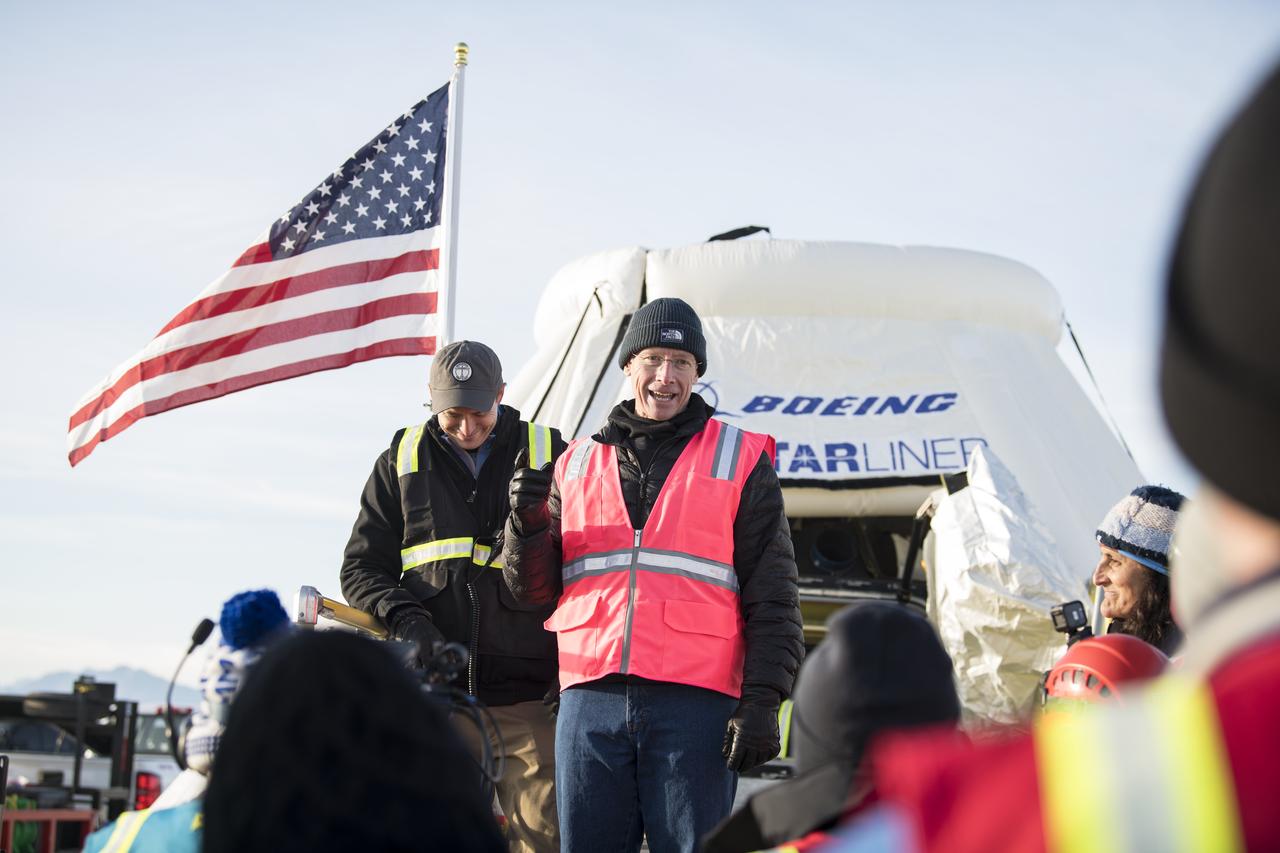

Former NASA astronaut and test flight pilot for the first manned flight of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft, Chris Ferguson, speaks after the capsule landed in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The NASA insignia has faded on the 50-year-old Mission Control Center on the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Out of use for many years, and with no valid operational or other use for the facility, NASA plans to demolish the site. The facility once controlled all manned Mercury space flights and the first two unmanned Gemini flights from May 1961-1963. It provided launch, orbital, re-entry and landing control for the flights. That function was later transferred to NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
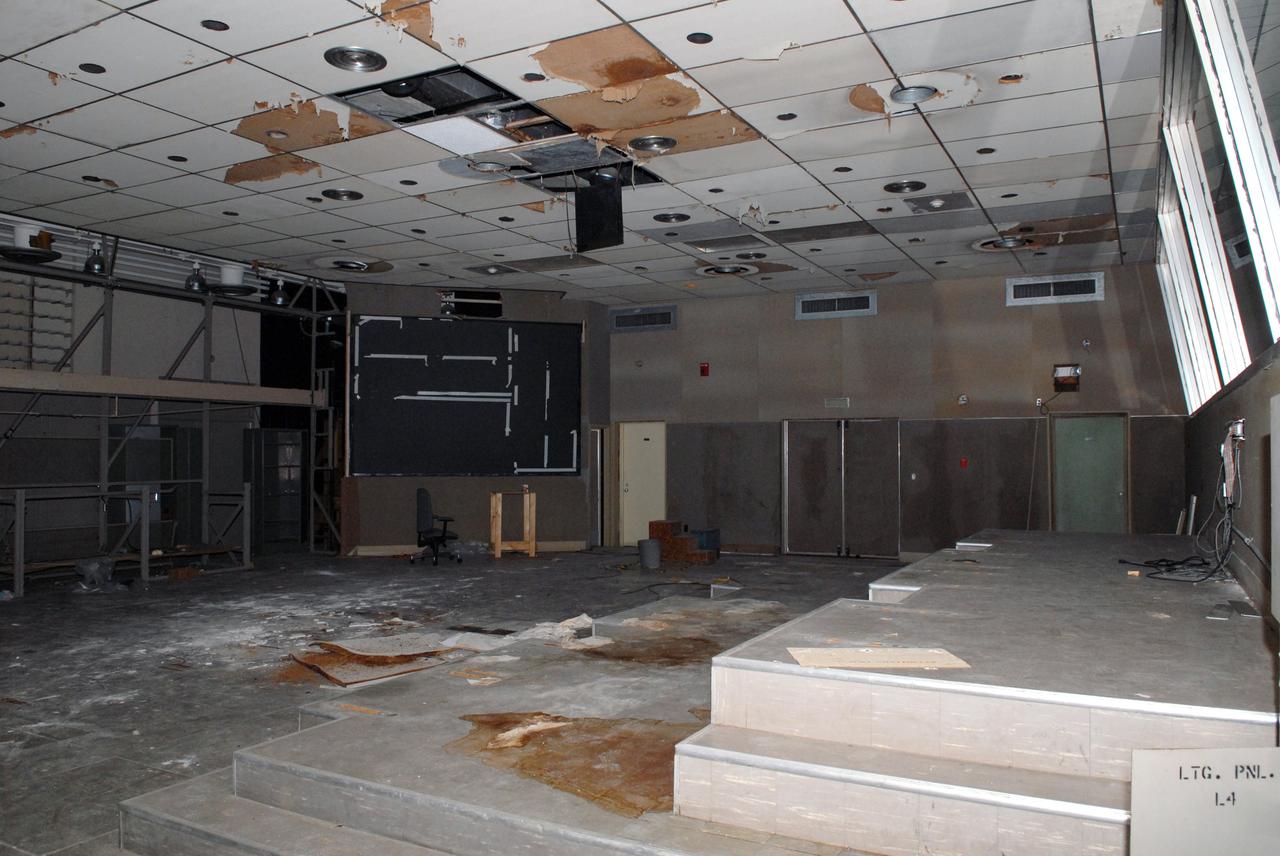

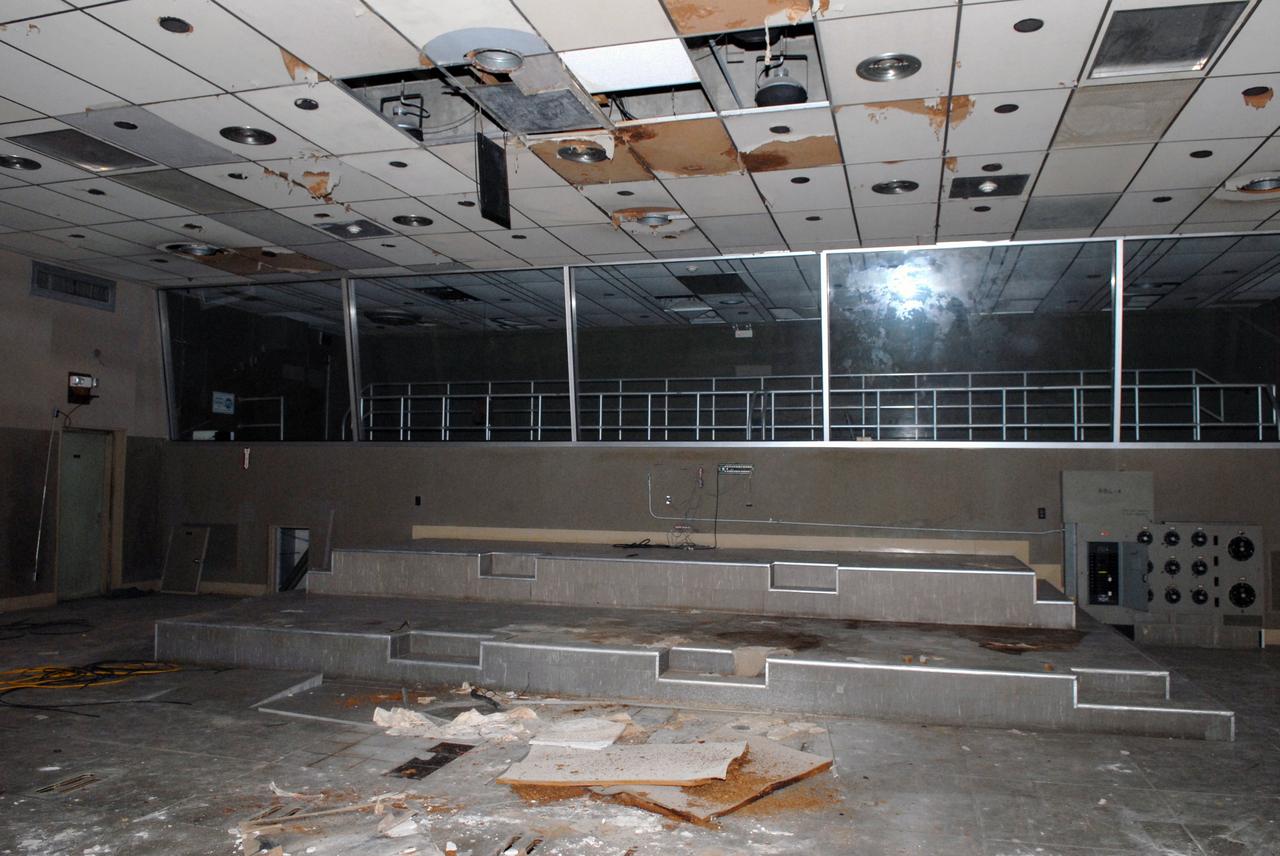
