
Student Assistant Antoinette Davis (left) of Utica; Carmella Forsythe, 13, of Clinton; Terri Henderson, 14, of Clinton; Tyra Greer, 12, of Port Gibson; and Kala Battle, 14, of Edwards, answer curriculum questions about NASA's Return to Flight mission exhibit at StenniSphere, the visitor center at NASA's Stennis Space Center (SSC) near Bay St. Louis, Miss. The girls were on a field trip to StenniSphere with fellow participants in Hinds Community College's MSEIP (Minority Science Engineering Improvement Program) summer program. MSEIP encourages students to pursue and prepare for careers in science, technology, engineering and math.
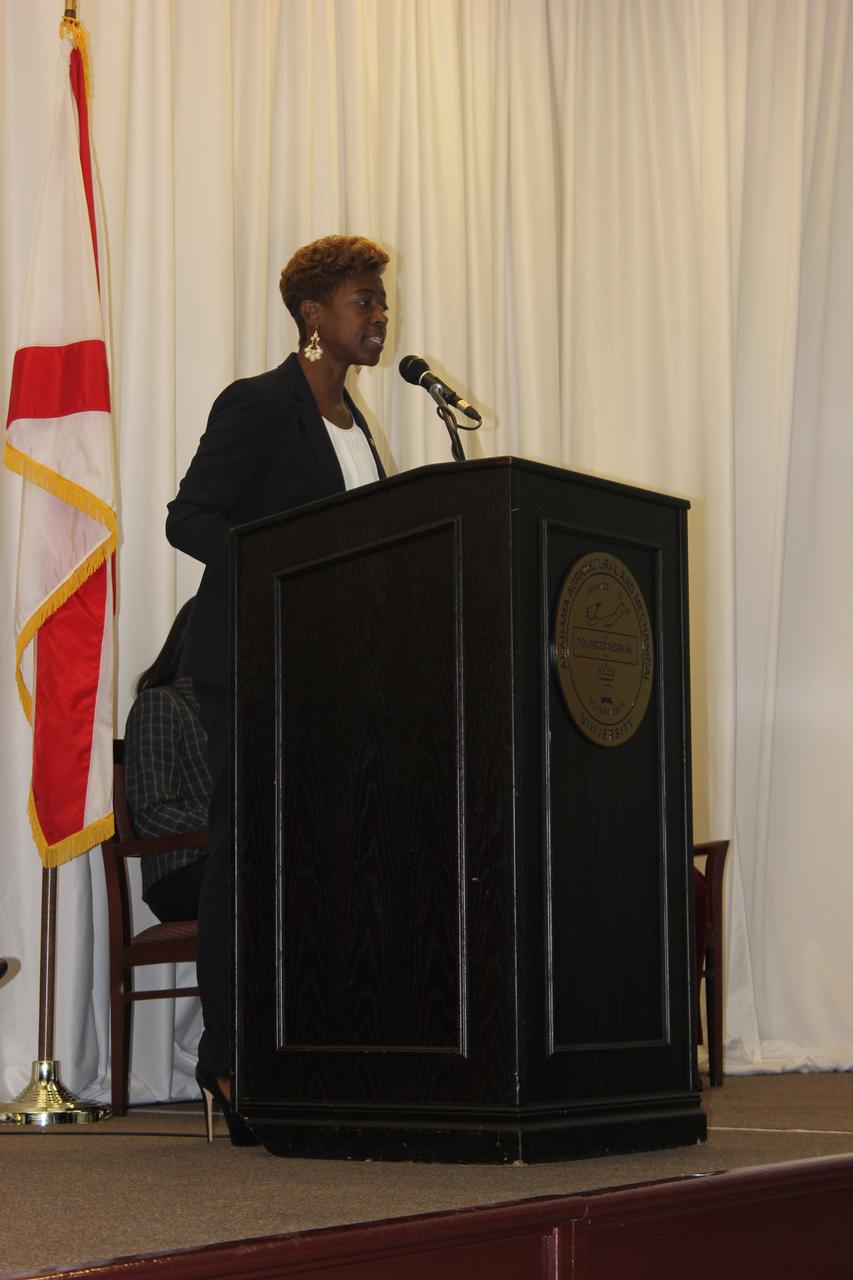

Marshall’s Ruth Jones, a mishap investigation specialist, told her NASA story and spoke about minority statistics in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). Jones also led a panel discussing how to engage, encourage and draw more minority students in to STEM fields and careers.
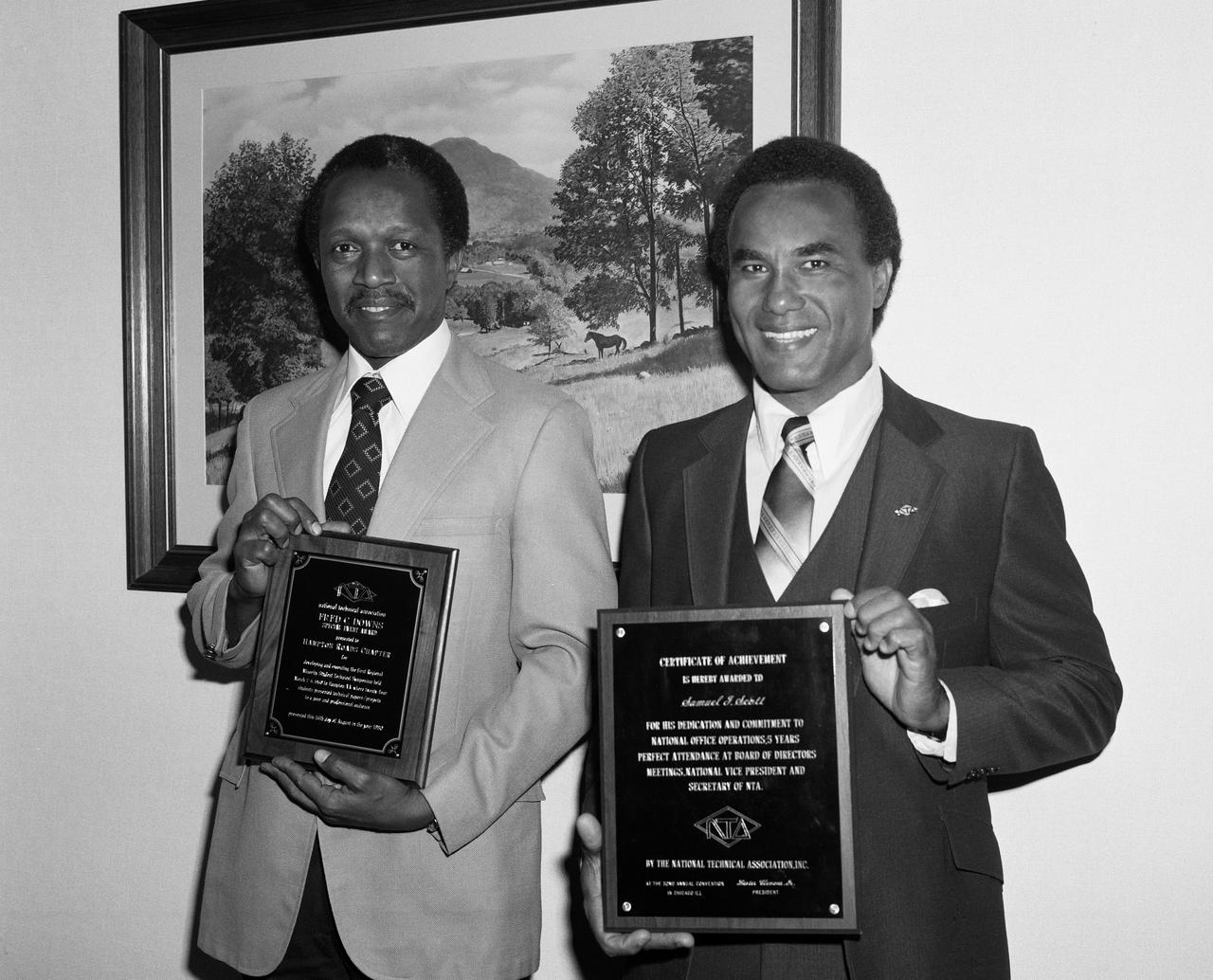

From left to right; Gilbert A. Haynes holding the NTA Fred C. Downs Special Event Award and Samuel J. Scott with award for their participation in the local Hampton Roads Chapter of the (NTA) National Technical Association. The guidance and counseling of minority youth is one of NTA's prime objectives. Formed in 1925, NTA has 15 chapters comprised of architects,engineers, scientists, and educators. NTA activities are directed toward encouraging and assisting public and private institutions in identifying potential minority technical talent.

Lorenzo L. Esters, Vice President, APLU (Association of Public and Land-grant Universities), and Project Director, MMSI (Minority Male STEM Initiative) addresses STEM initiative report findings at the Symposium on Supporting Underrepresented Minority Males in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), Tuesday, February 28, 2012 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Lorenzo L. Esters, Vice President, APLU (Association of Public and Land-grant Universities), and Project Director, MMSI (Minority Male STEM Initiative) addresses STEM initiative report findings at the Symposium on Supporting Underrepresented Minority Males in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), Tuesday, February 28, 2012 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
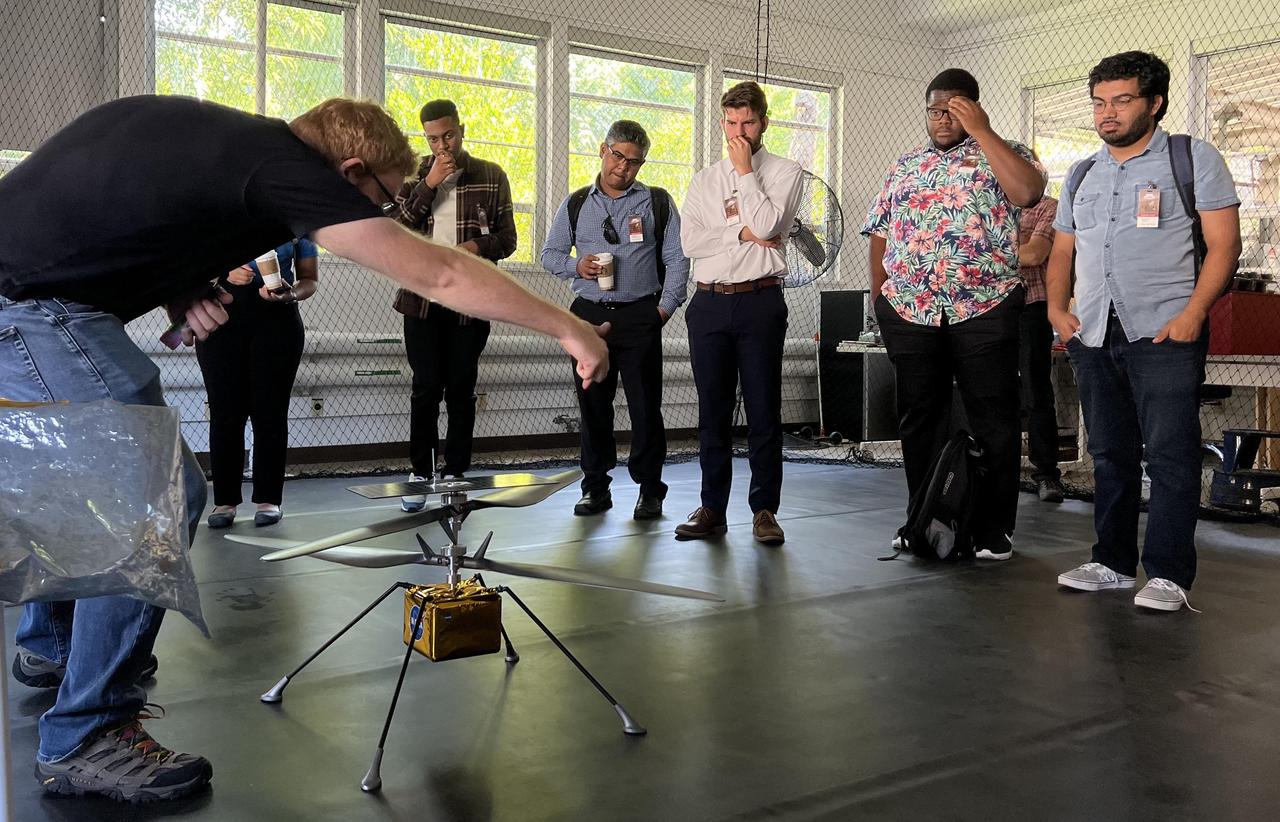

Participants in NASA's Minority Serving Institutions Space Accelerator program surround a full-scale model of NASA's Mars Ingenuity Helicopter as engineer Michael Starch discusses the mission. The group was visiting NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on Aug. 18, 2022. These participants were members of three teams named as awardees in the first-of-its-kind accelerator program, a competition to advance the NASA's goals and meet its needs in the areas of machine learning, artificial intelligence, and development of autonomous systems while also engaging underrepresented academic institutions and reducing barriers for them to submit ideas to the agency. The program provides funding, business training through a 10-week accelerator course, and mentorship to help the teams develop ideas for systems that can operate without human oversight for future science missions in space and on Earth. The teams were made up of professors and students from Fayetteville State University in North Carolina, University of Massachusetts Boston, and California State University, Northridge. At the conclusion of the accelerator, participants arrived in Southern California for a variety of events, including two days at JPL. The program is a partnership between NASA's Science Mission Directorate, its Earth Science Technology Office, the Minority University Research Education Project within the agency's Office of STEM Engagement, JPL, and Starburst, a global aerospace accelerator company based in Los Angeles. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25315

Carl Wieman, Associate Director, Office of Science and Technology Policy, The White House, speaks at the Symposium on Supporting Underrepresented Minority Males in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), Tuesday, February 28, 2012 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Christine Keller, right, Director of Research, APLU (Association of Public and Land-grant Universities) presents STEM initiative report findings at the Symposium on Supporting Underrepresented Minority Males in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), Tuesday, February 28, 2012 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Leland Melvin, Associate Administrator, Office of Education and former astronaut, gives opening remarks at the Symposium on Supporting Underrepresented Minority Males in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), Tuesday, February 28, 2012 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
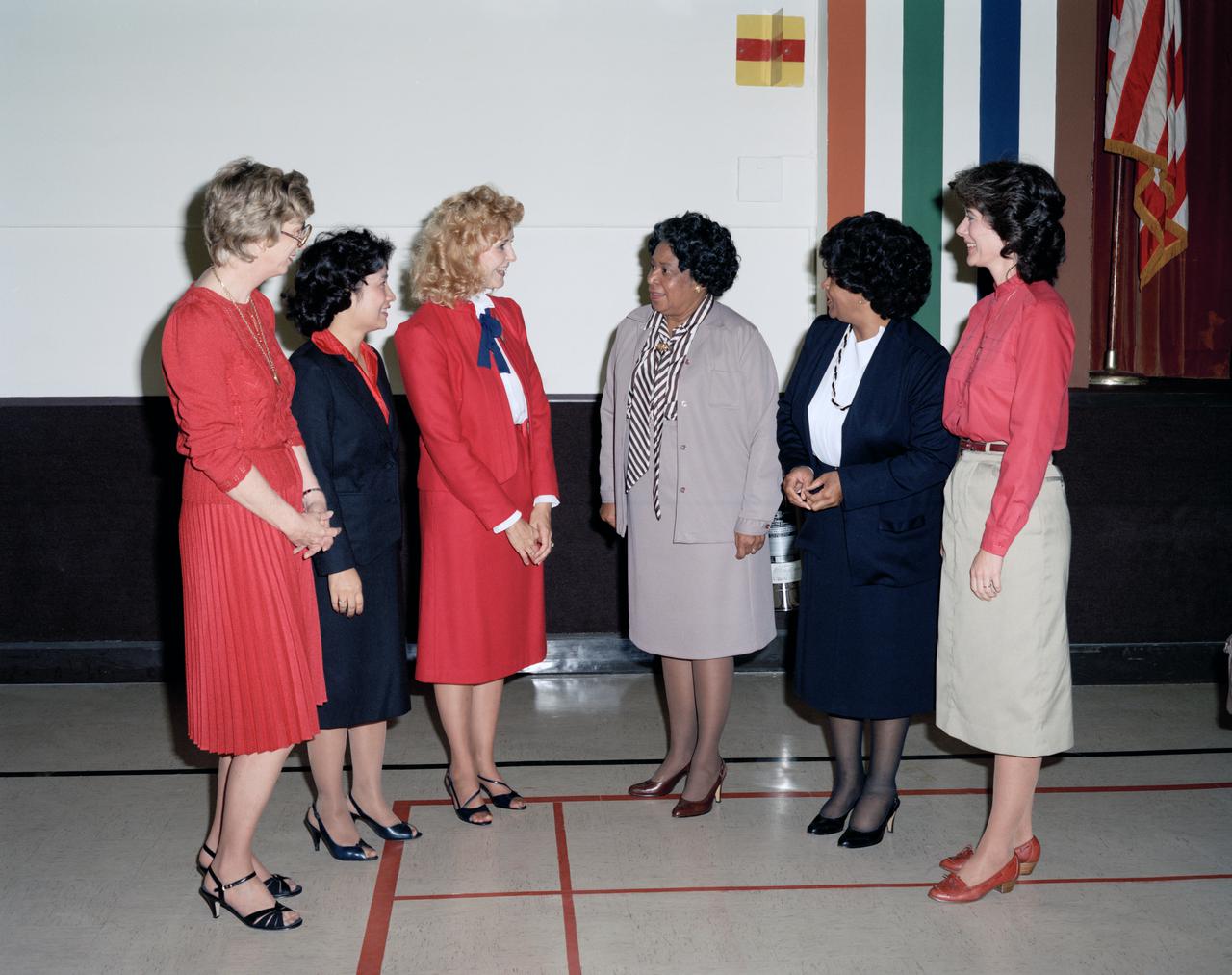

Members of the Langley Federal Women's Program surround Mary Jackson in the brown suit, of the Office of Equal Opportunity Programs. Mary Jackson NASA's first African-American female engineer, and subsequent career supporting the hiring and promotion of other deserving female and minority employees.
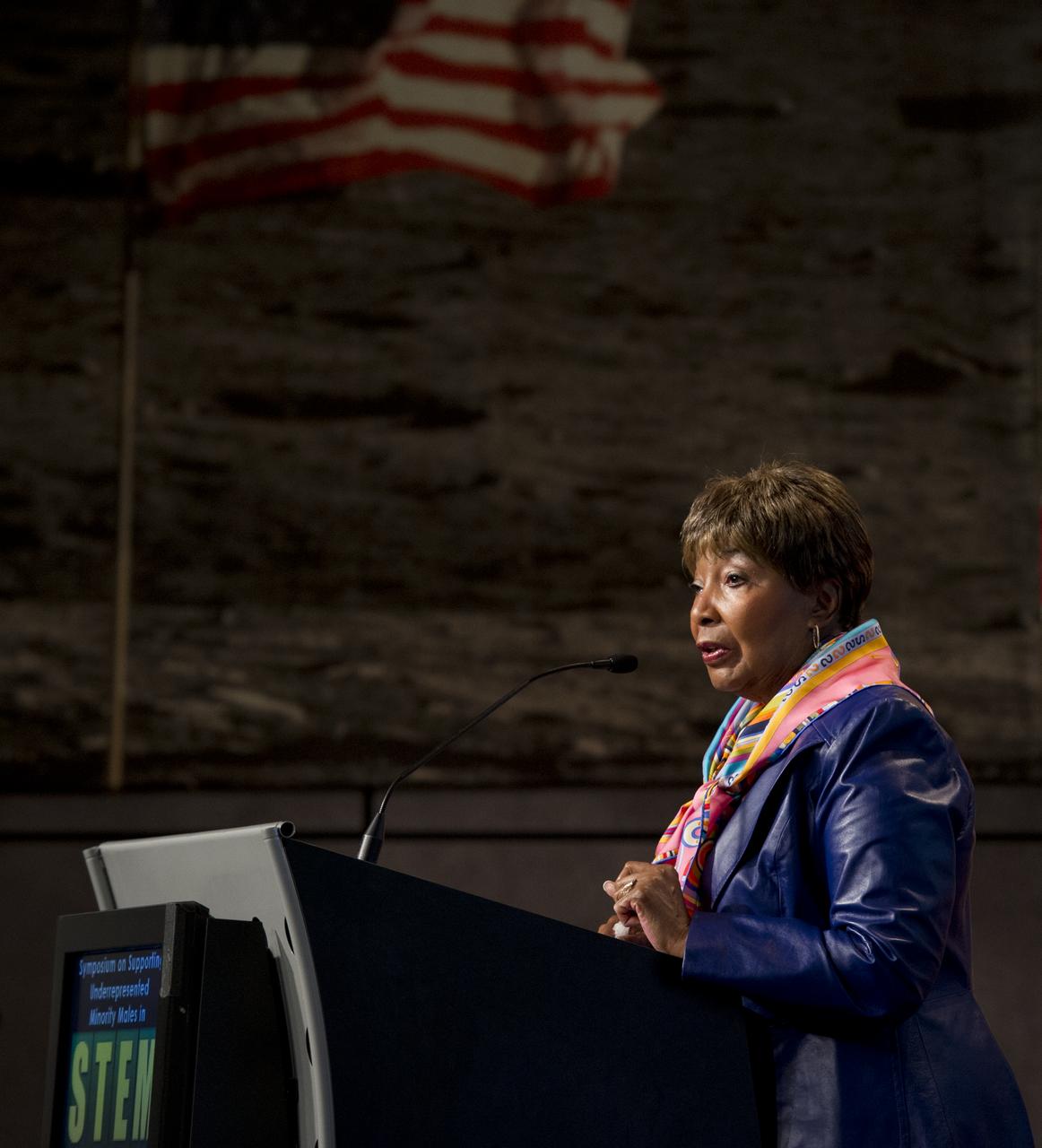

U.S. Congresswoman Eddie Bernice Johnson (D-TX) addresses the Symposium on Supporting Underrepresented Minority Males in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), Tuesday, February 28, 2012 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
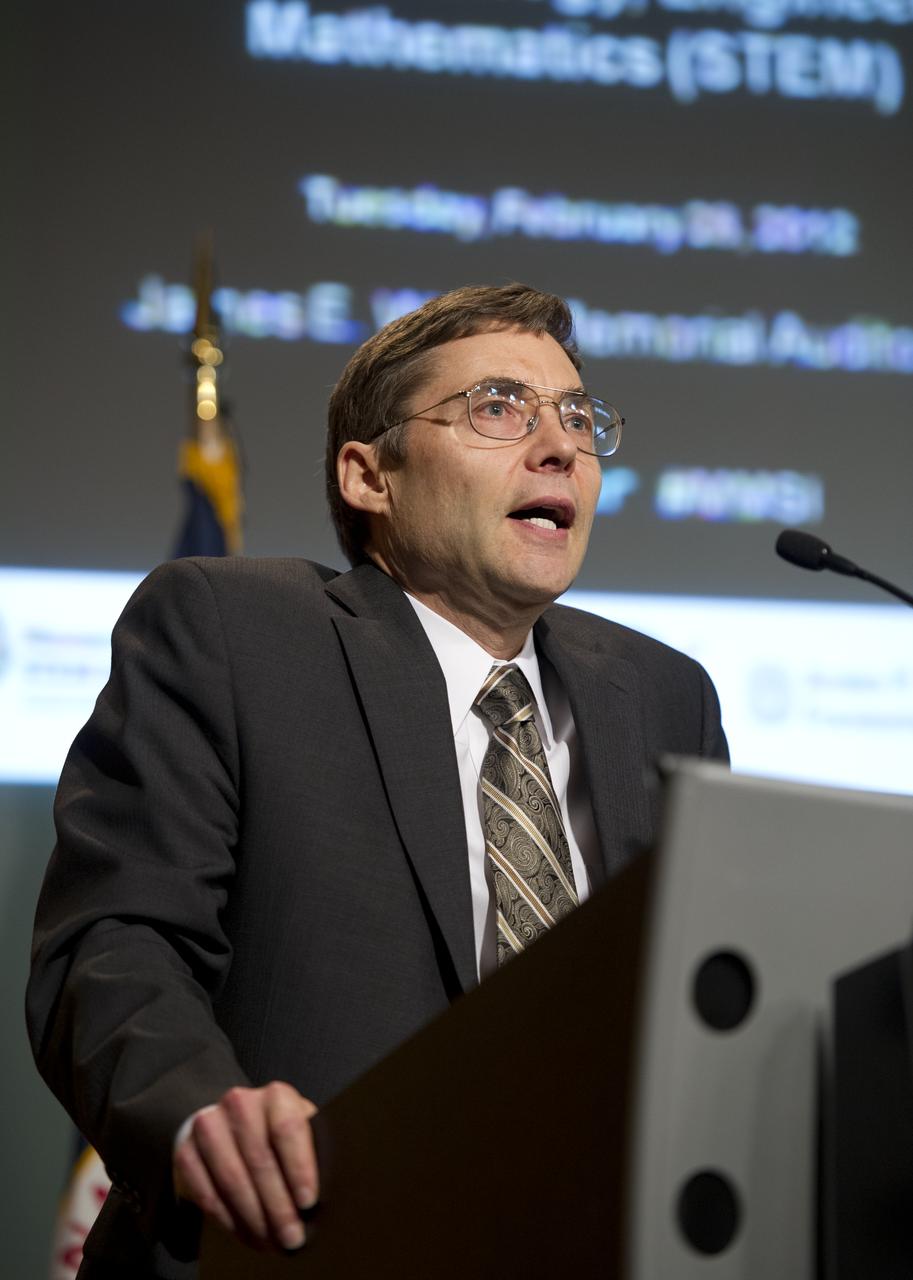

