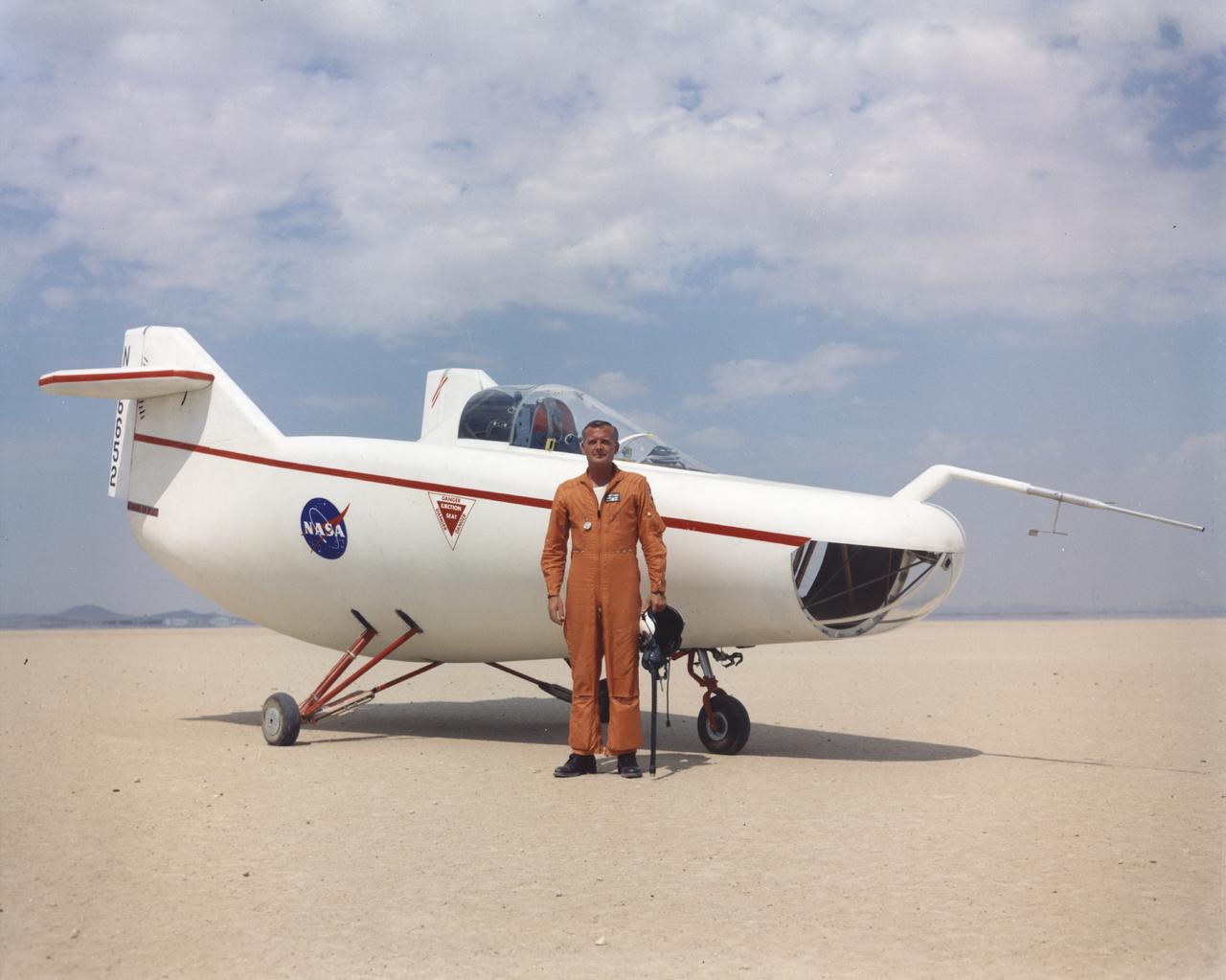

NASA Flight Research Pilot Milt Thompson, shown here on the lakebed with the M2-F1 lifting body, was an early backer of R. Dale Reed's lifting-body proposal. He urged Flight Research Center director Paul Bikle to approve the M2-F1's construction. Thompson also made the first glide flights in both the M2-F1 and its successor, the heavyweight M2-F2.
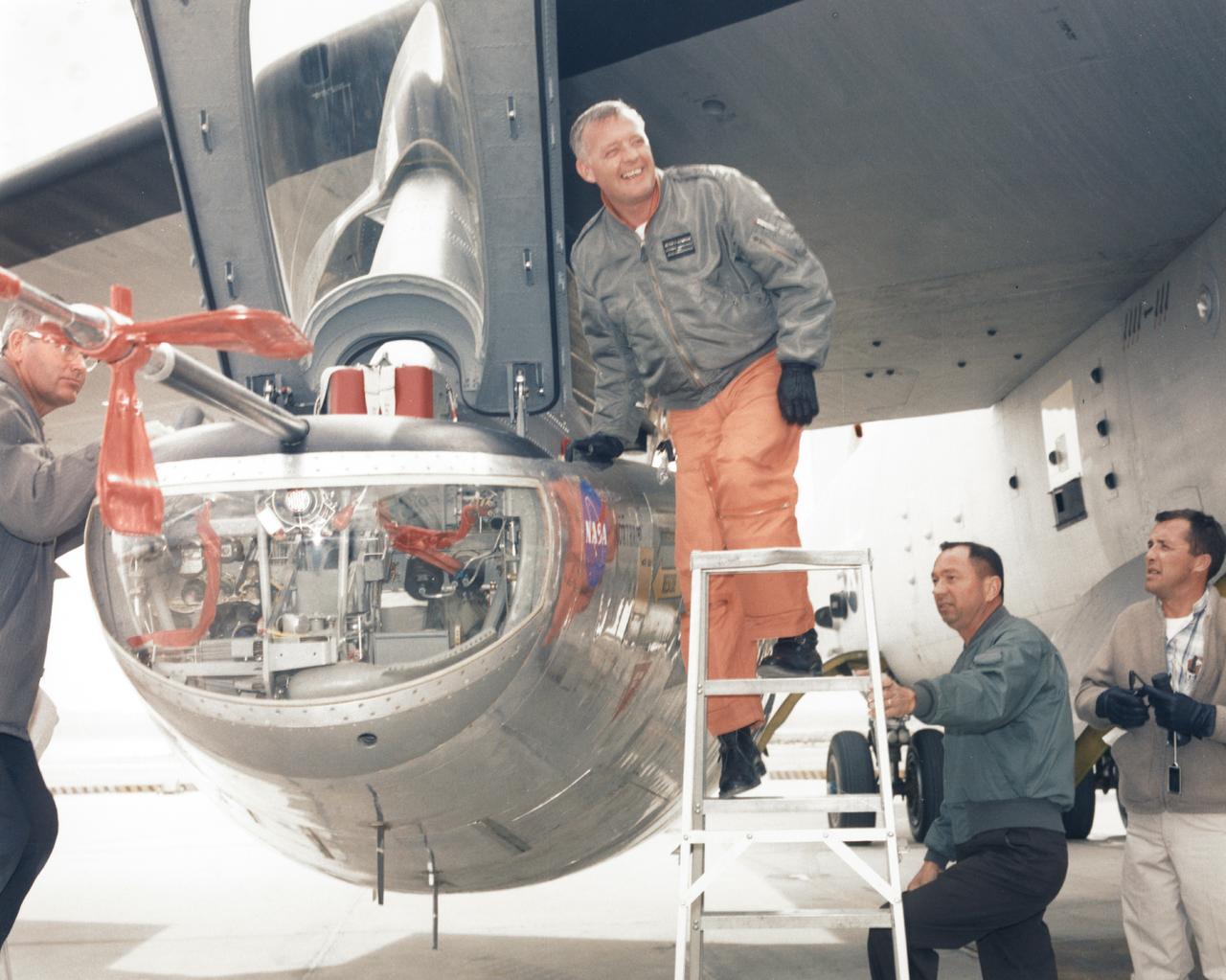

NASA research pilot Milt Thompson is helped into the cockpit of the M2-F2 lifting body research aircraft at NASA’s Flight Research Center (now the Dryden Flight Research Center). The M2-F2 is attached to a wing pylon under the wing of NASA’s B-52 mothership. The flight was a captive flight with the pilot on-board. Milt Thompson flew in the lifting body throughout the flight, but it was never dropped from the mothership.
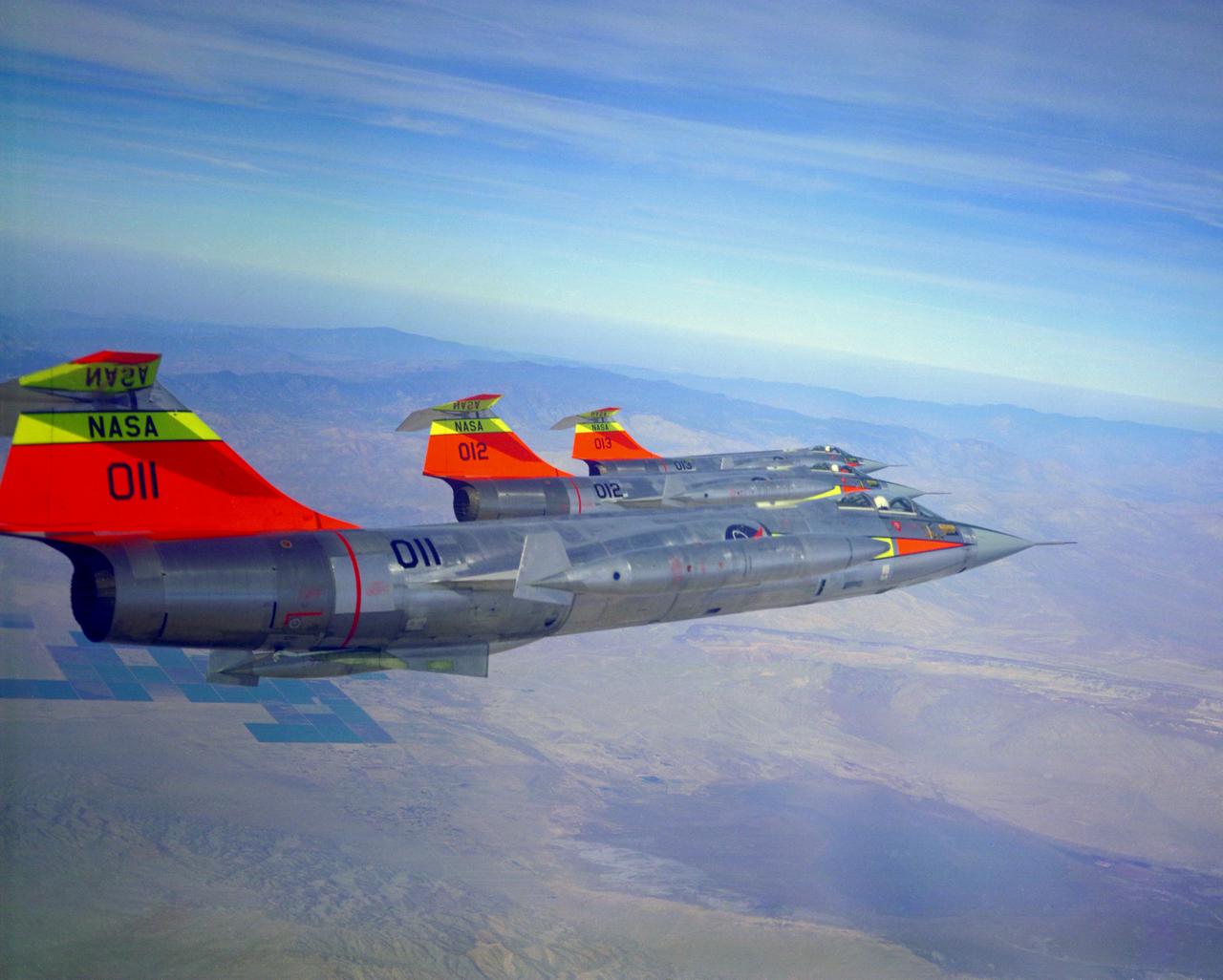

