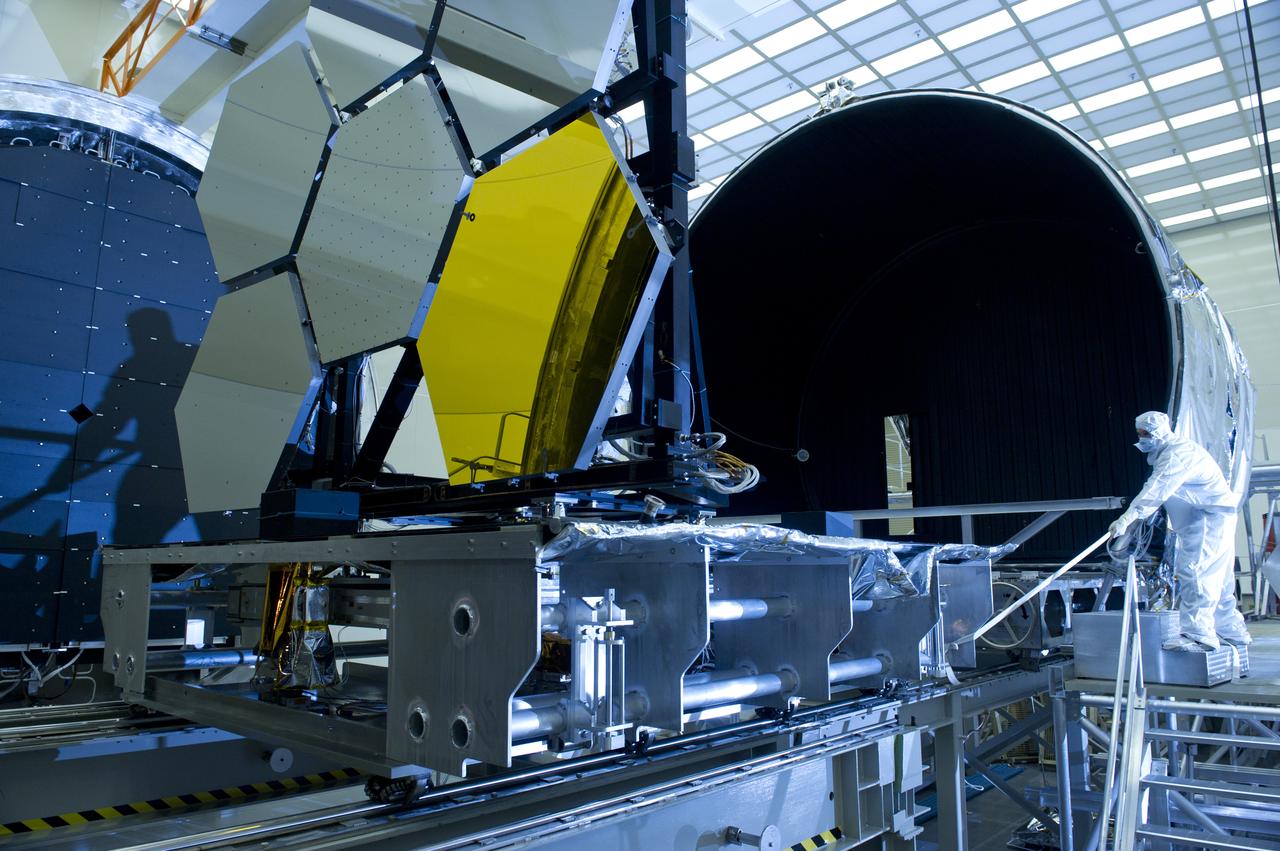

MARSHALL TEST ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT HELPS PULL JWST MIRROR ARRAY FROM CRYOGENICS CHAMBER.
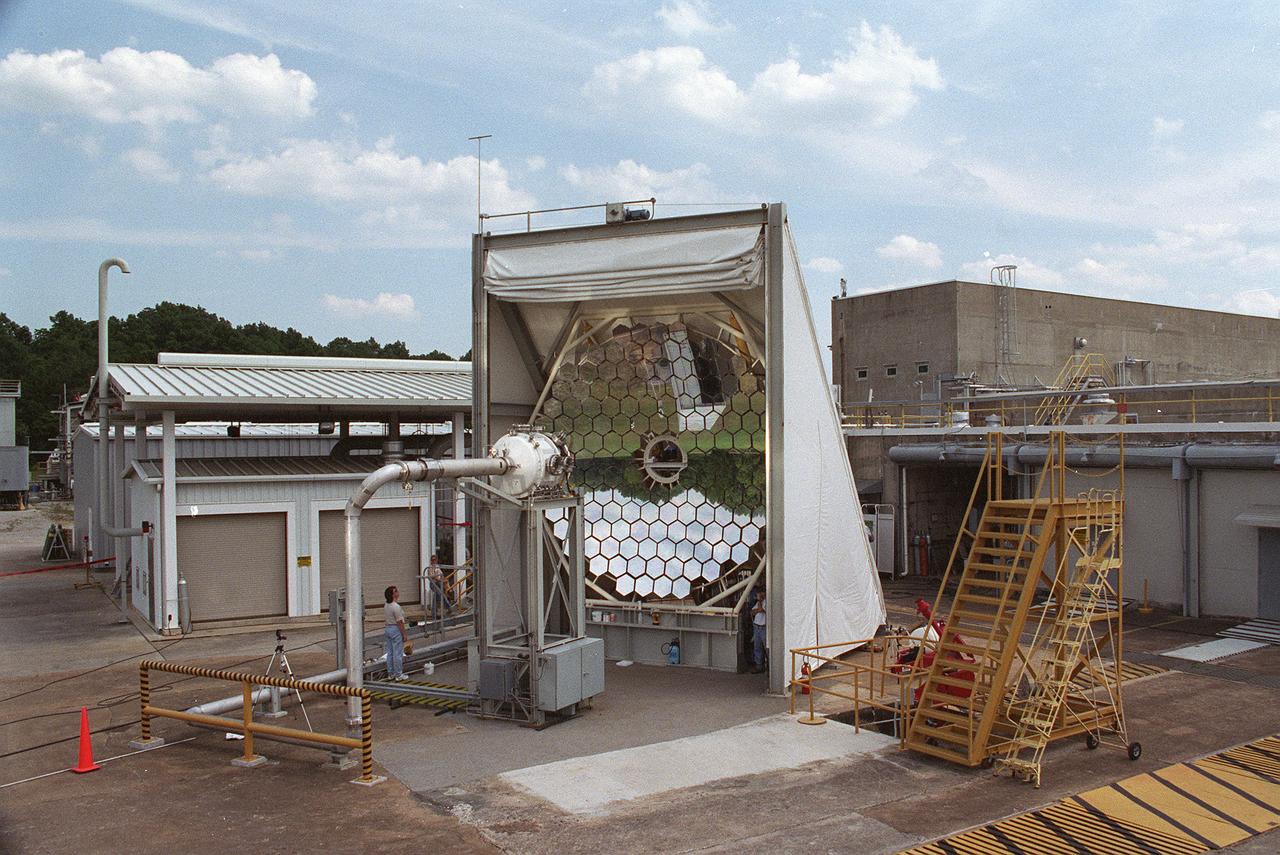

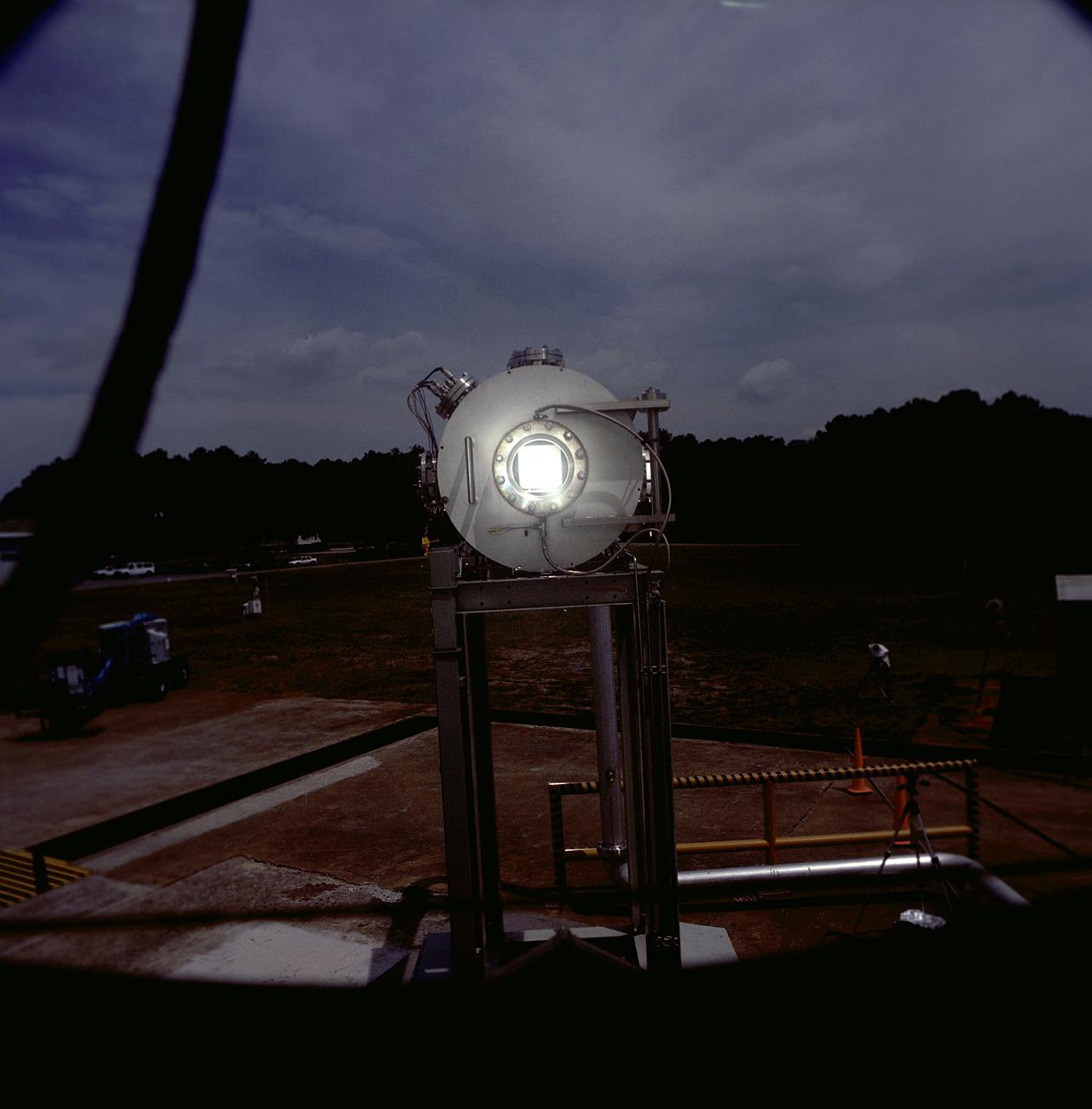
Researchers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) have designed, fabricated and tested the first solar thermal engine, a non-chemical rocket engine that produces lower thrust but has better thrust efficiency than a chemical combustion engine. MSFC turned to solar thermal propulsion in the early 1990s due to its simplicity, safety, low cost, and commonality with other propulsion systems. Solar thermal propulsion works by acquiring and redirecting solar energy to heat a propellant. This photograph, taken at MSFC's Solar Thermal Propulsion Test Facility, shows a concentrator mirror, a combination of 144 mirrors forming this 18-ft diameter concentrator, and a vacuum chamber that houses the focal point. The 20- by 24-ft heliostat mirror (not shown in this photograph) has a dual-axis control that keeps a reflection of the sunlight on the 18-foot diameter concentrator mirror, which then focuses the sunlight to a 4-in focal point inside the vacuum chamber. The focal point has 10 kilowatts of intense solar power. As part of MSFC's Space Transportation Directorate, the Propulsion Research Center serves as a national resource for research of advanced, revolutionary propulsion technologies. The mission is to move the Nation's capabilities beyond the confines of conventional chemical propulsion into an era of aircraft-like access to Earth-orbit, rapid travel throughout the solar system, and exploration of interstellar space.
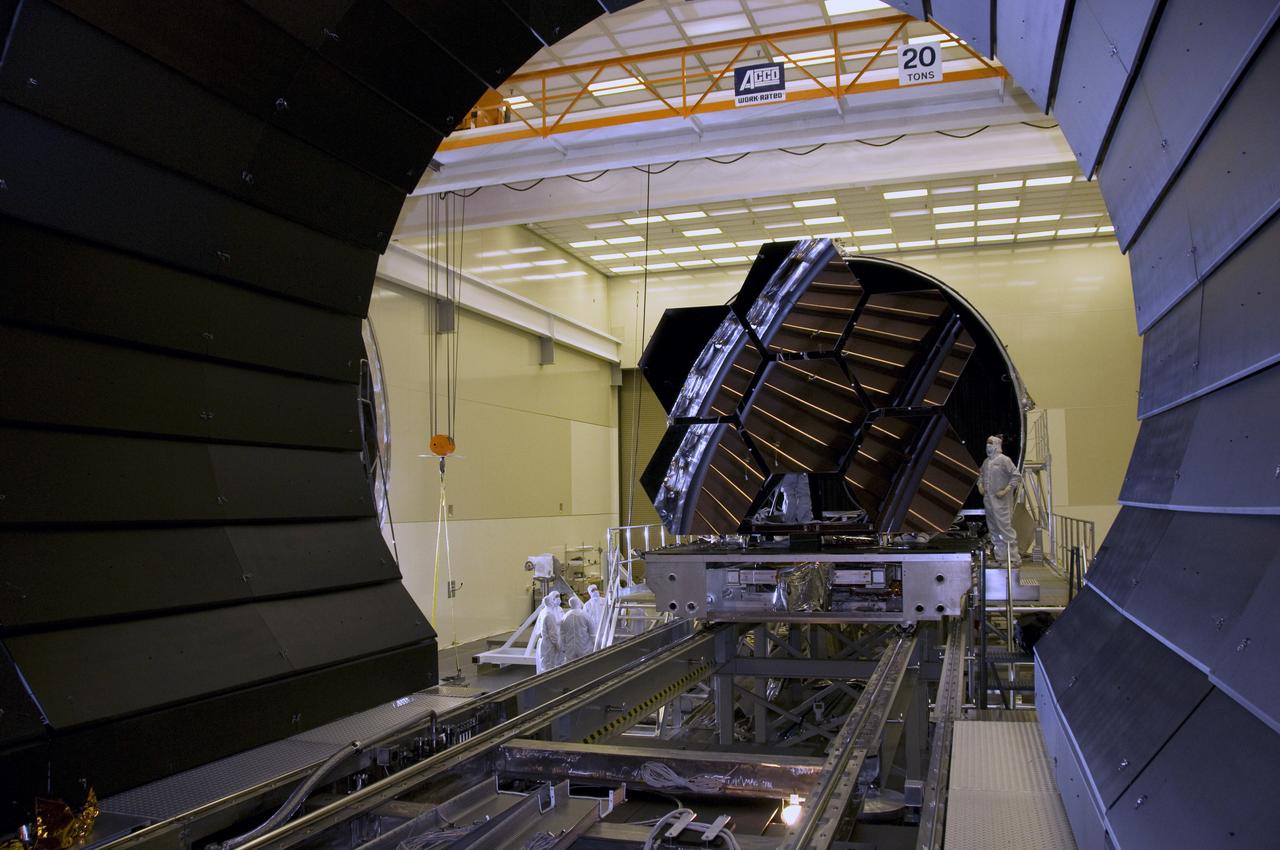

SIX MIRROR SEGMENTS OF THE JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE ARE REMOVED FROM THE CRYOGENIC TEST CHAMBER

In this photograph, the composite material mirror is tested in the X-Ray Calibration Facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The mirror test conducted was to check the ability to accurately model and predict the cryogenic performance of complex mirror systems, and the characterization of cryogenic dampening properties of beryllium. The JWST, a next generation successor to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), was named in honor of James W. Webb, NASA's second administrator, who led NASA in the early days of the fledgling Aerospace Agency. Scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle, the JWST will be able to look deeper into the universe than the HST because of the increased light-collecting power of its larger mirror and the extraordinary sensitivity of its instrument to infrared light.

Researchers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) have designed, fabricated, and tested the first solar thermal engine, a non-chemical rocket engine that produces lower thrust but has better thrust efficiency than a chemical combustion engine. MSFC turned to solar thermal propulsion in the early 1990s due to its simplicity, safety, low cost, and commonality with other propulsion systems. Solar thermal propulsion works by acquiring and redirecting solar energy to heat a propellant. The 20- by 24-ft heliostat mirror (not shown in this photograph) has dual-axis control that keeps a reflection of the sunlight on an 18-ft diameter concentrator mirror, which then focuses the sunlight to a 4-in focal point inside the vacuum chamber. The focal point has 10 kilowatts of intense solar power. This photograph is a close-up view of a 4-in focal point inside the vacuum chamber at the MSFC Solar Thermal Propulsion Test facility. As part of MSFC's Space Transportation Directorate, the Propulsion Research Center serves as a national resource for research of advanced, revolutionary propulsion technologies. The mission is to move the Nation's capabilities beyond the confines of conventional chemical propulsion into an era of aircraft-like access to Earth orbit, rapid travel throughout the solar system, and exploration of interstellar space.
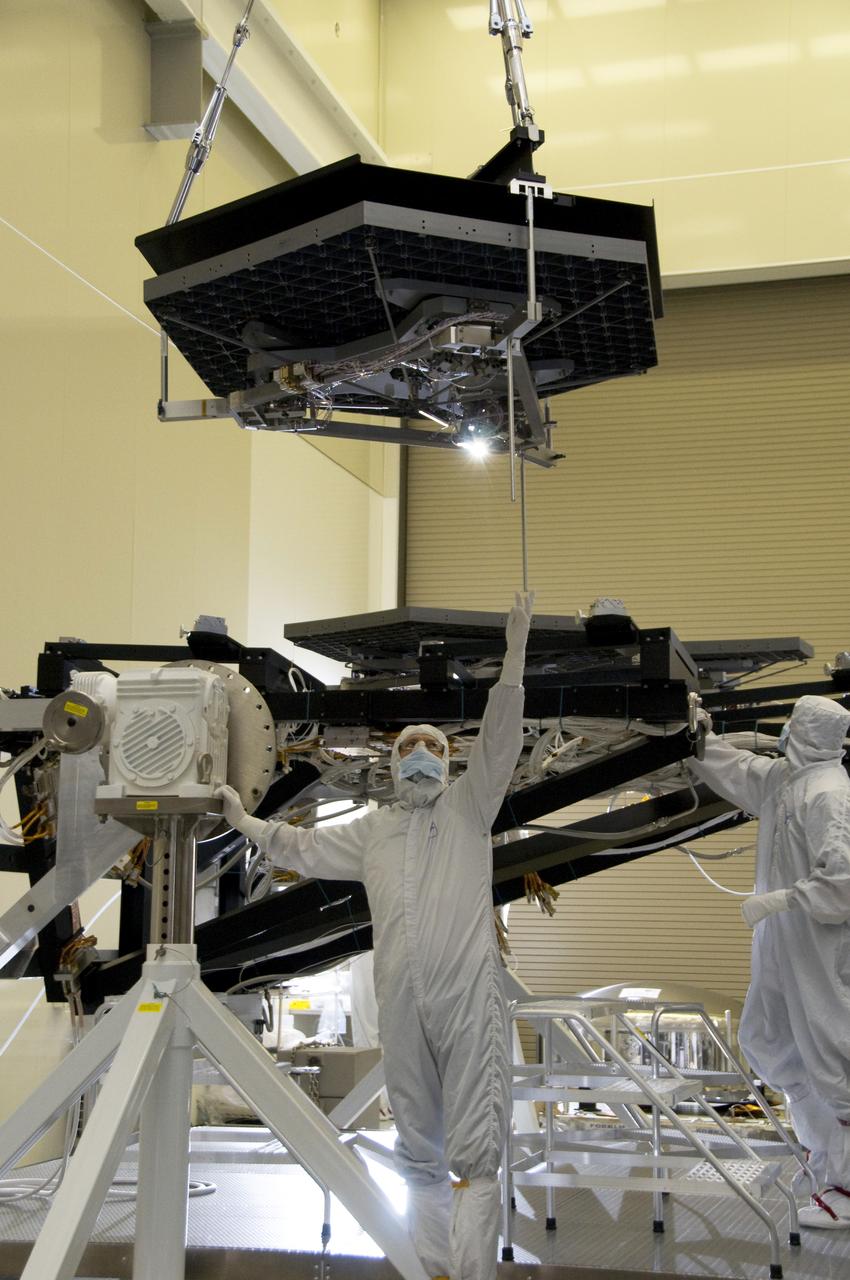

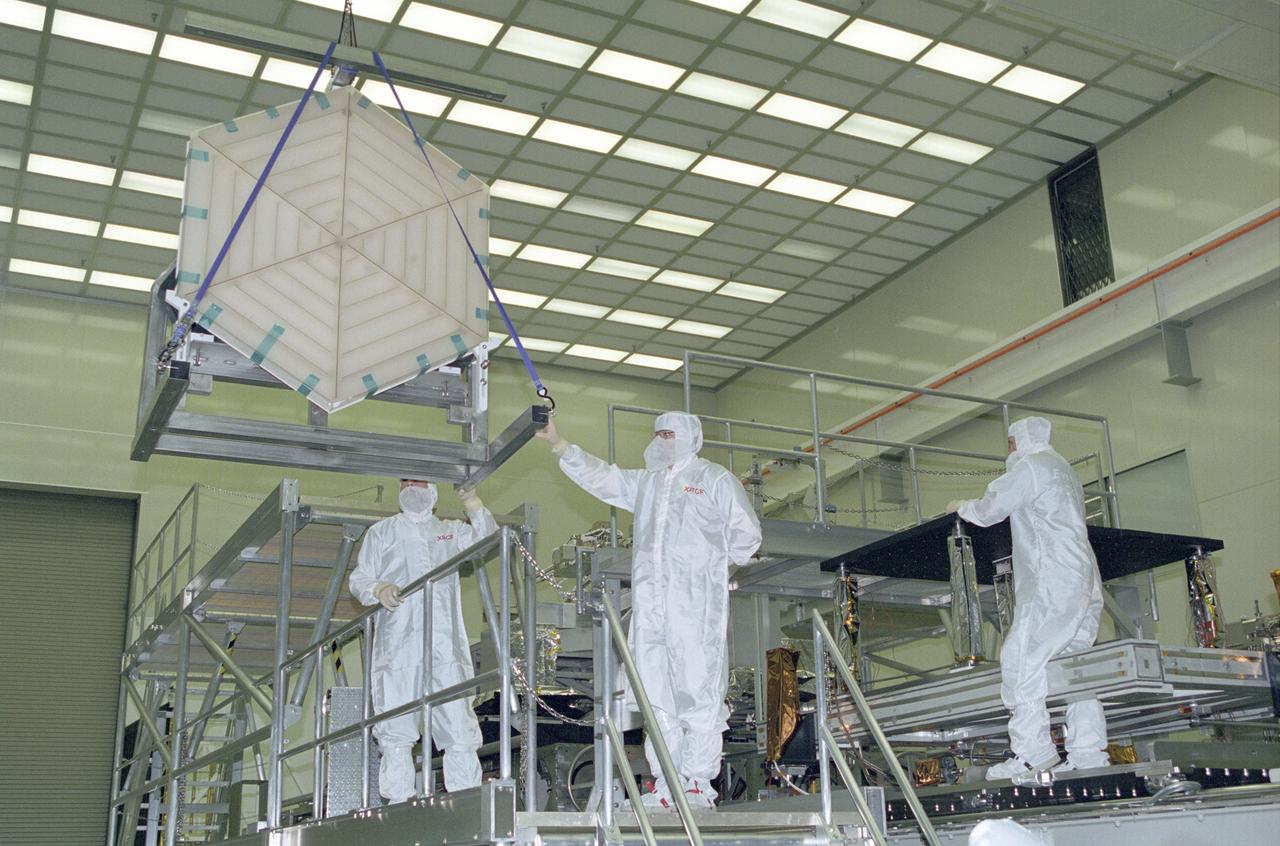
A PRIMARY MIRROR SEGMENT ASSEMBLY BEING CAREFULLY LOWERED TO ITS TEST STAND POSITION ALONGSIDE PREVIOUSLY INSTALLED MIRRORS

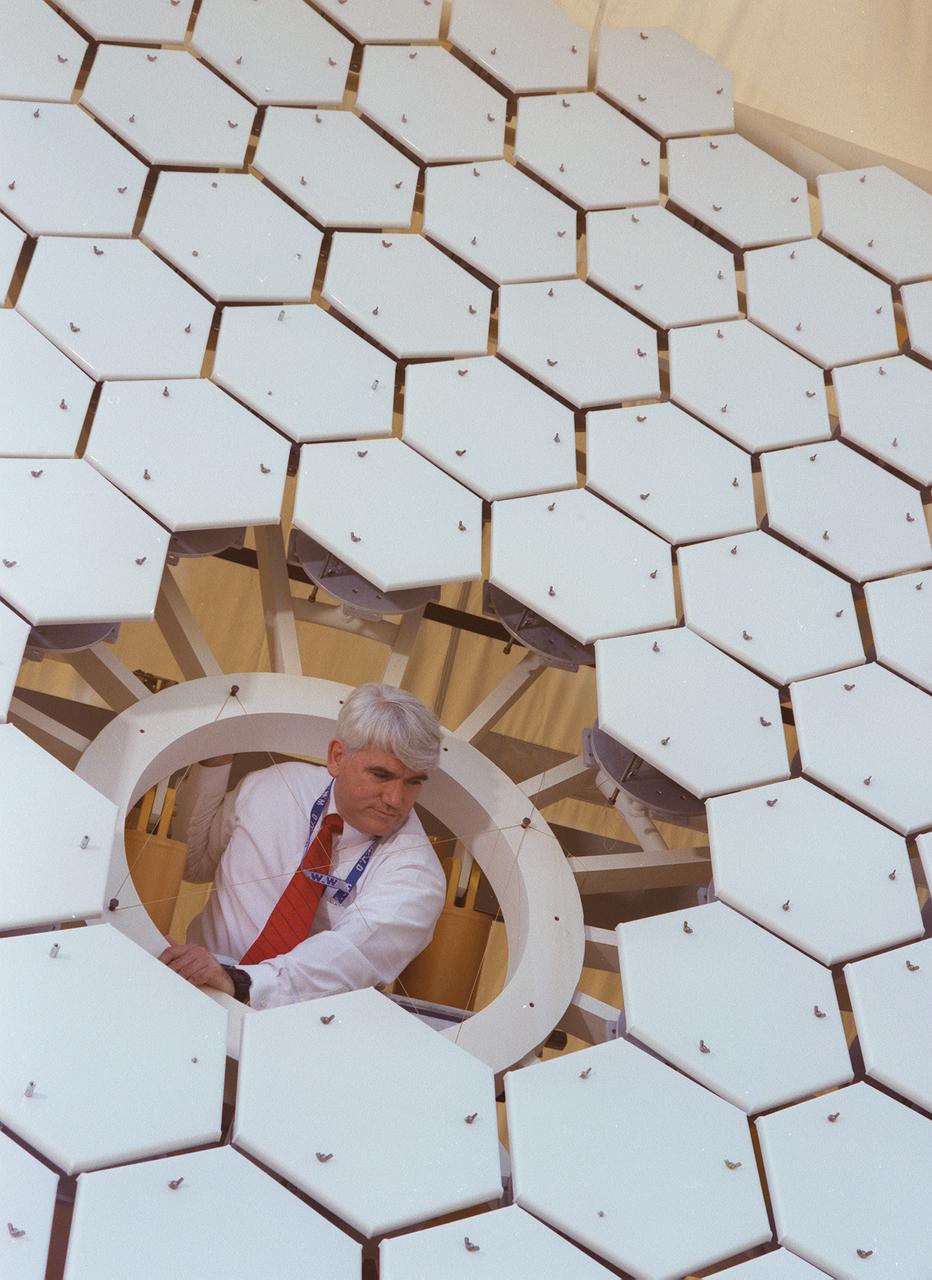
TESTING OF THE KODAK ADVANCE MIRROR SYSTEM DEMONSTRATOR IN THE X-RAY CALIBRATION FACILITY
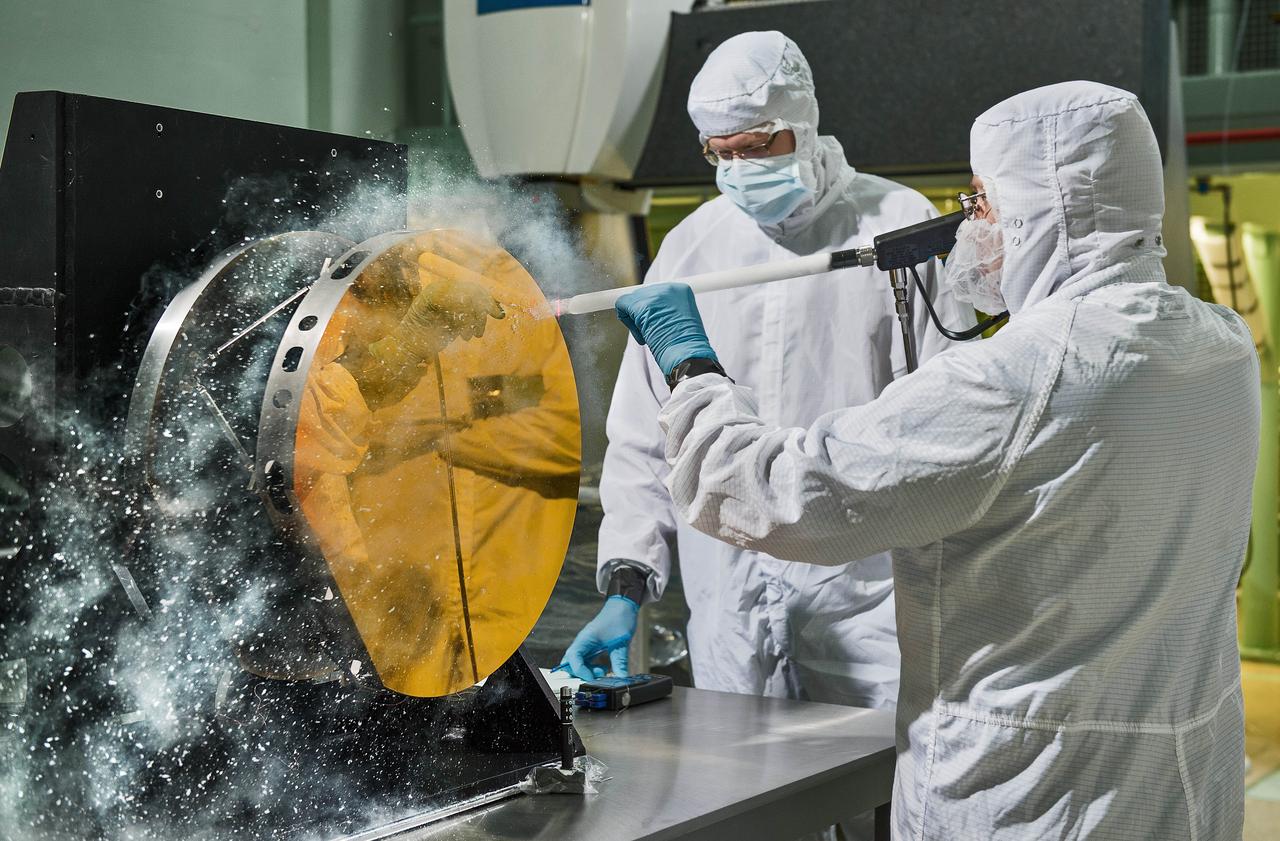

Just like drivers sometimes use snow to clean their car mirrors in winter, two Exelis Inc. engineers are practicing "snow cleaning'" on a test telescope mirror for the James Webb Space Telescope at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. By shooting carbon dioxide snow at the surface, engineers are able to clean large telescope mirrors without scratching them. "The snow-like crystals (carbon dioxide snow) knock contaminate particulates and molecules off the mirror," said Lee Feinberg, NASA optical telescope element manager. This technique will only be used if the James Webb Space Telescope's mirror is contaminated during integration and testing. The Webb telescope is the scientific successor to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. It will be the most powerful space telescope ever built. With a mirror seven times as large as Hubble's and infrared capability, Webb will be capturing light from 13.5 billion light years away. To do this, its mirror must be kept super clean. "Small dust particles or molecules can impact the science that can be done with the Webb," said Feinberg. "So cleanliness especially on the mirrors is critical." Webb is an international project led by NASA with its partners, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. Image credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn
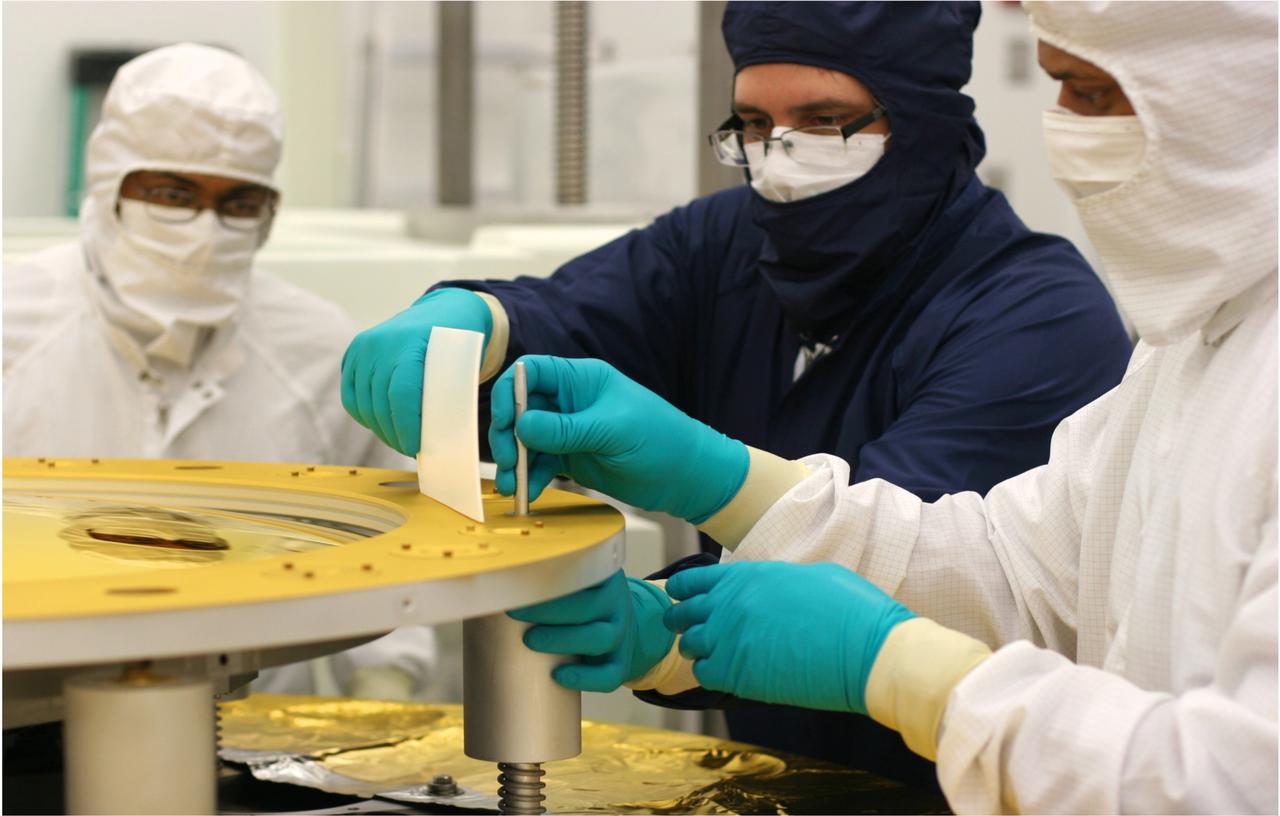

NASA release July 19, 2011 <b>Click here to learn about the <a href="http://www.jwst.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> James Webb Space Telescope</a></b> The secondary mirror (shown here) was polished at the L3 Integrated Optical Systems - Tinsley in Richmond, Calif. to accuracies of less than one millionth of an inch. That accuracy is important for forming the sharpest images when the mirrors cool to -400°F (-240°C) in the cold of space. The Webb's secondary mirror was recently completed, following polishing and gold-coating. "Secondary" may not sound as important as "primary" but when it comes to the next-generation James Webb Space Telescope a secondary mirror plays a critical role in ensuring the telescope gathers information from the cosmos. The Webb's secondary mirror was recently completed, following polishing and gold-coating. There are four different types of mirrors that will fly on the James Webb Space Telescope, and all are made of a light metal called beryllium. It is very strong for its weight and holds its shape across a range of temperatures. There are primary mirror segments (18 total that combined make the large primary mirror providing a collecting area of 25 meters squared/269.1 square feet), the secondary mirror, tertiary mirror and the fine steering mirror. Unlike the primary mirror, which is molded into the shape of a hexagon, the secondary mirror is perfectly rounded. The mirror is also convex, so the reflective surface bulges toward a light source. It looks much like a curved mirror that you'll see on the wall near the exit of a parking garage that lets motorists see around a corner. This mirror is coated with a microscopic layer of gold to enable it to efficiently reflect infrared light (which is what the Webb telescope's cameras see). The quality of the secondary mirror surface is so good that the final convex surface at cold temperatures does not deviate from the design by more than a few millionths of a millimeter - or about one ten thousandth the diameter of a human hair. "As the only convex mirror on the Webb telescope, the secondary mirror has always been recognized to be the hardest of all of the mirrors to polish and test, so we are delighted that its performance meets all specifications," said Lee Feinberg, Webb Optical Telescope manager at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Convex mirrors are particularly hard to test because light that strikes them diverges away from the mirror. Feinberg noted, "The Webb telescope convex secondary mirror is approximately the size of the Spitzer Space Telescope's primary mirror and is by far the largest convex cryogenic mirror ever built for a NASA program." It was data from the Spitzer's mirrors that helped make the decision to use beryllium for the Webb telescope mirrors. Spitzer's mirrors were also made of beryllium. So why is this mirror so critical? Because the secondary mirror captures light from the 18 primary mirror segments and relays those distant images of the cosmos to the telescope's science cameras. The secondary mirror is mounted on folding "arms" that position it in front of the 18 primary mirror segments. The secondary mirror will soon come to NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. where it will be installed on the telescope structure. Then, as a complete unit, the telescope structure and mirrors will undergo acoustic and vibration testing. The secondary mirror was developed at Ball Aerospace & Technology Corp. of Boulder, Colo. and the mirror recently completed polishing at the L3–IOS-Tinsley facility in Richmond, Calif. Northrop Grumman space Systems is the prime contractor on the Webb telescope program. The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s next-generation space observatory and successor to the Hubble Space Telescope. The most powerful space telescope ever built, Webb will observe the most distant objects in the universe, provide images of the very first galaxies ever formed and see unexplored planets around distant stars. The Webb Telescope is a joint project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. Credit:NASA/Ball Aerospace/Tinsley <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
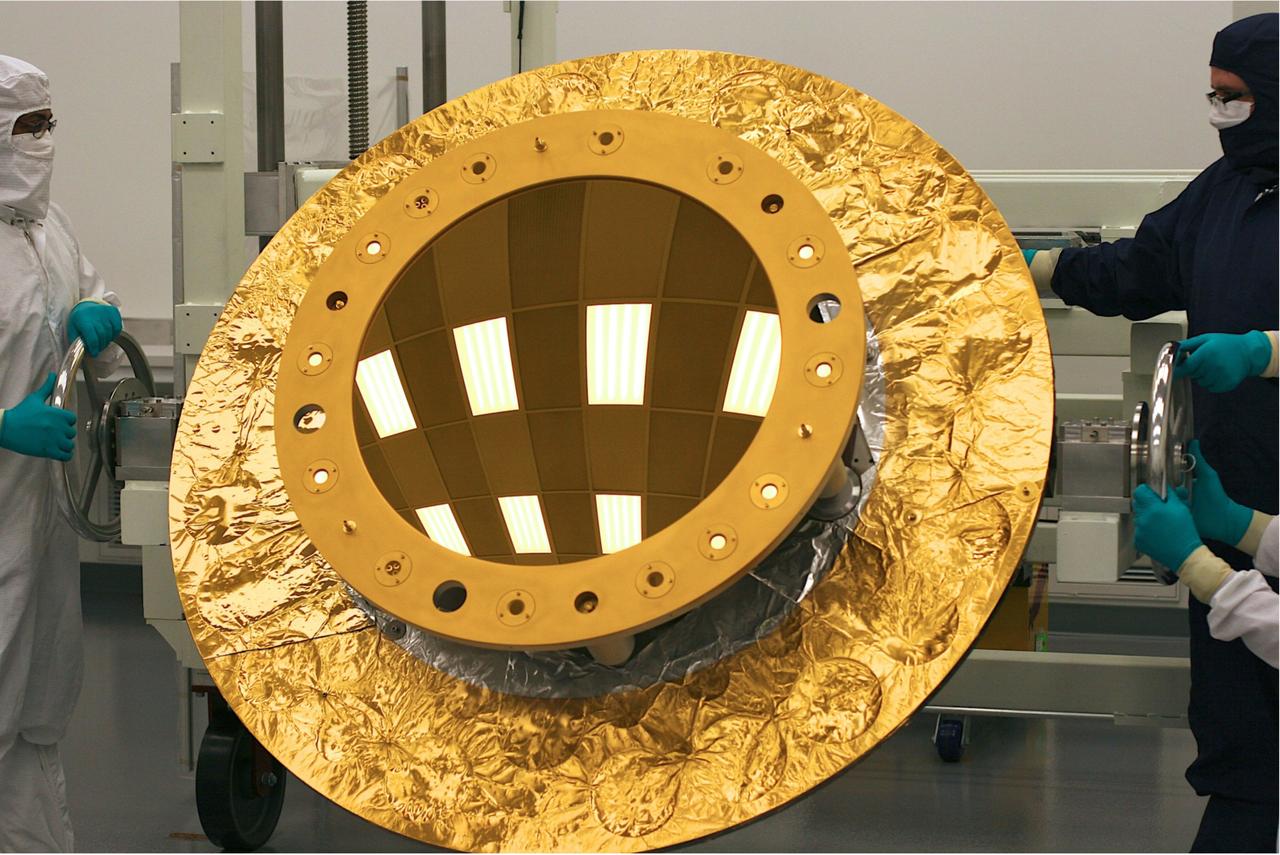