Carl Wieman, Associate Director, Office of Science and Technology Policy, The White House, speaks at the Symposium on Supporting Underrepresented Minority Males in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), Tuesday, February 28, 2012 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
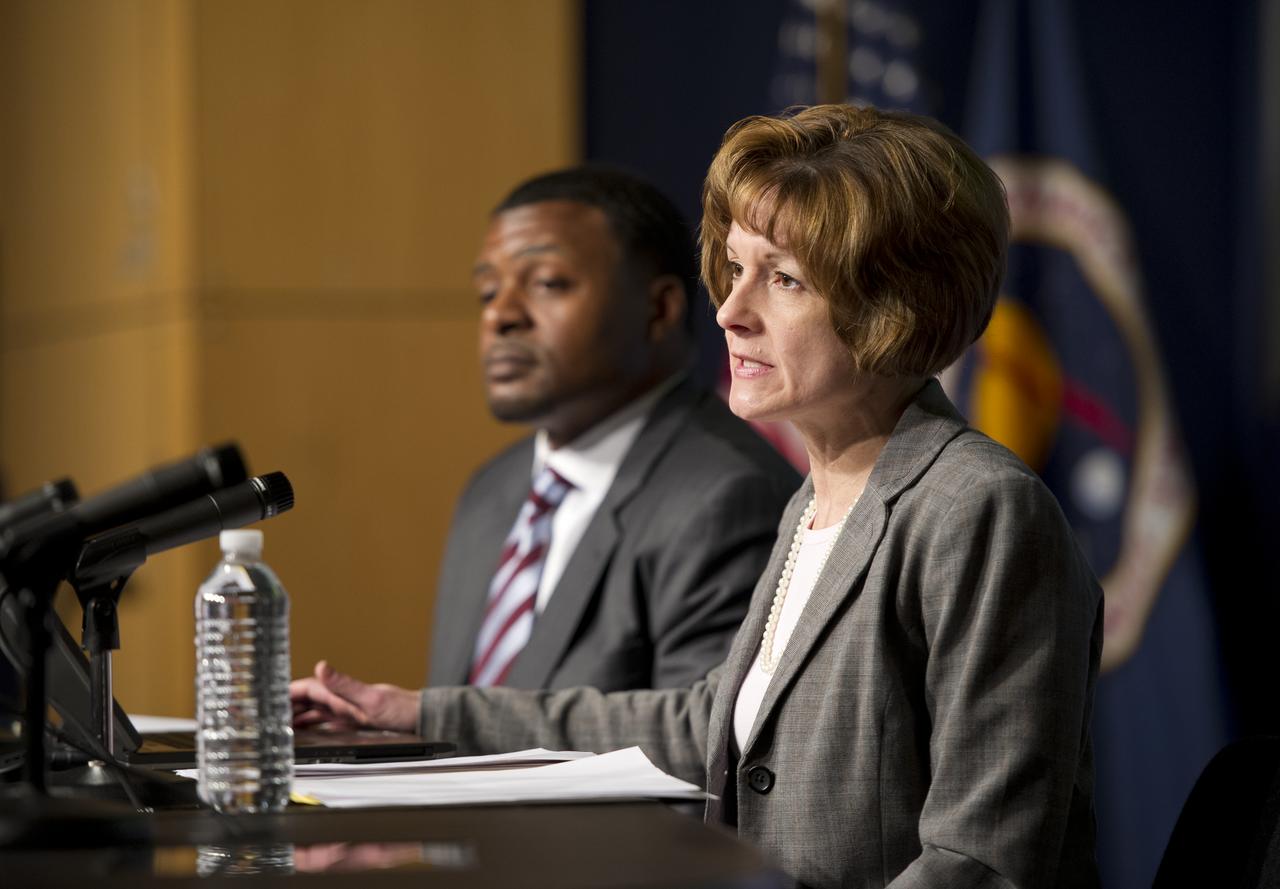

Christine Keller, Director of Research, APLU (Association of Public and Land-grant Universities) presents STEM initiative report findings at the Symposium on Supporting Underrepresented Minority Males in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), Tuesday, February 28, 2012 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
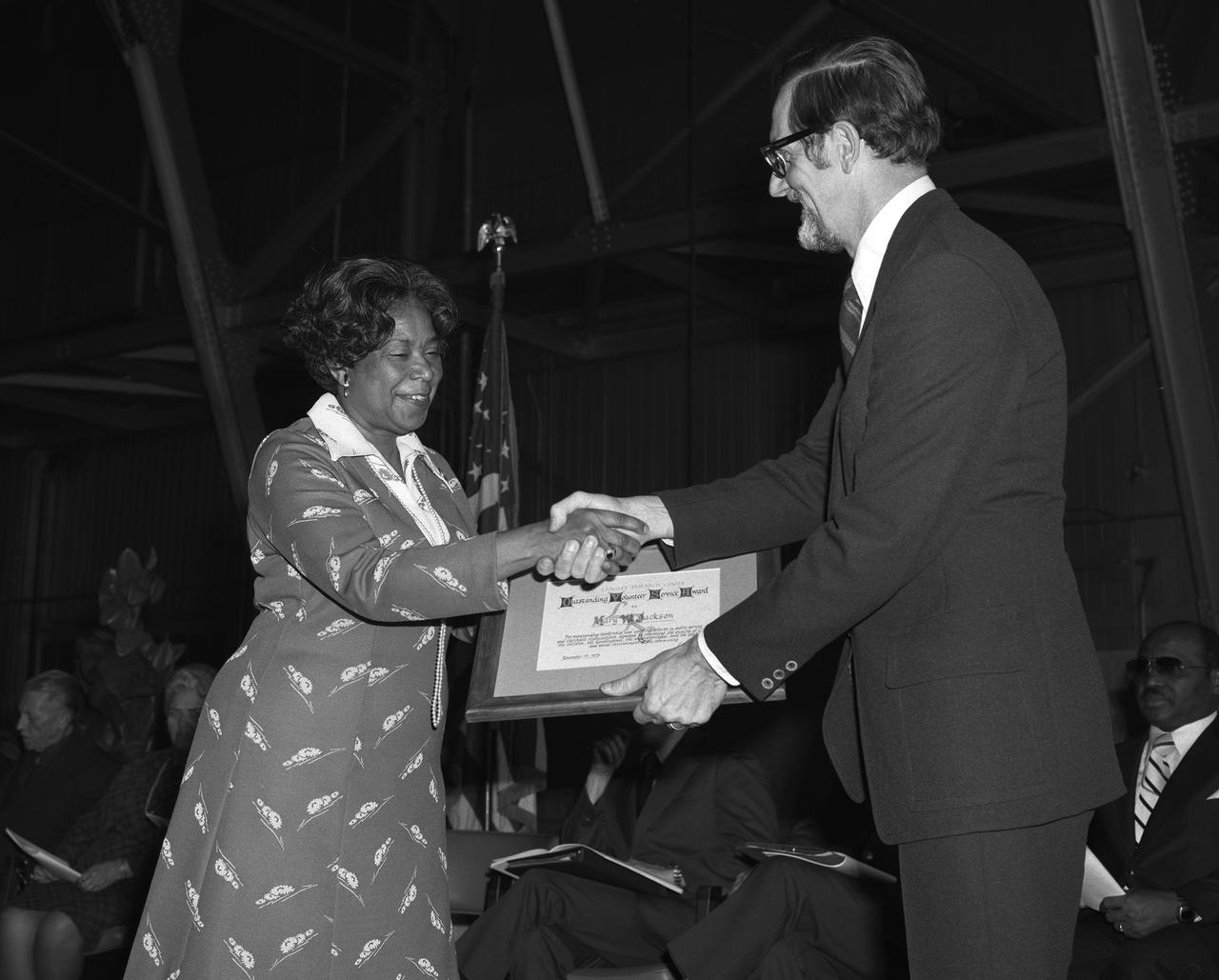

Langley Center Director Donald P. Hearth (right) presenting Mary Jackson with Outstanding Volunteer Service Award. Mary Jackson was NASA's first African-American female engineer,and subsequent career supporting the hiring and promotion of other deserving female and minority employees.

U.S. Congresswoman Eddie Bernice Johnson (D-TX) addresses the Symposium on Supporting Underrepresented Minority Males in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), Tuesday, February 28, 2012 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Woodrow Whitlow, NASA Associate Administrator, Mission Support Directorate, gives opening remarks at the Symposium on Supporting Underrepresented Minority Males in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), Tuesday, February 28, 2012 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
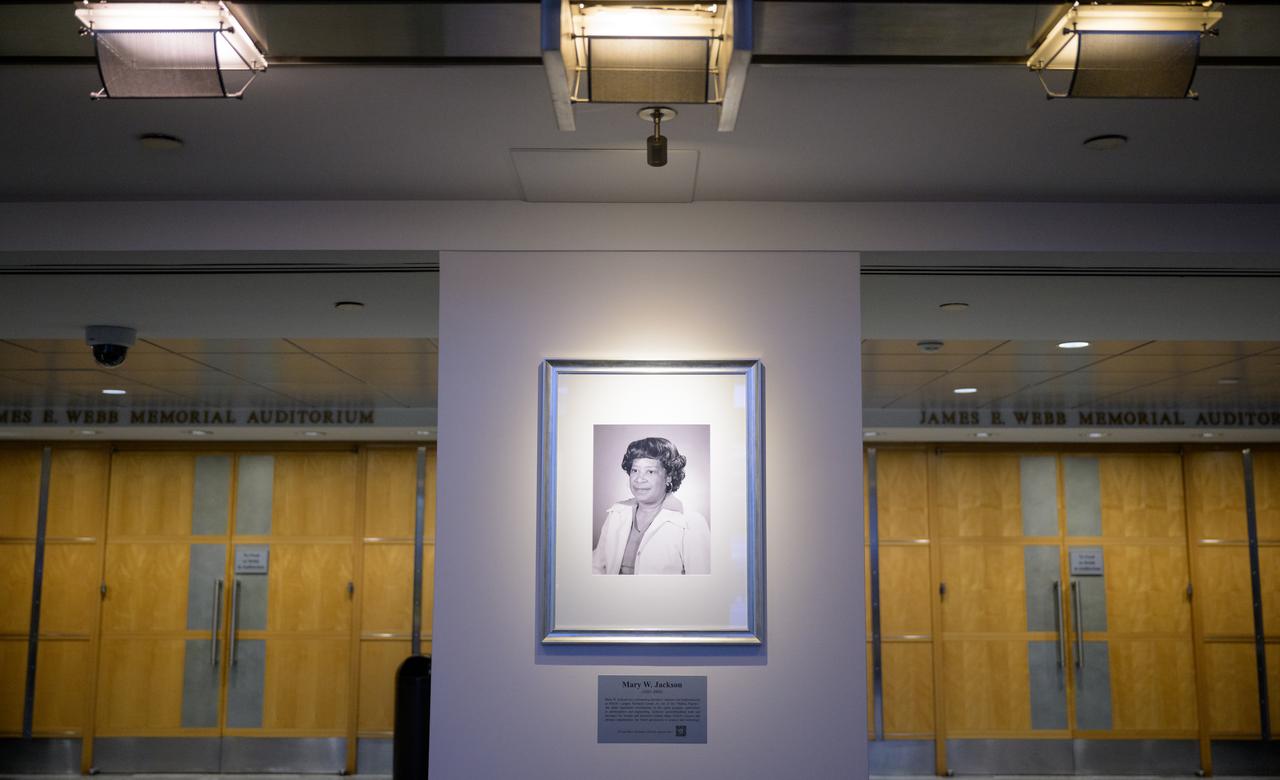

A portrait of Mary W. Jackson is seen after it was unveiled, Friday, Dec. 6, 2024, at the NASA Headquarters Mary W. Jackson Building in Washington. Mary W. Jackson was a pioneering aerospace engineer and mathematician at NASA’s Langley Research Center. As one of the “Hidden Figures,” she made significant contributions to the space program, particularly in aerodynamics and engineering. Jackson’s groundbreaking work and advocacy for women and minorities helped shape NASA’s success and advance opportunities for future generations in science and technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
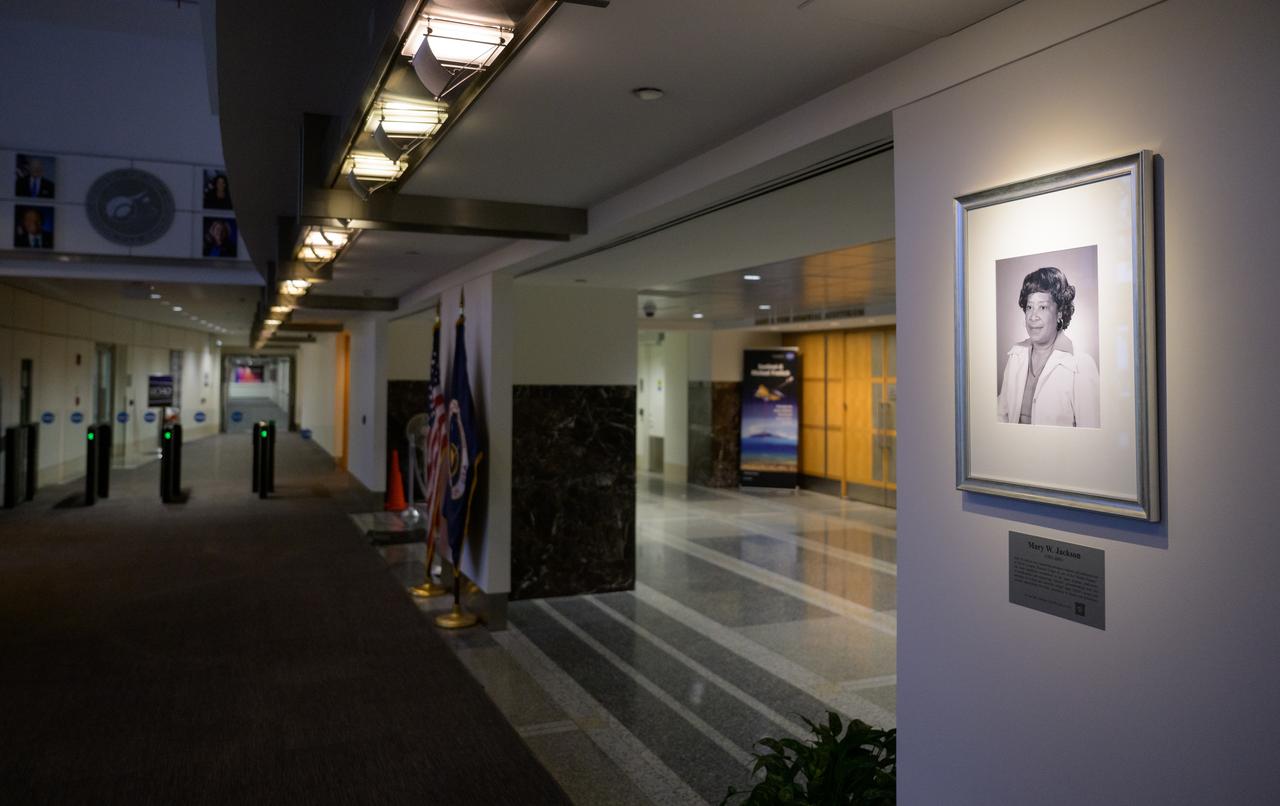

A portrait of Mary W. Jackson is seen after it was unveiled, Friday, Dec. 6, 2024, at the NASA Headquarters Mary W. Jackson Building in Washington. Mary W. Jackson was a pioneering aerospace engineer and mathematician at NASA’s Langley Research Center. As one of the “Hidden Figures,” she made significant contributions to the space program, particularly in aerodynamics and engineering. Jackson’s groundbreaking work and advocacy for women and minorities helped shape NASA’s success and advance opportunities for future generations in science and technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
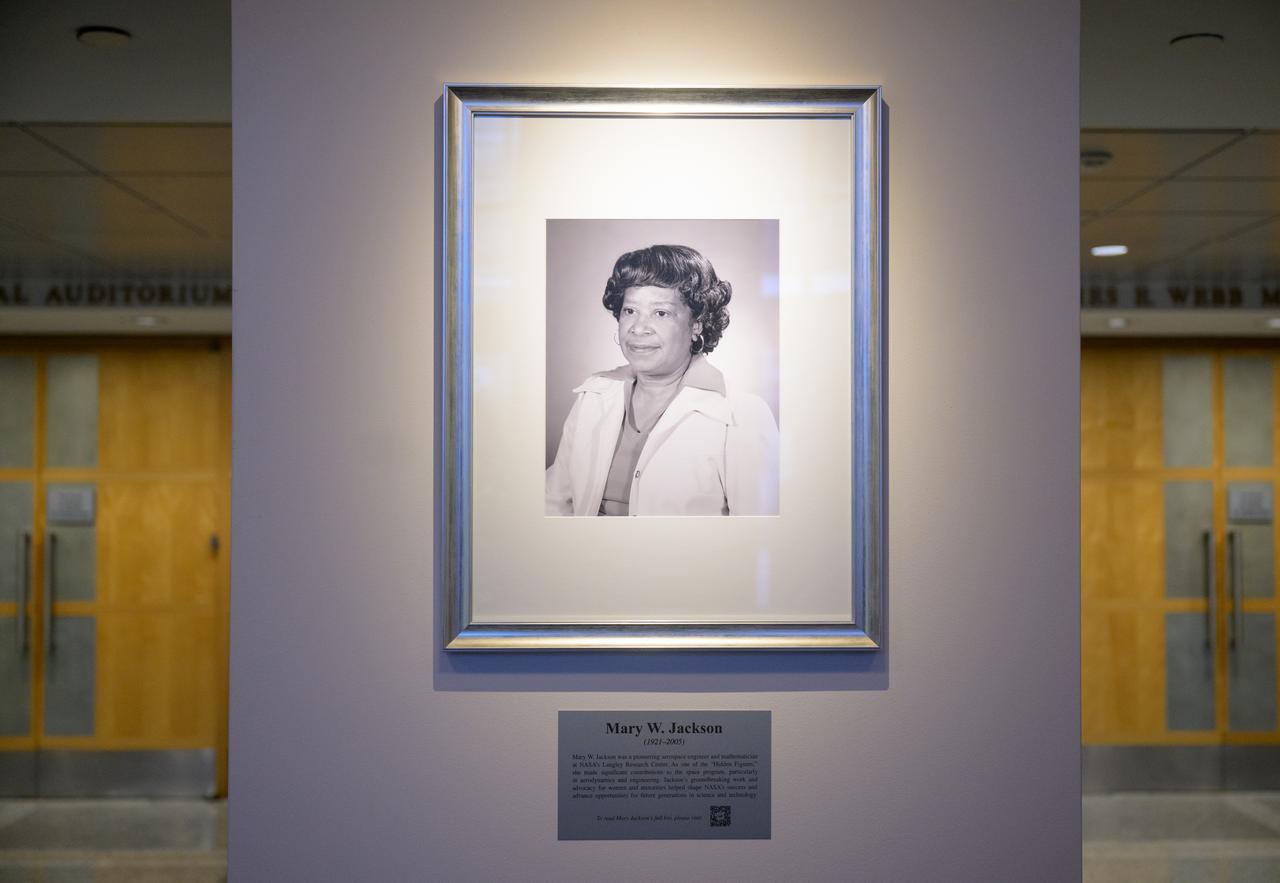

A portrait of Mary W. Jackson is seen after it was unveiled, Friday, Dec. 6, 2024, at the NASA Headquarters Mary W. Jackson Building in Washington. Mary W. Jackson was a pioneering aerospace engineer and mathematician at NASA’s Langley Research Center. As one of the “Hidden Figures,” she made significant contributions to the space program, particularly in aerodynamics and engineering. Jackson’s groundbreaking work and advocacy for women and minorities helped shape NASA’s success and advance opportunities for future generations in science and technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
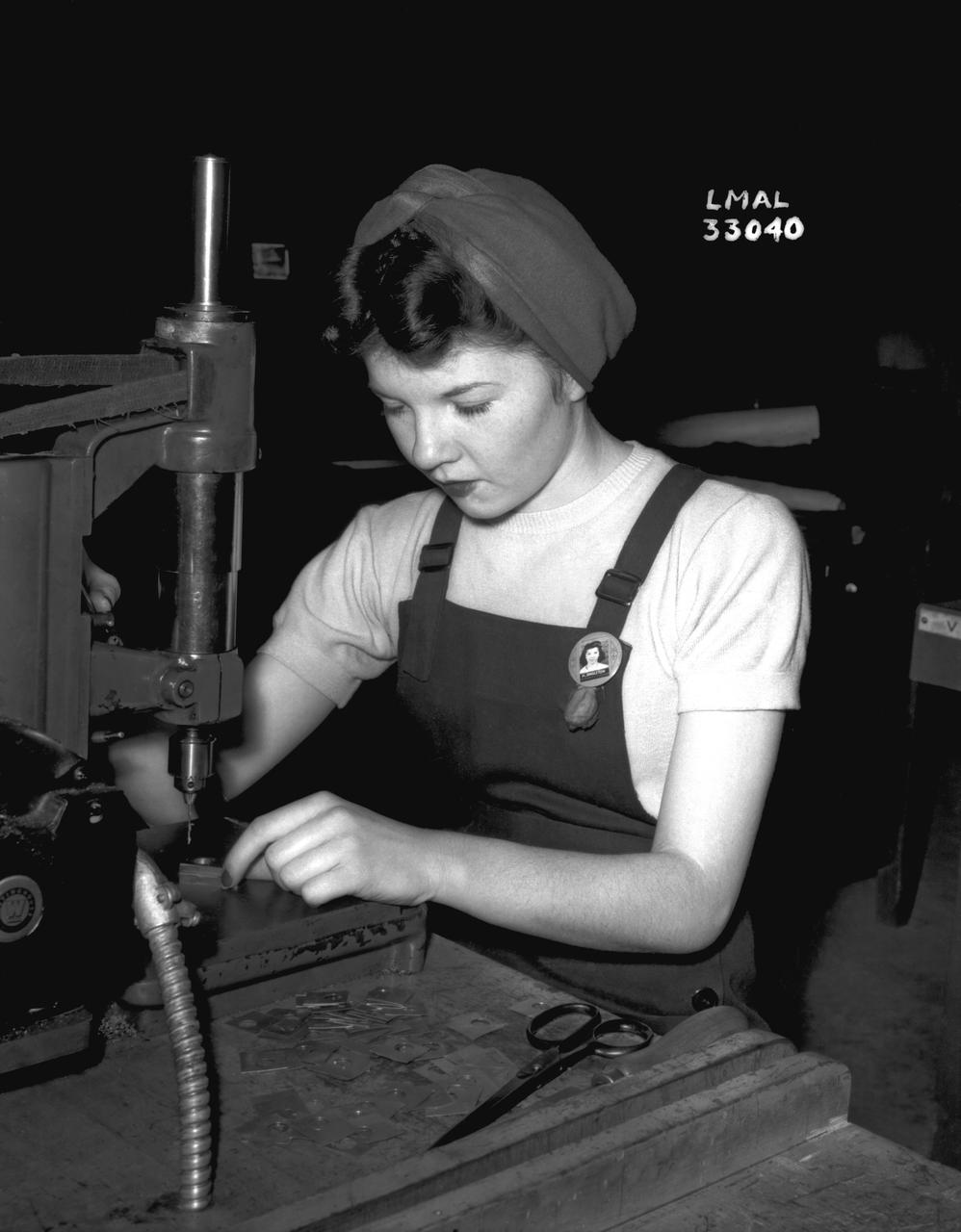