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Water damage and mold in rooms in the 50-year-old Mission Control Center on the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida are part of the reason for NASA's decision to demolish the site. The center has been out of use for many years, and NASA has found no valid operational or other use for the facility. The facility once controlled all manned Mercury space flights and the first two unmanned Gemini flights from May 1961-1963. It provided launch, orbital, re-entry and landing control for the flights. That function was later transferred to NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
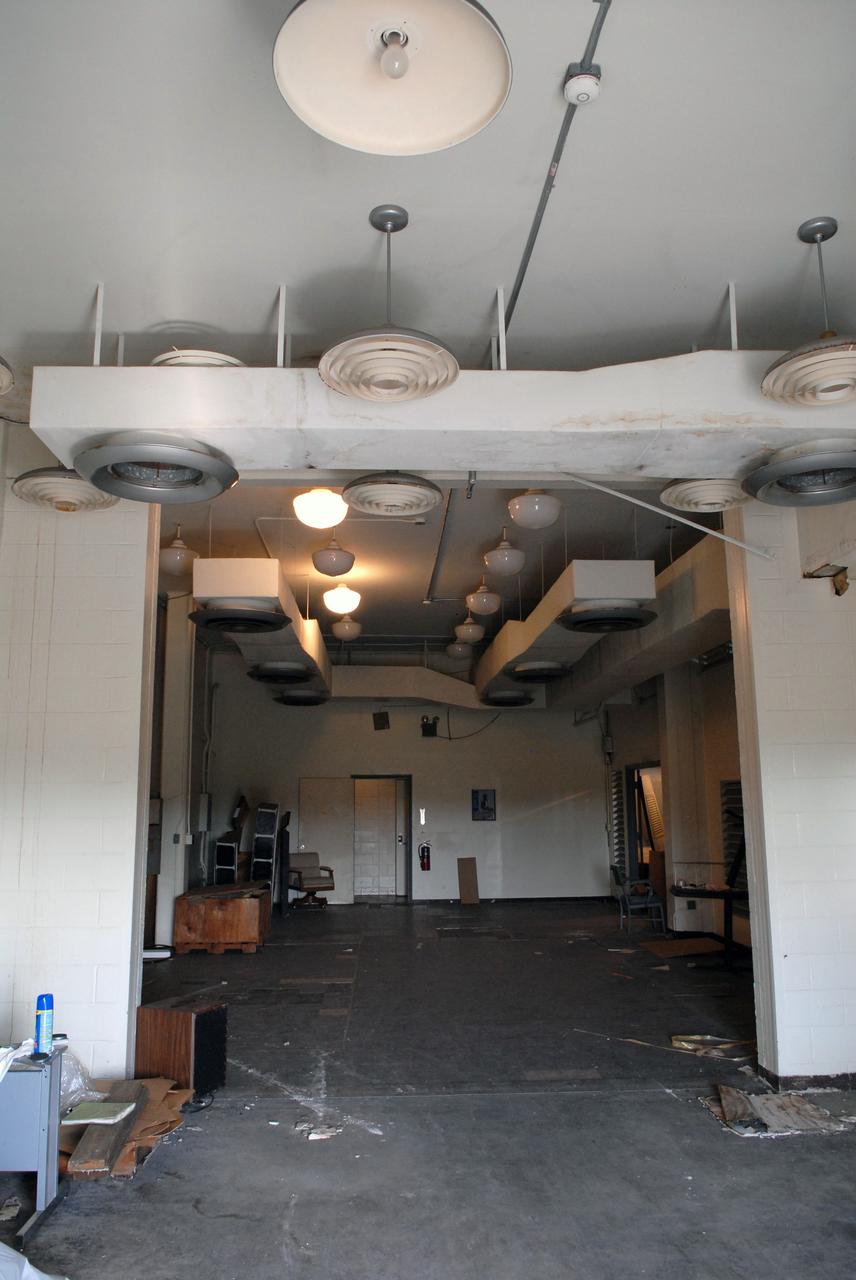

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Furniture and equipment is being moved out of the 50-year-old Mission Control Center on the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Out of use for many years, and with no valid operational or other use for the