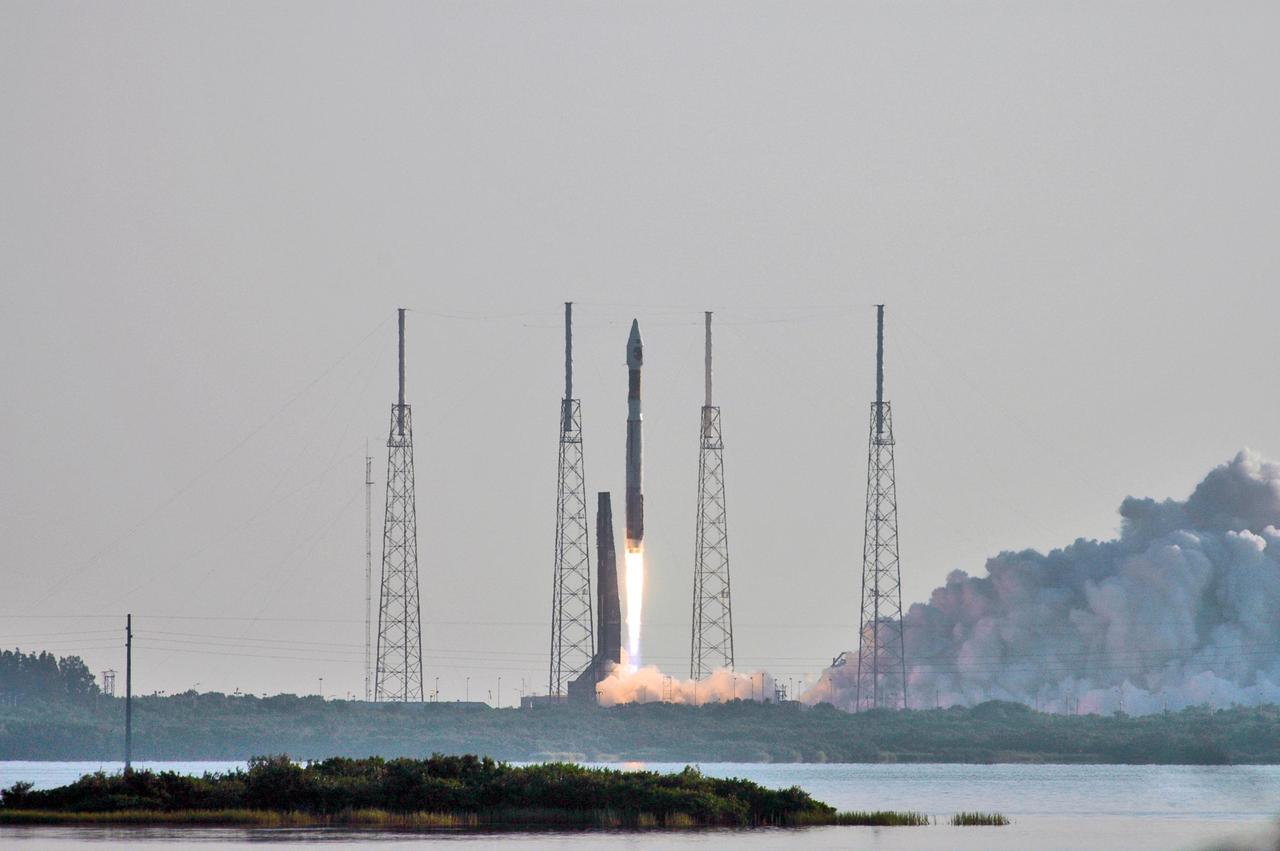

NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter MRO launched at 7:43 a.m. EDT atop a Lockheed Martin Atlas V rocket from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Aug. 12, 2005.
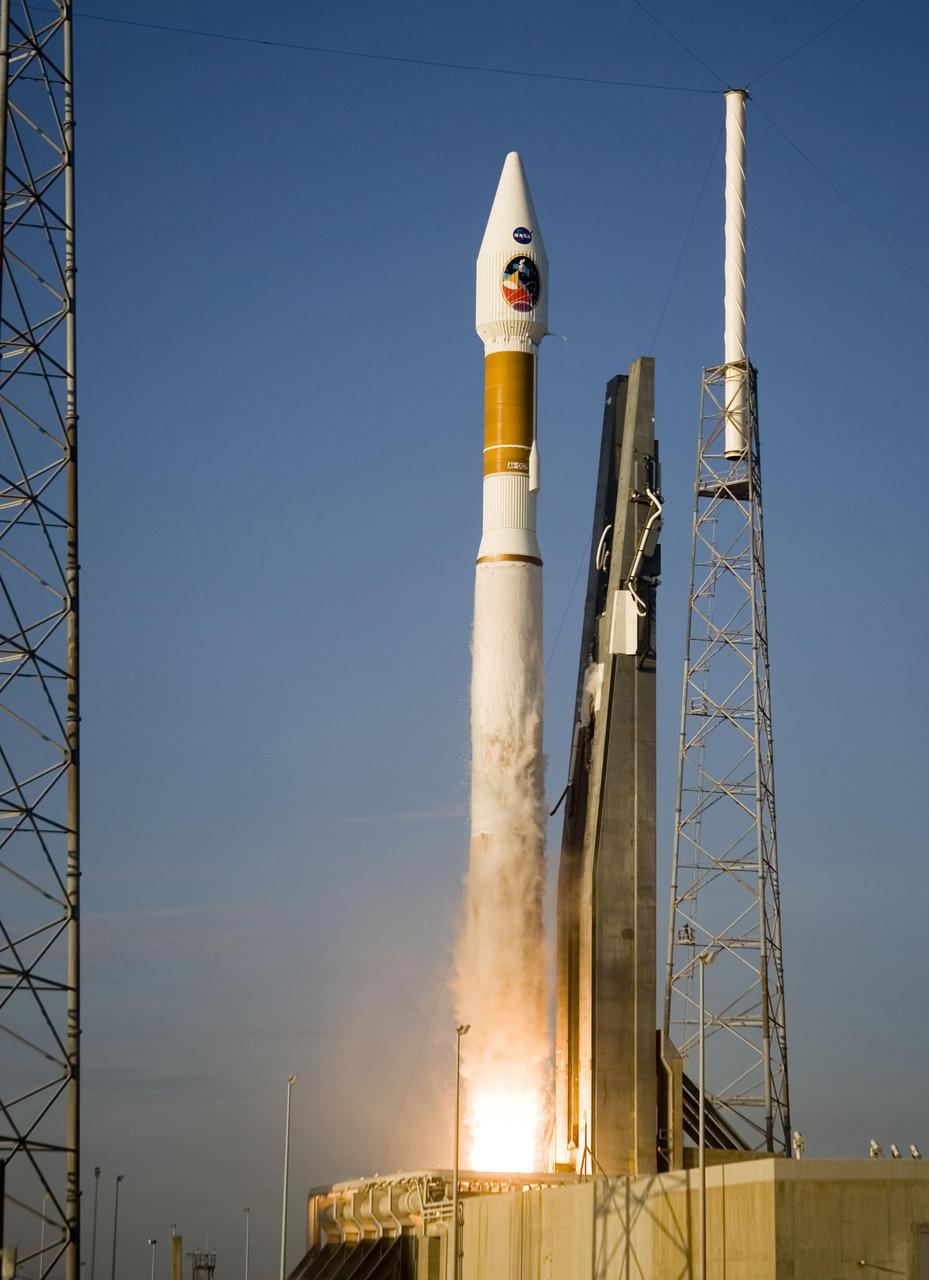

Atlas V launch vehicle, 19 stories tall, with a two-ton NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter MRO on top, lifts off the pad on Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Aug. 12, 2005.
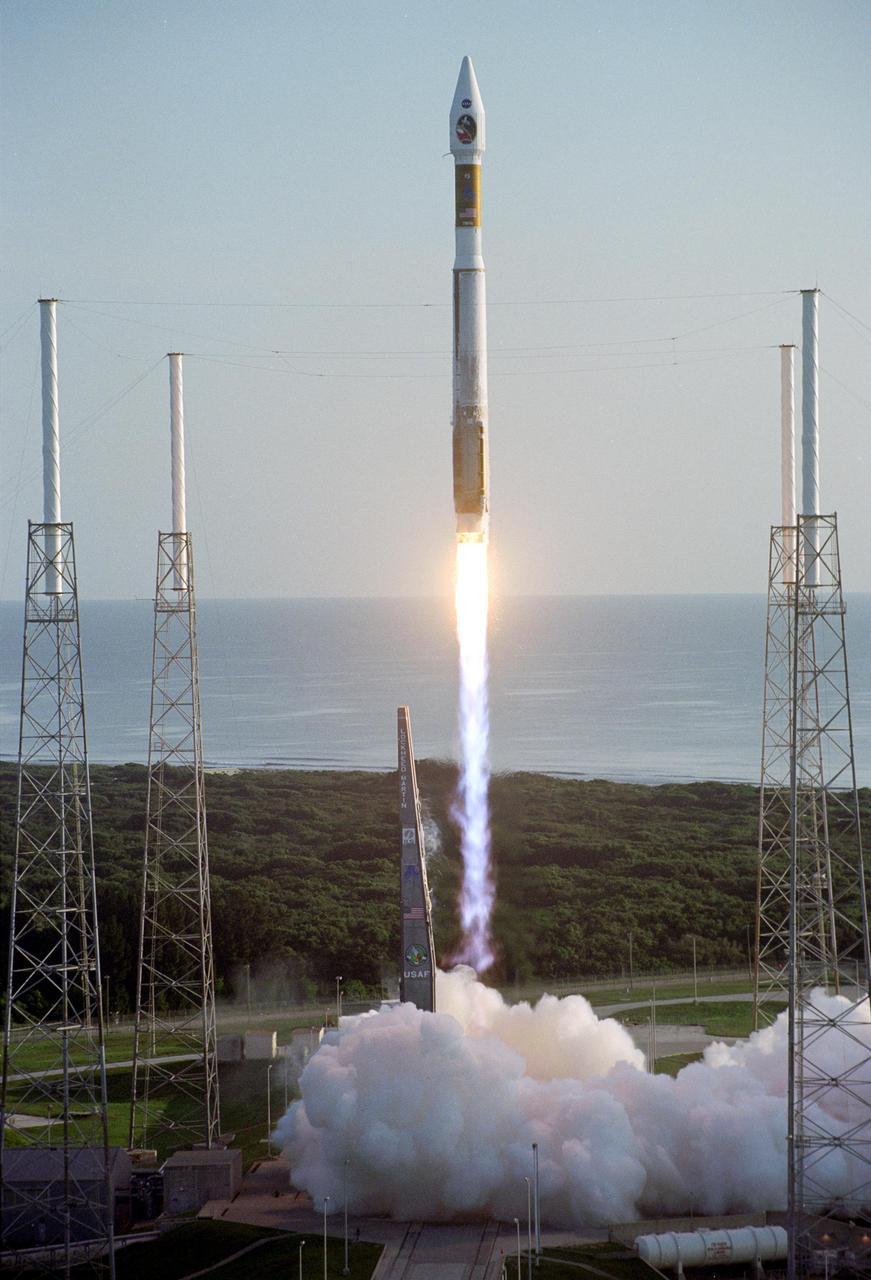

With the Atlantic Ocean as a backdrop, an Atlas V launch vehicle, 19 stories tall, with a two-ton NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter MRO on top, roars away from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter MRO launched at 7:43 a.m. EDT atop a Lockheed Martin Atlas V rocket from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Aug. 12, 2005.
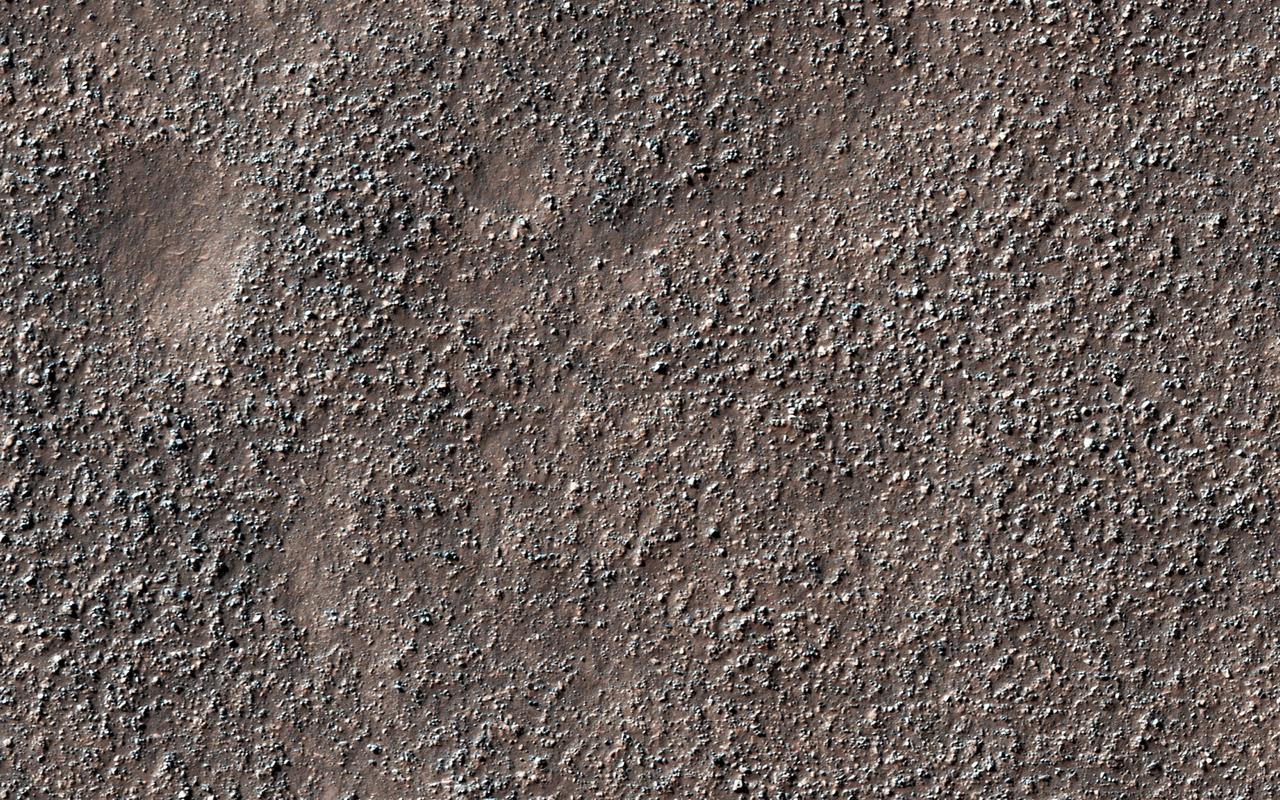

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows a field of boulders. More information is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22433

This image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter MRO is part of simulated flyover showing rhythmic layers of sedimentary rock inside Becquerel crater on Mars.
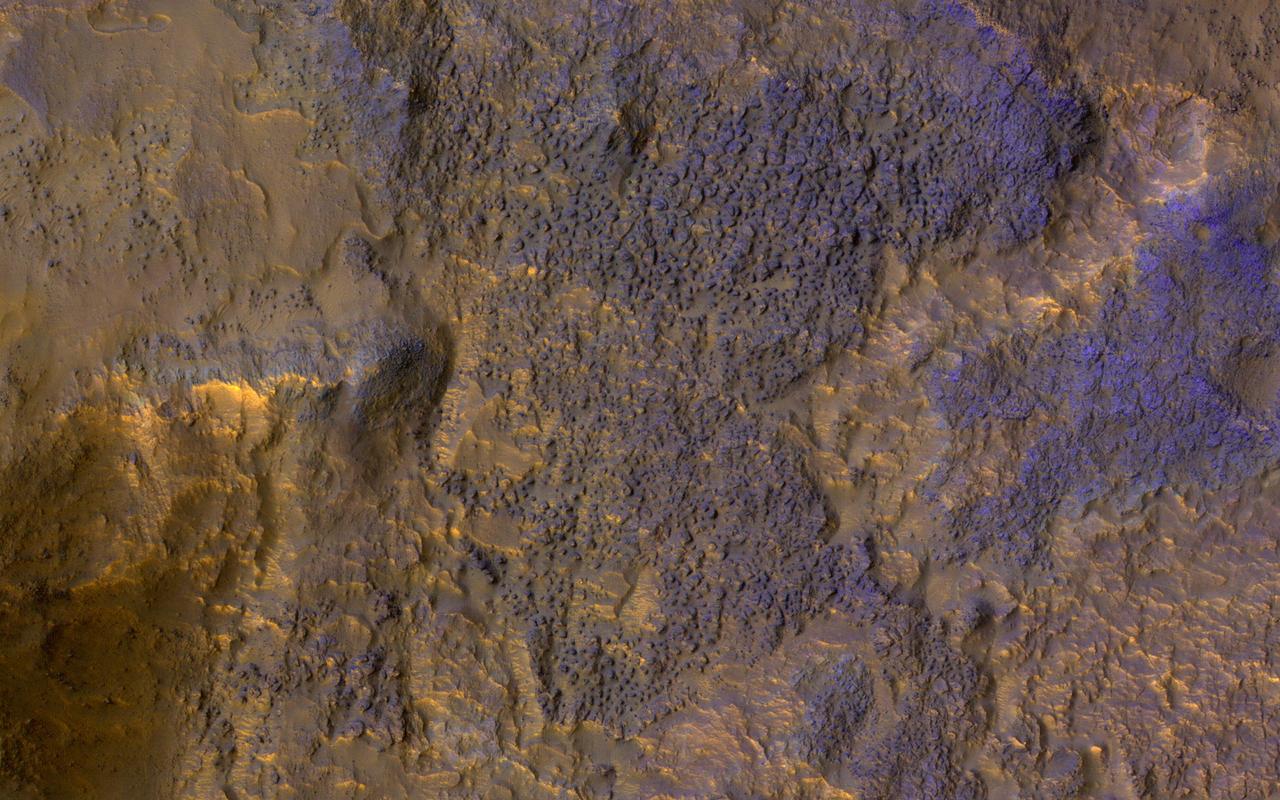

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows chaos terrain on Mars' equator. More information is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22435

Imaged by MRO NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Context Camera, this observation shows one of two odd, rounded mesas with a knobby, pitted texture.
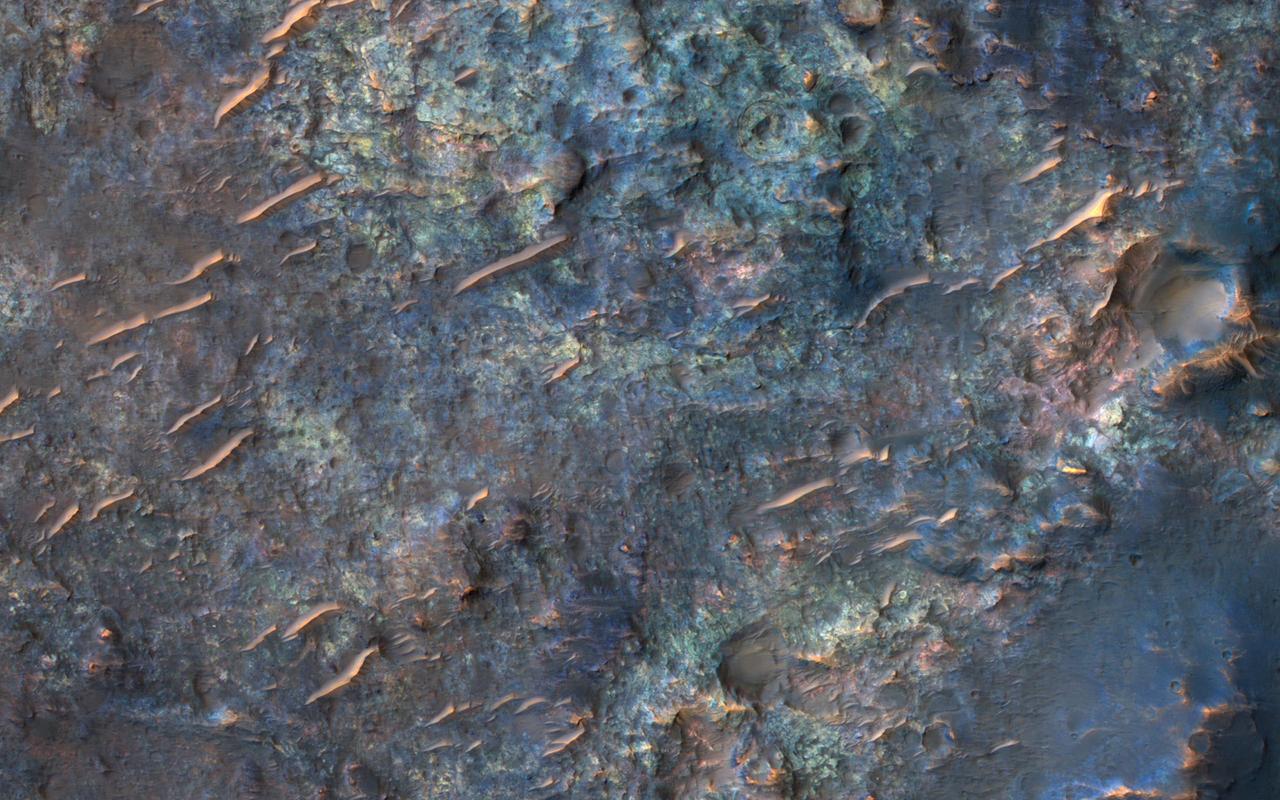

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows bedrock units with diverse colors indicating different mineral concentrations. More information is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22434
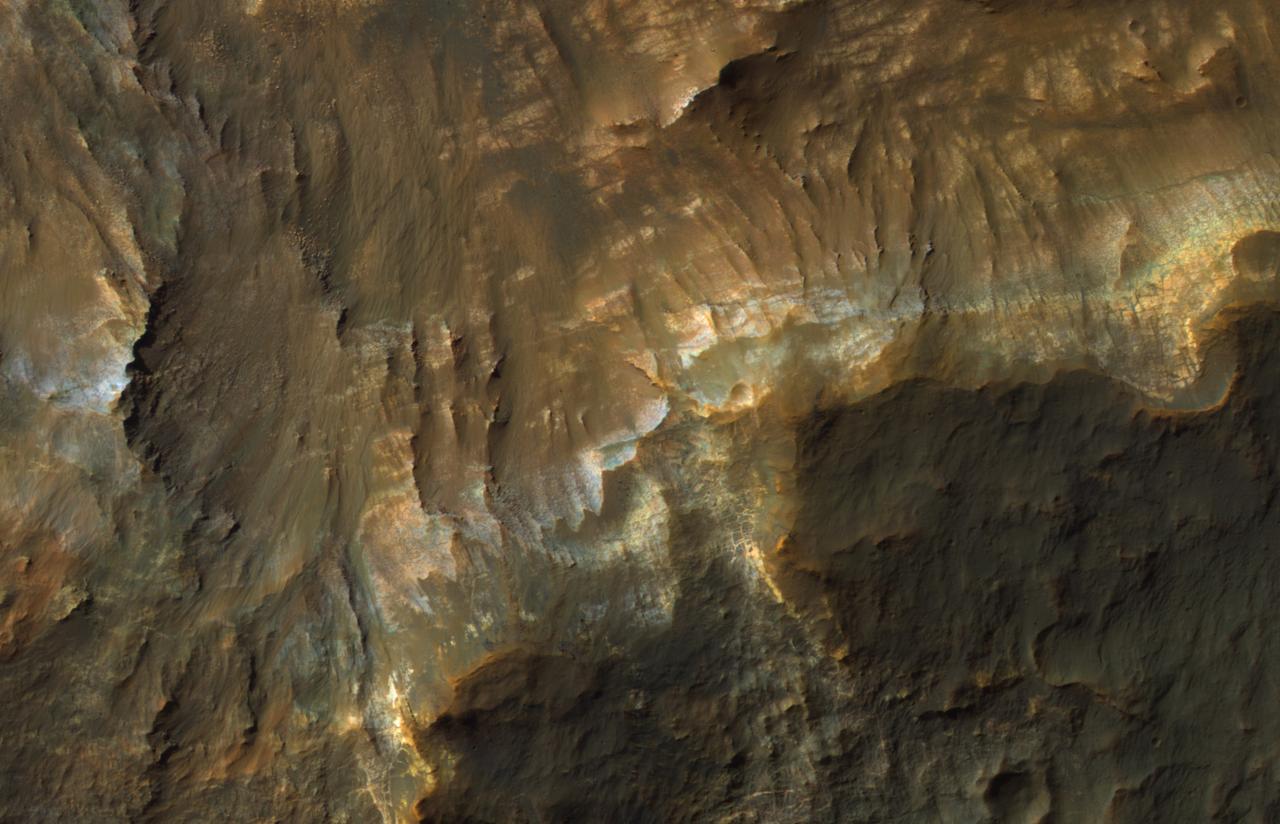

This color image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows bedrock layers of diverse colors and composition. For more information see https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22437
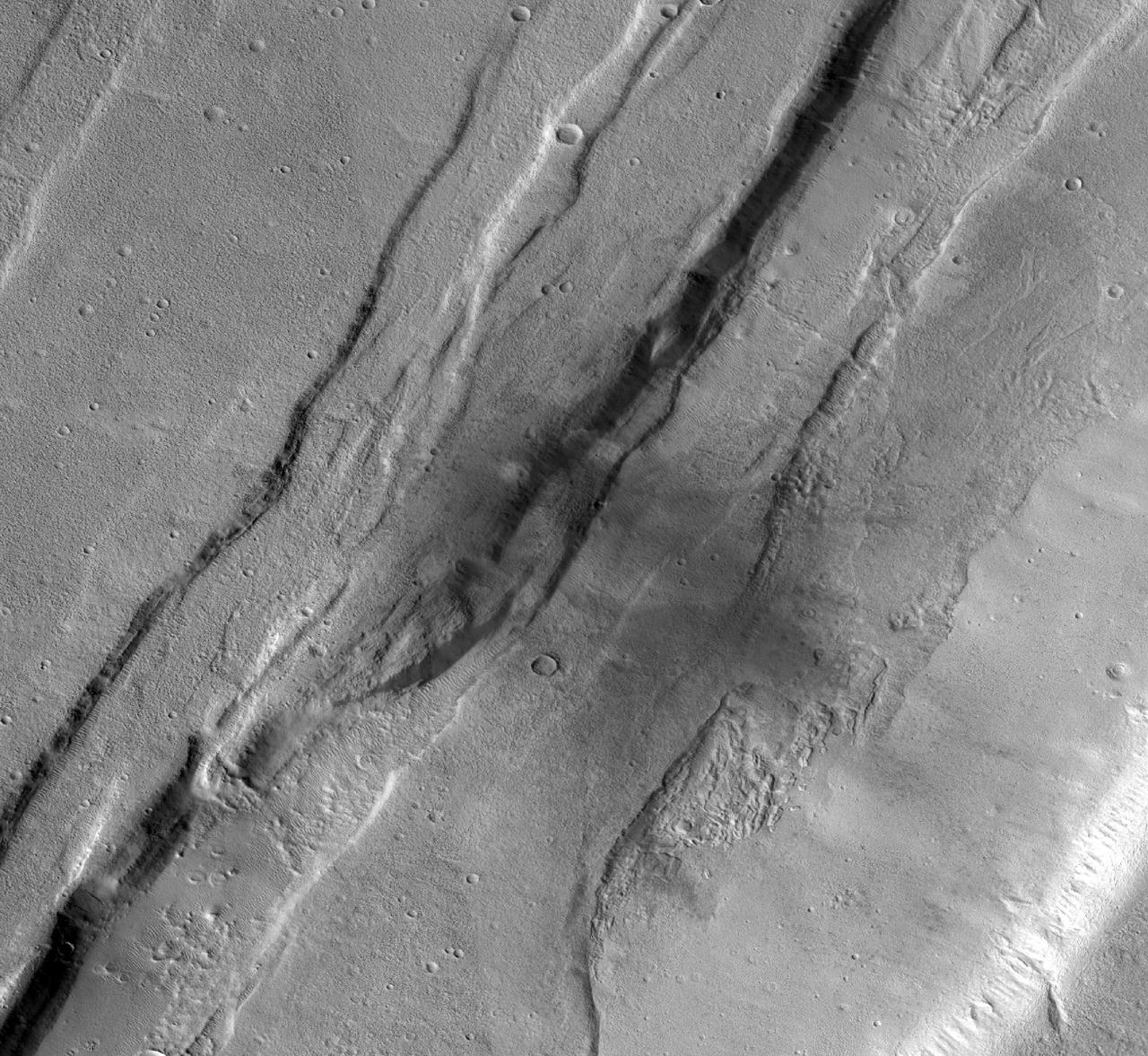
This meteoroid impact crater on Mars was captured using the black-and-white Context Camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The Context Camera took this image showing the impact, which occurred Sept. 18, 2021, in a region called Tempe Terra. The meteoroid struck the side of a graben – a depression created by faults. The impact crater left behind is roughly 427 feet (130 meters) across. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25587
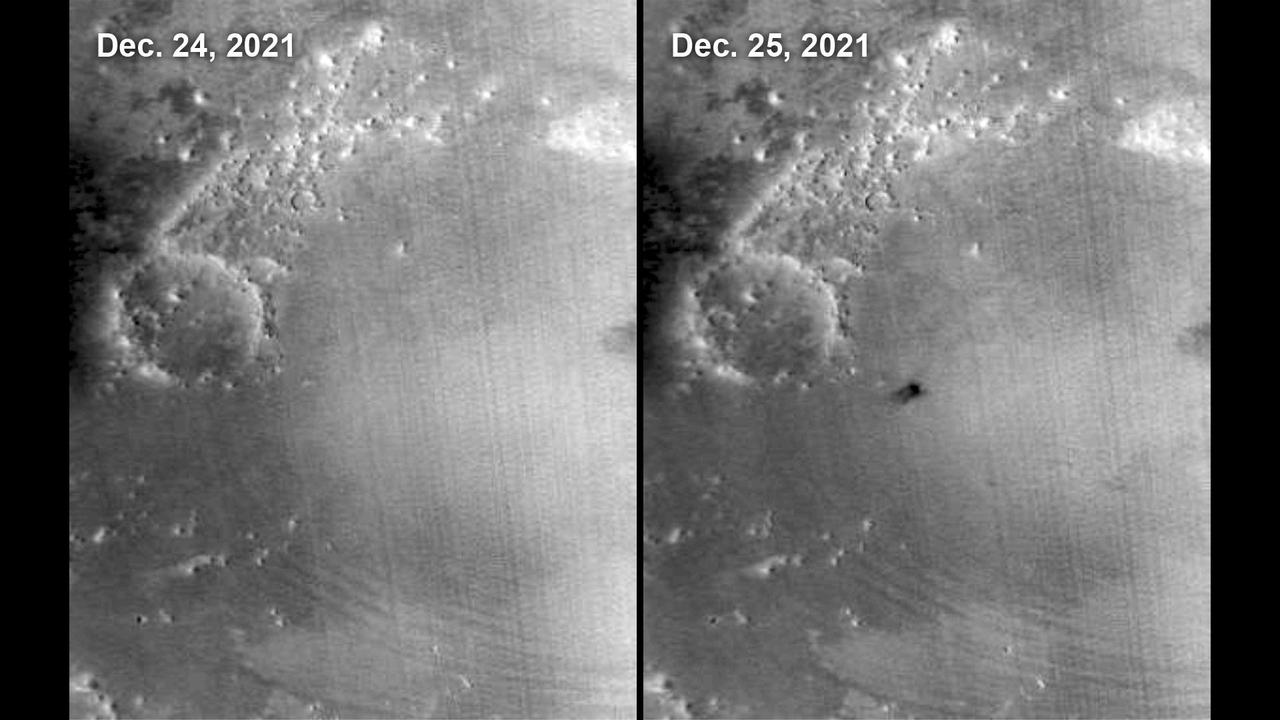

