
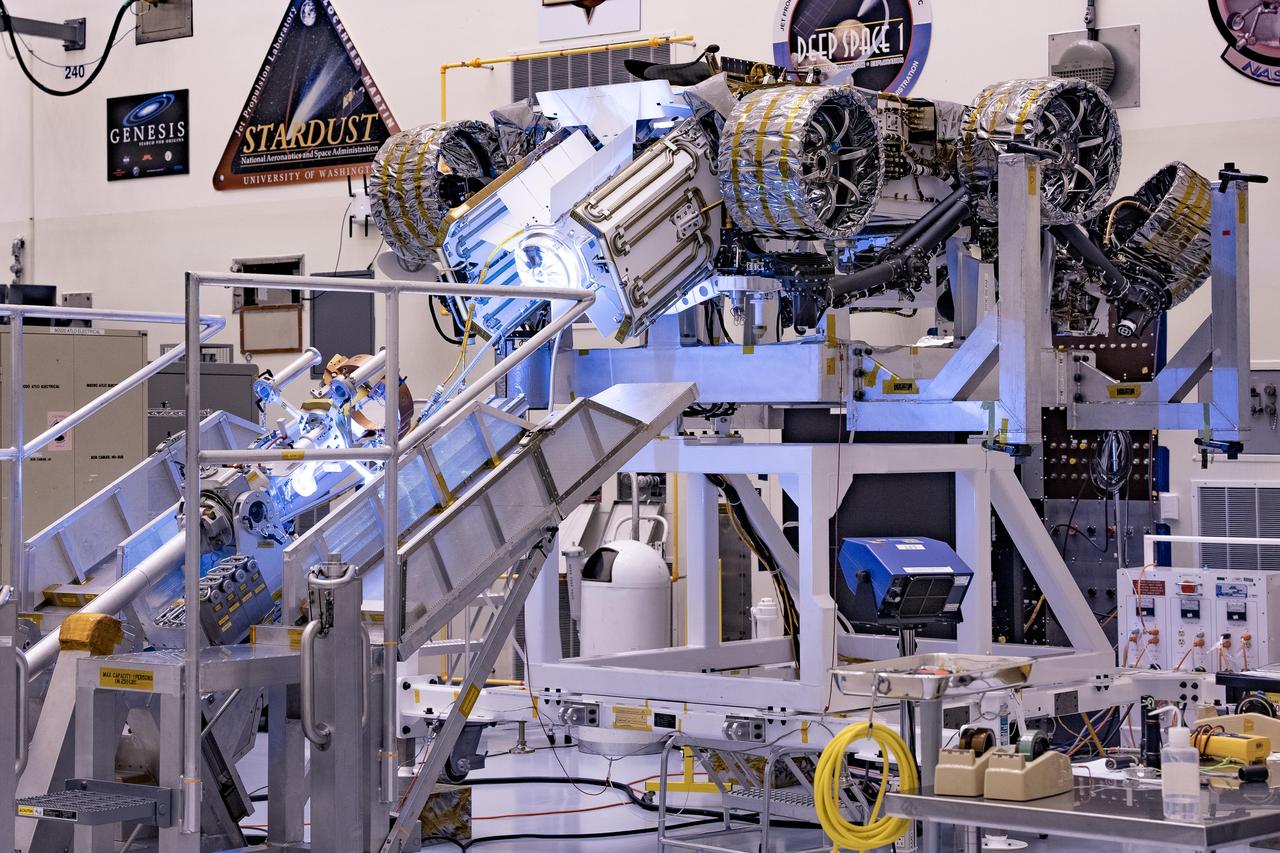
Members of NASA's Mars 2020 project take a moment after attaching the remote sensing mast to the Mars 2020 rover. The image was taken on June 5, 2019, in the Spacecraft Assembly Facility's High Bay 1 clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23267
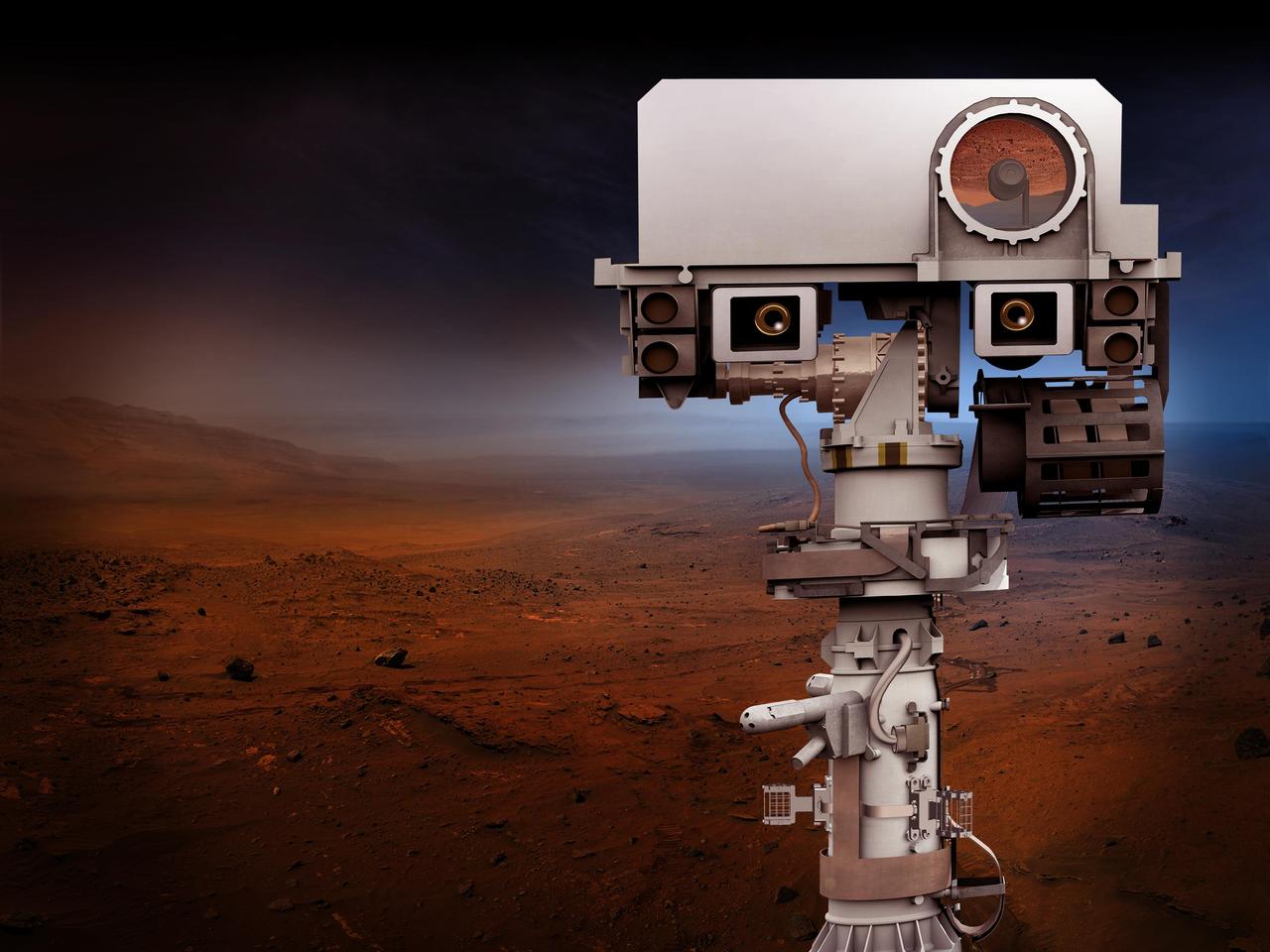

NASA's Mars 2020 Project will re-use the basic engineering of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory/Curiosity to send a different rover to Mars, with new objectives and instruments. This artist's concept depicts the top of the 2020 rover's mast. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20760
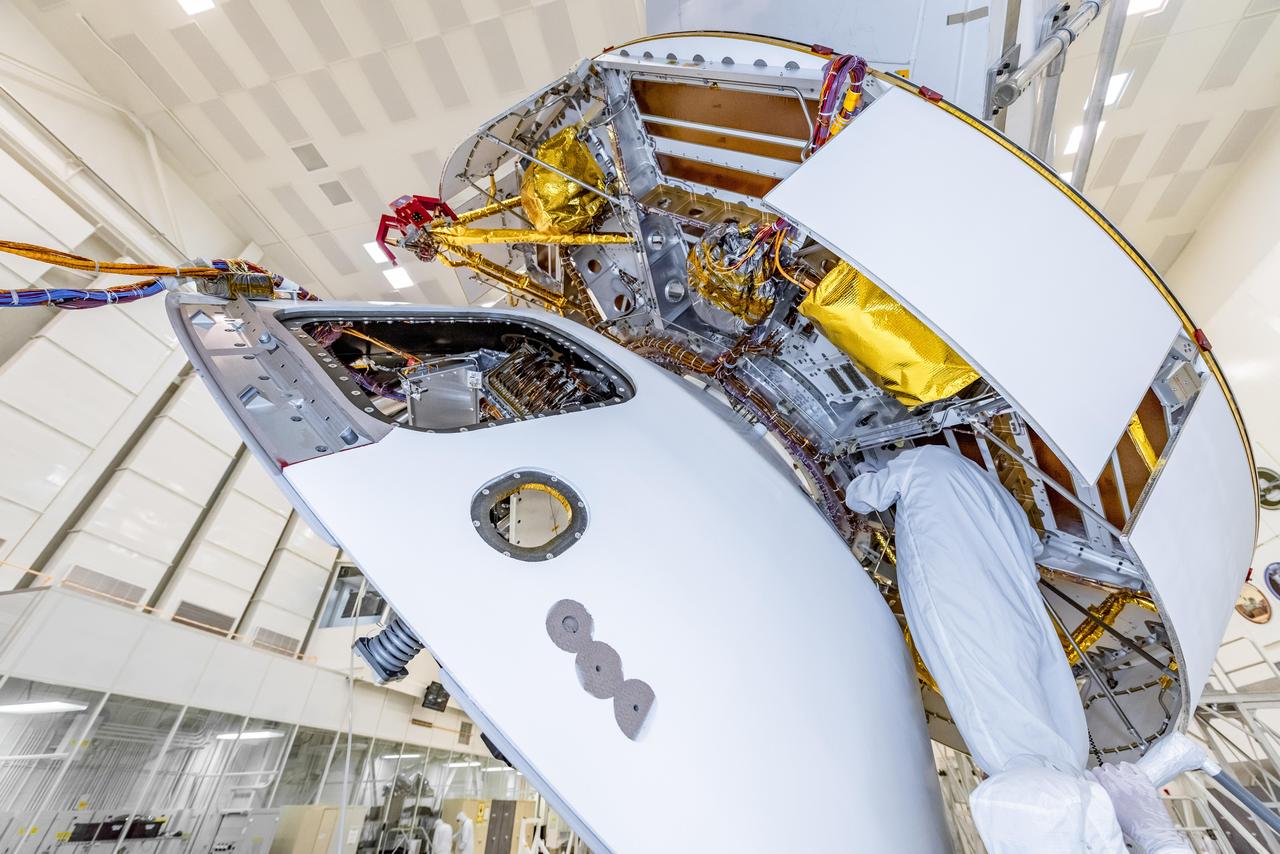

A member of NASA's Mars 2020 project checks connections between the spacecraft's back shell and cruise stage. The image was taken on March 26, 2019, in the Spacecraft Assembly Facility's High Bay 1 clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in Pasadena, California. During the mission's voyage to Mars, the cruise stage houses the hardware that steers and provides power to the spacecraft. The back shell, along with the heatshield (not pictured), protects the 2020 rover and the sky crane landing system during Mars atmospheric entry. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23163
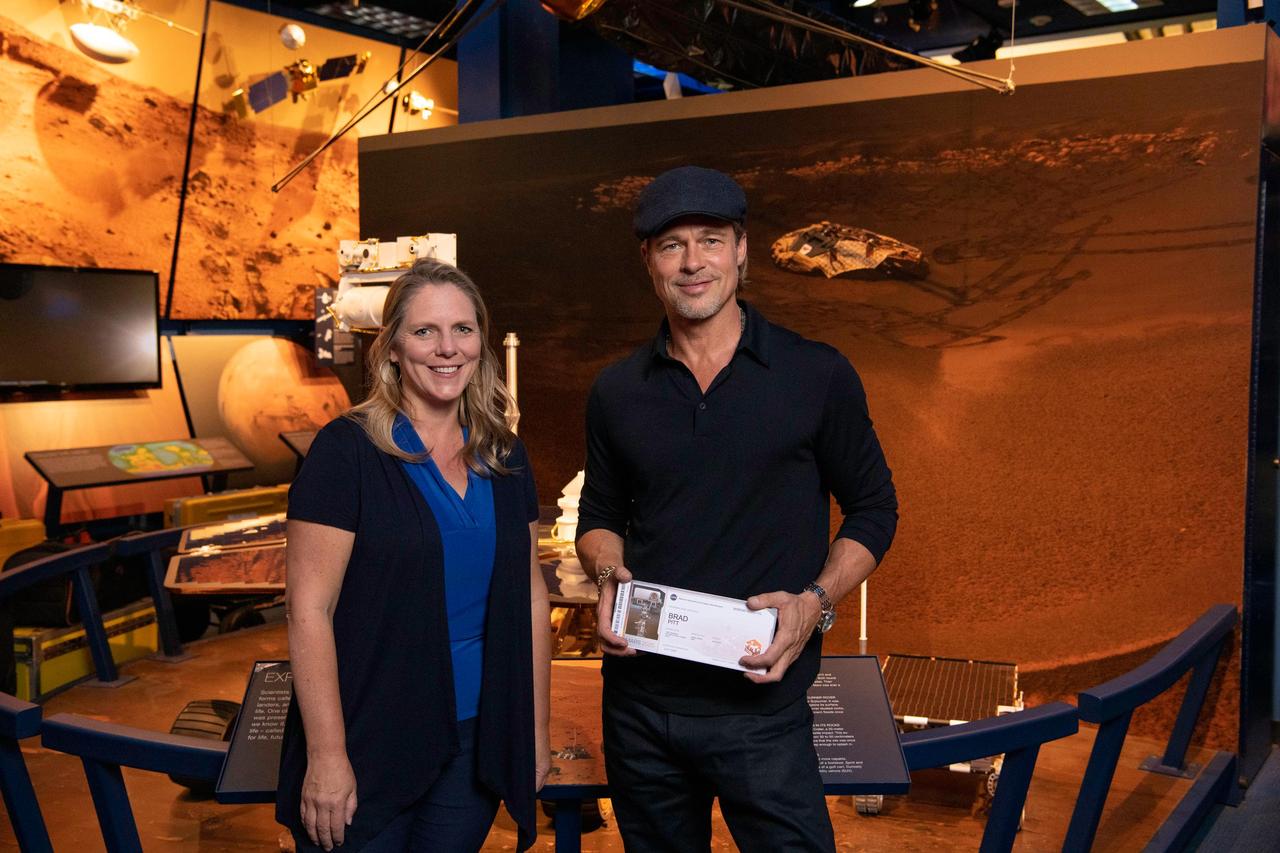

The actor Brad Pitt (right) shows off his "boarding pass" for Mars with Jennifer Trosper (left), the Mars 2020 project systems engineer and a veteran of several NASA Mars missions, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, on Sept. 6, 2019. Members of the public can join the actor in sending their names to Mars aboard NASA's Mars 2020 rover at https://go.nasa.gov/mars2020pass. Names can be submitted until Sept. 30, 2019. Pitt visited JPL to learn about real space technology after filming his space-themed movie "Ad Astra." https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23279
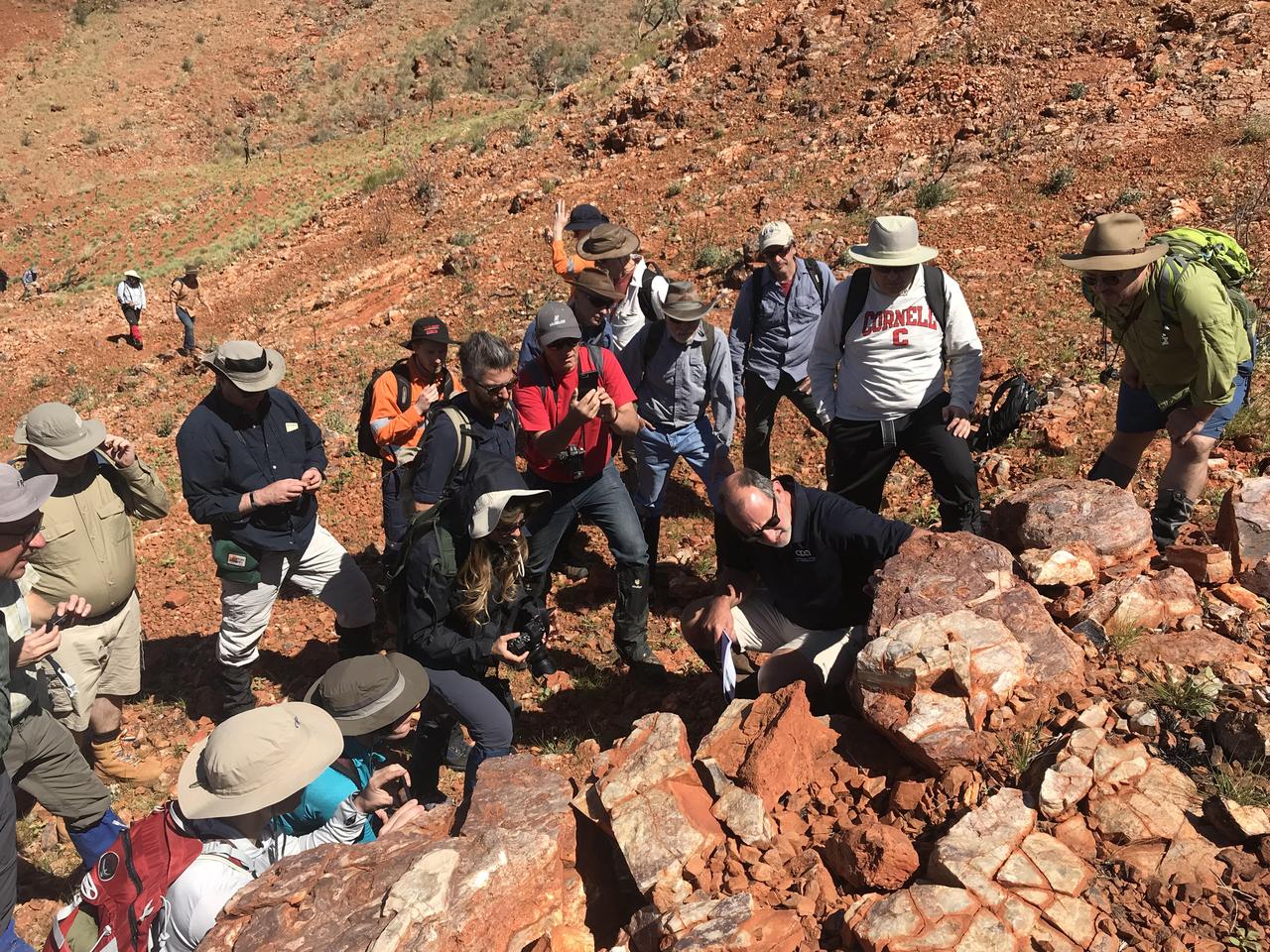

Scientists from NASA's Mars 2020 and ESA's ExoMars projects study stromatolites, the oldest confirmed fossilized lifeforms on Earth, in the Pilbara region of North West Australia. The image was taken on Aug. 19, 2019. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23551
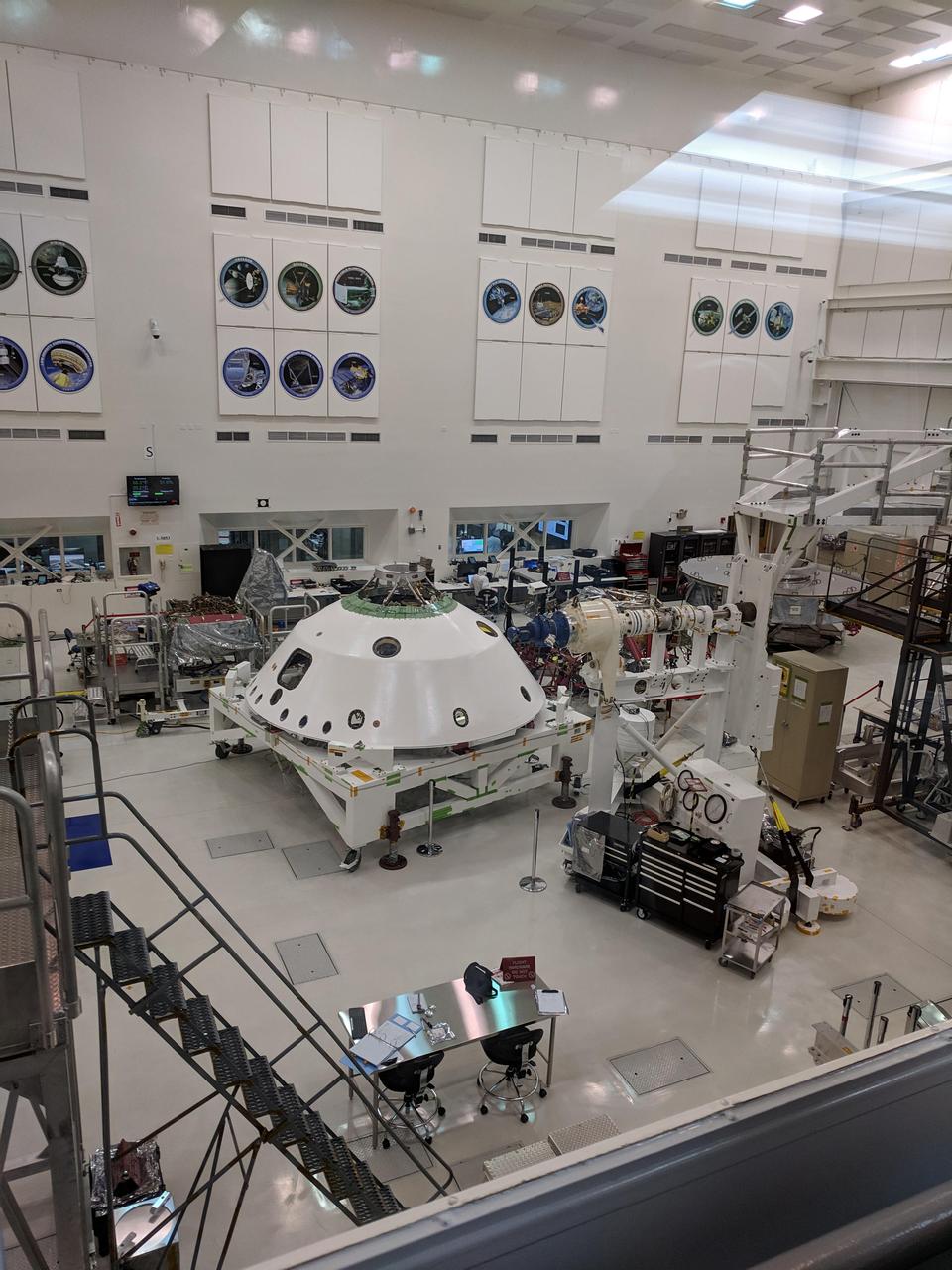

With the backshell that will help protect the Mars 2020 rover during its descent into the Martian atmosphere visible in the foreground, a technician on the project monitors the progress of Systems Test 1. Over two weeks in January 2019, 72 engineers and technicians assigned to the 2020 mission took over the High Bay 1 cleanroom in JPL's Spacecraft Assembly Facility to put the software and electrical systems aboard the mission's cruise, entry capsule, descent stage and rover through their paces. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22966
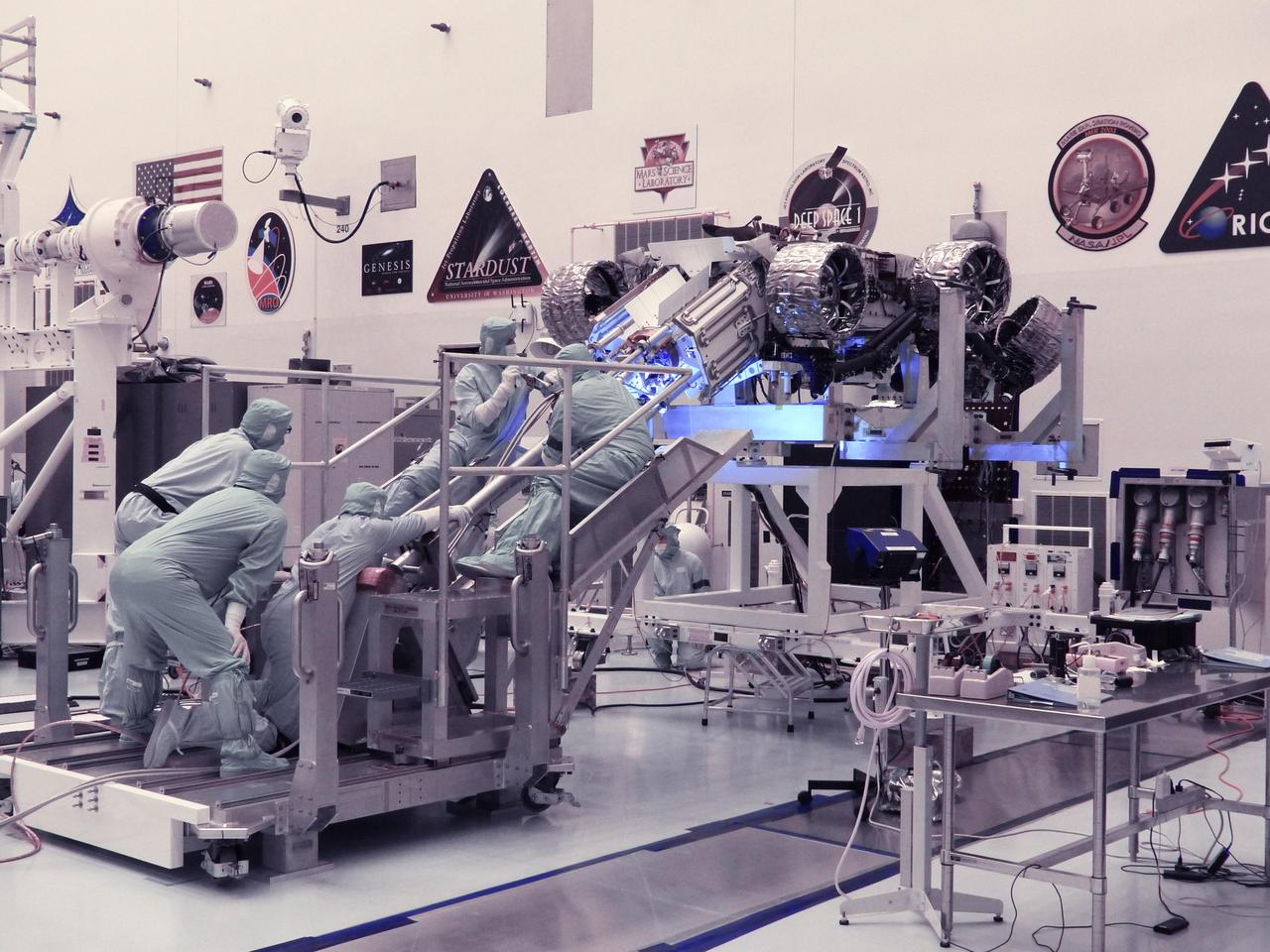
Technicians in the payload processing facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida perform a fit check between NASA'S Mars 2020 Perseverance rover and its Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator on April 16-17, 2020. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is designed and built by the U.S. Department of Energy, and provided to NASA as part of the space agency's Radioisotope Power Systems Program. It arrived at NASA KSC in April 2020 following its final assembly and transport from the Department of Energy's Idaho National Laboratory. The fit check is the first time that the fueled flight generator is connected to the rover. After the successful fit check, the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator was disconnected; it will be connected to the rover for the final time on the launch pad atop the mission's Atlas V launch vehicle in July, before the planned launch of the Mars 2020 mission. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is a space nuclear power system that produces about 110 watts of electrical power to run the rover's systems and science instruments, and extra heat to keep them warm during the frigid Martian nights and winter seasons. It converts the heat from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium dioxide into electricity using thermocouples with no moving parts. The choice of a Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator as the rover's power system gave mission planners significantly more flexibility in selecting the rover's landing site and in planning its surface operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23827
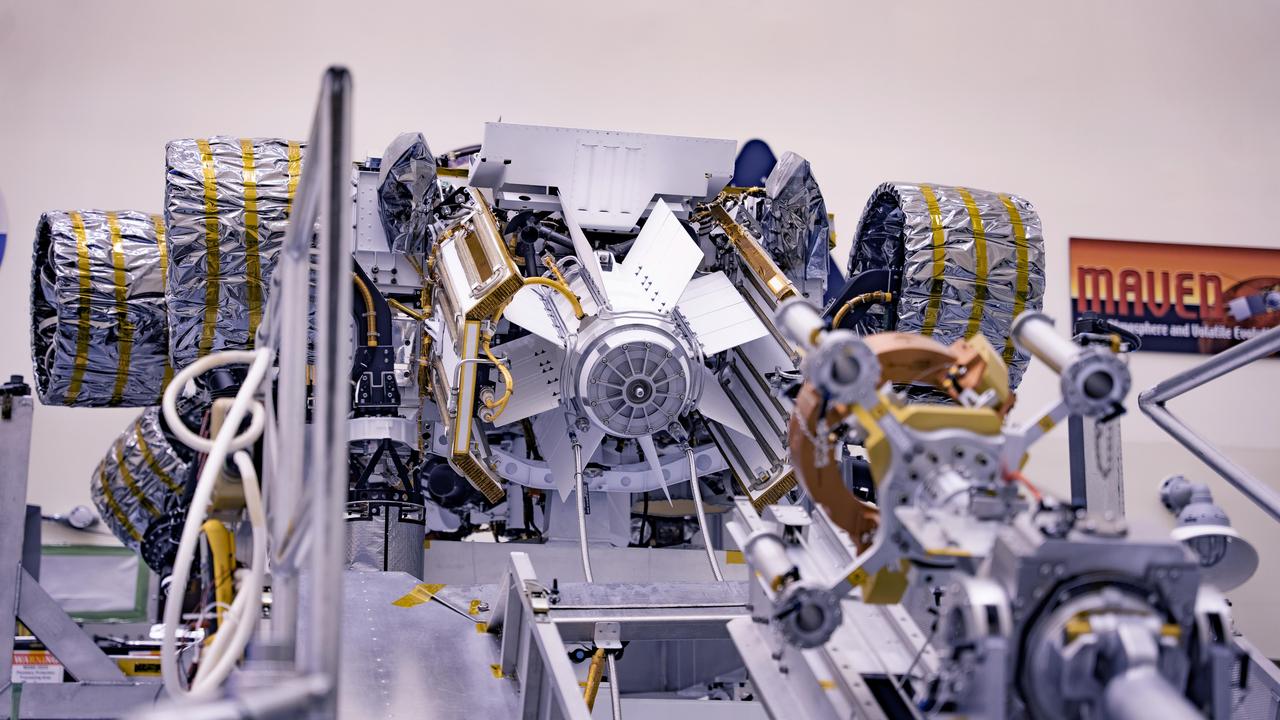
The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator for NASA'S Mars 2020 Perseverance rover is shown during a fit check with the rover in a payload processing facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 16-17, 2020. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is designed and built by the U.S. Department of Energy, and provided to NASA as part of the space agency's Radioisotope Power Systems Program. It arrived at NASA KSC in April 2020 following its final assembly and transport from the Department of Energy's Idaho National Laboratory. The fit check is the first time that the fueled flight generator is connected to the rover. After the successful fit check, the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator was disconnected; it will be connected to the rover for the final time on the launch pad atop the mission's Atlas V launch vehicle in July, before the planned launch of the Mars 2020 mission. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is a space nuclear power system that produces about 110 watts of electrical power to run the rover's systems and science instruments, and extra heat to keep them warm during the frigid Martian nights and winter seasons. It converts the heat from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium dioxide into electricity using thermocouples with no moving parts. The choice of a Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator as the rover's power system gave mission planners significantly more flexibility in selecting the rover's landing site and in planning its surface operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23981