NASA release July 19, 2011 <b>Click here to learn about the <a href="http://www.jwst.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> James Webb Space Telescope</a></b> The secondary mirror (shown here) was polished at the L3 Integrated Optical Systems - Tinsley in Richmond, Calif. to accuracies of less than one millionth of an inch. That accuracy is important for forming the sharpest images when the mirrors cool to -400°F (-240°C) in the cold of space. The Webb's secondary mirror was recently completed, following polishing and gold-coating. "Secondary" may not sound as important as "primary" but when it comes to the next-generation James Webb Space Telescope a secondary mirror plays a critical role in ensuring the telescope gathers information from the cosmos. The Webb's secondary mirror was recently completed, following polishing and gold-coating. There are four different types of mirrors that will fly on the James Webb Space Telescope, and all are made of a light metal called beryllium. It is very strong for its weight and holds its shape across a range of temperatures. There are primary mirror segments (18 total that combined make the large primary mirror providing a collecting area of 25 meters squared/269.1 square feet), the secondary mirror, tertiary mirror and the fine steering mirror. Unlike the primary mirror, which is molded into the shape of a hexagon, the secondary mirror is perfectly rounded. The mirror is also convex, so the reflective surface bulges toward a light source. It looks much like a curved mirror that you'll see on the wall near the exit of a parking garage that lets motorists see around a corner. This mirror is coated with a microscopic layer of gold to enable it to efficiently reflect infrared light (which is what the Webb telescope's cameras see). The quality of the secondary mirror surface is so good that the final convex surface at cold temperatures does not deviate from the design by more than a few millionths of a millimeter - or about one ten thousandth the diameter of a human hair. "As the only convex mirror on the Webb telescope, the secondary mirror has always been recognized to be the hardest of all of the mirrors to polish and test, so we are delighted that its performance meets all specifications," said Lee Feinberg, Webb Optical Telescope manager at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Convex mirrors are particularly hard to test because light that strikes them diverges away from the mirror. Feinberg noted, "The Webb telescope convex secondary mirror is approximately the size of the Spitzer Space Telescope's primary mirror and is by far the largest convex cryogenic mirror ever built for a NASA program." It was data from the Spitzer's mirrors that helped make the decision to use beryllium for the Webb telescope mirrors. Spitzer's mirrors were also made of beryllium. So why is this mirror so critical? Because the secondary mirror captures light from the 18 primary mirror segments and relays those distant images of the cosmos to the telescope's science cameras. The secondary mirror is mounted on folding "arms" that position it in front of the 18 primary mirror segments. The secondary mirror will soon come to NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. where it will be installed on the telescope structure. Then, as a complete unit, the telescope structure and mirrors will undergo acoustic and vibration testing. The secondary mirror was developed at Ball Aerospace & Technology Corp. of Boulder, Colo. and the mirror recently completed polishing at the L3–IOS-Tinsley facility in Richmond, Calif. Northrop Grumman space Systems is the prime contractor on the Webb telescope program. The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s next-generation space observatory and successor to the Hubble Space Telescope. The most powerful space telescope ever built, Webb will observe the most distant objects in the universe, provide images of the very first galaxies ever formed and see unexplored planets around distant stars. The Webb Telescope is a joint project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. Credit:NASA/Ball Aerospace/Tinsley <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
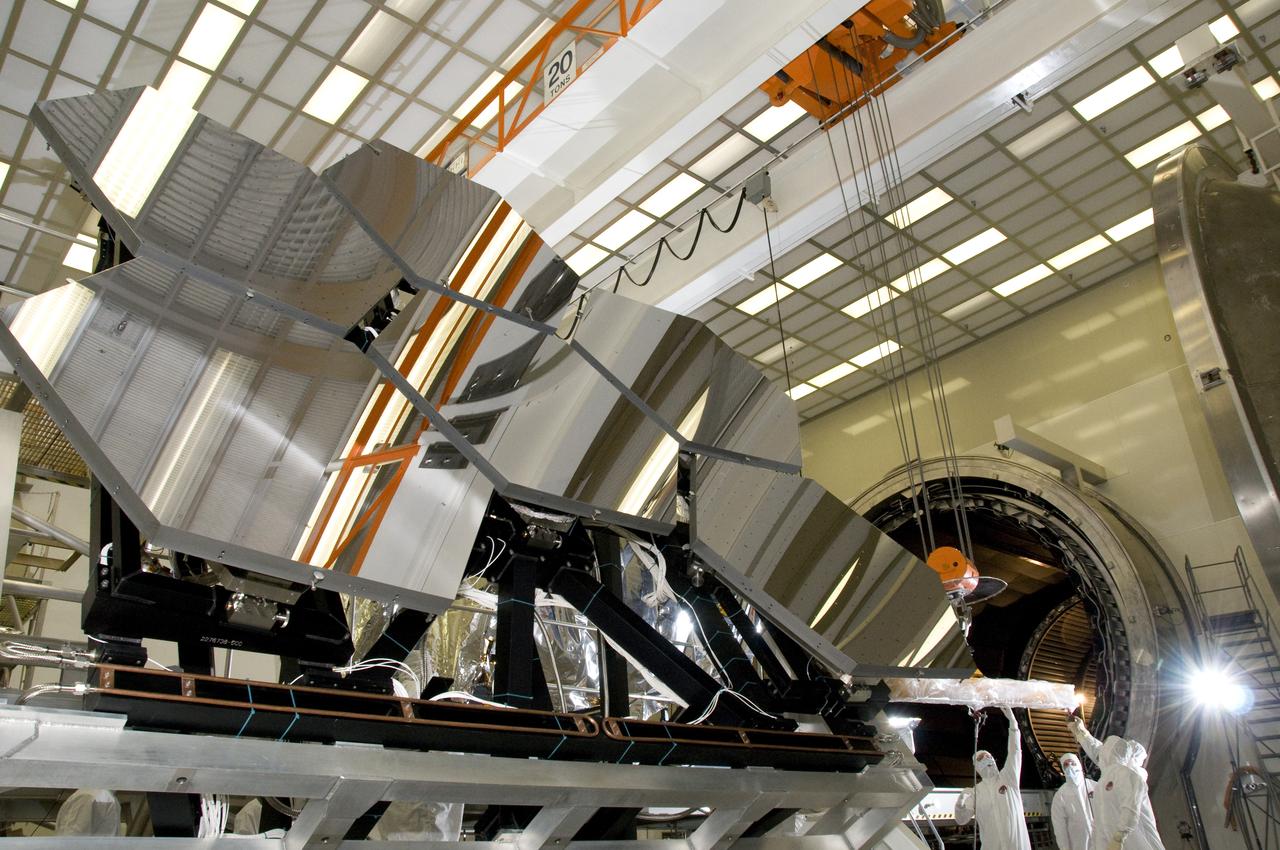

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
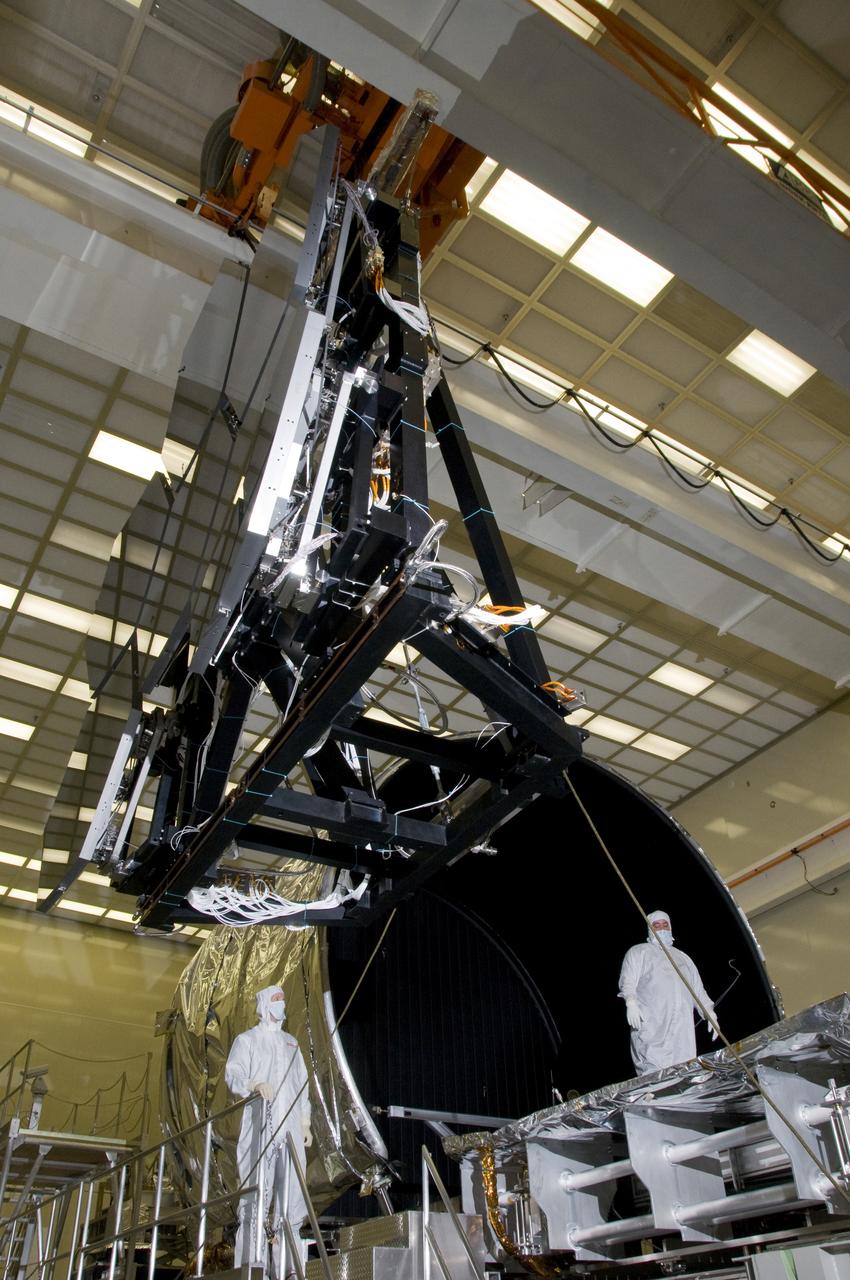

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
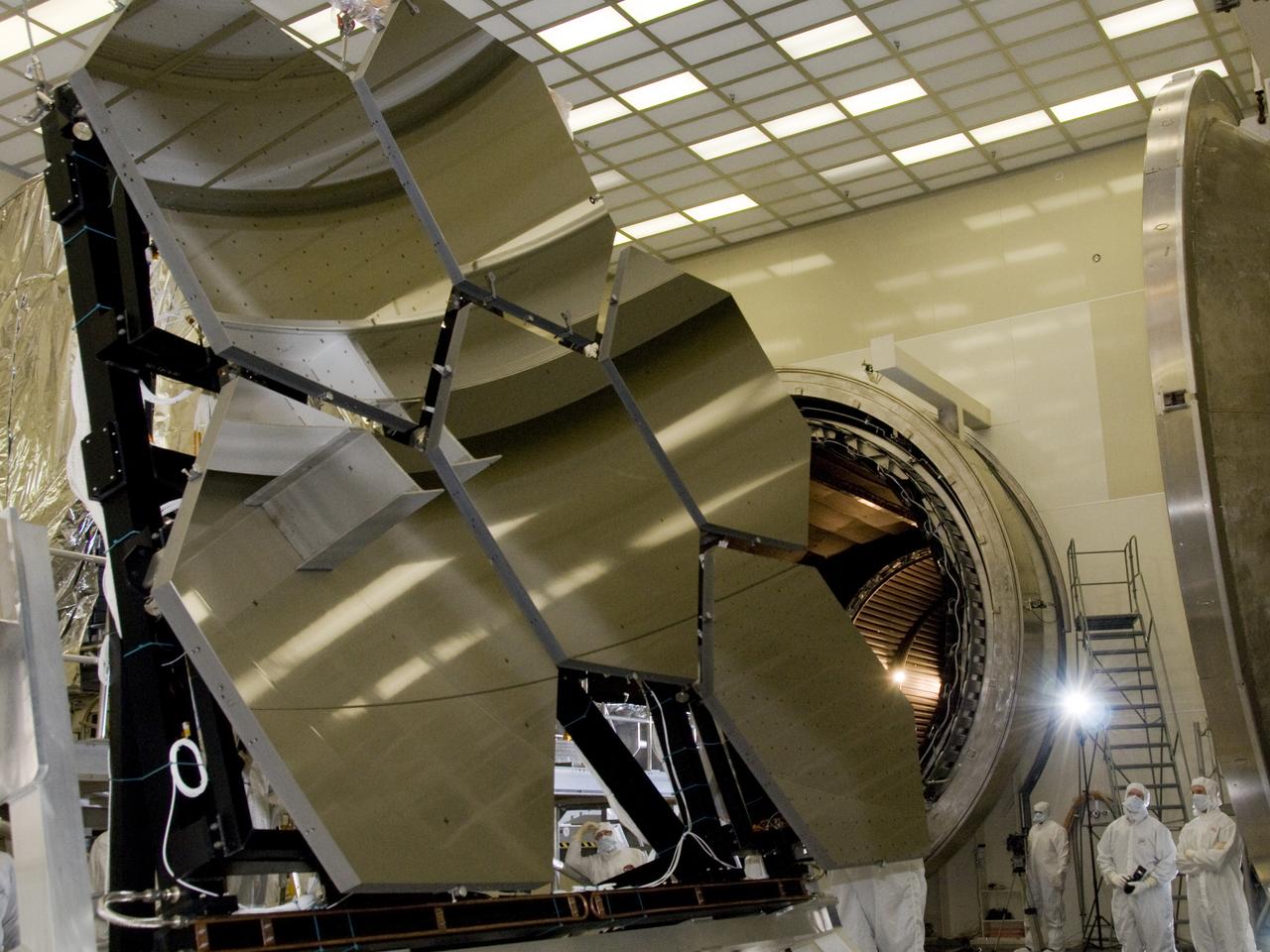

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
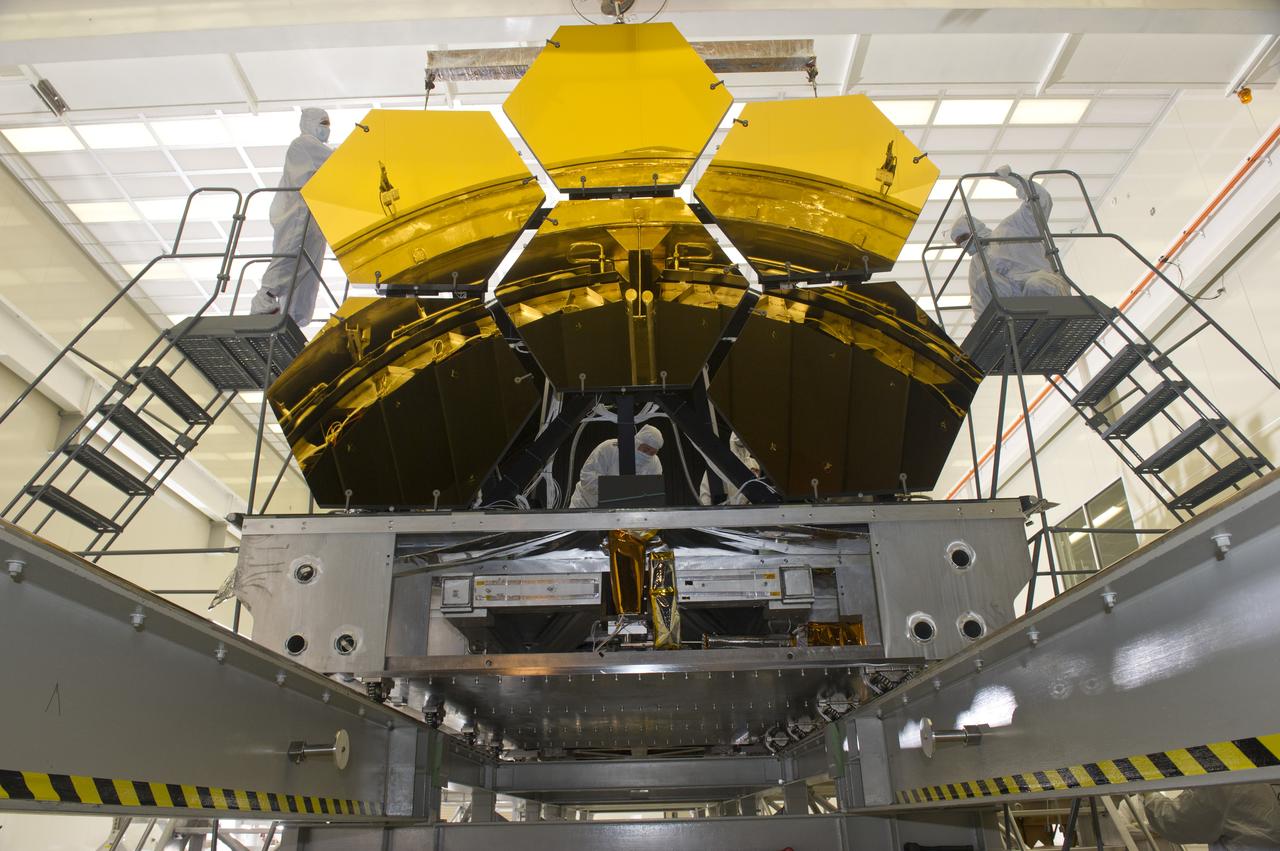

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
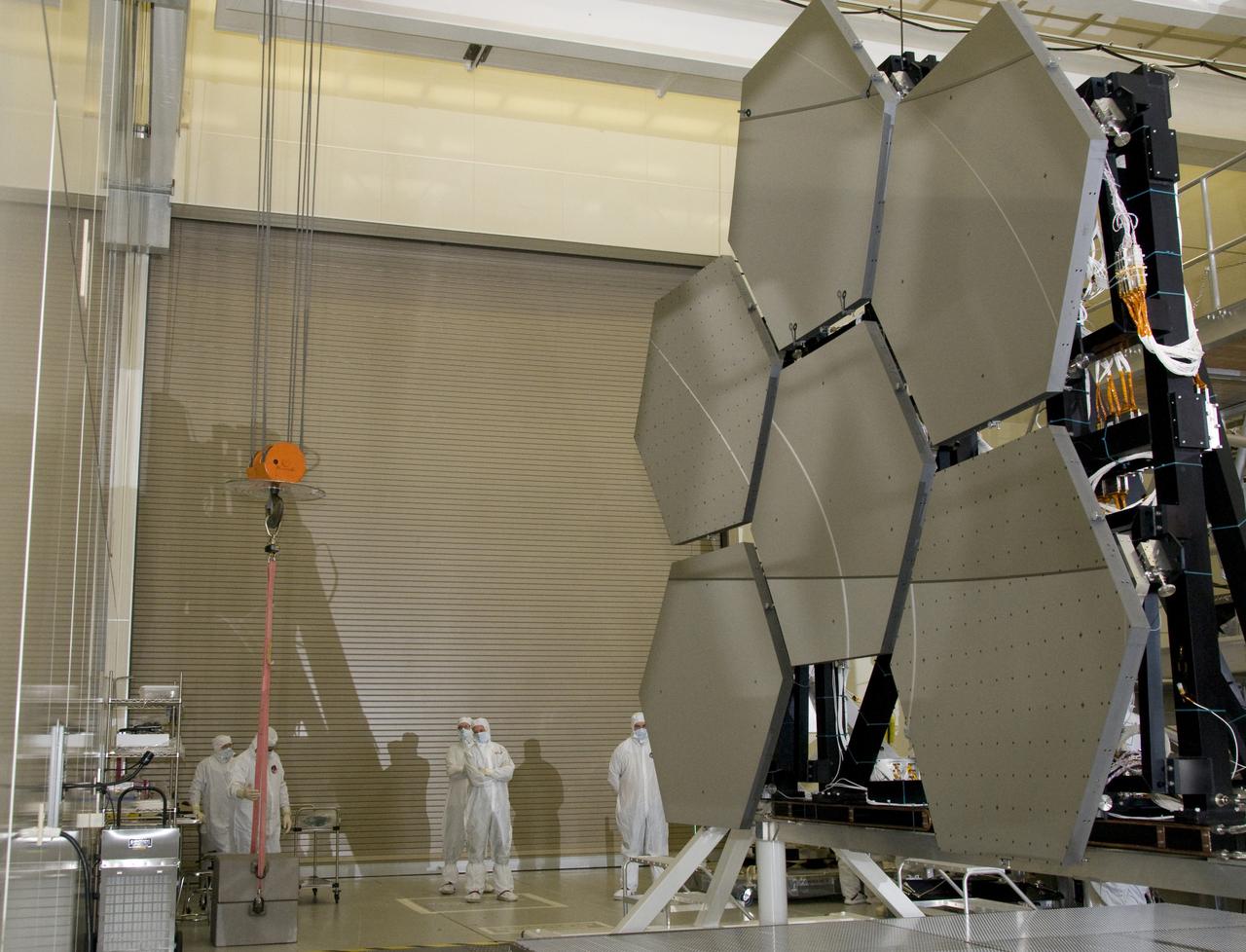

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
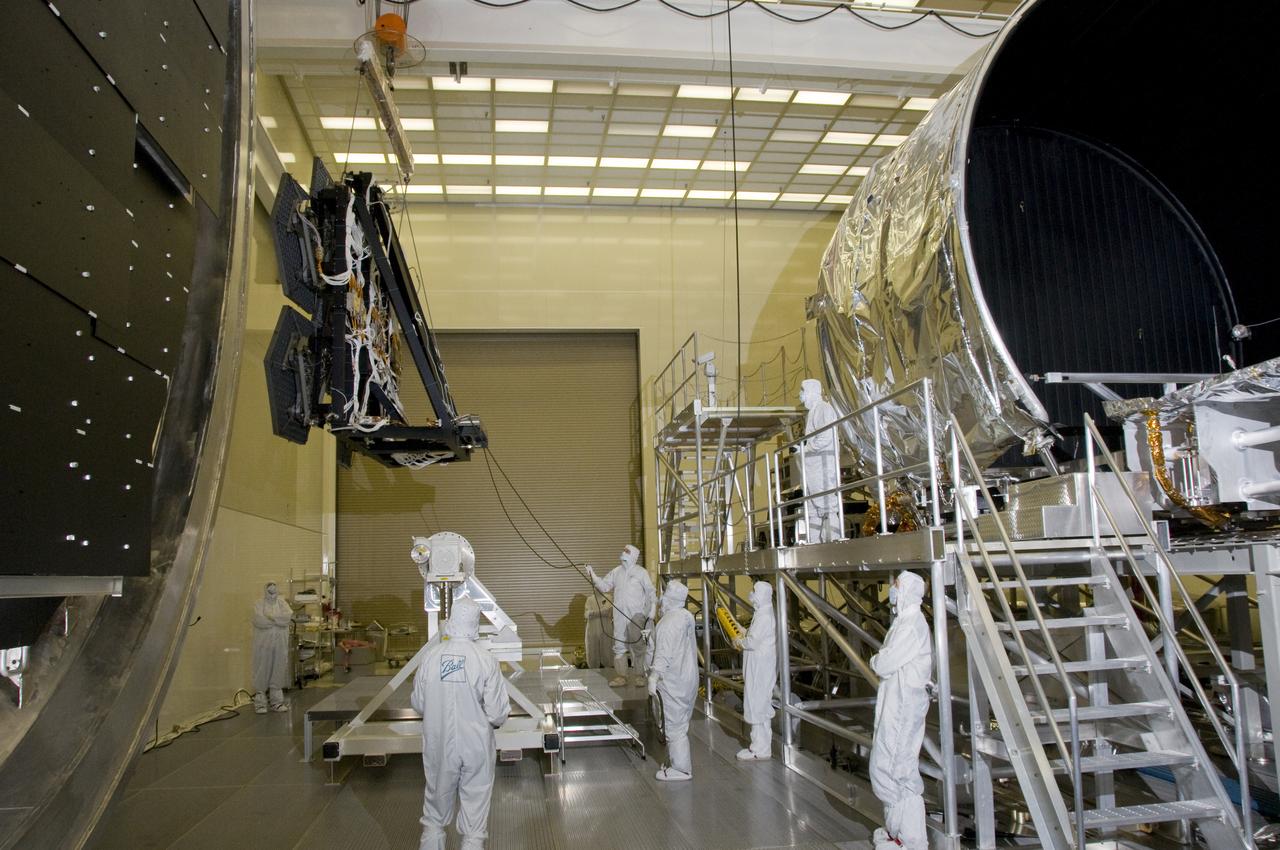

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
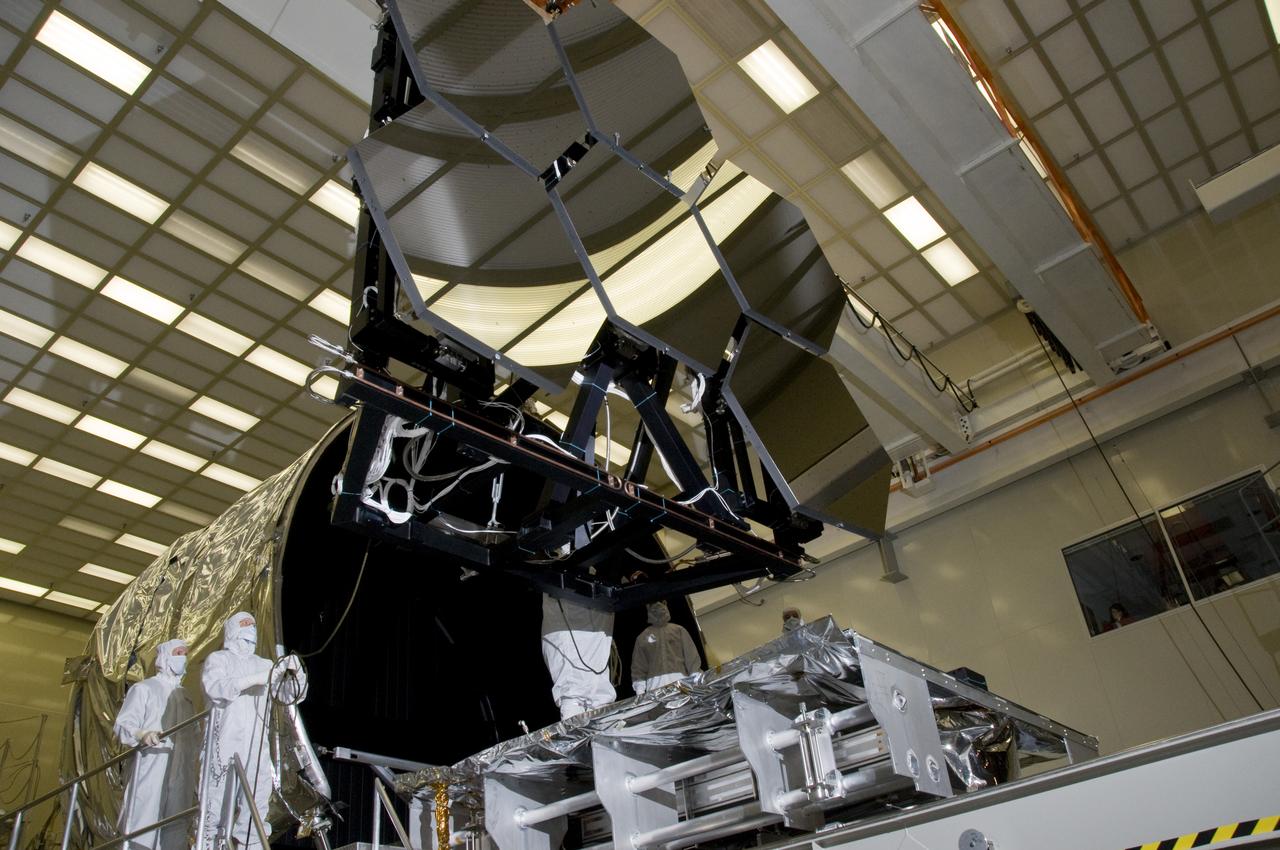

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
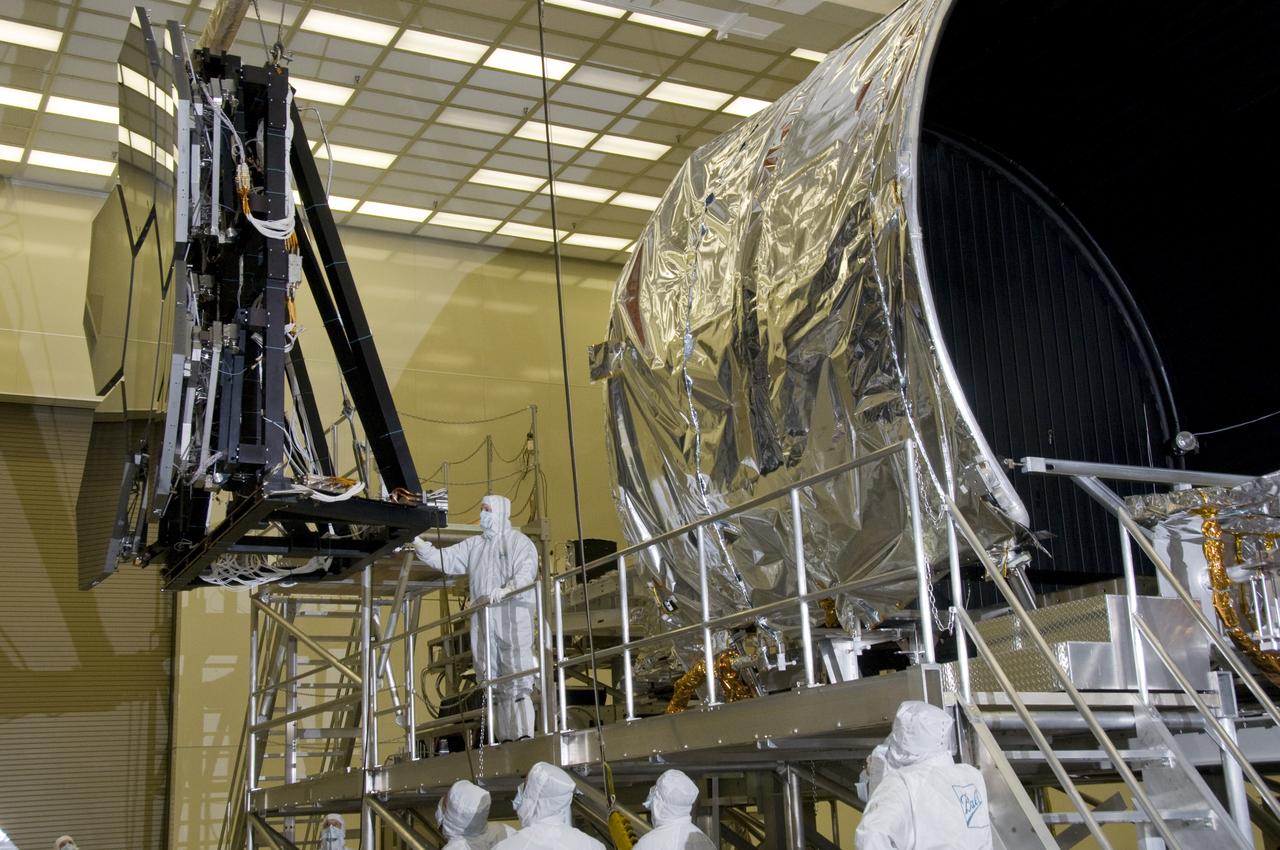

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
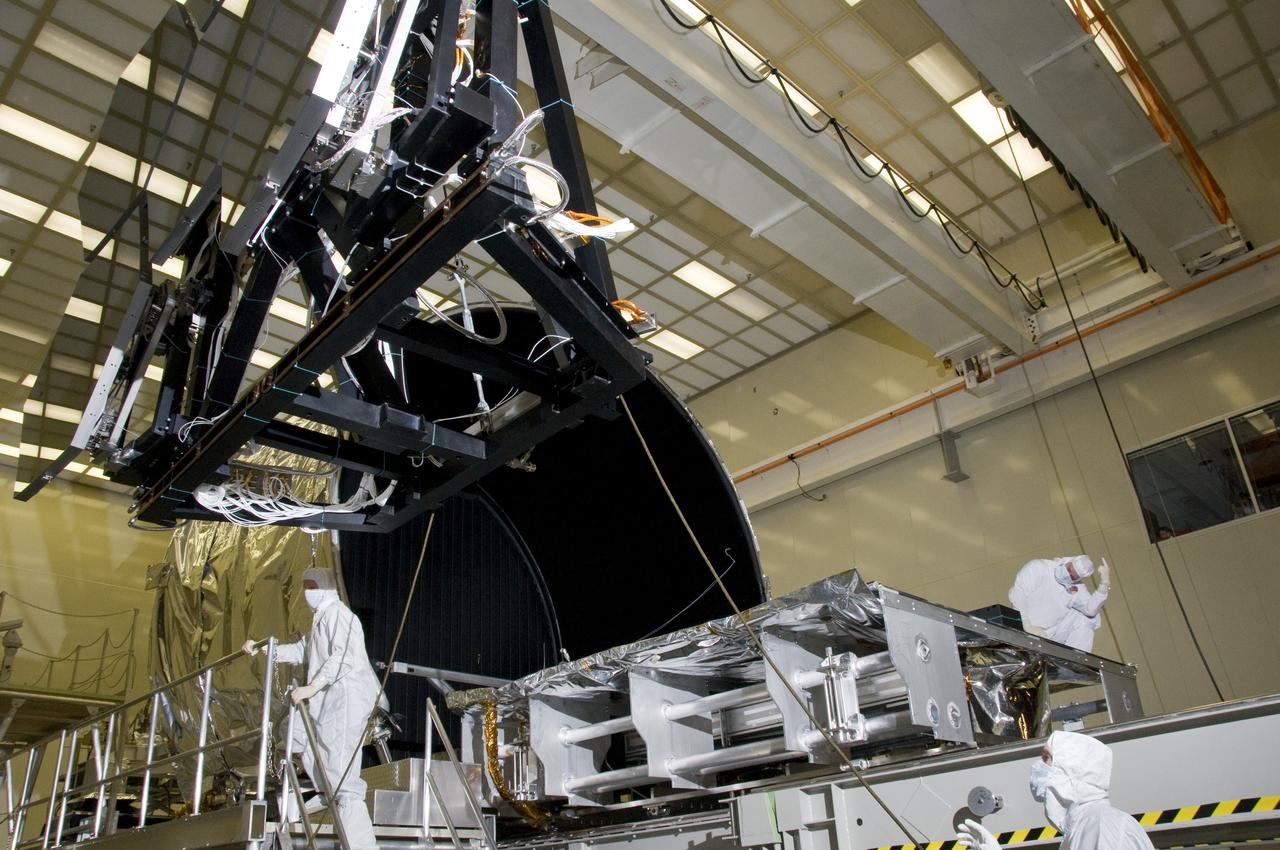

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
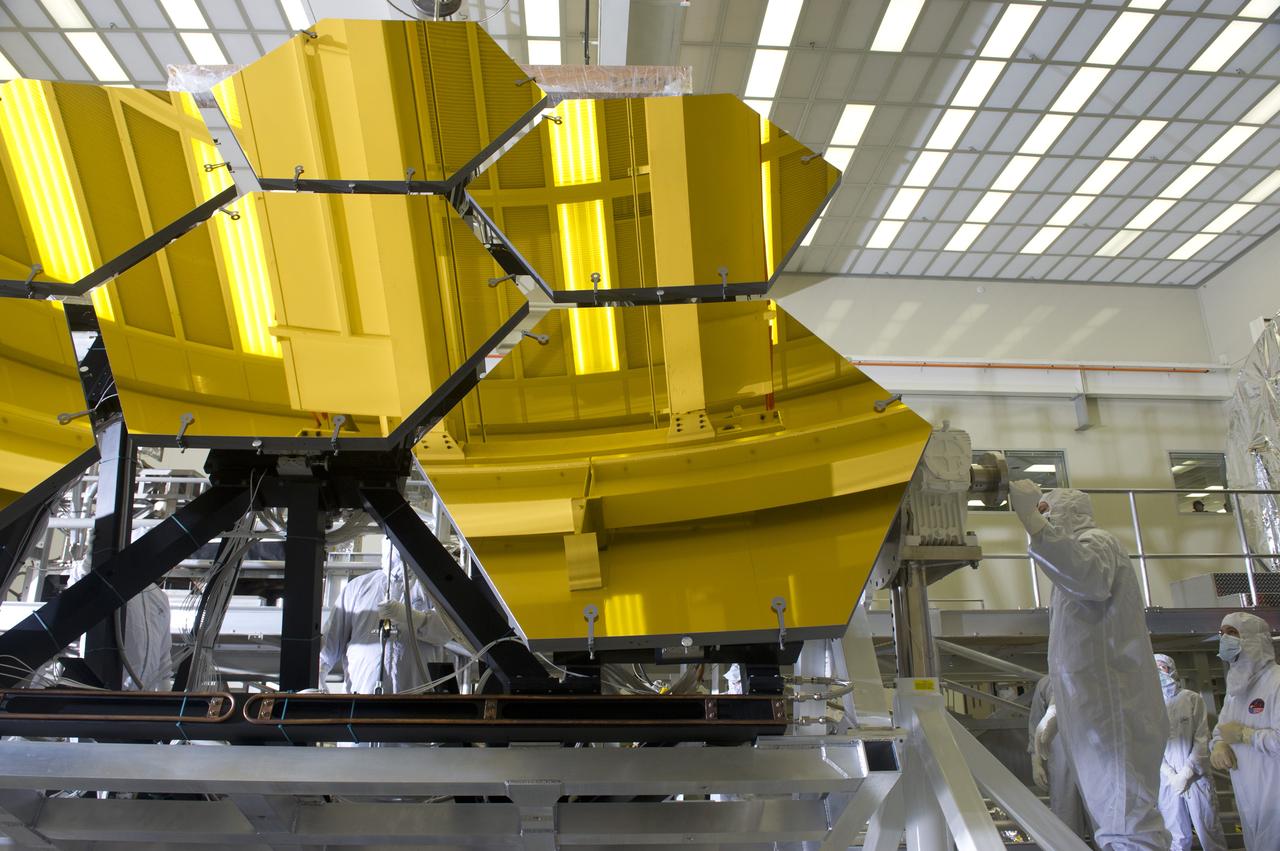

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
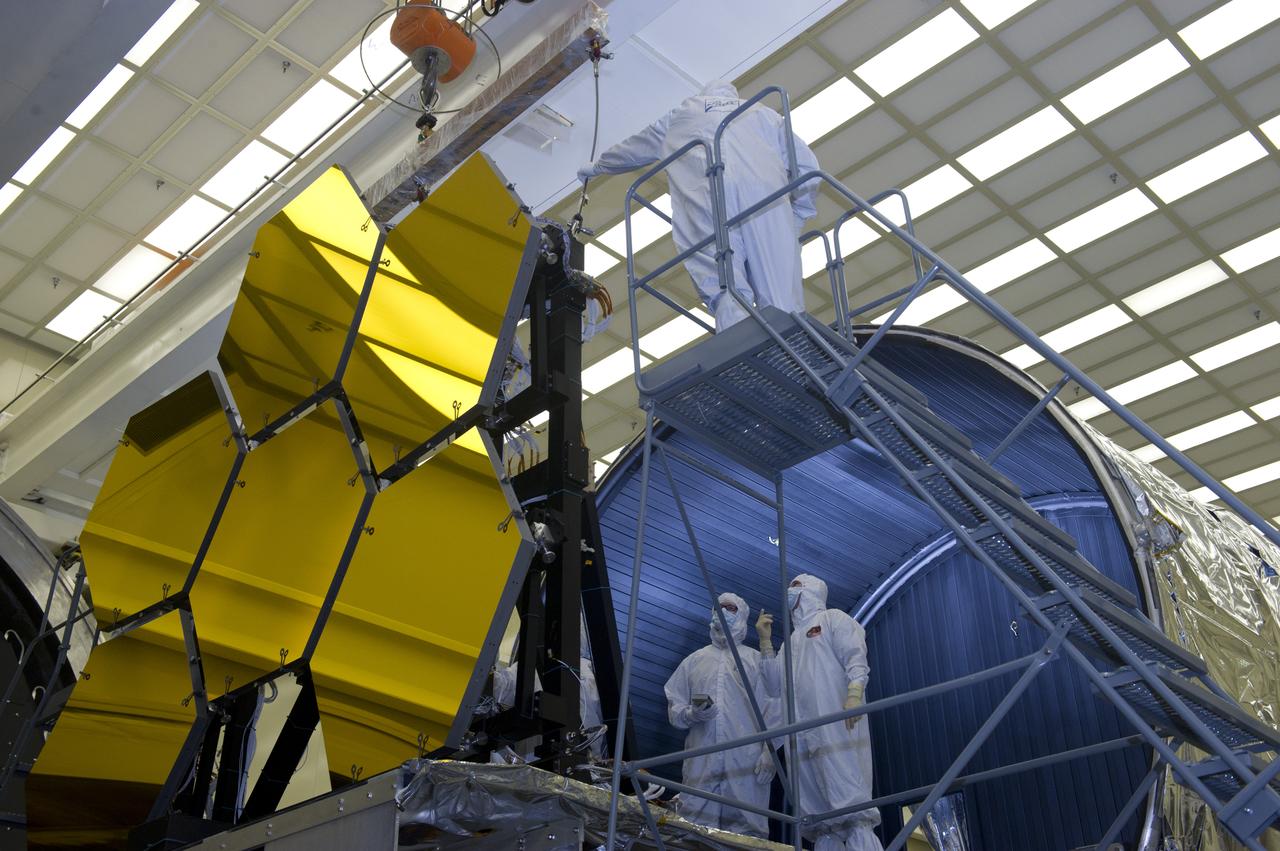

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
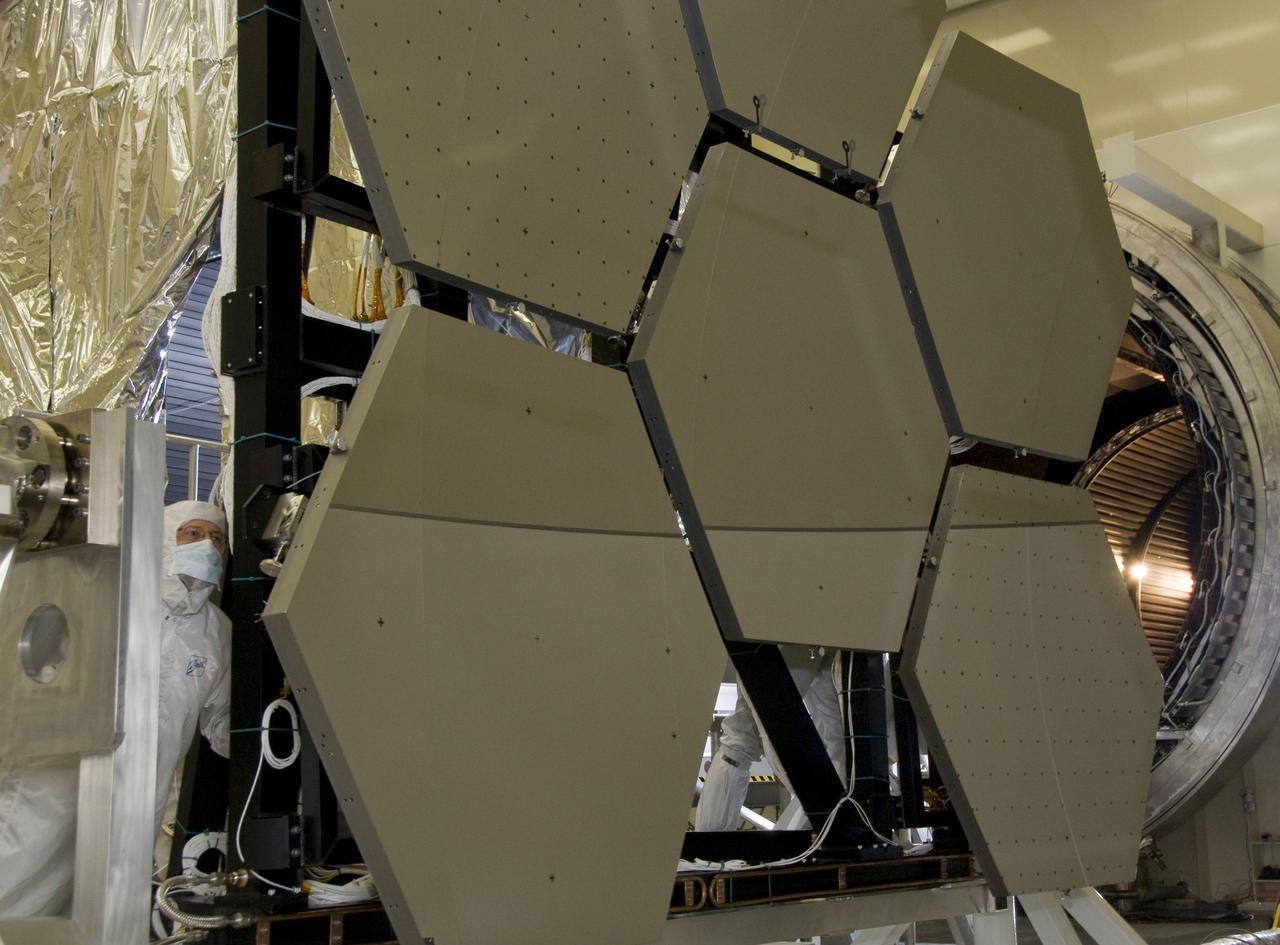

