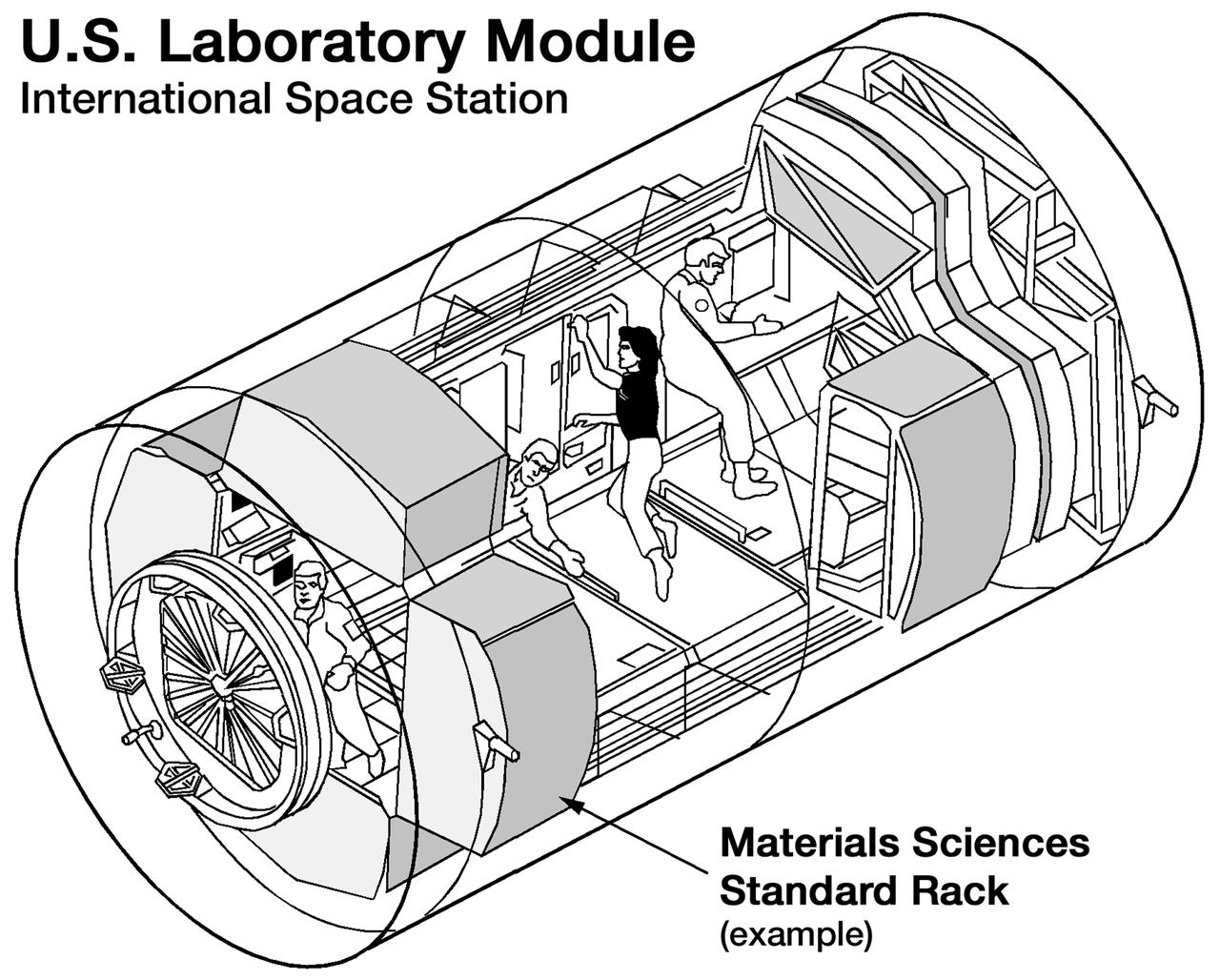
Line drawing depicts the location of one of three racks that will make up the Materials Science Research Facility in the U.S. Destiny laboratory module to be attached to the International Space Station (ISS). Other positions will be occupied by a variety of racks supporting research in combustion, fluids, biotechnology, and human physiology, and racks to support lab and station opertions. The Materials Science Research Facility is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center
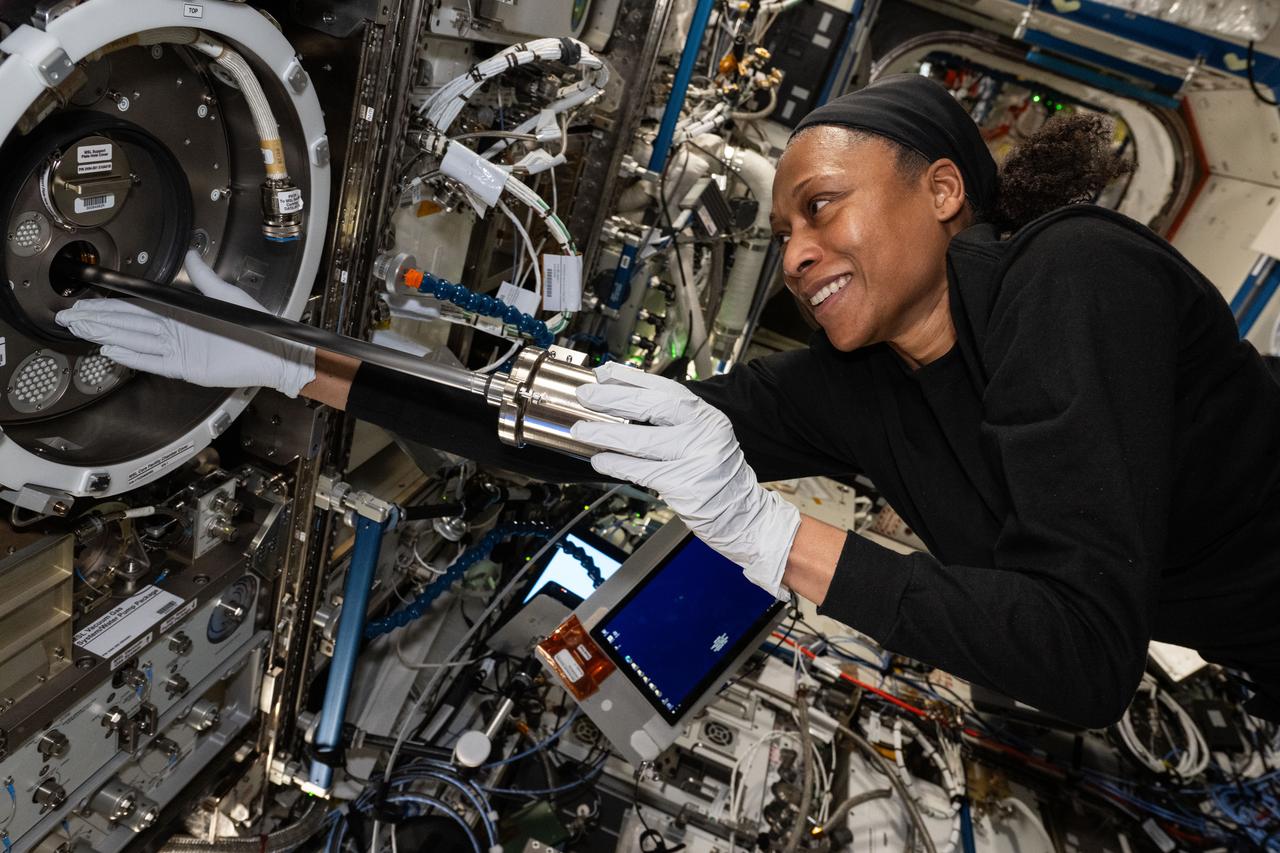

iss071e195867 (June 17, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 71 Flight Engineer Jeanette Epps works on the Materials Science Laboratory (MSL), a component of the Destiny laboratory module's Materials Science Research Rack. The MSL is a research facility used to discover new applications for existing materials and new or improved materials.

iss071e195867 (June 17, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 71 Flight Engineer Jeanette Epps works on the Materials Science Laboratory (MSL), a component of the Destiny laboratory module's Materials Science Research Rack. The MSL is a research facility used to discover new applications for existing materials and new or improved materials.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Life Sciences Lab, Lanfang Levine, with Dynamac Corp., transfers material into a sample bottle for analysis. She is standing in front of new equipment in the lab that will provide gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. The equipment will enable analysis of volatile compounds, such as from plants. The 100,000 square-foot facility houses labs for NASA’s ongoing research efforts, microbiology/microbial ecology studies and analytical chemistry labs. Also calling the new lab home are facilities for space flight-experiment and flight-hardware development, new plant growth chambers, and an Orbiter Environment Simulator that will be used to conduct ground control experiments in simulated flight conditions for space flight experiments. The SLS Lab, formerly known as the Space Experiment Research and Processing Laboratory or SERPL, provides space for NASA’s Life Sciences Services contractor Dynamac Corporation, Bionetics Corporation, and researchers from the University of Florida. NASA’s Office of Biological and Physical Research will use the facility for processing life sciences experiments that will be conducted on the International Space Station. The SLS Lab is the magnet facility for the International Space Research Park at KSC being developed in partnership with Florida Space Authority.

The Electrostatic Levitator (ESL) Facility established at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) supports NASA's Microgravity Materials Science Research Program. NASA materials science investigations include ground-based, flight definition and flight projects. Flight definition projects, with demanding science concept review schedules, receive highest priority for scheduling experiment time in the Electrostatic Levitator (ESL) Facility.
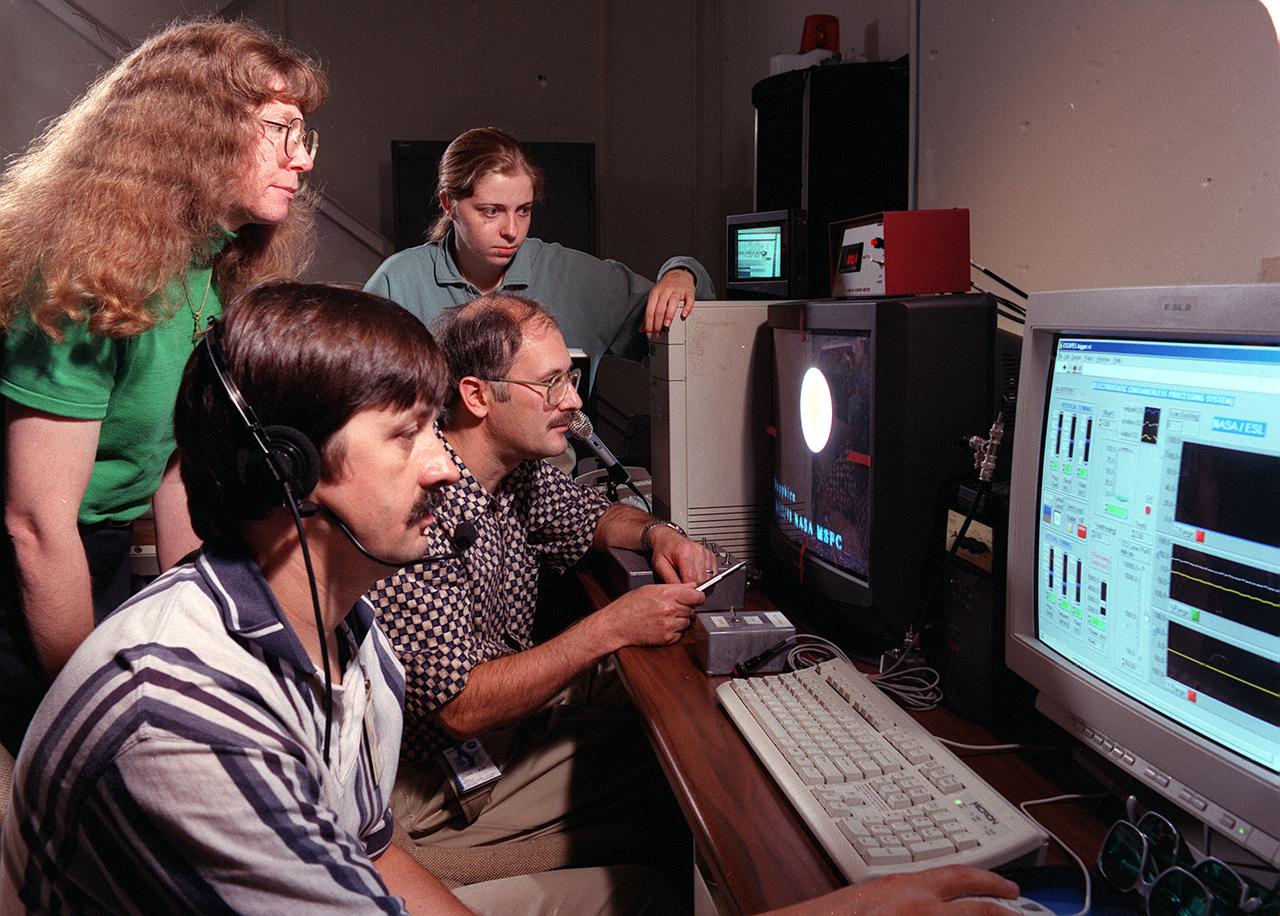

Dr. Jan Rogers (left) and Larry Savage (foreground) of the Science Directorate at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) are joined by Dr. Richard Weber (center) and April Hixon of Containerless Research Inc. of Evanston, Ill., in conducting an experiment run of the Electrostatic Levitator (ESL) using insulating materials. Materials researchers use unique capabilities of the facility to levitate and study the properties of various materials important in manufacturing processes.

NASA Space Science Advisory Committee Chairman Ed Wiler visit to Ames Research Center: checks out test material while on tour of the Arc Jet Facility
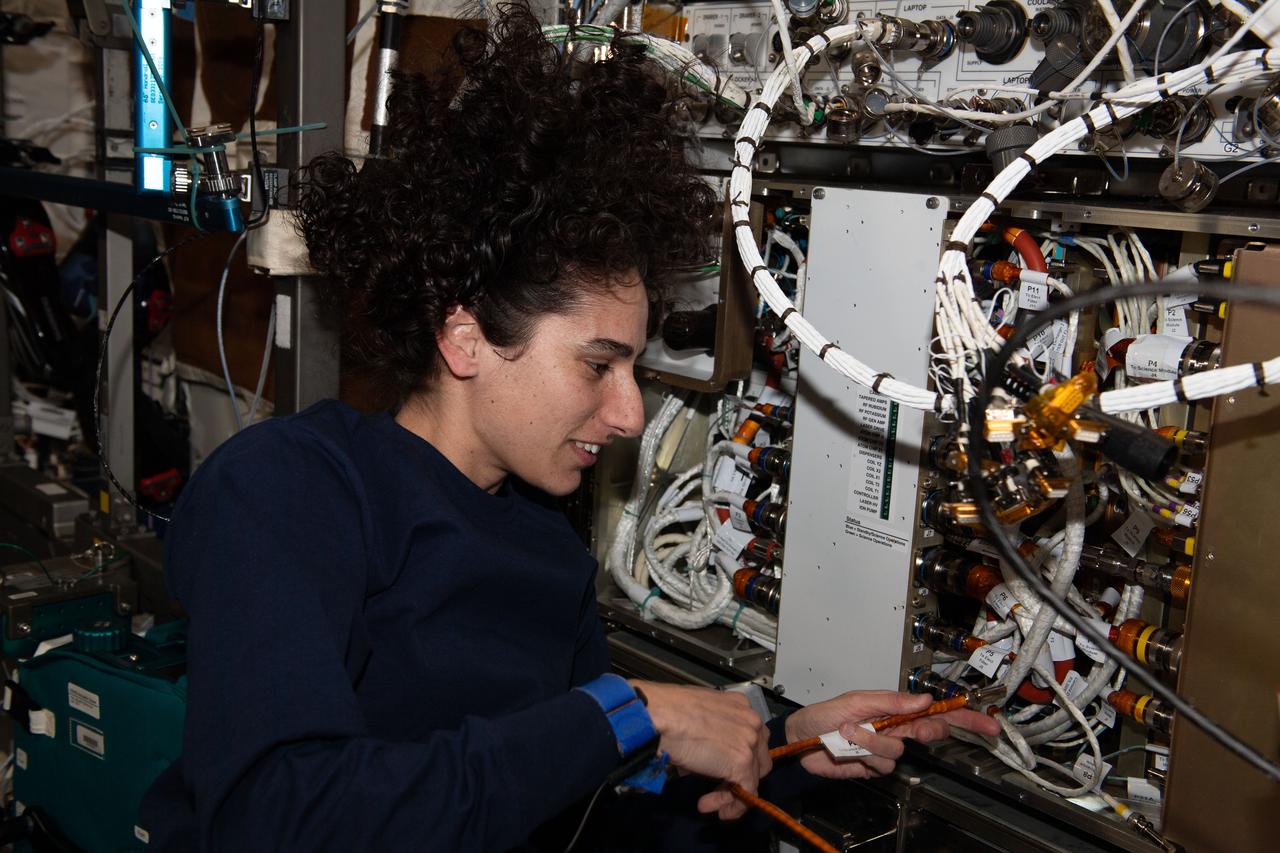

iss070e030810 (Nov. 27, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 70 Flight Engineer Jasmin Moghbeli works on the Materials Science Laboratory, a physics research facility, located in the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module.
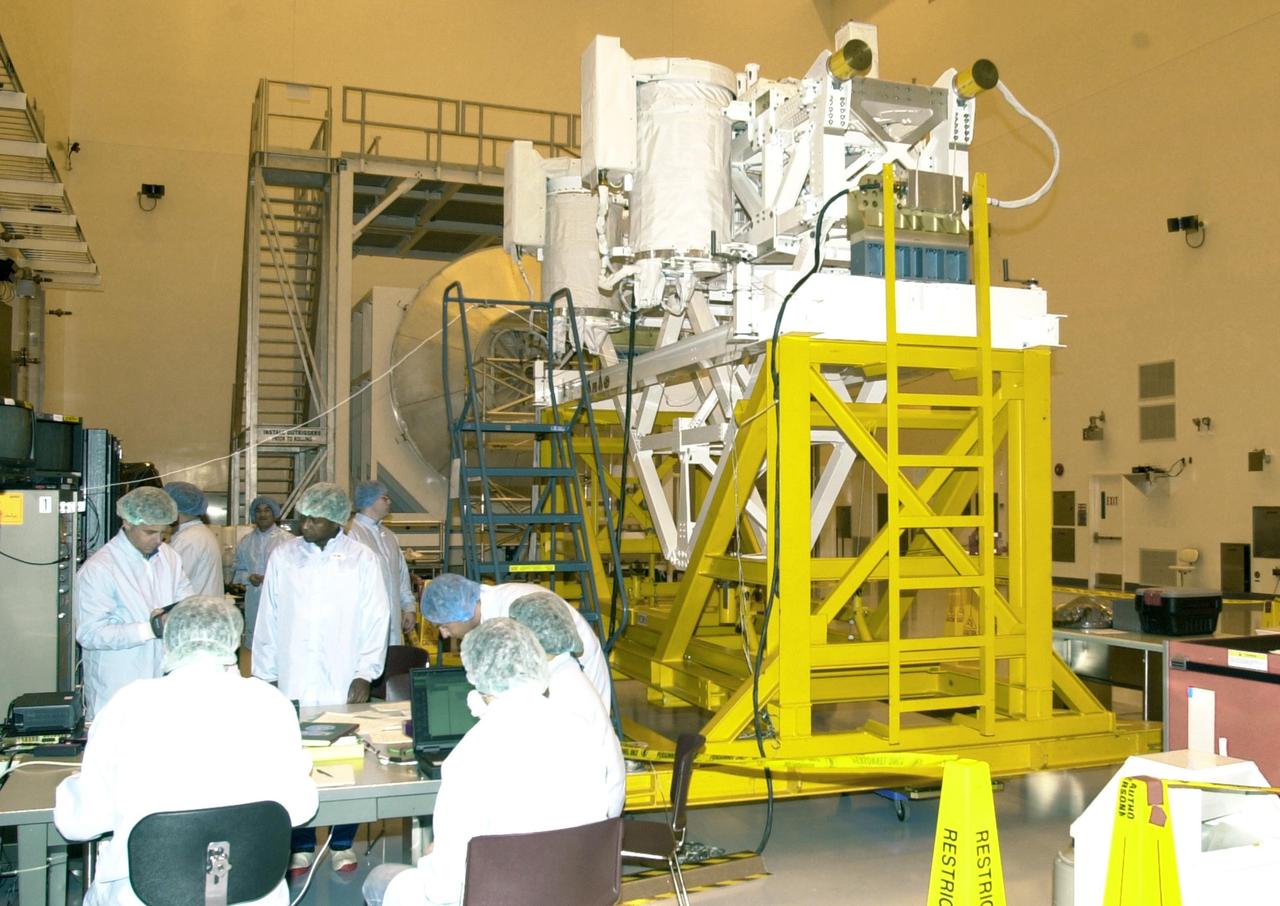

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, members of the STS-107 crew run tests on the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) experiments, part of the payload on their mission. A research mission, the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM), also known as SPACEHAB. The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 11, 2002
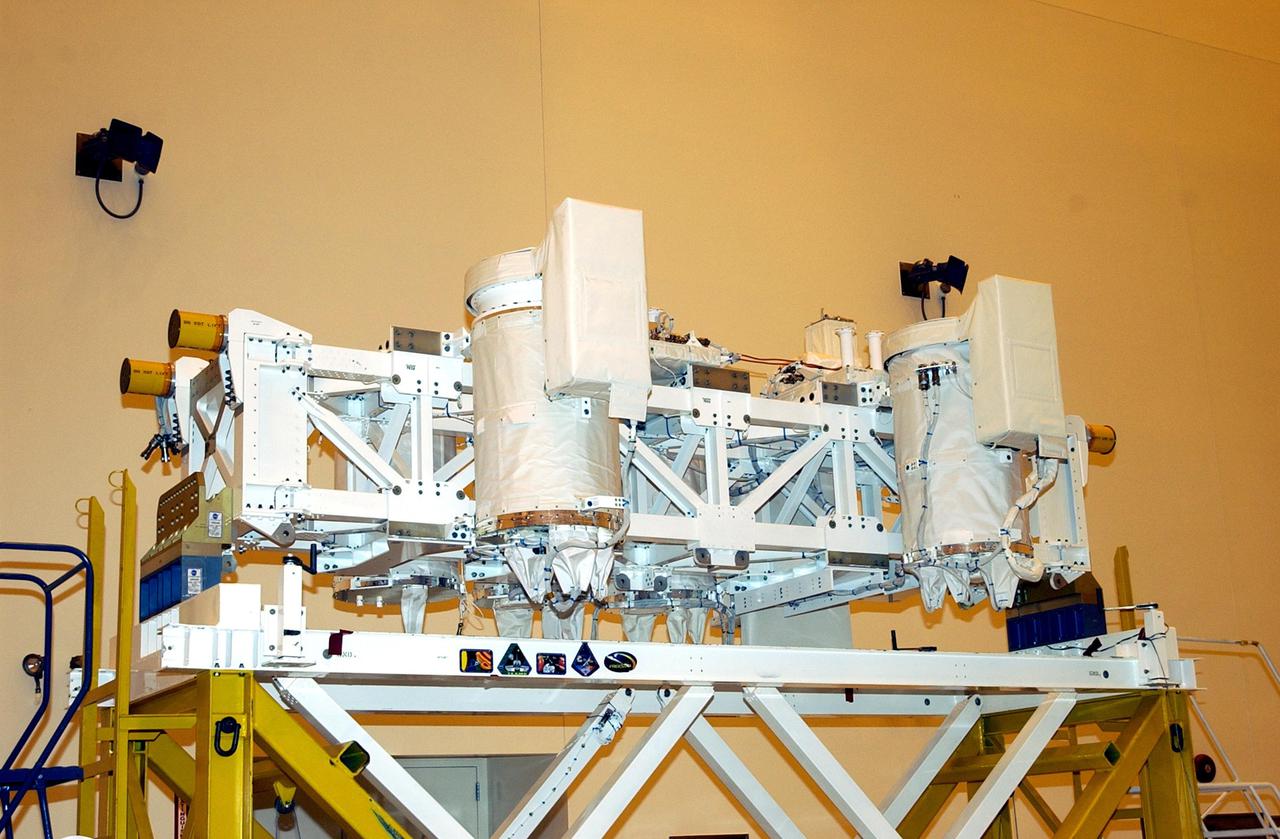

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Hitchhiker Bridge rests on a workstand in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF). The bridge is a carrier for the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments on mission STS-107. A research mission, the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI_RDM), also known as SPACEHAB. The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences. STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 11, 2002
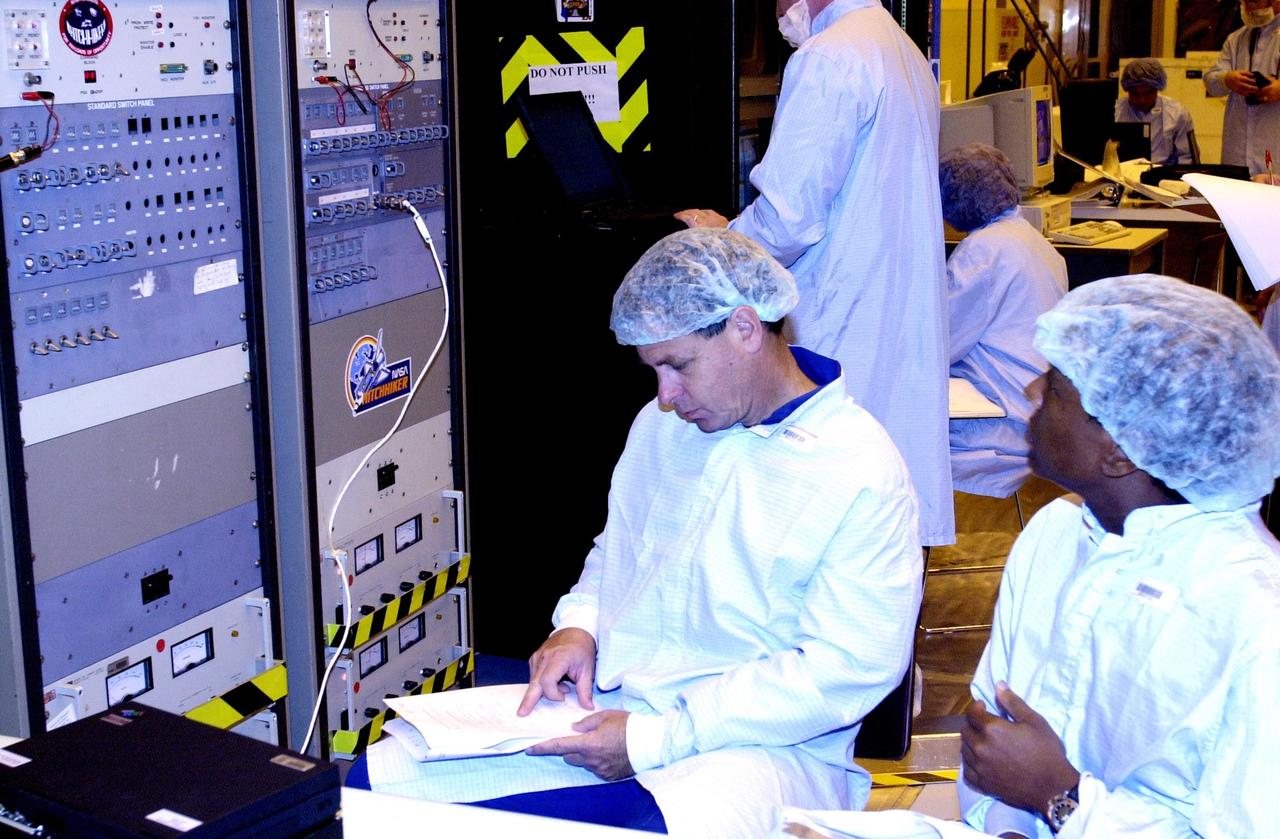

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, members of the STS-107 crew look at test results on the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) experiments, part of the payload on their mission. A research mission, the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM), also known as SPACEHAB. The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 11, 2002
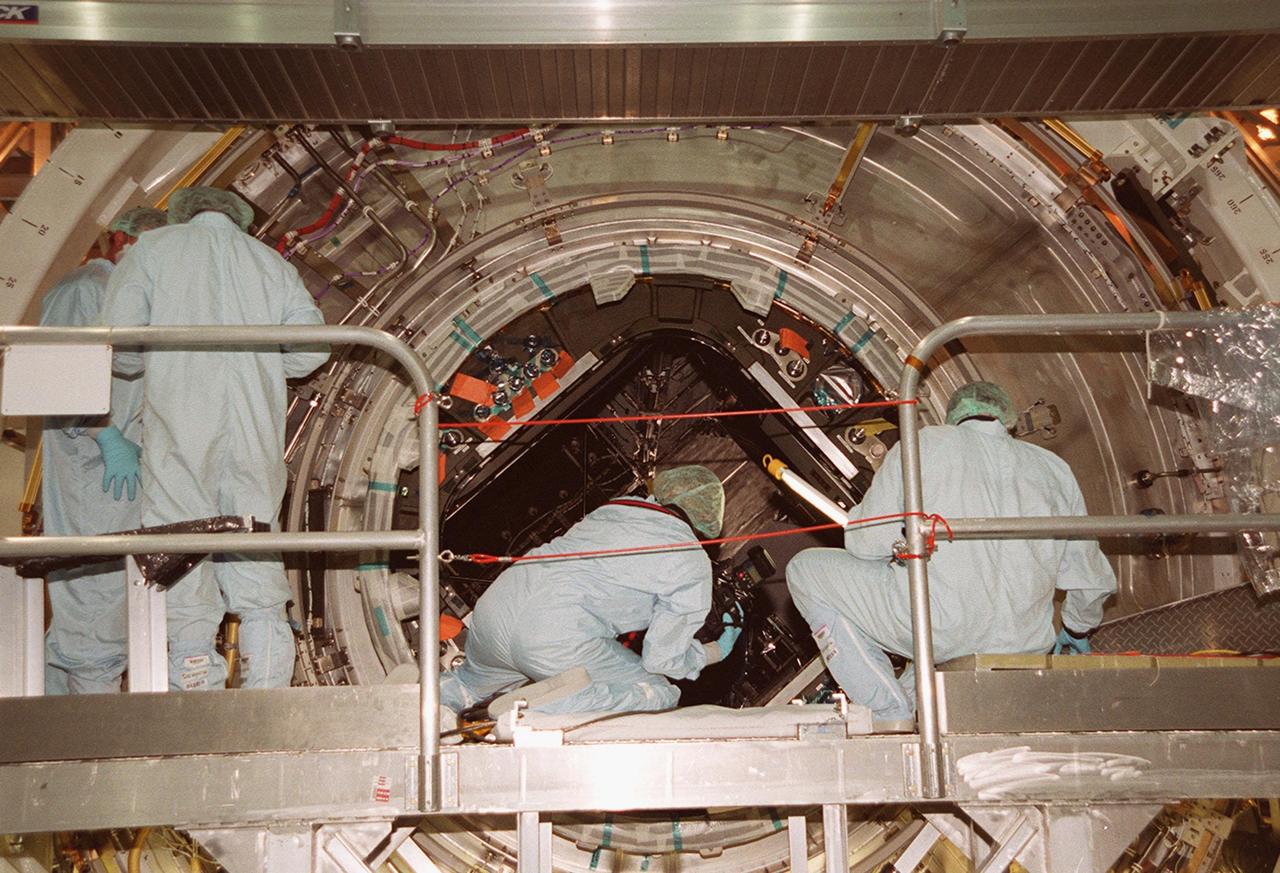

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, technicians watch closely as the U.S. Laboratory Destiny rotates. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the U.S. Lab Destiny comes to rest on the weigh stand. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
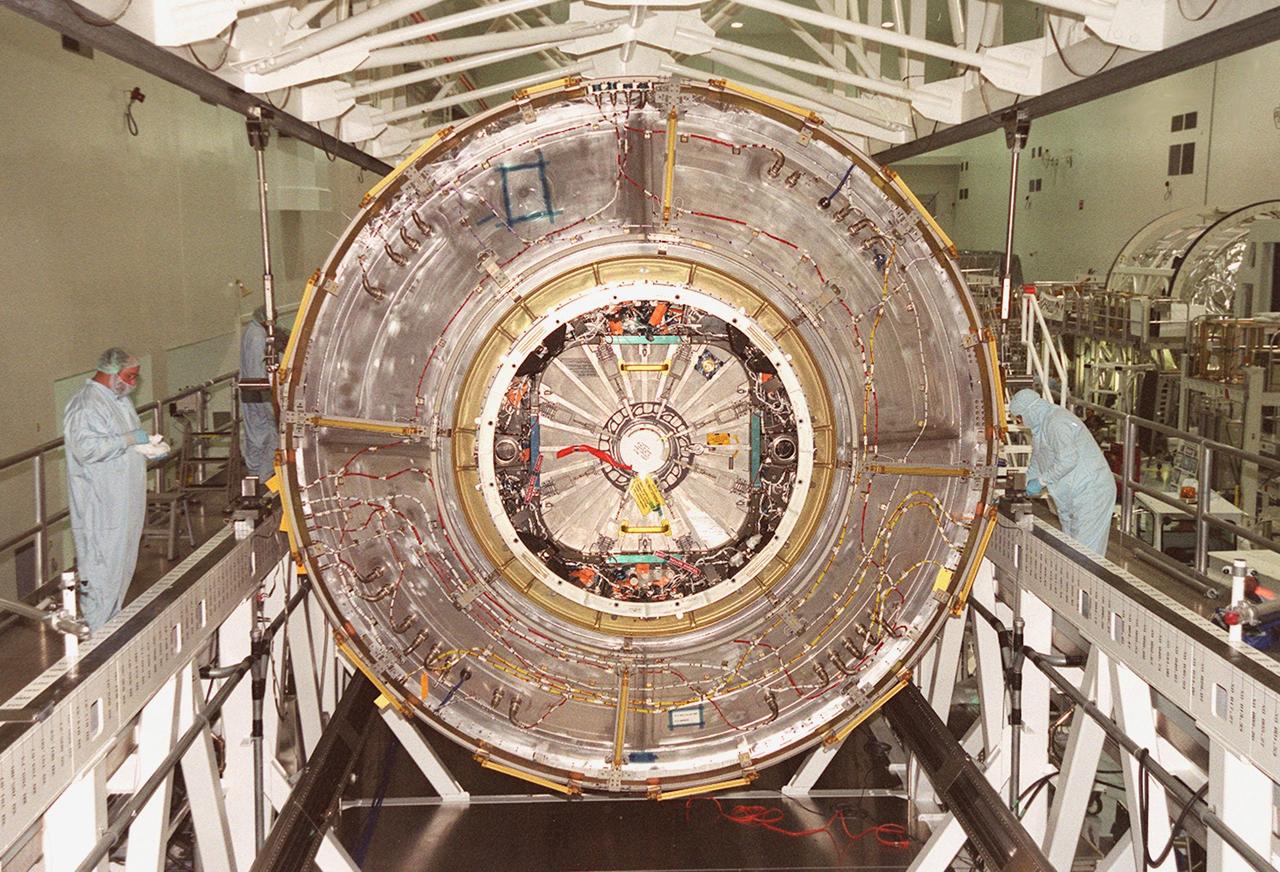

