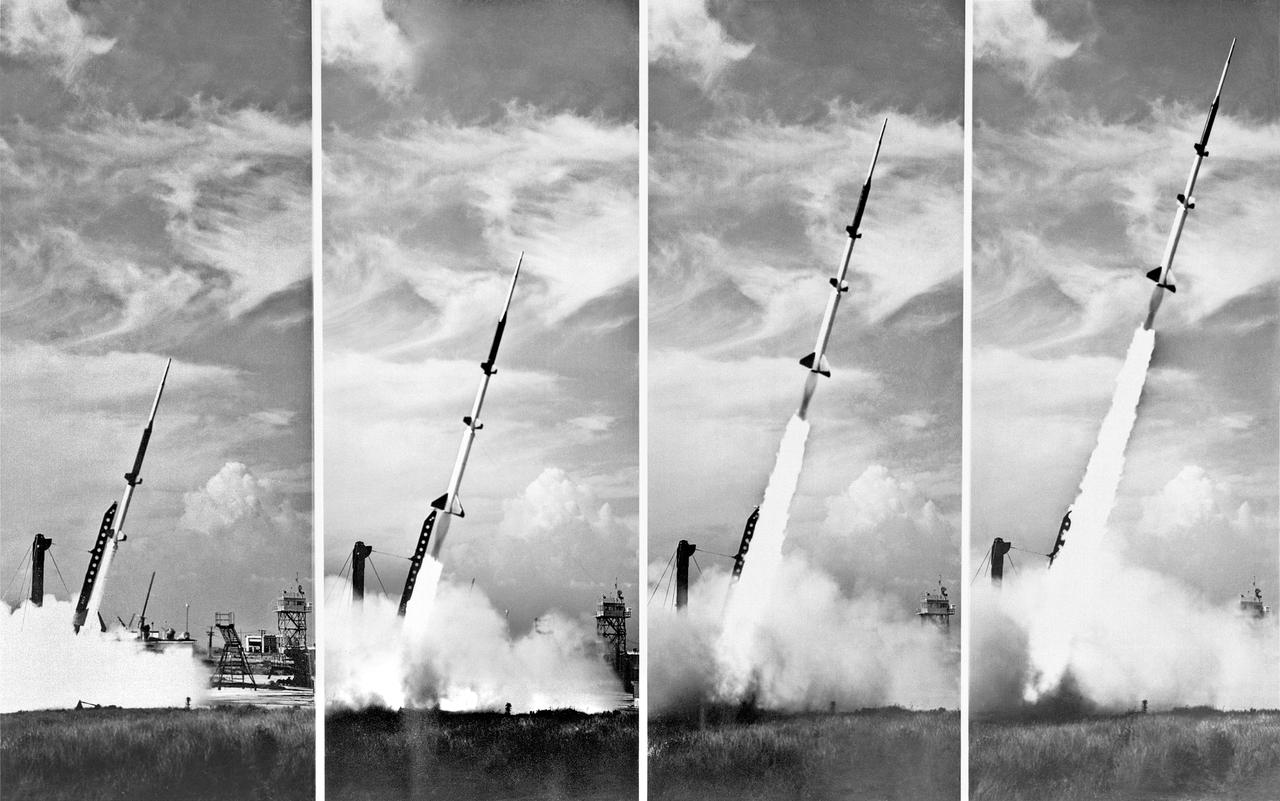

**Note also copied and numbered as L90-3749. -- L57-4827 caption: Take off of a five-stage missile research rocket from Wallops Island in 1957. The first two stages propelled the model to about 100,000 feet the last three stages were fired on a descending path to simulate the reentry conditions of ballistic missiles. -- Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication (page 72), by James Schultz. -- Photograph also published in Engineer in Charge: A History of the Langley Aeronautical Laboratory, 1917-1958 by James R. Hansen (page 380).
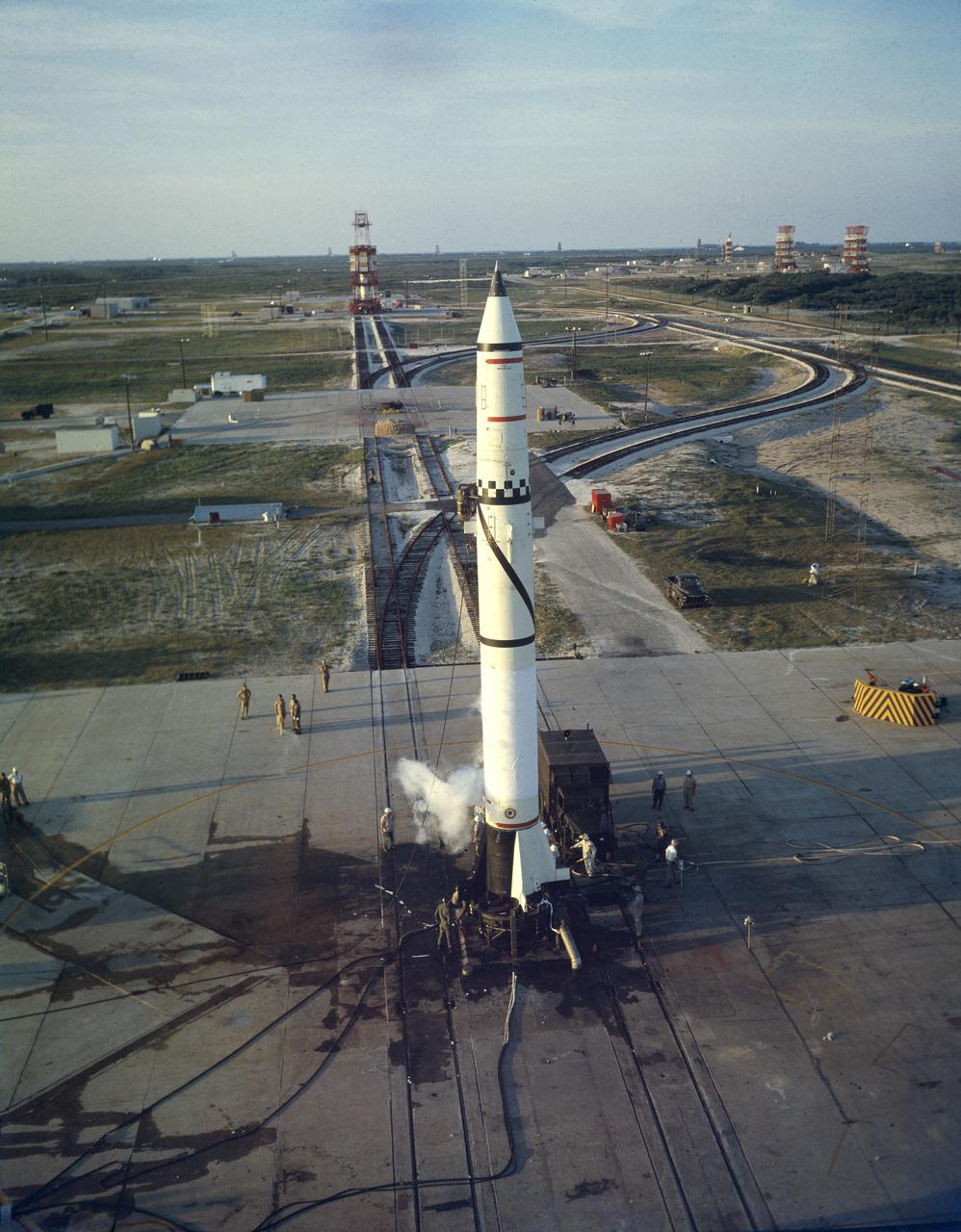

Redstone missile No. 1002 on the launch pad at Cape Canaveral, Florida, on May 16, 1958. The Redstone ballistic missile was a high-accuracy, liquid-propelled, surface-to-surface missile developed by the Army Ballistic Missile Agency, Redstone Arsenal, in Huntsville, Alabama, under the direction of Dr. von Braun. The Redstone engine was a modified and improved version of the Air Force's Navaho cruise missile engine of the late forties. The A-series, as this would be known, utilized a cylindrical combustion chamber as compared with the bulky, spherical V-2 chamber. By 1951, the Army was moving rapidly toward the design of the Redstone missile, and production was begun in 1952. Redstone rockets became the "reliable workhorse" for America's early space program. As an example of the versatility, Redstone was utilized in the booster for Explorer 1, the first American satellite, with no major changes to the engine or missile
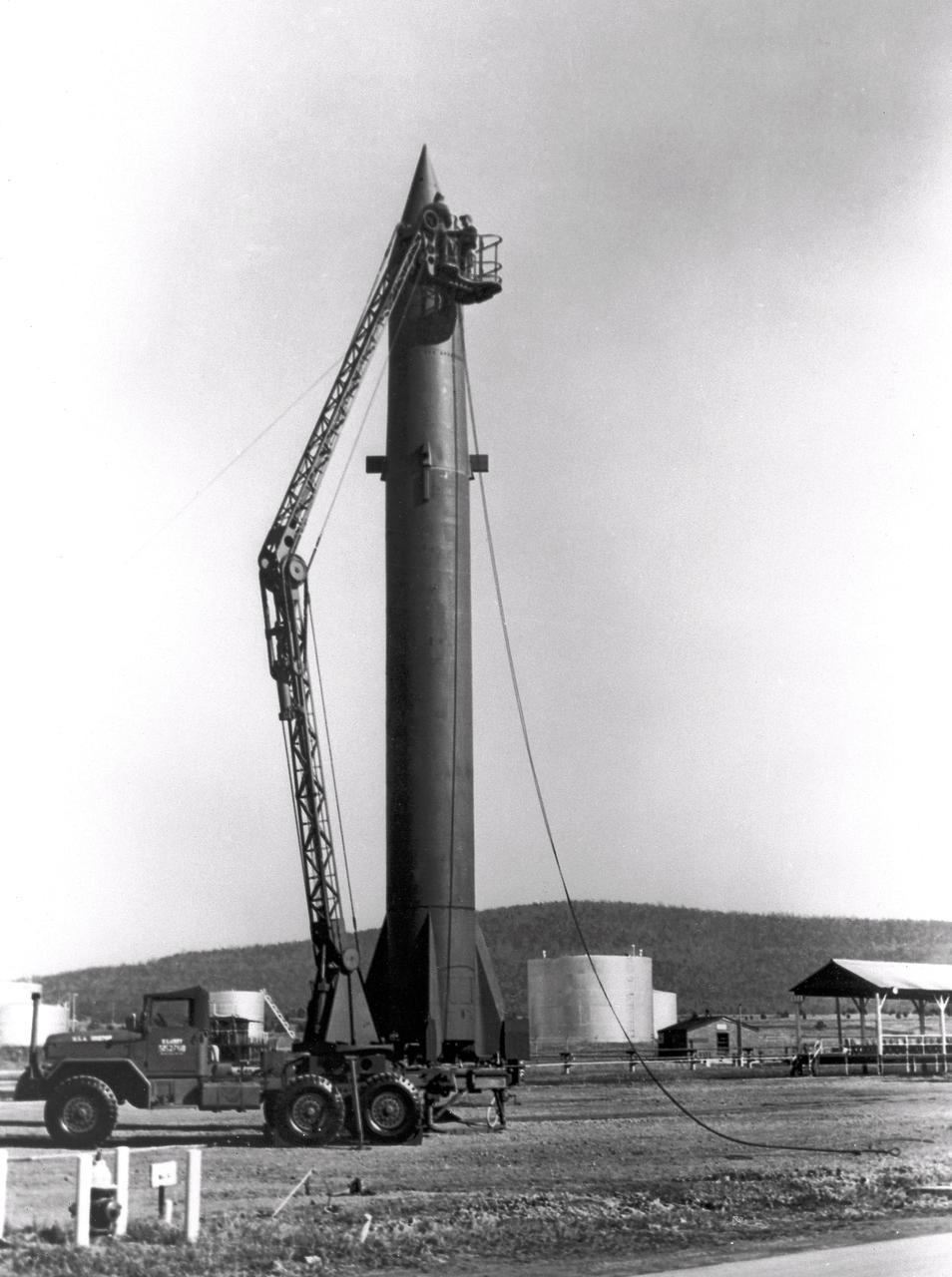

The image depicts Redstone missile being erected. The Redstone ballistic missile was a high-accuracy, liquid-propelled, surface-to-surface missile developed by Army Ballistic Missile Agency, Redstone Arsenal, in Huntsville, Alabama, under the direction of Dr. von Braun. The Redstone engine was a modified and improved version of the Air Force's Navaho cruise missile engine of the late forties. The A-series, as this would be known, utilized a cylindrical combustion chamber as compared with the bulky, spherical V-2 chamber. By 1951, the Army was moving rapidly toward the design of the Redstone missile, and the production was begun in 1952. Redstone rockets became the "reliable workhorse" for America's early space program. As an example of the versatility, Redstone was utilized in the booster for Explorer 1, the first American satellite, with no major changes to the engine or missile
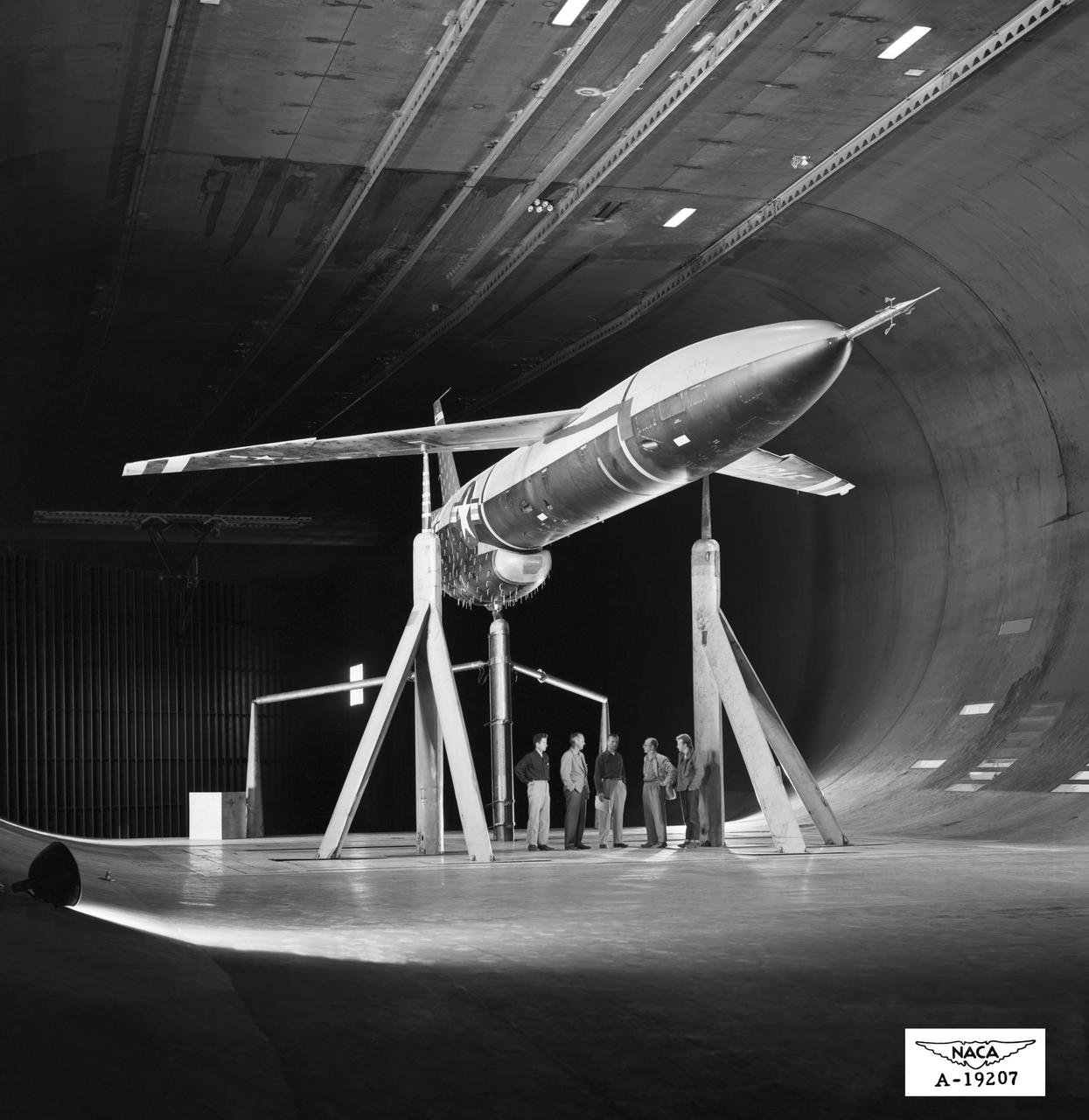

3/4 front view in Ames 40x80 foot Wind Tunnel investigation of the Lockheed T-33 modified for area-suction leading-edge and trailing edge flaps.
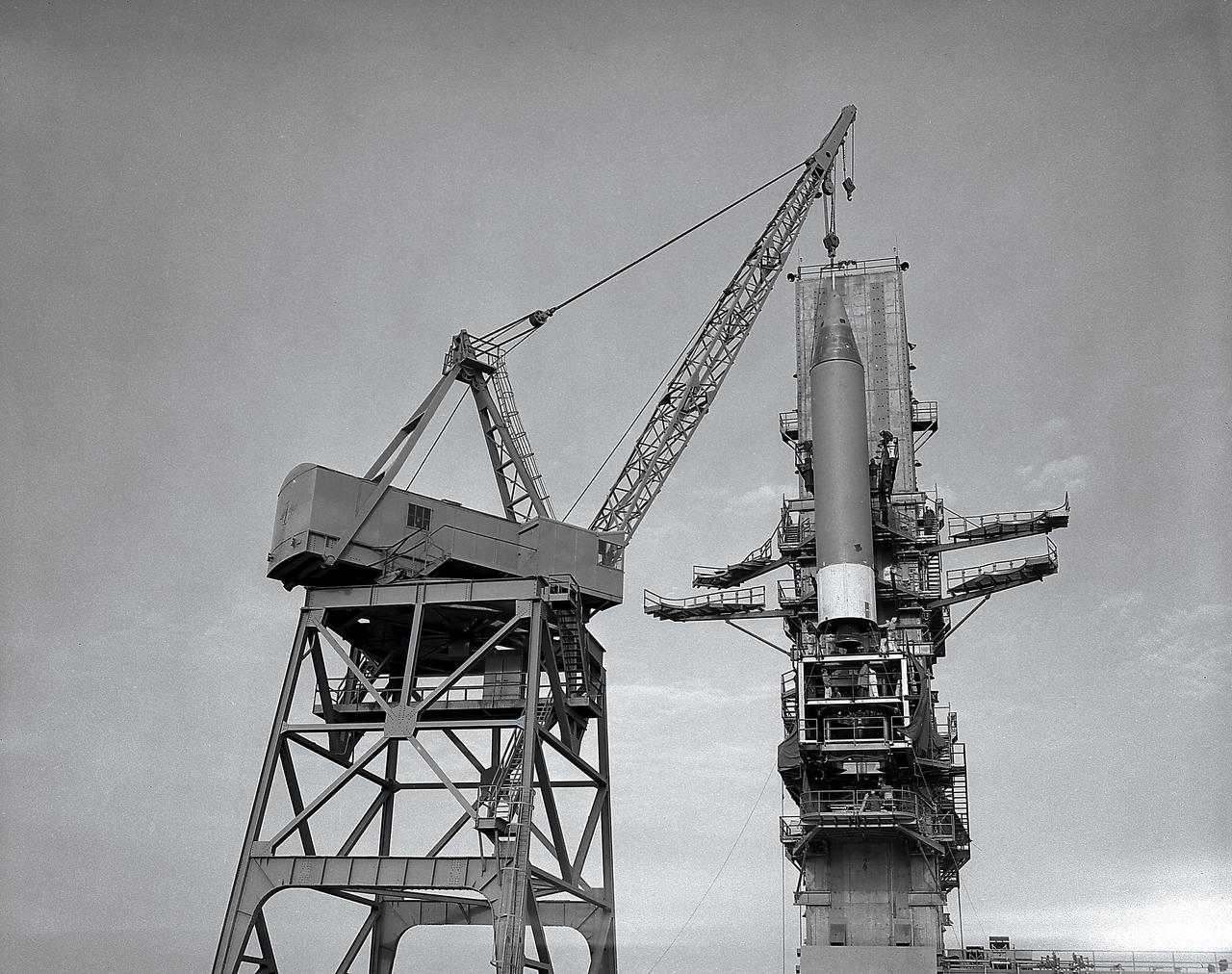

Installation of a Jupiter missile in ABMA (Army Ballistic Missile Agency) West Test Stand, Jan. 16, 1957. Jupiter was a 1500-mile range missile
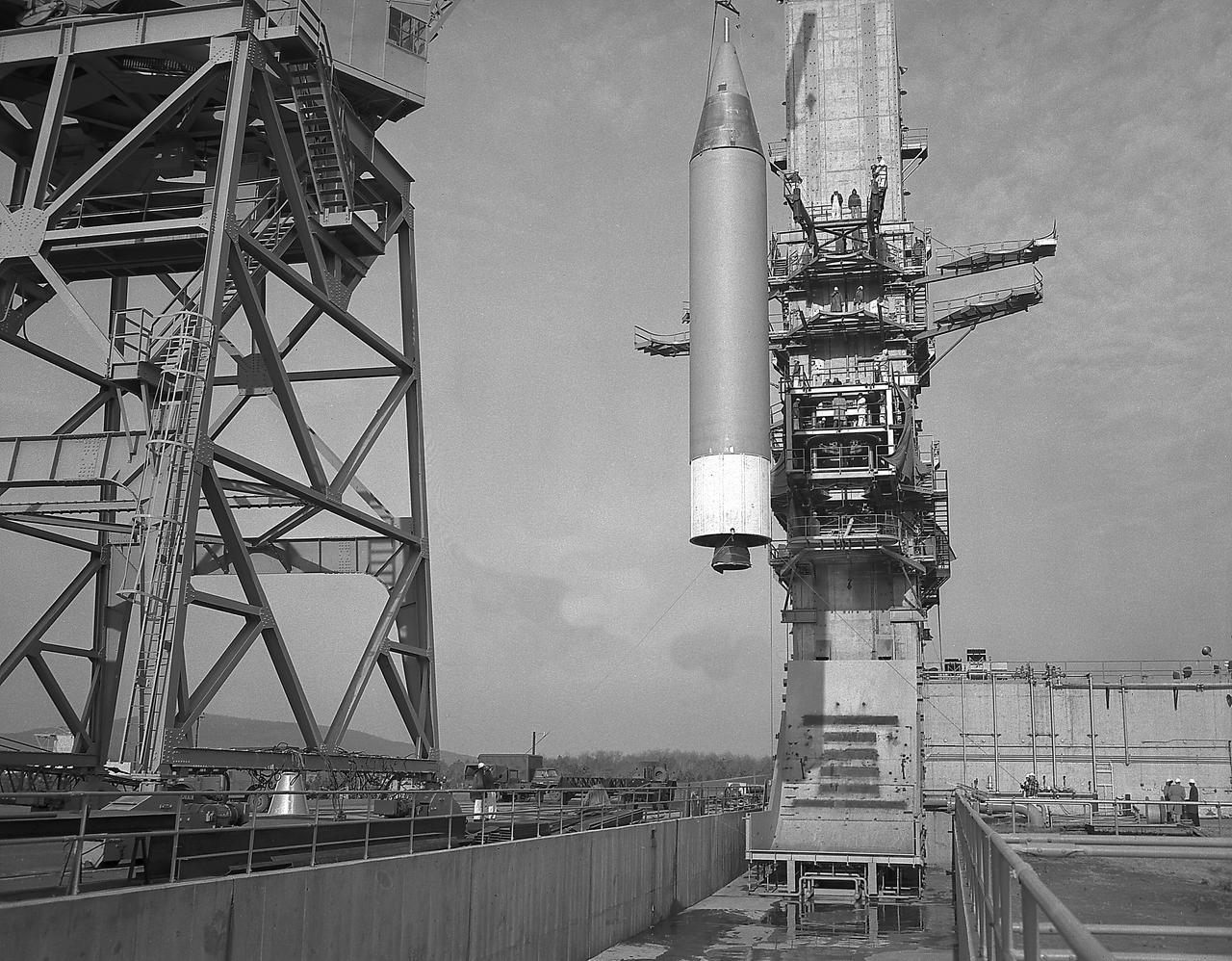

Installation of a Jupiter Missile in ABMA (Army Ballistic Missile Agency) West Test Stand, Jan. 16, 1957. Jupiter was a 1500-mile range missile
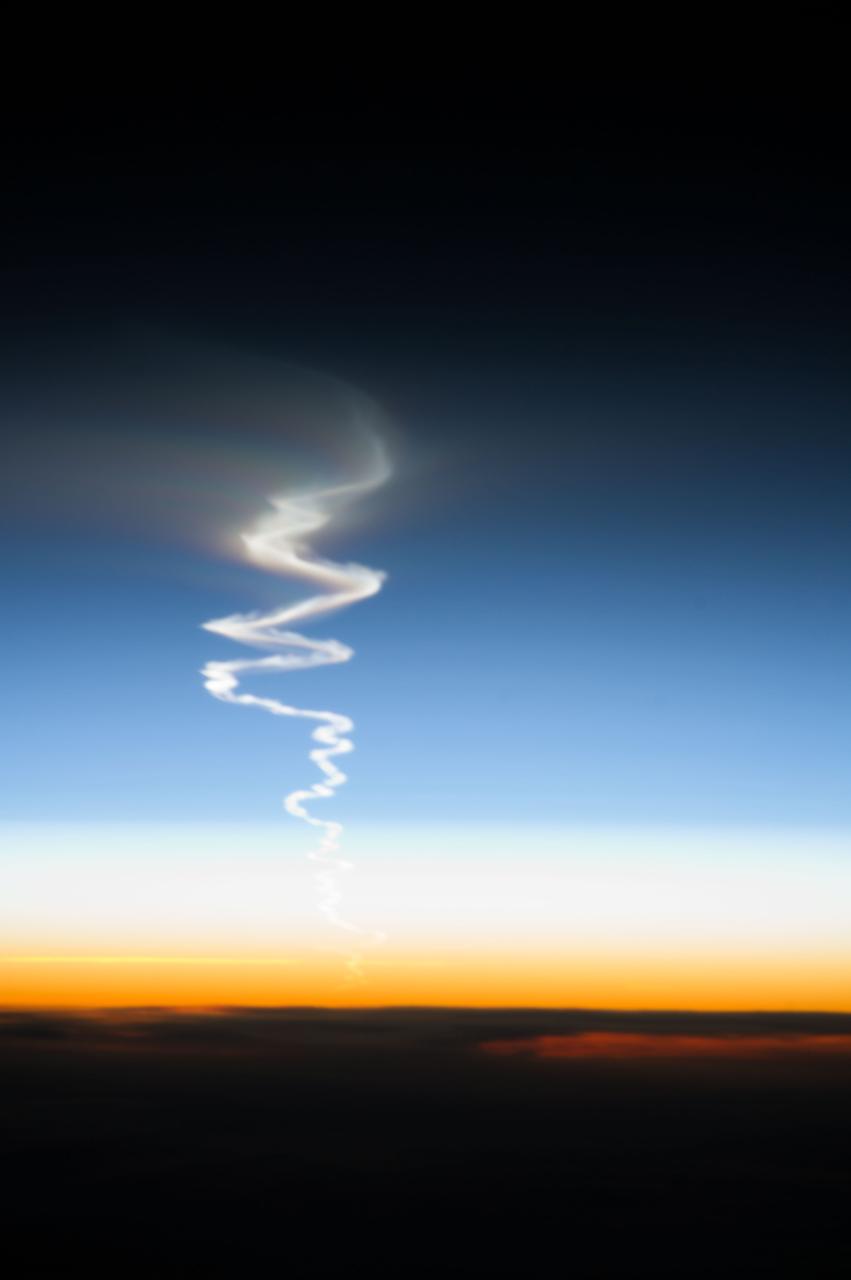

View of test launch of a Topol/SS-25 missile on Oct. 10, 2013 as seen by the Expedition 37 crew aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The missile was launched at 17:39 MSK (13:39 UTC) from Kapustin Yar to the Sary Shagan test site in Kazakhstan. Also sent as Twitter message.