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
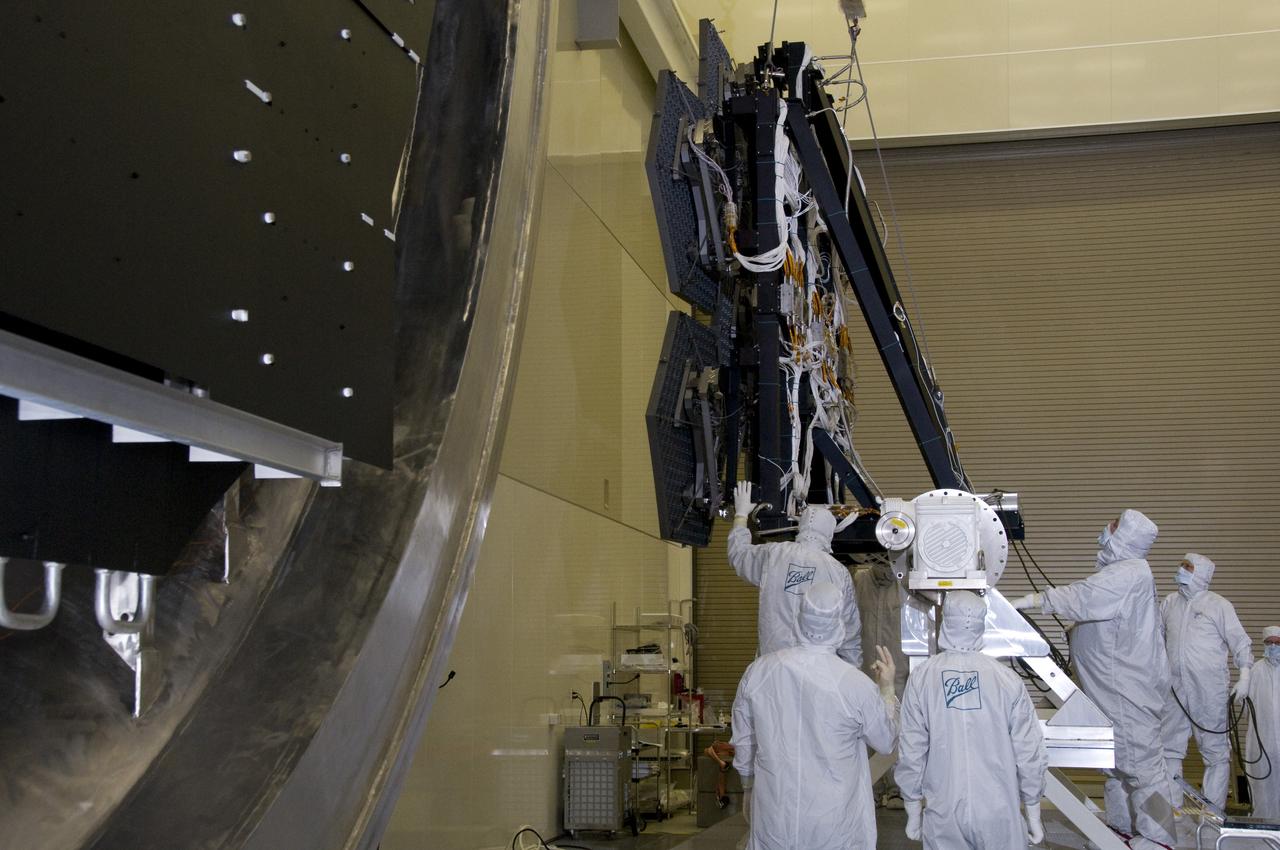

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
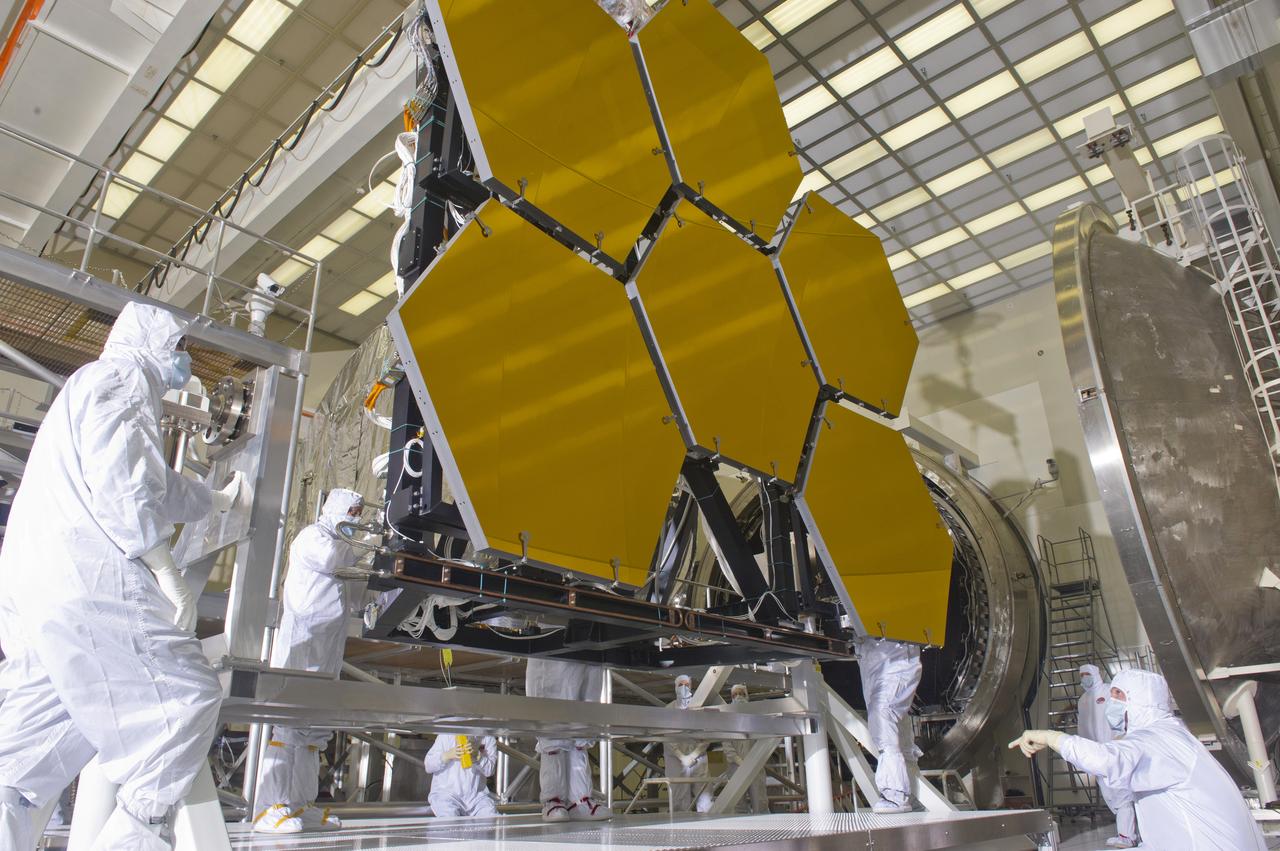

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
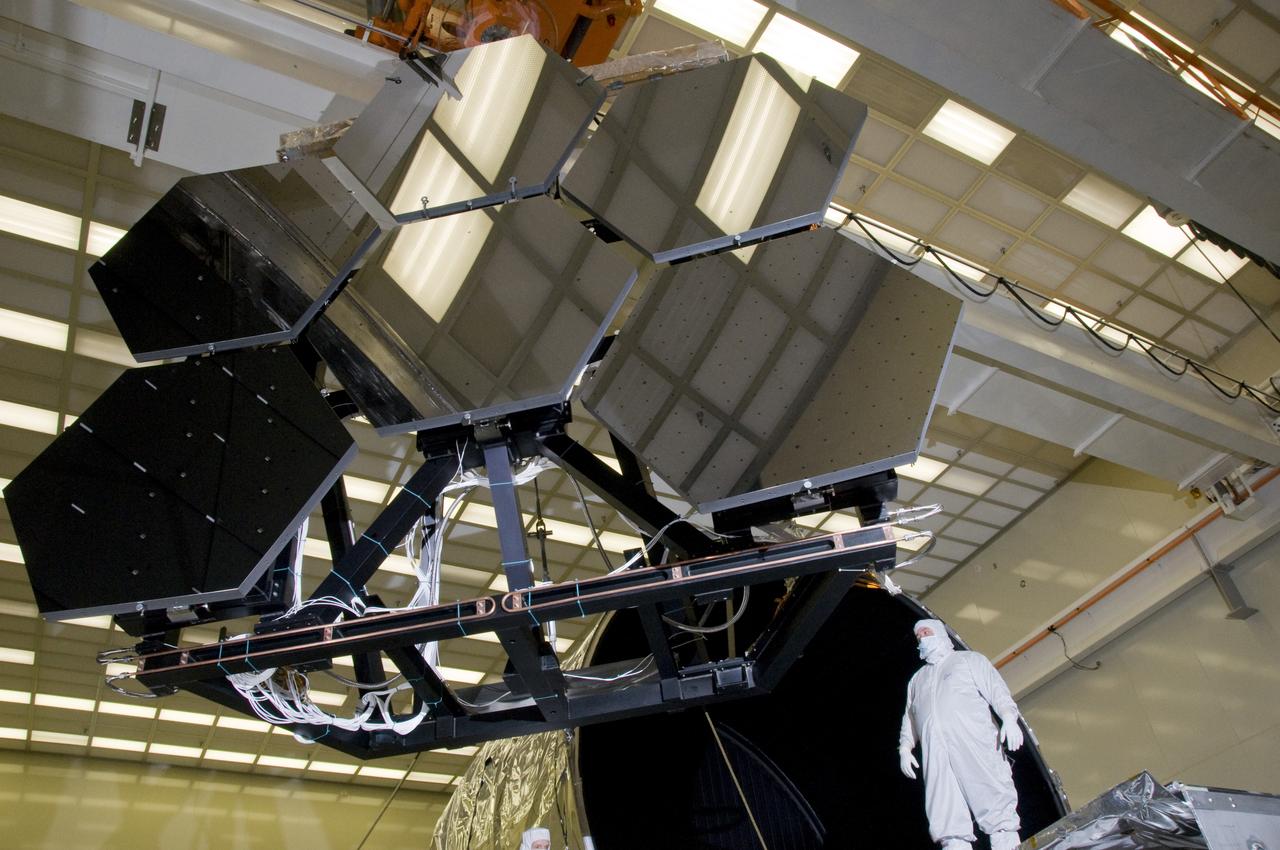

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
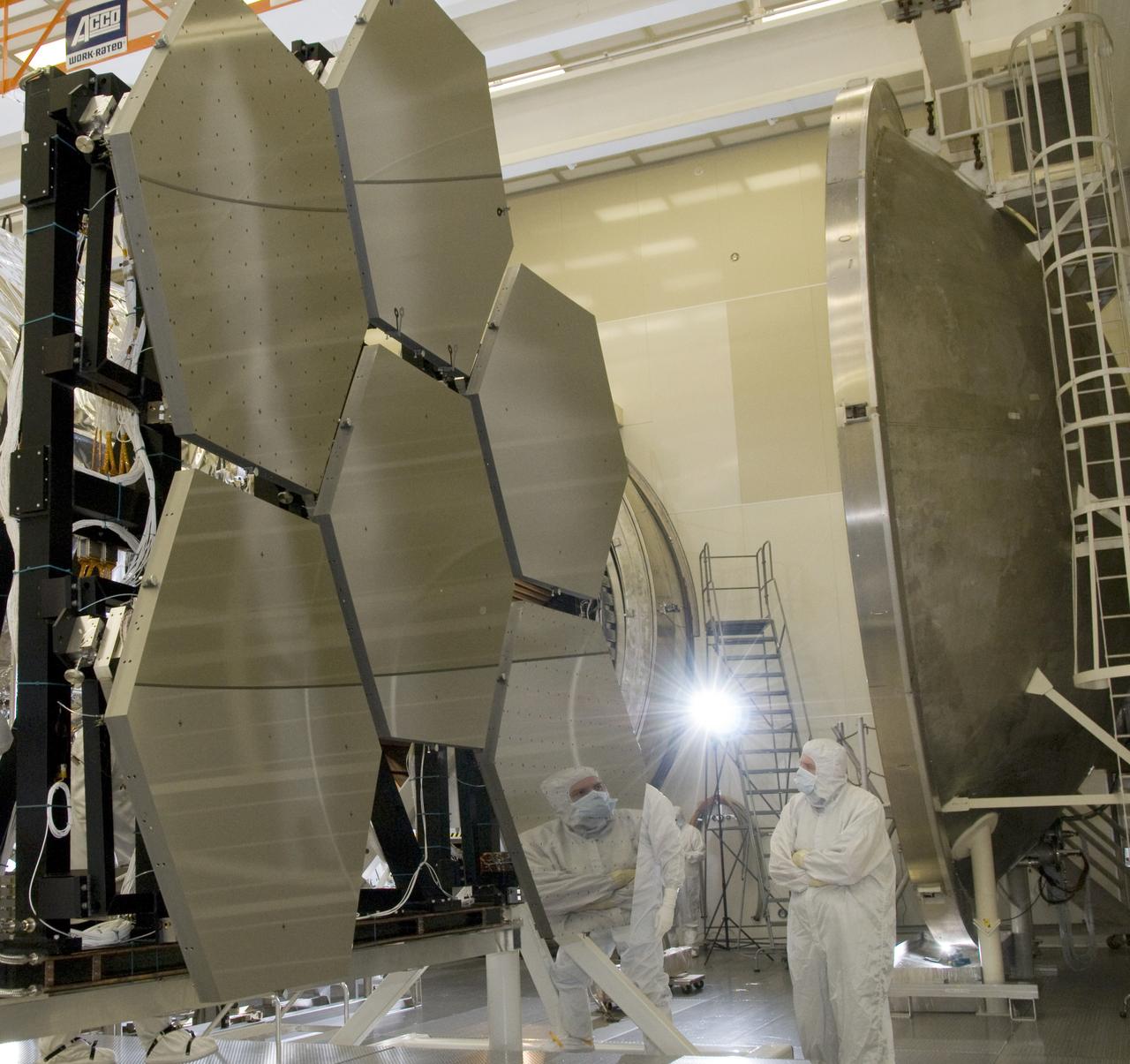

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
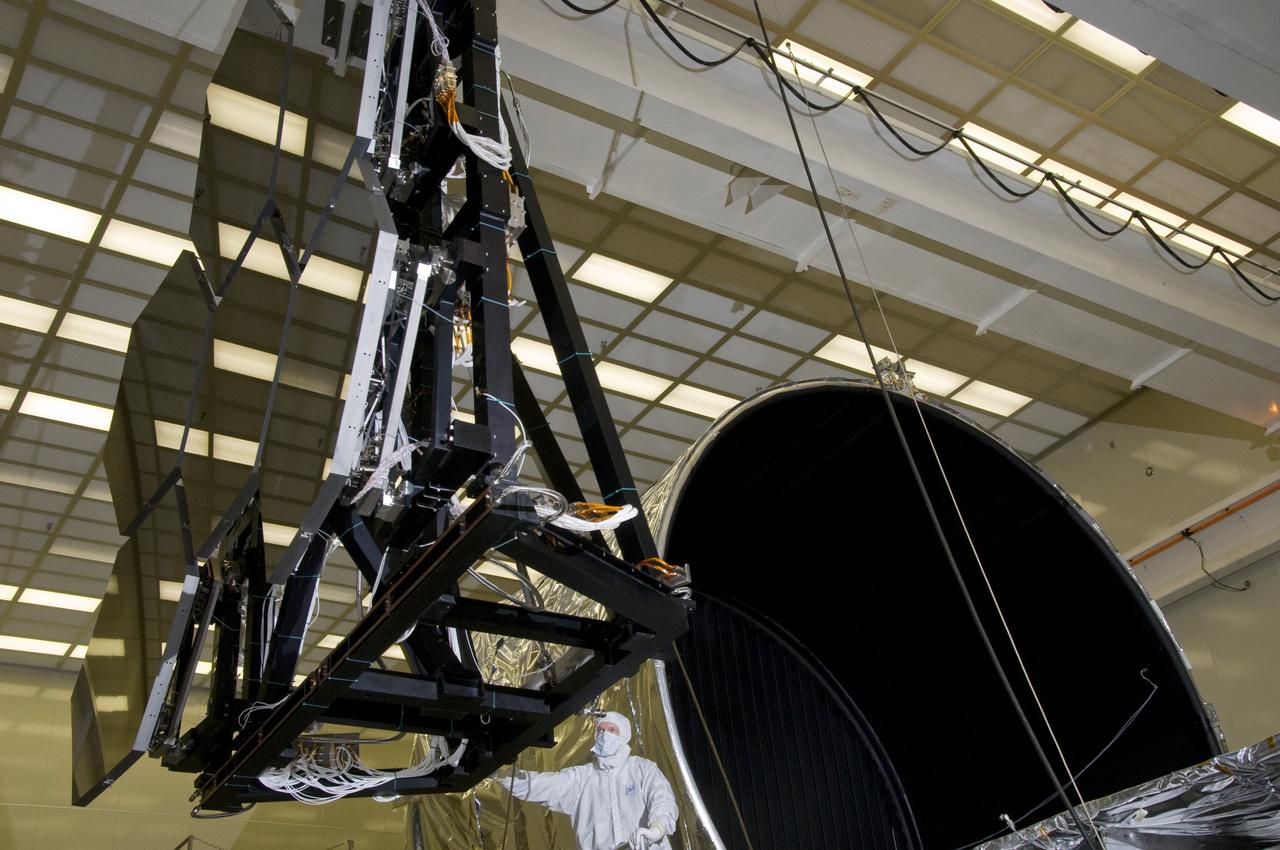

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.

Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility-S (AXAF-S) nickel prototype mirror optical test setup.
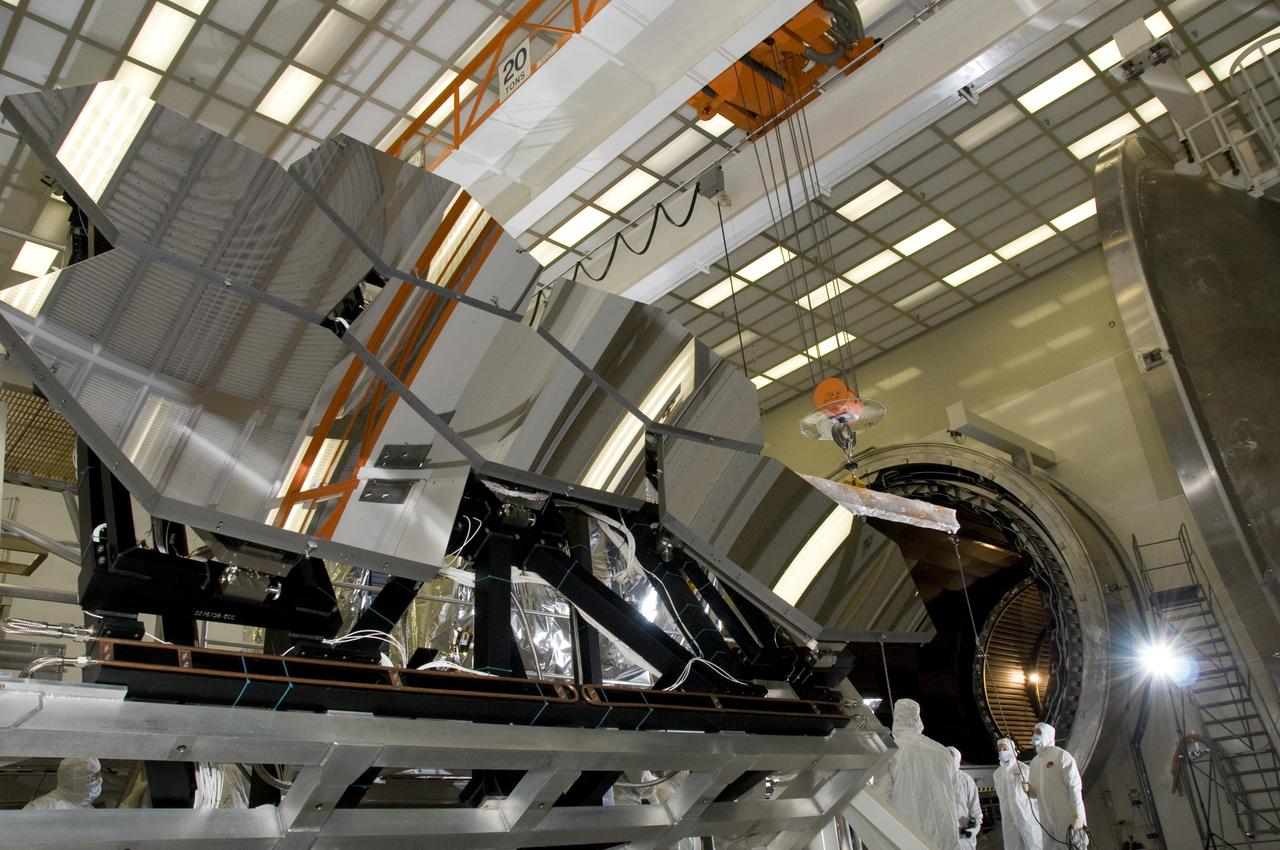

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
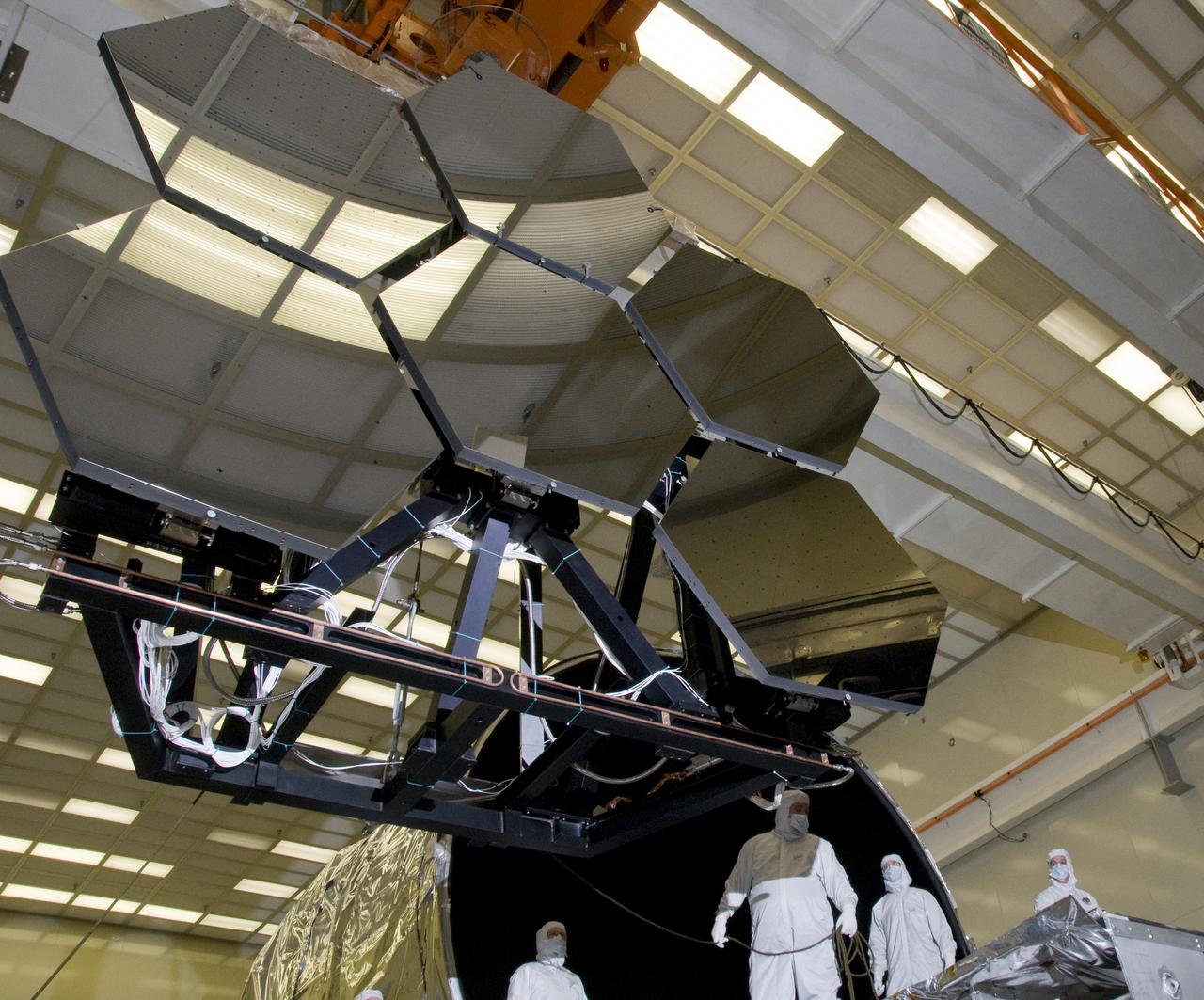

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
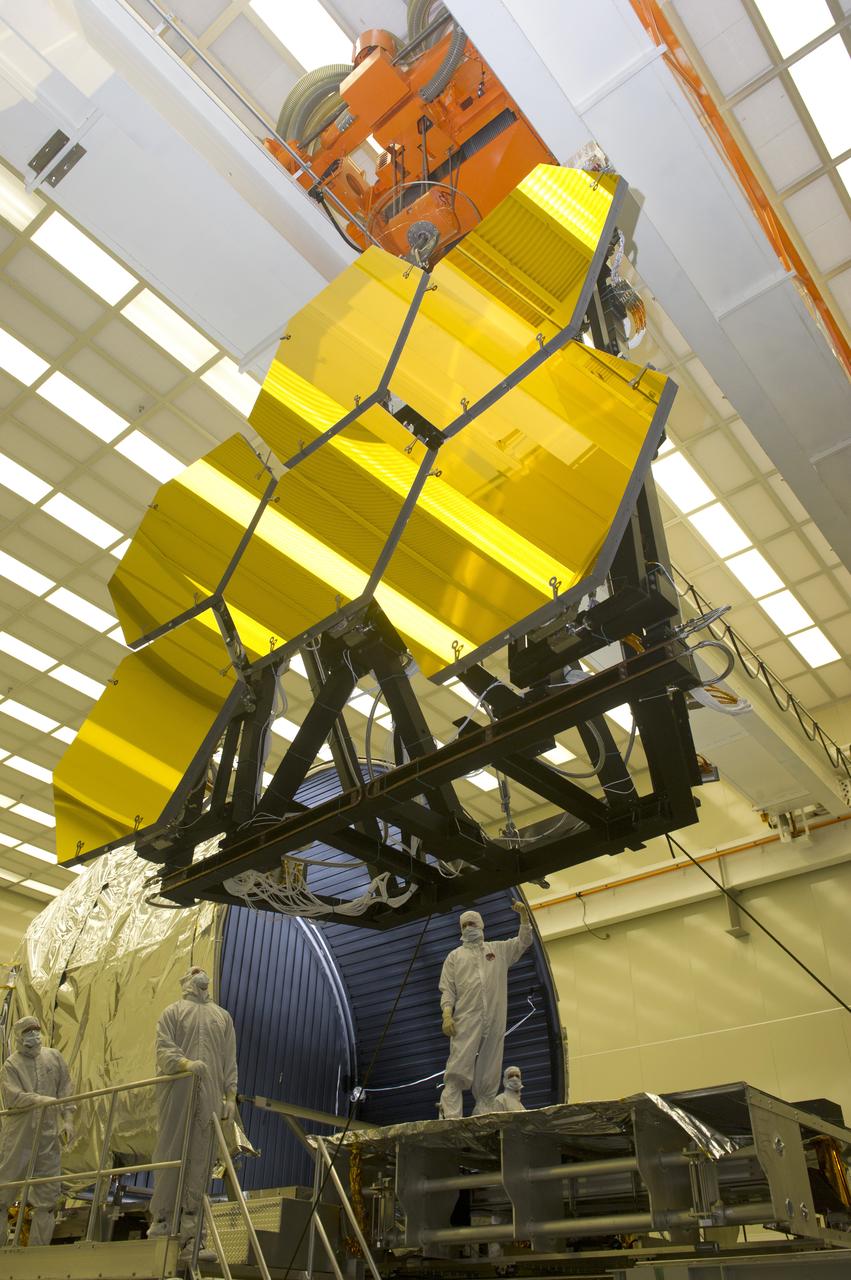

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
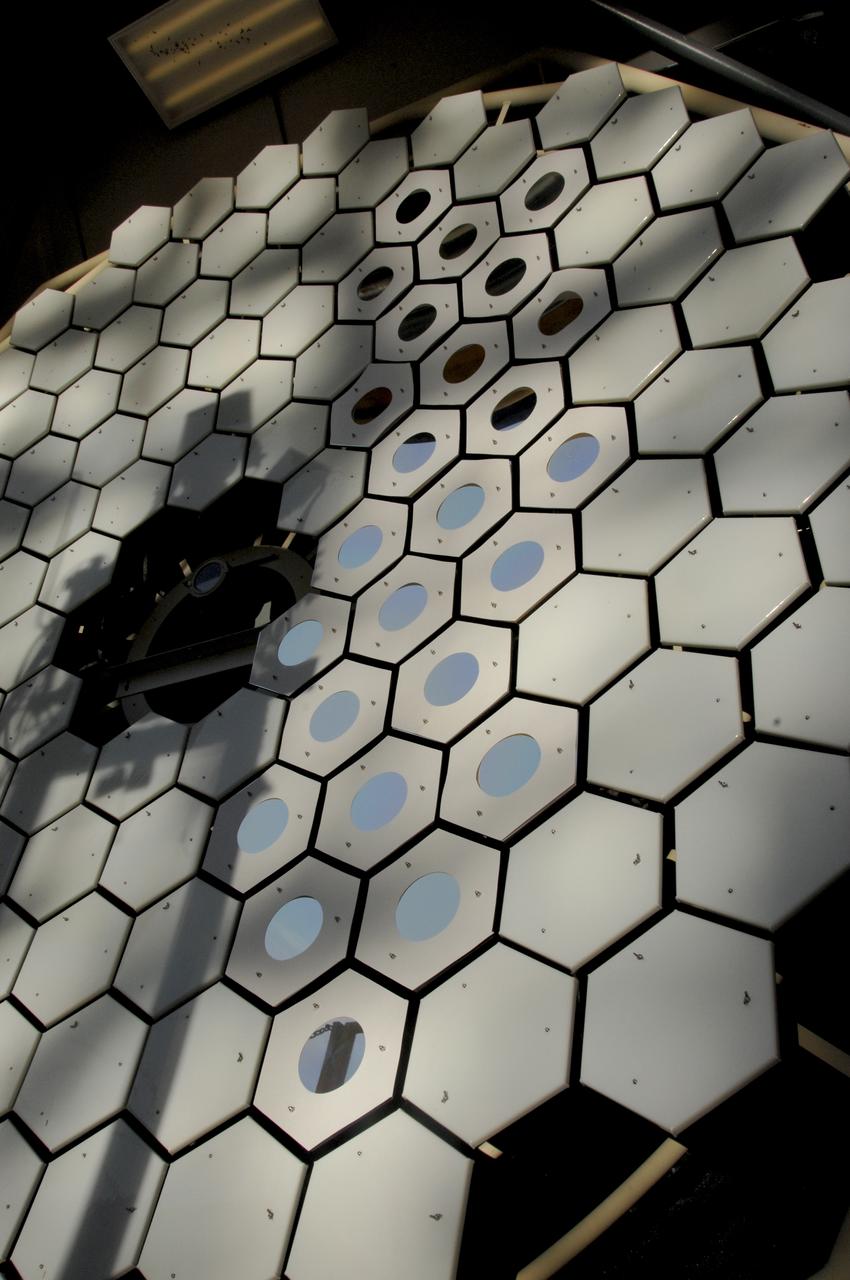

PA084 SOLAR THERMAL PROPULSION. BLDG 4590 STROFIO THERMAL BALANCE TEST, MIRROR VIEW
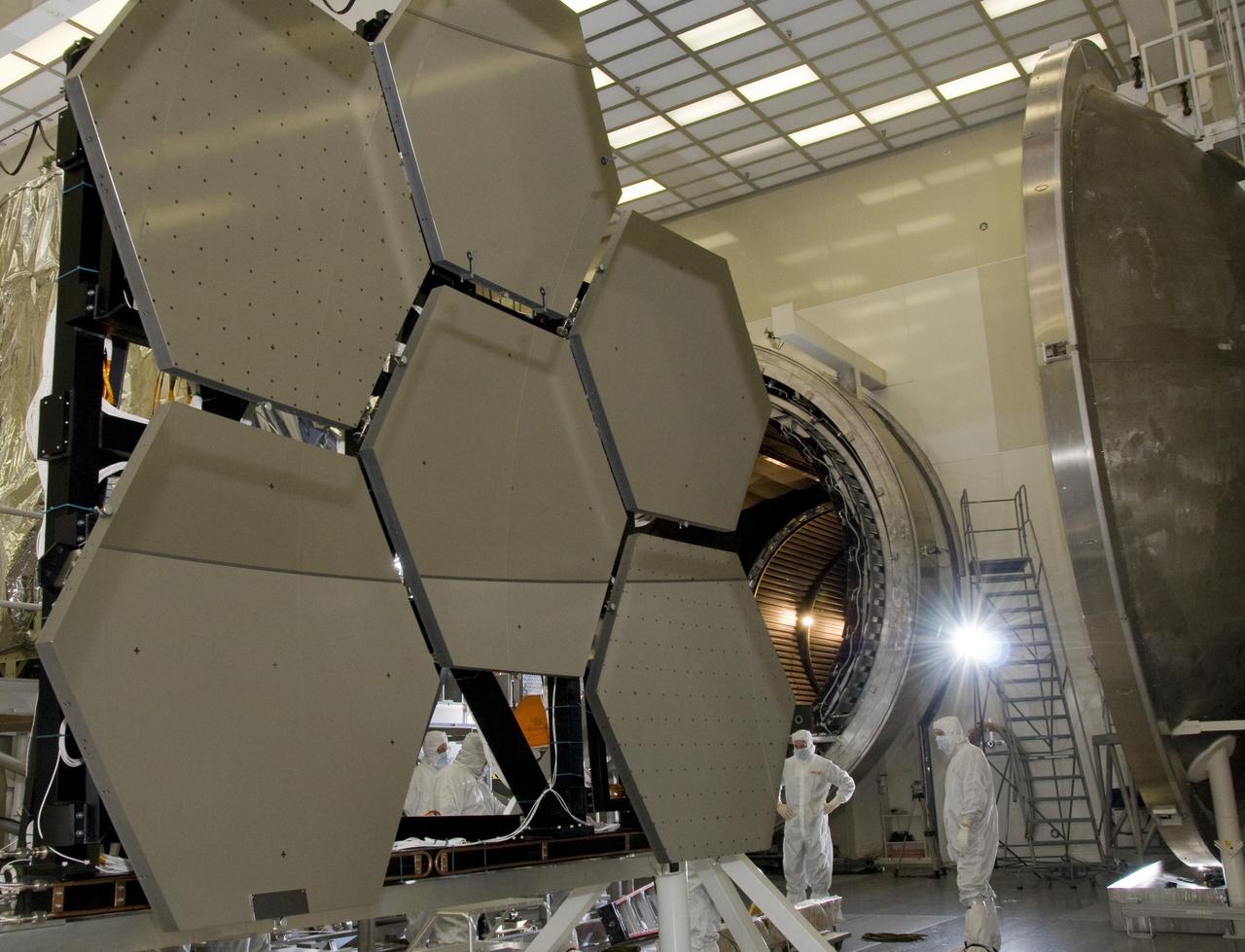

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
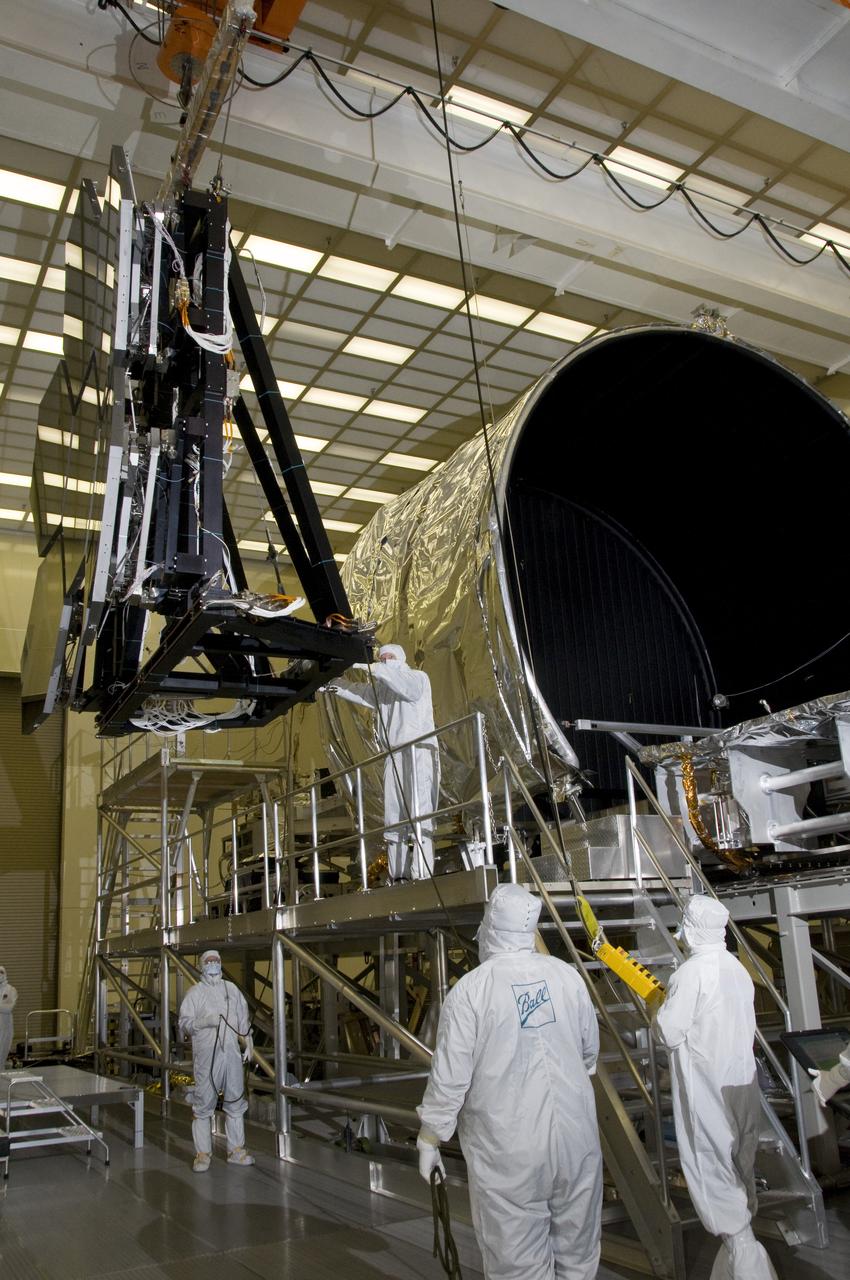

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
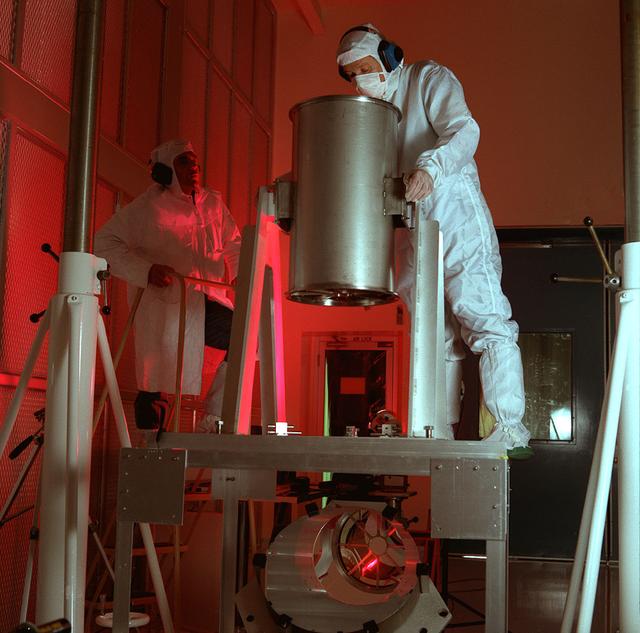

Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility-S (AXAF-S) nickel prototype mirror optical test setup.
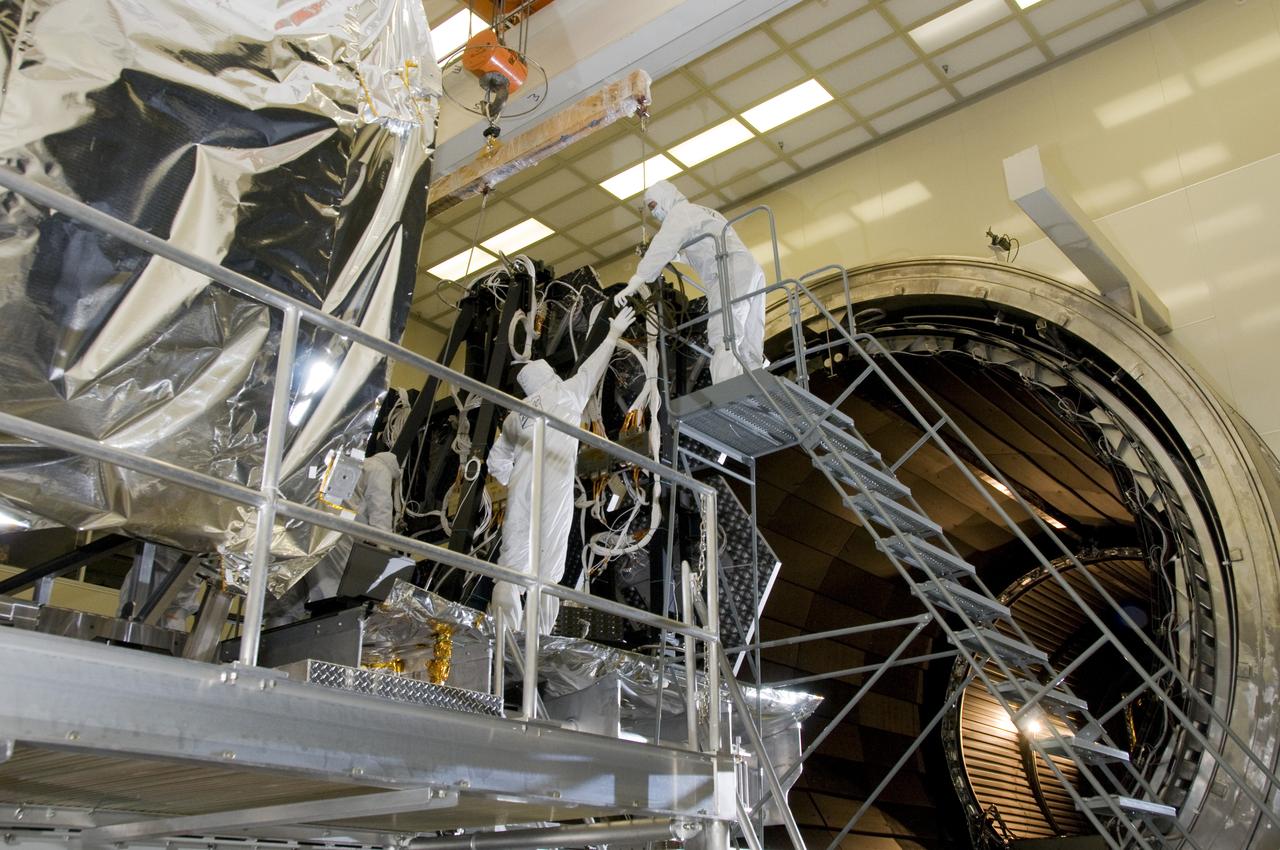

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
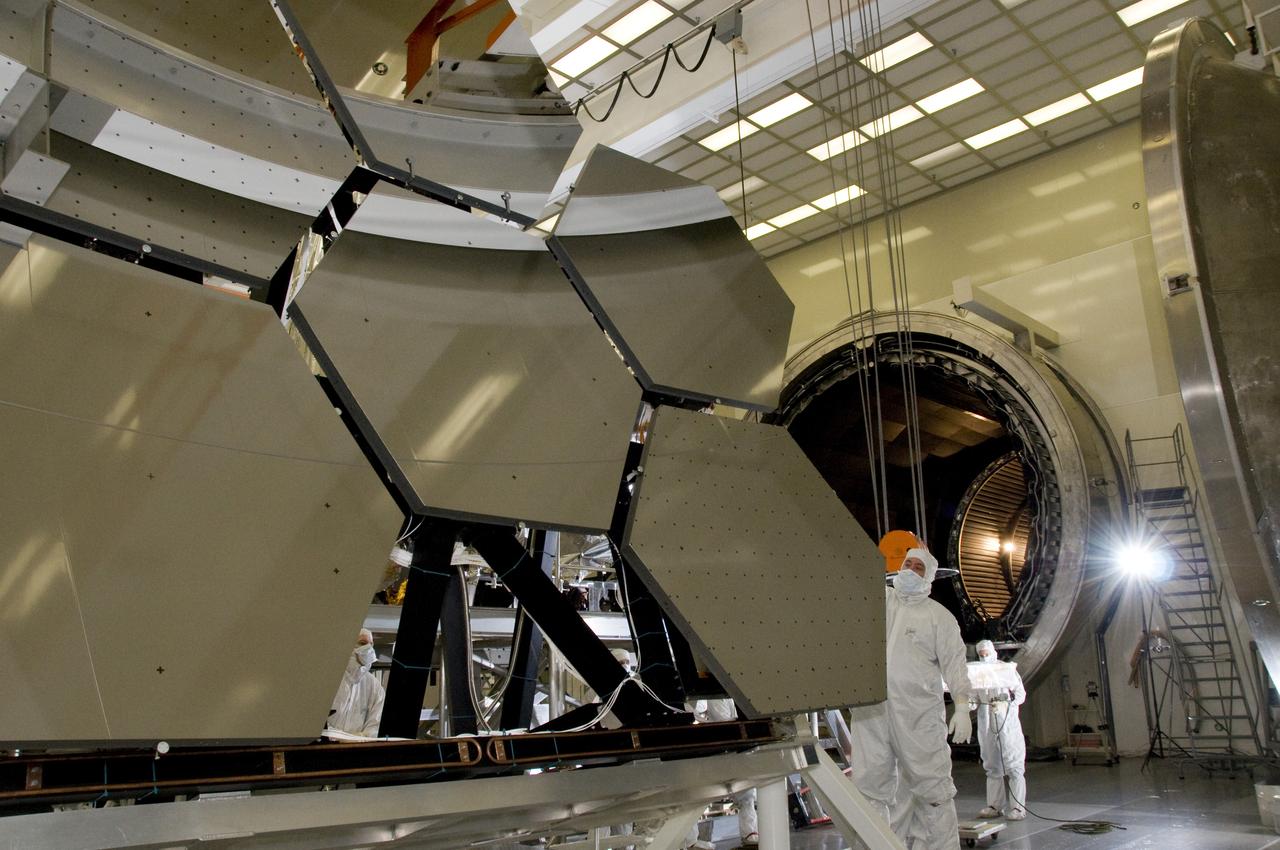

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
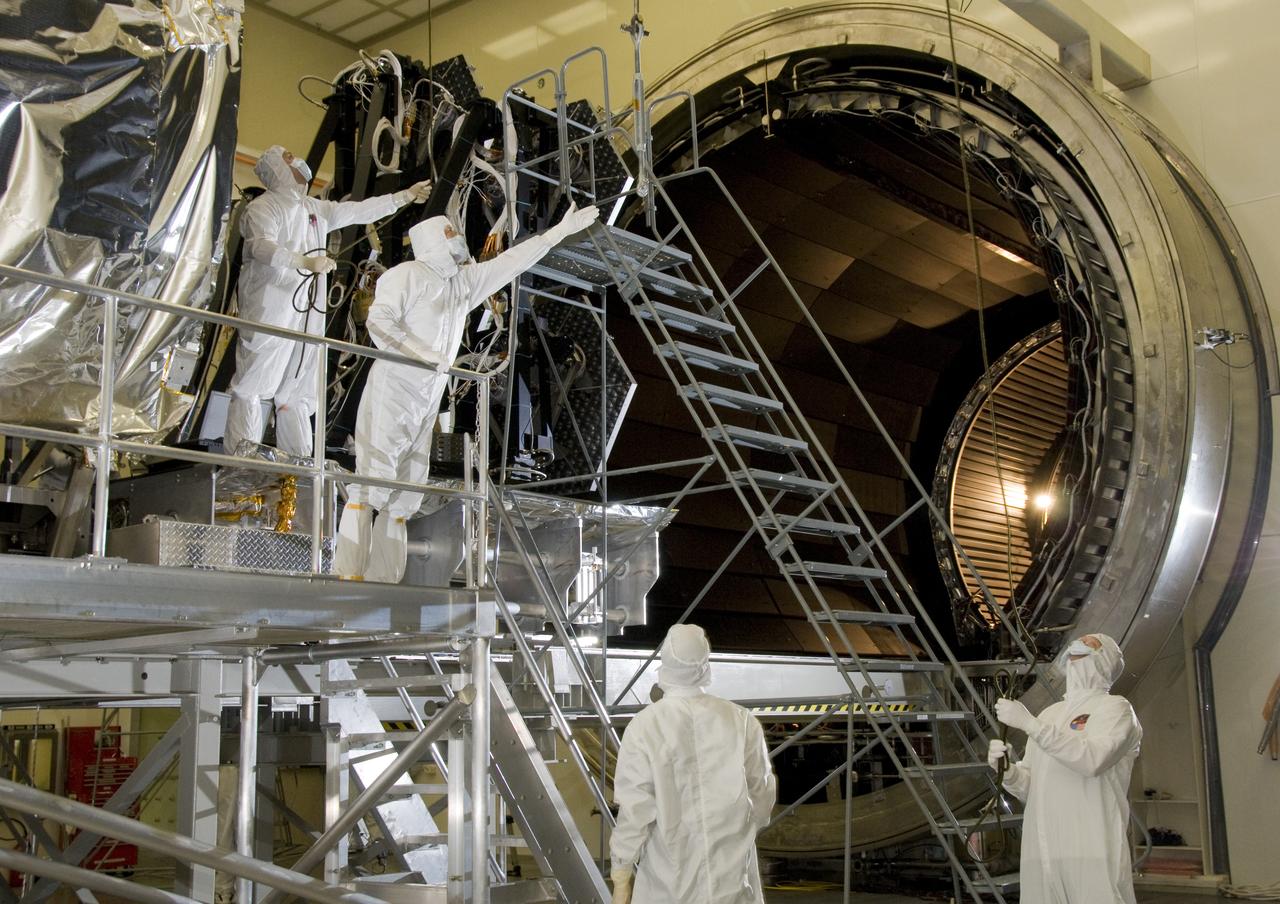

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
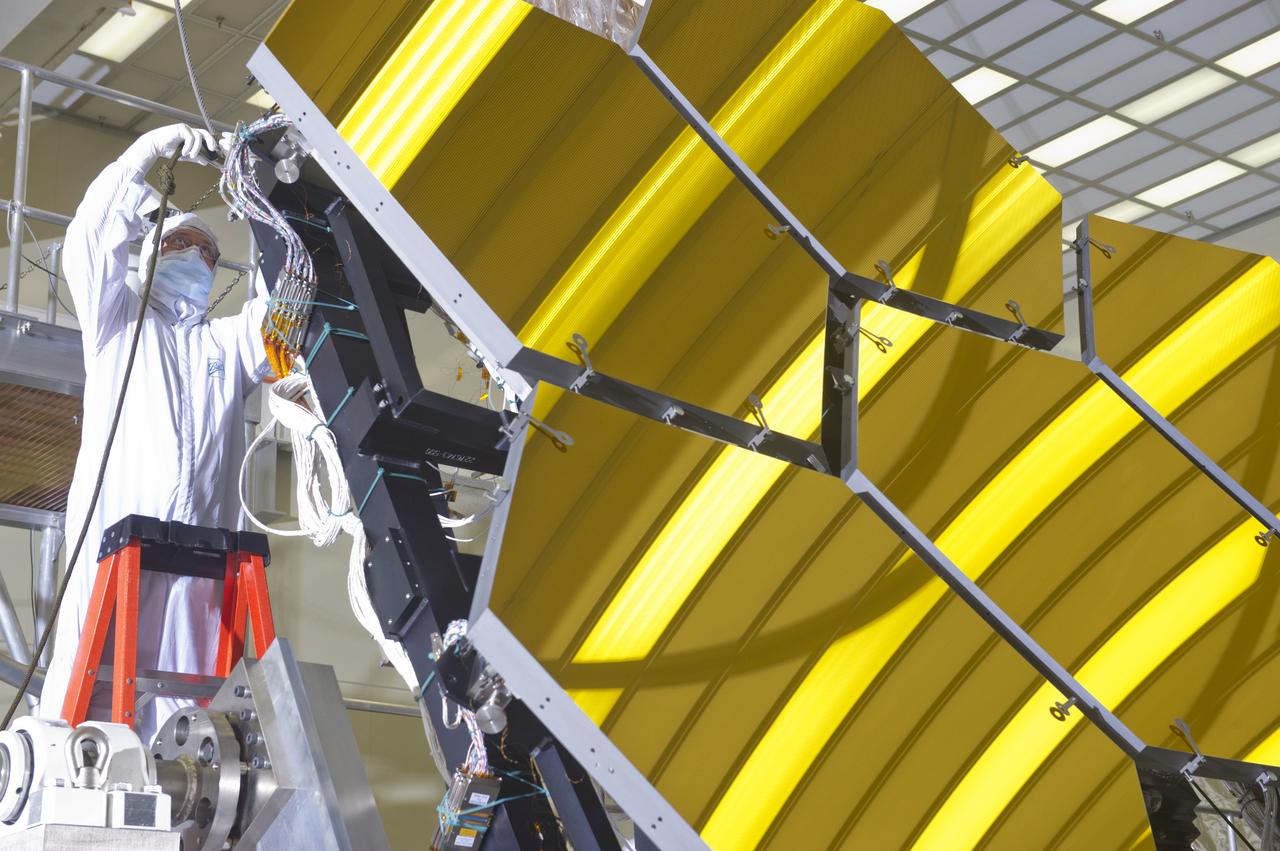

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
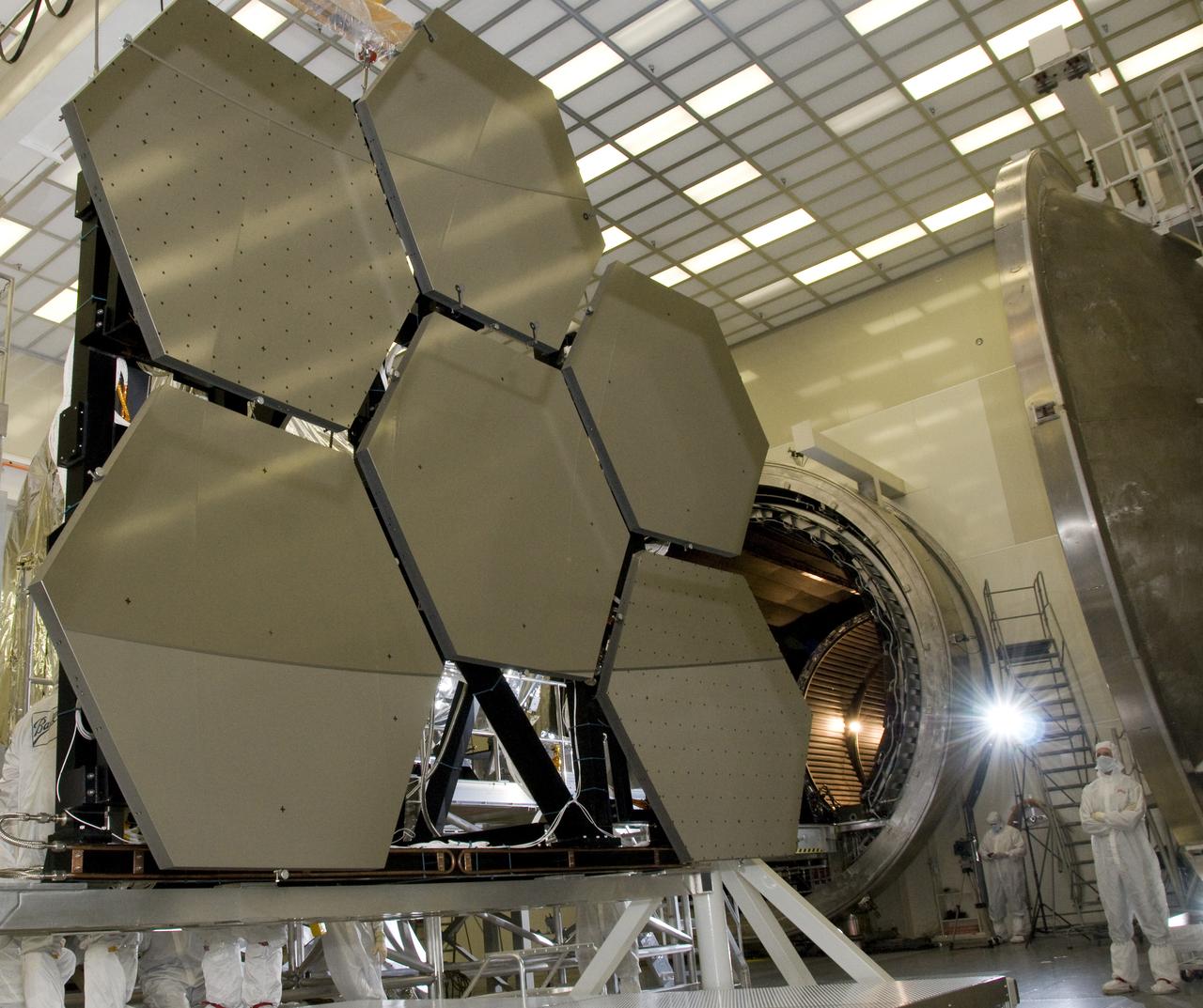

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
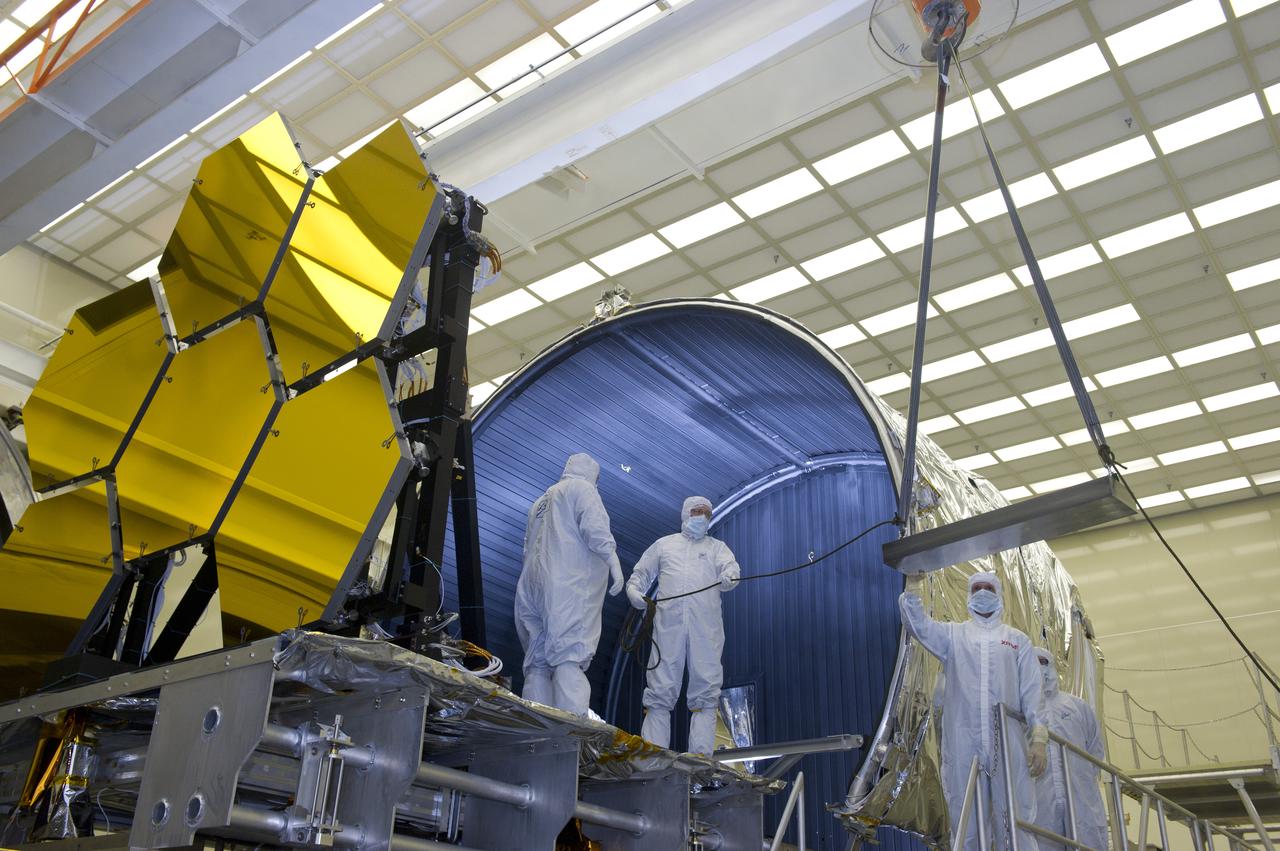

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
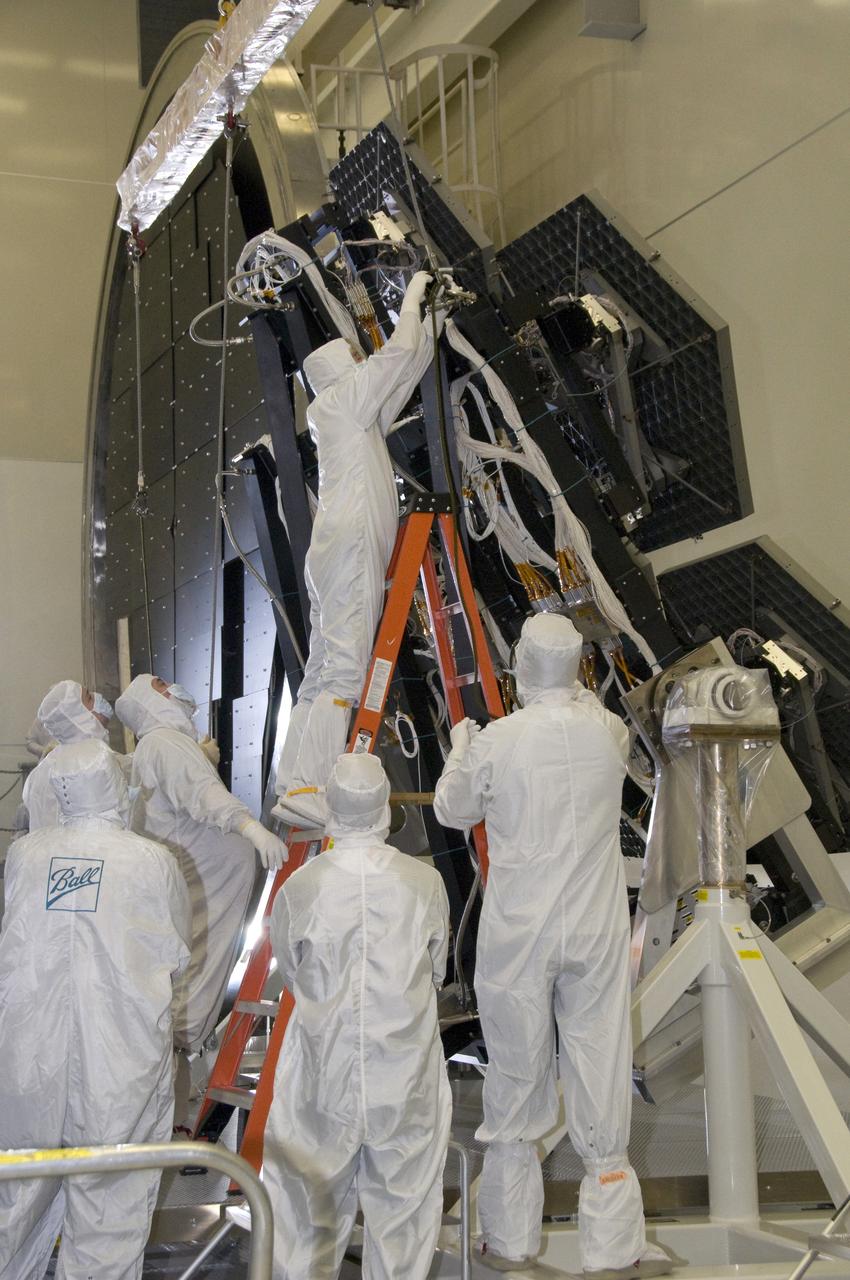

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
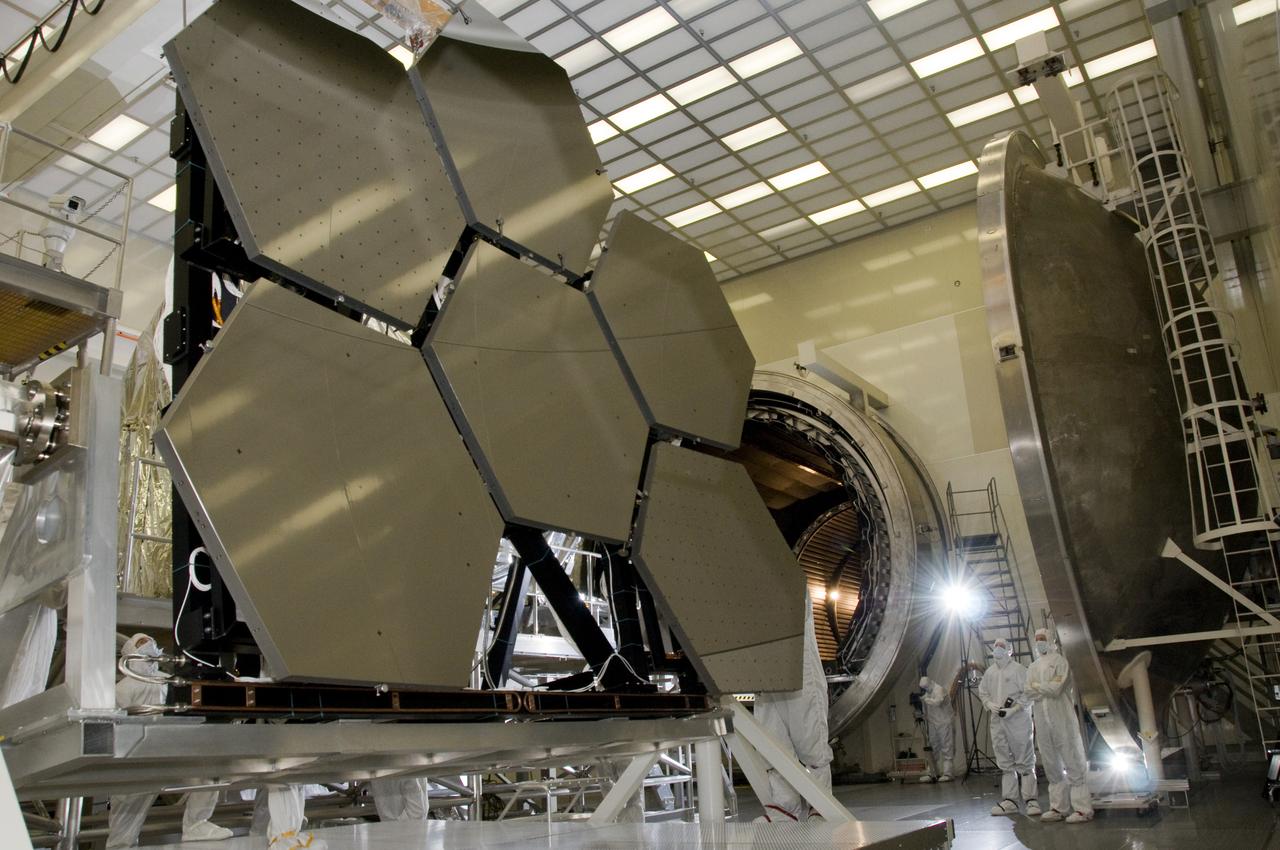

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
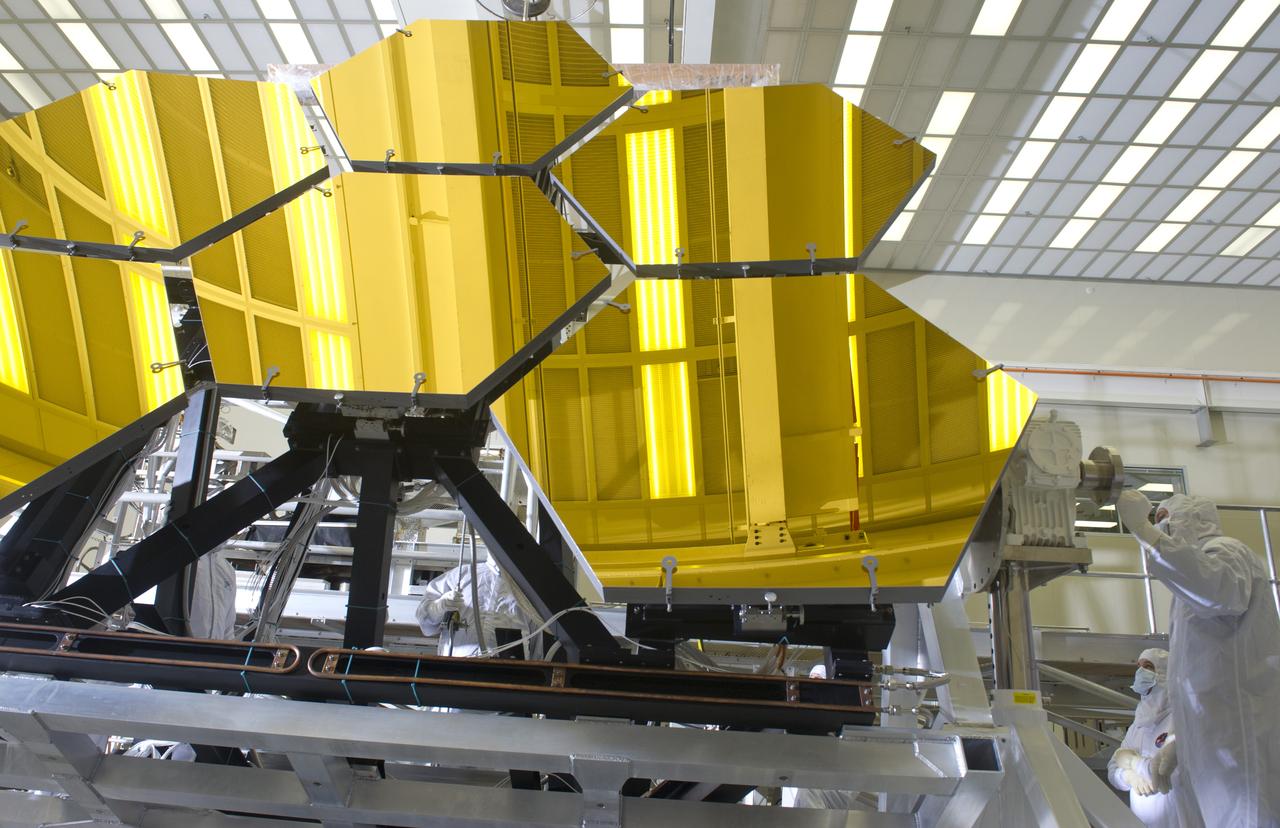

BALL AEROSPACE TECHNICIANS REMOVE FINAL SIX JWST MIRRORS TESTED AT MSFC X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
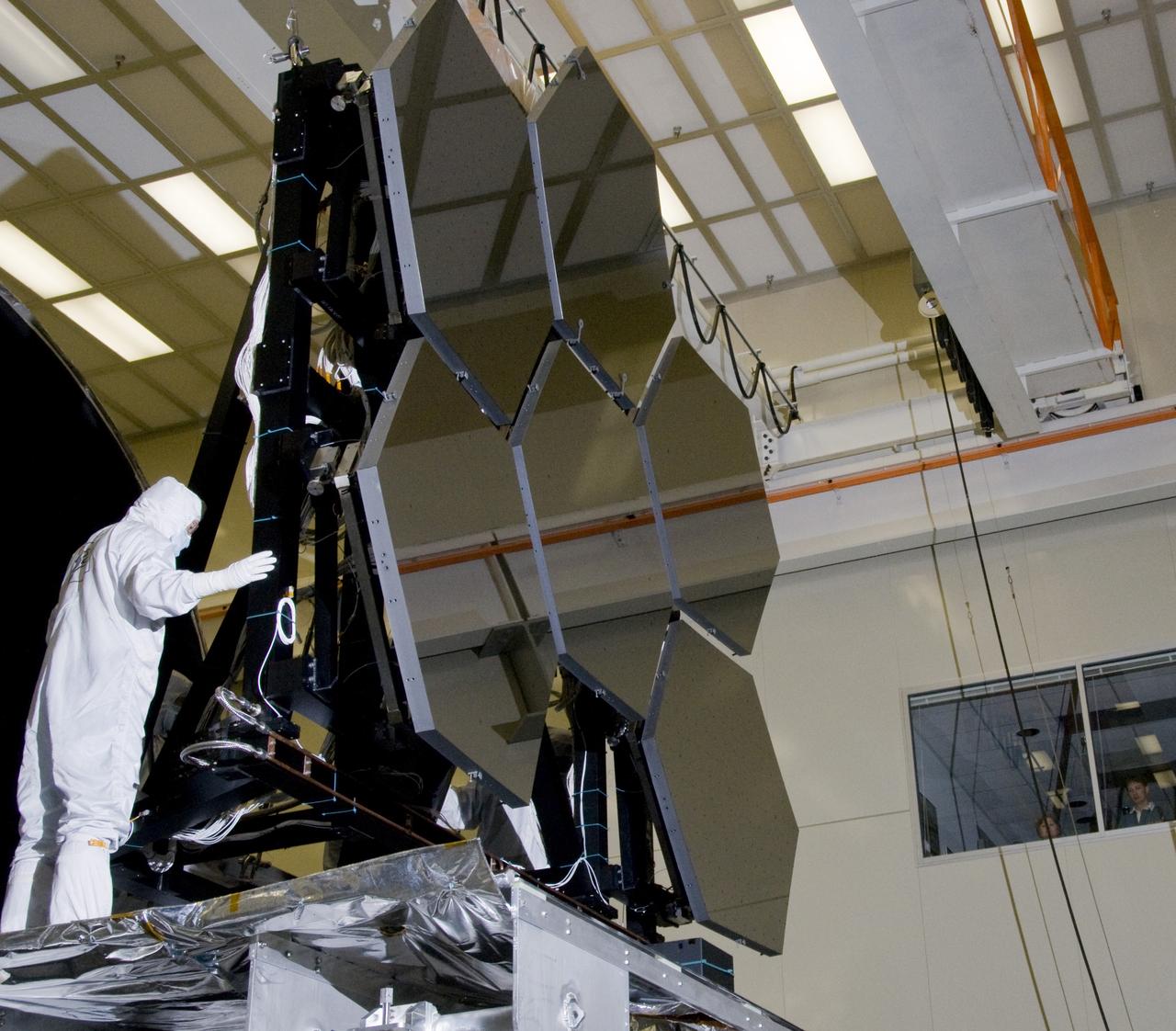

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
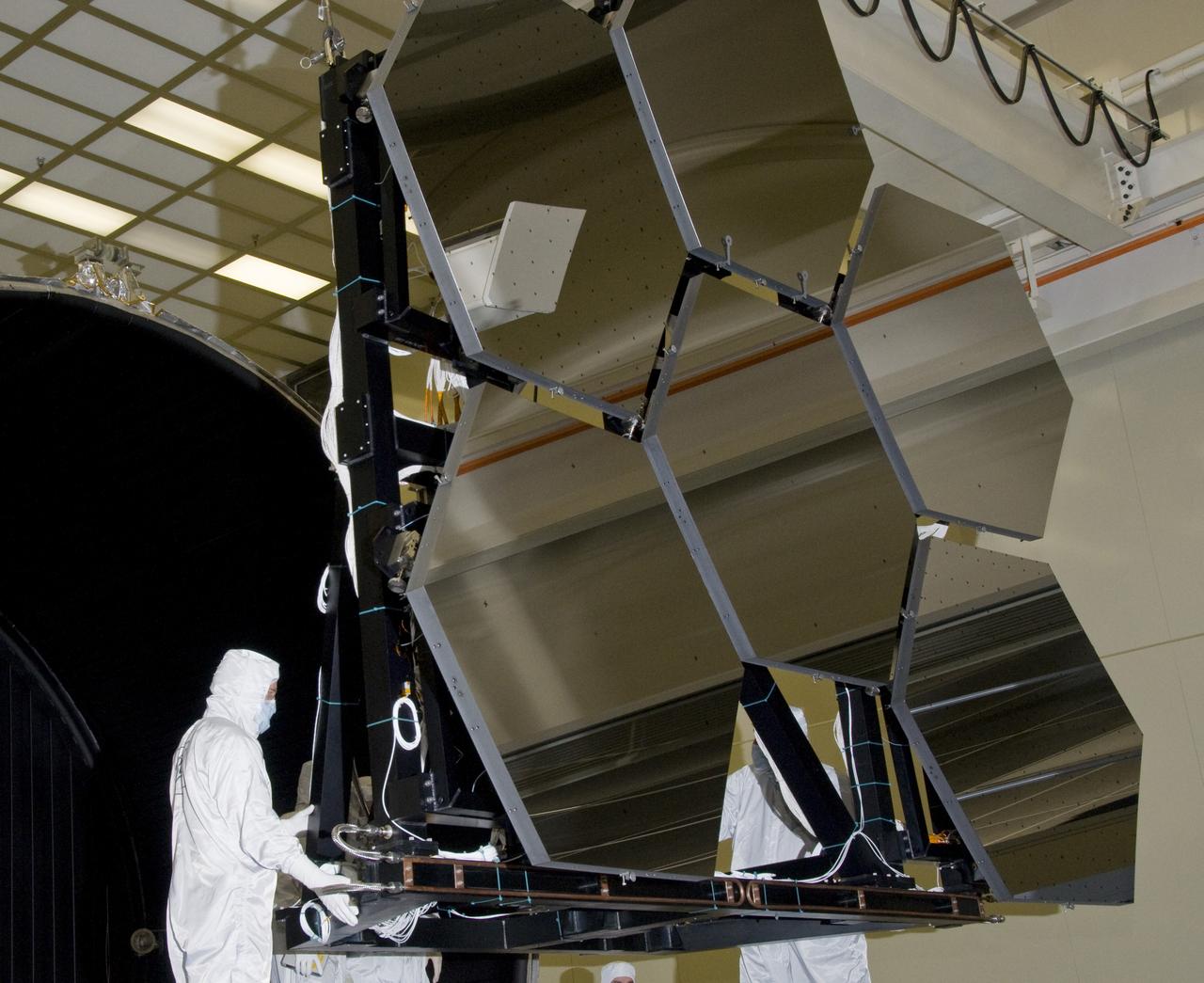

SIX OF THE EIGHTEEN JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRROR SEGMENTS ARE BEING PREPPED TO MOVE INTO THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING.
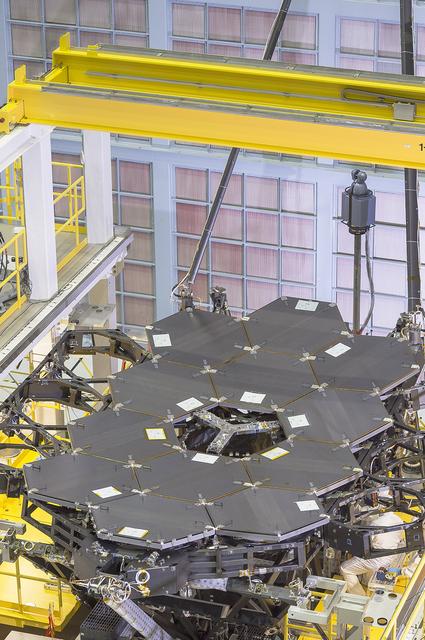

A view of the one dozen (out of 18) flight mirror segments that make up the primary mirror on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have been installed at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn More: Since December 2015, the team of scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to install all the primary mirror segments onto the telescope structure in the large clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The twelfth mirror was installed on January 2, 2016. "This milestone signifies that all of the hexagonal shaped mirrors on the fixed central section of the telescope structure are installed and only the 3 mirrors on each wing are left for installation," said Lee Feinberg, NASA's Optical Telescope Element Manager at NASA Goddard. "The incredibly skilled and dedicated team assembling the telescope continues to find ways to do things faster and more efficiently." Each hexagonal-shaped segment measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). After being pieced together, the 18 primary mirror segments will work together as one large 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) mirror. The primary mirror will unfold and adjust to shape after launch. The mirrors are made of ultra-lightweight beryllium. The mirrors are placed on the telescope's backplane using a robotic arm, guided by engineers. The full installation is expected to be completed in a few months. The mirrors were built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. Ball is the principal subcontractor to Northrop Grumman for the optical technology and lightweight mirror system. The installation of the mirrors onto the telescope structure is performed by Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York. Harris Corporation leads integration and testing for the telescope. While the mirror assembly is a very significant milestone, there are many more steps involved in assembling the Webb telescope. The primary mirror and the tennis-court-sized sunshield are the largest and most visible components of the Webb telescope. However, there are four smaller components that are less visible, yet critical. The instruments that will fly aboard Webb - cameras and spectrographs with detectors able to record extremely faint signals — are part of the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), which is currently undergoing its final cryogenic vacuum test and will be integrated with the mirror later this year.
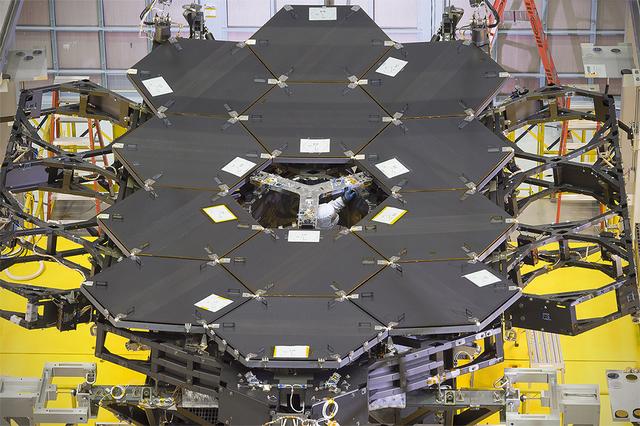

Caption: One dozen (out of 18) flight mirror segments that make up the primary mirror on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have been installed at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn More: Since December 2015, the team of scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to install all the primary mirror segments onto the telescope structure in the large clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The twelfth mirror was installed on January 2, 2016. "This milestone signifies that all of the hexagonal shaped mirrors on the fixed central section of the telescope structure are installed and only the 3 mirrors on each wing are left for installation," said Lee Feinberg, NASA's Optical Telescope Element Manager at NASA Goddard. "The incredibly skilled and dedicated team assembling the telescope continues to find ways to do things faster and more efficiently." Each hexagonal-shaped segment measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). After being pieced together, the 18 primary mirror segments will work together as one large 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) mirror. The primary mirror will unfold and adjust to shape after launch. The mirrors are made of ultra-lightweight beryllium. The mirrors are placed on the telescope's backplane using a robotic arm, guided by engineers. The full installation is expected to be completed in a few months. The mirrors were built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. Ball is the principal subcontractor to Northrop Grumman for the optical technology and lightweight mirror system. The installation of the mirrors onto the telescope structure is performed by Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York. Harris Corporation leads integration and testing for the telescope. While the mirror assembly is a very significant milestone, there are many more steps involved in assembling the Webb telescope. The primary mirror and the tennis-court-sized sunshield are the largest and most visible components of the Webb telescope. However, there are four smaller components that are less visible, yet critical. The instruments that will fly aboard Webb - cameras and spectrographs with detectors able to record extremely faint signals — are part of the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), which is currently undergoing its final cryogenic vacuum test and will be integrated with the mirror later this year.

