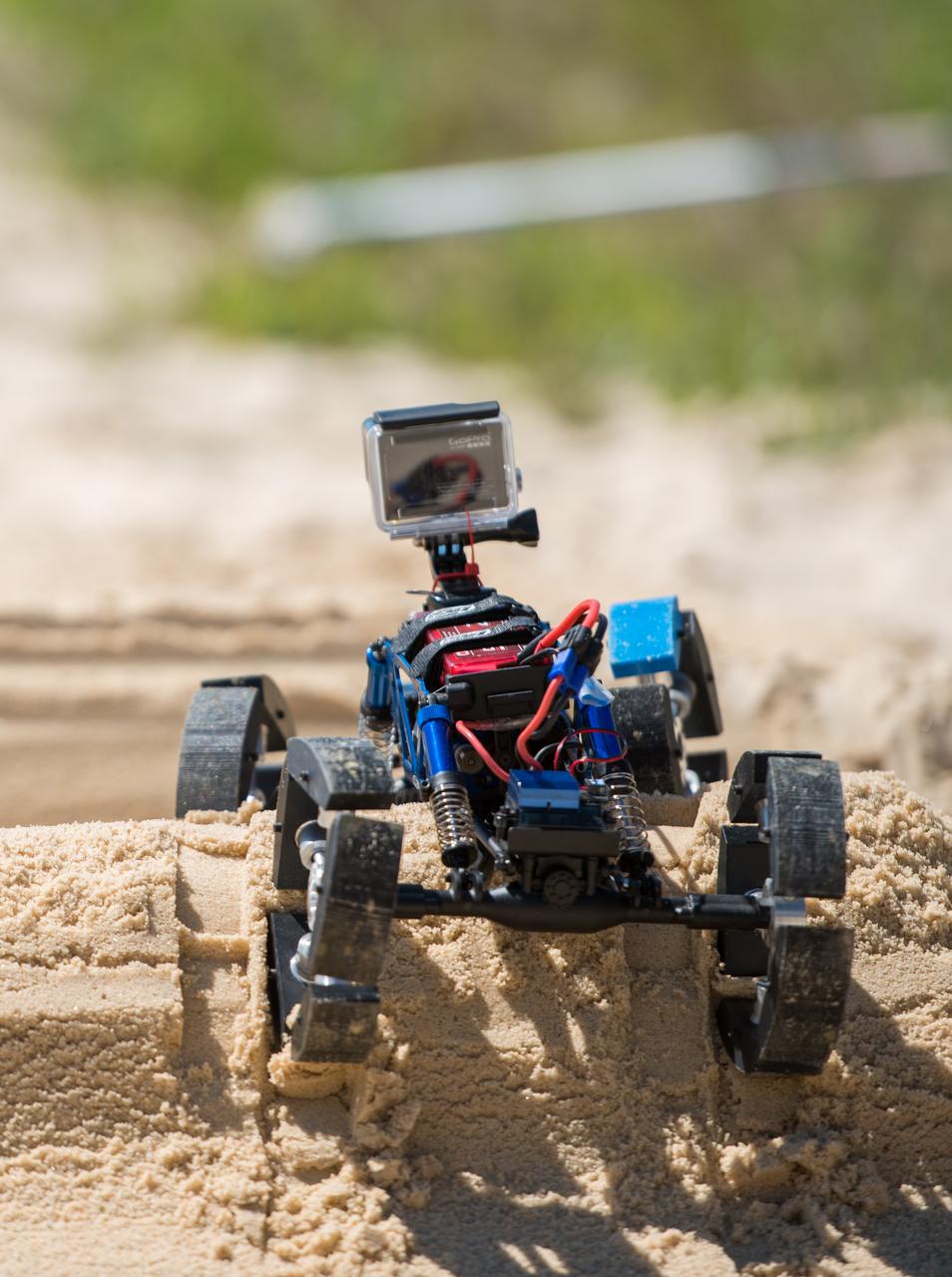

Toledo, Bowser and Scott High School Students, Mars and Moon Wheel, Engineering Design Project, Hardware Test on the Dunes
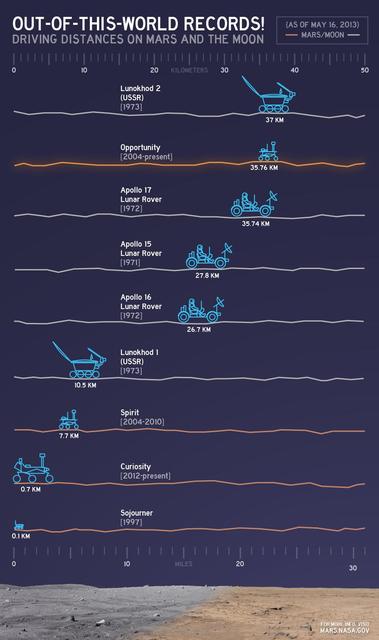
This chart illustrates comparisons among the distances driven by various wheeled vehicles on the surface of Earth moon and Mars. Of the vehicles shown, the NASA Mars rovers Opportunity and Curiosity are still active.

