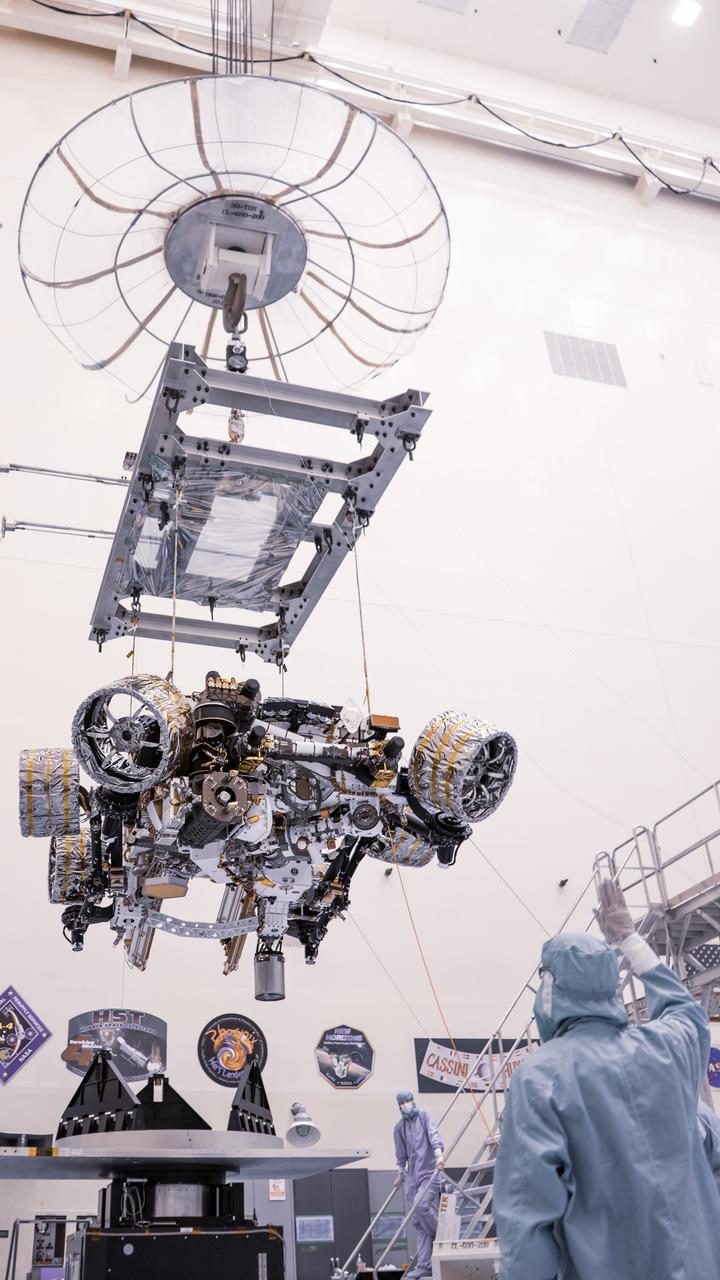

Engineers perform mass properties testing on NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on April 7, 2020. The rover was rotated clockwise and counterclockwise on a spin table to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides. Establishing the rover’s center of gravity will help ensure the spacecraft will land on Mars as calculated. Perseverance will touch down on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
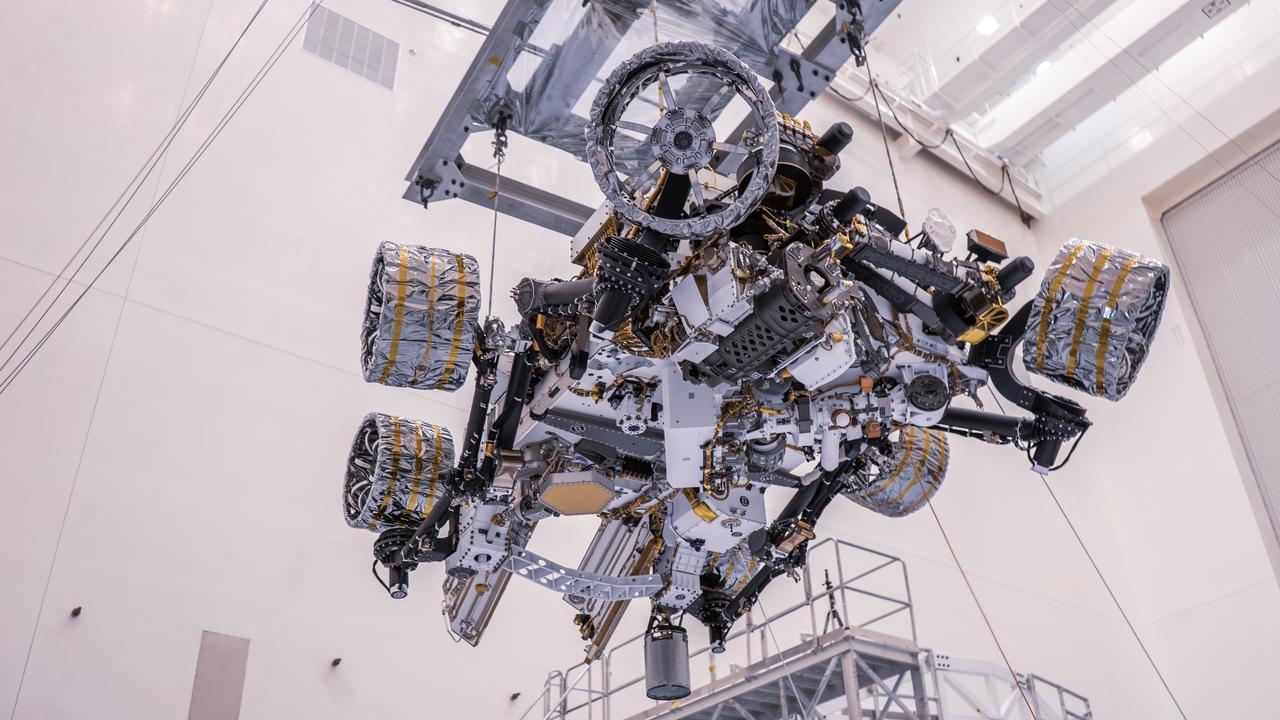
Engineers perform mass properties testing on NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on April 7, 2020. The rover was rotated clockwise and counterclockwise on a spin table to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides. Establishing the rover’s center of gravity will help ensure the spacecraft will land on Mars as calculated. Perseverance will touch down on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
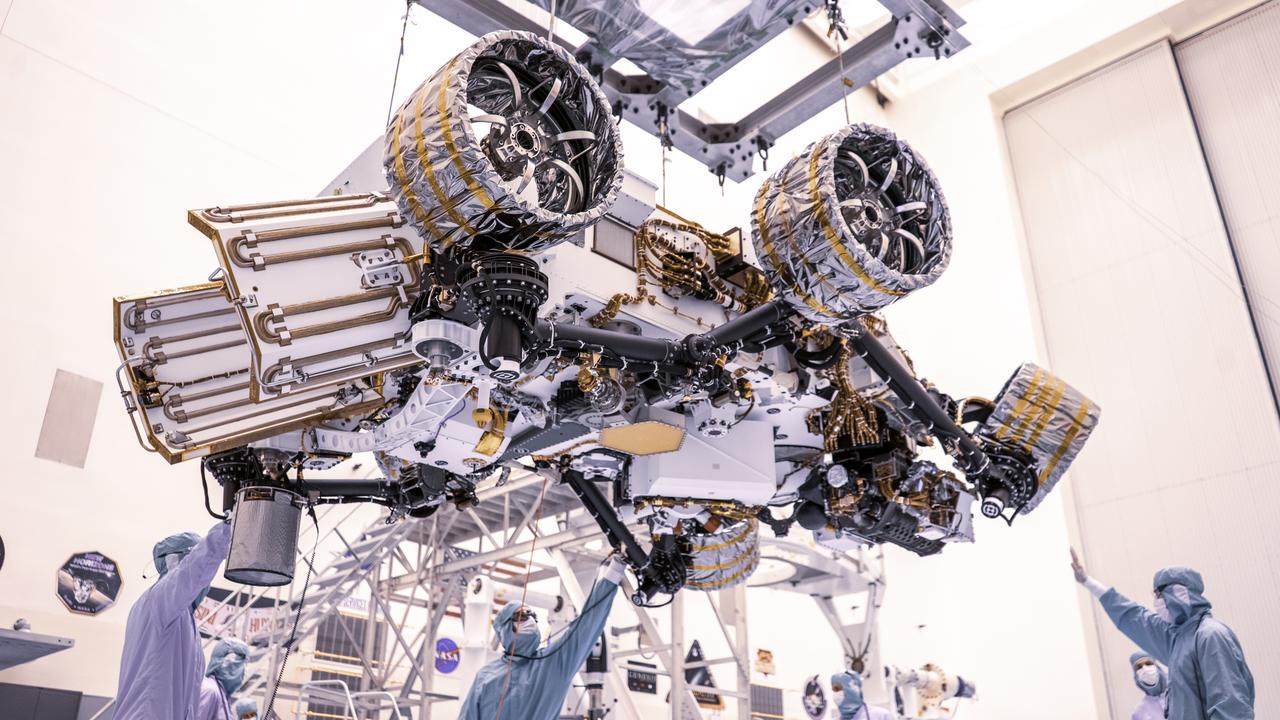

Engineers perform mass properties testing on NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on April 7, 2020. The rover was rotated clockwise and counterclockwise on a spin table to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides. Establishing the rover’s center of gravity will help ensure the spacecraft will land on Mars as calculated. Perseverance will touch down on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
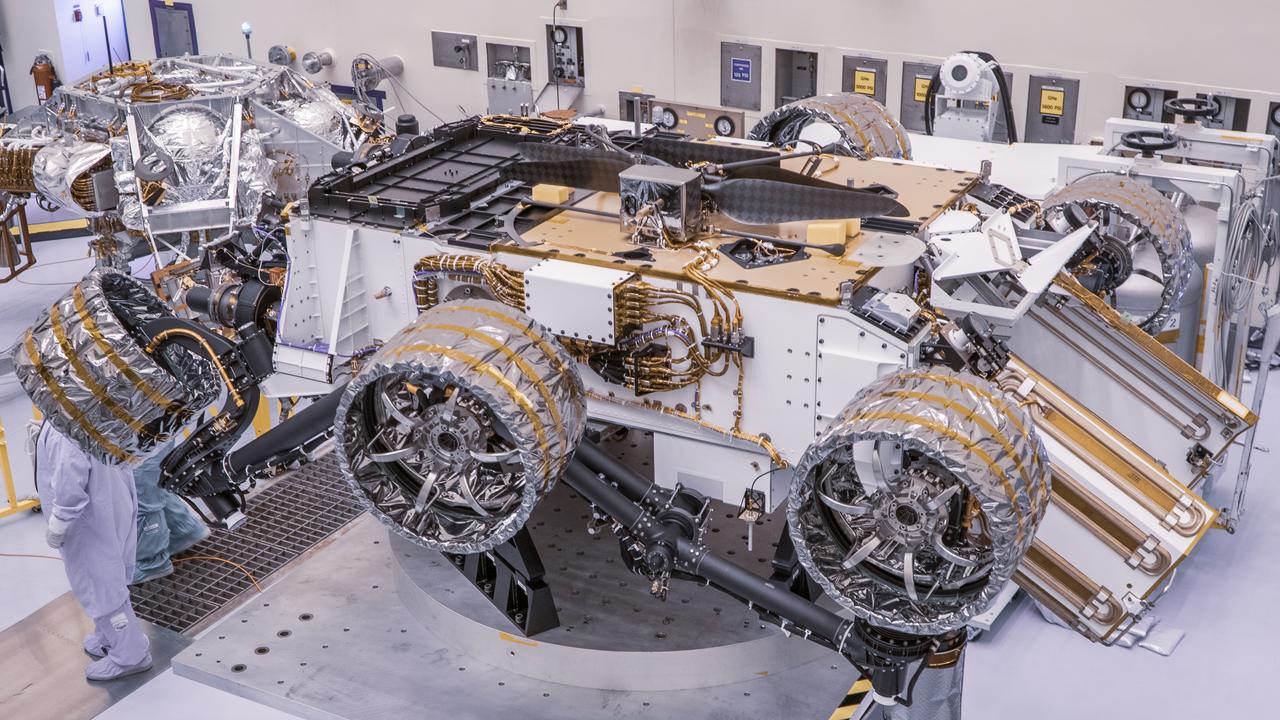
Engineers perform mass properties testing on NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on April 7, 2020. The rover was rotated clockwise and counterclockwise on a spin table to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides. Establishing the rover’s center of gravity will help ensure the spacecraft will land on Mars as calculated. Perseverance will touch down on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
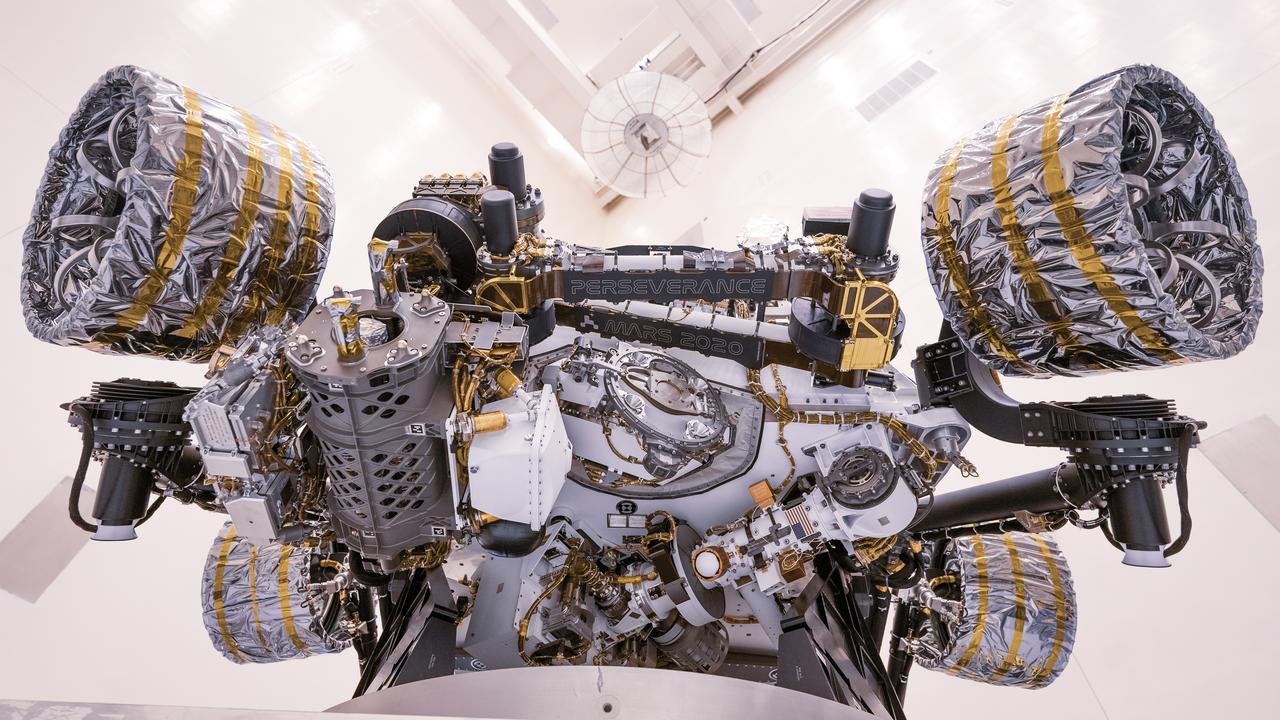
Engineers perform mass properties testing on NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on April 7, 2020. The rover was rotated clockwise and counterclockwise on a spin table to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides. Establishing the rover’s center of gravity will help ensure the spacecraft will land on Mars as calculated. Perseverance will touch down on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
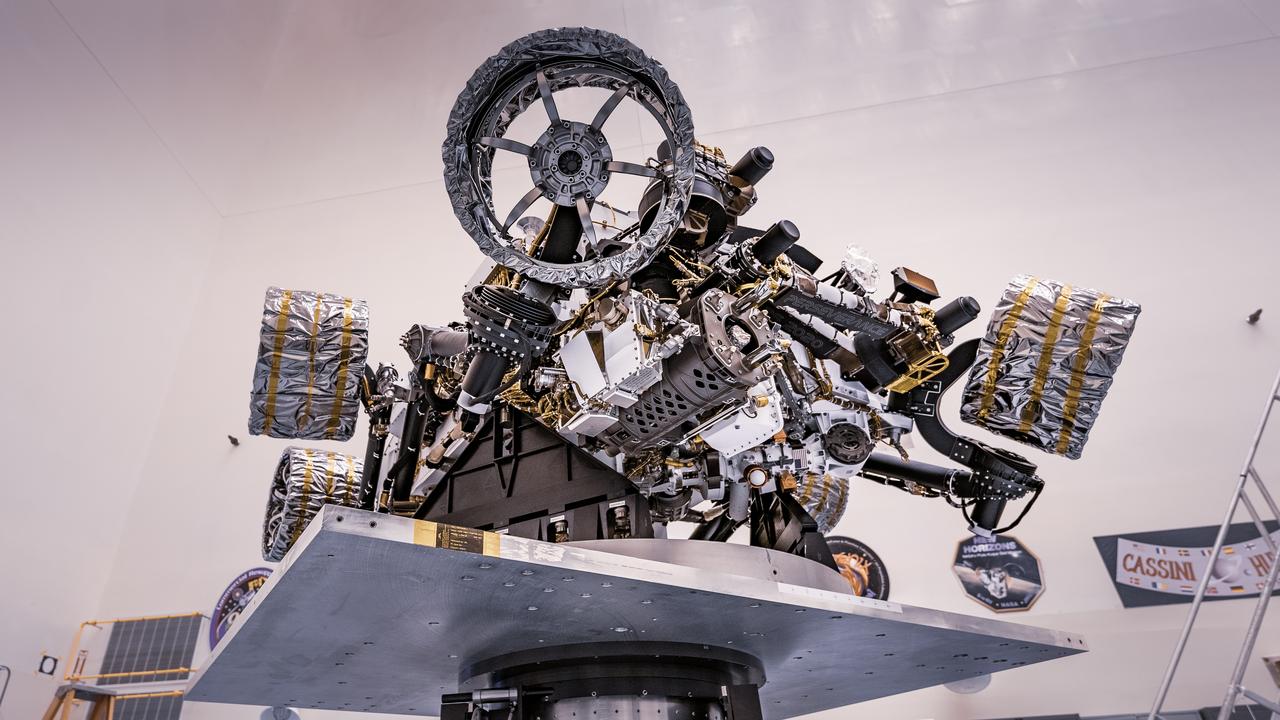
Engineers perform mass properties testing on NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on April 7, 2020. The rover was rotated clockwise and counterclockwise on a spin table to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides. Establishing the rover’s center of gravity will help ensure the spacecraft will land on Mars as calculated. Perseverance will touch down on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
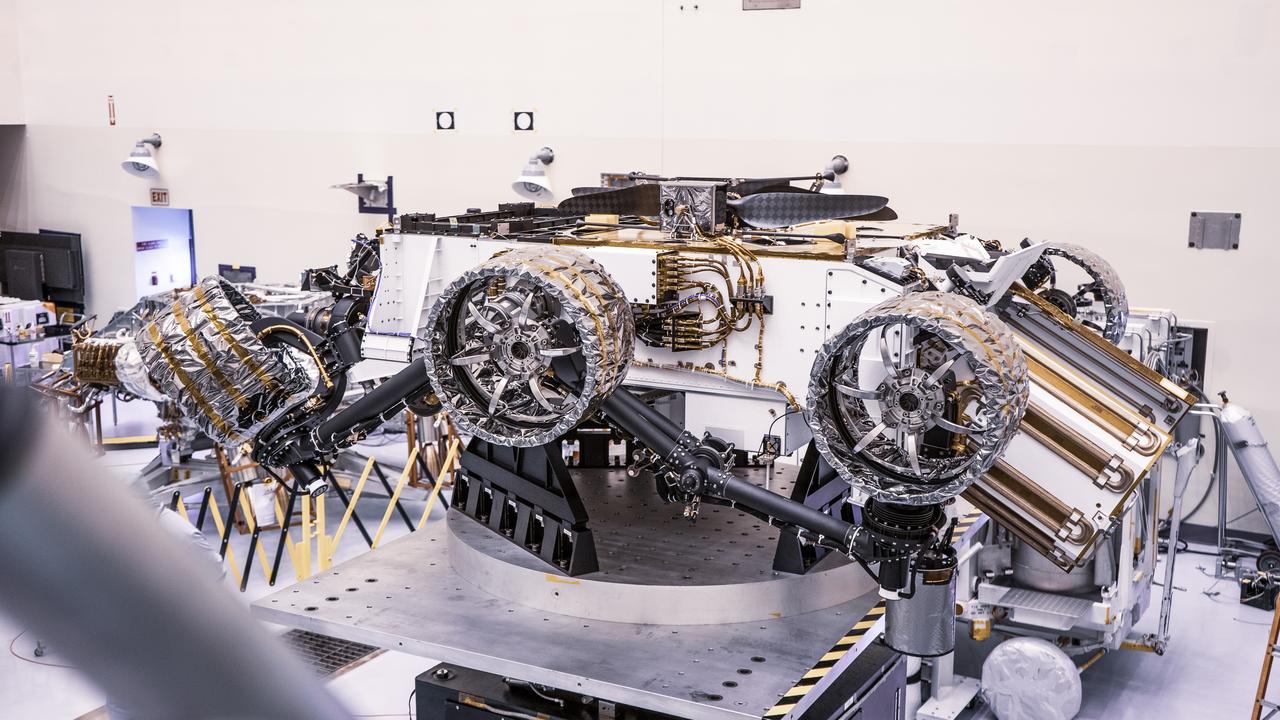