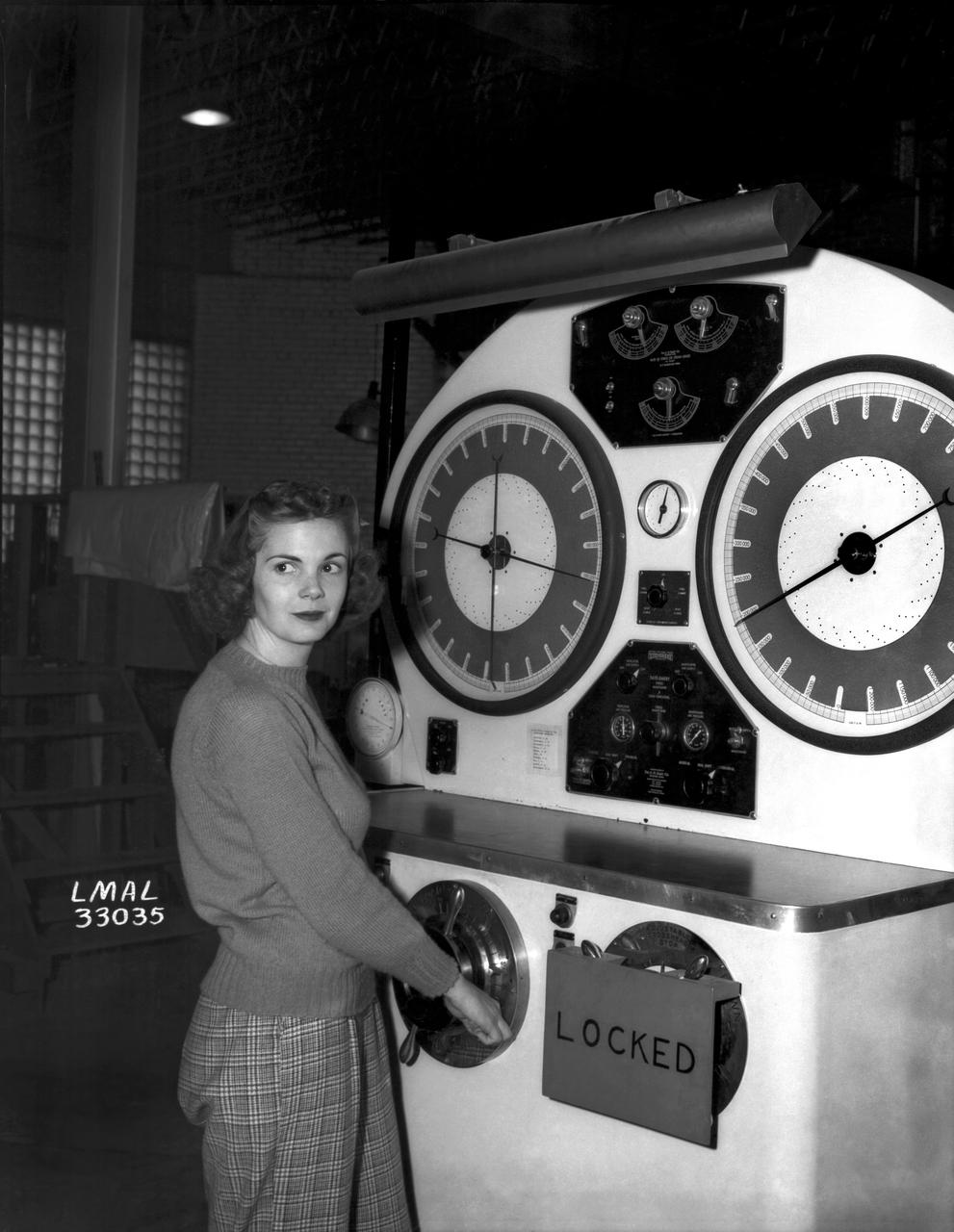
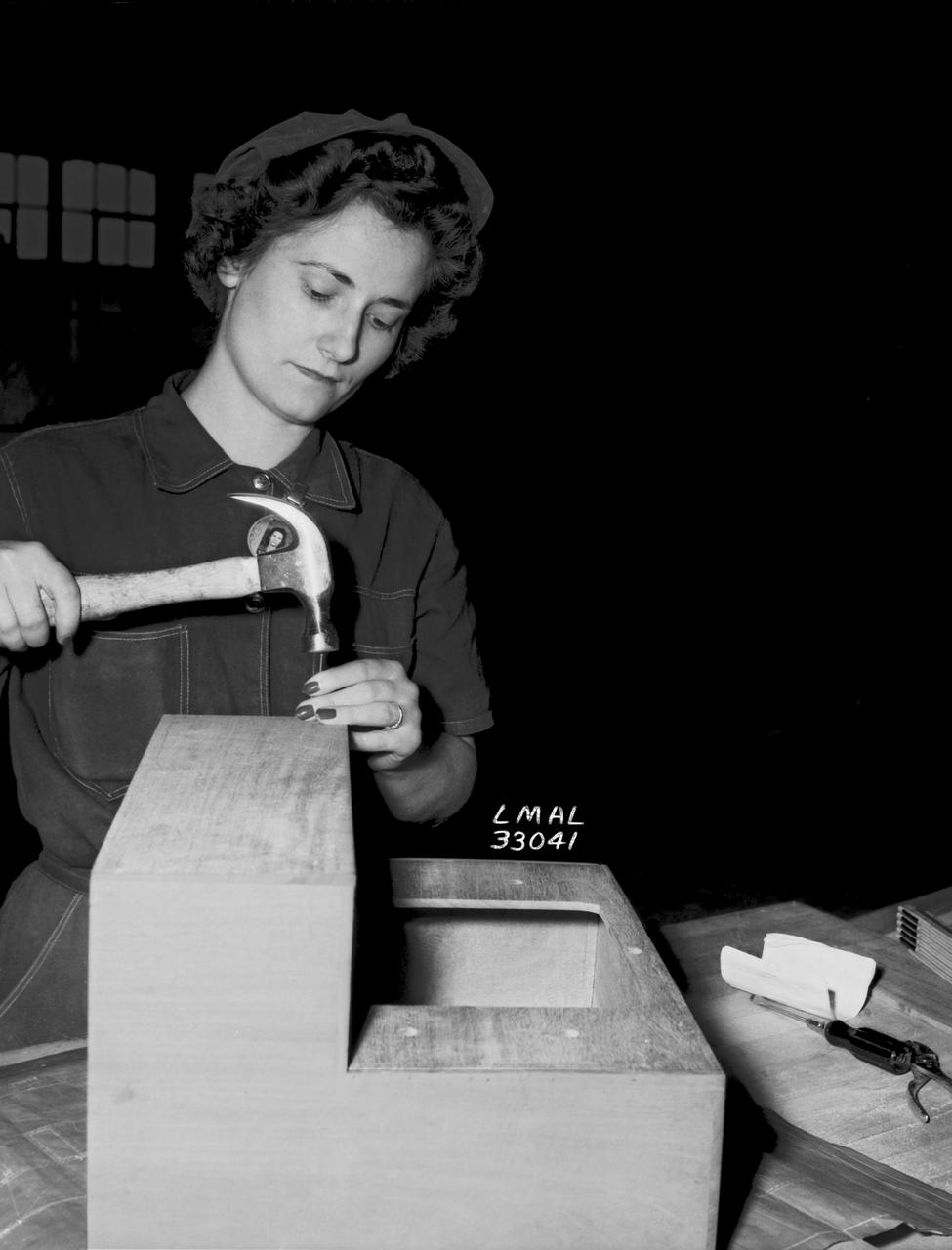
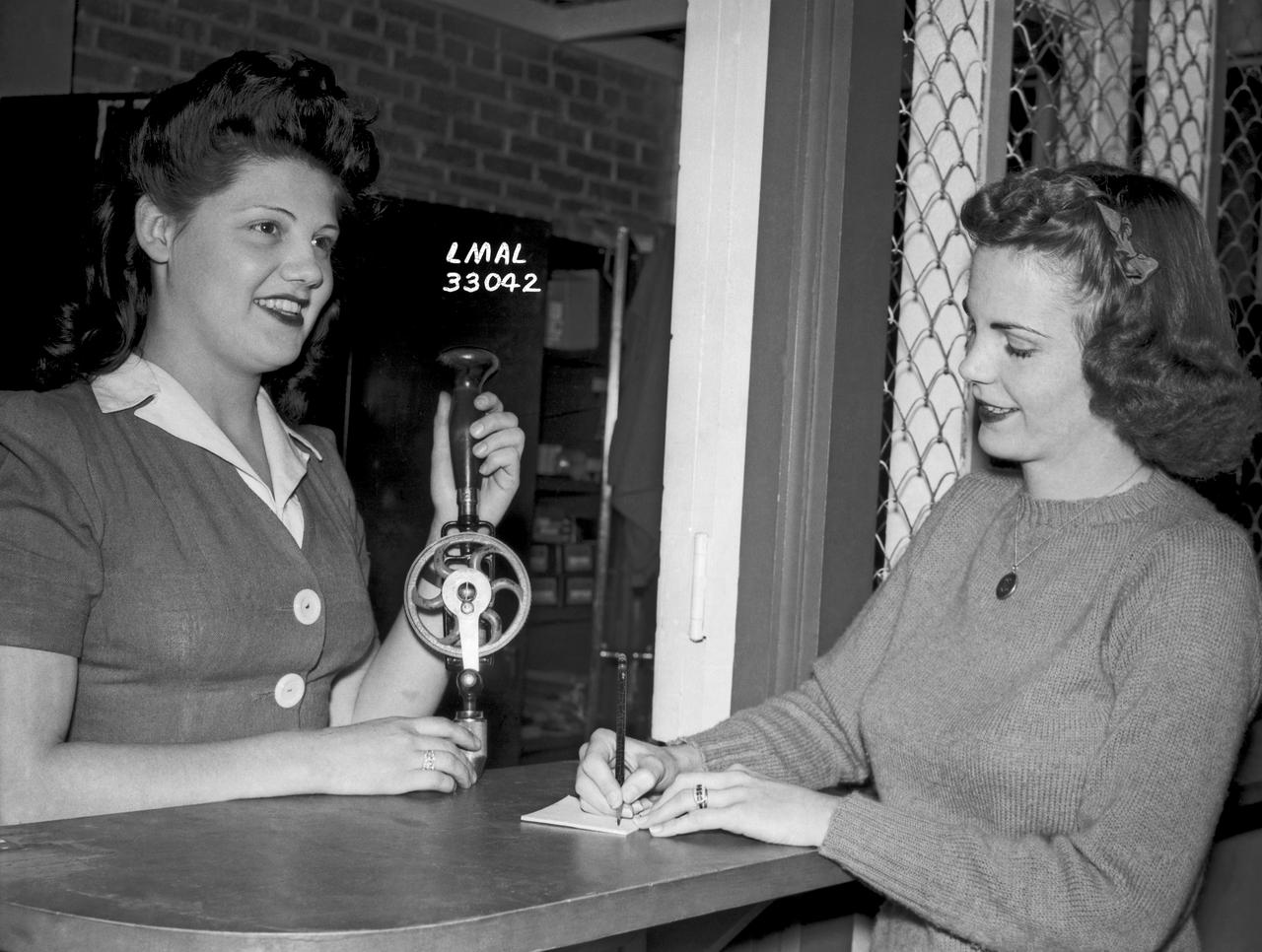
Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
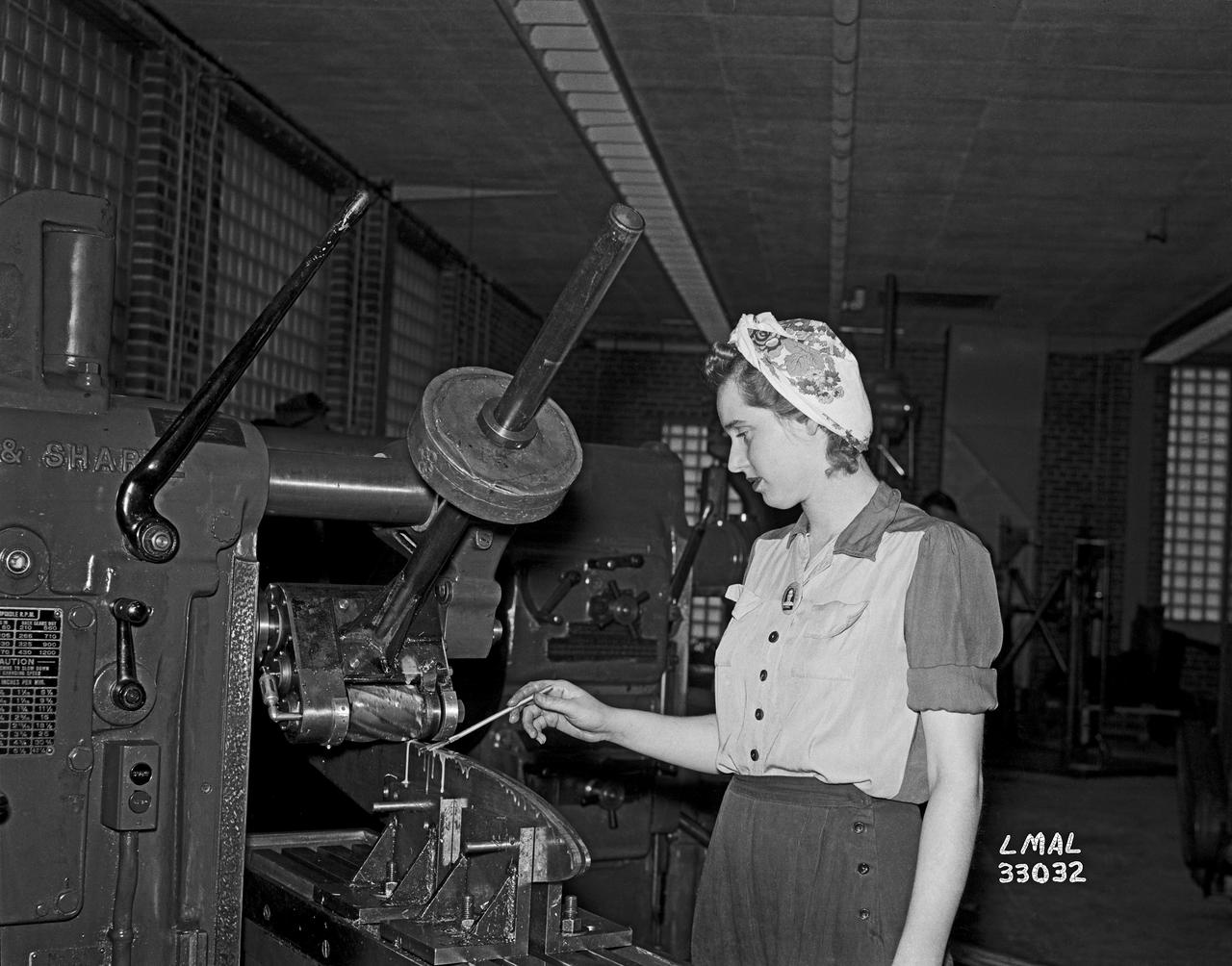

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
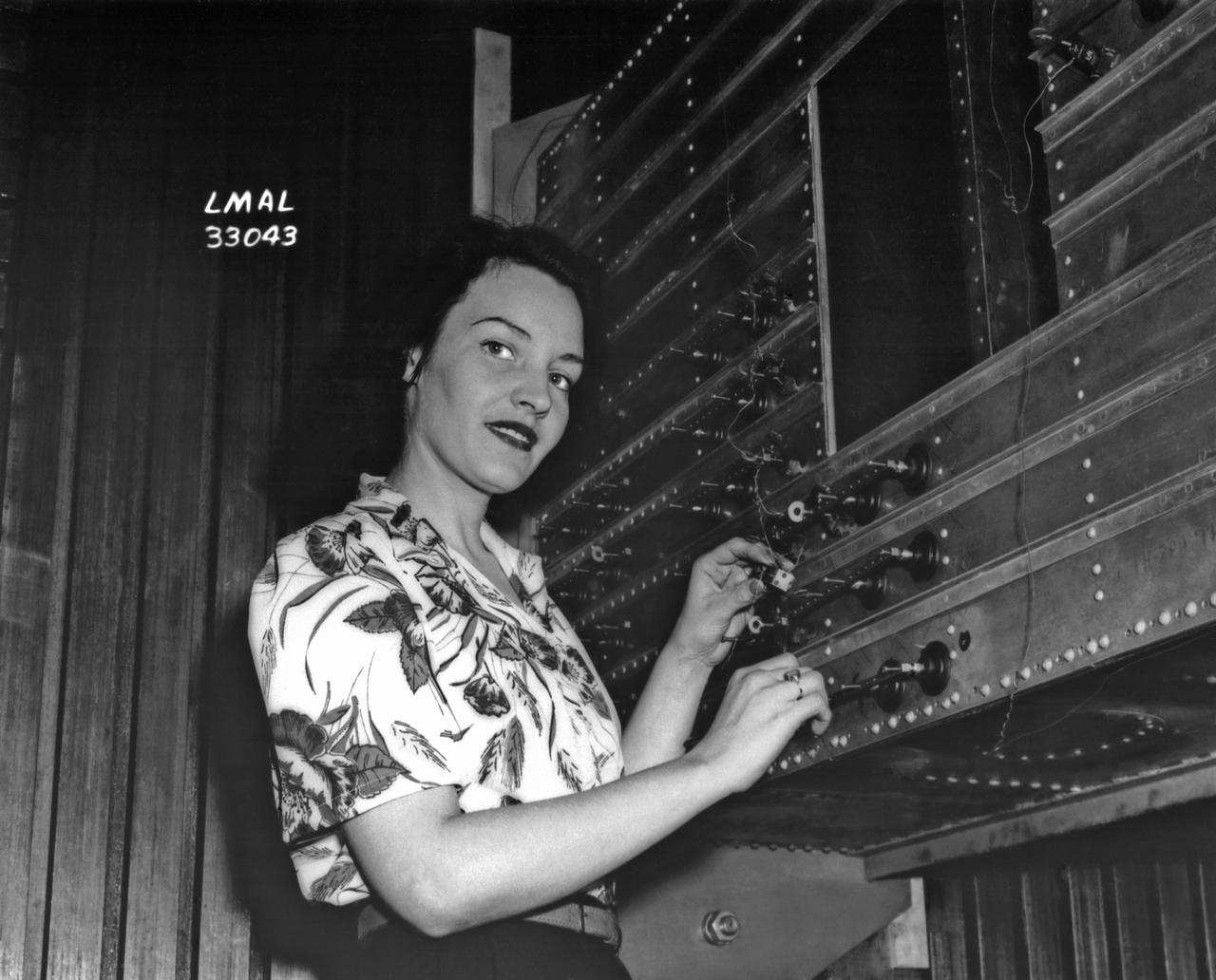

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
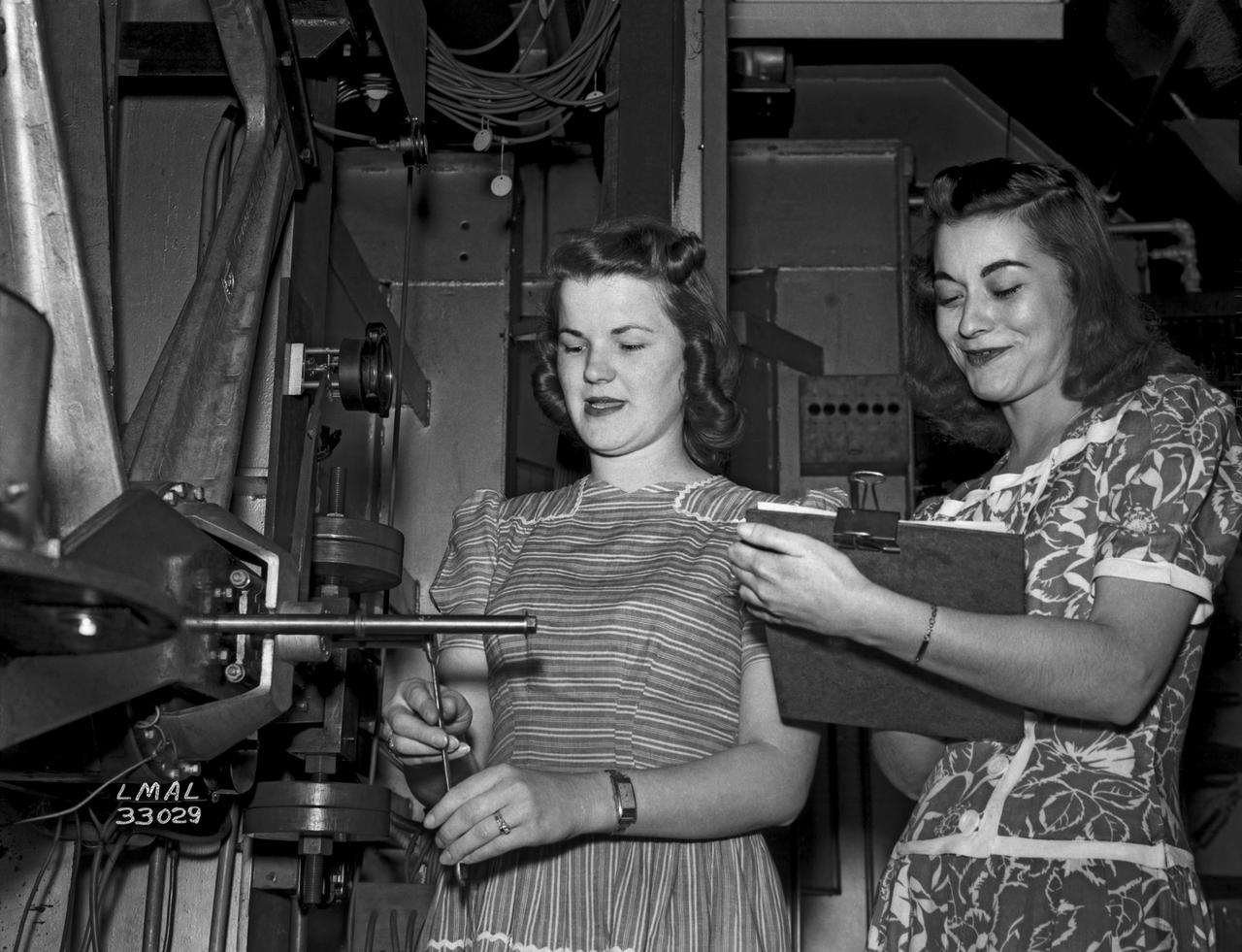

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
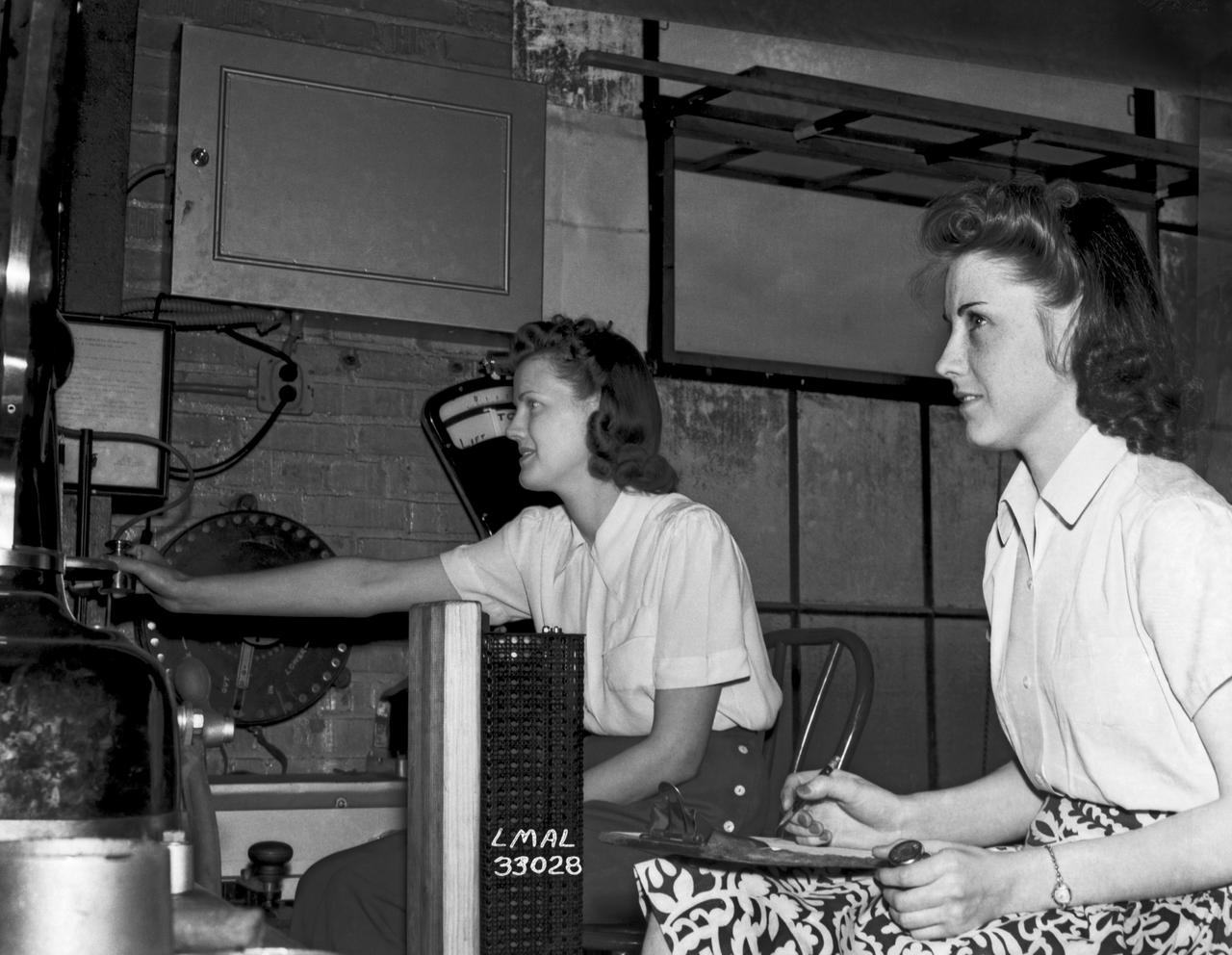