All three NASA F-104N's fly in formation. Aircraft numbers 011, 012 and 013. These would be changed to 811, 812 and 813 in 1965. Pilots are Bruce Peterson in 011, Milt Thompson in 012 and Joe Walker in 013. October 24, 1963
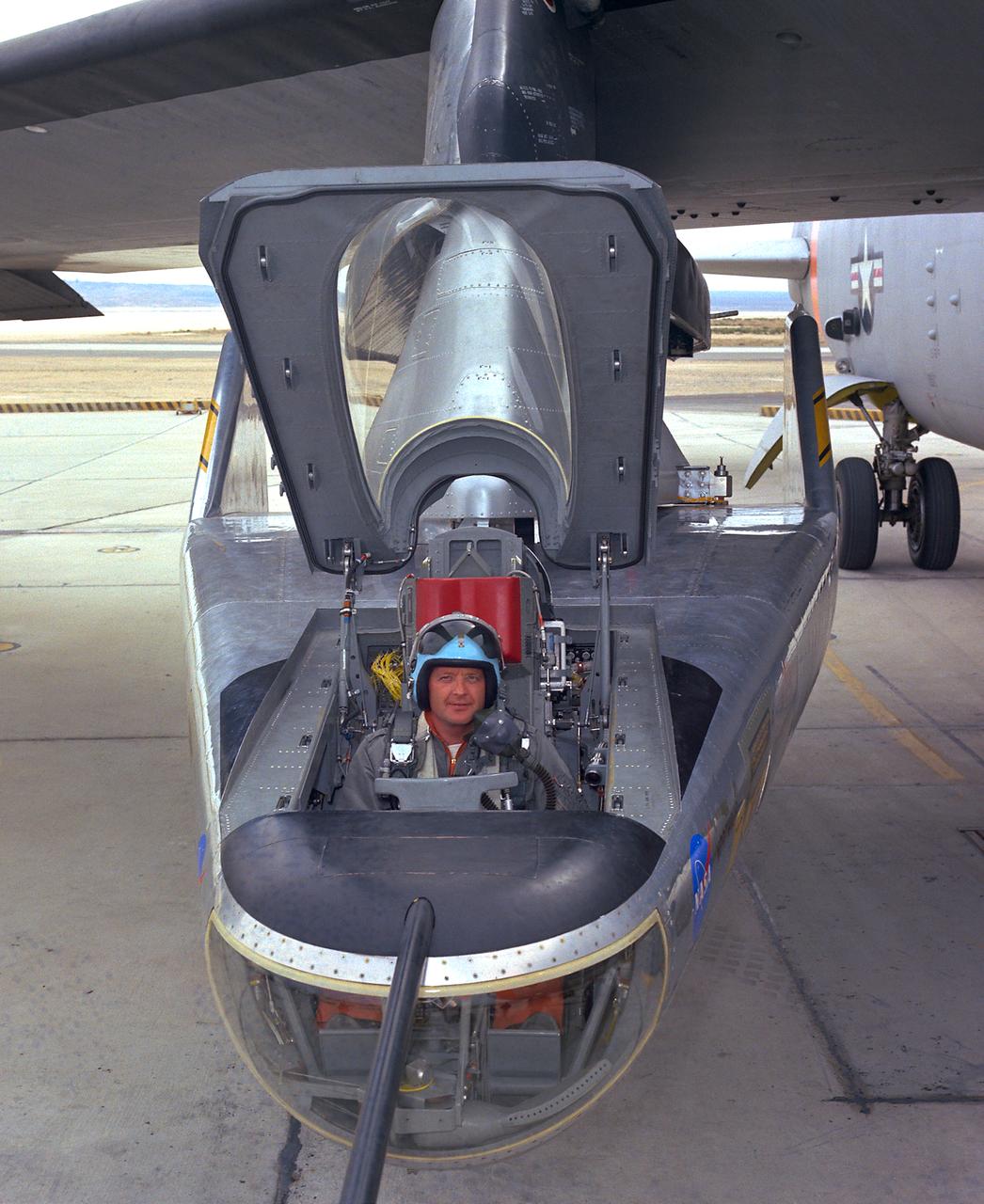

NASA research pilot Milt Thompson sits in the M2-F2 "heavyweight" lifting body research vehicle before a 1966 test flight. The M2-F2 and the other lifting-body designs were all attached to a wing pylon on NASA’s B-52 mothership and carried aloft. The vehicles were then drop-launched and, at the end of their flights, glided back to wheeled landings on the dry lake or runway at Edwards AFB. The lifting body designs influenced the design of the Space Shuttle and were also reincarnated in the design of the X-38 in the 1990s.
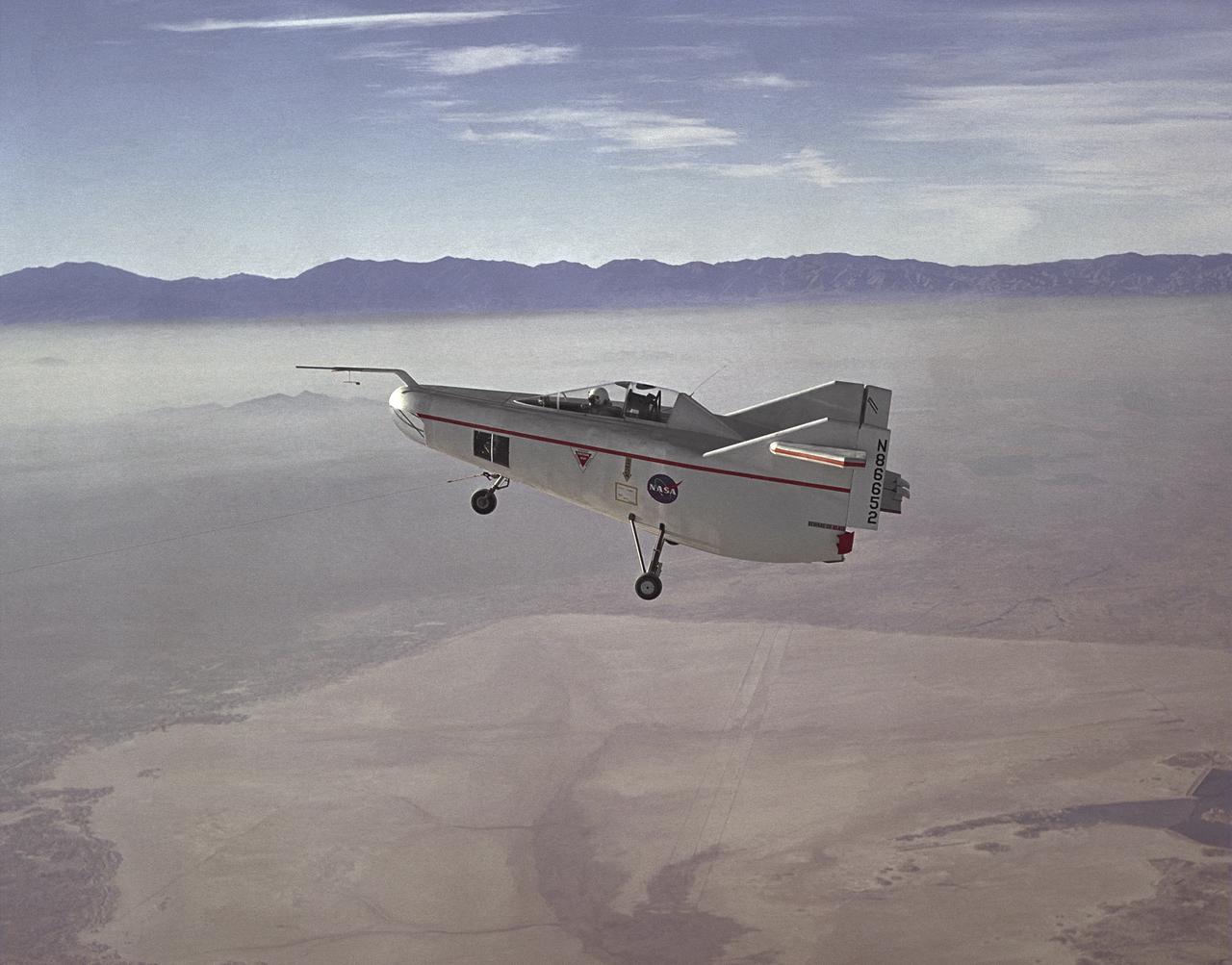

The M2-F1 Lifting Body is seen here under tow, high above Rogers Dry Lake near the Flight Research Center (later redesignated the Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California. R. Dale Reed effectively advocated the project with the support of NASA research pilot Milt Thompson. Together, they gained the support of Flight Research Center Director Paul Bikle. After a six-month feasibility study, Bikle gave approval in the fall of 1962 for the M2-F1 to be built.
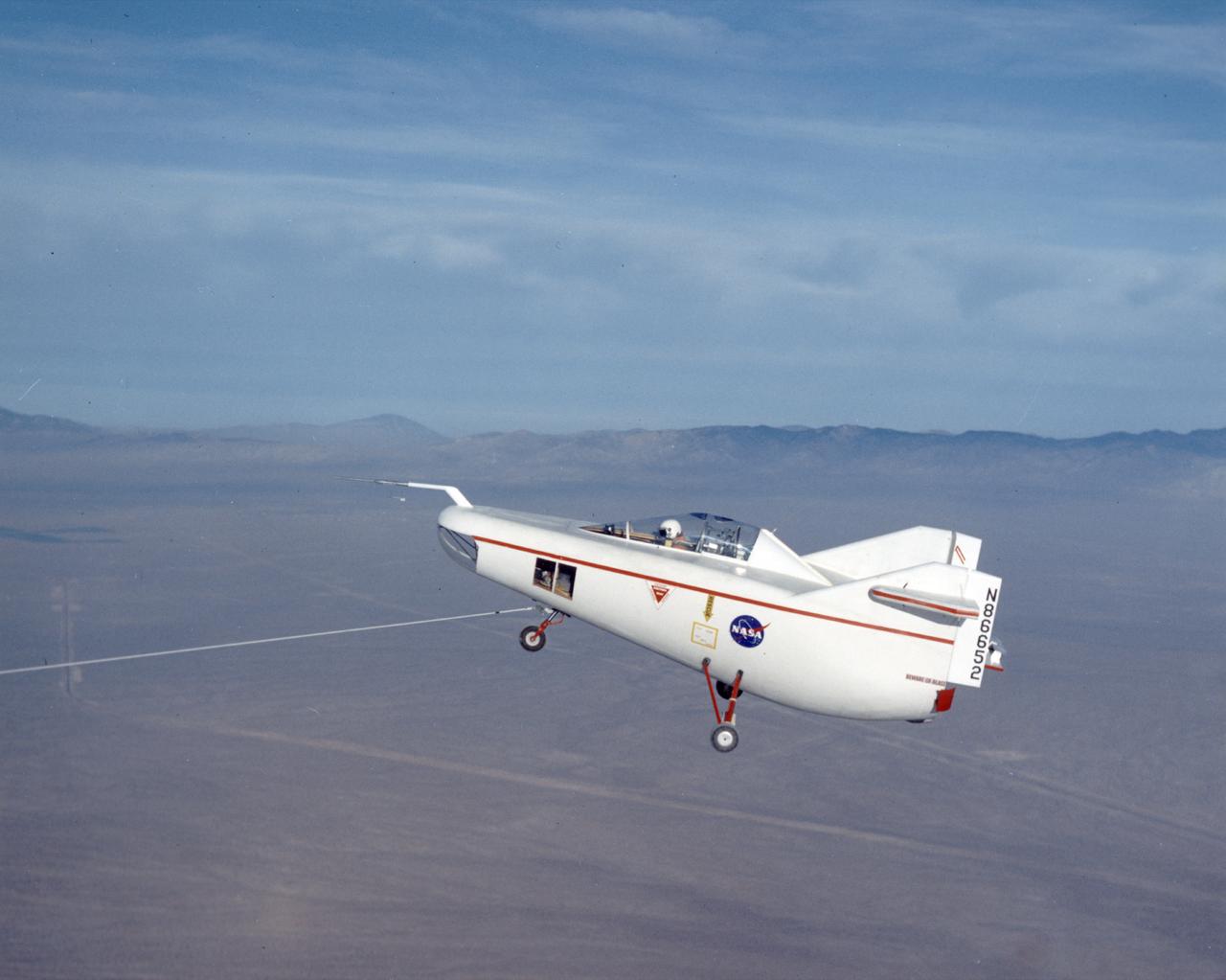