facility, NASA plans to demolish the site. The facility once controlled all manned Mercury space flights and the first two unmanned Gemini flights from May 1961-1963. It provided launch, orbital, re-entry and landing control for the flights. That function was later transferred to NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
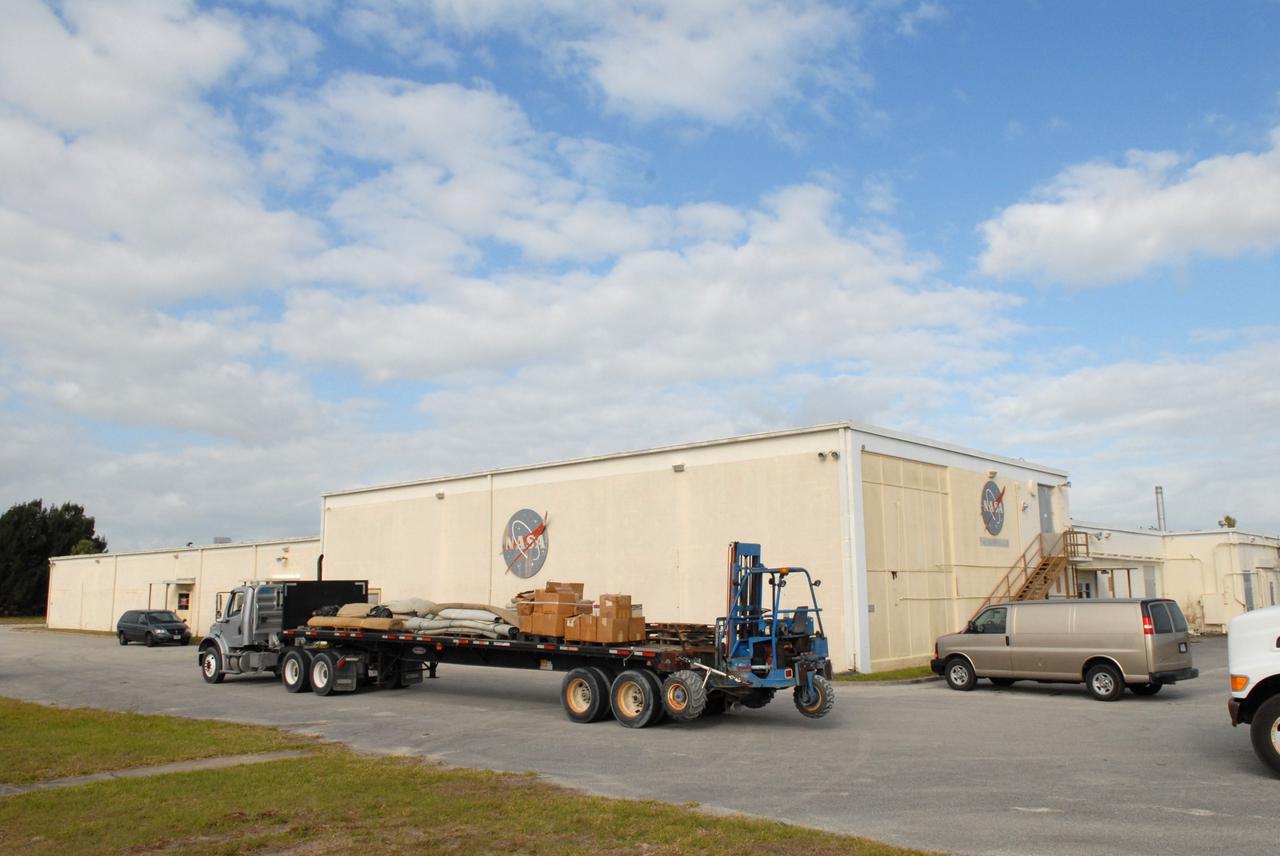

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A trailer hauls boxes and equipment from the 50-year-old Mission Control Center on the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Out of use for many years, and with no valid operational or other use for the facility, NASA plans to demolish the site. The facility once controlled all manned Mercury space flights and the first two unmanned Gemini flights from May 1961-1963. It provided launch, orbital, re-entry and landing control for the flights. That function was later transferred to NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Water damage and mold in rooms in the 50-year-old Mission Control Center on the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida are part of the reason for NASA's decision to demolish the site. The center has been out of use for many years, and NASA has found no valid operational or other use for the facility. The facility once controlled all manned Mercury space flights and the first two unmanned Gemini flights from May 1961-1963. It provided launch, orbital, re-entry and landing control for the flights. That function was later transferred to NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
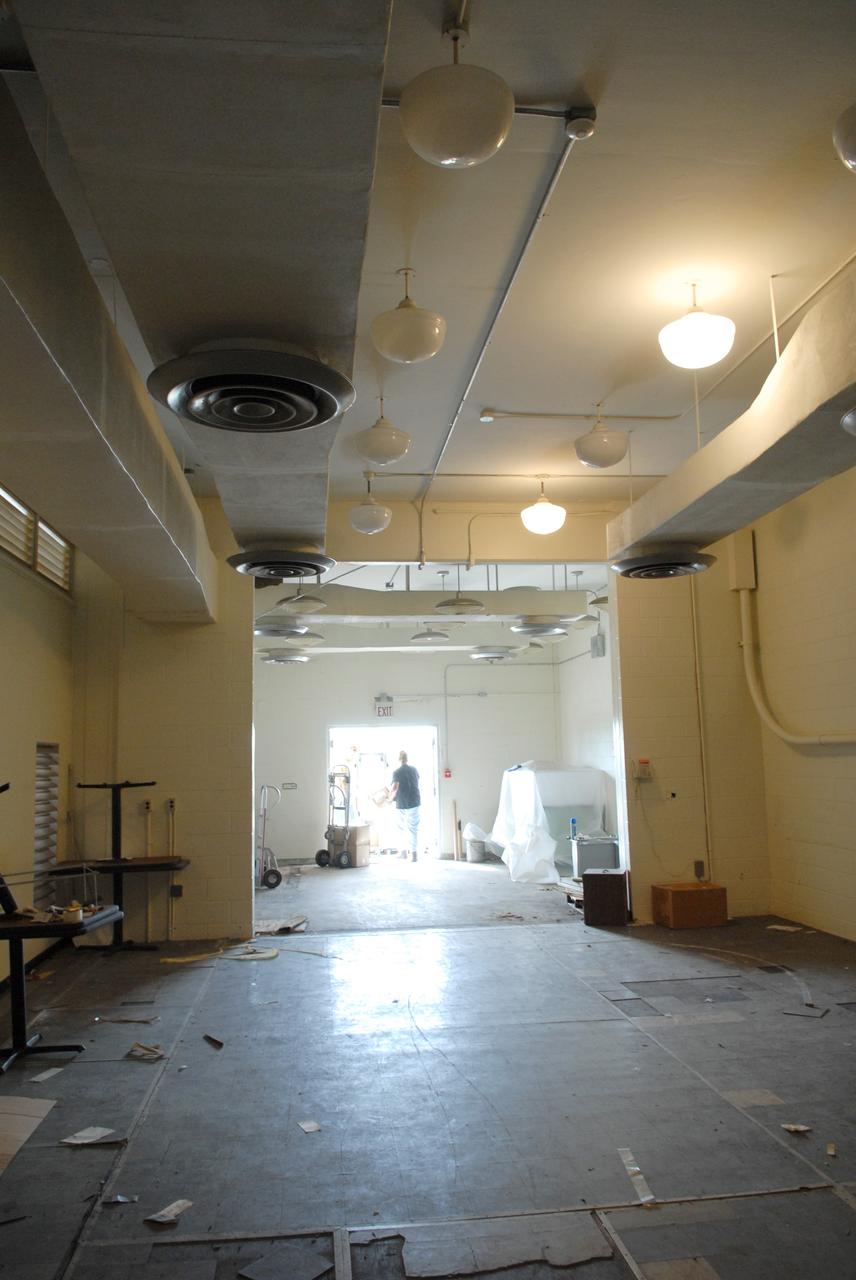

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Furniture and equipment is being moved out of the 50-year-old Mission Control Center on the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Out of use for many years, and with no valid operational or