Engineers perform mass properties testing on NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover inside Kennedy Space Center’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on April 7, 2020. The rover was rotated clockwise and counterclockwise on a spin table to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides. Establishing the rover’s center of gravity will help ensure the spacecraft will land on Mars as calculated. Perseverance will touch down on the Red Planet on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
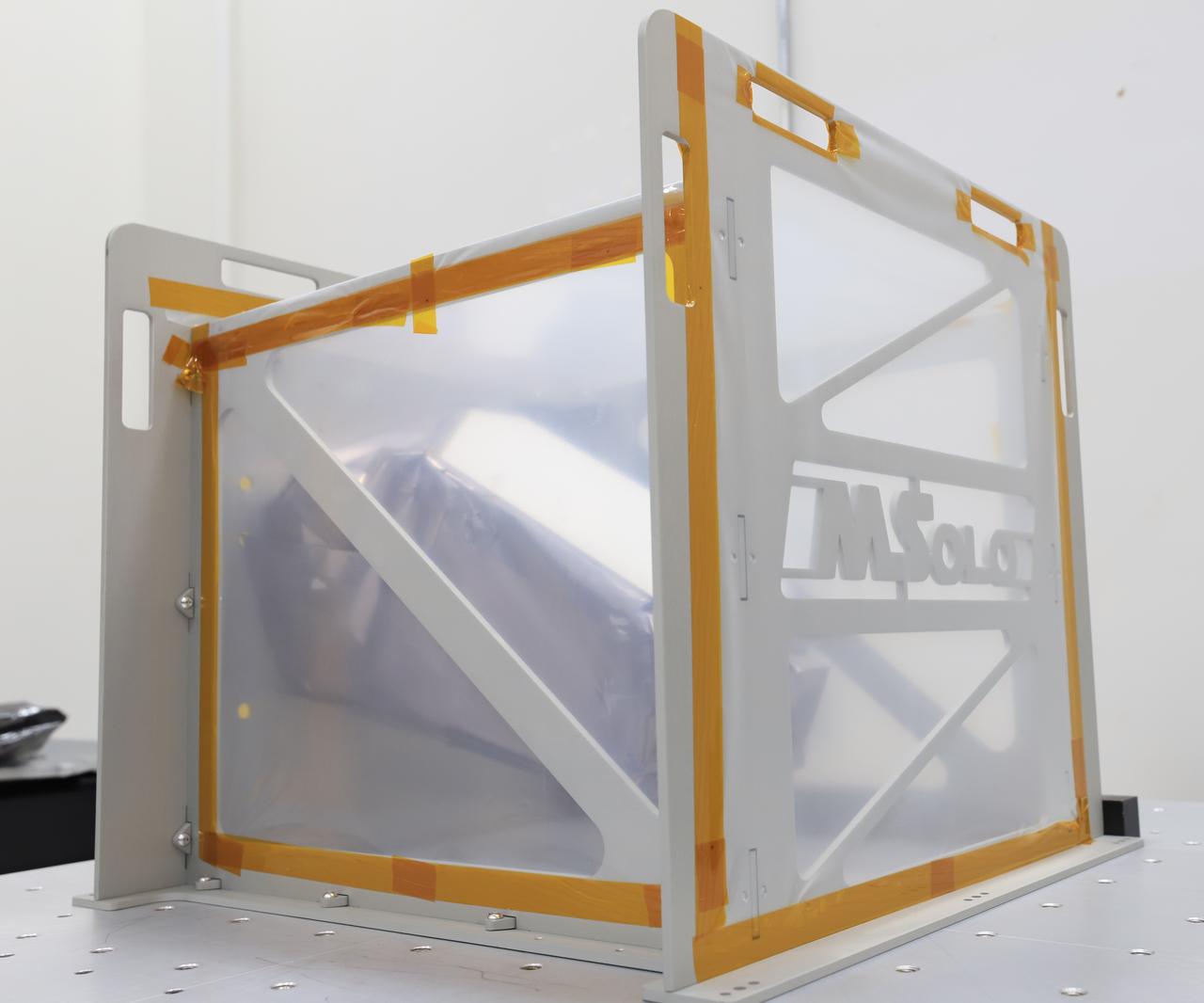

Engineers conduct a mass properties test on the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility in Florida on Nov. 22, 2022. Mass properties determines the mass and center of gravity of the flight unit. The lander uses this information, from all payloads, to improve stability and performance of the lander – and to a lesser degree, the stability and performance of the rocket. This marks the end of testing at Kennedy for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) MSolo instrument. It will soon be shipped to Intuitive Machines in Houston for integration on the NOVA-C landing platform. Launching in 2023, the PRIME-1 mission will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon.
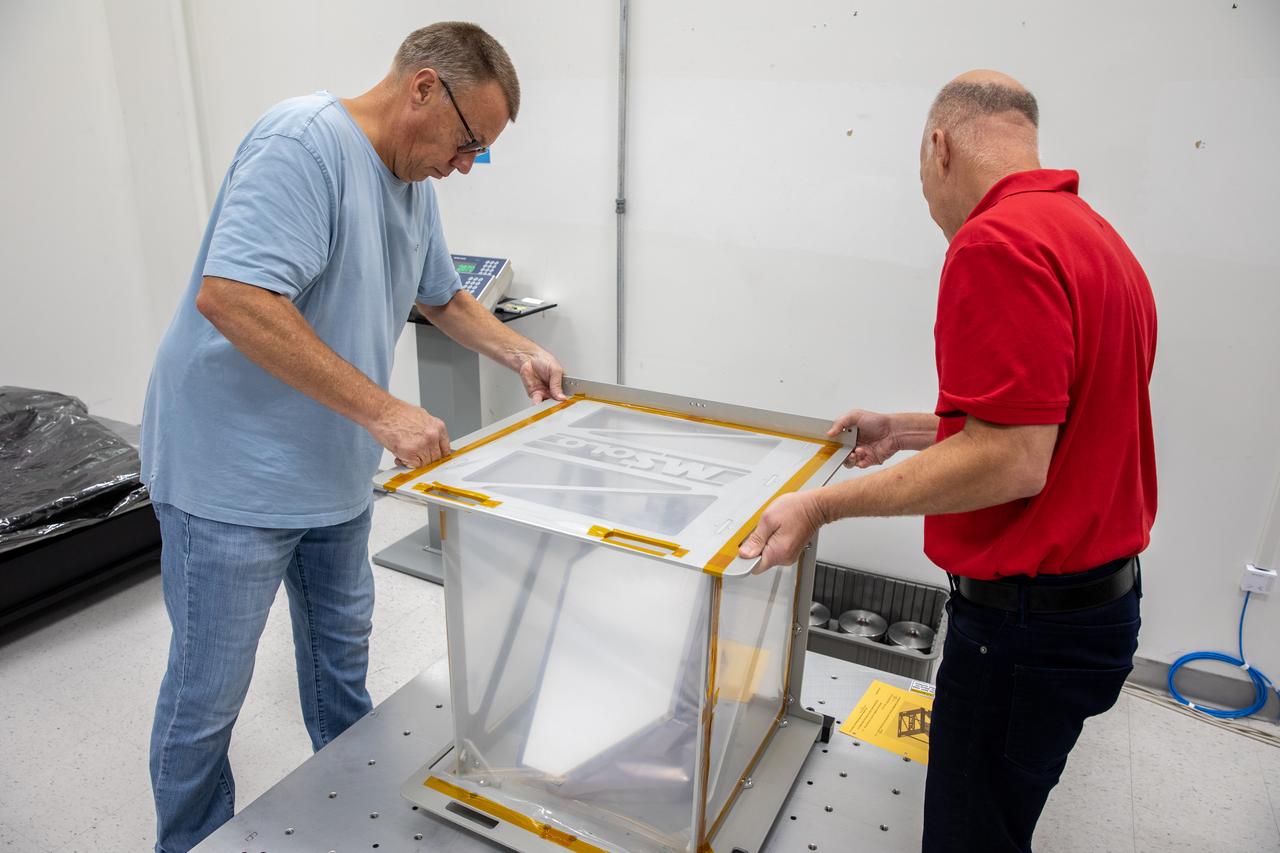

Engineers conduct a mass properties test on the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility in Florida on Nov. 22, 2022. Mass properties determines the mass and center of gravity of the flight unit. The lander uses this information, from all payloads, to improve stability and performance of the lander – and to a lesser degree, the stability and performance of the rocket. This marks the end of testing at Kennedy for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) MSolo instrument. It will soon be shipped to Intuitive Machines in Houston for integration on the NOVA-C landing platform. Launching in 2023, the PRIME-1 mission will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon.

Engineers conduct a mass properties test on the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility in Florida on Nov. 22, 2022. Mass properties determines the mass and center of gravity of the flight unit. The lander uses this information, from all payloads, to improve stability and performance of the lander – and to a lesser degree, the stability and performance of the rocket. This marks the end of testing at Kennedy for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) MSolo instrument. It will soon be shipped to Intuitive Machines in Houston for integration on the NOVA-C landing platform. Launching in 2023, the PRIME-1 mission will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon.
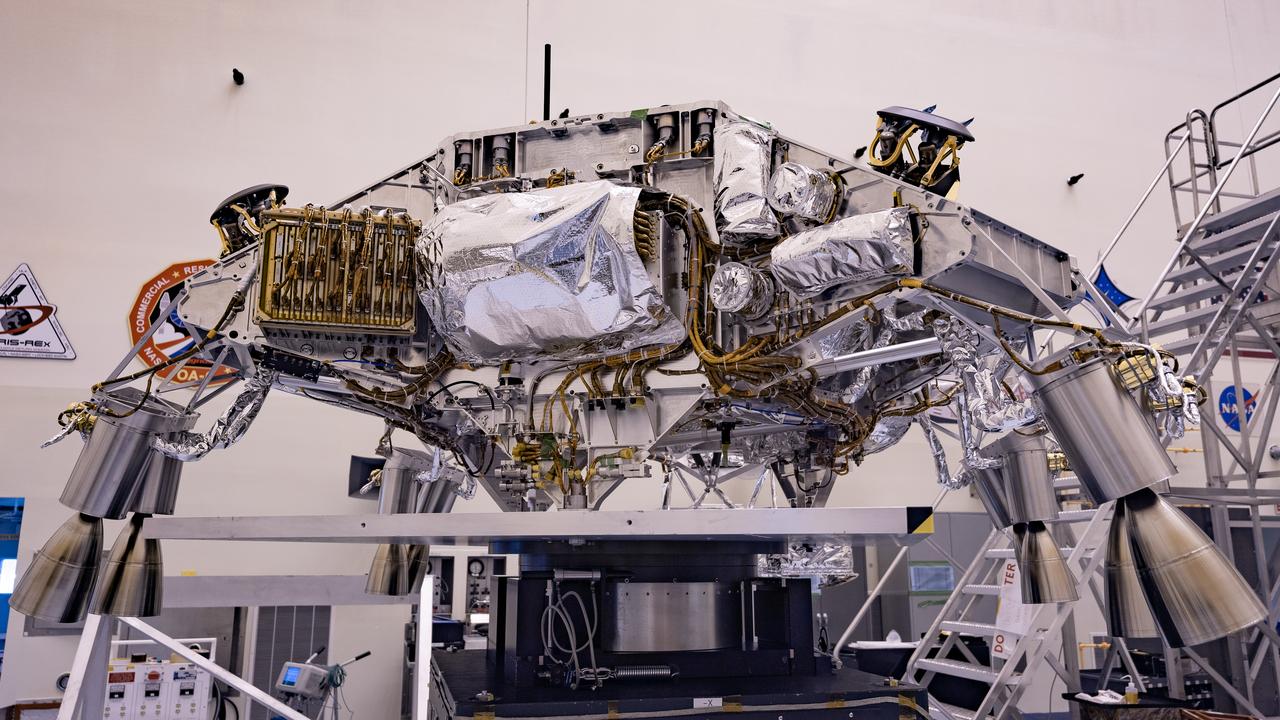
Engineers perform mass properties testing on the rocket-powered descent stage of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center on April 12, 2020. The testing to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides, was performed inside the Florida spaceport’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The descent stage will lower the rover through the thin Martian atmosphere and onto the surface on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The rover will seek signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for possible return to Earth.
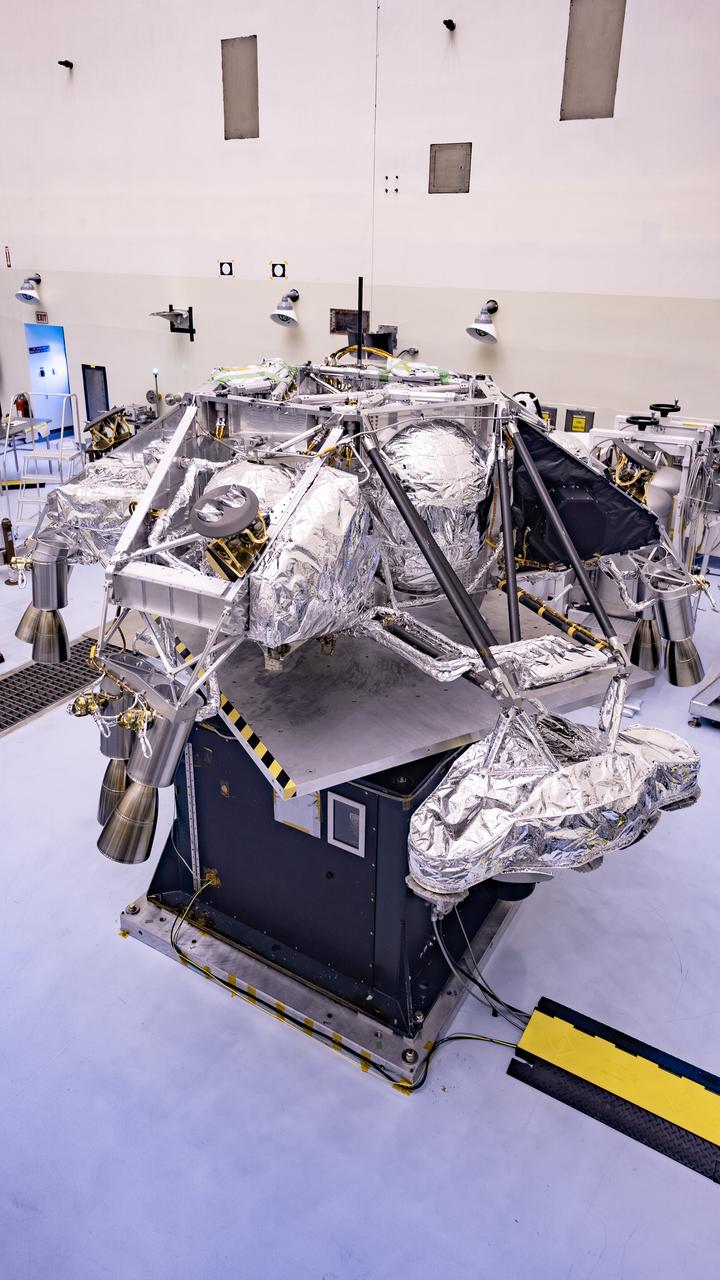

