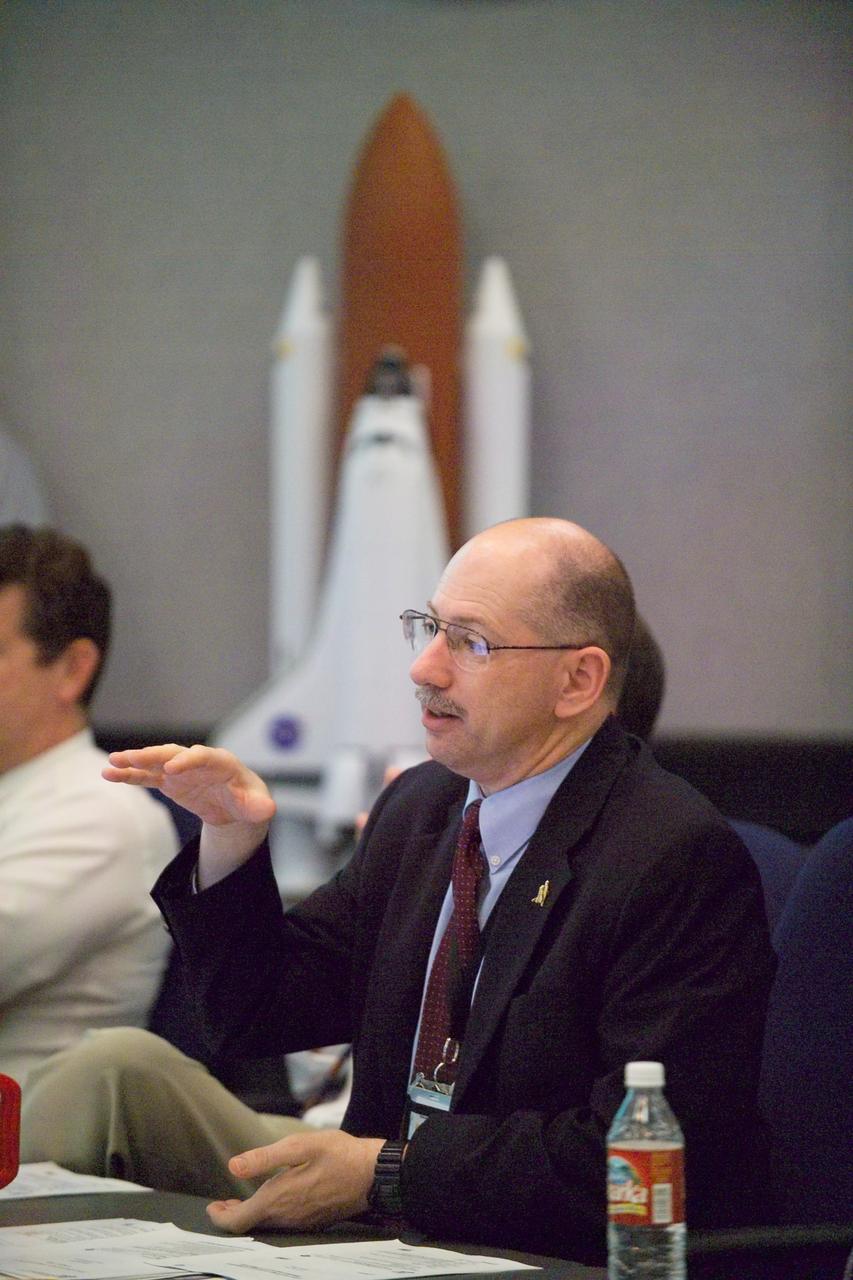

JSC2005-E-32012 (4 August 2005) --- John Muratore, Manager of Space Shuttle Systems Engineering & Integration Office, discusses a key STS-114 issue during the Mission Management Team (MMT) session of the afternoon of August 4. The MMT meets daily in Houston's Mission Control Center.
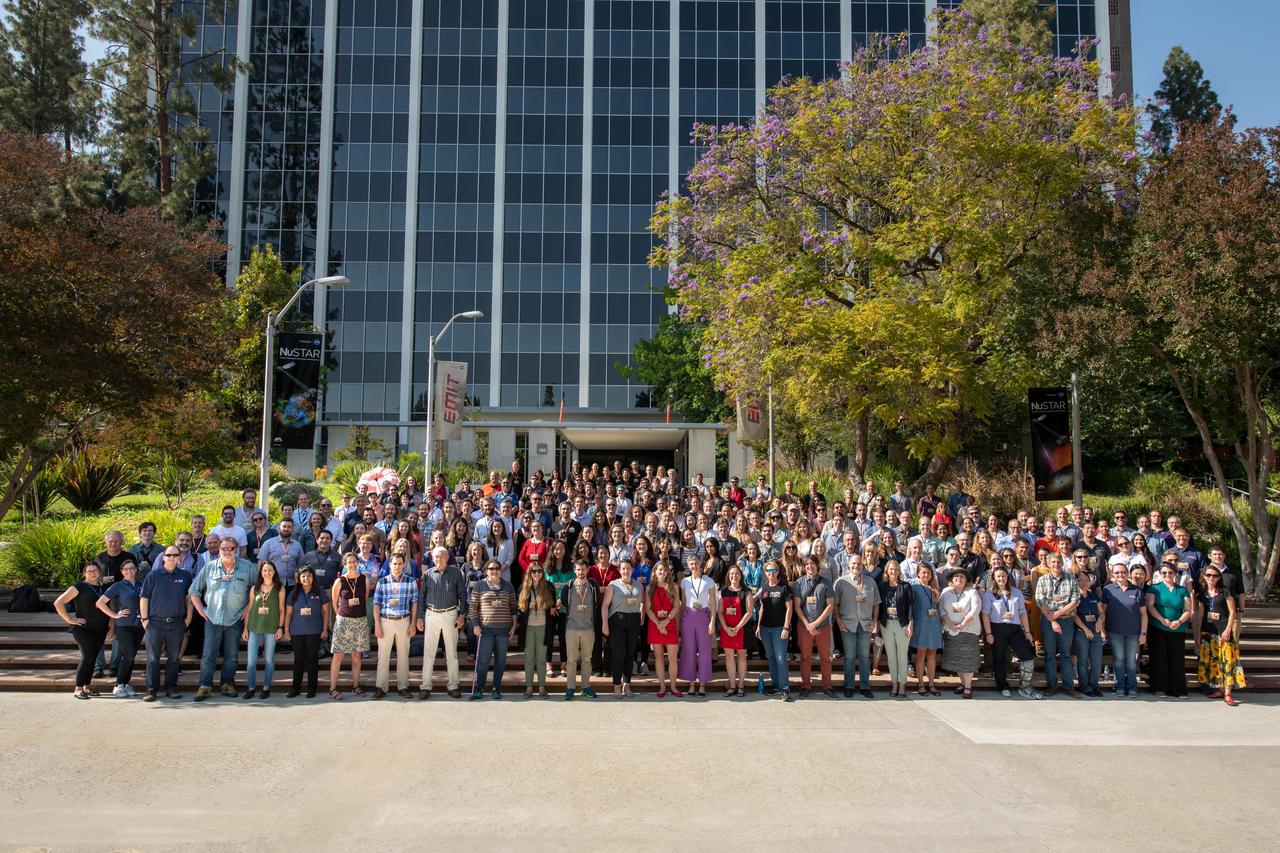

Members of the Perseverance rover Science Team pose on June 7, 2022, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which manages the mission. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25328

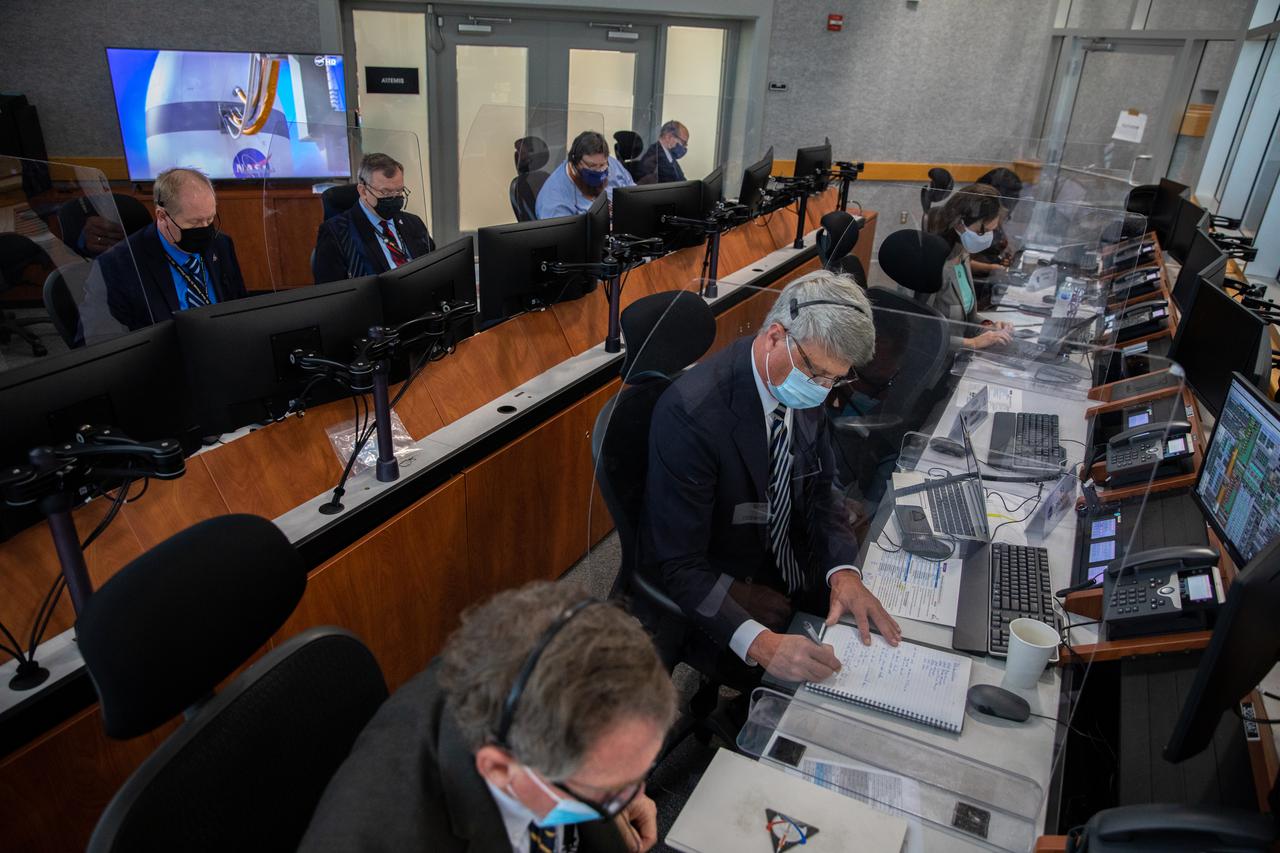
Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
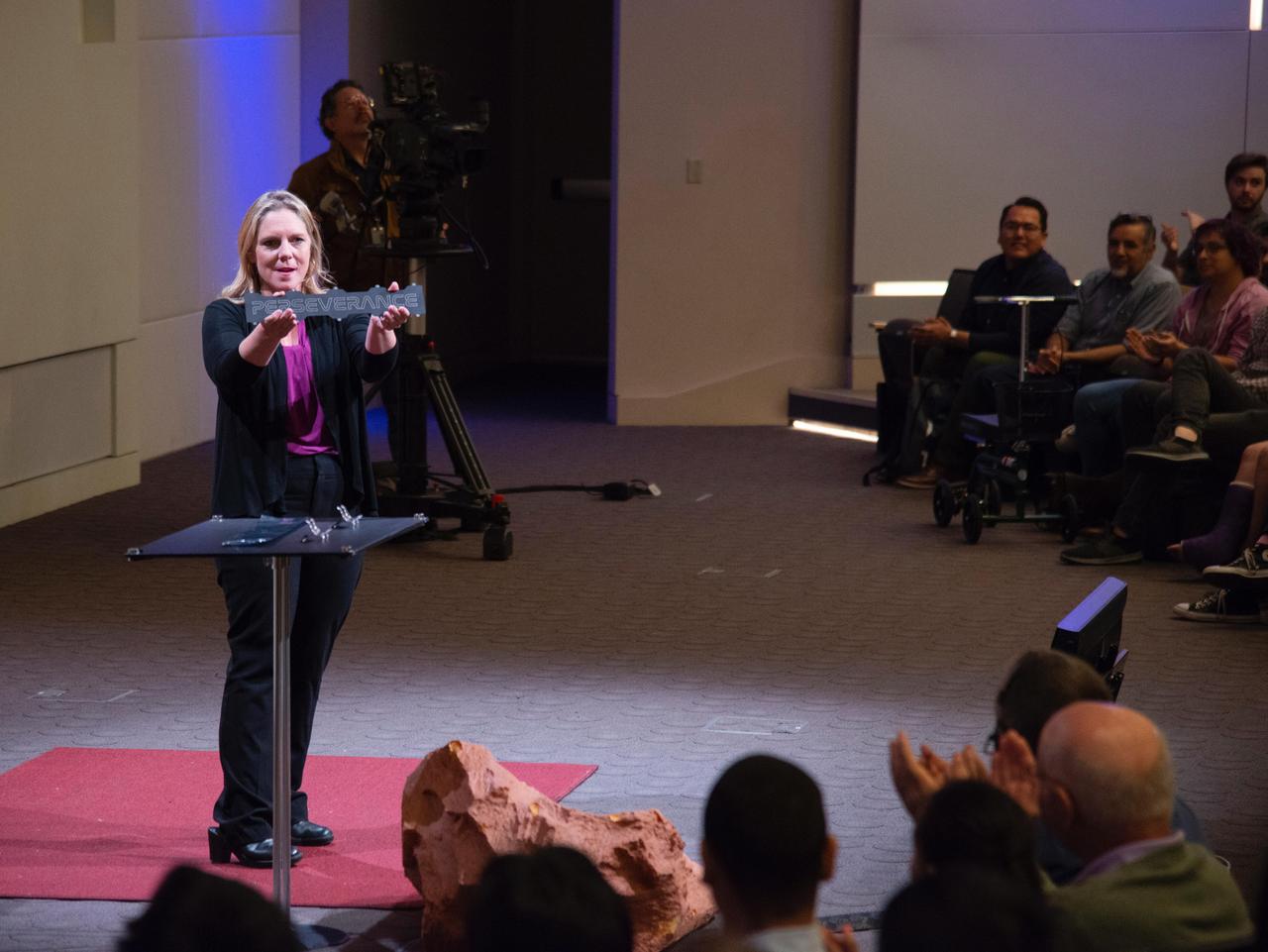

Team members of NASA's next Mars mission applaud as mission manager Jennifer Trosper unveils a nameplate with "Perseverance" laser-etched into its surface. The image was taken at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on March 5, 2020. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23763

John Honeycutt, Space Launch System program manager, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
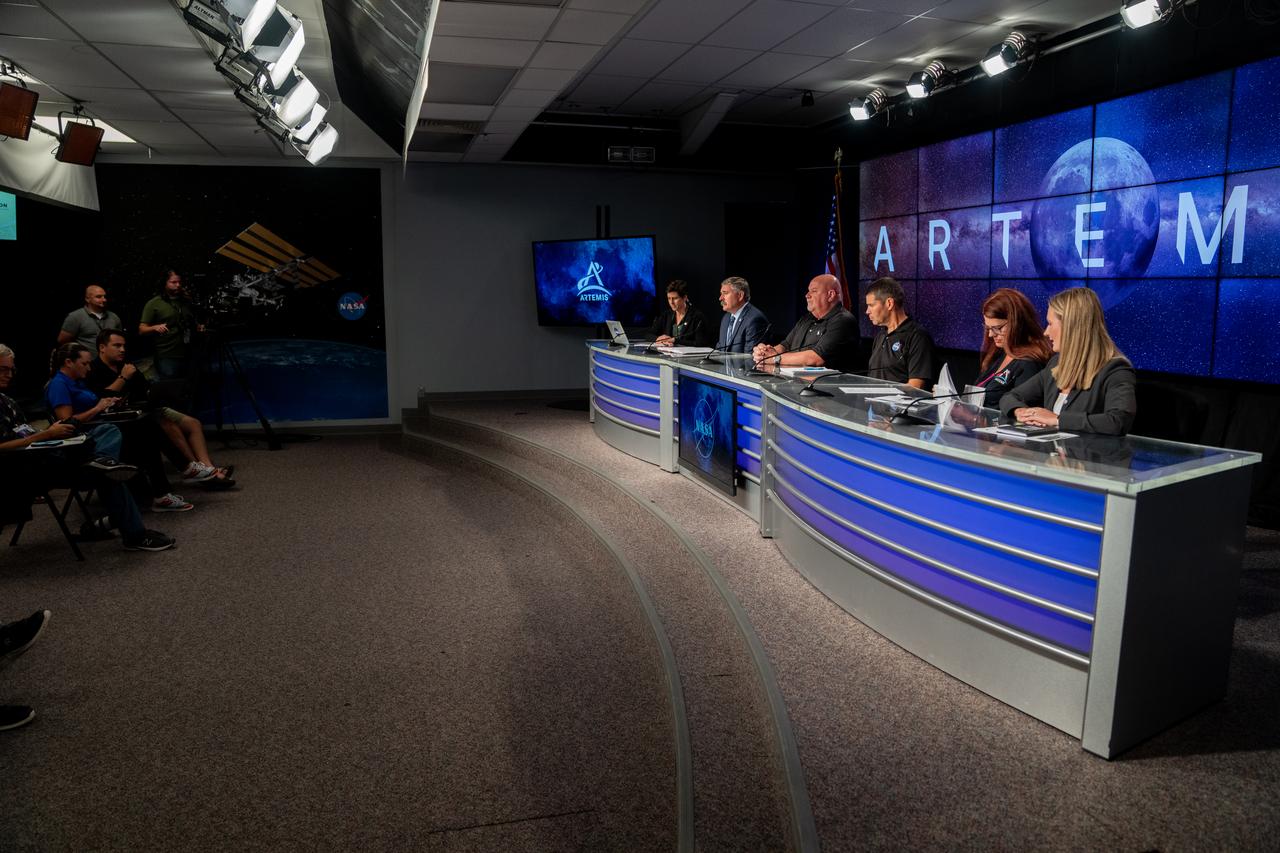

A prelaunch media briefing is held following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Participants are, from left, Rachel Kraft, NASA Communications; Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager; John Honeycutt, Space Launch System (SLS) program manager; John Blevins, SLS chief engineer; Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis launch director; and Melody Lovin, Space Launch Delta 45 weather officer. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

A prelaunch media briefing is held following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Participants are, from left, John Honeycutt, Space Launch System (SLS) program manager; John Blevins, SLS chief engineer; Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis launch director; and Melody Lovin, Space Launch Delta 45 weather officer. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Melody Lovin, Space Launch Delta 45 weather officer, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
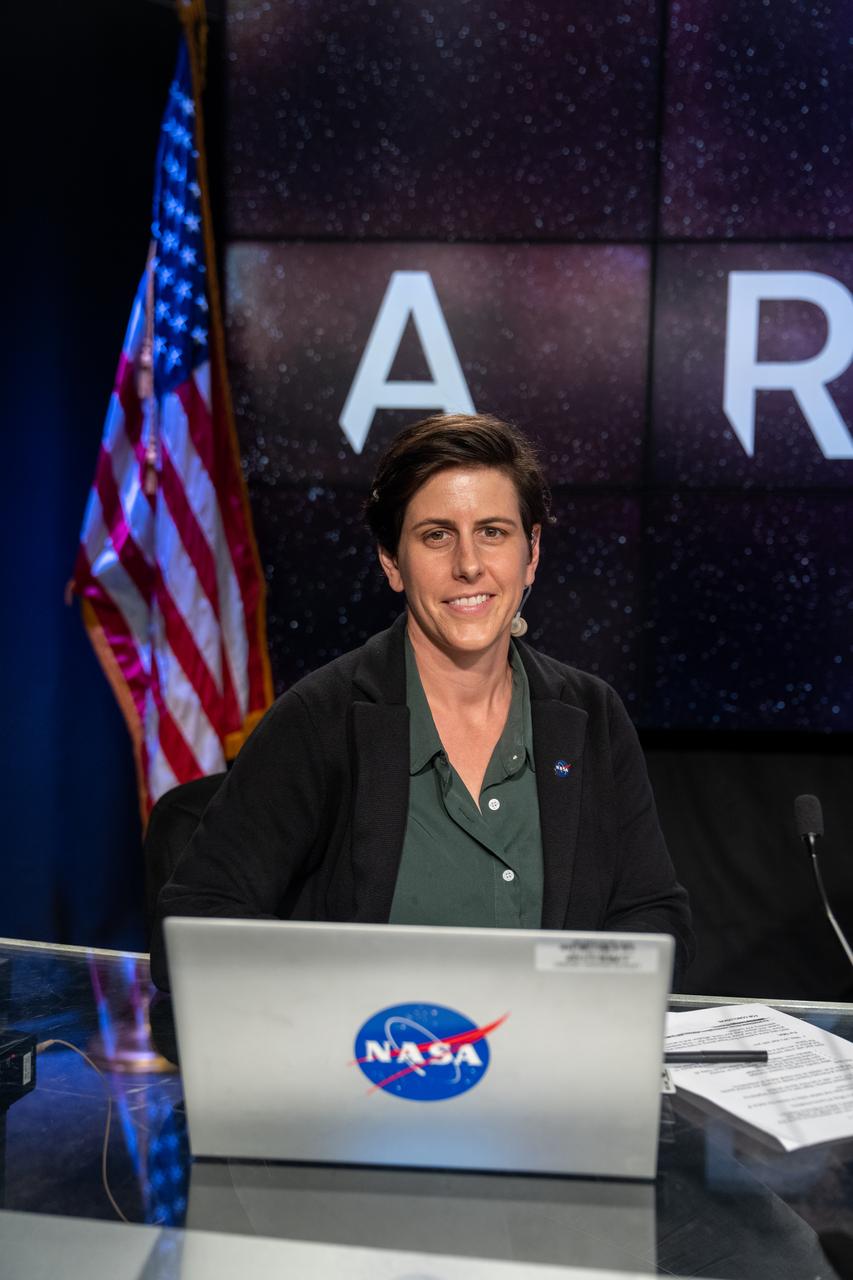

Rachel Kraft, NASA Communications, moderates a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
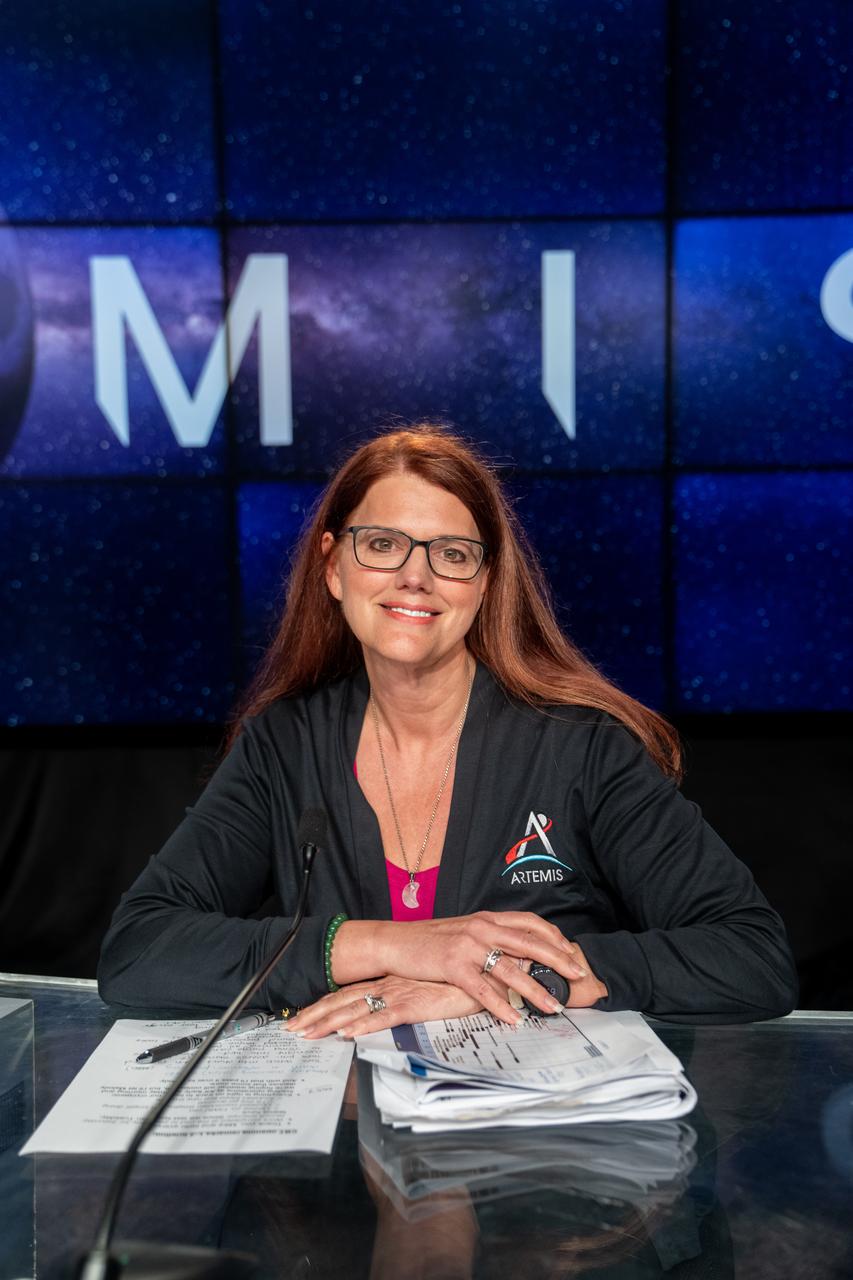

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis I launch director, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
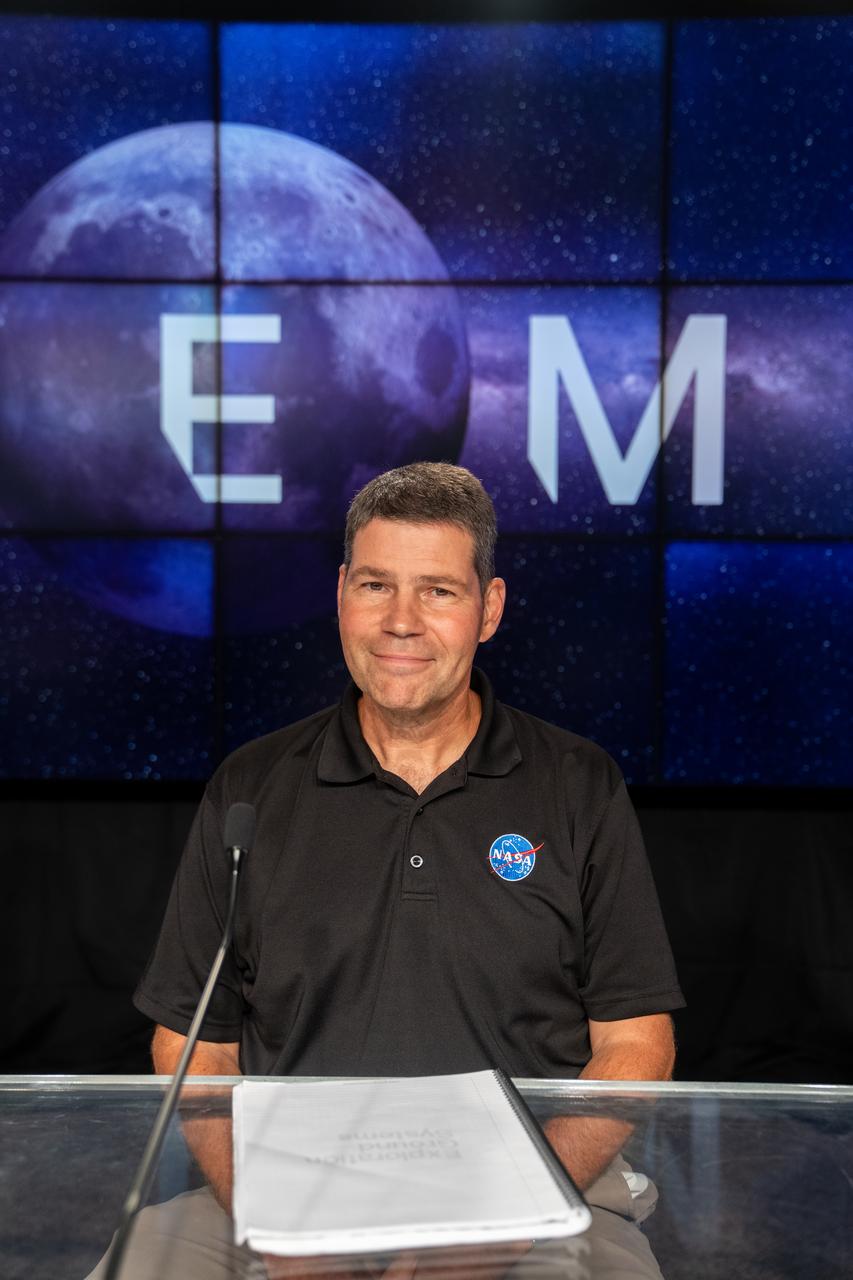

John Blevins, Space Launch System chief engineer, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
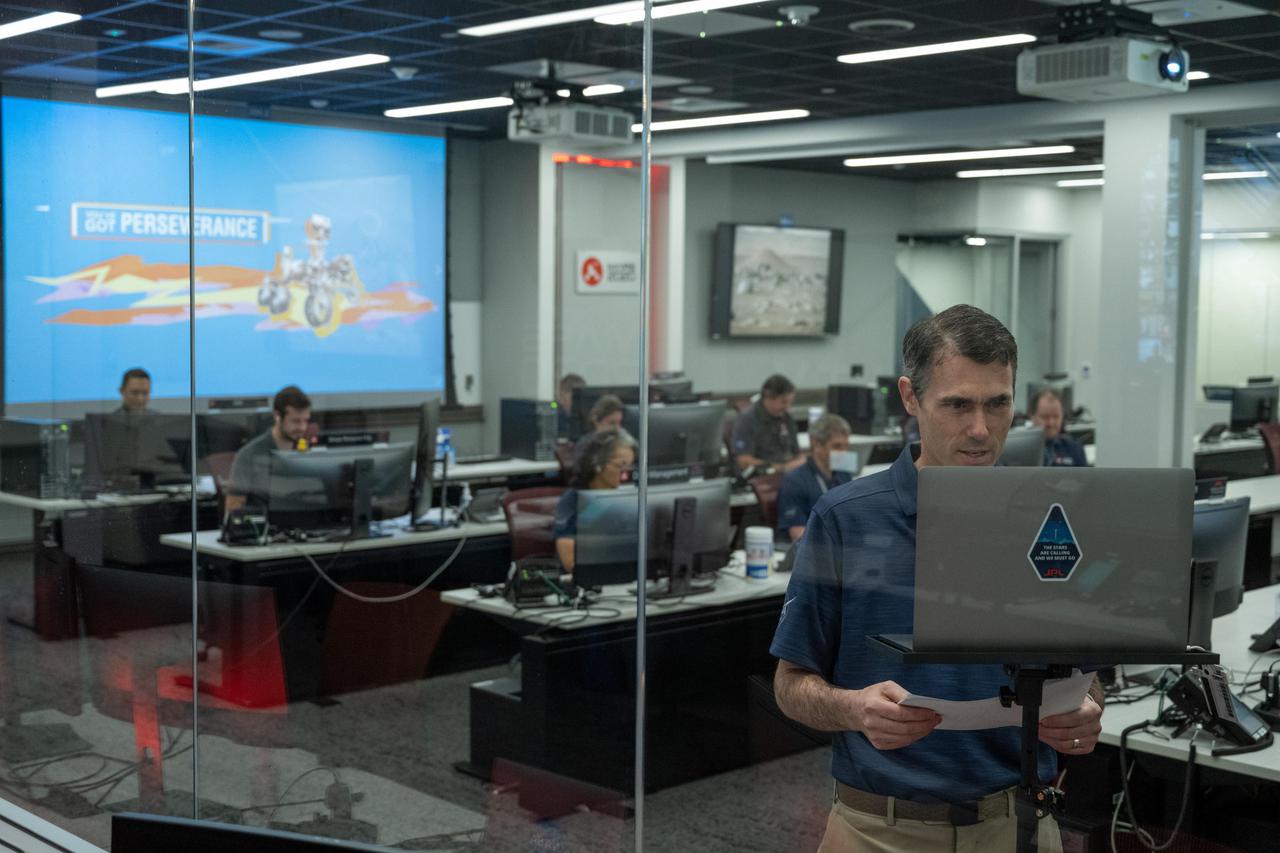

On April 5, 2022, inside the Mars Perseverance rover control room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, the rover team's deputy mission manager, Robert Hogg, and other team members interacted virtually with students who have overcome academic obstacles. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25274
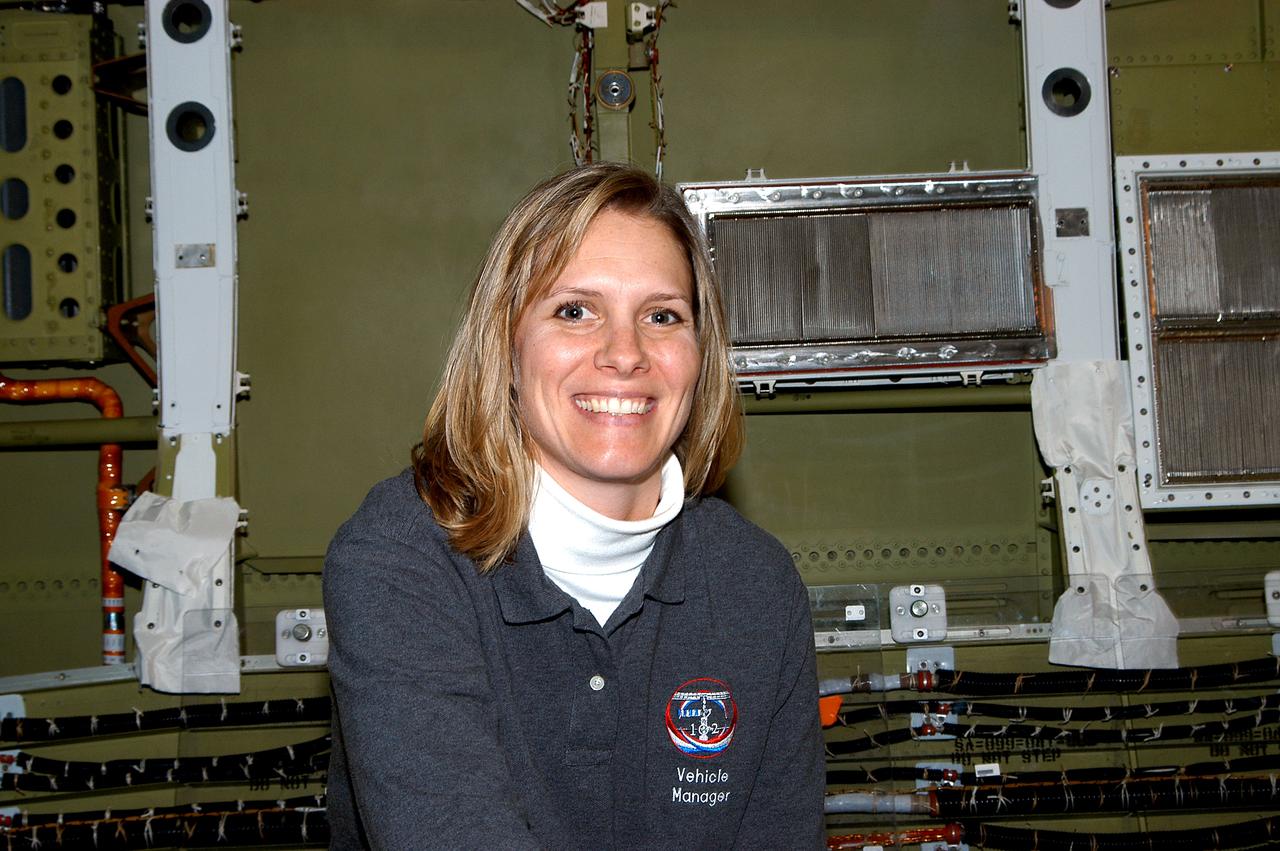

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA Vehicle Manager for Discovery, Stephanie Stilson poses for a photo after working with a KSC Web team who were filming a special feature for the KSC Web. Stilson explained her role in the recent Orbiter Major Modification period, which included inspection, modifications and reservicing of most systems onboard. The work on Discovery also included the installation of a Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem (MEDS) - a state-of-the-art “glass cockpit.” The orbiter is now being prepared for eventual launch on a future mission.
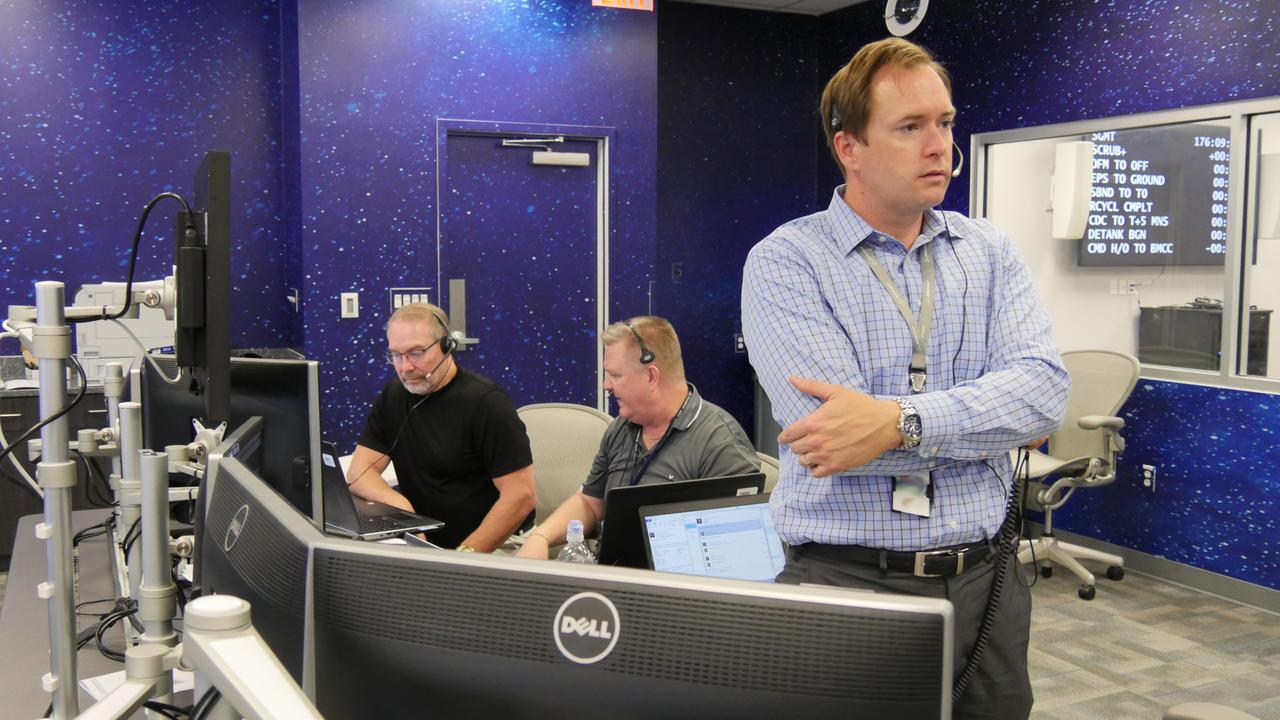

