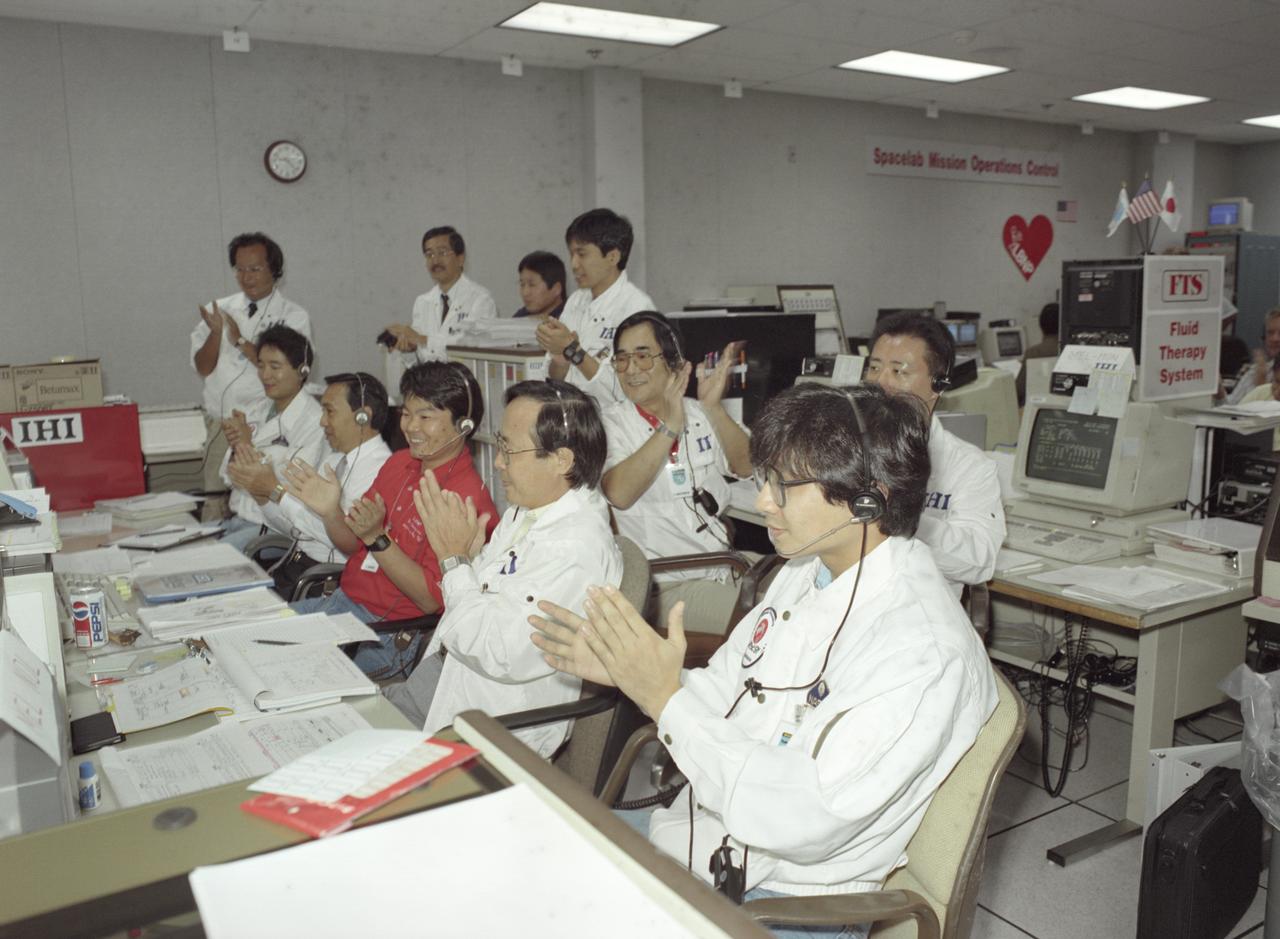

The science laboratory, Spacelab-J (SL-J), flown aboard the STS-47 flight was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a manned Spacelab module. The mission conducted 24 materials science and 20 life science experiments, of which 35 were sponsored by NASDA, 7 by NASA, and two collaborative efforts. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, and frogs and frog eggs. Featured together in the Science Operation Area (SOA) are payload specialists’ first Materials Processing Test during NASA/NASDA joint ground activities at the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
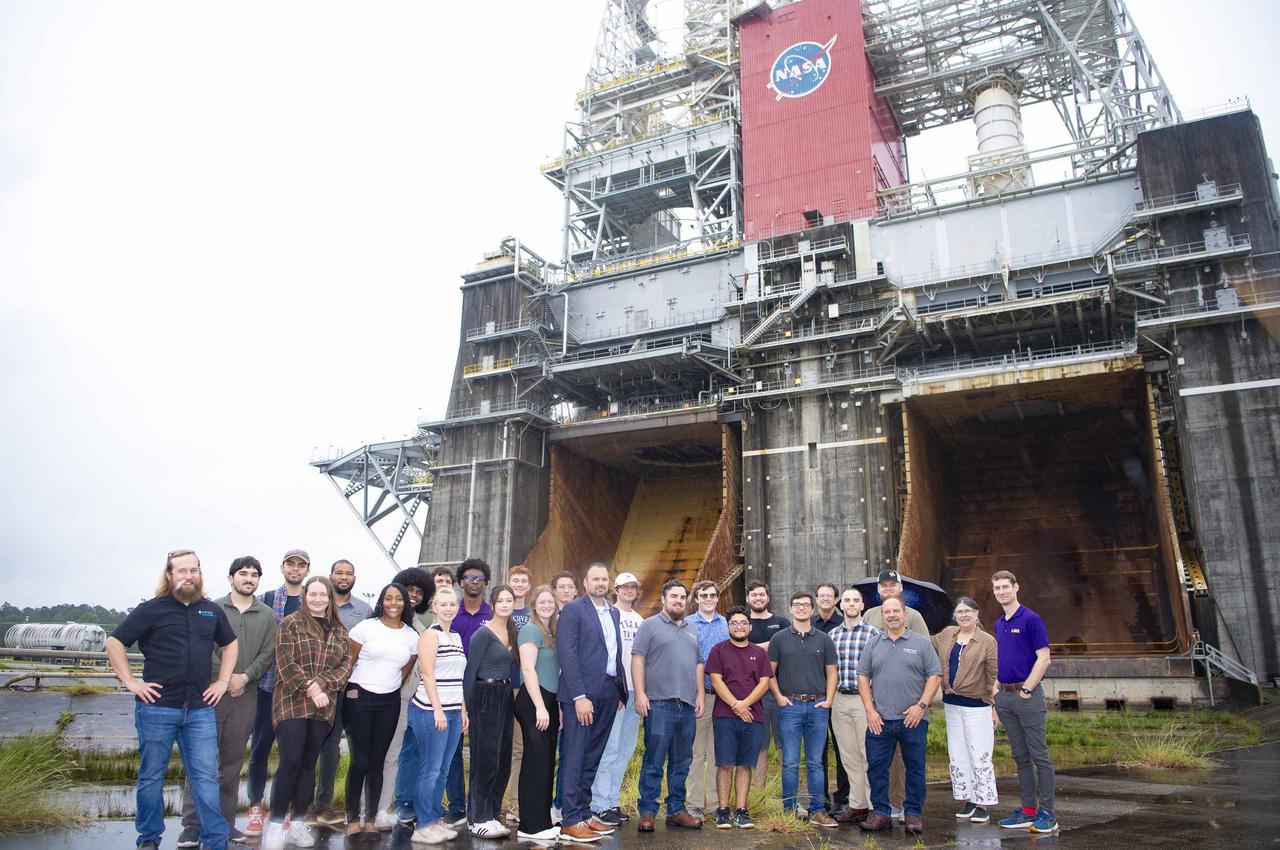

Members of the Society for the Advancement of Material and Process Engineering at Louisiana State University stand at the Thad Cochran Test Stand during a visit to NASA Stennis on Oct. 4. The Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-2) is where future Green Run testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage will take place ahead of future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. The mission of the Society for the Advancement of Material and Process Engineering at LSU is to provide enhanced educational opportunities by delivering information on new and advanced materials and processing technology.
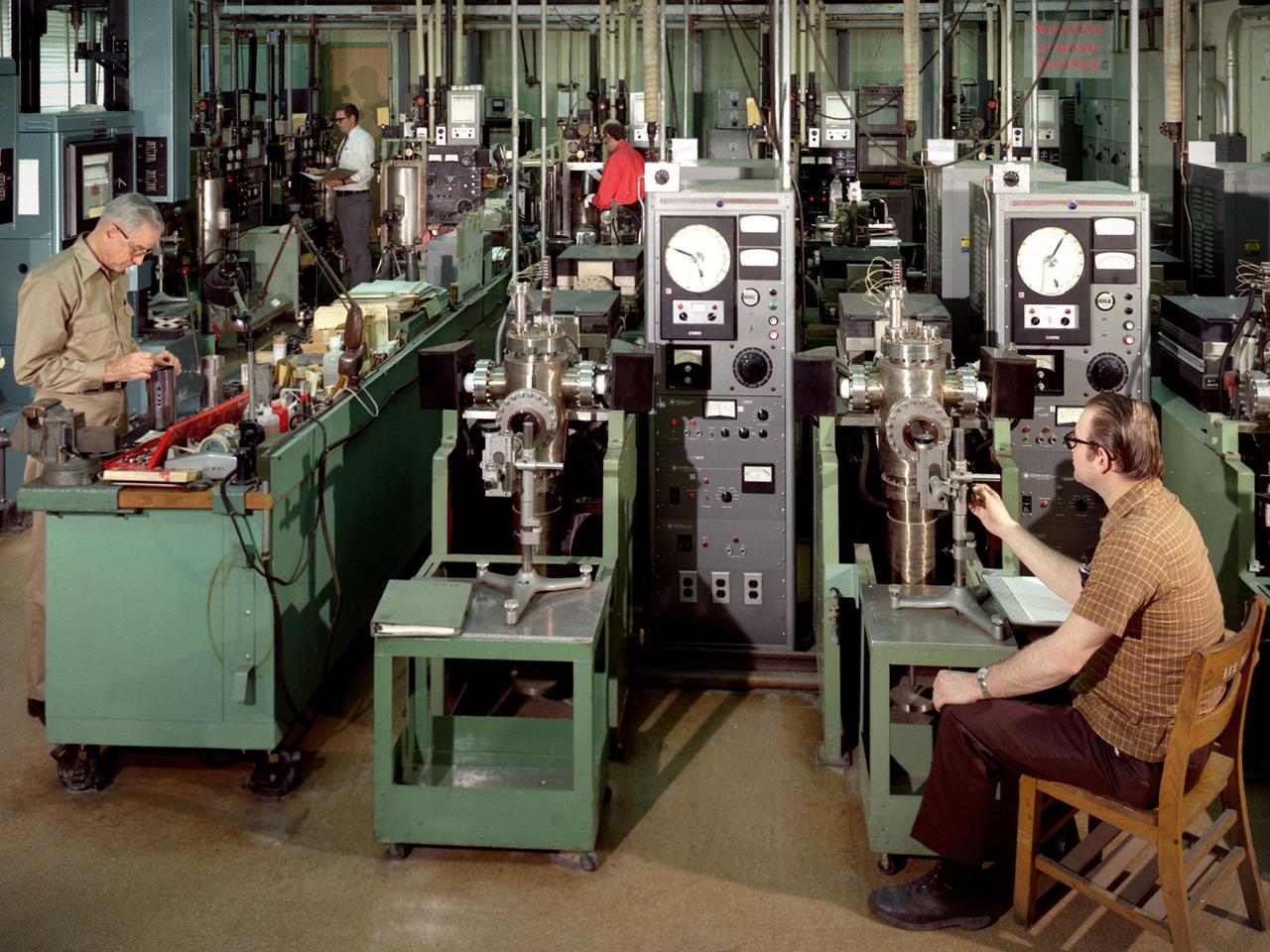

Technicians at work in the Materials Processing Laboratory’s Creep Facility at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The technicians supported the engineers’ studies of refractory materials, metals, and advanced superalloys. The Materials Processing Laboratory contained laboratories and test areas equipped to prepare and develop these metals and materials. The ultra-high vacuum lab, seen in this photograph, contained creep and tensile test equipment. Creep testing is used to study a material’s ability to withstand long durations under constant pressure and temperatures. The equipment measured the strain over a long period of time. Tensile test equipment subjects the test material to strain until the material fails. The two tests were used to determine the strength and durability of different materials. The Materials Processing Laboratory also housed arc and electron beam melting furnaces, a hydraulic vertical extrusion press, compaction and forging equipment, and rolling mills and swagers. There were cryogenic and gas storage facilities and mechanical and oil diffusion vacuum pumps. The facility contained both instrumental and analytical chemistry laboratories for work on radioactive or toxic materials and the only shop to machine toxic materials in the Midwest.
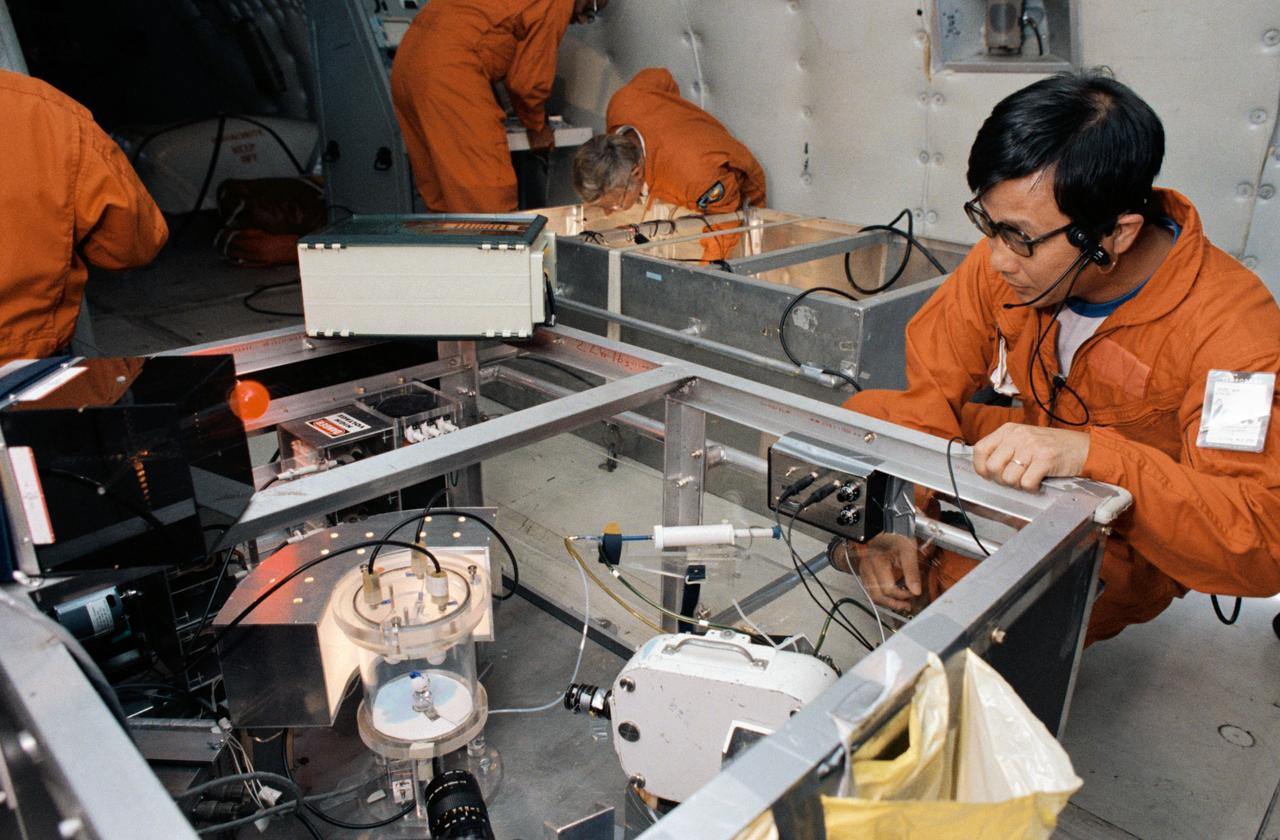

Weightless testing of the MSFC Materials Processing in Space Experiment onboard the KC-135, NASA 930, 10/26/1983.
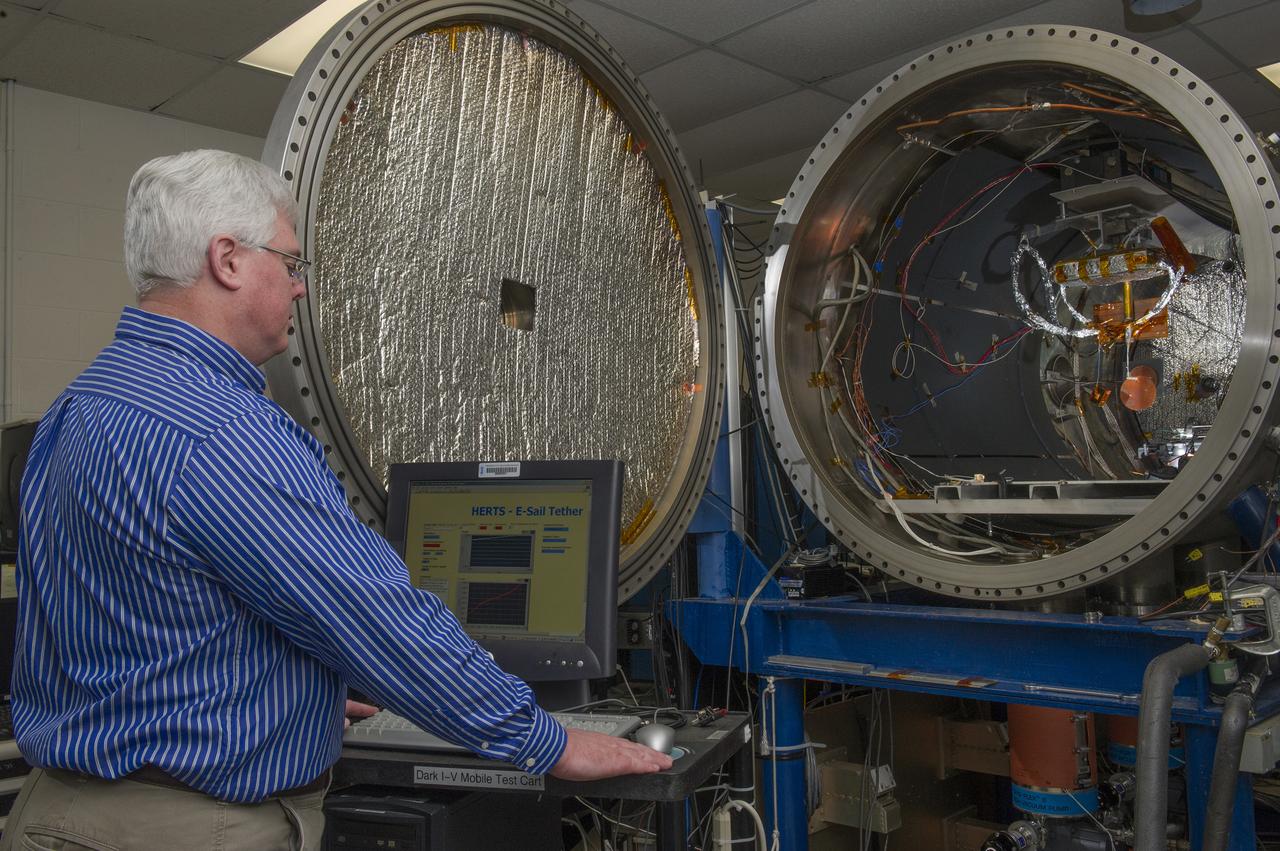

TODD SCHNEIDER PREPARES A PLASMA CHAMBER IN BUILDING 4605 AT MSFC FOR AN UPCOMING TEST. SCHNEIDER IS A PHYSICIST IN THE MATERIALS AND PROCESSES DEPARTMENT AT MSFC.
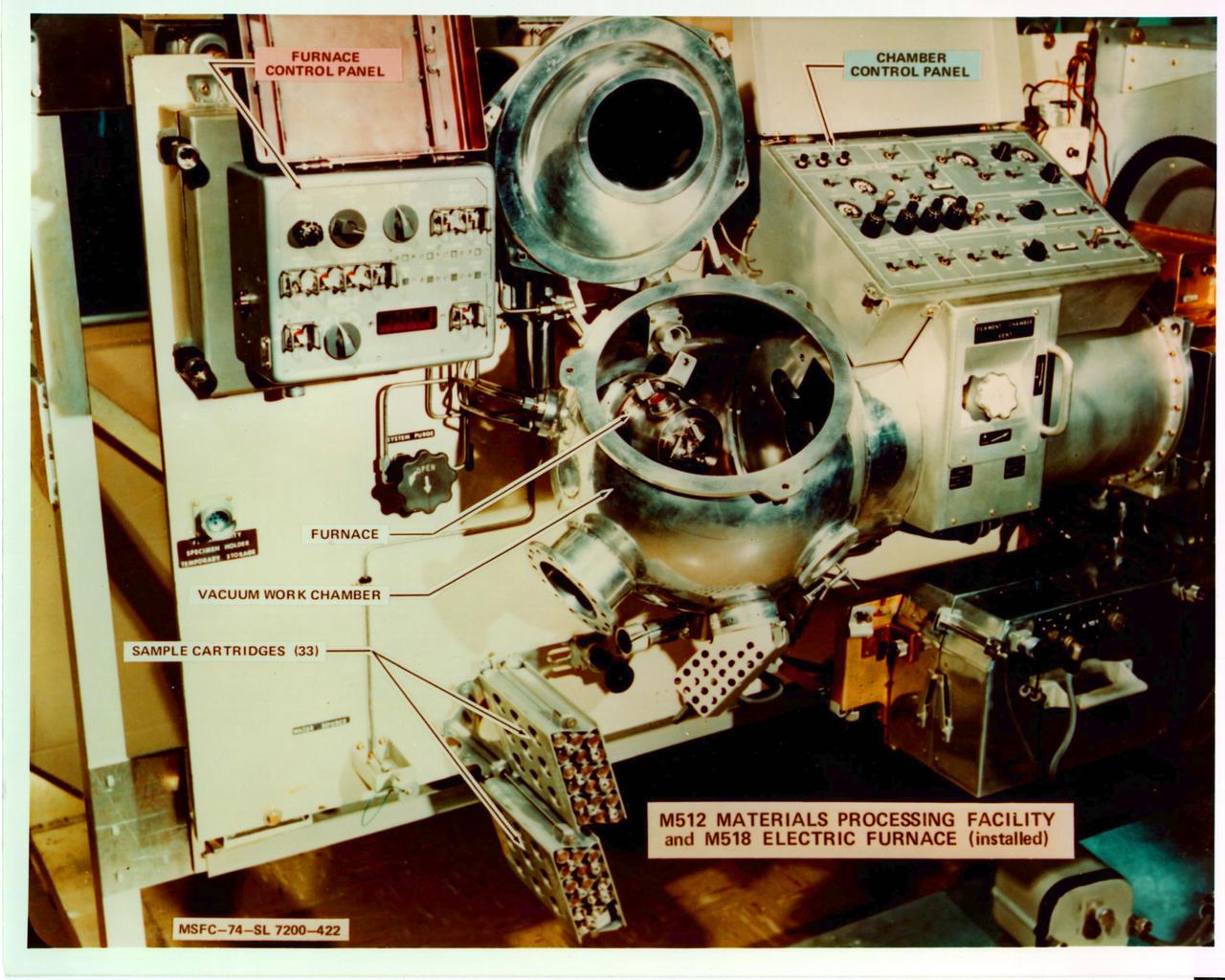
The M512 Materials Processing Facility (MPF) with the M518 Multipurpose Electric Facility (MEF) tested and demonstrated a facility approach for materials process experimentation in space. It also provided a basic apparatus and a common interface for a group of metallic and nonmetallic materials experiments. The MPF consisted of a vacuum work chamber and associated mechanical and electrical controls. The M518 Multipurpose Electric Furnace (MEF) was an electric furnace system in which solidification, crystal growth, and other experiments involving phase changes were performed.
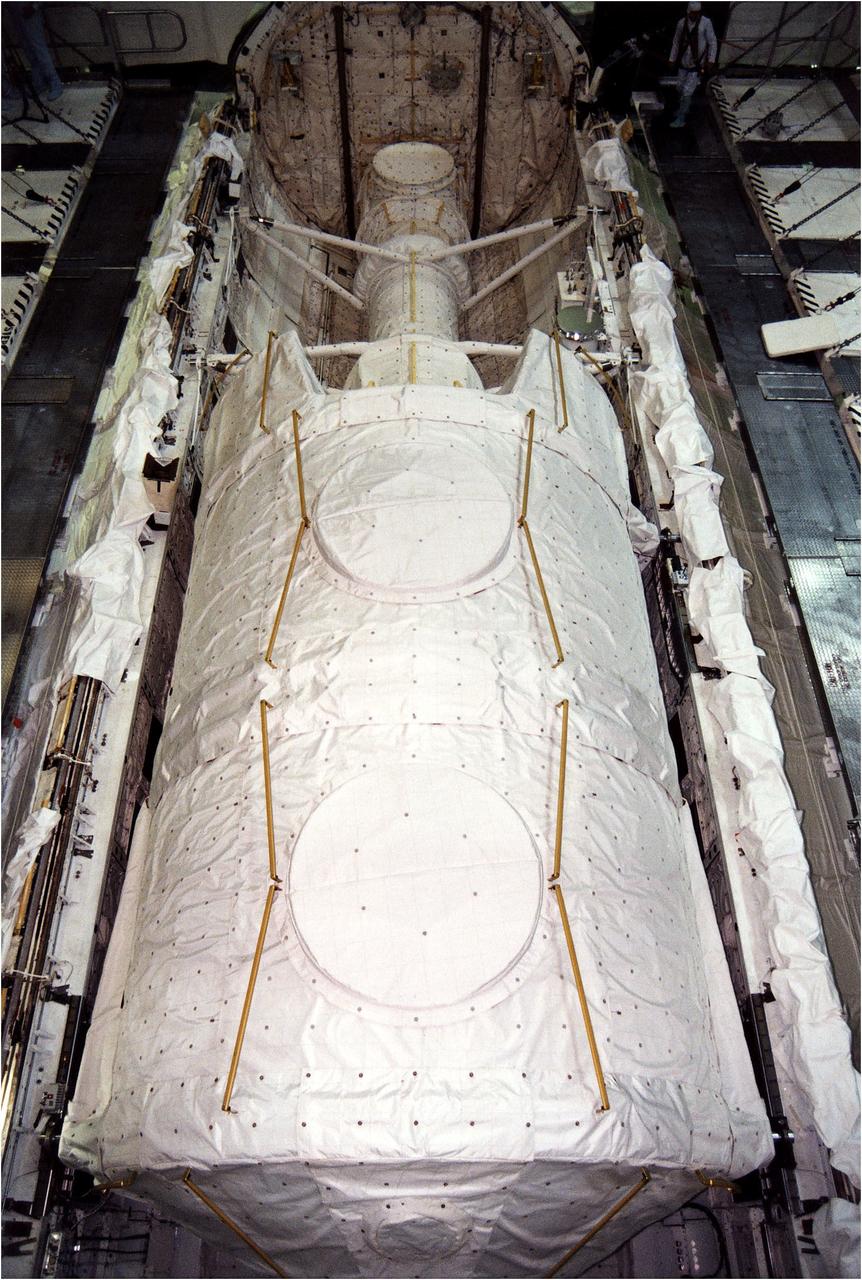
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is installed into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia in Orbiter Processing Facility 1. The Spacelab long crew transfer tunnel that leads from the orbiter's crew airlock to the module is also aboard, as well as the Hitchhiker Cryogenic Flexible Diode (CRYOFD) experiment payload, which is attached to the right side of Columbia's payload bay. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments.
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is installed into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia in Orbiter Processing Facility 1. The Spacelab long crew transfer tunnel that leads from the orbiter's crew airlock to the module is also aboard, as well as the Hitchhiker Cryogenic Flexible Diode (CRYOFD) experiment payload, which is attached to the right side of Columbia's payload bay. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, packing material is placed over the nose cap that was removed from Atlantis. The reinforced carbon-carbon (RCC) nose cap is being sent to the original manufacturing company, Vought in Ft. Worth, Texas, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, to undergo non-destructive testing such as CAT scan and thermography.
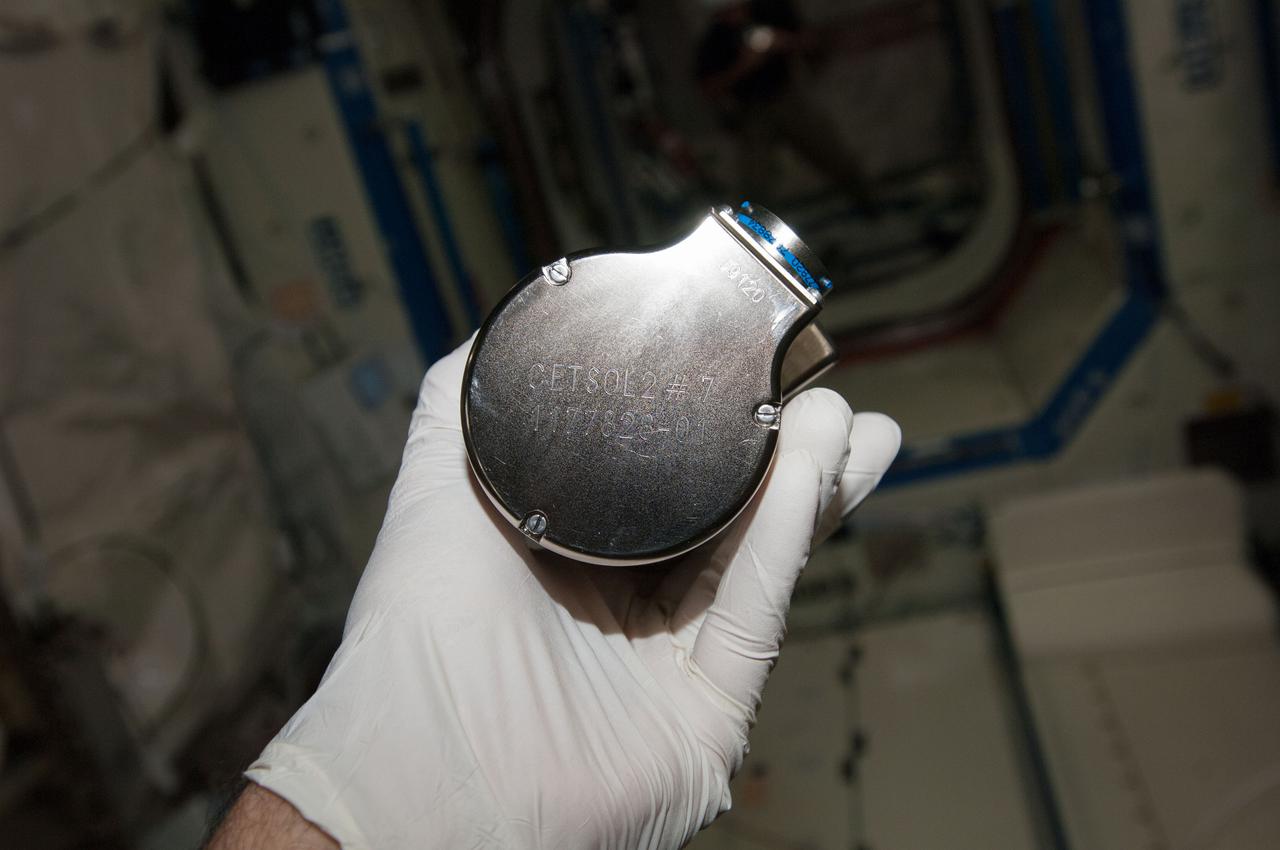

iss038e045758 (2/12/2014) --- A view of Columnar-to-Equiaxed Transition in Solidification Processing-2 (CETSOL-2) test sample 7 which is to be installed into the Material Science Laboratory (MSL) Solidification and Quench Furnace (SQF). This investigation aims to deepen the understanding of the physical principles that govern solidification processes in metal alloys. The patterns of the crystals resulting from transitions of liquids to solids is important for processes used to produce materials such as solar cells, thermoelectrics, and metal alloys.
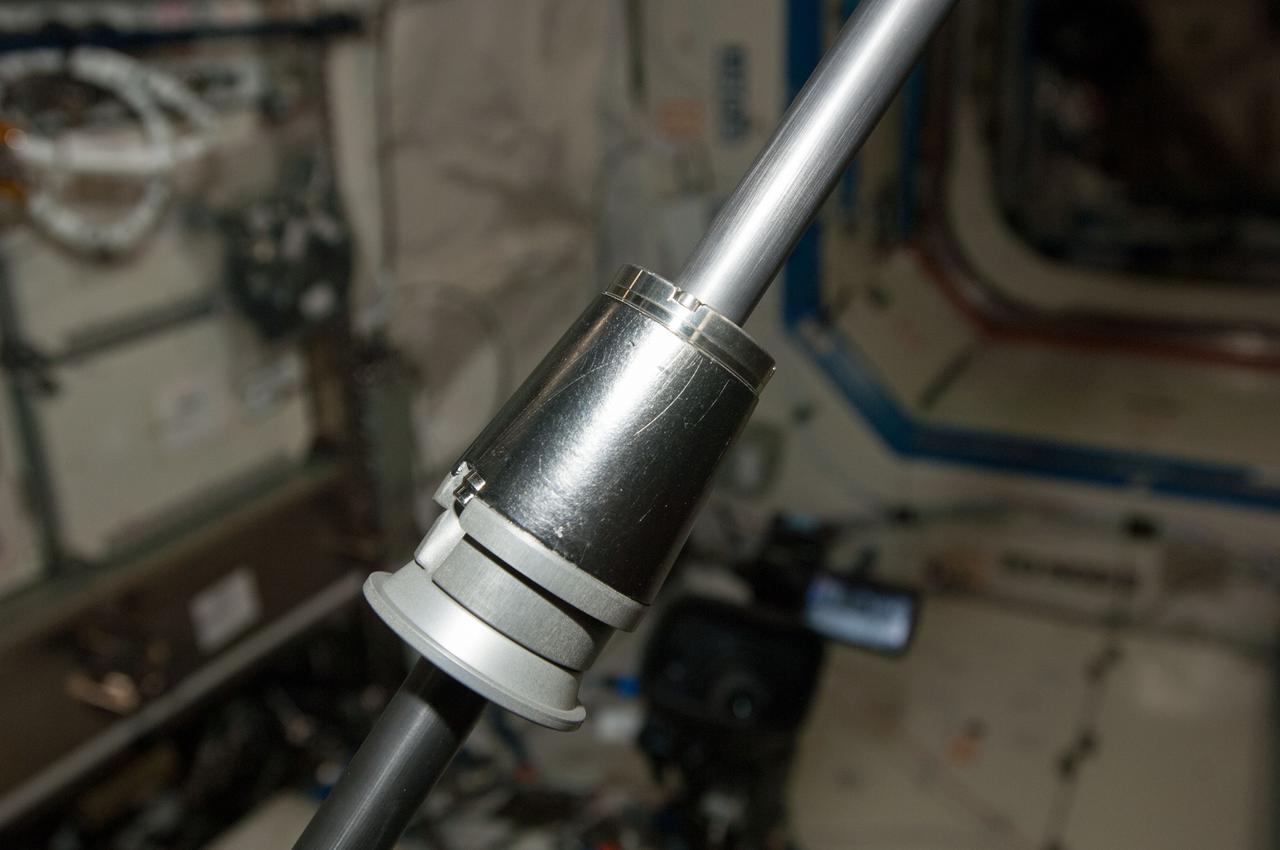

iss038e045760 92/12/2014) --- A view of Columnar-to-Equiaxed Transition in Solidification Processing-2 (CETSOL-2) test sample 7 which is to be installed into the Material Science Laboratory (MSL) Solidification and Quench Furnace (SQF). This investigation aims to deepen the understanding of the physical principles that govern solidification processes in metal alloys. The patterns of the crystals resulting from transitions of liquids to solids is important for processes used to produce materials such as solar cells, thermoelectrics, and metal alloys.
TODD SCHNEIDER LOOKS UP FROM WORK AT THE DOOR OF T HE HIGH INTENSITY SOLAR ENVIRONMENT TEST SYSTEM IN BUILDING 4605. SCHNEIDER IS A PHYSICIST IN THE MATERIALS AND PROCESSES DEPARTMENT AT MSFC AND IS PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR FOR HISET.
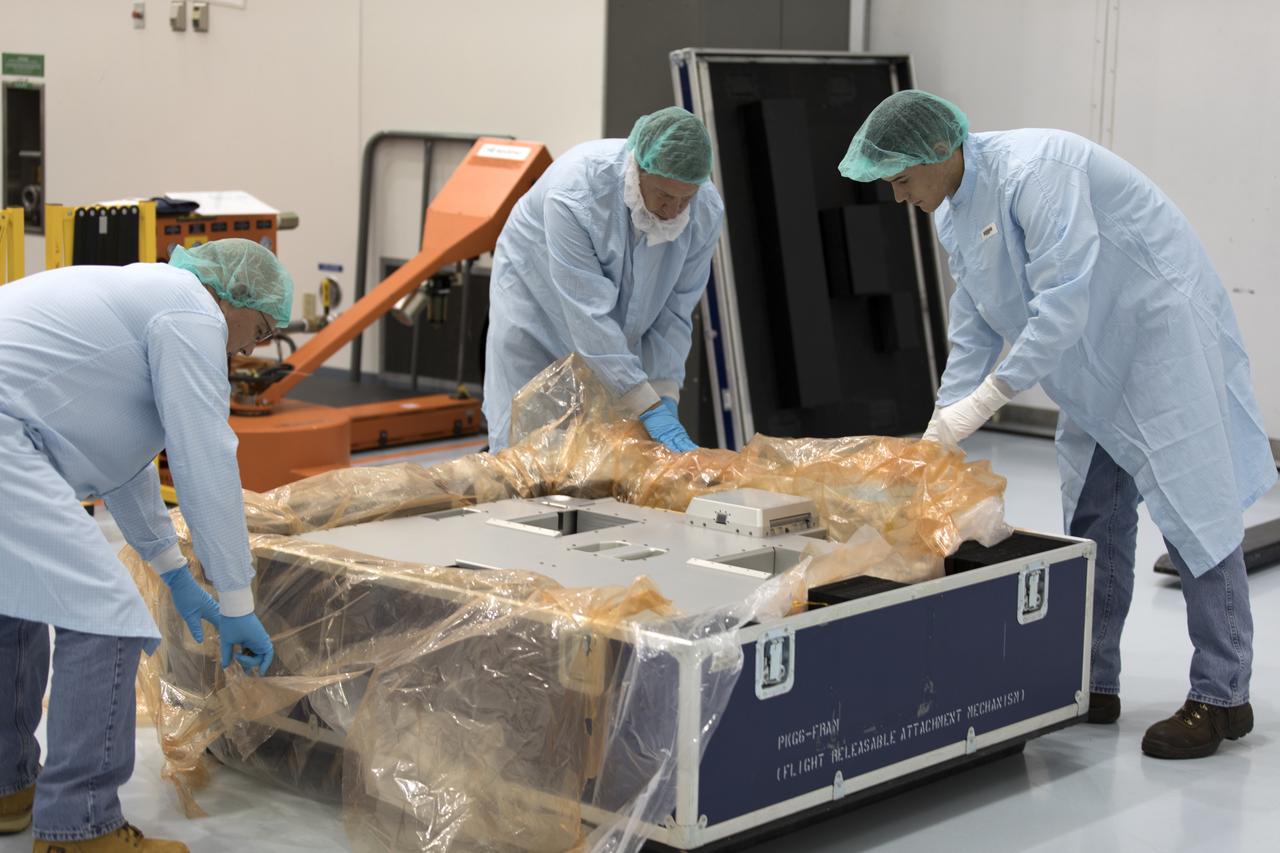

