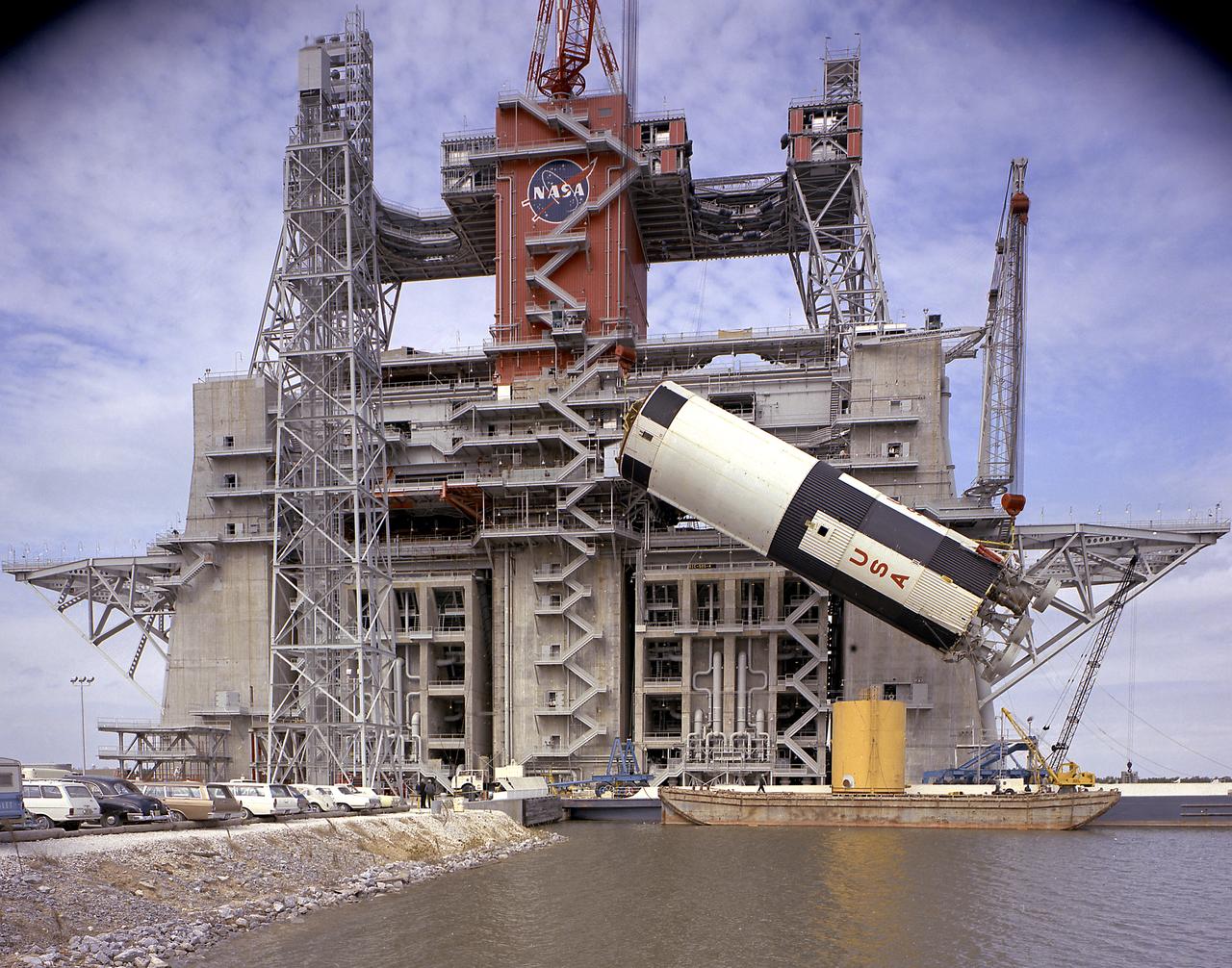

This photograph is a view of the Saturn V S-IC (first) test stage being hoisted into the S-IC-B1 test stand at the Mississippi Test Facility (MTF), Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. This stage was used to prove the operational readiness of the stand. Begirning operations in 1966, the MTF has two test stands; a dual-position structure for running the S-IC stage at full throttle, and two separate stands for the S-II (Saturn V third) stage. It became the focus of the static test firing program. The completed S-IC stage was shipped from the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) to the MTF. The stage was then installed into the 124-meter-high test stand for static firing tests before shipment to the Kennedy Space Center for final assembly of the Saturn V vehicle. The MTF was renamed to the National Space Technology Laboratory (NSTL) in 1974 and later to the Stennis Space Center (SSC) in May 1988.
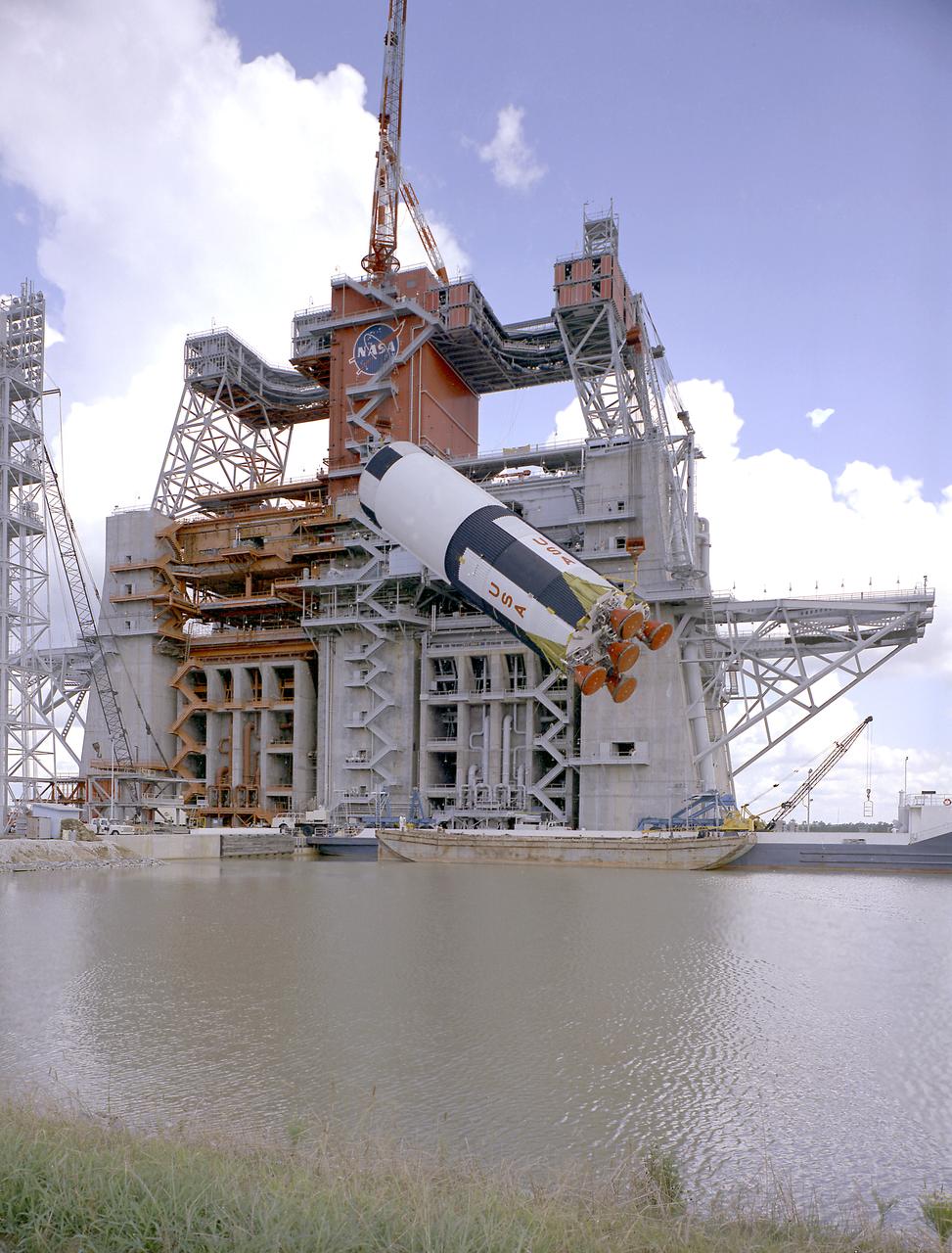

This photograph is a view of the Saturn V S-IC-5 (first) flight stage being hoisted into the S-IC-B1 test stand at the Mississippi Test Facility (MTF), Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Begirning operations in 1966, the MTF has two test stands, a dual-position structure for running the S-IC stage at full throttle, and two separate stands for the S-II (Saturn V third) stage. It became the focus of the static test firing program. The completed S-IC stage was shipped from Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) to the MTF. The stage was then installed into the 124-meter-high test stand for static firing tests before shipment to the Kennedy Space Center for final assembly of the Saturn V vehicle. The MTF was renamed to the National Space Technology Laboratory (NSTL) in 1974 and later to the Stennis Space Center (SSC) in May 1988.
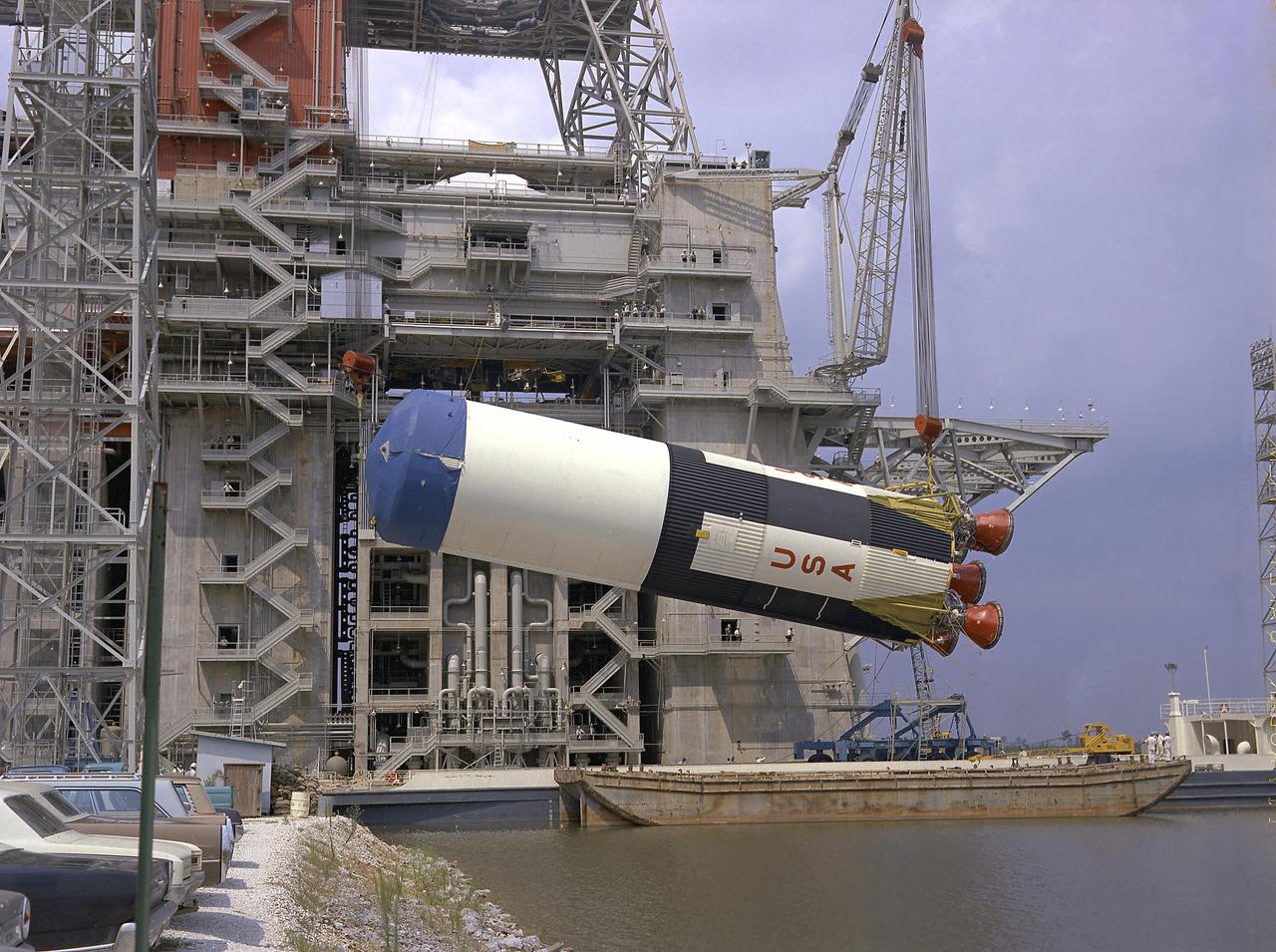

This photograph is a view of the Saturn V S-IC-5 (first) flight stage being hoisted into the S-IC-B1 test stand at the Mississippi Test Facility (MTF), Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Begirning operations in 1966, the MTF has two test stands, a dual-position structure for running the S-IC stage at full throttle, and two separate stands for the S-II (Saturn V third) stage. It became the focus of the static test firing program. The completed S-IC stage was shipped from Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) to the MTF. The stage was then installed into the 124-meter-high test stand for static firing tests before shipment to the Kennedy Space Center for final assembly of the Saturn V vehicle. The MTF was renamed to the National Space Technology Laboratory (NSTL) in 1974 and later to the Stennis Space Center (SSC) in May 1988.

This photograph shows the Saturn V S-II (second) stage being hoisted at the S-II-A2 test stand at the Mississippi Test Facility (MTF). When the Saturn V booster stage (S-IC) burns out and drops away, power for the Saturn will be provided by the 82-foot-long and 33-foot-diameter S-II stage. Developed by the Space Division of North American Aviation under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the stage utilized five J-2 engines, each producing 200,000 pounds of thrust. The engines used liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen as propellants. Static test of ground test versions of the S-II stage were conducted at North American Aviation's Santa Susana, California test site. All flight stages were tested at the Mississippi Test Facility, Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. MTF was renamed to the National Space Technology Laboratory (NSTL) in 1974 and later to the Sternis Space Center in May 1988.
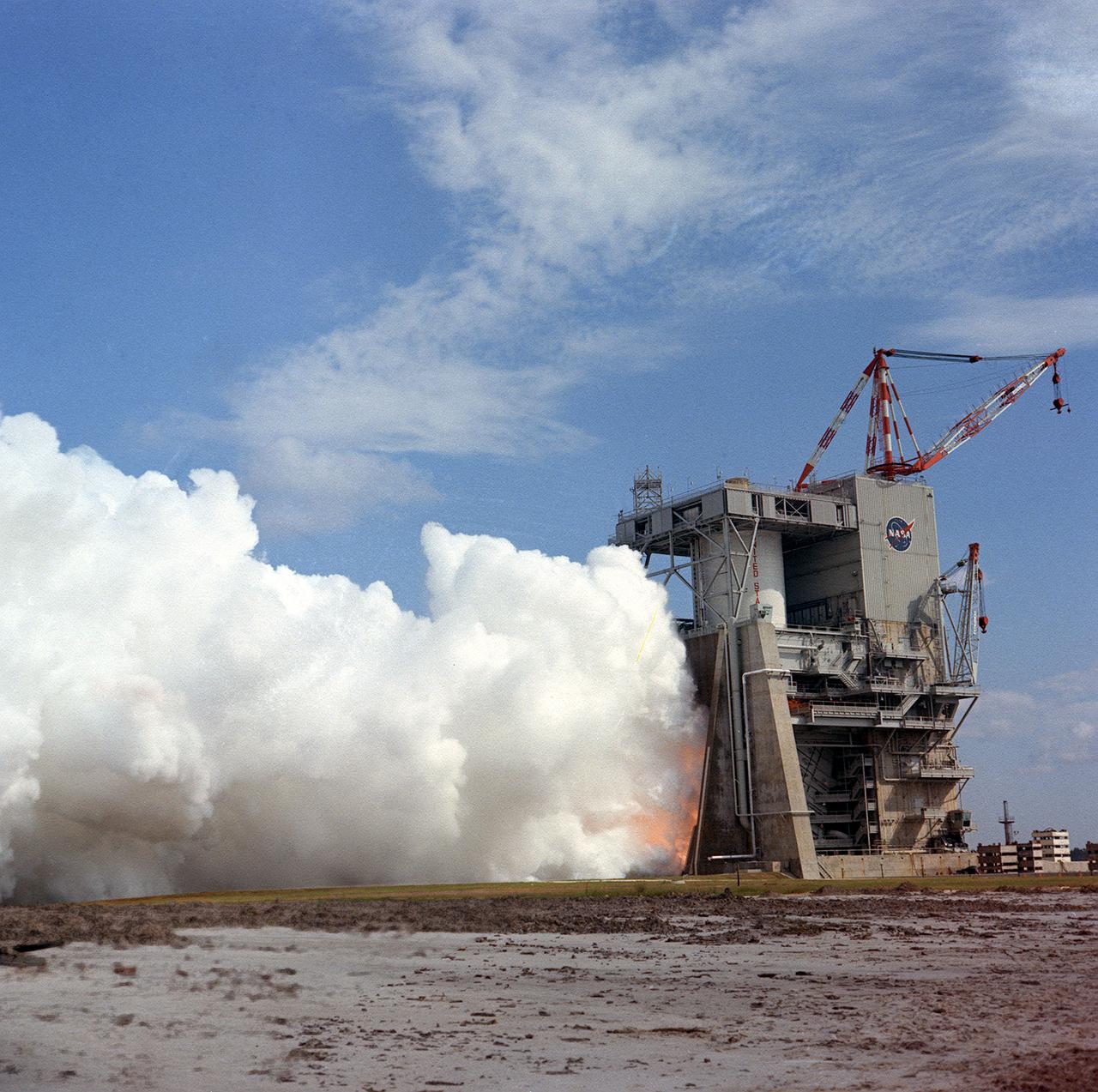

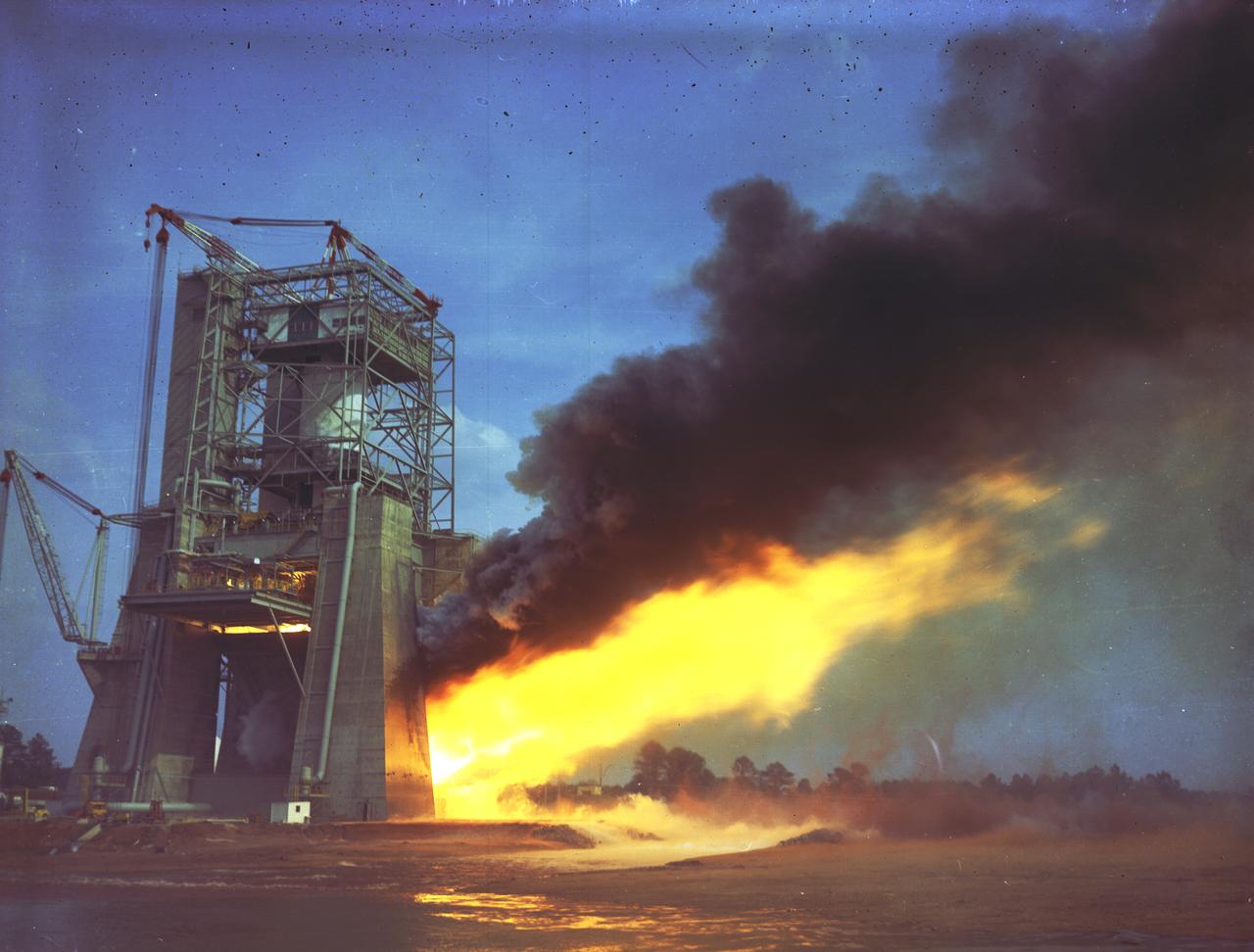
This photograph shows a test firing of the the Saturn V S-II (second) stage at the Mississippi Test Facility's (MTF) S-II test stand. When the Saturn V booster stage (S-IC) burns out and drops away, power for the Saturn will be provided by the 82-foot-long and 33-foot-diameter S-II stage. Developed by the Space Division of North American Aviation under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the stage utilized five J-2 engines, each producing 200,000 pounds of thrust. The engines used liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen as propellants. Static test of ground test versions of the S-II stage were conducted at North American Aviation's Santa Susana, California test site. All flight stages were tested at the Mississippi Test Facility, Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. MTF was renamed to the National Space Technology Laboratory (NSTL) in 1974 and later to the Sternis Space Center in May 1988.
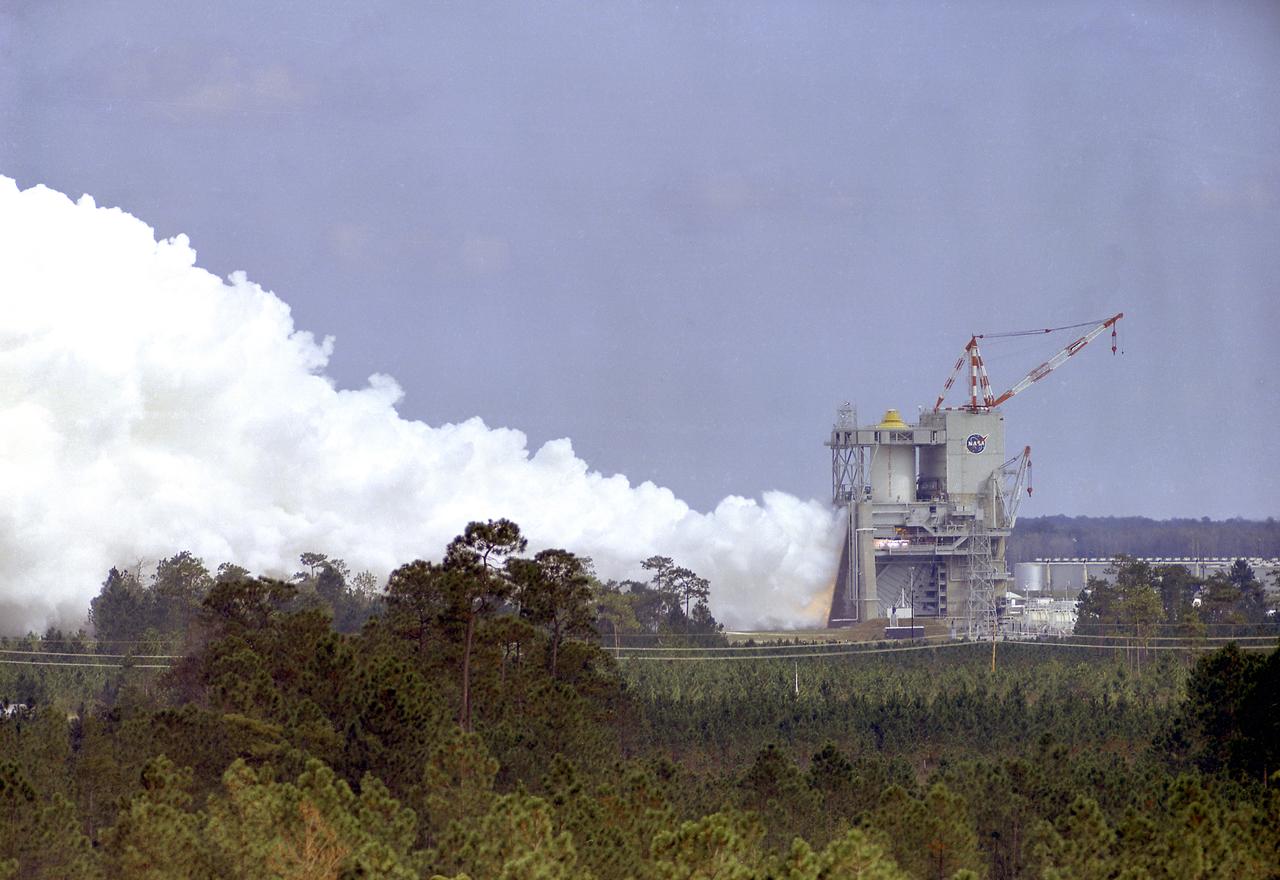

This photograph shows a test firing of the the Saturn V S-II (second) stage at the Mississippi Test Facility's (MTF) S-II test stand. When the Saturn V booster stage (S-IC) burns out and drops away, power for the Saturn will be provided by the 82-foot-long and 33-foot-diameter S-II stage. Developed by the Space Division of North American Aviation under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the stage utilized five J-2 engines, each producing 200,000 pounds of thrust. The engine used liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen as its propellants. Static test of ground test versions of the S-II stage were conducted at North American Aviation's Santa Susana, California test site. All flight stages were tested at the Mississippi Test Facility, Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The MTF was renamed to the National Space Technology Laboratory (NSTL) in 1974 and later to the Sternis Space Center (SSC) in May 1988.
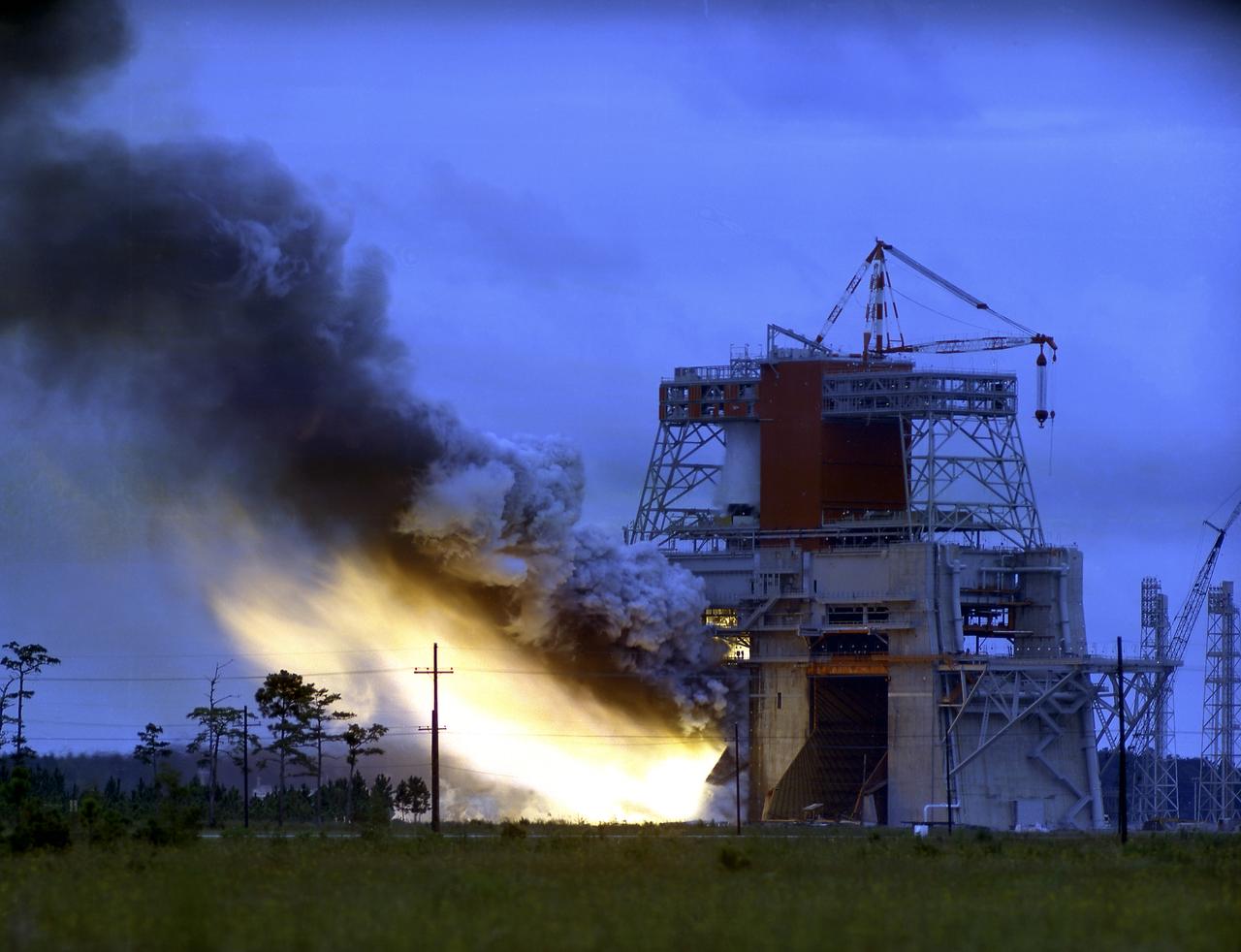

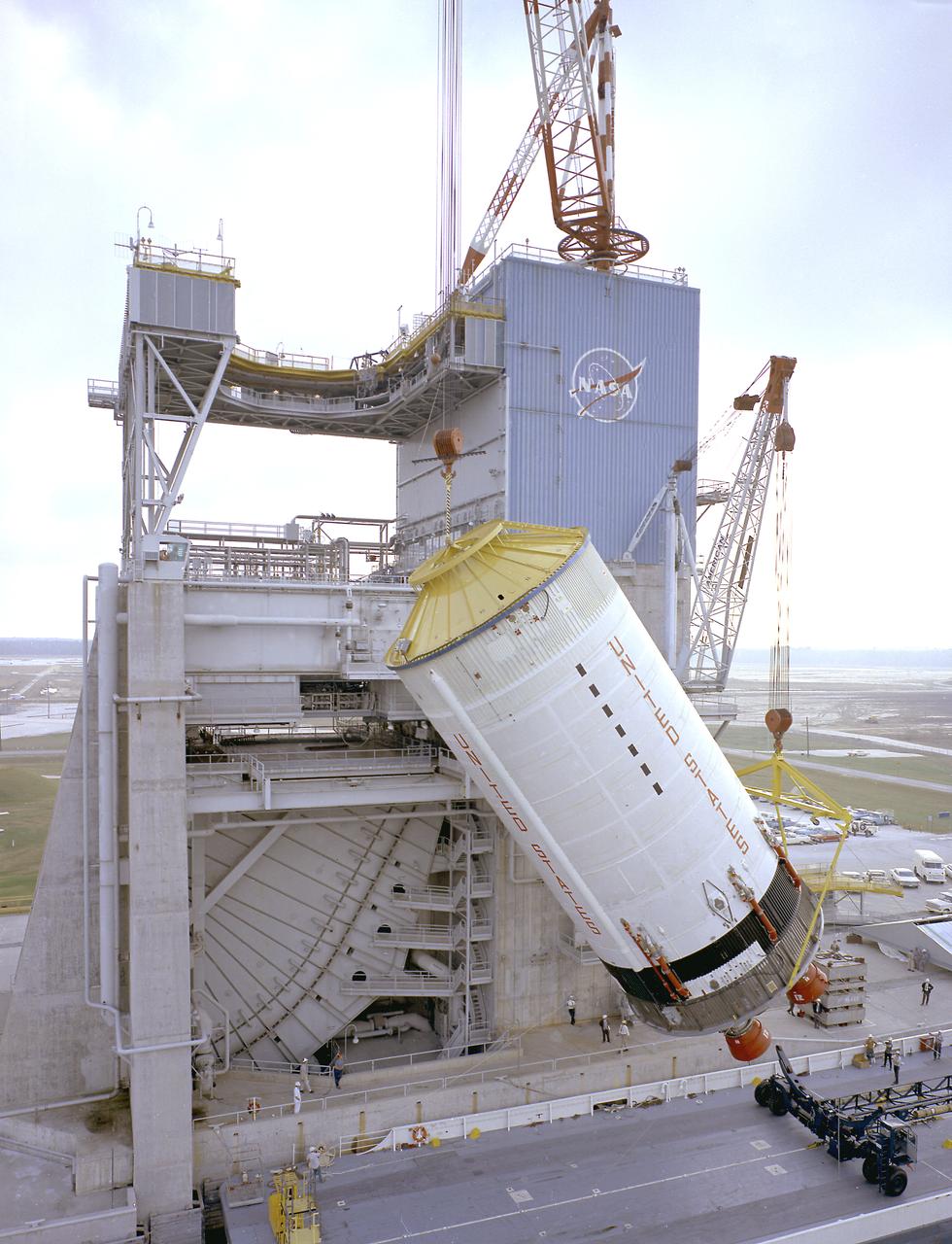
This photograph is a view of the Saturn V S-IC-5 (first) flight stage static test firing at the S-IC-B1 test stand at the Mississippi Test Facility (MTF), Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Begirning operations in 1966, the MTF has two test stands, a dual-position structure for running the S-IC stage at full throttle, and two separate stands for the S-II (Saturn V third) stage. It became the focus of the static test firing program. The completed S-IC stage was shipped from Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) to the MTF. The stage was then installed into the 407-foot-high test stand for the static firing tests before shipment to the Kennedy Space Center for final assembly of the Saturn V vehicle. The MTF was renamed to the National Space Technology Laboratory (NSTL) in 1974 and later to the Stennis Space Center (SSC) in May 1988.
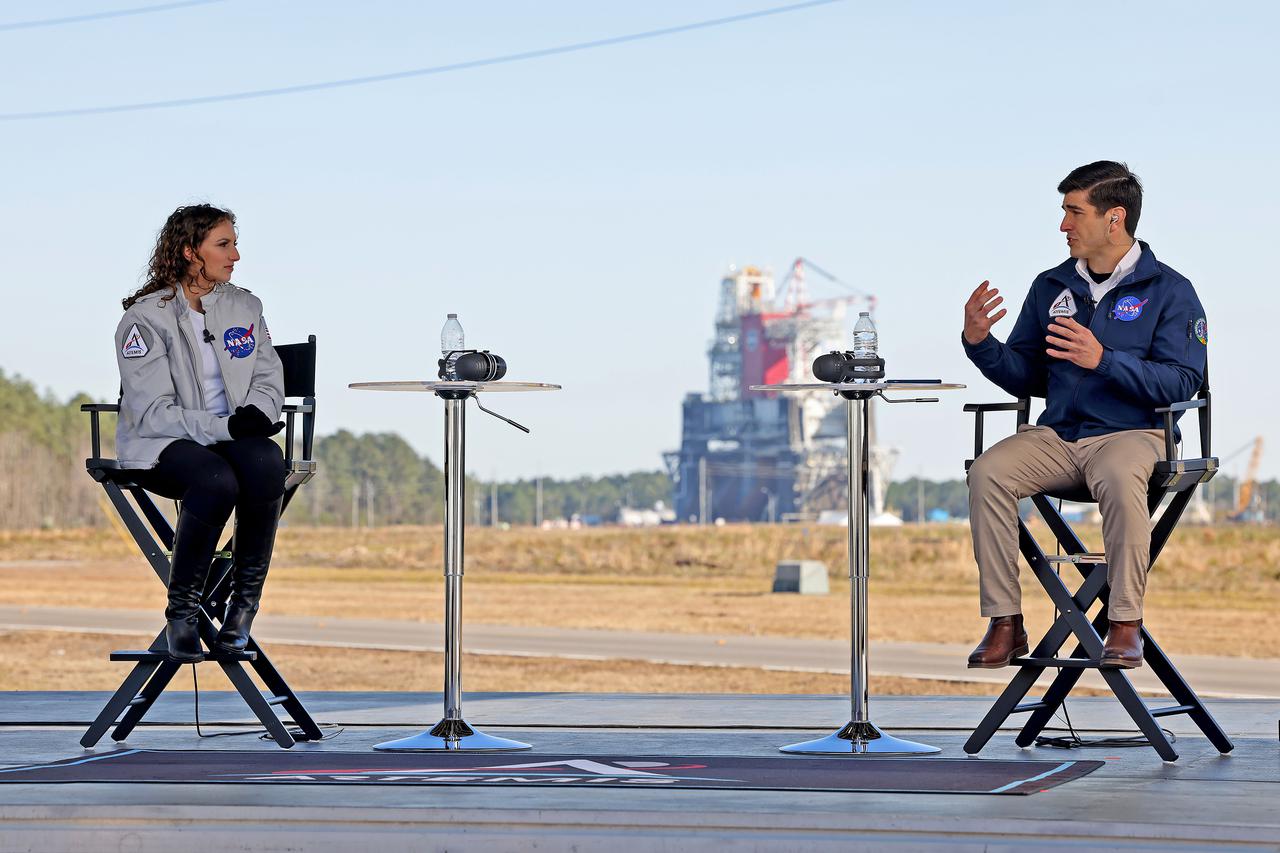

Host Leigh D’Angelo (left) talks with NASA Space Launch System core stage engineer Alex Cagnola from Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, during NASA TV live coverage from Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Jan. 16, 2021. D’Angelo, also from Michoud Assembly Facility, hosted the NASA TV coverage prior to the hot fire test of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
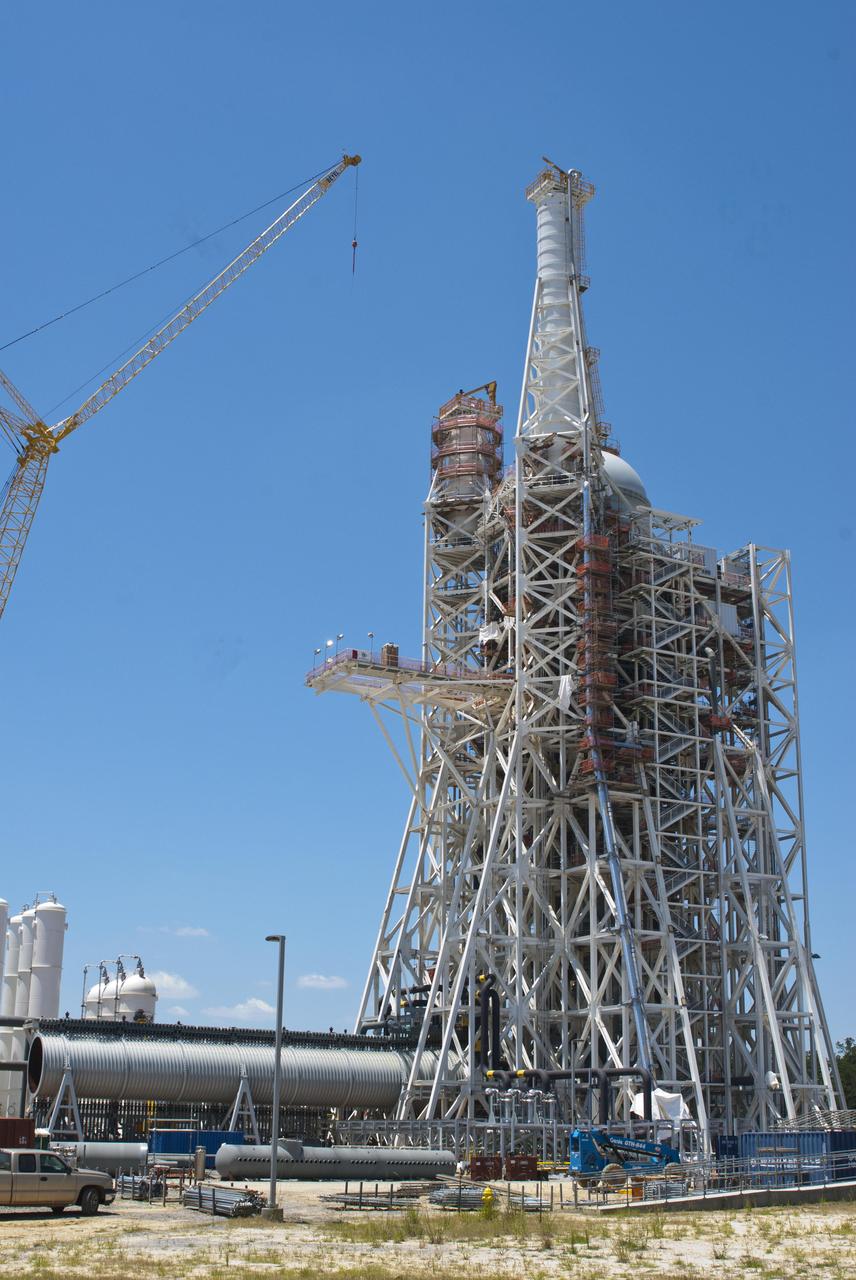