other use for the facility, NASA plans to demolish the site. The facility once controlled all manned Mercury space flights and the first two unmanned Gemini flights from May 1961-1963. It provided launch, orbital, re-entry and landing control for the flights. That function was later transferred to NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
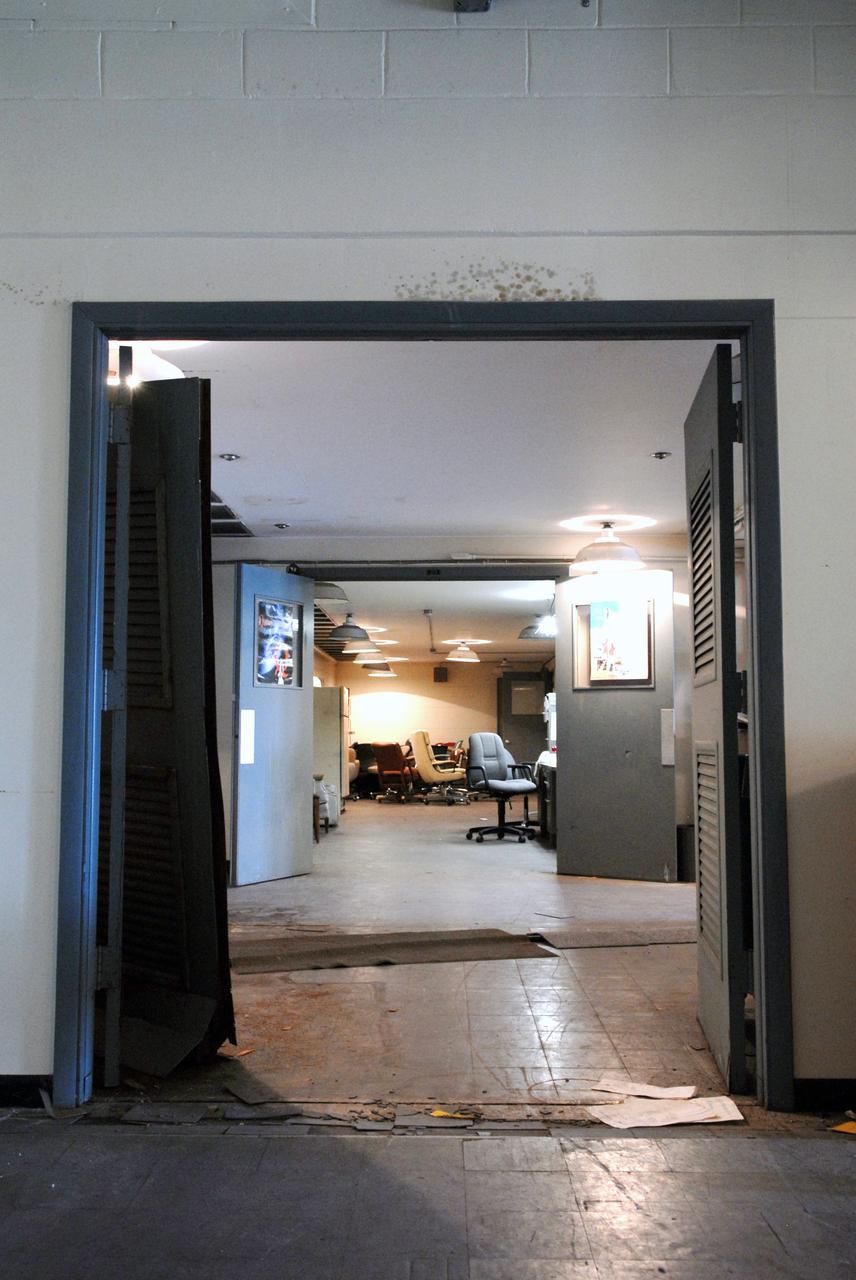

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Furniture no longer in use is stored in the far room of the 50-year-old Mission Control Center on the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Out of use for many years, and with no valid operational or other use for the facility, NASA plans to demolish the site. The facility once controlled all manned Mercury space flights and the first two unmanned Gemini flights from May 1961-1963. It provided launch, orbital, re-entry and landing control for the flights. That function was later transferred to NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