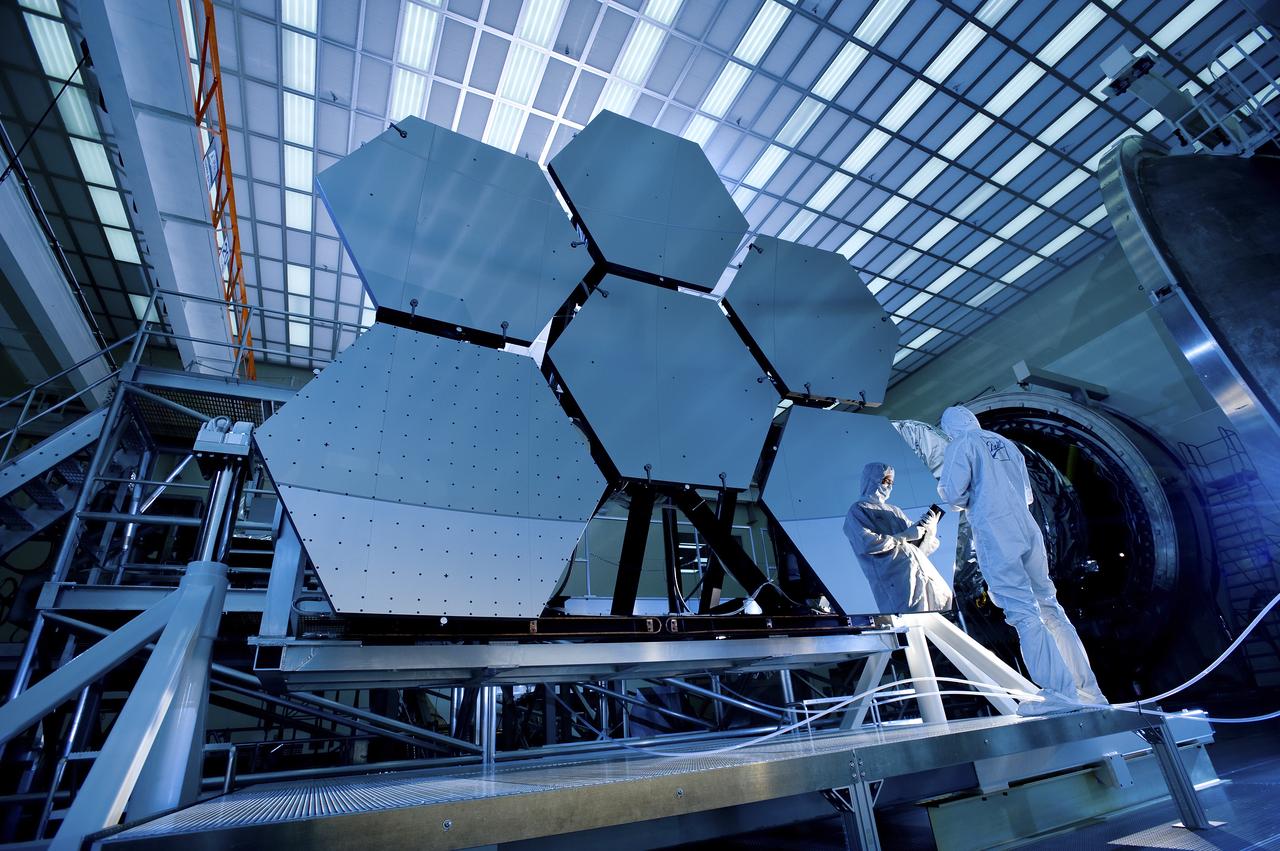
A team of engineers at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) has designed, fabricated, and tested the first solar thermal engine, a non-chemical rocket that produces lower thrust but has better thrust efficiency than the chemical combustion engines. This segmented array of mirrors is the solar concentrator test stand at MSFC for firing the thermal propulsion engines. The 144 mirrors are combined to form an 18-foot diameter array concentrator. The mirror segments are aluminum hexagons that have the reflective surface cut into it by a diamond turning machine, which is developed by MSFC Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center.

BALL AEROSPACE'S JAKE LEWIS IS REFLECTED IN ONE OF THE MIRRORS ON A JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE ARRAY THAT WAS IN THE X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY FOR TESTING
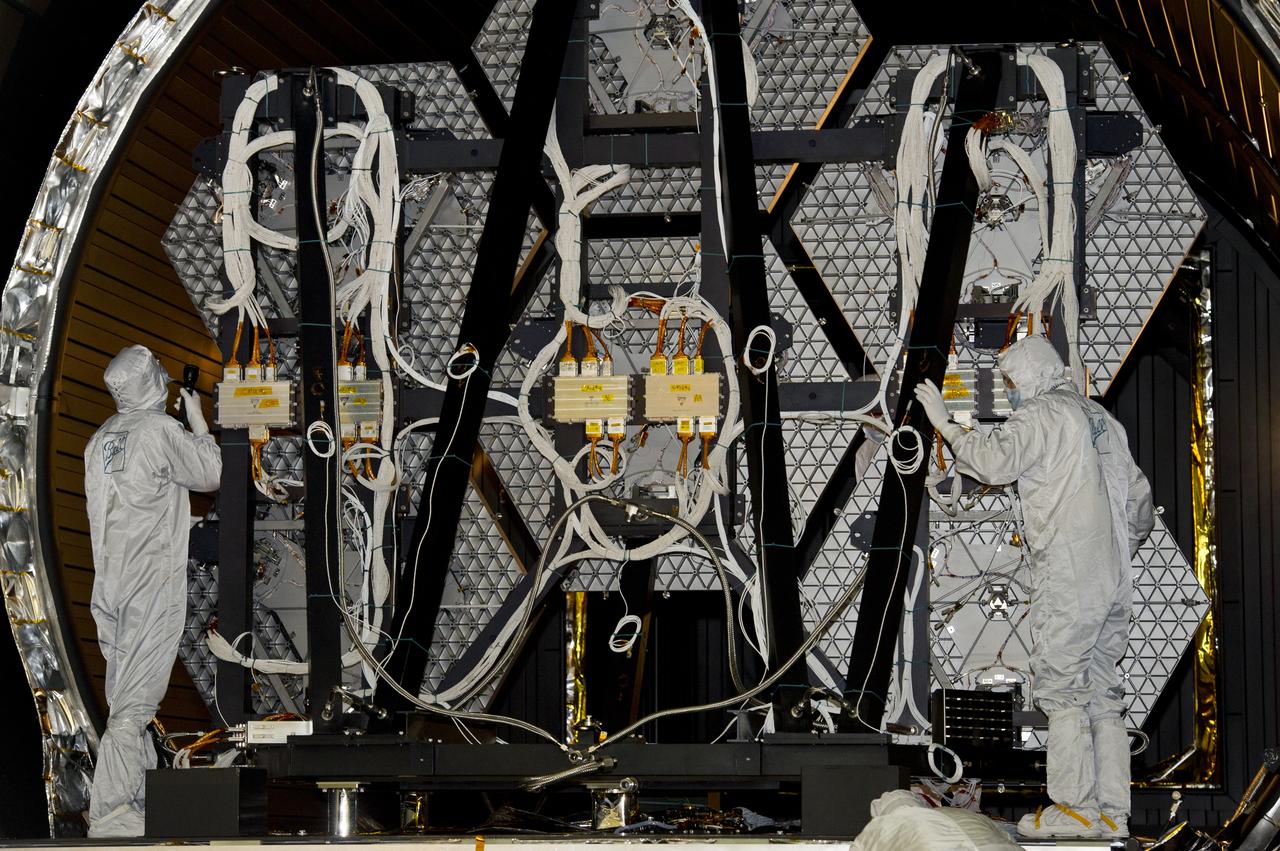
JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
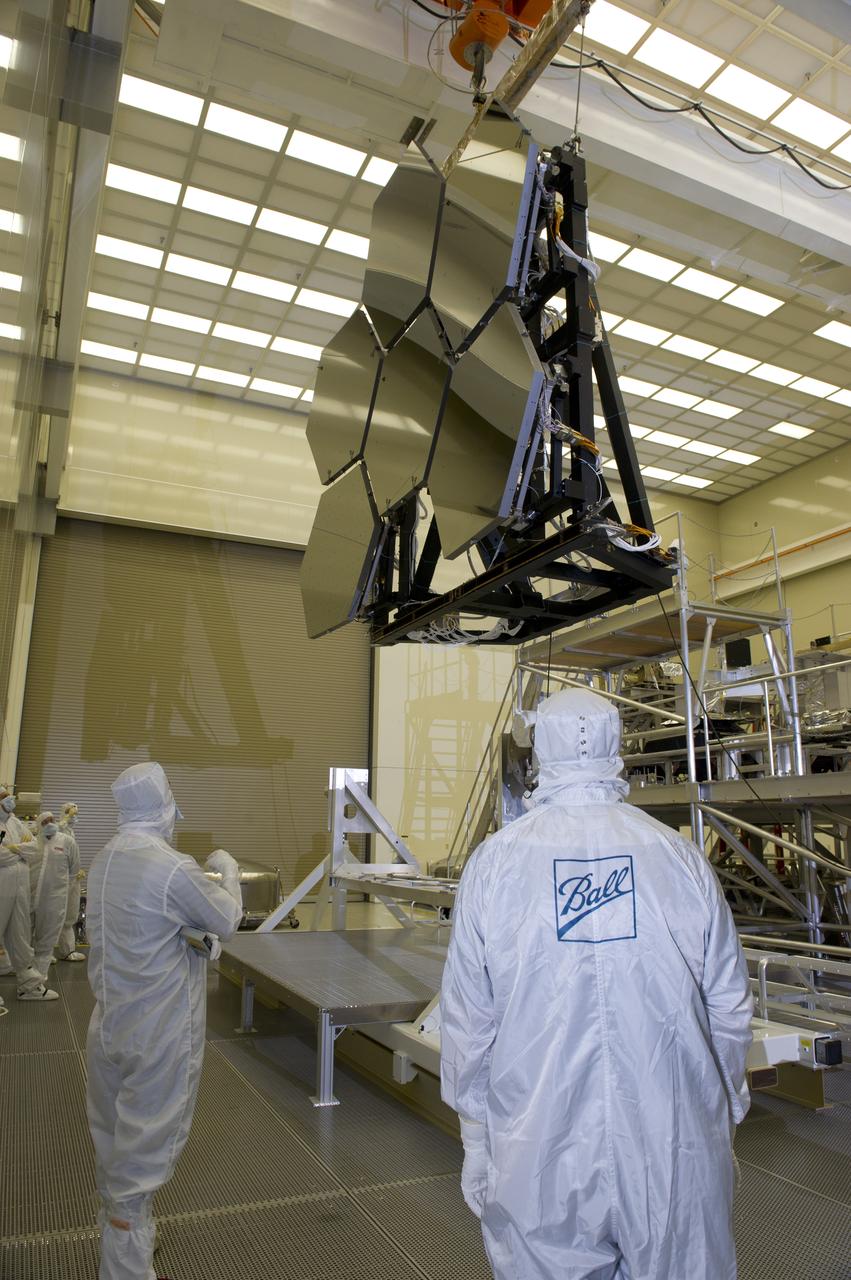

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
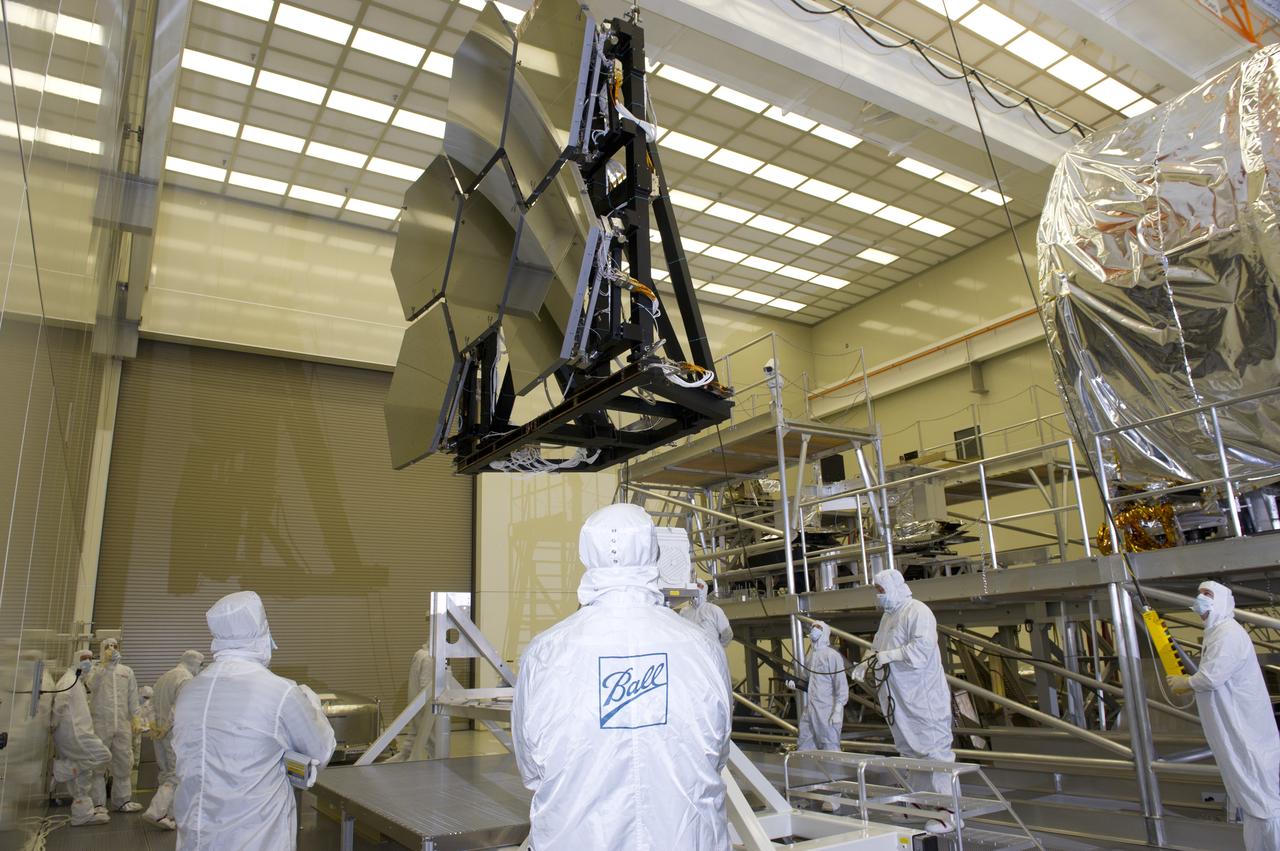

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
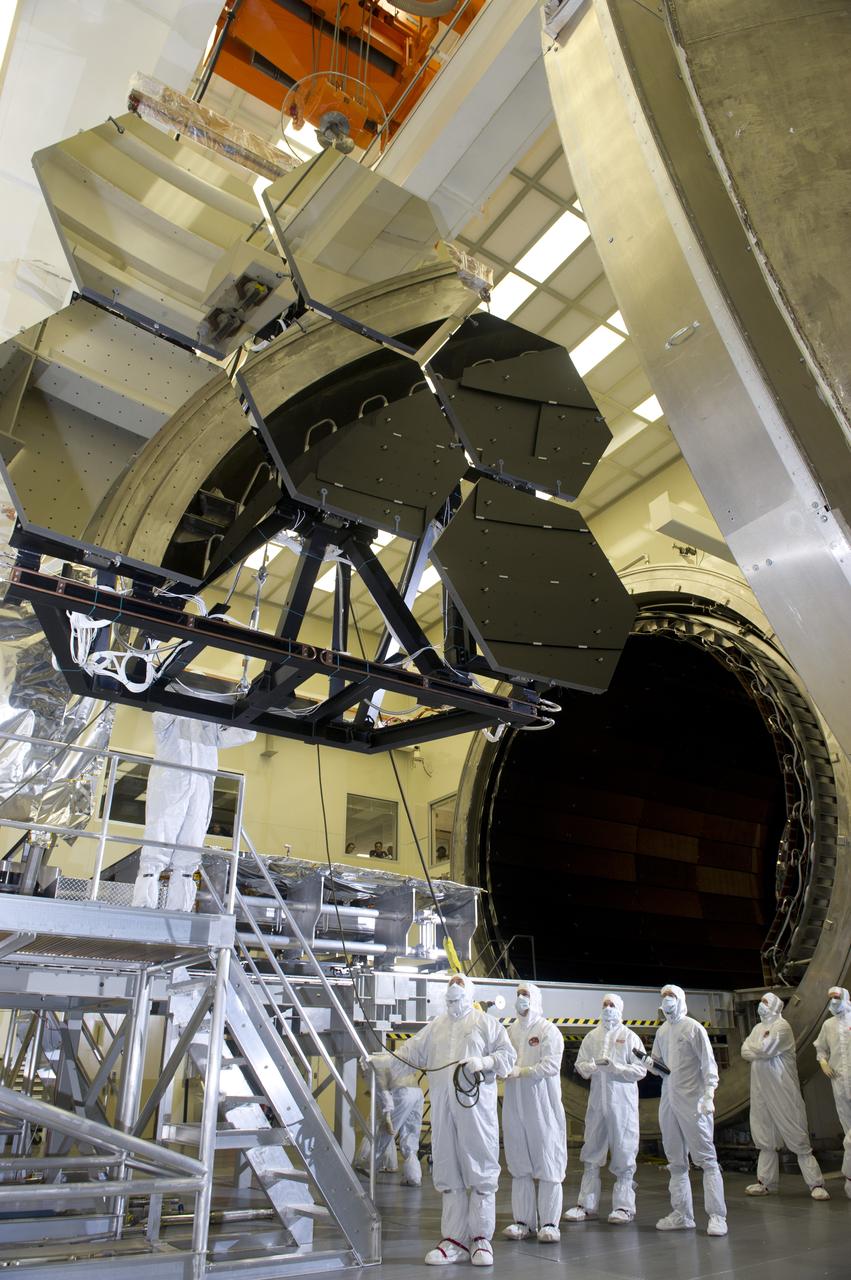

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
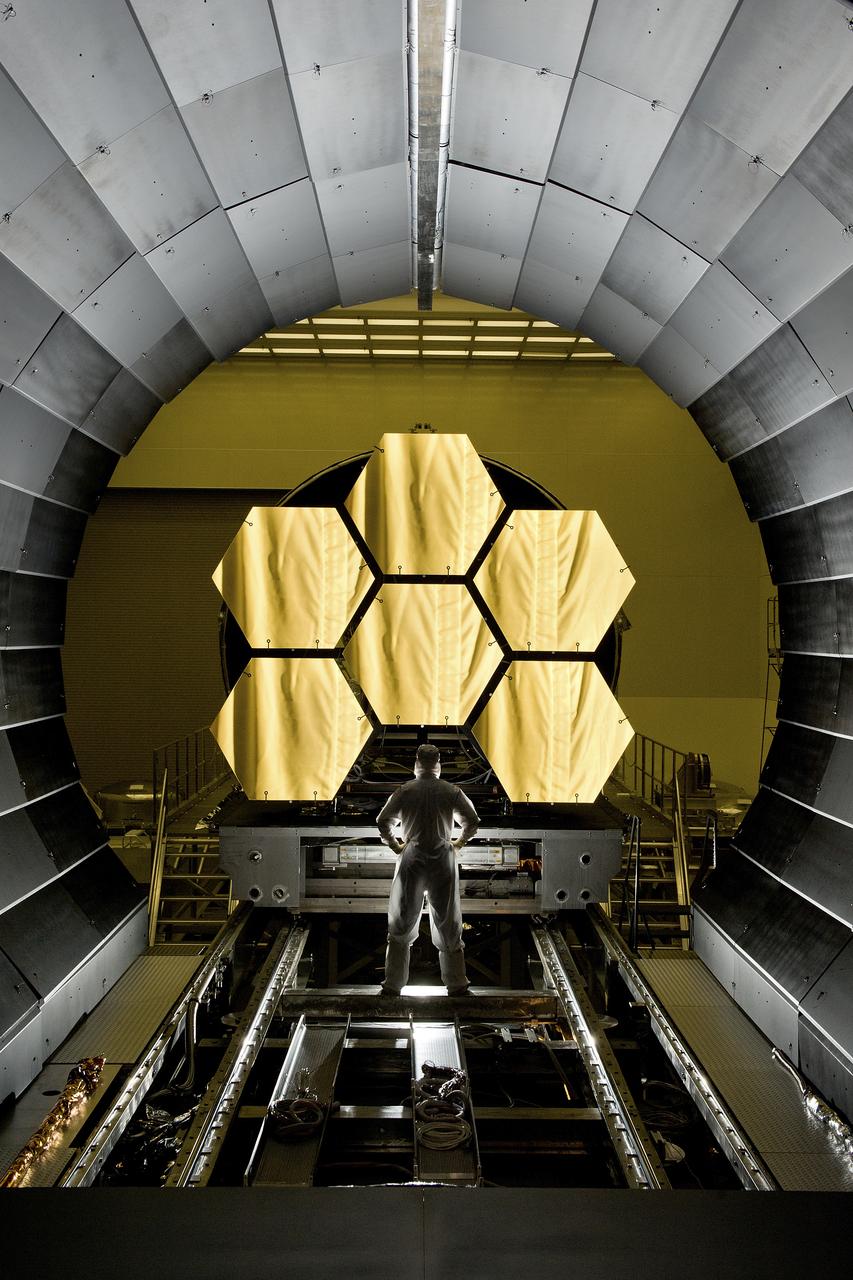

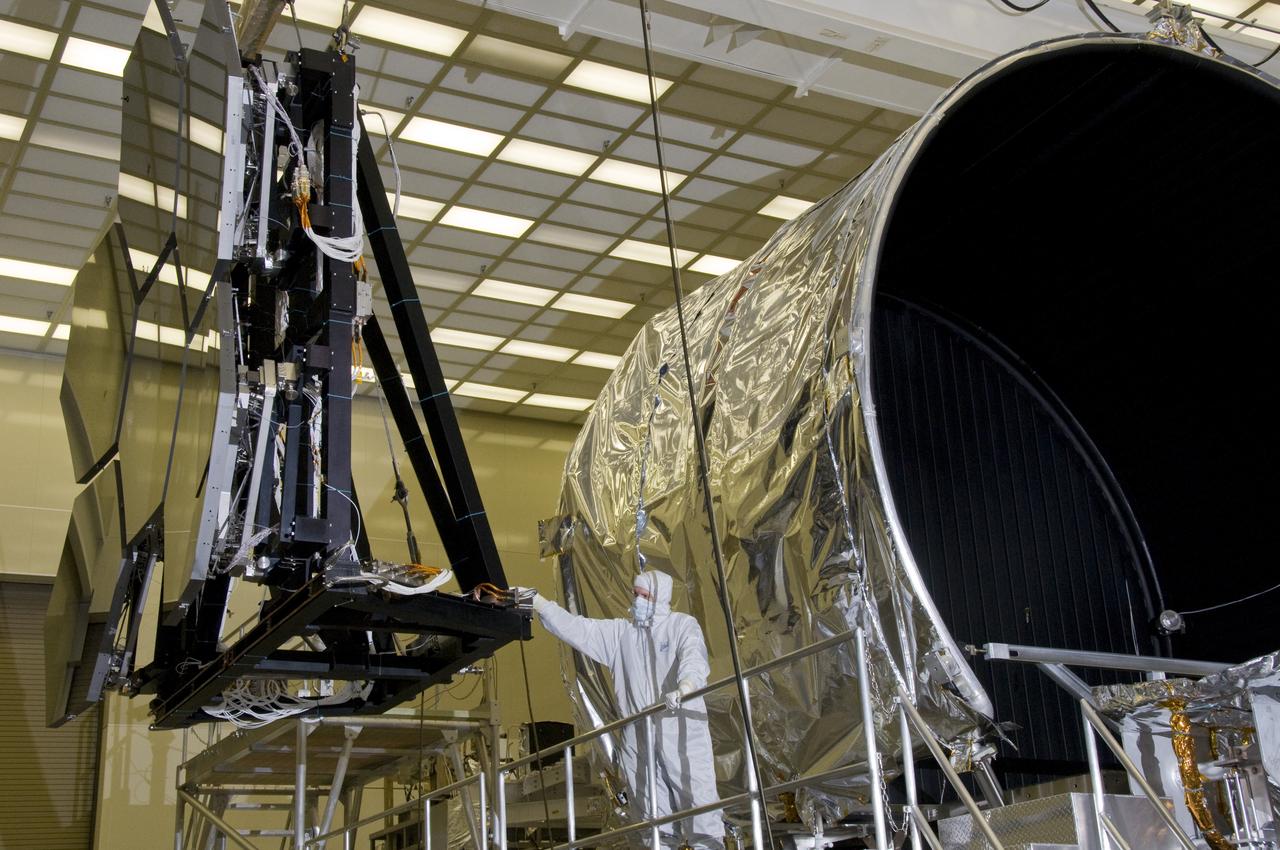
ERNIE WRIGHT STANDS NEAR THE JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AS THEY SIT JUST OUTSIDE THE TESTING CHAMBER IN THE XRAY CALIBRATION FACILITY AT MSFC
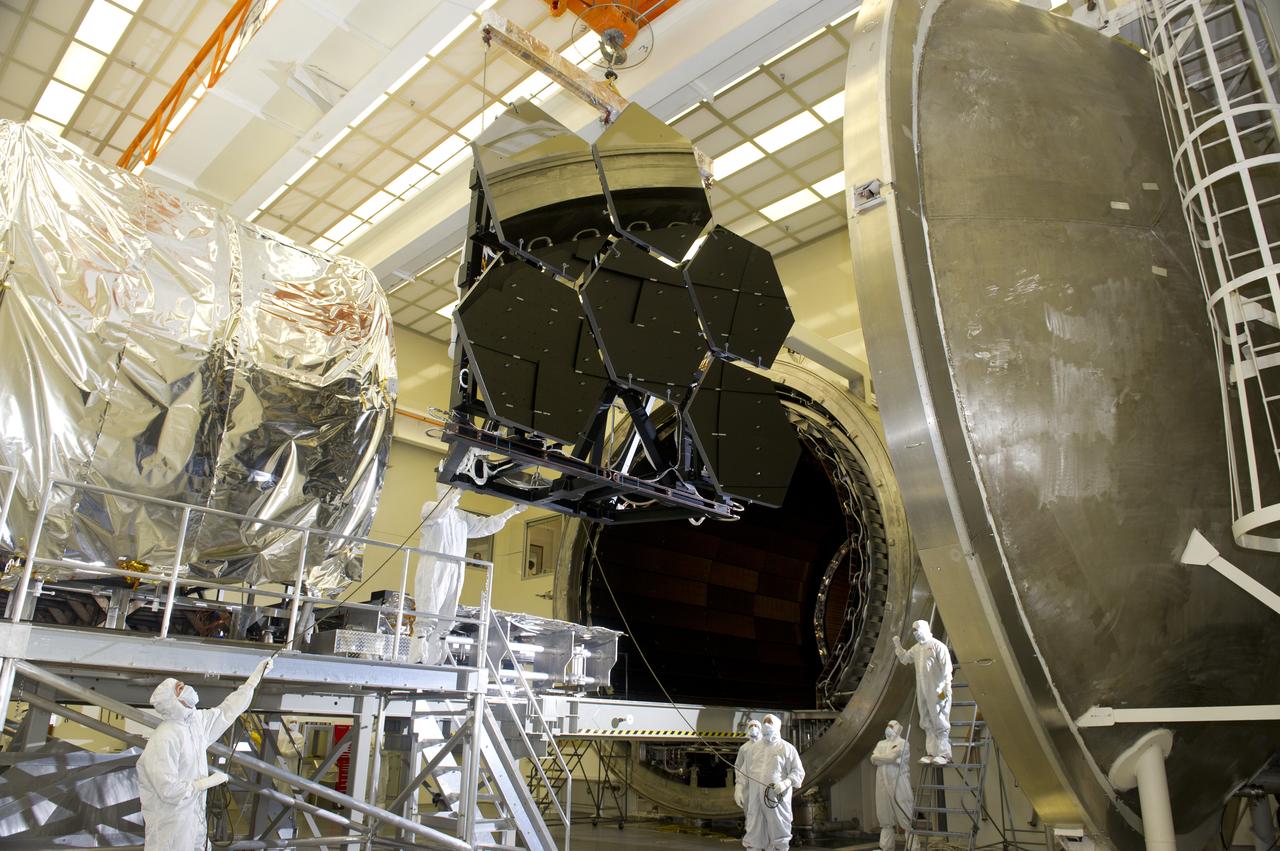

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
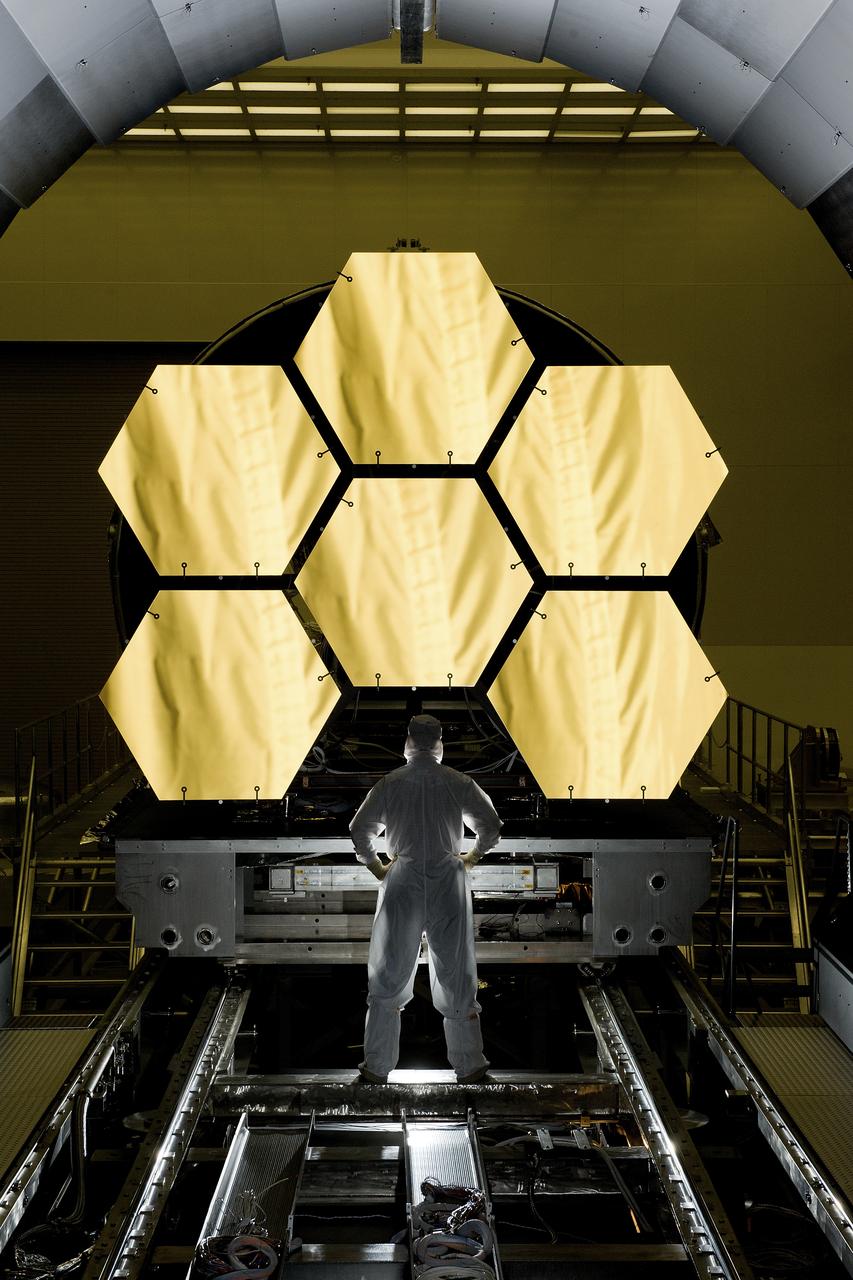

ERNIE WRIGHT STANDS NEAR THE JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AS THEY SIT JUST OUTSIDE THE TESTING CHAMBER IN THE XRAY CALIBRATION FACILITY AT MSFC
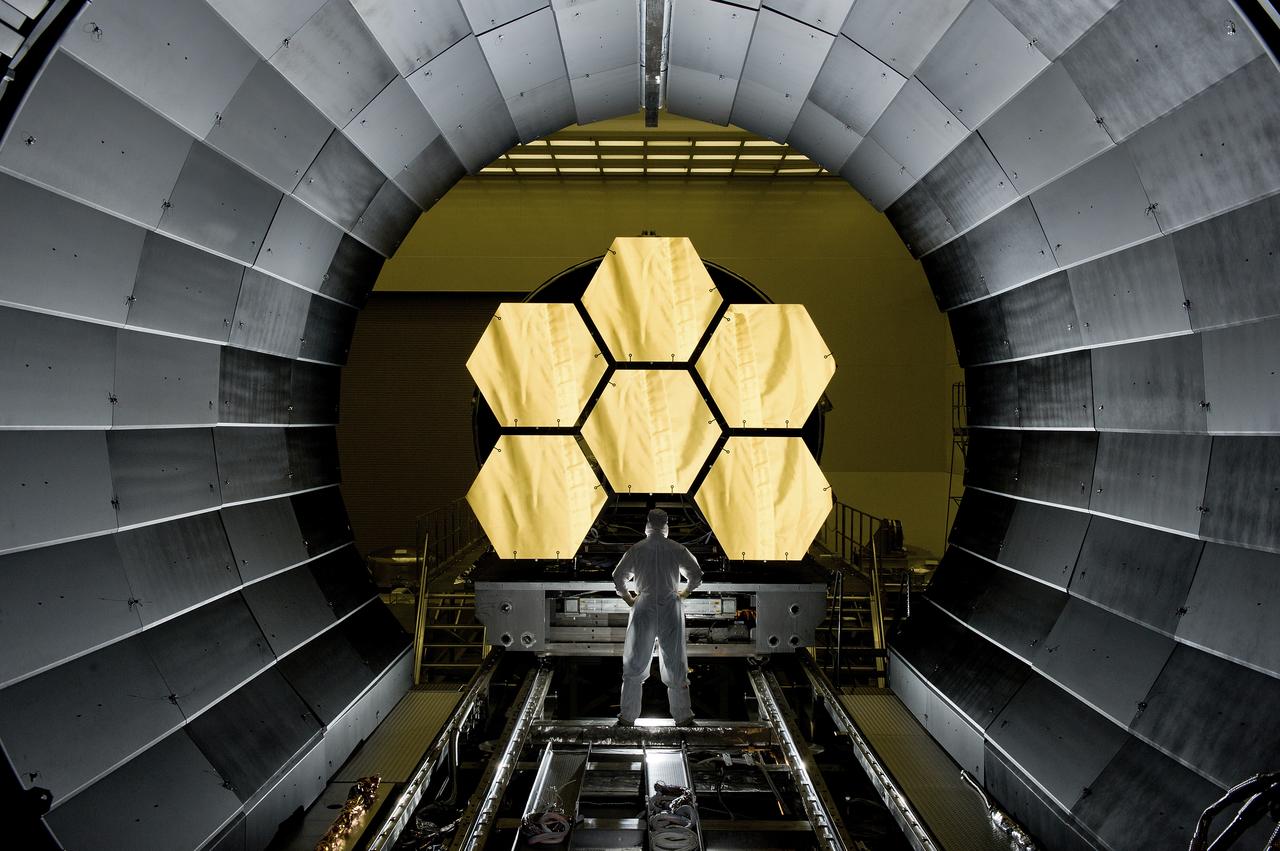

ERNIE WRIGHT STANDS NEAR THE JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AS THEY SIT JUST OUTSIDE THE TESTING CHAMBER IN THE XRAY CALIBRATION FACILITY AT MSFC
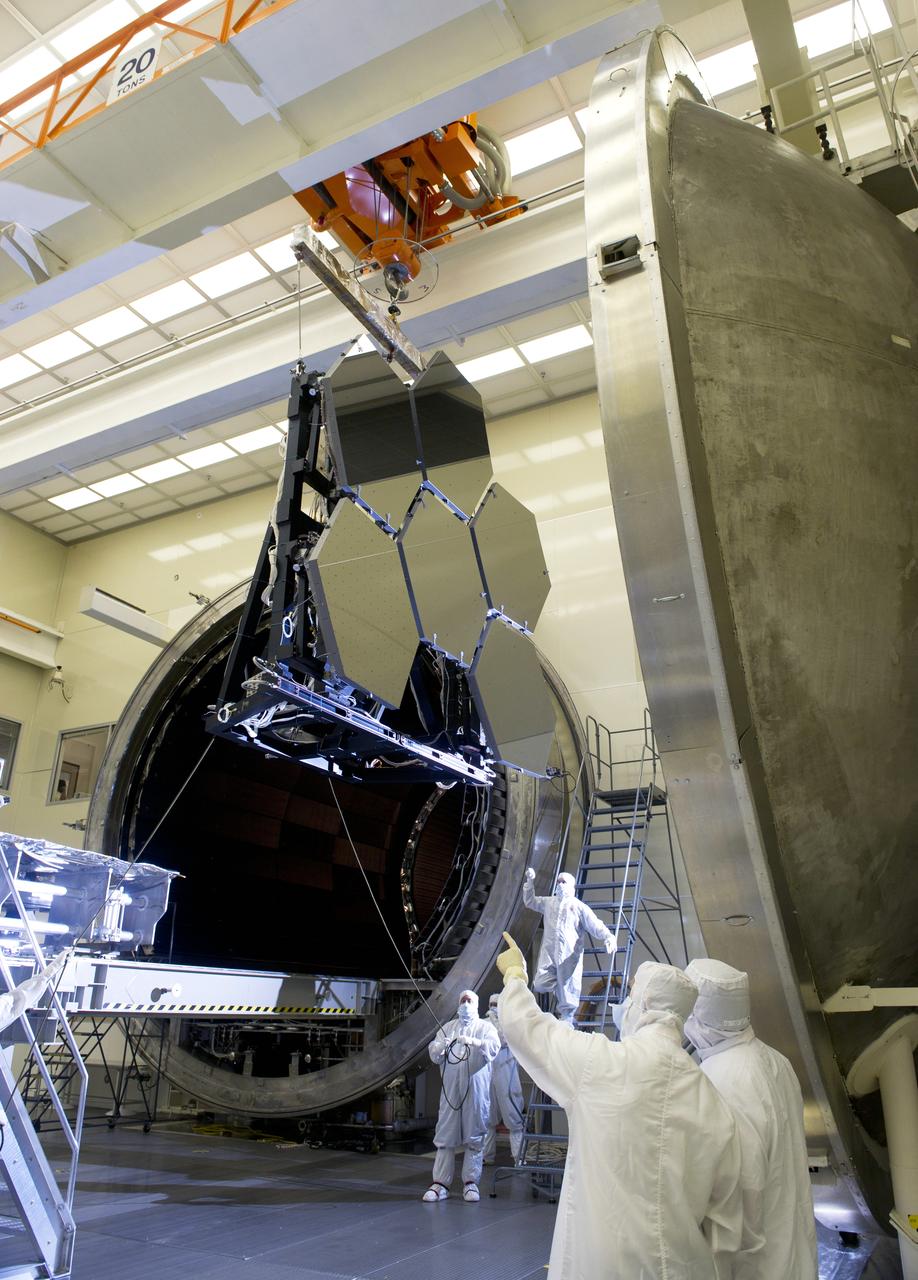

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
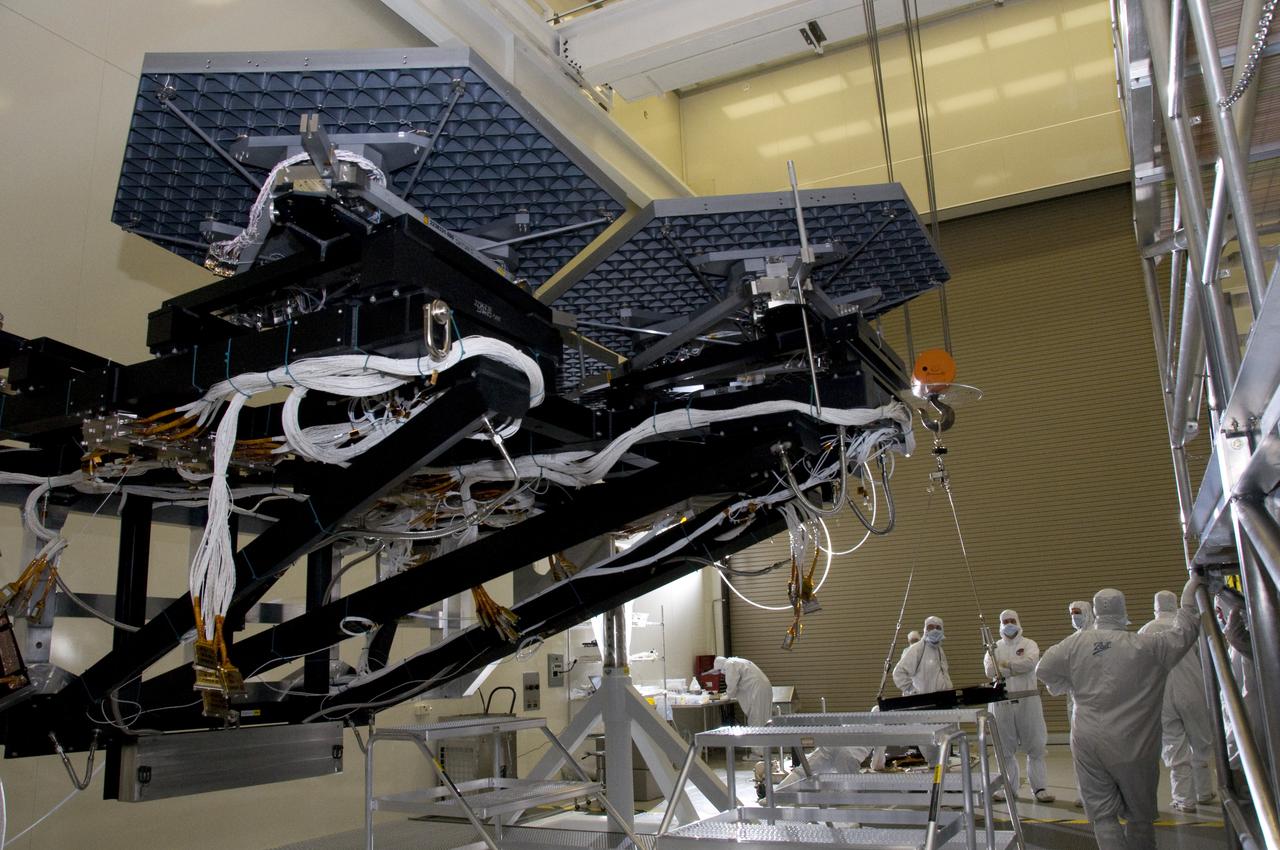