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
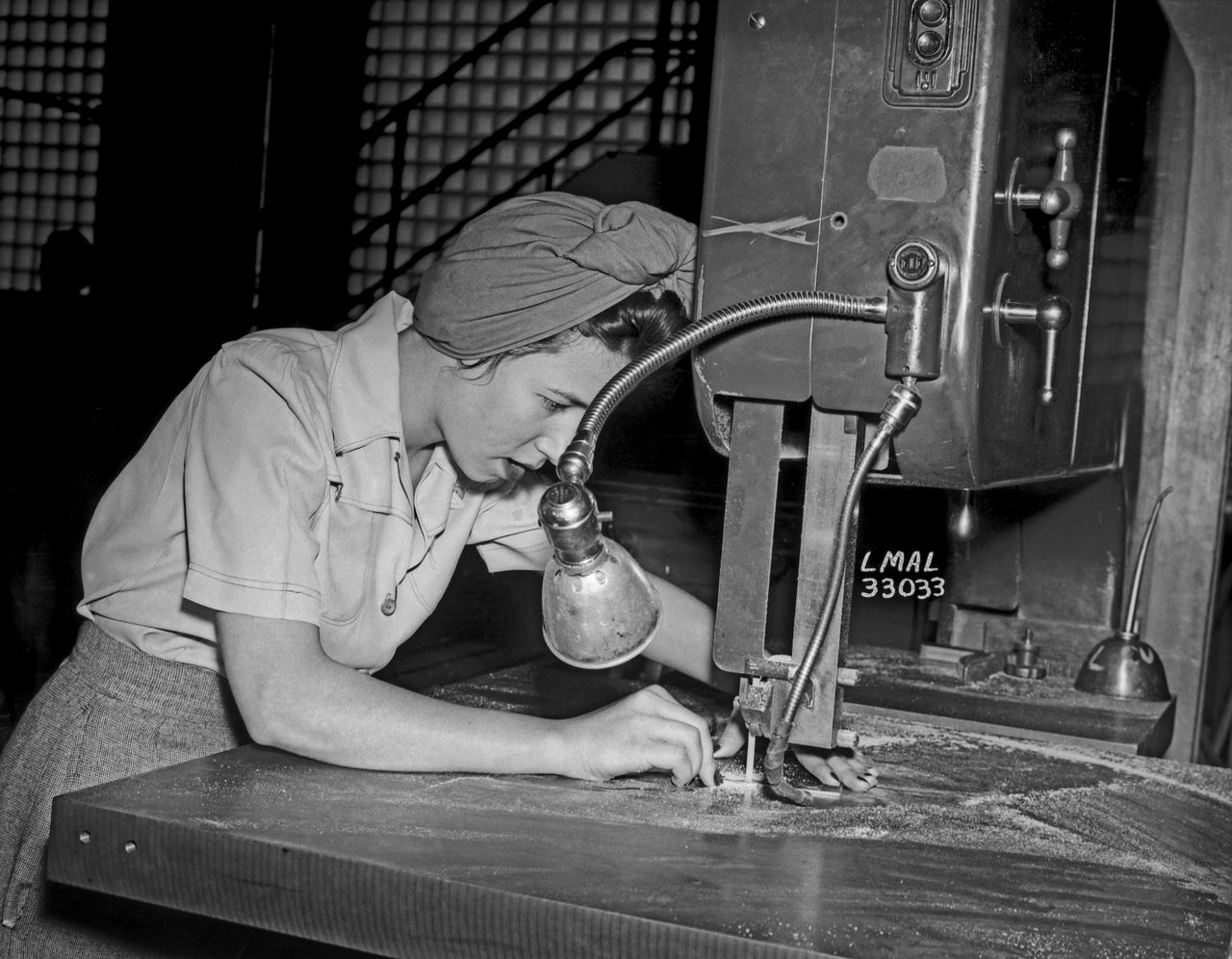

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
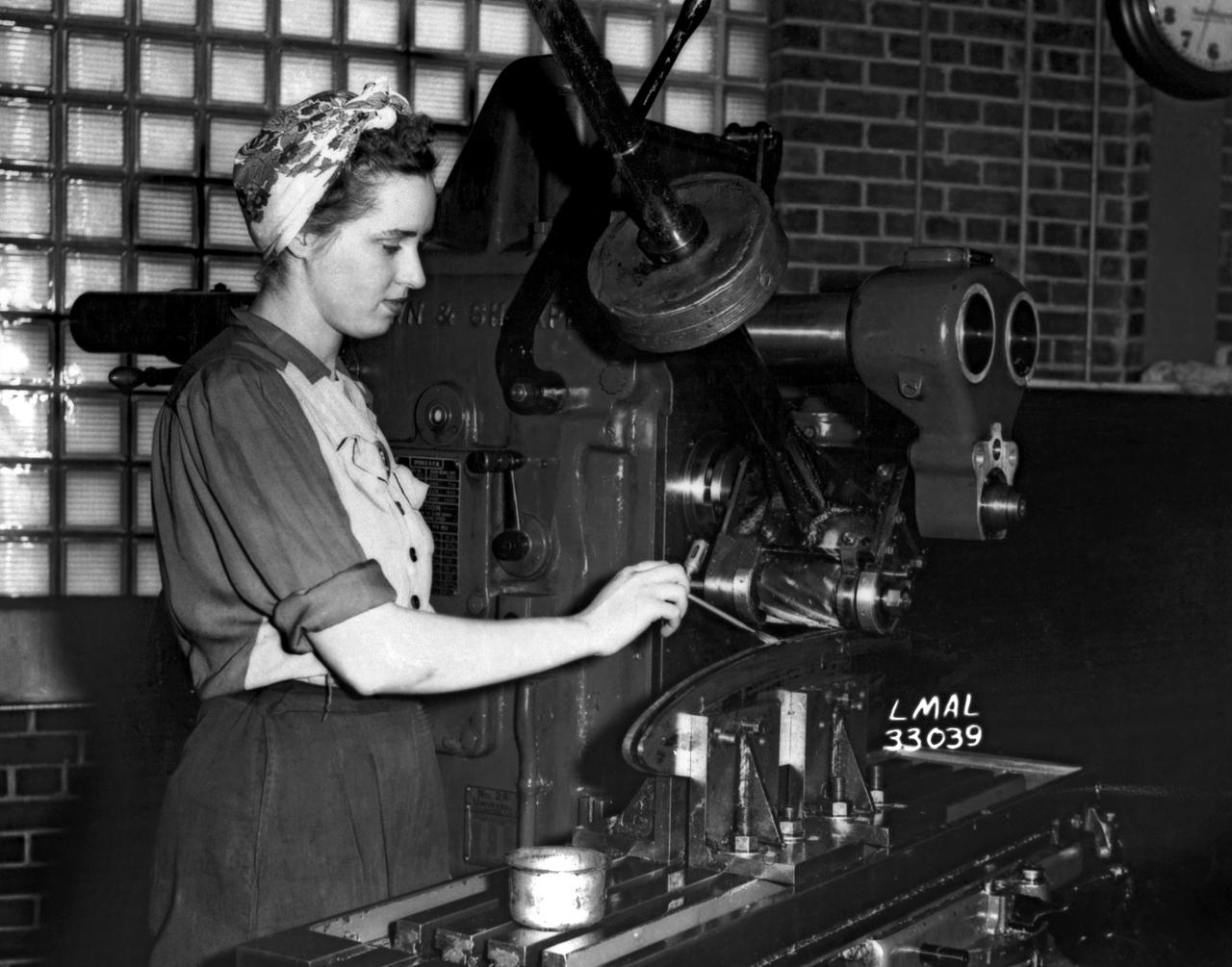

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
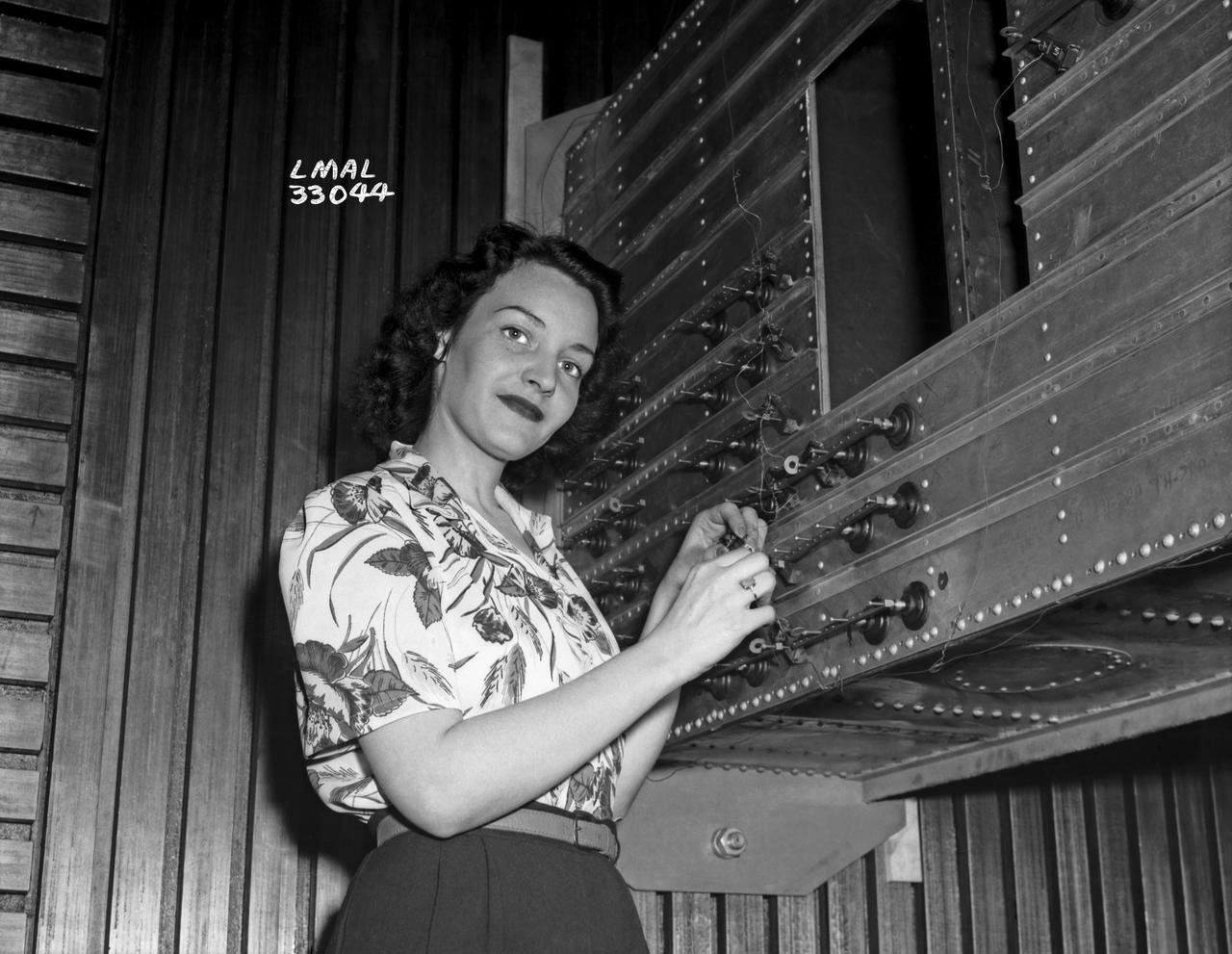

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
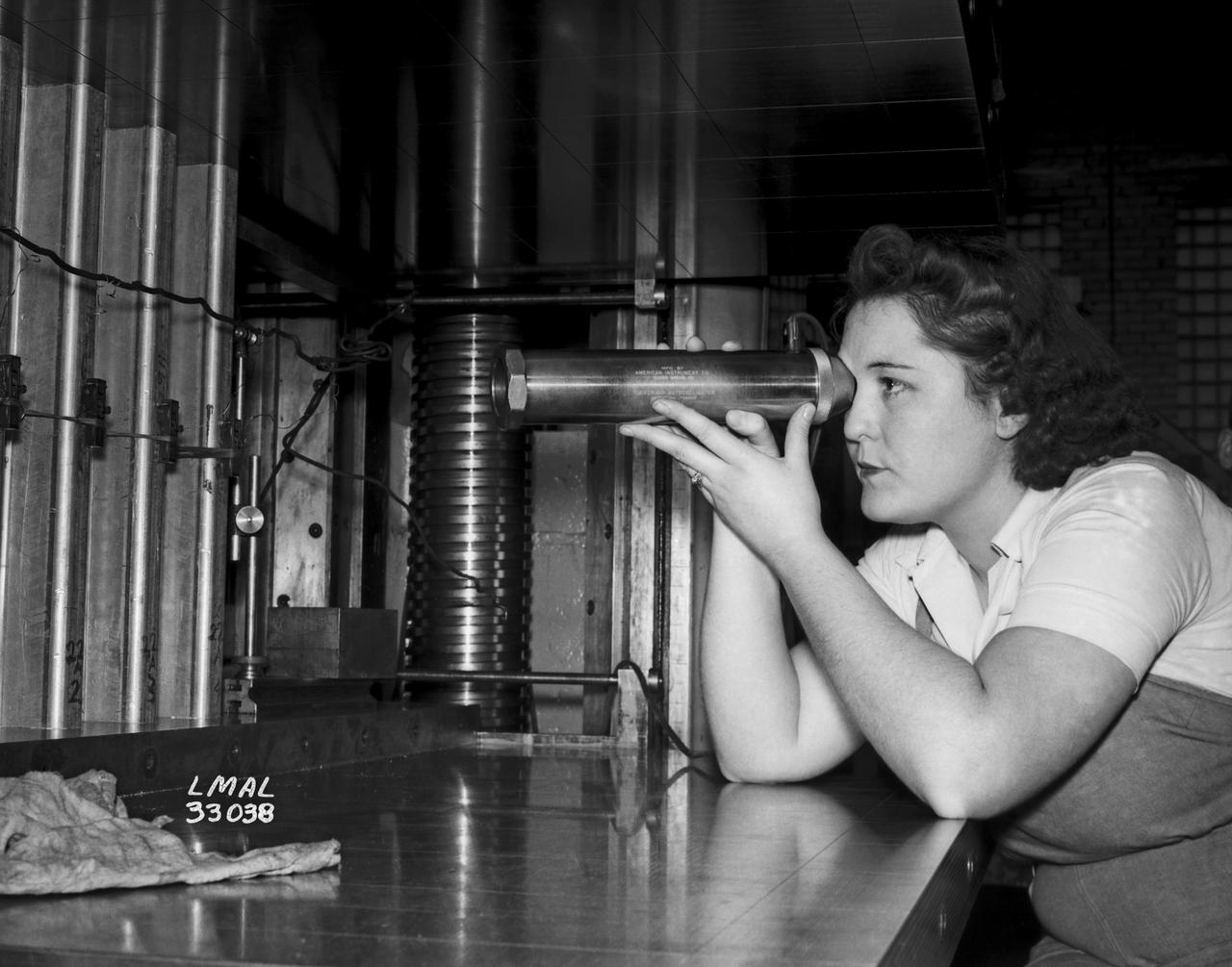

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
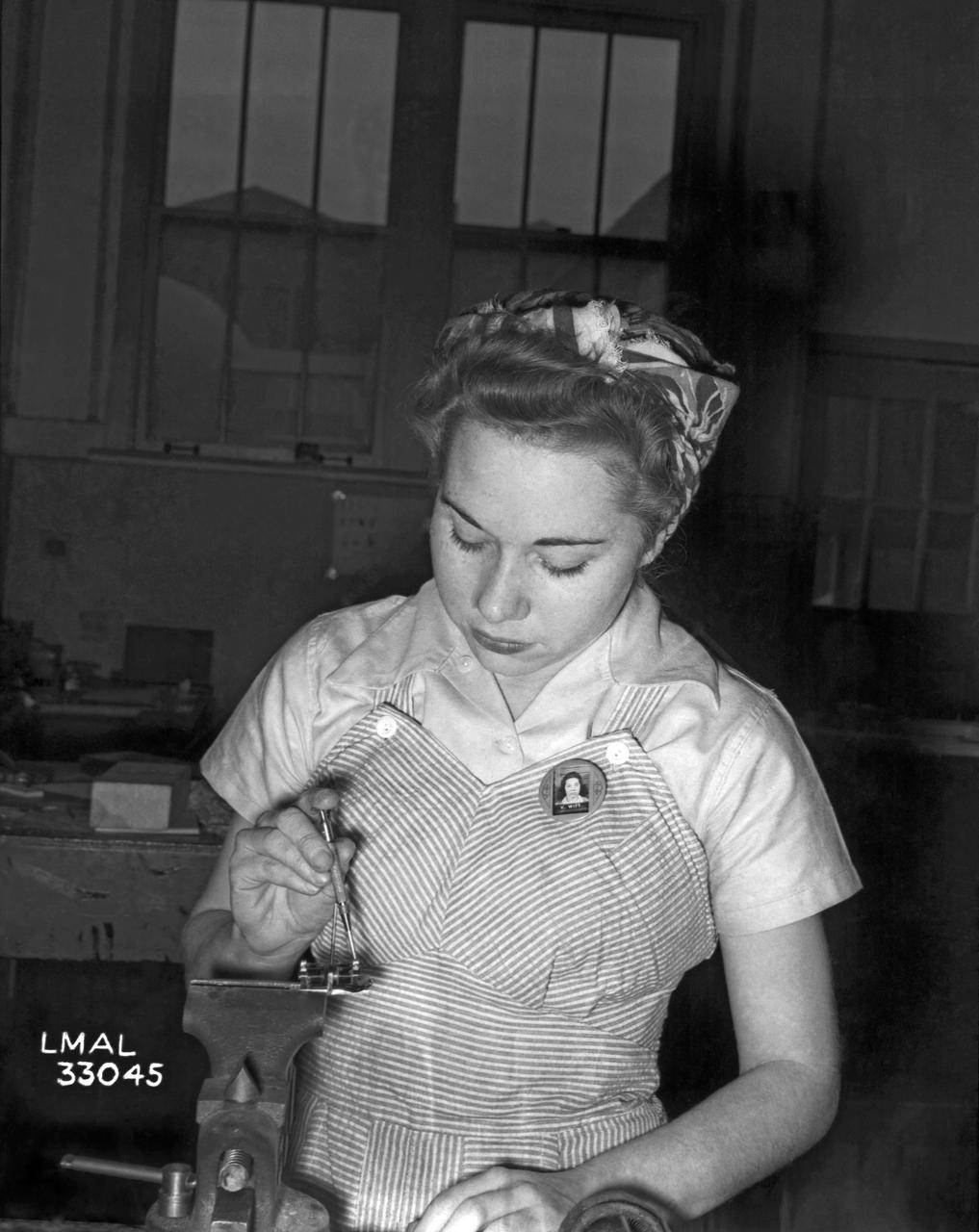

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
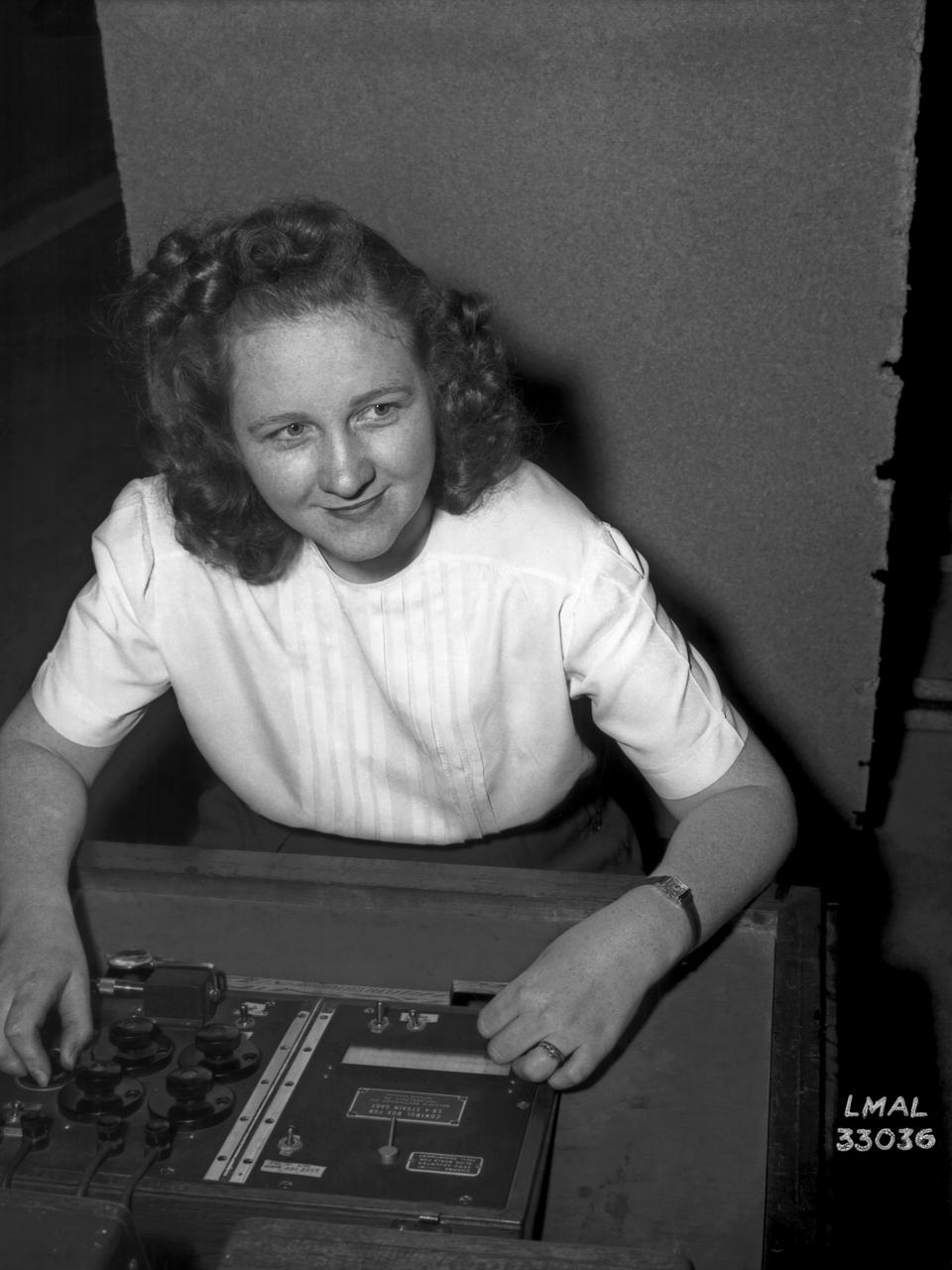