These sets of animated GIFs show seven views of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover wiggling its wheels on March 4, 2021, the day Perseverance completed its first drive on Mars. The first three sets of GIFs come from the Navigation Cameras (Navcams). The first view shows the front left wheel; the second the front right wheel; the third the rear right wheel. The next four sets come from the Hazard Avoidance Cameras (Hazcams). The fourth GIF shows the front left wheel again; the fifth the front right wheel again; the sixth the rear left wheel; and the seventh the rear right wheel again. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animations available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24489

Sophia Bogat from NASA Headquarters talks about the various wheels used on Mars rovers during the Mars celebration Saturday, June 1, 2019, in Mars, Pennsylvania. NASA is in the small town to celebrate Mars exploration and share the agency’s excitement about landing astronauts on the Moon in five years. The celebration includes a weekend of Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts and Mathematics (STEAM) activities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
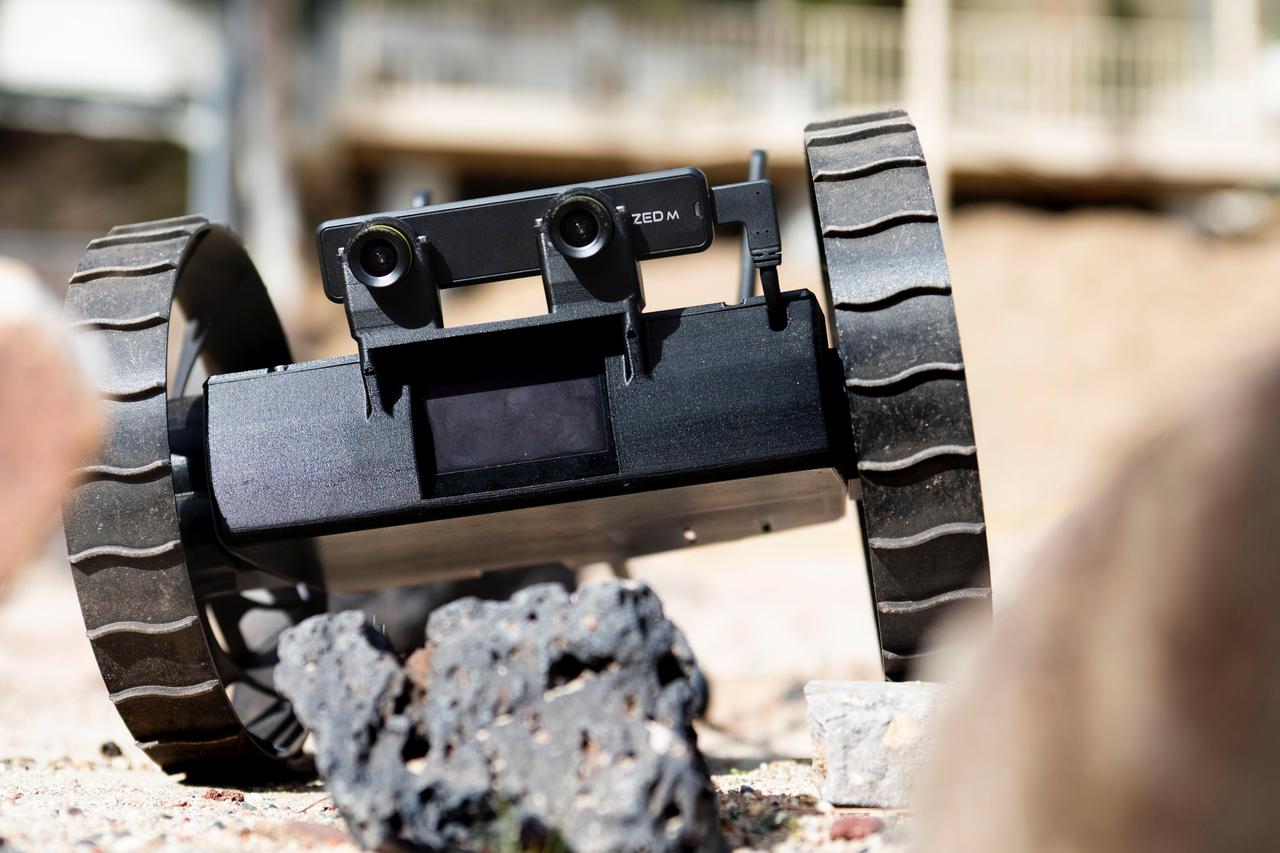

A shoebox-sized wheeled robot explores the rugged terrain on the surface of the Mars Yard at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory during recent tests of the Autonomous Pop-Up Flat Folding Explorer Robot (A-PUFFER) project. The robots are designed to work in groups, and could form roving teams of small robots that might one day explore the surface of the Moon or Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23793