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. MISSE will be unpacked for integration and processing. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
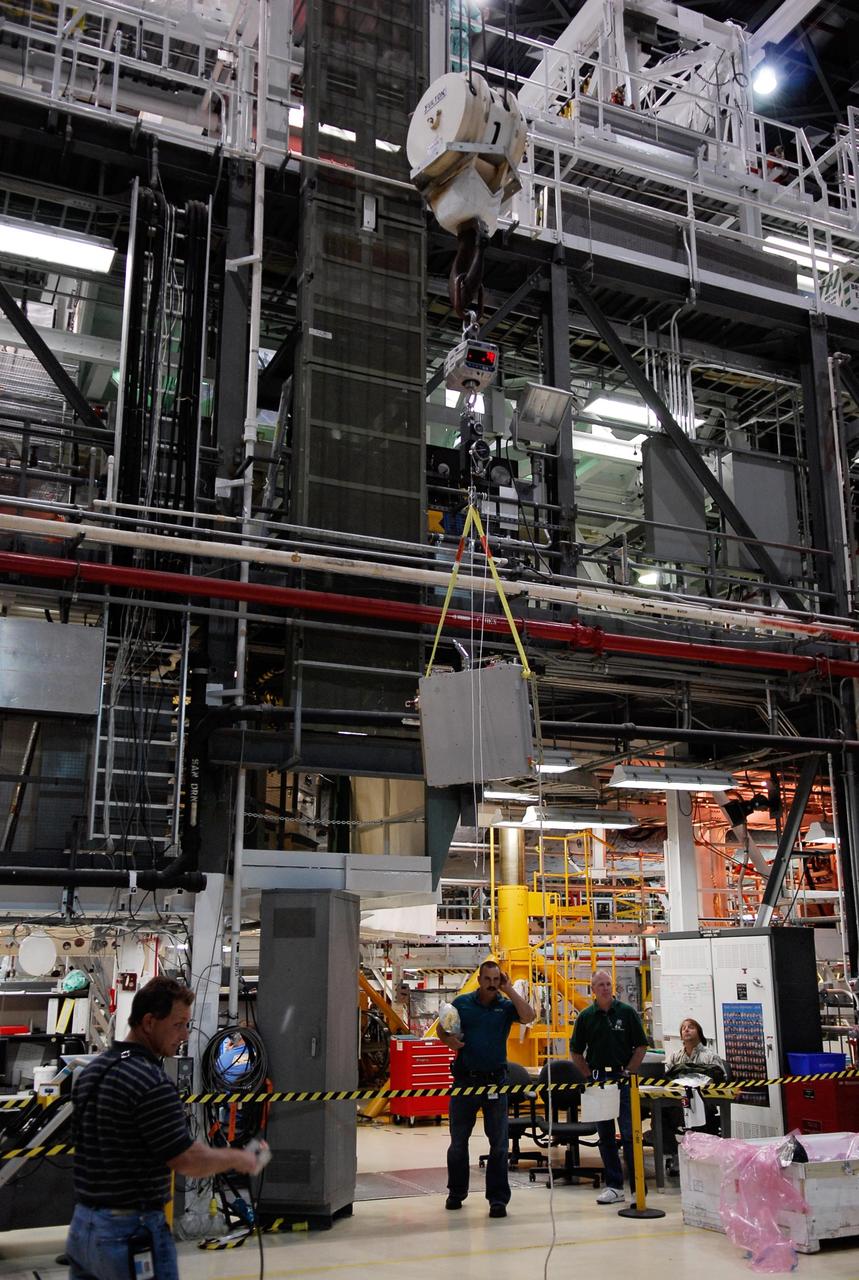

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, one of two Materials International Space Station Experiments, or MISSE, is moved across facility toward space shuttle Endeavour. The MISSE is part of the payload onboard Endeavour for mission STS-123 and will be installed in the payload bay. The MISSE project is a NASA/Langley Research Center-managed cooperative endeavor to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the International Space Station. The objective is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components planned for use on future spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
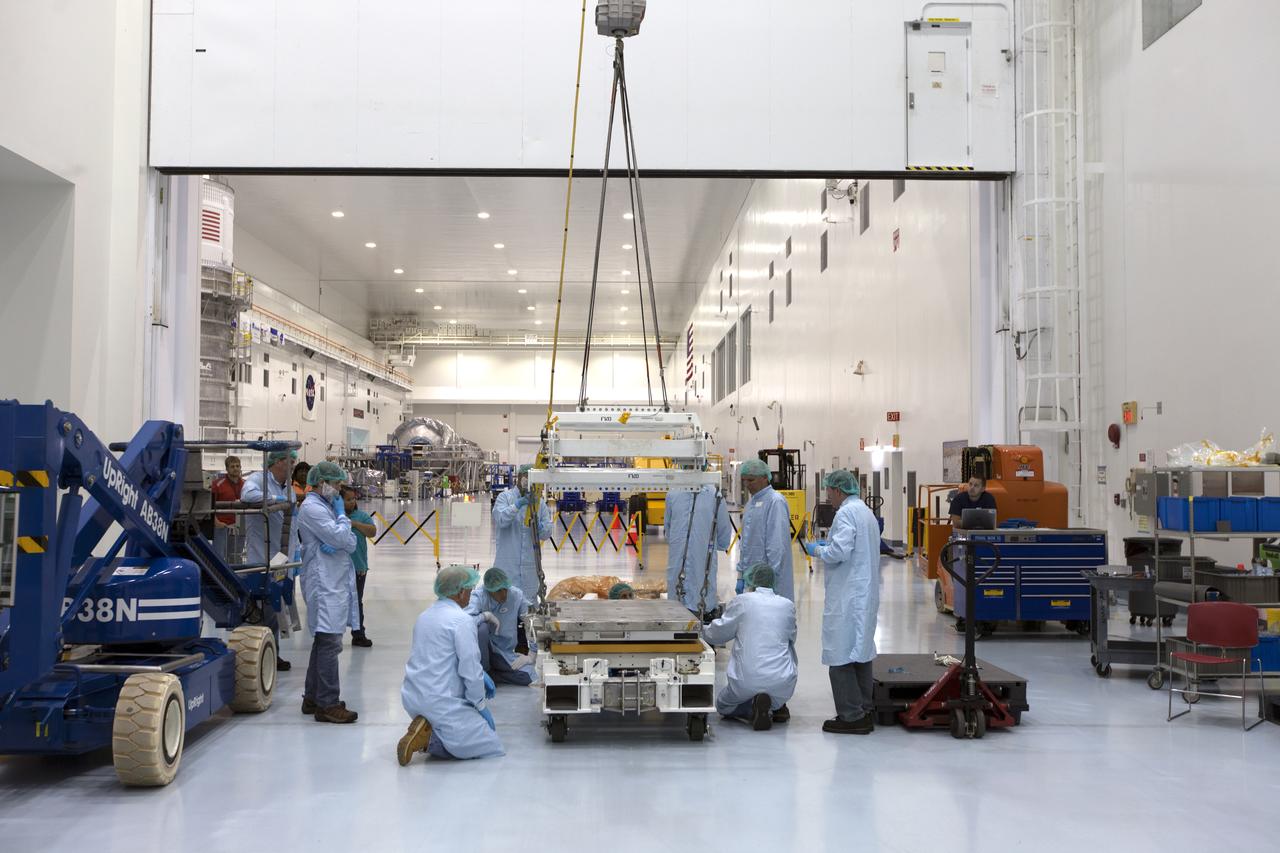

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as one of the components is lowered onto another MISSE component. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
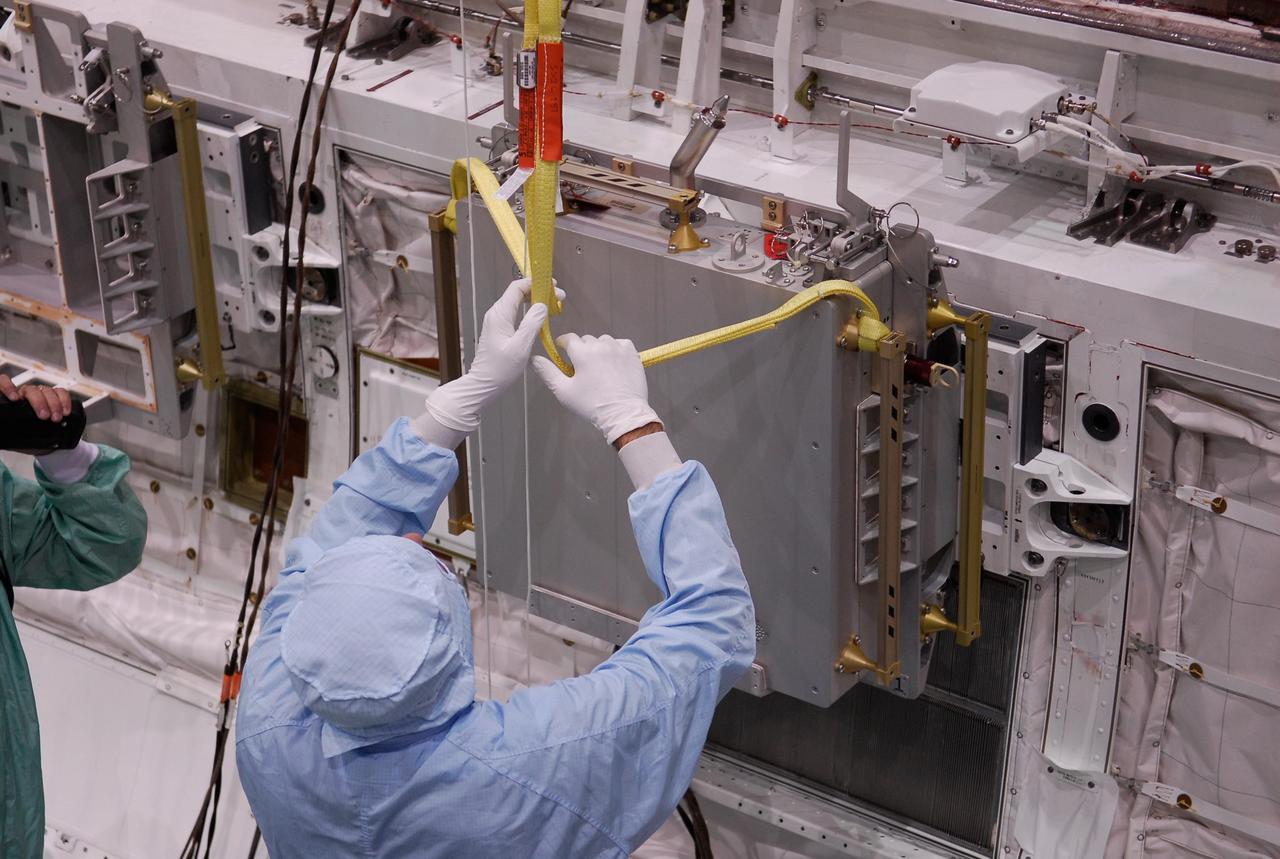

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, one of two Materials International Space Station Experiments, or MISSE, is lowered into space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay for installation. The MISSE is part of the payload onboard Endeavour for mission STS-123. The MISSE project is a NASA/Langley Research Center-managed cooperative endeavor to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the International Space Station. The objective is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components planned for use on future spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
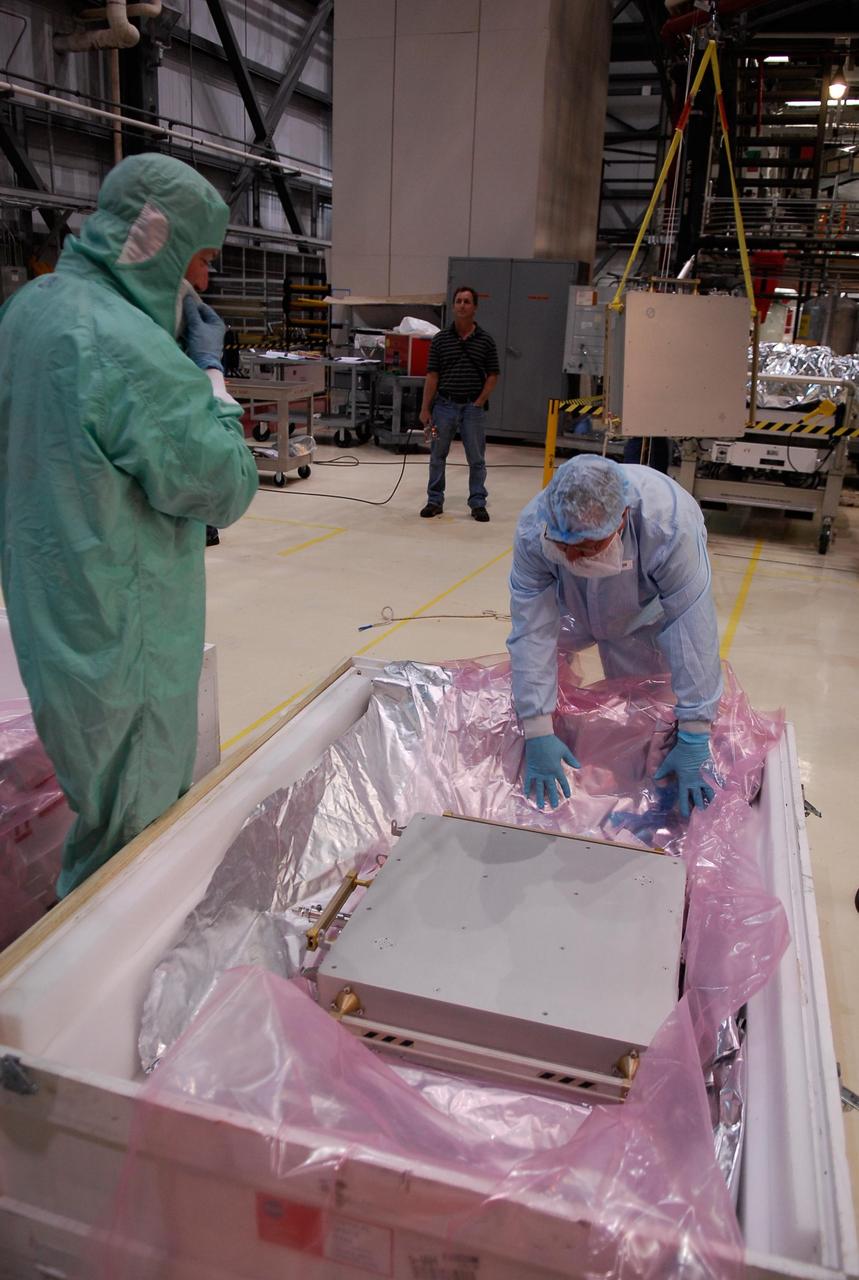

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, technicians get ready to remove another Materials International Space Station Experiments, or MISSE, from a shipping container. The MISSE is part of the payload onboard space shuttle Endeavour for mission STS-123. It will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. The MISSE project is a NASA/Langley Research Center-managed cooperative endeavor to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the International Space Station. The objective is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components planned for use on future spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, technicians help lift the first of the Materials International Space Station Experiments, or MISSE, from a shipping container. The MISSE is part of the payload onboard space shuttle Endeavour for mission STS-123. It will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. The MISSE project is a NASA/Langley Research Center-managed cooperative endeavor to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the International Space Station. The objective is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components planned for use on future spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the second of two Materials International Space Station Experiments, or MISSE, is lowered into space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay for installation. The MISSE is part of the payload onboard Endeavour for mission STS-123. The MISSE project is a NASA/Langley Research Center-managed cooperative endeavor to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the International Space Station. The objective is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components planned for use on future spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
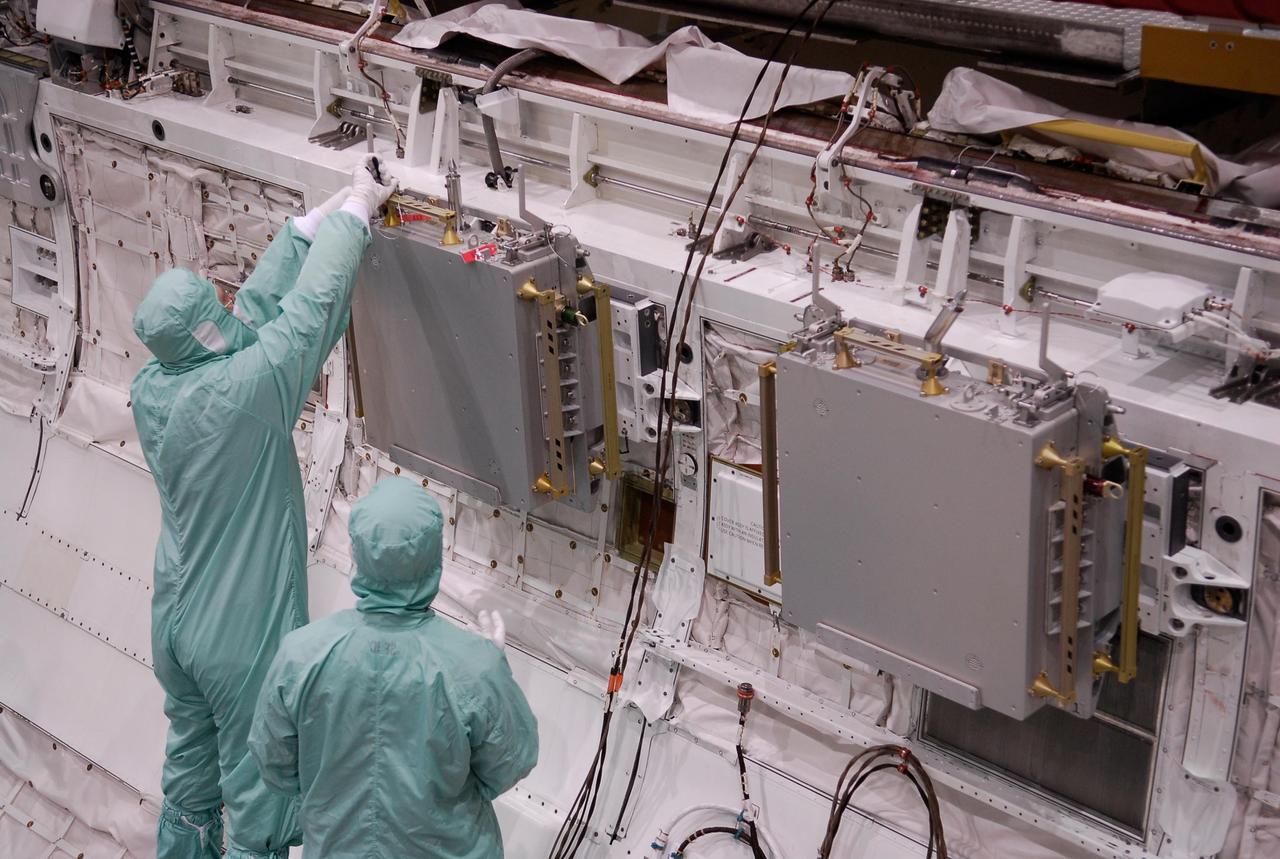

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, technicians install the second Materials International Space Station Experiments, or MISSE, in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The MISSE is part of the payload onboard Endeavour for mission STS-123. The MISSE project is a NASA/Langley Research Center-managed cooperative endeavor to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the International Space Station. The objective is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components planned for use on future spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
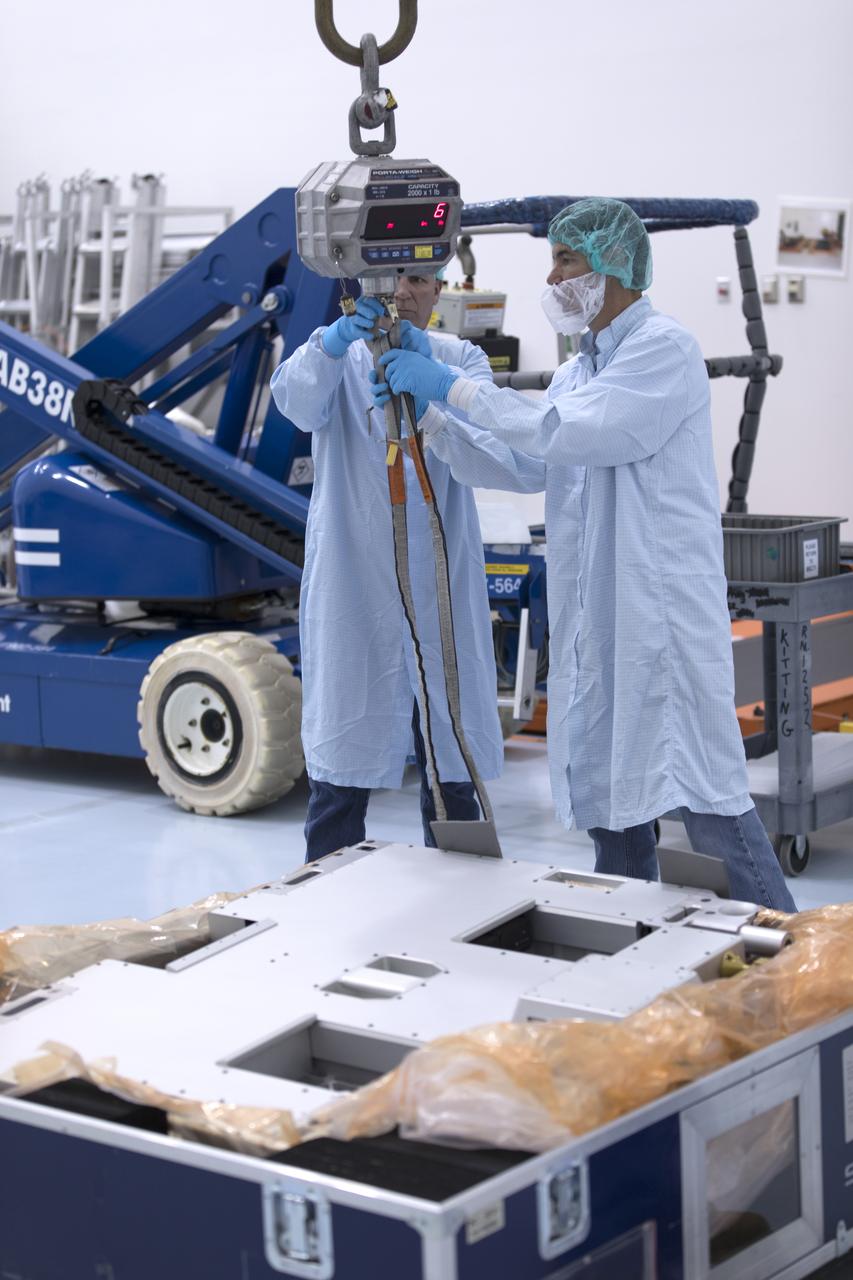

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians work to attach a crane to MISSE for lifting out of its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
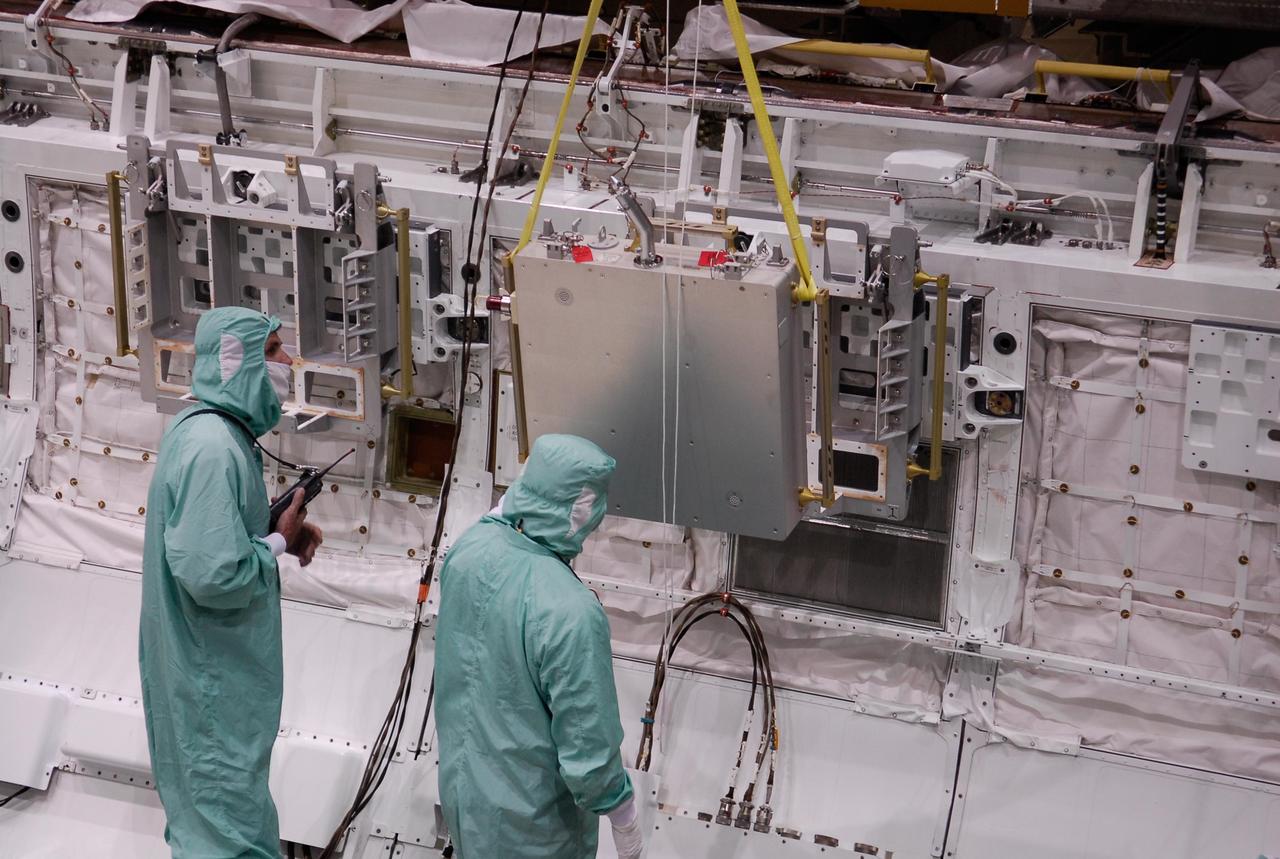

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, one of two Materials International Space Station Experiments, or MISSE, is lowered into space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay for installation. The MISSE is part of the payload onboard Endeavour for mission STS-123. The MISSE project is a NASA/Langley Research Center-managed cooperative endeavor to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the International Space Station. The objective is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components planned for use on future spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
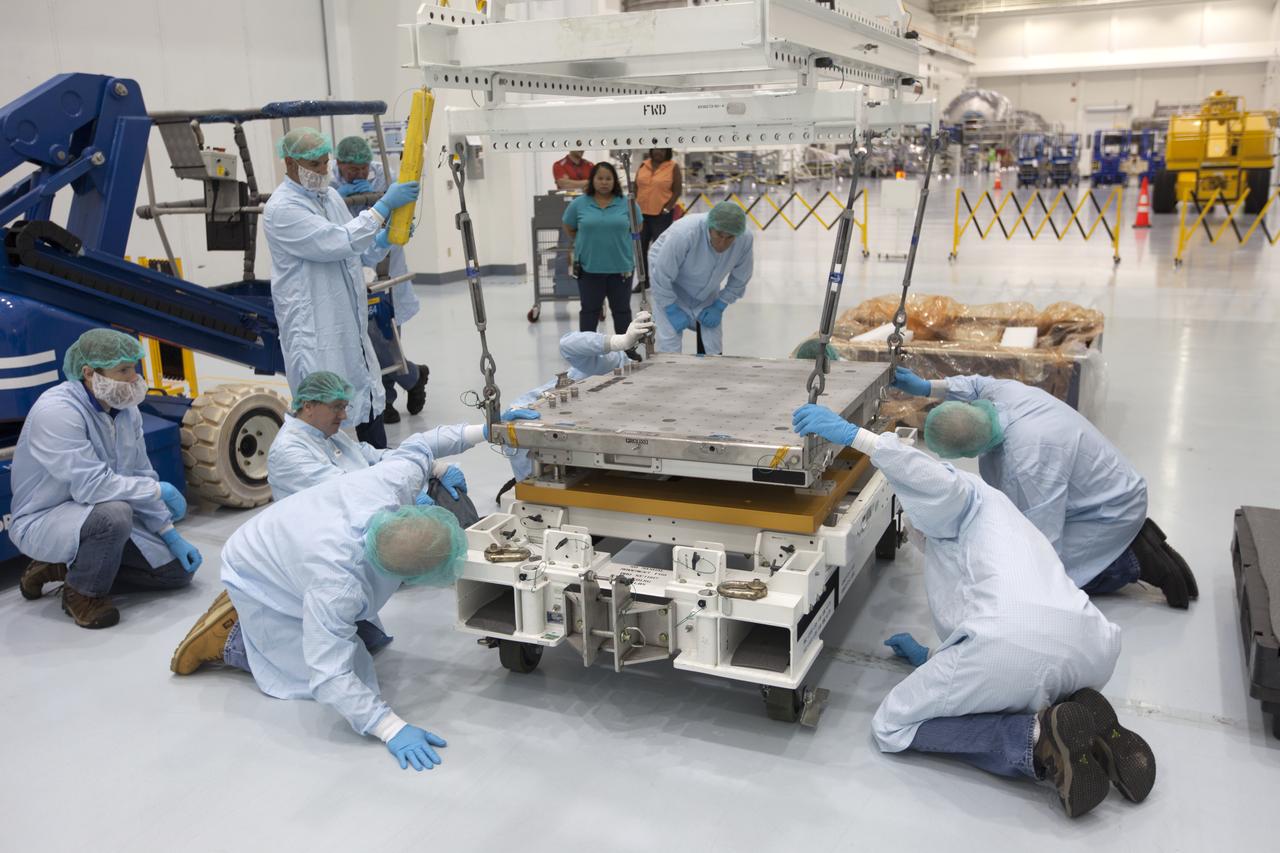

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as one of the components is lowered onto another MISSE component. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
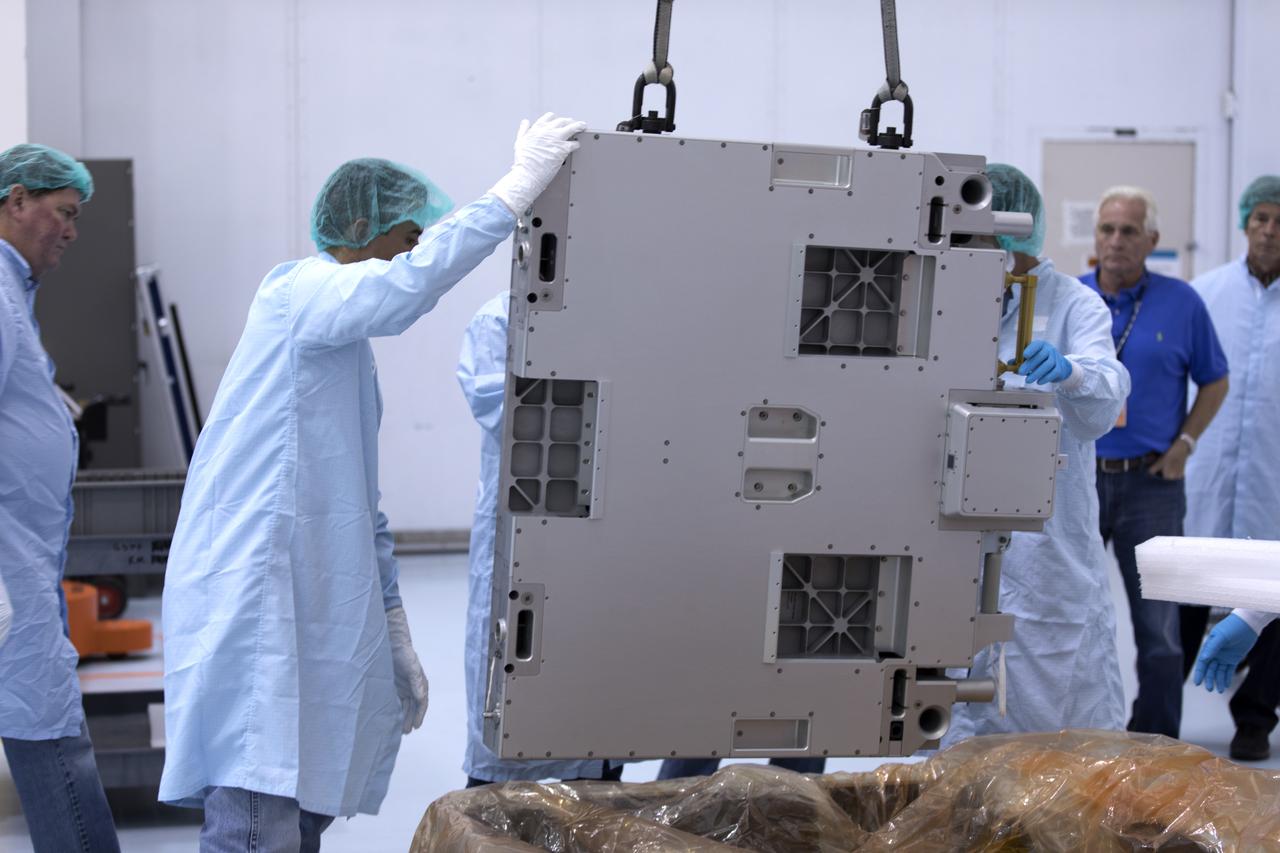

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as a crane is used to lift MISSE out of its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
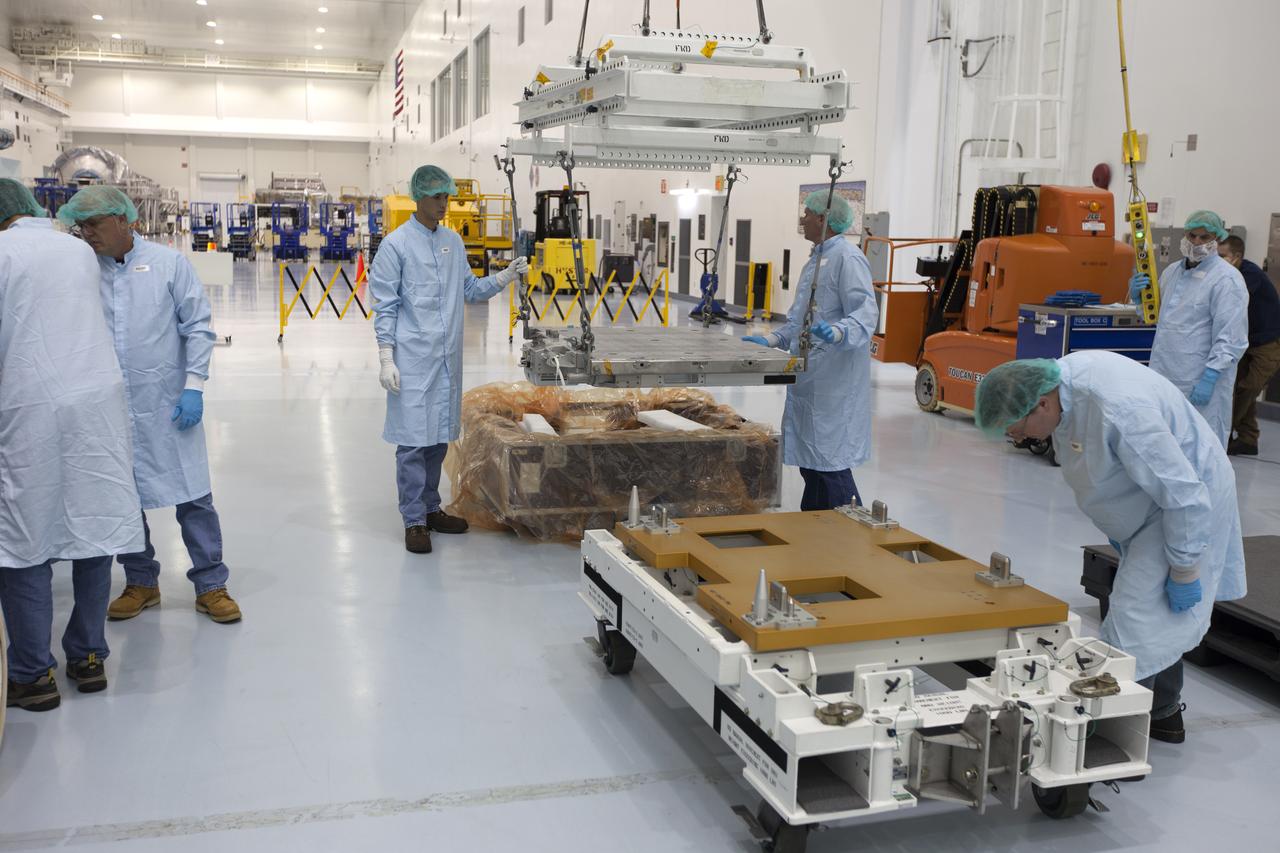

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as MISSE is lifted by crane from its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
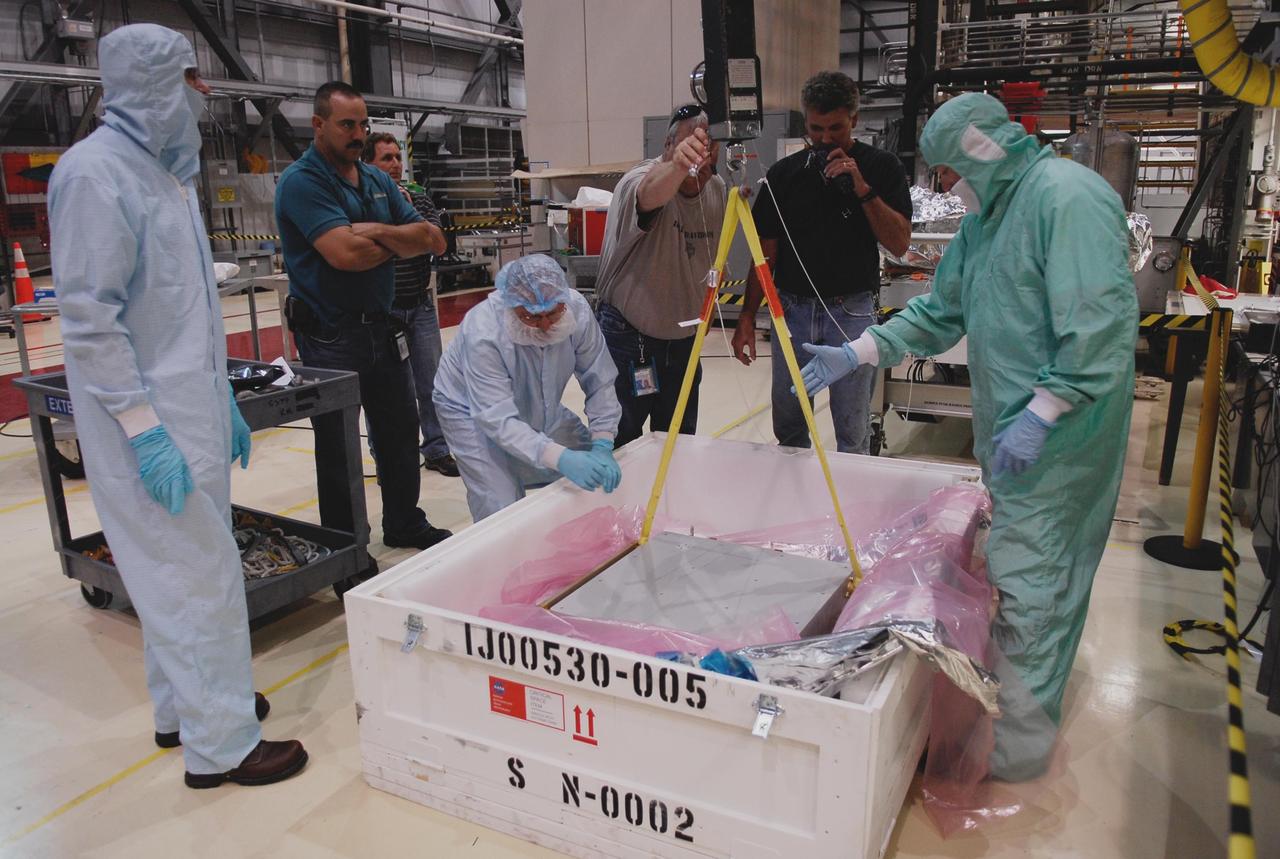

