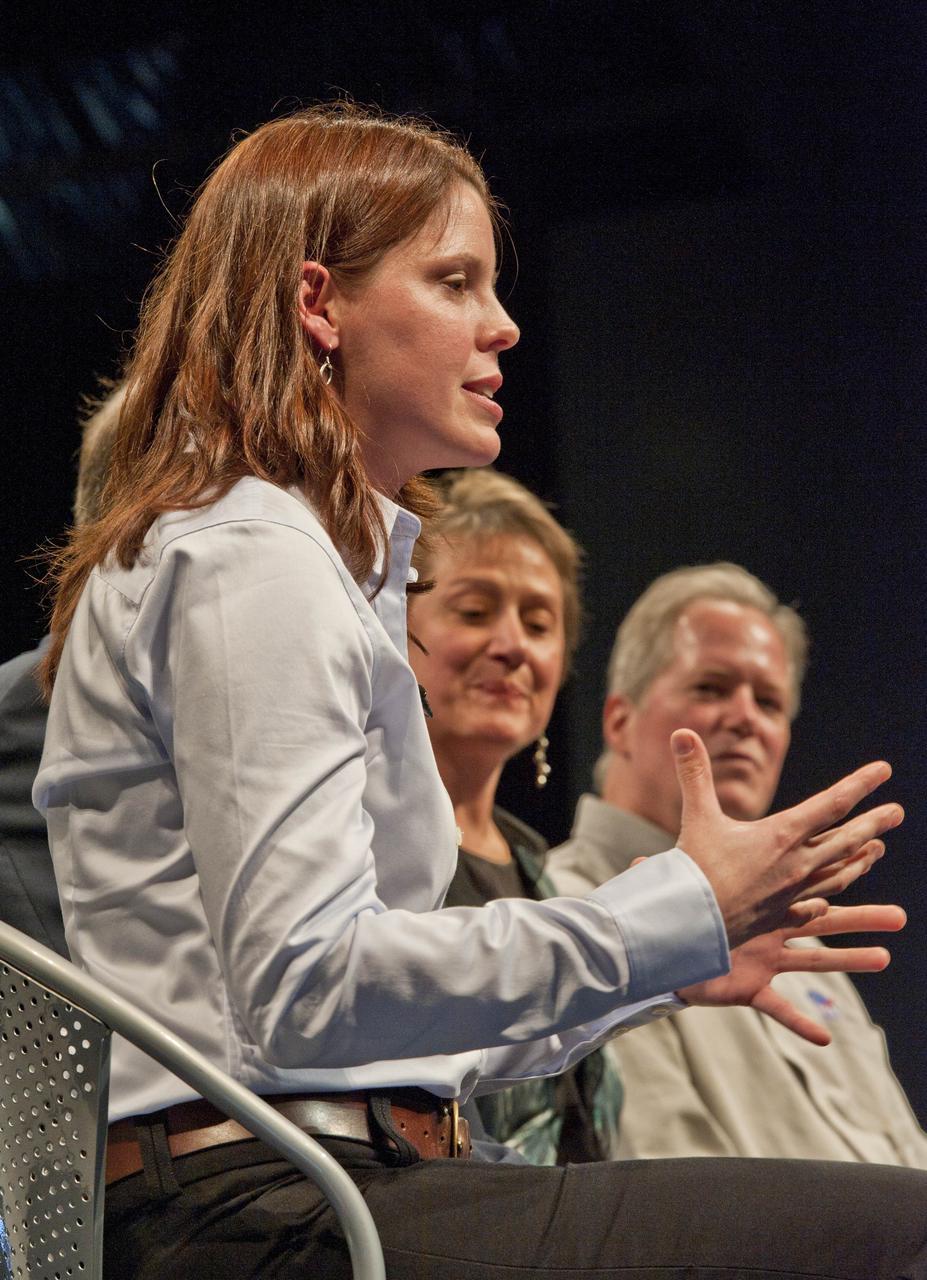

Dr. Jennifer Elgenbrode, from Goddard Space Flight Center, foreground, talks as Dr. Mary Voytek and Dr. Michael Meyer, far right, look on during a Mars Program Update where prominent scientists discussed evidence of water on Mars, current Program status, including the 7th Anniversary of the Mars rovers and the upcoming Mars Science Laboratory mission and previewing exciting discoveries to come, Thursday, Jan. 13, 2011, at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

Steven Benner, a distinguished fellow at the Foundation for Applied Molecular Evolution, right, speaks during a press conference as Mary Voytek, director of the Astrobiology Program at NASA looks on, Thursday, Dec. 2, 