Construction continues on NASA's A-3 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center. The stand is the first large test structure built at the south Mississippi facility since the 1960s.
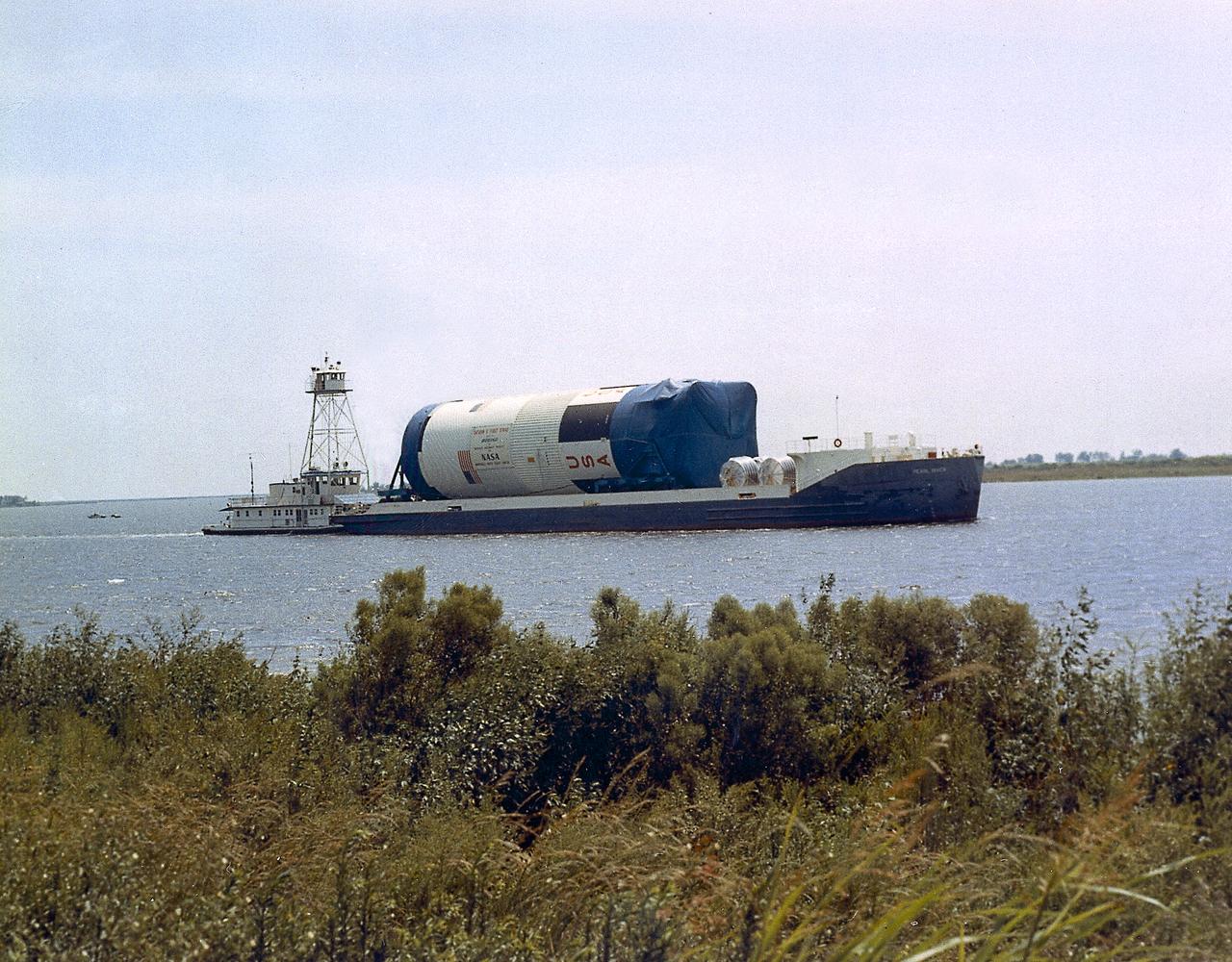

This is a view of the Saturn V S-IC (first) stage aboard the NASA barge, Pearl River, returning from the Mississippi Test Facility to the Michoud Assembly Facility.
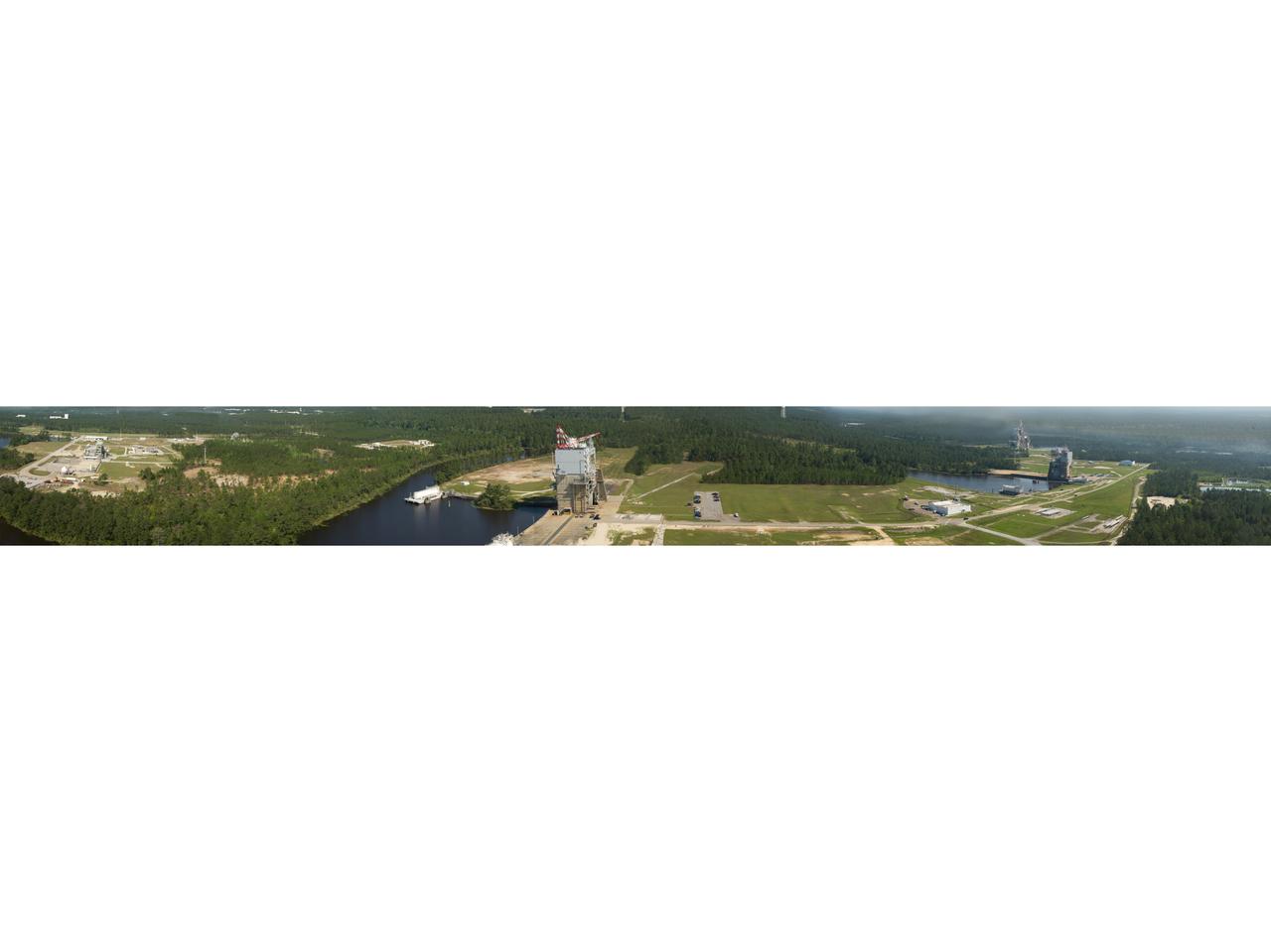

A photo taken from the top of the new A-3 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center offers a panoramic view of the A, B and E test complexes at the south Mississippi facility.
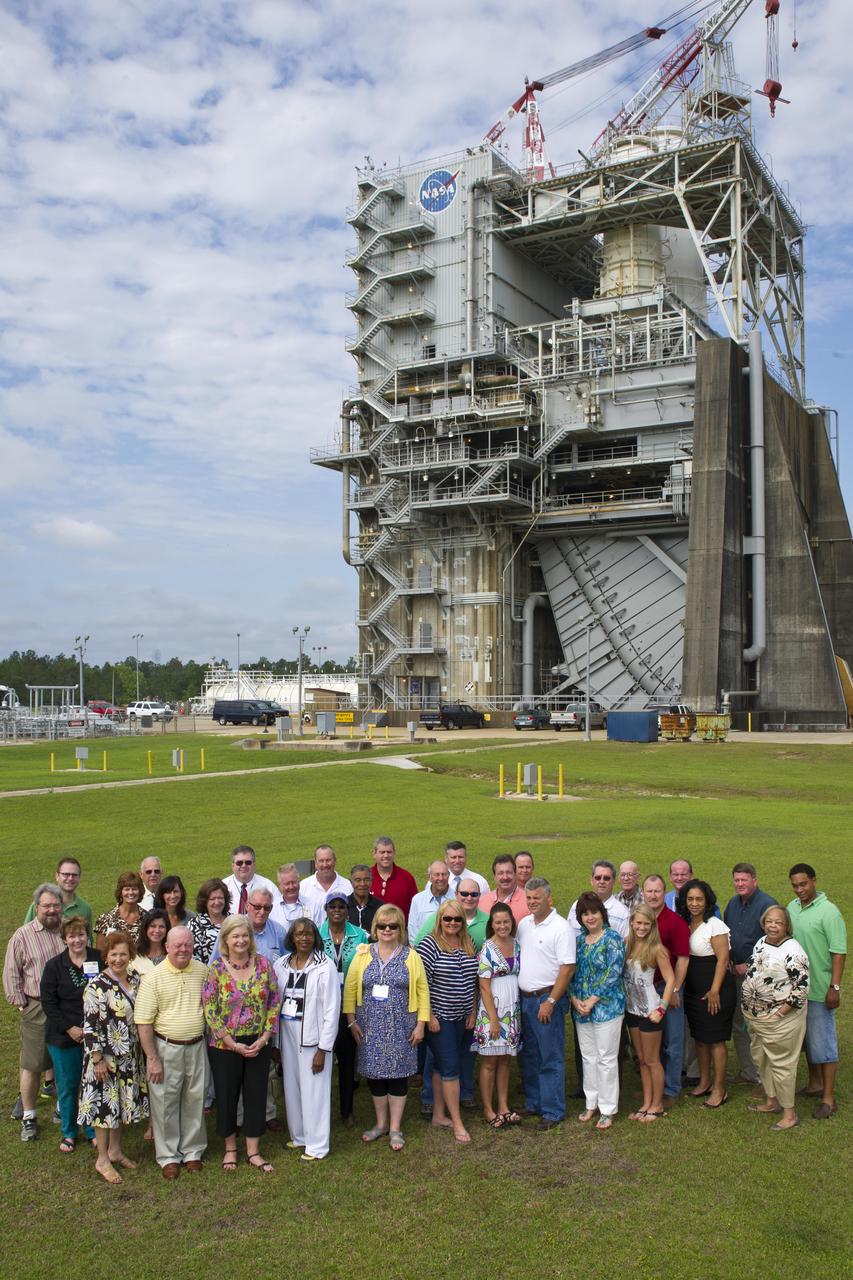

Legislators from across Mississippi visited Stennis Space Center on May 7, 2012, touring various facilities, including the A-1 Test Stand, and learning about work under way at the facility. The legislators also toured the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility and met with Apollo 13 astronaut Fred Haise.
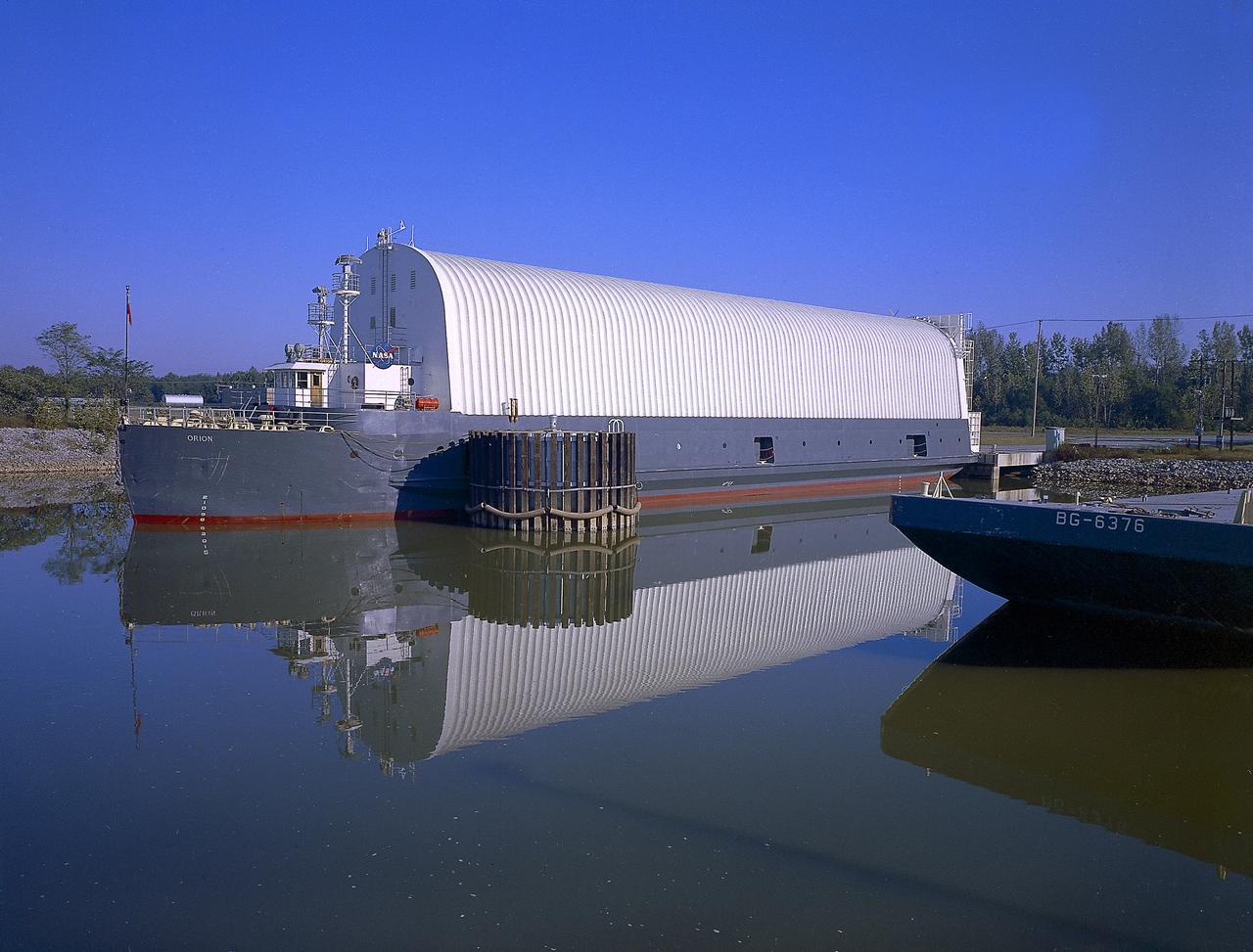

NASA used barges for transporting full-sized stages for the Saturn I, Saturn IB, and Saturn V vehicles between the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the manufacturing plant at the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF), the Mississippi Test Facility for testing, and the Kennedy Space Center. The barges traveled from the MSFC dock to the MAF, a total of 1,086.7 miles up the Tennessee River and down the Mississippi River. The barges also transported the assembled stages of the Saturn vehicle from the MAF to the Kennedy Space Center, a total of 932.4 miles along the Gulf of Mexico and up along the Atlantic Ocean, for the final assembly and the launch. This photograph shows the barge Orion at the MSFC dock.
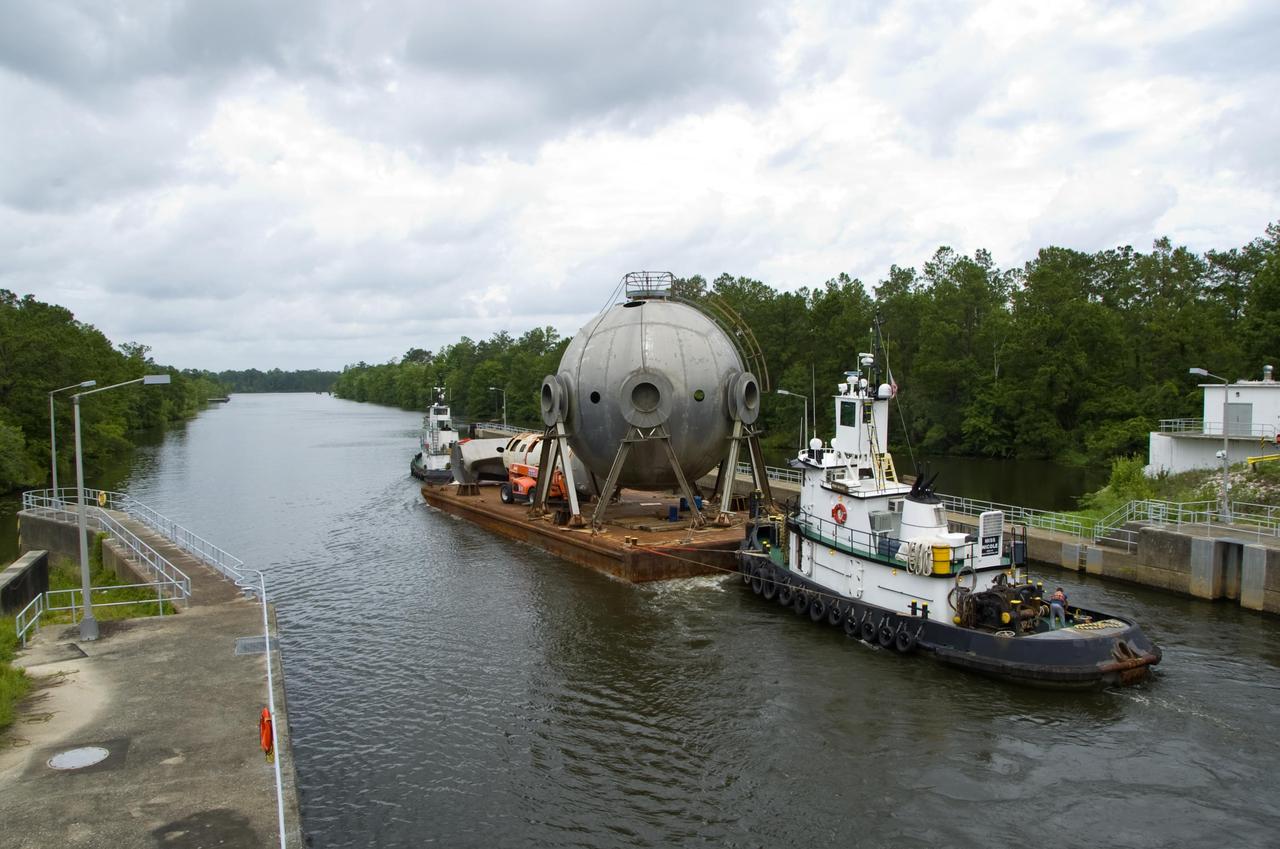

A 107,000-gallon liquid hydrogen sphere no longer needed at Stennis Space Center is barged through the facility locks June 21. The rocket engine test facility has teamed with the Mississippi Department of Marine Resource to place the sphere in offshore waters as an artificial reef.
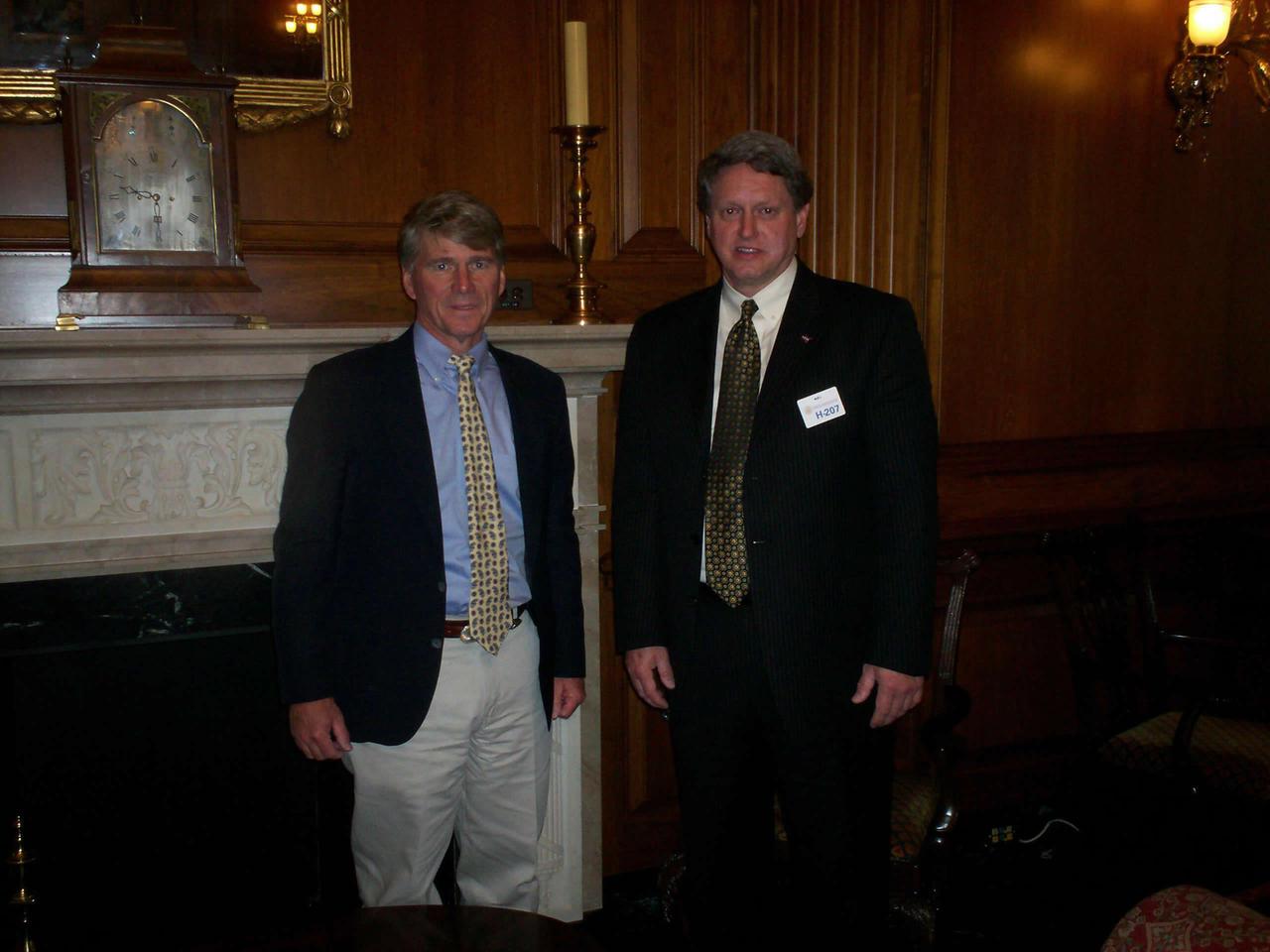

Stennis Space Center Director Gene Goldman (right) visited Washington, D.C,. last month, where he called on Louisiana and Mississippi leaders to update them on work at the rocket engine testing facility. Rep. Gene Taylor, D-Miss., was among those visited by Goldman on March 24.

NASA's Pegasus barge arrived at Stennis Space Center on Nov. 16, delivering space shuttle main engine ground support equipment to the south Mississippi facility. Stennis tested every main engine used on all 135 space shuttle flights.

A space shuttle main engine test April 21, 2006, at NASA Stennis Space Center marked the 40th anniversary of the first rocket engine test at the site. The firing also marked the 25th anniversary of NASA's STS-1, the first space shuttle mission. Then called the Mississippi Test Facility, the center conducted its first test on April 23, 1966. That historic test was on an S-II (second) stage, a cluster of five J-2 engines that powered the Saturn V rockets that took America's Apollo missions to the moon.
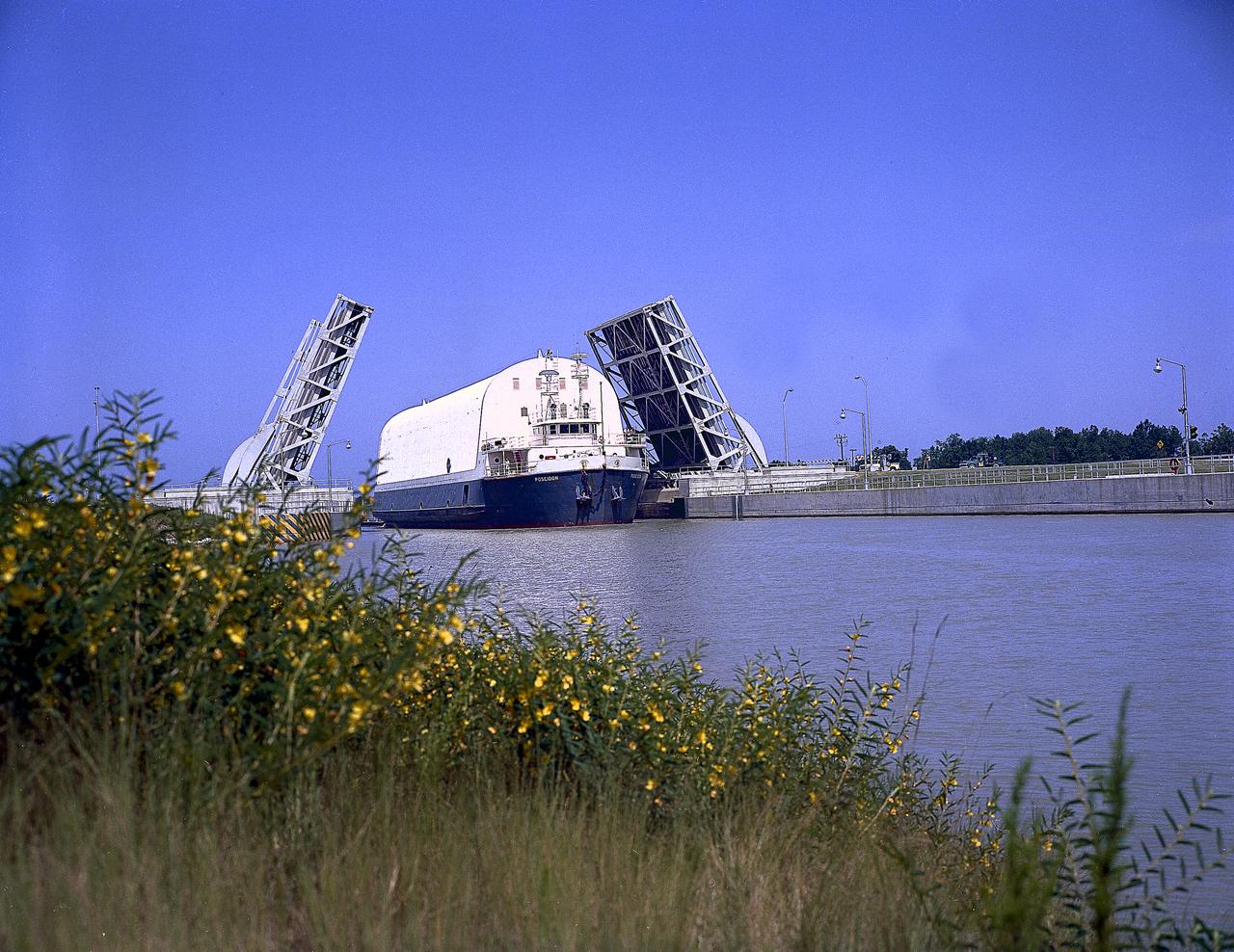

NASA used barges for transporting full-sized stages for the Saturn I, Saturn IB, and Saturn V vehicles between the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the manufacturing plant at the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF), the Mississippi Test Facility for testing, and the Kennedy Space Center. The barges traveled from the MSFC dock to the MAF, a total of 1,086.7 miles up the Tennessee River and down the Mississippi River. The barges also transported the assembled stages of the Saturn vehicle from the MAF to the Kennedy Space Center, a total of 932.4 miles along the Gulf of Mexico and up along the Atlantic Ocean, for the final assembly and the launch. This photograph shows the barge Poseidon loaded with the Saturn V S-II (second) stage passing through a bascule bridge.
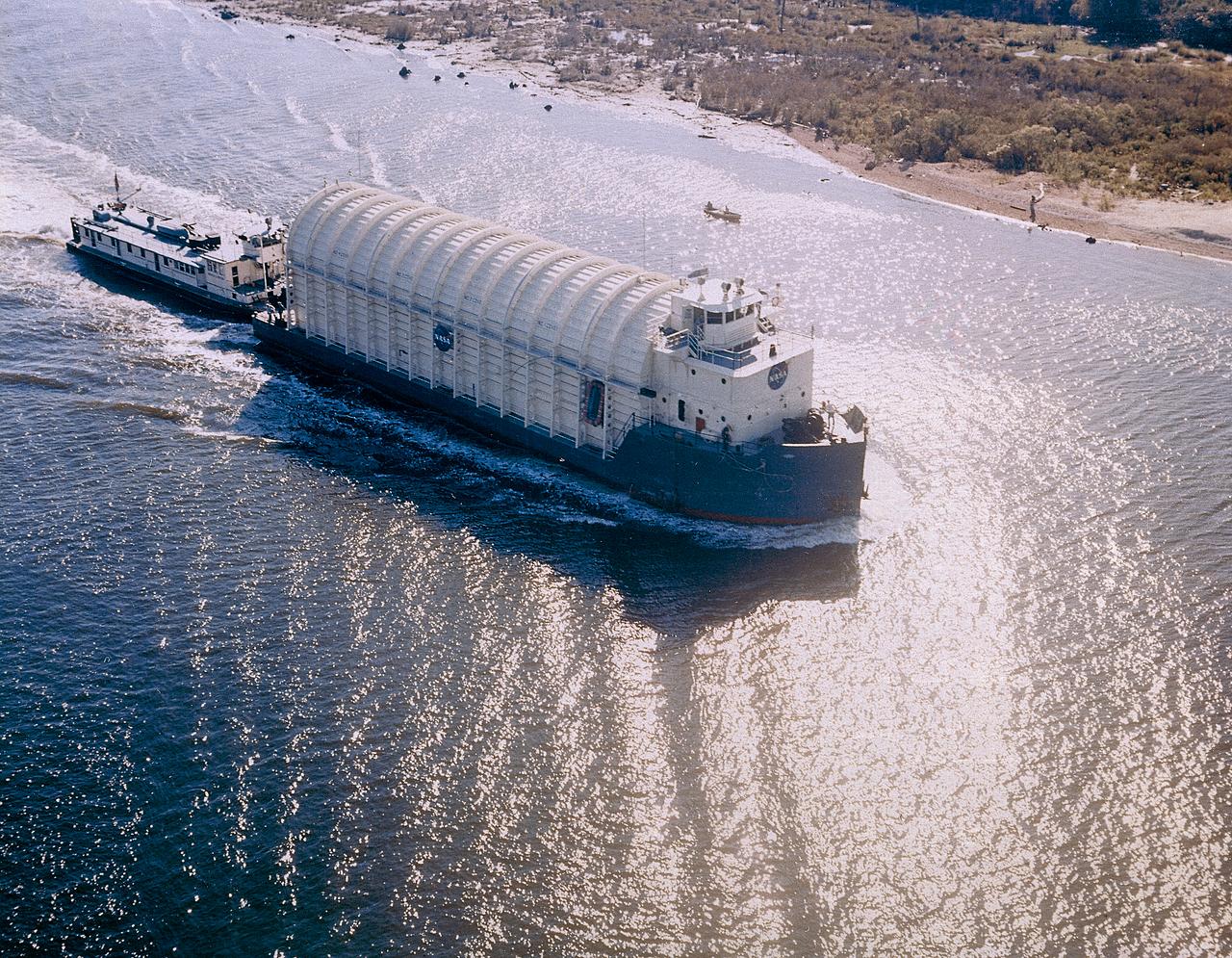

NASA used barges for transporting full-sized stages for the Saturn I, Saturn IB, and Saturn V vehicles between the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the manufacturing plant at the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF), the Mississippi Test Facility for testing, and the Kennedy Space Center. The barges traveled from the MSFC dock to the MAF, a total of 1,086.7 miles up the Tennessee River and down the Mississippi River. The barges also transported the assembled stages of the Saturn vehicle from the MAF to the Kennedy Space Center, a total of 932.4 miles along the Gulf of Mexico and up along the Atlantic Ocean, for the final assembly and the launch. Pictured is the barge Palaemon carrying Saturn IV S-IB flight stage enroute to MSFC.

Officials cut the ribbon during dedication ceremonies of the George A. Knauer Marine Science Building on Oct. 17 at NASA Stennis Space Center (SSC). The $2.75 million facility, the first building at the test site funded by the state of Mississippi, houses six science labs, classrooms and office space for 40 faculty and staff. Pictured are, from left, Rear Adm. Thomas Donaldson, commander of the Naval Meteorology and Oceanography Command; SSC Assistant Director David Throckmorton; Dr. George A. Knauer, founder of the Center of Marine Science at the University of Southern Mississippi (USM); Lt. Gov. Amy Tuck; and USM President Dr. Shelby Thames.

The Saturn V first stages were test fired at the Mississippi Test Facility and at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Five F-1 engines powered the first stage, each developing 1.5 million pounds of thrust. The first stage, known as the S-IC stage, burned over 15 tons of propellant per second during its 2.5 minutes of operation to take the vehicle to a height of about 36 miles and to a speed of about 6,000 miles per hour. The stage was 138 feet long and 33 feet in diameter. This photograph shows the test firing of an F-1 engine at the MSFC's S-IC Static Test Firing Facility.
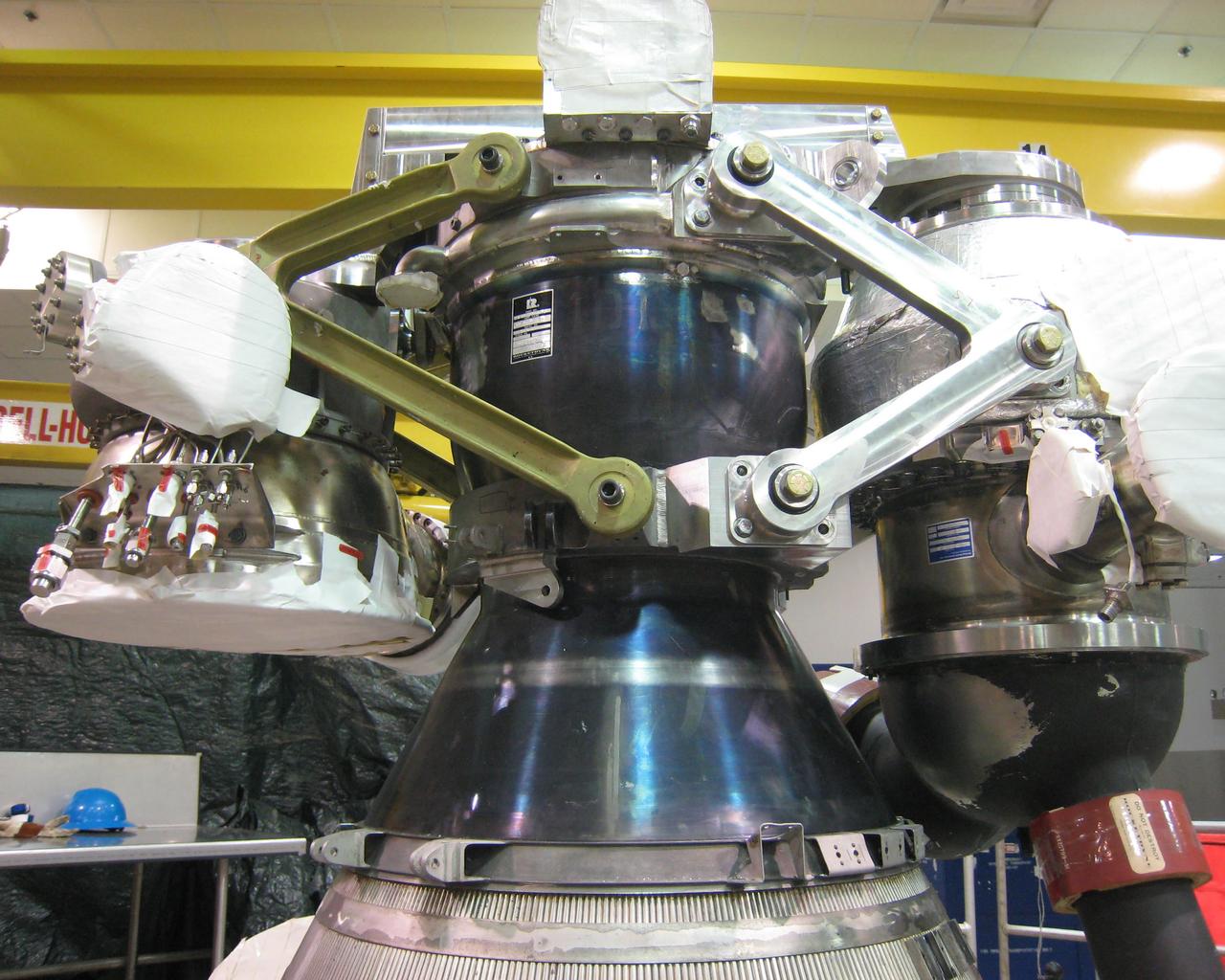

A vintage 1960 J-2 thrust chamber is fitted with brackets and pumps recently at the Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne assembly facility in Stennis Space Center's Building 9101. Together, the parts comprise the J-2X Powerpack 1A test article. Mississippi Space Services machined the new bracket (the V-shaped arm on the right), making this the first time parts for an engine test article were machined, welded and assembled on site at SSC.
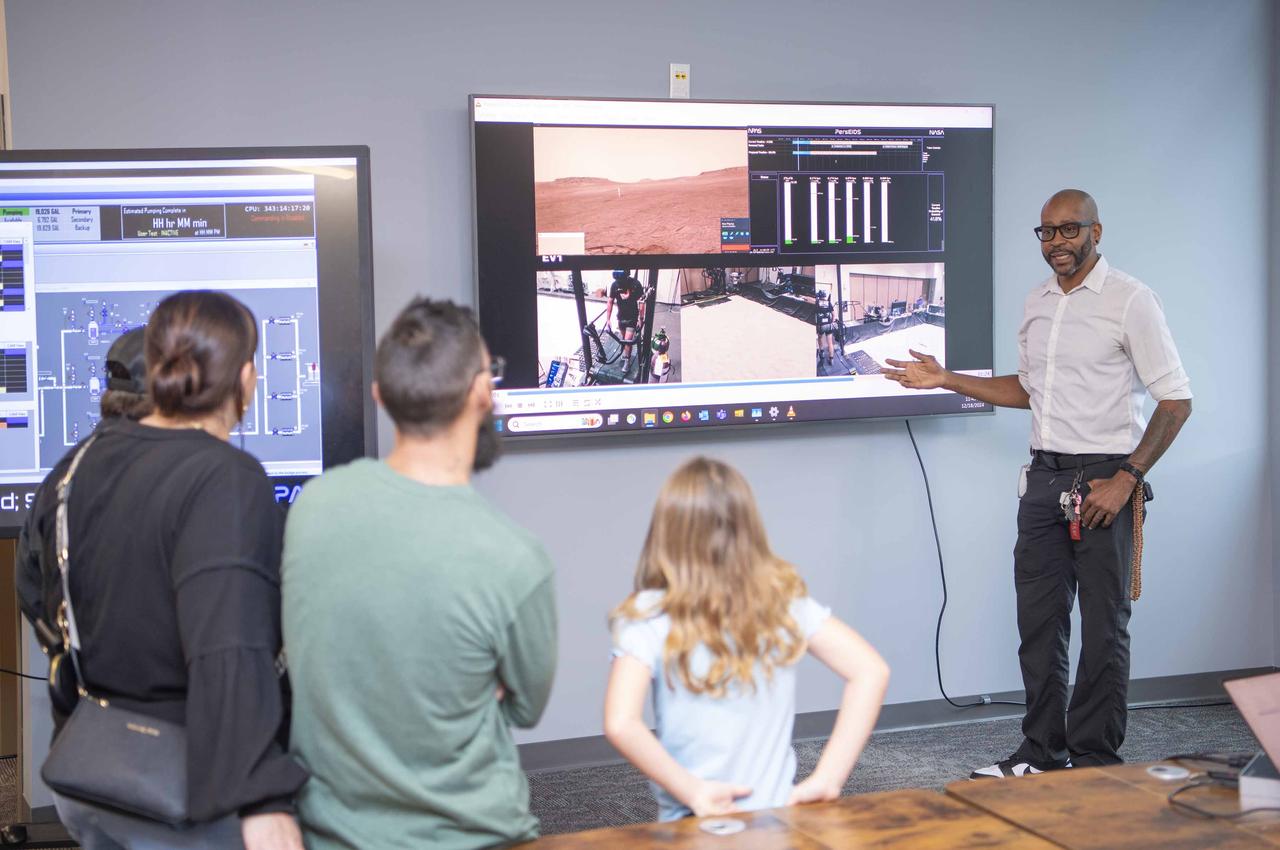

