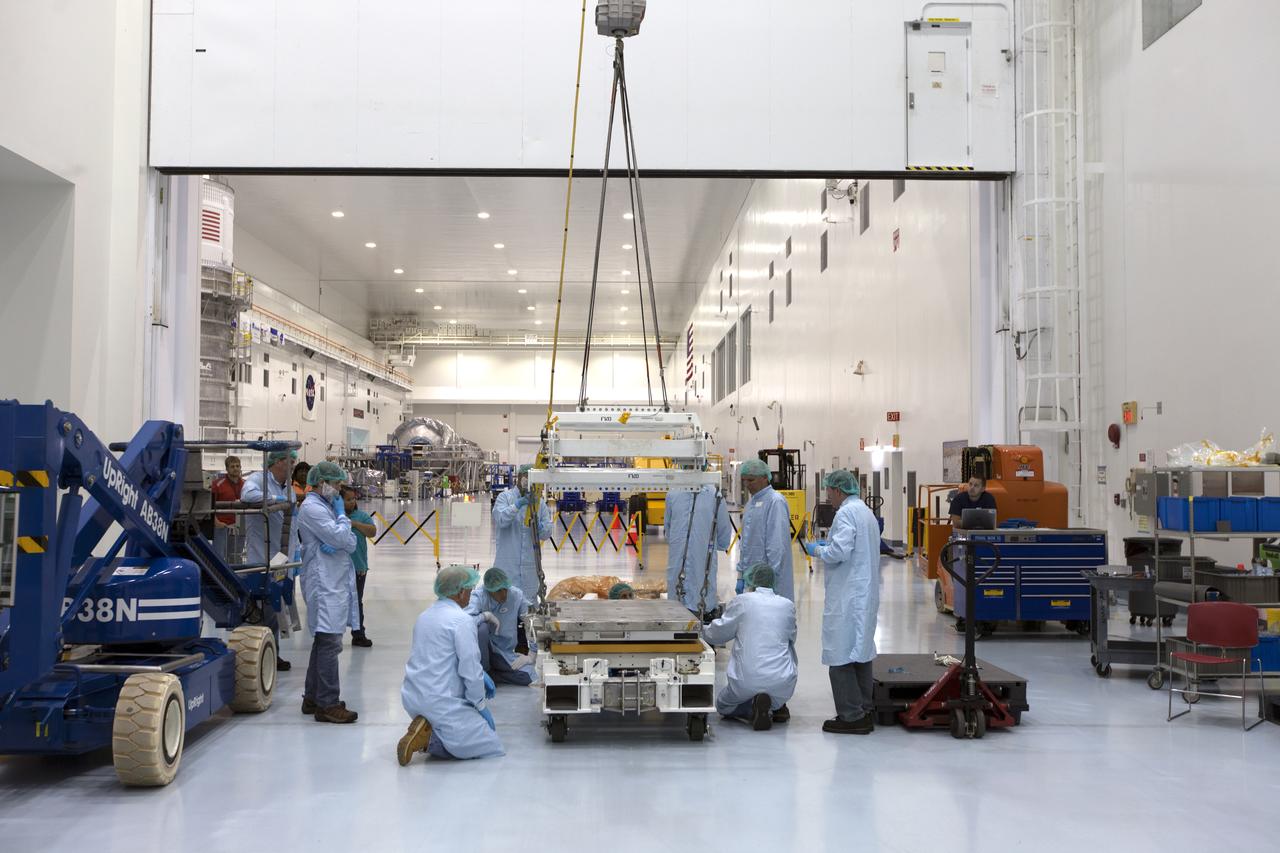

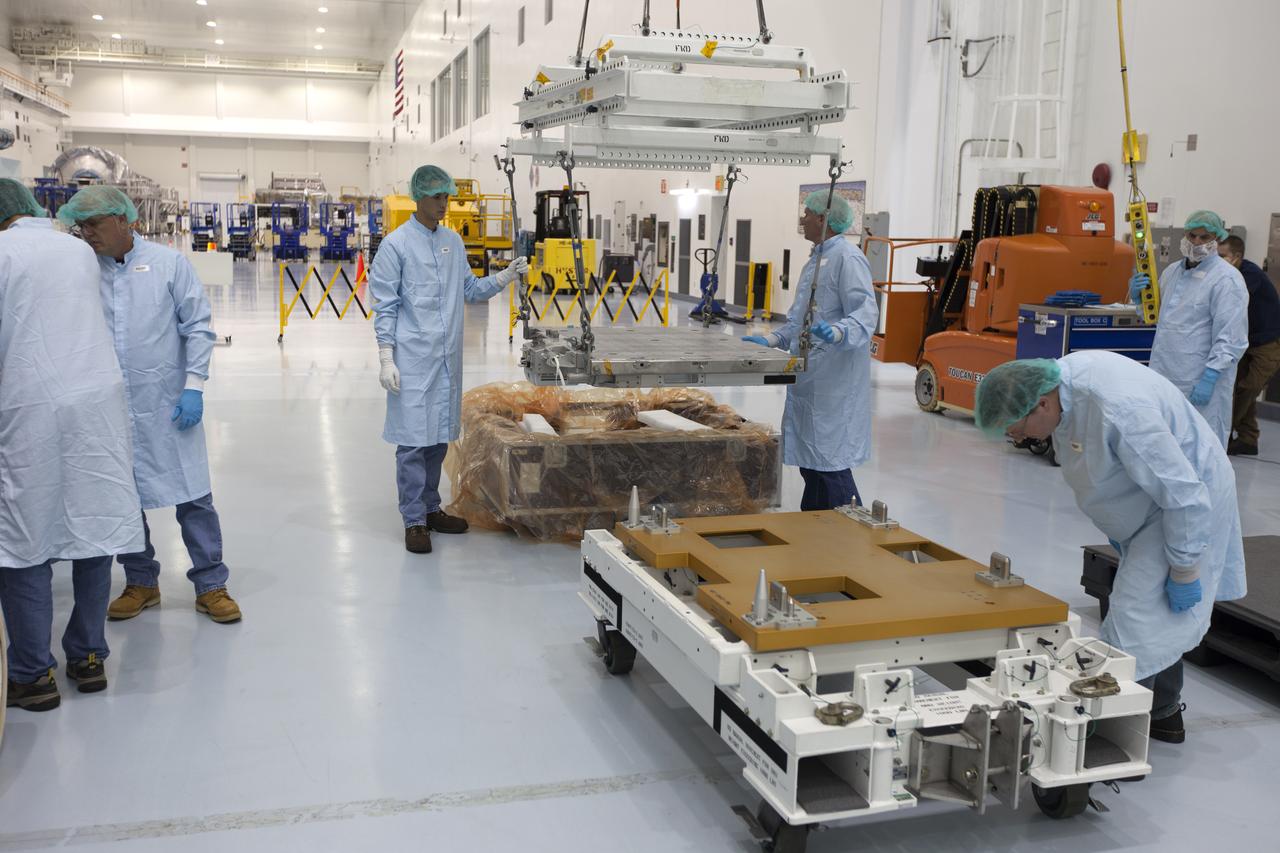
The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as one of the components is lowered onto another MISSE component. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
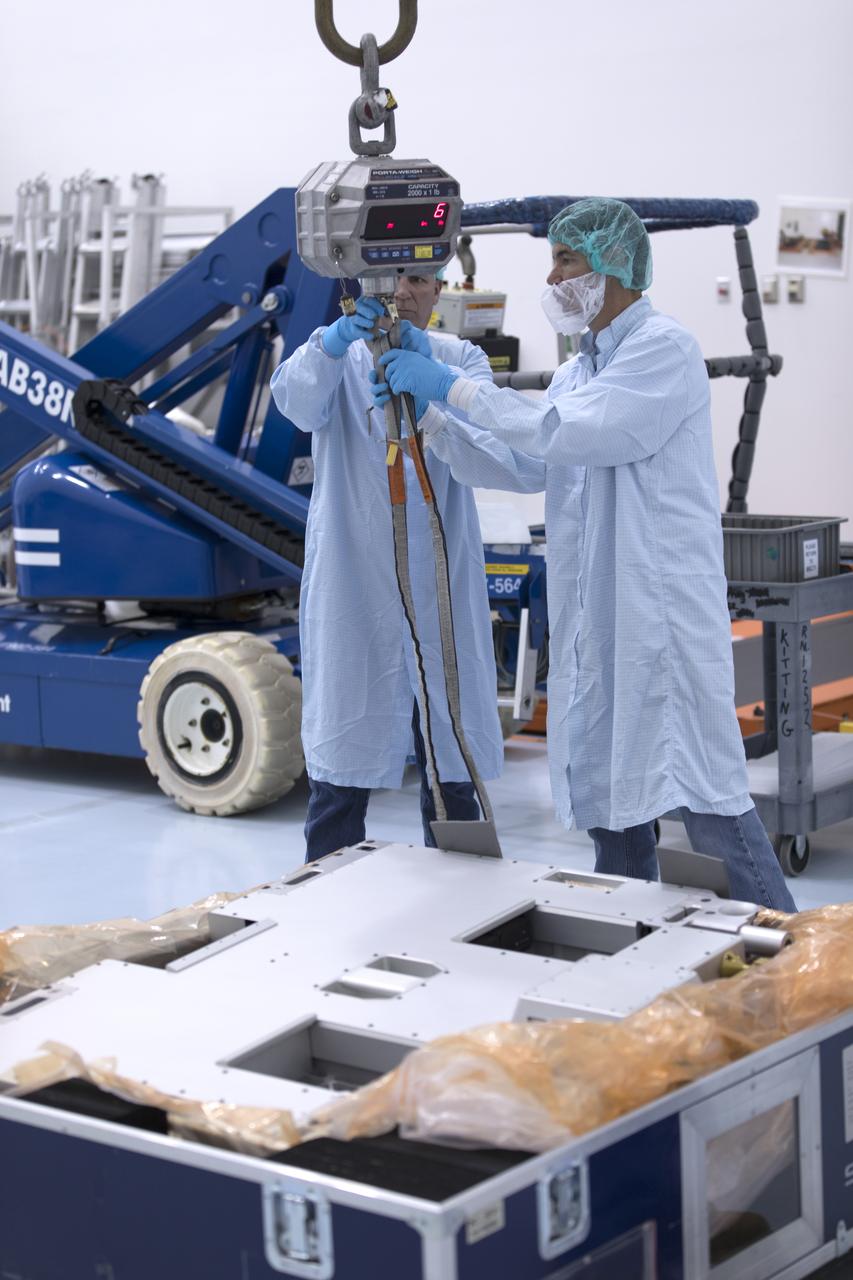

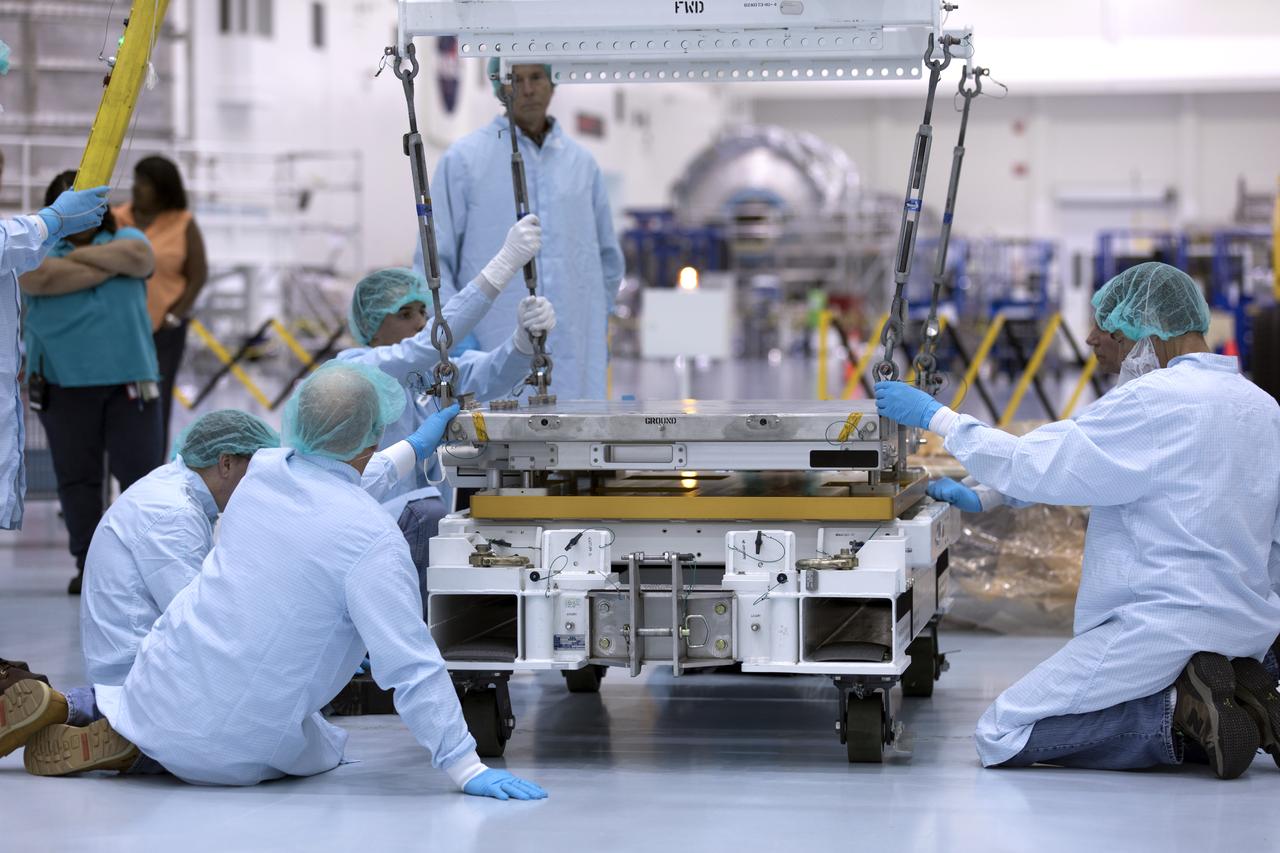
The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians work to attach a crane to MISSE for lifting out of its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as one of the components is lowered onto another MISSE component. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
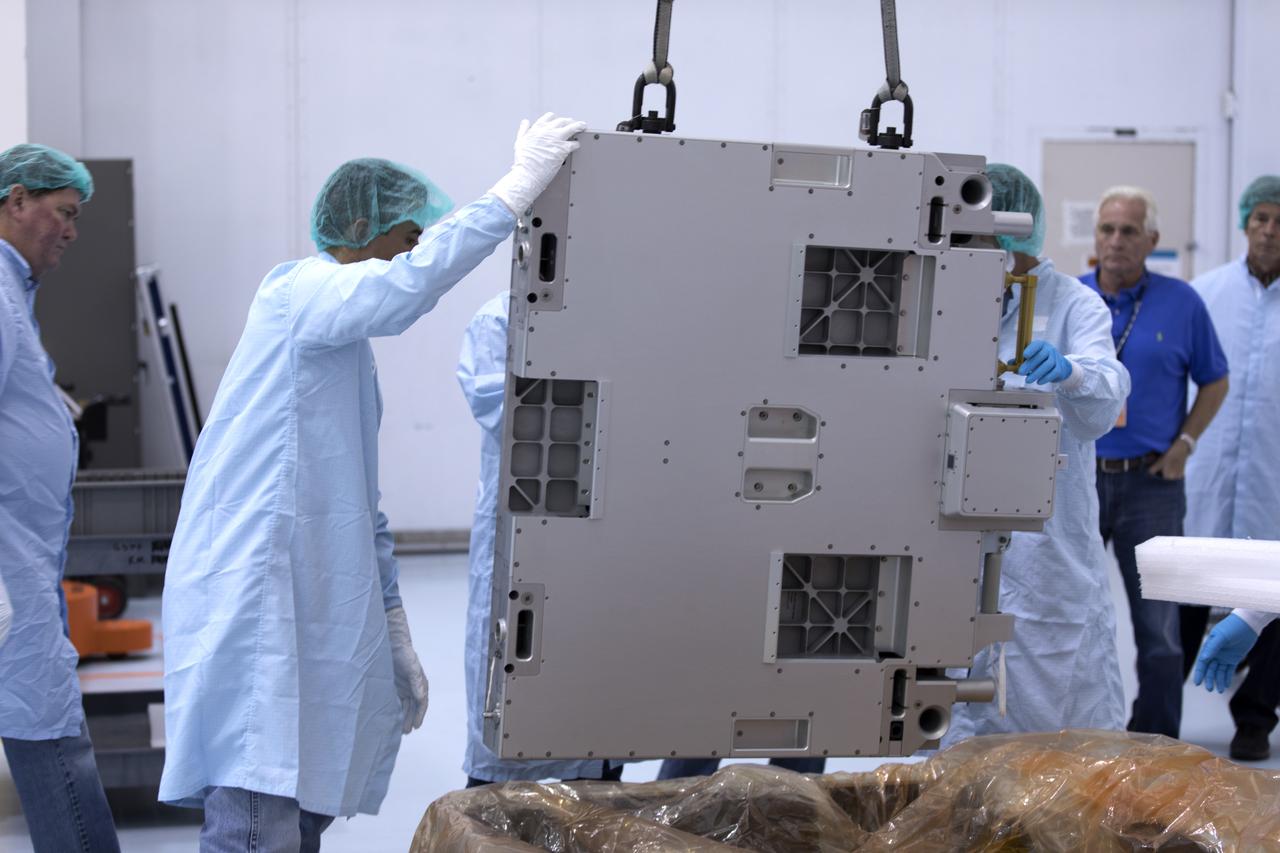

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as a crane is used to lift MISSE out of its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as MISSE is lifted by crane from its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.

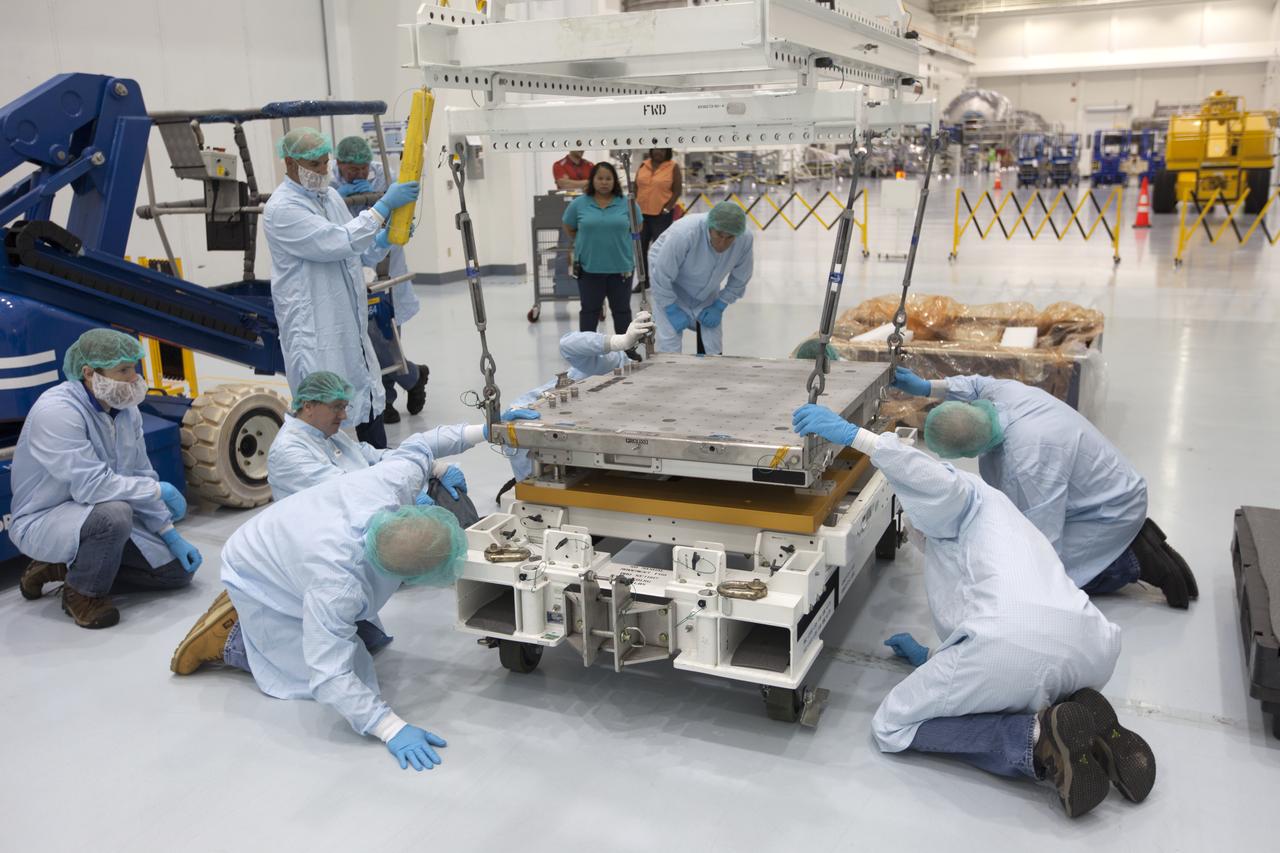
The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as one of the components is lowered and secured onto another MISSE component. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
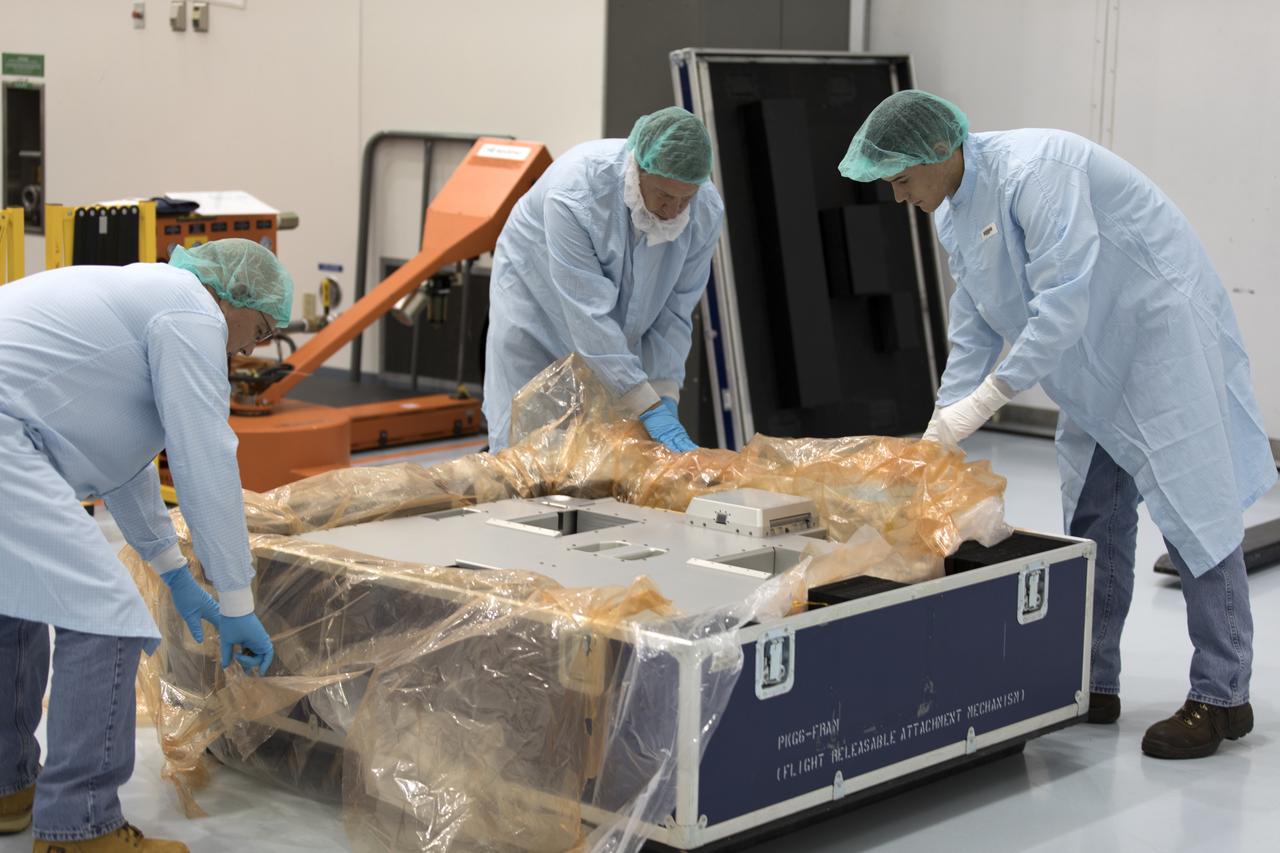

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. MISSE will be unpacked for integration and processing. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
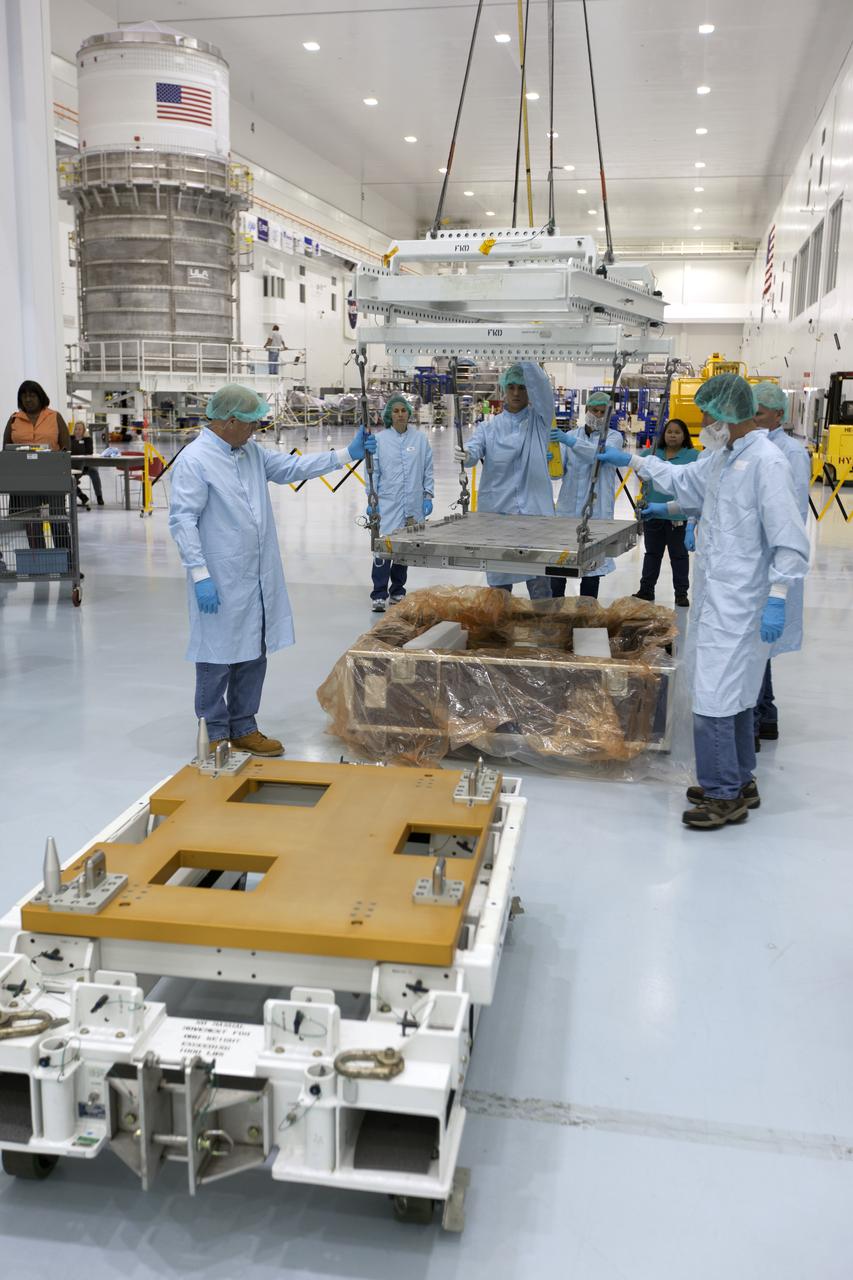

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as MISSE is lifted by crane from its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
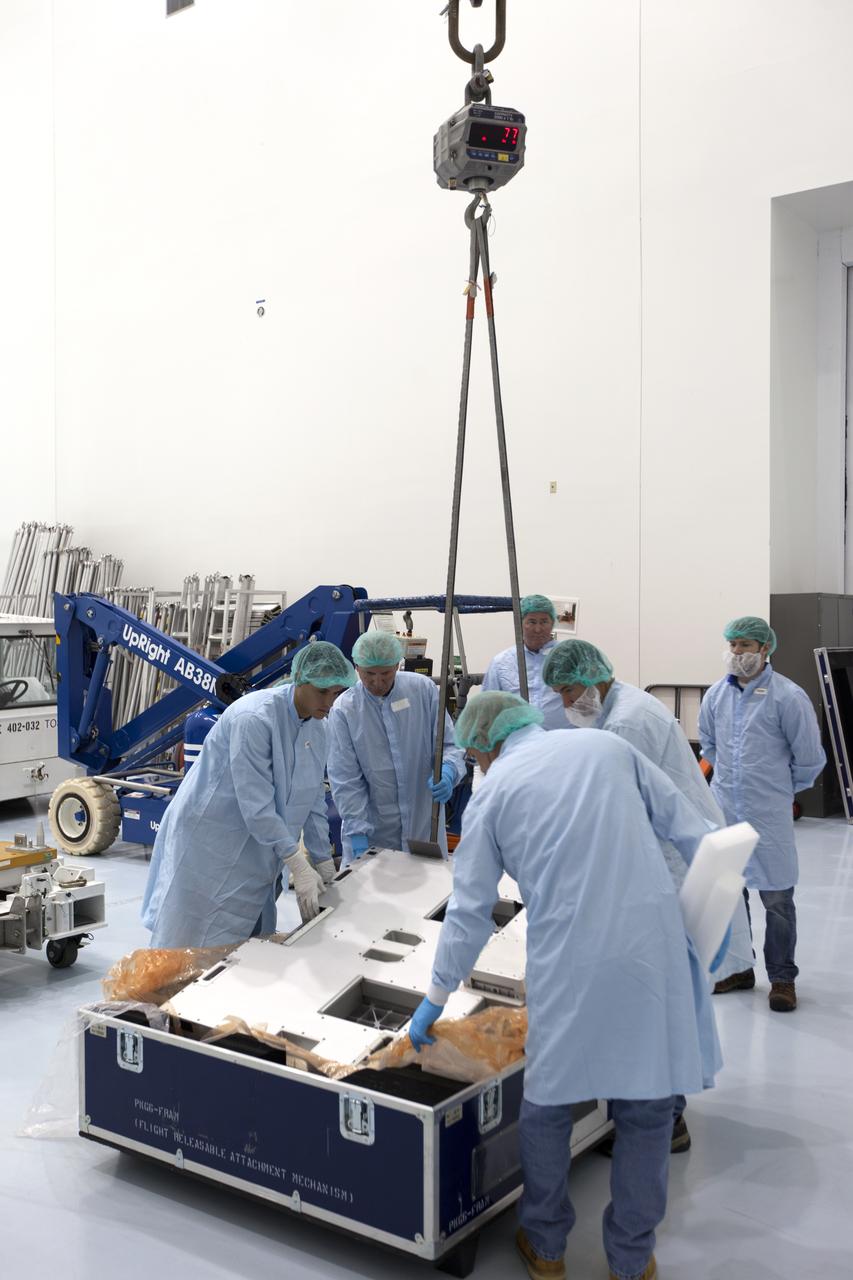

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians attach a crane to MISSE for lifting out of its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
Backdropped by a sunrise, the newly installed Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) is visible on this image. MISSE would expose 750 material samples for about 18 months and collect information on how different materials weather the space environment. The objective of MISSE is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components plarned for use on future spacecraft. The experiment was the first externally mounted experiment conducted on the International Space Station (ISS) and was installed on the outside of the ISS Quest Airlock during extravehicular activity (EVA) of the STS-105 mission. MISSE was launched on August 10, 2001 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery.
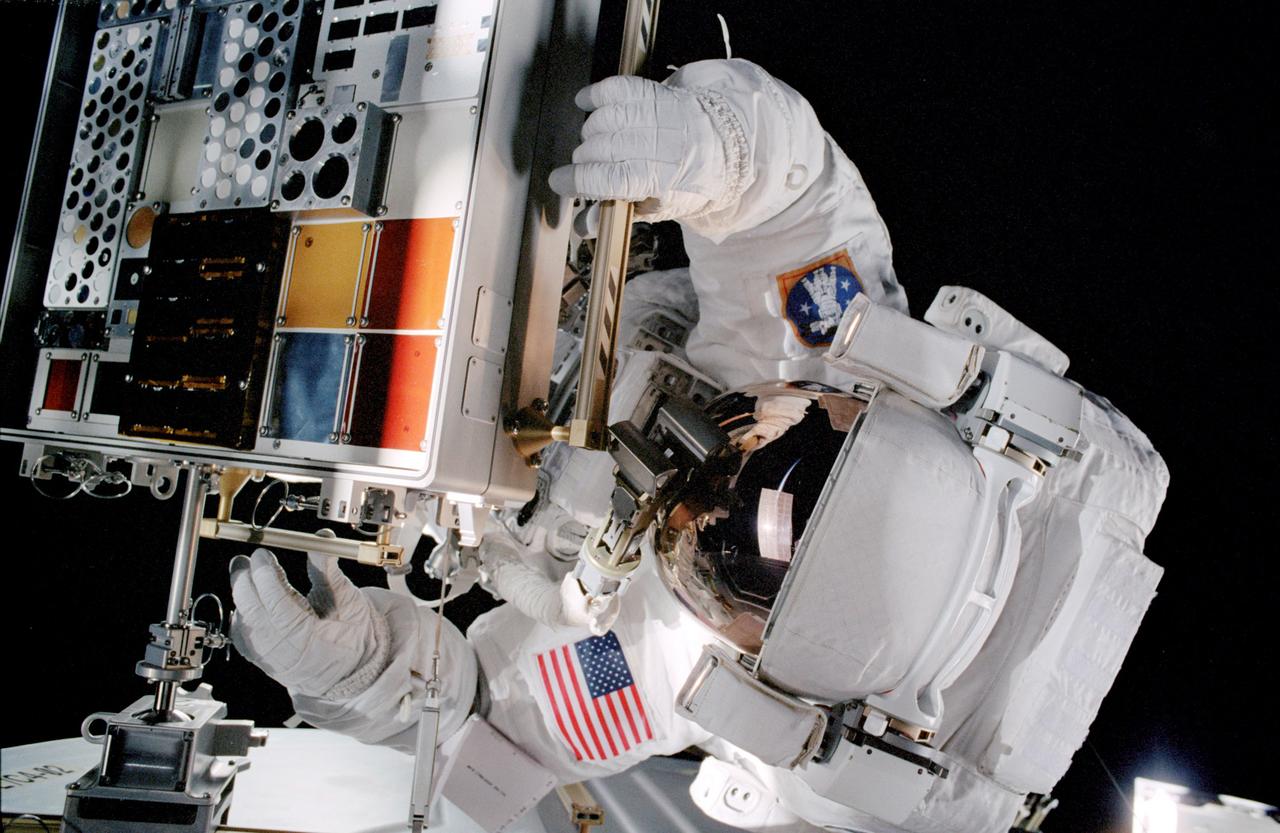

Astronaut Patrick G. Forrester works with the the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) during extravehicular activity (EVA). MISSE would expose 750 material samples for about 18 months and collect information on how different materials weather the space environment The objective of MISSE is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components plarned for use on future spacecraft. The experiment was the first externally mounted experiment conducted on the International Space Station (ISS) and was installed on the outside of the ISS Quest Airlock. MISSE was launched on August 10, 2001 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery.
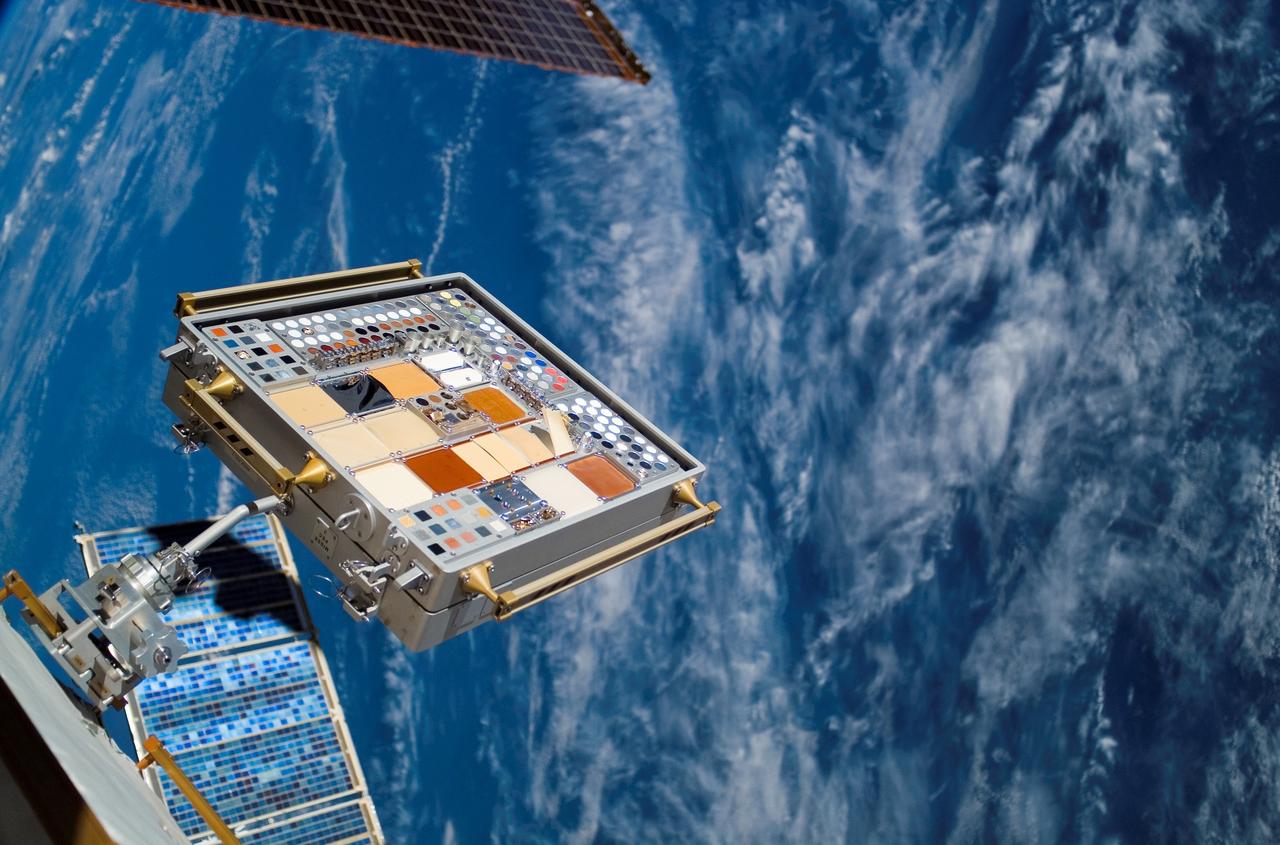

Back dropped by the blue and white Earth is a Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) on the exterior of the Station. The photograph was taken during the second bout of STS-118 Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA). MISSE collects information on how different materials weather in the environment of space.
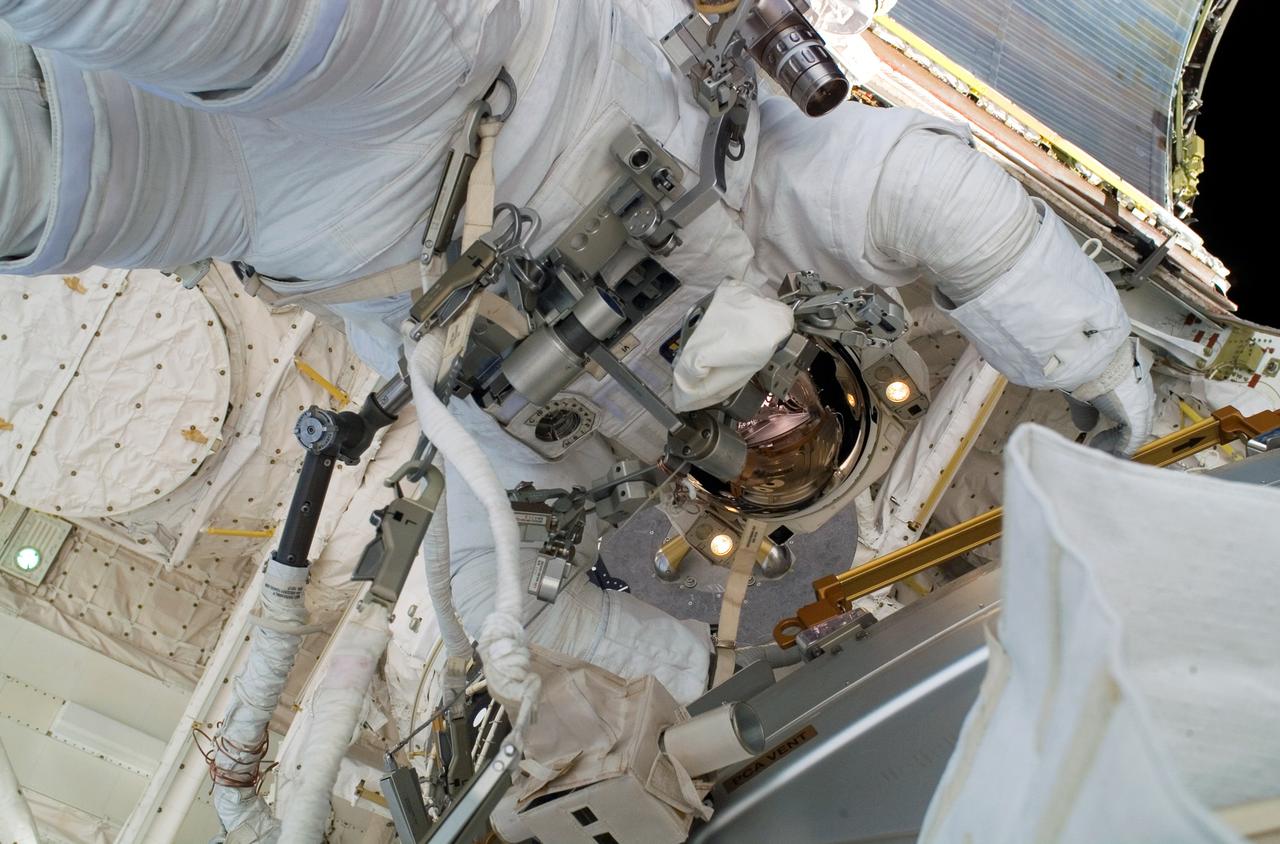

As the construction continued on the International Space Station (ISS), STS-118 Astronaut Dave Williams, representing the Canadian Space Agency, participated in the fourth and final session of Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA). During the 5 hour space walk, Williams and Expedition 15 engineer Clay Anderson (out of frame) installed the External Wireless Instrumentation System Antenna, attached a stand for the shuttle robotic arm extension boom, and retrieved the two Materials International Space Station Experiments (MISSE) for return to Earth. MISSE collects information on how different materials weather in the environment of space.