The Mars Color Imager (MARCI) camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) captured this before-and-after comparison of a region of Mars called Amazonis Planitia, which was struck by a meteoroid on Dec. 24, 2021. The impact was so large that MARCI can view it from space. As MRO passes over the planet, MARCI takes linear images – essentially strips – of the planet's circumference each day. The images are then stitched together to create a daily global map of the planet, data that's typically used to monitor atmospheric changes and Martian weather. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25585
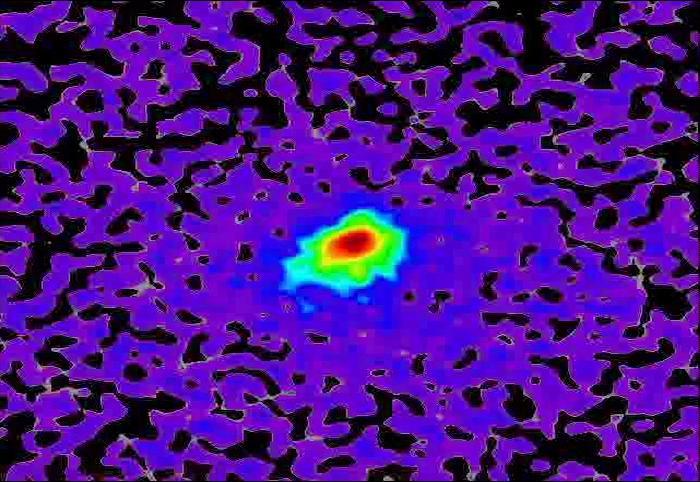

This frame from a movie sequence of images from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter MRO shows comet C/2013 A1 Siding Spring before and after its close pass by Mars in October 2014. False color enhances subtle variations in brightness in the comet coma.
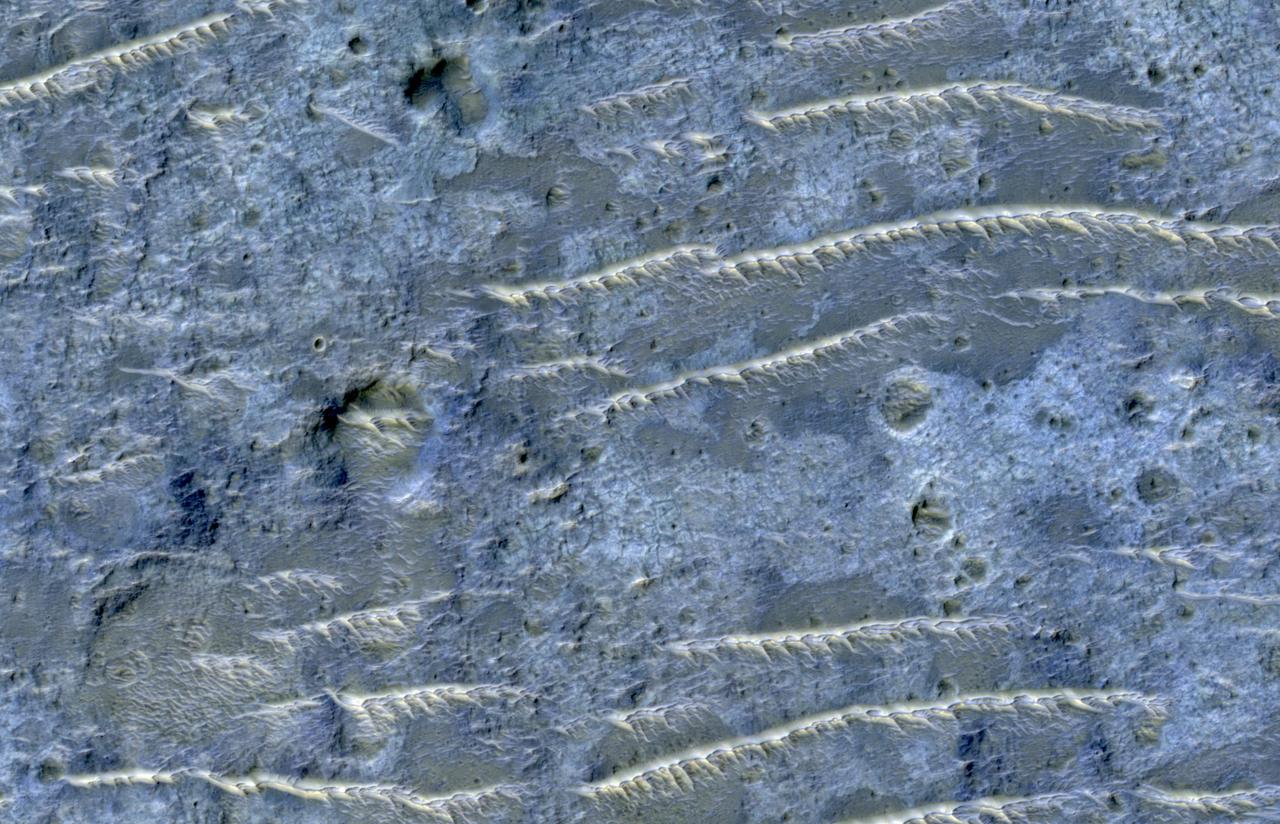

This enhanced color image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows the heavily channeled and ancient southern highlands of Mars. The elongated and jagged features are windblown dunes, perhaps hardened and eroded. For more information see https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22436
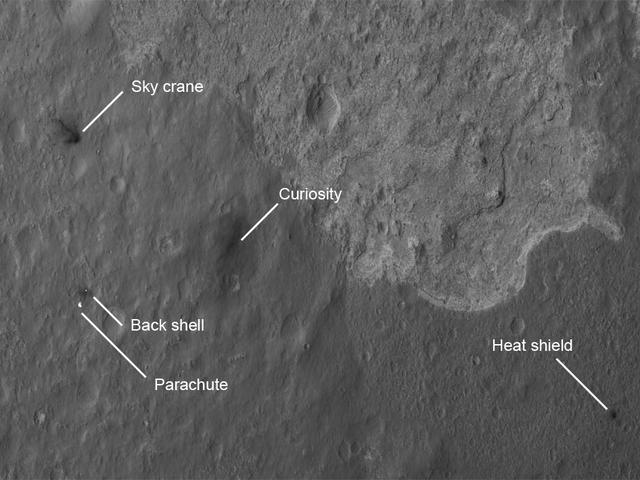

The four main pieces of hardware that arrived on Mars with NASA Curiosity rover were spotted by NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter MRO which captured this image about 24 hours after landing.
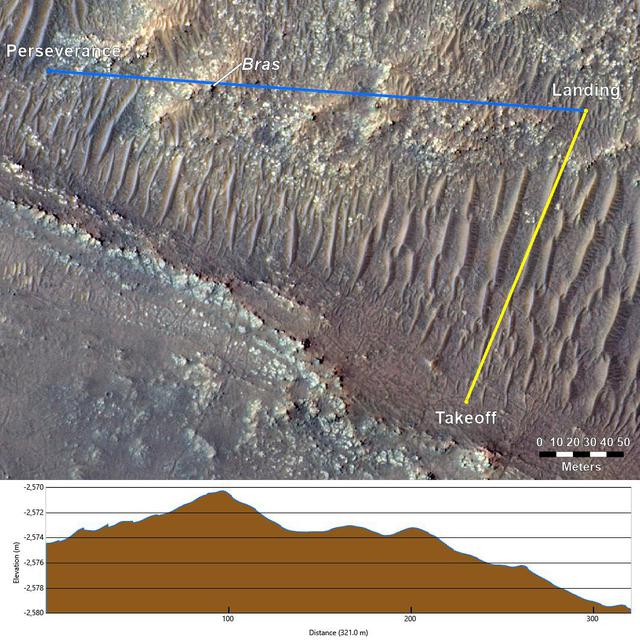
This annotated image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), and the topographic map below it, provide a look at the altitude of surface features standing between the agency's Perseverance Mars rover and Ingenuity helicopter at the conclusion of the rotorcraft's 17th flight at Mars on Dec. 5, 2021. In the image of the surface – taken by MRO's High Resolution Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera – Ingenuity's flight path is depicted in yellow. Perseverance's location is indicated in the upper left, with the blue line delineating its line of sight to the helicopter's landing spot. The location of the tallest point on Mars' surface between rover and helicopter during its final descent is the hill near the center of image that the Perseverance science team has nicknamed "Bras," after a city in France. The topographic map below the orbital image provides the elevation of surface features along the blue line, or Perseverance's line of sight to helicopter. The height measurements to the left of the map are derived by comparing local elevations to the areoid (a model for an equipotential surface of Mars, analogous to "sea level" on Earth). The Ingenuity team believes the 13-foot (4-meter) height difference between the Perseverance rover and the top of Bras contributed to the loss of communications when the helicopter descended toward the surface at the end of its flight. The image's background terrain was generated using data collected by the HiRISE camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24980

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover appears as a dark speck in this image captured from directly overhead by the agency's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, or MRO. The orbiter is equipped with a camera capable of viewing objects the size of a dinner table on the Red Planet's surface. The camera, called the High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE), has viewed spacecraft on the surface many times before. Here, it captured Curiosity driving up a steep slope on Dec. 29, 2023, the 4,051st Martian day, or sol, of the rover's mission. Curiosity is seen in an area striped with alternating dark and light bands. Scientists are interested in learning what differentiated the materials on the surface to form these different bands. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26245
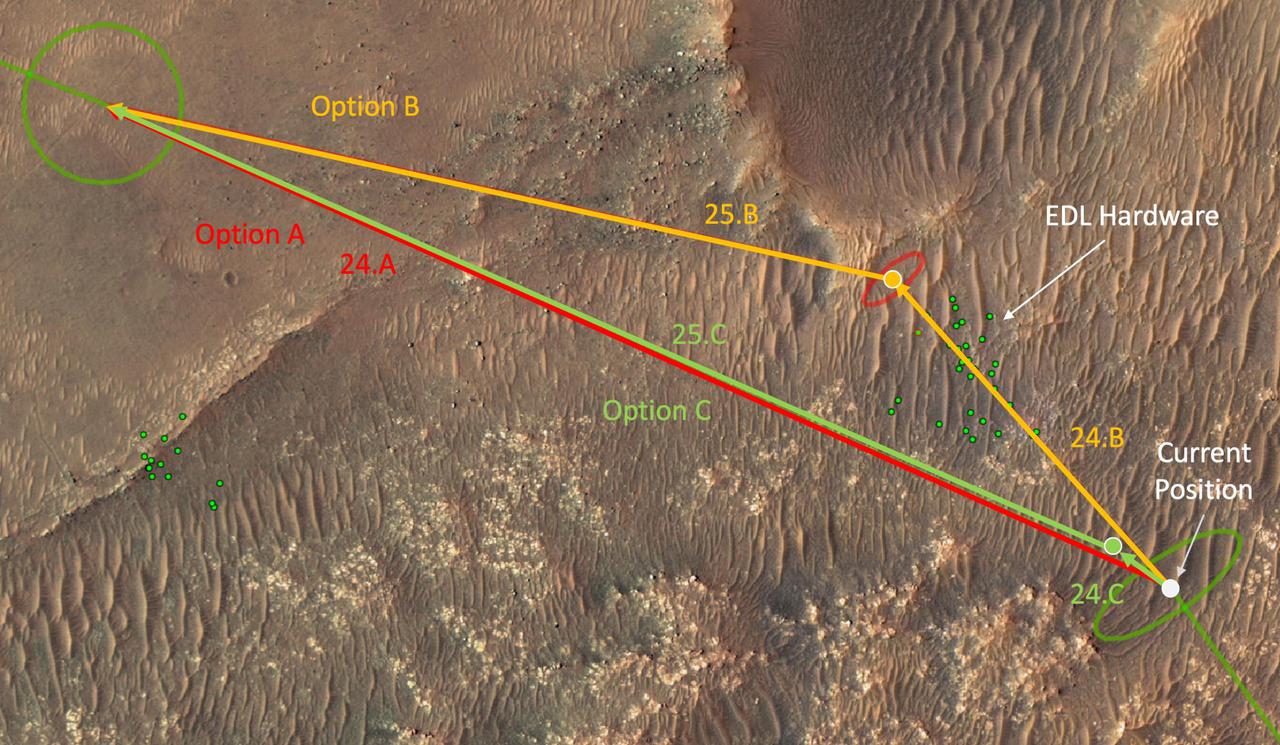
This annotated overhead image from the HiRISE camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) depicts three options for the agency's Mars Ingenuity Helicopter to take on flights out of the "Séítah" region, as well as the location of the entry, descent, and landing (EDL) hardware. The size and location of the landing ellipses have been analyzed to be safe for landing – free of hazards such as rocks, dunes, and large slopes. See an interactive map with Perseverance and Ingenuity location updates here: https://mars.nasa.gov/mars2020/mission/where-is-the-rover/ https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25029

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows the location with the most impressive known gully activity in Mars' northern hemisphere. Gullies are active in the winter due to carbon dioxide frost, but northern winters are shorter and warmer than southern winters, so there is less frost and less gully activity.. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21593
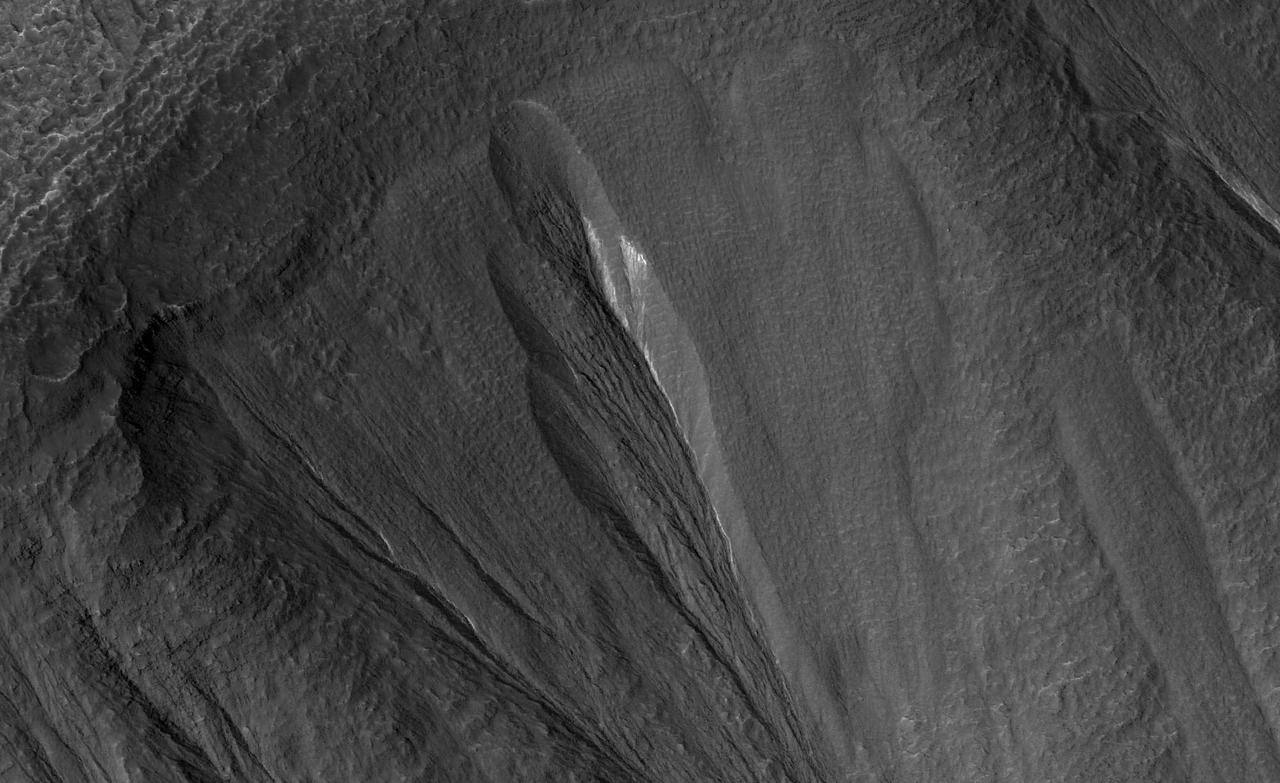

The white material seen within this gully is believed to be dusty water ice in a Martian region called Dao Vallis, captured by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Scientists believe dust particles within this ice act similarly to dust that falls on to glaciers on Earth, warming up in sunlight and causing subsurface pockets of meltwater to form. On Earth, the dust that forms these pockets are called cryoconite, and the pockets are called cryoconite holes. These Earth-based pockets of water are often teeming with simple life, including algae, fungi and cyanobacteria. Scientists believe similar shallow pools of water could exist on Mars, and may also be excellent places to search for life on the Red Planet today. This black-and-white image was captured by MRO using its HiRISE (High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) camera on May 10, 2009. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26408
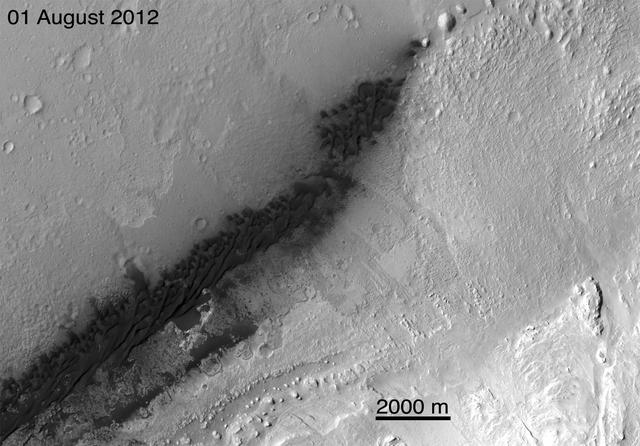

This image from an animation is from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter MRO showing the landing effects of the descent stage, the rover lander, the back shell and parachute, and the heat shield, all found on the left side of the image.

In early Martian summer, at the time NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) acquired this image, the dunes are almost free of their seasonal ice cover. Only pockets of ice protected in the shade most of the day remain. The North Pole of Mars is surrounded by a vast sea of sand dunes. In this dune field, the dunes are covered by a seasonal cap of dry ice in the winter. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22463
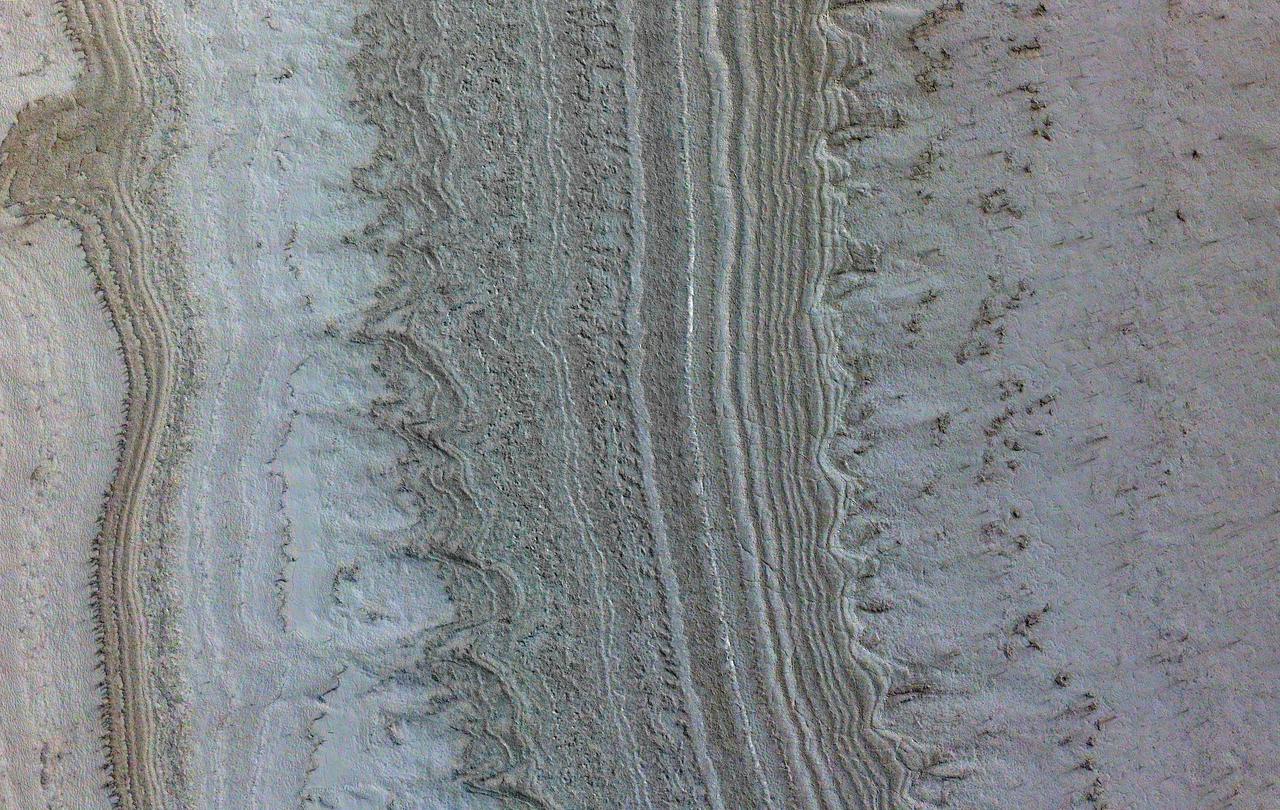

This image taken by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows ice sheets at Mars' south pole. The spacecraft detected clays near this ice; scientists have proposed such clays are the source of radar reflections that have been previously interpreted as liquid water using data from the ESA (European Space Agency) Mars Express orbiter. Flying 186 miles (300 kilometers) above the Martian surface, MRO used its High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera to study the ice sheets while using its Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer (CRISM) to map out clay minerals near the ice. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24763
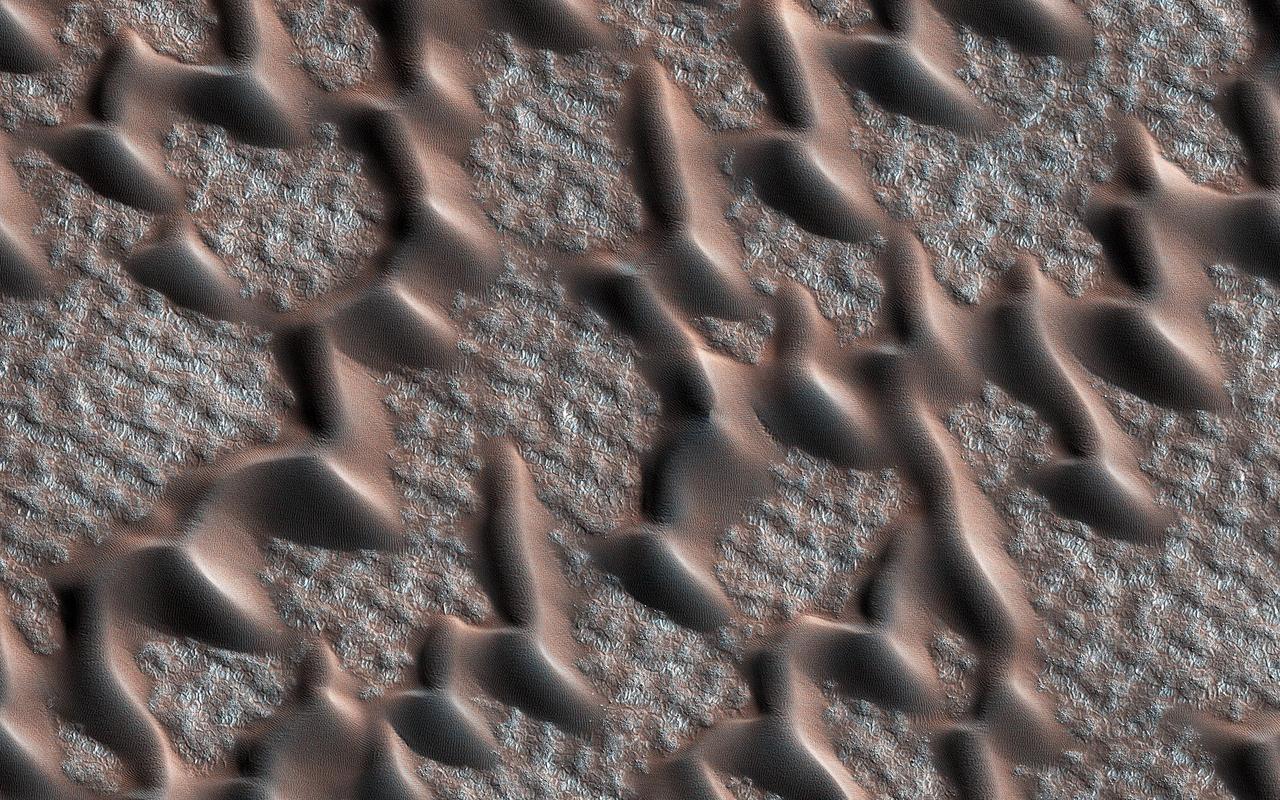