Cookbook author and culinary content creator Caroline Davis, popularly known as Mississippi Kween, and her family enjoy touring facilities and learning about NASA Stennis and its frontline work during a site visit Dec. 18. Davis, husband Joe, and children Zeke and Zoey, met with NASA Stennis leadership before touring the L3Harris (formerly Aerojet Rocketdyne) Engine Assembly Facility, Thad Cochran Test Stand, Autonomous Systems Laboratory, and the NASA Stennis rocket engine garden. The tour highlighted the NASA Stennis story and how the south Mississippi NASA center has the ingredients for a recipe that accelerates the exploration and commercialization of space, innovates to benefit NASA and industry, and leverages assets to stimulate the economy.
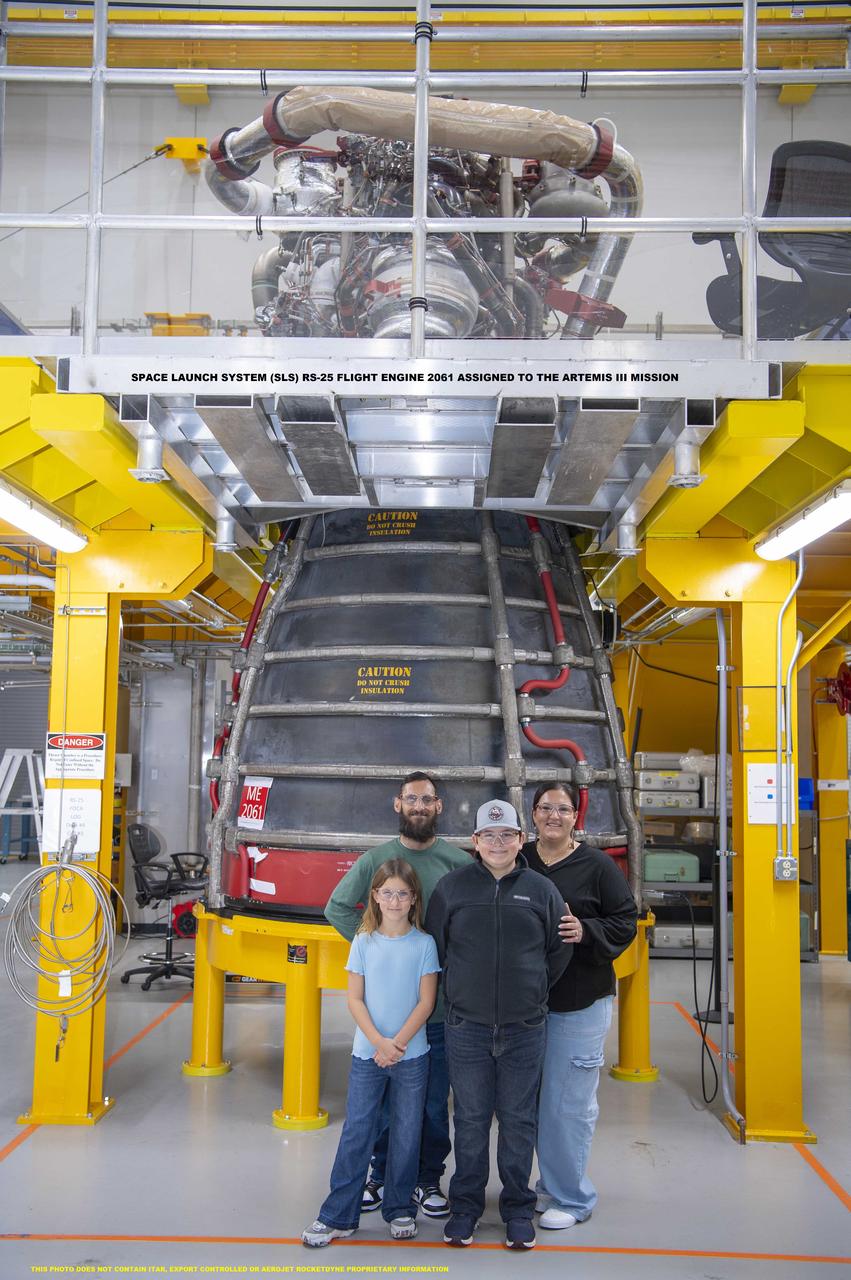

Cookbook author and culinary content creator Caroline Davis, popularly known as Mississippi Kween, and her family enjoy touring facilities and learning about NASA Stennis and its frontline work during a site visit Dec. 18. Davis, husband Joe, and children Zeke and Zoey, met with NASA Stennis leadership before touring the L3Harris (formerly Aerojet Rocketdyne) Engine Assembly Facility, Thad Cochran Test Stand, Autonomous Systems Laboratory, and the NASA Stennis rocket engine garden. The tour highlighted the NASA Stennis story and how the south Mississippi NASA center has the ingredients for a recipe that accelerates the exploration and commercialization of space, innovates to benefit NASA and industry, and leverages assets to stimulate the economy.
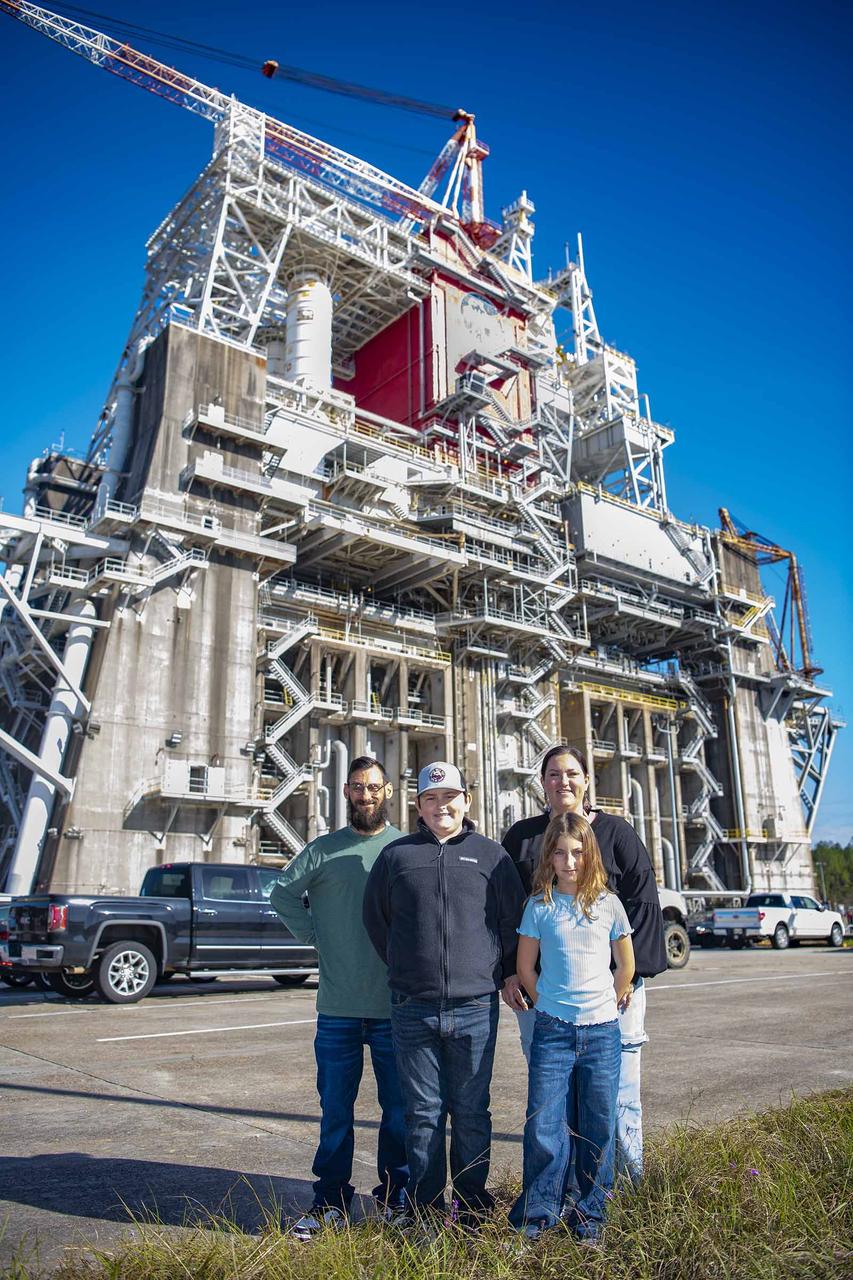

Cookbook author and culinary content creator Caroline Davis, popularly known as Mississippi Kween, and her family enjoy touring facilities and learning about NASA Stennis and its frontline work during a site visit Dec. 18. Davis, husband Joe, and children Zeke and Zoey, met with NASA Stennis leadership before touring the L3Harris (formerly Aerojet Rocketdyne) Engine Assembly Facility, Thad Cochran Test Stand, Autonomous Systems Laboratory, and the NASA Stennis rocket engine garden. The tour highlighted the NASA Stennis story and how the south Mississippi NASA center has the ingredients for a recipe that accelerates the exploration and commercialization of space, innovates to benefit NASA and industry, and leverages assets to stimulate the economy.

Cookbook author and culinary content creator Caroline Davis, popularly known as Mississippi Kween, and her family enjoy touring facilities and learning about NASA Stennis and its frontline work during a site visit Dec. 18. Davis, husband Joe, and children Zeke and Zoey, met with NASA Stennis leadership before touring the L3Harris (formerly Aerojet Rocketdyne) Engine Assembly Facility, Thad Cochran Test Stand, Autonomous Systems Laboratory, and the NASA Stennis rocket engine garden. The tour highlighted the NASA Stennis story and how the south Mississippi NASA center has the ingredients for a recipe that accelerates the exploration and commercialization of space, innovates to benefit NASA and industry, and leverages assets to stimulate the economy.
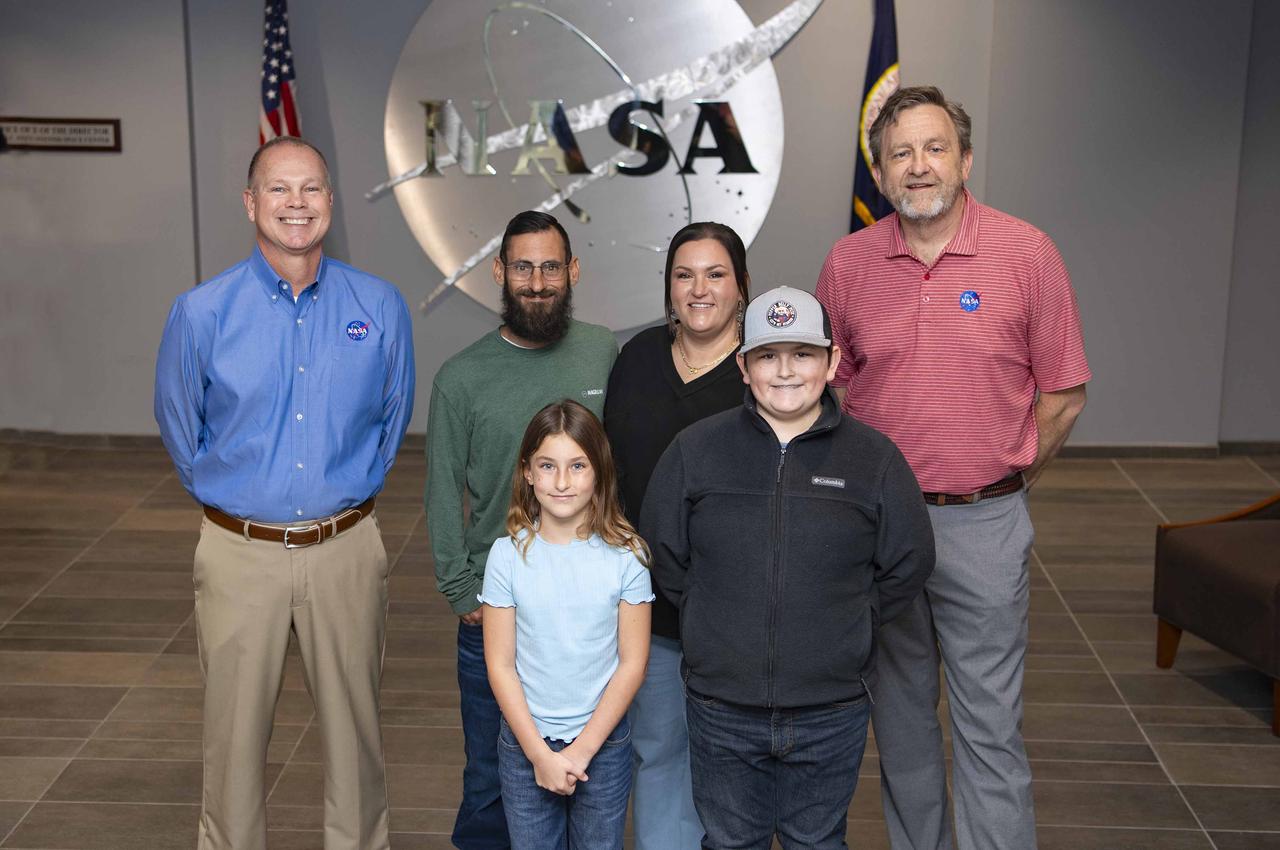

Cookbook author and culinary content creator Caroline Davis, popularly known as Mississippi Kween, and her family enjoy touring facilities and learning about NASA Stennis and its frontline work during a site visit Dec. 18. Davis, husband Joe, and children Zeke and Zoey, met with NASA Stennis leadership before touring the L3Harris (formerly Aerojet Rocketdyne) Engine Assembly Facility, Thad Cochran Test Stand, Autonomous Systems Laboratory, and the NASA Stennis rocket engine garden. The tour highlighted the NASA Stennis story and how the south Mississippi NASA center has the ingredients for a recipe that accelerates the exploration and commercialization of space, innovates to benefit NASA and industry, and leverages assets to stimulate the economy.
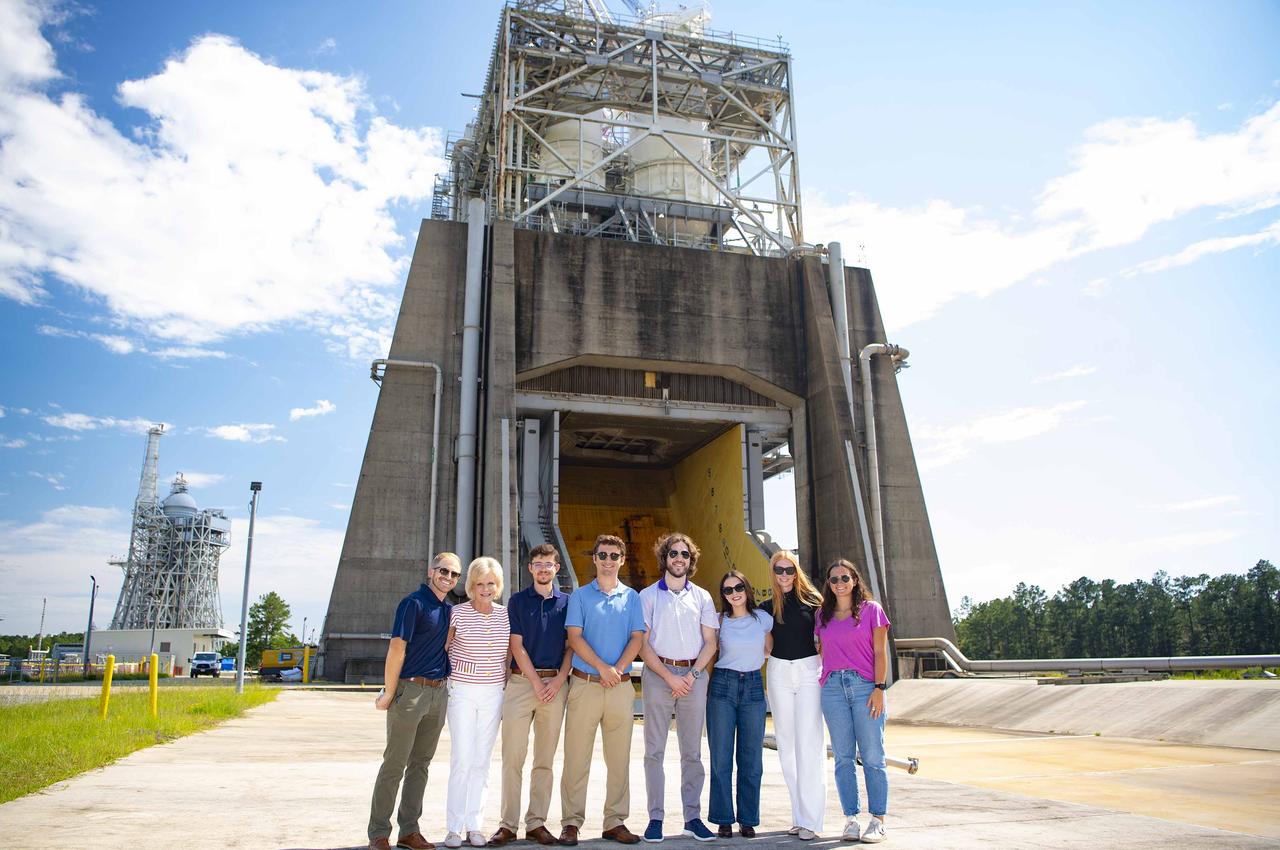

Legislative staff and interns from the office of U.S. Rep. Garrett Graves of Louisiana are pictured at the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA Stennis on July 11. During the visit to the south Mississippi site, the group learned more about internship opportunities with NASA and NASA Stennis. In addition to touring the test complex where RS-25 engines are tested for future Artemis missions, the group visited the Aerojet Rocketdyne Engine Assembly Facility onsite. Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, manufactures RS-25 engines to help power NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
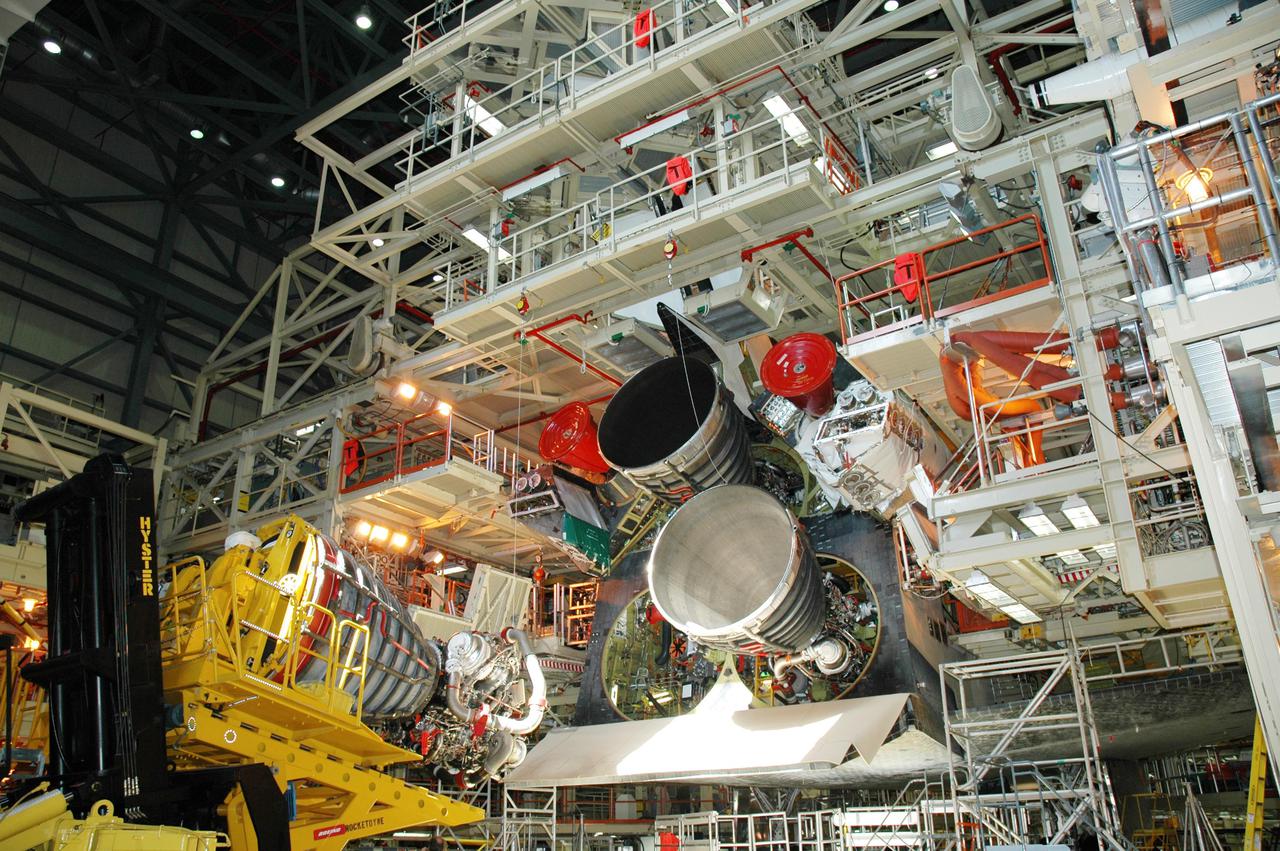

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The third Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) arrives in the Orbiter Processing Facility for installation on Discovery. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114. Recent improvements to the SSME include the introduction of redesigned high-pressure turbopumps into the SSME fleet. The new pumps are designed and built by Pratt and Whitney at West Palm Beach, Fla. SSMEs and the Pratt and Whitney turbopumps are tested at Stennis Space Center in Mississippi. Engines and engine components are delivered to Kennedy Space Center to be prepared for flight.
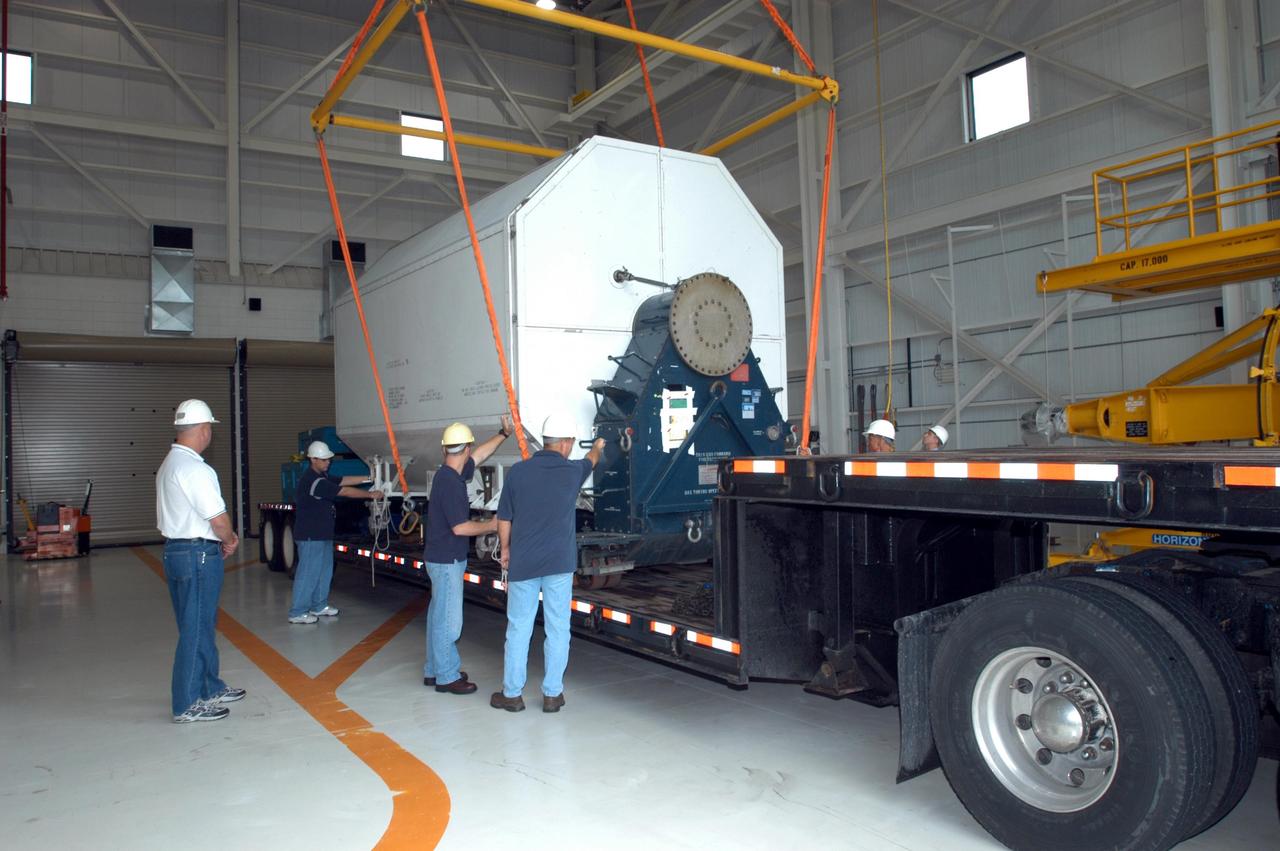

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the KSC Engine Shop, Boeing-Rocketdyne technicians attach an overhead crane to the container enclosing the third Space Shuttle Main Engine for Discovery’s Return to Flight mission STS-114 arrives at the KSC Engine Shop aboard a trailer. The engine is returning from NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi where it underwent a hot fire acceptance test. Typically, the engines are installed on an orbiter in the Orbiter Processing Facility approximately five months before launch.

Mississippi Gov. Haley Barbour speaks to members of the World Presidents' Organization during the group's visit to NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center on Jan. 26. WPO members from several states spent the day touring Stennis facilities and learning about the work of the nation's premier rocket engine testing site. Barbour visited with group members during a morning session in StenniSphere, the center's visitors center and museum.
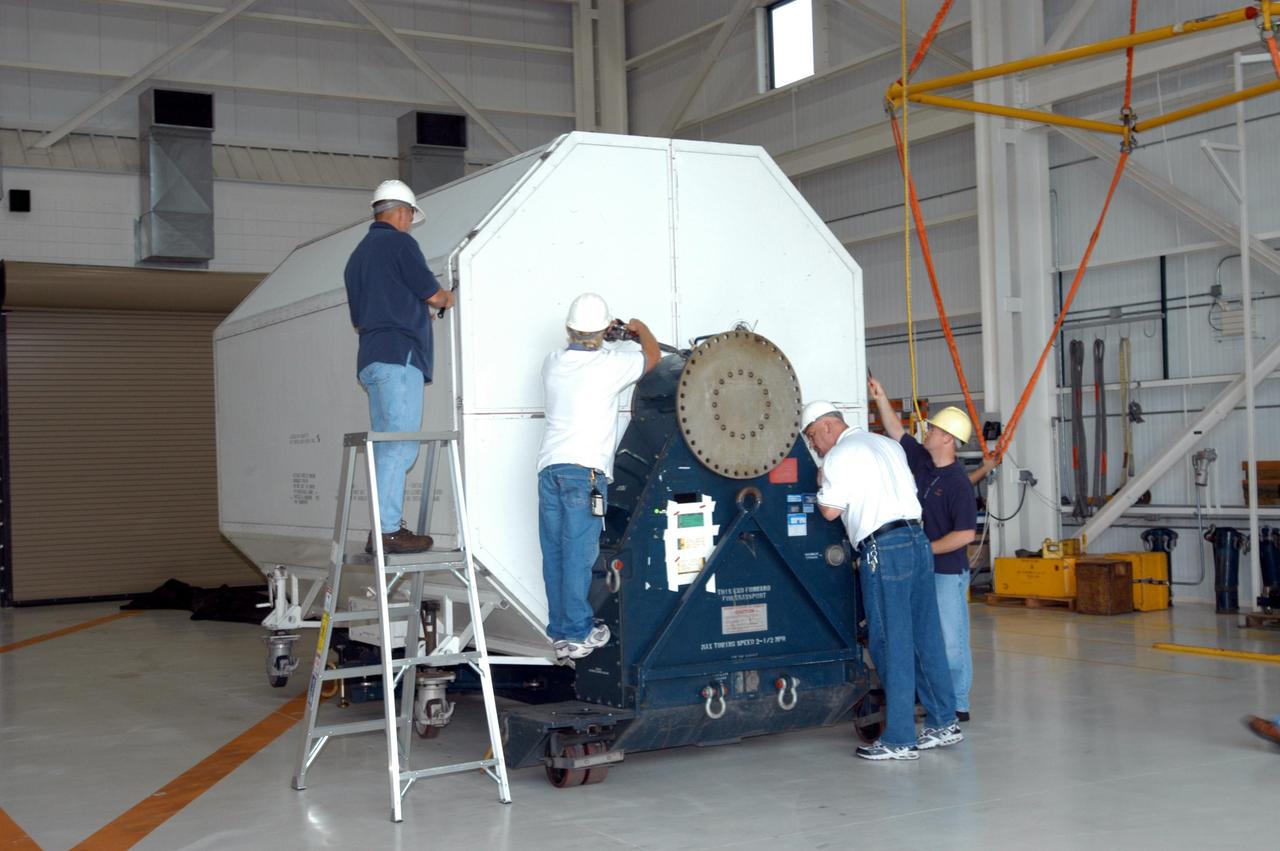

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the KSC Engine Shop, Boeing-Rocketdyne technicians begin removing the end of the container enclosing the third Space Shuttle Main Engine for Discovery’s Return to Flight mission STS-114. The engine is returning from NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi where it underwent a hot fire acceptance test. Typically, the engines are installed on an orbiter in the Orbiter Processing Facility approximately five months before launch.
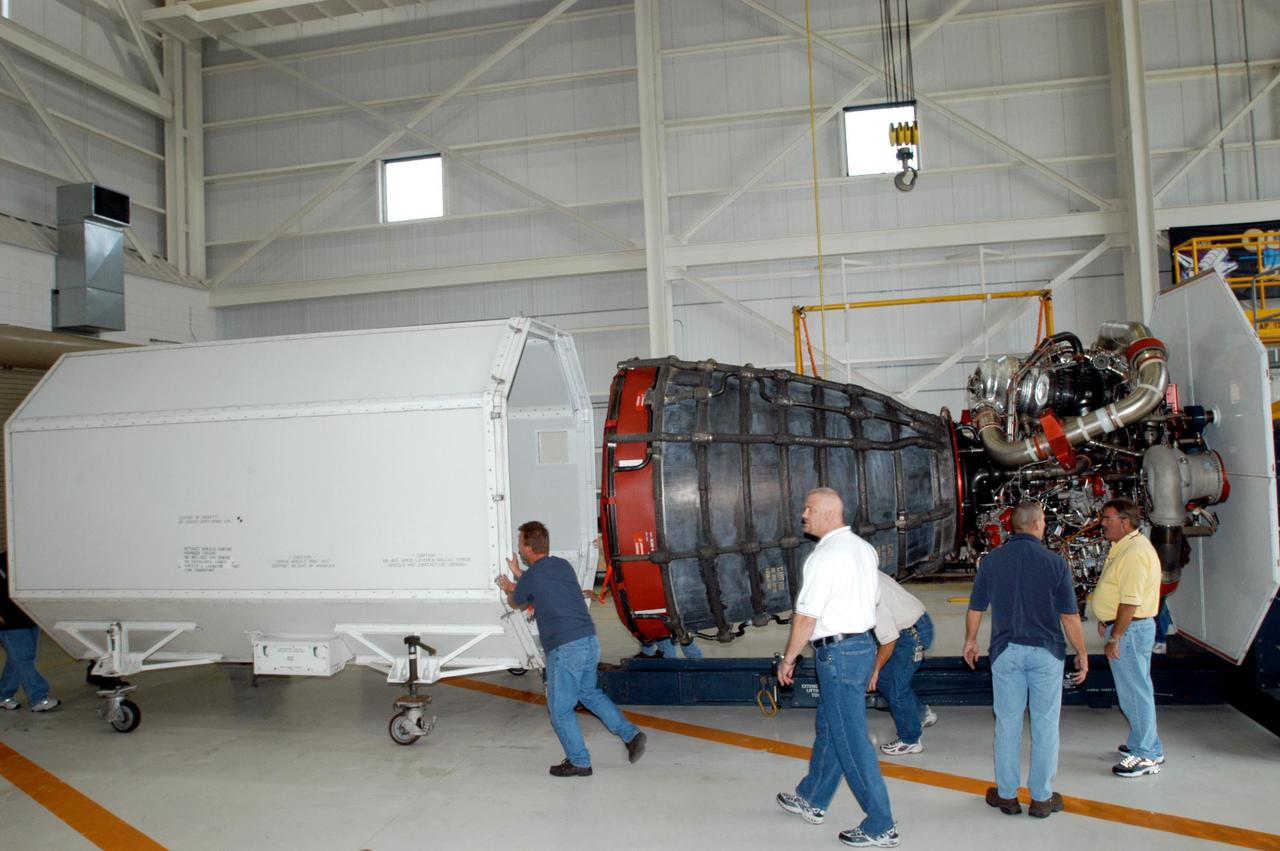

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the KSC Engine Shop, Boeing-Rocketdyne technicians remove the container that enclosed the third Space Shuttle Main Engine for Discovery’s Return to Flight mission STS-114. The engine is returning from NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi where it underwent a hot fire acceptance test. Typically, the engines are installed on an orbiter in the Orbiter Processing Facility approximately five months before launch.
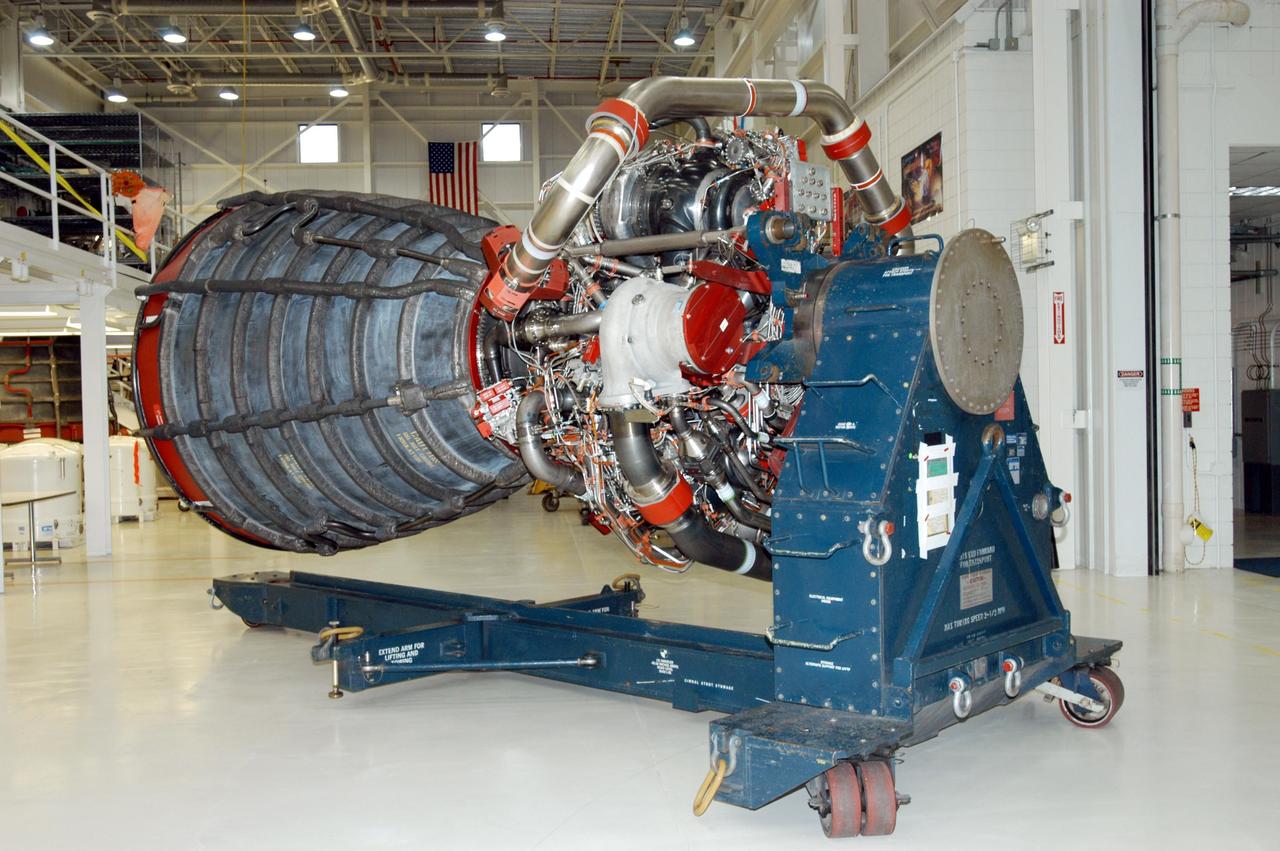

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the KSC Engine Shop, the third Space Shuttle Main Engine for Discovery’s Return to Flight mission STS-114 is secure on a stand. The engine has been returned from NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi where it underwent a hot fire acceptance test. Typically, the engines are installed on an orbiter in the Orbiter Processing Facility approximately five months before launch.
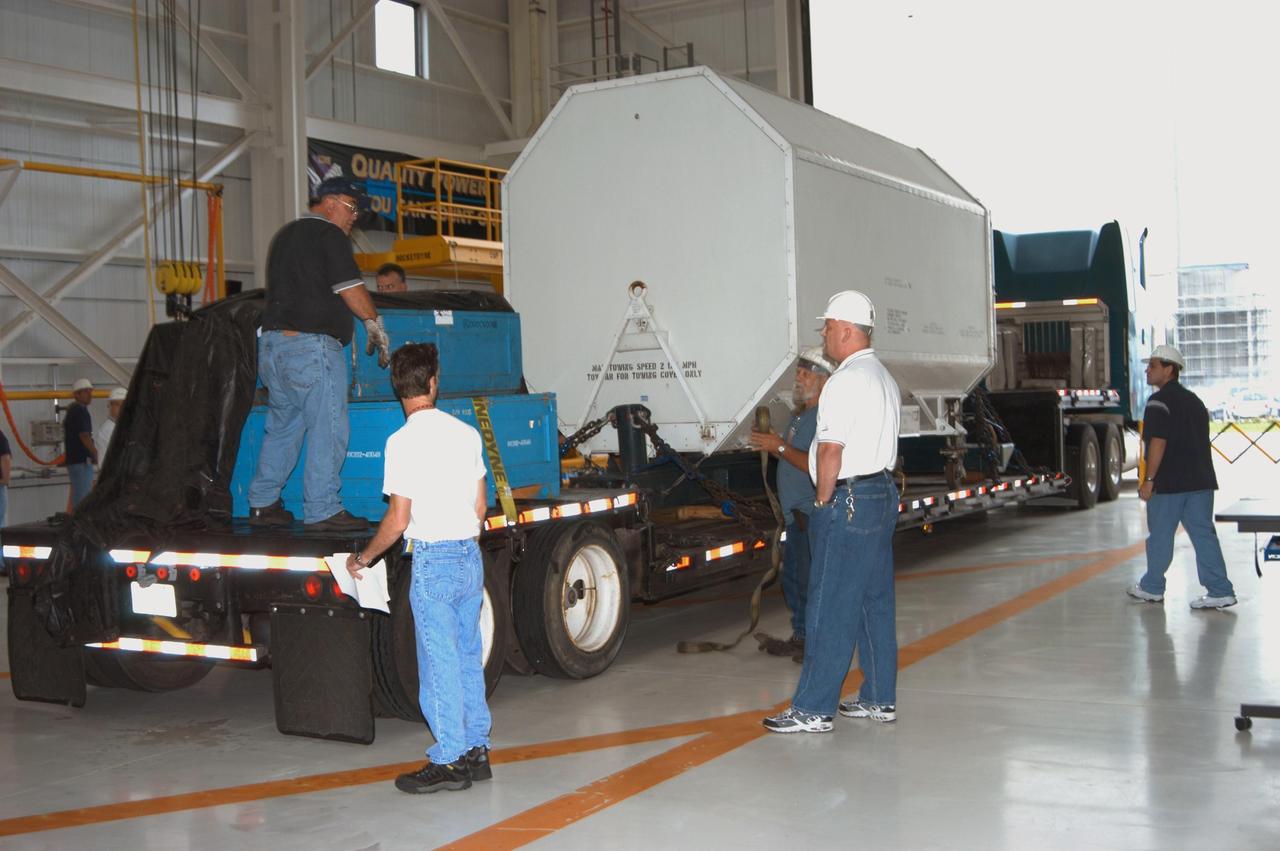

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Enclosed inside the shipping container, the third Space Shuttle Main Engine for Discovery’s Return to Flight mission STS-114 arrives at the KSC Engine Shop aboard a trailer. The engine is returning from NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi where it underwent a hot fire acceptance test. Typically, the engines are installed on an orbiter in the Orbiter Processing Facility approximately five months before launch.
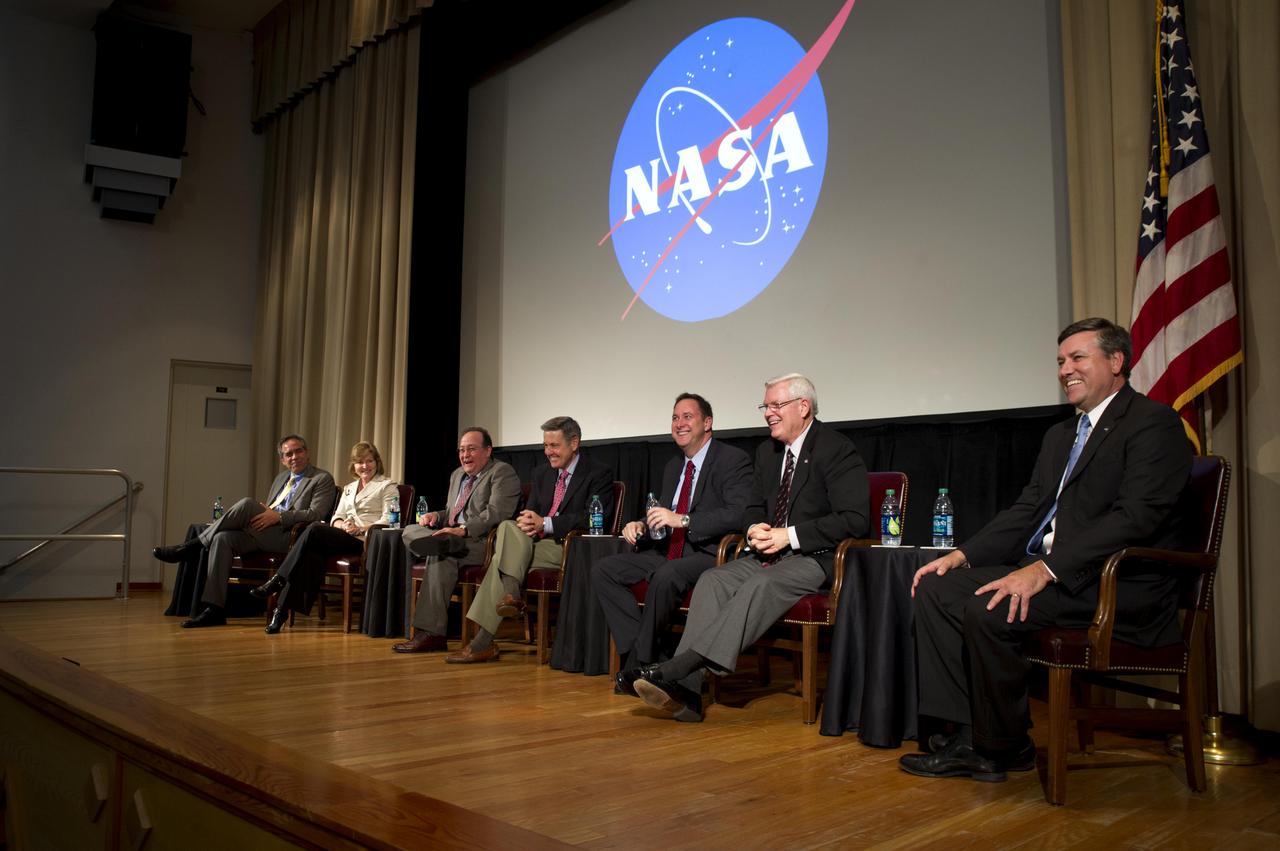