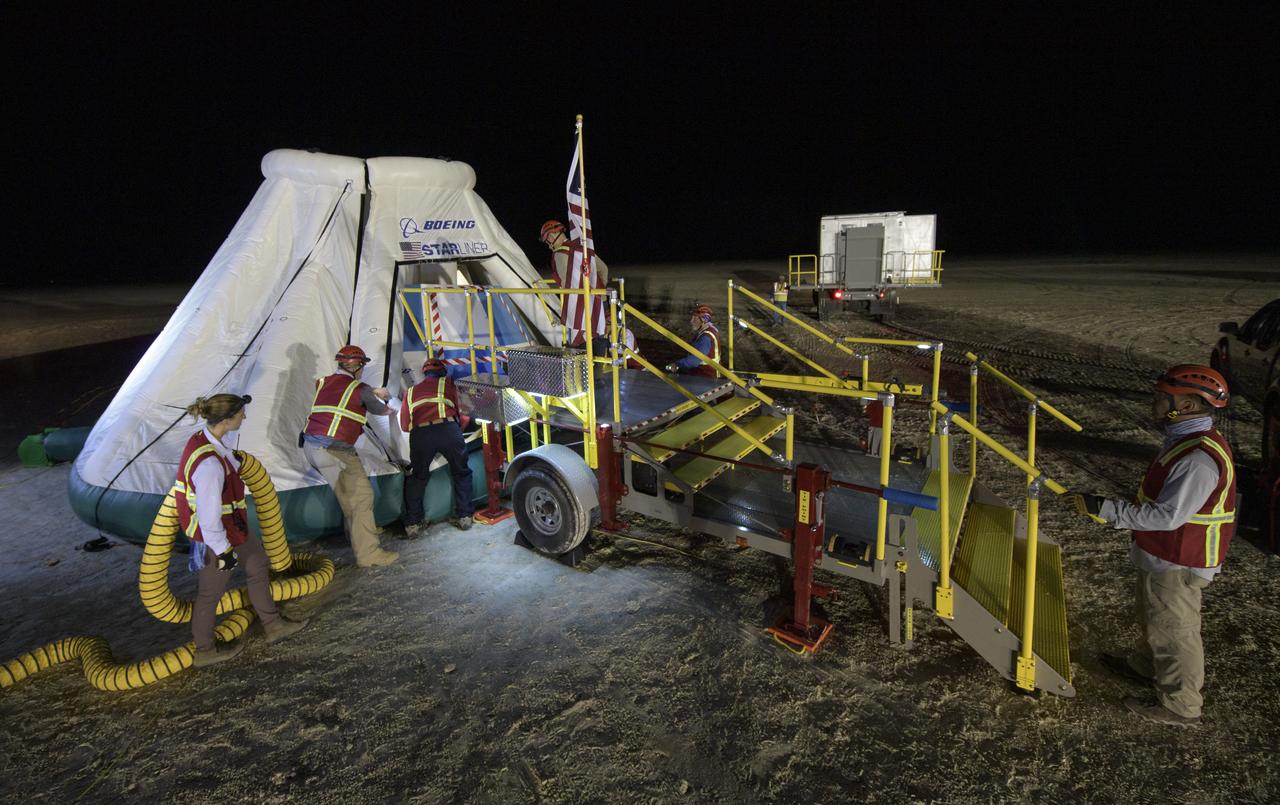
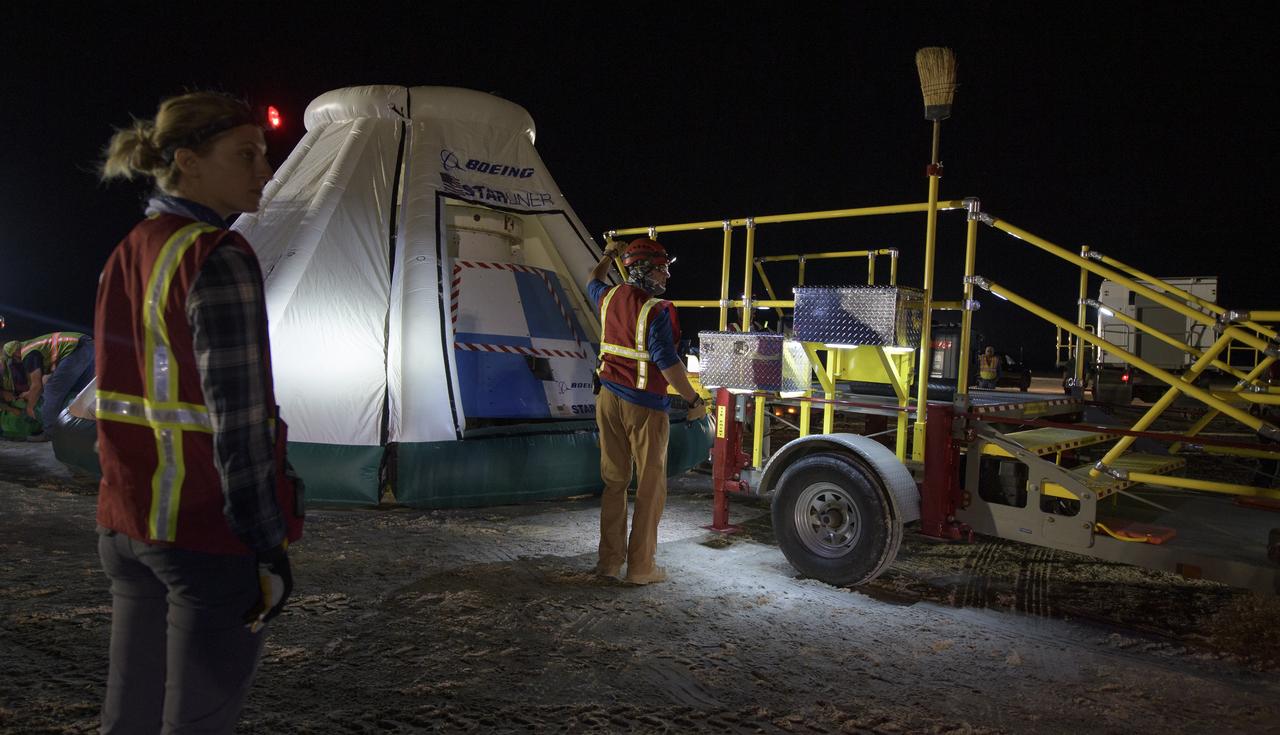
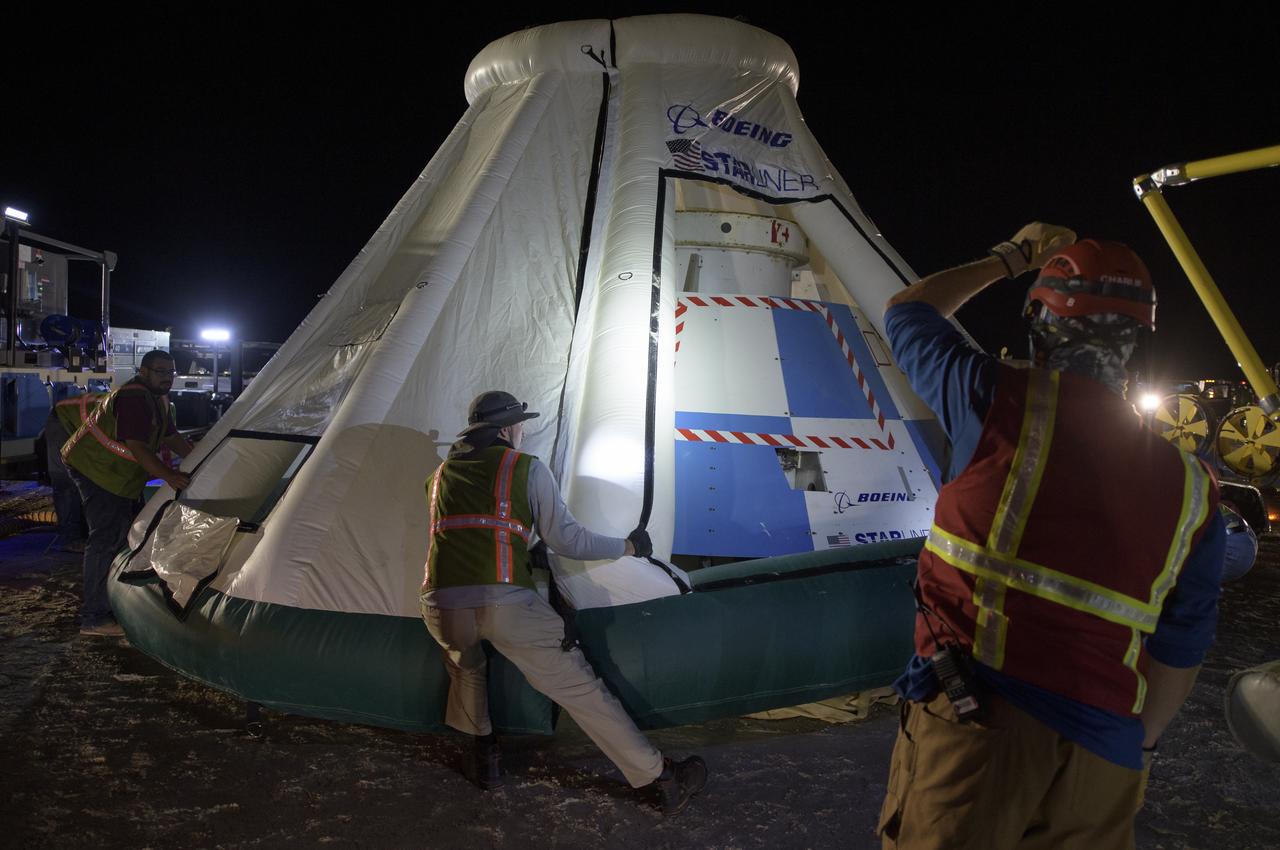
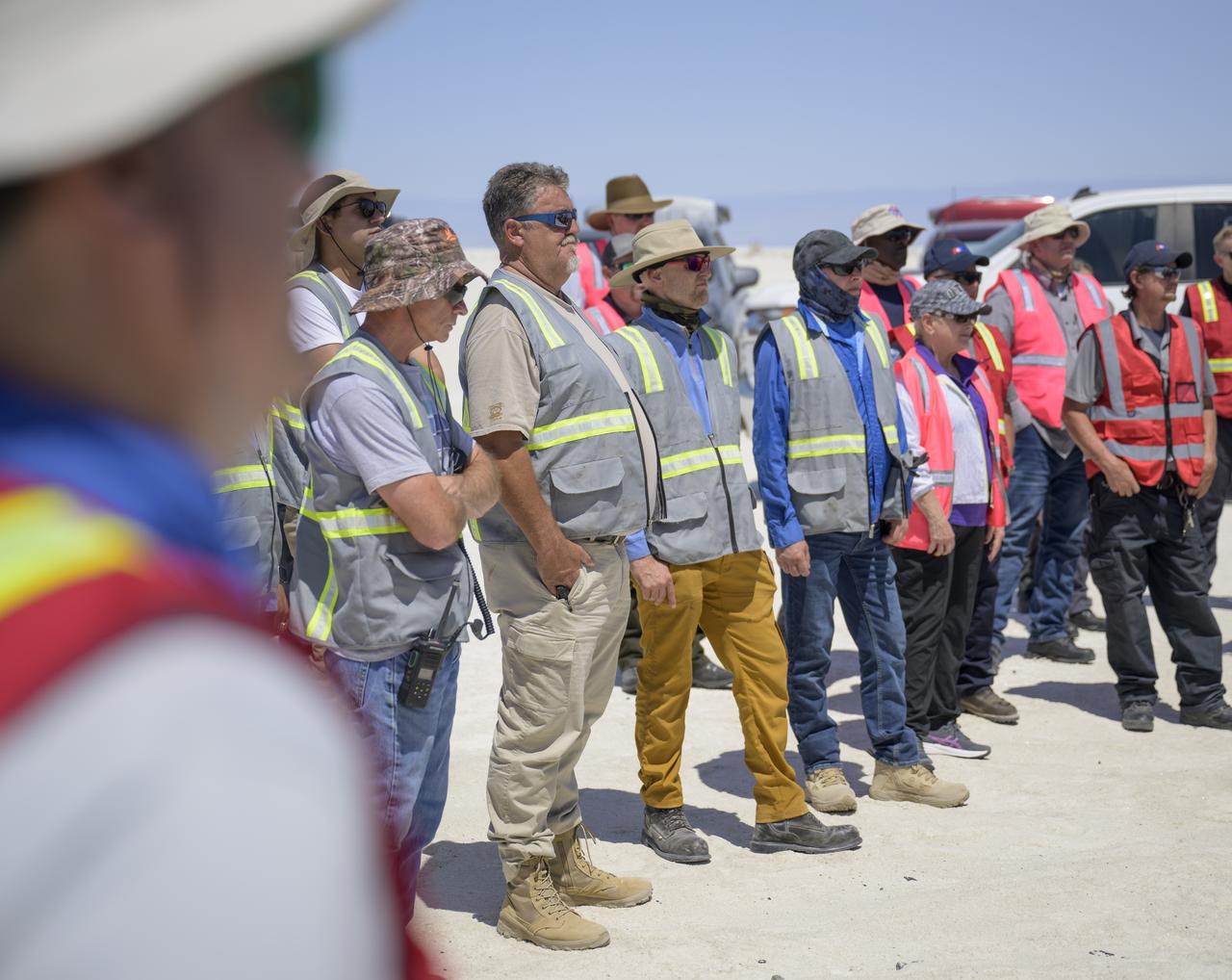
White Sands Missile Range Fire Department team members listen to a pretending briefing as they, NASA, and Boeing teams prepare for the landing of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
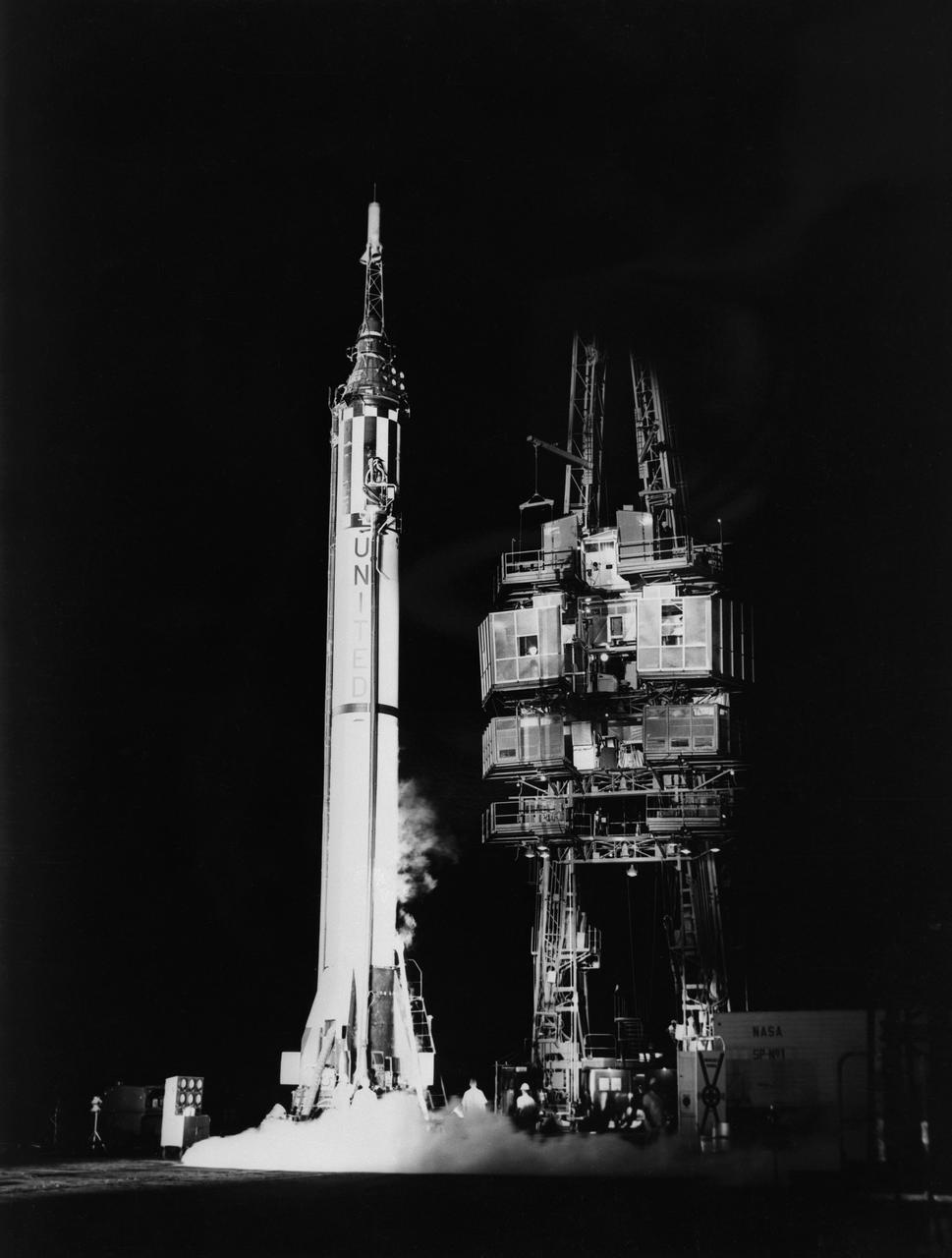
S61-03158 (1961) --- Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) missile standing alone on launch pad. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
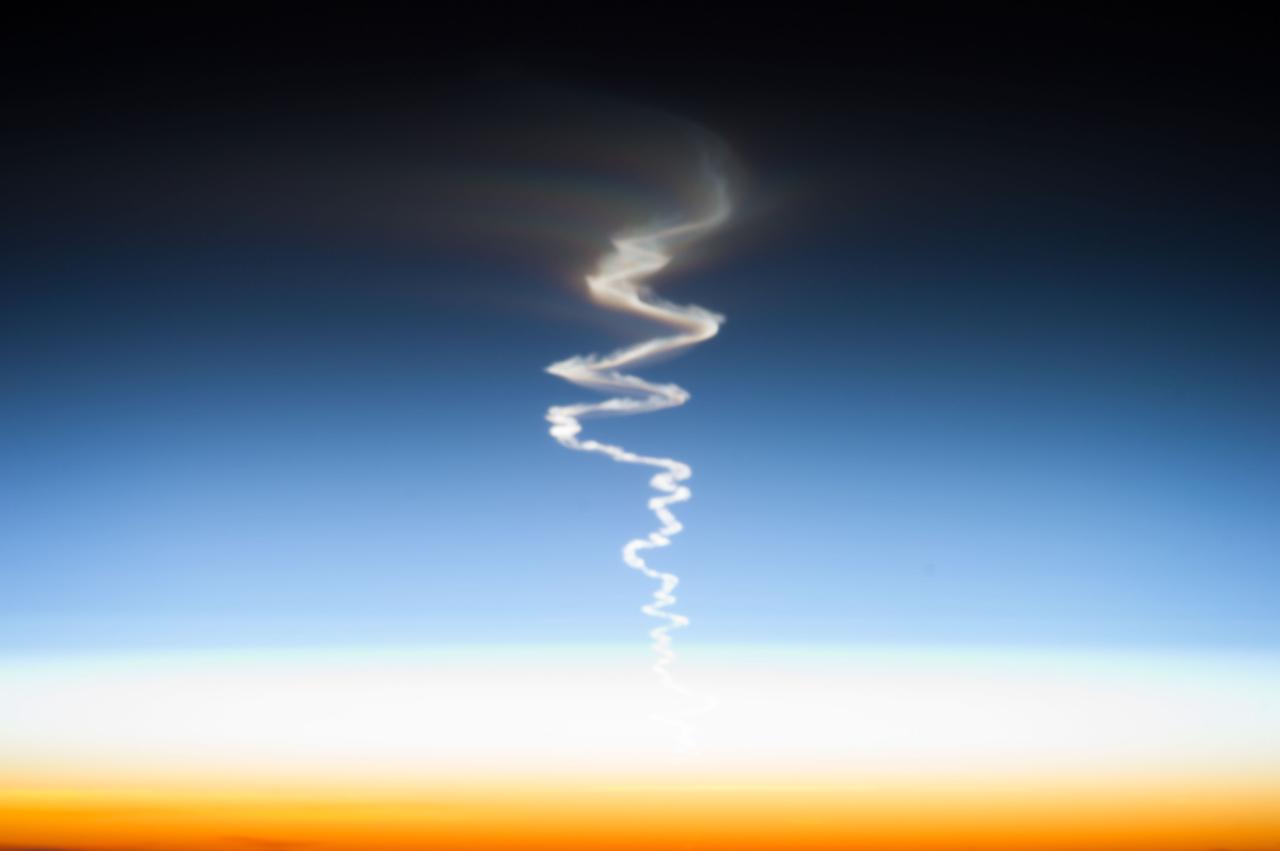

ISS037-E-009203 (10 Oct. 2013) --- This is one of a series of views that captured a missile launch from Earth as seen on Oct. 10, 2013 by the Expedition 37 crew aboard the International Space Station.
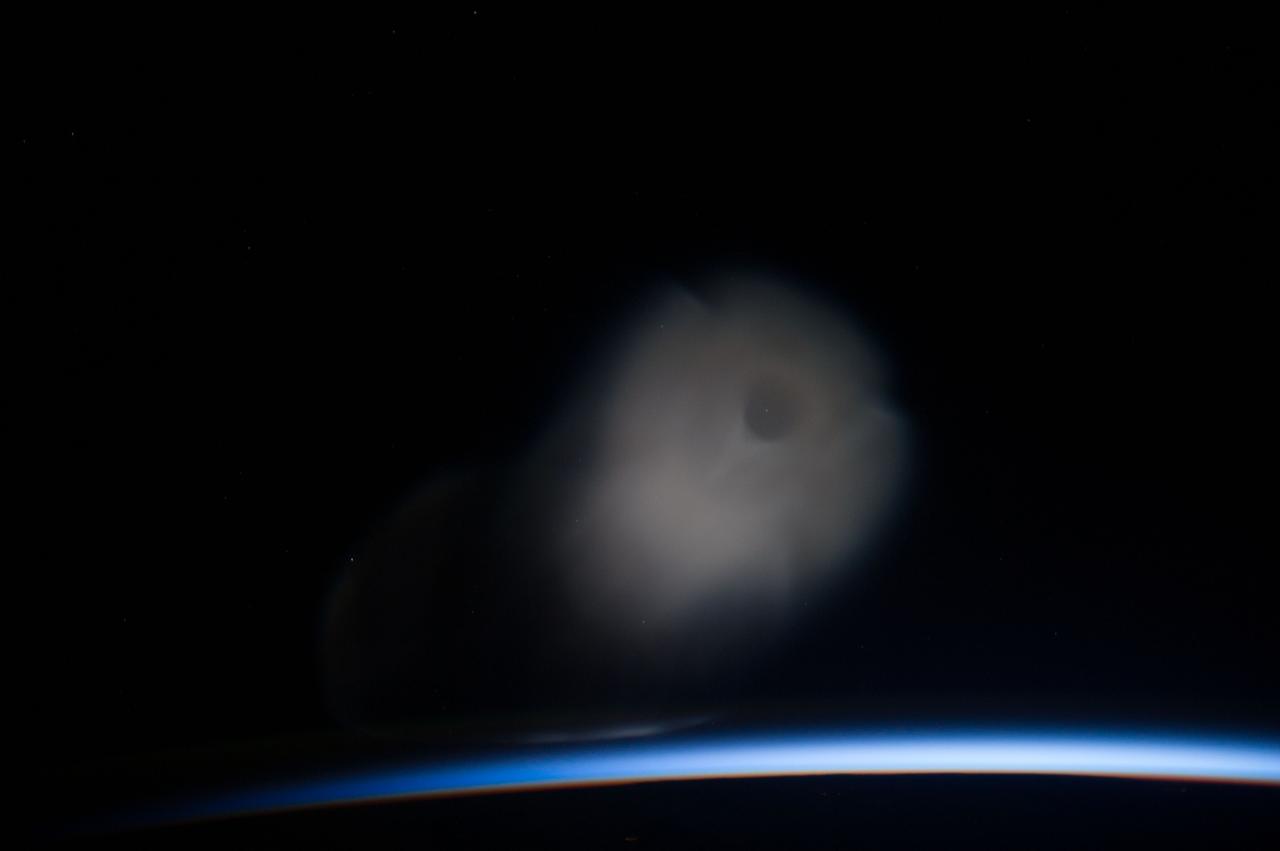

ISS037-E-009251 (10 Oct. 2013) --- This is one of a series of photos that captured a missile launch from Earth as seen on Oct. 10, 2013 by the Expedition 37 crew aboard the International Space Station.
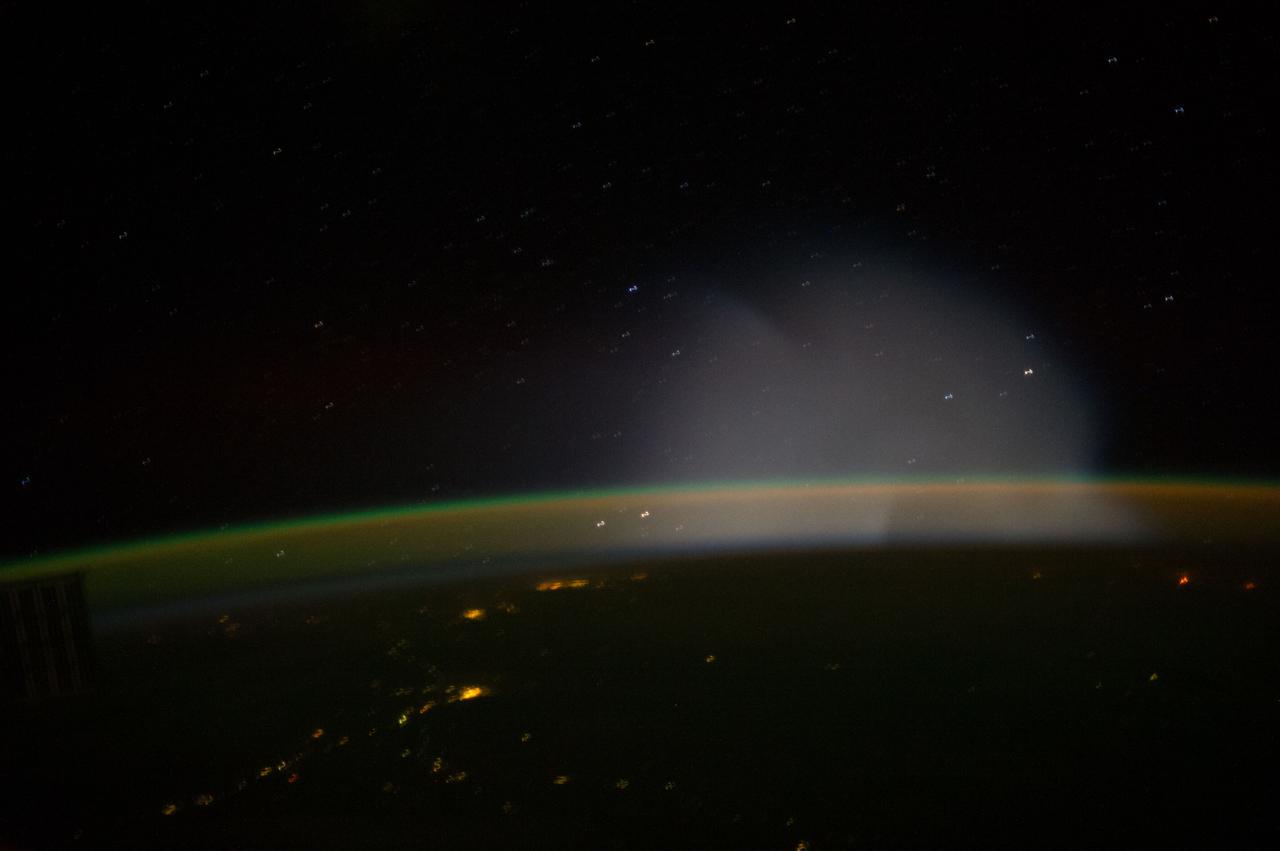

ISS037-E-009321 (10 Oct. 2013) --- This is one of a series of views that captured a missile launch from Earth as seen on Oct. 10, 2013 by the Expedition 37 crew aboard the International Space Station.
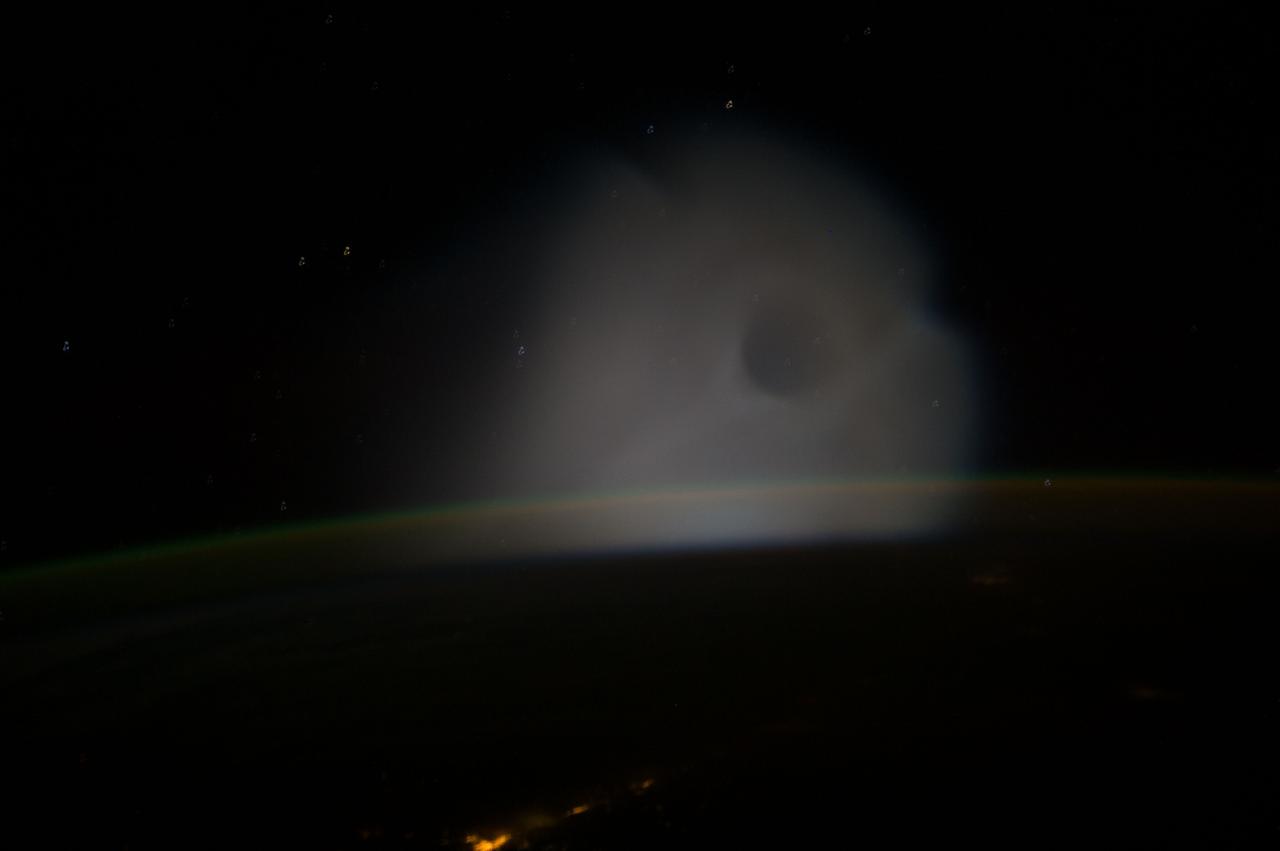

ISS037-E-009296 (10 Oct. 2013) --- This is one of a series of views that captured a missile launch from Earth as seen on Oct. 10, 2013 by the Expedition 37 crew aboard the International Space Station.
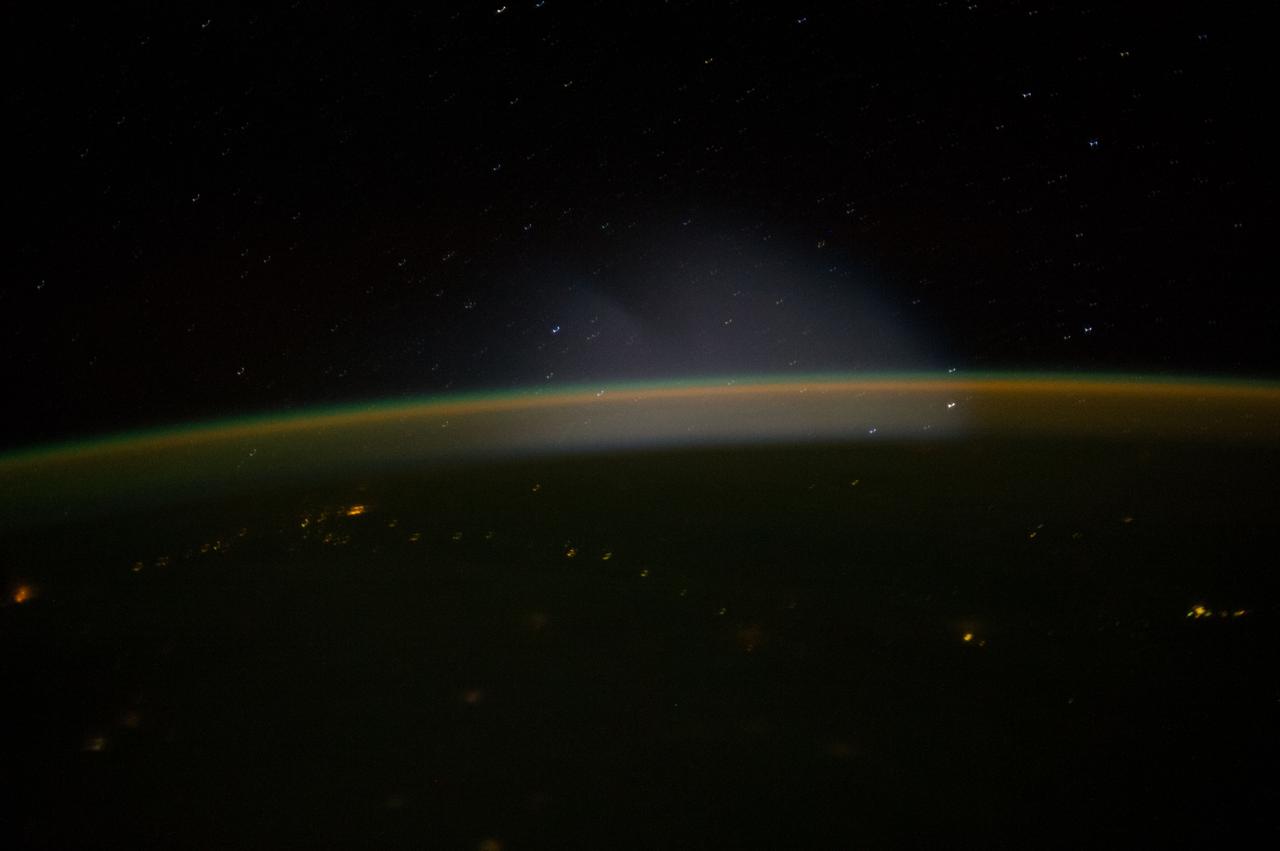

ISS037-E-009333 (10 Oct. 2013) --- This is one of a series of views that captured a missile launch from Earth as seen on Oct. 10, 2013 by the Expedition 37 crew aboard the International Space Station.
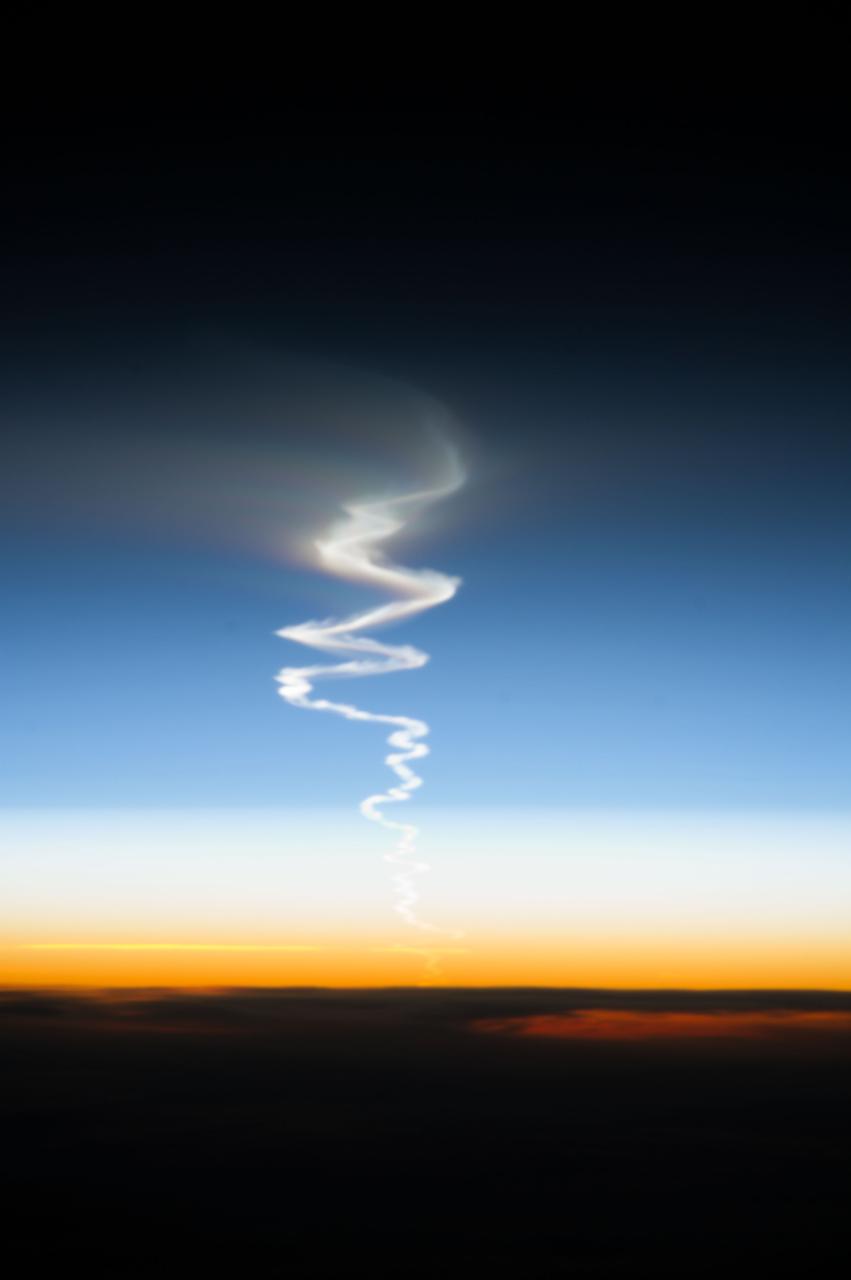

ISS037-E-009224 (10 Oct. 2013) --- This is one of a series of views that captured a missile launch from Earth as seen on Oct. 10, 2013 by the Expedition 37 crew aboard the International Space Station.
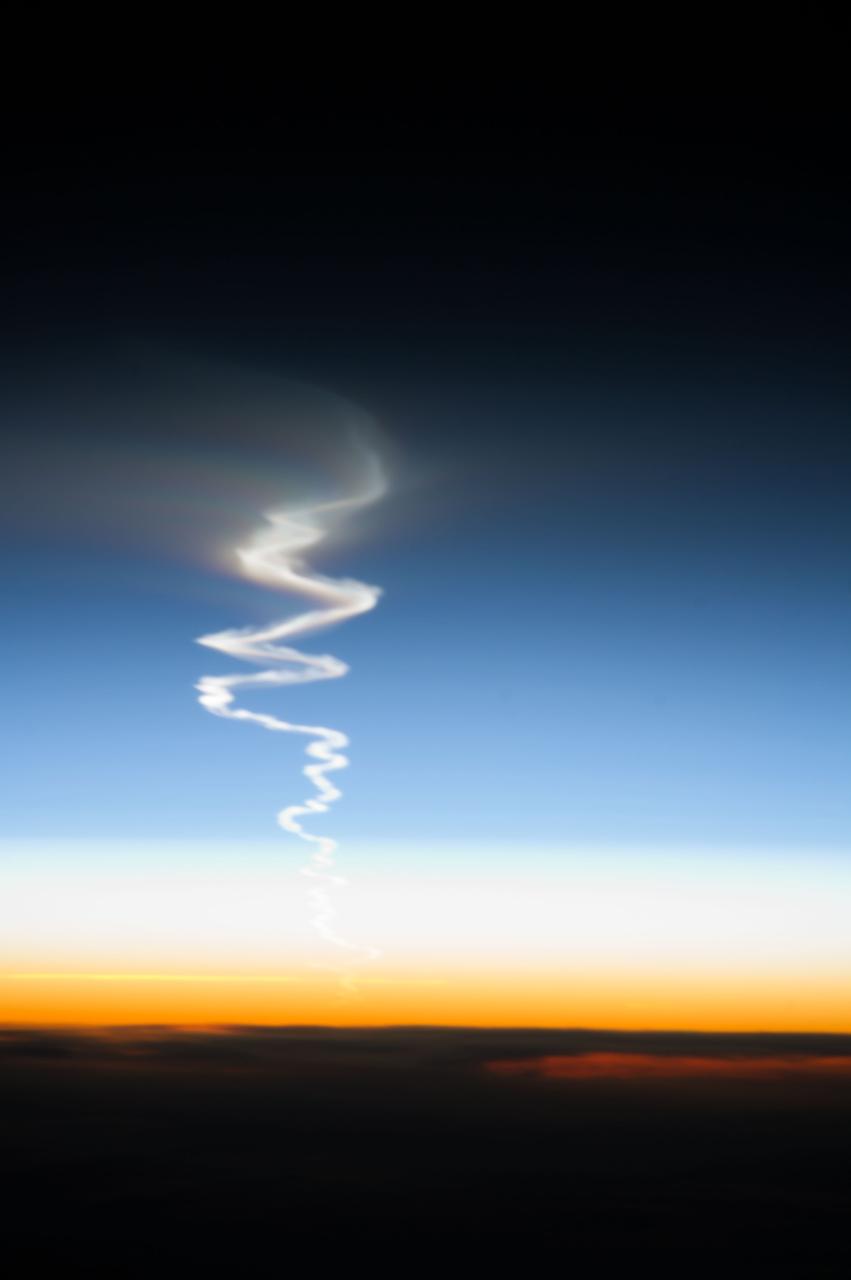

ISS037-E-009212 (10 Oct. 2013) --- This is one of a series of views that captured a missile launch from Earth as seen on Oct. 10, 2013 by the Expedition 37 crew aboard the International Space Station.
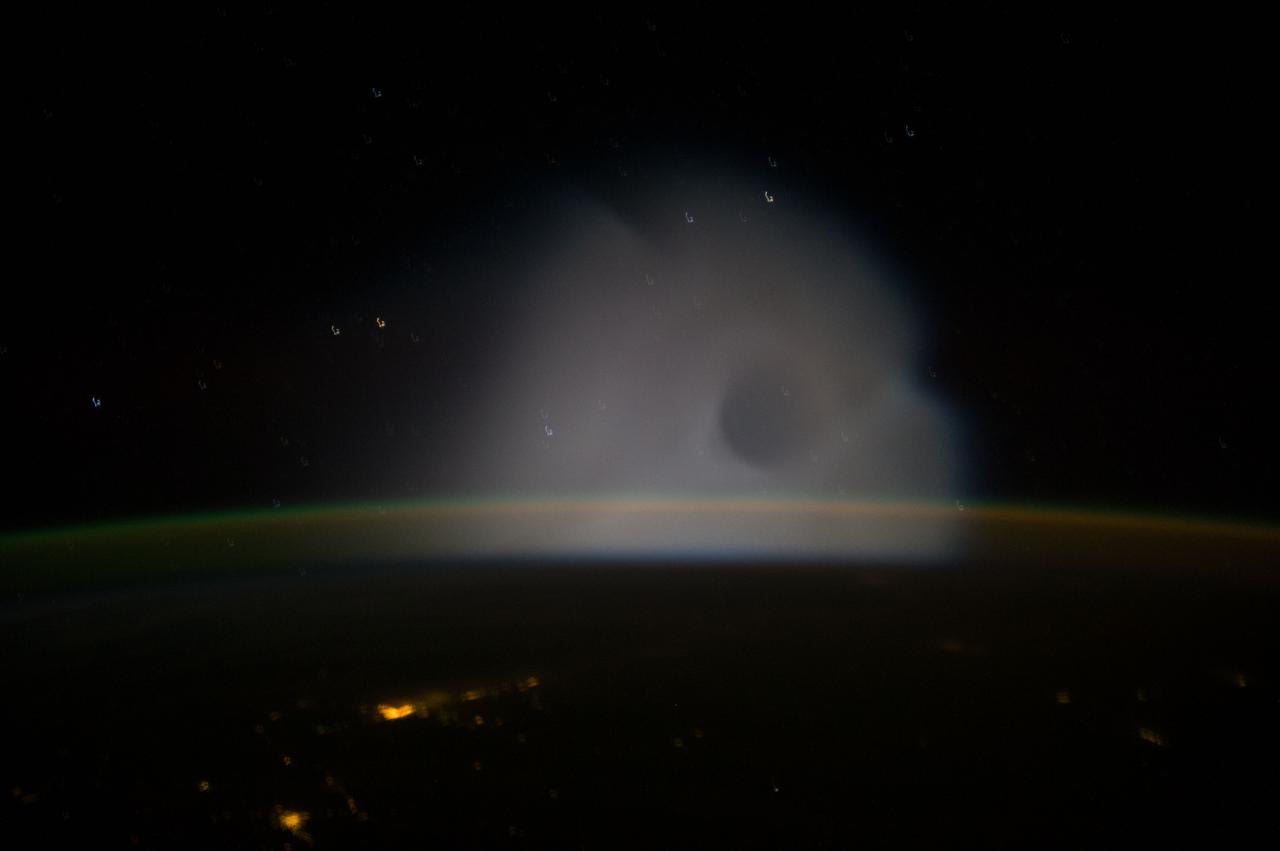