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
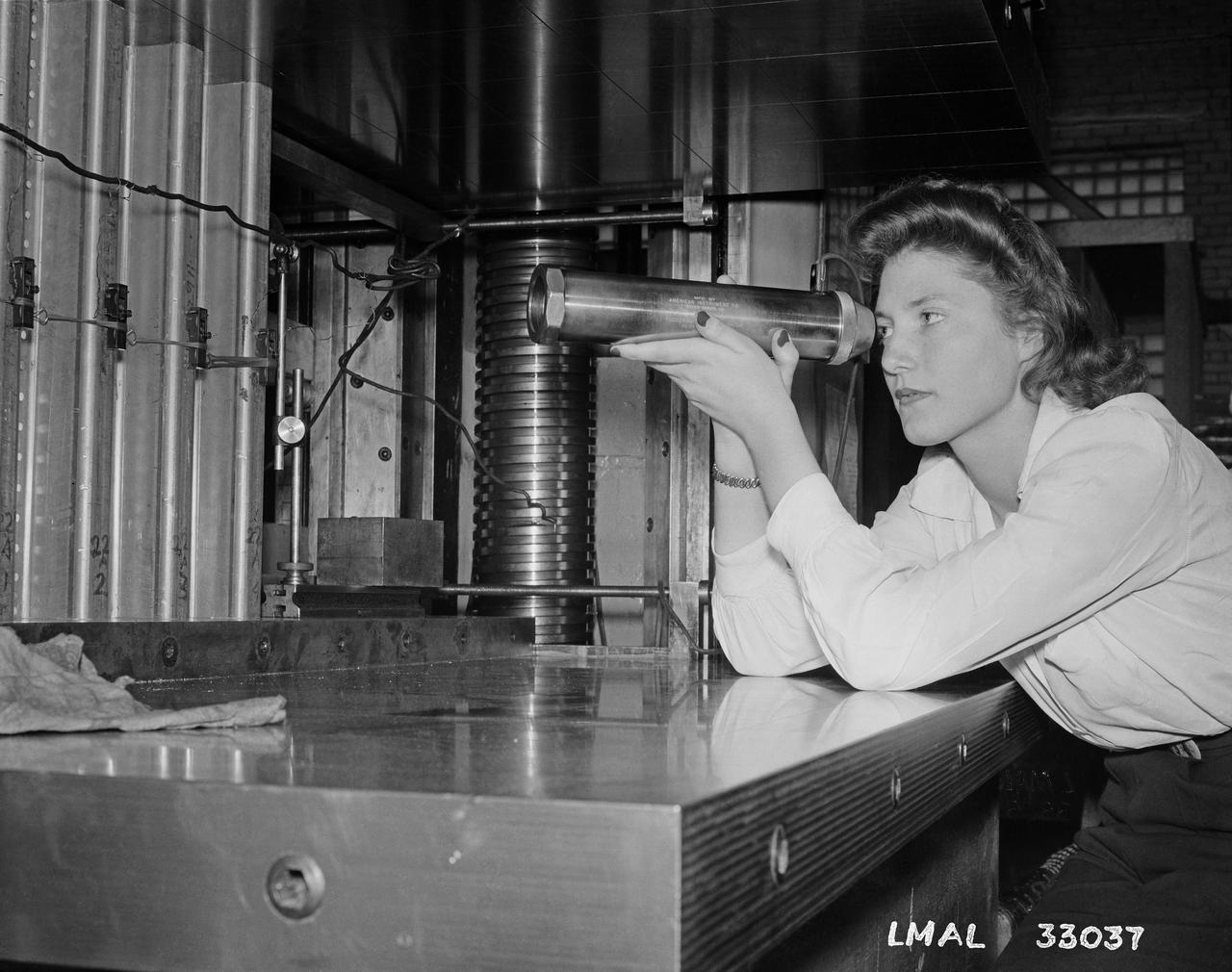

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
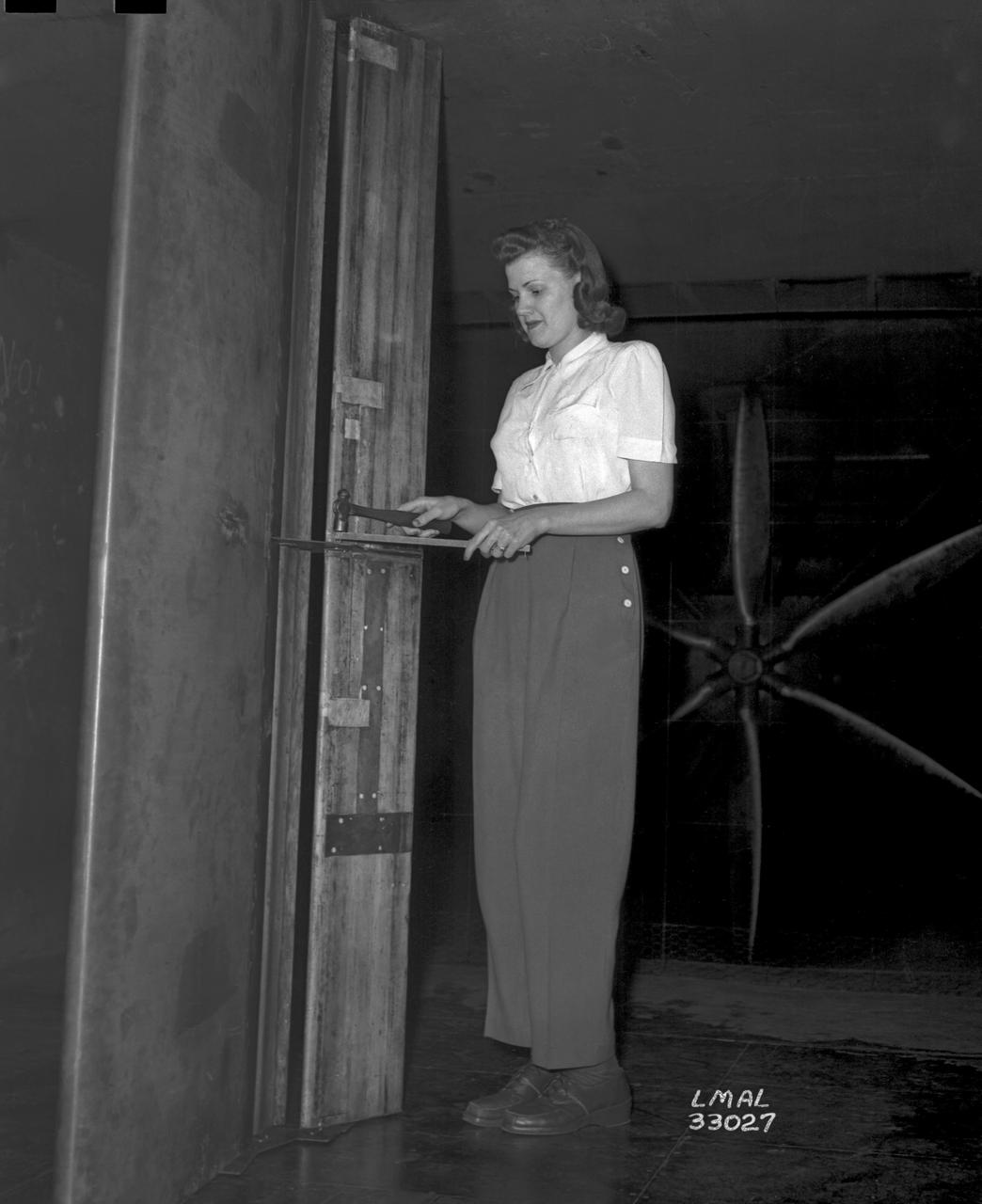

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
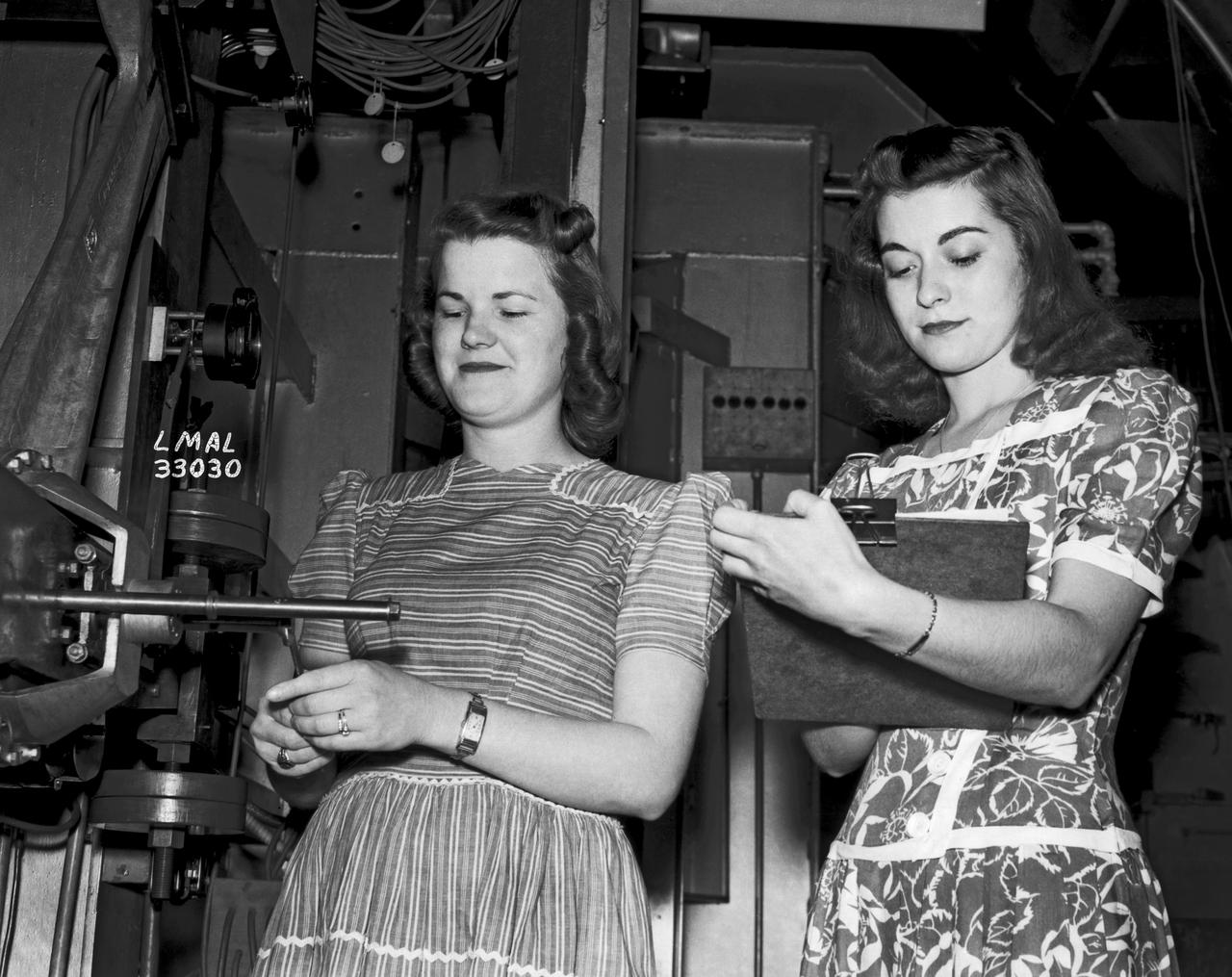

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
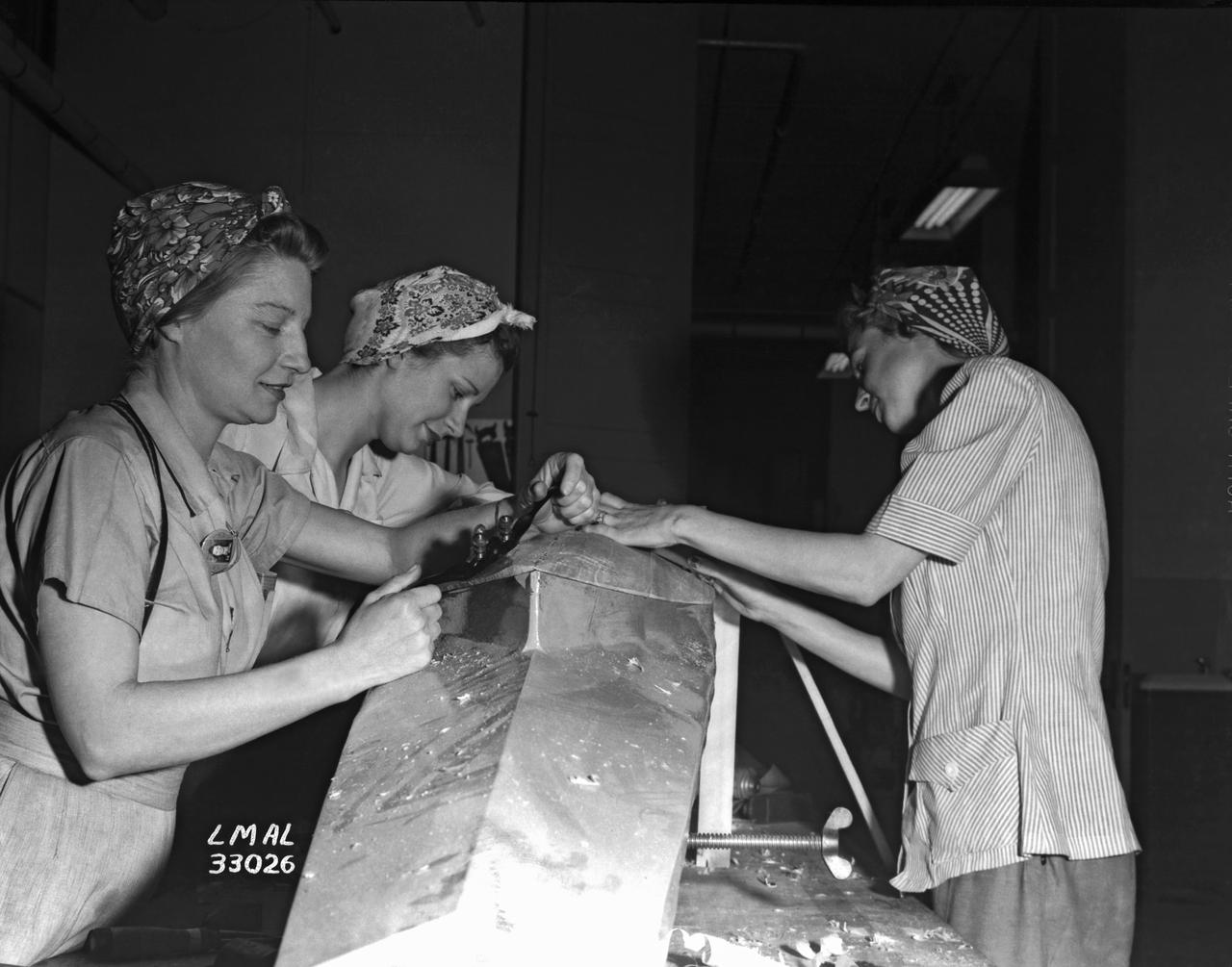

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During a Minority Student Education Forum, former NASA Associate Administrator for Aeronautics Dr. Wesley Harris talks to hundreds of fifth- through 12th-grade students. The forum focused on encouraging students to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, by featuring some of NASA's greatest legends and trailblazers. NASA's Education Office sponsored the forum as part of the agency's 'Summer of Innovation' initiative and the federal 'Education to Innovate' campaign. Photo credit: NASA_Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During a Minority Student Education Forum, NASA's Associate Deputy Administrator Charles Scales talks to hundreds of fifth- through 12th-grade students. The forum focused on encouraging students to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, by featuring some of NASA's greatest legends and trailblazers. NASA's Education Office sponsored the forum as part of the agency's 'Summer of Innovation' initiative and the federal 'Education to Innovate' campaign. Photo credit: NASA_Cory Huston
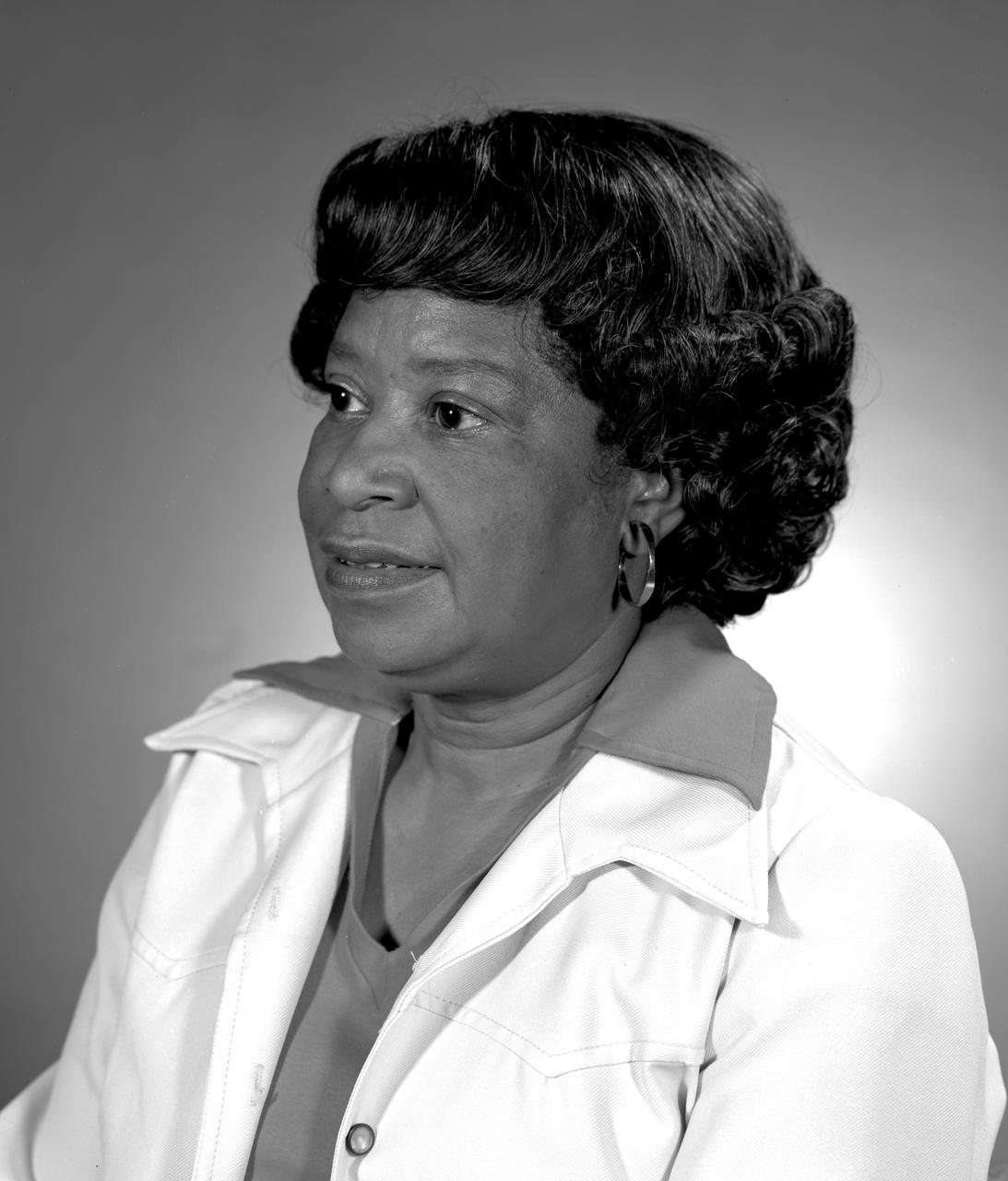

Portrait of Mary Jackson. 2017 Hall of Honor inductee. Langley Research Center NACA and NASA Hall of Honor. In honor and recognition of the ambition and motivation that enabled her career progression from human computer to NASA' s first African-American female engineer, and subsequent career supporting the hiring and promotion of other deserving female and minority employees.
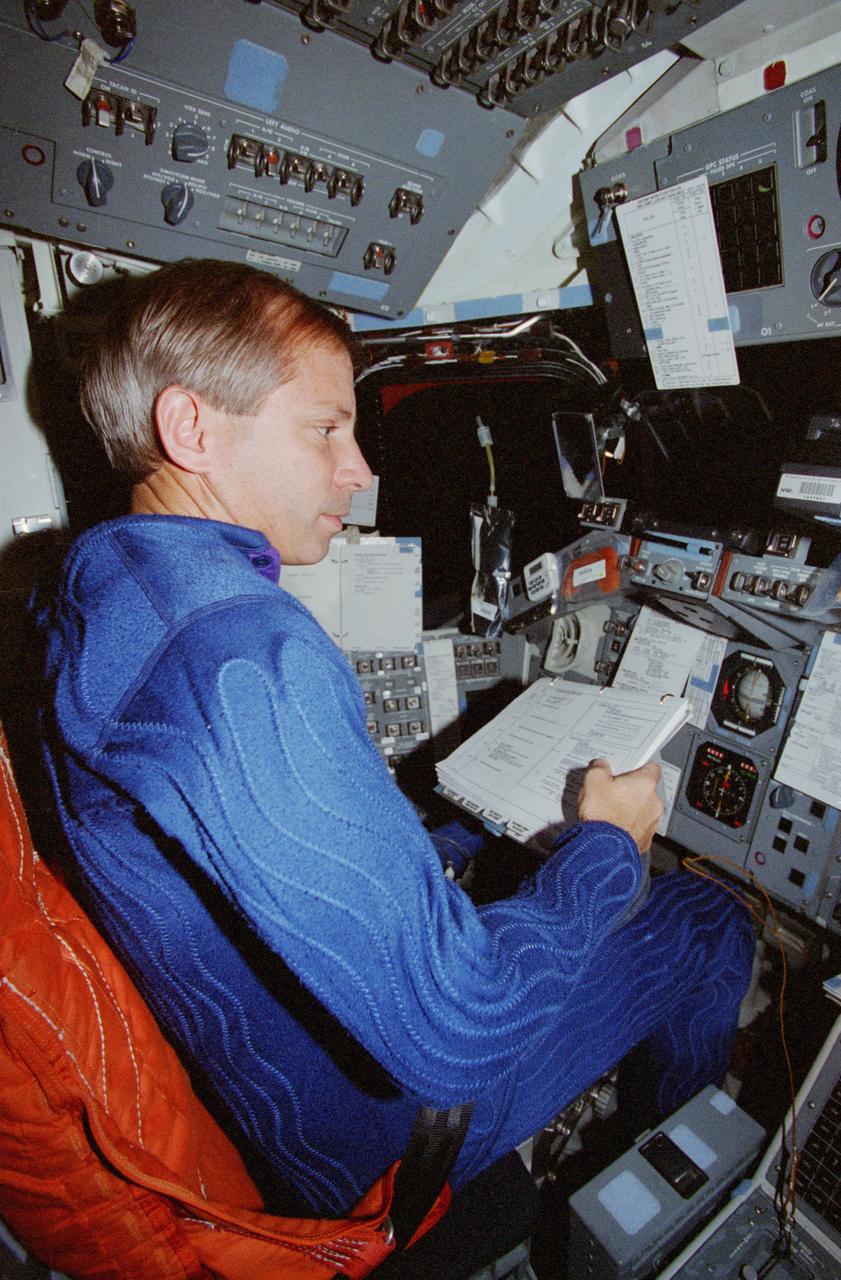

STS080-360-002 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- From the commander's station on the port side of the space shuttle Columbia's forward flight deck, astronaut Kenneth D. Cockrell prepares for a minor firing of Reaction Control System (RCS) engines during operations with the Wake Shield Facility (WSF). The activity was recorded with a 35mm camera on flight day seven. The commander is attired in a liquid-cooled biological garment.