Stennis Space Center Director Patrick Scheuermann (right) hosted directors from six other NASA centers during a forum discussion at the south Mississippi rocket engine test facility Nov. 9. The directors discussed the future of the American space program from their perspectives during an all hands session with Stennis employees. Participants were: (l to r) David McBride, Lesa Roe, Ray Lugo, Bob Cabana, Robert Lightfoot, Mike Coats and Scheuermann.
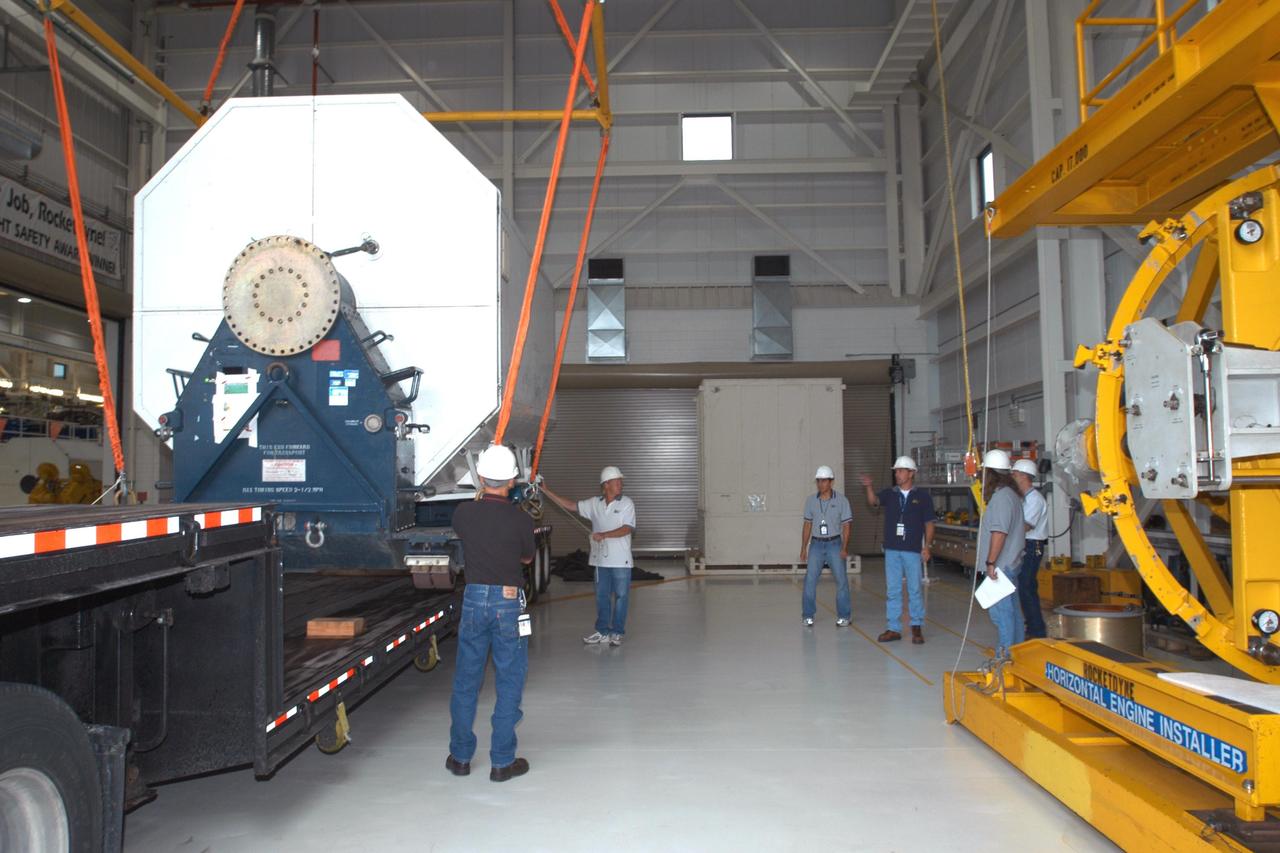

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the KSC Engine Shop, the third Space Shuttle Main Engine for Discovery’s Return to Flight mission STS-114 is ready to be lifted off the trailer. The engine is returning from NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi where it underwent a hot fire acceptance test. Typically, the engines are installed on an orbiter in the Orbiter Processing Facility approximately five months before launch.
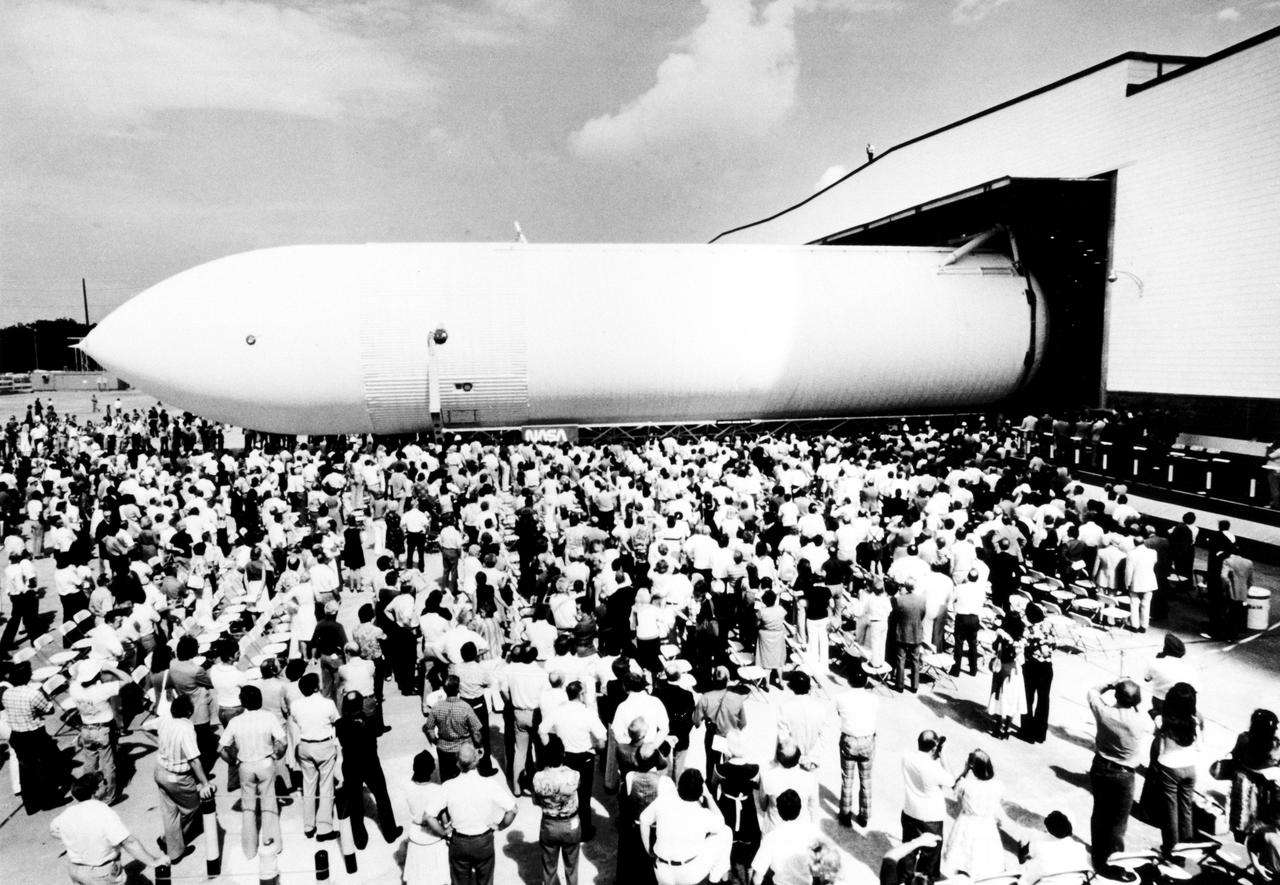

The first Space Shuttle External Tank, the Main Propulsion Test Article (MPTA), rolls off the assembly line September 9, 1977 at the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The MPTA was then transported to the National Space Technology Laboratories in southern Mississippi where it was used in the first static firing of the three main engines. Marshall Space Flight Center had management responsibility for Space Shuttle propulsion elements, including the External Tank. Martin Marietta was the prime contractor who designed and assembled the tanks at Michoud.
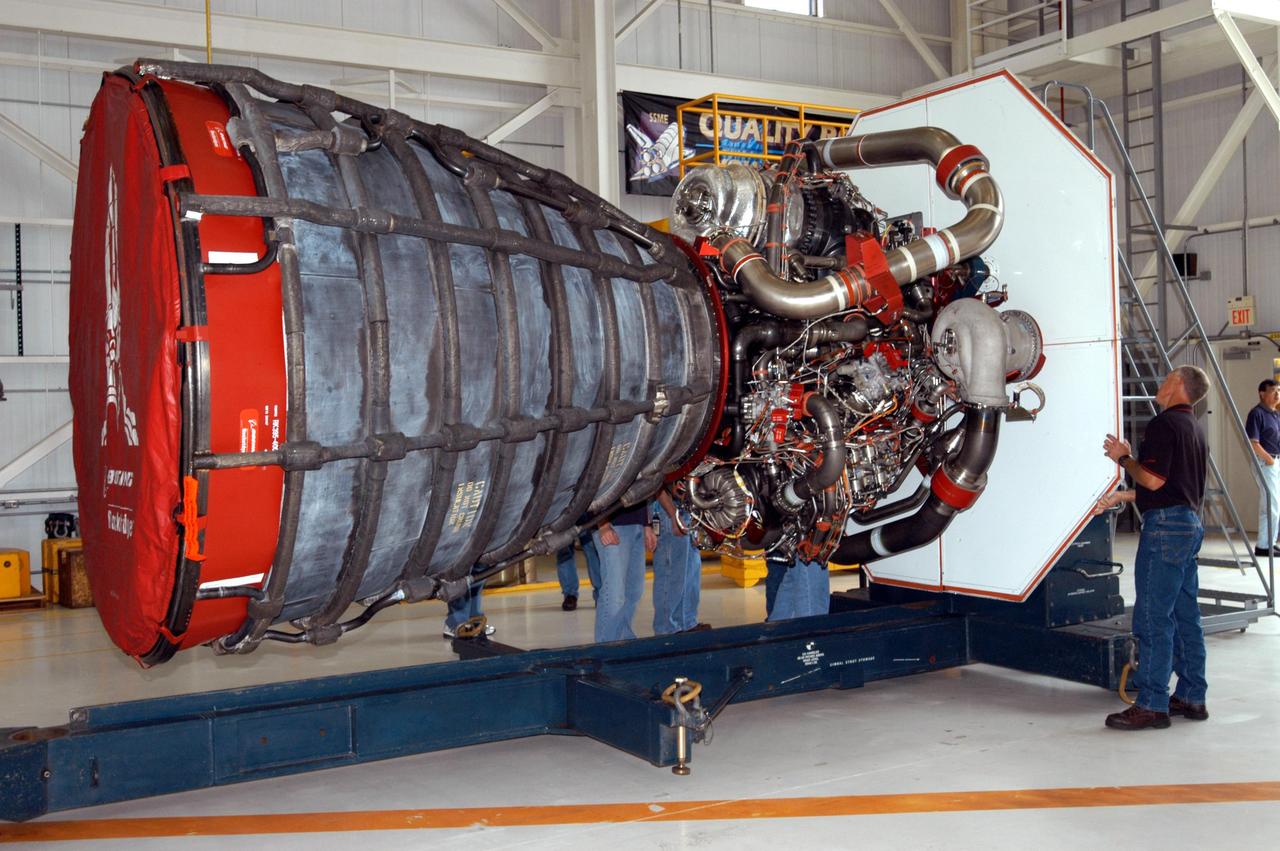
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the KSC Engine Shop, Boeing-Rocketdyne technicians secure on a stand the third Space Shuttle Main Engine for Discovery’s Return to Flight mission STS-114. The engine is returning from NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi where it underwent a hot fire acceptance test. Typically, the engines are installed on an orbiter in the Orbiter Processing Facility approximately five months before launch.
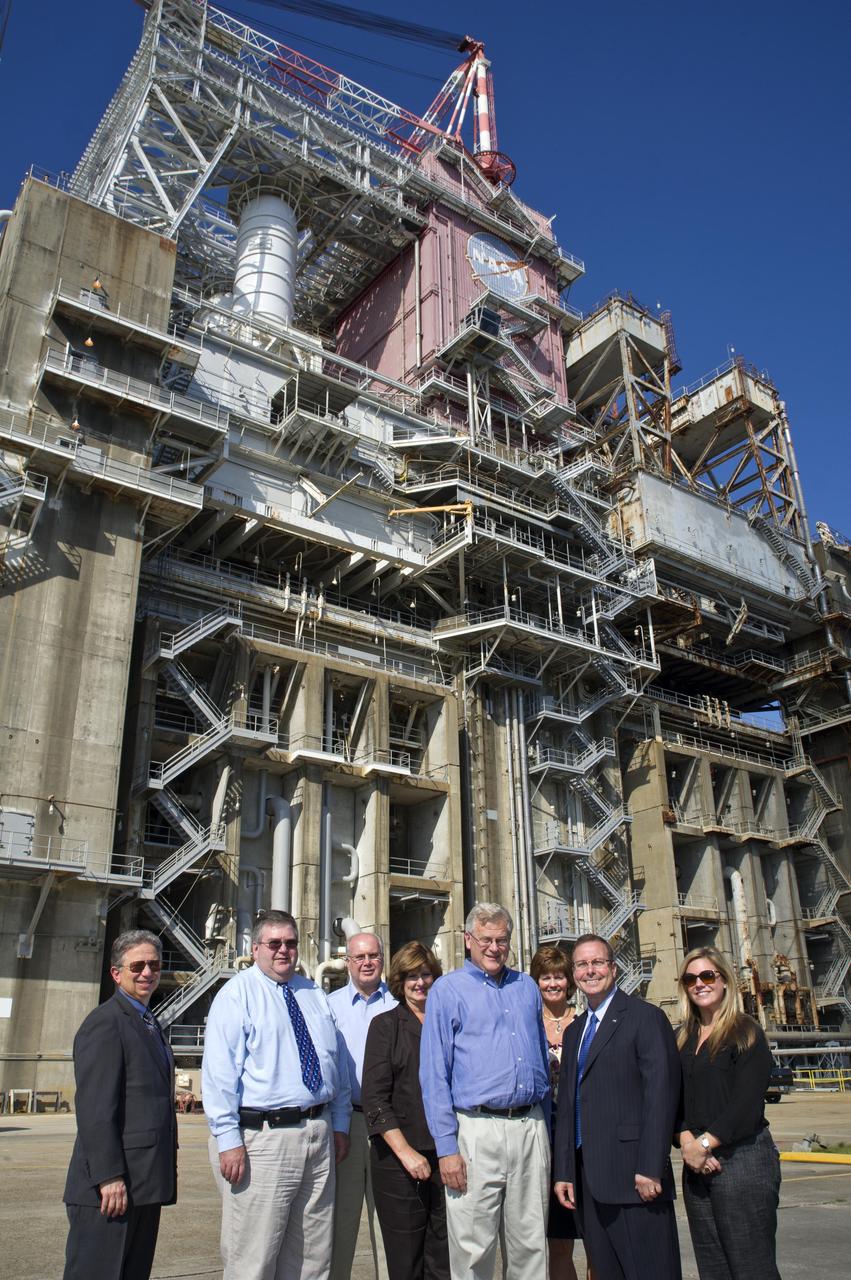

U.S. Rep. Alan Nunnelee, R-Miss., visited Stennis Space Center on Oct. 5, meeting with leaders and touring facilities to learn about ongoing work at the south Mississippi site. Joining Nunnelee during a stop at the B-1/B-2 Test Stand were: (l to r) Ken Human, Stennis associate director; Randy Galloway, director of the Stennis Engineering and Test Directorate; Ted Maness, chief of staff for Nunnelee; Nunnelee's wife, Toni; Nunnelee; Myron Webb, Stennis legislative affairs officer; Gilbrech; and Meyer Seligman, legislative director for Nunnelee. A Tupelo native, Nunnelee serves Mississipi's 1st Congressional District.
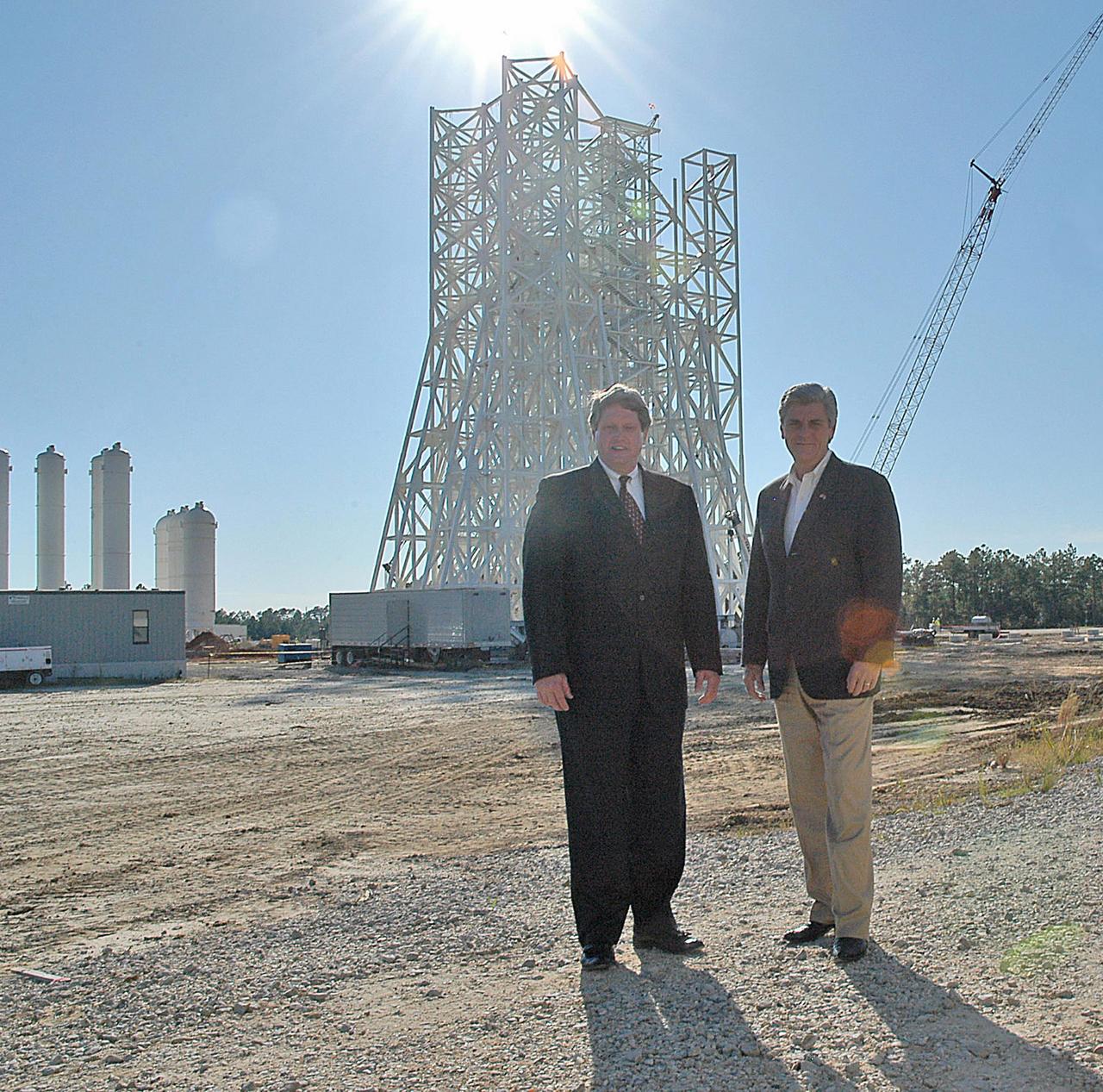

Stennis Space Center Director Gene Goldman (left) stands with Mississippi Lt. Gov. Phil Bryant at the A-3 Test Stand construction site during an Oct. 1 visit by the state official. During his tour, Bryant was updated on construction of the first large test stand at Stennis since the 1960s. The A-3 stand will be used to conduct simulated high-altitude testing on the next generation of rocket engines that will take humans back to the moon and possibly beyond. In addition to touring Stennis facilities, Bryant visited the INFINITY Science Center construction site, where he was updated on work under way to construct a 72,000-square-foot facility that will showcase the science underpinning the missions of NASA and resident agencies at Stennis.
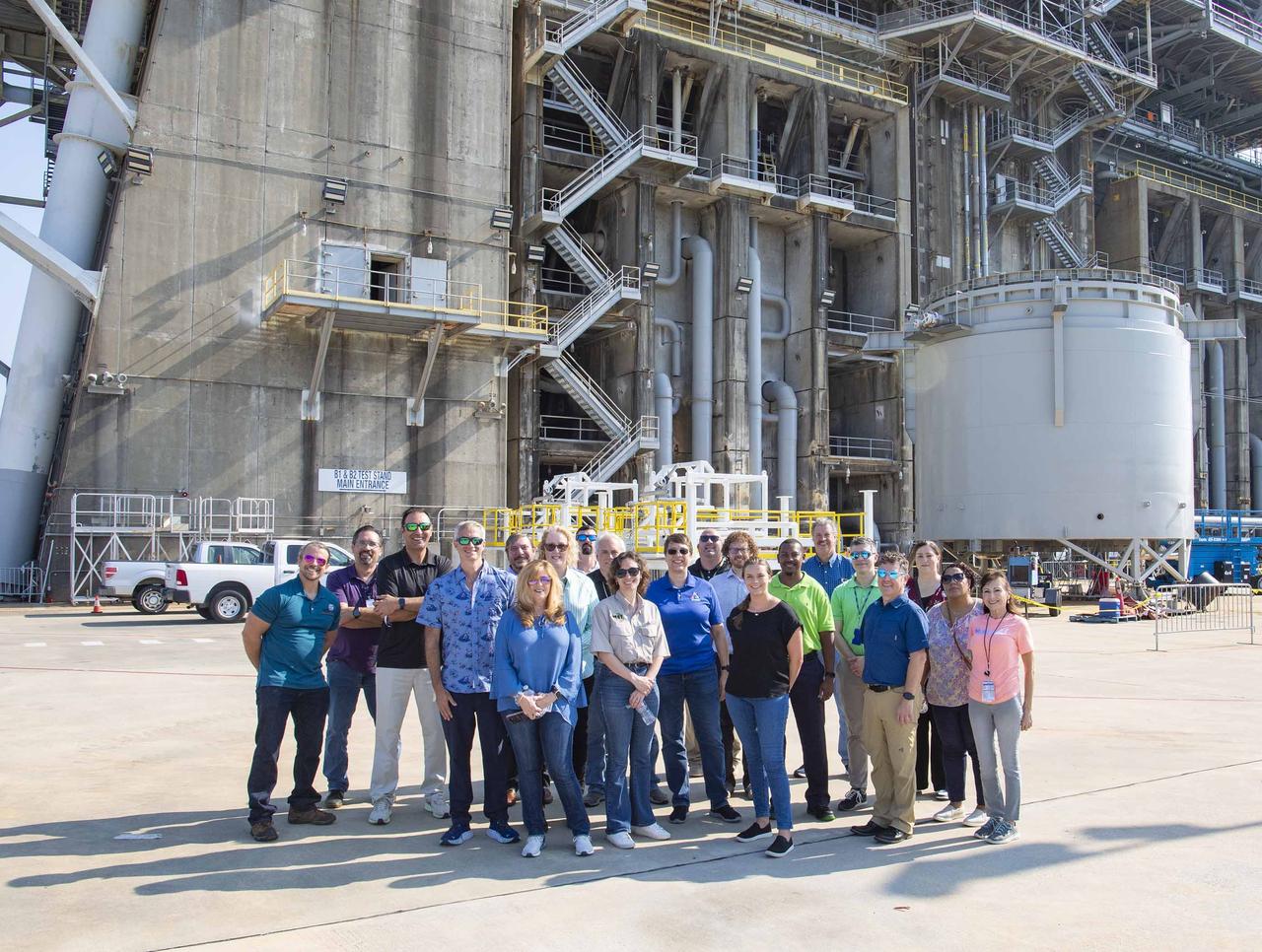

NASA and contractor representatives working with NASA’s Rocket Propulsion Test Program Office stand at the base of the Thad Cochran Test Stand during a tour of the test complex on Aug. 15 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The program office hosted a Risk Workshop and Program Management Review meeting at NASA Stennis on Aug. 13-15. The representatives are from NASA Stennis; NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio; NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans; NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama; NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia; and NASA Headquarters in Washington. NASA Stennis is preparing the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-2) to test the exploration upper stage, which will fly on future SLS (Space Launch System) missions as NASA continues its mission of exploring the secrets of the universe for the benefit of all. The upper stage is being built at NASA Michoud as a more powerful second stage to send the Orion spacecraft to deep space. It is expected to fly on the Artemis IV mission. Before that, it will be installed on the test stand at NASA Stennis to undergo a series of Green Run tests of its integrated systems to demonstrate it is ready to fly.
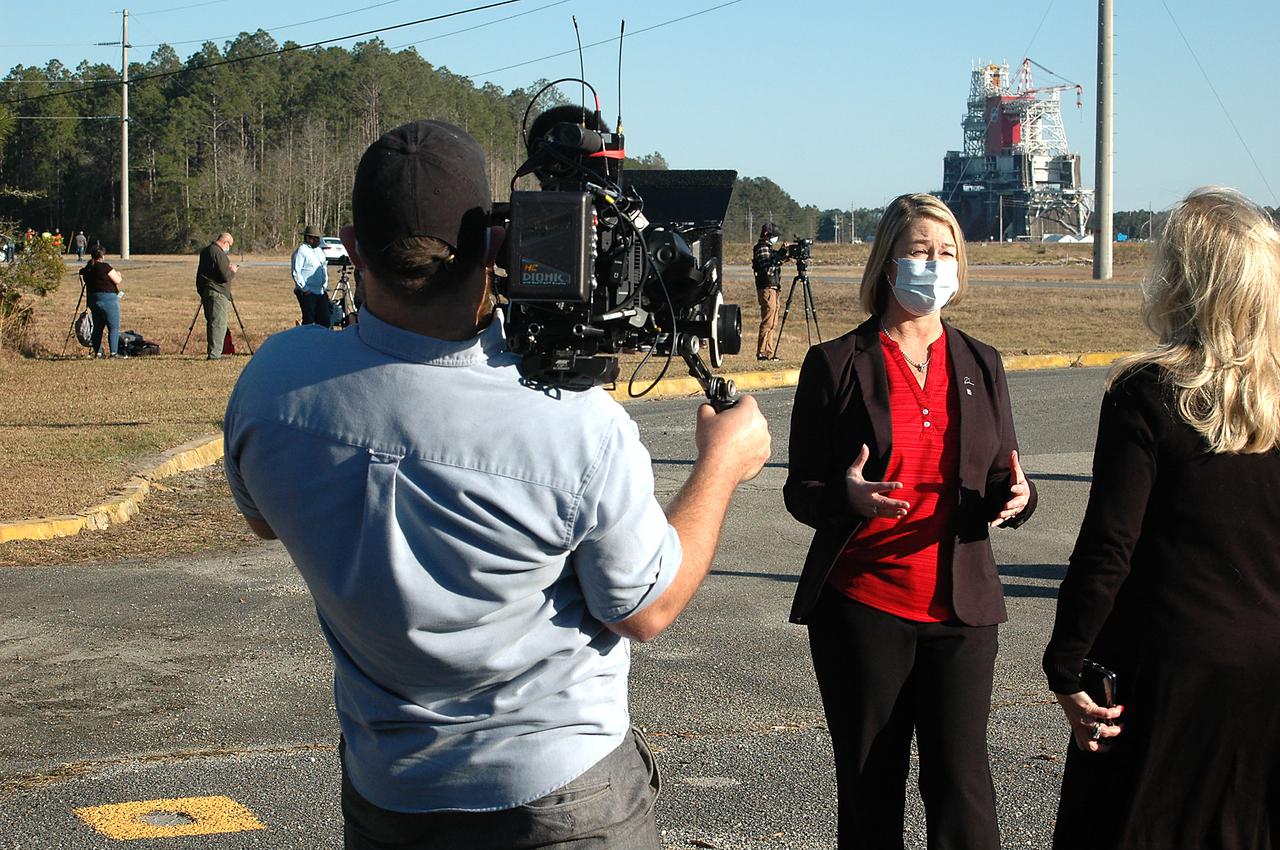

Jennifer Boland-Masterson, director of Boeing Operations at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, talks with media prior to the Green Run hot fire test of the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Jan. 16, 2021. NASA conducted a hot fire test of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis. Scheduled for as long as eight minutes, the engines fired for a little more than one minute to generate a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
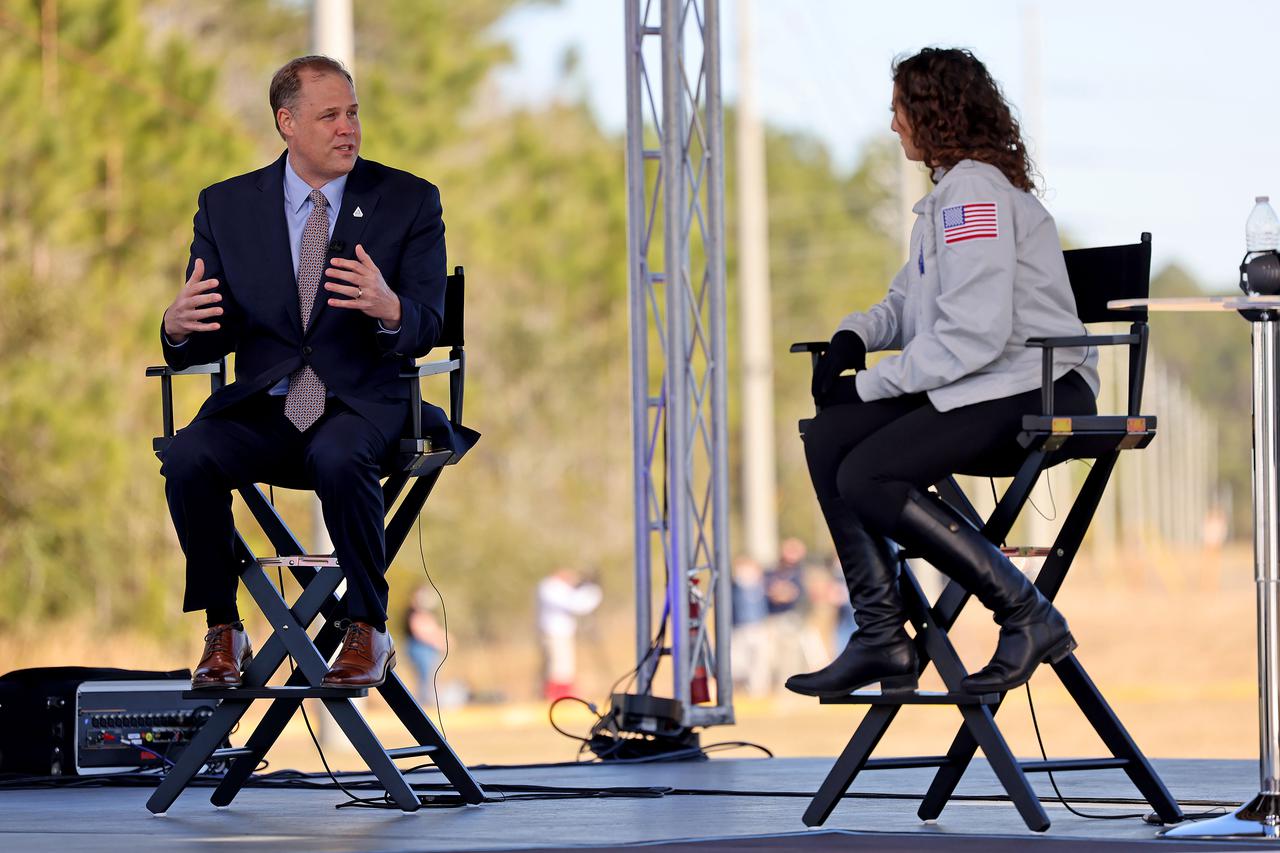

Outgoing NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine (left) talks with host Leigh D’Angelo during NASA TV live coverage from Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on Jan. 16, 2021. D’Angelo, from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in nearby New Orleans, hosted the NASA TV coverage prior to the hot fire test of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
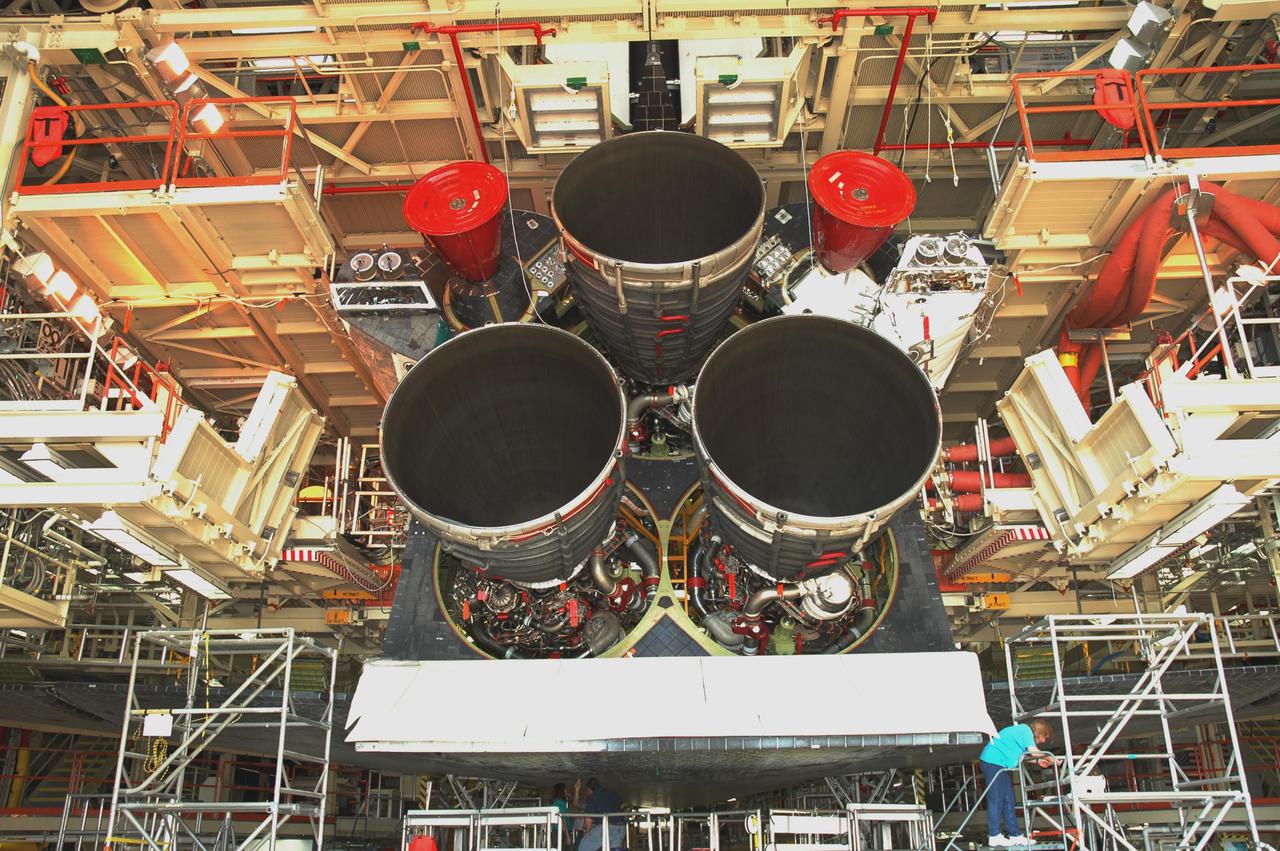
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the aft of Discovery is shown with all three Space Shuttle Main Engines (SSMEs) installed. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114. Recent improvements to the SSME include the introduction of redesigned high-pressure turbopumps into the SSME fleet. The new pumps are designed and built by Pratt and Whitney at West Palm Beach, Fla. SSMEs and the Pratt and Whitney turbopumps are tested at Stennis Space Center in Mississippi. Engines and engine components are delivered to Kennedy Space Center to be prepared for flight.
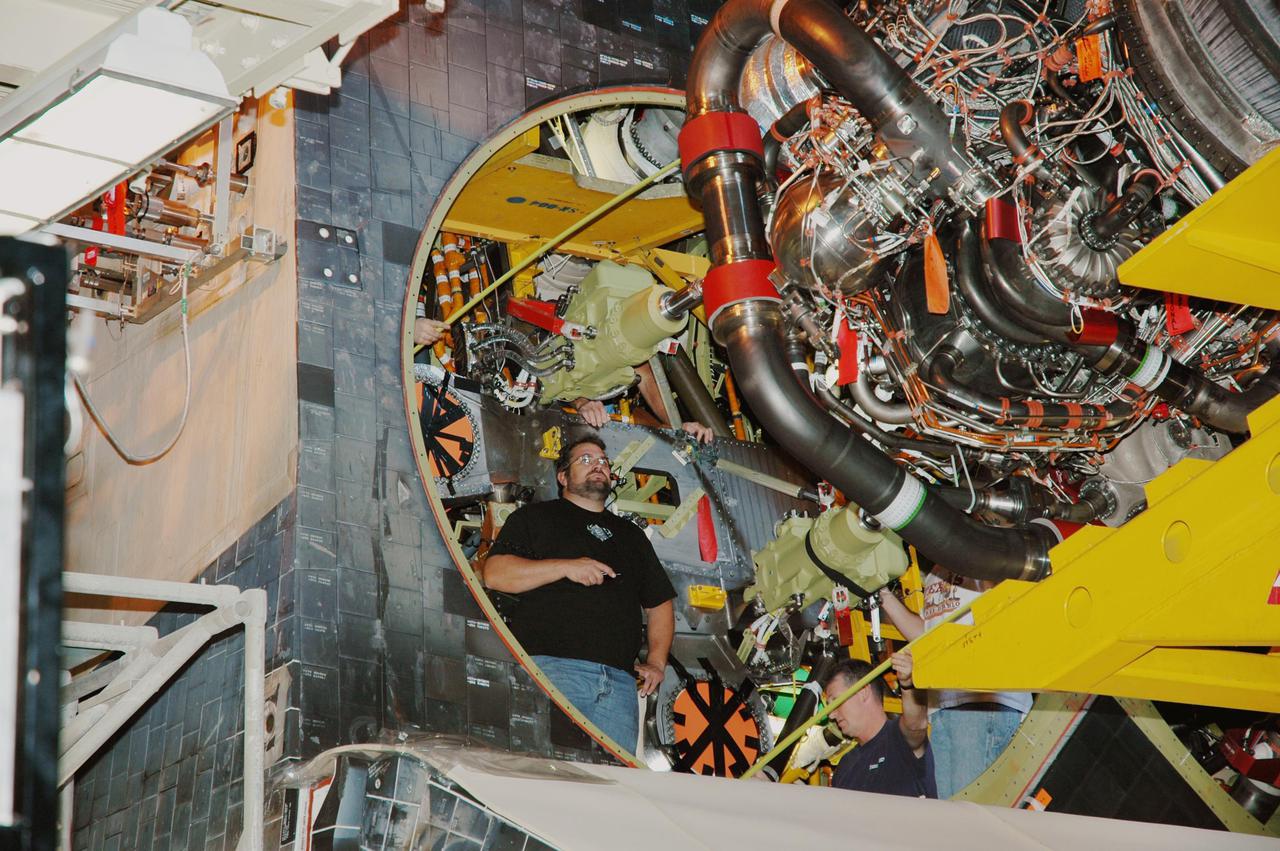

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, a technician watches closely as the third Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) is moved into position behind Discovery for installation. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114. Recent improvements to the SSME include the introduction of redesigned high-pressure turbopumps into the SSME fleet. The new pumps are designed and built by Pratt and Whitney at West Palm Beach, Fla. SSMEs and the Pratt and Whitney turbopumps are tested at Stennis Space Center in Mississippi. Engines and engine components are delivered to Kennedy Space Center to be prepared for flight.
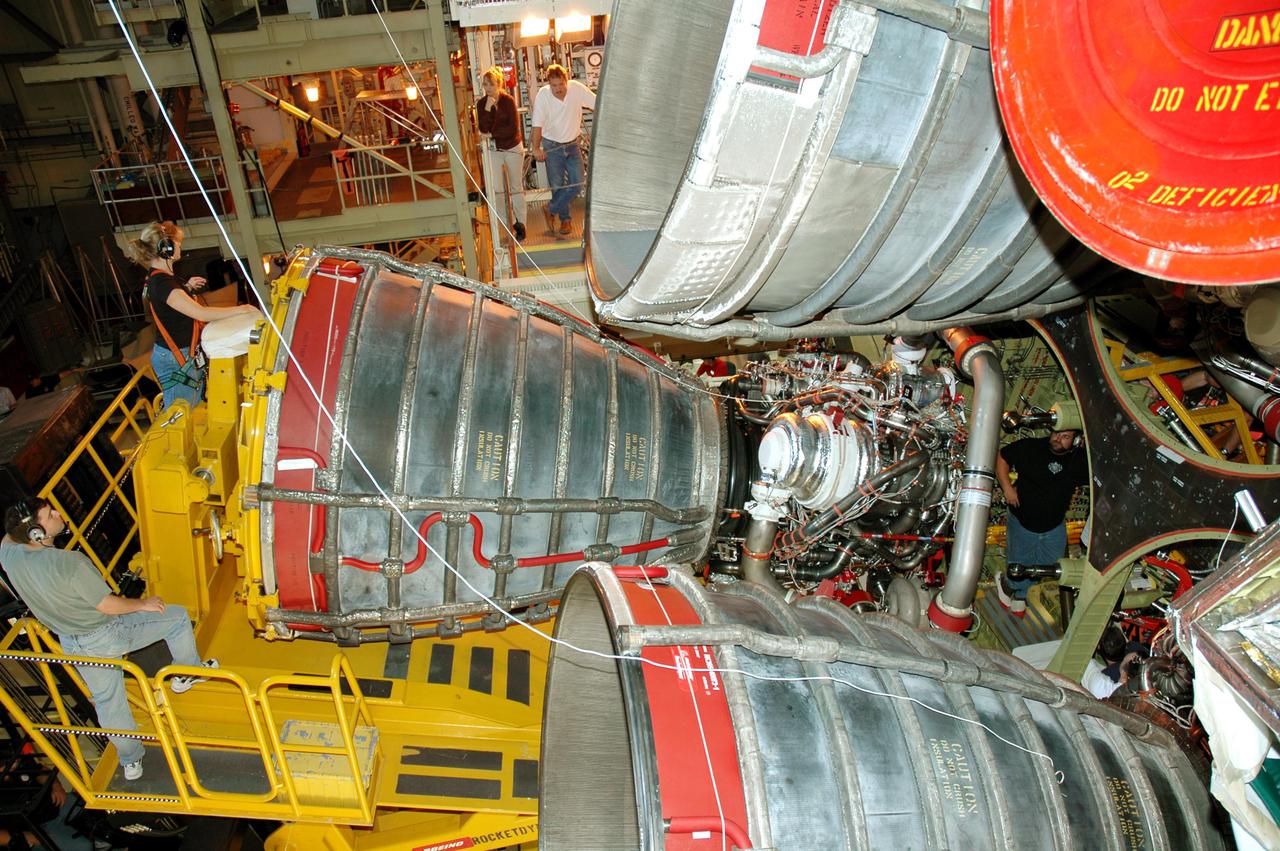