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, technicians get ready to remove one of two Materials International Space Station Experiments, or MISSE, from a shipping container. The MISSE is part of the payload onboard space shuttle Endeavour for mission STS-123. It will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. The MISSE project is a NASA/Langley Research Center-managed cooperative endeavor to fly materials and other types of space exposure experiments on the International Space Station. The objective is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components planned for use on future spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
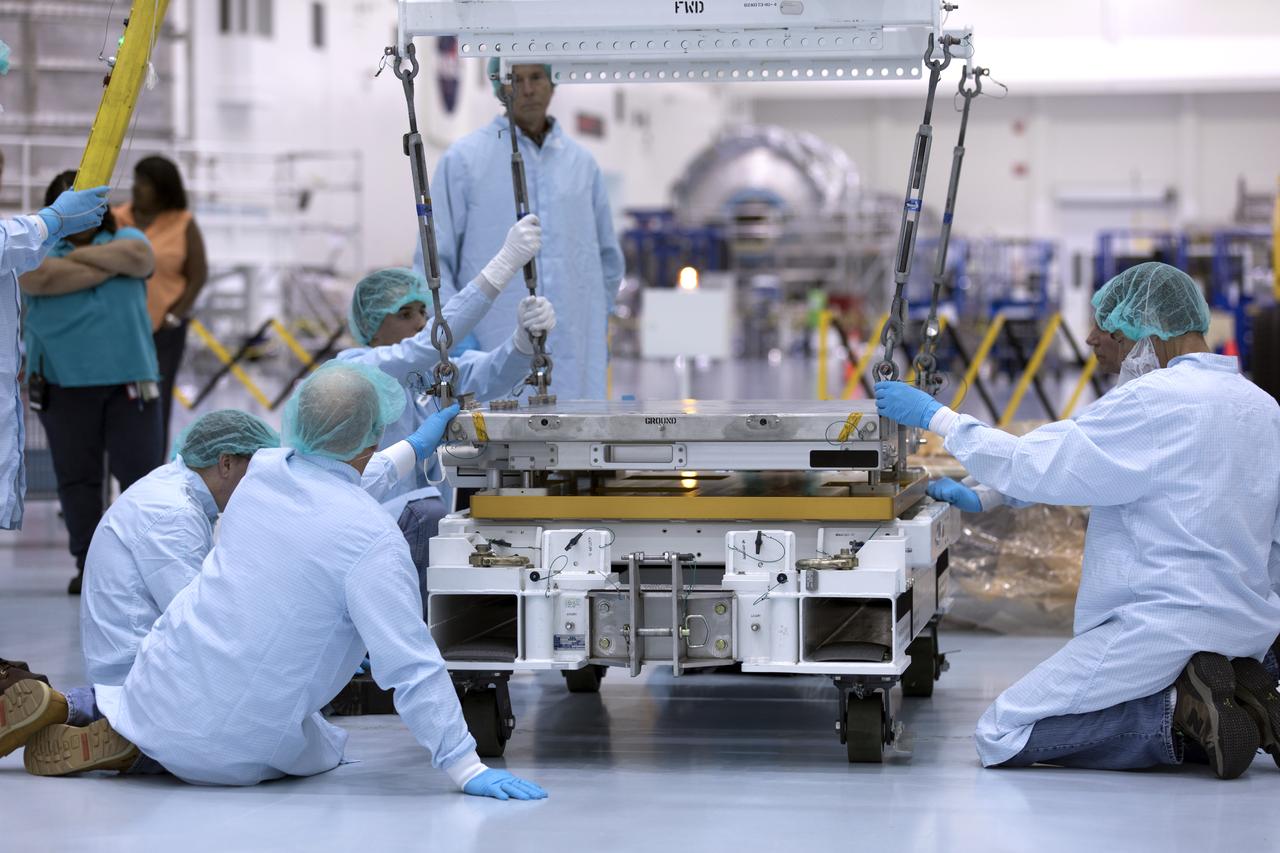

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as one of the components is lowered and secured onto another MISSE component. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
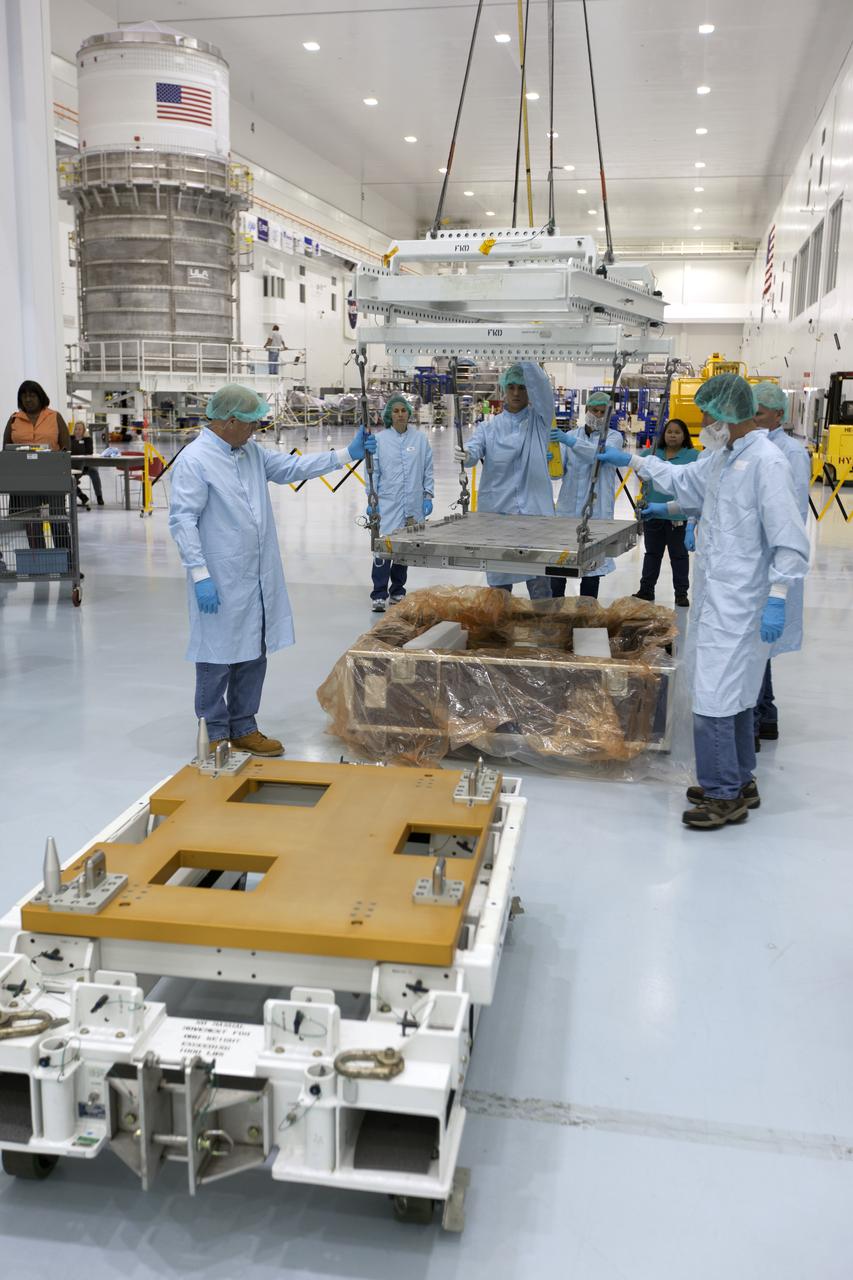

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as MISSE is lifted by crane from its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
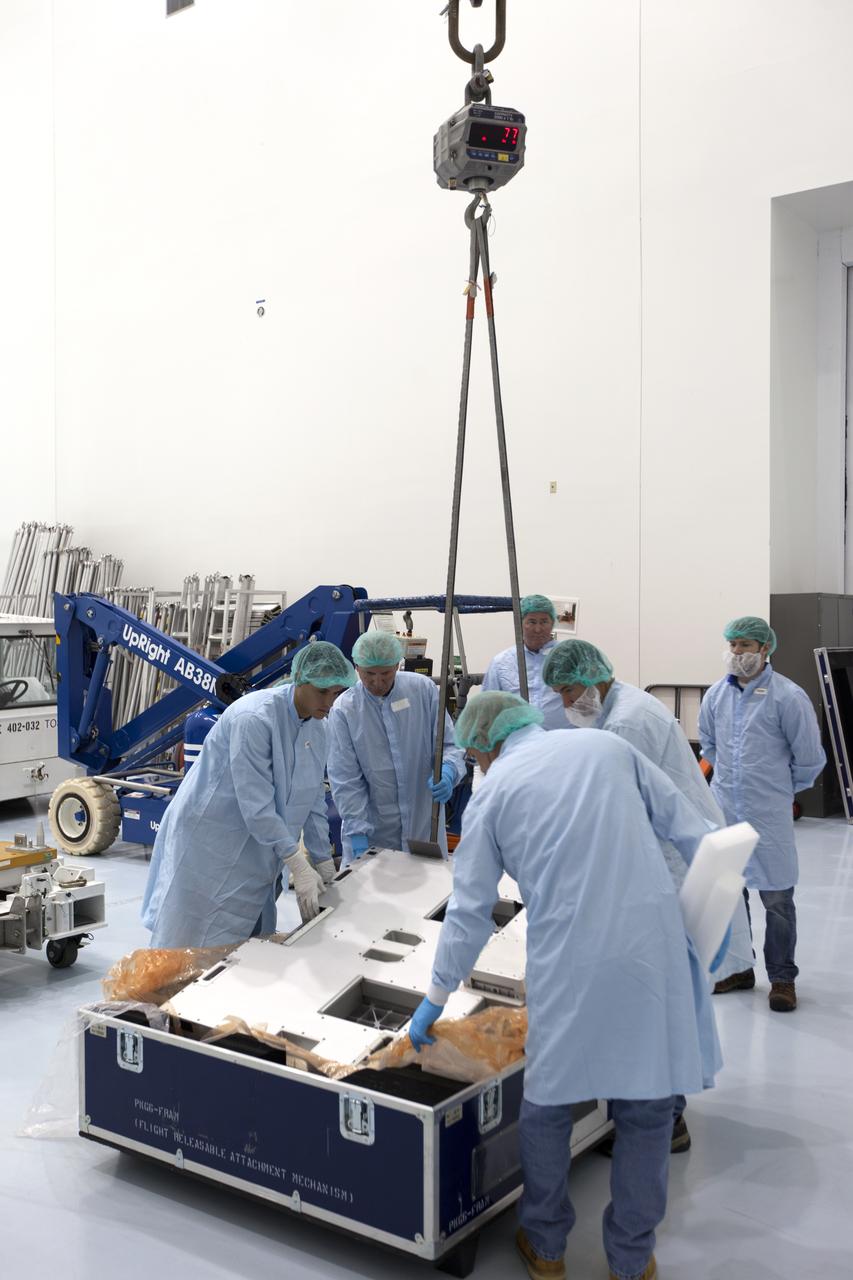

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians attach a crane to MISSE for lifting out of its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.

The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is lowered into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia in Orbiter Processing Facility 1. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments
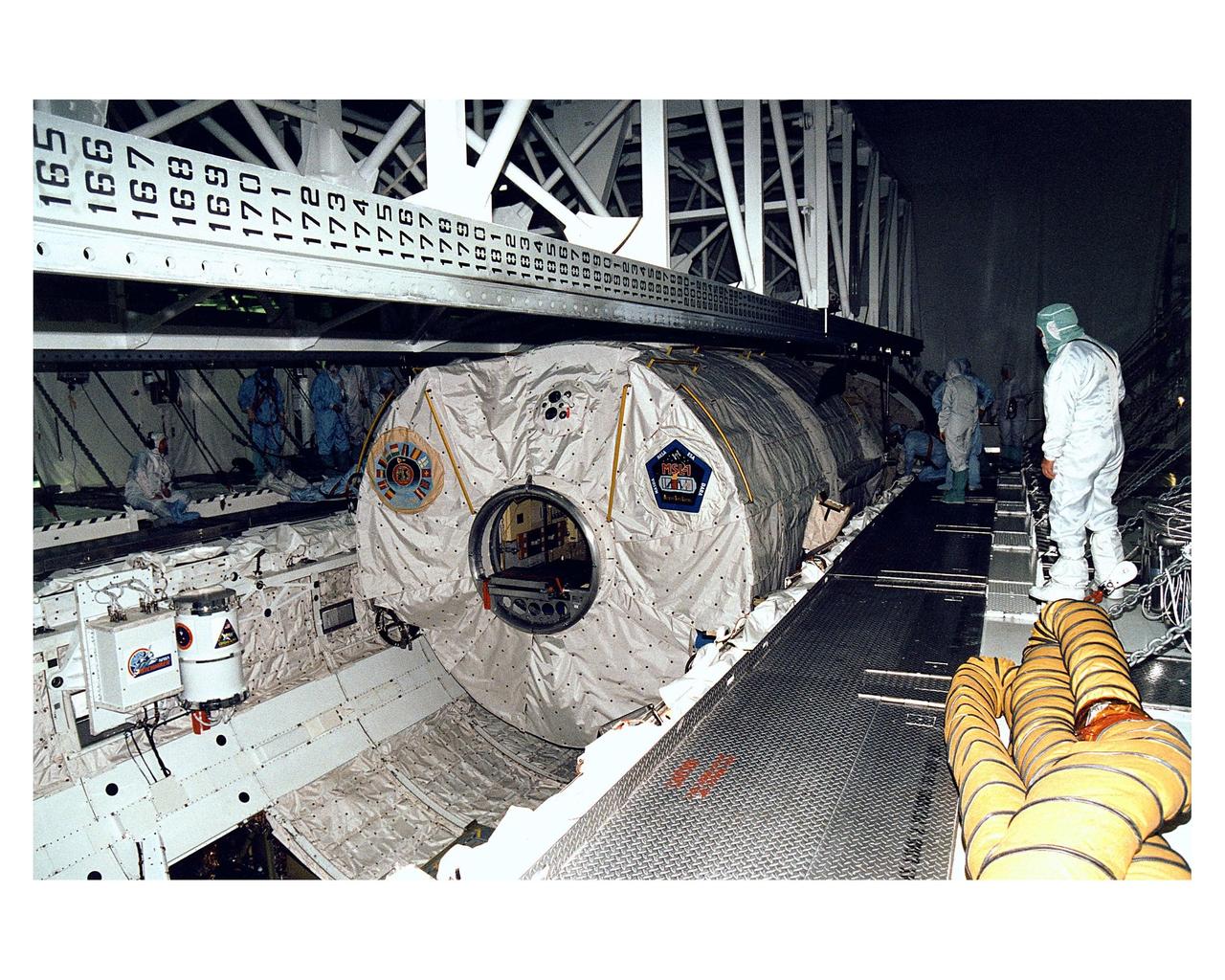

The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is lowered into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia in Orbiter Processing Facility 1. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments
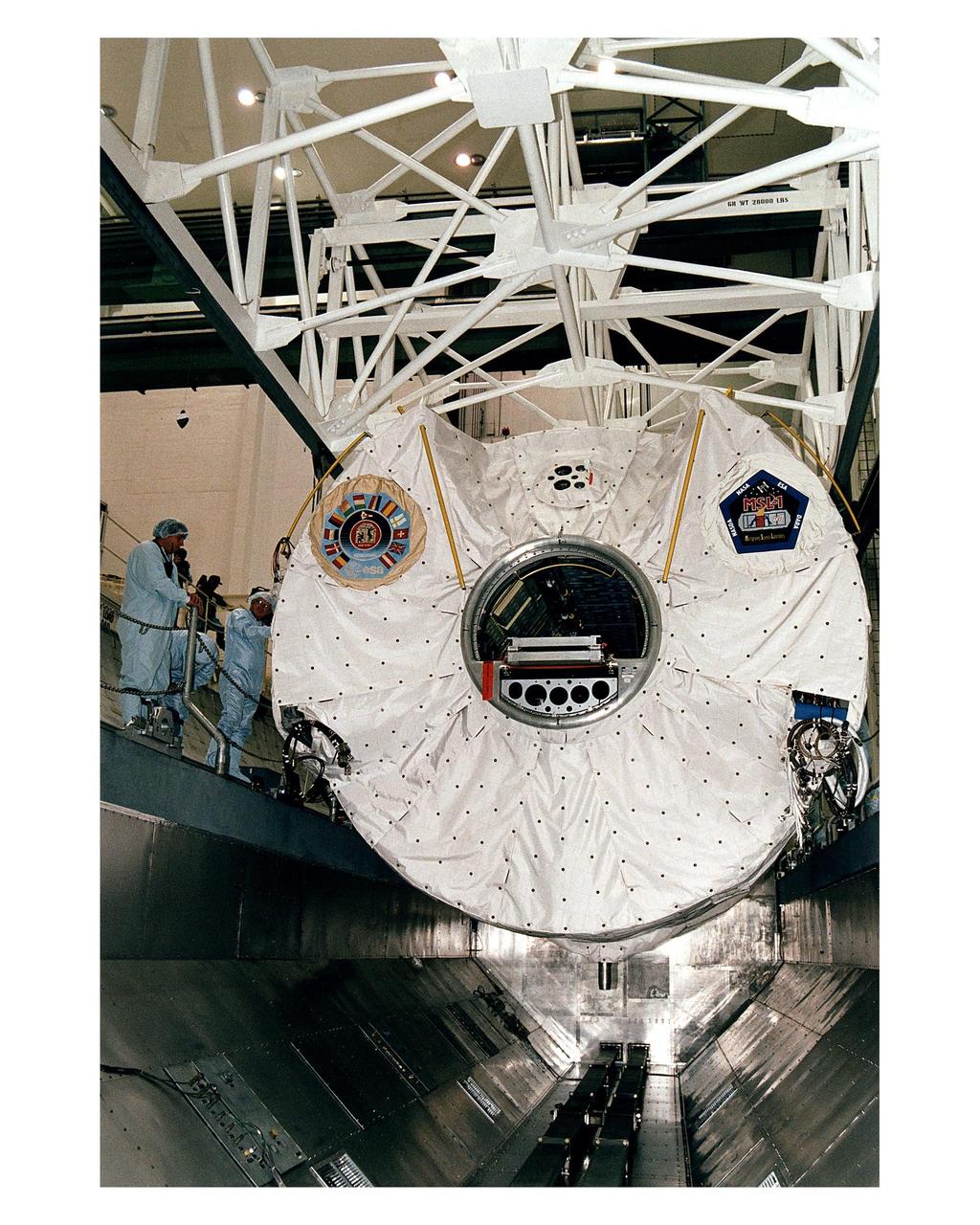

The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is moved to be installed into a payload canister in the Operations and Checkout Building. Once in the canister, the MSL-1 will be transported to Orbiter Processing Bay 1 where it will be integrated into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments
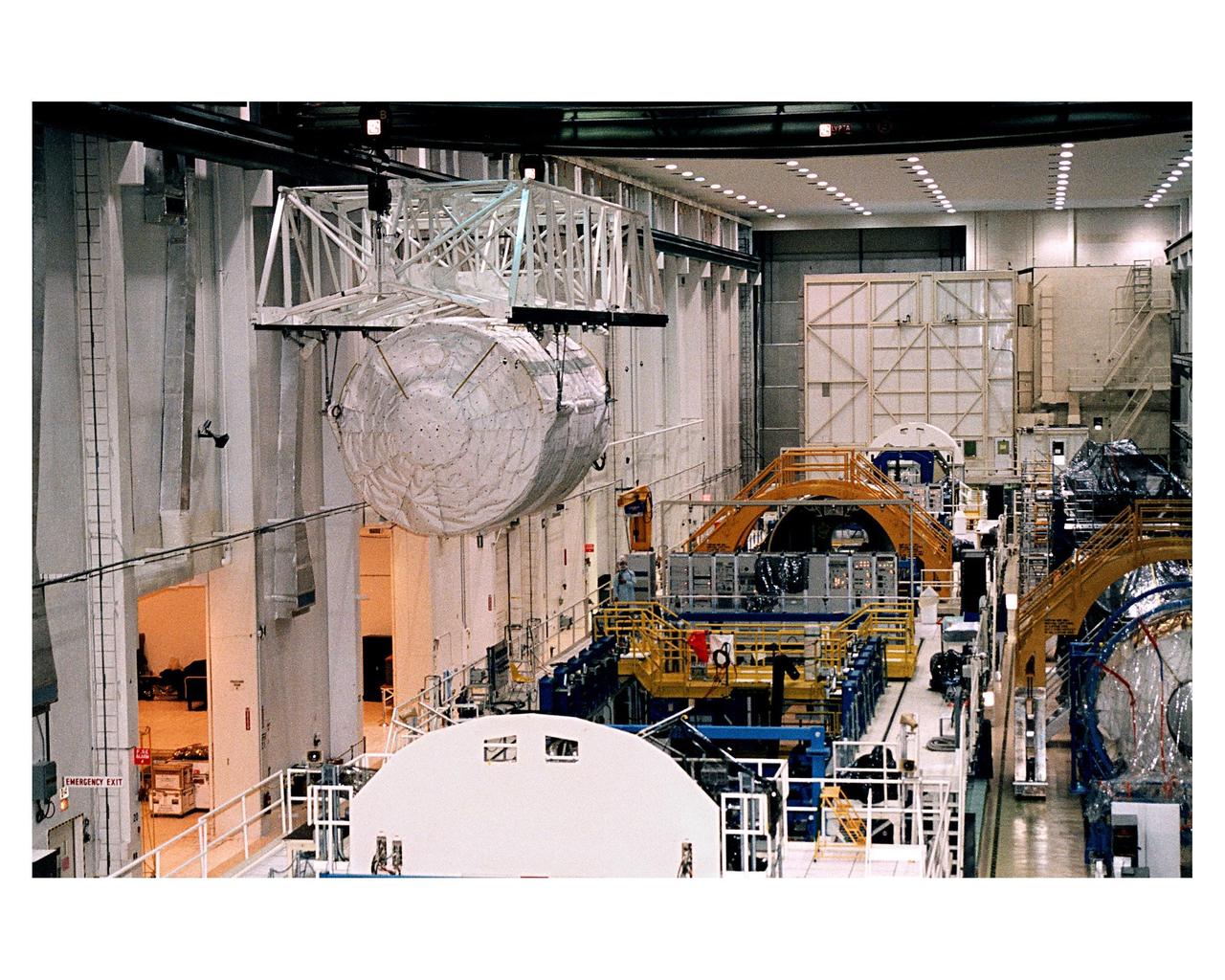
The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is moved to be installed into a payload canister in the Operations and Checkout Building. Once in the canister, the MSL-1 will be transported to Orbiter Processing Bay 1 where it will be integrated into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments

The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is moved to be installed into a payload canister in the Operations and Checkout Building. Once in the canister, the MSL-1 will be transported to Orbiter Processing Bay 1 where it will be integrated into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments

A scaled-down 24-inch version of the Space Shuttle's Reusable Solid Rocket Motor was successfully fired for 21 seconds at a Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Test Stand. The motor was tested to ensure a replacement material called Lycocel would meet the criteria set by the Shuttle's Solid Motor Project Office. The current material is a heat-resistant, rayon-based, carbon-cloth phenolic used as an insulating material for the motor's nozzle. Lycocel, a brand name for Tencel, is a cousin to rayon and is an exceptionally strong fiber made of wood pulp produced by a special "solvent-spirning" process using a nontoxic solvent. It will also be impregnated with a phenolic resin. This new material is expected to perform better under the high temperatures experienced during launch. The next step will be to test the material on a 48-inch solid rocket motor. The test, which replicates launch conditions, is part of Shuttle's ongoing verification of components, materials, and manufacturing processes required by MSFC, which oversees the Reusable Solid Rocket Motor project. Manufactured by the ATK Thiokol Propulsion Division in Promontory, California, the Reusable Solid Rocket Motor measures 126 feet (38.4 meters) long and 12 feet (3.6 meters) in diameter. It is the largest solid rocket motor ever flown and the first designed for reuse. During its two-minute burn at liftoff, each motor generates an average thrust of 2.6 million pounds (1.2 million kilograms).
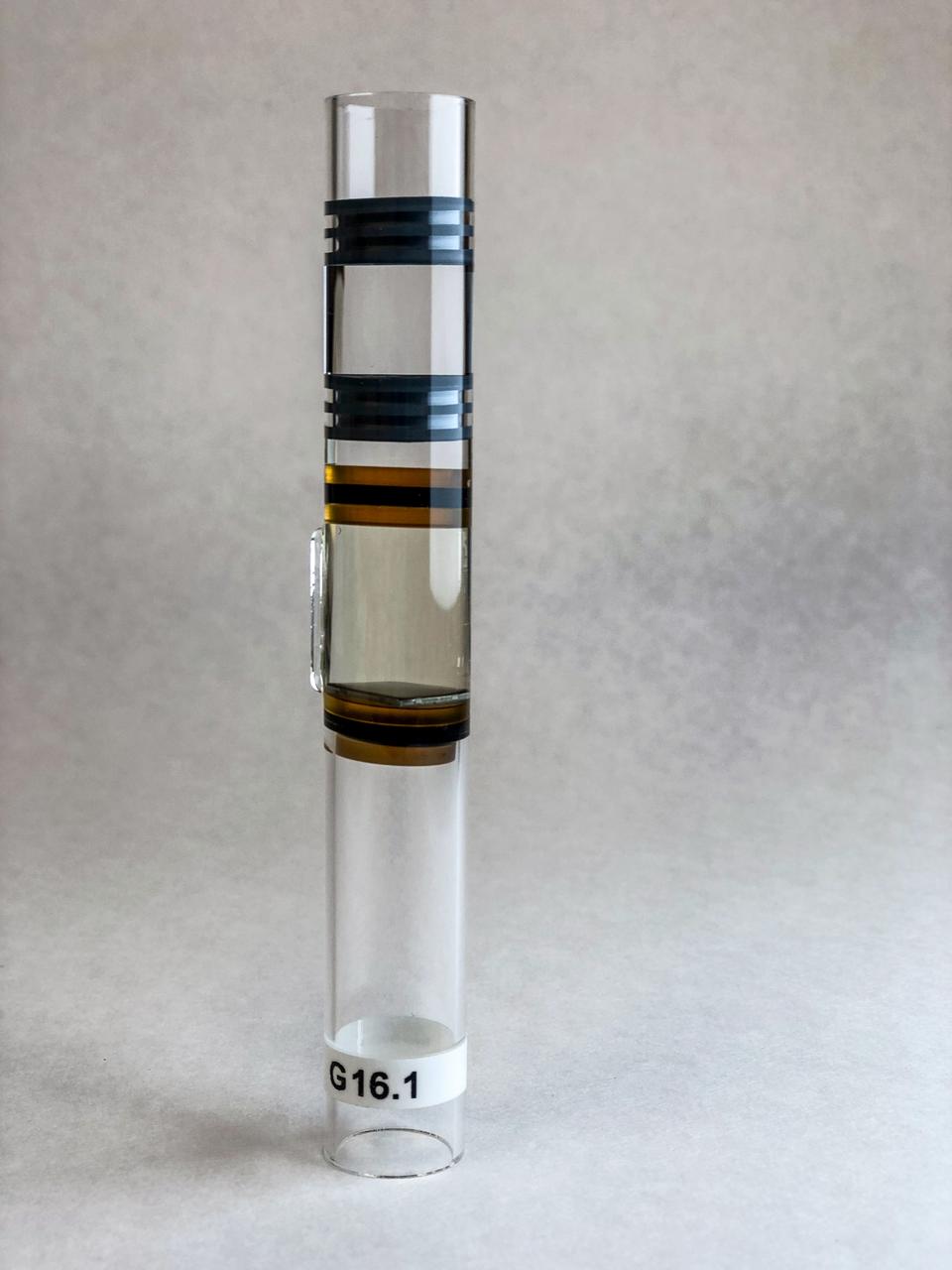

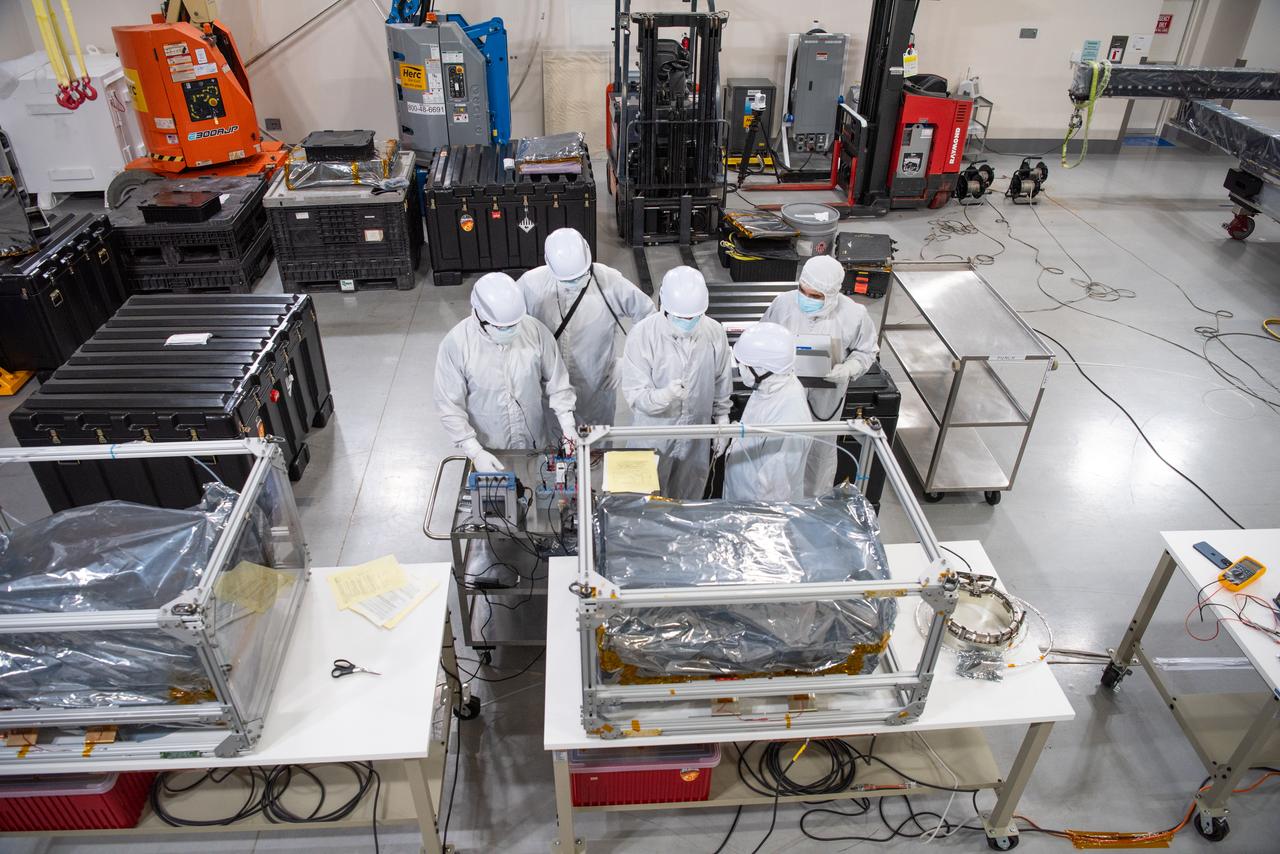
jsc2020e003405 (10/30/2019) --- A preflight view of BioServe’s Fluid Processing Apparatus (FPA) in a three-chamber configuration. From bottom to top: sterile growth medium and 1 cm2 material coupon, bacteria in stasis (inoculum), and fixative for controlled experiment termination. FPAs were used to house the bacterial component of this experiment, where six different materials were tested. The Characterization of Biofilm Formation, Growth, and Gene Expression on Different Materials and Environmental Conditions in Microgravity (Space Biofilms) investigation characterizes the mass, thickness, structure, and associated gene expression of biofilms that form in space by analyzing different microbial species grown on different materials. Biofilm formation can cause equipment malfunction and human illnesses, and could be a serious problem on future long-term human space missions.
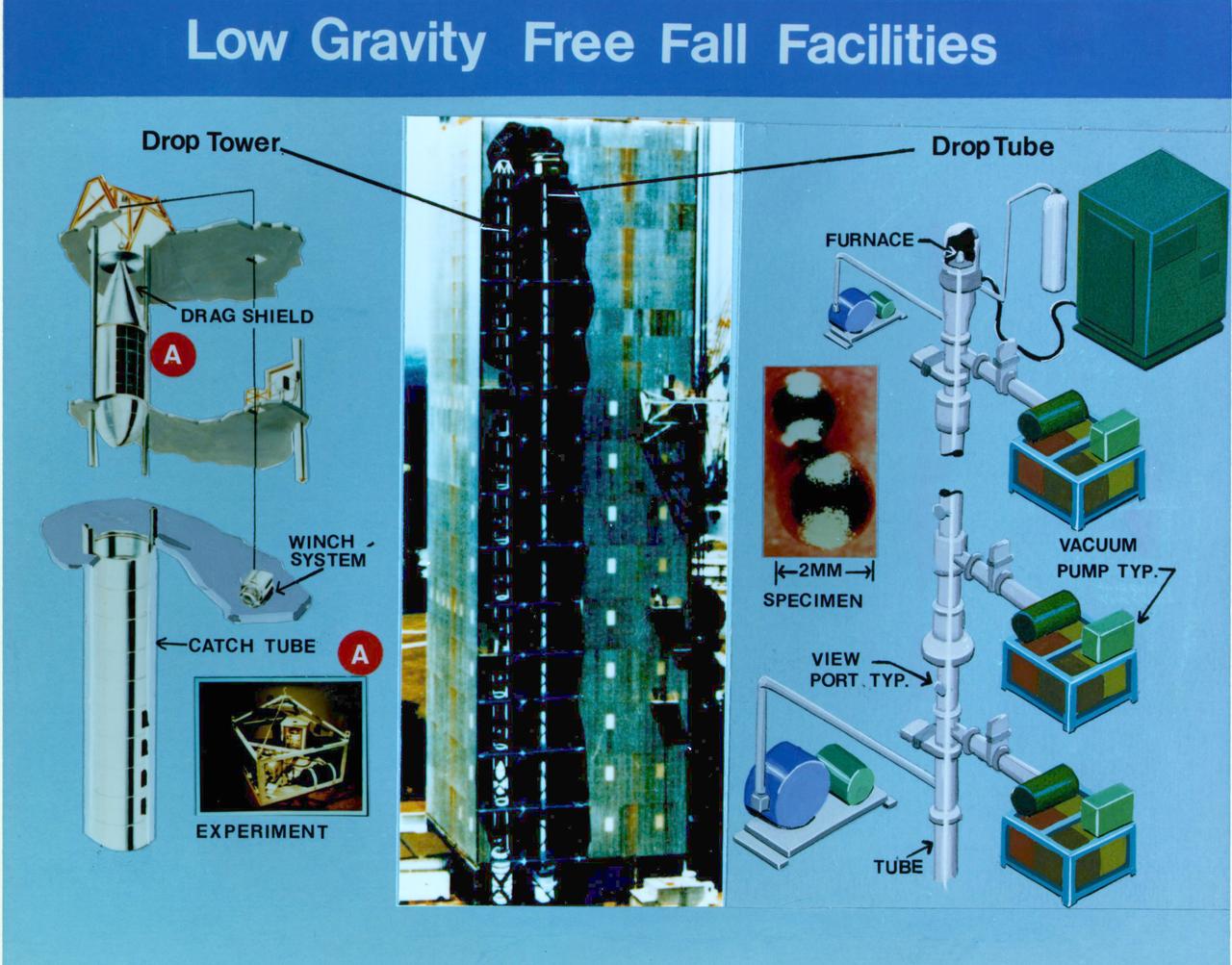
Composite of Marshall Space Flight Center's Low-Gravity Free Fall Facilities.These facilities include a 100-meter drop tower and a 100-meter drop tube. The drop tower simulates in-flight microgravity conditions for up to 4.2 seconds for containerless processing experiments, immiscible fluids and materials research, pre-flight hardware design test and flight experiment simulation. The drop tube simulates in-flight microgravity conditions for up to 4.6 seconds and is used extensively for ground-based microgravity convection research in which extremely small samples are studied. The facility can provide deep undercooling for containerless processing experiments that require materials to remain in a liquid phase when cooled below the normal solidification temperature.
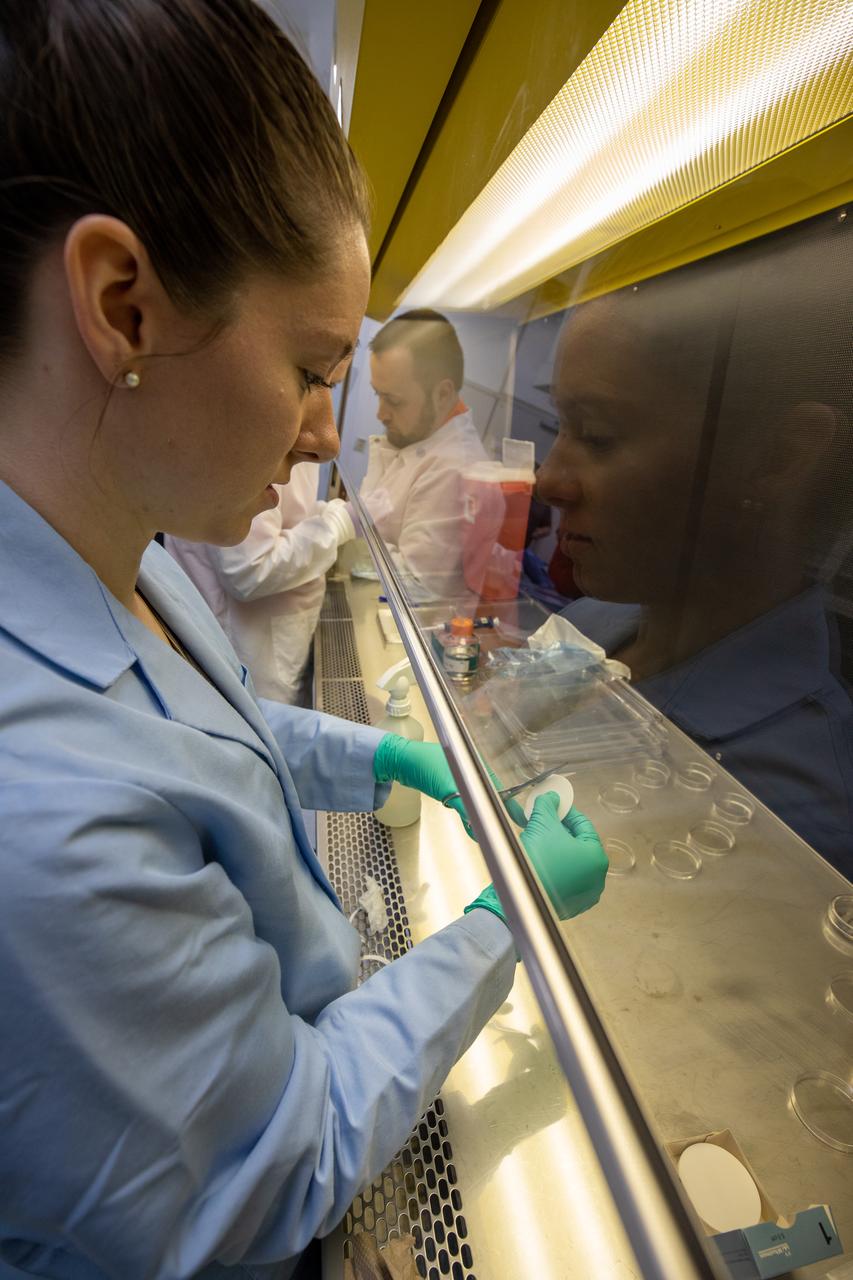
Jess Bunchek, a pseudonaut and associate scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares the materials needed for a germination test of plant seeds inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 15, 2020. The test will verify that the seeds can successfully grow here on Earth before they are sent to the International Space Station for testing in a microgravity environment as part of the VEG-03 series of experiments. The experiments will launch aboard a Northrop Grumman Antares rocket and Cygnus spacecraft on the company’s 13th resupply services mission to the space station. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia.
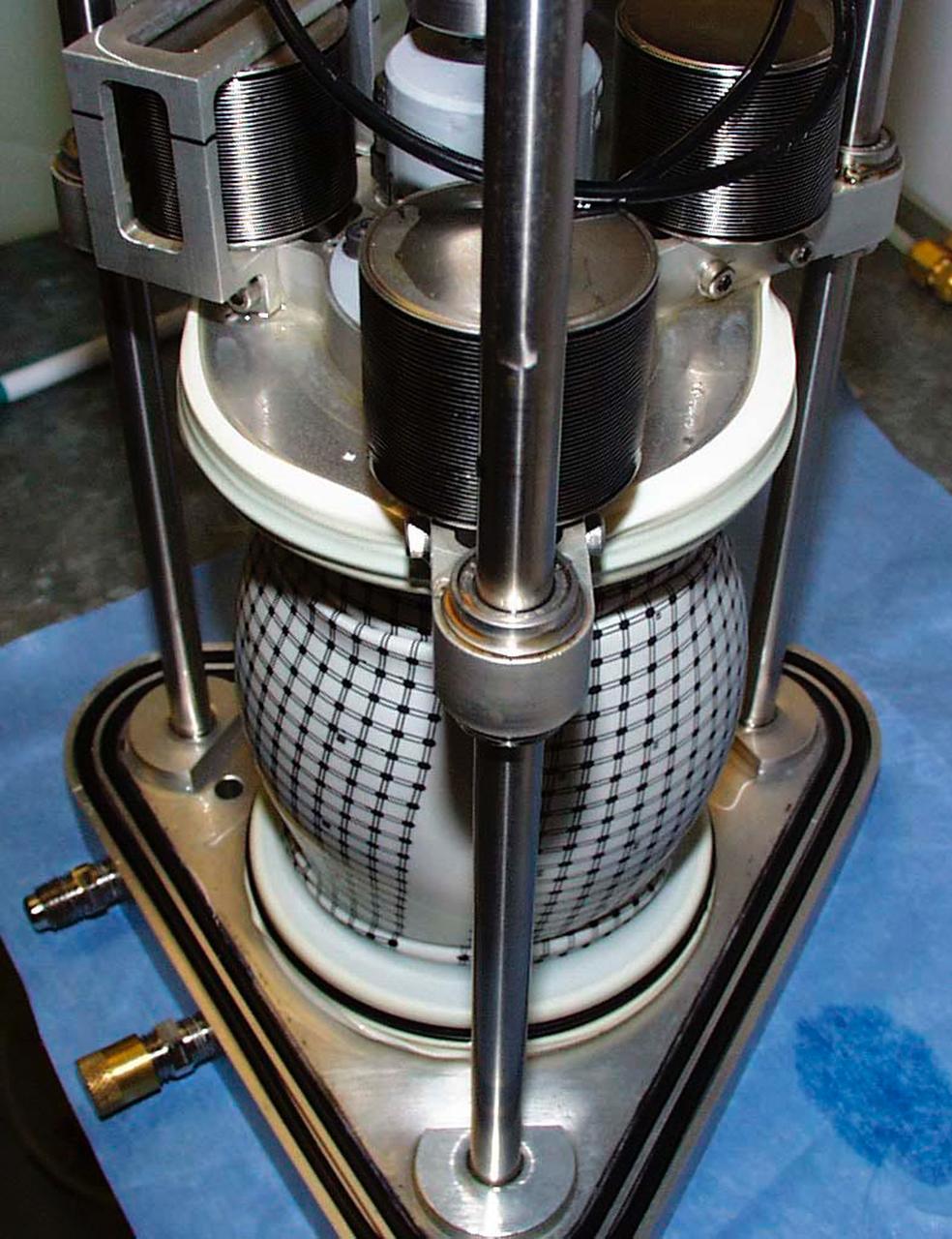