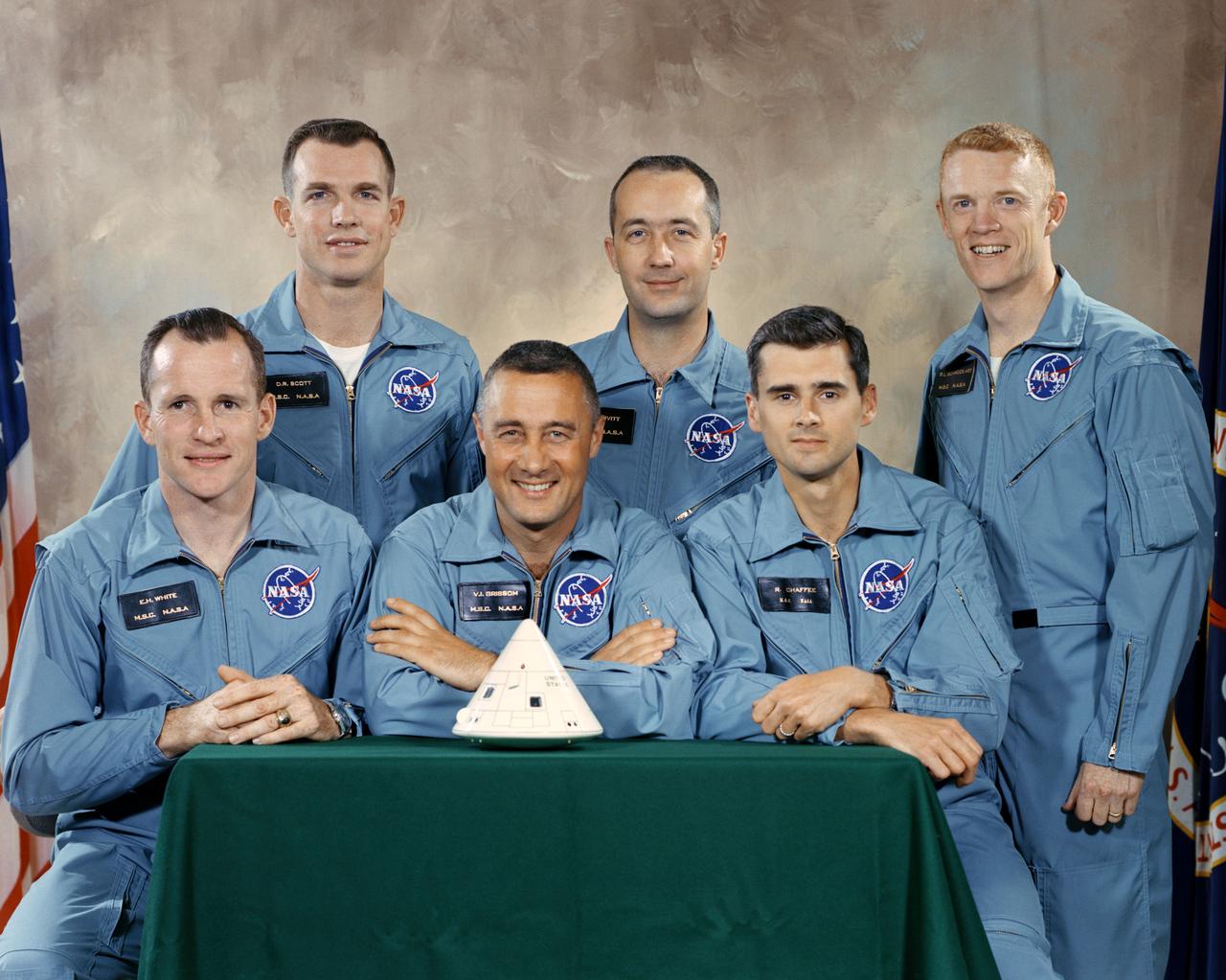

S66-30238 (1 April 1966) --- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has named these astronauts as the prime crew of the first manned Apollo Space Flight. Left to right, are Edward H. White II, command module pilot; Virgil I. Grissom, mission commander; and Roger B. Chaffee, lunar module pilot. On the second row are the Apollo 1 backup crew members, astronauts David R. Scott, James A. McDivitt and Russell L. Schweickart. EDITOR'S NOTE: Astronauts Grissom, White and Chaffee lost their lives in a Jan. 27, 1967 fire in the Apollo CM during testing at Cape Canaveral. McDivitt, Scott and Schweickart later served as crewmembers for the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission, which was one of the important stair-step missions leading up to the Apollo 11 manned lunar landing mission of July 1969.