ISS037-E-009302 (10 Oct. 2013) --- This is one of a series of views that captured a missile launch from Earth as seen on Oct. 10, 2013 by the Expedition 37 crew aboard the International Space Station.
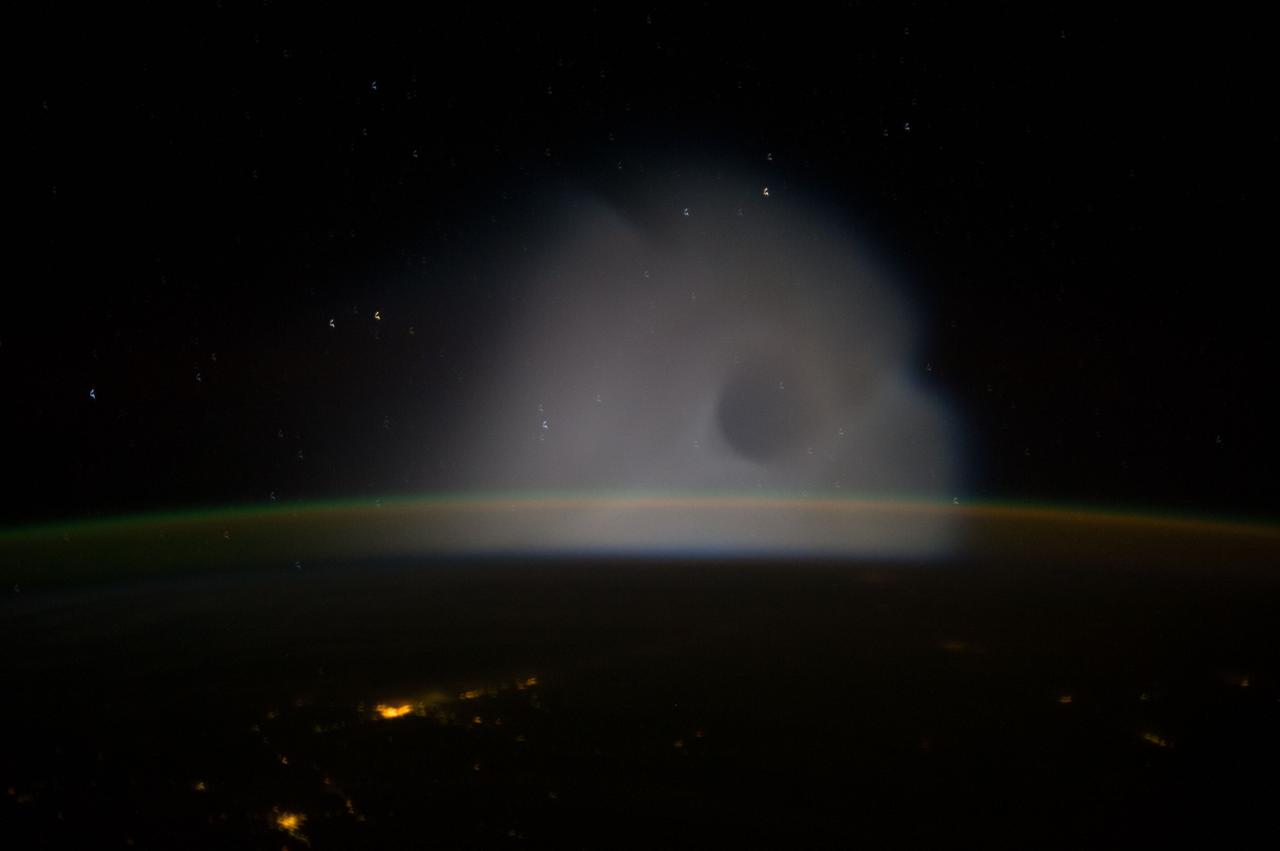

ISS037-E-009301 (10 Oct. 2013) --- This is one of a series of views that captured a missile launch from Earth as seen on Oct. 10, 2013 by the Expedition 37 crew aboard the International Space Station.
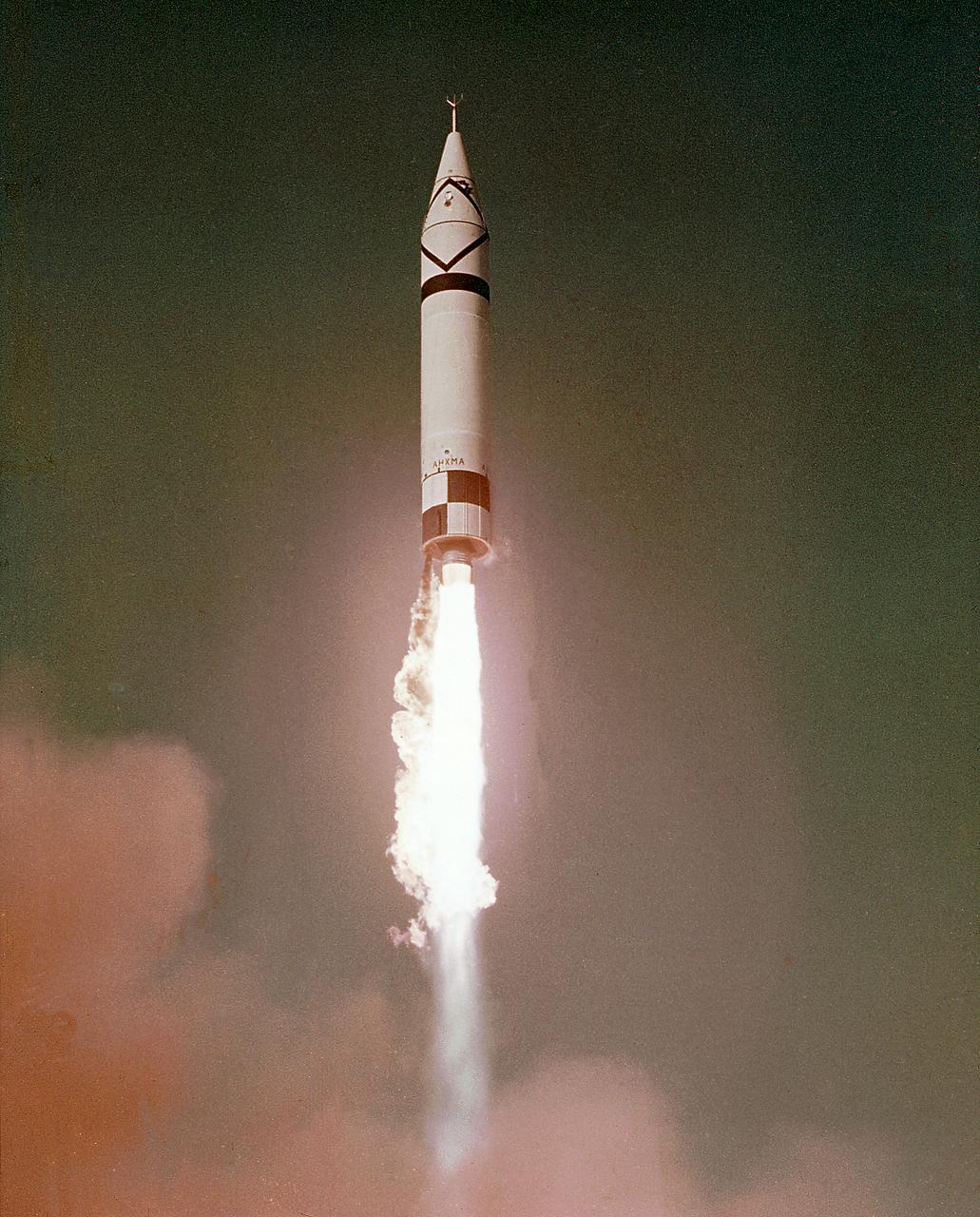

The Jupiter rocket was designed and developed by the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA). ABMA launched the Jupiter-A at Cape Canaveral, Florida, on March 1, 1957. The Jupiter vehicle was a direct derivative of the Redstone. The Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) at Redstone Arsenal, Alabama, continued Jupiter development into a successful intermediate ballistic missile, even though the Department of Defense directed its operational development to the Air Force. ABMA maintained a role in Jupiter RD, including high-altitude launches that added to ABMA's understanding of rocket vehicle operations in the near-Earth space environment. It was knowledge that paid handsome dividends later.
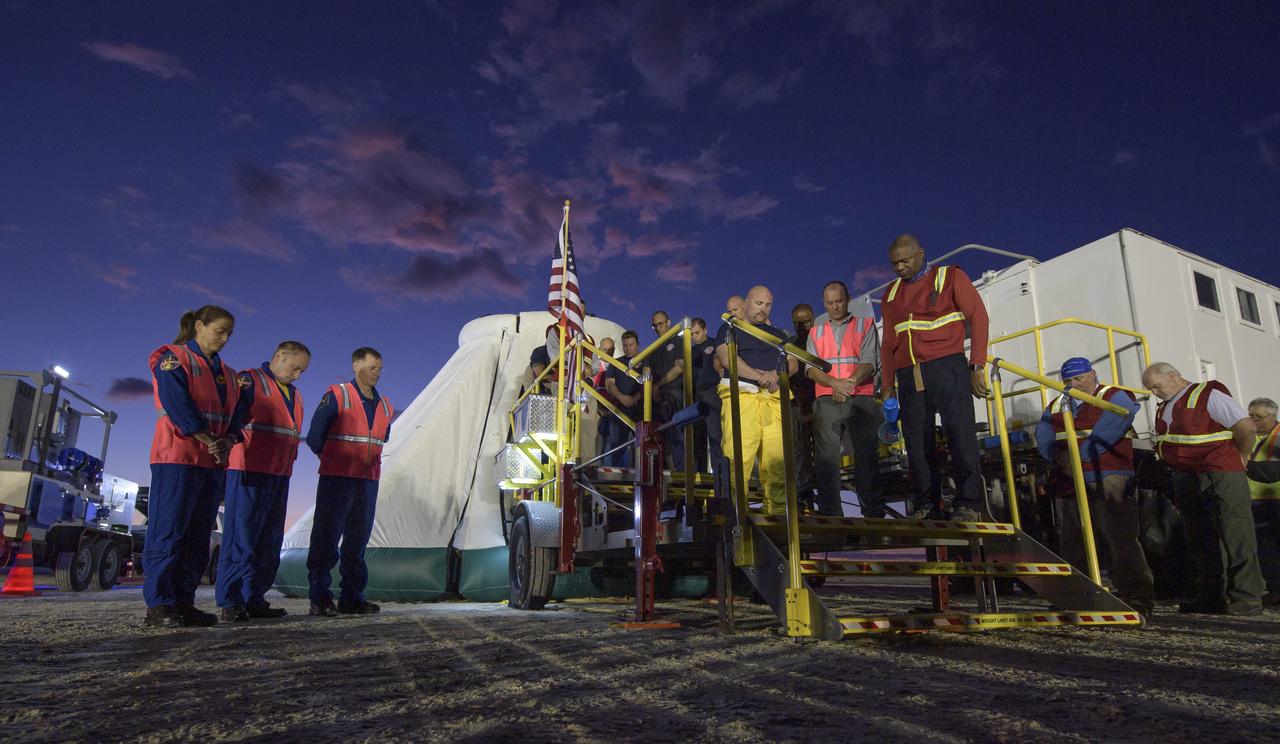

NASA astronauts Nicole Mann and Mike Fincke and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson observe a moment of silence with teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, honoring the victims of the Sept. 11 terrorist attacks, Wednesday, Sept. 11, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. The joint teams gathered in the desert to rehearse landing and crew extrication from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station. Mann, Fincke and Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

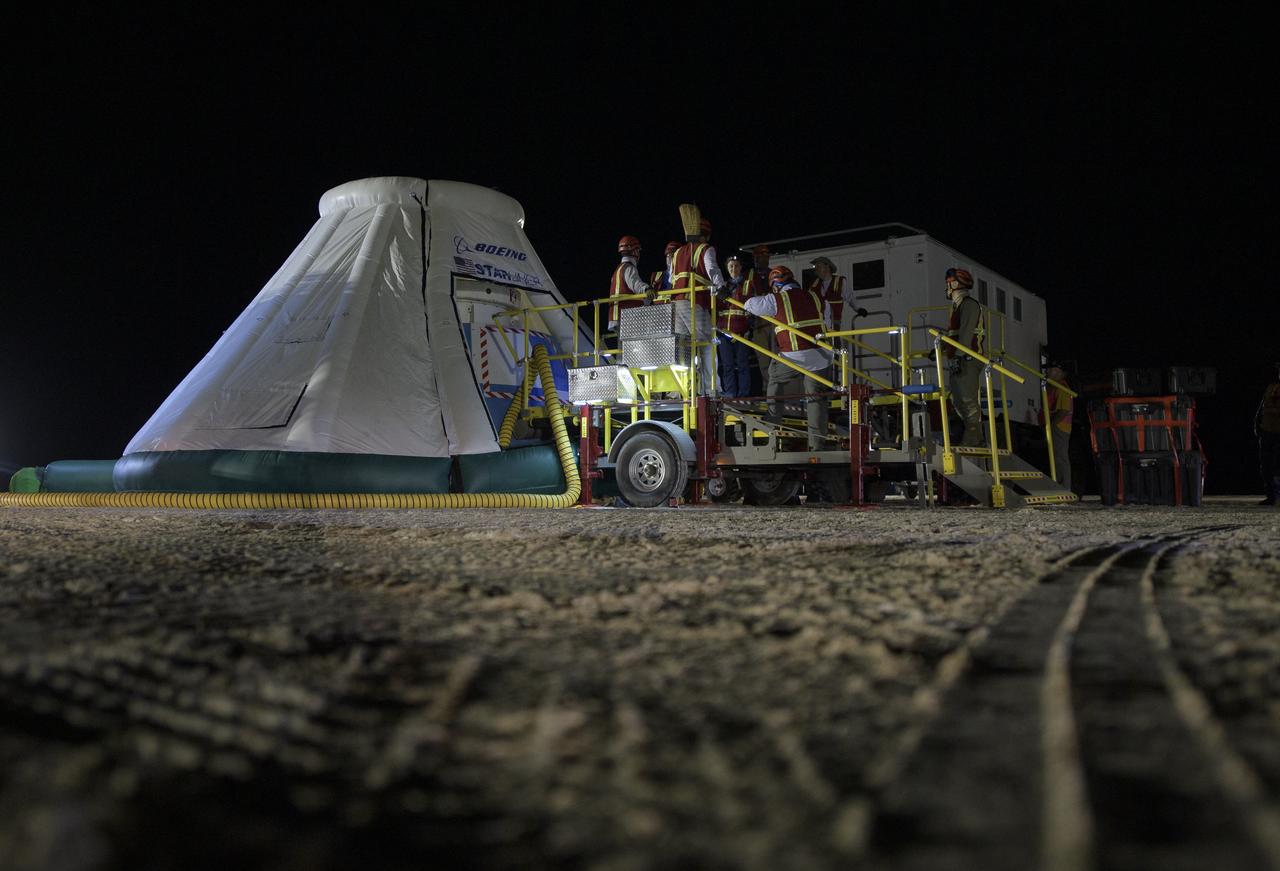
Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Wednesday, Sept. 11, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Wednesday, Sept. 11, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Thursday, Sept. 12, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Wednesday, Sept. 11, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Wednesday, Sept. 11, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Wednesday, Sept. 11, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Thursday, Sept. 12, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Wednesday, Sept. 11, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Thursday, Sept. 12, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Wednesday, Sept. 11, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Monday, Sept. 9, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Wednesday, Sept. 11, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Monday, Sept. 9, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Wednesday, Sept. 11, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Tuesday, Sept. 10, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
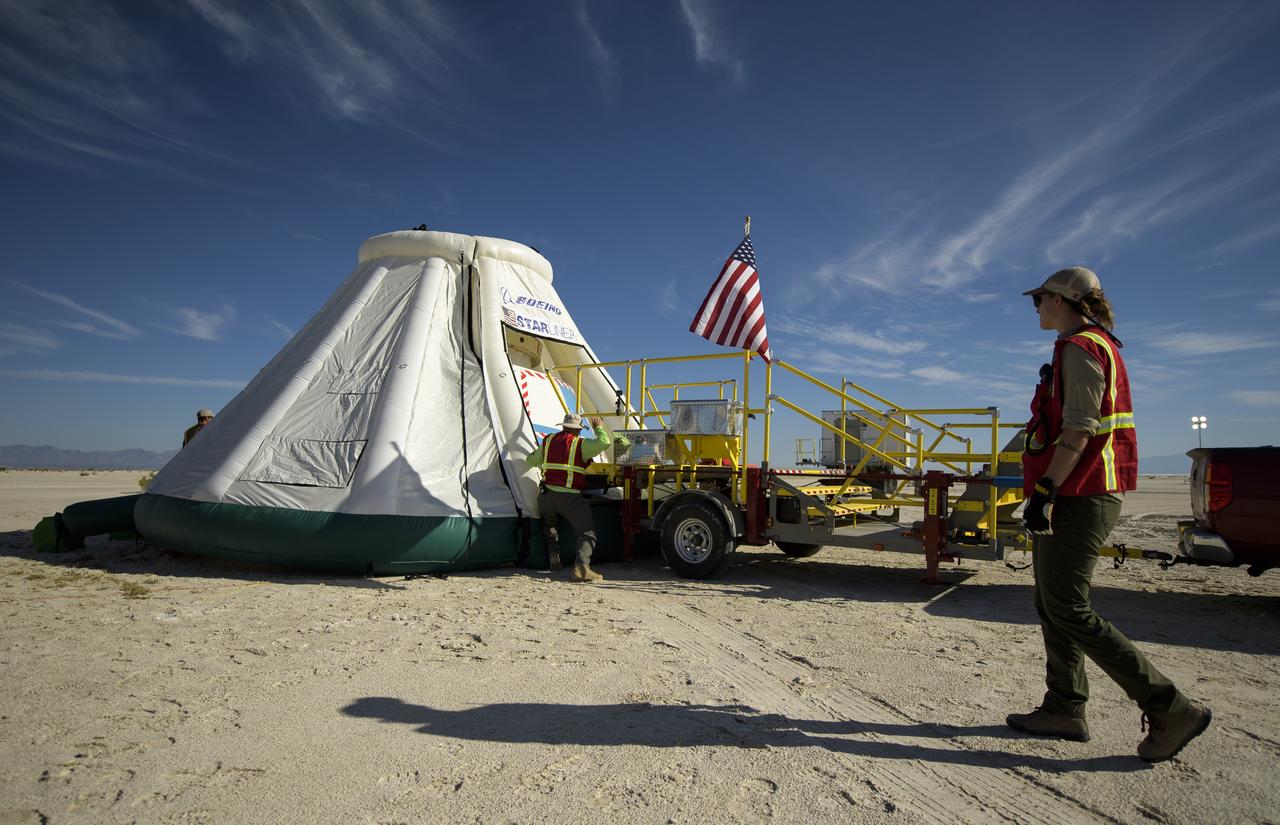

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Thursday, Sept. 12, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
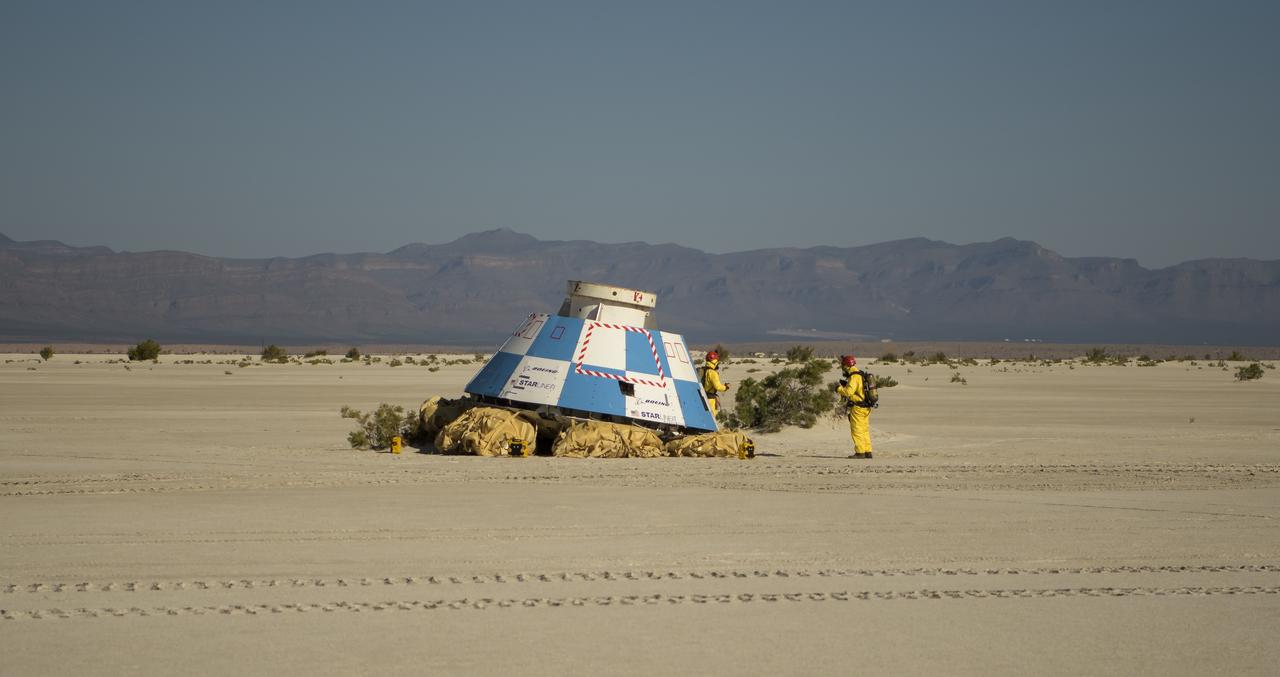

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Thursday, Sept. 12, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
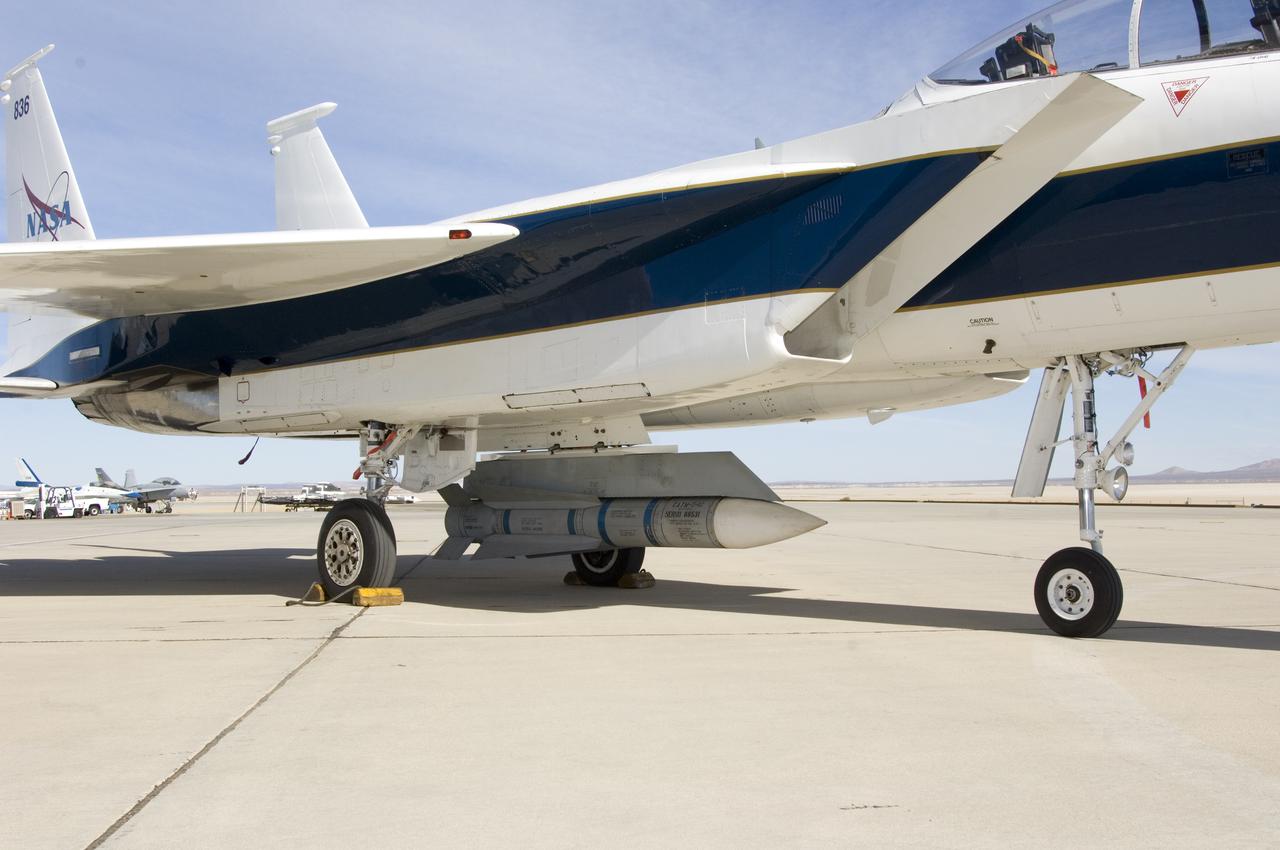

An inert AIM-54 Phoenix missile nestled under the fuselage of NASA Dryden's F-15B aircraft is being studied as a possible test vehicle to obtain hypersonic data.

NASA Dryden aircraft and avionics technicians (from left) Bryan Hookland, Art Cope, Herman Rijfkogel and Jonathan Richards install the nose cone on a Phoenix missile prior to a fit check on the center's F-15B research aircraft.
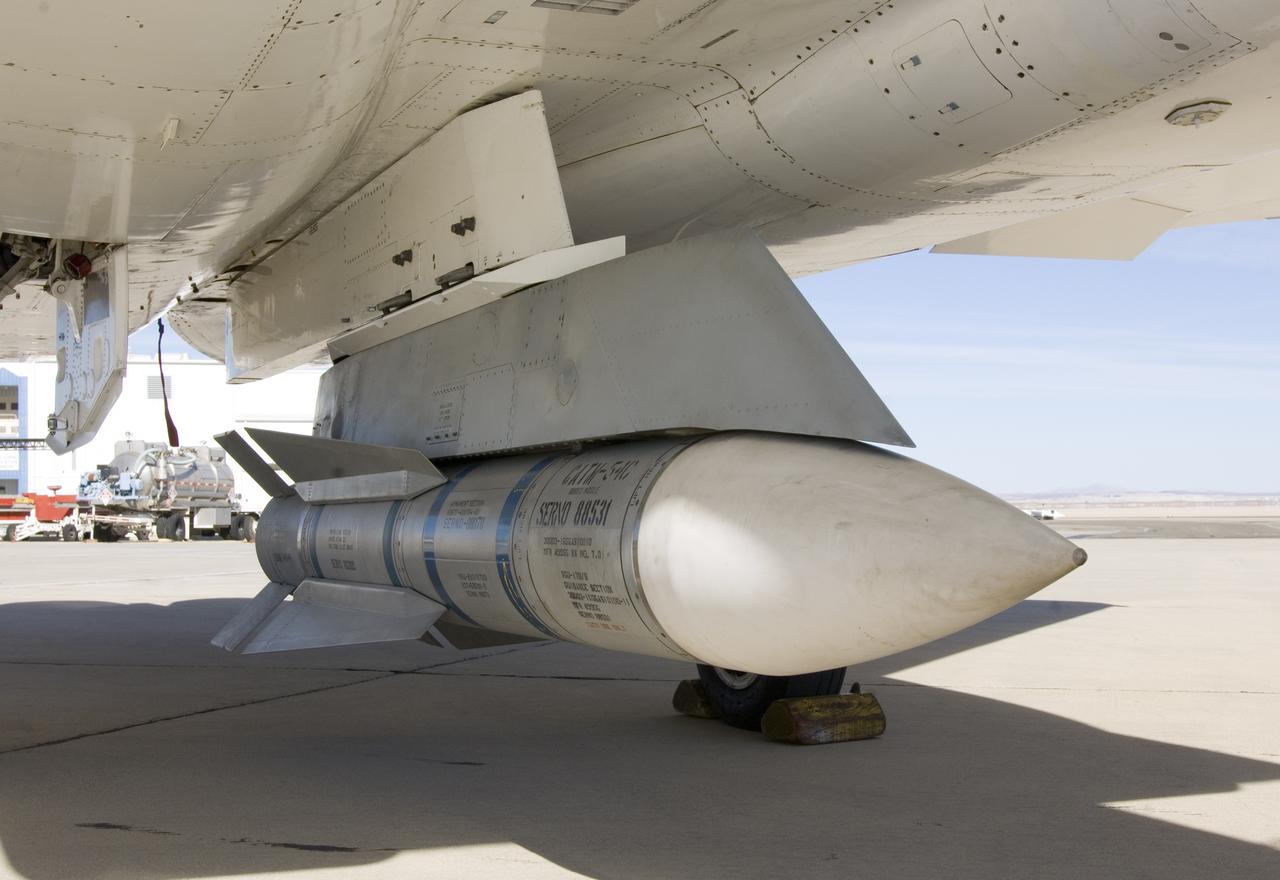

Surplus Navy Phoenix missiles like this one mounted on the centerline pylon of NASA's F-15B research aircraft may be used to acquire hypersonic flight test data.
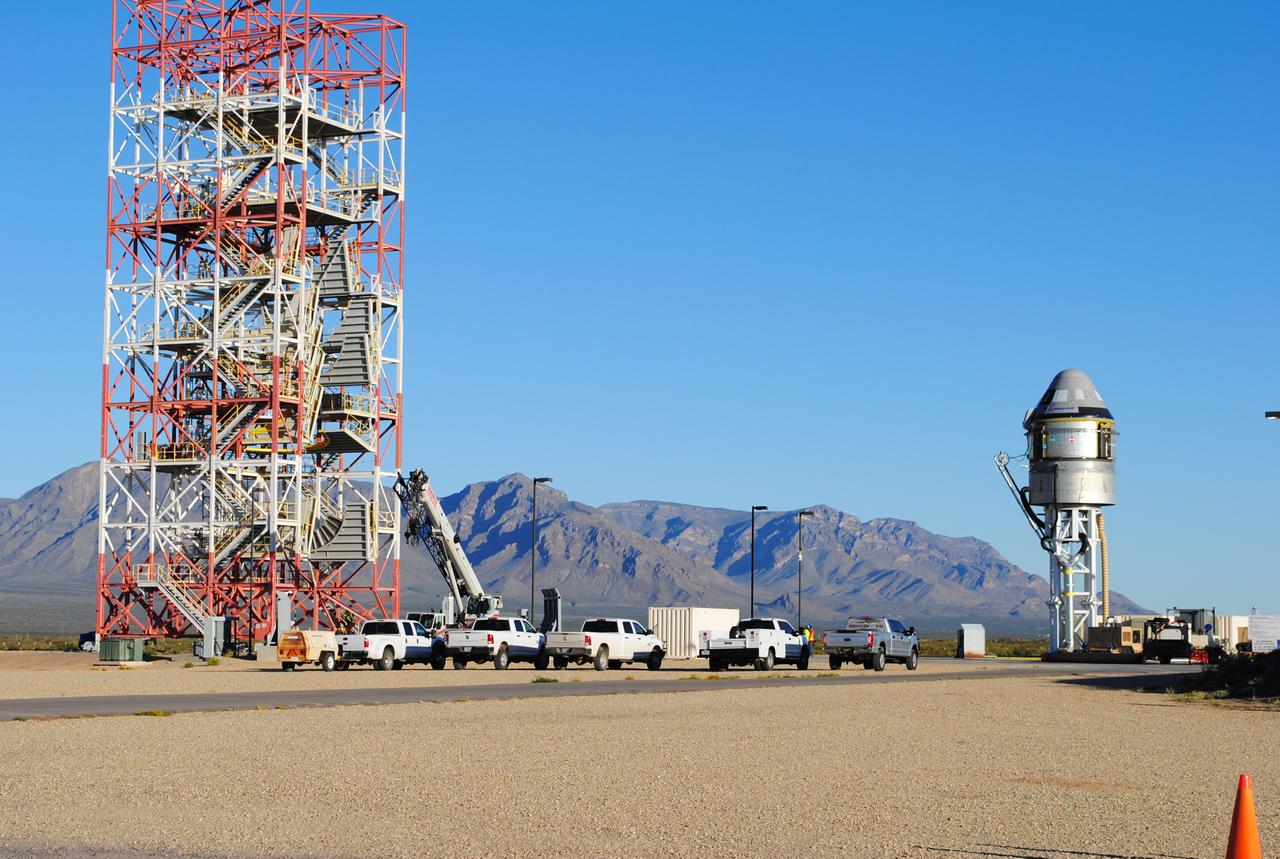

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft and its service module stand atop the test stand at Launch Complex 32, White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico, in preparation for the Pad Abort Test. Boeing’s Pad Abort Test is designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. This will be Boeing’s first flight test as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The Pad Abort Test is scheduled for Nov. 4, 2019.

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner’s airbags inflate in preparation for landing in the New Mexico desert in the company’s Pad Abort Test for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The test, conducted Nov. 4 at the White Sands Missile Range, was designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. This is Boeing’s first test flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working to launch astronauts on American rockets and spacecraft from American soil for the first time since 2011.
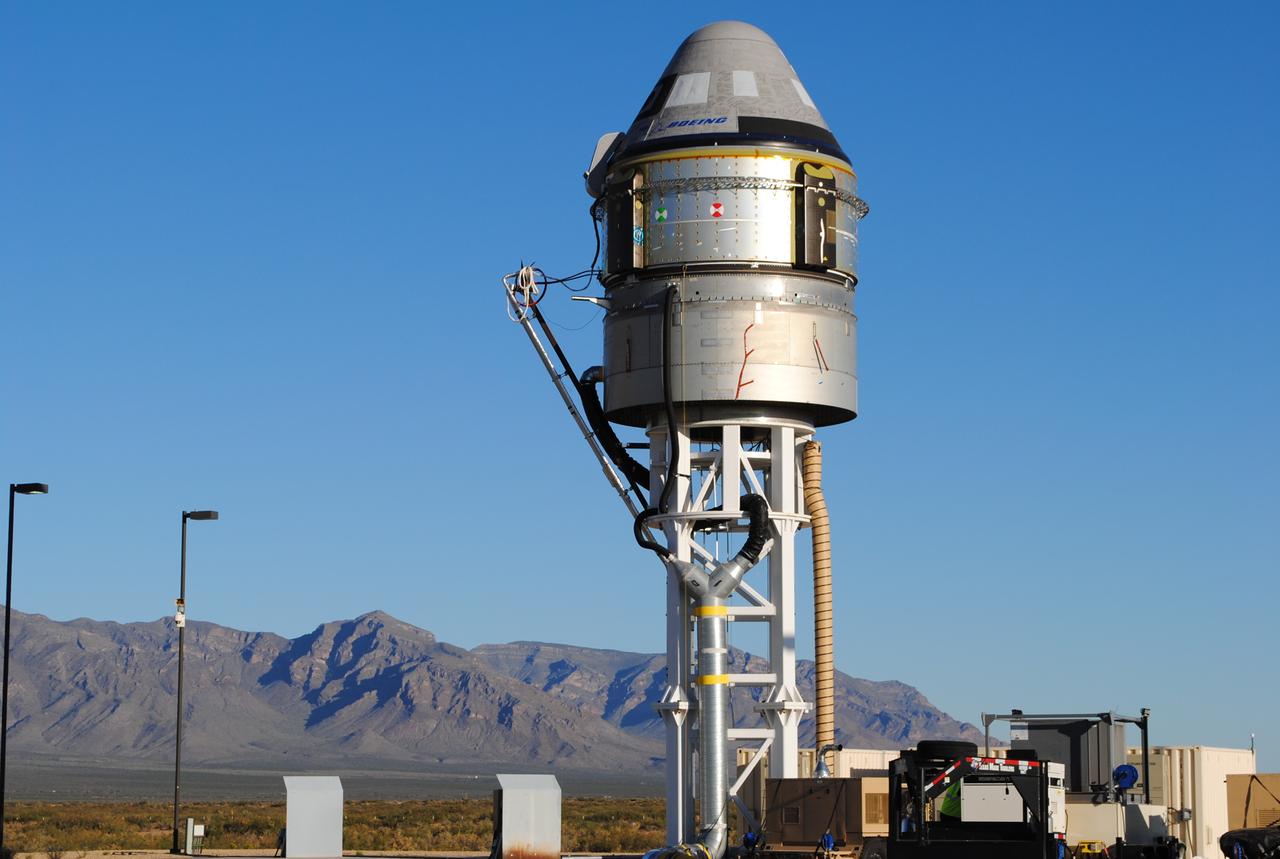

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft and its service module stand atop the test stand at Launch Complex 32, White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico, in preparation for the Pad Abort Test. Boeing’s Pad Abort Test is designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. This will be Boeing’s first flight test as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The Pad Abort Test is scheduled for Nov. 4, 2019.