Miria Finckenor, a researcher at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, shows off the 15th Materials International Space Station Experiment, or MISSE, an external science payload berthed on the International Space Station since 2001
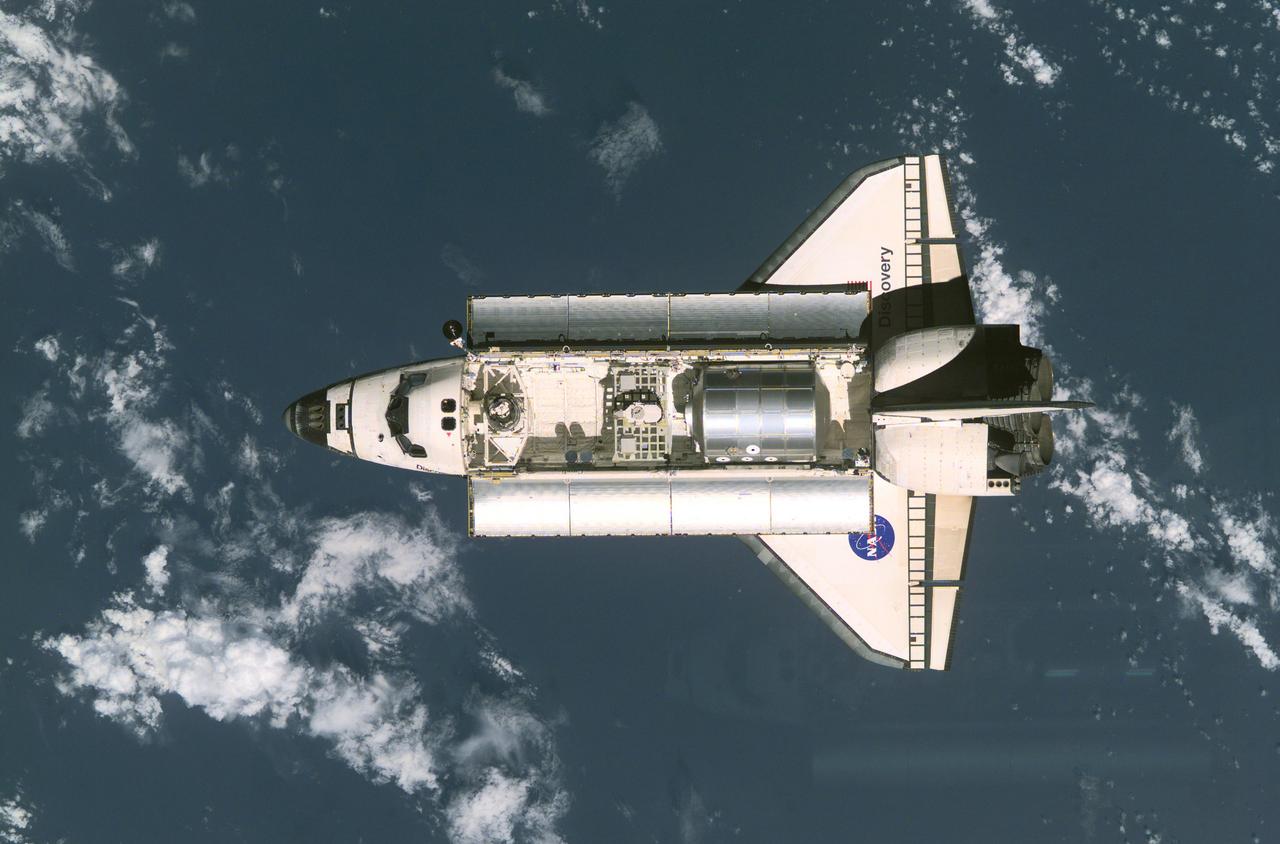

This is a view of the Space Shuttle Discovery as it approaches the International Space Station (ISS) during the STS-105 mission. Visible in the payload bay of Discovery are the Multipurpose Logistics Module (MPLM) Leonardo at right, which stores various supplies and experiments to be transferred into the ISS; at center, the Integrated Cargo Carrier (ICC) which carries the Early Ammonia Servicer (EAS); and two Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) containers at left. Aboard Discovery were the ISS Expedition Three crew, who were to replace the Expedition Two crew that had been living on the ISS for the past five months.

Containers carrying set of seeds for a Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) are shown Feb. 11, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The containers will fly aboard Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft as part of NG-15, a NASA commercial resupply mission to the orbiting laboratory targeted for Feb. 20, 2021. They will be placed in the MISSE testing facility, located near the space station’s solar arrays, where they will be exposed to the extreme environment of space for six months before returning to Earth for further study.
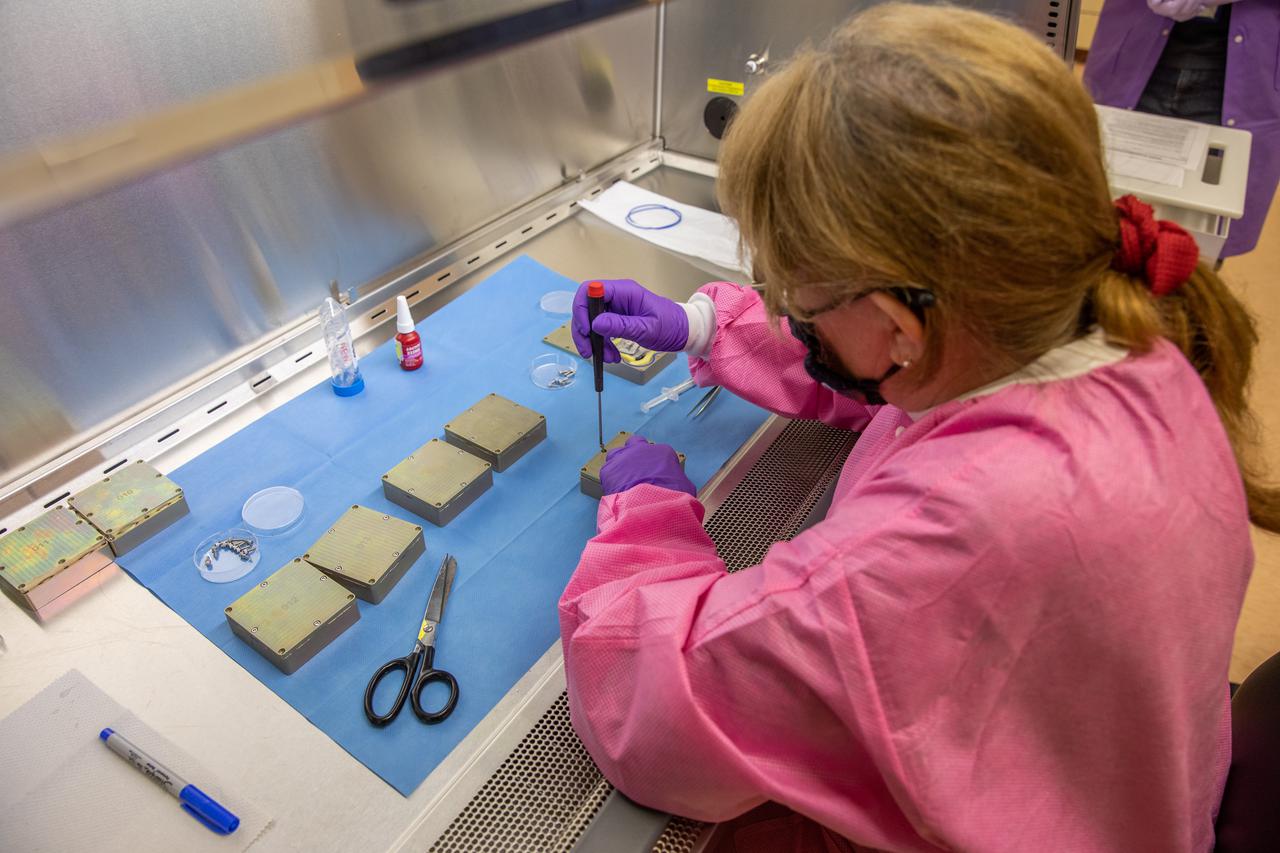

Christina Khodada, a research scientist working with the Exploration Research and Technology Programs, prepares containers Feb. 11, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for a Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE). The containers, carrying sets of seeds, will fly aboard Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft as part of NG-15, a NASA commercial resupply mission to the orbiting laboratory targeted for Feb. 20, 2021. They will be placed in the MISSE testing facility, located near the space station’s solar arrays, where they will be exposed to the extreme environment of space for six months before returning to Earth for further study.
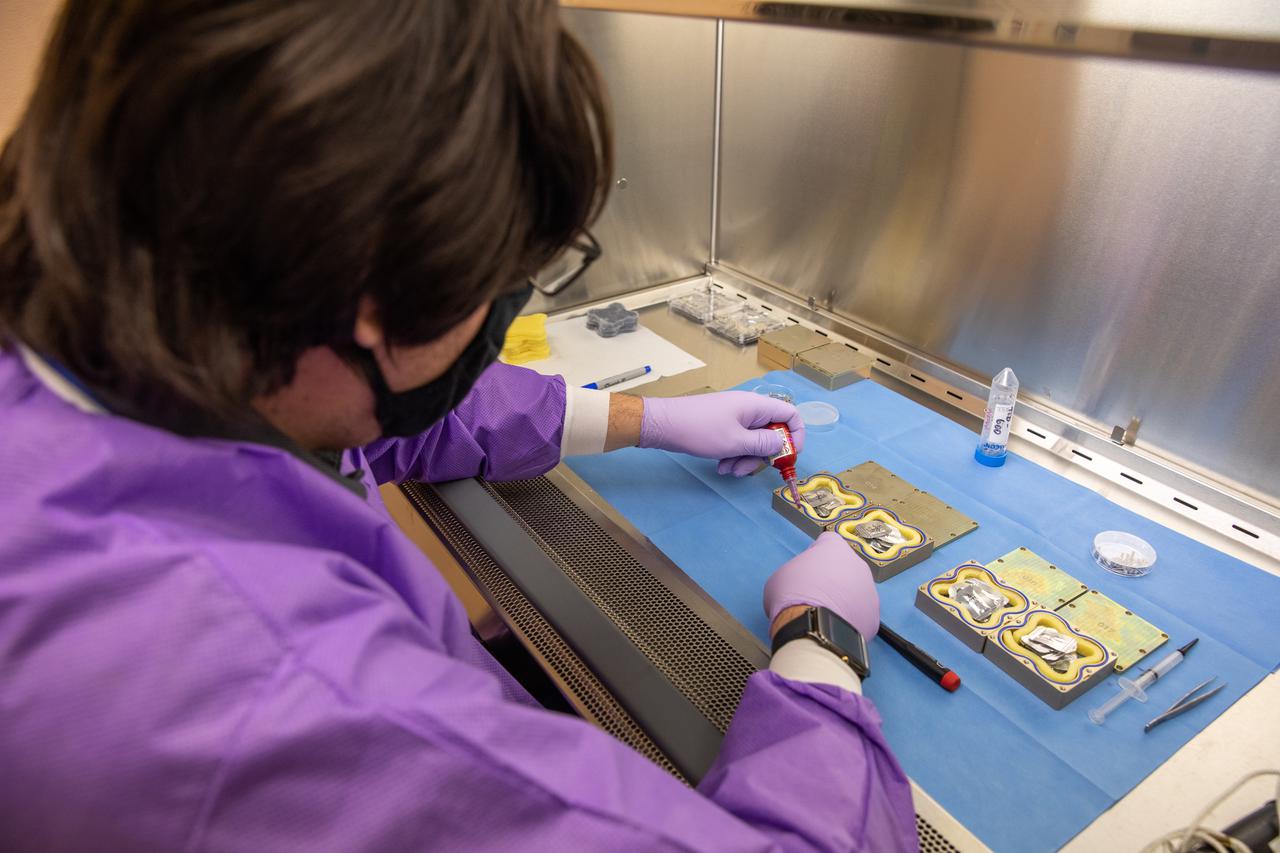

Cory Spern, a research scientist working with the Exploration Research and Technology programs at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares containers Feb. 11, 2021, for a Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE). The containers, carrying sets of seeds, will fly aboard Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft as part of NG-15, a NASA commercial resupply mission to the orbiting laboratory targeted for Feb. 20, 2021. They will be placed in the MISSE testing facility, located near the space station’s solar arrays, where they will be exposed to the extreme environment of space for six months before returning to Earth for further study.
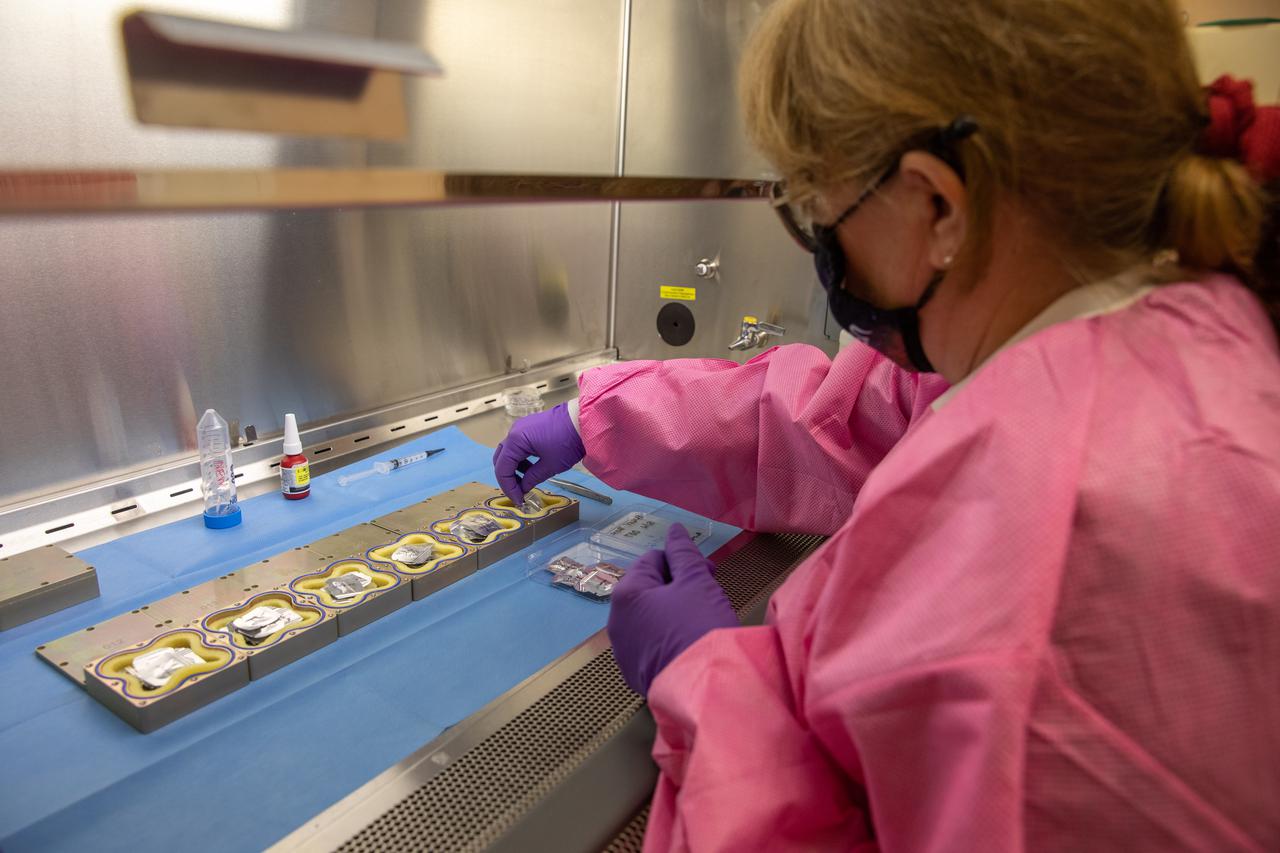

Christina Khodada, a research scientist working with the Exploration Research and Technology Programs, prepares containers Feb. 11, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for a Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE). The containers, carrying sets of seeds, will fly aboard Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft as part of NG-15, a NASA commercial resupply mission to the orbiting laboratory targeted for Feb. 20, 2021. They will be placed in the MISSE testing facility, located near the space station’s solar arrays, where they will be exposed to the extreme environment of space for six months before returning to Earth for further study.
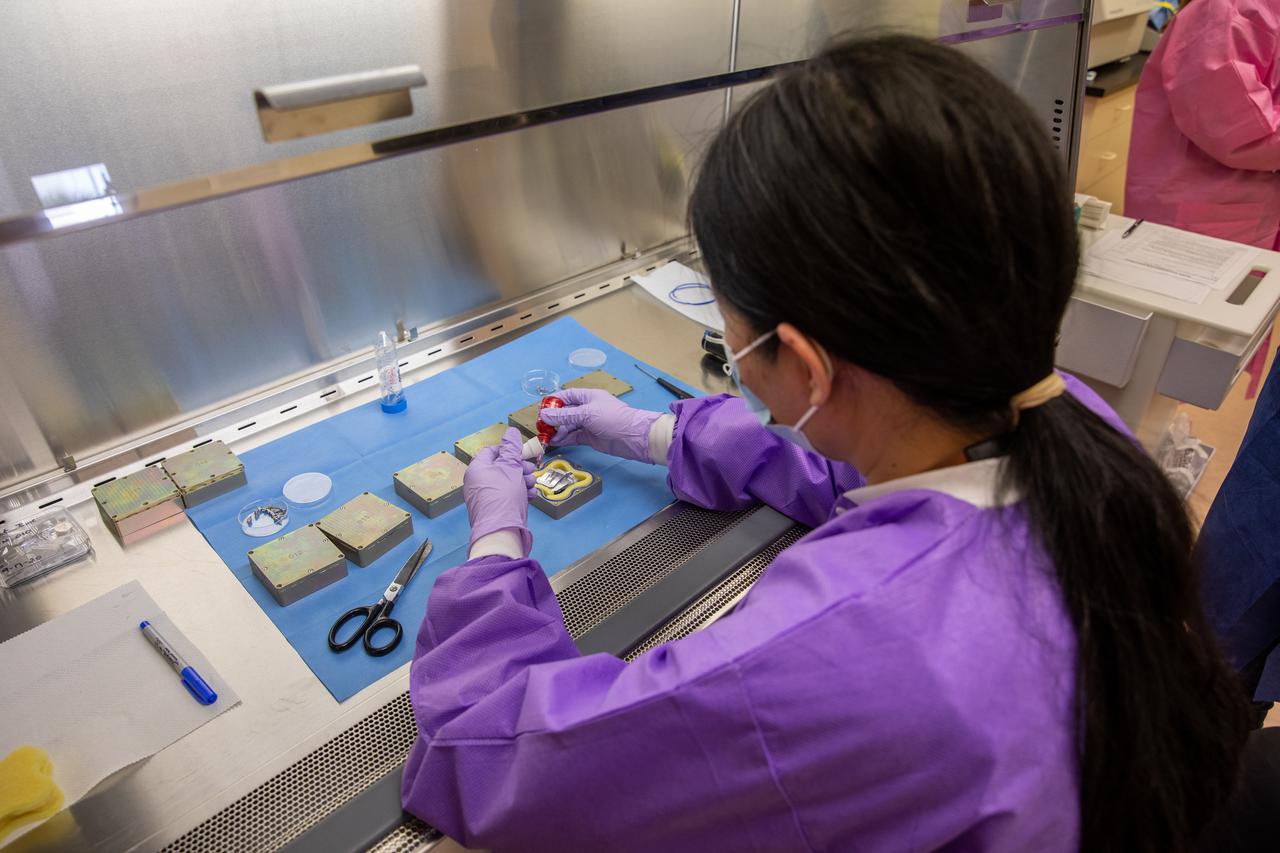

Ye Zhang, project scientist for the Exploration Research and Technology programs at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares containers for a Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE). The containers, carrying sets of seeds, will fly aboard Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft as part of NG-15, a NASA commercial resupply mission to the orbiting laboratory targeted for Feb. 20, 2021. They will be placed in the MISSE testing facility, located near the space station’s solar arrays, where they will be exposed to the extreme environment of space for six months before returning to Earth for further study.
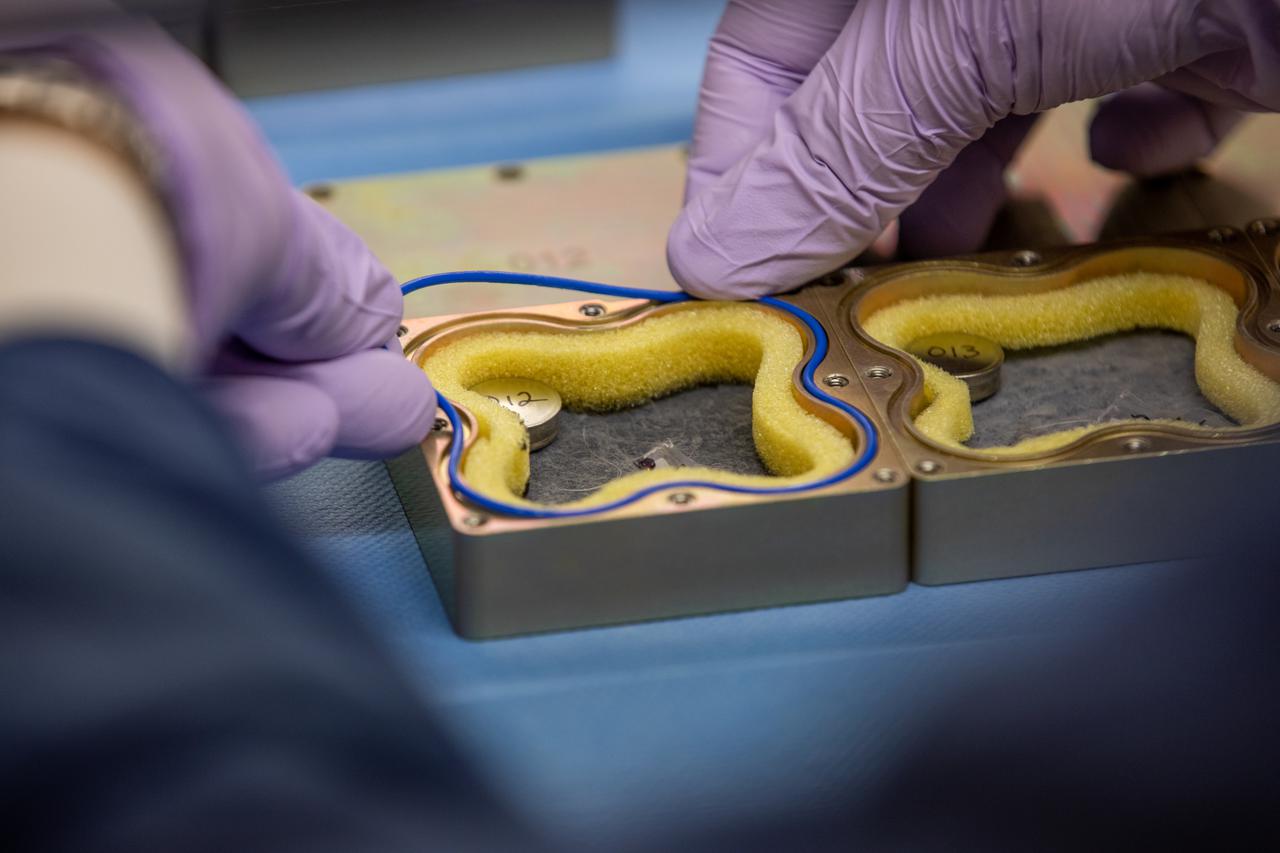
Jeffrey Richards, a project science coordinator working with the Exploration Research and Technology programs at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares containers Feb. 11, 2021, for a Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE). The containers, carrying sets of seeds, will fly aboard Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft as part of NG-15, a NASA commercial resupply mission to the orbiting laboratory targeted for Feb. 20, 2021. They will be placed in the MISSE testing facility, located near the space station’s solar arrays, where they will be exposed to the extreme environment of space for six months before returning to Earth for further study.

Jeffrey Richards, a project science coordinator working with the Exploration Research and Technology programs at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares containers Feb. 11, 2021, for a Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE). The containers, carrying sets of seeds, will fly aboard Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft as part of NG-15, a NASA commercial resupply mission to the orbiting laboratory targeted for Feb. 20, 2021. They will be placed in the MISSE testing facility, located near the space station’s solar arrays, where they will be exposed to the extreme environment of space for six months before returning to Earth for further study.
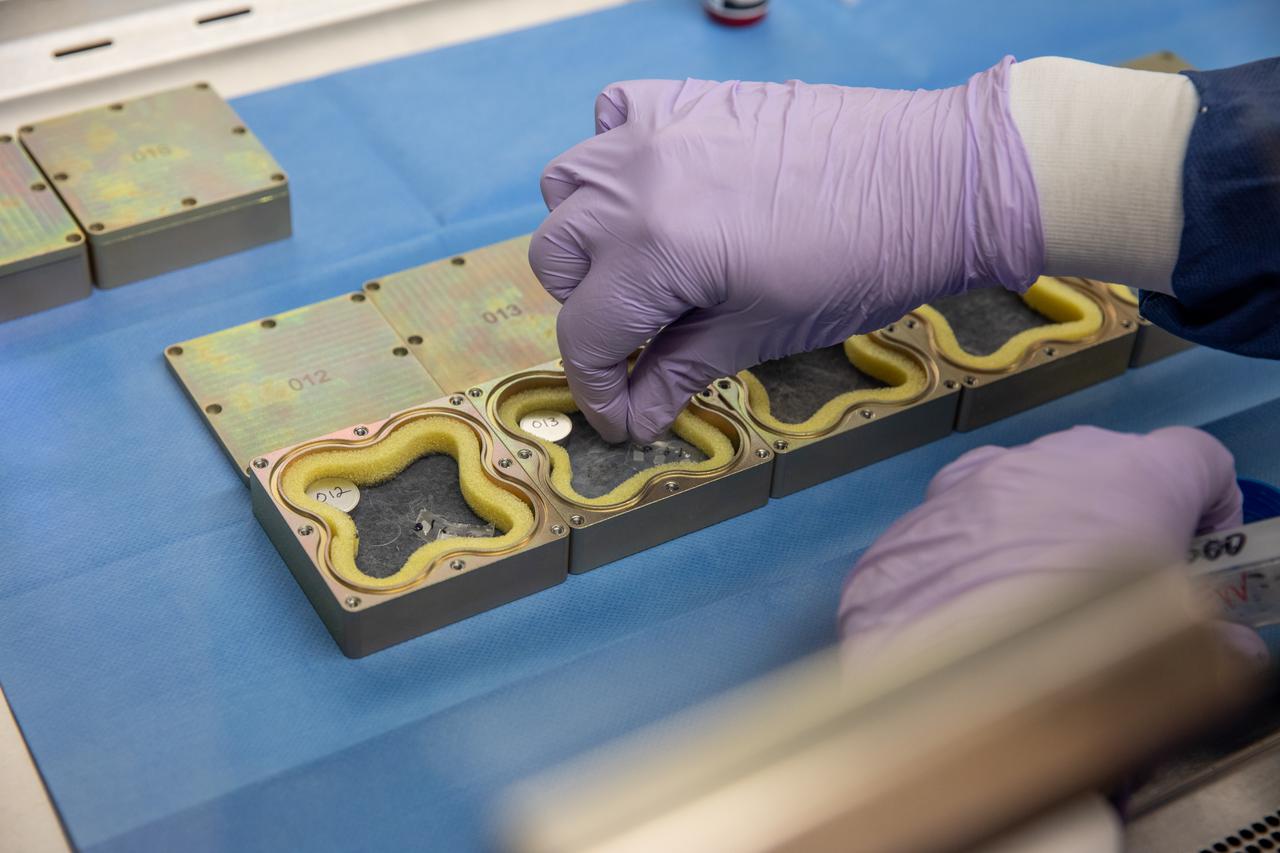

Jeffrey Richards, a project science coordinator working with the Exploration Research and Technology programs at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares containers Feb. 11, 2021, for a Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE). The containers, carrying sets of seeds, will fly aboard Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft as part of NG-15, a NASA commercial resupply mission to the orbiting laboratory targeted for Feb. 20, 2021. They will be placed in the MISSE testing facility, located near the space station’s solar arrays, where they will be exposed to the extreme environment of space for six months before returning to Earth for further study.

Jeffrey Richards, a project science coordinator working with the Exploration Research and Technology programs at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares containers Feb. 11, 2021, for a Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE). The containers, carrying sets of seeds, will fly aboard Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft as part of NG-15, a NASA commercial resupply mission to the orbiting laboratory targeted for Feb. 20, 2021. They will be placed in the MISSE testing facility, located near the space station’s solar arrays, where they will be exposed to the extreme environment of space for six months before returning to Earth for further study.