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility carefully guide the placement of the third Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) for installation on Discovery. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114. Recent improvements to the SSME include the introduction of redesigned high-pressure turbopumps into the SSME fleet. The new pumps are designed and built by Pratt and Whitney at West Palm Beach, Fla. SSMEs and the Pratt and Whitney turbopumps are tested at Stennis Space Center in Mississippi. Engines and engine components are delivered to Kennedy Space Center to be prepared for flight.
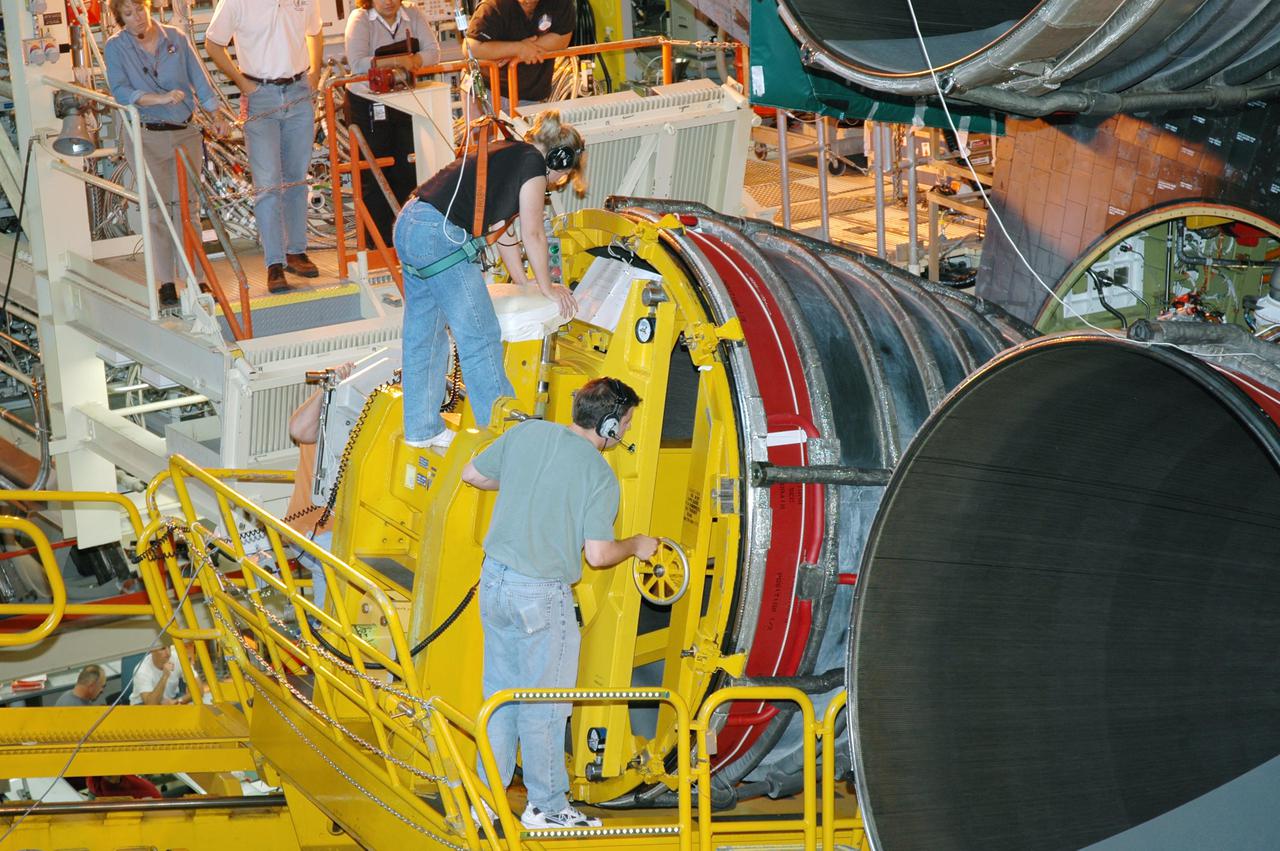

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians in the Orbiter Processing Facility carefully maneuver the third Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) into place on Discovery. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114. Recent improvements to the SSME include the introduction of redesigned high-pressure turbopumps into the SSME fleet. The new pumps are designed and built by Pratt and Whitney at West Palm Beach, Fla. SSMEs and the Pratt and Whitney turbopumps are tested at Stennis Space Center in Mississippi. Engines and engine components are delivered to Kennedy Space Center to be prepared for flight.
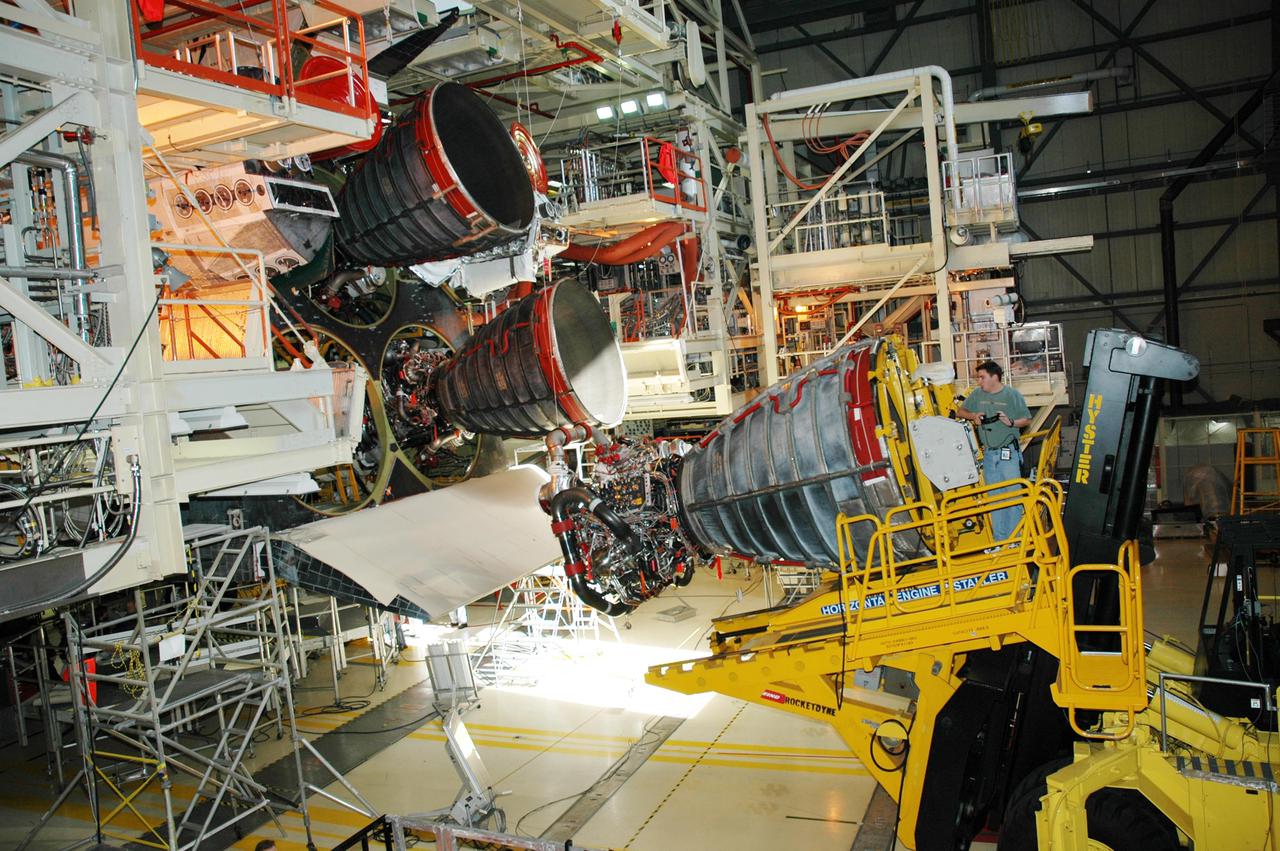

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the Hyster lift at right moves the third Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) into position behind Discovery for installation. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114. Recent improvements to the SSME include the introduction of redesigned high-pressure turbopumps into the SSME fleet. The new pumps are designed and built by Pratt and Whitney at West Palm Beach, Fla. SSMEs and the Pratt and Whitney turbopumps are tested at Stennis Space Center in Mississippi. Engines and engine components are delivered to Kennedy Space Center to be prepared for flight.
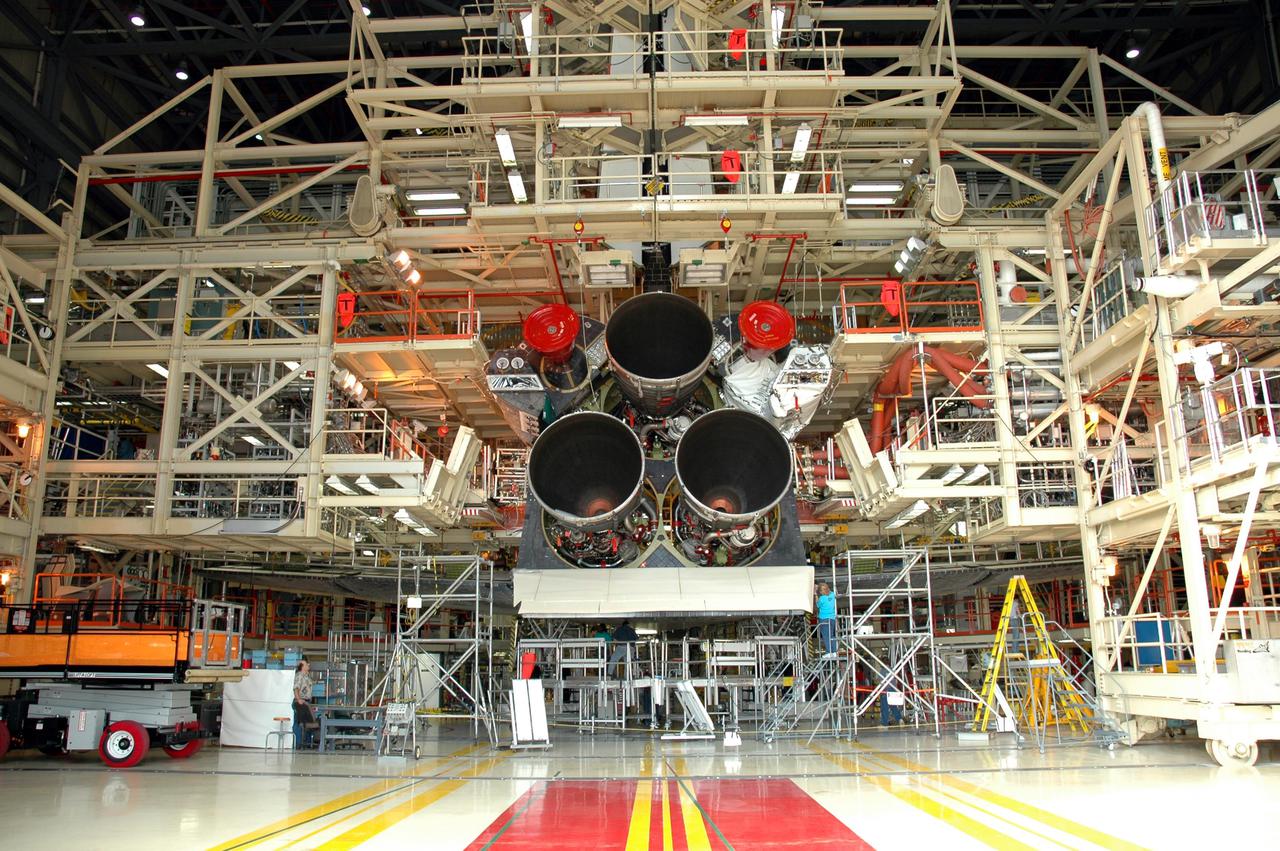

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the aft of Discovery is shown after the third Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) was installed. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114. Recent improvements to the SSME include the introduction of redesigned high-pressure turbopumps into the SSME fleet. The new pumps are designed and built by Pratt and Whitney at West Palm Beach, Fla. SSMEs and the Pratt and Whitney turbopumps are tested at Stennis Space Center in Mississippi. Engines and engine components are delivered to Kennedy Space Center to be prepared for flight.
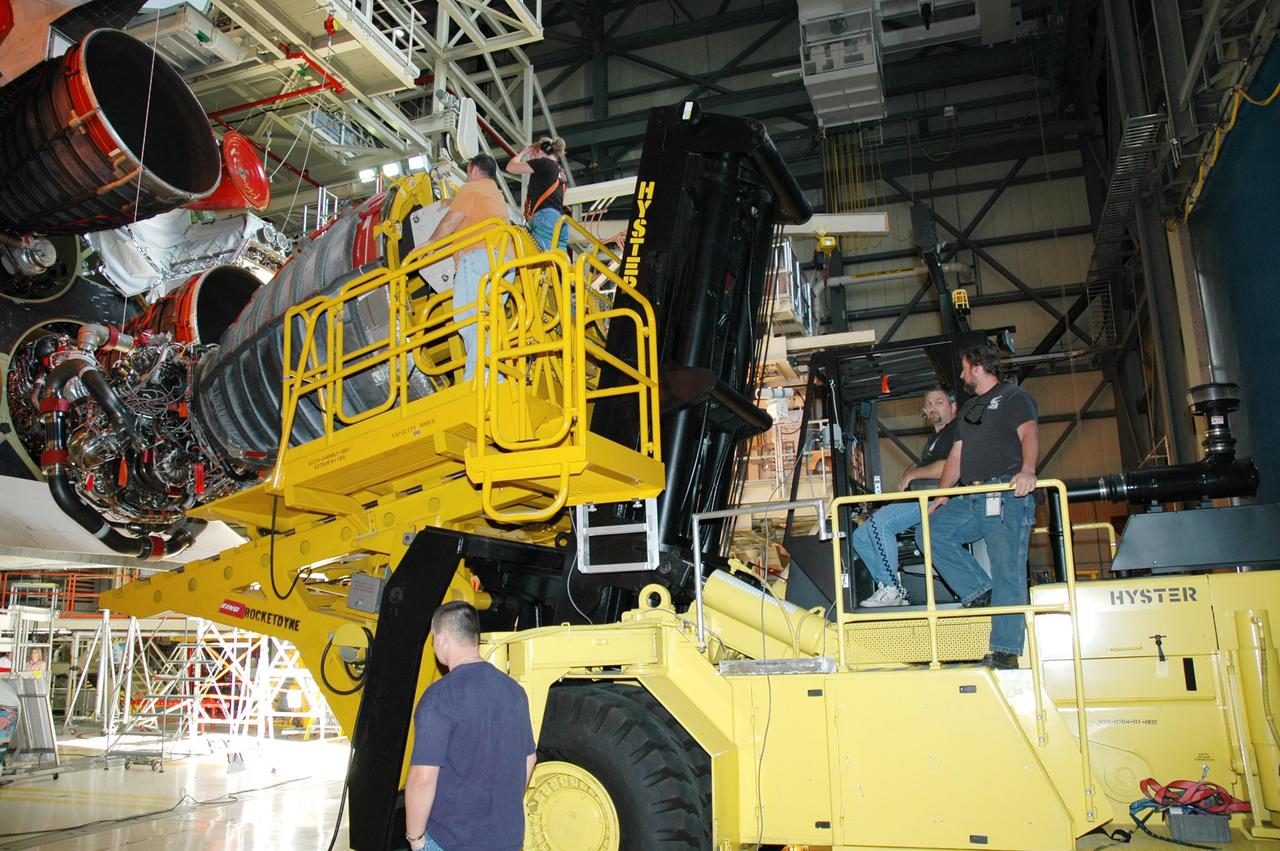

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the Hyster lift raises the third Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) into position behind Discovery for installation. Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114. Recent improvements to the SSME include the introduction of redesigned high-pressure turbopumps into the SSME fleet. The new pumps are designed and built by Pratt and Whitney at West Palm Beach, Fla. SSMEs and the Pratt and Whitney turbopumps are tested at Stennis Space Center in Mississippi. Engines and engine components are delivered to Kennedy Space Center to be prepared for flight.
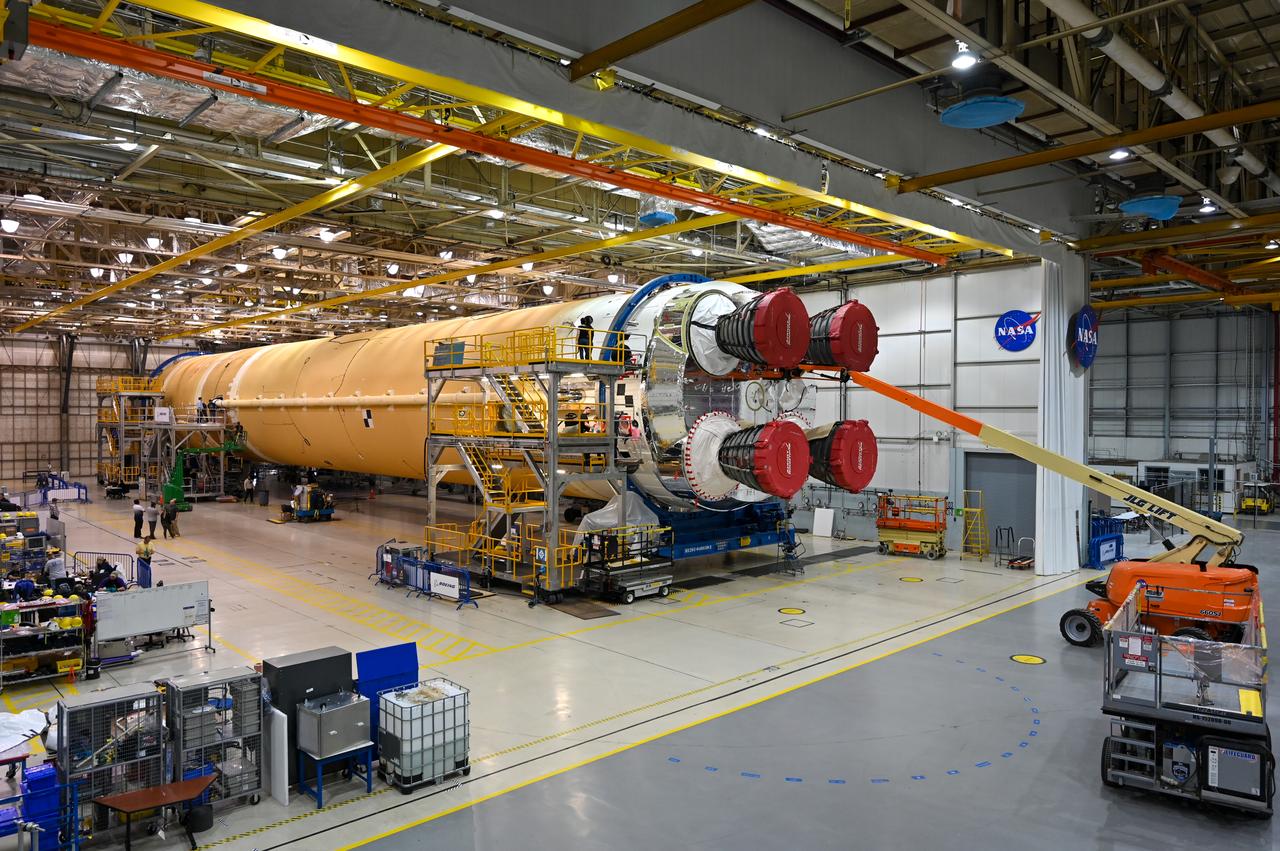

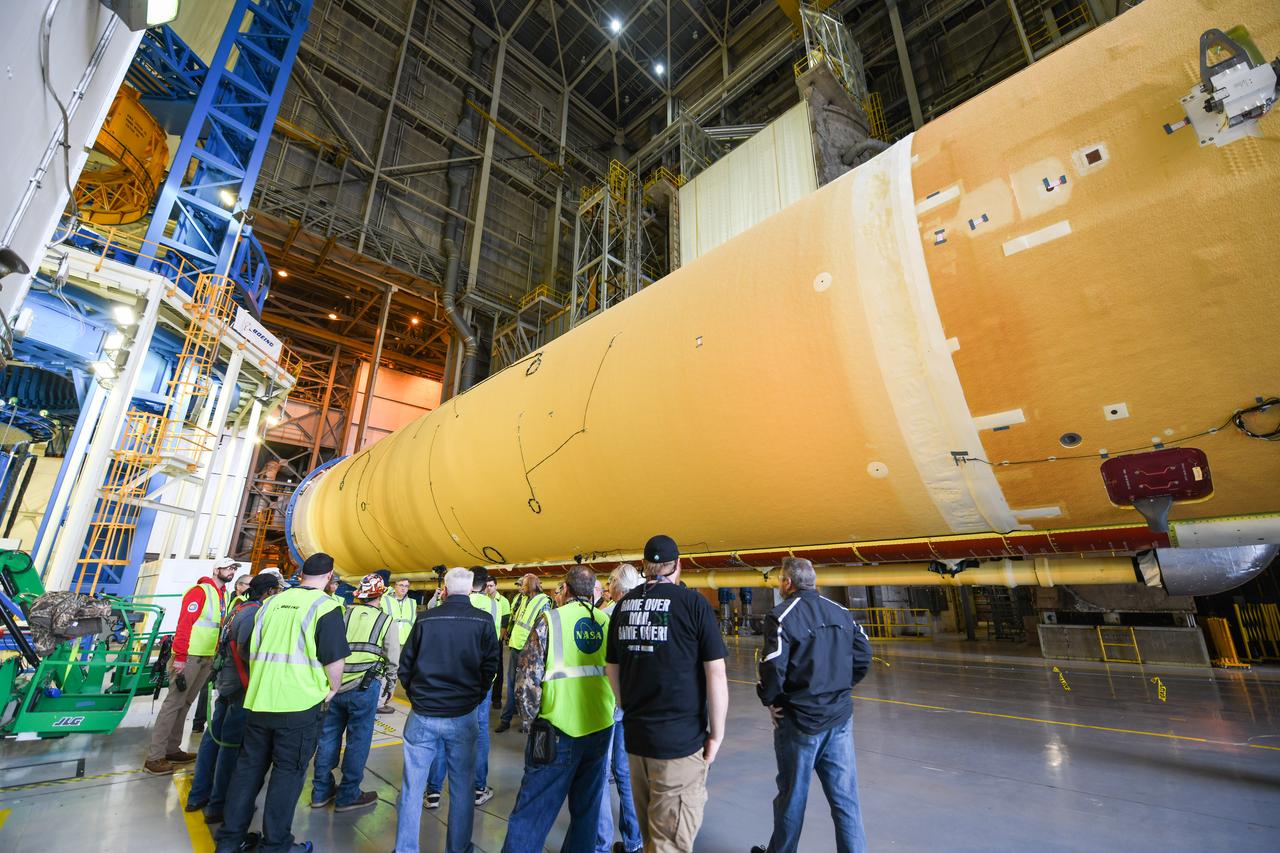
This image shows the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket without scaffolding at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. NASA and the contractor team used the scaffolding previously positioned around the 212-foot core stage to assess the stage’s inside and check out the electronic systems distributed throughout the stage, including avionics and propulsion systems, that will enable the stage to operate during launch and flight. The team will continue to check out these systems at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, where it will undergo the core stage Green Run testing.
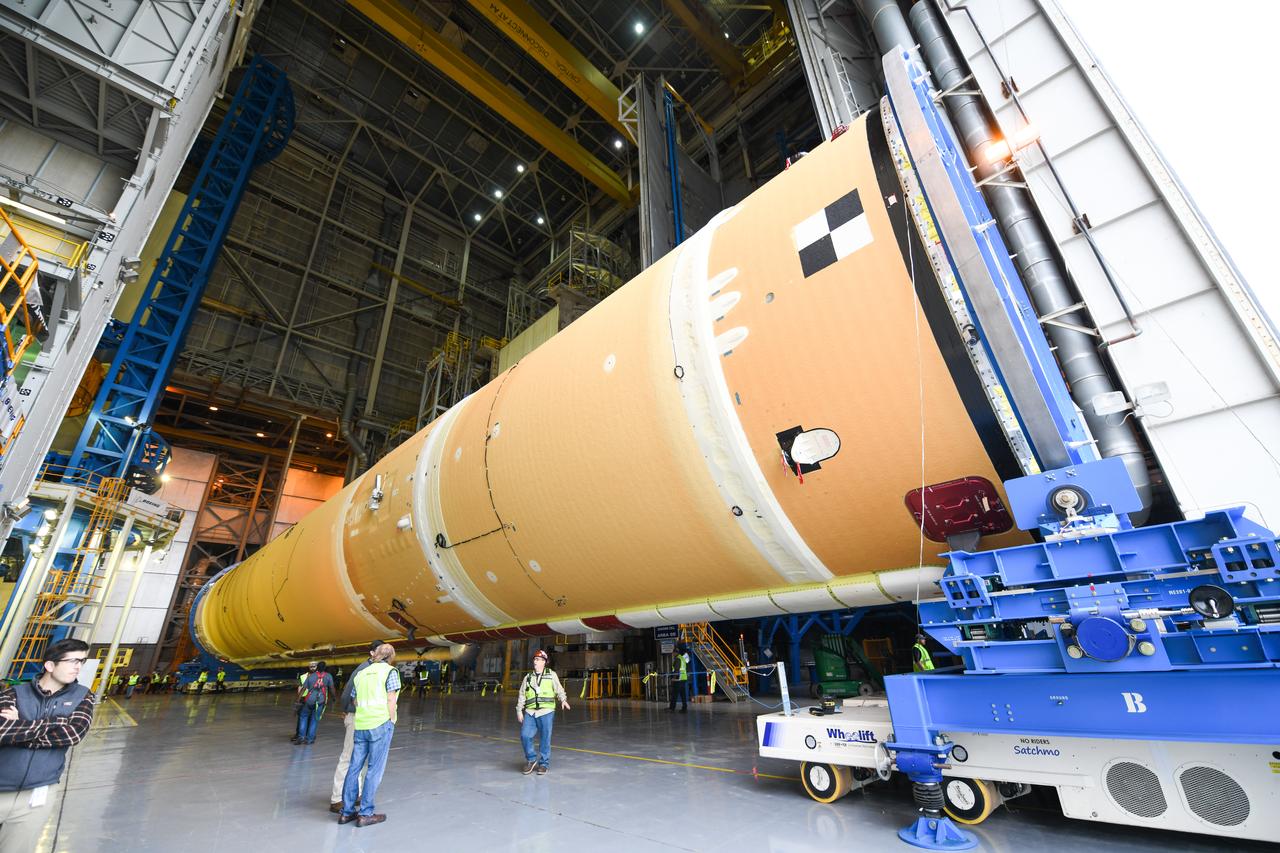

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
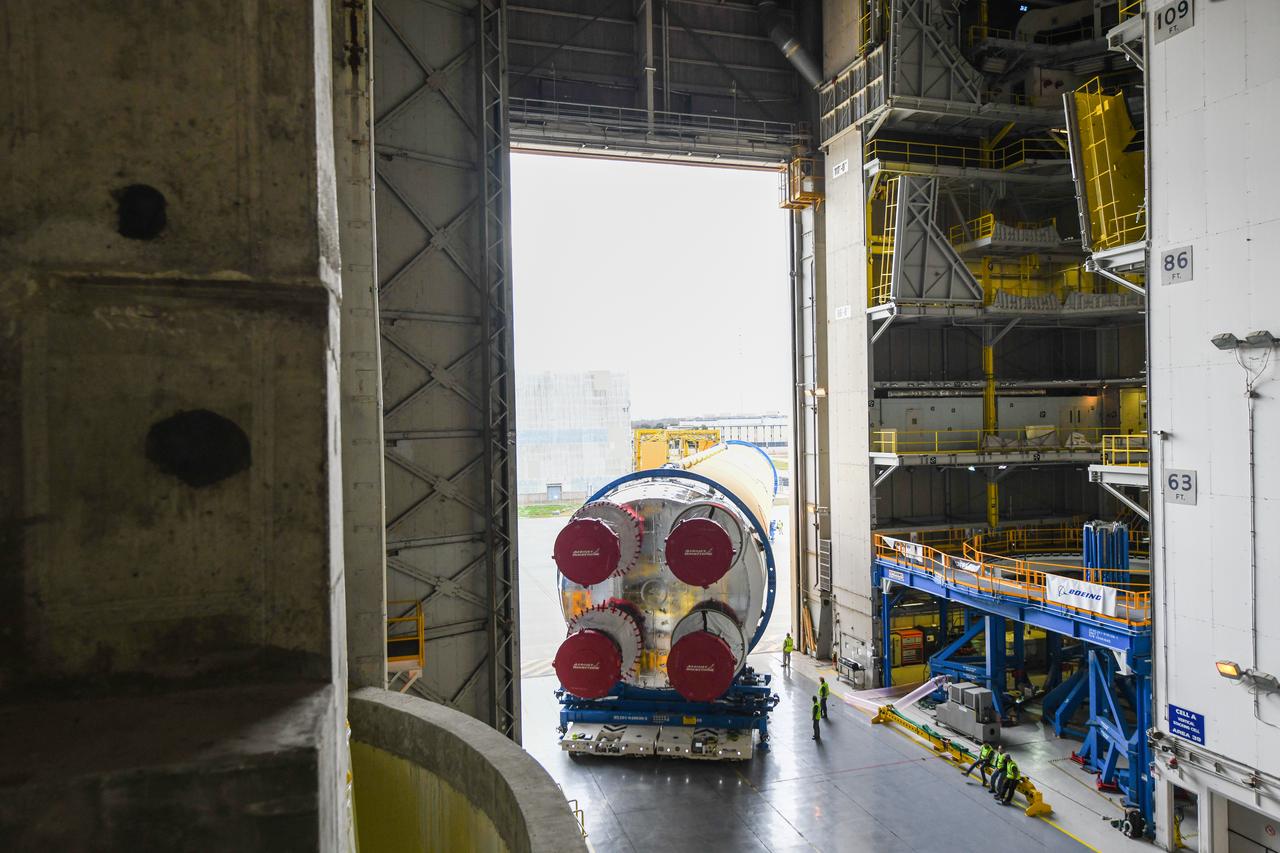

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
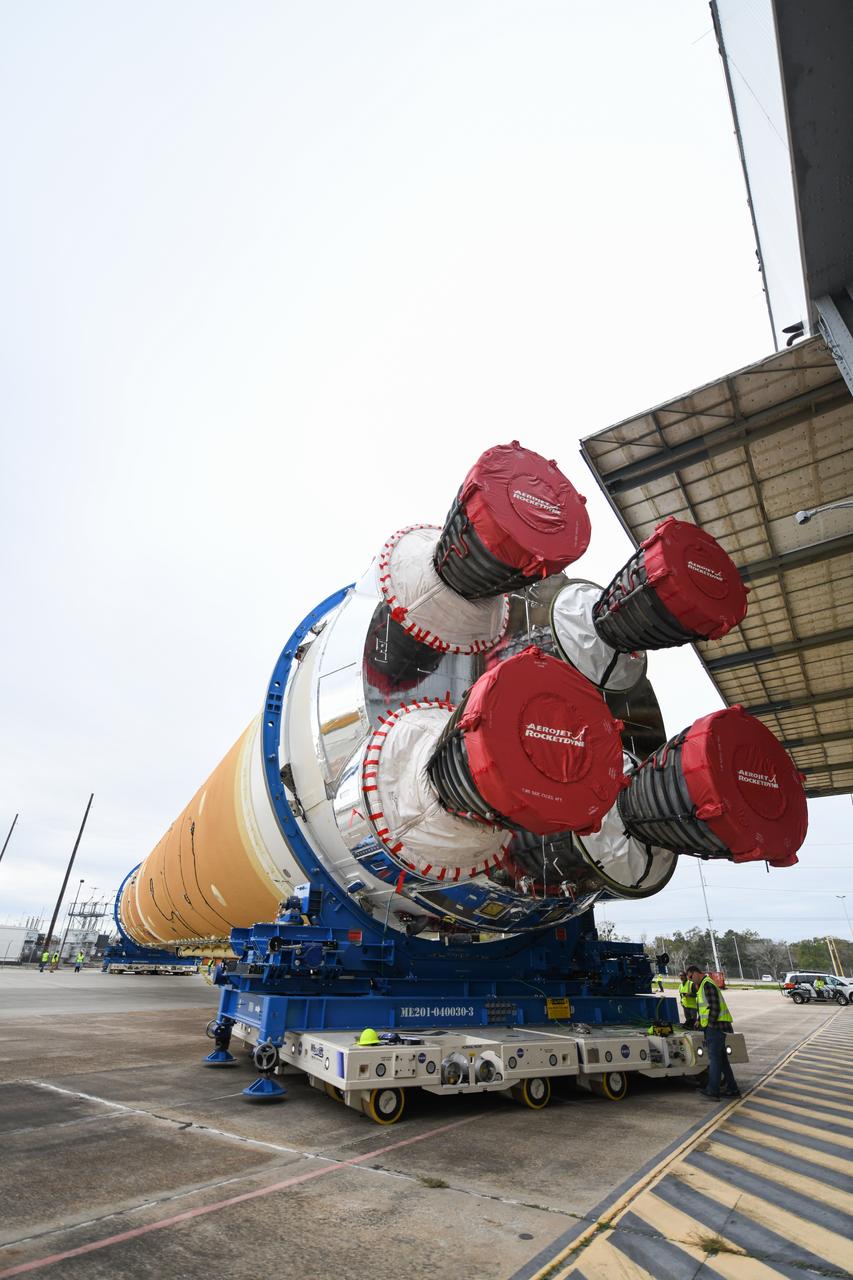

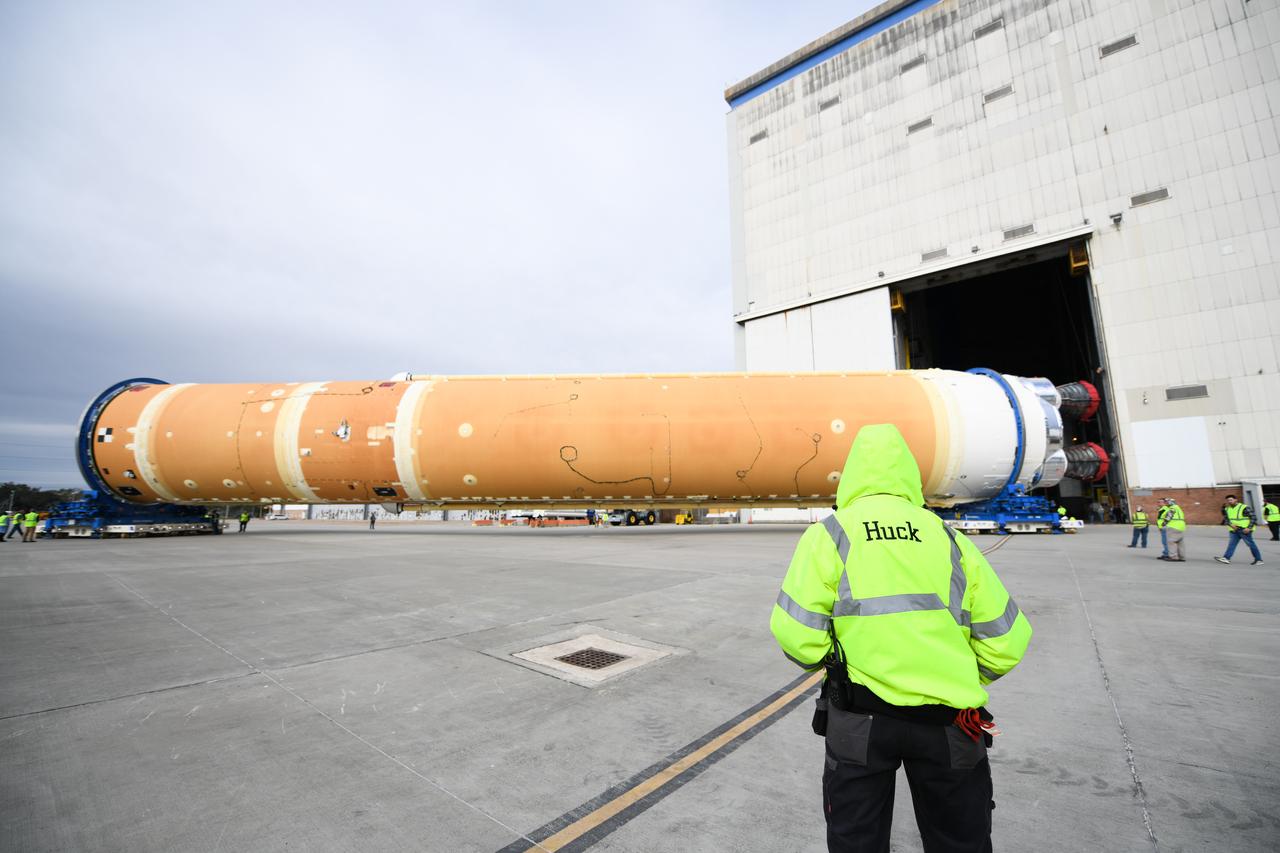
These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
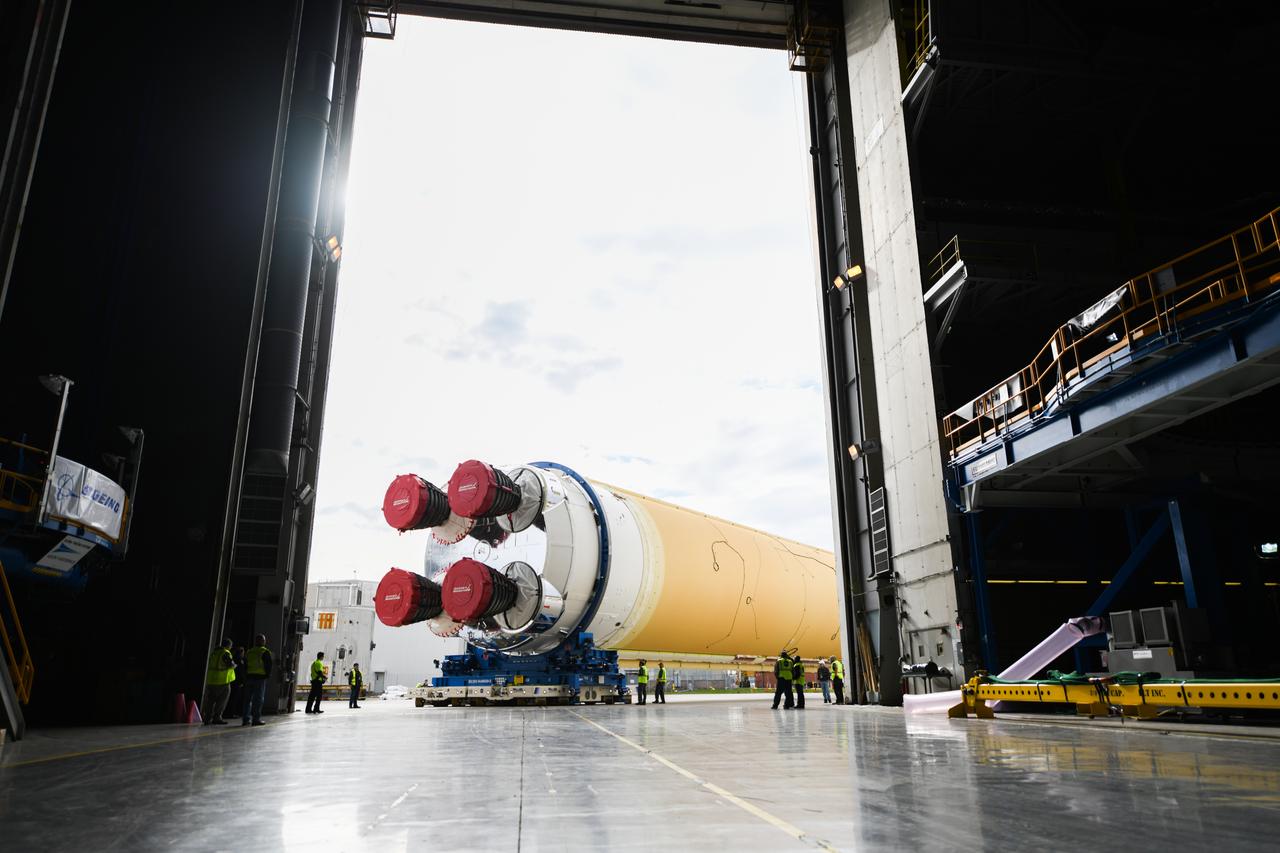