This image shows the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator for NASA'S Mars 2020 Perseverance rover during a fit check with the rover in the payload processing facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 16-17, 2020. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is designed and built by the U.S. Department of Energy, and provided to NASA as part of the space agency's Radioisotope Power Systems Program. It arrived at NASA KSC in April 2020 following its final assembly and transport from the Department of Energy's Idaho National Laboratory. The fit check is the first time that the fueled flight generator is connected to the rover. After the successful fit check, the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator was disconnected; it will be connected to the rover for the final time on the launch pad atop the mission's Atlas V launch vehicle in July, before the planned launch of the Mars 2020 mission. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is a space nuclear power system that produces about 110 watts of electrical power to run the rover's systems and science instruments, and extra heat to keep them warm during the frigid Martian nights and winter seasons. It converts the heat from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium dioxide into electricity using thermocouples with no moving parts. The choice of a Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator as the rover's power system gave mission planners significantly more flexibility in selecting the rover's landing site and in planning its surface operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23982
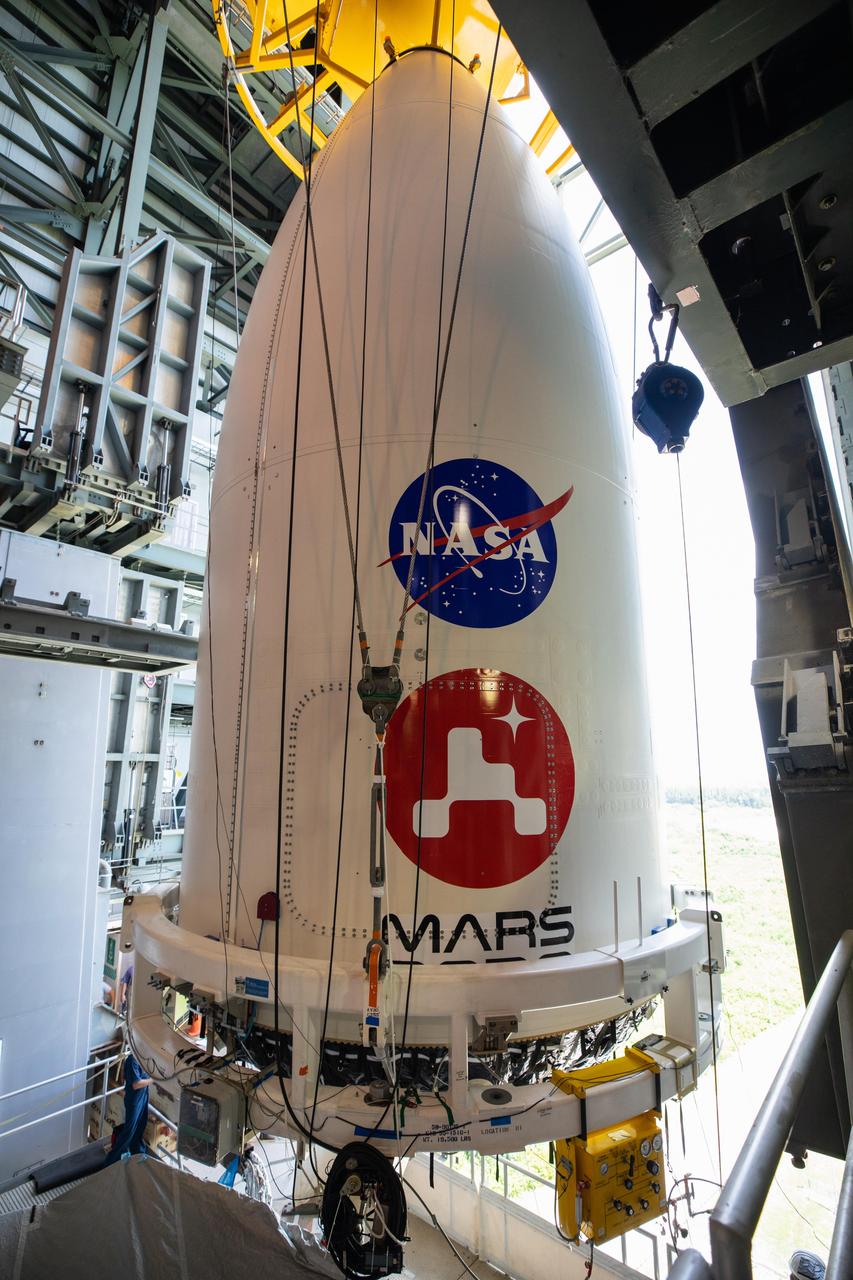

The payload fairing, or nose cone, containing NASA's Mars 2020 Perseverance rover is maneuvered into place atop the Atlas V rocket that will hurl it toward Mars. The image was taken on July 7, 2020, inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23986
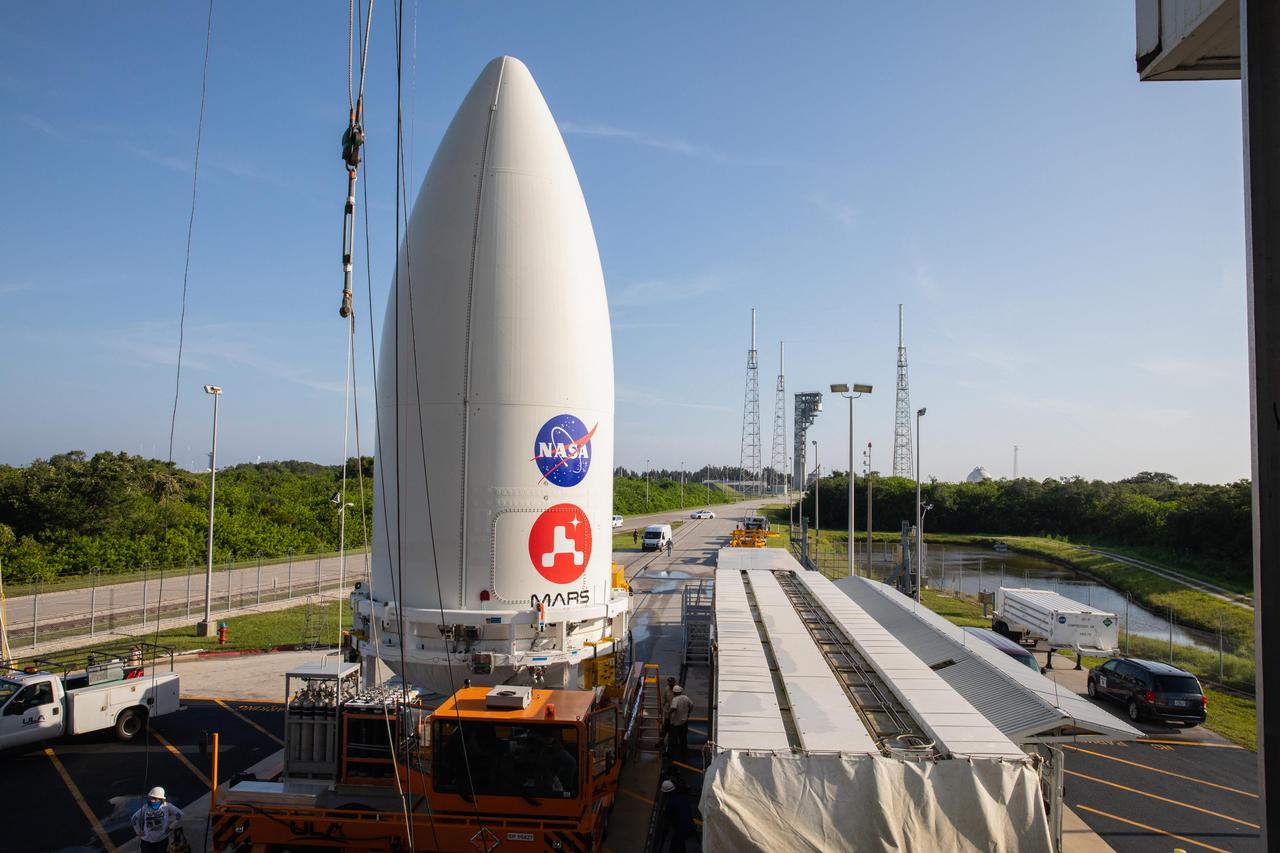

The payload fairing, or nose cone, containing the Mars 2020 Perseverance rover sits atop the motorized payload transporter that will carry it to Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The image was taken on July 7, 2020. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23985

One investigation on NASA's Mars 2020 rover will extract oxygen from the Martian atmosphere. It is called MOXIE, for Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment. In this image, MOXIE Principal Investigator Michael Hecht, of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, is in the MOXIE development laboratory at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California. Mars' atmosphere is mostly carbon dioxide. Demonstration of the capability for extracting oxygen from it, under Martian environmental conditions, will be a pioneering step toward how humans on Mars will use the Red Planet's natural resources. Oxygen can be used in the rocket http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20761
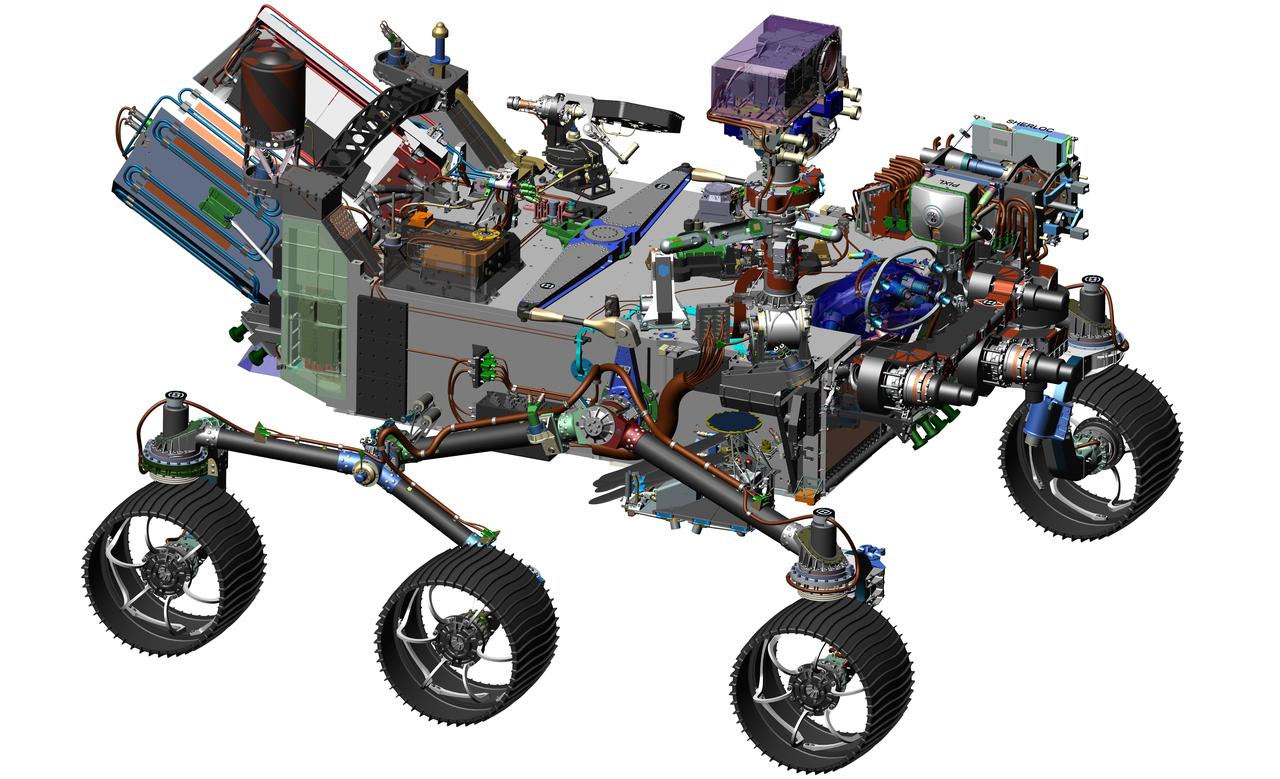
NASA's 2020 Mars rover mission will go to a region of Mars thought to have offered favorable conditions long ago for microbial life, and the rover will search for signs of past life there. It will also collect and cache samples for potential return to Earth, for many types of laboratory analysis. As a pioneering step toward how humans on Mars will use the Red Planet's natural resources, the rover will extract oxygen from the Martian atmosphere. This 2016 image comes from computer-assisted-design work on the 2020 rover. The design leverages many successful features of NASA's Curiosity rover, which landed on Mars in 2012, but it adds new science instruments and a sampling system to carry out the new goals for the mission. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20759
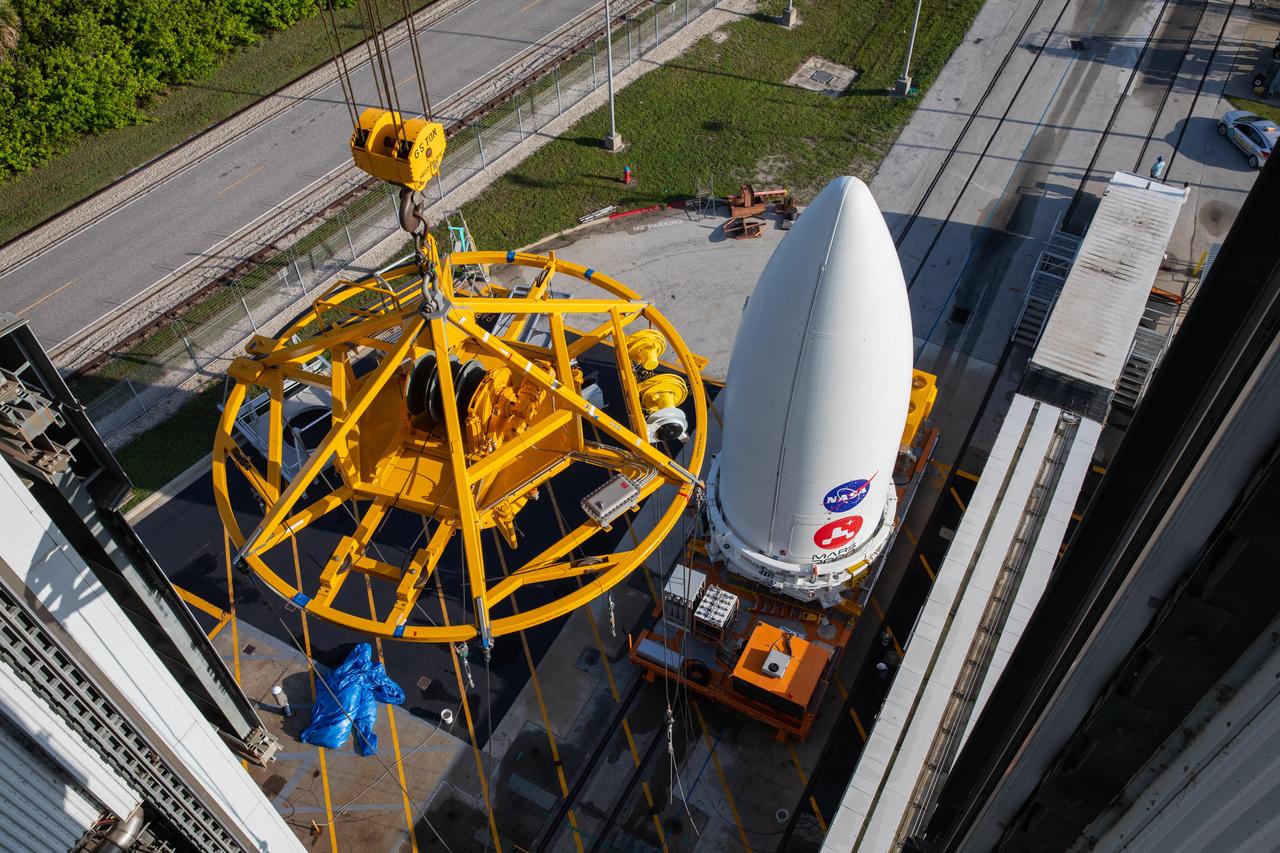

A crane stands at the ready to hoist the payload fairing, or nose cone, containing NASA's Mars 2020 Perseverance rover onto the top of an Atlas V launch vehicle. The image was taken at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23984
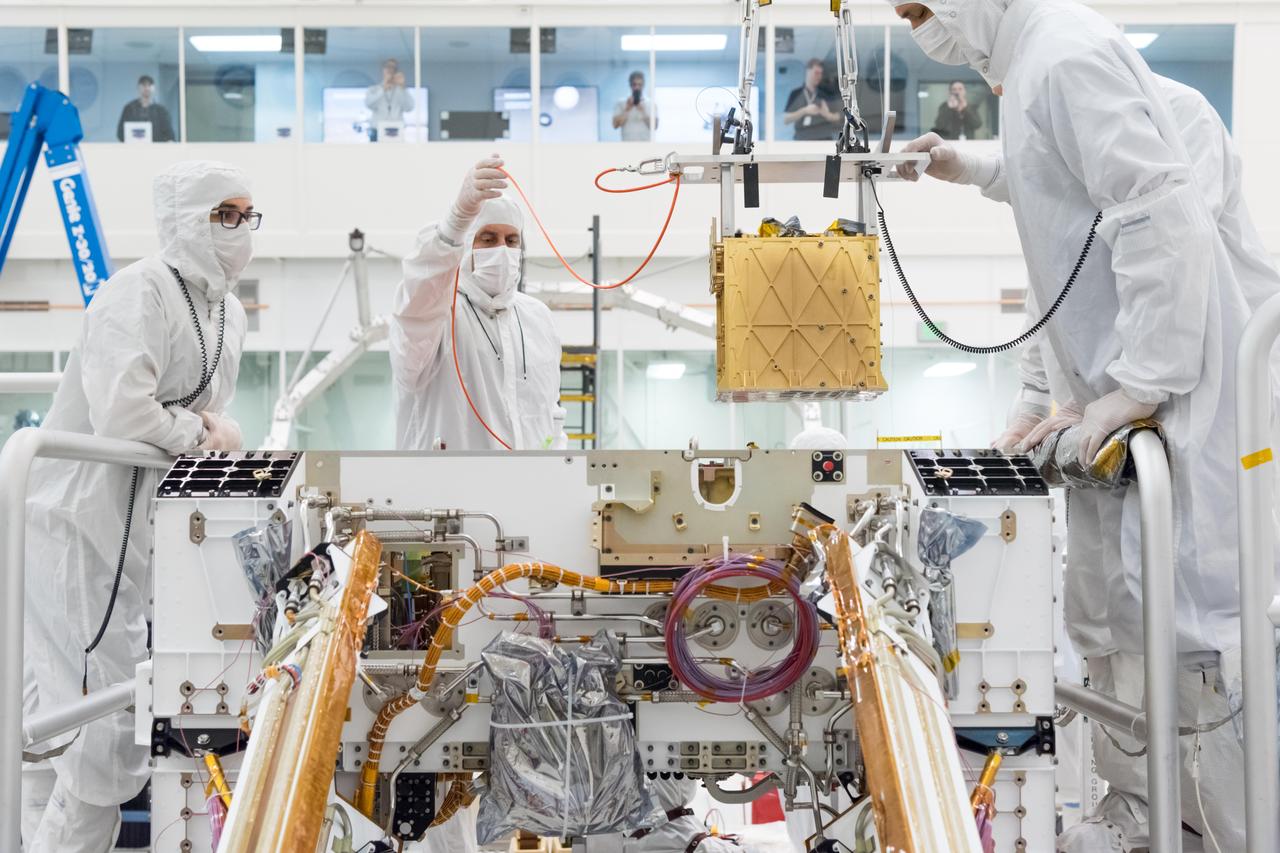
Members of NASA's Mars 2020 project install the Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE) into the chassis of NASA's next Mars rover. MOXIE will demonstrate a way that future explorers might produce oxygen from the Martian atmosphere for propellant and for breathing. The car-battery-sized instrument does this by collecting carbon dioxide (CO2) from the Martian atmosphere and electrochemically splitting the carbon dioxide molecules into oxygen and carbon monoxide molecules. The oxygen is then analyzed for purity before being vented back out to the Martian atmosphere along with the carbon monoxide and other exhaust products. The image was taken on March 20, 2019, in the Spacecraft Assembly Facility's High Bay 1 Cleanroom at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in Pasadena, California. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23154
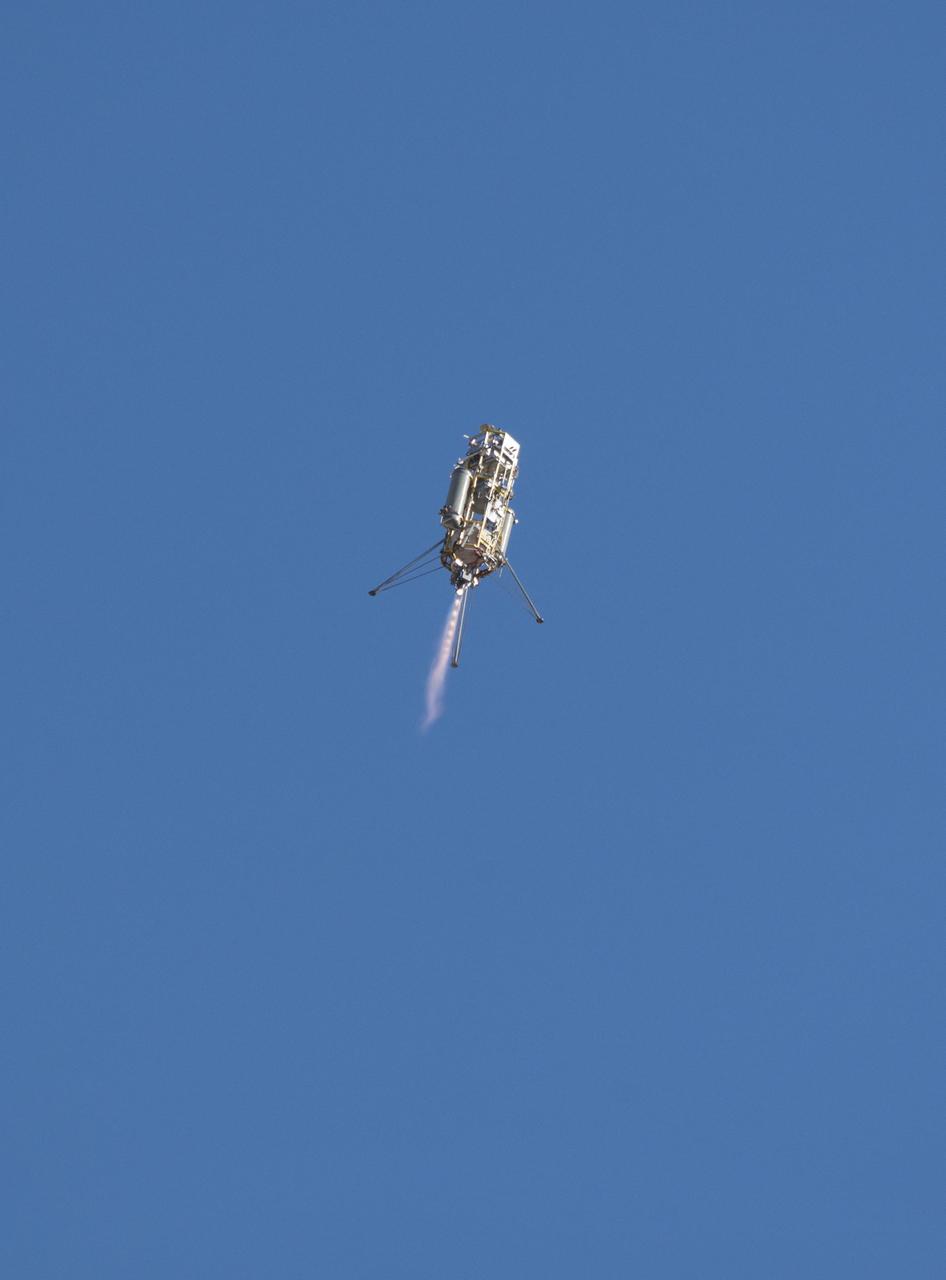