After initial ground-tow flights of the M2-F1 using the Pontiac as a tow vehicle, the way was clear to make air tows behind a C-47. The first air tow took place on 16 August 1963. Pilot Milt Thompson found that the M2-F1 flew well, with good control. This first flight lasted less than two minutes from tow-line release to touchdown. The descent rate was 4,000 feet per minute.
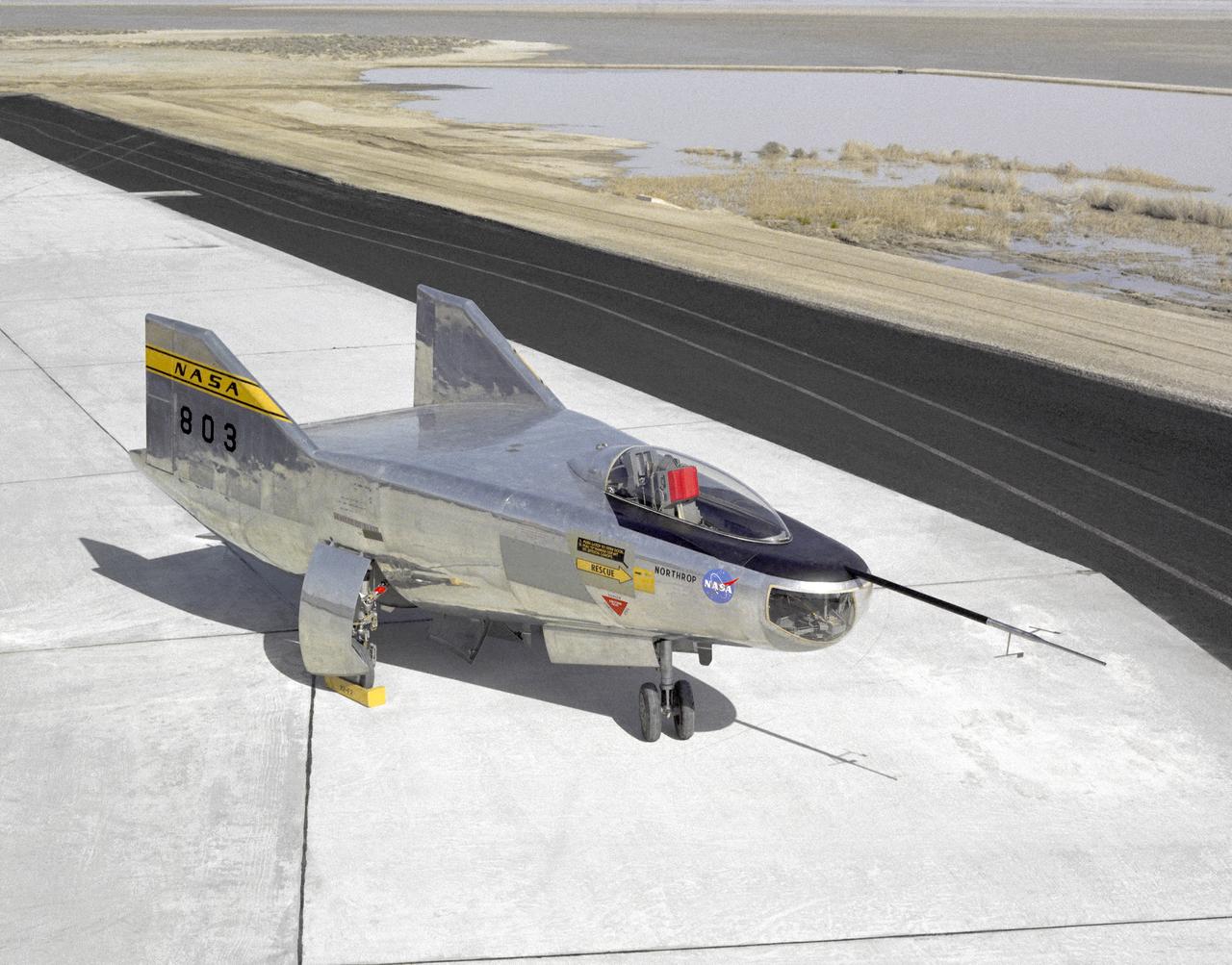

The M2-F2 Lifting Body is seen here on the ramp at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center. The success of Dryden's M2-F1 program led to NASA's development and construction of two heavyweight lifting bodies based on studies at NASA's Ames and Langley research centers -- the M2-F2 and the HL-10, both built by the Northrop Corporation. The "M" refers to "manned" and "F" refers to "flight" version. "HL" comes from "horizontal landing" and 10 is for the tenth lifting body model to be investigated by Langley. The first flight of the M2-F2 -- which looked much like the "F1" -- was on July 12, 1966. Milt Thompson was the pilot. By then, the same B-52 used to air launch the famed X-15 rocket research aircraft was modified to also carry the lifting bodies. Thompson was dropped from the B-52's wing pylon mount at an altitude of 45,000 feet on that maiden glide flight. The M2-F2 weighed 4,620 pounds, was 22 feet long, and had a width of about 10 feet. On May 10, 1967, during the sixteenth glide flight leading up to powered flight, a landing accident severely damaged the vehicle and seriously injured the NASA pilot, Bruce Peterson. NASA pilots and researchers realized the M2-F2 had lateral control problems, even though it had a stability augmentation control system. When the M2-F2 was rebuilt at Dryden and redesignated the M2-F3, it was modified with an additional third vertical fin -- centered between the tip fins -- to improve control characteristics. The M2-F2/F3 was the first of the heavy-weight, entry-configuration lifting bodies. Its successful development as a research test vehicle answered many of the generic questions about these vehicles. NASA donated the M2-F3 vehicle to the Smithsonian Institute in December 1973. It is currently hanging in the Air and Space Museum along with the X-15 aircraft number 1, which was its hangar partner at Dryden from 1965 to 1969.
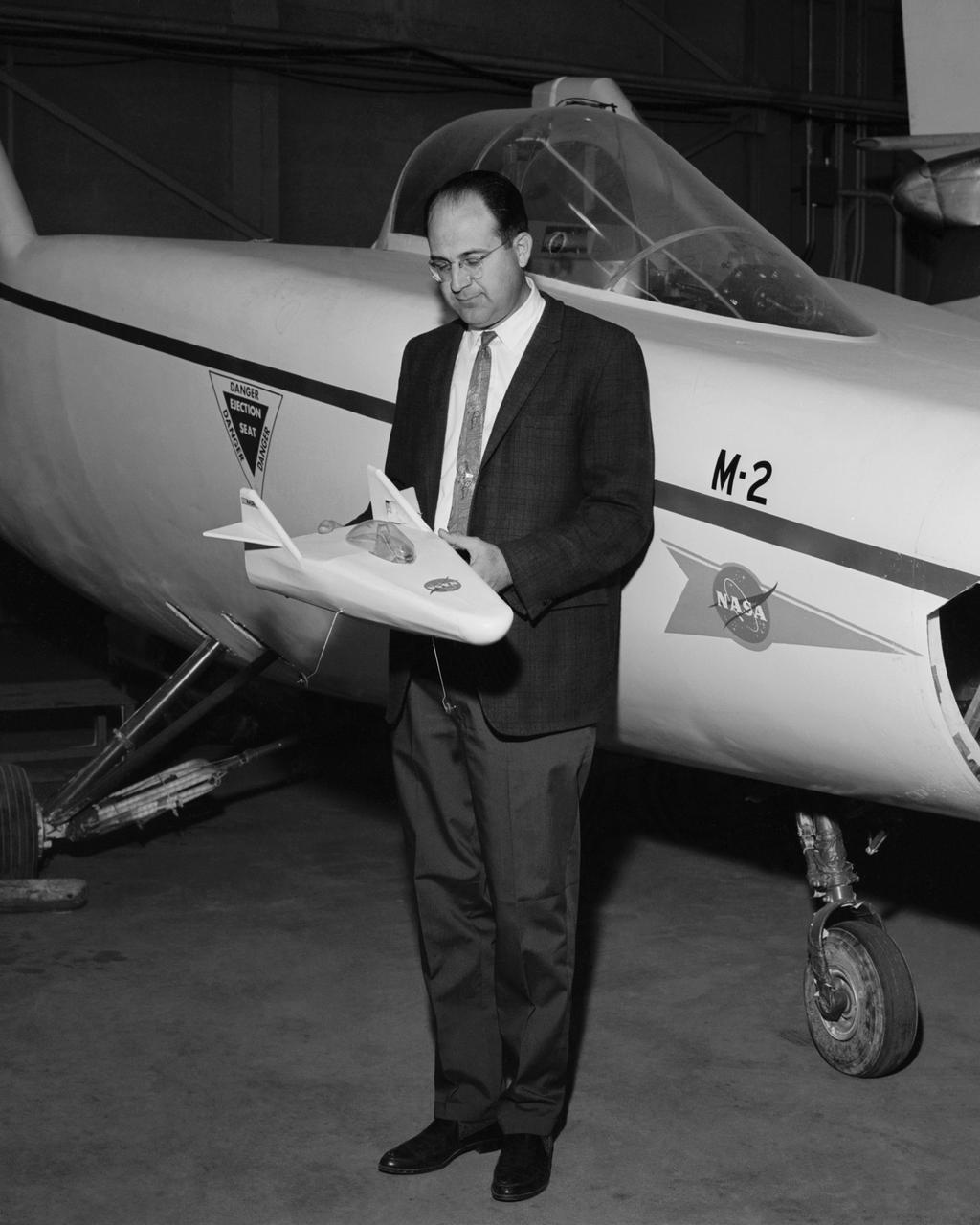