Inside the Boeing Mission Control Center at Kennedy Space Center, Fla., launch control teams for the CST-100 Starliner rehearse a fully integrated prelaunch simulation of the spacecraft’s upcoming Orbital Flight Test. Boeing Spacecraft Launch Conductor Louis Atchison speaks on console to the Mission Management Team as the countdown in the launch simulation progresses.
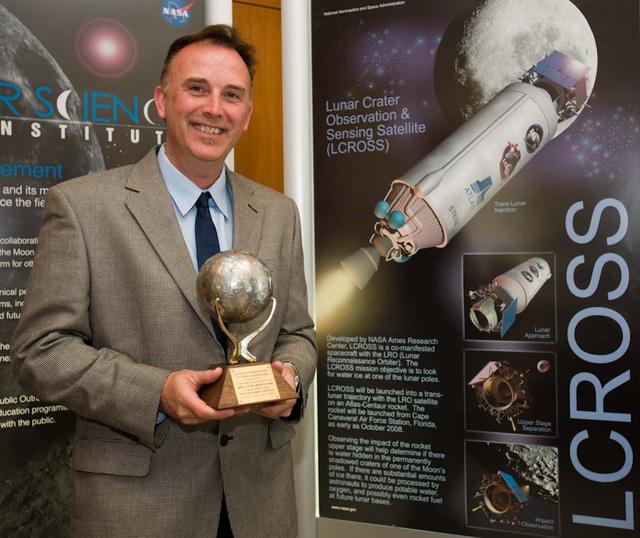

John Marmie, deputy project manager of the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite Mission with the 2010 National Space Society Space Pioneer Award, which he accepted on behalf of the NASA Ames LCROSS mission team.
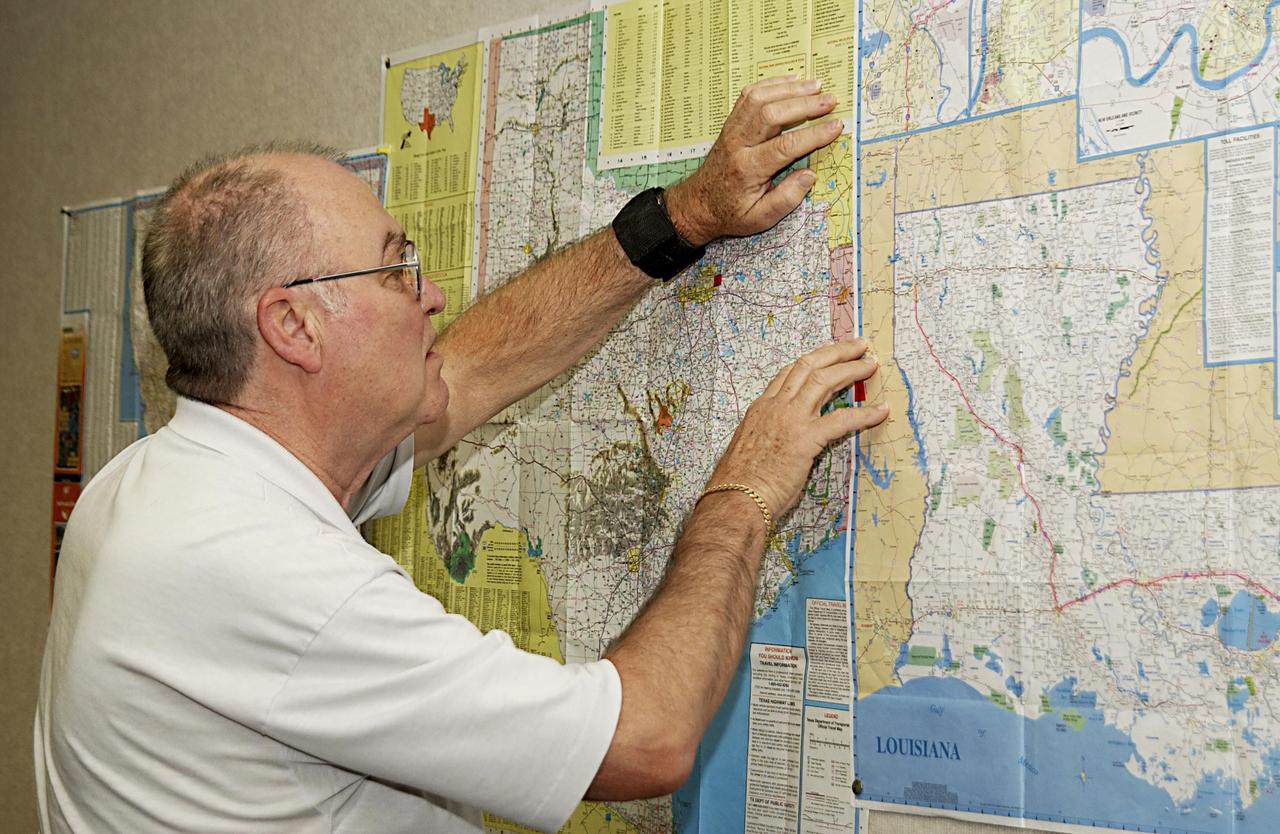
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Don Maxwell, Safety, United Space Alliance, checks a map of Texas during a meeting of the Recovery Management Team at KSC. The team is part of the investigation into the accident that claimed orbiter Columbia and her crew of seven on Feb. 1, 2003, over East Texas as they returned to Earth after a 16-day research mission. Other team members are Russ DeLoach, chief, Shuttle Mission Assurance Branch, NASA; George Jacobs, Shuttle Engineering; Jeff Campbell, Shuttle Engineering; Dave Rainer, Launch and Landing Operations; the two co-chairs of the Response Management Team, Denny Gagen, Landing Recovery Manager, Chris Hasselbring, Landing Operations, USA; and Larry Ulmer, Safety, NASA. The team is coordinating KSC technical support and assets to the Mishap Investigation Team in Barksdale, La., and providing support for the Recovery teams in Los Angeles, Texas, New Mexico, Arizona and California. In addition, the team is following up on local leads pertaining to potential debris in the KSC area. .

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the Recovery Management Team at KSC are at work in the Operations Support Building. They are part of the investigation into the accident that claimed orbiter Columbia and her crew of seven on Feb. 1, 2003, over East Texas as they returned to Earth after a 16-day research mission. Seated around the table (clockwise from far left) are Chris Hasselbring, Landing Operations, USA (co-chair of the Response Management Team); Don Maxwell, Safety, United Space Alliance (USA); Russ DeLoach, chief, Shuttle Mission Assurance Branch, NASA; George Jacobs, Shuttle Engineering; Jeff Campbell, Shuttle Engineering; Denny Gagen, Landing Recovery Manager (second co-chair of the team); and Dave Rainer, Launch and Landing Operations. The team is coordinating KSC technical support and assets to the Mishap Investigation Team in Barksdale, La., and providing support for the Recovery teams in Los Angeles, Texas, New Mexico, Arizona and California. In addition, the team is following up on local leads pertaining to potential debris in the KSC area. .
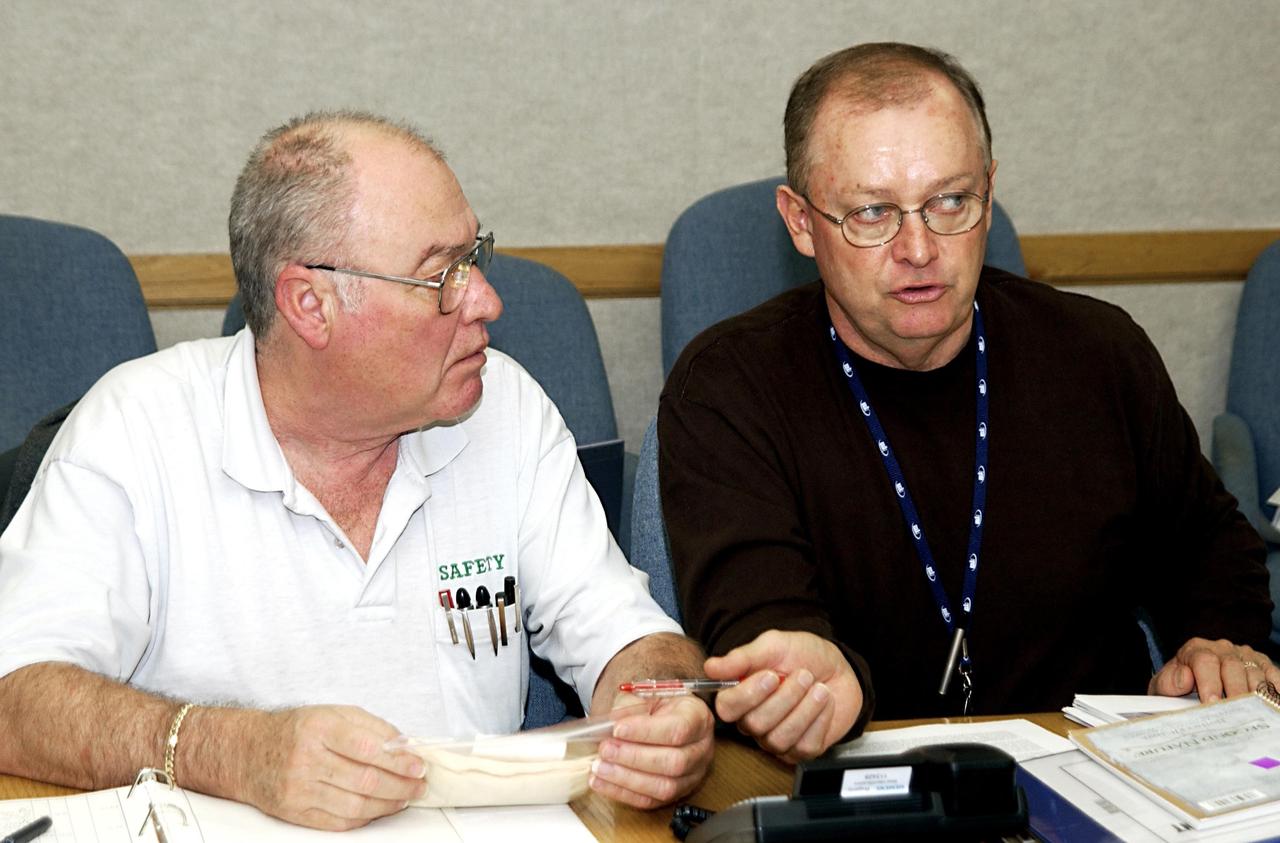

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Two members of the Recovery Management Team at KSC are at work in the Operations Support Building. At left is Don Maxwell, Safety, United Space Alliance, and at right is Larry Ulmer, Safety, NASA. They are part of the investigation into the accident that claimed orbiter Columbia and her crew of seven on Feb. 1, 2003, over East Texas as they returned to Earth after a 16-day research mission. Other team members are Russ DeLoach, chief, Shuttle Mission Assurance Branch, NASA; George Jacobs, Shuttle Engineering; Jeff Campbell, Shuttle Engineering; Dave Rainer, Launch and Landing Operations; and the two co-chairs of the Response Management Team, Denny Gagen, Landing Recovery Manager, and Chris Hasselbring, Landing Operations, USA. The team is coordinating KSC technical support and assets to the Mishap Investigation Team in Barksdale, La., and providing support for the Recovery teams in Los Angeles, Texas, New Mexico, Arizona and California. In addition, the team is following up on local leads pertaining to potential debris in the KSC area. .
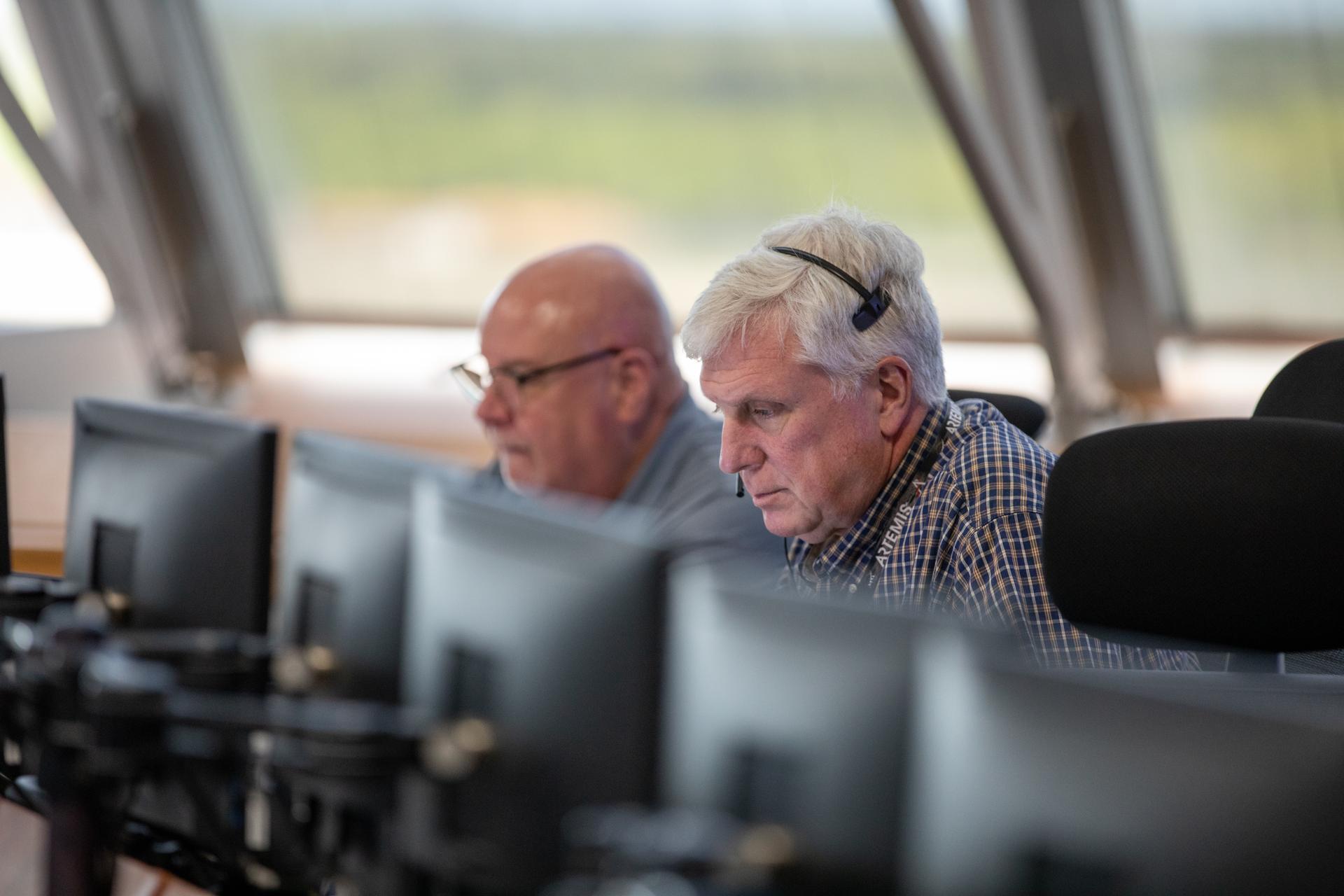

From left, John Honeycutt, Artemis II mission management team chair and Matthew Ramsey, Artemis II mission manager with NASA’s Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, participate in an Artemis II launch countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 5, 2025. The simulations go through launch day scenarios to help launch team members test software and make adjustments if needed during countdown operations. For Artemis II, four astronauts will venture around the Moon, the first crewed mission on NASA’s path to establishing a long-term presence for science and exploration through Artemis.

LEWIS WOOTEN MANAGES THE MISSION OPERATIONS LABORATORY. MORE THAN 1600 INVESTIGATIONS AND STUDENT EXPERIMENTS FOR OVER 80 COUNTRIES HAVE BEEN COMPLETED WITH THE HELP OF WOOTEN'S TEAM AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA.
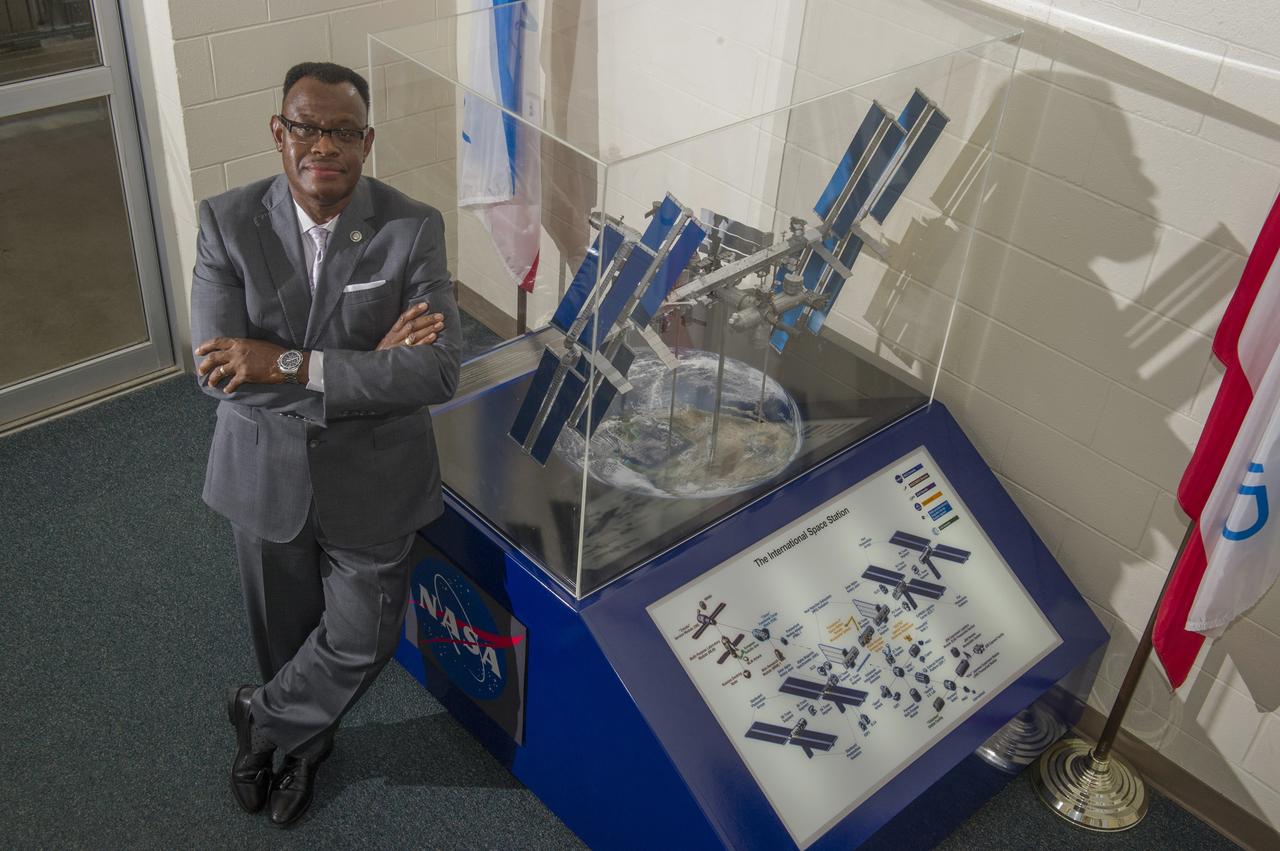

LEWIS WOOTEN MANAGES THE MISSION OPERATIONS LABORATORY. MORE THAN 1600 INVESTIGATIONS AND STUDENT EXPERIMENTS FOR OVER 80 COUNTRIES HAVE BEEN COMPLETED WITH THE HELP OF WOOTEN'S TEAM AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA.
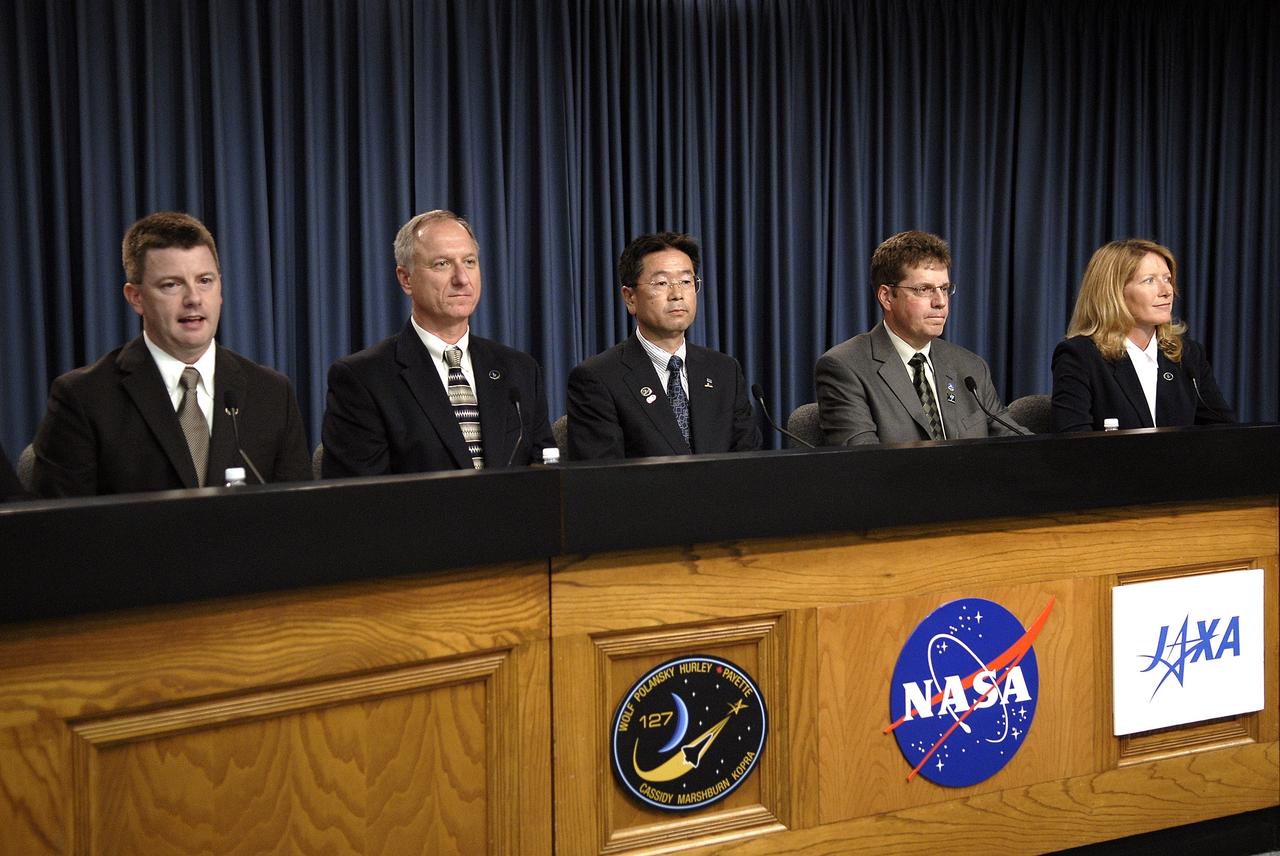

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Taking part in a prelaunch news conference at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida about the STS-127 mission are (from left) Mike Moses, launch integration manager and chair of the Mission Management Team; Pete Nickolenko, STS-127 shuttle launch director; Koki Oikawa, Japan Experiment Module, or JEM, Project Team function manager; Pierre Jean, director of Operations Engineering and program manager for the Canadian Space Station Program, Canadian Space Agency; and Kathy Winters, shuttle weather officer. In the final of three flights dedicated to the assembly of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory complex on the International Space Station, space shuttle Endeavour will deliver the JEM Exposed Facility and the Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES. STS-127 is the 29th flight for the assembly of the space station and the 127th flight in the Space Shuttle Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the Recovery Management Team at KSC are at work in the Operations Support Building. They are part of the investigation into the accident that claimed orbiter Columbia and her crew of seven on Feb. 1, 2003, over East Texas as they returned to Earth after a 16-day research mission. From left around the table are Don Maxwell, Safety, United Space Alliance (USA); Russ DeLoach, chief, Shuttle Mission Assurance Branch, NASA; George Jacobs, Shuttle Engineering; Jeff Campbell, Shuttle Engineering; Dave Rainer, Launch and Landing Operations; and the two co-chairs of the Response Management Team, Denny Gagen, Landing Recovery Manager, and Chris Hasselbring, Landing Operations, USA. The team is coordinating KSC technical support and assets to the Mishap Investigation Team in Barksdale, La., and providing support for the Recovery teams in Los Angeles, Texas, New Mexico, Arizona and California. In addition, the team is following up on local leads pertaining to potential debris in the KSC area. .

Catherine Koerner, second from left, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion, Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and TOSC, tours the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 5, 2020. Accompanying her, from left are Skip Williams, operations manager for the MPPF spacecraft offline element integration team; Mike Bolger, EGS manager; Nicolas Kindred, TOSC flow manager; Annette Hasbrook, Orion Program assistant manager; Jeremy Parsons, EGS deputy manager; and Scott Wilson, Orion Production Operations manager. Koerner viewed spacecraft hardware and processing facilities for the Artemis I and II missions. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Tim Dunn, NASA launch manager, center, monitors the countdown for the launch of the TDRS-K spacecraft on an Atlas V rocket. Omar Baez, assistant NASA launch manager, left, and Diana Calero, NASA mission manager, right, also participate in the countdown procedures before the liftoff. The launch teams for NASA and the United Launch Alliance work inside the Atlas Space Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., known as the ASOC. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Tim Dunn, NASA launch manager, center, monitors the countdown for the launch of the TDRS-K spacecraft on an Atlas V rocket. Omar Baez, assistant NASA launch manager, left, and Diana Calero, NASA mission manager, right, also participate in the countdown procedures before the liftoff. The launch teams for NASA and the United Launch Alliance work inside the Atlas Space Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., known as the ASOC. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett

Mike Bolger; front; manager; NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems; and Chris Cianciola; NASA’s Space Launch System Program deputy manager at Marshall Space Flight Center; participate in the 11th terminal countdown simulation for the Artemis I launch inside Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Control Center on Oct. 14; 2021. The event marked the first time members of NASA’s mission management team; launch team; and contractor Jacobs conducted the simulation together. During Artemis I; the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions; the agency; along with commercial and international partners; will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
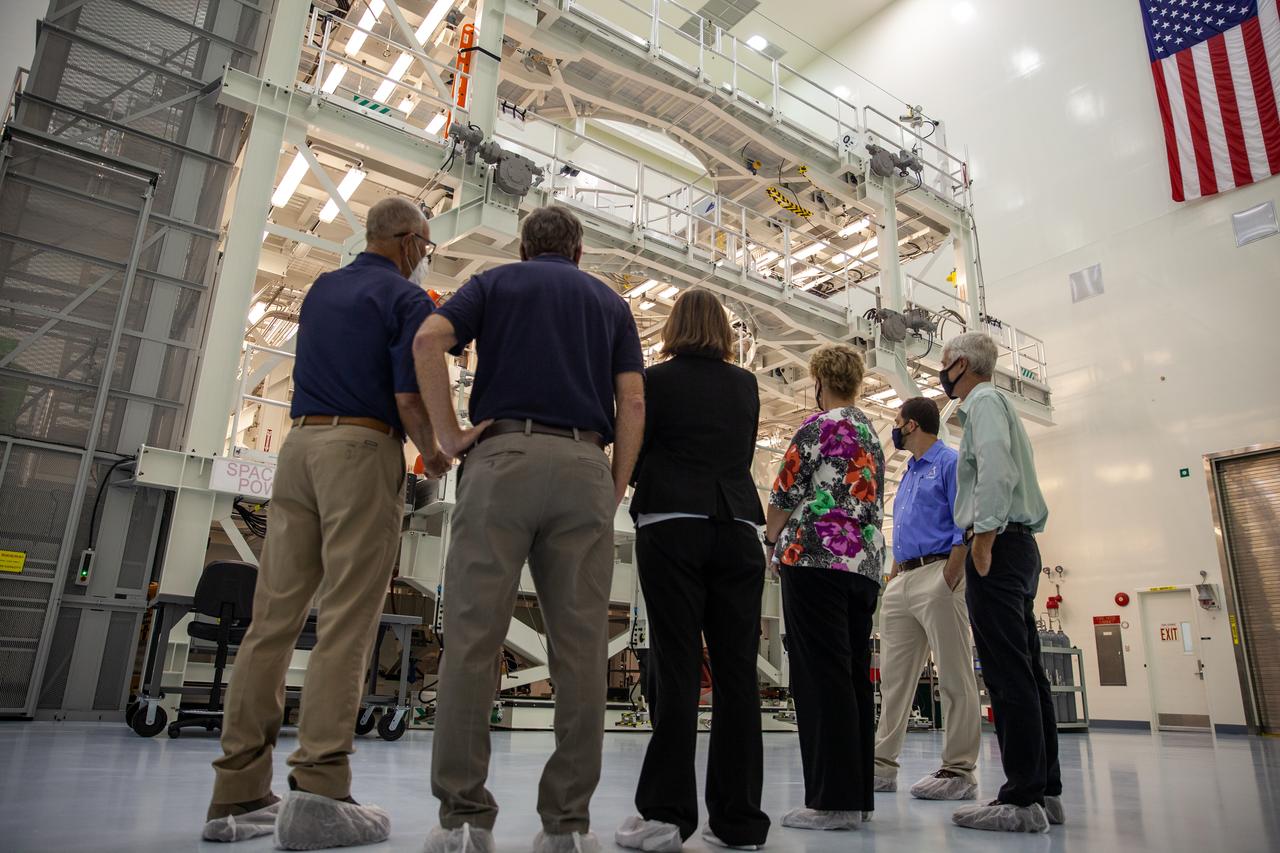

Catherine Koerner, third from left, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion, and Exploration Ground Systems (EGS), visits the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 5, 2020. Accompanying her, from left are Skip Williams, operations manager for the MPPF spacecraft offline element integration team; Mike Bolger, EGS manager; Annette Hasbrook, Orion Program assistant manager; Scott Wilson, Orion Production Operations manager; and Jeremy Parsons, EGS deputy manager. Koerner viewed spacecraft hardware and processing facilities for the Artemis I and II missions. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

Catherine Koerner, in front, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion, Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and TOSC, tours the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 5, 2020. Accompanying her, from left are Nicolas Kindred, (partically hidden), TOSC flow manager; Jeremy Parsons, EGS deputy manager; Scott Wilson, Orion Production Operations manager; Mike Bolger, (partially hidden), EGS manager; and Skip Williams, operations manager for the MPPF spacecraft offline element integration team. Koerner viewed spacecraft hardware and processing facilities for the Artemis I and II missions. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
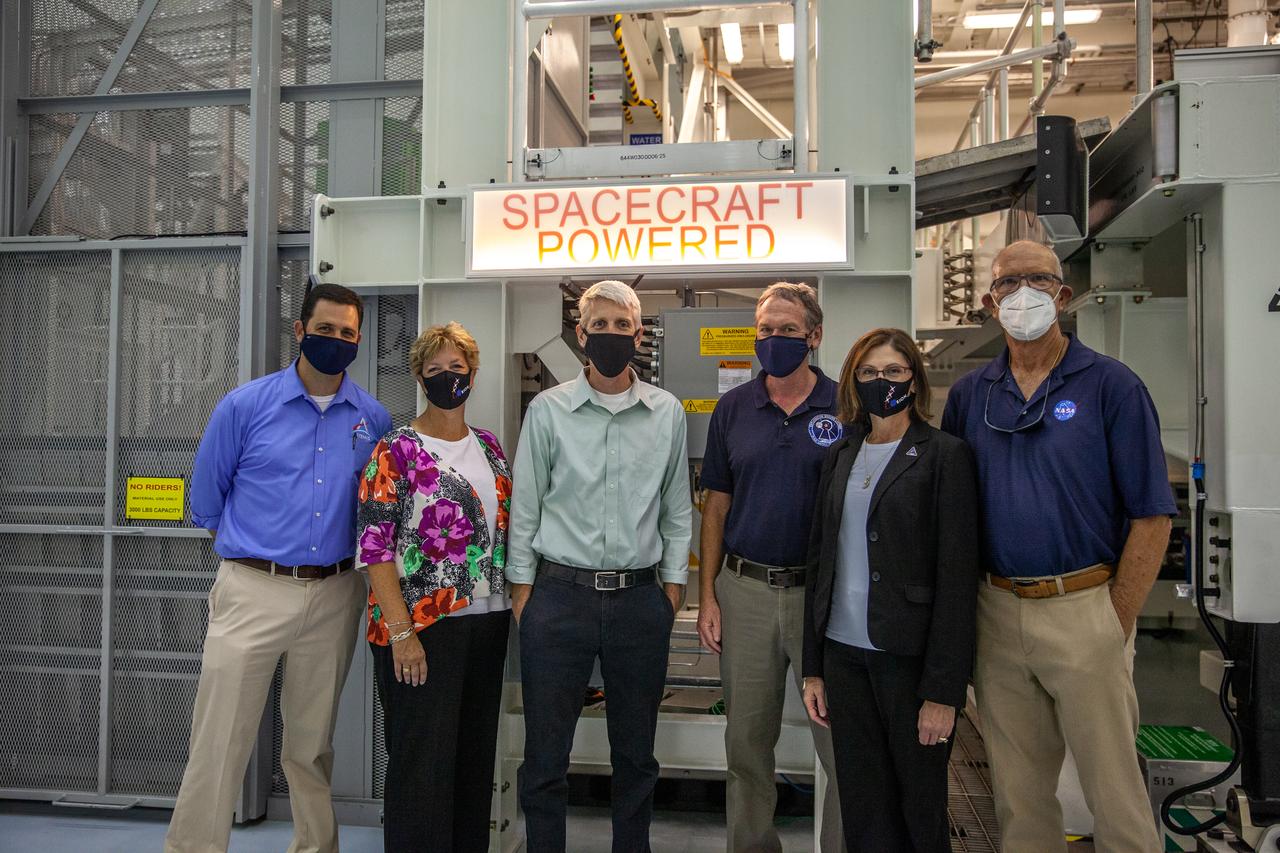

Catherine Koerner, second from right, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion, and Exploration Ground Systems (EGS), tours the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 5, 2020. Accompanying her, from left are Jeremy Parsons, EGS deputy manager; Annette Hasbrook, Orion Program assistant manager; Scott Wilson, Orion Production Operations manager; and Mike Bolger, EGS manager. At far right is Skip Williams, operations manager for the MPPF spacecraft offline element integration team. Koerner viewed spacecraft hardware and processing facilities for the Artemis I and II missions. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
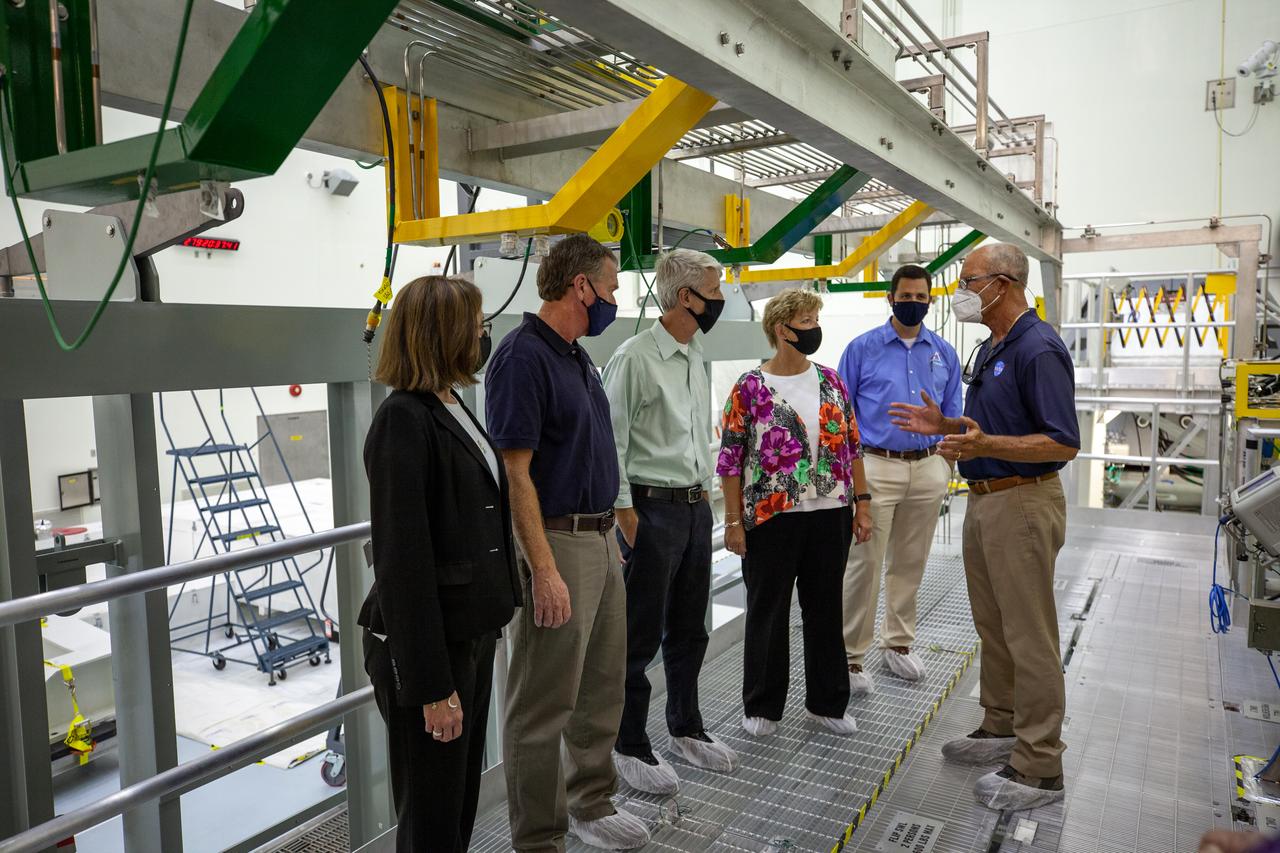