2010, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. NASA-funded astrobiology research has changed the fundamental knowledge about what comprises all known life on Earth. Researchers conducting tests in the harsh environment of Mono Lake in California have discovered the first known microorganism on Earth able to thrive and reproduce using the toxic chemical arsenic. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

Felisa Wolfe-Simon, a lead researcher and NASA astrobiology research fellow, speaks during a press conference, as Mary Voytek, Steven Benner and Pamela Conrad look on, Thursday, Dec. 2, 2010, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. NASA-funded astrobiology research has changed the fundamental knowledge about what comprises all known life on Earth. Researchers conducting tests in the harsh environment of Mono Lake in California have discovered the first known microorganism on Earth able to thrive and reproduce using the toxic chemical arsenic. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
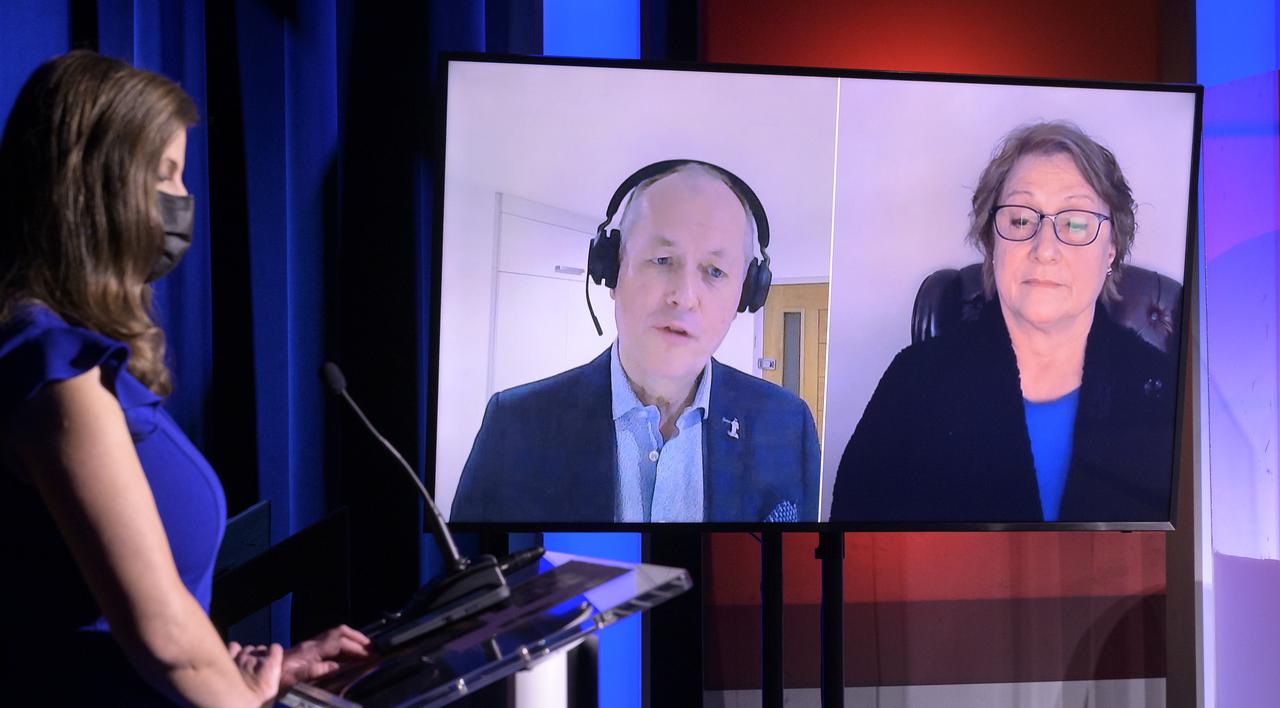
Director of human and robotic exploration, ESA’s European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC), Netherlands, David Parker, , screen left, and Director of NASA’s astrobiology program, Mary Voytek, give remarks via remote during a NASA Perseverance rover press briefing about the search for ancient life at Mars and about samples to be brought back to Earth on a future mission, Wednesday, Feb. 17, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The Perseverance Mars rover is due to land on Mars Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