Representatives of the state of Alabama, academia, and industry listen and take part in a panel discussion led by NASA Marshall Space Flight Center's Ruth Jones as part of the first Alabama Historically Black Colleges and Universities Roundtable Discussion. The event focused on drawing more minorities, specifically women, into academic fields and careers in science, technology, engineering and mathematics.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During a Minority Student Education Forum, fifth- through 12th-grade students perform a hands-on activity. The forum focused on encouraging students to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, by featuring some of NASA's greatest legends and trailblazers. NASA's Education Office sponsored the forum as part of the agency's 'Summer of Innovation' initiative and the federal 'Education to Innovate' campaign. Photo credit: NASA_Cory Huston
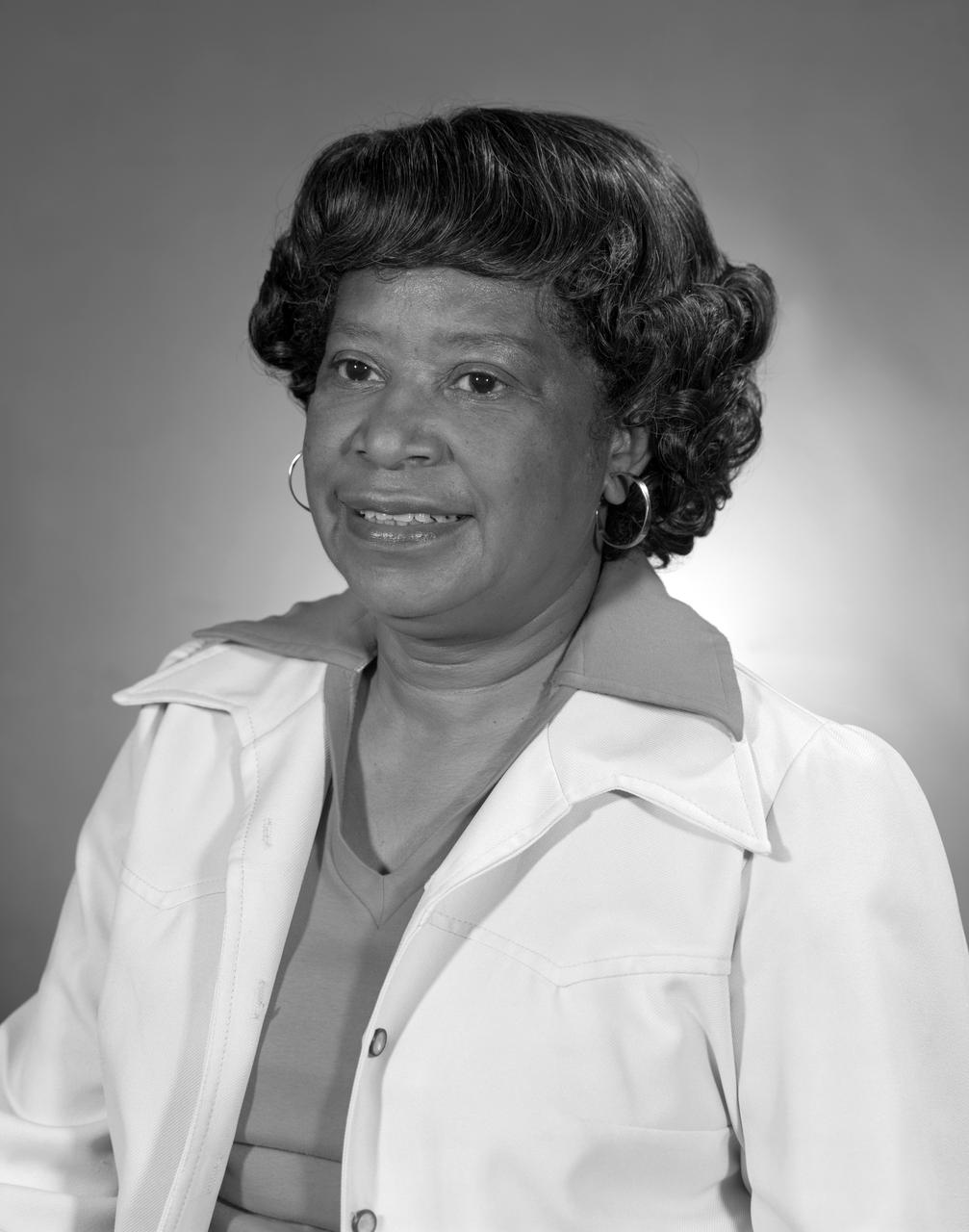

Portrait of Mary Jackson. 2017 Hall of Honor inductee. Langley Research Center NACA and NASA Hall of Honor. In honor and recognition of the ambition and motivation that enabled her career progression from human computer to NASA' s first African-American female engineer, and subsequent career supporting the hiring and promotion of other deserving female and minority employees.
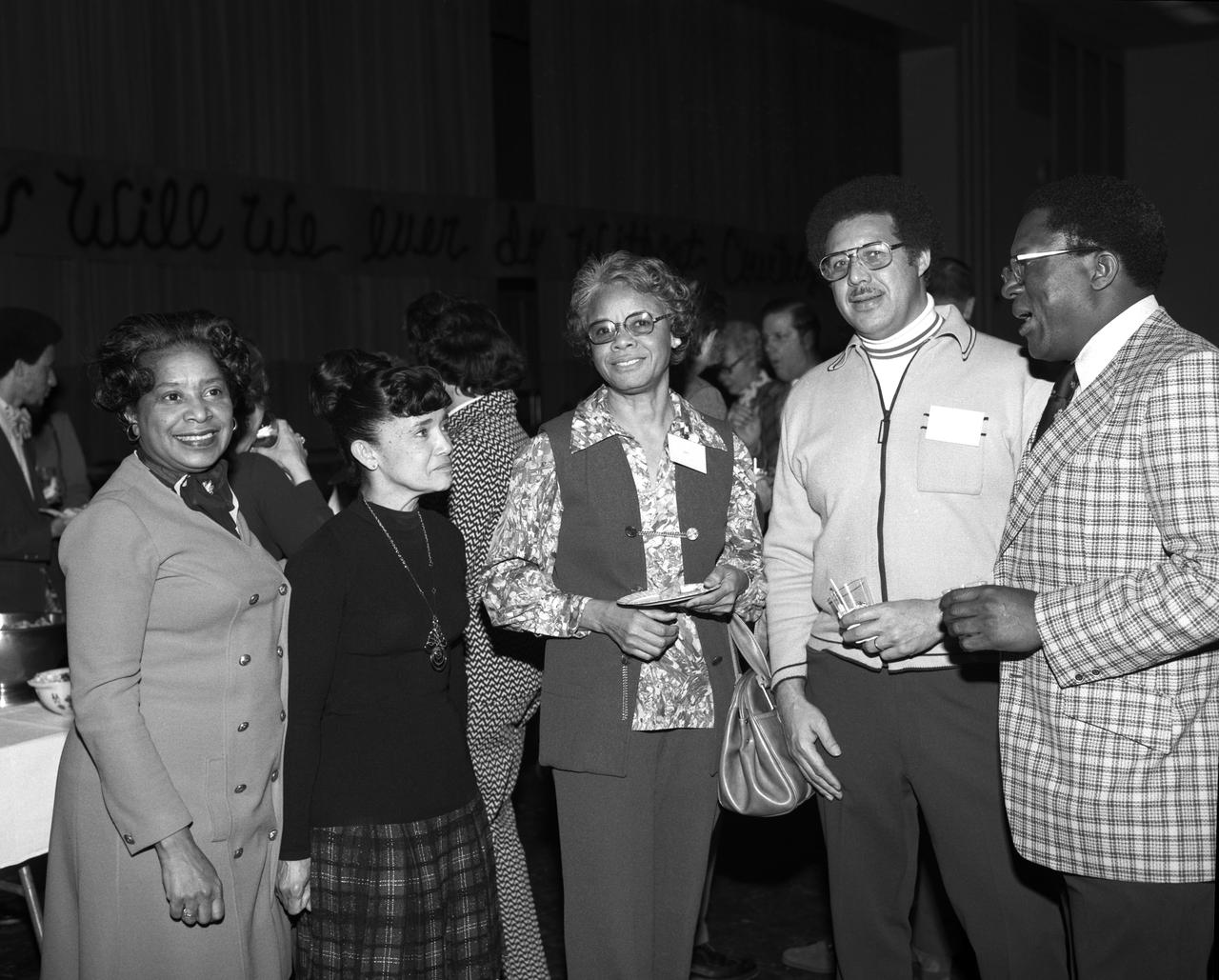

Photograph taken on February 5, 1975. Guests attending a retirement party for Vernon Courtney, of the MSD Communications Section. Mary Jackson standing on left with human computer Christine B. Richie next to her, another from the west computers group mentioned in the book "Hidden Figures" by author Margot Lee Shetterly. Mary Jackson from NASA Langley was NASA' s first African-American female engineer, and subsequent career supporting the hiring and promotion of other deserving female and minority employees.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During a Minority Student Education Forum, Kennedy Space Center's Associate Director Kelvin Manning talks to hundreds of fifth- through 12th-grade students. The forum focused on encouraging students to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, by featuring some of NASA's greatest legends and trailblazers. NASA's Education Office sponsored the forum as part of the agency's 'Summer of Innovation' initiative and the federal 'Education to Innovate' campaign. Photo credit: NASA_Cory Huston

J. Keith Motley, Chancellor, University of Massachusetts Boston, and Chair, APLU (Association of Public and Land-grant Universities) Commission on Access, Diversity and Excellence, speaks at the Symposium on Supporting Underrepresented Minority Males in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), Tuesday, February 28, 2012 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
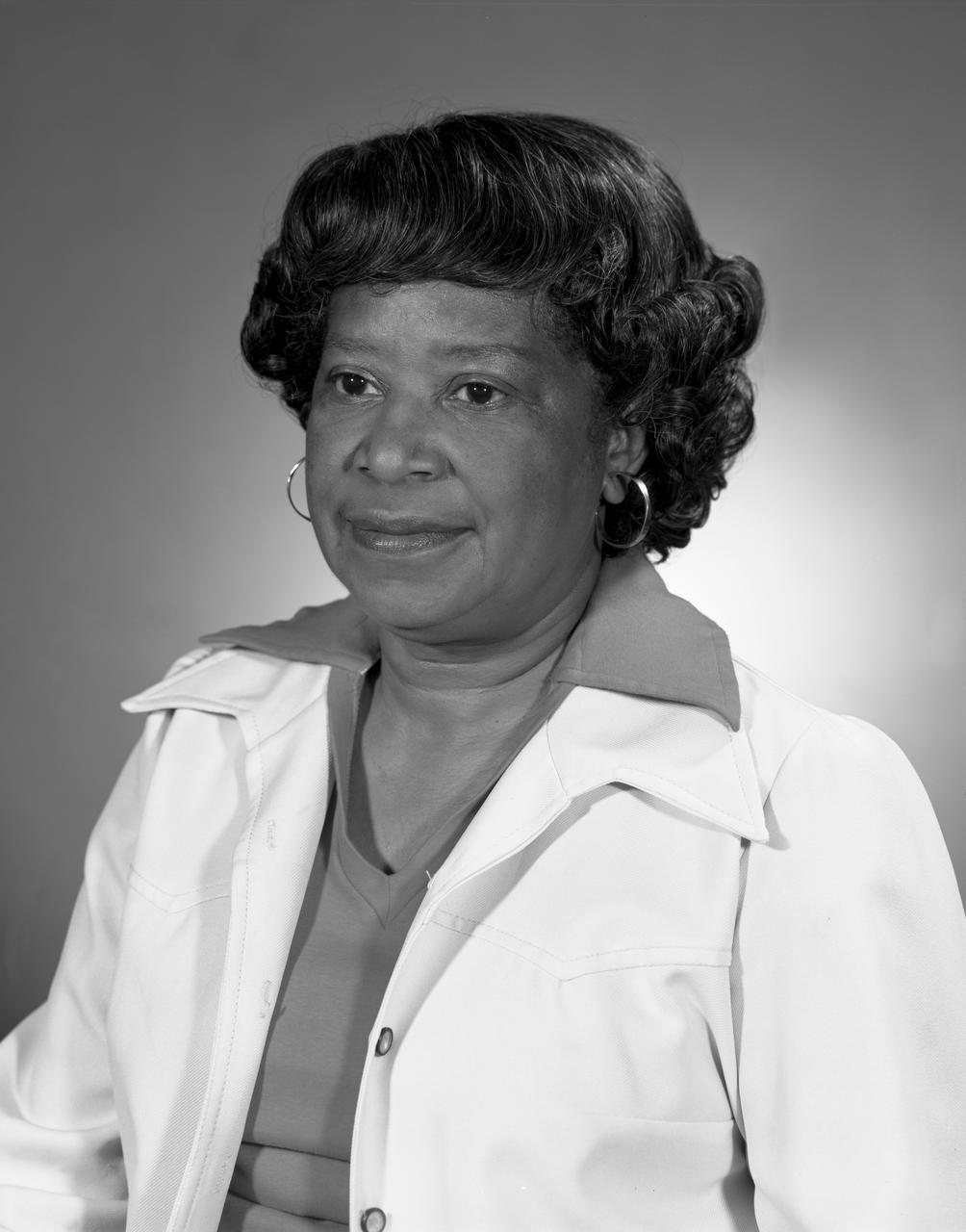

Portrait of Mary Jackson. 2017 Hall of Honor inductee. Langley Research Center NACA and NASA Hall of Honor. In honor and recognition of the ambition and motivation that enabled her career progression from human computer to NASA' s first African-American female engineer, and subsequent career supporting the hiring and promotion of other deserving female and minority employees.

J. Keith Motley, Chancellor, University of Massachusetts Boston, and Chair, APLU (Association of Public and Land-grant Universities) Commission on Access, Diversity and Excellence, speaks at the Symposium on Supporting Underrepresented Minority Males in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), Tuesday, February 28, 2012 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During a Minority Student Education Forum, Glenn Research Center's Associate Director Vernon Wessell talks to hundreds of fifth- through 12th-grade students. The forum focused on encouraging students to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, by featuring some of NASA's greatest legends and trailblazers. NASA's Education Office sponsored the forum as part of the agency's 'Summer of Innovation' initiative and the federal 'Education to Innovate' campaign. Photo credit: NASA_Cory Huston
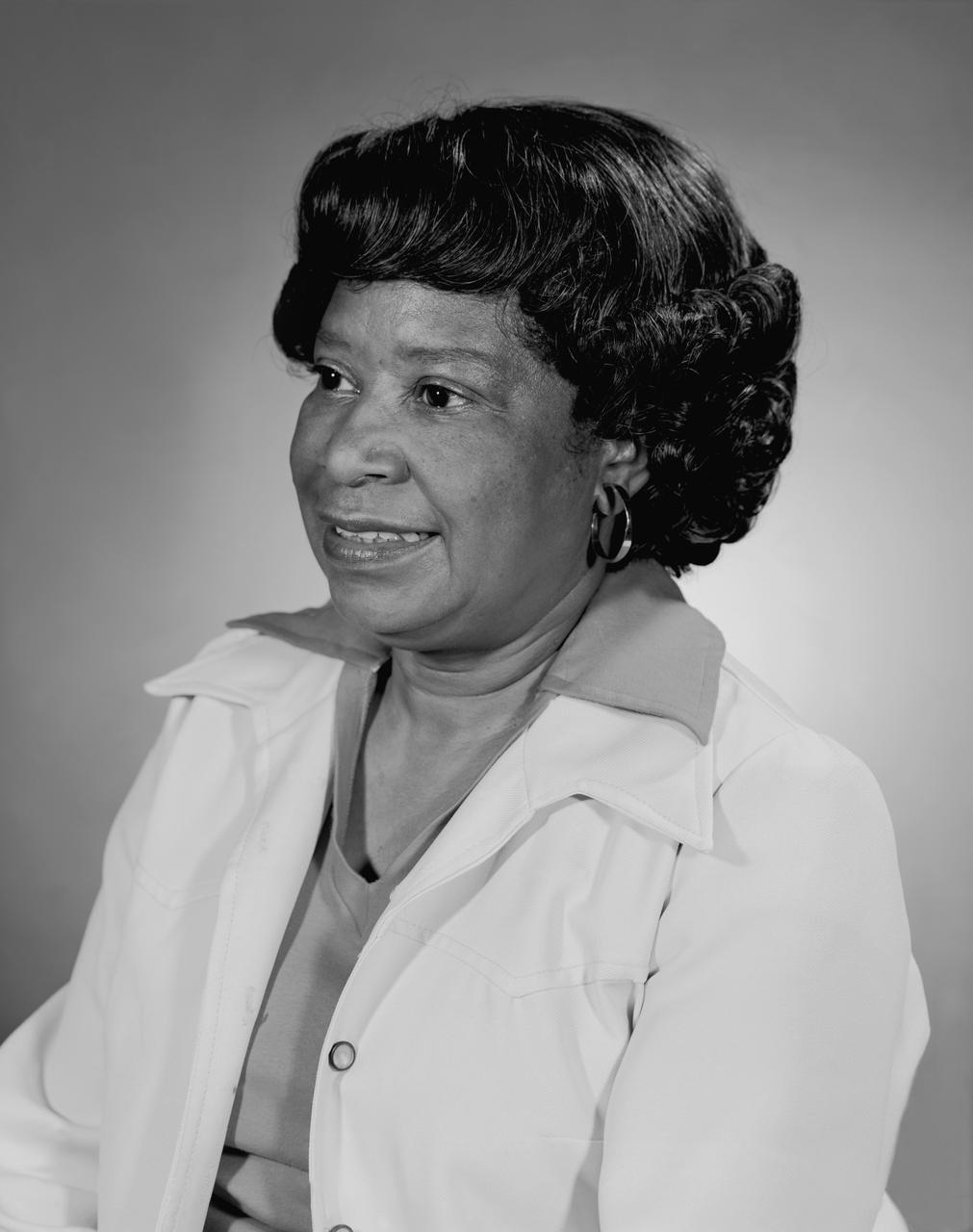

Portrait of Mary Jackson. 2017 Hall of Honor inductee. Langley Research Center NACA and NASA Hall of Honor. In honor and recognition of the ambition and motivation that enabled her career progression from human computer to NASA's s first African-American female engineer, and subsequent career supporting the hiring and promotion of other deserving female and minority employees.
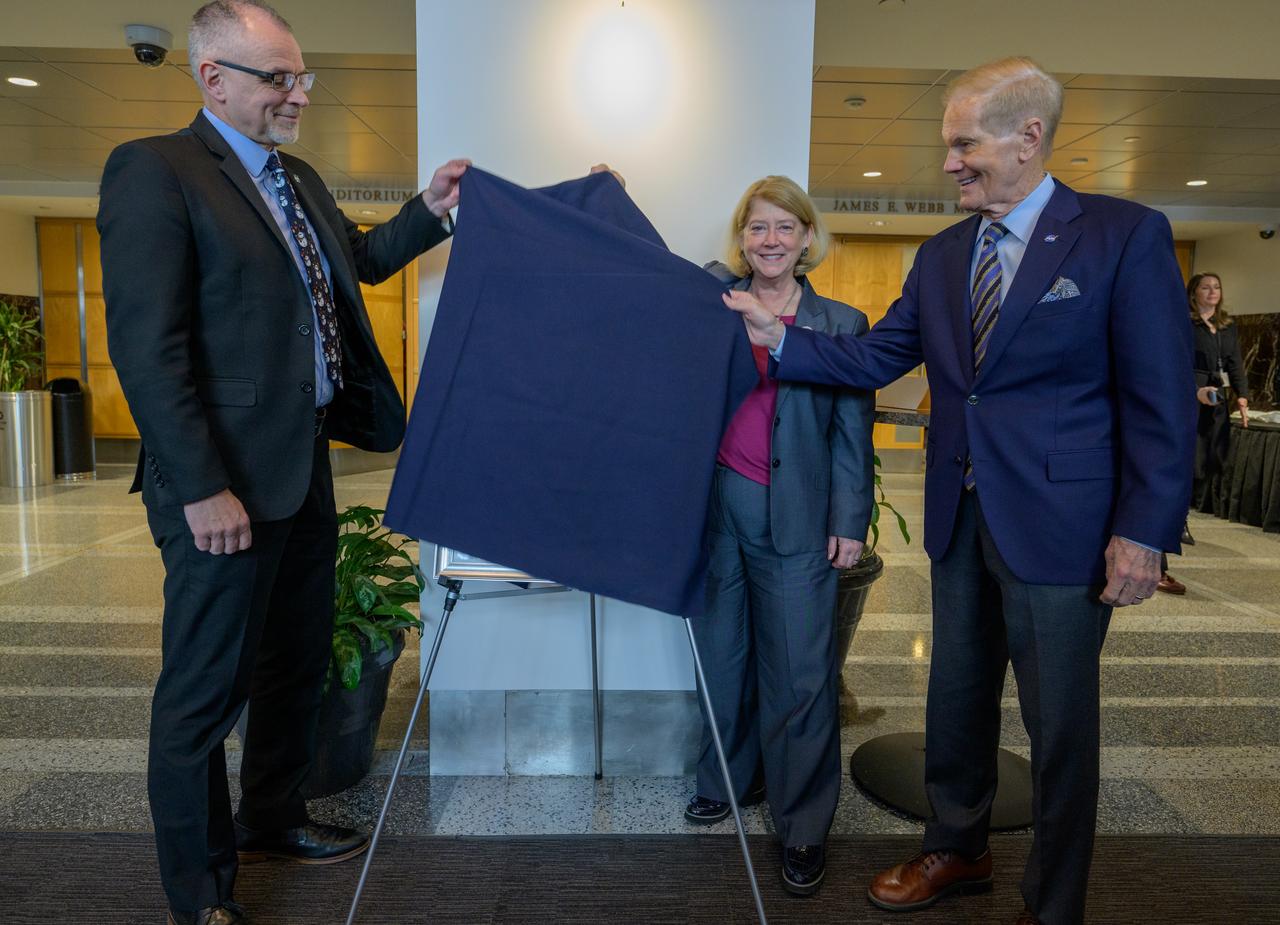

A portrait of Mary W. Jackson is unveiled, by NASA Associate Administrator Jim Free, left, NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, and, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, right, Friday, Dec. 6, 2024, at the NASA Headquarters Mary W. Jackson Building in Washington. Mary W. Jackson was a pioneering aerospace engineer and mathematician at NASA’s Langley Research Center. As one of the “Hidden Figures,” she made significant contributions to the space program, particularly in aerodynamics and engineering. Jackson’s groundbreaking work and advocacy for women and minorities helped shape NASA’s success and advance opportunities for future generations in science and technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
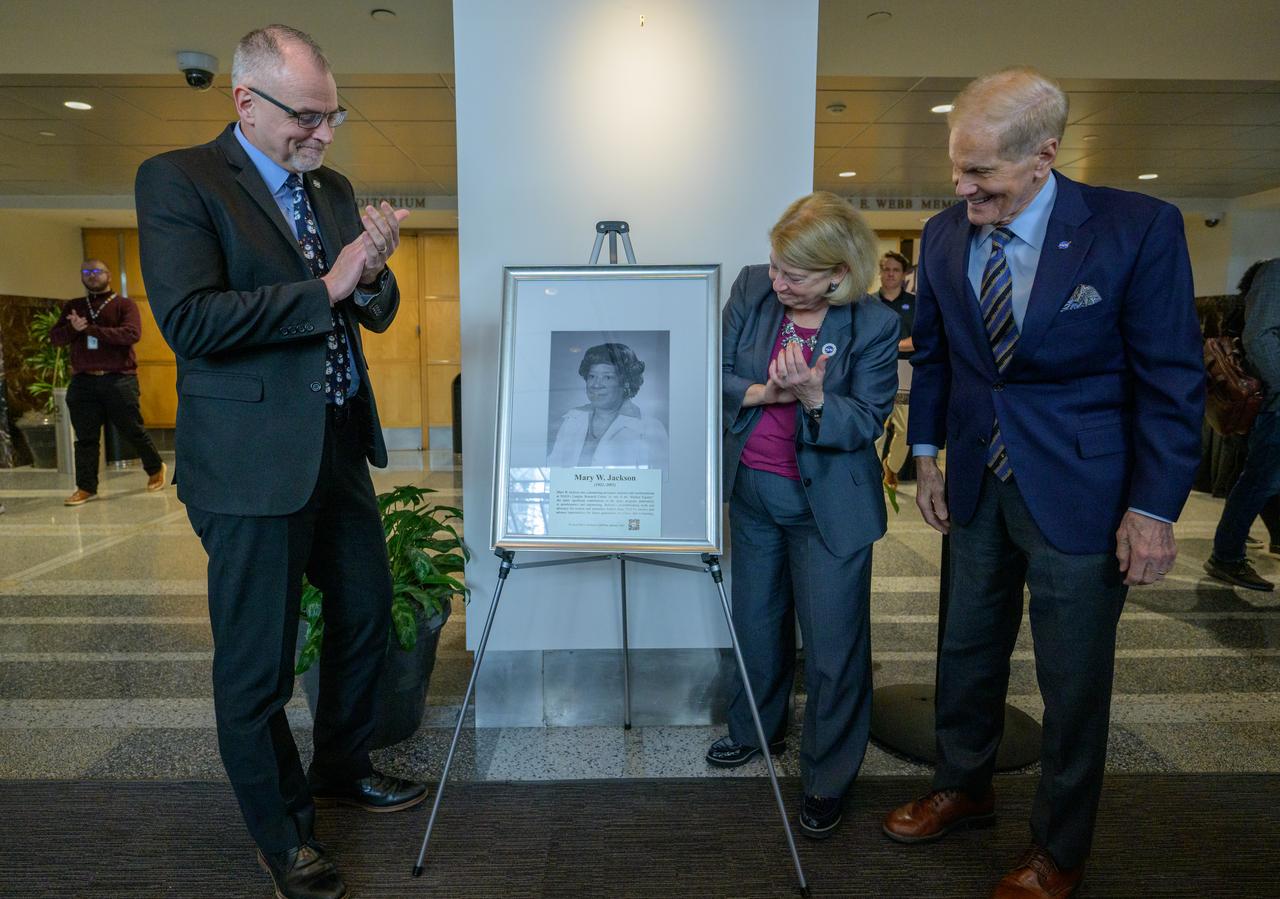