Catherine Koerner, far left, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion, and Exploration Ground Systems (EGS), tours the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 5, 2020. Accompanying her, from left are Mike Bolger, EGS manager; Scott Wilson, Orion Production Operations manager; Annette Hasbrook, Orion Program assistant manager; and Jeremy Parsons, EGS deputy manager. Speaking to the group is Skip Williams, operations manager for the MPPF spacecraft offline element integration team. Koerner viewed spacecraft hardware and processing facilities for the Artemis I and II missions. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
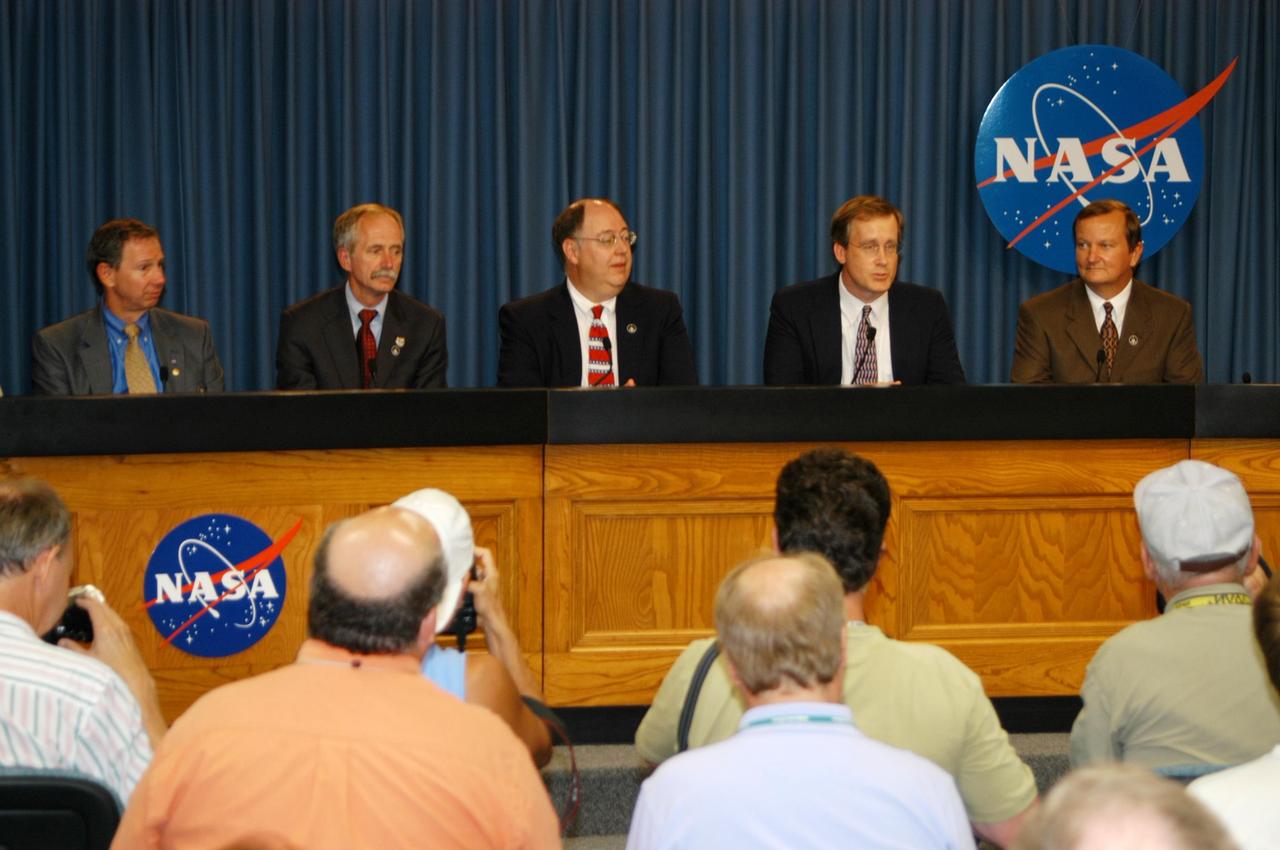

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a post-launch briefing, Shuttle Program Manager Wayne Hale, center, briefs the media about the successful launch of Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-121. Seated with him are, left to right, NASA Administrator Mike Griffin, NASA Associate Administrator for Space Operations Mission Bill Gerstenmaier, Chief of the Mission Management Team John Shannon, and Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach. Liftoff of Discovery was on time at 2:30 p.m. EDT.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA managers brief the media about the Flight Readiness Review for STS-129. From left are Associate Administrator for NASA Space Operations Bill Gerstenmaier, Mission Management Team Chair Mike Moses and Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach. The session confirmed a Nov. 16 launch date for space shuttle Atlantis is to fly the resupply mission to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett.
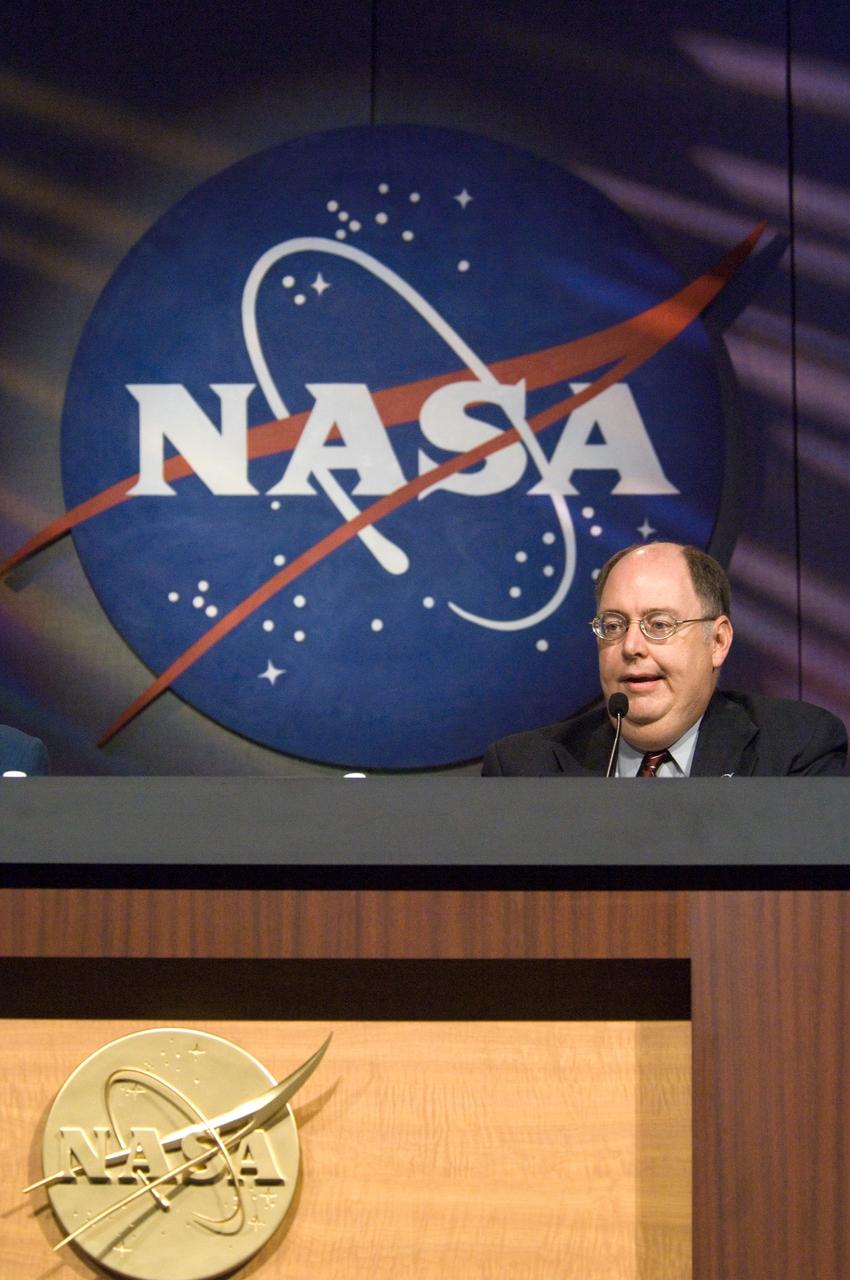

JSC2005-E-32015 (4 August 2005) --- Wayne Hale, Deputy Manager of the Shuttle Program Office, fields questions from news media represetatives during a press conference in the Olin Teague Auditorium at the Johnson Space Center. Hale had just come from a meeting of the Mission Management Team, and he passed onto the news reporters the decision of not planning for a fourth spacewalk on Discovery's STS-114 mission.
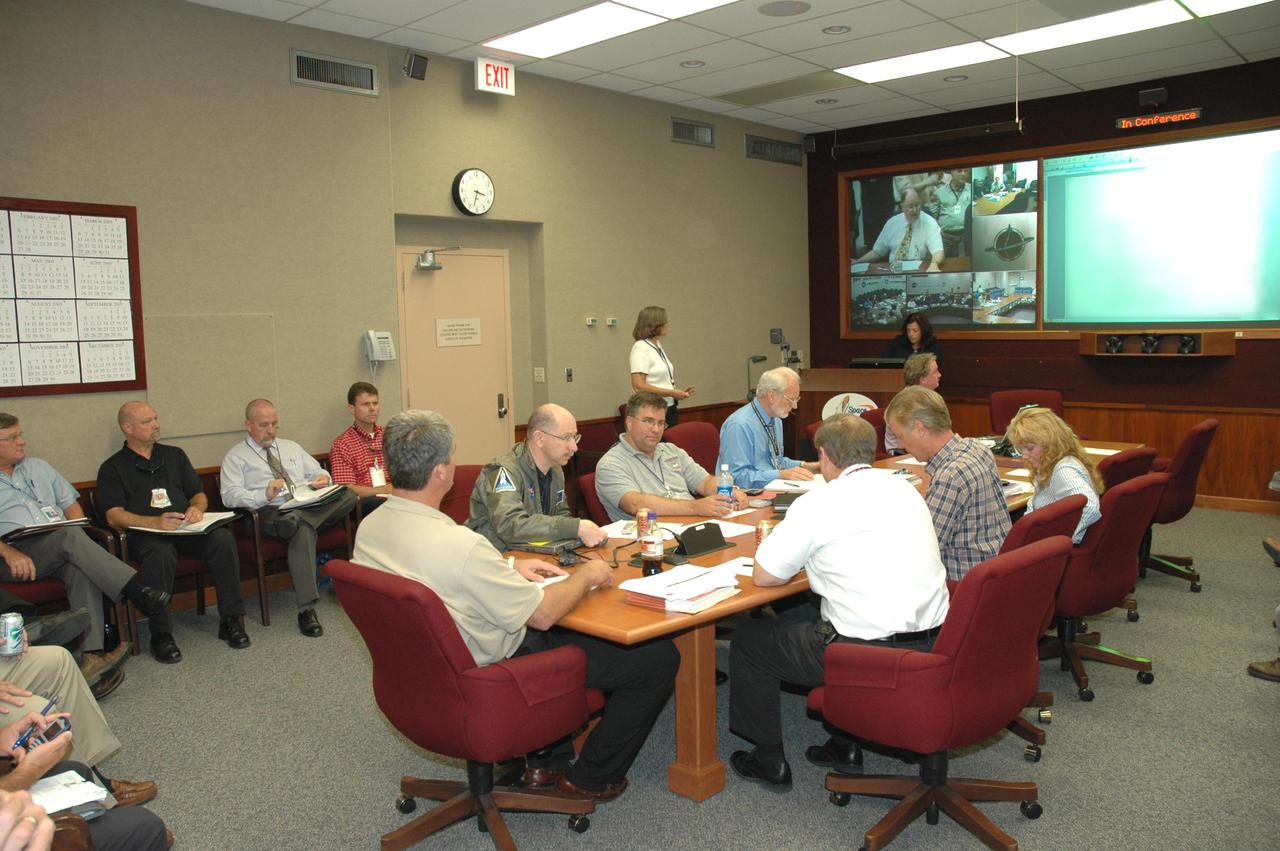

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Mission Management Team gathers in NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Headquarters Building to review the findings about the faulty Engine Cut-Off sensor reading in last week’s launch attempt for Return to Flight mission STS-114. Seated at the head of the table at left is Bill Parsons, Space Shuttle program manager. A press briefing is scheduled for late in the day.
Mike Collins, NASA Operations manager for Spacecraft Offline Operations, left, and Skip Williams, operations manager for the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) spacecraft offline element integration team, stand in front of the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission, as the capsule moves out from Kennedy Space Center’s MFFP on July 10, 2021. Orion is being transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility, where teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.

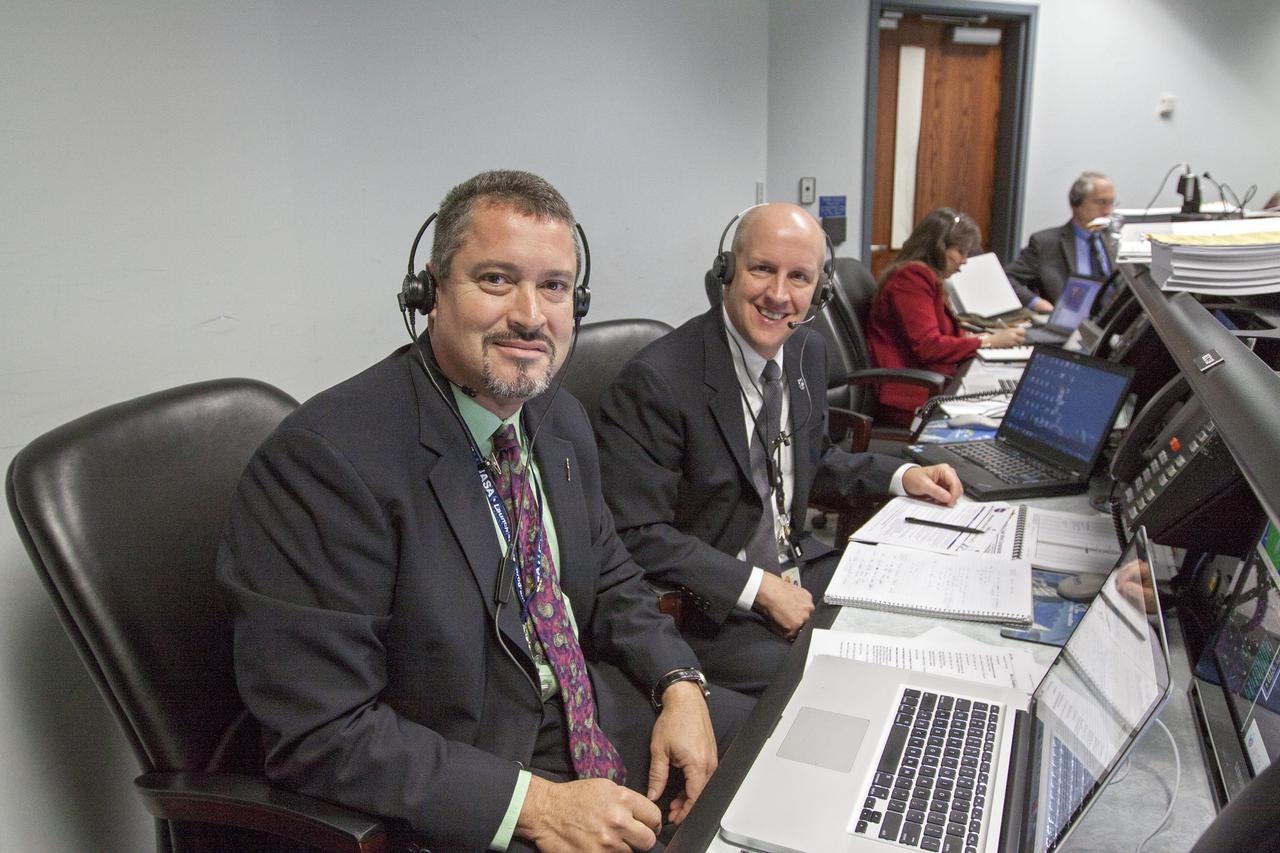
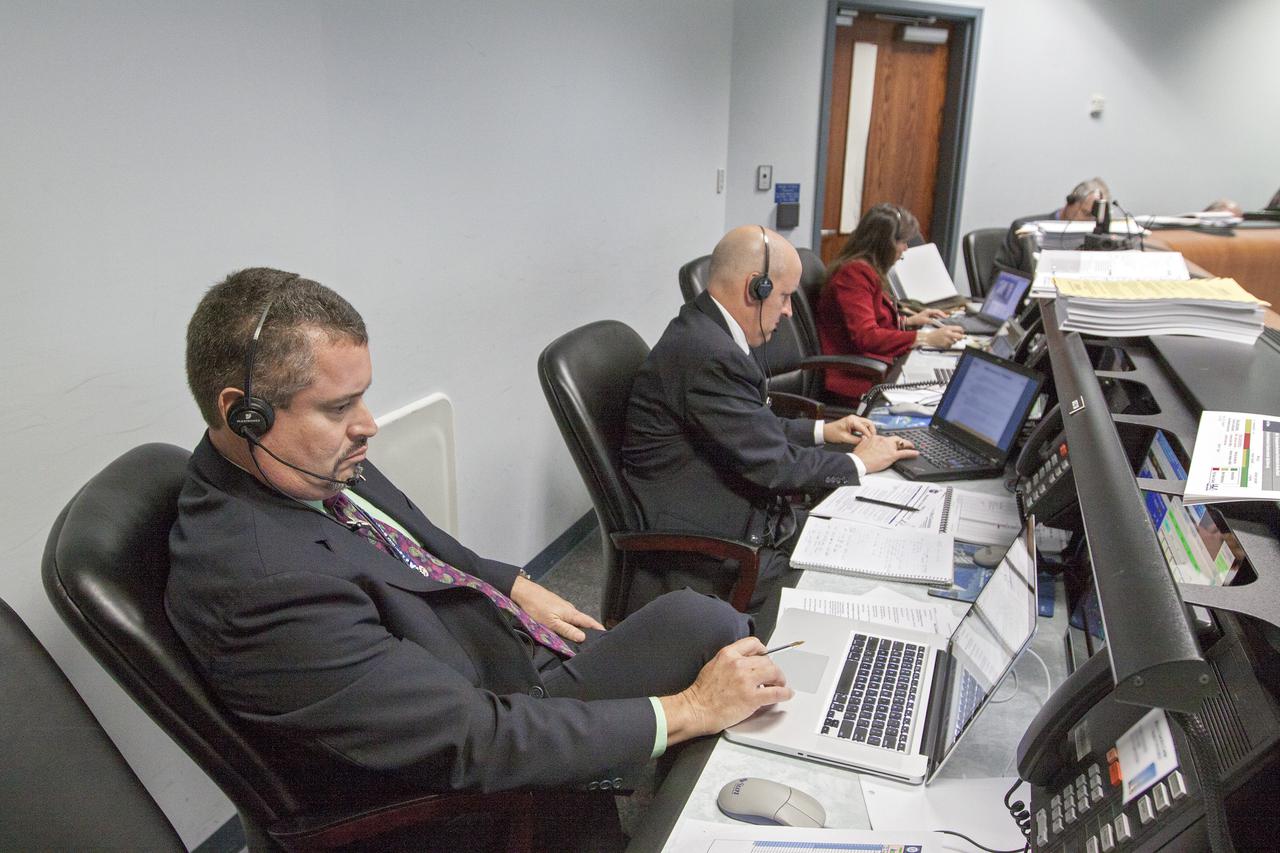
Members of NASA’s mission management team, launch team, and contractor Jacobs participate in the 11th terminal countdown simulation for the Artemis I launch inside Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Control Center on Oct. 14, 2021. It marked the first time these teams conducted the simulation together. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
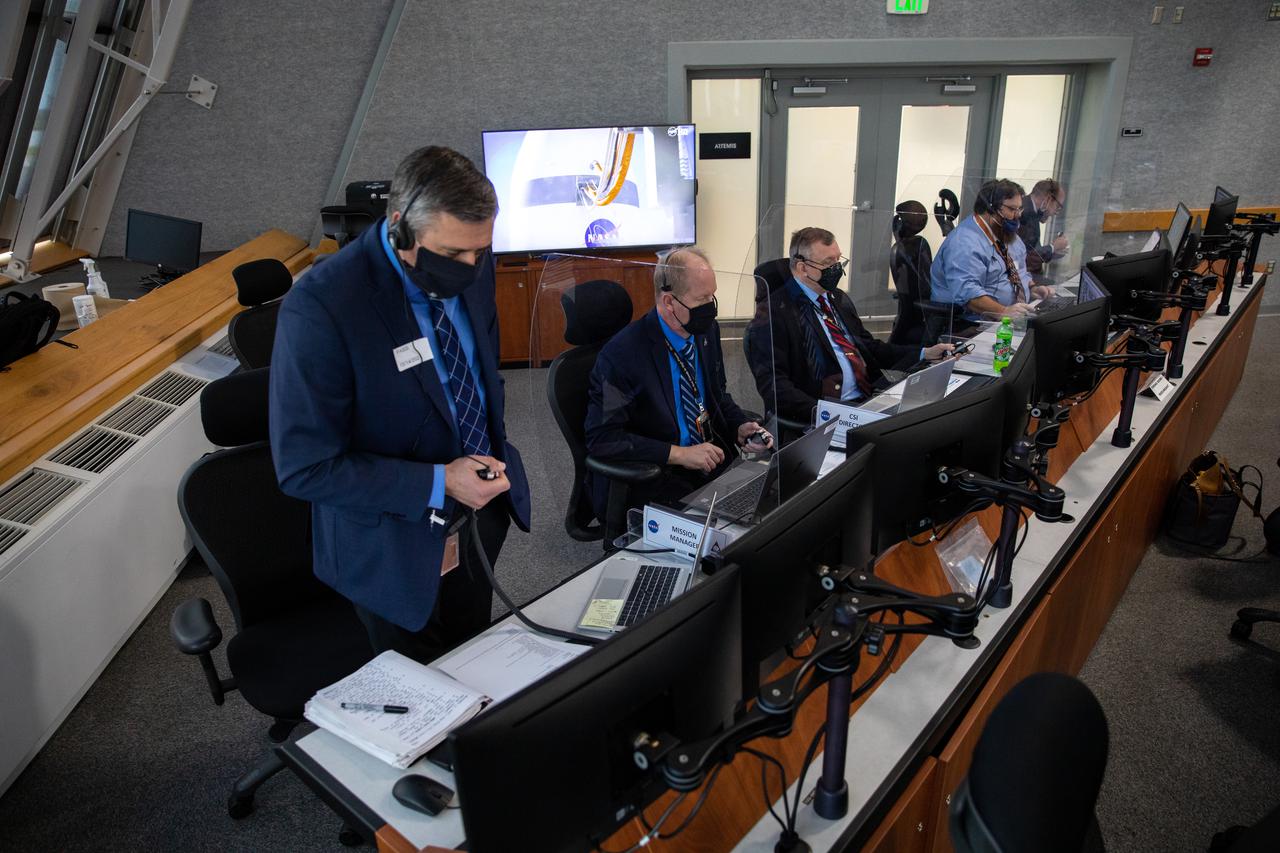

Members of NASA’s mission management team, launch team, and contractor Jacobs participate in the 11th terminal countdown simulation for the Artemis I launch inside Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Control Center on Oct. 14, 2021. It marked the first time these teams conducted the simulation together. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
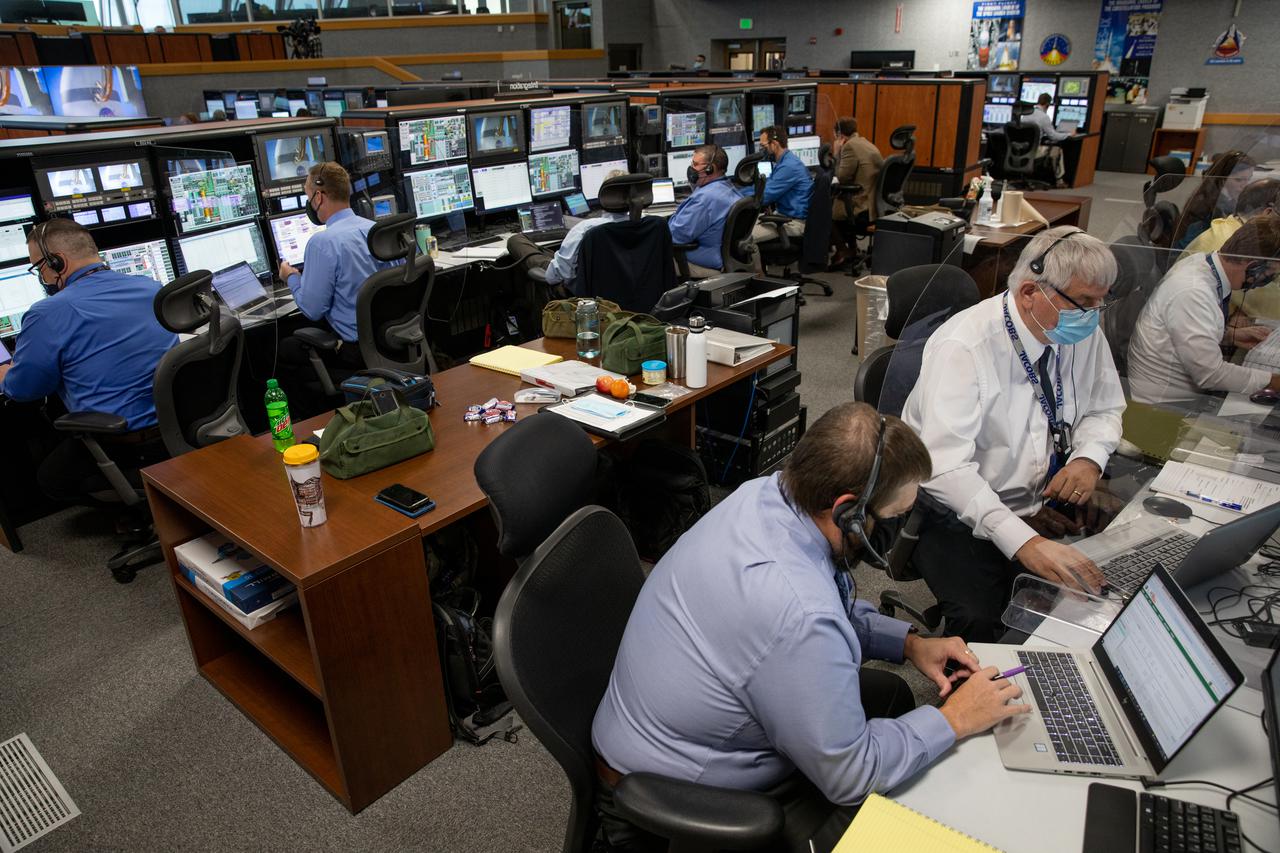

Members of NASA’s mission management team, launch team, and contractor Jacobs participate in the 11th terminal countdown simulation for the Artemis I launch inside Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Control Center on Oct. 14, 2021. It marked the first time these two teams conducted the simulation together. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
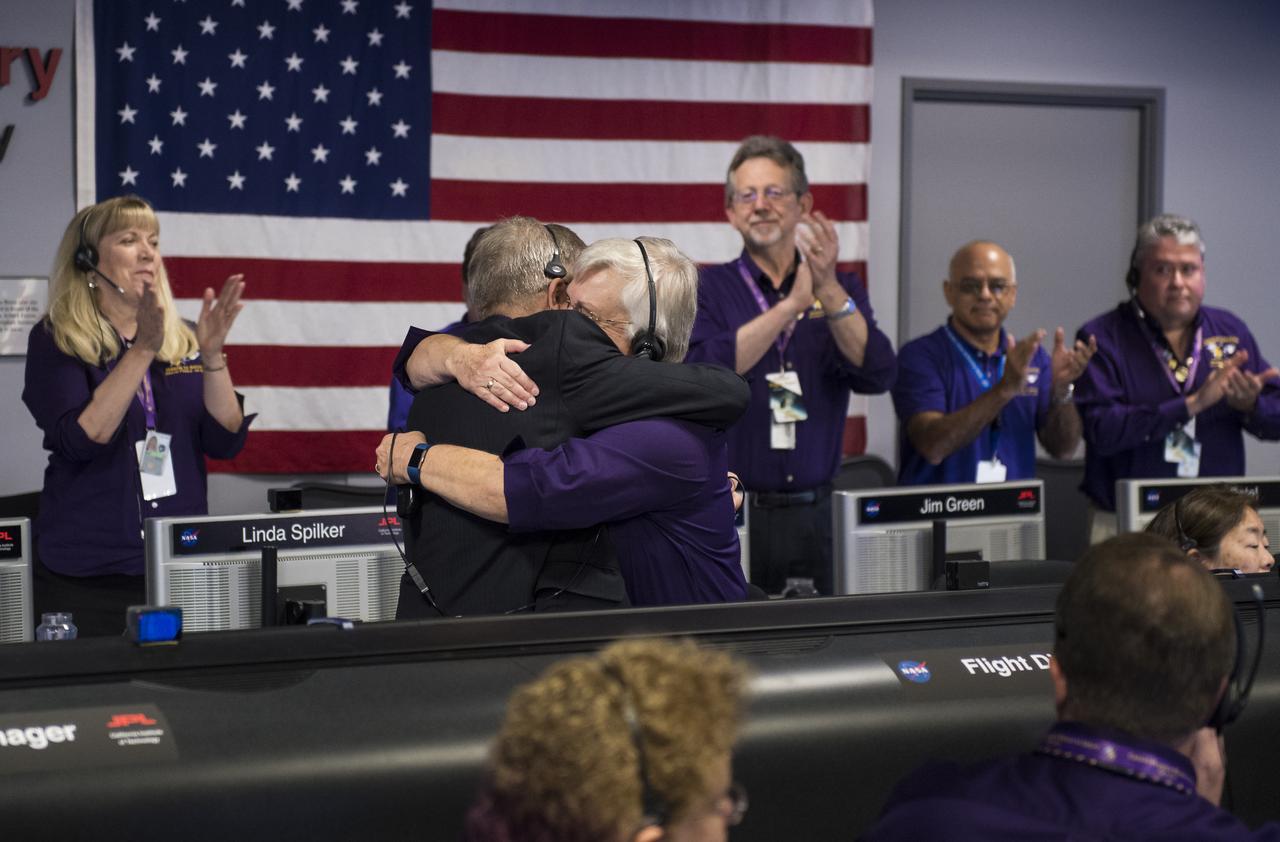

Cassini program manager at JPL, Earl Maize, left, and spacecraft operations team manager for the Cassini mission at Saturn, Julie Webster, right, embrace after the Cassini spacecraft plunged into Saturn, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
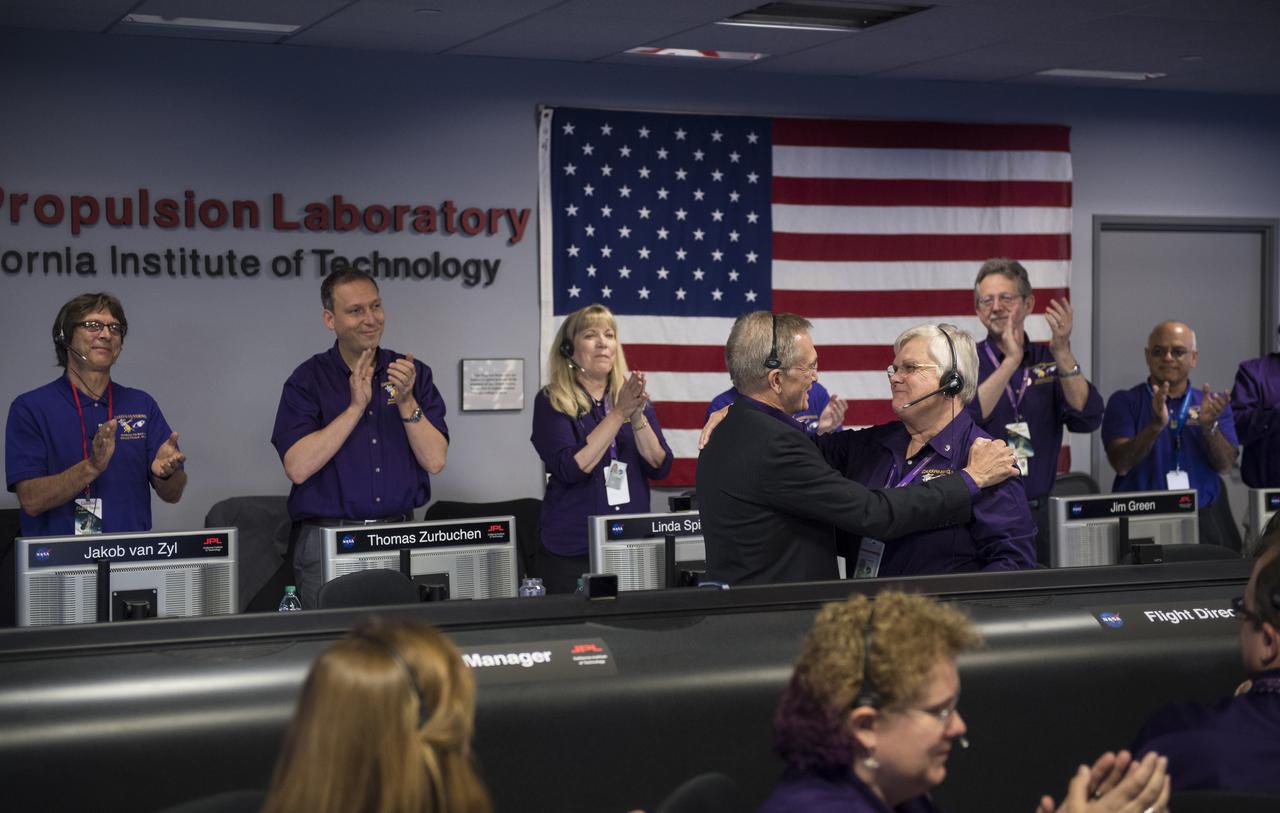

Cassini program manager at JPL, Earl Maize, left, and spacecraft operations team manager for the Cassini mission at Saturn, Julie Webster, right, embrace after the Cassini spacecraft plunged into Saturn, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

MORE THAN 250 PEOPLE FROM ACROSS NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER PARTICIPATED IN THE SPACE LAUNCH SYSTEM (SLS) POST-PRELIMINARY DESIGN REVIEW REPORT, HELD AUG. 5 IN ACTIVITIES BUILDING 4316. DISCUSSING THE REVIEW AND THANKING THE MARSHALL TEAM FOR A JOB WELL DONE, ARE FROM LEFT, GARRY LYLES, SLS CHIEF ENGINEER; TODD MAY, MANAGER OF THE SLS PROGRAM; STEVE CASH, DIRECTOR OF MARSHALL’S SAFETY & MISSION ASSURANCE DIRECTORATE; AND CHRIS SINGER, MANAGER OF MARSHALL’S ENGINEERING DIRECTORATE
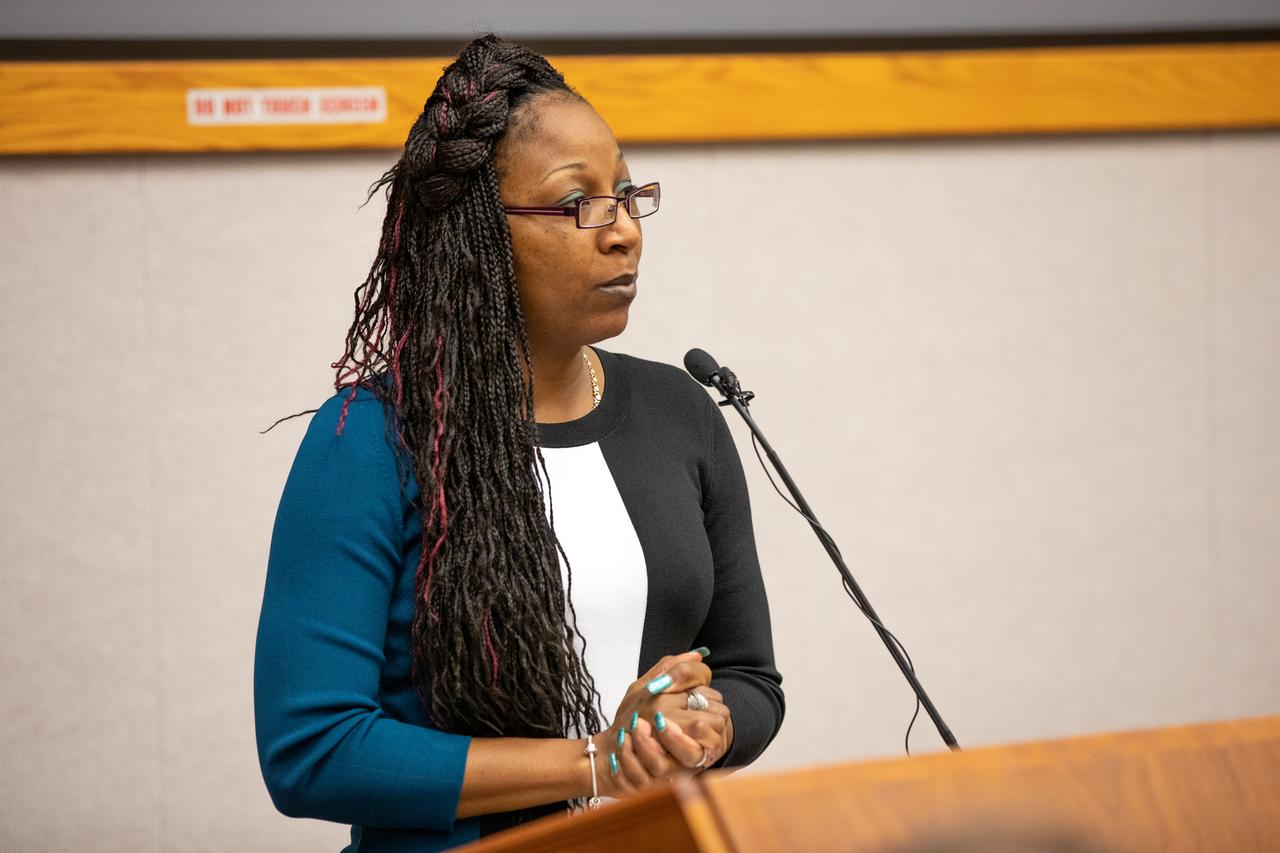

Henrietta Hanner, an administrative assistant in Safety and Mission Assurance, speaks about the theme of this year’s Black History Month celebration at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 18, 2020. The program was organized by the Black Employee Strategy Team (BEST), one of the center’s employee resource groups. This year’s theme was “African Americans and the Vote.” Keynote speaker was James Jennings, former NASA associate administrator for Institutions and Management and Kennedy’s former deputy director. Jennings shared advice with workers and managers.
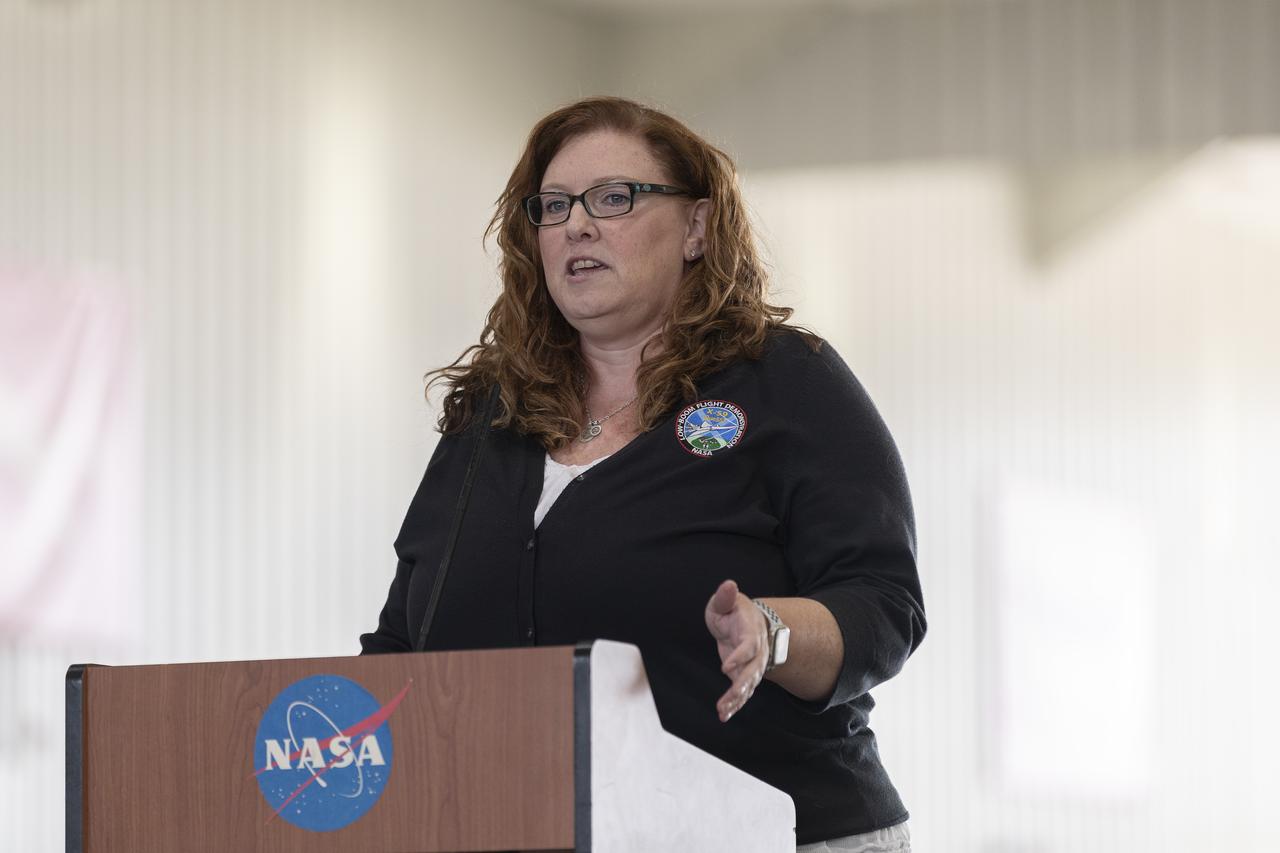

Cathy Bahm, Low Boom Flight Demonstrator project manager at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, presents a look at how the X-59 aircraft team addresses safety. Bahm manages the effort to design, build, and test the X-59 aircraft, which will use quiet supersonic technologies to fly over communities as part of NASA’s Quesst mission.
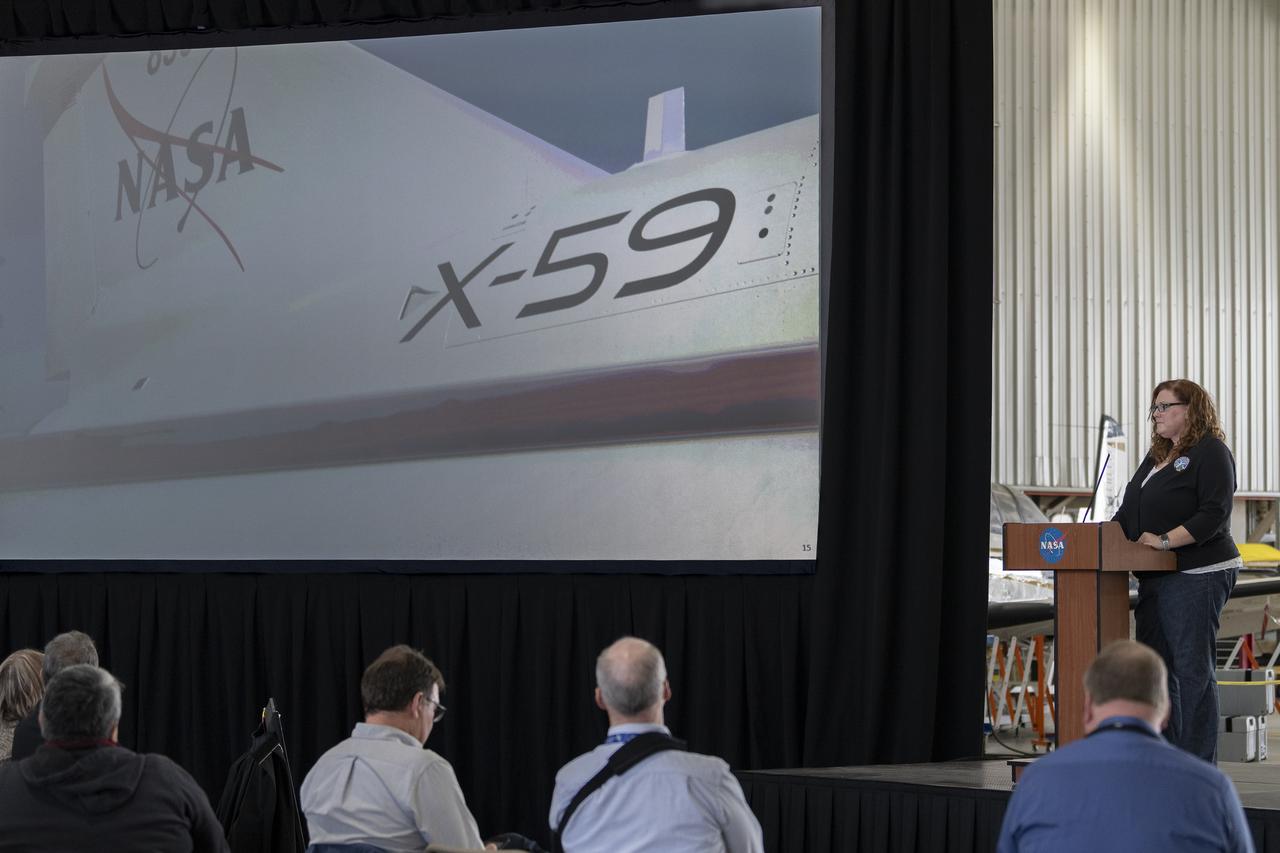

Cathy Bahm, Low Boom Flight Demonstrator project manager at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, presents a look at how the X-59 aircraft team addresses safety. Bahm manages the effort to design, build, and test the X-59 aircraft, which will use quiet supersonic technologies to fly over communities as part of NASA’s Quesst mission.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA managers brief the media about the Space Shuttle Program and mission STS-121 from the press site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Public Information Officer Jessica Rye moderated. Seated at her right are Space Shuttle Program Manager Wayne Hale, NASA Launch Director Mike Leinbach and STS-114 External Tank Tiger Team lead Tim Wilson, with the NASA Engineering & Safety Center. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
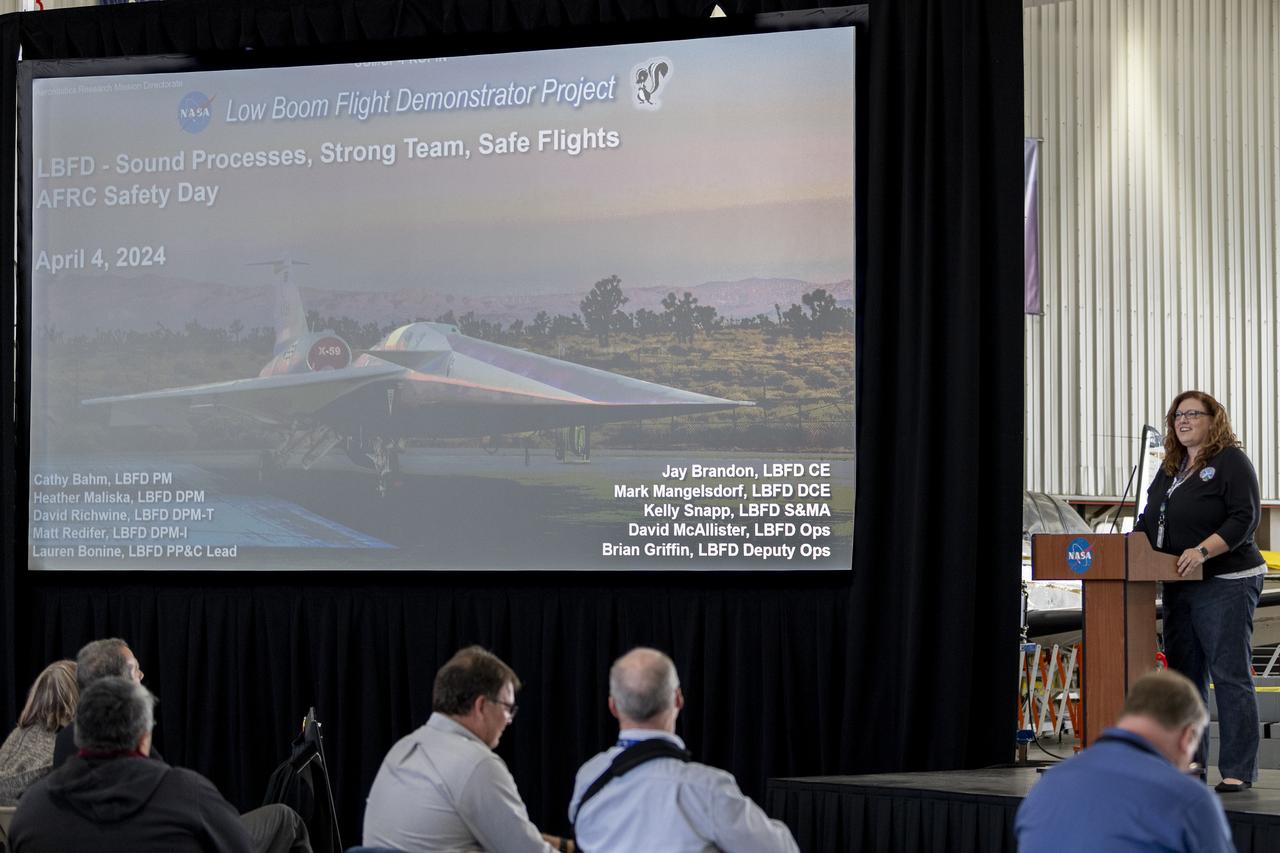

Cathy Bahm, Low Boom Flight Demonstrator project manager at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, presents a look at how the X-59 aircraft team addresses safety. Bahm manages the effort to design, build, and test the X-59 aircraft, which will use quiet supersonic technologies to fly over communities as part of NASA’s Quesst mission.
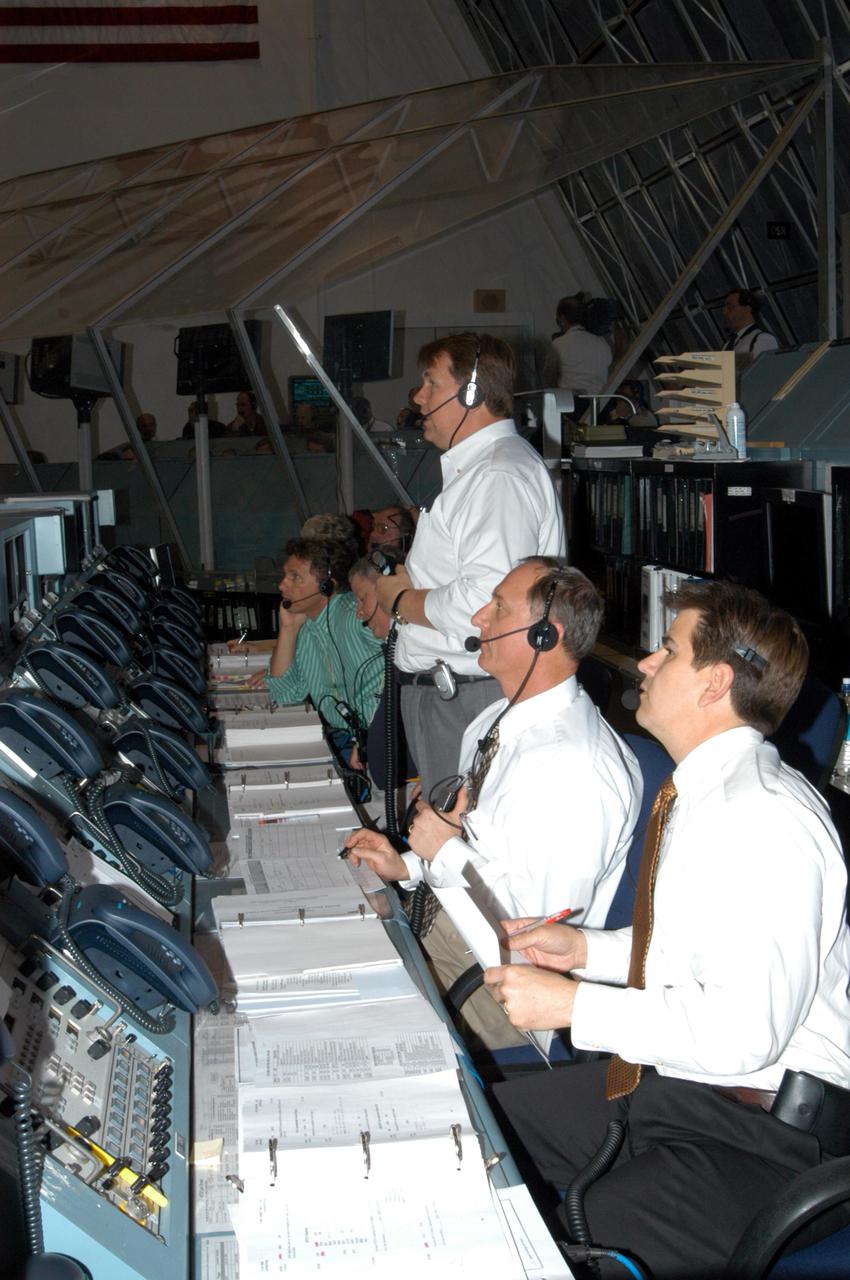

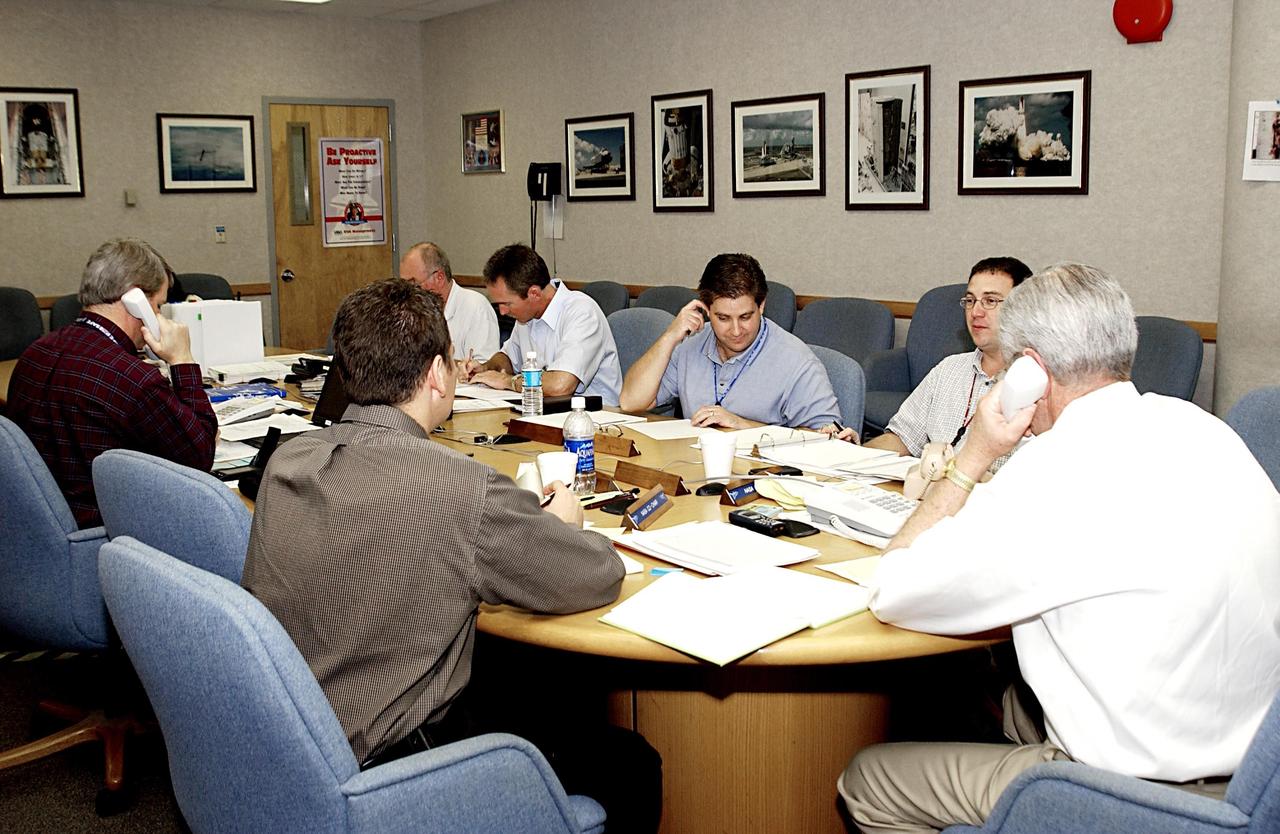
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle Program managers, directors and engineers man the consoles in the Launch Control Center. They are taking part in an End-to-End (ETE) Mission Management Team (MMT) launch simulation at KSC. In Firing Room 1 at KSC, Shuttle launch team members put the Shuttle system through an integrated simulation. The control room is set up with software used to simulate flight and ground systems in the launch configuration. The ETE MMT simulation included L-2 and L-1 day Prelaunch MMT meetings, an external tanking_weather briefing, and a launch countdown. The ETE transitioned to the Johnson Space Center for the flight portion of the simulation, with the STS-114 crew in a simulator at JSC. Such simulations are common before a launch to keep the Shuttle launch team sharp and ready for liftoff.
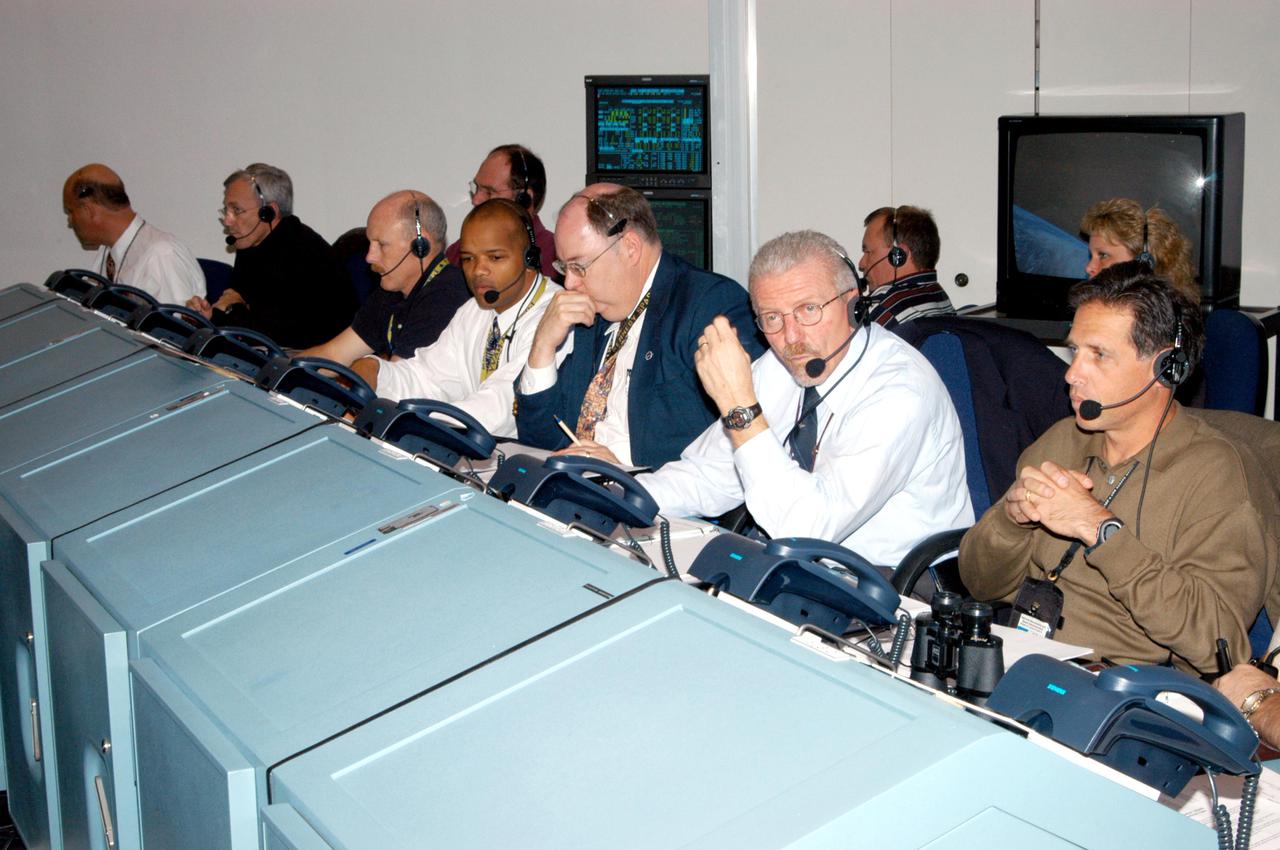

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle Program managers, directors and engineers work the consoles in the Launch Control Center. They are taking part in an End-to-End (ETE) Mission Management Team (MMT) launch simulation at KSC. In Firing Room 1 at KSC, Shuttle launch team members put the Shuttle system through an integrated simulation. The control room is set up with software used to simulate flight and ground systems in the launch configuration. The ETE MMT simulation included L-2 and L-1 day Prelaunch MMT meetings, an external tanking_weather briefing, and a launch countdown. The ETE transitioned to the Johnson Space Center for the flight portion of the simulation, with the STS-114 crew in a simulator at JSC. Such simulations are common before a launch to keep the Shuttle launch team sharp and ready for liftoff.
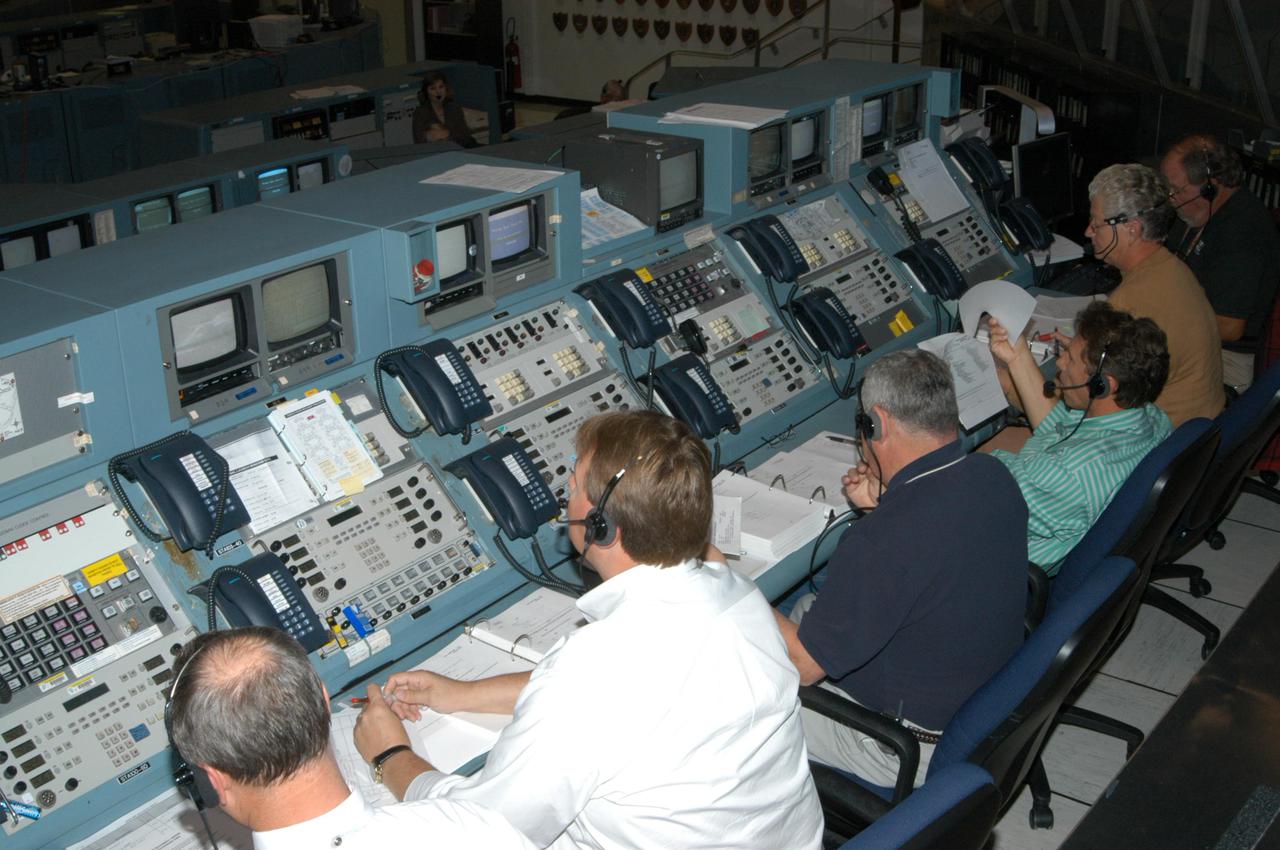

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle Program managers, directors and engineers work the consoles in the Launch Control Center. They are taking part in an End-to-End (ETE) Mission Management Team (MMT) launch simulation at KSC. In Firing Room 1 at KSC, Shuttle launch team members put the Shuttle system through an integrated simulation. The control room is set up with software used to simulate flight and ground systems in the launch configuration. The ETE MMT simulation included L-2 and L-1 day Prelaunch MMT meetings, an external tanking_weather briefing, and a launch countdown. The ETE transitioned to the Johnson Space Center for the flight portion of the simulation, with the STS-114 crew in a simulator at JSC. Such simulations are common before a launch to keep the Shuttle launch team sharp and ready for liftoff.

Mike Bolger, manager, Exploration Ground Systems, participates in the 11th terminal countdown simulation for the Artemis I launch inside Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Control Center on Oct. 14, 2021. The event marked the first time members of NASA’s mission management team, launch team, and contractor Jacobs conducted the simulation together. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
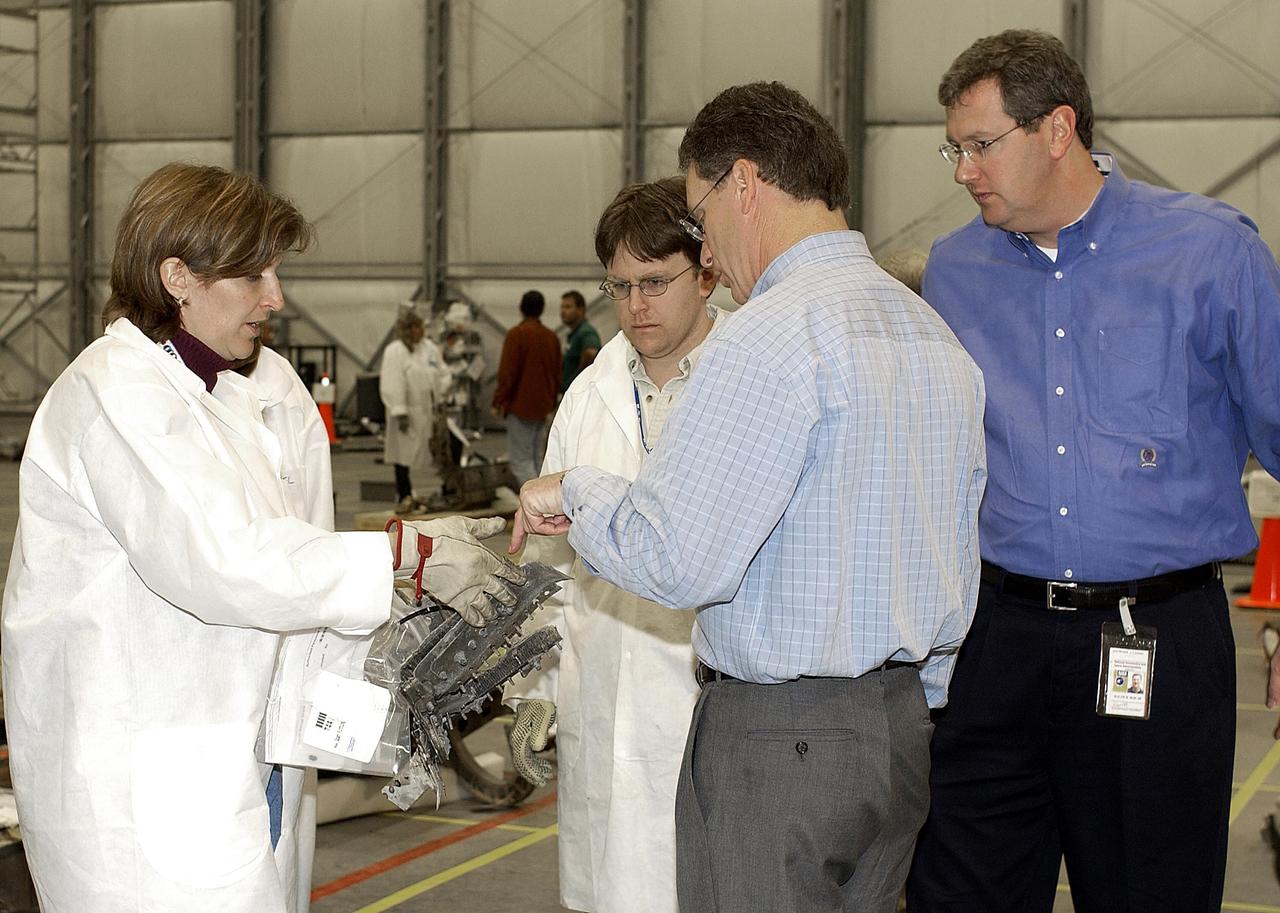

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the RLV Hangar at KSC, members of the Columbia Restoration Project Team show Shuttle Program Manager Ron Dittemore (third from left) and Ralph Roe, with the Orbiter Work Group at JSC, a piece of Columbia debris. The team is examining pieces and attempting to reconstruct the orbiter as part of the investigation into the accident that caused the destruction of Columbia on its return to Earth from mission STS-107. To date, four shipments have arrived from Barksdale AFB, Shreveport, La., the collection point for debris.
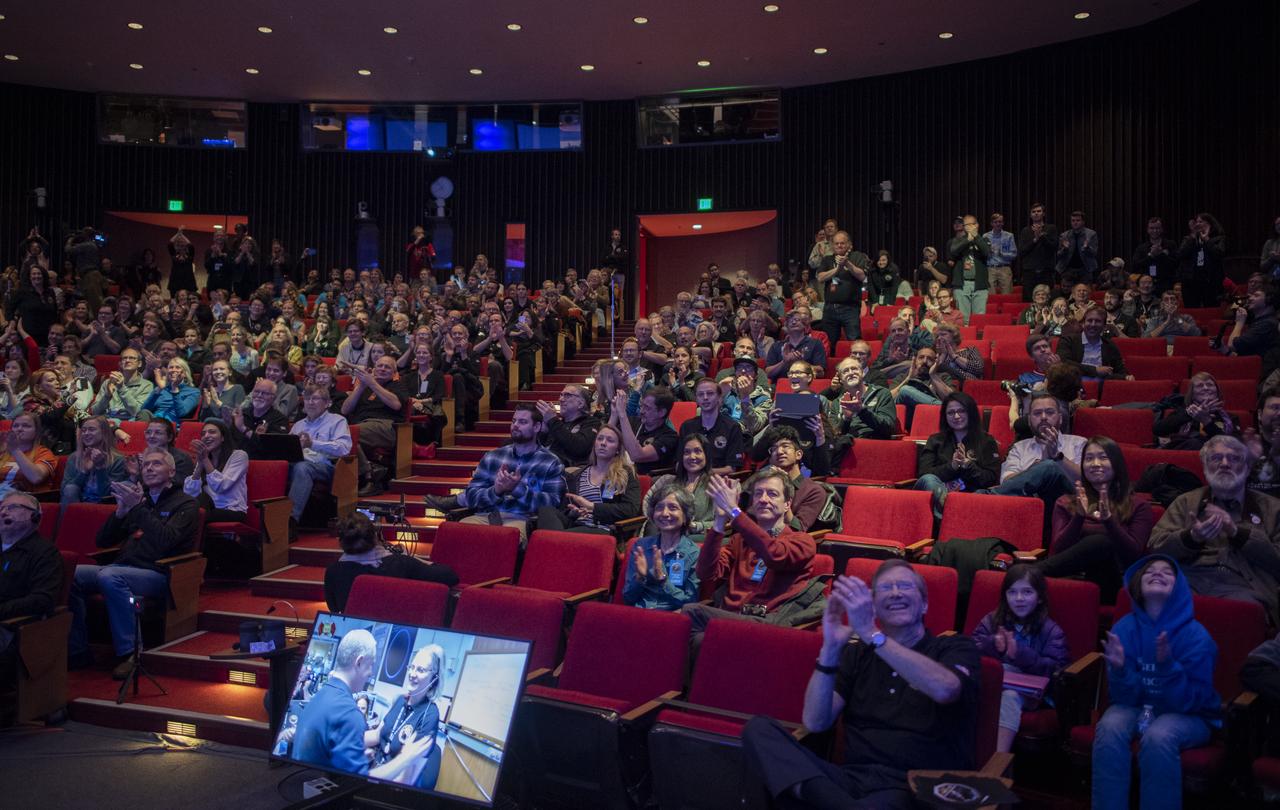

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO and New Horizons Mission Operations Manager Alice Bowman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory are seen on a television screen as New Horizons team members and guests cheer as the team receives confirmation from the spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
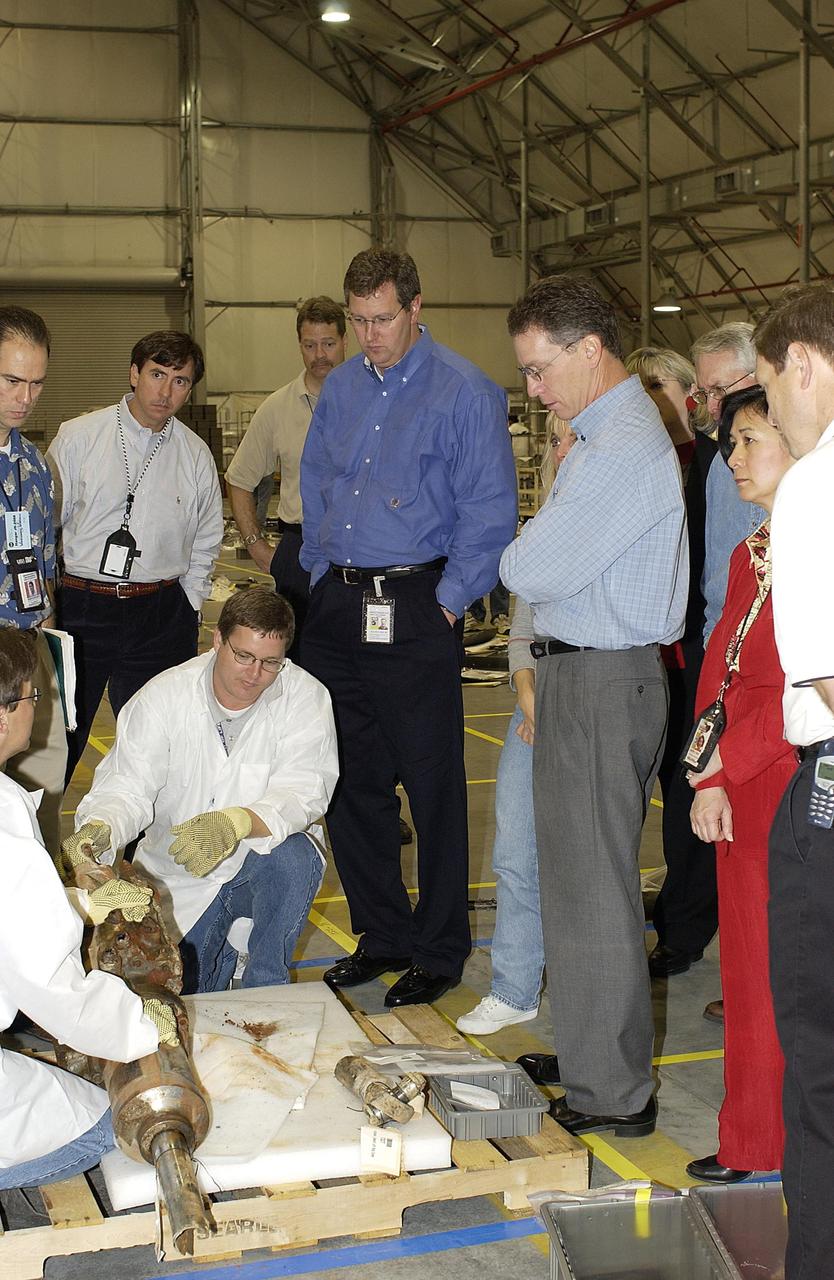

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Shuttle Program Manager Ron Dittemore (third from right) and Ralph Roe (fourth from right), with the Orbiter Work Group, JSC, look at Columbia debris being held my a member of the Columbia Restoration Project Team. The team is examining pieces and attempting to reconstruct the orbiter as part of the investigation into the accident that caused the destruction of Columbia on its return to Earth from mission STS-107. To date, four shipments have arrived from Barksdale AFB, Shreveport, La., the collection point for debris.
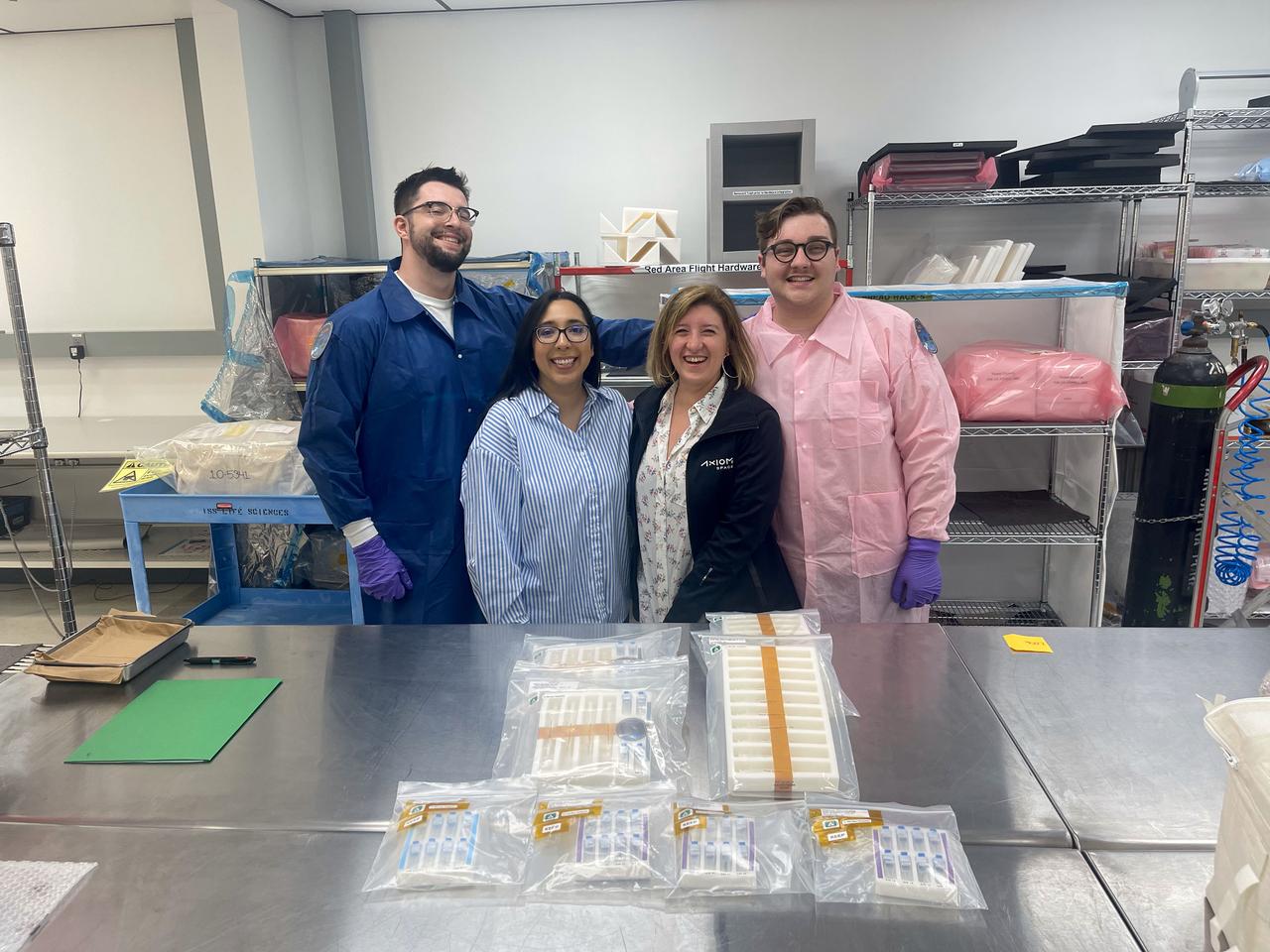

jsc2025e036193 (4/4/2025) --- Our team is pictured turning over samples for SpX-30 (Demo 2) to the NASA Packaging team. From left to right, we see Maxwell Landolina (UCONN PhD Student), Alexis Rios (Payload Mission Integrator, Axiom Space), Pinar Mesci (Senior Program Manager, Axiom Space), and Trystin Cote (UCONN PhD Student).
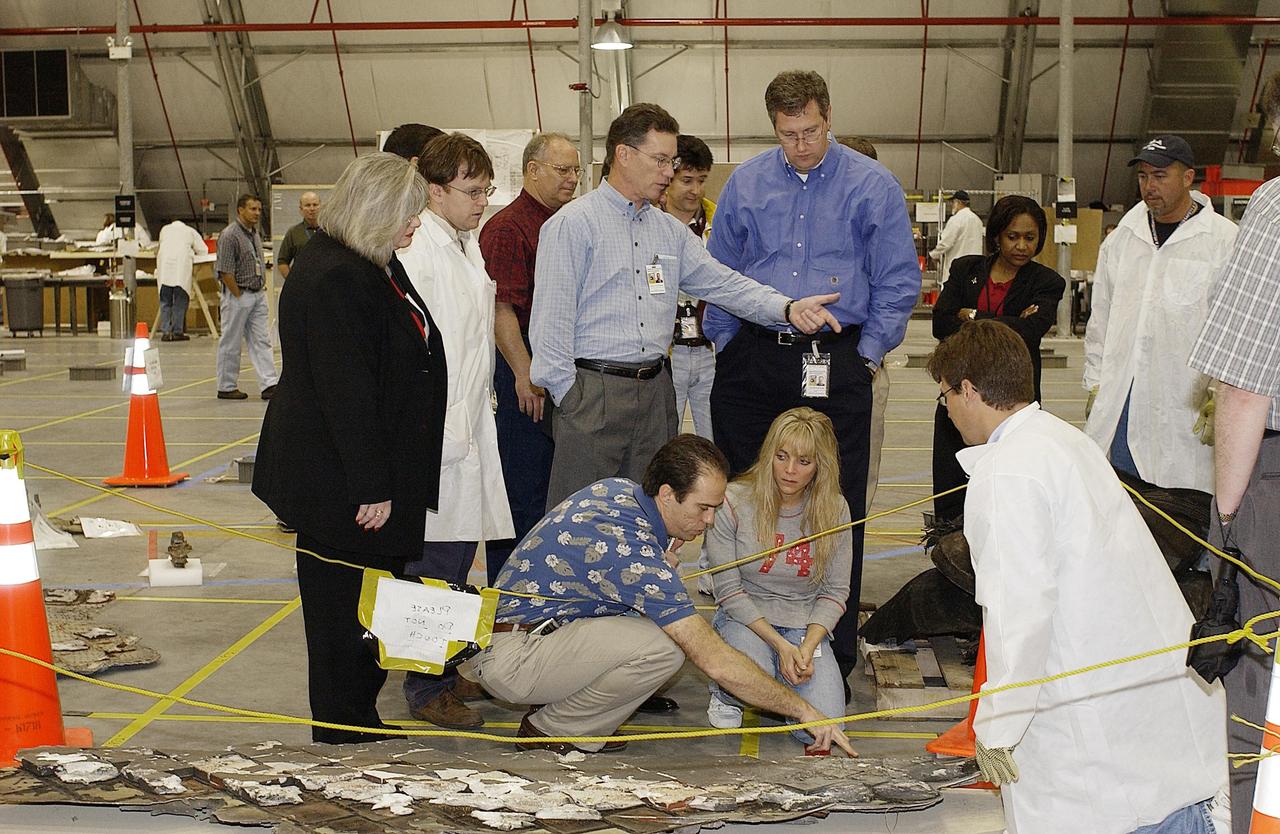

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Shuttle Program Manager Ron Dittemore (center, pointing) looks over Columbia debris with members of the Columbia Restoration Project Team. To his right is Ralph Roe, with the Orbiter Work Group, JSC. The team is examining pieces and attempting to reconstruct the orbiter as part of the investigation into the accident that caused the destruction of Columbia on its return to Earth from mission STS-107. To date, four shipments have arrived from Barksdale AFB, Shreveport, La., the collection point for debris.
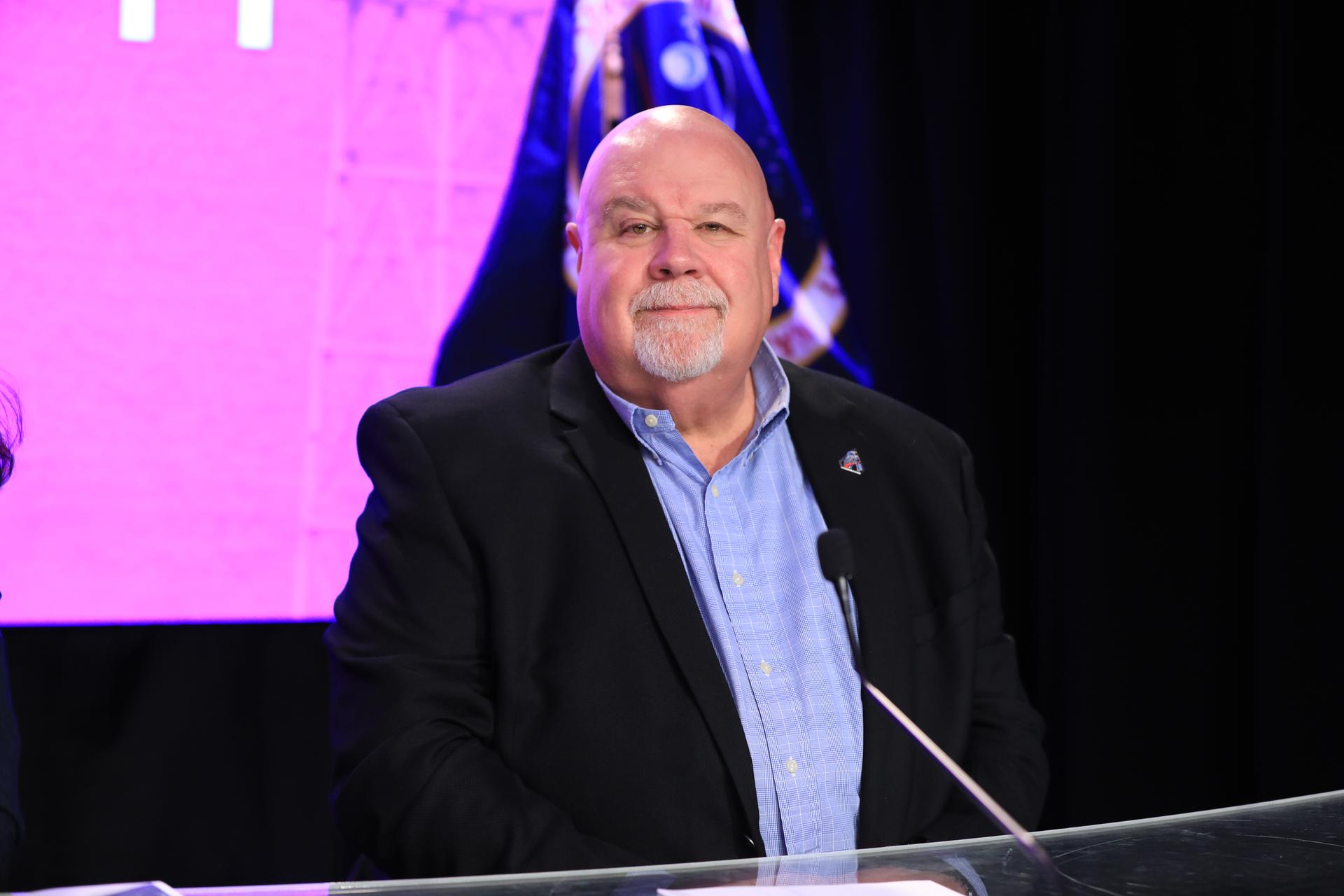

John Honeycutt, chair, Artemis II mission management team, participates in a news conference on Tuesday, Feb. 3, 2026, to discuss the completion of Artemis II wet dress rehearsal at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The wet dress rehearsal allows the Artemis II launch team to run through operations to load propellant, conduct a full launch countdown, demonstrate the ability to recycle the countdown clock, and drain the tanks to practice timelines and procedures for launch.
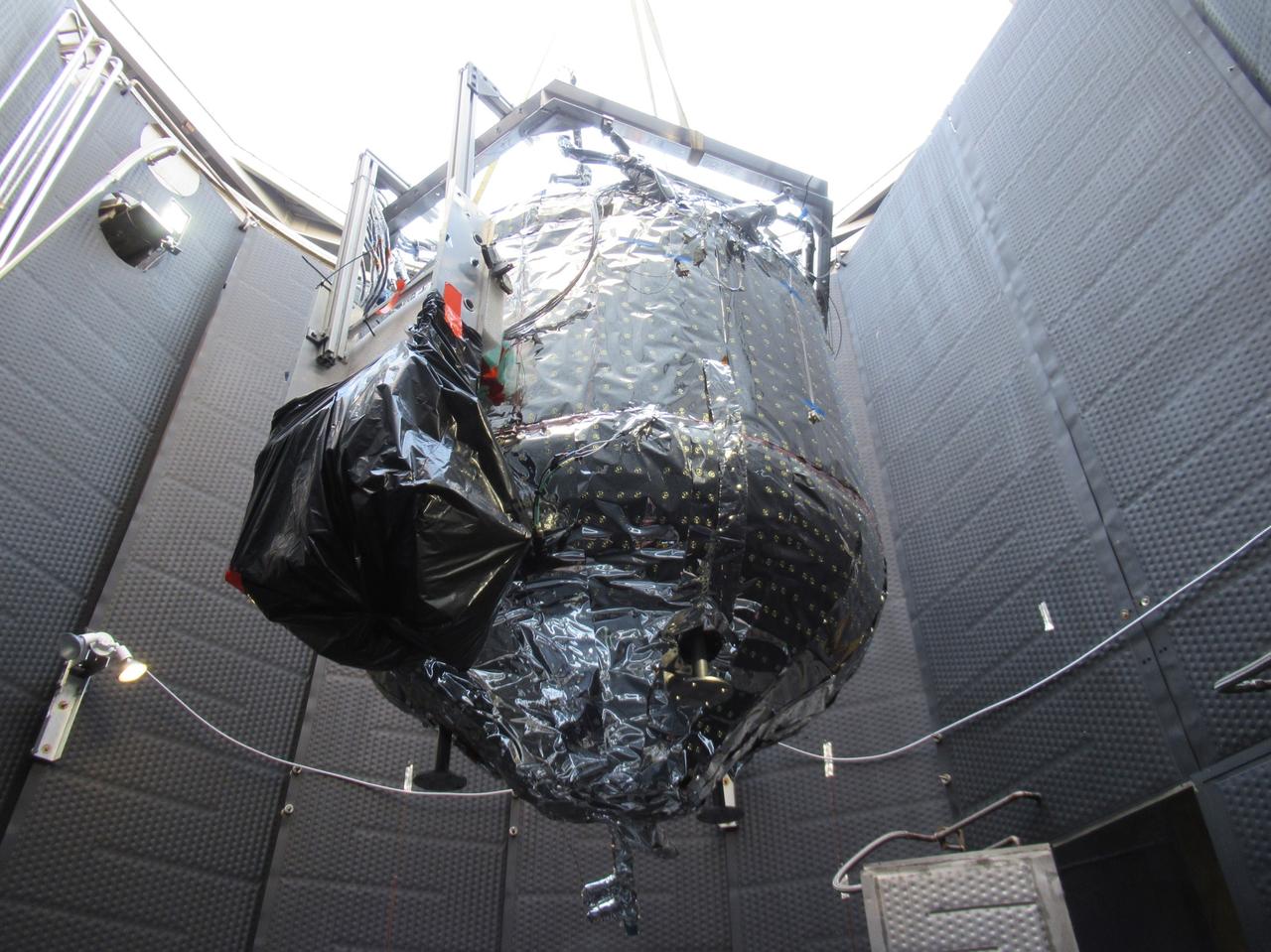

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are testing an innovative approach to achieve zero boiloff storage of liquid hydrogen using two stages of active cooling, which could prevent the loss of valuable propellant during future long-duration spaceflight missions. Test teams installed the propellant tank in Test Stand 300 at NASA Marshall in early June, and the 90-day test campaign is scheduled to conclude in September. The tank is wrapped in a multi-layer insulation blanket that includes a thin aluminum heat shield fitted between layers. A second set of tubes, carrying helium at about minus 298 Fahrenheit, is integrated into the shield. This intermediate cooling layer intercepts and rejects incoming heat before it reaching the tank, easing the heat load on the tube-on-tank system. The Cryogenic Fluid Management Portfolio Project is a cross-agency team based at NASA Marshall and the agency’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland. The cryogenic portfolio’s work is under NASA’s Technology Demonstration Missions Program, part of NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate, and is comprised of more than 20 individual technology development activities. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are testing an innovative approach to achieve zero boiloff storage of liquid hydrogen using two stages of active cooling, which could prevent the loss of valuable propellant during future long-duration spaceflight missions. Test teams installed the propellant tank in Test Stand 300 at NASA Marshall in early June, and the 90-day test campaign is scheduled to conclude in September. The tank is wrapped in a multi-layer insulation blanket that includes a thin aluminum heat shield fitted between layers. A second set of tubes, carrying helium at about minus 298 Fahrenheit, is integrated into the shield. This intermediate cooling layer intercepts and rejects incoming heat before it reaching the tank, easing the heat load on the tube-on-tank system. The Cryogenic Fluid Management Portfolio Project is a cross-agency team based at NASA Marshall and the agency’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland. The cryogenic portfolio’s work is under NASA’s Technology Demonstration Missions Program, part of NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate, and is comprised of more than 20 individual technology development activities. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
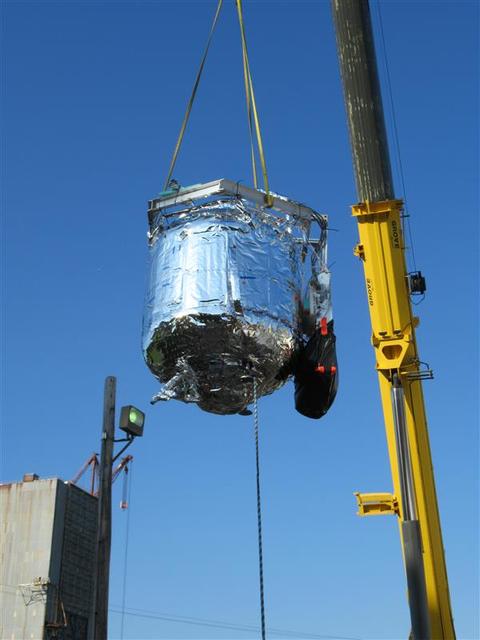

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are testing an innovative approach to achieve zero boiloff storage of liquid hydrogen using two stages of active cooling, which could prevent the loss of valuable propellant during future long-duration spaceflight missions. Test teams installed the propellant tank in Test Stand 300 at NASA Marshall in early June, and the 90-day test campaign is scheduled to conclude in September. The tank is wrapped in a multi-layer insulation blanket that includes a thin aluminum heat shield fitted between layers. A second set of tubes, carrying helium at about minus 298 Fahrenheit, is integrated into the shield. This intermediate cooling layer intercepts and rejects incoming heat before it reaching the tank, easing the heat load on the tube-on-tank system. The Cryogenic Fluid Management Portfolio Project is a cross-agency team based at NASA Marshall and the agency’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland. The cryogenic portfolio’s work is under NASA’s Technology Demonstration Missions Program, part of NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate, and is comprised of more than 20 individual technology development activities. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
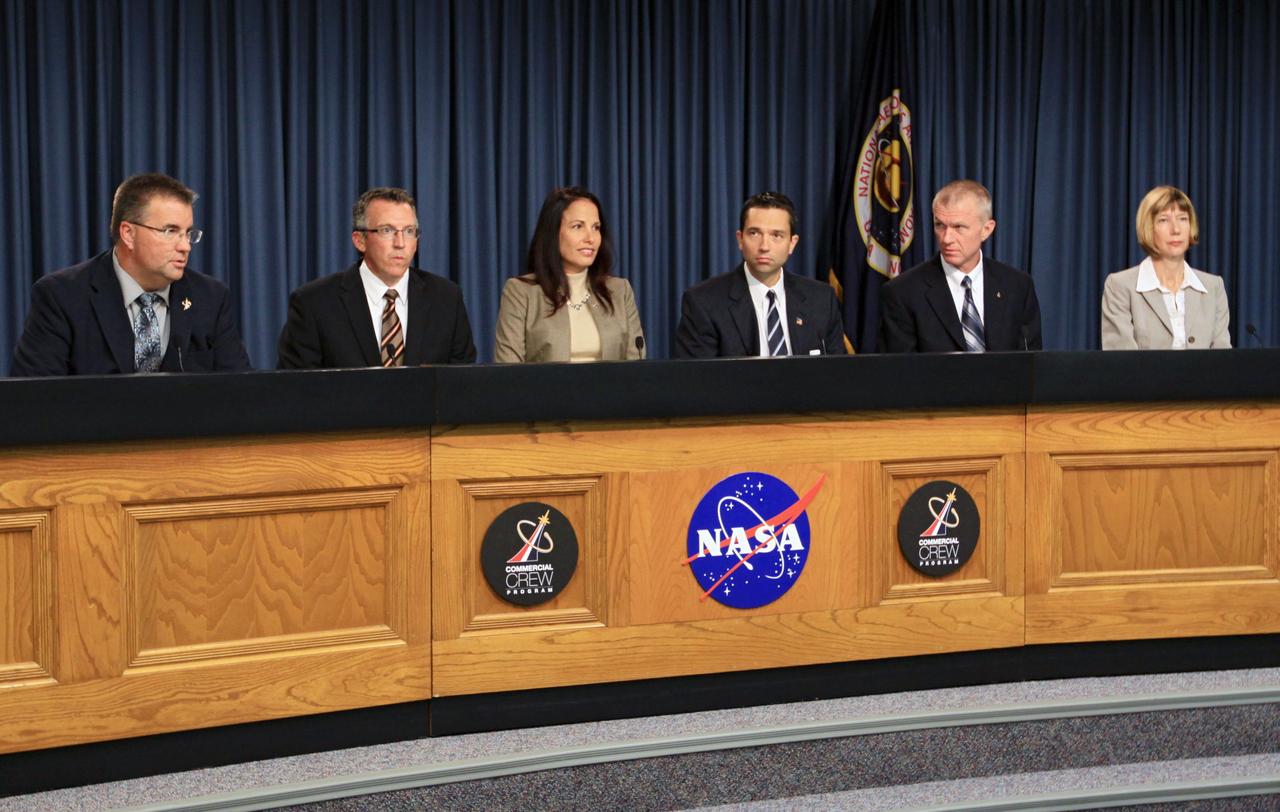

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, hosts a pre-proposal conference to inform prospective companies about the recently released request for contract proposals and updates to the certification requirements for crewed missions to the International Space Station, or ISS. The two-phase certification process, called Certification Products Contract, or CPC, will enable NASA to eventually purchase service missions to fly astronauts to and from the ISS. From left, Ed Mango, CCP's program manager Steve Janney, CPC contracting officer Maria Collura, CCP certification manager Tom Simon, CPC Evaluation Team chair Brent Jett, CCP deputy program manager and Kathy Lueders, manager of the ISS Transportation Integration Office. To learn more about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
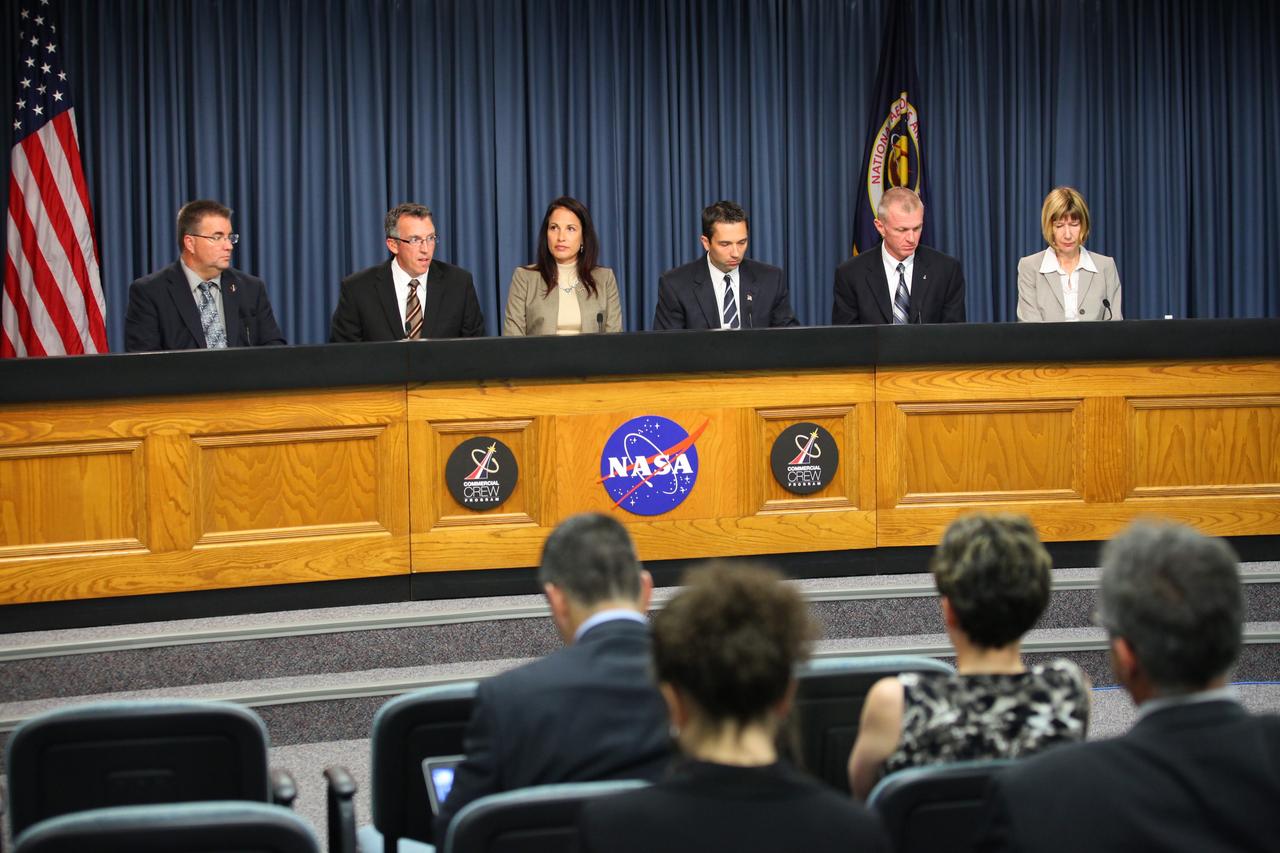

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, hosts a pre-proposal conference to inform prospective companies about the recently released request for contract proposals and updates to the certification requirements for crewed missions to the International Space Station, or ISS. The two-phase certification process, called Certification Products Contract, or CPC, will enable NASA to eventually purchase service missions to fly astronauts to and from the ISS. From left, Ed Mango, CCP's program manager Steve Janney, CPC contracting officer Maria Collura, CCP certification manager Tom Simon, CPC Evaluation Team chair Brent Jett, CCP deputy program manager and Kathy Lueders, manager of the ISS Transportation Integration Office. To learn more about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
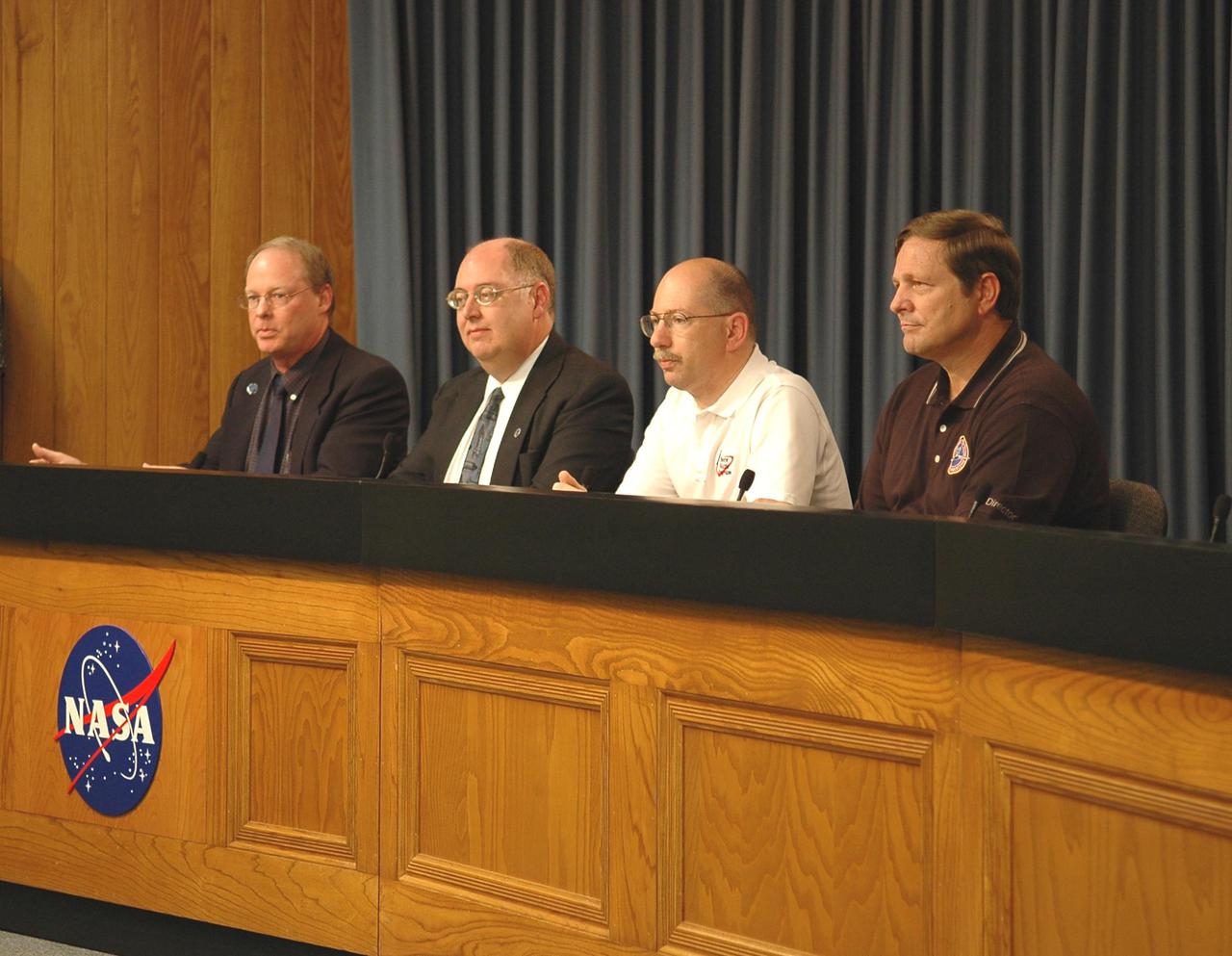

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a press conference, members of the Mission Management Team reveal aspects of the troubleshooting and testing being done on the liquid hydrogen tank low-level fuel cut-off sensor. From left are moderator Bruce Buckingham, NASA news chief; Wayne Hale, Space Shuttle deputy program manager; John Muratore, manager of Systems Engineering and Integration for the Space Shuttle Program; and Mike Wetmore, director of Space Shuttle Processing. The sensor failed a routine prelaunch check during the launch countdown July 13, causing mission managers to scrub Discovery's first launch attempt. The sensor protects the Shuttle's main engines by triggering their shutdown in the event fuel runs unexpectedly low. The sensor is one of four inside the liquid hydrogen section of the External Tank (ET).
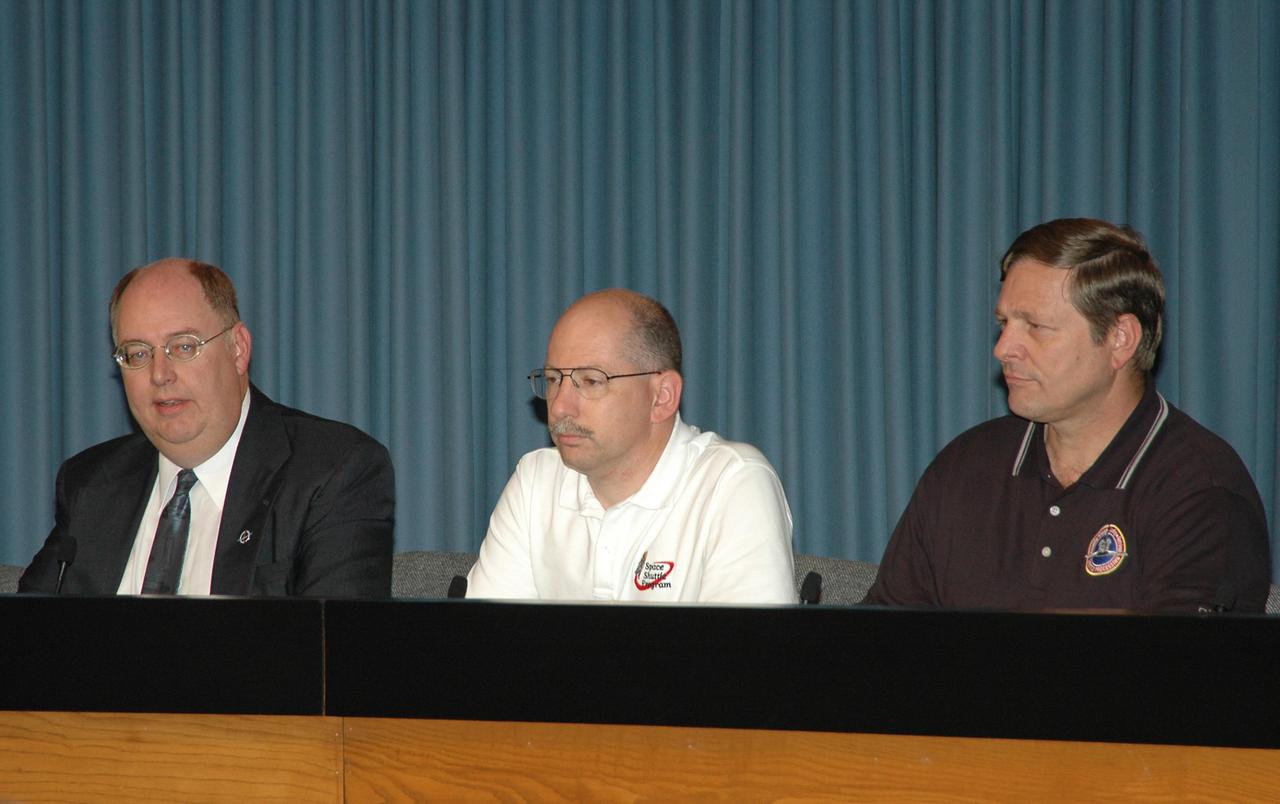

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a press conference, members of the Mission Management Team reveal aspects of the troubleshooting and testing being done on the liquid hydrogen tank low-level fuel cut-off sensor. From left are Wayne Hale, Space Shuttle deputy program manager; John Muratore, manager of Systems Engineering and Integration for the Space Shuttle Program; and Mike Wetmore, director of Space Shuttle Processing. The sensor failed a routine prelaunch check during the launch countdown July 13, causing mission managers to scrub Discovery's first launch attempt. The sensor protects the Shuttle's main engines by triggering their shutdown in the event fuel runs unexpectedly low. The sensor is one of four inside the liquid hydrogen section of the External Tank (ET).

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Media gather in the television studio at the NASA News Center to hear members of the Mission Management Team reveal aspects of the troubleshooting and testing being done on the liquid hydrogen tank low-level fuel cut-off sensor. On the stage at right are (from left) Bruce Buckingham, NASA news chief; Wayne Hale, Space Shuttle deputy program manager; John Muratore, manager of Systems Engineering and Integration for the Space Shuttle Program; and Mike Wetmore, director of Space Shuttle Processing. The sensor failed a routine prelaunch check during the launch countdown July 13, causing mission managers to scrub Discovery's first launch attempt. The sensor protects the Shuttle's main engines by triggering their shutdown in the event fuel runs unexpectedly low. The sensor is one of four inside the liquid hydrogen section of the External Tank (ET).
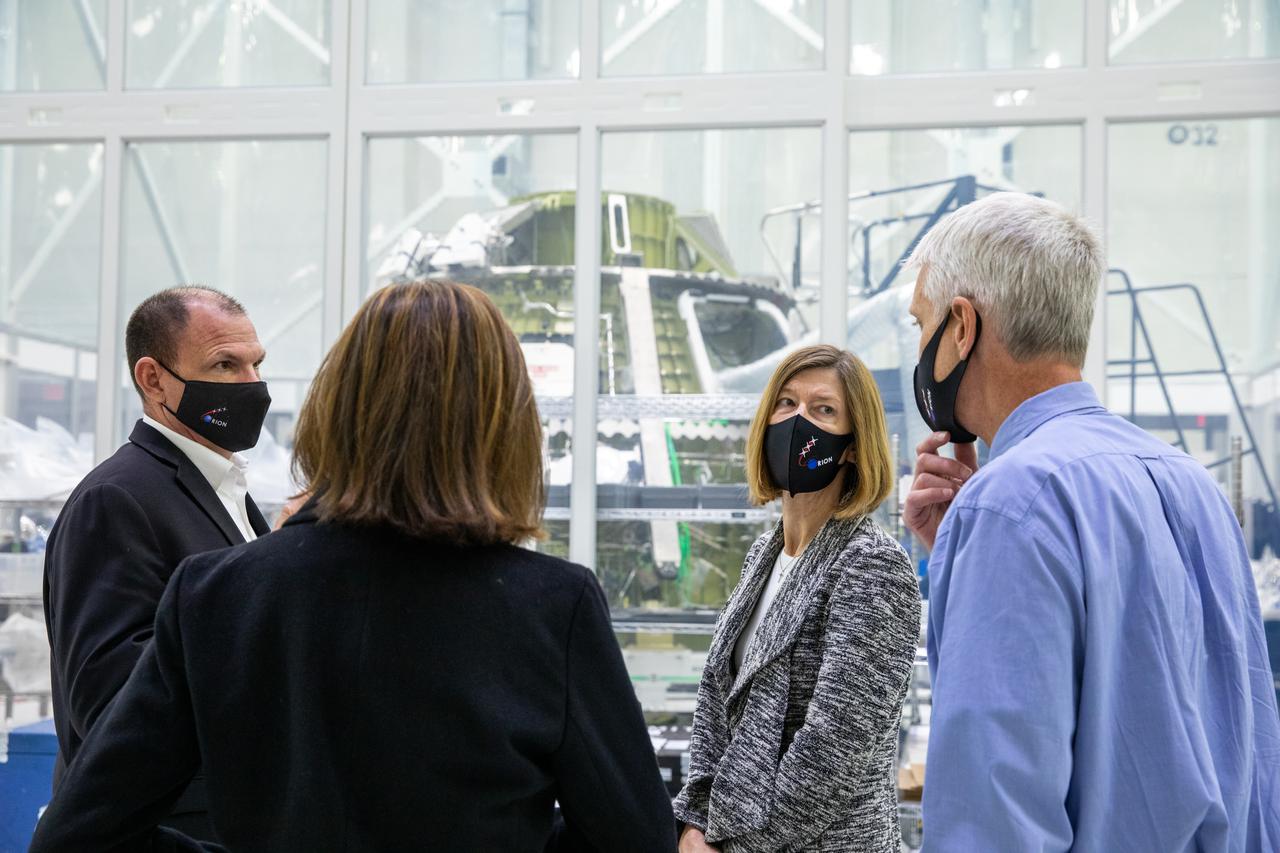

Kathy Lueders, second from right, associate administrator of the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate, tours the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. In the background is the Orion crew module for the Artemis II mission. From left are Tony Antonelli, Lockheed Martin Orion Program director and Artemis II Mission director; Cathy Koerner, Orion Program manager; and Scott Wilson, Orion Production Operations manager. The group also viewed the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I as it was lowered onto a transporter for the move to the Multi-Payload Processing Facility to begin ground processing by the Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs teams.
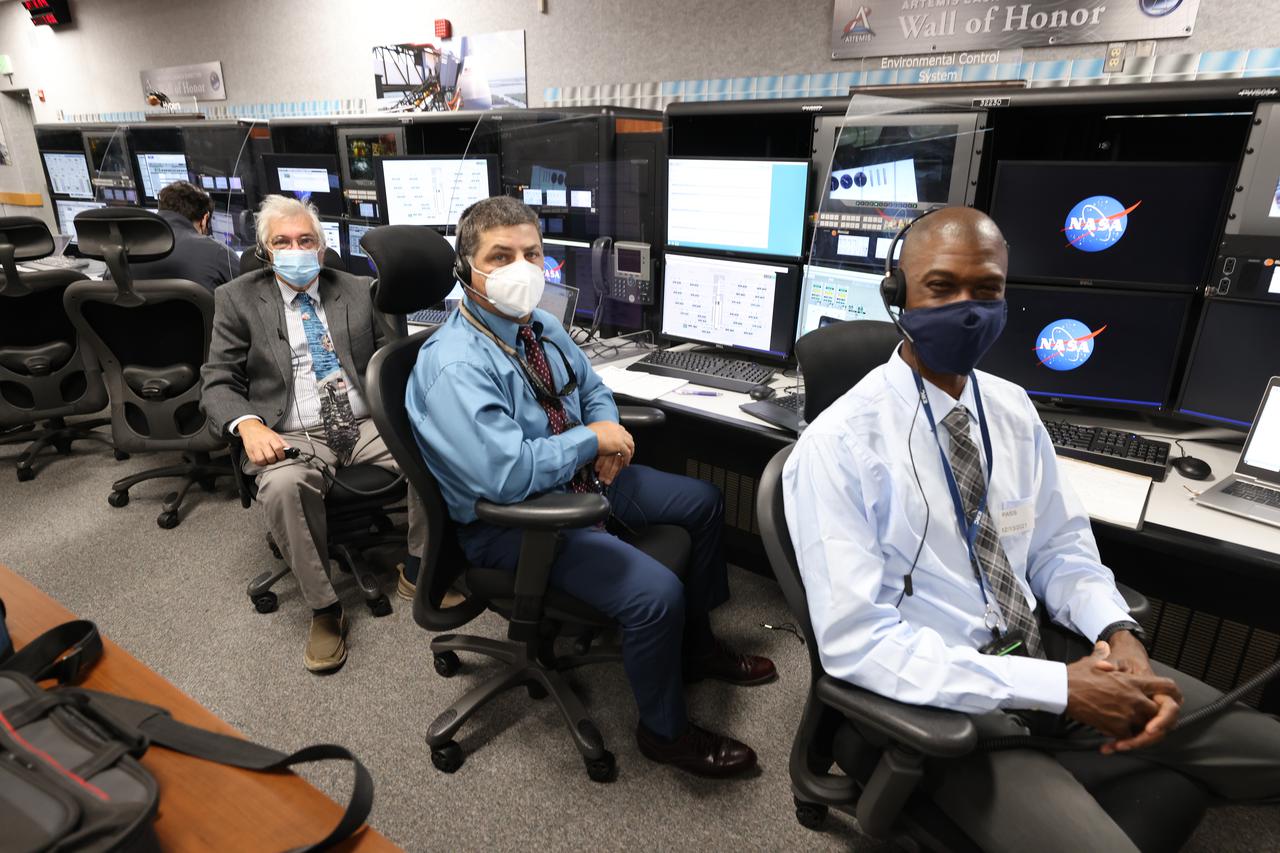

Launch team members are seated at the Environment Control System consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
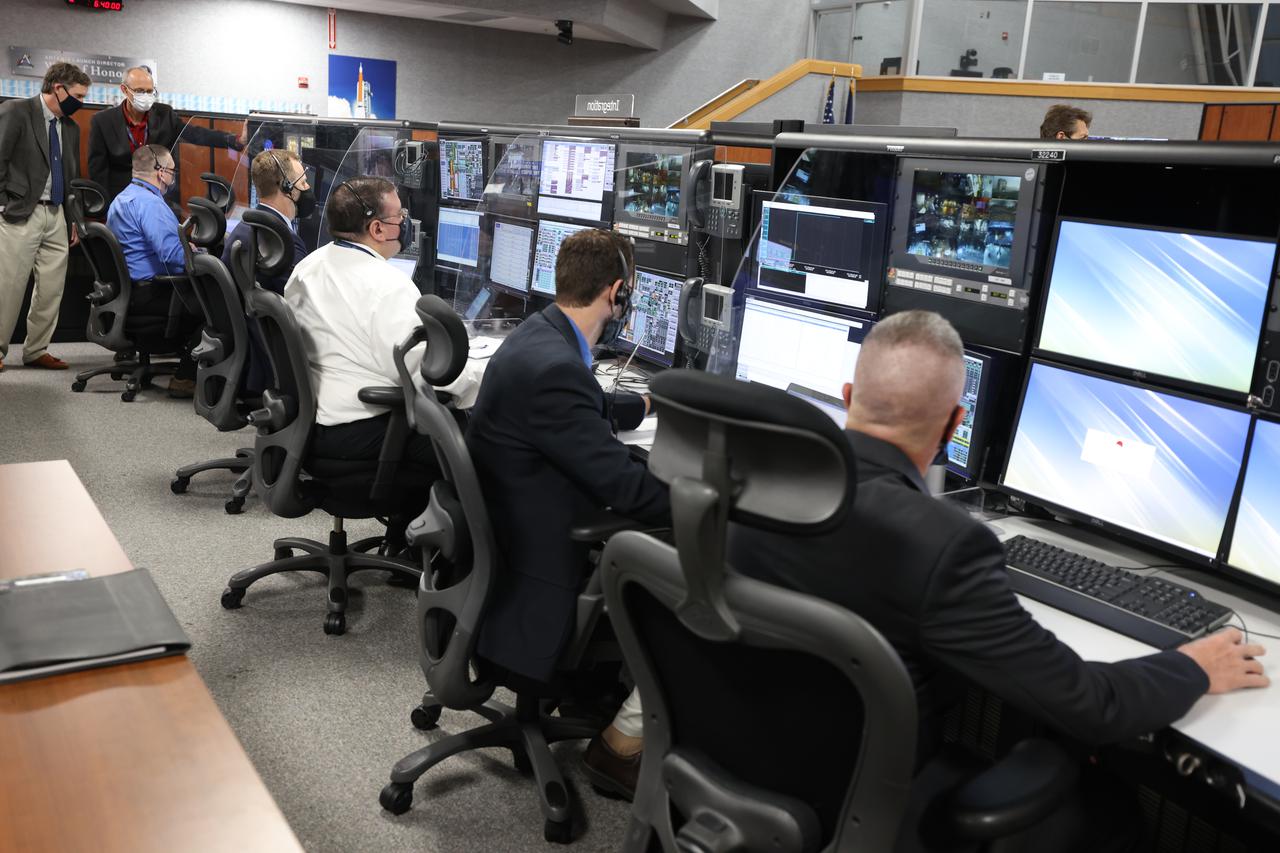

Launch team members are seated at the Integration consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
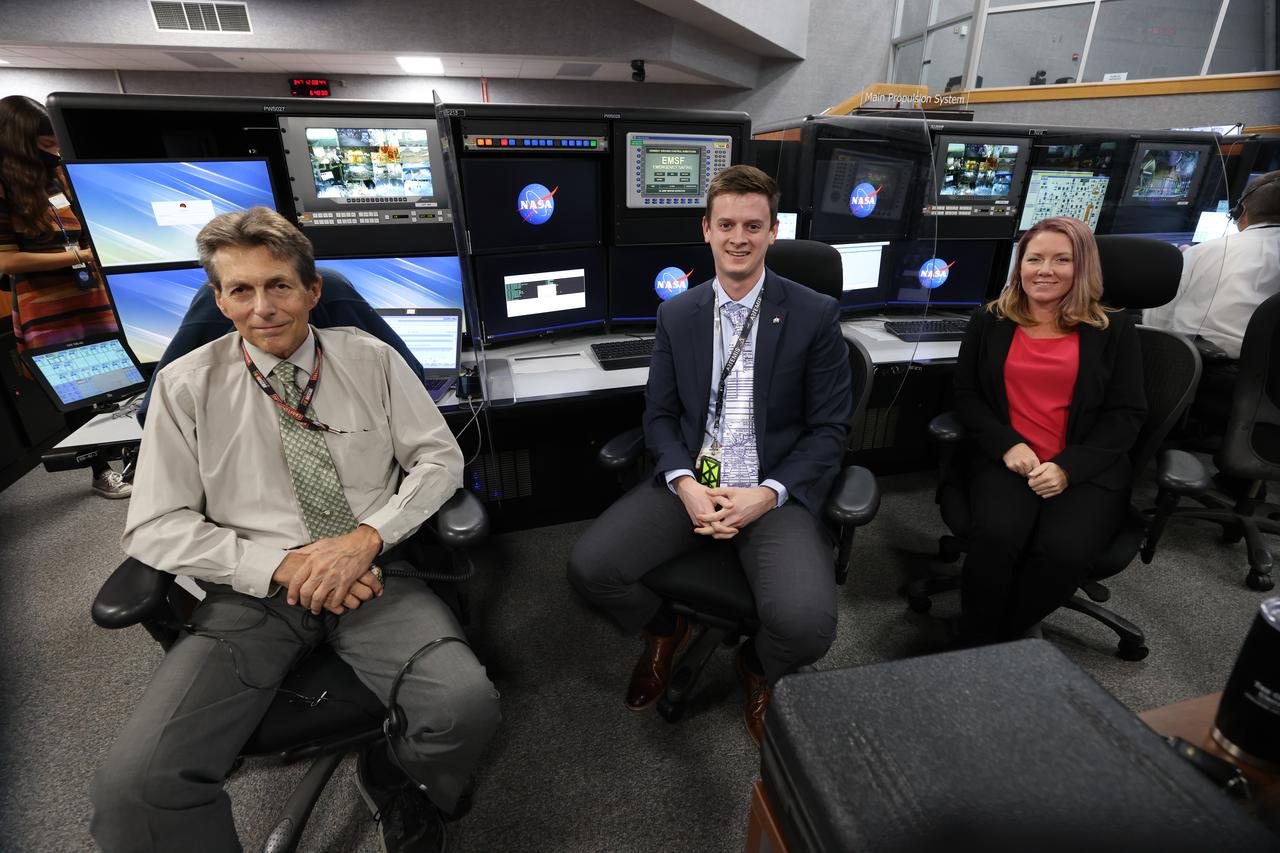

Launch team members are seated at the Main Propulsion consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.

Launch team members are seated the Integration consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
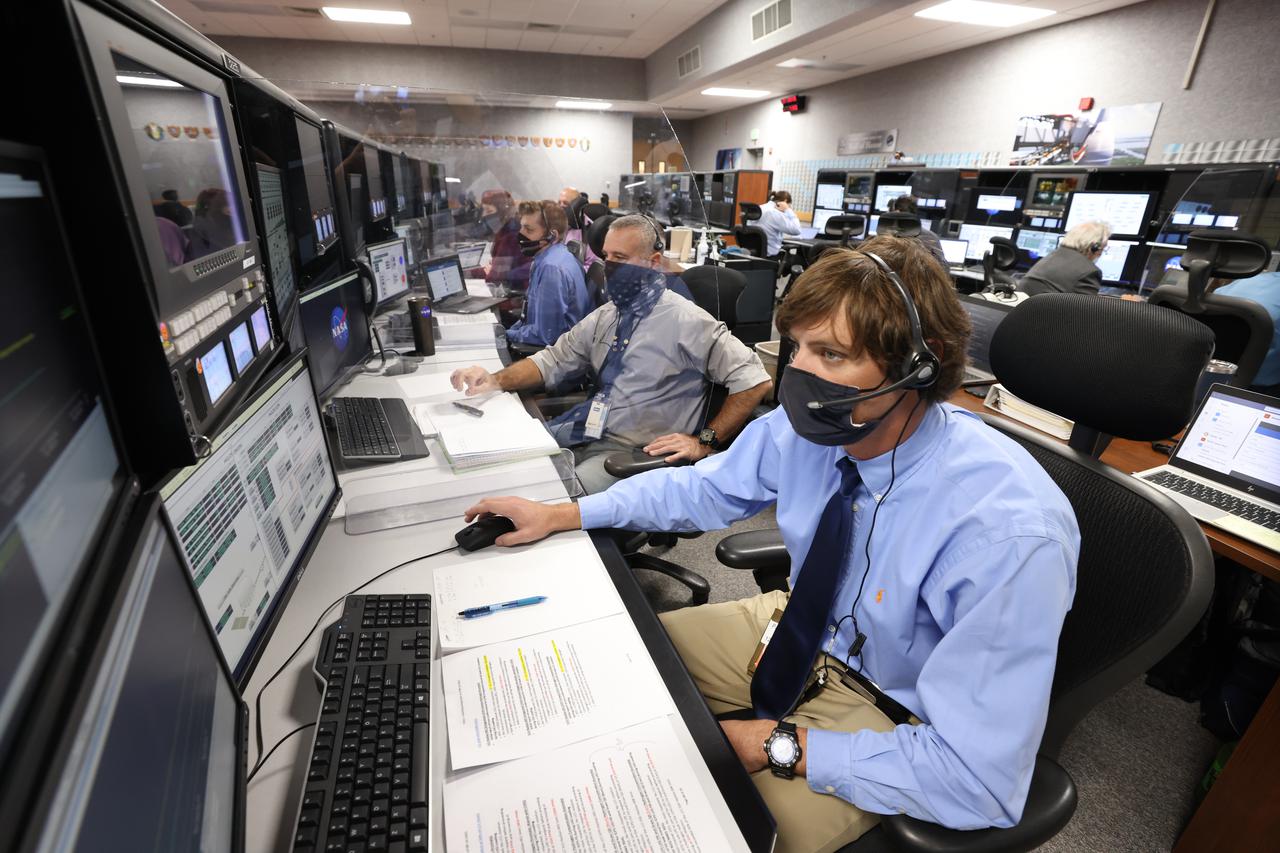

Launch team members are seated at the Hazardous Gas consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
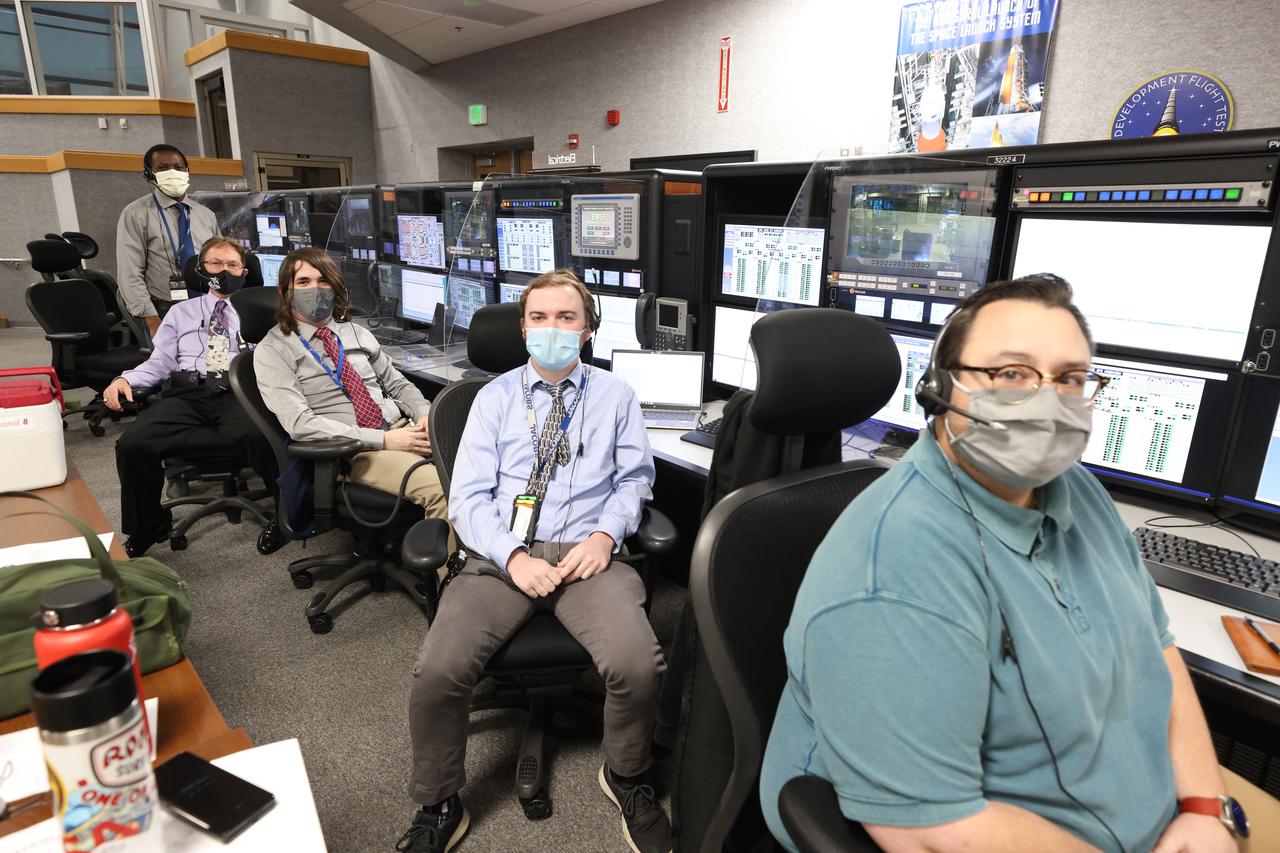

Launch team members are seated at the Electrical System consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
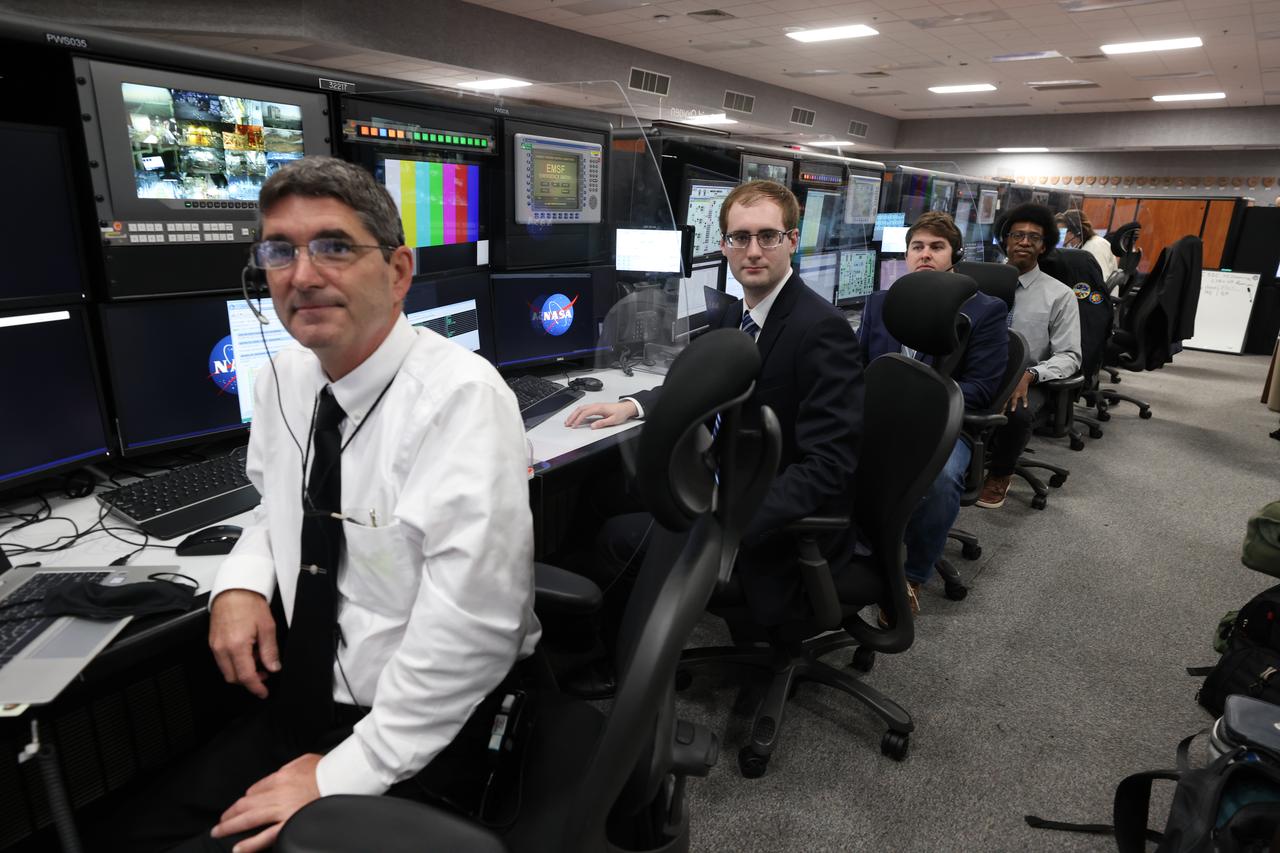

Launch team members are seated at the Liquid Oxygen consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
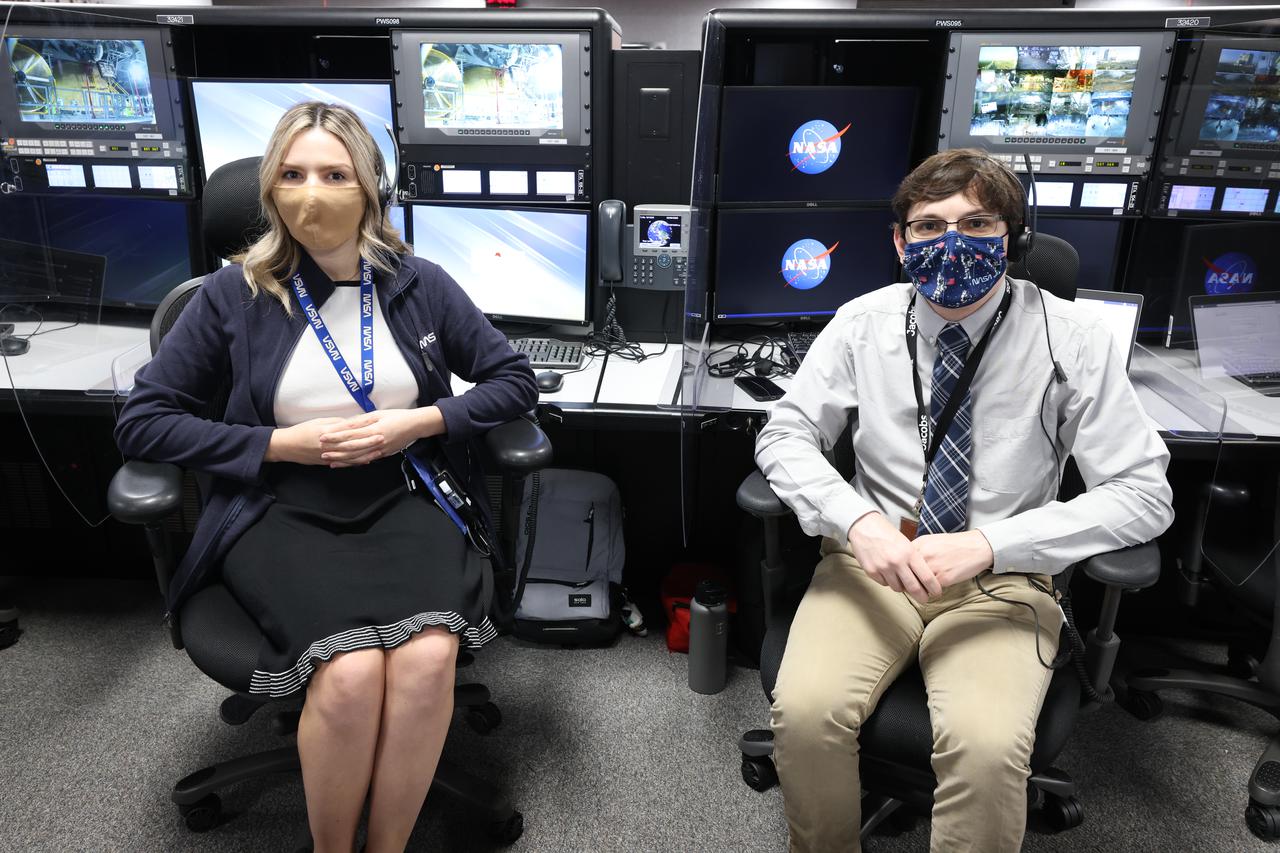

Launch team members are seated at the Communication and Tracking consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
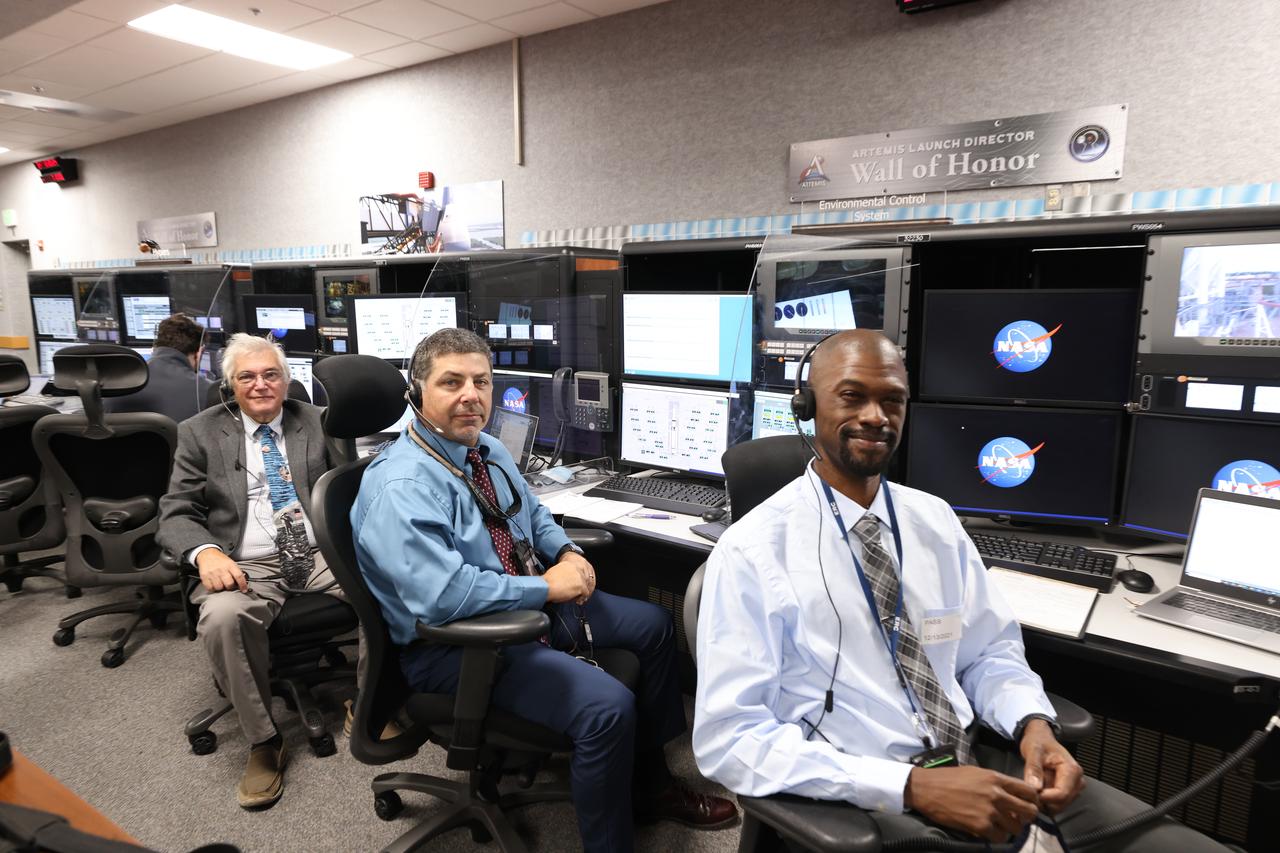

Launch team members are seated at the Environment Control System consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
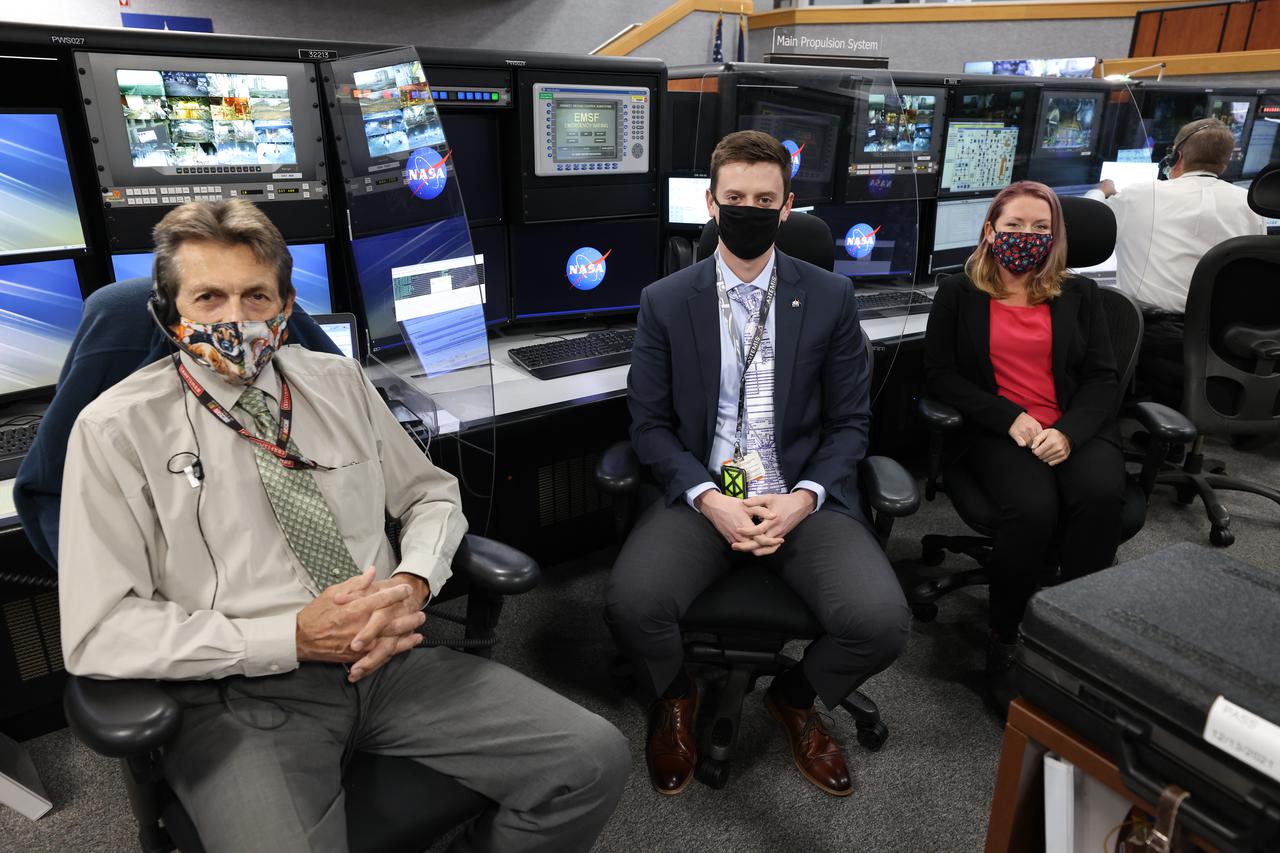

Launch team members are seated at the Main Propulsion System consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
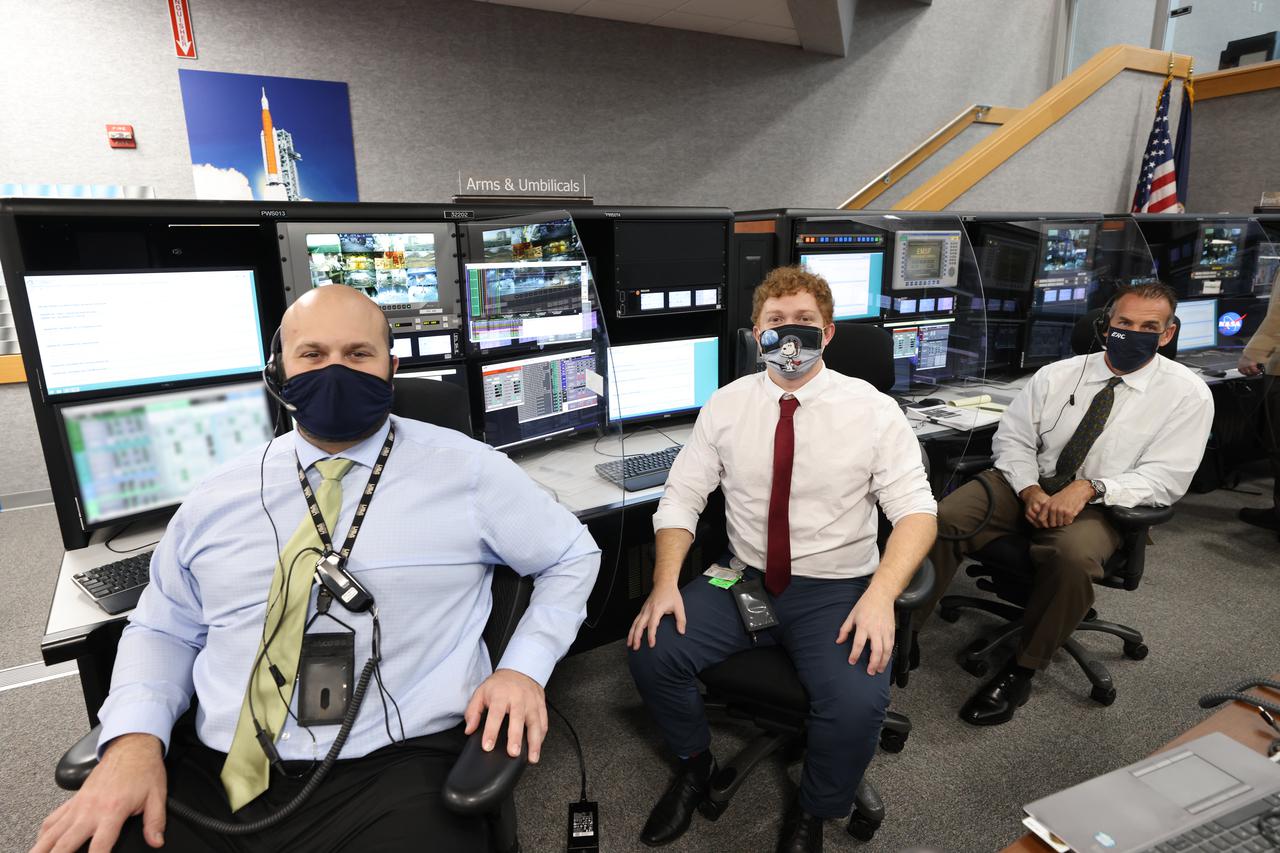