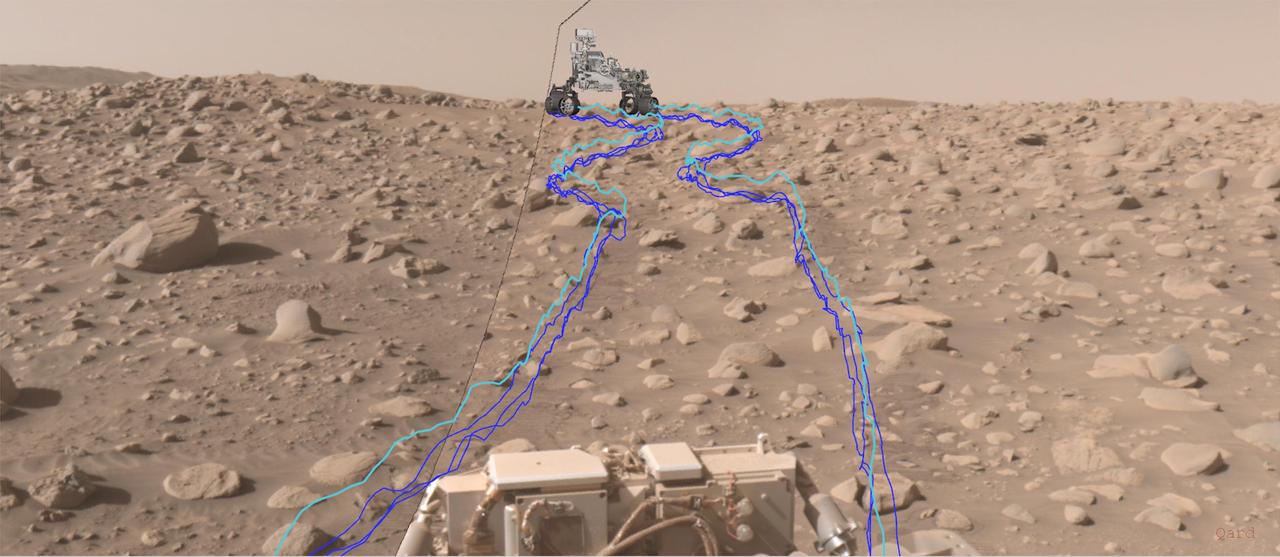
This annotated composite image shows the path NASA's Perseverance Mars rover took through a dense section of boulders. It was acquired on June 29, 2023, the 838th day, or sol, of the mission, by one of the rover's navigation cameras and was annotated using the Robot Sequencing and Visualization Program. The pale blue line indicates the course of the center of the rover's front wheel hubs, while the darker blue lines show the paths taken by the bottom of the rover's six wheels. With the help of its self-driving autonomous navigation system, AutoNav, Perseverance traversed the boulder field much more quickly than previous rovers could have. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26071
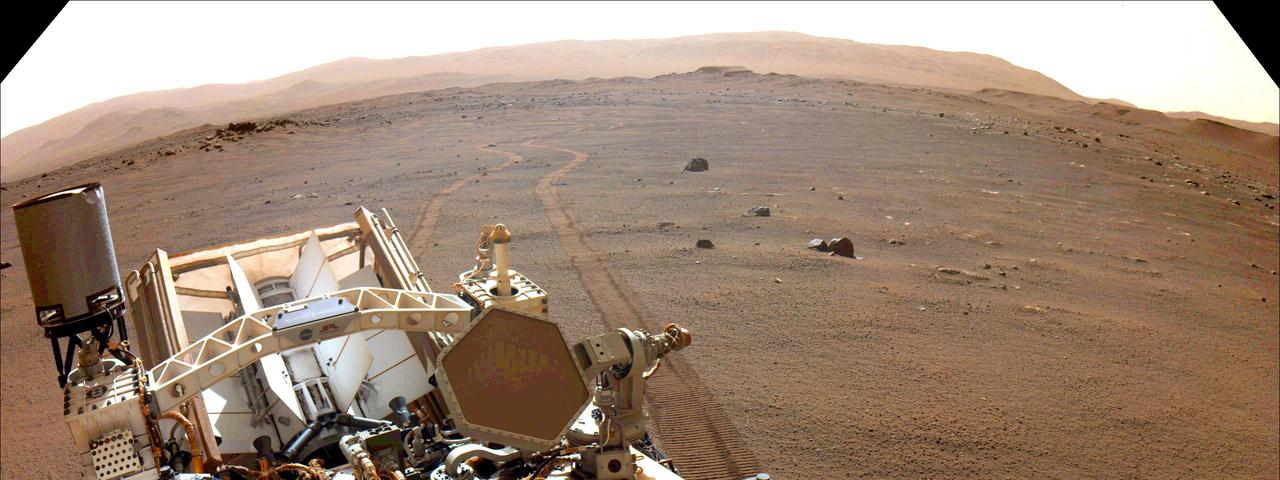
NASA's Perseverance Mars rover looks back at its wheel tracks on March 17, 2022, the 381st Martian day, or sol, of the mission. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25171

NASA's Perseverance rover wiggles one of its wheels in this set of images obtained by the rover's left Navigation Camera on March 4, 2021. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24340
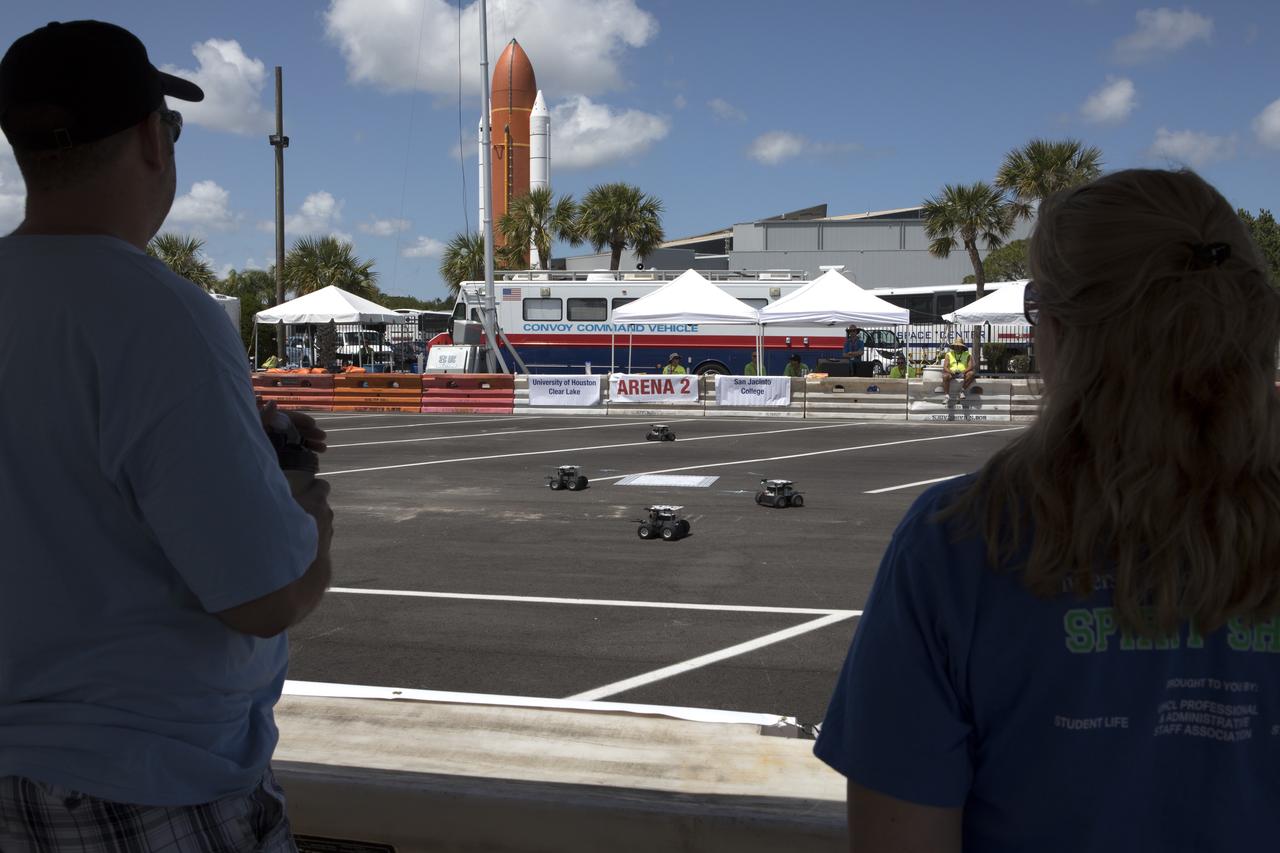

At the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex, students monitor progress as their Swarmie robots as they search for "resources." The goal is for the robots to pick up cubes with AprilTags, which are similar to bar codes. The Swarmies then move the cubes to a white square in the center of the completion arena. The small, four-wheeled robots are designed to effectively and efficiently locate hidden resources while astronauts explore distant destinations such as the moon or Mars.