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the U.S. Lab Destiny comes to rest on the weigh stand. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
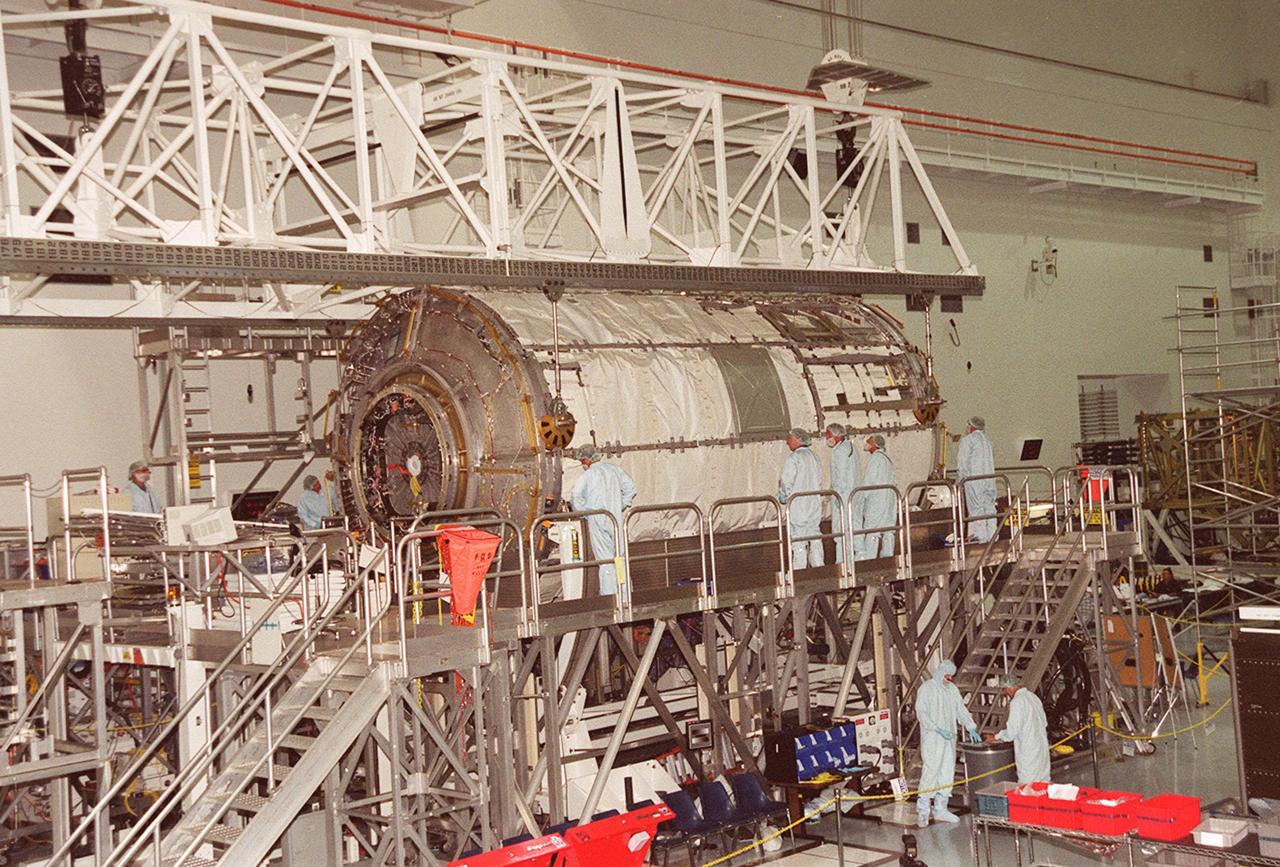
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, technicians watch closely as the U.S. Laboratory Destiny rotates. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research.
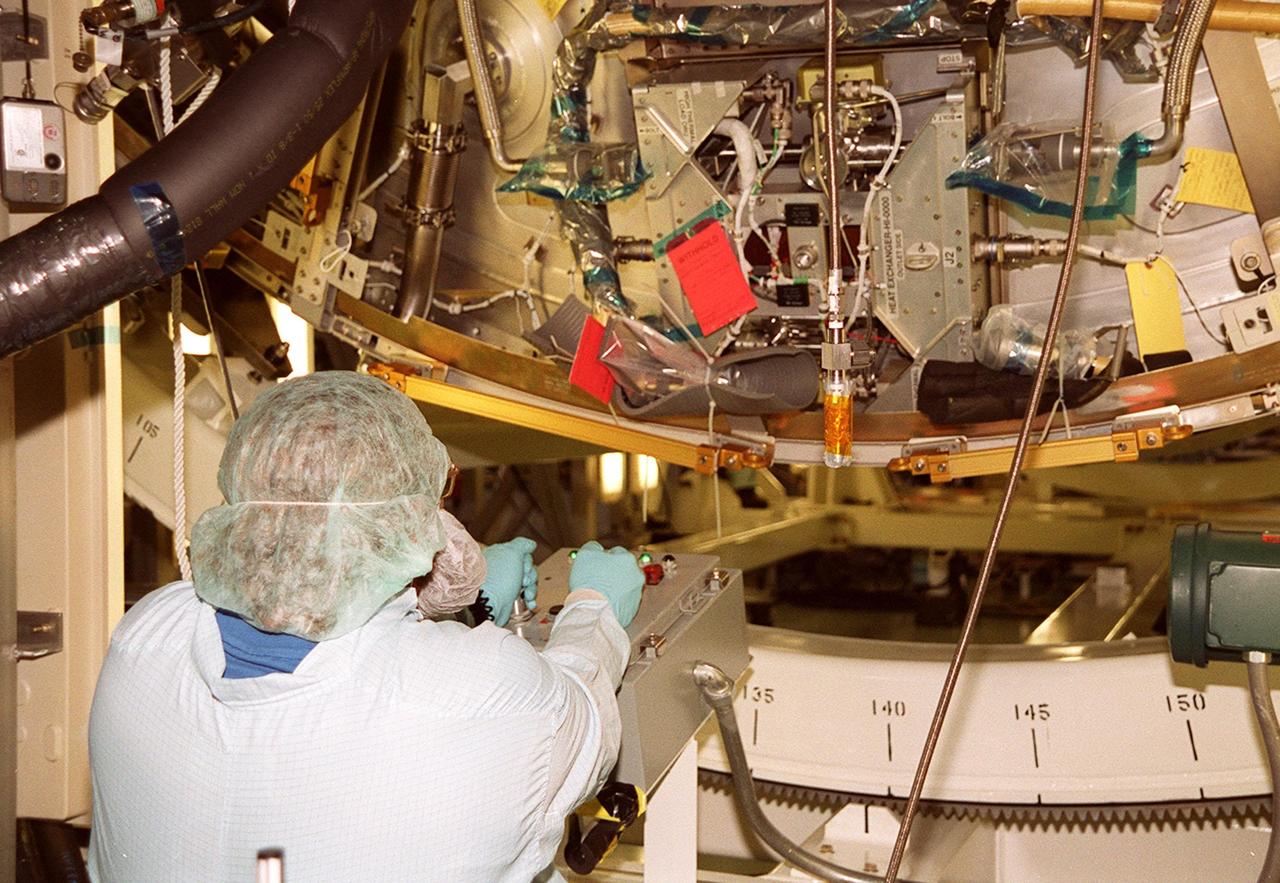

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, a worker controls the rotation of the U.S. Laboratory Destiny. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
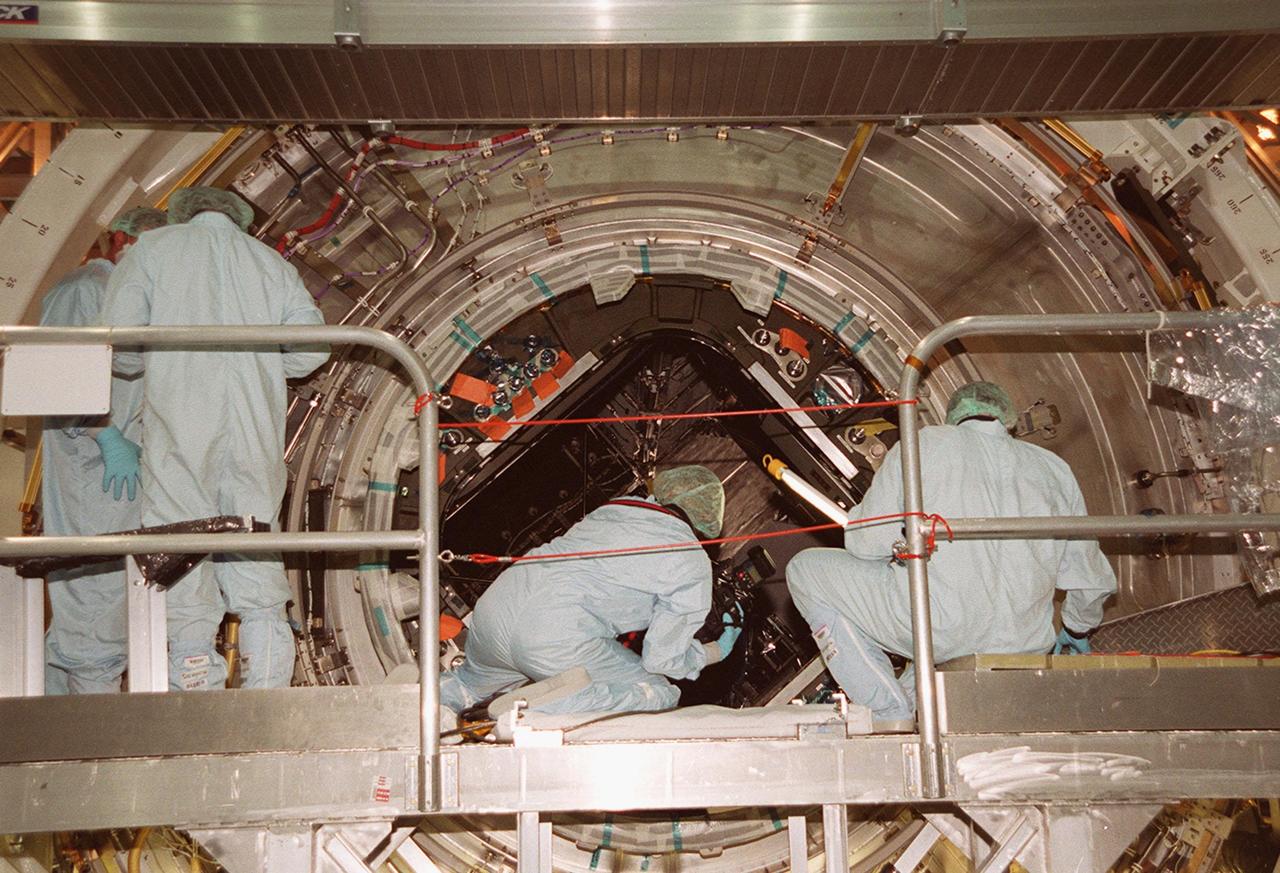

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, technicians watch closely as the U.S. Laboratory Destiny rotates. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
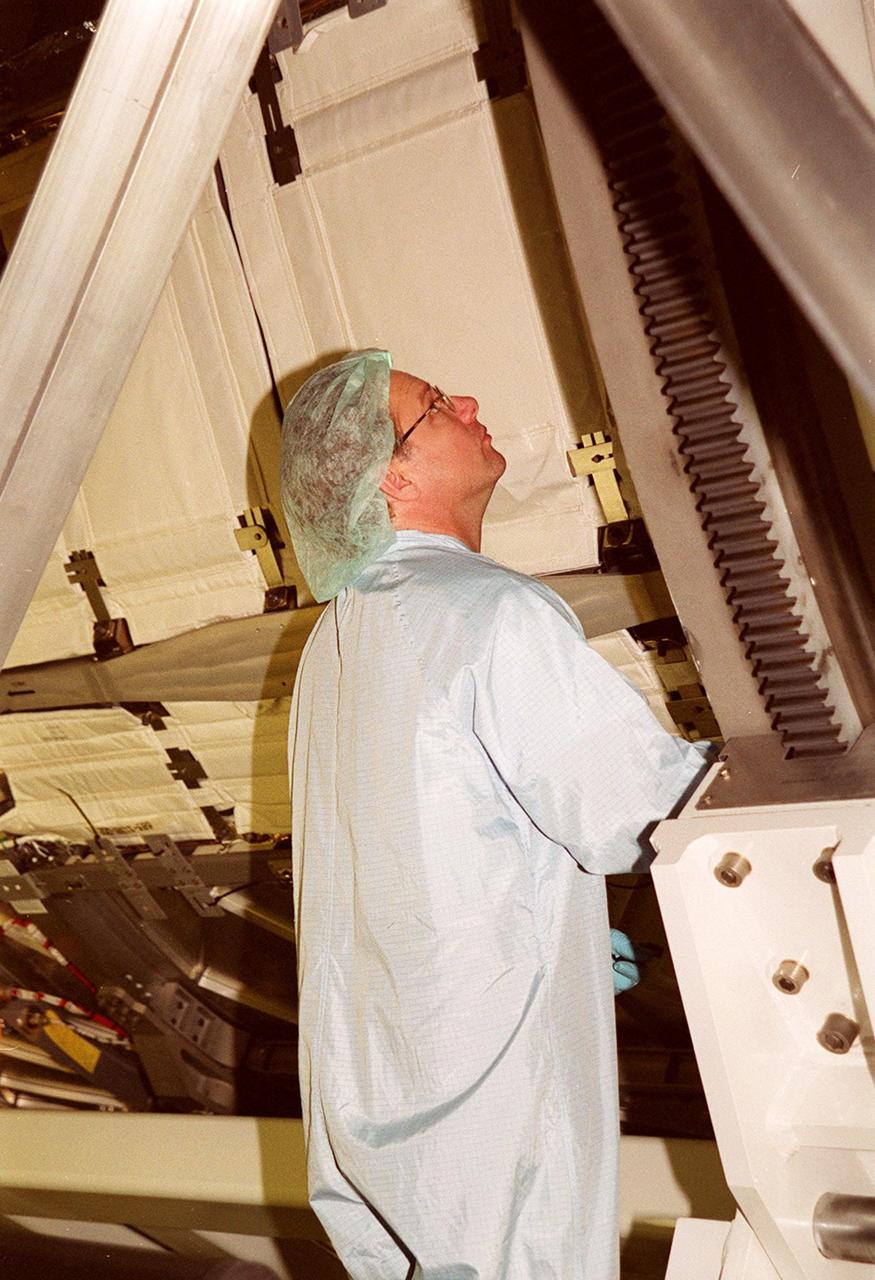

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, a worker checks the U.S. Laboratory Destiny as it rotates. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
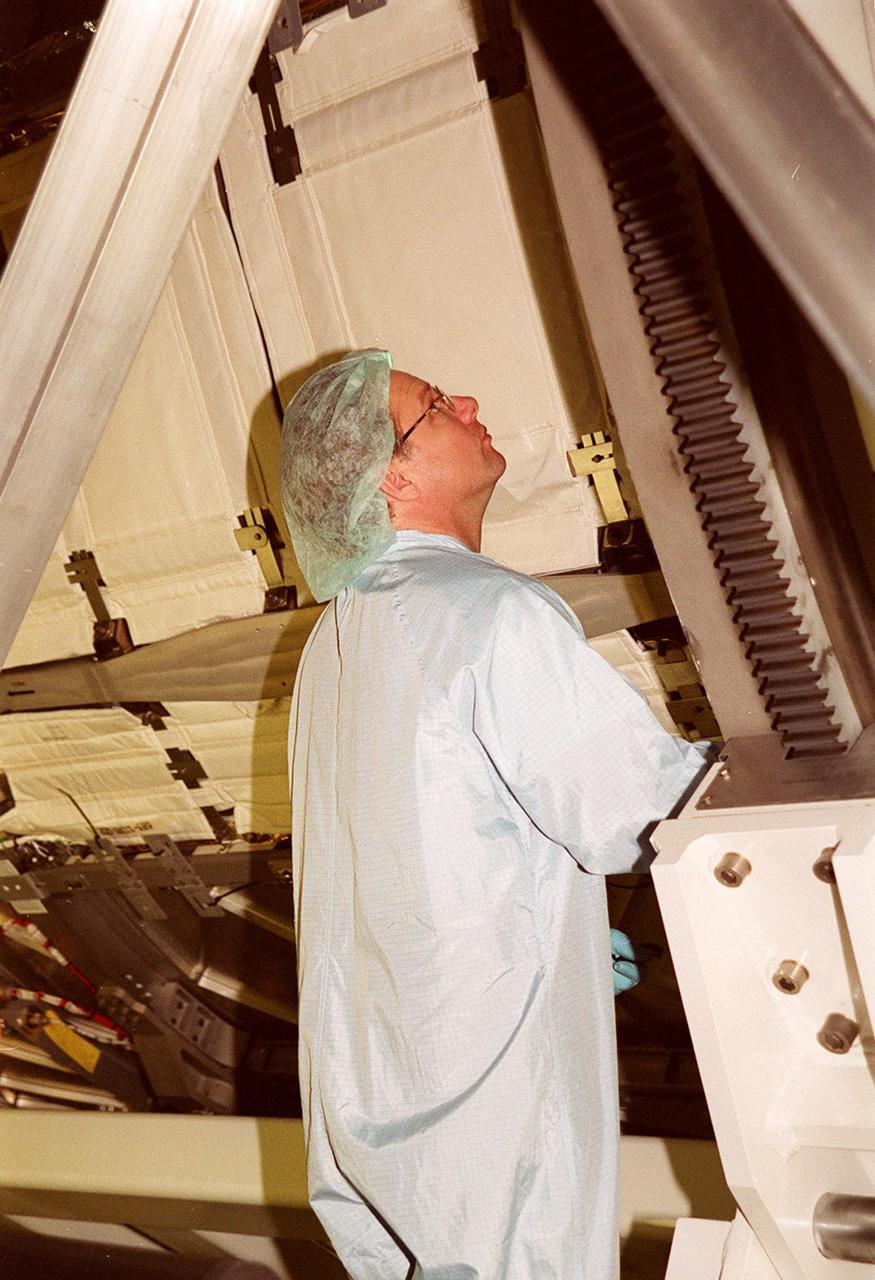

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, a worker checks the U.S. Laboratory Destiny as it rotates. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
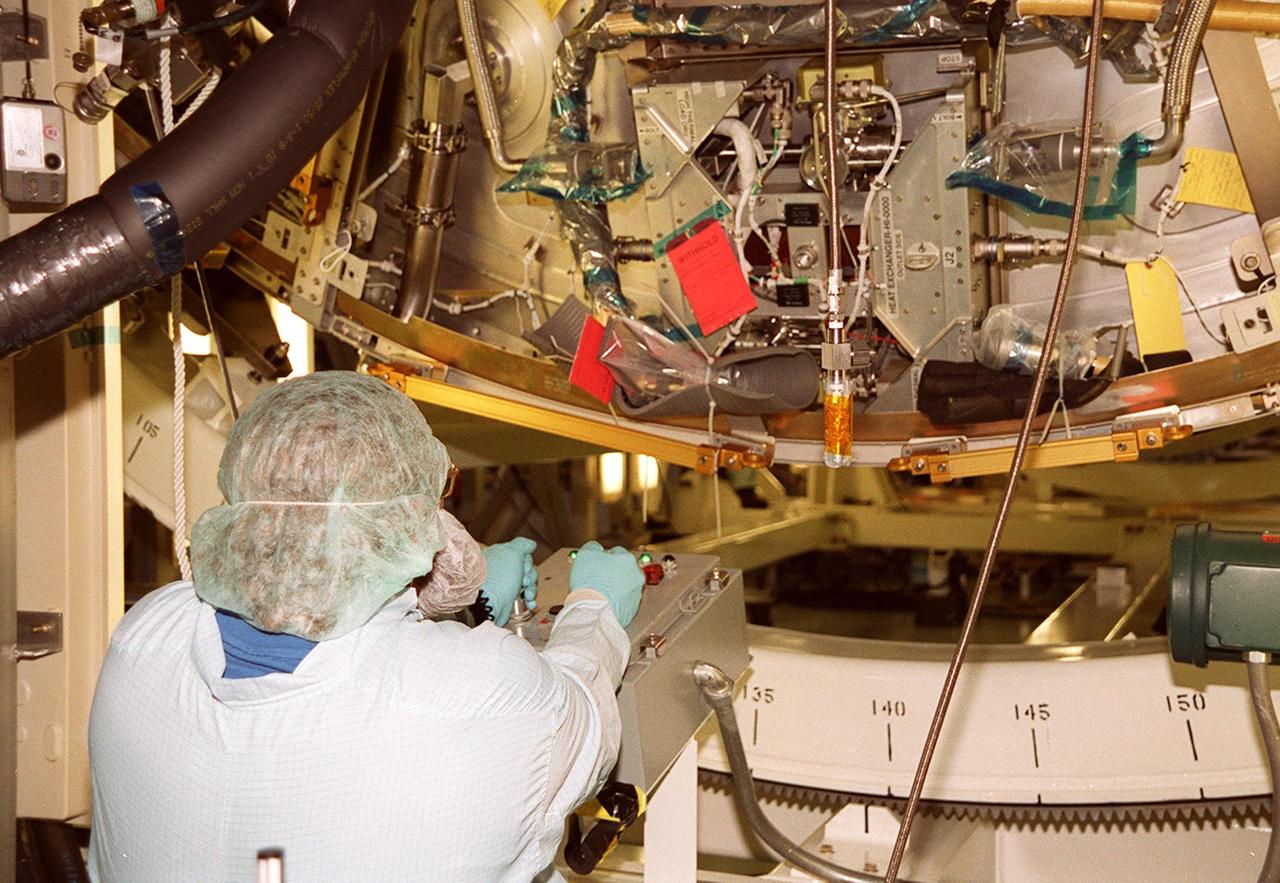

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, a worker controls the rotation of the U.S. Laboratory Destiny. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
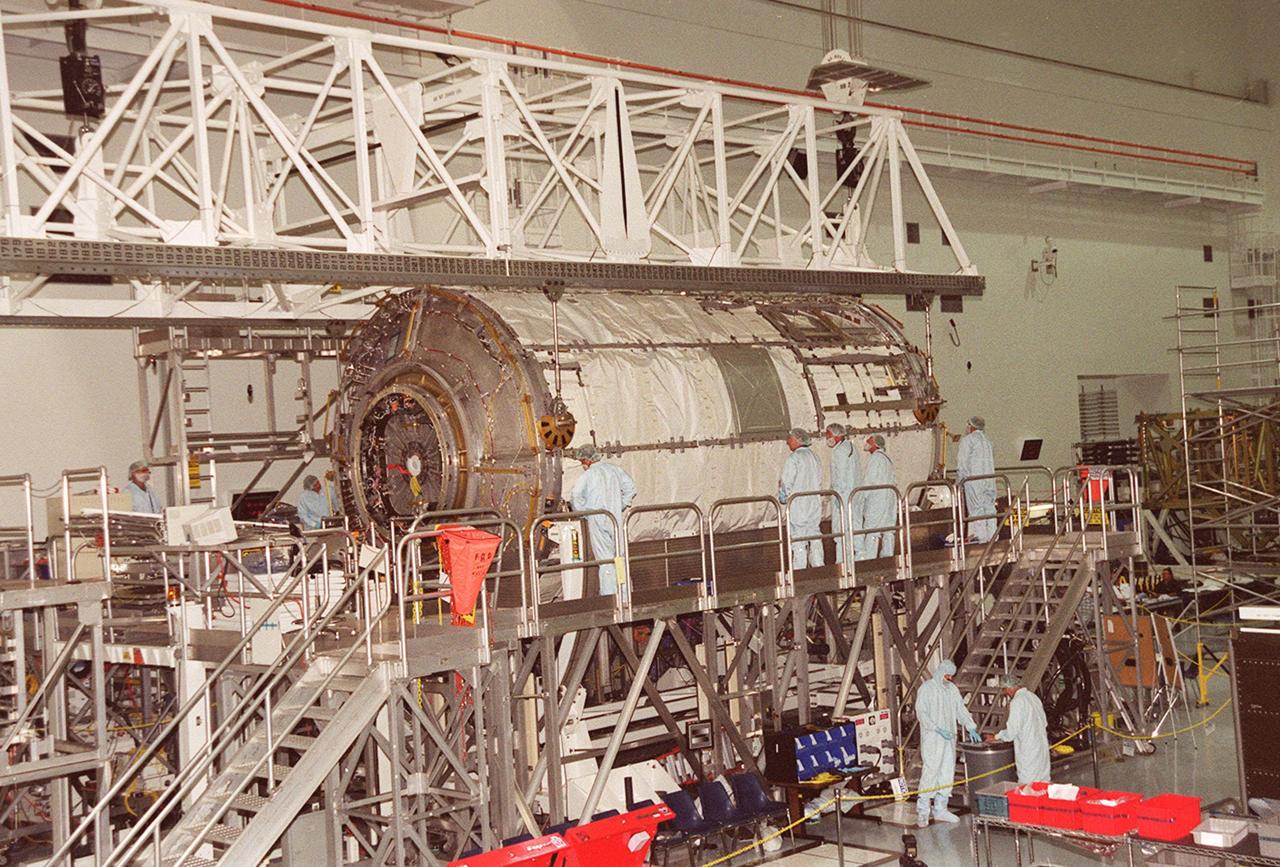
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, technicians watch closely as the U.S. Laboratory Destiny rotates. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research.
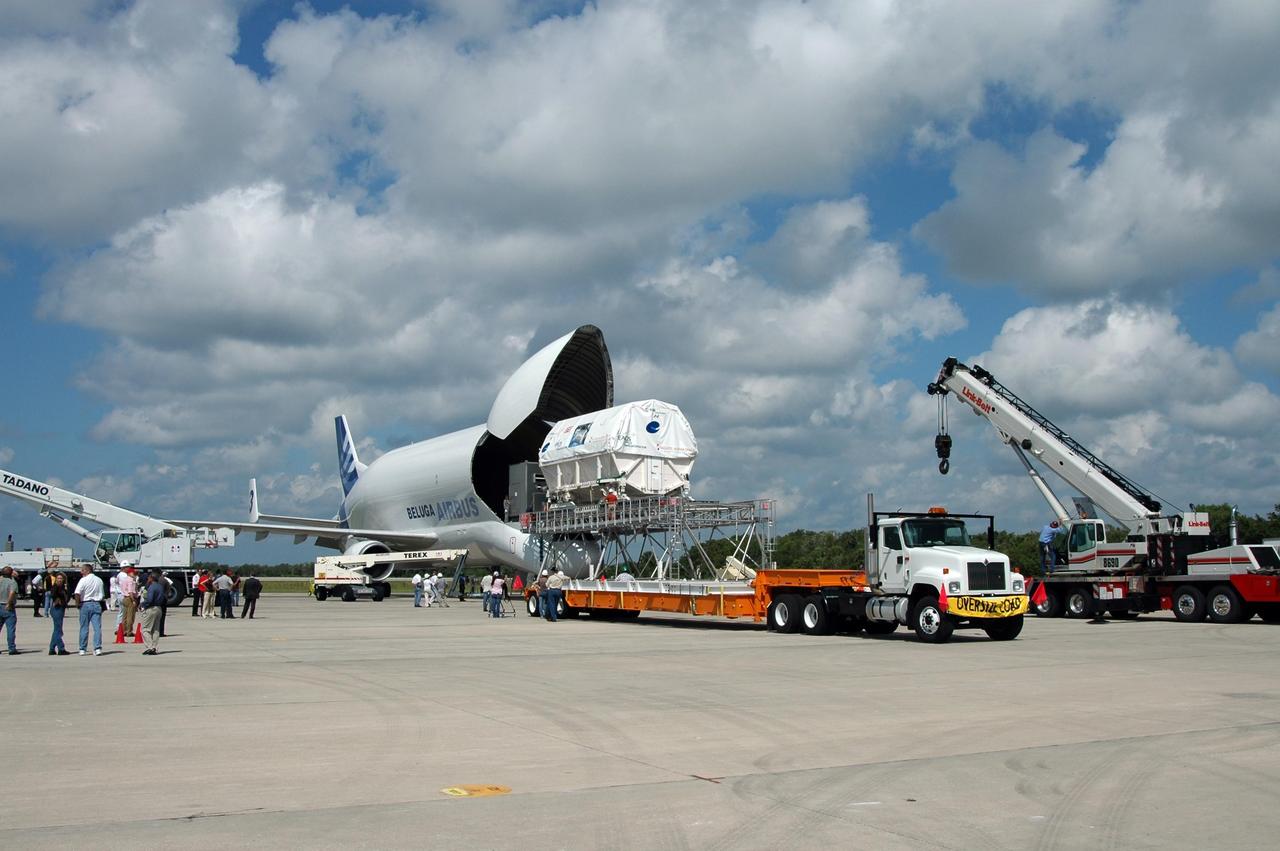

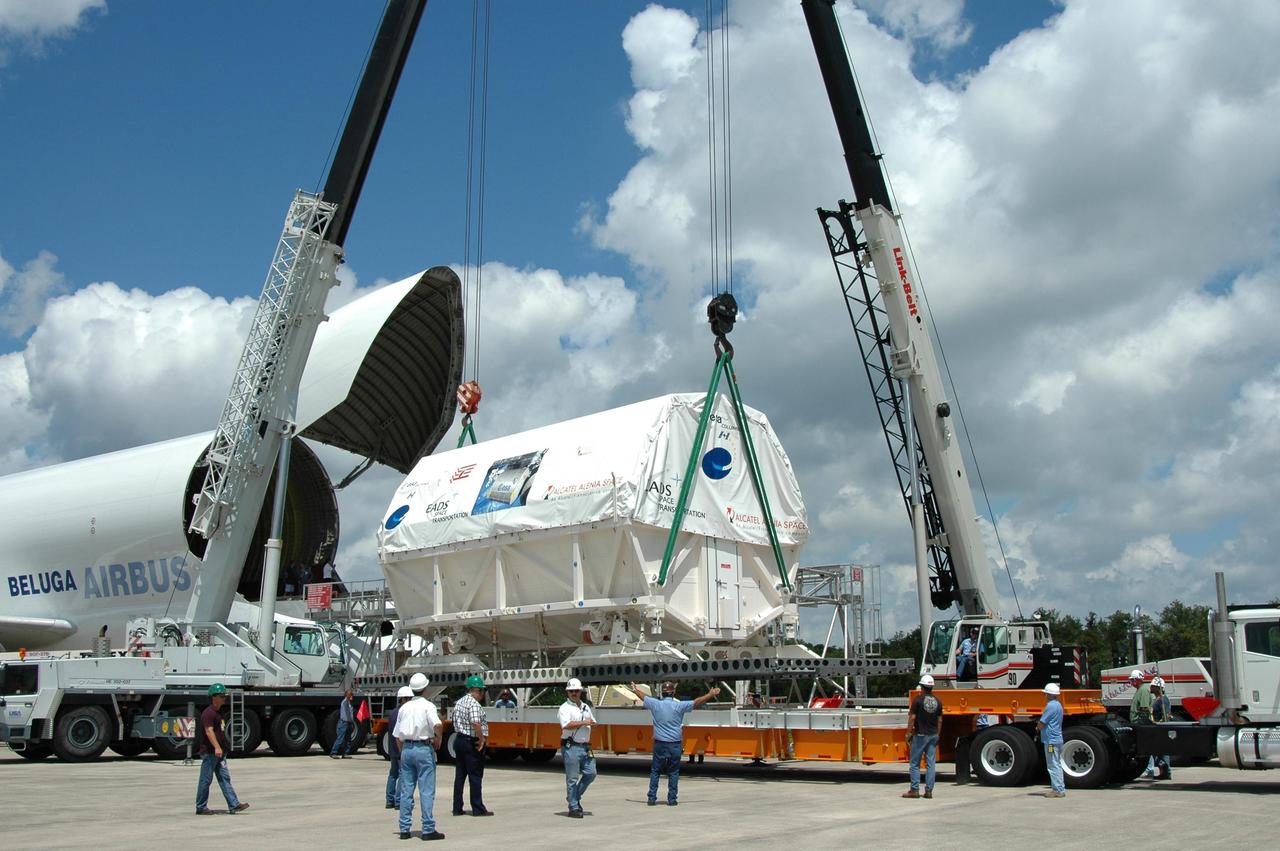
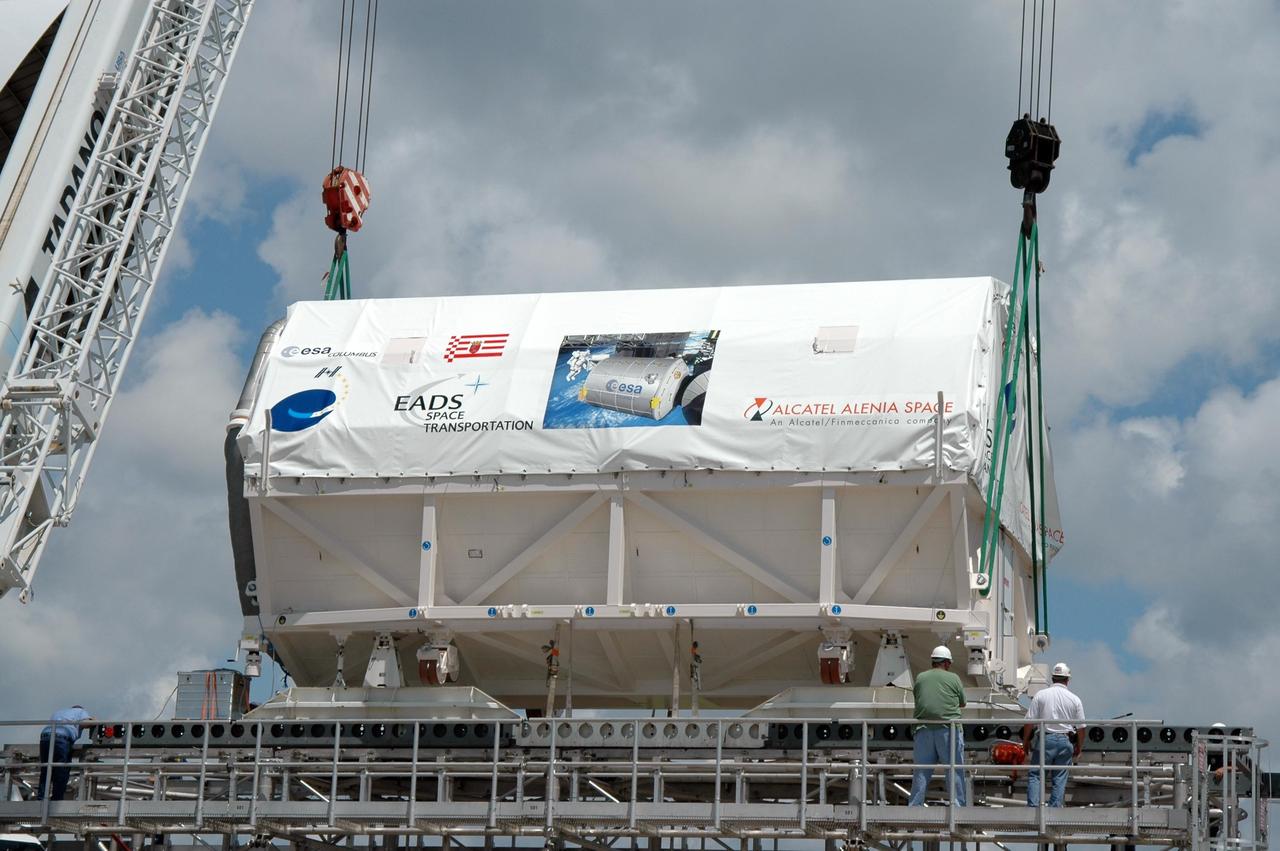
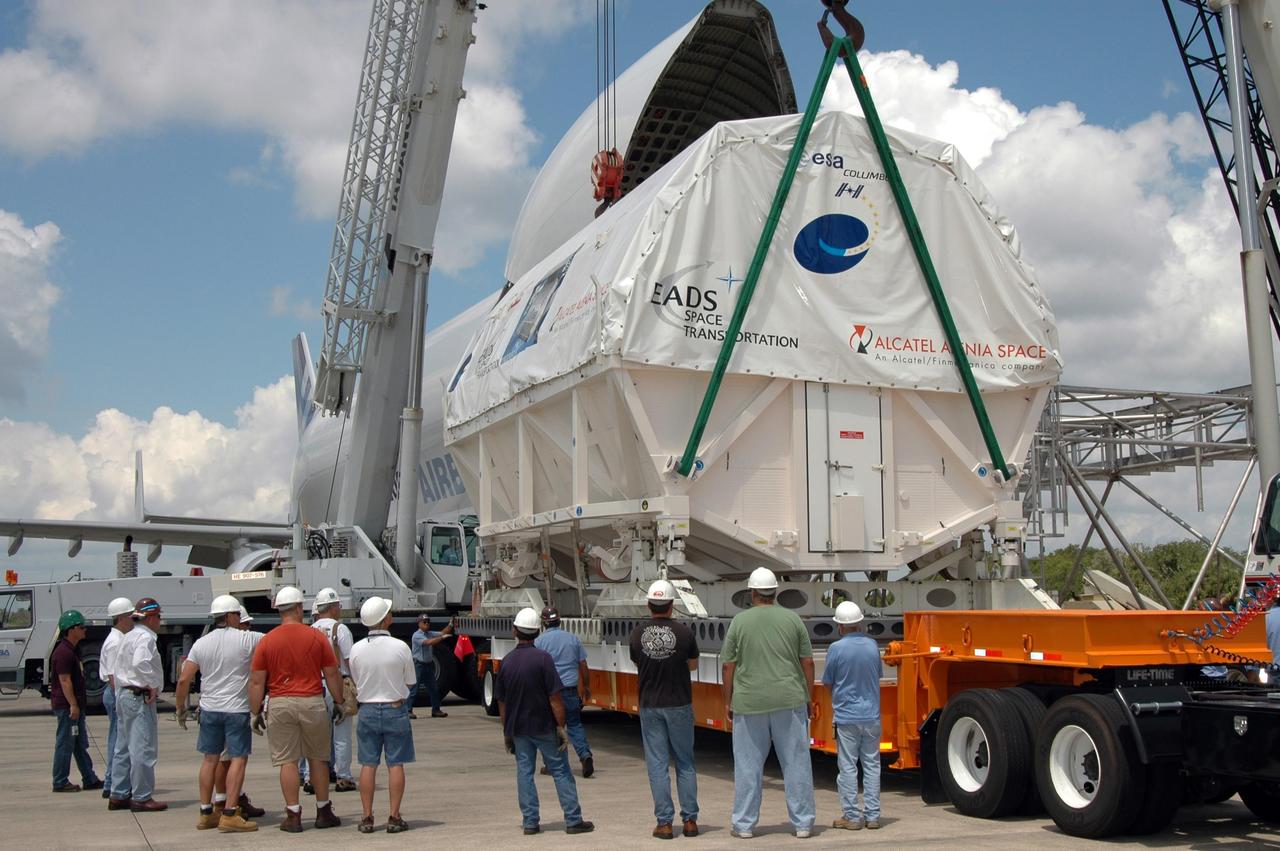
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Shuttle Landing Facility, the European Space Agency's research laboratory, designated Columbus, slides out onto an Airbus Transport International platform. The module will be lifted onto a flat bed truck and transported to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will be prepared for delivery to the International Space Station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
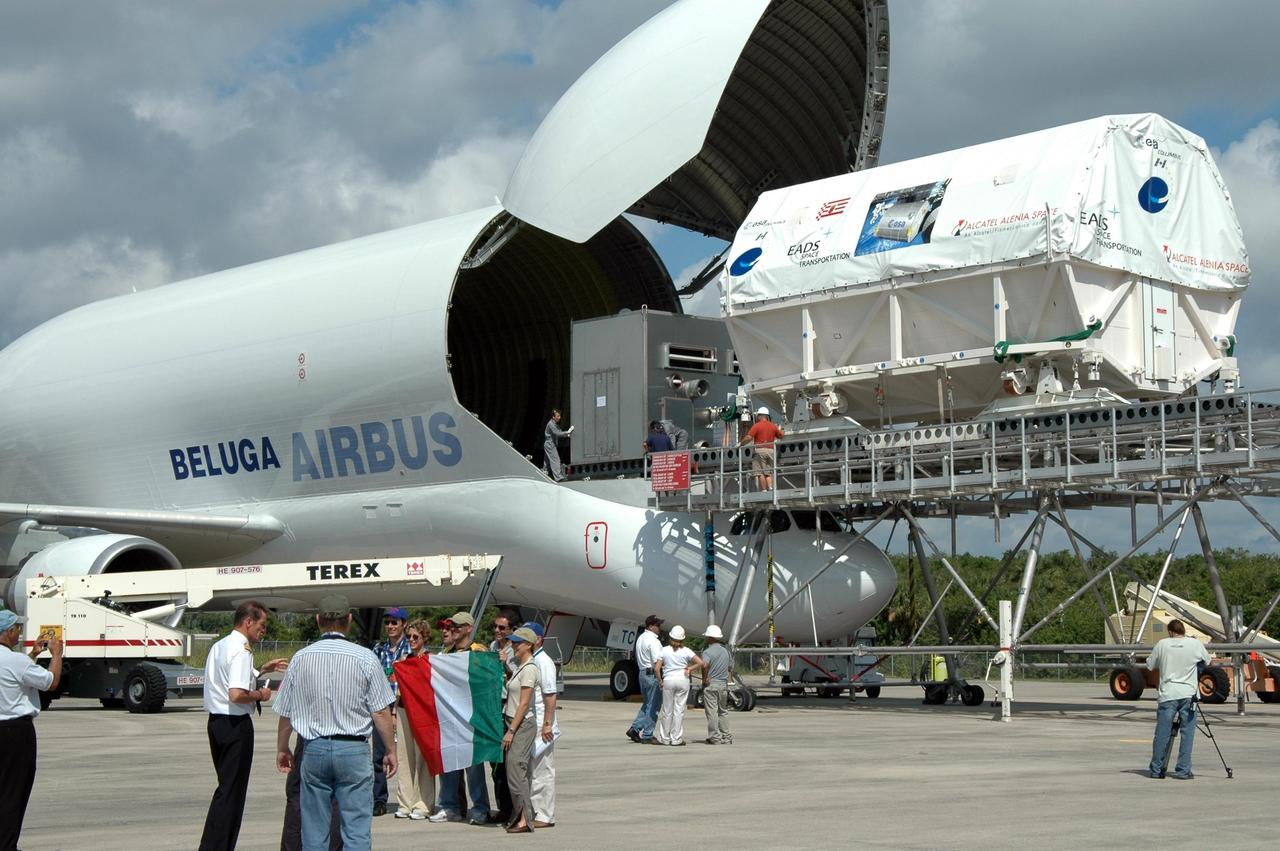