Dale Reed with a model of the M2-F1 in front of the actual lifting body. Reed used the model to show the potential of the lifting bodies. He first flew it into tall grass to test stability and trim, then hand-launched it from buildings for longer flights. Finally, he towed the lifting-body model aloft using a powered model airplane known as the "Mothership." A timer released the model and it glided to a landing. Dale's wife Donna used a 9 mm. camera to film the flights of the model. Its stability as it glided--despite its lack of wings--convinced Milt Thompson and some Flight Research Center engineers including the center director, Paul Bikle, that a piloted lifting body was possible.
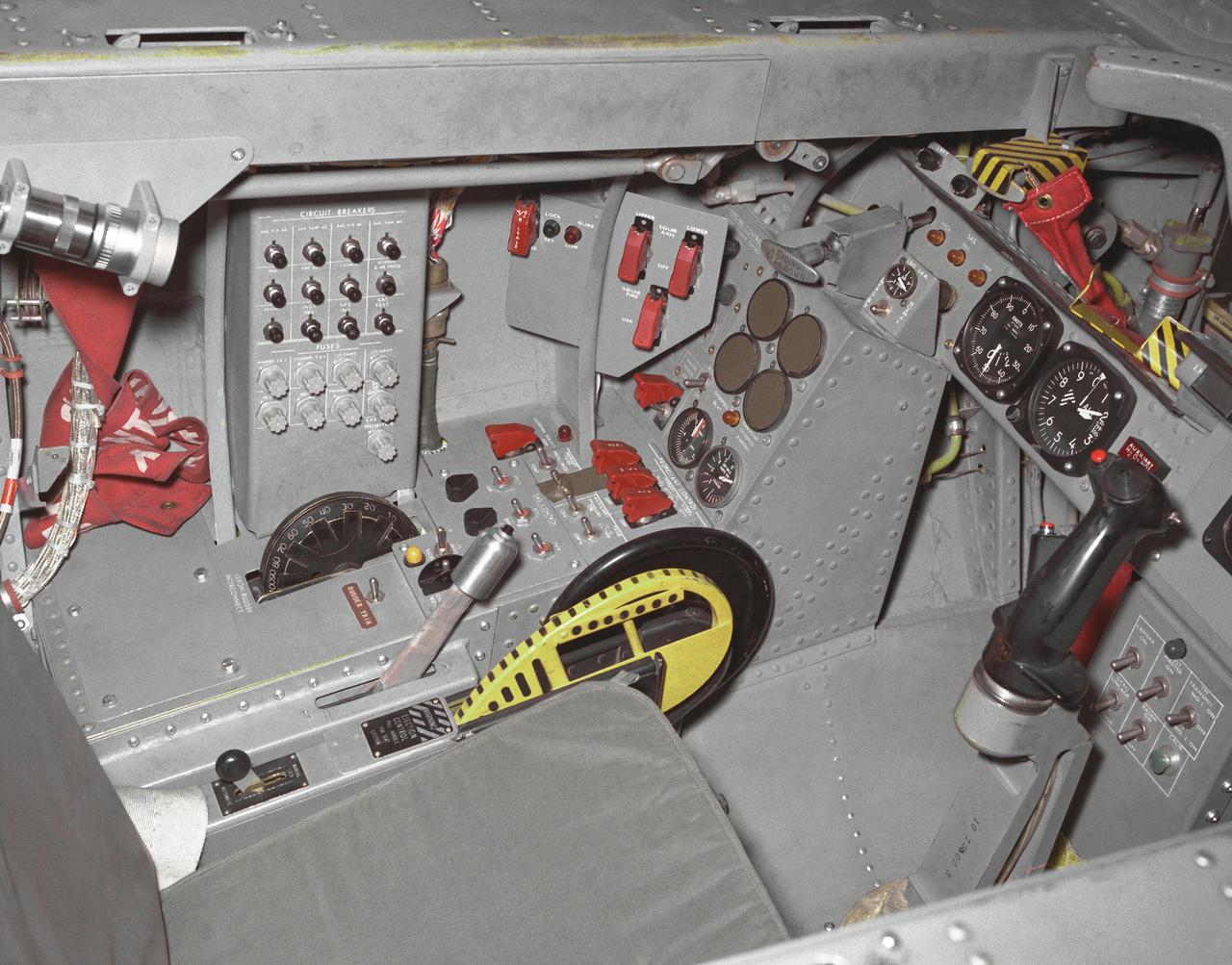

This photo shows the left side cockpit instrumentation panel of the M2-F2 Lifting Body. The success of Dryden's M2-F1 program led to NASA's development and construction of two heavyweight lifting bodies based on studies at NASA's Ames and Langley research centers -- the M2-F2 and the HL-10, both built by the Northrop Corporation. The "M" refers to "manned" and "F" refers to "flight" version. "HL" comes from "horizontal landing" and 10 is for the tenth lifting body model to be investigated by Langley. The first flight of the M2-F2 -- which looked much like the "F1" -- was on July 12, 1966. Milt Thompson was the pilot. By then, the same B-52 used to air launch the famed X-15 rocket research aircraft was modified to also carry the lifting bodies. Thompson was dropped from the B-52's wing pylon mount at an altitude of 45,000 feet on that maiden glide flight. The M2-F2 weighed 4,620 pounds, was 22 feet long, and had a width of about 10 feet. On May 10, 1967, during the sixteenth glide flight leading up to powered flight, a landing accident severely damaged the vehicle and seriously injured the NASA pilot, Bruce Peterson. NASA pilots and researchers realized the M2-F2 had lateral control problems, even though it had a stability augmentation control system. When the M2-F2 was rebuilt at Dryden and redesignated the M2-F3, it was modified with an additional third vertical fin -- centered between the tip fins -- to improve control characteristics. The M2-F2/F3 was the first of the heavy-weight, entry-configuration lifting bodies. Its successful development as a research test vehicle answered many of the generic questions about these vehicles. NASA donated the M2-F3 vehicle to the Smithsonian Institute in December 1973. It is currently hanging in the Air and Space Museum along with the X-15 aircraft number 1, which was its hangar partner at Dryden from 1965 to 1969.
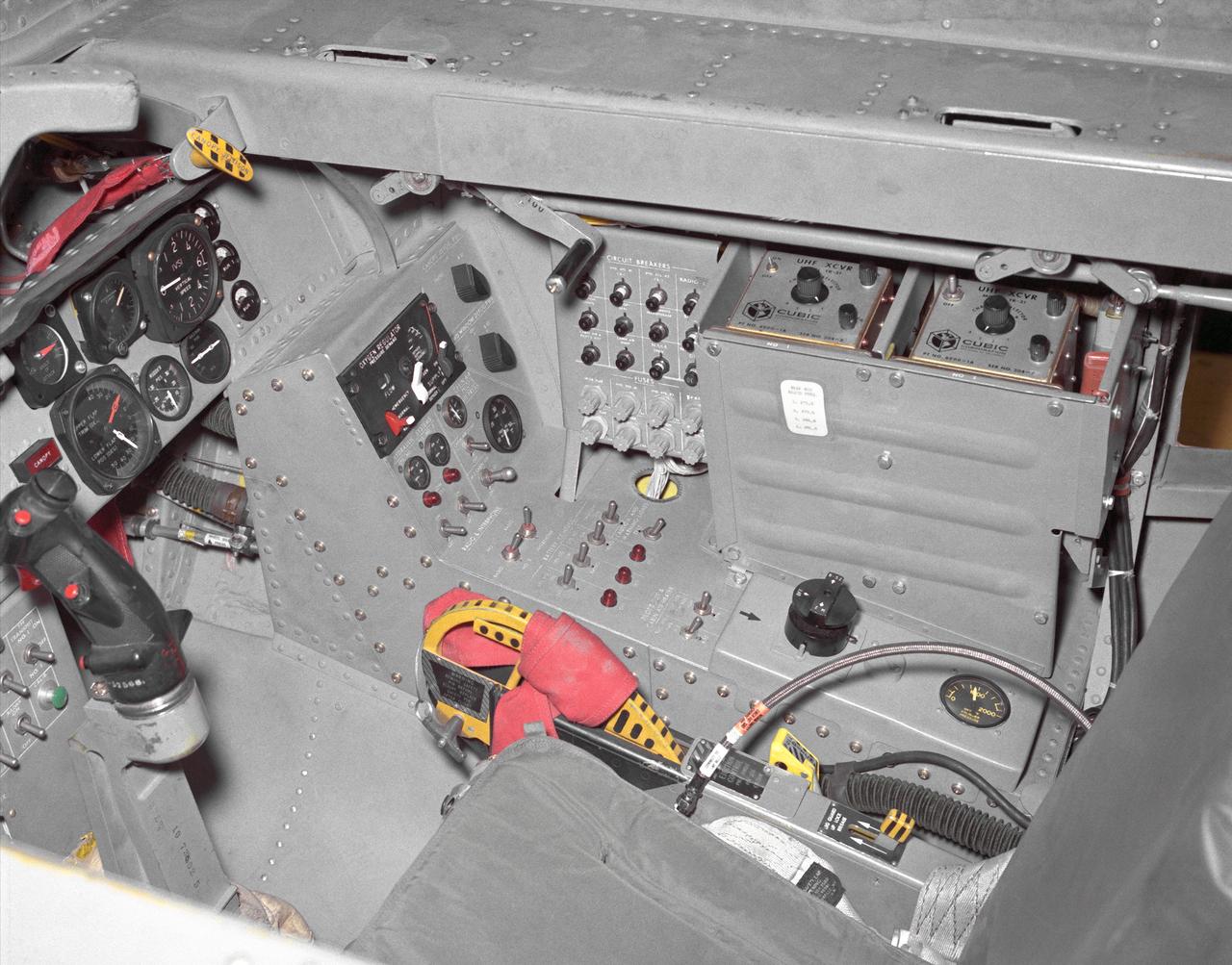

This photo shows the right side cockpit instrumentation panel of the M2-F2 Lifting Body. The success of Dryden's M2-F1 program led to NASA's development and construction of two heavyweight lifting bodies based on studies at NASA's Ames and Langley research centers -- the M2-F2 and the HL-10, both built by the Northrop Corporation. The "M" refers to "manned" and "F" refers to "flight" version. "HL" comes from "horizontal landing" and 10 is for the tenth lifting body model to be investigated by Langley. The first flight of the M2-F2 -- which looked much like the "F1" -- was on July 12, 1966. Milt Thompson was the pilot. By then, the same B-52 used to air launch the famed X-15 rocket research aircraft was modified to also carry the lifting bodies. Thompson was dropped from the B-52's wing pylon mount at an altitude of 45,000 feet on that maiden glide flight. The M2-F2 weighed 4,620 pounds, was 22 feet long, and had a width of about 10 feet. On May 10, 1967, during the sixteenth glide flight leading up to powered flight, a landing accident severely damaged the vehicle and seriously injured the NASA pilot, Bruce Peterson. NASA pilots and researchers realized the M2-F2 had lateral control problems, even though it had a stability augmentation control system. When the M2-F2 was rebuilt at Dryden and redesignated the M2-F3, it was modified with an additional third vertical fin -- centered between the tip fins -- to improve control characteristics. The M2-F2/F3 was the first of the heavy-weight, entry-configuration lifting bodies. Its successful development as a research test vehicle answered many of the generic questions about these vehicles. NASA donated the M2-F3 vehicle to the Smithsonian Institute in December 1973. It is currently hanging in the Air and Space Museum along with the X-15 aircraft number 1, which was its hangar partner at Dryden from 1965 to 1969.
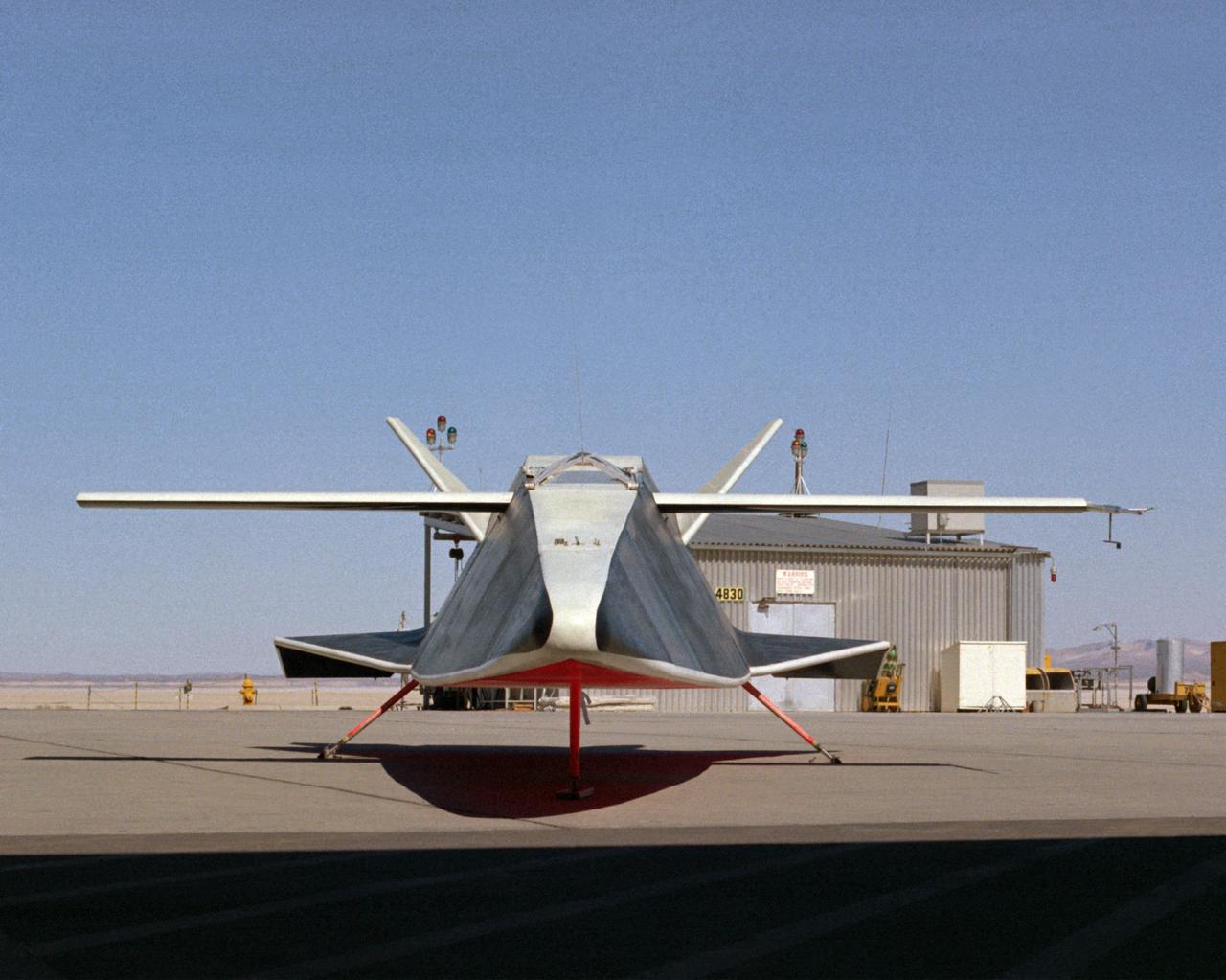