A test cell for Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiment is tested for long-term storage with water in the system as plarned for STS-107. This view shows the compressed sand column with the protective water jacket removed. Sand and soil grains have faces that can cause friction as they roll and slide against each other, or even cause sticking and form small voids between grains. This complex behavior can cause soil to behave like a liquid under certain conditions such as earthquakes or when powders are handled in industrial processes. Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiments aboard the Space Shuttle use the microgravity of space to simulate this behavior under conditons that cannot be achieved in laboratory tests on Earth. MGM is shedding light on the behavior of fine-grain materials under low effective stresses. Applications include earthquake engineering, granular flow technologies (such as powder feed systems for pharmaceuticals and fertilizers), and terrestrial and planetary geology. Nine MGM specimens have flown on two Space Shuttle flights. Another three are scheduled to fly on STS-107. The principal investigator is Stein Sture of the University of Colorado at Boulder. Credit: University of Colorado at Boulder
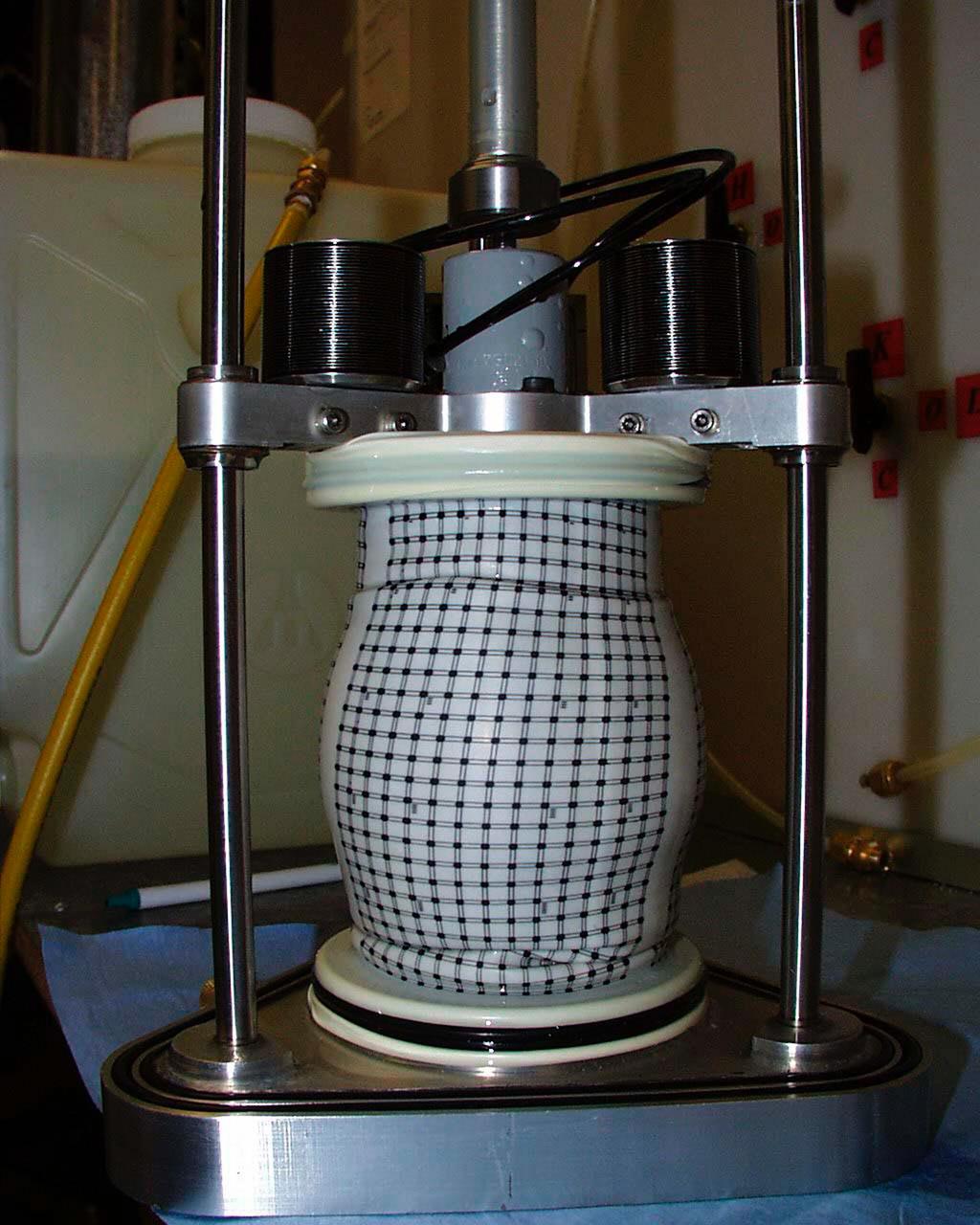
A test cell for Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiment is tested for long-term storage with water in the system as plarned for STS-107. This view shows the compressed sand column with the protective water jacket removed. Sand and soil grains have faces that can cause friction as they roll and slide against each other, or even cause sticking and form small voids between grains. This complex behavior can cause soil to behave like a liquid under certain conditions such as earthquakes or when powders are handled in industrial processes. Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiments aboard the Space Shuttle use the microgravity of space to simulate this behavior under conditons that cannot be achieved in laboratory tests on Earth. MGM is shedding light on the behavior of fine-grain materials under low effective stresses. Applications include earthquake engineering, granular flow technologies (such as powder feed systems for pharmaceuticals and fertilizers), and terrestrial and planetary geology. Nine MGM specimens have flown on two Space Shuttle flights. Another three are scheduled to fly on STS-107. The principal investigator is Stein Sture of the University of Colorado at Boulder. Credit: University of Colorado at Boulder
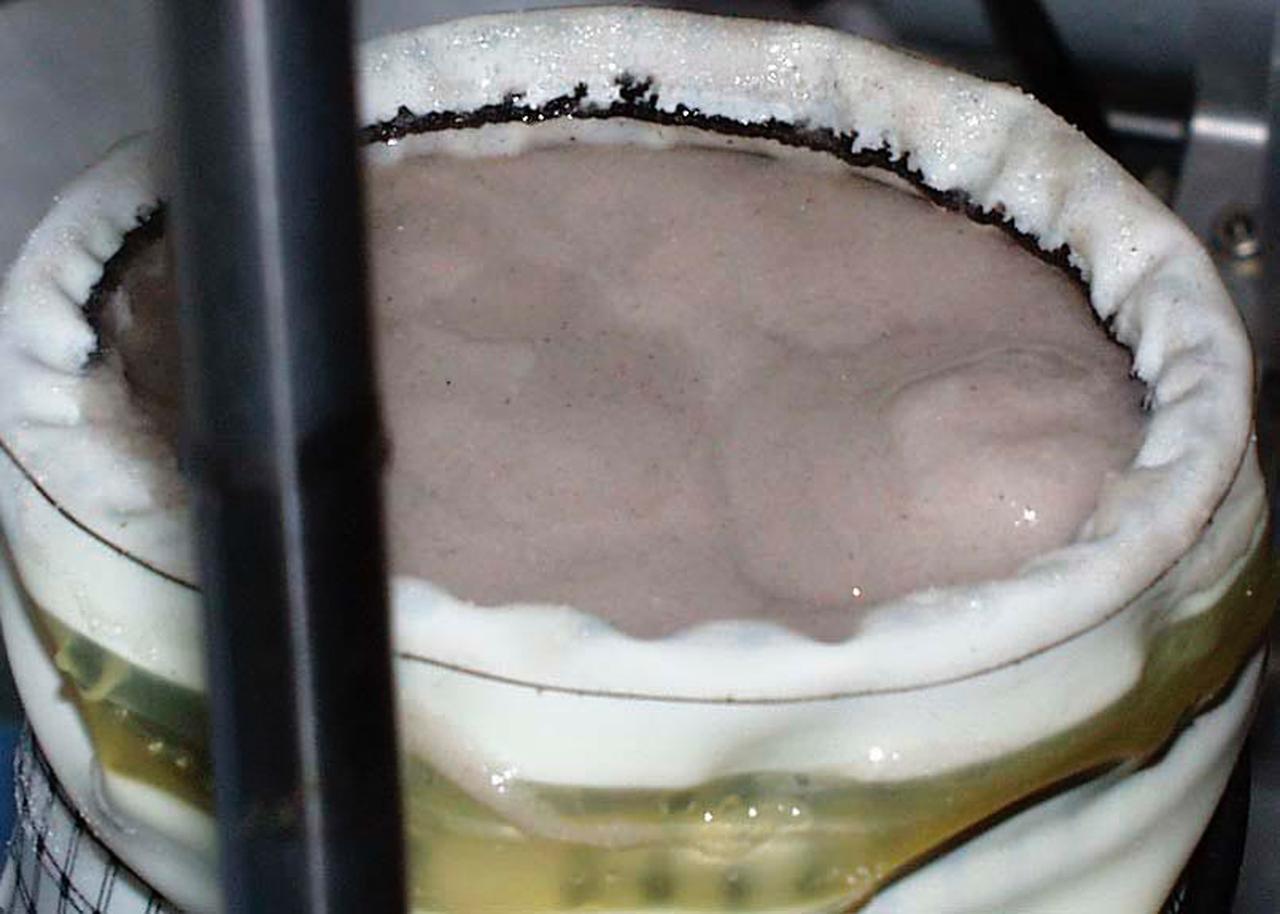

A test cell for Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiment is tested for long-term storage with water in the system as plarned for STS-107. This view shows the top of the sand column with the metal platten removed. Sand and soil grains have faces that can cause friction as they roll and slide against each other, or even cause sticking and form small voids between grains. This complex behavior can cause soil to behave like a liquid under certain conditions such as earthquakes or when powders are handled in industrial processes. Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiments aboard the Space Shuttle use the microgravity of space to simulate this behavior under conditons that cannot be achieved in laboratory tests on Earth. MGM is shedding light on the behavior of fine-grain materials under low effective stresses. Applications include earthquake engineering, granular flow technologies (such as powder feed systems for pharmaceuticals and fertilizers), and terrestrial and planetary geology. Nine MGM specimens have flown on two Space Shuttle flights. Another three are scheduled to fly on STS-107. The principal investigator is Stein Sture of the University of Colorado at Boulder. Credit: University of Colorado at Boulder
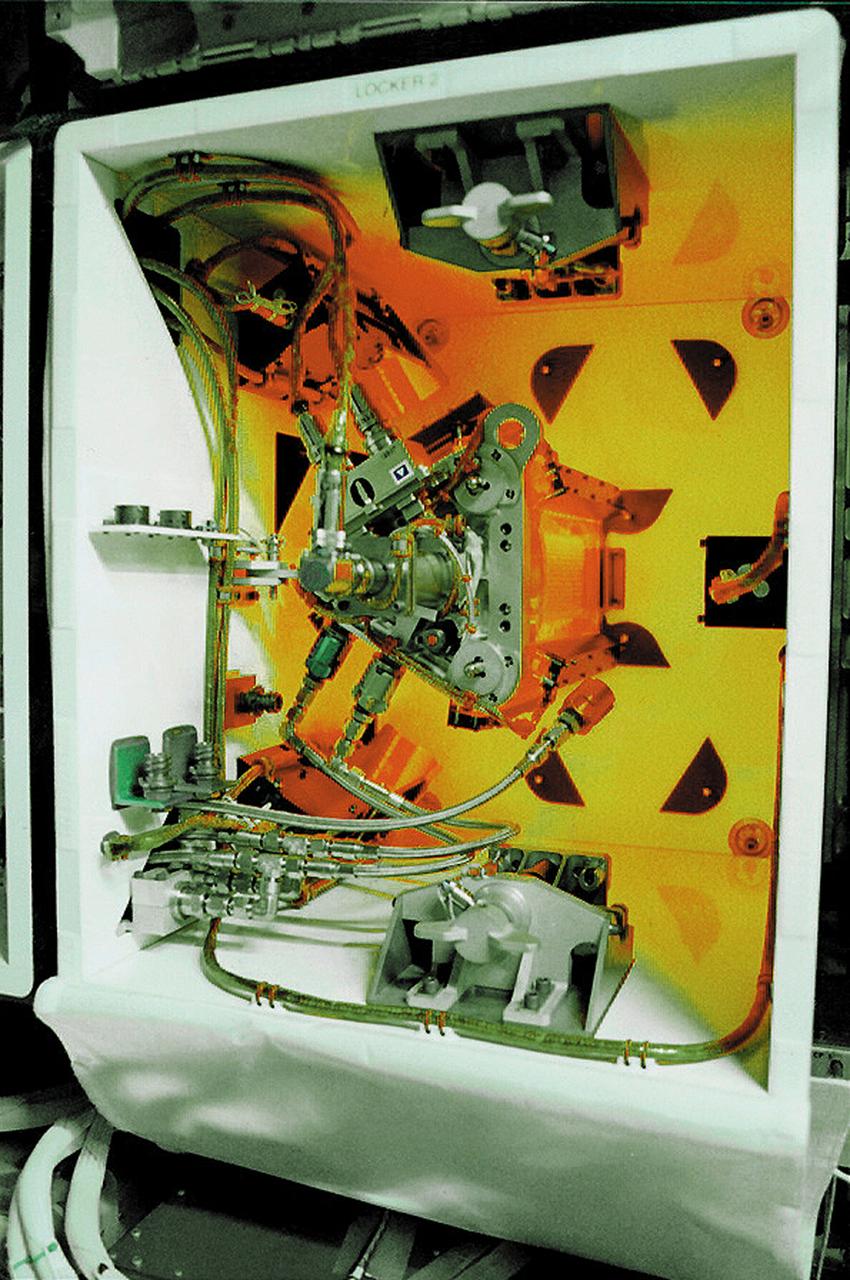
A test cell for the Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiment is shown in its on-orbit configuration in Spacehab during preparations for STS-89. The twin locker to the left contains the hydraulic system to operate the experiment. Sand and soil grains have faces that can cause friction as they roll and slide against each other, or even cause sticking and form small voids between grains. This complex behavior can cause soil to behave like a liquid under certain conditions such as earthquakes or when powders are handled in industrial processes. Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiments aboard the Space Shuttle use the microgravity of space to simulate this behavior under conditons that carnot be achieved in laboratory tests on Earth. MGM is shedding light on the behavior of fine-grain materials under low effective stresses. Applications include earthquake engineering, granular flow technologies (such as powder feed systems for pharmaceuticals and fertilizers), and terrestrial and planetary geology. Nine MGM specimens have flown on two Space Shuttle flights. Another three are scheduled to fly on STS-107. The principal investigator is Stein Sture of the University of Colorado at Boulder. Note: Because the image on the screen was muted in the original image, its brightness and contrast are boosted in this rendering to make the test cell more visible. Credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)
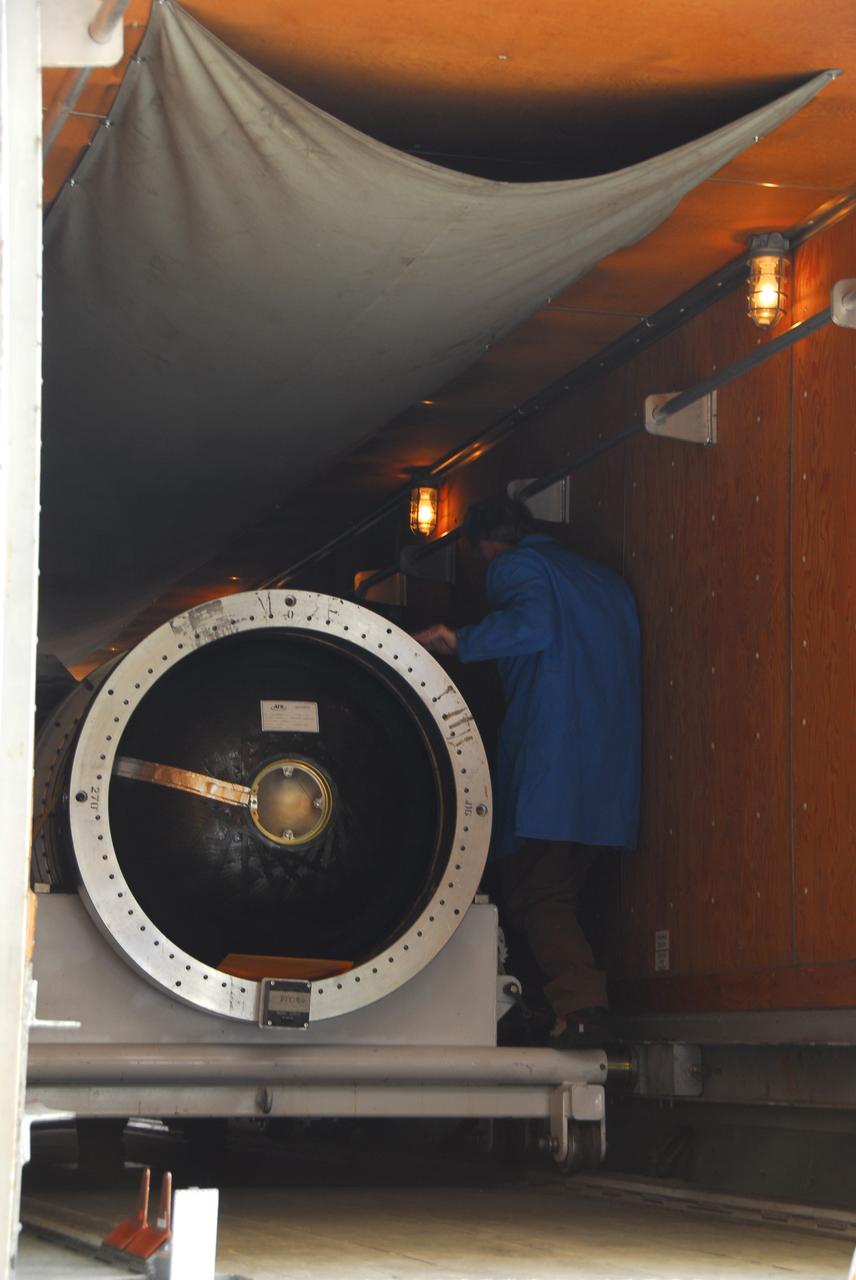

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the third stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit arrives at Building 1555 for processing. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean's Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Dan Liberotti, VAFB
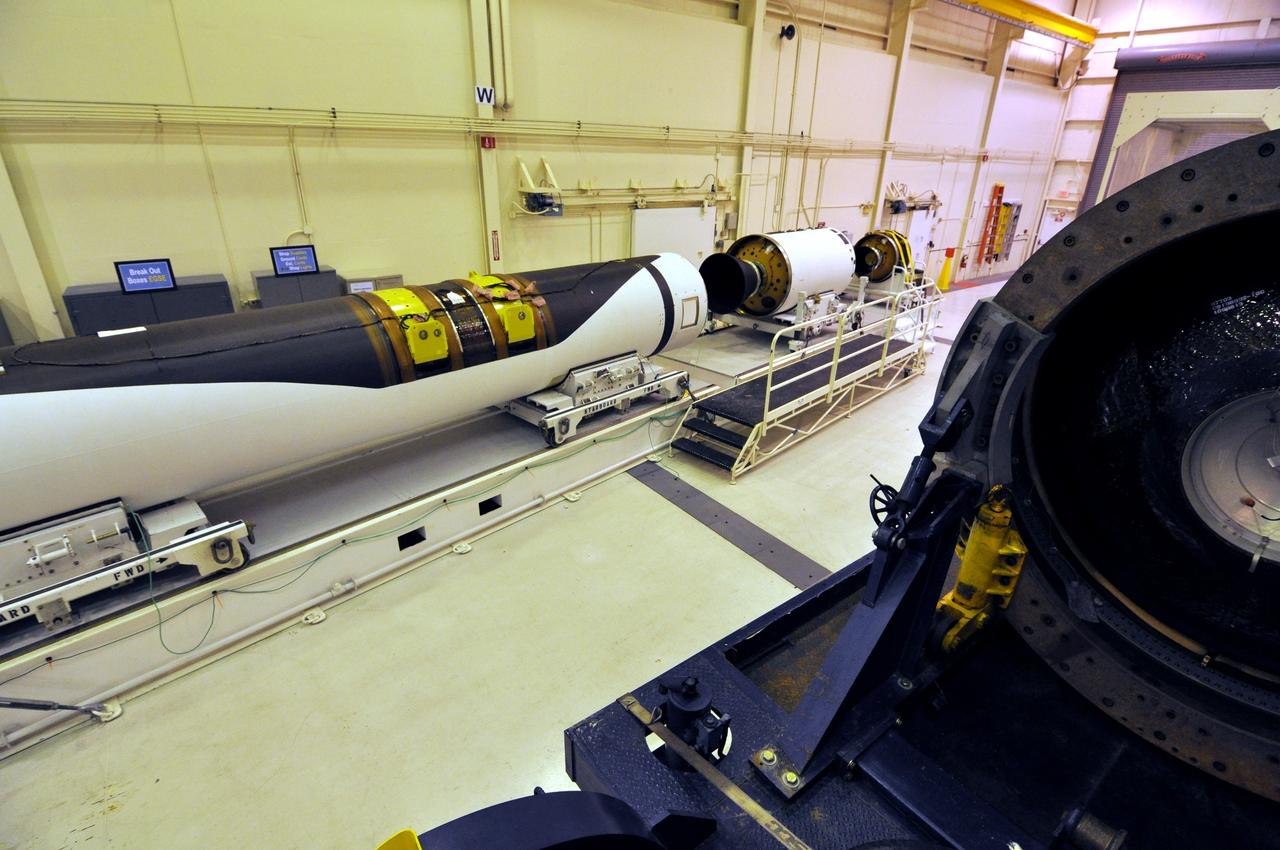

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the first, second and third stages of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit are being processed in the west high bay of Building 1555. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
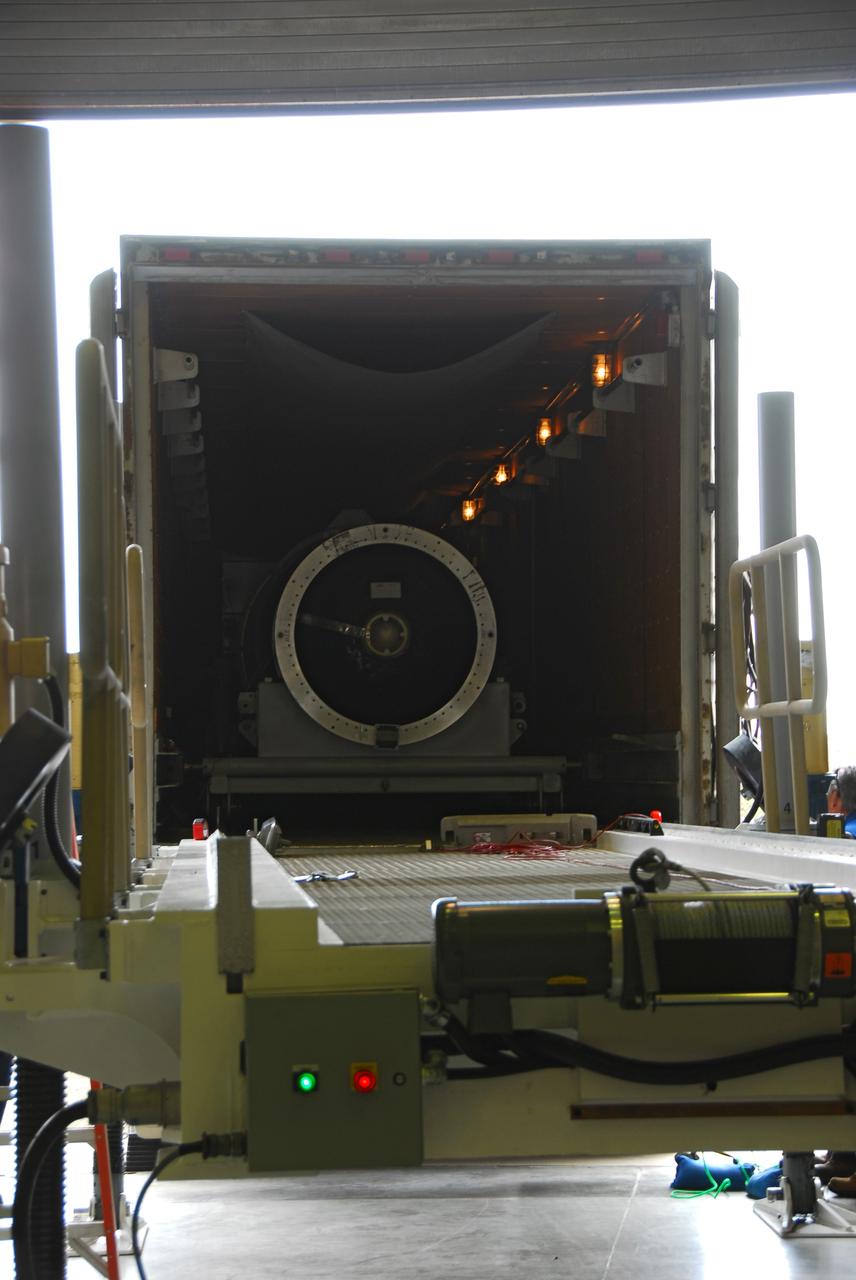

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the third stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit arrives at Building 1555 for processing. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Dan Liberotti, VAFB
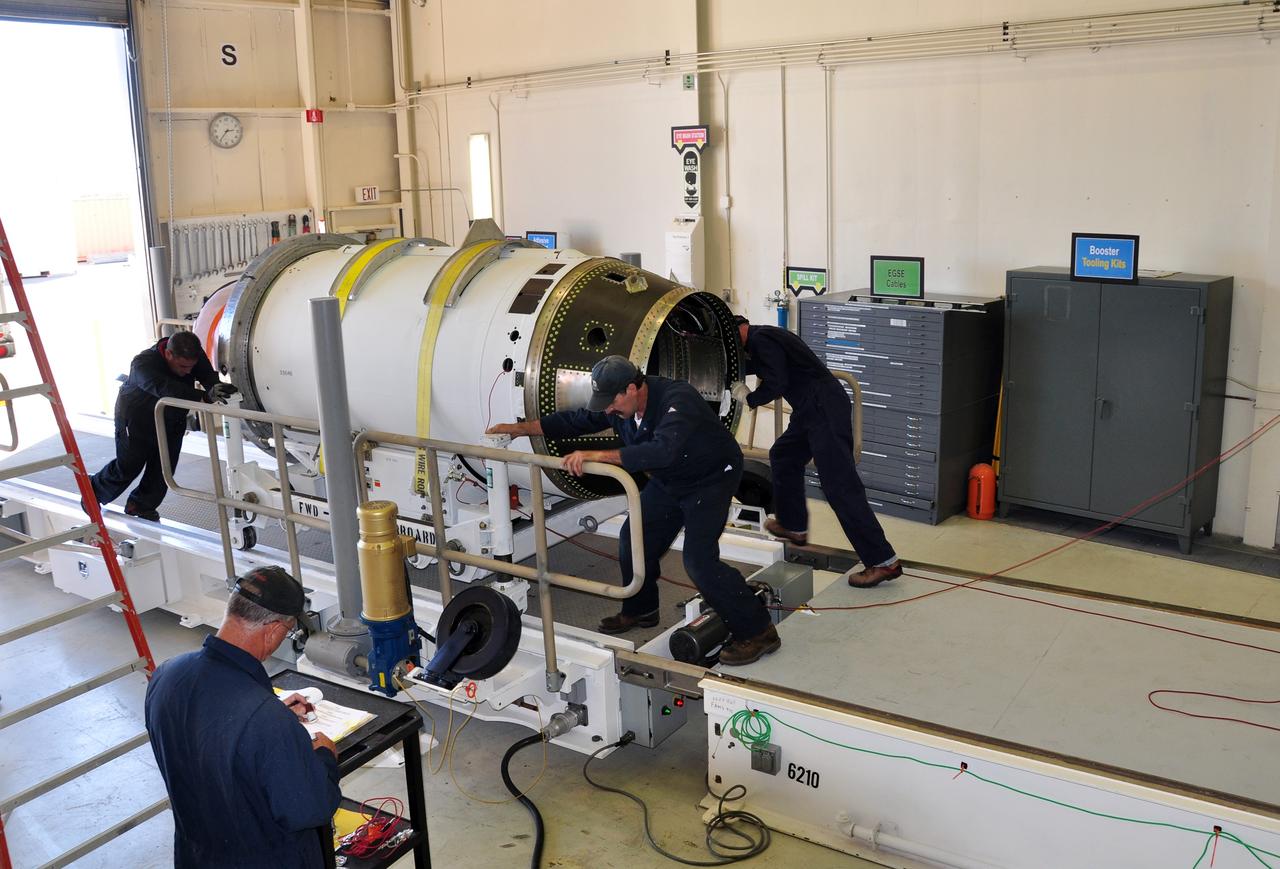

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the second stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit is moved to a stationary rail in Building 1555 for processing. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
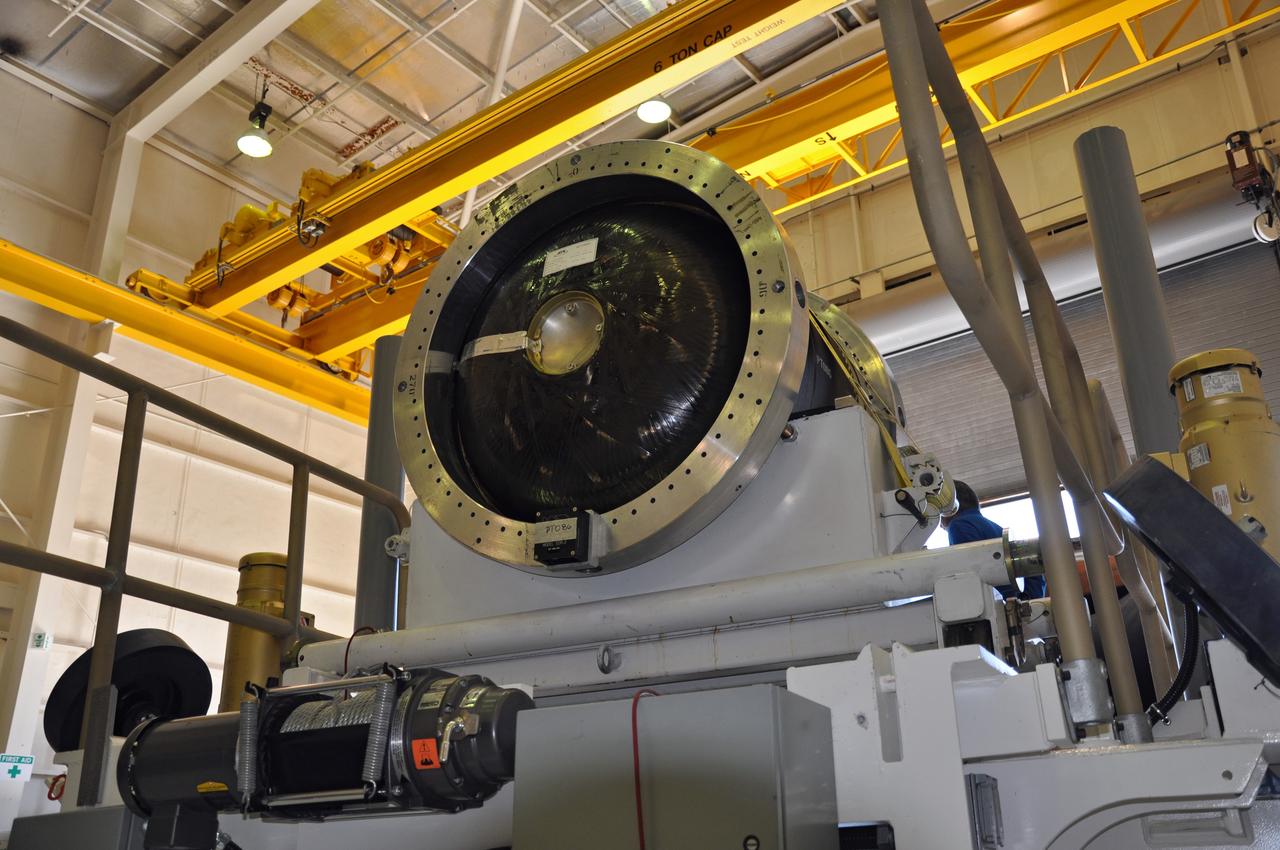

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the third stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit is offloaded for processing in Building 1555. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the first, second and third stages of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit are being processed in the west high bay of Building 1555. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the first stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit is offloaded for processing in Building 1555. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the third stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit is offloaded for processing in Building 1555. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Dan Liberotti, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the second stage of the Pegasus XL rocket, left, that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit is moved onto a jackable rail for processing in Building 1555. On the right is the rocket's third stage. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Dan Liberotti, VAFB
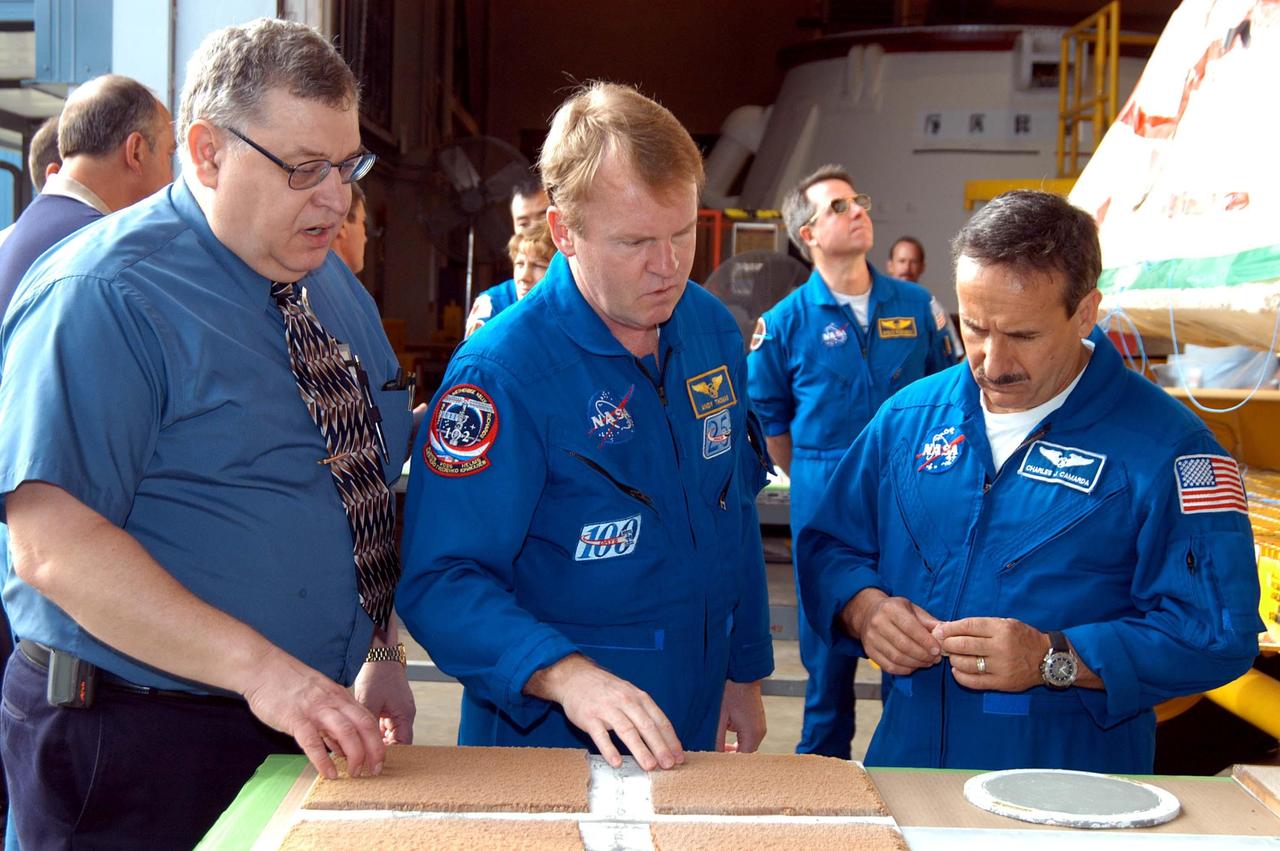