Launch team members are seated at the Arms and Umbilicals consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
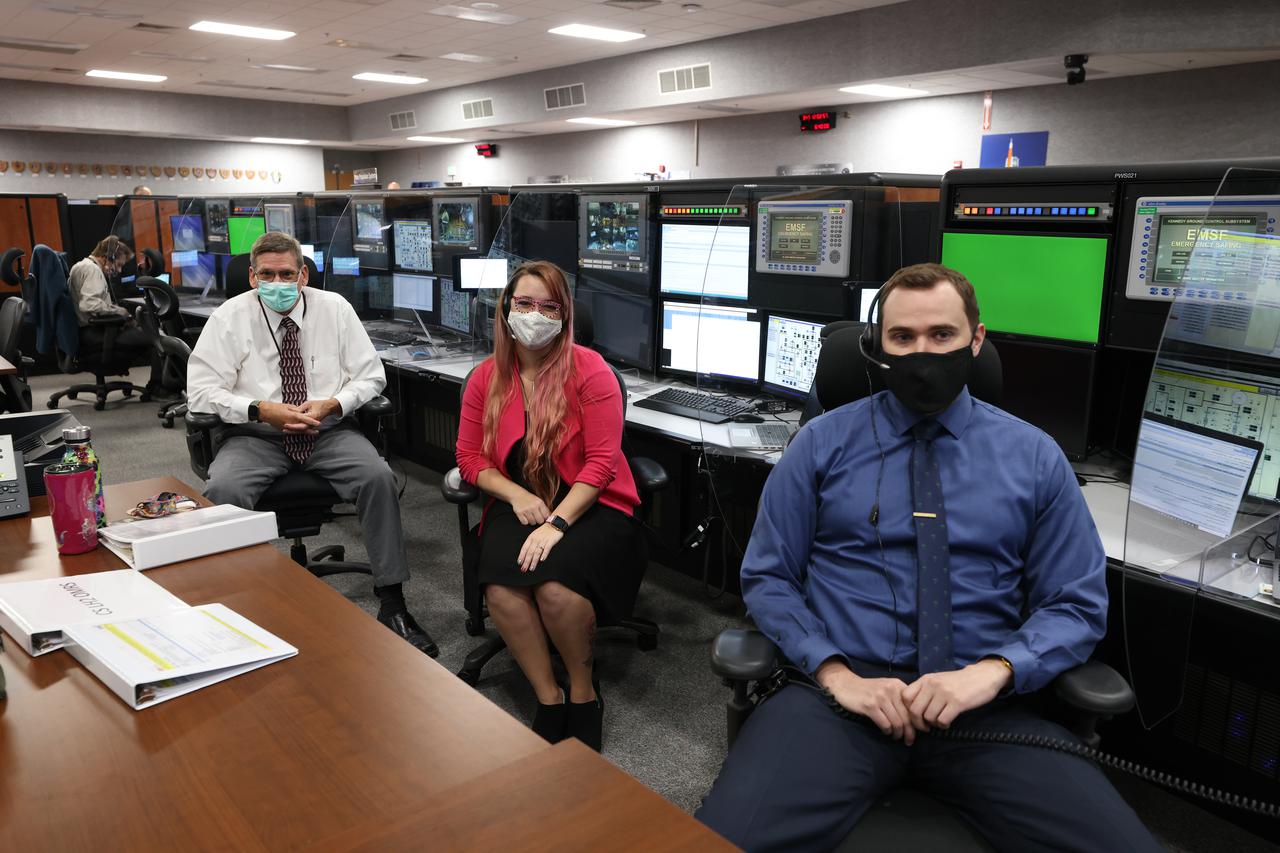

Launch team members are seated at Liquid Hydrogen consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
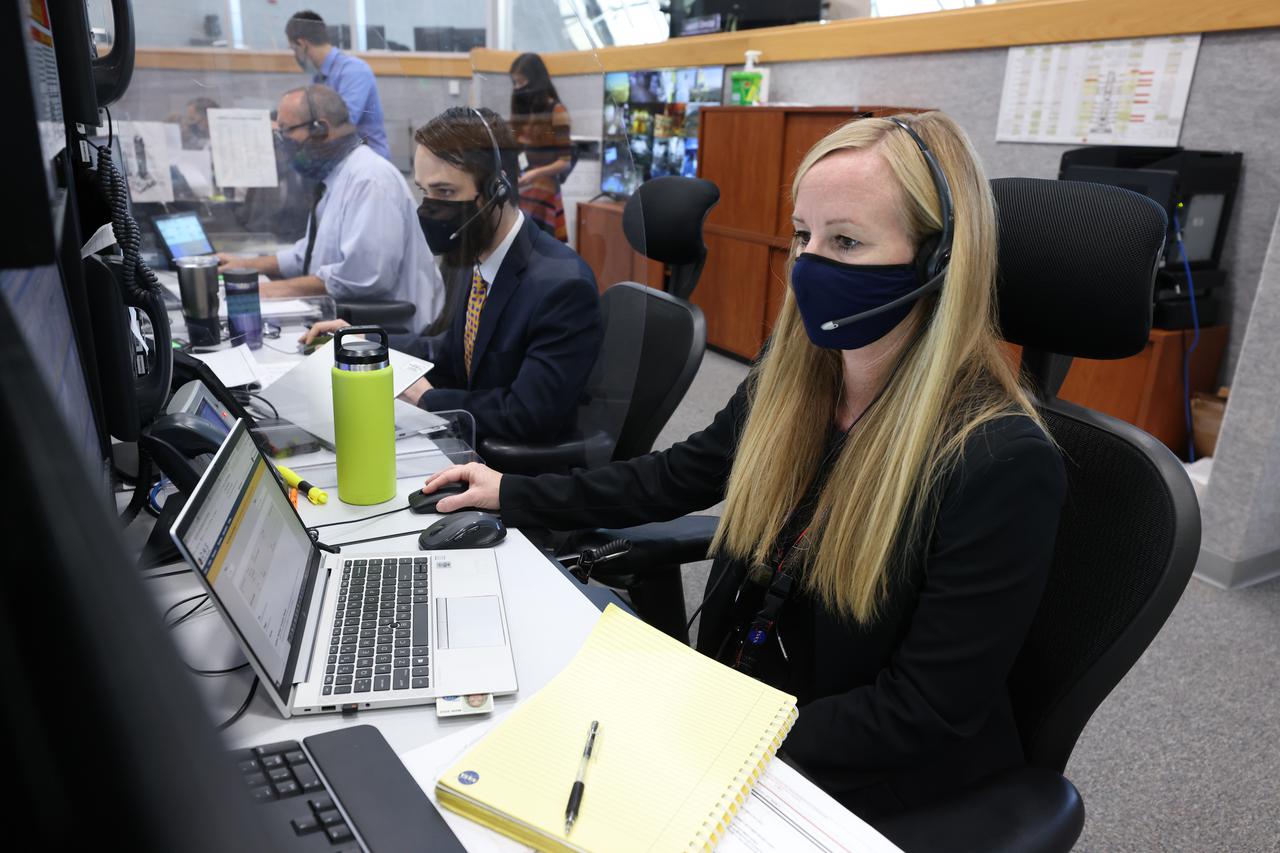

Launch team members are seated at the Orion Test Conductor consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. From right are Carla Rekucki, Joshua Coleman, John Kracsun, and Dan Florez. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
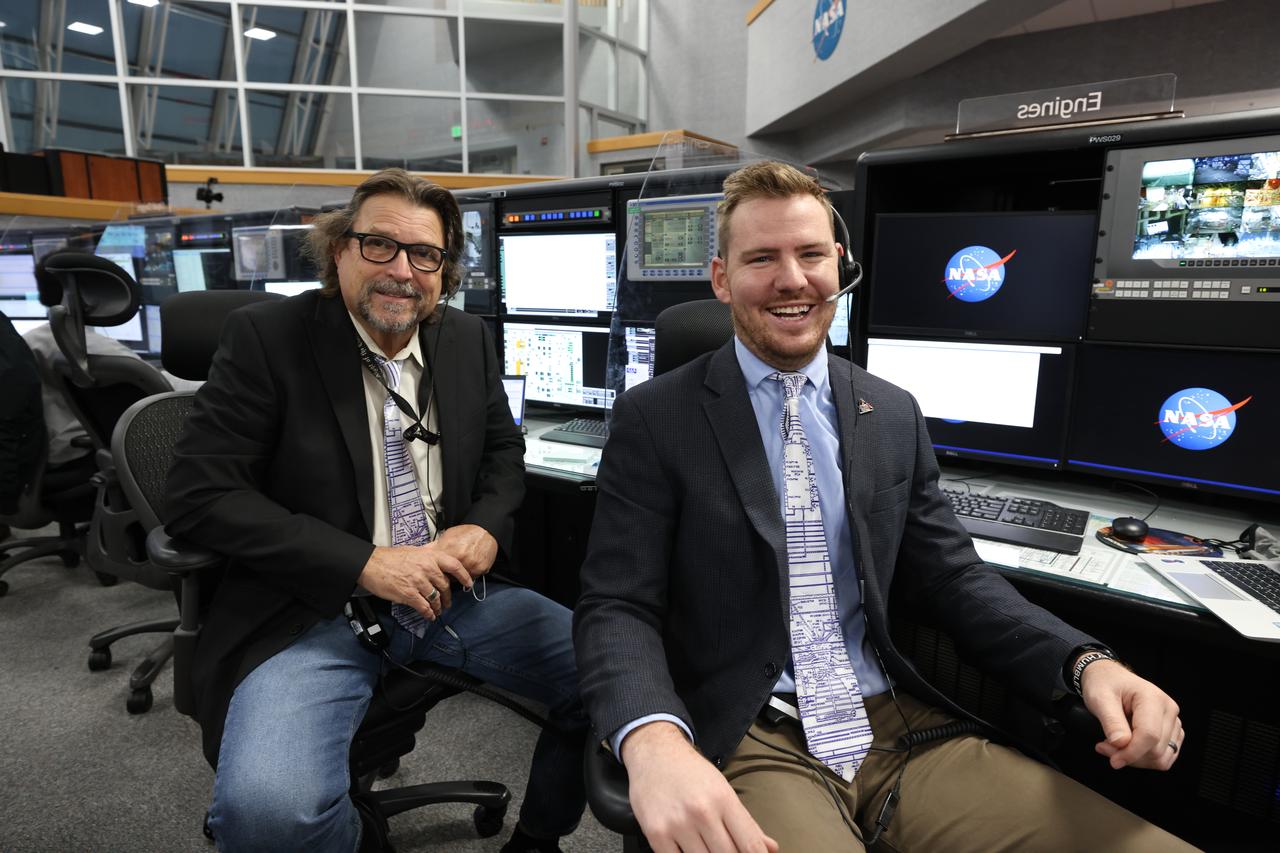

Launch team members are seated the Main Engine consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.

Launch team members are seated at the Flight Controls consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
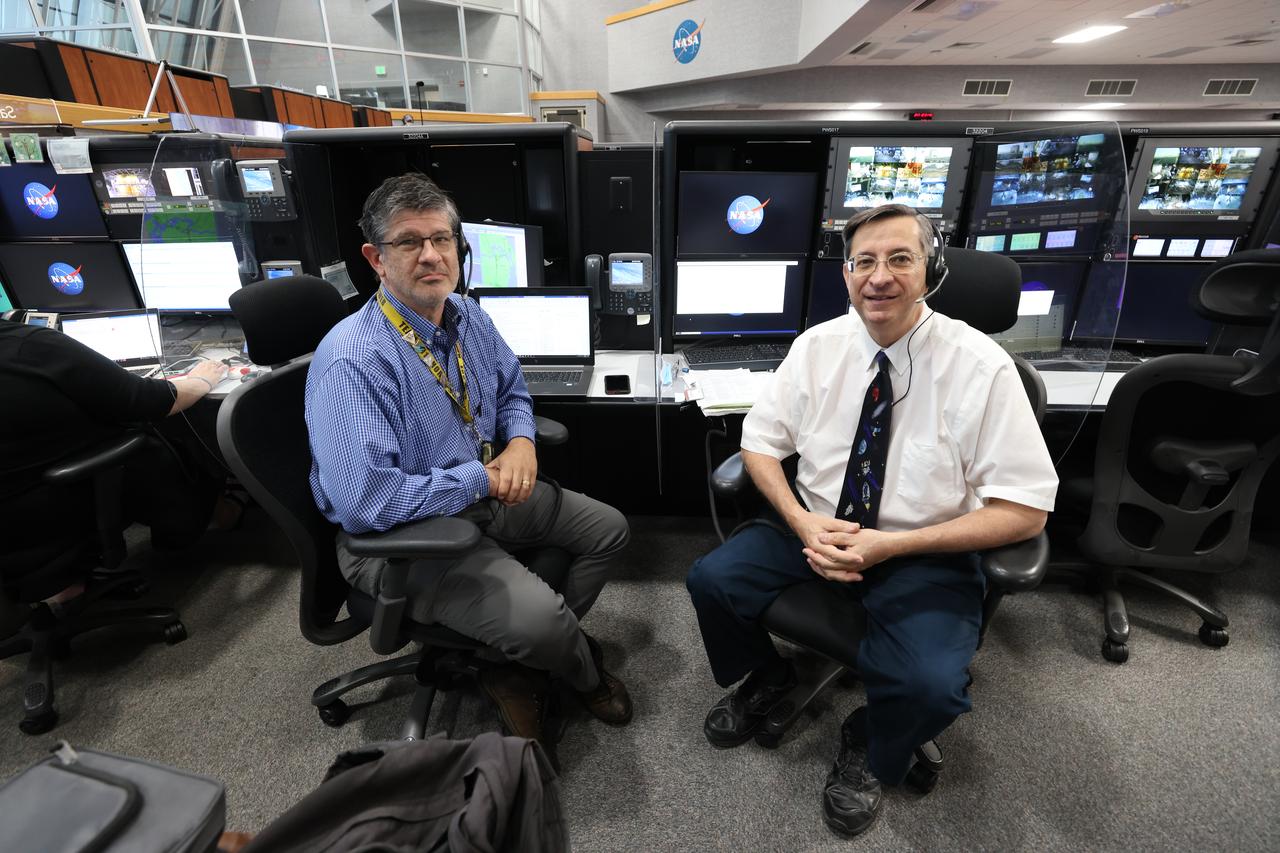

Launch team members are seated at the Biomedical/Emergency Medical Services consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars

Launch team members are seated at the Guidance, Navigation, and Control consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
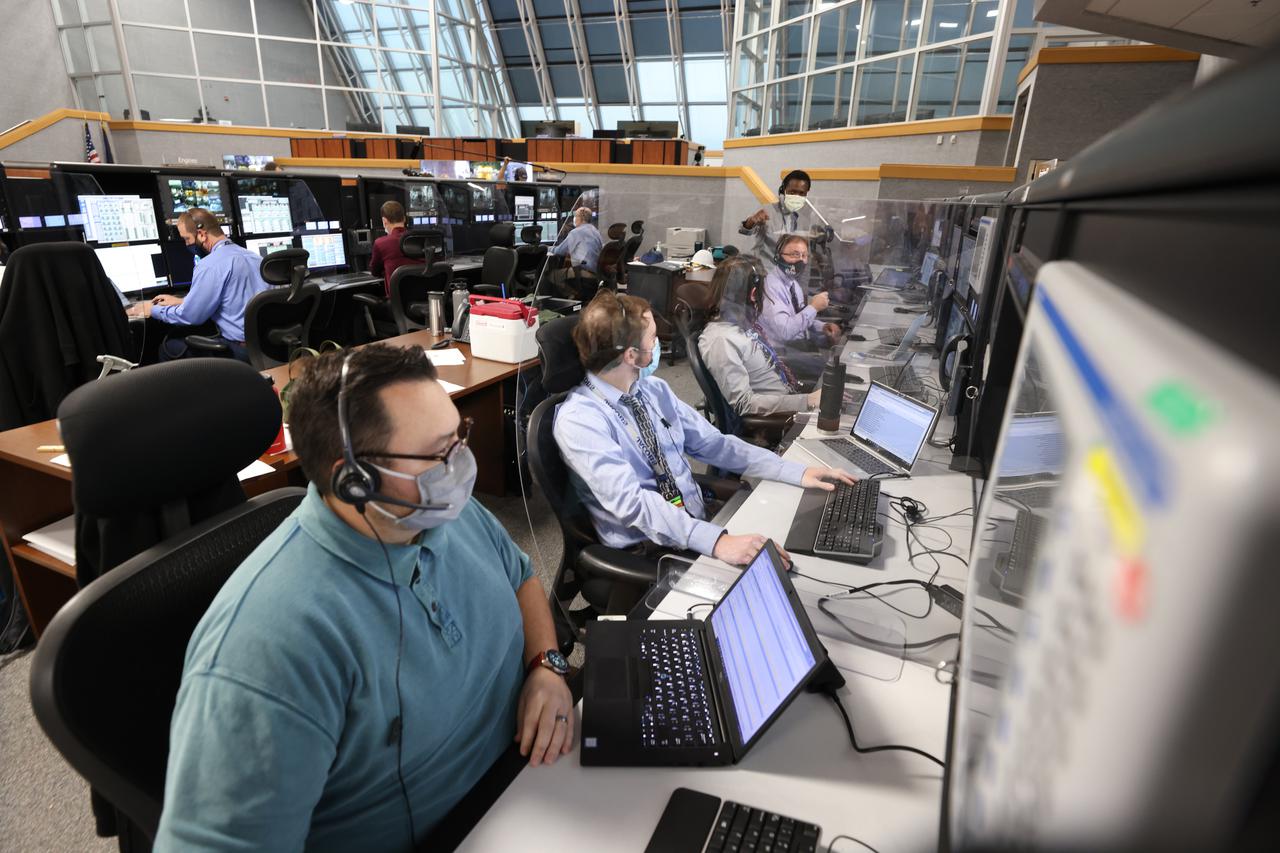

Launch team members are seated at the Electrical System consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
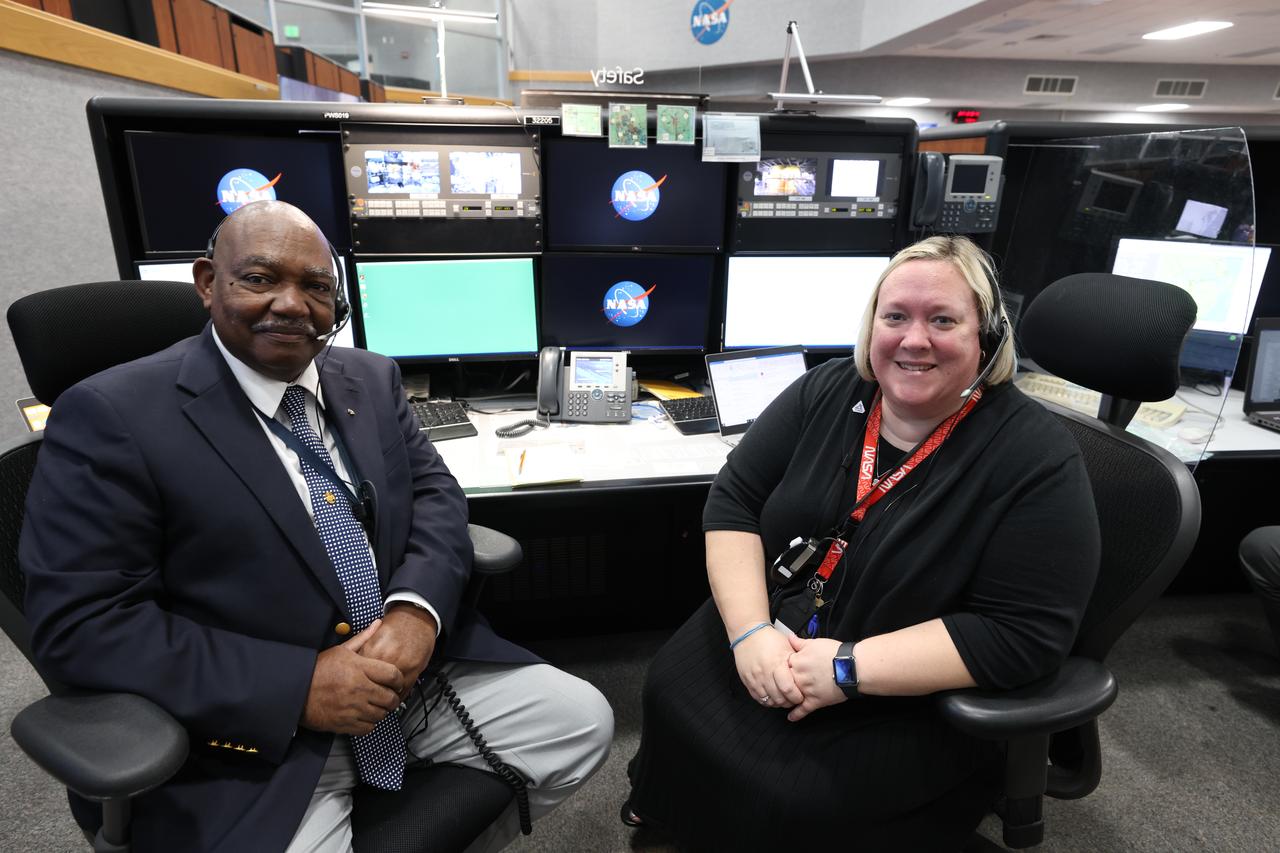

Launch team members are seated at the Safety consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
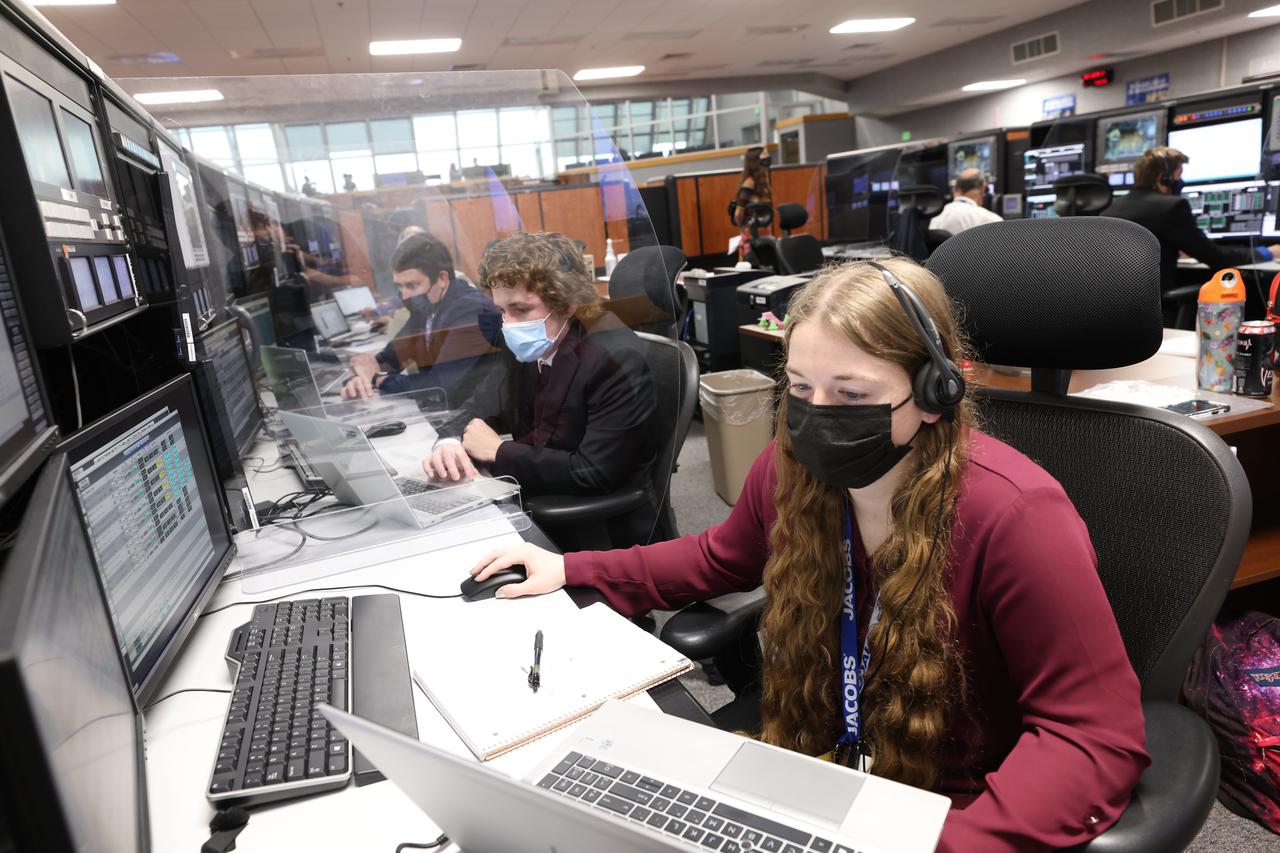

Launch team members are seated at the Environmental Control and Life Support system consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
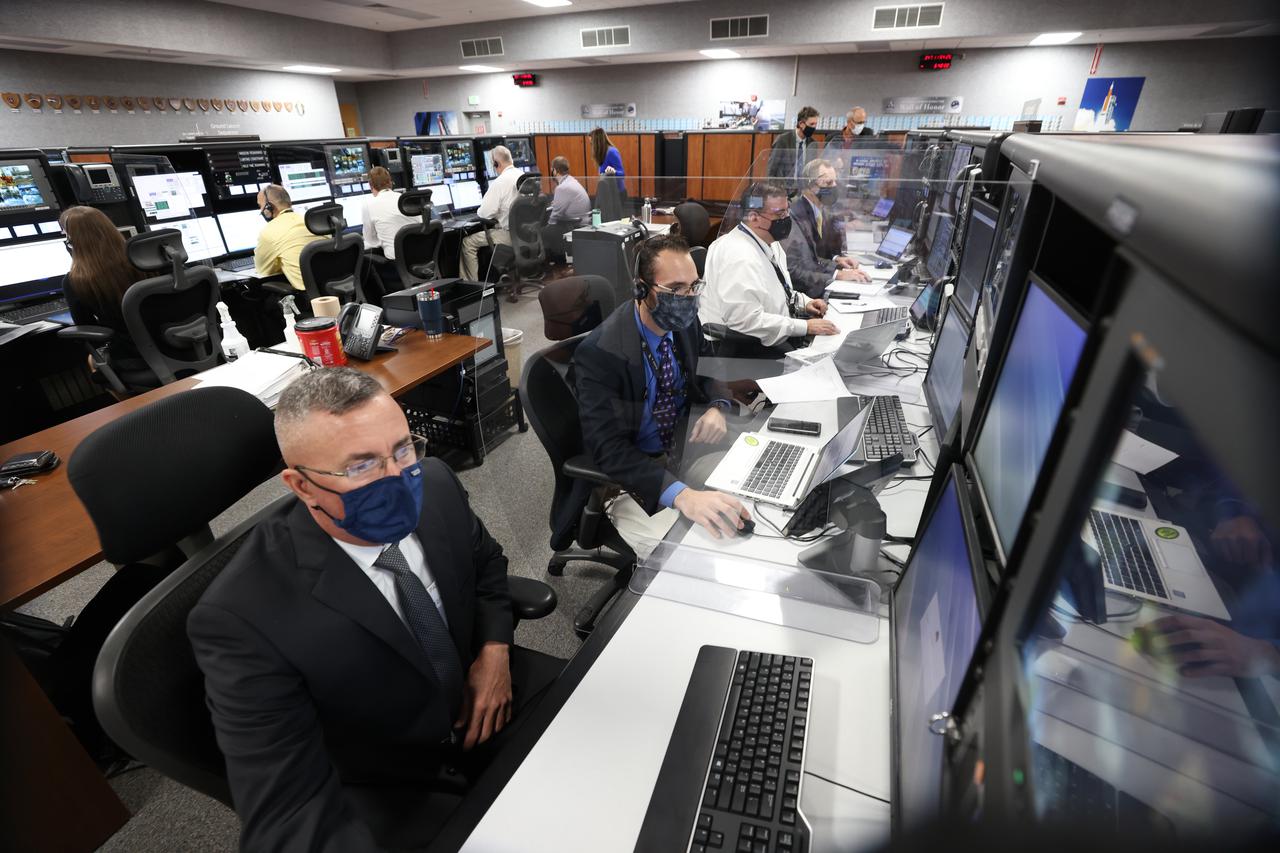

Launch team members are seated at the Integration consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
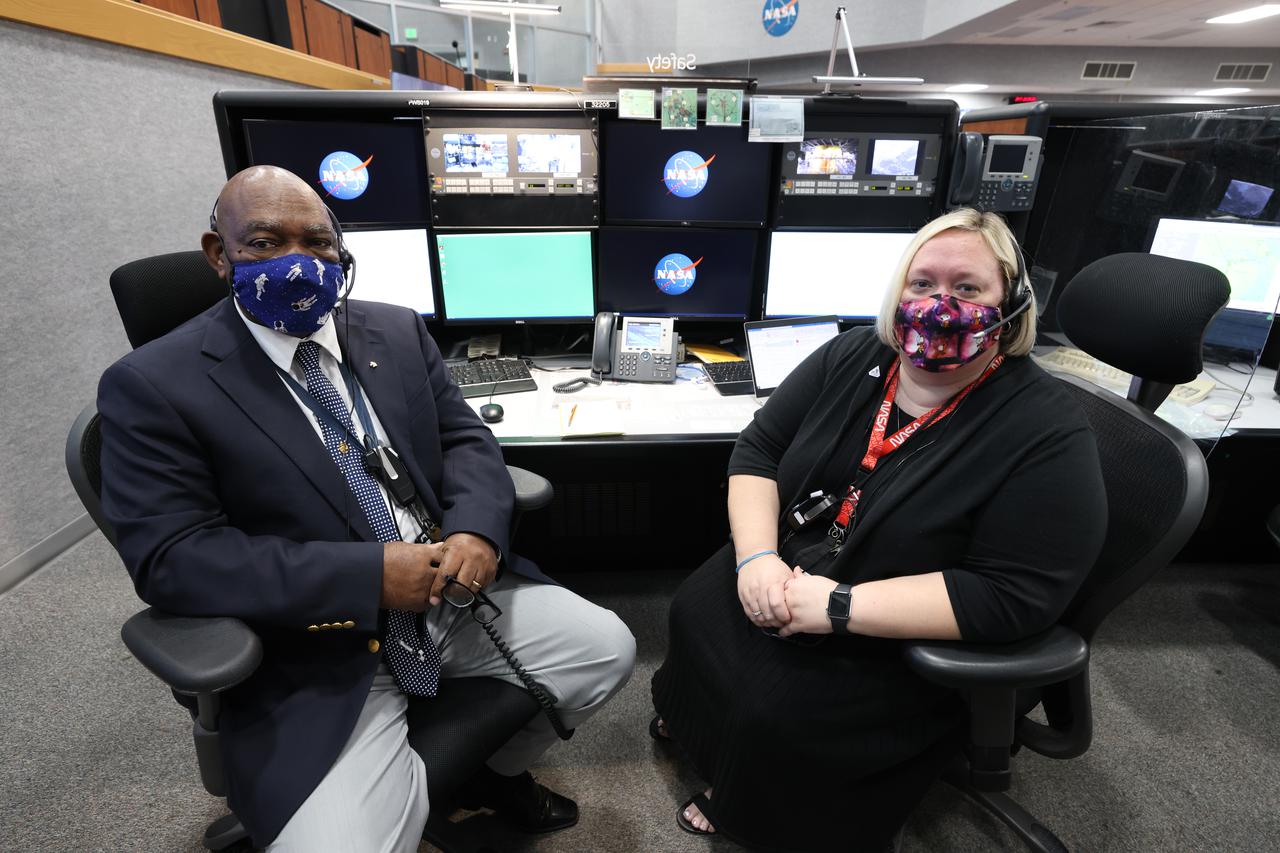

Launch team members are seated at the Safety consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
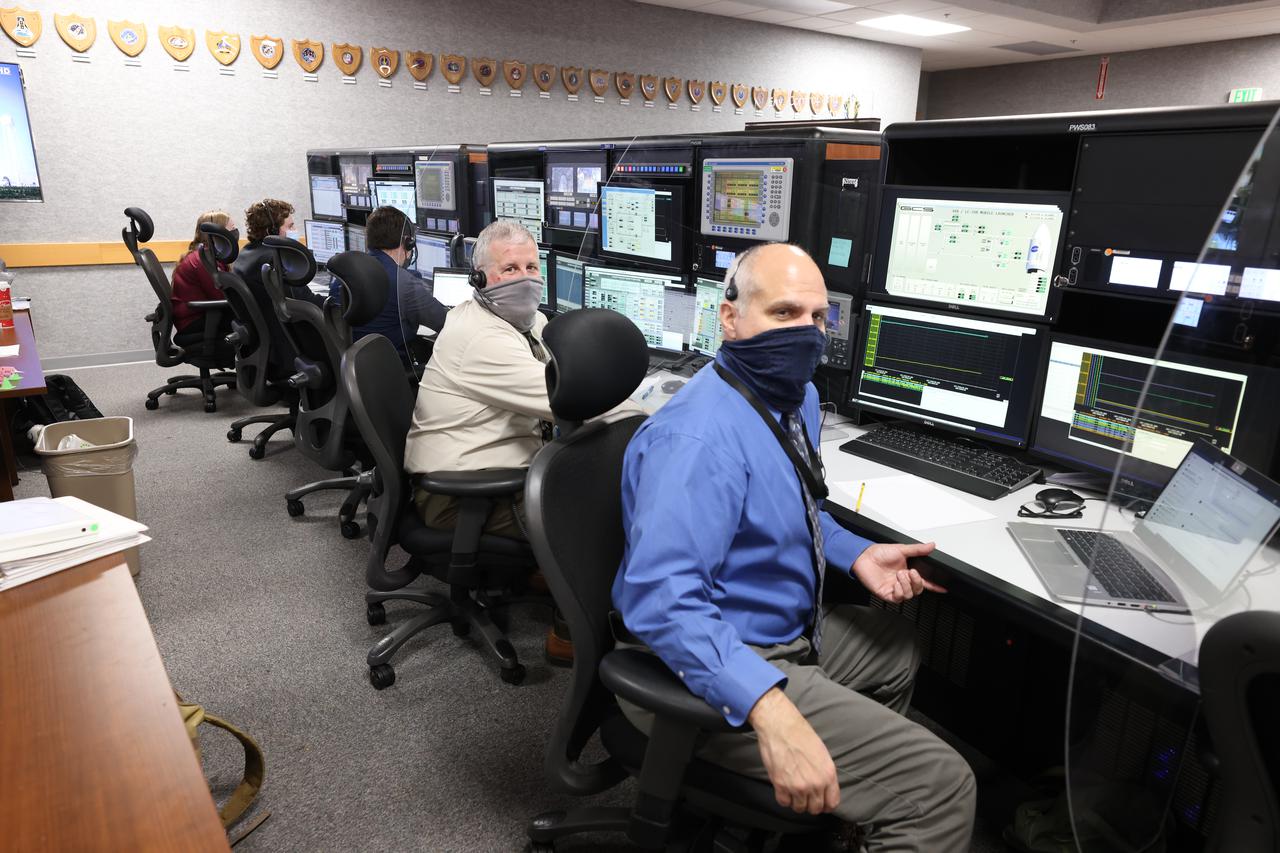