A prototype of the Lander Vision System for NASA Mars 2020 mission was tested in this Dec. 9, 2014, flight of a Masten Space Systems Xombie vehicle at Mojave Air and Space Port in California. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20848
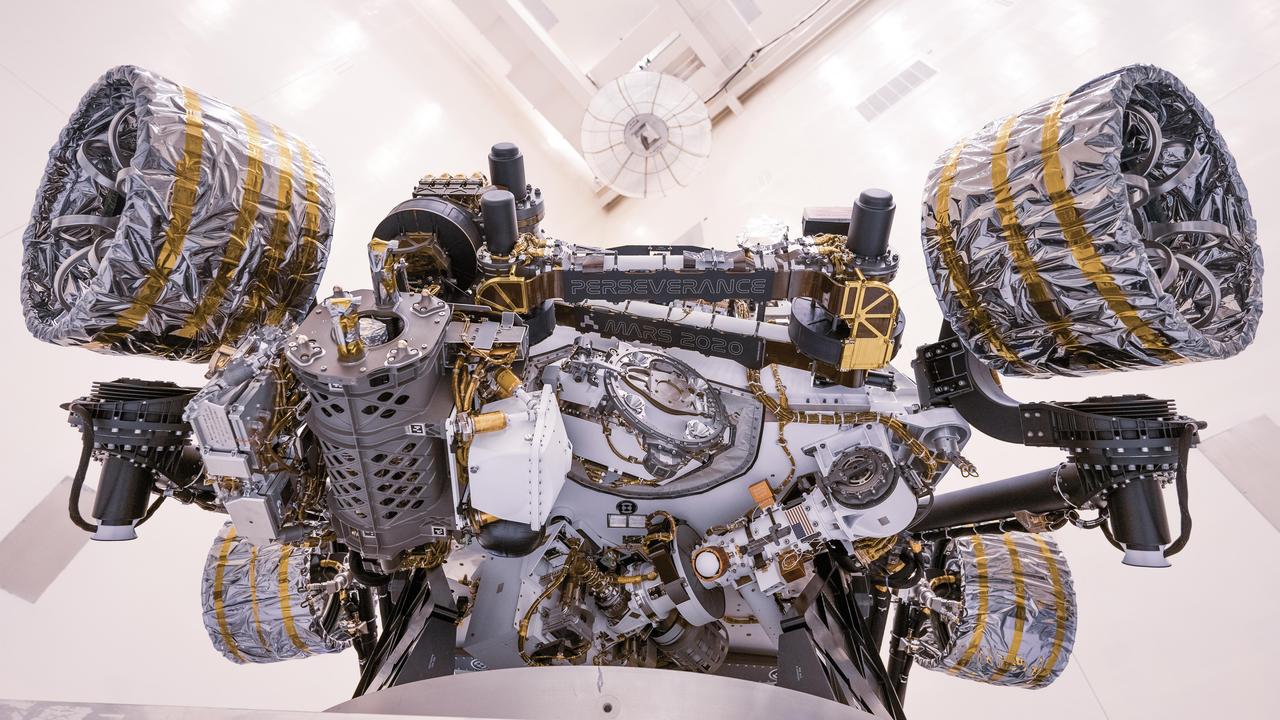
This image of the Perseverance Mars rover was taken at NASA's Kennedy Space Center on April 7, 2020, during a test of the vehicle's mass properties. The rover was rotated clockwise and counterclockwise on a spin table to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides. In the image, the project name "Mars 2020" and rover name "Perseverance" can be seen on name plates that have been attached to the rover's robotic arm. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23828
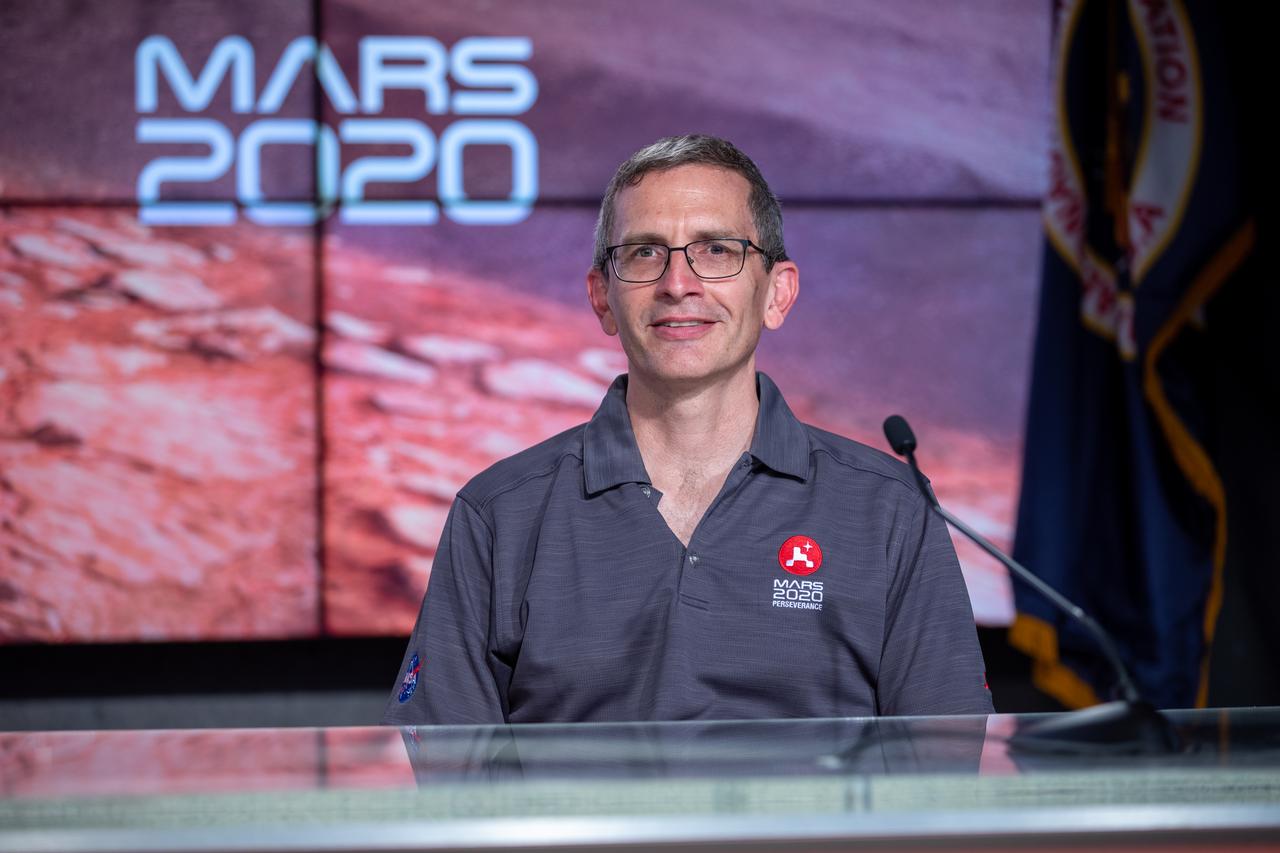

Ken Farley, project scientist, California Institute of Technology, participates in a Mars 2020 Mission Engineering and Science Briefing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 27, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch July 30, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
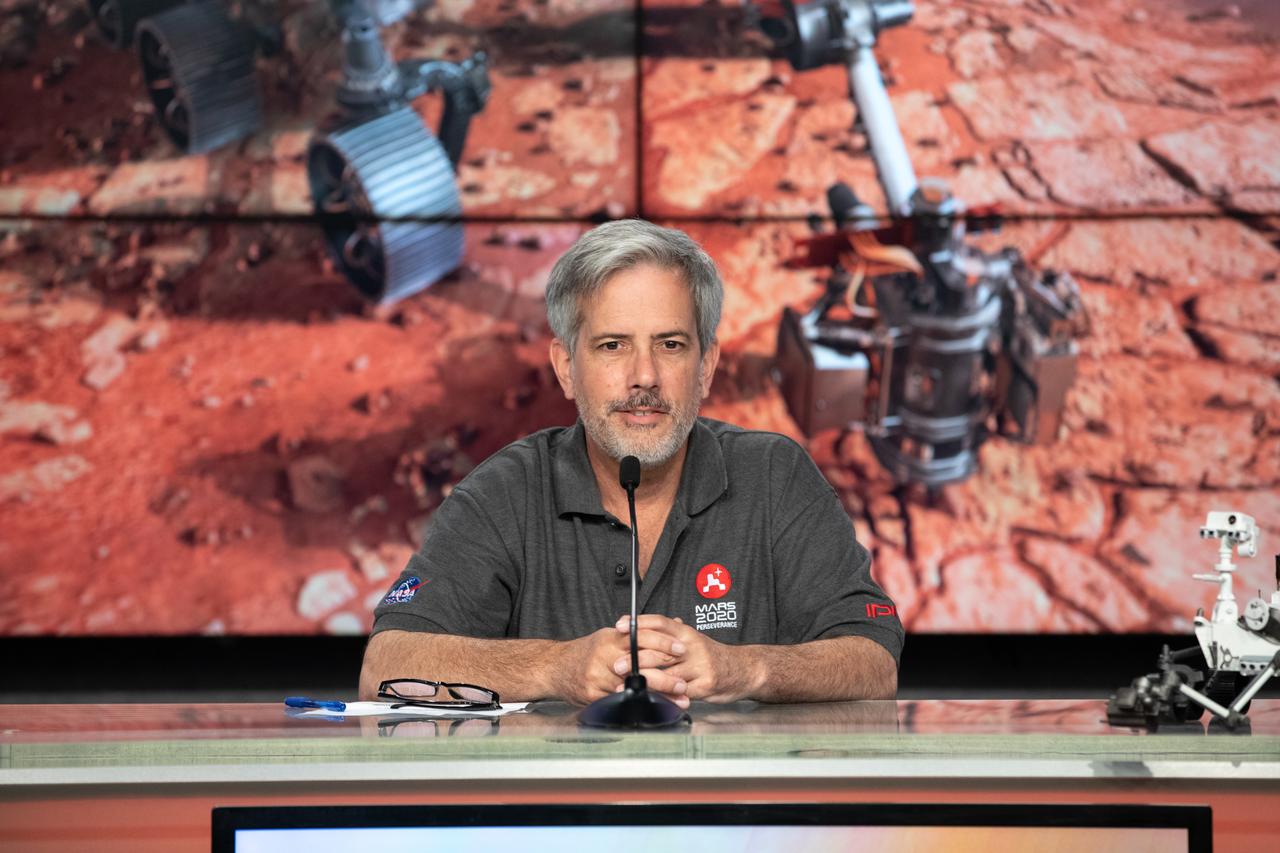

Matt Wallace, deputy project manager, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, participates in a Mars 2020 prelaunch news briefing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 27, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch on July 30, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
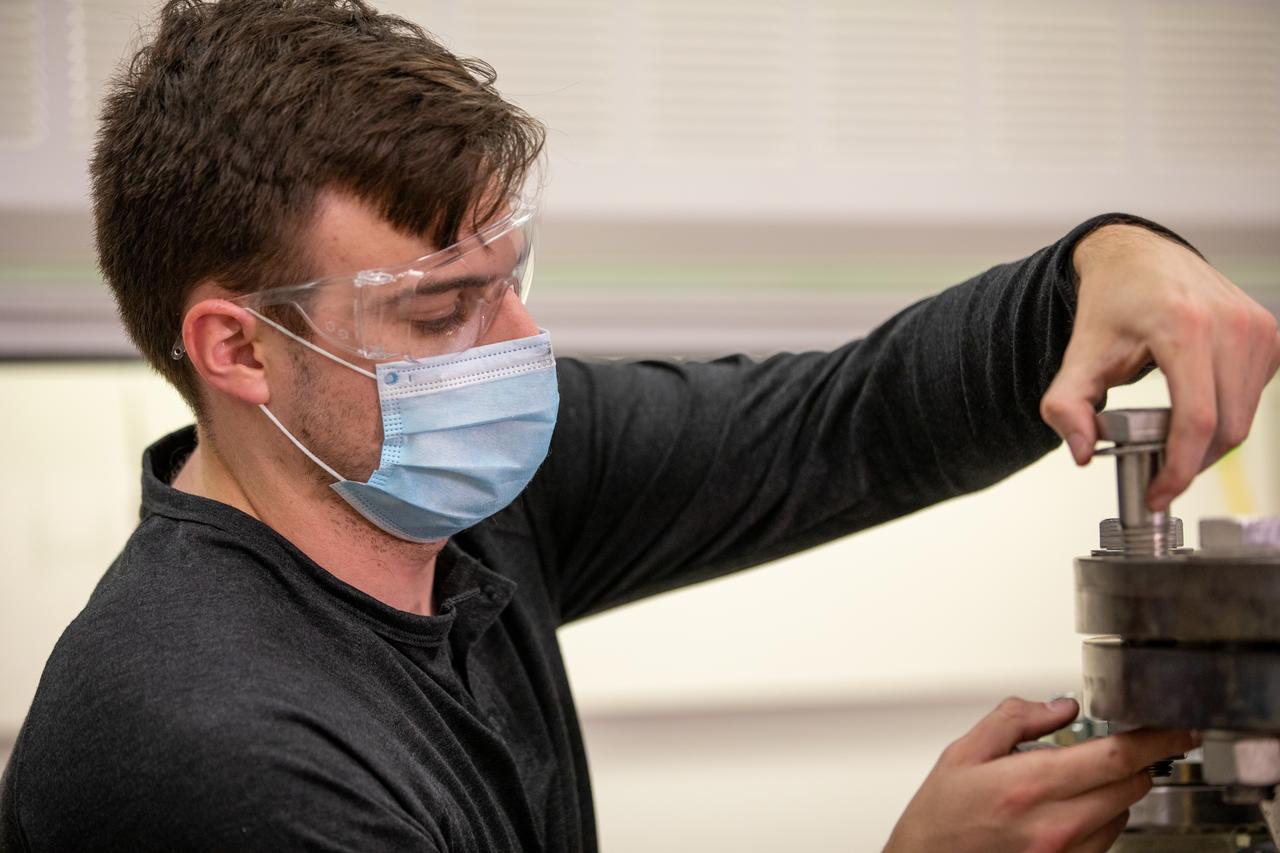
Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, checks the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
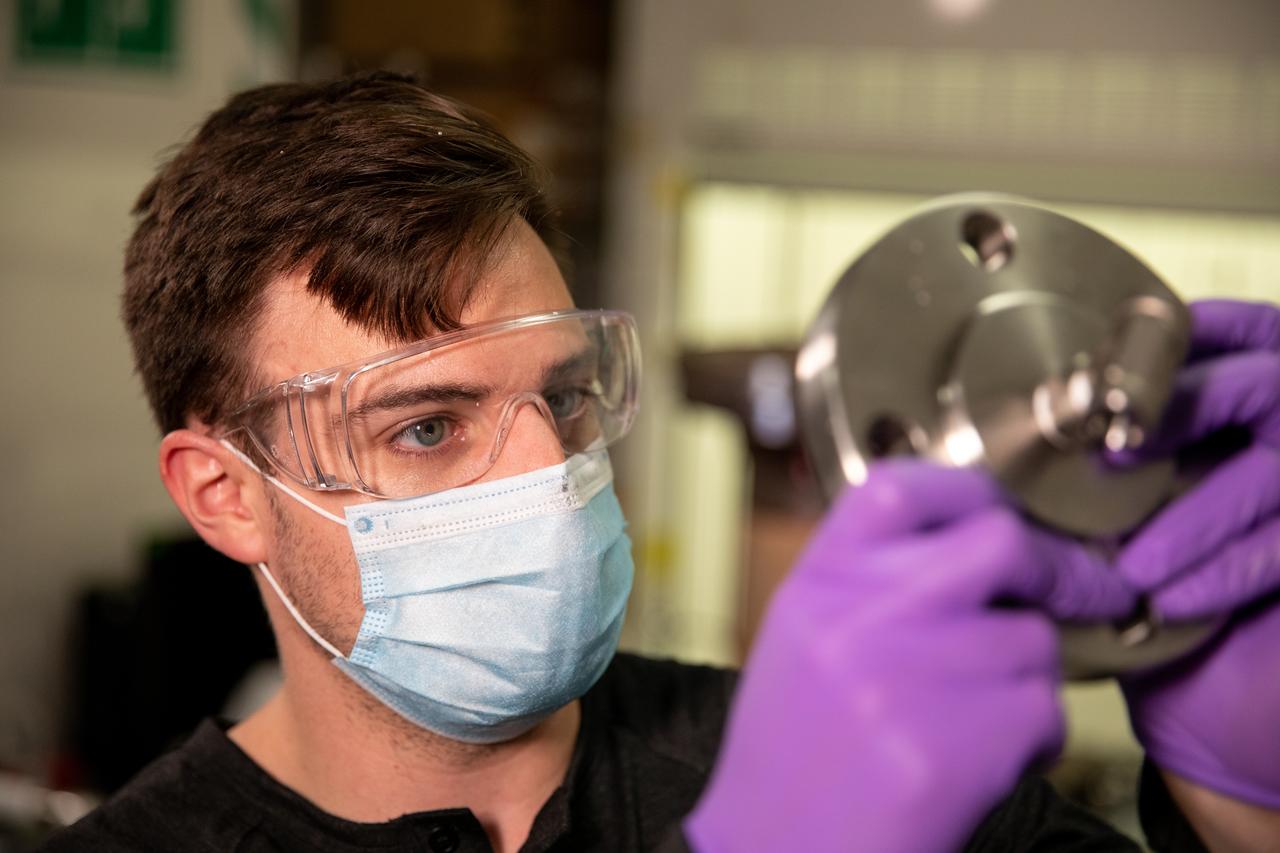

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
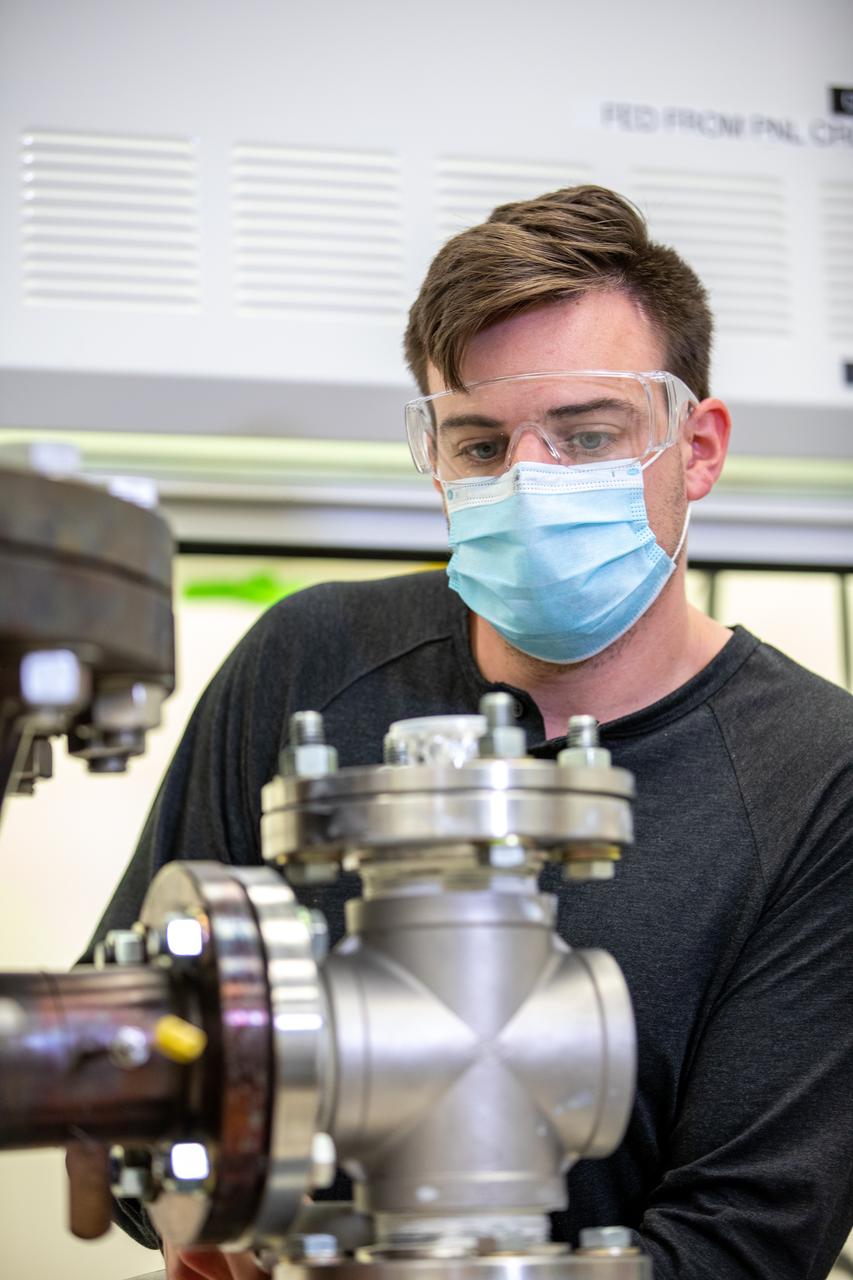

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
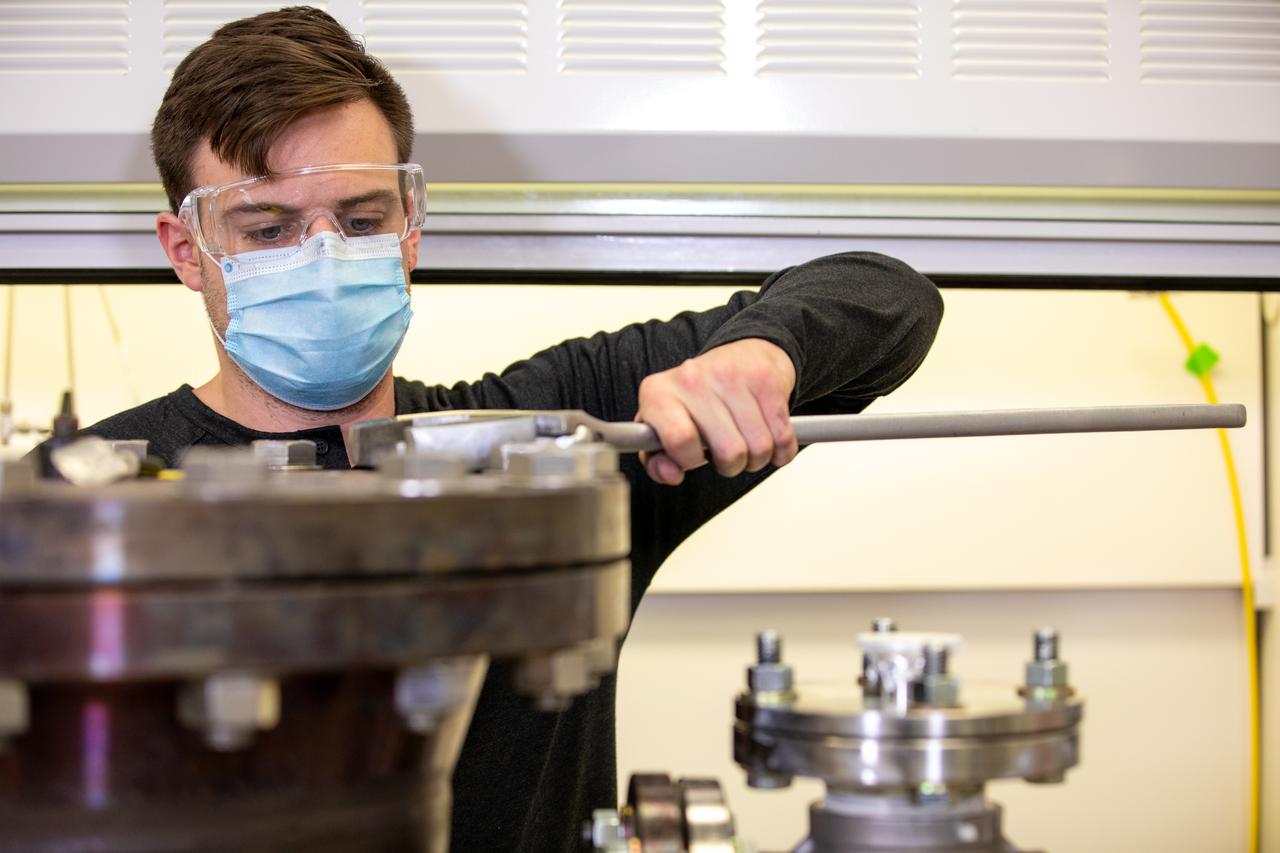

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
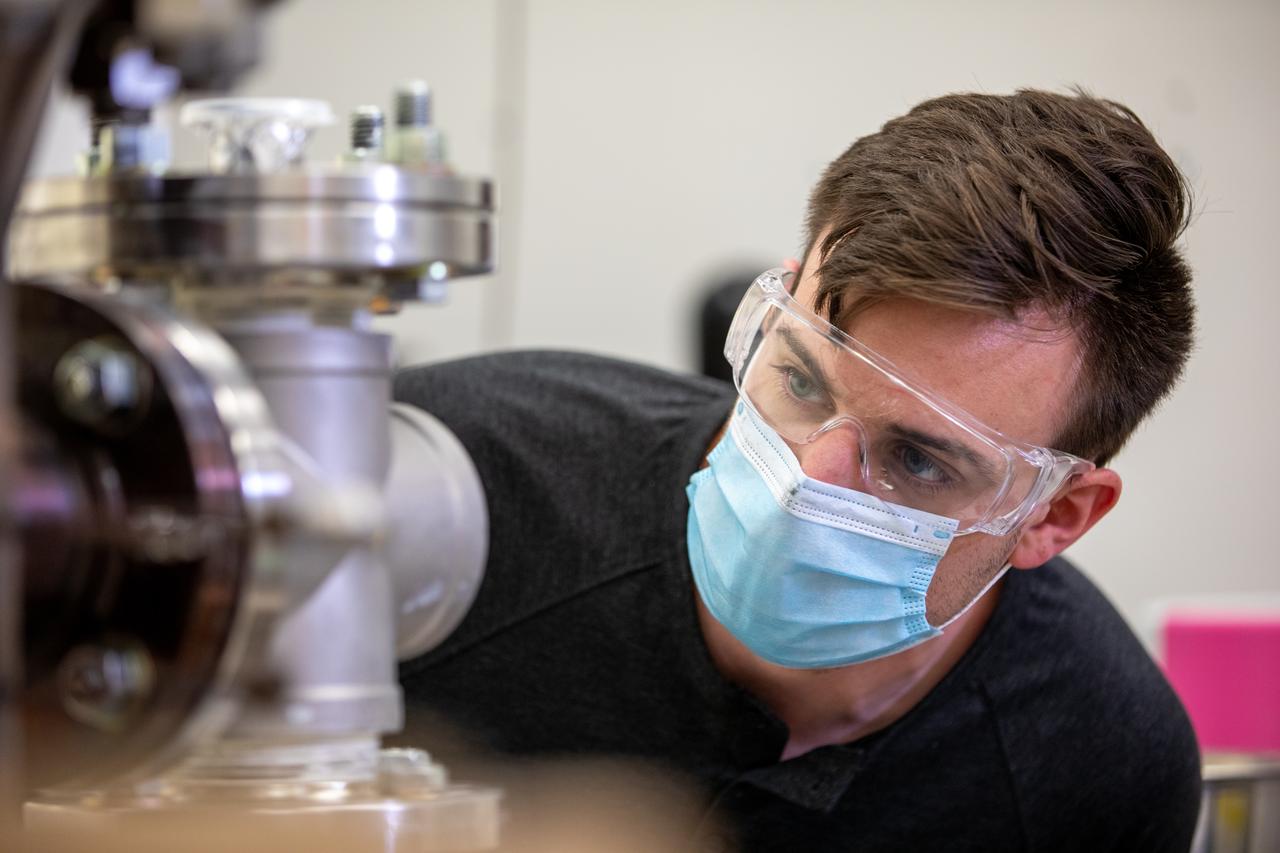