Jeffrey Richards, a project science coordinator working with the Exploration Research and Technology programs at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares containers Feb. 11, 2021, for a Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE). The containers, carrying sets of seeds, will fly aboard Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft as part of NG-15, a NASA commercial resupply mission to the orbiting laboratory targeted for Feb. 20, 2021. They will be placed in the MISSE testing facility, located near the space station’s solar arrays, where they will be exposed to the extreme environment of space for six months before returning to Earth for further study.
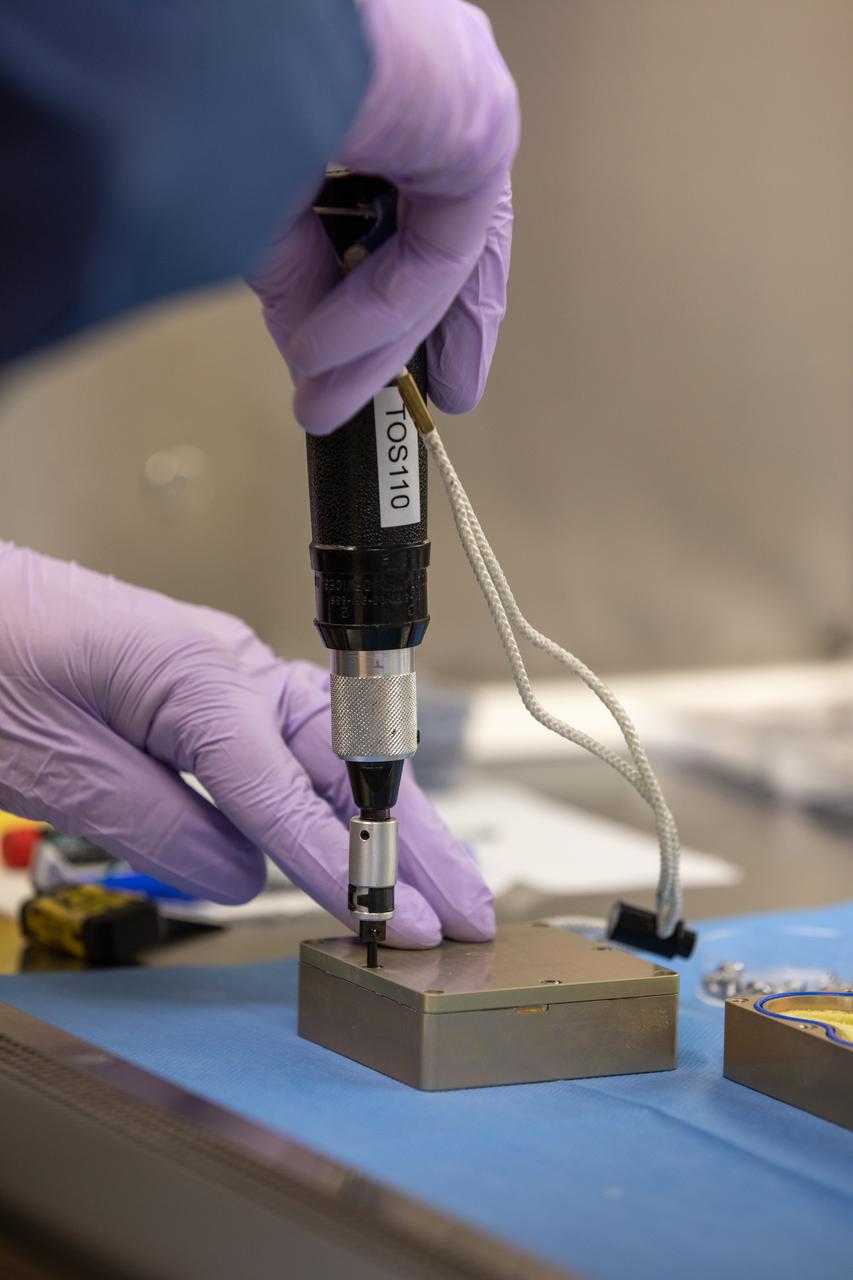

Jeffrey Richards, a project science coordinator working with the Exploration Research and Technology programs at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares containers Feb. 11, 2021, for a Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE). The containers, carrying sets of seeds, will fly aboard Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft as part of NG-15, a NASA commercial resupply mission to the orbiting laboratory targeted for Feb. 20, 2021. They will be placed in the MISSE testing facility, located near the space station’s solar arrays, where they will be exposed to the extreme environment of for six months before returning to Earth for further study.
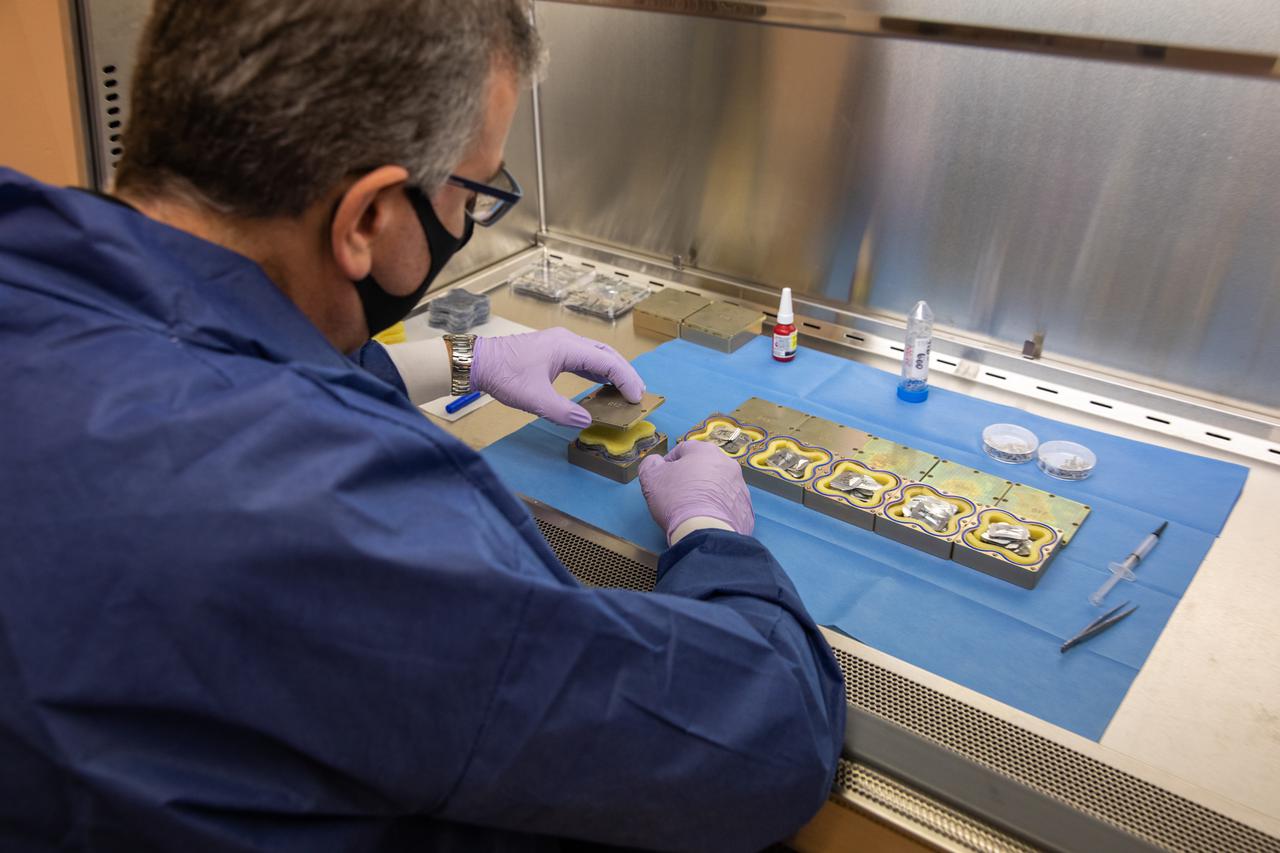

Jeffrey Richards, a project science coordinator working with the Exploration Research and Technology programs at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares containers Feb. 11, 2021, for a Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE). The containers, carrying sets of seeds, will fly aboard Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft as part of NG-15, a NASA commercial resupply mission to the orbiting laboratory targeted for Feb. 20, 2021. They will be placed in the MISSE testing facility, located near the space station’s solar arrays, where they will be exposed to the extreme environment of for six months before returning to Earth for further study.
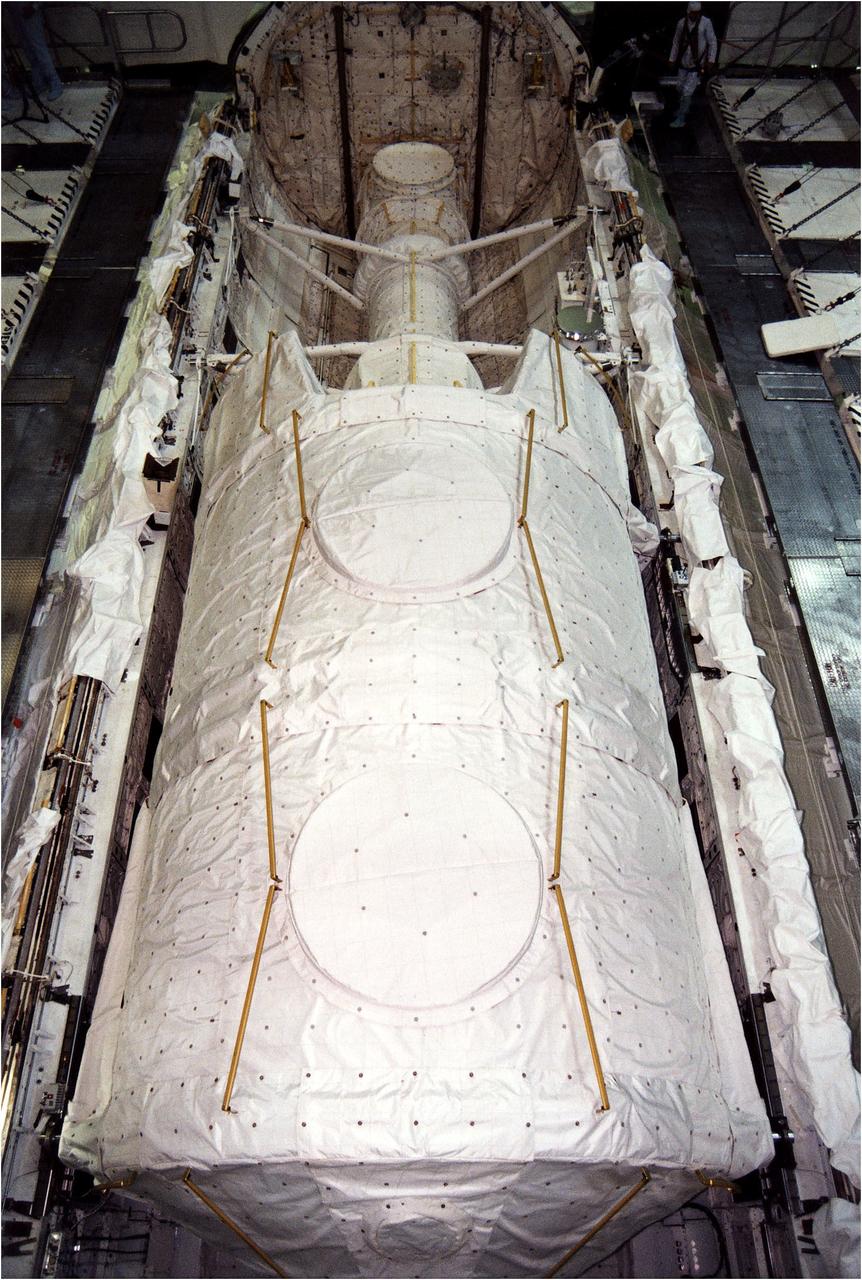
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is installed into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia in Orbiter Processing Facility 1. The Spacelab long crew transfer tunnel that leads from the orbiter's crew airlock to the module is also aboard, as well as the Hitchhiker Cryogenic Flexible Diode (CRYOFD) experiment payload, which is attached to the right side of Columbia's payload bay. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments.
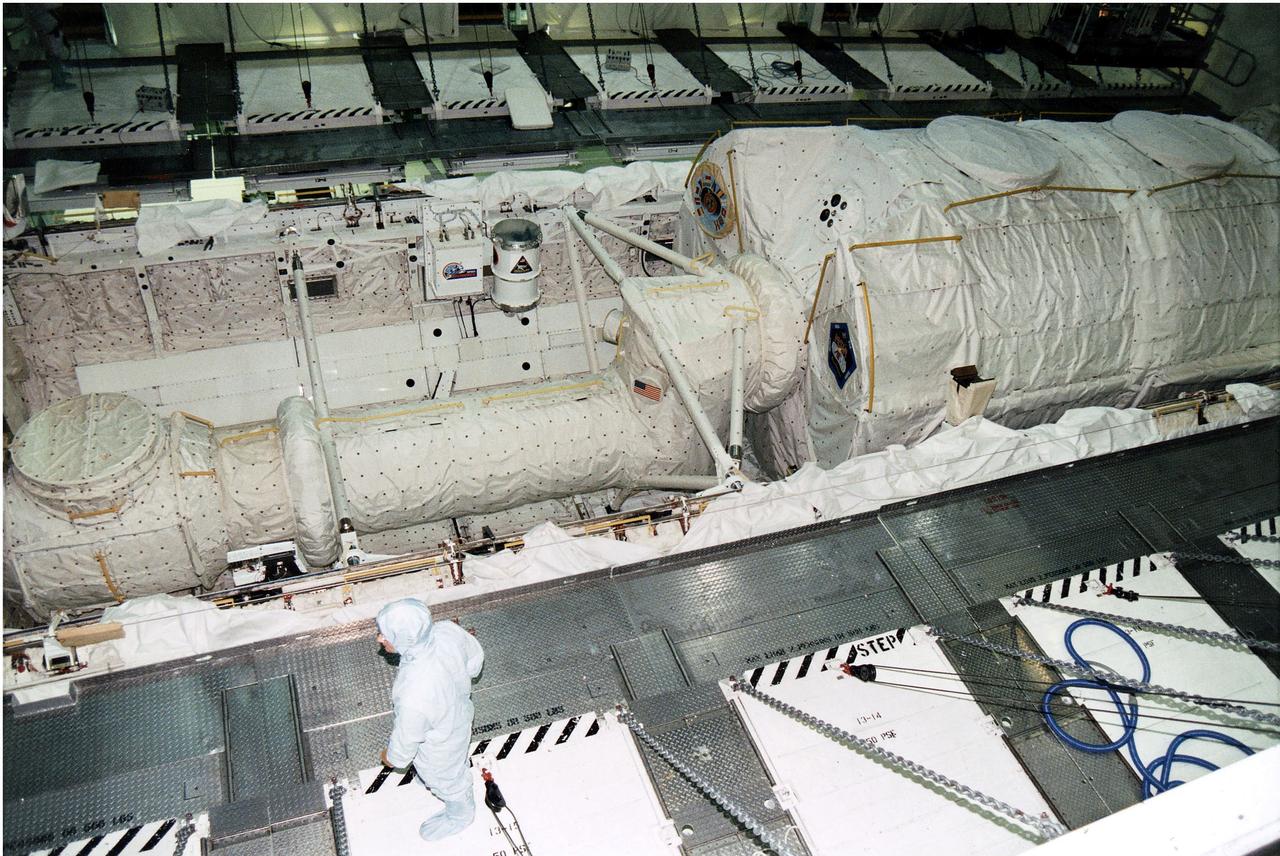
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is installed into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia in Orbiter Processing Facility 1. The Spacelab long crew transfer tunnel that leads from the orbiter's crew airlock to the module is also aboard, as well as the Hitchhiker Cryogenic Flexible Diode (CRYOFD) experiment payload, which is attached to the right side of Columbia's payload bay. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments.
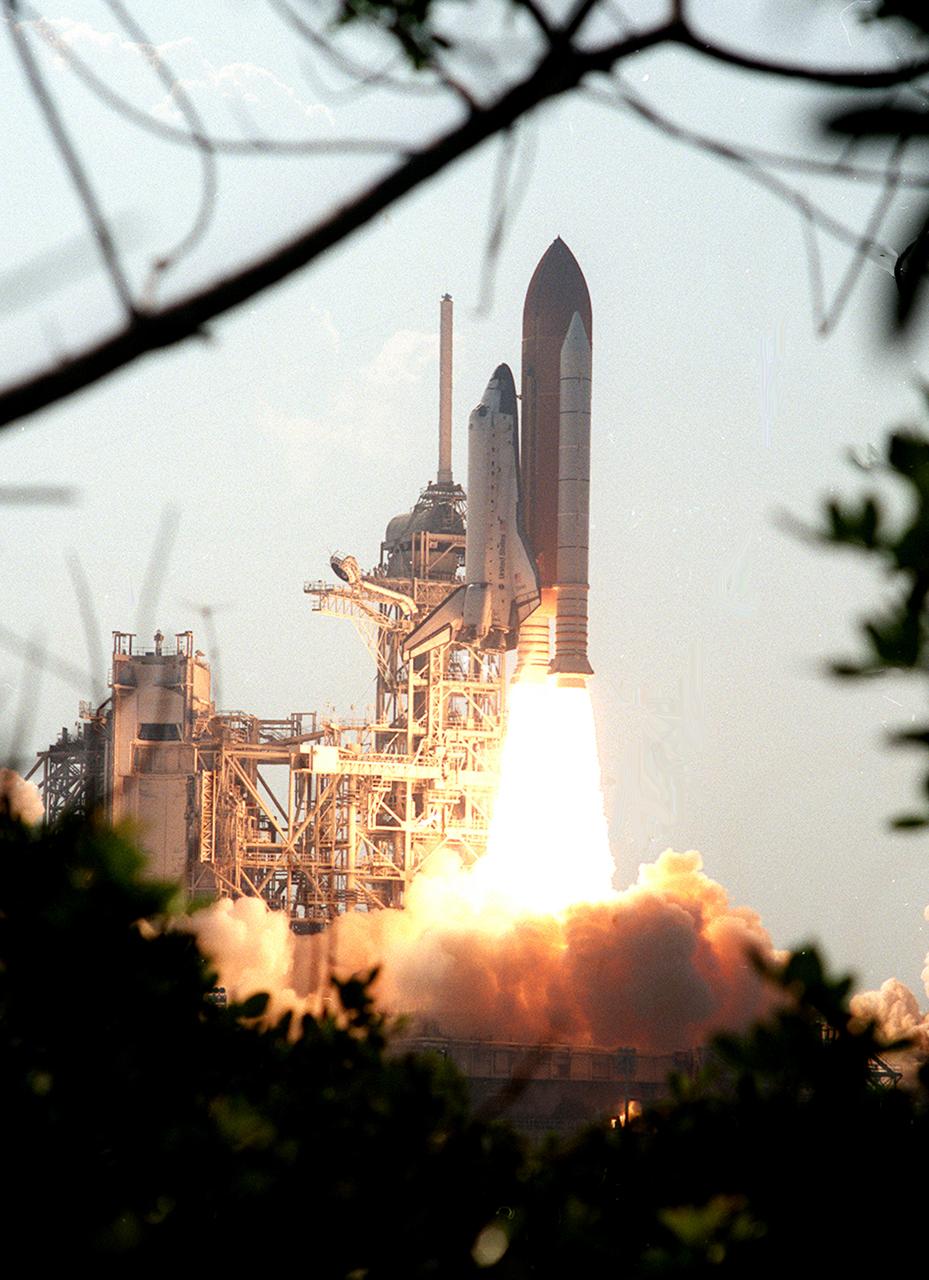

Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery lifted off for the STS-105 mission on August 10, 2001. The main purpose of the mission was the rotation of the International Space Station (ISS) Expedition Two crew with the Expedition Three crew and the delivery of supplies utilizing the Italian-built Multipurpose Logistics Module (MPLM) Leonardo. Another payload was the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE). The MISSE experiment was to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the Space Station and was the first externally mounted experiment conducted on the ISS.
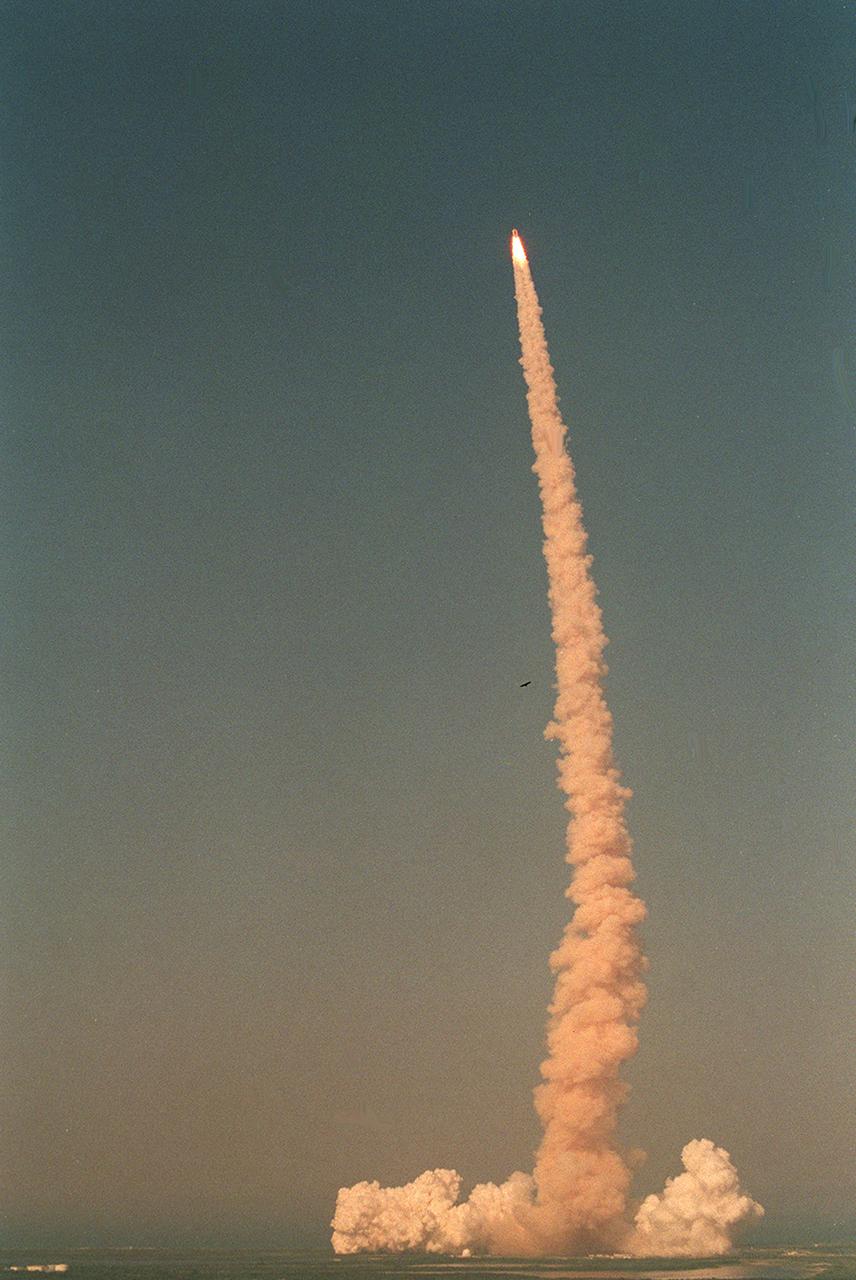

Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery lifted off for the STS-105 mission on August 10, 2001. The main purpose of the mission was the rotation of the International Space Station (ISS) Expedition Two crew with the Expedition Three crew, and the delivery of supplies utilizing the Italian-built Multipurpose Logistics Module (MPLM) Leonardo. Another payload was the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE). The MISSE experiment was to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the Space Station and was the first externally mounted experiment conducted on the ISS.
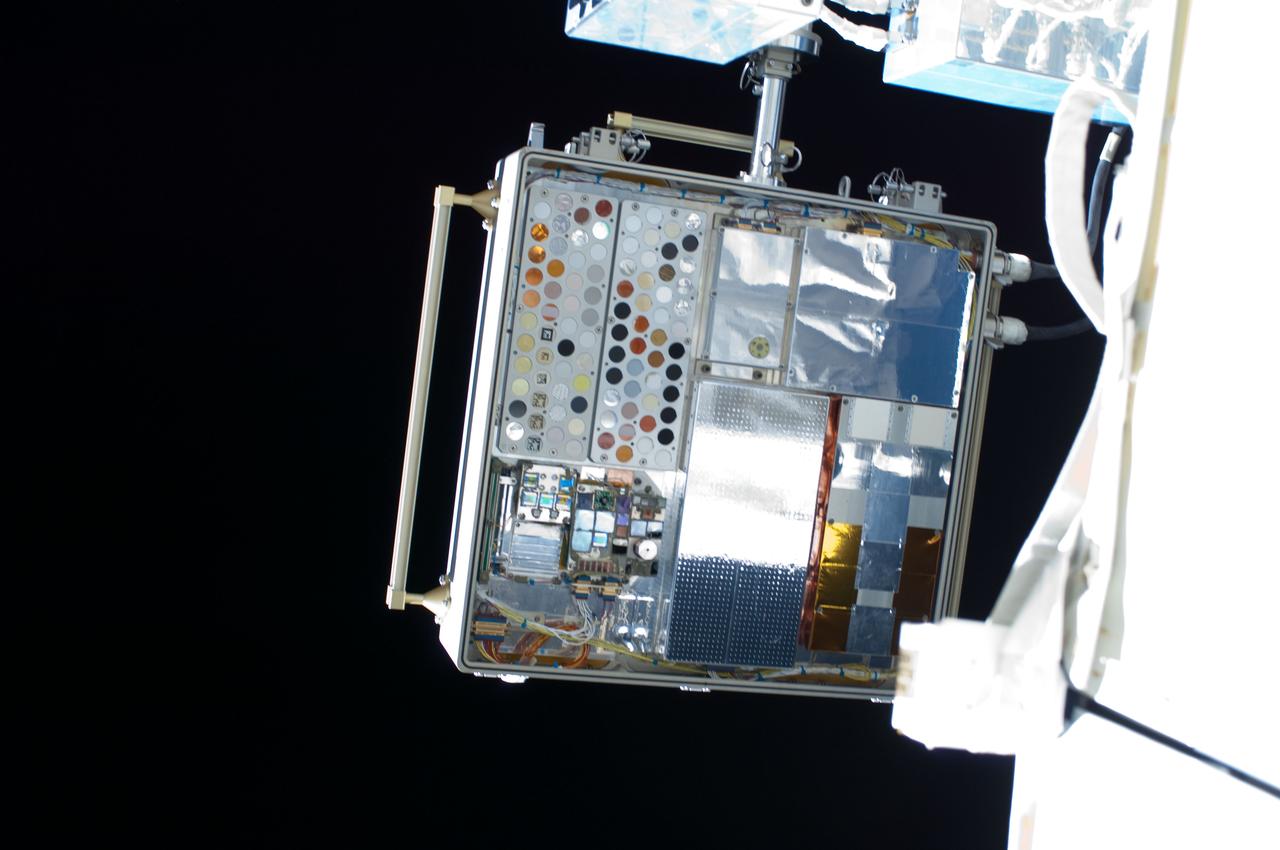

iss028e016106 (7/12/2011) --- View of a Materials on International Space Station Experiment - 8 (MISSE-8) installed on the starboard truss. The Materials on International Space Station Experiment - 8 (MISSE-8) tests various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. The payload container is mounted so one side faces the Earth and the other faces space.
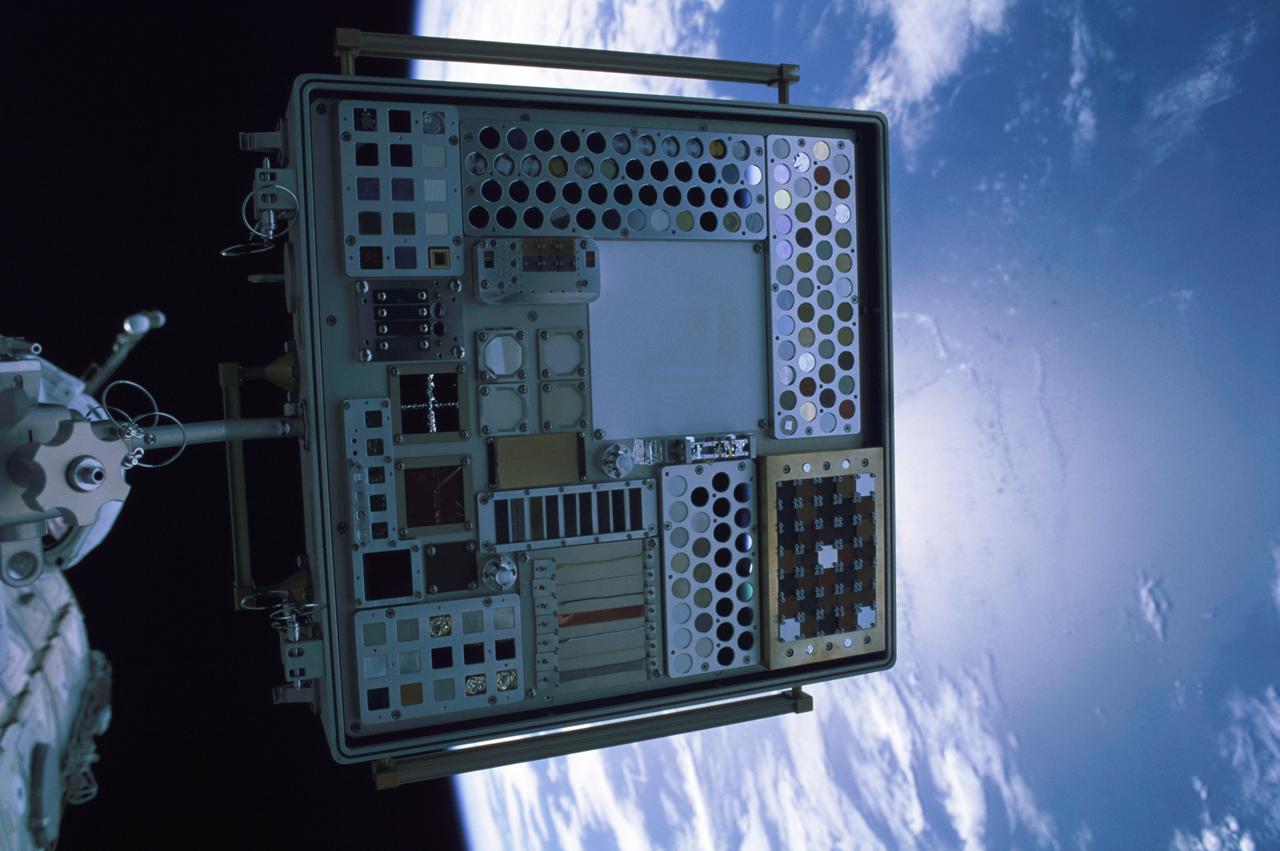

ISS006-348-019 (January 2003) ---- Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE), a suitcase-sized experiment attached to the outside of the space station to expose hundreds of potential space construction materials to the environment, leading to stronger, more durable spacecraft construction. Photographed by one of the Expedition 6 crew members with a 35mm camera.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Life Sciences Lab, Lanfang Levine, with Dynamac Corp., transfers material into a sample bottle for analysis. She is standing in front of new equipment in the lab that will provide gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. The equipment will enable analysis of volatile compounds, such as from plants. The 100,000 square-foot facility houses labs for NASA’s ongoing research efforts, microbiology/microbial ecology studies and analytical chemistry labs. Also calling the new lab home are facilities for space flight-experiment and flight-hardware development, new plant growth chambers, and an Orbiter Environment Simulator that will be used to conduct ground control experiments in simulated flight conditions for space flight experiments. The SLS Lab, formerly known as the Space Experiment Research and Processing Laboratory or SERPL, provides space for NASA’s Life Sciences Services contractor Dynamac Corporation, Bionetics Corporation, and researchers from the University of Florida. NASA’s Office of Biological and Physical Research will use the facility for processing life sciences experiments that will be conducted on the International Space Station. The SLS Lab is the magnet facility for the International Space Research Park at KSC being developed in partnership with Florida Space Authority.
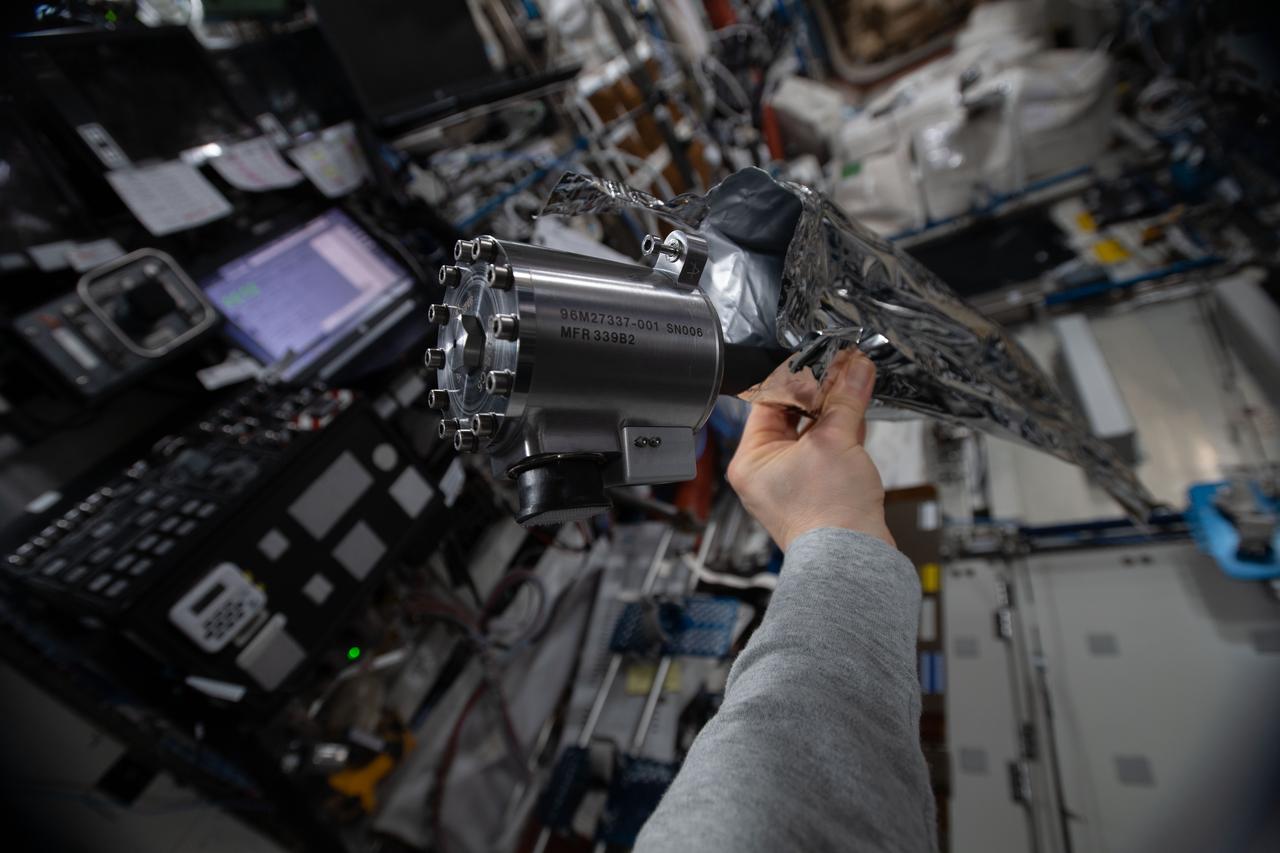

iss061e092274 (12/18/2019) --- A view of the Materials Science Laboratory (MSL) Sample Cartridge Assembly (SCA) in the Destiny module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Materials Science Laboratory (MSL) is used for basic materials research in the microgravity environment of the International Space Station (ISS). The MSL can accommodate and support diverse Experiment Modules. In this way many material types, such as metals, alloys, polymers, semiconductors, ceramics, crystals, and glasses, can be studied to discover new applications for existing materials and new or improved materials.
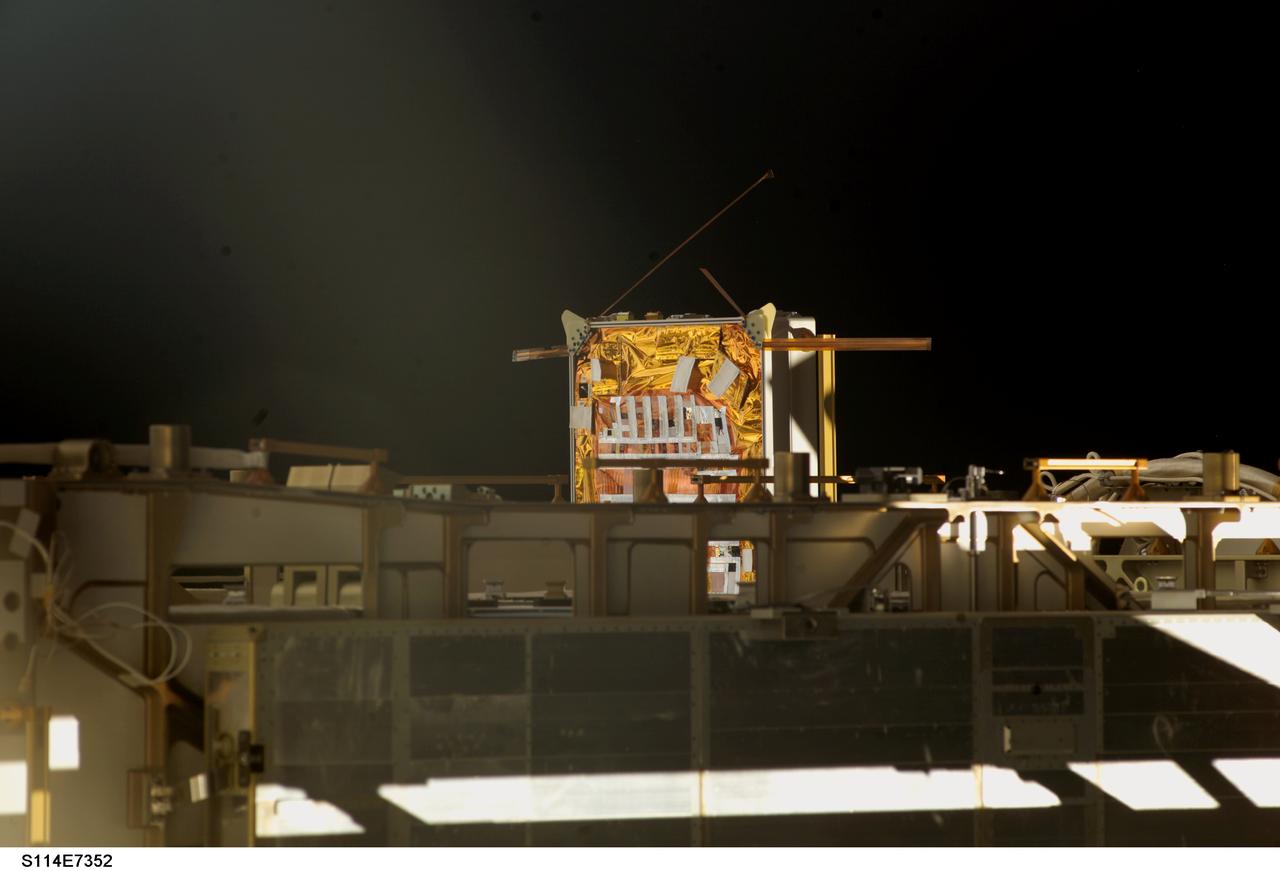

s114e7352 (8/6/2005) --- A view of the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) 5 Passive Experiment Containter (PEC) mounted on the P6 Truss during one of the STS-114 missions Extravehicular Activities (EVAs). The Materials International Space Station Experiment-5 (MISSE-5) was an external payload that flew on-board the ISS from August 2005 until September 2006. MISSE-5 provided an opportunity for researchers to test a wide range of samples in the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) environment.
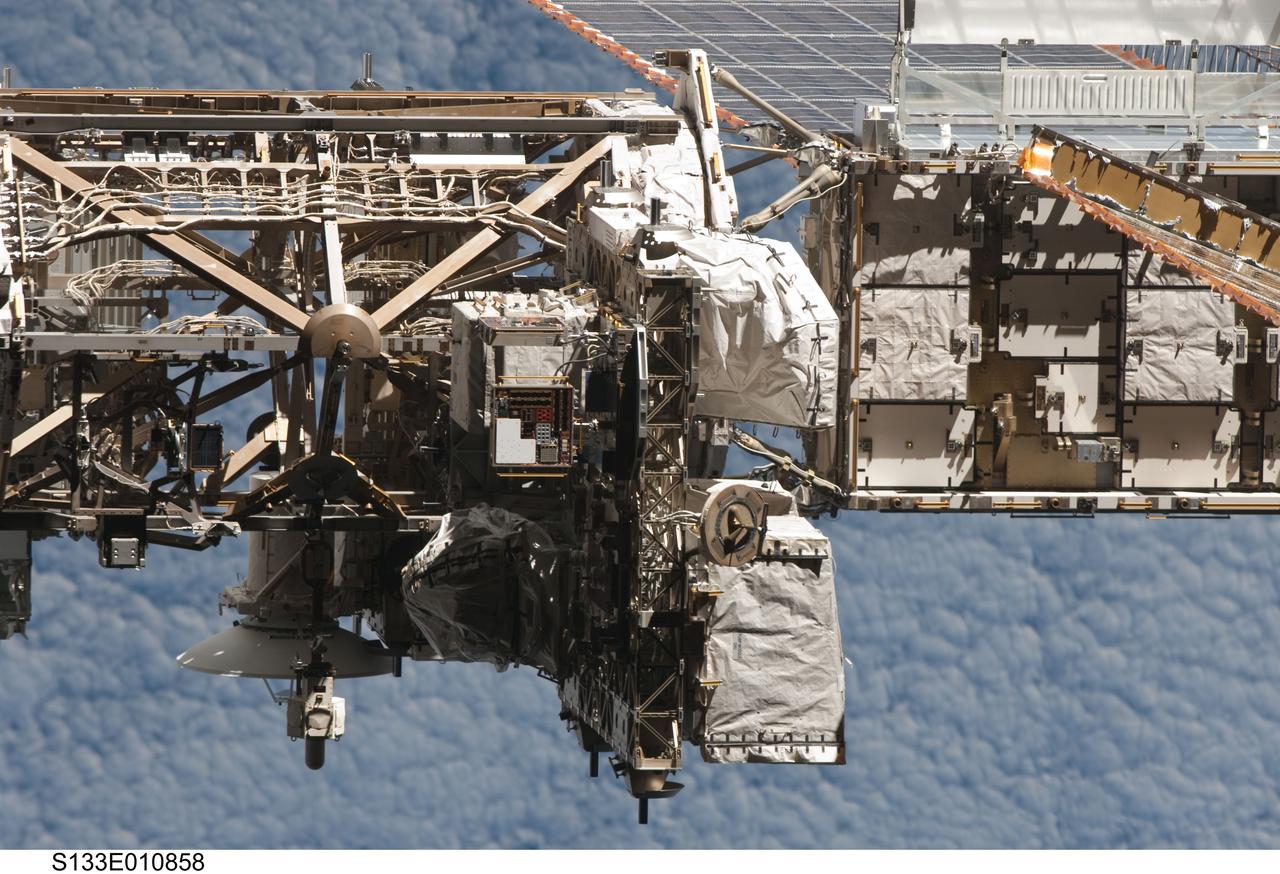

