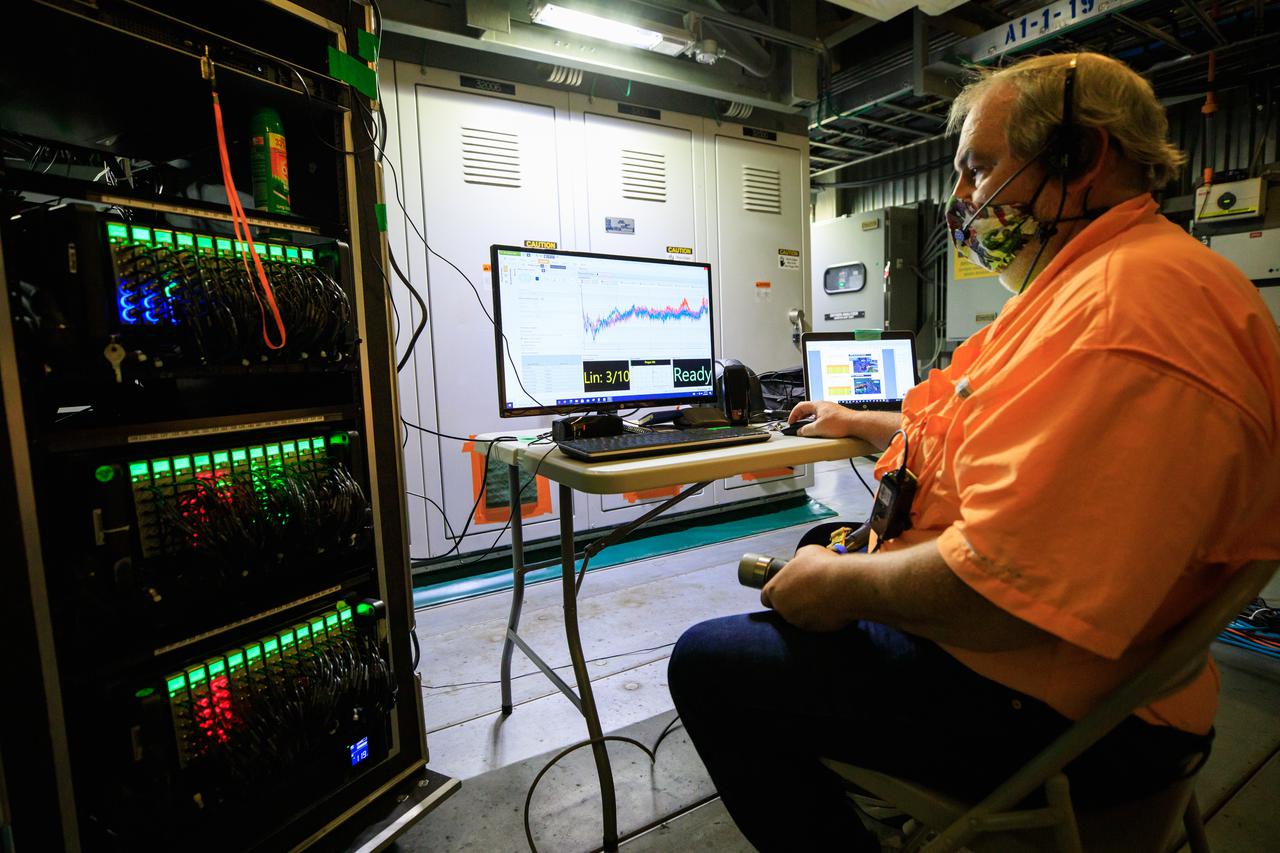
An engineer with contractor Jacobs prepares for a modal tap test on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis I in a room under the zero deck of the mobile launcher inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 16, 2021. The Exploration Ground systems and Jacobs team, along with the SLS team from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are performing the tests with support from personnel at other NASA centers. Engineers are using the mass simulator for Orion and the Orion stage adapter structural test article for the modal test. The tests will determine the different modes of vibration with the recently stacked and integrated SLS rocket before launch of the Artemis I mission. Artemis I will be an uncrewed test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
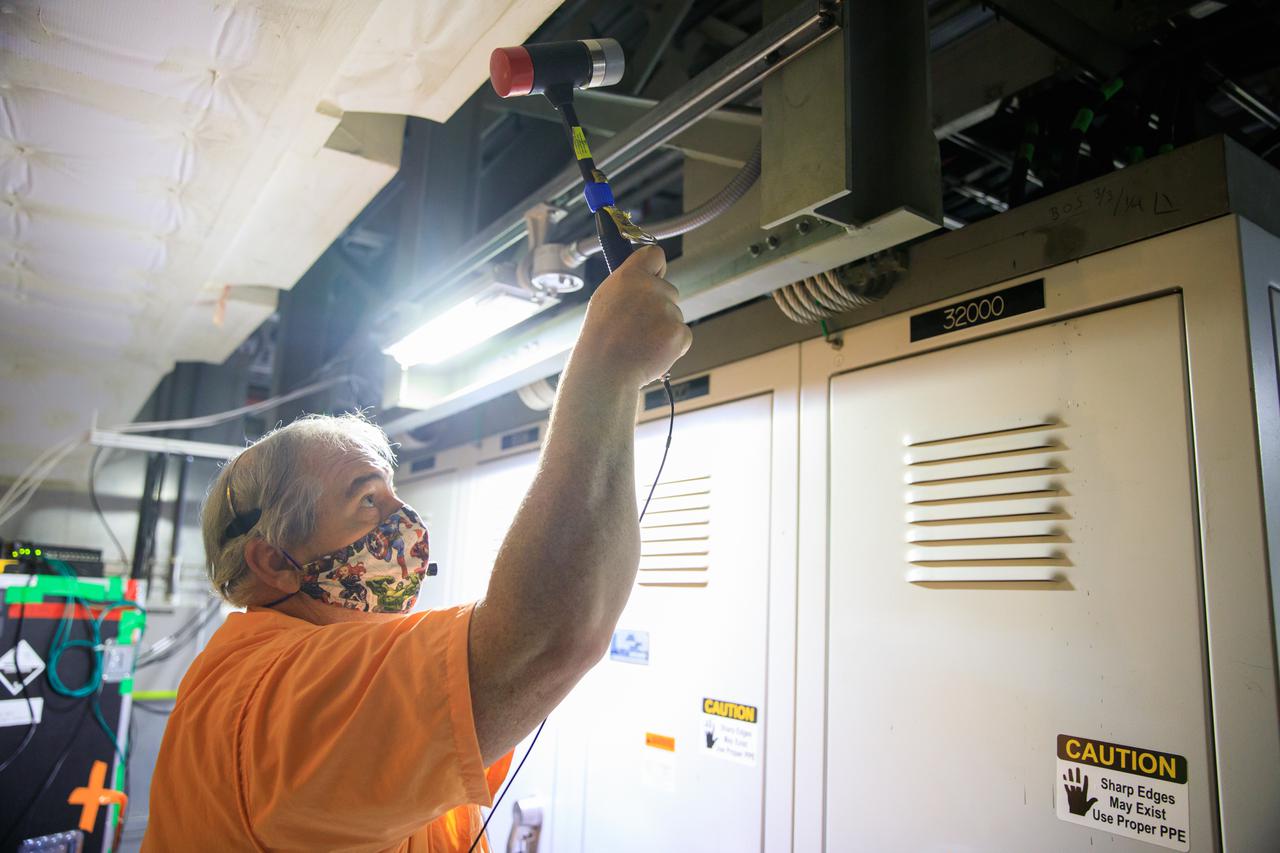

An engineer with contractor Jacobs prepares for a modal tap test on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis I in a room under the zero deck of the mobile launcher inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 16, 2021. The Exploration Ground systems and Jacobs team, along with the SLS team from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are performing the tests with support from personnel at other NASA centers. Engineers are using the mass simulator for Orion and the Orion stage adapter structural test article for the modal test. The tests will determine the different modes of vibration with the recently stacked and integrated SLS rocket before launch of the Artemis I mission. Artemis I will be an uncrewed test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
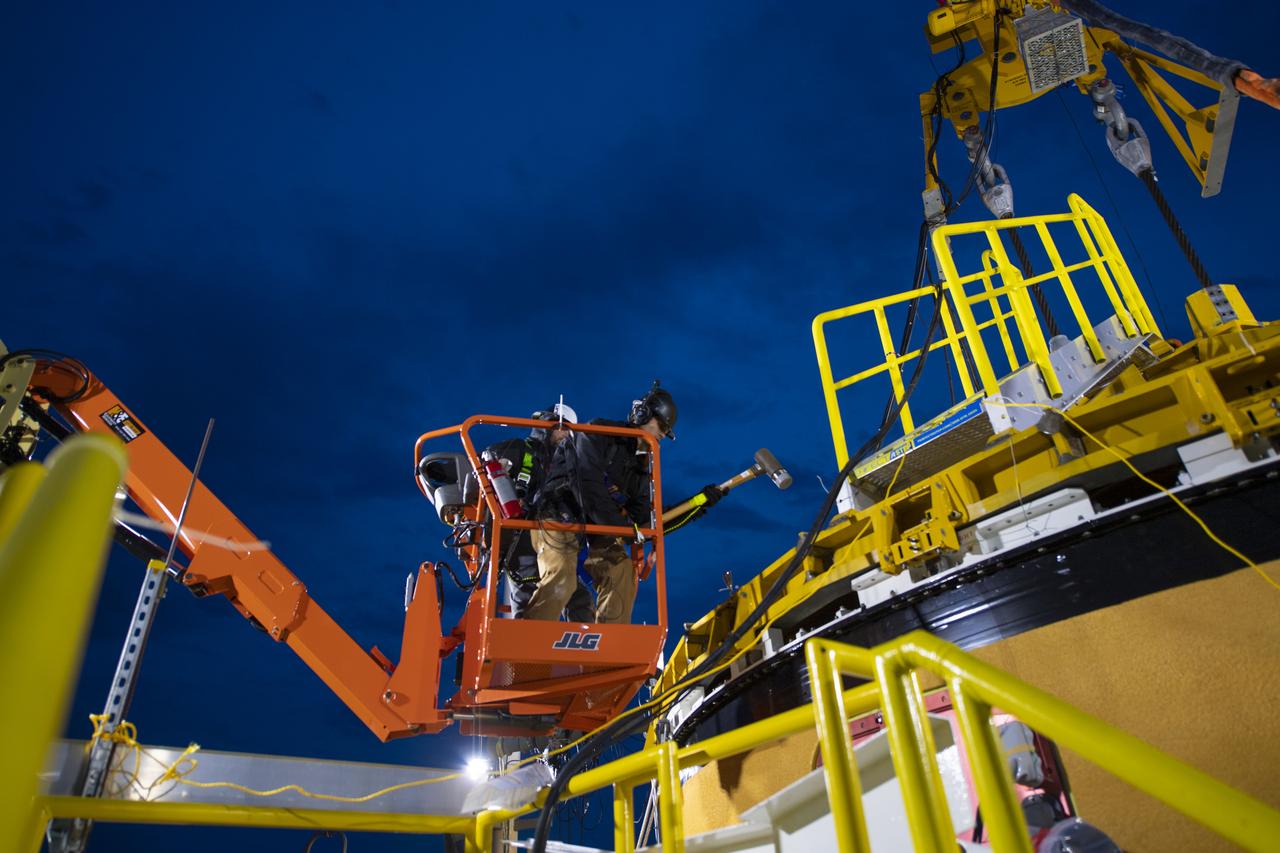

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
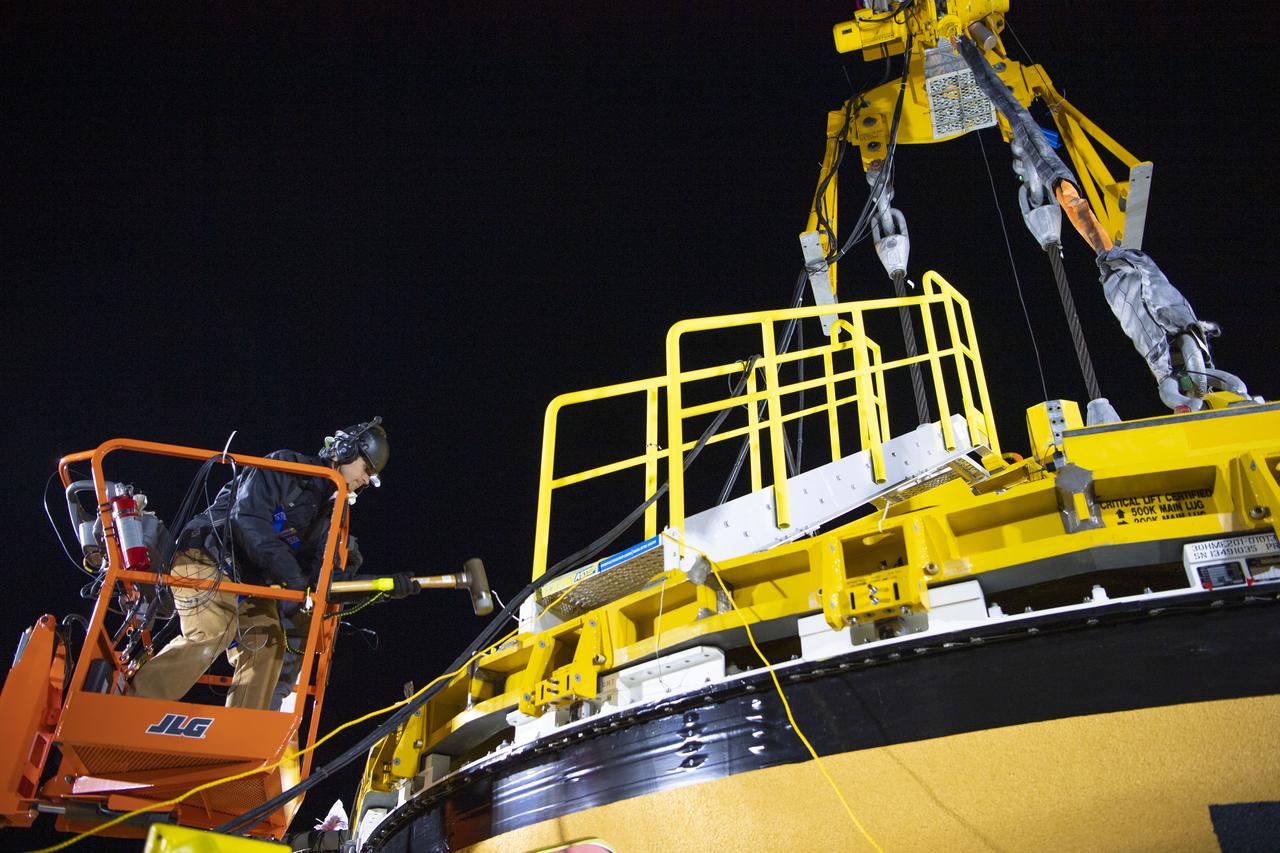

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
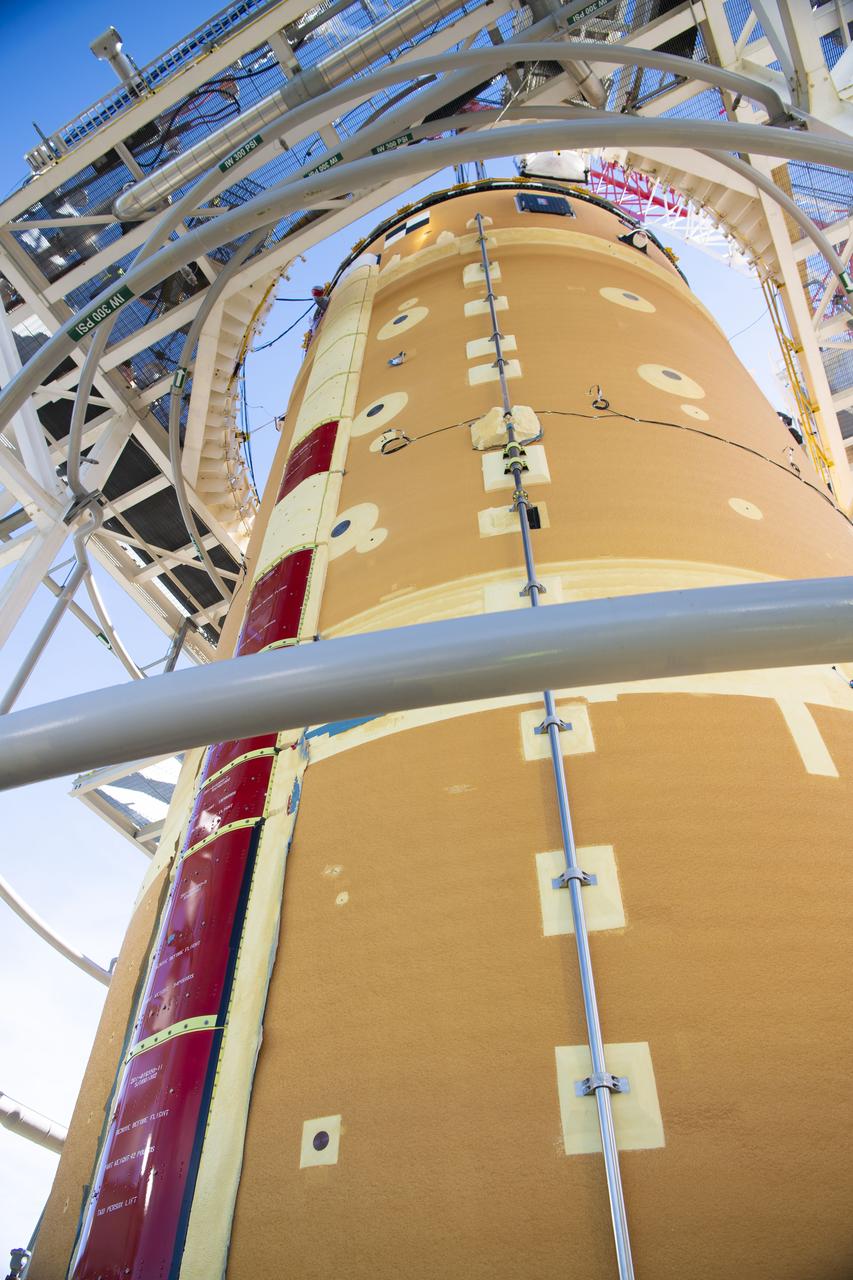

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
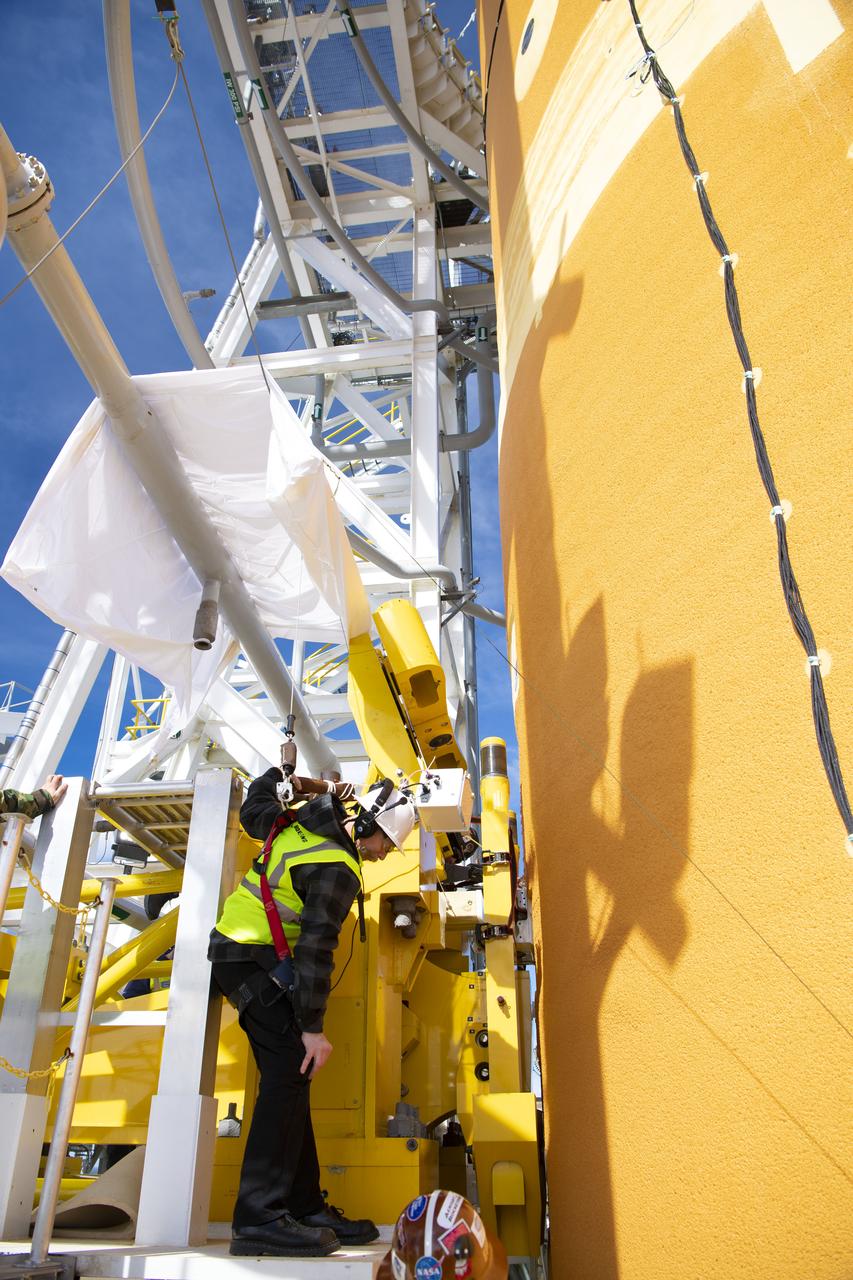