Engineers perform mass properties testing on the rocket-powered descent stage of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center on April 12, 2020. The testing to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides, was performed inside the Florida spaceport’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The descent stage will lower the rover through the thin Martian atmosphere and onto the surface on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The rover will seek signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for possible return to Earth.
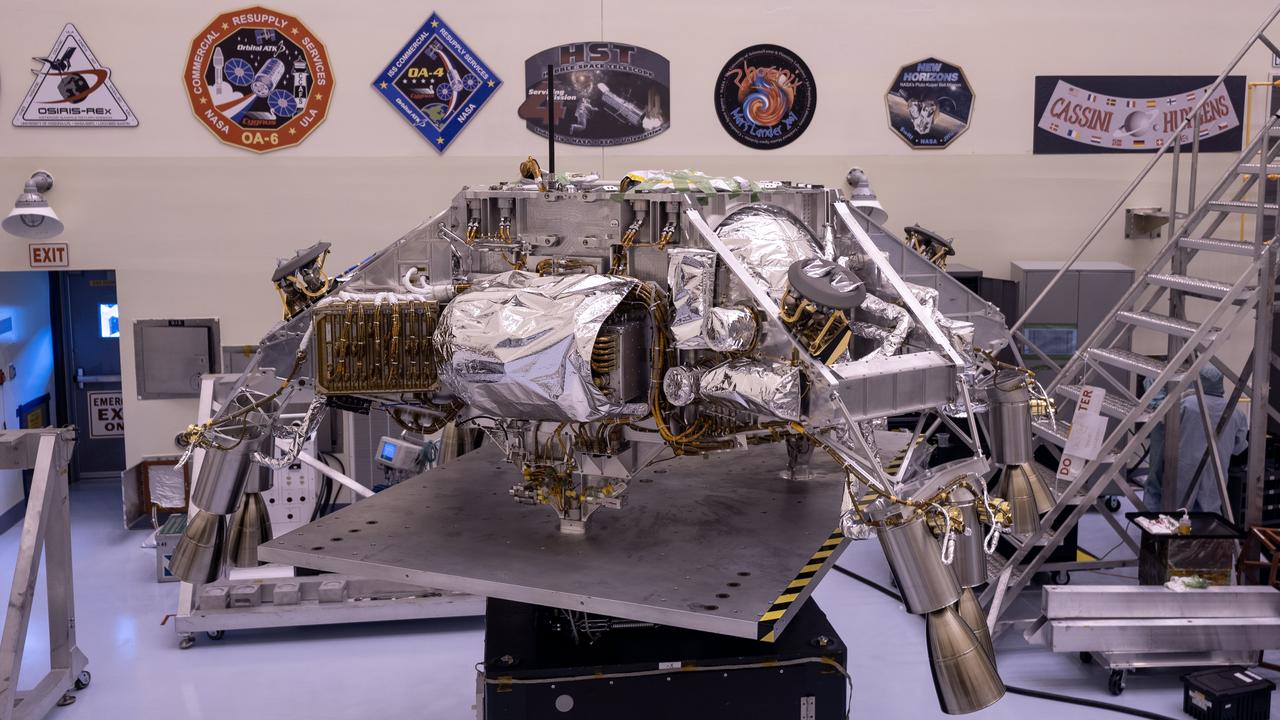

Engineers perform mass properties testing on the rocket-powered descent stage of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center on April 12, 2020. The testing to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides, was performed inside the Florida spaceport’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The descent stage will lower the rover through the thin Martian atmosphere and onto the surface on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The rover will seek signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for possible return to Earth.
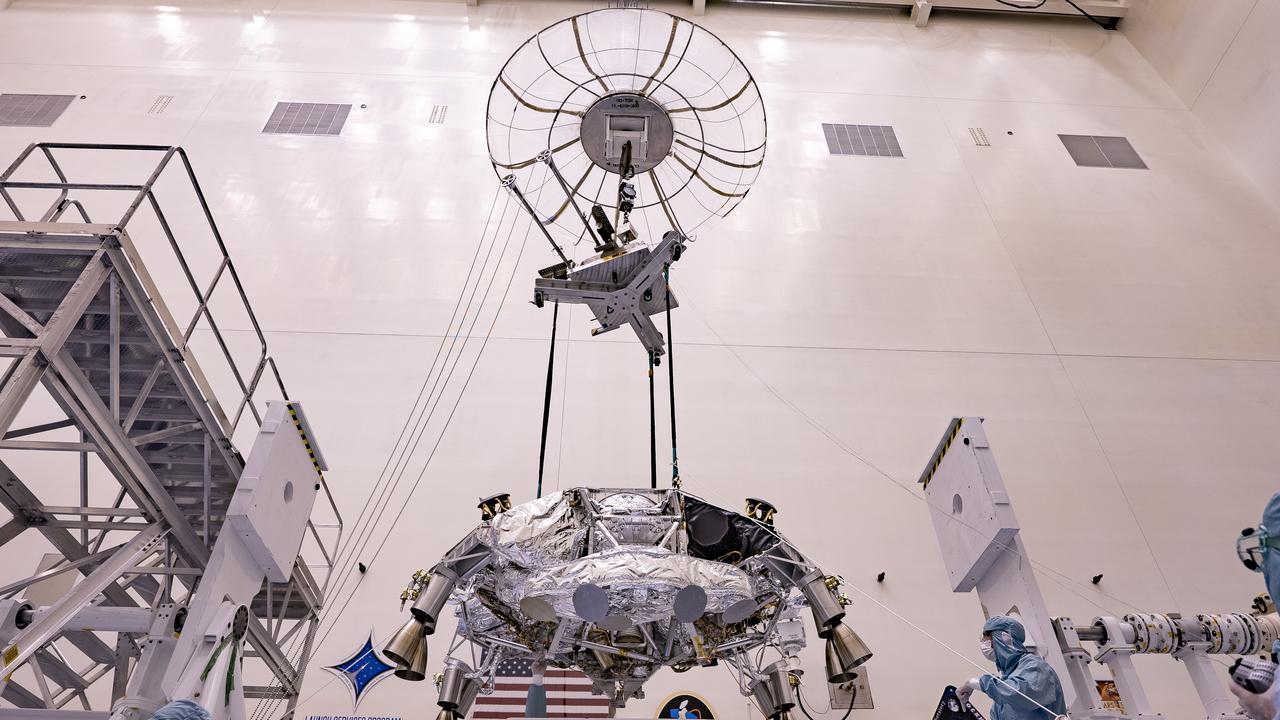
Engineers perform mass properties testing on the rocket-powered descent stage of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center on April 9, 2020. The testing to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides, was performed inside the Florida spaceport’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The descent stage will lower the rover through the thin Martian atmosphere and onto the surface on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The rover will seek signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for possible return to Earth.
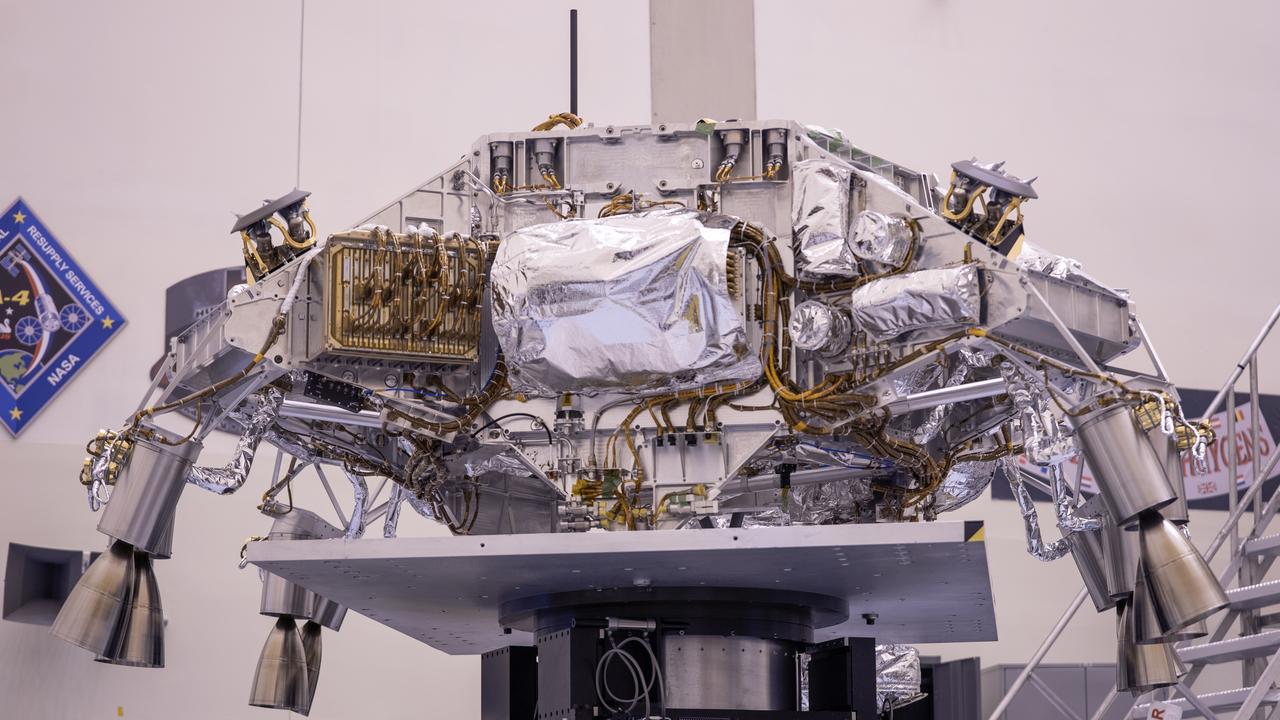
Engineers perform mass properties testing on the rocket-powered descent stage of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center on April 12, 2020. The testing to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides, was performed inside the Florida spaceport’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The descent stage will lower the rover through the thin Martian atmosphere and onto the surface on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The rover will seek signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for possible return to Earth.
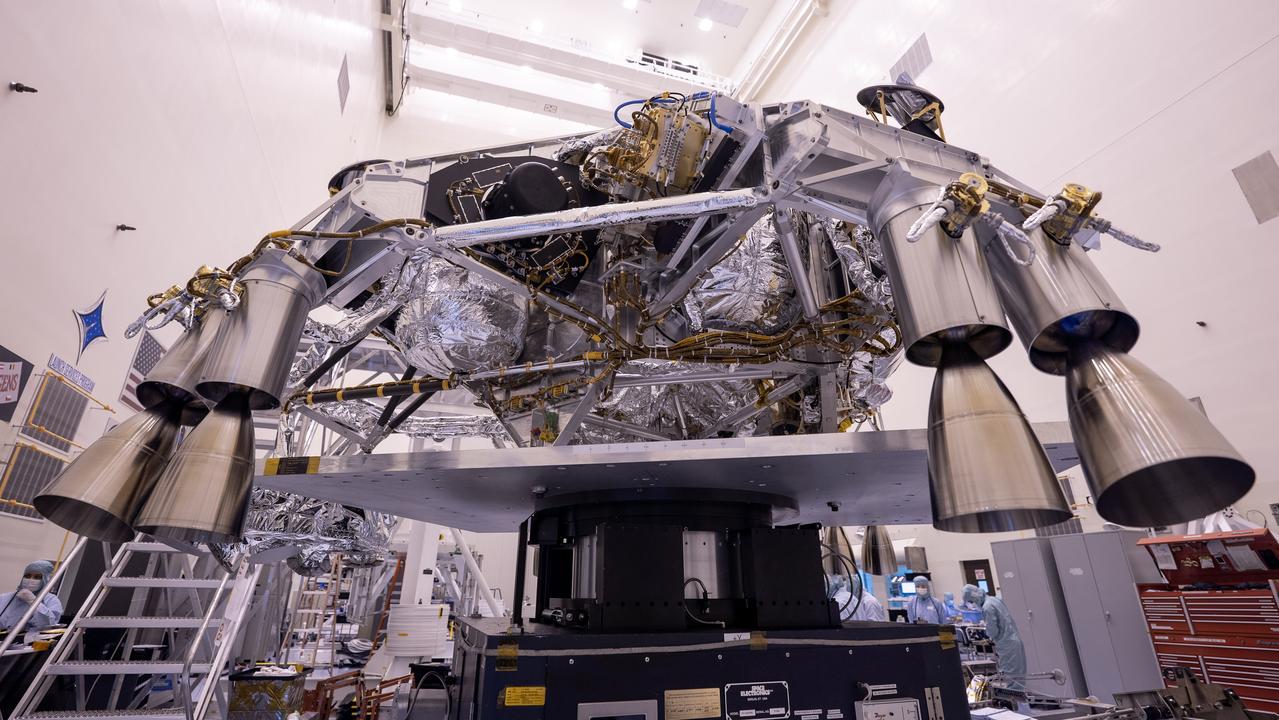

Engineers perform mass properties testing on the rocket-powered descent stage of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center on April 12, 2020. The testing to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides, was performed inside the Florida spaceport’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The descent stage will lower the rover through the thin Martian atmosphere and onto the surface on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The rover will seek signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for possible return to Earth.
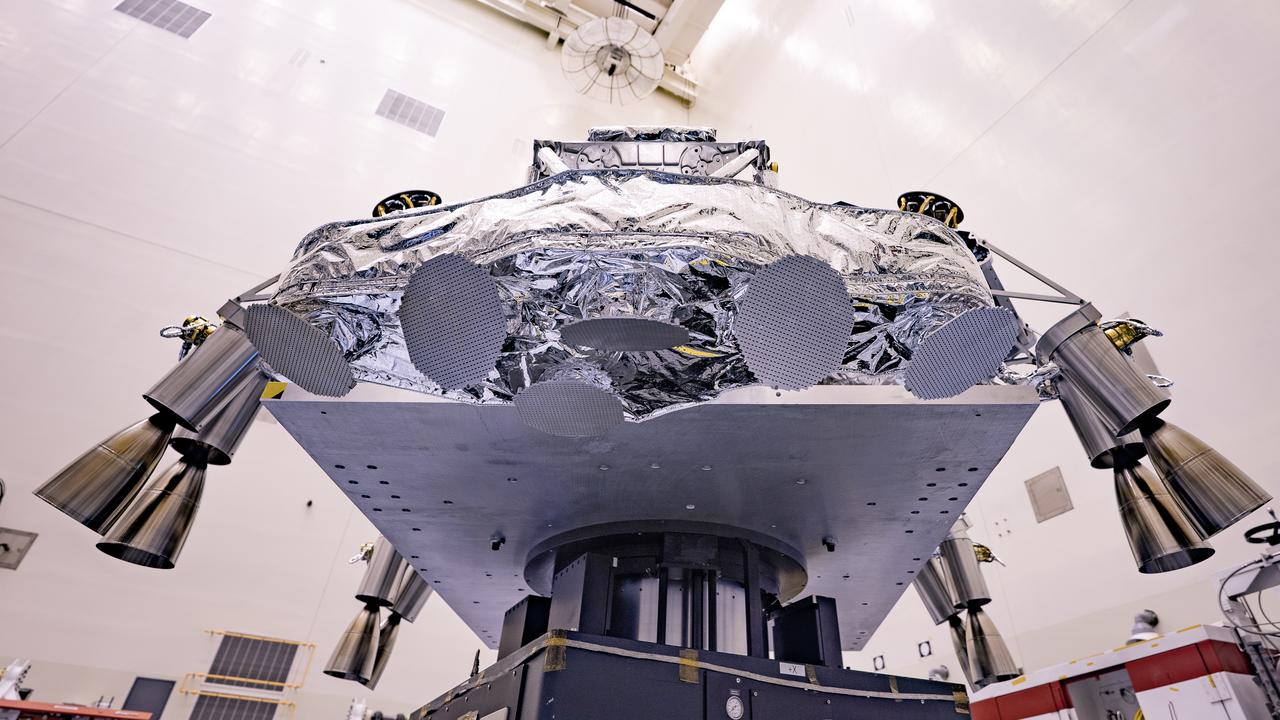

Engineers perform mass properties testing on the rocket-powered descent stage of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center on April 12, 2020. The testing to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides, was performed inside the Florida spaceport’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The descent stage will lower the rover through the thin Martian atmosphere and onto the surface on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The rover will seek signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for possible return to Earth.
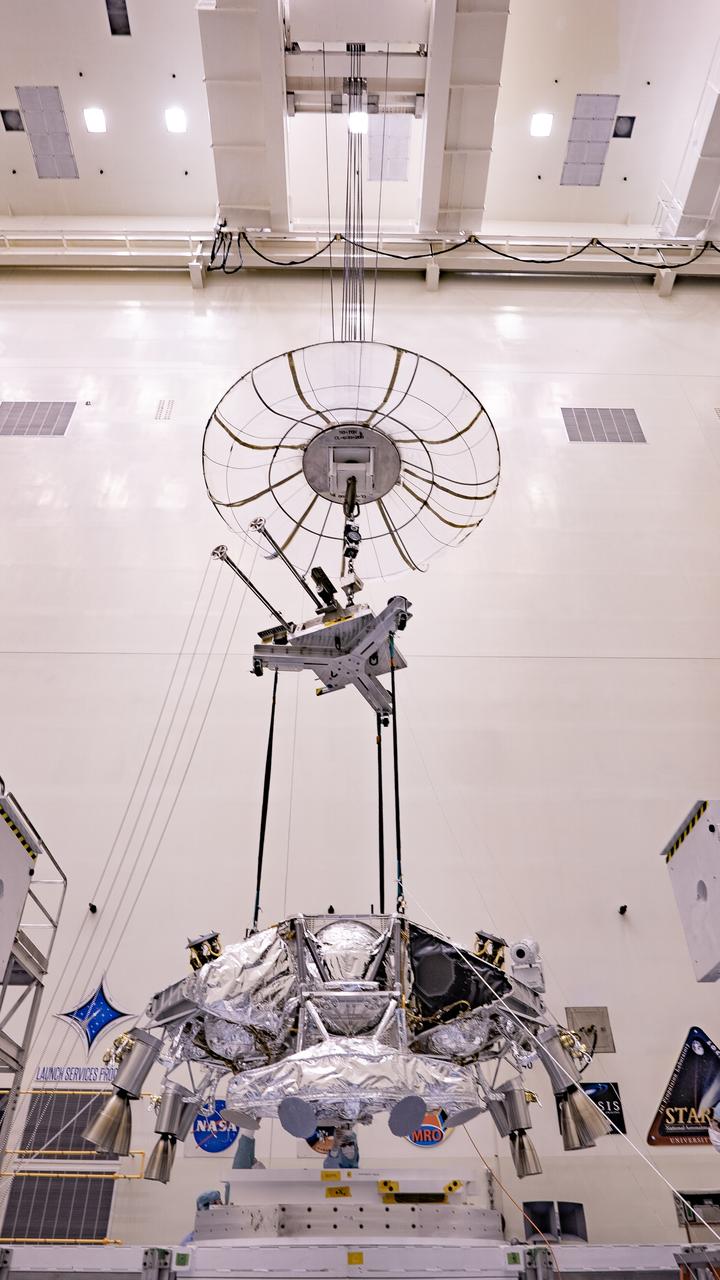

Engineers perform mass properties testing on the rocket-powered descent stage of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center on April 9, 2020. The testing to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides, was performed inside the Florida spaceport’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The descent stage will lower the rover through the thin Martian atmosphere and onto the surface on Feb. 18, 2021. Liftoff, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, is targeted between July 17 and Aug. 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The rover will seek signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for possible return to Earth.
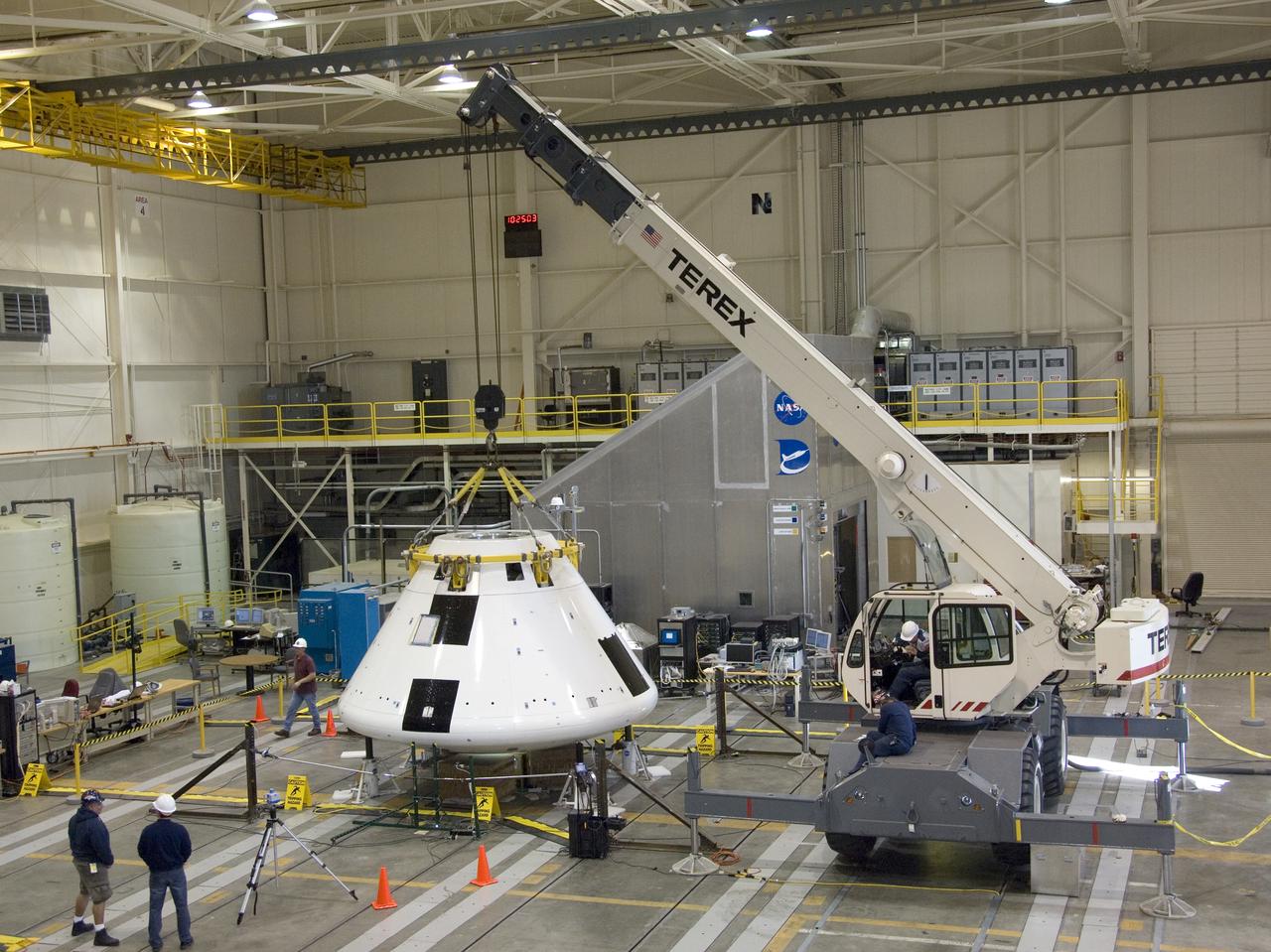

Under the watchful eyes of technicians, a crane positions the Orion PA-1 Abort Flight Test module for mass properties testing in NASA Dryden's Flight Loads Lab.
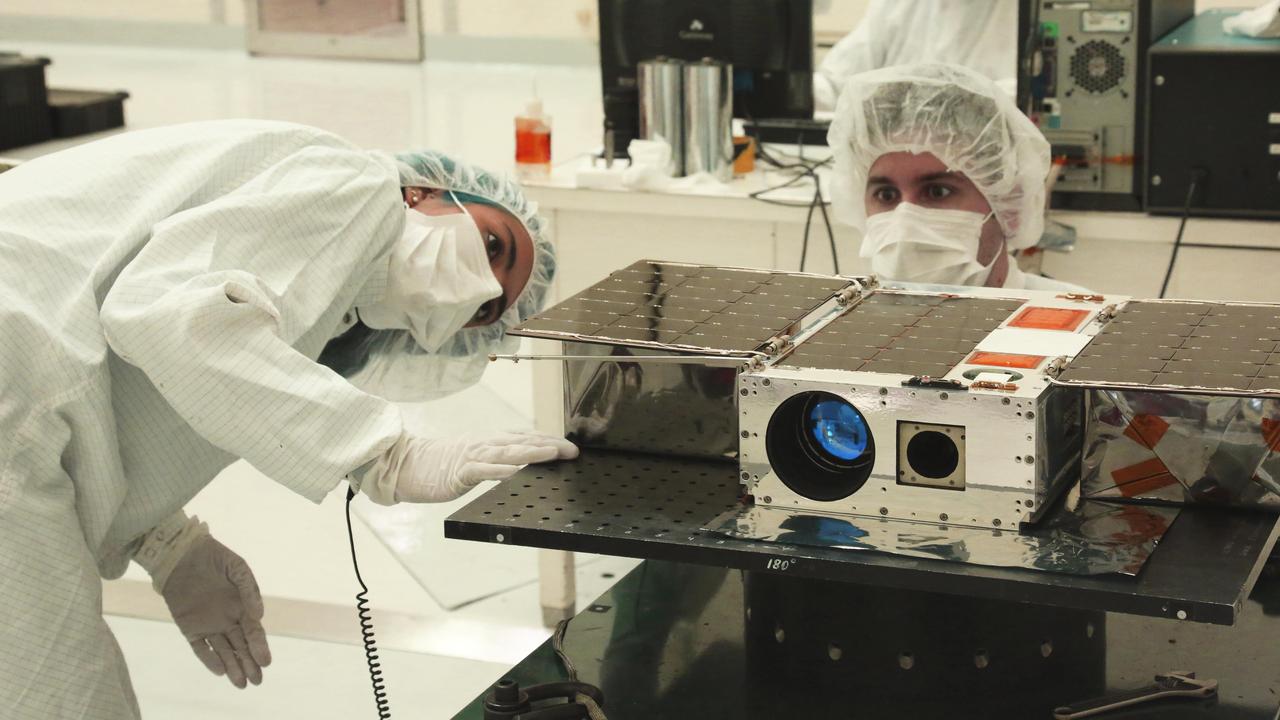