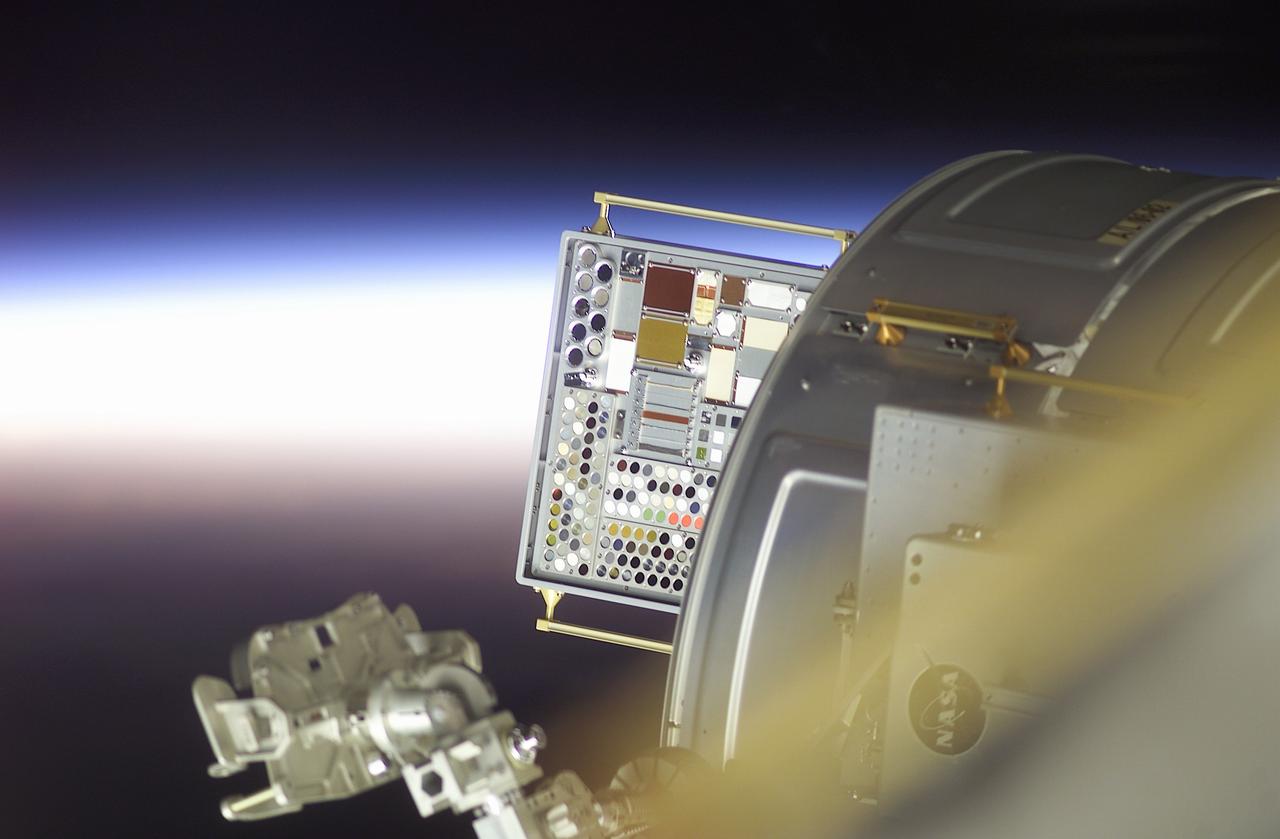
s133e010858 (3/7/2011) --- The Materials International Space Station Experiment-7 (MISSE-7) is a test bed for materials and coatings attached to the outside of the International Space Station being evaluated for the effects of atomic oxygen, ultraviolet, direct sunlight, radiation and extremes of heat and cold.
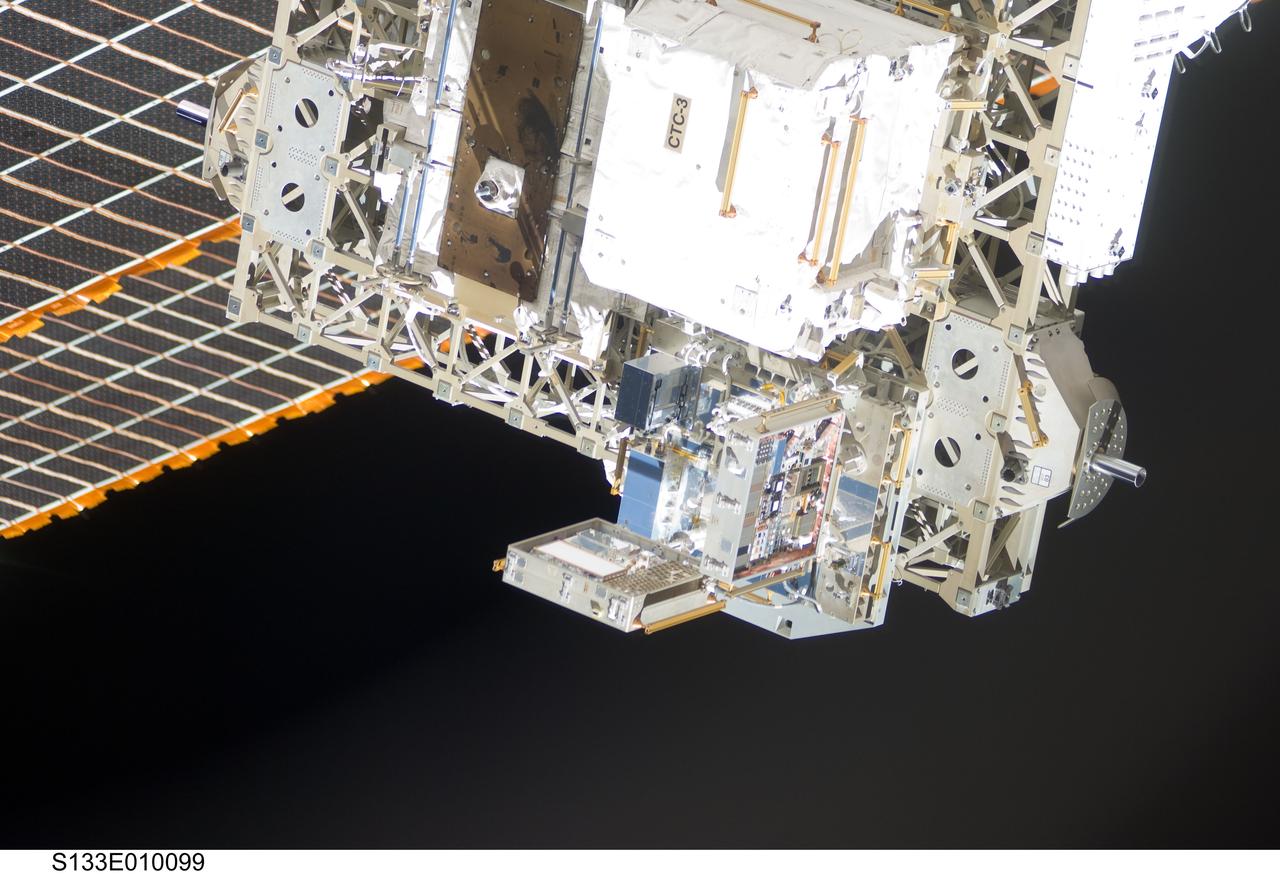
s133e010099 (3/7/2011) --- The Materials International Space Station Experiment-7 (MISSE-7) is a test bed for materials and coatings attached to the outside of the International Space Station being evaluated for the effects of atomic oxygen, ultraviolet, direct sunlight, radiation and extremes of heat and cold.
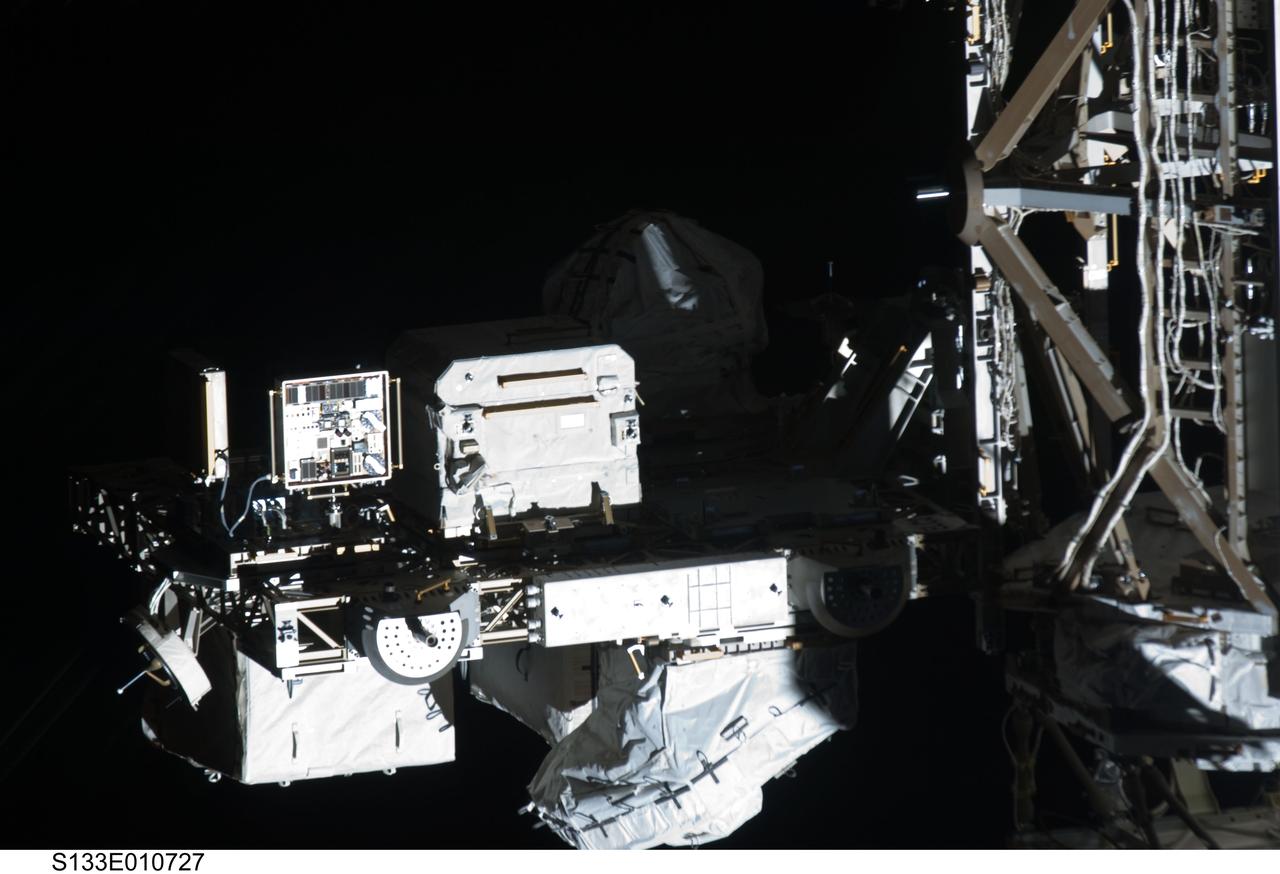
s133e010727 (3/7/2011) --- The Materials International Space Station Experiment-7 (MISSE-7) is a test bed for materials and coatings attached to the outside of the International Space Station being evaluated for the effects of atomic oxygen, ultraviolet, direct sunlight, radiation and extremes of heat and cold.
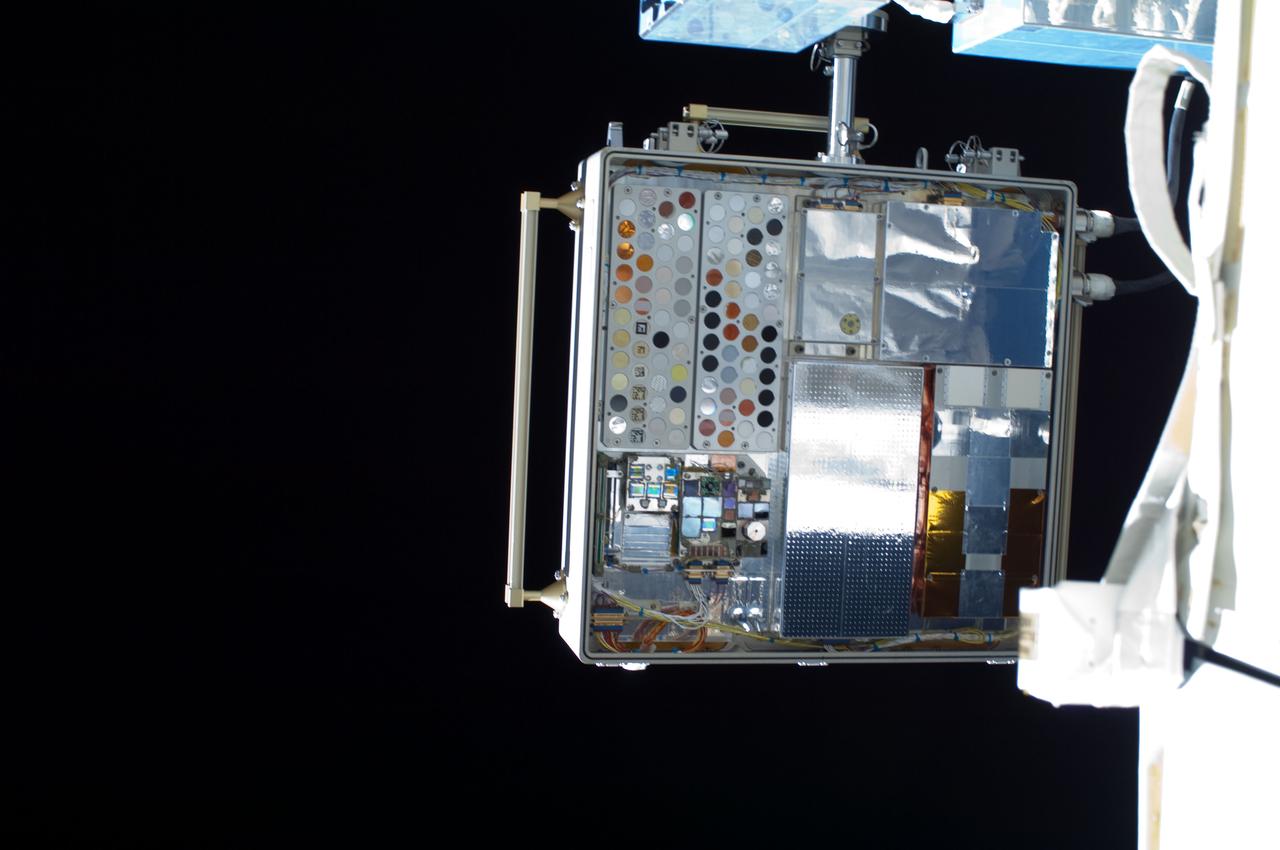
ISS028-E-016107 (12 July 2011) --- This medium close-up image, recorded during a July 12 spacewalk, shows the Materials on International Space Station Experiment - 8 (MISSE-8). The experiment package is a test bed for materials and computing elements attached to the outside of the orbiting complex. These materials and computing elements are being evaluated for the effects of atomic oxygen, ultraviolet, direct sunlight, radiation, and extremes of heat and cold. This experiment allows the development and testing of new materials and computing elements that can better withstand the rigors of space environments. Results will provide a better understanding of the durability of various materials and computing elements when they are exposed to the space environment, with applications in the design of future spacecraft.
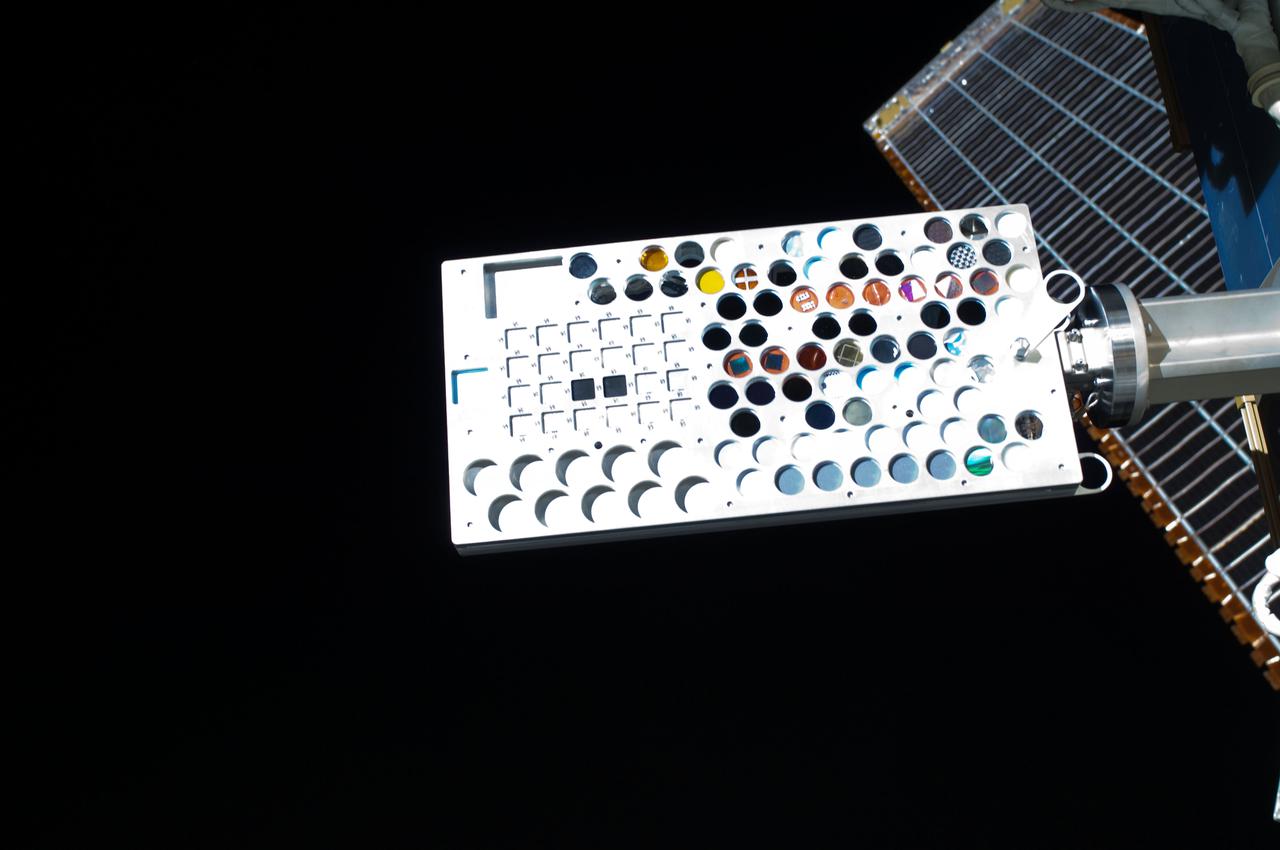
ISS028-E-016111 (12 July 2011) --- This close-up image, recorded during a July 12 spacewalk, shows the Materials on International Space Station Experiment - 8 (MISSE-8). The experiment package is a test bed for materials and computing elements attached to the outside of the orbiting complex. These materials and computing elements are being evaluated for the effects of atomic oxygen, ultraviolet, direct sunlight, radiation, and extremes of heat and cold. This experiment allows the development and testing of new materials and computing elements that can better withstand the rigors of space environments. Results will provide a better understanding of the durability of various materials and computing elements when they are exposed to the space environment, with applications in the design of future spacecraft.
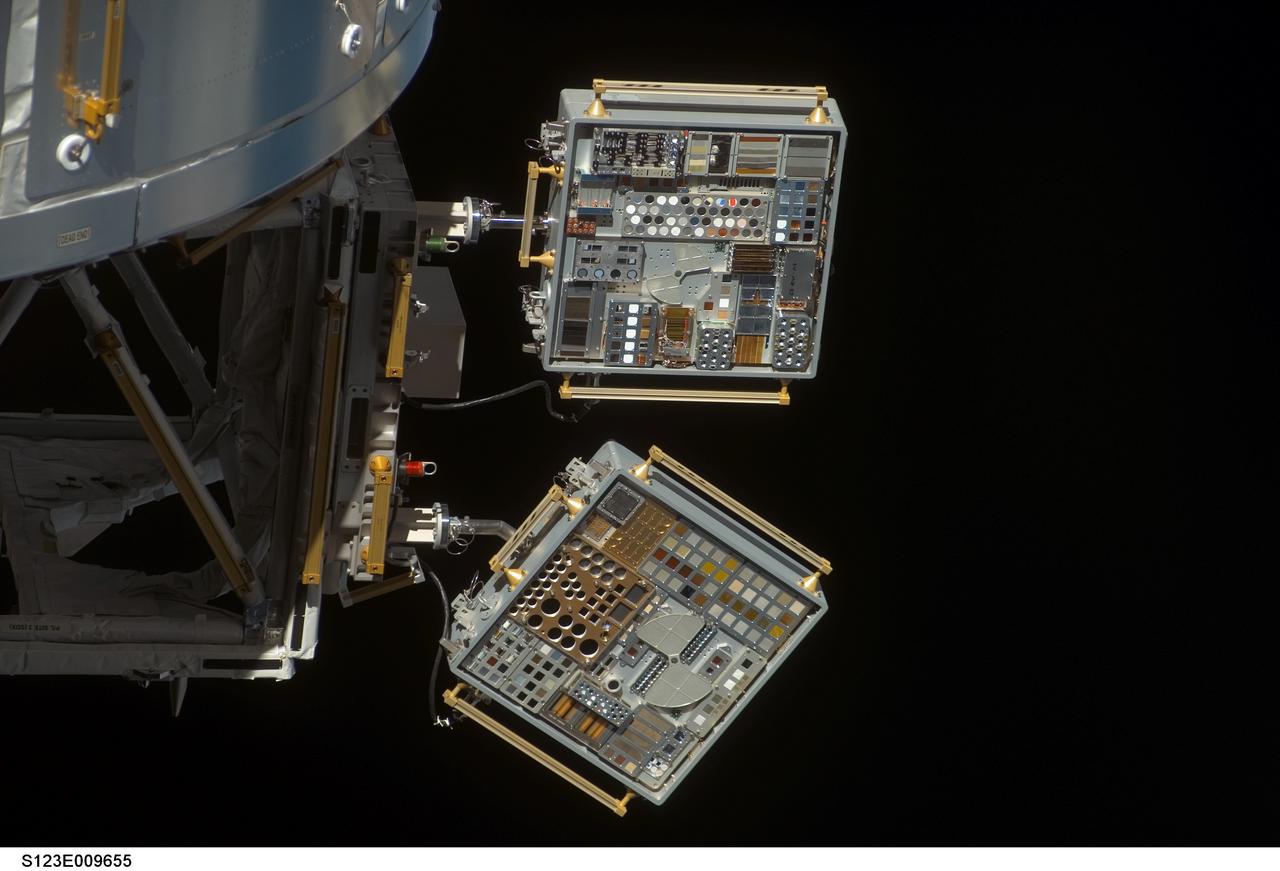
s123e009655 (3/25/2008) --- View of Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) 6 Passive Experiment Container (PEC) on European Laboratory/Columbus. Photo was taken during flyaround of STS-123 Space Shuttle Endeavor.

iss013e63407 (8/3/2006) --- View of a Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) Passive Experiment Container 3 (PEC 3) mounted on the Airlock Crewlock endcone of the International Space Station (ISS). Photo taken during Expedition 13. Materials on the International Space Station Experiment 3 and 4 (MISSE - 3 and 4) are the third and fourth in a series of five suitcase-sized test beds attached to the outside of the space station. The beds were deployed during a spacewalk by the station crew in August 2006. They are exposing hundreds of potential space construction materials and different types of solar cells to the harsh environment of space. Mounted to the space station for about a year, the equipment then will be returned to Earth for study. Investigators will use the resulting data to design stronger, more durable spacecraft.
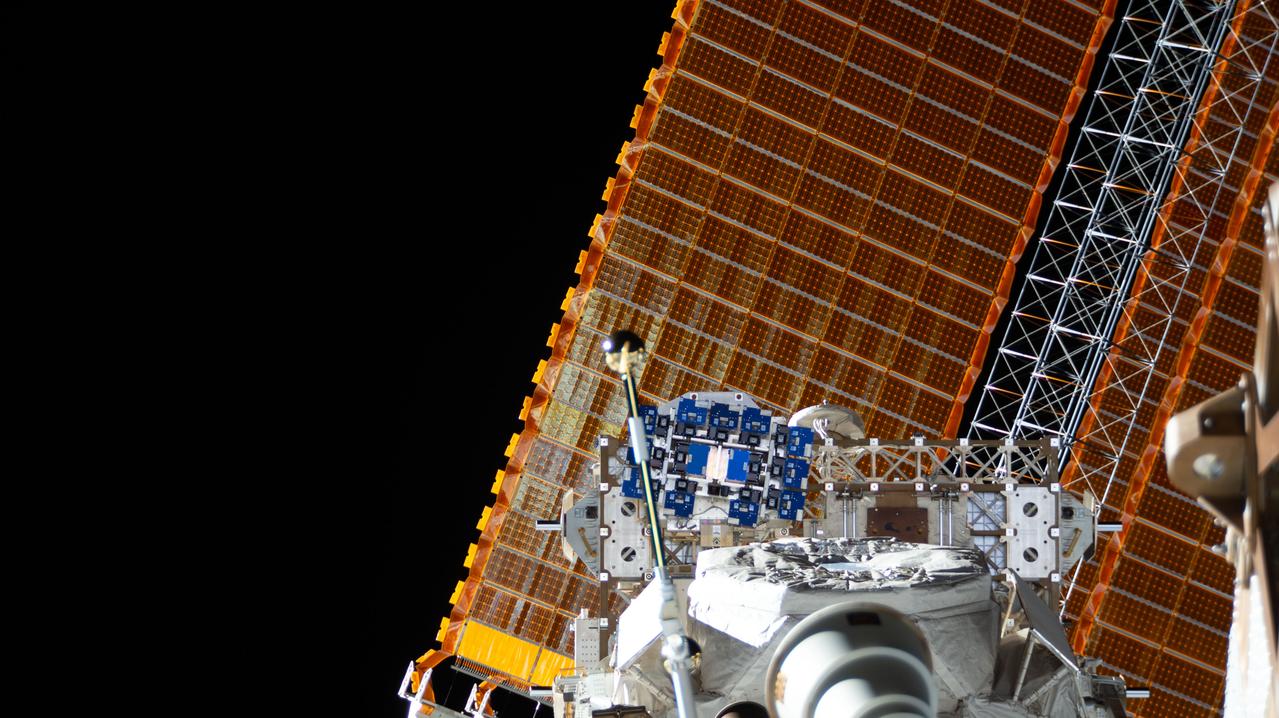

iss059e036747 (4/26/2019) --- --- Photo documentation of the Materials ISS Experiment Flight Facility (MISSE-FF) platform aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
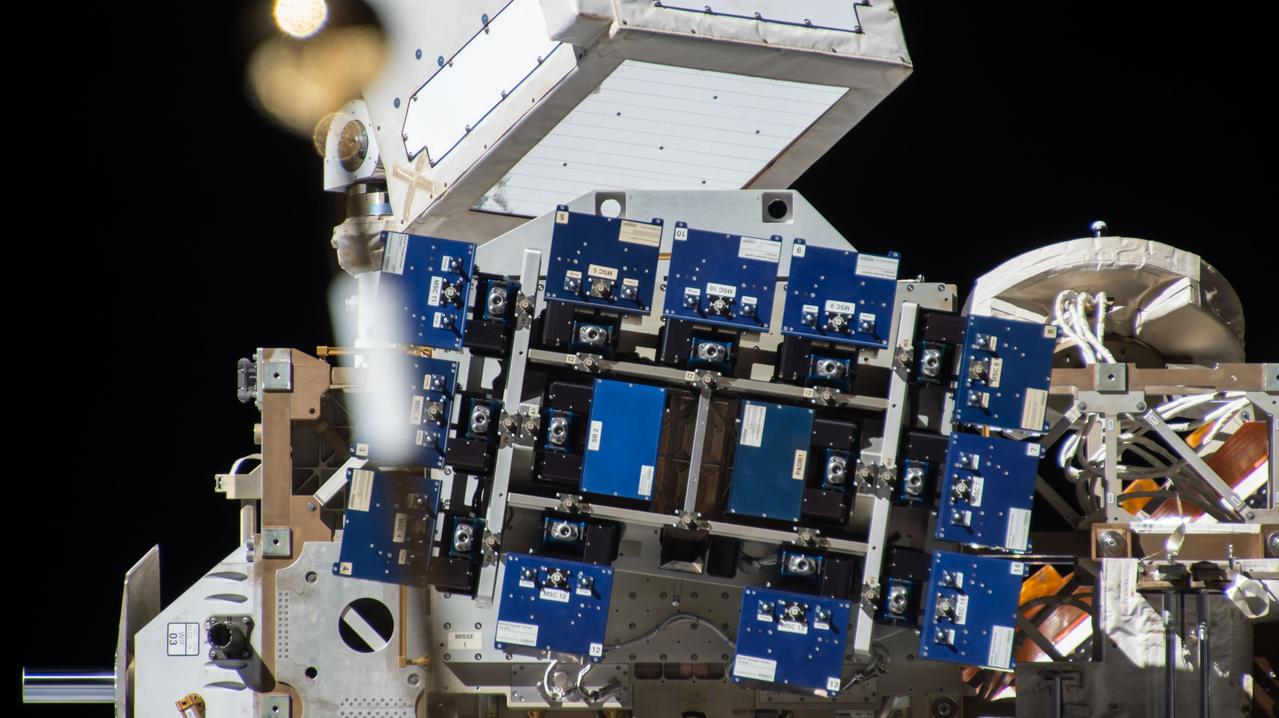
iss058e003972 (1/26/2019) --- Photo documentation of the Materials ISS Experiment Flight Facility (MISSE-FF) platform aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
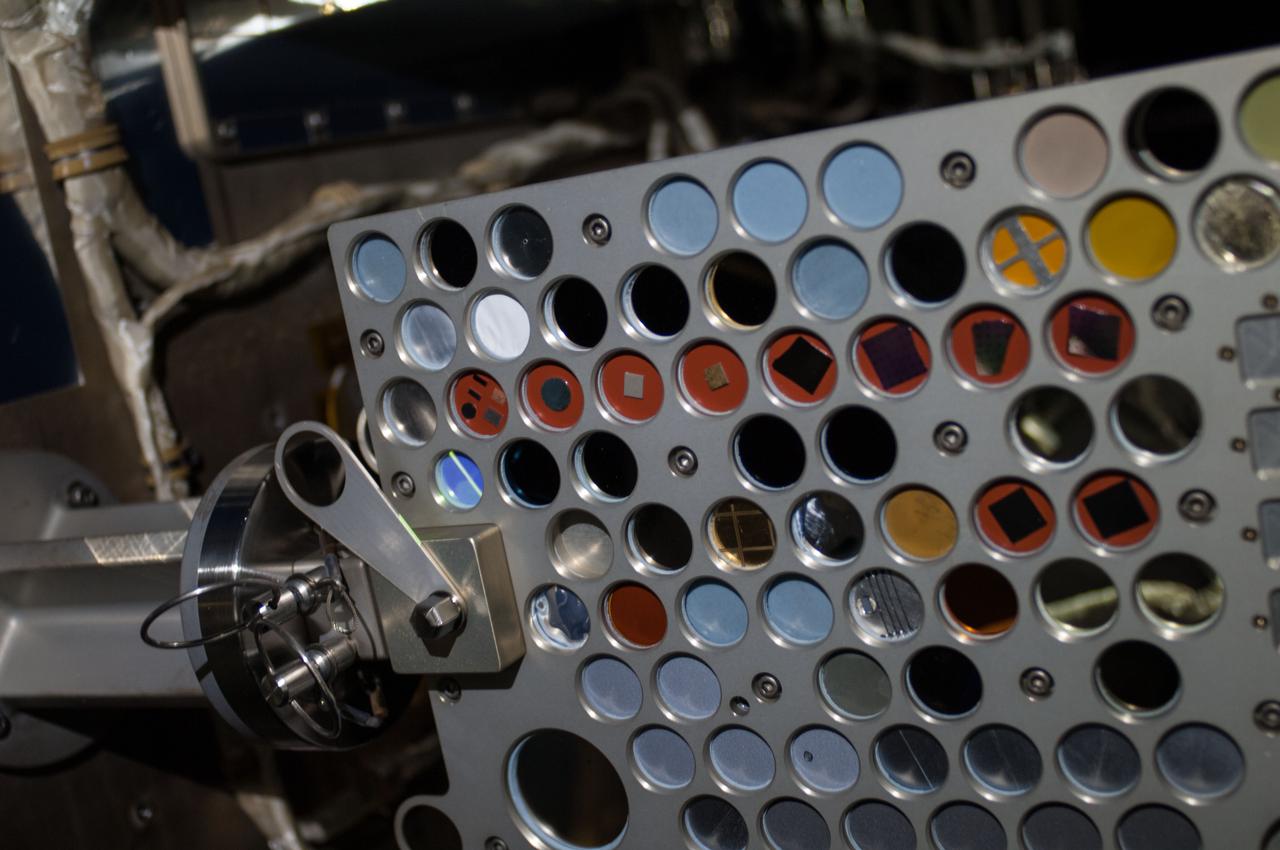
iss036e016736 (7/9/2013) --- Close-up view of the Optical Reflector Materials Experiment III Ram/Wake (ORMatE-III R/W) which is part of the Materials on International Space Station Experiment - 8 (MISSE-8) installed on the starboard truss. View was taken during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) 22 as work continues on the International Space Station.
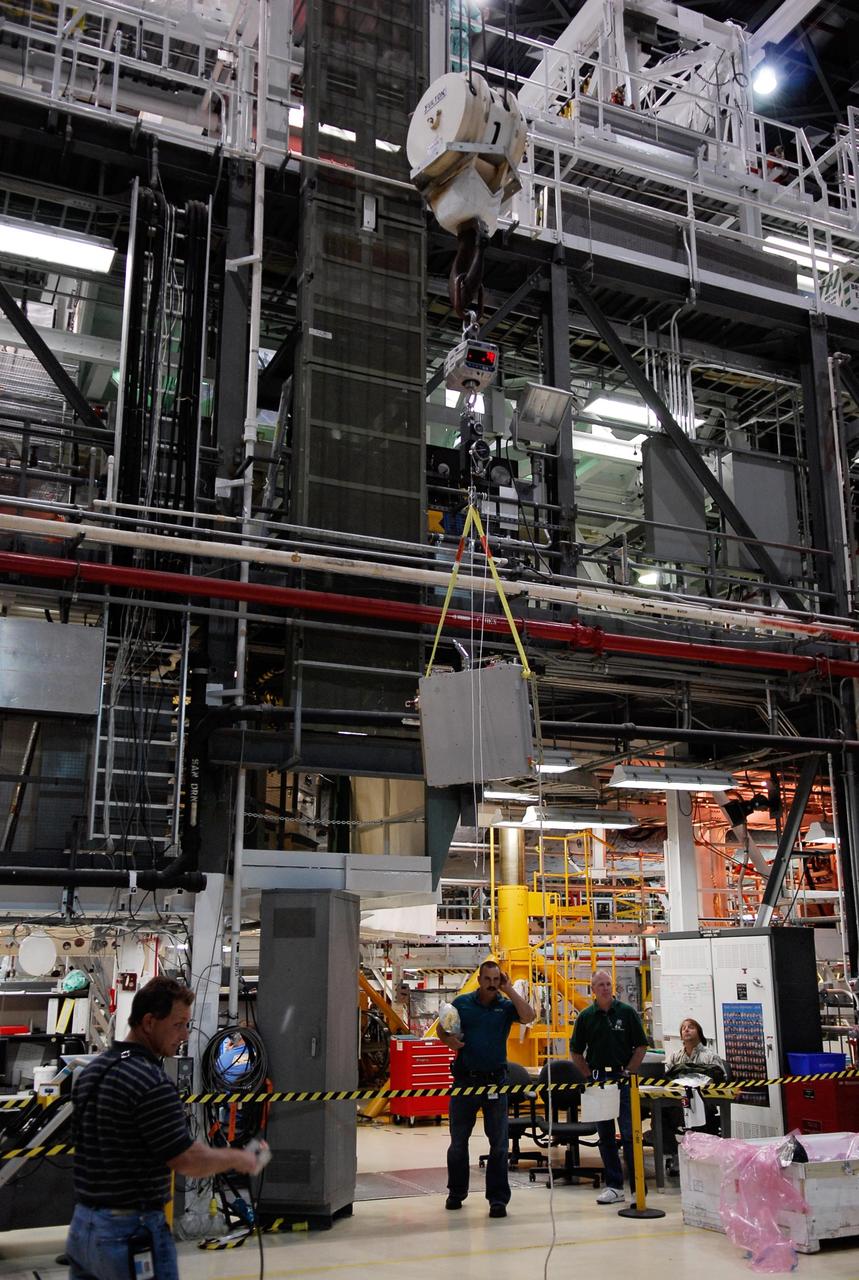