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Shuttle Landing Facility, the European Space Agency's research laboratory, designated Columbus, has been offloaded onto an Airbus Transport International platform. The module will be lifted onto a flat bed truck and transported to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will be prepared for delivery to the International Space Station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
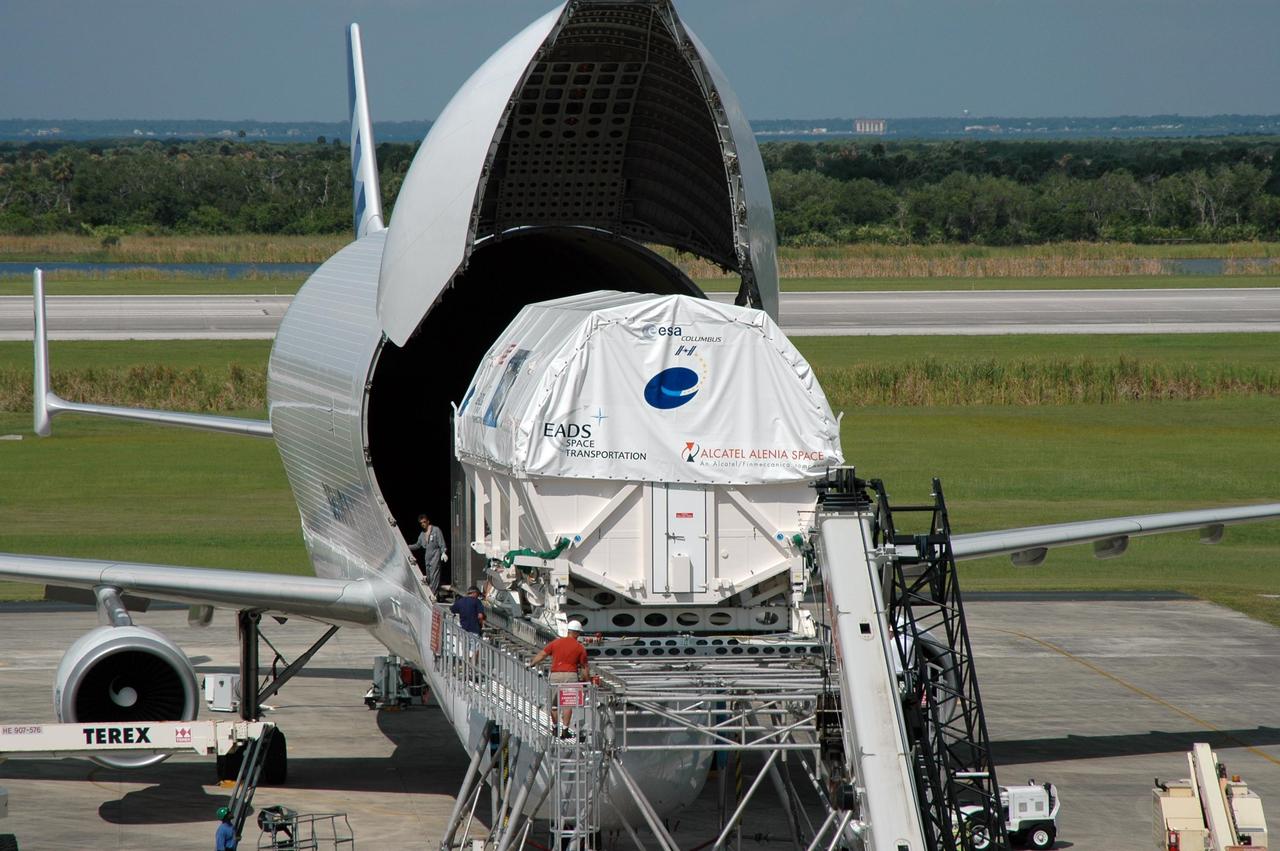

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Shuttle Landing Facility, the European Space Agency's research laboratory, designated Columbus, slides out onto an Airbus Transport International platform. The module will be lifted onto a flat bed truck and transported to the Space Station Processing Facility. In the SSPF, the module will be prepared for delivery to the International Space Station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
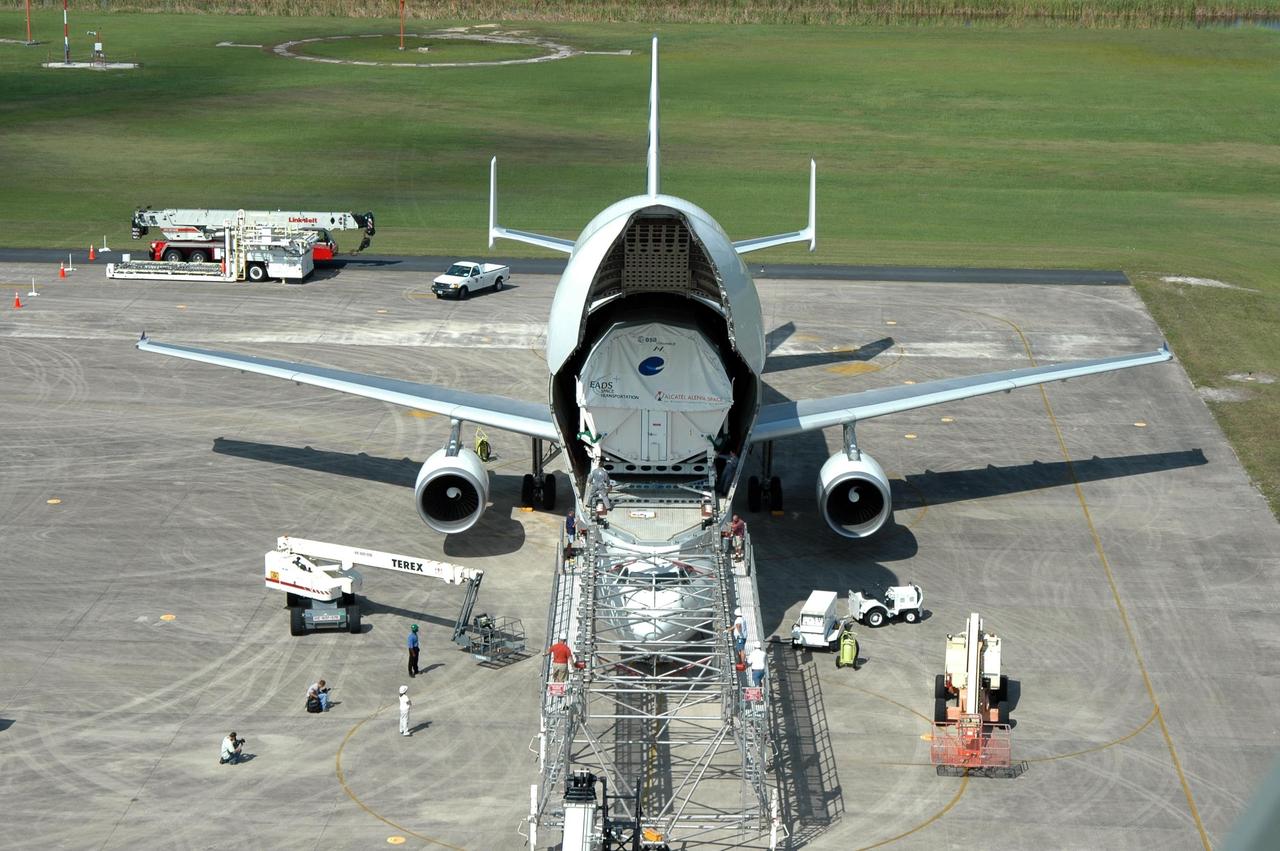

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Shuttle Landing Facility, the European Space Agency's research laboratory, designated Columbus, is being offloaded onto an Airbus Transport International platform. The module will be lifted onto a flat bed truck and transported to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will be prepared for delivery to the International Space Station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
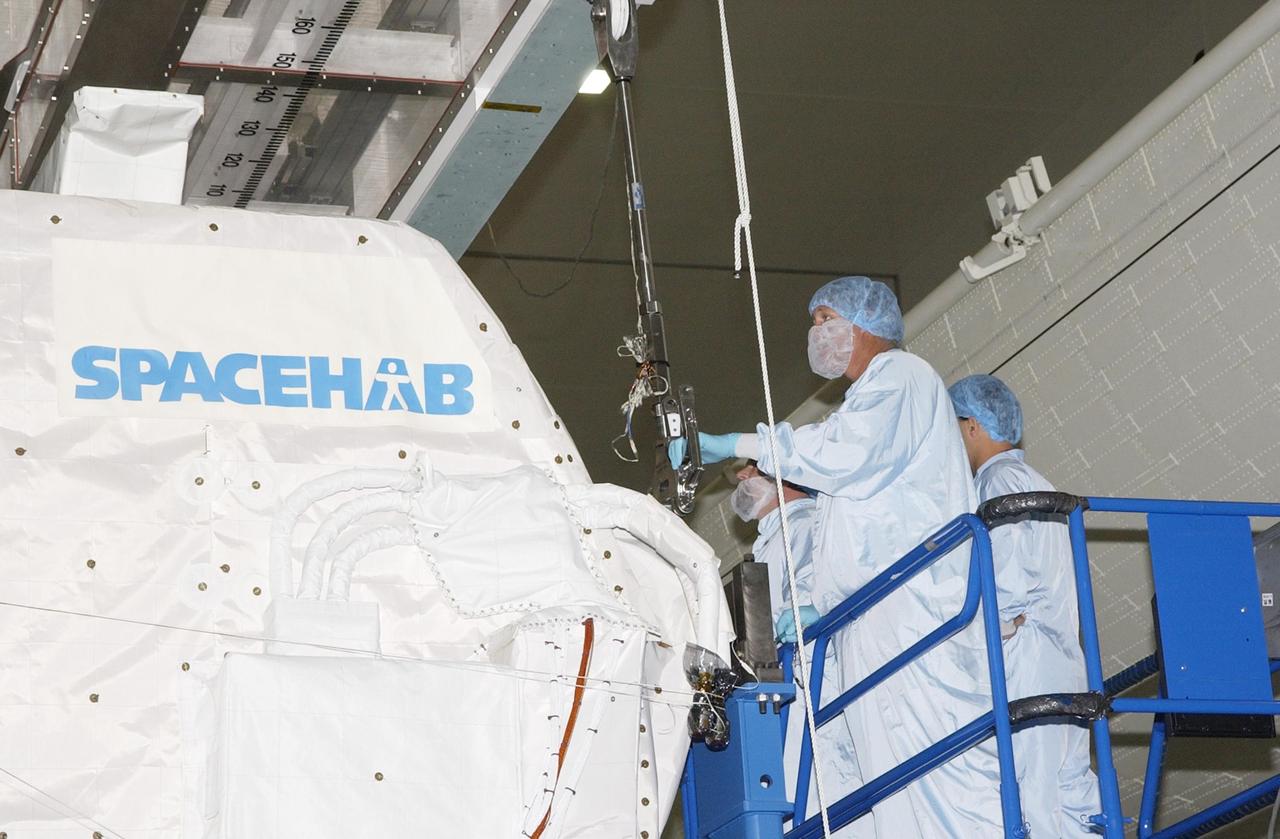

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Space Station Processing Facility attach the overhead crane to the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM) to lift it off the workstand. The module is being transferred to the payload canister for transport to the Orbiter Processing Facility where it will be installed in Columbia's payload bay for mission STS-107. SHI/RDM is the primary payload of the research mission, with experiments ranging from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). Also part of the payload is the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments. STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 19, 2002
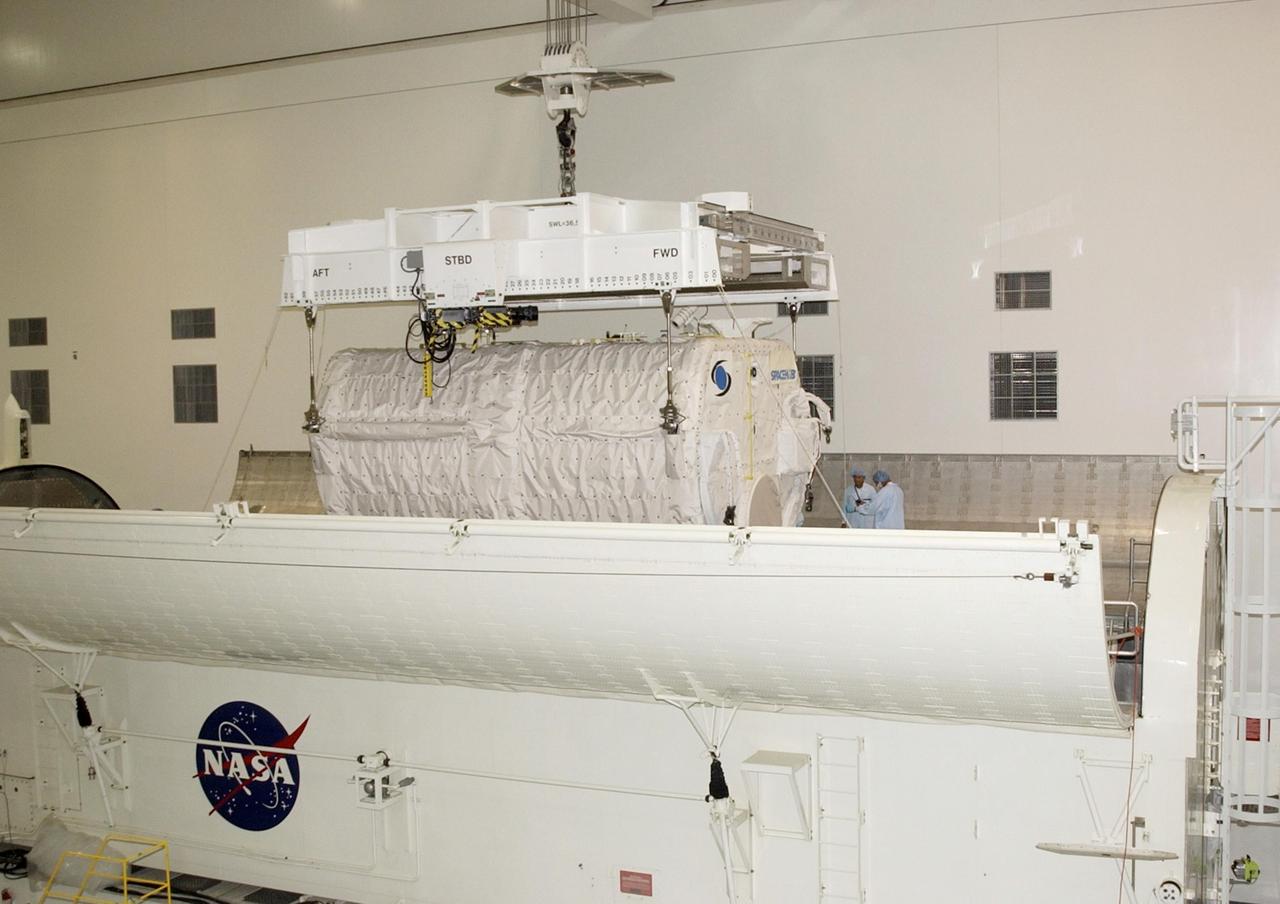

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the overhead crane lowers the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM) into the payload canister. The canister will transport it to the Orbiter Processing Facility where it will be installed in Columbia's payload bay for mission STS-107. SHI/RDM is the primary payload of the research mission, with experiments ranging from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). Also part of the payload is the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments. STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 19, 2002
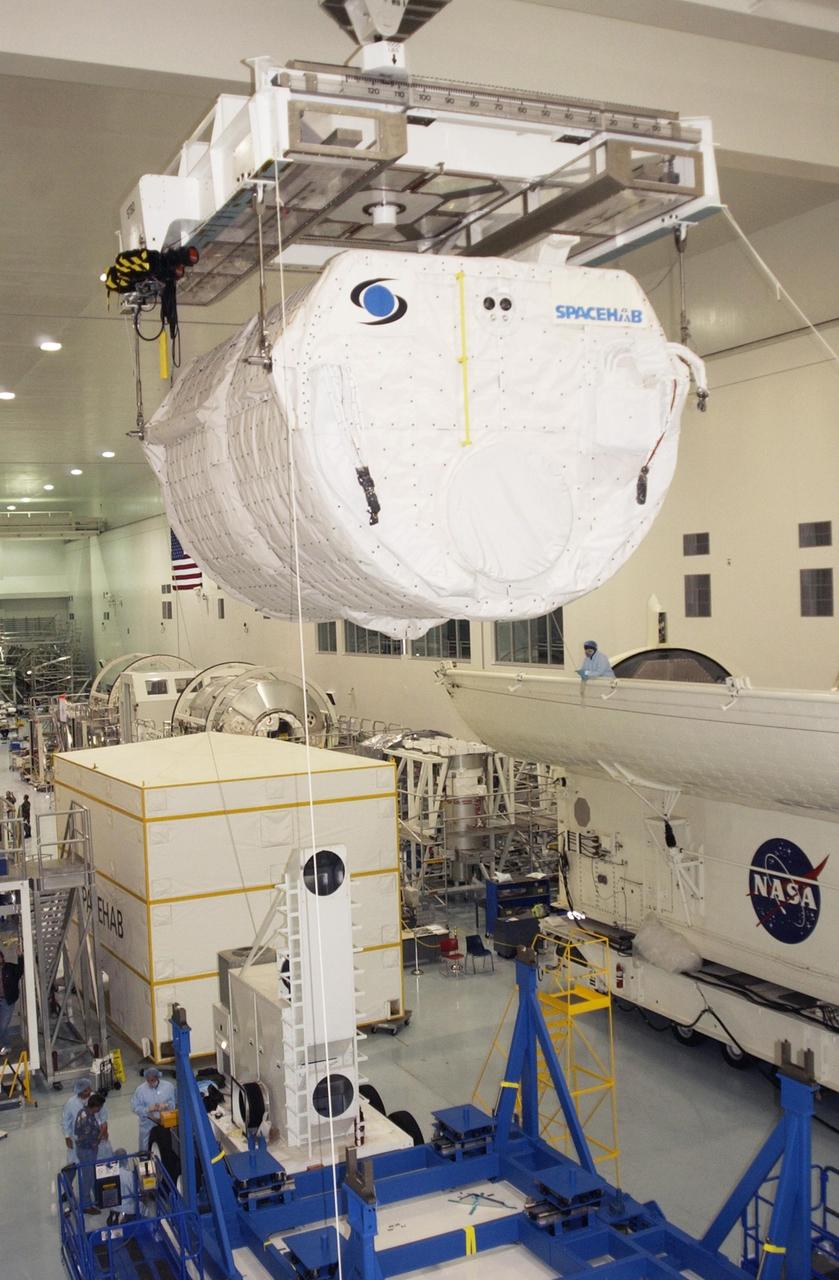

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Suspended from the overhead crane, the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM) travels across the Space Station Processing Facility to the payload canister waiting at right. The module will be placed in the canister for transport to the Orbiter Processing Facility where it will be installed in Columbia's payload bay for mission STS-107. SHI/RDM is the primary payload of the research mission, with experiments ranging from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). Also part of the payload is the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments. STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 19, 2002
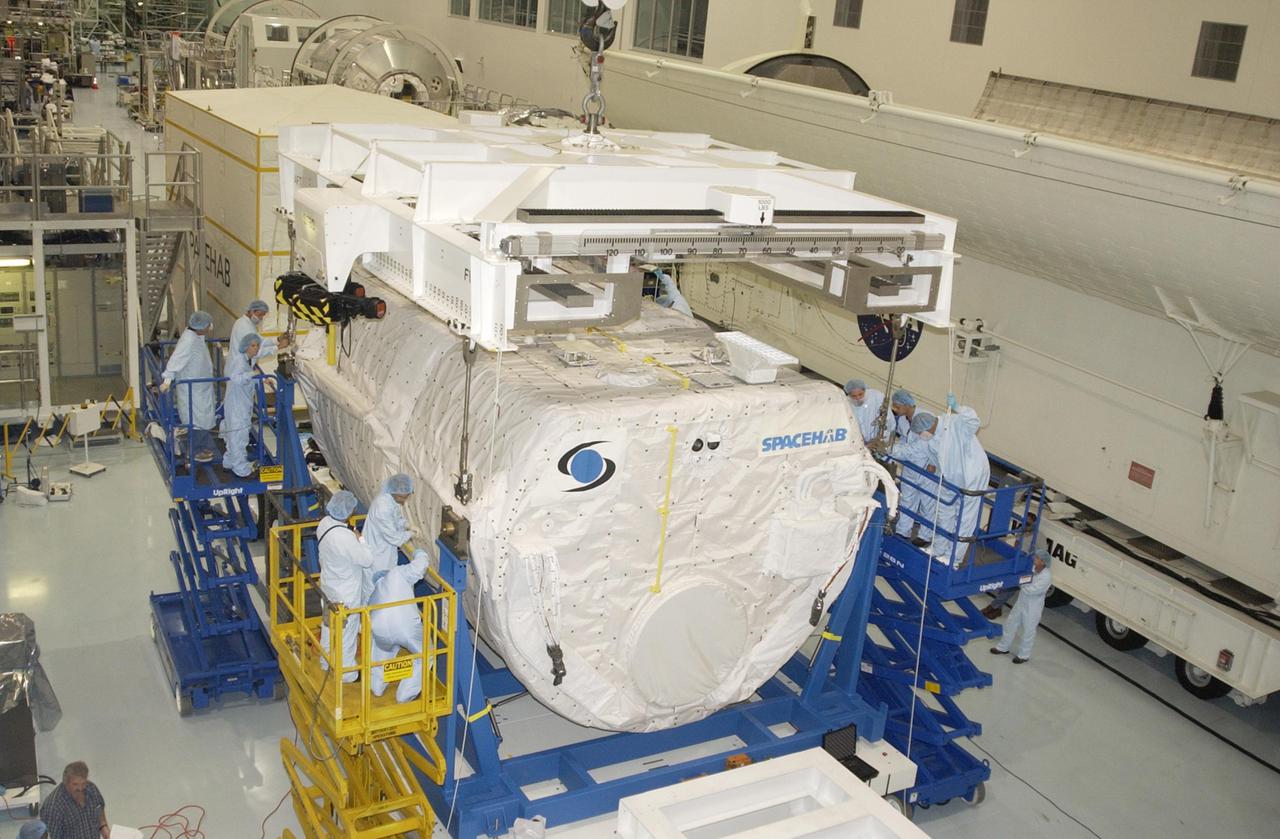

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, the overhead crane lifts the SHI Research Double Module (SHI_RDM) from its workstand. The module is being transferred to the payload canister for transport to the Orbiter Processing Facility where it will be installed in Columbia's payload bay for mission STS-107. SHI_RDM is the primary payload of the research mission, with experiments ranging from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). Also part of the payload is the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments. STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 19, 2002
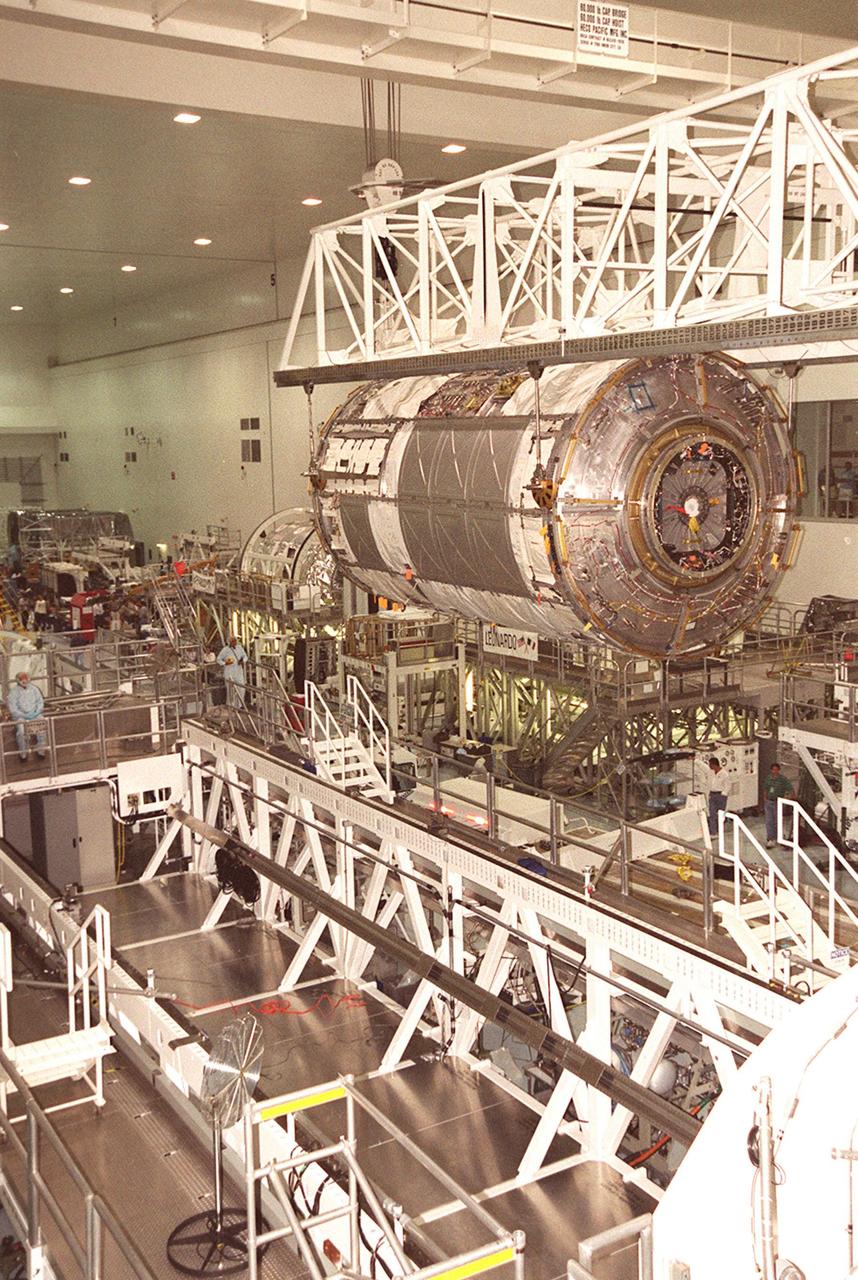
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Suspended under an overhead crane, the U.S. Lab Destiny nears the weigh stand at left. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
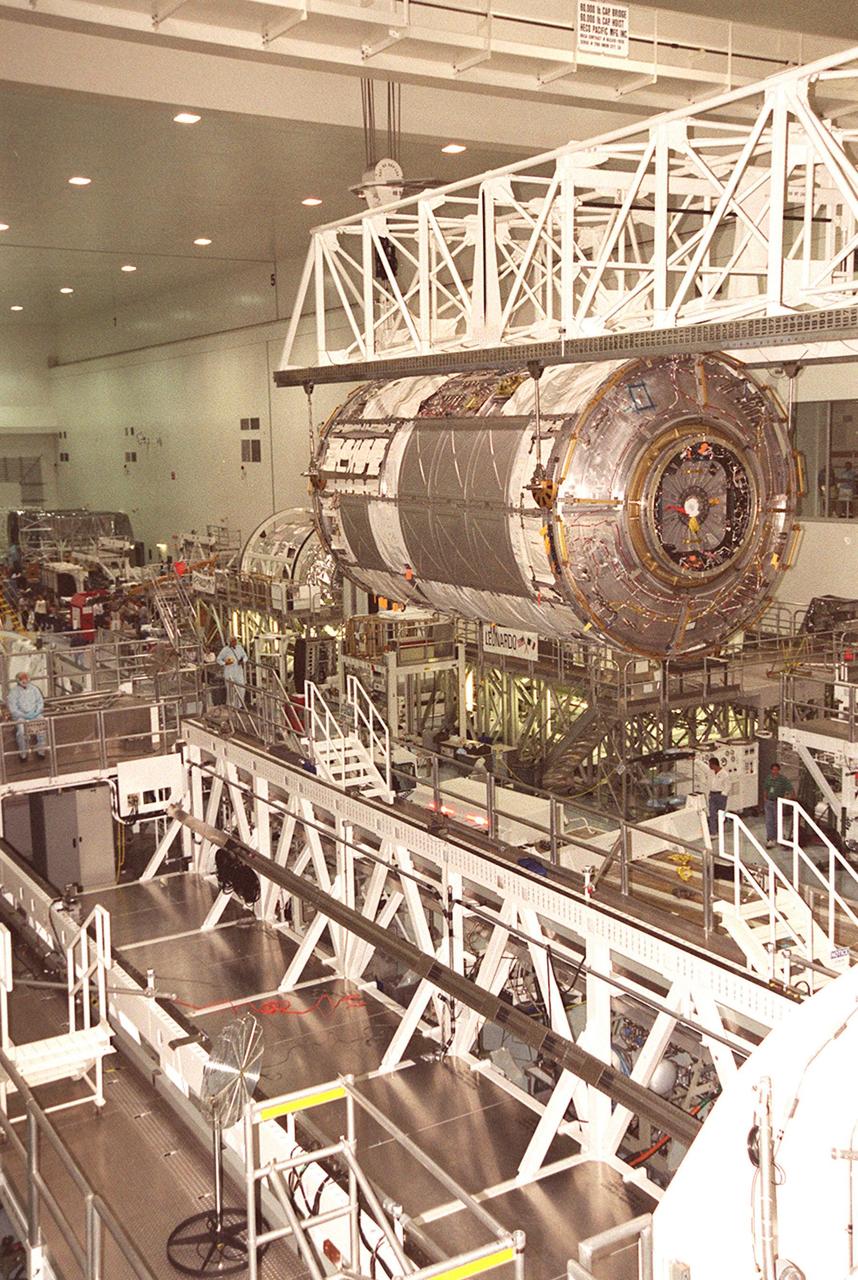
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Suspended under an overhead crane, the U.S. Lab Destiny nears the weigh stand at left. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
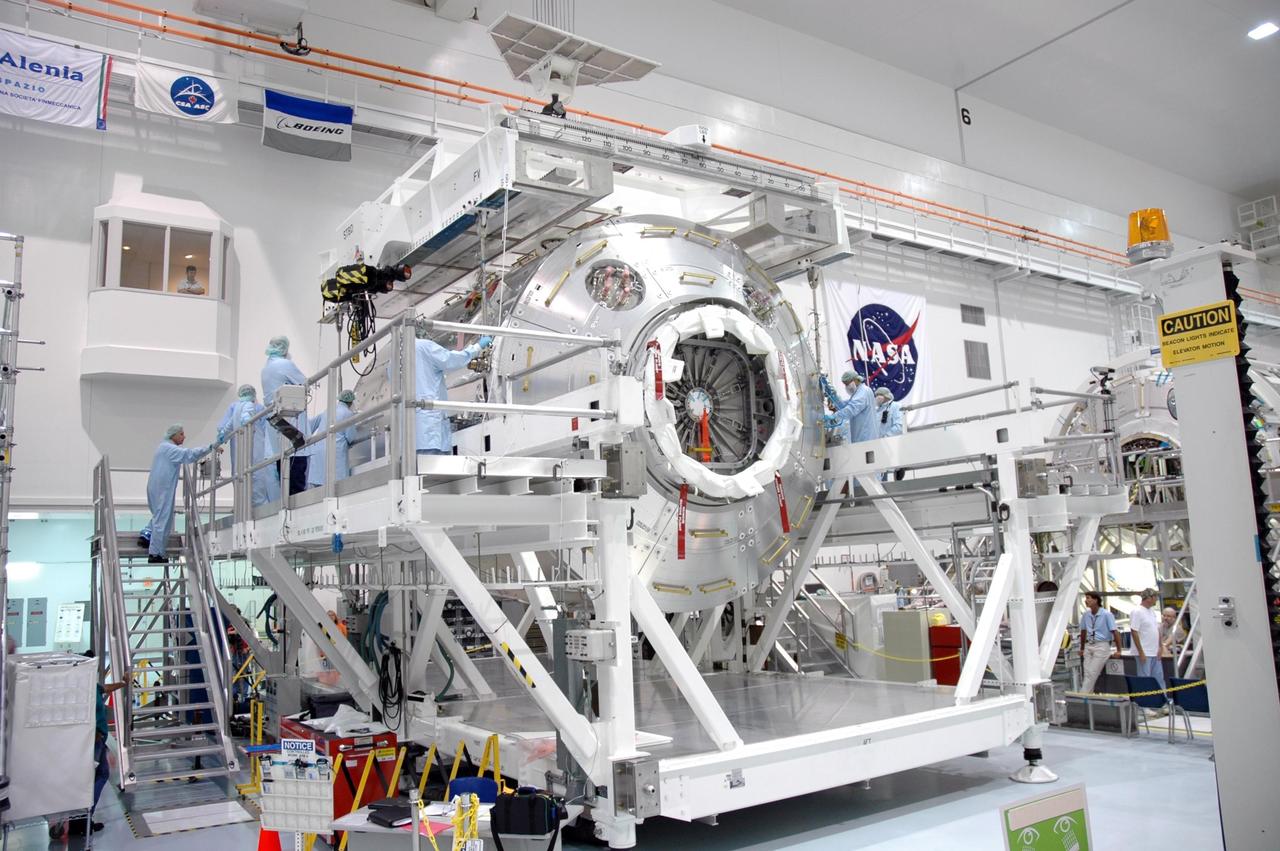

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers release the cables around the Columbus module from the overhead crane. Columbus is the European Space Agency's research laboratory for the International Space Station. The module will be prepared for delivery to the space station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
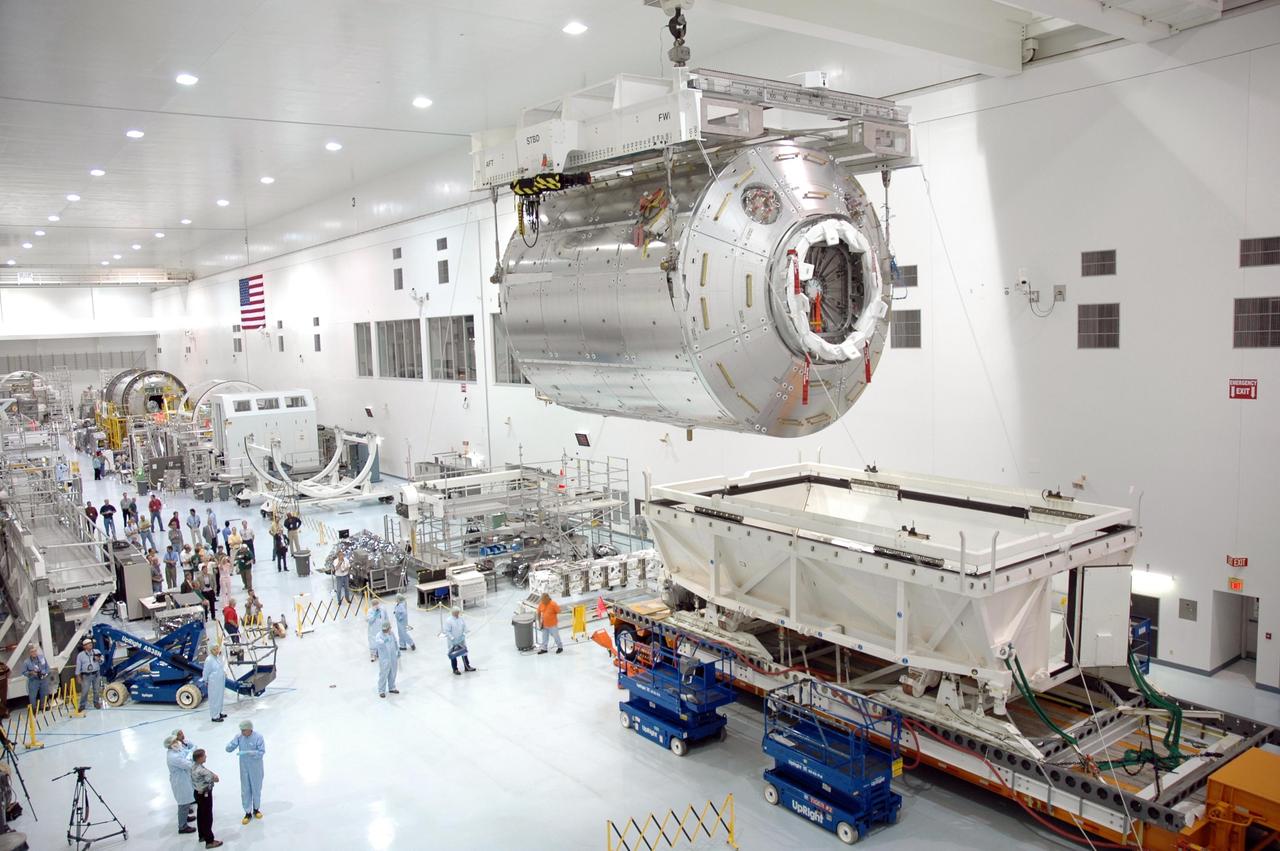