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
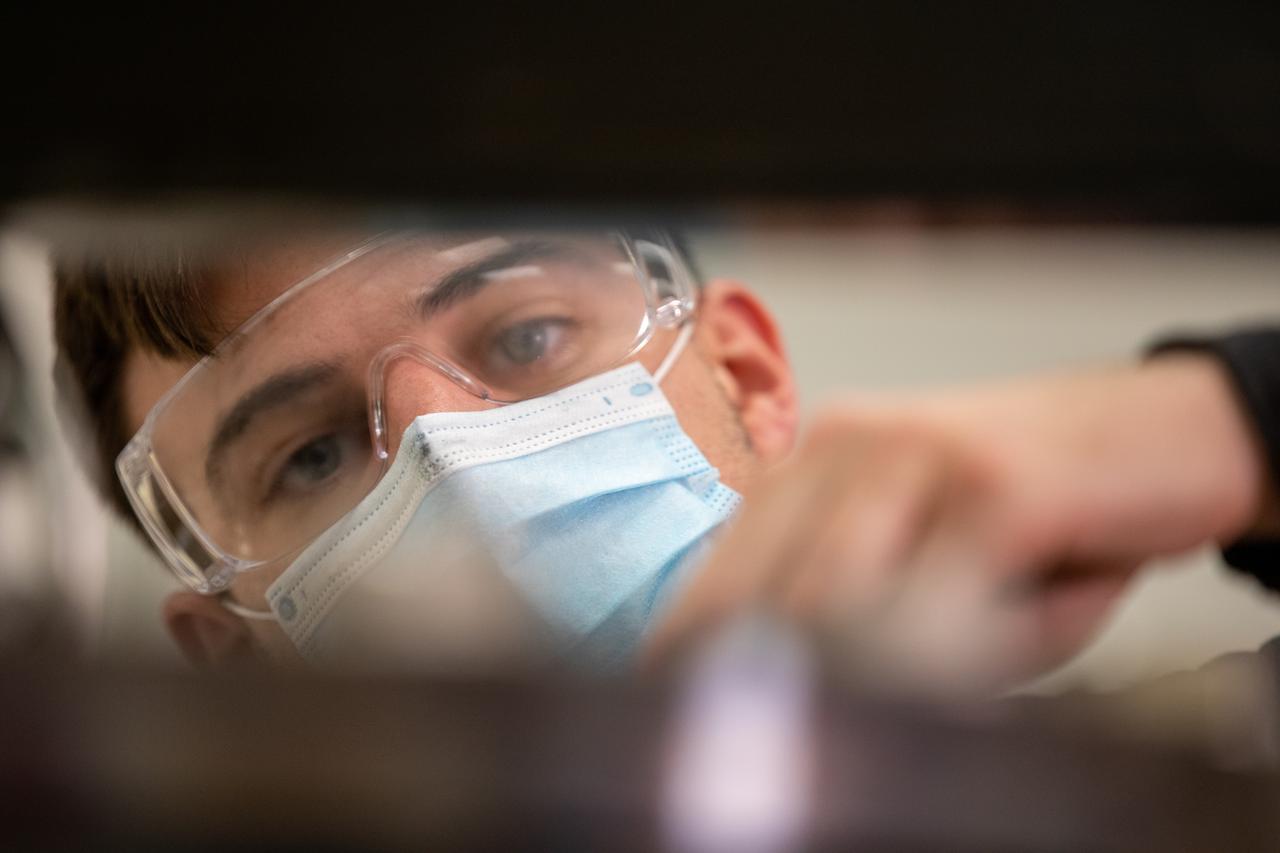

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
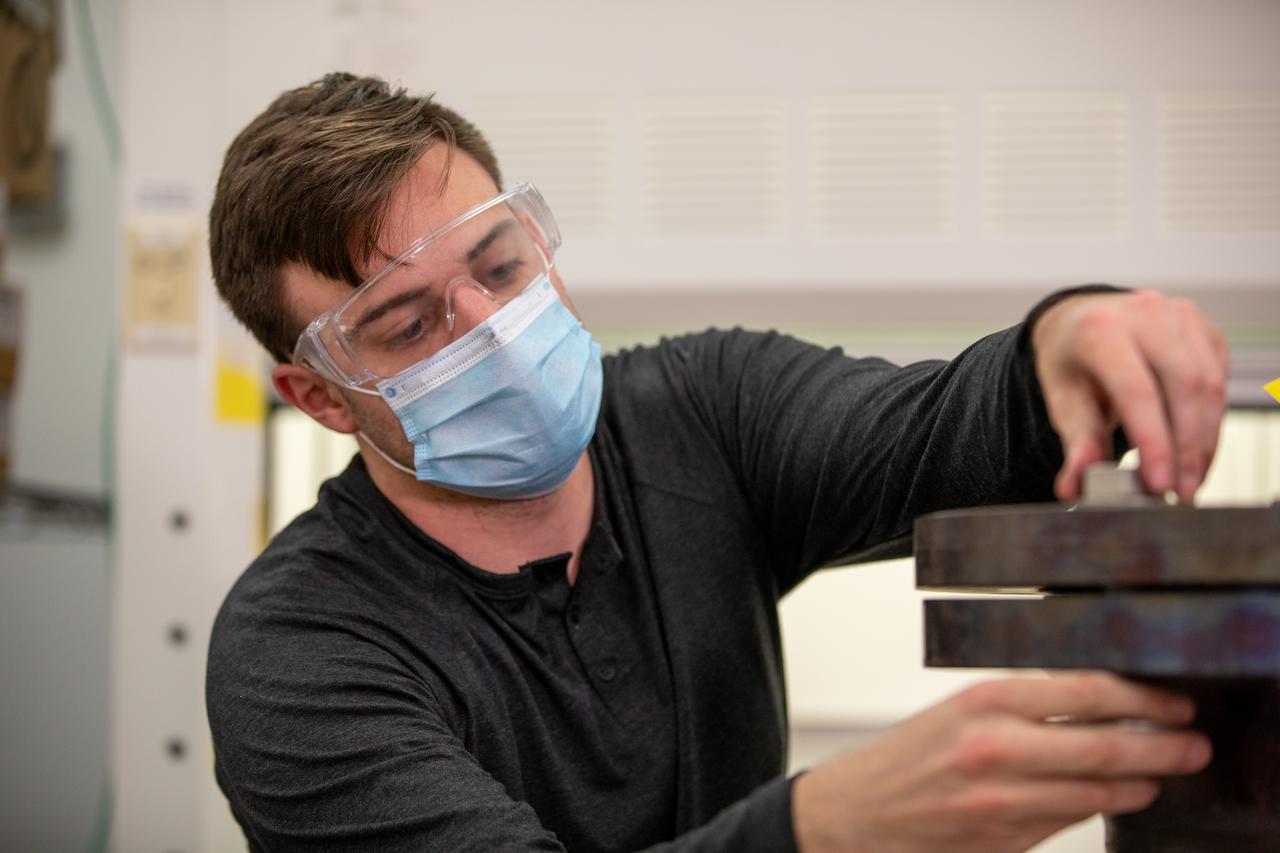

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, checks the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
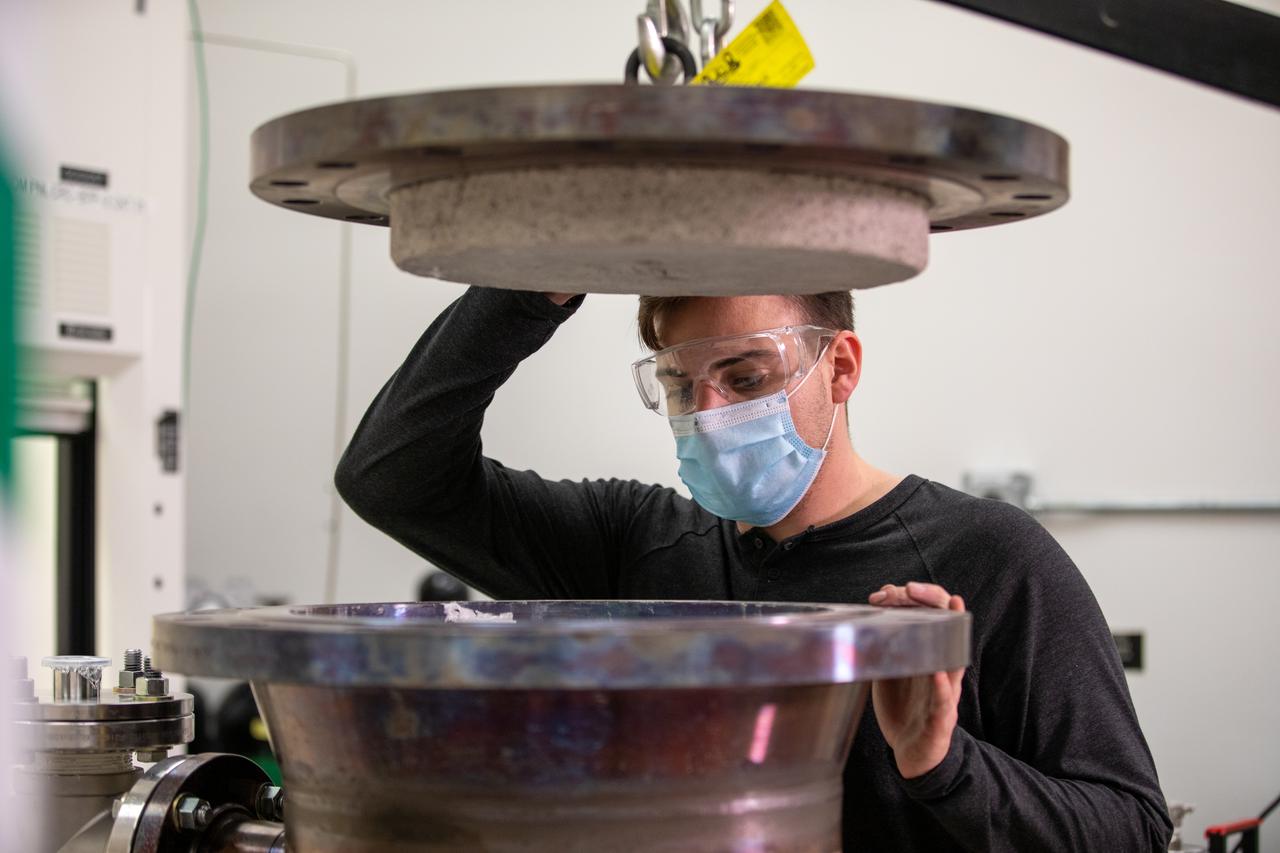

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, checks the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
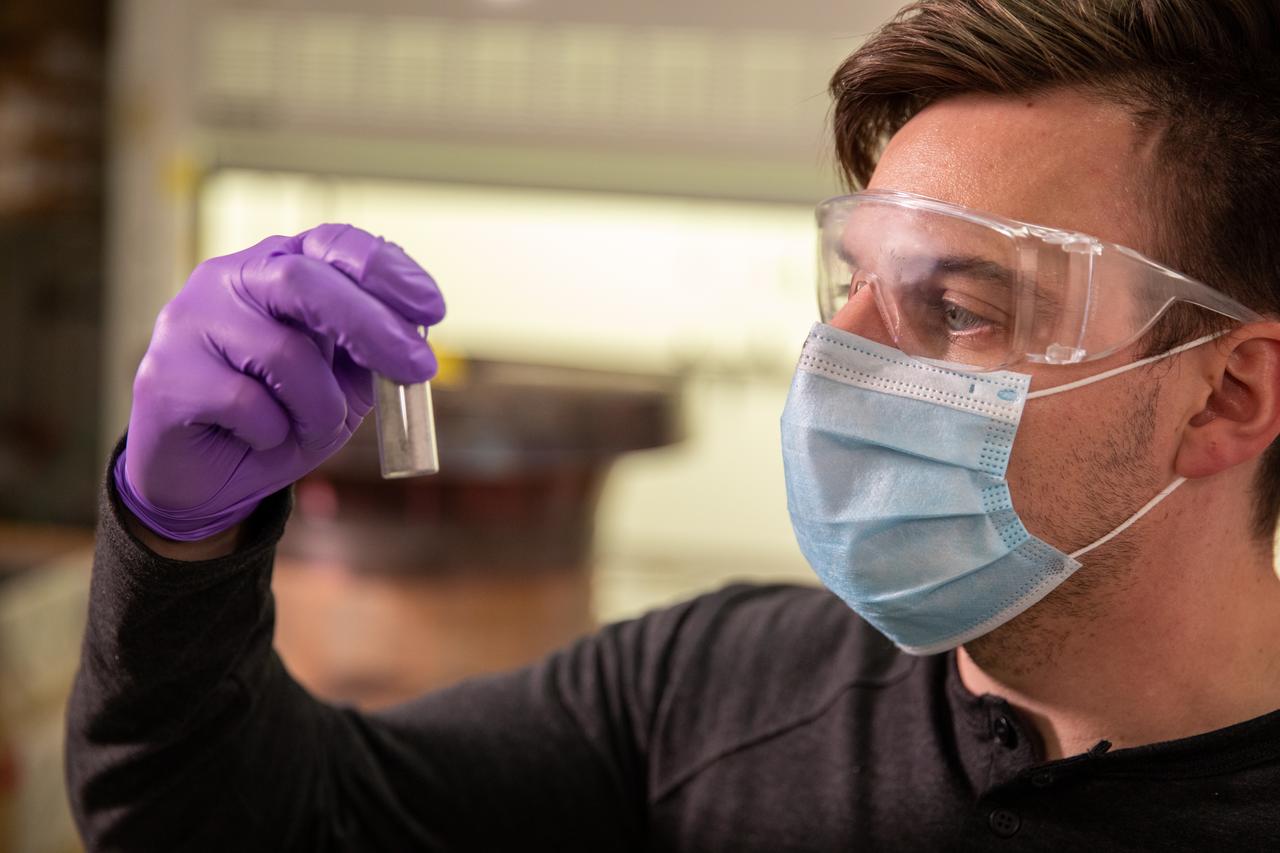

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
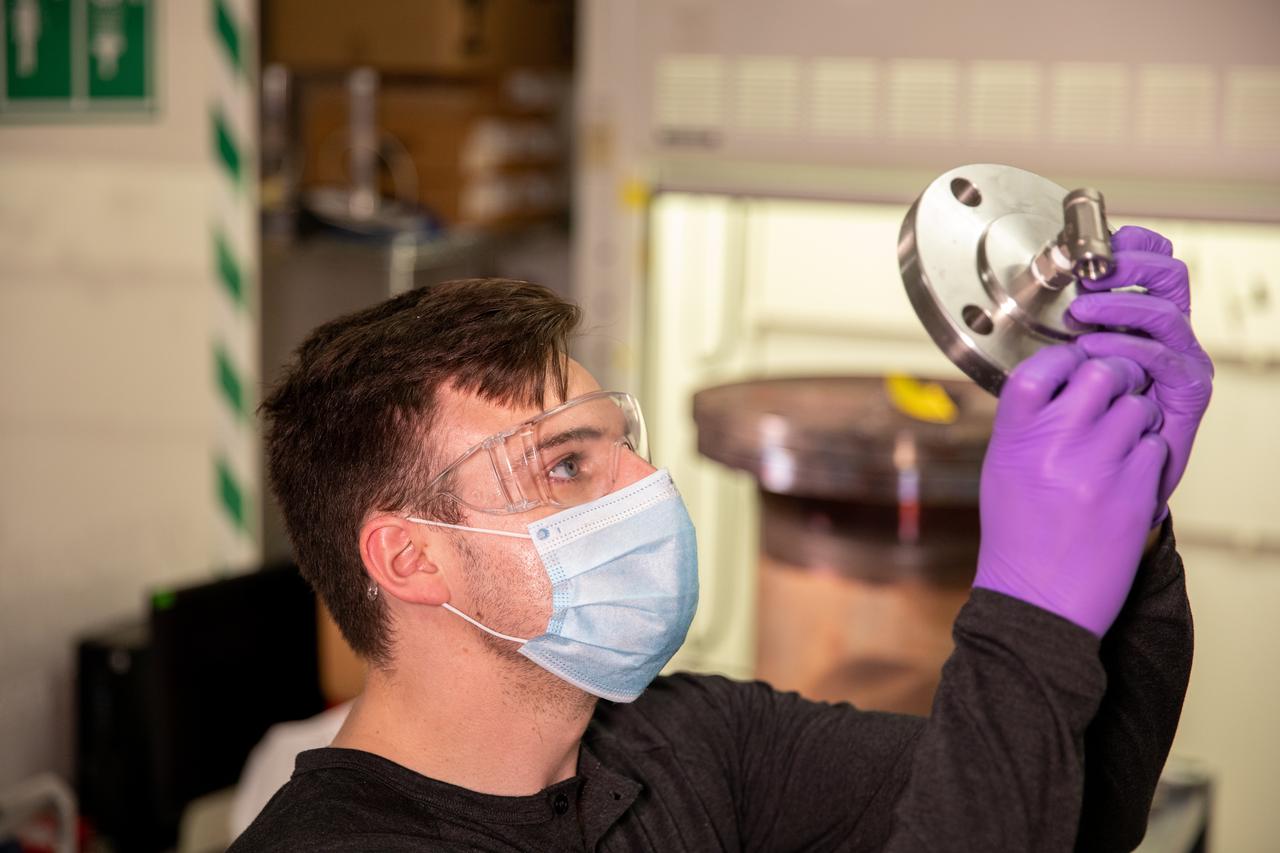

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
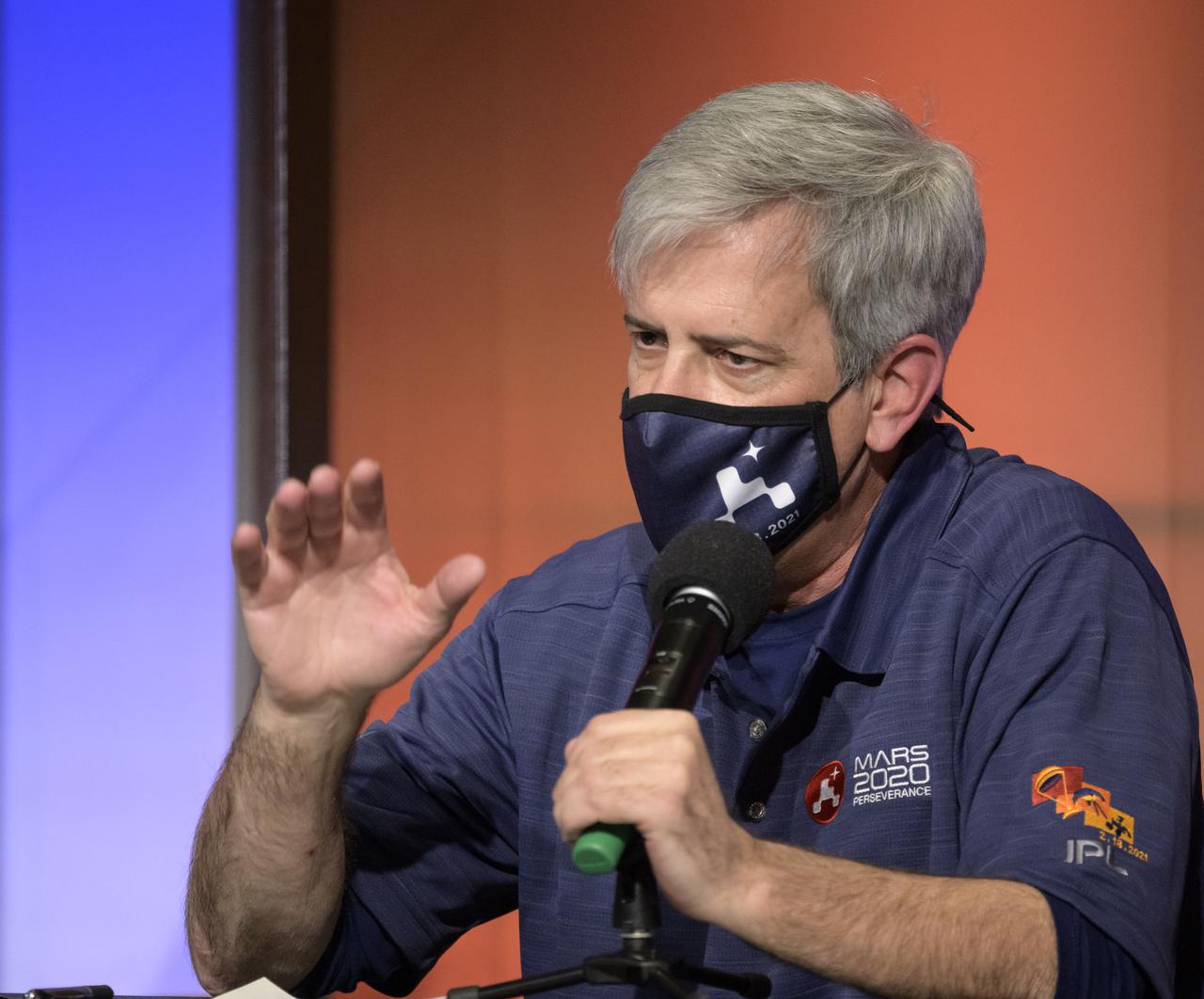

Mars 2020 Deputy Project Manager Matt Wallace, gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission post-landing update, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Mars 2020 Deputy Project Manager Matt Wallace, gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission post-landing update, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Dr. Kenneth Farley, a project scientist with Caltech, gave a science overview at the Mars 2020 VIP briefing at the Operations and Support Building II at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, before launch of the Mars Perseverance rover and Ingenuity helicopter on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Liftoff occurred at 7:50 a.m. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

The location where NASA's Mars 2020 Perseverance rover will observe the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter's attempt at powered controlled flight at Mars is called "Van Zyl Overlook," after Jakob van Zyl. Van Zyl was the team's longtime colleague, mentor, and leader at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. He passed away unexpectedly in August 2020, about a month after the launch of Perseverance. Van Zyl joined JPL in 1986 and served in crucial roles at the Lab over a 33-year career, including as director for the Astronomy and Physics Directorate, associate director for project formulation and strategy, and finally director for the Solar System Exploration Directorate. As leader of solar system exploration at JPL, he oversaw successful operations of such NASA missions as Juno, Dawn, and Cassini, the implementation of the Mars InSight lander and MarCO CubeSats, as well as ongoing development of Europa Clipper, Psyche, and all of JPL's instruments and Ingenuity. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24435
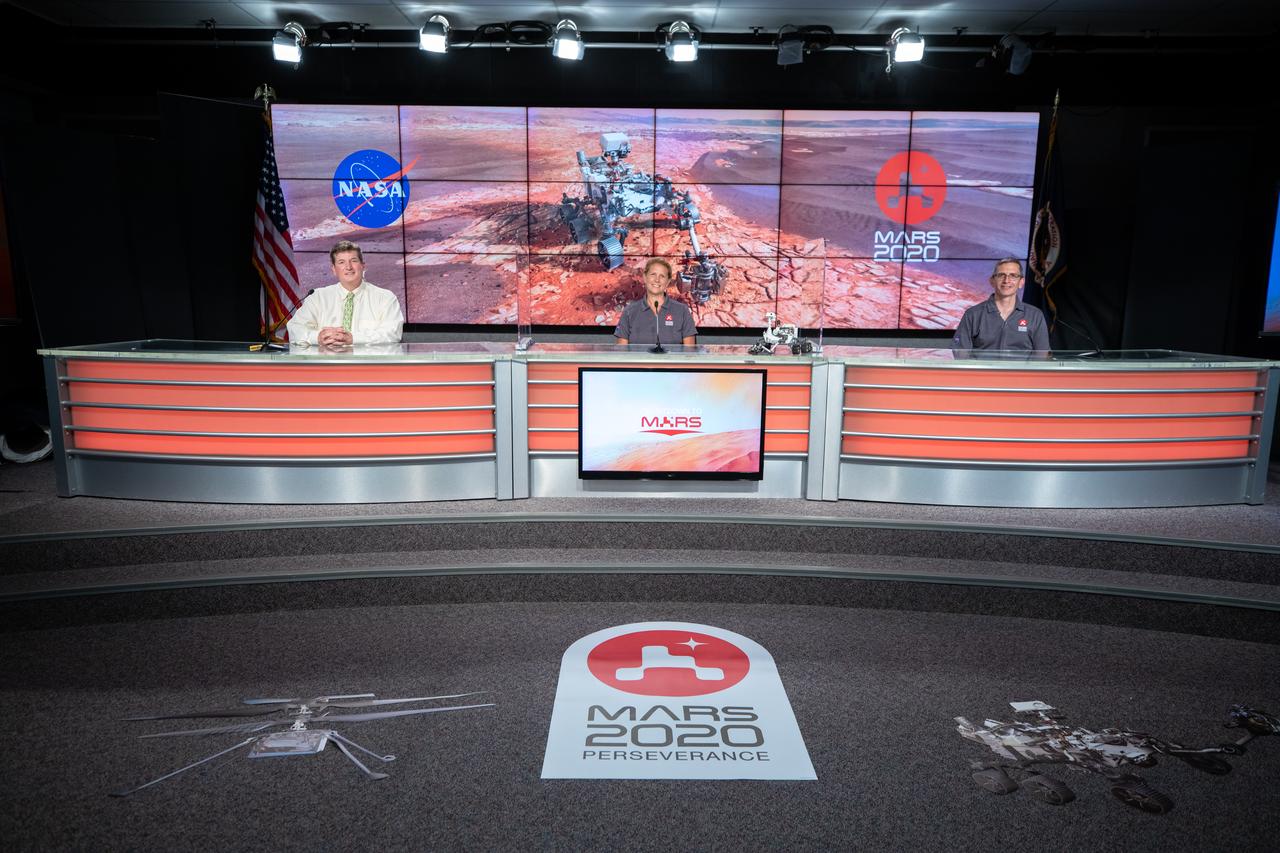

A Mars 2020 Mission Engineering and Science Briefing is held at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 27, 2020. Participating in the briefing from left, are Moderator DC Agle, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory; Lori Glaze, Planetary Science Division director, NASA Headquarters; and Ken Farley, project scientist, California Institute of Technology. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch July 30, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

Matt Wallace, deputy project manager, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, participates in a Mars 2020 post-launch news conference at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020. The United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket lifted off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 7:50 a.m. EDT, carrying the agency’s Mars Perseverance rover and Ingenuity helicopter. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

A Mars 2020 Mission Engineering and Science Briefing is held at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 27, 2020. Participating in the briefing from left, are Moderator DC Agle, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory; Lori Glaze, Planetary Science Division director, NASA Headquarters; and Ken Farley, project scientist, California Institute of Technology. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch July 30, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

Mars 2020 Deputy Project Manager Matt Wallace, , left, and Perseverance entry, descent, and landing lead, JPL, Allen Chen, give remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission landing update, Wednesday, Feb. 17, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The Perseverance Mars rover is due to land on Mars Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Mars 2020 Deputy Project Manager Matt Wallace, gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission landing update, Wednesday, Feb. 17, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The Perseverance Mars rover is due to land on Mars Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
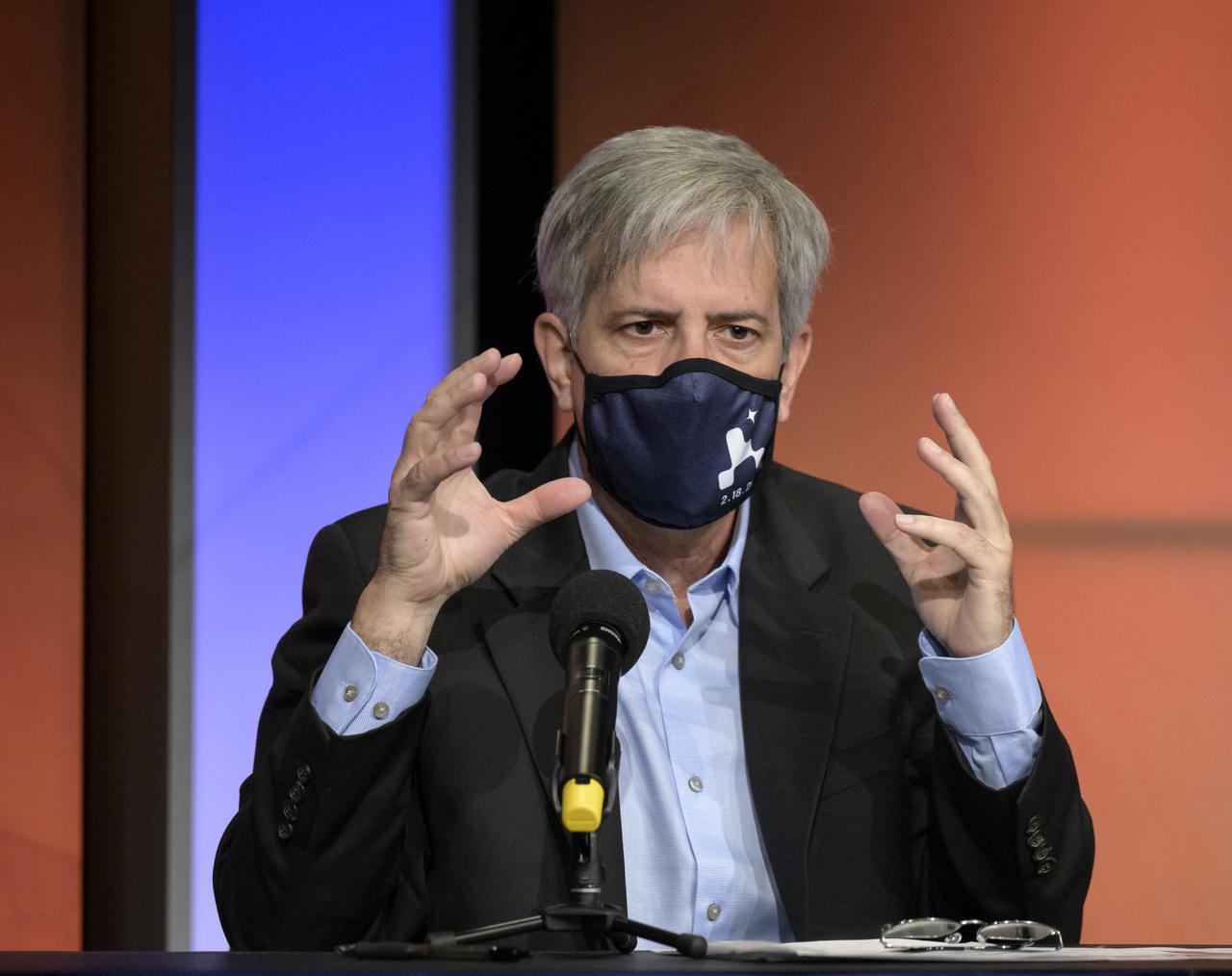