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
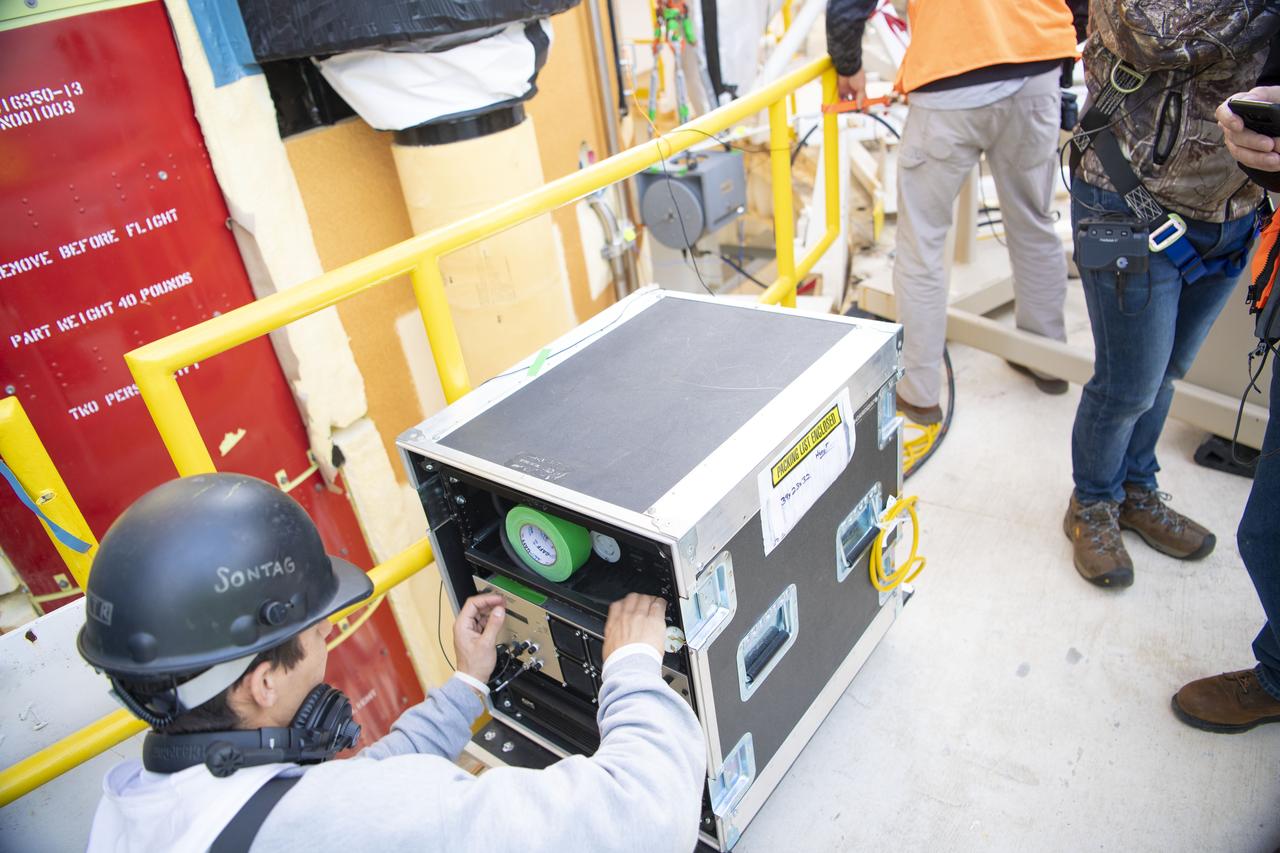

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
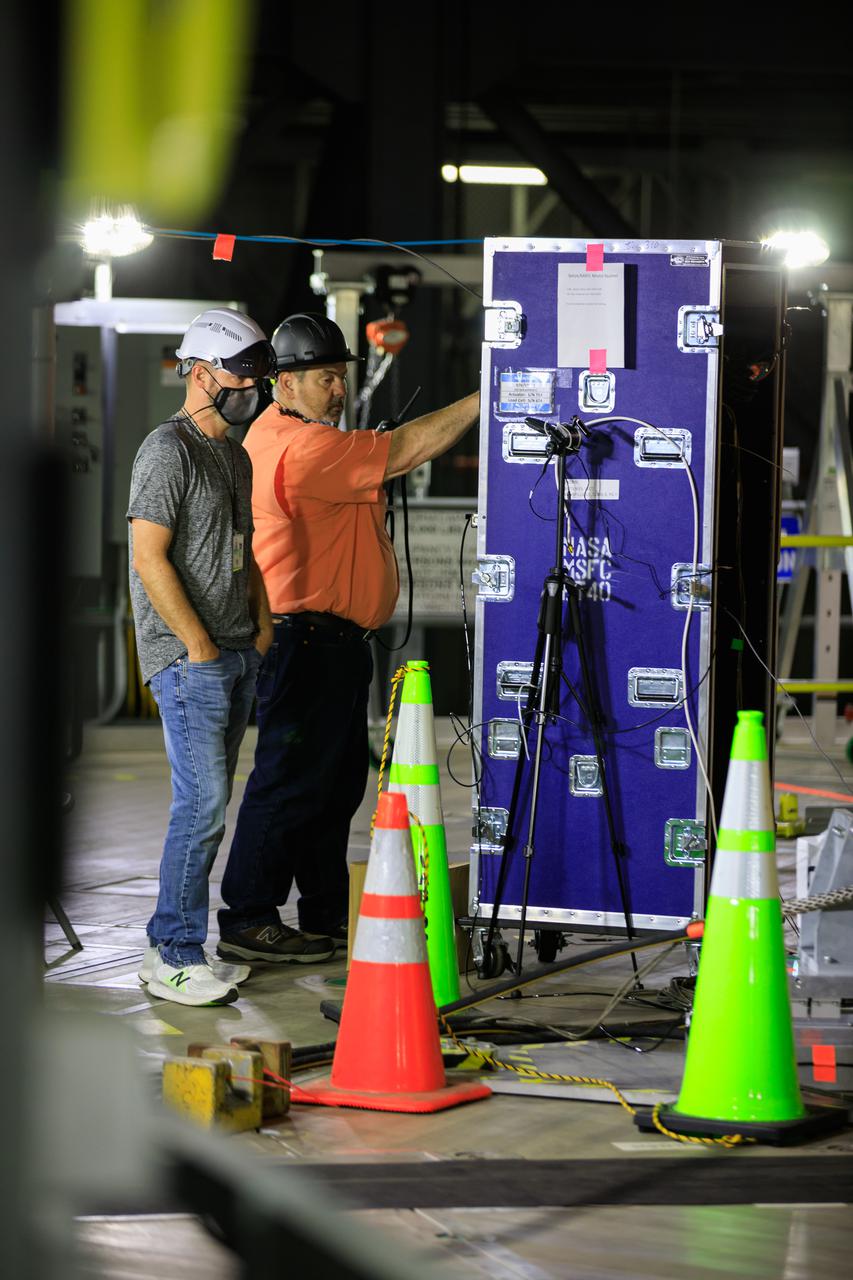

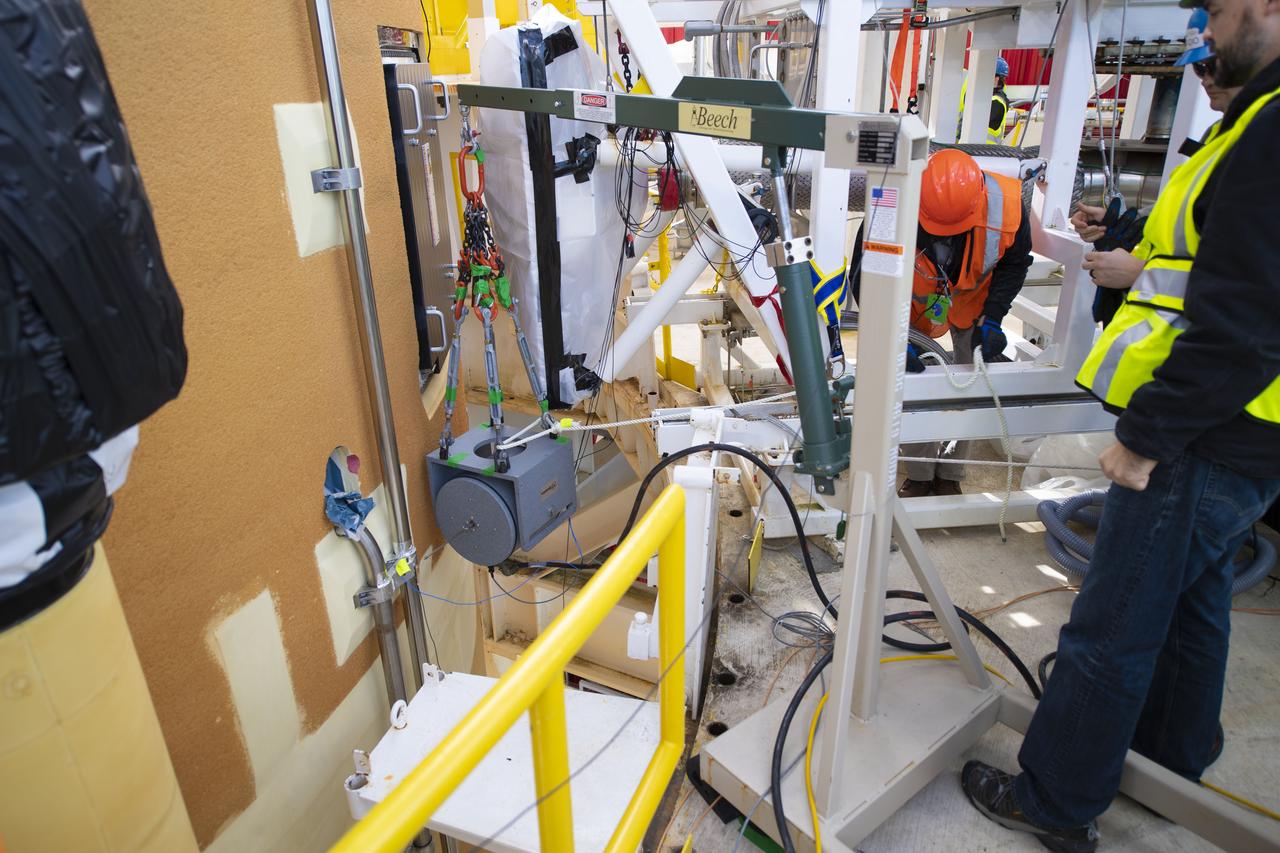
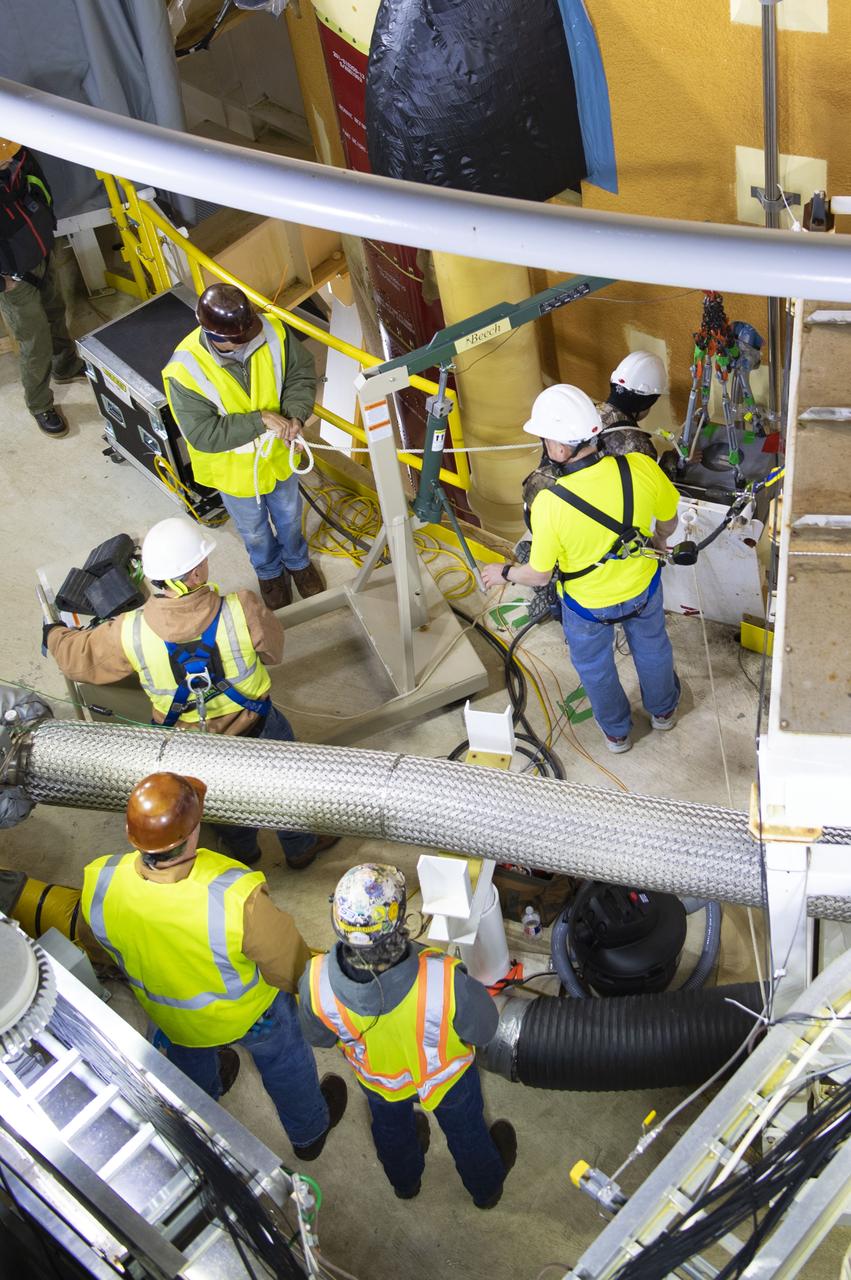
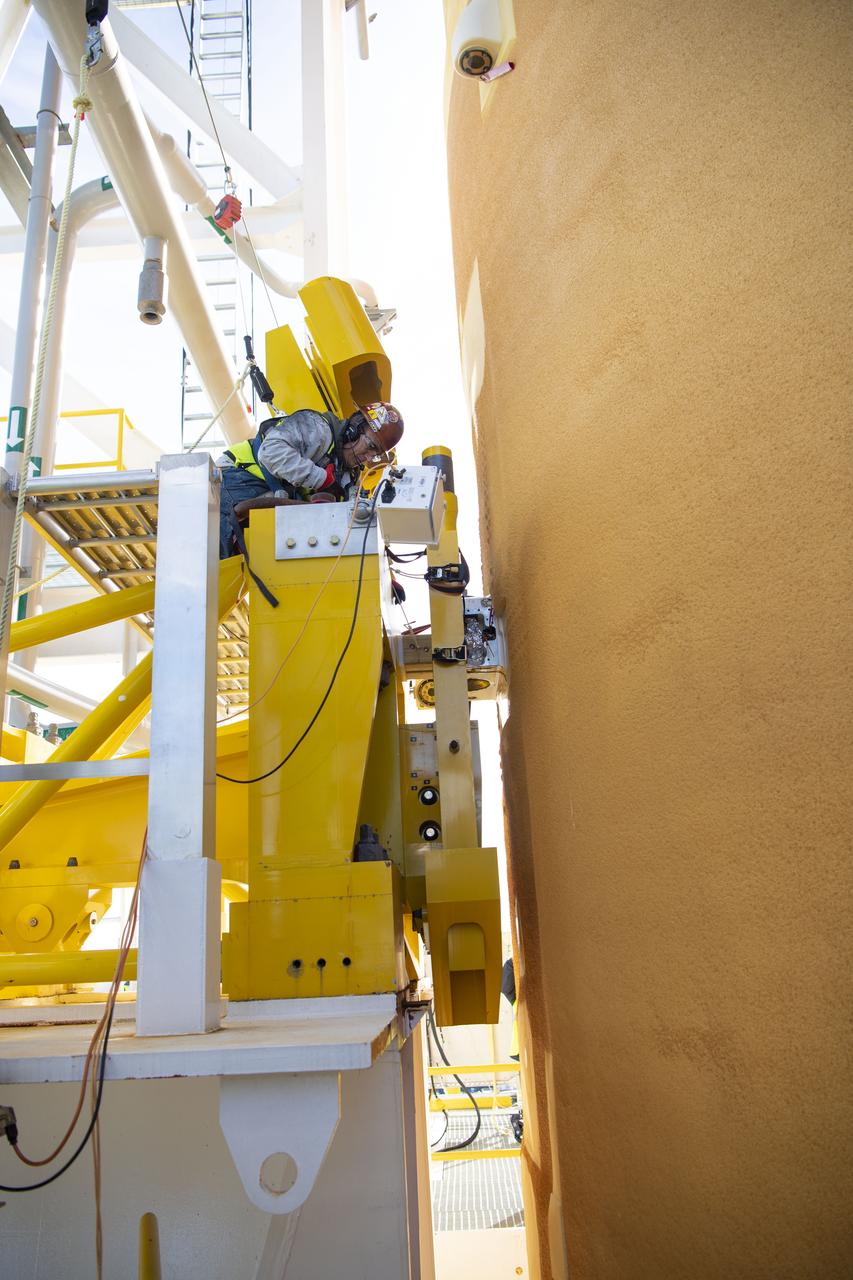
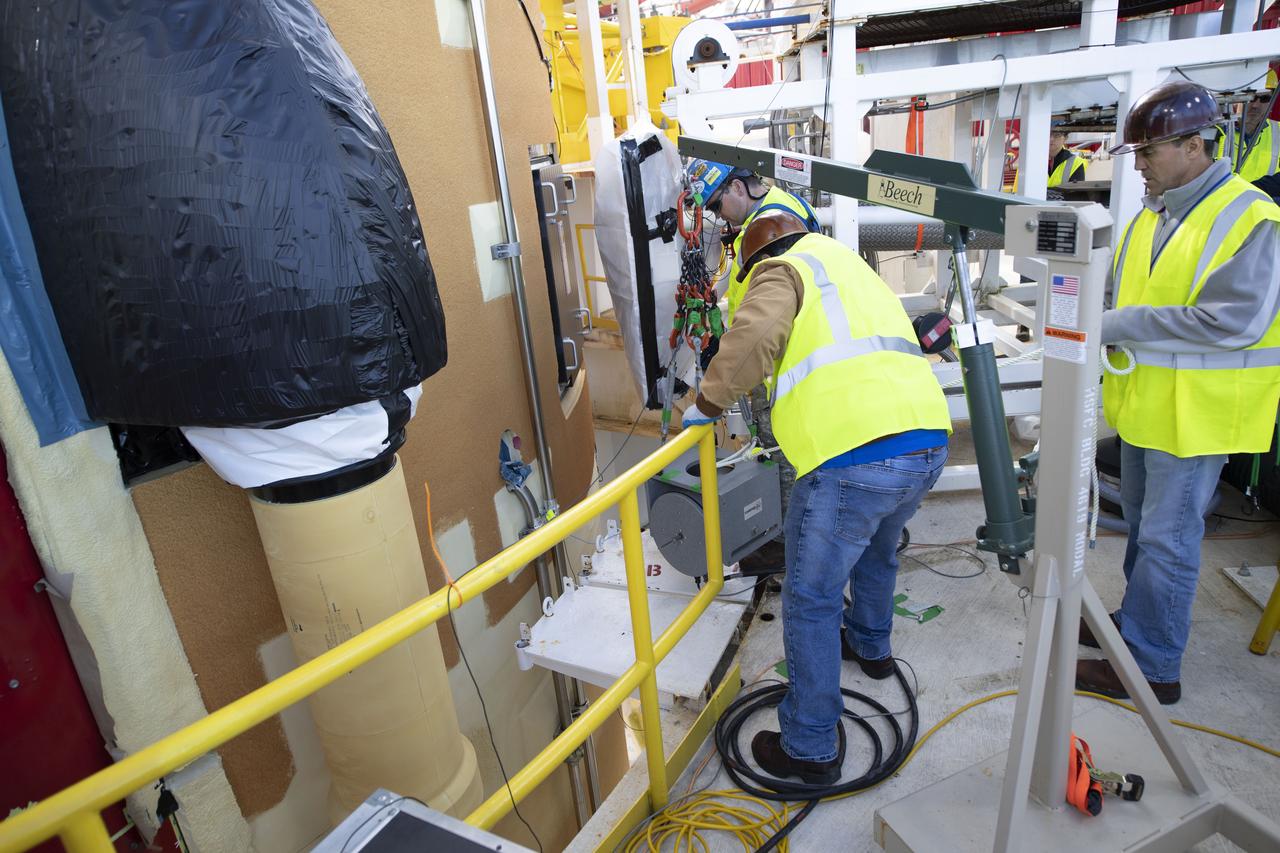
Artemis teams members perform the integrated modal test of the Space Launch System and mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 24, 2021. The tests will help determine the natural frequencies of the recently stacked rocket before launch of the Artemis I mission. The data also will be used to help steer the rocket during flight. To identify the rocket’s natural frequencies, the team placed about 300 sensors on it and the mobile launcher to detect, record, and transmit the information, along with hydraulic shakers attached to seven locations on the rocket. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In later missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
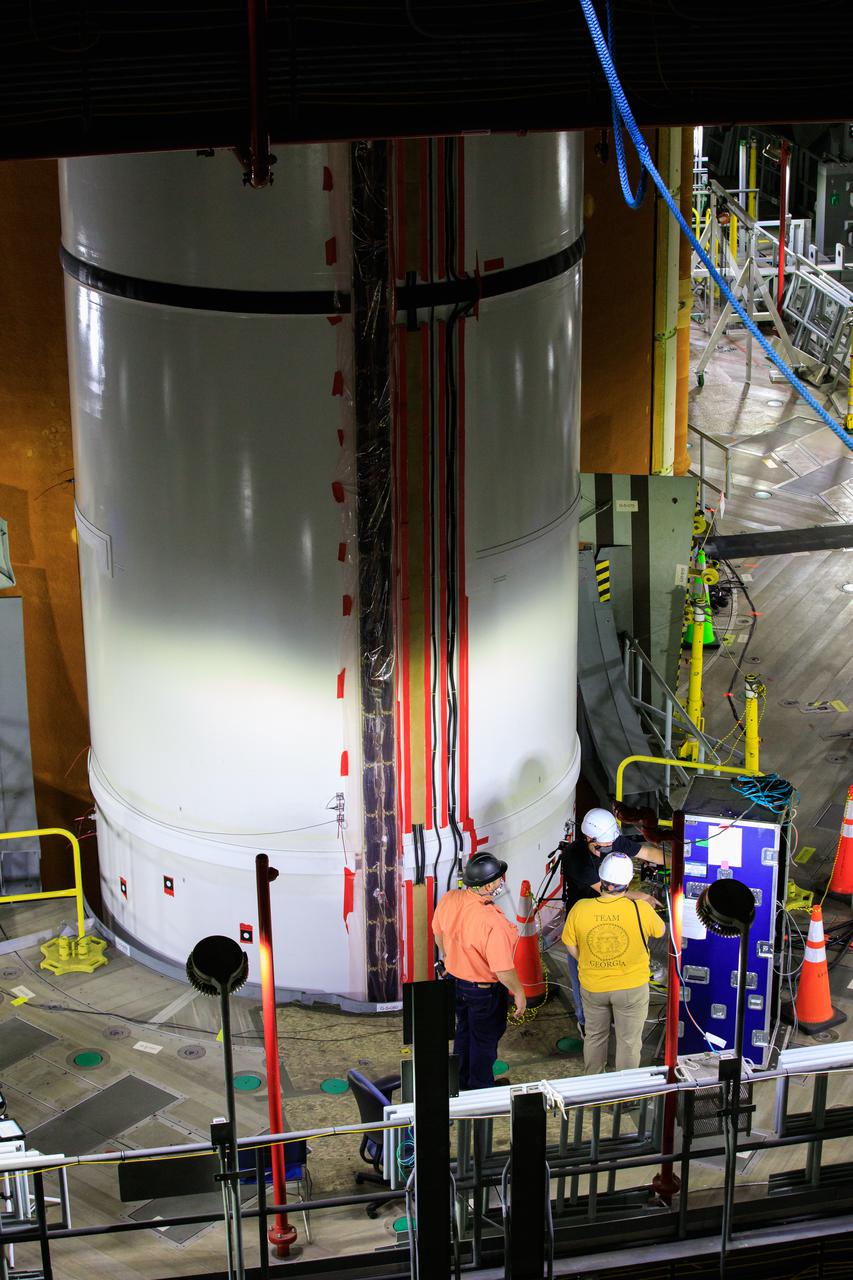