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane carries the Columbus module toward a work stand. Columbus is the European Space Agency's research laboratory for the International Space Station. Once on the work stand , it will be prepared for delivery to the space station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
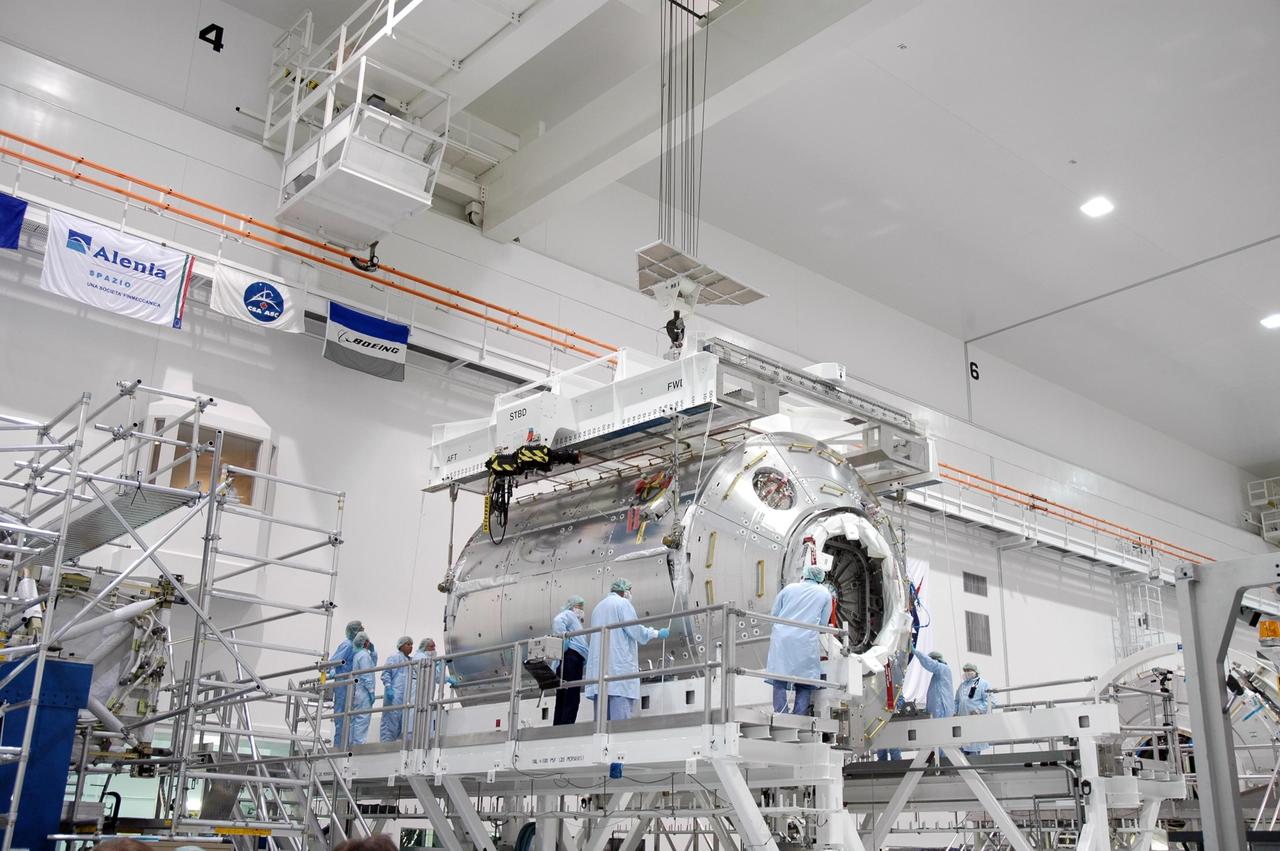

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane settles the Columbus module onto a work stand. Columbus is the European Space Agency's research laboratory for the International Space Station. The module will be prepared for delivery to the space station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
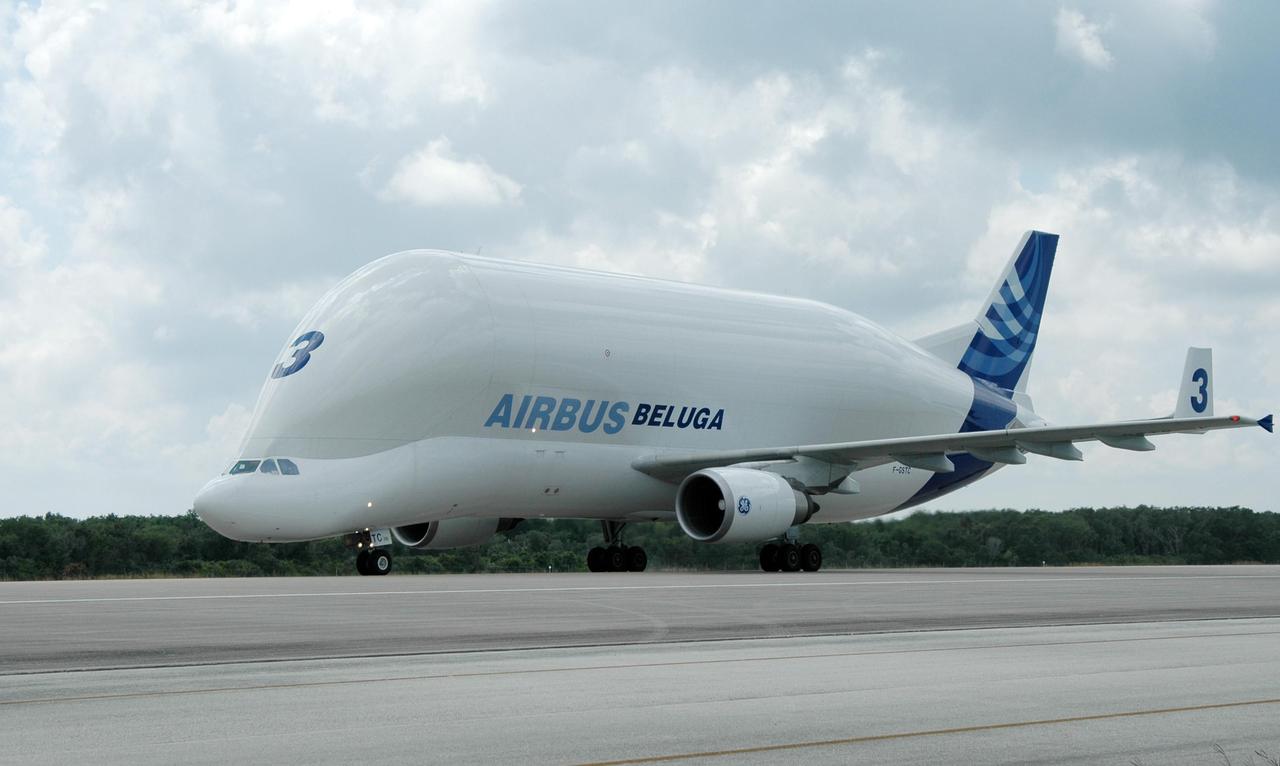

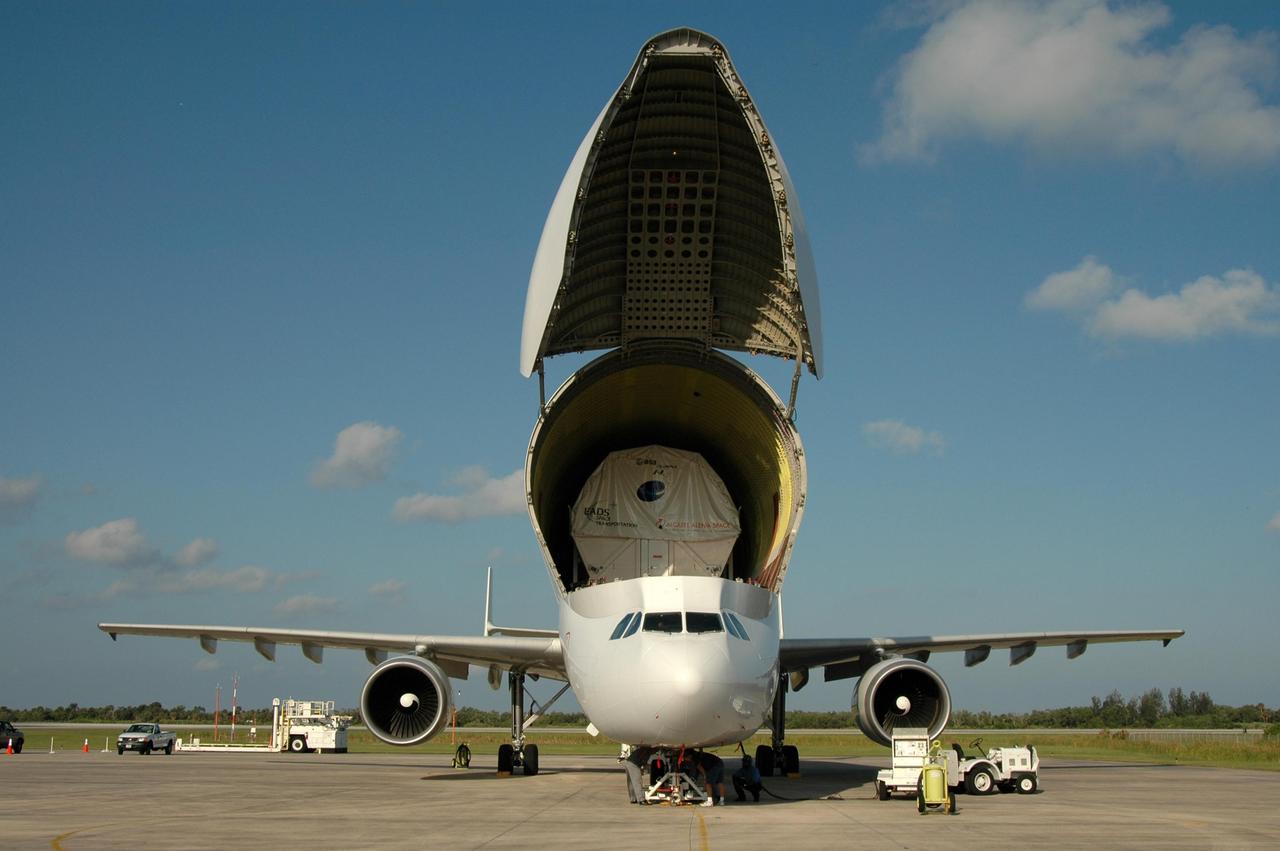
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A Beluga aircraft taxis on the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility on NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The Beluga carries the European Space Agency's research laboratory, designated Columbus, flown to Kennedy from its manufacturer in Germany. The module will be prepared for delivery to the International Space Station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Jim Kennedy, director of NASA's Kennedy Space Center, addresses the audience attending a ceremony in the Space Station Processing Facility to welcome the European Space Agency's Columbus module. Columbus is the European Space Agency's research laboratory for the International Space Station. The module will be prepared in the SSPF for delivery to the space station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
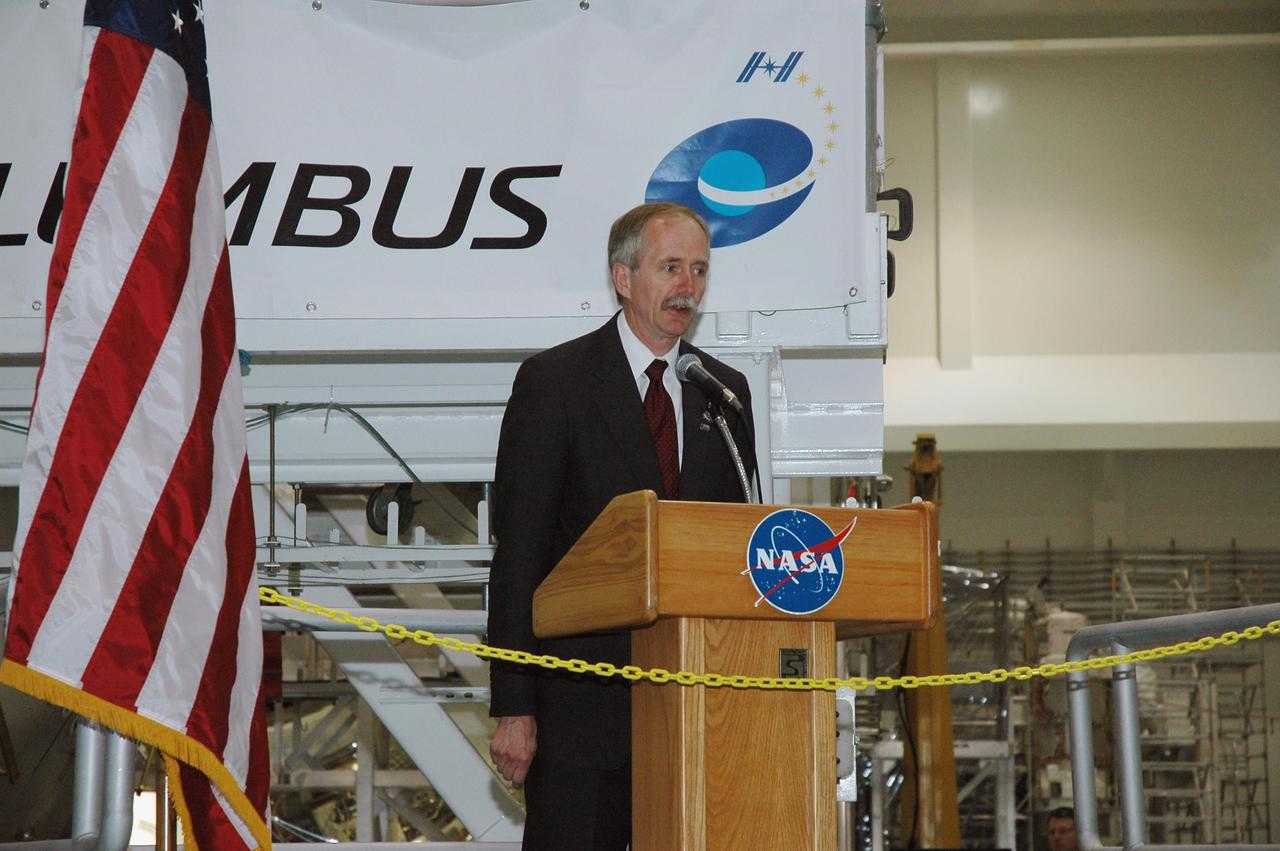

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - William Gerstenmaier, NASA associate administrator for Space Operations, welcomes the delivery of the European Space Agency's Columbus module at a ceremony in the Space Station Processing Facility. Columbus is the European Space Agency's research laboratory for the International Space Station. The module will be prepared in the SSPF for delivery to the space station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A Beluga aircraft parks near the mate/demate device at the Shuttle Landing Facility on NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The Beluga carries the European Space Agency's research laboratory, designated Columbus, flown to Kennedy from its manufacturer in Germany. The module will be prepared for delivery to the International Space Station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
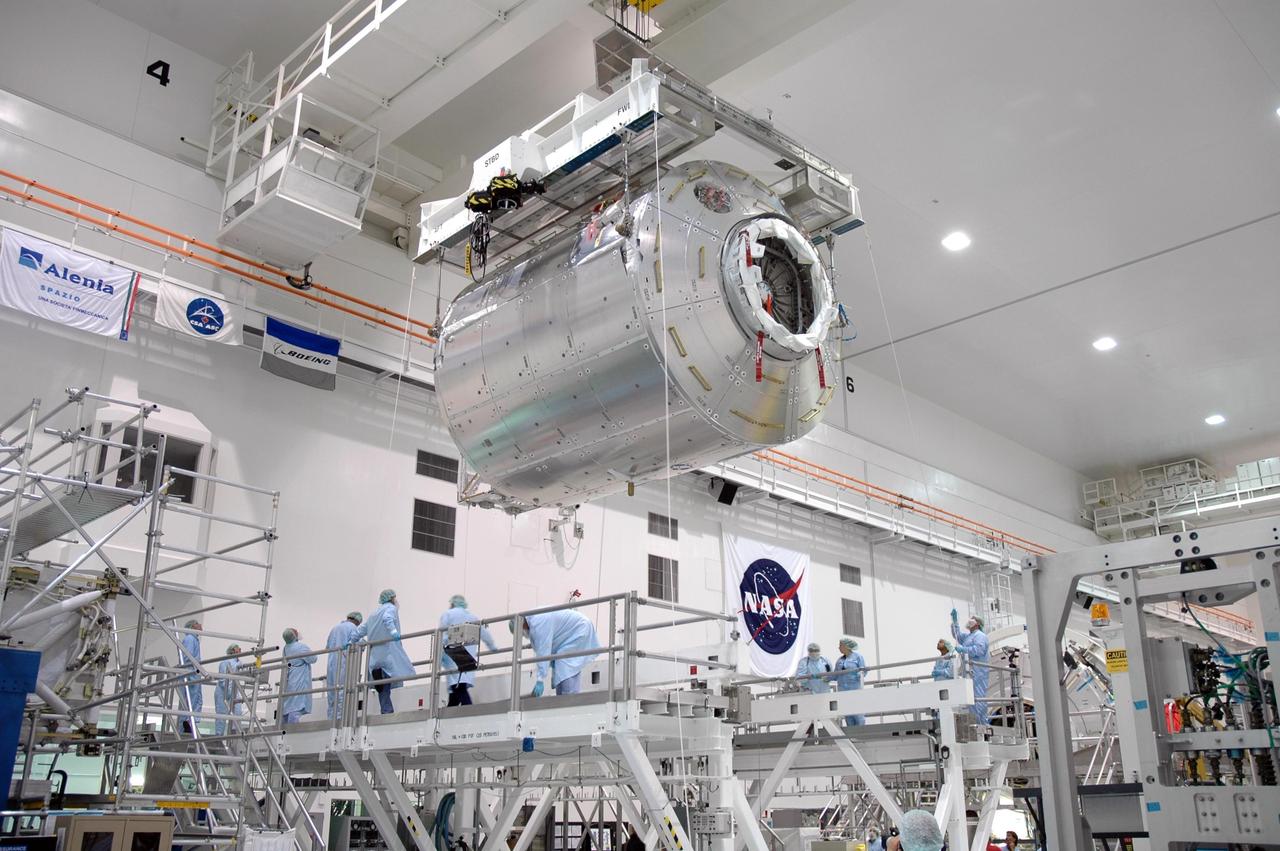

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lowers the Columbus module toward a work stand. Columbus is the European Space Agency's research laboratory for the International Space Station. The module will be prepared for delivery to the space station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
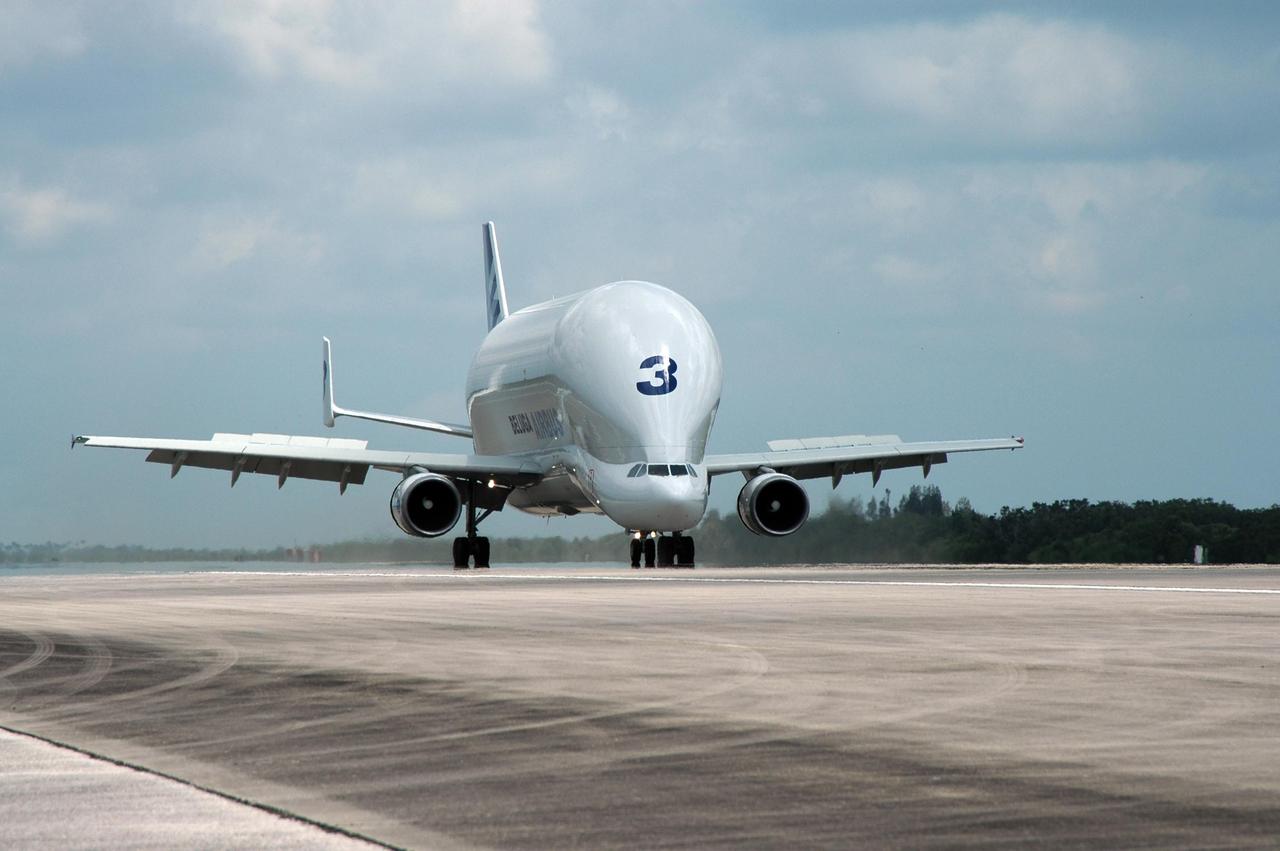

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A Beluga aircraft arrives at the Shuttle Landing Facility on NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The Beluga carries the European Space Agency's research laboratory, designated Columbus, flown to Kennedy from its manufacturer in Germany. The module will be prepared for delivery to the International Space Station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

iss065e442803 (10/7/2021) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet gathers fluid physics and materials research hardware inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module. Device for the Study of Critical Liquids and Crystallization (DECLIC) is a multi-user facility developed by the agency Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (French Space Agency, CNES) and flown in collaboration with NASA. It is designed to support experiments in the fields of fluid physics and materials science. Special inserts allow researchers to study both ambient temperature critical point fluids and high temperature super-critical fluids. Another class of insert studies the dynamics and morphology of the fronts that form as a liquid material solidifies.

An experiment vehicle plunges into the deceleration pit at the end of a 5.18-second drop in the Zero-Gravity Research Facility at NASA's Glenn Research Center. The Zero-Gravity Research Facility was developed to support microgravity research and development programs that investigate various physical sciences, materials, fluid physics, and combustion and processing systems. Payloads up to 1 meter in diameter and 455 kg in weight can be accommodated. The facility has a 145-meter evacuated shaft to ensure a disturbance-free drop. This is No.1 of a sequence of 4 images. (Credit: NASA/Glenn Research Center)

An experiment vehicle plunges into the deceleration at the end of a 5.18-second drop in the Zero-Gravity Research Facility at NASA's Glenn Research Center. The Zero-Gravity Research Facility was developed to support microgravity research and development programs that investigate various physical sciences, materials, fluid physics, and combustion and processing systems. Payloads up to one-meter in diameter and 455 kg in weight can be accommodated. The facility has a 145-meter evacuated shaft to ensure a disturbance-free drop. This is No. 3 of a sequence of 4 images. (Credit: NASA/Glenn Research Center)
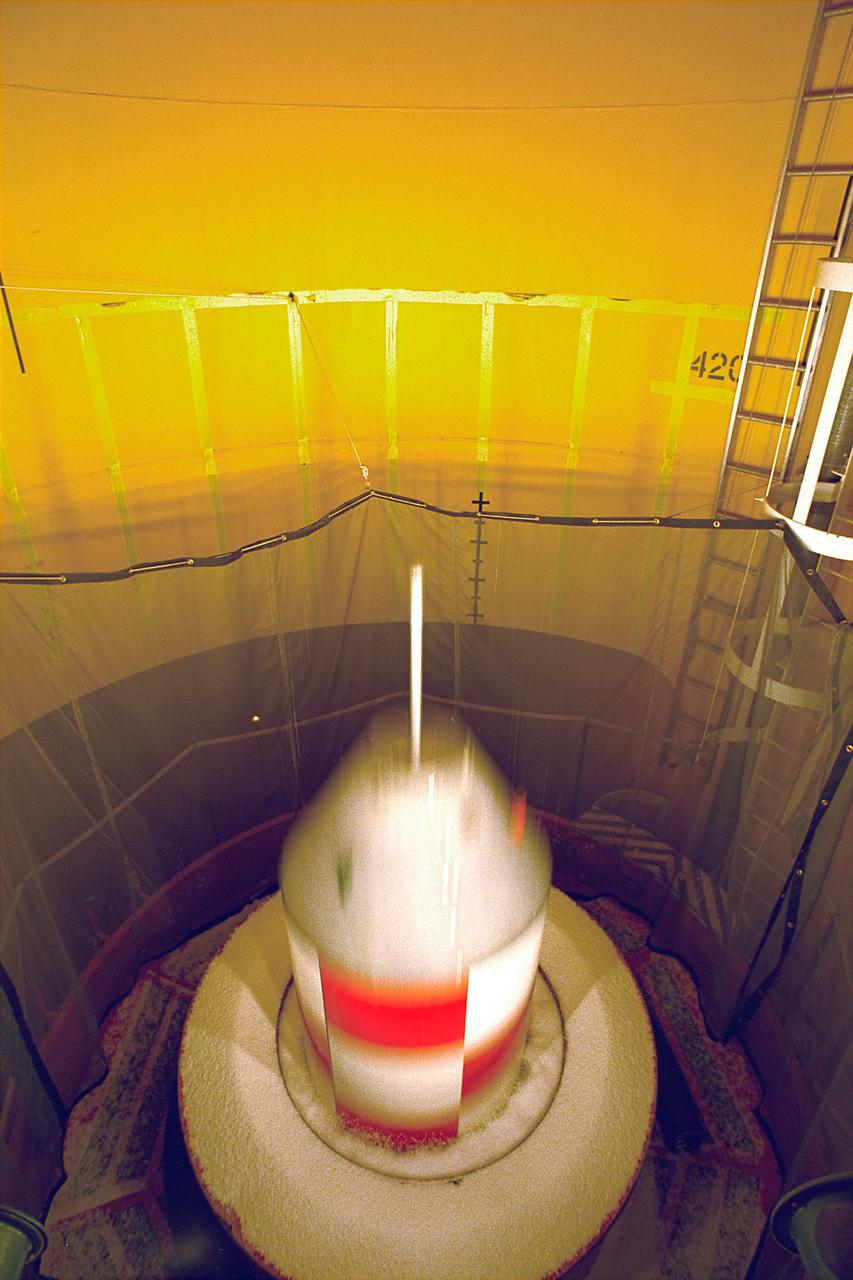
An experiment vehicle plunges into the deceleration pit at the end of a 5.18-second drop in the Zero-Gravity Research Facility at NASA's Glenn Research Center. The Zero-Gravity Research Facility was developed to support microgravity research and development programs that investigate various physical sciences, materials, fluid physcis, and combustion and processing systems. Payloads up to 1 meter in diameter and 455 kg in weight can be accommodated. The facility has a 145-meter evacuated shaft to ensure a disturbance-free drop. This is No. 2 of a sequence of 4 images. (Credit: NASA/Glenn Research Center)

An experiment vehicle plunges into the deceleration pit at the end of a 5.18-second drop in the Zero-Gravity Research Facility at NASA's Glenn Research Center. The Zero-Gravity Research Facility was developed to support microgravity research and development programs that investigate various physical sciences, materials, fluid physics, and combustion and processing systems. Payloads up to one meter in diameter and 455 kg in weight can be accommodated. The facility has a 145-meter evacuated shaft to ensure a disturbance-free drop. This is No. 4 of a sequence of 4 images. (Credit: NASA/Glenn Research Center)
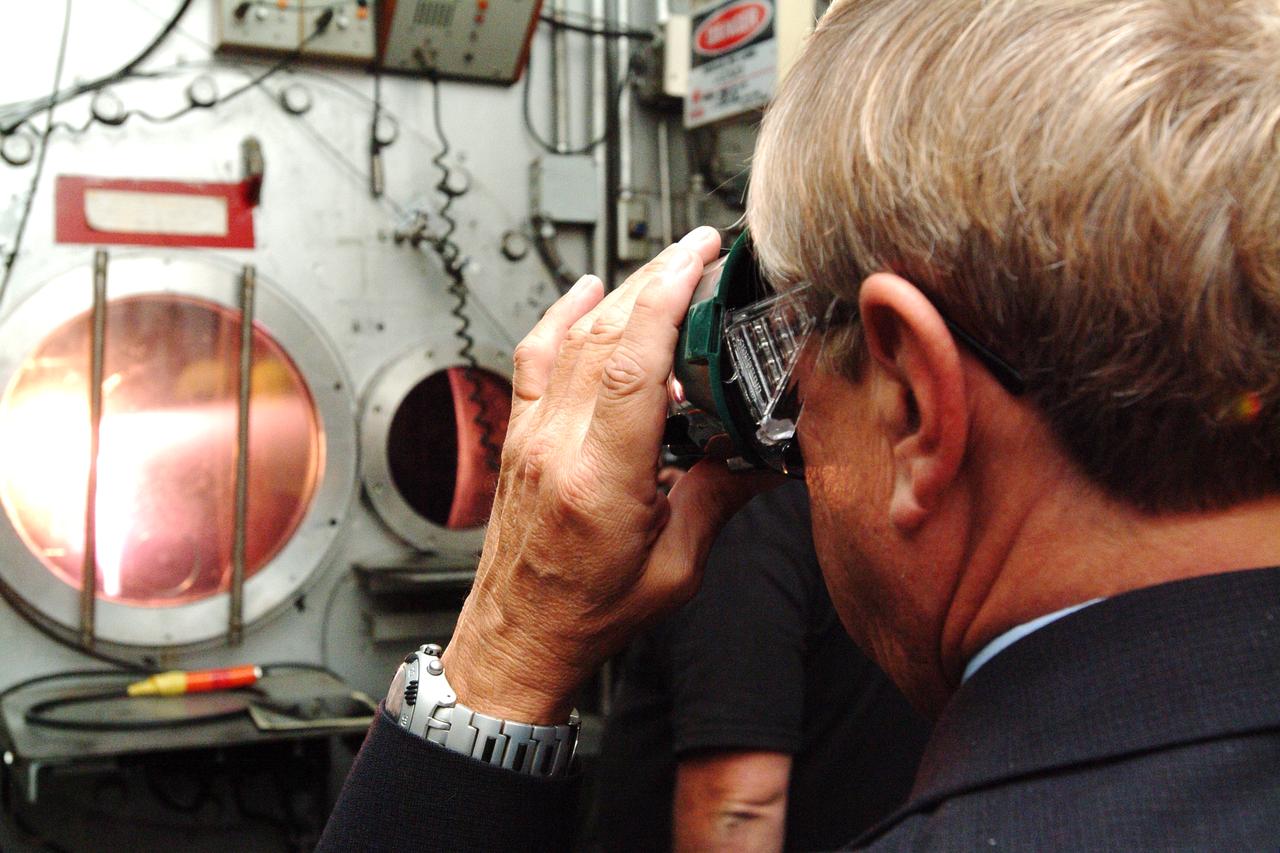
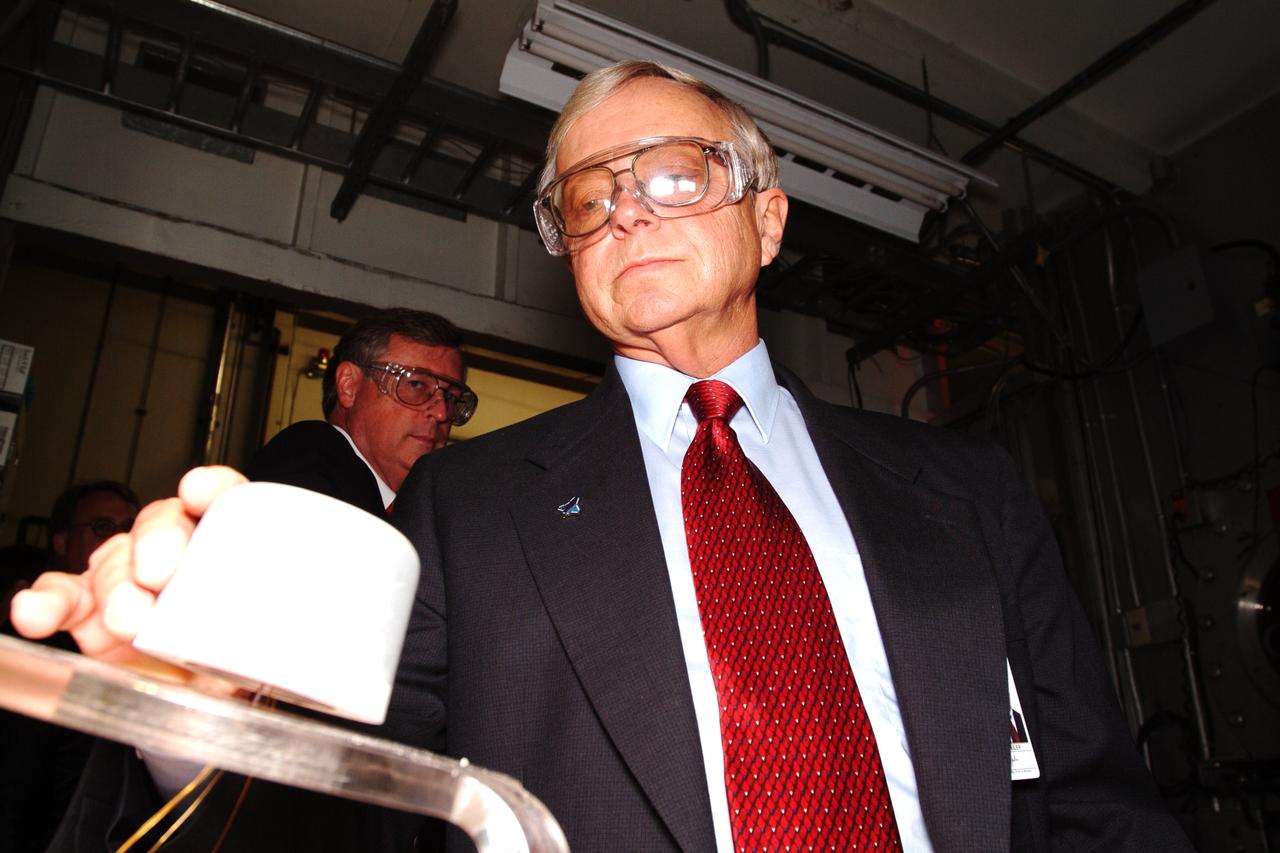
NASA Space Science Advisory Committee Chairman Ed Wiler (r) visit to Ames Research Center: while on tour of the Arc Jet Facility with G. Scott Hubbard, Raj Venkatapathy and entourage. Wiler uses special viewing glasses to observe a test run of Thermal Protection Materials.
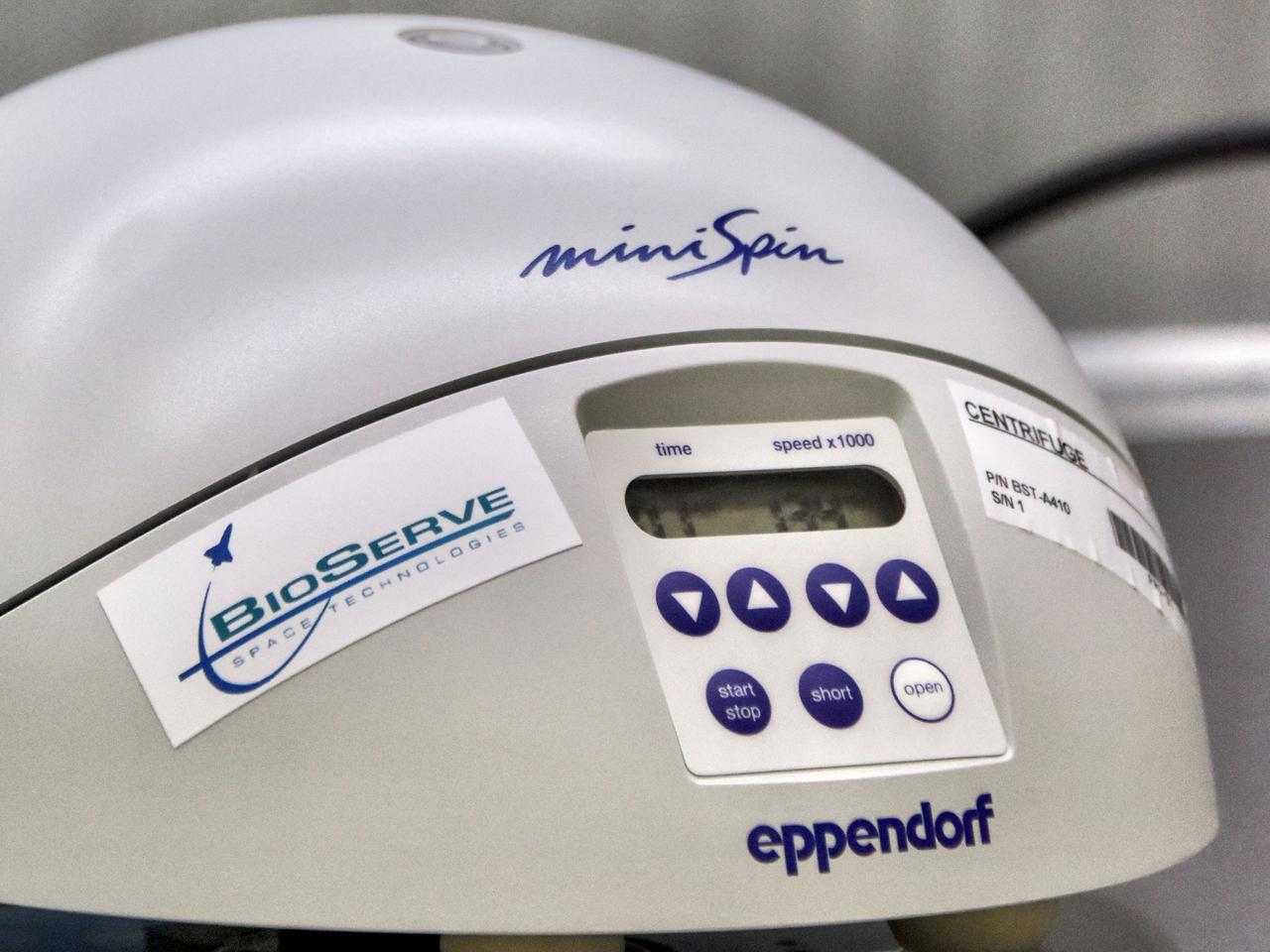