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
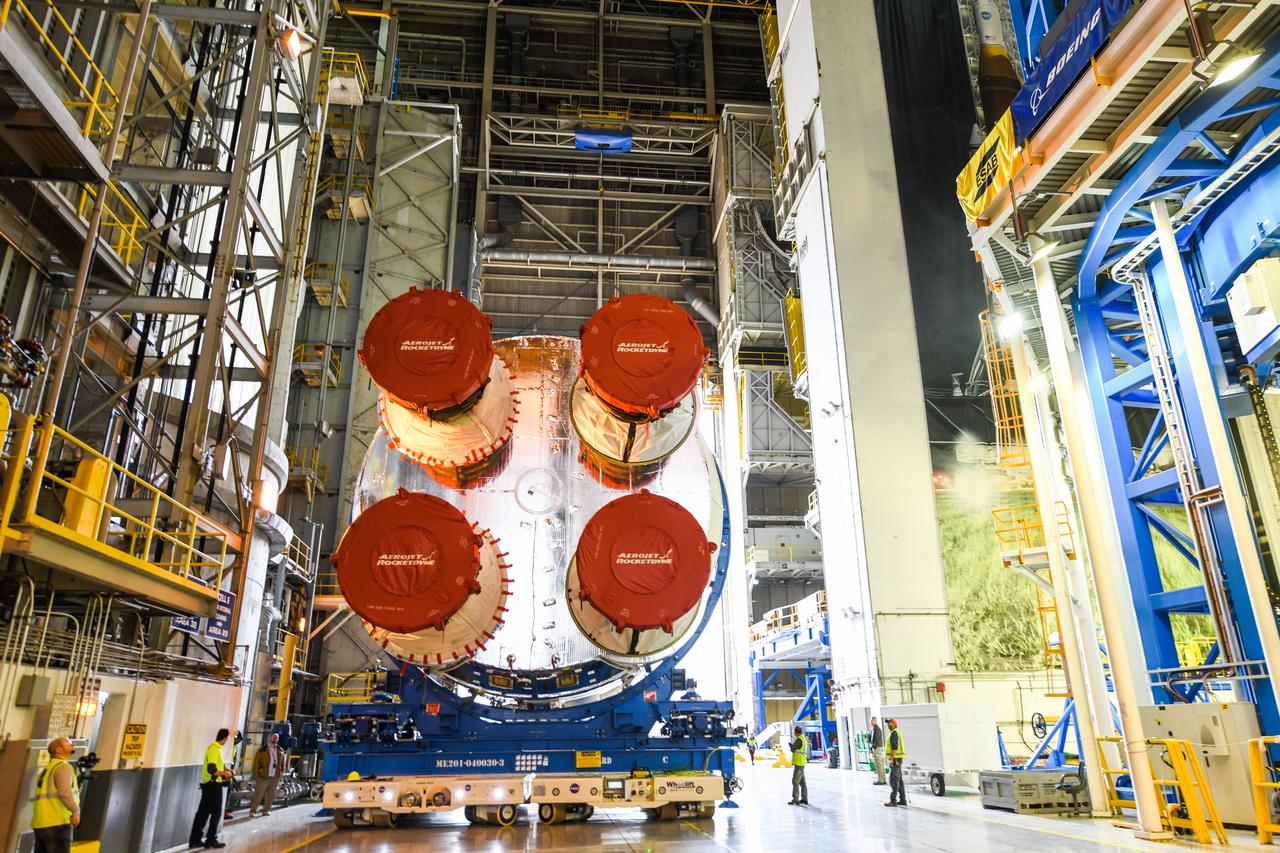
These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
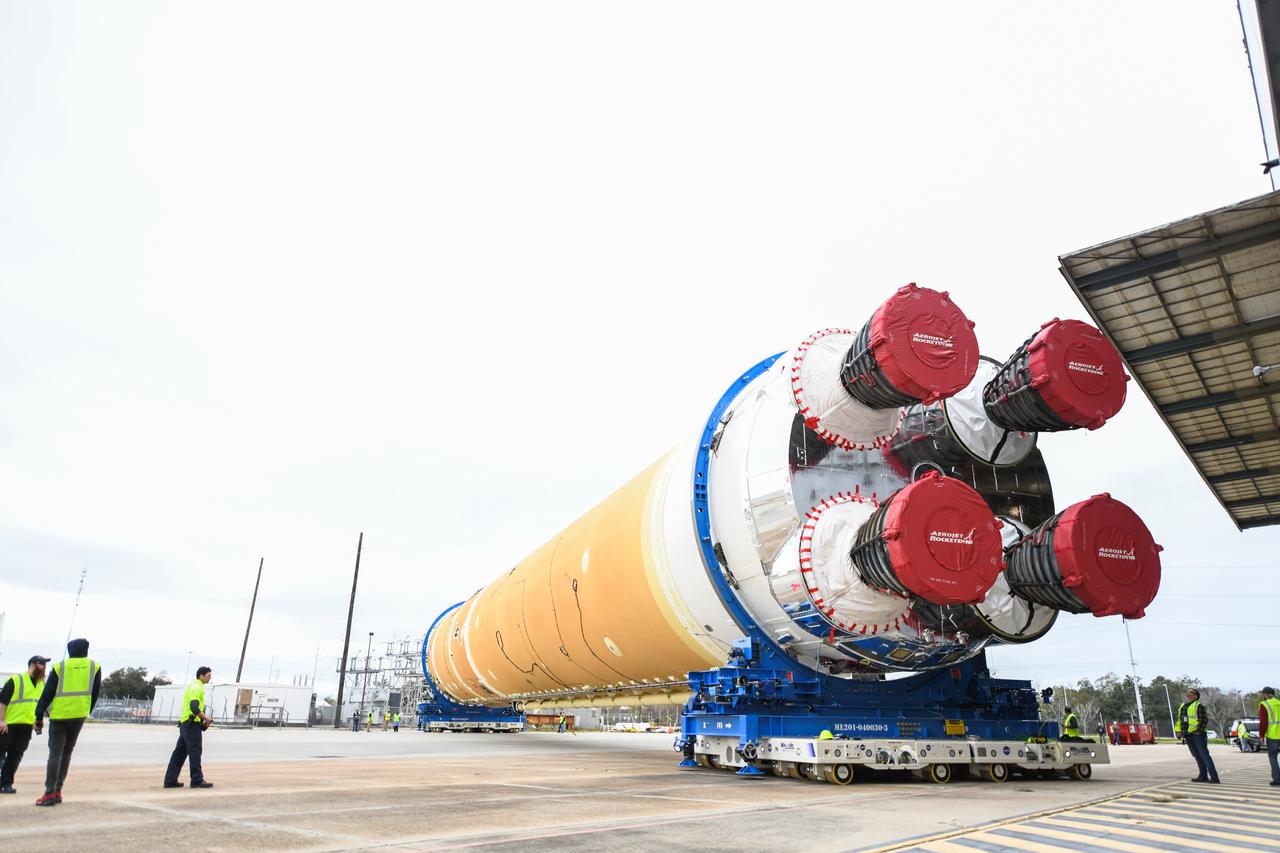

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
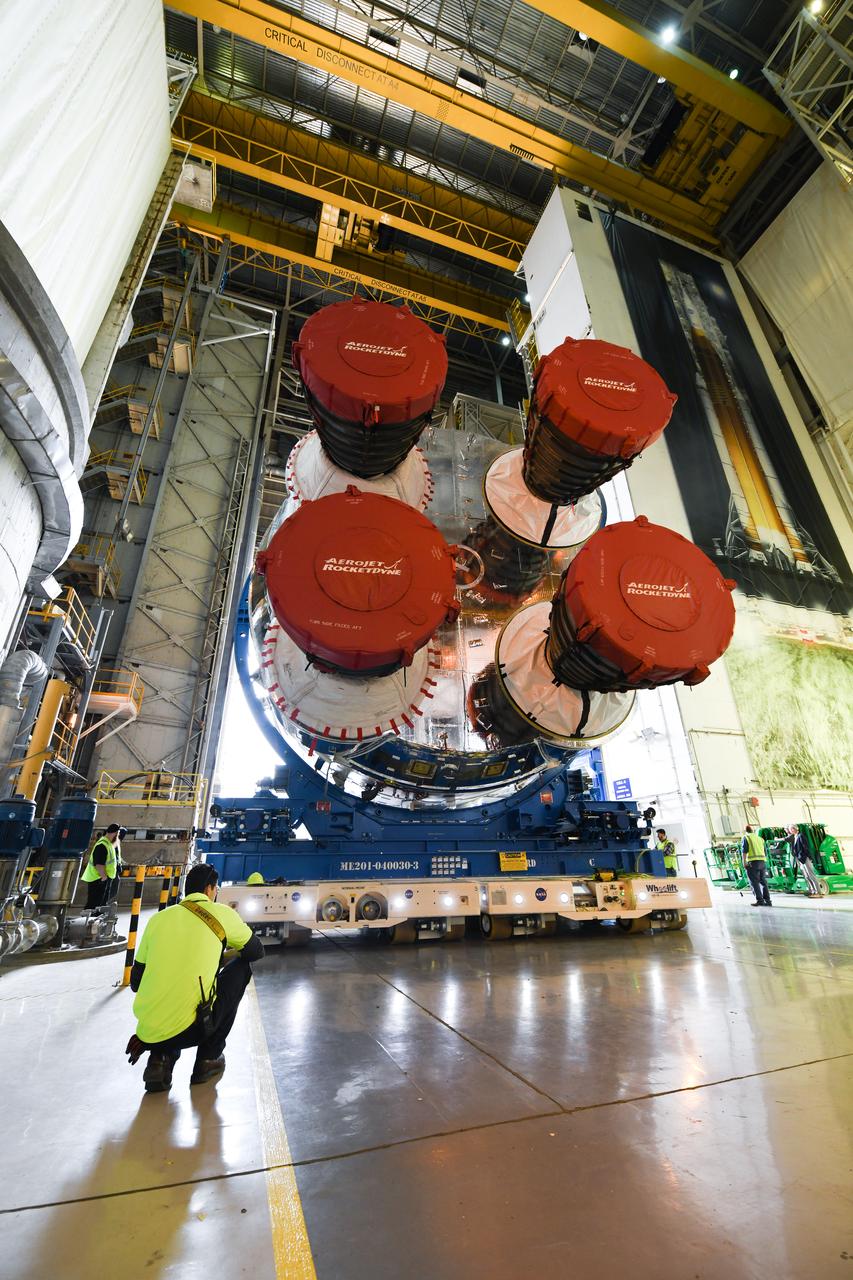

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
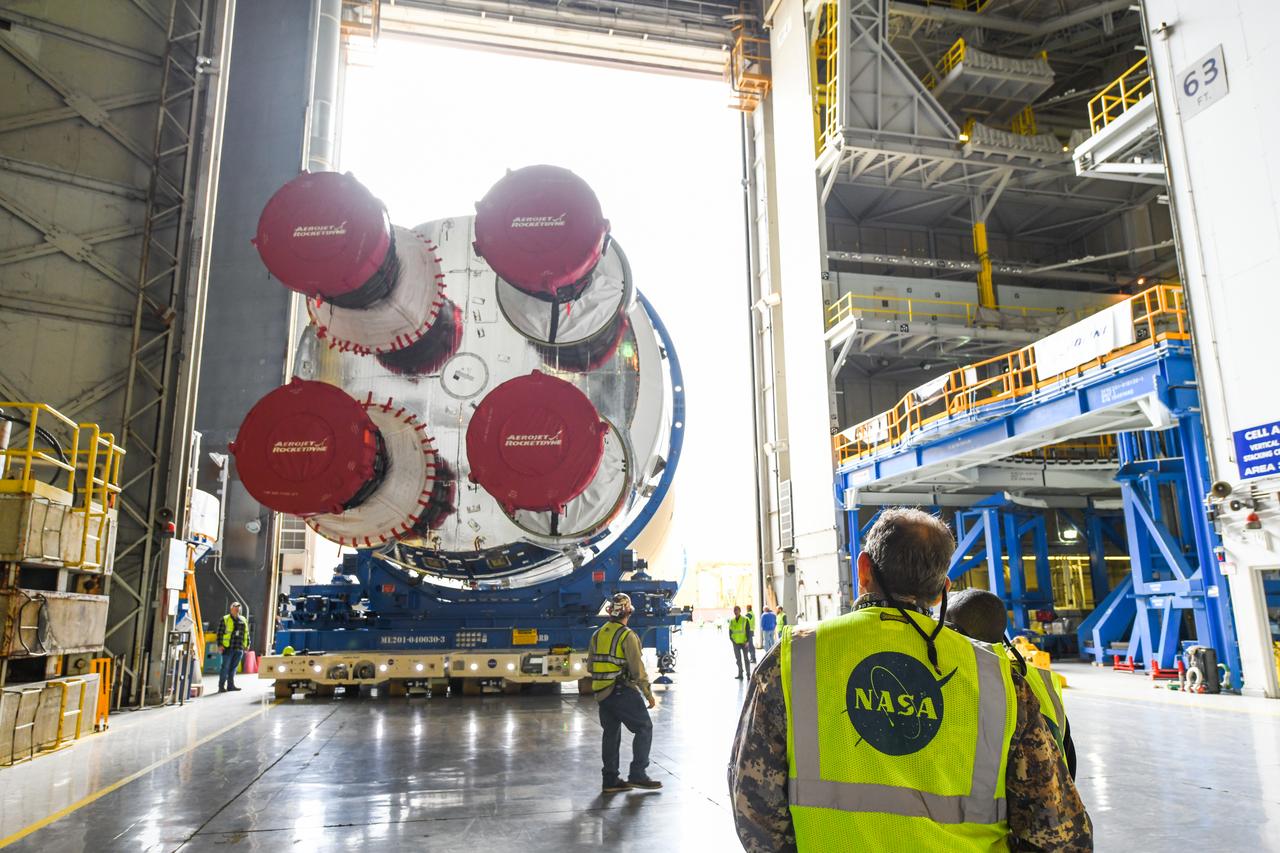

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
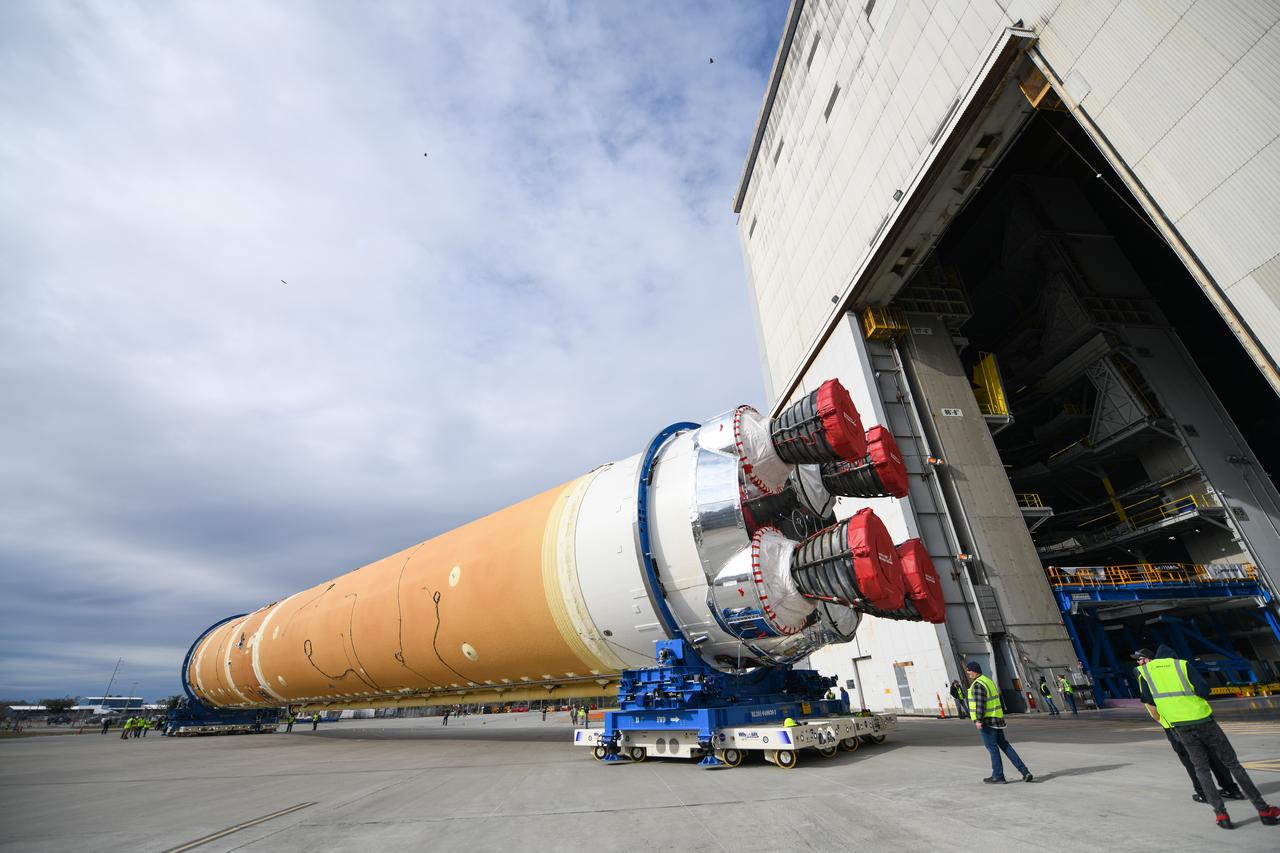

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
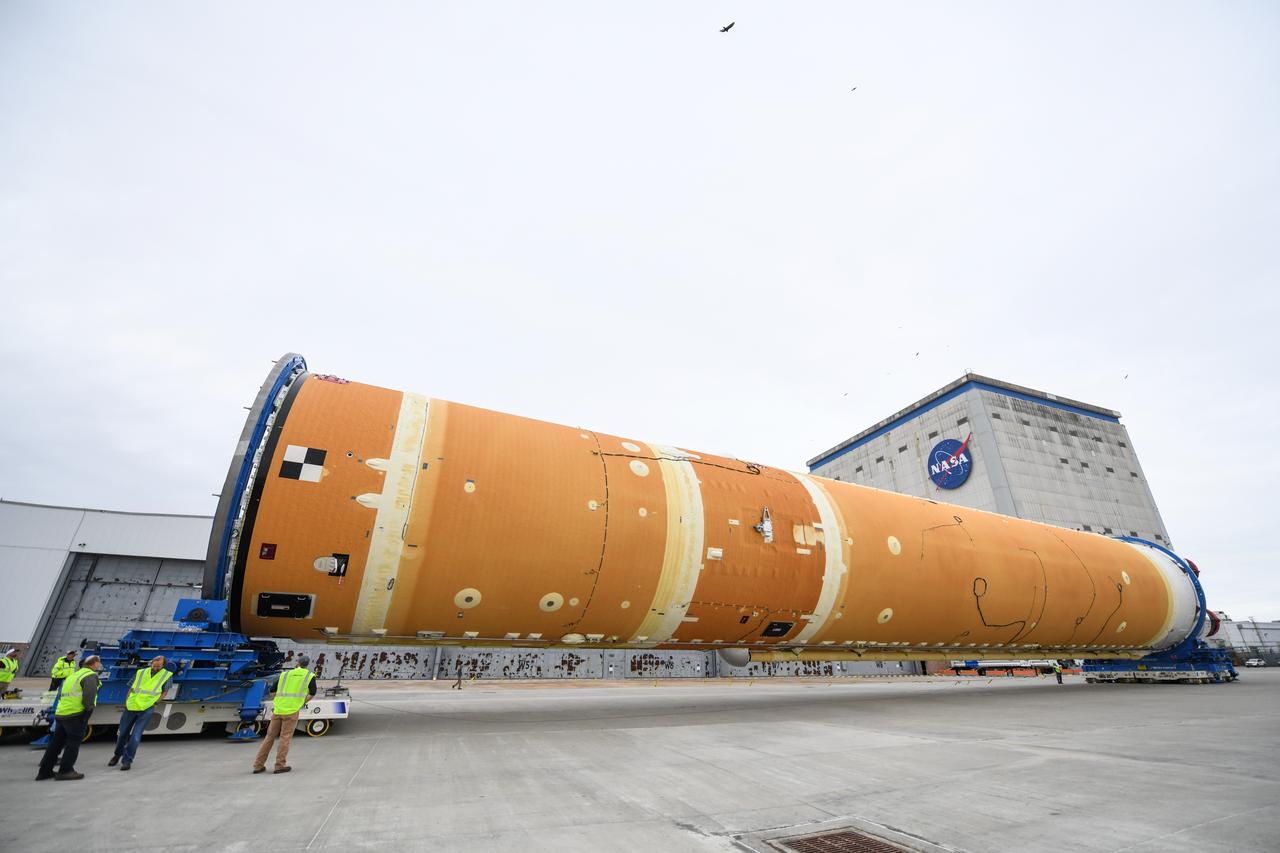

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
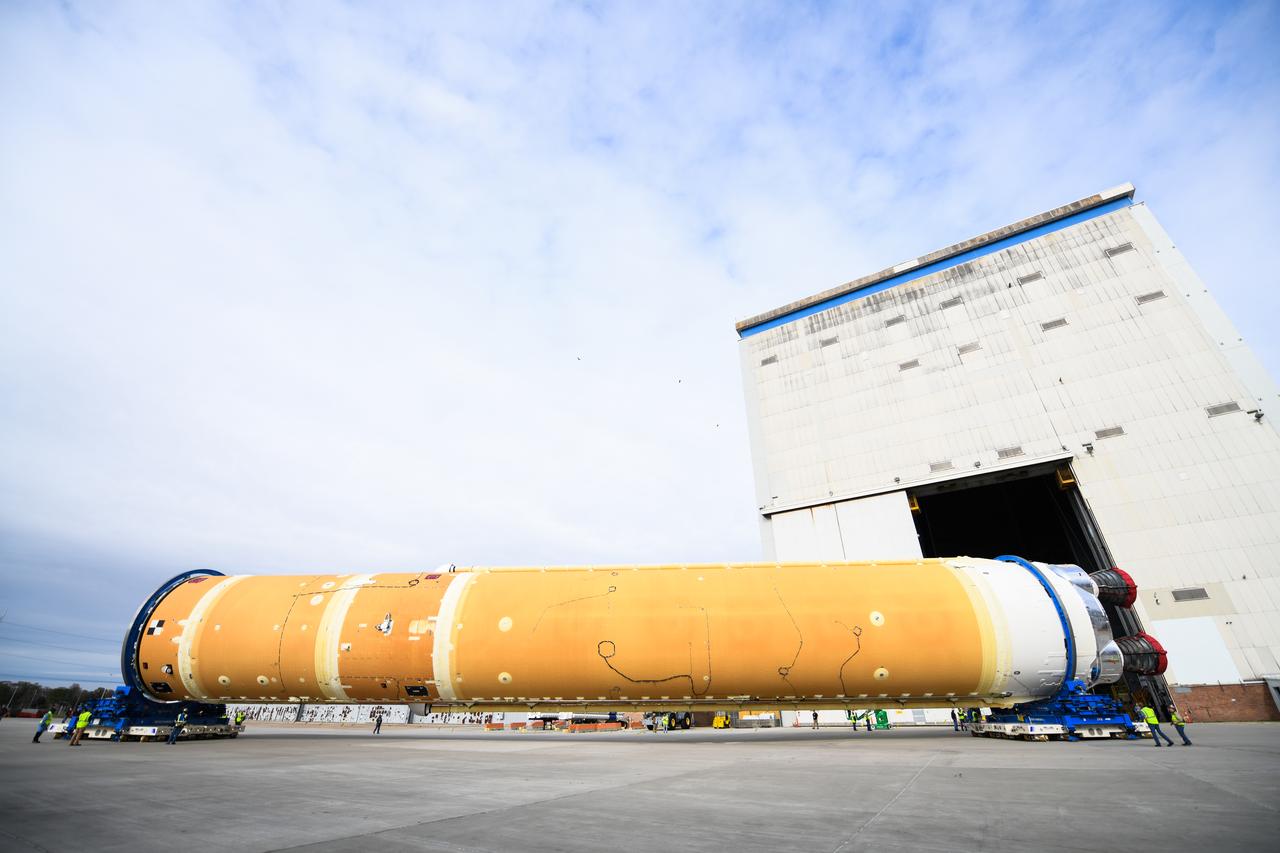

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
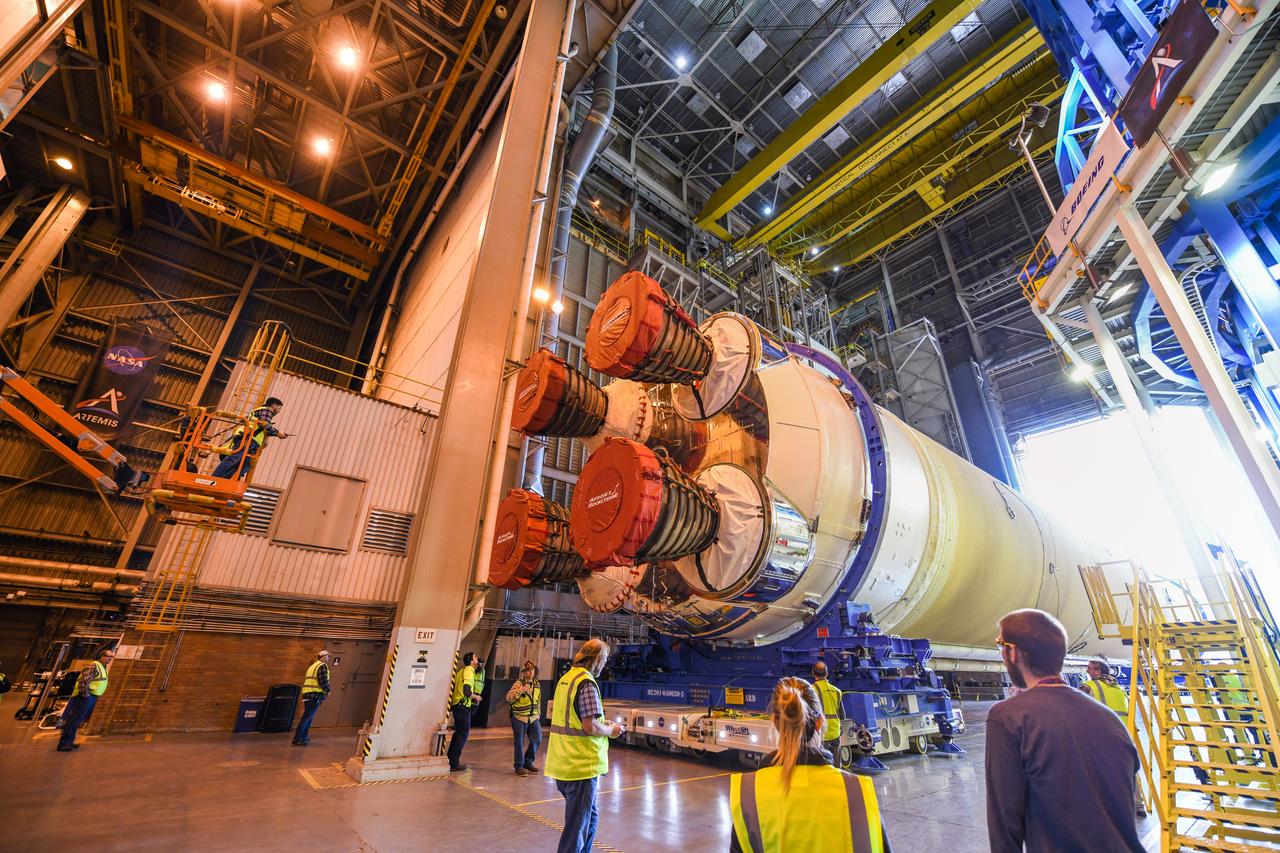

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
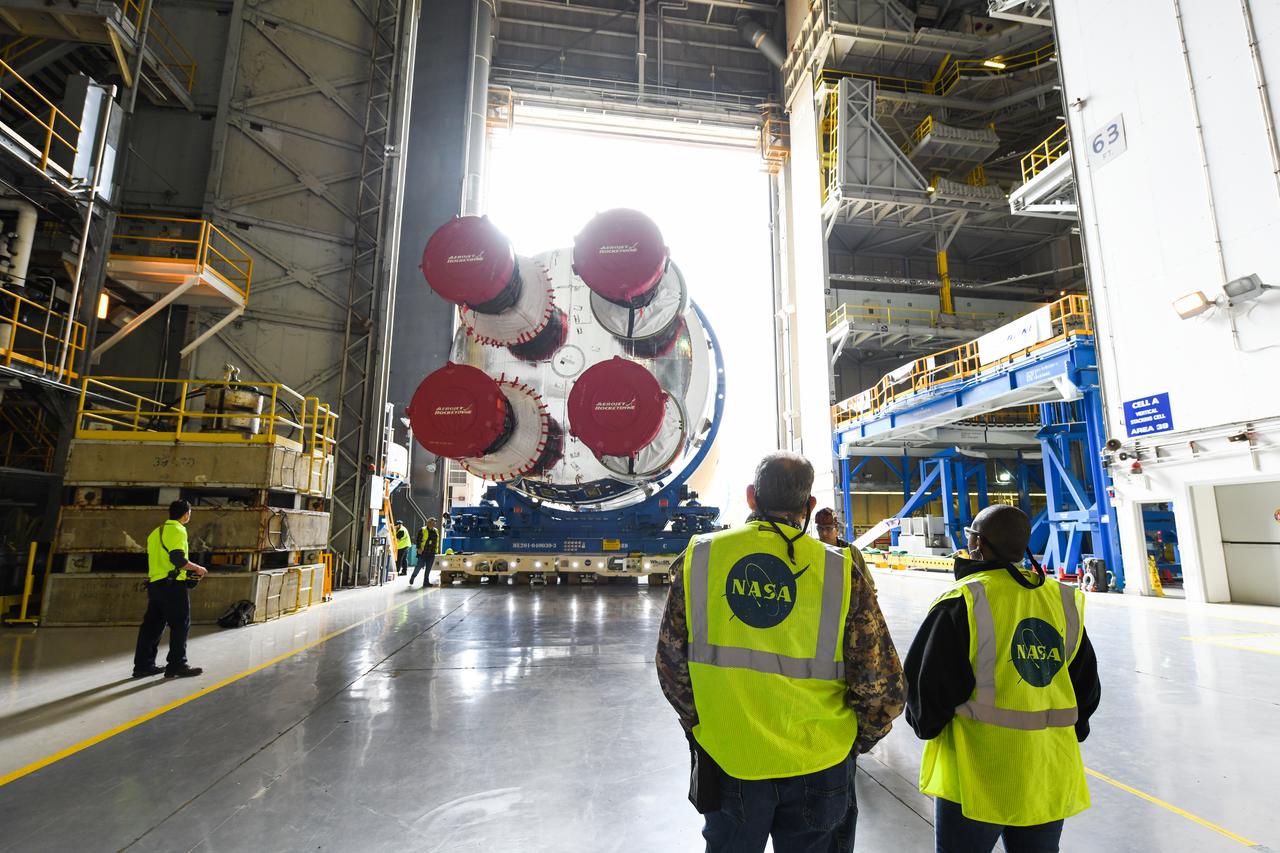

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
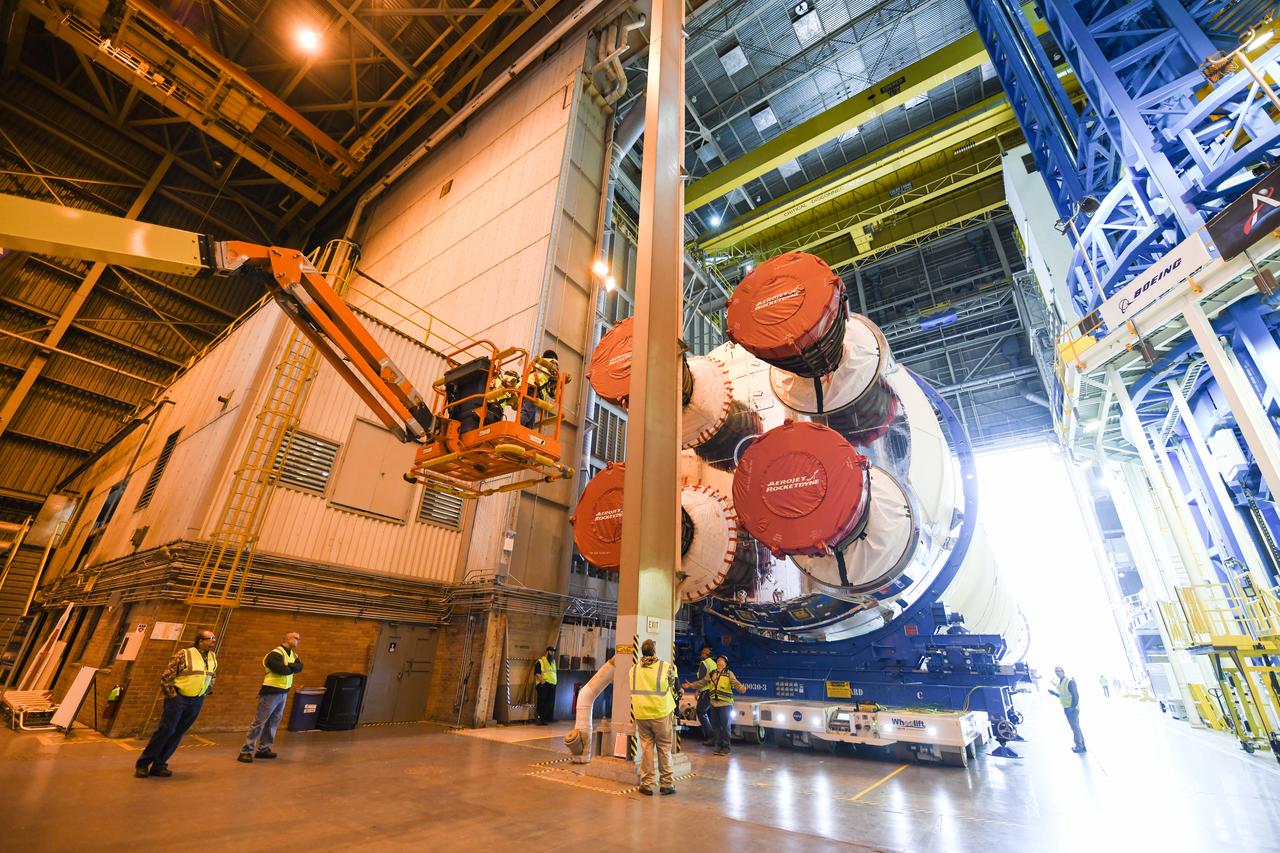

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
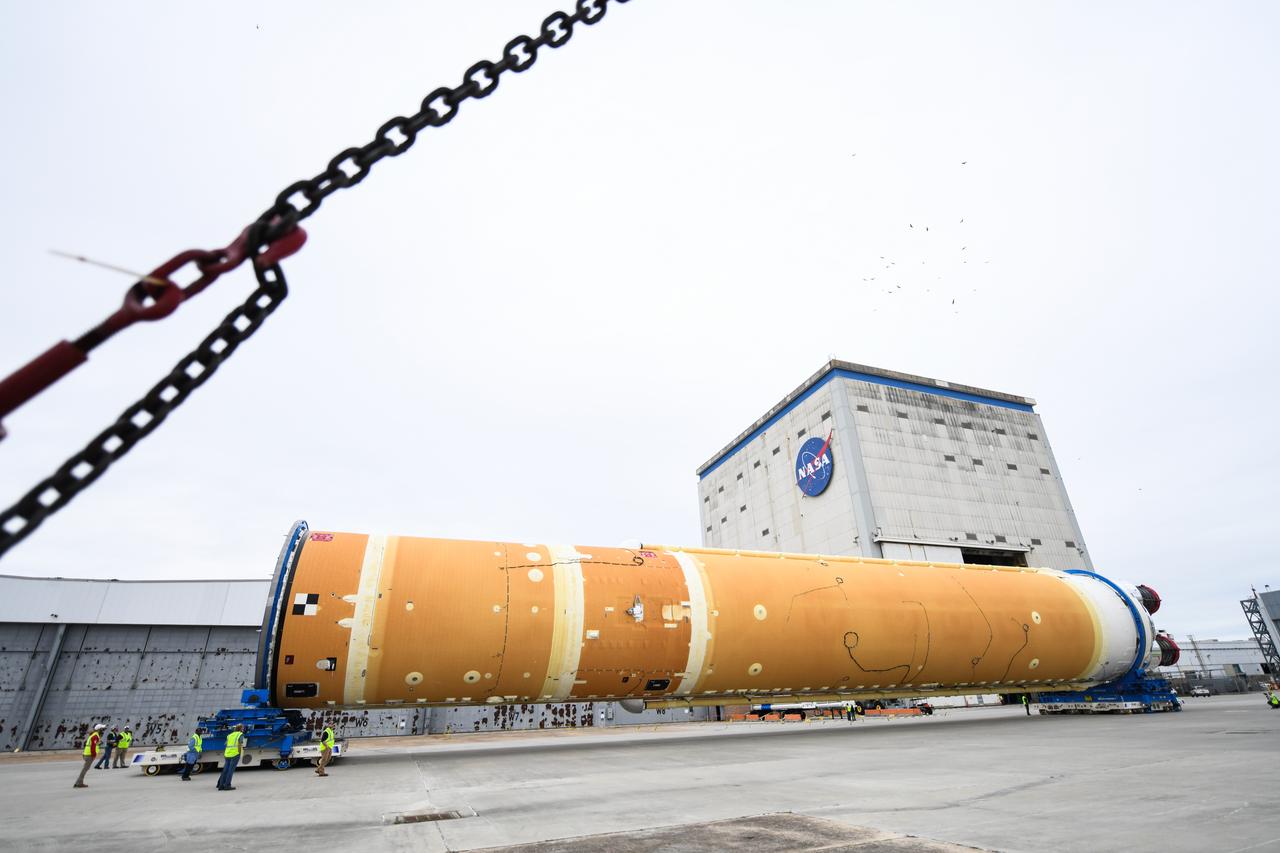

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
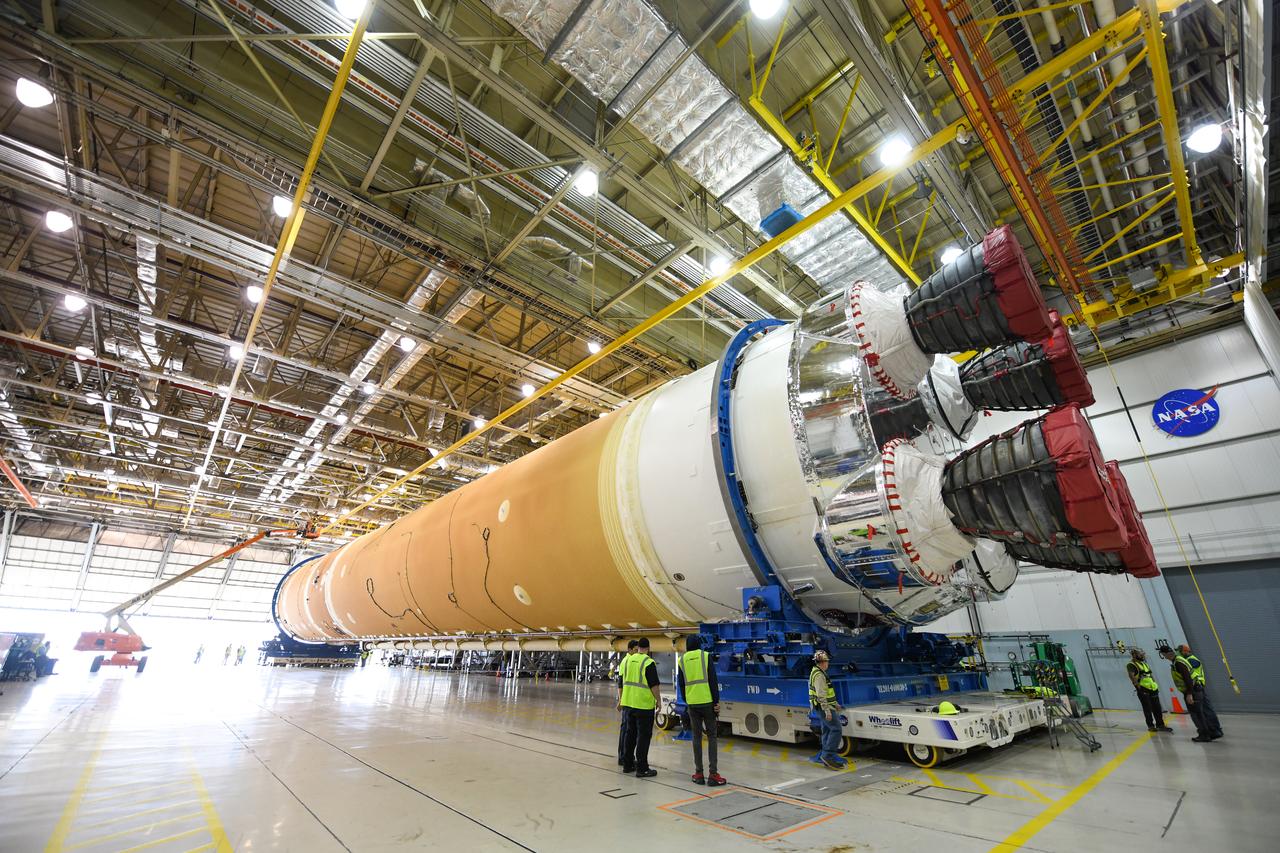

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
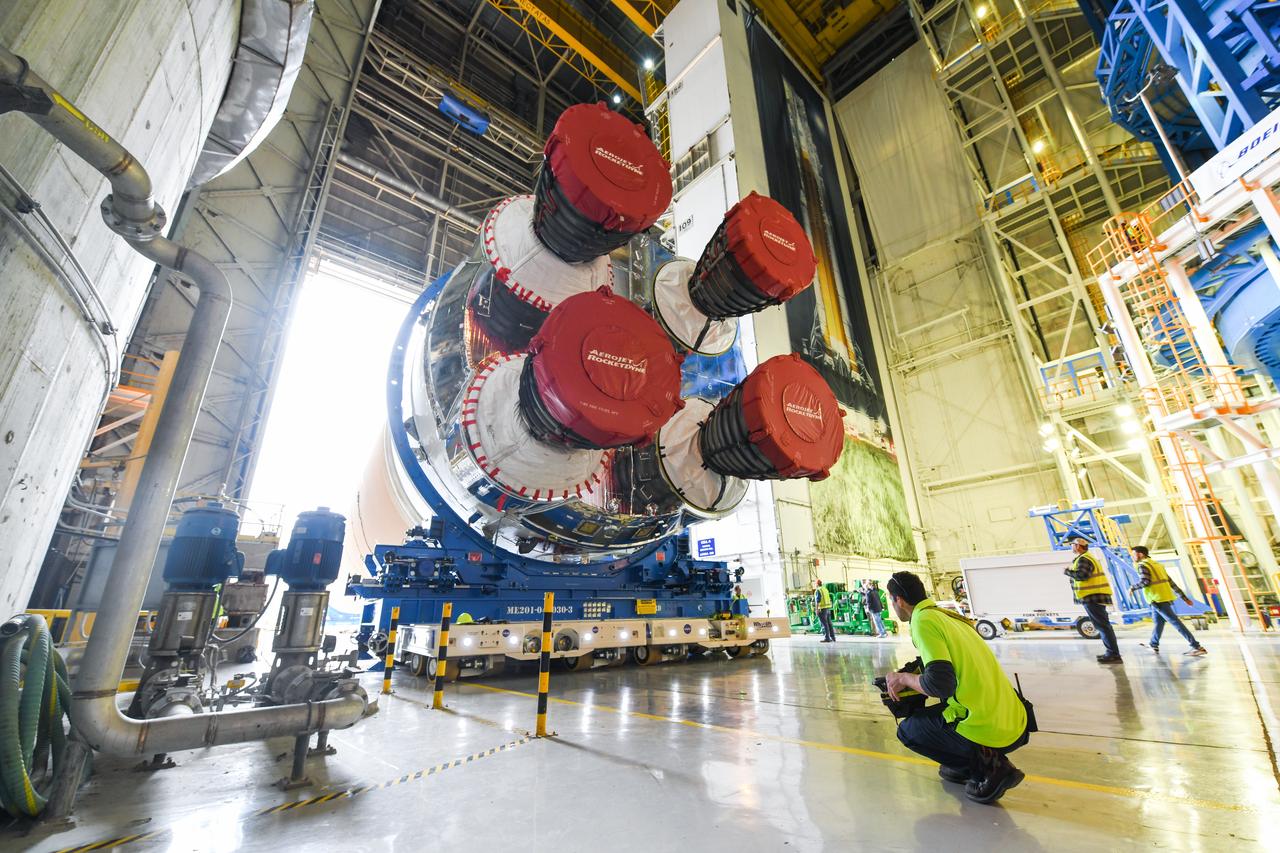