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner’s airbags inflate in preparation for landing in the New Mexico desert in the company’s Pad Abort Test for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The test, conducted Nov. 4 at the White Sands Missile Range, was designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. This is Boeing’s first test flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working to launch astronauts on American rockets and spacecraft from American soil for the first time since 2011.

Parachutes deploy in in Boeing’s Pad Abort Test of its CST-100 Starliner spacecraft over the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico, slowing the descent of the vehicle. The test, conducted Nov. 4, 2019, was designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. This is Boeing’s first test flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working to launch astronauts on American rockets and spacecraft from American soil for the first time since 2011.
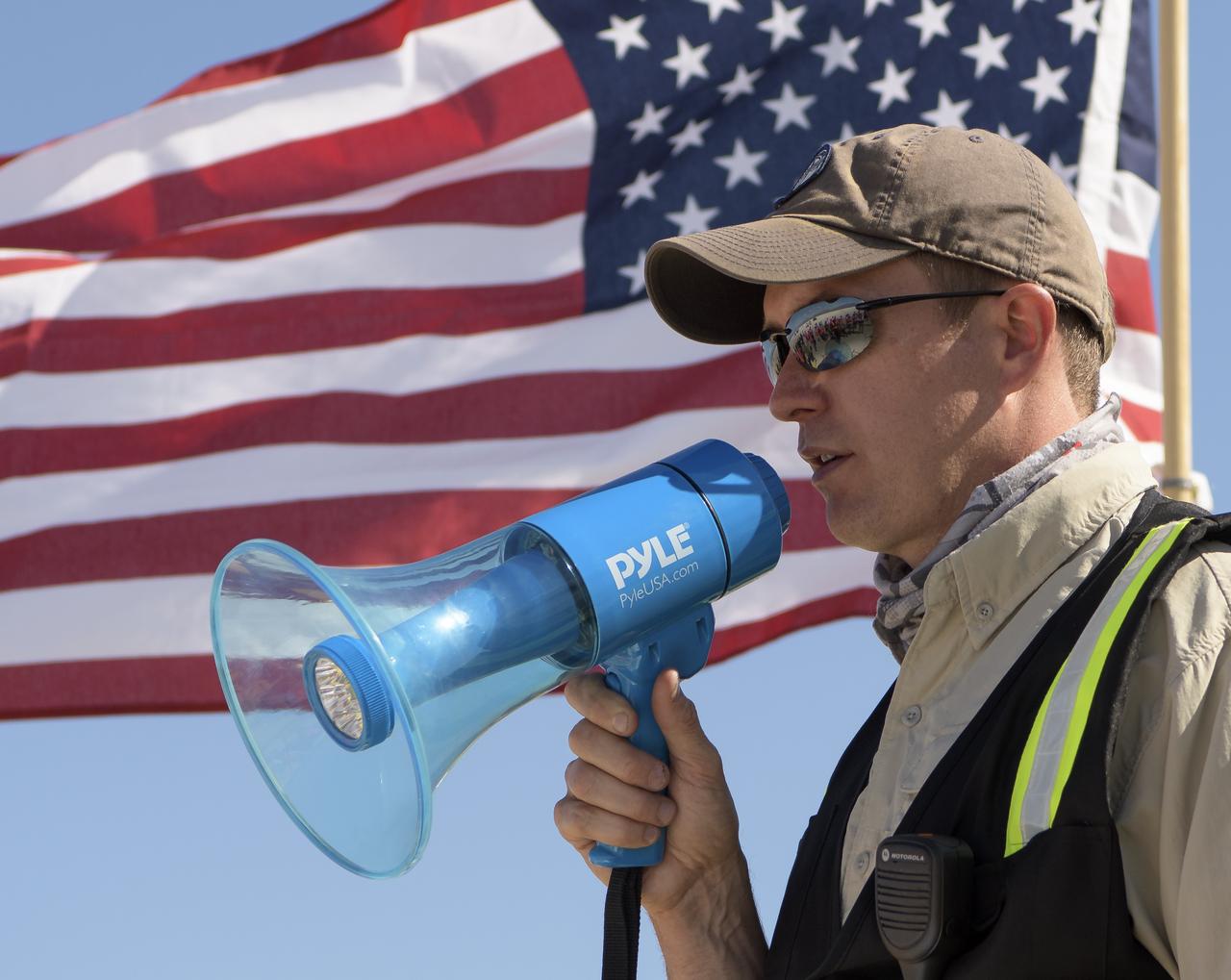

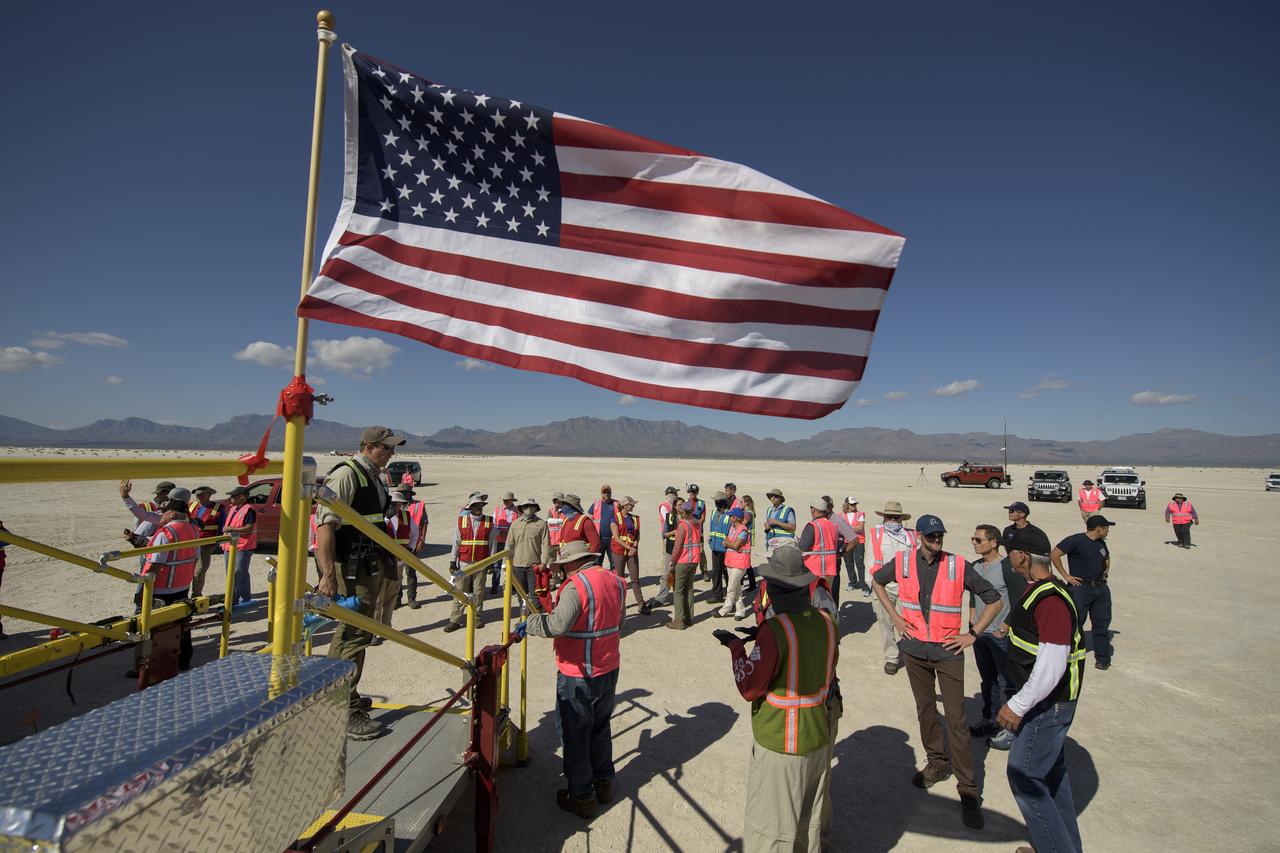
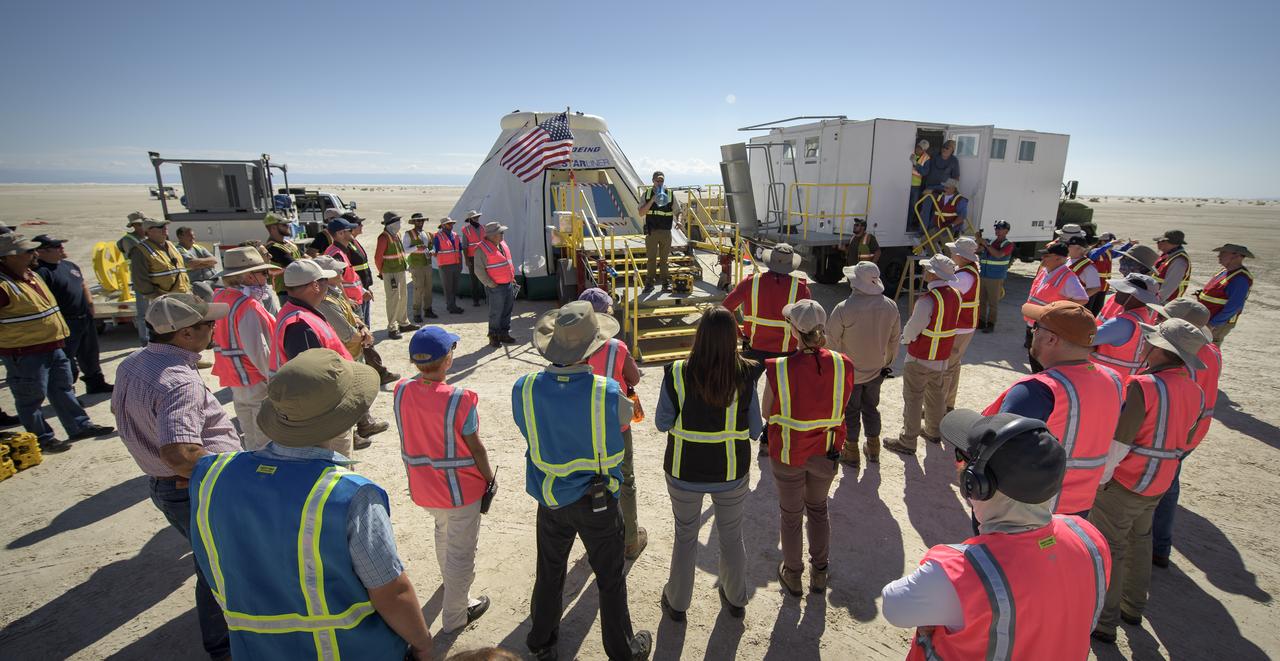
Louis Atchison chief of launch and recovery operations for Boeing Commercial Crew Program addresses teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range during rehearsals for landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Wednesday, Sept. 11, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
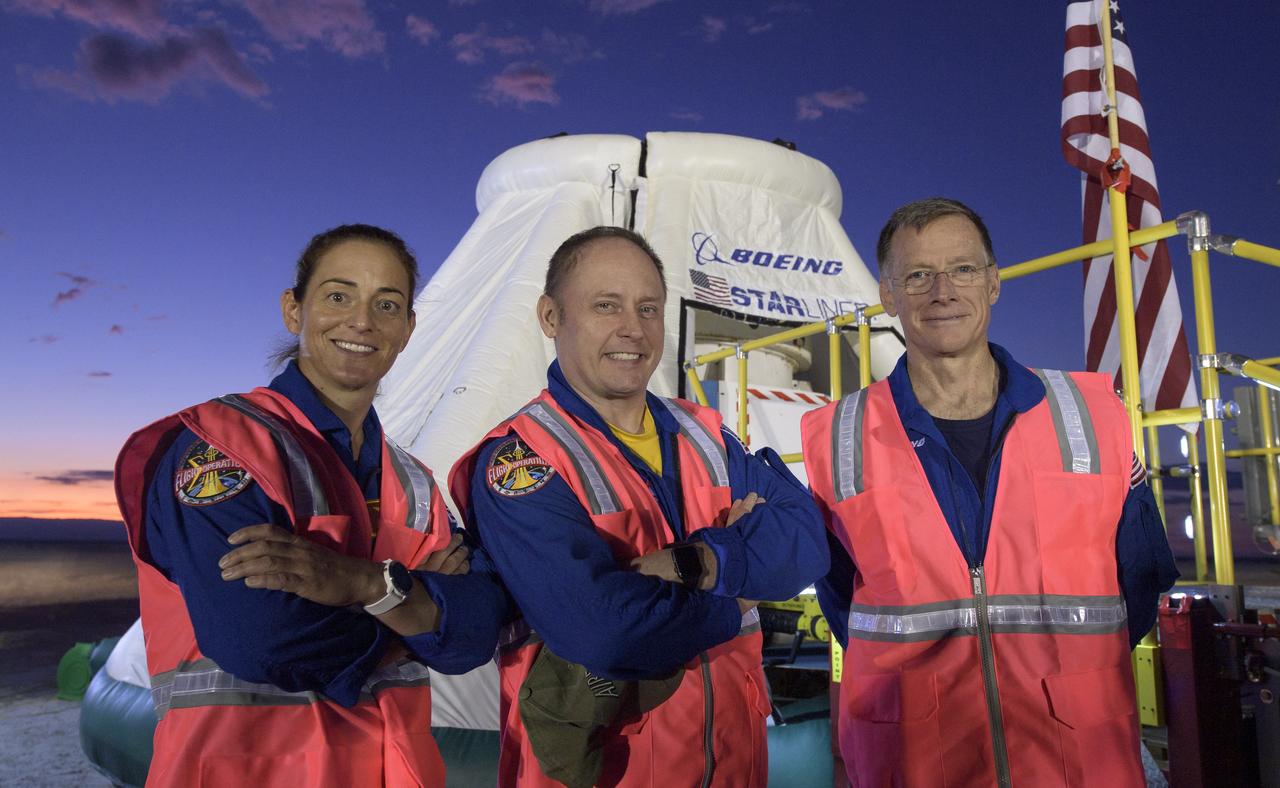

NASA astronauts Nicole Mann, left, Mike Fincke, and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, right, pose for photograph as they and teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Wednesday, Sept. 11, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. Fincke, Mann and Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
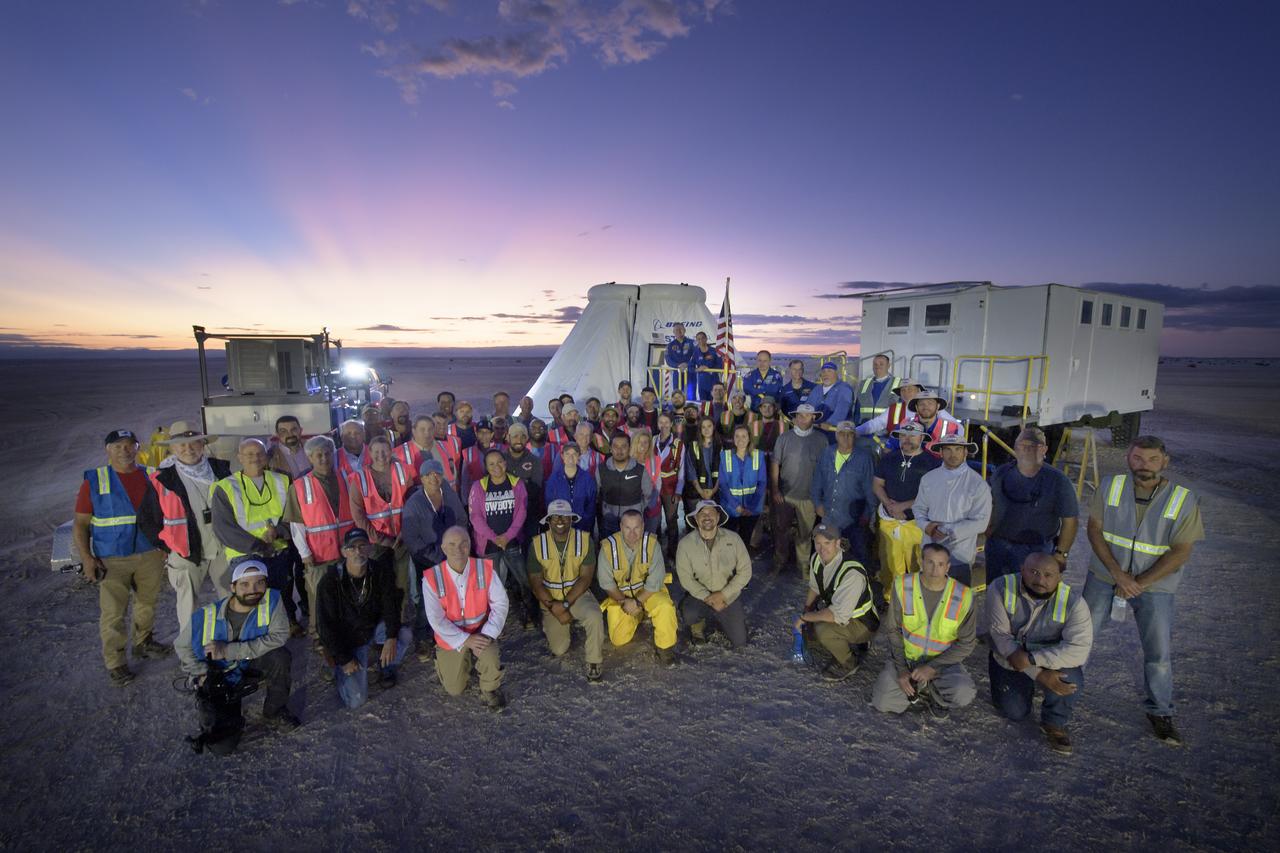

Teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, pose for a group photograph during rehearsals for landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Wednesday, Sept. 11, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
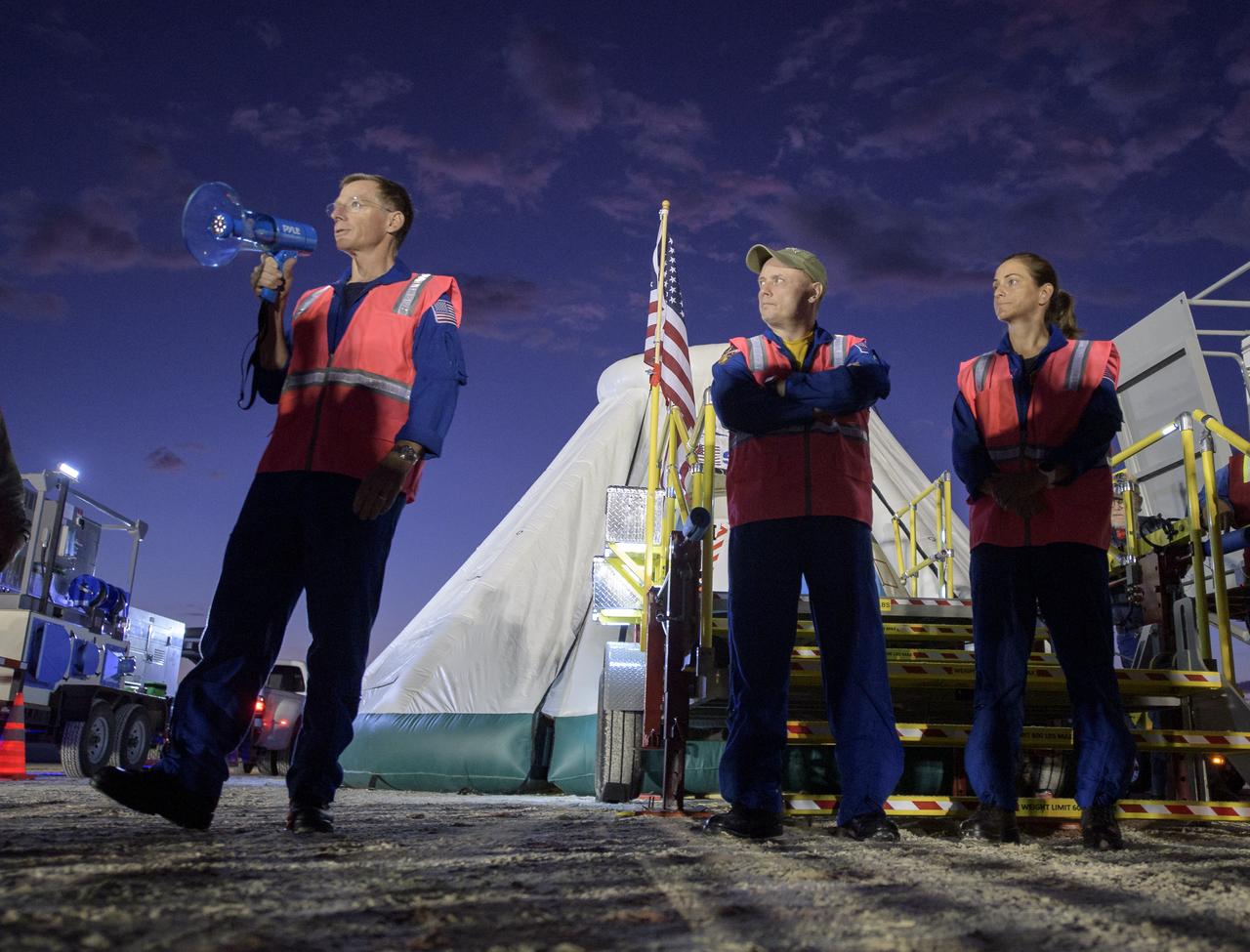

Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, left, and NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann, along with teams from NASA, Boeing and the White Sands Missile Range, rehearse landing and crew extraction from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, which will be used to carry humans to the International Space Station, on Wednesday, Sept. 11, 2019 at the White Sands Missile Range outside Las Cruces, New Mexico. Using a convoy of vehicles Boeing uses to recover their spacecraft after landing and a boiler plate test article of the Starliner capsule, the teams worked through the steps necessary to safe the vehicle and get future crew members out of the Starliner to return home. Fincke, Mann and Ferguson will fly to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Boeing Crew Flight Test mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
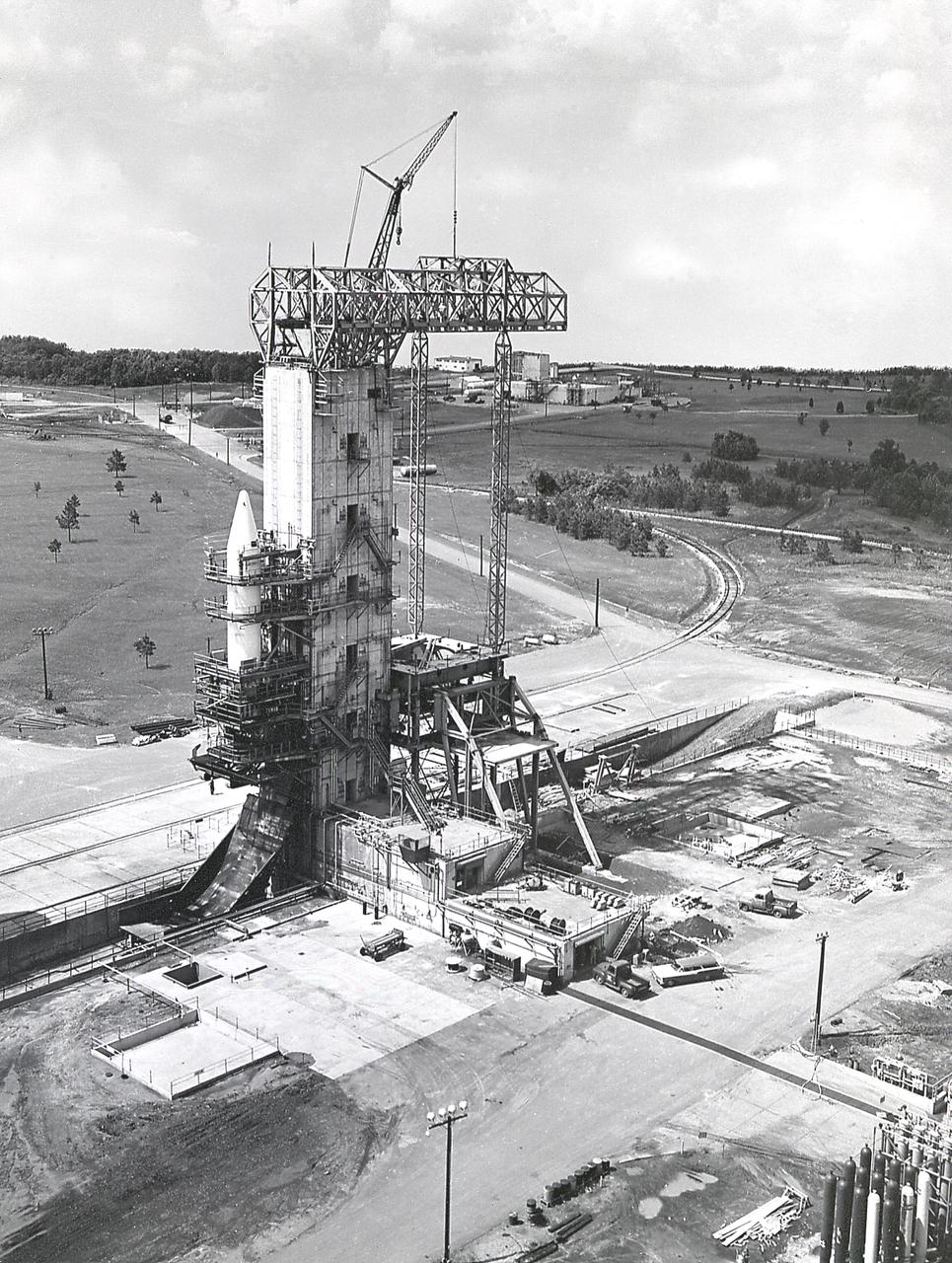
The Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) test tower being modified for testing the Saturn booster.
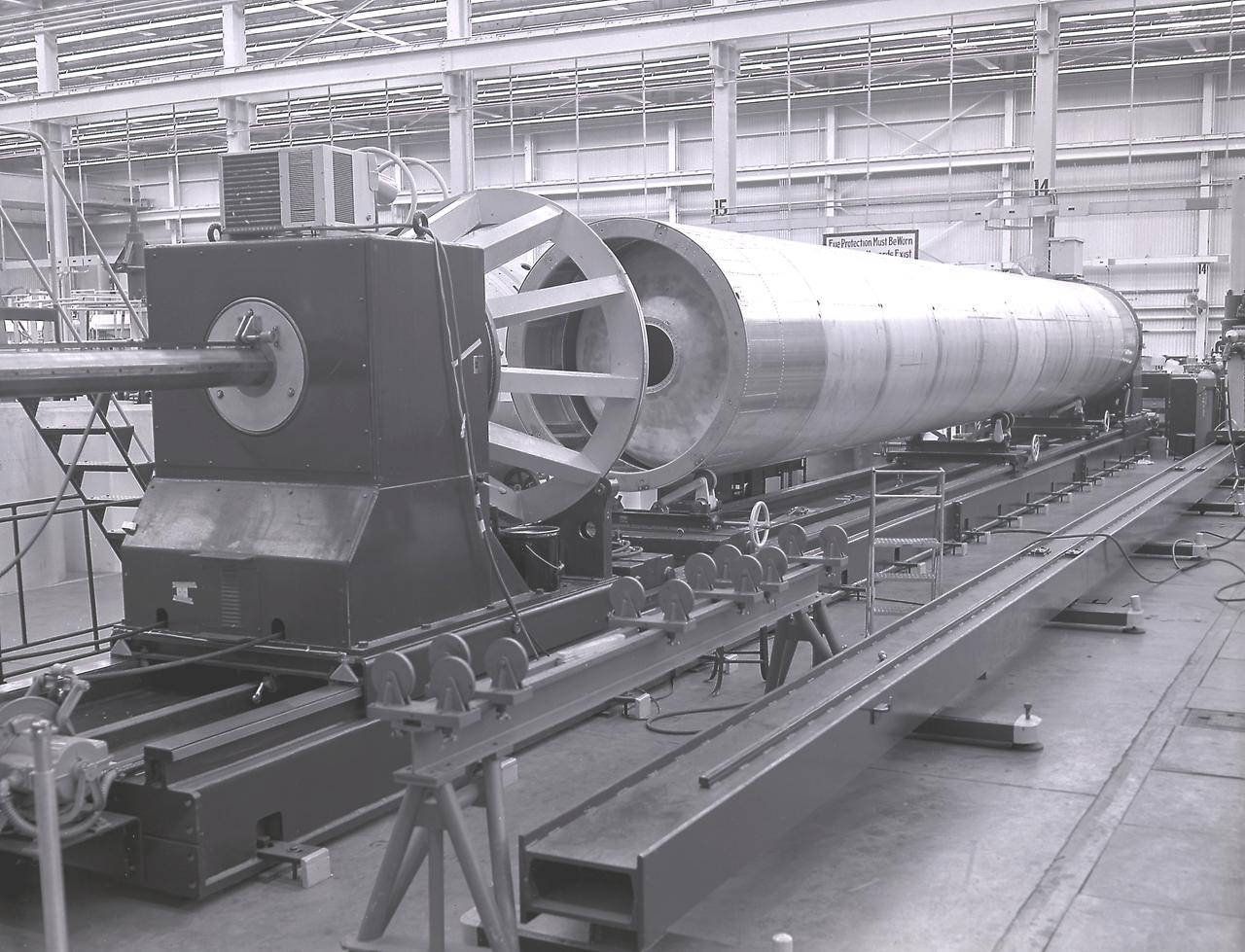
The first circumferential welding being applied on a Saturn fuel container in the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) fabrication laboratory, Building 4707, in May 1959.
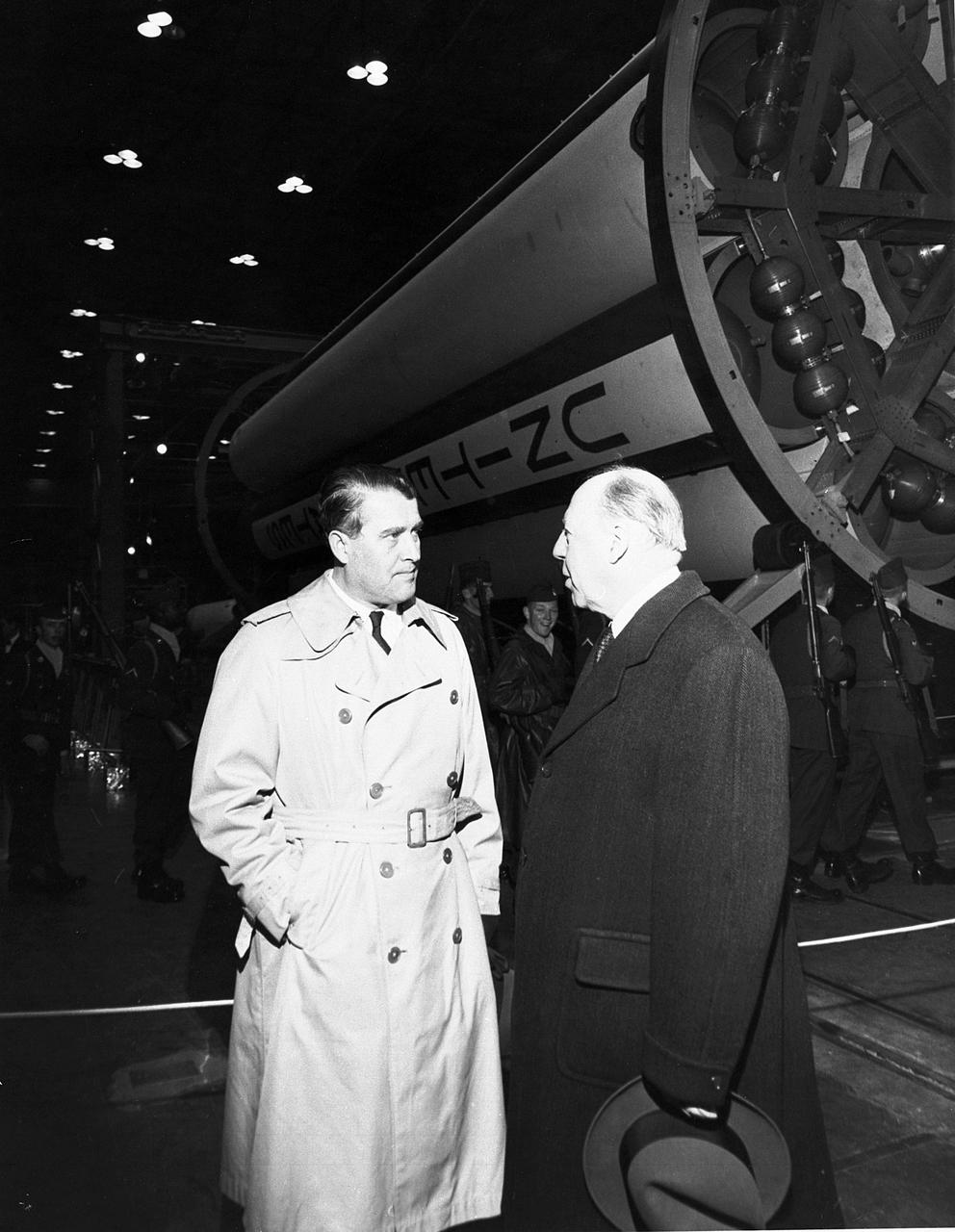

This photograph was taken in 1960 and shows Dr. von Braun, left, and Secretary of the Army, Wilbur Brucker in the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) Fabrication Laboratory.

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner’s four launch abort engines and several orbital maneuvering and attitude control thrusters ignite in the company’s Pad Abort Test, pushing the spacecraft away from the test stand with a combined 160,000 pounds of thrust, from Launch Complex 32 on White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico. The test, conducted Nov. 4, 2019, was designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. The Pad Abort Test is Boeing’s first test flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working to launch astronauts on American rockets and spacecraft from American soil for the first time since 2011.

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner lands in the New Mexico desert in the company’s Pad Abort Test for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The test, conducted Nov. 4 at the White Sands Missile Range, was designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. Starliner touched down on land approximately 90 seconds after the test began, about one mile from the test stand at Launch Complex 32. This is Boeing’s first test flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working to launch astronauts on American rockets and spacecraft from American soil for the first time since 2011.

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner’s four launch abort engines and several orbital maneuvering and attitude control thrusters ignite in the company’s Pad Abort Test, pushing the spacecraft away from the test stand with a combined 160,000 pounds of thrust, from Launch Complex 32 on White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico. The test, conducted Nov. 4, 2019, was designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. The Pad Abort Test is Boeing’s first test flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working to launch astronauts on American rockets and spacecraft from American soil for the first time since 2011.

