NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer took this near ultraviolet image of Messier 101 on June 20, 2003. Messier 101 is a large spiral galaxy located 20 million light-years from Earth. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04631
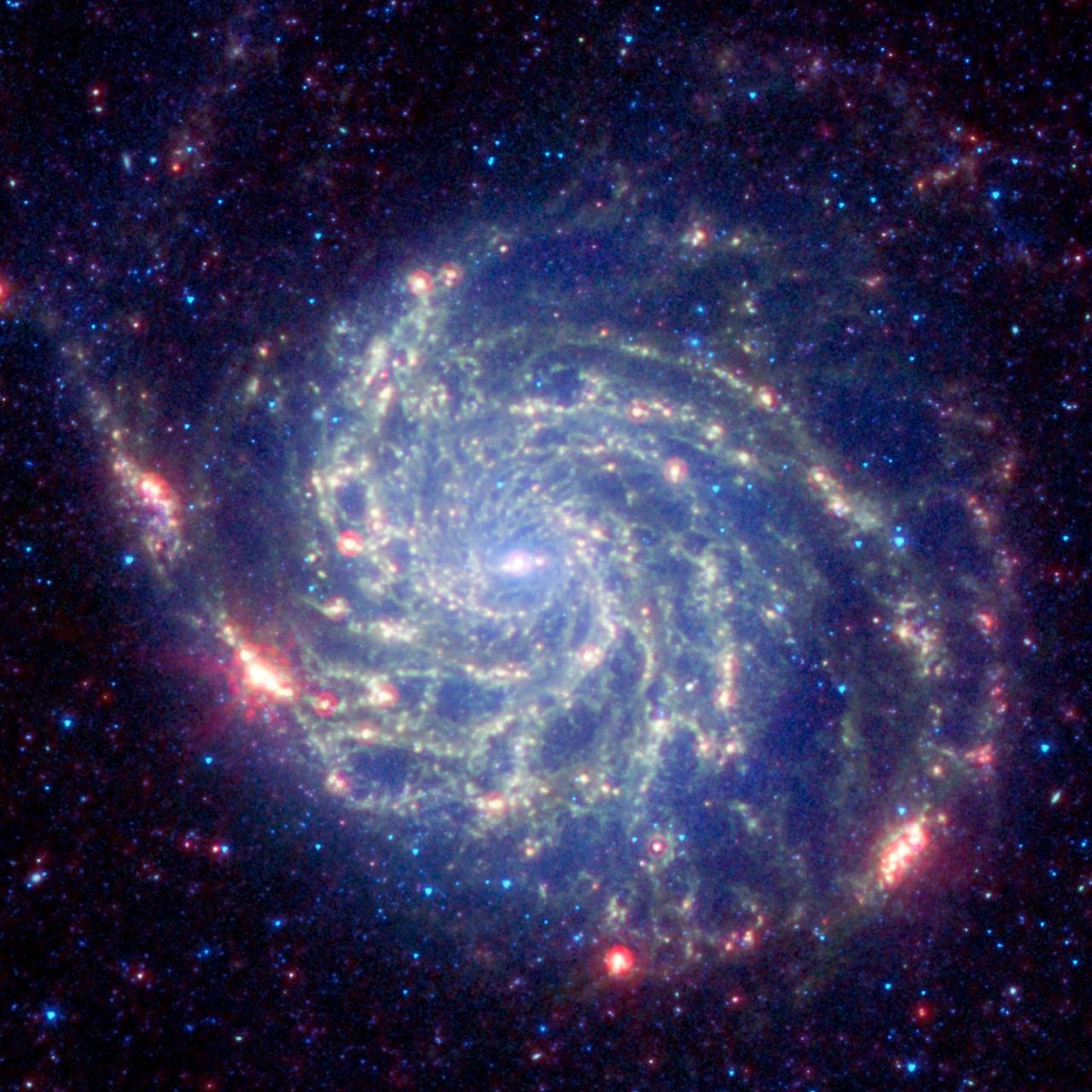

The galaxy Messier 101 is a swirling spiral of stars, gas, and dust. Messier 101 is nearly twice as wide as our Milky Way galaxy in this image as seen by NASA Spitzer Space Telescope.