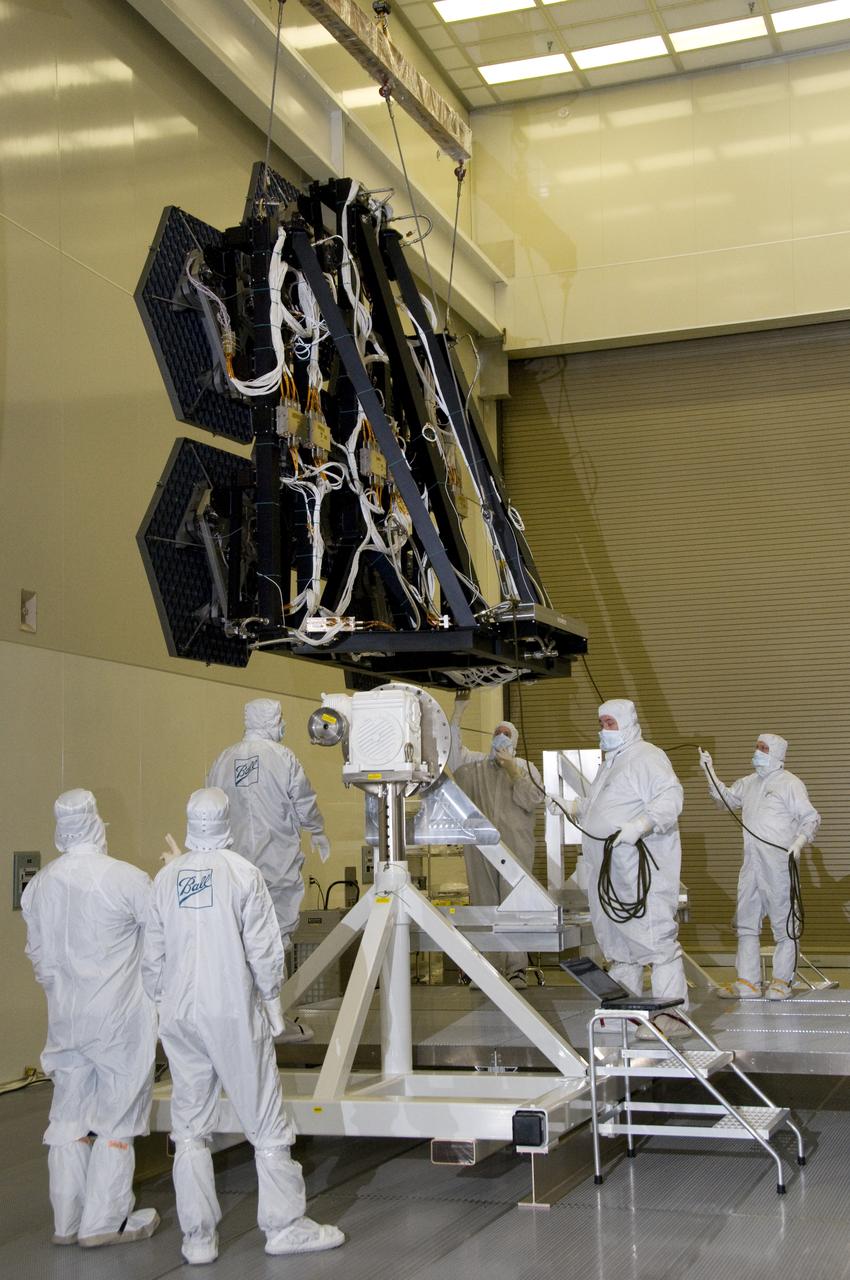
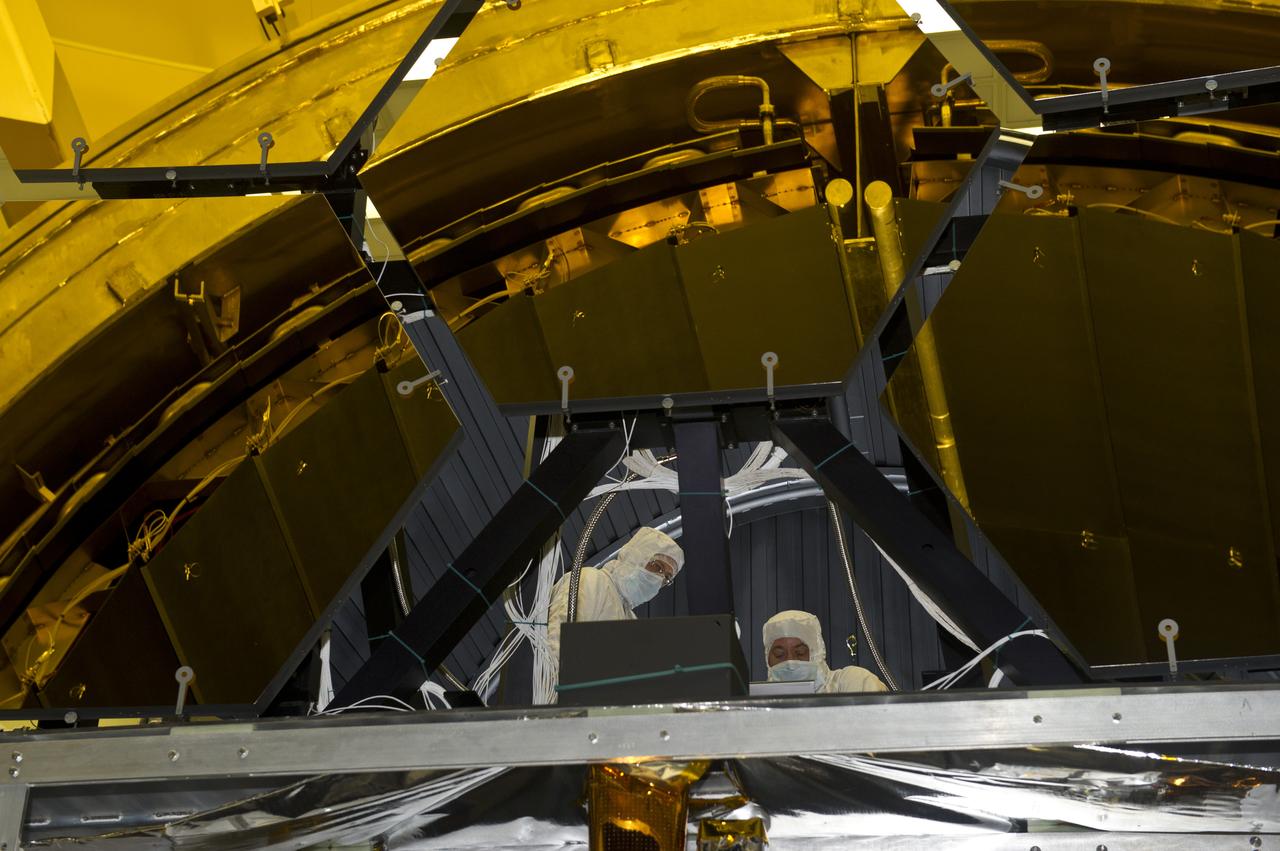
BALL AEROSPACE AND NASA ENGINEERS & TECHNICIANS INSTALL MIRRORS ON THE ROTATABLE CRYOGENIC OPTICAL TEST STAND IN MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER’S XRCF CLEAN ROOM
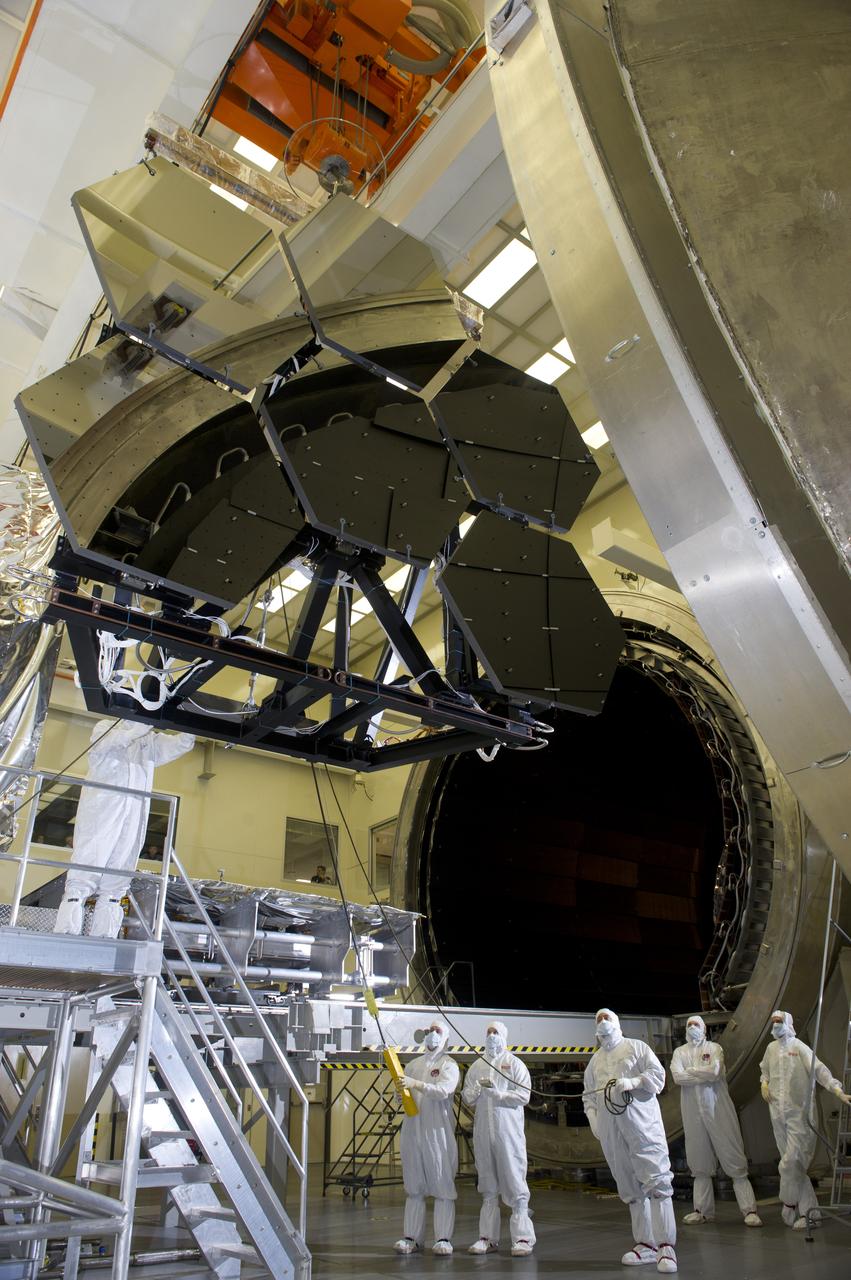

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
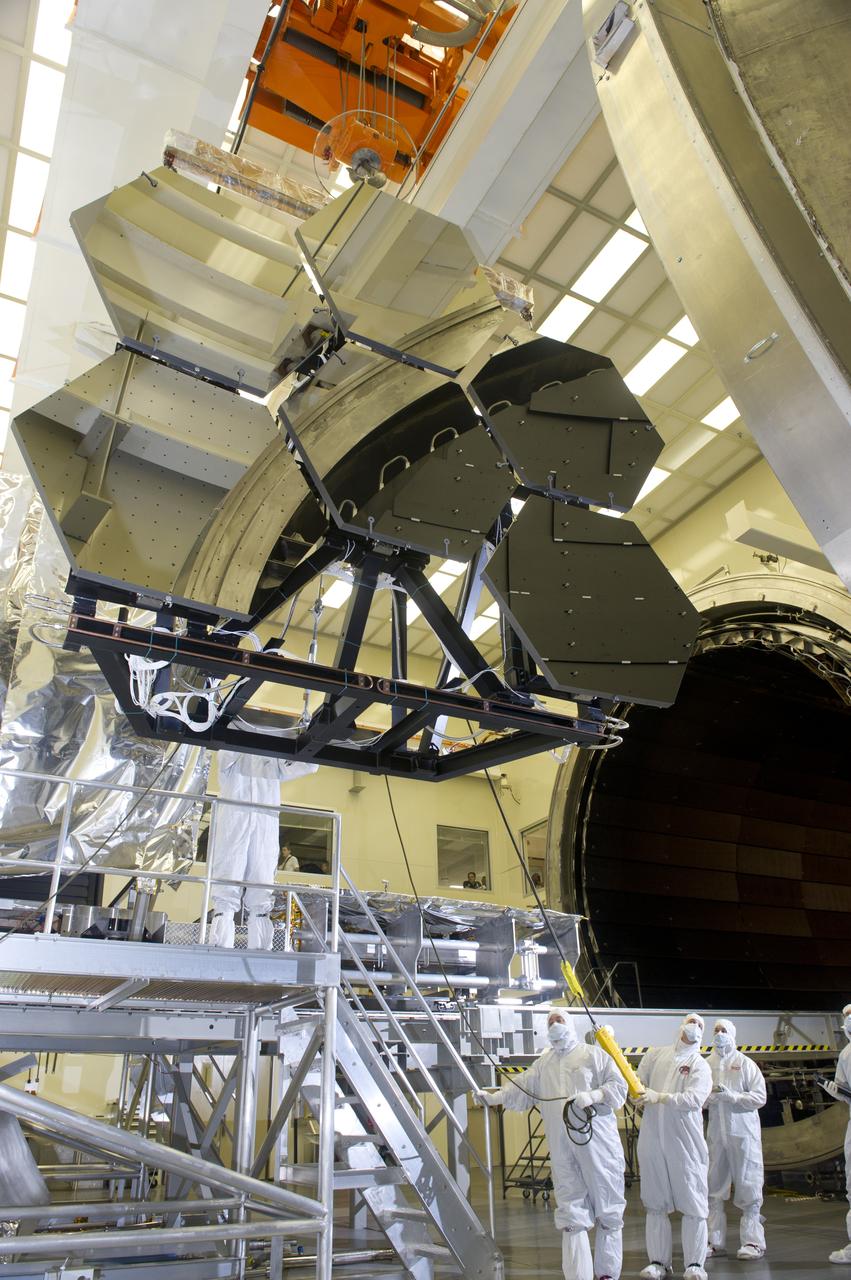

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
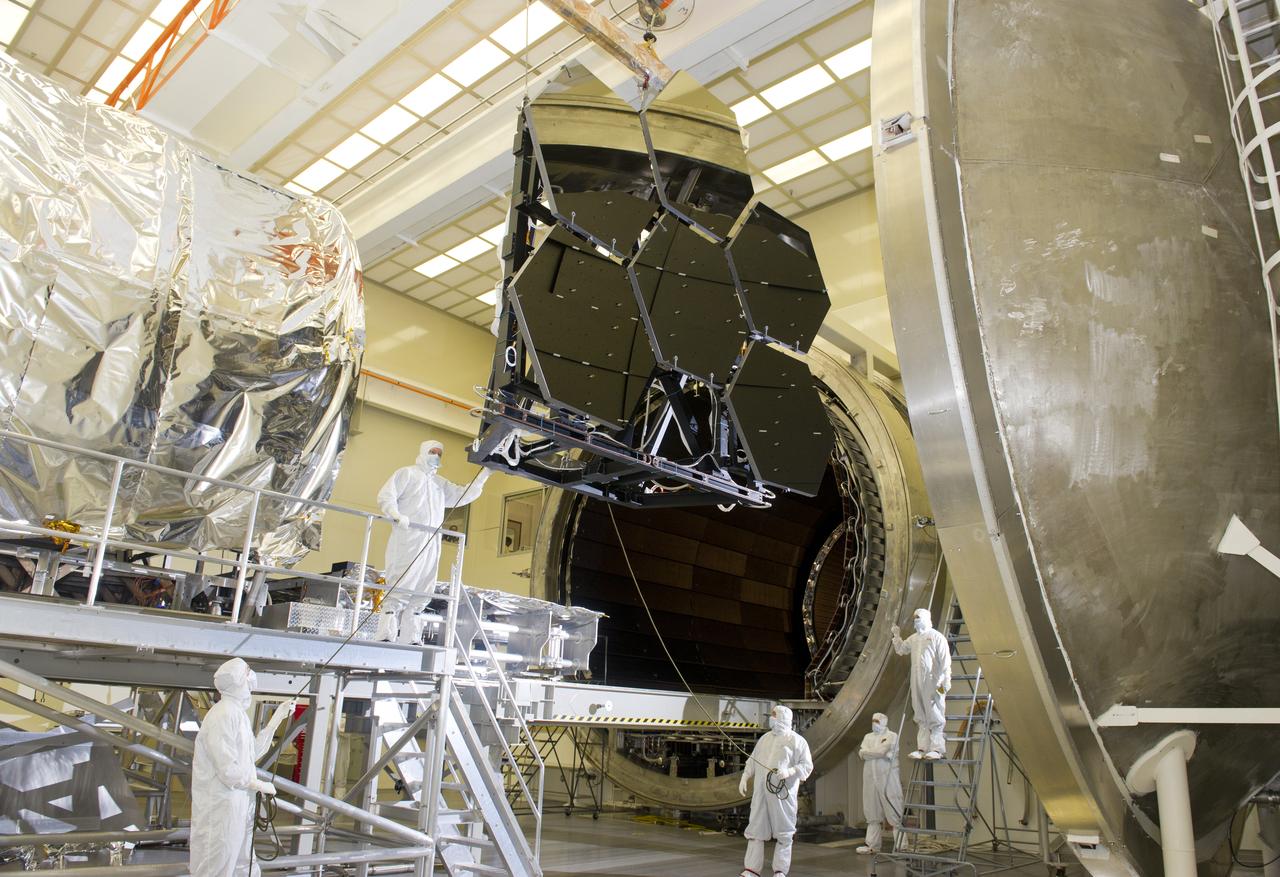

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
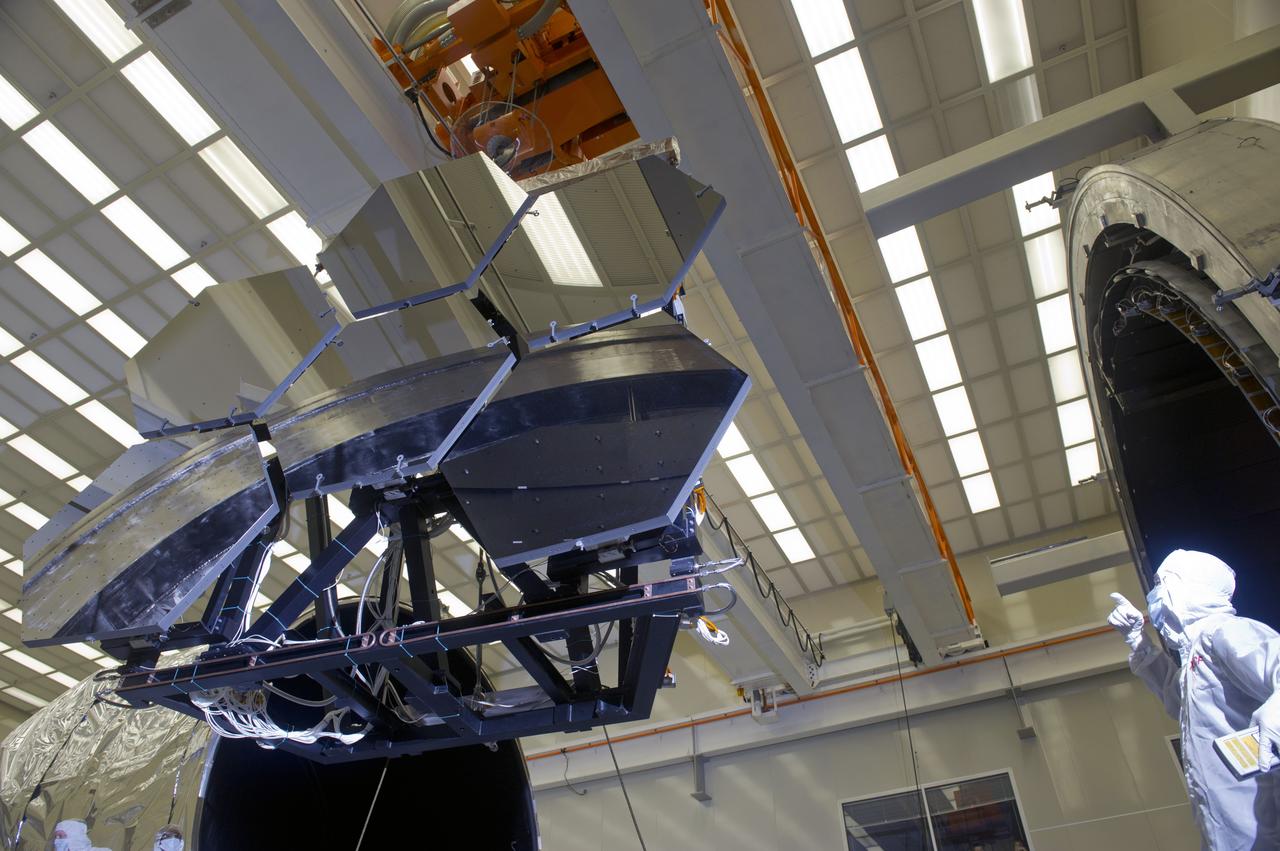

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
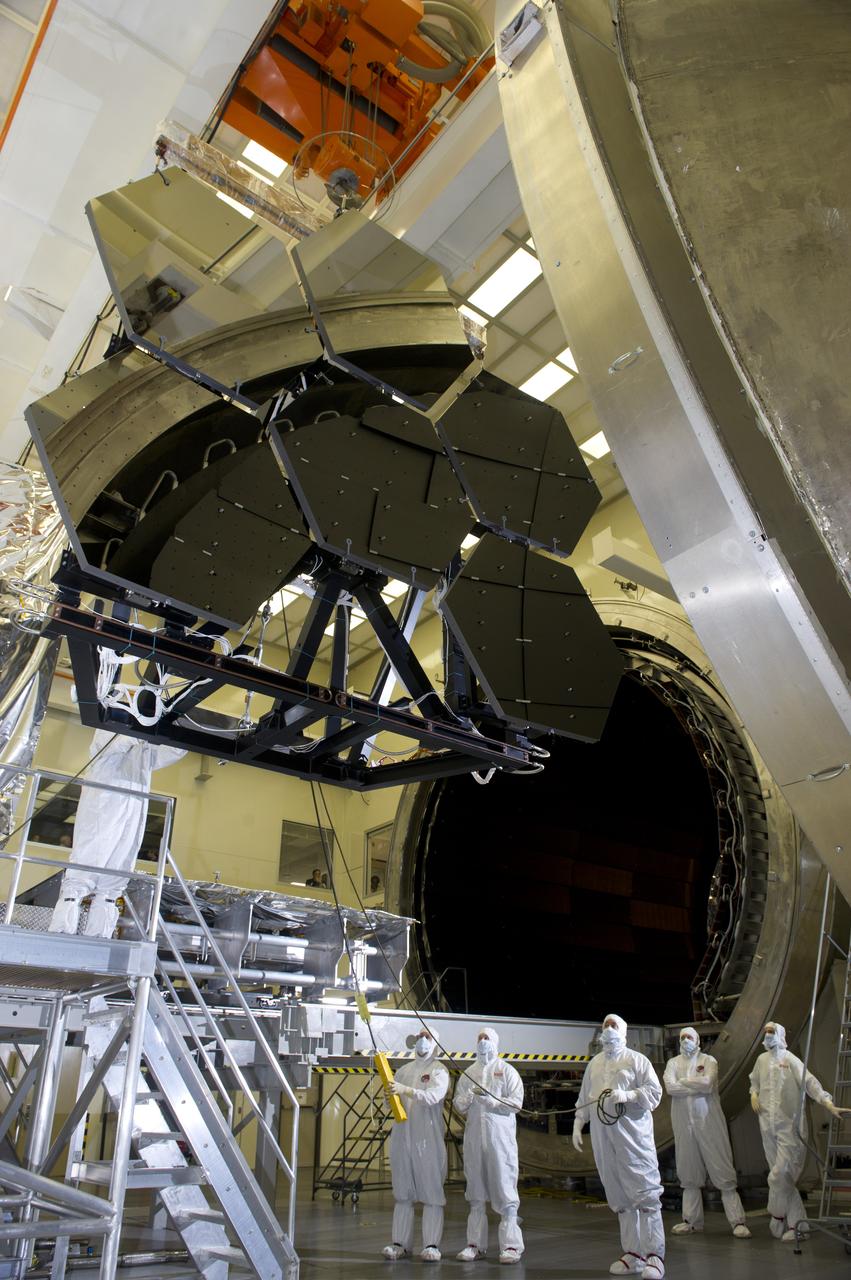

JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE CRYOGENIC TEST #4 SIX MIRROR DE-INTEGRATION, JULY 13, 2010, MSFC X-RAY & CRYOGENIC FACILITY
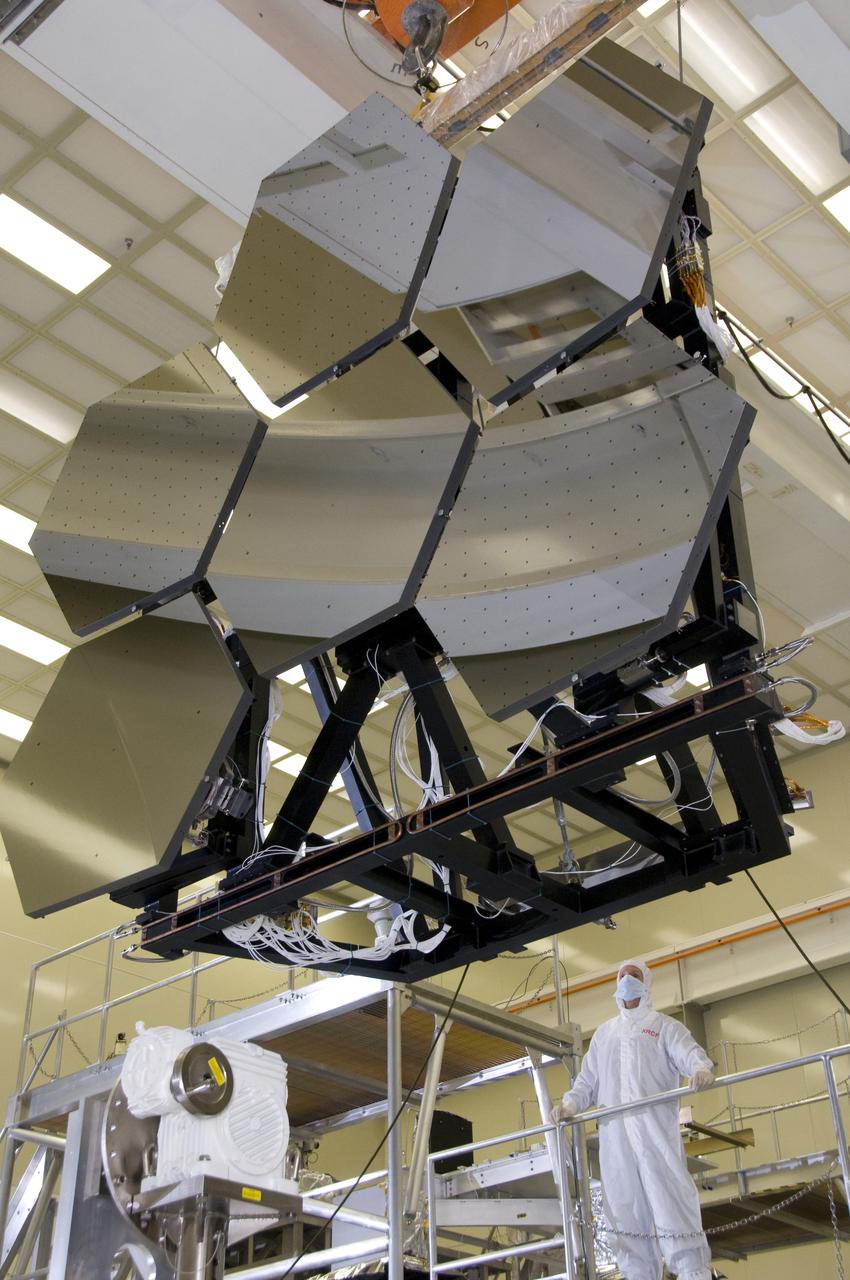

ERNIE WRIGHT, TEST DIRECTOR, MONITORS MOVE OF TEST STAND WITH SIX JWST (JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE) PRIMARY MIRROR SEGMENT ASSEMBLIES AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY.
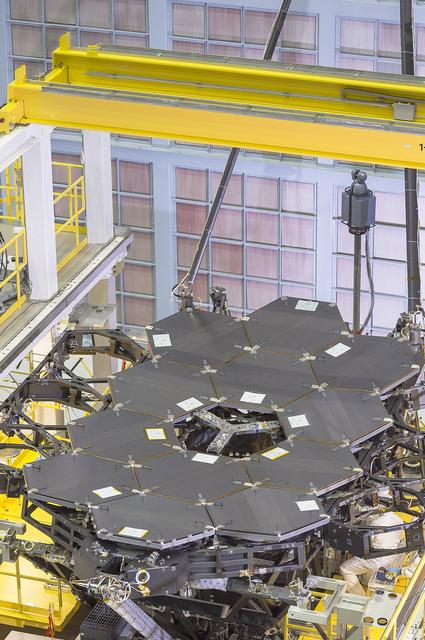

A view of the one dozen (out of 18) flight mirror segments that make up the primary mirror on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have been installed at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn More: Since December 2015, the team of scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to install all the primary mirror segments onto the telescope structure in the large clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The twelfth mirror was installed on January 2, 2016. "This milestone signifies that all of the hexagonal shaped mirrors on the fixed central section of the telescope structure are installed and only the 3 mirrors on each wing are left for installation," said Lee Feinberg, NASA's Optical Telescope Element Manager at NASA Goddard. "The incredibly skilled and dedicated team assembling the telescope continues to find ways to do things faster and more efficiently." Each hexagonal-shaped segment measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). After being pieced together, the 18 primary mirror segments will work together as one large 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) mirror. The primary mirror will unfold and adjust to shape after launch. The mirrors are made of ultra-lightweight beryllium. The mirrors are placed on the telescope's backplane using a robotic arm, guided by engineers. The full installation is expected to be completed in a few months. The mirrors were built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. Ball is the principal subcontractor to Northrop Grumman for the optical technology and lightweight mirror system. The installation of the mirrors onto the telescope structure is performed by Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York. Harris Corporation leads integration and testing for the telescope. While the mirror assembly is a very significant milestone, there are many more steps involved in assembling the Webb telescope. The primary mirror and the tennis-court-sized sunshield are the largest and most visible components of the Webb telescope. However, there are four smaller components that are less visible, yet critical. The instruments that will fly aboard Webb - cameras and spectrographs with detectors able to record extremely faint signals — are part of the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), which is currently undergoing its final cryogenic vacuum test and will be integrated with the mirror later this year. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/by-the-dozen-nasas-james-webb-space-telescope-mirrors" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/by-the-dozen-nasas-jame...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
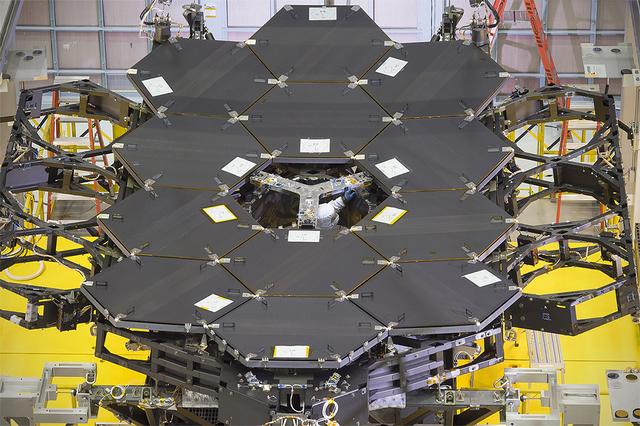

Caption: One dozen (out of 18) flight mirror segments that make up the primary mirror on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have been installed at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn More: Since December 2015, the team of scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to install all the primary mirror segments onto the telescope structure in the large clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The twelfth mirror was installed on January 2, 2016. "This milestone signifies that all of the hexagonal shaped mirrors on the fixed central section of the telescope structure are installed and only the 3 mirrors on each wing are left for installation," said Lee Feinberg, NASA's Optical Telescope Element Manager at NASA Goddard. "The incredibly skilled and dedicated team assembling the telescope continues to find ways to do things faster and more efficiently." Each hexagonal-shaped segment measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). After being pieced together, the 18 primary mirror segments will work together as one large 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) mirror. The primary mirror will unfold and adjust to shape after launch. The mirrors are made of ultra-lightweight beryllium. The mirrors are placed on the telescope's backplane using a robotic arm, guided by engineers. The full installation is expected to be completed in a few months. The mirrors were built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. Ball is the principal subcontractor to Northrop Grumman for the optical technology and lightweight mirror system. The installation of the mirrors onto the telescope structure is performed by Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York. Harris Corporation leads integration and testing for the telescope. While the mirror assembly is a very significant milestone, there are many more steps involved in assembling the Webb telescope. The primary mirror and the tennis-court-sized sunshield are the largest and most visible components of the Webb telescope. However, there are four smaller components that are less visible, yet critical. The instruments that will fly aboard Webb - cameras and spectrographs with detectors able to record extremely faint signals — are part of the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), which is currently undergoing its final cryogenic vacuum test and will be integrated with the mirror later this year. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/by-the-dozen-nasas-james-webb-space-telescope-mirrors" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/by-the-dozen-nasas-jame...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
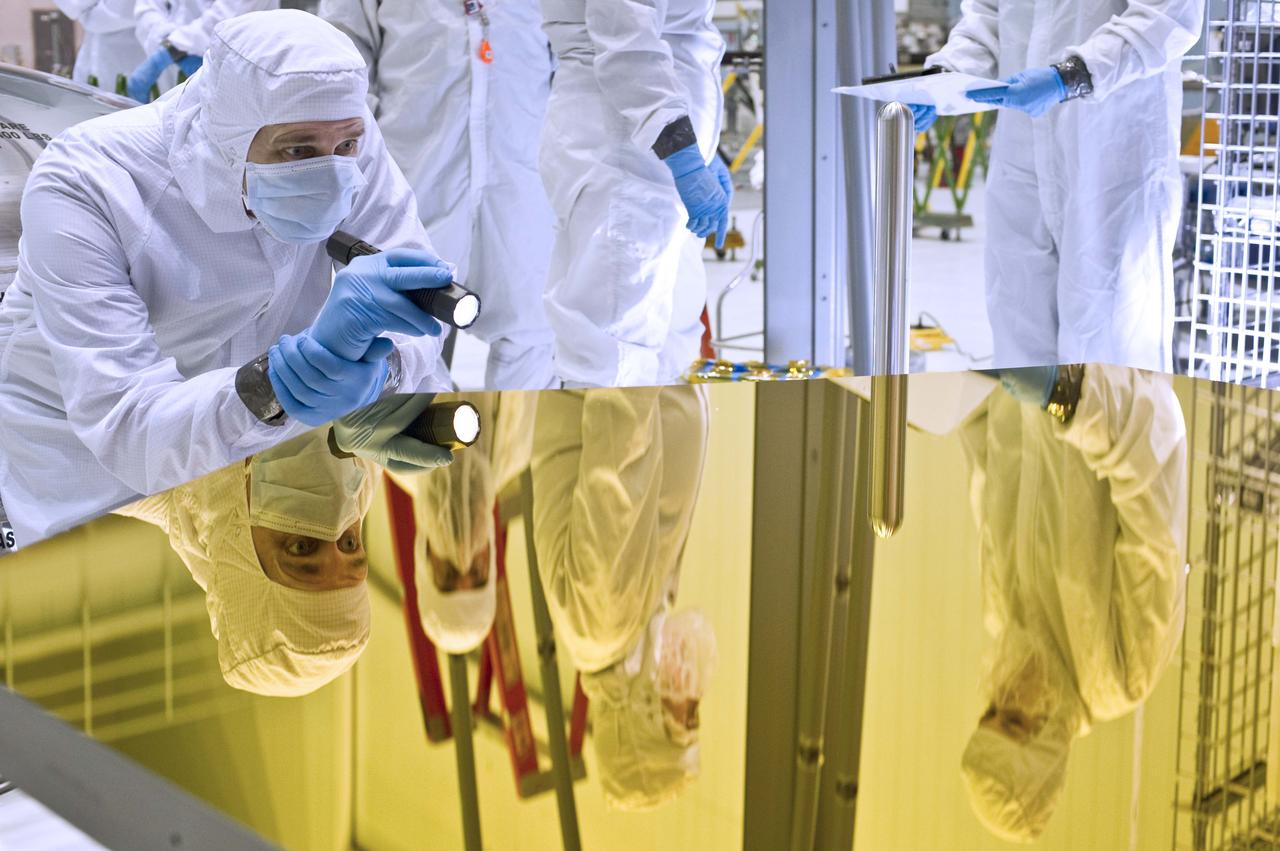

NASA image release April 13, 2011 An engineer examines the Webb telescope primary mirror Engineering Design Unit segment in the clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. It takes two unique types of mirrors working together to see farther back in time and space than ever before, and engineers at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center have just received one of each type. Primary and Secondary Mirror Engineering Design Units (EDUs) have recently arrived at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. from Northrop Grumman Aerospace Systems in Redondo Beach, Calif. and are undergoing examination and testing. When used on the James Webb Space Telescope those two types of mirrors will allow scientists to make those observations. "The Primary mirror EDU will be used next year to check out optical test equipment developed by Goddard and slated to be used to test the full Flight Primary mirror," said Lee Feinberg, the Optical Telescope Element Manager for the Webb telescope at NASA Goddard. "Following that, the primary and secondary EDU's will actually be assembled onto the Pathfinder telescope. The Pathfinder telescope includes two primary mirror segments (one being the Primary EDU) and the Secondary EDU and allows us to check out all of the assembly and test procedures (that occur both at Goddard and testing at Johnson Space Center, Houston, Texas) well in advance of the flight telescope assembly and test." To read more about this image go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/technology/features/two-webb-mirrors.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/technology/features/two-webb-mirrors....</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
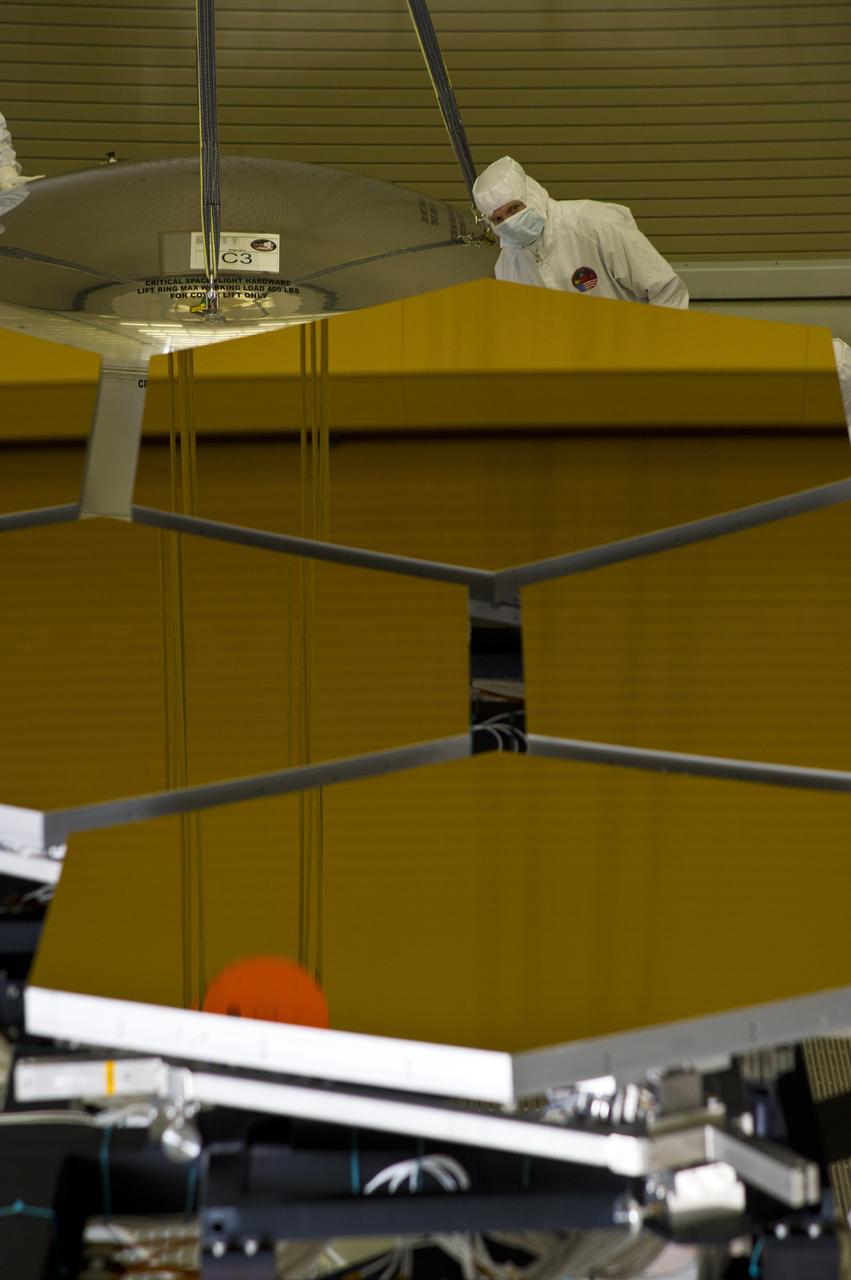

BALL ENGINEERS DISMANTLE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS FOR TRANSPORT TO BALL AEROSPACE AFTER CRYOGENIC TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY.
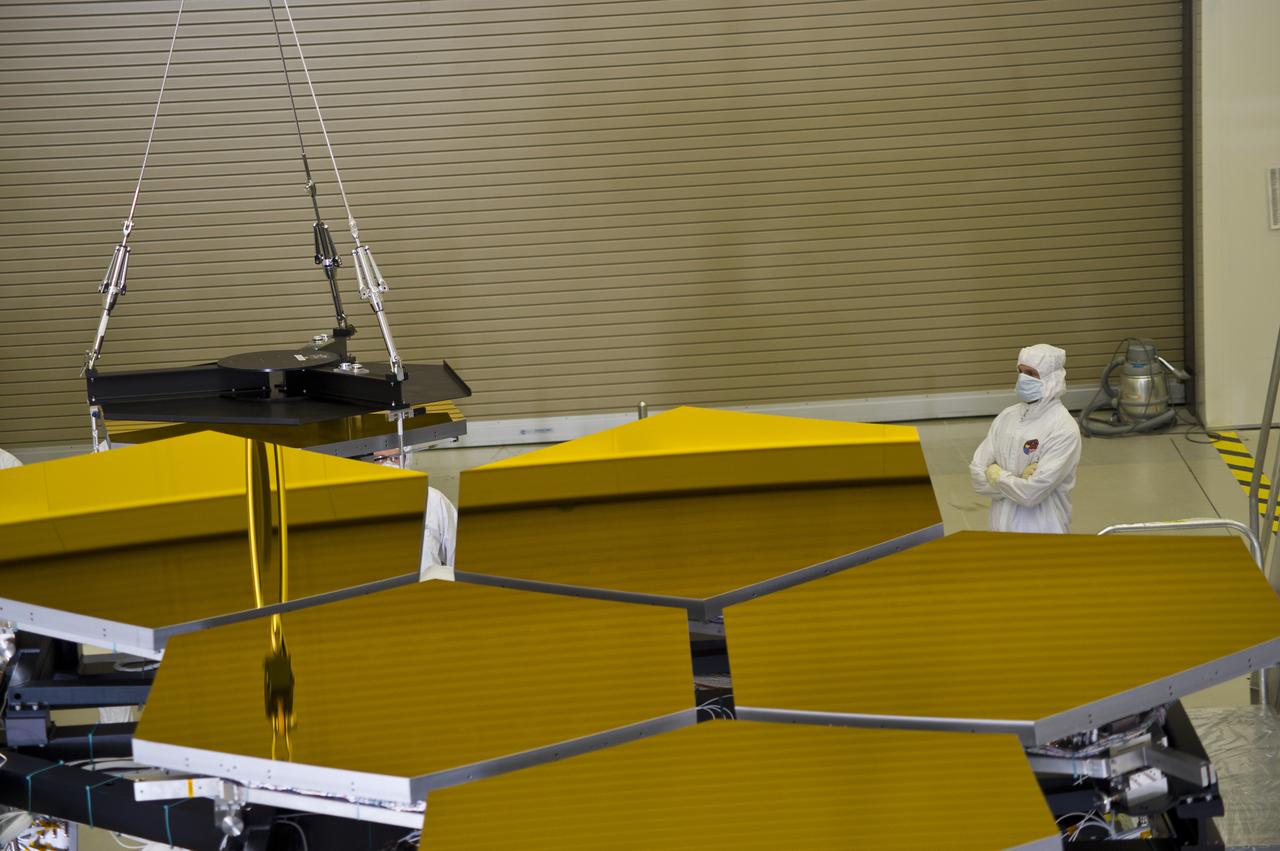