Artemis teams members perform the integrated modal test of the Space Launch System and mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 24, 2021. The tests will help determine the natural frequencies of the recently stacked rocket before launch of the Artemis I mission. The data also will be used to help steer the rocket during flight. To identify the rocket’s natural frequencies, the team placed about 300 sensors on it and the mobile launcher to detect, record, and transmit the information, along with hydraulic shakers attached to seven locations on the rocket. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In later missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
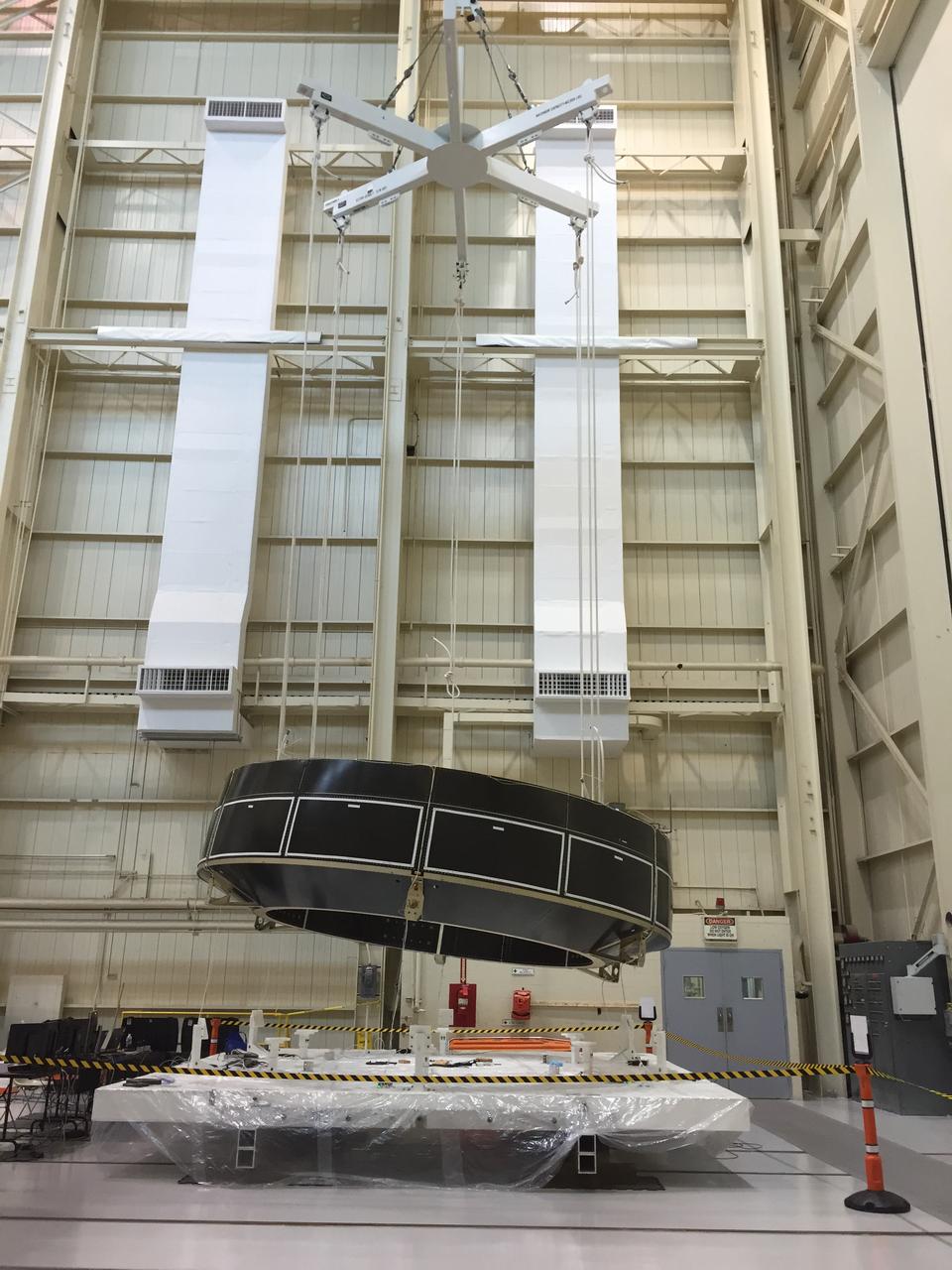

Engineers at the NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio, begin the first of a series of modal tests on an Orion service module structural test article provided by the European Space Agency on July 20, 2015. This test vibrates spacecraft structural elements at various frequencies to simulate how launch vibrations and acoustics will affect the vehicle. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
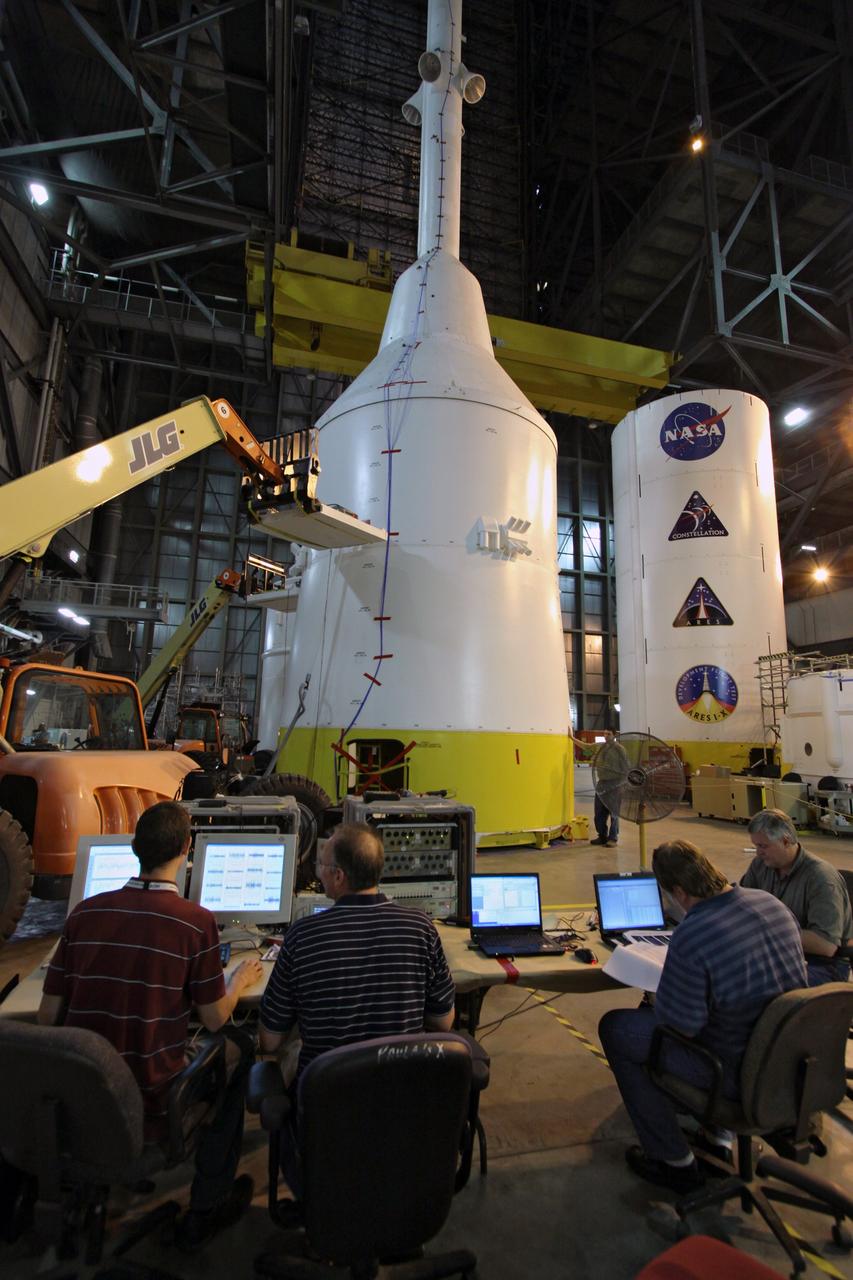

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians begin the modal survey testing on the top part of the Ares I-X (center) after sensors were placed on the stack. The top consists of the launch abort tower, crew module, service module and spacecraft adaptor. Shakers will impose random loads/vibrations to determine the flight test vehicle’s first several bending modes and the strategically located sensors throughout the stacks will measure the amount, acceleration and direction of movement. The purpose of the testing is to confirm that Ares I-X will behave as predicted as it lifts off the pad and powers through the initial stage of flight in a demonstration flight later this year. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
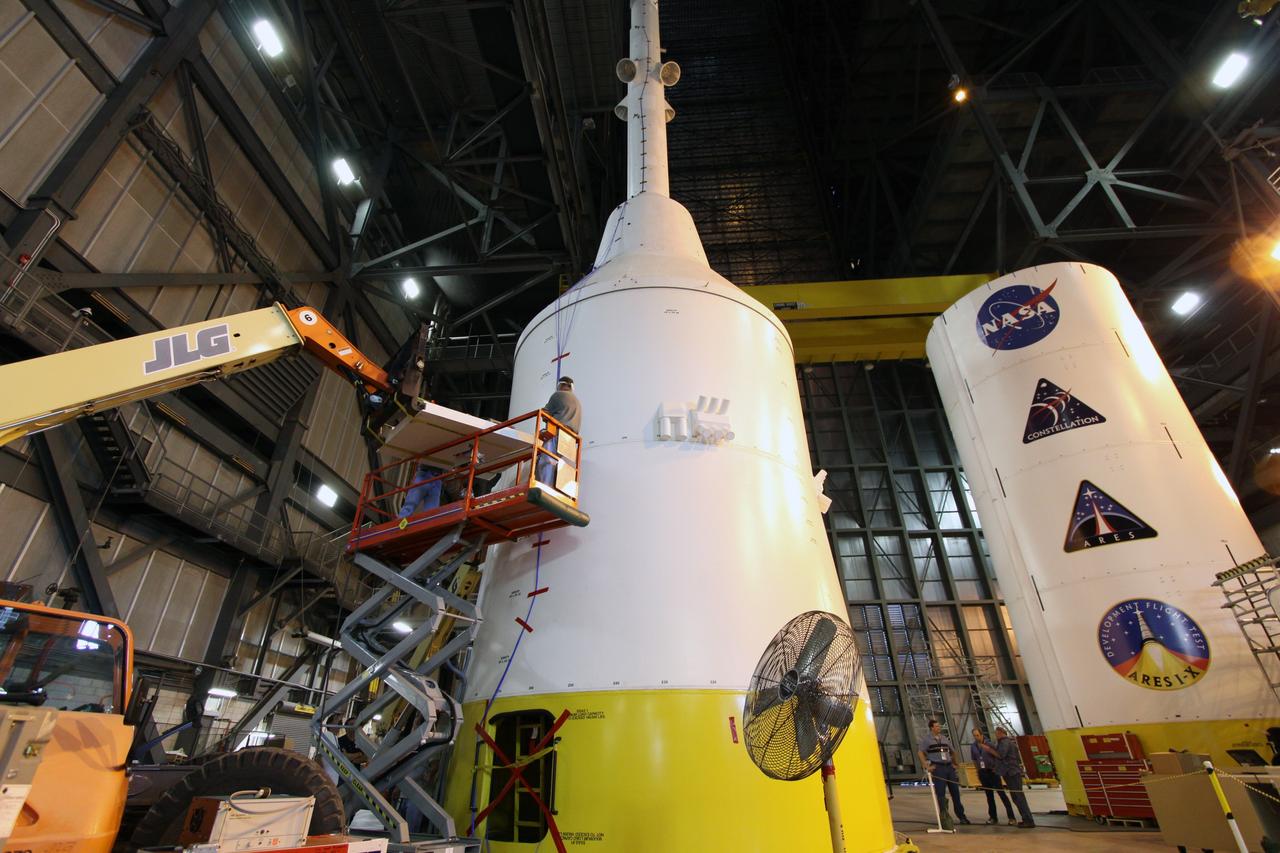

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians place sensors on the top part of the Ares I-X for modal survey testing. The top consists of the launch abort tower, crew module, service module and spacecraft adaptor. Shakers will impose random loads/vibrations to determine the flight test vehicle’s first several bending modes and the strategically located sensors throughout the stacks will measure the amount, acceleration and direction of movement. The purpose of the testing is to confirm that Ares I-X will behave as predicted as it lifts off the pad and powers through the initial stage of flight in a demonstration flight later this year. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
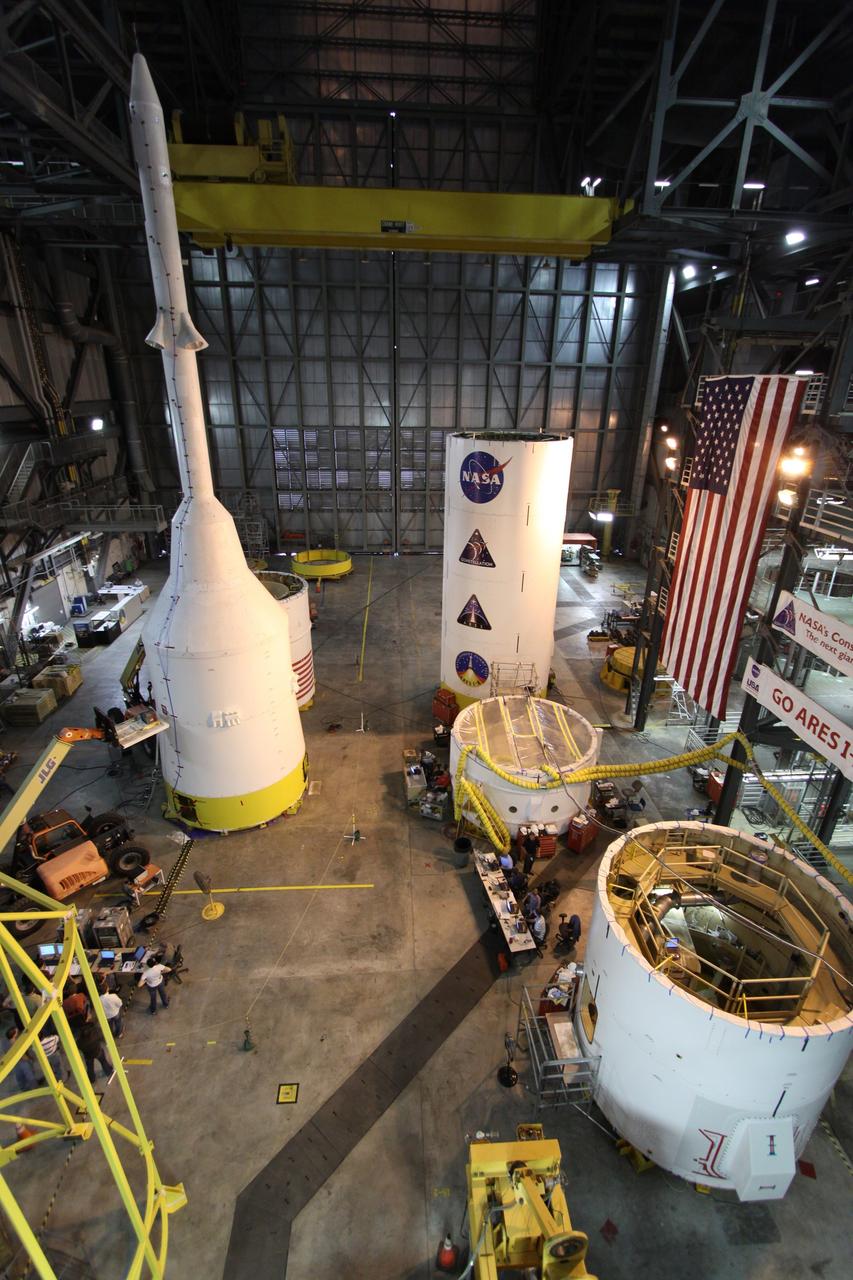

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians begin the modal survey testing on the top part of the Ares I-X (upper left) after sensors were placed on the stack. The top consists of the launch abort tower, crew module, service module and spacecraft adaptor. Other segments are stacked nearby. Shakers will impose random loads/vibrations to determine the flight test vehicle’s first several bending modes and the strategically located sensors throughout the stacks will measure the amount, acceleration and direction of movement. The purpose of the testing is to confirm that Ares I-X will behave as predicted as it lifts off the pad and powers through the initial stage of flight in a demonstration flight later this year. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
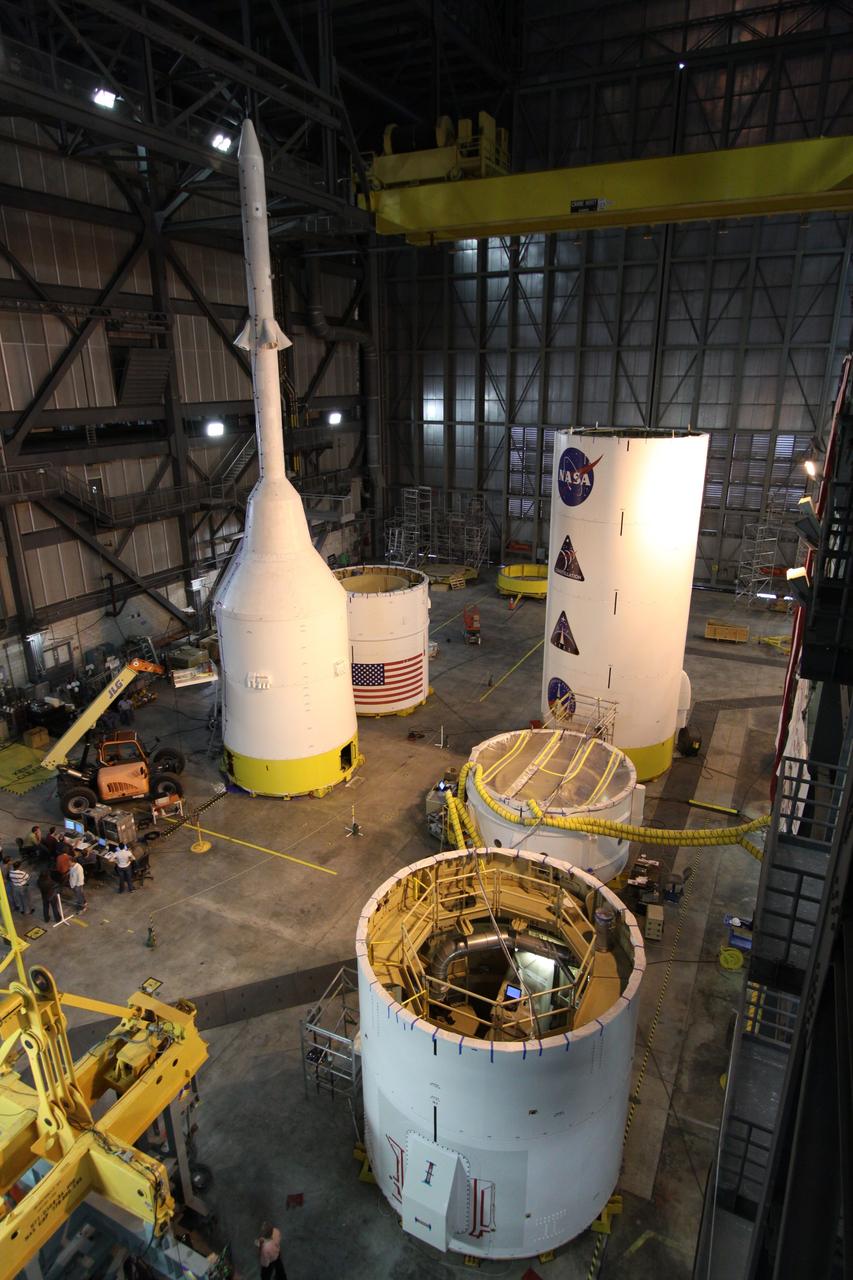

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the top part of the Ares I-X (upper left) undergoes modal survey testing after sensors were placed on the stack. The top consists of the launch abort tower, crew module, service module and spacecraft adaptor. Other segments are stacked nearby. Shakers will impose random loads/vibrations to determine the flight test vehicle’s first several bending modes and the strategically located sensors throughout the stacks will measure the amount, acceleration and direction of movement. The purpose of the testing is to confirm that Ares I-X will behave as predicted as it lifts off the pad and powers through the initial stage of flight in a demonstration flight later this year. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
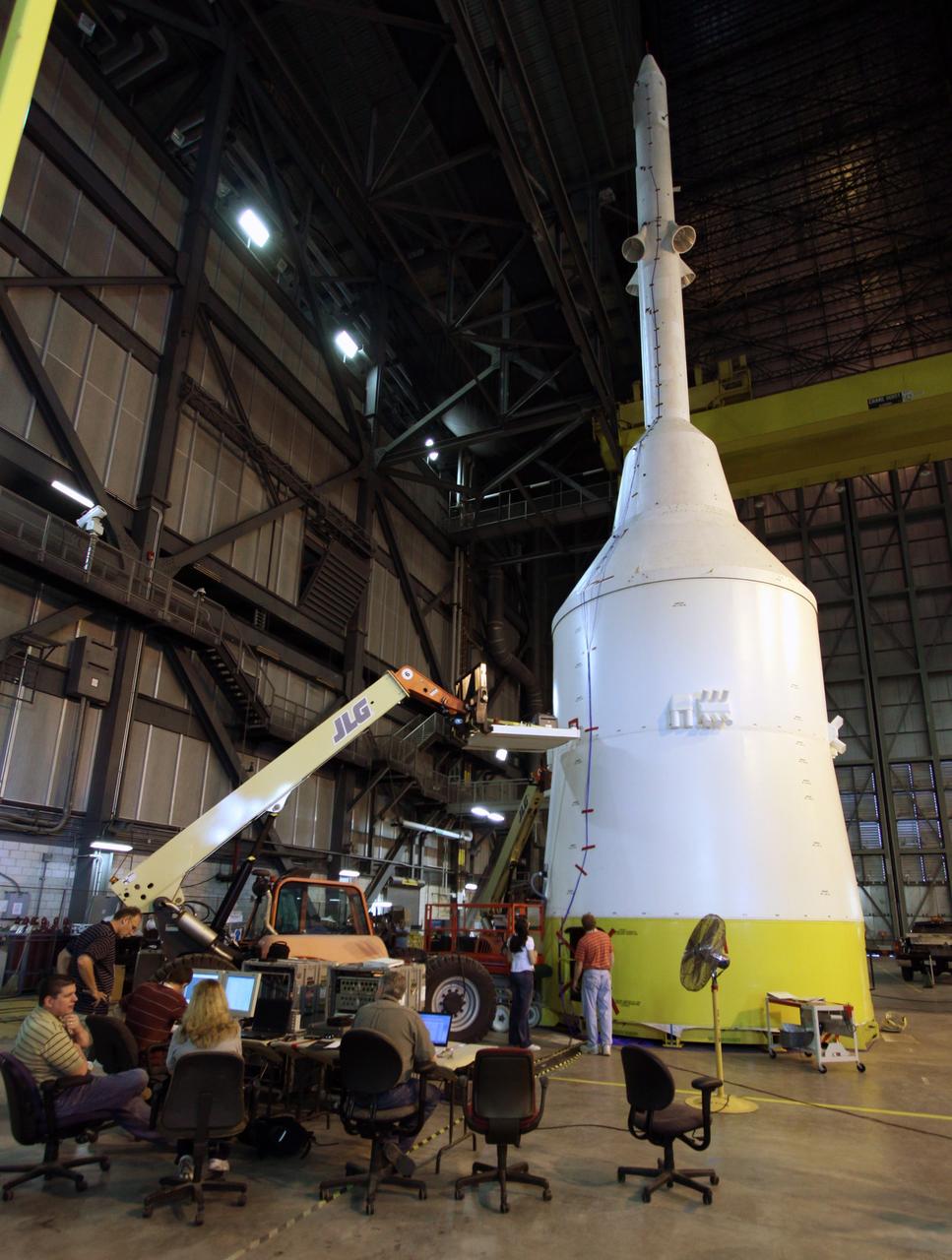