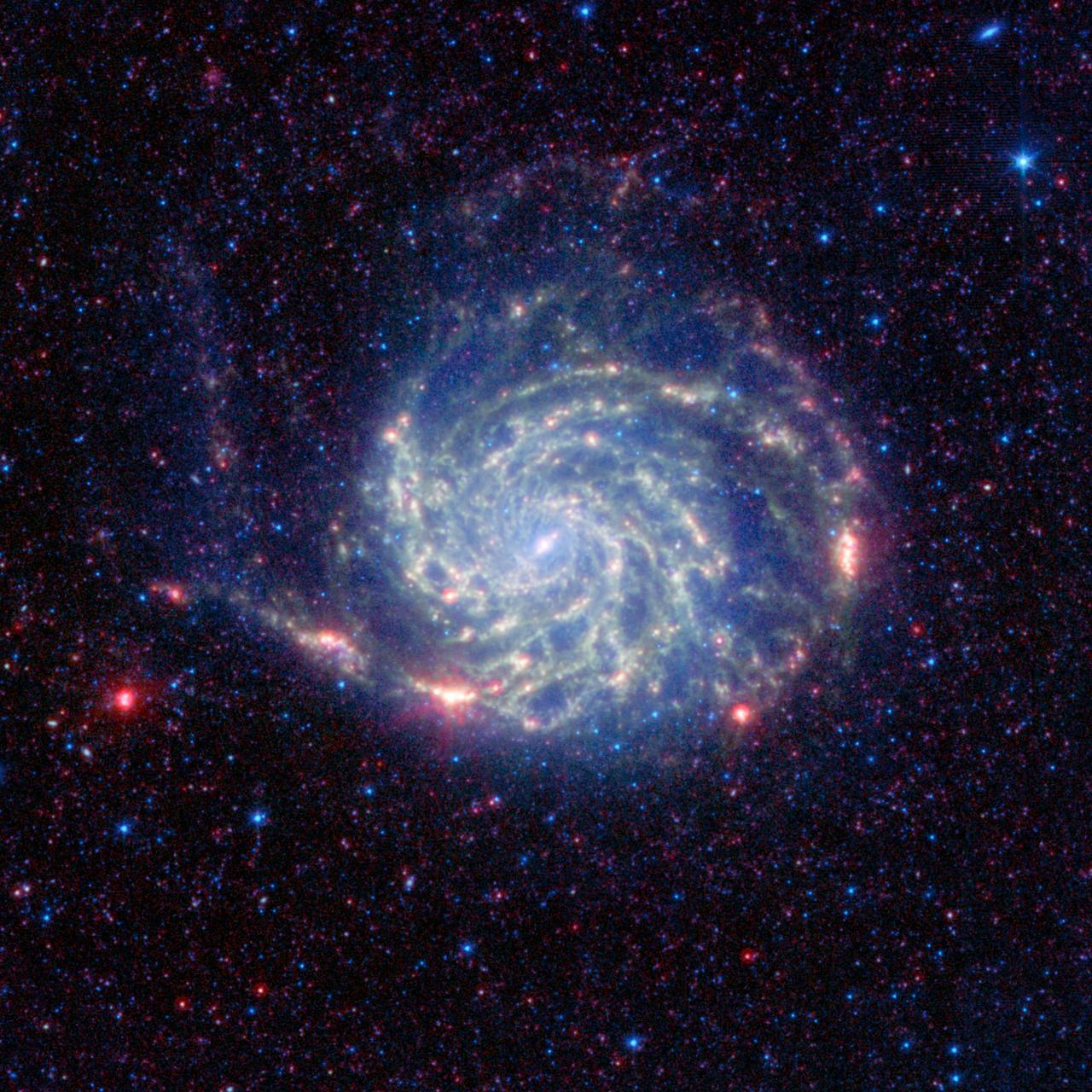

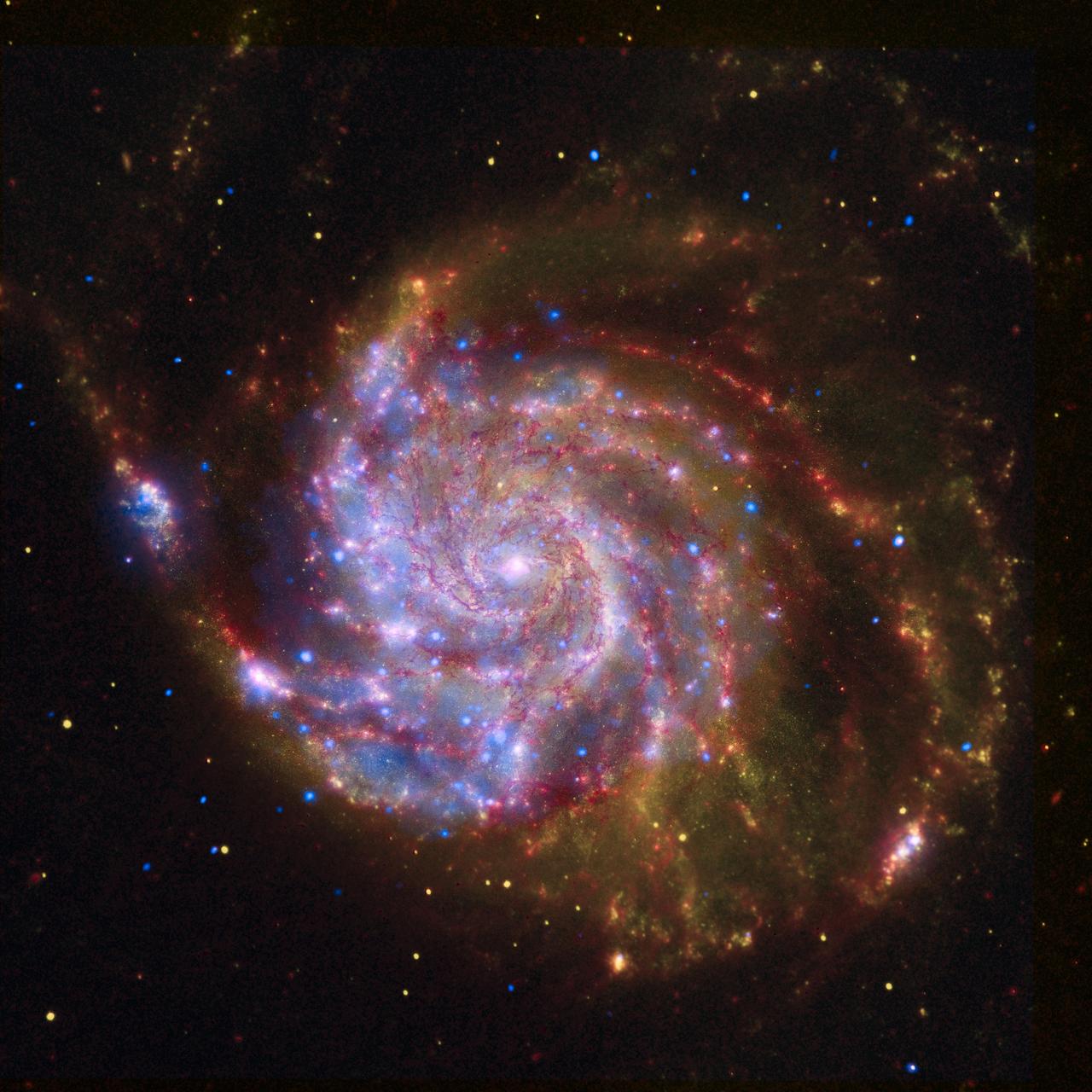
The Pinwheel galaxy, otherwise known as Messier 101, sports bright reddish edges in this new infrared image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope.