BALL ENGINEERS DISMANTLE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS FOR TRANSPORT TO BALL AEROSPACE AFTER CRYOGENIC TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY.
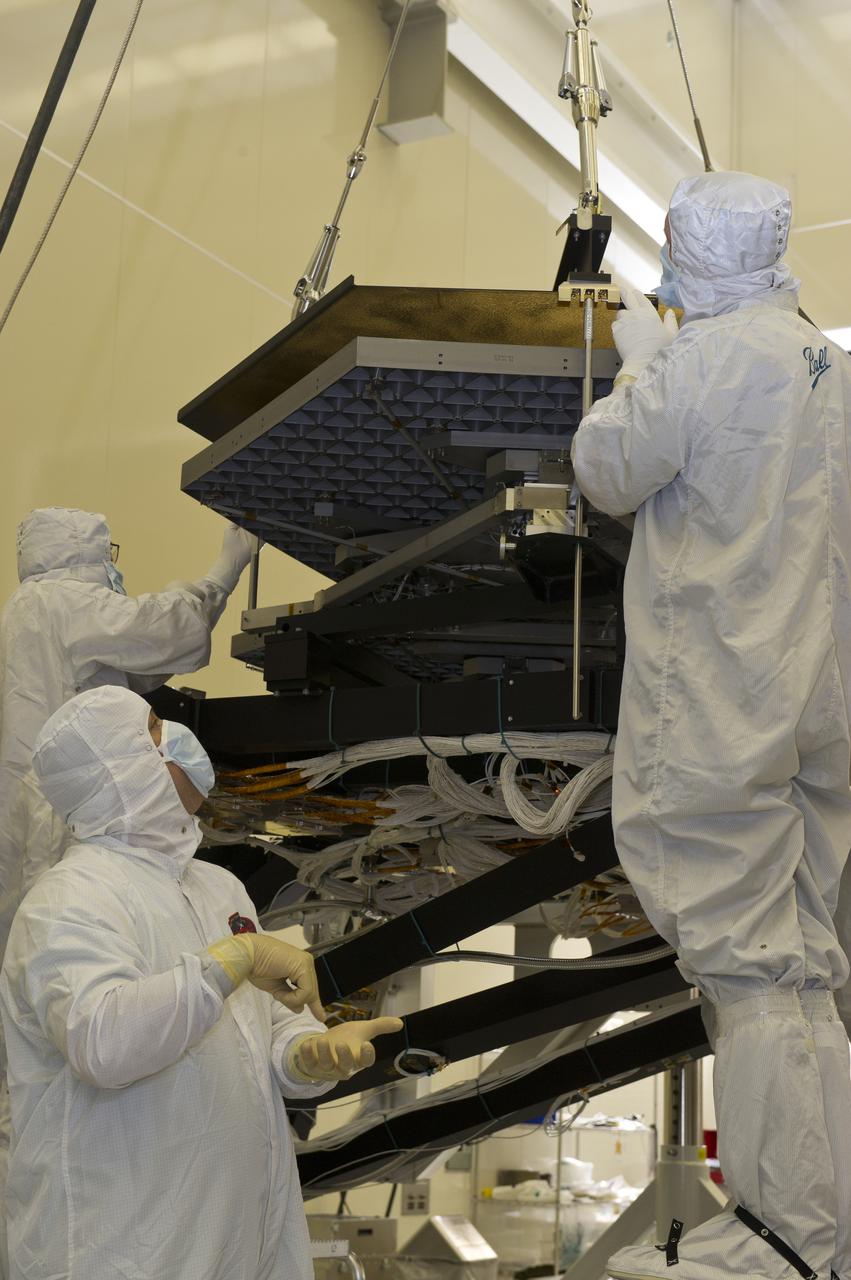

BALL ENGINEERS DISMANTLE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS FOR TRANSPORT TO BALL AEROSPACE AFTER CRYOGENIC TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY.
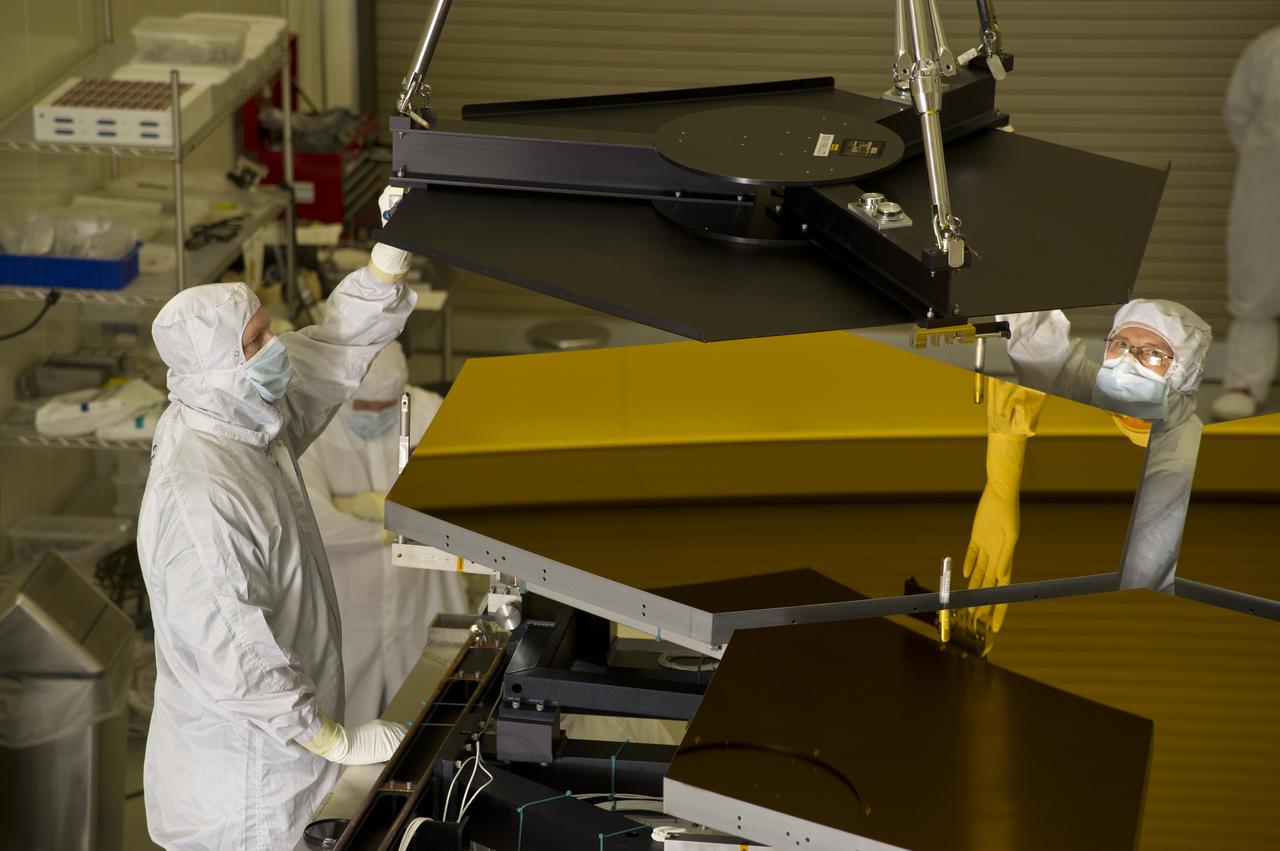

BALL ENGINEERS DISMANTLE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS FOR TRANSPORT TO BALL AEROSPACE AFTER CRYOGENIC TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY.
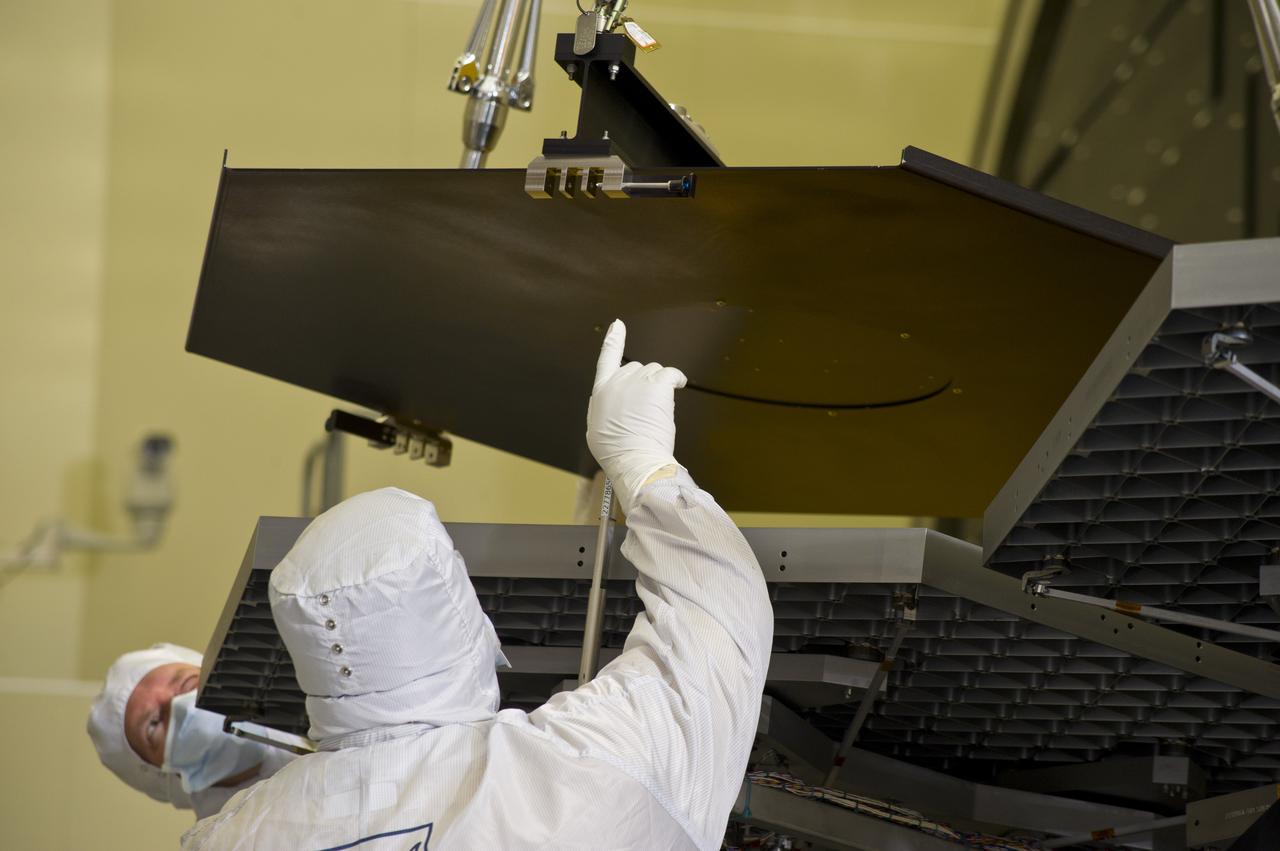

BALL ENGINEERS DISMANTLE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS FOR TRANSPORT TO BALL AEROSPACE AFTER CRYOGENIC TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY.
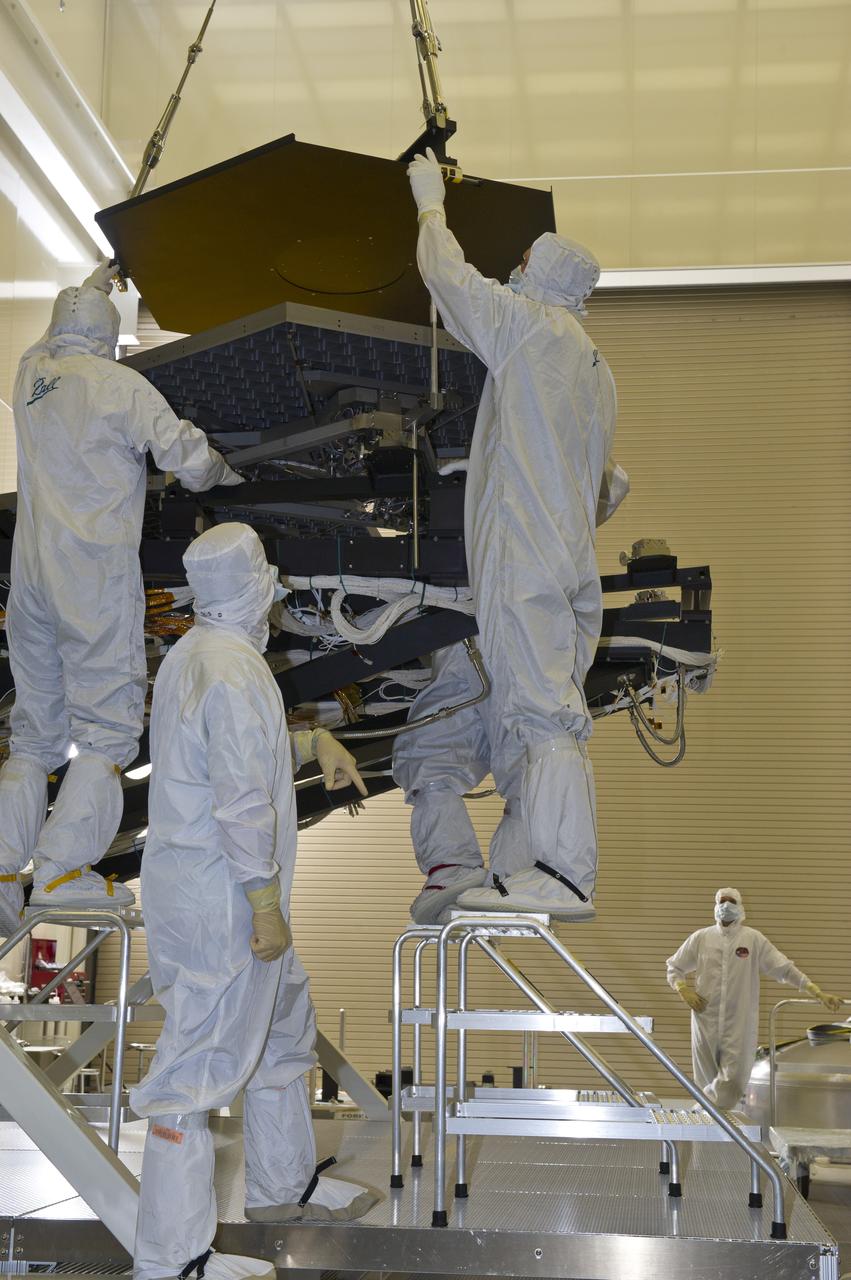

BALL ENGINEERS DISMANTLE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS FOR TRANSPORT TO BALL AEROSPACE AFTER CRYOGENIC TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY.

Engineers at Ball Aerospace test the Wavefront Sensing and Control testbed to ensure that the 18 primary mirror segments and one secondary mirror on JWST work as one. The test is performed on a 1/6 scale model of the JWST mirrors. Credit: NASA/Northrop Grumman/Ball Aerospace To read more about the James Webb Space Telescope go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/technology/features/partnerships.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/technology/features/partnerships.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
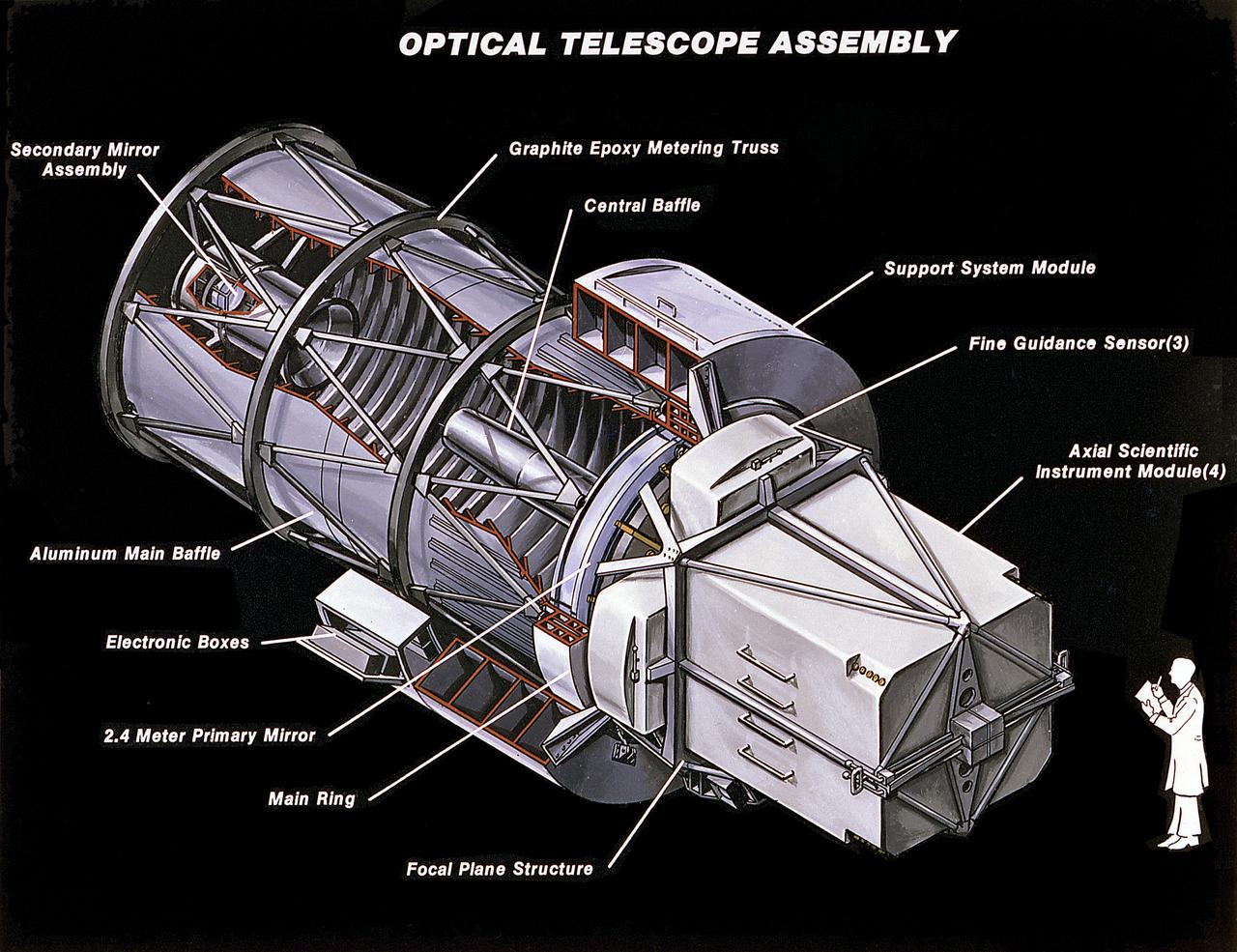
This image illustrates the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA). One of the three major elements of the HST, the OTA consists of two mirrors (a primary mirror and a secondary mirror), support trusses, and the focal plane structure. The mirrors collect and focus light from selected celestial objects and are housed near the center of the telescope. The primary mirror captures light from objects in space and focuses it toward the secondary mirror. The secondary mirror redirects the light to a focal plane where the Scientific Instruments are located. The primary mirror is 94.5 inches (2.4 meters) in diameter and the secondary mirror is 12.2 inches (0.3 meters) in diameter. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth Orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from the Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The spacecraft is 42.5 feet (13 meters) long and weighs 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
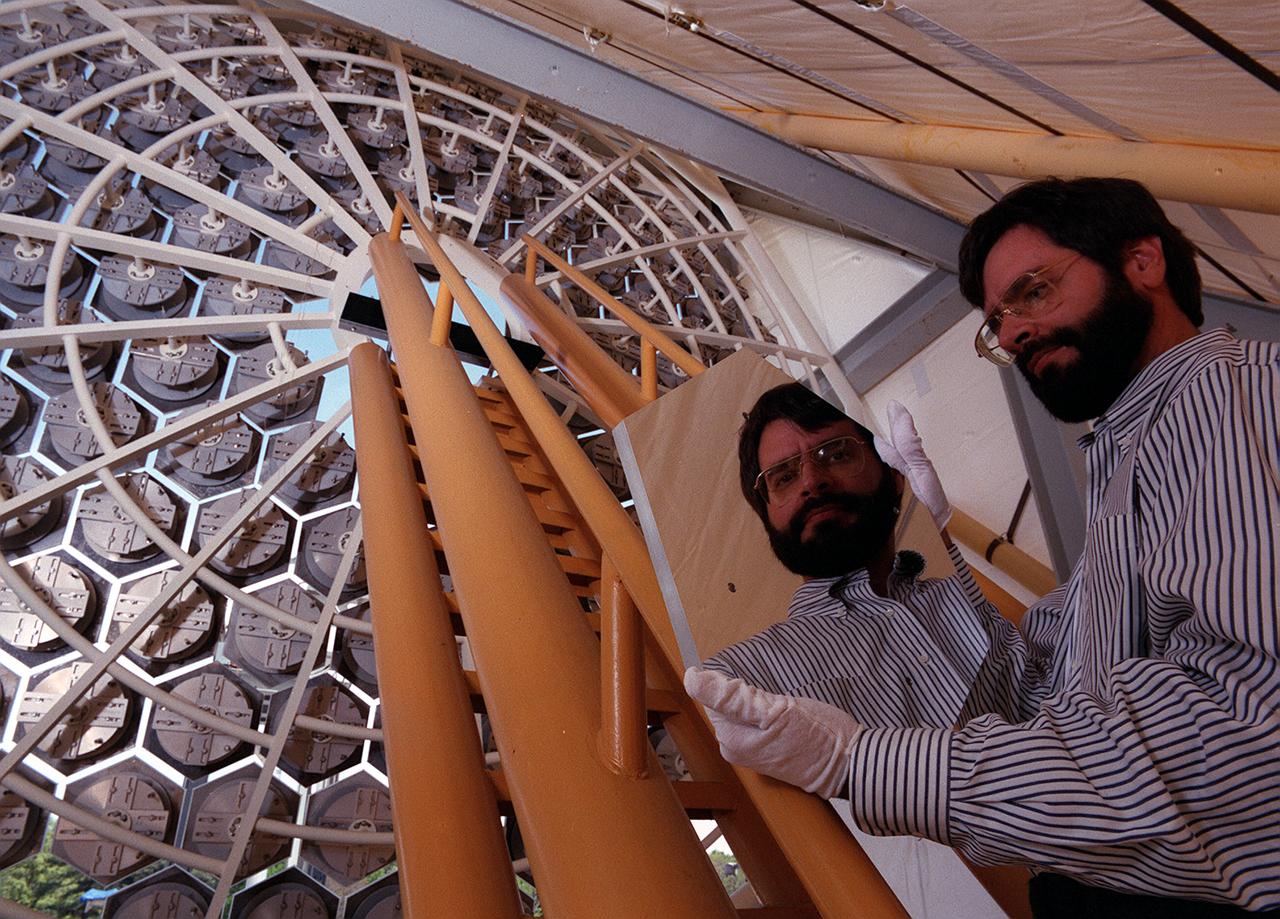

NASA's Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center has been working to expand our view of the universe via sophisticated new telescopes. The Optics Center's goal is to develop low-cost, advanced space optics technologies for the NASA program in the 21st century, including the long-term goal of imaging Earth-like planets in distant solar systems. A segmented array of mirrors was designed by the Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center for solar the concentrator test stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) for powering solar thermal propulsion engines. Each hexagon mirror has a spherical surface to approximate a parabolic concentrator when combined into the entire 18-foot diameter array. The aluminum mirrors were polished with a diamond turning machine, that creates a glass-like reflective finish on metal. The precision fabrication machinery at the Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center at MSFC can polish specialized optical elements to a world class quality of smoothness. This image shows optics physicist, Vince Huegele, examining one of the 144-segment hexagonal mirrors of the 18-foot diameter array at the MSFC solar concentrator test stand.
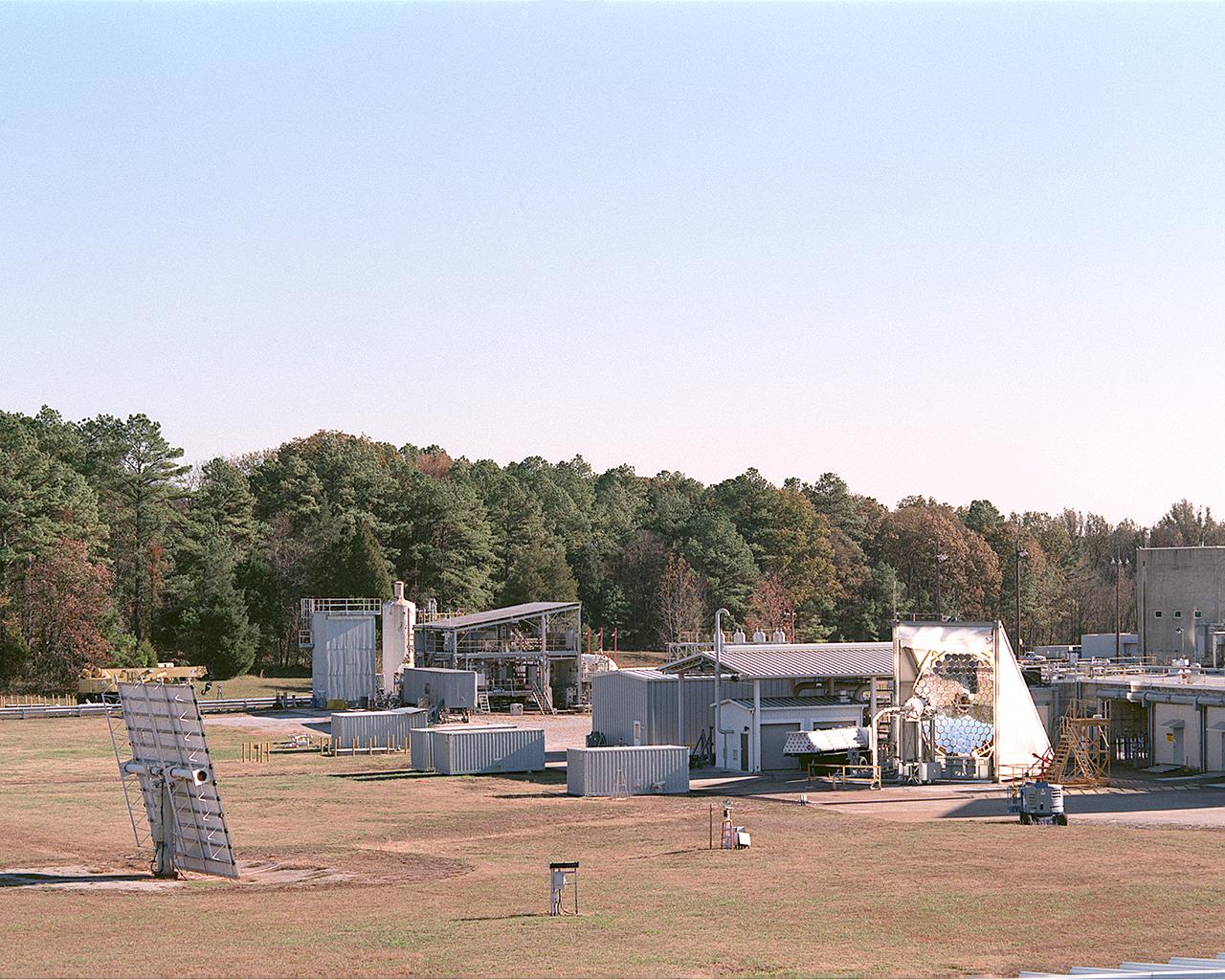

This photograph shows an overall view of the Solar Thermal Propulsion Test Facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The 20-by 24-ft heliostat mirror, shown at the left, has dual-axis control that keeps a reflection of the sunlight on an 18-ft diameter concentrator mirror (right). The concentrator mirror then focuses the sunlight to a 4-in focal point inside the vacuum chamber, shown at the front of concentrator mirror. Researchers at MSFC have designed, fabricated, and tested the first solar thermal engine, a non-chemical rocket engine that produces lower thrust but has better thrust efficiency than chemical a combustion engine. MSFC turned to solar thermal propulsion in the early 1990s due to its simplicity, safety, low cost, and commonality with other propulsion systems. Solar thermal propulsion works by acquiring and redirecting solar energy to heat a propell nt. As part of MSFC's Space Transportation Directorate, the Propulsion Research Center serves as a national resource for research of advanced, revolutionary propulsion technologies. The mission is to move the Nation's capabilities beyond the confines of conventional chemical propulsion into an era of aircraft-like access to Earth-orbit, rapid travel throughout the solar system, and exploration of interstellar space.
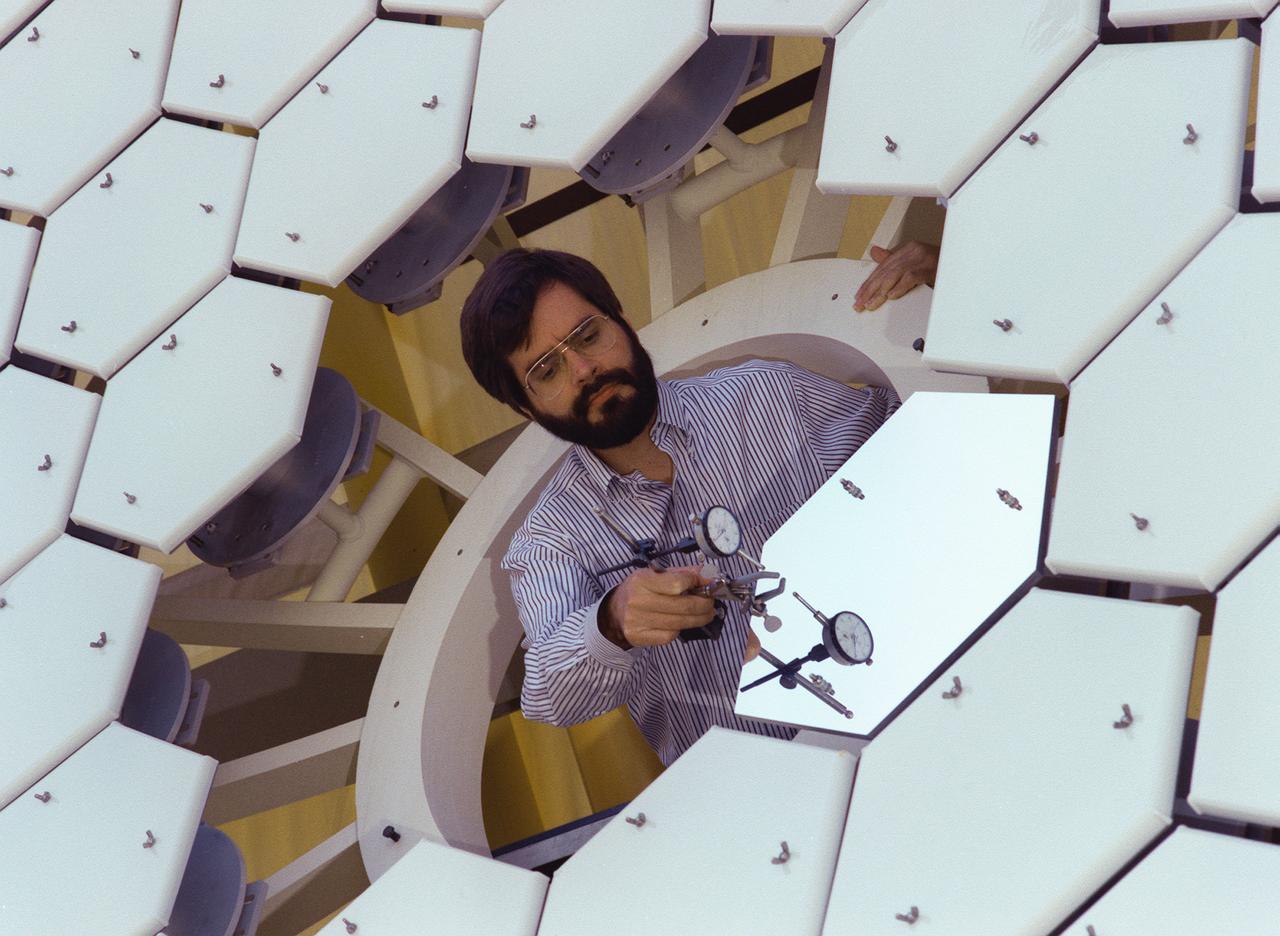

NASA's Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center has been working to expand our view of the universe via sophisticated new telescopes. The Optics Center's goal is to develop low-cost, advanced space optics technologies for the NASA program in the 21st century, including the long-term goal of imaging Earth-like planets in distant solar systems. A segmented array of mirrors was designed by the Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center for the solar concentrator test stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) for powering solar thermal propulsion engines. Each hexagon mirror has a spherical surface to approximate a parabolic concentrator when combined into the entire 18-foot diameter array. The aluminum mirrors were polished with a diamond turning machine that creates a glass-like reflective finish on metal. The precision fabrication machinery at the Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center at MSFC can polish specialized optical elements to a world class quality of smoothness. This image shows optics physicist, Vince Huegele, examining one of the 144-segment hexagonal mirrors of the 18-foot diameter array at the MSFC solar concentrator test stand.
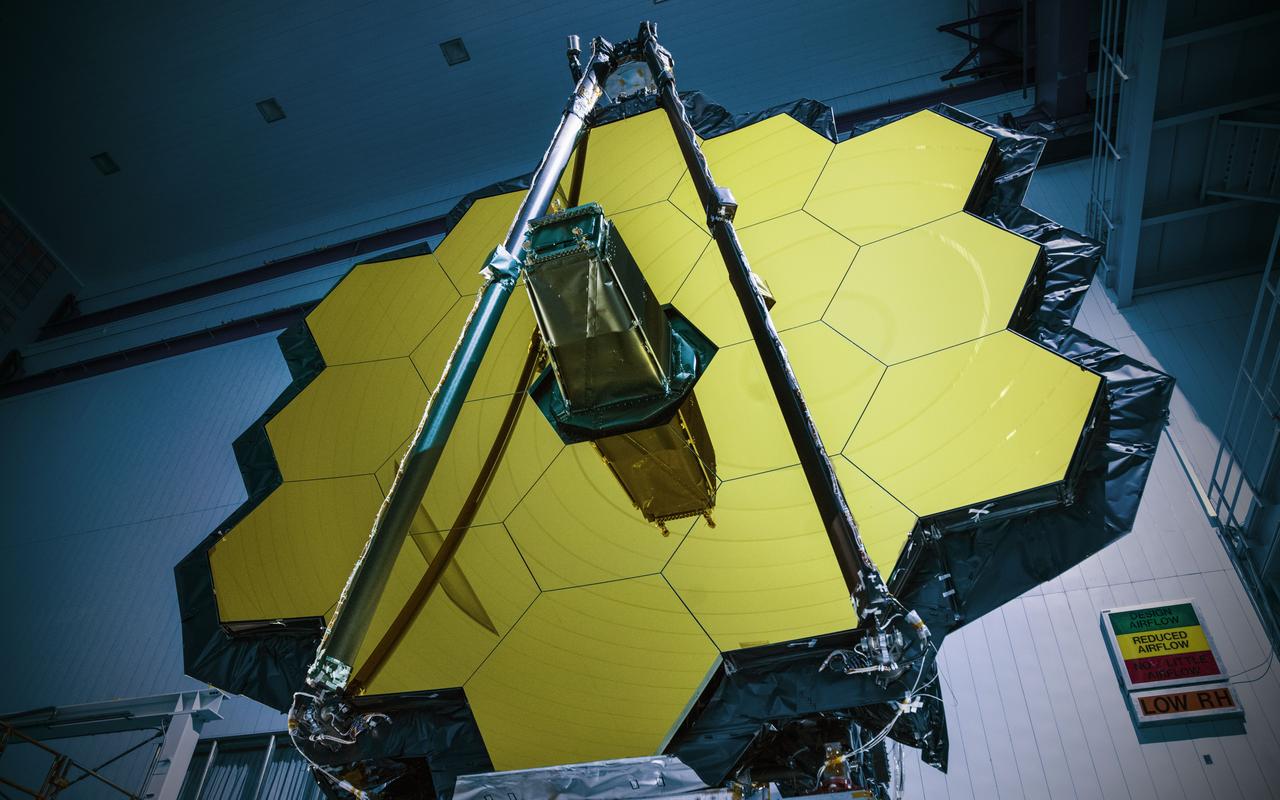

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has successfully passed the center of curvature test, an important optical measurement of Webb’s fully assembled primary mirror prior to cryogenic testing, and the last test held at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, before the spacecraft is shipped to NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston for more testing. After undergoing rigorous environmental tests simulating the stresses of its rocket launch, the Webb telescope team at Goddard analyzed the results from this critical optical test and compared it to the pre-test measurements. The team concluded that the mirrors passed the test with the optical system unscathed. “The Webb telescope is about to embark on its next step in reaching the stars as it has successfully completed its integration and testing at Goddard. It has taken a tremendous team of talented individuals to get to this point from all across NASA, our industry and international partners, and academia,” said Bill Ochs, NASA’s Webb telescope project manager. “It is also a sad time as we say goodbye to the Webb Telescope at Goddard, but are excited to begin cryogenic testing at Johnson.” Rocket launches create high levels of vibration and noise that rattle spacecraft and telescopes. At Goddard, engineers tested the Webb telescope in vibration and acoustics test facilities that simulate the launch environment to ensure that functionality is not impaired by the rigorous ride on a rocket into space. Before and after these environmental tests took place, optical engineers set up an interferometer, the main device used to measure the shape of the Webb telescope’s mirror. An interferometer gets its name from the process of recording and measuring the ripple patterns that result when different beams of light mix and their waves combine or “interfere.” Waves of visible light are less than a thousandth of a millimeter long and optics on the Webb telescope need to be shaped and aligned even more accurately than that to work correctly. Making measurements of the mirror shape and position by lasers prevents physical contact and damage (scratches to the mirror). So, scientists use wavelengths of light to make tiny measurements. By measuring light reflected off the optics using an interferometer, they are able to measure extremely small changes in shape or position that may occur after exposing the mirror to a simulated launch or temperatures that simulate the subfreezing environment of space. During a test conducted by a team from Goddard, Ball Aerospace of Boulder, Colorado, and the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, temperature and humidity conditions in the clean room were kept incredibly stable to minimize fluctuations in the sensitive optical measurements over time. Even so, tiny vibrations are ever-present in the clean room that cause jitter during measurements, so the interferometer is a “high-speed” one, taking 5,000 “frames” every second, which is a faster rate than the background vibrations themselves. This allows engineers to subtract out jitter and get good, clean results on any changes to the mirror's shape. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn Read more: <a href="https://go.nasa.gov/2oPqHwR" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2oPqHwR</a> NASA’s Webb Telescope Completes Goddard Testing
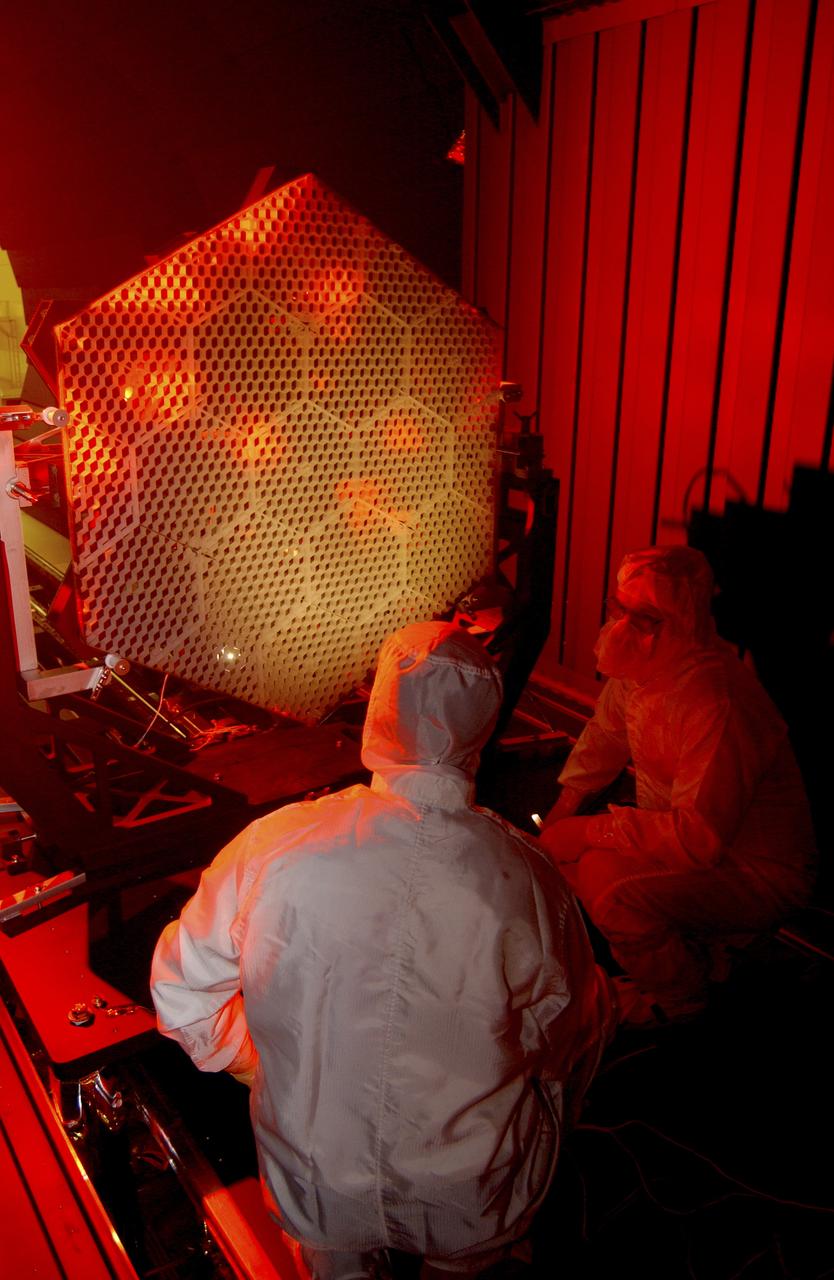