The Hyper III was a low-cost test vehicle for an advanced lifting-body shape. Like the earlier M2-F1, it was a "homebuilt" research aircraft, i.e., built at the Flight Research Center (FRC), later redesignated the Dryden Flight Research Center. It had a steel-tube frame covered with Dacron, a fiberglass nose, sheet aluminum fins, and a wing from an HP-11 sailplane. Construction was by volunteers at the FRC. Although the Hyper III was to be flown remotely in its initial tests, it was fitted with a cockpit for a pilot. On the Hyper III's only flight, it was towed aloft attached to a Navy SH-3 helicopter by a 400-foot cable. NASA research pilot Bruce Peterson flew the SH-3. After he released the Hyper III from the cable, NASA research pilot Milt Thompson flew the vehicle by radio control until the final approach when Dick Fischer took over control using a model-airplane radio-control box. The Hyper III flared, then landed and slid to a stop on Rogers Dry Lakebed.
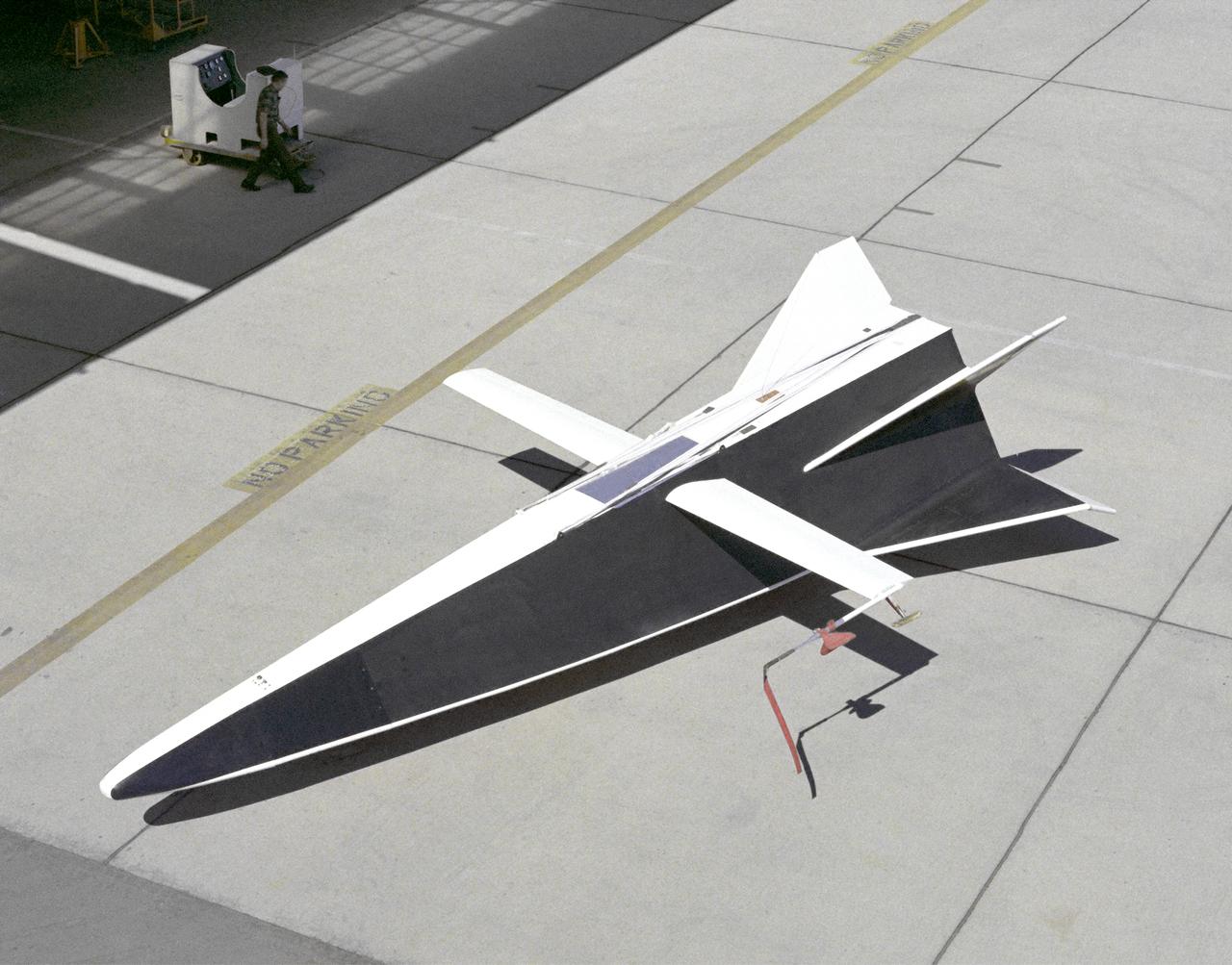
The Hyper III was a full-scale lifting-body remotely piloted research vehicle (RPRV) built at what was then the NASA Flight Research Center located at Edwards Air Force Base in Southern California.
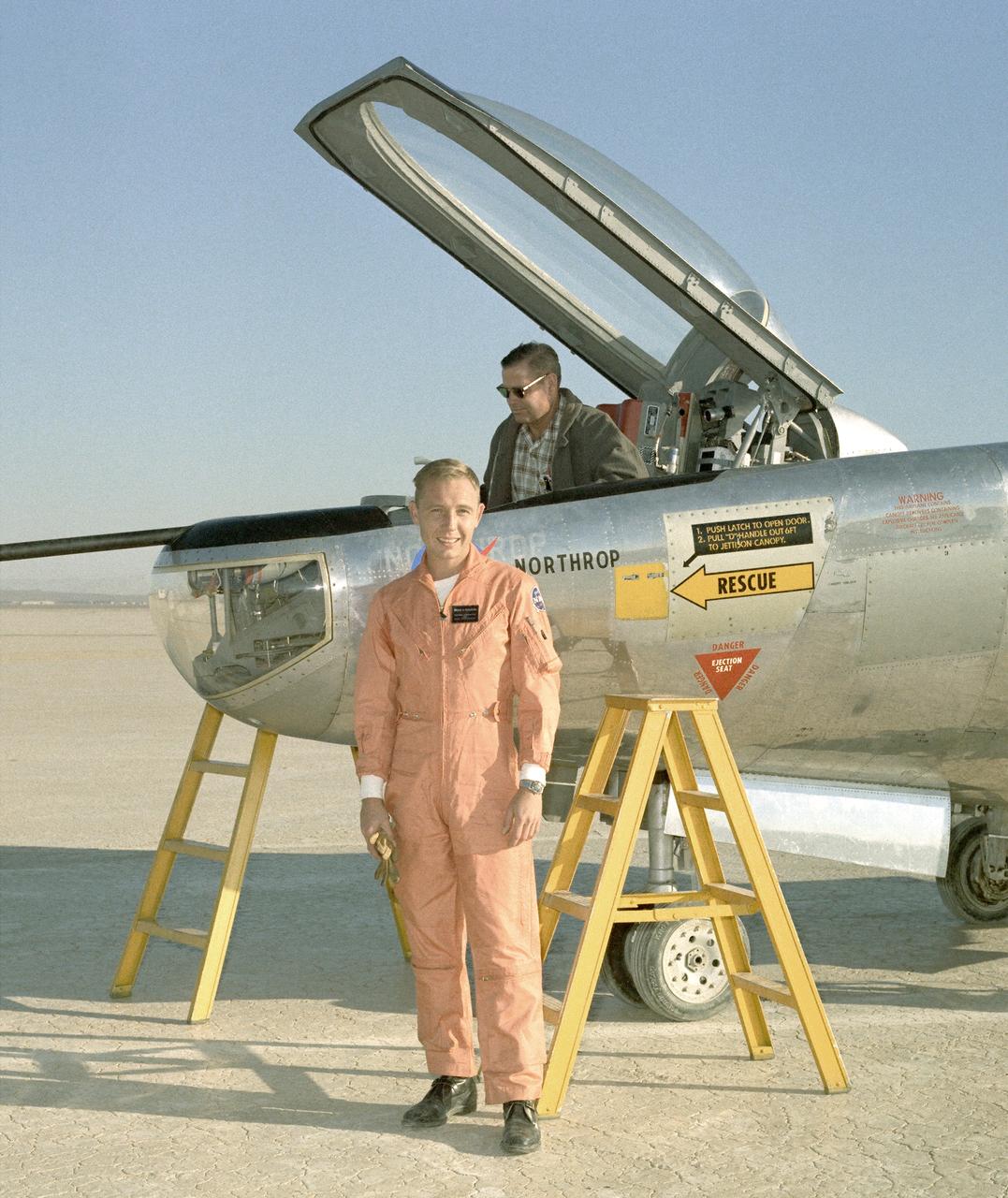