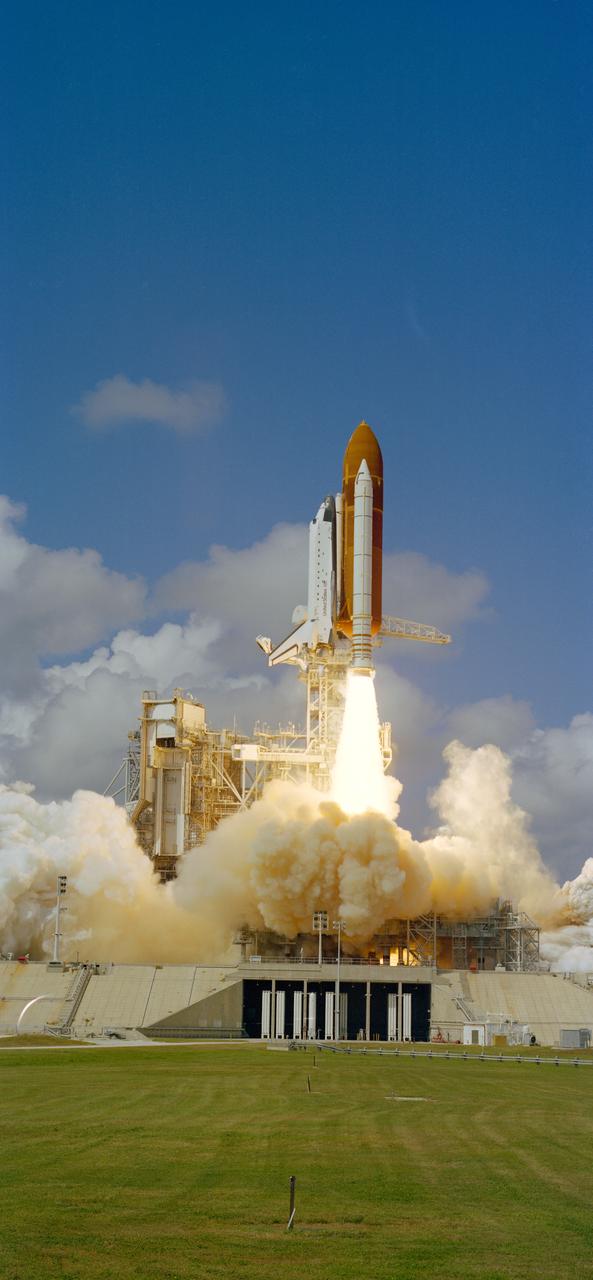

STS026-S-031 (29 Sept 1988) --- Just moments after ignition, the Space Shuttle Discovery, mated to two solid rocket boosters and an external fuel tank, heads, toward Earth orbit. The mission marks Discovery?s first flight since September of 1985 and NASA?s first manned mission since September of 1985 and NASA?s first manned mission since the 51L Challenger accident of January 28, 1986. Onboard the spacecraft are Astronauts Frederick H. (Rick) Hauck, commander; Richard O. Covey, pilot; and George D. Nelson, John M. (Mike) Lounge and David C. Hilmers, mission specialists. Discovery?s dry weight is 171,419 pounds. The tracking and data relay satellite and its inertial upper stage total about 37,000 pounds.
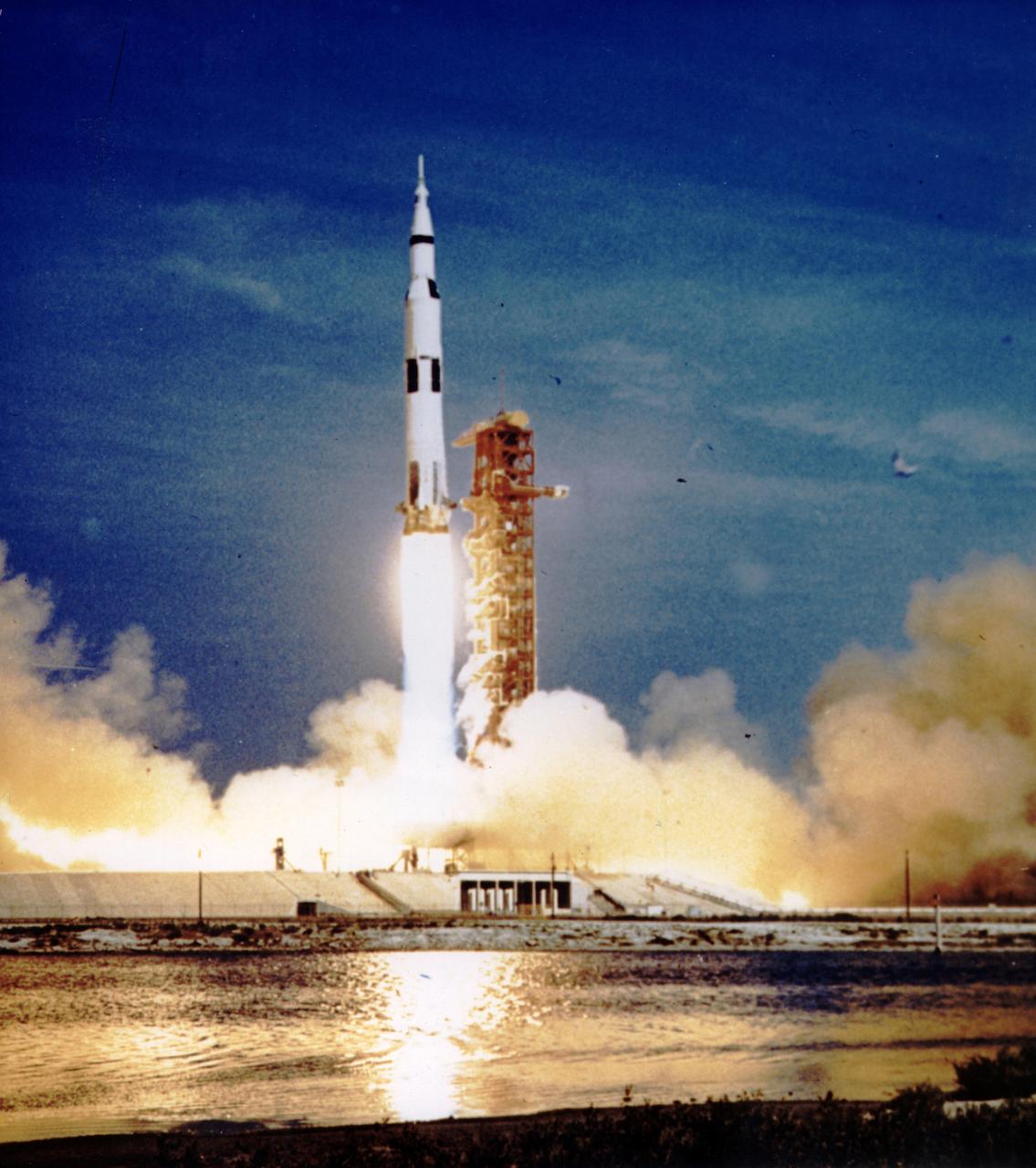