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner lands in the New Mexico desert in the company’s Pad Abort Test for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The test, conducted Nov. 4 at the White Sands Missile Range, was designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. Starliner touched down on land approximately 90 seconds after the test began, about one mile from the test stand at Launch Complex 32. This is Boeing’s first test flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working to launch astronauts on American rockets and spacecraft from American soil for the first time since 2011.
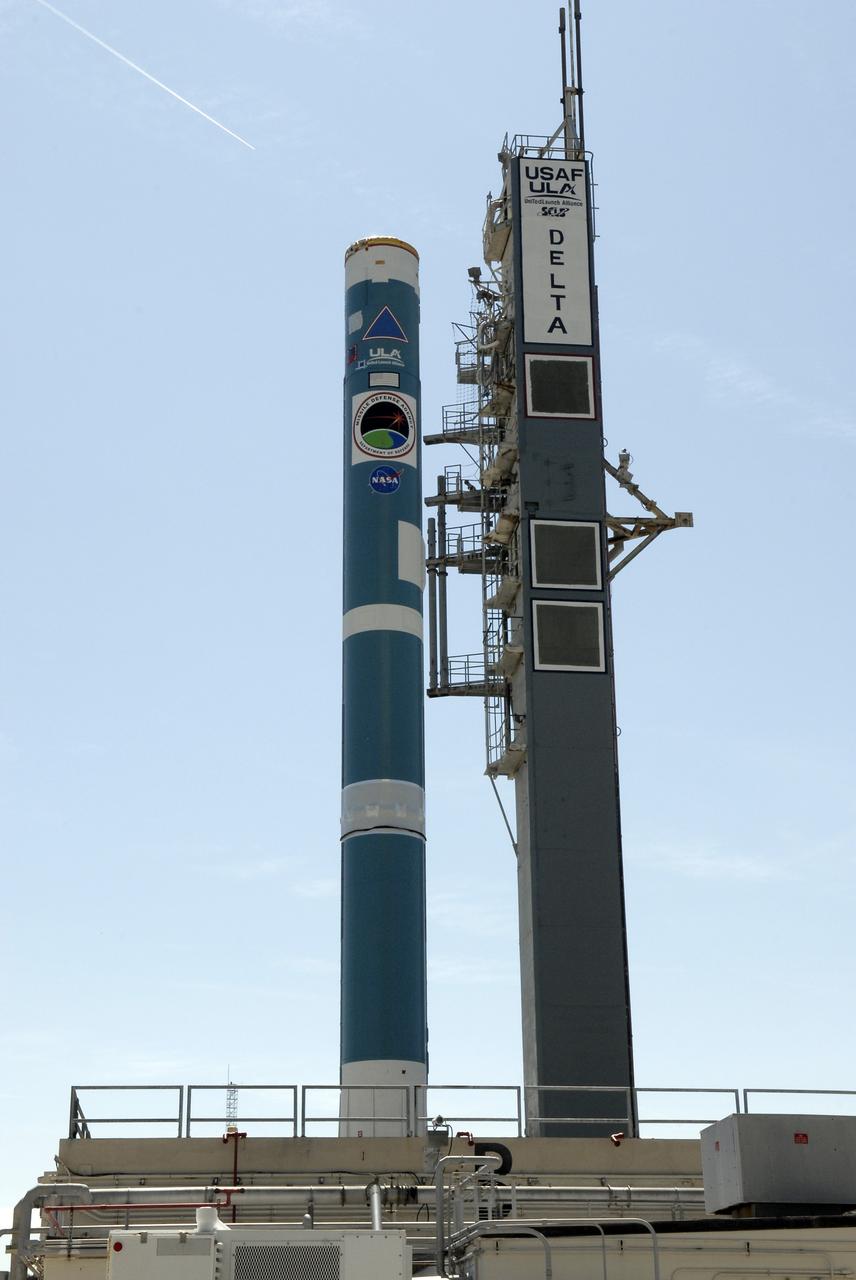

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the first stage of the Delta II rocket waits on the gantry for the solid rocket boosters. The STSS Demonstrators is a midcourse tracking technology demonstrator and is part of an evolving ballistic missile defense system. STSS is capable of tracking objects after boost phase and provides trajectory information to other sensors. It will be launched by NASA for the Missile Defense Agency on July 29. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
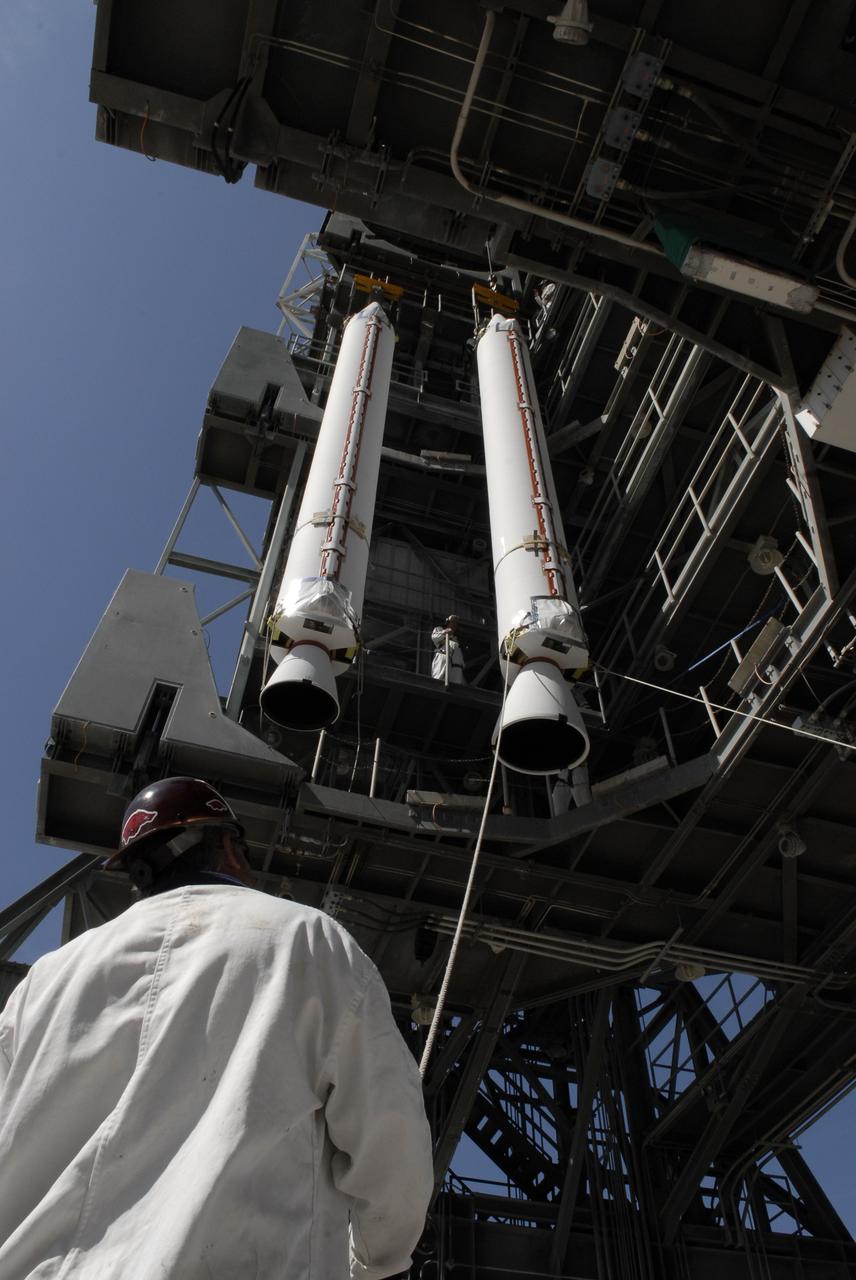

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, solid rocket boosters are lifted into the mobile service tower. The boosters will be attached to the Delta II rocket that will launch the STSS Demonstrator spacecraft. The STSS Demonstrators is a midcourse tracking technology demonstrator and is part of an evolving ballistic missile defense system. STSS is capable of tracking objects after boost phase and provides trajectory information to other sensors. It will be launched by NASA for the Missile Defense Agency on July 29. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, solid rocket boosters are lifted into the mobile service tower. The boosters will be attached to the Delta II rocket that will launch the STSS Demonstrator spacecraft. The STSS Demonstrators is a midcourse tracking technology demonstrator and is part of an evolving ballistic missile defense system. STSS is capable of tracking objects after boost phase and provides trajectory information to other sensors. It will be launched by NASA for the Missile Defense Agency on July 29. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

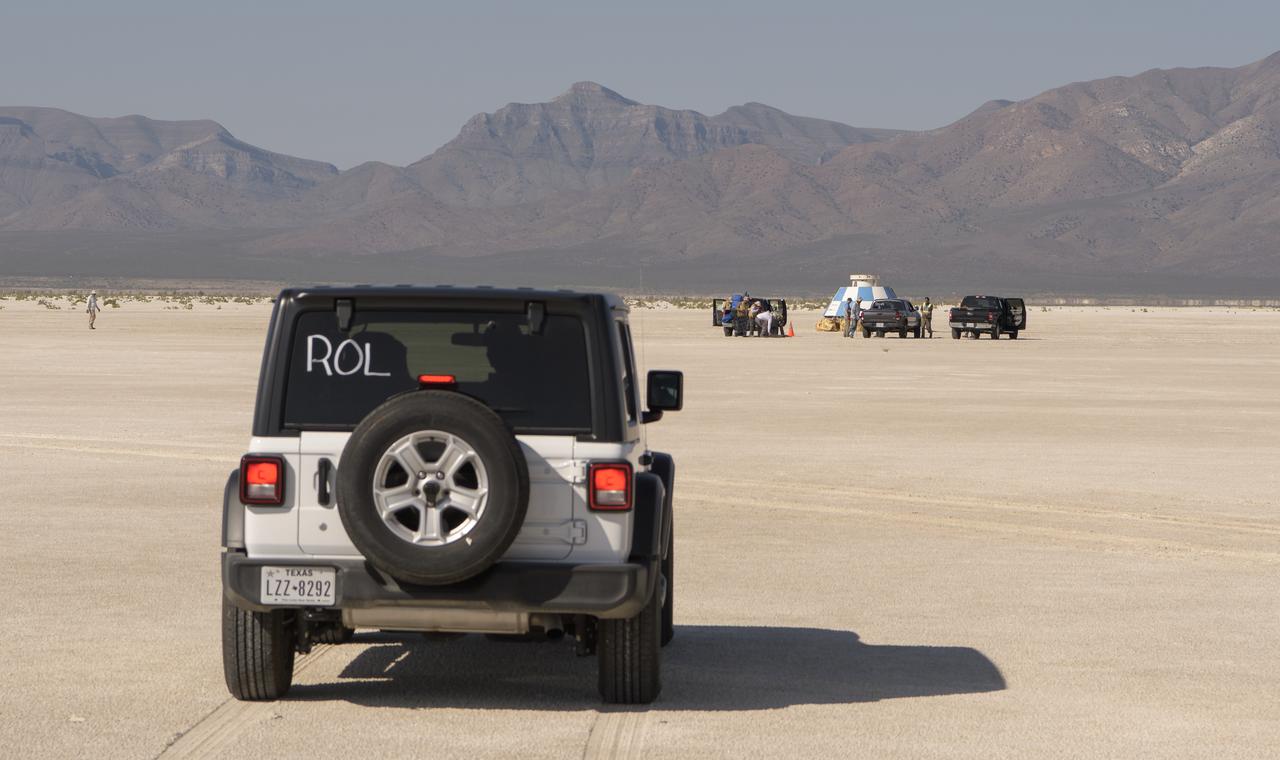
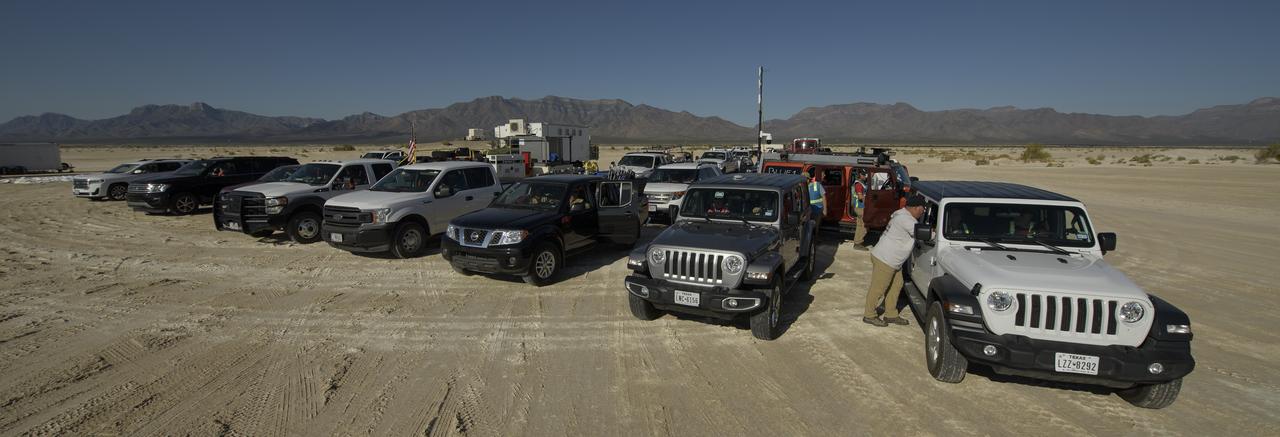
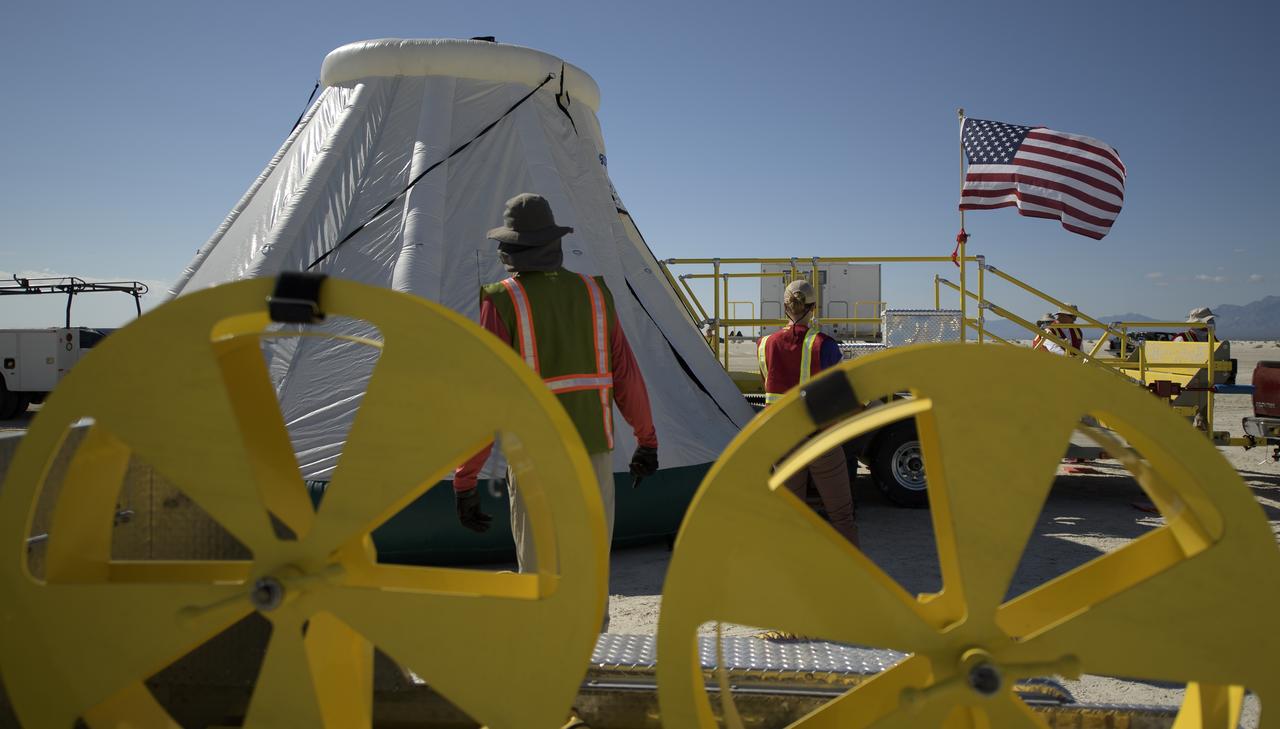
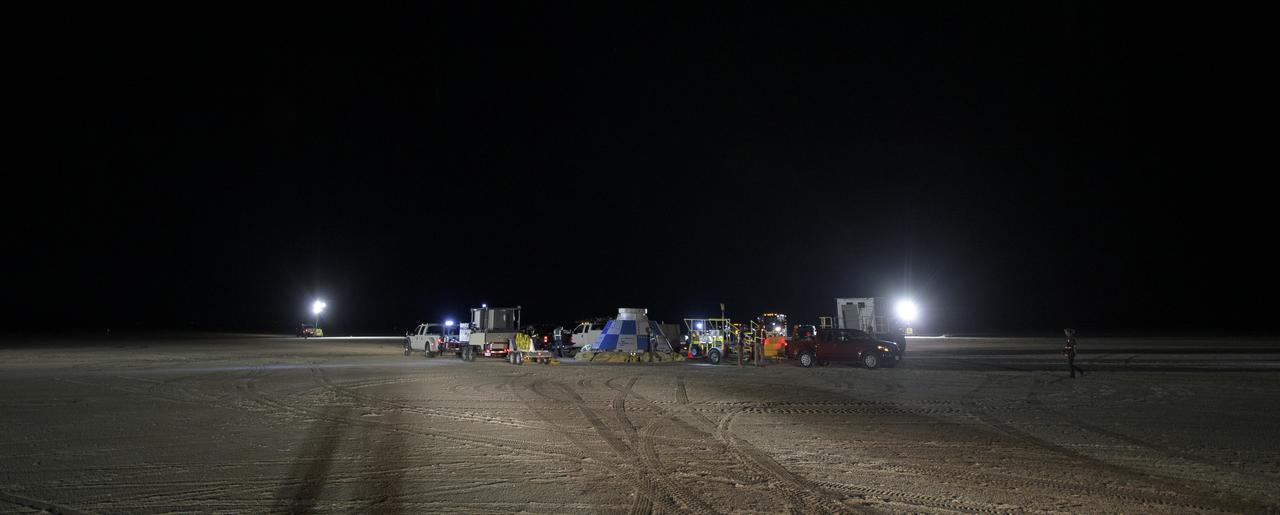
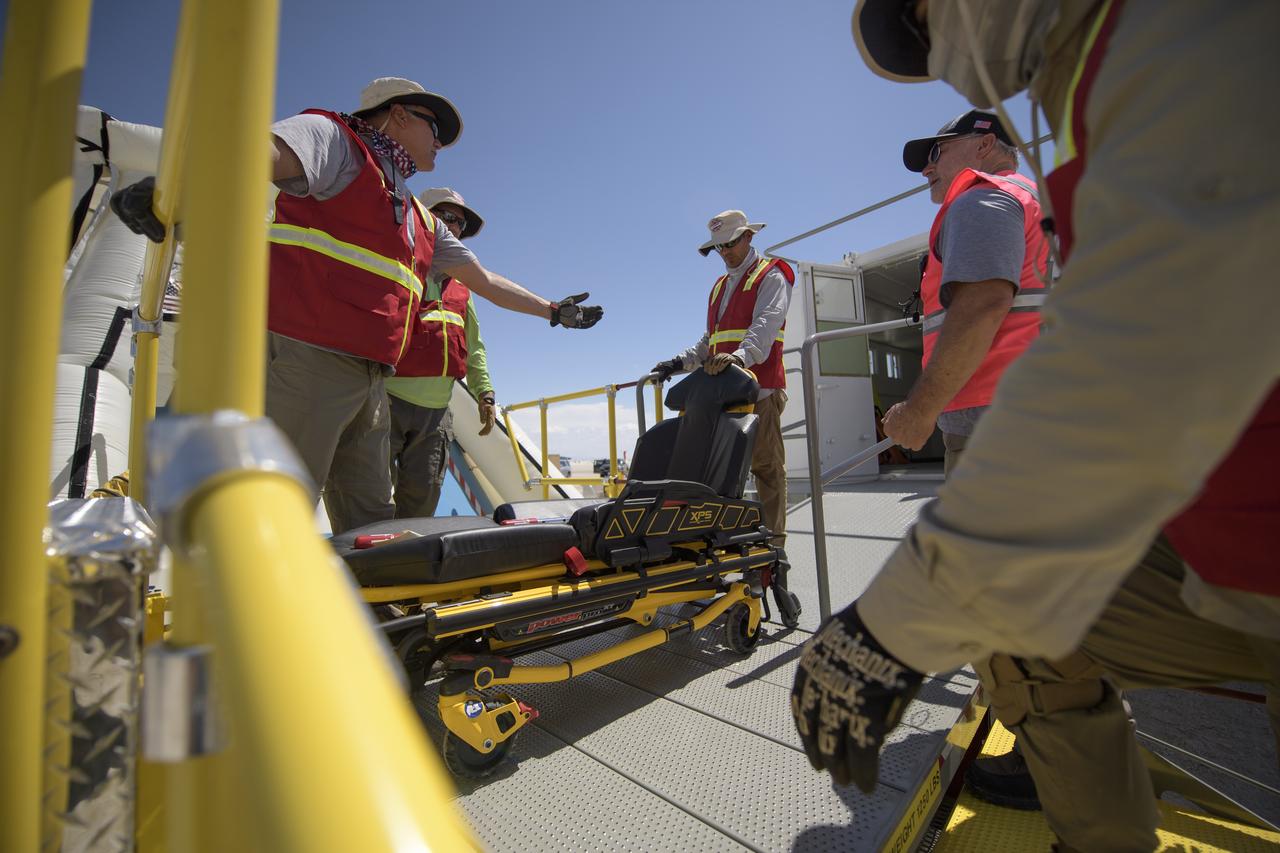
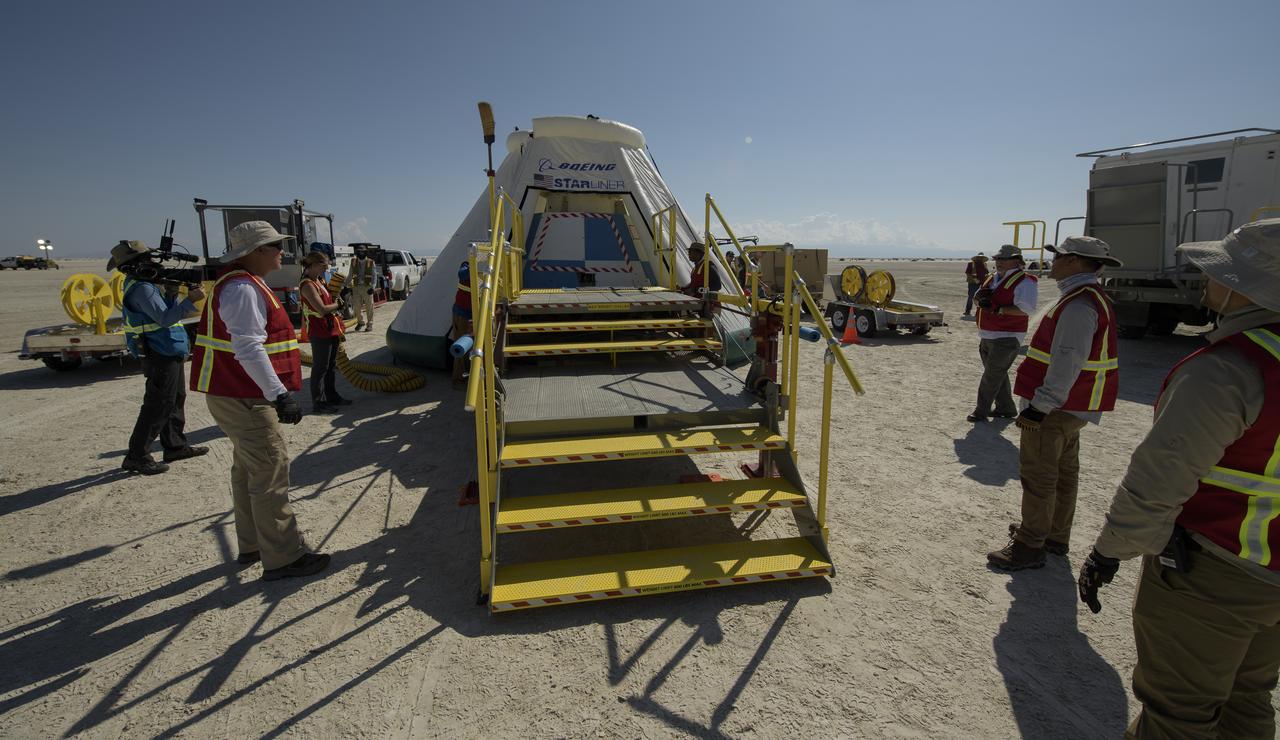
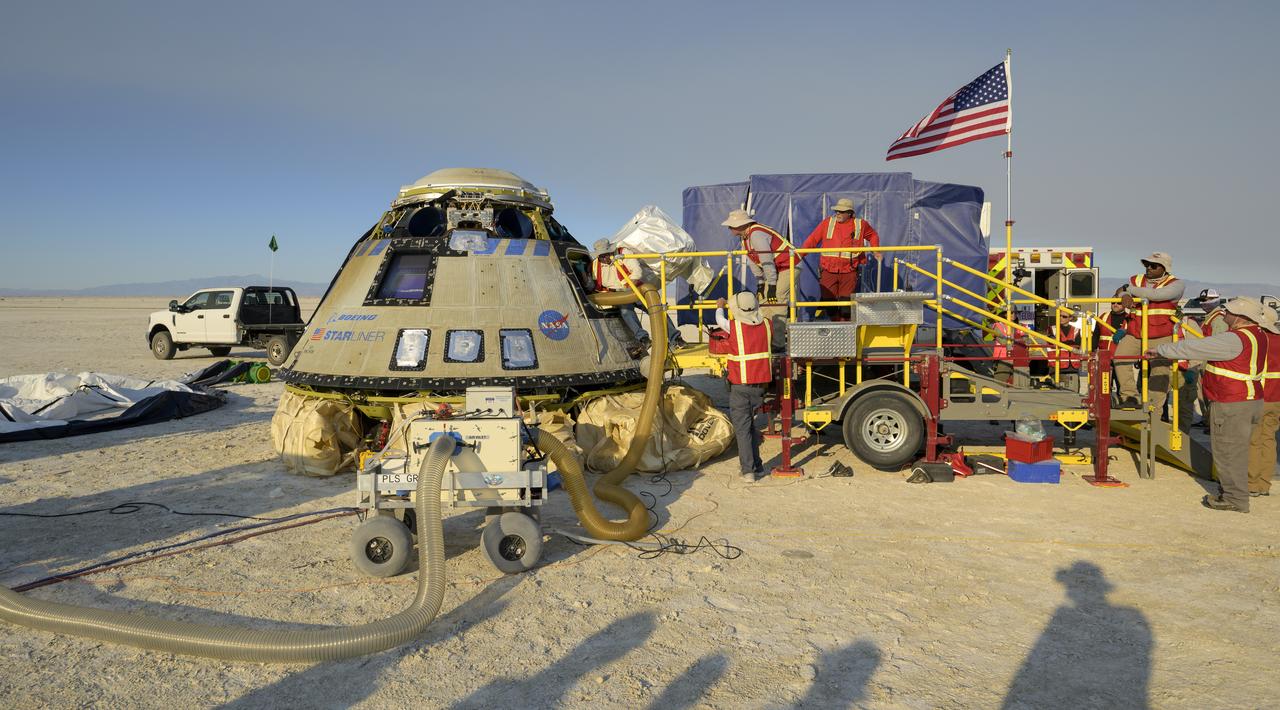
NASA and Boeing teams prepare for the landing of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
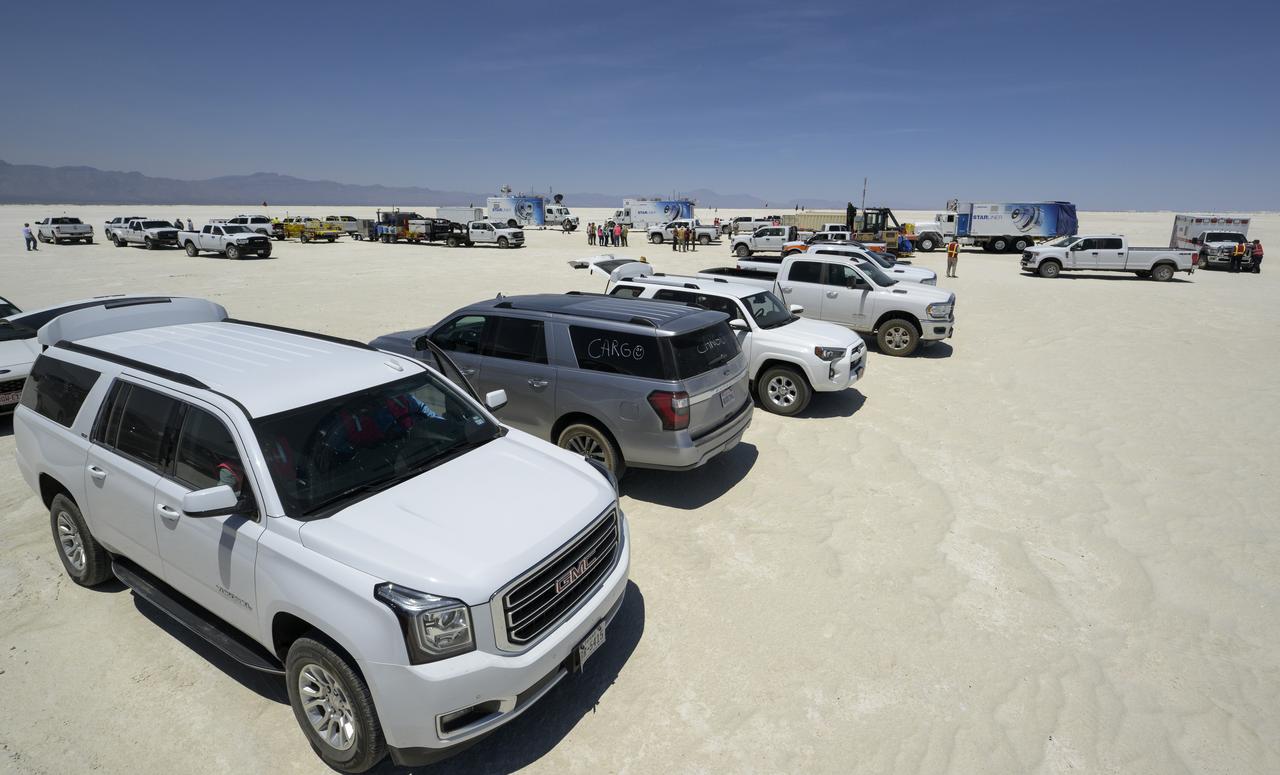

NASA and Boeing teams prepare for the landing of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
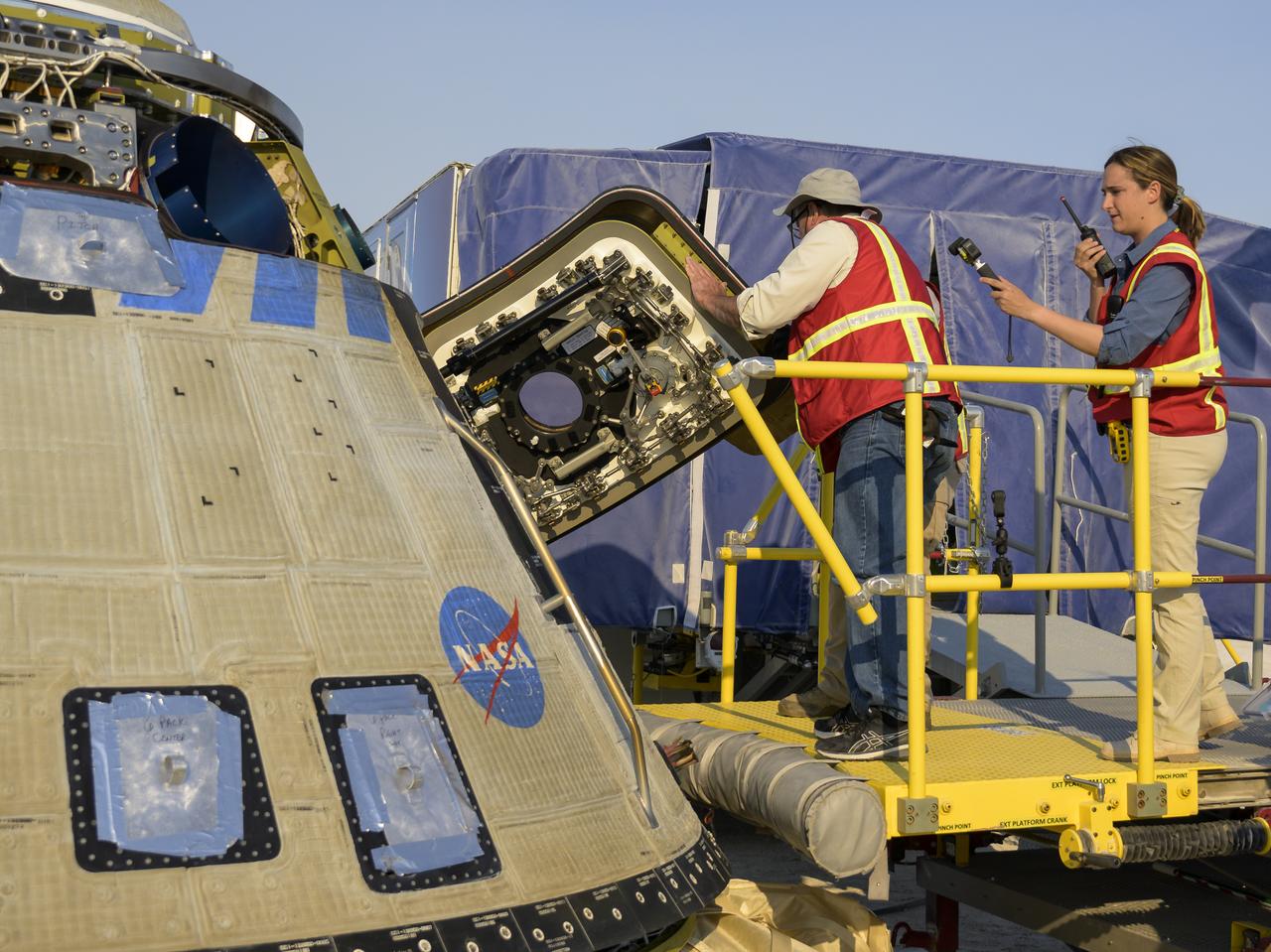