Left to right: Electrical Test Engineer Esha Murty and Integration and Test Lead Cody Colley prepare the ASTERIA spacecraft for mass-properties measurements in April 2017 prior to spacecraft delivery ahead of launch. ASTERIA was deployed from the International Space Station in November 2017. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23406
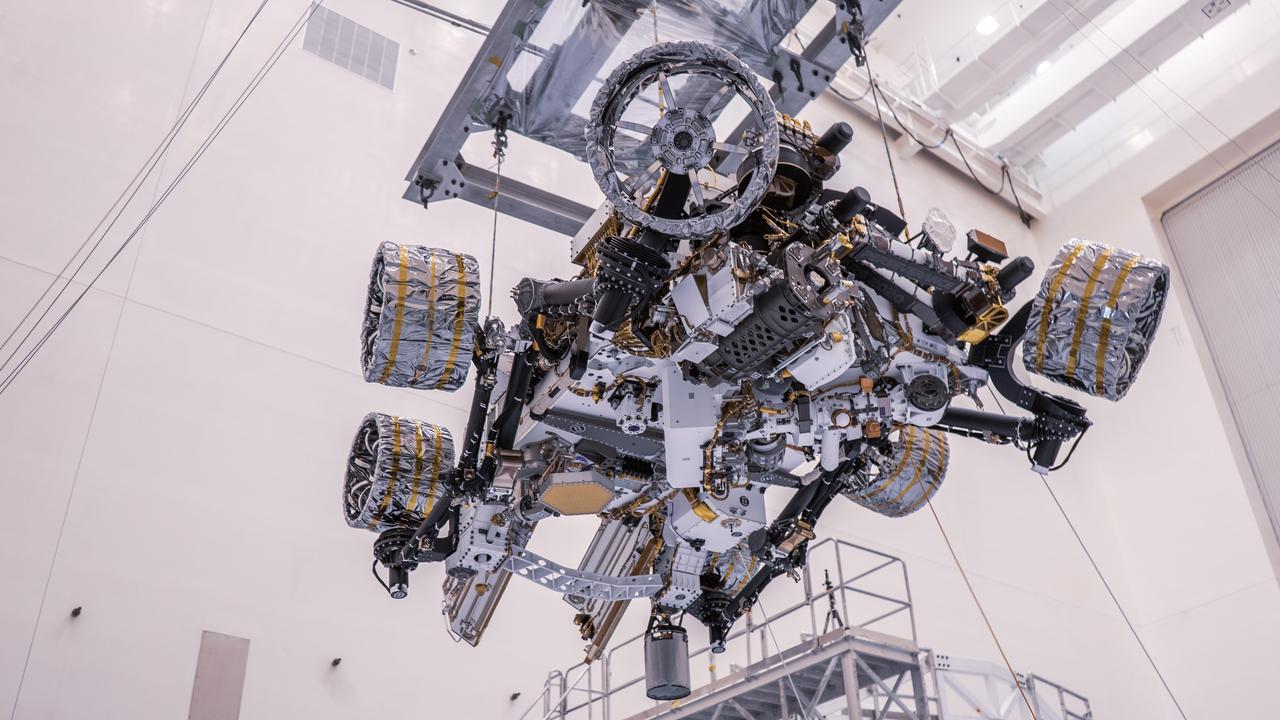
NASA's Perseverance rover is moved during a test of its mass properties at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The image was taken on April 7, 2020. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23829
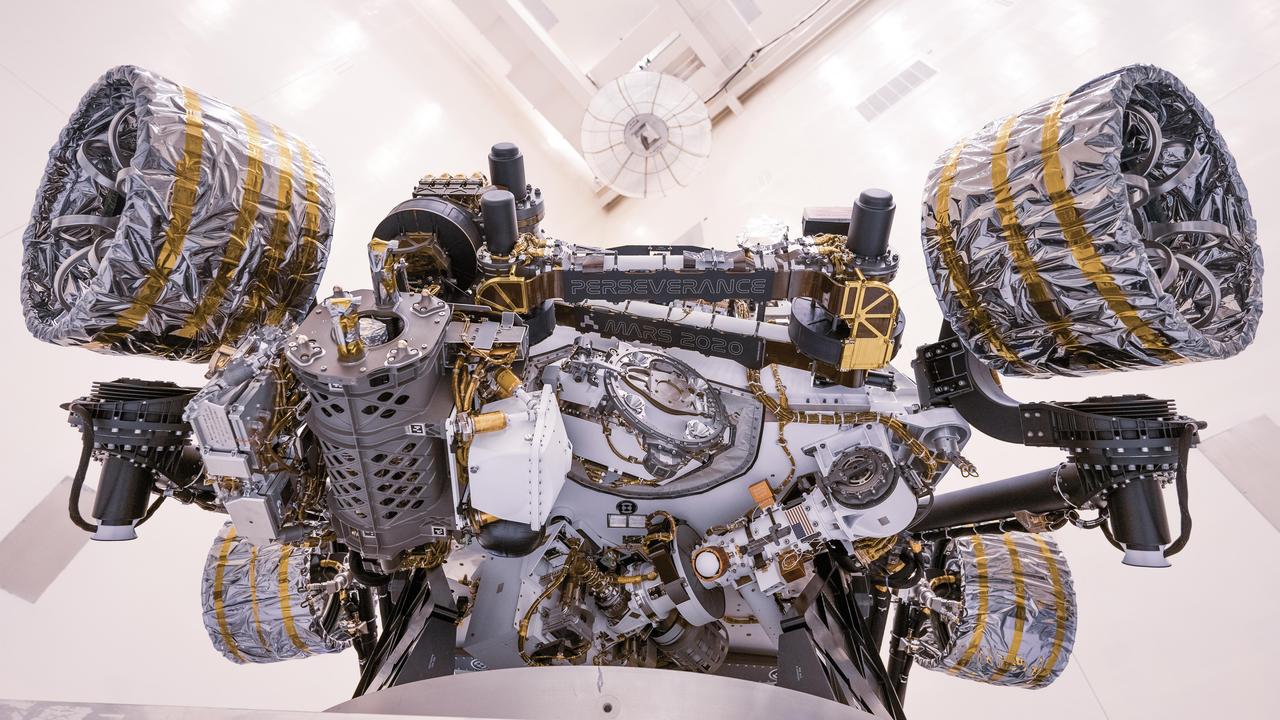
This image of the Perseverance Mars rover was taken at NASA's Kennedy Space Center on April 7, 2020, during a test of the vehicle's mass properties. The rover was rotated clockwise and counterclockwise on a spin table to determine the center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides. In the image, the project name "Mars 2020" and rover name "Perseverance" can be seen on name plates that have been attached to the rover's robotic arm. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23828
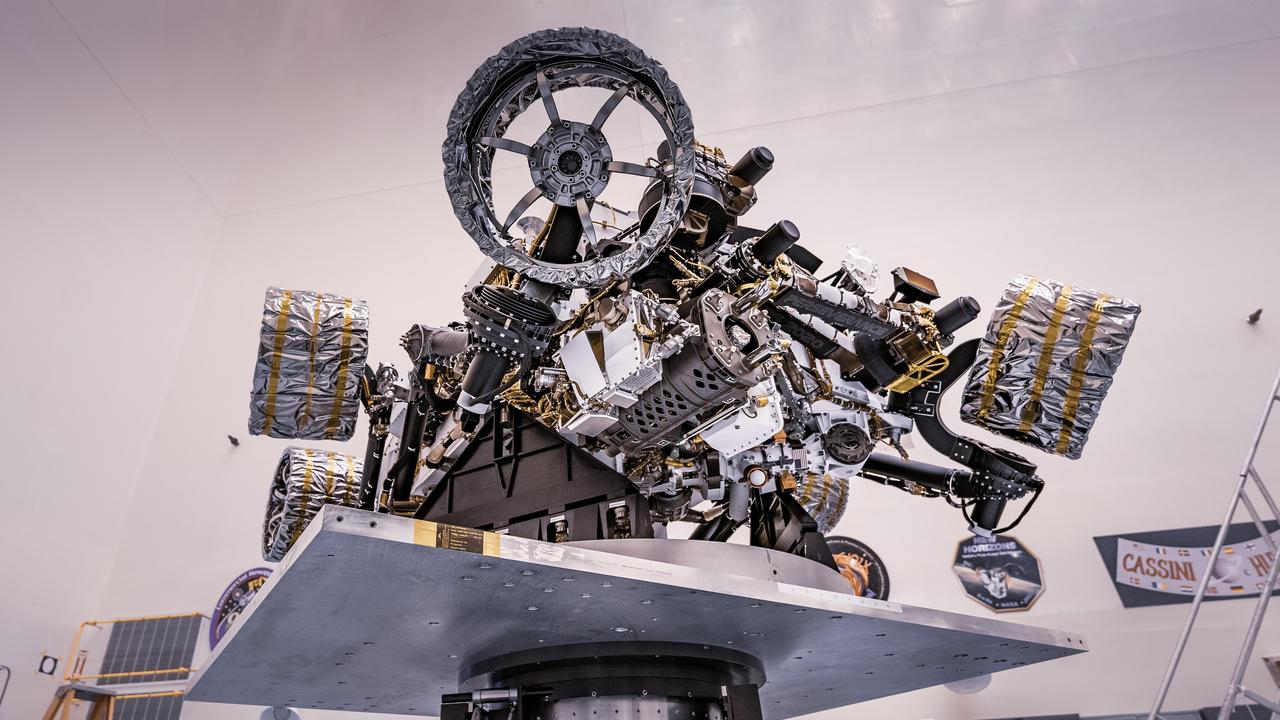
NASA's Perseverance rover can be seen attached to a spin table during a test of its mass properties at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. During the test, the rover was rotated clockwise and counterclockwise to determine its center of gravity, or the point at which weight is evenly dispersed on all sides. The image was taken on April 7, 2020. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23826
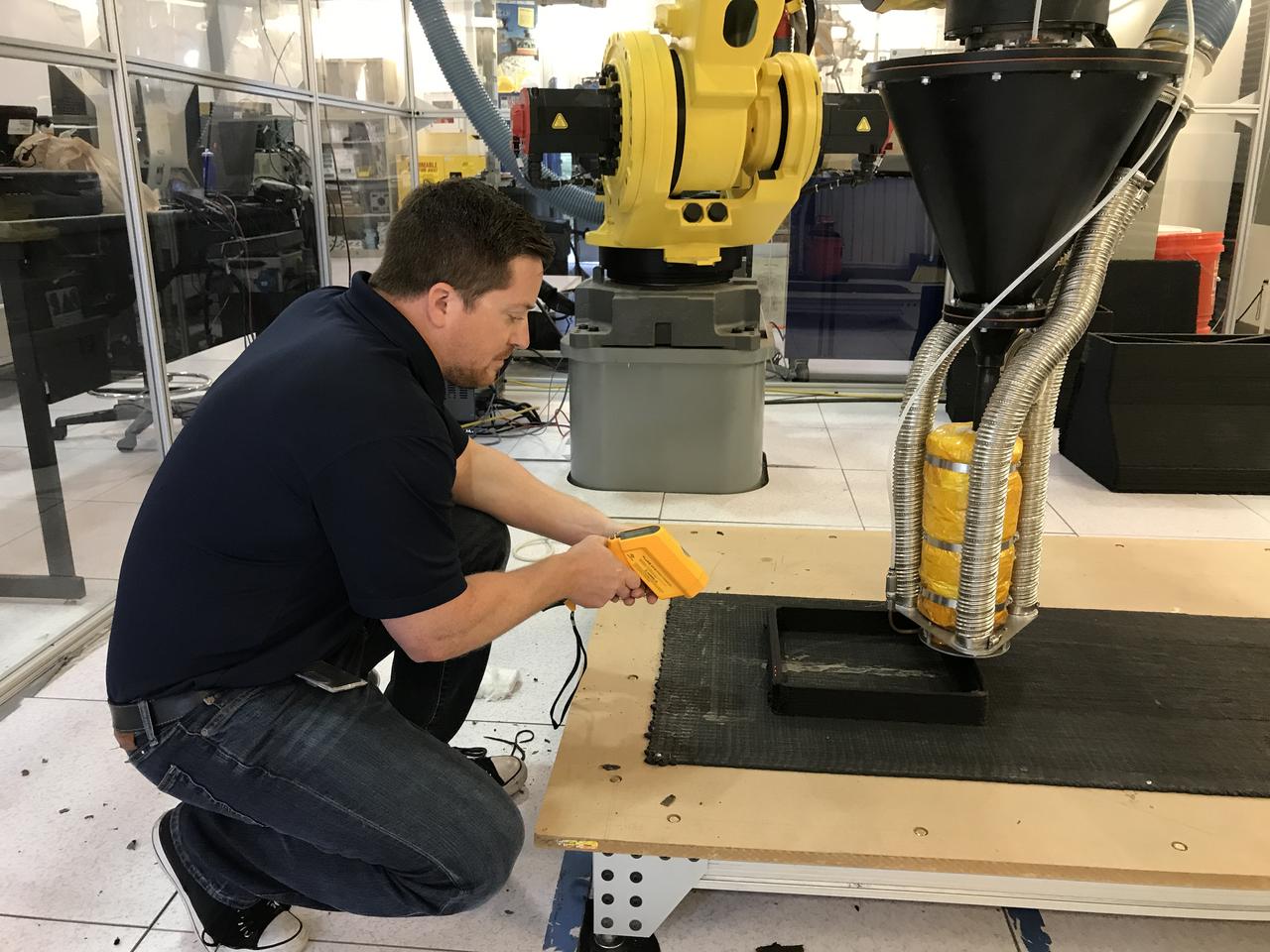

Packing light is the idea behind the Zero Launch Mass 3-D Printer. Instead of loading up on heavy building supplies, a large scale 3-D printer capable of using recycled plastic waste and dirt at the destination as construction material would save mass and money when launching robotic precursor missions to build infrastructure on the Moon or Mars in preparation for human habitation. To make this a reality, Nathan Gelino, a researcher engineer with NASA’s Swamp Works at Kennedy Space Center, measured the temperature of a test specimen from the 3-D printer Tuesday as an early step in characterizing printed material strength properties. Material temperature plays a large role in the strength of bonds between layers.
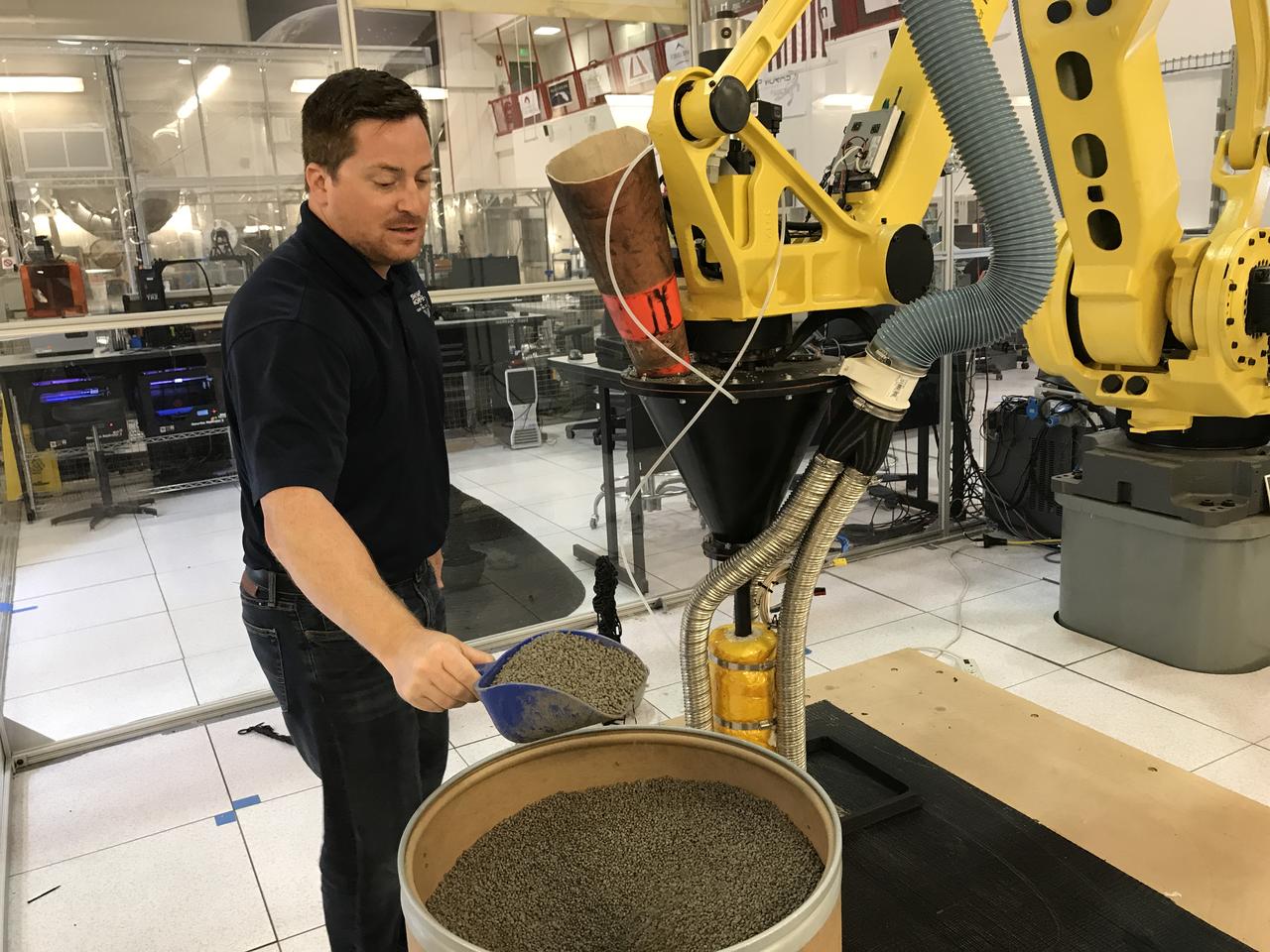

Nathan Gelino, a research engineer, manually loads materials into the Zero Launch Mass 3-D Printer at Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works Tuesday. The 3-D printer heated the pellets to about 600 degrees F and extruded them to produce specimens for material strength properties testing. Automated pellet delivery system will be added to the printer soon.
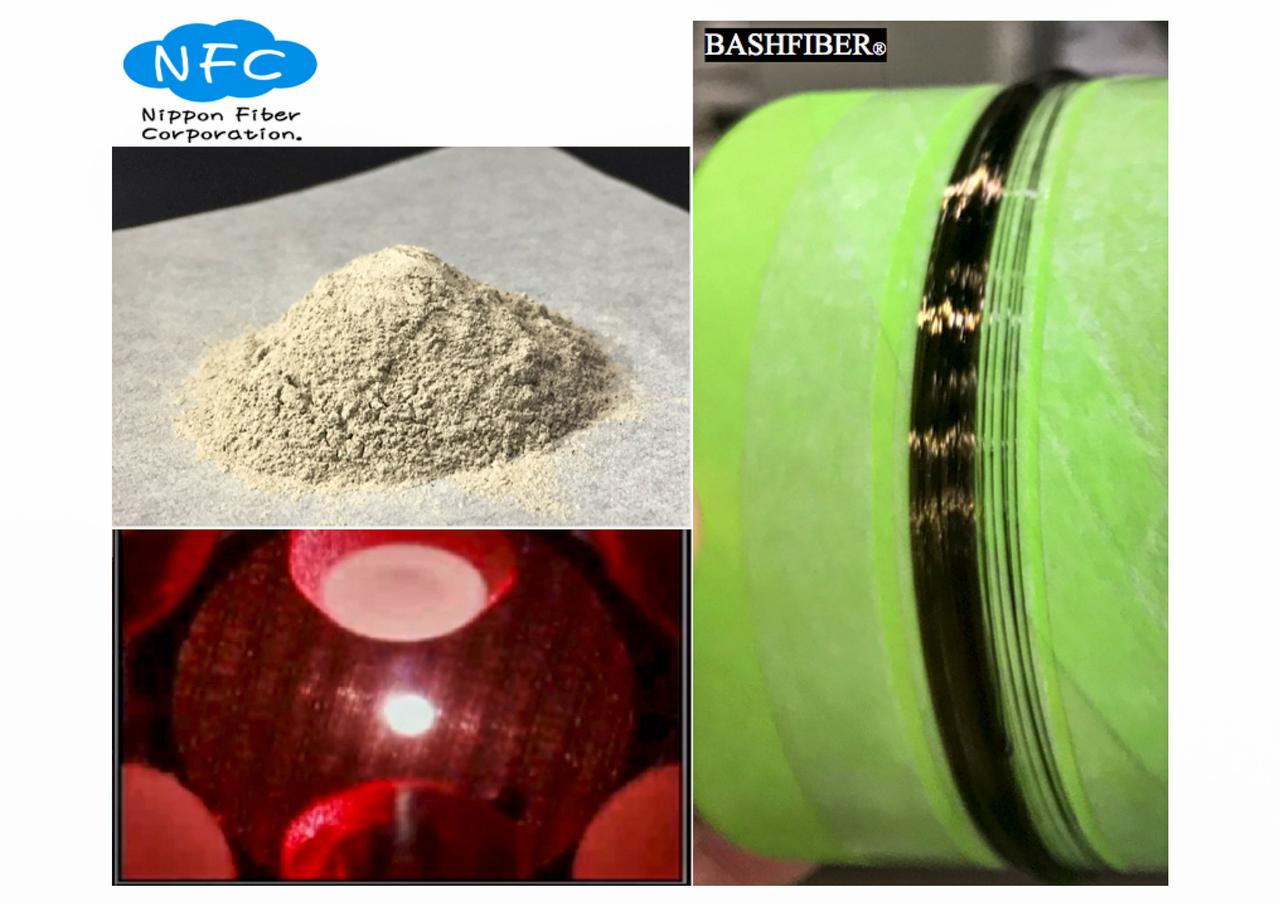