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
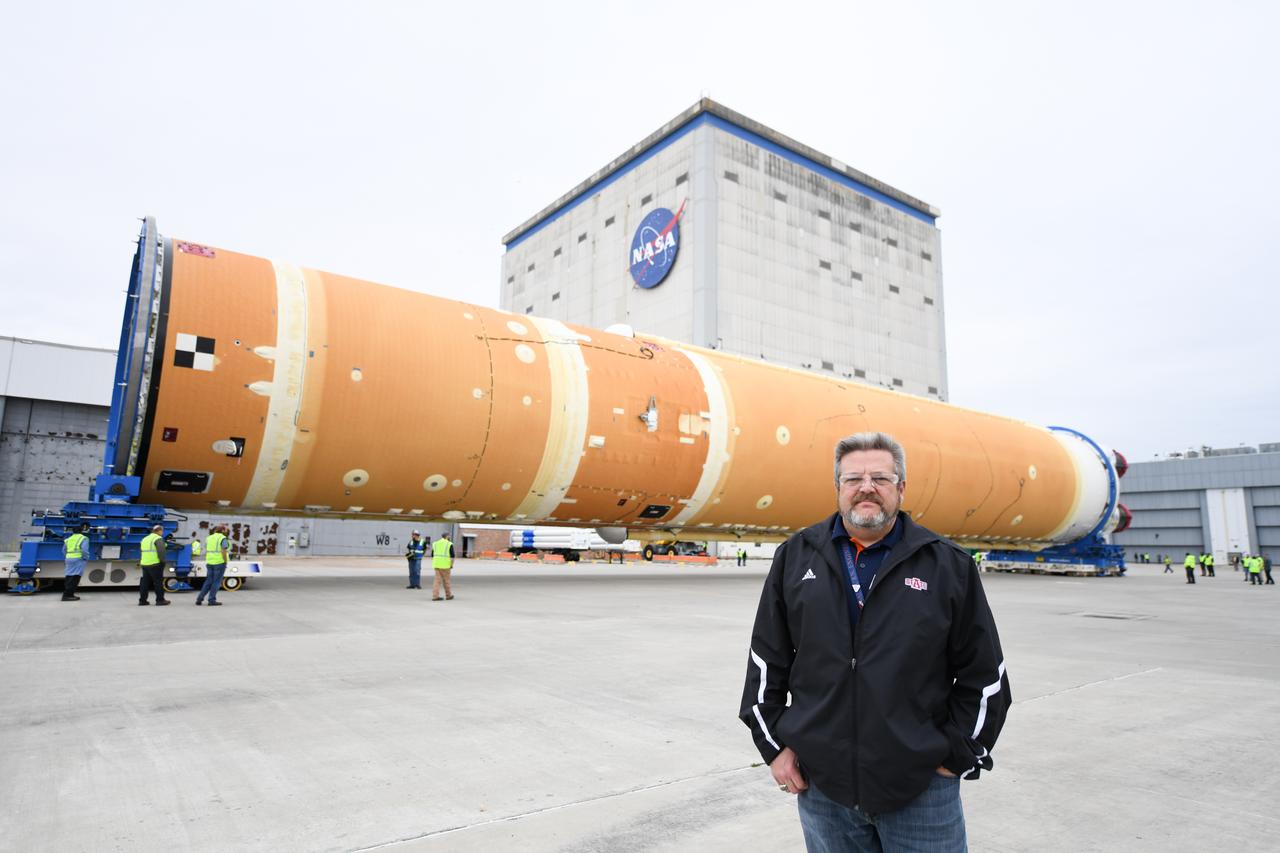

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
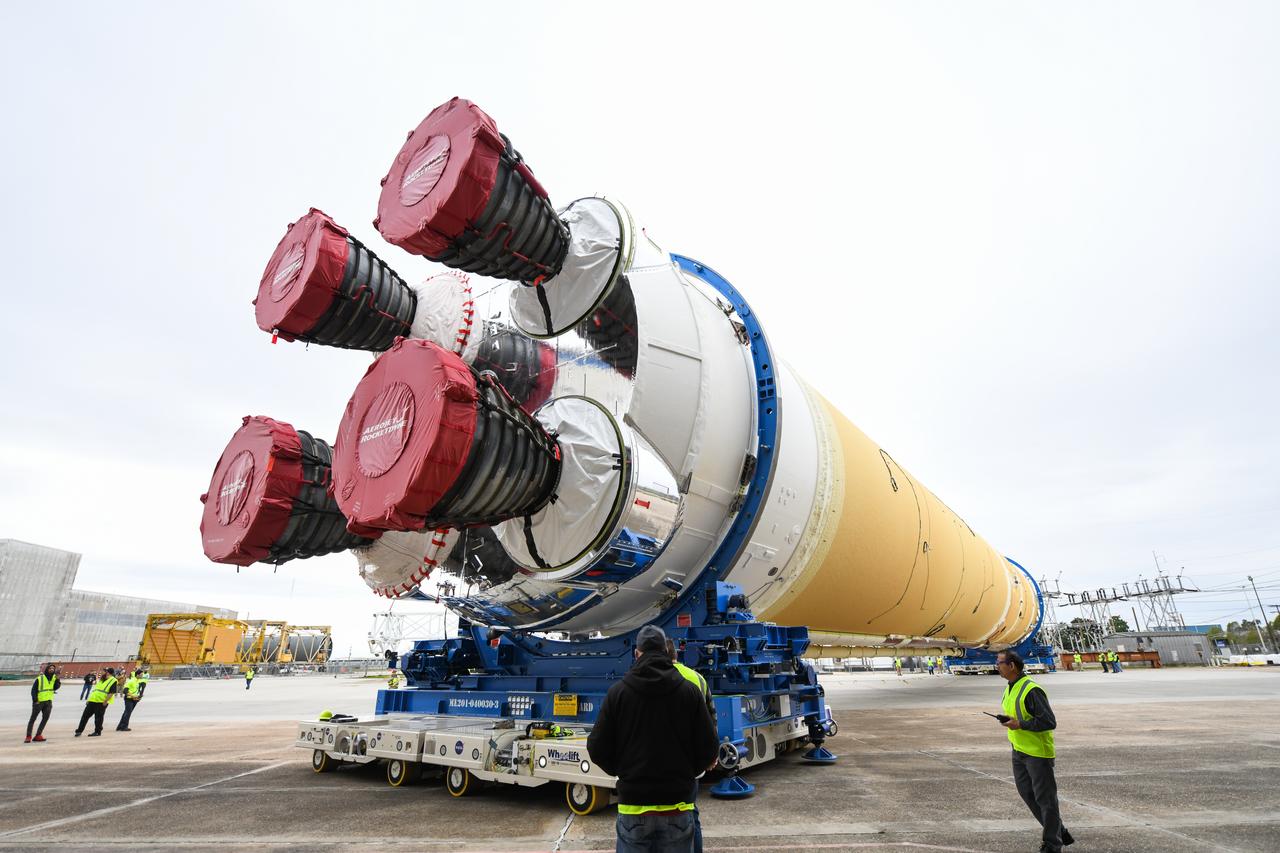

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
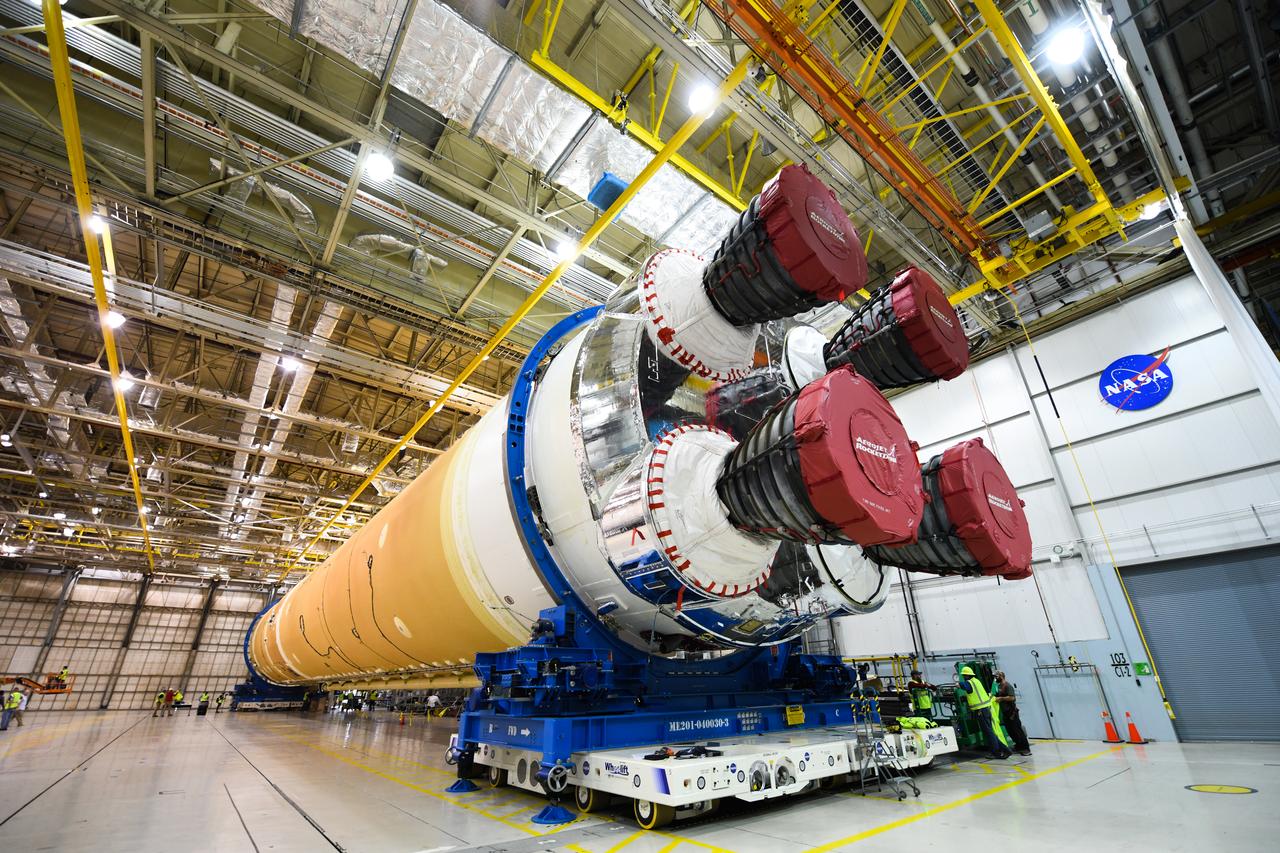

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
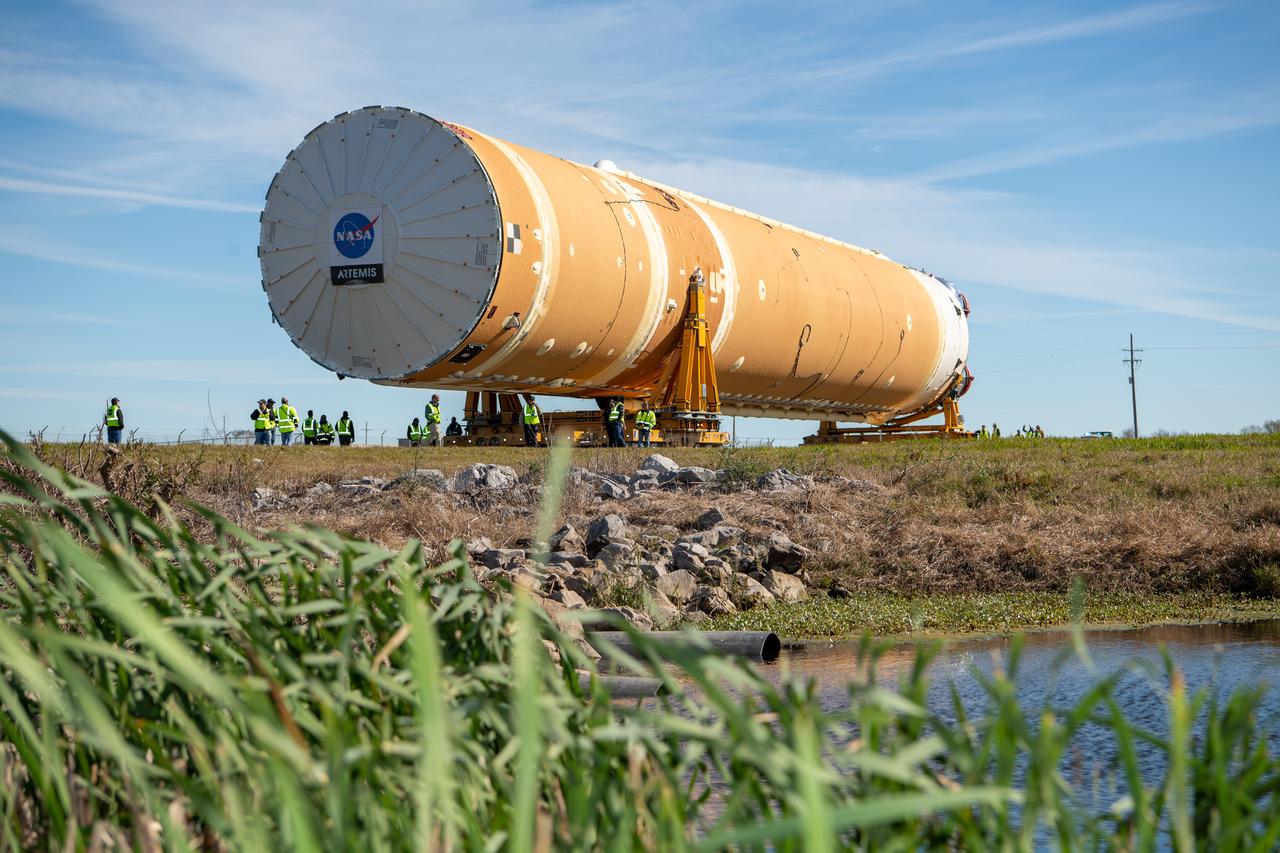

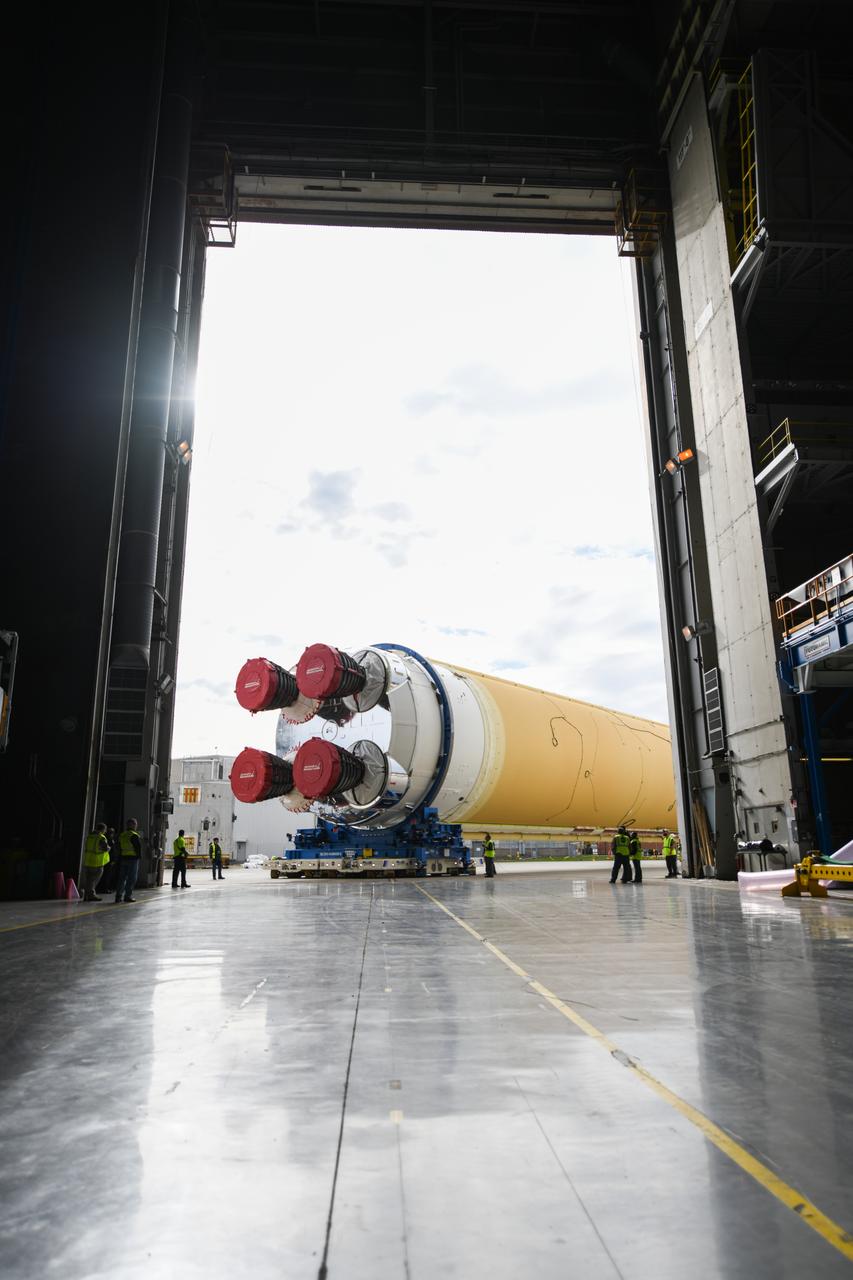
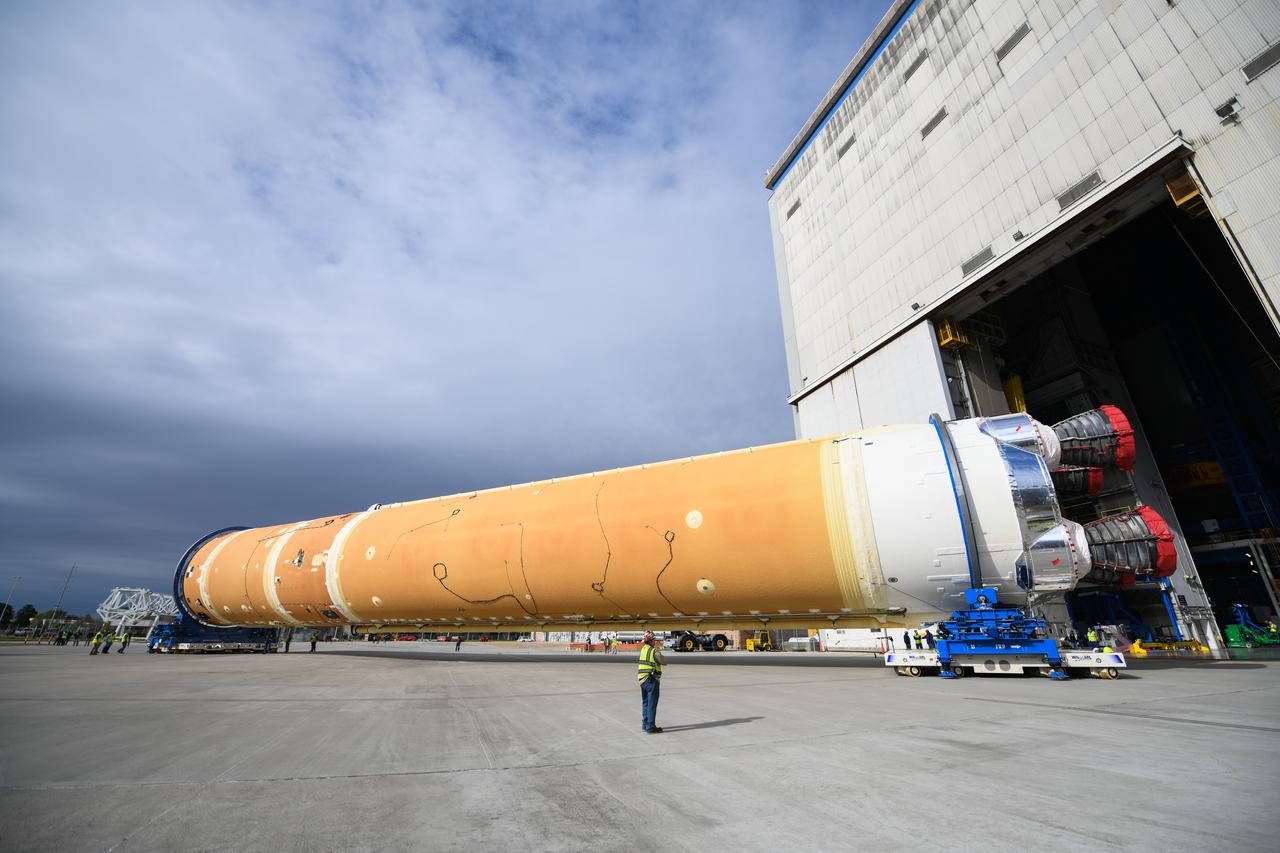
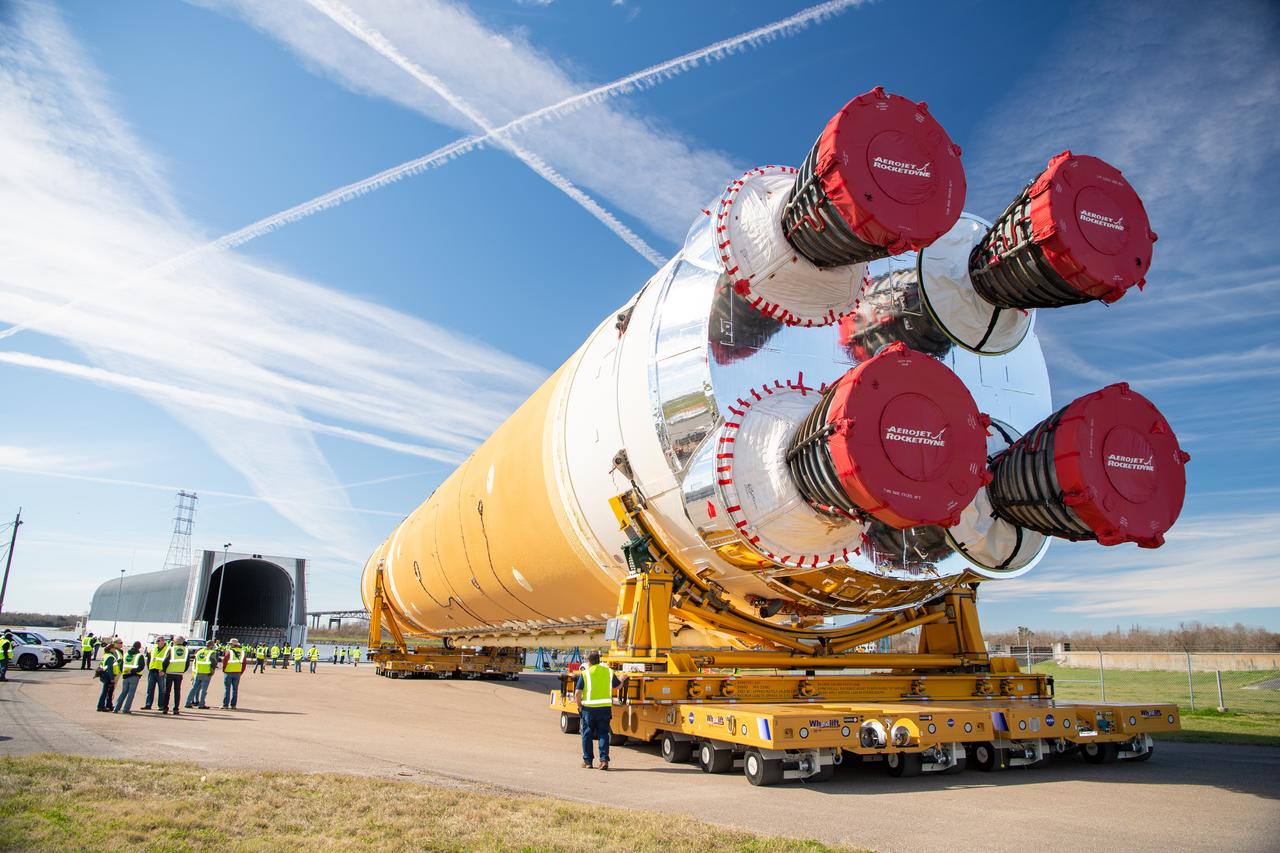
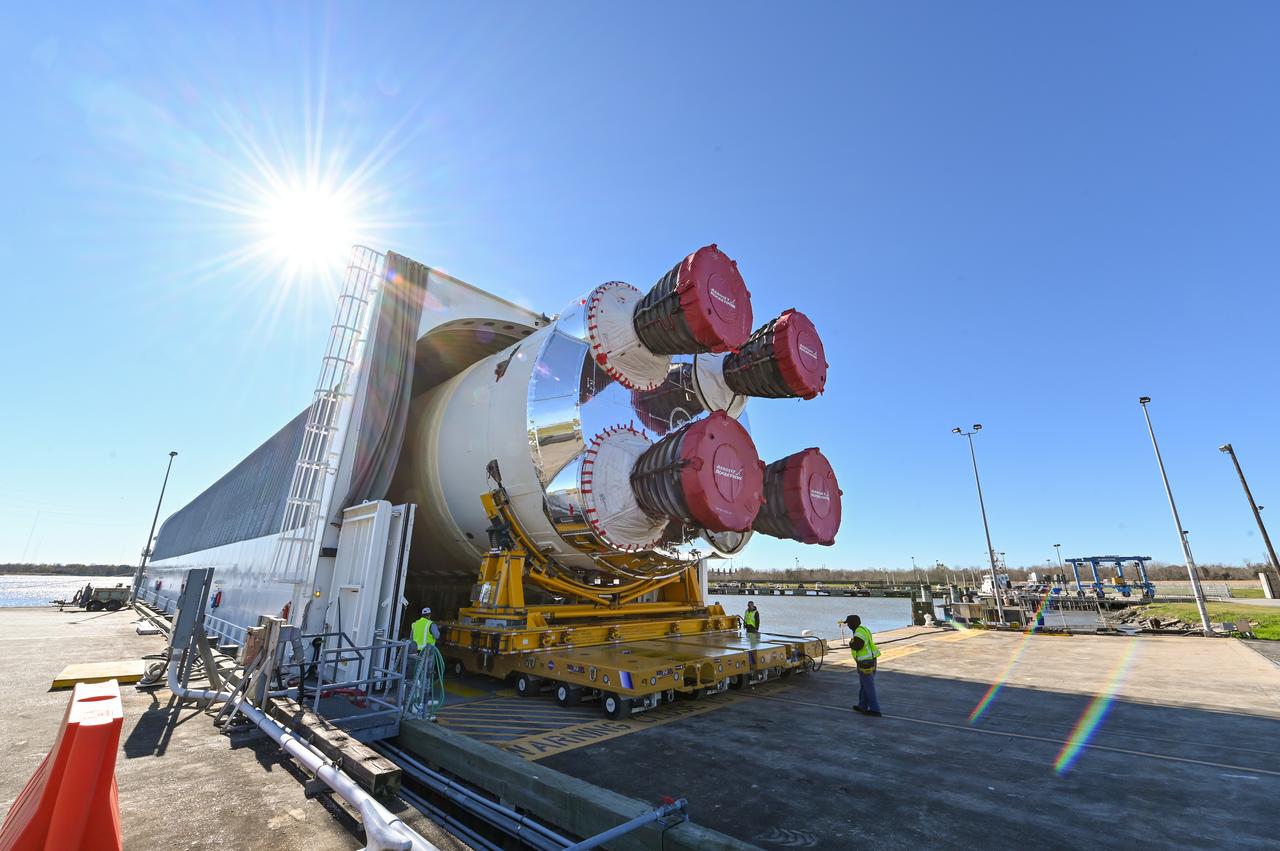
These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
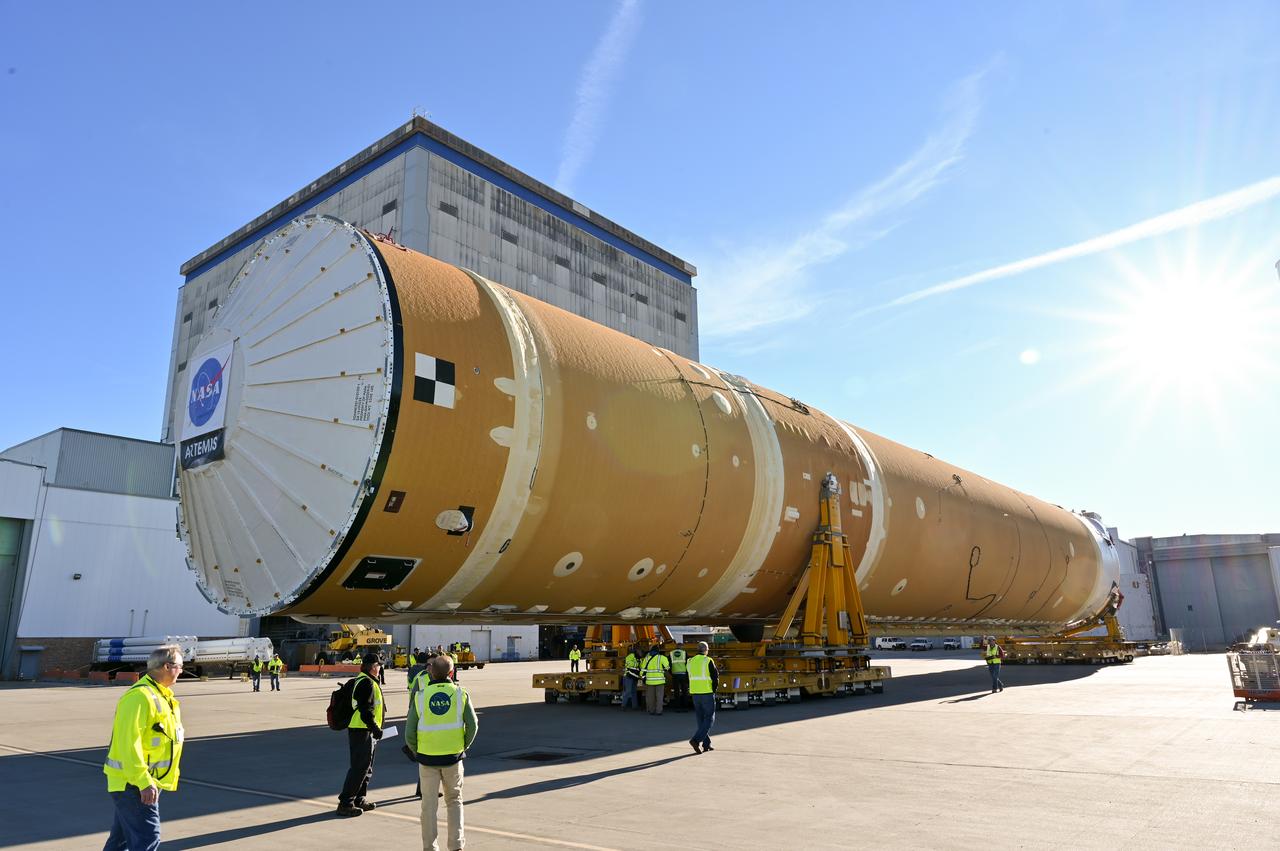

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
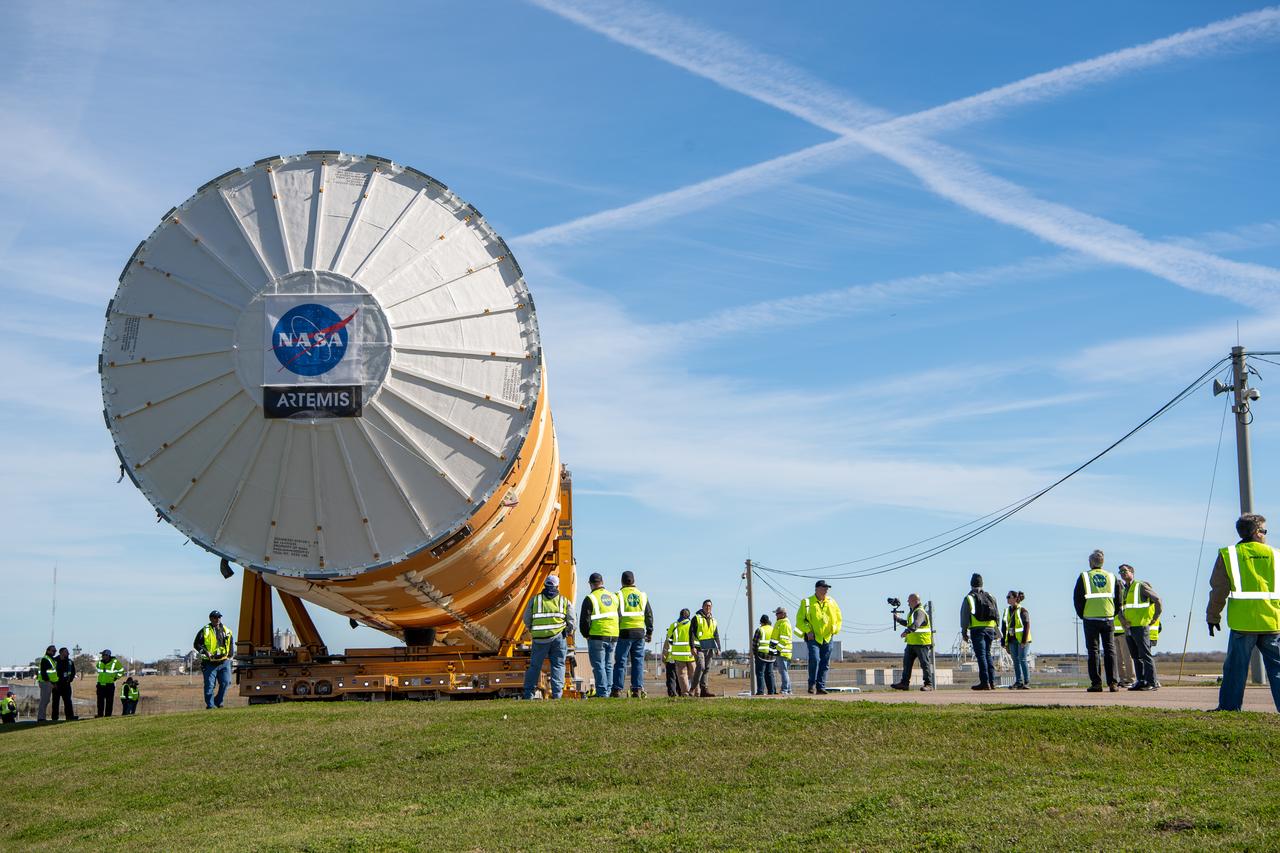

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
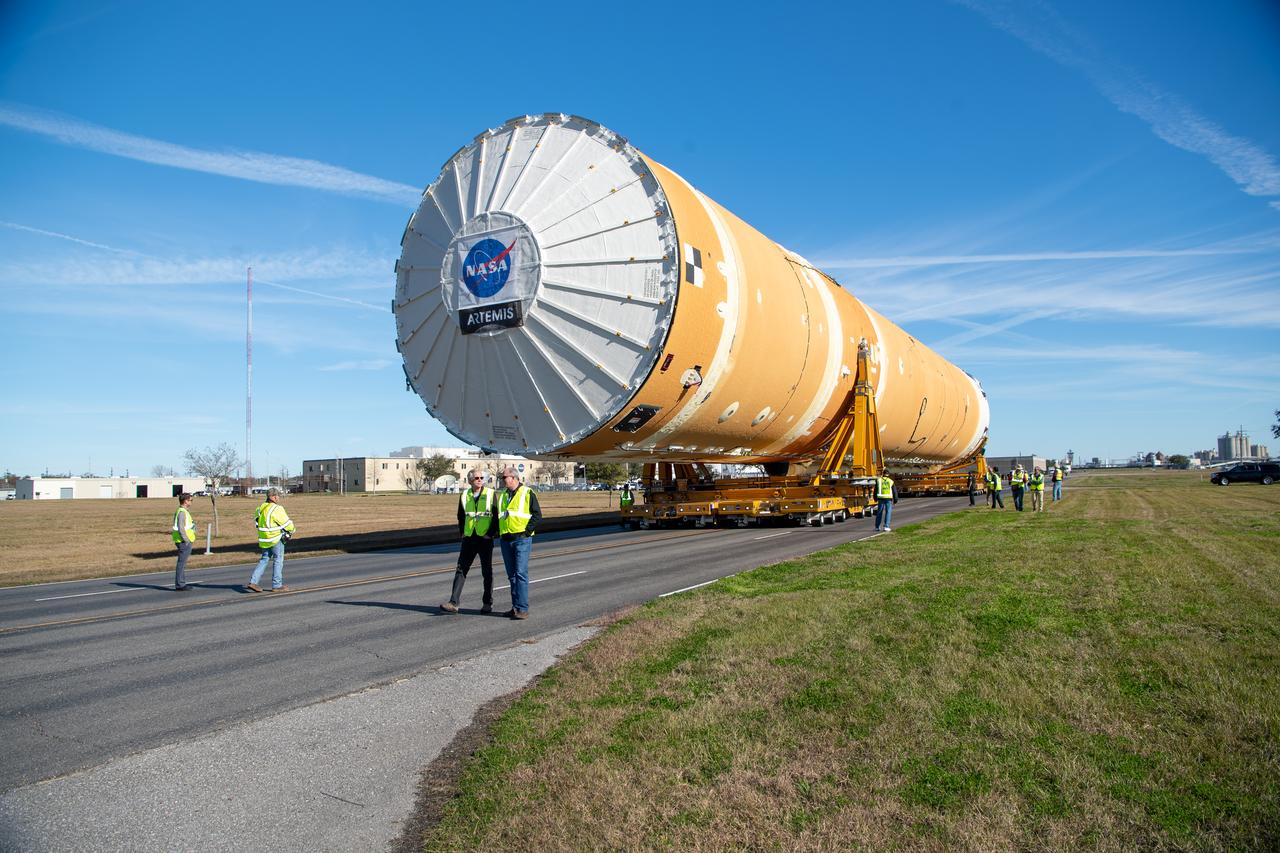

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
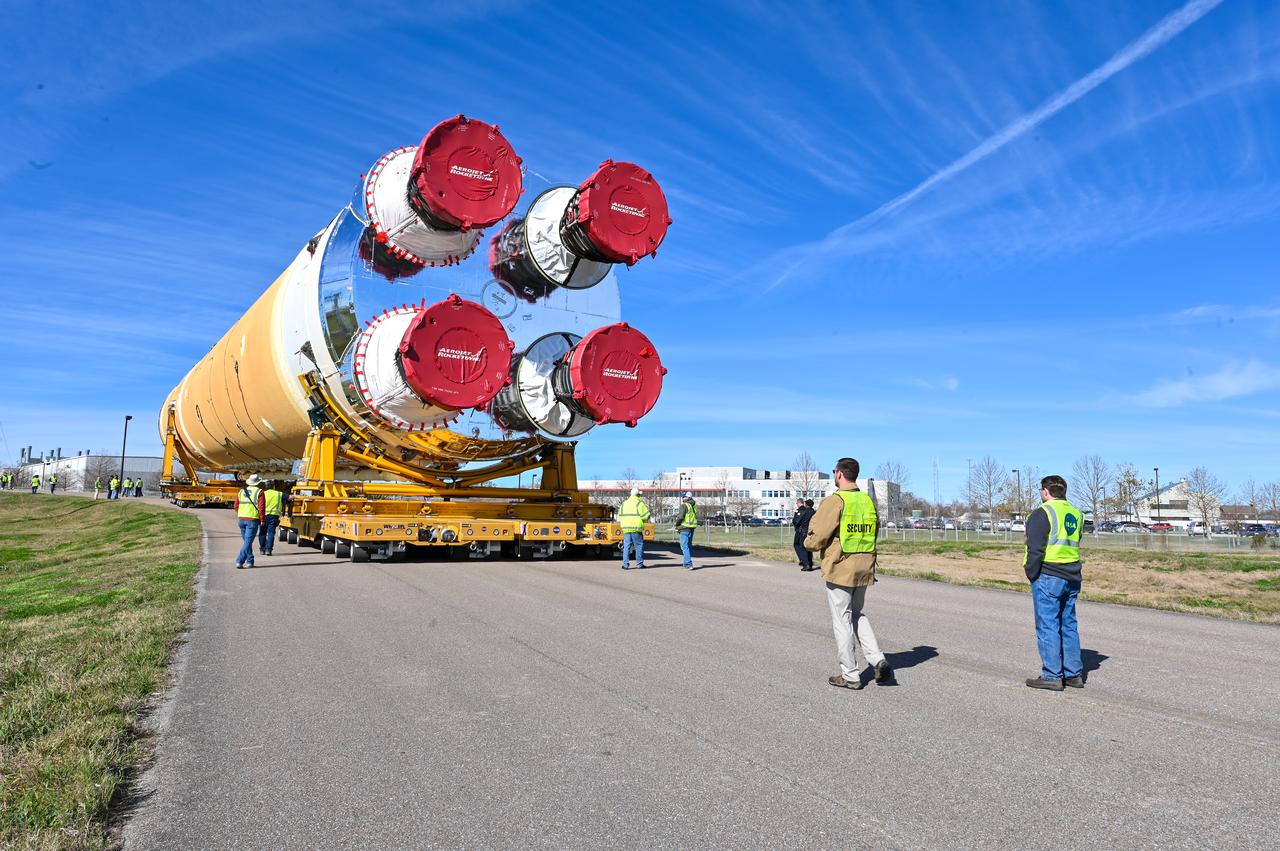