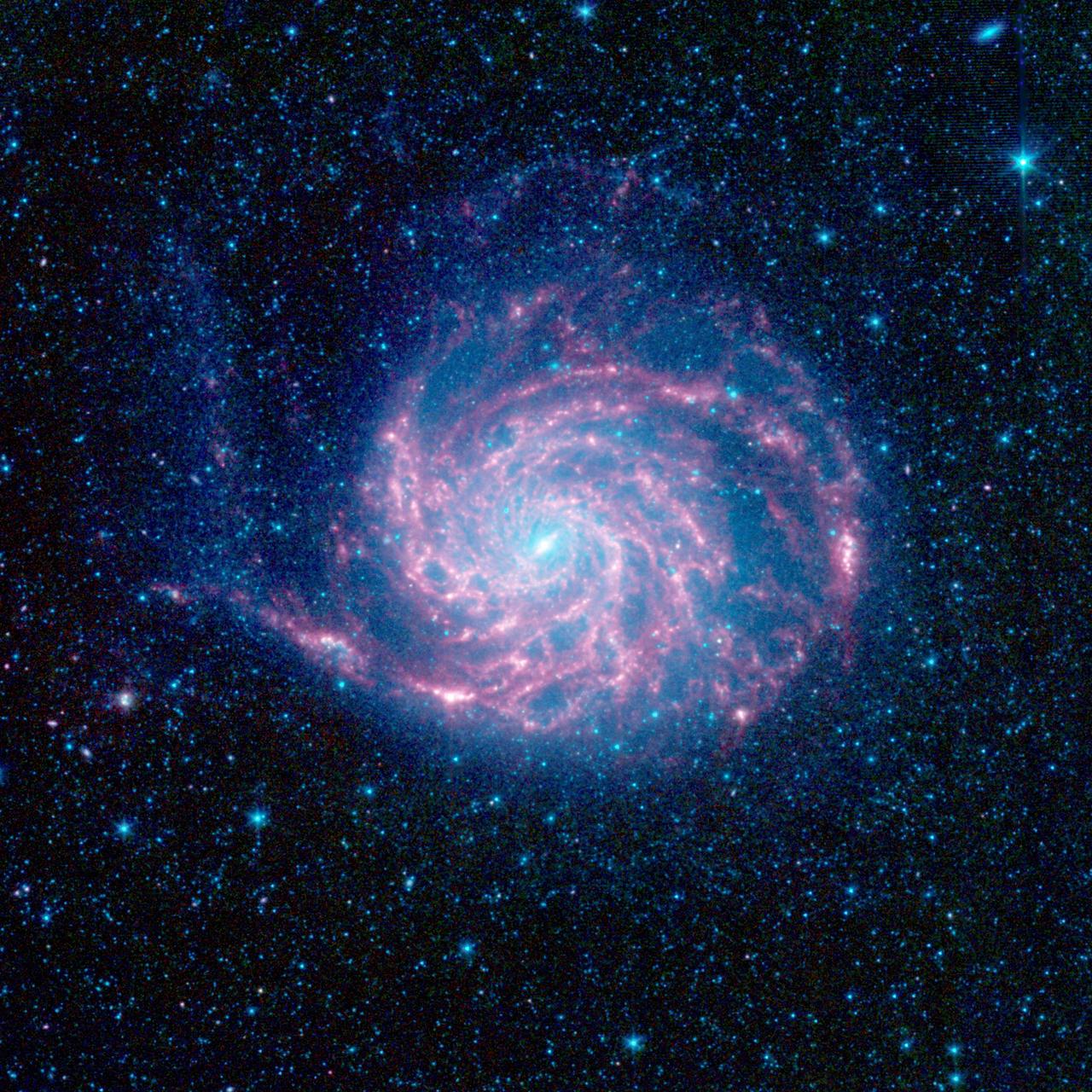

The tangled arms of the Pinwheel galaxy, otherwise known as Messier 101, are decked out in red in this new infrared image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope.
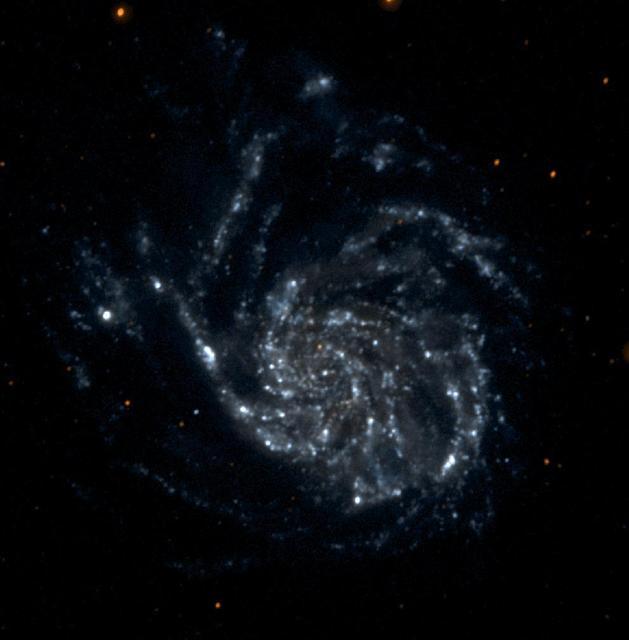

This single orbit exposure, ultraviolet color image of Messier 101 was taken by NASA's Galaxy Evolution Explorer on June 20, 2003. Messier 101 is a large spiral galaxy located 20 million light-years from Earth. This image is a short and medium "exposure" picture of the evolution of star formation in a spiral galaxy. The far ultraviolet emission detects the younger stars as concentrated in tight spiral arms, while the near ultraviolet emission, which traces stars living for more than 100 million years, displays the movement of the spiral pattern over a 100 million year period. The red stars in the foreground of the image are Milky Way stars. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04632
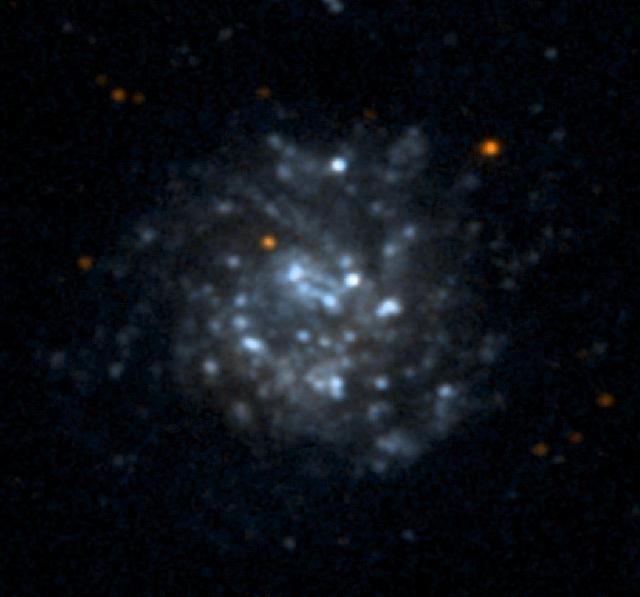

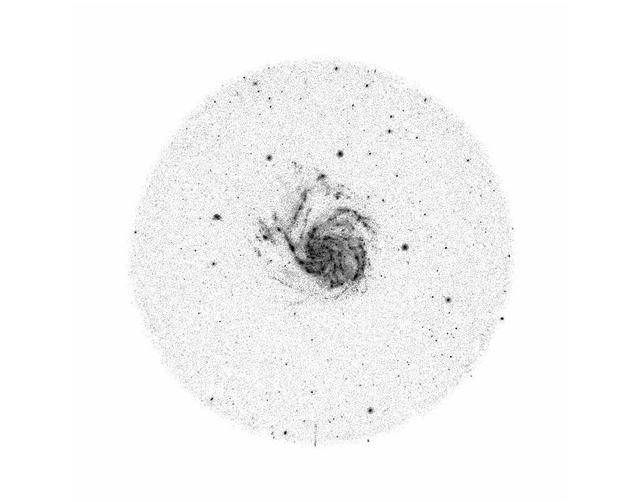
NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer took this ultraviolet color image of the galaxy NGC5474 on June 7, 2003. NGC5474 is located 20 million light-years from Earth and is within a group of galaxies dominated by the Messier 101 galaxy. Star formation in this galaxy shows some evidence of a disturbed spiral pattern, which may have been induced by tidal interactions with Messier 101. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04634
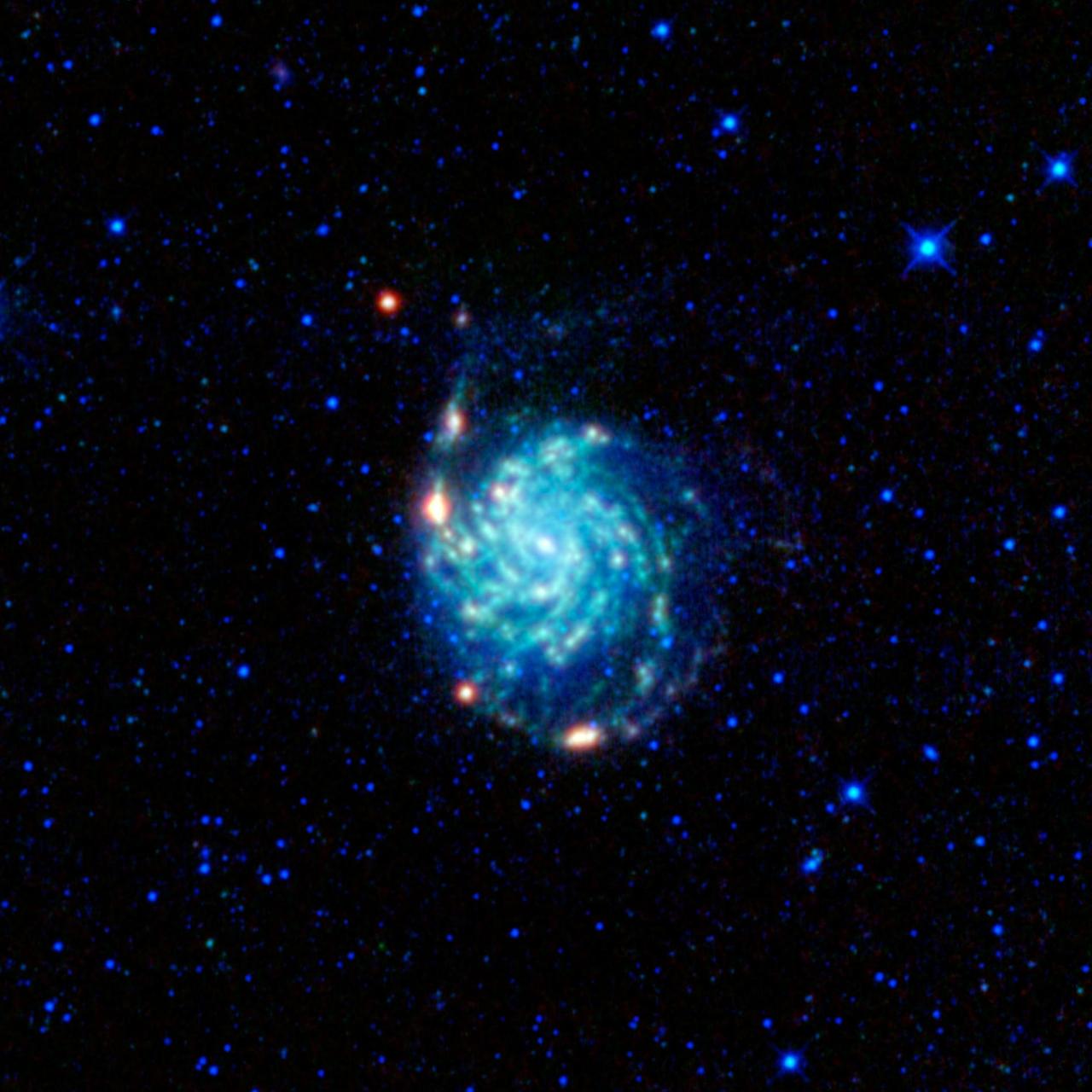

A large spiral galaxy dominates this view from NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer. The galaxy, often called the Pinwheel galaxy, was designated object 101 in astronomer Charles Messier catalog of fuzzy things in the sky that are not comets.
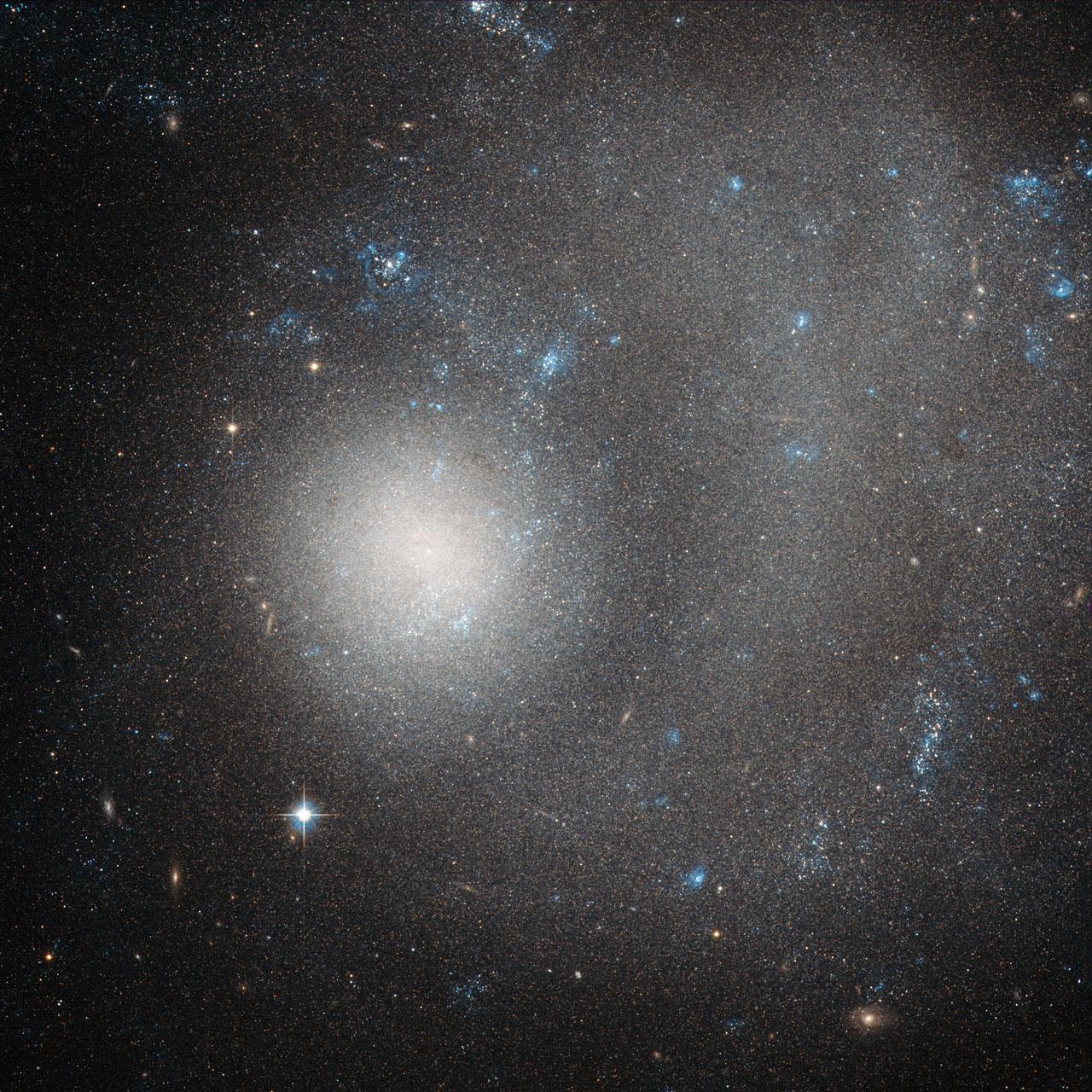

The subject of this Hubble image is NGC 5474, a dwarf galaxy located 21 million light-years away in the constellation of Ursa Major (The Great Bear). This beautiful image was taken with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). The term "dwarf galaxy" may sound diminutive, but don't let that fool you — NGC 5474 contains several billion stars! However, when compared to the Milky Way with its hundreds of billions of stars, NGC 5474 does indeed seem relatively small. NGC 5474 itself is part of the Messier 101 Group. The brightest galaxy within this group is the well-known spiral Pinwheel Galaxy (also known as Messier 101). This galaxy's prominent, well-defined arms classify it as a "grand design galaxy," along with other spirals Messier 81 and Messier 74. Also within this group are Messier 101's galactic neighbors. It is possible that gravitational interactions with these companion galaxies have had some influence on providing Messier 101 with its striking shape. Similar interactions with Messier 101 may have caused the distortions visible in NGC 5474. Both the Messier 101 Group and our own Local Group reside within the Virgo Supercluster, making NGC 5474 something of a neighbor in galactic terms. Credit: ESA/NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA Great Observatories continue Galileo legacy with stunning images and breakthrough science from the Hubble Space Telescope, the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Chandra X-ray Observatory.

The constellation of Ursa Major (The Great Bear) is home to Messier 101, the Pinwheel Galaxy. Messier 101 is one of the biggest and brightest spiral galaxies in the night sky. Like the Milky Way, Messier 101 is not alone, with smaller dwarf galaxies in its neighborhood. NGC 5477, one of these dwarf galaxies in the Messier 101 group, is the subject of this image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. Without obvious structure, but with visible signs of ongoing star birth, NGC 5477 looks much like an typical dwarf irregular galaxy. The bright nebulae that extend across much of the galaxy are clouds of glowing hydrogen gas in which new stars are forming. These glow pinkish red in real life, although the selection of green and infrared filters through which this image was taken makes them appear almost white. The observations were taken as part of a project to measure accurate distances to a range of galaxies within about 30 million light-years from Earth, by studying the brightness of red giant stars. In addition to NGC 5477, the image includes numerous galaxies in the background, including some that are visible right through NGC 5477. This serves as a reminder that galaxies, far from being solid, opaque objects, are actually largely made up of the empty space between their stars. This image is a combination of exposures taken through green and infrared filters using Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys. The field of view is approximately 3.3 by 3.3 arcminutes. ESA/Hubble & NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>