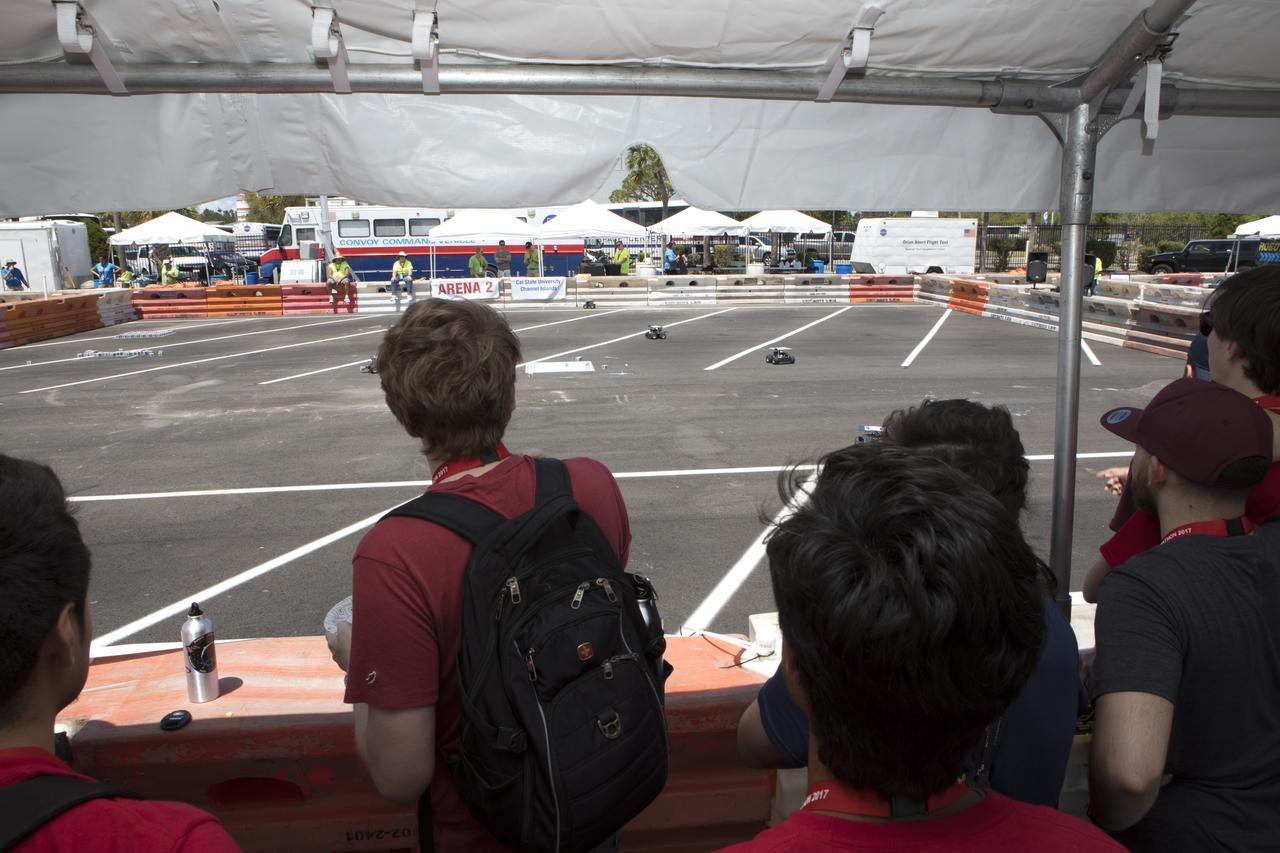

At the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex, students monitor progress as their Swarmie robots as they search for "resources." The goal is for the robots to pick up cubes with AprilTags, which are similar to bar codes. The Swarmies then move the cubes to a white square in the center of the completion arena. The small, four-wheeled robots are designed to effectively and efficiently locate hidden resources while astronauts explore distant destinations such as the moon or Mars.
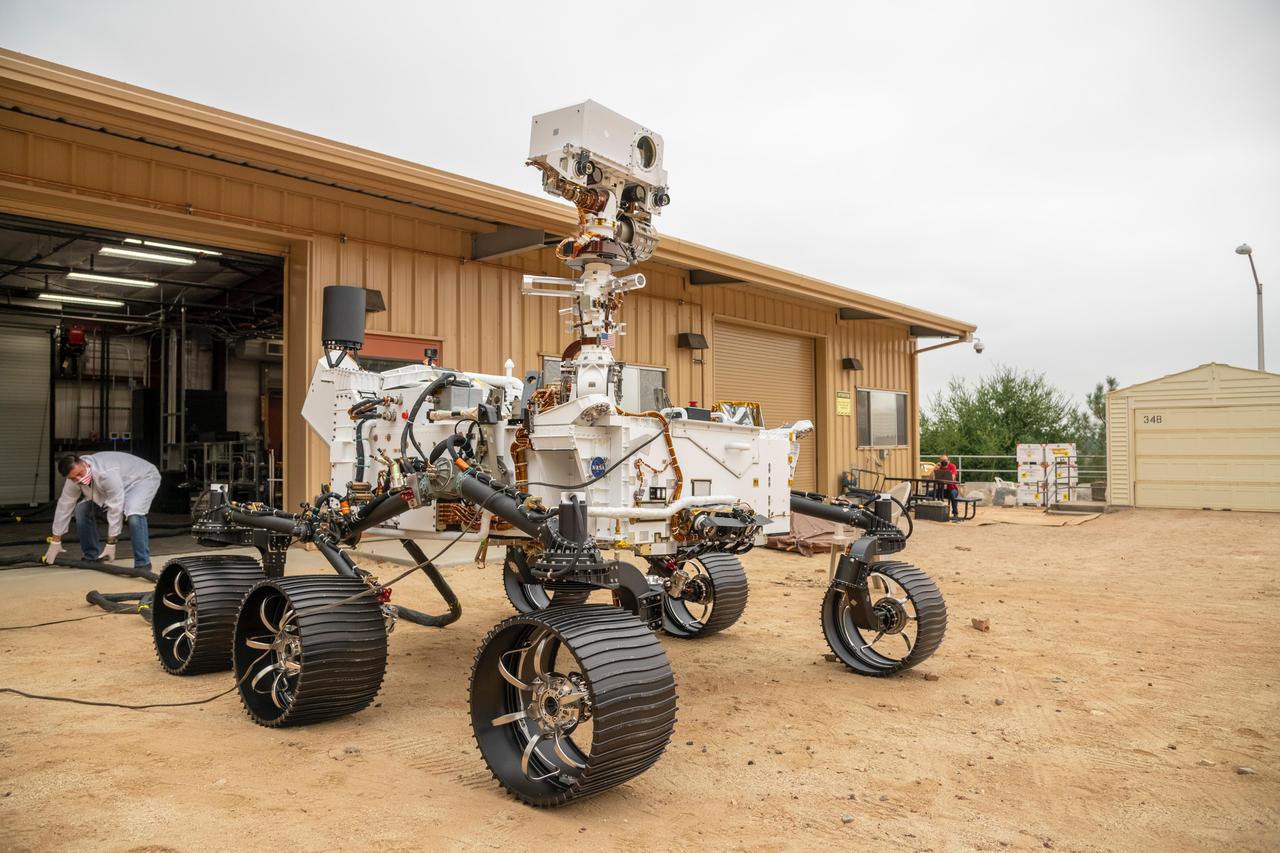

The full-scale engineering model of NASA's Perseverance rover has put some dirt on its wheels. This vehicle system test bed (VSTB) rover moved into its home — a garage facing the Mars Yard at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California — on Sept. 4, 2020. It drove onto simulated Martian surface of the Mars Yard — a dirt field at JPL studded with rocks and other obstacles — for the first time on Sept. 8. The VSTB rover is also known as OPTIMISM (Operational Perseverance Twin for Integration of Mechanisms and Instruments Sent to Mars). A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will also characterize the planet's climate and geology, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first planetary spacecraft to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent missions, currently under consideration by NASA in cooperation with the European Space Agency, would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these cached samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 mission is part of a larger program that includes missions to the Moon as a way to prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Charged with returning astronauts to the Moon by 2024, NASA will establish a sustained human presence on and around the Moon by 2028 through NASA's Artemis lunar exploration plans. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23966
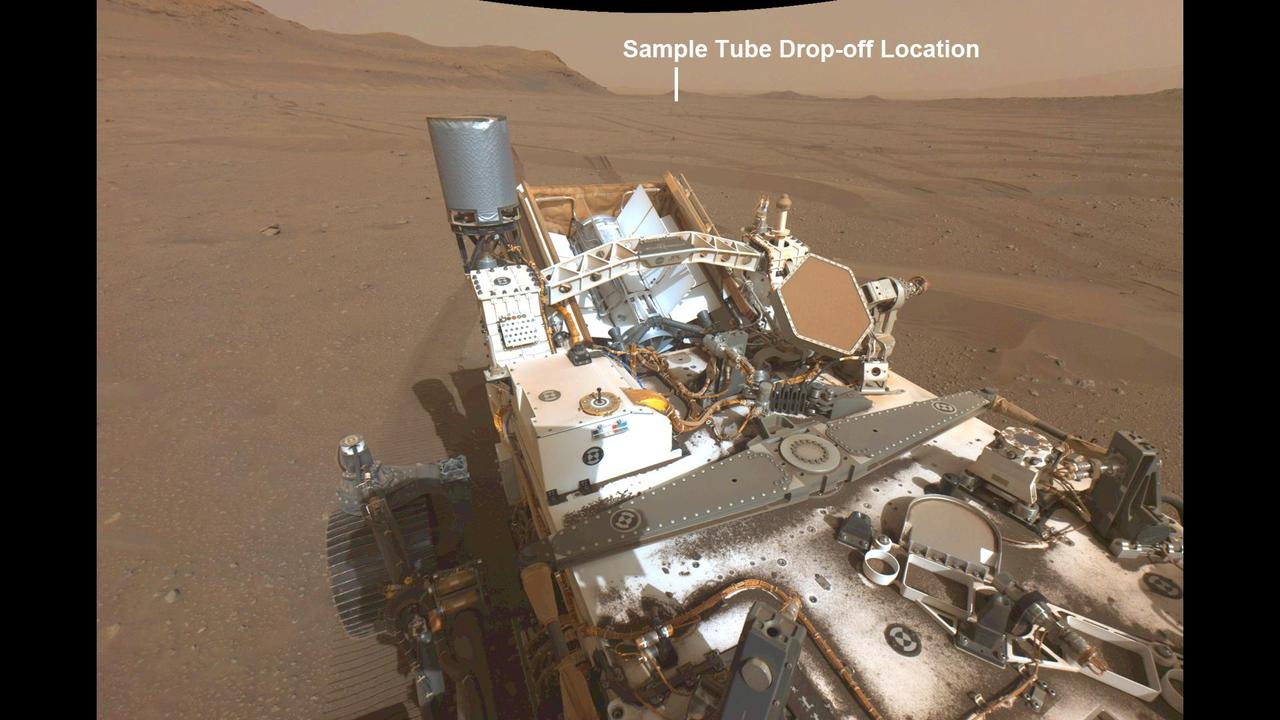