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows the permanent polar cap of Mars, encircled by sand dunes and looking like pulled threads, these dunes march across a fabric of patterned ground. At this time of the Martian year the dunes are free of the seasonal dry ice that forms a temporary cover every winter. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22464
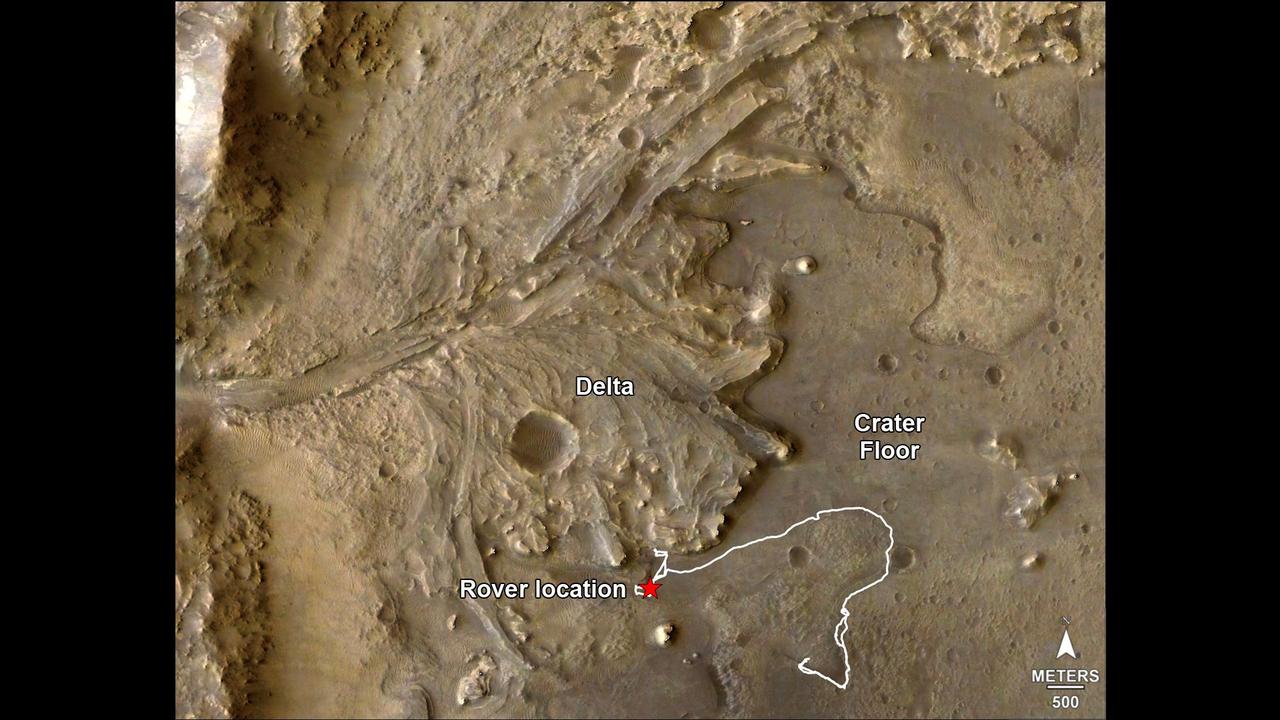
The route of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover – from its landing site on the floor of Jezero Crater to the ancient river delta, which it is currently exploring – is shown in this annotated image composed of overhead views from the agency's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The red star indicates the location of the rover in September 2022. Perseverance touched down at "Octavia E. Butler Landing" on Feb. 18, 2021, and explored formations (abbreviated "fm" in the annotation) known as "Séítah" and "Máaz" on the floor of Jezero Crater before driving toward the delta region. The delta, which Perseverance reached in April 2022, is a fan-shaped area where, billions of years ago, a river once flowed into a lake and deposited rocks and sediment. Scientists consider it one of the best places on Mars to search for potential signs of ancient microbial life. For this image, the Perseverance team and the U.S. Geological Survey collaborated on the base map, combining multiple images from the High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE) camera with color from the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM), both instruments aboard MRO. The HiRISE images used span a period from 2007 to 2017. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24922
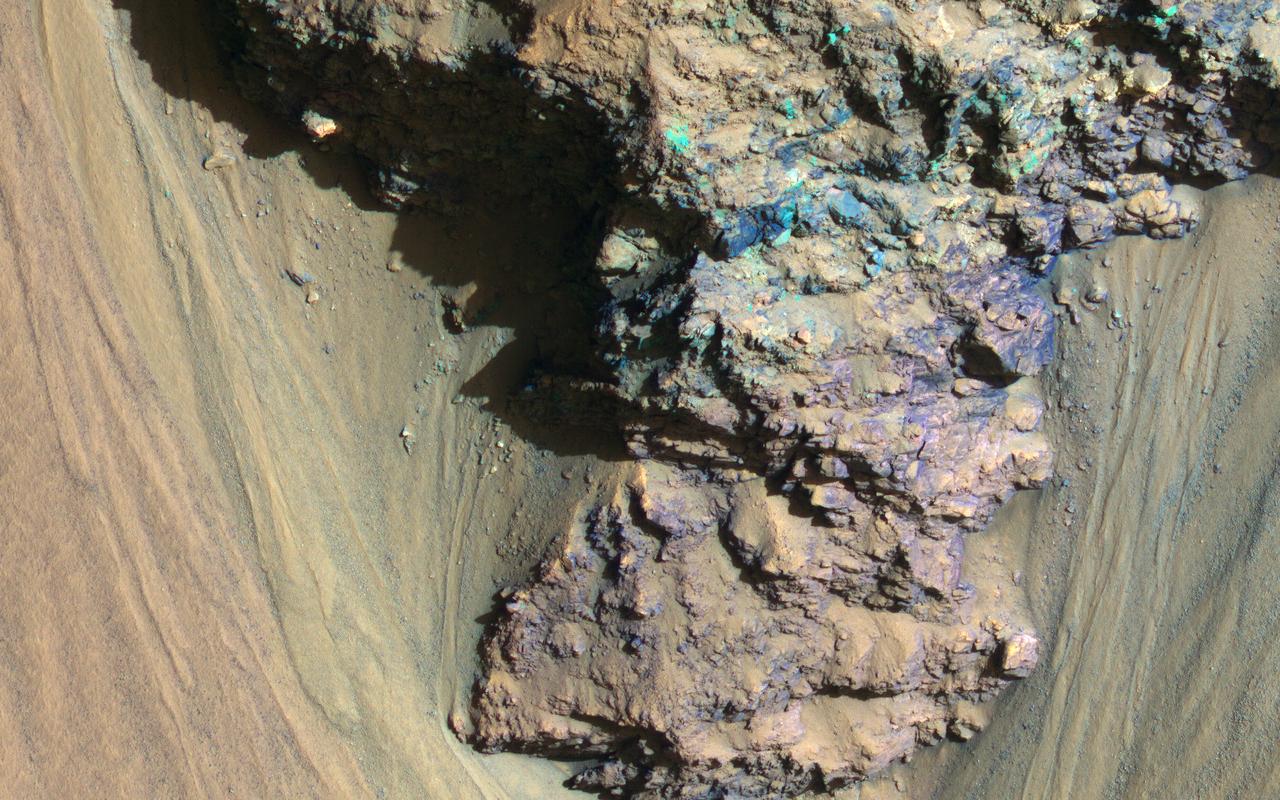

An enhanced-color image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) reveals bedrock that is several kilometers below the top of the giant Valles Marineris canyons. The upper layers have relatively little diversity of colors and textures, but deeper levels show more complex processes. The upper layers could be mostly volcanic while the lower layers were influenced by the period of heavy bombardment and greater interactions with water. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22238

This annotated image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows the journey NASA's Perseverance rover has taken and will take in the future as it heads toward Jezero Crater's delta on Mars. The white line depicts the route the rover has taken since it touched down at the "Octavia E. Butler Landing" site on Feb. 18, 2021, to its current location in the "South Séítah" geologic unit (light-blue dot). The rover will return to the landing site along the same route and then continue to the delta along the line in blue. This map is composed of images from the MRO's High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE). A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25027
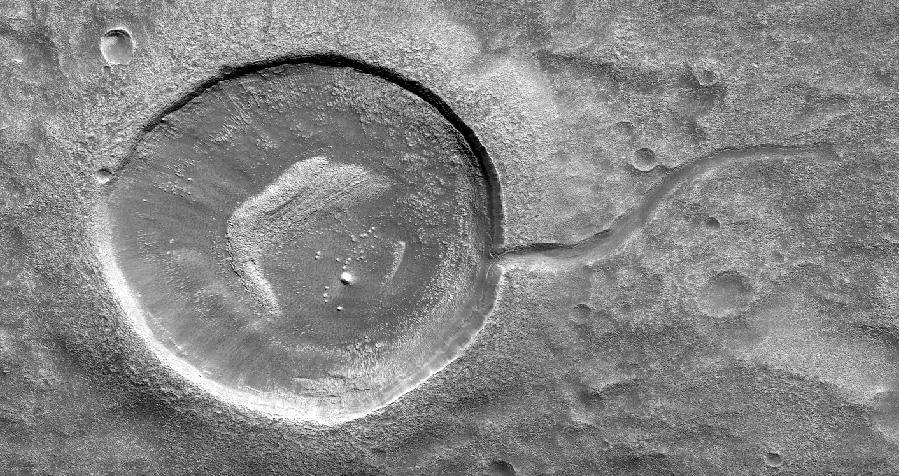

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows an impact crater looking amusingly like a tadpole because of the valley that was carved by water that used to fill it. It is often difficult to differentiate between inlet and outlet channels, but water always flows downhill. In this particular case, we can infer that water is flowing outward because we have the necessary terrain-height information. When studying these images in detail, scientists can gain a better understanding of the strength of the flooding water that carved the channels, and better understand the history of water activity in this region of Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22241
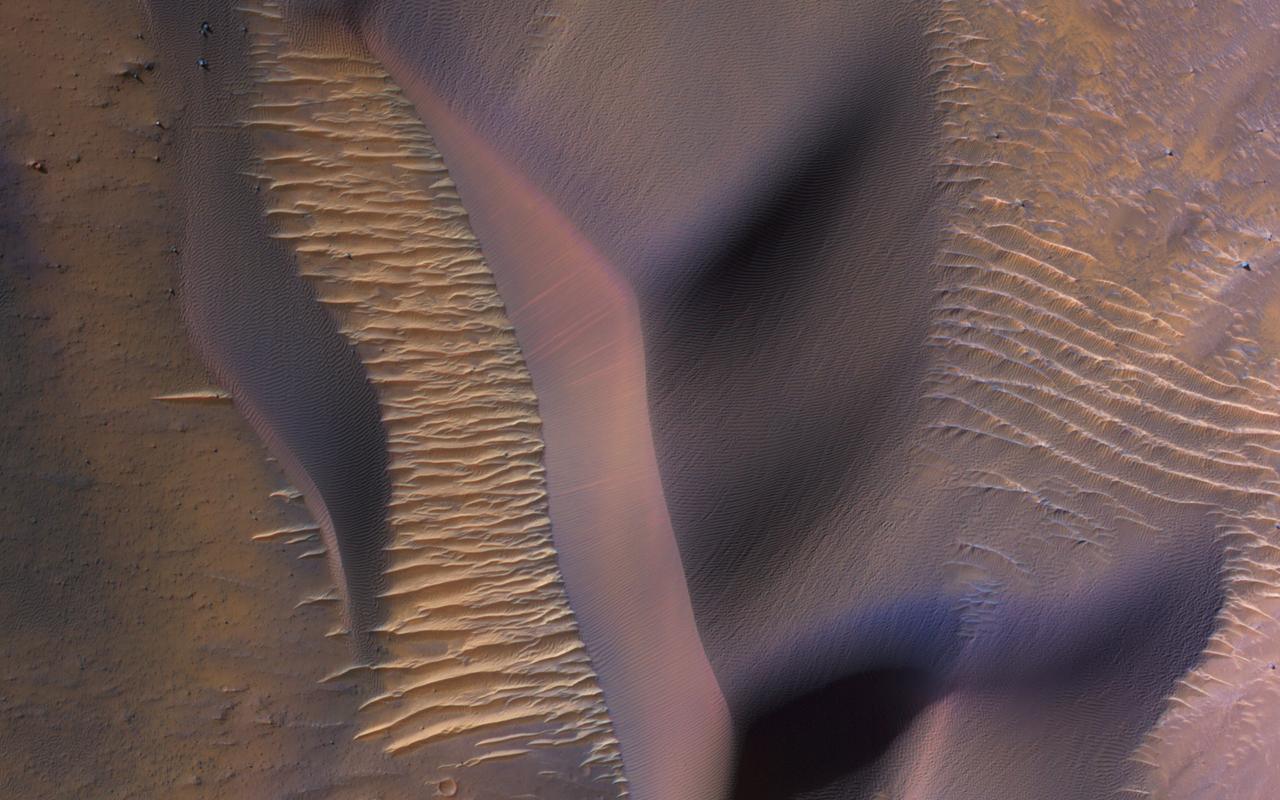

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows some of these on the slopes of Nectaris Montes within Coprates Chasma. Sand dunes in Valles Marineris can be impressive in size, with steep slopes that seem to climb and descend. The brighter bedforms are inactive while the bigger dunes move over the landscape, burying and exhuming the surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22455
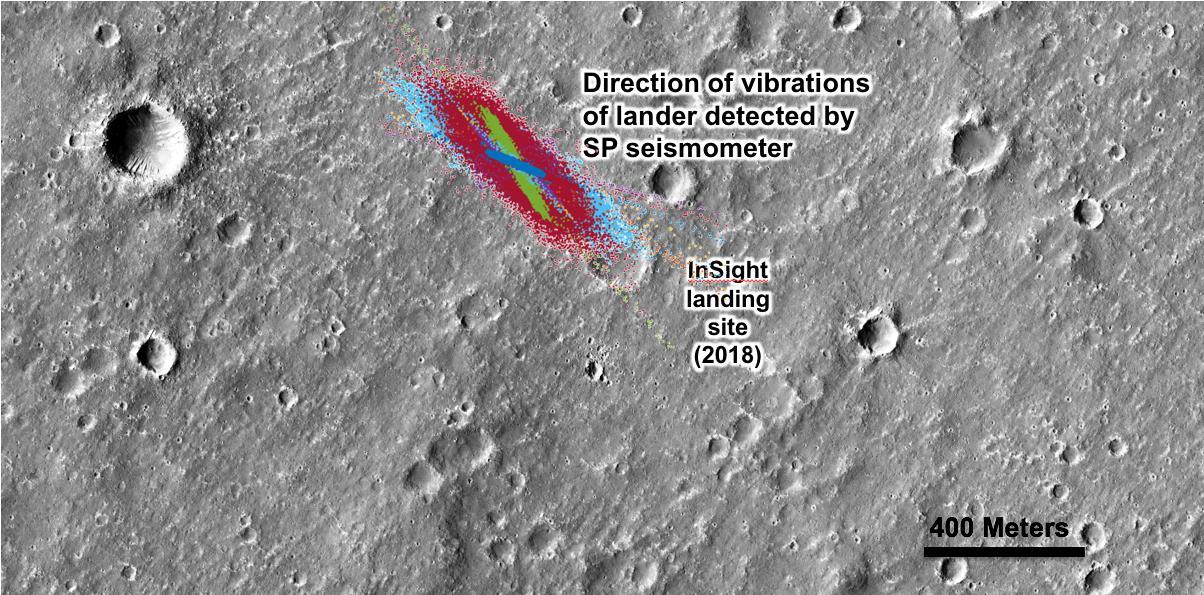
An annotated image of the surface of Mars, taken by the HiRISE camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) on May 30, 2014. The contrast has been enhanced in this image to better show the region where InSight landed on Nov. 26, 2018. The labels show the approximate position of NASA's InSight lander in Elysium Planitia. Overlaid on top are the direction of the vibrations detected by InSight's science instruments. The diagonal lines, faintly seen moving from upper left corner to the lower right corner of the image, show the paths of dust devils on the Martian surface. The vibrations recorded by InSight line up with the direction of the dust devil motion. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22927
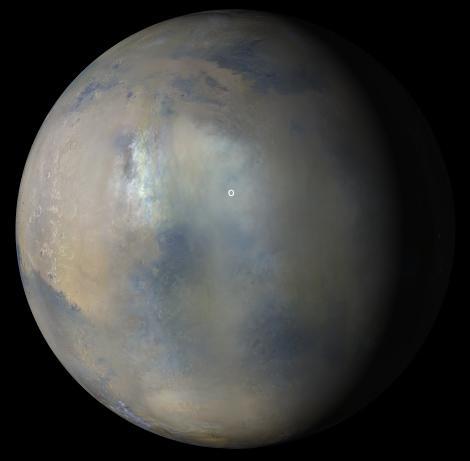

Multiple images from the Mars Color Imager (MARCI) aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) were used to generate this view of a regional dust storm obscuring Syrtis Major and Jezero Crater (white circle). The images were acquired on Jan. 9, 2022. MRO creates global maps of Mars but roll maneuvers for targeted observations produce gaps in the coverage, which appear as black gores in the maps. On some days there are data drops where partial or full orbits of coverage are missing. Green and purple observed in the south polar region indicate saturated pixels. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25068

This enhanced color image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows eroded bedrock on the floor of a large ancient crater. For more information see https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22439
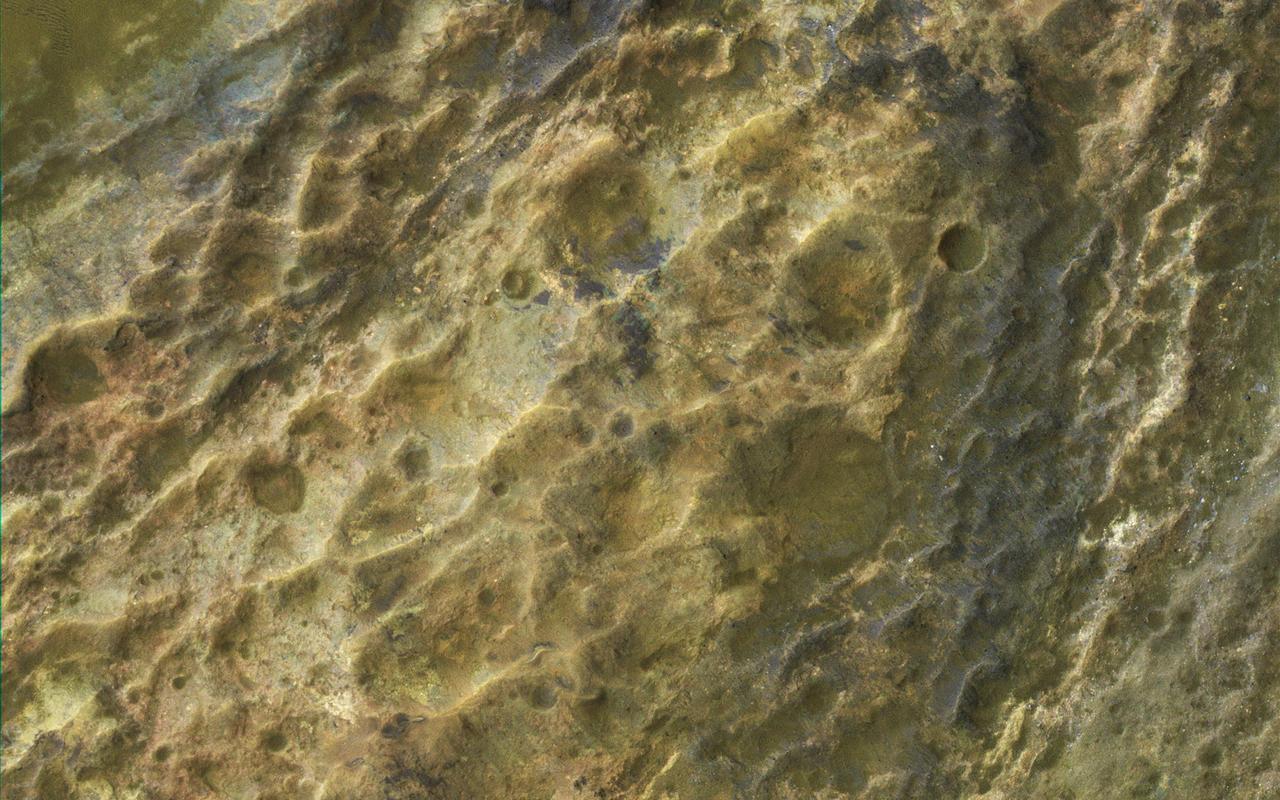

This image captured by NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter MRO covers diverse surface units on the floor of eastern Coprates Chasma in eastern Valles Marineris. The bedrock has diverse minerals producing wonderful color contrasts. In over 10 years of orbiting Mars, HiRISE has acquired nearly 50,000 large images, but they cover less than 3 percent of the Martian surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21606
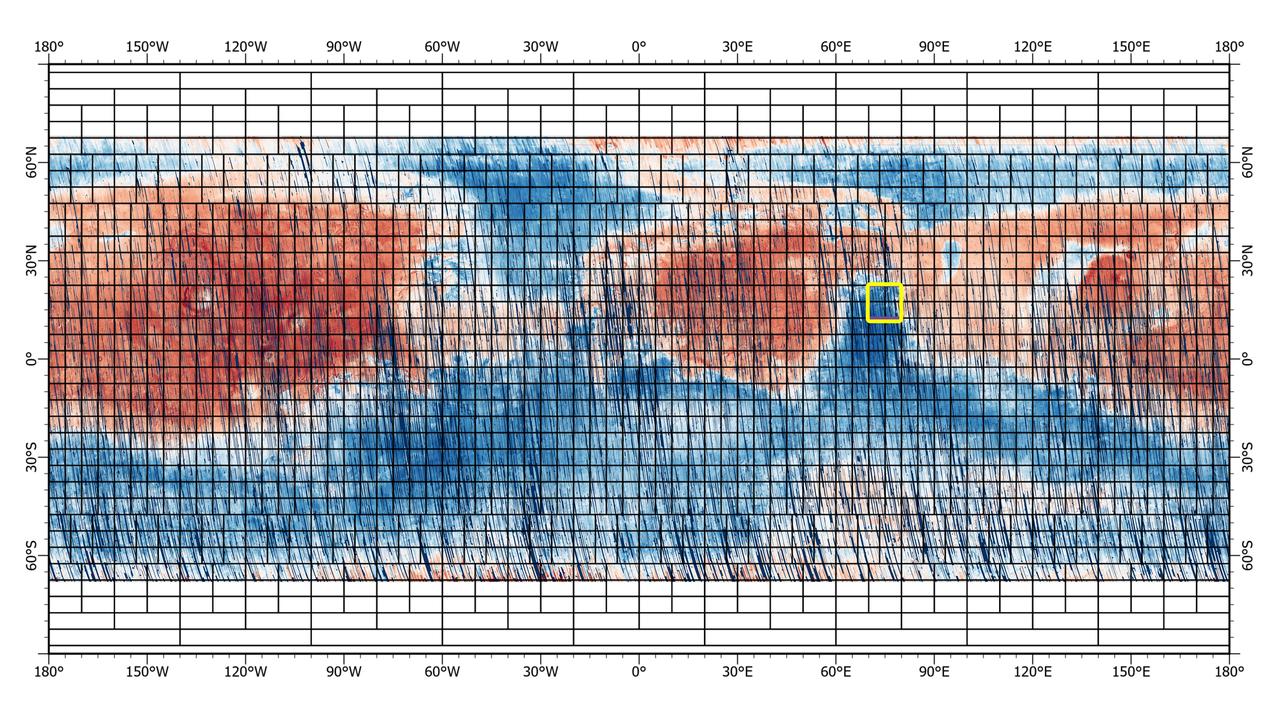
This 72-color near-global map of the Red Planet was captured by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) using its Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars, or CRISM. The yellow square indicates the Nili Fossae region of Mars, which is highlighted in six views in PIA25364. The map is one of the last major datasets CRISM will ever produce; the instrument will be decommissioned by the end of 2022. Data for the 6.3-gigapixel map was collected over 11 years of CRISM operations. The instrument arrived at Mars with three cryocoolers that allowed it to see in a range of wavelengths, including infrared; in 2017, the last of those cryocoolers stopped working, severely limiting the number of wavelengths CRISM could "see." https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25363
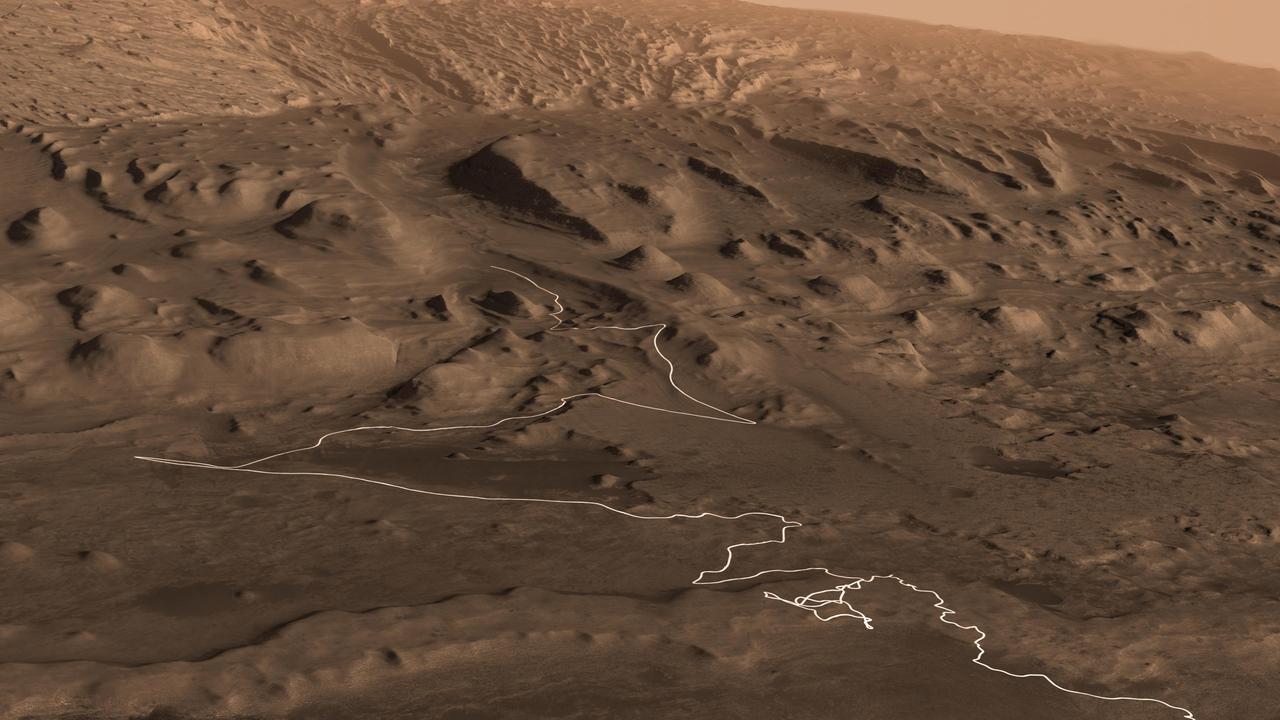