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians place sensors on the top part of the Ares I-X for modal survey testing. The top consists of the launch abort tower, crew module, service module and spacecraft adaptor. Shakers will impose random loads/vibrations to determine the flight test vehicle’s first several bending modes and the strategically located sensors throughout the stacks will measure the amount, acceleration and direction of movement. The purpose of the testing is to confirm that Ares I-X will behave as predicted as it lifts off the pad and powers through the initial stage of flight in a demonstration flight later this year. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
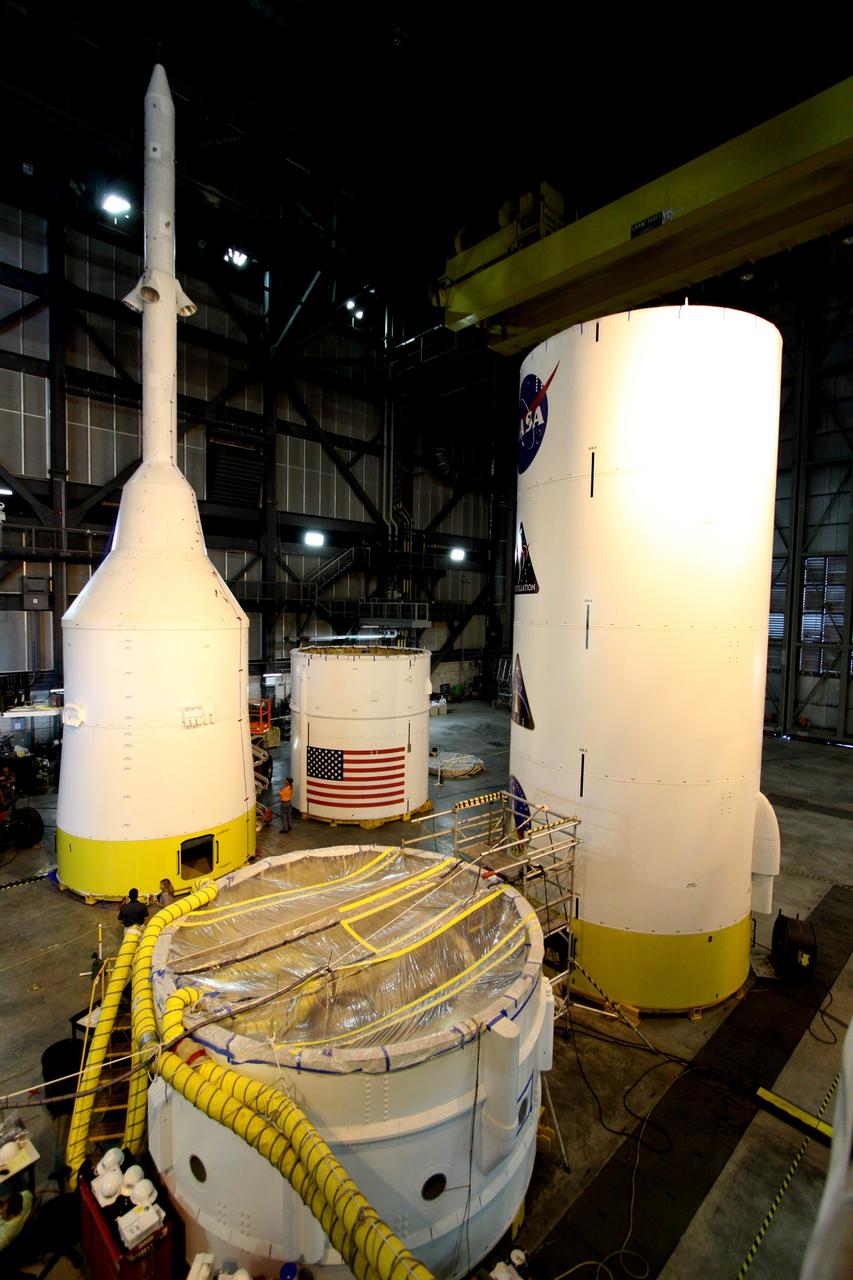

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the top part of the Ares I-X (upper left) is ready for modal survey testing. The top consists of the launch abort tower, crew module, service module and spacecraft adaptor. Other segments are stacked nearby. Shakers will impose random loads/vibrations to determine the flight test vehicle’s first several bending modes and the strategically located sensors throughout the stacks will measure the amount, acceleration and direction of movement. The purpose of the testing is to confirm that Ares I-X will behave as predicted as it lifts off the pad and powers through the initial stage of flight in a demonstration flight later this year. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

A view of one of the RS-25 engines on the Space Launch System rocket as seen from the zero deck of the mobile launcher inside the Vehicle Assembly Building on Aug. 16, 2021. Four RS-25 engines will fire for over eight minutes at liftoff of the Artemis I mission to help get the Orion spacecraft to orbit. Artemis I will be an uncrewed test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
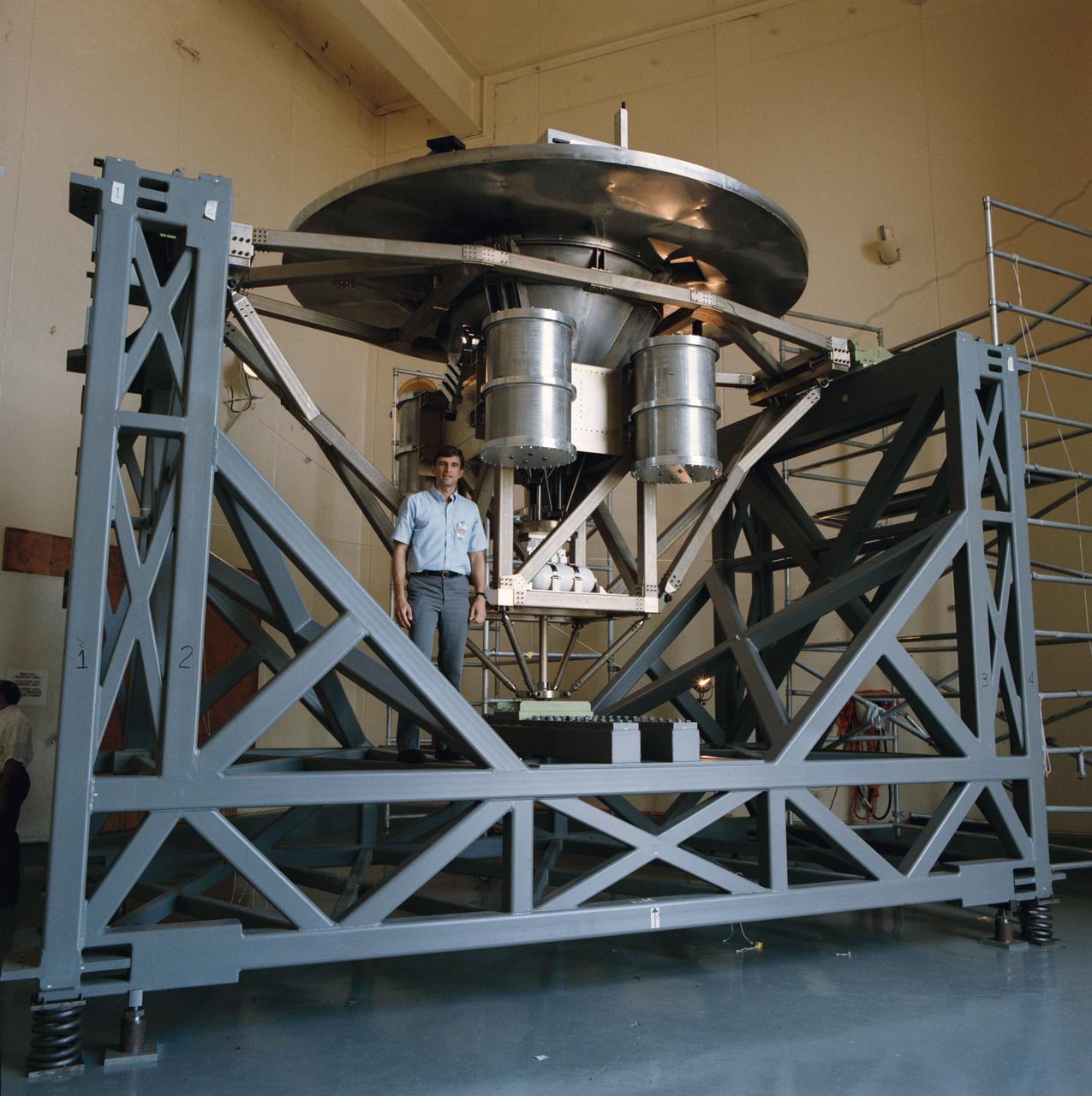

Astronaut Ronald M. Sega stands beside the University of Houston's Wake Shield Facility before it undergoes a Modal Survey Test in the Vibration and Acoustic Test Facility Building 49, prior to being flown on space shuttle mission STS-60.
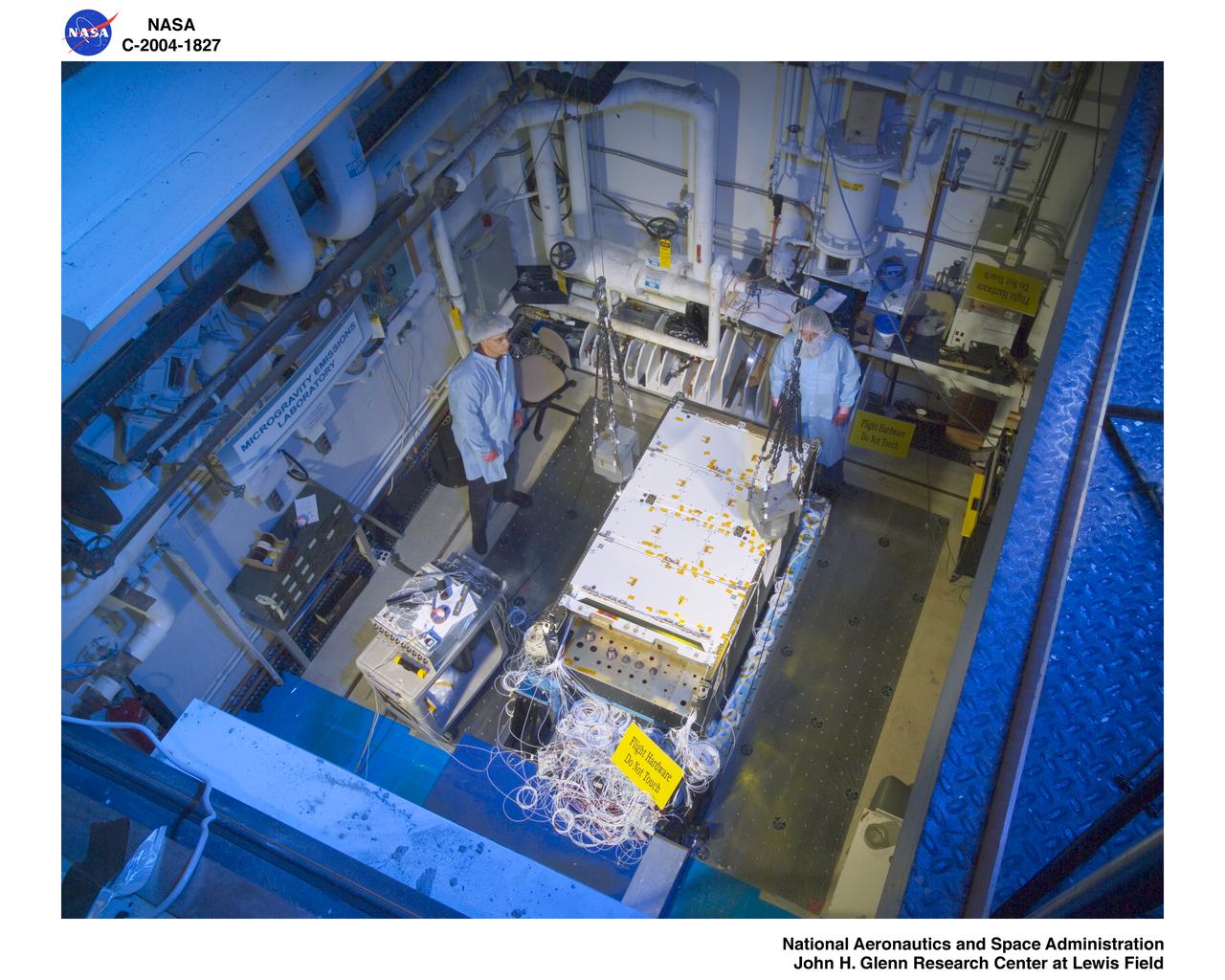

Fluids and Combustion Facility (FCF) Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) Ground Integration Unit (GIU) Modal Test in the Structural Dynamics Laboratory at NASA Glenn
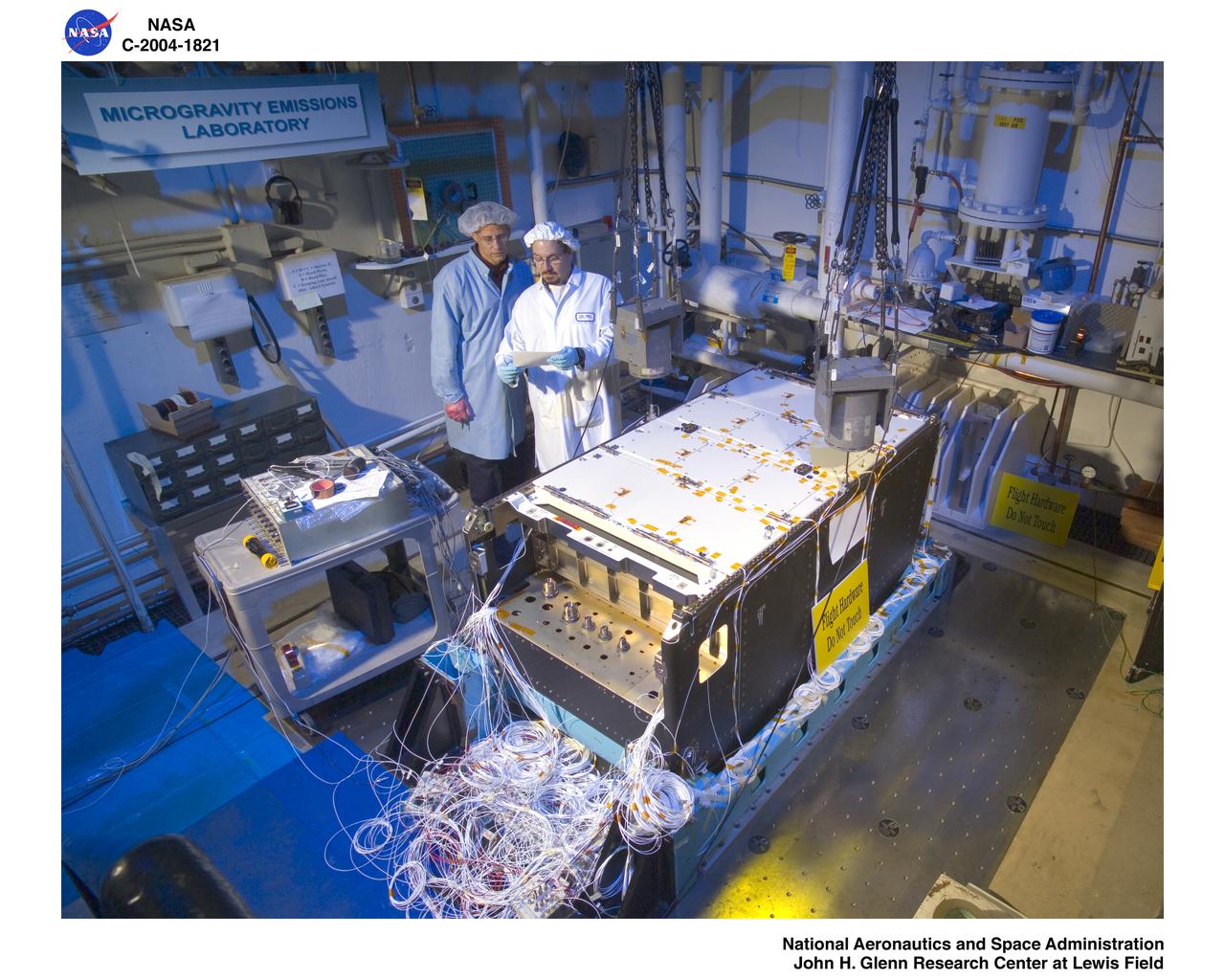

Fluids and Combustion Facility (FCF) Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) Ground Integration Unit (GIU) Modal Test in the Structural Dynamics Laboratory at NASA Glenn
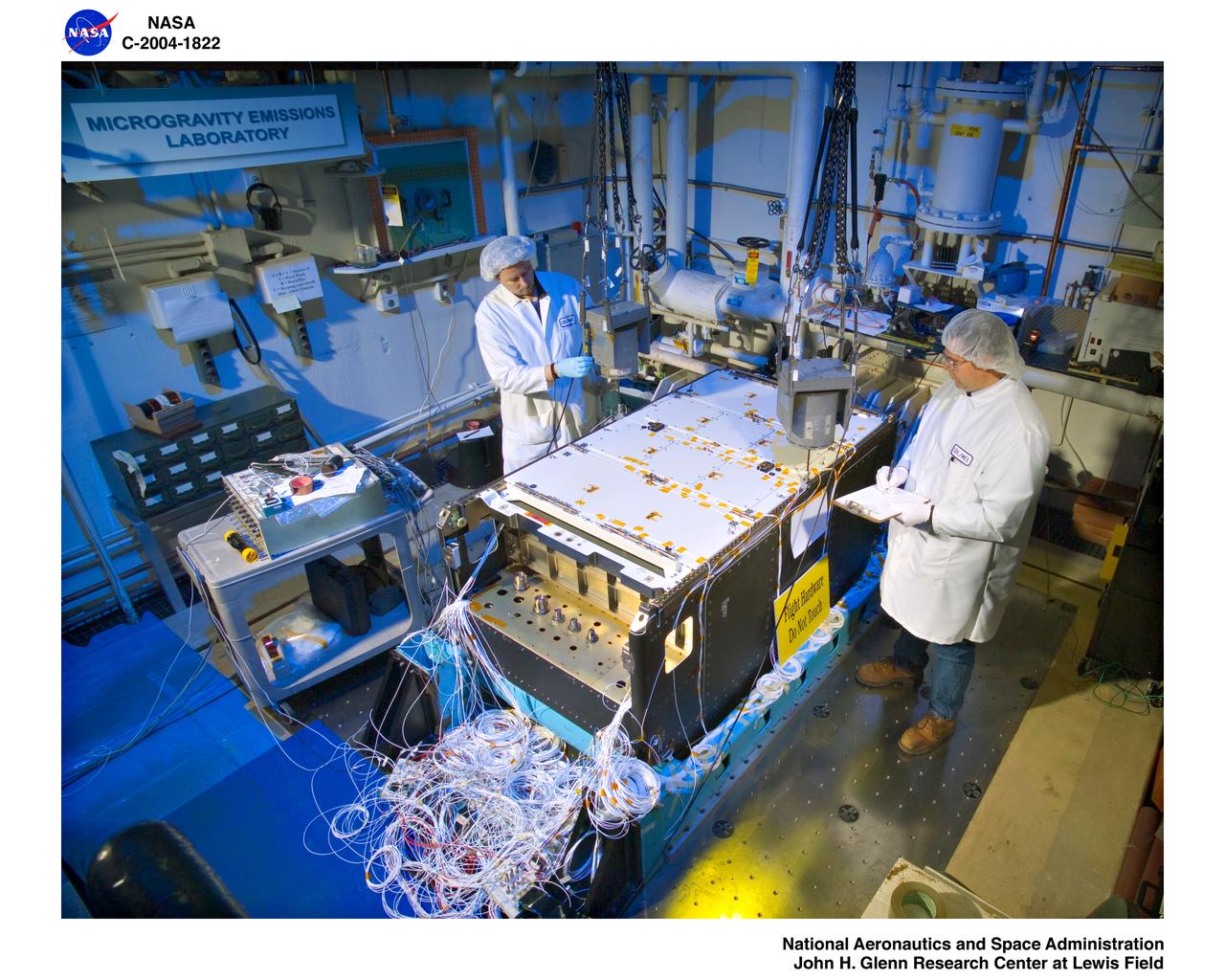

Fluids and Combustion Facility (FCF) Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) Ground Integration Unit (GIU) Modal Test in the Structural Dynamics Laboratory at NASA Glenn
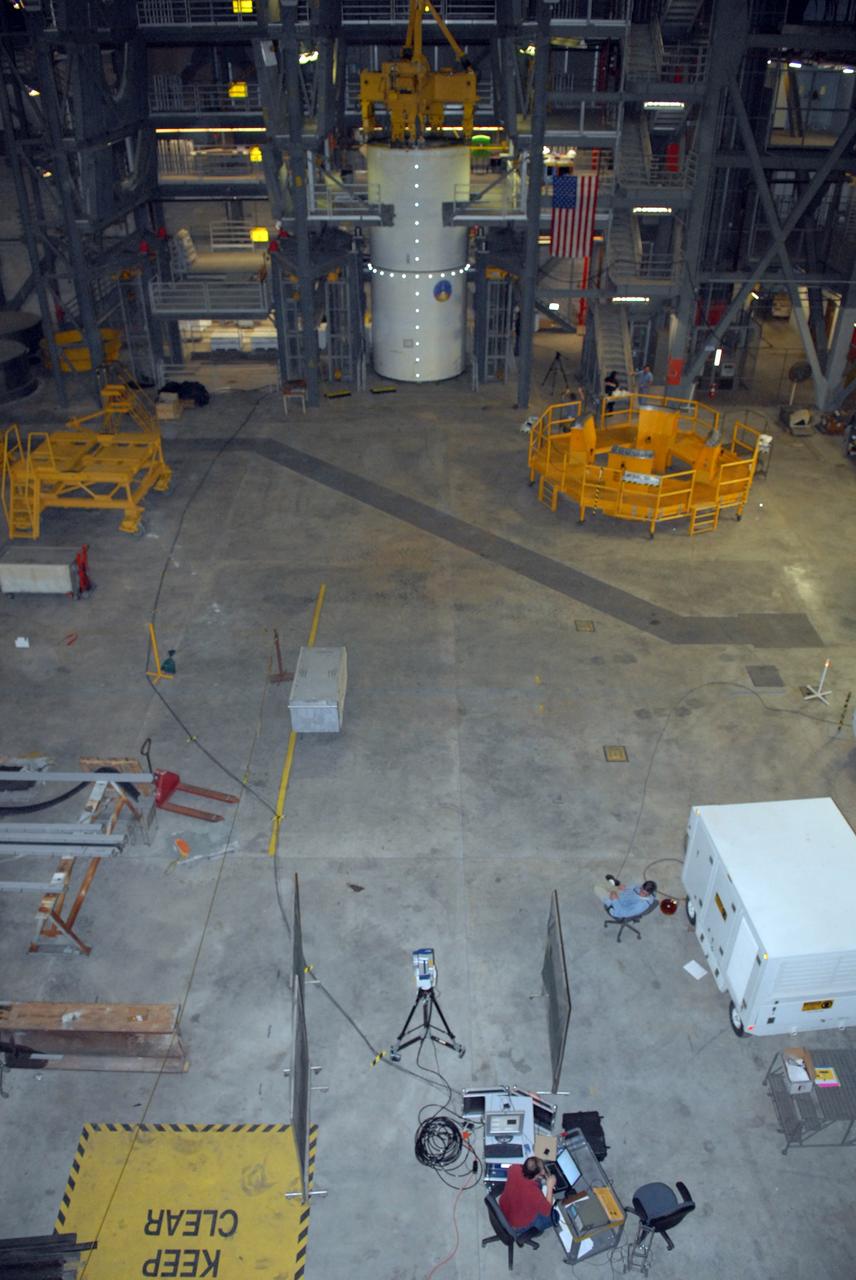