This annotated image from NASA's Perseverance Mars rover shows its wheel tracks in Jezero Crater and a distant view of the first potential location it could deposit a group of sample tubes for possible future return to Earth. The image was taken on Aug. 29, 2022, the 542nd Martian day, or sol, of the rover's mission, by Perseverance's navigation camera. Sample tubes already filled with rock are currently stored in the rover's Sampling and Caching System. Perseverance will deposit select samples in designated locations. Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis as part of the Mars Sample Return campaign. This image has been linearized to remove optical lens distortion effects. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25243
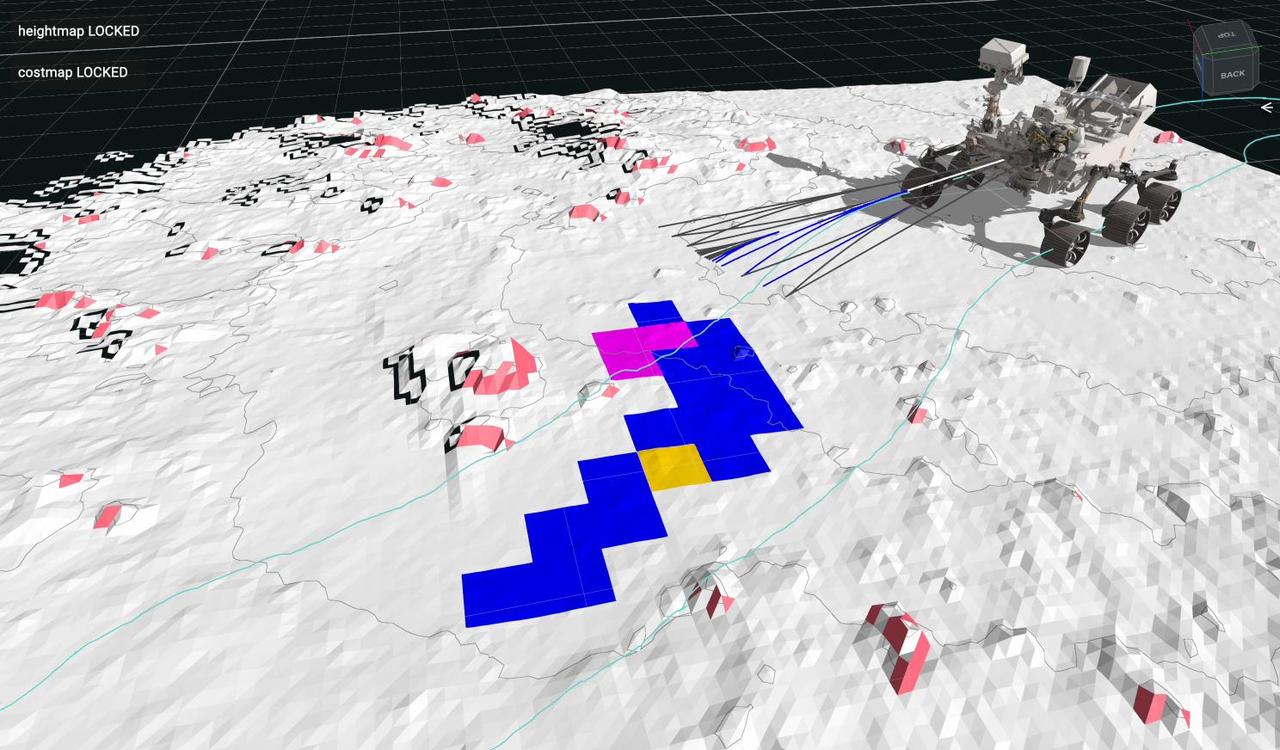
This animation is a playback of data recorded by NASA's Perseverance Mars rover during an autonomous drive on July 15, 2023, the 854th day, or sol, of the mission. During this drive, the rover identified and navigated around the 14-inch (35-centimeter) rock seen at center-left. The self-driving autonomous navigation system, AutoNav, allows the rover to autonomously re-plan its route around rocks or other obstacles on its way to a pre-established destination. Engineers driving the rover at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California use visualization software to plan how the rover moves around on Mars and to evaluate its performance. The lines seen emanating from the front of the rover are 20 feet (6 meters) long and indicate the paths the rover is evaluating for safety in real time, while driving. Lines that turn blue show where the rover identified a "wheel drop" hazard – where a wheel could drop more than 14 inches (35 centimeters). Magenta lines indicate where the rover saw a belly pan clearance issue – where a terrain feature could get too close to the belly pan underneath the rover. The surrounding white terrain is a digital elevation model that the rover creates onboard using navigation camera images. The animation has been sped up compared to real time. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26073

This computer animation shows a replay of telemetry from NASA's Perseverance Mars rover as it carried out its first drive using AutoNav, it's auto-navigation feature, which allows it to avoid rocks and other hazards without input from engineers back on Earth. The rover's progress here has been sped up by 50 times. The entire drive was roughly 102 feet (31 meters) and took 45 minutes. The terrain is created from height maps, which is how the rover navigates surrounding terrain. The map is created incrementally from stereo imagery taken from the rover's navigation cameras. Auto-navigation software uses a height map to evaluate possible drive paths for safety. The paths are represented by arcs emanating from the front of the rover. Different-colored arcs denote different results of the hazard evaluation. Blue arcs represent arcs that failed due to "wheel drop," where the terrain could allow for a wheel to fall more than a certain height. Pink arcs fail the belly-pan clearance check, where the terrain is at risk of high-centering the rover. Yellow arcs fail by driving onto unknown terrain. Gray arcs are safe. The white arc is the actual path selected by auto-navigation. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24723
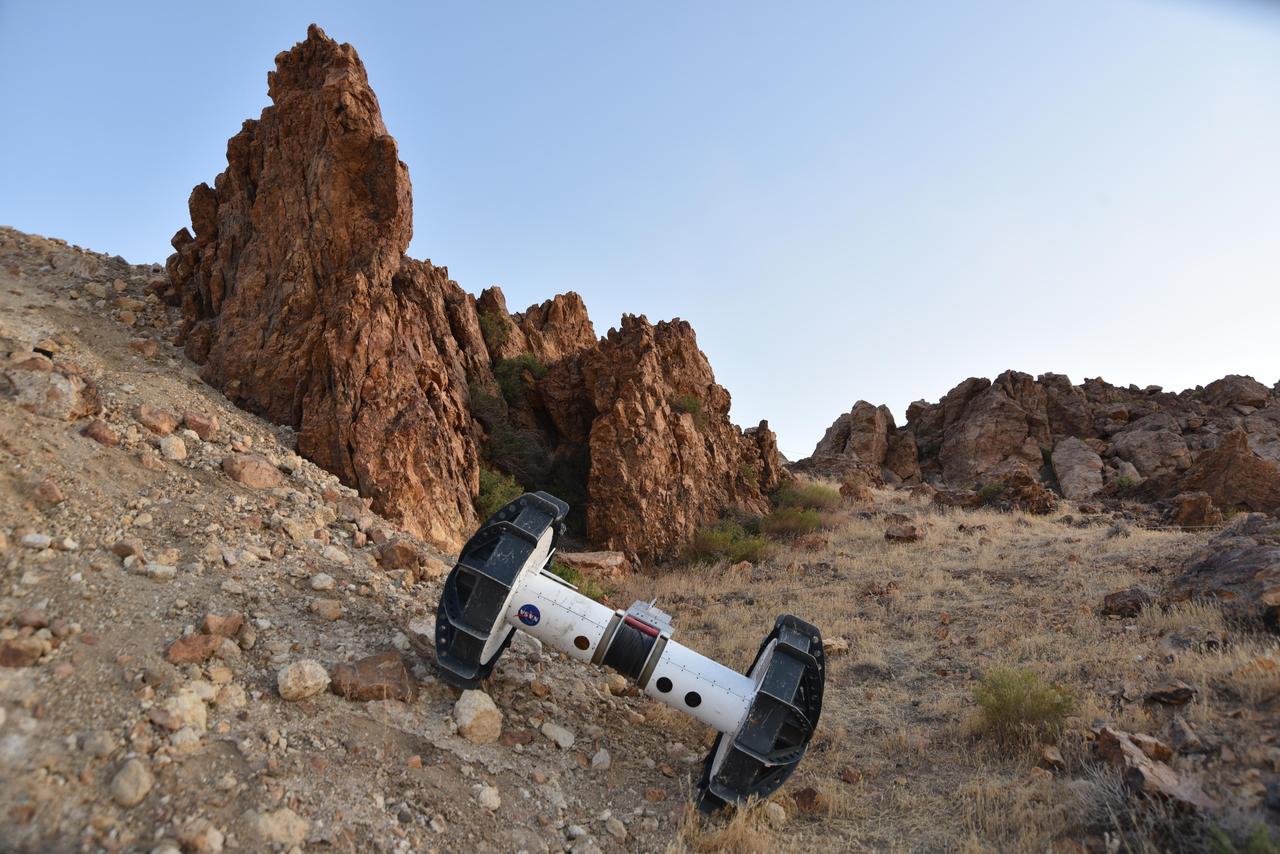

In this photograph, a tethered Axel robot — part of the four-wheeled DuAxel rover — navigates a steep slope during a field test in the Mojave Desert. The tether, which connects to the rover's other half, serves as a climbing rope of sorts while also providing power and a means of communication. This flexibility was built with crater walls, pits, scarps, vents, and other extreme terrain in mind. That's because on Earth, some of the best locations to study geology can be found in rocky outcrops and cliff faces, where many layers of the past are neatly exposed. They're hard enough to reach here, let alone on the Moon, Mars, and other celestial bodies. The DuAxel project is a technology demonstration being developed by roboticists at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California to see how this unconventional rover might fill a niche in planetary exploration. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24110
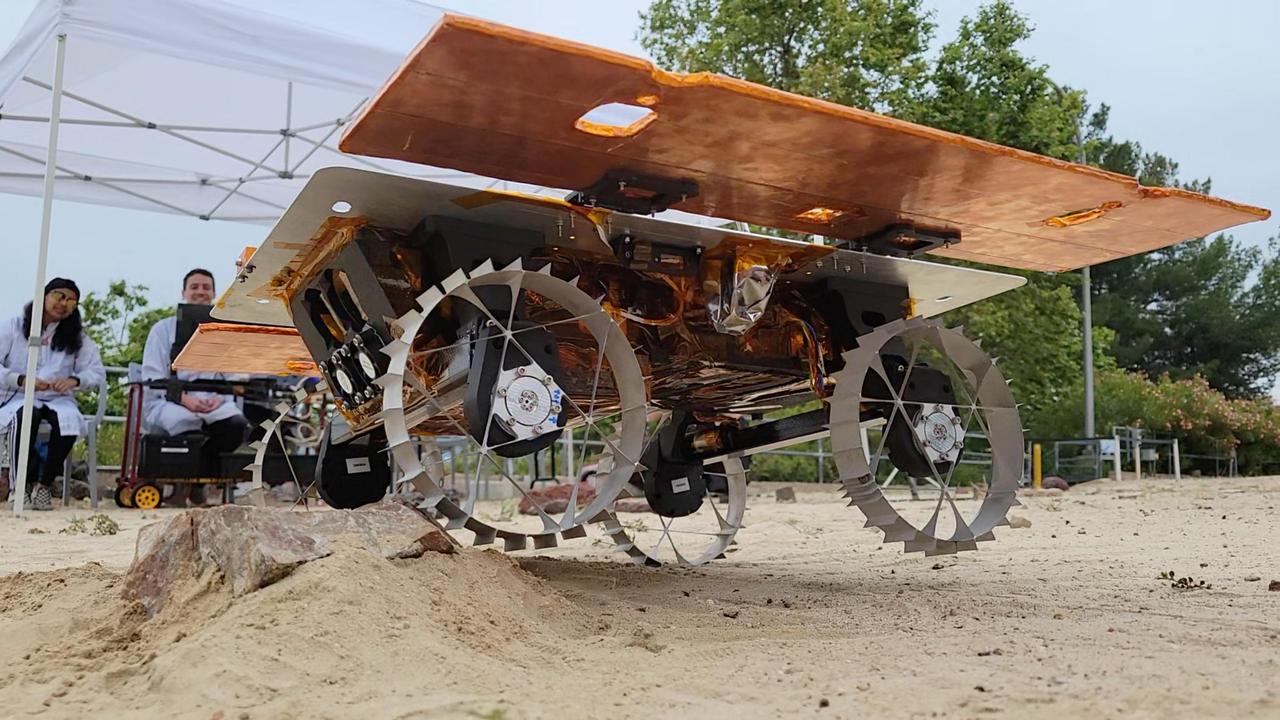

A development rover that is part of NASA's CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration) technology demonstration drives over a rock during its first autonomous drive around the Mars Yard at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in June 2023. Under a canopy behind the rover are, from left, graduate student intern Natalie Deo and CADRE verification and validation lead Sawyer Brooks of JPL. The CADRE team successfully tested a new wheel design, surface navigation software, and mobility capabilities, among other aspects of the project. The rover being tested is similar in size and appearance to the flight models of the CADRE rovers, which are still being built. Slated to arrive at the Moon in spring 2024 as part of NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, CADRE is designed to demonstrate that multiple robots can cooperate and explore together autonomously – without direct input from human mission controllers. A trio of the miniature solar-powered rovers, each about the size of a carry-on suitcase, will explore the Moon as a team, communicating via radio with each other and a base station aboard a lunar lander. By taking simultaneous measurements from multiple locations, CADRE will also demonstrate how multirobot missions can record data impossible for a single robot to achieve – a tantalizing prospect for future missions. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25667

A development model rover that is part of NASA's CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration) technology demonstration took its first autonomous drive around the Mars Yard at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in June 2023. The CADRE team tested a new wheel design, surface navigation software, and mobility capabilities, among other aspects of the project. Engineer Kristopher Sherrill is shown recording video of the test. The rover being tested is similar in size and appearance to the flight models of the CADRE rovers, which are still being built. Slated to arrive at the Moon in spring 2024 as part of NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, CADRE is designed to demonstrate that multiple robots can cooperate and explore together autonomously – without direct