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle produced a holocaust of flames as it rose from its pad at Launch complex 39. The 363 foot tall, 6,400,000 pound rocket hurled the spacecraft into Earth parking orbit and then placed it on the trajectory to the moon for man’s first lunar landing. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module pilot. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
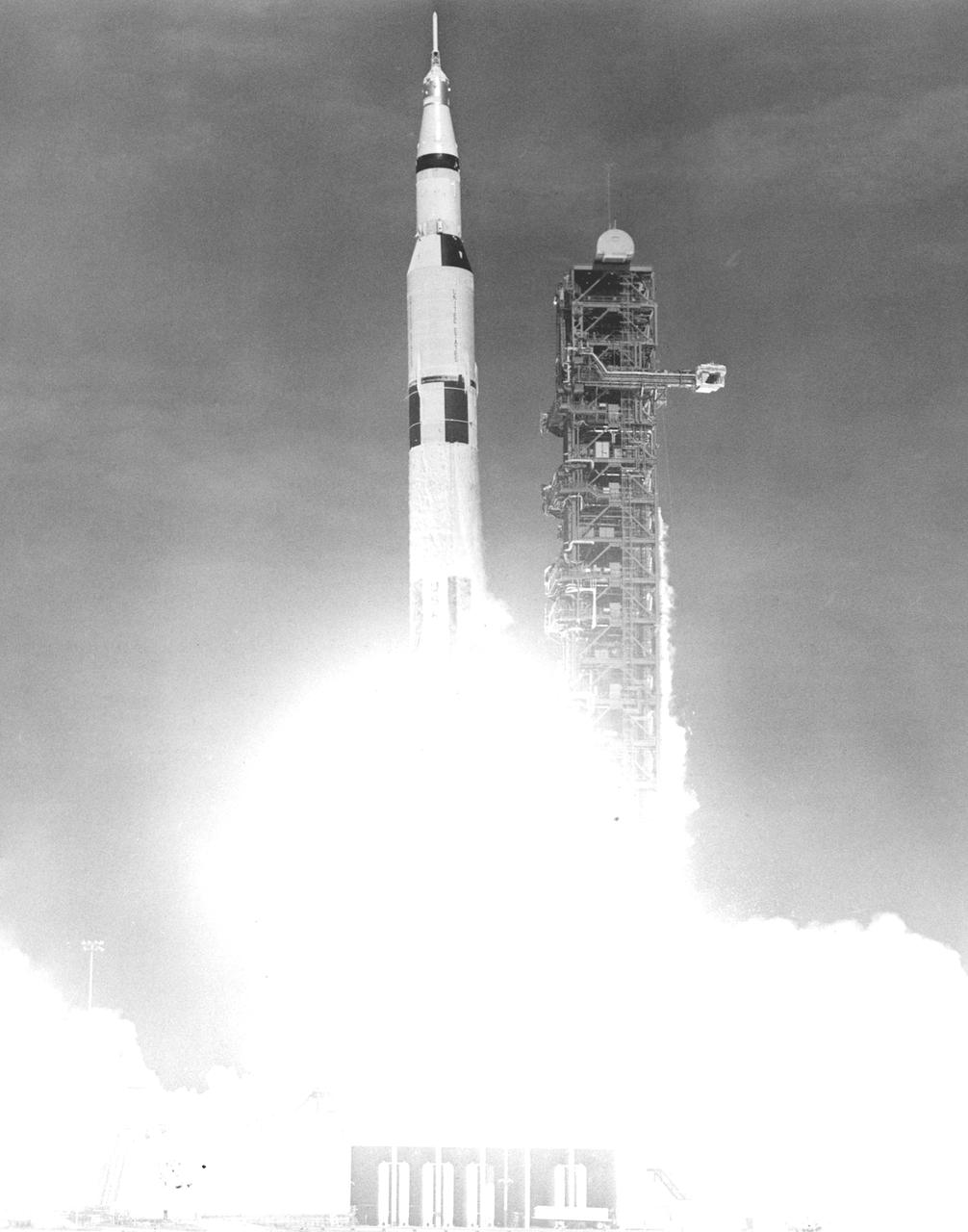

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle produced a holocaust of flames as it rose from its pad at Launch complex 39. The 363 foot tall, 6,400,000 pound rocket hurled the spacecraft into Earth parking orbit and then placed it on the trajectory to the moon for man’s first lunar landing. The Saturn V was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard the spacecraft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module pilot. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.