Mars 2020 Deputy Project Manager Matt Wallace, gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission landing update, Wednesday, Feb. 17, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The Perseverance Mars rover is due to land on Mars Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
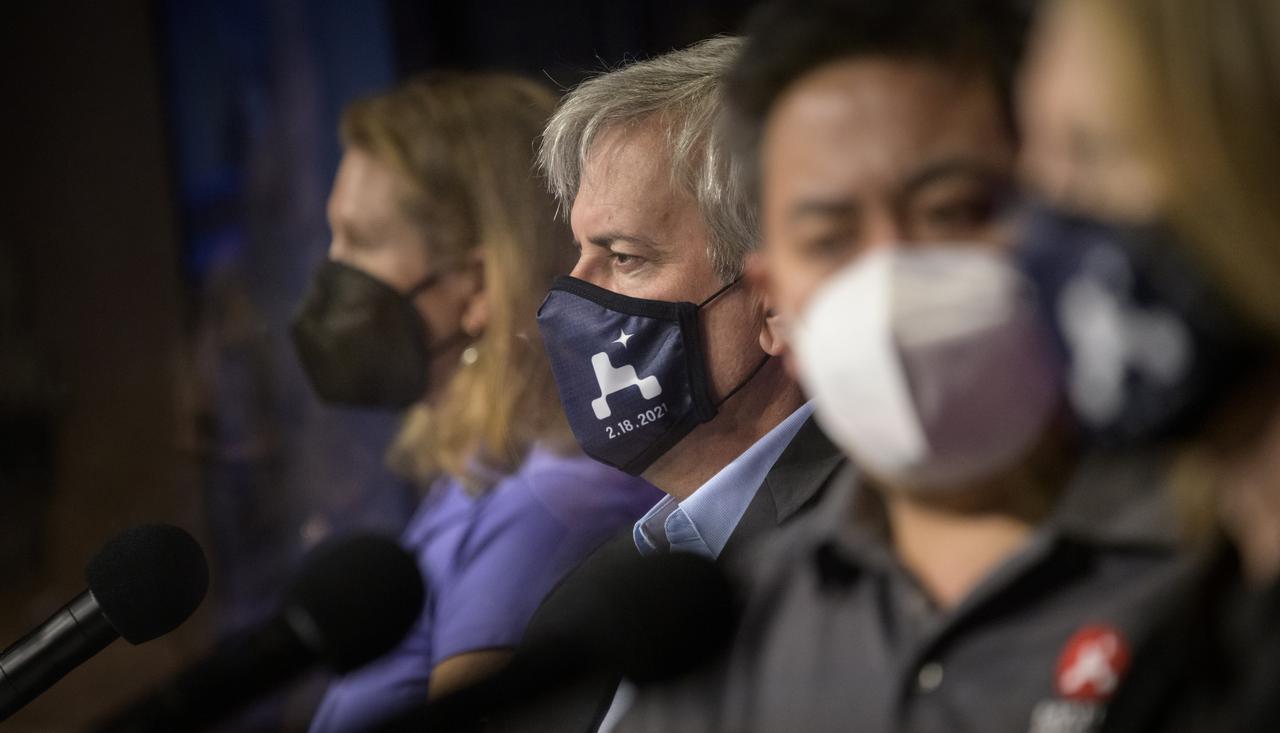

Mars 2020 Deputy Project Manager Matt Wallace, gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission landing update, Wednesday, Feb. 17, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The Perseverance Mars rover is due to land on Mars Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
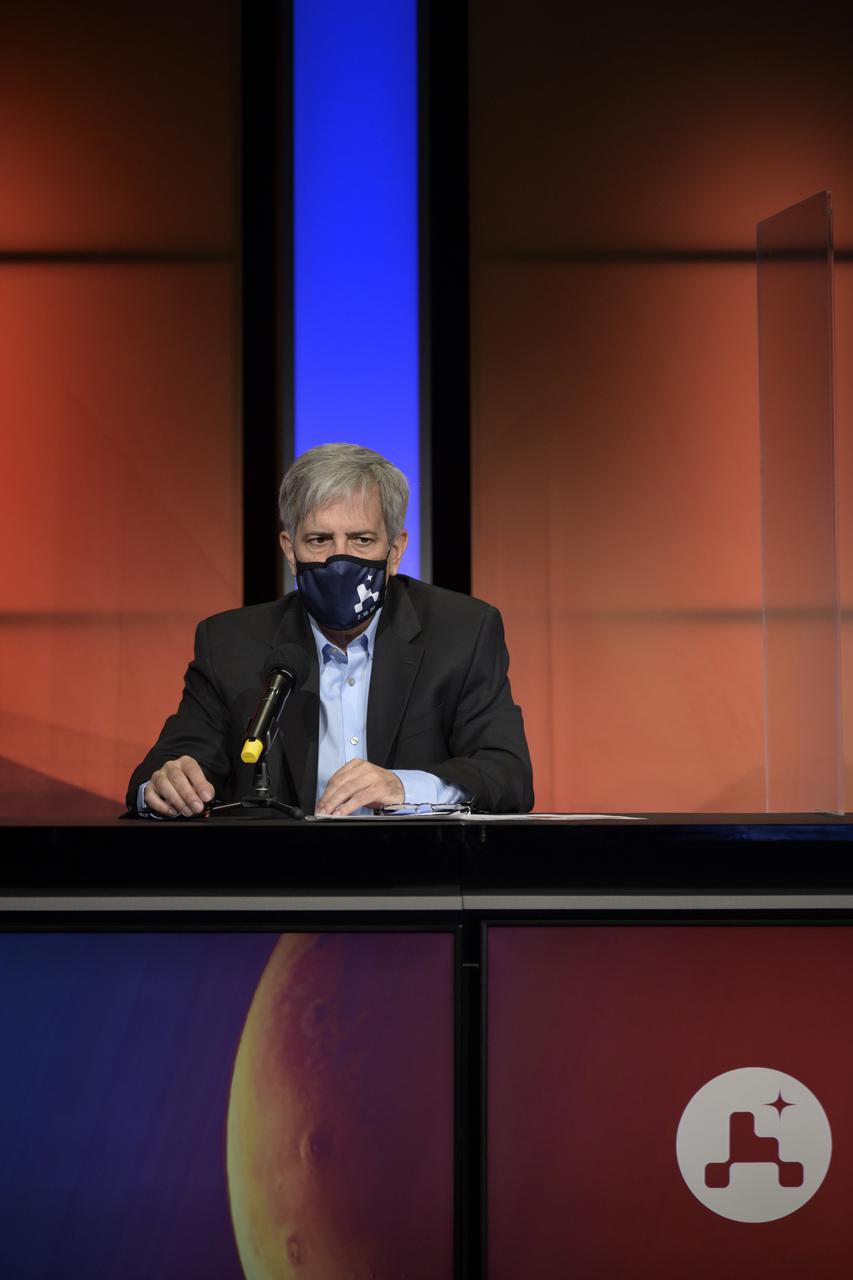

Mars 2020 Deputy Project Manager Matt Wallace, gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission landing update, Wednesday, Feb. 17, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The Perseverance Mars rover is due to land on Mars Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
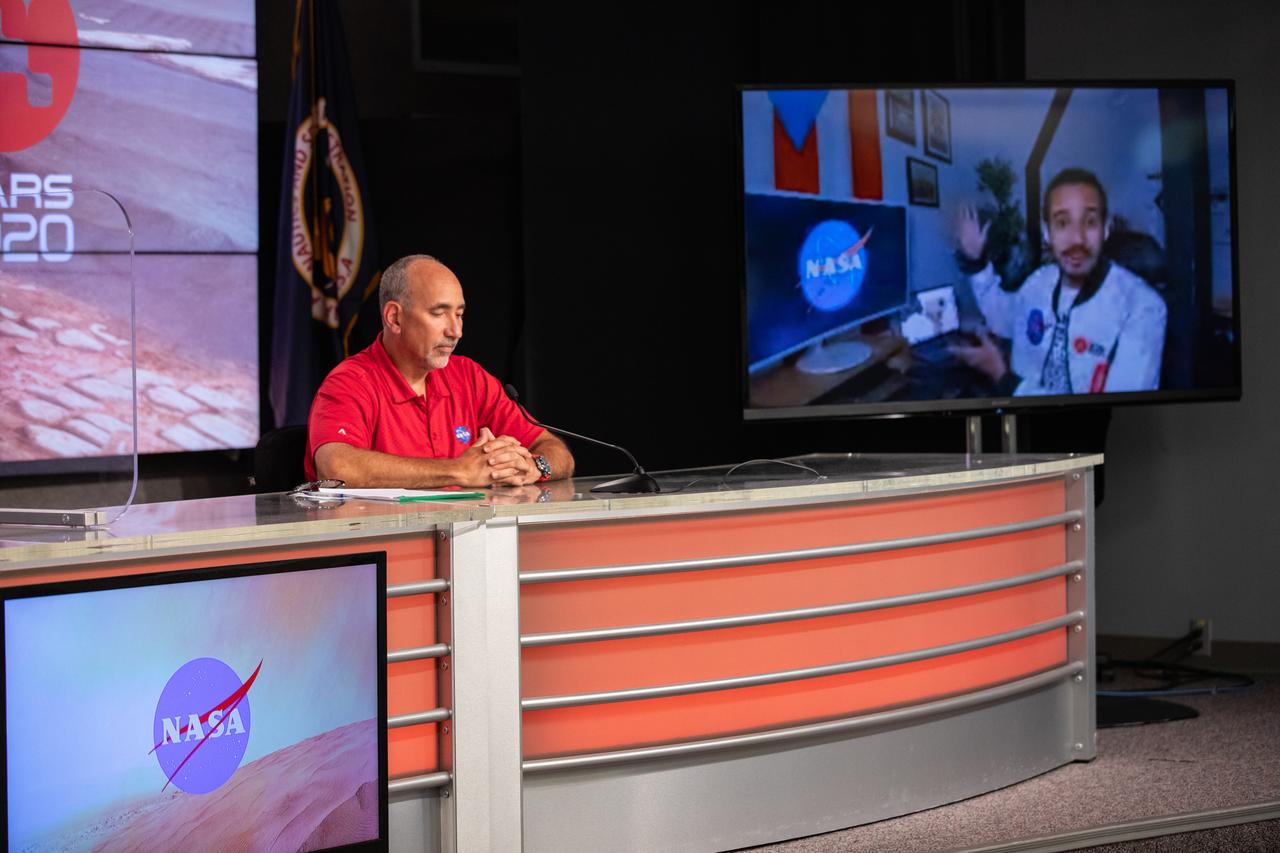

Elio Morillo, a Mars 2020 system testbed engineer from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, speaks remotely while Albert Sierra, NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) chief of Flight Projects Office, listens during a “Mars 2020 Social Media Q&A: En Español” program on Wednesday, July 22, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The event featured representatives from LSP and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to lift off aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Thursday, July 30. The two-hour window opens at 7:50 a.m. EDT. LSP, based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
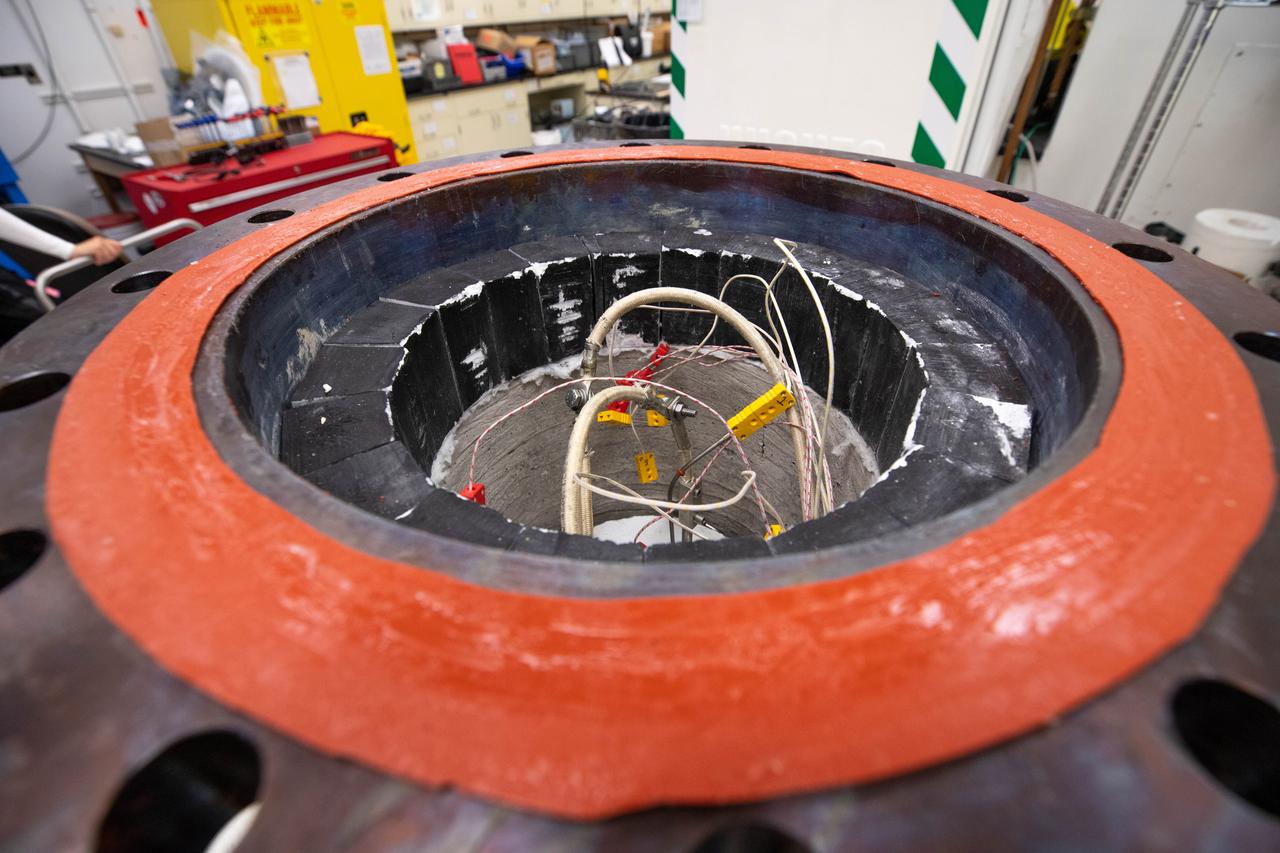

A team investigating molten regolith electrolysis prepares to test a reactor inside a laboratory in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 29, 2020. The Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project seeks to develop technology to extract oxygen and metals from the crushed rock, or regolith, that covers the Moon’s surface. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate.

With the launch period for the Perseverance mission opening July 17, 2020, members of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover project continue the mission's march to the launch pad while working from their home offices during the coronavirus outbreak. Clockwise from upper left: lead mobility systems engineer Rich Rieber (with son Ben); deputy project scientist Katie Stack Morgan; mission system verification and validation supervisor Ruth Fragoso; mission design and navigation manager Fernando Abilleira (below mission logo); staff assistant Monica Hopper; systems engineer Heather Bottom; project chief engineer Adam Steltzner; guidance and control systems engineer Swati Mohan; entry, Descent and Landing Phase Lead Al Chen (with son Max); project manager John McNamee; and Entry, Descent and Landing Systems Engineer Cj Giovingo. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23881

NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Chief of Flight Projects Office Albert Sierra participates in a “Mars 2020 Social Media Q&A: En Español” program on Wednesday, July 22, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The event featured representatives from LSP and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to lift off aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Thursday, July 30. The two-hour window opens at 7:50 a.m. EDT. LSP, based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.

NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Chief of Flight Projects Office Albert Sierra participates in a “Mars 2020 Social Media Q&A: En Español” program on Wednesday, July 22, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The event featured representatives from LSP and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to lift off aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Thursday, July 30. The two-hour window opens at 7:50 a.m. EDT. LSP, based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
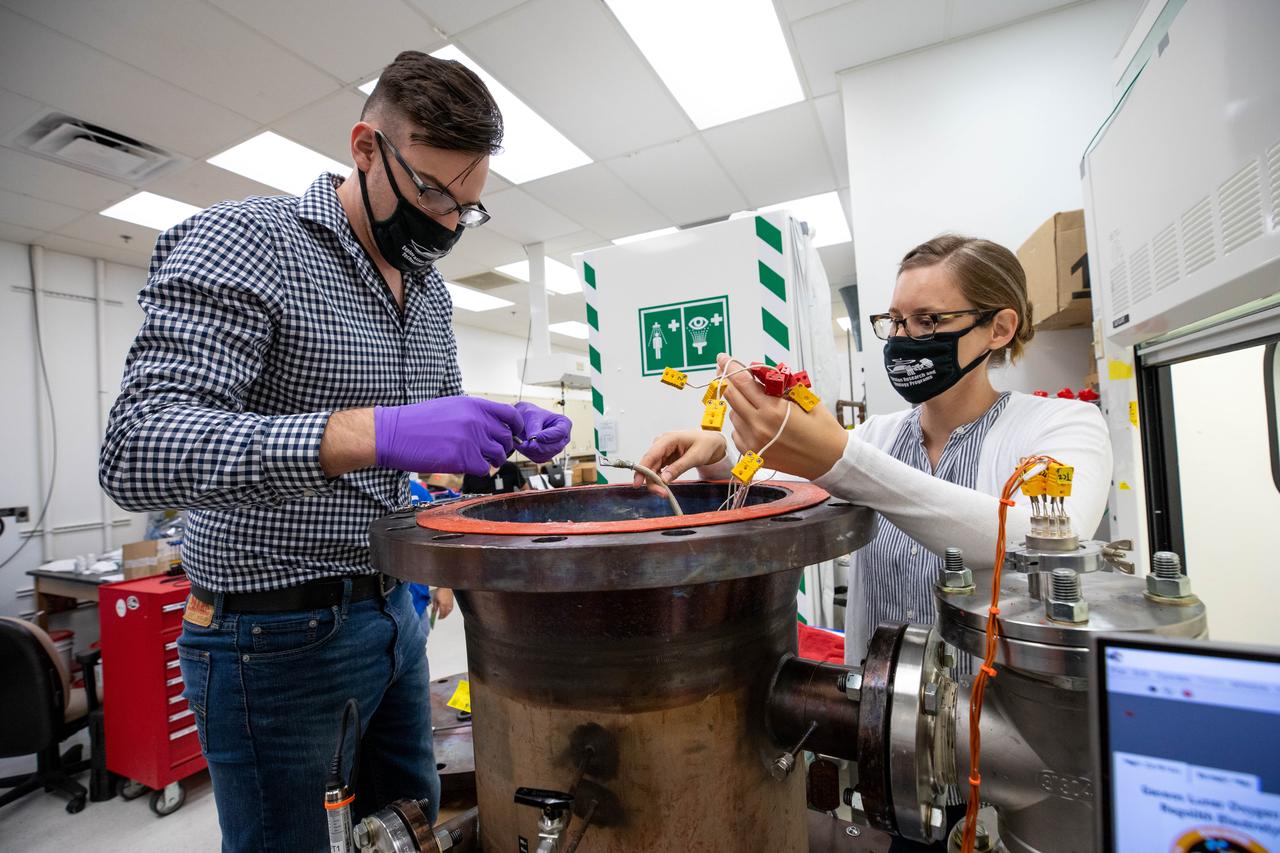

Kevin Grossman, left, principal investigator of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project, and Elspeth Petersen, a chemical engineer and member of the GaLORE team, check some of the project’s hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
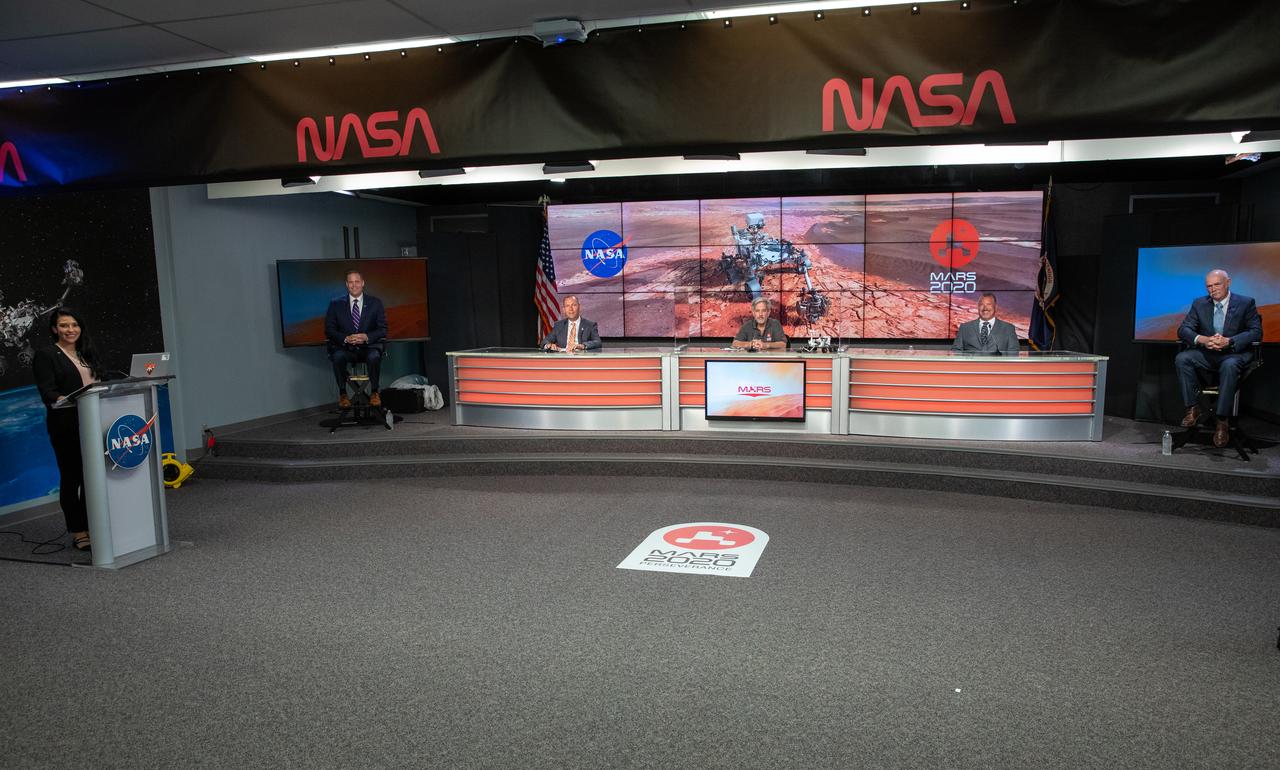

A Mars 2020 prelaunch news conference is held at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 27, 2020. Participating in the briefing from left, are Moderator Bettina Inclan, NASA Headquarters; NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine; Thomas Zurbuchen, NASA associate administrator, Science Mission Directorate; Matt Wallace, deputy project manager, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory; Launch Director Omar Baez, NASA’s Launch Services Program; and Tory Bruno, CEO, United Launch Alliance. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch on July 30, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
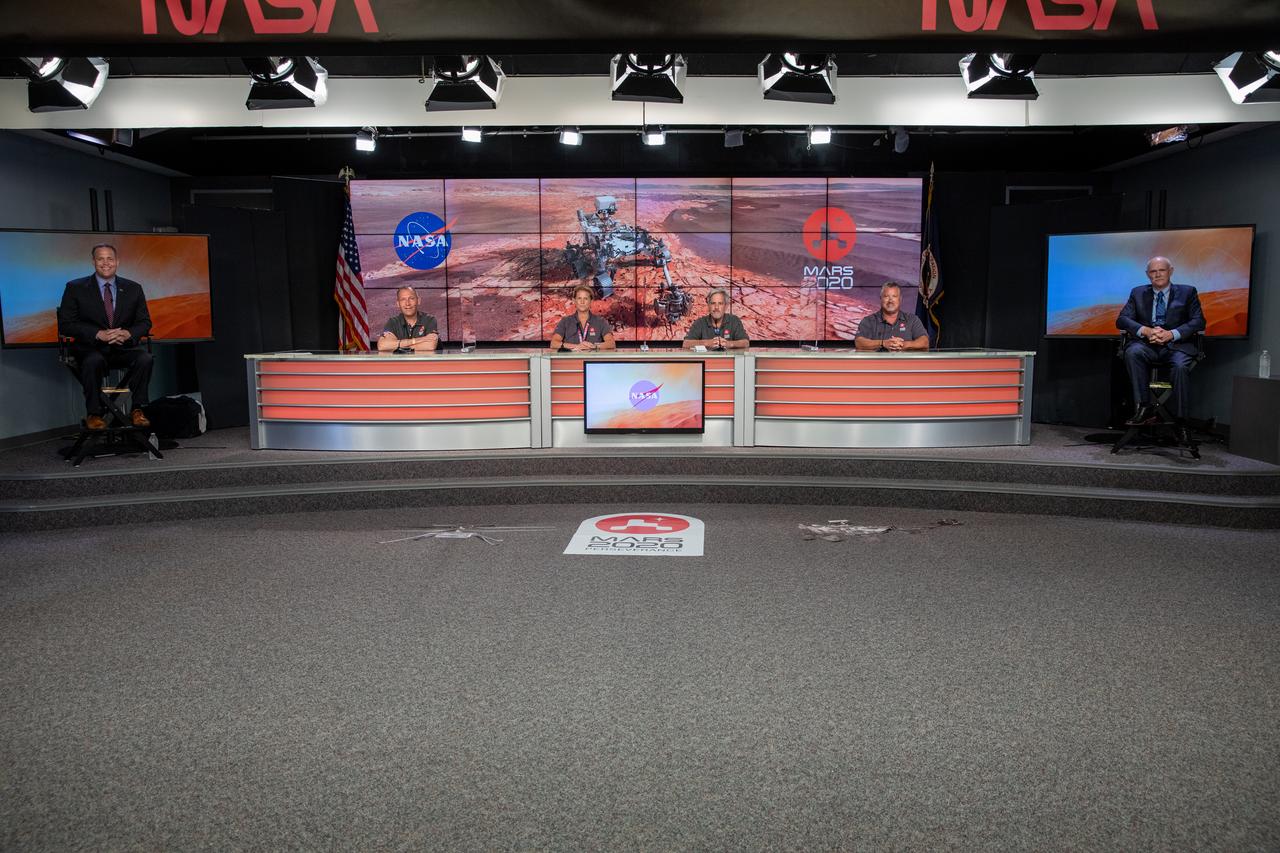