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, one of two Materials International Space Station Experiments, or MISSE, is moved across facility toward space shuttle Endeavour. The MISSE is part of the payload onboard Endeavour for mission STS-123 and will be installed in the payload bay. The MISSE project is a NASA/Langley Research Center-managed cooperative endeavor to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the International Space Station. The objective is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components planned for use on future spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
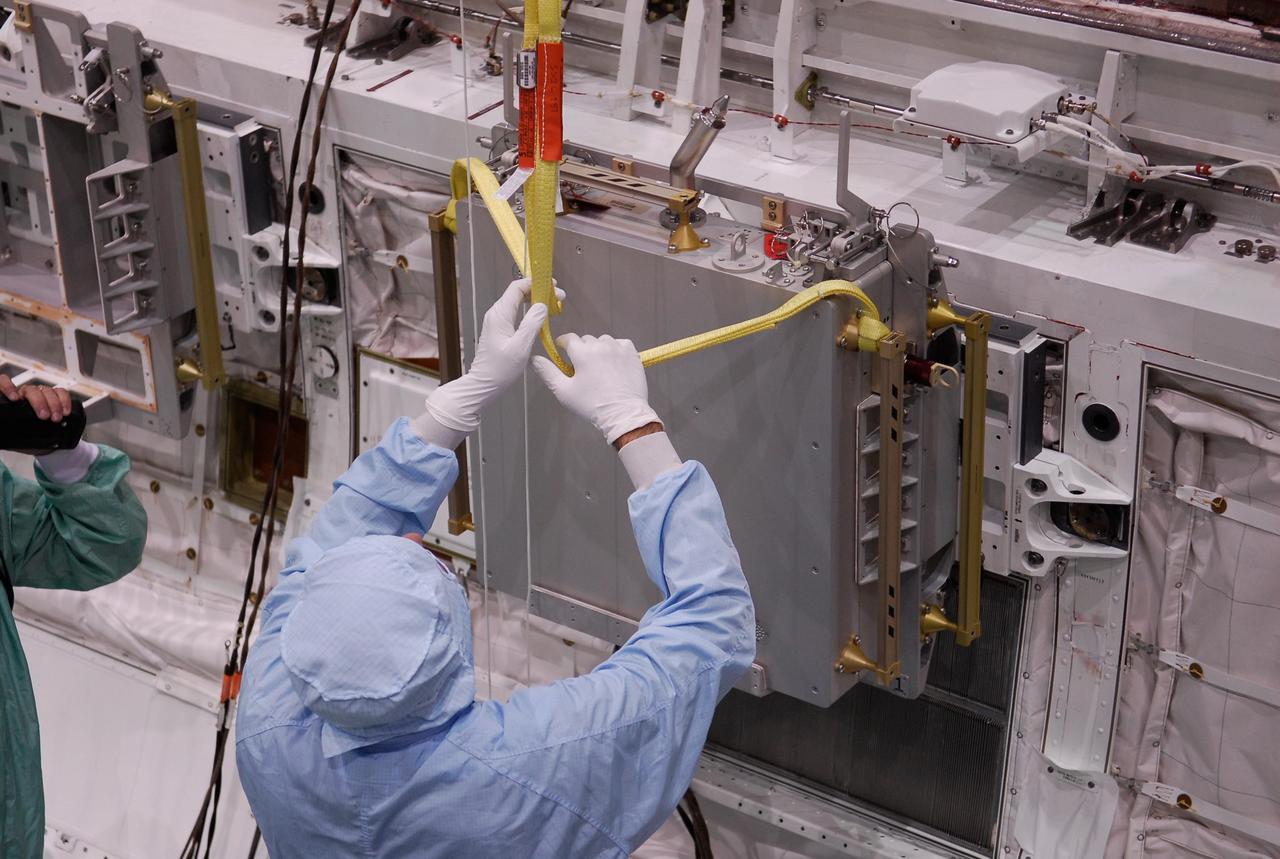

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, one of two Materials International Space Station Experiments, or MISSE, is lowered into space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay for installation. The MISSE is part of the payload onboard Endeavour for mission STS-123. The MISSE project is a NASA/Langley Research Center-managed cooperative endeavor to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the International Space Station. The objective is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components planned for use on future spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
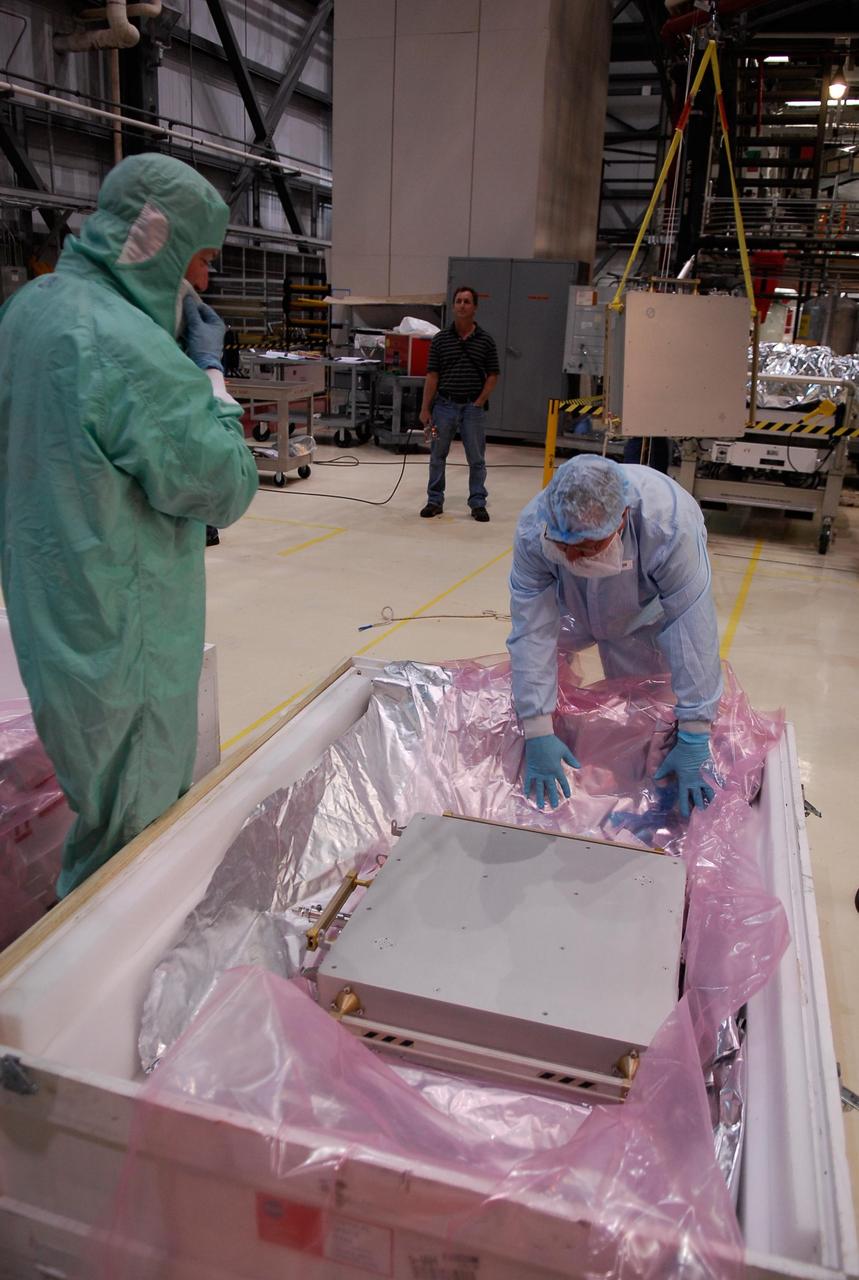

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, technicians get ready to remove another Materials International Space Station Experiments, or MISSE, from a shipping container. The MISSE is part of the payload onboard space shuttle Endeavour for mission STS-123. It will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. The MISSE project is a NASA/Langley Research Center-managed cooperative endeavor to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the International Space Station. The objective is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components planned for use on future spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, technicians help lift the first of the Materials International Space Station Experiments, or MISSE, from a shipping container. The MISSE is part of the payload onboard space shuttle Endeavour for mission STS-123. It will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. The MISSE project is a NASA/Langley Research Center-managed cooperative endeavor to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the International Space Station. The objective is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components planned for use on future spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the second of two Materials International Space Station Experiments, or MISSE, is lowered into space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay for installation. The MISSE is part of the payload onboard Endeavour for mission STS-123. The MISSE project is a NASA/Langley Research Center-managed cooperative endeavor to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the International Space Station. The objective is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components planned for use on future spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
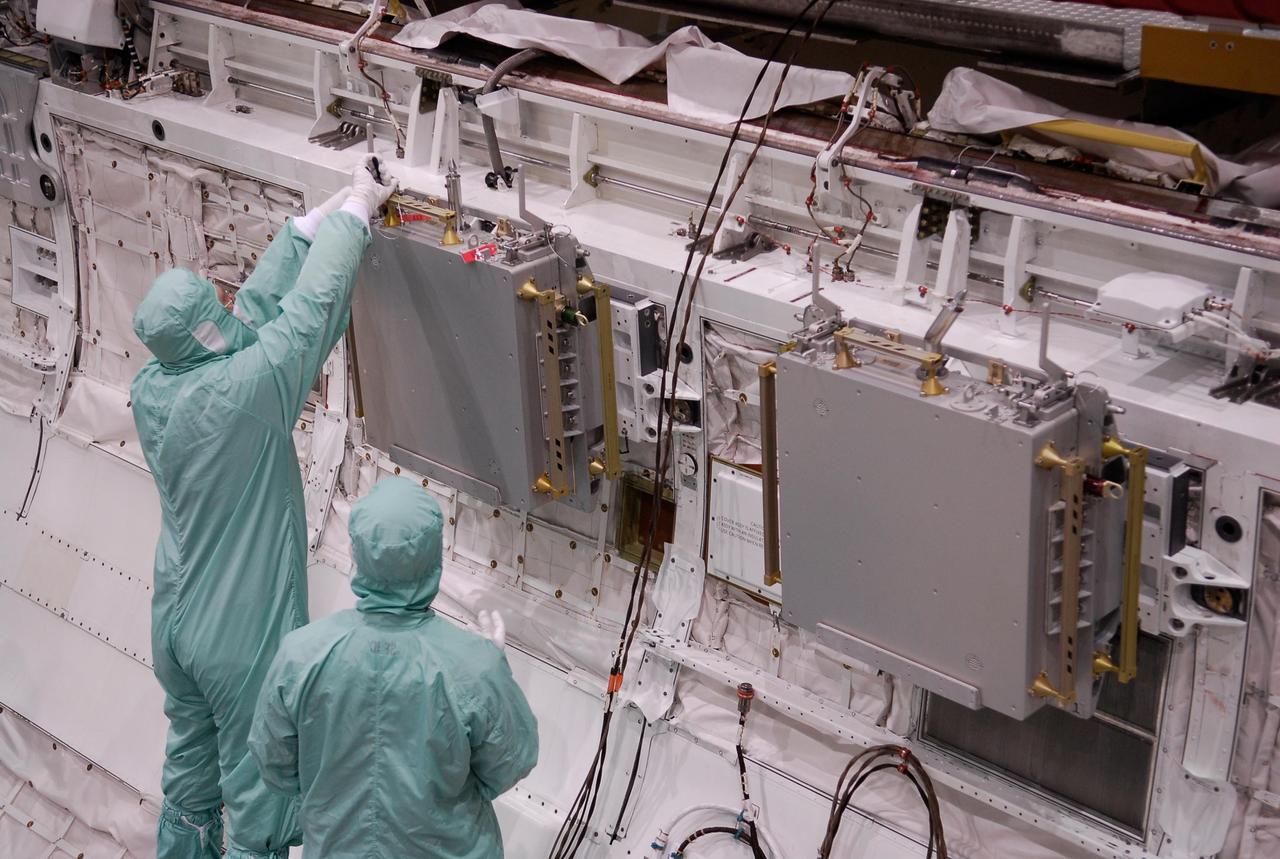

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, technicians install the second Materials International Space Station Experiments, or MISSE, in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The MISSE is part of the payload onboard Endeavour for mission STS-123. The MISSE project is a NASA/Langley Research Center-managed cooperative endeavor to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the International Space Station. The objective is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components planned for use on future spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
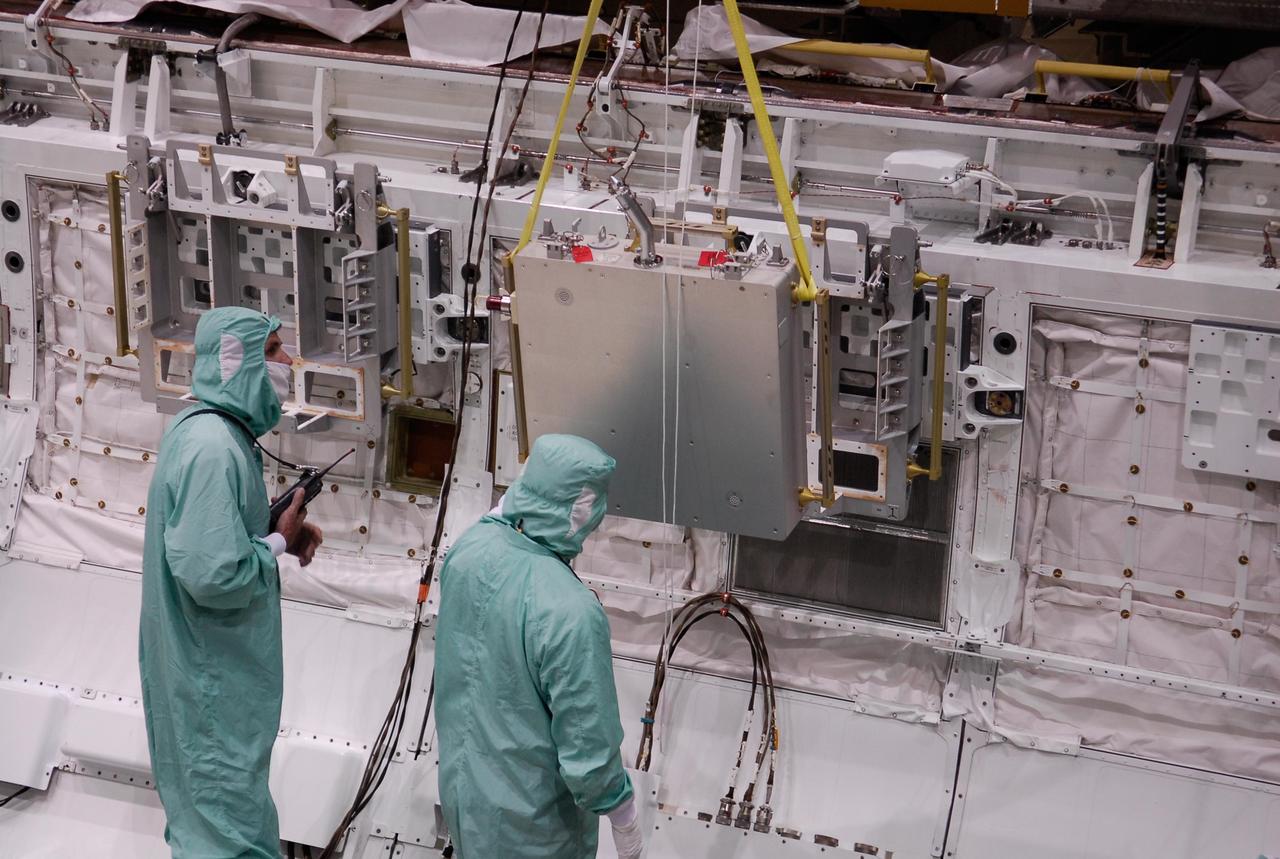

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, one of two Materials International Space Station Experiments, or MISSE, is lowered into space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay for installation. The MISSE is part of the payload onboard Endeavour for mission STS-123. The MISSE project is a NASA/Langley Research Center-managed cooperative endeavor to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the International Space Station. The objective is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components planned for use on future spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
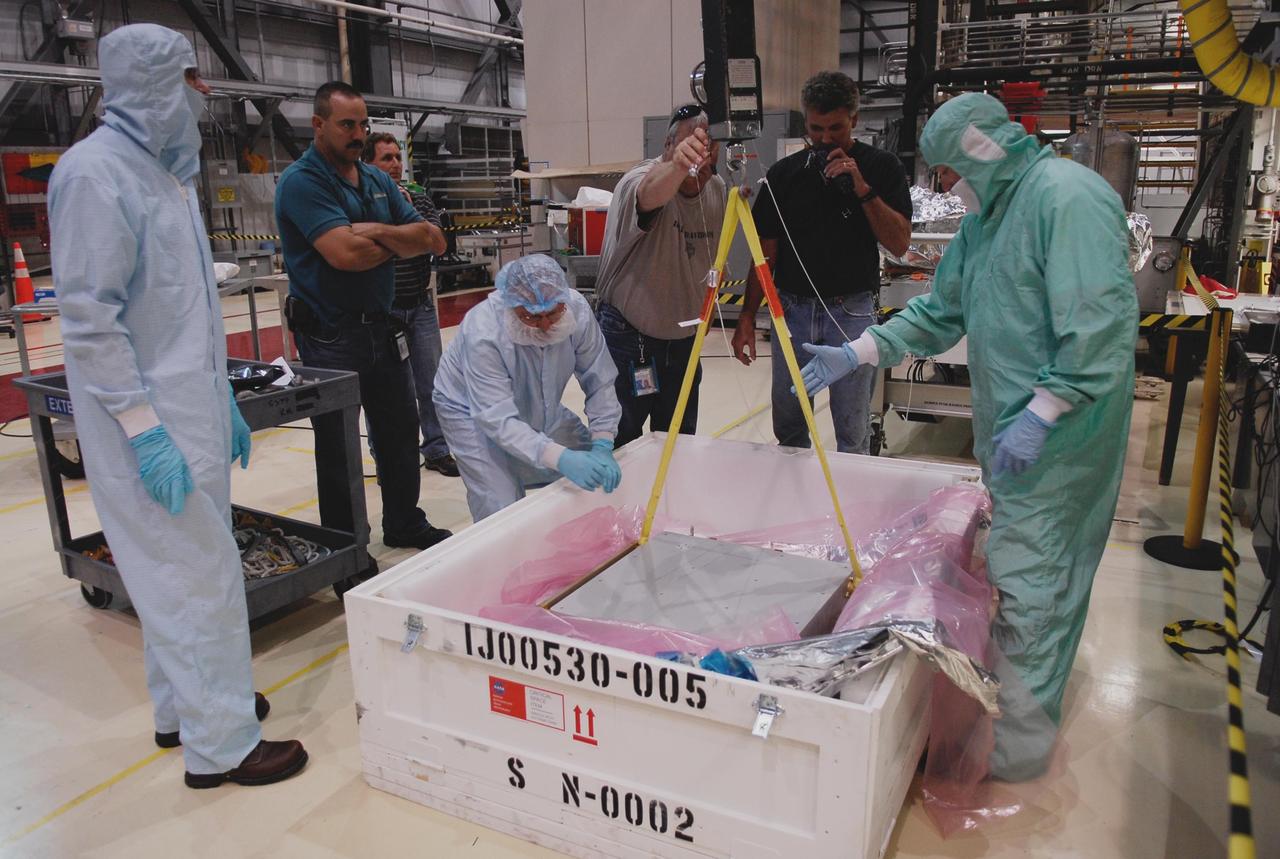

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, technicians get ready to remove one of two Materials International Space Station Experiments, or MISSE, from a shipping container. The MISSE is part of the payload onboard space shuttle Endeavour for mission STS-123. It will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. The MISSE project is a NASA/Langley Research Center-managed cooperative endeavor to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the International Space Station. The objective is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components planned for use on future spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
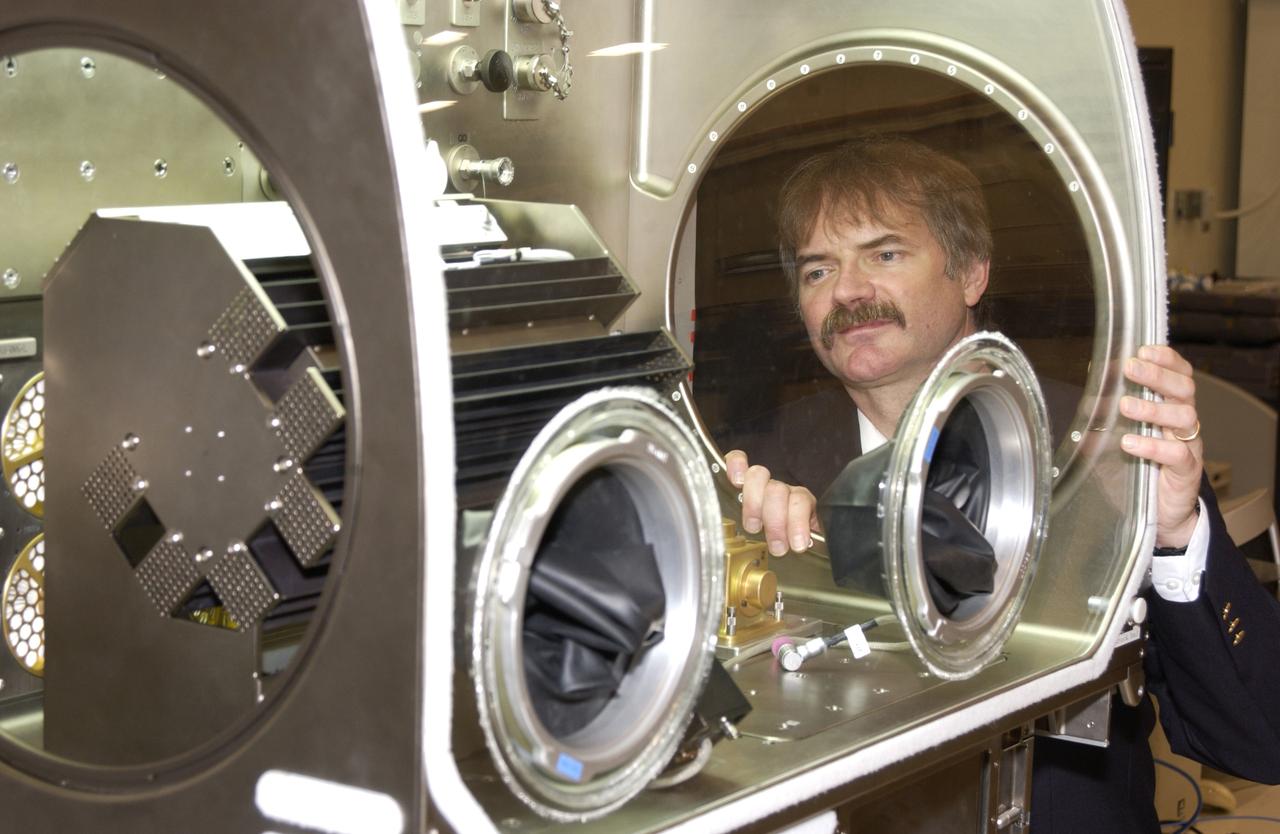

Dr. Richard Grugel, a materials scientist at NASA's Marshall Space Flight in Huntsville, Ala., examines the furnace used to conduct his Pore Formation and Mobility Investigation -- one of the first two materials science experiments to be conducted on the International Space Station. This experiment studies materials processes similar to those used to make components used in jet engines. Grugel's furnace was installed in the Microgravity Science Glovebox through the circular port on the side. In space, crewmembers are able to change out samples using the gloves on the front of the facility's work area.
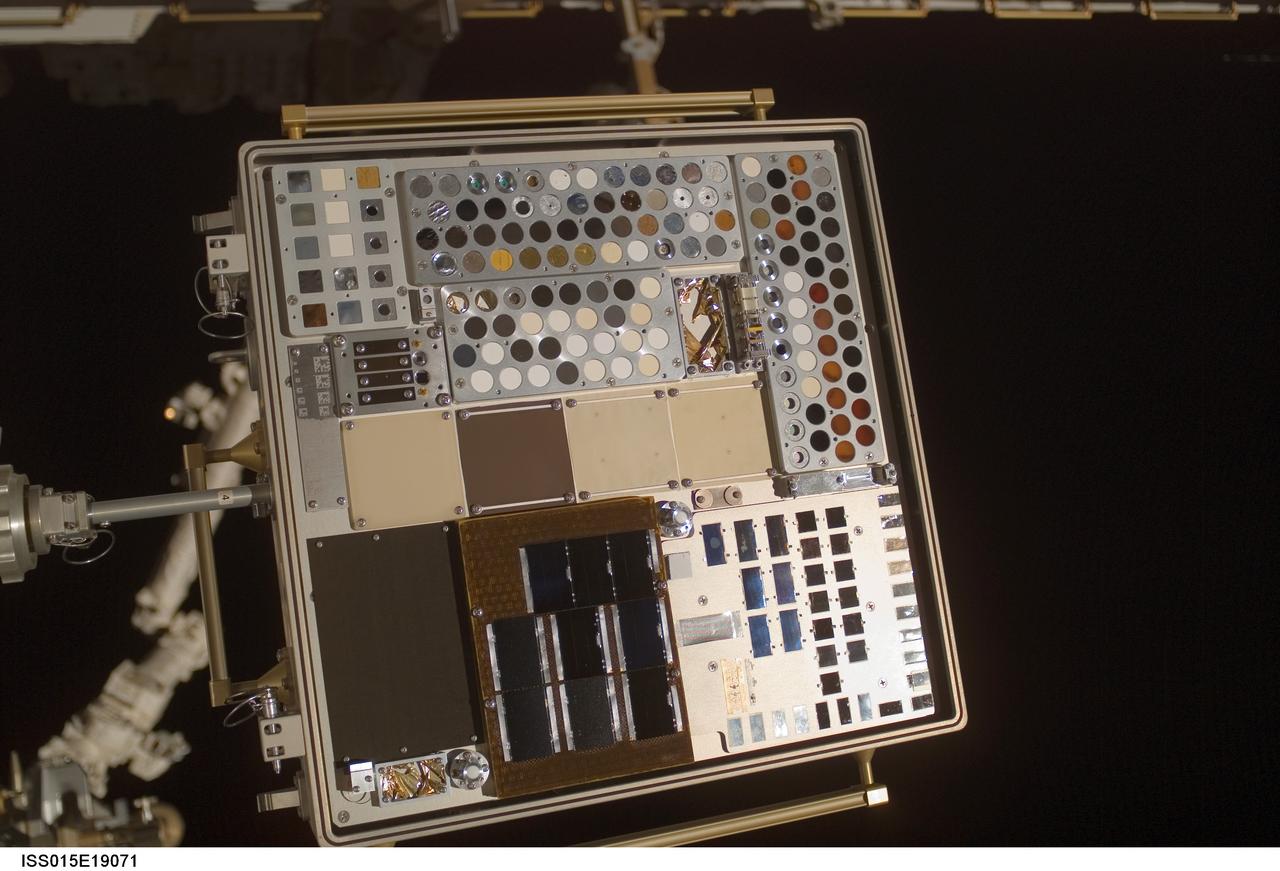

iss015e19071 (7/23/2007) --- View of Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) Passive Experiment Container (PEC) mounted to the exterior of the Quest/Airlock (A/L). Photo taken during a session of Extravehicular Activity (EVA) on Expedition 15. Materials on the International Space Station Experiment 3 and 4 (MISSE - 3 and 4) are the third and fourth in a series of five suitcase-sized test beds attached to the outside of the space station. The beds were deployed during a spacewalk by the station crew in August 2006. They are exposing hundreds of potential space construction materials and different types of solar cells to the harsh environment of space. Mounted to the space station for about a year, the equipment then will be returned to Earth for study. Investigators will use the resulting data to design stronger, more durable spacecraft.
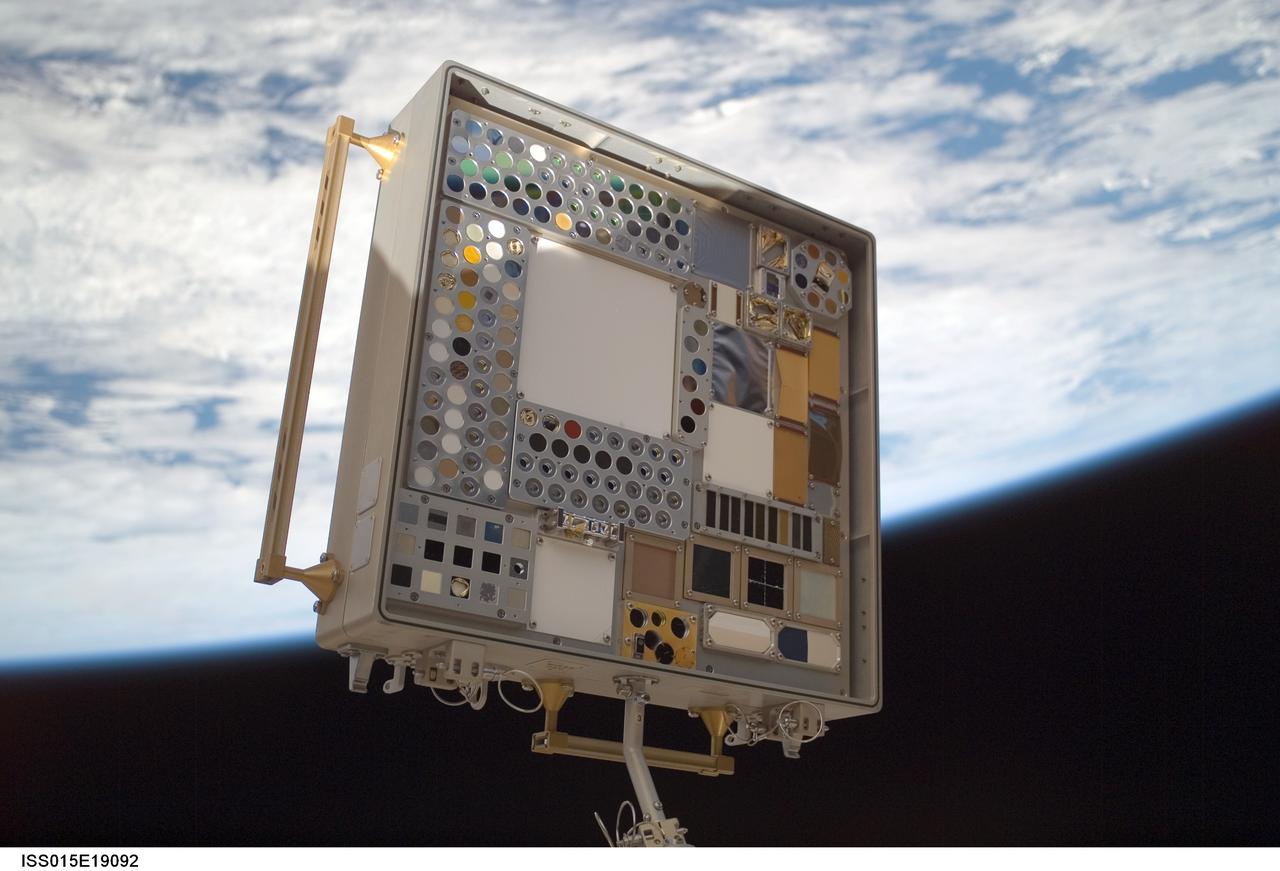

iss015e19092 (7/23/2007) --- View of Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) Passive Experiment Container (PEC) mounted to the exterior of the Quest/Airlock (A/L). Photo taken during a session of Extravehicular Activity (EVA) on Expedition 15. Materials on the International Space Station Experiment 3 and 4 (MISSE - 3 and 4) are the third and fourth in a series of five suitcase-sized test beds attached to the outside of the space station. The beds were deployed during a spacewalk by the station crew in August 2006. They are exposing hundreds of potential space construction materials and different types of solar cells to the harsh environment of space. Mounted to the space station for about a year, the equipment then will be returned to Earth for study. Investigators will use the resulting data to design stronger, more durable spacecraft.
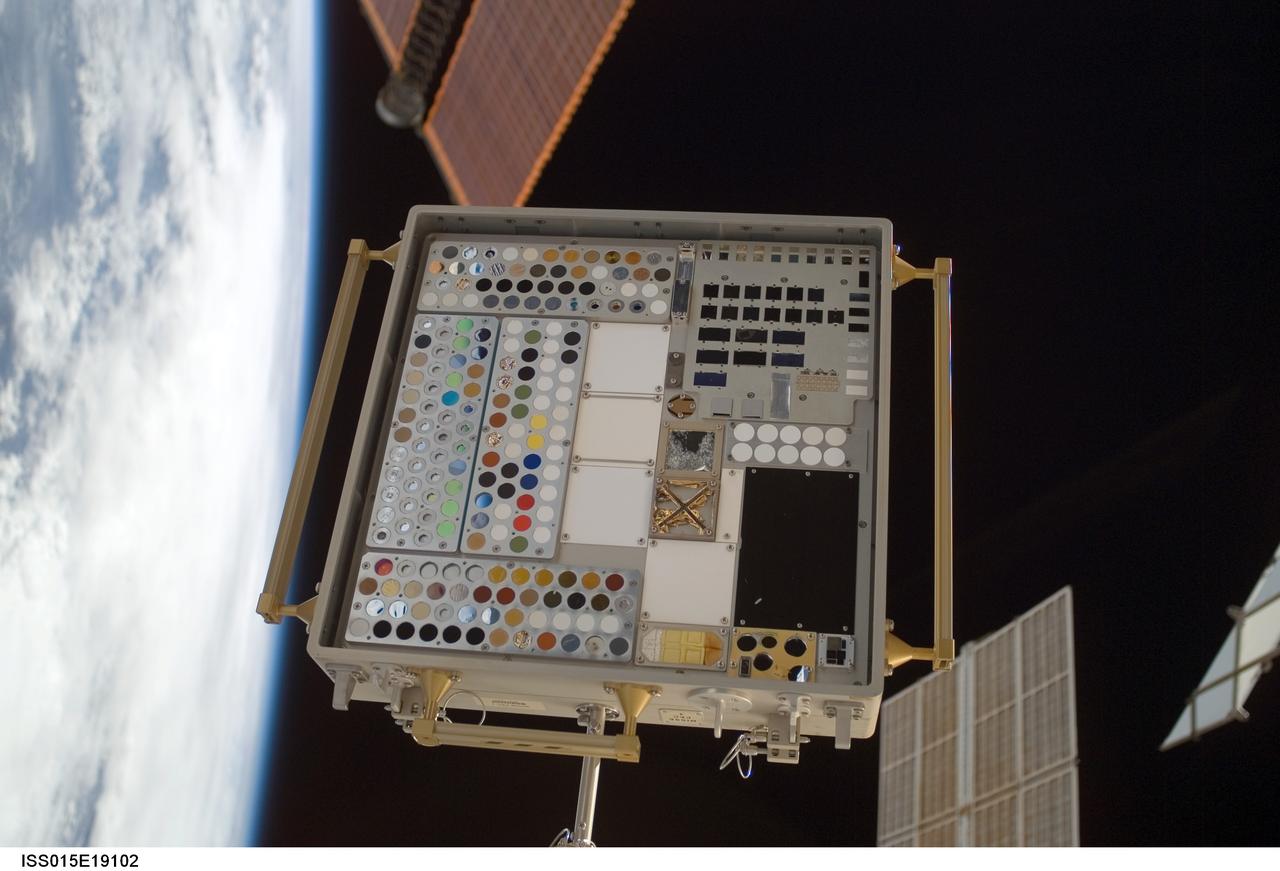

iss015e19102 (7/23/2007) --- View of Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) Passive Experiment Container (PEC) mounted to the exterior of the Quest/Airlock (A/L). Photo taken during a session of Extravehicular Activity (EVA) on Expedition 15. Materials on the International Space Station Experiment 3 and 4 (MISSE - 3 and 4) are the third and fourth in a series of five suitcase-sized test beds attached to the outside of the space station. The beds were deployed during a spacewalk by the station crew in August 2006. They are exposing hundreds of potential space construction materials and different types of solar cells to the harsh environment of space. Mounted to the space station for about a year, the equipment then will be returned to Earth for study. Investigators will use the resulting data to design stronger, more durable spacecraft.
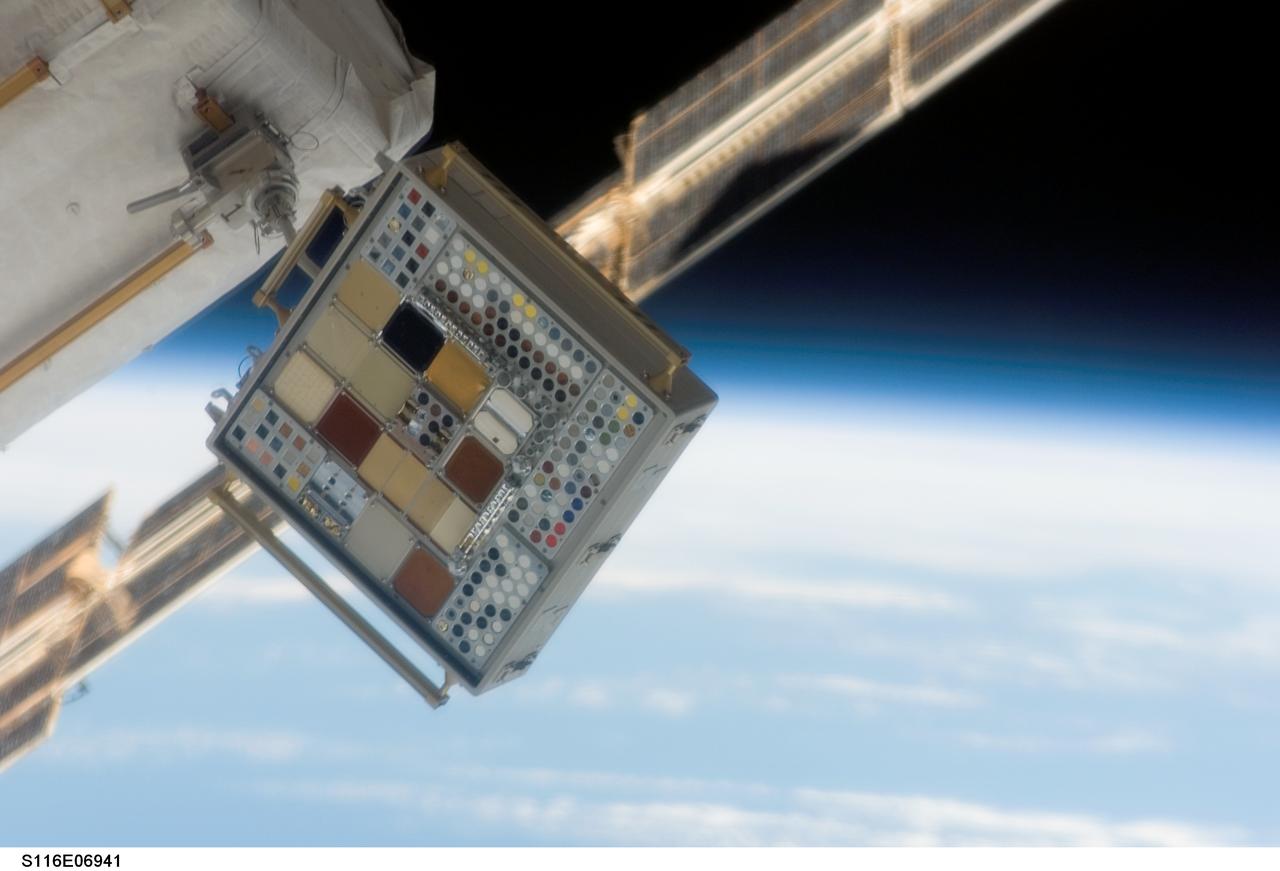