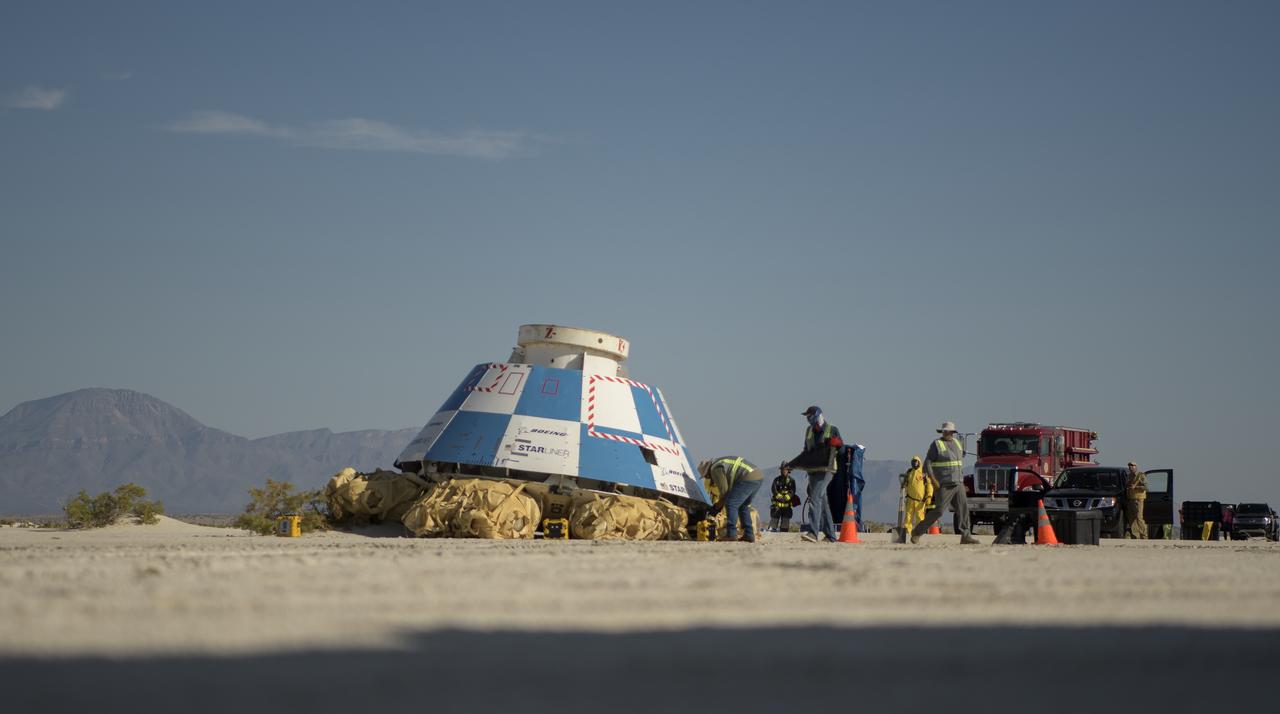
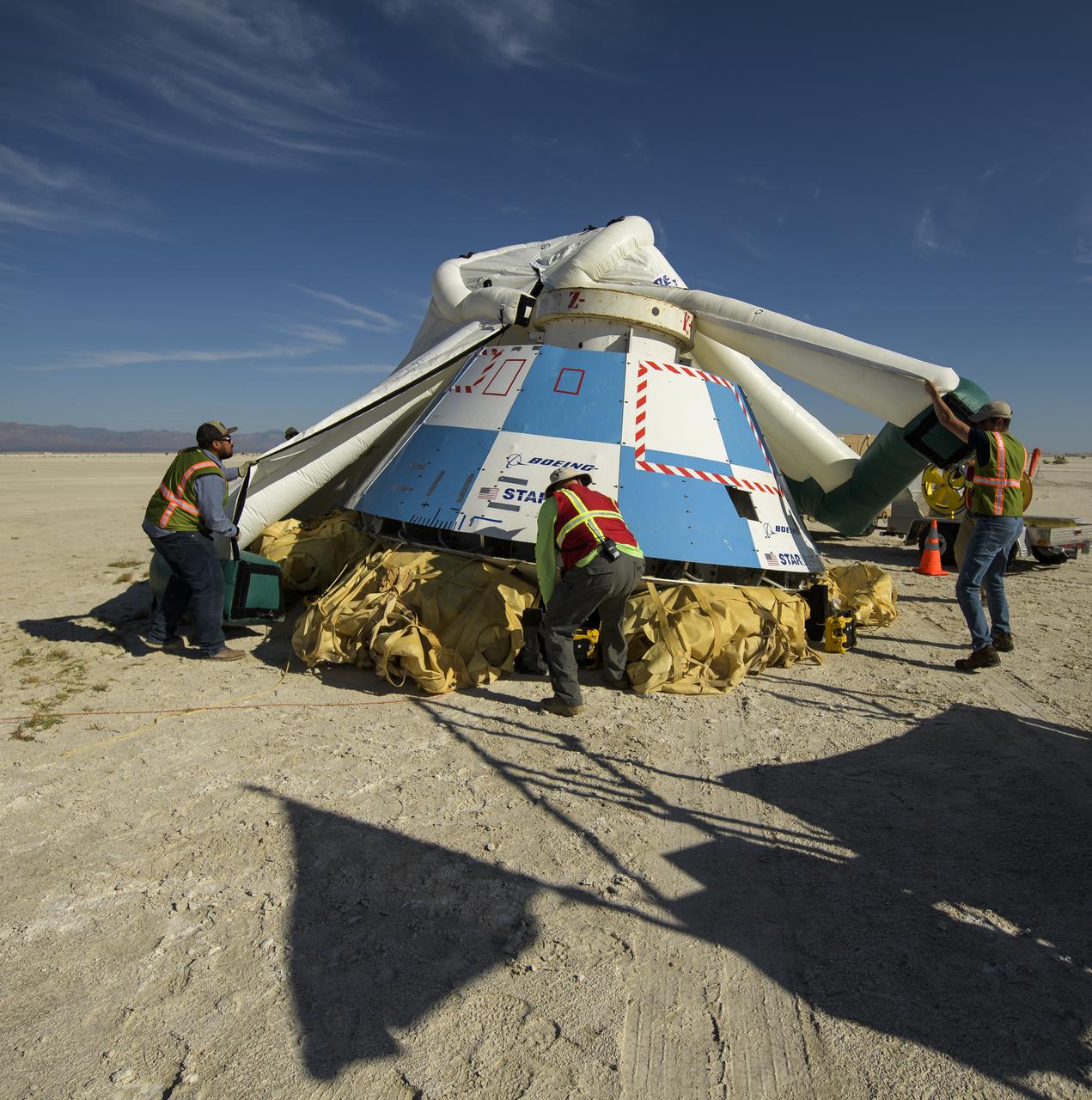
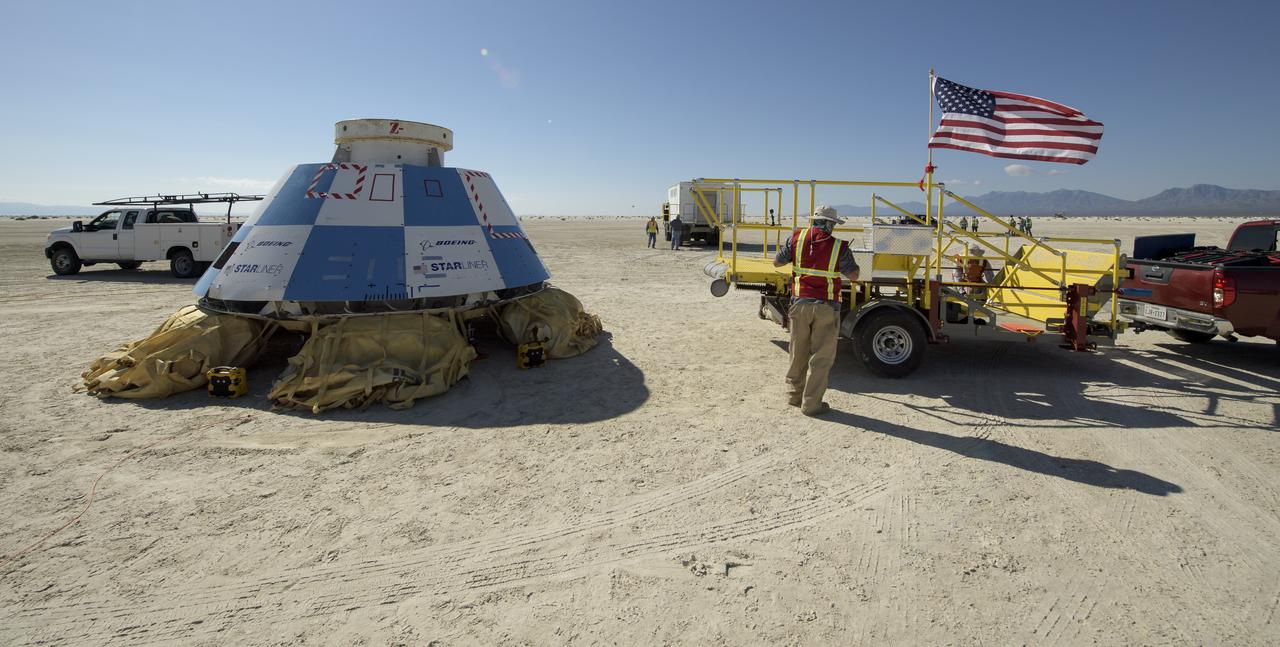
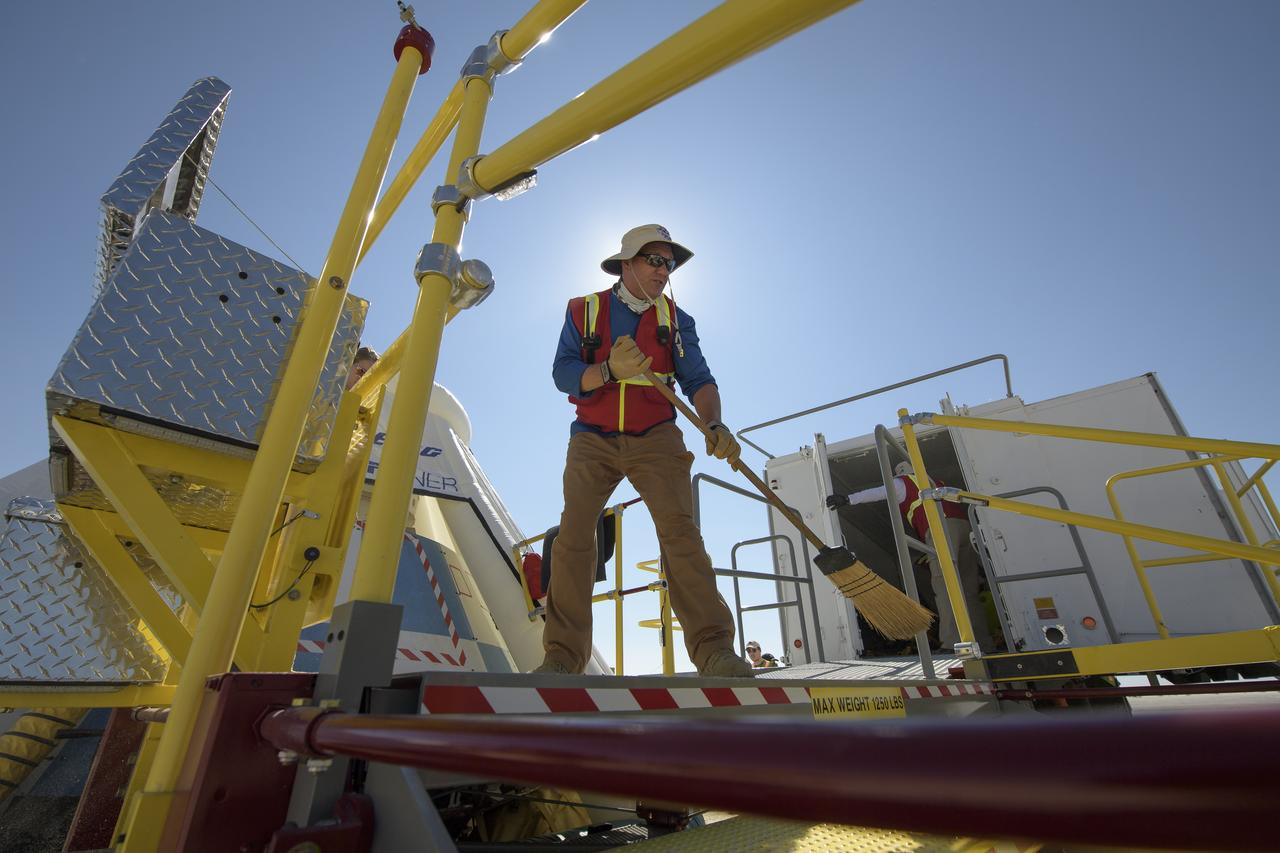
Boeing and NASA teams work around Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A member of the range safety team labels her convoy vehicle as they prepare for the landing of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
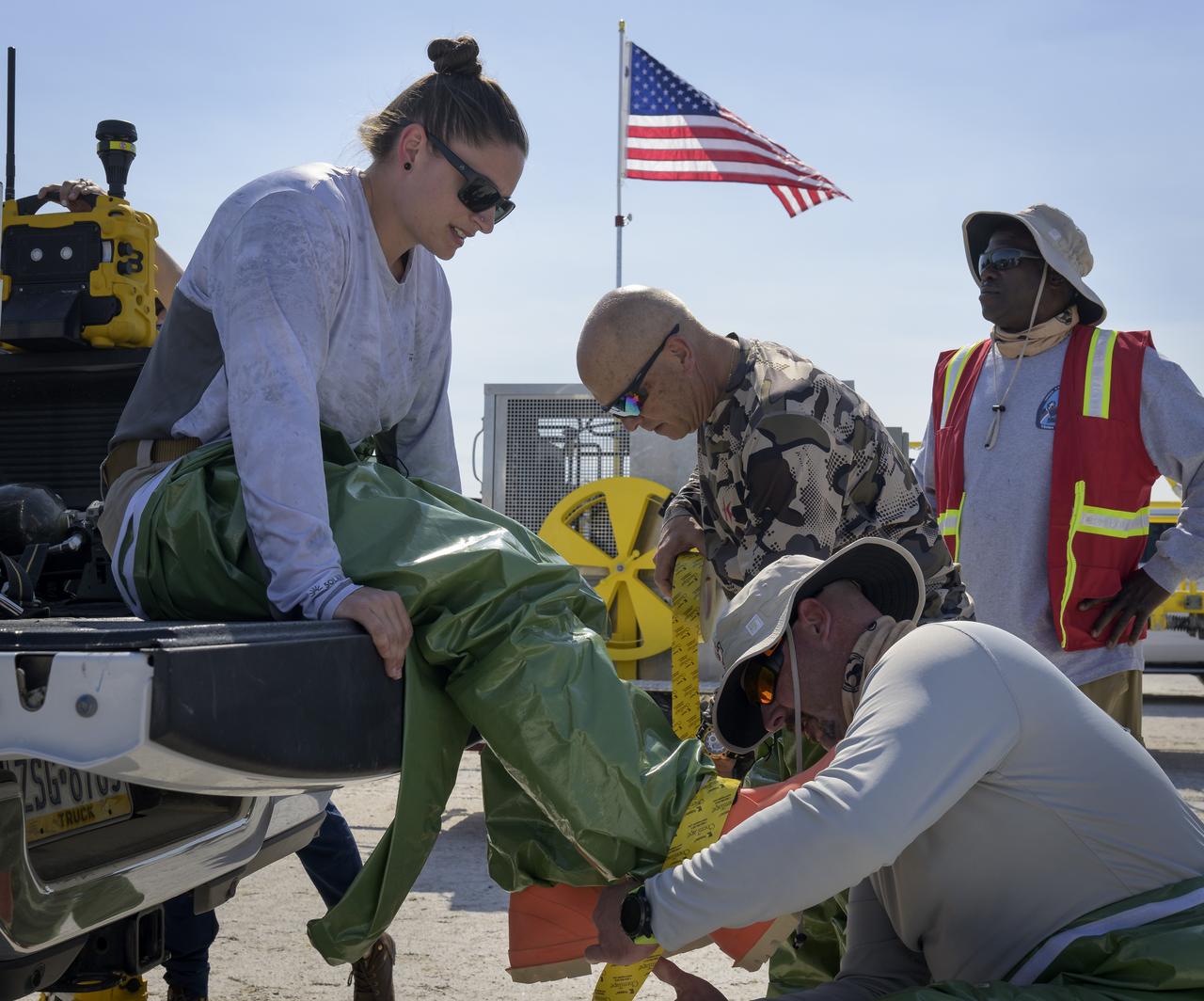

Boeing team members don hazmat suits as they prepare for the landing of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
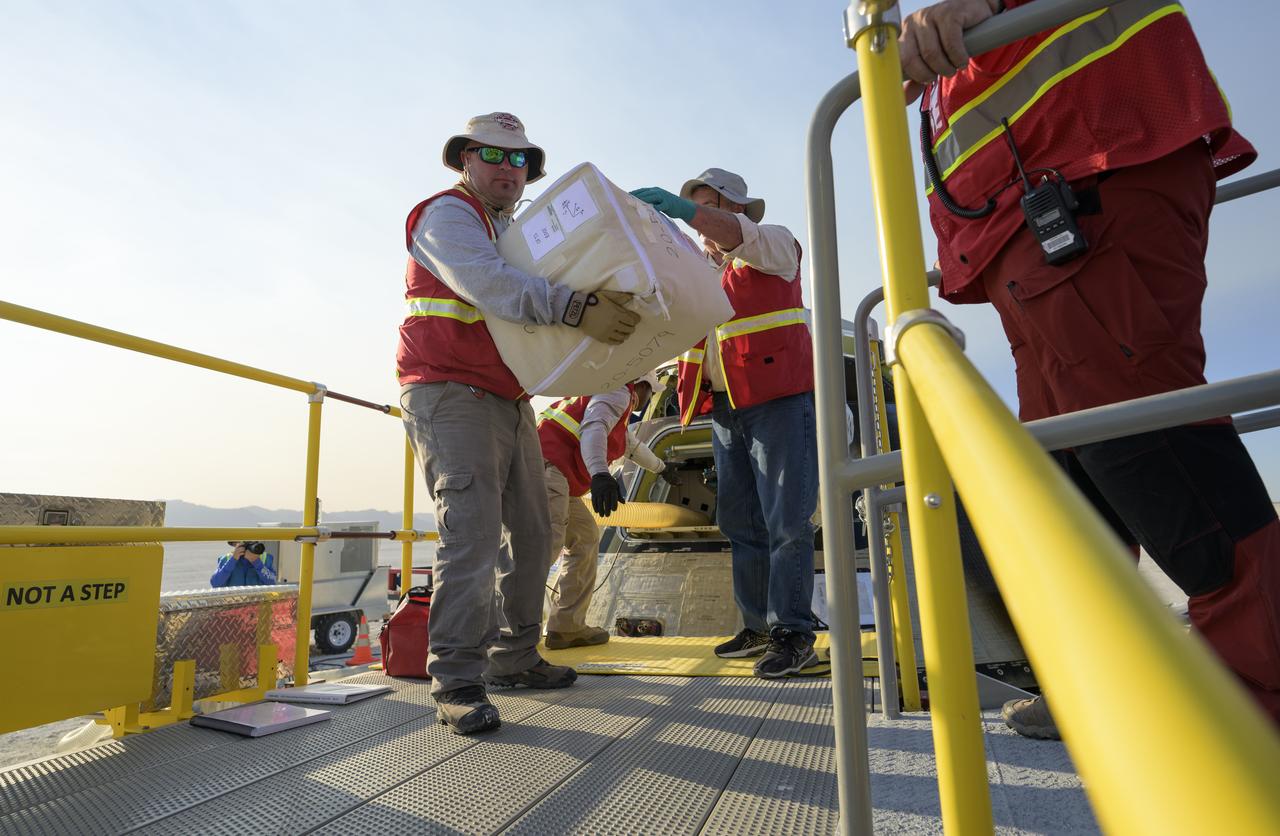

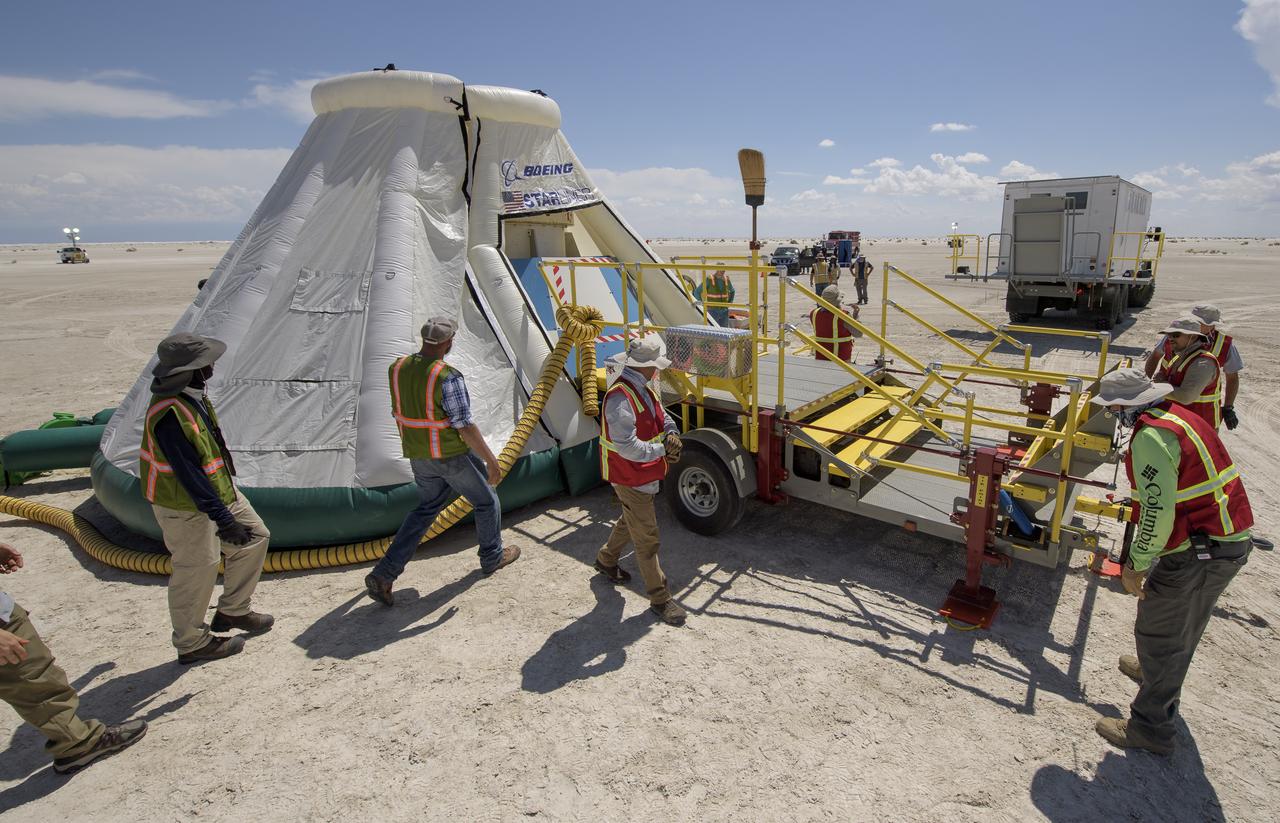
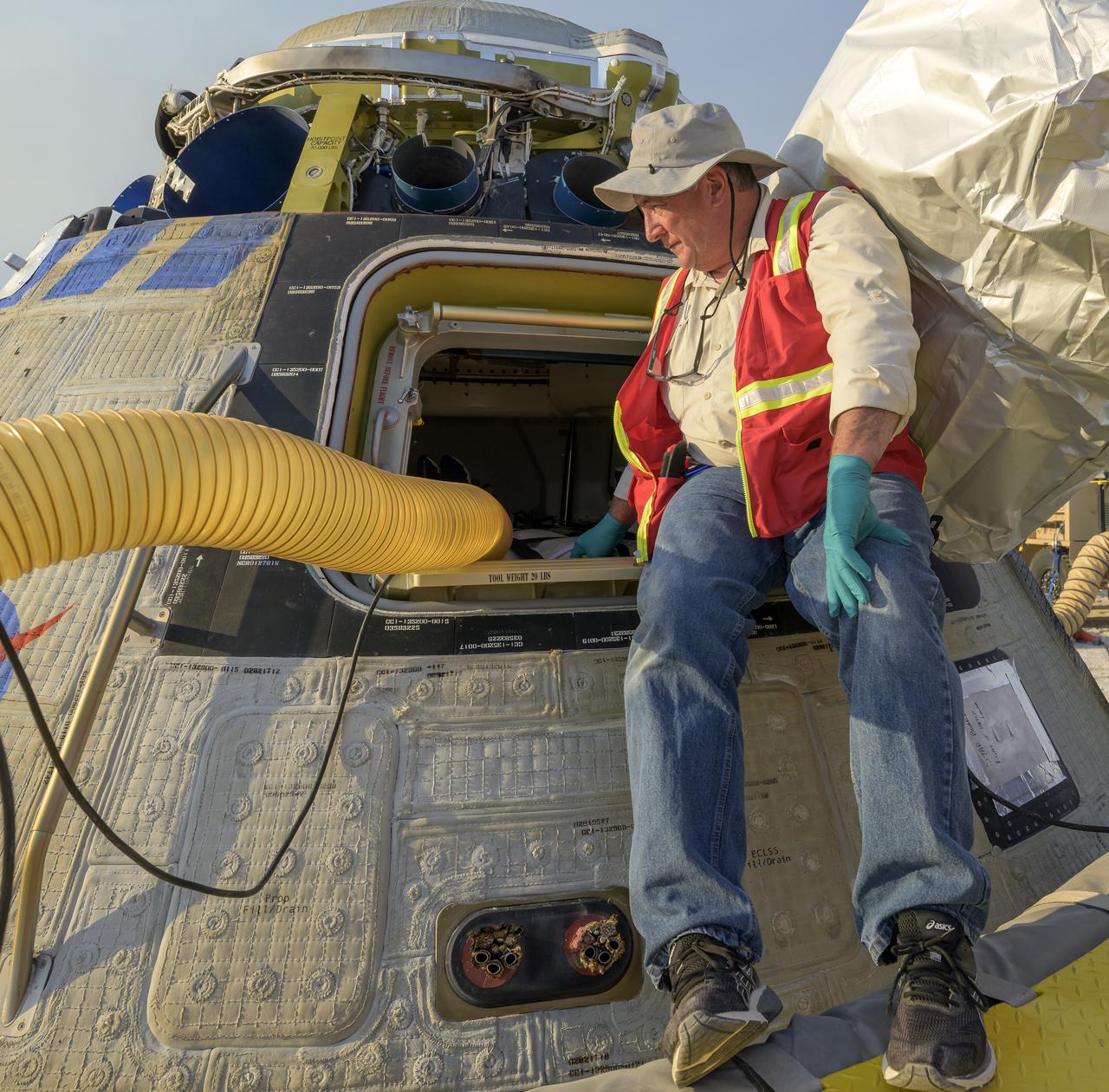
Boeing and NASA teams unload cargo from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
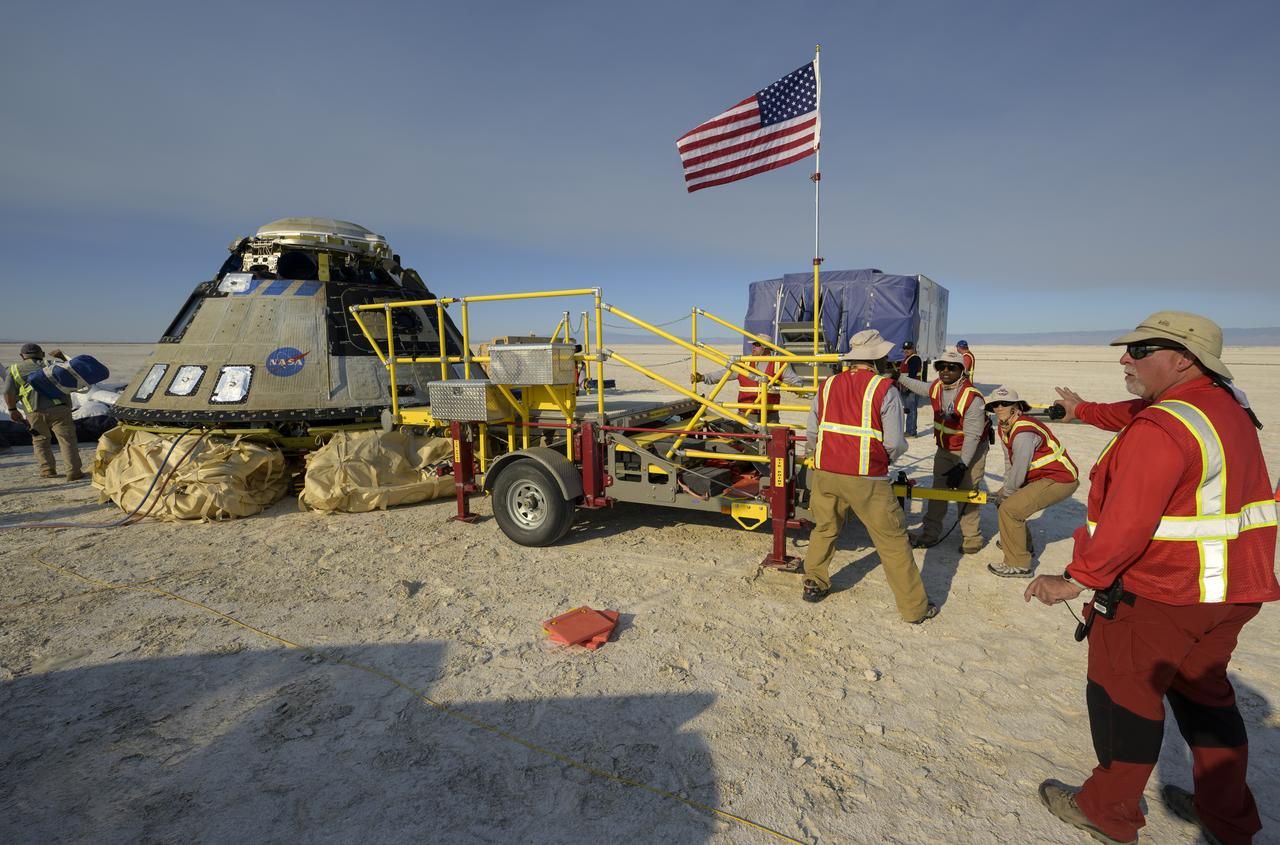

Boeing and NASA teams work around Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
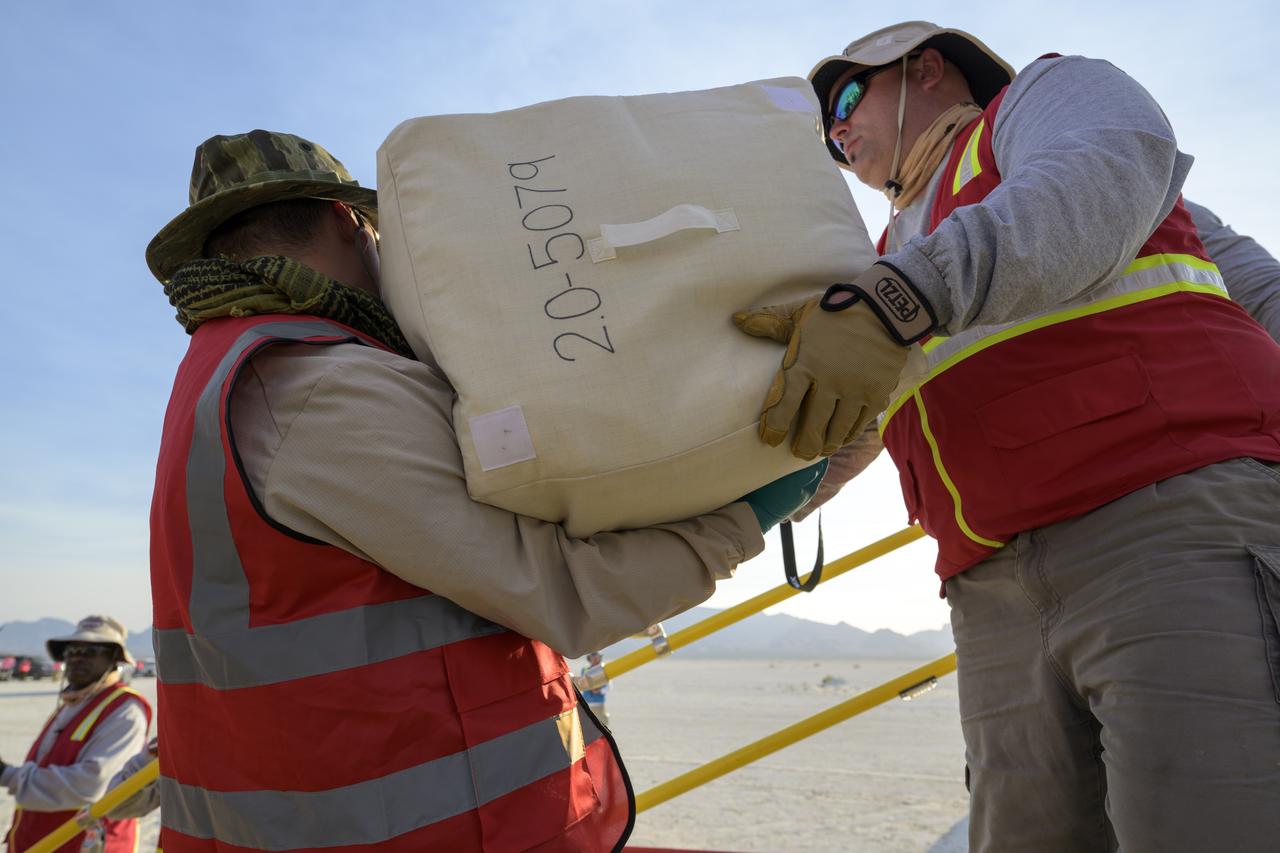

Boeing and NASA teams unload cargo from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
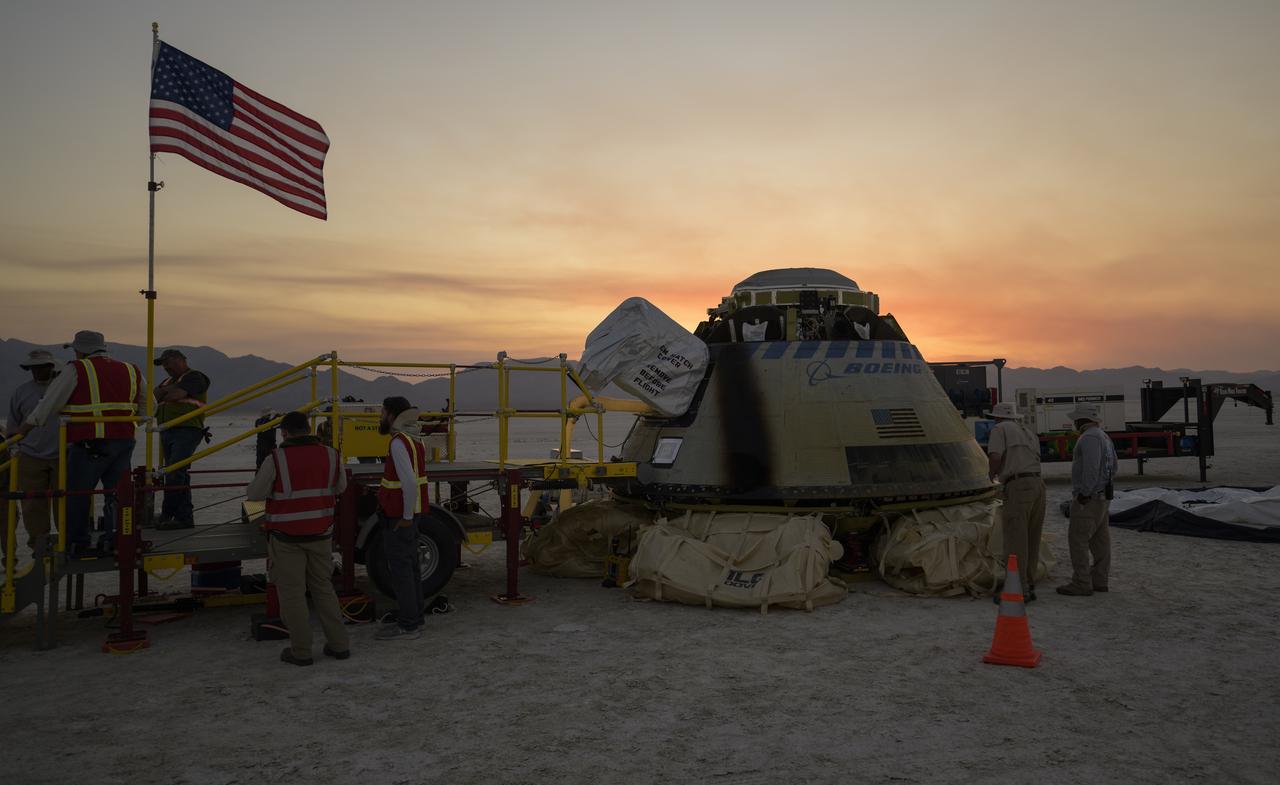

Boeing and NASA teams work around Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
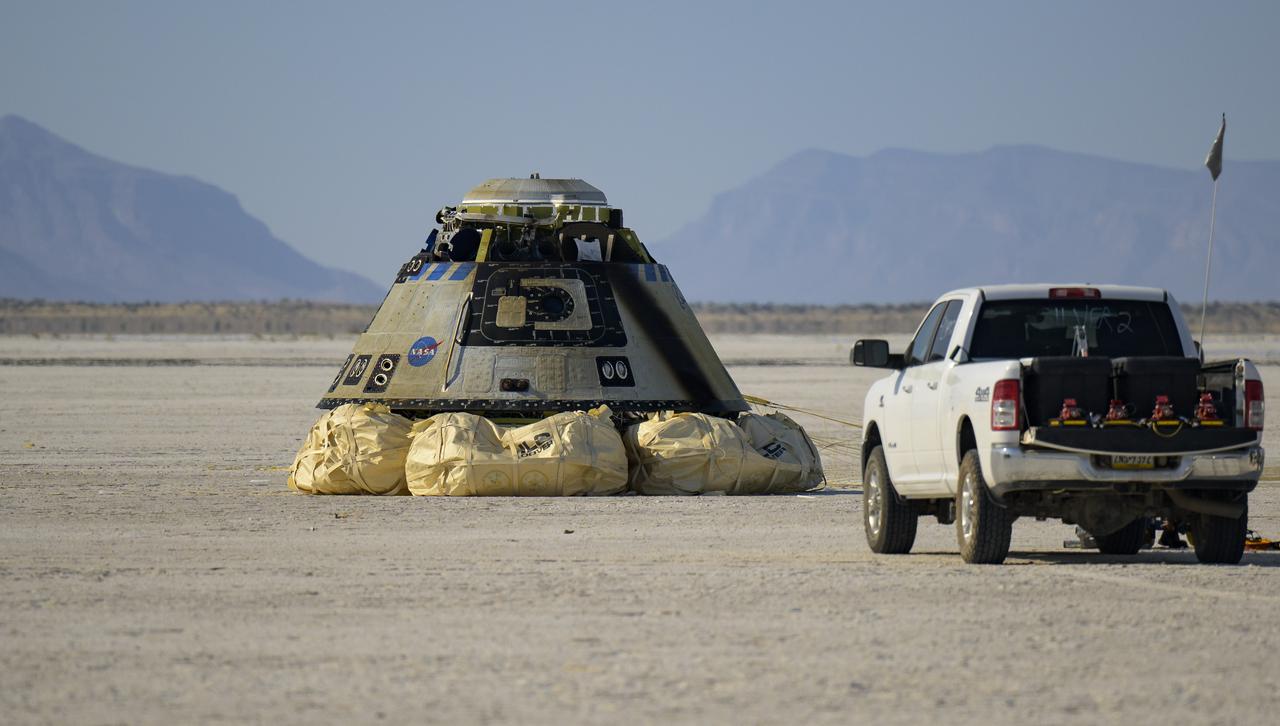