input from human mission controllers. A trio of the miniature solar-powered rovers, each about the size of a carry-on suitcase, will explore the Moon as a team, communicating via radio with each other and a base station aboard a lunar lander. By taking simultaneous measurements from multiple locations, CADRE will also demonstrate how multirobot missions can record data impossible for a single robot to achieve – a tantalizing prospect for future missions. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25665
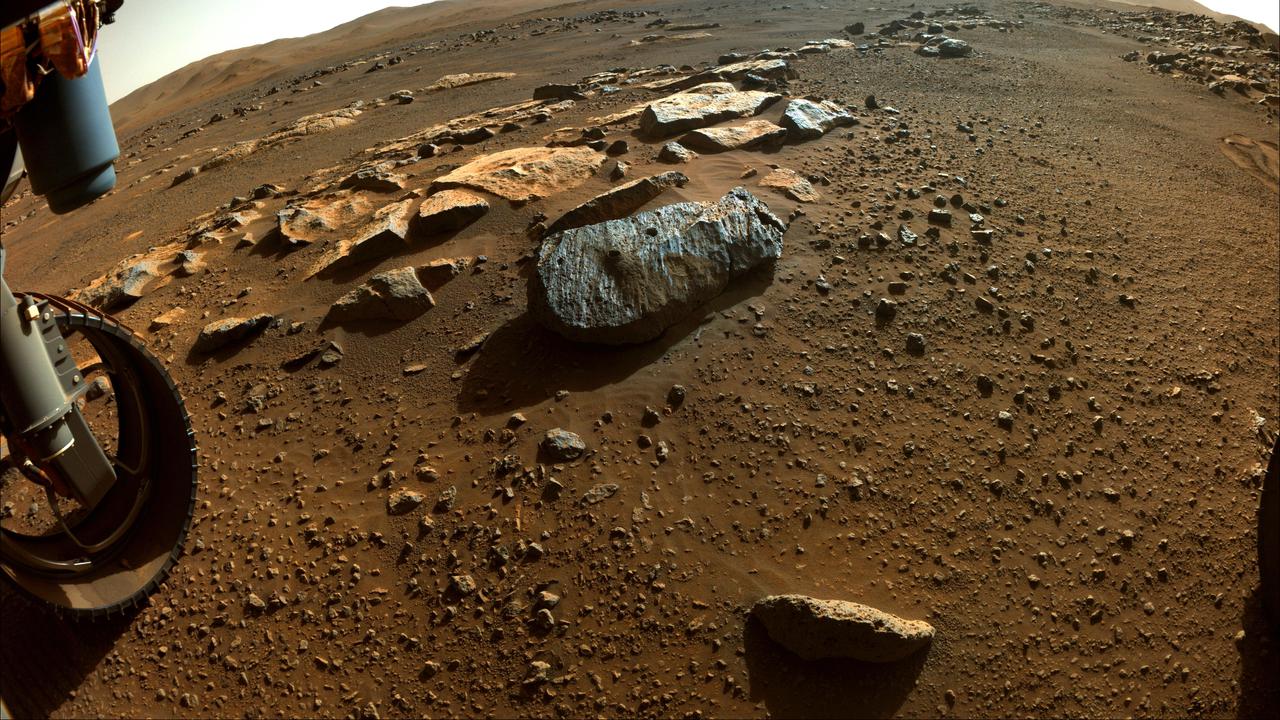

This image taken by NASA's Perseverance rover on Sept. 7, 2021, PDT (Sept. 8, EDT), shows two holes where the rover's drill obtained chalk-size samples from rock nicknamed "Rochette." The hole on the left side is known as "Montagnac" (drilled on Sept. 7), and the hole on the right is known as "Montdenier" (drilled on Sept. 1). A round spot where the rover abraded part of the rock's surface, nicknamed "Bellegarde," is visible under the hole on the right. Tailings (or cuttings) from the Montdenier coring activity slid over Bellegarde. This image in which a rover wheel is visible was taken by one of Perseverance's Hazard Avoidance Cameras on the 196th sol (Martian day) of the rover's mission and processed to enhance contrast. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24840
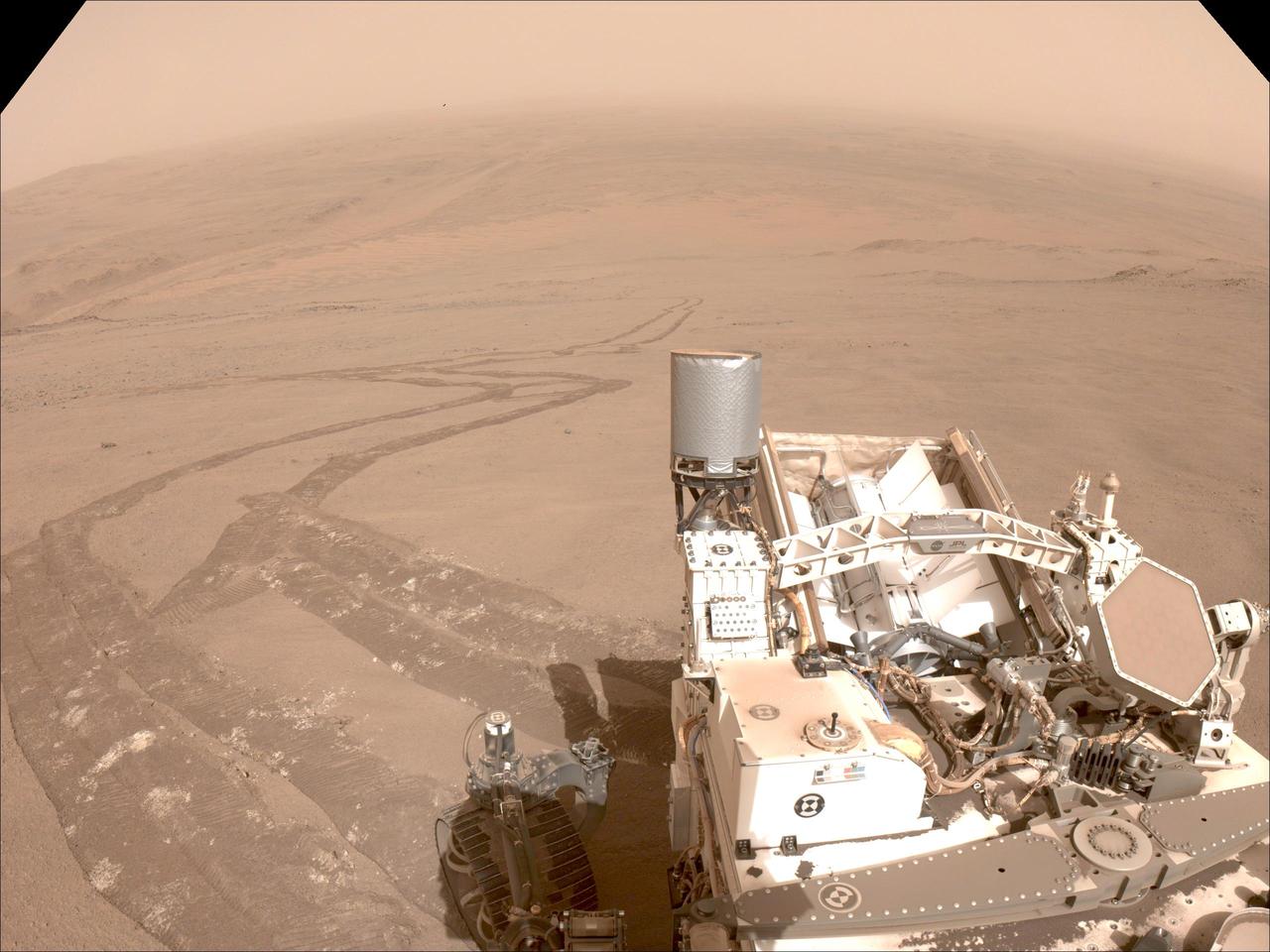

One of the navigation cameras aboard NASA's Perseverance captured this image of the tracks made by the rover during its climb up the rim of Jezero Crater on Oct. 11, 2024, the 1,295th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The rover's tracks, seen disappearing into the distance, have churned up the regolith (broken rock and sand) on the surface, indicating high slip. The edges of the tracks are not straight or smooth, which indicates cross-track sliding during the drive. On less slippery terrain, the tracks have well defined lines from the grousers on the rover wheels. The distant river channel seen at the upper left of image is Neretva Vallis, which fed Jezero Crater with fresh water billions of years ago. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26379