The Eastman-Kodak mirror assembly is being tested for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) project at the X-Ray Calibration Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). In this photo, one of many segments of the mirror assembly is being set up inside the 24-ft vacuum chamber where it will undergo x-ray calibration tests. MSFC is supporting Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in developing the JWST by taking numerous measurements to predict its future performance. The tests are conducted in a vacuum chamber cooled to approximate the super cold temperatures found in space. During its 27 years of operation, the facility has performed testing in support of a wide array of projects, including the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Solar A, Chandra technology development, Chandra High Resolution Mirror Assembly and science instruments, Constellation X-Ray Mission, and Solar X-Ray Imager, currently operating on a Geostationary Operational Environment Satellite. The JWST is NASA's next generation space telescope, a successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, named in honor of NASA's second administrator, James E. Webb. It is scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle. It will take about 3 months for the spacecraft to reach its destination, an orbit of 940,000 miles in space.
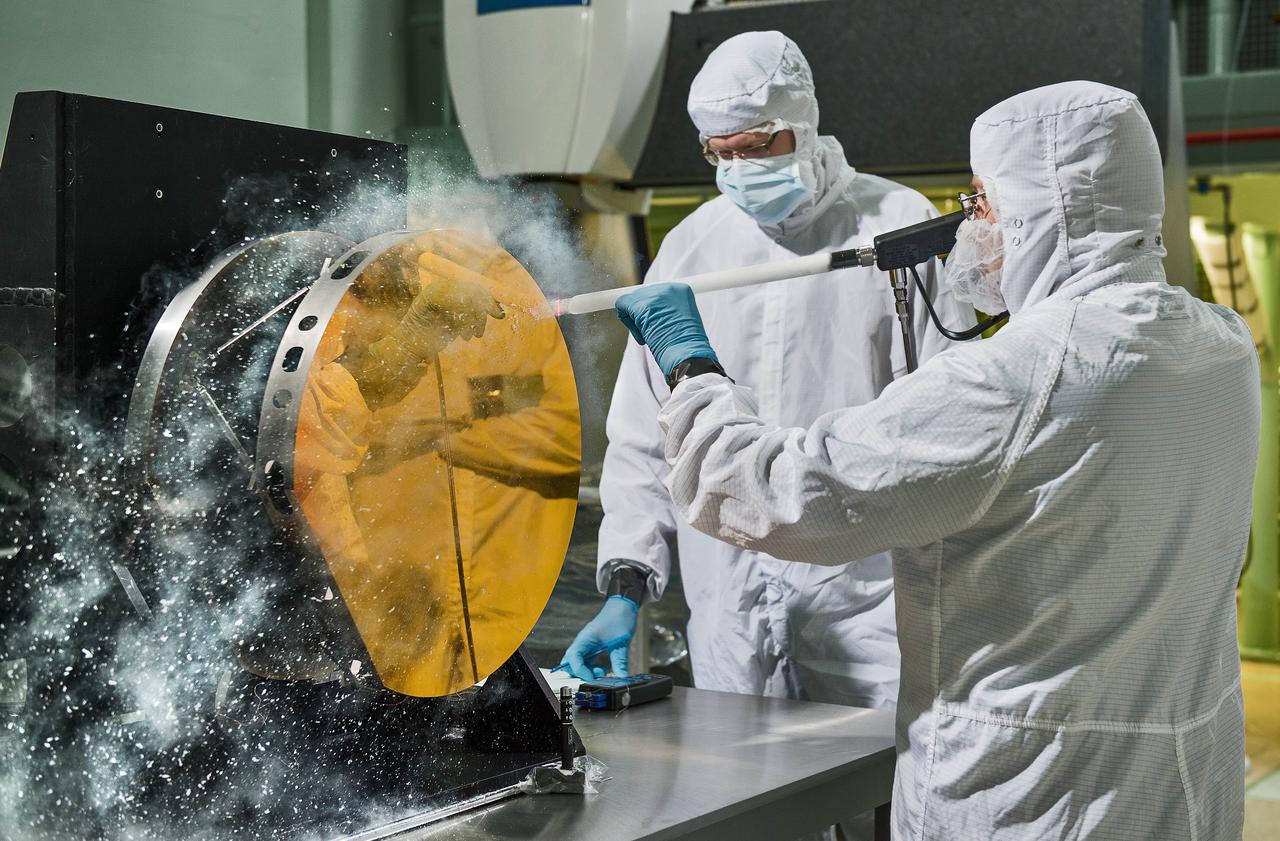

Just like drivers sometimes use snow to clean their car mirrors in winter, two Exelis Inc. engineers are practicing "snow cleaning'" on a test telescope mirror for the James Webb Space Telescope at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. By shooting carbon dioxide snow at the surface, engineers are able to clean large telescope mirrors without scratching them. "The snow-like crystals (carbon dioxide snow) knock contaminate particulates and molecules off the mirror," said Lee Feinberg, NASA optical telescope element manager. This technique will only be used if the James Webb Space Telescope's mirror is contaminated during integration and testing. The Webb telescope is the scientific successor to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. It will be the most powerful space telescope ever built. With a mirror seven times as large as Hubble's and infrared capability, Webb will be capturing light from 13.5 billion light years away. To do this, its mirror must be kept super clean. "Small dust particles or molecules can impact the science that can be done with the Webb," said Feinberg. "So cleanliness especially on the mirrors is critical." Webb is an international project led by NASA with its partners, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. Image credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn Text credit: Laura Betz, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
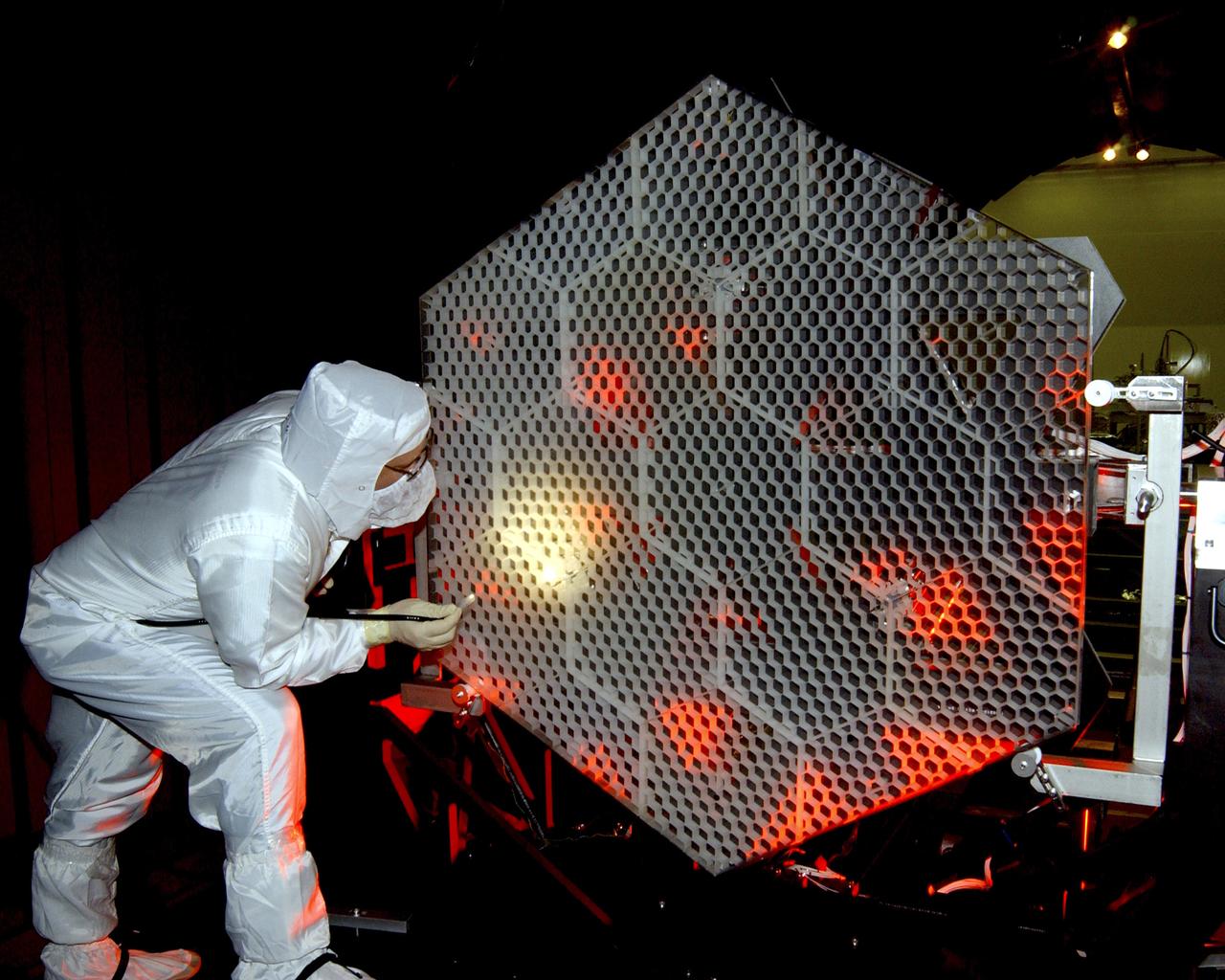

The Eastman-Kodak mirror assembly is being tested for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) project at the X-Ray Calibration Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). In this photo, an MSFC employee is inspecting one of many segments of the mirror assembly for flaws. MSFC is supporting Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in developing the JWST by taking numerous measurements to predict its future performance. The tests are conducted in a vacuum chamber cooled to approximate the super cold temperatures found in space. During its 27 years of operation, the facility has performed testing in support of a wide array of projects, including the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Solar A, Chandra technology development, Chandra High Resolution Mirror Assembly and science instruments, Constellation X-Ray Mission, and Solar X-Ray Imager, currently operating on a Geostationary Operational Environment Satellite. The JWST is NASA's next generation space telescope, a successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, named in honor of NASA's second administrator, James E. Webb. It is scheduled for launch in 2010 aboard an expendable launch vehicle. It will take about 3 months for the spacecraft to reach its destination, an orbit of 940,000 miles in space.

The primary mirror of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope consisting of 18 hexagonal mirrors looks like a giant puzzle piece standing in the massive clean room of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Appropriately, combined with the rest of the observatory, the mirrors will help piece together puzzles scientists have been trying to solve throughout the cosmos. Webb's primary mirror will collect light for the observatory in the scientific quest to better understand our solar system and beyond. Using these mirrors and Webb's infrared vision scientists will peer back over 13.5 billion years to see the first stars and galaxies forming out of the darkness of the early universe. Unprecedented infrared sensitivity will help astronomers to compare the faintest, earliest galaxies to today's grand spirals and ellipticals, helping us to understand how galaxies assemble over billions of years. Webb will see behind cosmic dust clouds to see where stars and planetary systems are being born. It will also help reveal information about atmospheres of planets outside our solar system, and perhaps even find signs of the building blocks of life elsewhere in the universe. The Webb telescope was mounted upright after a "center of curvature" test conducted at Goddard. This initial center of curvature test ensures the integrity and accuracy, and test will be repeated later to verify those same properties after the structure undergoes launch environment testing. In the photo, two technicians stand before the giant primary mirror. For information on the Webb's Center of Curvature test, visit: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2fidD9S" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2fidD9S</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
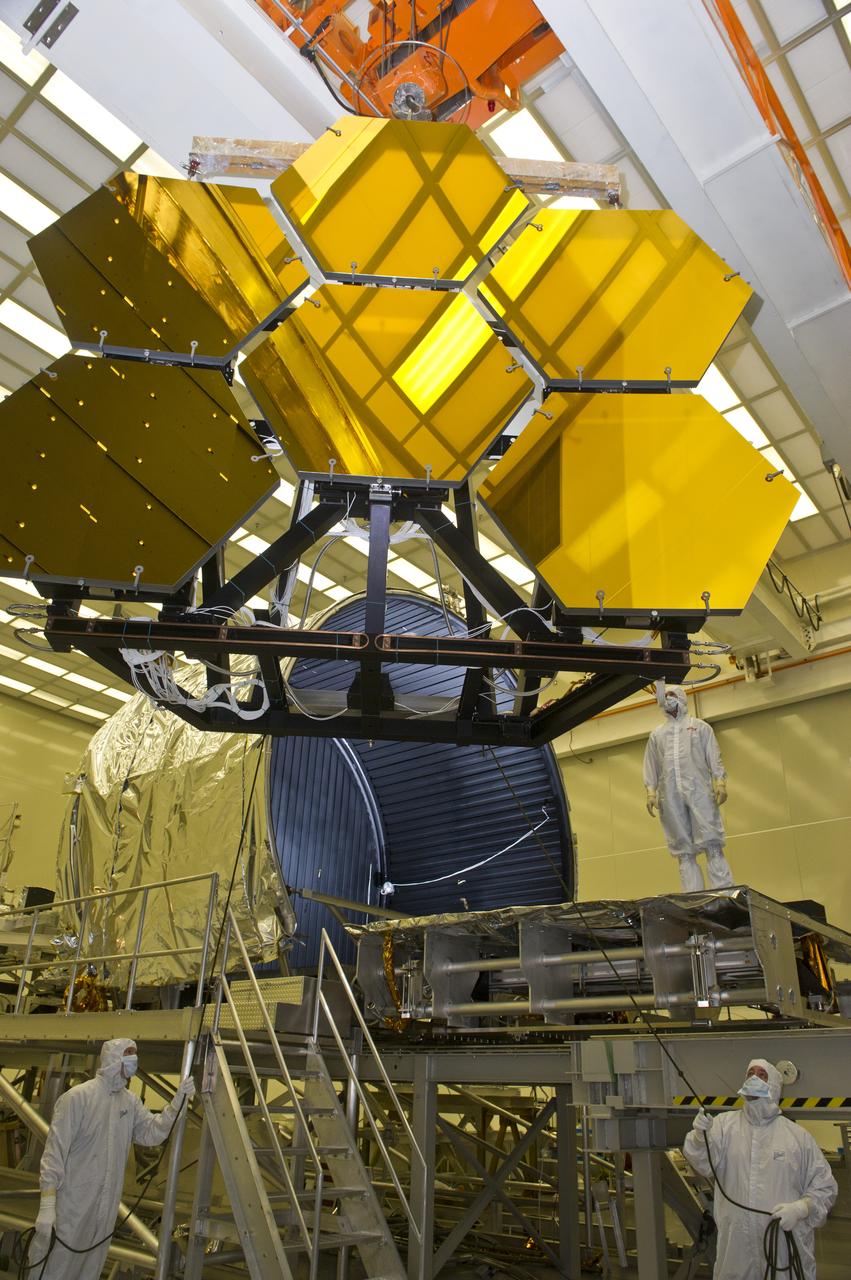

BALL AEROSPACE ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY, (L), AND MARSHALL ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT, (R), GUIDE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AFTER FINAL ACCEPTANCE TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY

BALL AEROSPACE ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY, (L), AND MARSHALL ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT, (R), GUIDE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AFTER FINAL ACCEPTANCE TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
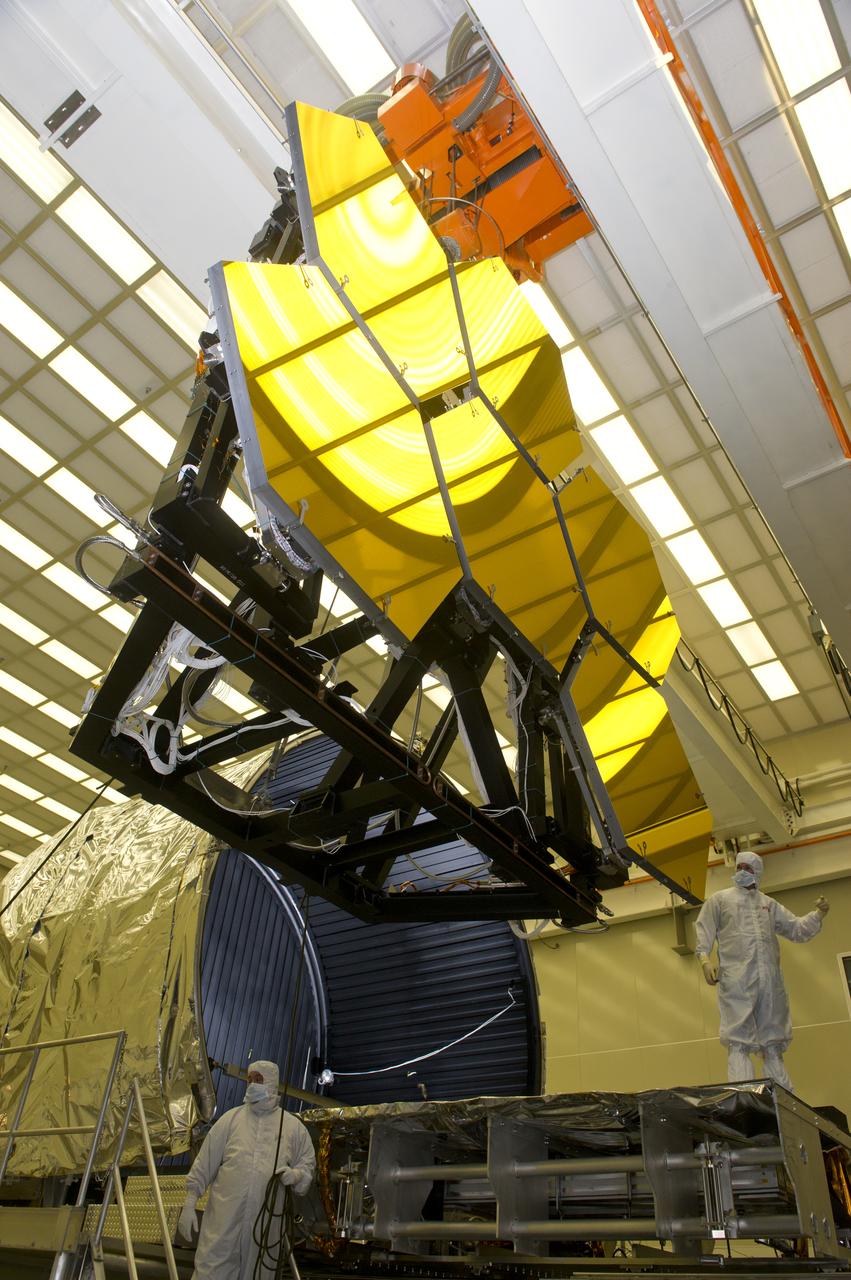

BALL AEROSPACE ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY, (L), AND MARSHALL ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT, (R), GUIDE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AFTER FINAL ACCEPTANCE TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
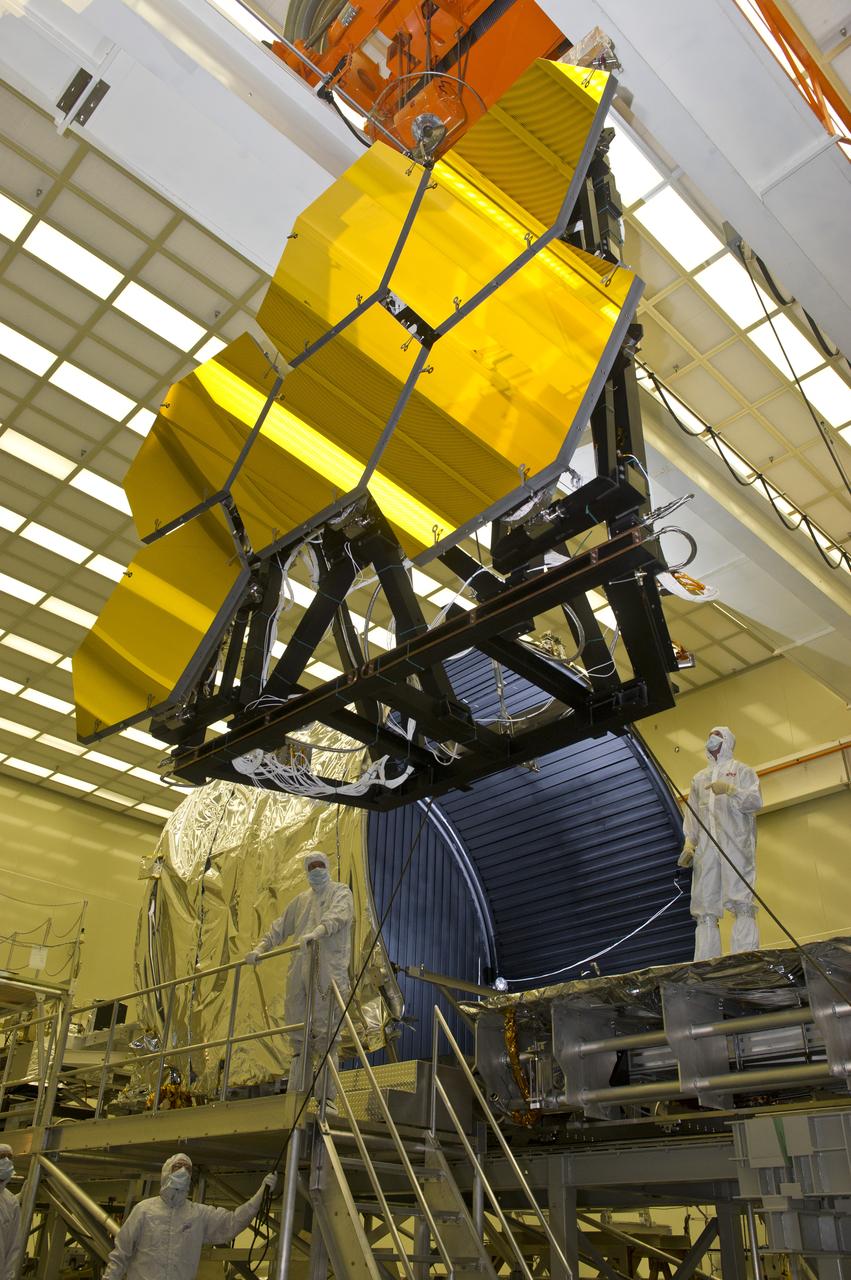

BALL AEROSPACE ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY, (L), AND MARSHALL ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT, (R), GUIDE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AFTER FINAL ACCEPTANCE TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
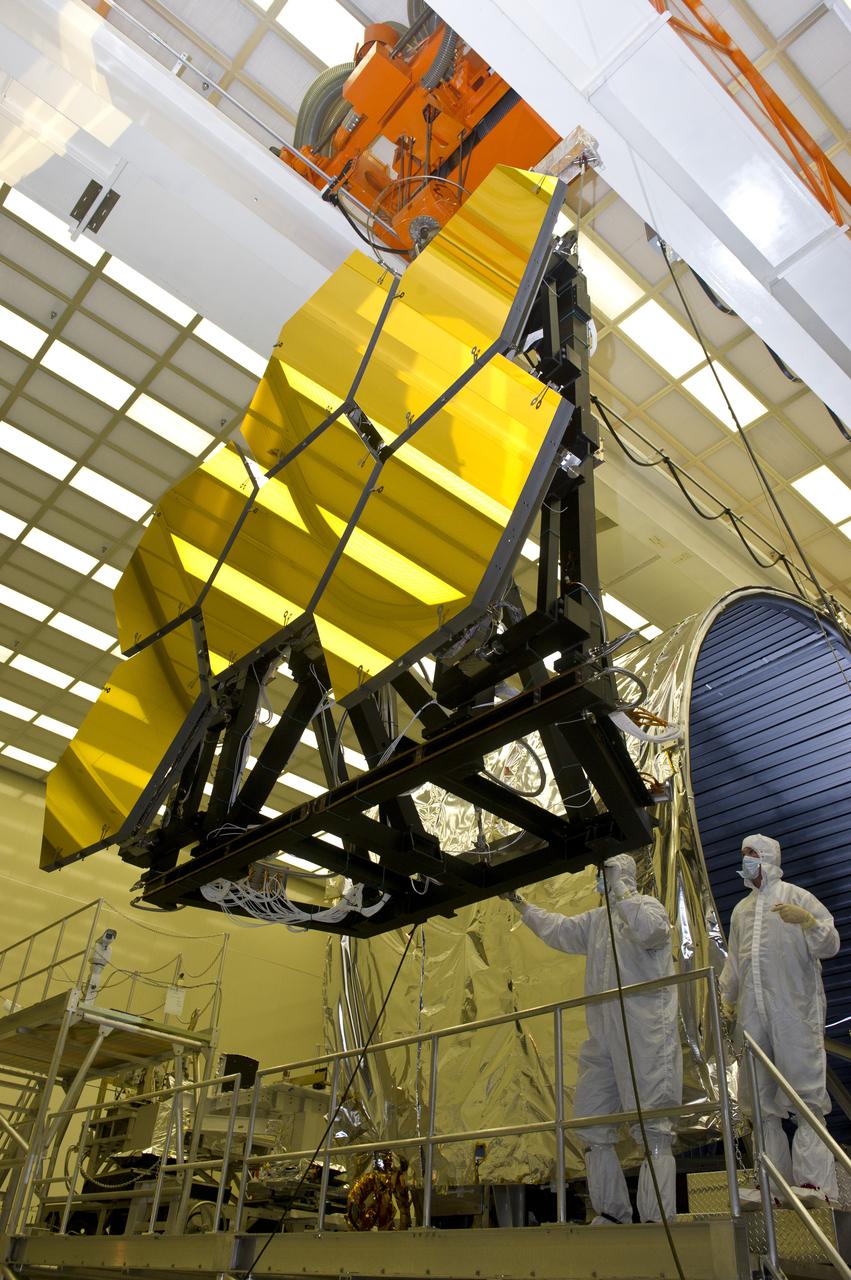

BALL AEROSPACE ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY, (L), AND MARSHALL ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT, (R), GUIDE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AFTER FINAL ACCEPTANCE TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
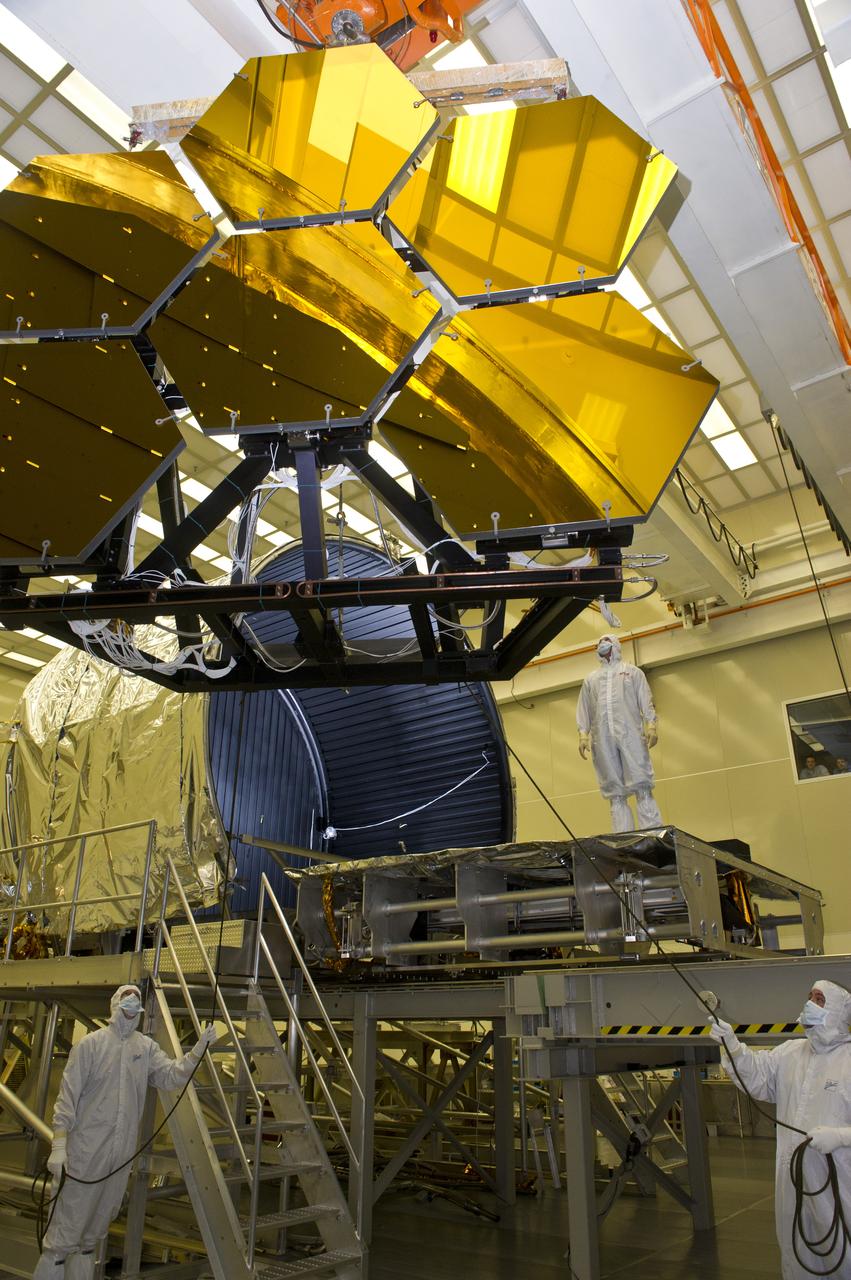

BALL AEROSPACE ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY, (L), AND MARSHALL ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT, (R), GUIDE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AFTER FINAL ACCEPTANCE TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
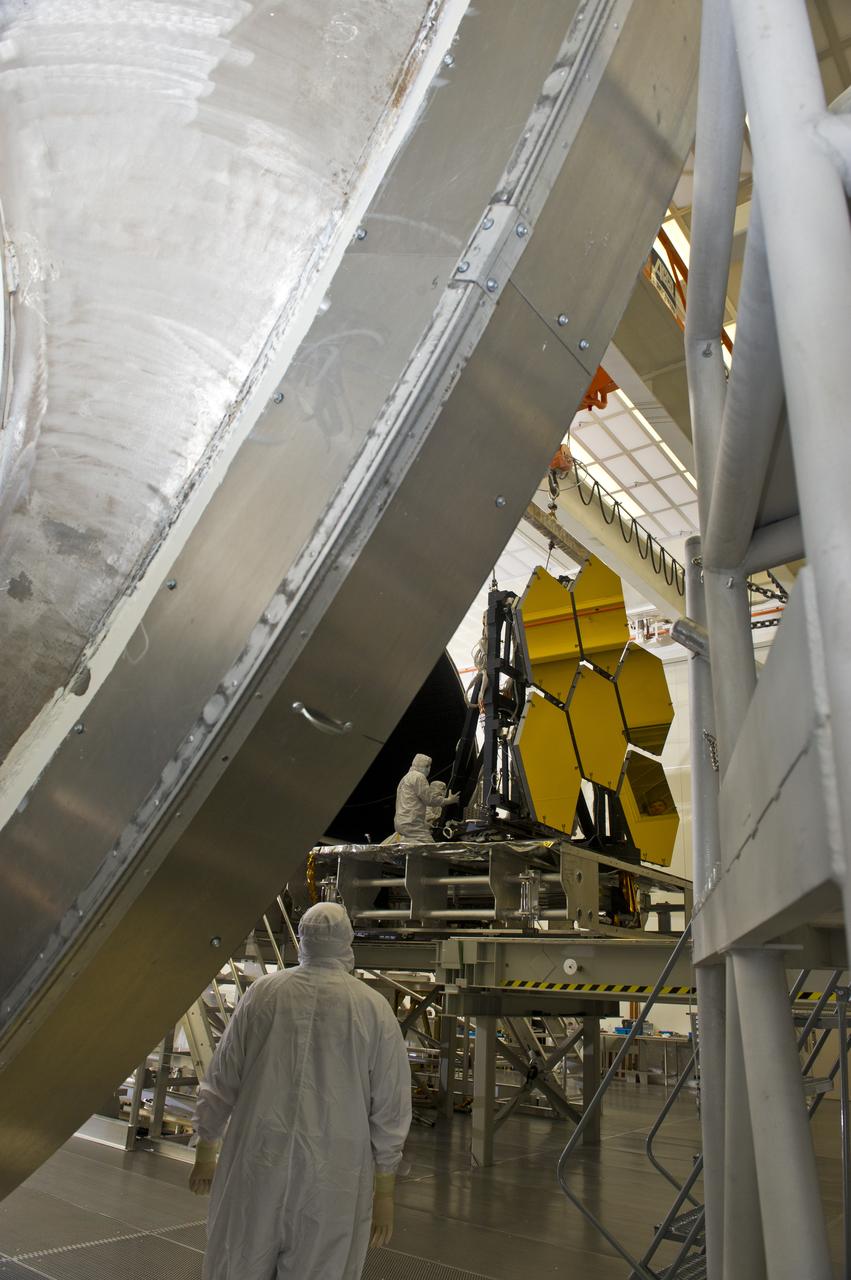

BALL AEROSPACE ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY, (L), AND MARSHALL ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT, (R), GUIDE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AFTER FINAL ACCEPTANCE TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
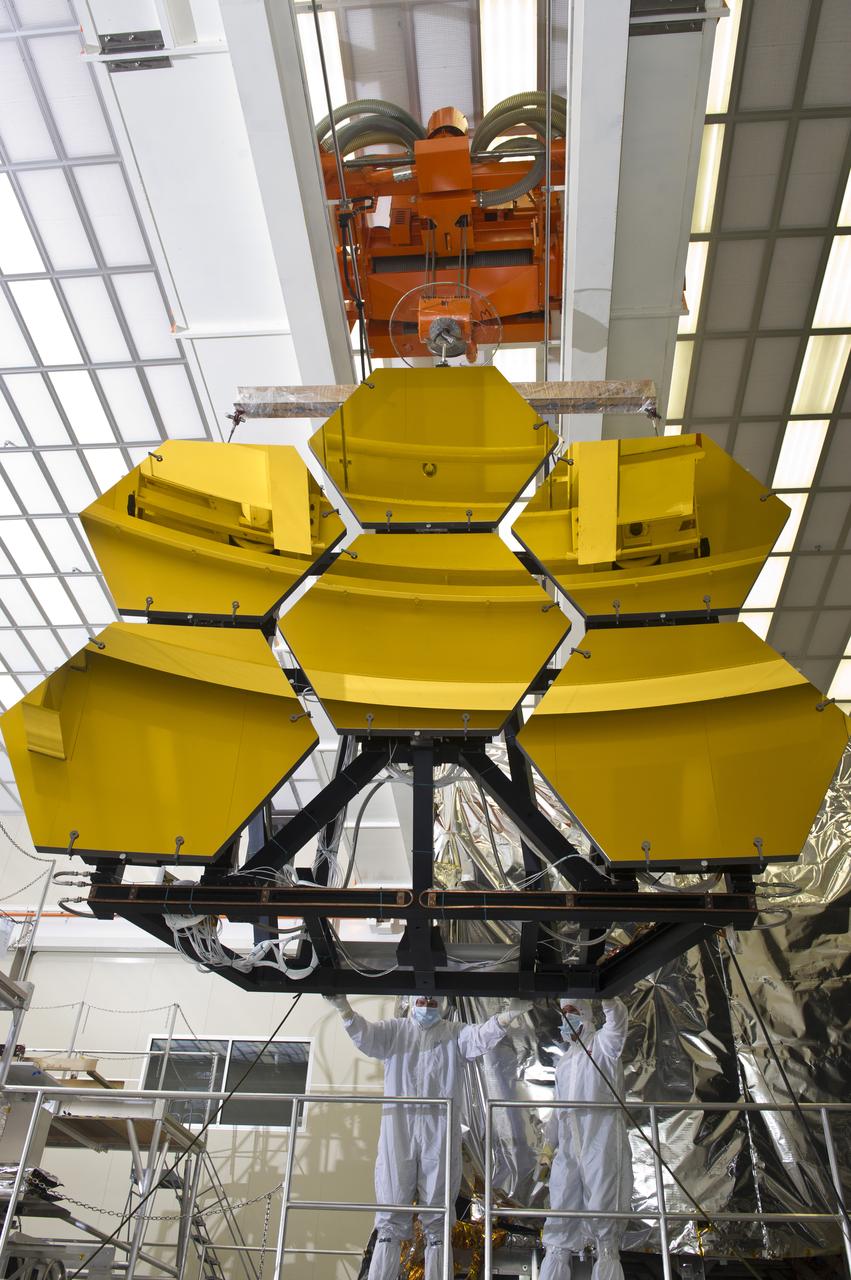

BALL AEROSPACE ENGINEER DAVE CHANEY, (L), AND MARSHALL ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT, (R), GUIDE ARRAY OF SIX GOLD-PLATED JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE MIRRORS AFTER FINAL ACCEPTANCE TESTING AT MARSHALL'S X-RAY AND CRYOGENIC FACILITY
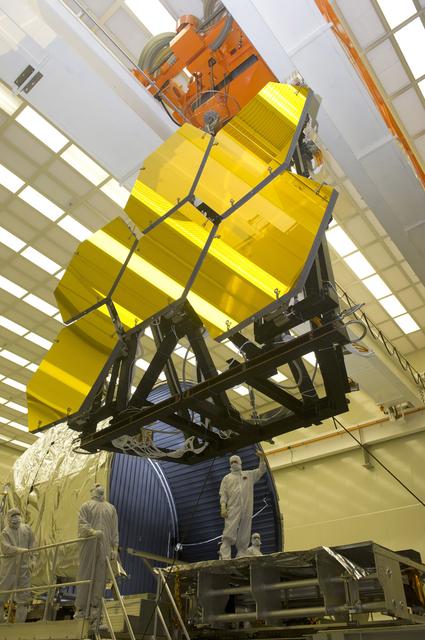

The James Webb Space Telescope mirrors have completed deep-freeze tests and are removed from the X-ray and Cryogenic test Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center. To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/technology/features/webb-mirror-cryo.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/technology/features/webb-mirror-cryo....</a> Credit: Emmett Given, NASA Marshall <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
This photograph shows the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), High Resolution Mirror Assembly (HRMA) being removed from the test structure in the X-Ray Calibration Facility (XRCF) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The AXAF was renamed CXO in 1999. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most powerful x-ray telescope ever built. It observes x-rays from high-energy regions of the universe, such as hot gas in the remnants of exploded stars. The HRMA, the heart of the telescope system, is contained in the cylindrical "telescope" portion of the observatory. Since high-energy x-rays would penetrate a normal mirror, special cylindrical mirrors were created. The two sets of four nested mirrors resemble tubes within tubes. Incoming x-rays graze off the highly polished mirror surface and are furneled to the instrument section for detection and study. MSFC's XRCF is the world's largest, most advanced laboratory for simulating x-ray emissions from distant celestial objects. It produces a space-like environment in which components related to x-ray telescope imaging are tested and the quality of their performances in space is predicted. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development of the CXO and NASA's MSFC was responsible for its project management. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations of the CXO for NASA from Cambridge, Massachusetts. The CXO was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-93).
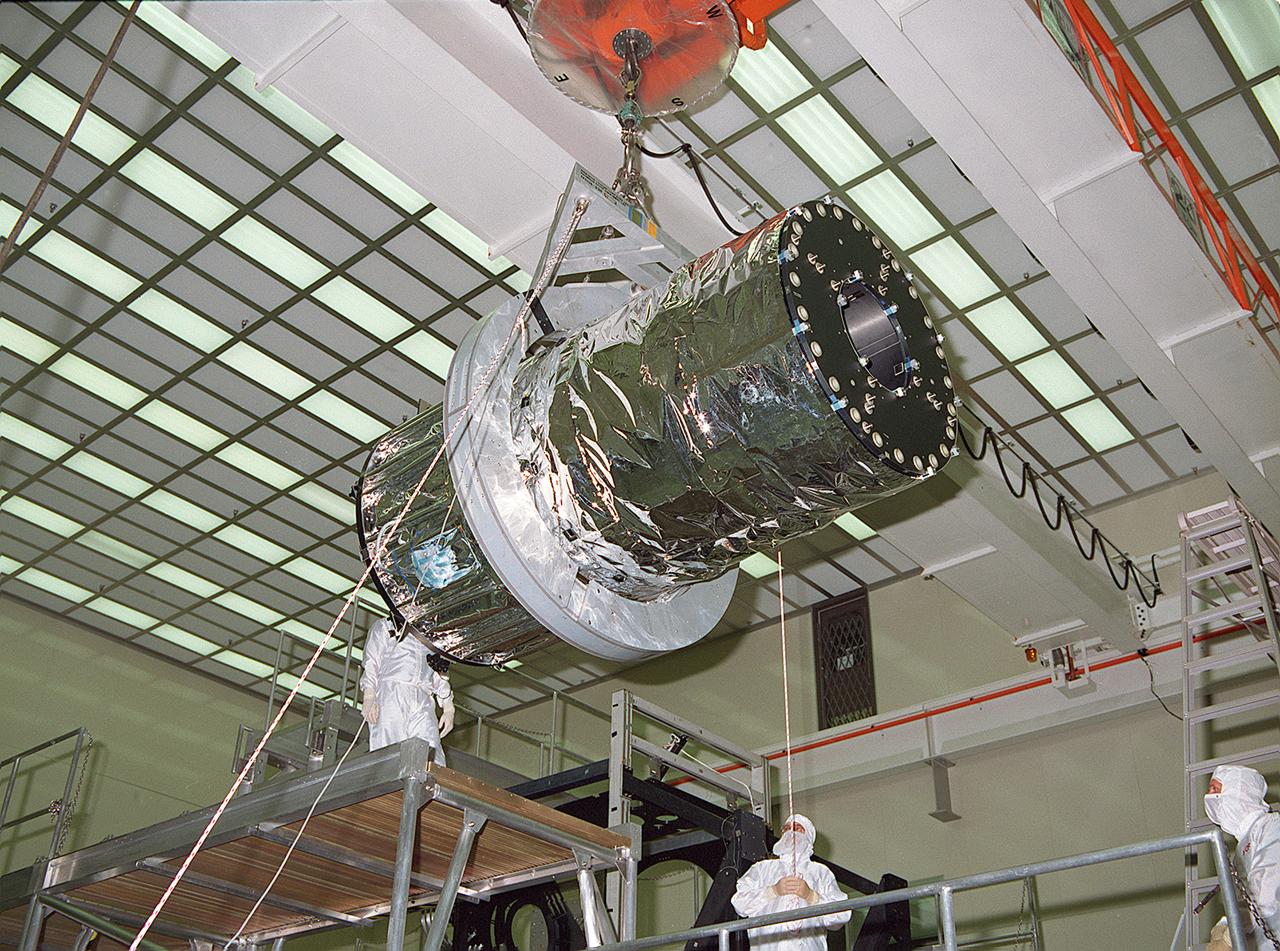

This photograph shows the Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), High Resolution Mirror Assembly (HRMA) being removed from the test structure in the X-Ray Calibration Facility (XRCF) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The AXAF was renamed CXO in 1999. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most powerful x-ray telescope ever built. It observes x-rays from high-energy regions of the universe, such as hot gas in the remnants of exploded stars. The HRMA, the heart of the telescope system, is contained in the cylindrical "telescope" portion of the observatory. Since high-energy x-rays would penetrate a normal mirror, special cylindrical mirrors were created. The two sets of four nested mirrors resemble tubes within tubes. Incoming x-rays graze off the highly polished mirror surface and are furneled to the instrument section for detection and study. MSFC's XRCF is the world's largest, most advanced laboratory for simulating x-ray emissions from distant celestial objects. It produces a space-like environment in which components related to x-ray telescope imaging are tested and the quality of their performances in space is predicted. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development of the CXO and NASA's MSFC was responsible for its project management. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations of the CXO for NASA from Cambridge, Massachusetts. The CXO was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-93).