s116e06941 (12/18/2006) --- View of Materials International Space Station Experiment Passive Experiment Container (MISSE PEC) on the Quest/Airlock Crewlock during STS-116 Extravehicular Activity - 4 (EVA-4). Materials on the International Space Station Experiment 3 and 4 (MISSE - 3 and 4) are the third and fourth in a series of five suitcase-sized test beds attached to the outside of the space station. The beds were deployed during a spacewalk by the station crew in August 2006. They are exposing hundreds of potential space construction materials and different types of solar cells to the harsh environment of space. Mounted to the space station for about a year, the equipment then will be returned to Earth for study. Investigators will use the resulting data to design stronger, more durable spacecraft.
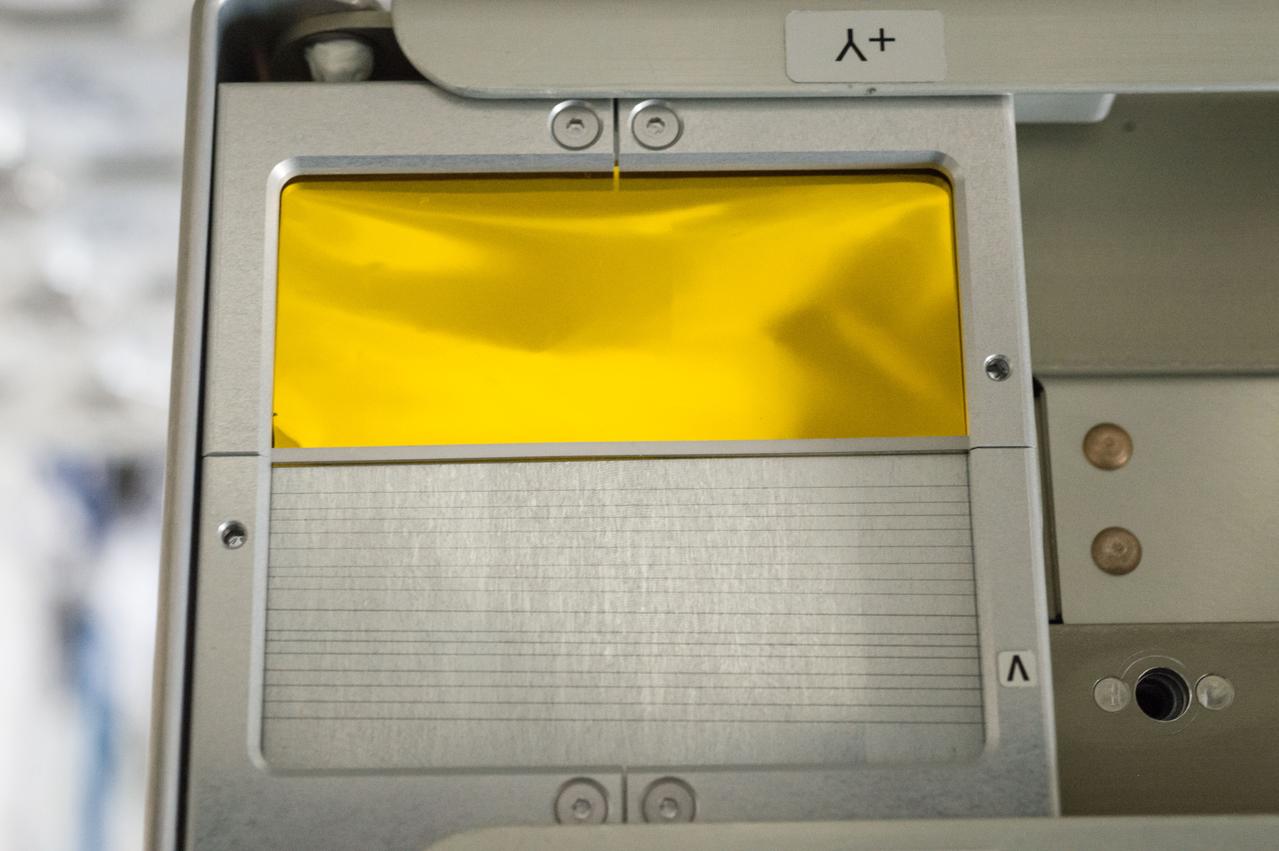

iss045e083552 (10/30/2015) --- Photo documentation of the Carbon Nanotube sample attached to the V position on the Handhold Experiment Platform (HXP) for ExHAM-MDM2 experiment operations aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Space Environment Exposure Experiment of CNT Material for Space Application (Carbon Nanotube) tests an advanced carbon-based material for its ability to withstand the withering radiation of space.
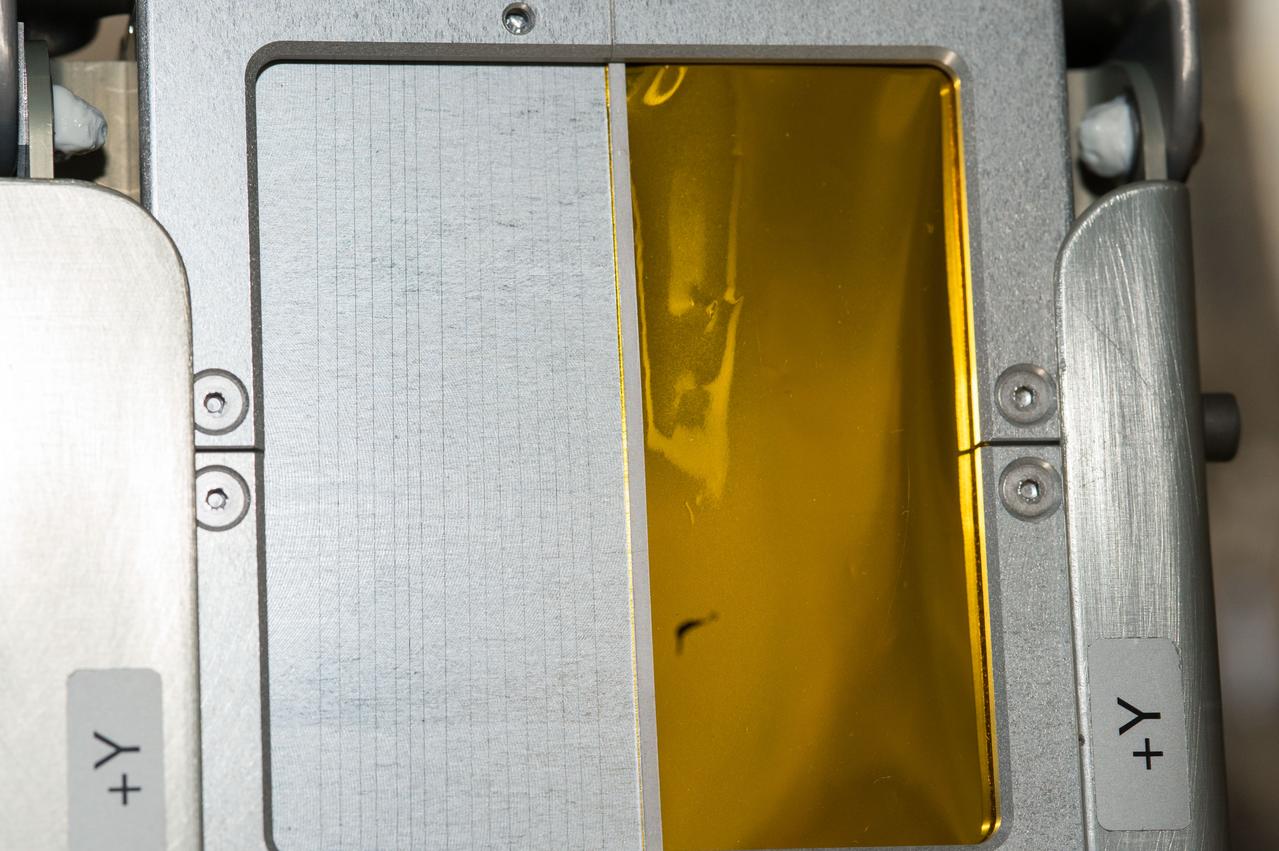
iss045e083367 (10/30/2015) --- Photo documentation of the Carbon Nanotube sample attached to the V position on the Handhold Experiment Platform (HXP) for ExHAM-MDM2 experiment operations aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Space Environment Exposure Experiment of CNT Material for Space Application (Carbon Nanotube) tests an advanced carbon-based material for its ability to withstand the withering radiation of space.

iss003e5863 (9/22/2001) --- A view of the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) on the Quest / Airlock taken during Expedition 3. MISSE-1 and 2 are a test bed for materials and coatings attached to the outside of the ISS is being evaluated for the effects of atomic oxygen, direct sunlight, and extremes of heat and cold. This experiment allows the development and testing of new materials to better withstand the rigors of space environments. Results will provide a better understanding of the durability of various materials when they are exposed to the space environment. Many of the materials may have applications in the design of future spacecraft.
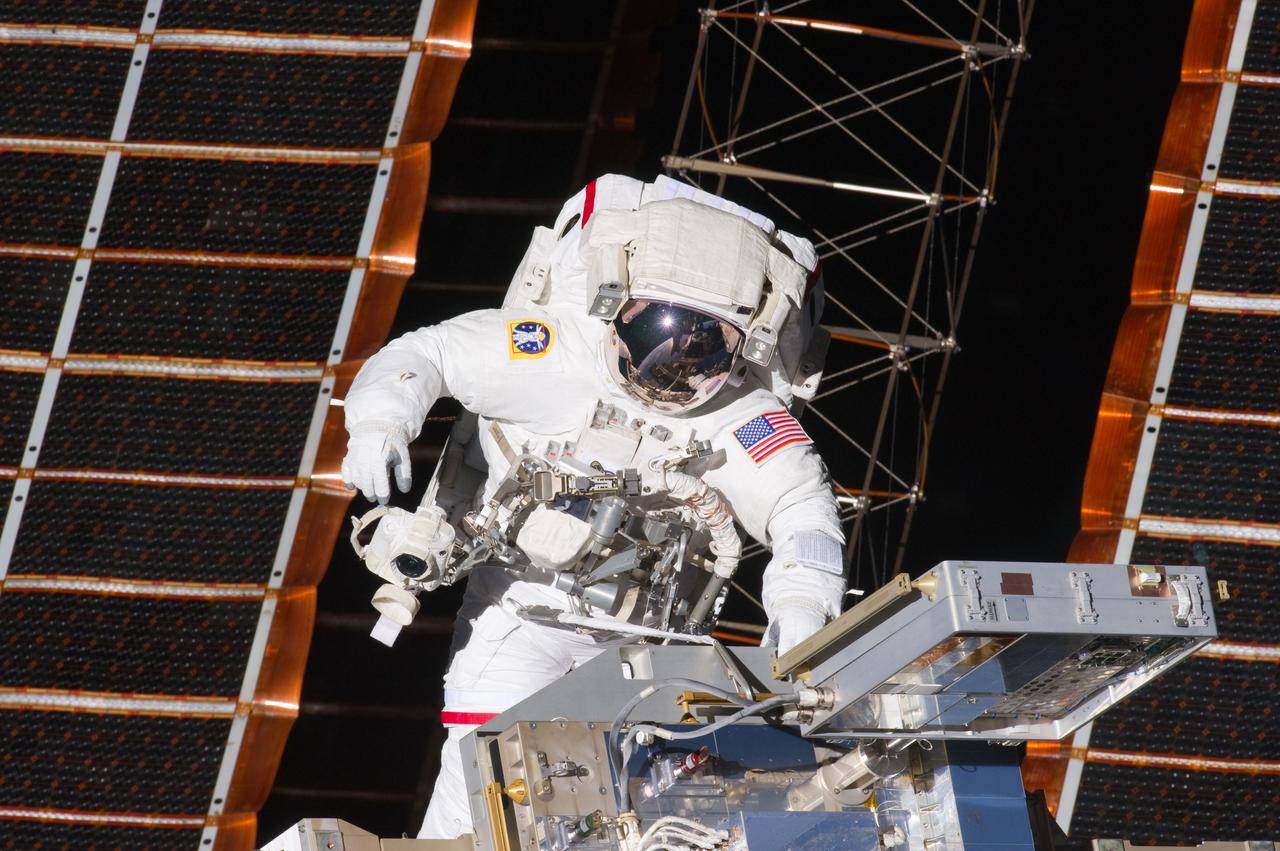

s134e007603 (5/20/2011) --- View of STS-134 Mission Specialist (MS-3) Andrew Feustel working to install a new Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) on the EXPRESS (Expedite the Processing of Experiments to Space Station) Logistics Carrier 2 (ELC2) during the first session of Extravehicular Activity (EVA-1).

jsc2021e009430 (3/2/2021) --- Materials International Space Station Experiment-14-NASA (MISSE-14-NASA) continues a series of tests by NASA Glenn Research Center on how the harsh environment of space affects the performance and durability of various materials. MISSE-Seed sample containers ready for turnover. Image courtesy of Jeff Richards.

jsc2021e009429 (3/2/2021) --- Materials International Space Station Experiment-14-NASA (MISSE-14-NASA) continues a series of tests by NASA Glenn Research Center on how the harsh environment of space affects the performance and durability of various materials. Seed packets in the Equipment (EUE) container. Image courtesy of Jeff Richards.
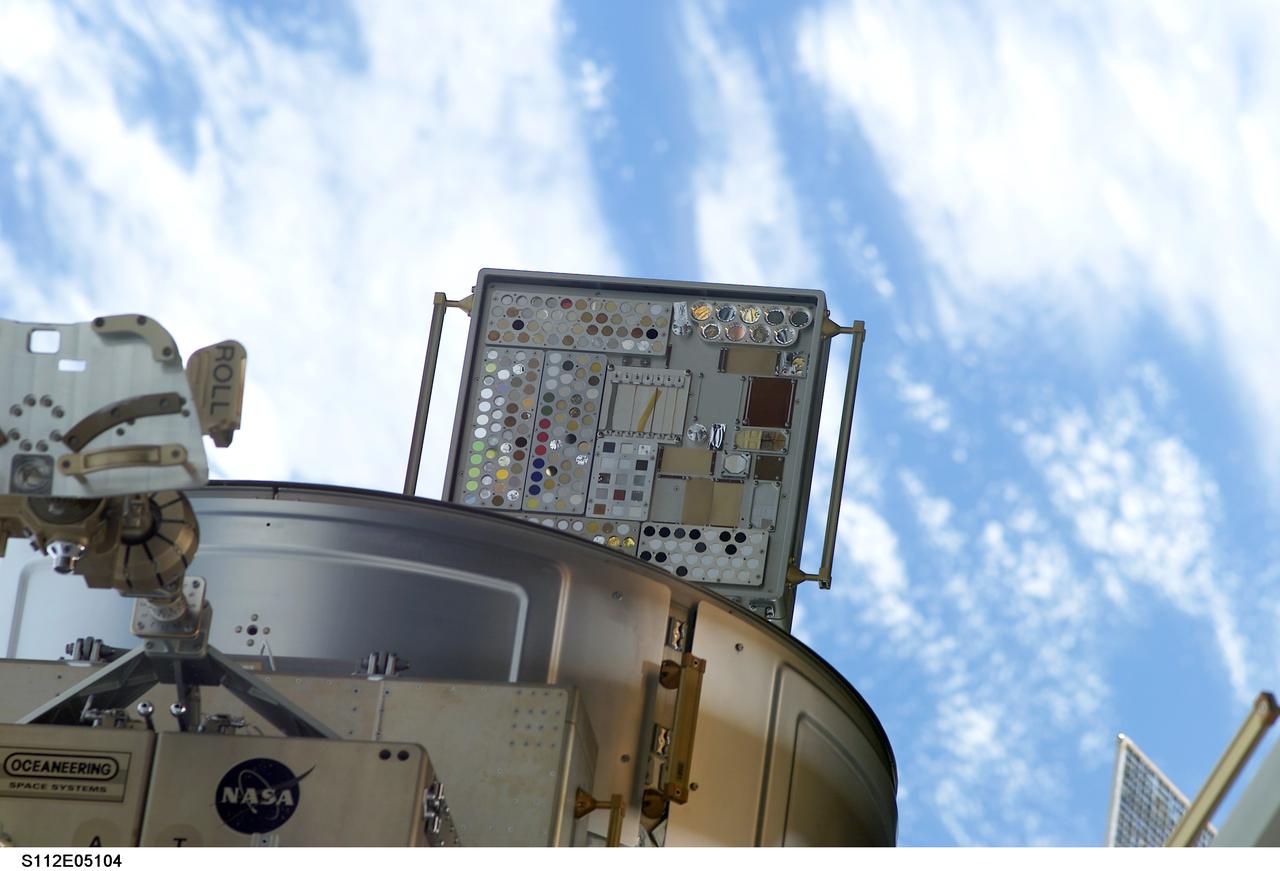

STS112-E-05104 (10 October 2002) --- Backdropped by a blue and white Earth, the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) and a portion of the Quest Airlock are visible. MISSE collects information on how different materials weather in the environment of space.
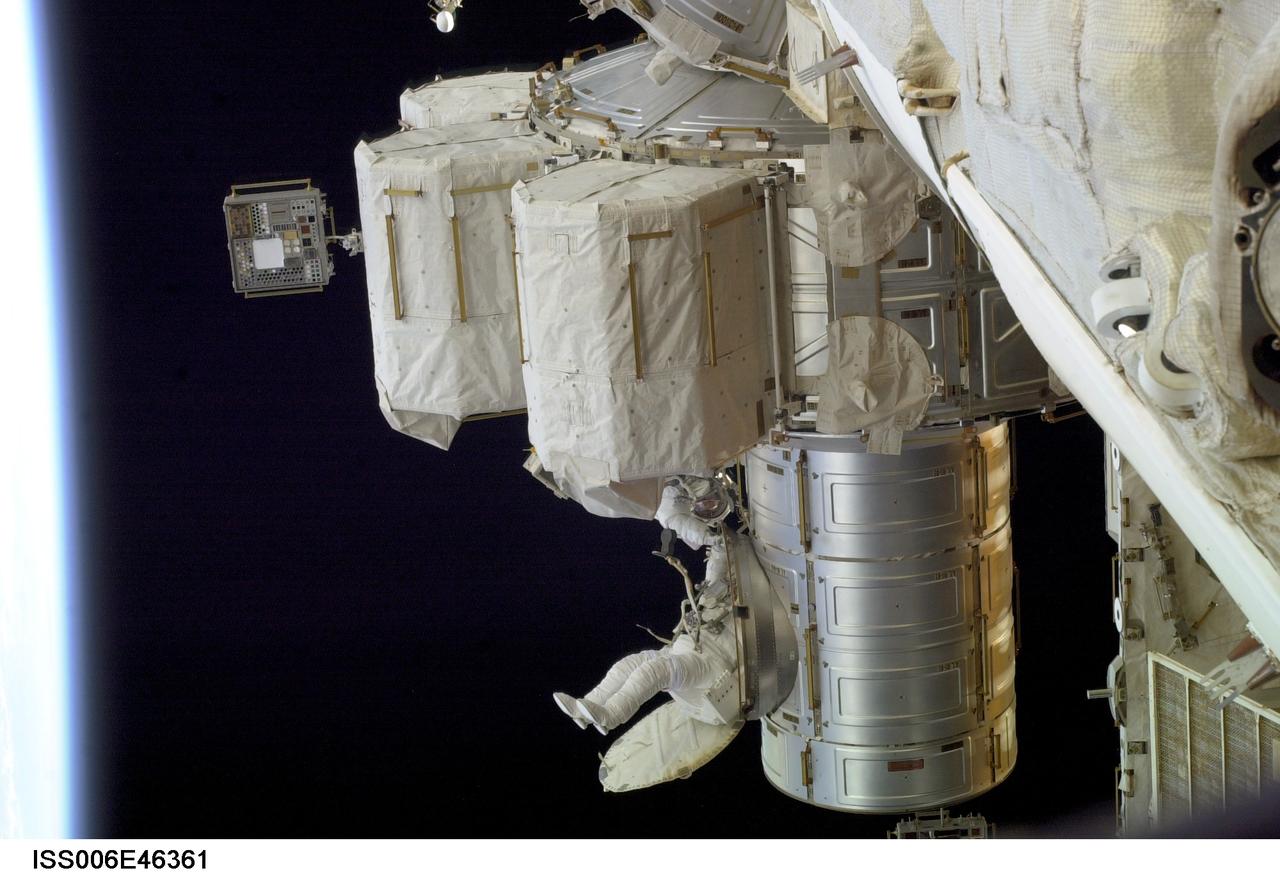

iss006e46361 (4/24/2003) --- A view of NASA astronaut Donald Pettit emerging from the Quest/Airlock (A/L) to perform a variety of maintenance tasks. Bowersox is working in the background. Also in view is Materials International Space Station Experiments (MISSE) attached to A/L. Photo was taken during Expedition Six on the International Space Station (ISS). MISSE-1 and 2 are a test bed for materials and coatings attached to the outside of the ISS is being evaluated for the effects of atomic oxygen, direct sunlight, and extremes of heat and cold. This experiment allows the development and testing of new materials to better withstand the rigors of space environments. Results will provide a better understanding of the durability of various materials when they are exposed to the space environment. Many of the materials may have applications in the design of future spacecraft.
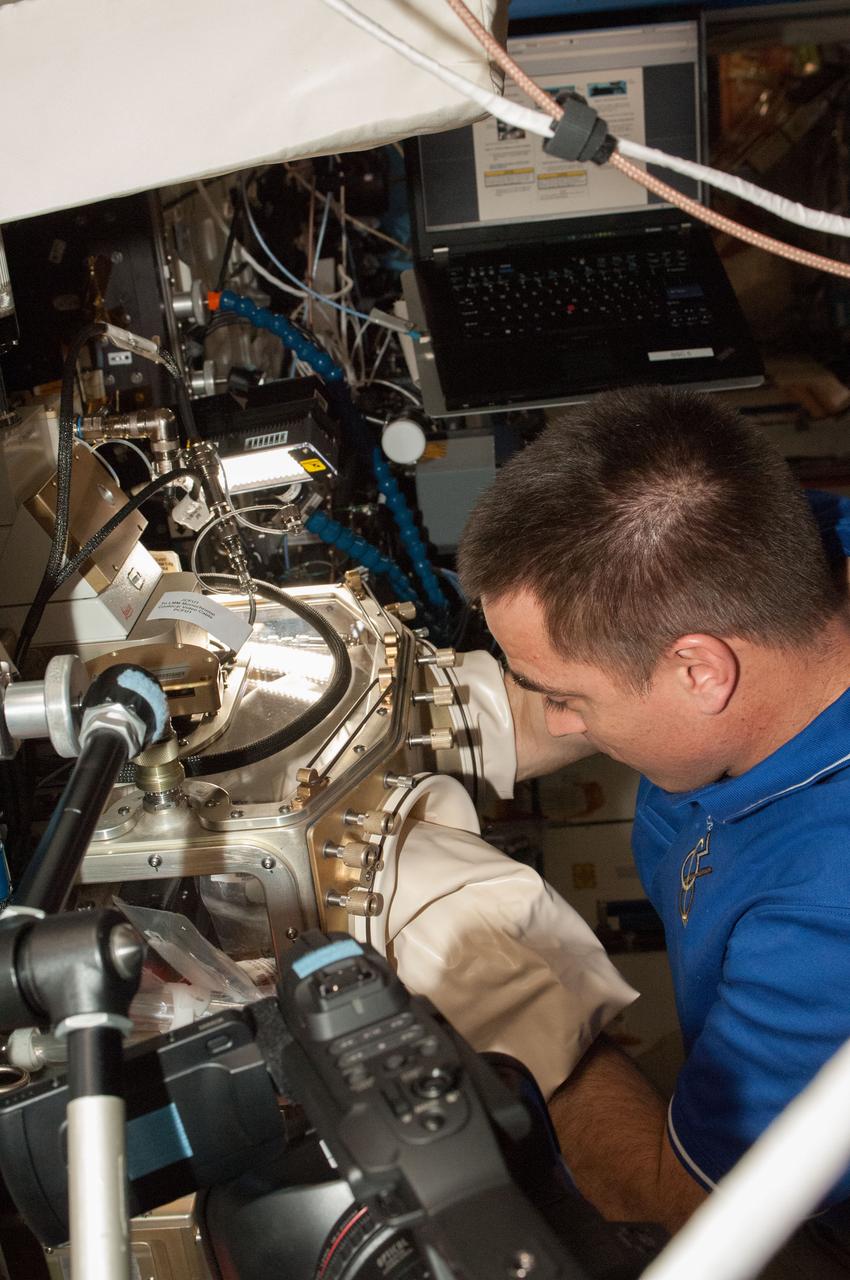

ISS036-E-023770 (22 July 2013) --- NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy, Expedition 36 flight engineer, conducts science work with the ongoing experiment Advanced Colloids Experiment-1 (ACE-1) inside the Fluids Integrated Rack. The experiment observes colloids, microscopic particles evenly dispersed throughout materials, with the potential for manufacturing improved materials and products on Earth. Cassidy is working at the Light Microscopy Module (LMM) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
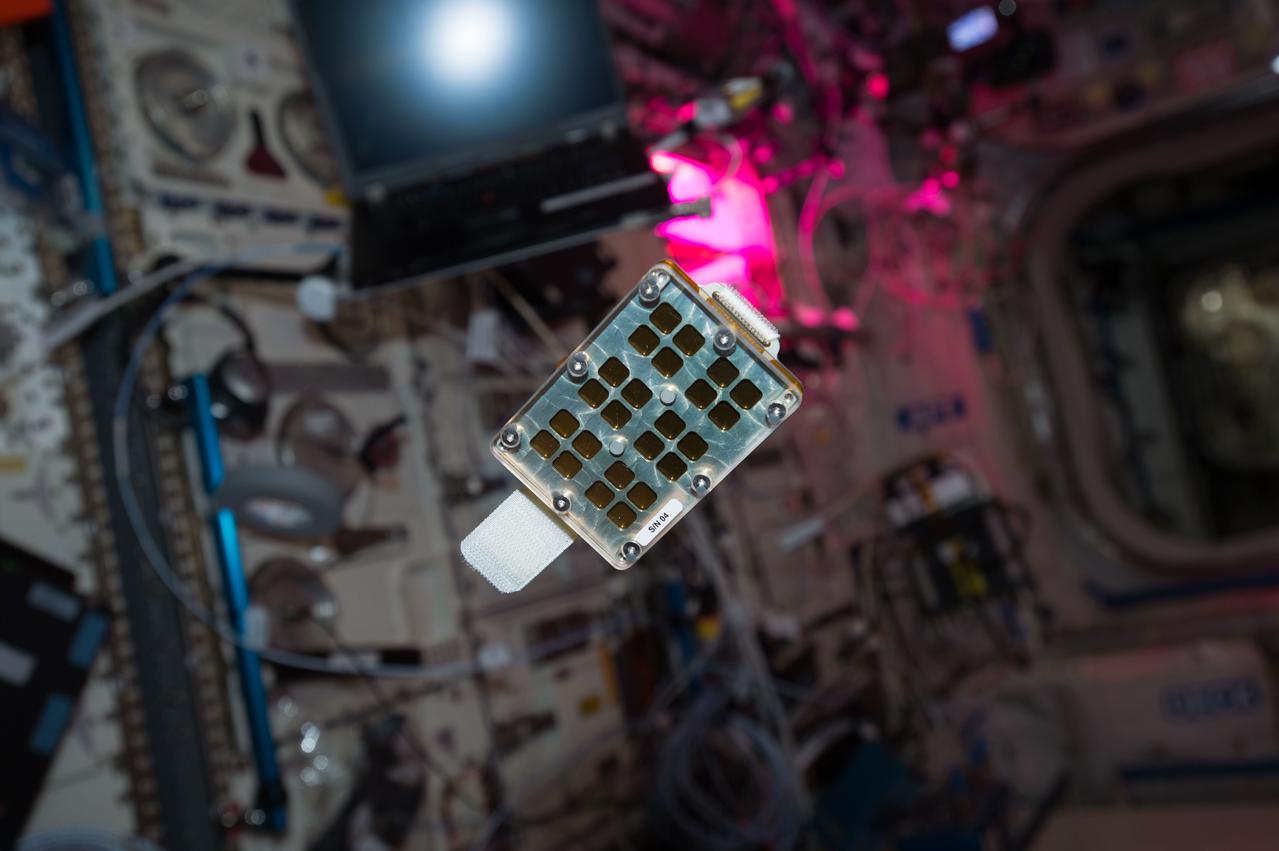
iss050e010908 911/21/2016) --- A view of Matiss floating in the Columbus Module. The Microbial Aerosol Tethering on Innovative Surfaces in the International Space Station (MATISS) experiment investigates the antibacterial properties of materials in space to see if future spacecraft could be made easier to clean. The experiment aims to understand the mechanisms of attachment of biofilms in microgravity conditions.
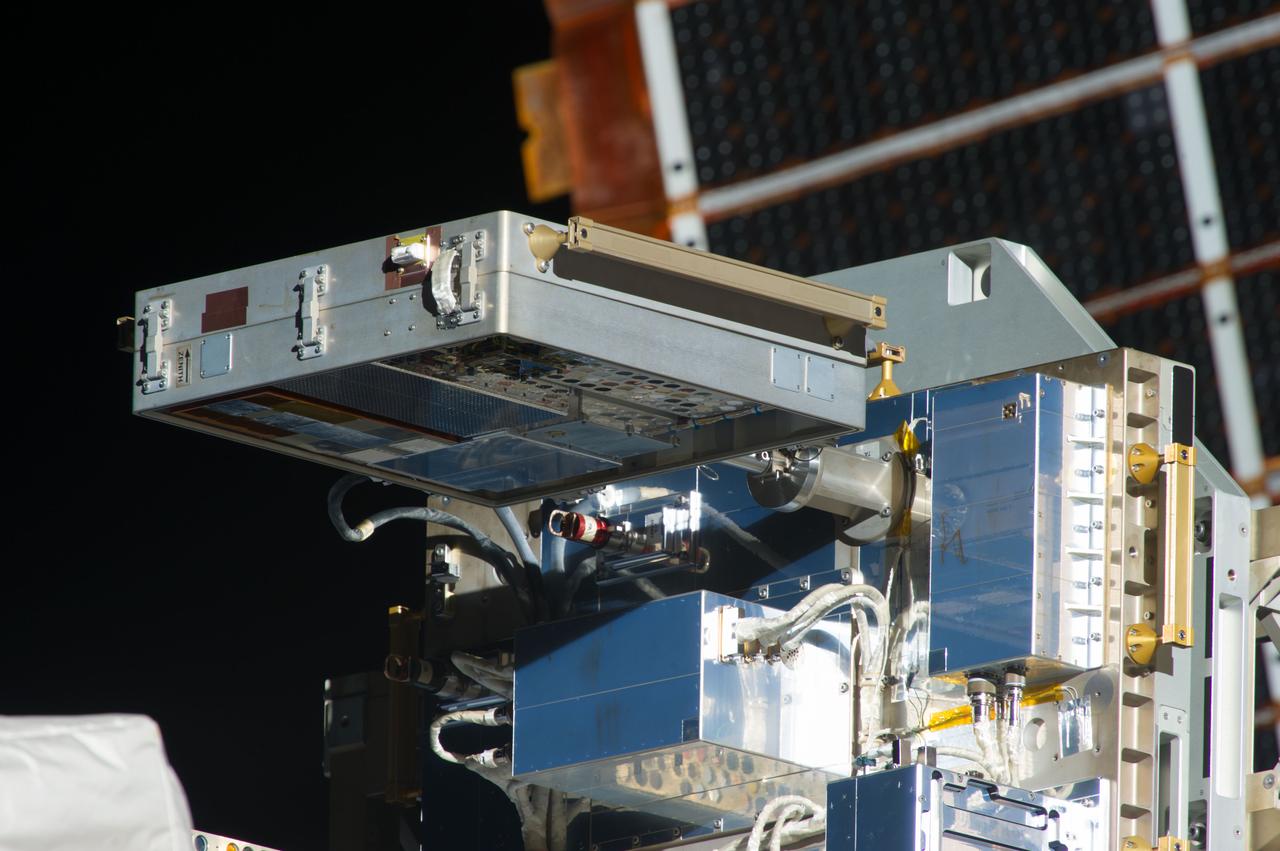
iss036e004042 (5/24/2013) --- View of Materials on International Space Station Experiment - 8 (MISSE-8) which is installed on the ExPRESS Logistics Carrier 2 (ELC-2),located on the S3 Truss Outboard Zenith site.

STS105-346-011 (18 August 2001) --- Astronaut Patrick G. Forrester, during the second STS-105 extravehicular activity, prepares to work with the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE, almost out of frame at left). The experiment was installed on the outside of the Quest Airlock during the first extravehicular activity (EVA) of the STS-105 mission. MISSE will collect information on how different materials weather in the environment of space.
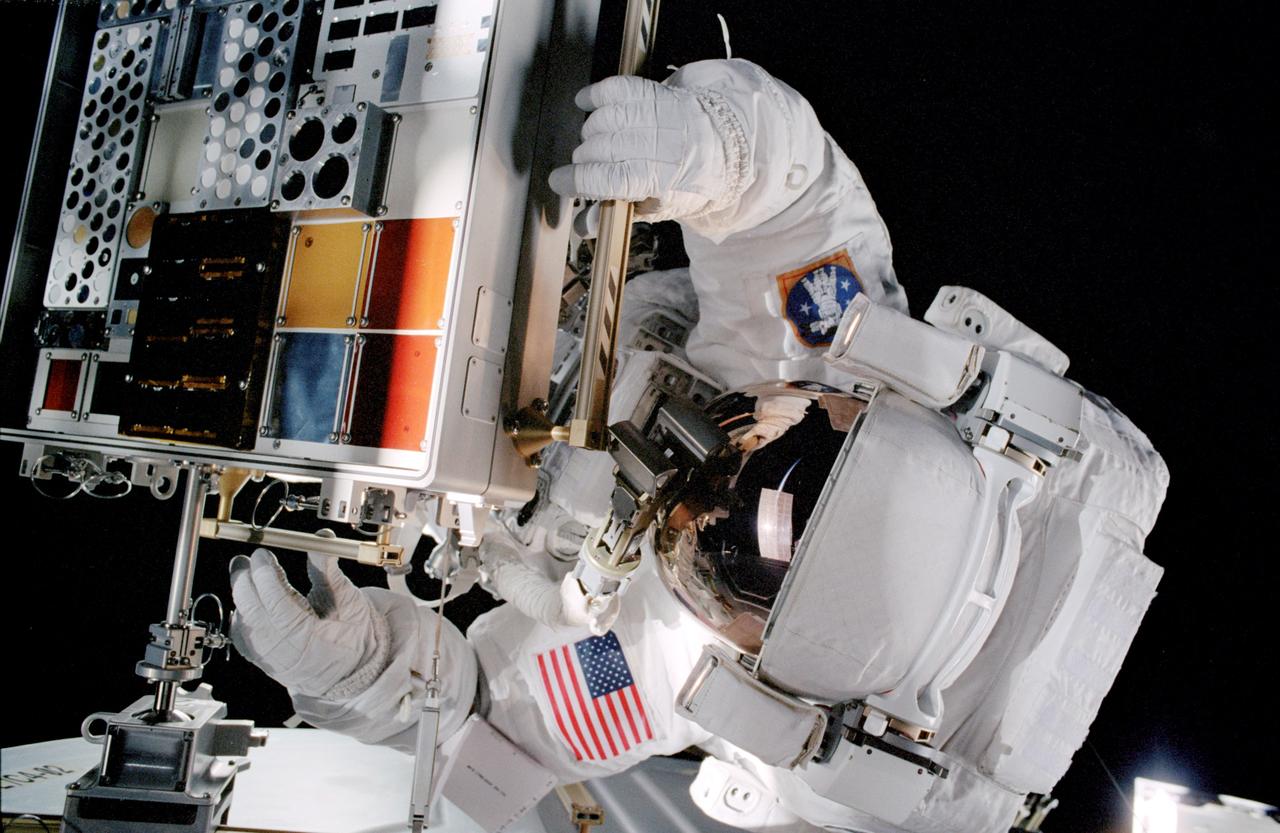

STS105-346-007 (18 August 2001) --- Astronaut Patrick G. Forrester, during the second STS-105 extravehicular activity, prepares to work with the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE). The experiment was installed on the outside of the Quest Airlock during the first extravehicular activity (EVA) of the STS-105 mission. MISSE will collect information on how different materials weather in the environment of space.
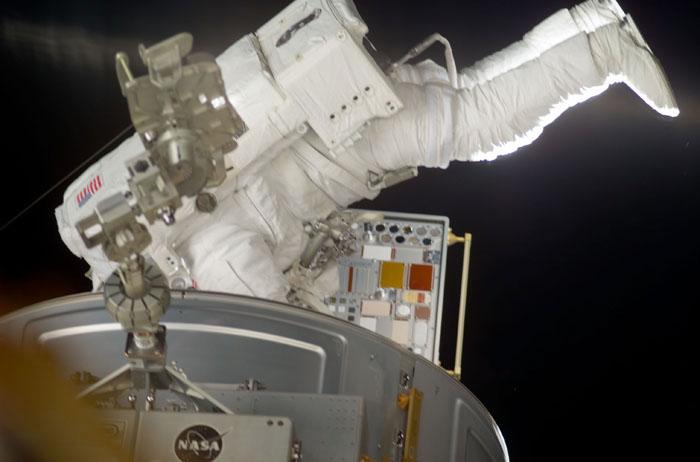

STS105-E-5306 (16 August 2001) --- Astronaut Patrick G. Forrester works with the first external experiment on the International Space Station's (ISS) hull. The Materials ISS Experiment (pronounced 'missy' by its acronym) will expose 750 material samples to the space environment for about 18 months before being returned home late next year. This image was recorded with a digital still camera.