jsc2022e031231 (8/13/2021) --- A preflight closeup view of the BioServe Centrifuge’s user interface. The BioServe Centrifuge facility supports a wide variety of life, physical, and materials science research. It enables separation of substances with differing densities, including cell cultures, DNA, protein, blood, and sedimentation samples. Image courtesy of BioServe Space Technologies.
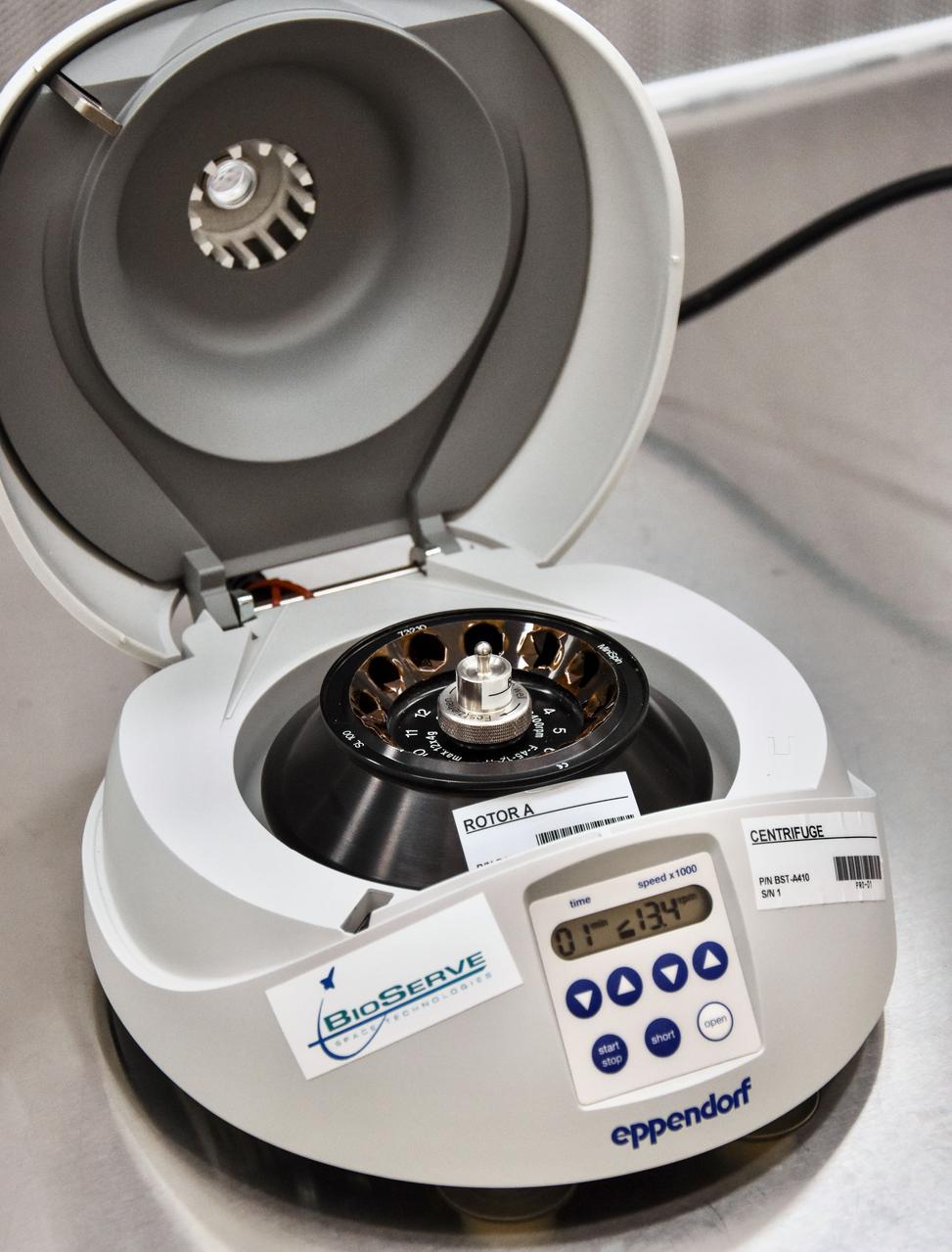

jsc2022e031230 (8/13/2021) --- A preflight view of the interior of the BioServe Centrifuge in nominal configuration with Rotor A. The BioServe Centrifuge facility supports a wide variety of life, physical, and materials science research. It enables separation of substances with differing densities, including cell cultures, DNA, protein, blood, and sedimentation samples.Image courtesy of BioServe Space Technologies.
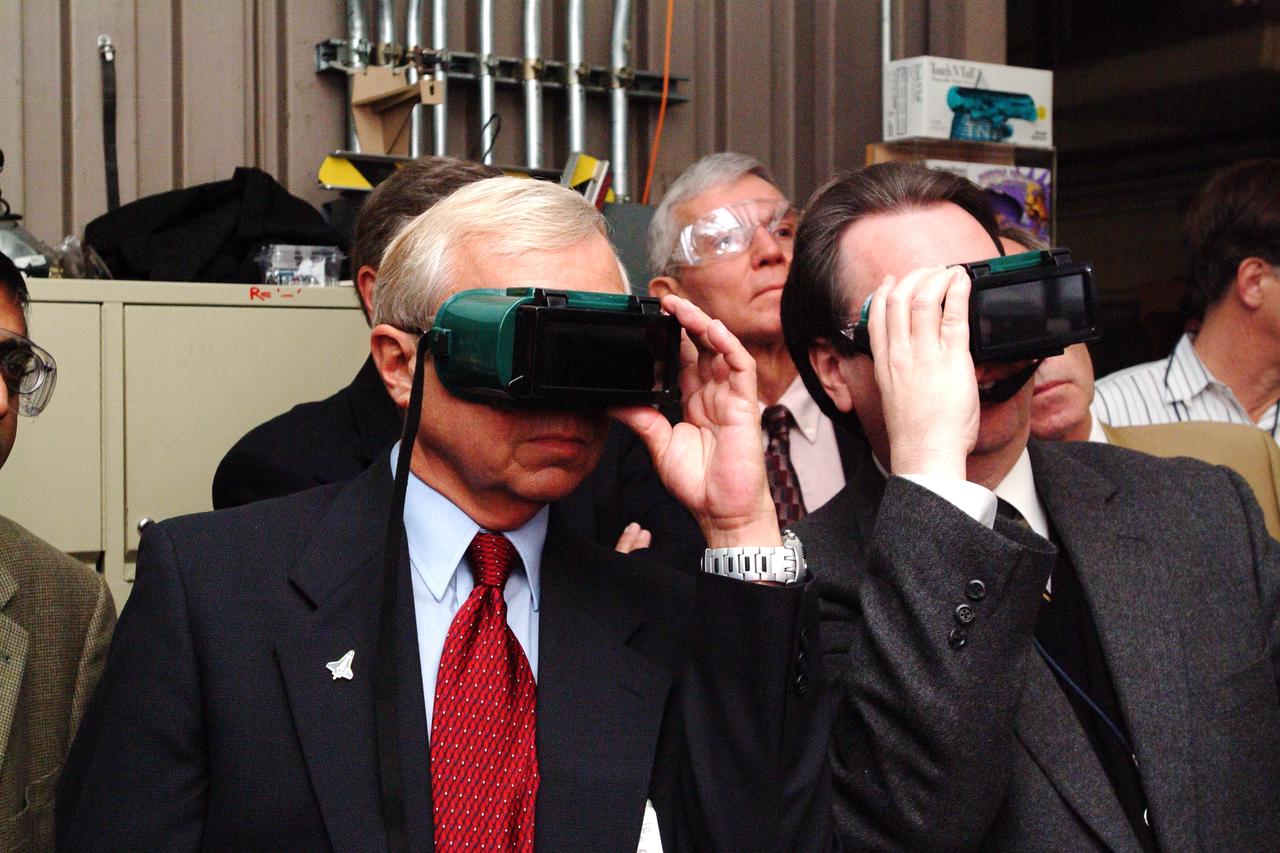

NASA Space Science Advisory Committee Chairman Ed Wiler (r) visit to Ames Research Center: on tour of the Arc Jet Facility with G. Scott Hubbard, Raj Venkatapathy and entourage. Wiler and Hubbard use special viewing glasses to observe a test run of Thermal Protection Materials.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, STS-107 crew members review test results on the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) experiments, part of the payload on their mission. A research mission, the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM), also known as SPACEHAB. The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 11, 2002. In the background, on the stand, are some of the experiments going on the mission
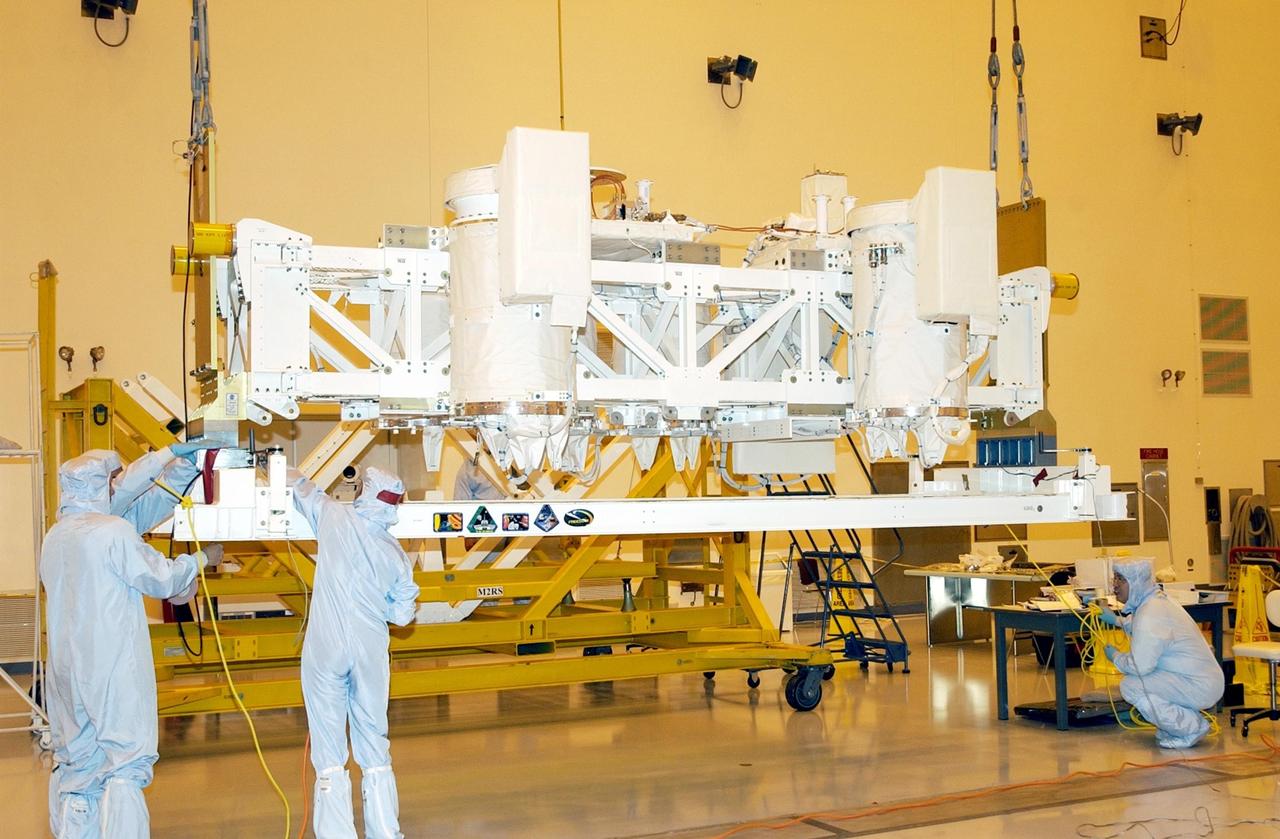

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF), workers check the Hitchhiker Bridge that is being lifted by a crane for transfer to a workstand. The bridge is a carrier for the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments on mission STS-107. A research mission, the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM), also known as SPACEHAB. The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences. STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 11, 2002
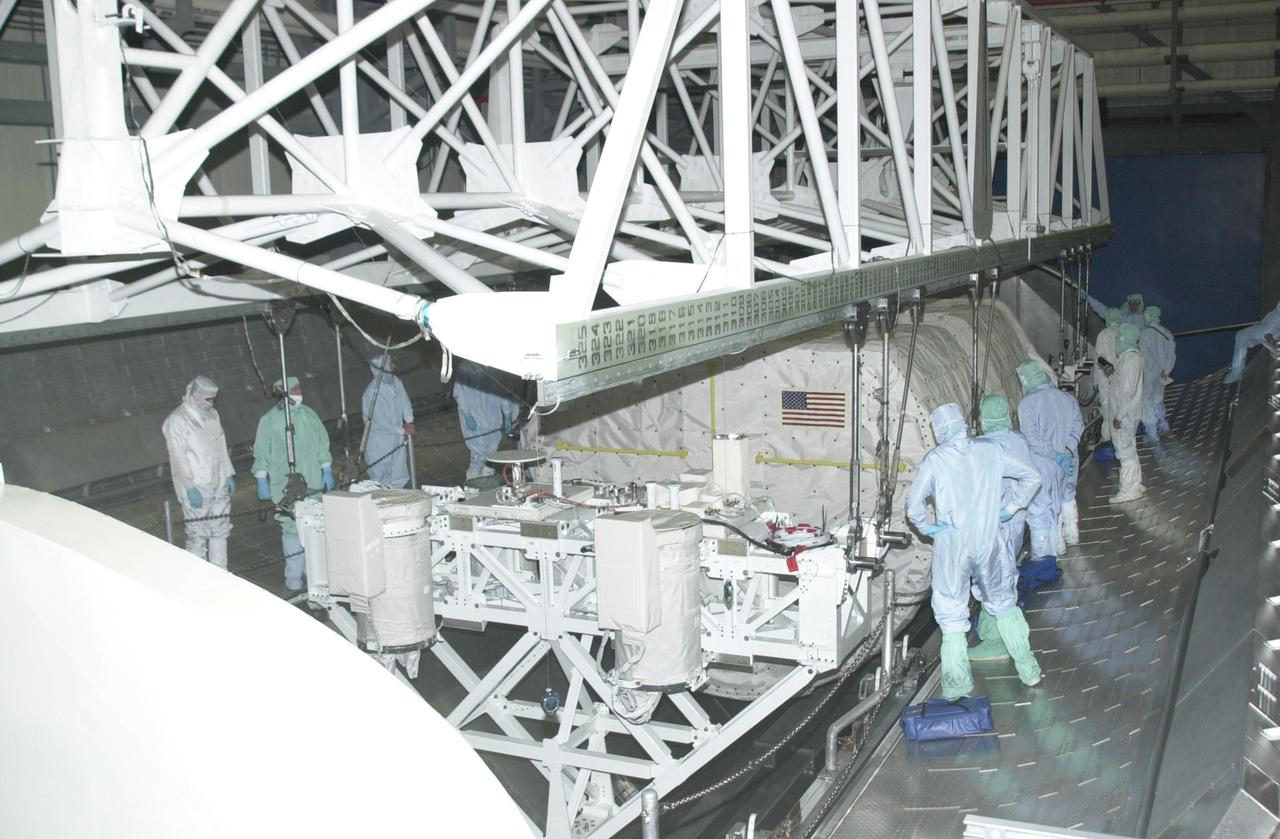

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, an overhead crane is attached to the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM) (right) and Hitchhiker Carrier (left) to lift them out of the payload canister. They will be installed in Columbia's payload bay. SHI/RDM is the primary payload of the STS-107 research mission, with experiments ranging from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). Also, the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that is on the Hitchhiker Carrier incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments. STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 19, 2002
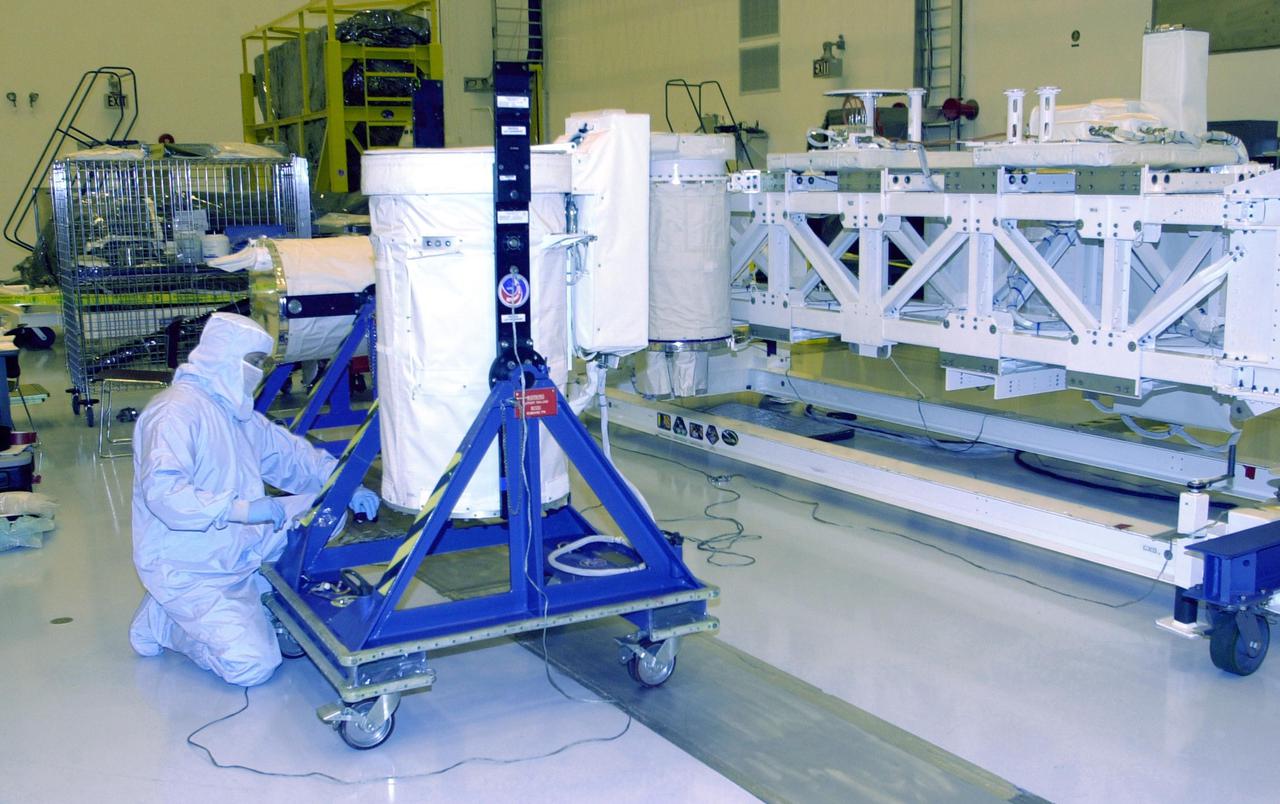

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A worker in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility prepares a GetAway Special canister (GAS can) for a move to the Hitchhiker Bridge. The bridge is a carrier for the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments on mission STS-107. A research mission, the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI_RDM), also known as SPACEHAB. The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 11, 2002
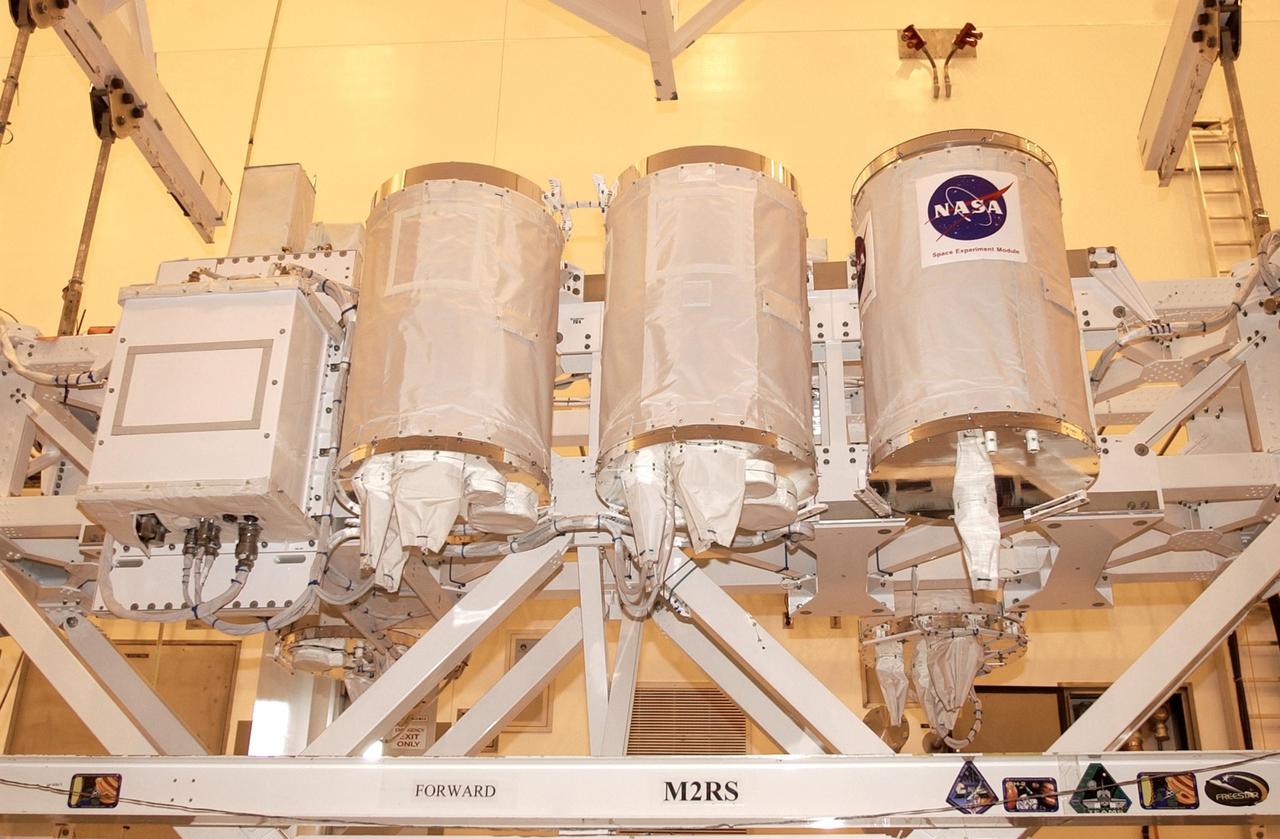

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, the Hitchhiker Bridge with GetAway Special canisters (GAS cans) are ready for transfer to the payload canister. The bridge is a carrier for the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments on mission STS-107. The bridge will be installed in Columbia's payload bay. A research mission, STS-107 will also carry the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM), known as SPACEHAB. Experiments on the module range from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 19, 2002
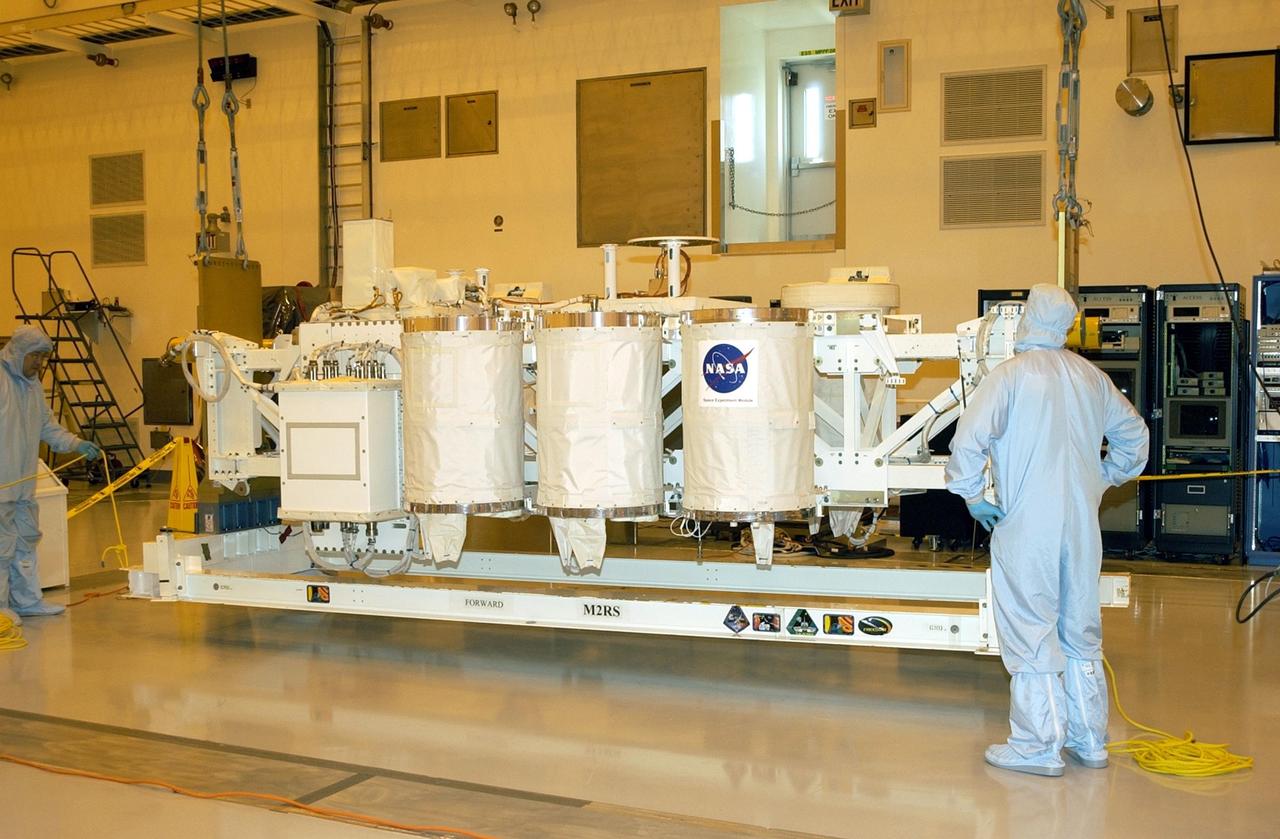

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF), workers watch as the Hitchhiker Bridge, with several Get-Away Special canisters (GAS cans) for mission ST-107, is lifted off the ground. The bridge is being moved to a workstand in the MPPF. The bridge is a carrier for the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments on mission STS-107. A research mission, the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM), also known as SPACEHAB. The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences. STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 11, 2002
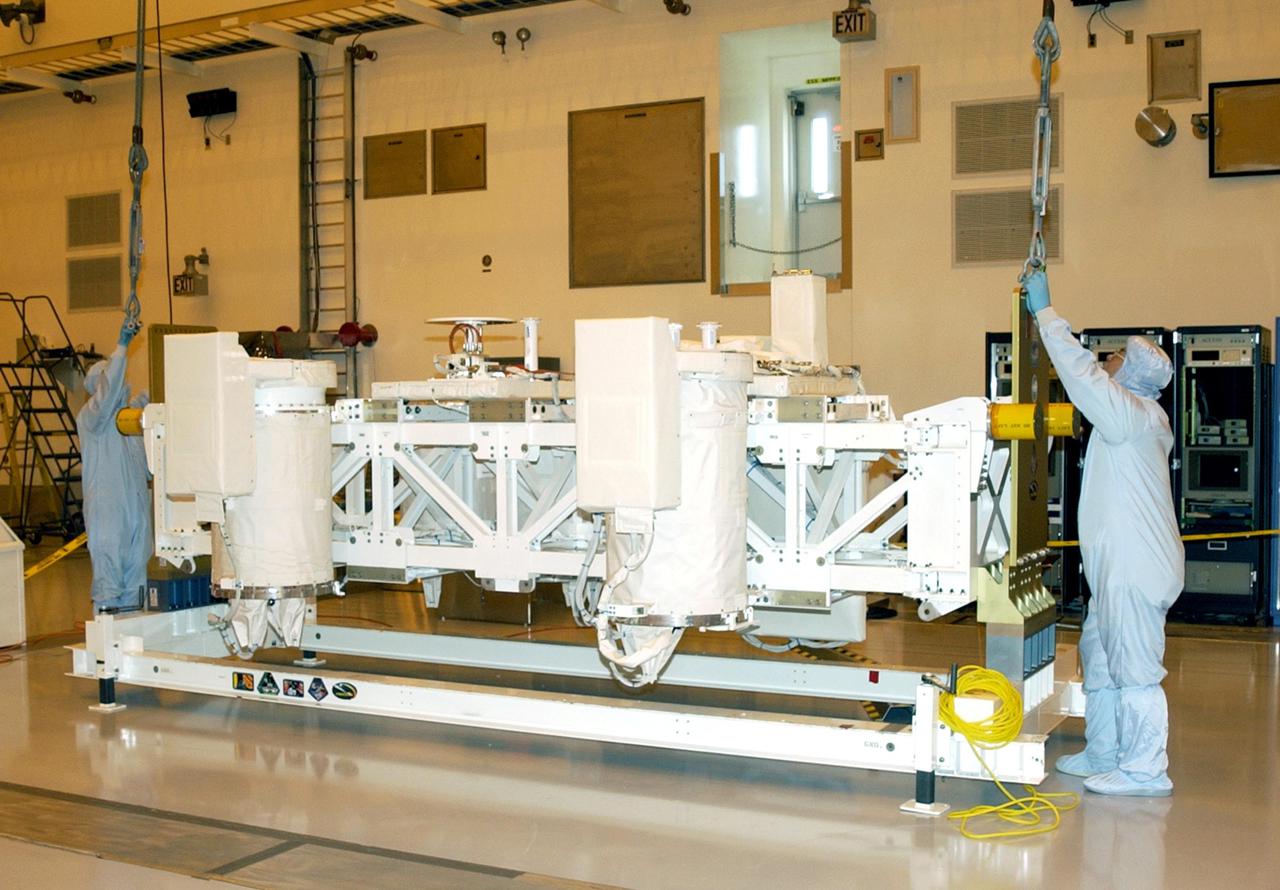

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF), workers attach a crane to the Hitchhiker Bridge that holds several Get-Away Special canisters (GAS cans) for mission ST-107. The bridge is being moved to a workstand in the MPPF. The bridge is a carrier for the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments on mission STS-107. A research mission, the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI_RDM), also known as SPACEHAB. The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences. STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 11, 2002
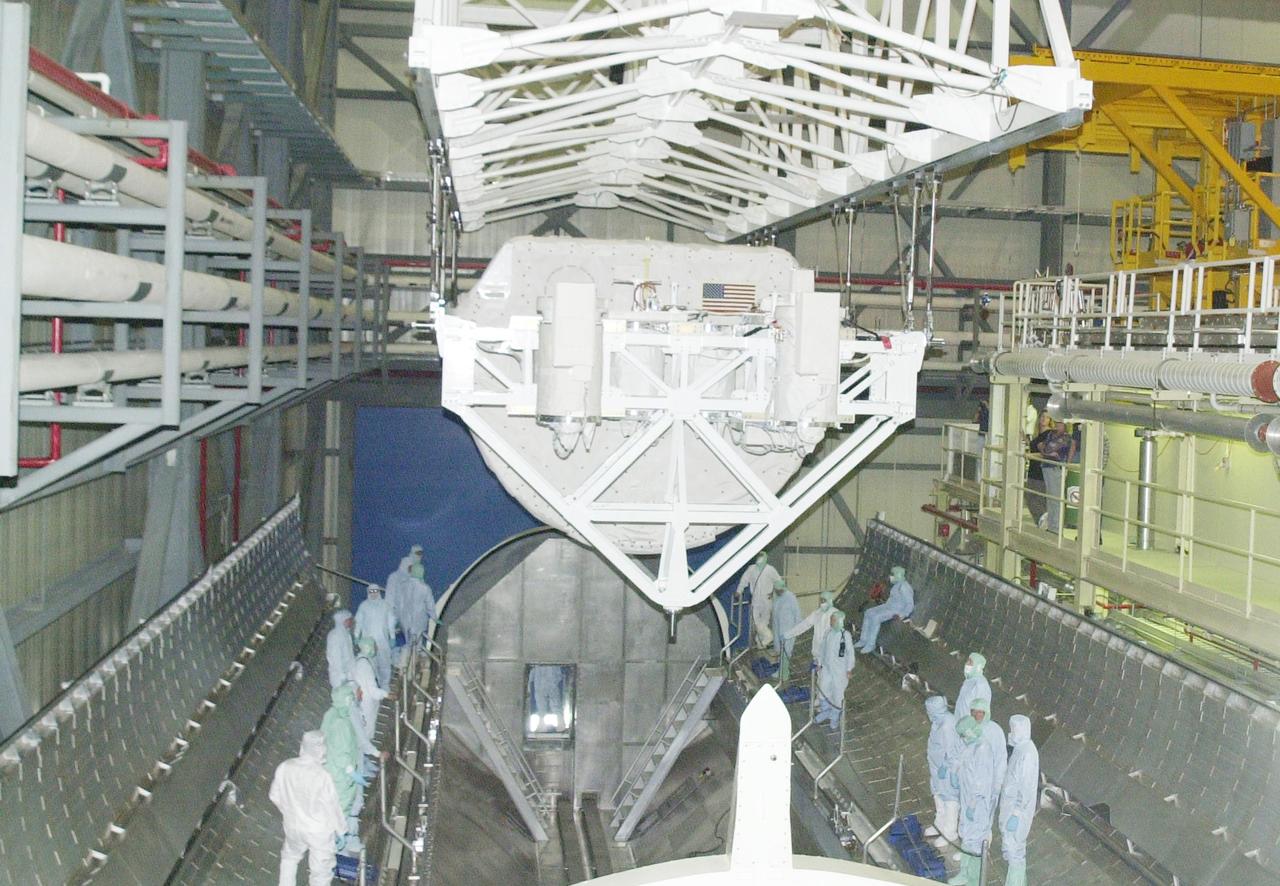

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM) and Hitchhiker Carrier behind it are suspended by an overhead crane during their move to Columbia's payload bay. SHI/RDM is the primary payload of the STS-107 research mission, with experiments ranging from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). Also, the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that is on the Hitchhiker Carrier incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments. STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 19, 2002
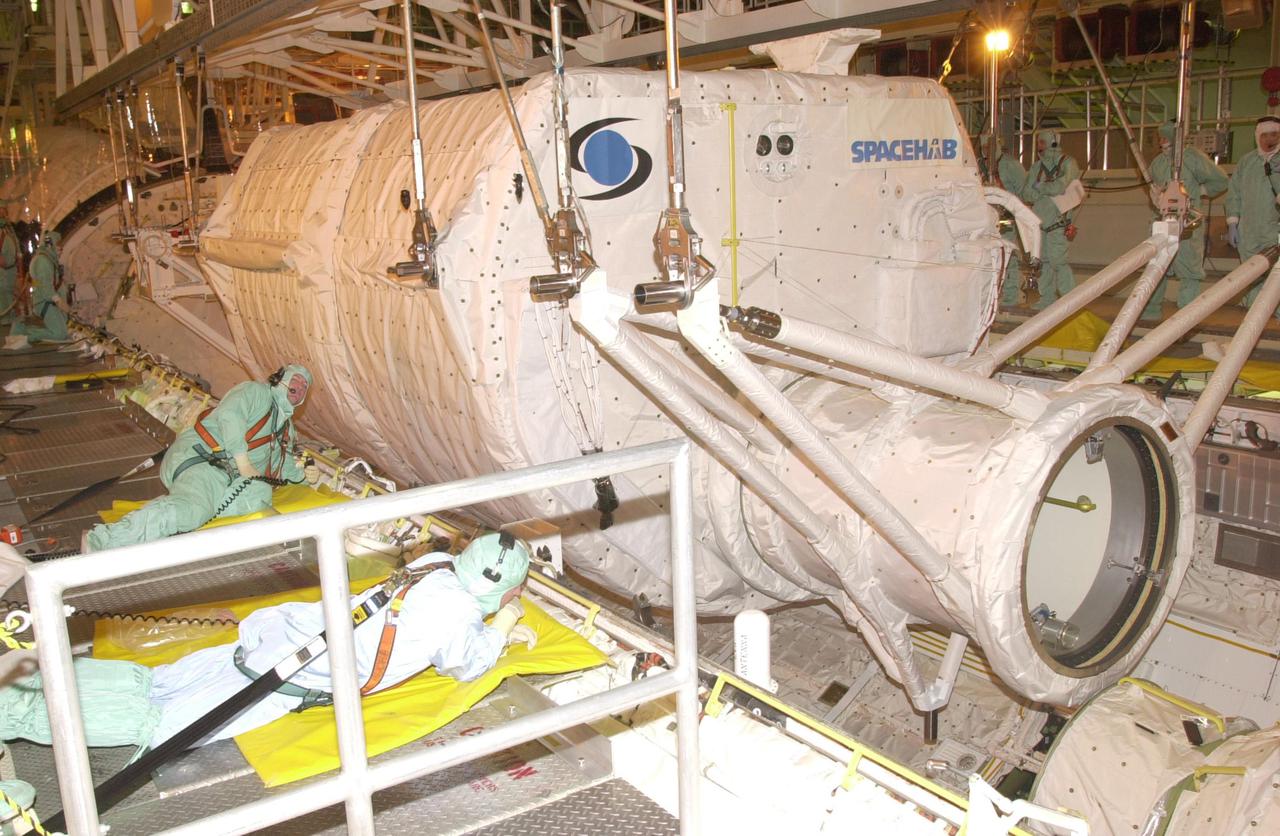