Boeing and NASA teams work around Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
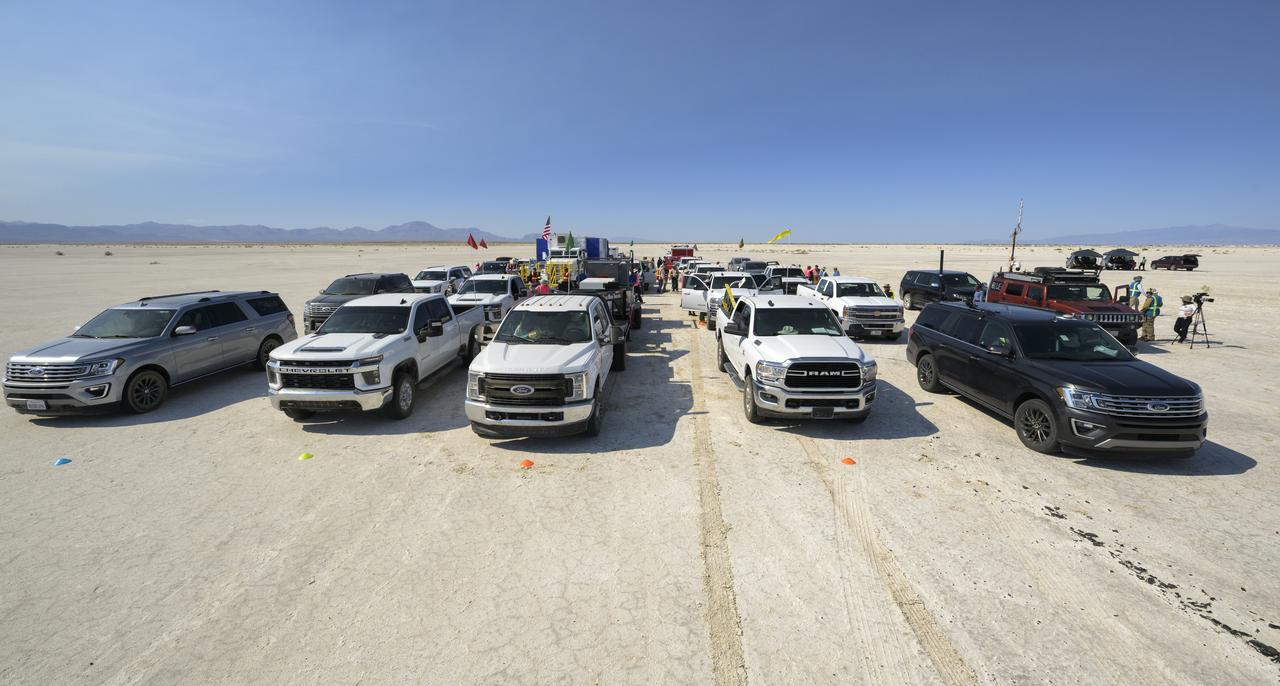

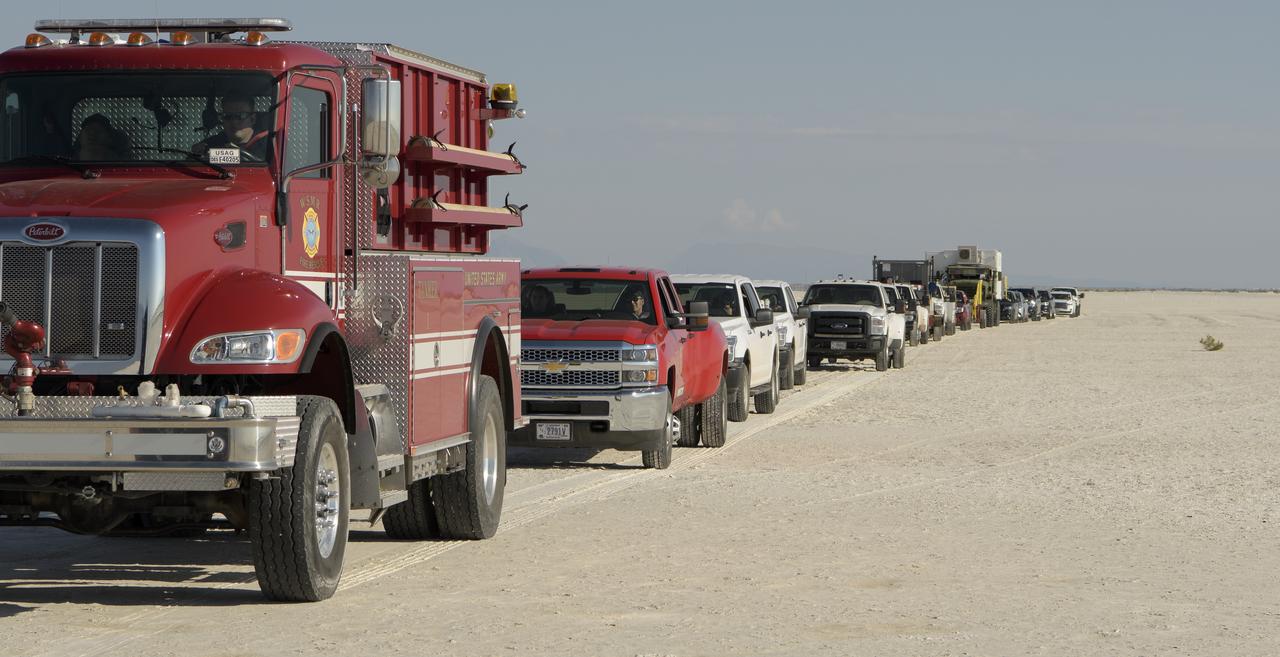
NASA and Boeing teams line up in a convoy as they prepare for the landing of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
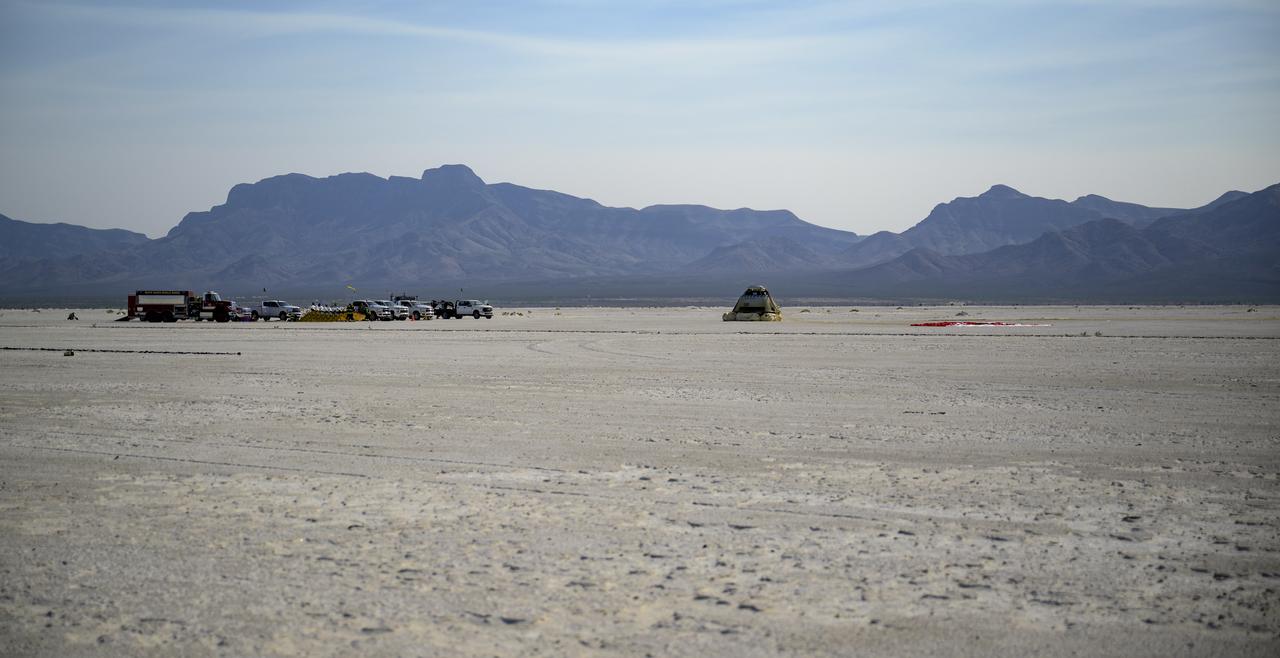

Boeing and NASA teams arrive at Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
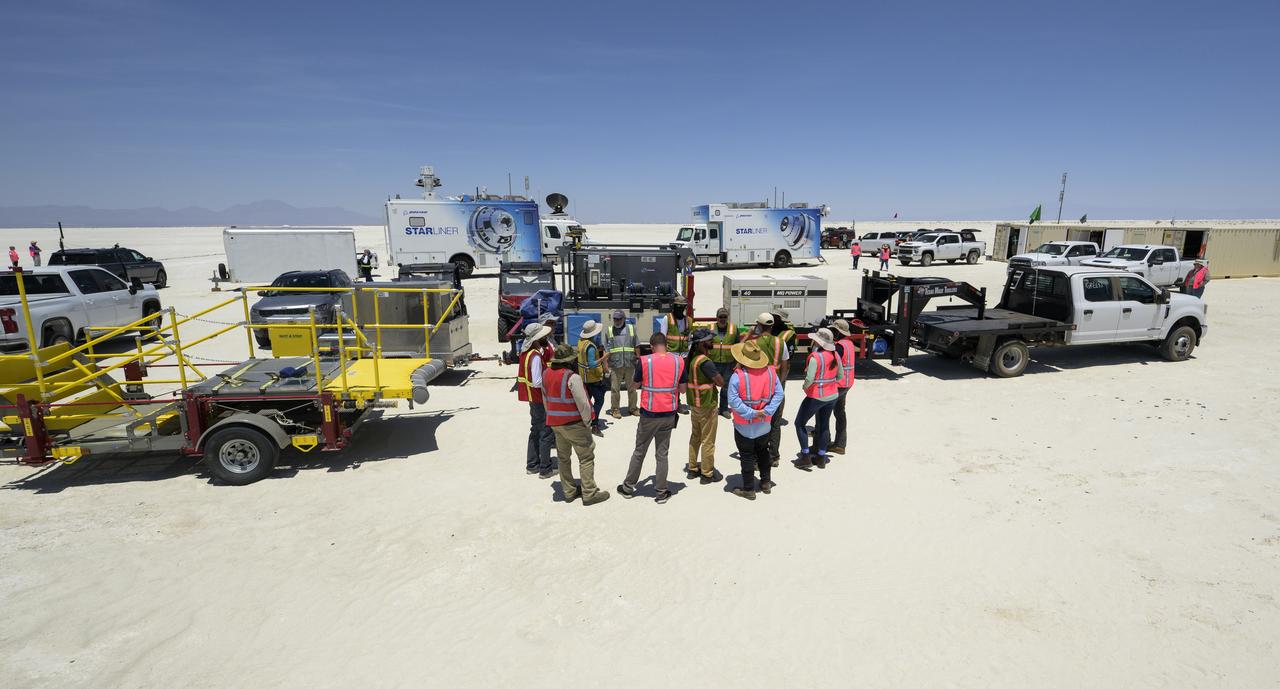

NASA and Boeing teams prepare for the landing of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
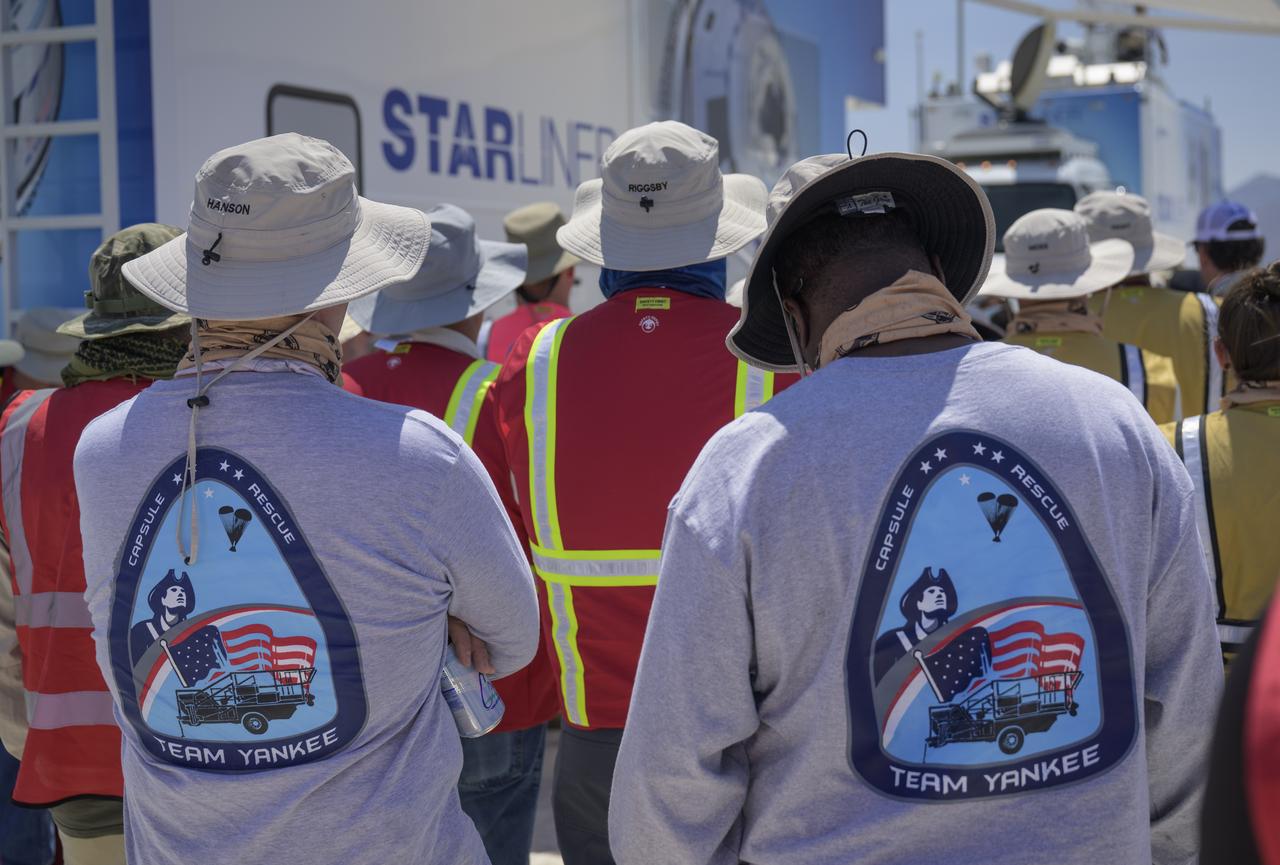

NASA and Boeing teams prepare for the landing of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
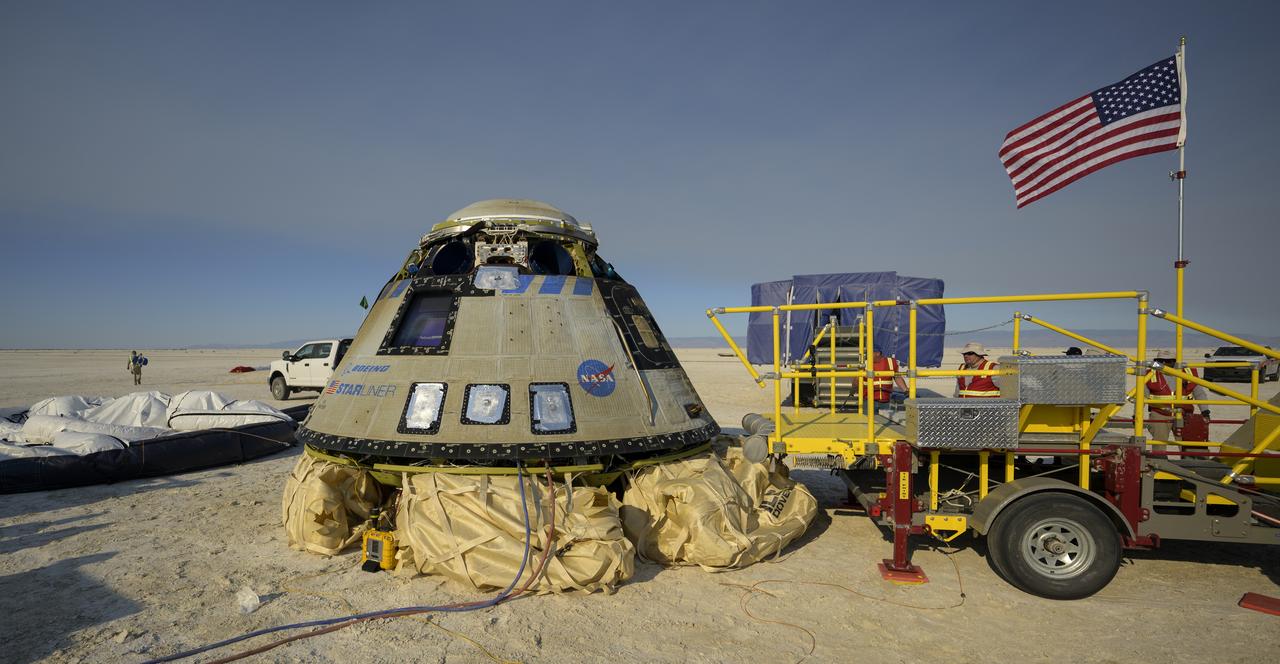

Boeing and NASA teams work around Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Boeing and NASA teams work around Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
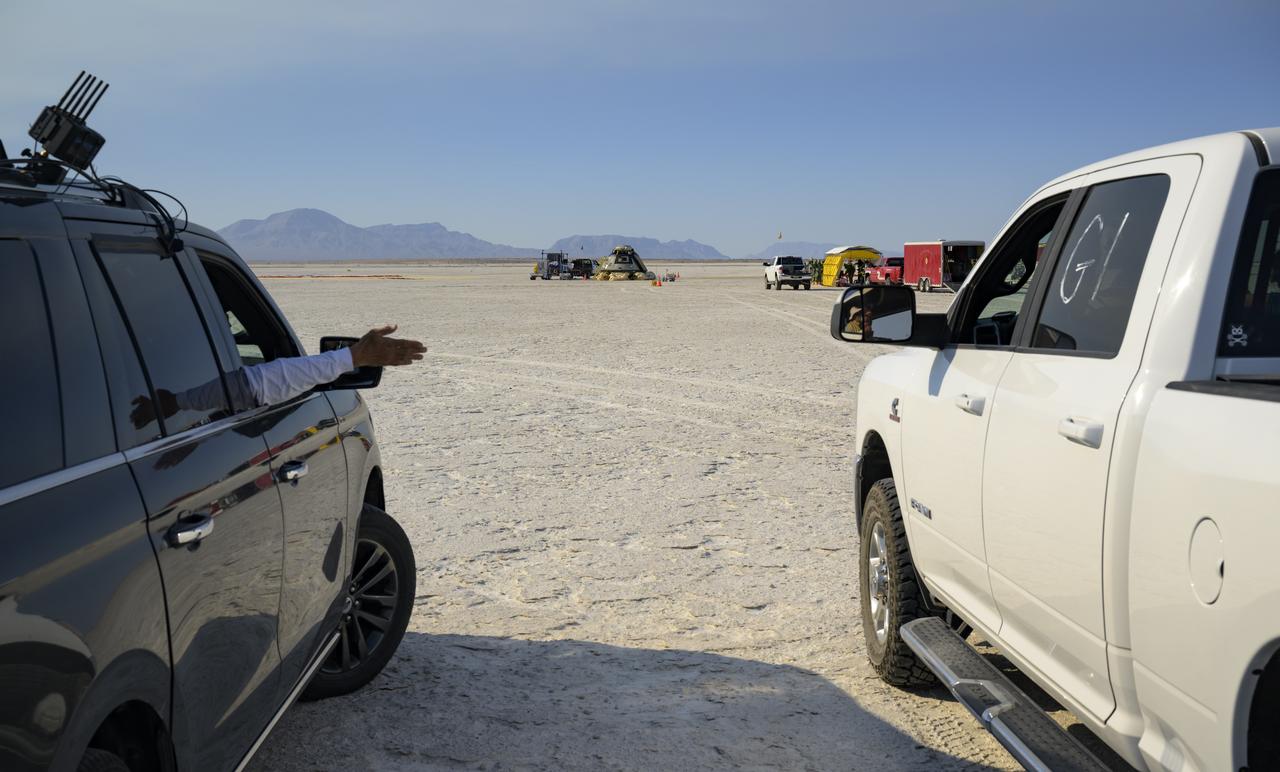

Boeing and NASA teams work around Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
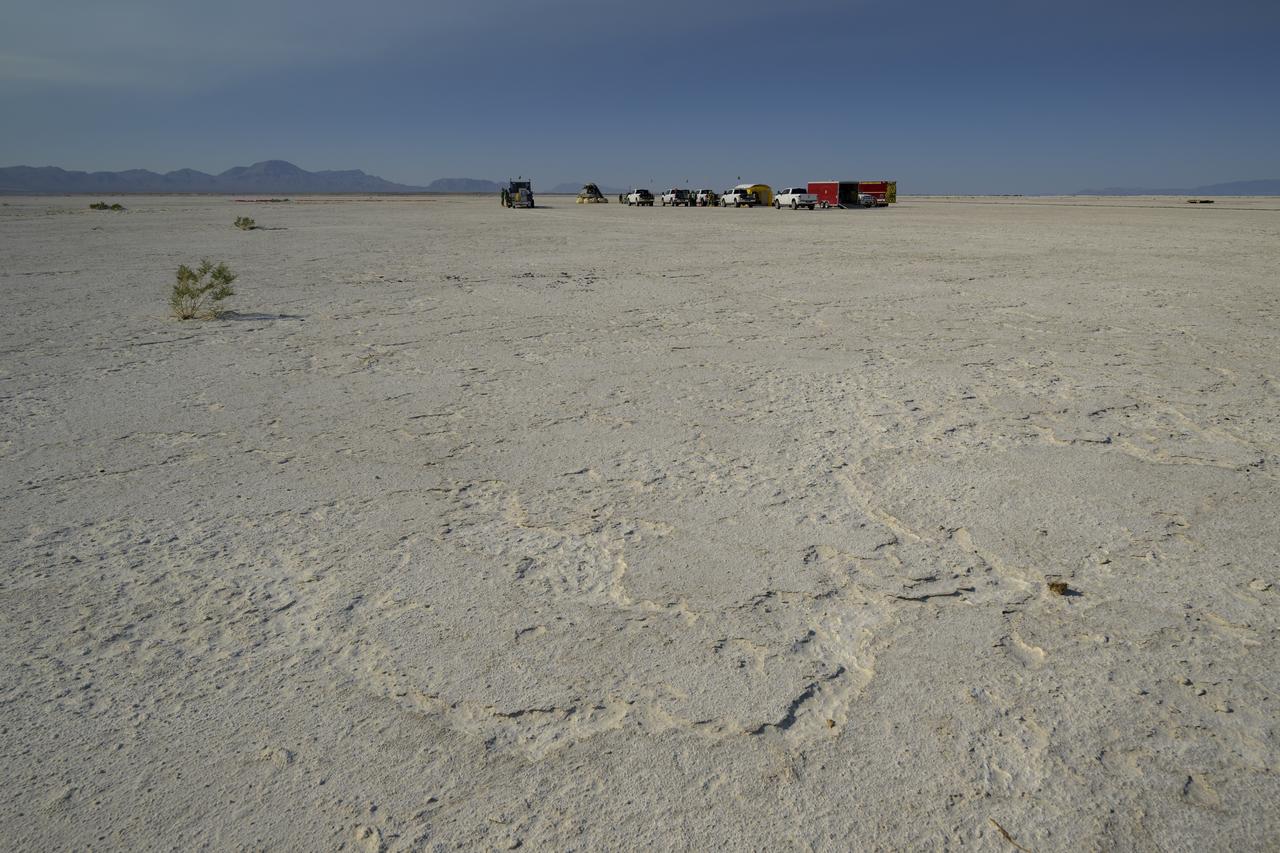

Boeing and NASA teams work around Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Boeing team members don hazmat suits as they prepare for the landing of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Boeing and NASA teams work around Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Boeing and NASA teams work around Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
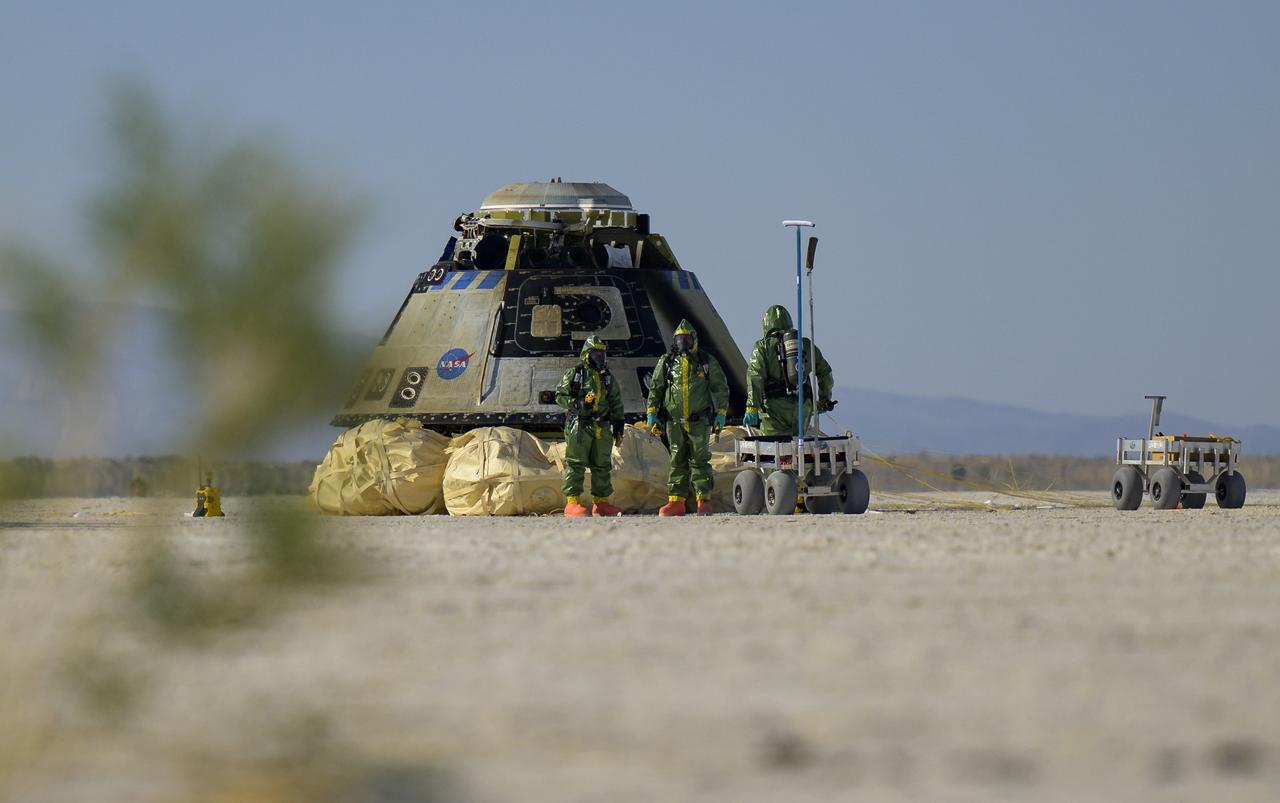

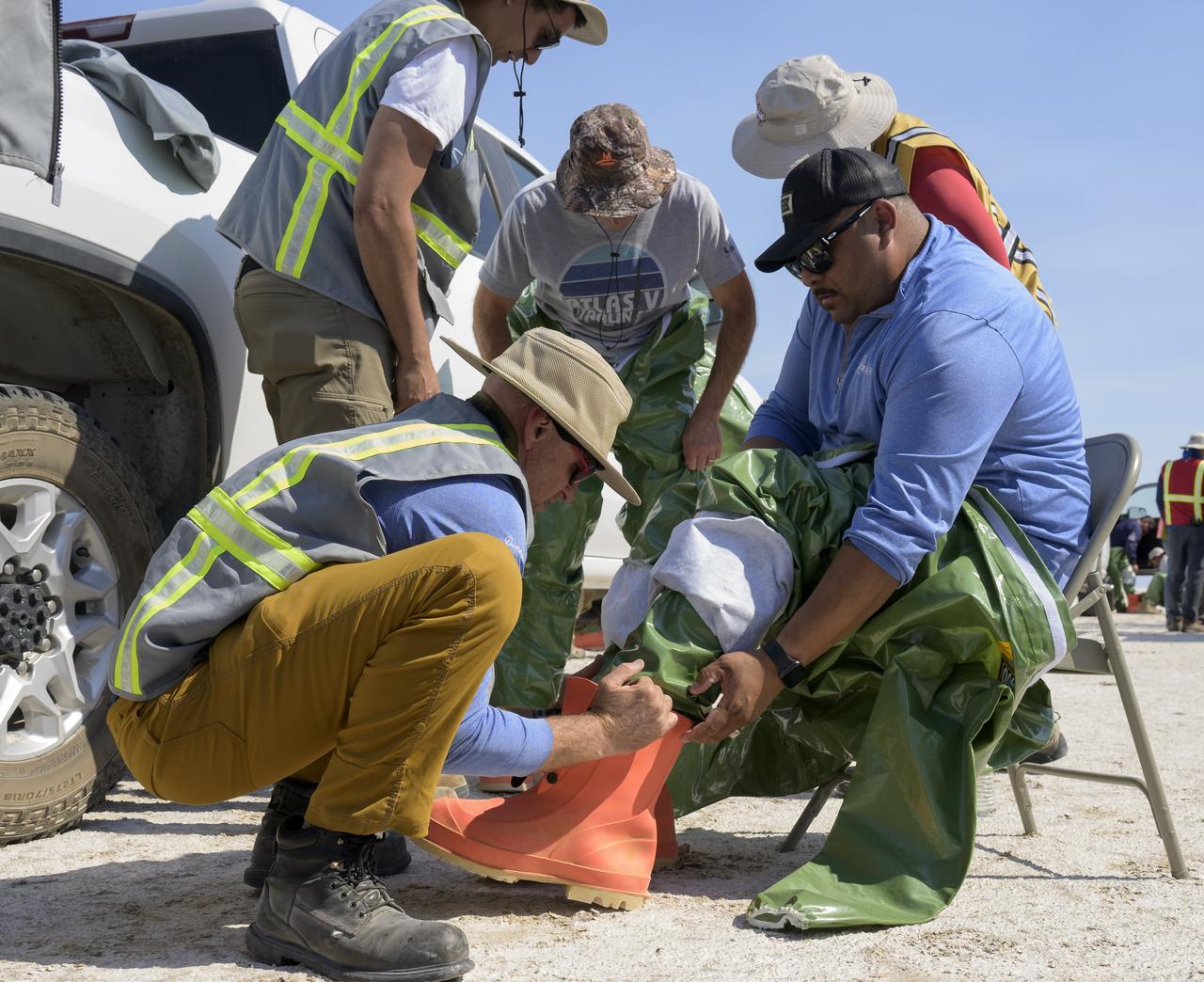
Boeing hazmat teams work around Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
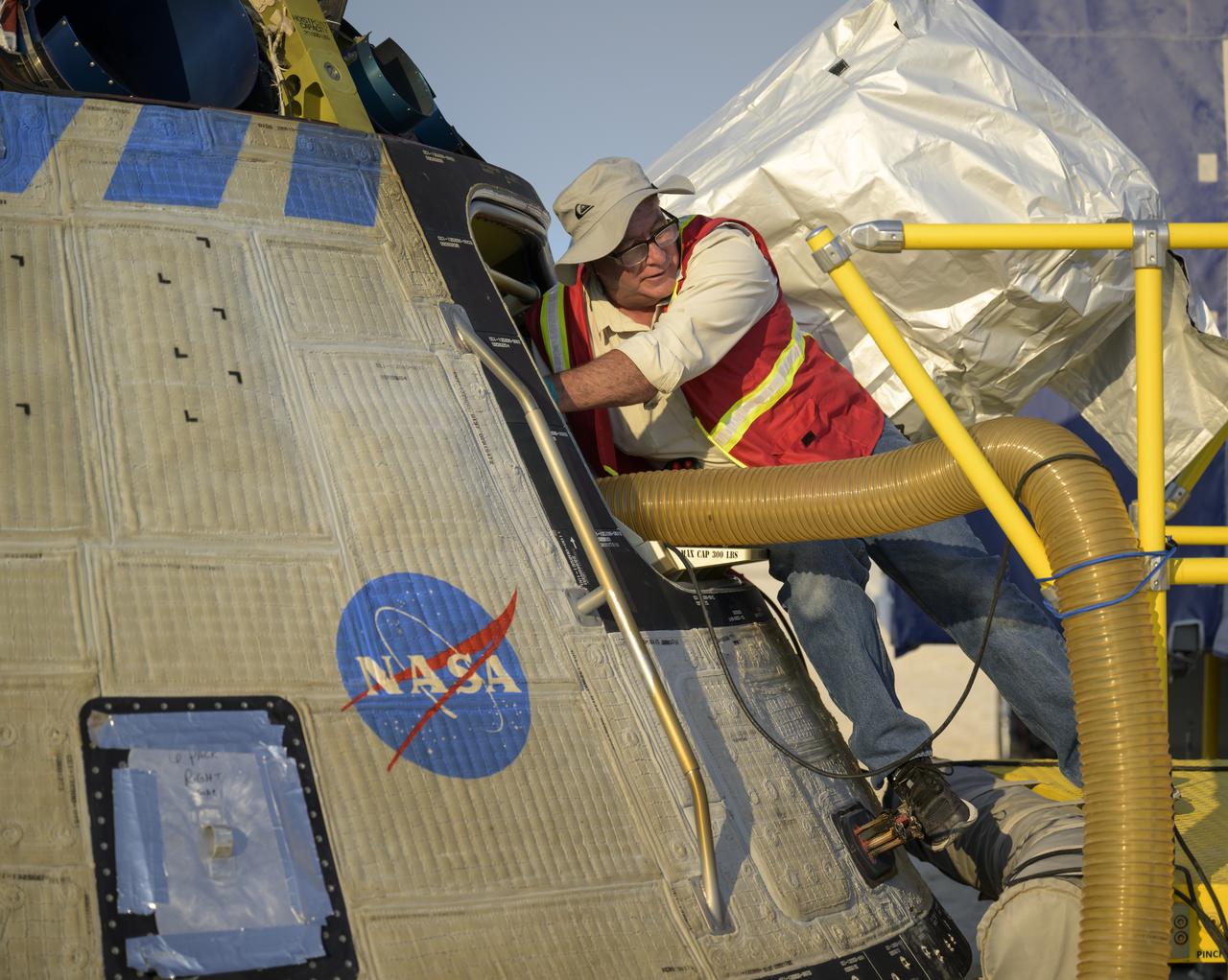

Boeing and NASA teams work around Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
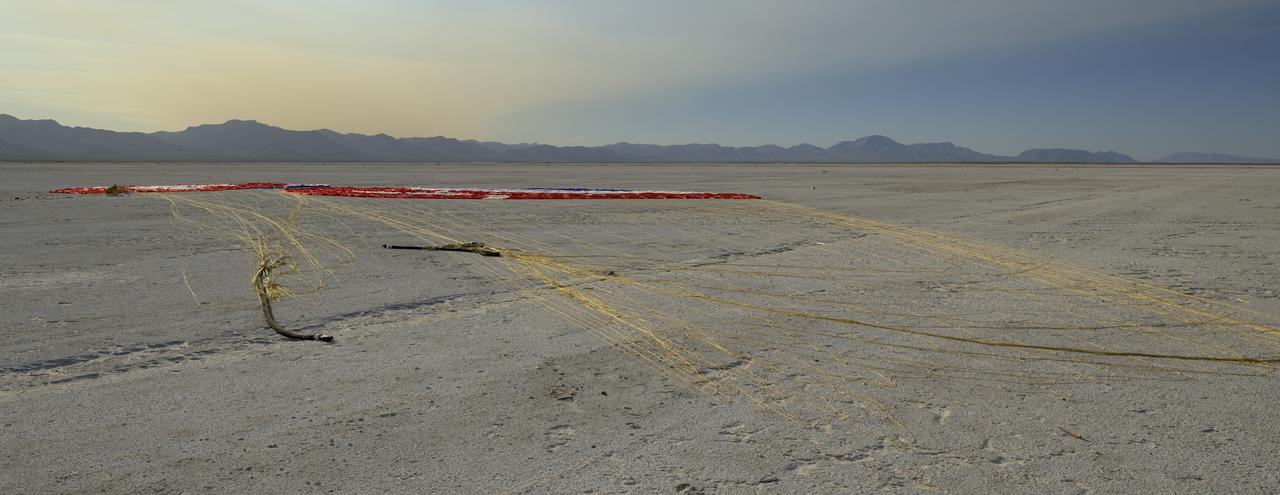