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the SRB Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, STS-114 Mission Specialists Andrew Thomas (center) and Charles Camarda (right) look at a test panel of insulation material (left) cut in a liquid nitrogen process and a round aft heat seal (right) also treated in a liquid nitrogen process. At left is Mike Leppert, Manufacturing Operations project lead with United Space Alliance. The crew is at KSC for familiarization with Shuttle and mission equipment. The STS-114 mission is Logistics Flight 1, which is scheduled to deliver supplies and equipment, plus the external stowage platform, to the International Space Station.
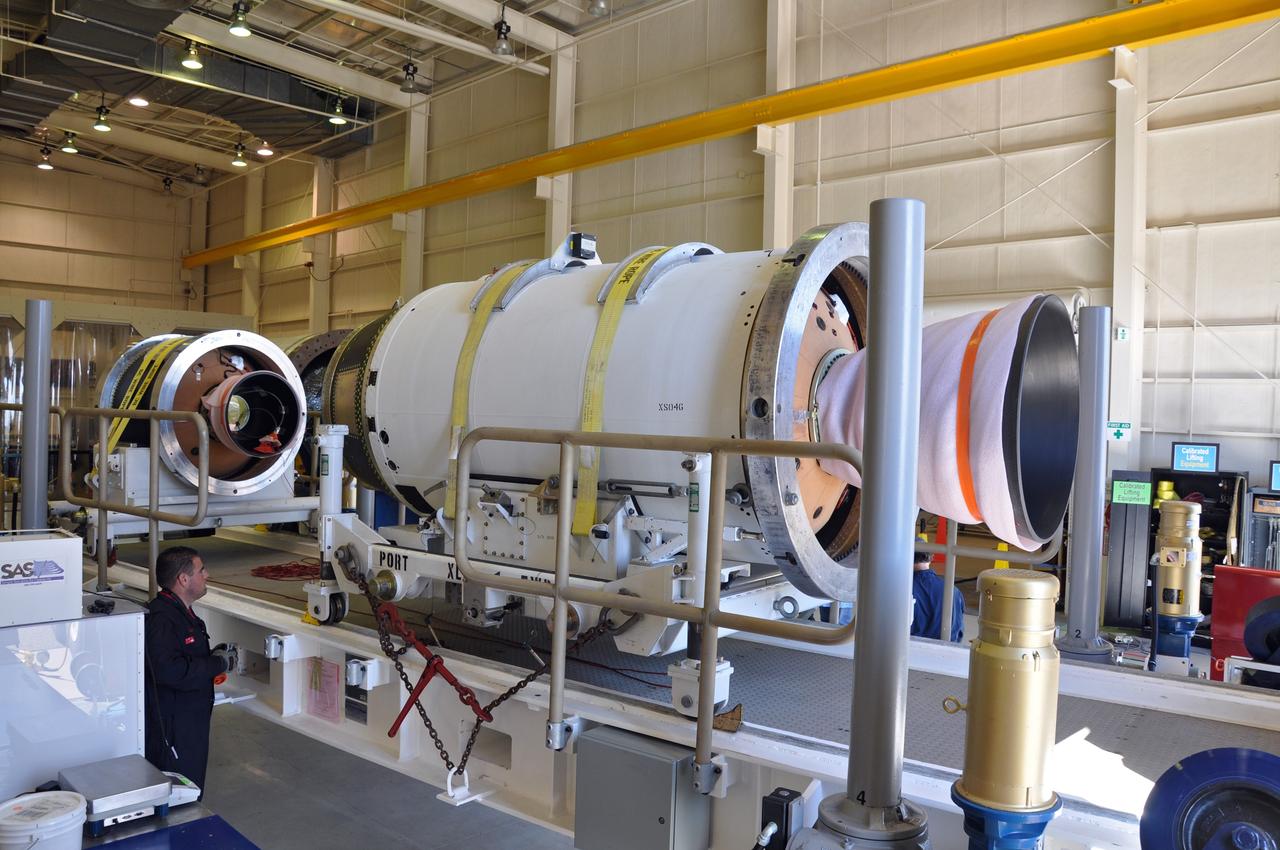

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the second stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit is ready to move from a jackable rail to a stationary one for processing in Building 1555. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
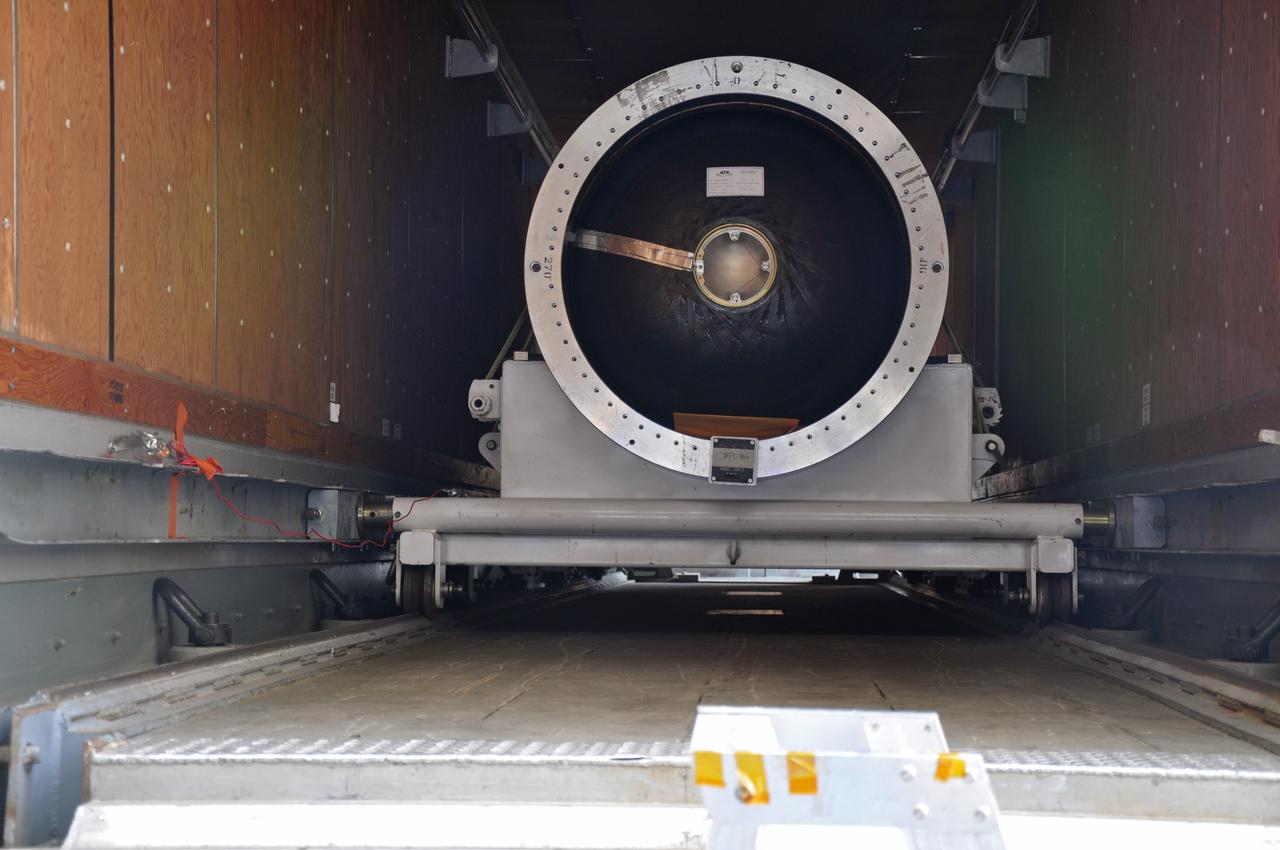

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the third stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit is offloaded for processing in Building 1555. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
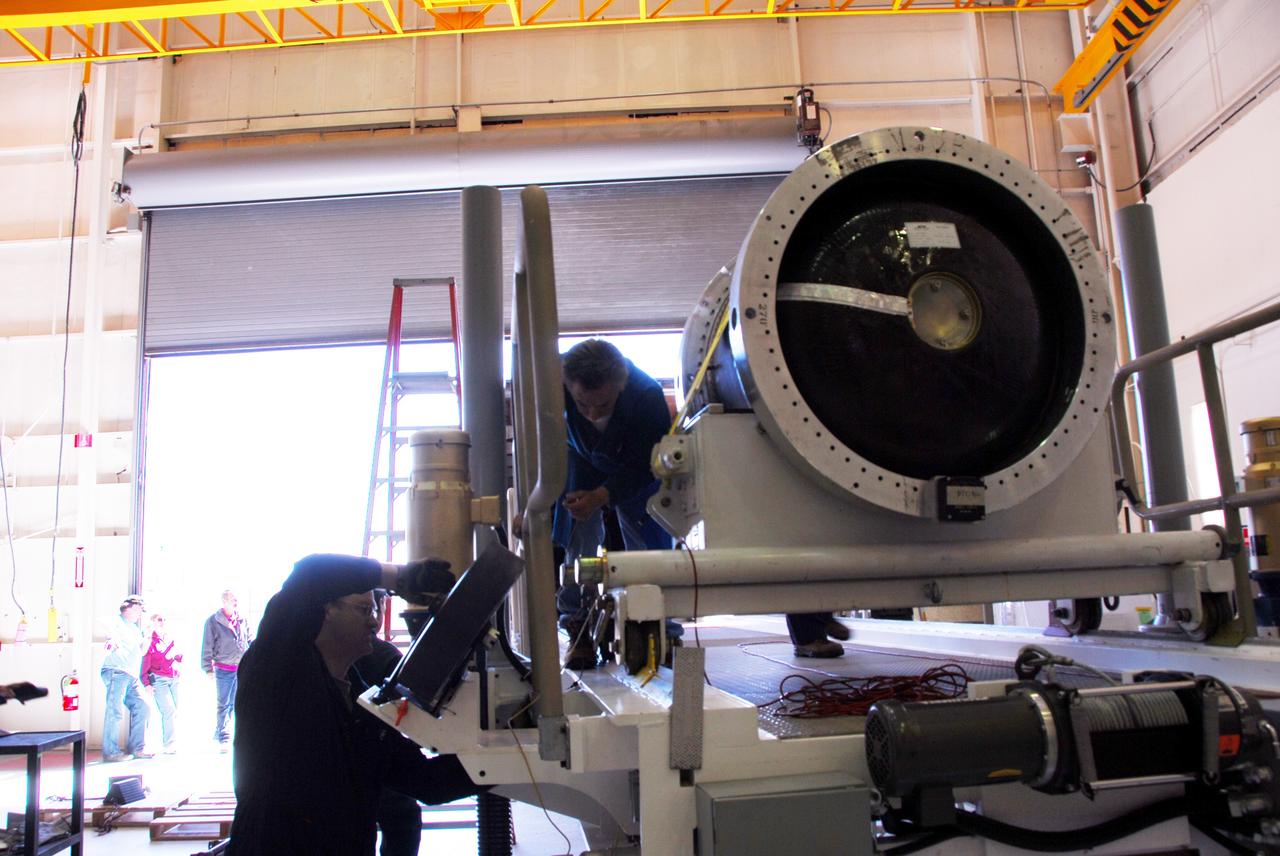

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the third stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit is moved onto a jackable rail for processing in Building 1555. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Dan Liberotti, VAFB
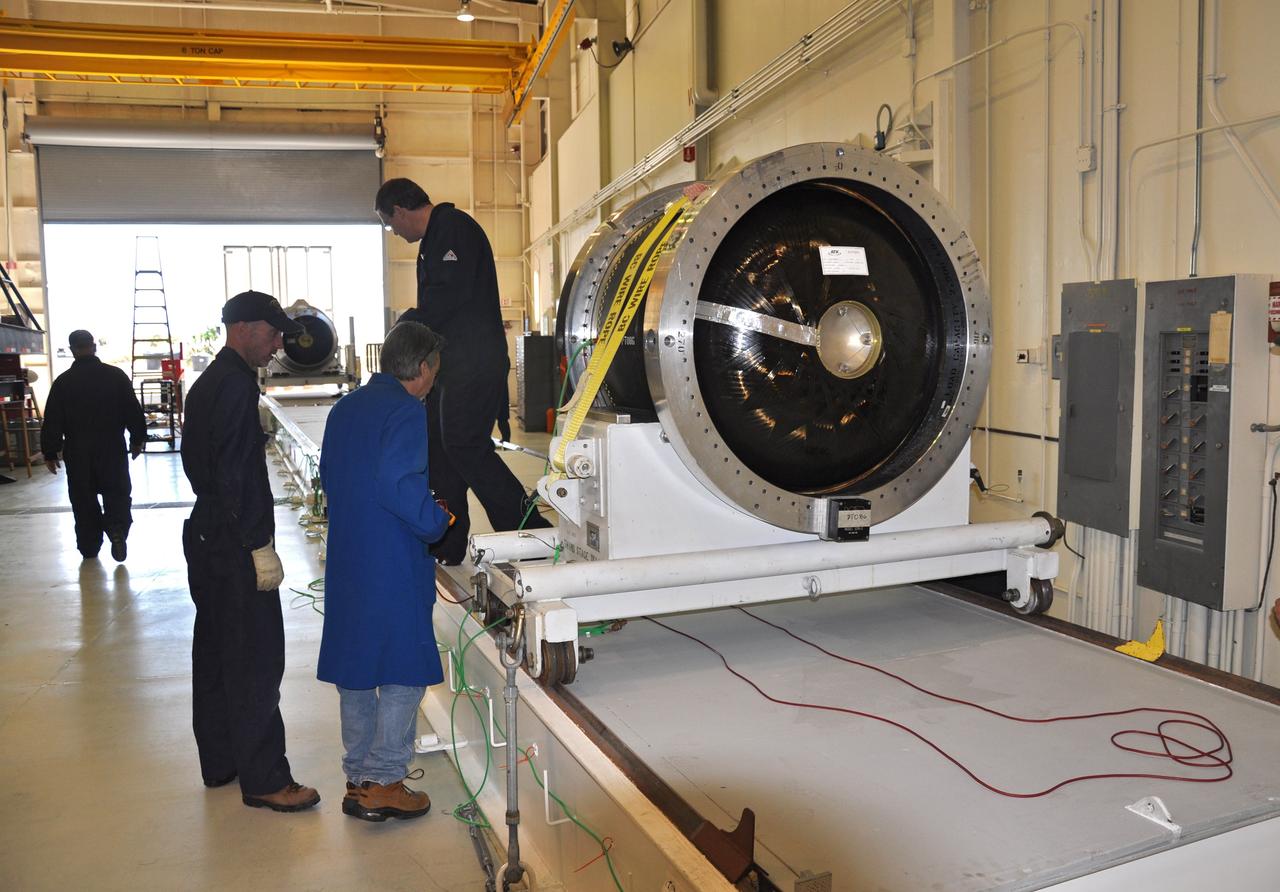

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the second stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit is moved to a stationary rail in Building 1555 for processing. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
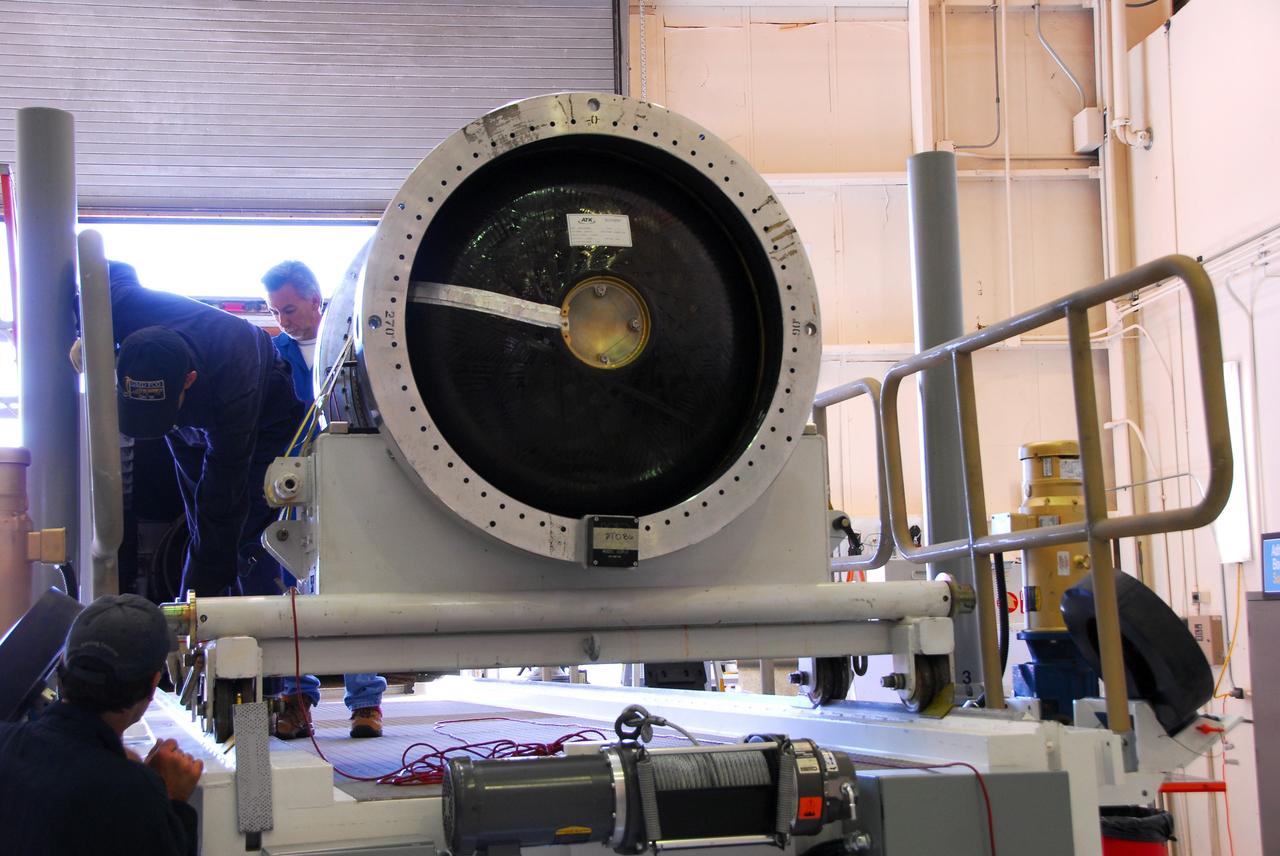

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the third stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit is moved onto a jackable rail for processing in Building 1555. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Dan Liberotti, VAFB
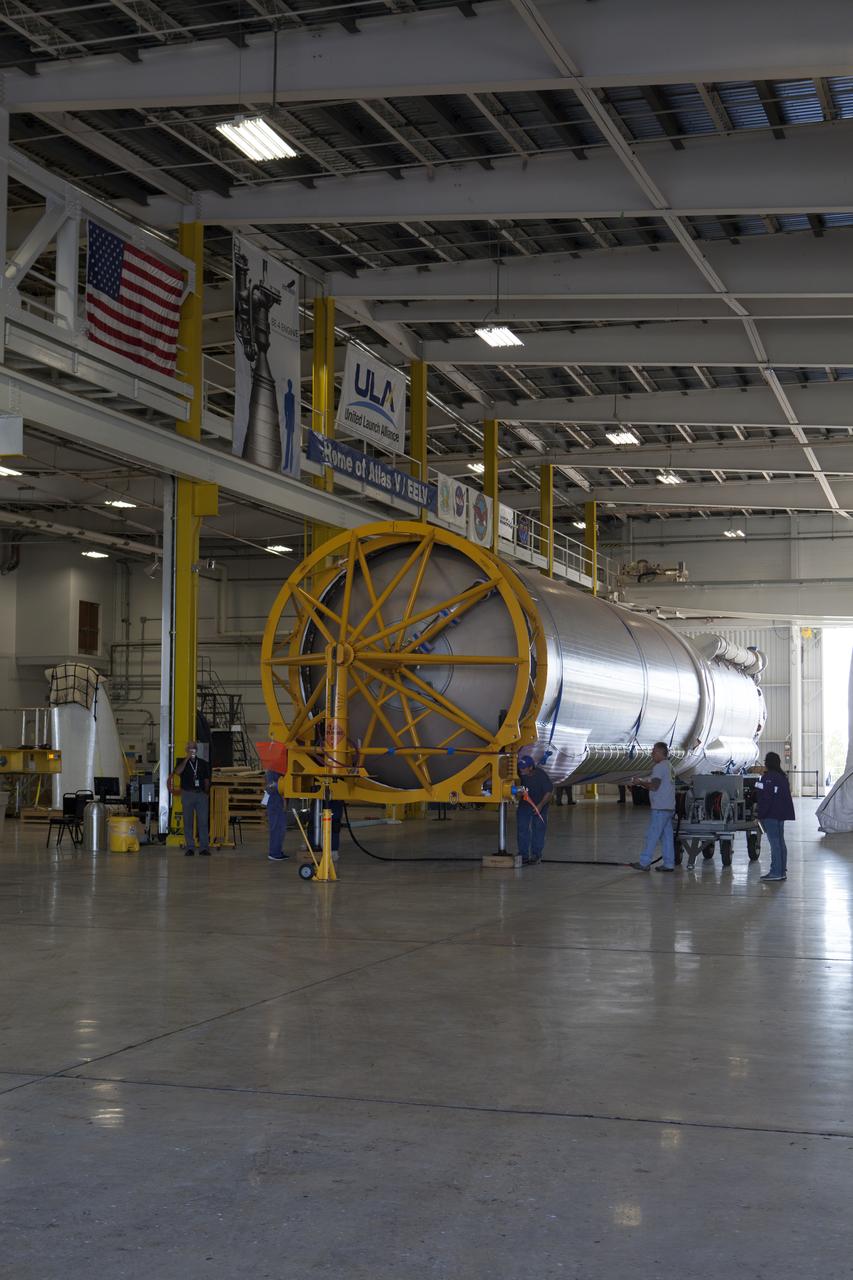

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC). The Atlas V will undergo final testing in that facility. When processing in the ASOC is complete, the Atlas booster will be moved to the Vertical Integration Facility for stacking at Space Launch Complex 41. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Atlas will launch a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the International Space Station.
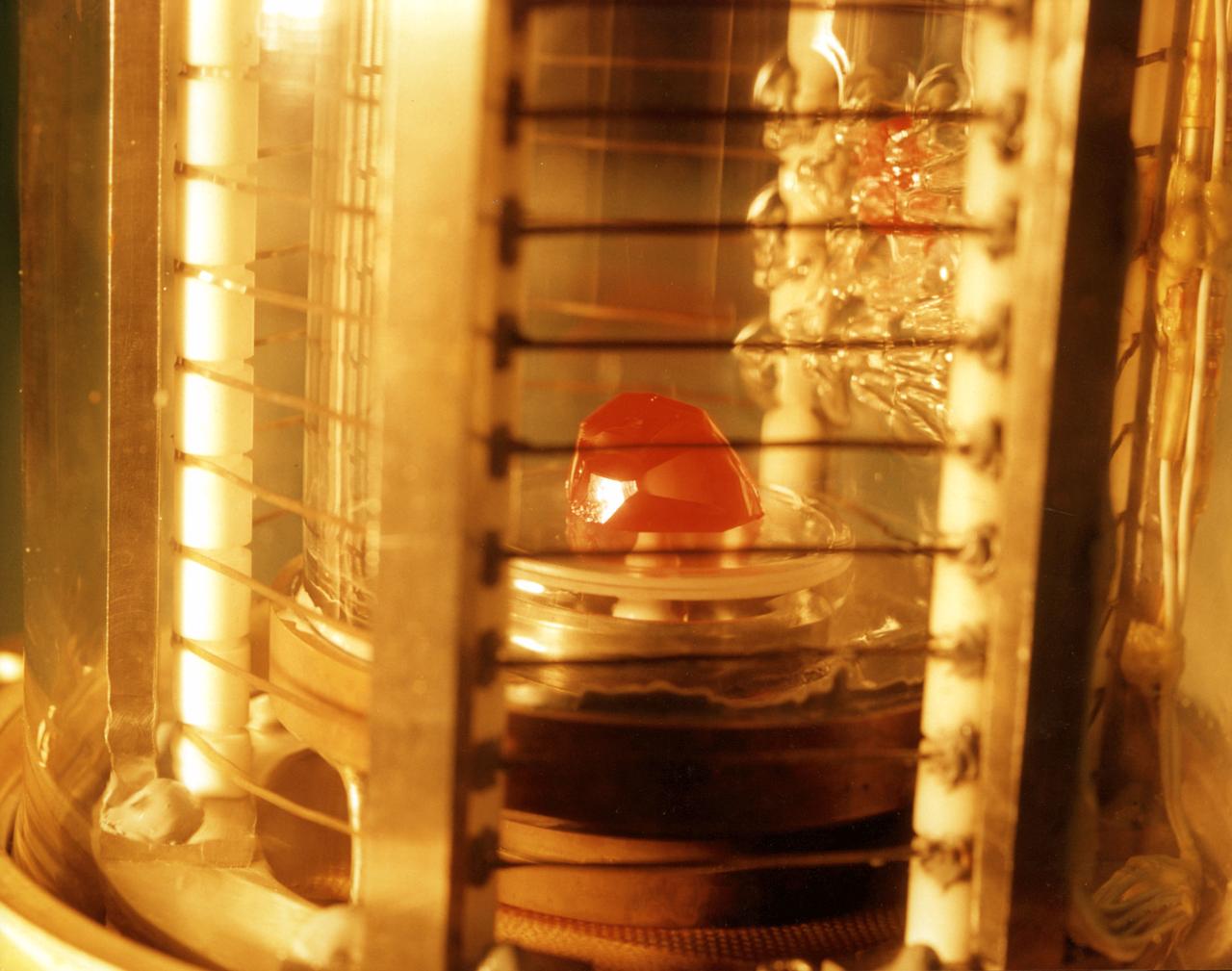

The image shows a test cell of Crystal Growth experiment inside the Vapor Crystal Growth System (VCGS) furnace aboard the STS-42, International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1), mission. The goal of IML-1, a pressurized marned Spacelab module, was to explore in depth the complex effects of weightlessness of living organisms and materials processing. More than 200 scientists from 16 countires participated in the investigations.
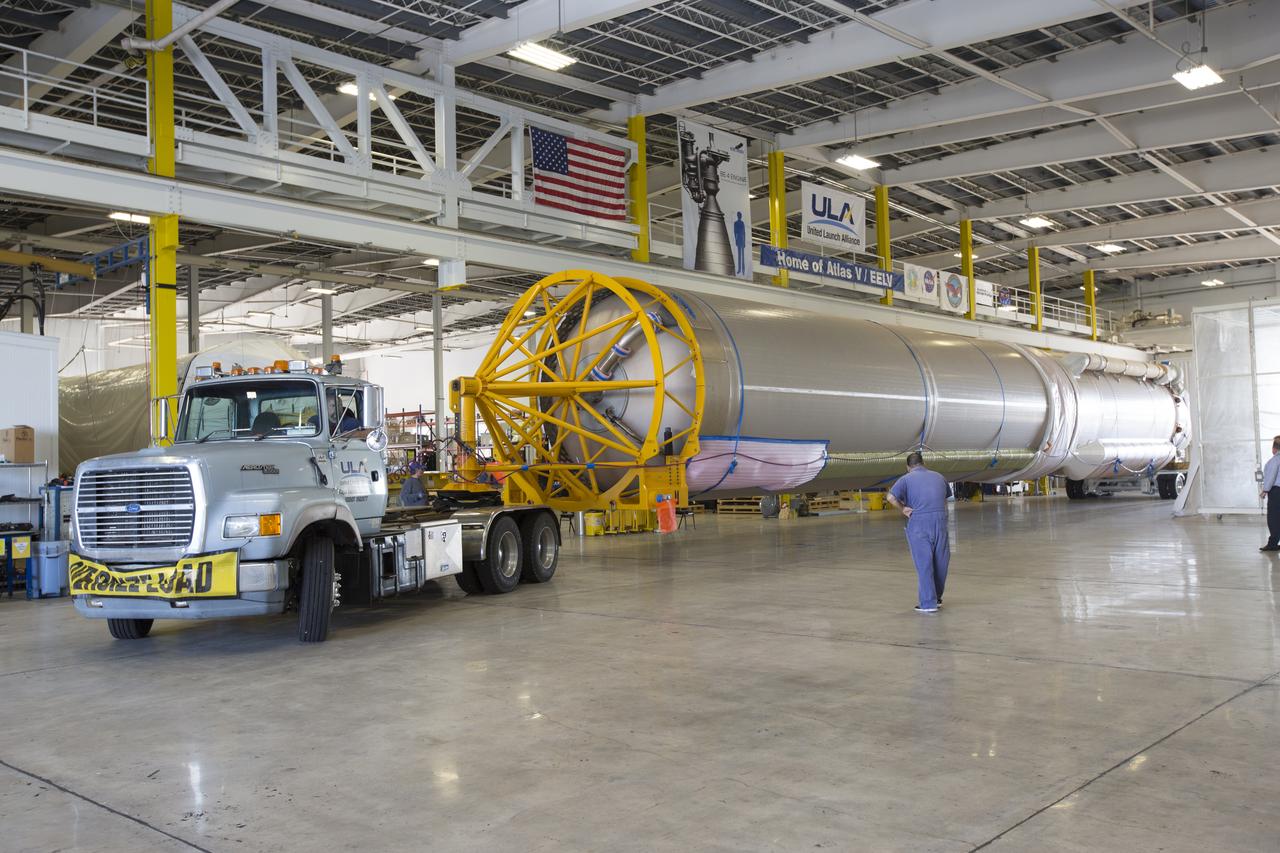

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC). The Atlas V will undergo final testing in that facility. When processing in the ASOC is complete, the Atlas booster will be moved to the Vertical Integration Facility for stacking at Space Launch Complex 41. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Atlas will launch a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the International Space Station.
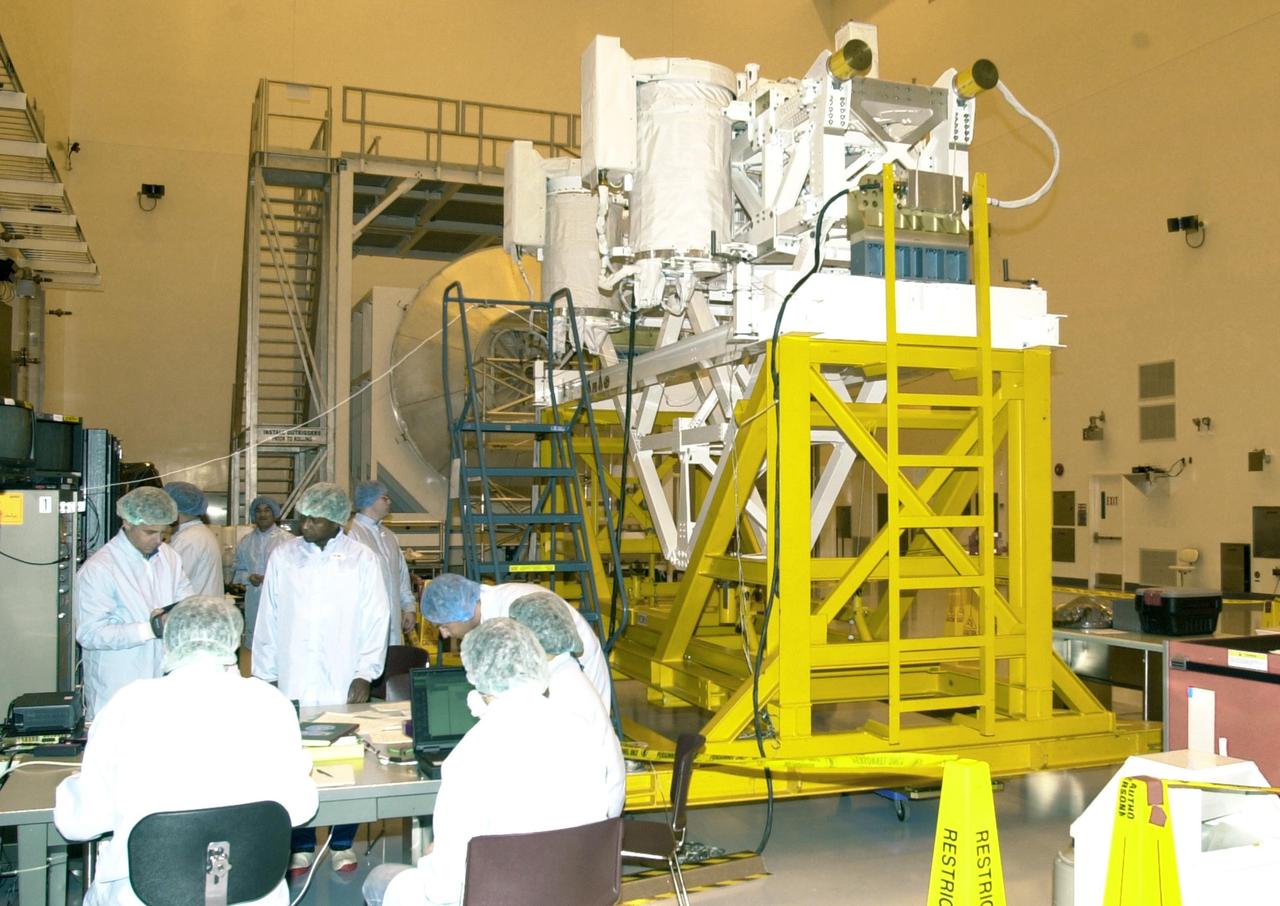

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, members of the STS-107 crew run tests on the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) experiments, part of the payload on their mission. A research mission, the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM), also known as SPACEHAB. The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 11, 2002
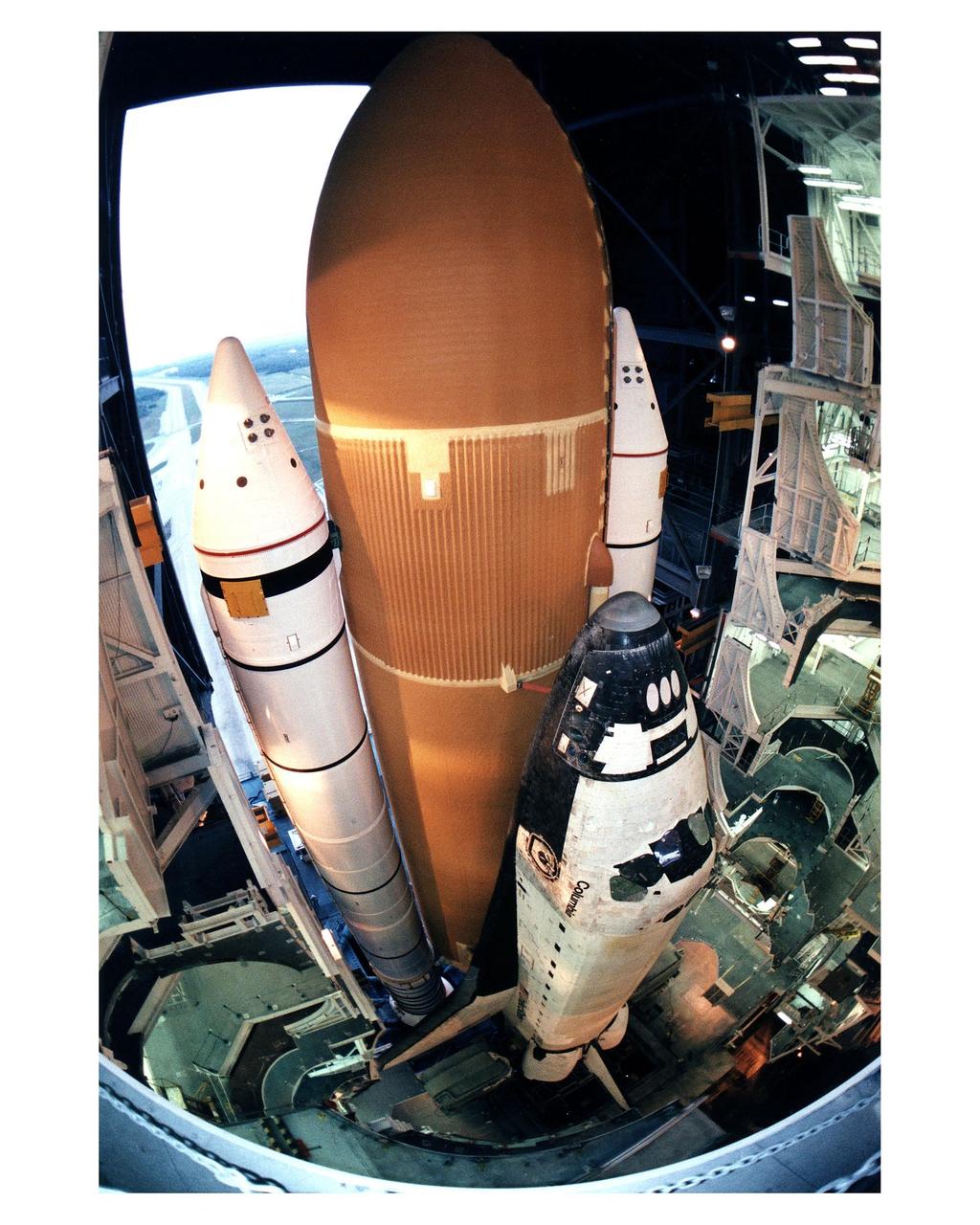

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia begins its rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39A in preparation for the STS-83 mission. The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is the primary payload on this 16-day spaceflight. The MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station, while the seven-member flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments
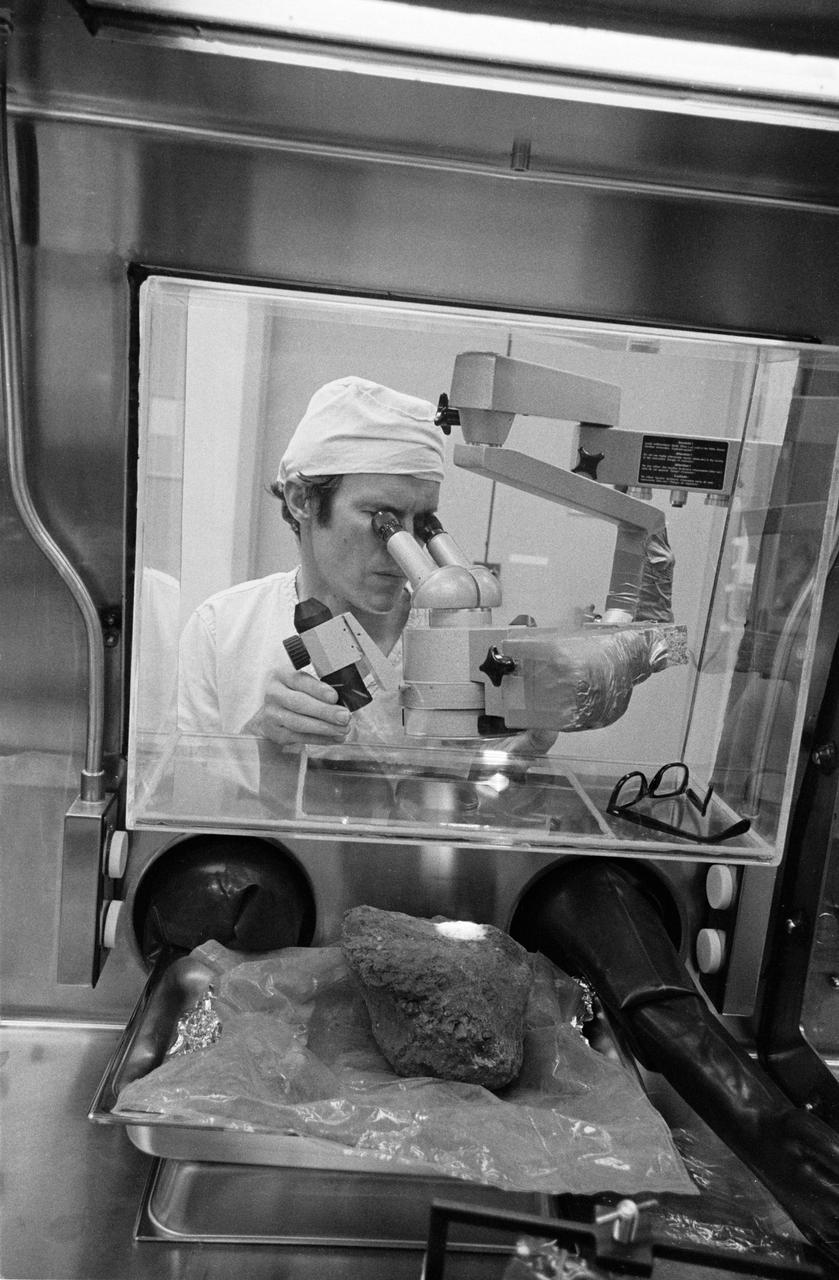