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility keep watch as the SHI Research Double Module (SHI_RDM) (right) and Hitchhiker Carrier (left) are lowered into Columbia's payload bay for mission STS-107, a research mission. SHI_RDM is the primary payload, with experiments ranging from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). Also, the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that is on the Hitchhiker Carrier incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments. STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 19, 2002
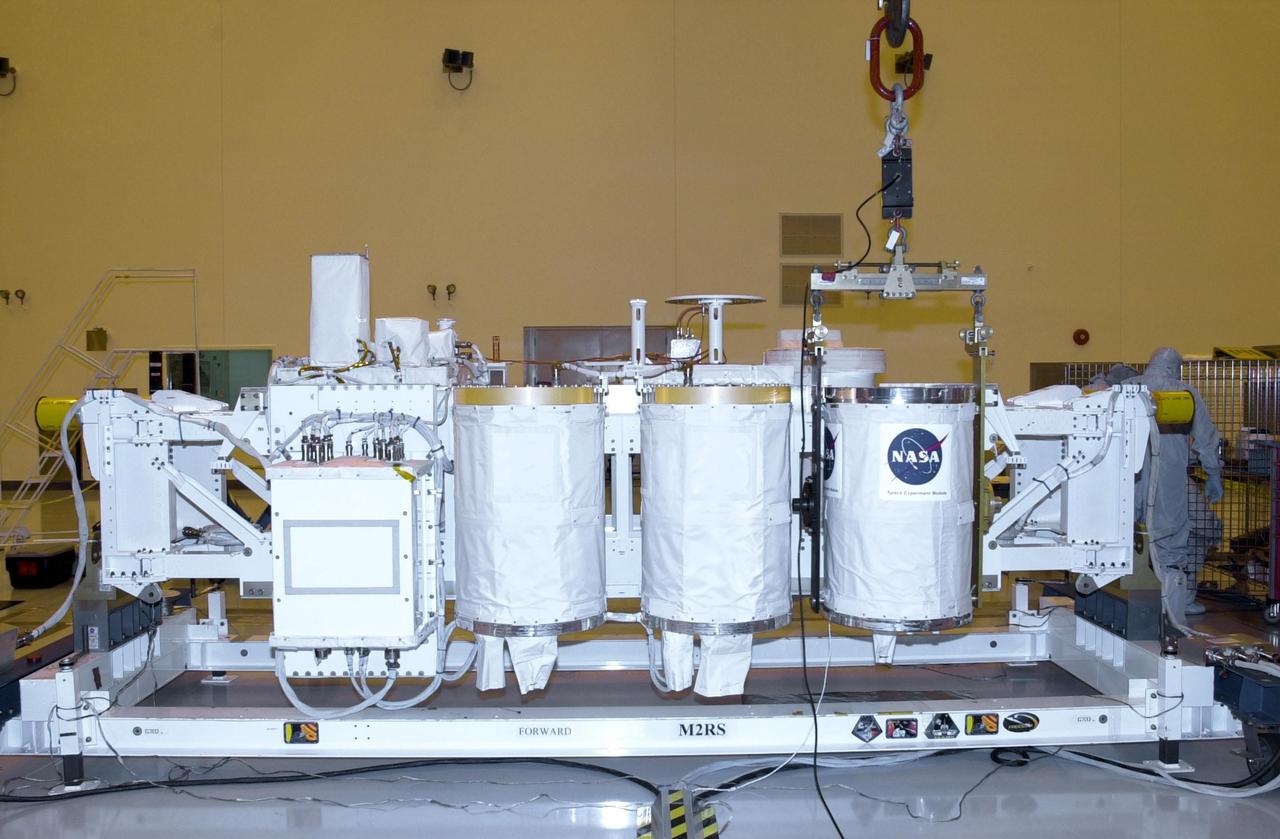

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, an overhead crane lowers a GetAway Special canister (GAS can) onto the Hitchhiker Bridge. The bridge is a carrier for the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments on mission STS-107. A research mission, the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM), also known as SPACEHAB. The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 11, 2002
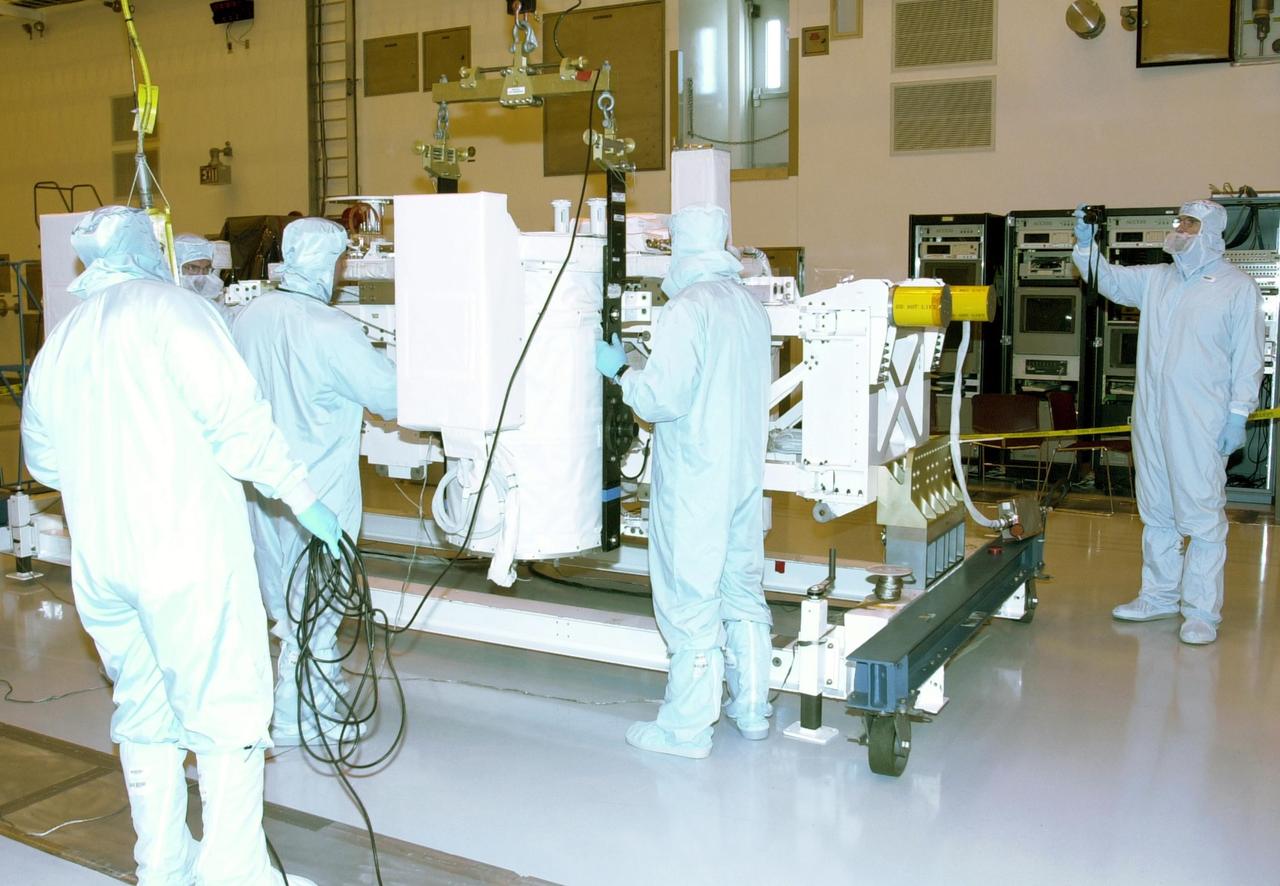

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, workers check a GetAway Special canister (GAS can) being moved onto the Hitchhiker Bridge. The bridge is a carrier for the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments on mission STS-107. A research mission, the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM), also known as SPACEHAB. The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 11, 2002
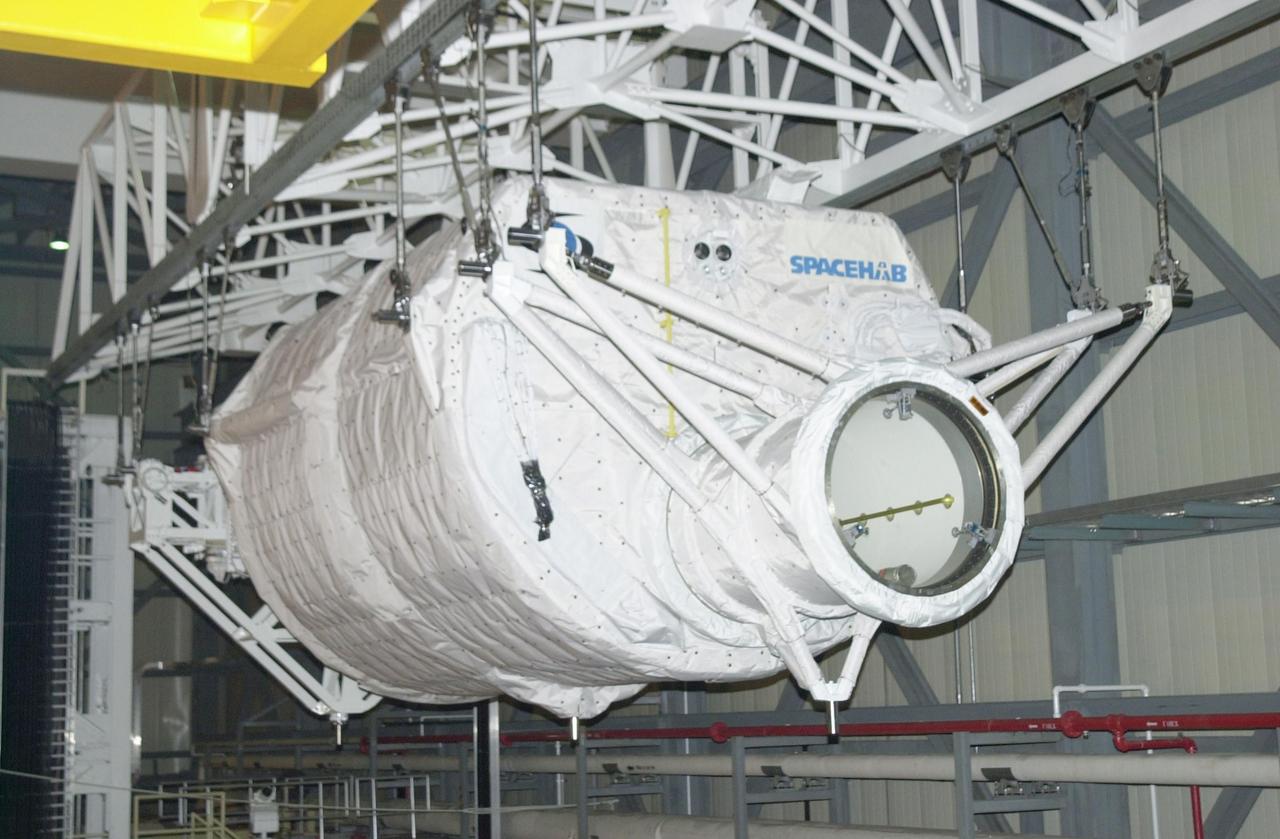

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the Hitchhiker Carrier (front) and the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM) behind it are suspended over Columbia's payload bay. The two payloads will be installed in the payload bay for mission STS-107, a research mission. SHI/RDM is the primary payload, with experiments ranging from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). Also, the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that is on the Hitchhiker Carrier incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments. STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 19, 2002
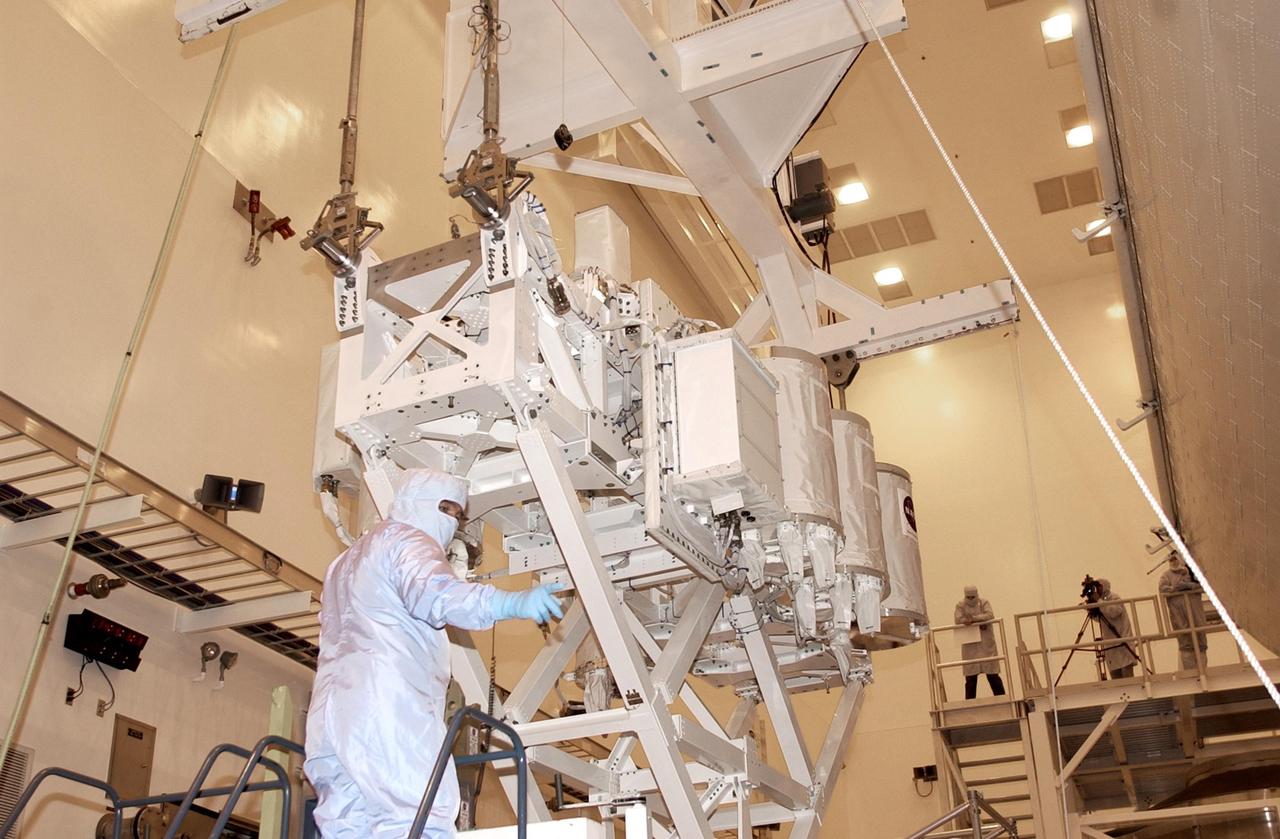

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, an overhead crane is attached to the Hitchhiker Bridge with GetAway Special canisters (GAS cans). The bridge, a carrier for the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments, is being transferred to the payload canister. The bridge will be installed in Columbia's payload bay as part of mission STS-107. A research mission, STS-107 will also carry the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM), known as SPACEHAB. Experiments on the module range from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 19, 2002
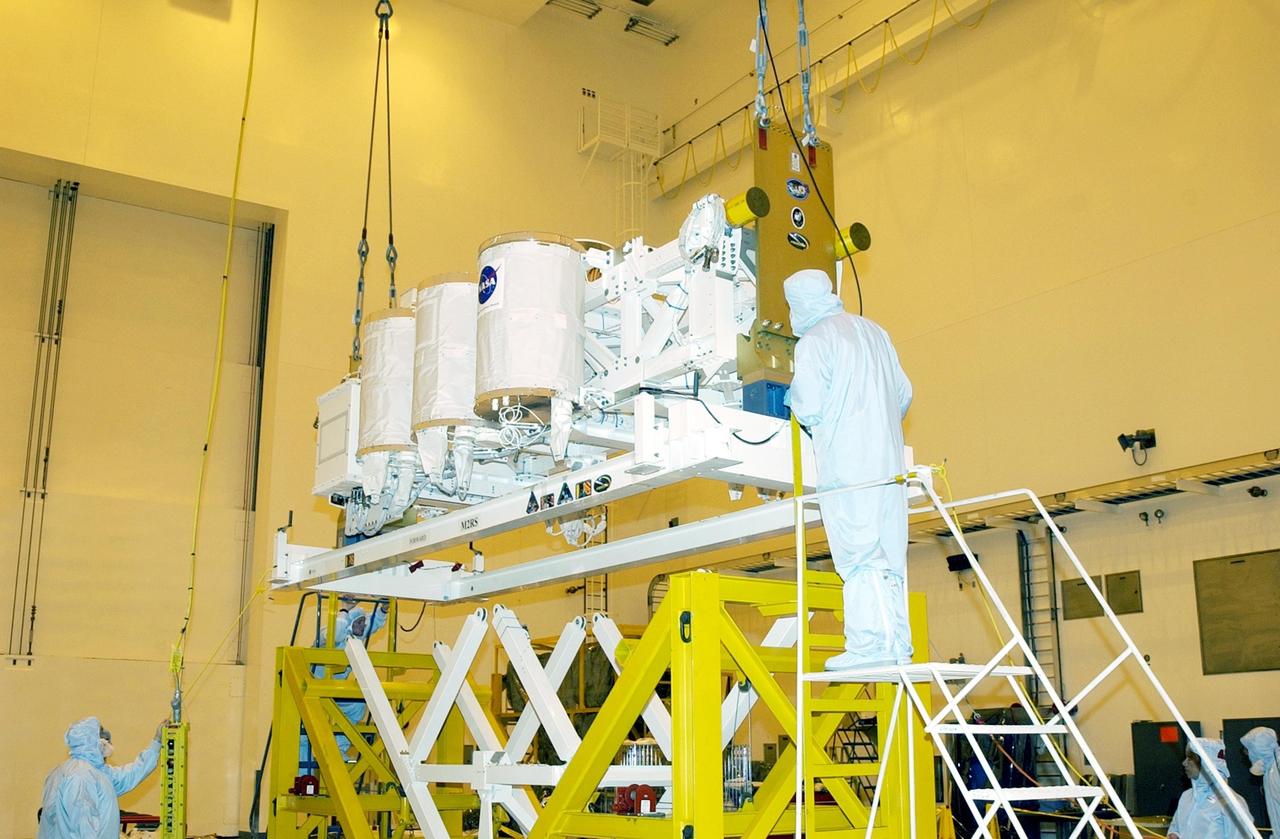

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- -- In the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF), the Hitchhiker Bridge is lowered onto a workstand. The bridge is a carrier for the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments on mission STS-107. A research mission, the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM), also known as SPACEHAB. The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences. STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 11, 2002
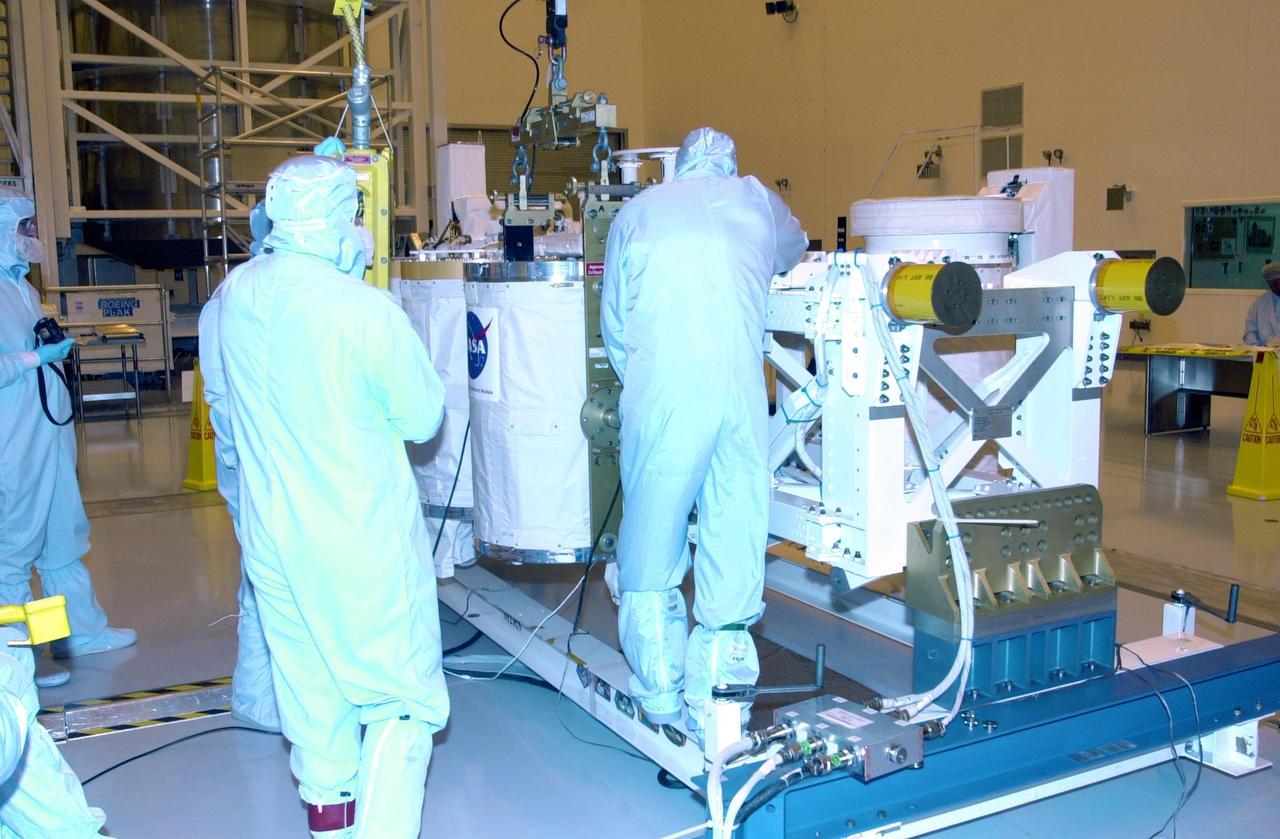

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, workers check the movement of a GetAway Special canister (GAS can) being lowered onto the Hitchhiker Bridge. The bridge is a carrier for the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) that incorporates eight high priority secondary attached shuttle experiments on mission STS-107. A research mission, the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM), also known as SPACEHAB. The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 11, 2002
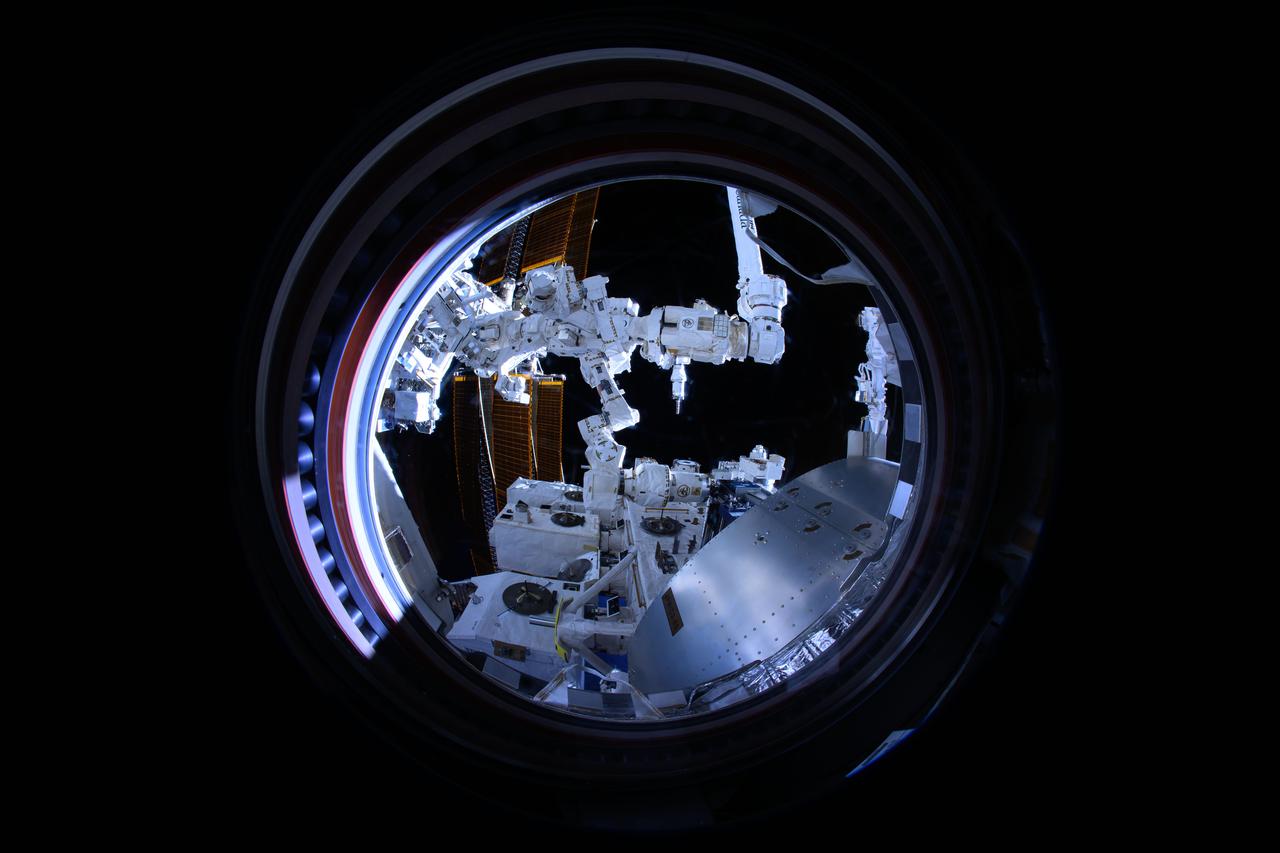

iss072e189571 (11/16/2024) --- The Canadarm2 robotic arm removes Materials ISS Experiment (MISSE) science carriers from the Kibo laboratory module's airlock. The MISSE Flight Facility mounted outside the International Space Station allows researchers to test the performance and durability of materials and devices. This is done by exposing items of interest to everything that makes the space environment harsh, including radiation, highly reactive atomic oxygen, microgravity, and extreme temperatures.
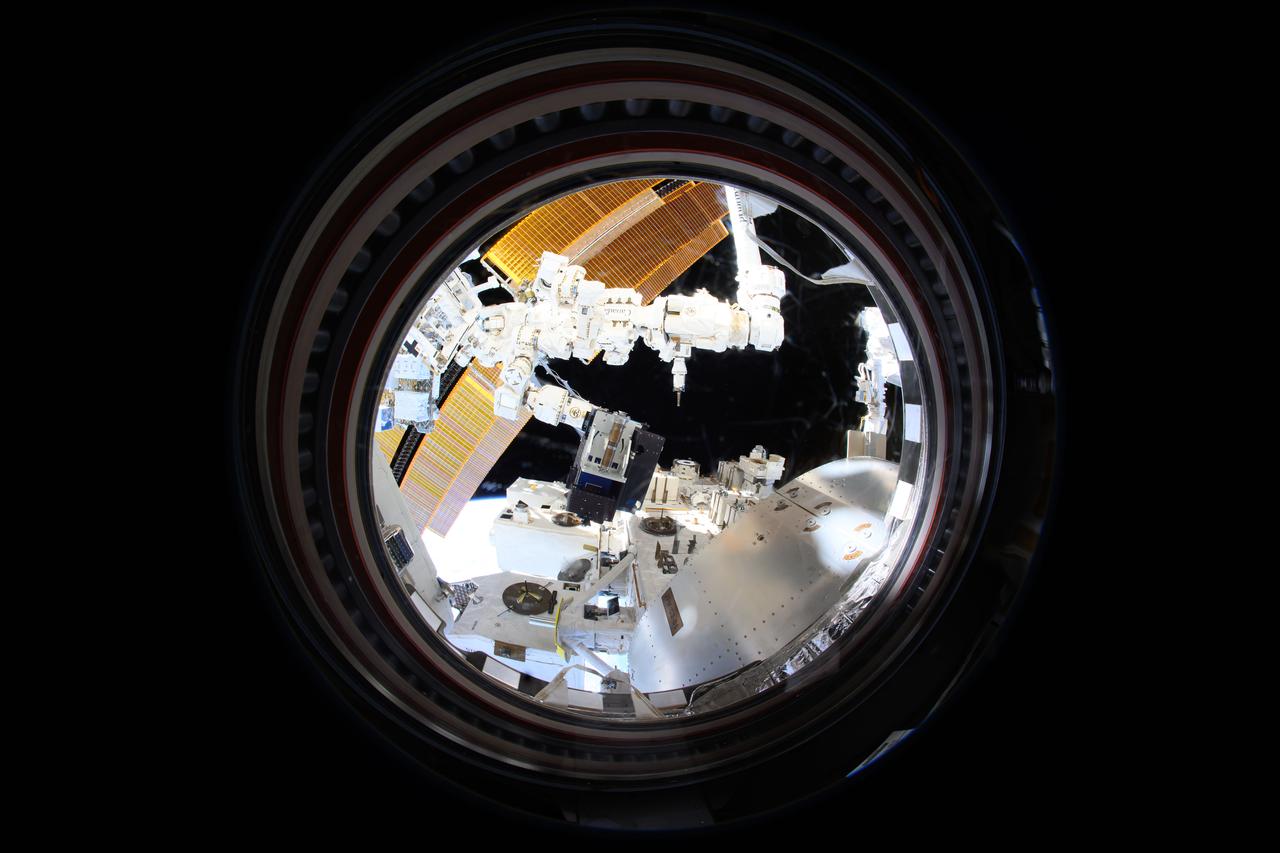

iss072e189789 (11/16/2024) --- The Canadarm2 robotic arm removes Materials ISS Experiment (MISSE) science carriers from the Kibo laboratory module's airlock. The MISSE Flight Facility mounted outside the International Space Station allows researchers to test the performance and durability of materials and devices. This is done by exposing items of interest to everything that makes the space environment harsh, including radiation, highly reactive atomic oxygen, microgravity, and extreme temperatures.
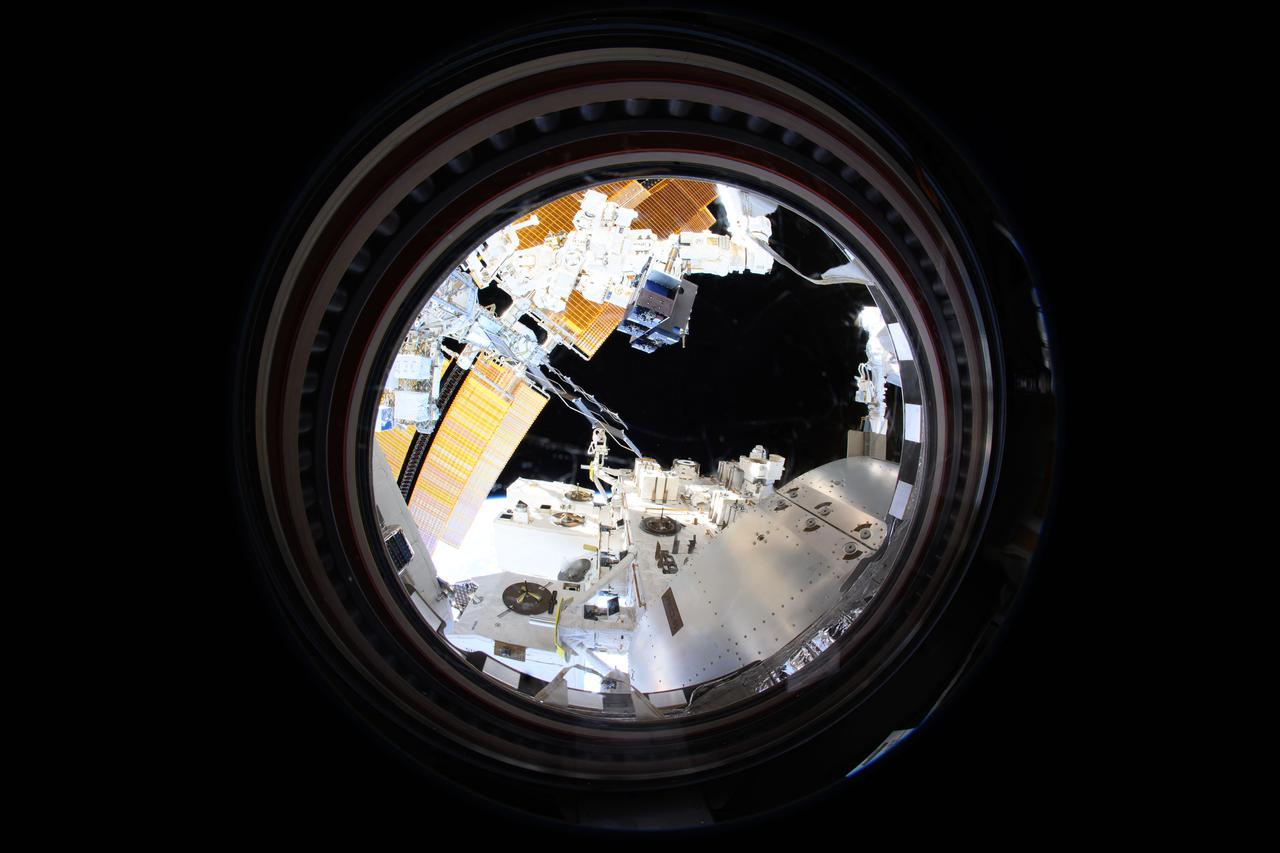

iss072e189797 (11/16/2024) --- The Canadarm2 robotic arm removes Materials ISS Experiment (MISSE) science carriers from the Kibo laboratory module's airlock. The MISSE Flight Facility mounted outside the International Space Station allows researchers to test the performance and durability of materials and devices. This is done by exposing items of interest to everything that makes the space environment harsh, including radiation, highly reactive atomic oxygen, microgravity, and extreme temperatures.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Shuttle Landing Facility, the European Space Agency's research laboratory, designated Columbus, slides out onto an Airbus Transport International platform that will lower it to the ground. The module will then be lifted onto a flat bed truck and transported to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will be prepared for delivery to the International Space Station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Shuttle Landing Facility, a crane lowers Columbus, the European Space Agency's research laboratory, toward a flat bed truck. The truck will transport the module to the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The module arrived on a Beluga Airbus May 30 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center from the manufacturer in Germany. In the SSPF, the module will be prepared for delivery to the International Space Station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Shuttle Landing Facility, a crane lifts Columbus, the European Space Agency's research laboratory, off an Airbus Transport International platform to place it onto a flat bed truck. The module will be transported to the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The module arrived on a Beluga Airbus May 30 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center from the manufacturer in Germany. In the SSPF, the module will be prepared for delivery to the International Space Station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Shuttle Landing Facility, an Airbus Transport International platform is moved in front of the nose of the Beluga airbus in order to offload the European Space Agency's research laboratory, designated Columbus. After being unloaded, the module will be transported to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will be prepared for delivery to the International Space Station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Shuttle Landing Facility, a crane settles Columbus, the European Space Agency's research laboratory, onto a flat bed truck. The truck will transport the module to the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The module arrived on a Beluga Airbus May 30 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center from the manufacturer in Germany. In the SSPF, the module will be prepared for delivery to the International Space Station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
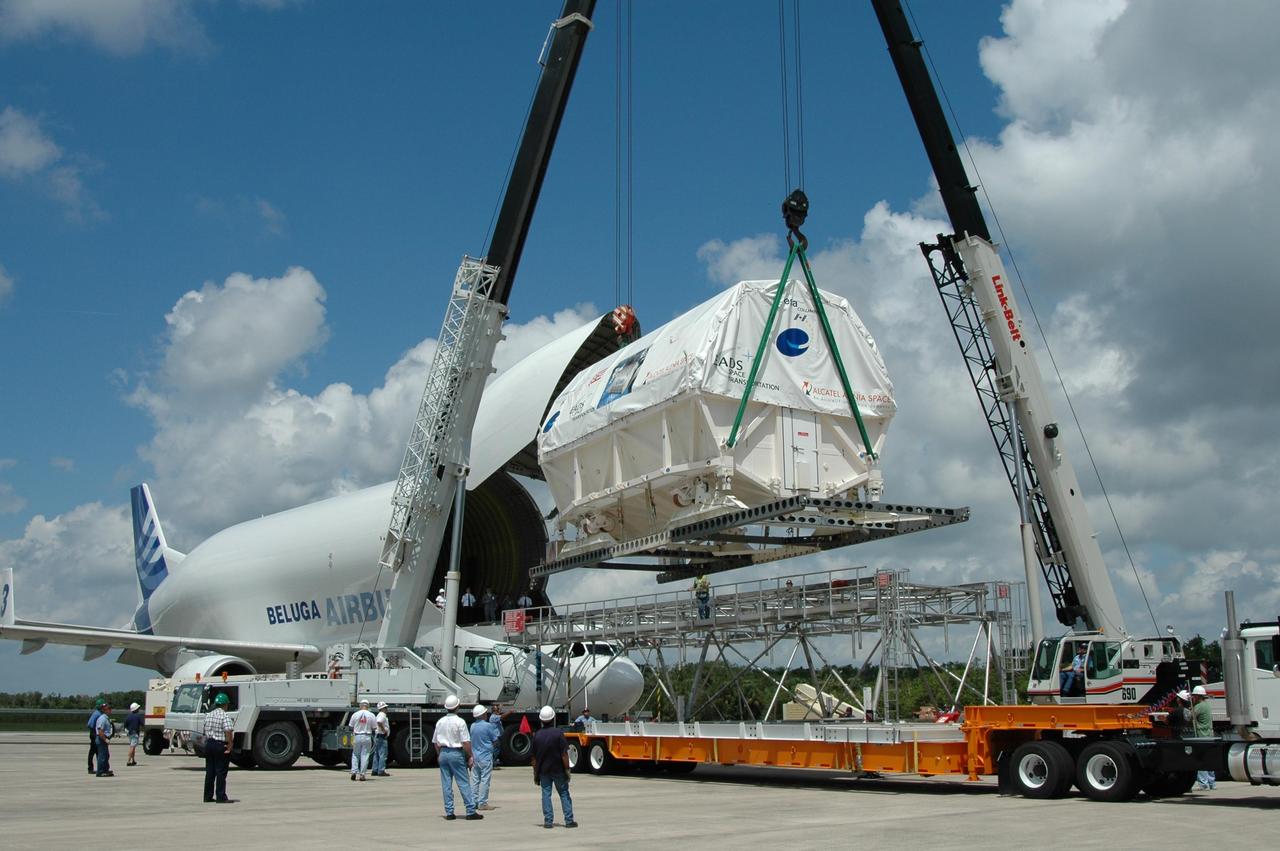