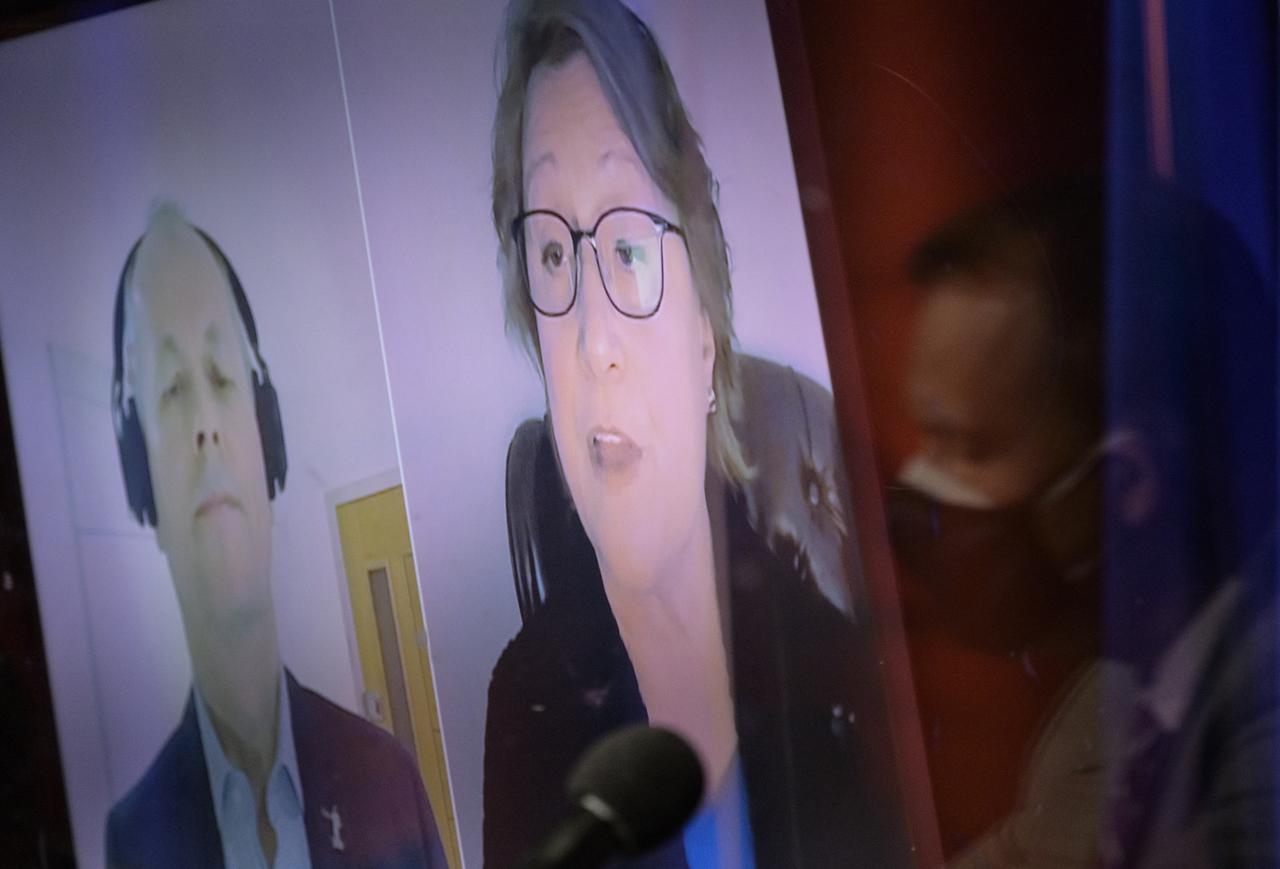

Director of human and robotic exploration, ESA’s European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC), Netherlands, David Parker, , screen left, and Director of NASA’s astrobiology program, Mary Voytek, give remarks via remote during a NASA Perseverance rover press briefing about the search for ancient life at Mars and about samples to be brought back to Earth on a future mission, Wednesday, Feb. 17, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The Perseverance Mars rover is due to land on Mars Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
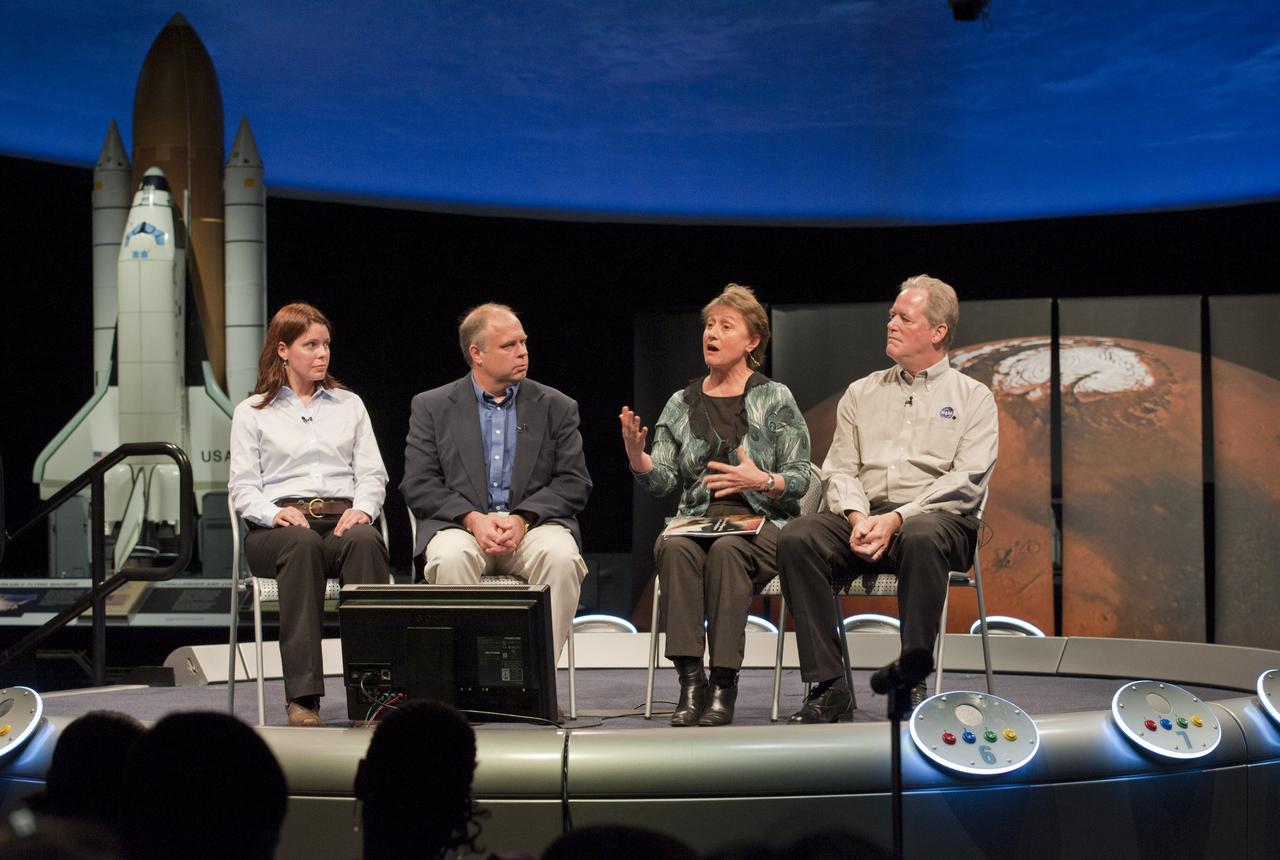