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Vibration and laser testing is being conducted on Ares I-X segments at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. This is an overall view of the modal testing setup using the Inert Solid Rocket Motor Segment and Laser Vibrometer in high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly building. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
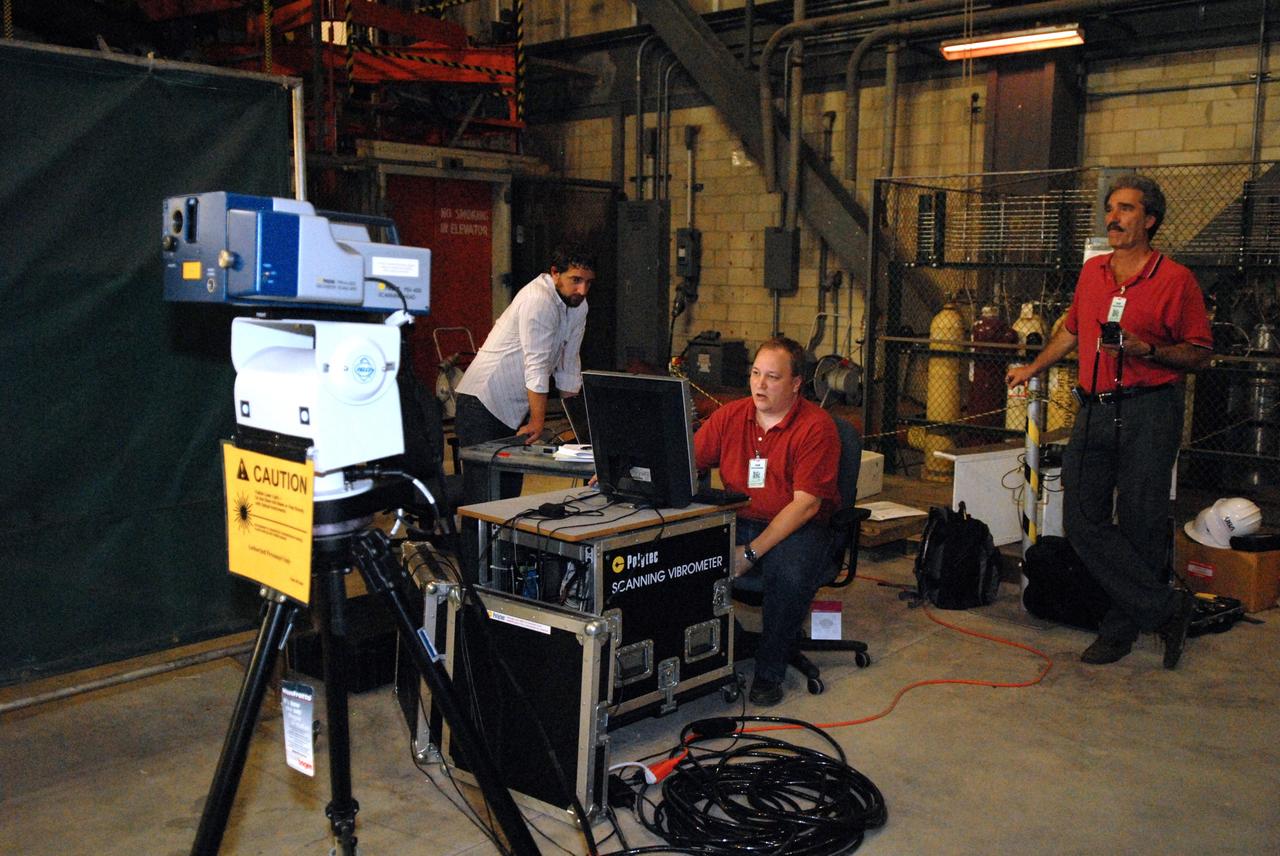

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Vibration and laser testing is being conducted on Ares I-X segments at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Team members (from left) Ryan Tuttle, with Aerospace Corporation, Jim Gaspar, with NASA's Langley Research Center, and Vaughn Behun, with Langley ATK, execute modal testing using a Laser Vibrometer to collect deflection data from the test article. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
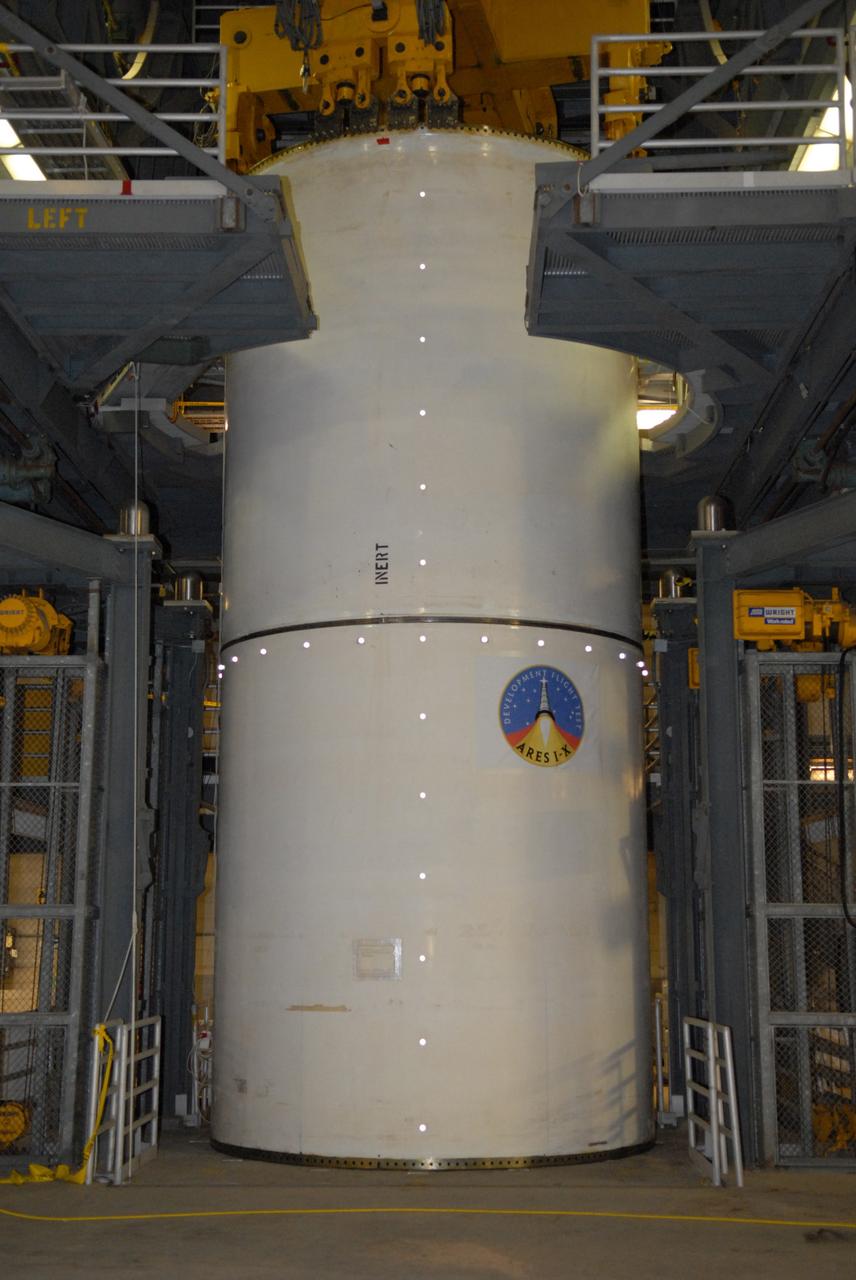

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Vibration and laser testing is being conducted on Ares I-X segments at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Here, the Inert Solid Rocket Motor Segment is configured with targets both vertically and horizontally in attempts to validate the predicted “Shell Modes” during the actual Modal Testing. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
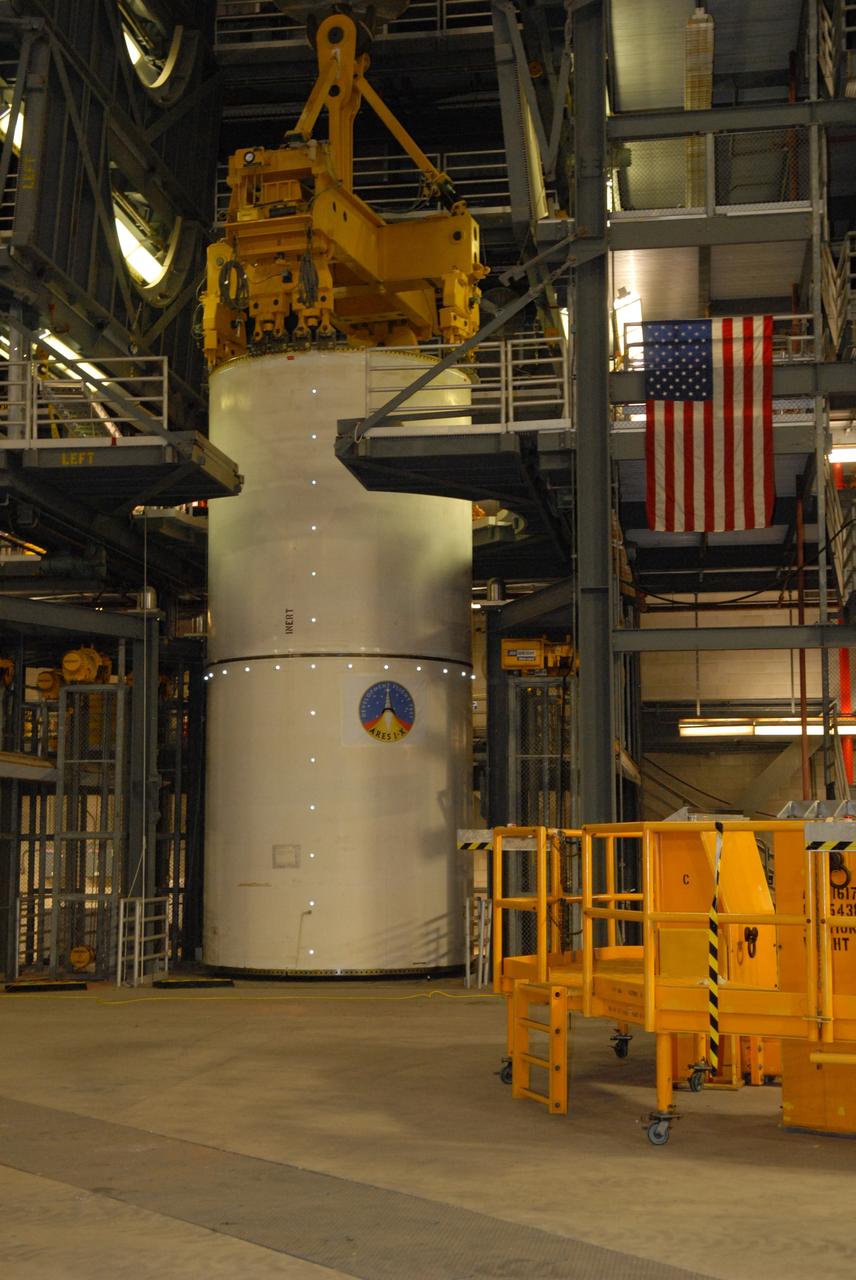

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Vibration and laser testing is being conducted on Ares I-X segments at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Here, actual modal testing is being performed on the Inert Solid Rocket Motor Segment while suspended from the 250-ton overhead crane in the Vehicle Assembly Building. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Vibration and laser testing is being conducted on Ares I-X segments at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Here, is a closeup of a special Ares I-X Logo, supplied by Jon Cowart of NASA Constellation, that the Inert Solid Rocket Motor Segment has received for the Modal Test. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
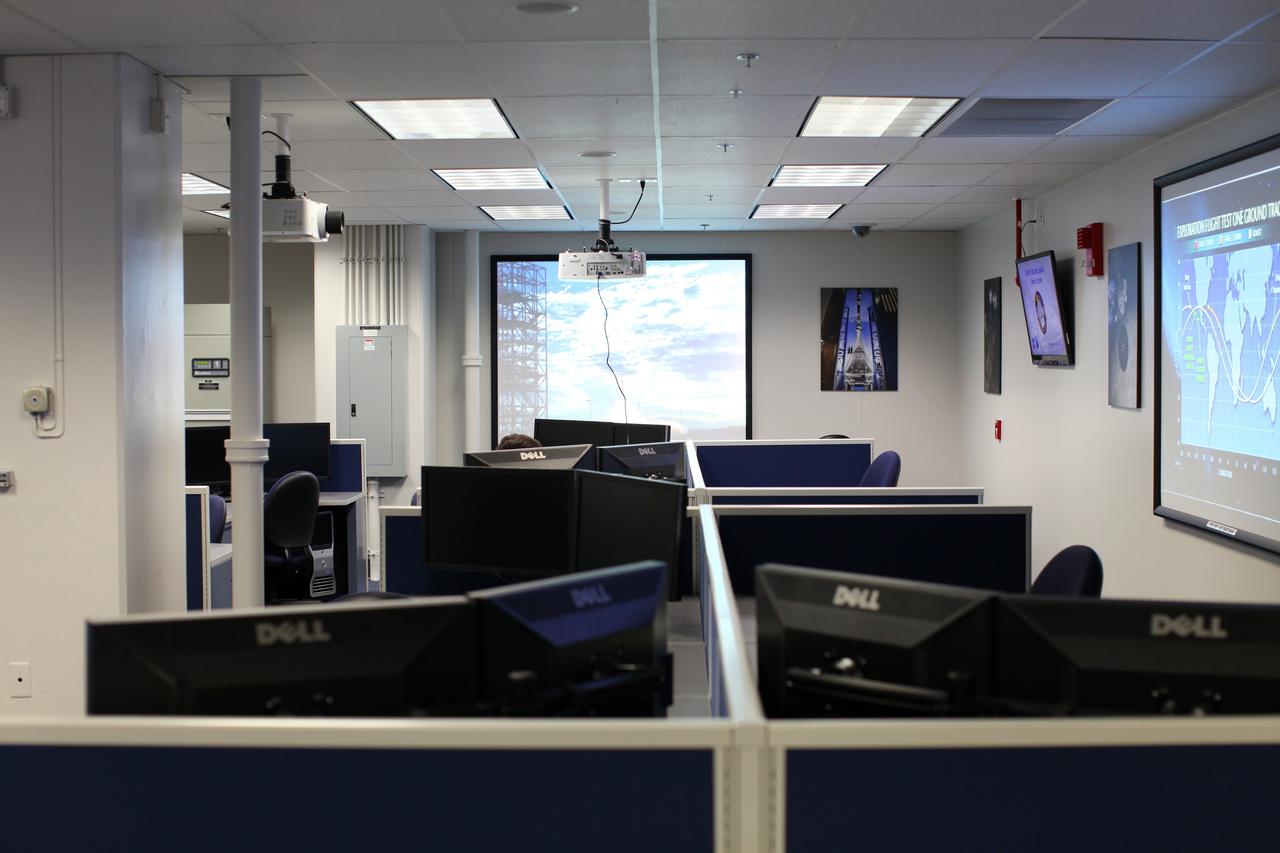

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, media tour the new Orion Test and Launch Control Center. During a tour of the facility, media representatives viewed Orion, several processing stations, and the Orion Test and Launch Control Center. The ground test vehicle will remain at Kennedy for acoustic and modal testing. The heat shield on the bottom of the module will be removed and replaced with a more flight-like heat shield that was built by Lockheed Martin in Denver and will be shipped to Kennedy for installation. The test vehicle will then be in its vehicle configuration for the splashdown test at Langley as NASA prepares for Exploration Flight Test-1. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
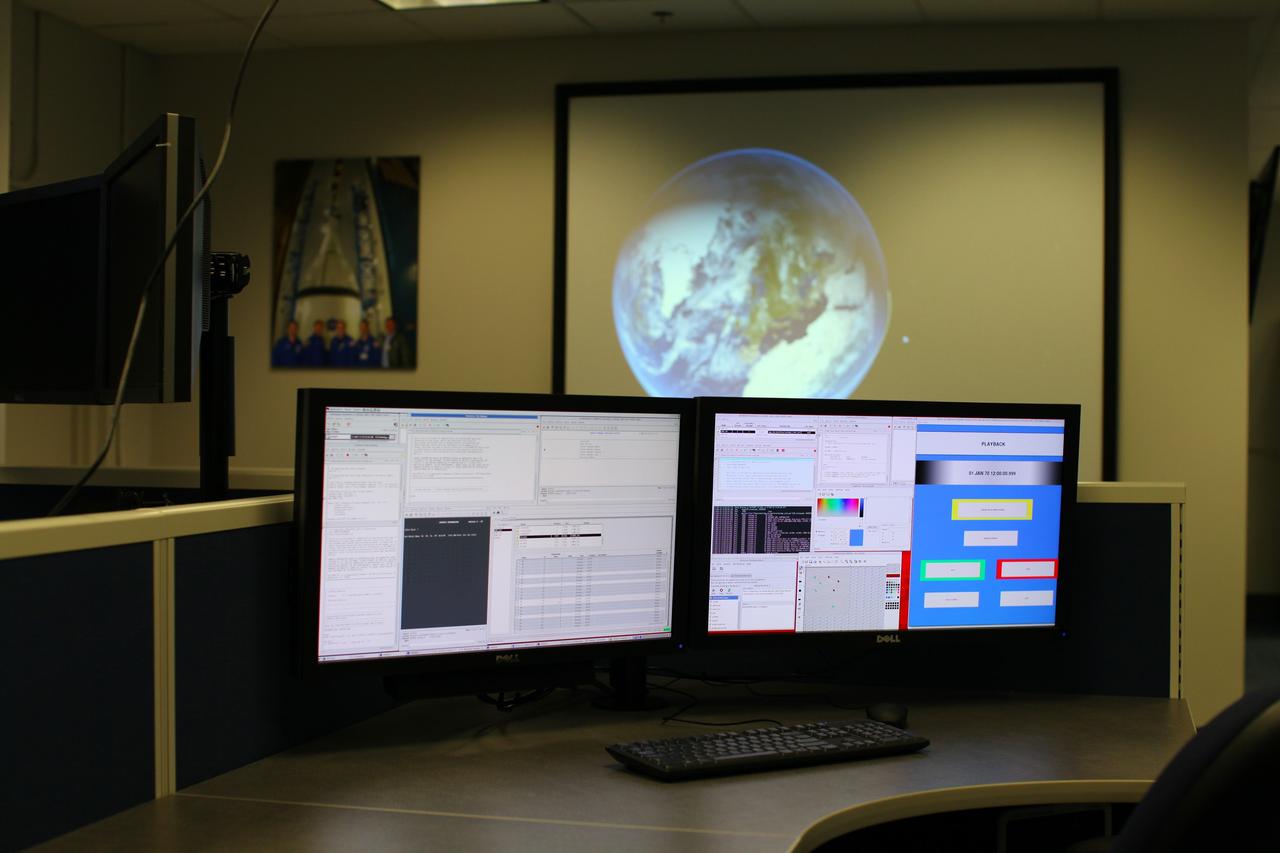
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, media tour the new Orion Test and Launch Control Center. During a tour of the facility, media representatives viewed Orion, several processing stations, and the Orion Test and Launch Control Center. The ground test vehicle will remain at Kennedy for acoustic and modal testing. The heat shield on the bottom of the module will be removed and replaced with a more flight-like heat shield that was built by Lockheed Martin in Denver and will be shipped to Kennedy for installation. The test vehicle will then be in its vehicle configuration for the splashdown test at Langley as NASA prepares for Exploration Flight Test-1. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, media tour the new Orion Test and Launch Control Center. During a tour of the facility, media representatives viewed Orion, several processing stations, and the Orion Test and Launch Control Center. The ground test vehicle will remain at Kennedy for acoustic and modal testing. The heat shield on the bottom of the module will be removed and replaced with a more flight-like heat shield that was built by Lockheed Martin in Denver and will be shipped to Kennedy for installation. The test vehicle will then be in its vehicle configuration for the splashdown test at Langley as NASA prepares for Exploration Flight Test-1. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine and NASA astronaut Raja Chari speak with workers involved modal testing of the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at the B-2 Test Stand,x3 Monday, Feb. 10, 2020, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Over the coming months, the first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket will be undergoing a series of integrated Green Run tests prior to its maiden flight. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
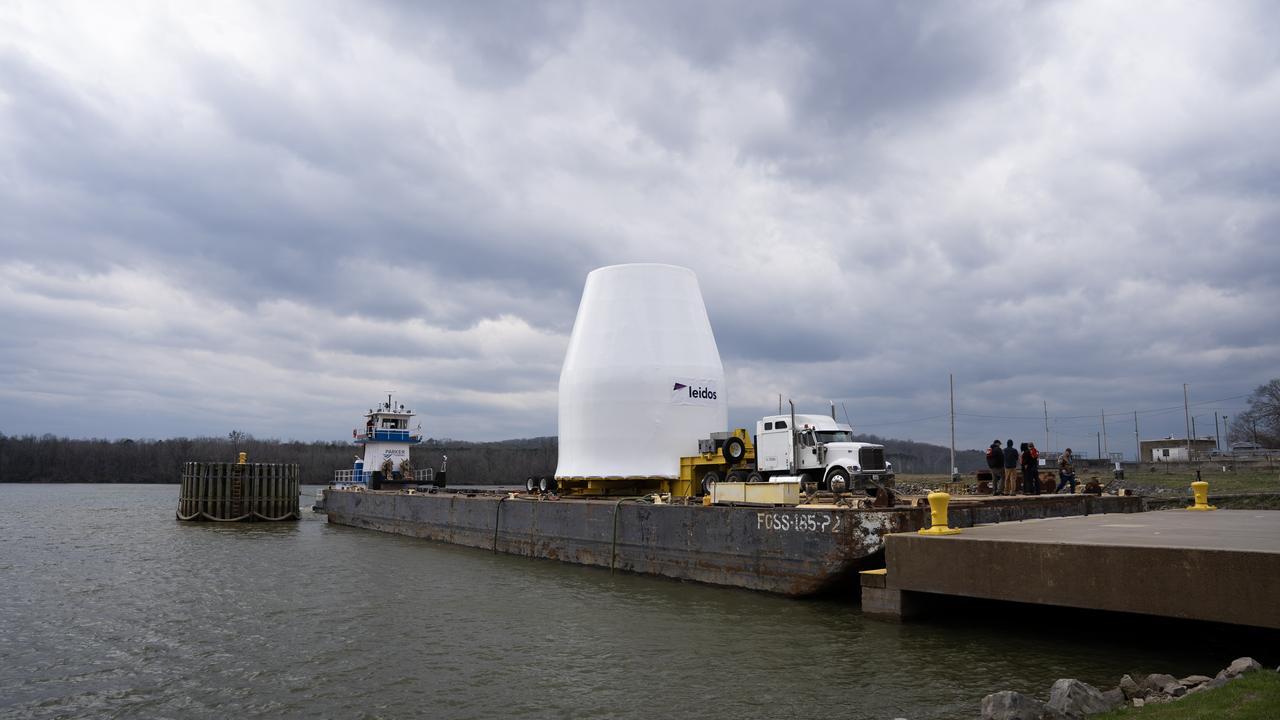