S71-21245 (24 Feb. 1971) --- Dr. Daniel H. Anderson, an aerospace technologist and test director in the Nonsterile Nitrogen Processing Laboratory in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) looks at much-discussed Apollo 14 basketball-size rock through a microscope. The two moon-exploring crew men of Apollo 14 brought back 90-odd pounds of lunar sample material from their two periods of extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface in the Fra Mauro area.
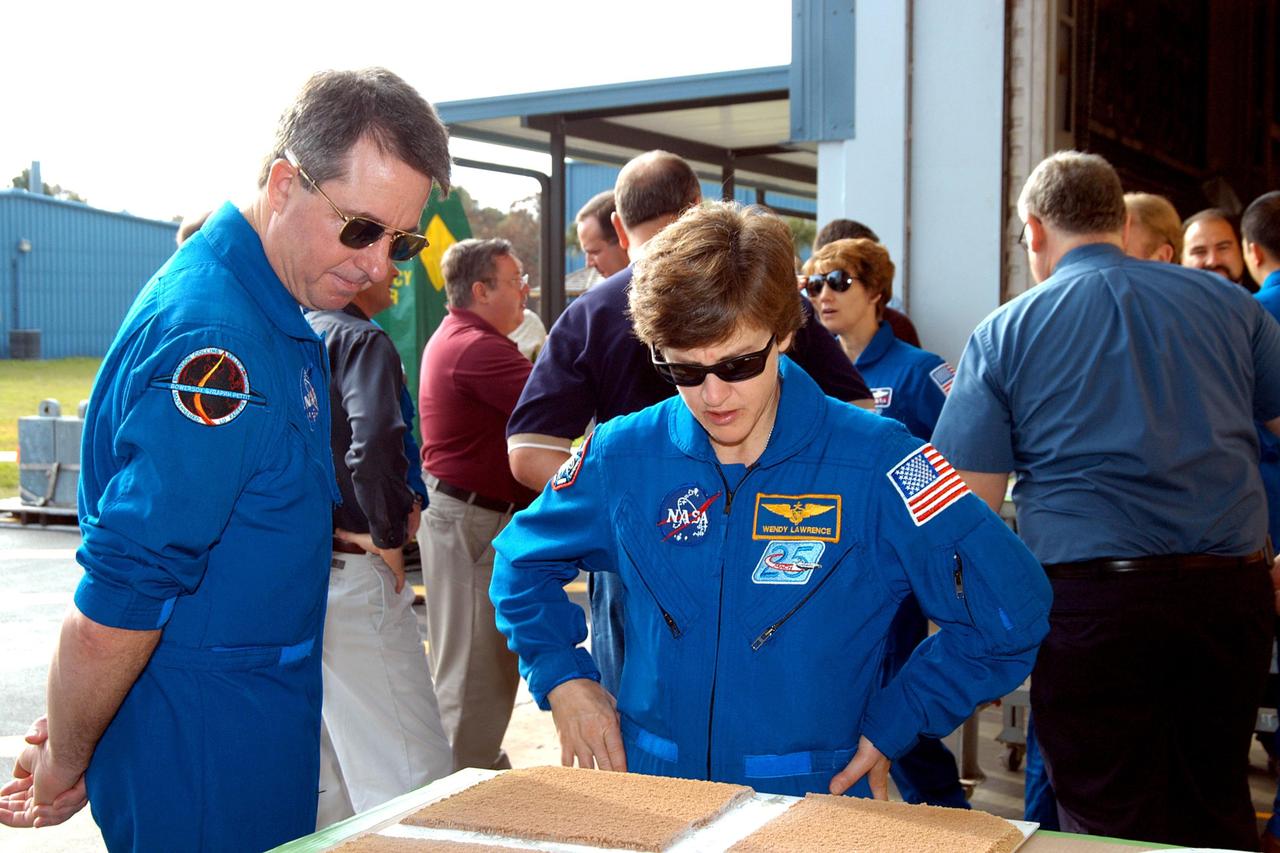

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the SRB Assembly and Refurbishment Facility, STS-114 Mission Specialists Stephen Robinson and Wendy Lawrence look at a test panel of insulation material cut in a liquid nitrogen process. The STS-114 crew is at KSC for familiarization with Shuttle and mission equipment. The mission is Logistics Flight 1, which is scheduled to deliver supplies and equipment, plus the external stowage platform, to the International Space Station.
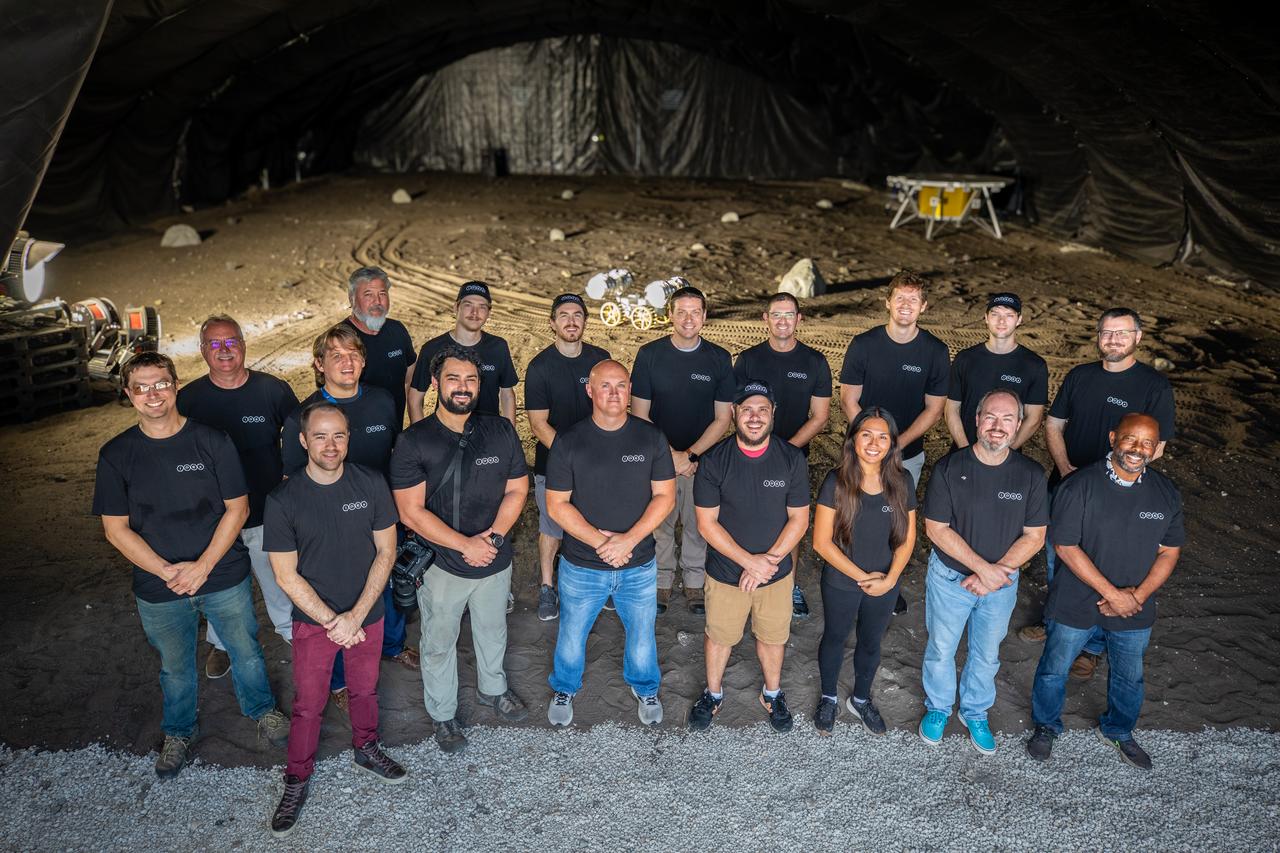

A team from the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations lab who developed and tested NASA’s ISRU Pilot Excavator (IPEx) pose for a photo on Friday, Aug. 30, 2024, in a testbed located at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IPEx functions as both an excavator and a dump truck to mine and transport lunar regolith, the loose rocky material on the Moon’s surface, which is crucial for future lunar missions and In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) processes. This dual capability makes IPEx an indispensable tool for sustainable lunar exploration.
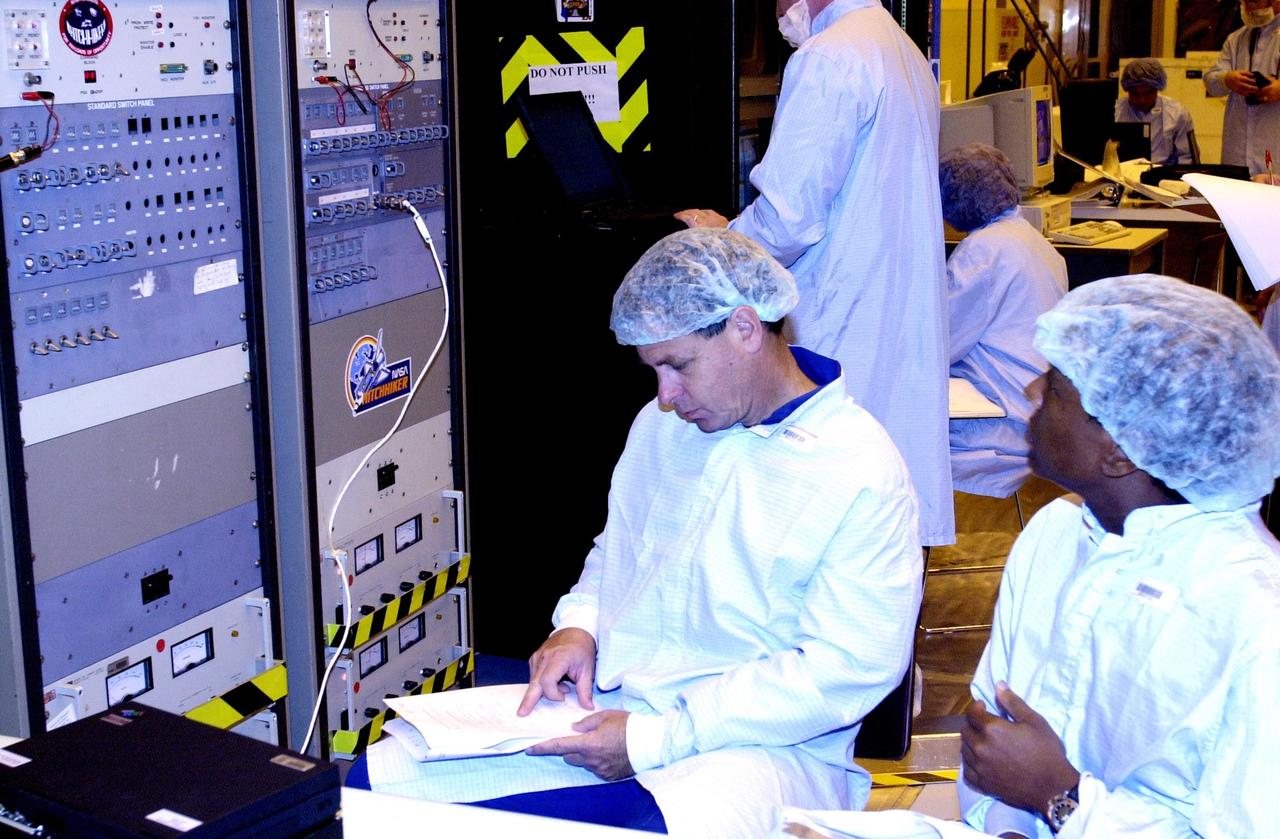

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, members of the STS-107 crew look at test results on the Fast Reaction Experiments Enabling Science, Technology, Applications and Research (FREESTAR) experiments, part of the payload on their mission. A research mission, the primary payload is the first flight of the SHI Research Double Module (SHI/RDM), also known as SPACEHAB. The experiments range from material sciences to life sciences (many rats). STS-107 is scheduled to launch July 11, 2002

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC). The Atlas V will undergo final testing in that facility. When processing in the ASOC is complete, the Atlas booster will be moved to the Vertical Integration Facility for stacking at Space Launch Complex 41. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Atlas will launch a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the International Space Station.
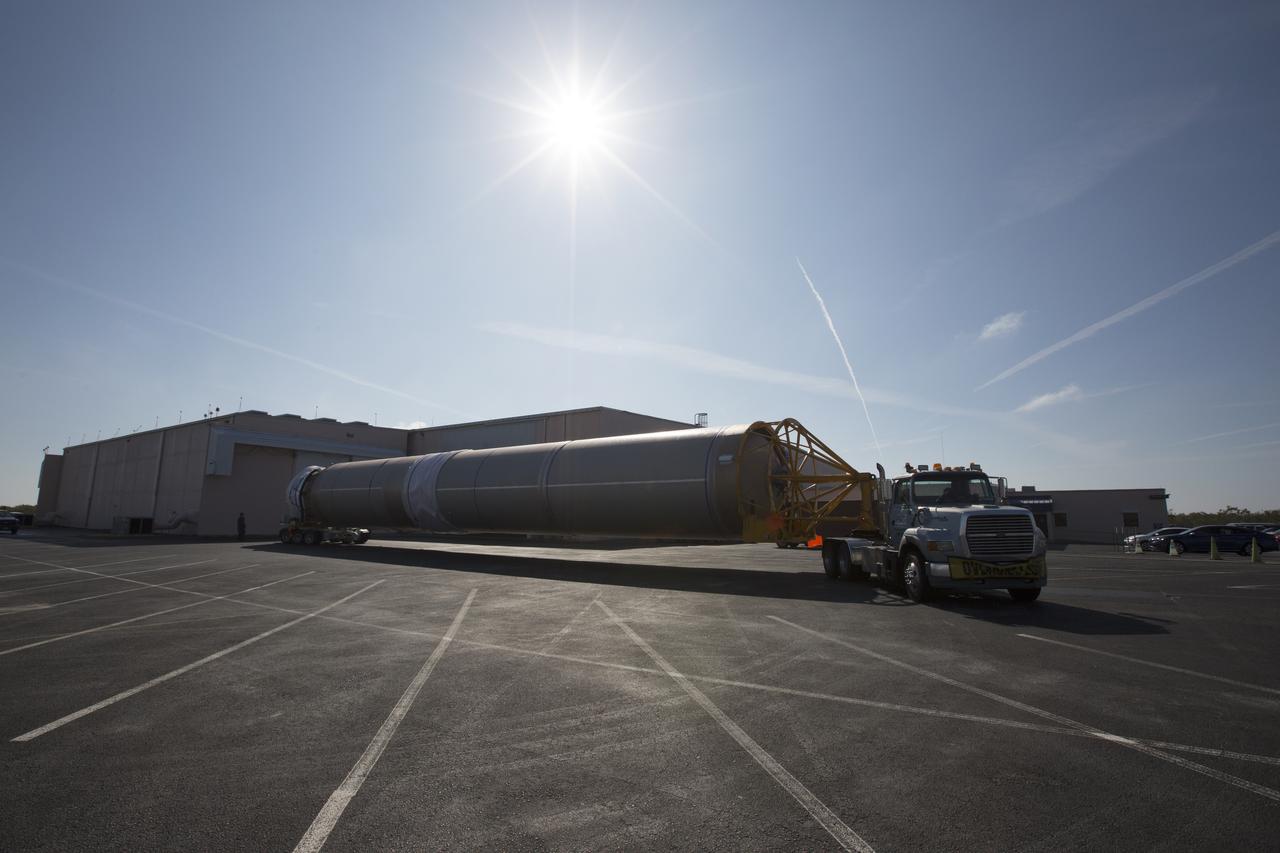

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC). The Atlas V will undergo final testing in that facility. When processing in the ASOC is complete, the Atlas booster will be moved to the Vertical Integration Facility for stacking at Space Launch Complex 41. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Atlas will launch a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the International Space Station.
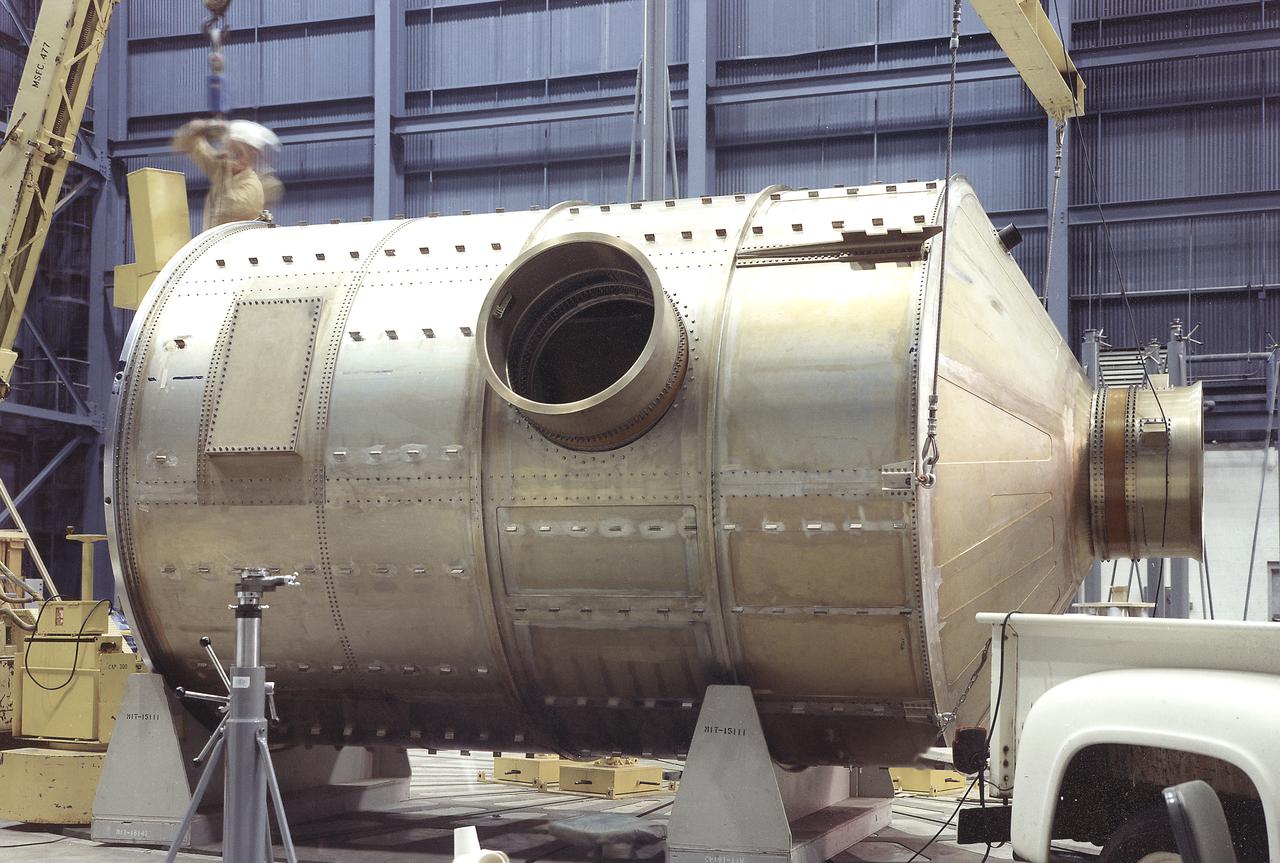
At Marshall Space Flight Center, Skylab's Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) flight article undergoes center-of-gravity testing. Developed and fabricated by MSFC, the MDA housed the control units for the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Earth Resources Experiment Package (EREP), and the Zero-Gravity Material Processing Facility and provided a docking port for the Apollo Command Module.
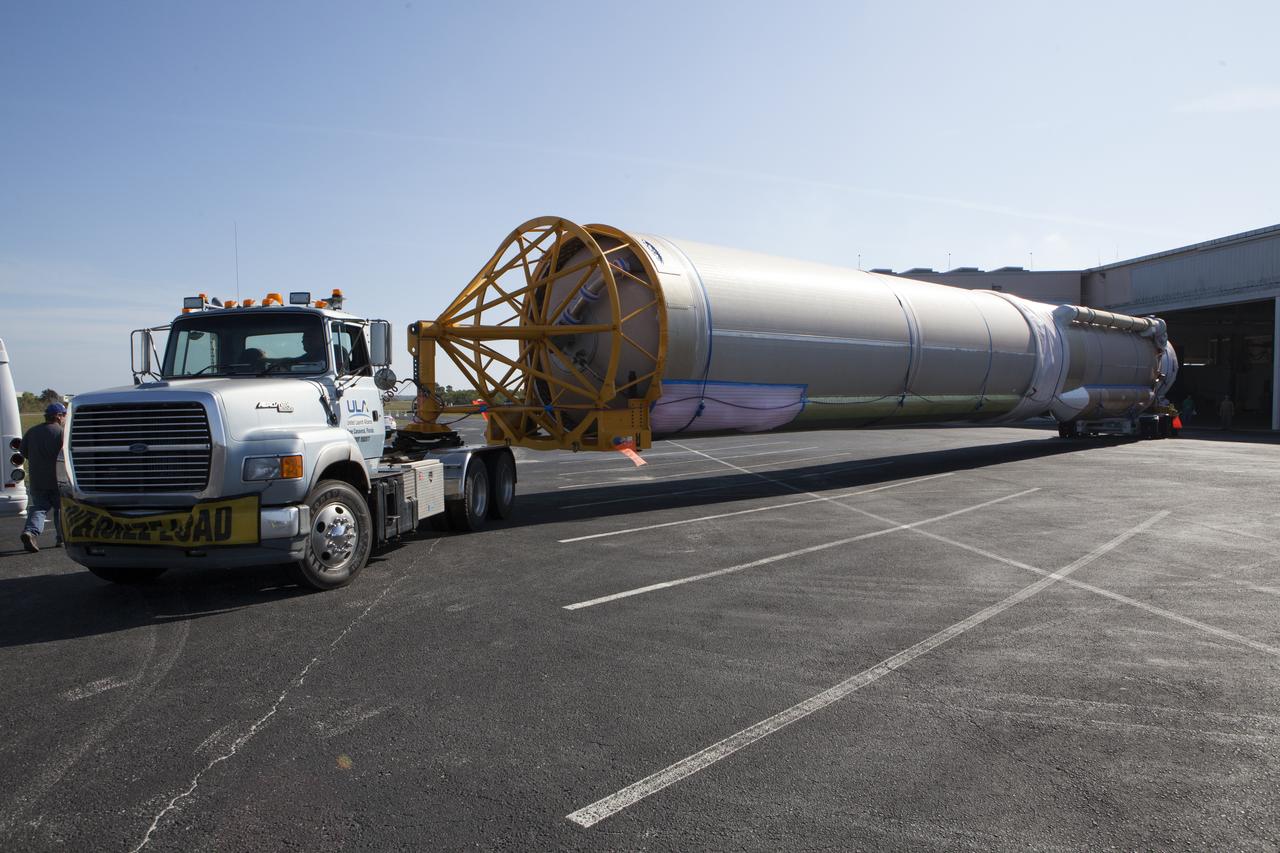

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC). The Atlas V will undergo final testing in that facility. When processing in the ASOC is complete, the Atlas booster will be moved to the Vertical Integration Facility for stacking at Space Launch Complex 41. Scheduled to launch March 19, 2017, the Atlas will launch a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-7 mission to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the International Space Station.
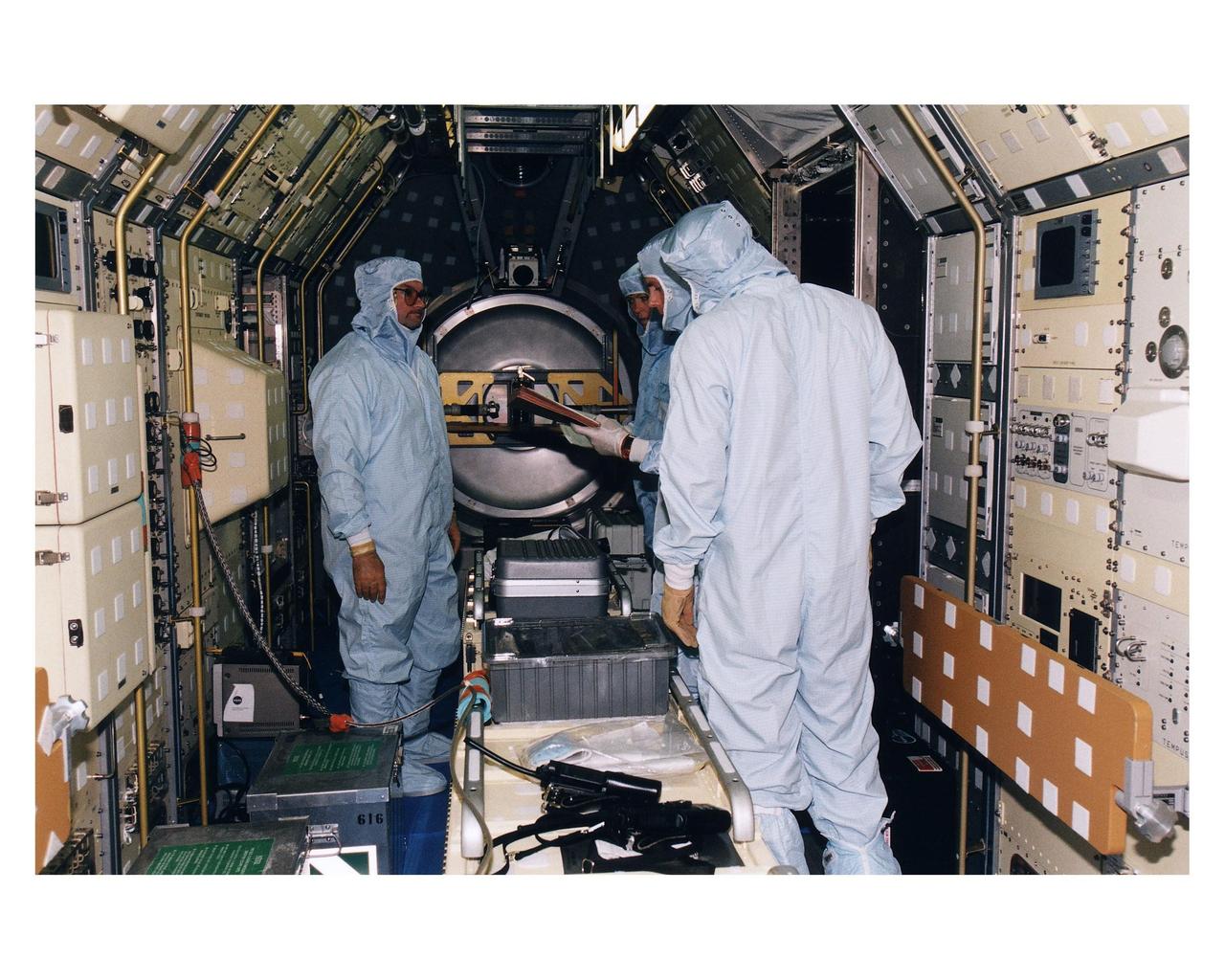

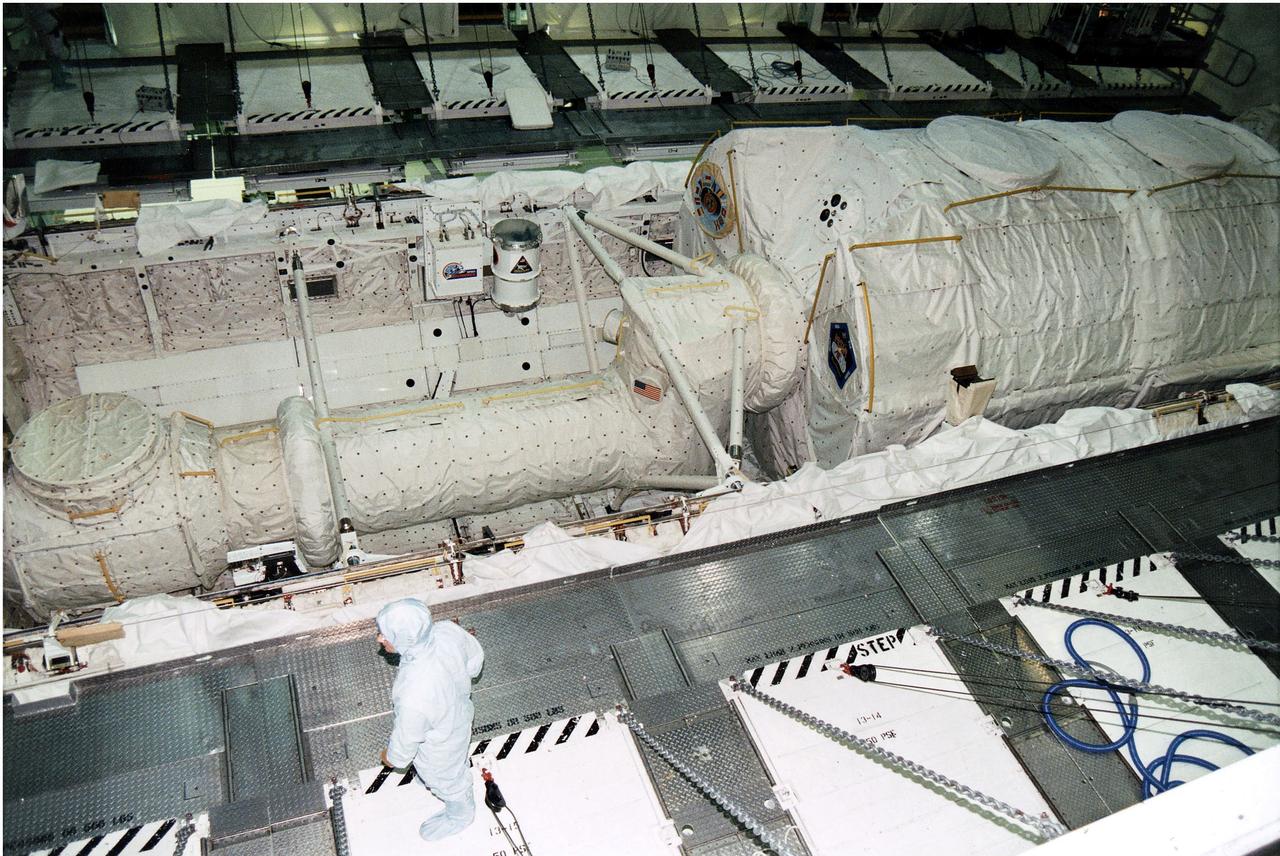
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- KSC payloads processing employees work to reservice the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module in the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia’s payload bay for the STS-94 mission in Orbiter Processing Facility 1. That mission is now scheduled to lift off in early July. This was the first time that this type of payload was reserviced without removing it from the payload bay. This new procedure pioneers processing efforts for quick relaunch turnaround times for future payloads. The Spacelab module was scheduled to fly again with the full complement of STS-83 experiments after that mission was cut short due to a faulty fuel cell. During the scheduled 16-day STS-94 mission, the experiments will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments
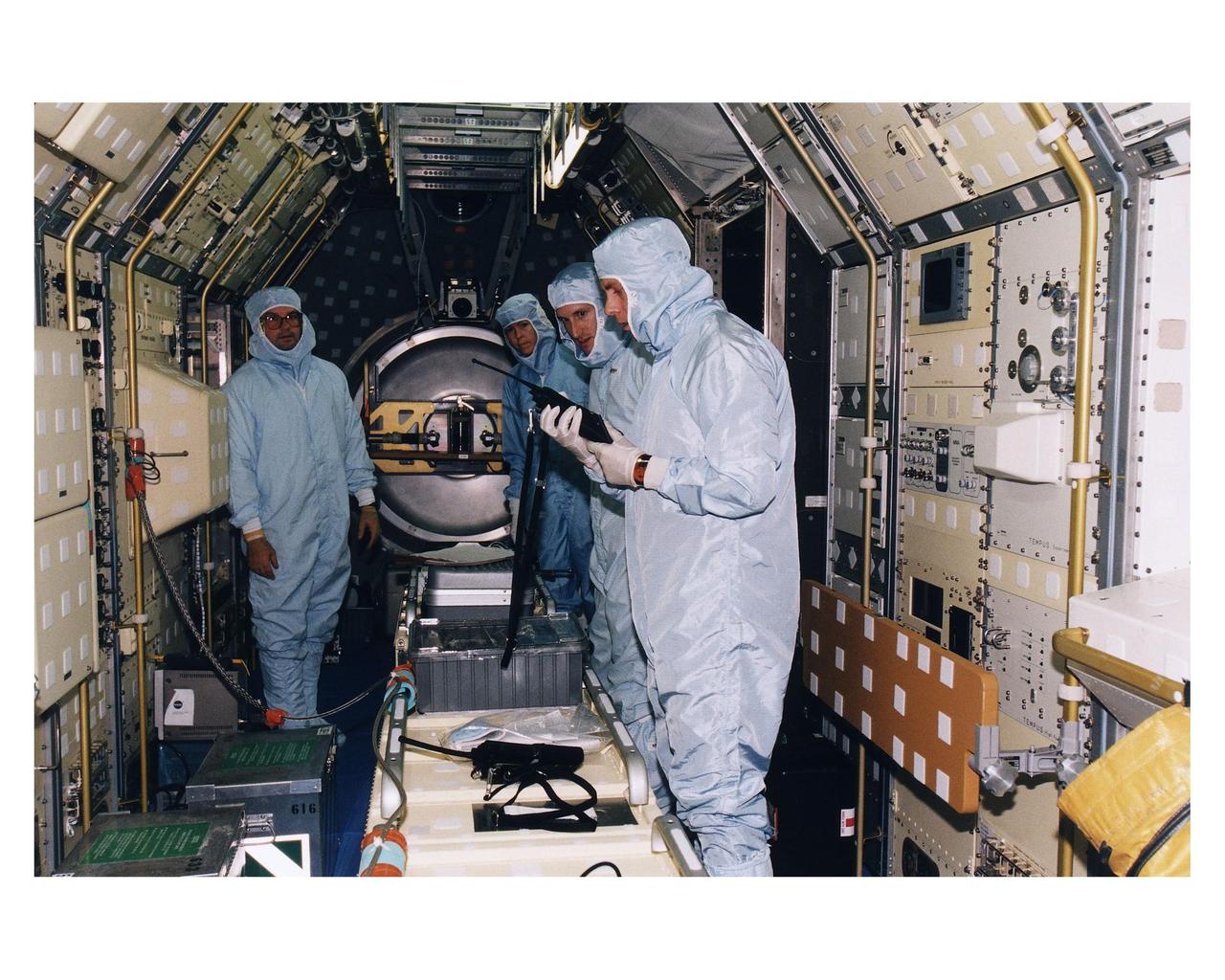

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- KSC payloads processing employees work to reservice the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module in the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia’s payload bay for the STS-94 mission in Orbiter Processing Facility 1. That mission is now scheduled to lift off in early July. This was the first time that this type of payload was reserviced without removing it from the payload bay. This new procedure pioneers processing efforts for quick relaunch turnaround times for future payloads. The Spacelab module was scheduled to fly again with the full complement of STS-83 experiments after that mission was cut short due to a faulty fuel cell. During the scheduled 16-day STS-94 mission, the experiments will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments

KSC payloads processing employees work to reservice the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module in the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia’s payload bay for the STS-94 mission in Orbiter Processing Facility 1. That mission is now scheduled to lift off in early July. This was the first time that this type of payload was reserviced without removing it from the payload bay. This new procedure pioneers processing efforts for quick relaunch turnaround times for future payloads. The Spacelab module was scheduled to fly again with the full complement of STS-83 experiments after that mission was cut short due to a faulty fuel cell. During the scheduled 16-day STS-94 mission, the experiments will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments
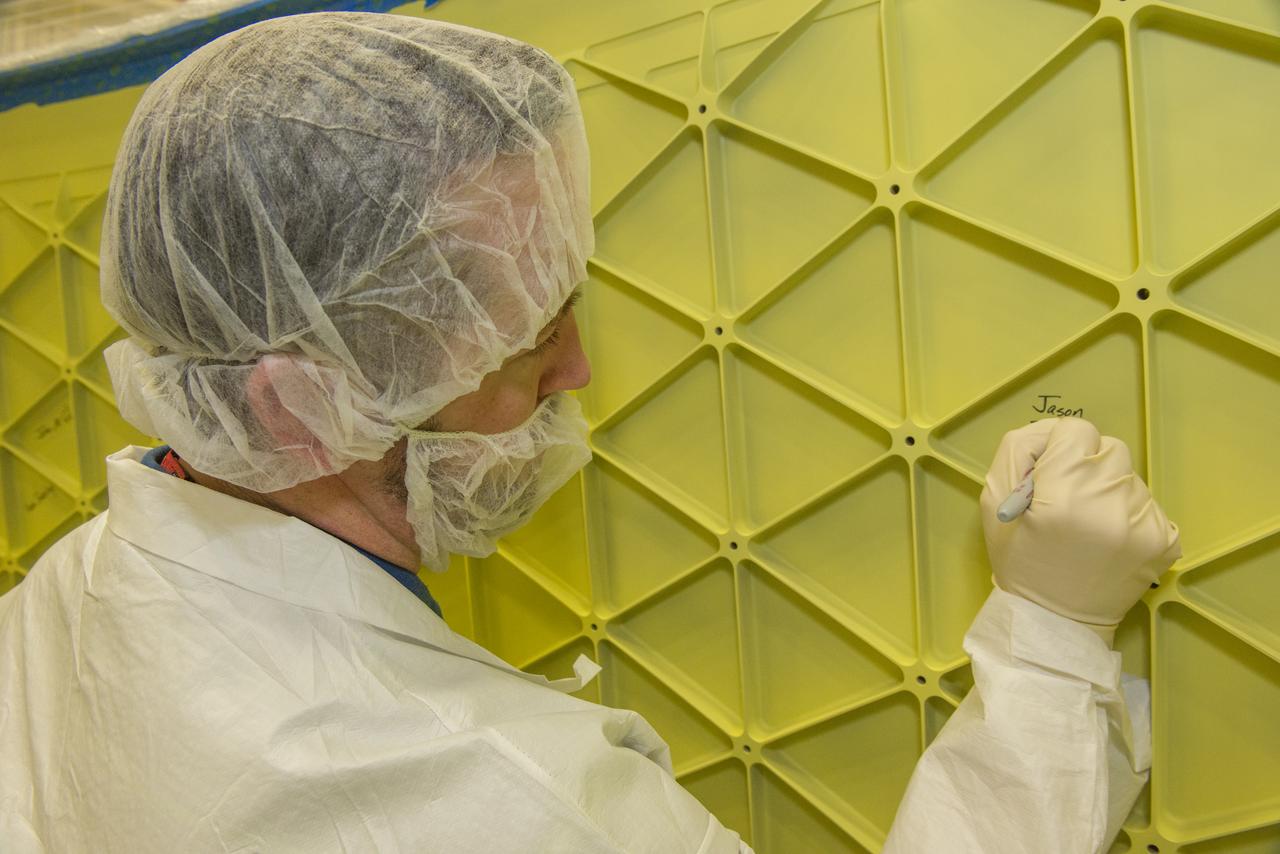

JASON ELDRIDGE, AN ERC INCORPORATED EMPLOYEE SUPPORTING THE MATERIALS & PROCESSES LABORATORY AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER, SIGNS HIS NAME ON THE INTERIOR OF THE ADAPTER THAT WILL CONNECT THE ORION SPACECRAFT TO A UNITED LAUNCH ALLIANCE DELTA IV ROCKET FOR EXPLORATION FLIGHT TEST (EFT)-1. MARSHALL CENTER TEAM MEMBERS WHO WERE INVOLVED IN THE DESIGN, CONSTRUCTION AND TESTING OF THE ADAPTER HAD THE OPPORTUNITY TO AUTOGRAPH IT BEFORE THE HARDWARE IS SHIPPED TO NASA'S KENNEDY SPACE CENTER IN FEBRUARY. ELDRIDGE WAS ON A TEAM THAT PERFORMED ULTRASONIC INSPECTIONS ON THE ADAPTER'S WELDS -- ENSURING THEY ARE STRUCTURALLY SOUND. EFT-1, SCHEDULED FOR 2014, WILL PROVIDE EARLY EXPERIENCE FOR NASA SPACE LAUNCH SYSTEM (SLS) HARDWARE AHEAD OF THE ROCKET'S FIRST FLIGHT IN 2017.
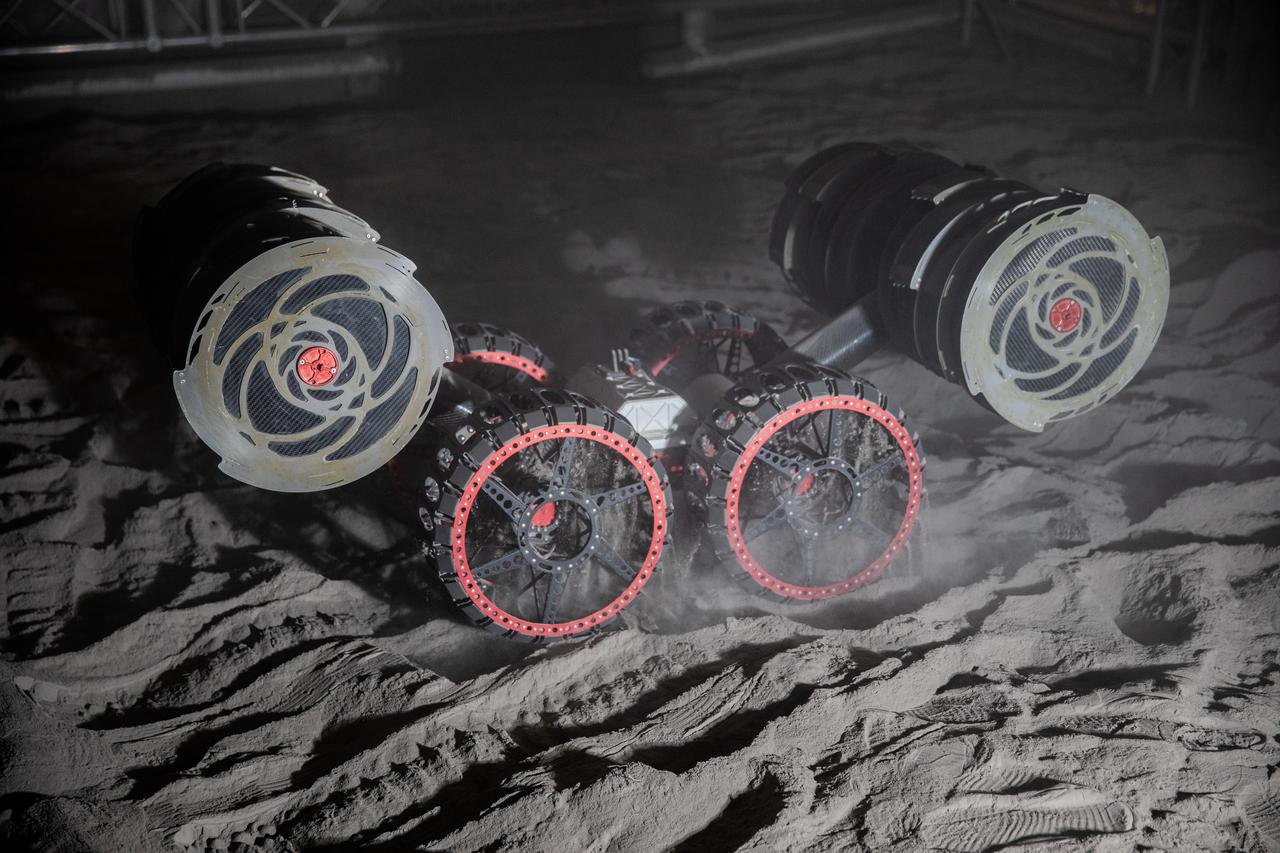