Dr. Mary Voytek, NASA Astrobiology Program Manager, second from right, talks during panel discussion as Dr. Jennifer Elgenbrode, from Goddard Space Flight Center, left, Dr. John Grant and Dr. Michael Meyer, NASA Mars lead scientist, right look on during a Mars Program Update where prominent scientists discussed evidence of water on Mars, current Program status, including the 7th Anniversary of the Mars rovers and the upcoming Mars Science Laboratory mission and previewing exciting discoveries to come, Thursday, Jan. 13, 2011, at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
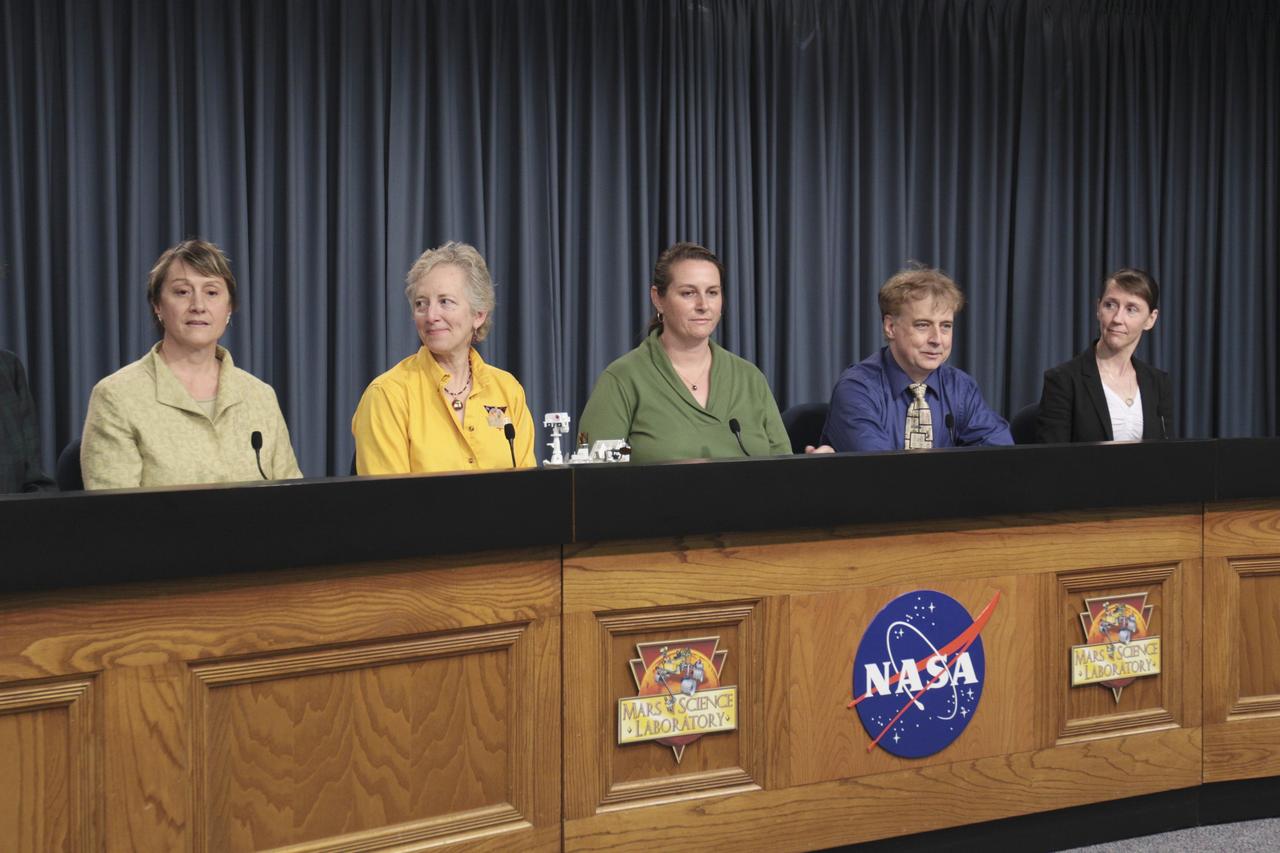

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, several scientists and researchers participate in a “Looking for Signs of Life