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Shuttle Landing Facility, a crane lifts Columbus, the European Space Agency's research laboratory, off an Airbus Transport International platform toward a flat bed truck. The truck will transport the module to the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The module arrived on a Beluga Airbus May 30 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center from the manufacturer in Germany. In the SSPF, the module will be prepared for delivery to the International Space Station on a future space shuttle mission. Columbus will expand the research facilities of the station and provide researchers with the ability to conduct numerous experiments in the area of life, physical and materials sciences. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
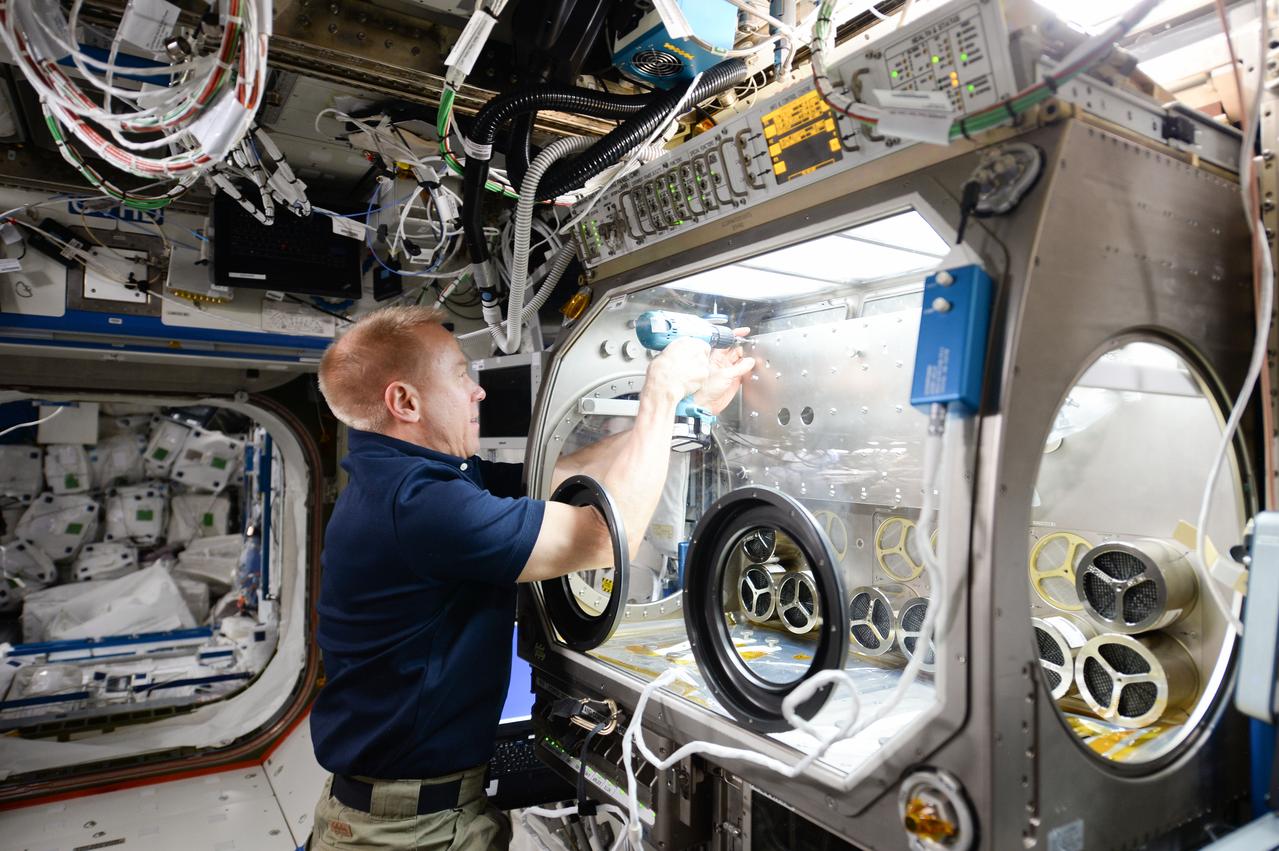

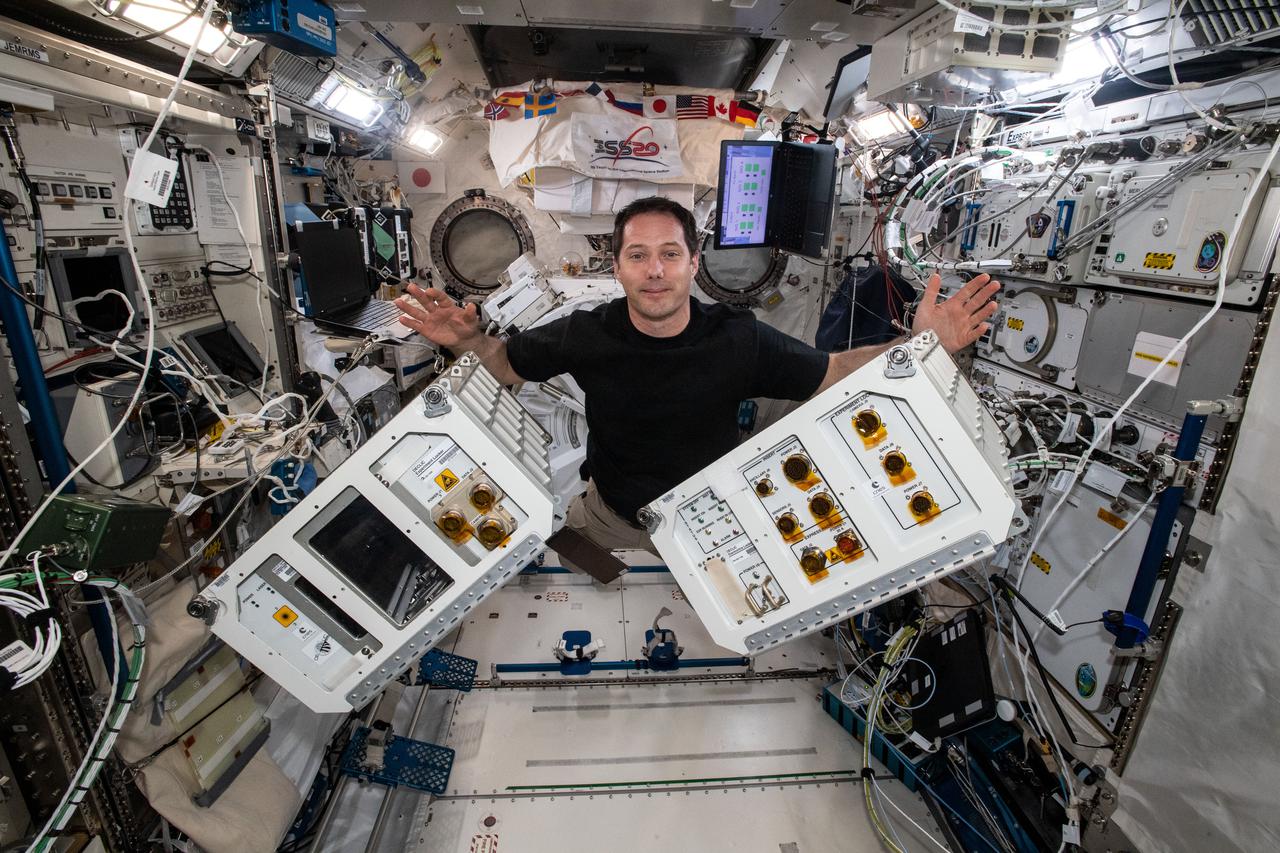
ISS047e050514 (04/07/2016) --- Expedition 47 Commander Tim Kopra configures the station’s Microgravity Science Glovebox for upcoming research operations. The glovebox is one of the major dedicated science facilities inside Destiny. It has a large front window and built-in gloves to provide a sealed environment for conducting science and technology experiments. The Glovebox is particularly suited for handling hazardous materials when the crew is present.
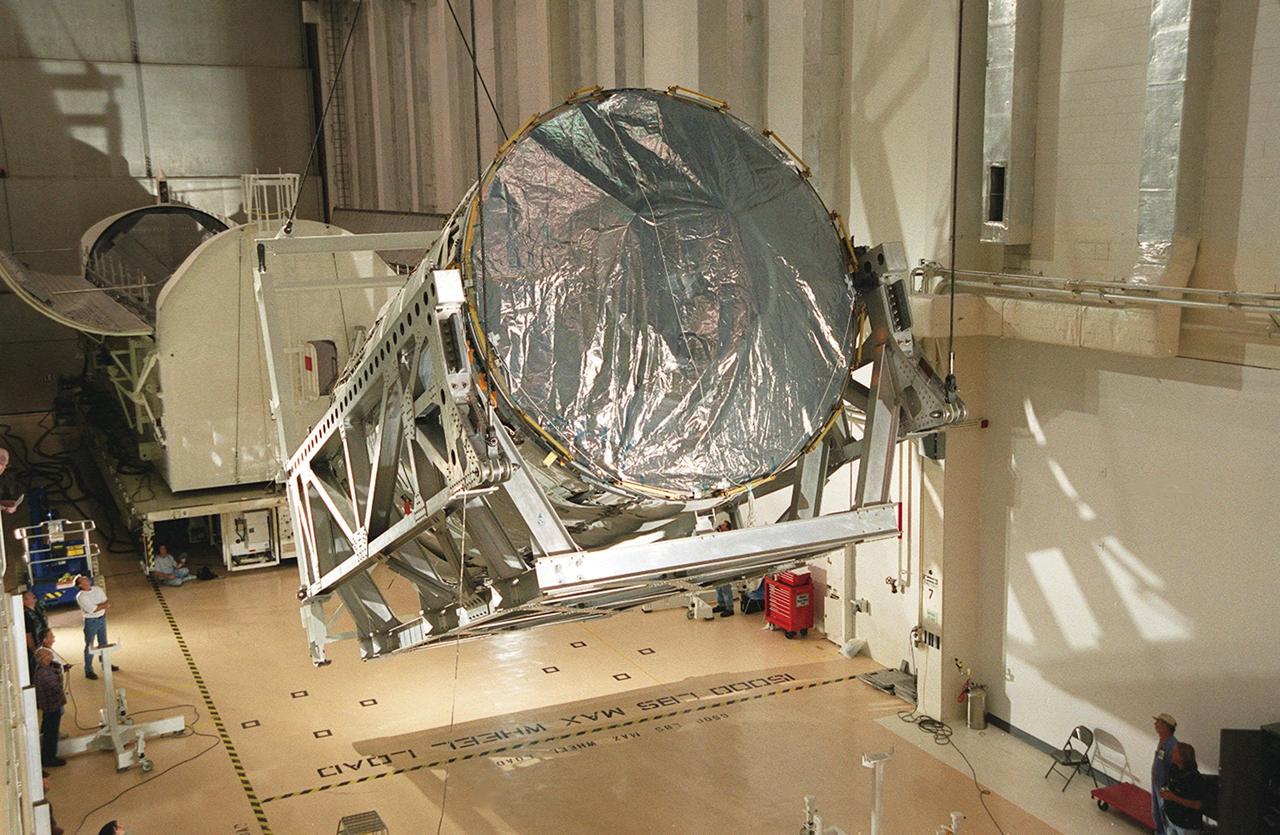

Resting in a rotation and handling fixture, the U.S. Lab, a component of the International Space Station, is lifted toward vertical. The Lab, named Destiny, will undergo testing in the altitude chamber in the Operations and Checkout Building. Behind the Lab is the payload canister which transported it from the Space Station Processing Facility. Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab in the Space Station during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the Station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Resting in a rotation and handling fixture, the U.S. Lab, a component of the International Space Station, is nearly vertical. The Lab, named Destiny, will undergo testing in the altitude chamber in the Operations and Checkout Building. Behind the Lab is the payload canister which transported it from the Space Station Processing Facility. Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab in the Space Station during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the Station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
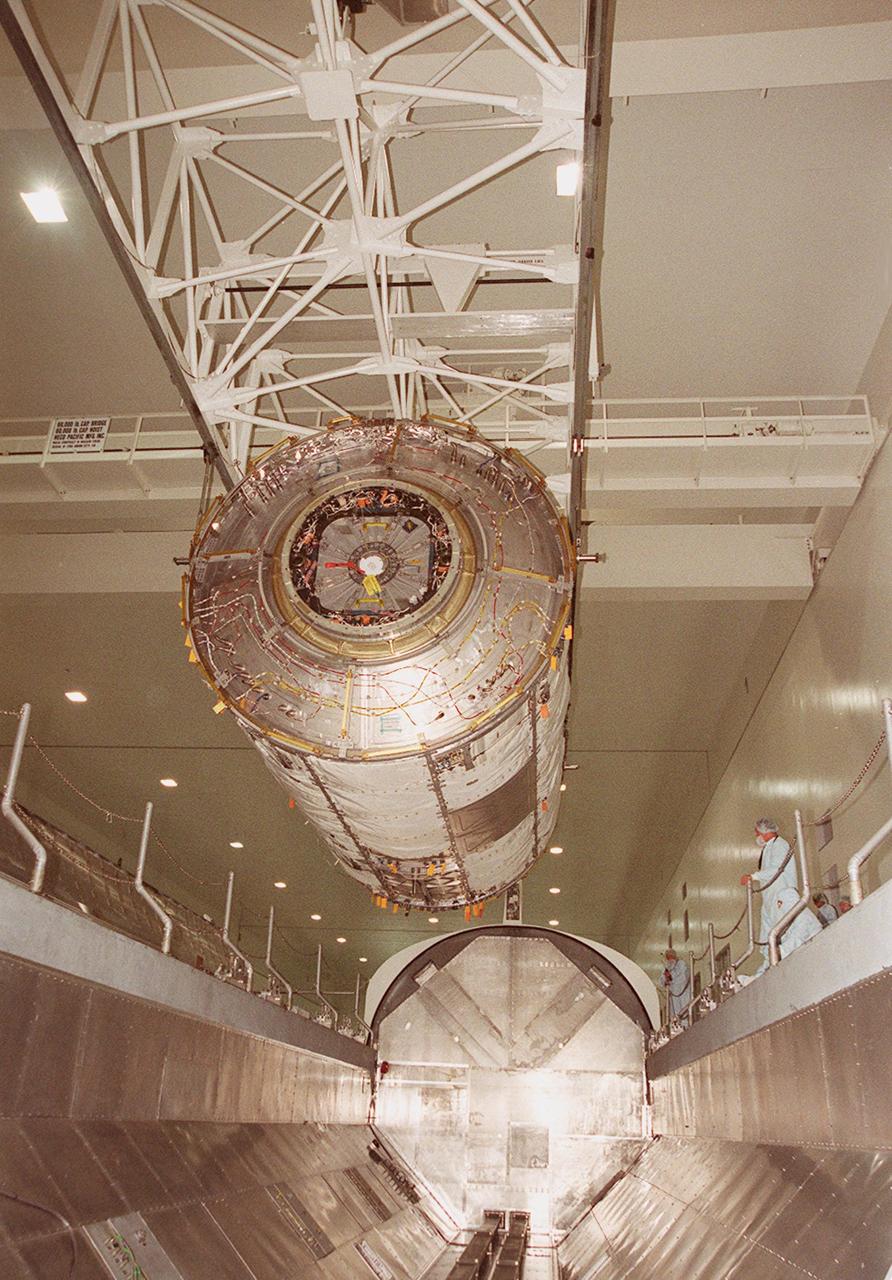
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a component of the International Space Station, is lowered into a payload canister for transfer to the Operations and Checkout Building where it will be tested in the altitude chamber. Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab in the Space Station during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the Station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
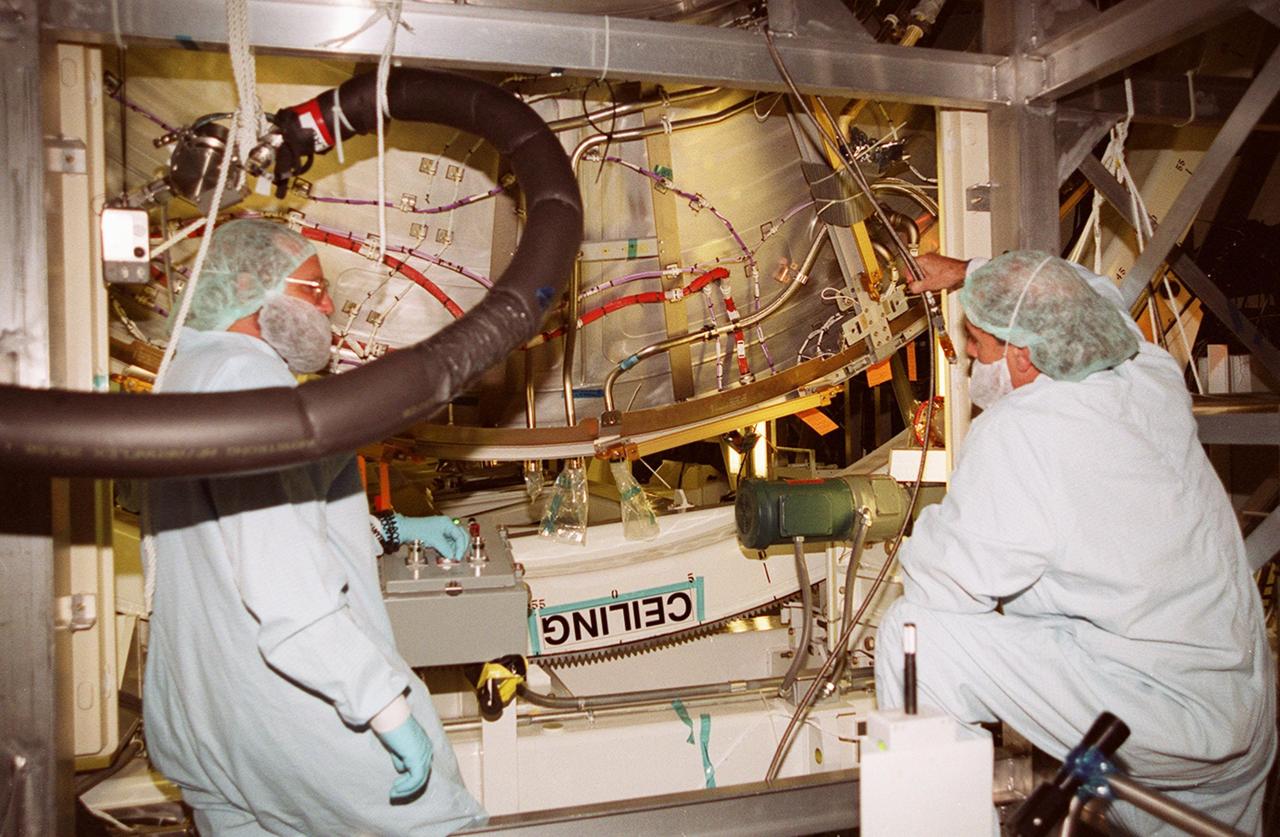
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers check the U.S. Laboratory Destiny as it rotates, with its ceiling now on the underside. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
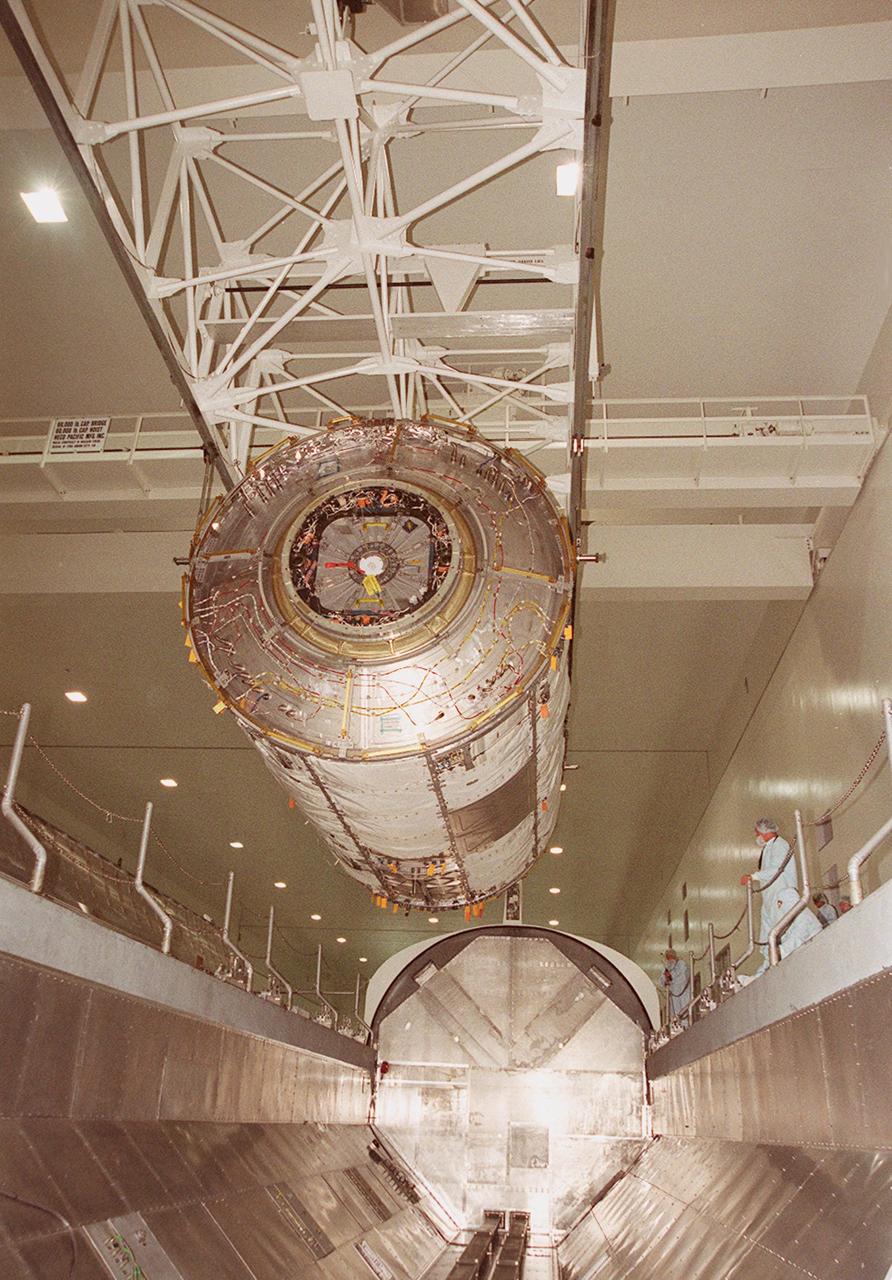
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a component of the International Space Station, is lowered into a payload canister for transfer to the Operations and Checkout Building where it will be tested in the altitude chamber. Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab in the Space Station during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the Station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Resting in a rotation and handling fixture, the U.S. Lab, a component of the International Space Station, is nearly vertical. The Lab, named Destiny, will undergo testing in the altitude chamber in the Operations and Checkout Building. Behind the Lab is the payload canister which transported it from the Space Station Processing Facility. Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab in the Space Station during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the Station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
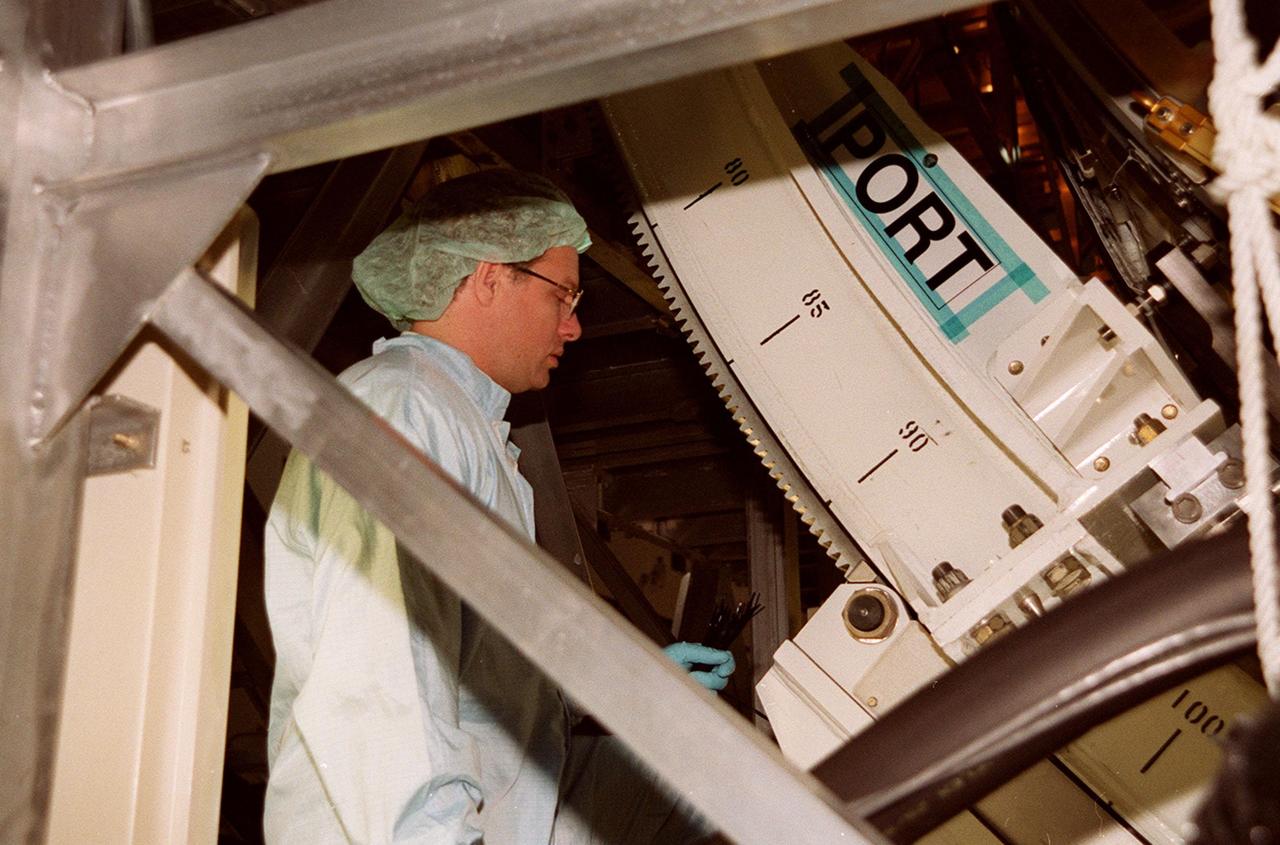

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, a worker checks the U.S. Laboratory Destiny as it rotates. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research.<font size="3"
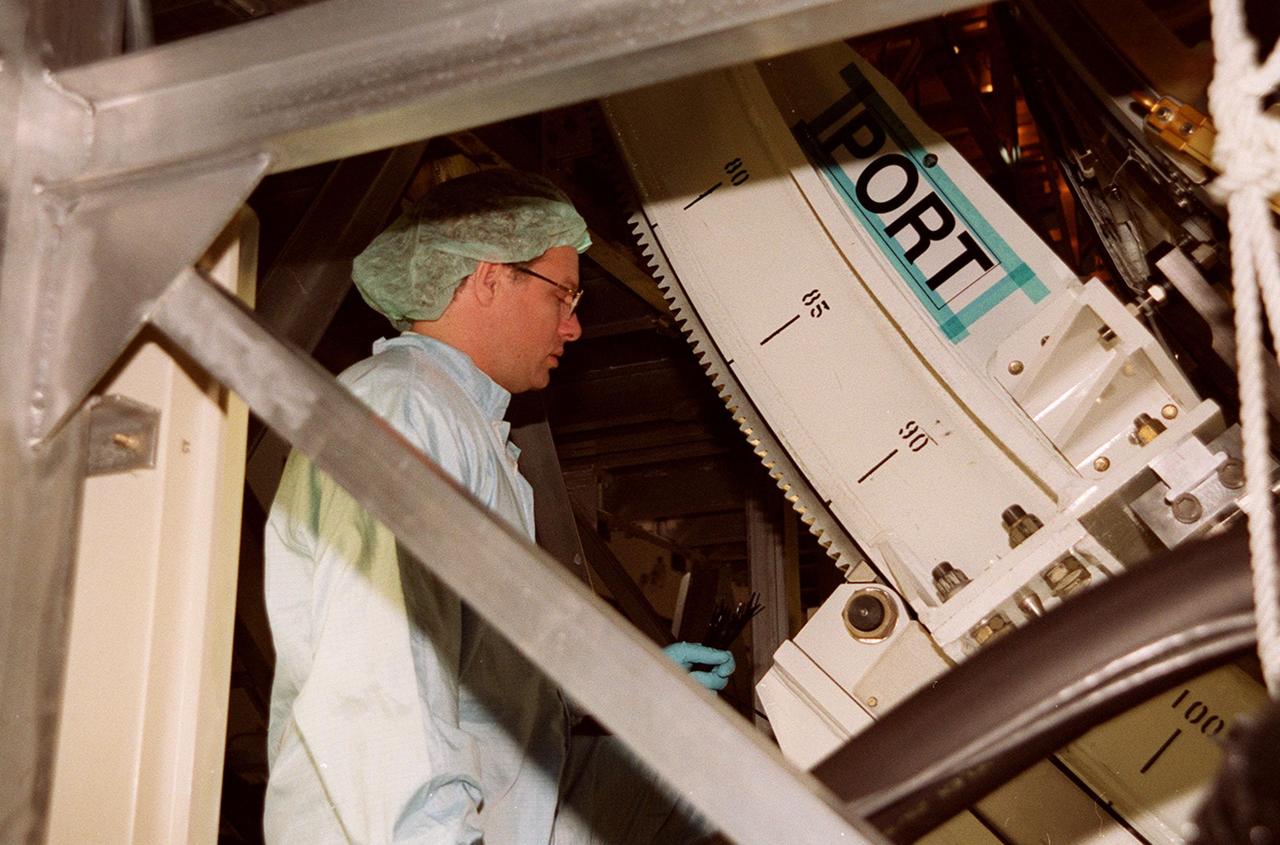

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, a worker checks the U.S. Laboratory Destiny as it rotates. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research.<font size="3"

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Resting in a rotation and handling fixture, the U.S. Lab, a component of the International Space Station, is nearly vertical. The Lab, named Destiny, will undergo testing in the altitude chamber in the Operations and Checkout Building. Behind the Lab is the payload canister which transported it from the Space Station Processing Facility. Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab in the Space Station during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the Station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
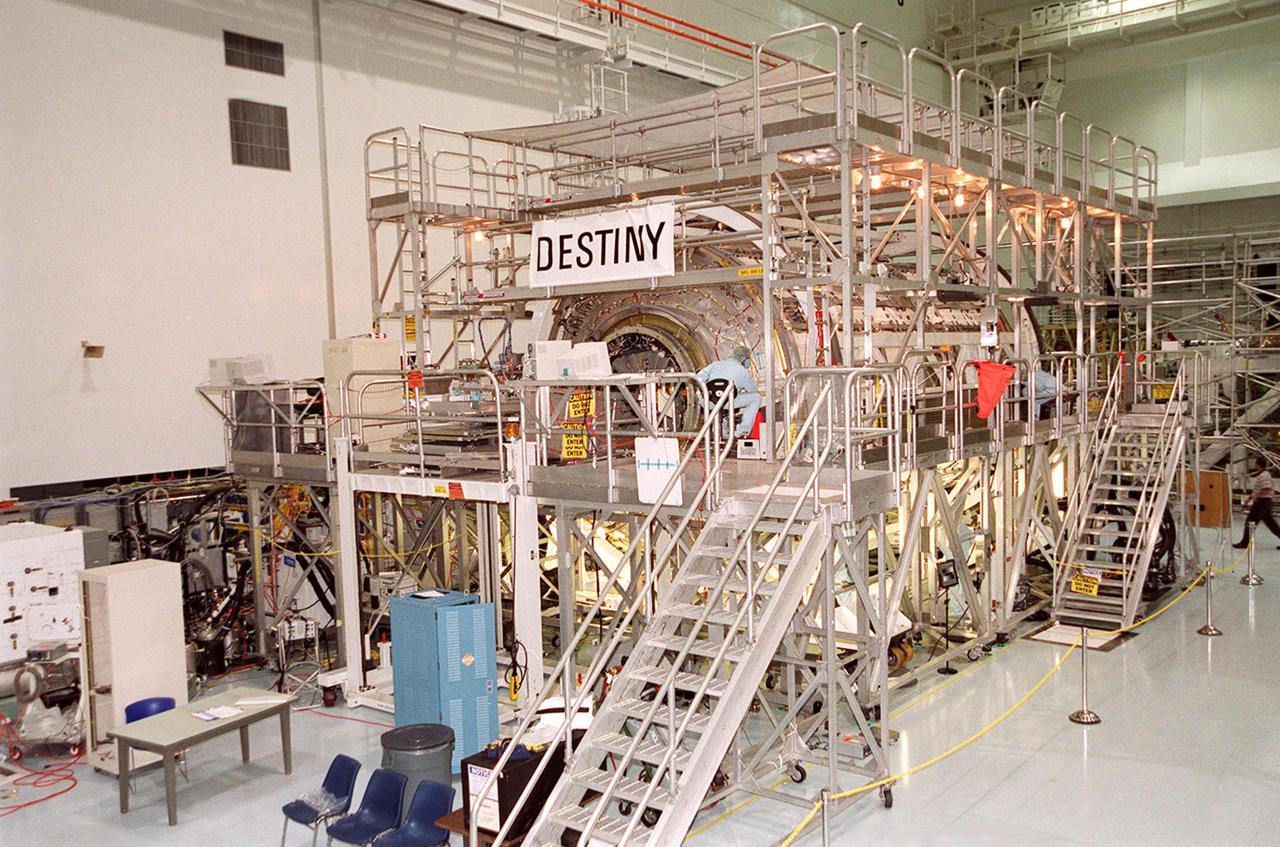