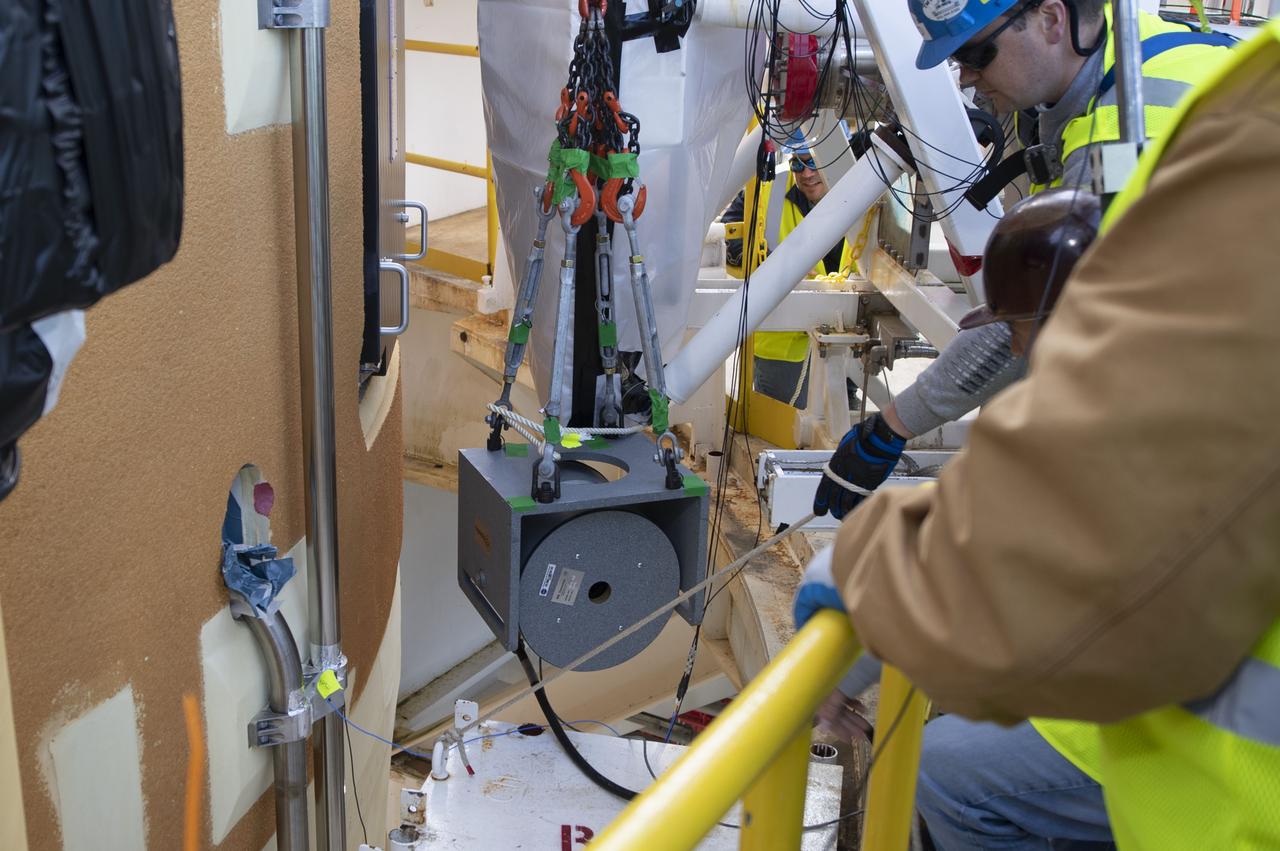
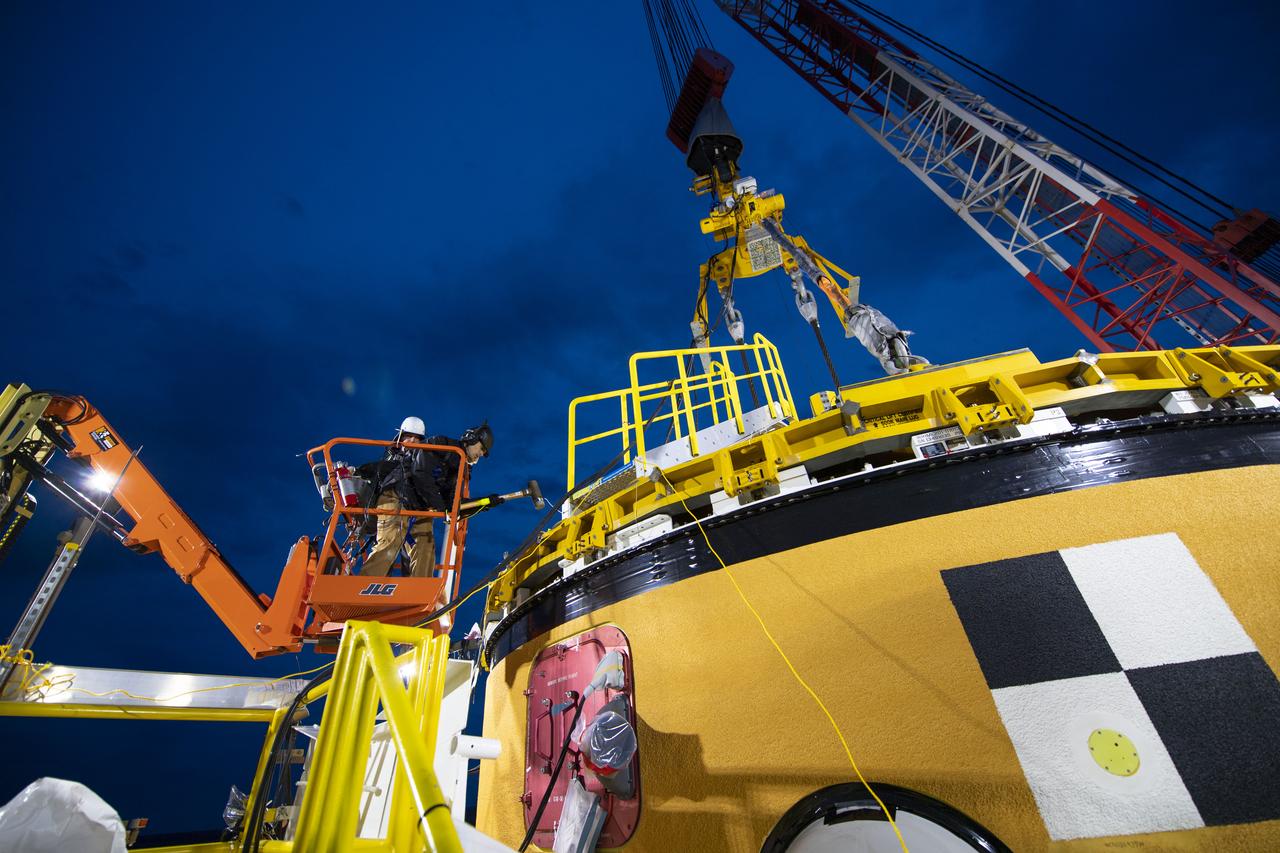
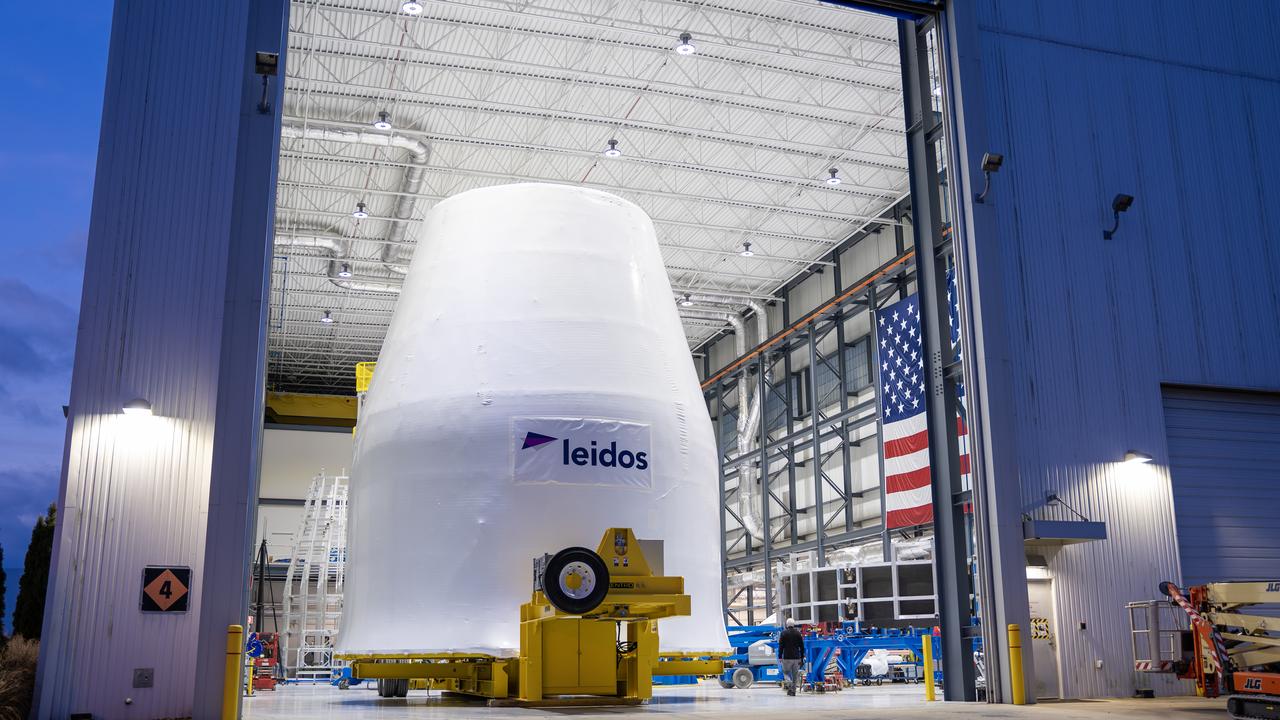
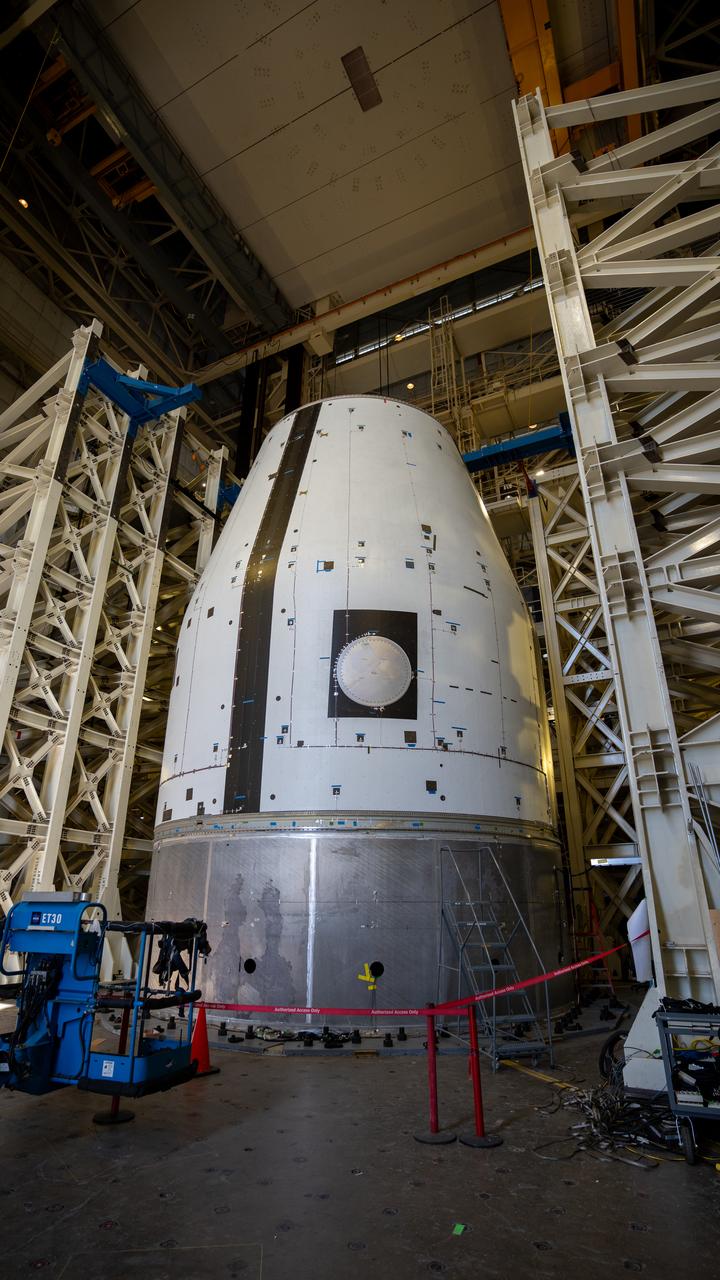
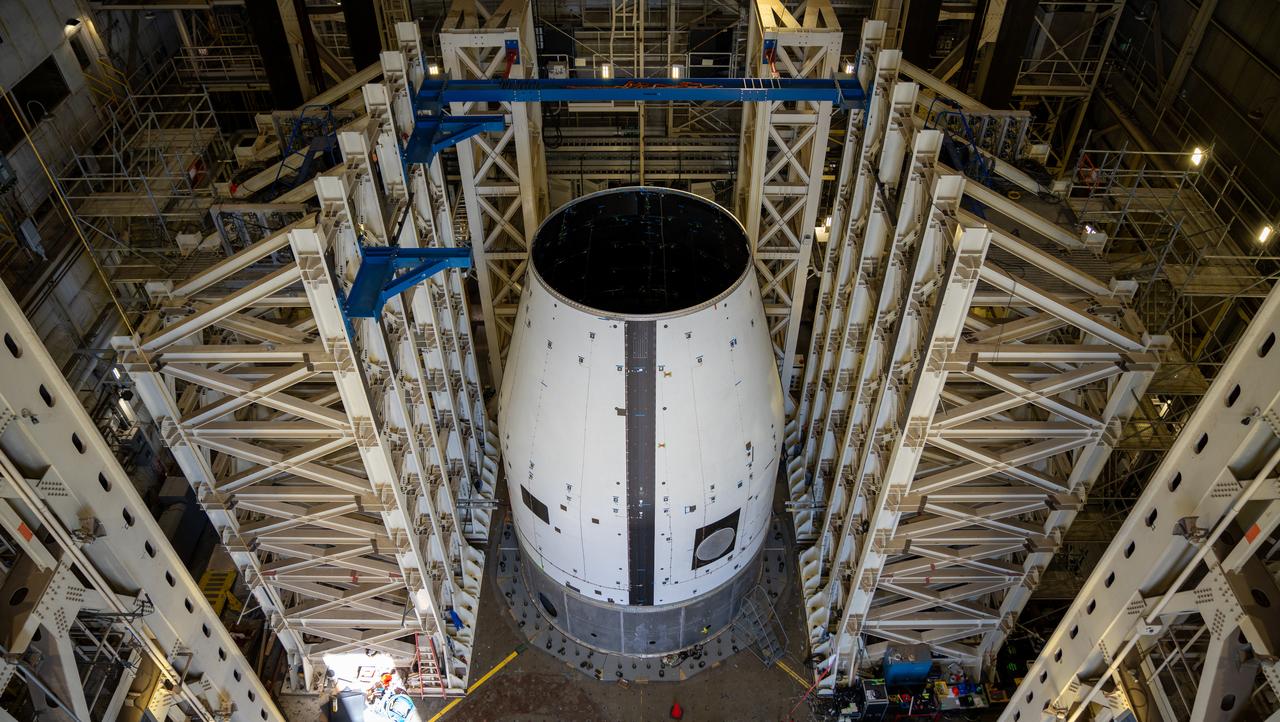
These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
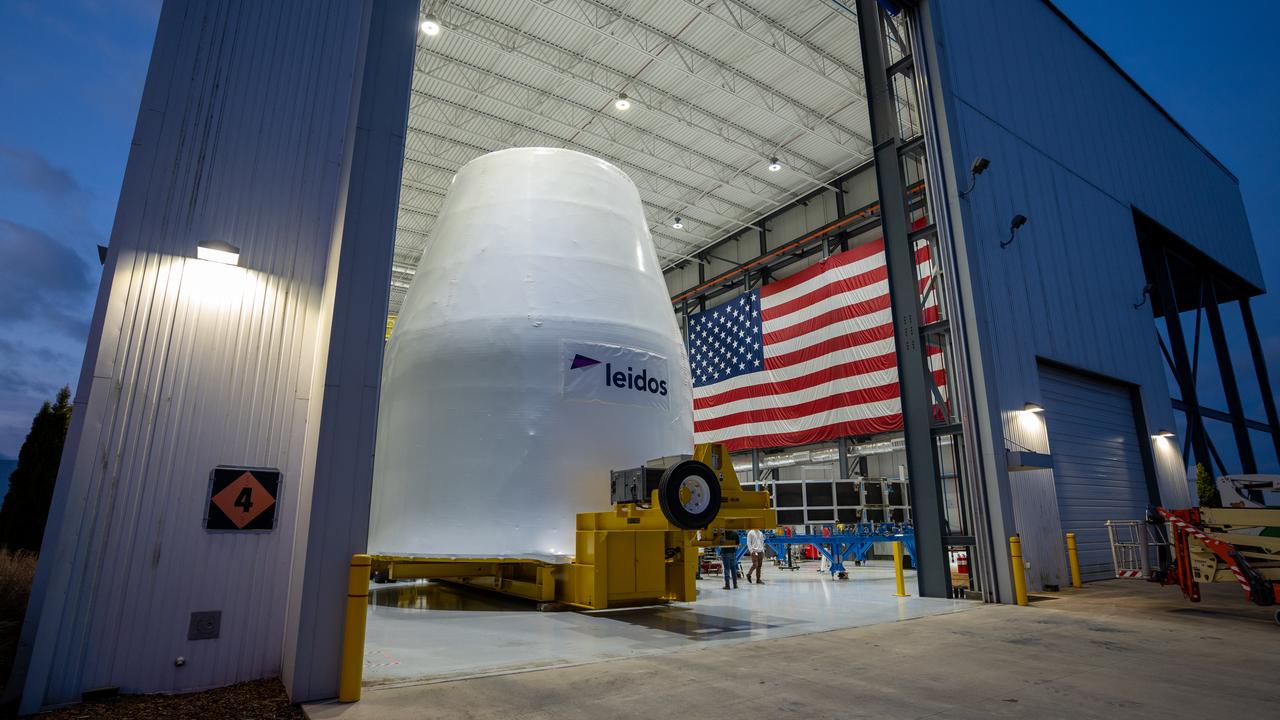

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
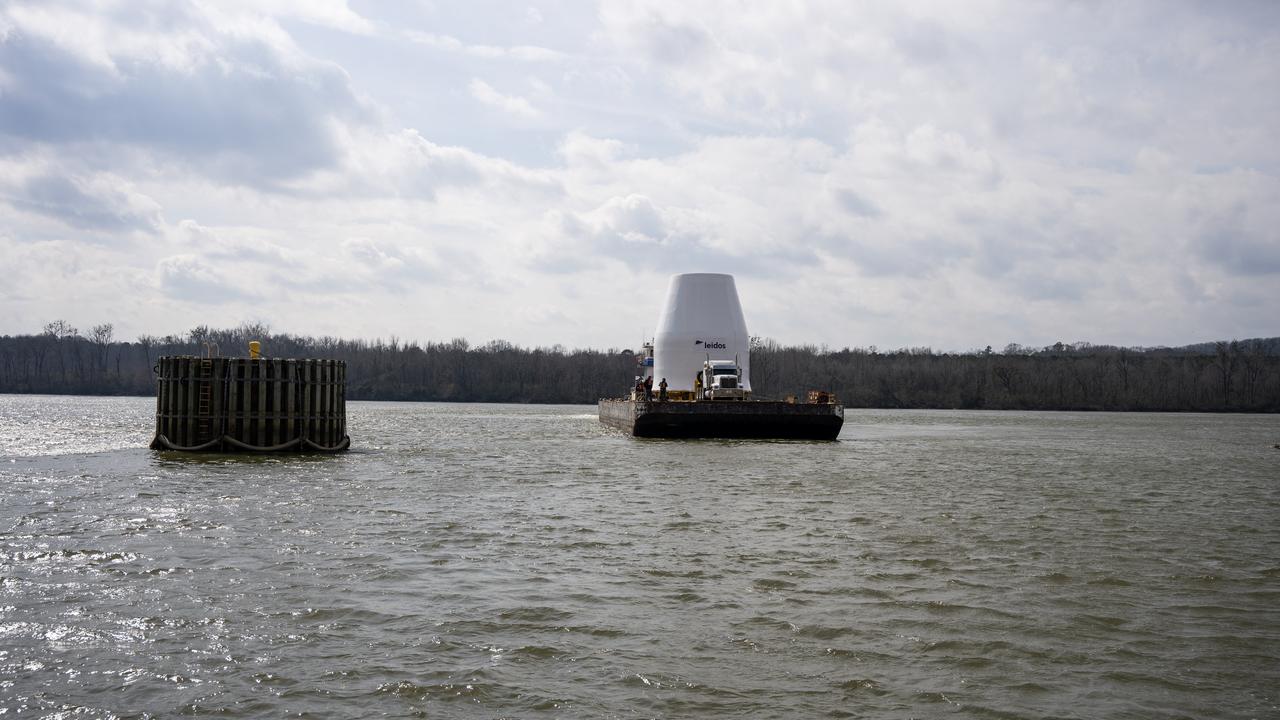