in the Universe” news conference, Nov. 22, as part of preflight activities for the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. From left, are NASA Astrobiology Director Mary Voytek; Professor Jamie Foster from the Department of Microbiology and Cell Science at the University of Florida in Gainesville; MSL Deputy Principal Investigator Pan Conrad; Director of the Foundation for Applied Molecular Evolution Steven Benner; and NASA Planetary Protection Officer Catharine Conley. MSL’s components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
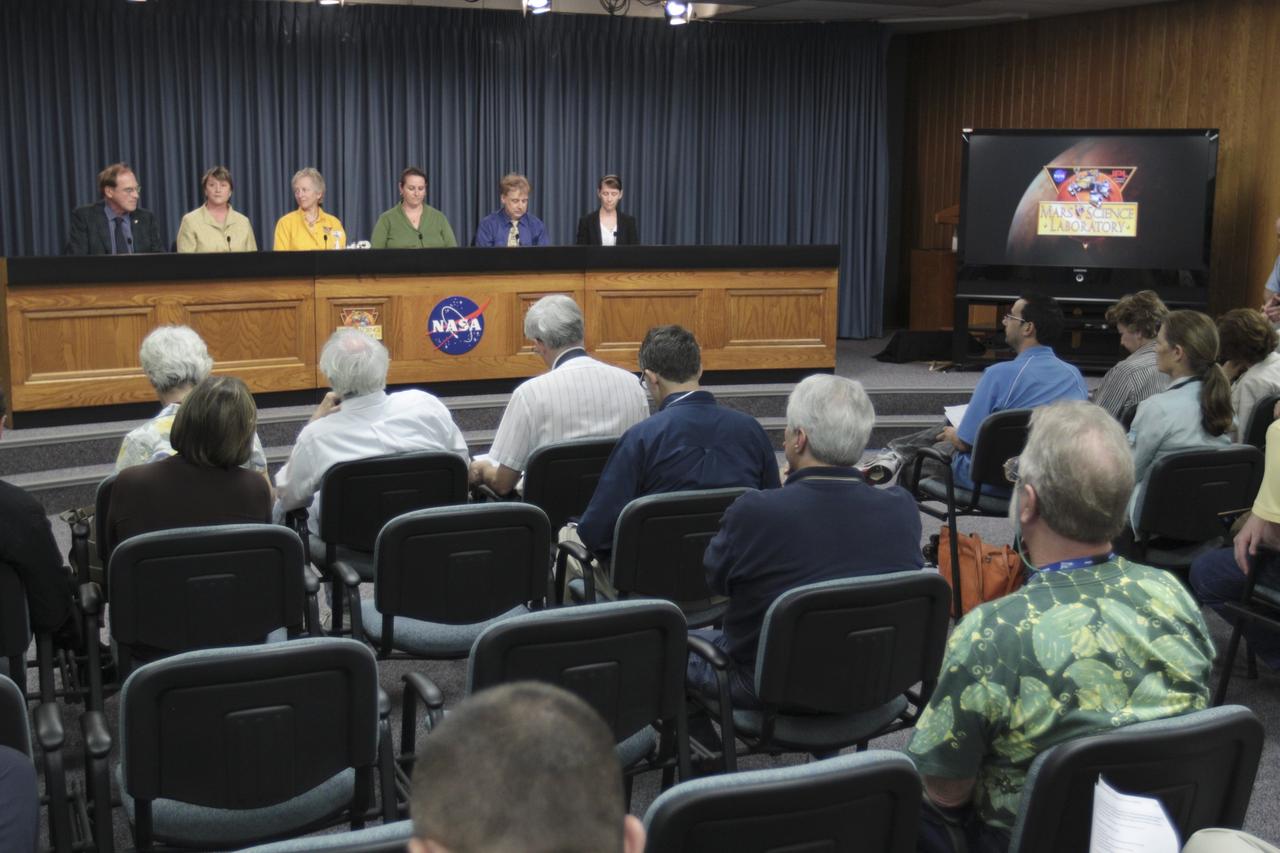

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, several scientists and researchers participate in a “Looking for Signs of Life in the Universe” news