A portrait of Mary W. Jackson is unveiled, by NASA Associate Administrator Jim Free, left, NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, and, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, right, Friday, Dec. 6, 2024, at the NASA Headquarters Mary W. Jackson Building in Washington. Mary W. Jackson was a pioneering aerospace engineer and mathematician at NASA’s Langley Research Center. As one of the “Hidden Figures,” she made significant contributions to the space program, particularly in aerodynamics and engineering. Jackson’s groundbreaking work and advocacy for women and minorities helped shape NASA’s success and advance opportunities for future generations in science and technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
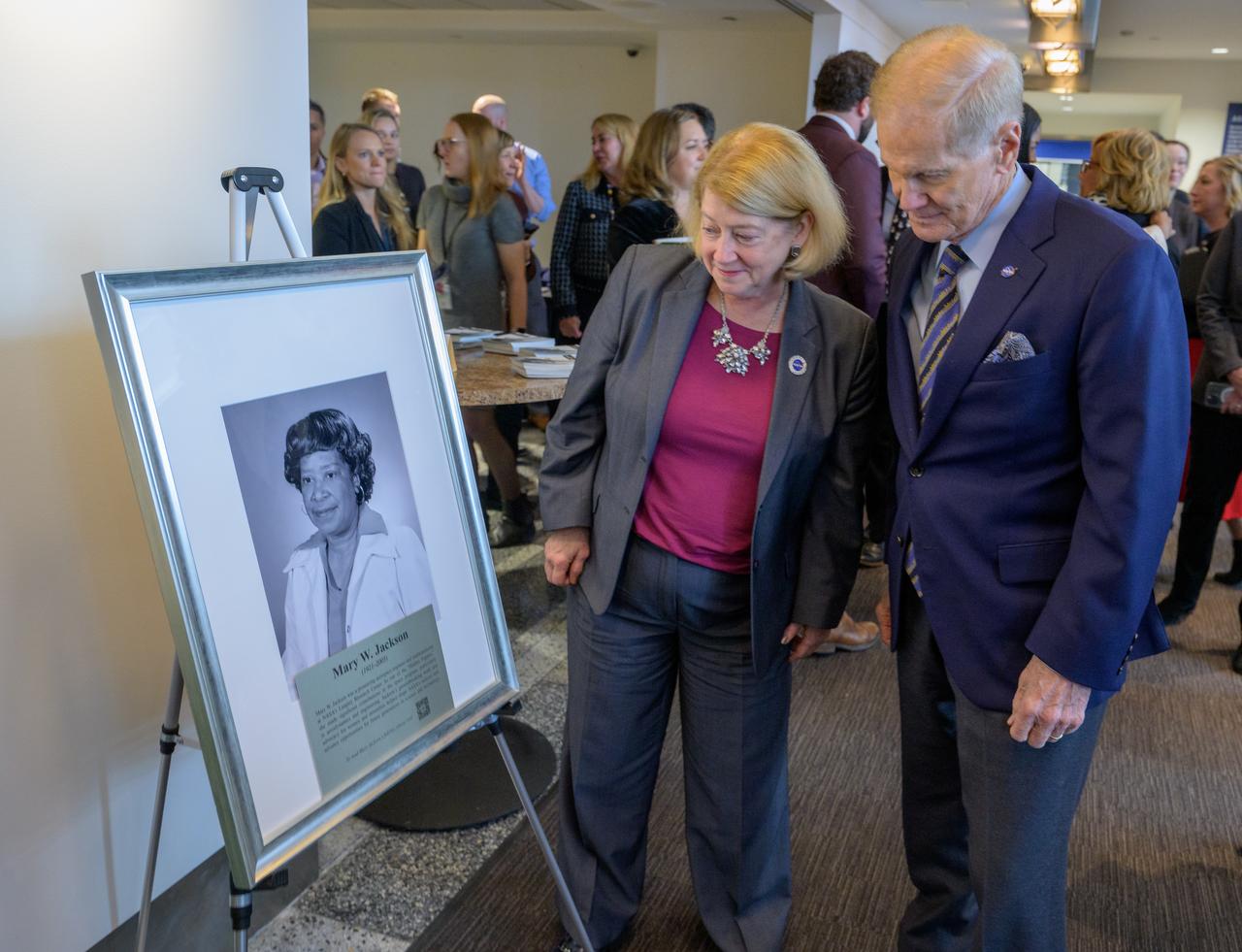

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, and, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, right, look at a portrait of Mary W. Jackson after it was unveiled, Friday, Dec. 6, 2024, at the NASA Headquarters Mary W. Jackson Building in Washington. Mary W. Jackson was a pioneering aerospace engineer and mathematician at NASA’s Langley Research Center. As one of the “Hidden Figures,” she made significant contributions to the space program, particularly in aerodynamics and engineering. Jackson’s groundbreaking work and advocacy for women and minorities helped shape NASA’s success and advance opportunities for future generations in science and technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During a Minority Student Education Forum, Kennedy Space Center Deputy Director Janet Petro, left, talks to hundreds of fifth- through 12th-grade students. The forum focused on encouraging students to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, by featuring some of NASA's greatest legends and trailblazers. Sitting, at right, is Glenn Research Center's Associate Director Vernon Wessell. NASA's Education Office sponsored the forum as part of the agency's 'Summer of Innovation' initiative and the federal 'Education to Innovate' campaign. Photo credit: NASA_Cory Huston

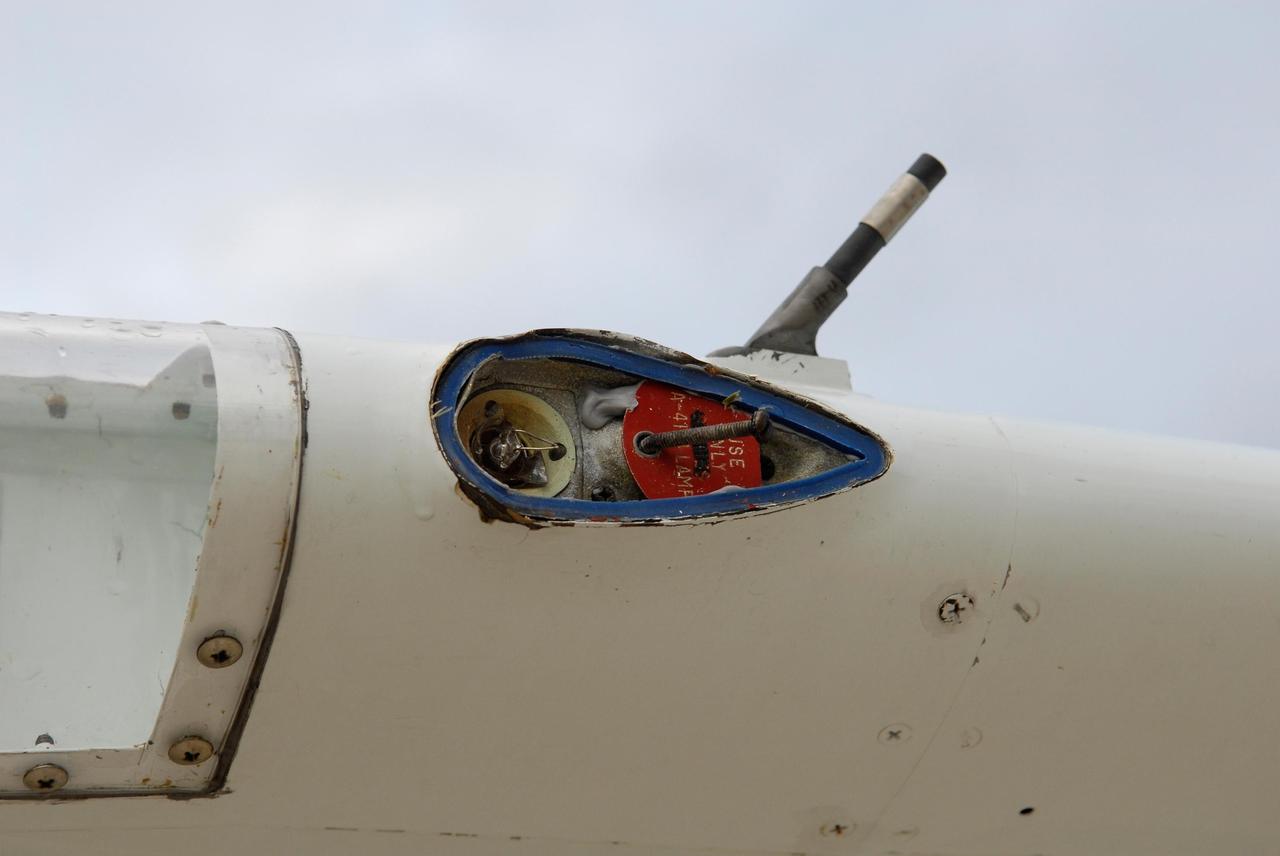
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The left position light, strobe light and wing tip of one of NASA's Shuttle Training Aircraft, or STAs, sustained minor damage from apparent contact with a tree near Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility. The incident occurred during landing about 6:30 p.m. EDT Oct. 19 following a training session. An STA flight instructor was piloting the aircraft. The flight crew was unaware of any contact with the tree, and there were no injuries. Thunderstorms were in the area at the time of the incident, which is under investigation. The STA is a twin-engine Gulfstream II jet that was modified to simulate a space shuttle during landing. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During a Minority Student Education Forum, Linda Dukes-Campbell, the chief of Community and Media Relations at Glenn Research Center, left, talks to hundreds of fifth- through 12th-grade students. Other NASA legends, sitting from left to right, are Glenn Research Center's former Director Dr. Julian Earls, Dryden Flight Research Center's former Director Isaac Gillam, Glenn's Director Donald Campbell, and former NASA Associate Administrator for Aeronautics Dr. Wesley Harris. The forum focused on encouraging students to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering and mathematics, or STEM, by featuring some of NASA's greatest legends and trailblazers. NASA's Education Office sponsored the forum as part of the agency's 'Summer of Innovation' initiative and the federal 'Education to Innovate' campaign. Photo credit: NASA_Cory Huston
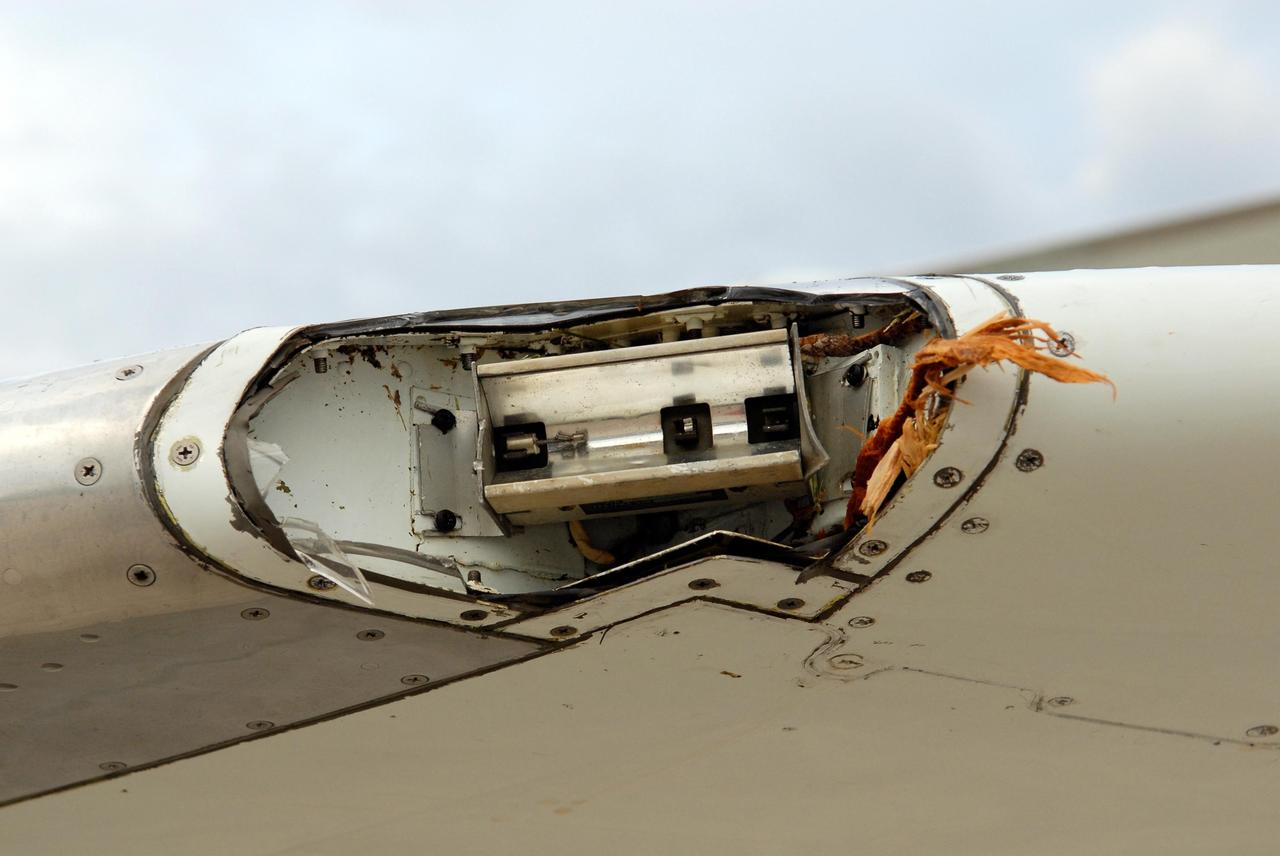

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Debris from apparent contact with a tree near Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility can be seen in the position light cavity on the left side of one of NASA's Shuttle Training Aircraft, or STA. The left strobe light and wing tip also received minor damage. The incident occurred during landing about 6:30 p.m. EDT Oct. 19 following a training session. An STA flight instructor was piloting the aircraft. The flight crew was unaware of any contact with the tree, and there were no injuries. Thunderstorms were in the area at the time of the incident, which is under investigation. The STA is a twin-engine Gulfstream II jet that was modified to simulate a space shuttle during landing. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Debris from apparent contact with a tree near Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility can be seen in the strobe light cavity on the left side of one of NASA's Shuttle Training Aircraft, or STA. The left position light and wing tip also received minor damage. The incident occurred during landing about 6:30 p.m. EDT Oct. 19 following a training session. An STA flight instructor was piloting the aircraft. The flight crew was unaware of any contact with the tree, and there were no injuries. Thunderstorms were in the area at the time of the incident, which is under investigation. The STA is a twin-engine Gulfstream II jet that was modified to simulate a space shuttle during landing. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
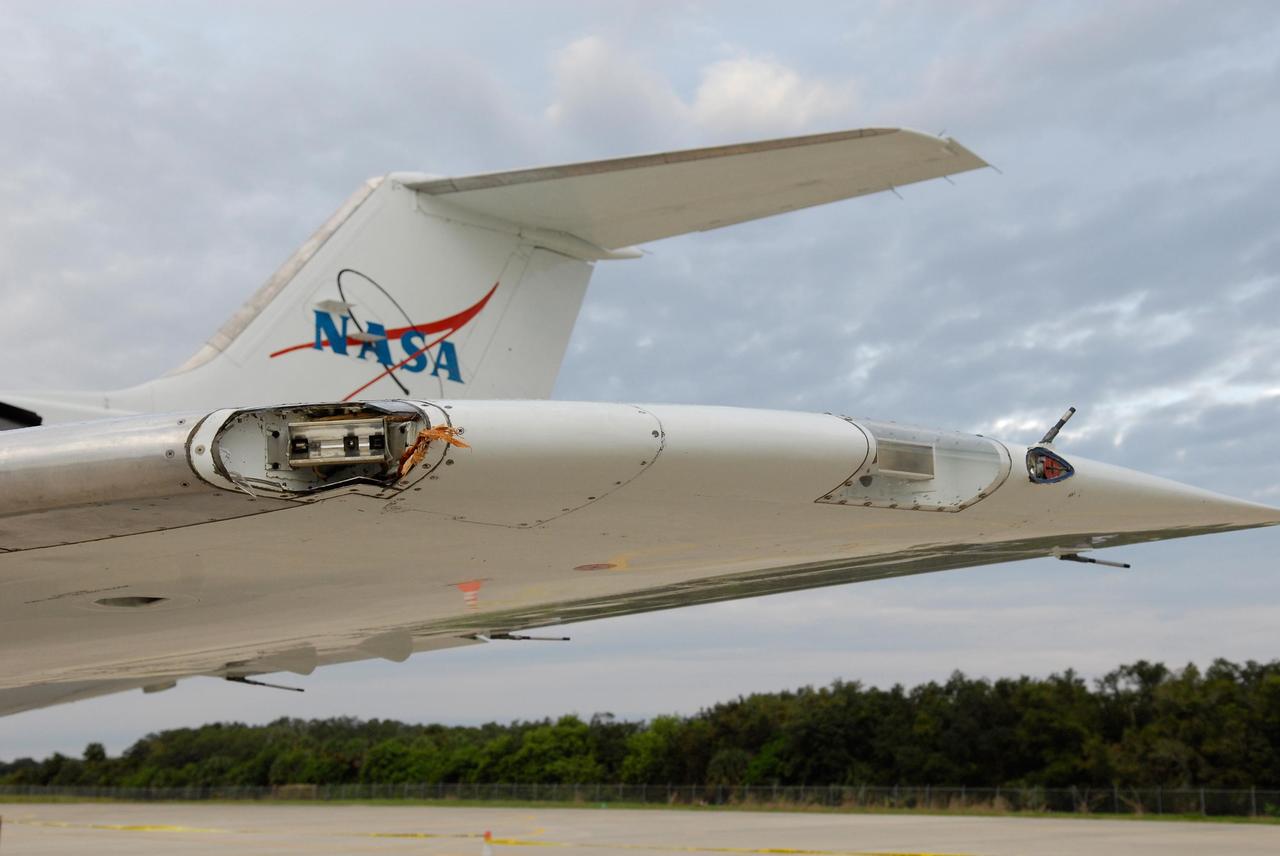

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The left position light, strobe light and wing tip of one of NASA's Shuttle Training Aircraft, or STA, show signs of minor damage from apparent contact with a tree near Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility. The incident occurred during landing about 6:30 p.m. EDT Oct. 19 following a training session. An STA flight instructor was piloting the aircraft. The flight crew was unaware of any contact with the tree, and there were no injuries. Thunderstorms were in the area at the time of the incident, which is under investigation. The STA is a twin-engine Gulfstream II jet that was modified to simulate a space shuttle during landing. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis, mounted on a mobile launch platform, finally rests on the hard stand of Launch Pad 39A after an early morning rollout. This is the second rollout for the shuttle. Seen on either side of the main engine exhaust hole on the launcher platform are the tail service masts. Their function is to provide umbilical connections for liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen lines to fuel the external tank from storage tanks adjacent to the launch pad. Other umbilical lines carry helium and nitrogen, as well as ground electrical power and connections for vehicle data and communications. First motion out of the Vehicle Assembly Building was at 5:02 a.m. EDT. In late February, while Atlantis was on the launch pad, Atlantis' external tank received hail damage during a severe thunderstorm that passed through the Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39 area. The hail caused visible divots in the giant tank's foam insulation, as well as minor surface damage to about 26 heat shield tiles on the shuttle's left wing. The shuttle was returned to the VAB for repairs. The launch of Space Shuttle Atlantis on mission STS-117 is now targeted for June 8. A flight readiness review will be held on May 30 and 31. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians and engineers will perform a walk down and detailed inspections of space shuttle Endeavour following severe storms over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The frontal system moved through Central Florida producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. During the inspections, teams found only minor damage to Endeavour's external fuel tank foam insulation and evaluations indicate there was no damage to the spacecraft. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew are targeted to launch April 29 at 3:47 p.m. EDT. They will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
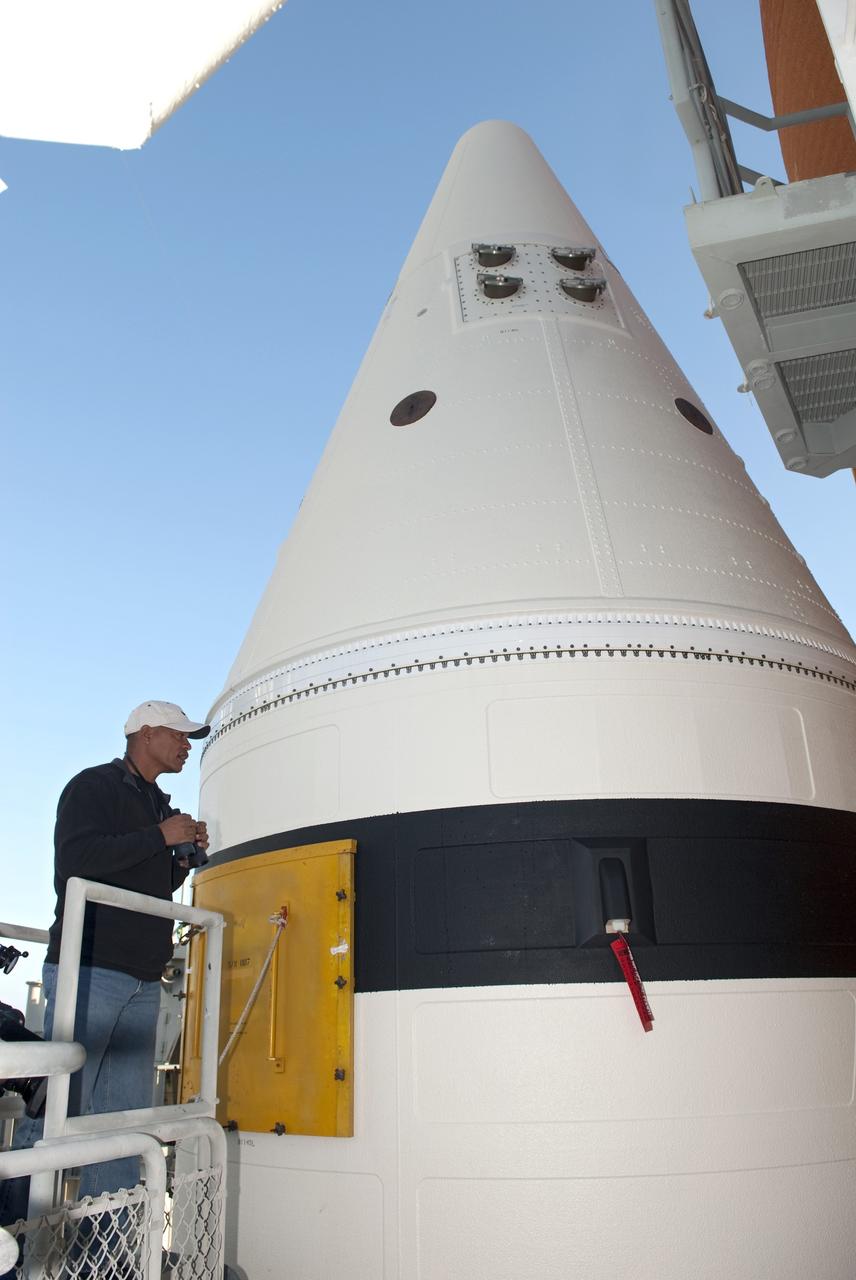