jsc2020e040946 (9/10/2020) --- A picture of roving fiber (right), which is made from fly ash (upper left) in a Japanese thermal power station. A mass production project for this fiber is in progress. Detailed properties are being investigated on the ISS. One of the tests was conducted at the Electrostatic Levitation Furnace (ELF) aboard the ISS from April to May 2020 (lower left). The Exposure test of of BASHFIBER® (ExHAM-Nippon Fiber-2) tests the resistance of a thread-like fiber to cosmic rays on the exterior of the International Space Station (ISS). BASHFIBER is a mixture of basalt rock and fly ash, with high resistance to acid and salt. The fiber has the potential for a variety of applications making use of an abundant byproduct.
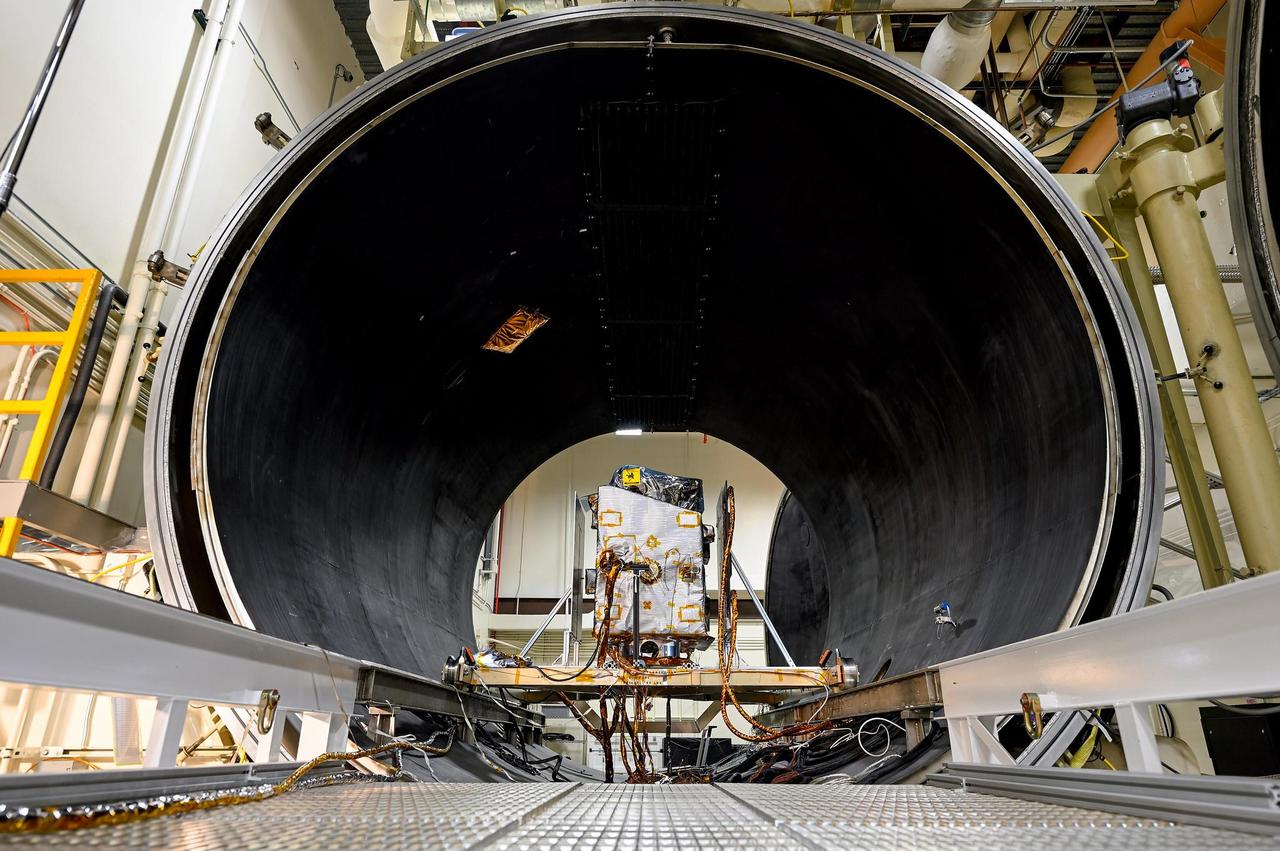

NASA's Lunar Trailblazer undergoes thermal vacuum chamber (TVAC) testing at Lockheed Martin Space in Littleton, Colorado, in June 2023. The extremely low pressures and temperatures during these tests simulate the conditions that the spacecraft will experience during in space. Lunar Trailblazer, which has a mass of about 440 pounds (200 kilograms) and measures only 11.5 feet (3.5 meters) wide with its solar panels deployed, has now completed TVAC testing and is nearing completion before its planned launch in early 2024. The spacecraft's two science instruments will map the form, abundance, and locations of water in on the lunar surface while also revealing the thermal properties and surface composition of those regions. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25836
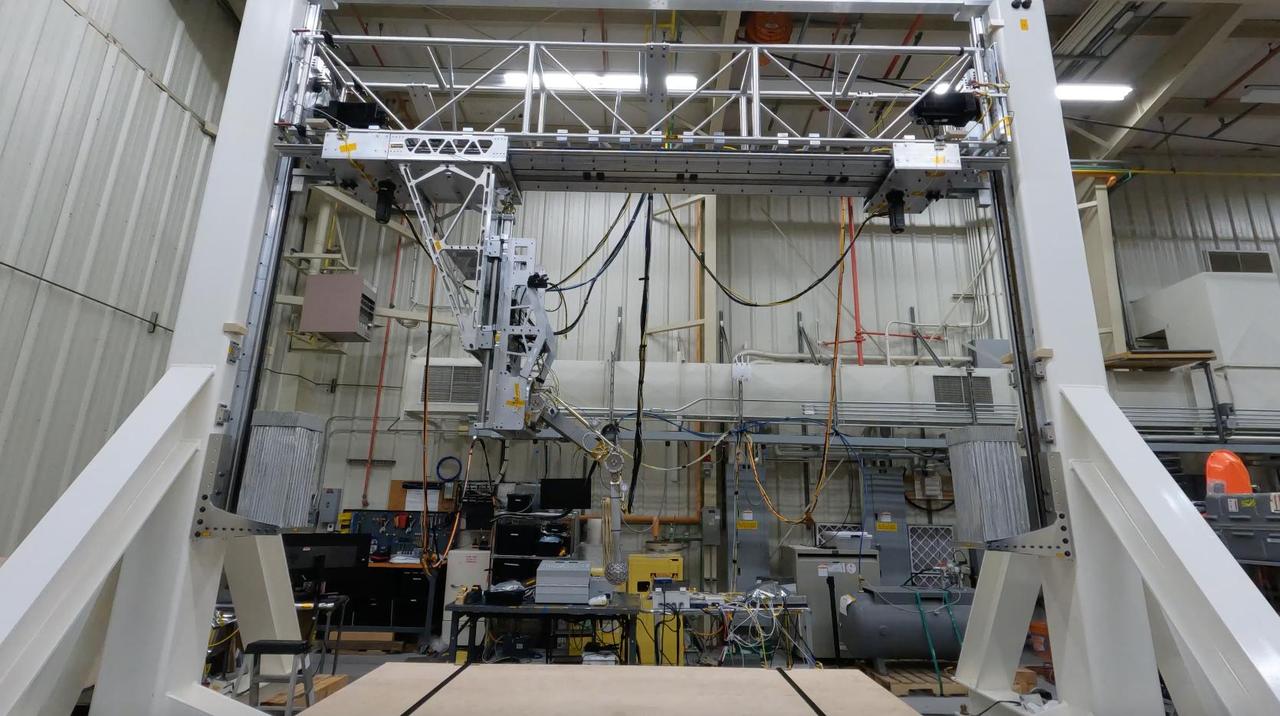

Engineers test the mechanical landing system for the proposed Europa Lander project at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on Sept. 15, 2022. This test, using the Europa Lander landing gear testbed, fully exercises the Europa Lander landing gear mechanism through a simulated dynamic landing. Europa Lander is a concept for a potential future mission that would look for signs of life in the icy surface material of Jupiter's moon Europa. The moon is thought to contain a global ocean of salty water beneath its frozen crust. If life exists in that ocean, signs of its existence called biosignatures could potentially find their way to the surface. In this mission concept, a spacecraft would land on Europa and collect and study samples from about 4 inches (10 centimeters) beneath the surface, looking for signs of life. The Europa Lander landing gear testbed was developed to test and inform the design of the landing gear for the spacecraft: It mimics the landing loads and ground interaction forces that a single flight landing gear would experience when touching down on the Europan surface. It does this by using gravity offloading to simulate the reduced gravity on Europa, and by replicating the mass and inertial properties of a flight lander as well as all the degrees of freedom that the landing gear would experience. Video available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26199
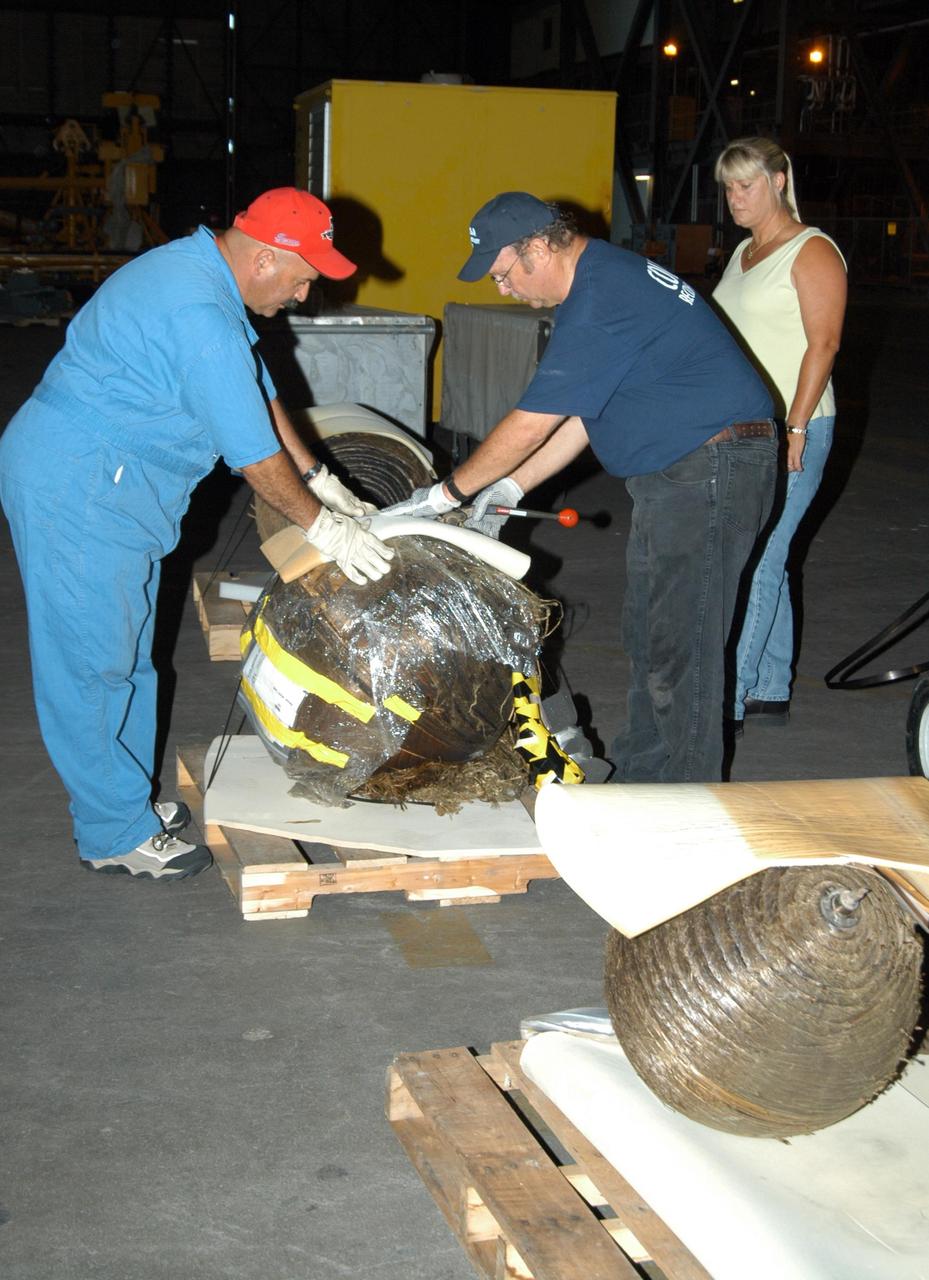

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - United Space Alliance workers begin packing pieces of Columbia debris for shipment to The Aerospace Corporation in El Segundo, Calif. The pieces have been released for loan to the non-governmental agency for testing and research. The Aerospace Corporation requested and will receive graphite/epoxy honeycomb skins from an Orbital Maneuvering System pod, Main Propulsion System Helium tanks, a Reaction Control System Helium tank and a Power Reactant Storage Distribution system tank. The company will use the parts to study re-entry effects on composite materials. NASA notified the Columbia crew’s families about the loan before releasing the items for study. Researchers believe the testing will show how materials are expected to respond to various heating and loads' environments. The findings will help calibrate tools and models used to predict hazards to people and property from reentering hardware. The Aerospace Corporation will have the debris for one year to perform analyses to estimate maximum temperatures during reentry based upon the geometry and mass of the recovered composite. Columbia’s debris is stored in the VAB.
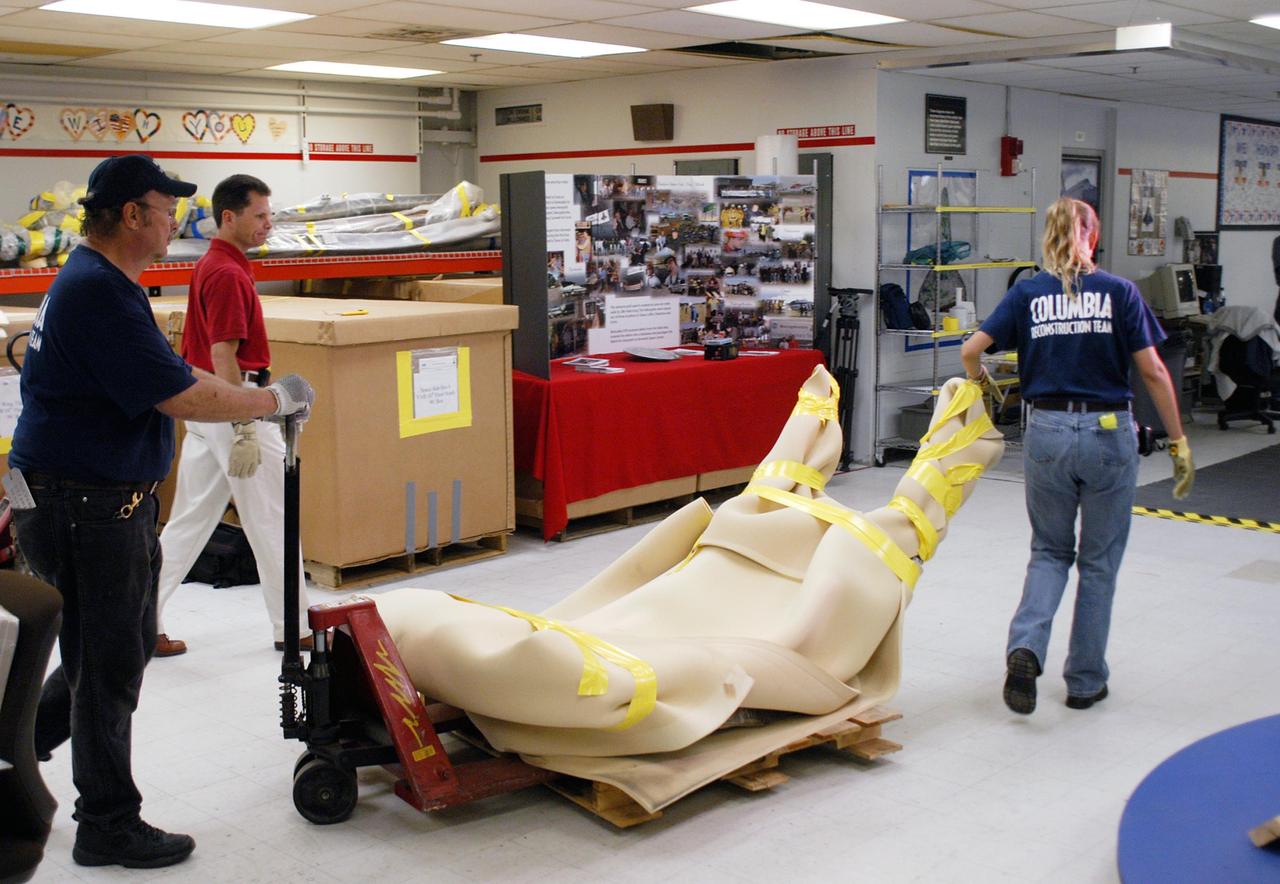