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
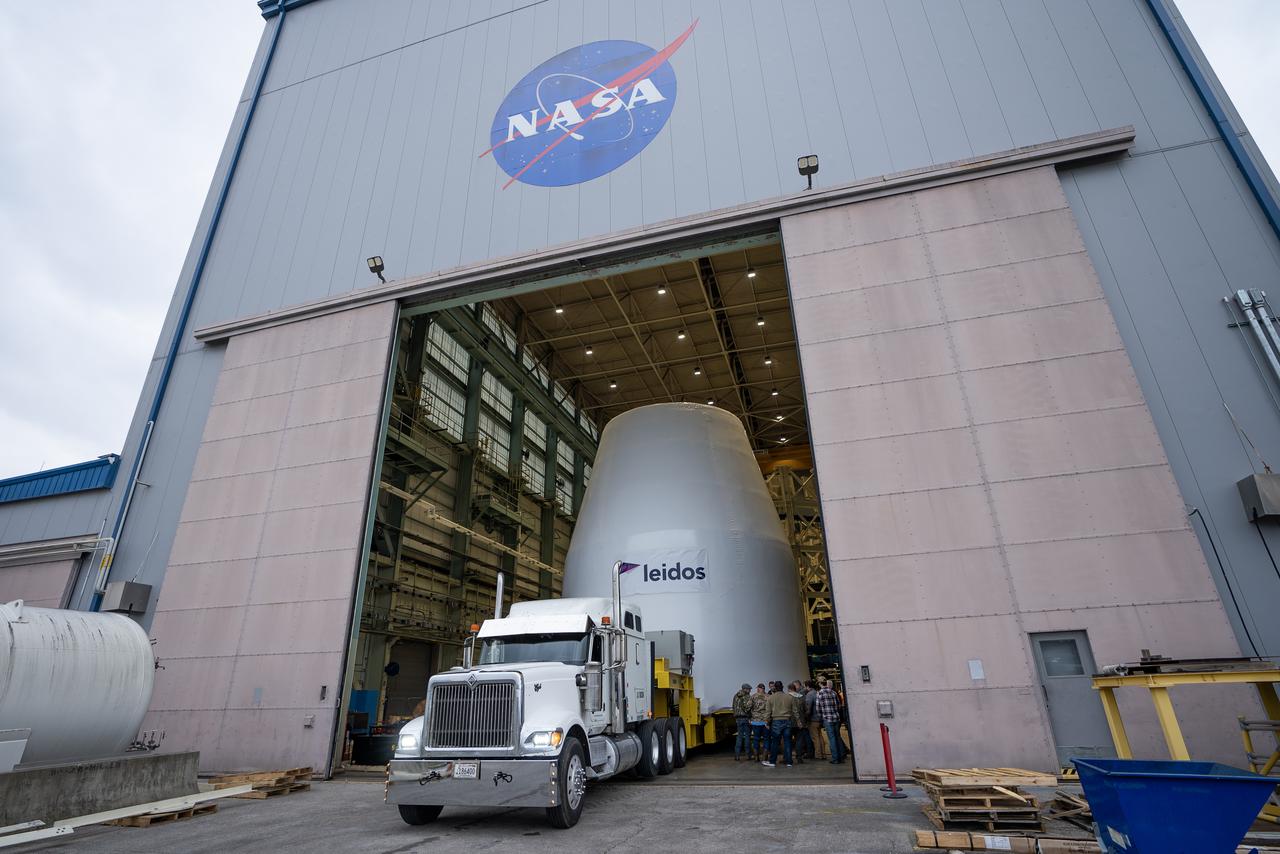

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
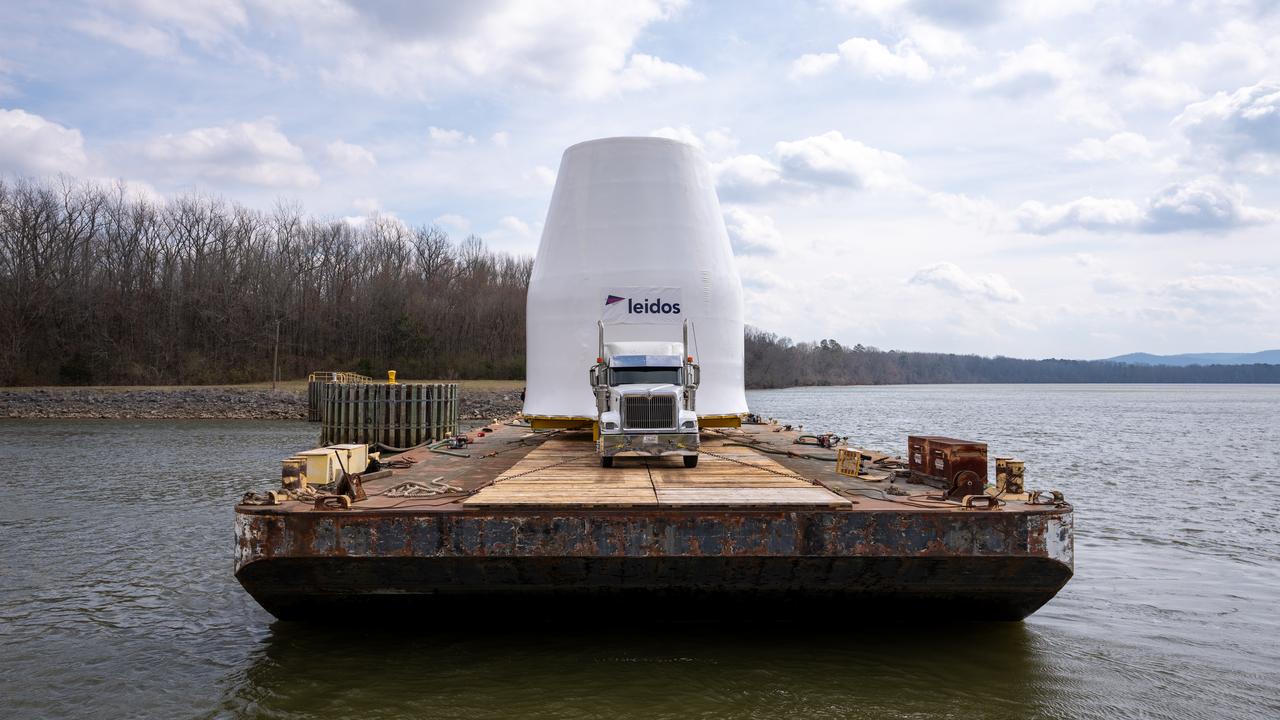

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
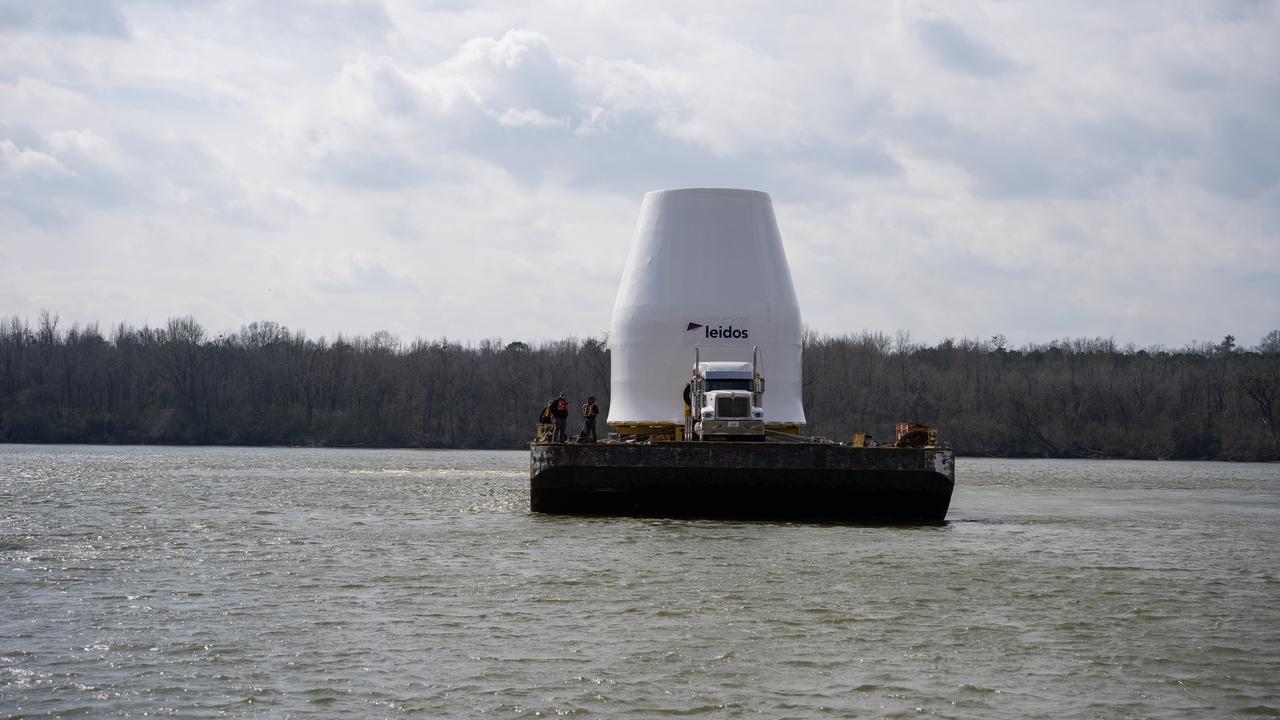

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
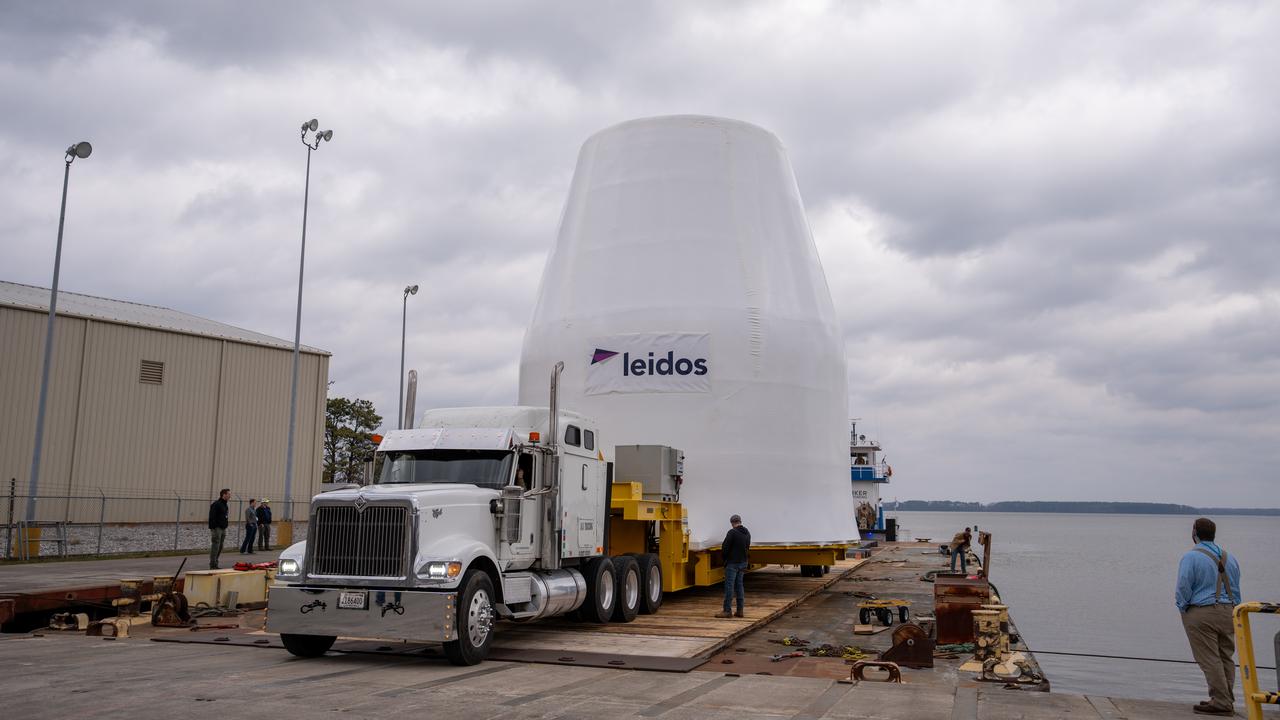

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
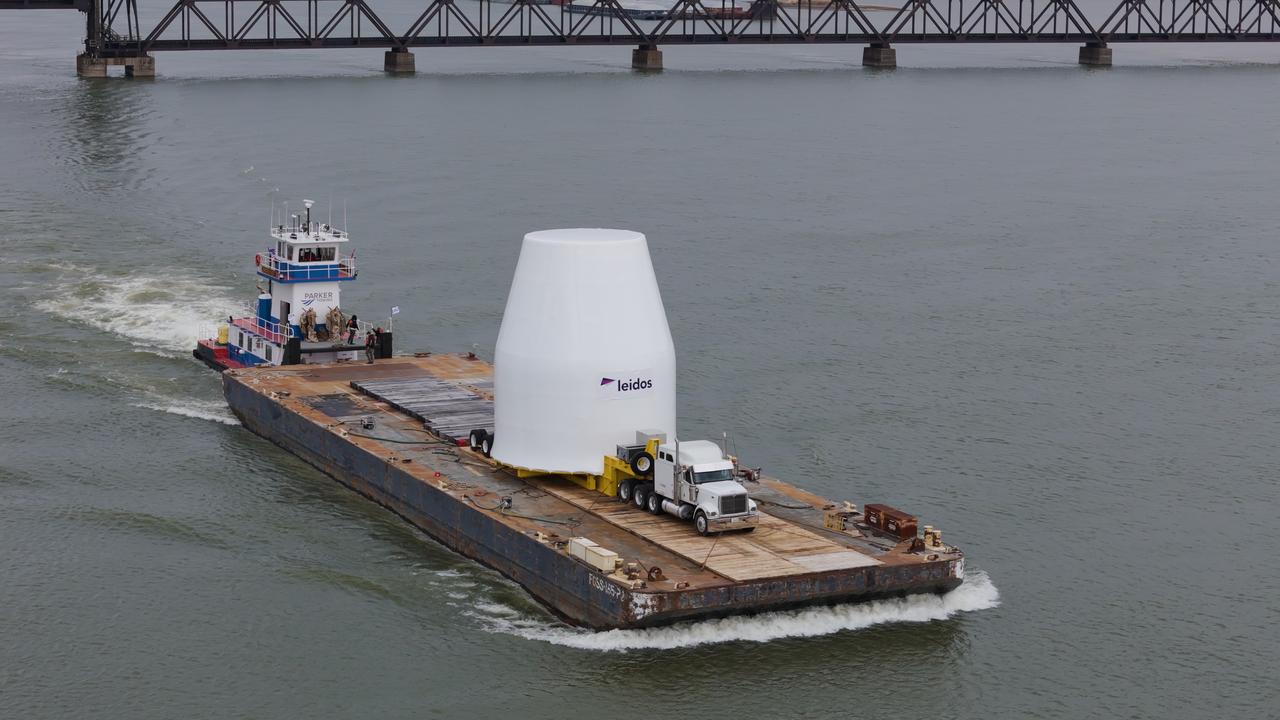

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
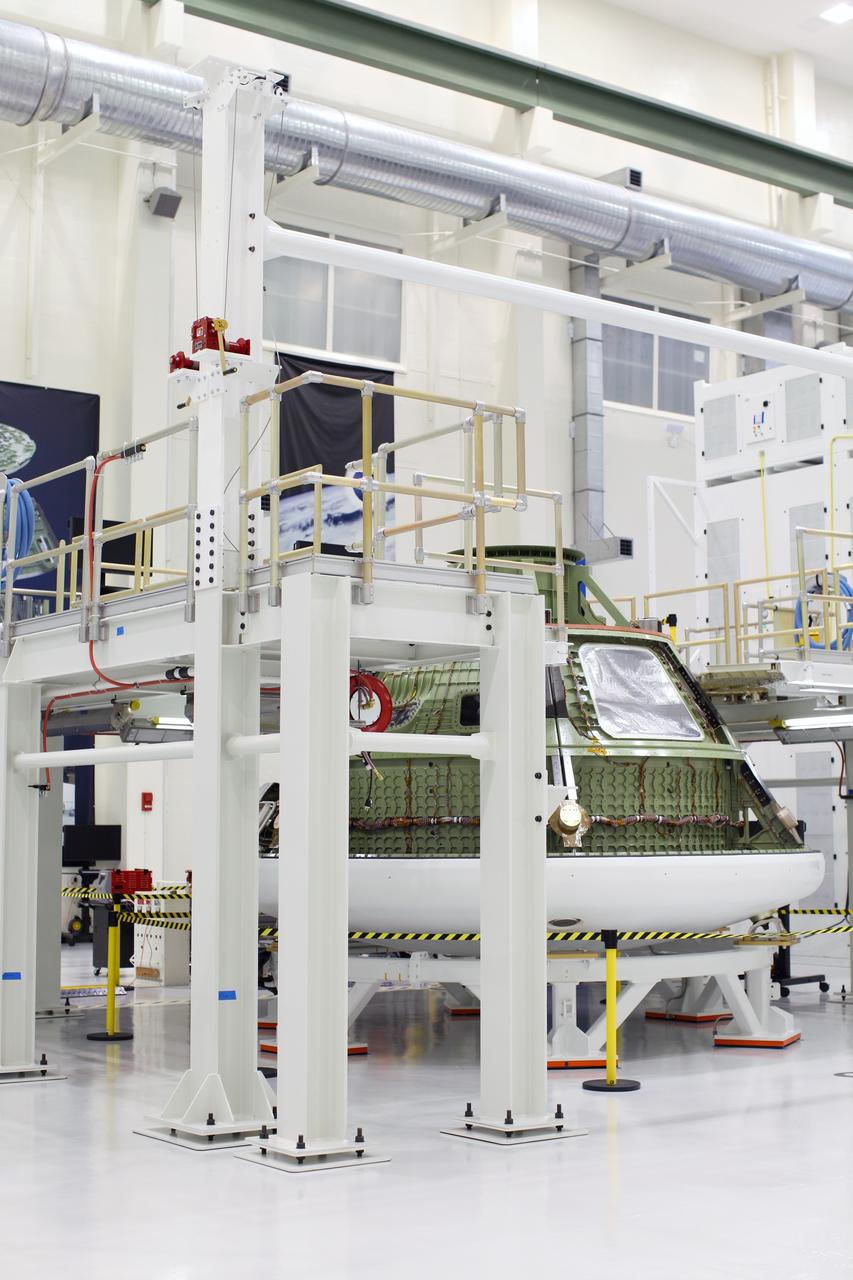

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion ground test vehicle sits in a work stand. The heat panels have been removed. During a tour of the facility, media representatives viewed Orion, several processing stations, and the Orion Test and Launch Control Center. The ground test vehicle will remain at Kennedy for acoustic and modal testing. The heat shield on the bottom of the module will be removed and replaced with a more flight-like heat shield that was built by Lockheed Martin in Denver and will be shipped to Kennedy for installation. The test vehicle will then be in its vehicle configuration for the splashdown test at Langley as NASA prepares for Exploration Flight Test-1. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion ground test vehicle sits in a work stand. The heat panels have been removed. During a tour of the facility, media representatives viewed Orion, several processing stations, and the Orion Test and Launch Control Center. The ground test vehicle will remain at Kennedy for acoustic and modal testing. The heat shield on the bottom of the module will be removed and replaced with a more flight-like heat shield that was built by Lockheed Martin in Denver and will be shipped to Kennedy for installation. The test vehicle will then be in its vehicle configuration for the splashdown test at Langley as NASA prepares for Exploration Flight Test-1. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
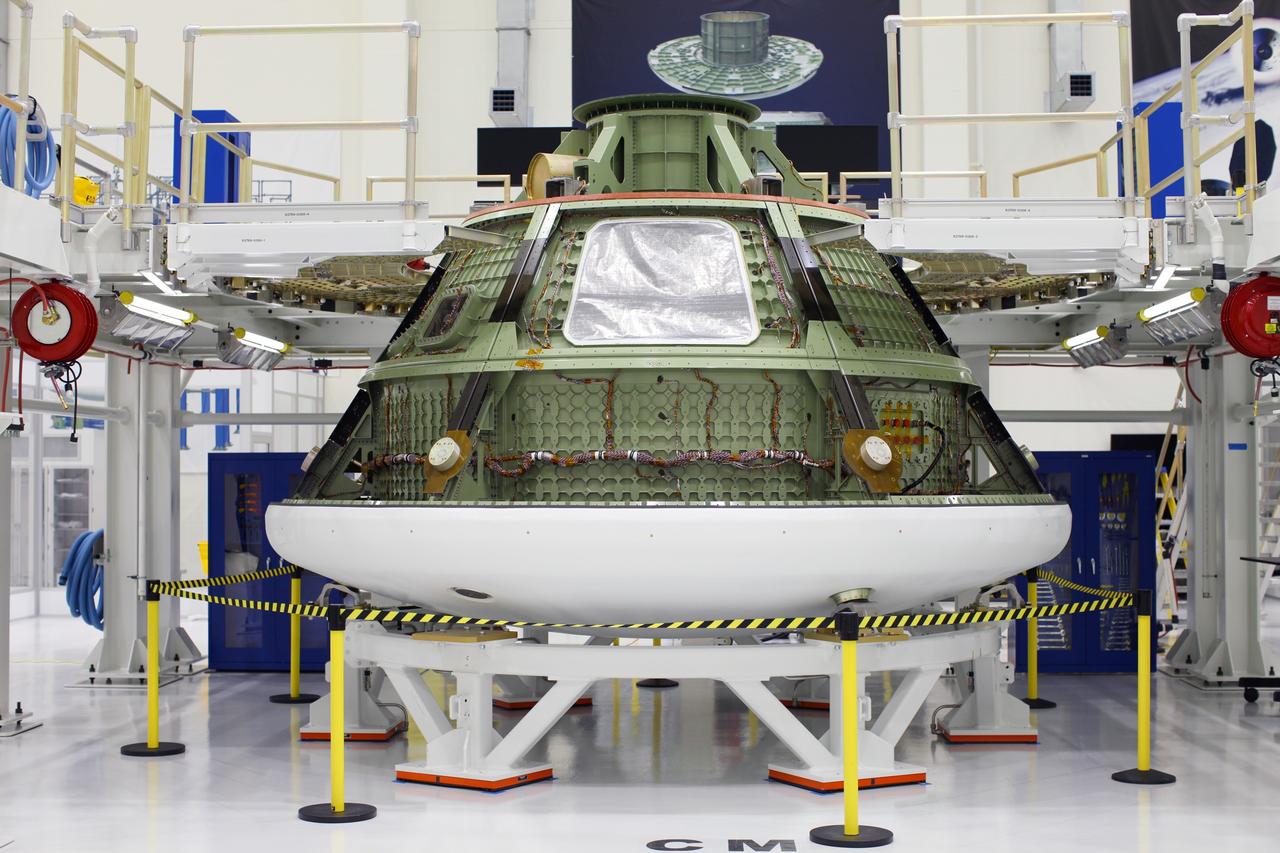

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion ground test vehicle sits in a work stand. The heat panels have been removed. During a tour of the facility, media representatives viewed Orion, several processing stations, and the Orion Test and Launch Control Center. The ground test vehicle will remain at Kennedy for acoustic and modal testing. The heat shield on the bottom of the module will be removed and replaced with a more flight-like heat shield that was built by Lockheed Martin in Denver and will be shipped to Kennedy for installation. The test vehicle will then be in its vehicle configuration for the splashdown test at Langley as NASA prepares for Exploration Flight Test-1. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
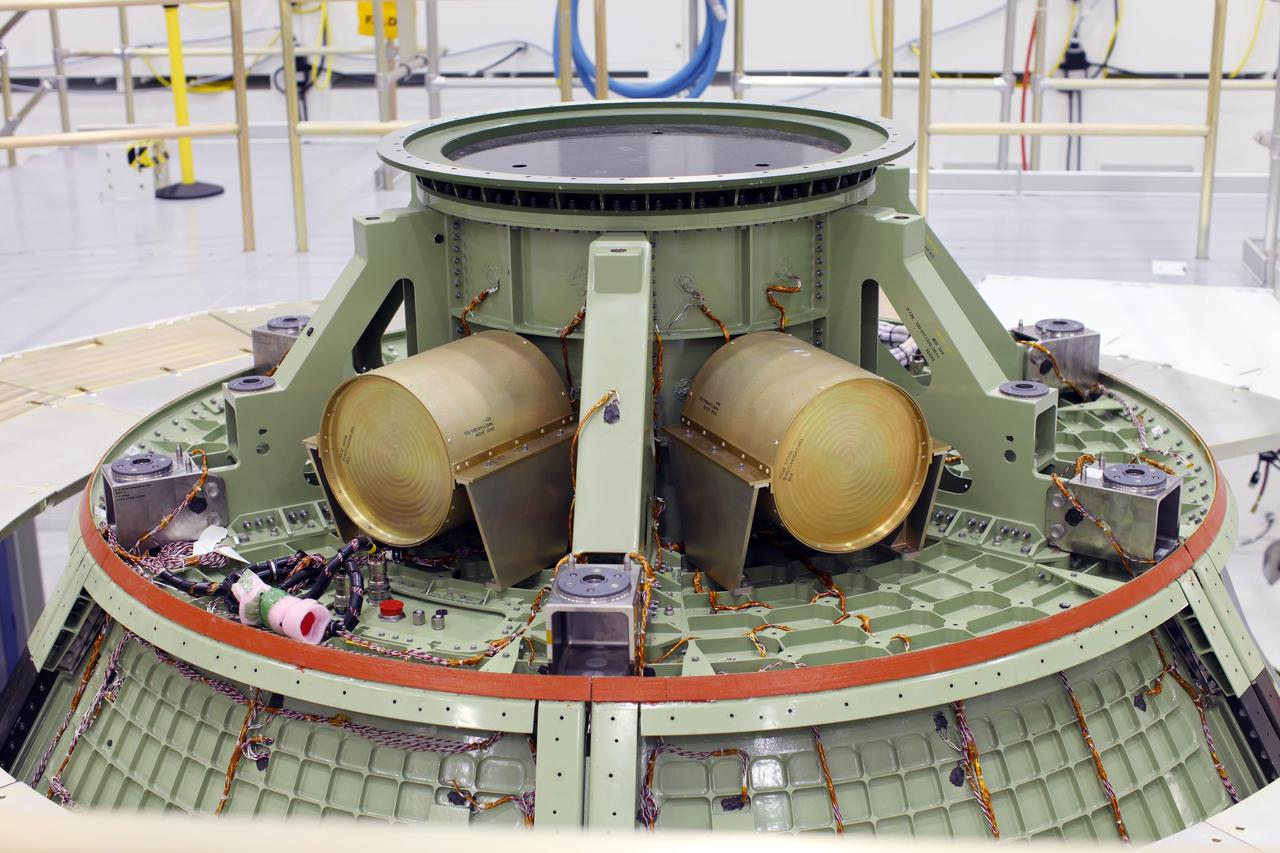
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion ground test vehicle sits in a work stand. The heat panels have been removed. During a tour of the facility, media representatives viewed Orion, several processing stations, and the Orion Test and Launch Control Center. The ground test vehicle will remain at Kennedy for acoustic and modal testing. The heat shield on the bottom of the module will be removed and replaced with a more flight-like heat shield that was built by Lockheed Martin in Denver and will be shipped to Kennedy for installation. The test vehicle will then be in its vehicle configuration for the splashdown test at Langley as NASA prepares for Exploration Flight Test-1. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
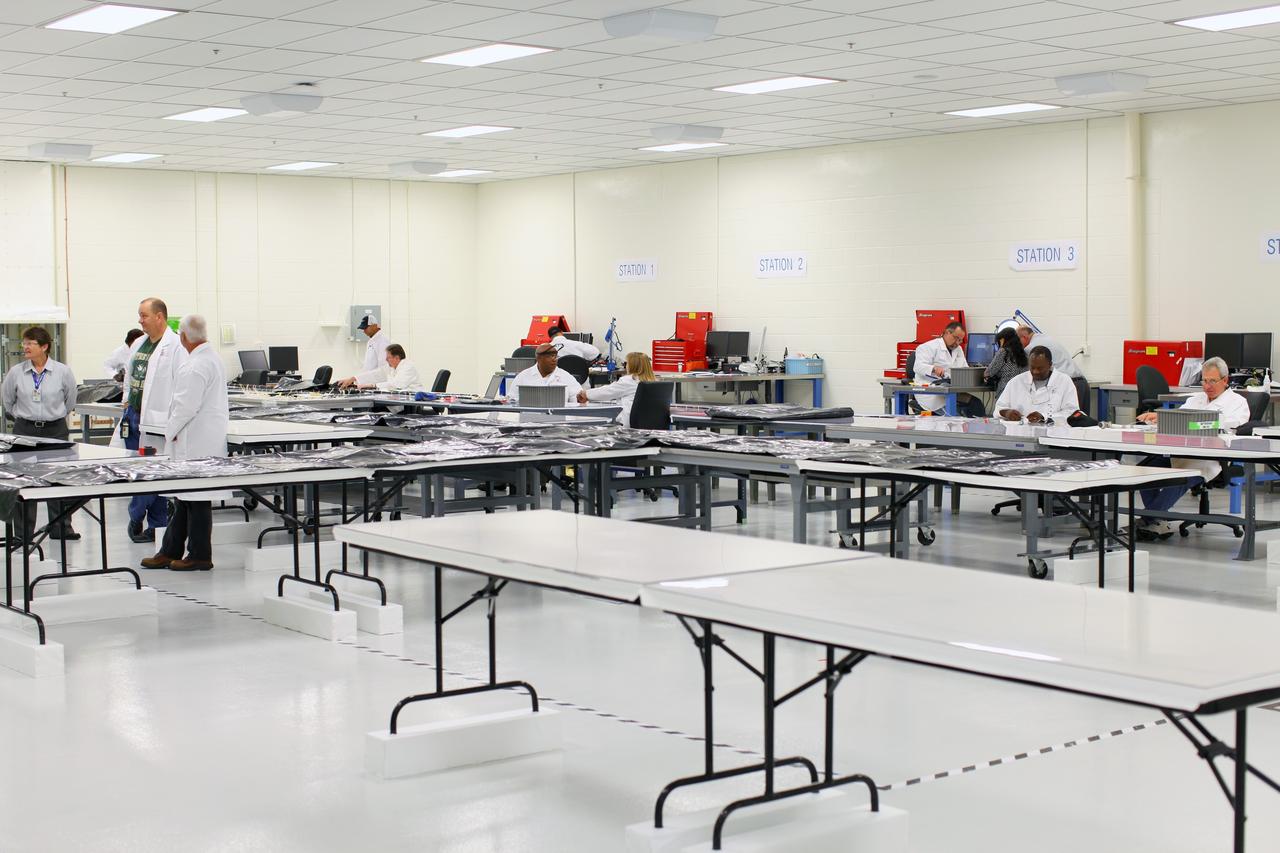

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United Space Alliance workers are manufacturing harnesses which will be used on NASA’s Orion multi-purpose crew vehicle, or MPCV. During a tour of the facility, media representatives viewed Orion, several processing stations, and the Orion Test and Launch Control Center. The ground test vehicle will remain at Kennedy for acoustic and modal testing. The heat shield on the bottom of the module will be removed and replaced with a more flight-like heat shield that was built by Lockheed Martin in Denver and will be shipped to Kennedy for installation. The test vehicle will then be in its vehicle configuration for the splashdown test at Langley as NASA prepares for Exploration Flight Test-1. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
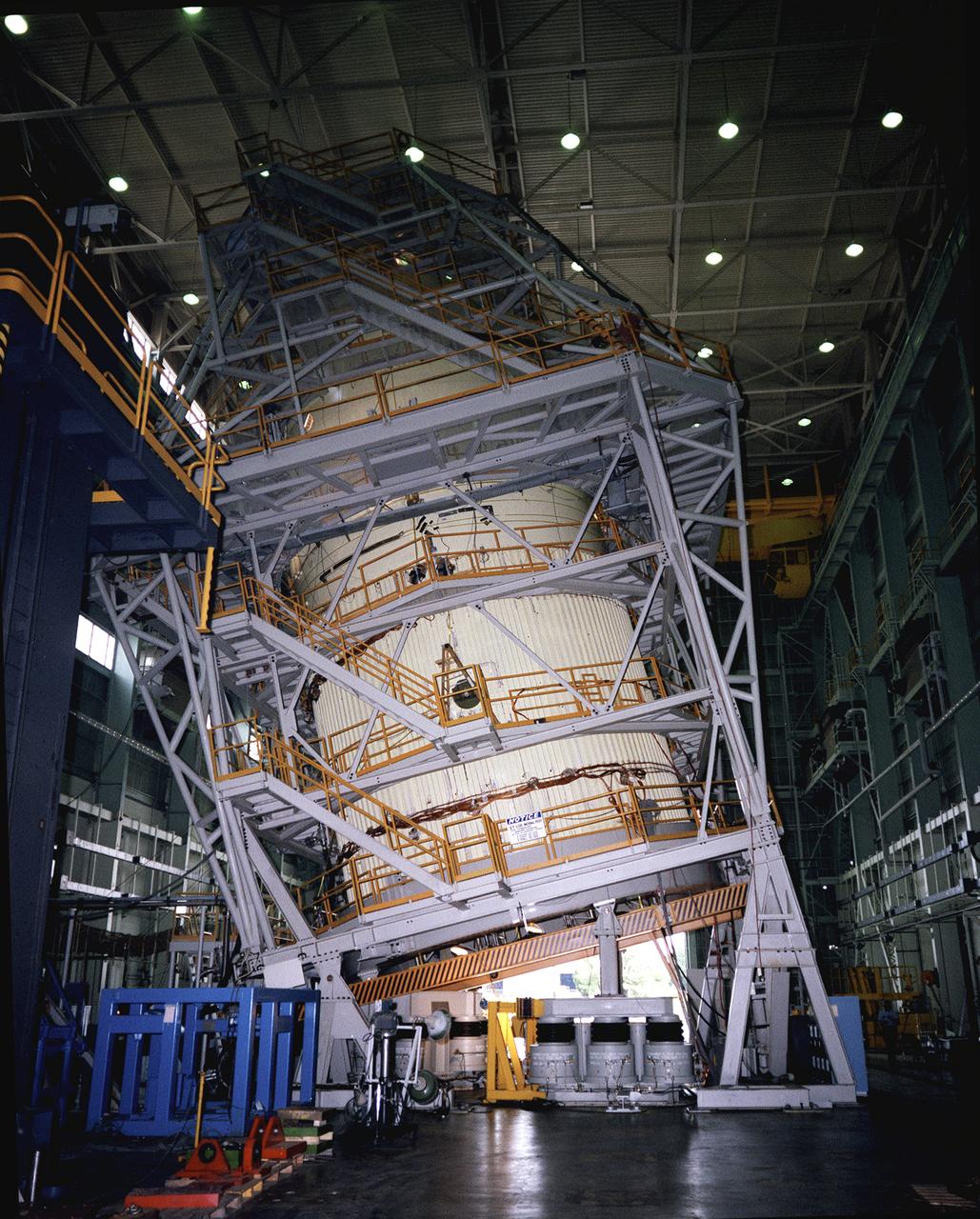

This photograph shows a liquid oxygen tank for the Shuttle External Tank (ET) during a hydroelastic modal survey test at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The ET provides liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen to the Shuttle's three main engines during the first 8.5 minutes of flight. At 154-feet long and more than 27-feet in diameter, the ET is the largest component of the Space Shuttle, the structural backbone of the entire Shuttle system, and is the only part of the vehicle that is not reusable. The ET is manufactured at the Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans, Louisiana, by the Martin Marietta Corporation under management of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
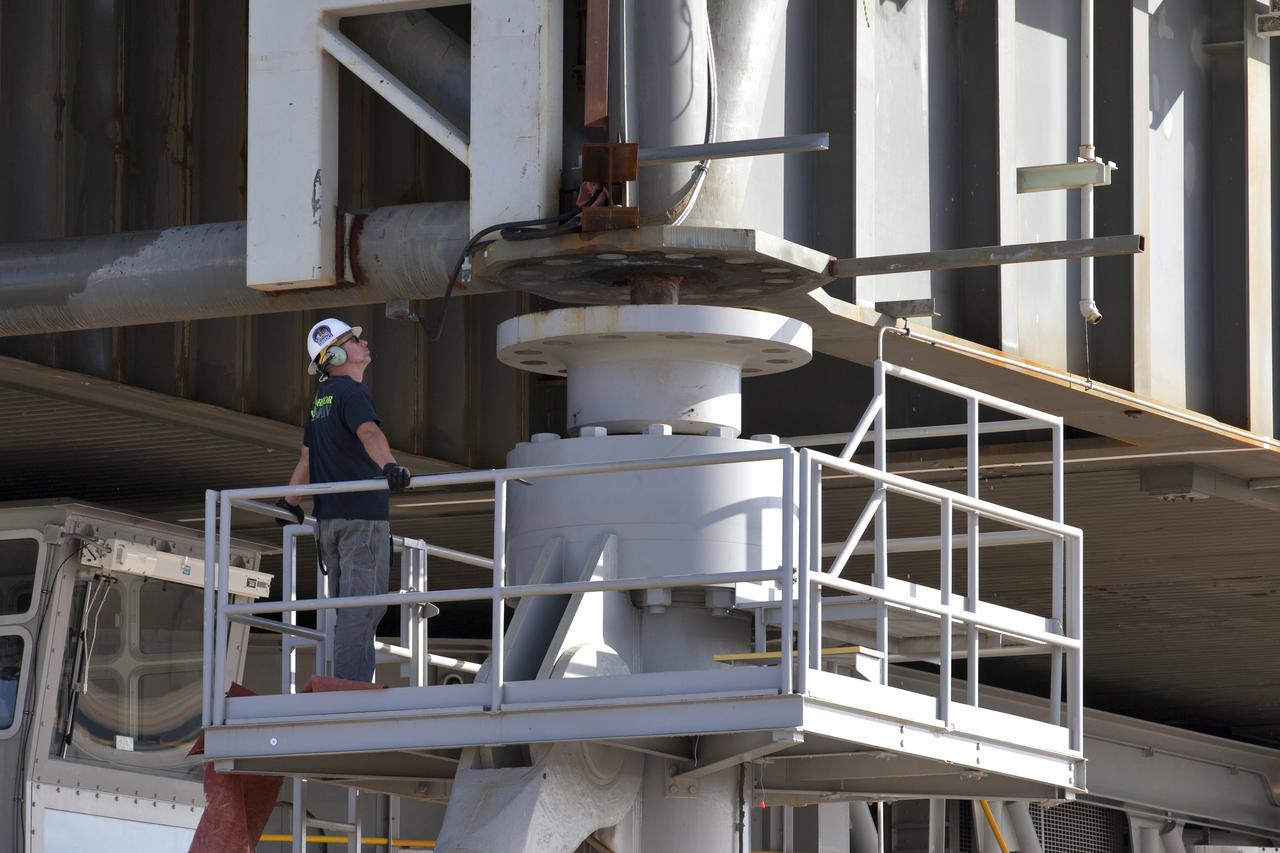

A construction worker monitors the progress as crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) lifts the mobile launcher up a few inches from its support posts June 1, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts were performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. The lift helped to test the capability of the upgraded CT-2 to handle the weight of the mobile launcher. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to support the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
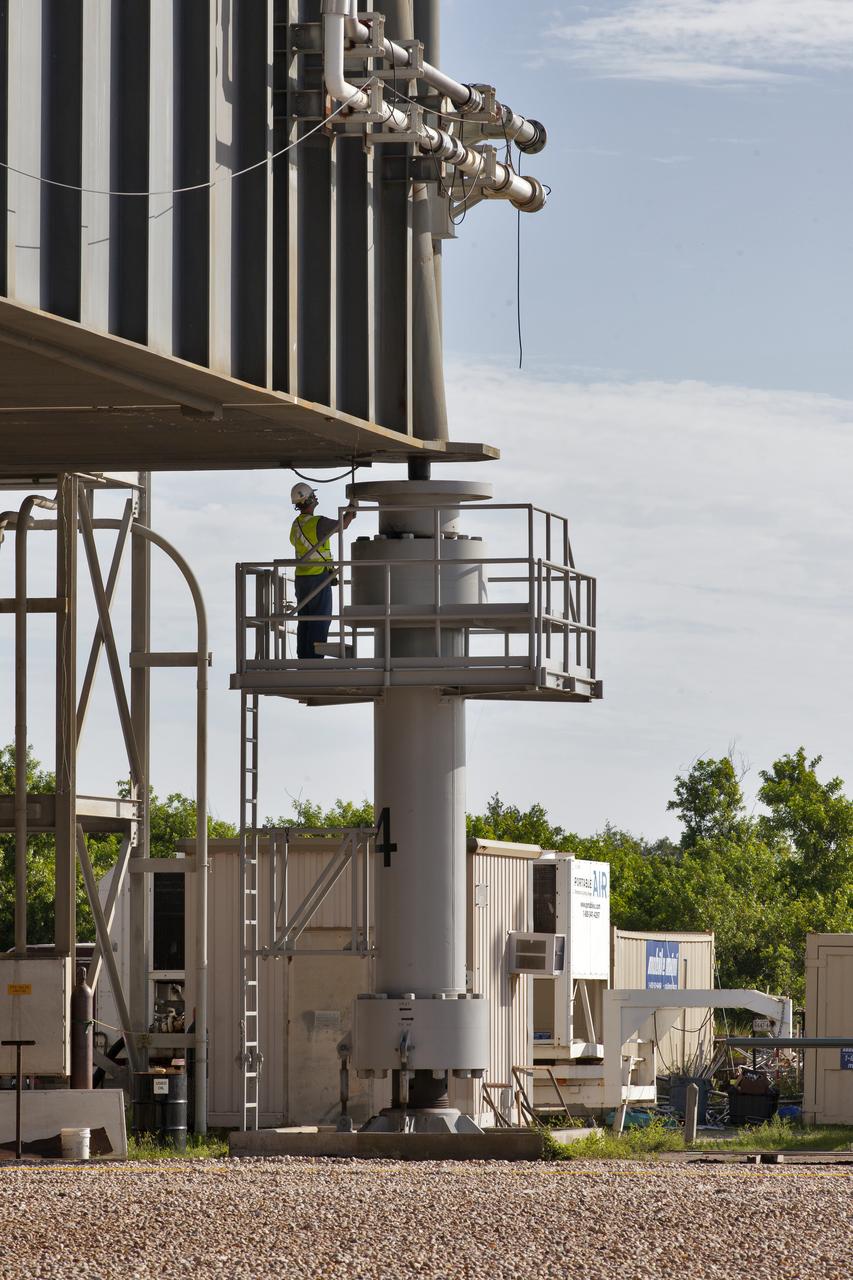

A construction worker monitors the progress as crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) lifts the mobile launcher up a few inches from its support posts June 1, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts were performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. The lift helped to test the capability of the upgraded CT-2 to handle the weight of the mobile launcher with SLS and Orion atop. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to support the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
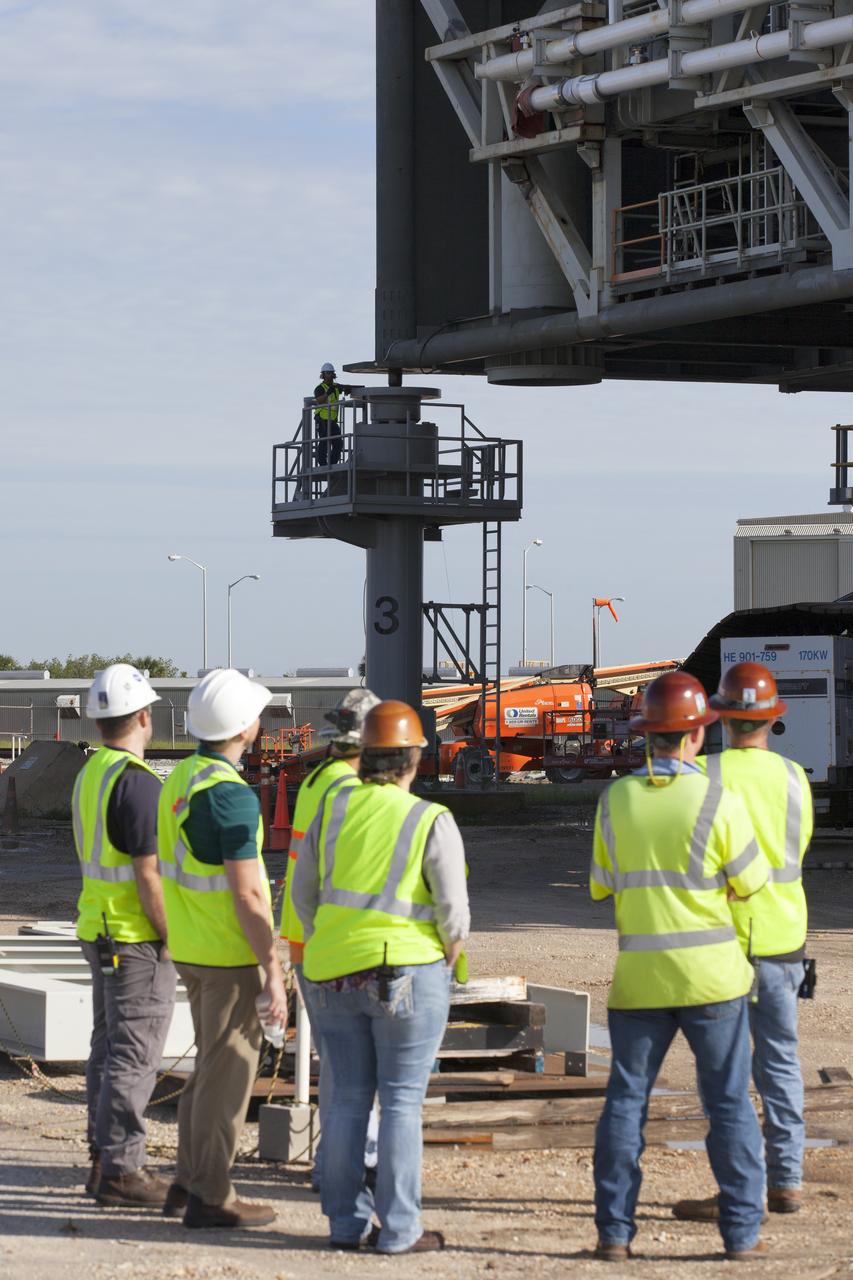

Workers watch as crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) lifts the mobile launcher up a few inches from its support posts June 1, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts were performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. The lift helped to test the capability of the upgraded CT-2 to handle the weight of the mobile launcher. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.