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A worker performs a walk down of space shuttle Endeavour following severe storms over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The frontal system moved through Central Florida producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. During detailed inspections, technicians and engineers found only minor damage to Endeavour's external fuel tank foam insulation and evaluations indicate there was no damage to the spacecraft. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew are targeted to launch April 29 at 3:47 p.m. EDT. They will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians and engineers will perform a walk down and detailed inspections of space shuttle Endeavour following severe storms over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The frontal system moved through Central Florida producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. During the inspections, teams found only minor damage to Endeavour's external fuel tank foam insulation and evaluations indicate there was no damage to the spacecraft. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew are targeted to launch April 29 at 3:47 p.m. EDT. They will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
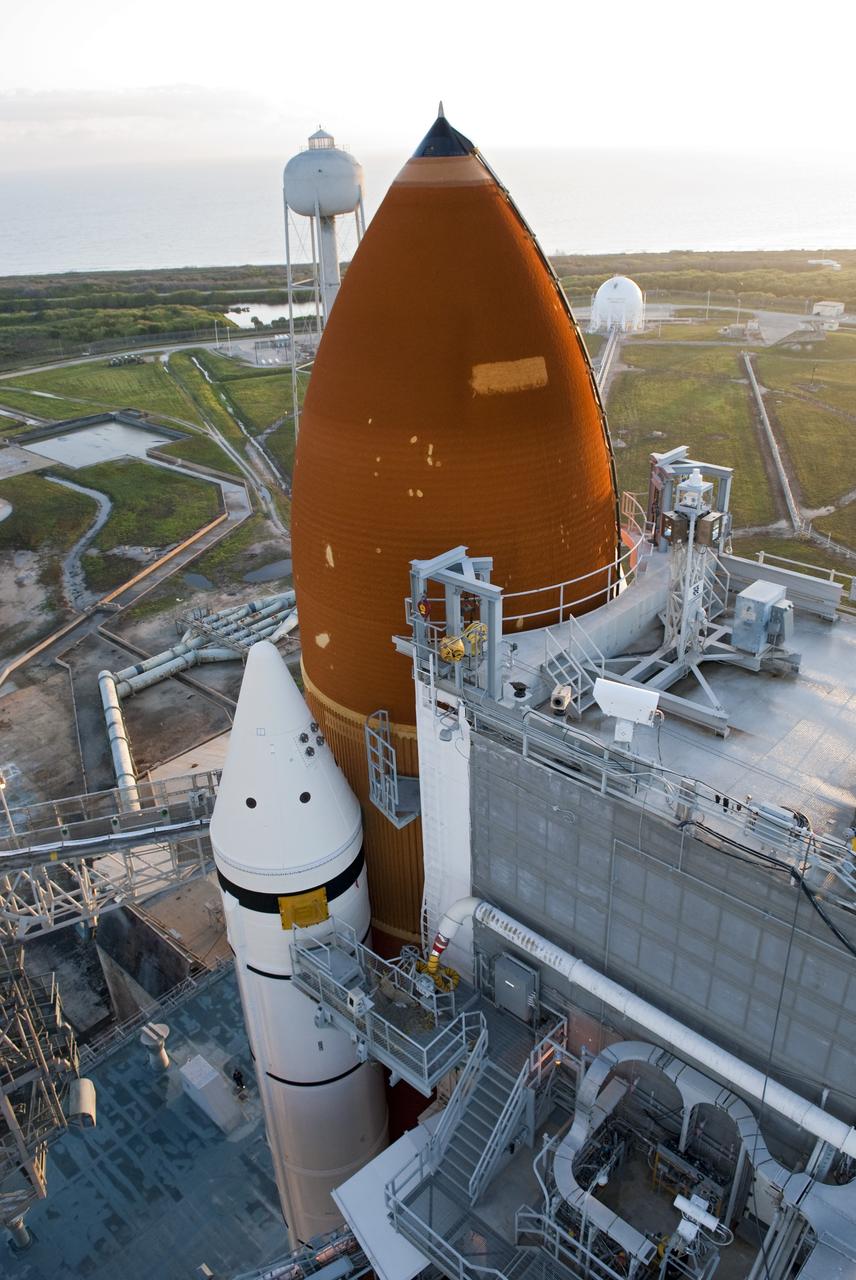

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians and engineers will perform a walk down and detailed inspections of space shuttle Endeavour following severe storms over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The frontal system moved through Central Florida producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. During the inspections, teams found only minor damage to Endeavour's external fuel tank foam insulation and evaluations indicate there was no damage to the spacecraft. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew are targeted to launch April 29 at 3:47 p.m. EDT. They will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
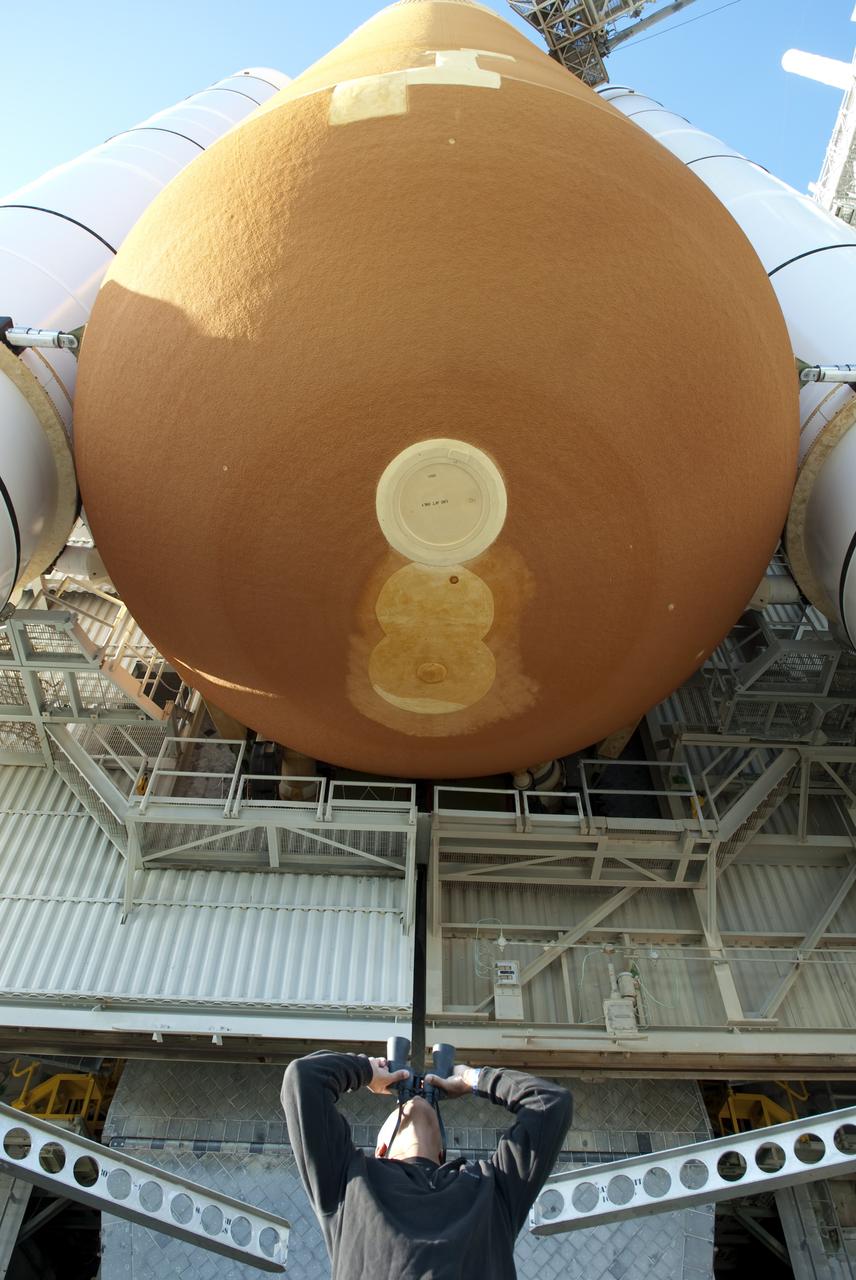

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A worker performs a walk down of space shuttle Endeavour following severe storms over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The frontal system moved through Central Florida producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. During detailed inspections, technicians and engineers found only minor damage to Endeavour's external fuel tank foam insulation and evaluations indicate there was no damage to the spacecraft. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew are targeted to launch April 29 at 3:47 p.m. EDT. They will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
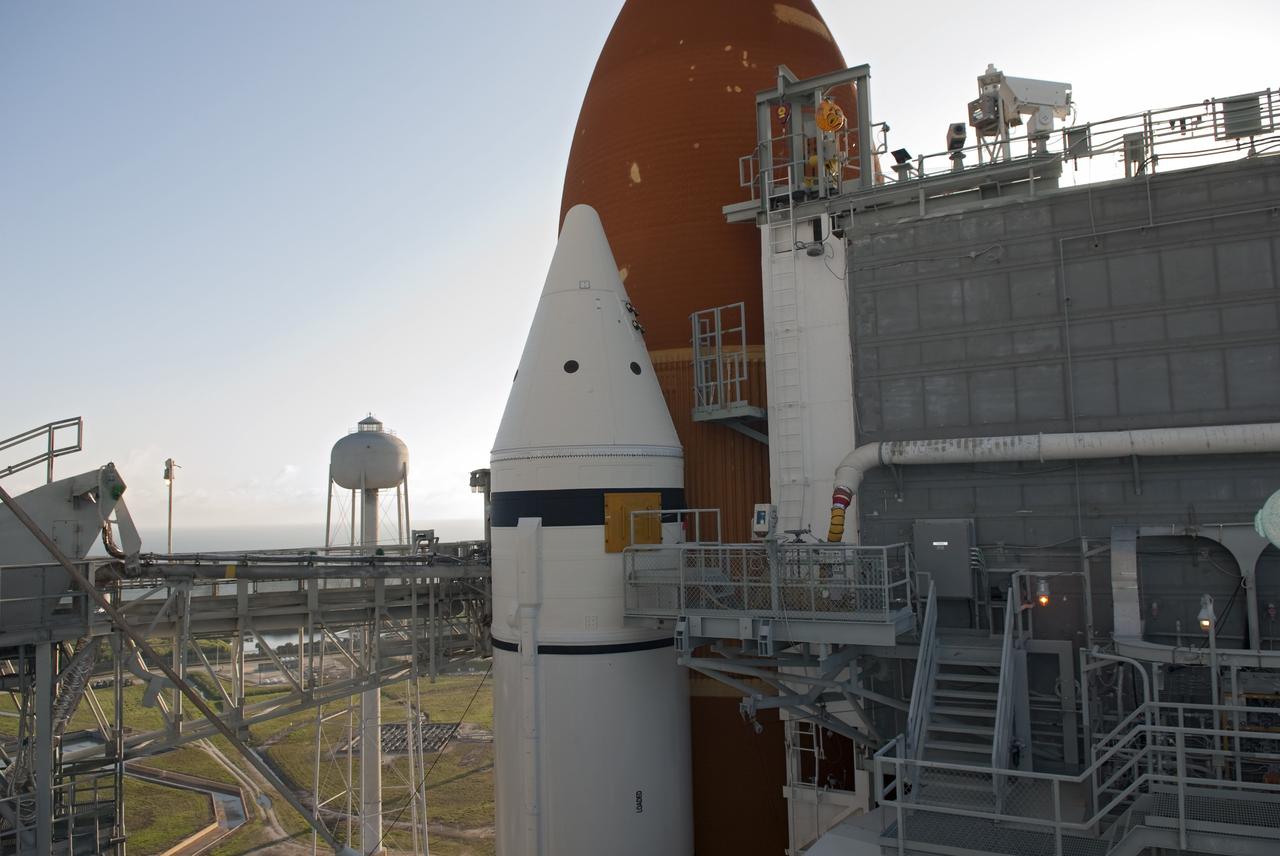

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians and engineers will perform a walk down and detailed inspections of space shuttle Endeavour following severe storms over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The frontal system moved through Central Florida producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. During the inspections, teams found only minor damage to Endeavour's external fuel tank foam insulation and evaluations indicate there was no damage to the spacecraft. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew are targeted to launch April 29 at 3:47 p.m. EDT. They will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
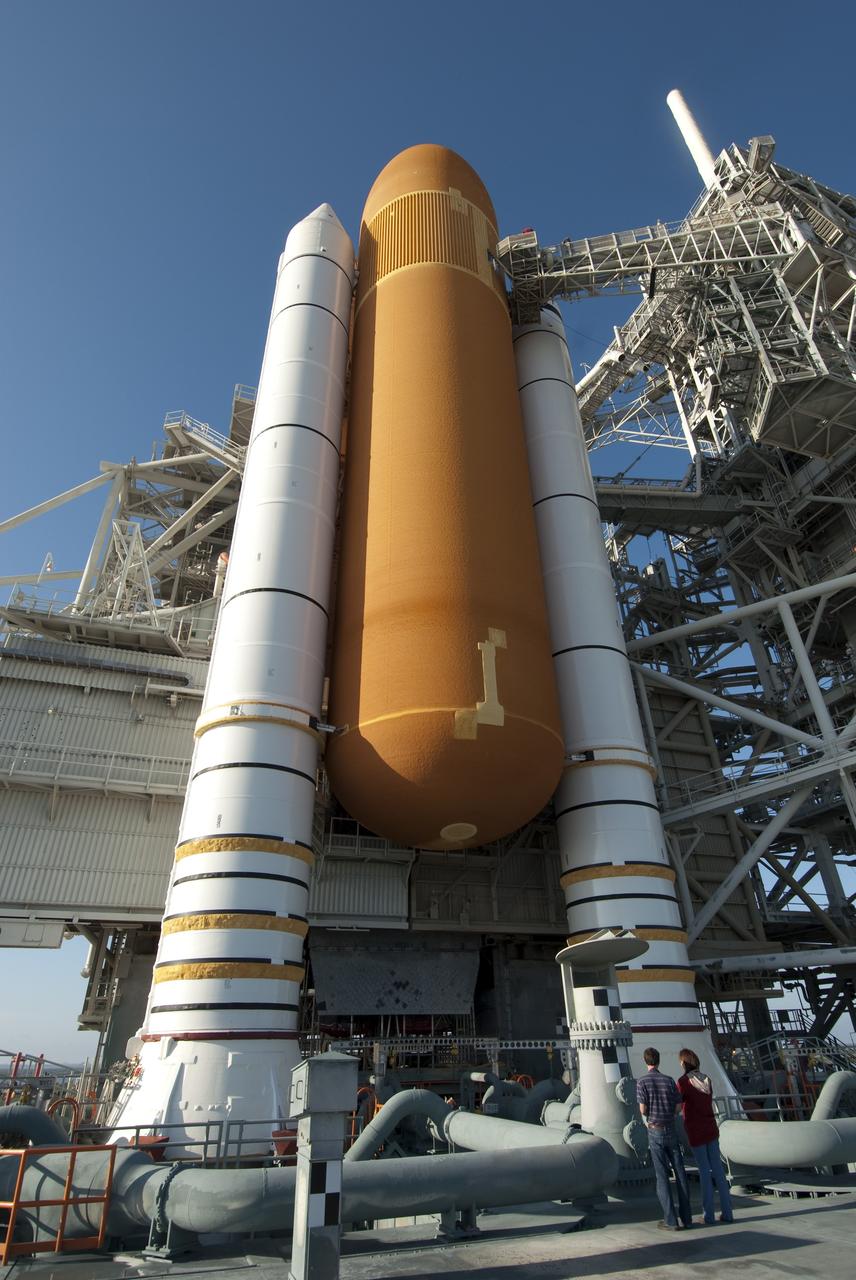

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers perform a walk down of space shuttle Endeavour following severe storms over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The frontal system moved through Central Florida producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. During detailed inspections, technicians and engineers found only minor damage to Endeavour's external fuel tank foam insulation and evaluations indicate there was no damage to the spacecraft. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew are targeted to launch April 29 at 3:47 p.m. EDT. They will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A walk down and detailed inspections of space shuttle Endeavour indicate that the external fuel tank foam insulation sustained only minor damage during severe storms over Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Seen here, the ET-122 logo is emblazoned on Endeavour's external tank. The frontal system moved through Central Florida producing strong winds, heavy rain, frequent lightning and even funnel clouds. Evaluations by technicians and engineers indicate there was no damage to the spacecraft. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew are targeted to launch April 29 at 3:47 p.m. EDT. They will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
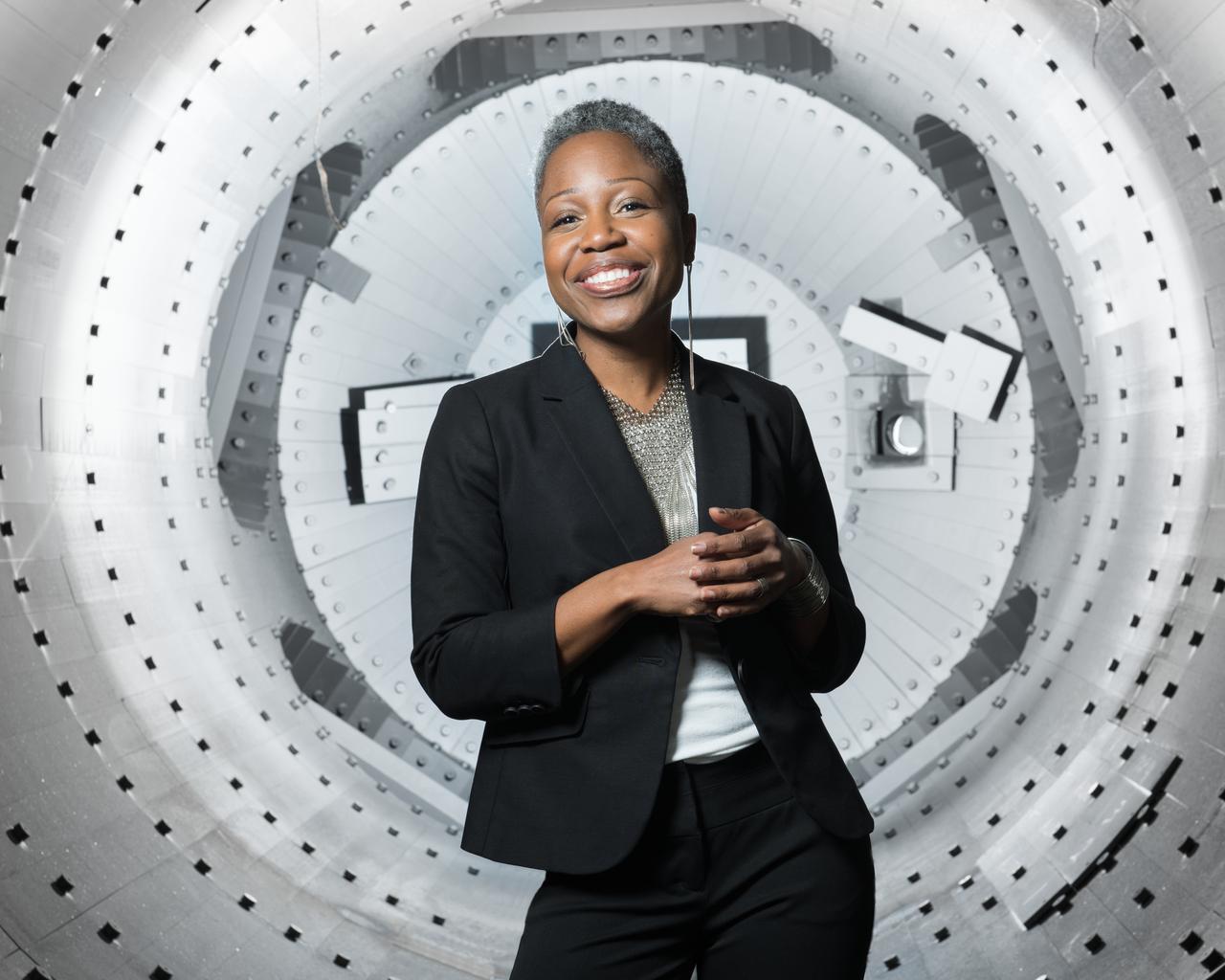

“I am a Black woman in STEM. And when I was growing up, I cannot say that I saw a lot of faces that looked like mine in STEM careers. I had some limited exposure to some notables, like Dr. Mae Jemison. But the names were few and far between of the great scientists or engineers that were Black — let alone Black females. So for me, if anybody sees my picture and says ‘yes, I see someone who looks like me working in STEM’ — that right there is very fulfilling. Just to be seen and to be visible makes a difference. "I also must provide words of encouragement because being in STEM can be difficult as is, let alone having to face the challenges of being a female in a male-dominated field. Or even being a double minority in the workplace. "It’s a matter of being really self-assured that you can do it, despite the fact that you’re going to have failures, that you’re going to have setbacks, and that you’re going have people who may not believe in you, for whatever reason. You have to be self-assured that this is what you want to do and that it can be done. This 4’11” Black woman achieved this, not knowing that STEM was going to be my path or that I was going to end up at NASA — I did it, and I believe that you can do it too — but you have to believe it for yourself.” — Mary Lobo, Director of Office of Technology Incubation and Innovation, Glenn Research Center The Facility Manager for the Space Simulation Facilities at Glenn Research Center, poses inside Vacuum Facility 16 (VF-16) for an Environmental Portrait. The lighting used in this portrait depicts the chamber as having an almost white interior when the chamber is actually almost black in color.
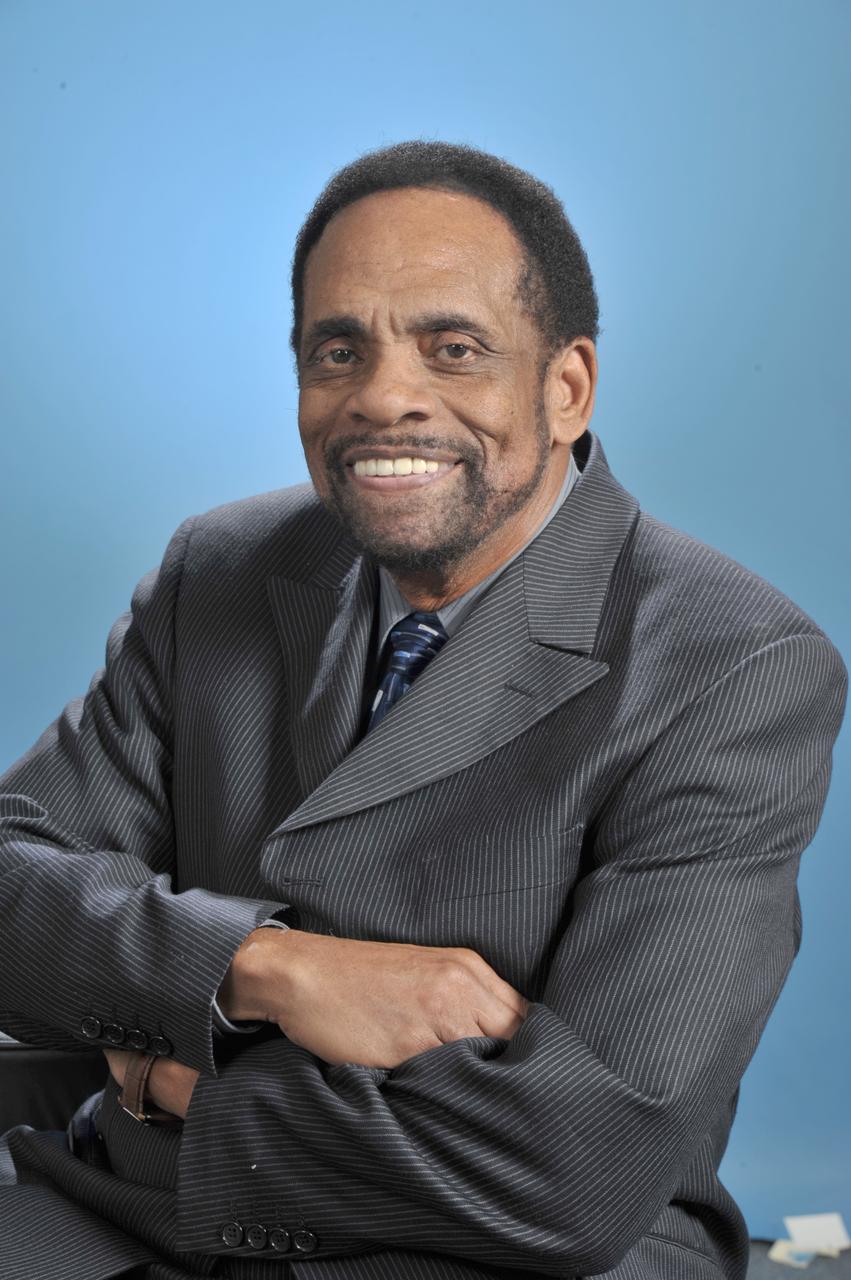

George Edward Alcorn, a pioneering African American physicist and engineer, is credited with dozens of inventions over the course of a distinguished career in private industry and at NASA, for which he earned eight patents. Alcorn joined Goddard Space Flight Center in 1978 and held numerous leadership roles in both research and administration until his retirement in 2012. One of Alcorn’s signature accomplishments at NASA was developing a smaller, more sensitive X-ray spectrometer, changing the way scientists were able to use the powerful tool in deep space exploration missions. His tool, which uses thermomigration of aluminum, can gather information about remote solar systems; for the invention, Alcorn was honored as the NASA Goddard Inventor of the Year in 1984. In addition to his groundbreaking contributions as an inventor and innovator, Alcorn also championed efforts to hire more women and minorities at Goddard, for which he was honored with the NASA Equal Opportunity Medal, and taught students at Howard University and the University of the District of Columbia. He also founded the Saturday Academy, an honors program in math and science for underserved middle school students. He earned many accolades over the years from NASA and beyond. These include, in 2010, the Robert H. Goddard Award for Merit, for his outstanding innovation and significant contributions to space science, technology, and NASA programs, as well as recognition in 1994 at Howard University’s Heritage of Greatness awards ceremony. He was also inducted into the National Inventor’s Hall of Fame in 2015. Alcorn passed away in 2024 at the age of 84.