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the U.S. Laboratory Destiny is about to undergo rotation in its workstand. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane lifts and moves the U.S. Laboratory Destiny to a weigh stand. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
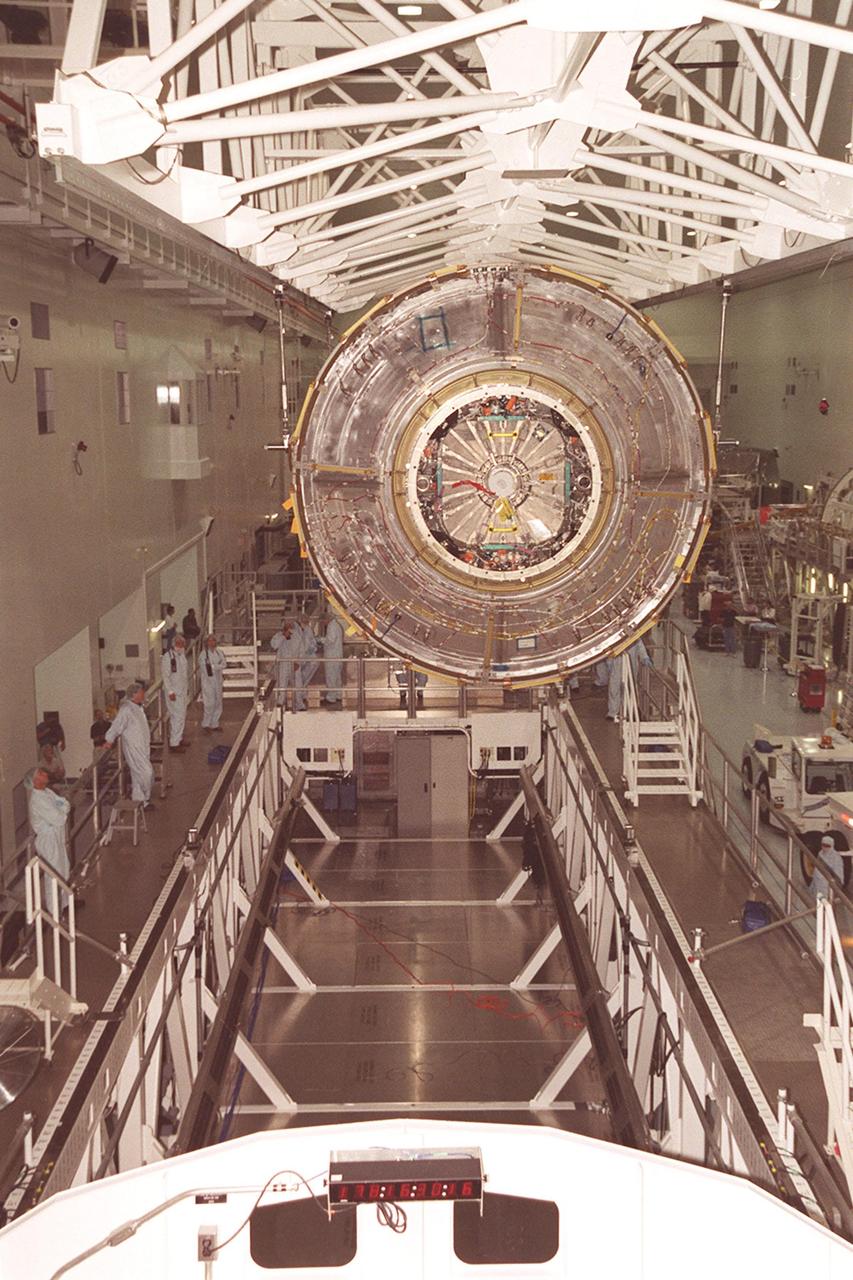
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the U.S. Lab Destiny is lowered toward the weigh stand below. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research.
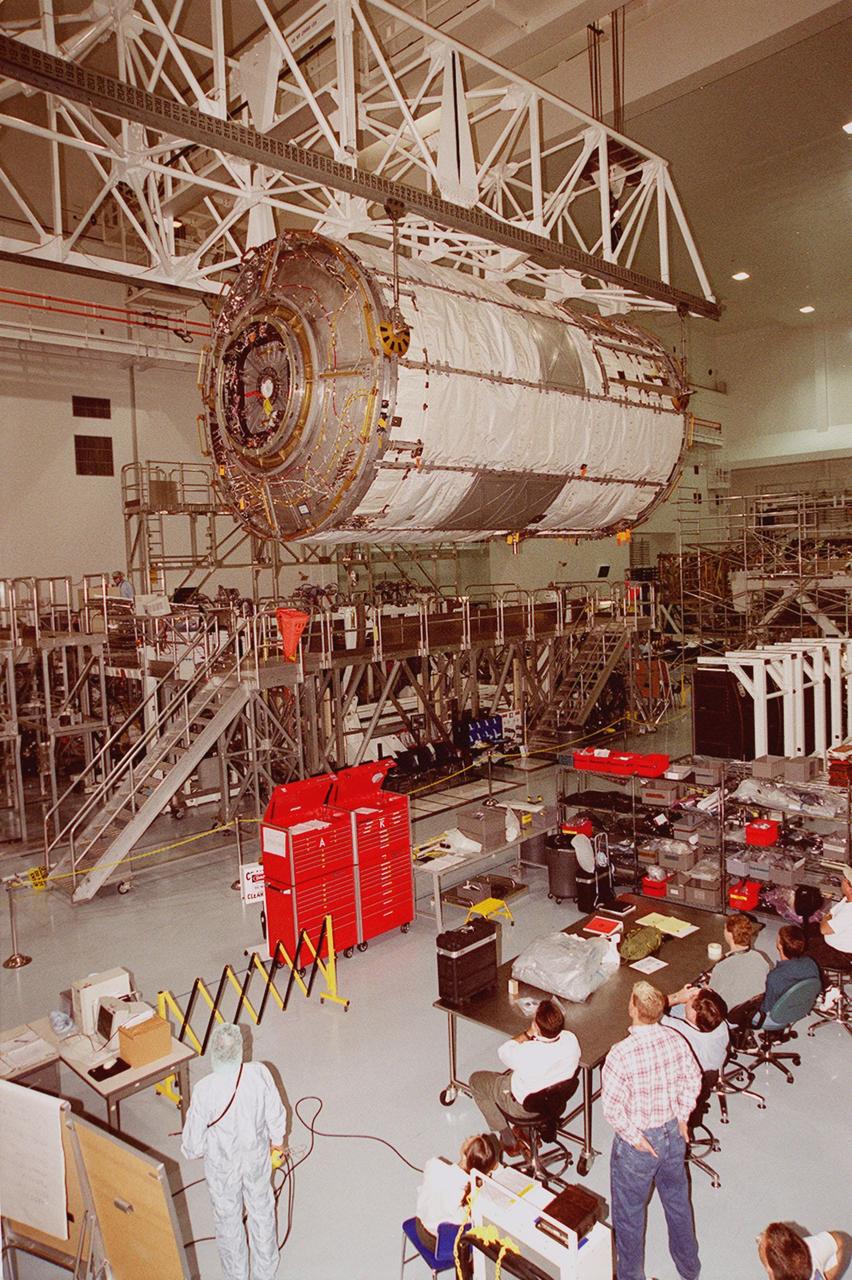
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the Space Station Processing Facility watch as the U.S. Lab Destiny, lifted by an overhead crane, glides through the air to a weigh stand. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
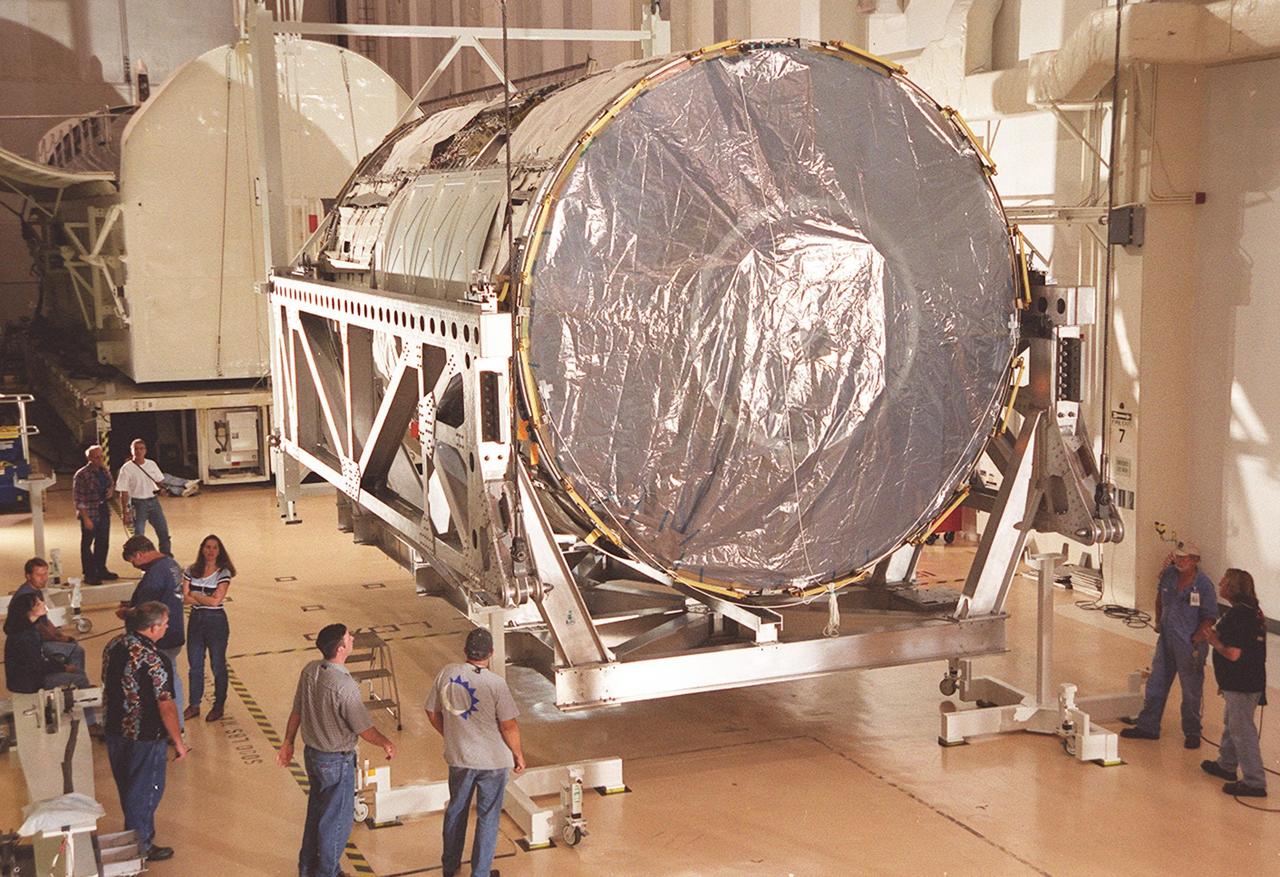

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building (O&C), the U.S. Lab, a component of the International Space Station, is lifted off the floor in order to be raised to a vertical position. The Lab, named Destiny, will undergo testing in the altitude chamber in the O&C. Behind the Lab is the payload canister which transported it from the Space Station Processing Facility. Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab in the Space Station during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the Station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
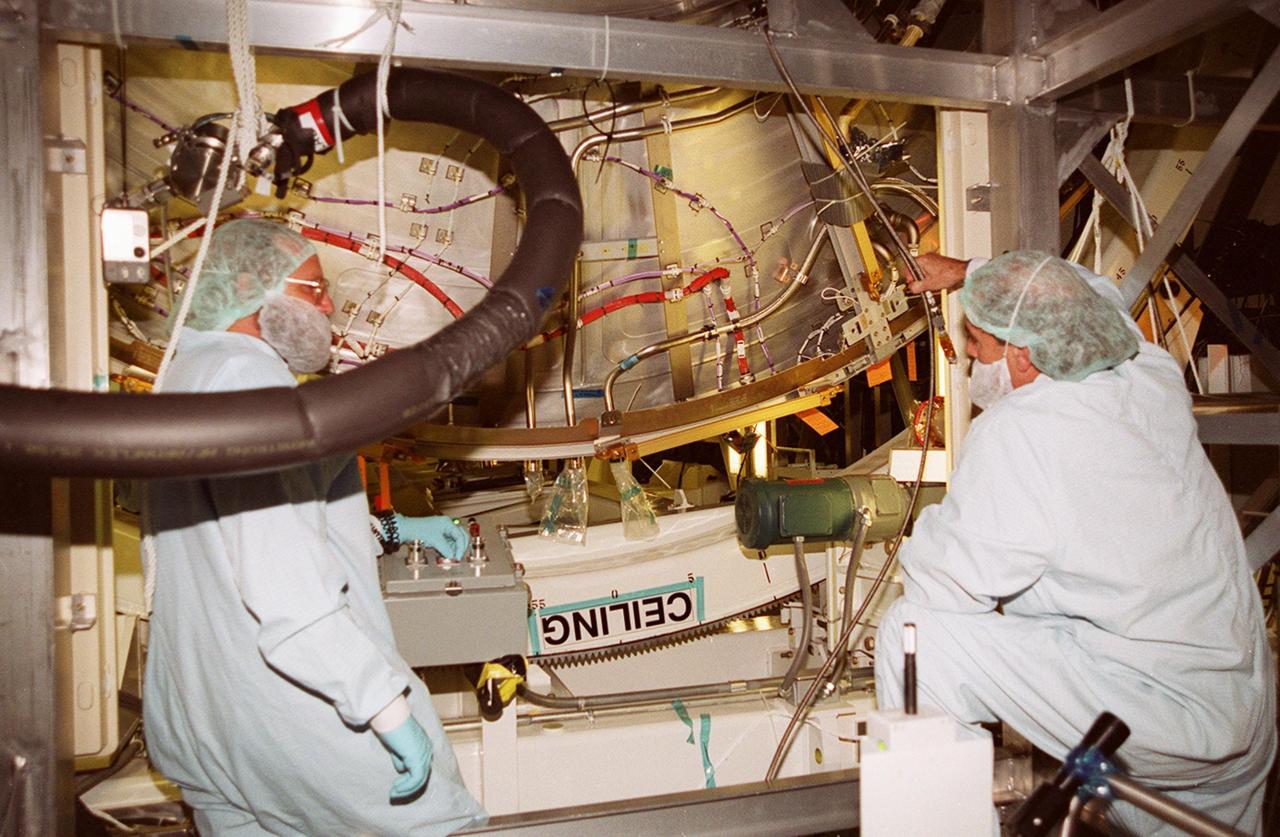
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers check the U.S. Laboratory Destiny as it rotates, with its ceiling now on the underside. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Resting in a rotation and handling fixture, the U.S. Lab, a component of the International Space Station, is nearly vertical. The Lab, named Destiny, will undergo testing in the altitude chamber in the Operations and Checkout Building. Behind the Lab is the payload canister which transported it from the Space Station Processing Facility. Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab in the Space Station during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the Station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
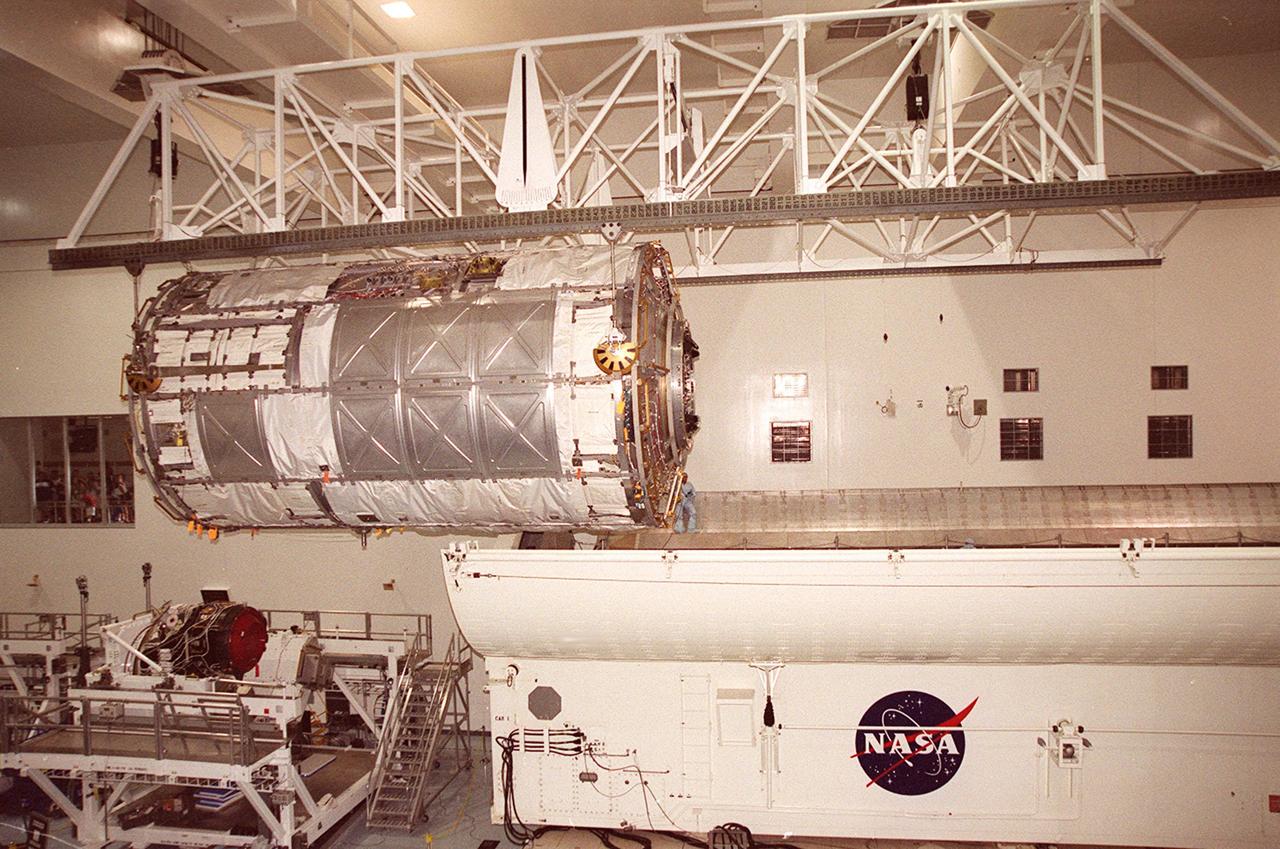
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF), the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a component of the International Space Station, is moved to a payload canister for transfer to the Operations and Checkout Building where it will be tested in the altitude chamber. On the floor of the SSPF, left, is a Pressurized Mating Adapter-3. Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab in the Space Station during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the Station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a component of the International Space Station, is lifted off a weigh stand (below) in the Space Station Processing Facility. The module is being moved to a payload canister for transfer to the Operations and Checkout Building where it will be tested in the altitude chamber. Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab in the Space Station during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the Station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building (O&C), the U.S. Lab, a component of the International Space Station, is lifted off the floor in order to be raised to a vertical position. The Lab, named Destiny, will undergo testing in the altitude chamber in the O&C. Behind the Lab is the payload canister which transported it from the Space Station Processing Facility. Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab in the Space Station during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the Station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
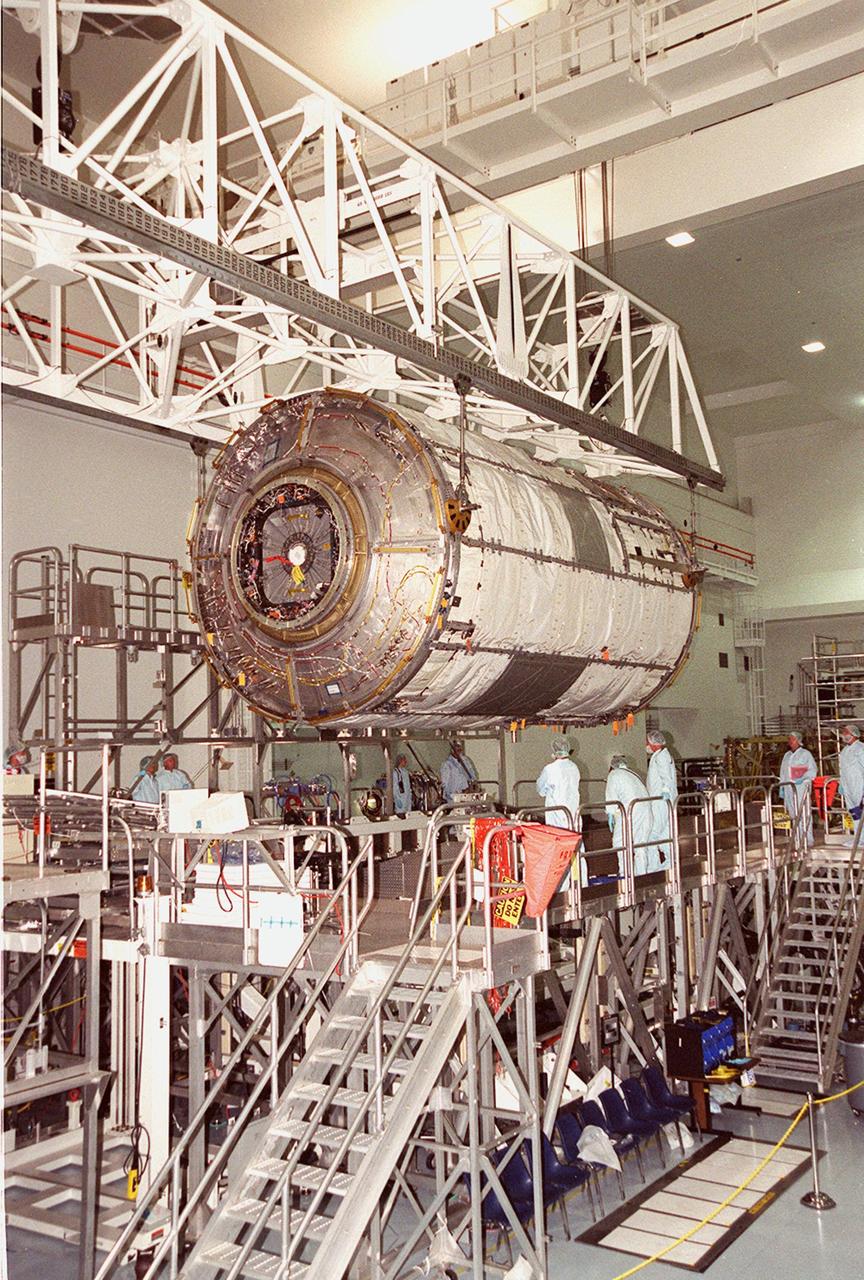
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane lifts and moves the U.S. Laboratory Destiny to a weigh stand. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
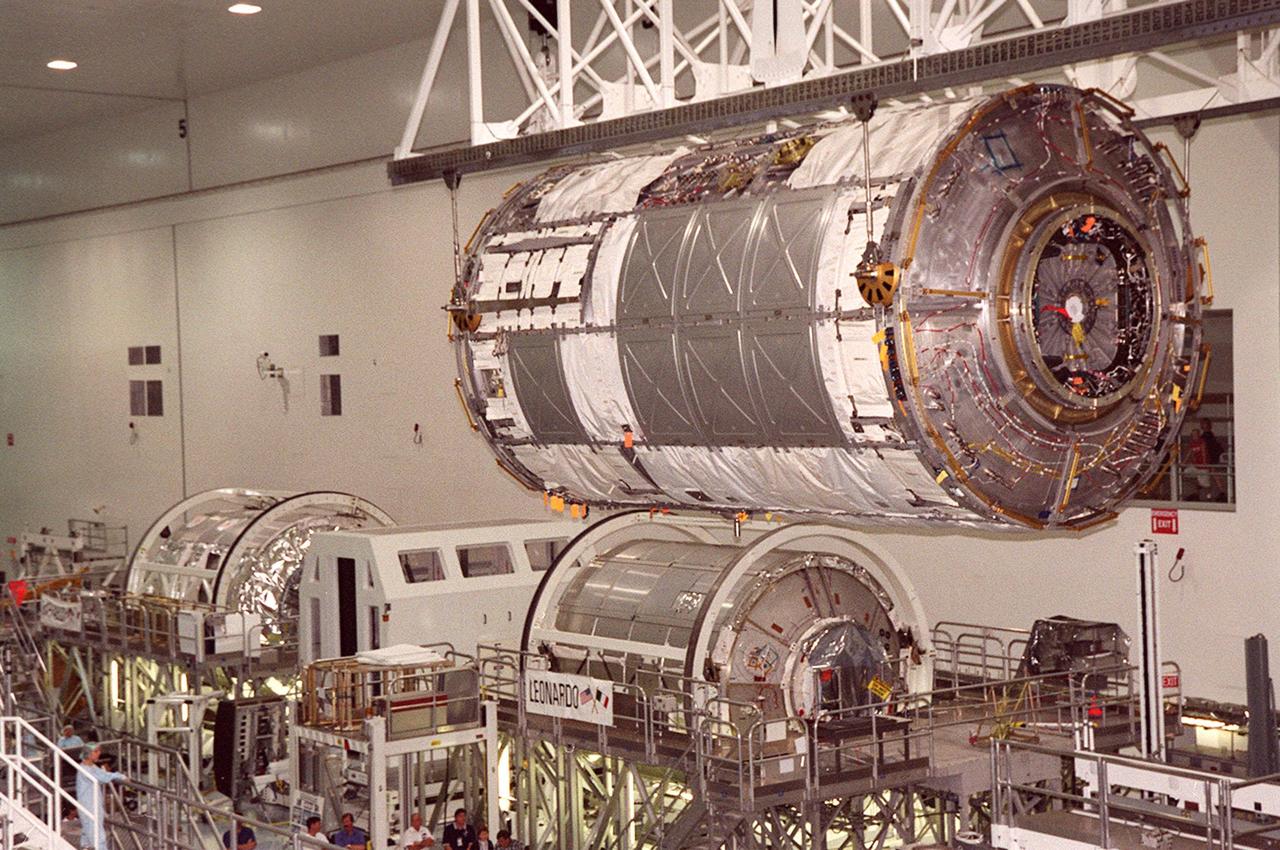
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a component of the International Space Station, glides above two Multi-Purpose Logistics Modules (MPLMs), Raffaello (far left) and Leonardo, in the Space Station Processing Facility. Destiny is being moved to a payload canister for transfer to the Operations and Checkout Building where it will be tested in the altitude chamber. Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab in the Space Station during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the Station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
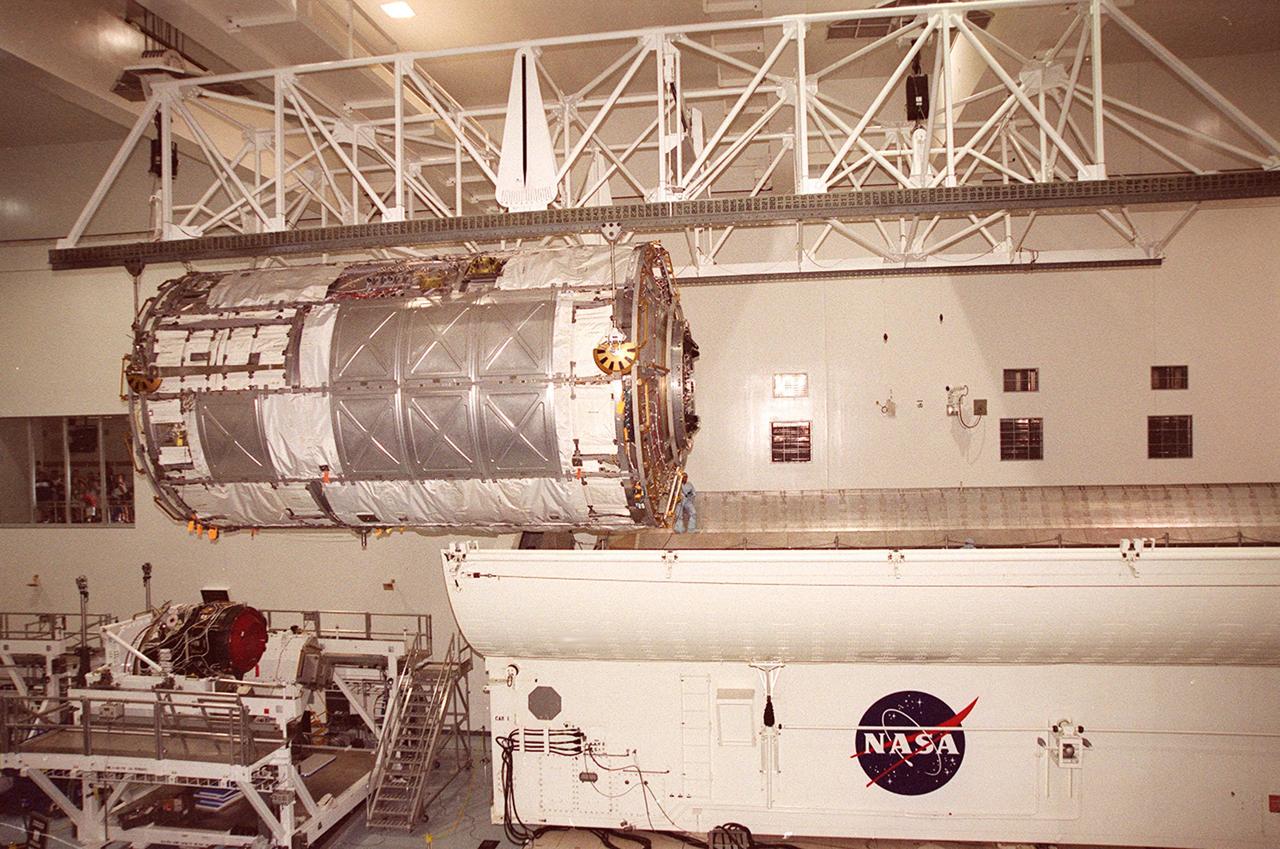
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF), the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a component of the International Space Station, is moved to a payload canister for transfer to the Operations and Checkout Building where it will be tested in the altitude chamber. On the floor of the SSPF, left, is a Pressurized Mating Adapter-3. Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab in the Space Station during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the Station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
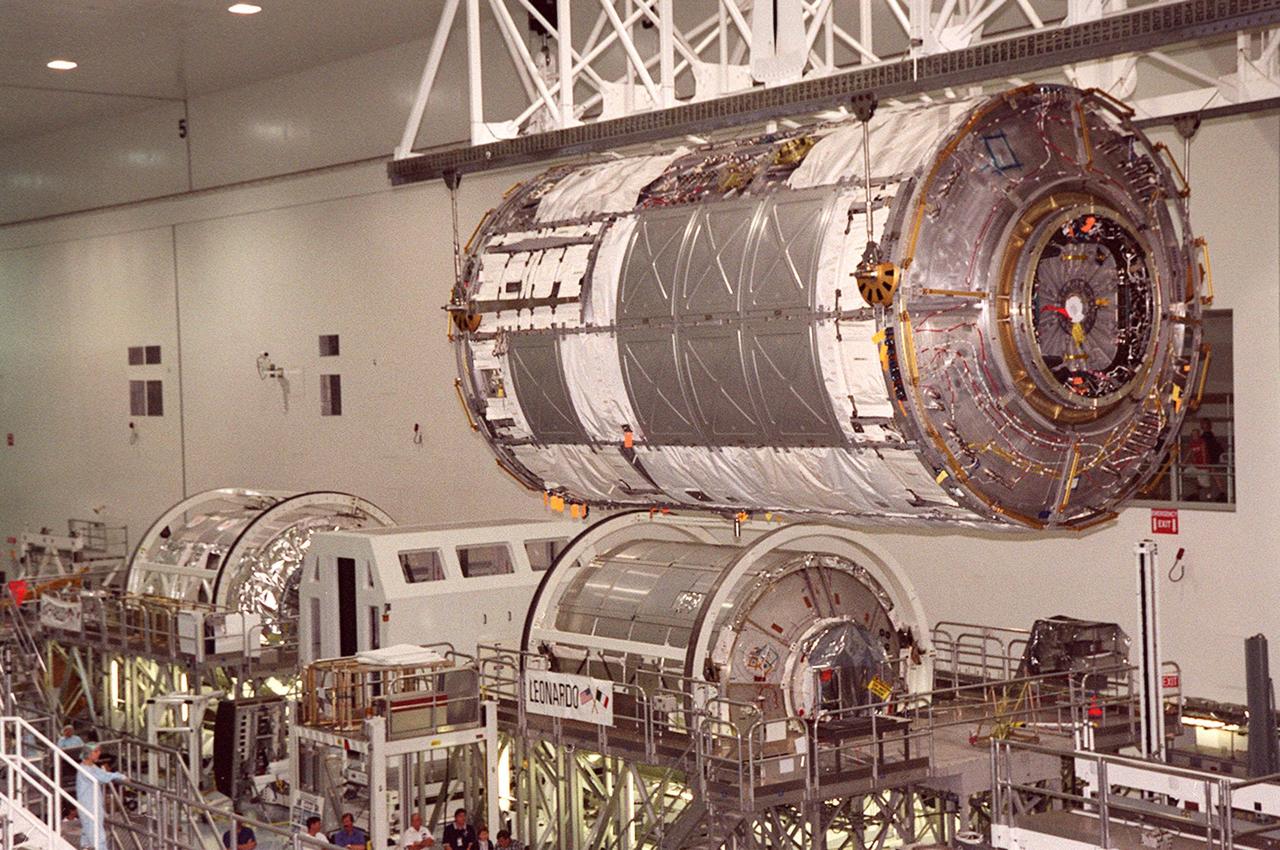
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a component of the International Space Station, glides above two Multi-Purpose Logistics Modules (MPLMs), Raffaello (far left) and Leonardo, in the Space Station Processing Facility. Destiny is being moved to a payload canister for transfer to the Operations and Checkout Building where it will be tested in the altitude chamber. Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab in the Space Station during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the Station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the U.S. Laboratory Destiny is about to undergo rotation in its workstand. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research
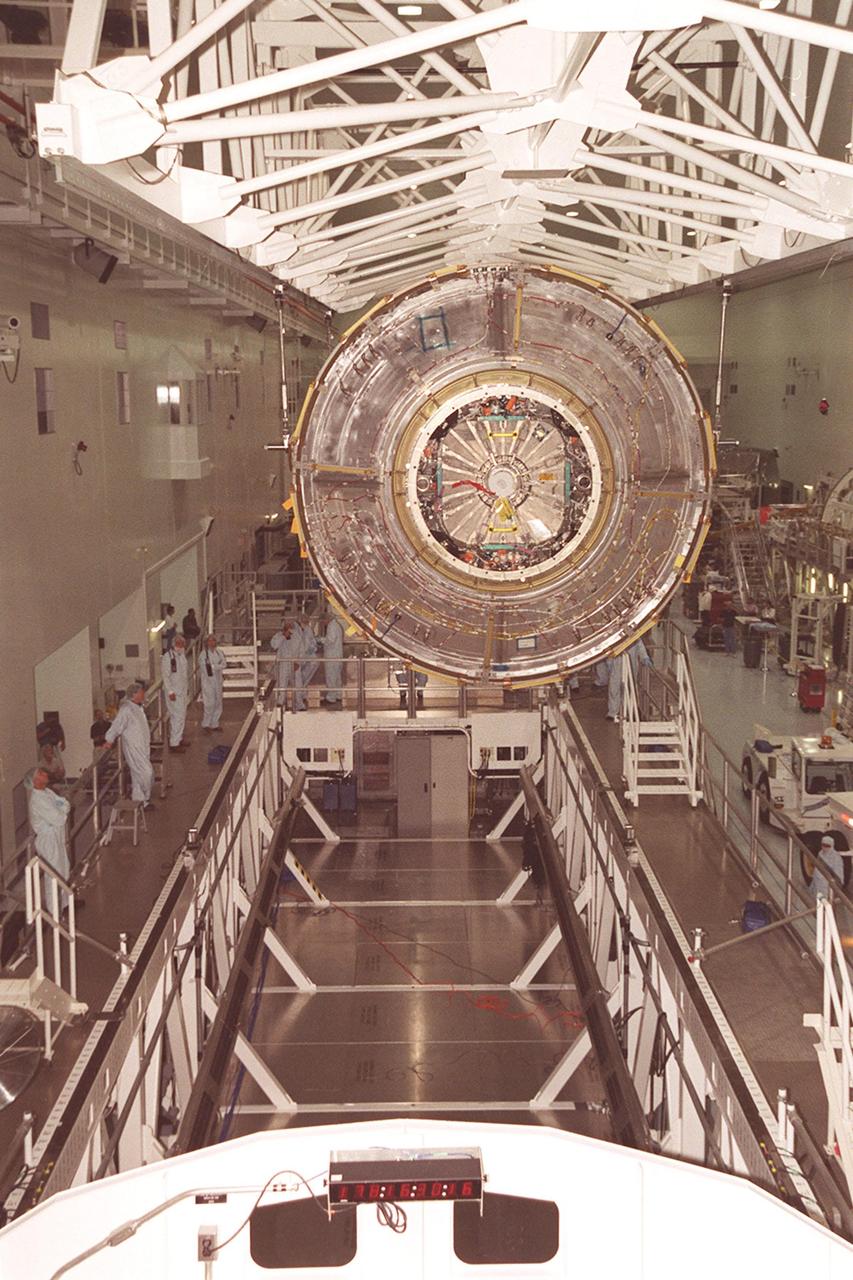
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the U.S. Lab Destiny is lowered toward the weigh stand below. A component of the International Space Station, Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research.
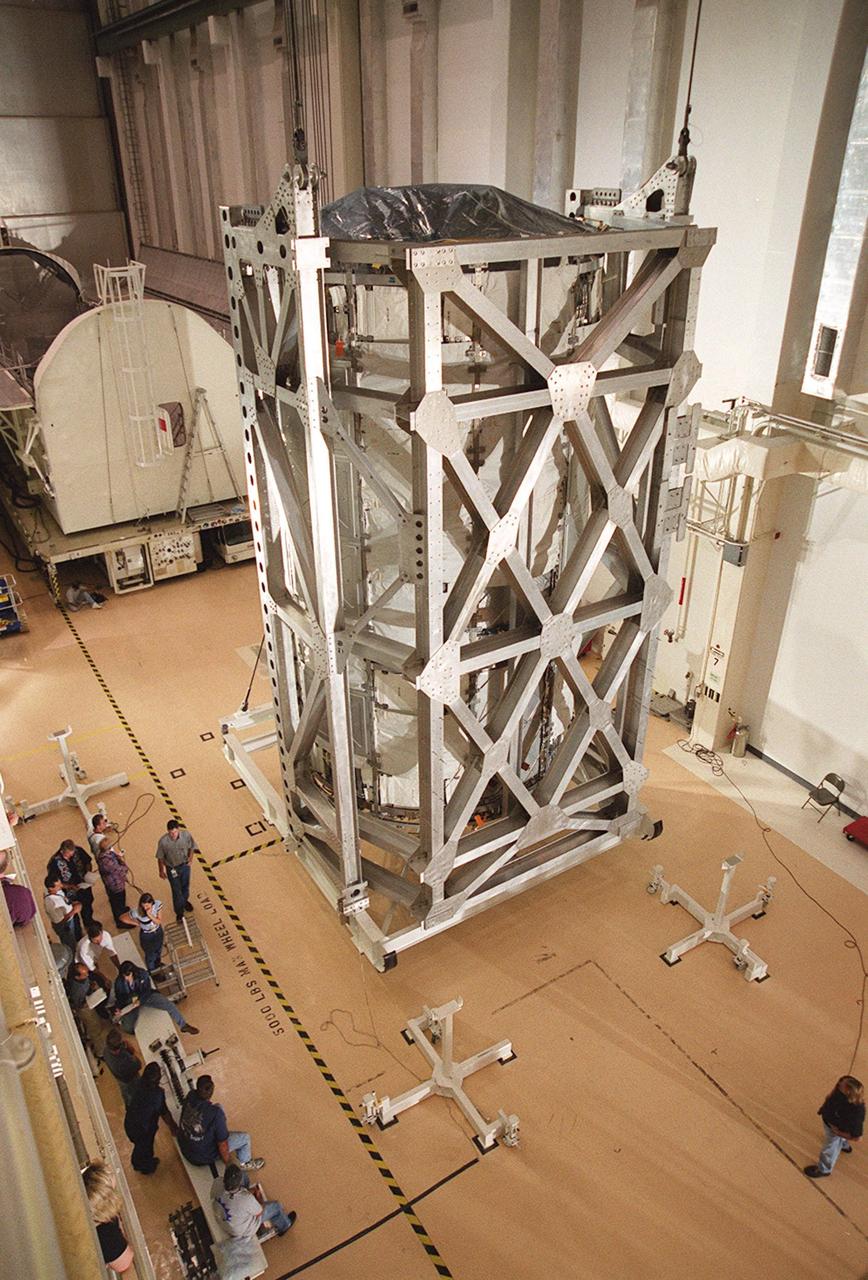

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The U.S. Lab, a component of the International Space Station, rests in a vertical position in the Operations and Checkout Building. The Lab, named Destiny, will undergo testing in the altitude chamber in the O&C. Behind the Lab is the payload canister which transported it from the Space Station Processing Facility. Destiny is scheduled to fly on mission STS-98 in early 2001. During the mission, the crew will install the Lab in the Space Station during a series of three space walks. The STS-98 mission will provide the Station with science research facilities and expand its power, life support and control capabilities. The U.S. Lab module continues a long tradition of microgravity materials research, first conducted by Skylab and later Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Destiny is expected to be a major feature in future research, providing facilities for biotechnology, fluid physics, combustion, and life sciences research