conference, Nov. 22, as part of preflight activities for the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. From left, are NASA Public Affairs Officer and conference moderator George Diller; NASA Astrobiology Director Mary Voytek; Professor Jamie Foster from the Department of Microbiology and Cell Science at the University of Florida in Gainesville; MSL Deputy Principal Investigator Pan Conrad; Director of the Foundation for Applied Molecular Evolution Steven Benner; and NASA Planetary Protection Officer Catharine Conley. MSL’s components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
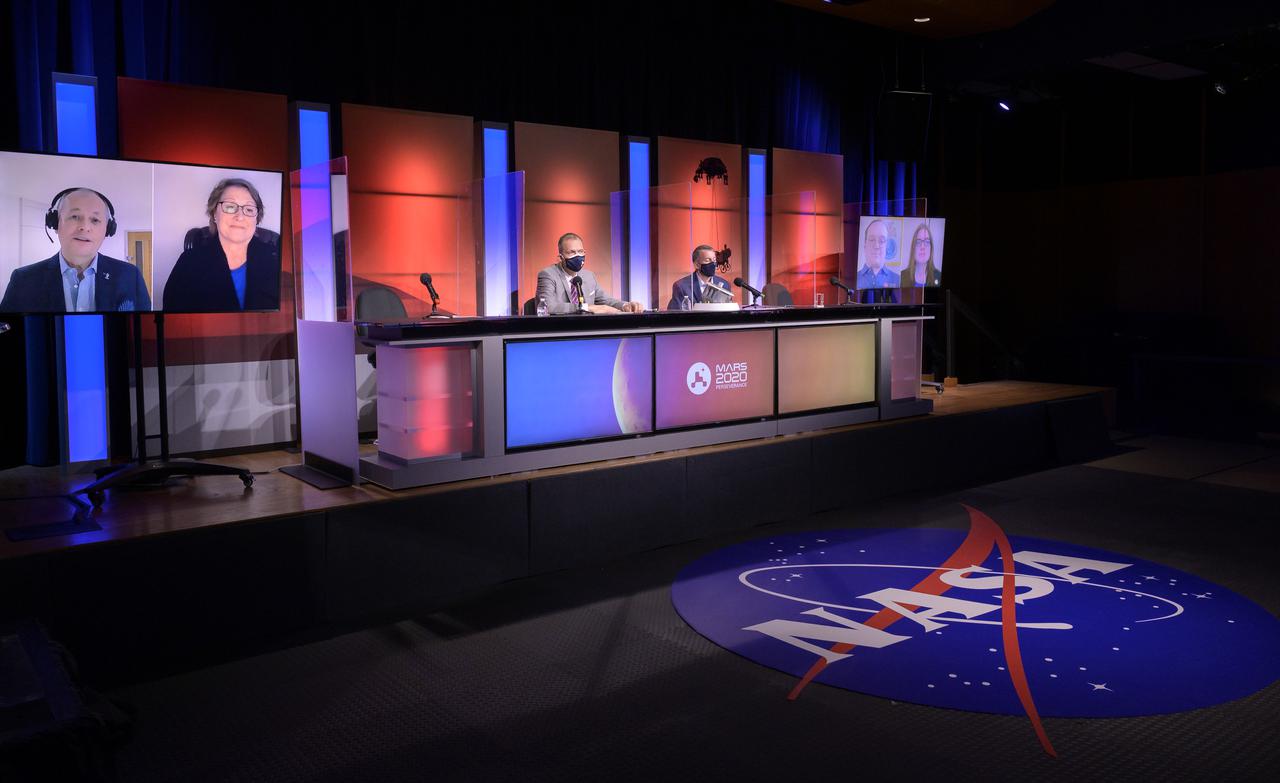

Perseverance Mars rover mission managers and scientist give remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover press briefing about the search for ancient life at Mars and about samples to be brought back to Earth on a future mission, Wednesday, Feb. 17, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The Perseverance Mars rover is due to land on Mars Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
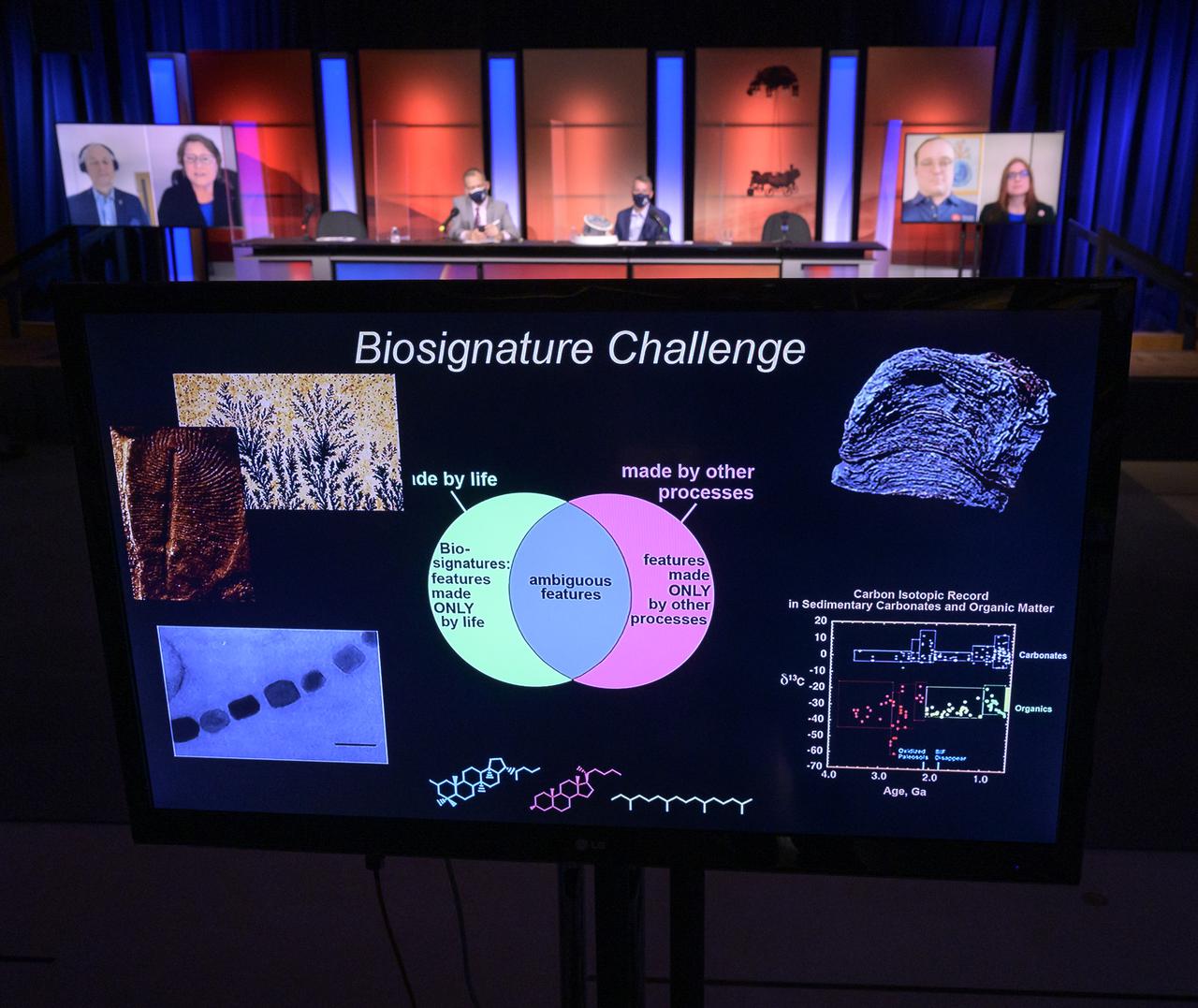
Perseverance Mars rover mission managers and scientist give remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover press briefing about the search for ancient life at Mars and about samples to be brought back to Earth on a future mission, Wednesday, Feb. 17, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The Perseverance Mars rover is due to land on Mars Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)