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
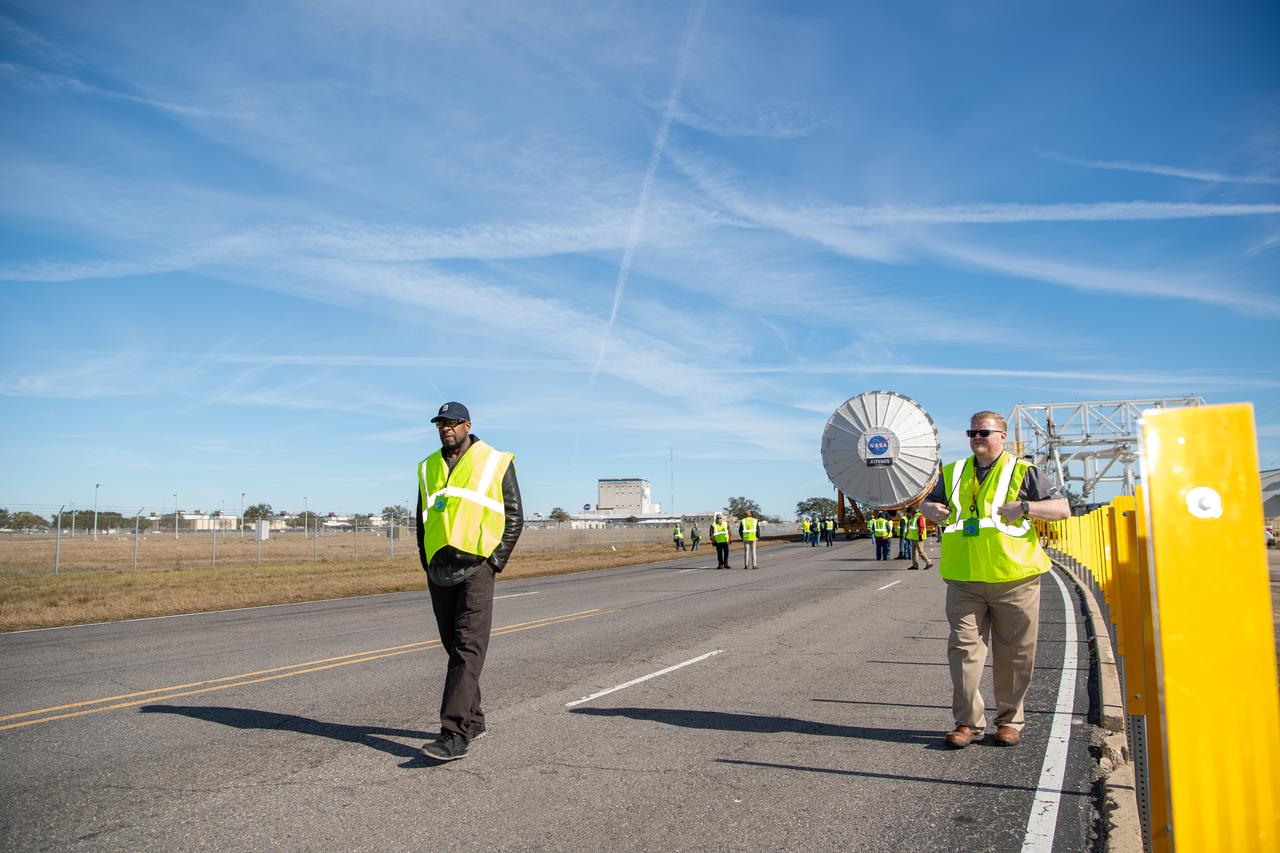

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
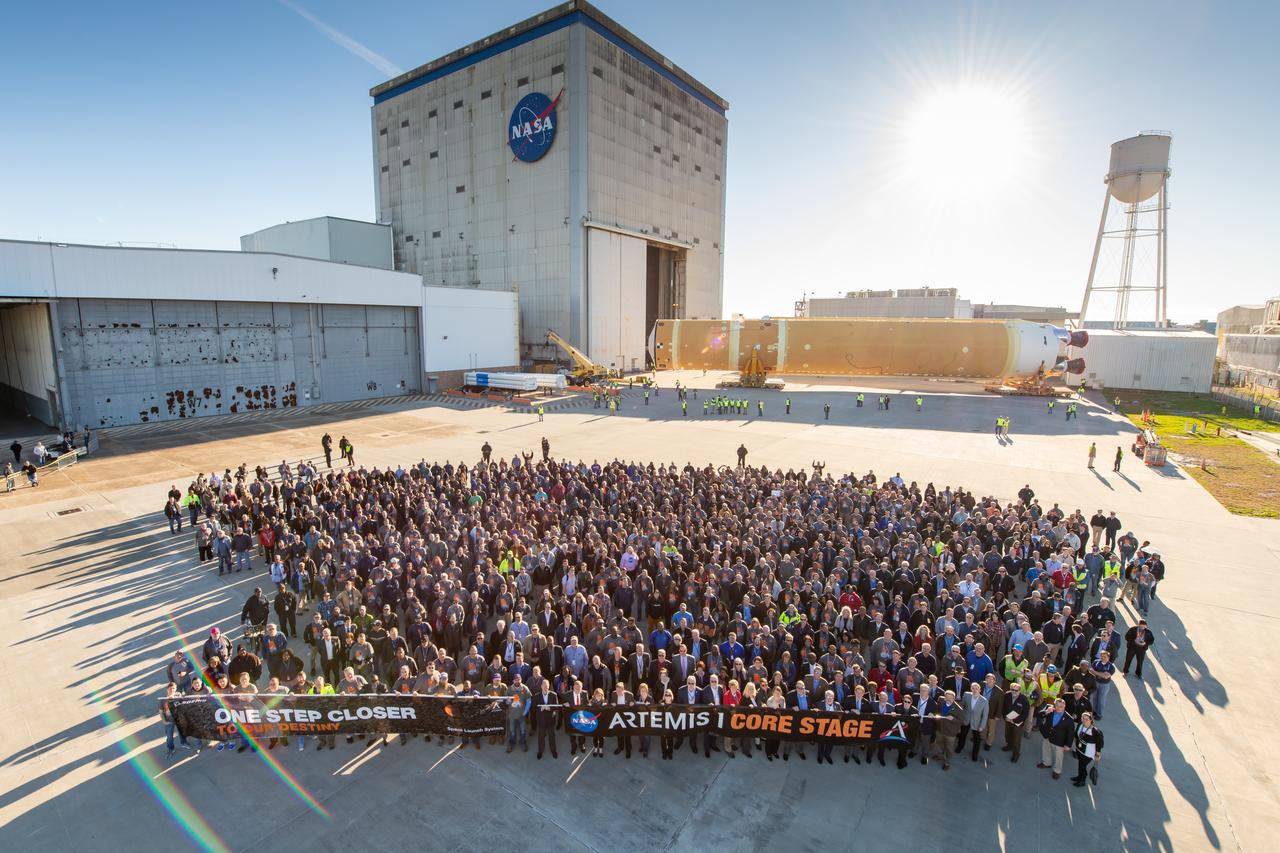

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
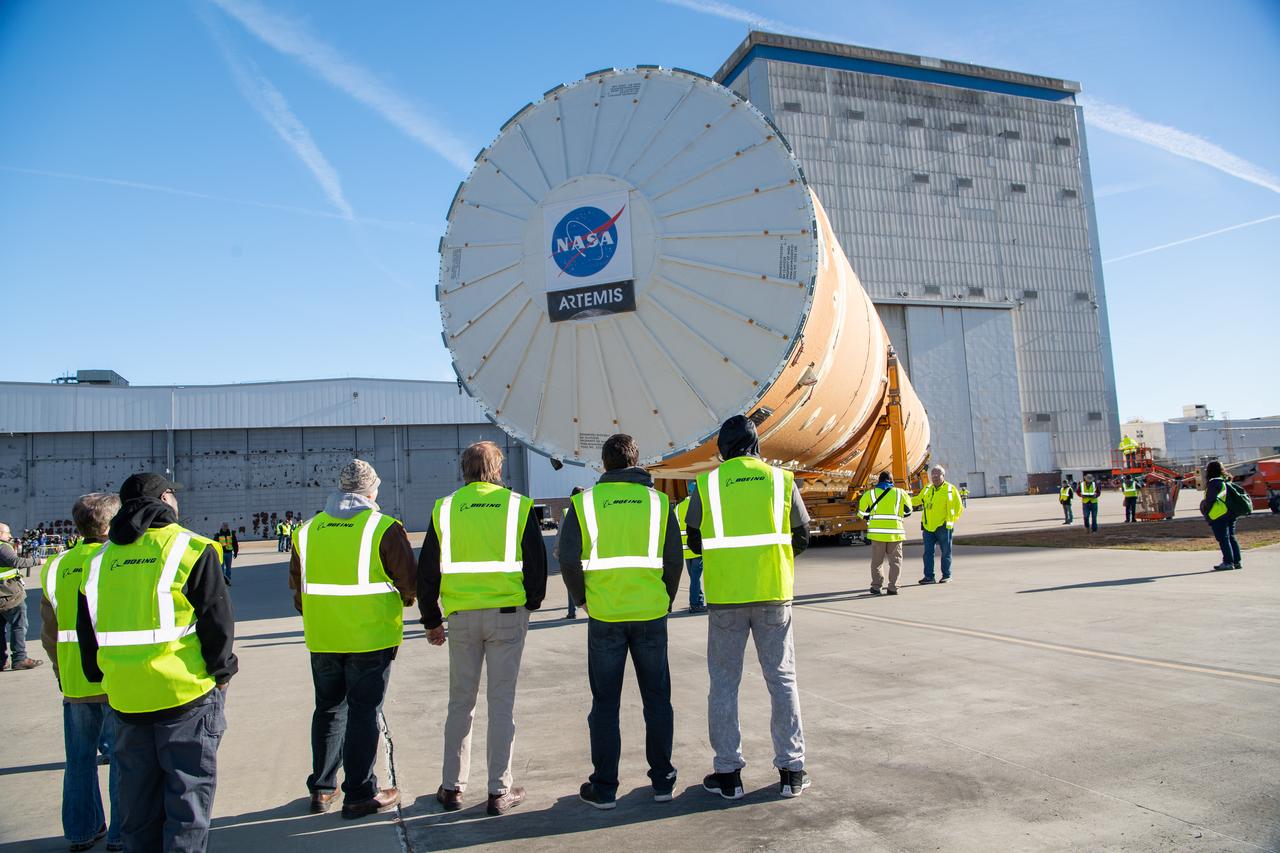

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
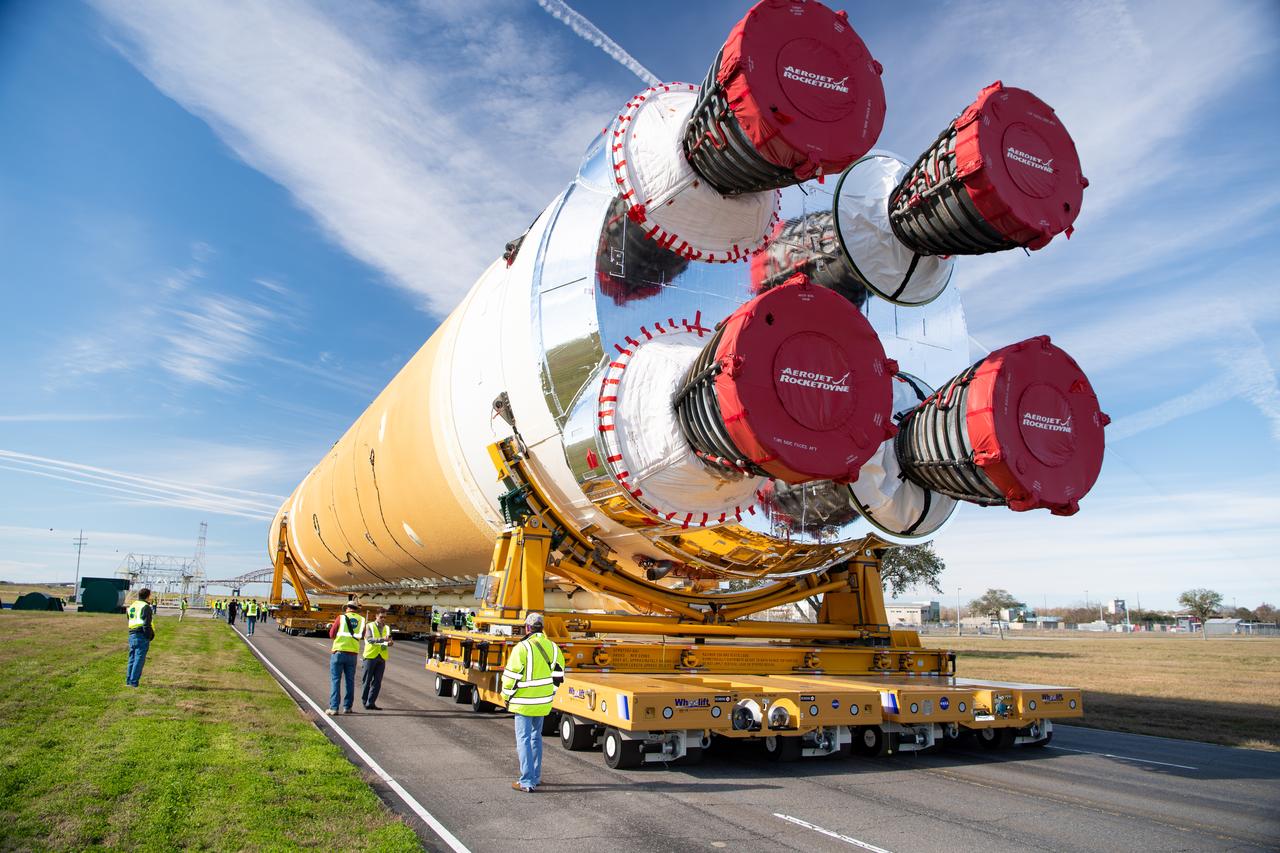

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
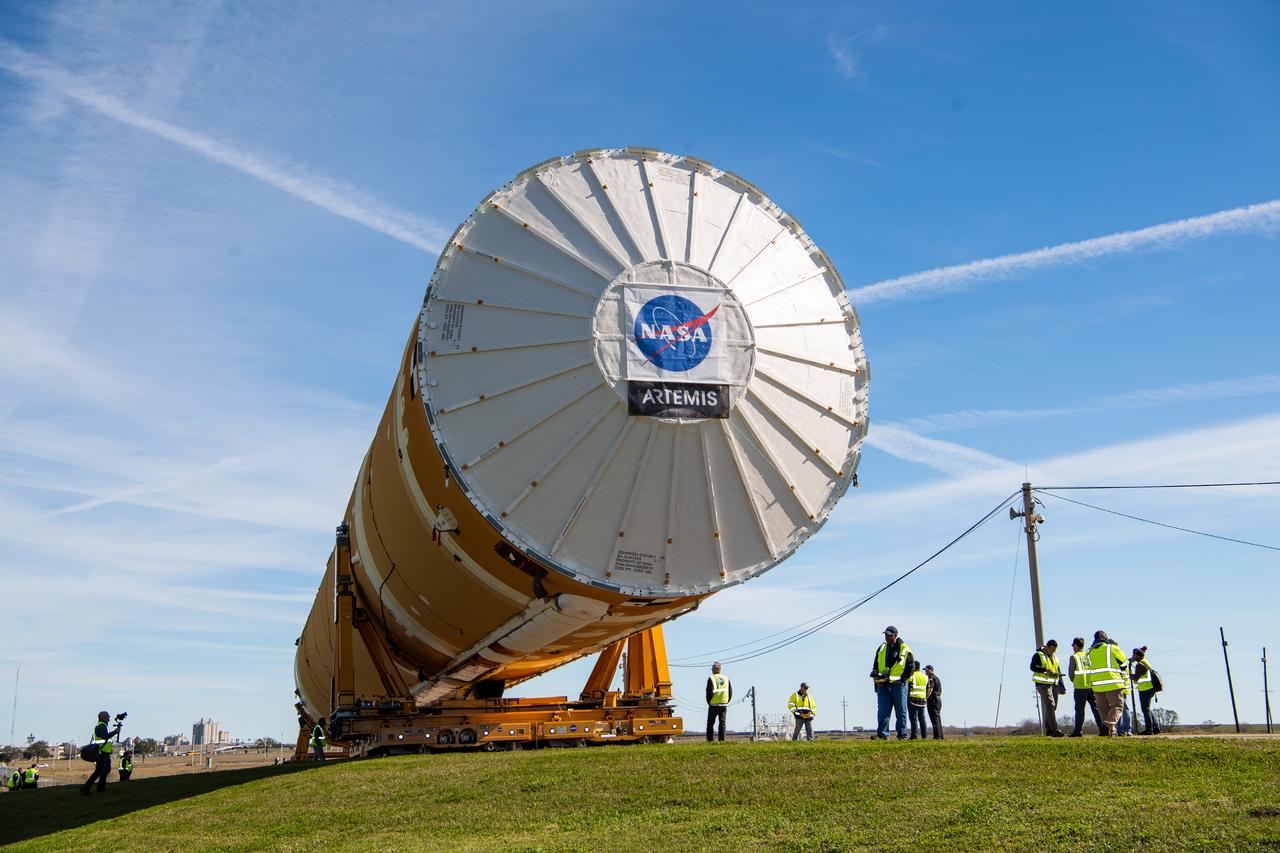

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
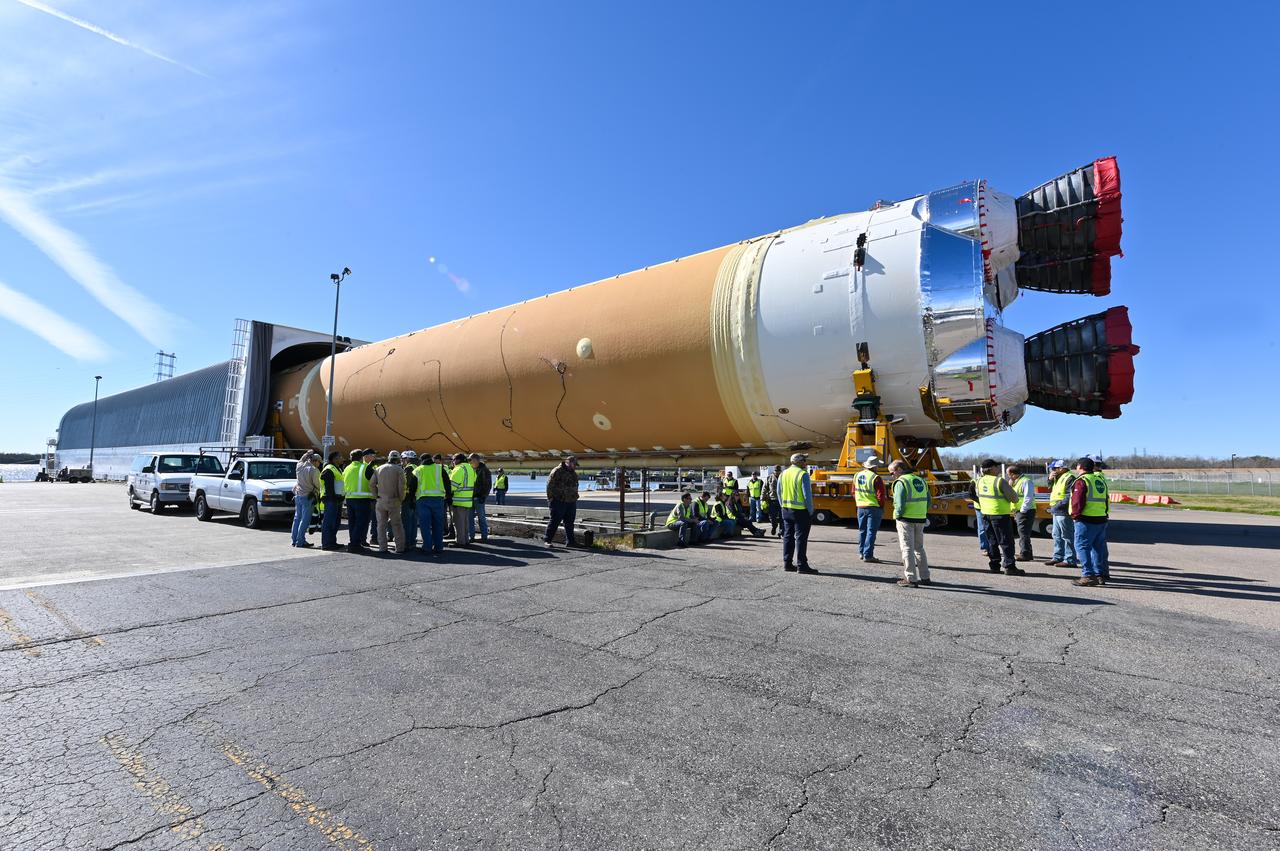

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
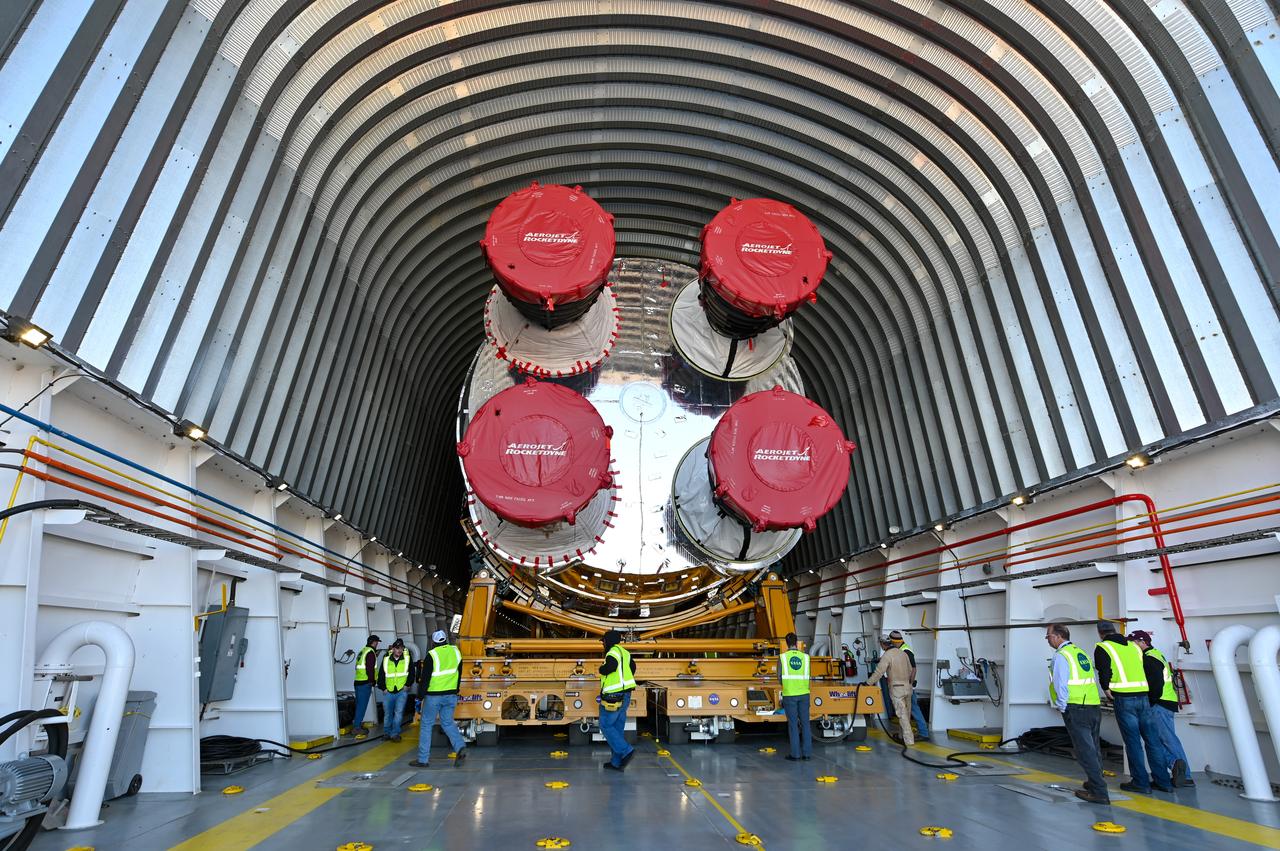

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
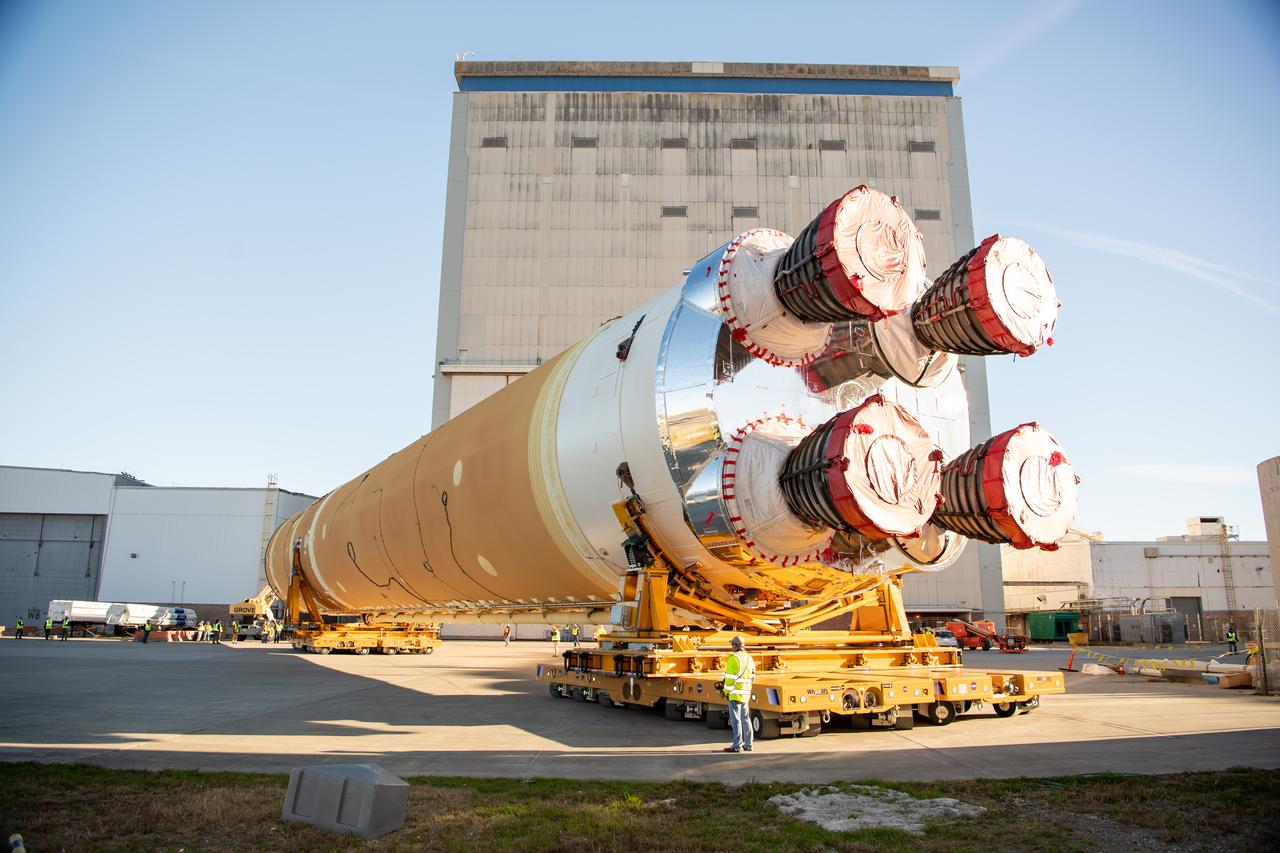

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
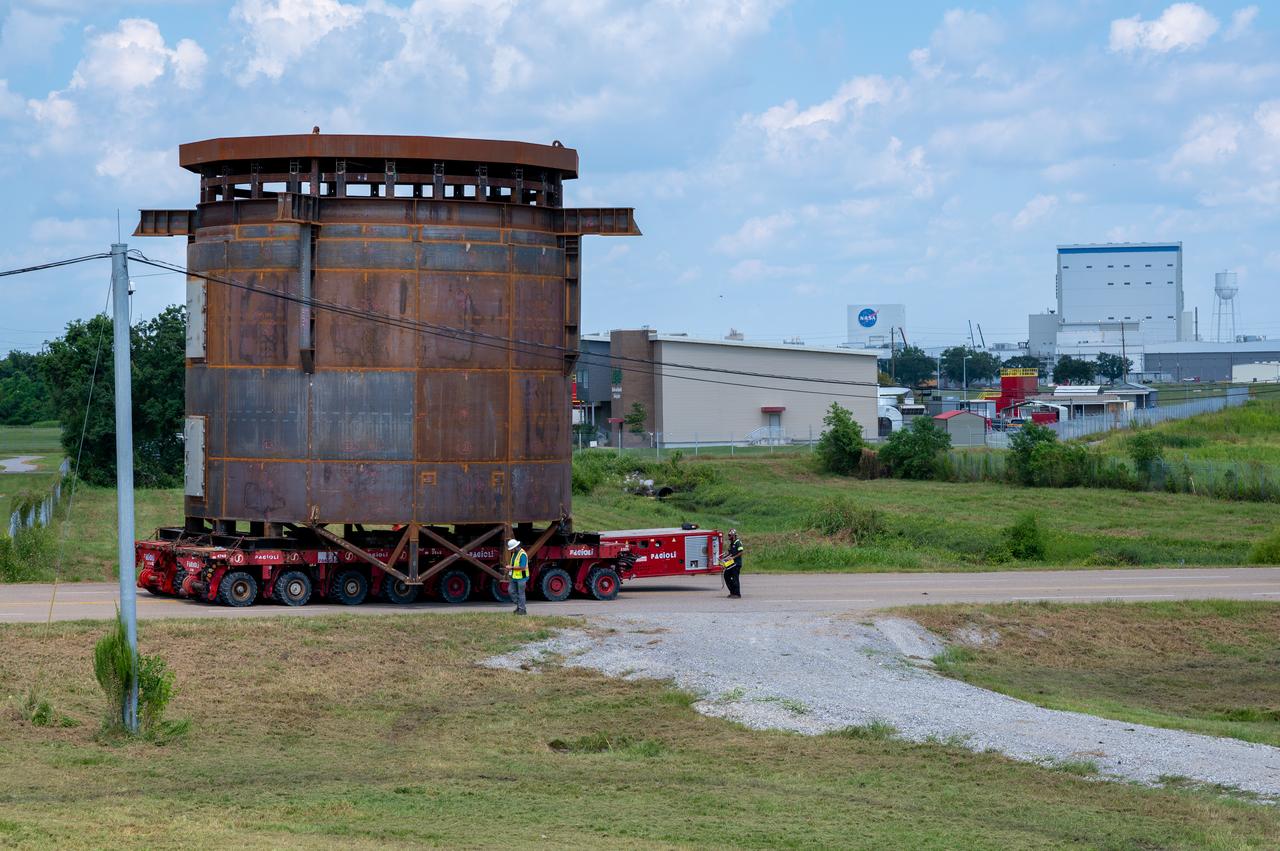

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Once it arrives at Stennis, the simulator will be lifted into the B2 Test Stand, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.
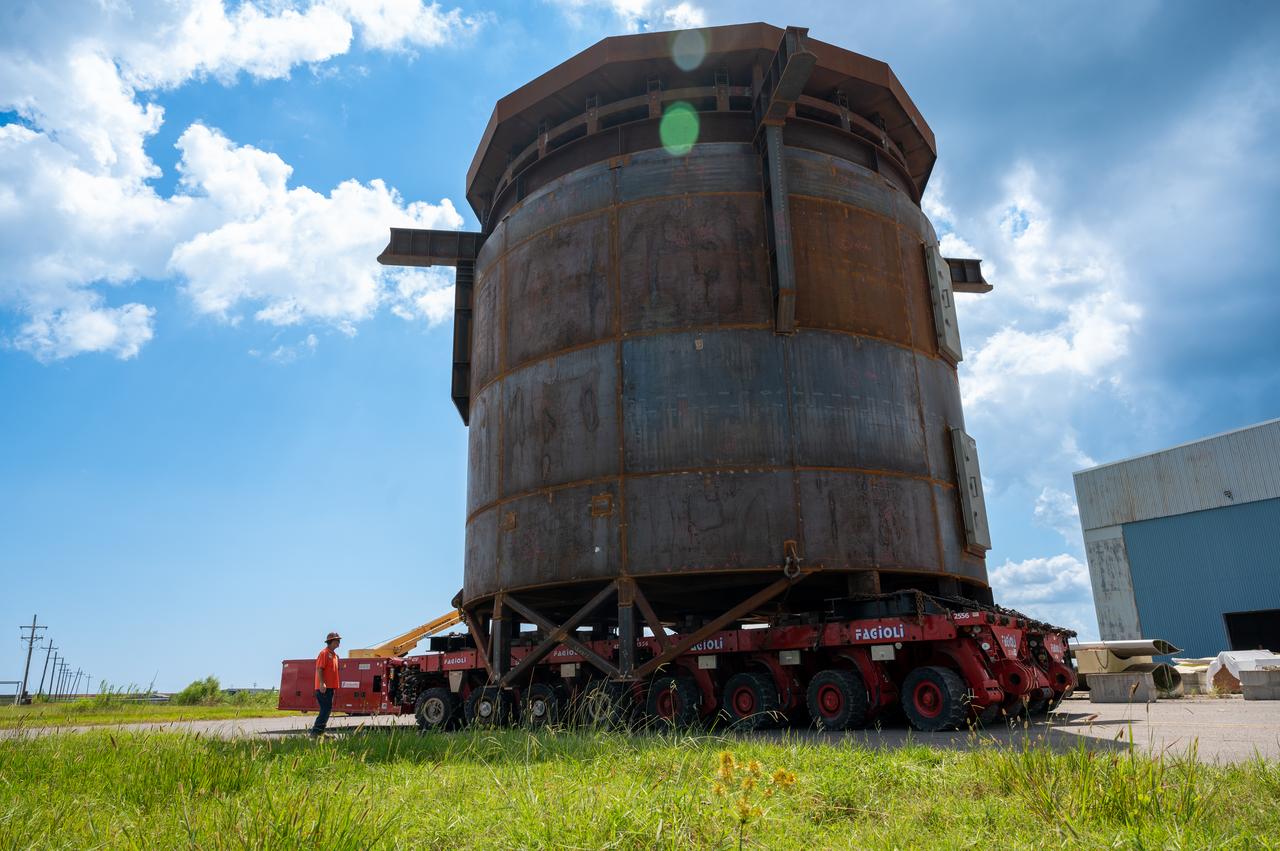

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Once it arrives at Stennis, the simulator will be lifted into the B2 Test Stand, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.
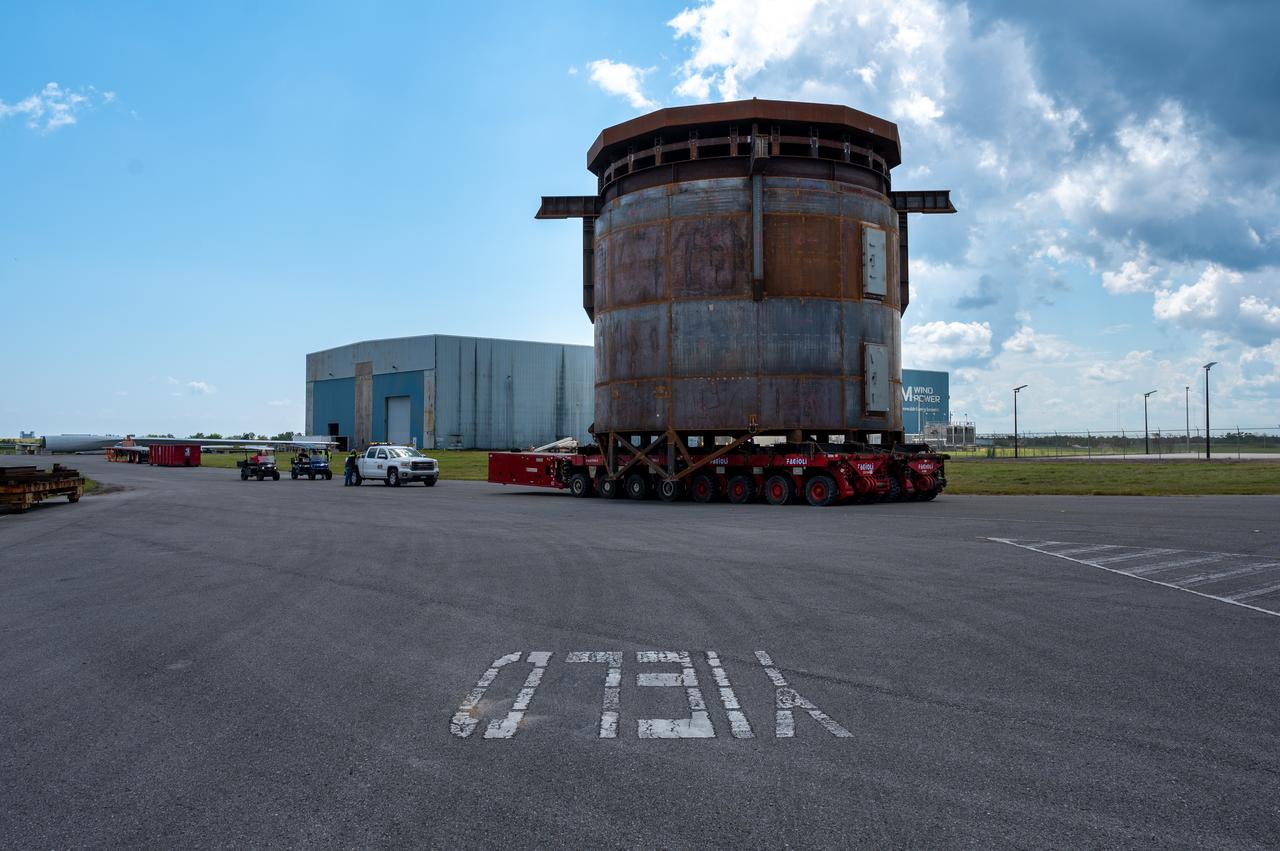

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Crews will lift the simulator into the B2 Test Stand at Stennis, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Crews will lift the simulator into the B2 Test Stand at Stennis, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.
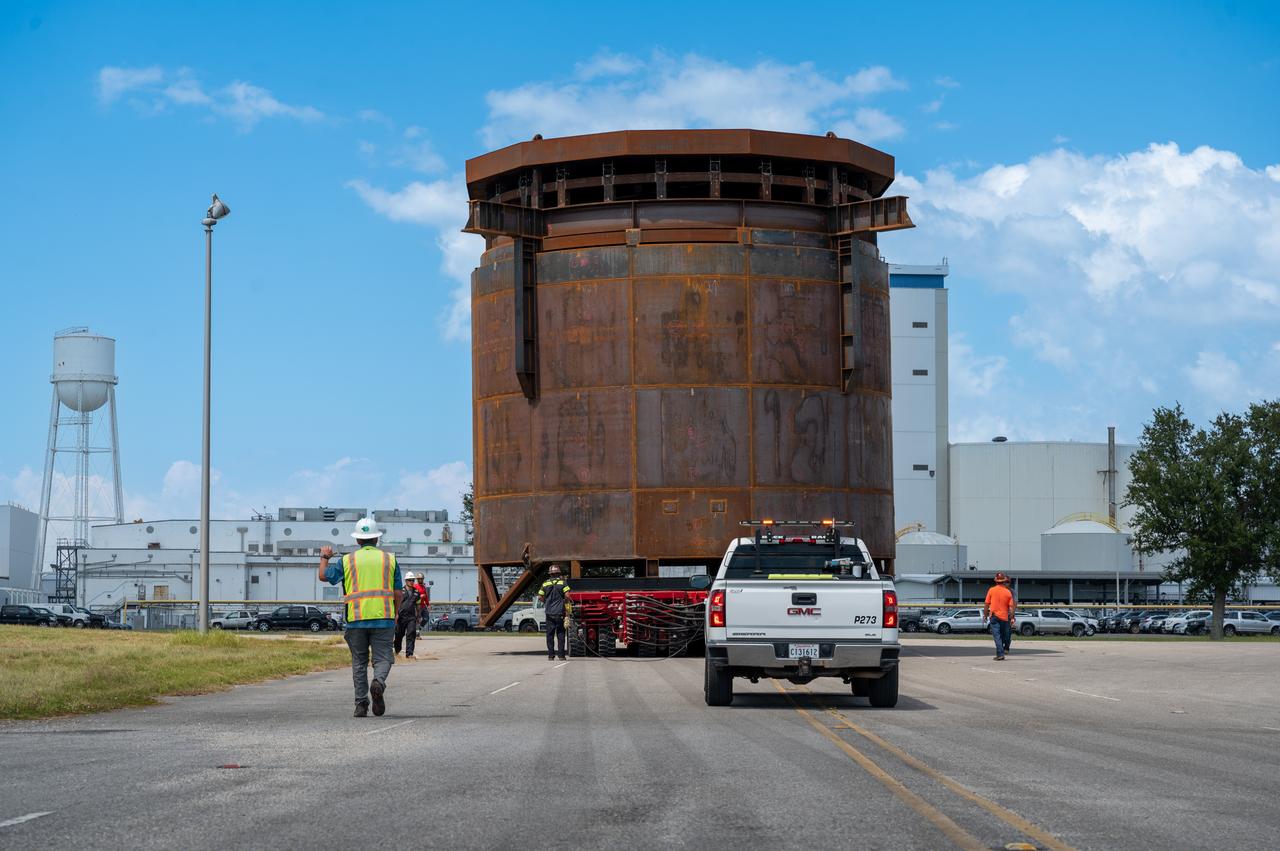

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Once it arrives at Stennis, the simulator will be lifted into the B2 Test Stand, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.