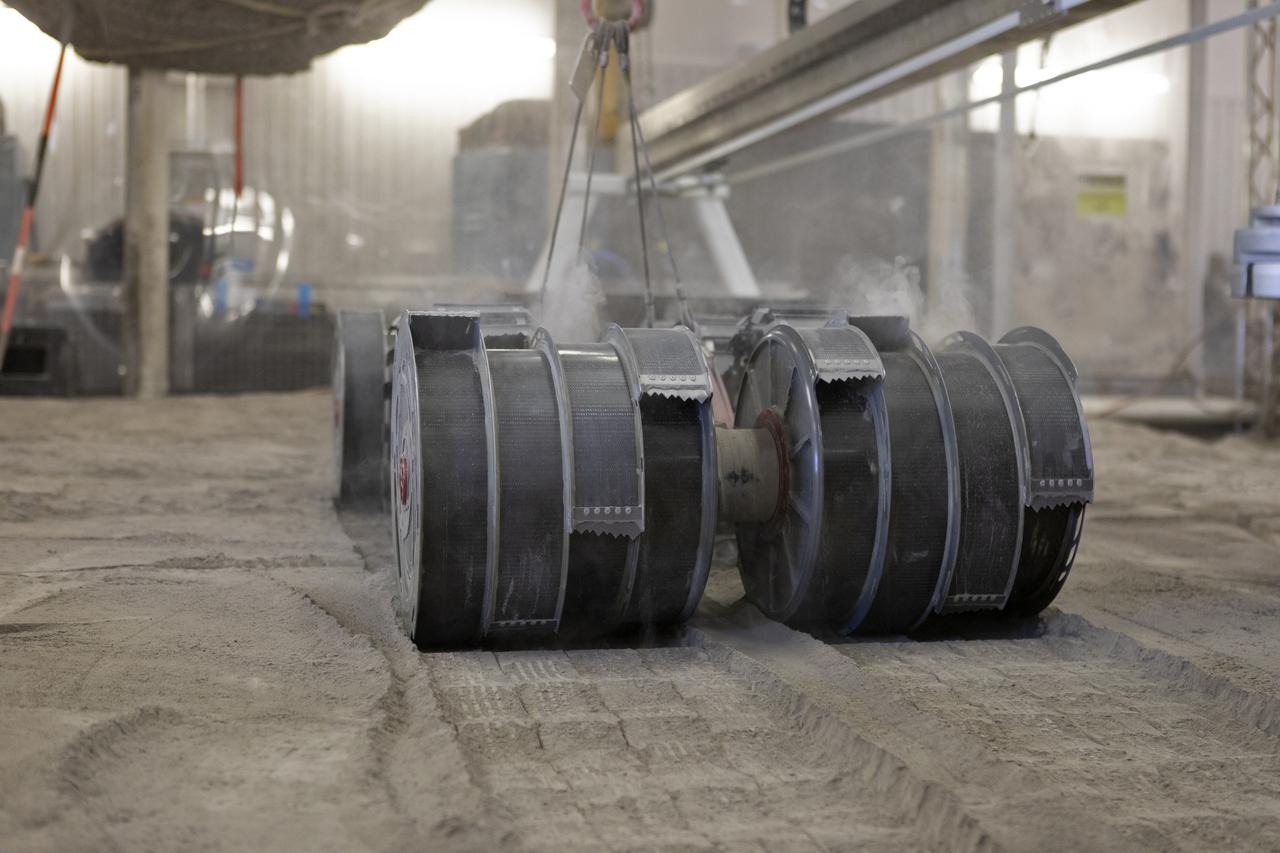
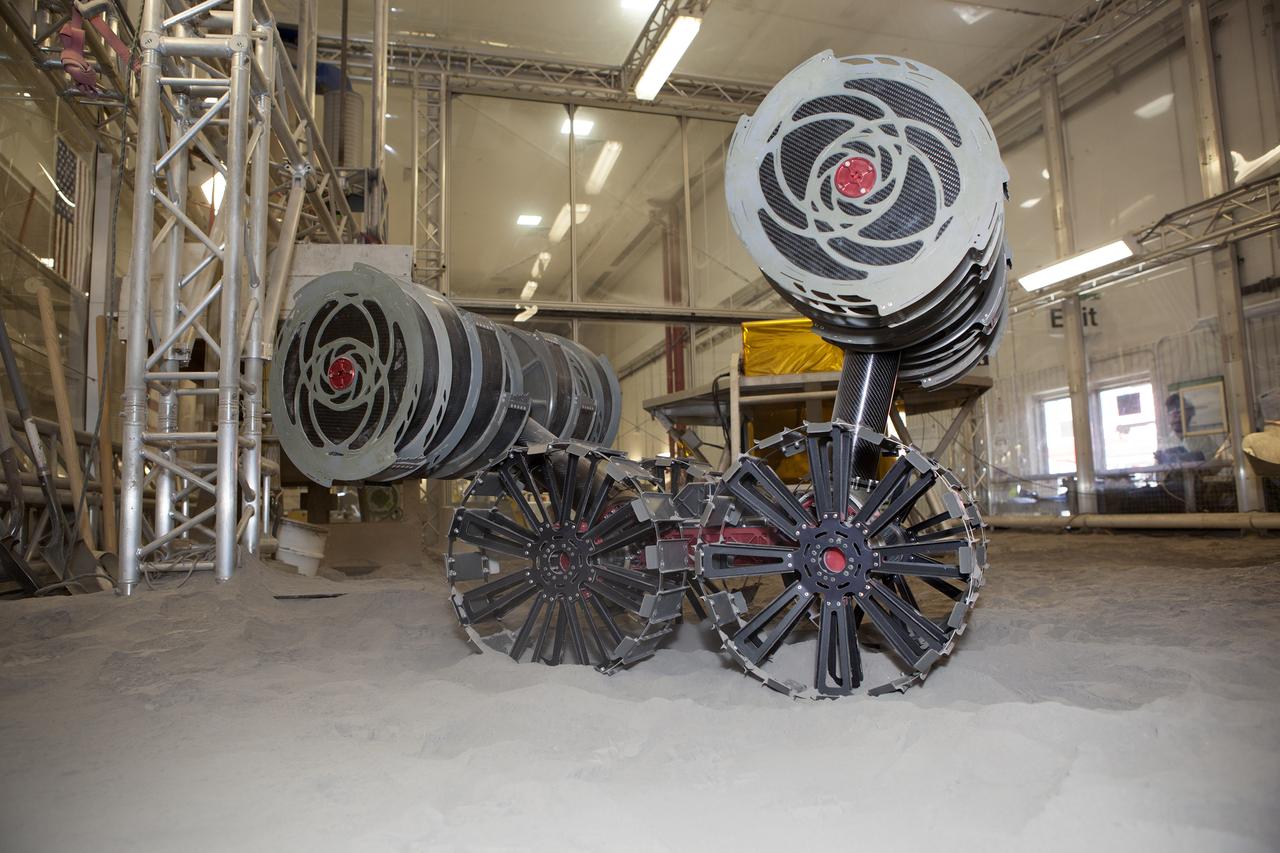
With the lights out, the ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
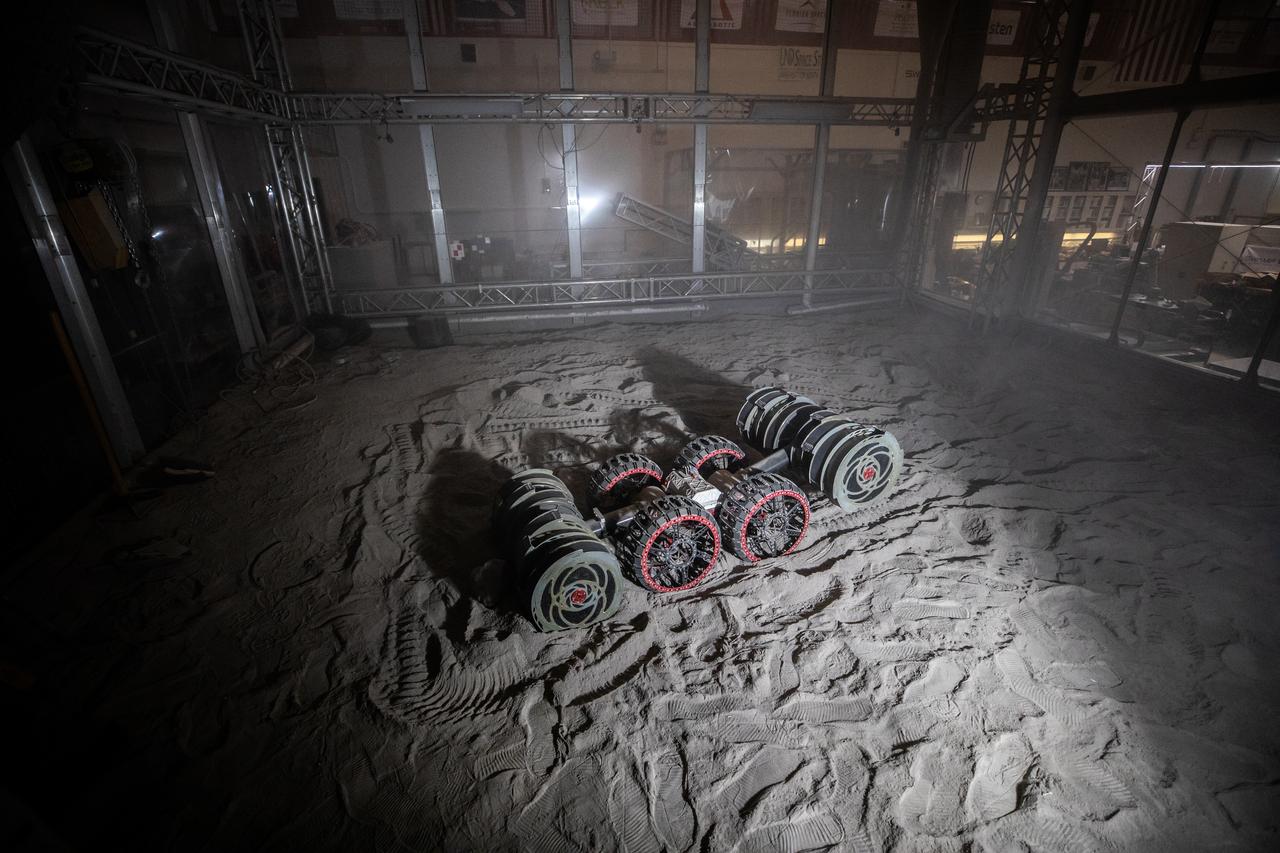

With the lights out, the ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.

A team from the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab tests the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot (RASSOR) in the regolith bin inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 5, 2019. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like RASSOR will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. RASSOR can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.

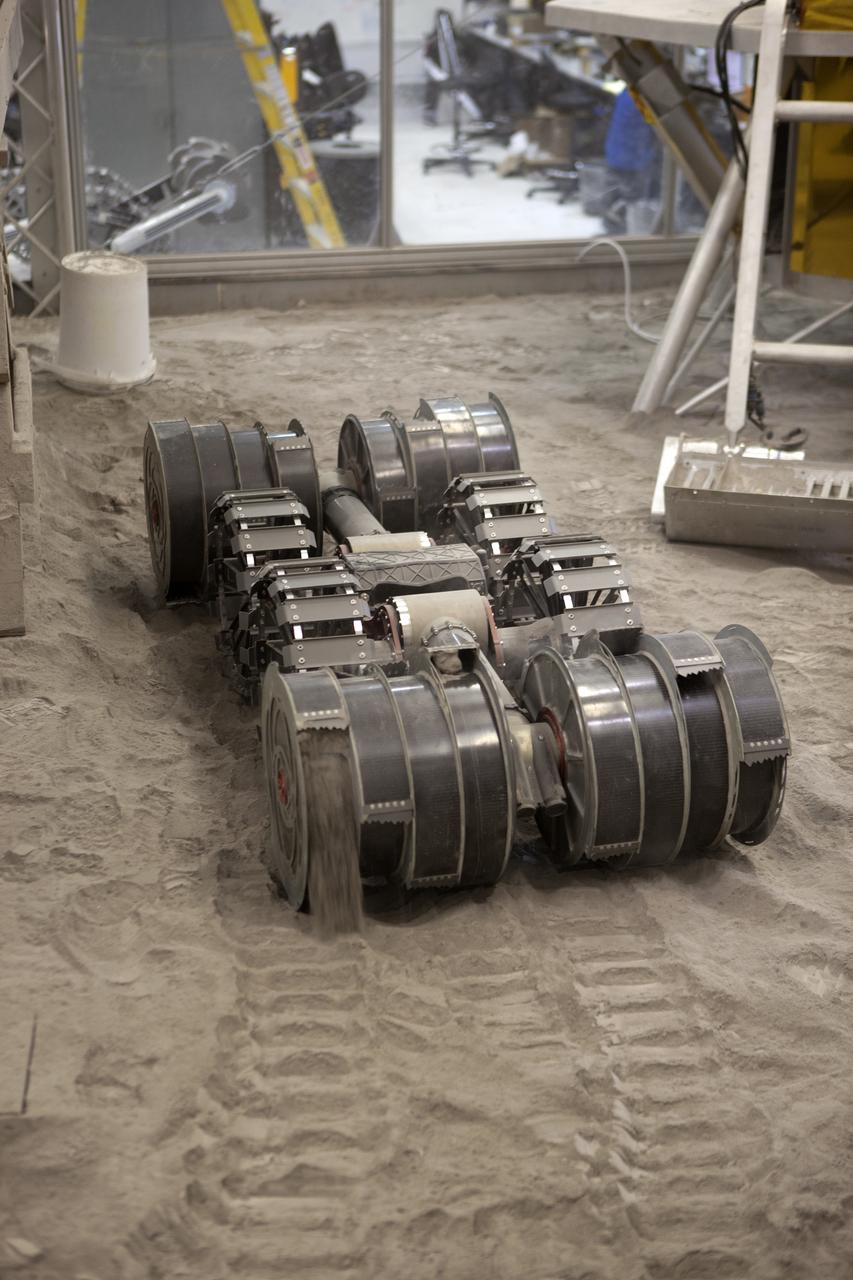
An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.

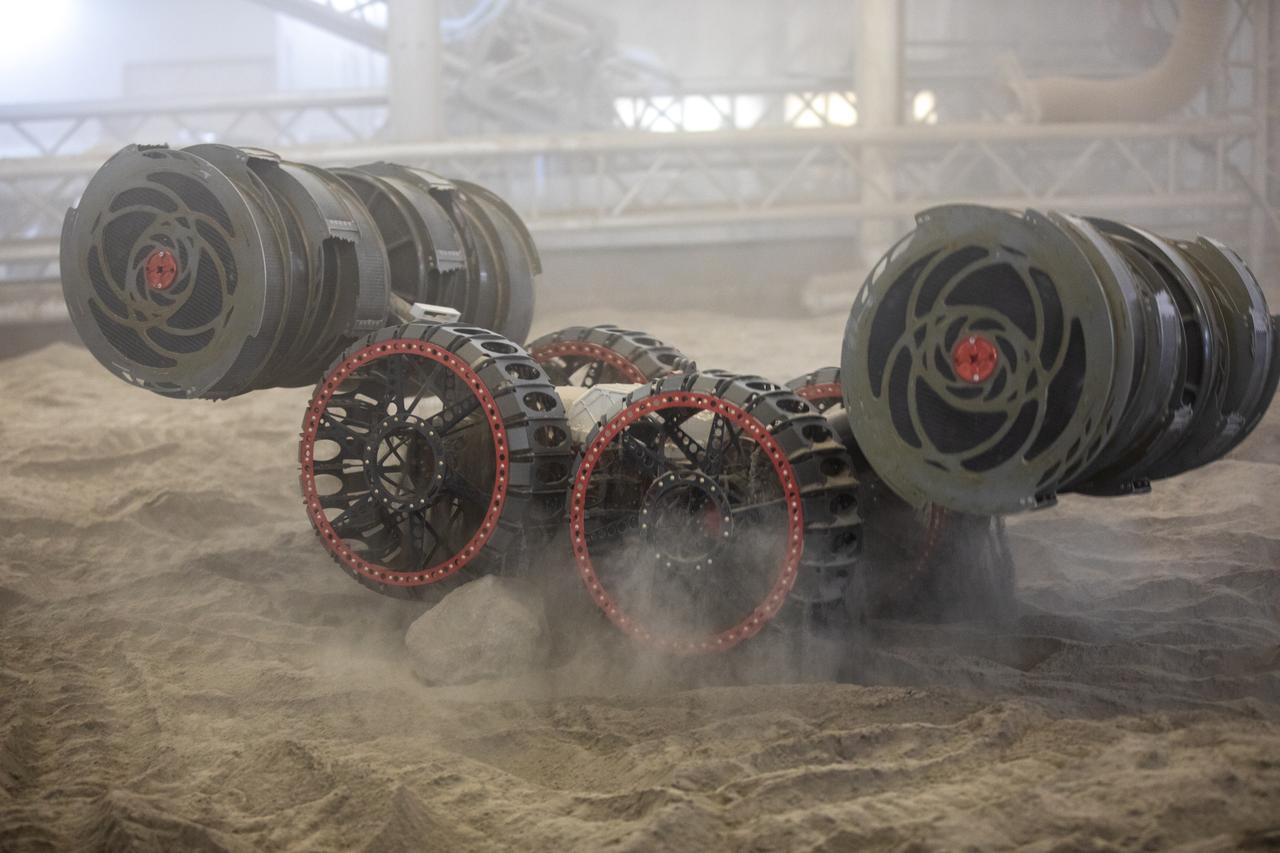
An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.

Technicians conduct testing operations on NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) spacecraft onto a work stand for testing operations at the Astrotech Processing Facility on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Jan. 19, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.

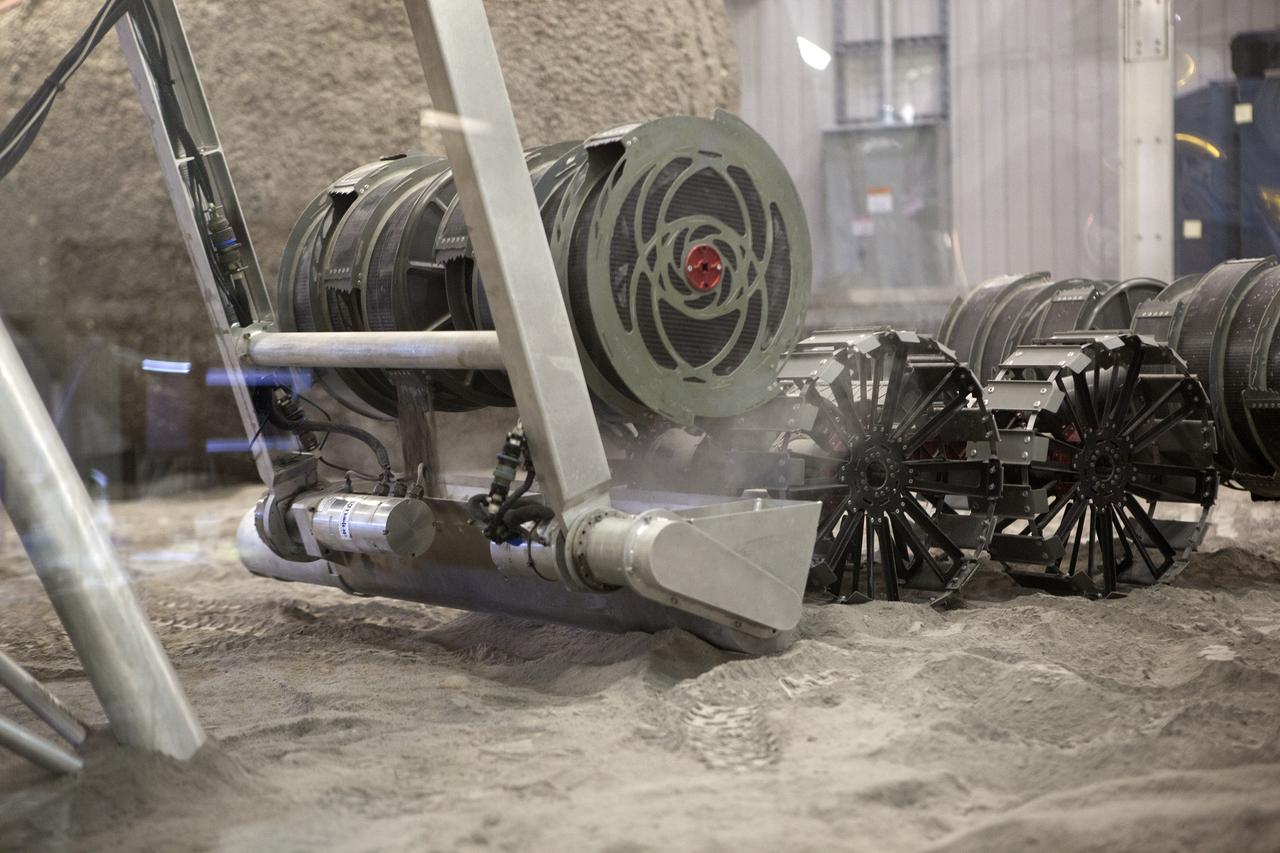
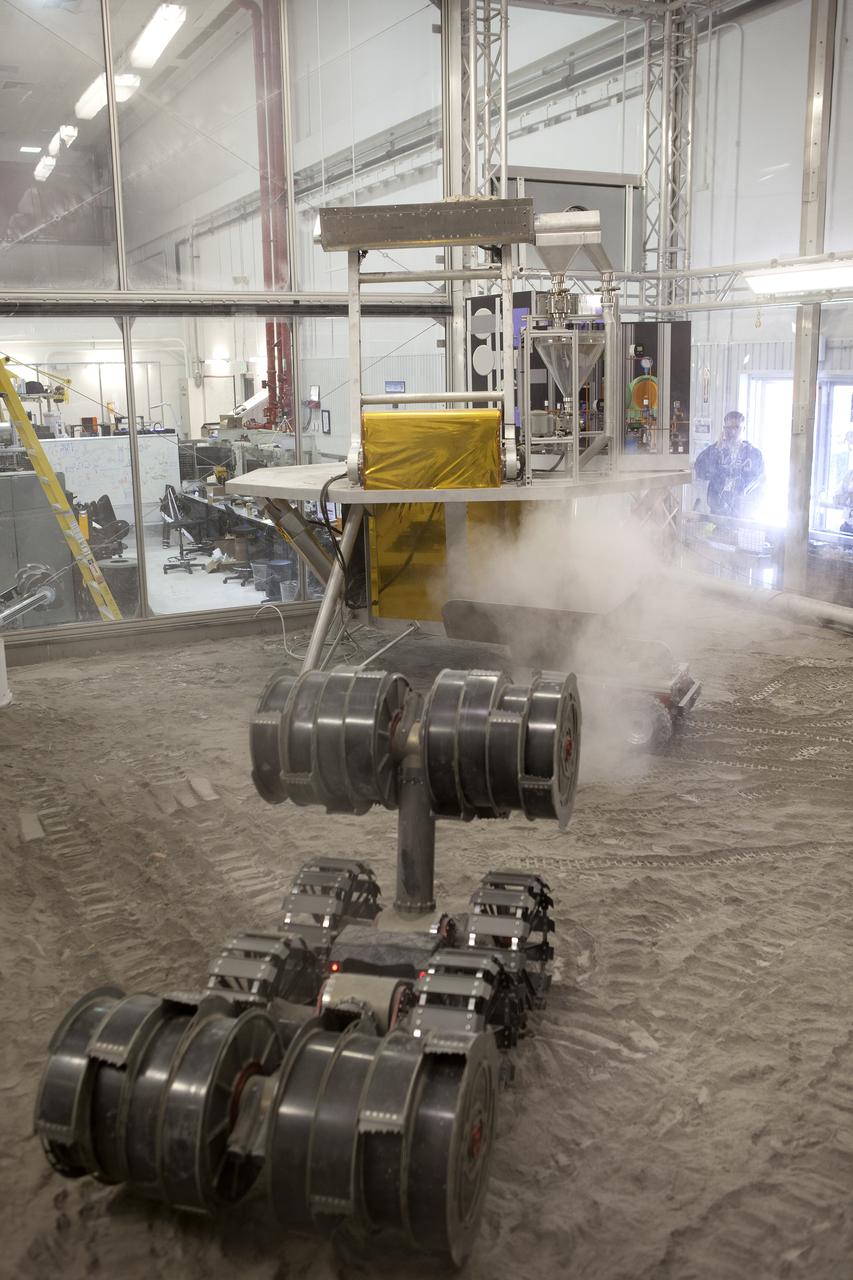
The ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in the regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.

An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.
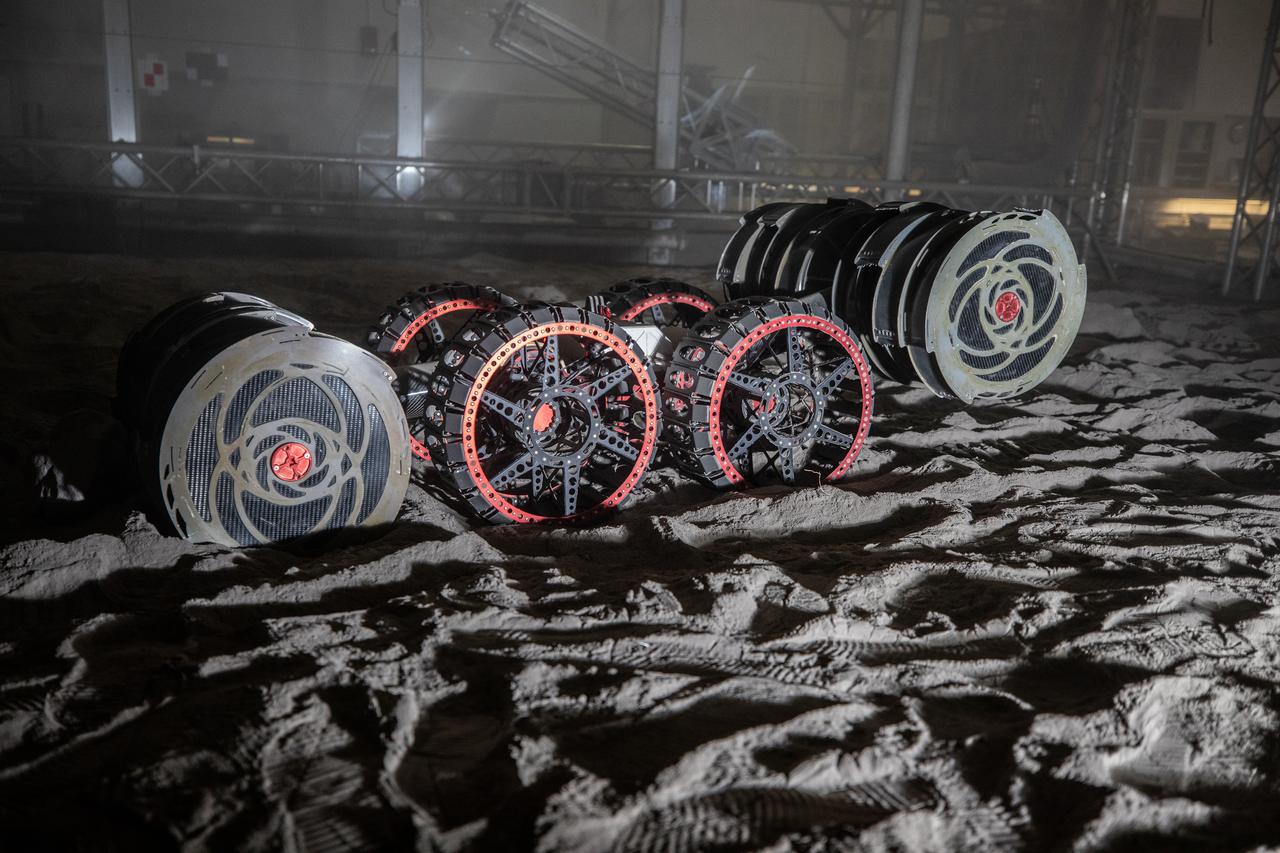

With the lights out, the ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in the regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.

An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.

A team from the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab tests the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot (RASSOR) in the regolith bin inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 5, 2019. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like RASSOR will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. RASSOR can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.

Technicians conduct testing operations on NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) spacecraft onto a work stand for testing operations at the Astrotech Processing Facility on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Jan. 19, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.

An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.
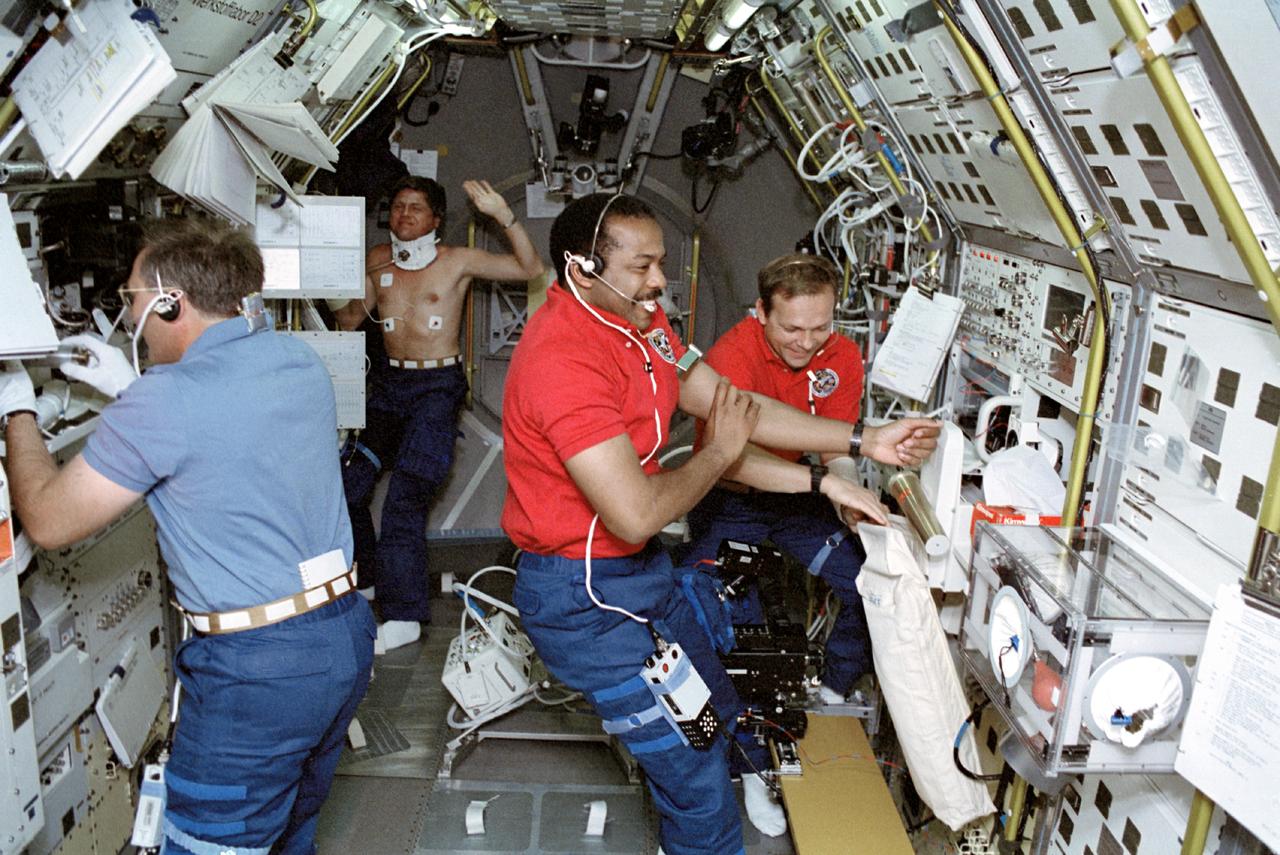

STS055-22-004 (26 April-6 May 1993) --- Four of the seven crew members who spent 10 days aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia are pictured during a brief shift overlap period in the Spacelab D-2 Science Module. Left to right are Jerry L. Ross, Ulrich Walter, Bernard A. Harris, Jr. and Hans Schlegel. Ross, STS-55 payload commander, is changing a sample in a materials processing furnace; Walter, a German payload specialist is in the midst of a baroreflex test and fellow payload specialist Schlegel assists mission specialist and physician Harris with a physiological test at the "Anthrorack".
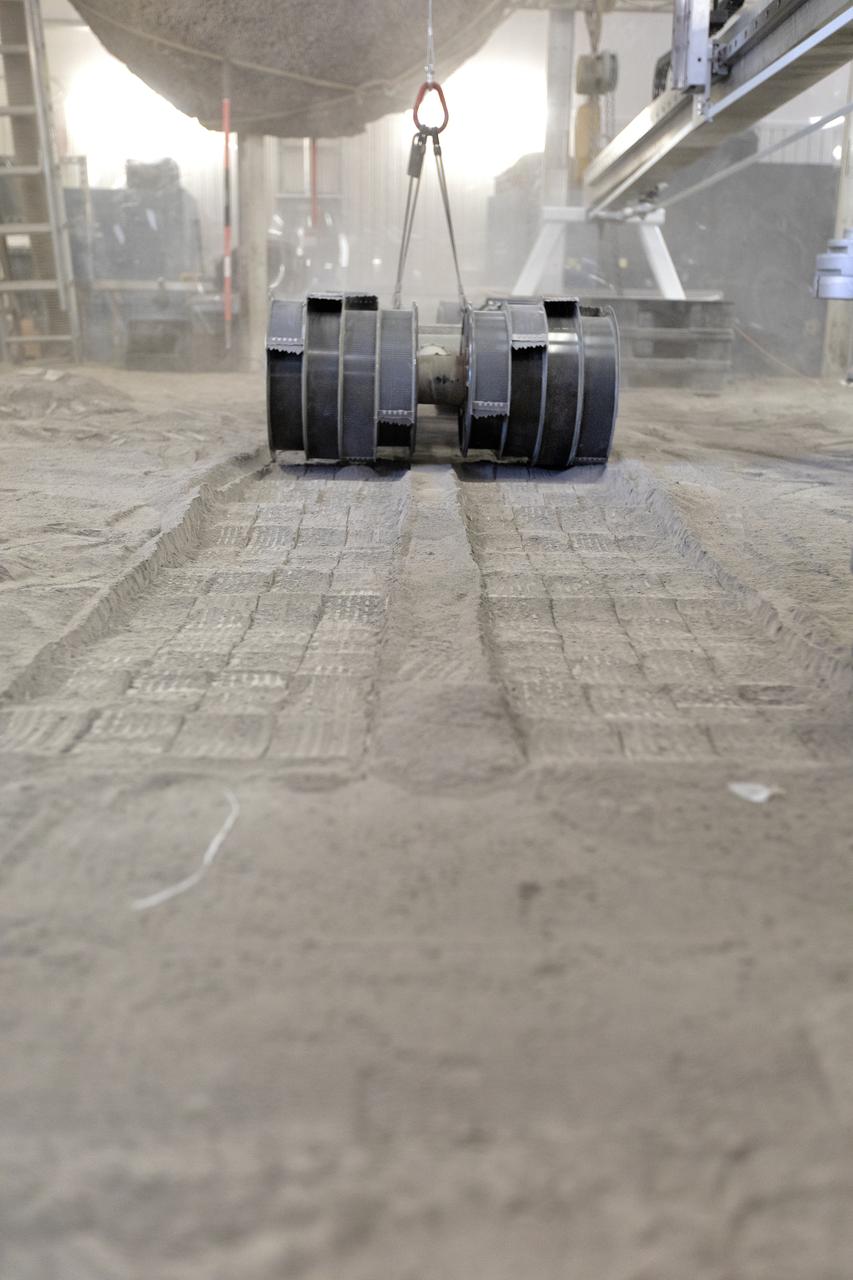

A team from the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab tests the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot (RASSOR) in the regolith bin inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 5, 2019. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like RASSOR will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. RASSOR can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
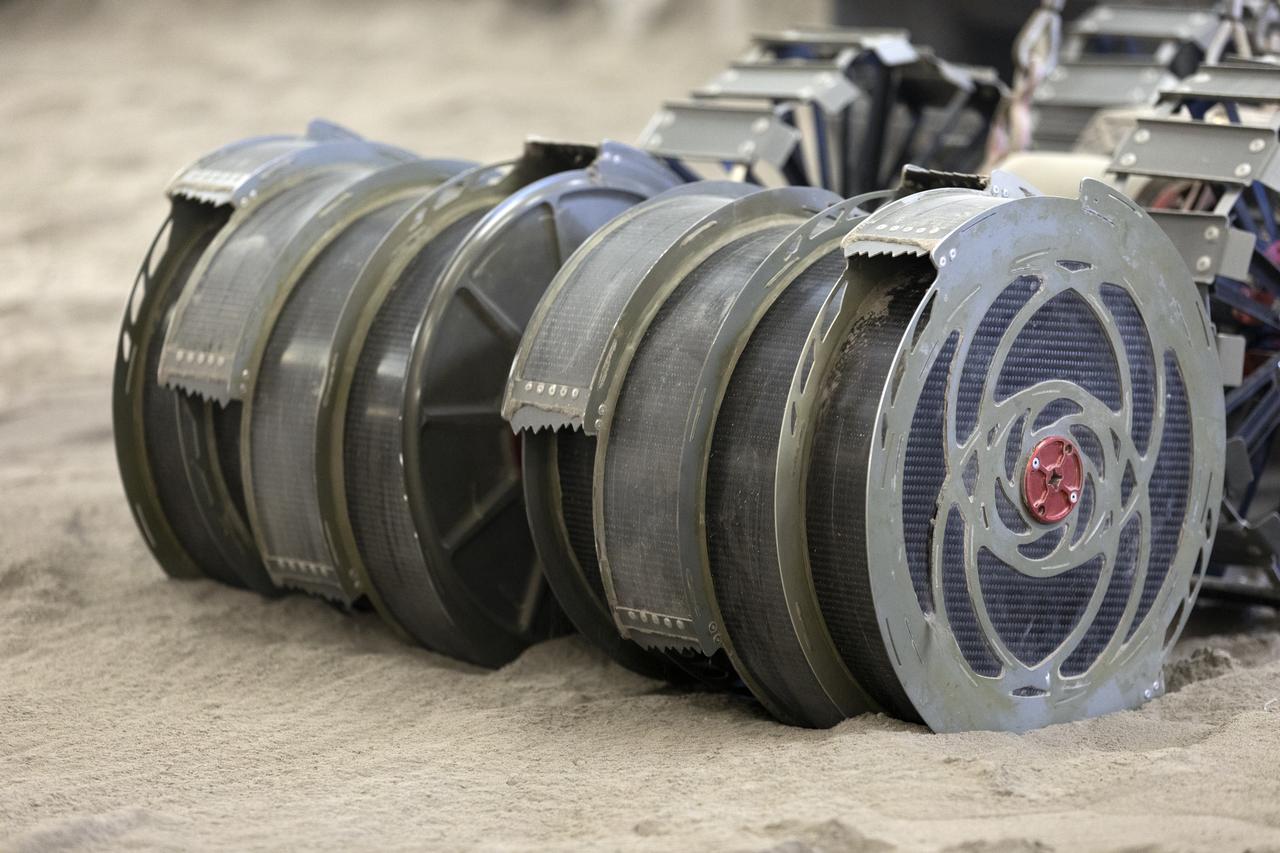