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - United Space Alliance workers J.C. Harrison (far left) and Amy Mangiacapra guide a wrapped piece of Columbia debris through the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it is stored. Alongside is NASA’s Scott Thurston, who is the Columbia debris coordinator. This piece is one of eight being released to The Aerospace Corporation in El Segundo, Calif., for testing and research. The Aerospace Corporation requested and will receive graphite/epoxy honeycomb skins from an Orbital Maneuvering System pod, Main Propulsion System Helium tanks, a Reaction Control System Helium tank and a Power Reactant Storage Distribution system tank. The company will use the parts to study re-entry effects on composite materials. NASA notified the Columbia crew’s families about the loan before releasing the items for study. Researchers believe the testing will show how materials are expected to respond to various heating and loads' environments. The findings will help calibrate tools and models used to predict hazards to people and property from reentering hardware. The Aerospace Corporation will have the debris for one year to perform analyses to estimate maximum temperatures during reentry based upon the geometry and mass of the recovered composite.
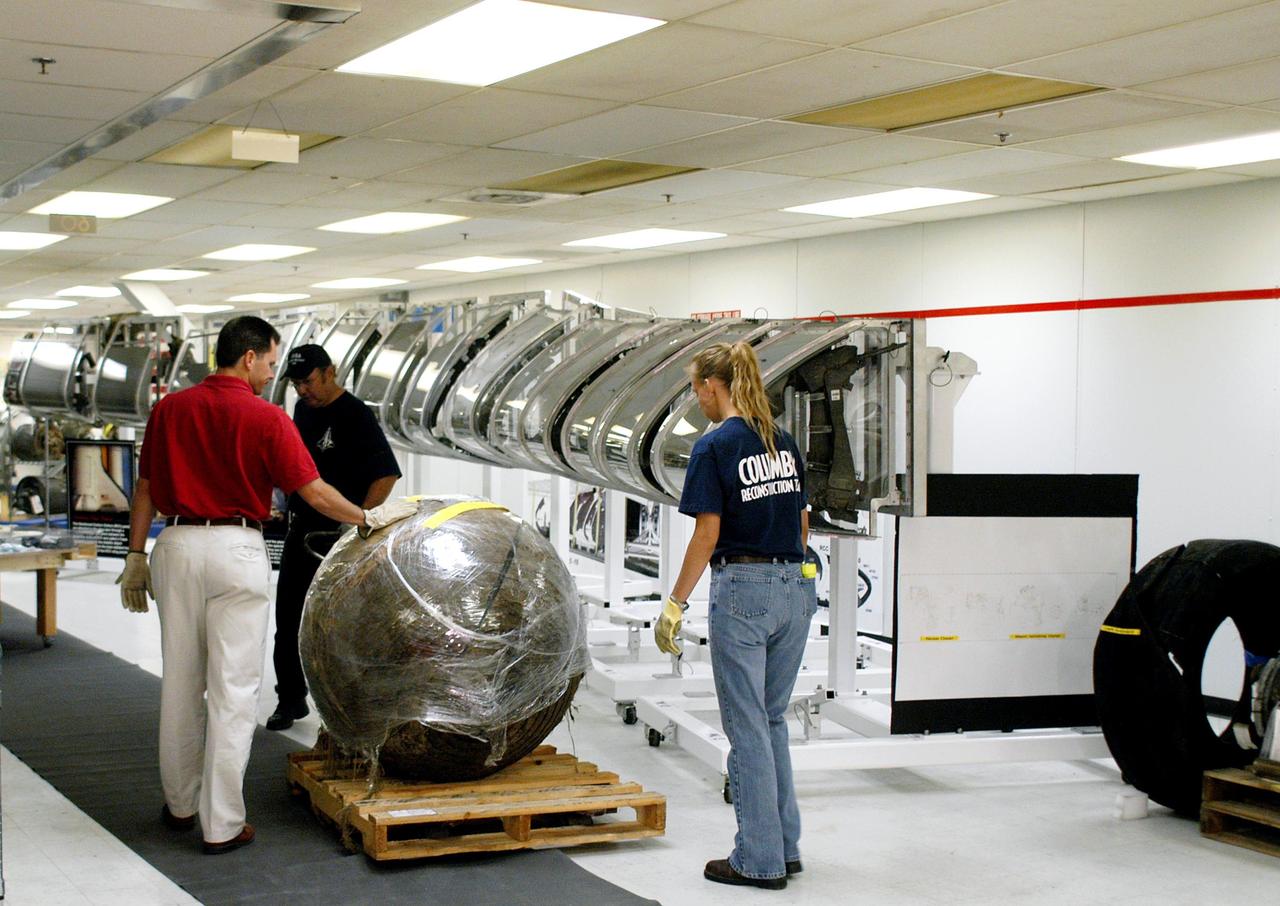

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - With NASA’s Scott Thurston (left) alongside, United Space Alliance workers J.C. Harrison (in cap) and Amy Mangiacapra (right) begin moving a piece of Columbia debris being shipped to The Aerospace Corporation in El Segundo, Calif. Thurston is the Columbia debris coordinator. The pieces have been released for loan to the non-governmental agency for testing and research. The Aerospace Corporation requested and will receive graphite/epoxy honeycomb skins from an Orbital Maneuvering System pod, Main Propulsion System Helium tanks, a Reaction Control System Helium tank and a Power Reactant Storage Distribution system tank. The company will use the parts to study re-entry effects on composite materials. NASA notified the Columbia crew’s families about the loan before releasing the items for study. Researchers believe the testing will show how materials are expected to respond to various heating and loads' environments. The findings will help calibrate tools and models used to predict hazards to people and property from reentering hardware. The Aerospace Corporation will have the debris for one year to perform analyses to estimate maximum temperatures during reentry based upon the geometry and mass of the recovered composite. Columbia’s debris is stored in the VAB.
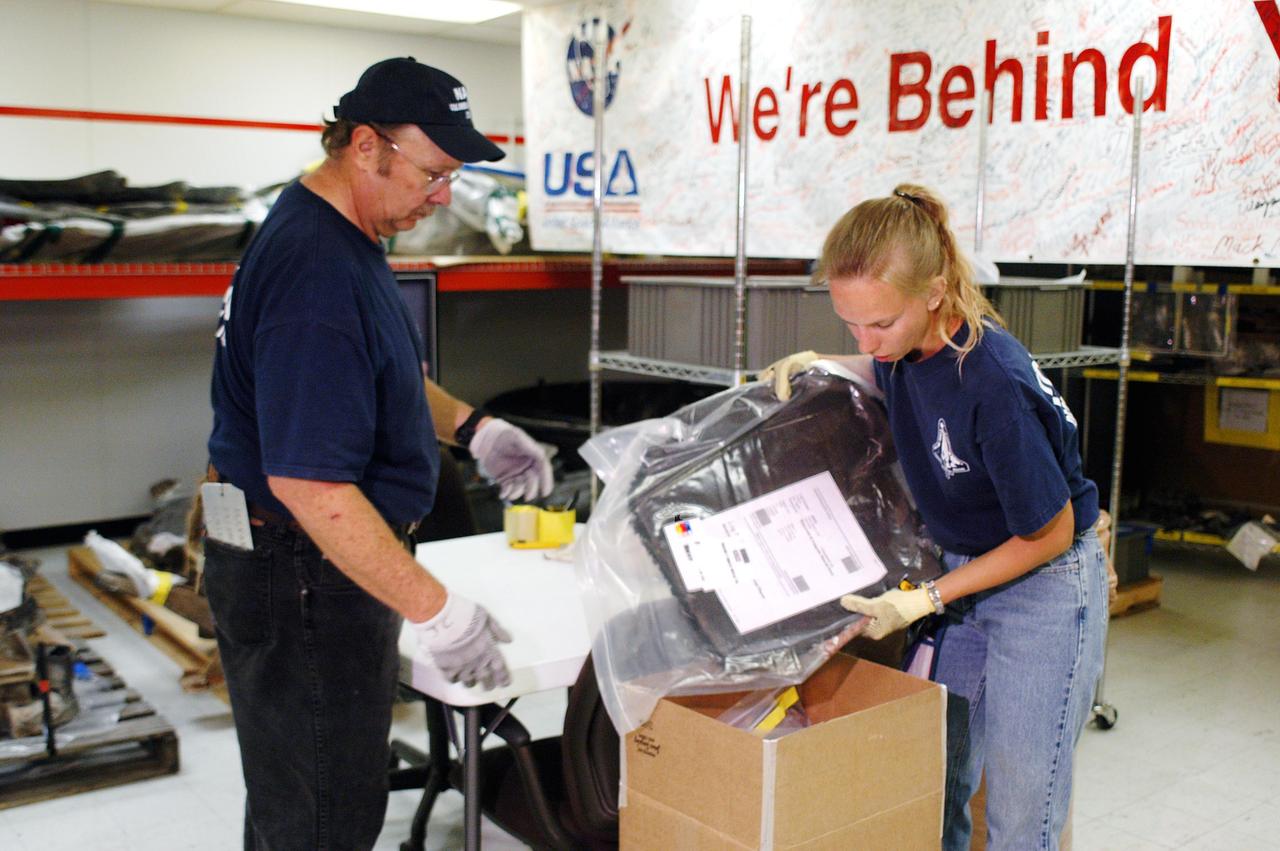

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - United Space Alliance workers J.C. Harrison (left) and Amy Mangiacapra (right) pack up pieces of Columbia debris for shipment to The Aerospace Corporation in El Segundo, Calif. The pieces have been released for loan to the non-governmental agency for testing and research. The Aerospace Corporation requested and will receive graphite/epoxy honeycomb skins from an Orbital Maneuvering System pod, Main Propulsion System Helium tanks, a Reaction Control System Helium tank and a Power Reactant Storage Distribution system tank. The company will use the parts to study re-entry effects on composite materials. NASA notified the Columbia crew’s families about the loan before releasing the items for study. Researchers believe the testing will show how materials are expected to respond to various heating and loads' environments. The findings will help calibrate tools and models used to predict hazards to people and property from reentering hardware. The Aerospace Corporation will have the debris for one year to perform analyses to estimate maximum temperatures during reentry based upon the geometry and mass of the recovered composite. Columbia’s debris is stored in the VAB.
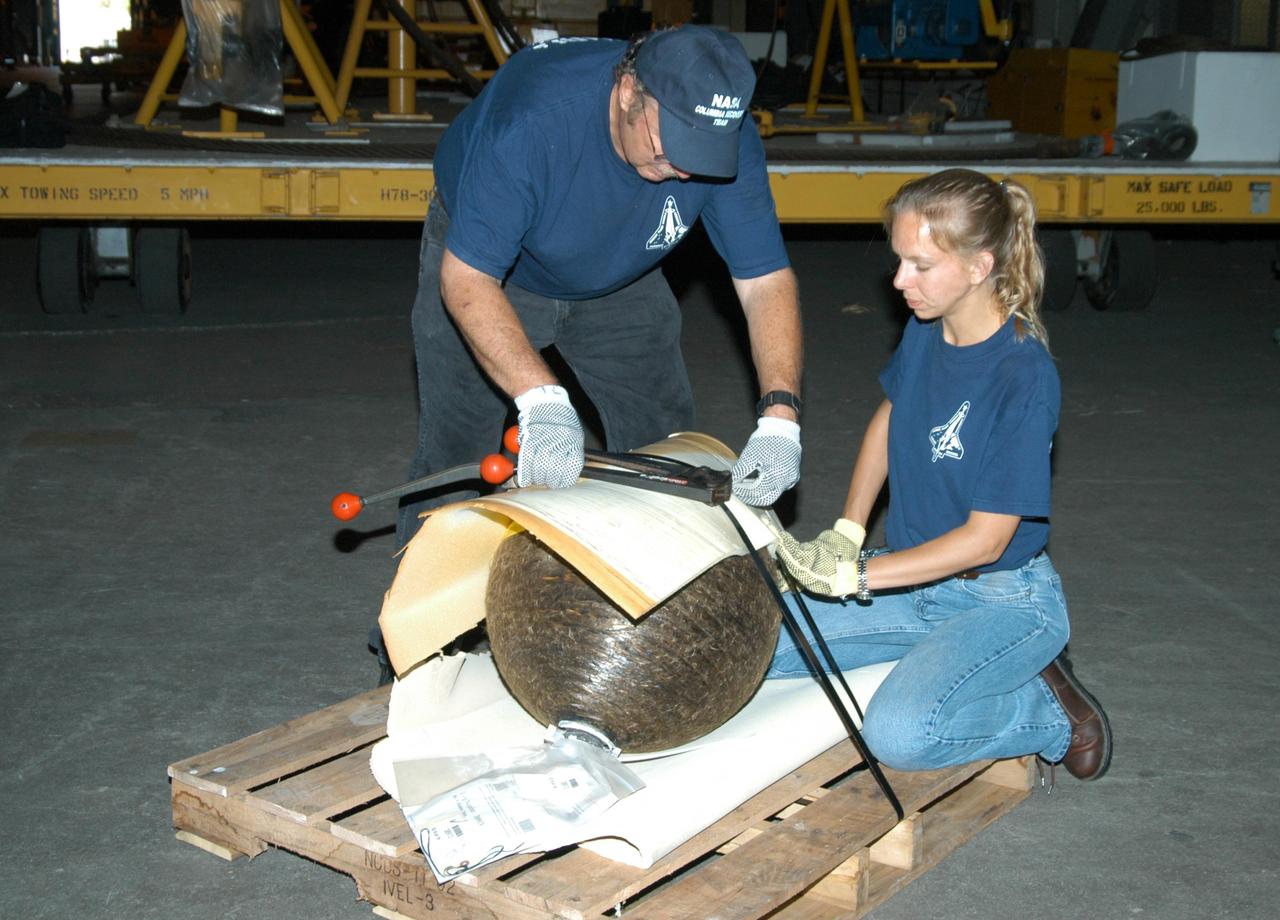

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - United Space Alliance workers J.C. Harrison (left) and Amy Mangiacapra pack pieces of Columbia debris for transfer to the shipping facility for travel to The Aerospace Corporation in El Segundo, Calif. The pieces have been released for loan to the non-governmental agency for testing and research. The Aerospace Corporation requested and will receive graphite/epoxy honeycomb skins from an Orbital Maneuvering System pod, Main Propulsion System Helium tanks, a Reaction Control System Helium tank and a Power Reactant Storage Distribution system tank. The company will use the parts to study re-entry effects on composite materials. NASA notified the Columbia crew’s families about the loan before releasing the items for study. Researchers believe the testing will show how materials are expected to respond to various heating and loads' environments. The findings will help calibrate tools and models used to predict hazards to people and property from reentering hardware. The Aerospace Corporation will have the debris for one year to perform analyses to estimate maximum temperatures during reentry based upon the geometry and mass of the recovered composite. Columbia’s debris is stored in the VAB.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), Scott Thurston (red shirt) stands by while a United Space Alliance worker (blue shirt) gets ready to start moving pieces of Columbia debris, such as the PRSD tank in front, for transfer to a shipping facility and delivery to The Aerospace Corporation in El Segundo, Calif. Thurston is the Columbia debris coordinator. The pieces have been released for loan to the non-governmental agency for testing and research. The Aerospace Corporation requested and will receive graphite/epoxy honeycomb skins from an Orbital Maneuvering System pod, Main Propulsion System Helium tanks, a Reaction Control System Helium tank and a Power Reactant Storage Distribution system tank. The company will use the parts to study re-entry effects on composite materials. NASA notified the Columbia crew’s families about the loan before releasing the items for study. Researchers believe the testing will show how materials are expected to respond to various heating and loads' environments. The findings will help calibrate tools and models used to predict hazards to people and property from reentering hardware. The Aerospace Corporation will have the debris for one year to perform analyses to estimate maximum temperatures during reentry based upon the geometry and mass of the recovered composite. Columbia’s debris is stored in the VAB.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - United Space Alliance technician J.C. Harrison steers while NASA’s Scott Thurston guides a piece of Columbia debris through a gate in the Vehicle Assembly Building, where the debris is stored. This piece is one of eight being released to The Aerospace Corporation in El Segundo, Calif., for testing and research. Thurston is the Columbia debris coordinator. The Aerospace Corporation requested and will receive graphite/epoxy honeycomb skins from an Orbital Maneuvering System pod, Main Propulsion System Helium tanks, a Reaction Control System Helium tank and a Power Reactant Storage Distribution system tank. The company will use the parts to study re-entry effects on composite materials. NASA notified the Columbia crew’s families about the loan before releasing the items for study. Researchers believe the testing will show how materials are expected to respond to various heating and loads' environments. The findings will help calibrate tools and models used to predict hazards to people and property from reentering hardware. The Aerospace Corporation will have the debris for one year to perform analyses to estimate maximum temperatures during reentry based upon the geometry and mass of the recovered composite.
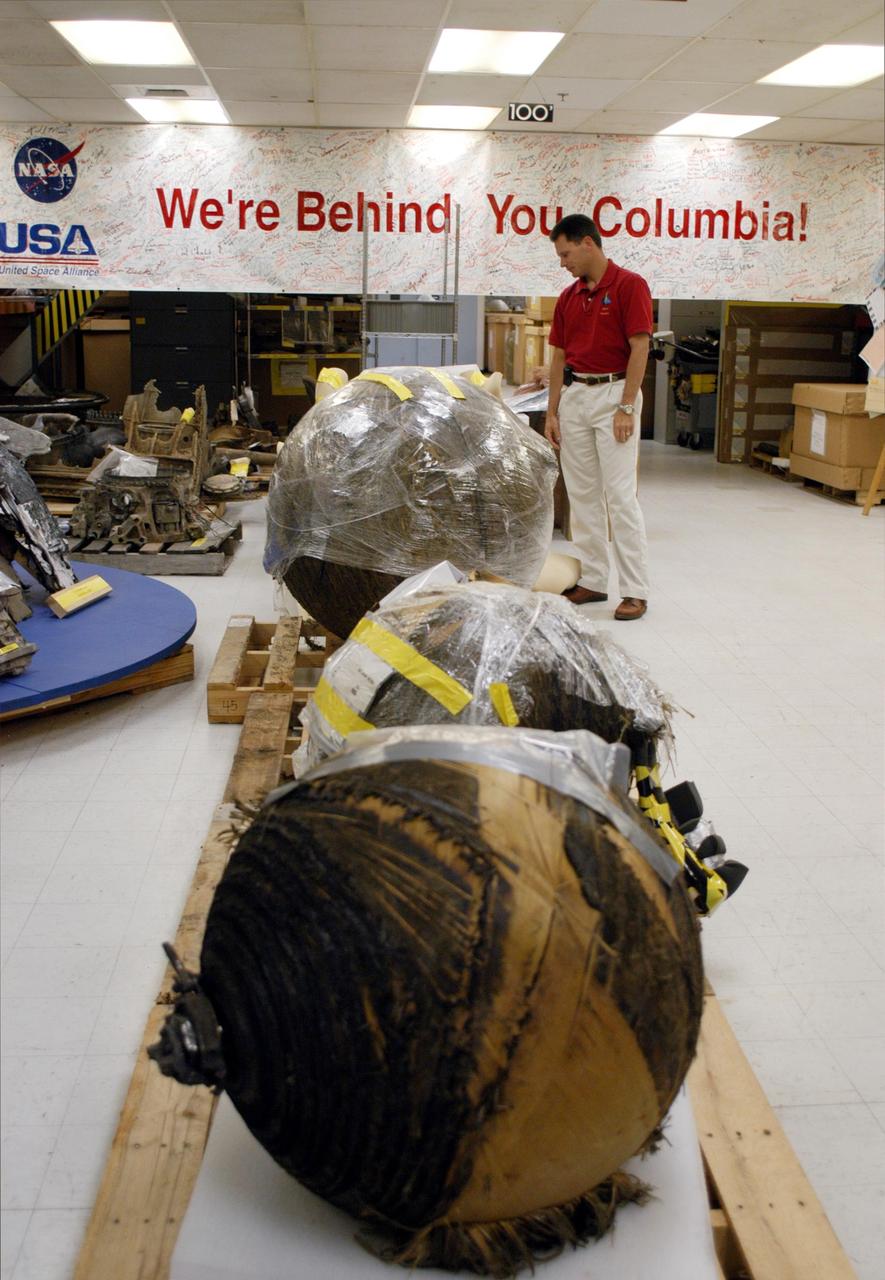