Launch team members are seated at the Environmental Control and Life Support system consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
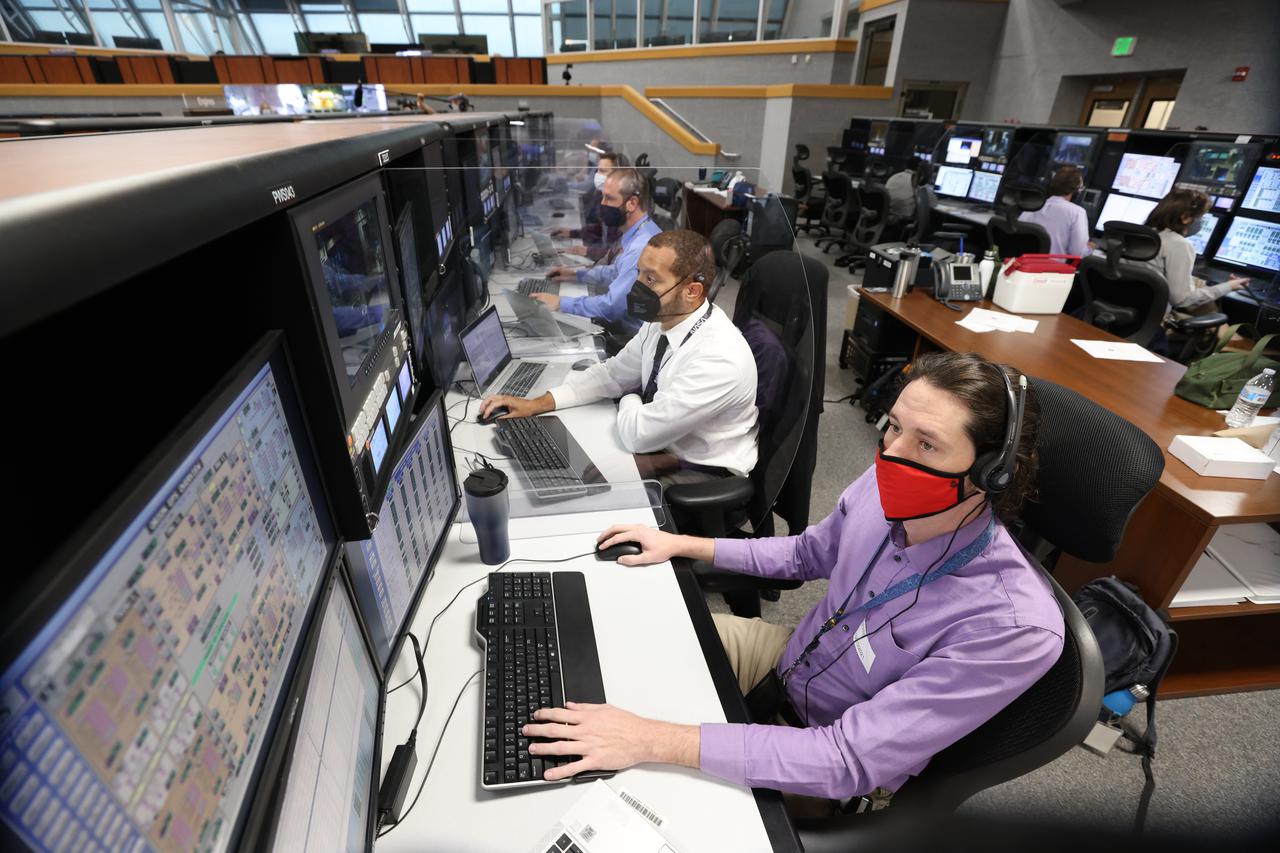

Launch team members are seated at consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
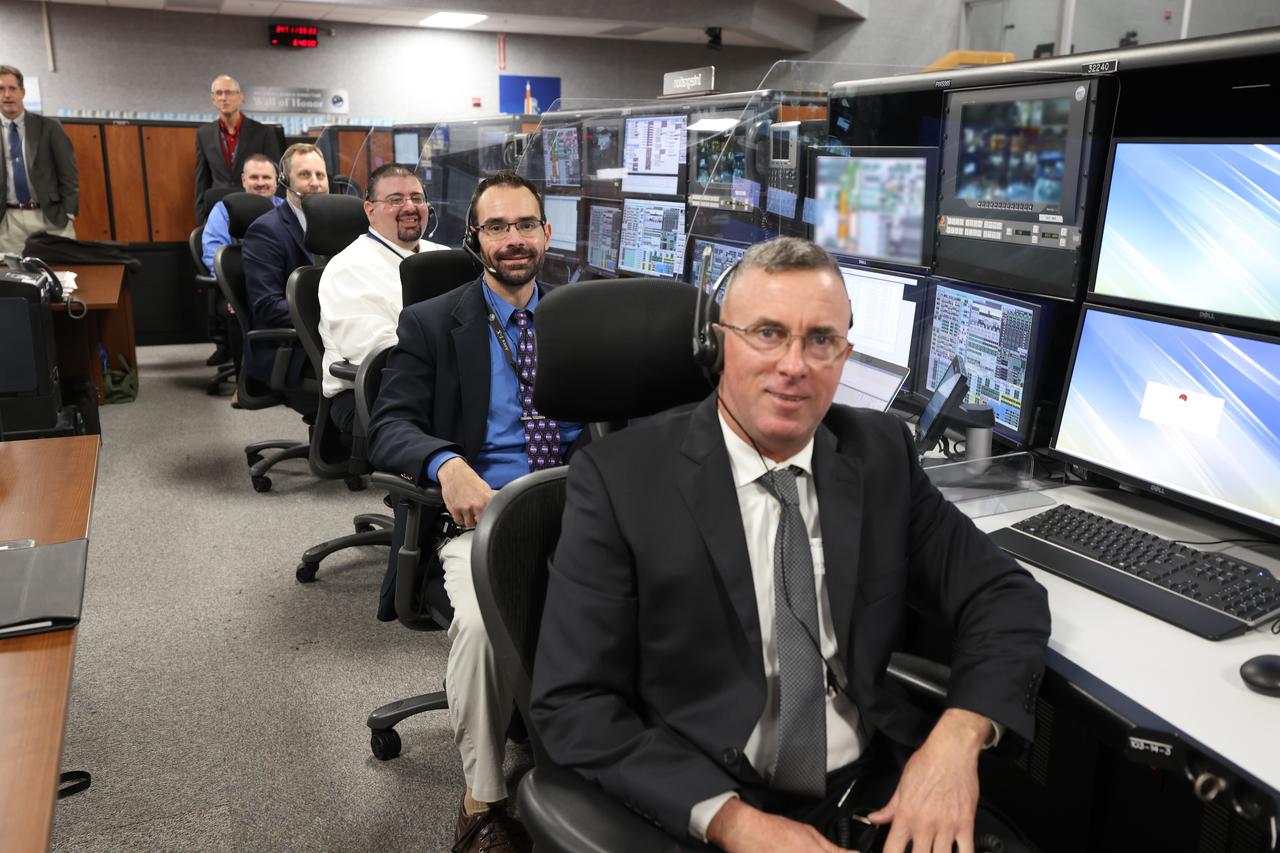

Launch team members are seated at the Integration consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
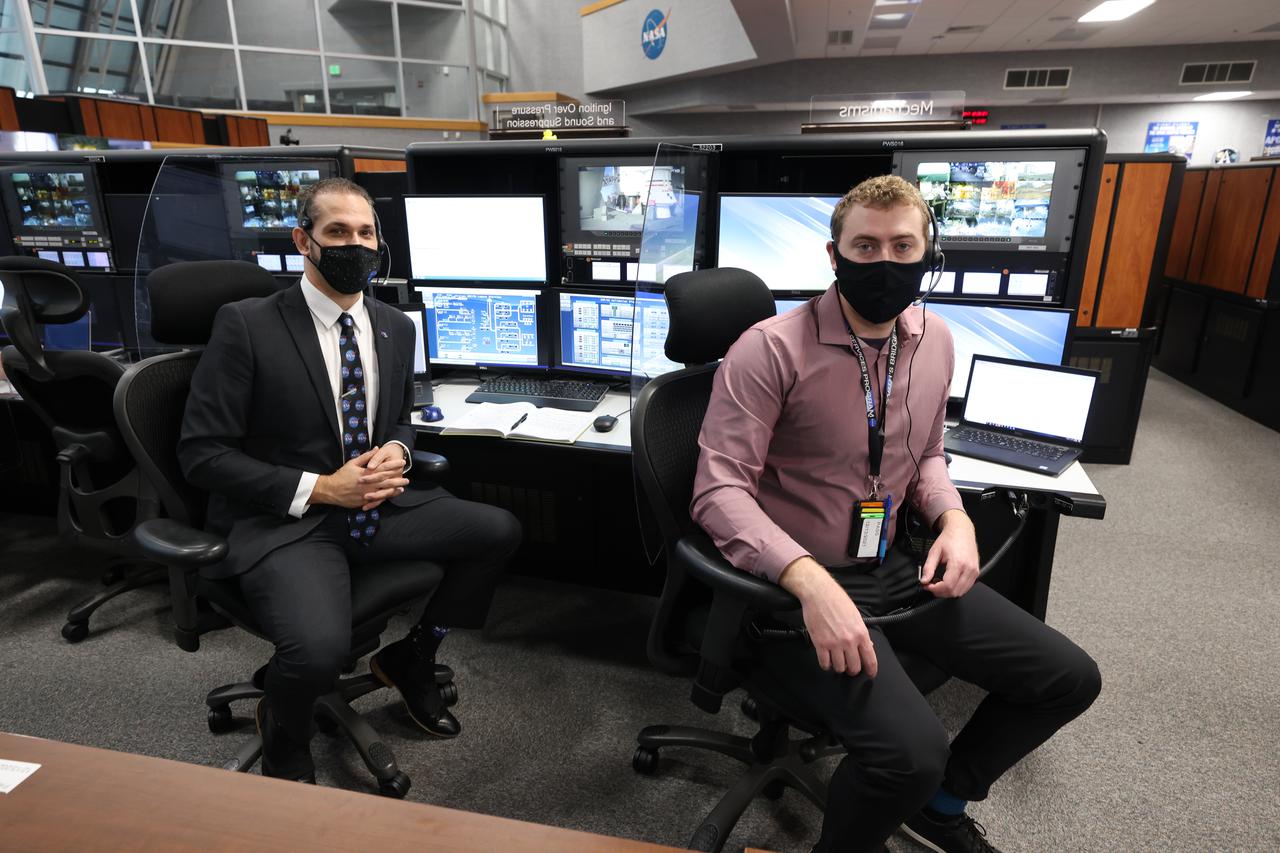

Launch team members are seated at the Mechanisms and Ignition Over Pressure and Sound Suppression System consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
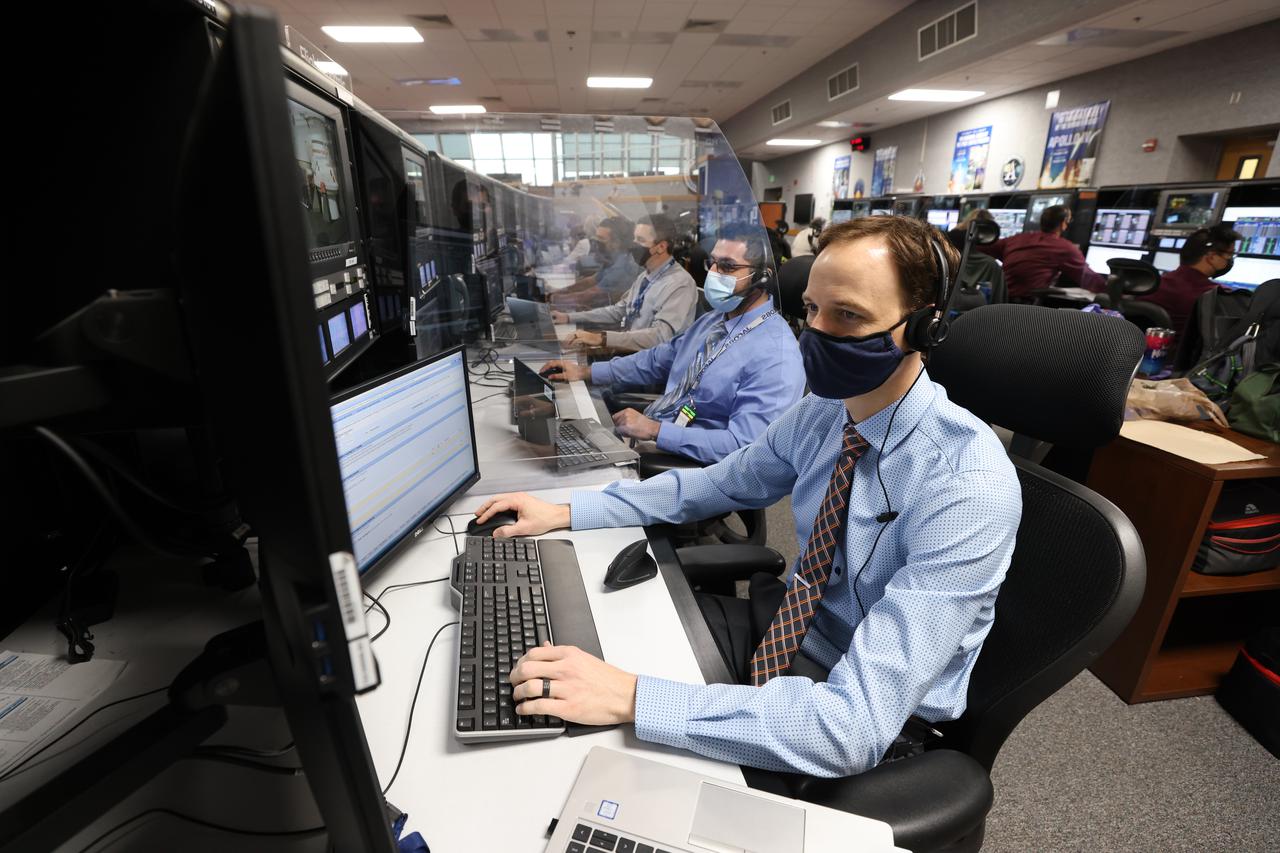

Launch team members are seated at the Flight Controls consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
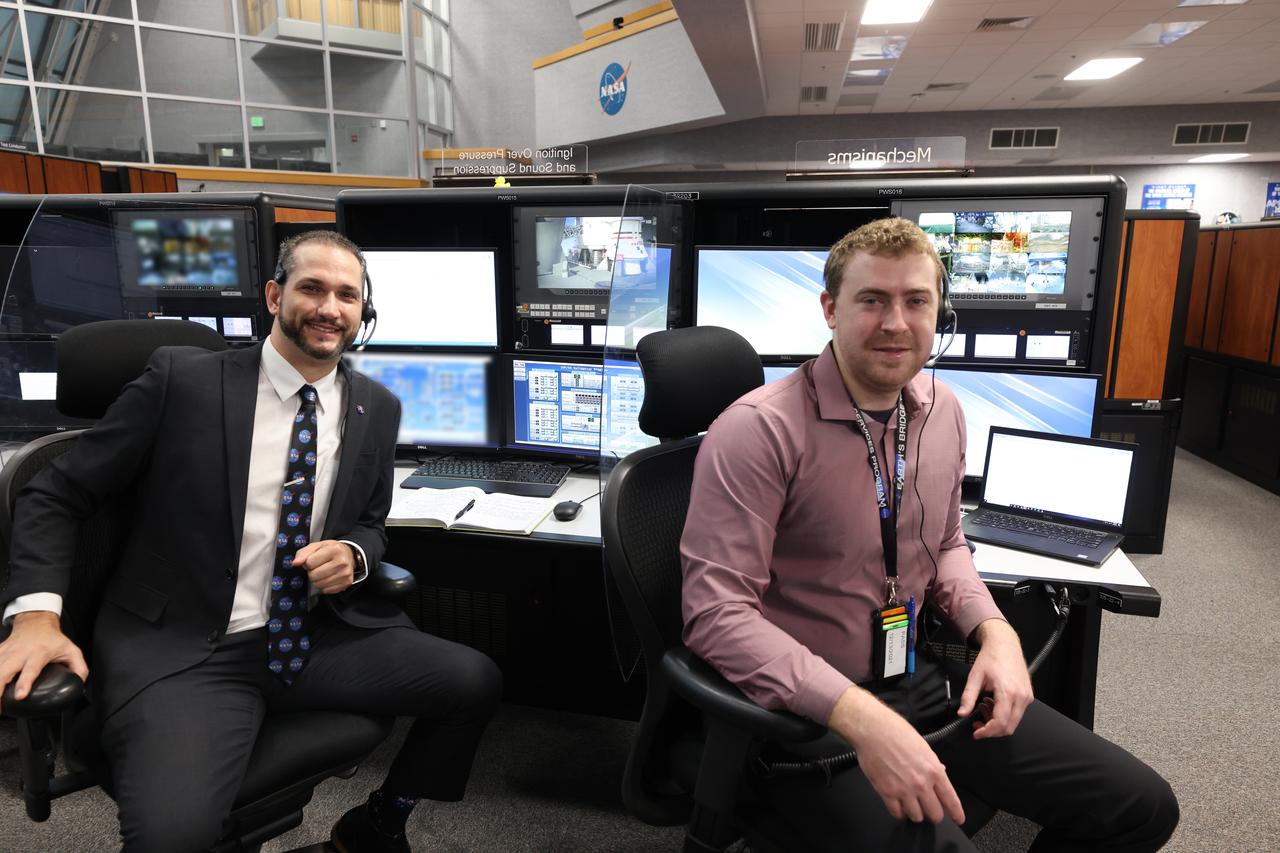

Launch team members are seated at the Mechanisms and Ignition Over Pressure and Sound Suppression System consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
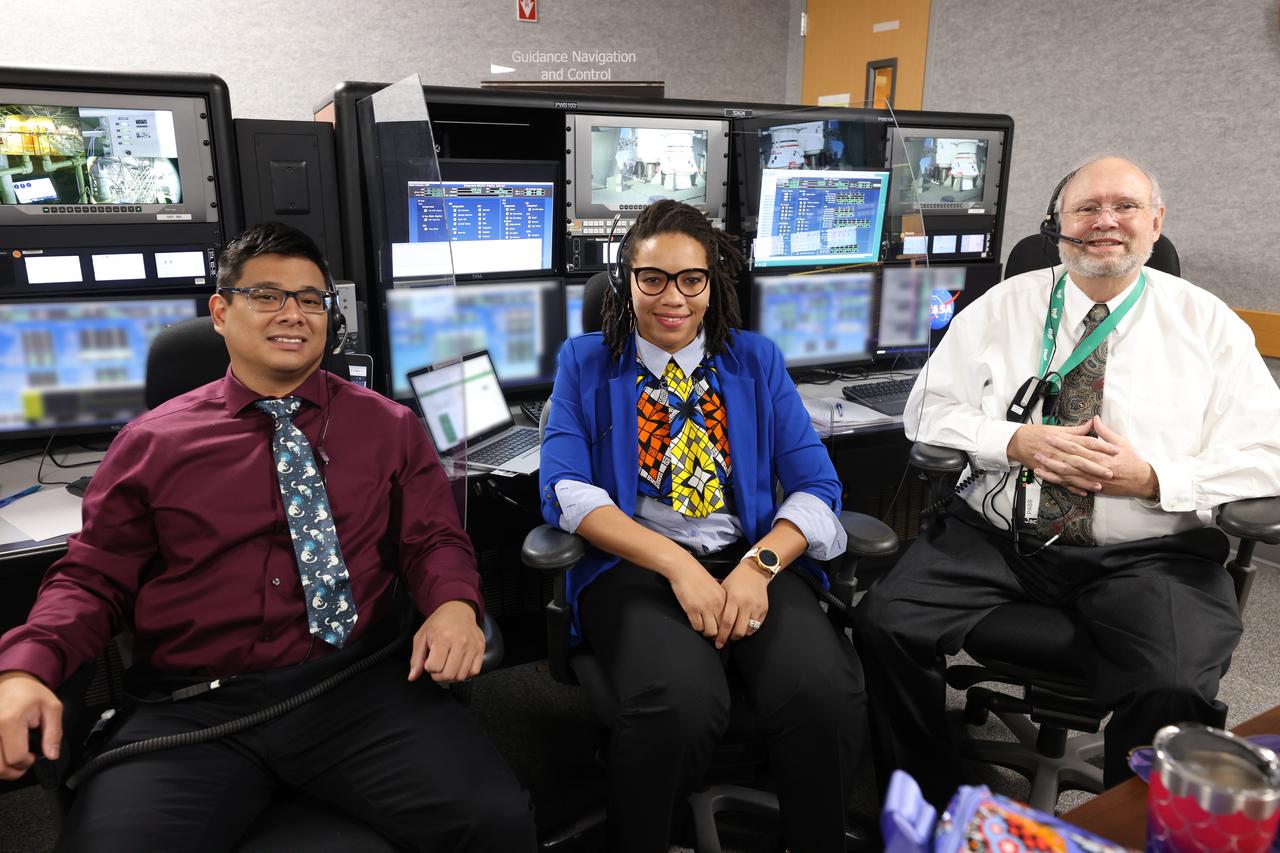

Launch team members are seated at the Guidance, Navigation, and Control consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
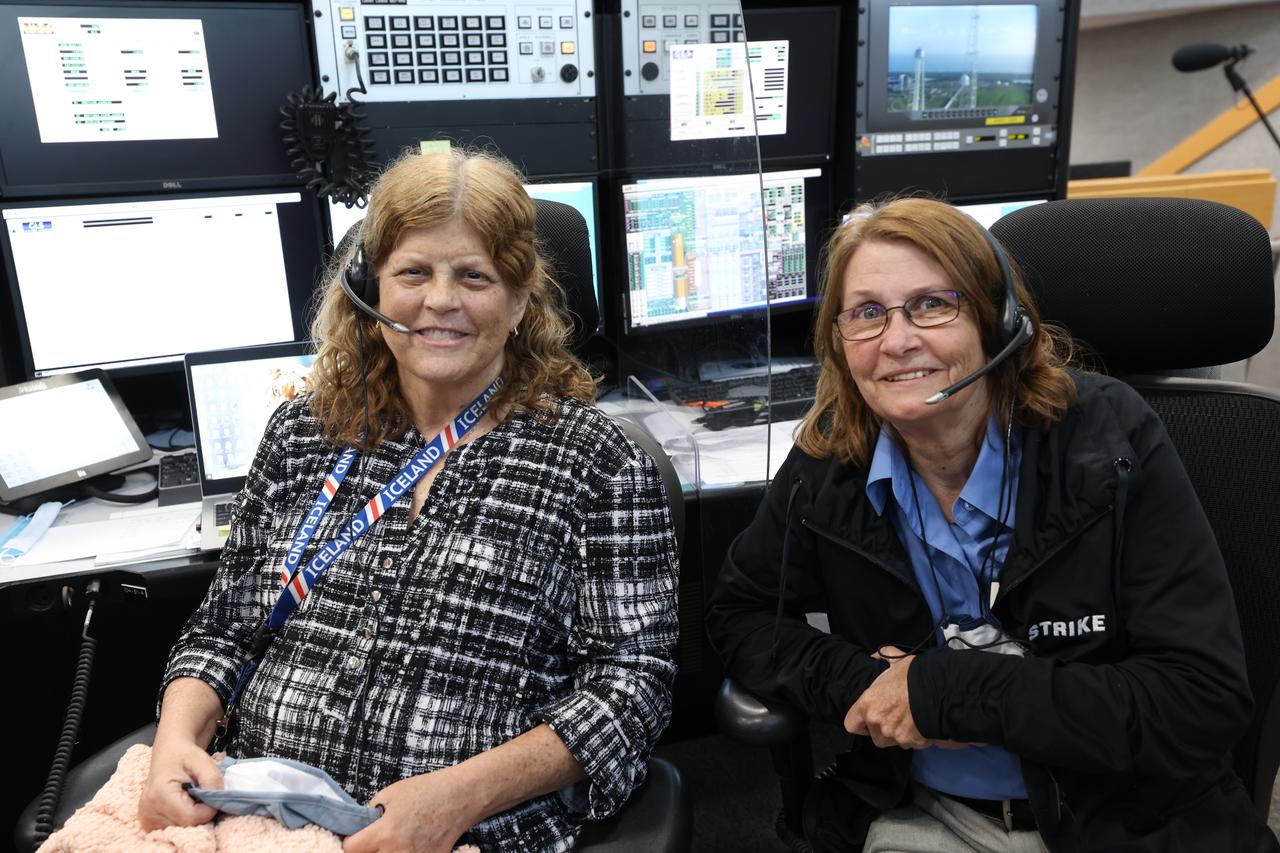

Launch team members Roberta Wyrick, at left, and Teresa Annulis, are seated at consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
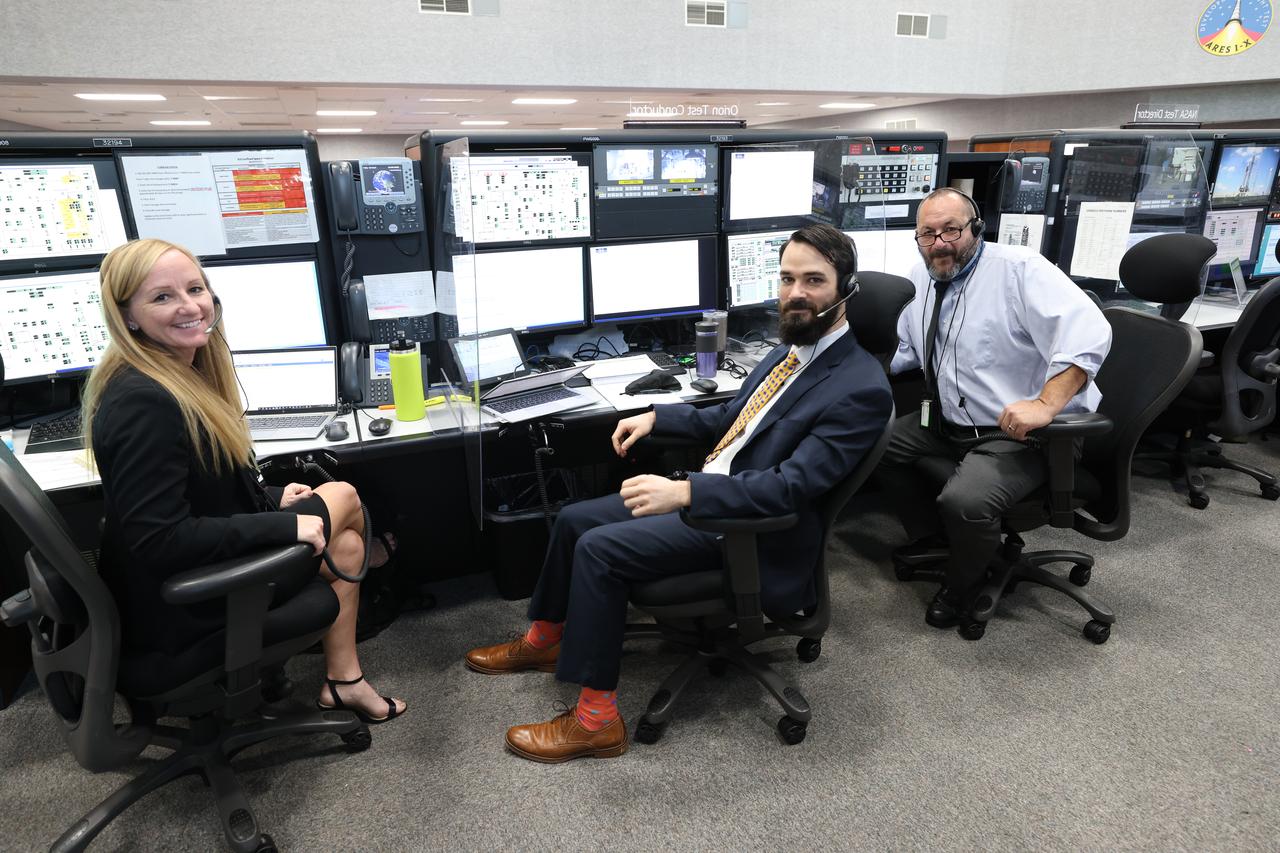

Launch team members, from left, Carla Rekucki, Joshua Coleman, and John Kracsun, are seated at consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
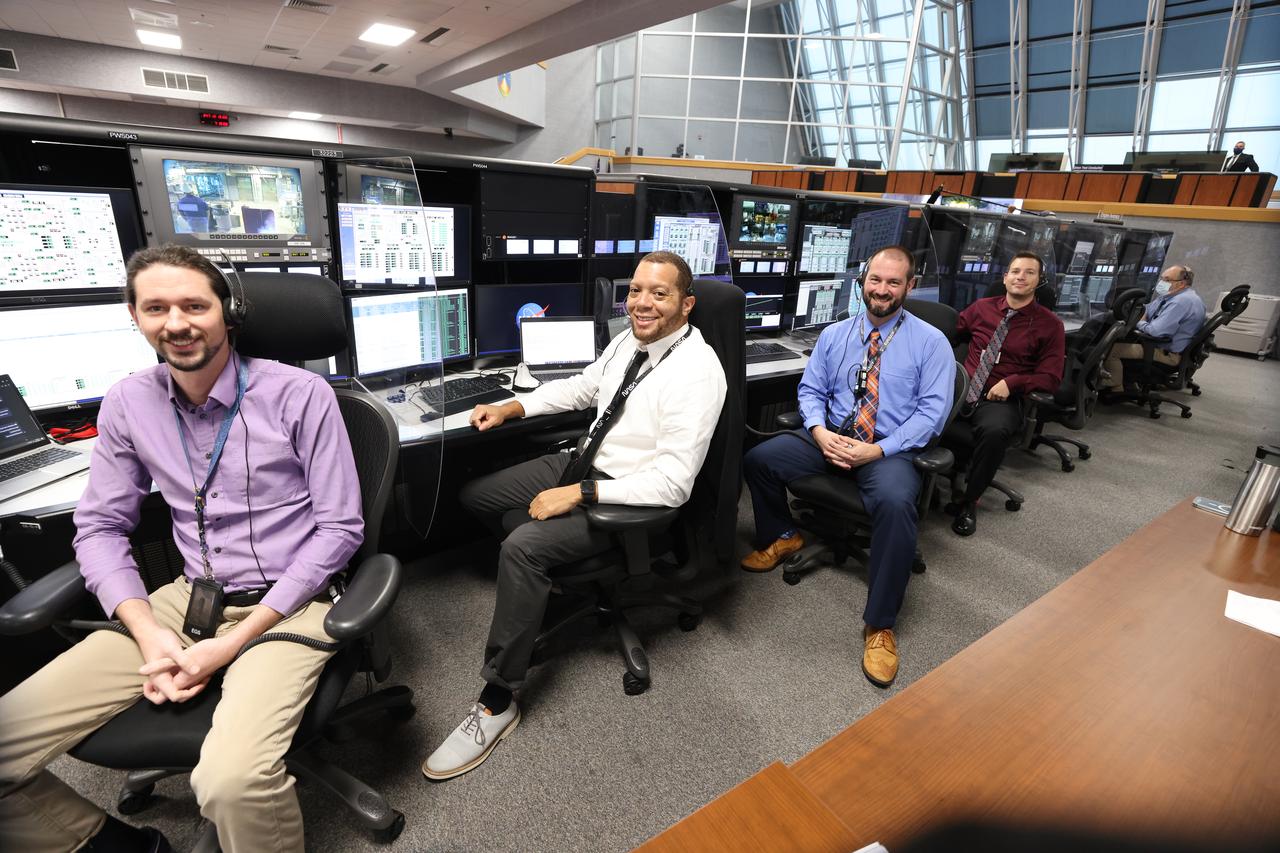

Launch team members are seated at consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
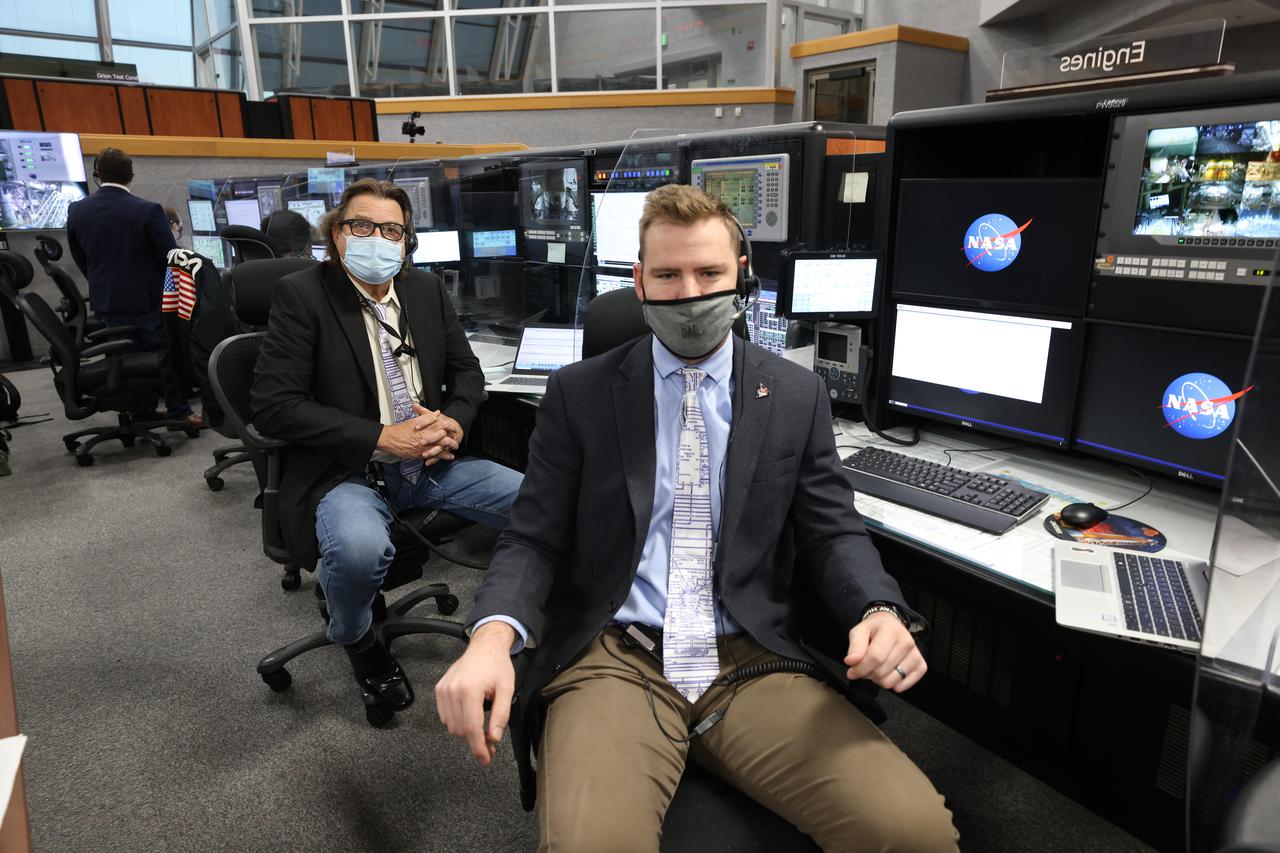

Launch team members are seated at the Main Engines consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.
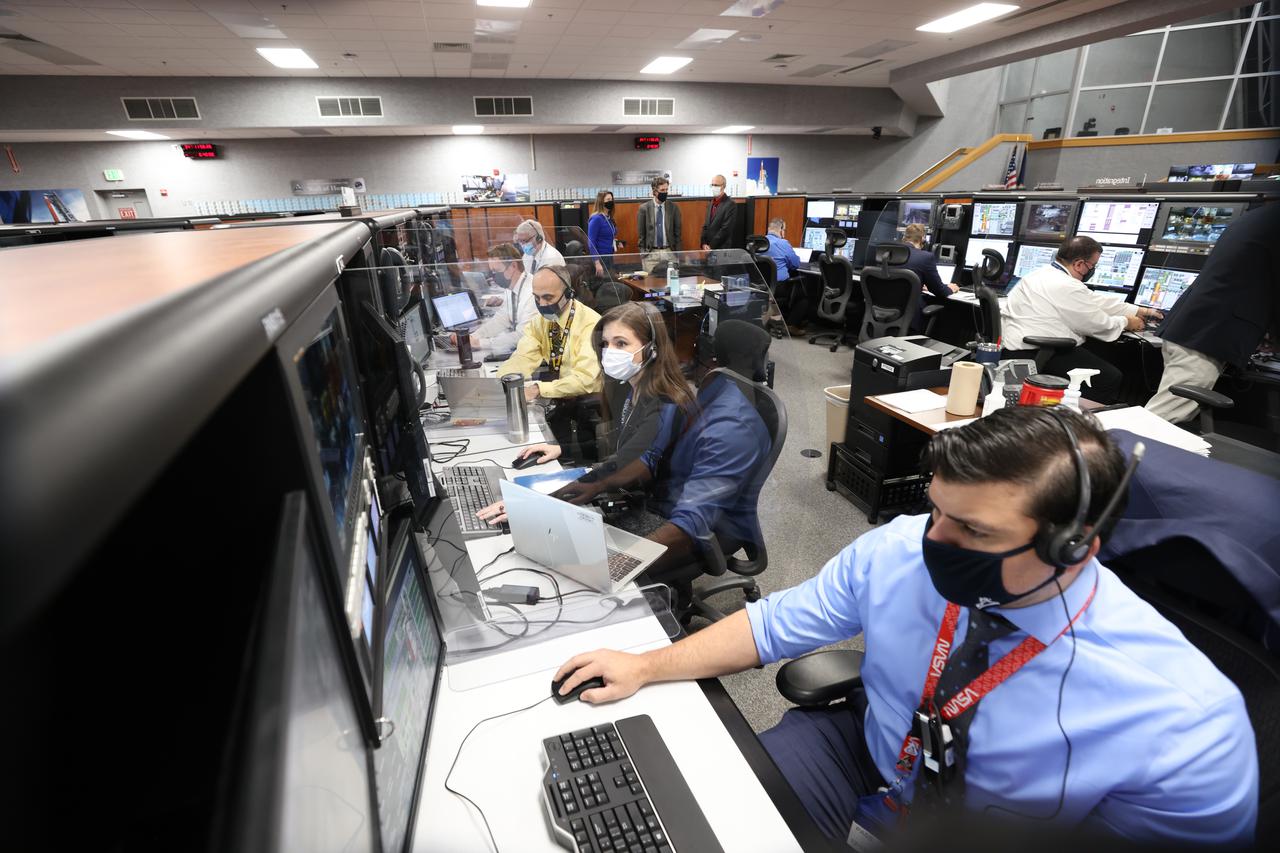

Launch team members are seated at the Integration consoles inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 13, 2021. They are participating in a joint integrated simulation for the Artemis I launch that covered both cryogenic loading and terminal countdown portions of prelaunch activities. Members of NASA’s mission management team and launch team conducted the simulation together. The Kennedy team was certified for the Artemis I launch. During Artemis I, the agency’s Orion spacecraft will lift off from Kennedy aboard NASA’s most powerful rocket – the Space Launch System – to fly farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown. Through NASA’s Artemis missions, the agency, along with commercial and international partners, will establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon to prepare for missions to Mars.