This animation shows a proposed route for NASA's Curiosity rover, which is climbing lower Mount Sharp on Mars. The annotated version of the map labels different regions that scientists working with the rover would like to explore in coming years. A flyover video explains them in more detail. Data used in creating this map came from several instruments on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), including the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE), Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) and the Context Camera (CTX). The High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) instrument on the European Space Agency's Mars Express also contributed data. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23179
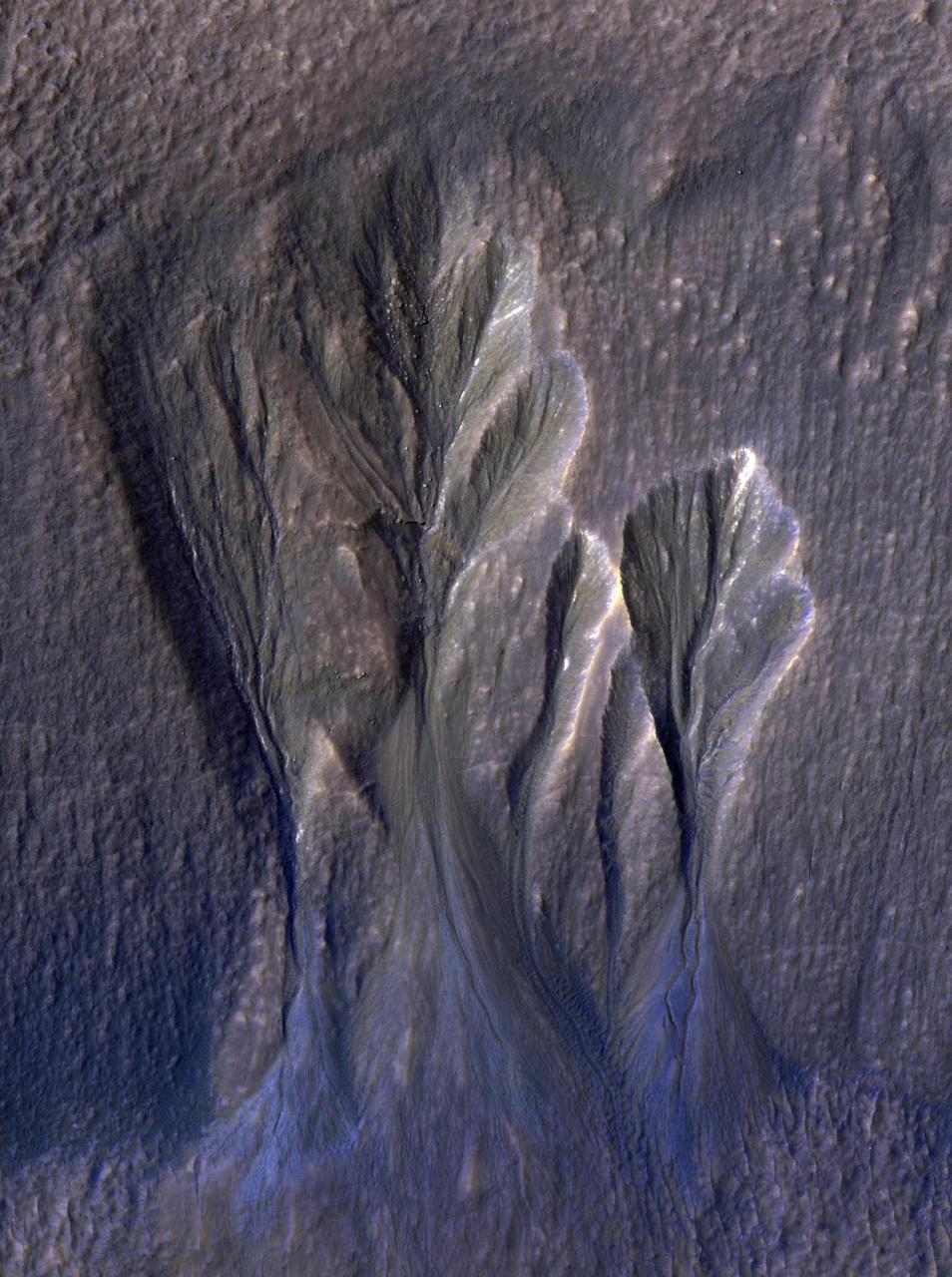

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows white material believed to be dusty water ice lining the edges of Martian gullies in a region named Terra Sirenum. Scientists believe dust particles within this ice act similarly to dust that falls onto glaciers on Earth, warming up in sunlight and causing subsurface pockets of meltwater to form. On Earth, the dust that builds up on glaciers is called cryoconite, and the pockets it forms are called cryoconite holes. These pockets of water on our planet are often teeming with simple life, including algae, fungi, and cyanobacteria. Scientists believe similar shallow pools of water could exist on Mars, and may also be excellent places to search for life on the Red Planet today. This enhanced-color image was captured by MRO's HiRISE (High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) camera on Dec. 25, 2016. The blue color at the bottom of the gullies is likely coarse sand (not ice); the hue would not actually be perceptible to the human eye. HiRISE is able to detect this color by looking at the scene in far-infrared wavelengths. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26407
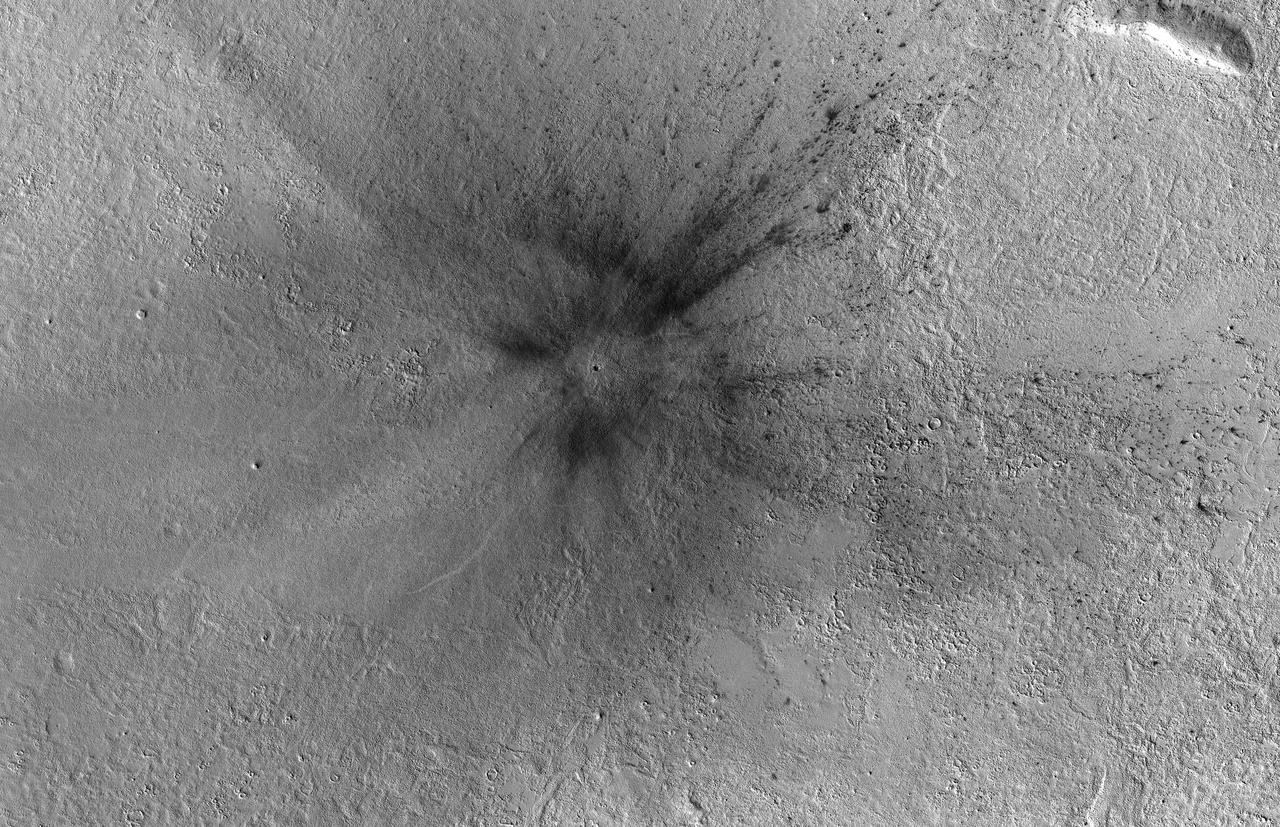

This meteoroid impact crater on Mars was discovered using the black-and-white Context Camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The Context Camera took this image showing the impact, which occurred Dec. 24, 2021, in a region called Amazonis Planitia. Relying on data from the Mars Color Imager camera, also aboard MRO, along with seismic data from NASA's InSight lander, scientists were able to determine when this particular crater formed. Looking closely at the crater's rim, white specks could be detected that suggested the presence of water ice (which was later confirmed by MRO's High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment, or HiRISE, camera). Debris thrown during the impact can be seen reaching as far as 23 miles (37 kilometers) away. The disturbance seen in the surface suggests the meteoroid was traveling towards the northeast when it hit the ground, throwing the longest streaks of debris in that direction. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25584
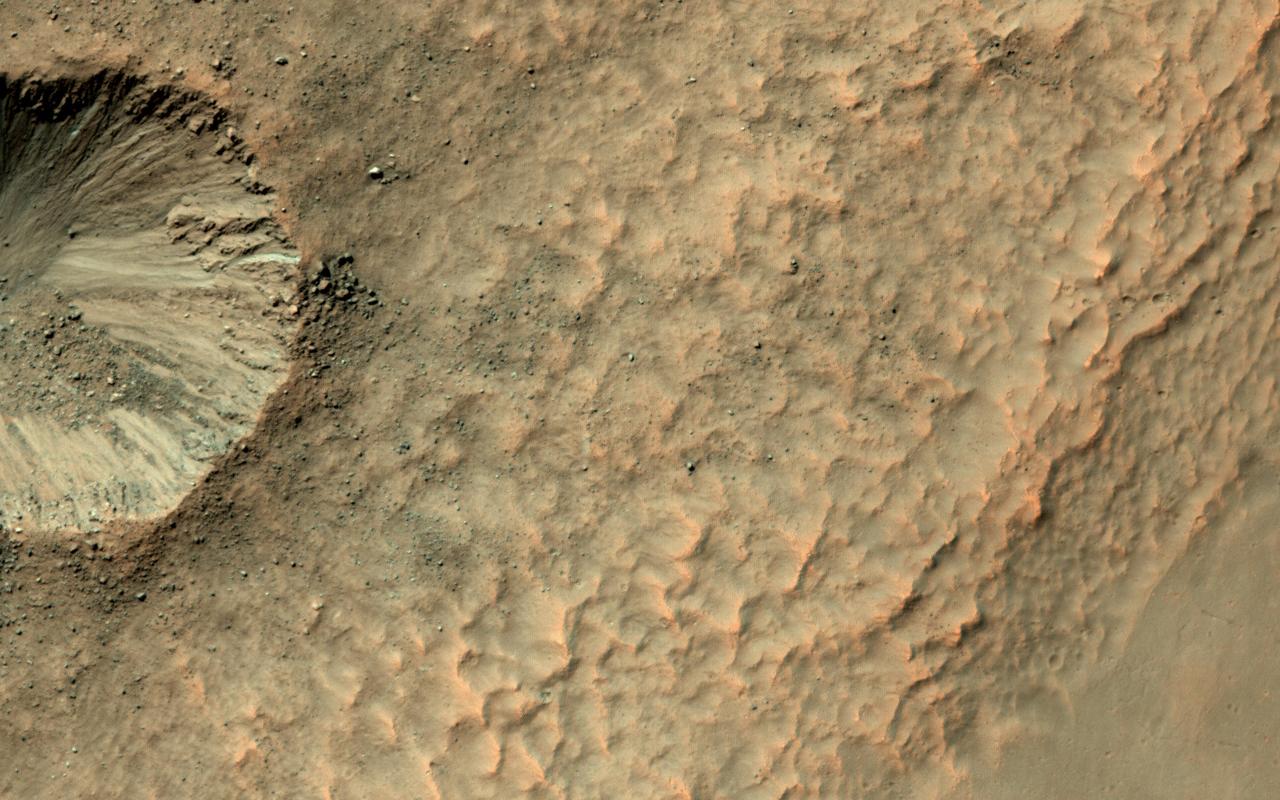

It's not that common to see craters on steep hills, partly because rocks falling downhill can quickly erase such craters. Here, however, NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) observes a small impact has occurred on the sloping wall of a larger crater and is well-preserved. Dark, blocky ejecta from the smaller crater has flowed downhill (to the west) toward the floor of the larger crater. Understanding the emplacement of such ejecta on steep hills is an area of ongoing research. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21758
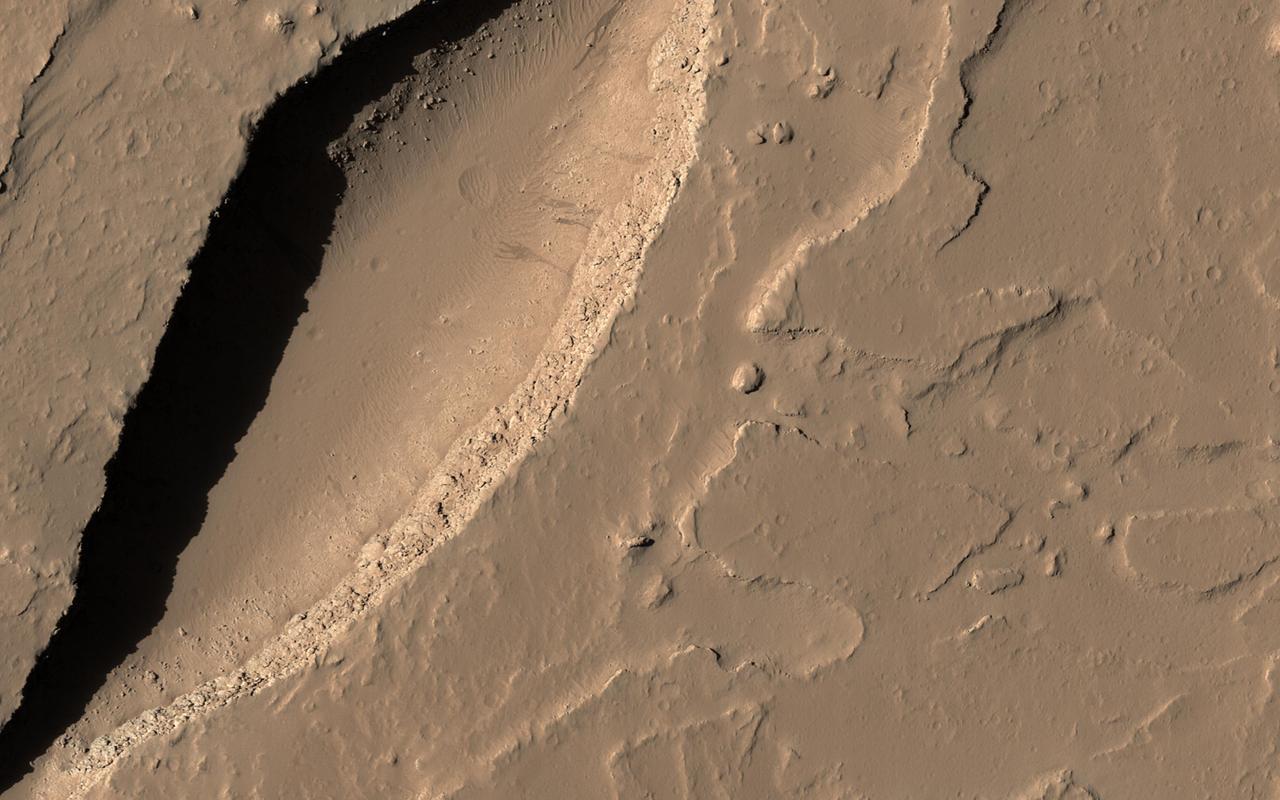

Although Mars is known for having the largest volcano in our solar system, Olympus Mons, we also find small-scale volcanic features on its surface, as shown in this image from HiRISE onboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). This fissure, less than 500 meters across at its widest point, lies in the Tharsis region and is believed to be a vent from which lava flowed in ancient eruptions. The total volume of lava released from this fissure is much less than what would erupt from nearby volcanoes, but the mark left on the landscape is dramatic nonetheless. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21601
![Ladon Basin was a large impact structure that was filled in by the deposits from Ladon Valles, a major ancient river on Mars as seen in this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). These wet sediments were altered into minerals such as various clay minerals. Clays imply chemistry that may have been favorable for life on ancient Mars, if anything lived there, so this could be a good spot for future exploration by rovers and perhaps return of samples to Earth. The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 52.1 centimeters (20.5 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 156 centimeters (61.4 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22183](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA22183/PIA22183~medium.jpg)
Ladon Basin was a large impact structure that was filled in by the deposits from Ladon Valles, a major ancient river on Mars as seen in this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). These wet sediments were altered into minerals such as various clay minerals. Clays imply chemistry that may have been favorable for life on ancient Mars, if anything lived there, so this could be a good spot for future exploration by rovers and perhaps return of samples to Earth. The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 52.1 centimeters (20.5 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 156 centimeters (61.4 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22183
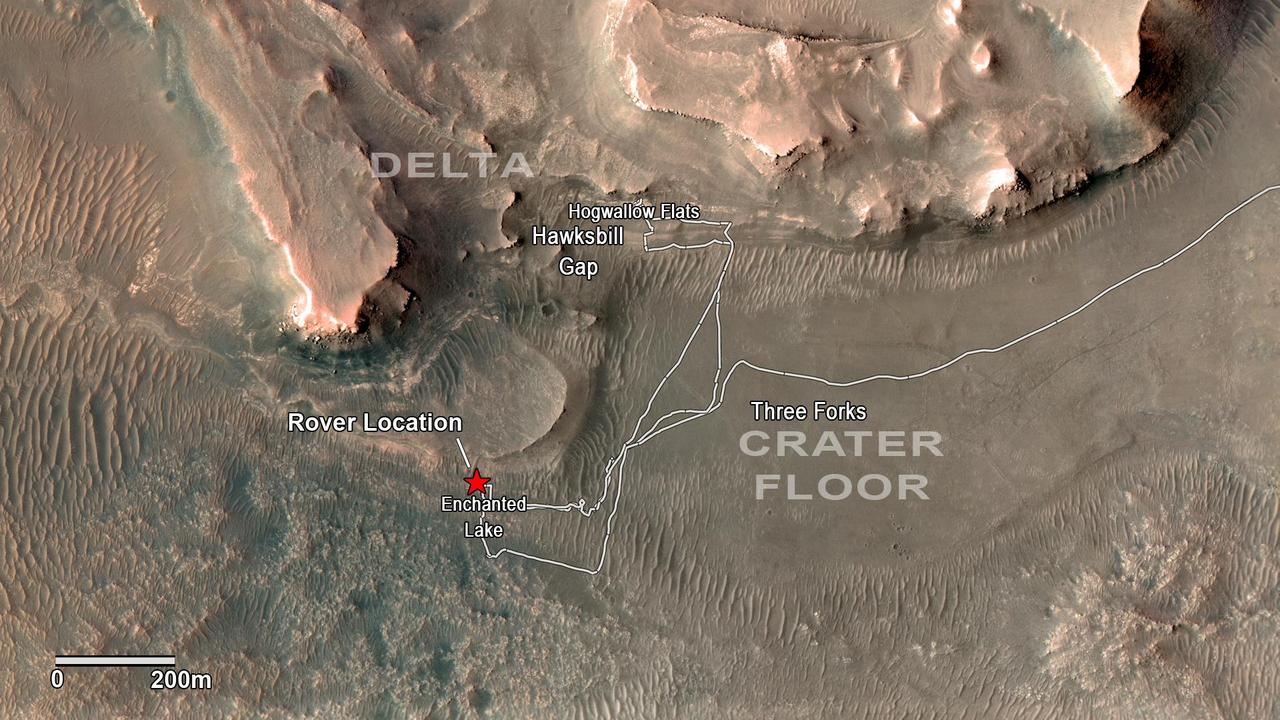
NASA's Perseverance rover has been investigating rocks at the front of the delta in Mars' Jezero Crater along the path indicated in this annotated image taken by the agency's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The red star indicates the location of the rover in September 2022. Perseverance touched down at "Octavia E. Butler Landing" on the floor of Jezero Crater on Feb. 18, 2021. It reached the delta in April 2022. The delta is a fan-shaped feature where, billions of years ago, a river flowed into a lake and deposited rocks and sediments. Scientists consider the delta one of the best places on Mars to search for potential signs of ancient microbial life. The annotations show the names of some of the key features Perseverance visited, such as "Enchanted Lake" and "Hogwallow Flats." Sample tubes already filled with rock are currently stored in the rover's Sampling and Caching System. Perseverance will deposit select samples in designated locations. MRO took this overhead image with its High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24923

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows streaks forming on slopes when dust cascades downhill. The dark streak is an area of less dust compared to the brighter and reddish surroundings. What triggers these avalanches is not known, but might be related to sudden warming of the surface. These streaks are often diverted by the terrain they flow down. This one has split into many smaller streaks where it encountered minor obstacles. These streaks fade away over decades as more dust slowly settles out of the Martian sky. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22240
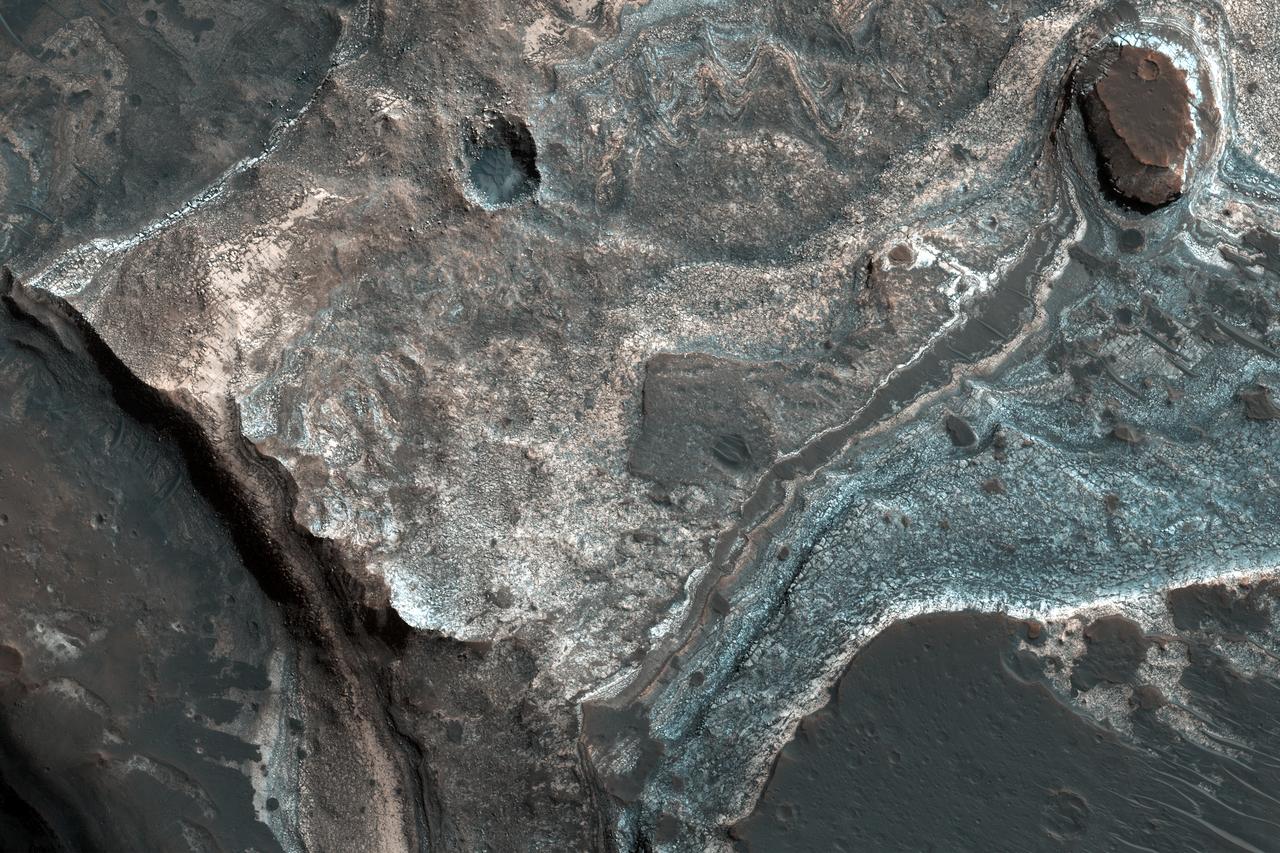

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows the western wall of a small pit that is located along the floor of a larger trough in Coprates Catena. Dark layers are exposed along the bottom of the pit wall while light-toned layers are near the top of the pit and the adjacent trough floor. Based upon where the layers are exposed, we can tell that the dark layers formed first followed by the light layers. The light layers could have been deposited when water filled part of the trough while the dark layers could be older lava flows. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22331
![Layers, probably sedimentary in origin, have undergone extensive erosion in this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) of Shalbatana Valles, a prominent channel that cuts through Xanthe Terra. This erosion has produced several small mesas and exposed light-toned material that may differ in composition from the surrounding material. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 27.5 centimeters (10.8 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 82 centimeters (32.3 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22182](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA22182/PIA22182~medium.jpg)
Layers, probably sedimentary in origin, have undergone extensive erosion in this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) of Shalbatana Valles, a prominent channel that cuts through Xanthe Terra. This erosion has produced several small mesas and exposed light-toned material that may differ in composition from the surrounding material. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 27.5 centimeters (10.8 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 82 centimeters (32.3 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22182

This annotated-composite graphic shows the entry of NASA's Perseverance rover into the "South Séítah" geologic unit from both an orbital and subsurface perspective. The annotated view from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbitor (MRO) depicts the route Perseverance took into Séítah. The image was provided by MRO's High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE). The graphic below the orbital image is the first "radargram" to be released by the Radar Imager for Mars' Subsurface Experiment (RIMFAX) instrument aboard Perseverance. It shows the subsurface as the rover drove across the "Artuby" ridgeline. The red lines link bright subsurface "reflectors" to erosion-resistant layers outcropping at the surface. The University of Arizona, in Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., in Boulder, Colorado. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25025
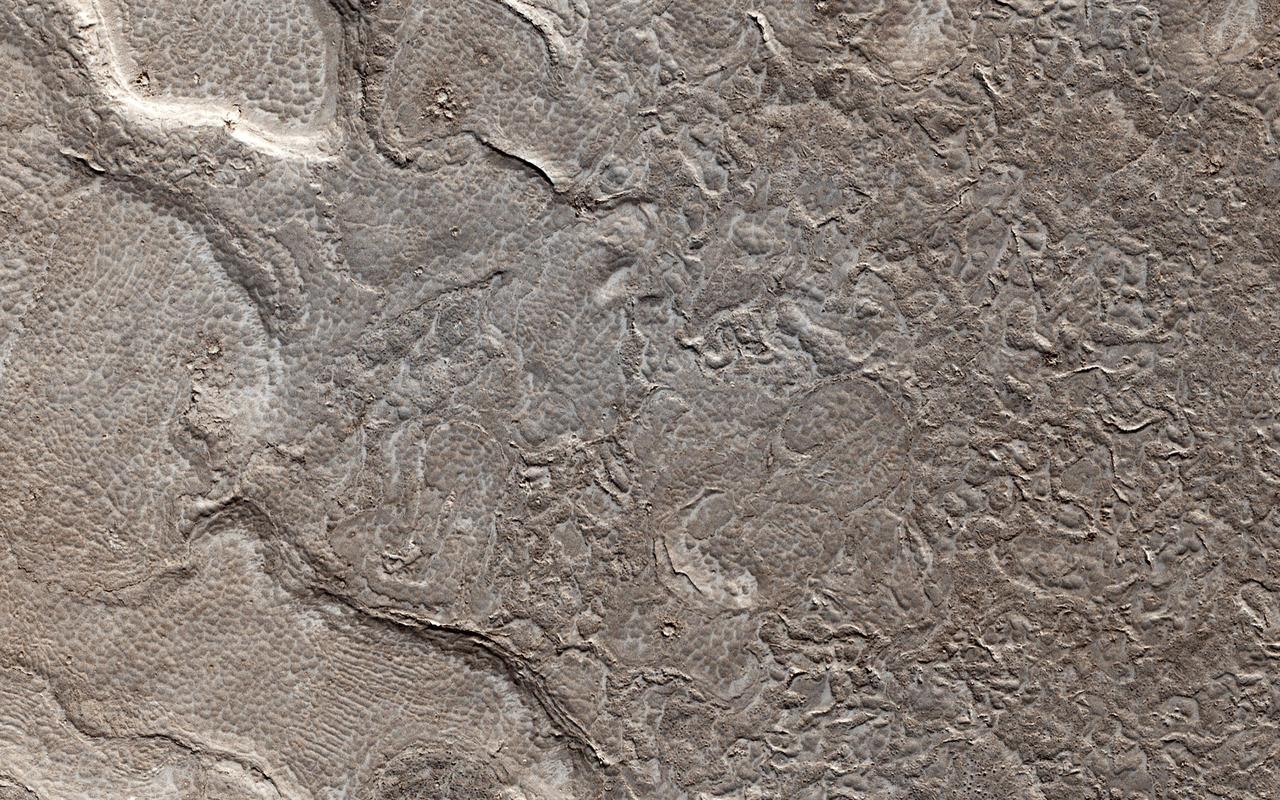

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows remarkably young lava flows in Elysium Planitia. There are almost no impact craters over this flow, indicating that it is probably only a few million years old -- practically an infant in geologic time. For more information see https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22432
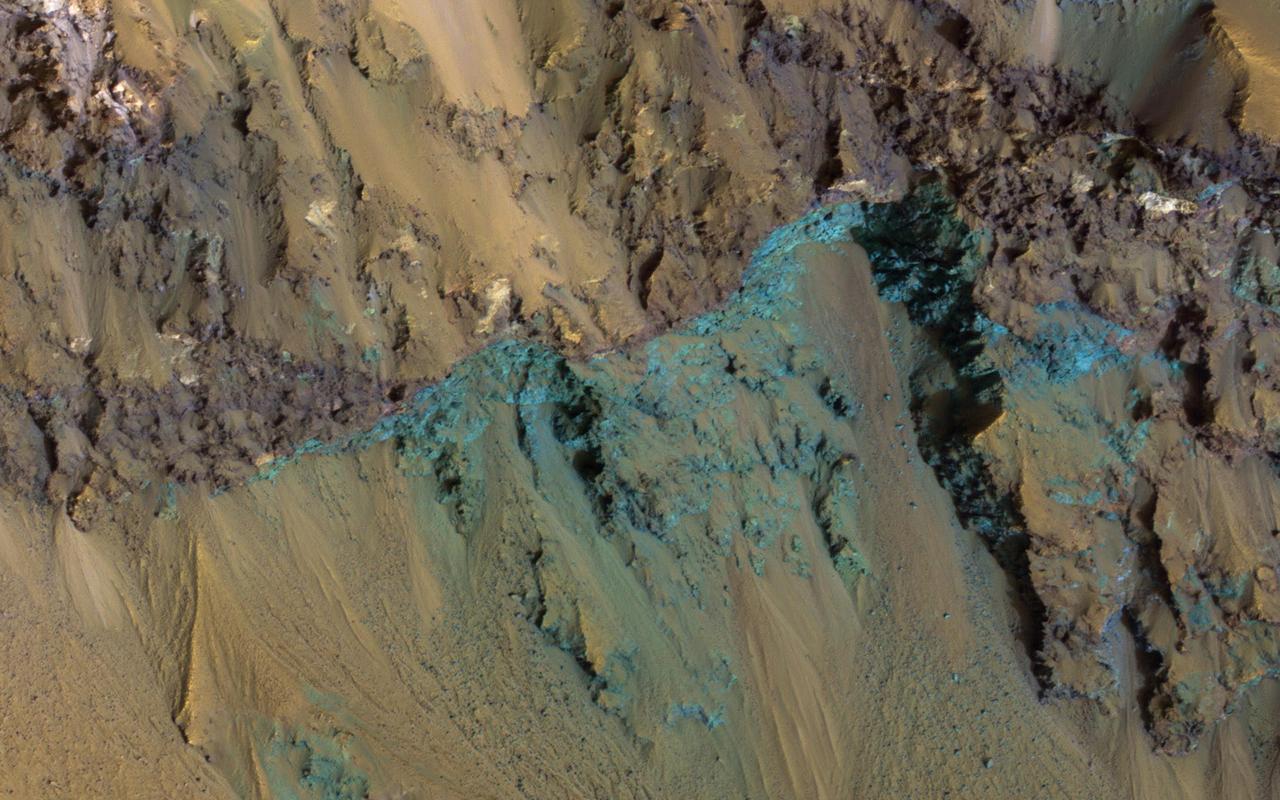

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows Hale Crater, a large impact crater (more than 100 kilometers) with a suite of interesting features such as active gullies, active recurring slope lineae, and extensive icy ejecta flows. There are also exposed diverse (colorful) bedrock units. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22465

The High-Resolution Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) took this image of the Perseverance rover on Feb. 24, 2021. The false-color image shows a ring of blast marks where thrusters from the rover's descent stage blew away dust during landing on Feb. 18, 2021. By rolling MRO to the side (18 degrees for this image) as it passes over Perseverance every few days, the mission team enables HiRISE to see the rover. Perseverance is about 10 feet by 9 feet (3 by 2.7 meters) in size and is about 180 miles (290 kilometers) away from HiRISE in this image. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24427
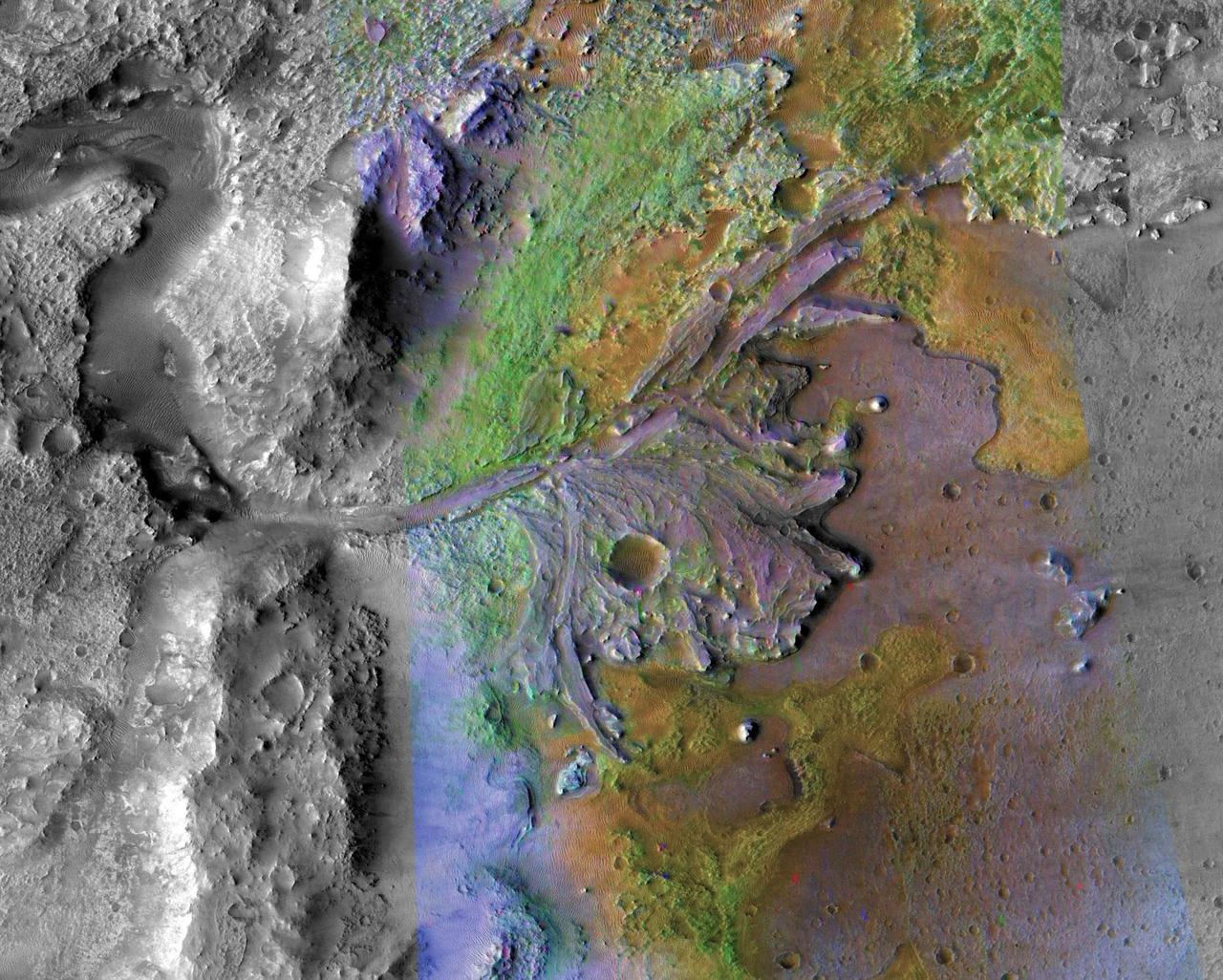

This image is of Jezero Crater on Mars, the landing site for NASA's Mars 2020 mission. It was taken by instruments on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), which regularly takes images of potential landing sites for future missions. On ancient Mars, water carved channels and transported sediments to form fans and deltas within lake basins. Examination of spectral data acquired from orbit show that some of these sediments have minerals that indicate chemical alteration by water. Here in Jezero Crater delta, sediments contain clays and carbonates. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23239

This set of images from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows a fierce, giant dust storm is kicking up on Mars, with rovers on the surface indicated as icons. The spread of the storm can be seen in the salmon-colored overlay. These images from MRO's Mars Color Imager start from May 31, when the dust event was first detected, and go through June 11, 2018. MRO creates global maps of Mars but roll maneuvers for targeted observations produce gaps in the coverage, which appear as black gores in the maps. On some days there are data drops where partial or full orbits of coverage are missing. Green and purple observed in the south polar region indicate saturated pixels. Latitude is indicated along the vertical axis. Longitude is indicated along the horizontal axis. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22519
![Lyot Crater (220-kilometers in diameter) is located in the Northern lowlands of Mars. The crater's floor marks the lowest elevation in the Northern Hemisphere as seen in this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). On the crater's floor, we see a network of channels. connecting a series of irregular shaped pits. These resemble terrestrial beaded streams, which are common in the Arctic regions of Earth and develop from uneven permafrost thawing. If terrestrial beaded streams are a good analog, these landforms suggest liquid water flow in the past. If not then these pits may result from the process of sublimation and would indicate pockets of easily accessible near-surface ground ice, which might have potentially preserved evidence of past habitability. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 12.2 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 93 centimeters (36.6 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22186](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA22187/PIA22187~medium.jpg)
Lyot Crater (220-kilometers in diameter) is located in the Northern lowlands of Mars. The crater's floor marks the lowest elevation in the Northern Hemisphere as seen in this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). On the crater's floor, we see a network of channels. connecting a series of irregular shaped pits. These resemble terrestrial beaded streams, which are common in the Arctic regions of Earth and develop from uneven permafrost thawing. If terrestrial beaded streams are a good analog, these landforms suggest liquid water flow in the past. If not then these pits may result from the process of sublimation and would indicate pockets of easily accessible near-surface ground ice, which might have potentially preserved evidence of past habitability. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 12.2 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 93 centimeters (36.6 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22186
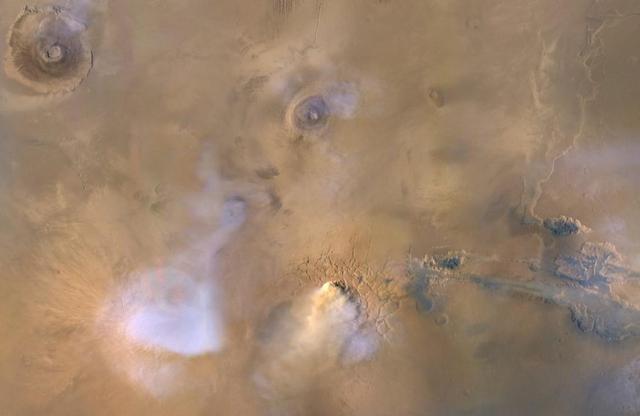

The yellow-white cloud in the bottom-center of this image is a Mars "dust tower" — a concentrated cloud of dust that can be lofted dozens of miles above the surface. The blue-white plumes are water vapor clouds. Olympus Mons, the tallest volcano in the solar system, is visible in the upper left corner, while Valles Marineris can be seen in the lower right. Heat-sensitive instruments like the Mars Climate Sounder, carried aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), can map the formation of these dust towers, which form almost continuously during global dust storms. Taken on Nov. 30, 2010, the image was produced by MRO's Mars Color Imager (MARCI), which was built and is operated by Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23513
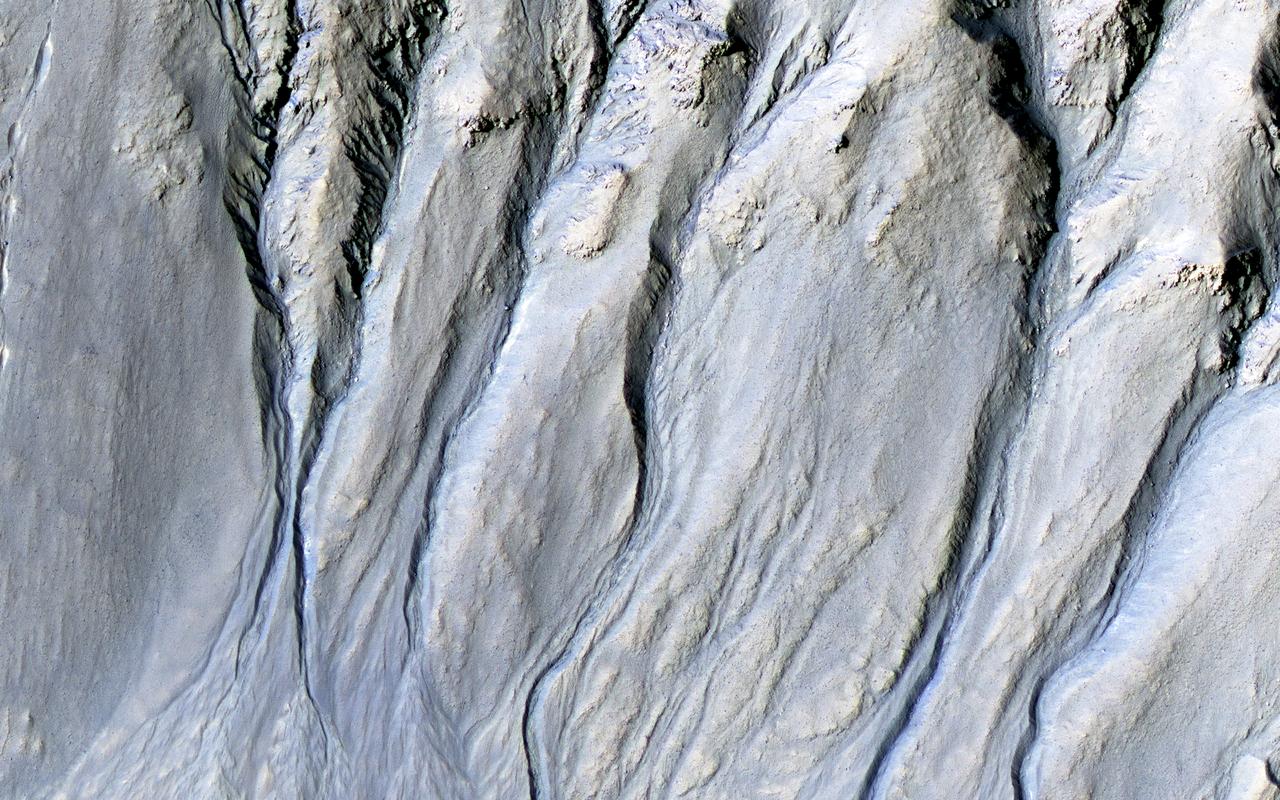

Intricate gullies have formed on the northern wall of this impact crater located in the Terra Cimmeria region in this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). This crater may have formed in a region rich in ground water. This ground water likely flowed down the wall, eventually eroding numerous gullies while carrying sediments to form fan deposits. Ultimately the water likely infiltrated and froze beneath the surface. Other hypotheses say gullies form through carbon dioxide frost avalanches that we can see today. What about this chain of pits snaking their way downhill? After material was transported, subsurface voids may have formed, removing support for the overlying material. The collapse of the surface into the cavities below likely resulted in the pits and troughs, perhaps beginning a new cycle of gully formation. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22239
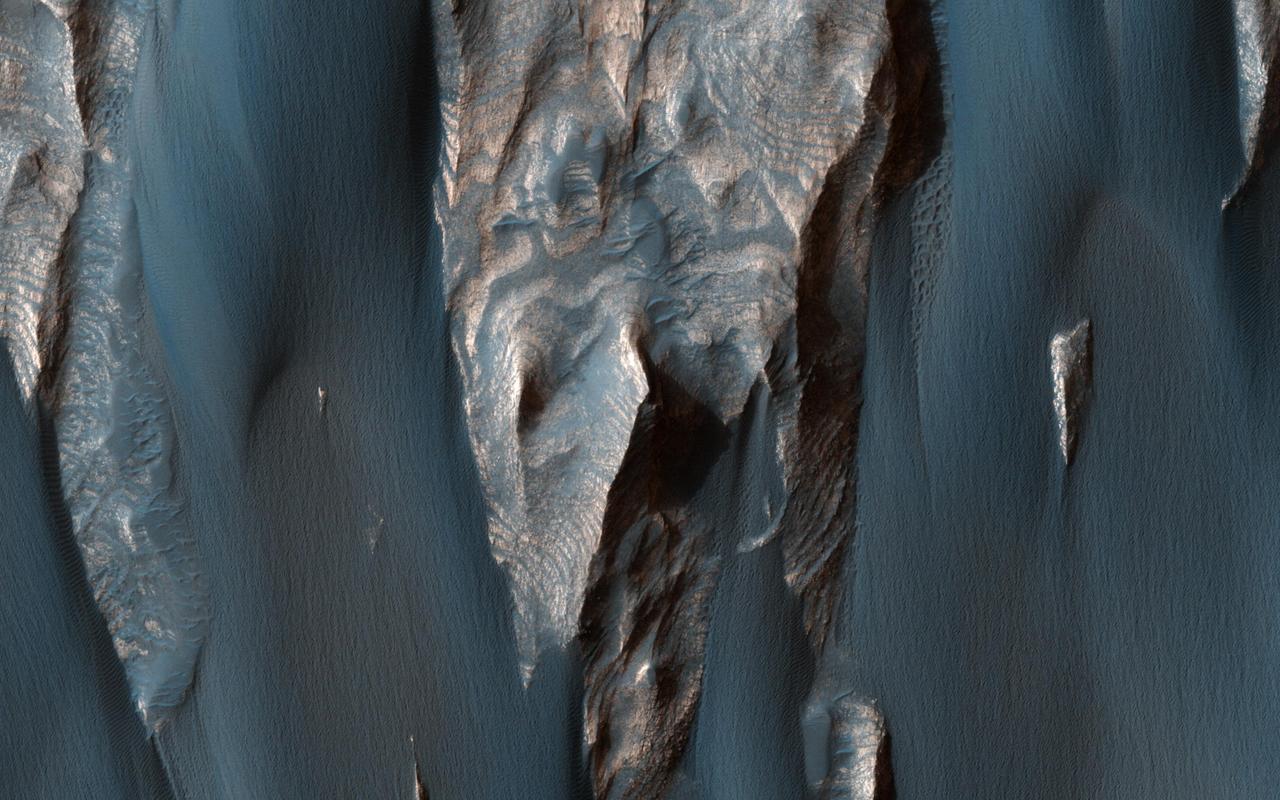

Dark, windblown sand covers intricate sedimentary rock layers in this image captured by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) from Ganges Chasma, a canyon in the Valles Marineris system. These features are at once familiar and unusual to those familiar with Earth's beaches and deserts. Most sand dunes on Earth are made of silica-rich sand, giving them a light color; these Martian dunes owe their dark color to the iron and magnesium-rich sand found in the region. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21600
![This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows Mars' surface in detail. Mars has captured the imagination of astronomers for thousands of years, but it wasn't until the last half a century that we were able to capture images of its surface in detail. This particular site on Mars was first imaged in 1965 by the Mariner 4 spacecraft during the first successful fly-by mission to Mars. From an altitude of around 10,000 kilometers, this image (the ninth frame taken) achieved a resolution of approximately 1.25 kilometers per pixel. Since then, this location has been observed by six other visible cameras producing images with varying resolutions and sizes. This includes HiRISE (highlighted in yellow), which is the highest-resolution and has the smallest "footprint." This compilation, spanning Mariner 4 to HiRISE, shows each image at full-resolution. Beginning with Viking 1 and ending with our HiRISE image, this animation documents the historic imaging of a particular site on another world. In 1976, the Viking 1 orbiter began imaging Mars in unprecedented detail, and by 1980 had successfully mosaicked the planet at approximately 230 meters per pixel. In 1999, the Mars Orbiter Camera onboard the Mars Global Surveyor (1996) also imaged this site with its Wide Angle lens, at around 236 meters per pixel. This was followed by the Thermal Emission Imaging System on Mars Odyssey (2001), which also provided a visible camera producing the image we see here at 17 meters per pixel. Later in 2012, the High-Resolution Stereo Camera on the Mars Express orbiter (2003) captured this image of the surface at 25 meters per pixel. In 2010, the Context Camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (2005) imaged this site at about 5 meters per pixel. Finally, in 2017, HiRISE acquired the highest resolution image of this location to date at 50 centimeters per pixel. When seen at this unprecedented scale, we can discern a crater floor strewn with small rocky deposits, boulders several meters across, and wind-blown deposits in the floors of small craters and depressions. This compilation of Mars images spanning over 50 years gives us a visual appreciation of the evolution of orbital Mars imaging over a single site. The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 52.2 centimeters (20.6 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 156 centimeters (61.4 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22115](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA22115/PIA22115~medium.jpg)
This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows Mars' surface in detail. Mars has captured the imagination of astronomers for thousands of years, but it wasn't until the last half a century that we were able to capture images of its surface in detail. This particular site on Mars was first imaged in 1965 by the Mariner 4 spacecraft during the first successful fly-by mission to Mars. From an altitude of around 10,000 kilometers, this image (the ninth frame taken) achieved a resolution of approximately 1.25 kilometers per pixel. Since then, this location has been observed by six other visible cameras producing images with varying resolutions and sizes. This includes HiRISE (highlighted in yellow), which is the highest-resolution and has the smallest "footprint." This compilation, spanning Mariner 4 to HiRISE, shows each image at full-resolution. Beginning with Viking 1 and ending with our HiRISE image, this animation documents the historic imaging of a particular site on another world. In 1976, the Viking 1 orbiter began imaging Mars in unprecedented detail, and by 1980 had successfully mosaicked the planet at approximately 230 meters per pixel. In 1999, the Mars Orbiter Camera onboard the Mars Global Surveyor (1996) also imaged this site with its Wide Angle lens, at around 236 meters per pixel. This was followed by the Thermal Emission Imaging System on Mars Odyssey (2001), which also provided a visible camera producing the image we see here at 17 meters per pixel. Later in 2012, the High-Resolution Stereo Camera on the Mars Express orbiter (2003) captured this image of the surface at 25 meters per pixel. In 2010, the Context Camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (2005) imaged this site at about 5 meters per pixel. Finally, in 2017, HiRISE acquired the highest resolution image of this location to date at 50 centimeters per pixel. When seen at this unprecedented scale, we can discern a crater floor strewn with small rocky deposits, boulders several meters across, and wind-blown deposits in the floors of small craters and depressions. This compilation of Mars images spanning over 50 years gives us a visual appreciation of the evolution of orbital Mars imaging over a single site. The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 52.2 centimeters (20.6 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 156 centimeters (61.4 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22115
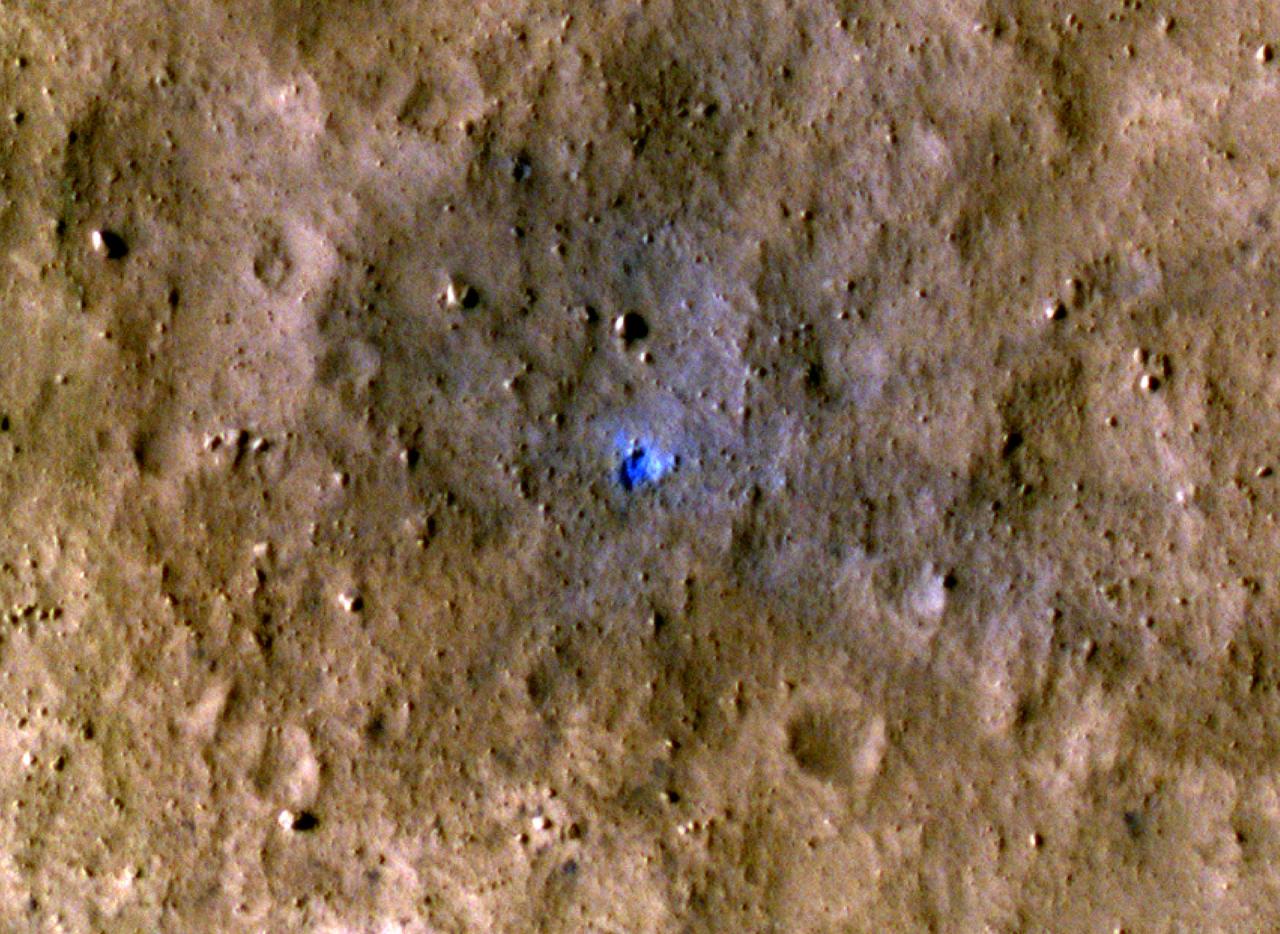

NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter captured this image of a meteoroid impact that was first detected by the agency's InSight lander using its seismometer. This crater was formed on Aug. 30, 2021. MRO's High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera captured this scene in color. The ground is not actually blue; this enhanced-color image highlights certain hues in the scene to make details more visible to the human eye – in this case, dust and soil disturbed by the impact. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25411
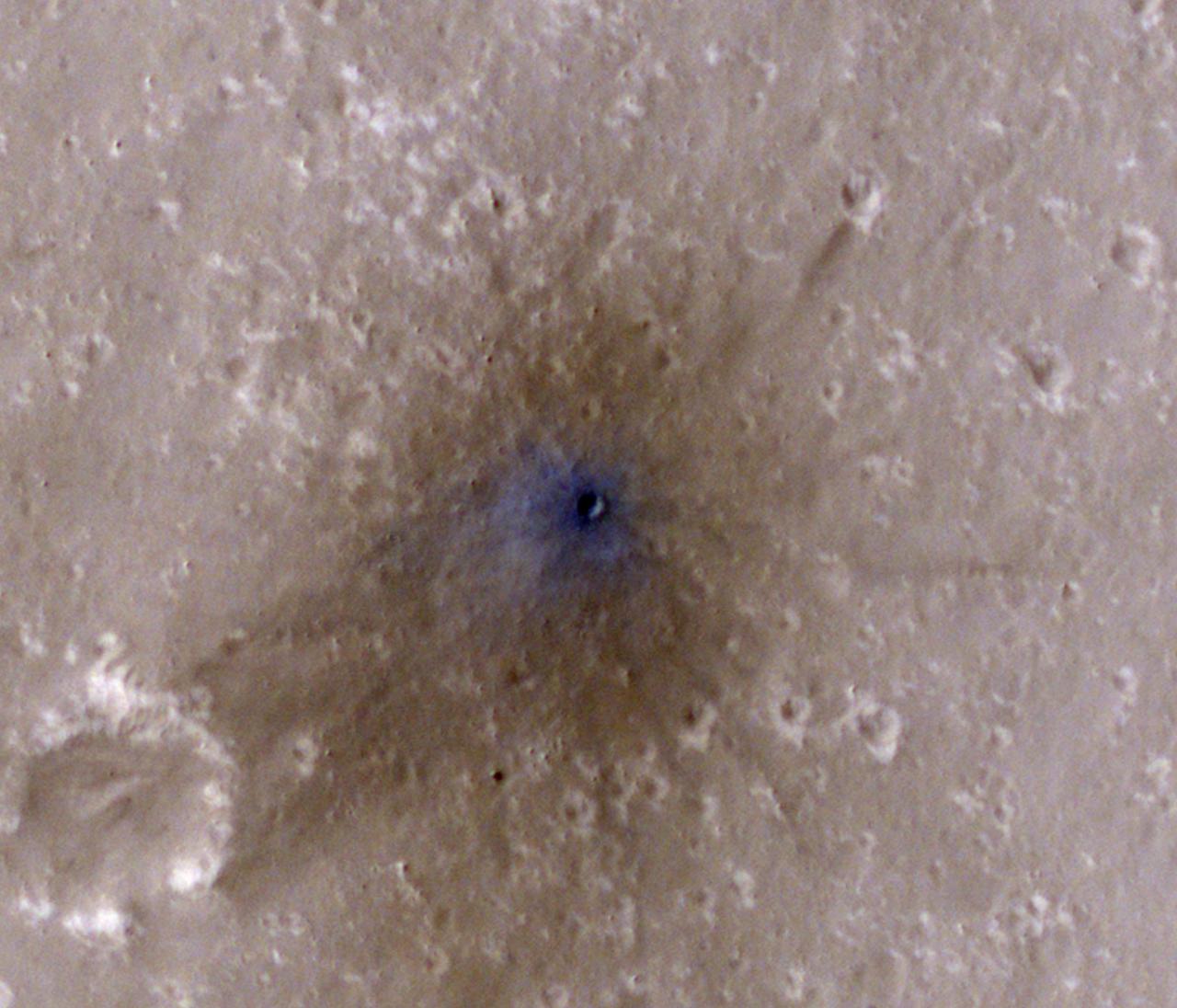
NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter captured this image of a meteoroid impact that was first detected by the agency's InSight lander using its seismometer. This crater was formed on Feb. 18, 2021. MRO's High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera captured this scene in color. The ground is not actually blue; this enhanced-color image highlights certain hues in the scene to make details more visible to the human eye – in this case, dust and soil disturbed by the impact. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25409

NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) captured this region of Mars, sprayed with secondary craters from 10-kilometer Zunil Crater to the northwest. Secondary craters form from rocks ejected at high speed from the primary crater, which then impact the ground at sufficiently high speed to make huge numbers of much smaller craters over a large region. In this scene, however, the secondary crater ejecta has an unusual raised-relief appearance like bas-relief sculpture. How did that happen? One idea is that the region was covered with a layer of fine-grained materials like dust or pyroclastics about 1 to 2 meters thick when the Zunil impact occurred (about a million years ago), and the ejecta served to harden or otherwise protect the fine-grained layer from later erosion by the wind. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21591

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows two new craters, both with the same distinctive pattern of relatively blue (less red) ejecta surrounded by a dark blast zone (where dust has been removed or disturbed), and with arcing patterns extending northwest and northeast. This pattern indicates an oblique impact angle with the bolide coming from the north. MRO has discovered over 700 new impact sites on Mars. Often, a bolide breaks apart in the atmosphere and makes a tight cluster of new craters. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22453
![NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) captured this crater featuring sand dunes and sand sheets on its floor. What are sand sheets? Snow fall on Earth is a good example of sand sheets: when it snows, the ground gets blanketed with up to a few meters of snow. The snow mantles the ground and "mimics" the underlying topography. Sand sheets likewise mantle the ground as a relatively thin deposit. This kind of environment has been monitored by HiRISE since 2007 to look for movement in the ripples covering the dunes and sheets. This is how scientists who study wind-blown sand can track the amount of sand moving through the area and possibly where the sand came from. Using the present environment is crucial to understanding the past: sand dunes, sheets, and ripples sometimes become preserved as sandstone and contain clues as to how they were deposited The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 75 centimeters (29.5 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21757](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA21757/PIA21757~medium.jpg)
NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) captured this crater featuring sand dunes and sand sheets on its floor. What are sand sheets? Snow fall on Earth is a good example of sand sheets: when it snows, the ground gets blanketed with up to a few meters of snow. The snow mantles the ground and "mimics" the underlying topography. Sand sheets likewise mantle the ground as a relatively thin deposit. This kind of environment has been monitored by HiRISE since 2007 to look for movement in the ripples covering the dunes and sheets. This is how scientists who study wind-blown sand can track the amount of sand moving through the area and possibly where the sand came from. Using the present environment is crucial to understanding the past: sand dunes, sheets, and ripples sometimes become preserved as sandstone and contain clues as to how they were deposited The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 75 centimeters (29.5 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21757
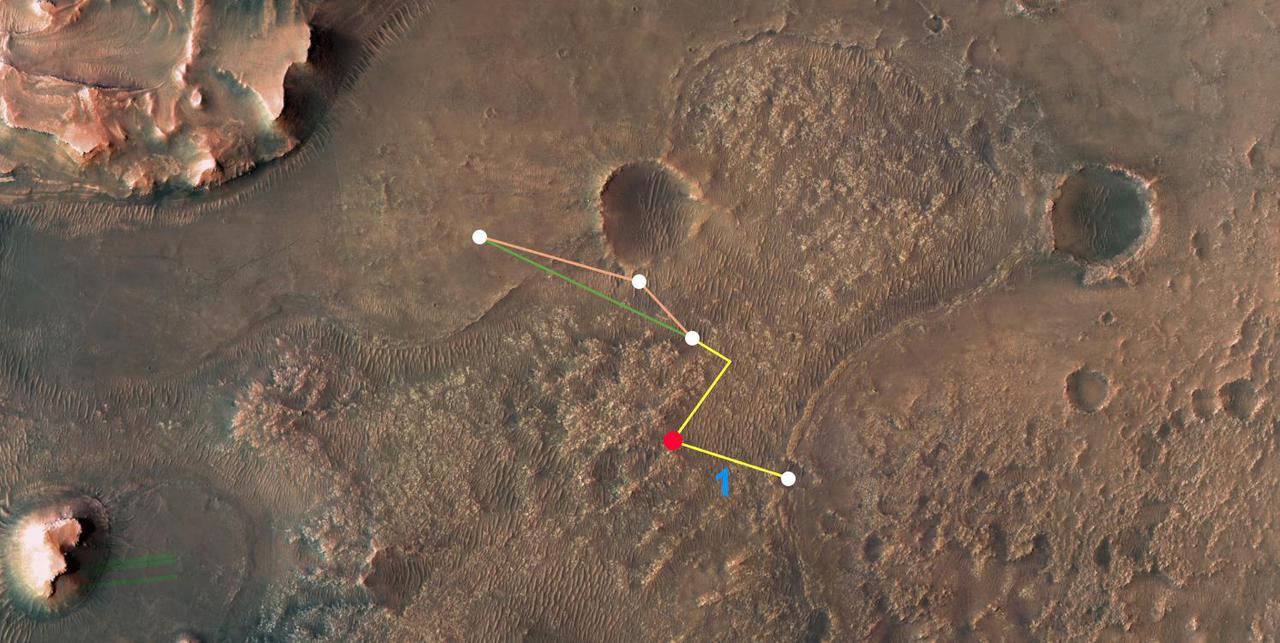
This annotated overhead image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) depicts the multiple flights – and two different routes – the agency's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter could take on its way to Jezero Crater's delta. The location of Ingenuity as of March 14, 2022, is indicated by the red dot. This map is made using images from MRO's High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE) camera. The first flight in this series (indicated by the number 1 in blue) occurred on March 10, 2022. After the next flight – which includes a sharp bend in the course to avoid a large hill – the helicopter team will consider which of two routes to take. The first option requires two flights to reach the base of the delta. The second option is more direct, necessitating only one final flight to reach the same location. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25080
![The two largest ice sheets in the inner solar system are here on Earth, Antarctica and Greenland. The third largest is at the South Pole of Mars and a small part of it is shown in this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Much like the terrestrial examples, this ice sheet is layered and scientists refer to it as the South Polar layered deposits. The ice layers contain information about past climates on Mars and deciphering this record has been a major goal of Mars science for decades. This slope, near the ice sheet's edge, shows the internal layers that have this climate record. With stereo images, we can tell the heights of these layers so we can measure their thickness and try to unravel the climatic information they contain. (Be sure to view the digital terrain model for this observation.) The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 25.0 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 75 centimeters (29.5 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22125](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA22125/PIA22125~thumb.jpg)
The two largest ice sheets in the inner solar system are here on Earth, Antarctica and Greenland. The third largest is at the South Pole of Mars and a small part of it is shown in this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Much like the terrestrial examples, this ice sheet is layered and scientists refer to it as the South Polar layered deposits. The ice layers contain information about past climates on Mars and deciphering this record has been a major goal of Mars science for decades. This slope, near the ice sheet's edge, shows the internal layers that have this climate record. With stereo images, we can tell the heights of these layers so we can measure their thickness and try to unravel the climatic information they contain. (Be sure to view the digital terrain model for this observation.) The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 25.0 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 75 centimeters (29.5 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22125

The tiny black speck in the lower left corner of this image within the red circle is a cluster of recently formed craters spotted on Mars using a new machine-learning algorithm. This image was taken by the Context Camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter in a region called Noctis Fossae, located at latitude -3.213, longitude: 259.415. The medium-angle Context Camera can view hundreds of miles of terrain in low resolution; scientists then scan the image for interesting features and can request another MRO camera, the High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE), to zoom in for a more detailed view. The HiRISE view of the black speck in this image can be seen in PIA24040. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24091
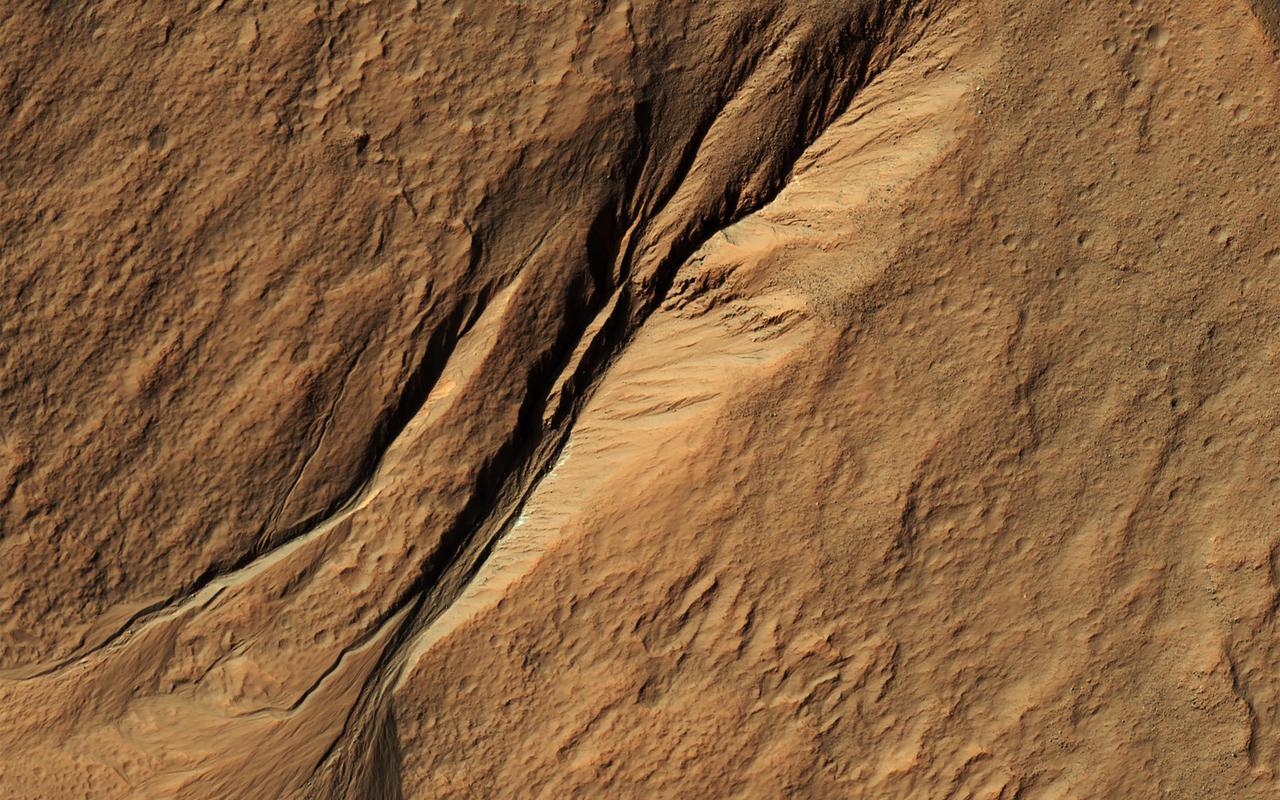

Gullies eroded into the steep inner slope of an impact crater at this location appear perfectly pristine in this image captured by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Although at first glance it may appear that there are craters superimposed on the gully fans, inspection of HiRISE stereo coverage shows that the craters lie only on the pre-gully terrain. Distinctive colors in the gully channels and alcoves offer another indication of youth and recent activity. The pre-gully landscape is covered by secondary craters from nearby Gasa Crater, estimated to be about 1 million years old. Although some have suggested that the Martian gullies are also about a million years old and formed in a different environment, we now know that they are continuing to form today. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21599
![The goal of this observation from NASA' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) is to determine the source of the ridge within a possible moraine that is also present in another HiRISE image. A moraine is a mass of rocks and sediment carried down and deposited by a glacier. If the structure is a moraine, we should expect to find two sources of debris converging in the valley. If the sources are carrying lots of debris, there is a good chance of finding more moraine features further up the valley. The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 59.5 centimeters (23.4 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 179 centimeters (70.5 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22124](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA22124/PIA22124~medium.jpg)
The goal of this observation from NASA' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) is to determine the source of the ridge within a possible moraine that is also present in another HiRISE image. A moraine is a mass of rocks and sediment carried down and deposited by a glacier. If the structure is a moraine, we should expect to find two sources of debris converging in the valley. If the sources are carrying lots of debris, there is a good chance of finding more moraine features further up the valley. The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 59.5 centimeters (23.4 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 179 centimeters (70.5 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22124

NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) keeps finding new impact sites on Mars. This one occurred within the dense secondary crater field of Corinto Crater, to the north-northeast. The new crater and its ejecta have distinctive color patterns. Once the colors have faded in a few decades, this new crater will still be distinctive compared to the secondaries by having a deeper cavity compared to its diameter. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22462

NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) observed sand dunes in the north polar regions of Mars showing light coatings of pale orange dust blown partially across the dark basaltic sand. Around the edges of the dunes, patches of seasonal dry ice remain. These patches will be gone soon as they sublimate (turn from ice to gas) in the summer sun. Some blocks of ice are visible at the foot of an alcove formed by a sand avalanche down the slipface of the dune. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22511
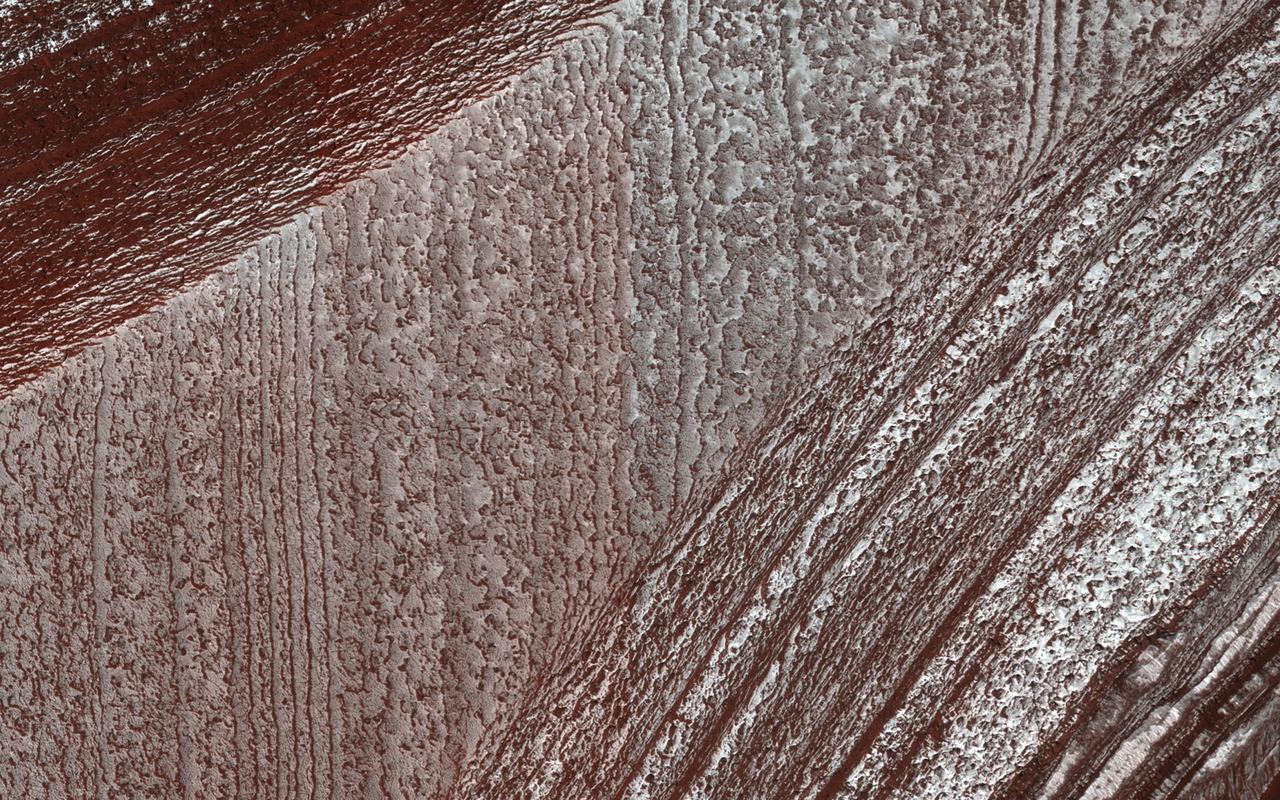
Mars' north polar layered deposits comprise a thick stack of icy layers. Part of this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) has lingering seasonal frost, which serves to accentuate those layers. An additional rationale for this observation is to document new activity in scarp erosion. More information is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22533
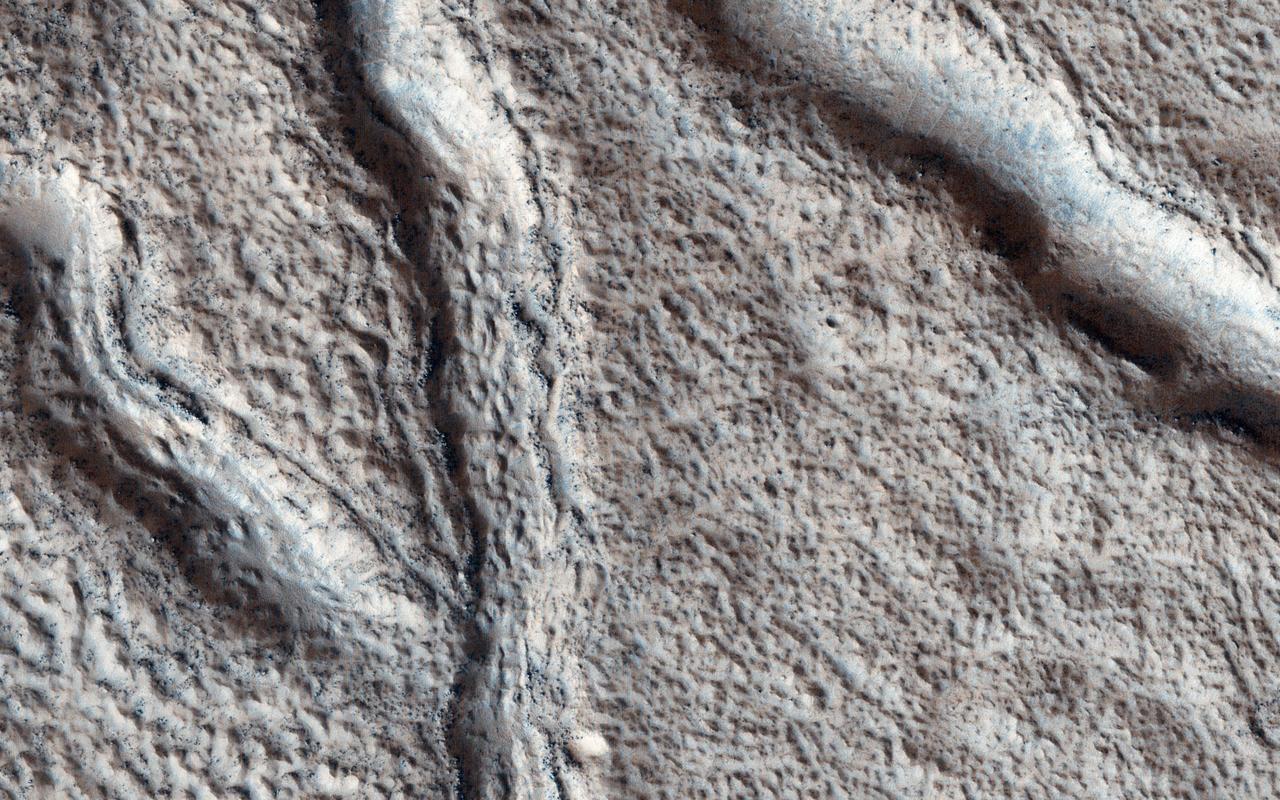

This observation from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows the nature of large fissures in a smooth apron around a mound in the Phlegra region. The apron could be (or could have been) ice-rich, so one possibility is that the fissures are related to ice loss. Based on radar data from MRO combined with studies of the region's geology from other orbiters, scientists think that extensive glaciers covered this region several hundred million years ago. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19307
![This enhanced color image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows what are called "recurring slope lineae"s in Tivat Crater. The narrow, dark flows descend downhill (towards the upper left). Analysis shows that the flows all end at approximately the same slope, which is similar to the angle of repose for sand. RSL are mostly found on steep rocky slopes in dark regions of Mars, such as the southern mid-latitudes, Valles Marineris near the equator, and in Acidalia Planitia on the northern plains. The appearance and growth of these features resemble seeping liquid water, but how they form remains unclear, and this research demonstrated that the RSL flows seen by HiRISE are likely moving granular material like sand and dust. These findings indicate that present-day Mars may not have a significant volume of liquid water. The water-restricted conditions that exist on Mars would make it difficult for Earth-like life to exist near the surface of the planet. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 25.6 centimeters (10.8 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 77 centimeters (30.3 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22114](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA22114/PIA22114~medium.jpg)
This enhanced color image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows what are called "recurring slope lineae"s in Tivat Crater. The narrow, dark flows descend downhill (towards the upper left). Analysis shows that the flows all end at approximately the same slope, which is similar to the angle of repose for sand. RSL are mostly found on steep rocky slopes in dark regions of Mars, such as the southern mid-latitudes, Valles Marineris near the equator, and in Acidalia Planitia on the northern plains. The appearance and growth of these features resemble seeping liquid water, but how they form remains unclear, and this research demonstrated that the RSL flows seen by HiRISE are likely moving granular material like sand and dust. These findings indicate that present-day Mars may not have a significant volume of liquid water. The water-restricted conditions that exist on Mars would make it difficult for Earth-like life to exist near the surface of the planet. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 25.6 centimeters (10.8 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 77 centimeters (30.3 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22114
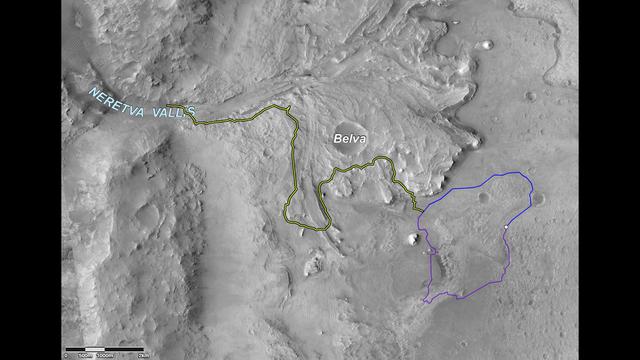
This image shows two possible routes (blue and purple) to the fan-shaped deposit of sediments known as a delta for NASA's Perseverance rover, which landed at the spot marked with a white dot in Mars' Jezero Crater. The yellow line marks a notional traverse exploring the delta. The base image is from the High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE) camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). MRO's mission is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate. Lockheed Martin Space in Denver built the spacecraft. The University of Arizona in Tucson provided and operates HiRISE. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24486
![This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) targets a portion of a group of honeycomb-textured landforms in northwestern Hellas Planitia, which is part of one of the largest and most ancient impact basins on Mars. In a larger Context Camera image, the individual "cells" are about 5 to 10 kilometers wide. With HiRISE, we see much greater detail of these cells, like sand ripples that indicate wind erosion has played some role here. We also see distinctive exposures of bedrock that cut across the floor and wall of the cells. These resemble dykes, which are usually formed by volcanic activity. Additionally, the lack of impact craters suggests that the landscape, along with these features, have been recently reshaped by a process, or number of processes that may even be active today. Scientists have been debating how these honeycombed features are created, theorizing from glacial events, lake formation, volcanic activity, and tectonic activity, to wind erosion. The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 53.8 centimeters (21.2 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 161 centimeters (23.5 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22118](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA22118/PIA22118~medium.jpg)
This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) targets a portion of a group of honeycomb-textured landforms in northwestern Hellas Planitia, which is part of one of the largest and most ancient impact basins on Mars. In a larger Context Camera image, the individual "cells" are about 5 to 10 kilometers wide. With HiRISE, we see much greater detail of these cells, like sand ripples that indicate wind erosion has played some role here. We also see distinctive exposures of bedrock that cut across the floor and wall of the cells. These resemble dykes, which are usually formed by volcanic activity. Additionally, the lack of impact craters suggests that the landscape, along with these features, have been recently reshaped by a process, or number of processes that may even be active today. Scientists have been debating how these honeycombed features are created, theorizing from glacial events, lake formation, volcanic activity, and tectonic activity, to wind erosion. The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 53.8 centimeters (21.2 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 161 centimeters (23.5 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22118
![Lyot Crater (220-kilometers in diameter) is located in the Northern lowlands of Mars. The crater's floor marks the lowest elevation in the Northern Hemisphere as seen in this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). On the crater's floor, we see a network of channels. connecting a series of irregular shaped pits. These resemble terrestrial beaded streams, which are common in the Arctic regions of Earth and develop from uneven permafrost thawing. If terrestrial beaded streams are a good analog, these landforms suggest liquid water flow in the past. If not then these pits may result from the process of sublimation and would indicate pockets of easily accessible near-surface ground ice, which might have potentially preserved evidence of past habitability. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 12.2 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 93 centimeters (36.6 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22186](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA22186/PIA22186~orig.jpg)
Lyot Crater (220-kilometers in diameter) is located in the Northern lowlands of Mars. The crater's floor marks the lowest elevation in the Northern Hemisphere as seen in this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). On the crater's floor, we see a network of channels. connecting a series of irregular shaped pits. These resemble terrestrial beaded streams, which are common in the Arctic regions of Earth and develop from uneven permafrost thawing. If terrestrial beaded streams are a good analog, these landforms suggest liquid water flow in the past. If not then these pits may result from the process of sublimation and would indicate pockets of easily accessible near-surface ground ice, which might have potentially preserved evidence of past habitability. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 12.2 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 93 centimeters (36.6 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22186

NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter captured this image of a meteoroid impact that was later associated with a seismic event detected by the agency's InSight lander using its seismometer. This crater was formed on May 27, 2020. MRO's Context Camera originally located the impact. Then, the spacecraft's High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera captured this scene in color. The ground is not actually blue; this enhanced-color image highlights certain hues in the scene to make details more visible to the human eye – in this case, dust and soil disturbed by the impact. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25410

This observation from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) is an oblique view of gully deposits from the steep slope of an impact crater. The deposits with anomalous (bluish) colors may reveal very recent activity, not yet homogenized by dust deposition, or there may be sand preferentially trapped in some places to give this appearance. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21602
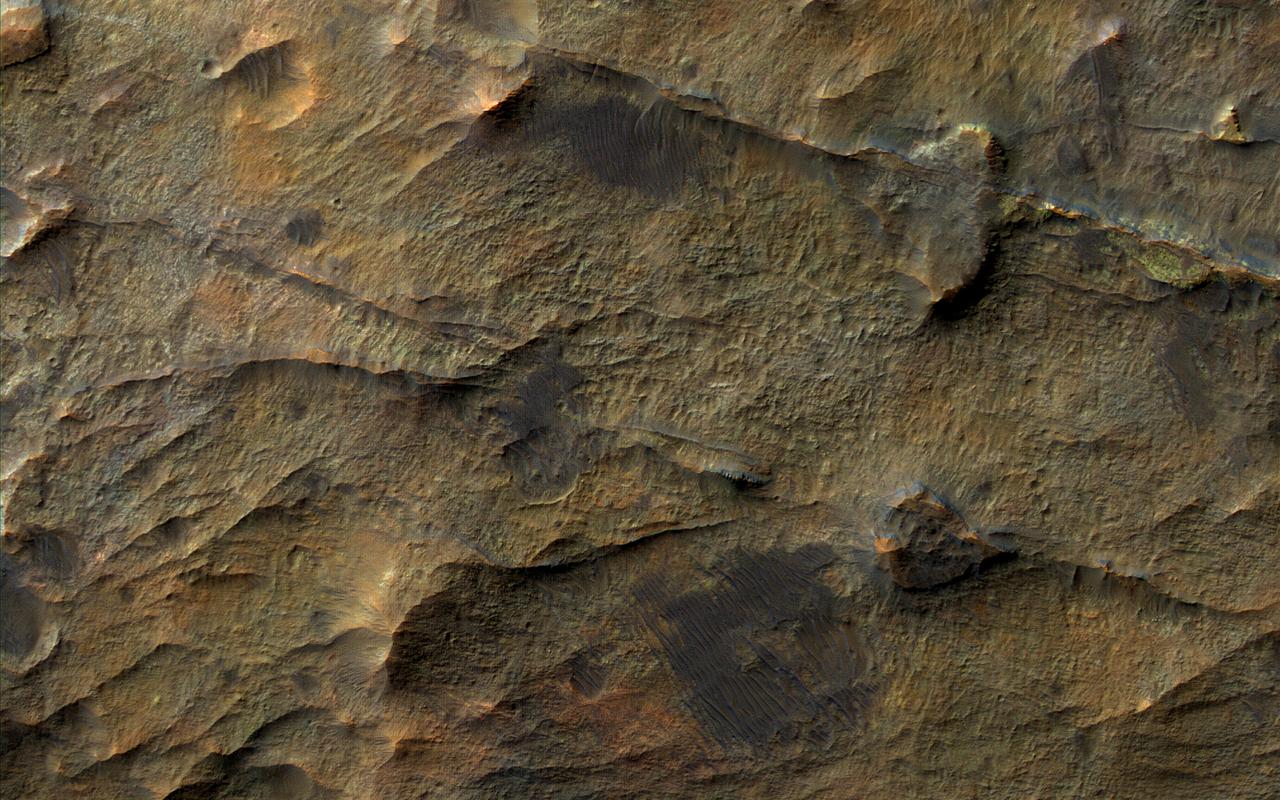

In this observation from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), we see a set of straight ridges in ancient bedrock near Nirgal Valles. The patterns indicate fractures from tectonic stresses, but how have they been hardened to now stand in positive relief after billions of years of erosion? It is possible that groundwater flowed through the fractures, depositing various durable minerals, some of which we see in diverse colors. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22333
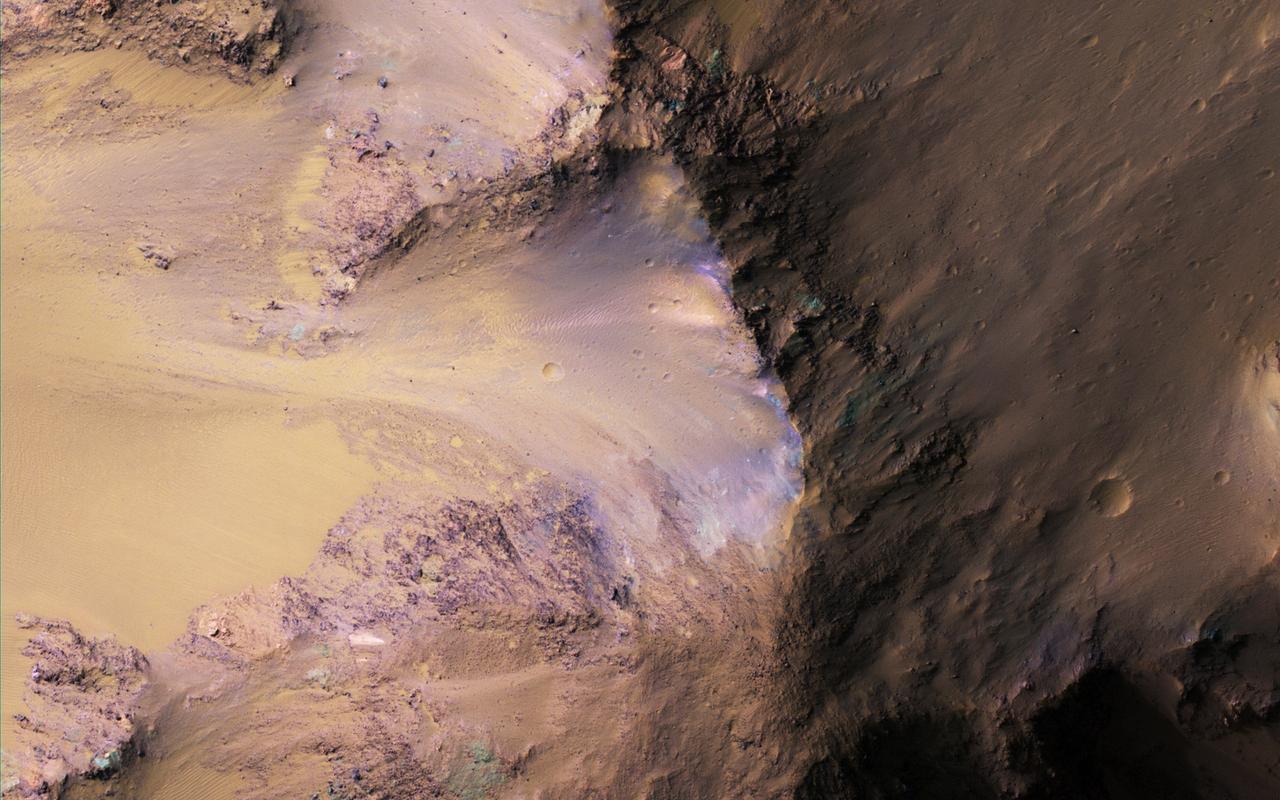
NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) observed this image of Ganges Chasma in the northeast portion of Valles Marineris, and opens into outflow channels that flowed to the north. Scattered hills on the canyon floor may be remnants of chaos terrain that formed from collapse of the canyon. Some of the bedrock has diverse colors. More information is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22536
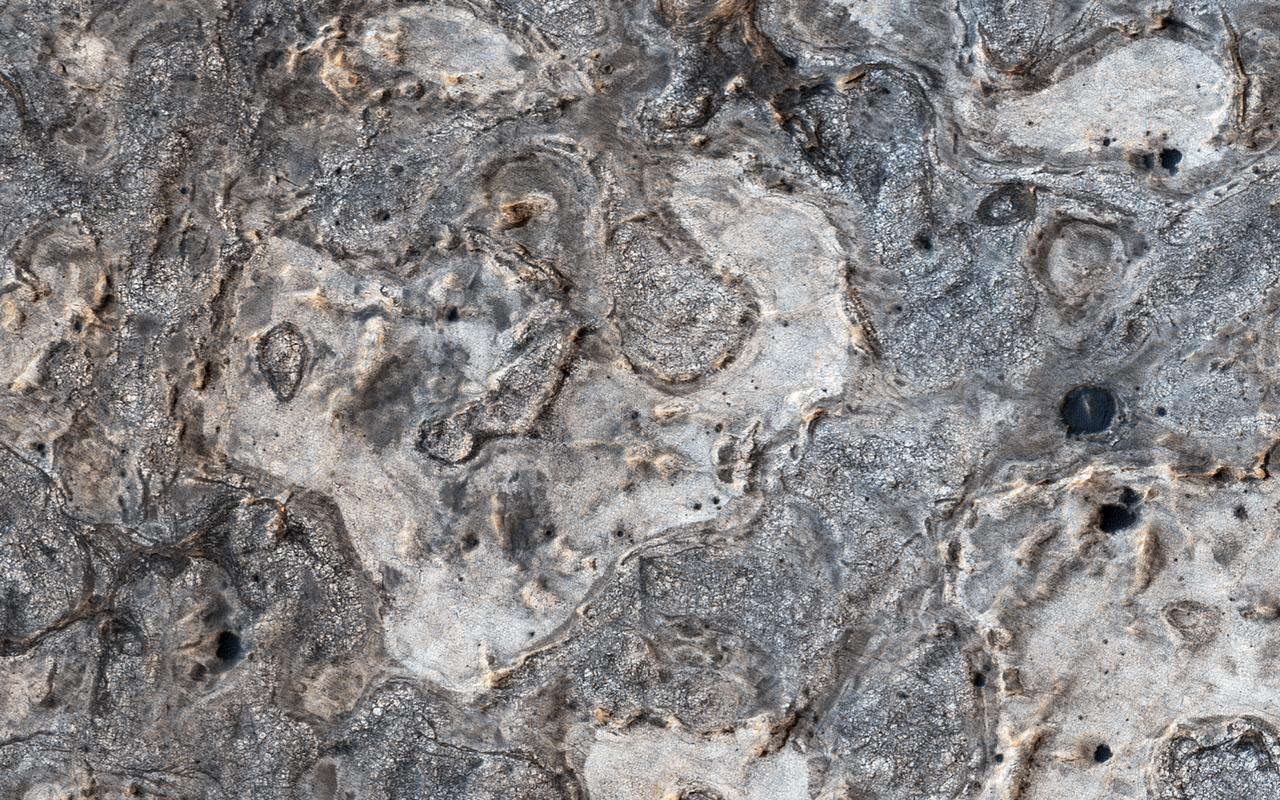

NASA's Opportunity rover has spent 13 years exploring a small region of Meridiani Planum which has a rather ordinary appearance as seen by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Other portions of Meridiani are much more interesting, with well-exposed layered bedrock eroded into strange patterns. For more information see https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22438

Sand dunes often accumulate in the floors of craters. In this region of Lyot Crater NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows a field of classic barchan dunes. Just to the south of the group of barchan dunes is one large dune with a more complex structure. This particular dune, appearing like turquoise blue in enhanced color, is made of finer material and/or has a different composition than the surrounding. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22512
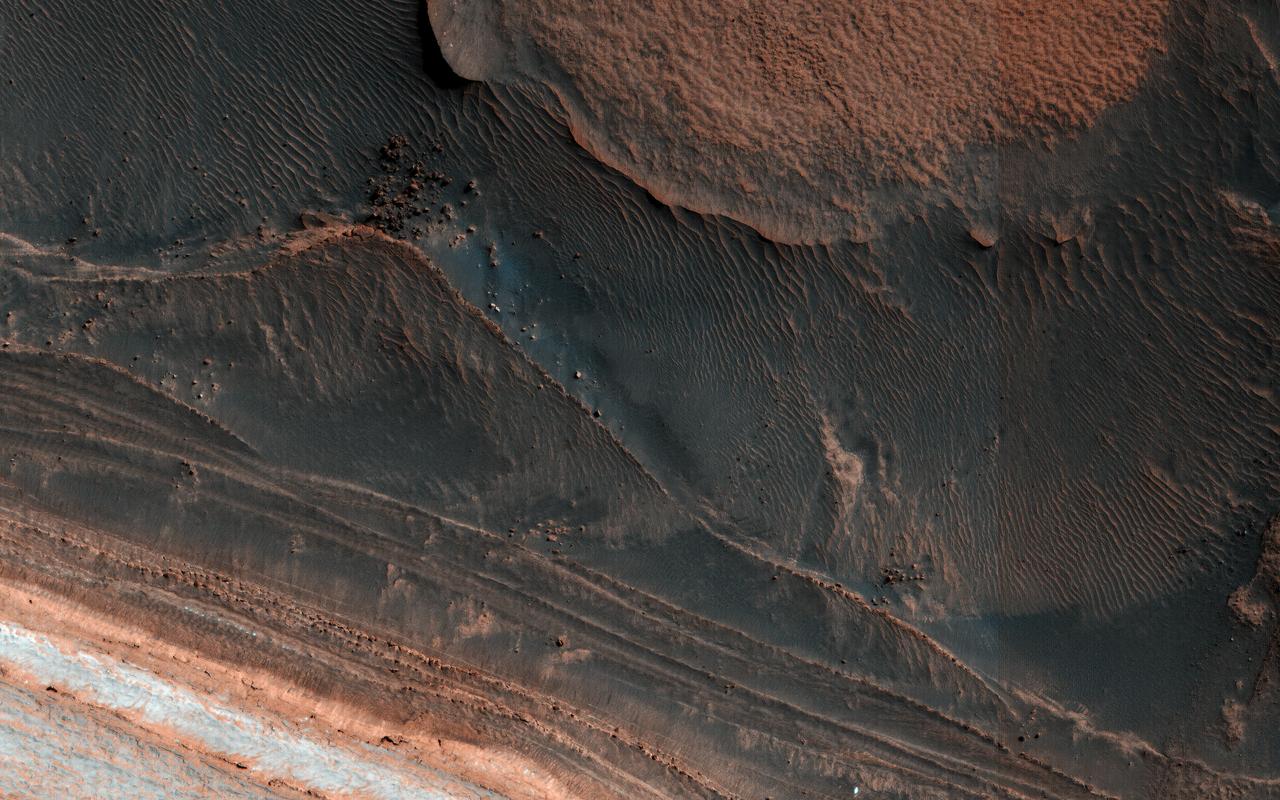

One of the most actively changing areas on Mars are the steep edges of the North Polar layered deposits. This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows many new ice blocks compared to an earlier image in December 2006. An animation shows one example, where a section of ice cliff collapsed. The older image (acquired in bin-2 mode) is not as sharp as the newer one. HiRISE has been re-imaging regions first photographed in 2006 through 2007, six Mars years ago. This long baseline allows us to see large, rare changes as well as many smaller changes. More information is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22535
![This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows the eastern rim of a small 3.5-kilometer crater which appears to have collapsed into a much larger crater (about 14-kilometers wide). The larger crater has a large ice flow around its central peak, and is non-circular, with large blocks further suggesting structural collapse of the terrain due to what are called periglacial processes. Understanding the composition of this small crater may inform us of the ice content of the surrounding terrain. The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 50.8 centimeters (20 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 152 centimeters (59.8 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22116](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA22116/PIA22116~medium.jpg)
This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows the eastern rim of a small 3.5-kilometer crater which appears to have collapsed into a much larger crater (about 14-kilometers wide). The larger crater has a large ice flow around its central peak, and is non-circular, with large blocks further suggesting structural collapse of the terrain due to what are called periglacial processes. Understanding the composition of this small crater may inform us of the ice content of the surrounding terrain. The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 50.8 centimeters (20 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 152 centimeters (59.8 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22116
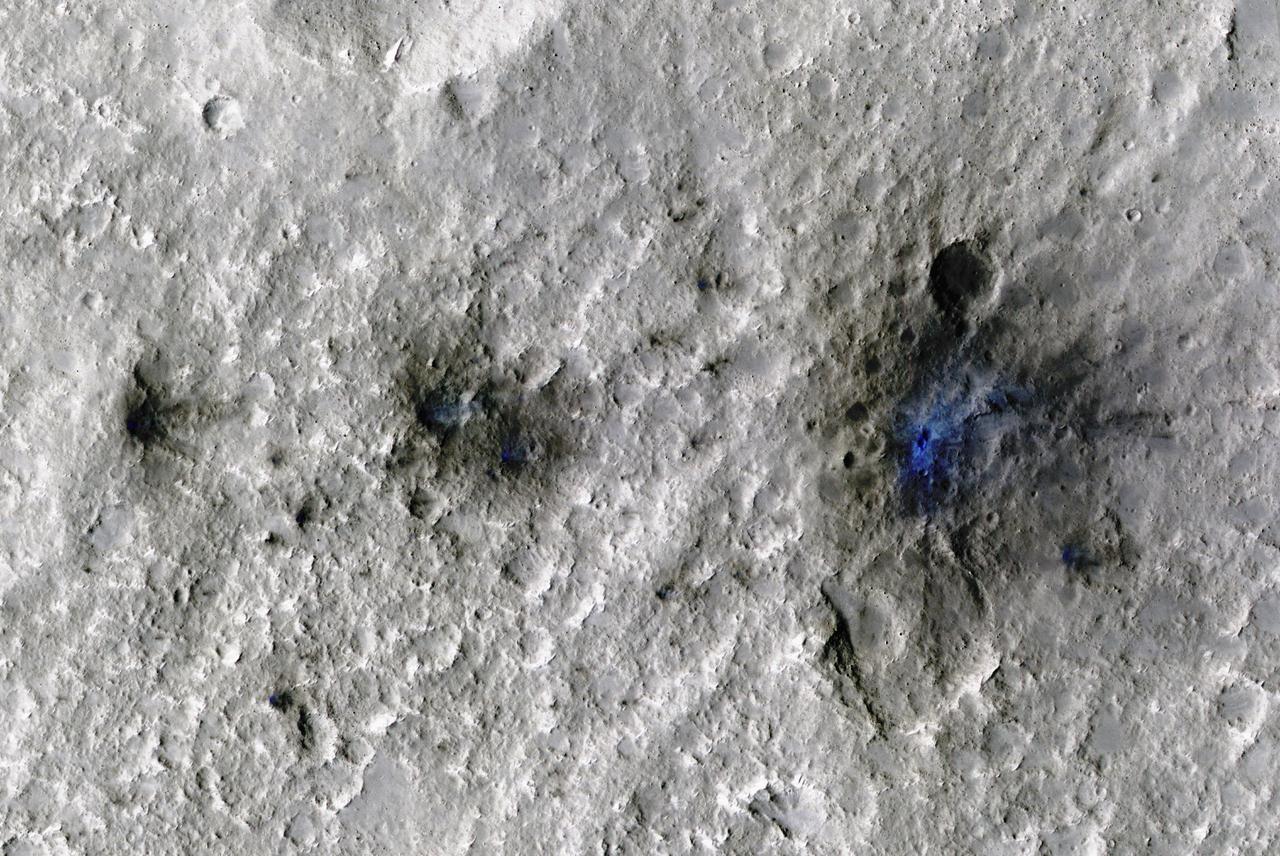

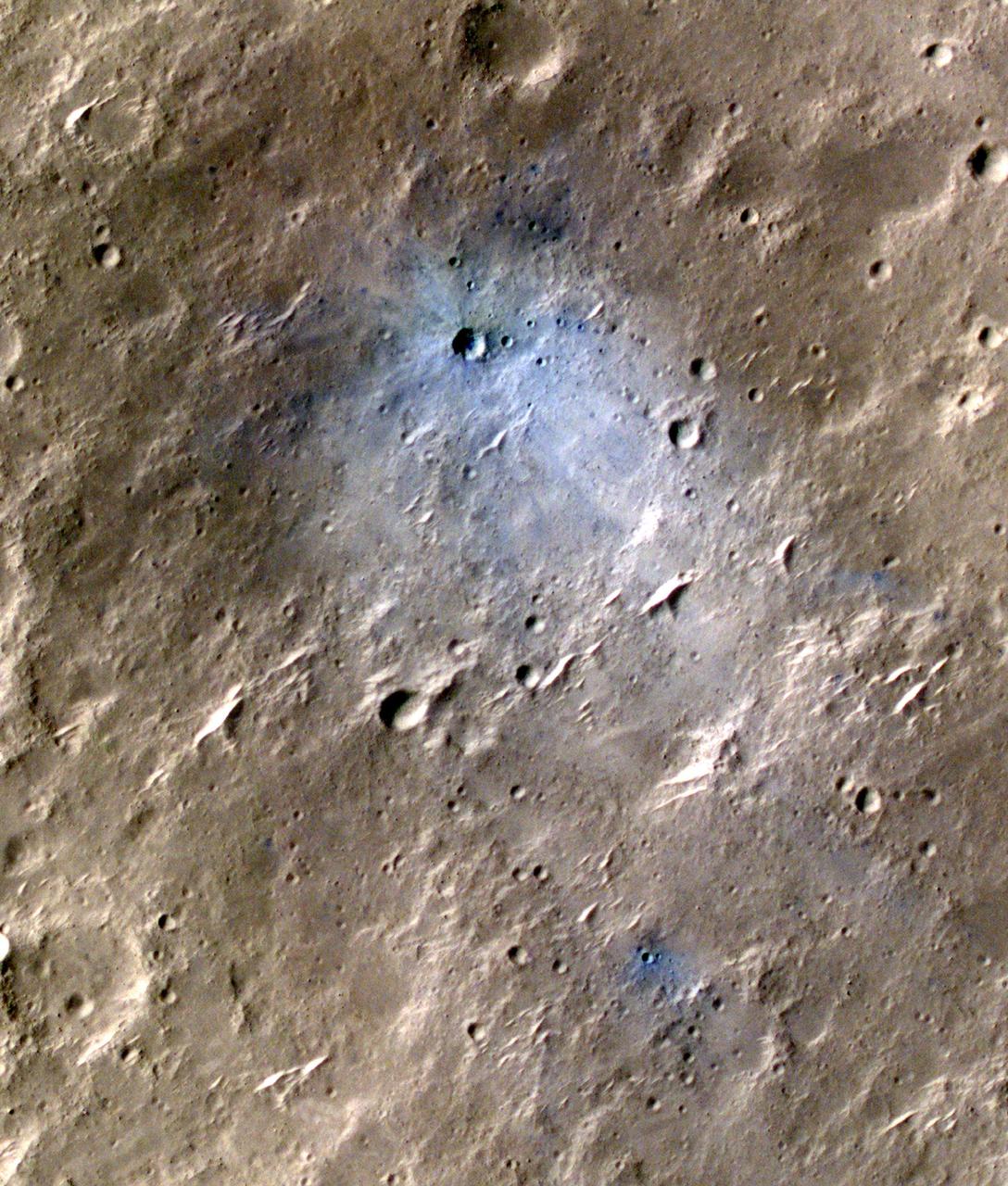
The craters seen here in blue were formed by a meteoroid impact on Mars on Sept. 5, 2021. The impact was the first to be detected by NASA's InSight mission; the image was taken later by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter using its High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera. The initial impact itself created a small marsquake that was detected by InSight's seismometer. The instrument recorded seismological data that showed the moment the meteoroid entered Mars' atmosphere, its explosion into pieces in the atmosphere, and finally, the impact that created a series of at least three craters in the surface. MRO then flew over the approximate site where the impact was "felt" to look for darkened patches of ground using its Context Camera. After finding this location, HiRISE captured the scene in color. The ground is not actually blue; this enhanced-color image highlights certain hues in the scene to make details more visible to the human eye – in this case, dust and soil disturbed by the impact. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25408
![The prominent tear-shaped features in this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) are erosional features called yardangs. Yardangs are composed of sand grains that have clumped together and have become more resistant to erosion than their surrounding materials. As the winds of Mars blow and erode away at the landscape, the more cohesive rock is left behind as a standing feature. (This Context Camera image shows several examples of yardangs that overlie the darker iron-rich material that makes up the lava plains in the southern portion of Elysium Planitia.) Resistant as they may be, the yardangs are not permanent, and will eventually be eroded away by the persistence of the Martian winds. For scientists observing the Red Planet, yardangs serve as a useful indicator of regional prevailing wind direction. The sandy structures are slowly eroded down and carved into elongated shapes that point in the downwind direction, like giant weathervanes. In this instance, the yardangs are all aligned, pointing towards north-northwest. This shows that the winds in this area generally gust in that direction. The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 55.8 centimeters (21 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 167 centimeters (65.7 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22119](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA22119/PIA22119~medium.jpg)
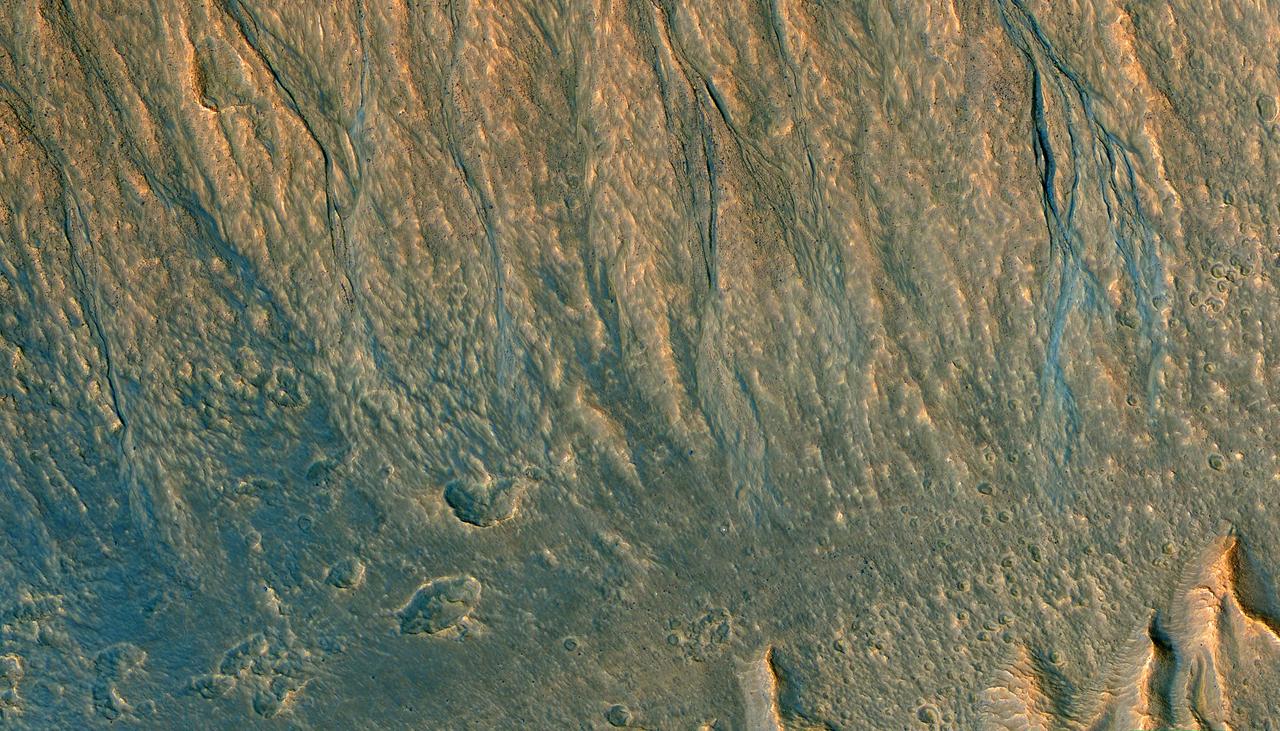
The prominent tear-shaped features in this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) are erosional features called yardangs. Yardangs are composed of sand grains that have clumped together and have become more resistant to erosion than their surrounding materials. As the winds of Mars blow and erode away at the landscape, the more cohesive rock is left behind as a standing feature. (This Context Camera image shows several examples of yardangs that overlie the darker iron-rich material that makes up the lava plains in the southern portion of Elysium Planitia.) Resistant as they may be, the yardangs are not permanent, and will eventually be eroded away by the persistence of the Martian winds. For scientists observing the Red Planet, yardangs serve as a useful indicator of regional prevailing wind direction. The sandy structures are slowly eroded down and carved into elongated shapes that point in the downwind direction, like giant weathervanes. In this instance, the yardangs are all aligned, pointing towards north-northwest. This shows that the winds in this area generally gust in that direction. The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 55.8 centimeters (21 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 167 centimeters (65.7 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22119

NASA has named the landing site of the agency's Perseverance rover "Octavia E. Butler Landing," after the science fiction author Octavia E. Butler. The landing location is marked with a star in this image from the High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE) camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). MRO's mission is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate. Lockheed Martin Space in Denver built the spacecraft. The University of Arizona in Tucson provided and operates HiRISE. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24483

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows two small impact craters located in Meridiani Planum. This is an example of the geologic principle of superposition: figuring out what happened first by looking at how features interact with each other. We can see that one of the craters must have hit the surface after the other was already there, but which came first? We can see that the ejecta blankets look rougher on the right side of the image than they do on the left. This could mean that the right side ejecta is newer, and has not been exposed to the wind as much as the left side has. Zooming in, we see small boulders on the floor and walls of the left-side crater, and they even seem to match the rough material in the ejecta on the right. With these clues, we can hypothesize that the crater on the left was here first. After some time another asteroid hit, formed the crater on the right, which threw material onto the floor of the left, where it remains to this day. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22454
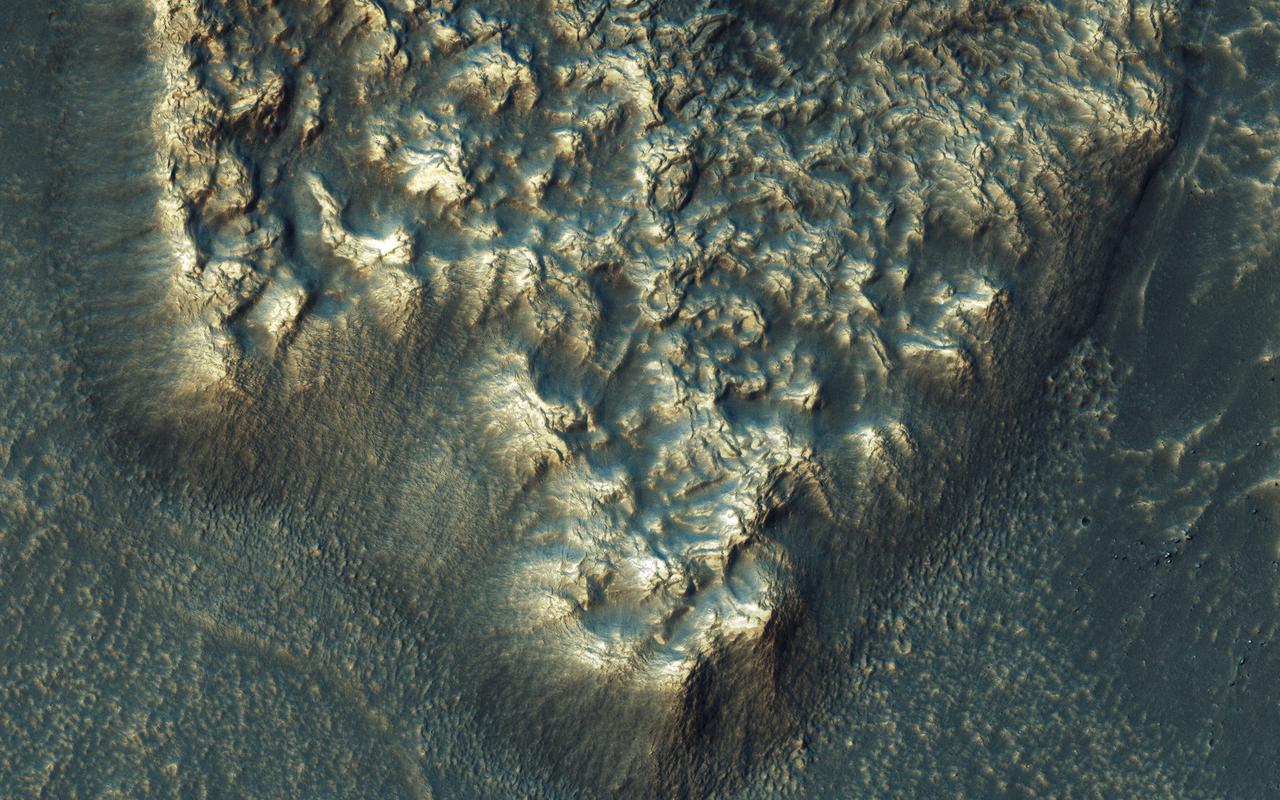

NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter observes many slopes in the middle latitudes of Mars showing icy flows or glaciers. The region shown here, in the south-facing slope of a crater, is unusual because the flows have bright highlights. The color and brightness variations are likely due to surface coatings of bright dust and dark sand. There is no evidence that these flows are currently active, but they may have been active only millions of years ago. These flows may well contain ice today in their interiors, as confirmed in places by the subsurface radar experiment on MRO. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21953

Shown in this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) are alluvial fans, fan-shaped deposits emerging from regions of steep topography. Alluvial fans on Mars are thought to be ancient and record past episodes of flowing water. This image shows part of one of those fans, which has been eroded. The old stream channels now stand above the rest of the fan as ridges, mostly in the southern (bottom) part of the image. This can occur because the channel materials are more resistant to erosion; perhaps they had larger grains (gravel) or because minerals deposited from the water cemented together. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22332
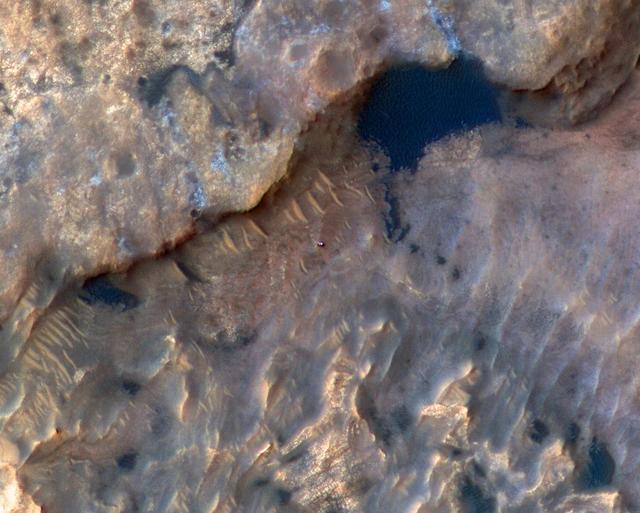

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover can be seen in this image taken from space on May 31, 2019, by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera aboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). In the image, Curiosity appears as a bluish speck. The image shows Curiosity at a location called "Woodland Bay." It's just one of many stops the rover has made in an area referred to as the "clay-bearing unit" on the side of Mount Sharp, a 3-mile-tall (5-kilometer-tall) mountain inside of Gale Crater. Look carefully, and you can make out what it is likely Curiosity's "head," technically known as the remote sensing mast. A bright spot appears in the upper-left corner of the rover. At the time this image was acquired, the rover was facing 65 degrees counterclockwise from north, which would put the mast in about the right location to produce this bright spot. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23341
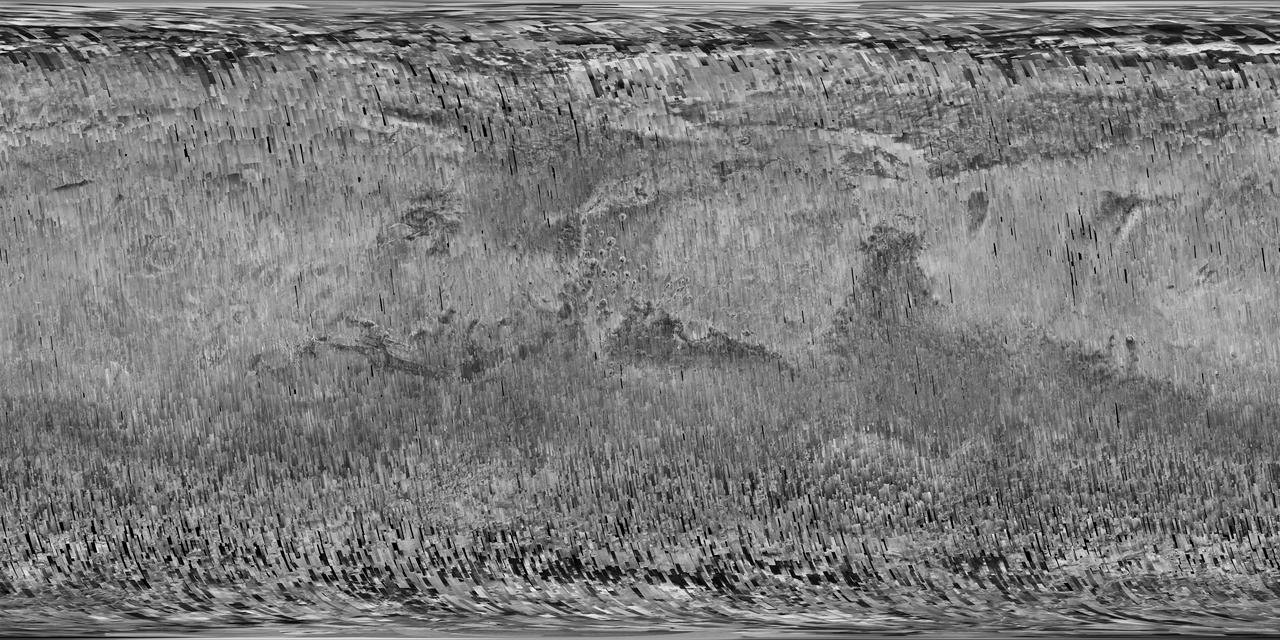
In early 2017, after more than a decade of observing Mars, the Context Camera (CTX) on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) surpassed 99 percent coverage of the entire planet. This mosaic shows that global coverage. No other camera has ever imaged so much of Mars in such high resolution. The mosaic offers a resolution that enables zooming in for more detail of any region of Mars. It is still far from the full resolution of individual CTX observations, which can reveal the shapes of features smaller than the size of a tennis court. As of March 2017, the Context Camera has taken about 90,000 images since the spacecraft began examining Mars from orbit in late 2006. In addition to covering 99.1 percent of the surface of Mars at least once, this camera has observed more than 60 percent of Mars more than once, checking for changes over time and providing stereo pairs for 3-D modeling of the surface. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21488
![This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) captures details of an approximately 1-kilometer inverted crater west of Mawrth Vallis. A Context Camera image provides context for the erosional features observed at this site. The location of this HiRISE image is north of the proposed landing ellipse for the ExoMars 2020 rover mission that will investigate diverse rocks and minerals related to ancient water-related activity in this region. Prolonged erosion removed less resistant rocks leaving behind other rocks that stand up locally such as the crater seen here and other nearby remnants. These resistant layers may belong to a phase of volcanism and/or water-related activity that carved Mawrth Vallis and filled in existing craters, and other lower-lying depressions, with darker materials. Erosion has also exposed these layers down to older, more resistant lighter rocks that are clay-bearing. The diversity of exposed bedrock made this location an ideal candidate for exploring a potentially water-rich ancient environment that might have once harbored life. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 28.7 centimeters (11.3 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 86 centimeters (33.9 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22117](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA22117/PIA22117~medium.jpg)
This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) captures details of an approximately 1-kilometer inverted crater west of Mawrth Vallis. A Context Camera image provides context for the erosional features observed at this site. The location of this HiRISE image is north of the proposed landing ellipse for the ExoMars 2020 rover mission that will investigate diverse rocks and minerals related to ancient water-related activity in this region. Prolonged erosion removed less resistant rocks leaving behind other rocks that stand up locally such as the crater seen here and other nearby remnants. These resistant layers may belong to a phase of volcanism and/or water-related activity that carved Mawrth Vallis and filled in existing craters, and other lower-lying depressions, with darker materials. Erosion has also exposed these layers down to older, more resistant lighter rocks that are clay-bearing. The diversity of exposed bedrock made this location an ideal candidate for exploring a potentially water-rich ancient environment that might have once harbored life. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 28.7 centimeters (11.3 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 86 centimeters (33.9 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22117

Although large gullies (ravines) are concentrated at higher latitudes, there are gullies on steep slopes in equatorial regions, as seen in this image captured by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The colors of the gully deposits match the colors of the eroded source materials. Krupac is a relatively young impact crater, but exposes ancient bedrock. Krupac Crater also hosts some of the most impressive recurring slope lineae (RSL) on equatorial Mars outside of Valles Marineris. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21605
The High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE) camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) was able to capture this image of the final location of the descent stage that helped fly NASA's Perseverance rover down to the surface of Mars. The image was taken on Feb. 19, 2021. It is a close-up version of a larger image showing several parts of the Mars 2020 mission landing system that got the rover safely on the ground. These close-ups of Mars 2020 hardware were processed to make them easier to see. The insets showing the descent stage and parachute have had color added and include data from the infrared band of light. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24335
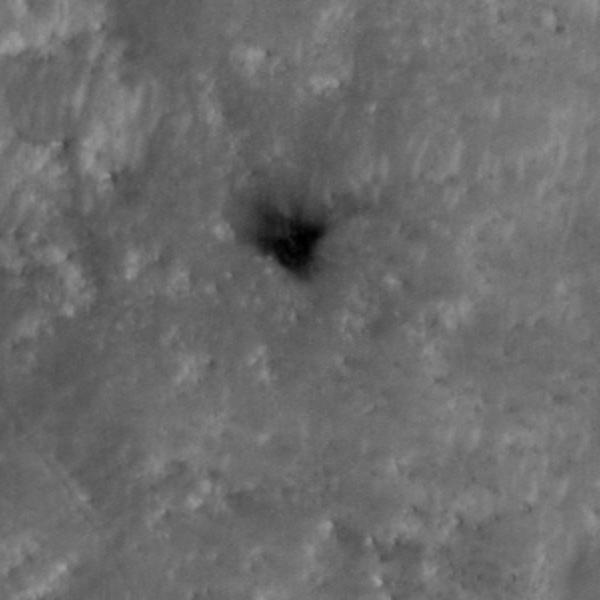

The High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE) camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) was able to capture this image of the final location of the heat shield that helped protect NASA's Perseverance rover during its landing on the surface of Mars. The image was taken on Feb. 19, 2021. It is a close-up version of a larger image showing several parts of the Mars 2020 mission landing system that got the rover safely on the ground. These close-ups of Mars 2020 hardware were processed to make them easier to see. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24337
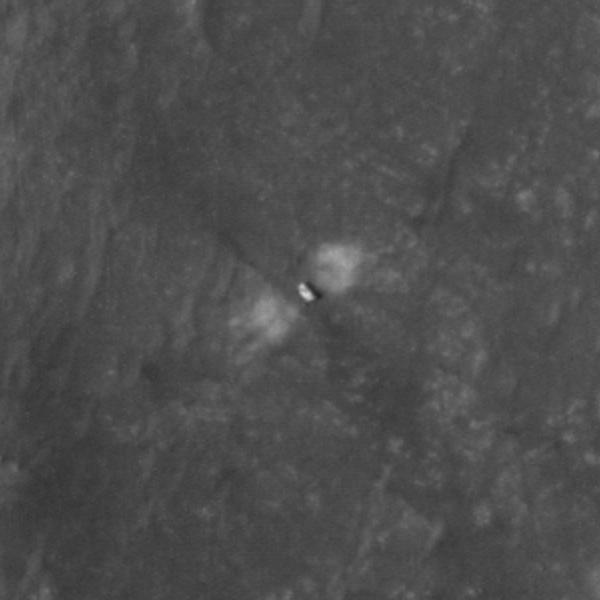

The High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE) camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) was able to capture this image of NASA's Perseverance rover on the surface of Mars. The image was taken on Feb. 19, 2021. It is a close-up version of a larger image showing several parts of the Mars 2020 mission landing system that got the rover safely on the ground. These close-ups of Mars 2020 hardware were processed to make them easier to see. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24334
The High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE) camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) was able to capture this image of the final location of the parachute that helped slow down NASA's Perseverance rover during its landing on the surface of Mars. It is a close-up version of a larger image showing several parts of the Mars 2020 mission landing system that got the rover safely on the ground. The image was taken on Feb. 19, 2021. These close-ups were processed to make them easier to see. The insets showing the descent stage and parachute have had color added and include data from the infrared band of light. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24336
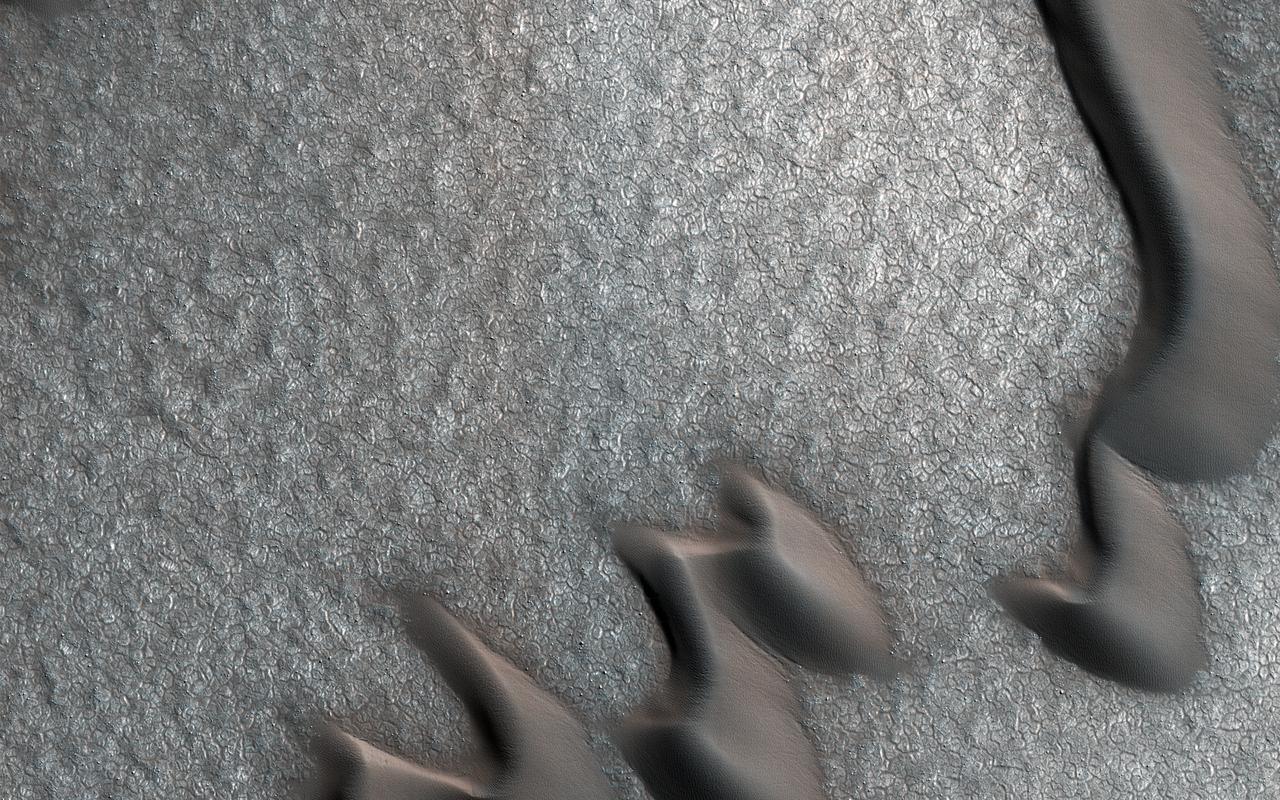

This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) was originally meant to track the movement of sand dunes near the North Pole of Mars, but what's on the ground in between the dunes is just as interesting! The ground has parallel dark and light stripes from upper left to lower right in this area. In the dark stripes, we see piles of boulders at regular intervals. What organized these boulders into neatly-spaced piles? In the Arctic back on Earth, rocks can be organized by a process called "frost heave." With frost heave, repeatedly freezing and thawing of the ground can bring rocks to the surface and organize them into piles, stripes, or even circles. On Earth, one of these temperature cycles takes a year, but on Mars it might be connected to changes in the planet's orbit around the Sun that take much longer. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22334
![This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows blocks of layered terrain within the Olympus Mons aureole. The aureole is a giant apron of chaotic material around the volcano, perhaps formed by enormous landslides off the flanks of the giant volcano. These blocks of layered material have been eroded by the wind into the scenic landscape we see here. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 28.3 centimeters (11.1 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 85 centimeters (33.5 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22181](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA22181/PIA22181~medium.jpg)
This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows blocks of layered terrain within the Olympus Mons aureole. The aureole is a giant apron of chaotic material around the volcano, perhaps formed by enormous landslides off the flanks of the giant volcano. These blocks of layered material have been eroded by the wind into the scenic landscape we see here. The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 28.3 centimeters (11.1 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 85 centimeters (33.5 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22181
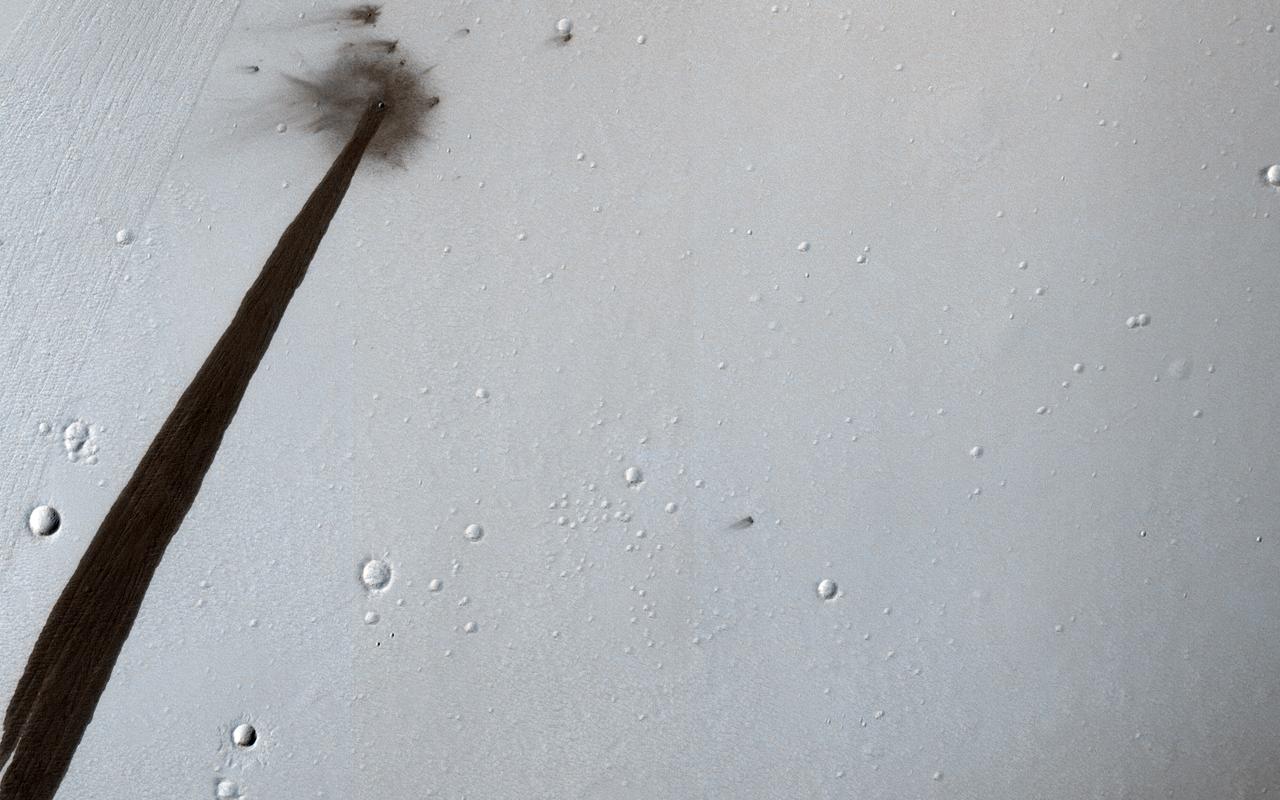

This HiRISE image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) captures a new, dated (within about a decade) impact crater that triggered a slope streak. When the meteoroid hit the surface and exploded to make the crater, it also destabilized the slope and initiated this avalanche. The crater itself is only 5 meters across, but the streak it started is 1 kilometer long! Slope streaks are created when dry dust avalanches leave behind dark swaths on dusty Martian hills. The faded scar of an old avalanche is also visible to the side of the new dark streak. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22513
![This image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows a new impact site originally detected by the Context Camera onboard MRO. The crater is on a dusty slope, which also has several dark slope streaks due to dust avalanches. A previous impact at another place on Mars triggered a major dust avalanche, but this one did not. This tells us that the dust here is more stable (stronger and/or on a lower slope). The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 27.1 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 81 centimeters (30 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21459](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA21459/PIA21459~medium.jpg)
This image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows a new impact site originally detected by the Context Camera onboard MRO. The crater is on a dusty slope, which also has several dark slope streaks due to dust avalanches. A previous impact at another place on Mars triggered a major dust avalanche, but this one did not. This tells us that the dust here is more stable (stronger and/or on a lower slope). The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 27.1 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel (with 1 x 1 binning); objects on the order of 81 centimeters (30 inches) across are resolved.] North is up. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21459
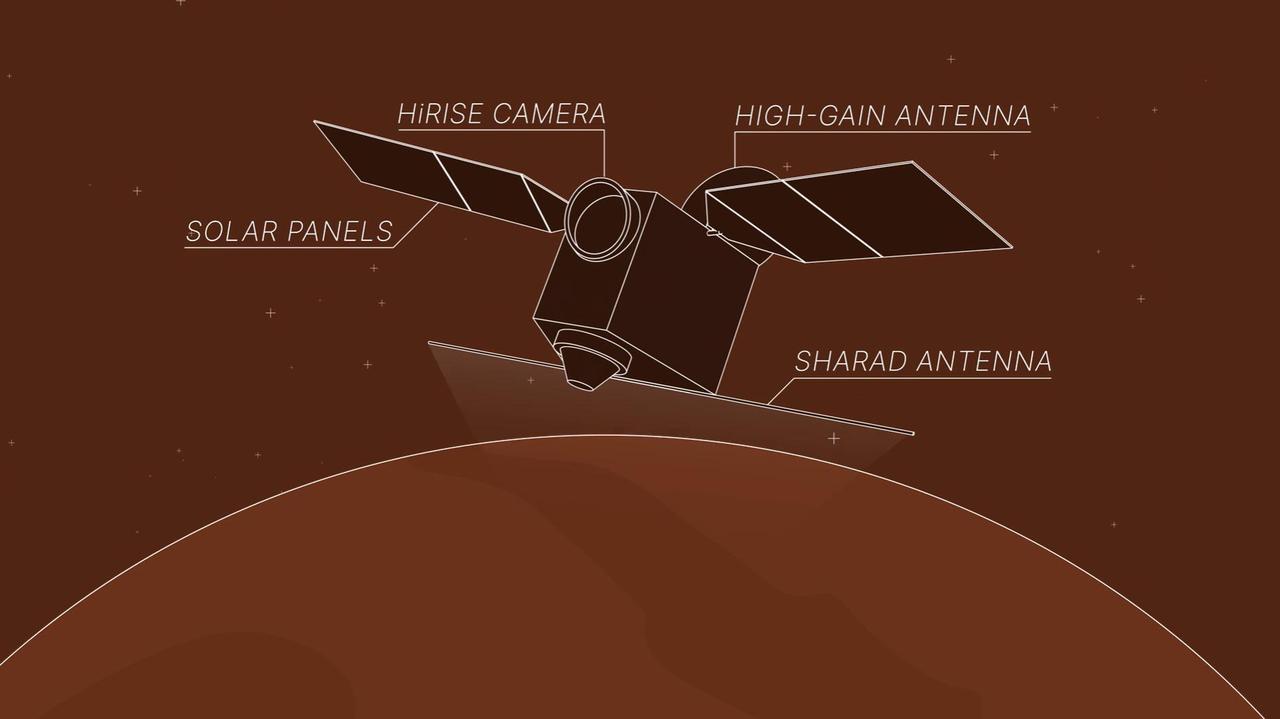
This animation depicts NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) performing what's called a "very large roll": a 120-degree roll that can increase the capabilities of the spacecraft's subsurface radar instrument, called Shallow Radar, or SHARAD. Very large rolls boost SHARAD's signal by 10 times or more, giving scientists a clearer and deeper look below the Martian surface than MRO has ever had before. The orbiter was designed to roll up to 30 degrees in any direction so that it can point its instruments at surface targets. These standard rolls give cameras like the High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) prime viewing at the front of MRO at the expense of SHARAD, which has an antenna mounted at the back of the orbiter. While this setup helps the cameras, it also means that radio signals SHARAD pings onto the surface below encounter parts of the spacecraft, interfering with the signals and resulting in images that are less clear. In 2023, the team decided to try developing 120-degree rolls – the very large rolls – that rotate SHARAD's antenna toward the planet and provide the radio waves an unobstructed path to the surface. That lets the radar's signals reach deeper and get a clearer picture of rocks, sand, and geologic layers underground. It also helps SHARAD look for water ice in the near-subsurface that could be accessed by astronauts to produce rocket propellant for the trip home and is important for learning more about the climate, geology, and potential for life at Mars. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26478