This image of the International Space Station (ISS) was photographed by one of the crewmembers of the STS-105 mission from the Shuttle Orbiter Discovery after separating from the ISS. The STS-105 mission was the 11th ISS assembly flight and its goals were the rotation of the ISS Expedition Two crew with Expedition Three crew, and the delivery of supplies utilizing the Italian-built Multipurpose Logistic Module (MPLM) Leonardo. Aboard Leonardo were six resupply stowage racks, four resupply stowage supply platforms, and two new scientific experiment racks, EXPRESS (Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station) Racks 4 and 5, which added science capabilities to the ISS. Another payload was the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE), which included materials and other types of space exposure experiments mounted on the exterior of the ISS.

iss072e188539 (Nov. 15, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Don Pettit unpacks and gathers research hardware to be placed outside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module. The scientific gear known as MISSE, or Materials International Space Station Experiment, places a variety of materials in the vacuum of space exposing them to the extreme thermal environment, different types of radiation, micrometeoroids, and more to promote the space industry.
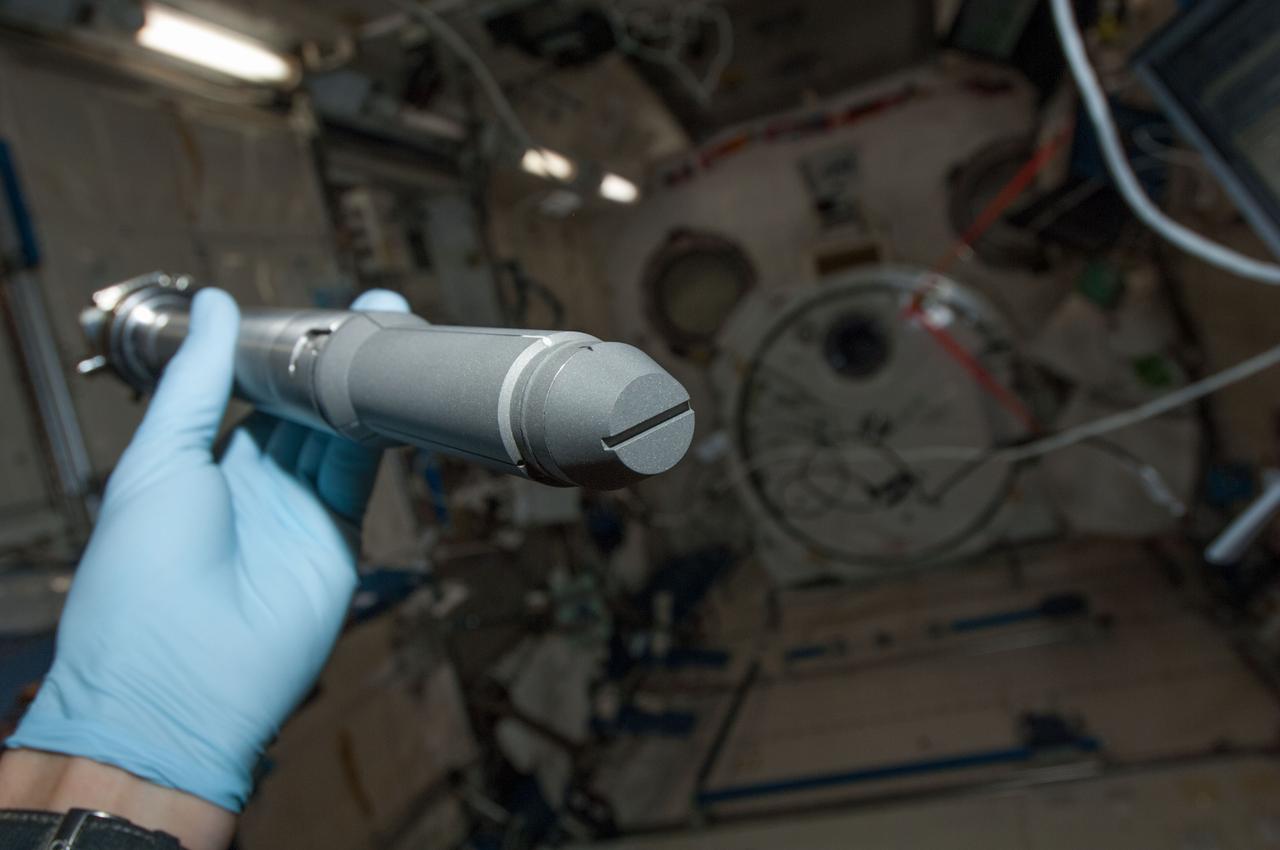

iss035e007095 (3/22/2013) --- A close-up view of an alloy cartridge to be installed in the Gradient Heating Furnace (GHF) of the Kobairo rack for the Alloy Semiconductor experiment. Image was taken in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Pressurized Module (JPM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Alloy Semiconductor investigation aims to develop a clear understanding of how semiconductor materials grow and crystallize in microgravity. The materials studied are also known to be useful as devices which convert heat into electricity (thermoelectrics).
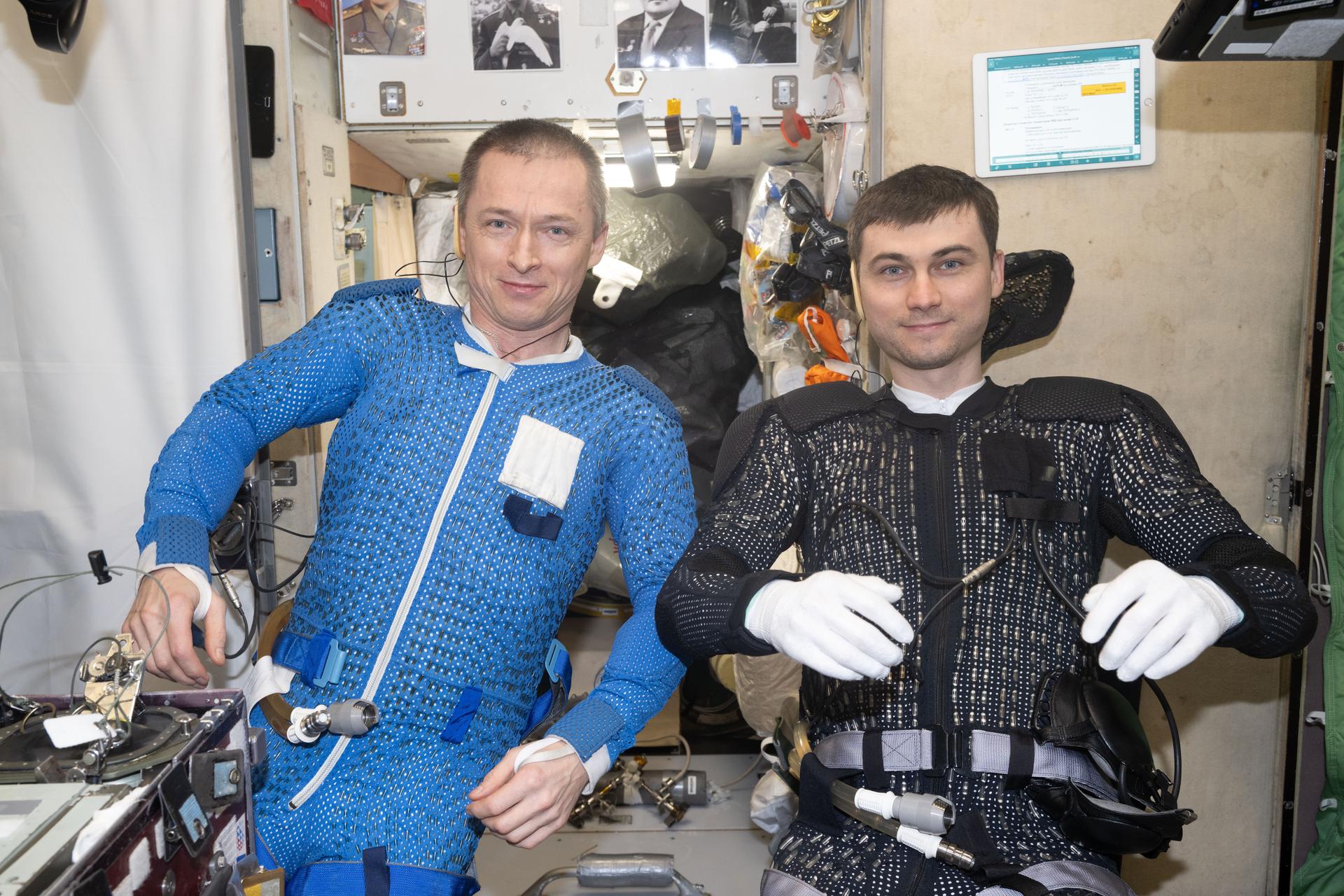

iss073e0880941 (Oct. 16, 2025) --- Roscosmos cosmonauts (from left) Sergey Ryzhikov and Alexey Zubritsky are pictured inside the International Space Station's Zvezda service module dressing up and preparing for a spacewalk. The duo would install a semiconductor materials experiment, remove a high-resolution camera monoblock, clean a window on the Zvezda service module, and remove a materials exposure experiment container during the six-hour and nine-minute excursion.
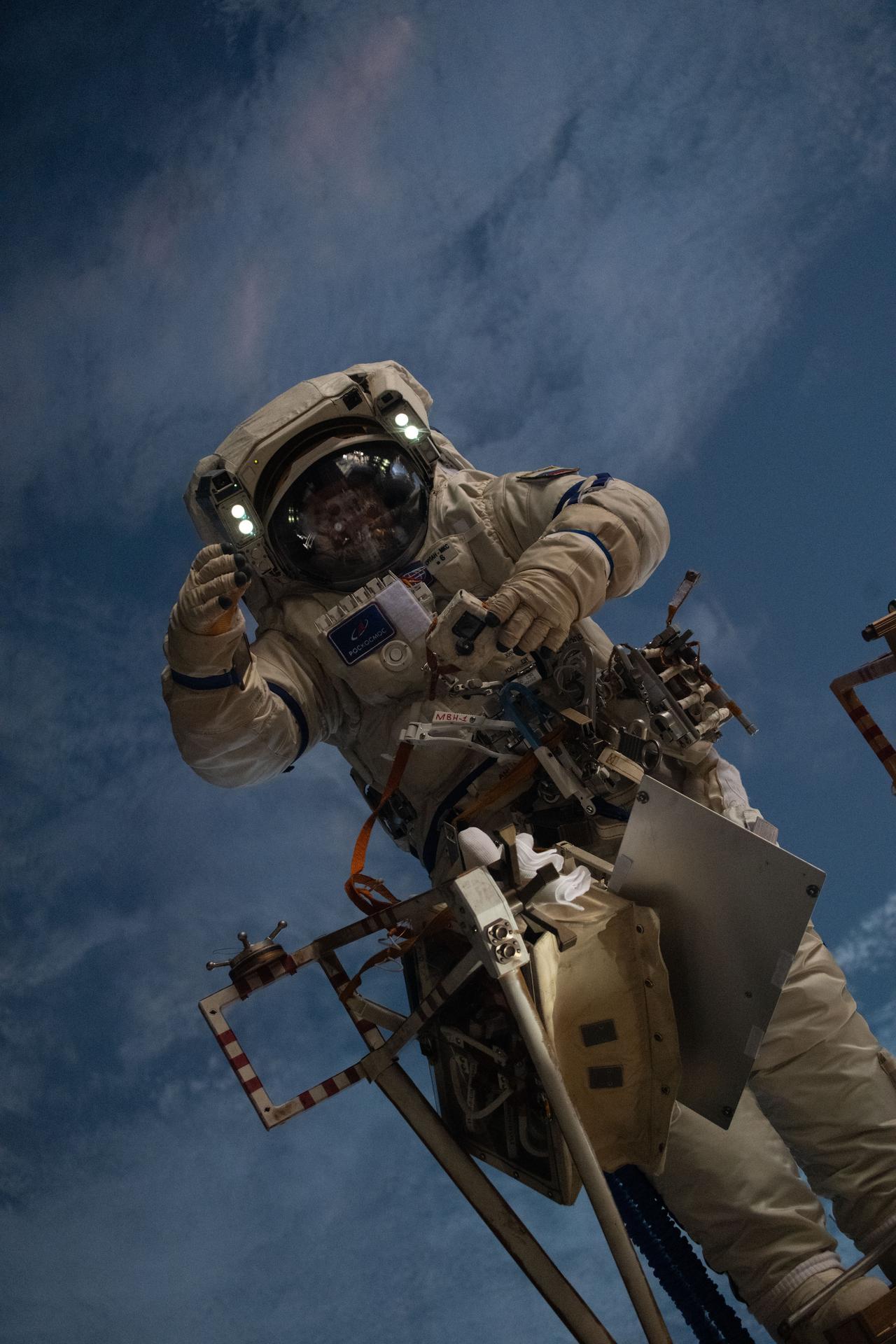

iss073e0881198 (Oct. 16, 2025) --- Roscosmos cosmonaut Alexey Zubritsky is pictured during a six-hour and nine-minute spacewalk on the International Space Station's Roscosmos segment 265 miles above Earth. Zubritsky helped install a semiconductor materials experiment, remove a high-resolution camera monoblock, clean a window on the Zvezda service module, and remove a materials exposure experiment container.

iss073e0881098 (Oct. 16, 2025) --- Roscosmos cosmonauts Alexey Zubritsky (left) and Sergey Ryzhikov (right) are pictured during a six-hour and nine-minute spacewalk outside the International Space Station's Roscosmos segment. The duo installed a semiconductor materials experiment, removed a high-resolution camera monoblock, cleaned a window on the Zvezda service module, and removed a materials exposure experiment container.
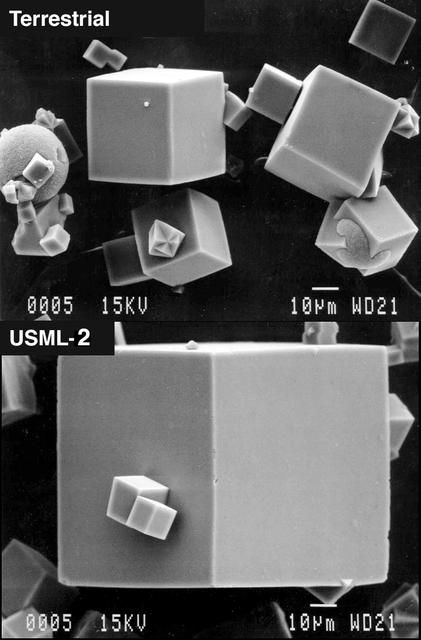
The Center for Advanced Microgravity Materials Processing (CAMMP), a NASA-sponsored Research Partnership Center, is working to improve zeolite materials for storing hydrogen fuel. CAMMP is also applying zeolites to detergents, optical cables, gas and vapor detection for environmental monitoring and control, and chemical production techniques that significantly reduce by-products that are hazardous to the environment. Shown here are zeolite crystals (top) grown in a ground control experiment and grown in microgravity on the USML-2 mission (bottom). Zeolite experiments have also been conducted aboard the International Space Station.
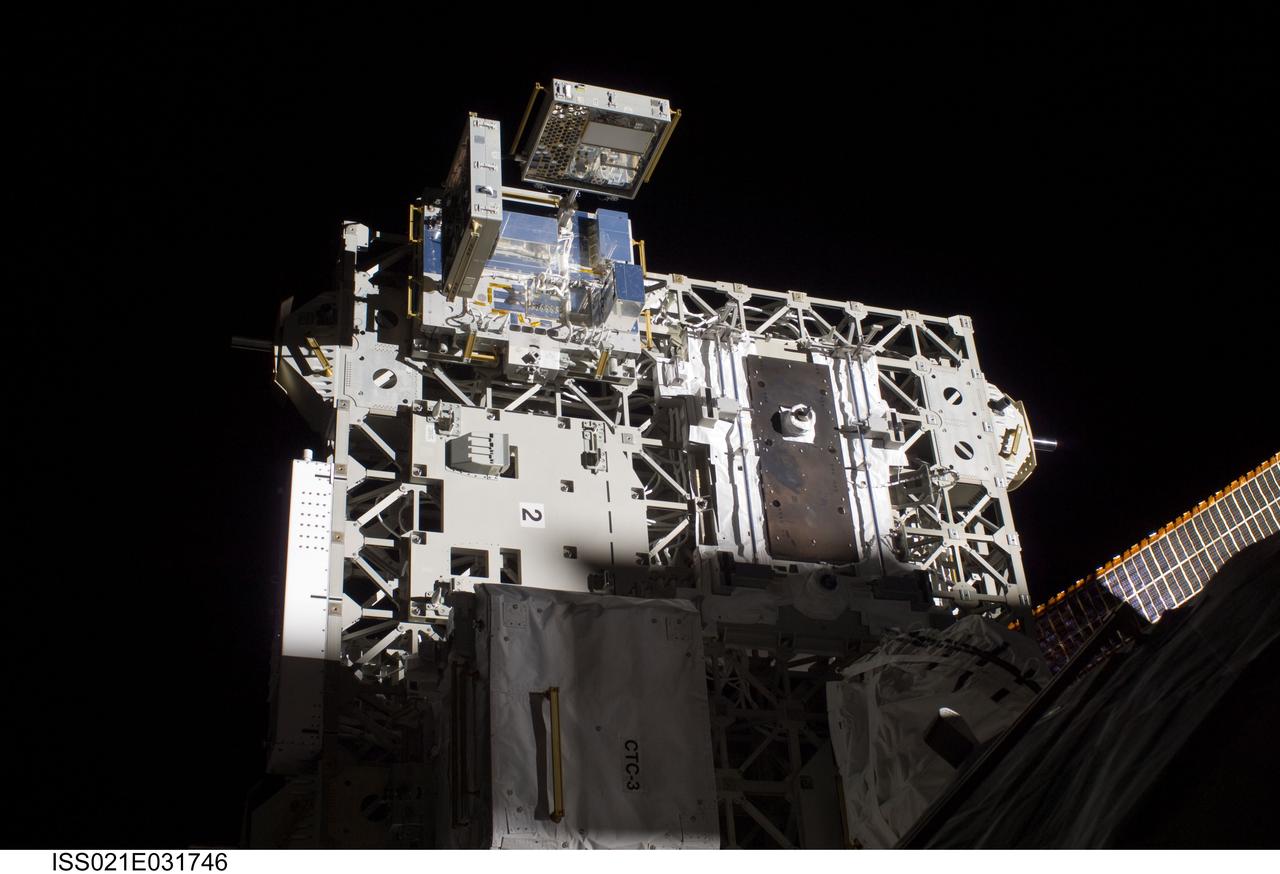

ISS021-E-031746 (23 Nov. 2009) --- The MISSE 7 experiment on the Express Logistics Carrier 2 of the International Space Station was photographed by a space-walking STS-129 astronaut during the mission's third and final session of extravehicular activity (EVA). This is the latest in a series of experiments that expose materials and composite samples to space for several months before they are returned for experts to analyze. This MISSE experiment actually is plugged into the space station’s power supply.

NASA's first Sample Cartridge Assembly (SCA) project designed and validated a payload containing a materials research sample in a sealed environment. The SCA was heated in the European Space Agency's (ESA) Low Gradient Furnace (LGF) that is housed inside the Material Science Research Rack (MSRR) located on the International Space Station (ISS). Sintered metals and crystal growth experiments in microgravity are examples of some of the types of materials research that may be performed with a SCA.
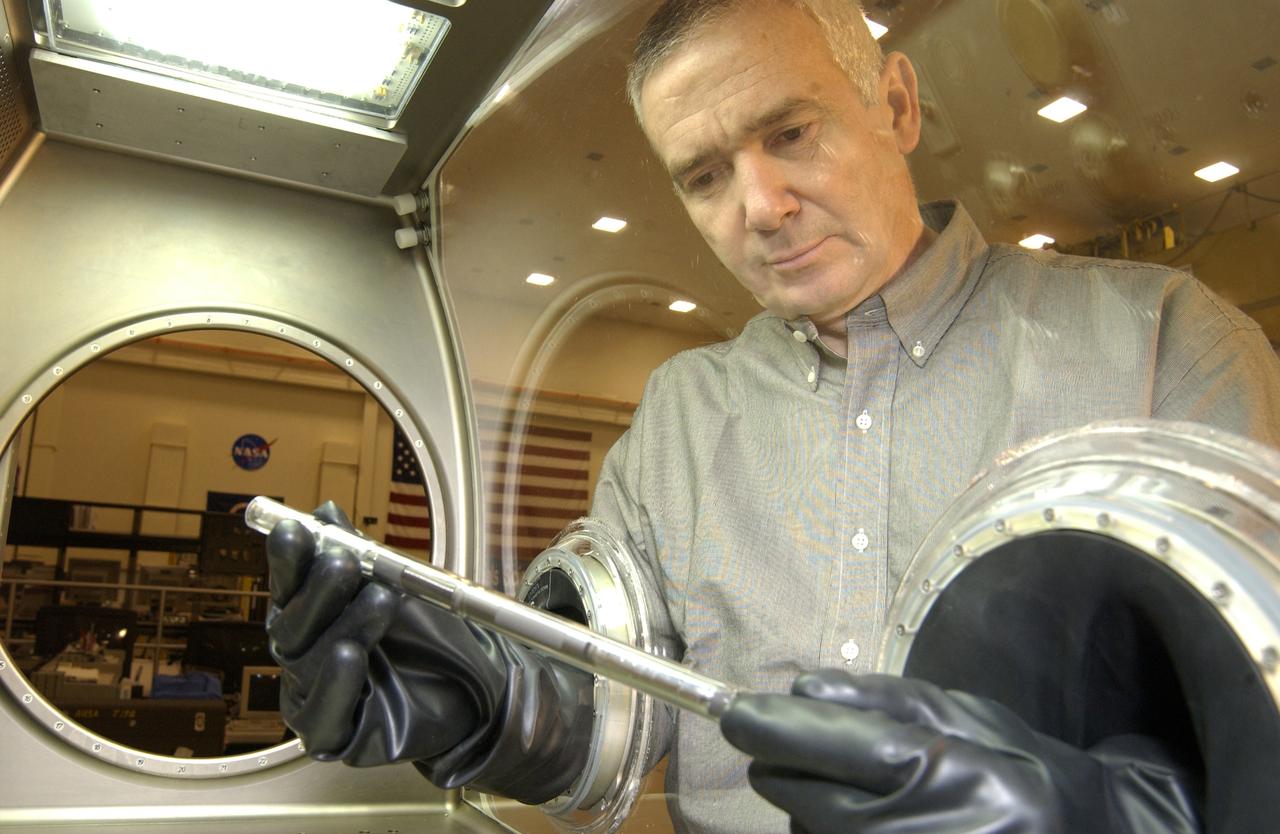

One of the first materials science experiments on the International Space Station -- the Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules (SUBSA) -- will be conducted during Expedition Five inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox. The glovebox is the first dedicated facility delivered to the Station for microgravity physical science research, and this experiment will be the first one operated inside the glovebox. The glovebox's sealed work environment makes it an ideal place for the furnace that will be used to melt semiconductor crystals. Astronauts can change out samples and manipulate the experiment by inserting their hands into a pair of gloves that reach inside the sealed box. Dr. Aleksandar Ostrogorsky, a materials scientist from the Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, N.Y., and the principal investigator for the SUBSA experiment, uses the gloves to examine an ampoule like the ones used for his experiment inside the glovebox's work area. The Microgravity Science Glovebox and the SUBSA experiment are managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala.
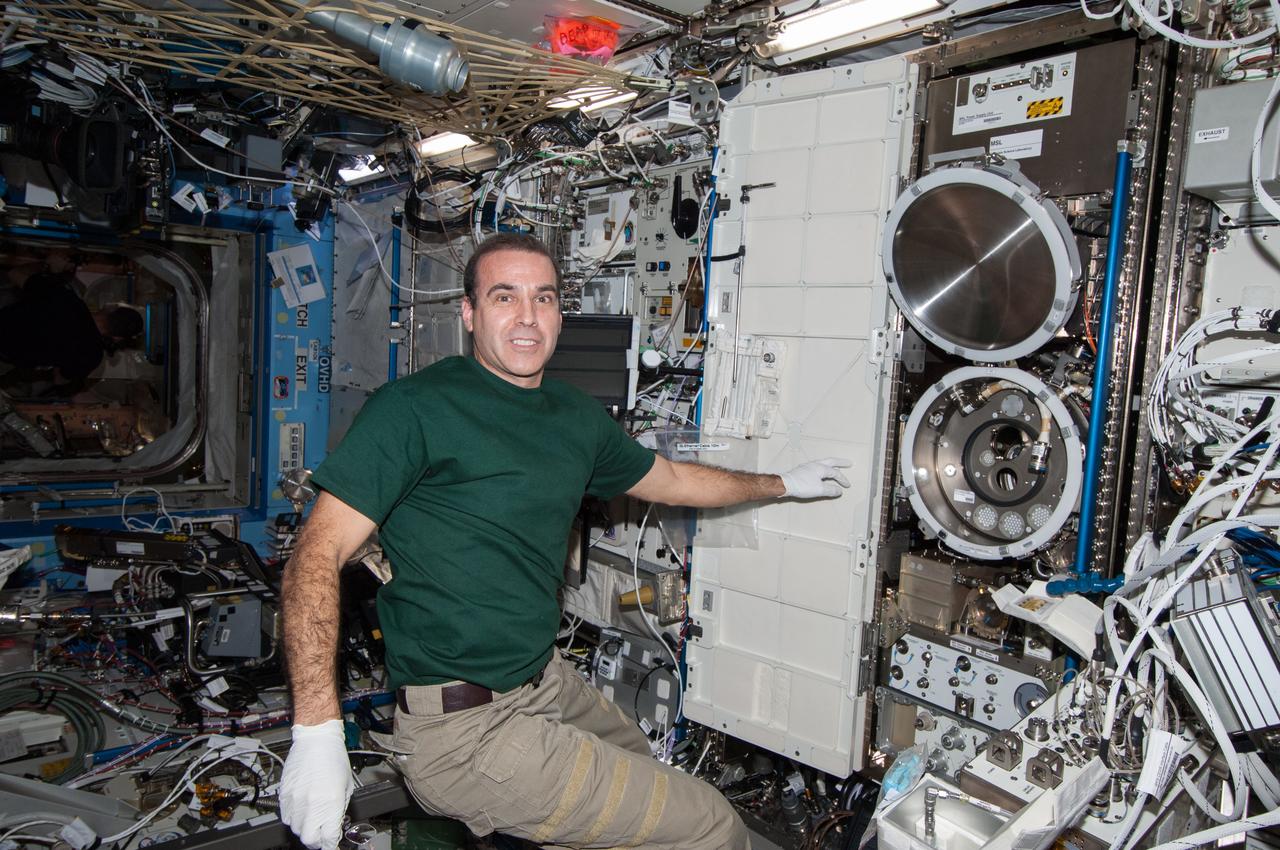

ss038e008298 (11/26/2013) --- A view of NASA astronaut Rick Mastracchio, during the Material Science Laboratory (MSL) Solidification and Quench Furnace (SQF) Sample Cartridge Exchange aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Materials Science Laboratory (MSL) is used for basic materials research in the microgravity environment of the ISS. The MSL can accommodate and support diverse Experiment Modules. In this way many material types, such as metals, alloys, polymers, semiconductors, ceramics, crystals, and glasses, can be studied to discover new applications for existing materials and new or improved materials.
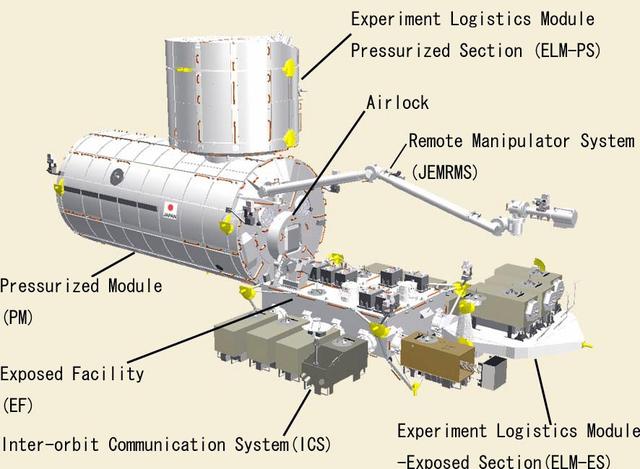
JSC2003-E-42552 (For Release: 18 June 2003) --- This artwork depicts the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), Japan's primary contribution to the International Space Station. The JEM, called Kibo, which means "hope" in Japanese, is Japan's first human space facility and enhances the unique research capabilities of the International Space Station. Experiments in Kibo focus on space medicine, biology, earth observations, material production, biotechnology, and communications research. Photo Credit: NASDA
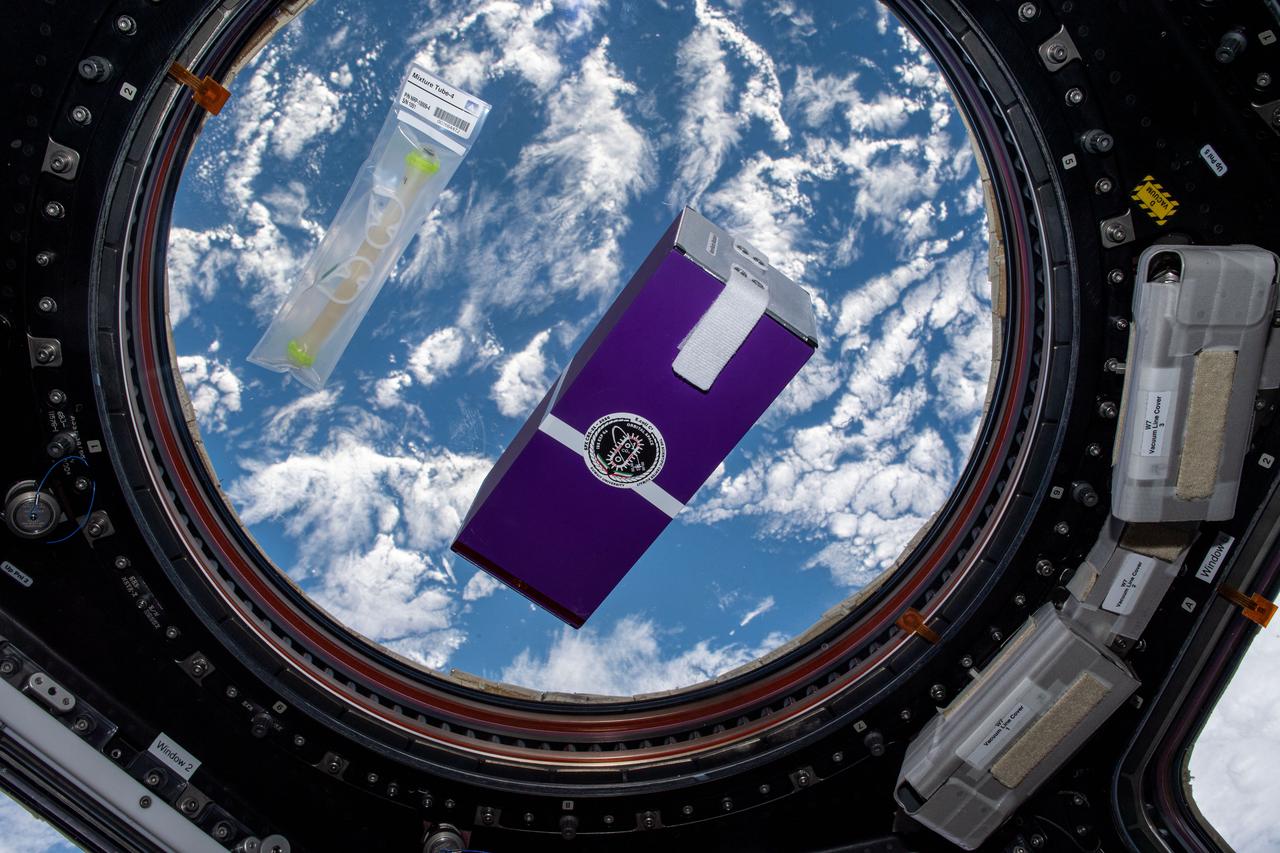

iss064e010985 (12/8/2020) --- A view of the NanoRacks Module-09 investigation in the Cupola module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). NanoRacks Module-09 is a combination of 35 experiments provided by school students from 5 different countries. The experiments are housed within a NanoRacks Module container and is a combination of biological static experiments and some experiments that require crew interaction to mix materials to activate. The experiments within the module are returned to the ground for analysis.
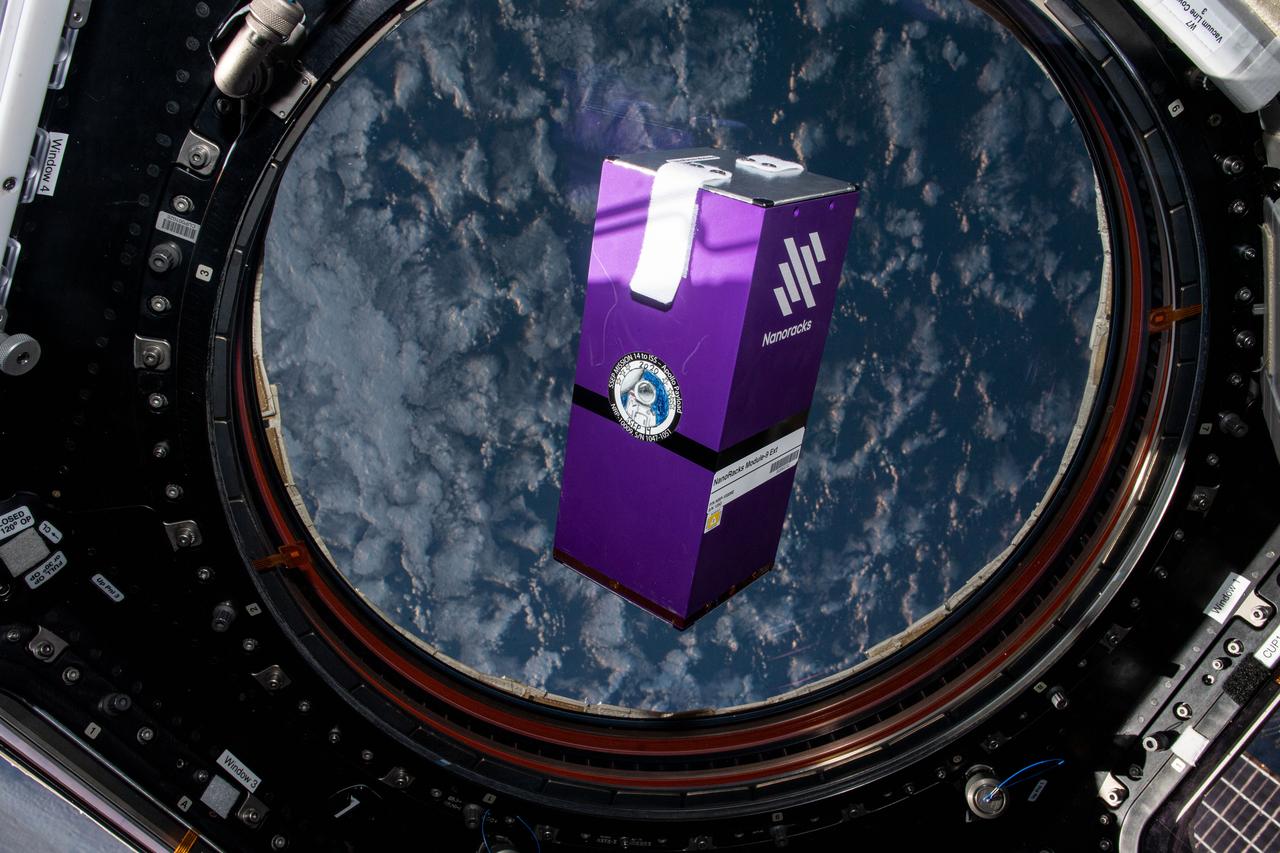