Bruce A. Peterson standing beside the M2-F2 lifting body on Rogers Dry Lake. Peterson became the NASA project pilot for the lifting body program after Milt Thompson retired from flying in late 1966. Peterson had flown the M2-F1, and made the first glide flight of the HL-10 heavy-weight lifting body in December 1966. On May 10, 1967, Peterson made his fourth glide flight in the M2-F2. This was also the M2-F2's 16th glide flight, scheduled to be the last one before the powered flights began. However, as pilot Bruce Peterson neared the lakebed, the M2-F2 suffered a pilot induced oscillation (PIO). The vehicle rolled from side to side in flight as he tried to bring it under control. Peterson recovered, but then observed a rescue helicopter that seemed to pose a collision threat. Distracted, Peterson drifted in a cross-wind to an unmarked area of the lakebed where it was very difficult to judge the height over the lakebed because of a lack of the guidance the markers provided on the lakebed runway. Peterson fired the landing rockets to provide additional lift, but he hit the lakebed before the landing gear was fully down and locked. The M2-F2 rolled over six times, coming to rest upside down. Pulled from the vehicle by Jay King and Joseph Huxman, Peterson was rushed to the base hospital, transferred to March Air Force Base and then the UCLA Hospital. He recovered but lost vision in his right eye due to a staph infection.
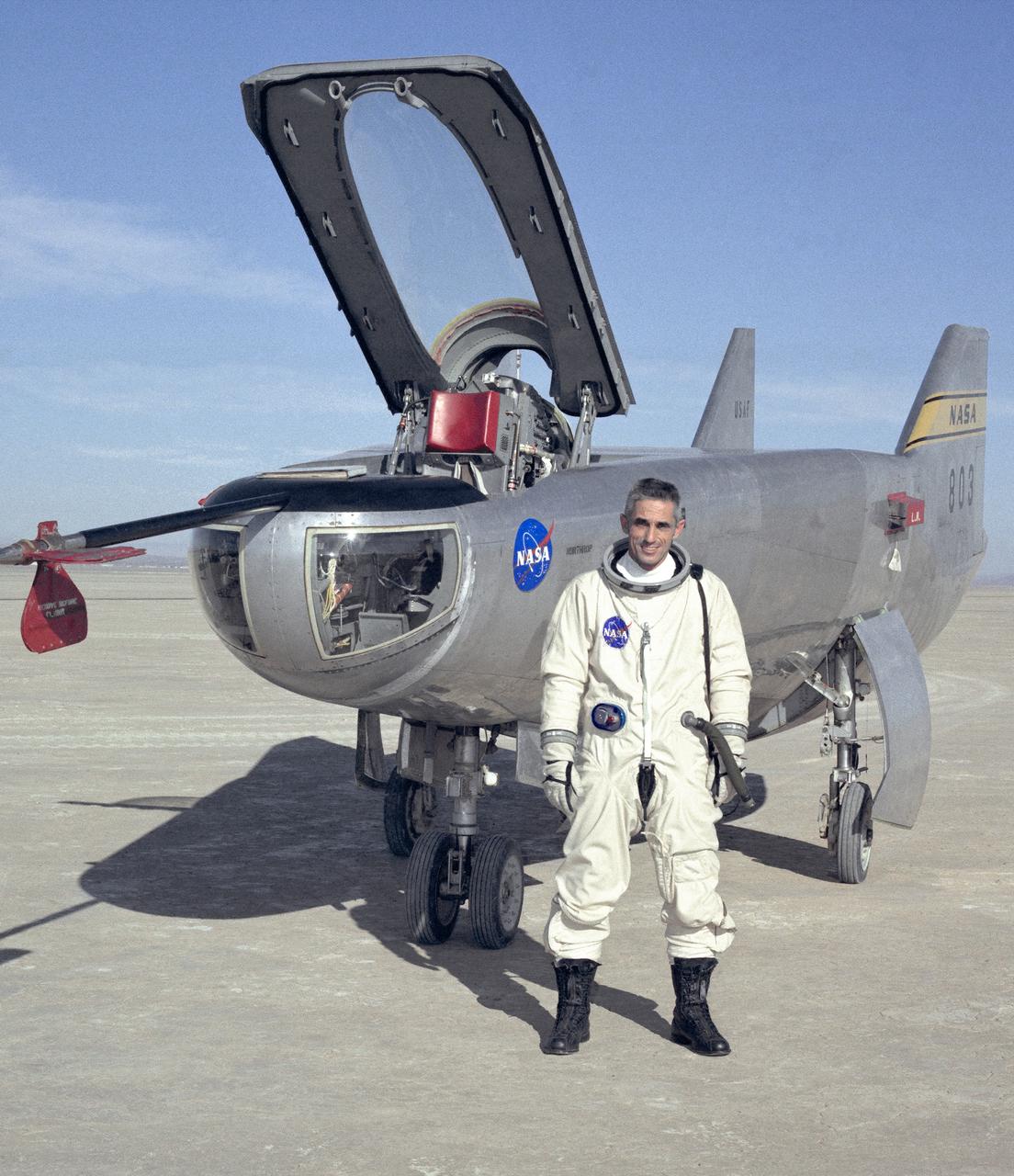

NASA research pilot John A. Manke is seen here in front of the M2-F3 Lifting Body. Manke was hired by NASA on May 25, 1962, as a flight research engineer. He was later assigned to the pilot's office and flew various support aircraft including the F-104, F5D, F-111 and C-47. After leaving the Marine Corps in 1960, Manke worked for Honeywell Corporation as a test engineer for two years before coming to NASA. He was project pilot on the X-24B and also flew the HL-10, M2-F3, and X-24A lifting bodies. John made the first supersonic flight of a lifting body and the first landing of a lifting body on a hard surface runway. Manke served as Director of the Flight Operations and Support Directorate at the Dryden Flight Research Center prior to its integration with Ames Research Center in October 1981. After this date John was named to head the joint Ames-Dryden Directorate of Flight Operations. He also served as site manager of the NASA Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility. John is a member of the Society of Experimental Test Pilots. He retired on April 27, 1984.
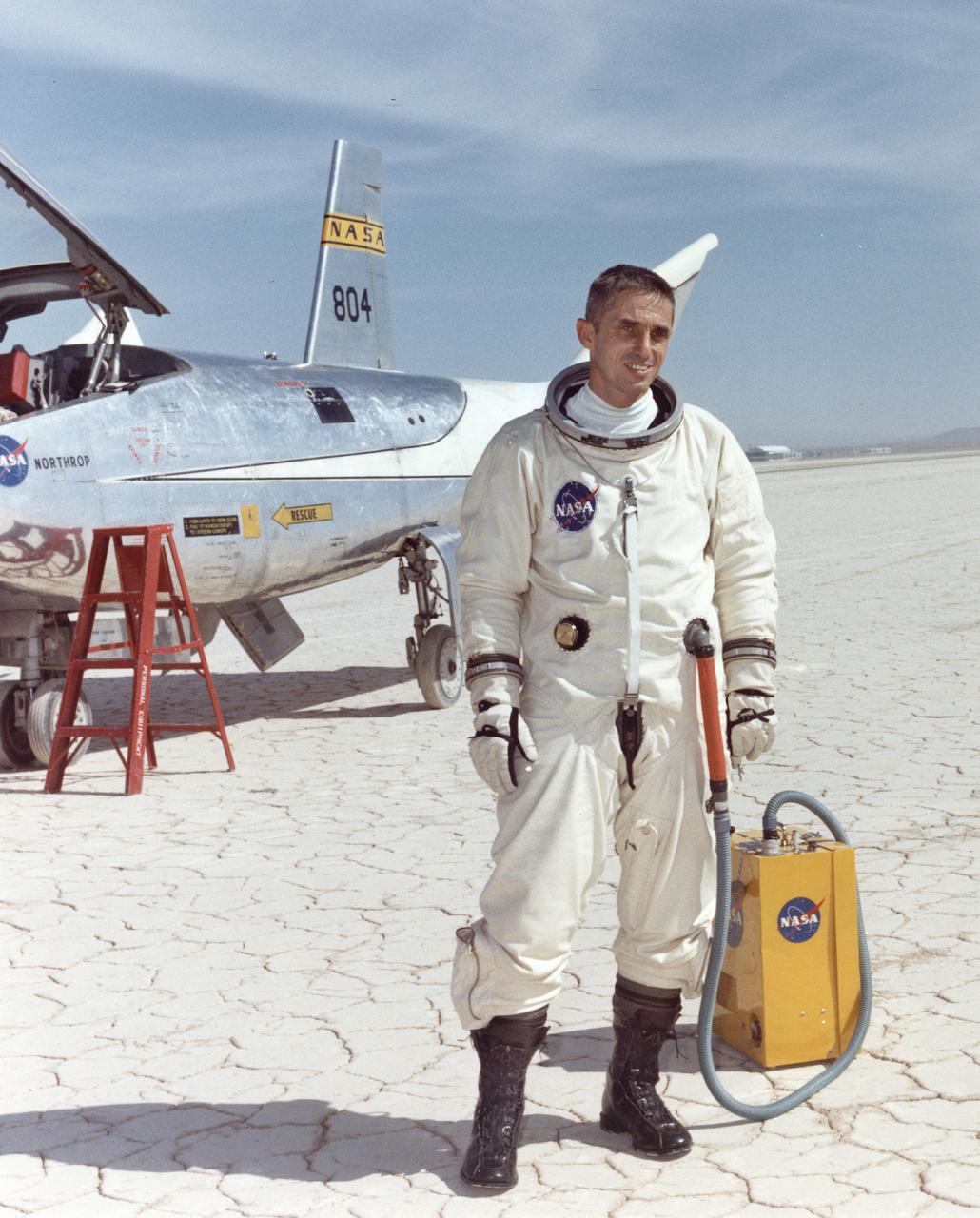

John Manke is shown here on the lakebed next to the HL-10, one of four different lifting-body vehicles he flew, including the X-24B, which he flew 16 times. His final total was 42 lifting-body flights.
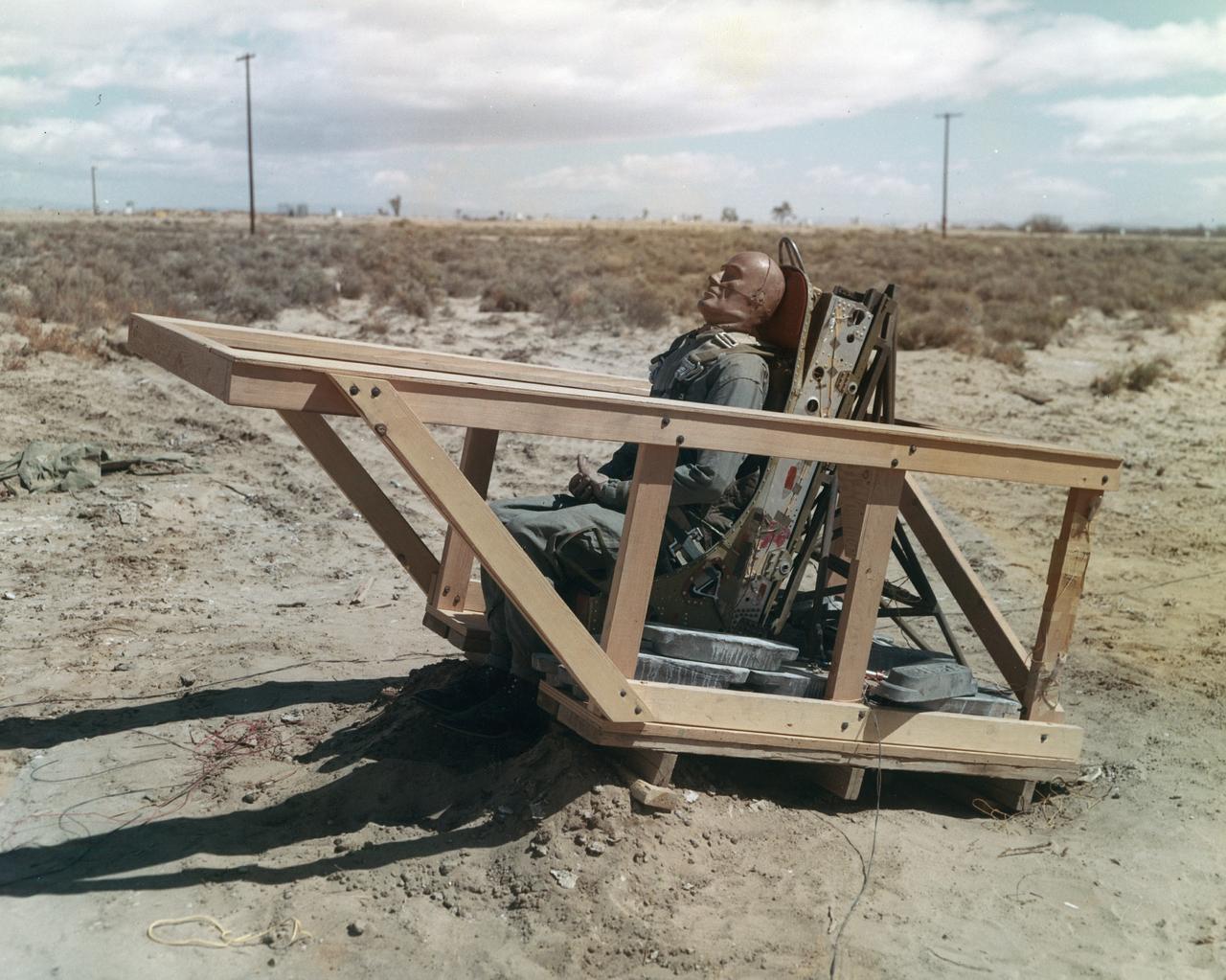