A Mars 2020 post-launch news conference is held at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020. Participants, from left, are NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine; Thomas Zurbuchen, NASA associate administrator, Science Mission Directorate; Lori Glaze, Planetary Science Division director, NASA Headquarters; Matt Wallace, deputy project manager, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory; Omar Baez, launch director, NASA’s Launch Services Program; and Tory Bruno, president and CEO of United Launch Alliance. The United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket lifted off from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 7:50 a.m. EDT, carrying the agency’s Mars Perseverance rover and Ingenuity helicopter. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
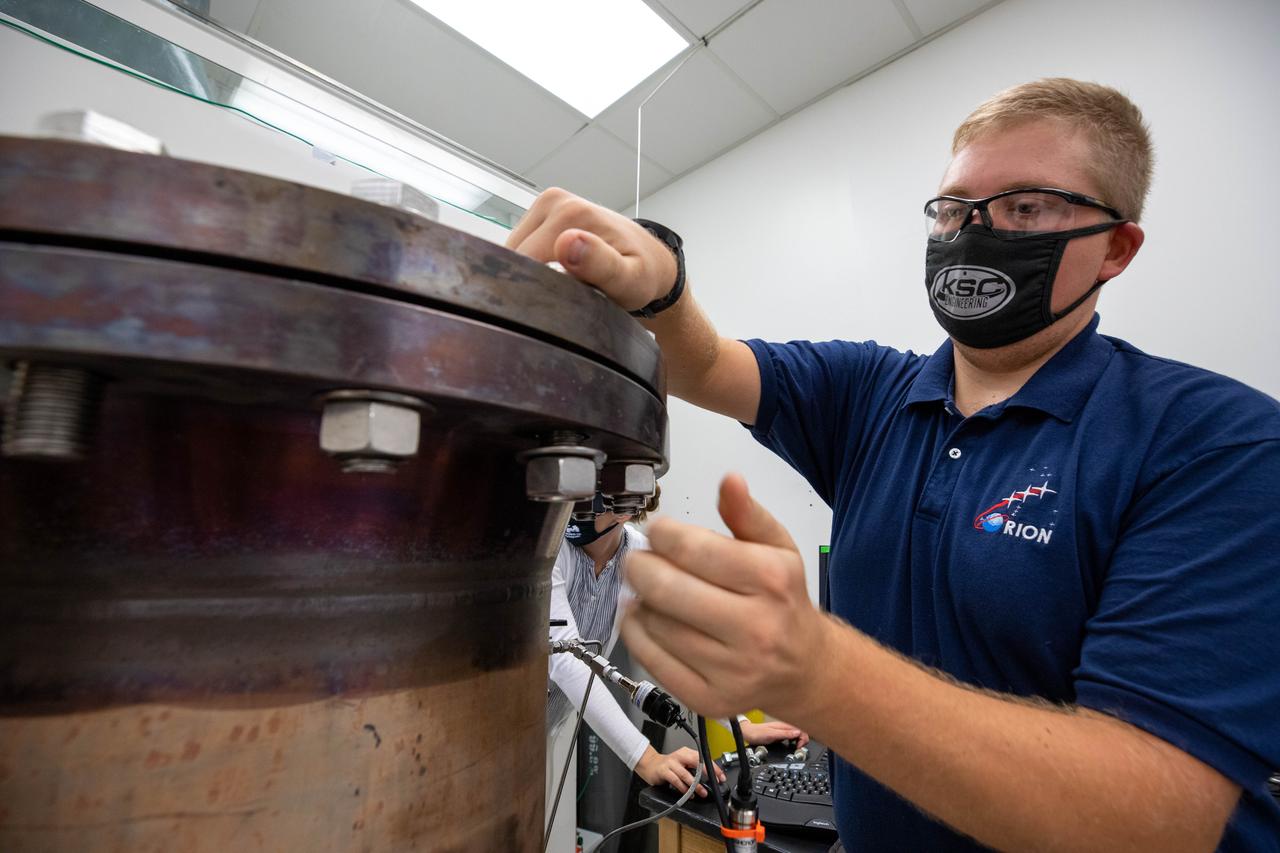

Evan Bell, a mechanical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
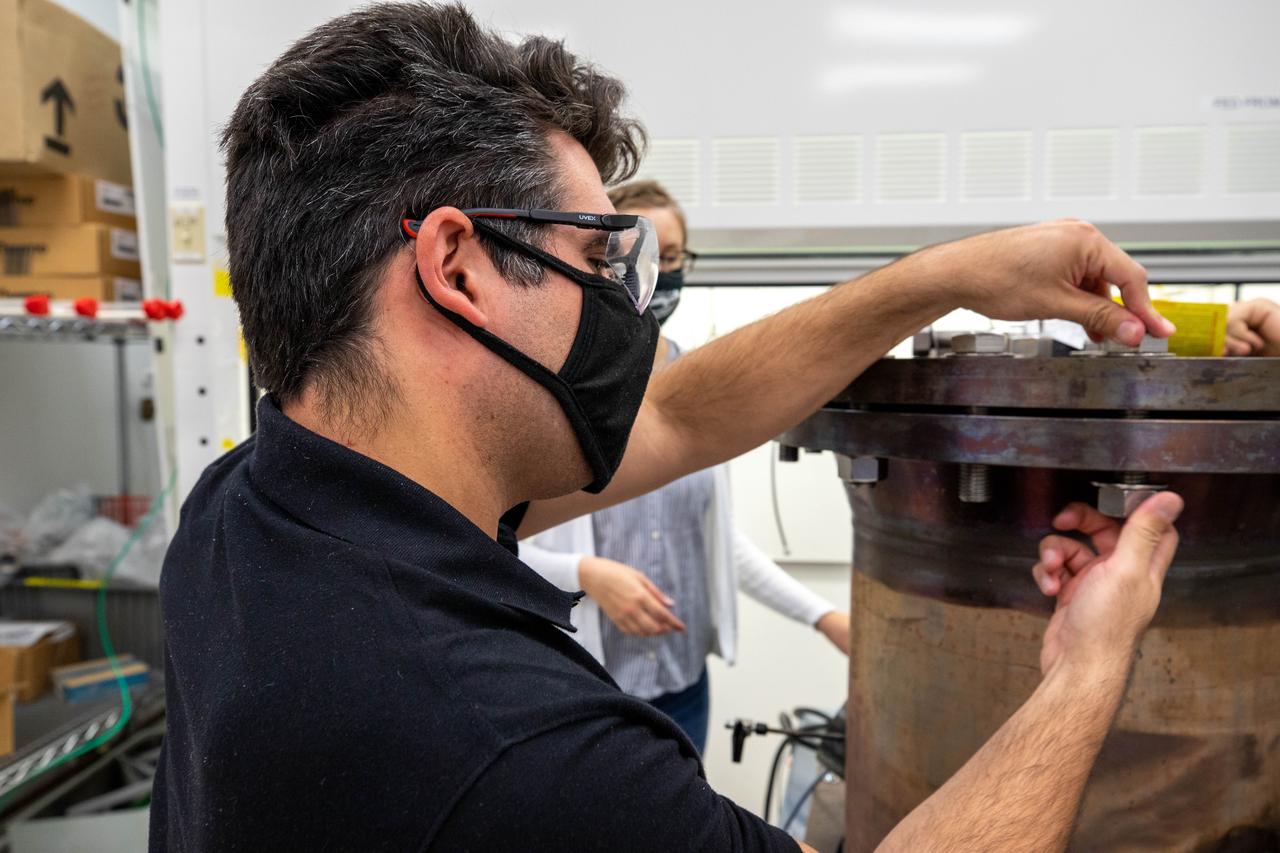

Jaime Toro, a mechanical engineer supporting the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
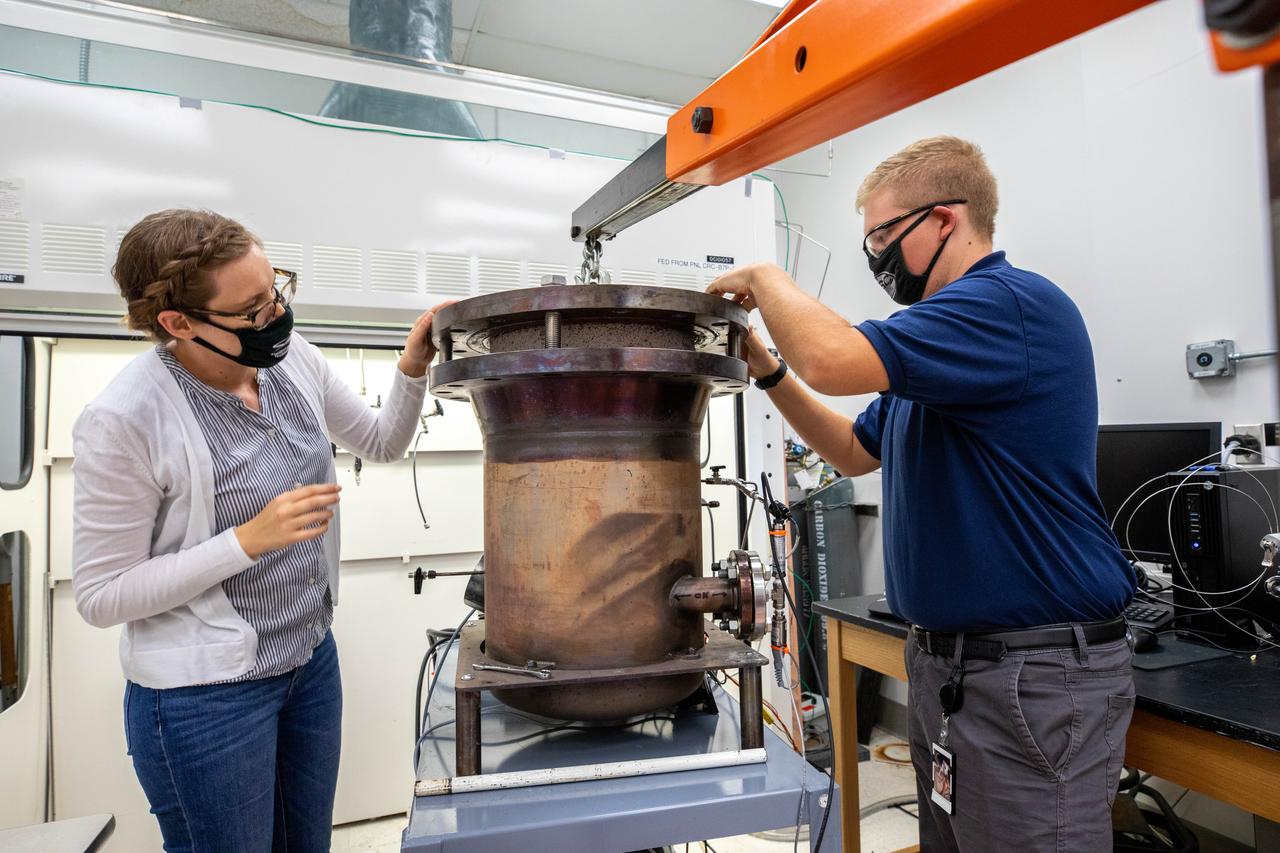

Elspeth Petersen, left, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, and Evan Bell, GaLORE mechanical engineer, inspect hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – stimulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
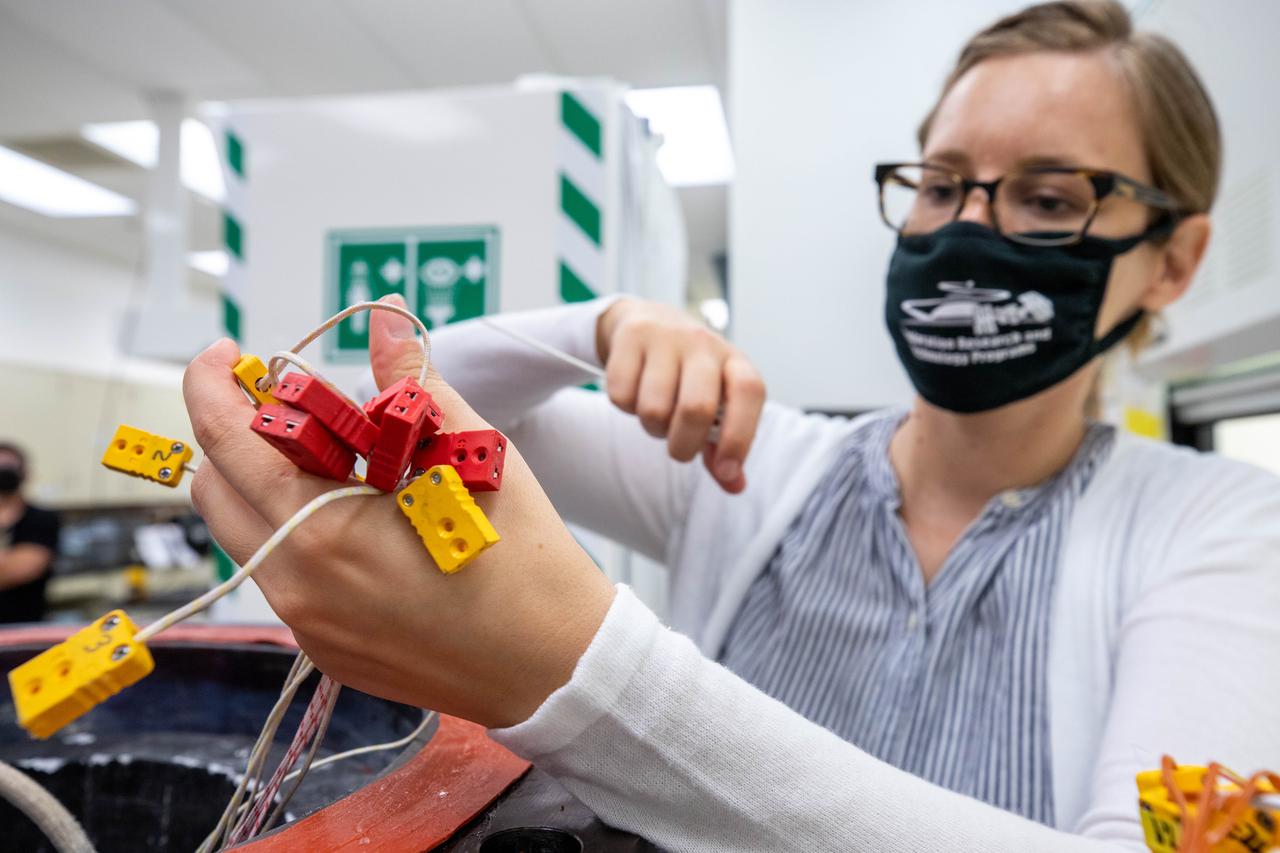

Elspeth Petersen, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, inspects some of the GaLORE hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
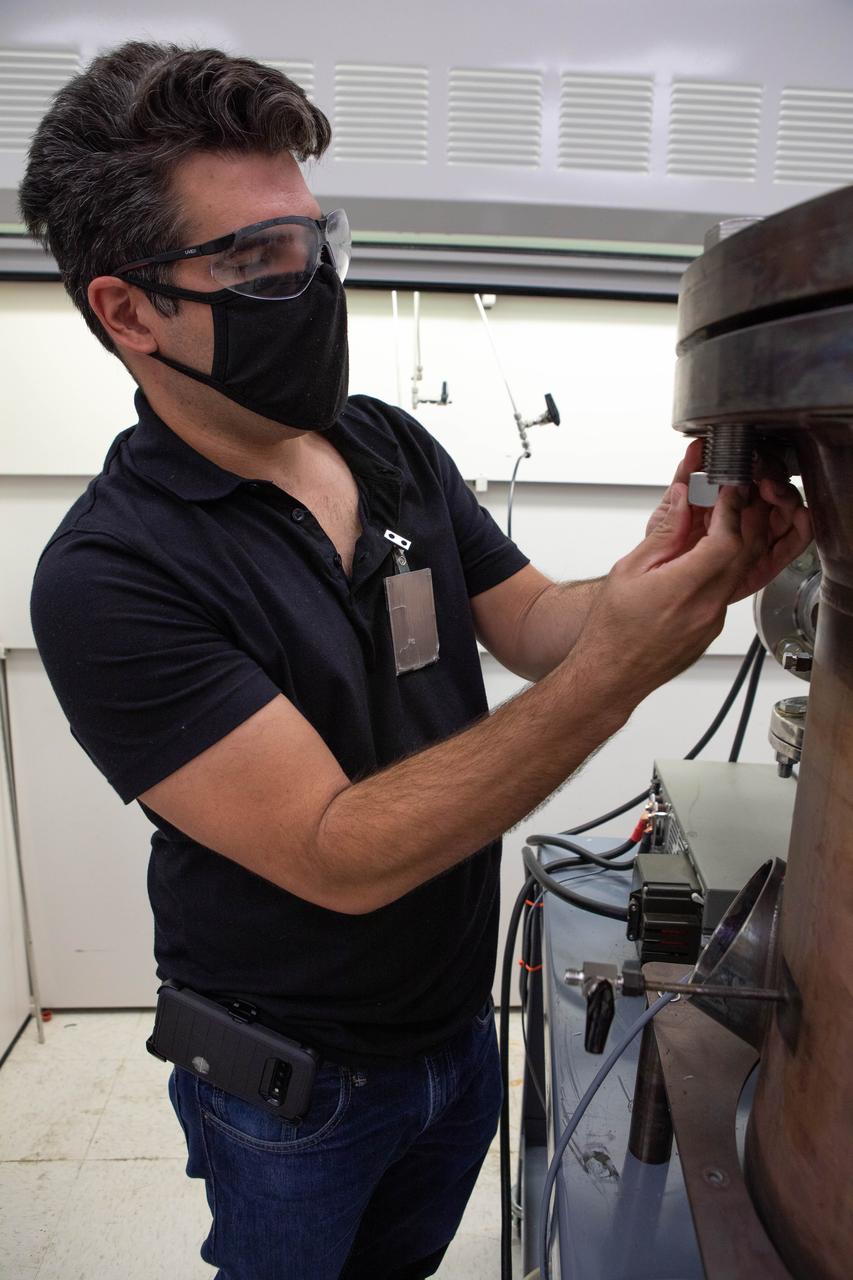

Jaime Toro, a mechanical engineer supporting the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
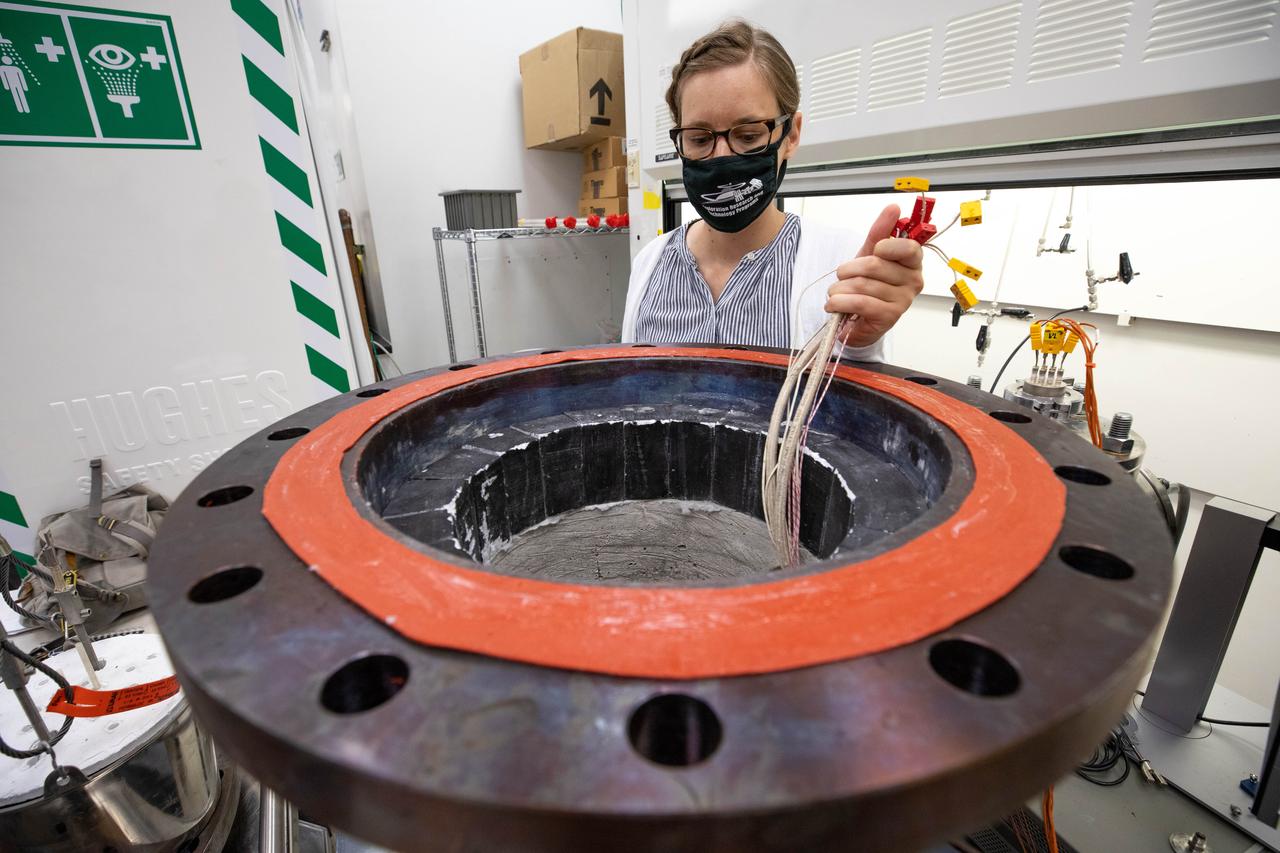

Elspeth Petersen, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, inspects hardware before a test to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.

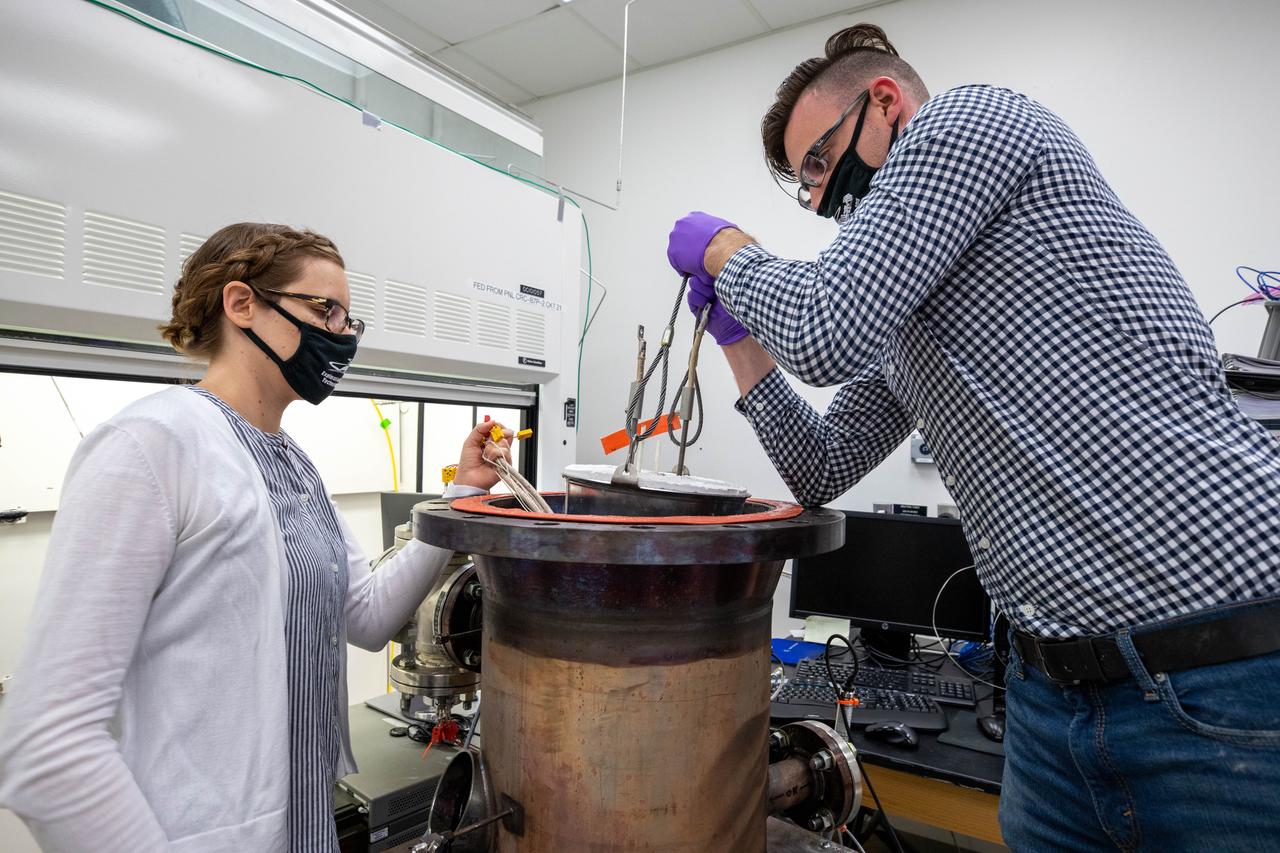
Members of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team inspect hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
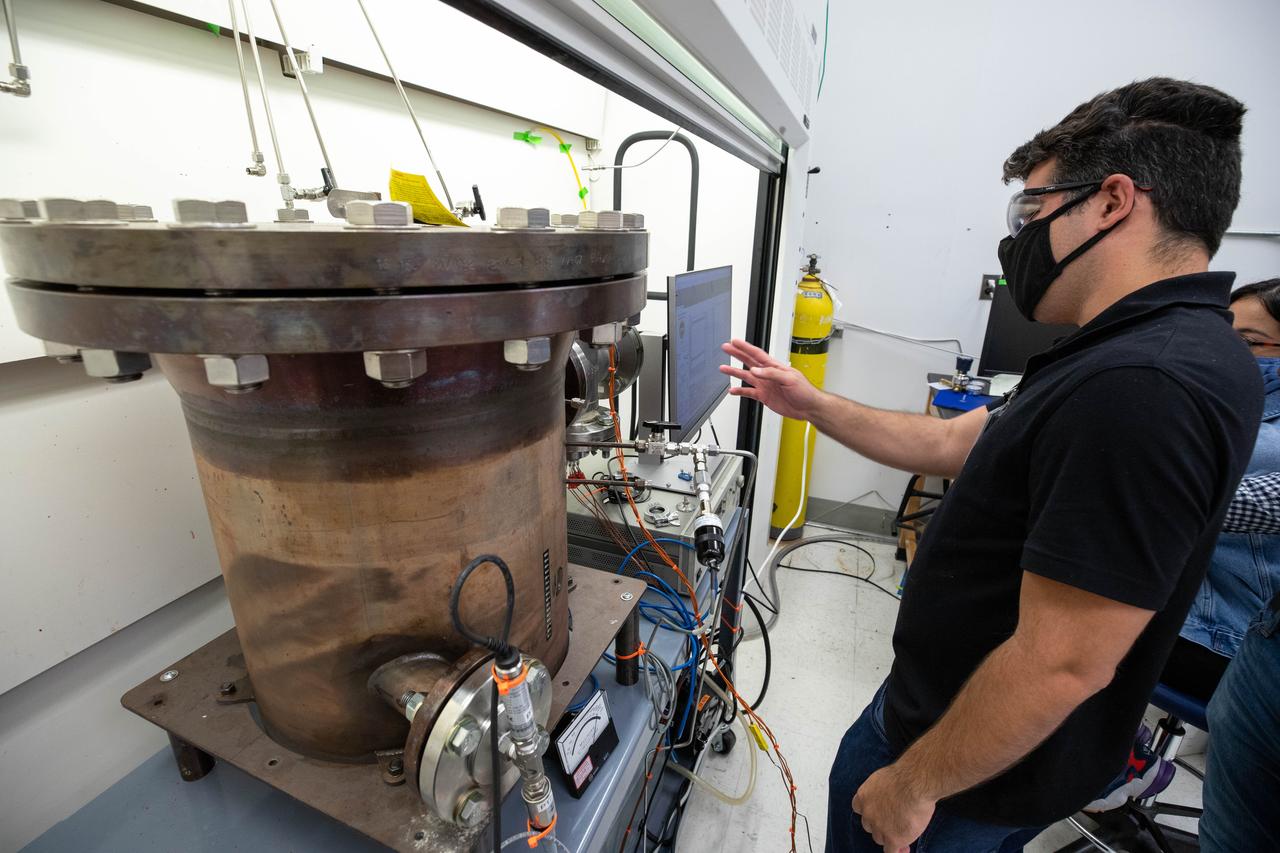

Jaime Toro, a mechanical engineer supporting the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.

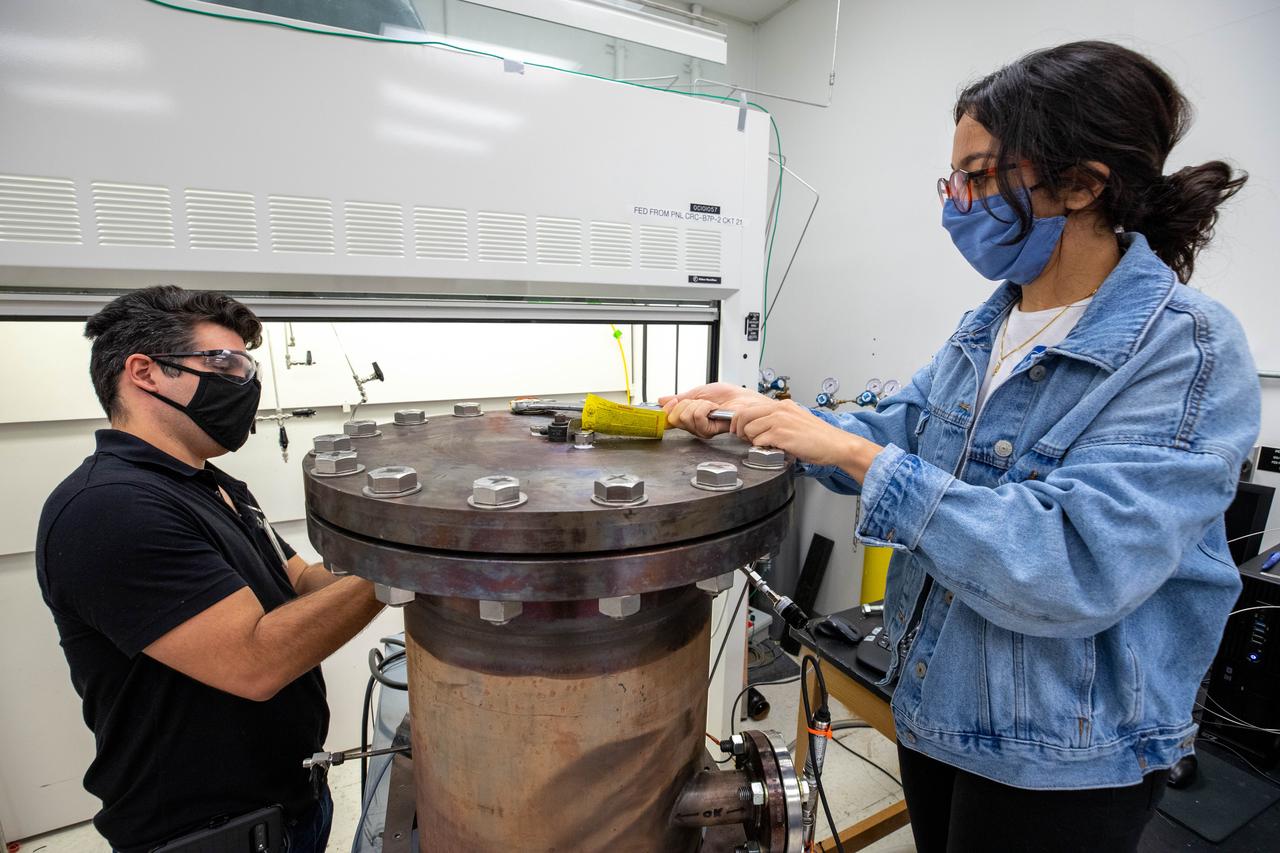
Elspeth Petersen, left, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team, and Kevin Grossman, GaLORE principal investigator, inspect a reactor before a test to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
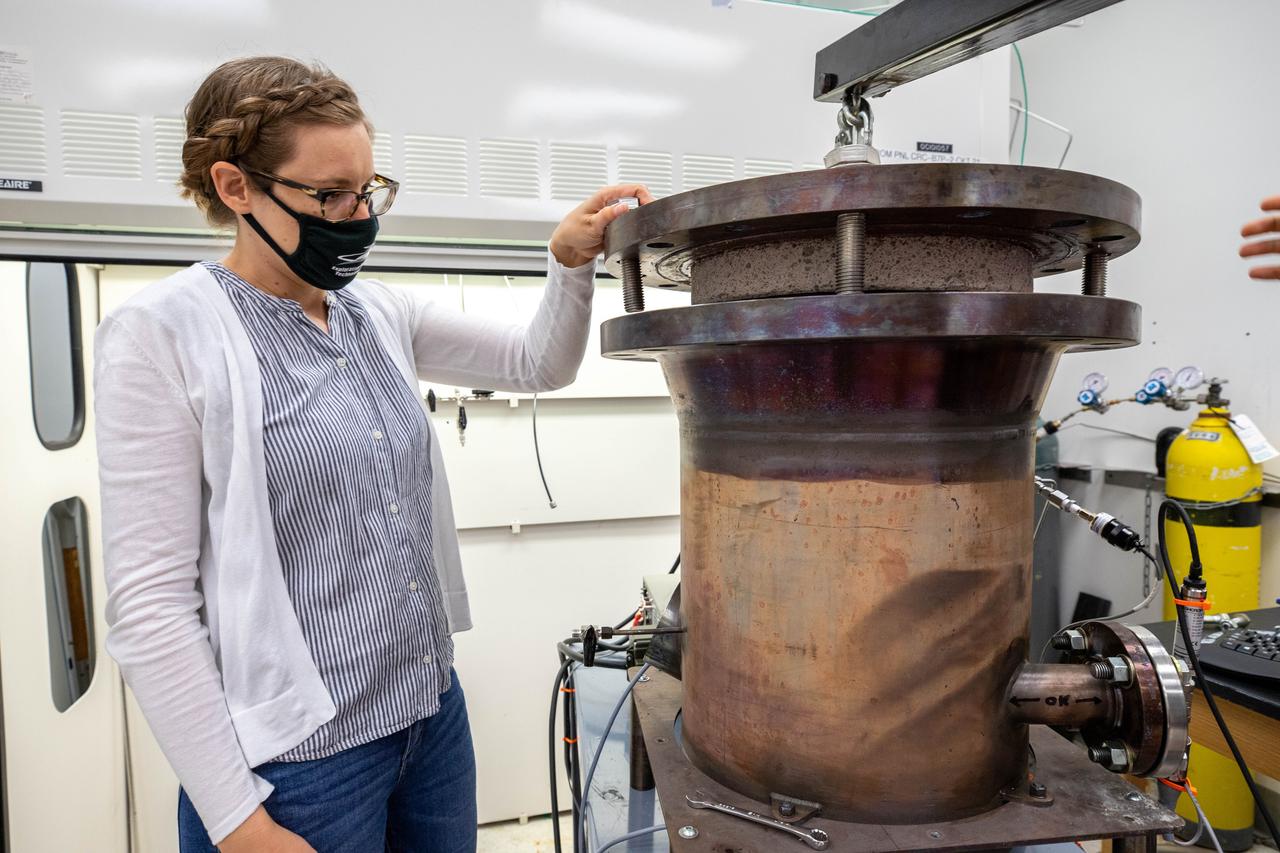

Elspeth Petersen, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, inspects the GaLORE hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
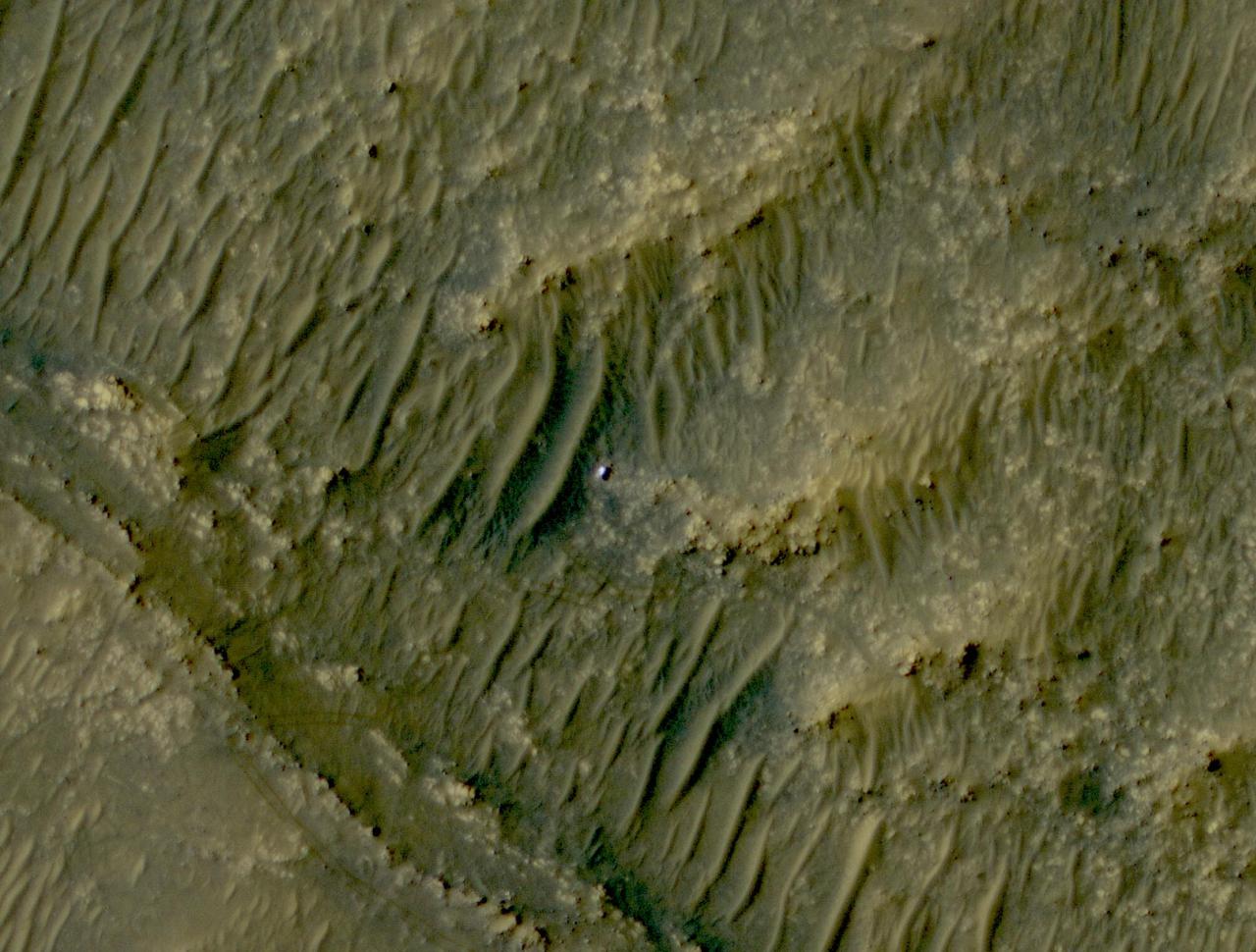

The white speck is NASA's Perseverance rover in the "South Séítah" area of Mars' Jezero Crater. The image was taken by the agency's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter using its High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment, or HiRISE, camera. The University of Arizona, in Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., in Boulder, Colorado. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24837
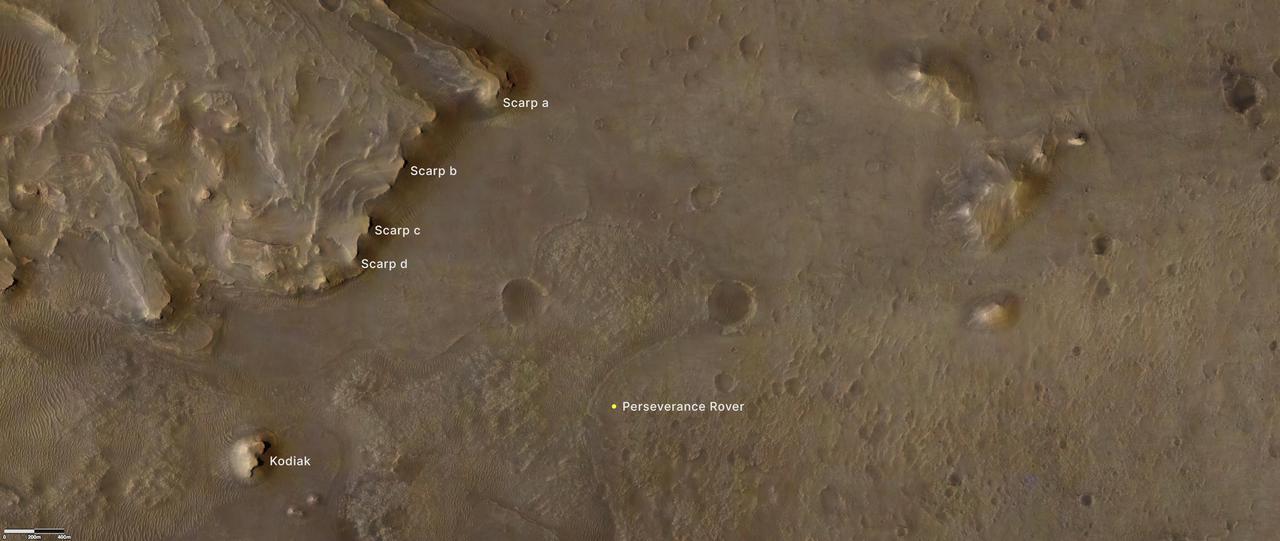

Provided by the High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE) aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance orbiter, this overhead image captures a portion of Mars' Jezero Crater. The yellow dot on lower right indicates the location of NASA's Perseverance rover. The remnant of Jezero Crater's rover delta the science team refers to as "Kodiak" is to the lower left. Long, steep slopes, called scarps, along the delta are on the upper left, labeled A through D. The University of Arizona, in Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., in Boulder, Colorado. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24814

NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter takes off and lands in this video captured on April 19, 2021, by Mastcam-Z, an imager aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. This video features only the moments of takeoff and the landing and not footage of the helicopter hovering for about 30 seconds. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24583
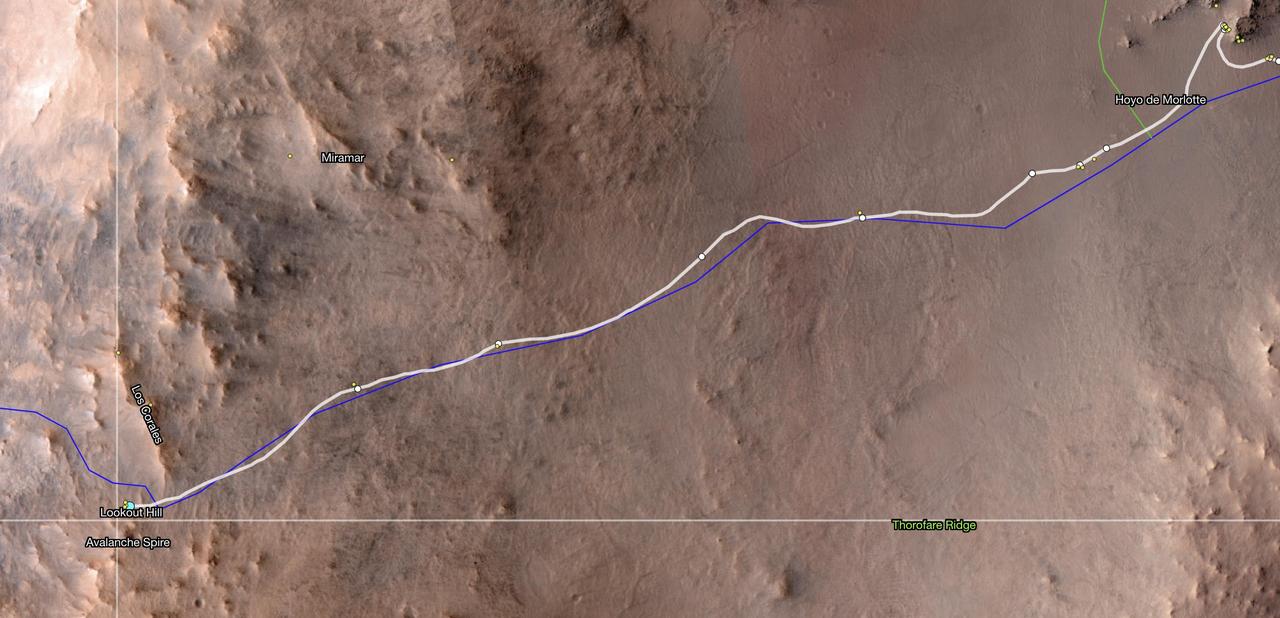

This map shows the location of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover as of Dec. 10, 2024, the 1,354th Martian day, or sol, of the mission, which it reached "Lookout Hill" at the top of Jezero Crater's rim after a monthslong climb. This map was made using data from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter's High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera as well as the European Space Agency's (ESA) High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC). The University of Arizona, in Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., in Boulder, Colorado, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26512

NASA's Ingenuity helicopter does a slow spin test of its blades on April 8, 2021, the 48th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This image was captured by the Mastcam-Z on NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie avaiable at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24582
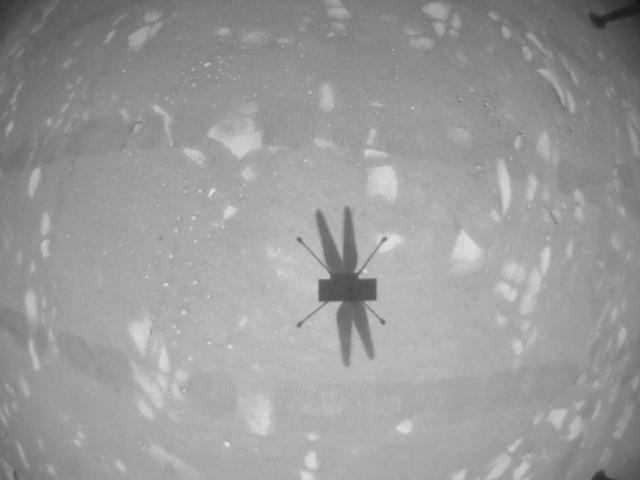

The downward-looking navigation camera aboard NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter took this image of the rotorcraft's shadow on the surface of Jezero Crater during helicopter's second experimental test flight on April 22, 2021. The helicopter's navigation camera autonomously tracks the ground during flight. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24592
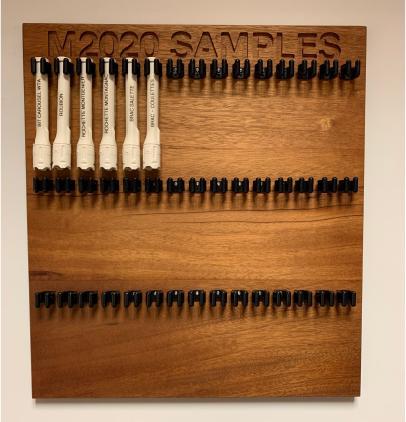

Six facsimile sample tubes hang on the sample tube board in the offices of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover mission at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. Each 3D-printed tube represents actual sample tubes the rover has filled on Mars, either with rock or atmosphere, and they are labeled with the names of the target from which they came. The board was handmade by Perseverance's deputy project manager, Rick Welch. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25026

Members of NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter team at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory react to data showing that the helicopter completed its second flight on the Red Planet on April 22, 2021. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24597

NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter took this shot, capturing its own shadow, while hovering over the Martian surface on April 19, 2021, during the first instance of powered, controlled flight on another planet. It used its navigation camera, which autonomously tracks the ground during flight. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24584
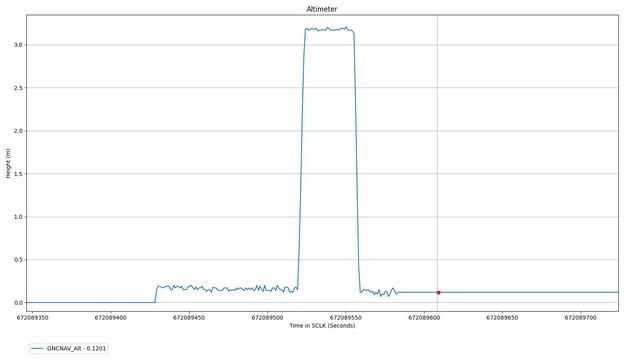
This altimeter chart shows data from the first flight of NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter, which occurred on April 19, 2021. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24587

NASA Public Affairs Specialist Kristi Irastorza, left, and NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Chief of Flight Projects Office Albert Sierra, participate in a “Mars 2020 Social Media Q&A: En Español” program on Wednesday, July 22, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The event featured representatives from LSP and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to lift off aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Thursday, July 30. The two-hour window opens at 7:50 a.m. EDT. LSP, based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.

NASA Public Affairs Specialist Kristi Irastorza, left, and NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Chief of Flight Projects Office Albert Sierra, participate in a “Mars 2020 Social Media Q&A: En Español” program on Wednesday, July 22, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The event featured representatives from LSP and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to lift off aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Thursday, July 30. The two-hour window opens at 7:50 a.m. EDT. LSP, based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
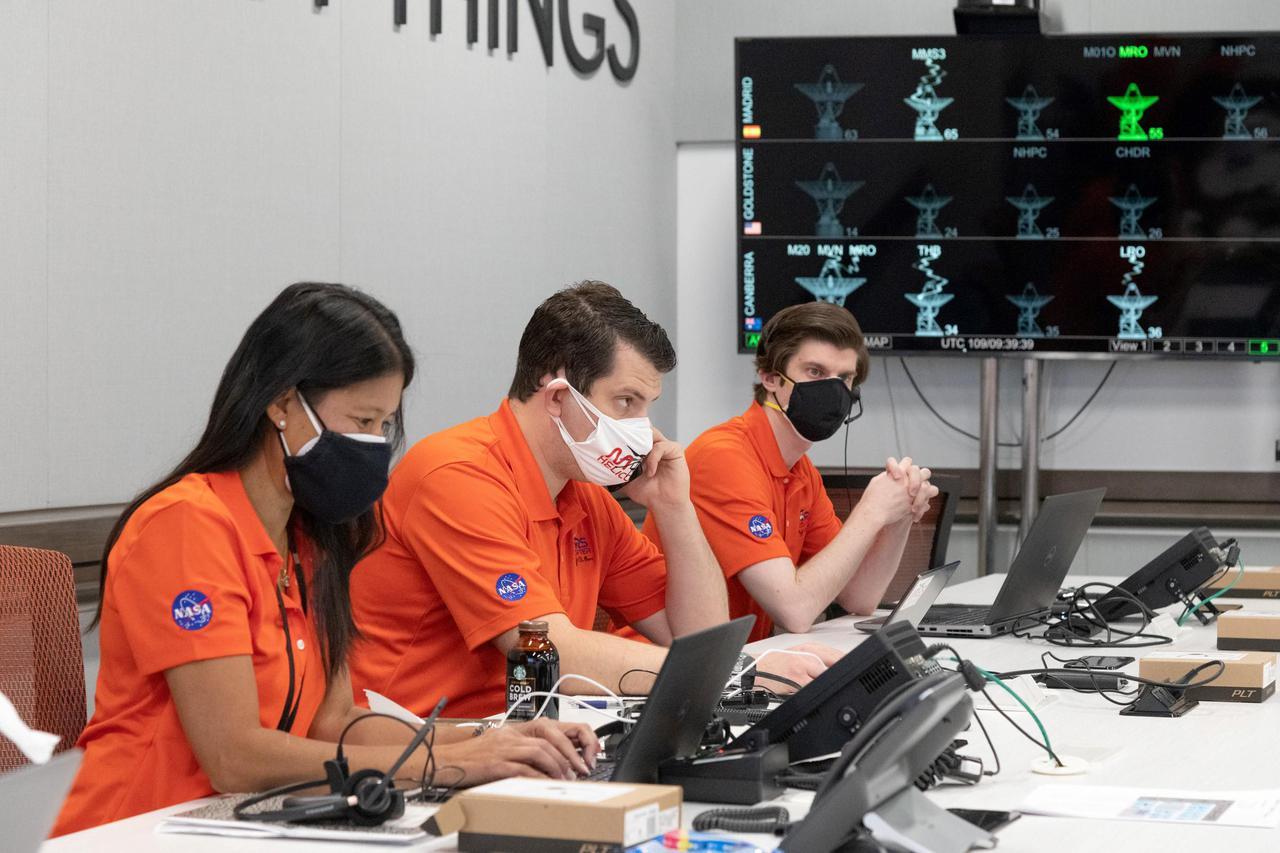

Members of NASA's Ingenuity helicopter team in the Space Flight Operations Facility at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory prepare to receive the data downlink showing whether the helicopter completed its first flight on April 19, 2021. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24585

Members of NASA's Ingenuity helicopter team in the Space Flight Operations Facility at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory react to data showing that the helicopter completed its first flight on April 19, 2021. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24499

This video animation made with data from the first flight of NASA's Ingenuity helicopter shows the flight from different angles. The flight occurred on April 19, 2021. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24588
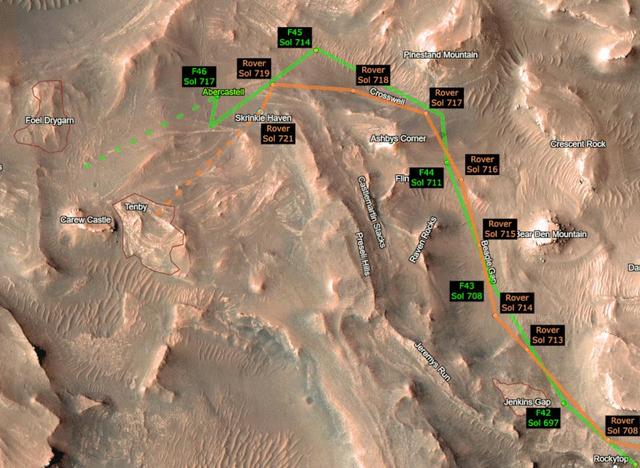
This animation shows the progress of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover and its Ingenuity Mars Helicopter as they make the climb up Jezero Crater's delta toward ancient river deposits. The helicopter's route is depicted in green, while the rover's progress is shown in orange. Black labels indicate which day, or sol, of the mission the rover and helicopter were on at each point. (Martian sols are counted from the date the Perseverance rover landed on Mars, Feb. 18, 2021). For the helicopter, the black labels also indicate which flight is shown; depicted here are Ingenuity's 42nd (F42) to 46th (F46) sorties. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, which also manages the project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center in California's Silicon Valley, and NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity’s development. AeroVironment Inc., Qualcomm, and SolAero also provided design assistance and major vehicle components. Lockheed Martin Space designed and manufactured the Mars Helicopter Delivery System. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25687
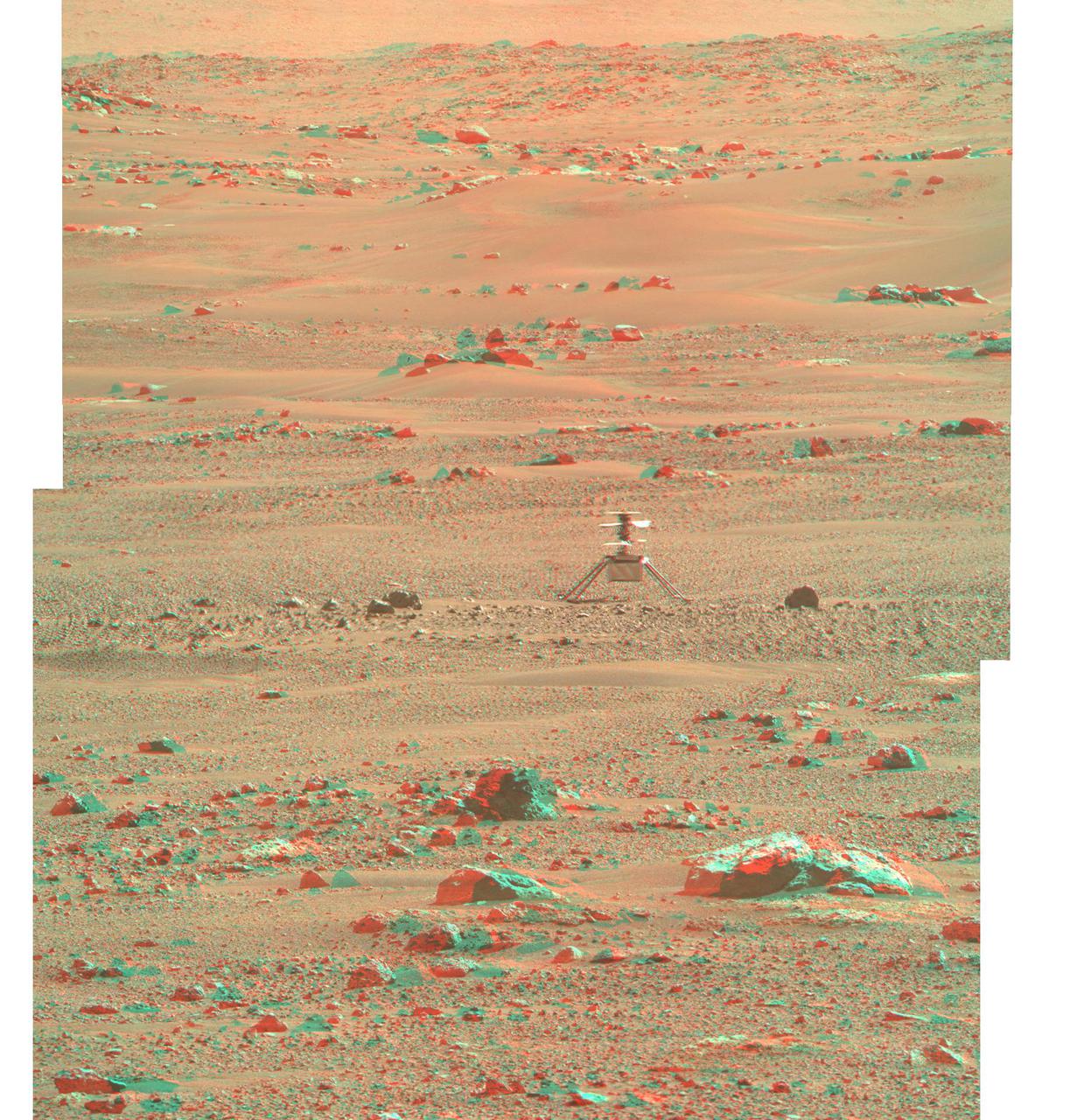

NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter is seen here in 3D using images taken June 6, 2021 (the 105 the Martian day, or sol, of the mission), by the left and right Mastcam-Z cameras aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages the technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science, Aeronautics Research, and Space Technology mission directorates. NASA's Ames Research Center in California's Silicon Valley, and NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. AeroVironment Inc., Qualcomm, and SolAero also provided design assistance and major vehicle components. Lockheed Martin Space designed and manufactured the Mars Helicopter Delivery System. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24670
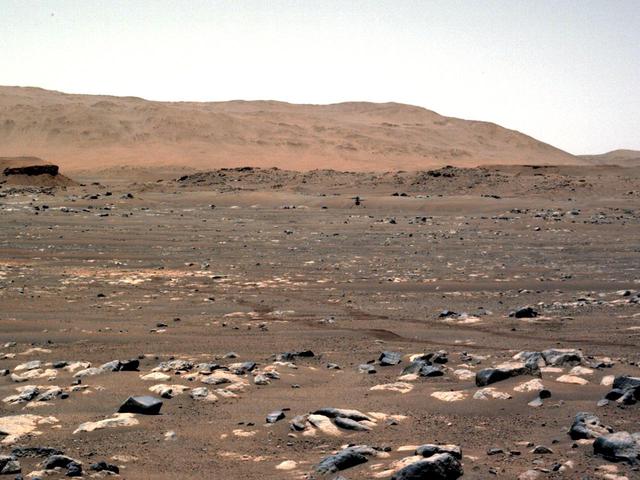

NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter achieves powered, controlled flight for the first time on another planet, hovering for several seconds before touching back down on April 19, 2021. The image was taken by the left Navigation Camera, or Navcam, aboard the agency's Perseverance Mars rover from a distance of 210 feet (64 meters). A short movie was also recorded and can be downloaded here as a GIF. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24586
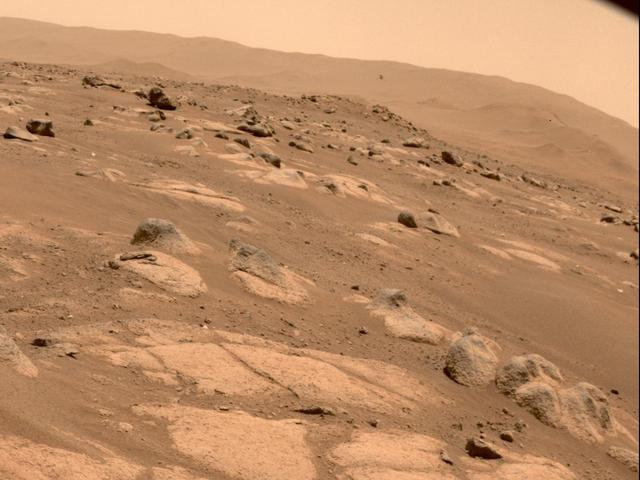

NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter is viewed by one of the hazard cameras aboard the Perseverance rover during the helicopter's fourth flight on April 30, 2021. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. AeroVironment Inc., Qualcomm, Snapdragon, and SolAero also provided design assistance and major vehicle components. The Mars Helicopter Delivery System was designed and manufactured by Lockheed Space Systems in Denver. More About the Mission A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24642
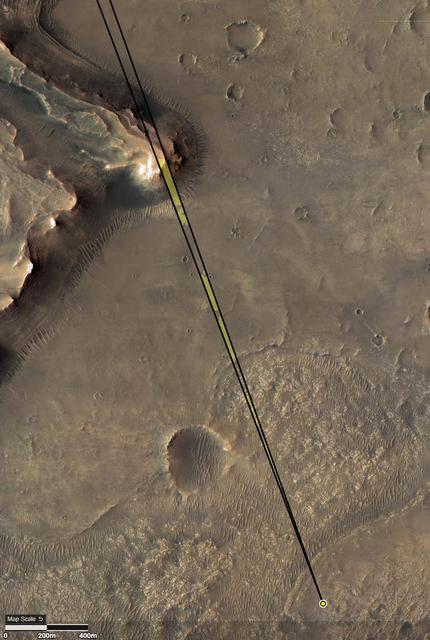

Provided by the High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE) aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance orbiter, this overhead image captures a portion of Mars' Jezero Crater. The yellow dot on lower right indicates the location of NASA's Perseverance rover. The field of view of the rover's Remote Microscopic Imager (RMI) camera is indicated with the diverging lines. The formation in the upper left is the "Delta Scarp," which the RMI camera photographed on March 17, 2021, from a distance of 1.4 miles (2.25 kilometers). The University of Arizona, in Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., in Boulder, Colorado. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24685
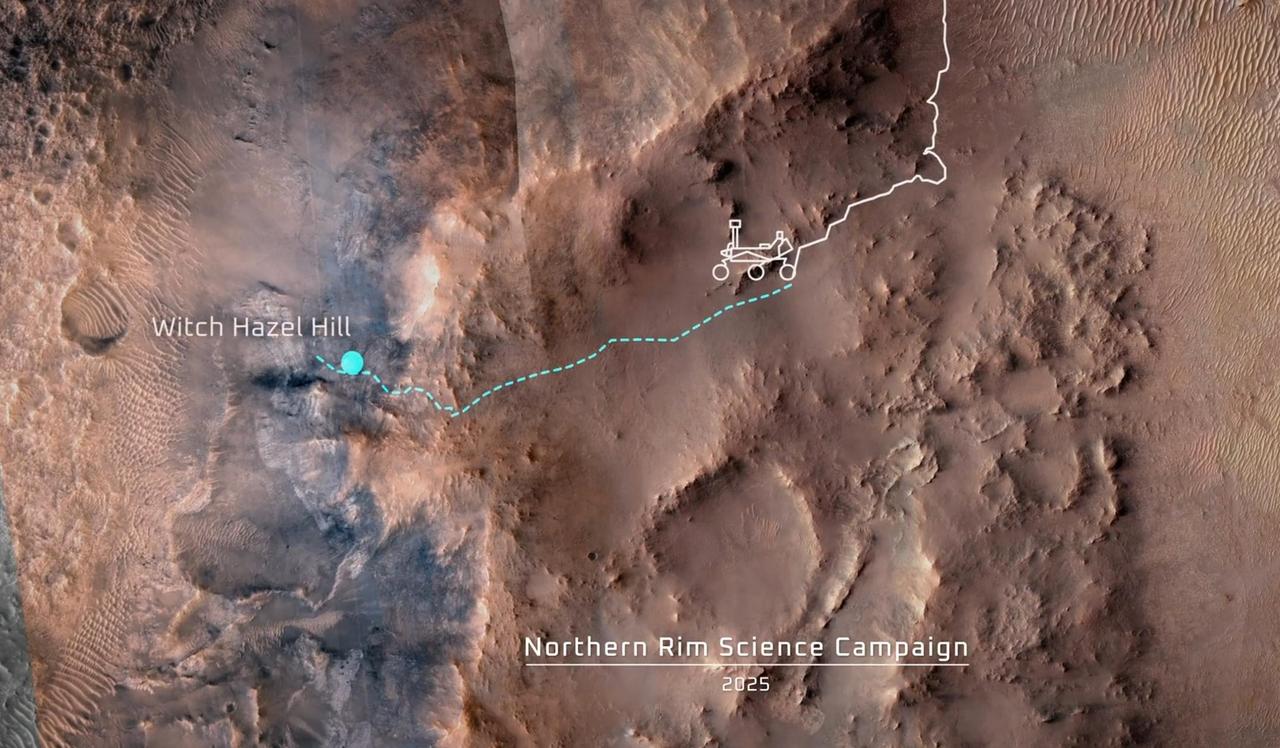
This animation shows the position of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover as of Dec. 4, 2024, the 1,347th Martian day, or sol, of the mission, along with the proposed route of the mission's fifth science campaign, dubbed Northern Rim, over the next several years. This map was made using data from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter's High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera as well as the European Space Agency's (ESA) High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC). The University of Arizona, in Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., in Boulder, Colorado. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26480
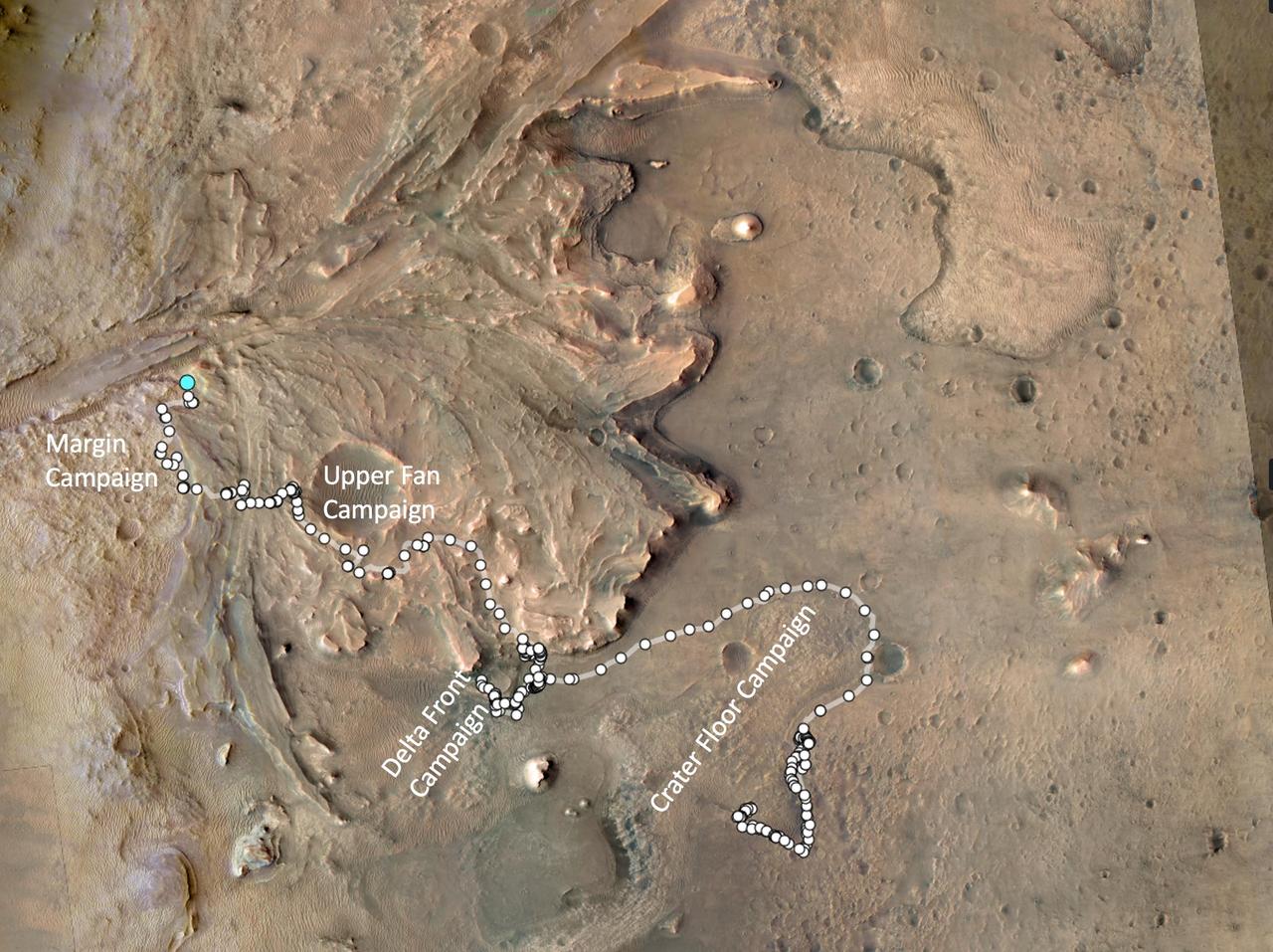

The path taken by NASA's Perseverance Mars rover during the first 1,000 sols (Martian days) of its mission at Jezero Crater is annotated on this overhead view taken by the HiRISE camera aboard the agency's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. White circles signify locations on the surface where the rover stopped after completing a traverse. The pale blue circle at upper left indicates the rover's position as of Dec. 12, 2023. The white text indicates the areas of the four rover science campaigns, from initial campaign to current: Crater Floor, Delta Front, Upper Fan, and Margin. Figure A, showing the same general area, is annotated to indicate the route and the two locations where the rover used its PIXL instrument to analyze abrasion patches "Ouzel Falls" and "Bills Bay" and its drill to core corresponding rock samples, "Otis Peak" and "Lefroy Bay." The University of Arizona, in Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., in Boulder, Colorado. JPL manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26231
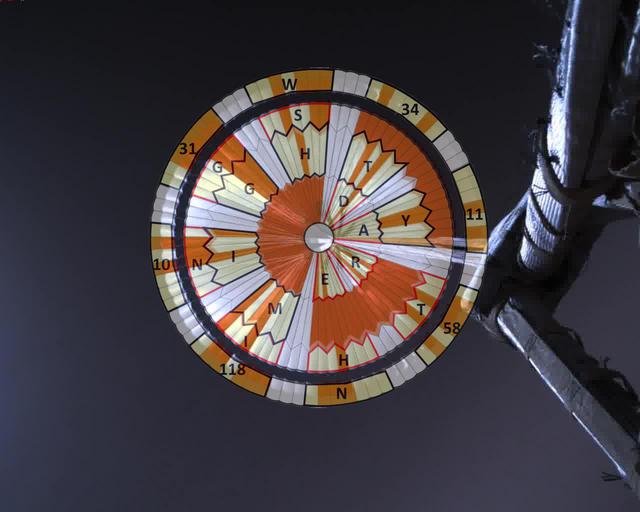

This annotated image was taken by a parachute-up-look camera aboard the protective back shell of NASA's Perseverance rover during its descent toward Mars' Jezero Crater on February 18, 2021. Using binary code, two messages have been encoded in the neutral white and international-orange parachute gores (the sections that make up the canopy's hemispherical shape). The inner portion spells out "DARE MIGHTY THINGS," with each word located on its own ring of gores. The outer band of the canopy provides GPS coordinates for NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, where the rover was built and the project is managed. Mars 2020 Perseverance Systems Engineer Ian Clark designed the binary code pattern. The saying is JPL's motto and is an abridgement of a quote from Teddy Roosevelt's "Strenuous Life" speech: "Far better is it to dare mighty things, to win glorious triumphs, even though checkered by failure ... than to rank with those poor spirits who neither enjoy nor suffer much, because they live in a gray twilight that knows not victory nor defeat." https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24431
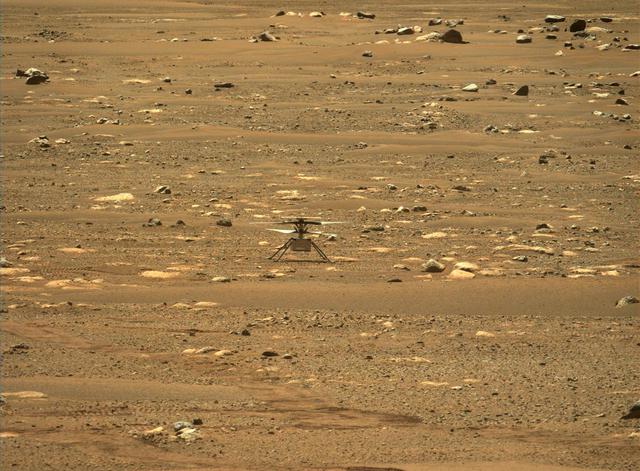

This image from NASA's Perseverance rover shows the agency's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter right after it successfully completed a high-speed spin-up test. It was captured by the Mastcam-Z instrument on Perseverance on April 16, 2021 (the 55th sol, or Martian day, of the rover's mission). The image has been slightly processed (stretched and cropped). The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24498
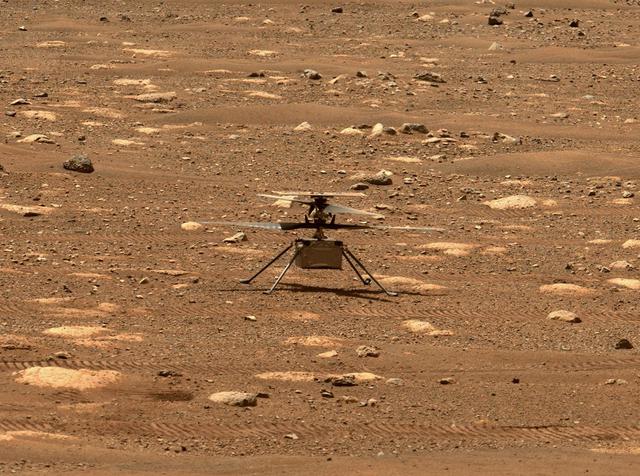

NASA's Ingenuity helicopter unlocked its rotor blades, allowing them to spin freely, on April 7, 2021, the 47th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. They had been held in place since before launch, and the unlocking is one of several milestones that must be met before the helicopter can attempt the first powered, controlled flight on another planet. This image was captured by the Mastcam-Z imager on NASA's Perseverance Mars rover on the following sol, April 8, 2021. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24581

NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter hovers over the Martian surface — the first instance of powered, controlled flight on another planet — as viewed by the Mastcam-Z imager aboard the Perseverance Mars rover on April 19, 2021. The solar-powered helicopter first became airborne at 3:34 a.m. EDT (12:34 a.m. PDT) — 12:33 Local Mean Solar Time (Mars time) — a time the Ingenuity team determined would have optimal energy and flight conditions. Altimeter data indicate Ingenuity climbed to its prescribed maximum altitude of 10 feet (3 meters) and maintained a stable hover for 30 seconds. It then descended, touching back down on the surface of Mars after logging a total of 39.1 seconds of flight. Flying in a controlled manner on Mars is far more difficult than flying on Earth. The Red Planet has significant gravity (about one-third that of Earth's), but its atmosphere is just 1% as dense as Earth's at the surface. Stitched together from multiple images, the mosaic is not white balanced; instead, it is displayed in a preliminary calibrated version of a natural-color composite, approximately simulating the colors of the scene as it would appear on Mars. Arizona State University in Tempe leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24590

In this footage captured by the Mastcam-Z imager aboard the Perseverance Mars rover on April 19, 2021, the agency's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter lifts of from the Martian surface, hovers for 30 seconds, then touches back down. Lasting a total of 39.1 seconds, the flight marks the first instance of powered, controlled flight on another planet. The solar-powered helicopter first became airborne at 3:34 a.m. EDT (12:34 a.m. PDT) — 12:33 Local Mean Solar Time (Mars time) — a time the Ingenuity team determined would have optimal energy and flight conditions. Altimeter data indicate Ingenuity climbed to its prescribed maximum altitude of 10 feet (3 meters) and maintained a stable hover for 30 seconds. It then descended. Flying in a controlled manner on Mars is far more difficult than flying on Earth. The Red Planet has significant gravity (about one-third that of Earth's), but its atmosphere is just 1% as dense as Earth's at the surface. Stitched together from multiple images, the mosaic is not white balanced; instead, it is displayed in a preliminary calibrated version of a natural-color composite, approximately simulating the colors of the scene as it would appear on Mars. Arizona State University in Tempe leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24521

NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter hovers and rotates over Jezero Crater during its second experimental flight test on April 22, 2021. The footage was captured by the Mastcam-Z imager, a pair of zoomable cameras aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. Altimeter data from the solar-powered helicopter indicates it climbed to its prescribed maximum altitude of 16 feet (5 meters), flew downrange 7 feet (2 meters) and returned, performed several turns while in a hover, and landed. Total flight time 51.9 seconds. Flying in a controlled manner on Mars is far more difficult than flying on Earth. The Red Planet has significant gravity (about one-third that of Earth's), but an atmosphere with only about 1% of the density at Earth's surface. Stitched together from multiple images, the mosaic is not white balanced; instead, it is displayed in a preliminary calibrated version of a natural-color composite, approximately simulating the colors of the scene as it would appear on Mars. Arizona State University in Tempe leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by JPL, which also manages this technology demonstration project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate, and Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center and Langley Research Center provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24595
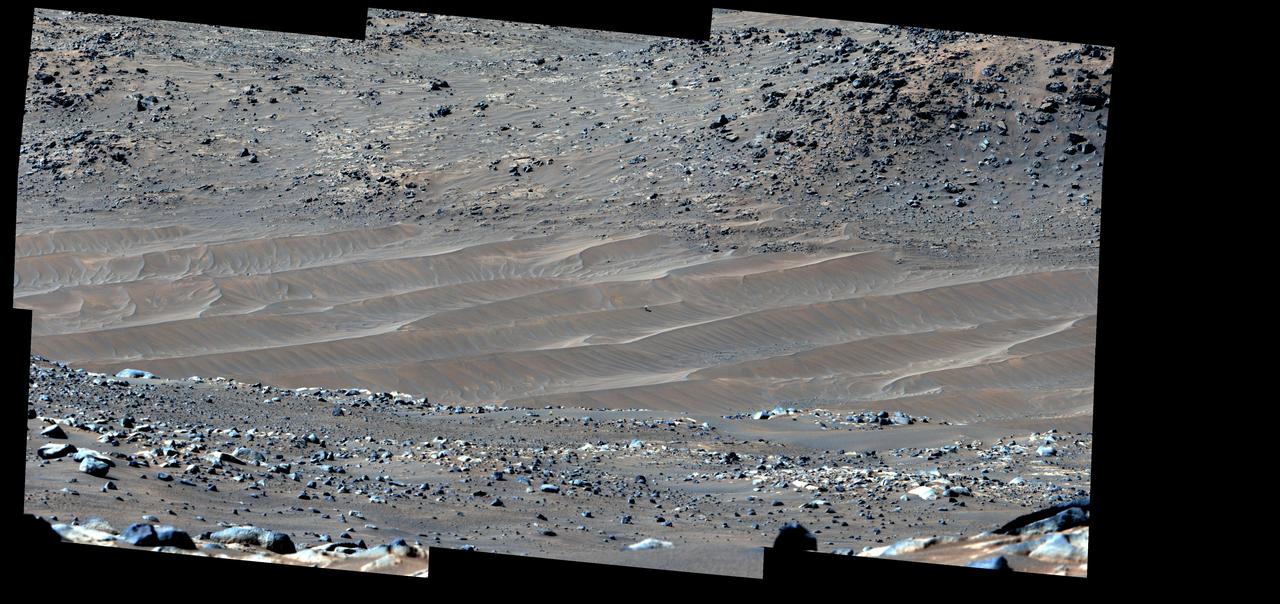

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover captured this mosaic showing the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter at its final airfield on Feb. 4, 2024. The helicopter damaged its rotor blades during landing on its 72nd flight on Jan. 18, 2024. The Ingenuity team has nicknamed the spot where the helicopter completed its final flight "Valinor Hills" after the fictional location in J.R.R. Tolkien's fantasy novels, which include "The Lord of the Rings" trilogy. The six images that were stitched together to make up this mosaic were captured from about 1,475 feet (450 meters) away by the rover's Mastcam-Z imager. Shown here is an enhanced-color view that exaggerates subtle color differences in the scene to show more detail. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which manages the project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center in California's Silicon Valley and NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. AeroVironment Inc., Qualcomm, and SolAero also provided design assistance and major vehicle components. Lockheed Martin Space designed and manufactured the Mars Helicopter Delivery System. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26236
![This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) captures details of an approximately 1-kilometer inverted crater west of Mawrth Vallis. A Context Camera image provides context for the erosional features observed at this site. The location of this HiRISE image is north of the proposed landing ellipse for the ExoMars 2020 rover mission that will investigate diverse rocks and minerals related to ancient water-related activity in this region. Prolonged erosion removed less resistant rocks leaving behind other rocks that stand up locally such as the crater seen here and other nearby remnants. These resistant layers may belong to a phase of volcanism and/or water-related activity that carved Mawrth Vallis and filled in existing craters, and other lower-lying depressions, with darker materials. Erosion has also exposed these layers down to older, more resistant lighter rocks that are clay-bearing. The diversity of exposed bedrock made this location an ideal candidate for exploring a potentially water-rich ancient environment that might have once harbored life. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 28.7 centimeters (11.3 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 86 centimeters (33.9 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22117](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA22117/PIA22117~medium.jpg)
This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) captures details of an approximately 1-kilometer inverted crater west of Mawrth Vallis. A Context Camera image provides context for the erosional features observed at this site. The location of this HiRISE image is north of the proposed landing ellipse for the ExoMars 2020 rover mission that will investigate diverse rocks and minerals related to ancient water-related activity in this region. Prolonged erosion removed less resistant rocks leaving behind other rocks that stand up locally such as the crater seen here and other nearby remnants. These resistant layers may belong to a phase of volcanism and/or water-related activity that carved Mawrth Vallis and filled in existing craters, and other lower-lying depressions, with darker materials. Erosion has also exposed these layers down to older, more resistant lighter rocks that are clay-bearing. The diversity of exposed bedrock made this location an ideal candidate for exploring a potentially water-rich ancient environment that might have once harbored life. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 28.7 centimeters (11.3 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 86 centimeters (33.9 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22117

A model of the new Aries I crew launch vehicle, for which NASA is designing, testing and evaluating hardware and related systems, is seen here on display at the Marshall Space Fight Center (MSFC), in Huntsville, Alabama. The Ares I crew launch vehicle is the rocket that will carry a new generation of space explorers into orbit. Under the goals of the Vision for Space Exploration, Ares I is a chief component of the cost-effective space transportation infrastructure being developed by NASA’s Constellation Program. These transportation systems will safely and reliably carry human explorers back to the moon, and then onward to Mars and other destinations in the solar system. The Ares I effort includes multiple project element teams at NASA centers and contract organizations around the nation, and is led by the Exploration Launch Projects Office at NASA’s MFSC. Together, these teams are developing vehicle hardware, evolving proven technologies, and testing components and systems. Their work builds on powerful, reliable space shuttle propulsion elements and nearly a half-century of NASA space flight experience and technological advances. Ares I is an inline, two-stage rocket configuration topped by the Crew Exploration Vehicle, its service module and a launch abort system. The launch vehicle’s first stage is a single, five-segment reusable solid rocket booster derived from the Space Shuttle Program’s reusable solid rocket motor that burns a specially formulated and shaped solid propellant called polybutadiene acrylonitrile (PBAN). The second or upper stage will be propelled by a J-2X main engine fueled with liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen. In addition to its primary mission of carrying crews of four to six astronauts to Earth orbit, the launch vehicle’s 25-ton payload capacity might be used for delivering cargo to space, bringing resources and supplies to the International Space Station or dropping payloads off in orbit for retrieval and transport to exploration teams on the moon. Crew transportation to the space station is planned to begin no later than 2014. The first lunar excursion is scheduled for the 2020 timeframe.

Psyche engineers adapted to COVID-19 social distancing and masking requirements while testing the Hall thrusters that will propel NASA's Psyche spacecraft on its journey to the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Set to launch in August 2022, the spacecraft will utilize this super-efficient electric propulsion system to travel to the asteroid Psyche. On May 20, 2020, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Flight System Engineer Steve Snyder (foreground) of JPL and a crew of engineers from Maxar Technologies worked together in the control room next to the vacuum chamber where the thruster was fired up. Snyder and his Maxar colleagues (from left: Faraz Aghazadeh, Taylor Kerl and Giovanni Lenguito) put the thruster and its power supply through a series of stress tests to ensure they can operate together in the extreme conditions of deep space. In the background, a monitor projects the image of the thruster firing. The thruster works by turning xenon gas, a neutral gas used in car headlights and plasma TVs, into xenon ions. As the xenon ions are accelerated out of the thruster, they create the thrust that will propel the spacecraft. The xenon plasma emits a blue glow, seen here on the screen, as it operates. Hall thrusters will be used for the first time beyond lunar orbit, demonstrating that they could play a role in supporting future missions to deep space. Maxar and JPL adapted the Hall thruster system for use with the main body of the spacecraft that Maxar is building at its facility in Palo Alto, California. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23878