iss064e010949 (12/8/2020) --- A view of the NanoRacks Module-09 investigation in the Cupola module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). NanoRacks Module-09 is a combination of 35 experiments provided by school students from 5 different countries. The experiments are housed within a NanoRacks Module container and is a combination of biological static experiments and some experiments that require crew interaction to mix materials to activate. The experiments within the module are returned to the ground for analysis.
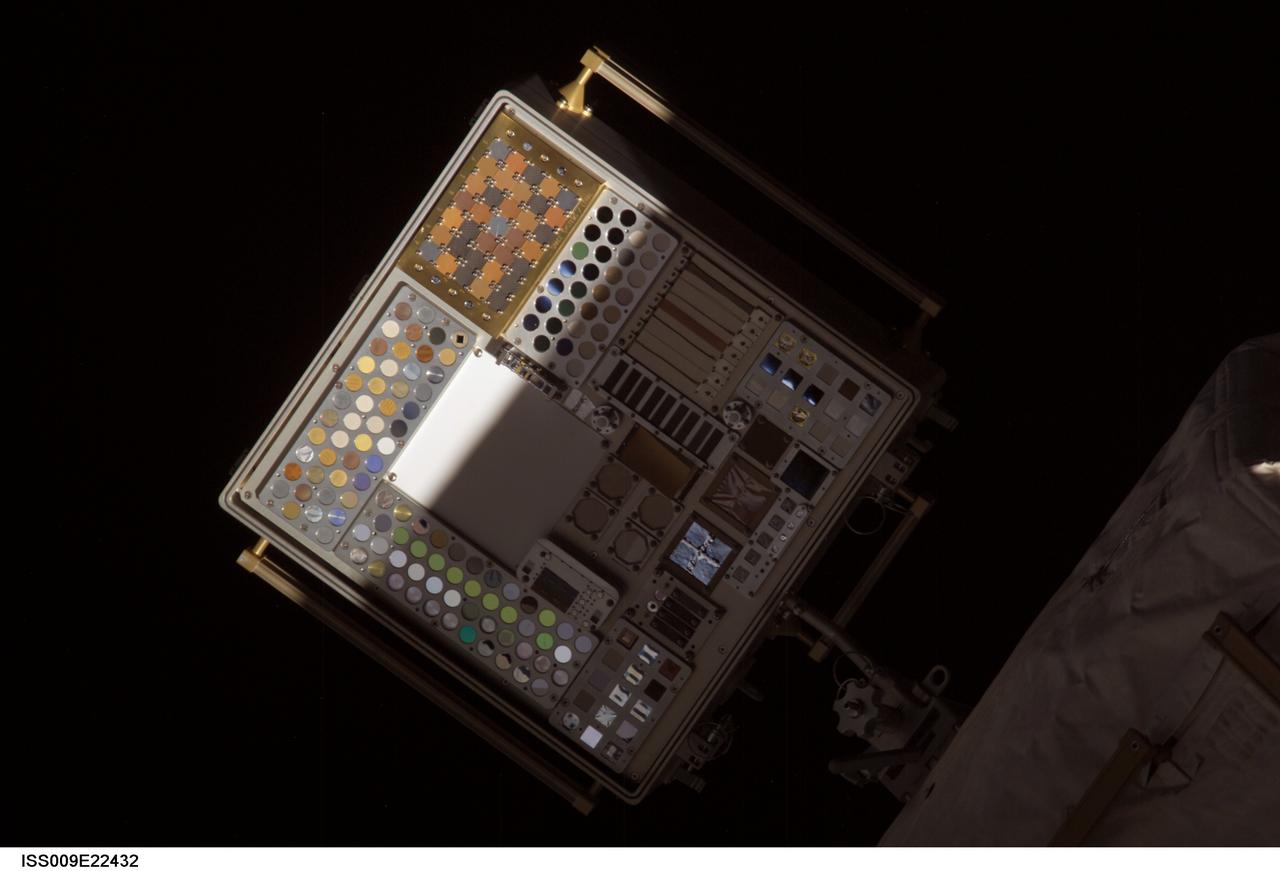

iss009e22432 (9/13/2004) --- A view of the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) #1, aft side. MISSE is attached to the outside of the Zvezda Service Module (SM). Image taken from the Pirs Docking Compartment forward port window during observation and photography of ISS External Structures on Expedition 9. MISSE-1 and 2 are a test bed for materials and coatings attached to the outside of the ISS is being evaluated for the effects of atomic oxygen, direct sunlight, and extremes of heat and cold. This experiment allows the development and testing of new materials to better withstand the rigors of space environments. Results will provide a better understanding of the durability of various materials when they are exposed to the space environment. Many of the materials may have applications in the design of future spacecraft.
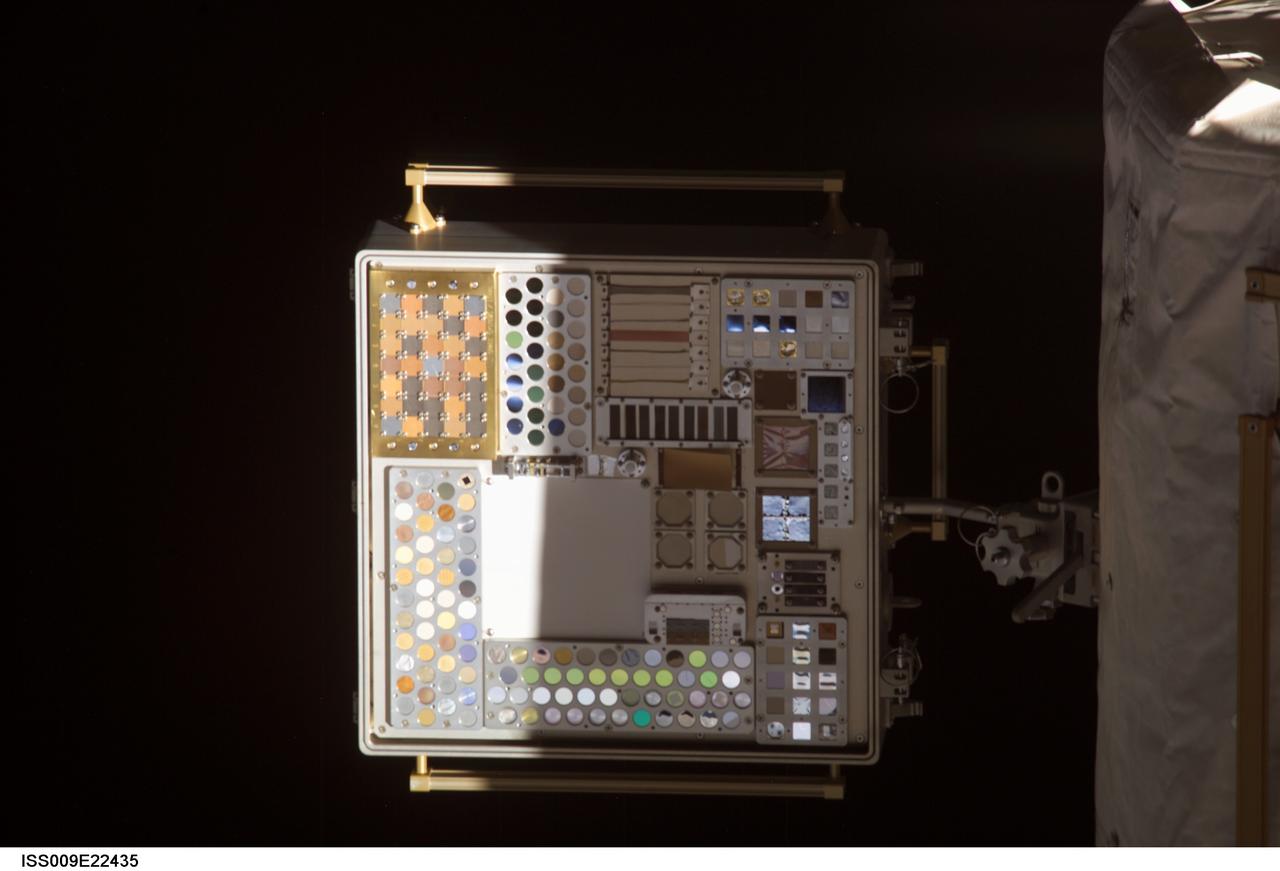

iss009e22435 (9/13/2004) --- A view of the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) #1,aft side. MISSE is attached to the outside of the Zvezda Service Module (SM). Image taken from the Pirs Docking Compartment forward port window during observation and photography of ISS External Structures on Expedition 9. MISSE-1 and 2 are a test bed for materials and coatings attached to the outside of the ISS is being evaluated for the effects of atomic oxygen, direct sunlight, and extremes of heat and cold. This experiment allows the development and testing of new materials to better withstand the rigors of space environments. Results will provide a better understanding of the durability of various materials when they are exposed to the space environment. Many of the materials may have applications in the design of future spacecraft.

Video images sent to the ground allow scientists to watch the behavior of the bubbles as they control the melting and freezing of the material during the Pore Formation and Mobility Investigation (PFMI) in the Microgravity Science Glovebox aboard the International Space Station. While the investigation studies the way that metals behave at the microscopic scale on Earth -- and how voids form -- the experiment uses a transparent material called succinonitrile that behaves like a metal to study this problem. The bubbles do not float to the top of the material in microgravity, so they can study their interactions.
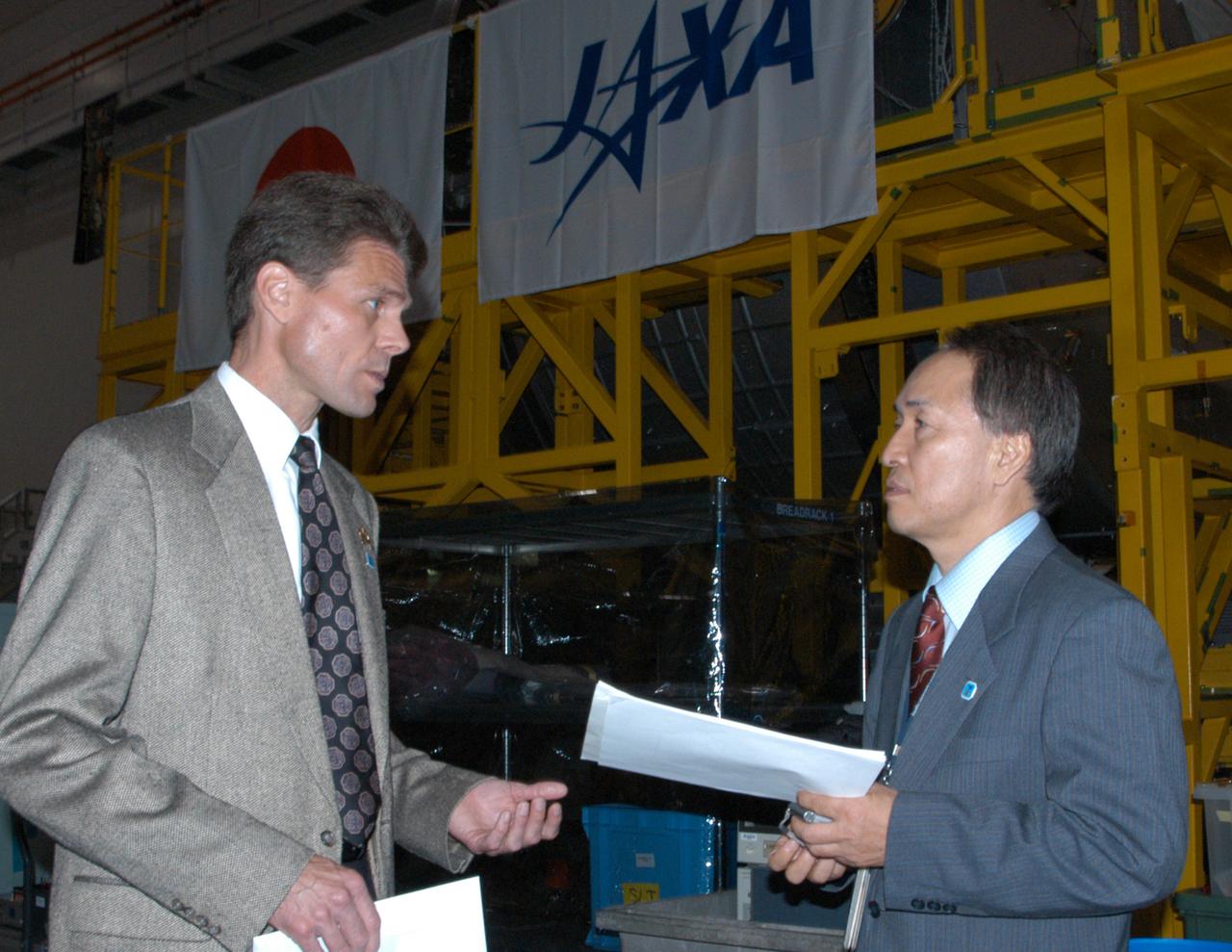

In the Space Station Processing Facility, Scott Higginbotham, payload manager for the International Space Station, discusses the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), with Dr. Hidetaka Tanaka, the JEM Project Team resident manager at KSC for the Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA). Earlier, NASA and JAXA officials welcomed the arrival of the module. The new International Space Station component arrived at Kennedy March 12 to begin preparations for its future launch on mission STS-123. It will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module.
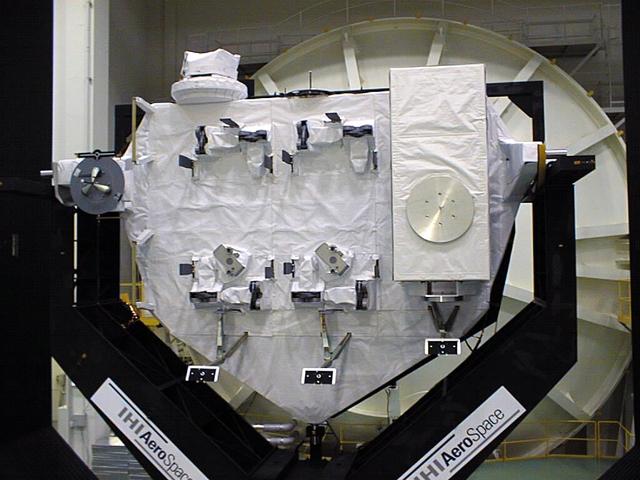
JSC2003-E-42549 (For Release: 18 June 2003) --- The Experiment Logistics Modules-Exposed (ELM-ES) of the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), Japan's primary contribution to the International Space Station (ISS), is shown in a processing facility. There are two JEM logistics modules, one each for the Pressurized Module and the Exposed Facility, that serve as on-orbit storage areas that house materials for experiments, maintenance tools and supplies. The ELM-ES is a pallet that can hold 3 experiment payloads for the JEM Exposed Facility. Photo Credit: NASDA
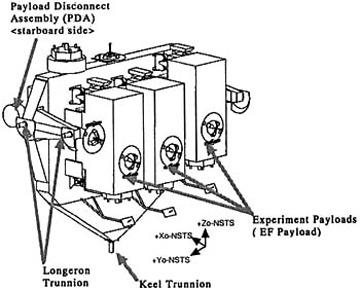
JSC2003-E-42551 (For Release: 18 June 2003) --- This graphic shows the Experiment Logistics Modules-Exposed (ELM-ES) of the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), Japan's primary contribution to the International Space Station (ISS), is shown in a processing facility. There are two JEM logistics modules, one each for the Pressurized Module and the Exposed Facility, that serve as on-orbit storage areas that house materials for experiments, maintenance tools and supplies. The ELM-ES is a pallet that can hold 3 experiment payloads for the JEM Exposed Facility. Photo Credit: NASDA
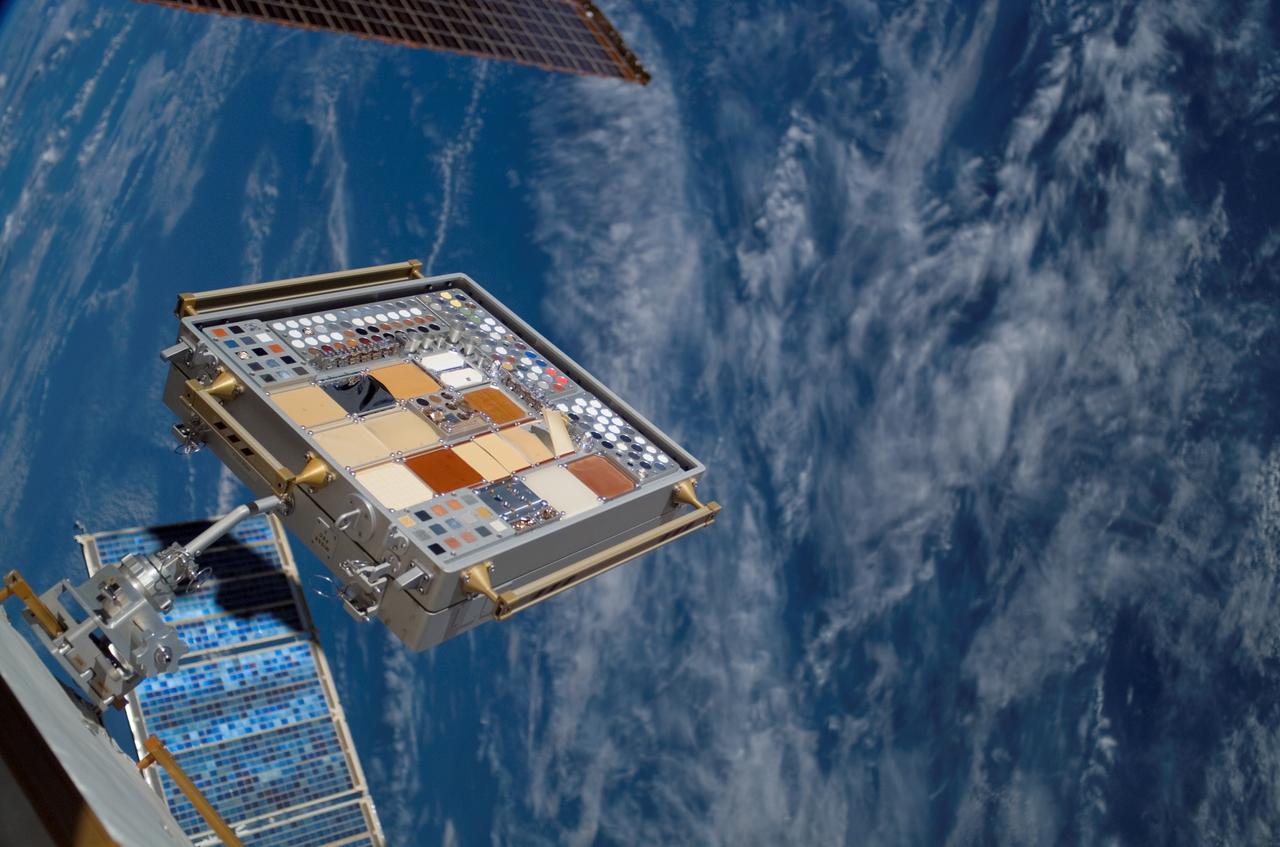

ISS015-E-22410 (13 Aug. 2007) --- Backdropped by a blue and white Earth, a Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) on the exterior of the station is featured in this image photographed by a crewmember during the STS-118 mission's second planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA). MISSE collects information on how different materials weather in the environment of space.
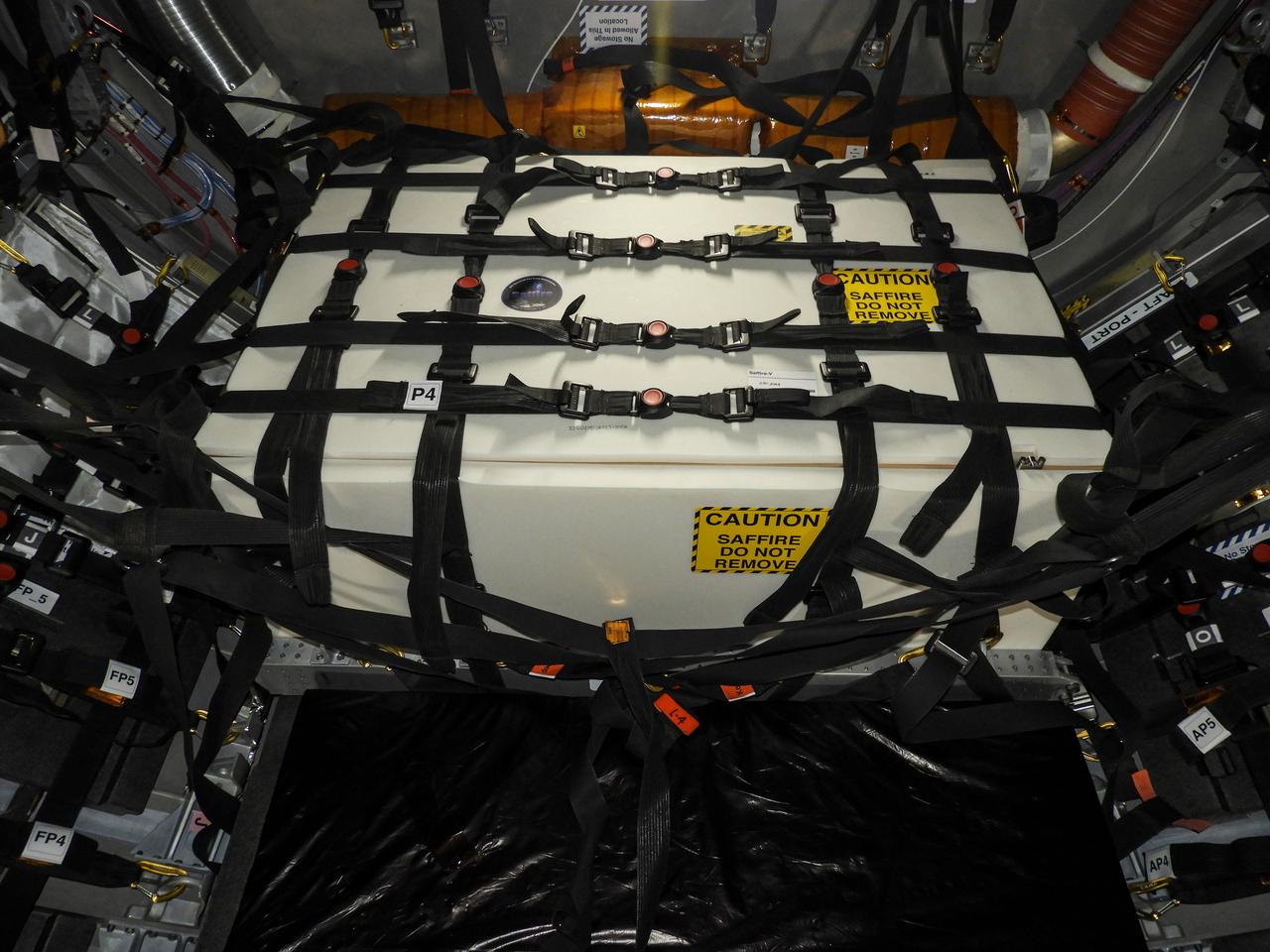

jsc2020e043815 (Sept. 10, 2020) --- A view of the Spacecraft Fire Safety Experiments (Saffire) V experiment hardware, loaded inside the Northrop Grumman(NG) Cygnus cargo vehicle for the 14th NG resupply mission to the International Space Station. Saffire is a series of experiments to investigate how fire spreads on a variety of combustible materials in the microgravity environment. The experiments are ignited in Cygnus cargo spacecraft after it departs the space station and before it reenters the Earth's atmosphere. Studying the development and growth of fire in a re-supply cargo vehicle eliminates the risk of exposure to humans in an occupied spacecraft. Understanding how fire behaves in microgravity, and how different materials propagate flames in space is immensely important for the development of future crew spacecraft.
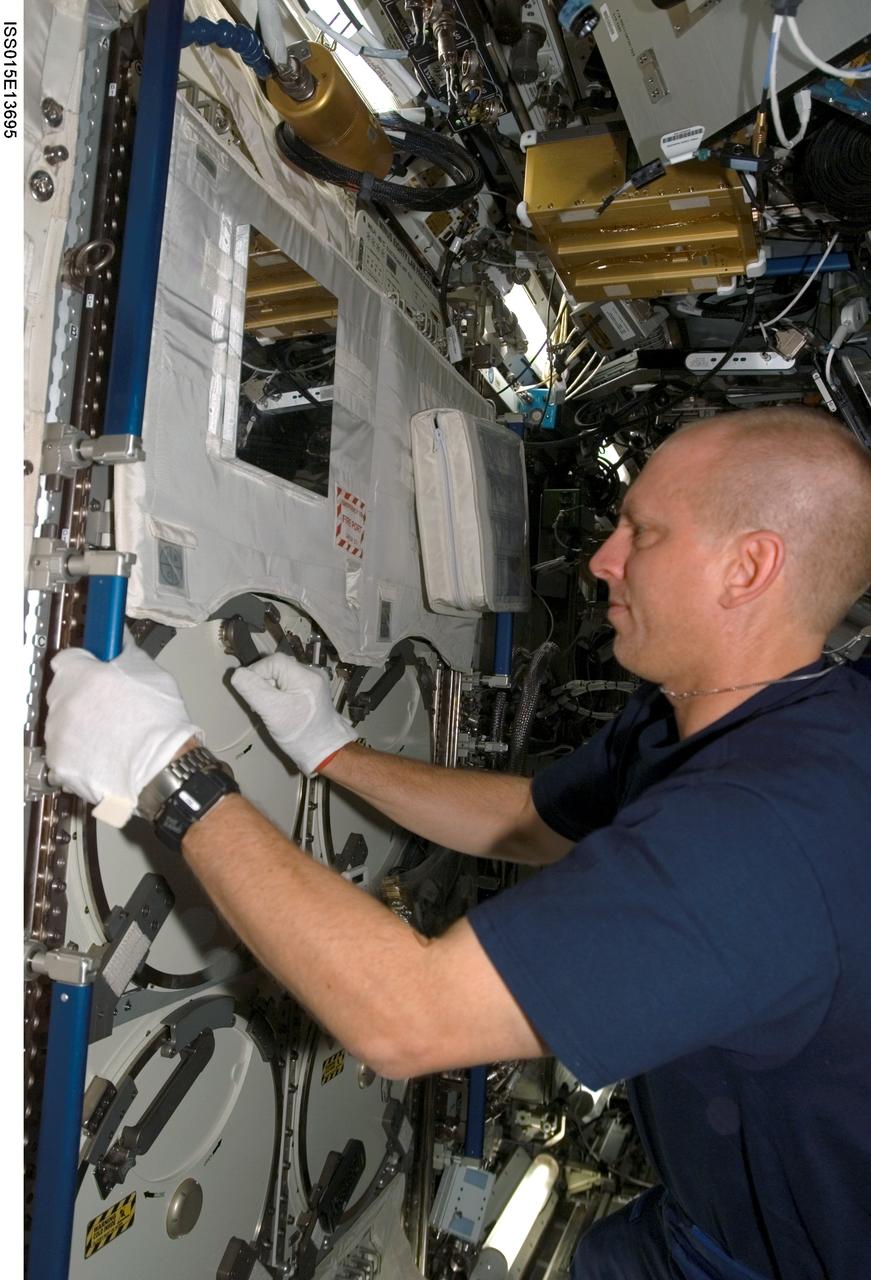

ISS015-E-13695 (25 June 2007) --- Astronaut Clayton Anderson, Expedition 15 flight engineer, works with the Minus Eighty Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) as part of the Nutritional Status Assessment (NUTRITION) experiment in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. MELFI is a low temperature freezer facility with nominal operating temperatures of -80, -26 and +4 degrees Celsius that will preserve experiment materials over long periods. The results of the Nutrition experiment will be used to better understand the time course effects of space flight on human physiology.
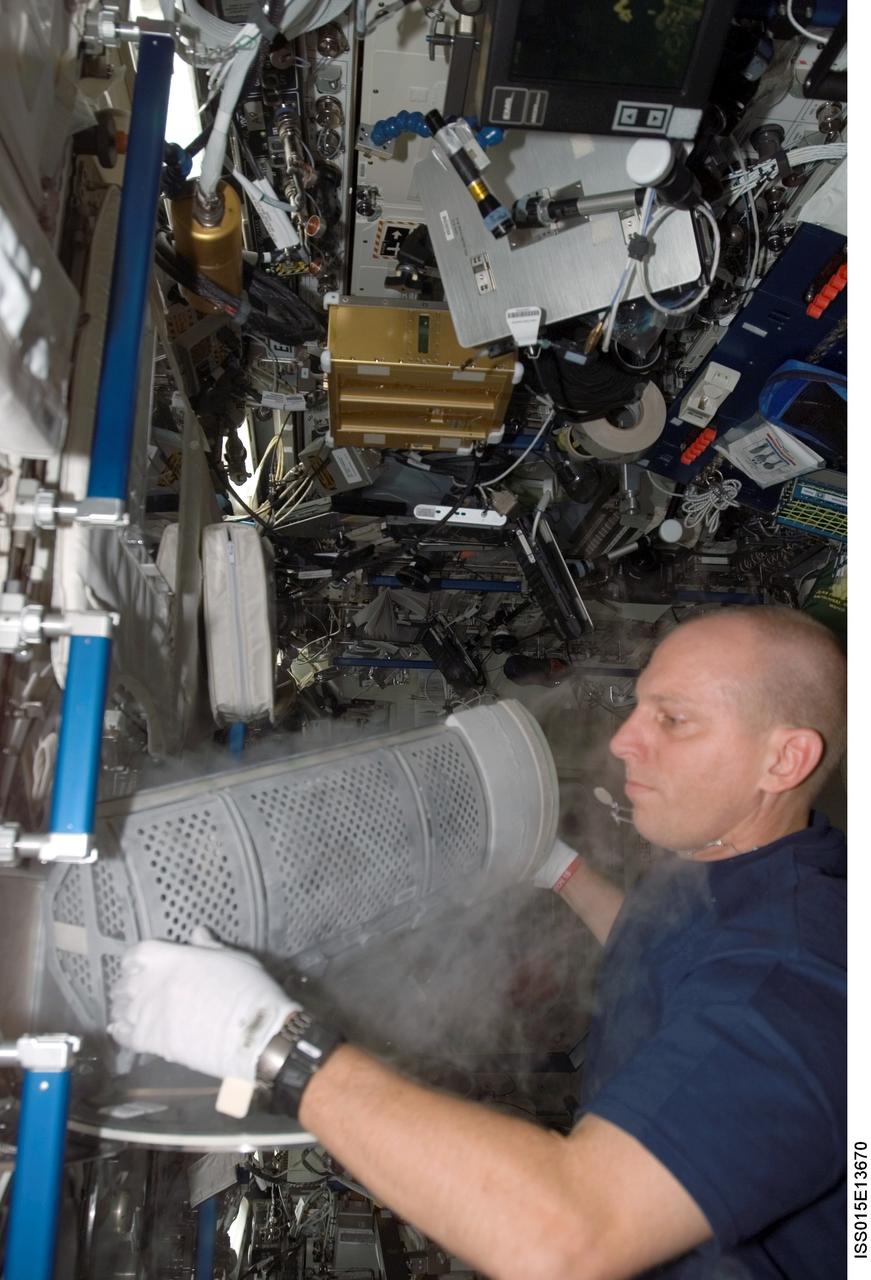

ISS015-E-13670 (25 June 2007) --- Astronaut Clayton Anderson, Expedition 15 flight engineer, works with the Minus Eighty Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) as part of the Nutritional Status Assessment (NUTRITION) experiment in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station. MELFI is a low temperature freezer facility with nominal operating temperatures of -80, -26 and +4 degrees Celsius that will preserve experiment materials over long periods. The results of the Nutrition experiment will be used to better understand the time course effects of space flight on human physiology.
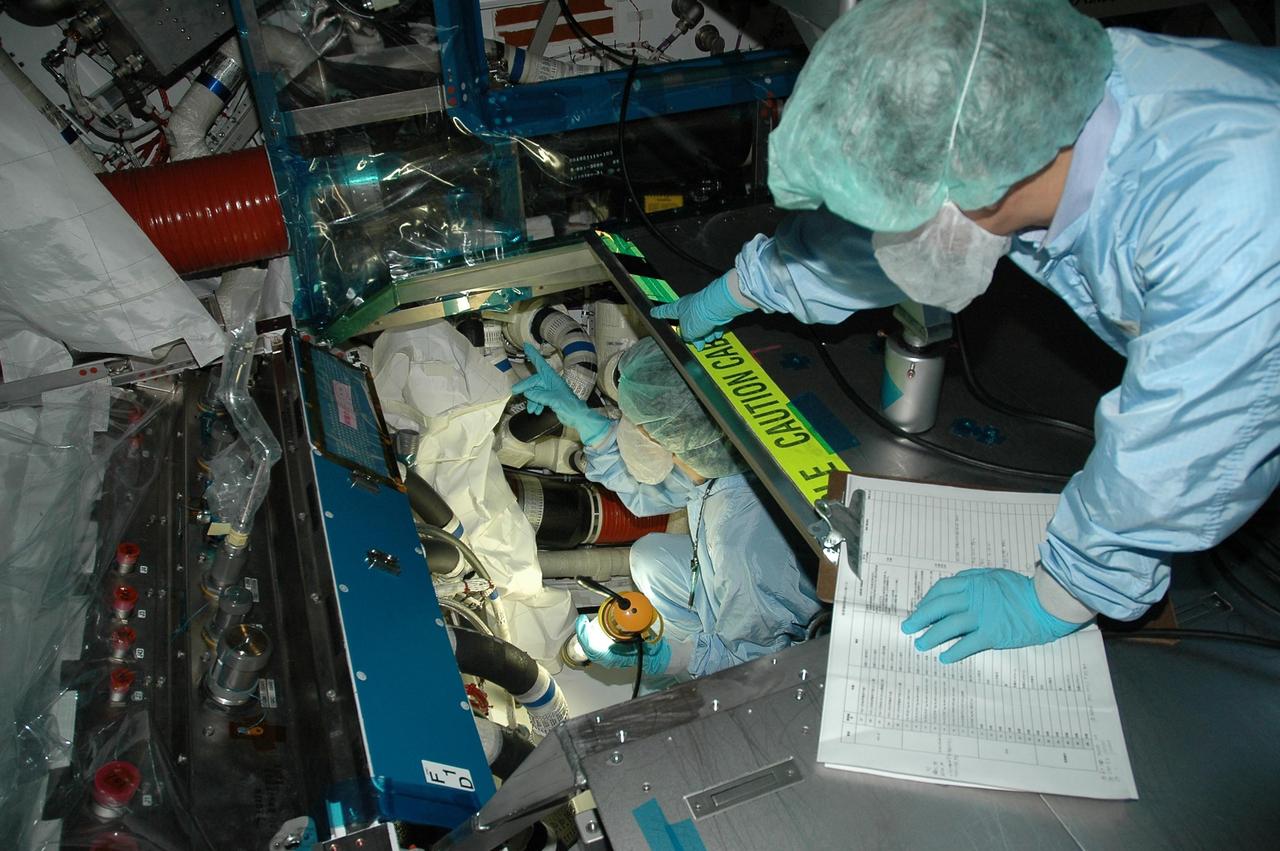

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) technician inspects the wiring on the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). The JEM, developed by JAXA for use on the International Space Station, is named Kibo -- which means "hope" in Japanese -- and will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. Research conducted in Kibo will focus on space medicine, biology, Earth observations, material production, biotechnology and communications. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
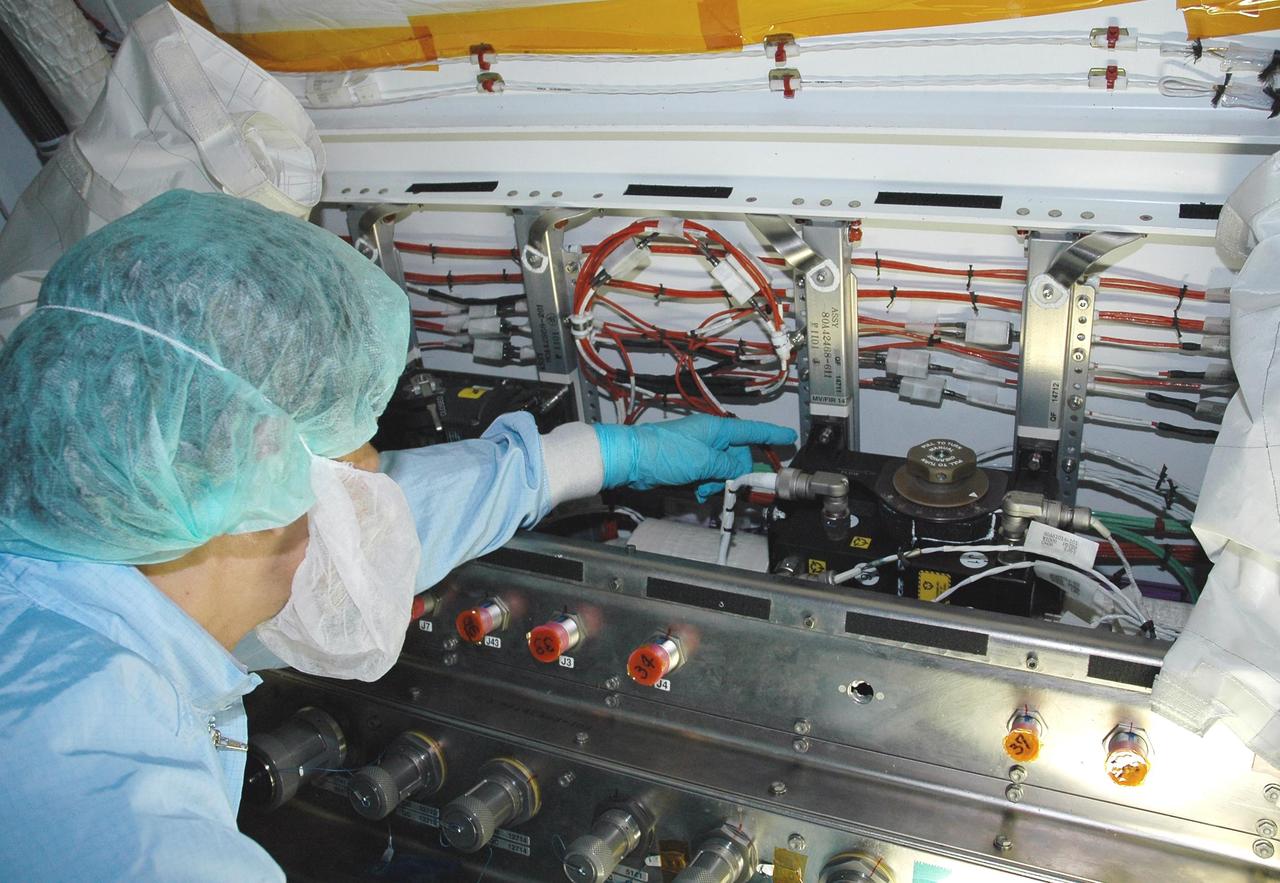

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) technicians inspect the wiring on the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). The JEM, developed by JAXA for use on the International Space Station, is named Kibo -- which means "hope" in Japanese -- and will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. Research conducted in Kibo will focus on space medicine, biology, Earth observations, material production, biotechnology and communications. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

S134-E-07608 (20 May 2011) --- NASA astronaut Andrew Feustel, STS-134 mission specialist, works to install a new Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) on the EXPRESS (Expedite the Processing of Experiments to Space Station) Logistics Carrier 2 (ELC2) during the first session of extravehicular activity (EVA-1) on NASA's next to last space shuttle flight. Photo credit: NASA