The M2-F1 was fitted with an ejection seat before the airtow flights began. The project selected the seat used in the T-37 as modified by the Weber Company to use a rocket rather than a ballistic charge for ejection. To test the ejection seat, the Flight Research Center's Dick Klein constructed a plywood mockup of the M2-F1's top deck and canopy. On the first firings, the test was unsuccessful, but on the final test the dummy in the seat landed safely. The M2-F1 ejection seat was later used in the two Lunar Landing Research Vehicles and the three Lunar Landing Training Vehicles. Three of them crashed, but in each case the pilot ejected from the vehicle successfully.
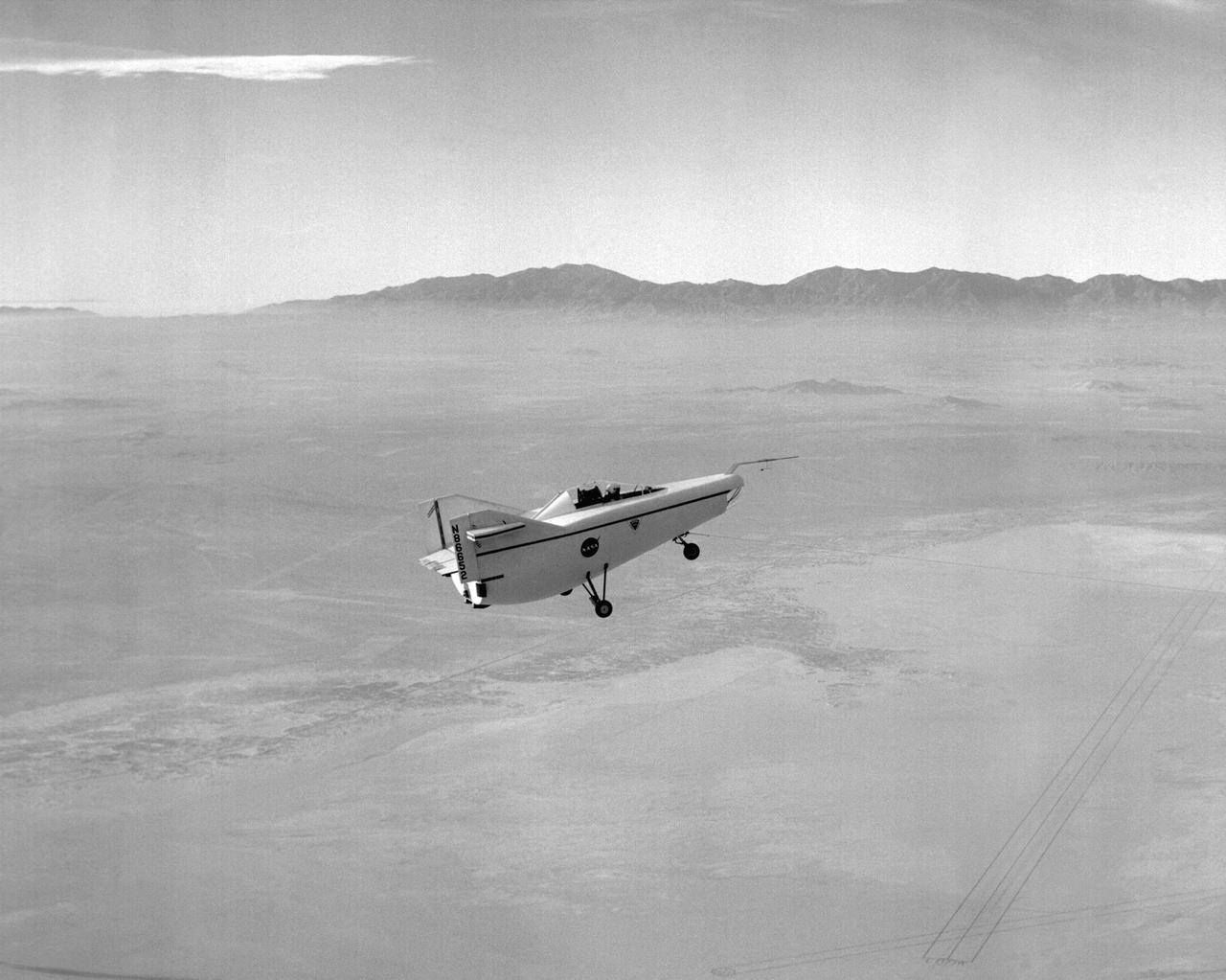

Following the first M2-F1 airtow flight on 16 August 1963, the Flight Research Center used the vehicle for both research flights and to check out new lifting-body pilots. These included Bruce Peterson, Don Mallick, Fred Haise, and Bill Dana from NASA. Air Force pilots who flew the M2-F1 included Chuck Yeager, Jerry Gentry, Joe Engle, Jim Wood, and Don Sorlie, although Wood, Haise, and Engle only flew on car tows. In the three years between the first and last flights of the M2-F1, it made about 400 car tows and 77 air tows.
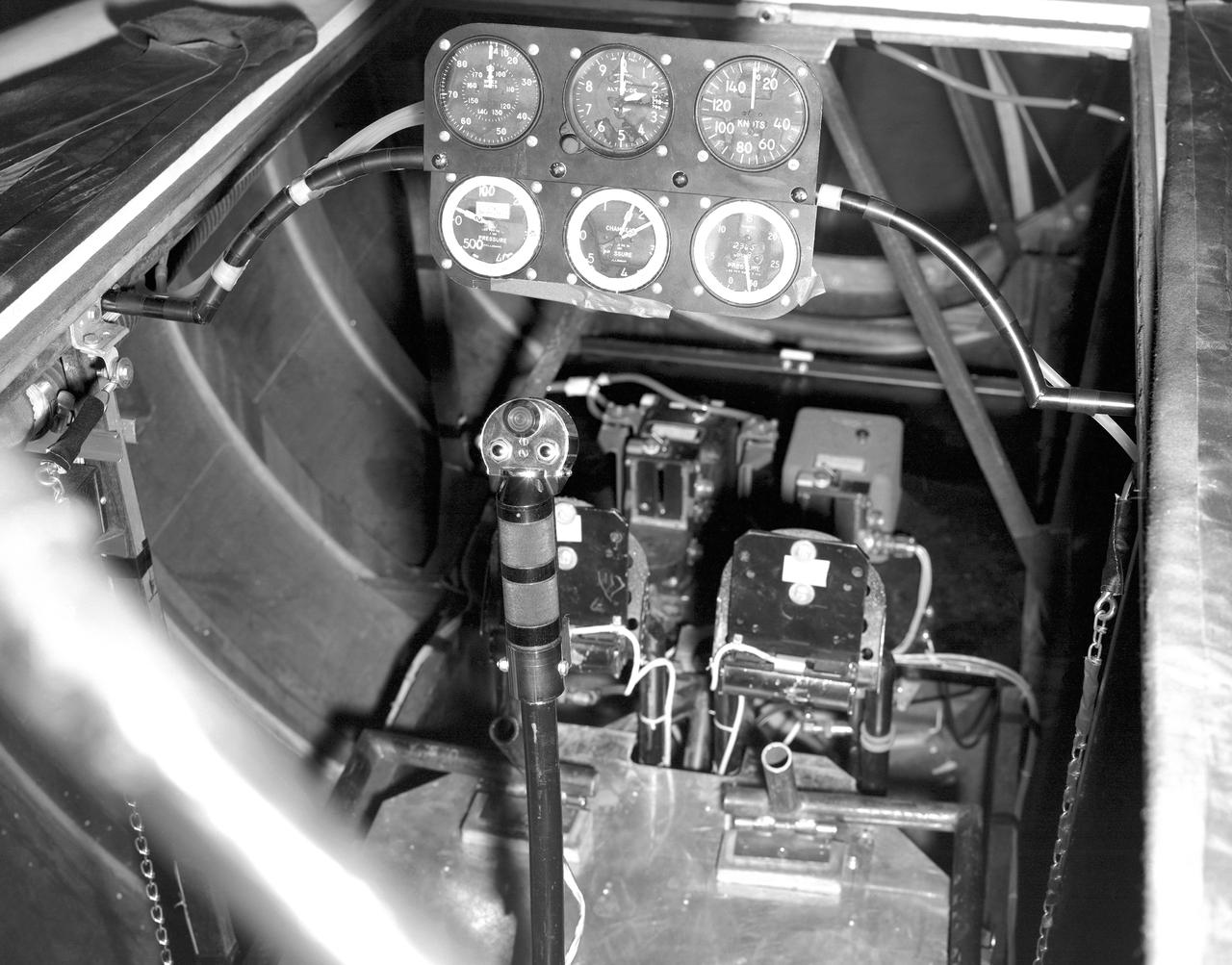