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), Scott Thurston looks at pieces of Columbia debris being prepared for transfer to the shipping facility before their delivery to The Aerospace Corporation in El Segundo, Calif. Thurston is the Columbia debris coordinator. The pieces have been released for loan to the non-governmental agency for testing and research. The Aerospace Corporation requested and will receive graphite/epoxy honeycomb skins from an Orbital Maneuvering System pod, Main Propulsion System Helium tanks, a Reaction Control System Helium tank and a Power Reactant Storage Distribution system tank. The company will use the parts to study re-entry effects on composite materials. NASA notified the Columbia crew’s families about the loan before releasing the items for study. Researchers believe the testing will show how materials are expected to respond to various heating and loads' environments. The findings will help calibrate tools and models used to predict hazards to people and property from reentering hardware. The Aerospace Corporation will have the debris for one year to perform analyses to estimate maximum temperatures during reentry based upon the geometry and mass of the recovered composite. Columbia’s debris is stored in the VAB.
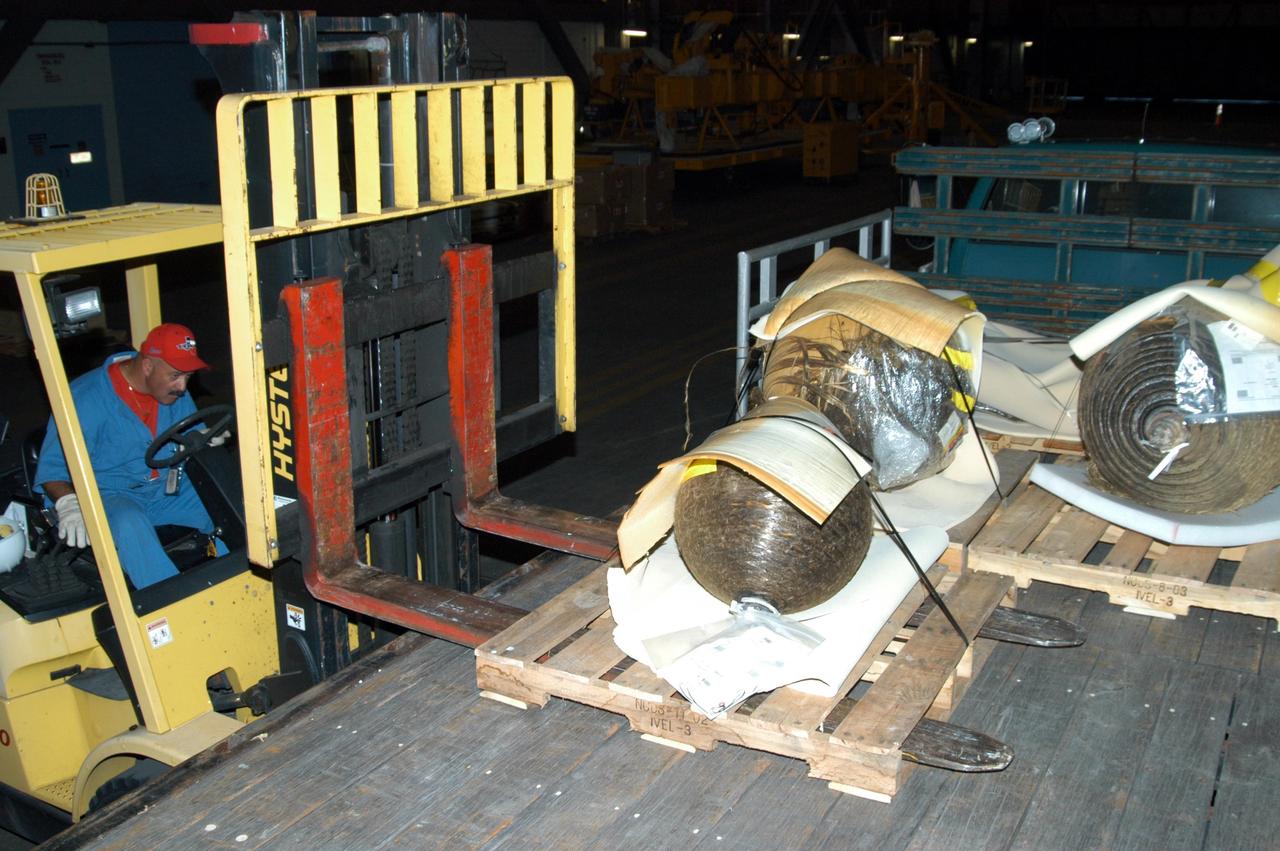

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After being wrapped and secured on pallets, pieces of Columbia debris are loaded onto a truck to transport them to the shipping facility for travel to The Aerospace Corporation in El Segundo, Calif. The pieces have been released for loan to the non-governmental agency for testing and research. The Aerospace Corporation requested and will receive graphite/epoxy honeycomb skins from an Orbital Maneuvering System pod, Main Propulsion System Helium tanks, a Reaction Control System Helium tank and a Power Reactant Storage Distribution system tank. The company will use the parts to study re-entry effects on composite materials. NASA notified the Columbia crew’s families about the loan before releasing the items for study. Researchers believe the testing will show how materials are expected to respond to various heating and loads' environments. The findings will help calibrate tools and models used to predict hazards to people and property from reentering hardware. The Aerospace Corporation will have the debris for one year to perform analyses to estimate maximum temperatures during reentry based upon the geometry and mass of the recovered composite. Columbia’s debris is stored in the VAB.
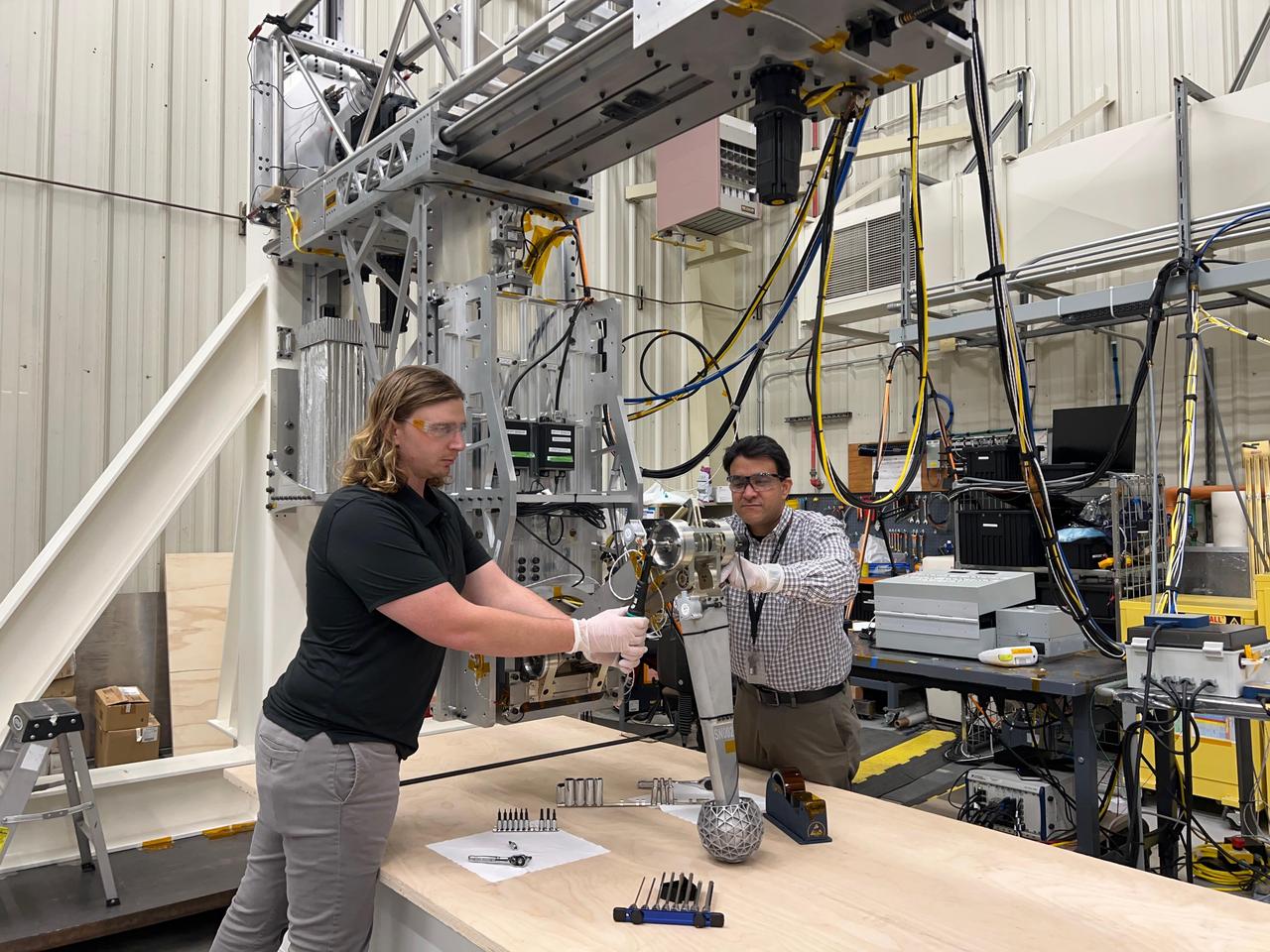

Engineers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory – from left, Matthew Cameron-Hooper, and Thomas Reynoso – prepare flight-like landing gear in the Europa Lander landing gear testbed in summer 2022. Europa Lander is a concept for a potential future mission that would look for signs of life in the icy surface material of Jupiter's moon Europa. The moon is thought to contain a global ocean of salty water beneath its frozen crust. If life exists in that ocean, signs of its existence called biosignatures could potentially find their way to the surface. In this mission concept, a spacecraft would land on Europa and collect and study samples from about 4 inches (10 centimeters) beneath the surface, looking for signs of life. The Europa Lander landing gear testbed was developed to test and inform the design of the landing gear for the spacecraft: It mimics the landing loads and ground interaction forces that a single flight landing gear would experience when touching down on the Europan surface. It does this by using gravity offloading to simulate the reduced gravity on Europa, and by replicating the mass and inertial properties of a flight lander as well as all the degrees of freedom that the landing gear would experience. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26198
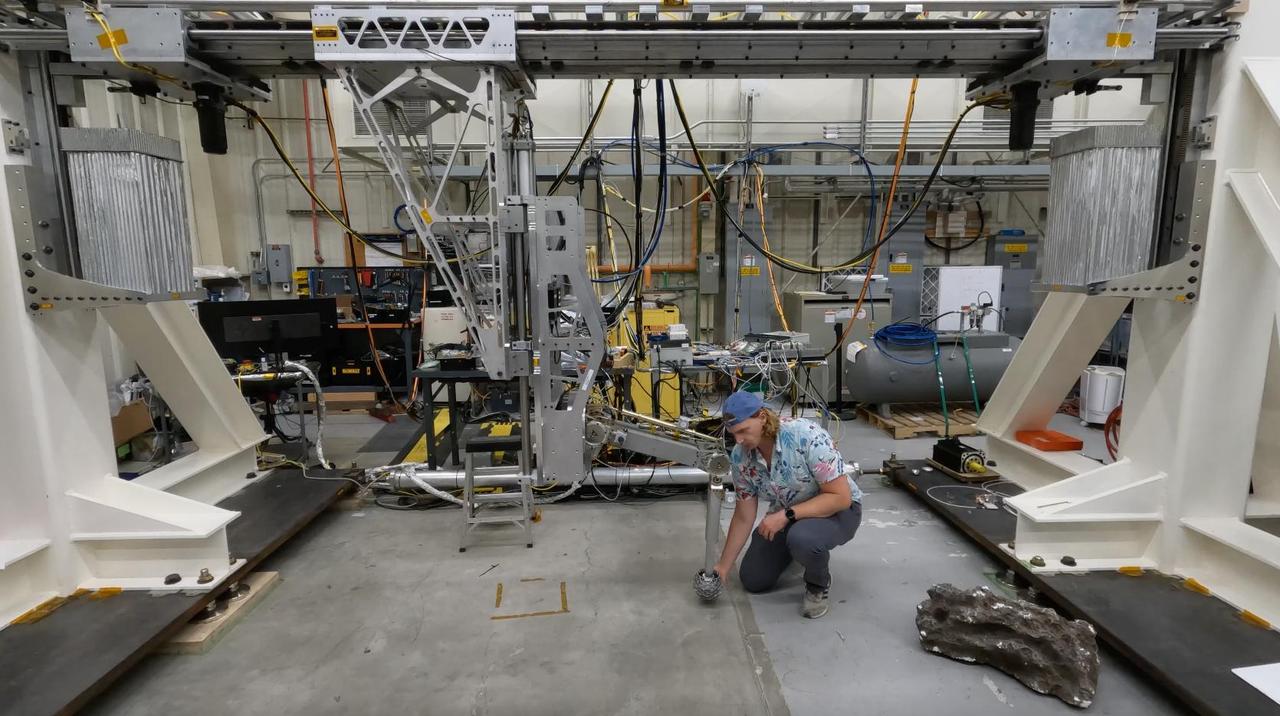

Engineer Matthew Cameron-Hooper performs a checkout on some systems of the Europa Lander landing gear testbed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on May 27, 2022. Europa Lander is a concept for a potential future mission that would look for signs of life in the icy surface material of Jupiter's moon Europa. The moon is thought to contain a global ocean of salty water beneath its frozen crust. If life exists in that ocean, signs of its existence called biosignatures could potentially find their way to the surface. In this mission concept, a spacecraft would land on Europa and collect and study samples from about 4 inches (10 centimeters) beneath the surface, looking for signs of life. The Europa Lander landing gear testbed was developed to test and inform the design of the landing gear for the spacecraft: It mimics the landing loads and ground interaction forces that a single flight landing gear would experience when touching down on the Europan surface. It does this by using gravity offloading to simulate the reduced gravity on Europa, and by replicating the mass and inertial properties of a flight lander as well as all the degrees of freedom that the landing gear would experience. This system checkout confirmed two critical functionalities of the testbed: low friction of the horizontal degree of freedom that carries the test landing gear, and proper functioning of the gravity offloading system. Together these functionalities ensure that only ground interaction forces cause the test landing gear to come to a stop during a test, just as a flight landing gear would experience when landing on the Europan surface. Video available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26200