A team from the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab tests the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot (RASSOR) in the regolith bin inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 5, 2019. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like RASSOR will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. RASSOR can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
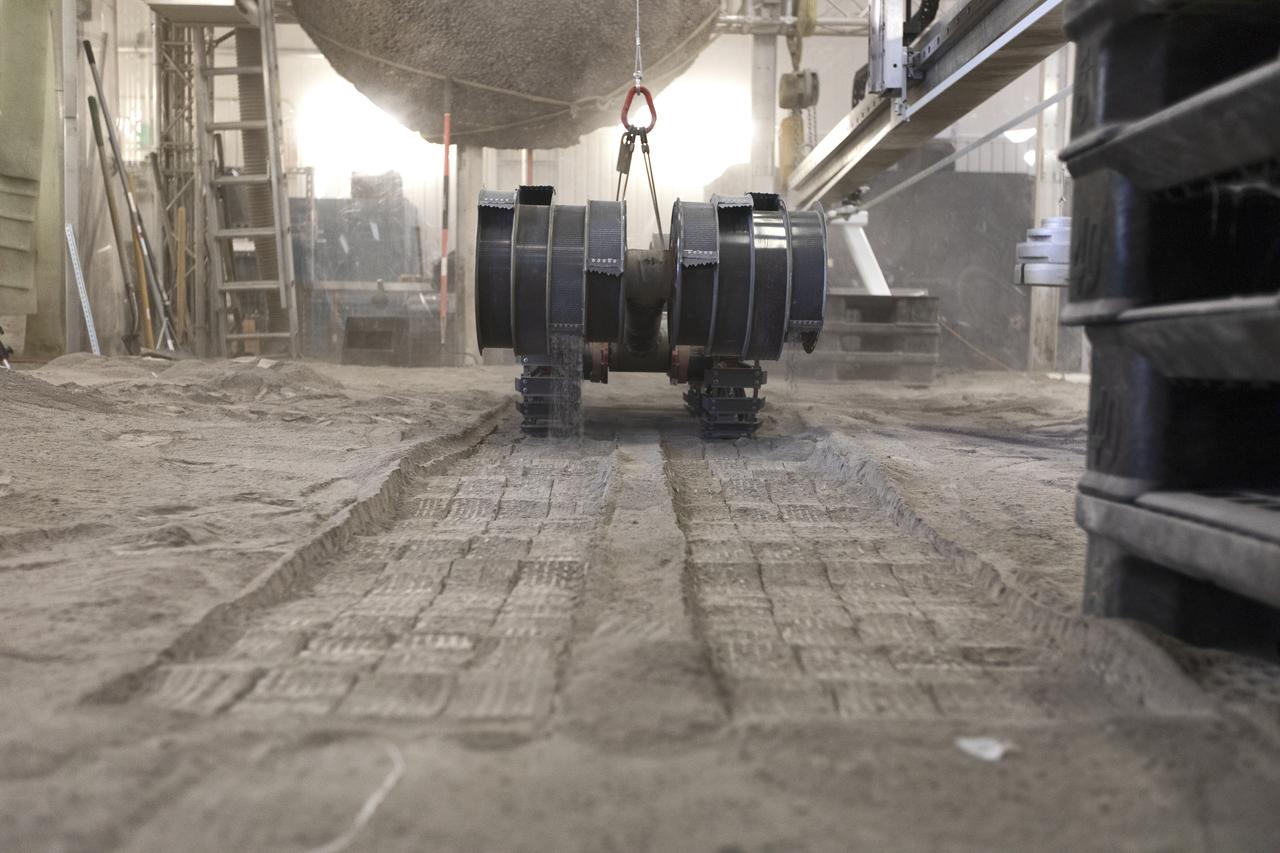

A team from the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab tests the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot (RASSOR) in the regolith bin inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 5, 2019. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like RASSOR will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. RASSOR can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
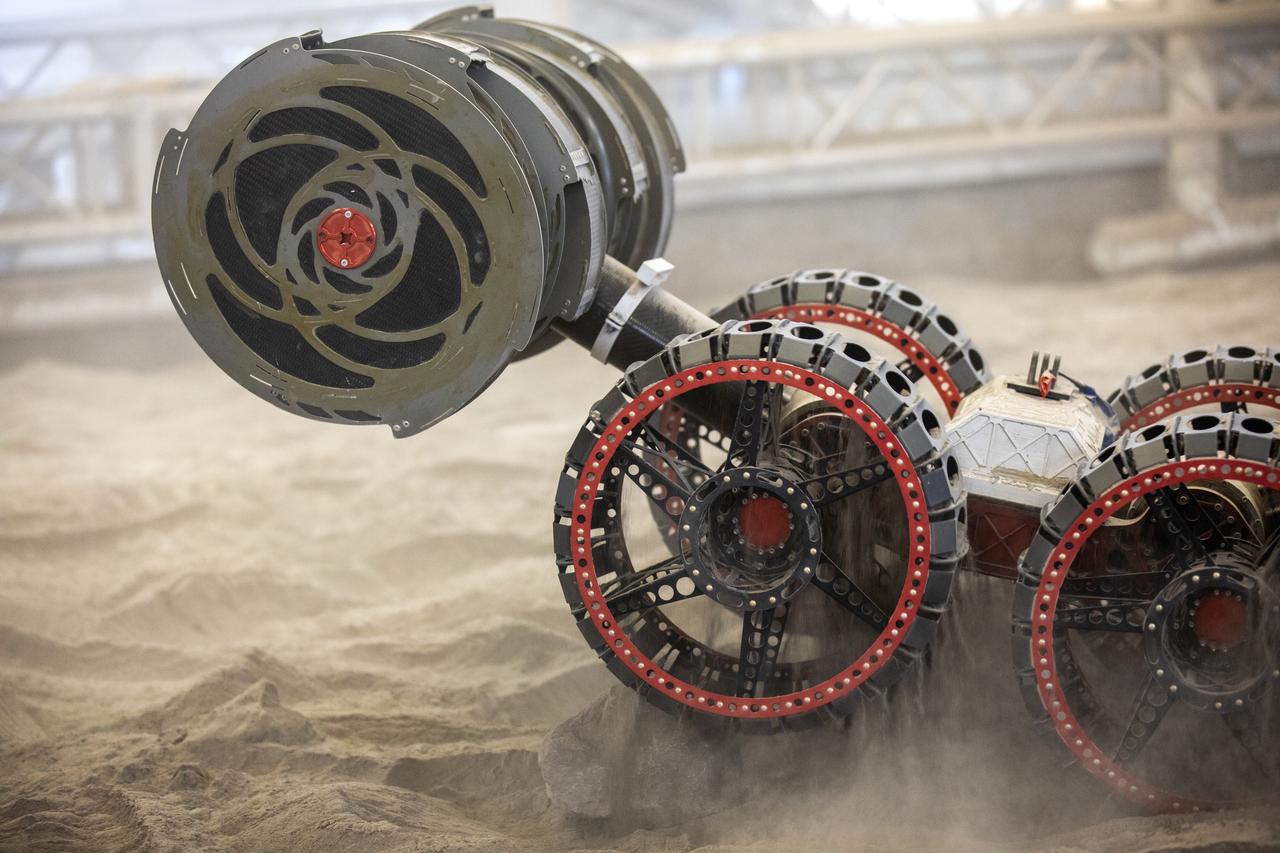

The ISRU Pilot Excavator digs its way through the regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.

An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.
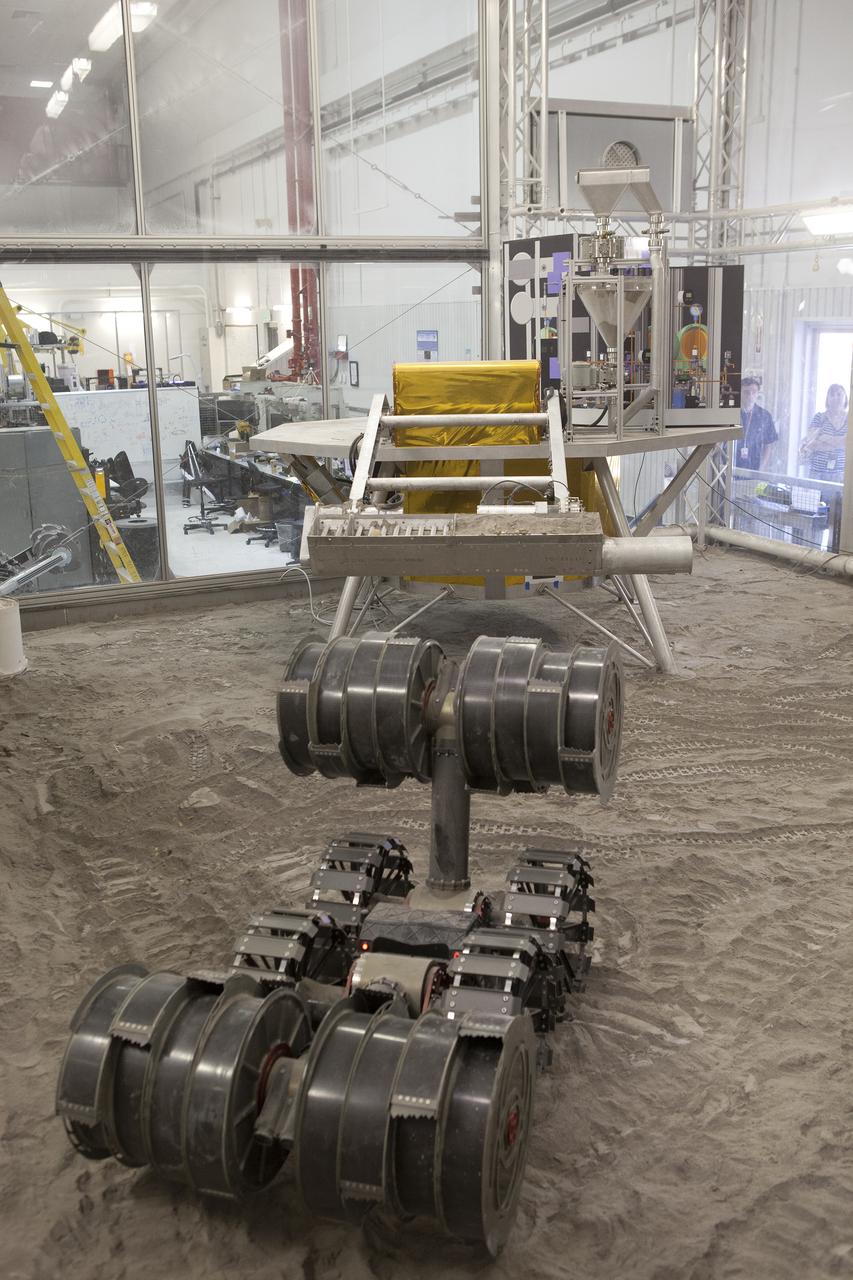

An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.
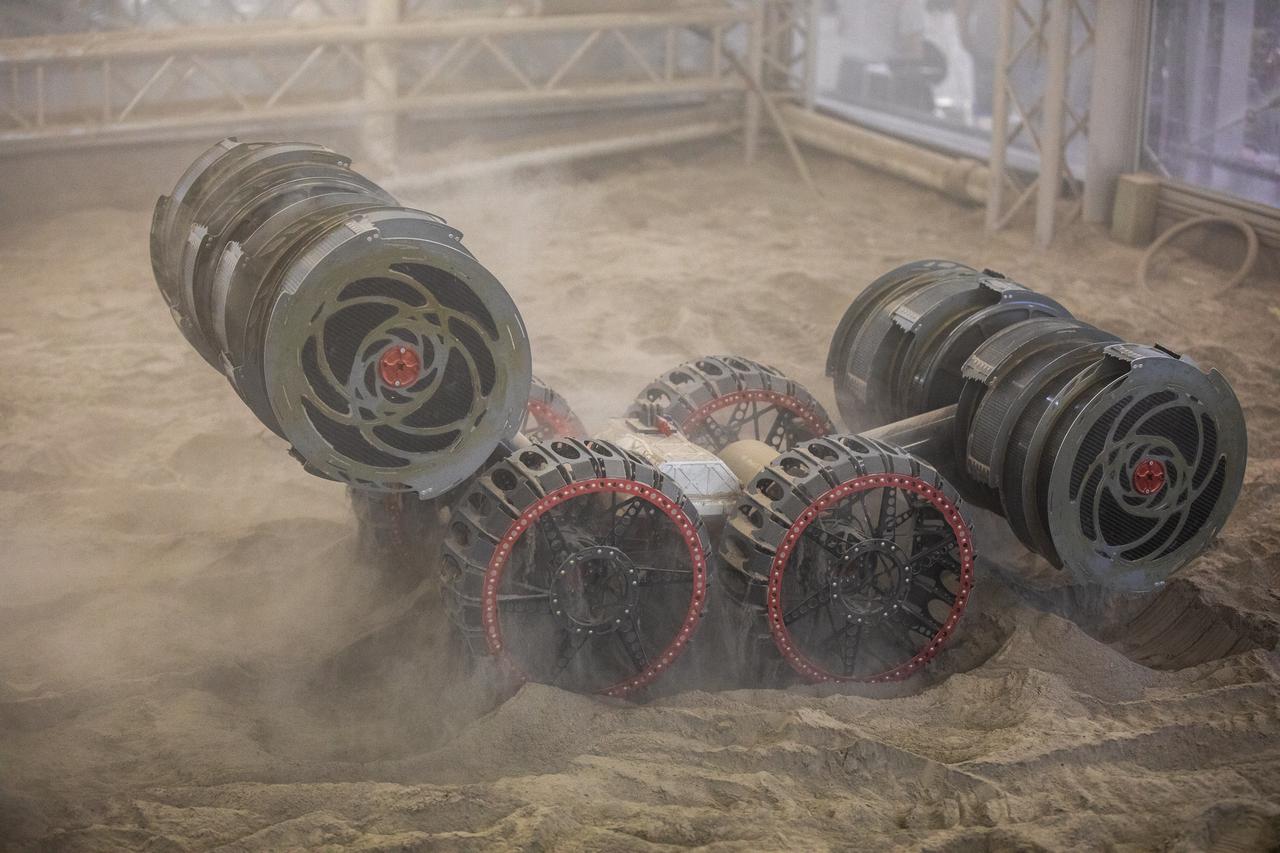

The ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in the regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
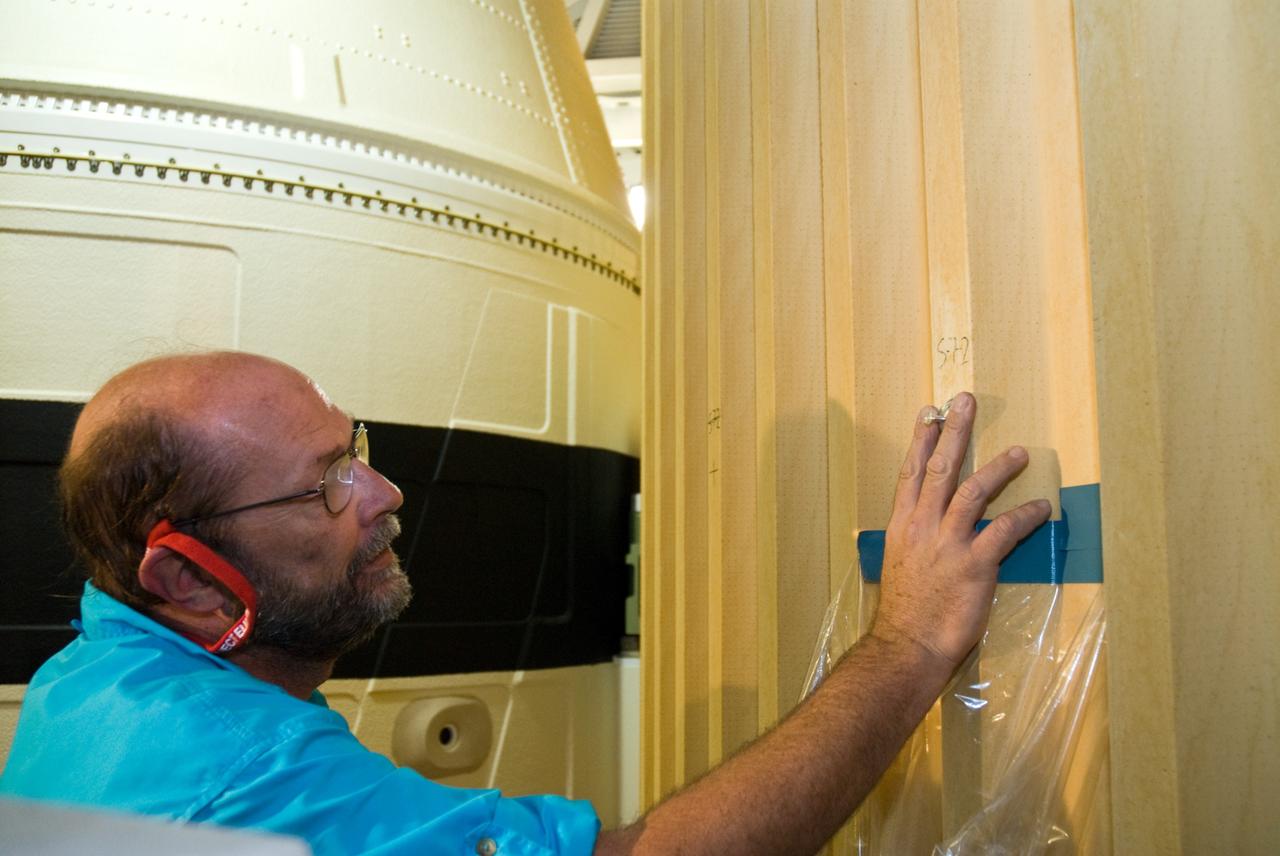

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 1 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, David Buras, a Material and Process engineer from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans where the fuel tanks are built, is testing foam adhesion on the intertank of space shuttle Discovery's external tank . He is collecting foam samples an inch-and-half in diameter for analysis to confirm the foam is bonded well to the metal primer underneath. The testing was prompted by the foam loss during launch of space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission July 15. Samples are being sent to Michoud for study. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
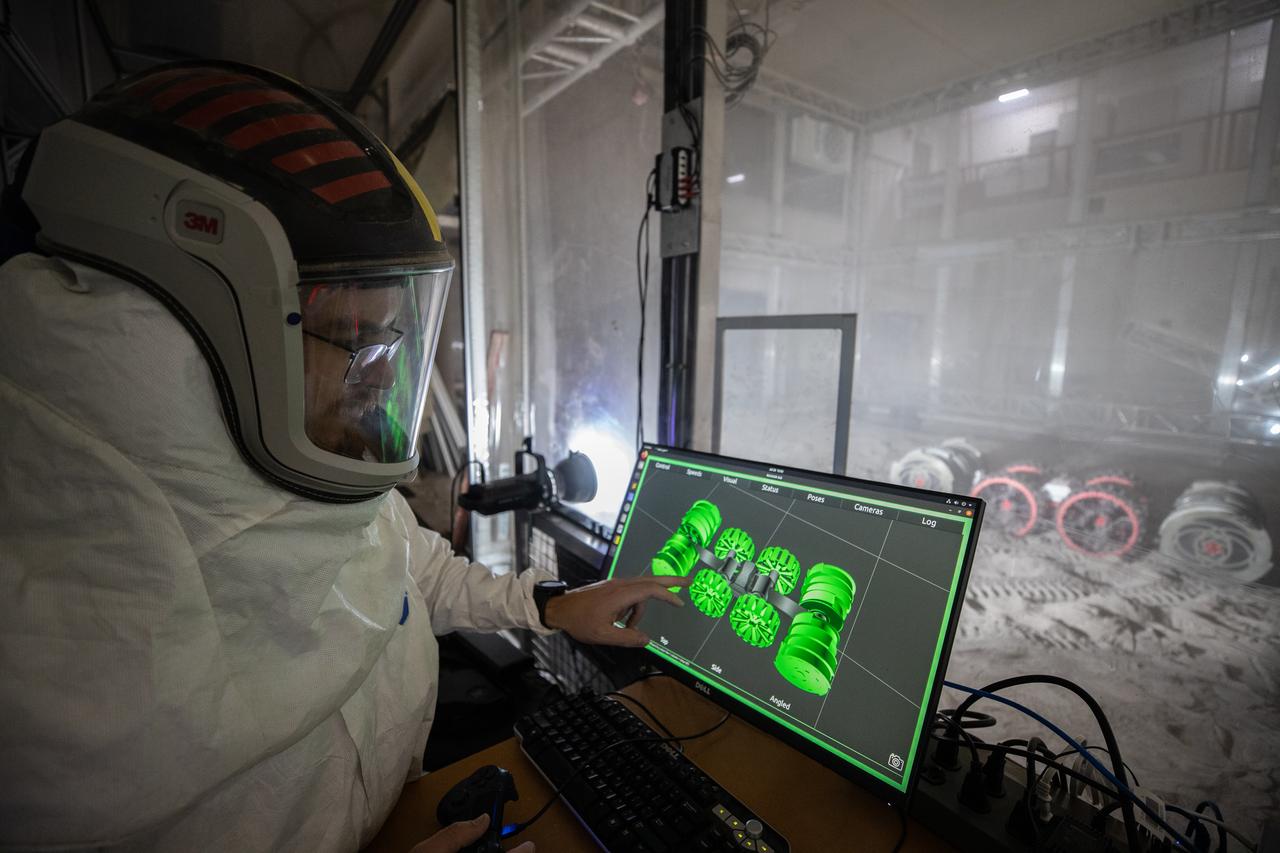

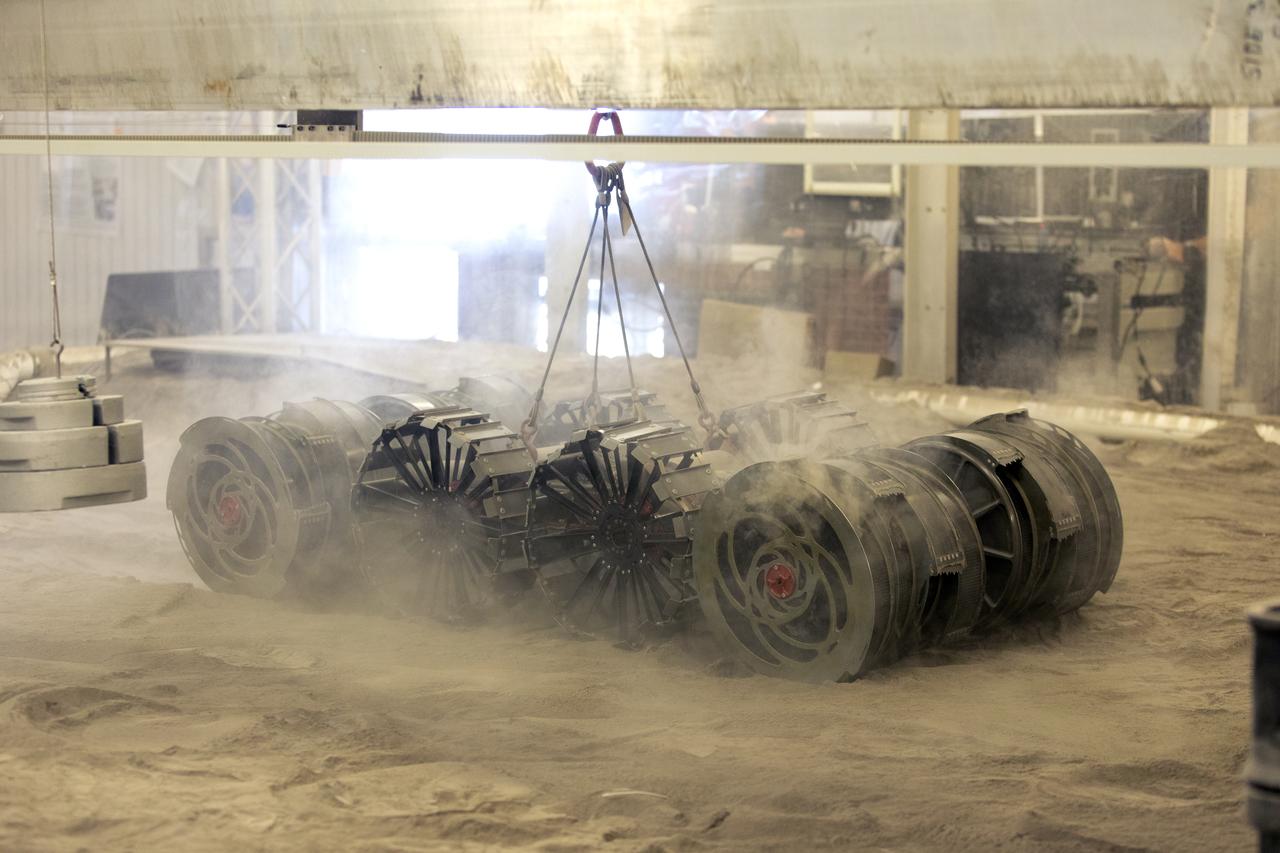
A team from the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab operates a test of the ISRU Pilot Excavator in regolith bin inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
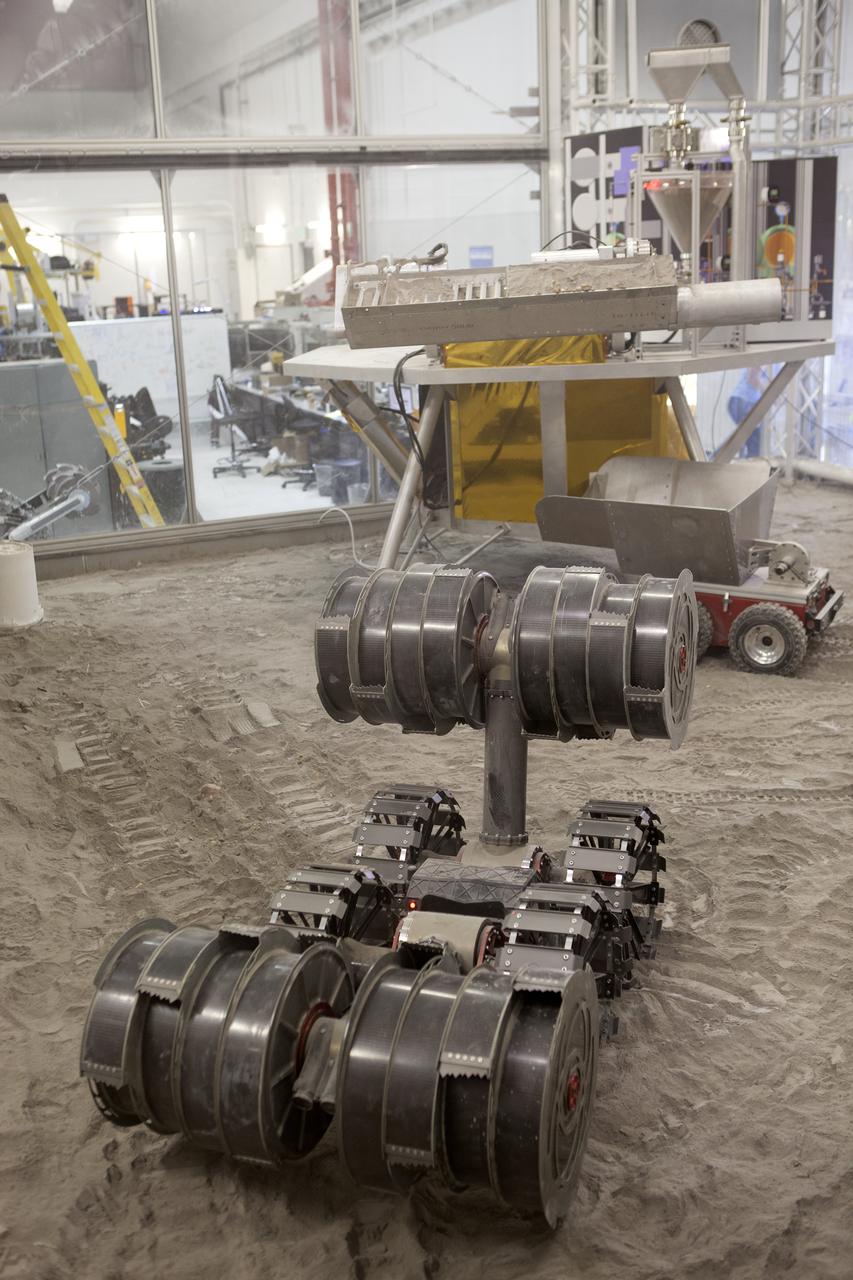
An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.
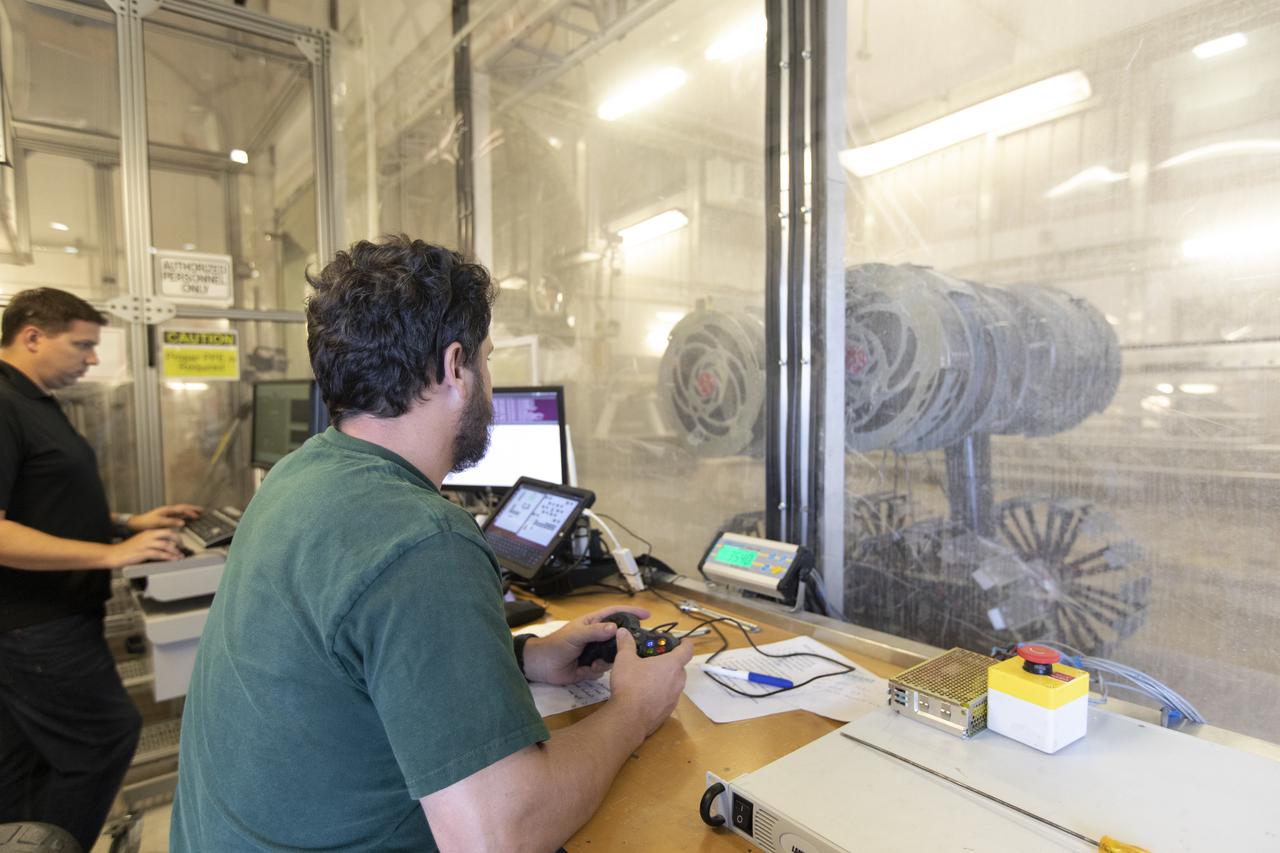

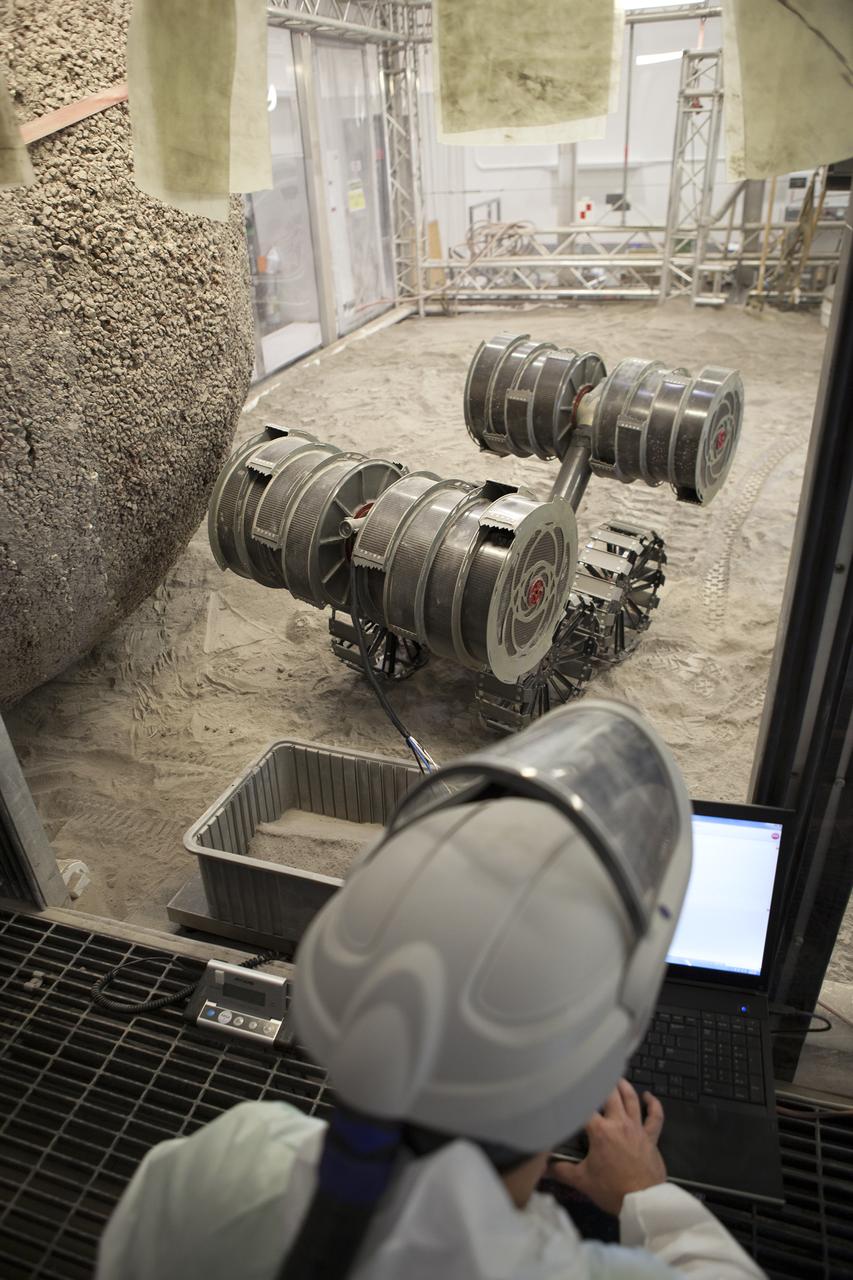
AJ Nick, a robotic engineer with the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab, monitors the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot (RASSOR) from a control room during testing in the regolith bin inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 5, 2019. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like RASSOR will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. RASSOR can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
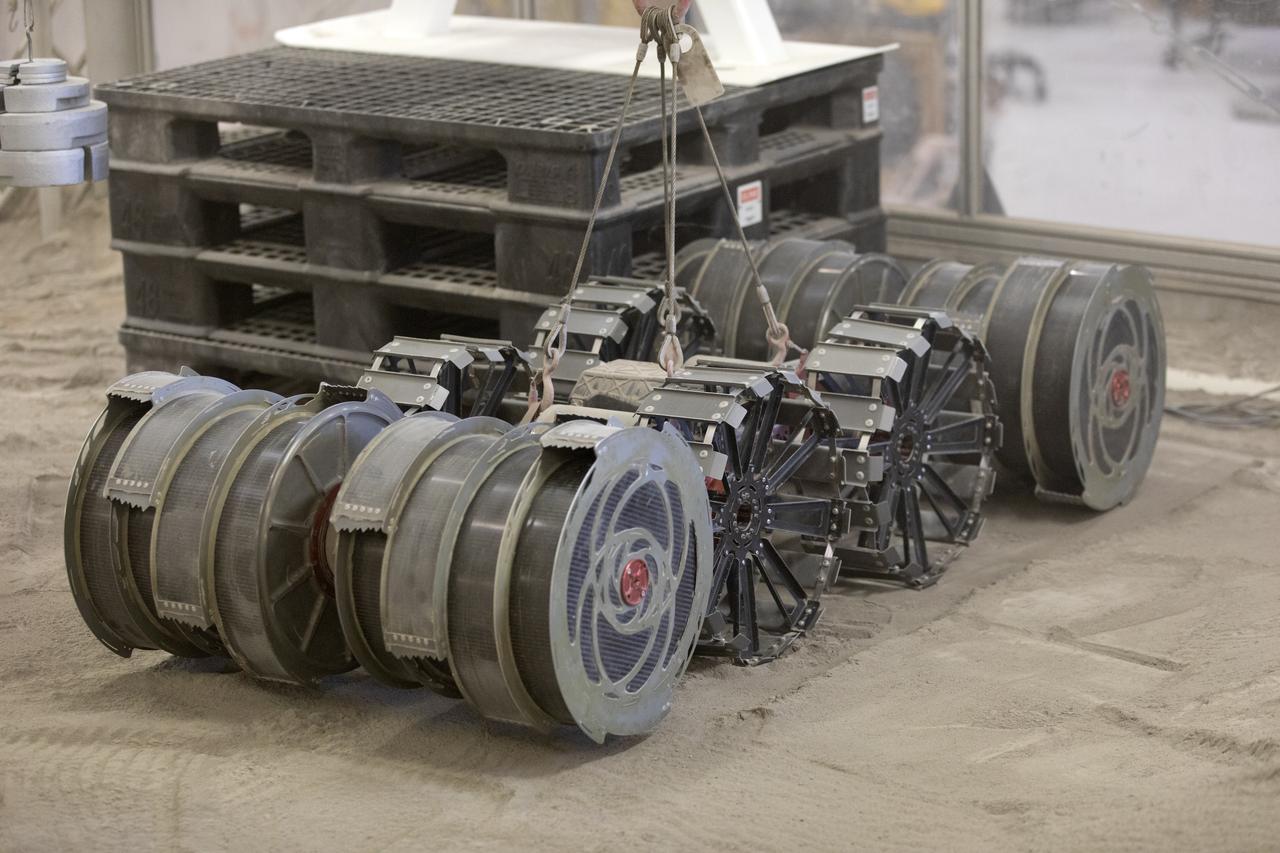

A team from the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab tests the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot (RASSOR) in the regolith bin inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 5, 2019. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like RASSOR will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. RASSOR can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.