This photo shows the cockpit configuration of the M2-F1 wingless lifting body. With a top speed of about 120 knots, the M2-F1 had a simple instrument panel. Besides the panel itself, the ribs of the wooden shell (left) and the control stick (center) are also visible.
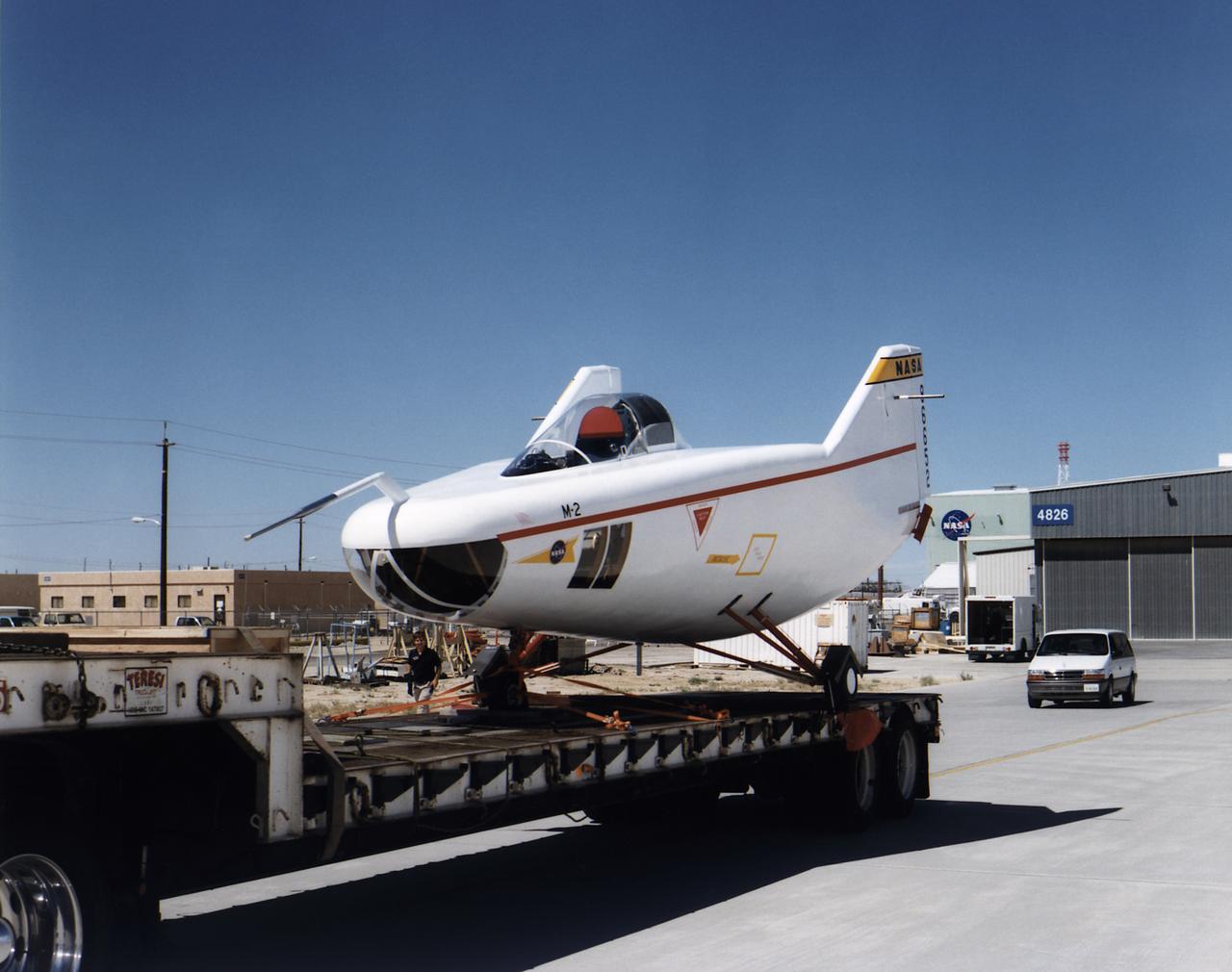

After the grounding of the M2-F1 in 1966, it was kept in outside storage on the Dryden complex. After several years, its fabric and plywood structure was damaged by the sun and weather. Restoration of the vehicle began in February 1994 under the leadership of NASA retiree Dick Fischer, with other retirees who had originally worked on the M2-F1's construction and flight research three decades before also participating. The photo shows the now-restored M2-F1 returning to the site of its flight research, now called the Dryden Flight Research Center, on 22 August 1997.
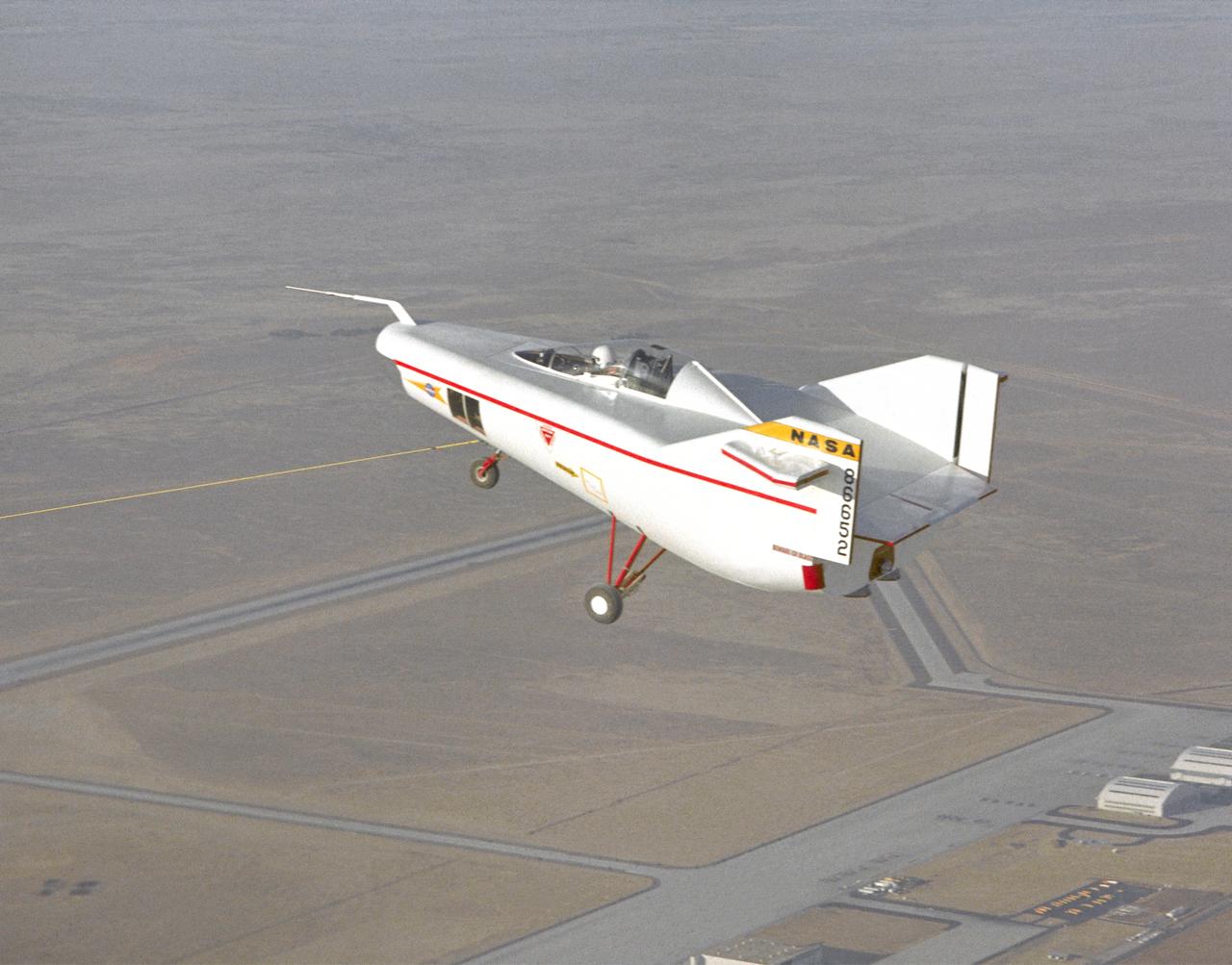

The M2-F1 Lifting Body is seen here under tow by an unseen C-47 at the NASA Flight Research Center (later redesignated the Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California. The low-cost vehicle was the first piloted lifting body to be test flown. The lifting-body concept originated in the mid-1950s at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics' Ames Aeronautical Laboratory, Mountain View California. By February 1962, a series of possible shapes had been developed, and R. Dale Reed was working to gain support for a research vehicle.
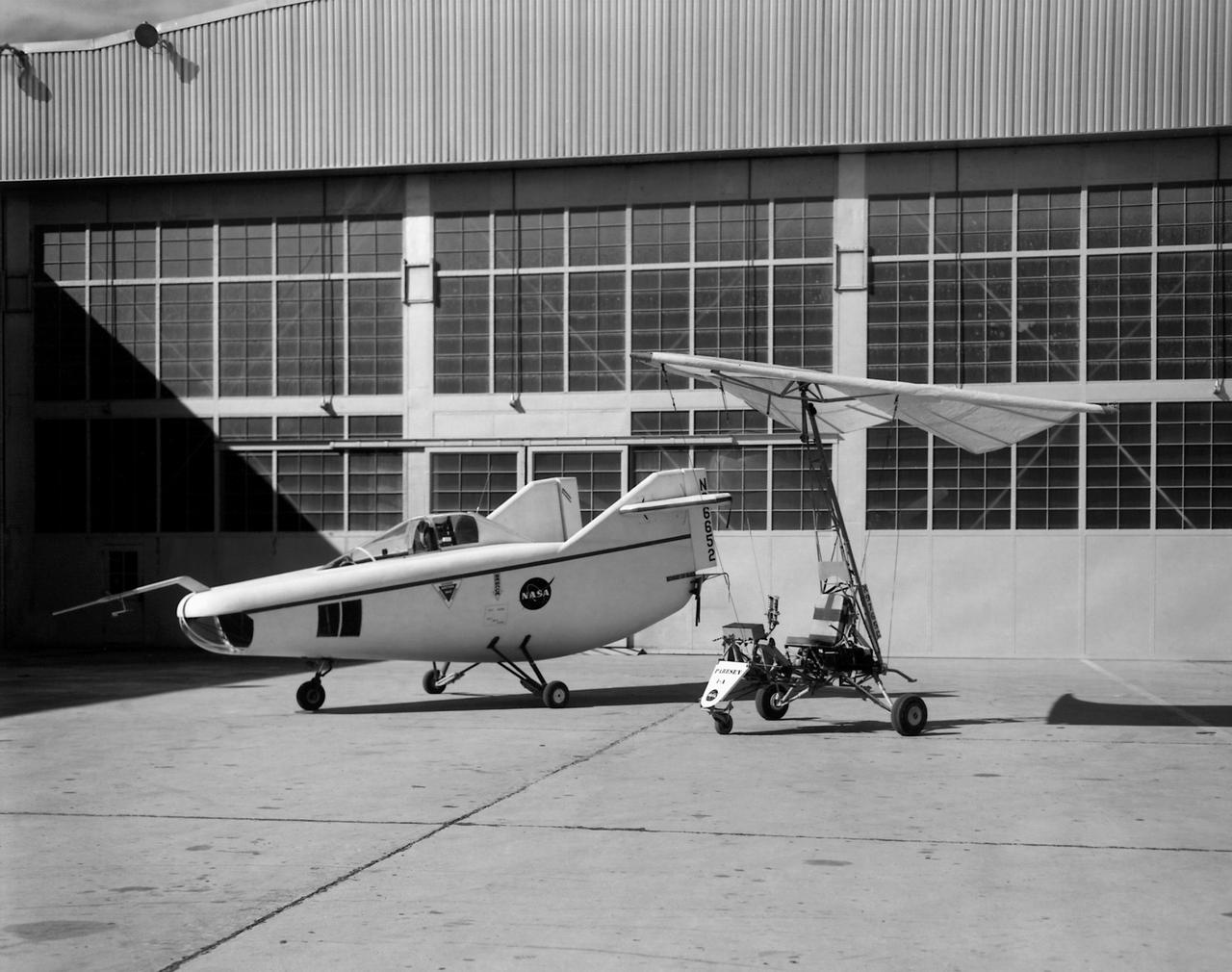

In this photo of the M2-F1 lifting body and the Paresev 1B on the ramp, the viewer sees two vehicles representing different approaches to building a research craft to simulate a spacecraft able to land on the ground instead of splashing down in the ocean as the Mercury capsules did. The M2-F1 was a lifting body, a shape able to re-enter from orbit and land. The Paresev (Paraglider Research Vehicle) used a Rogallo wing that could be (but never was) used to replace a conventional parachute for landing a capsule-type spacecraft, allowing it to make a controlled landing on the ground.