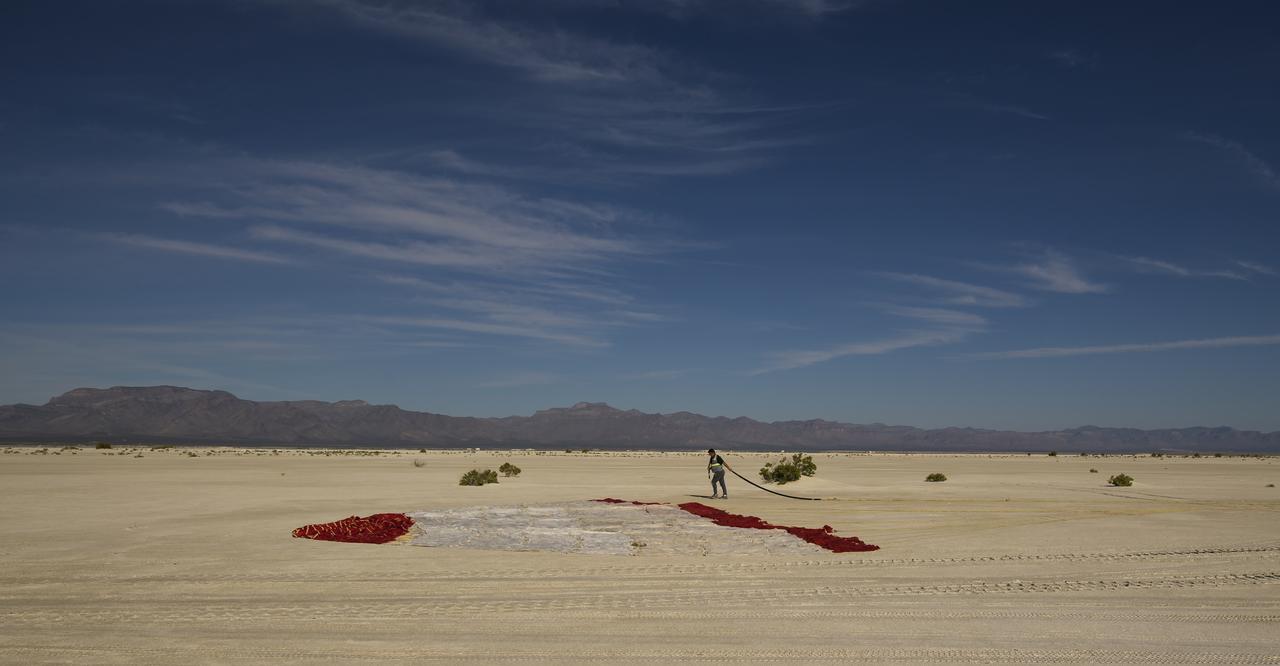
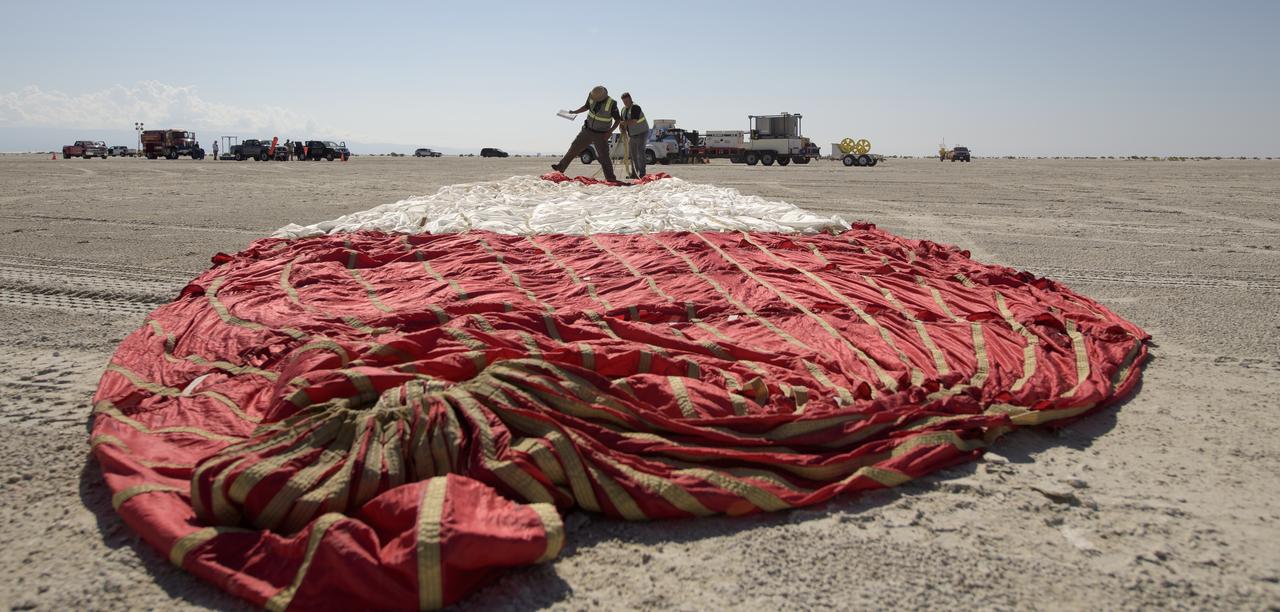
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner parachute is seen after the spacecraft landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
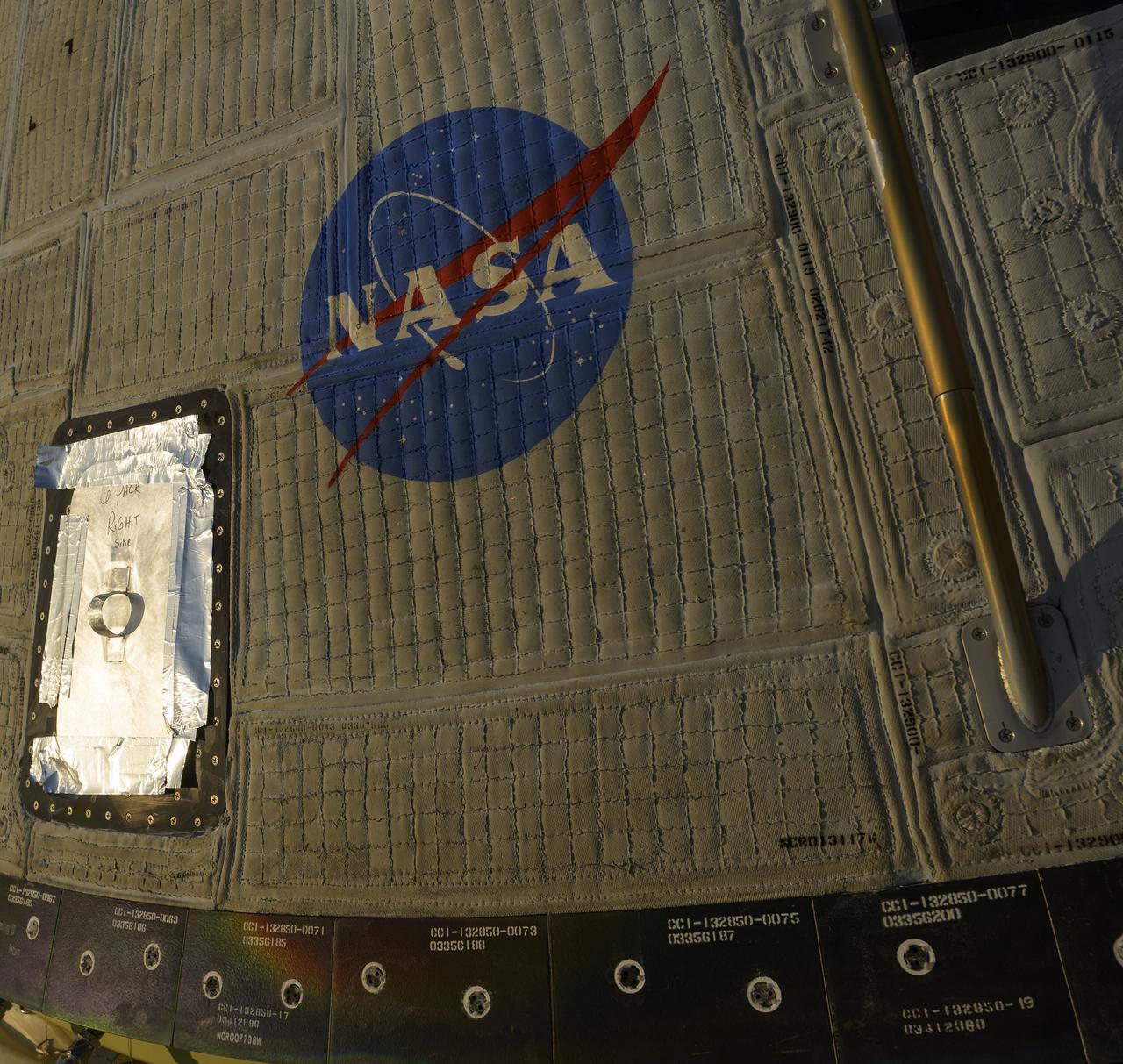

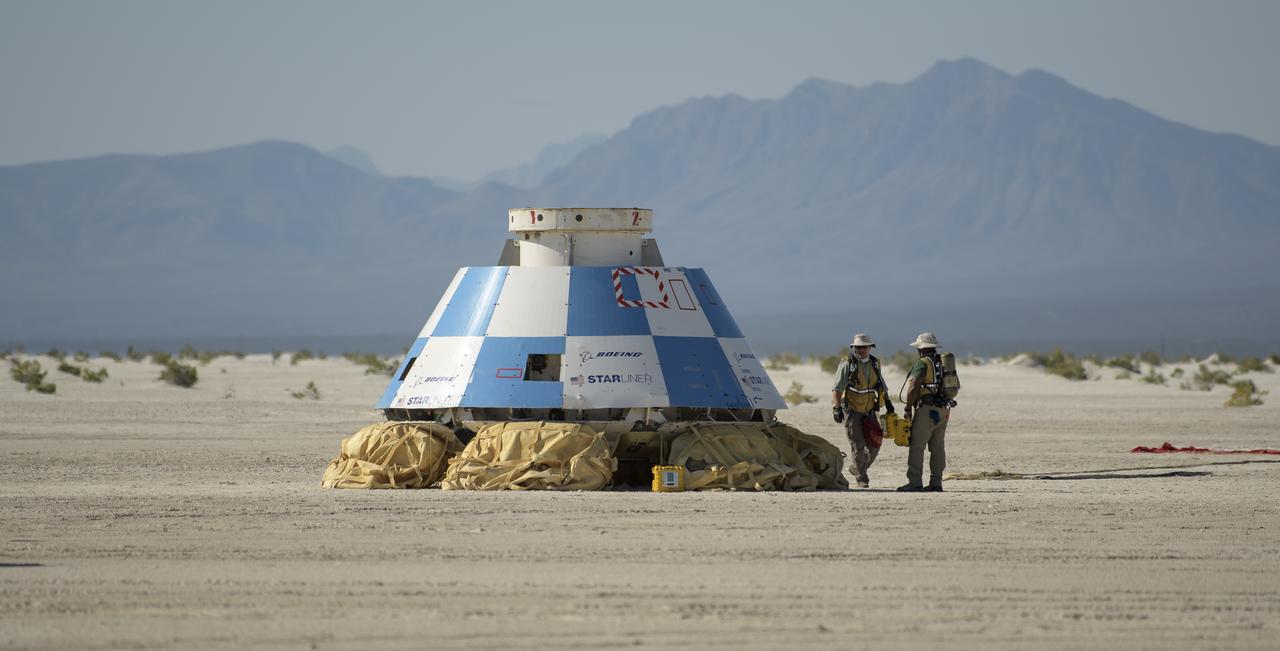
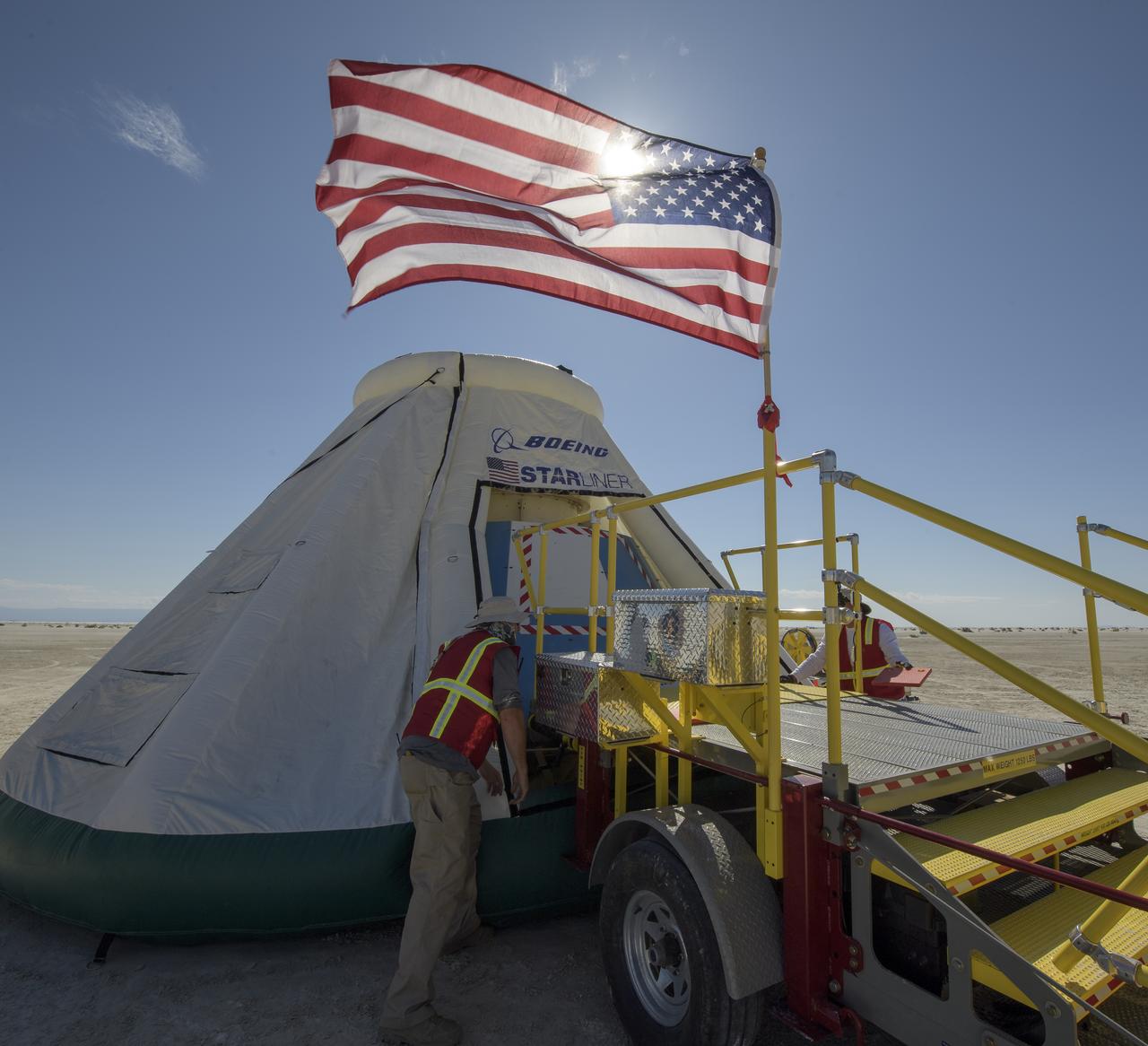
Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is seen after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
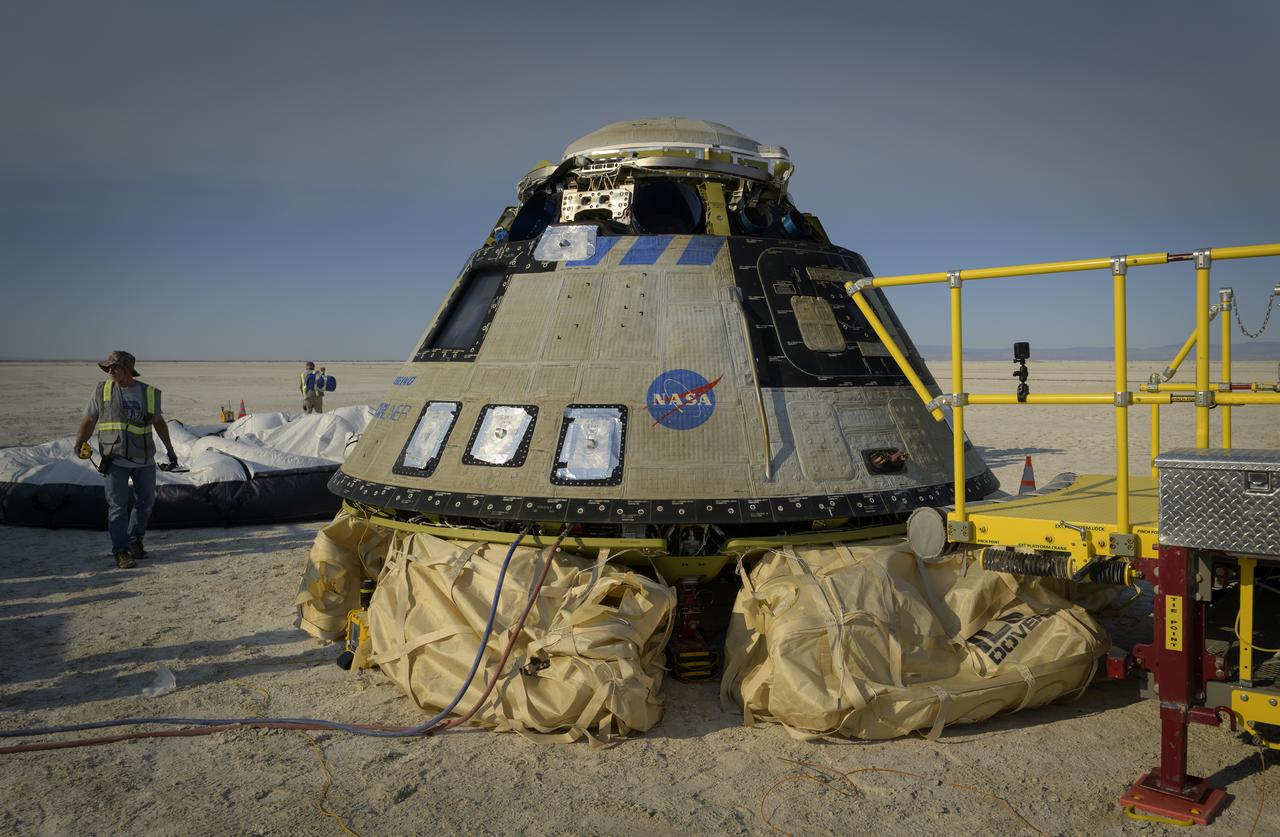

Boeing and NASA teams work around Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Boeing hazmat teams work around Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
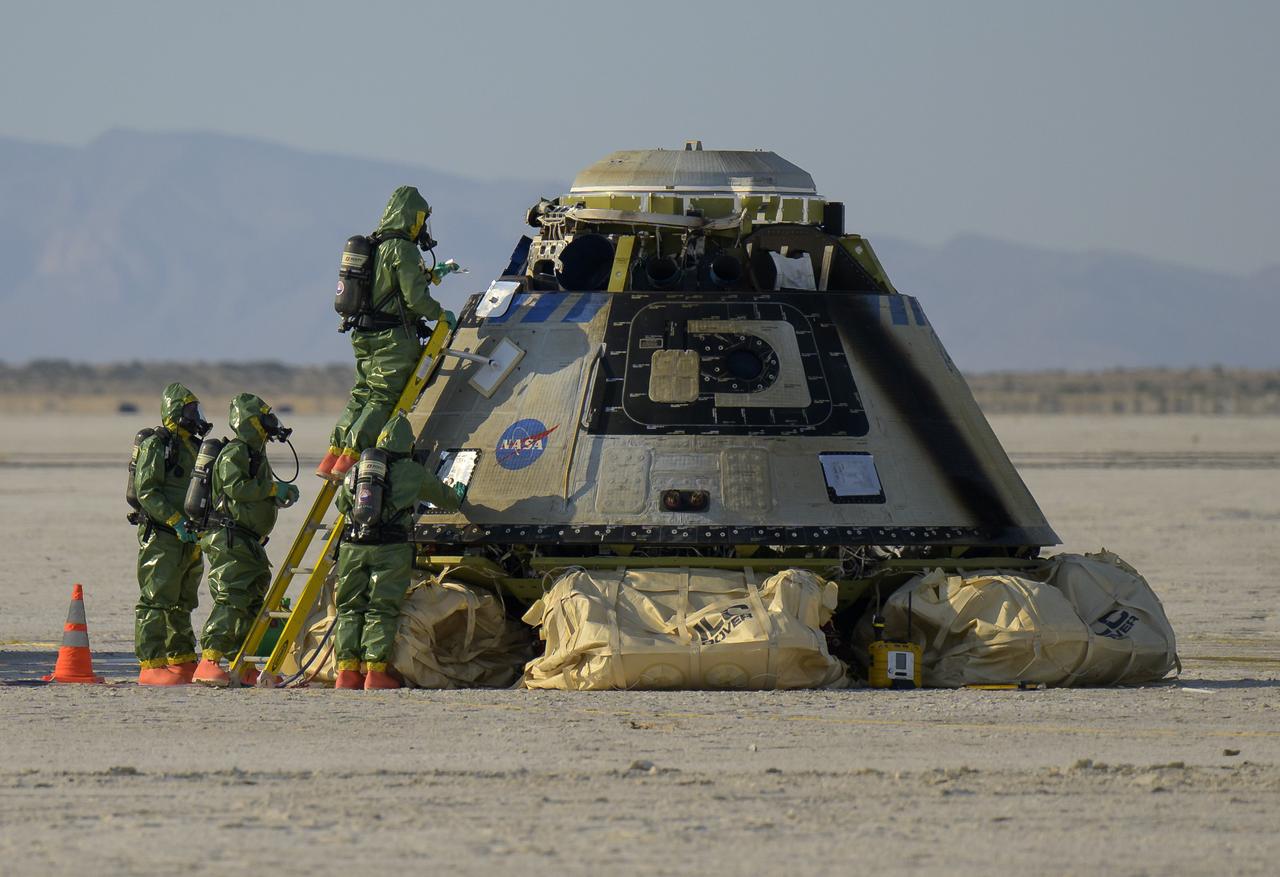

Boeing and NASA teams work around Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
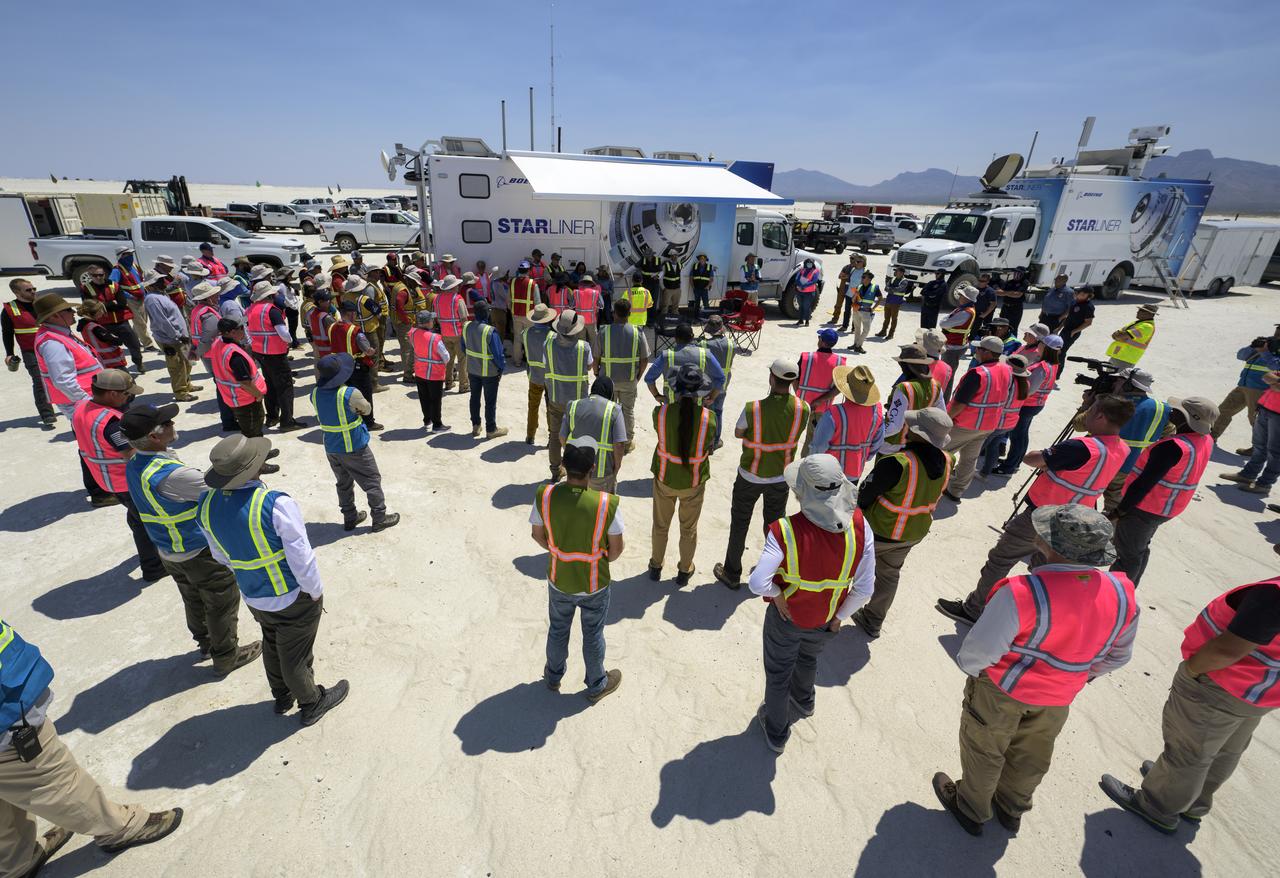

NASA and Boeing teams prepare for the landing of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

An engineer works on the Parachute Deployment Device of the Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator test vehicle in this image taken at the Missile Assembly Building at the U.S. Navy Pacific Missile Range Facility in Kauai, Hawaii.
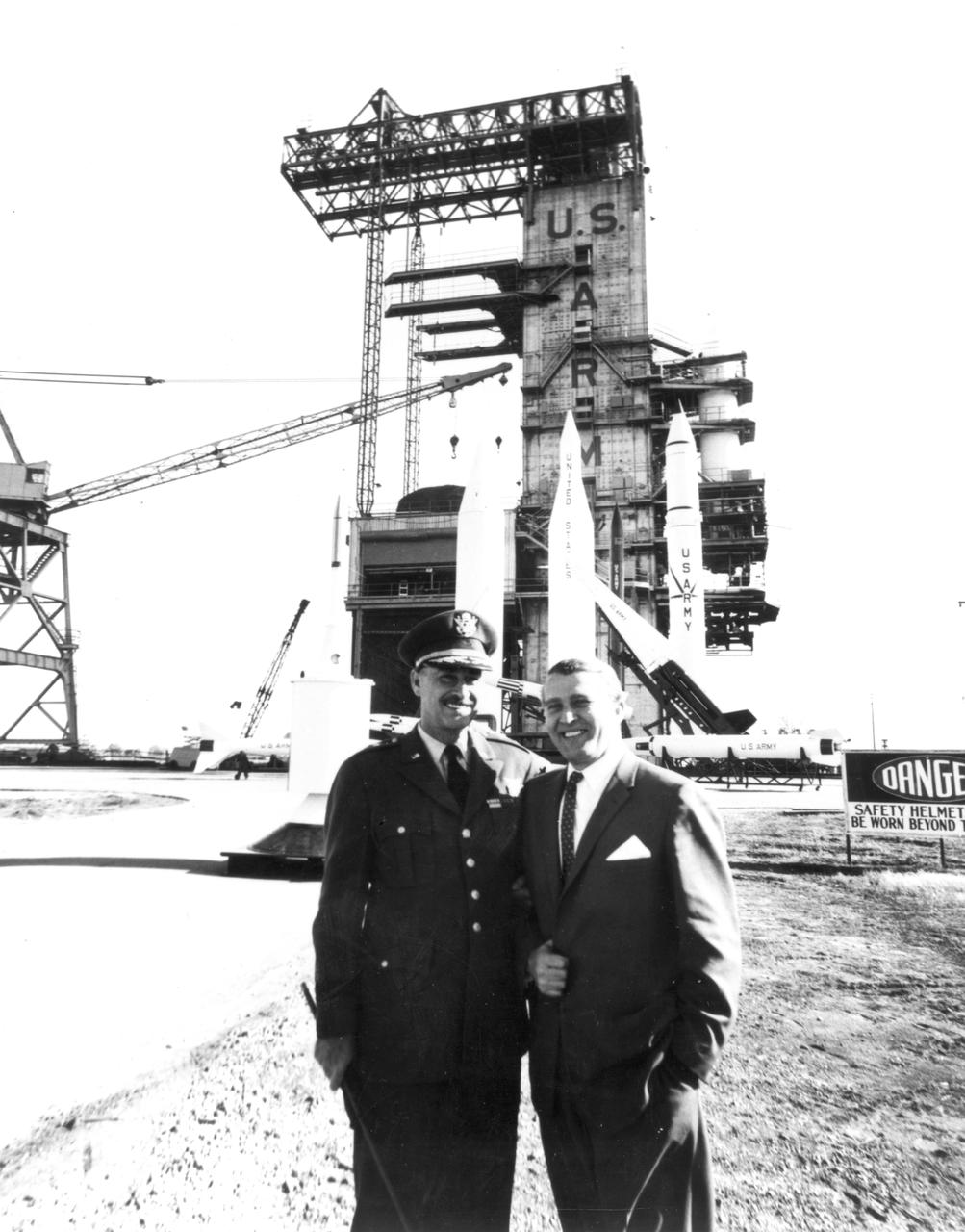

Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC) Director, Dr. Wernher von Braun, is pictured here with Army Ballistic Missile Agency’s (ABMA) Commanding General, J.B. Medaris, before a display of Army missles at the ABMA test lab.
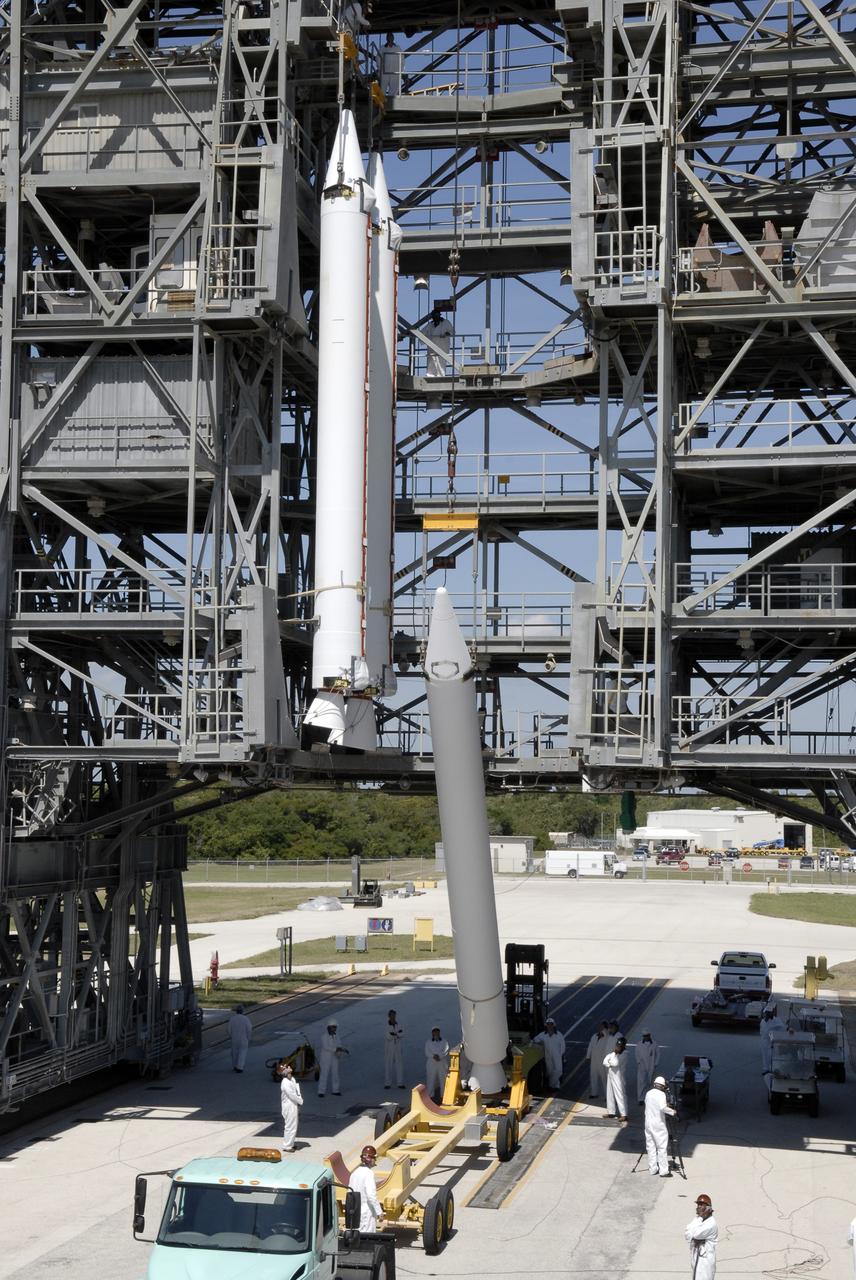

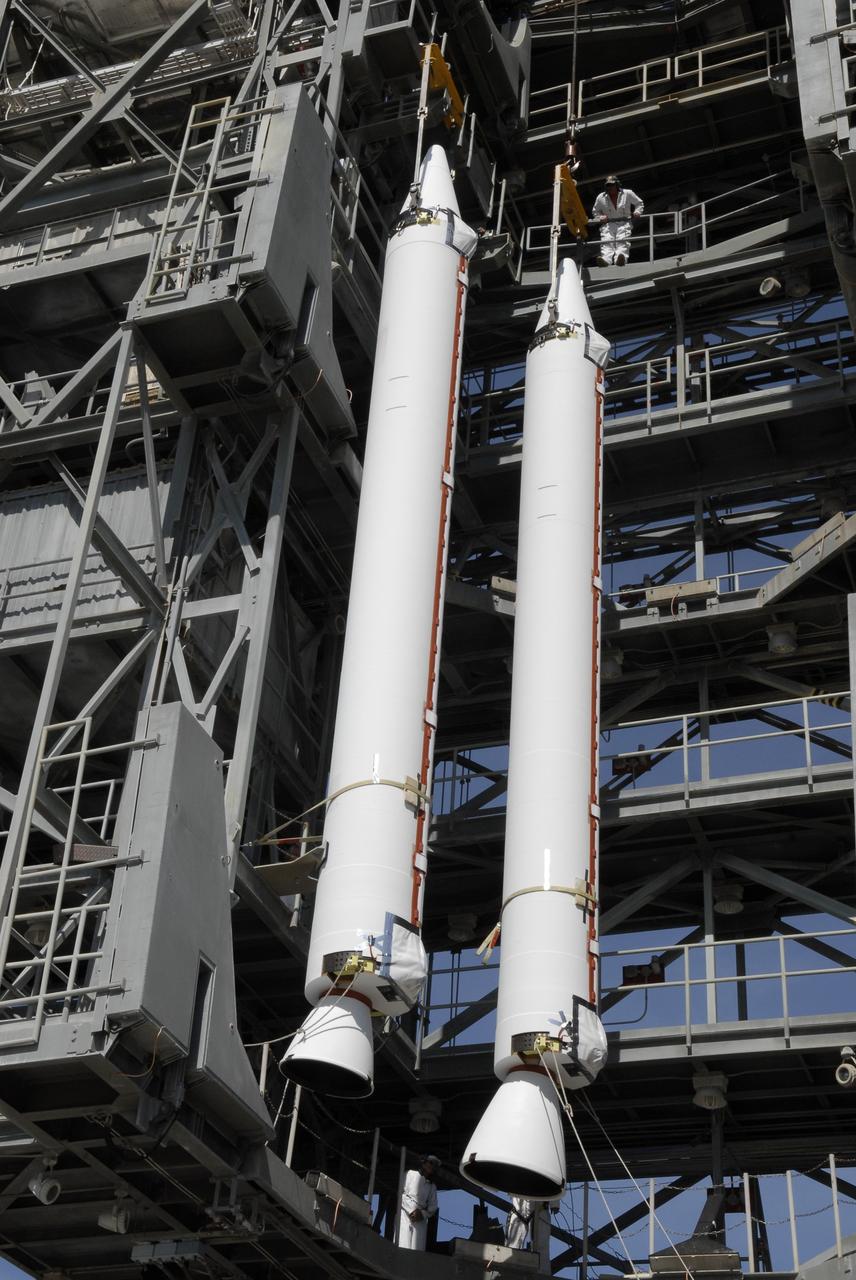
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a third solid rocket booster is raised from the transporter. It will join the others in the mobile service tower for attachment to the Delta II rocket that will launch the STSS Demonstrator spacecraft. The STSS Demonstrators is a midcourse tracking technology demonstrator and is part of an evolving ballistic missile defense system. STSS is capable of tracking objects after boost phase and provides trajectory information to other sensors. It will be launched by NASA for the Missile Defense Agency on July 29. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett