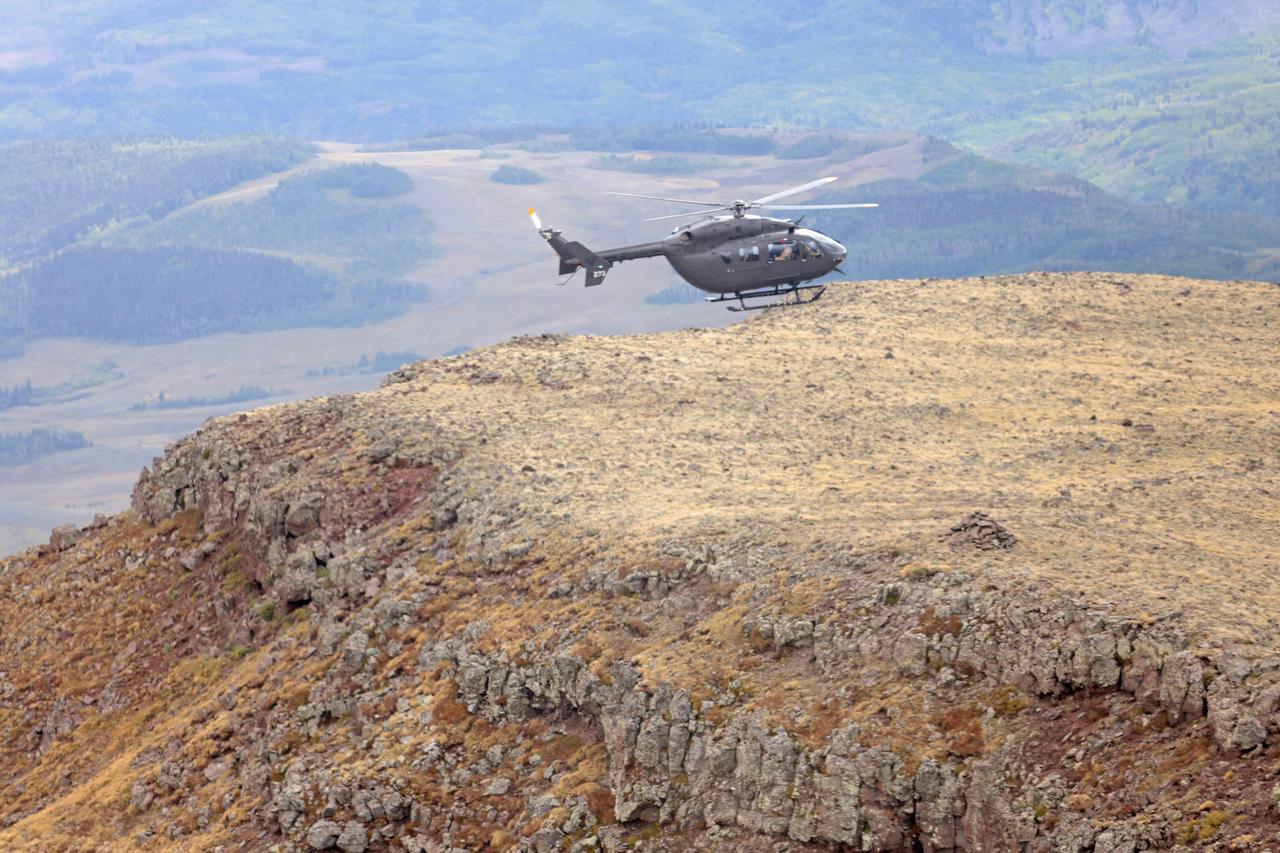

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
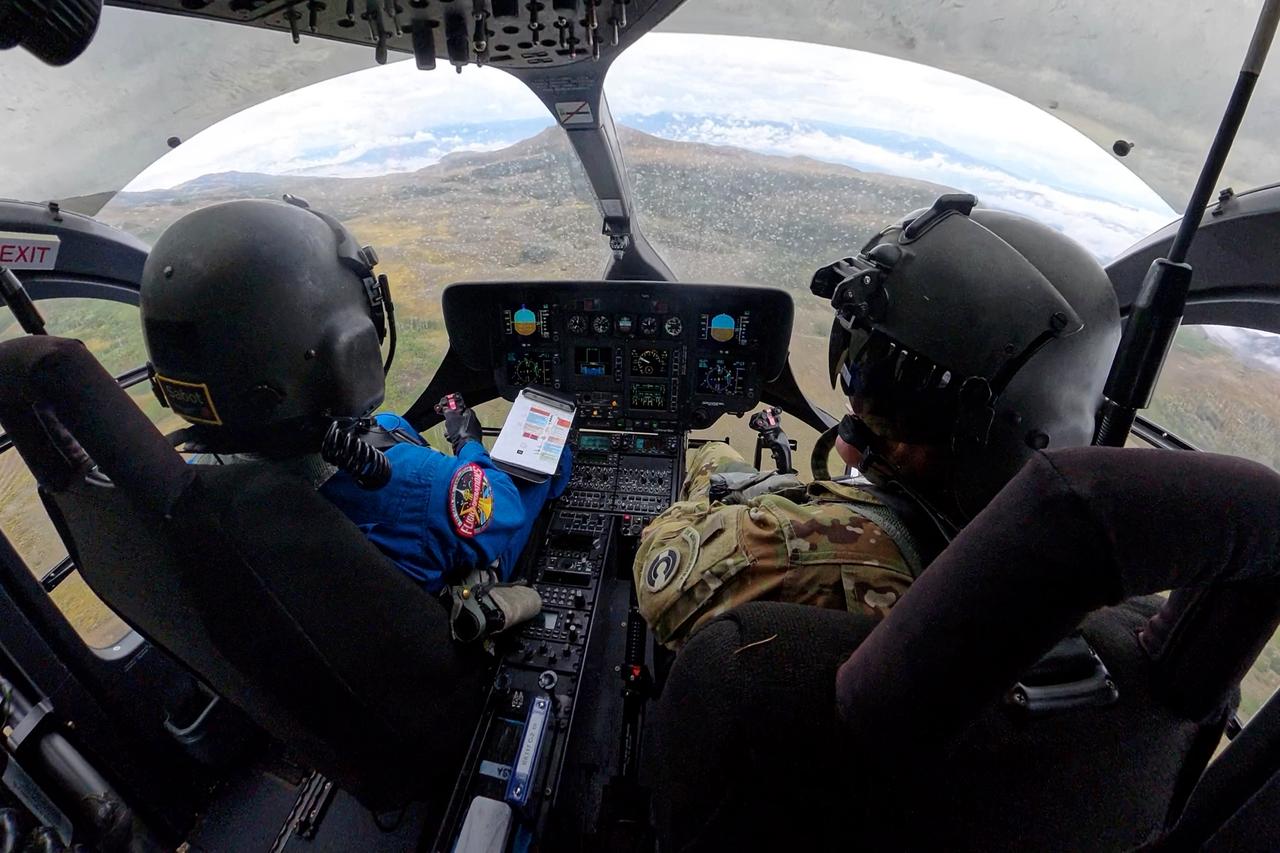

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
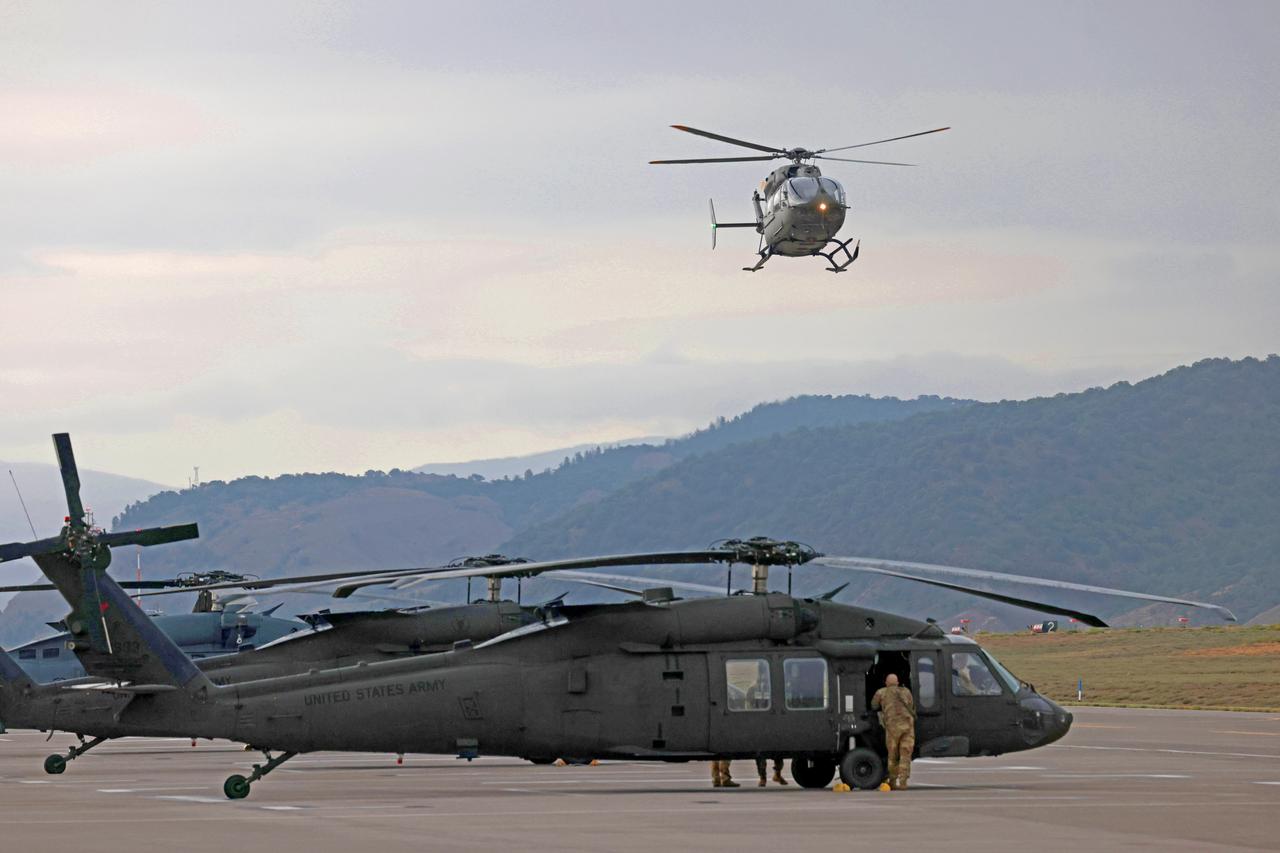

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
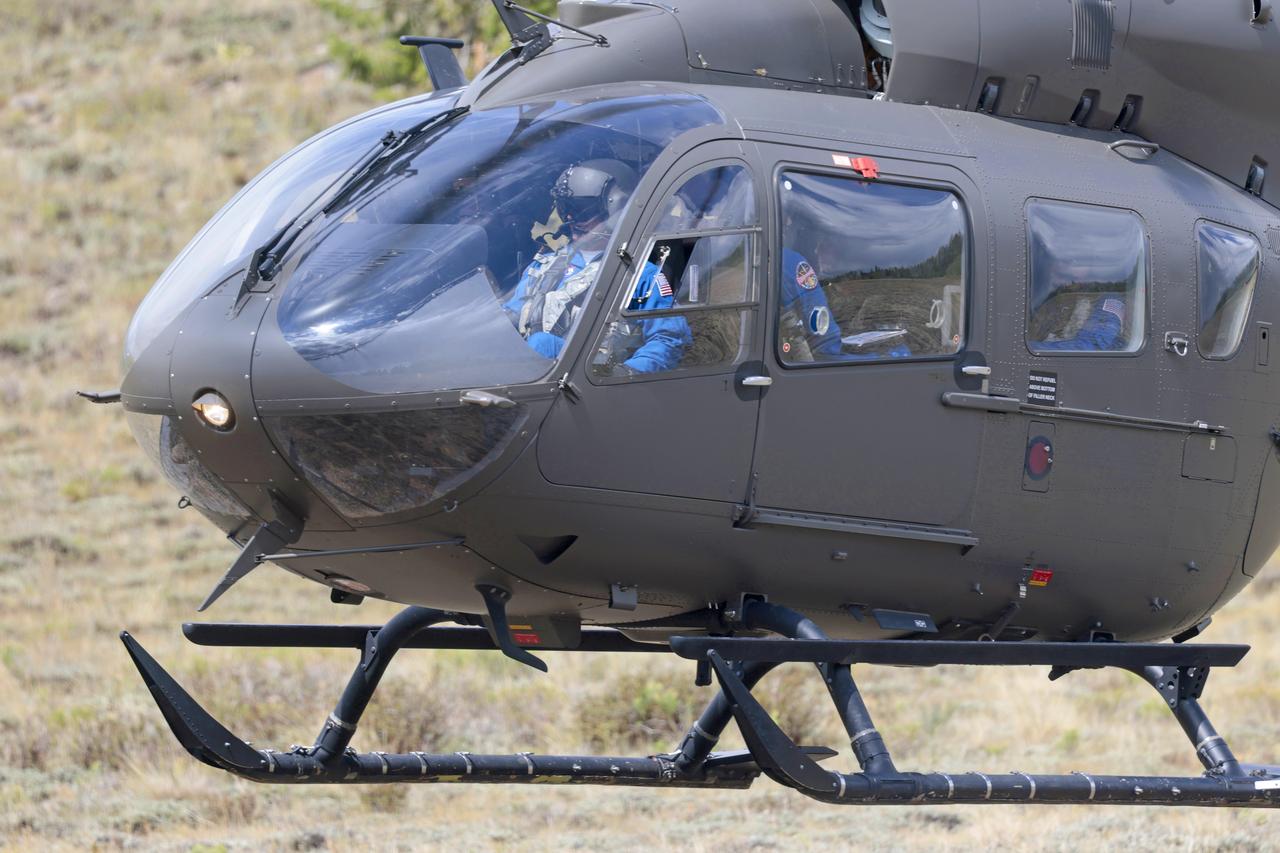

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
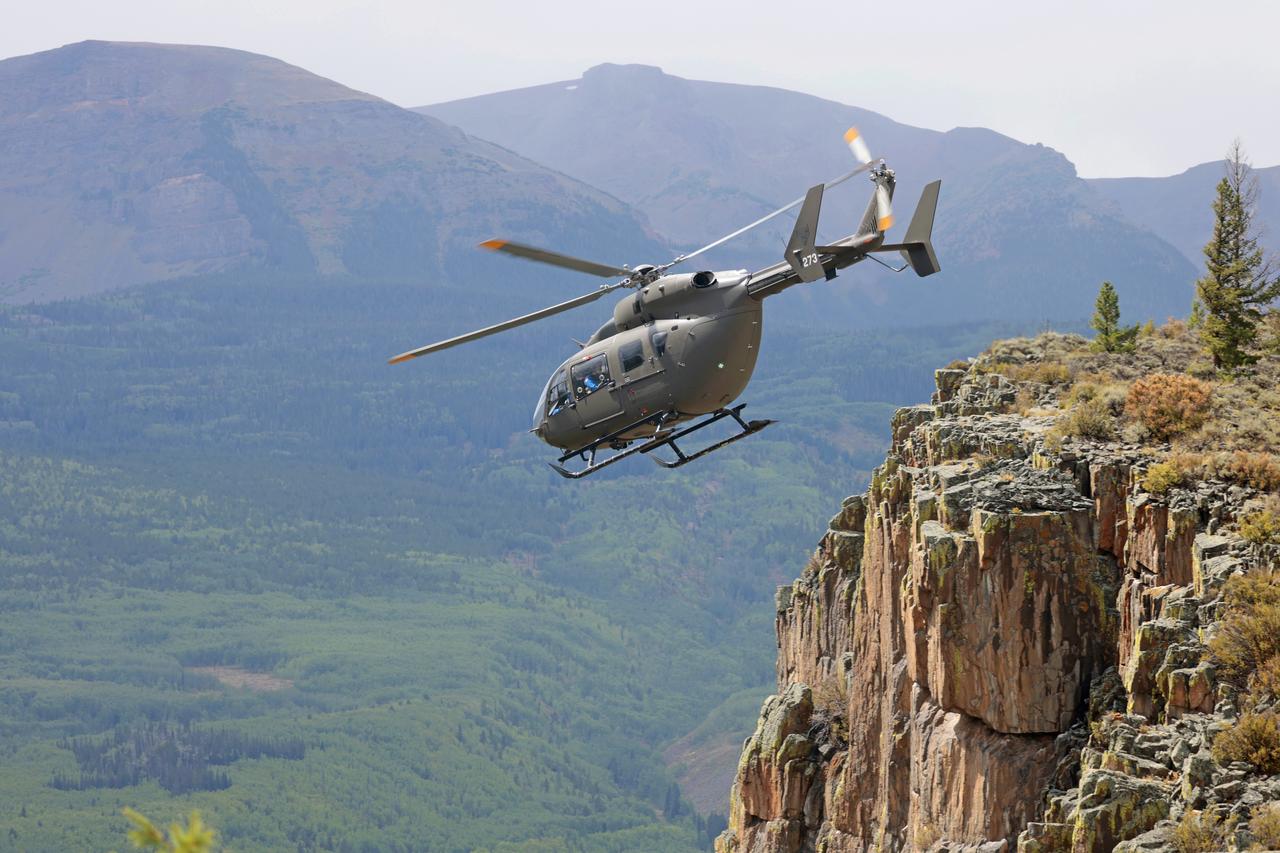

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
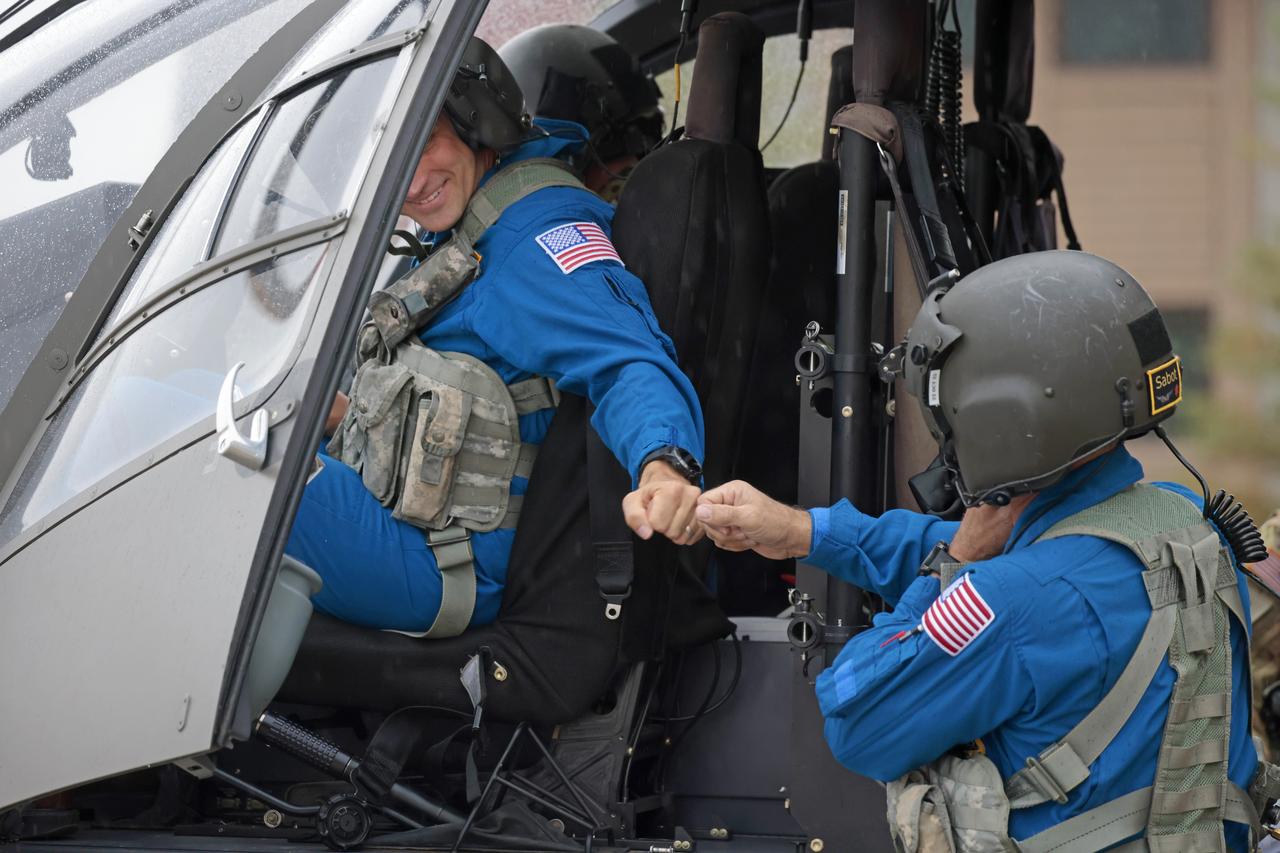

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
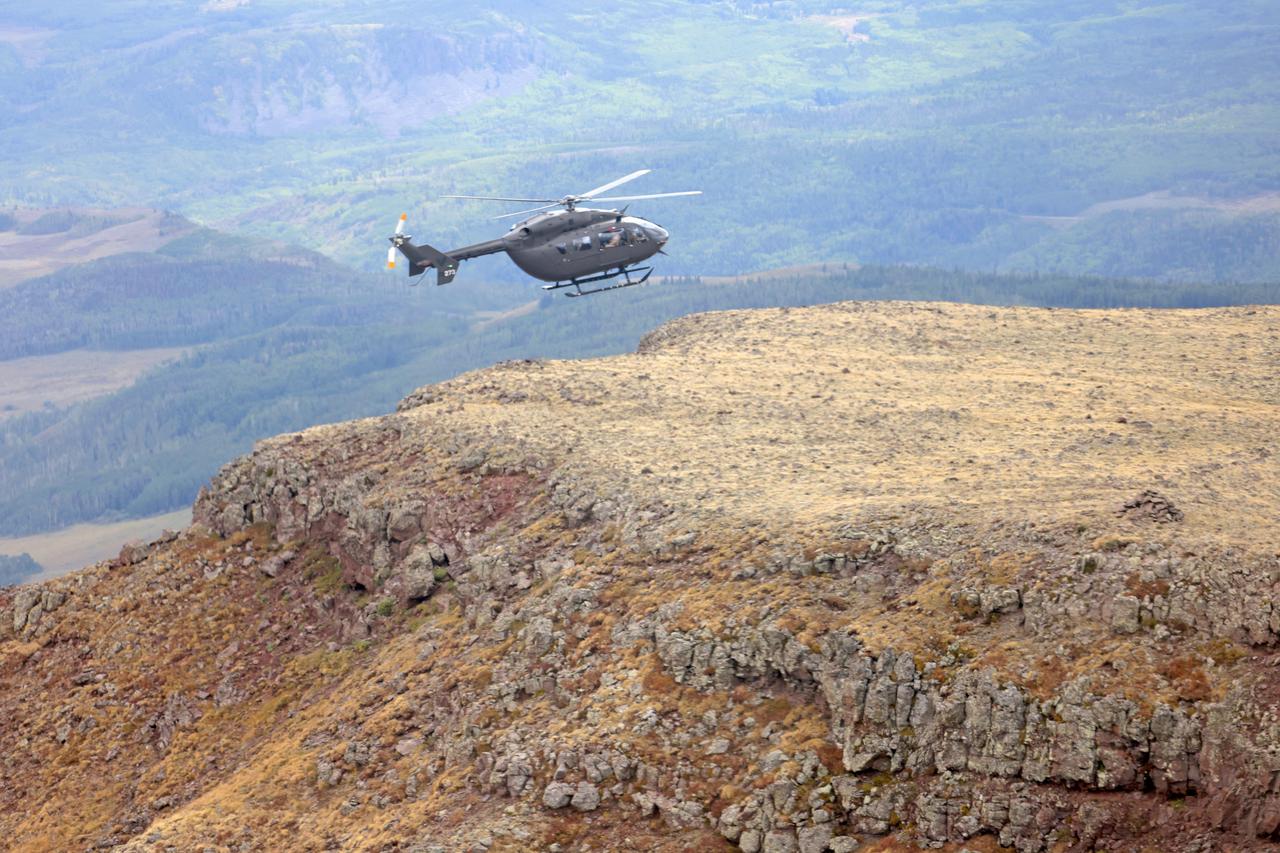

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
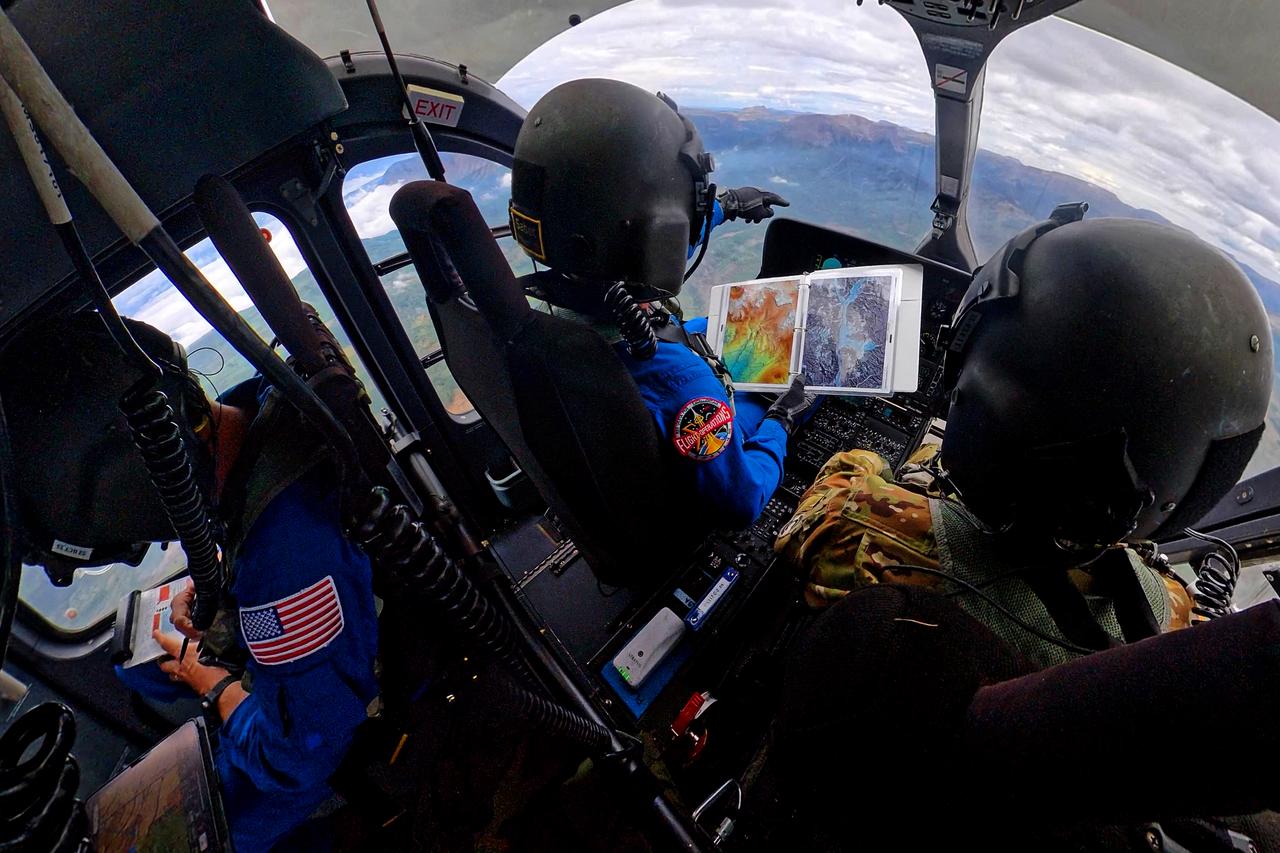

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
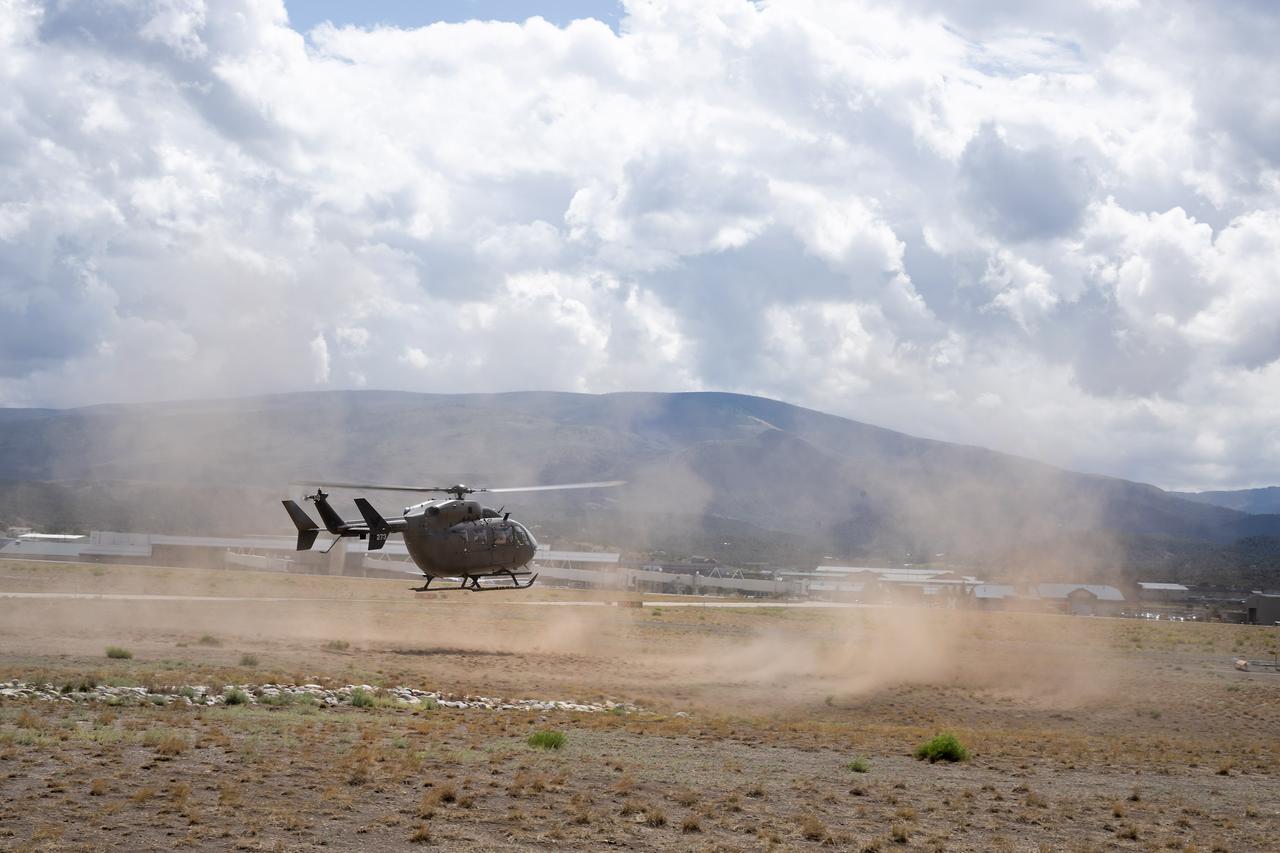

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
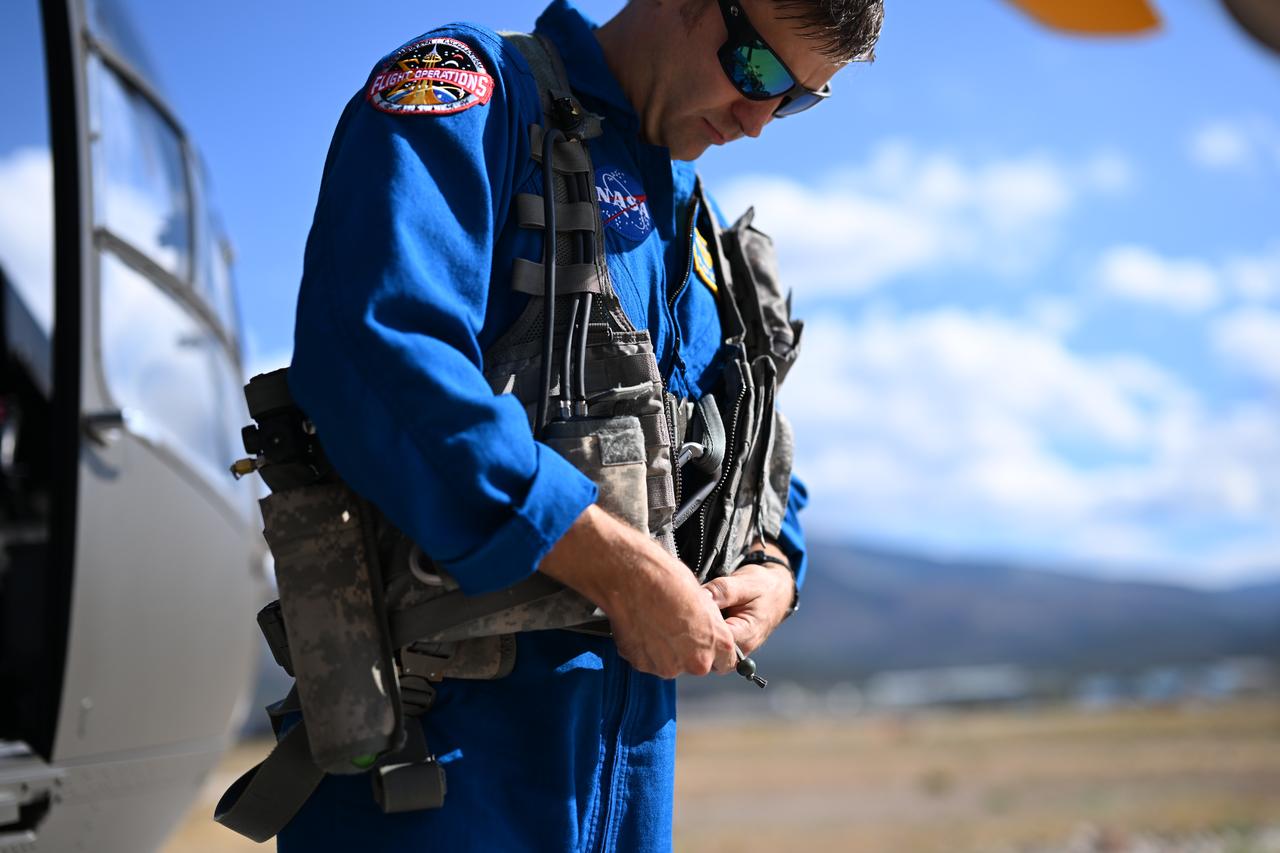

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
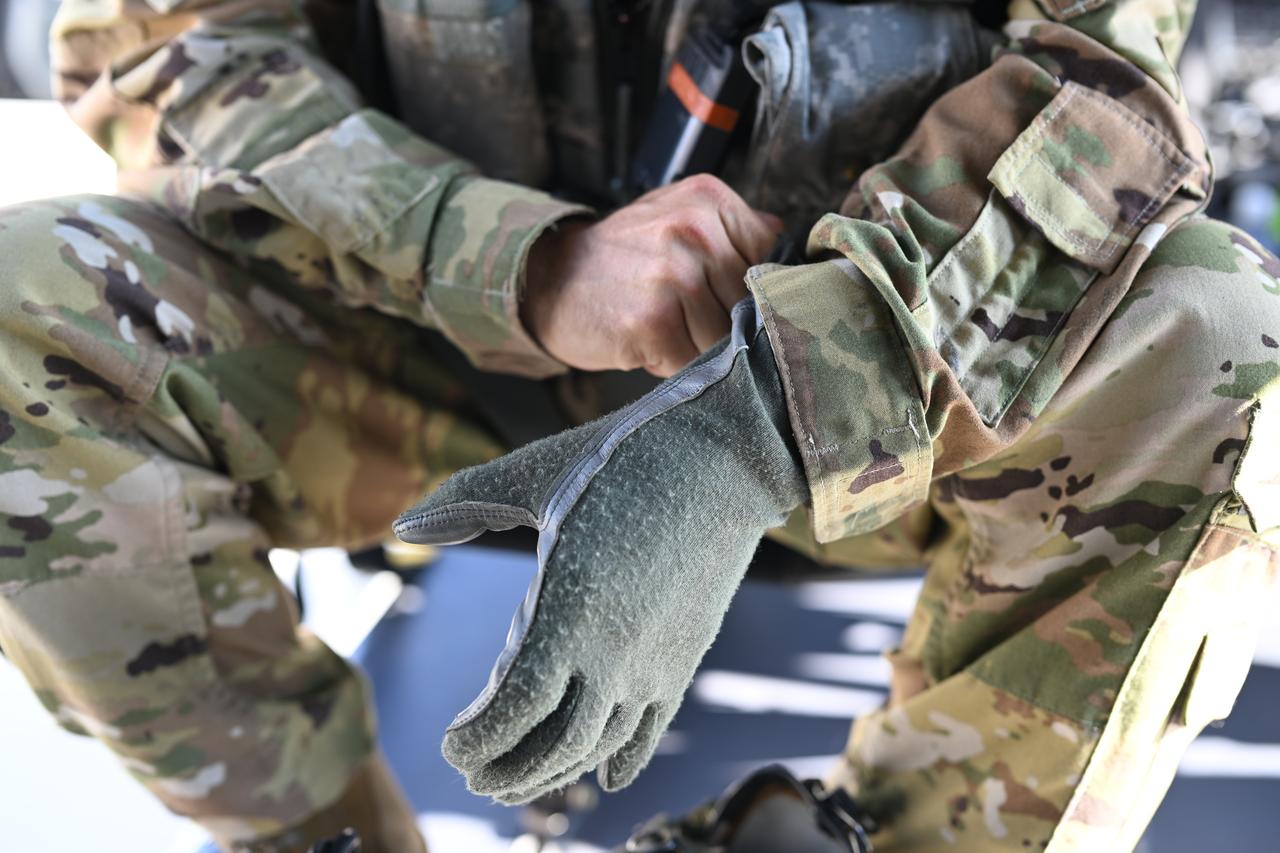

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
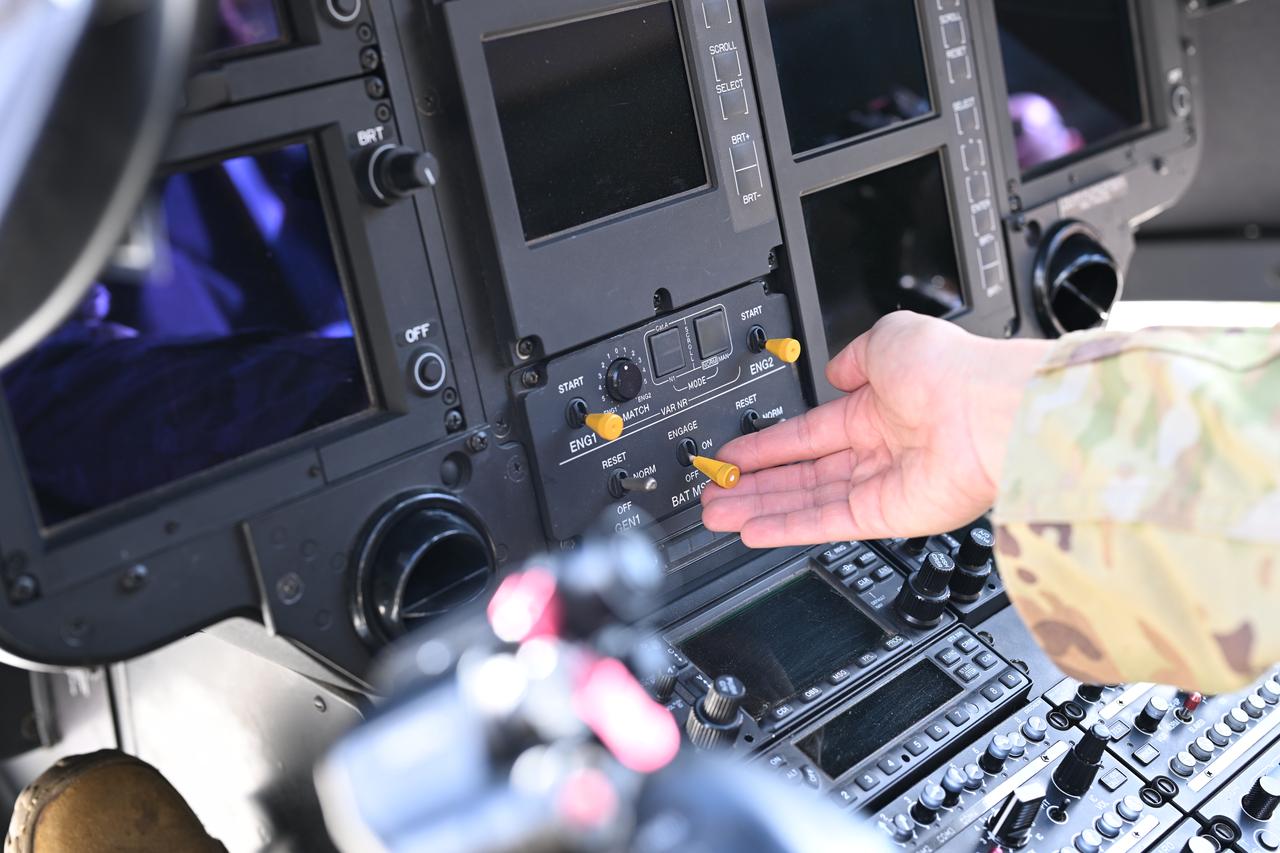

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
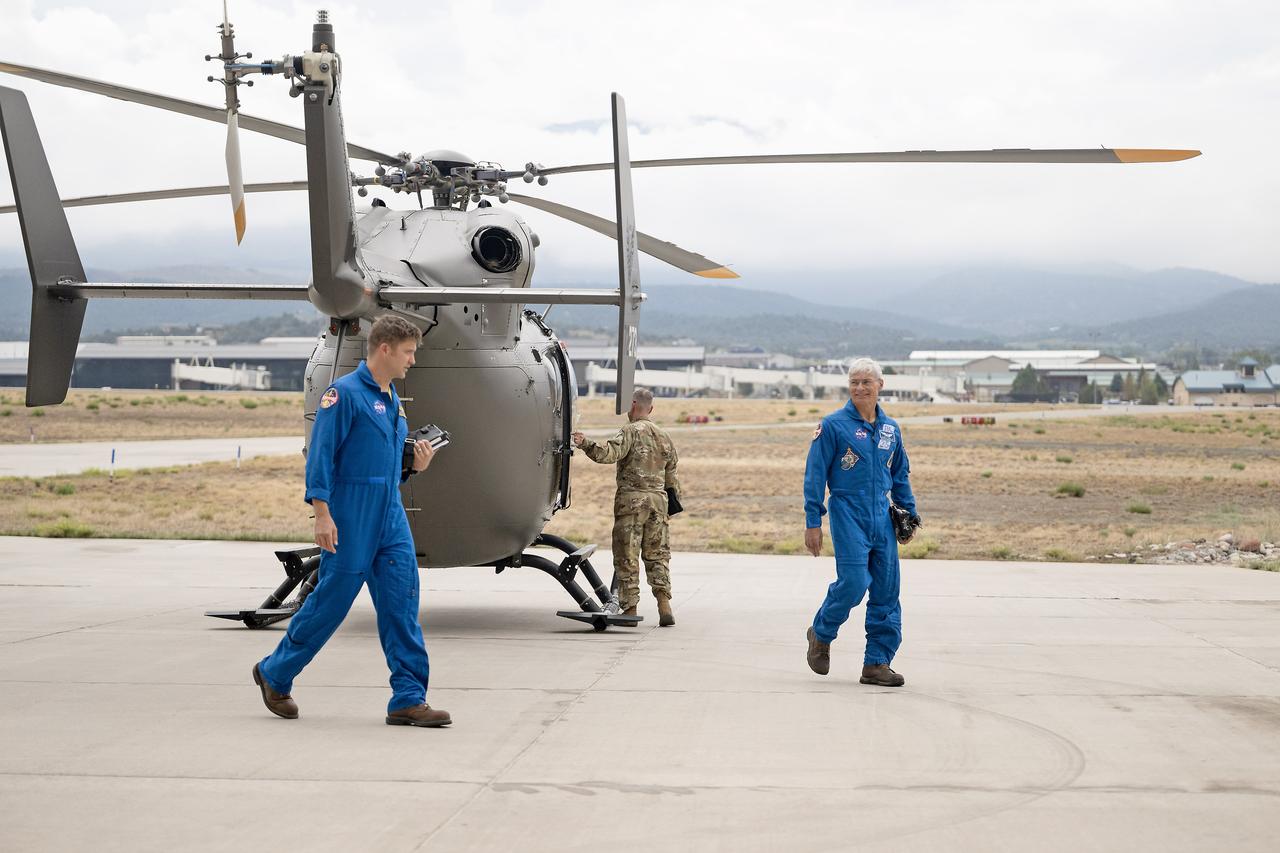

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
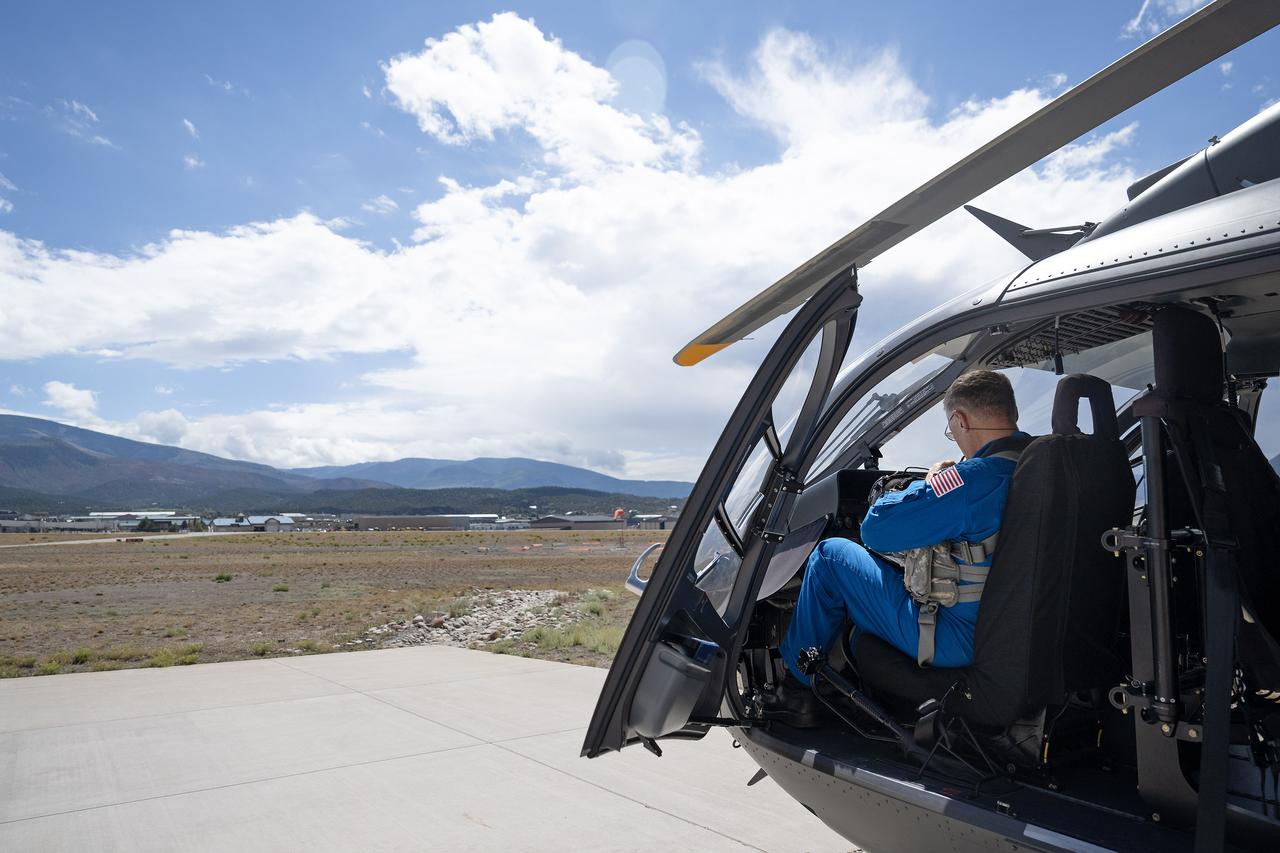

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
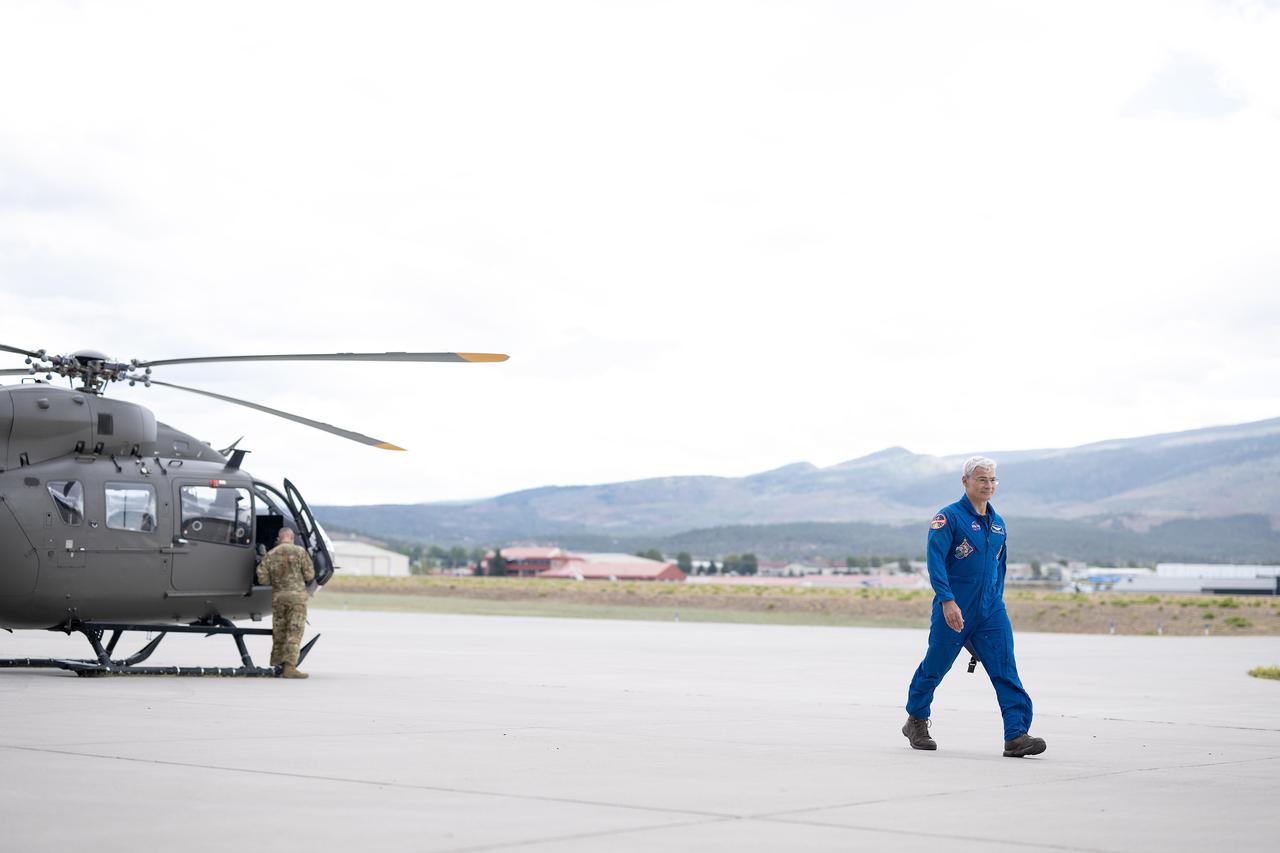

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
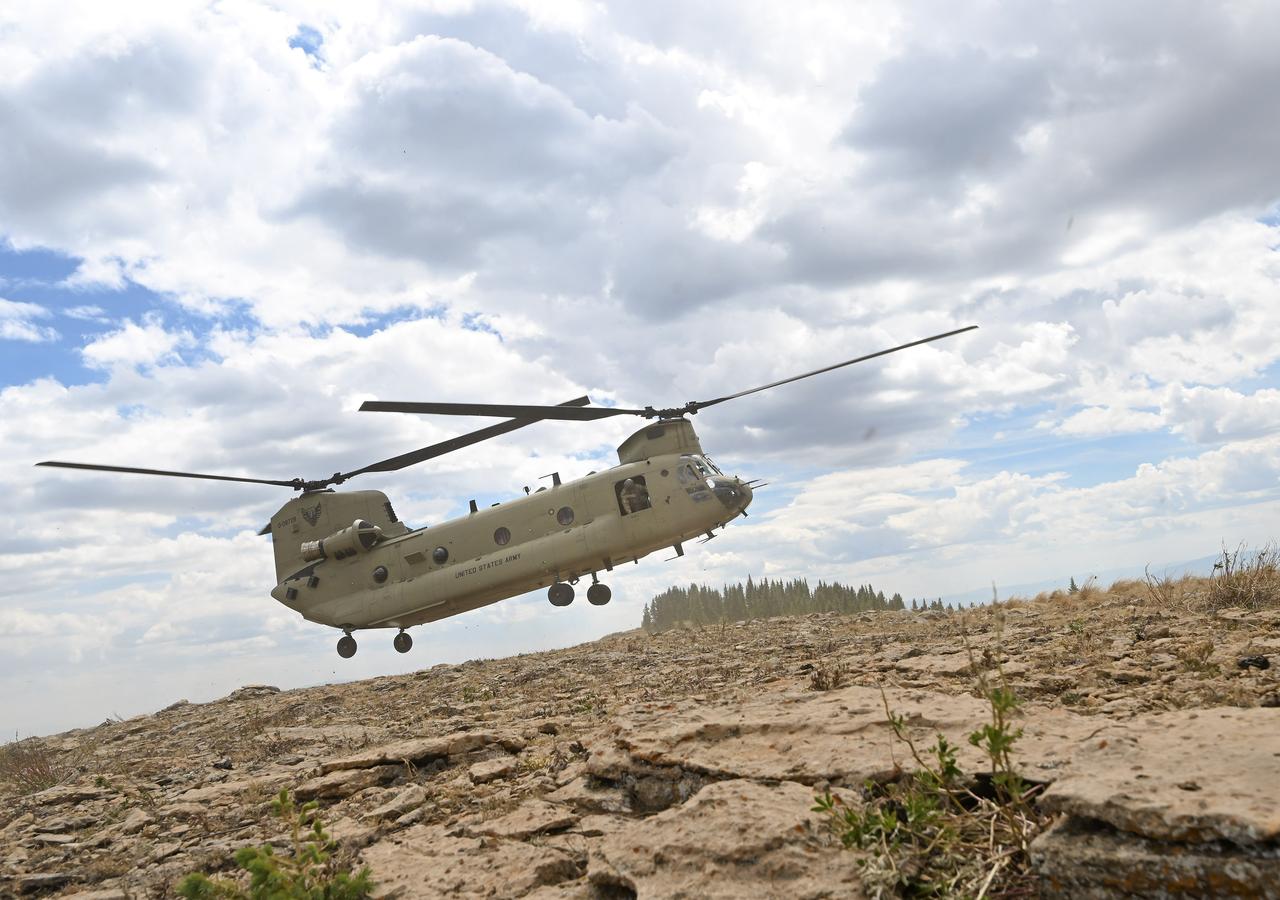

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
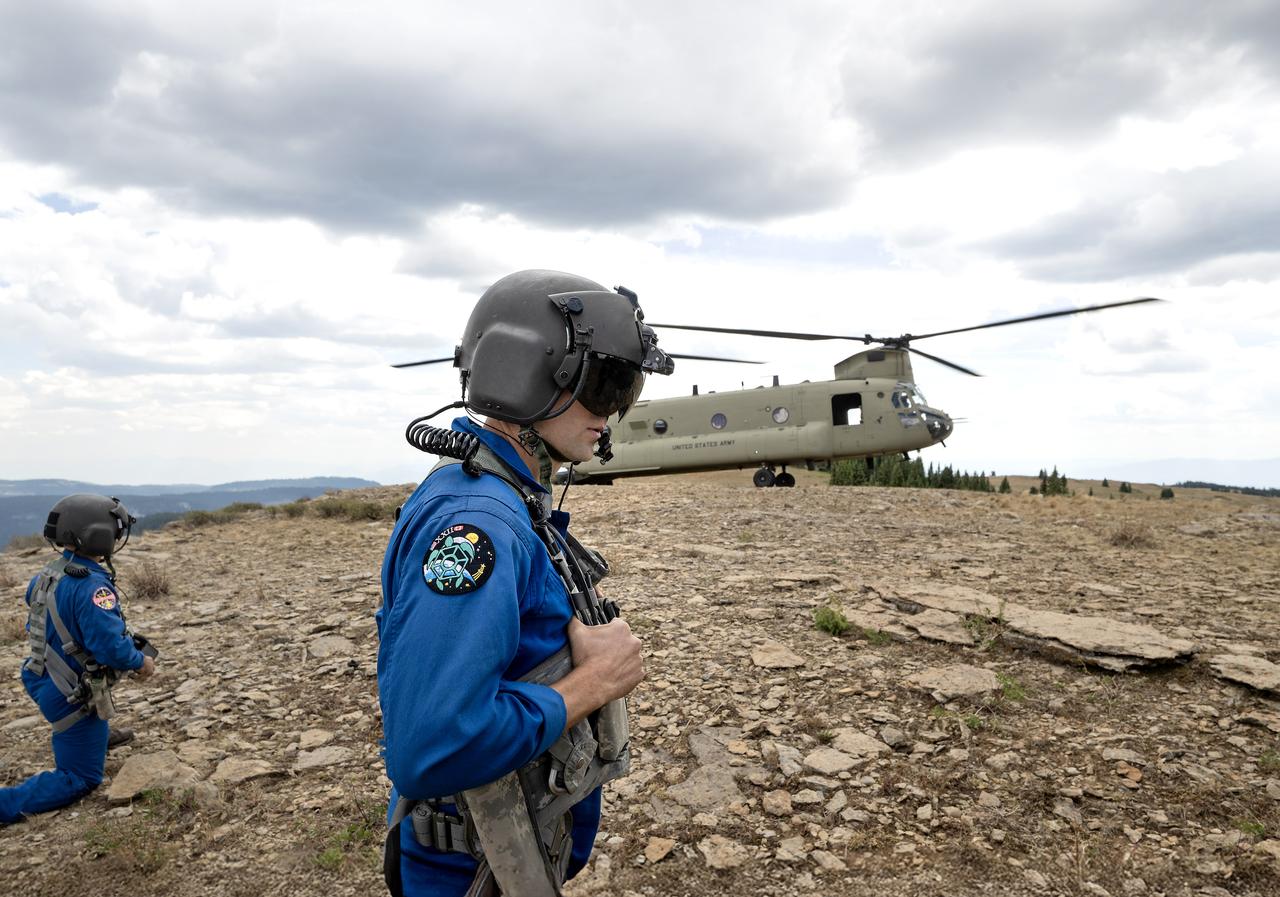

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
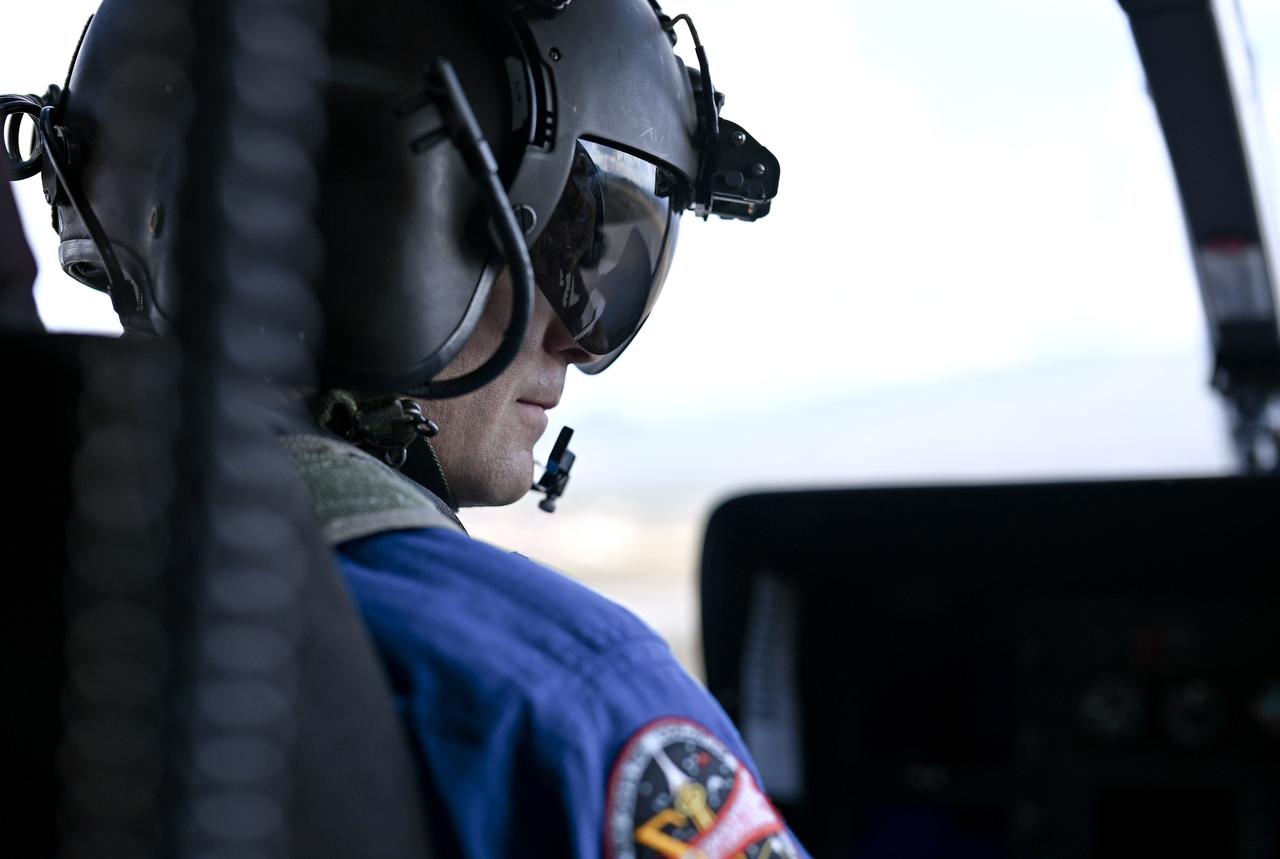

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
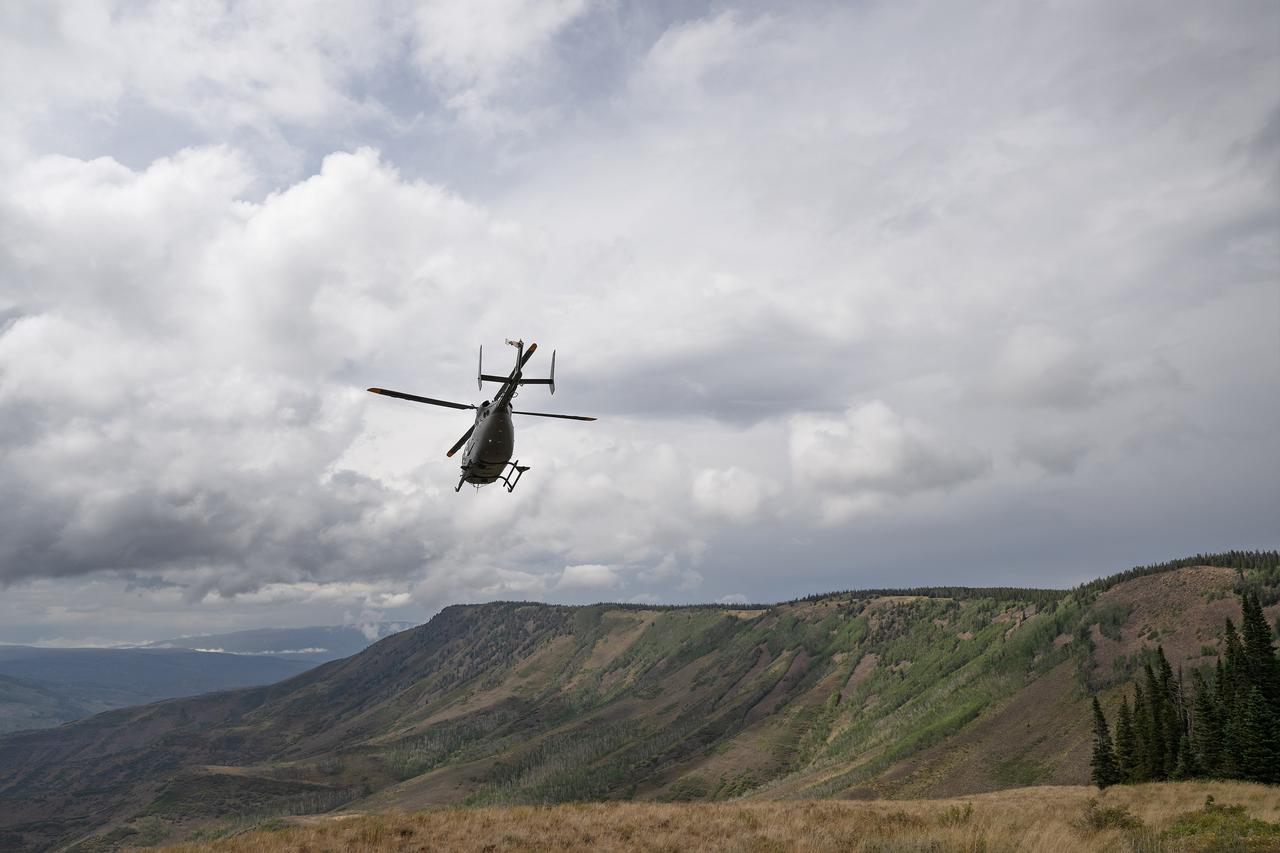

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
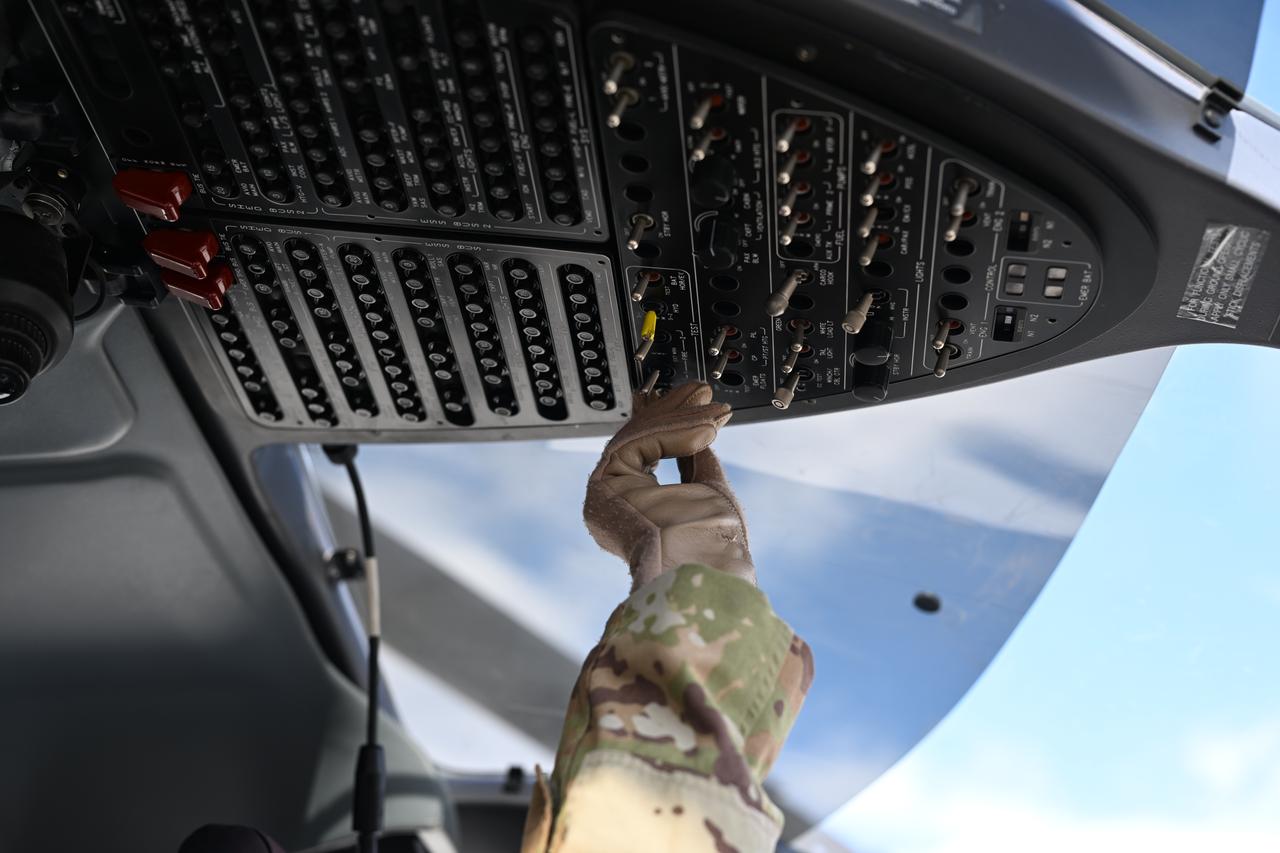

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
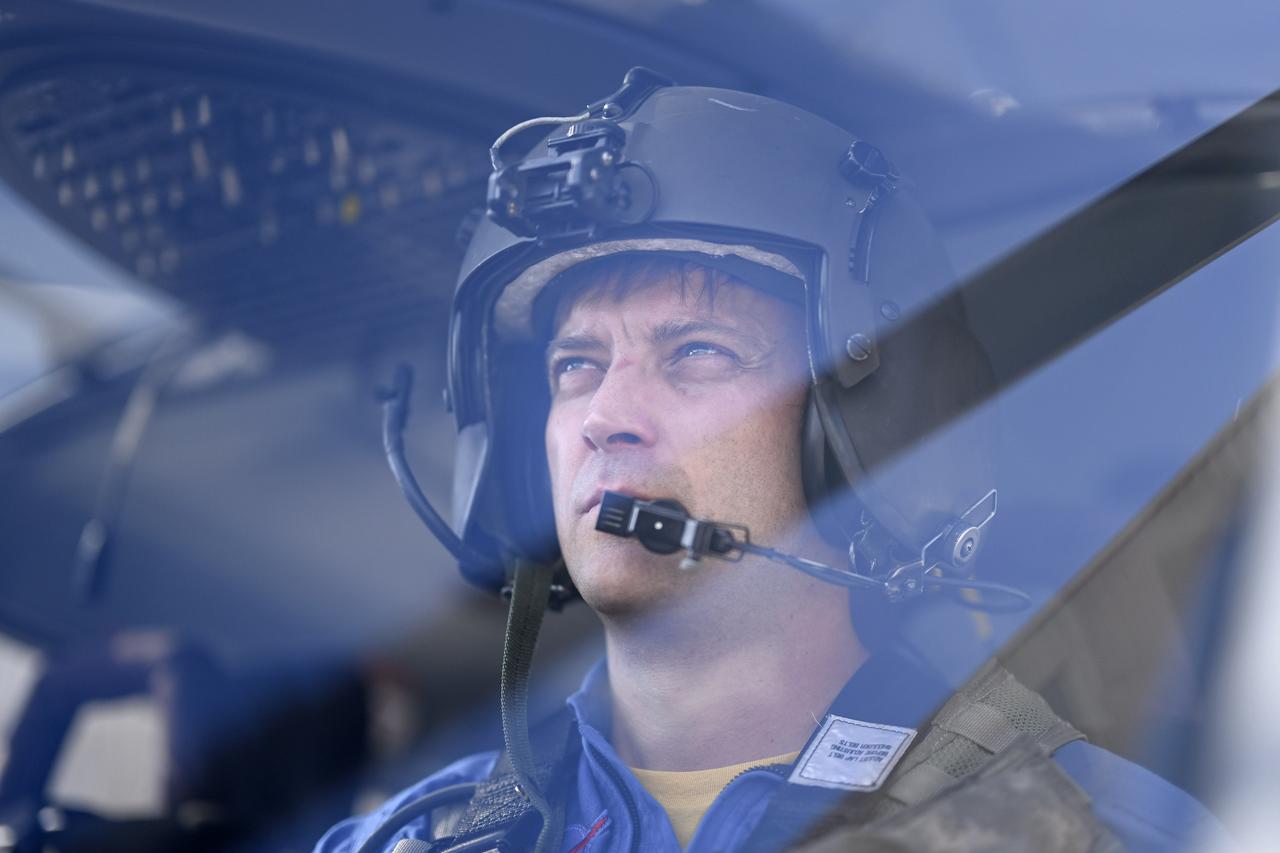

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
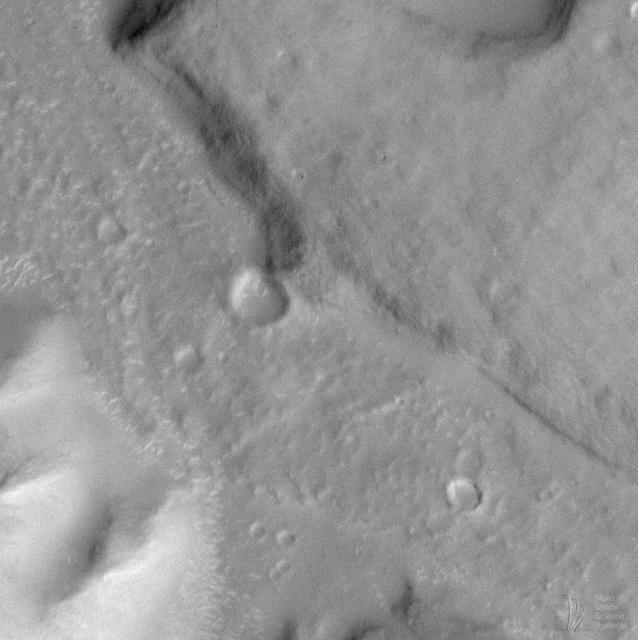

Moon/Mars Landing Commemorative Release: Gusev Crater and Maadim Vallis
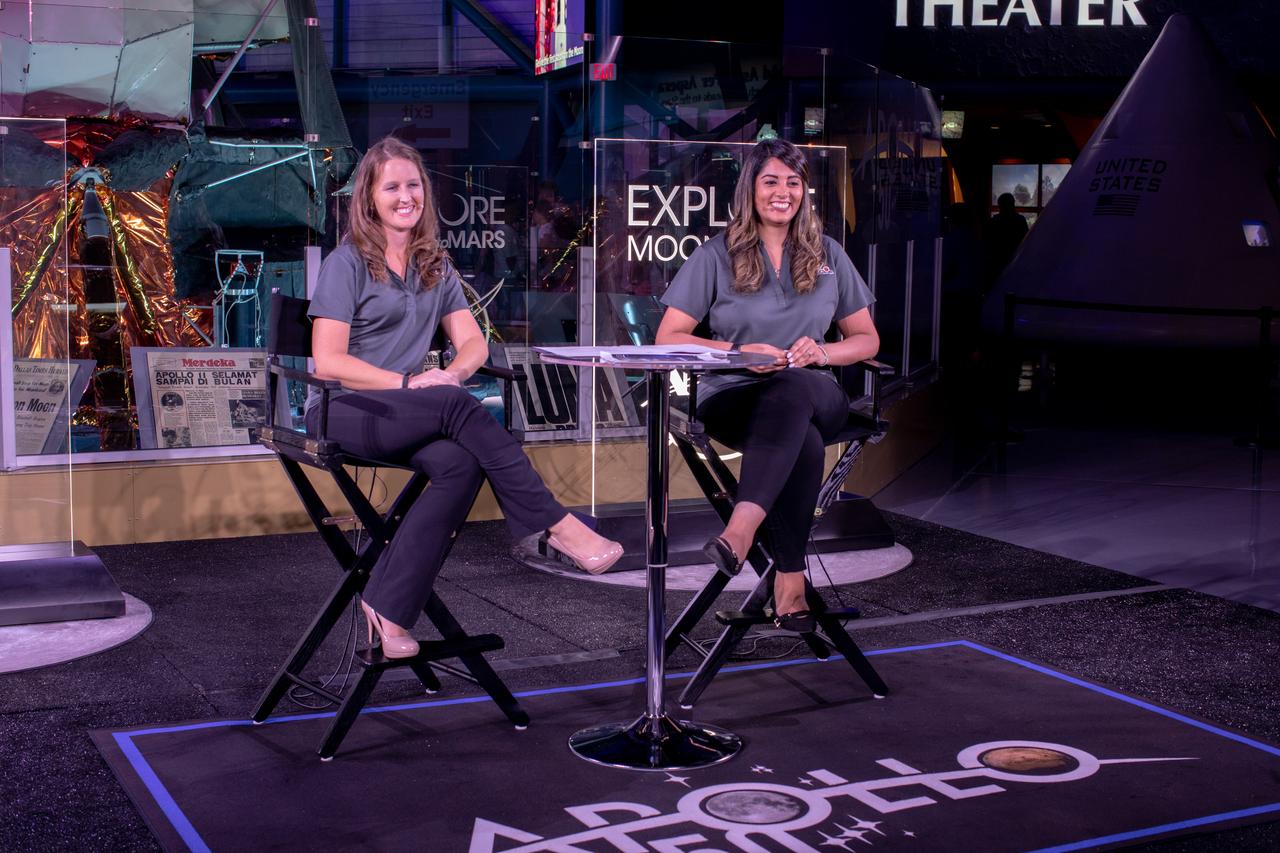

Stephanie Martin, left, NASA Office of Communications, and Nilufar Ramji, NASA Office of STEM Engagement, host a live broadcast of “STEM Forward to the Moon” on July 19, 2019 from Kennedy Space Center’s Apollo/Saturn V Center in Florida. The special program featured kids participating in Moon landing simulations at four museums throughout the country: Cosmosphere in Hutchinson, Kansas; Saint Louis Science Center; Columbia Memorial Space Center in Downey, California; and Arizona Science Center in Phoenix.
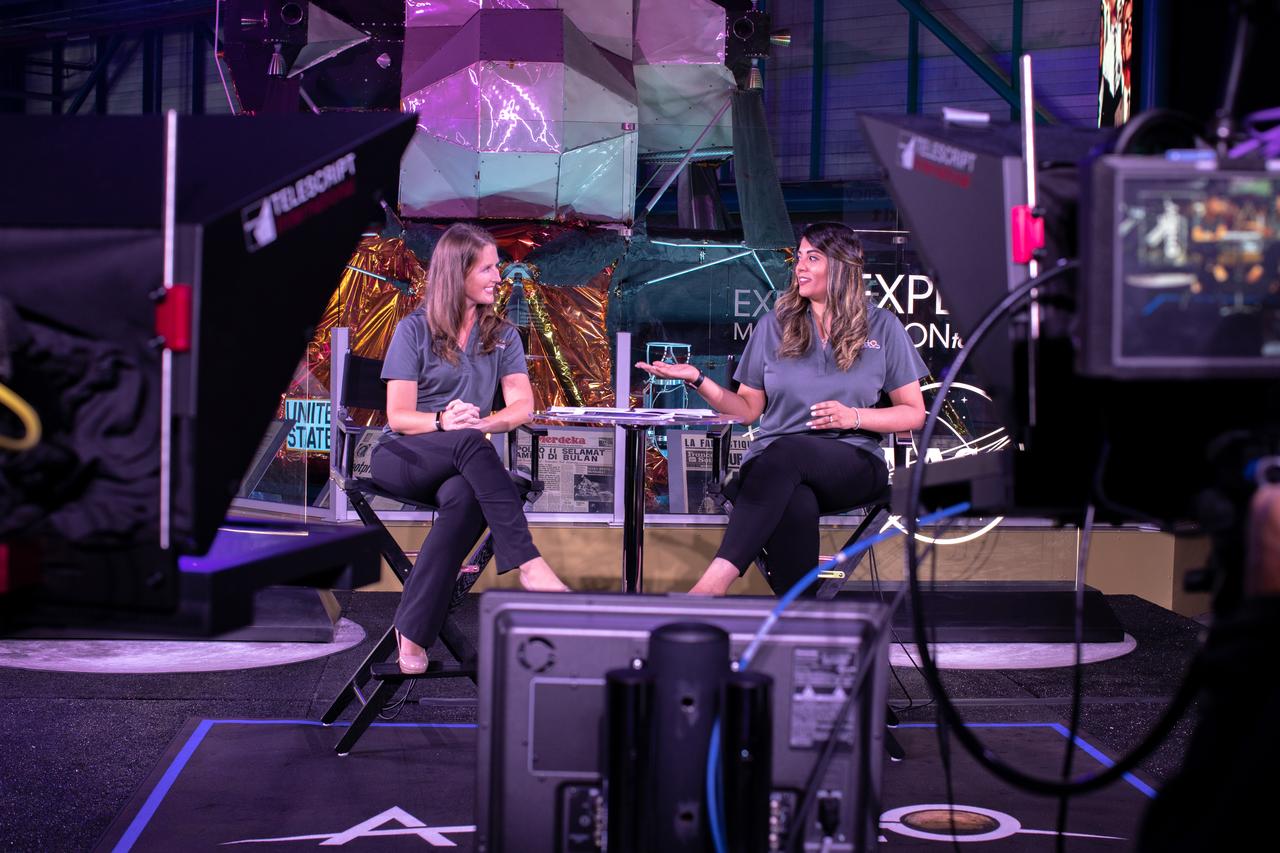

Stephanie Martin, left, NASA Office of Communications, and Nilufar Ramji, NASA Office of STEM Engagement, host a live broadcast of “STEM Forward to the Moon” on July 19, 2019 from Kennedy Space Center’s Apollo/Saturn V Center in Florida. The special program featured kids participating in Moon landing simulations at four museums throughout the country: Cosmosphere in Hutchinson, Kansas; Saint Louis Science Center; Columbia Memorial Space Center in Downey, California; and Arizona Science Center in Phoenix.
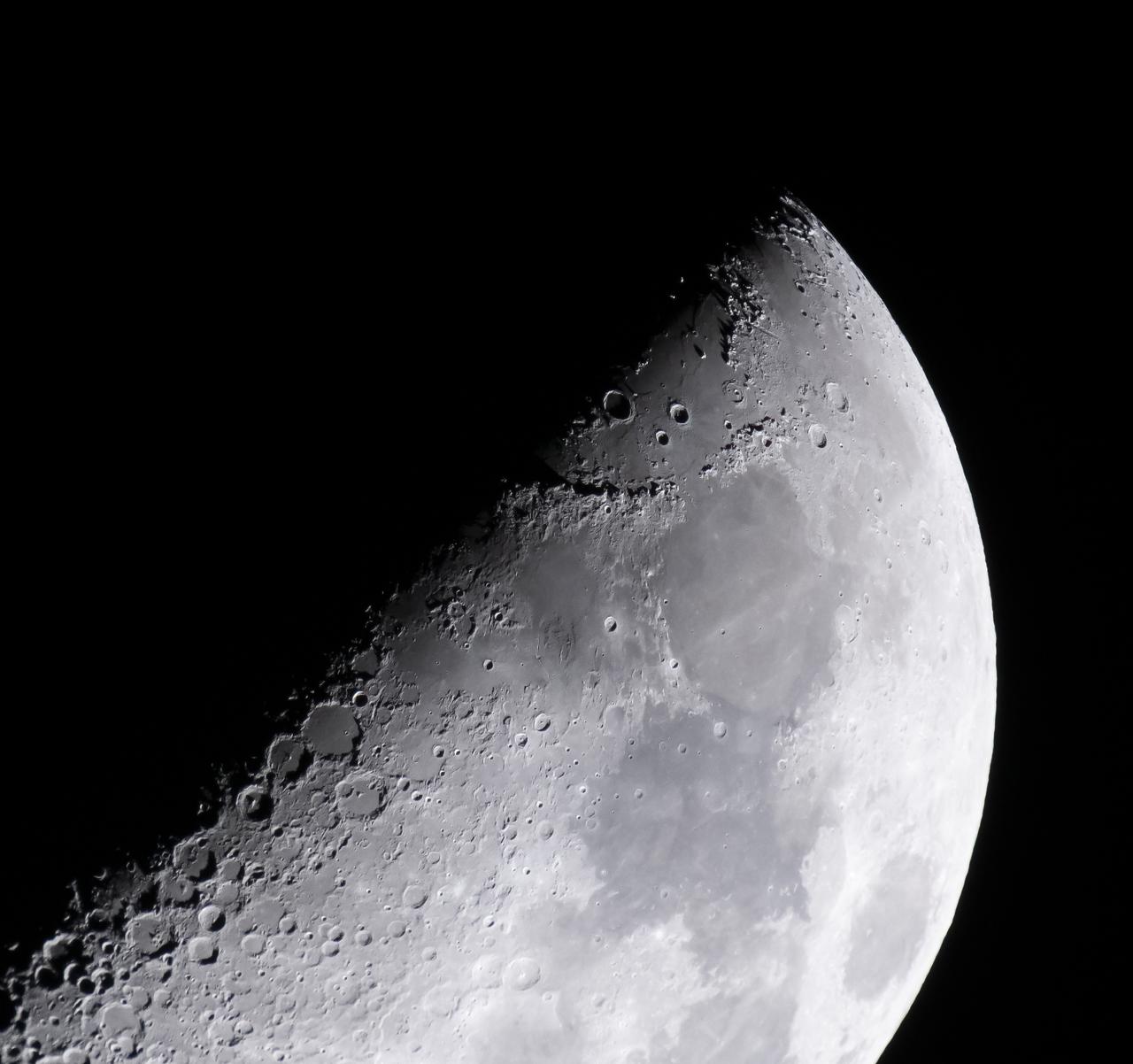

NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems’ Program Manager Shawn Quinn captured this image of the Hadley–Apennine region of the moon including the Apollo 15 landing site (very near the edge of the shadow of one of the lunar mountains in the area). Image is a crop of a full frame image. Apollo 11, 16 and 17 landing sites are also visible in this image. Hadley–Apennine is a region on the near side of Earth's Moon that served as the landing site for the American Apollo 15 mission, the fourth crewed landing on the Moon and the first of the "J-missions", in July 1971. The site is located on the eastern edge of Mare Imbrium on a lava plain known as Palus Putredinis. Hadley–Apennine is bordered by the Montes Apenninus (often referred to as "Apennine Front"), a mountain range, and Hadley Rille, a meandering channel, on the east and west, respectively.
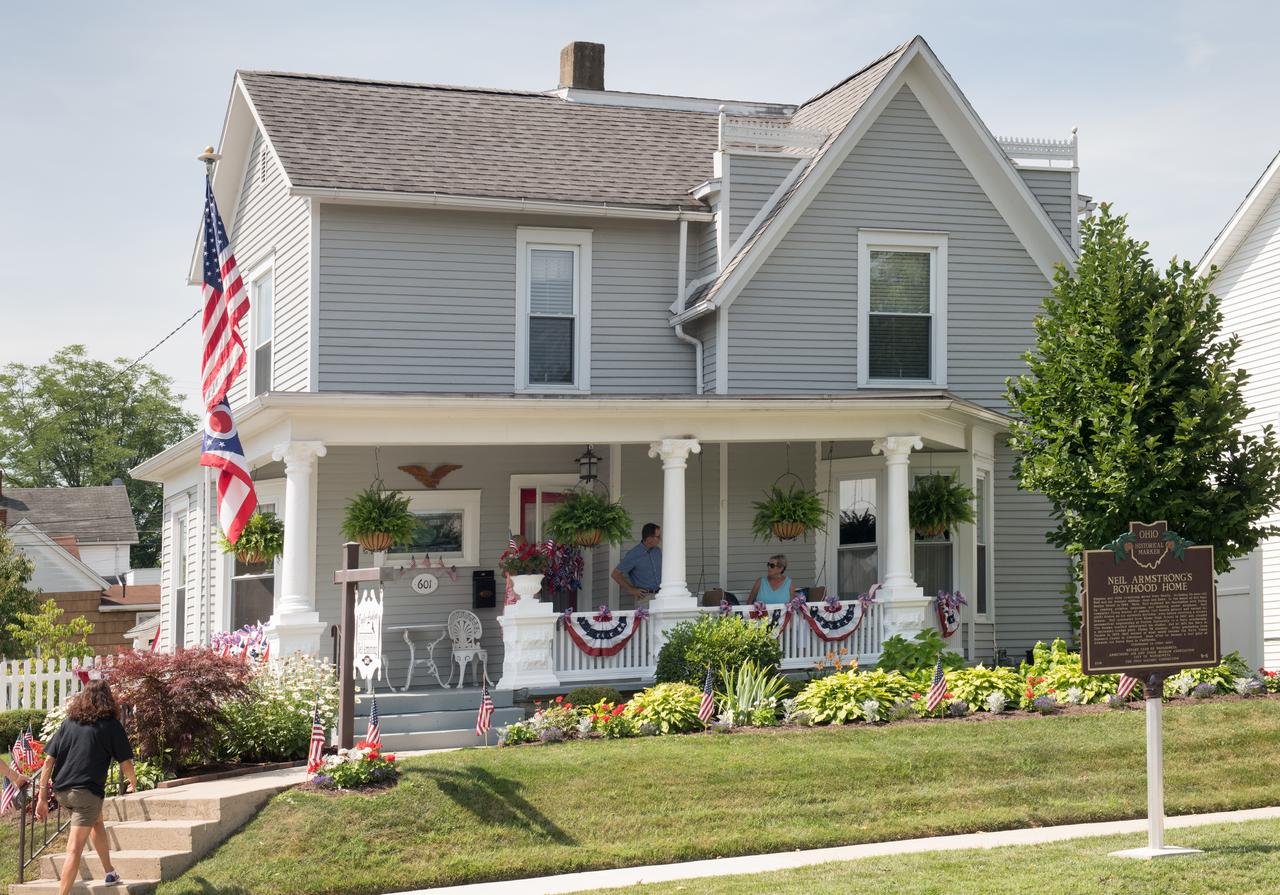

Summer Moon Festival, Wapakoneta, Ohio, Apollo 11 Moon Landing 50th Anniversary, Lunch Reception for Race Donors, held at Neil Armstrong's Boyhood Home, now the home of Karen Tullis
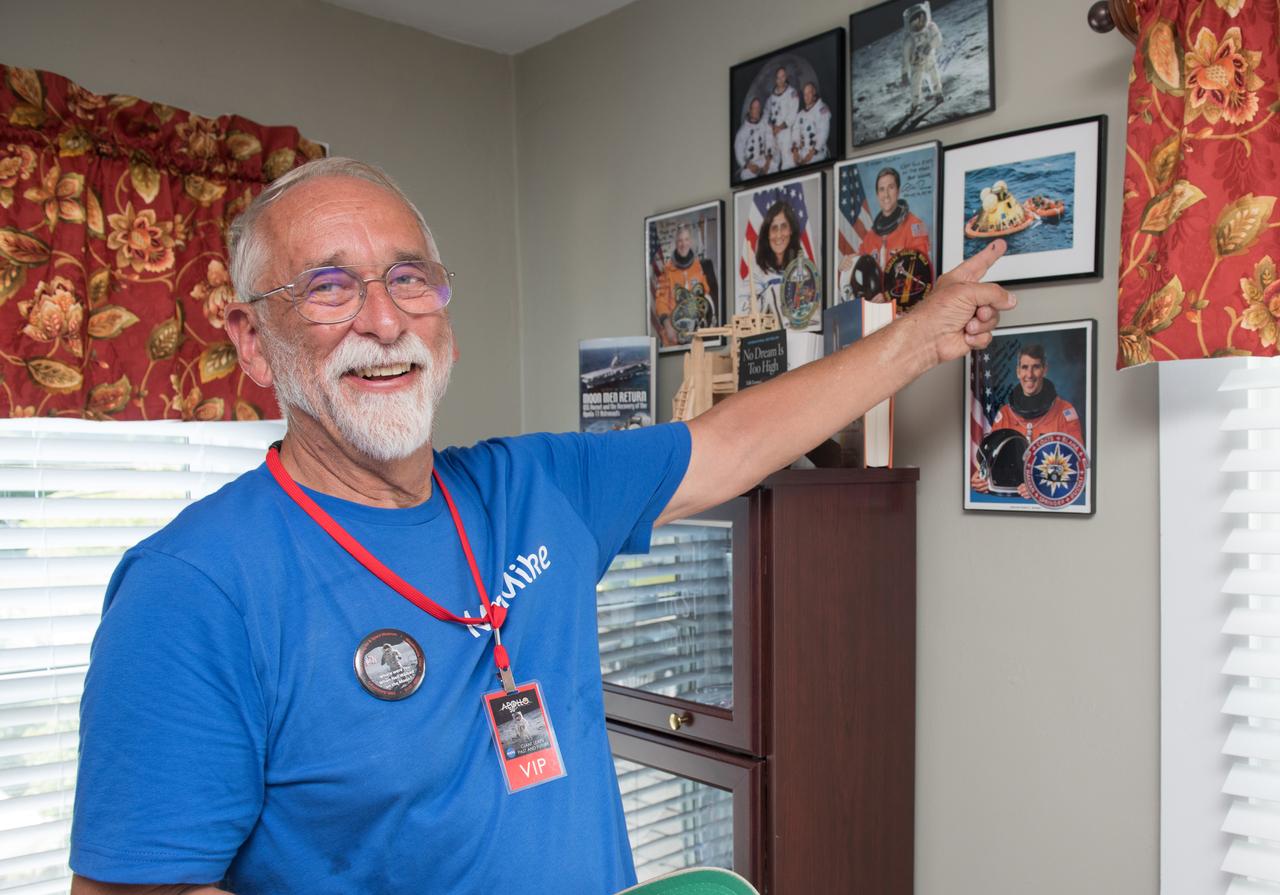

Summer Moon Festival, Wapakoneta, Ohio, Apollo 11 Moon Landing 50th Anniversary, Lunch Reception for Race Donors, held at Neil Armstrong's Boyhood Home, now the home of Karen Tullis
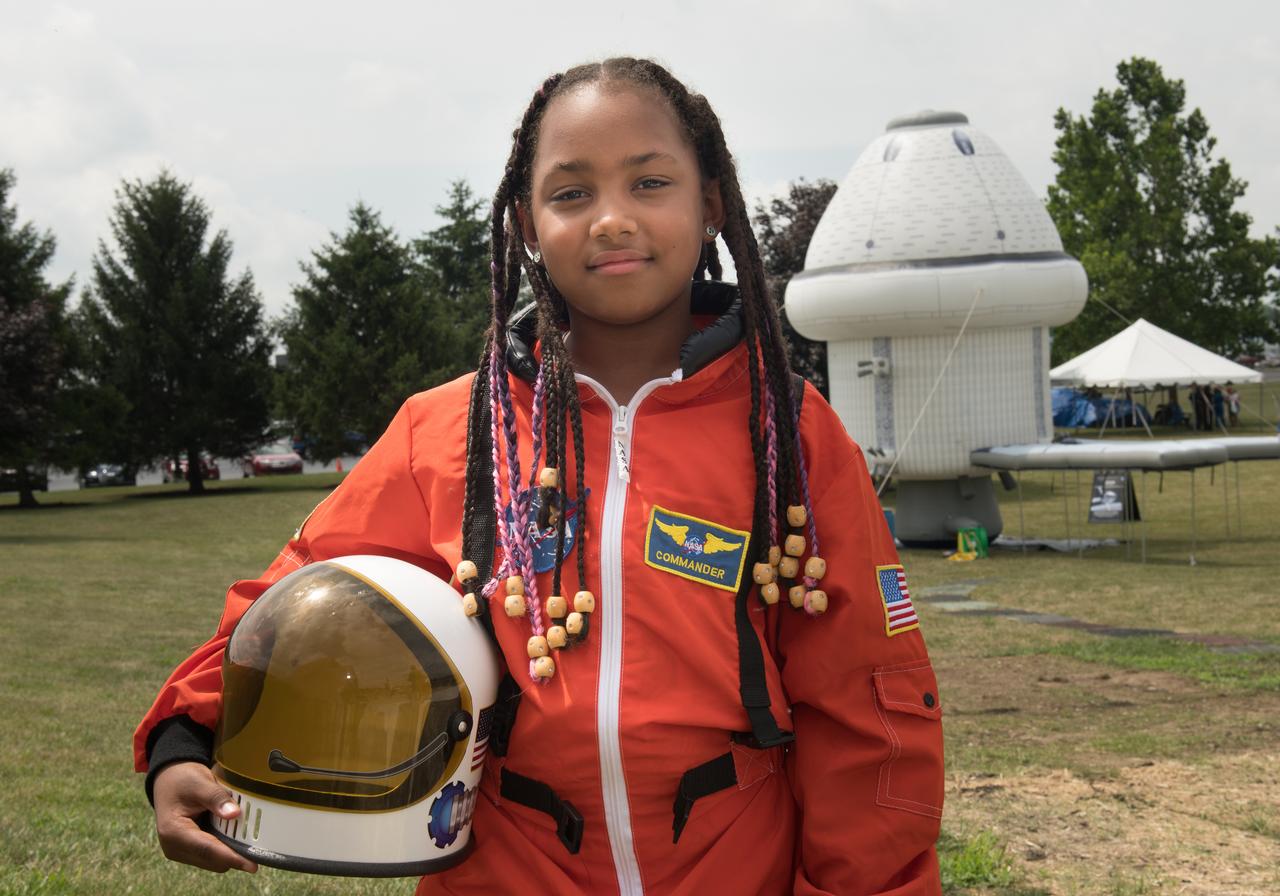

Summer Moon Festival, Wapakoneta, Ohio, Apollo 11 Moon Landing 50th Anniversary
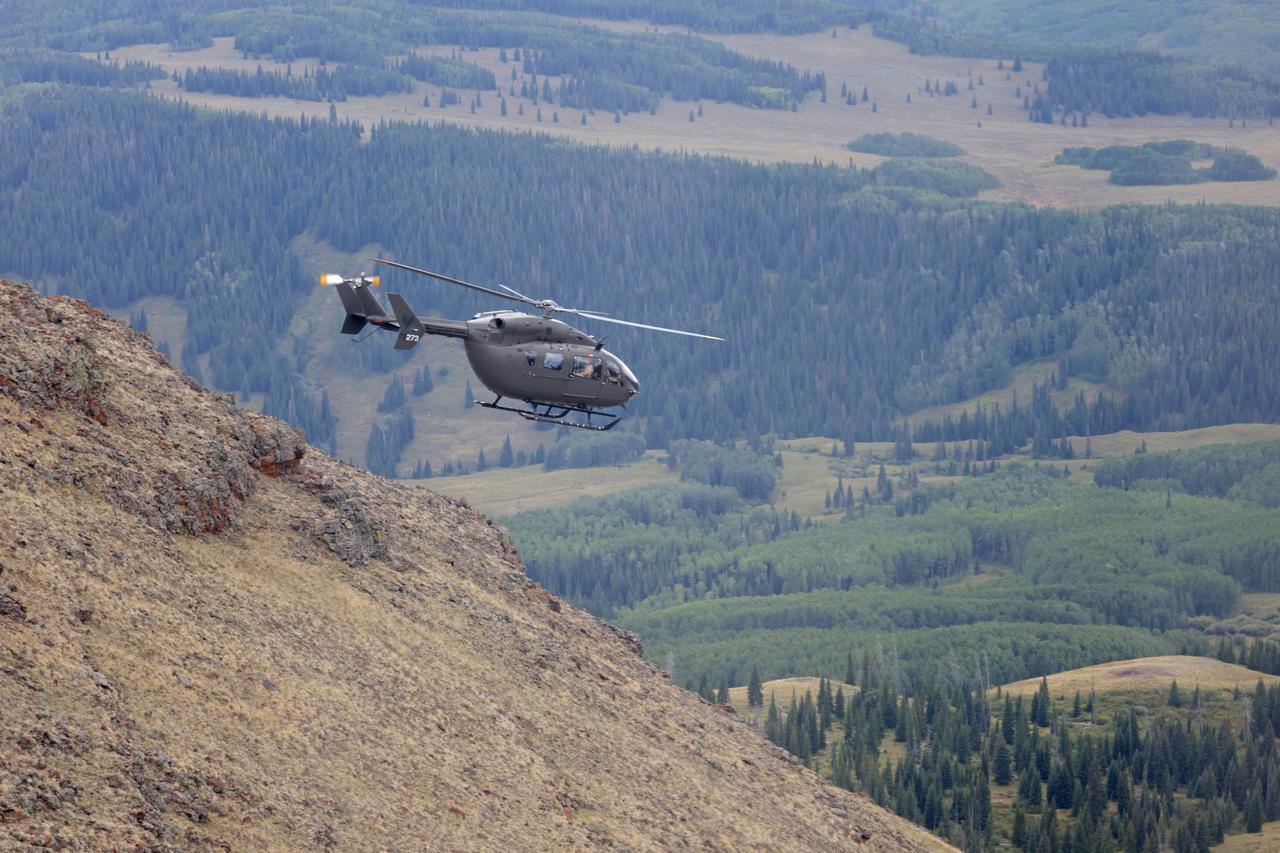

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
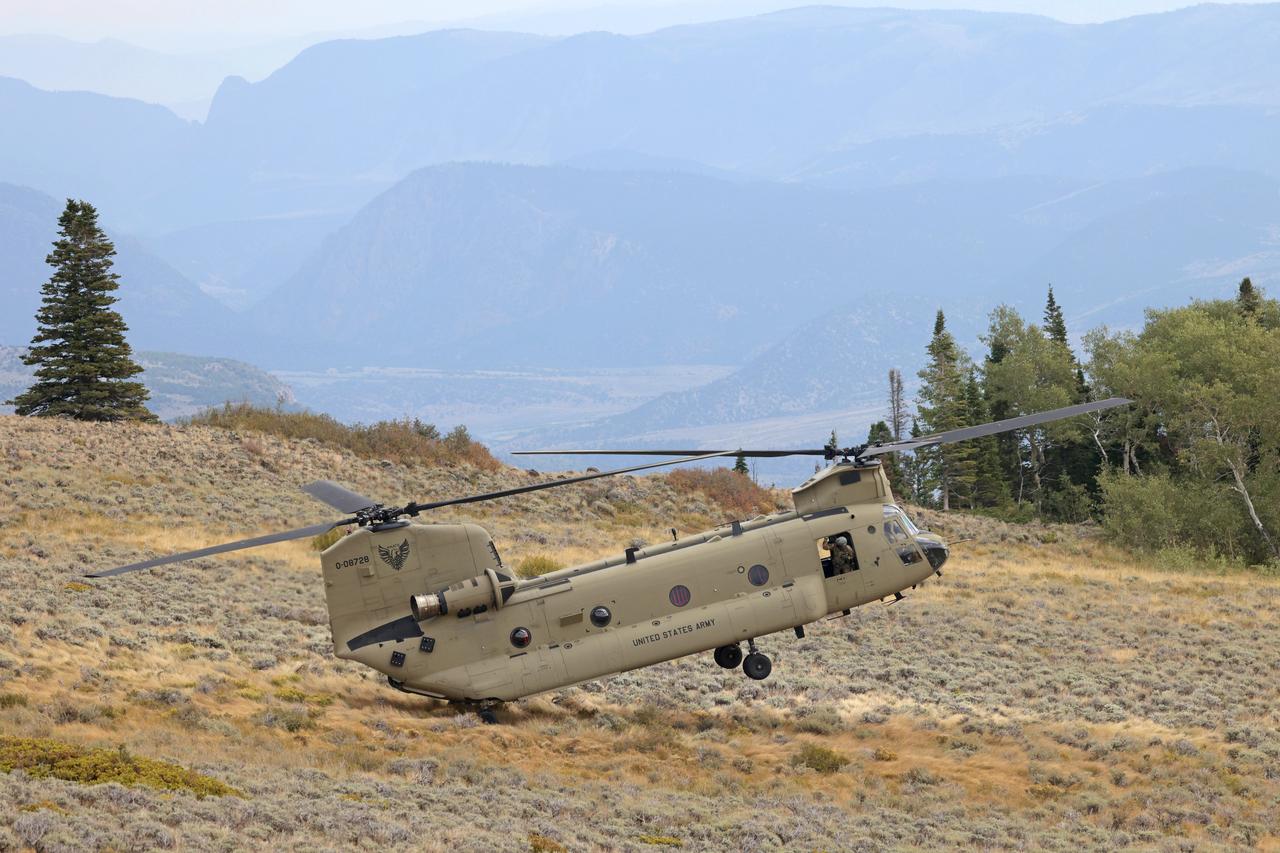

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
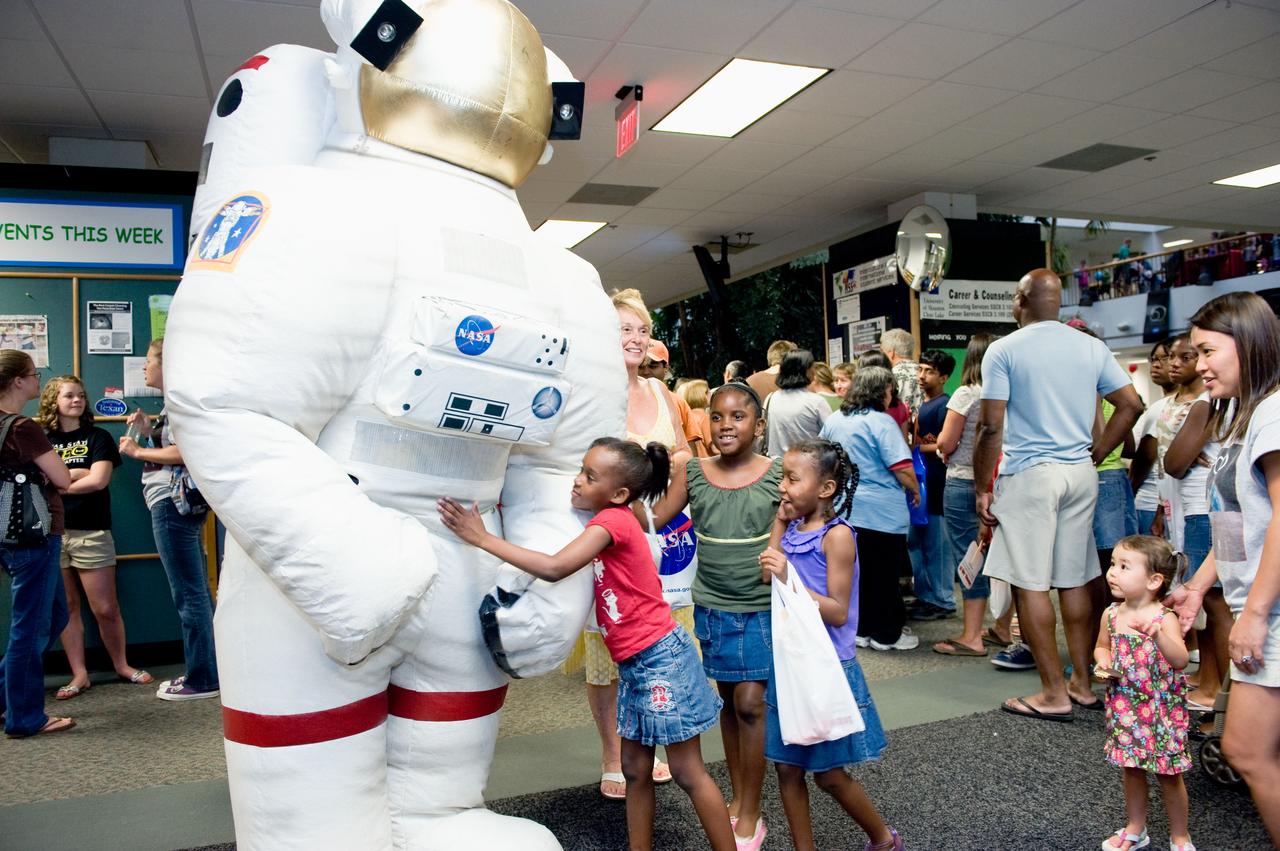

"Fly Me to the Moon: A Community Celebration of the First Lunar Landing" at University of Houston - Clear Lake

Astronaut Don Thomas and the crowd cheer at the moment of the Apollo 11 touchdown on the Moon during a replay of the 1969 television broadcast at the Summer Moon Festival, Wapakoneta, Ohio, Apollo 11 Moon Landing 50th Anniversary
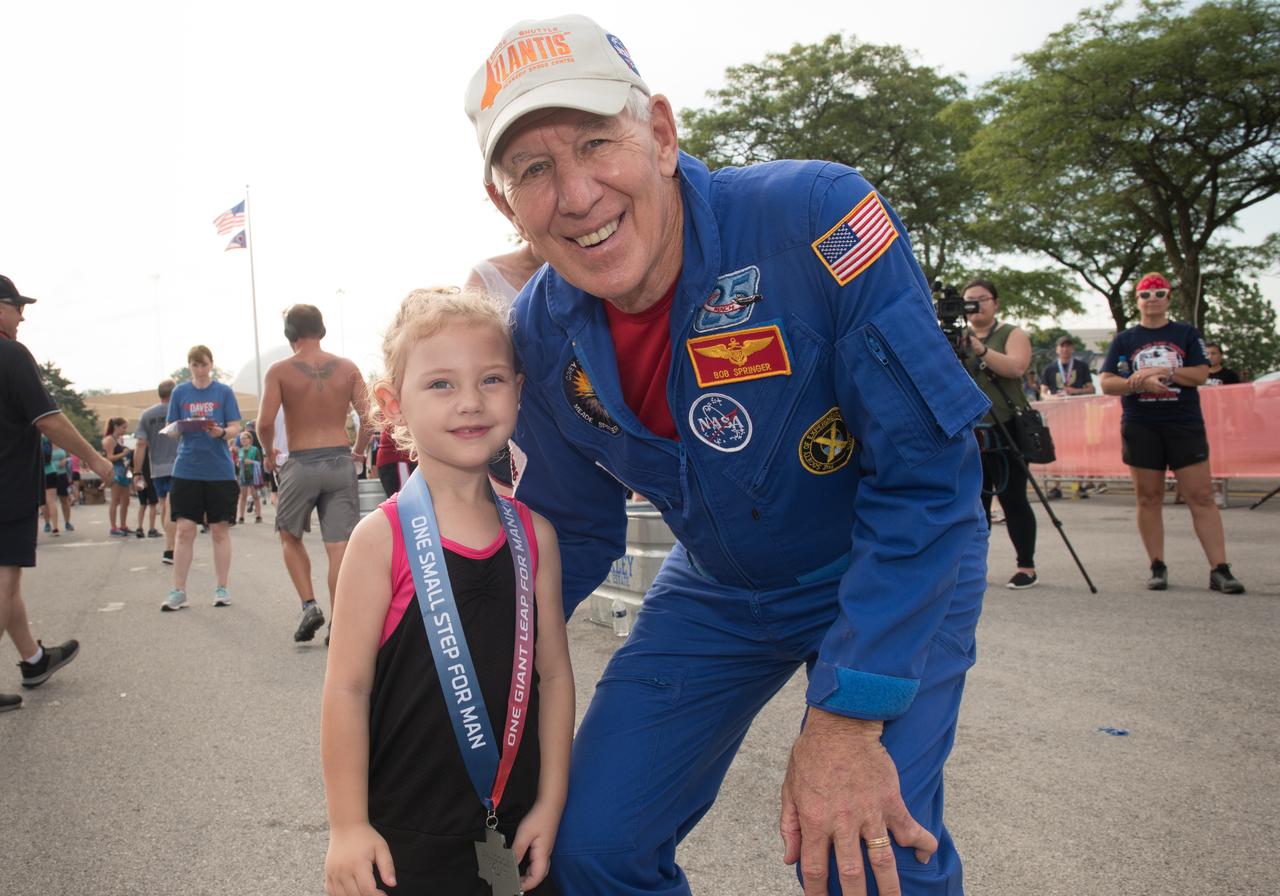

Astronaut Robert Springer congratulates who earned a medal in the 1-mile Fun Run during the Summer Moon Festival, Wapakoneta, Ohio, Apollo 11 Moon Landing 50th Anniversary, Run To The Moon Race
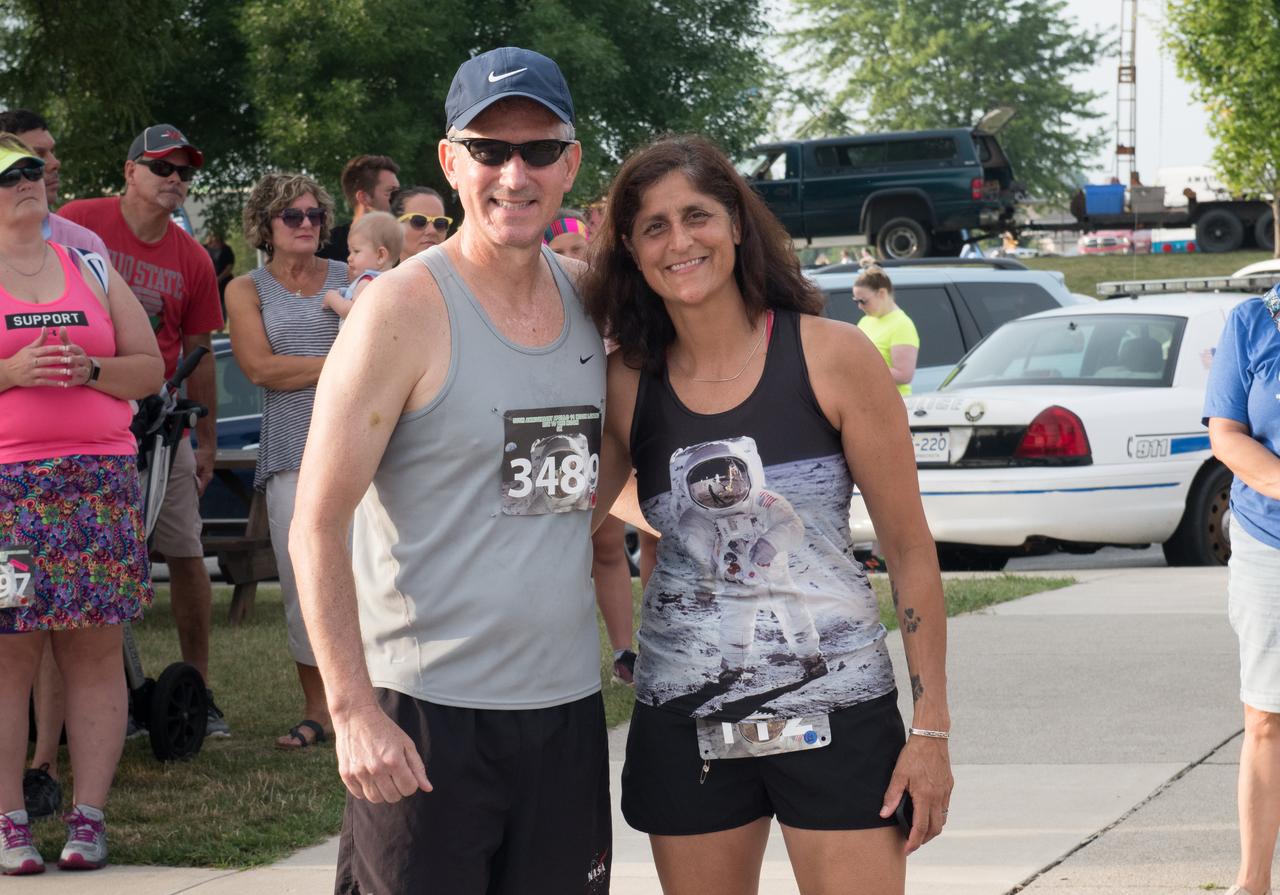

Astronaut Michael Good, Astronaut Sunita Williams prepare for the Run To The Moon Race during the Summer Moon Festival, Wapakoneta, Ohio, Apollo 11 Moon Landing 50th Anniversary
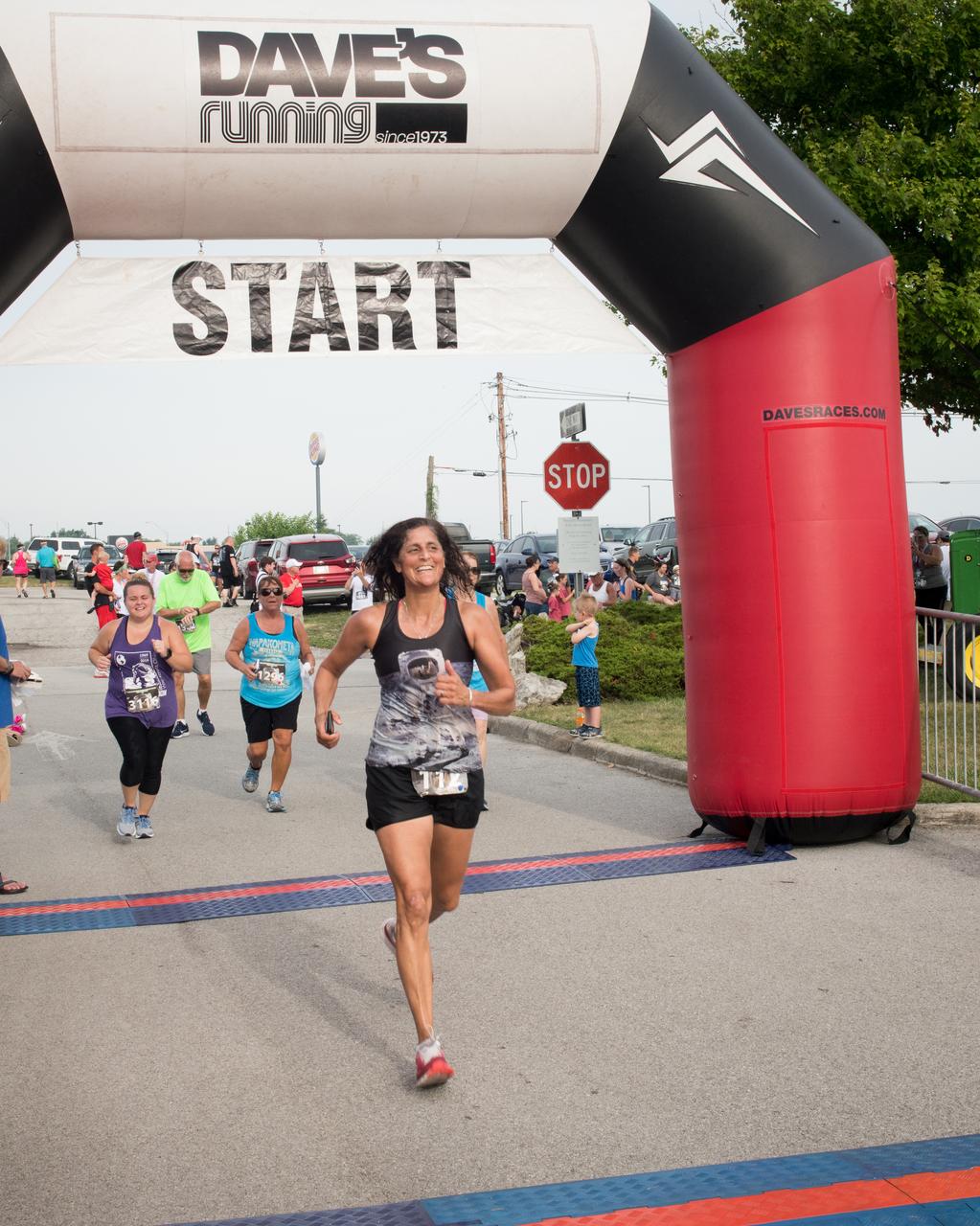

Astronaut Sunita Williams crosses the finish line of the Run To The Moon Race during the Summer Moon Festival, Wapakoneta, Ohio, Apollo 11 Moon Landing 50th Anniversary
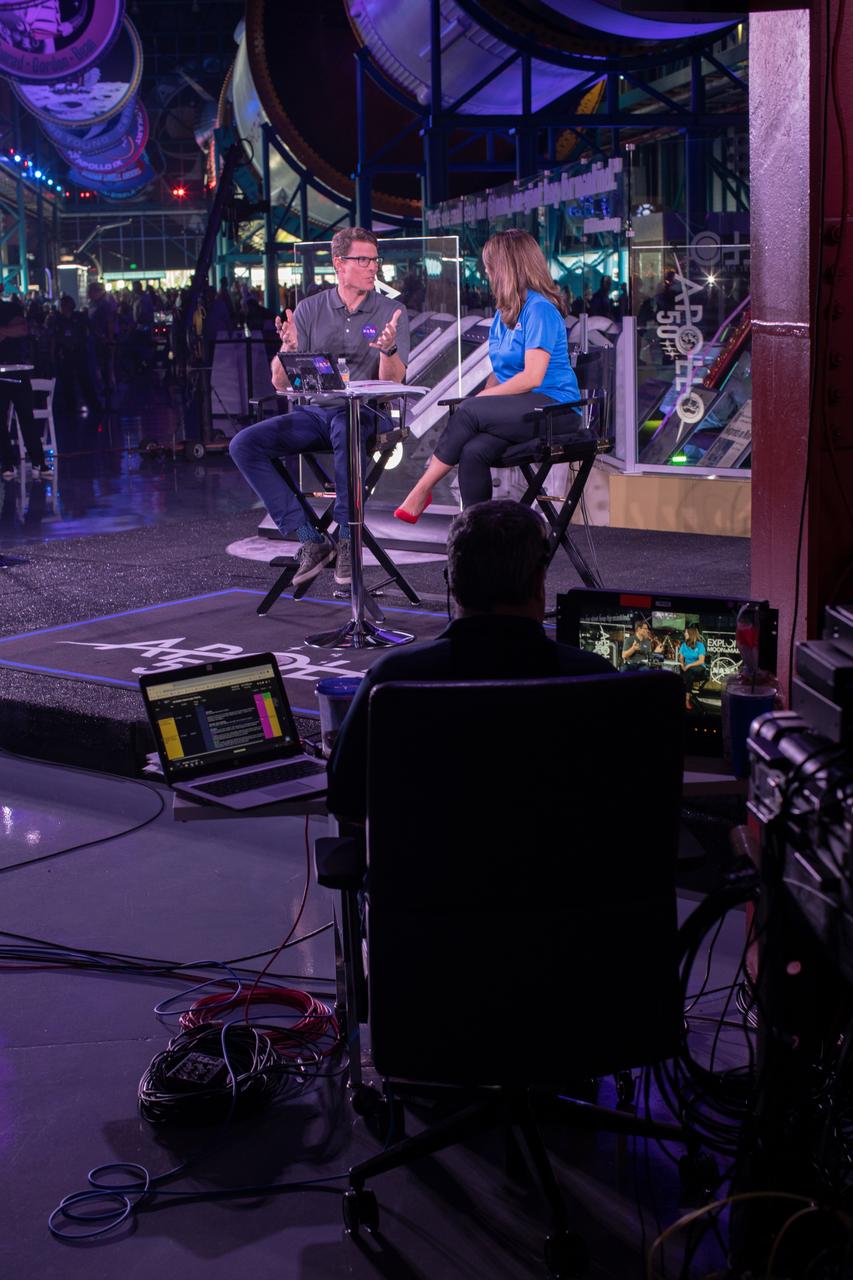

Derrol Nail, left, and Marie Lewis, NASA Office of Communications, host a special Apollo 11 show titled “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future” on July 19, 2019. The show, which honored the heroes of Apollo and examined NASA’s future plans, was broadcast live from Kennedy Space Center’s Apollo/Saturn V Center in Florida. It featured segments from across the nation, including The National Mall in Washington, NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Neil Armstrong’s hometown of Wapakoneta, Ohio, and the Apollo 11 command module on display at the Museum of Flight in Seattle.
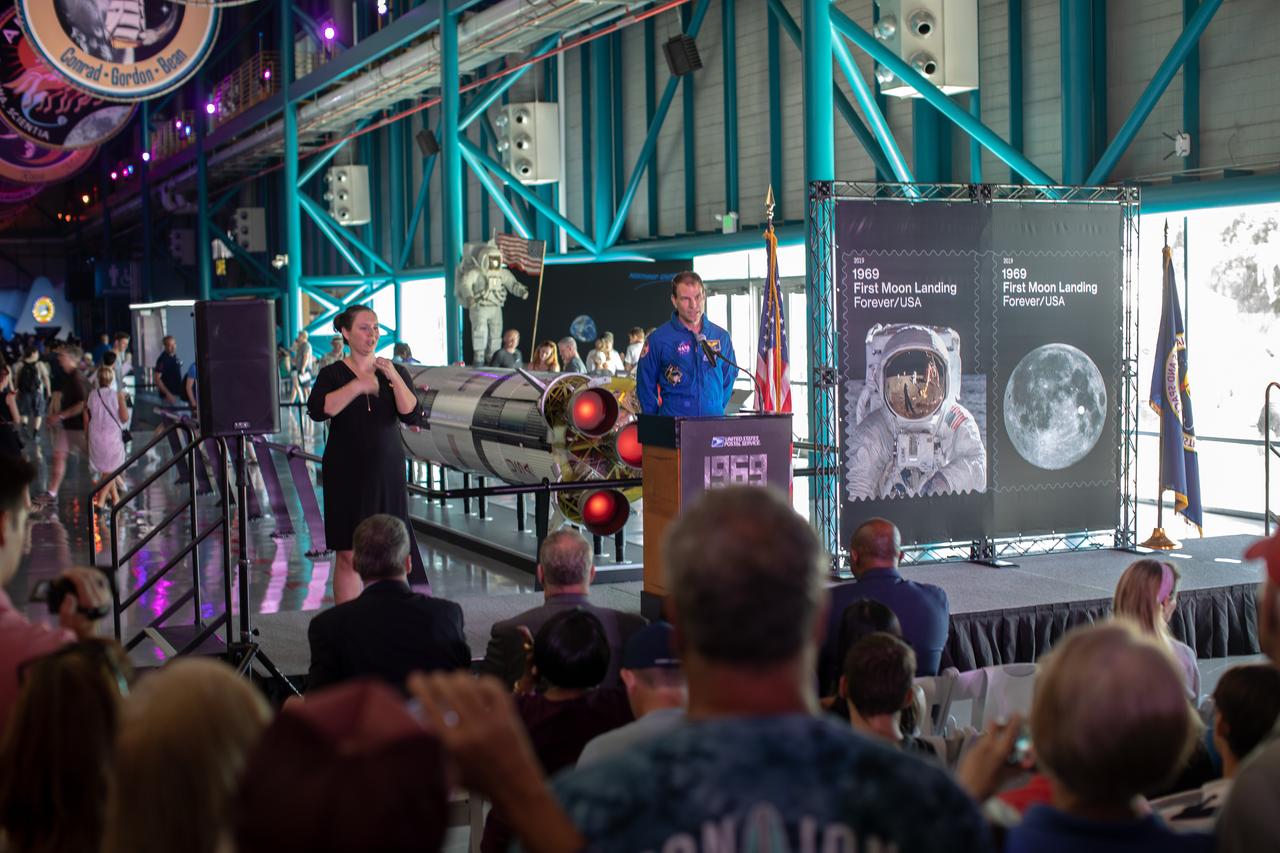

Astronaut Stan Love speaks at Kennedy Space Center’s Apollo/Saturn V Center on Friday, July 19, 2019. Love addressed a crowd at the Florida spaceport during a 50th Anniversary celebration of the Apollo 11 mission. The U.S. Postal Service issued two forever stamps to honor the historic moment. The event marked the first day of issue for the special stamps.
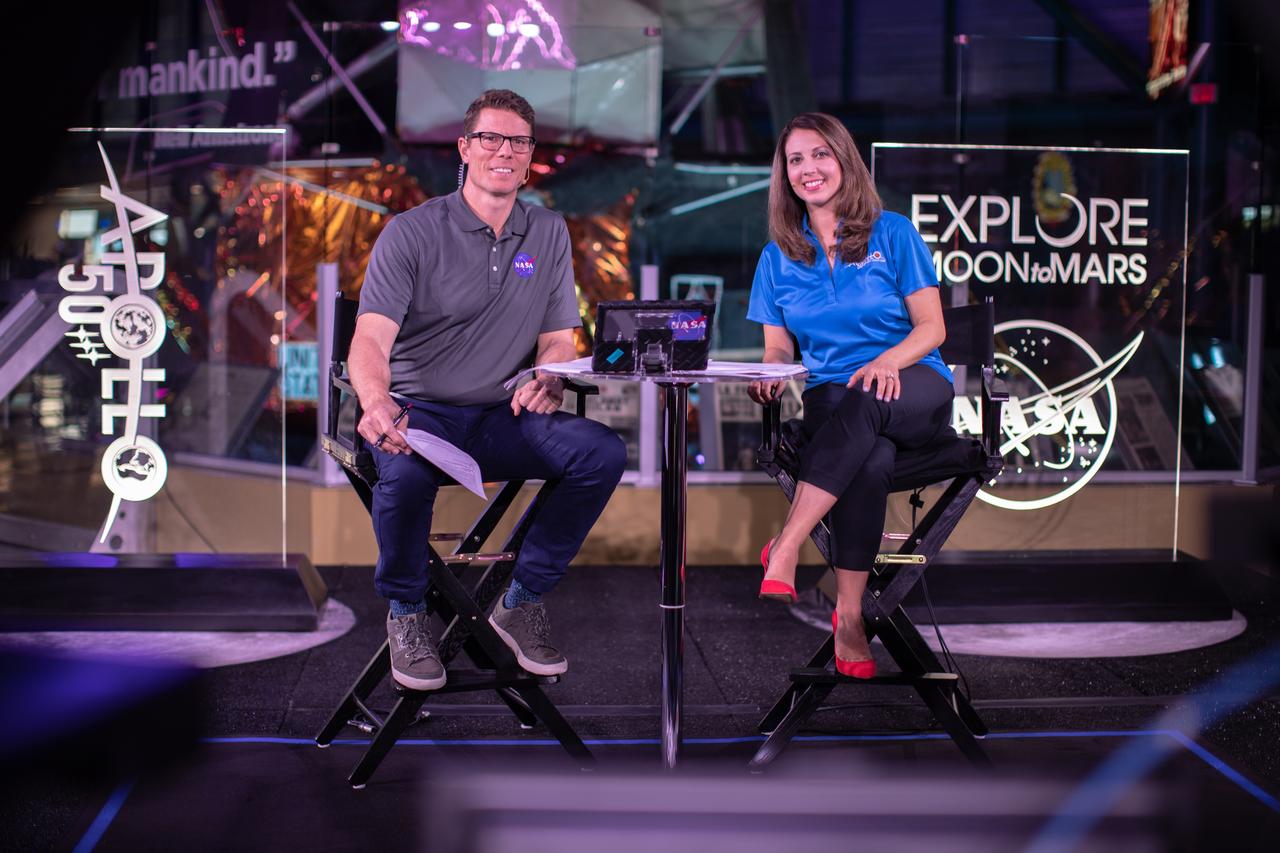

Derrol Nail, left, and Marie Lewis, NASA Office of Communications, host a special Apollo 11 show titled “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future” on July 19, 2019. The show, which honored the heroes of Apollo and examined NASA’s future plans, was broadcast live from Kennedy Space Center’s Apollo/Saturn V Center in Florida. It featured segments from across the nation, including The National Mall in Washington, NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Neil Armstrong’s hometown of Wapakoneta, Ohio, and the Apollo 11 command module on display at the Museum of Flight in Seattle.

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished. This logo represents the Commemorative 20th Anniversary of the Apollo 11 Lunar mission. Housed inside the zero of the numeral twenty is the original flight insignia in which an Eagle descending upon the lunar surface depicts the LM, named “Eagle’’.
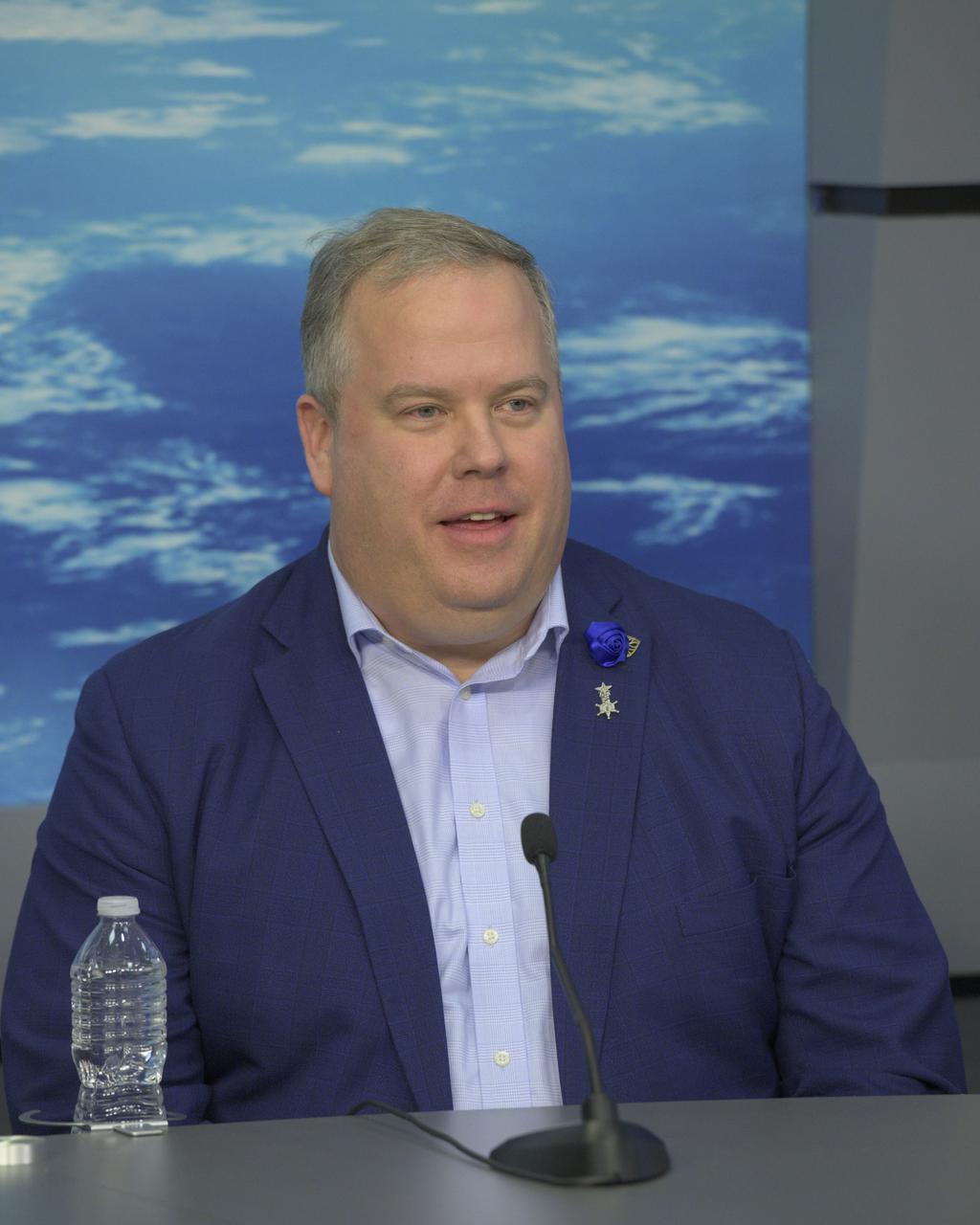

Tim Crain, chief technology officer and co-founder, Intuitive Machines, participates in a news conference Feb. 23, 2024, at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston to discuss the company’s Nova-C lander, called Odysseus, and its successful soft landing on the Moon Feb. 22, 2024. The mission is the first landing under NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, and the first American lunar landing in more than 50 years.
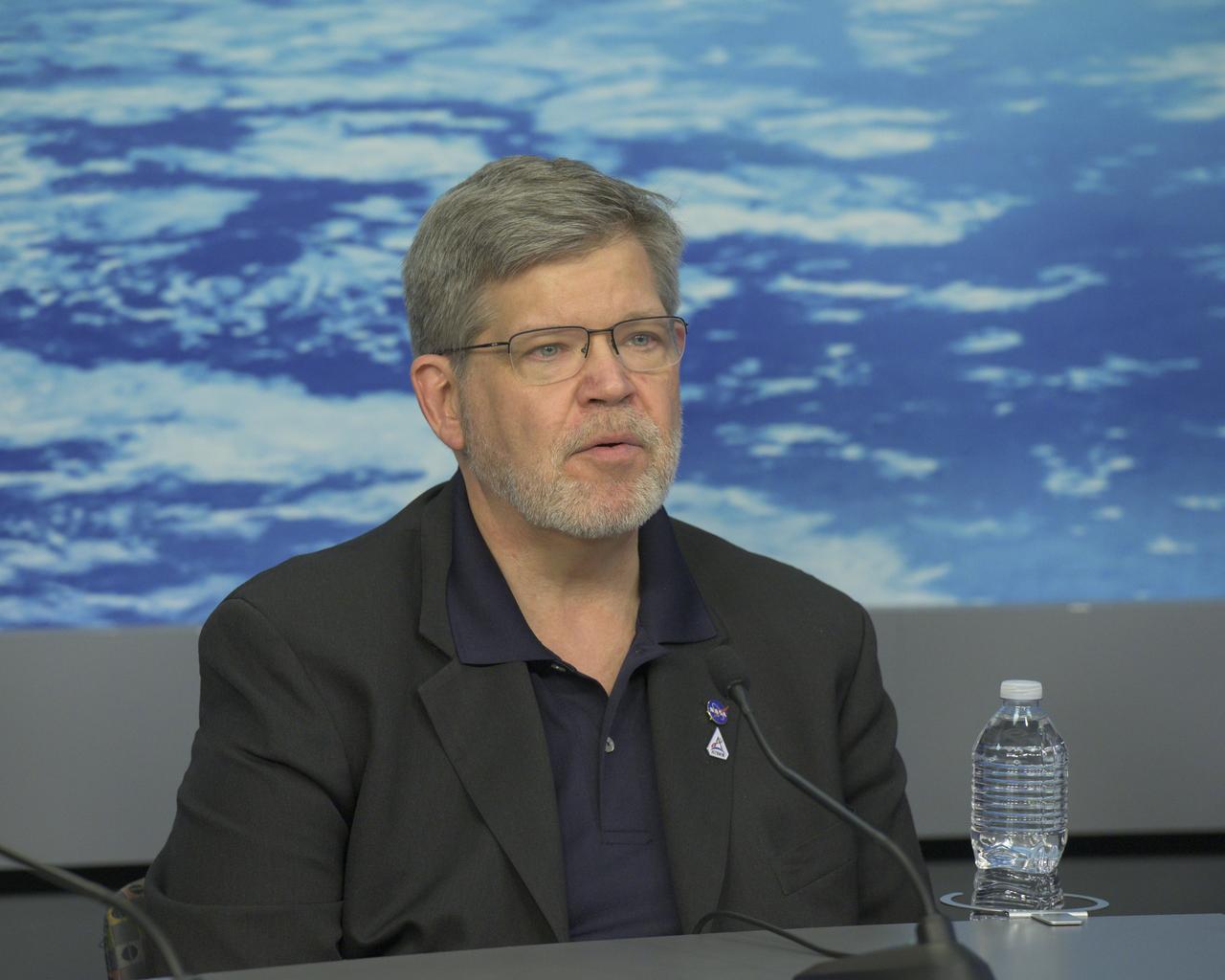

Joel Kearns, deputy associate administrator for Exploration, Science Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters, participates in a news conference Feb. 23, 2024, at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Kearns was on hand to discuss the NASA science and technology aboard Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lander, called Odysseus, and its successful soft landing on the Moon Feb. 22, 2024. The mission is the first landing under NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, and the first American lunar landing in more than 50 years.
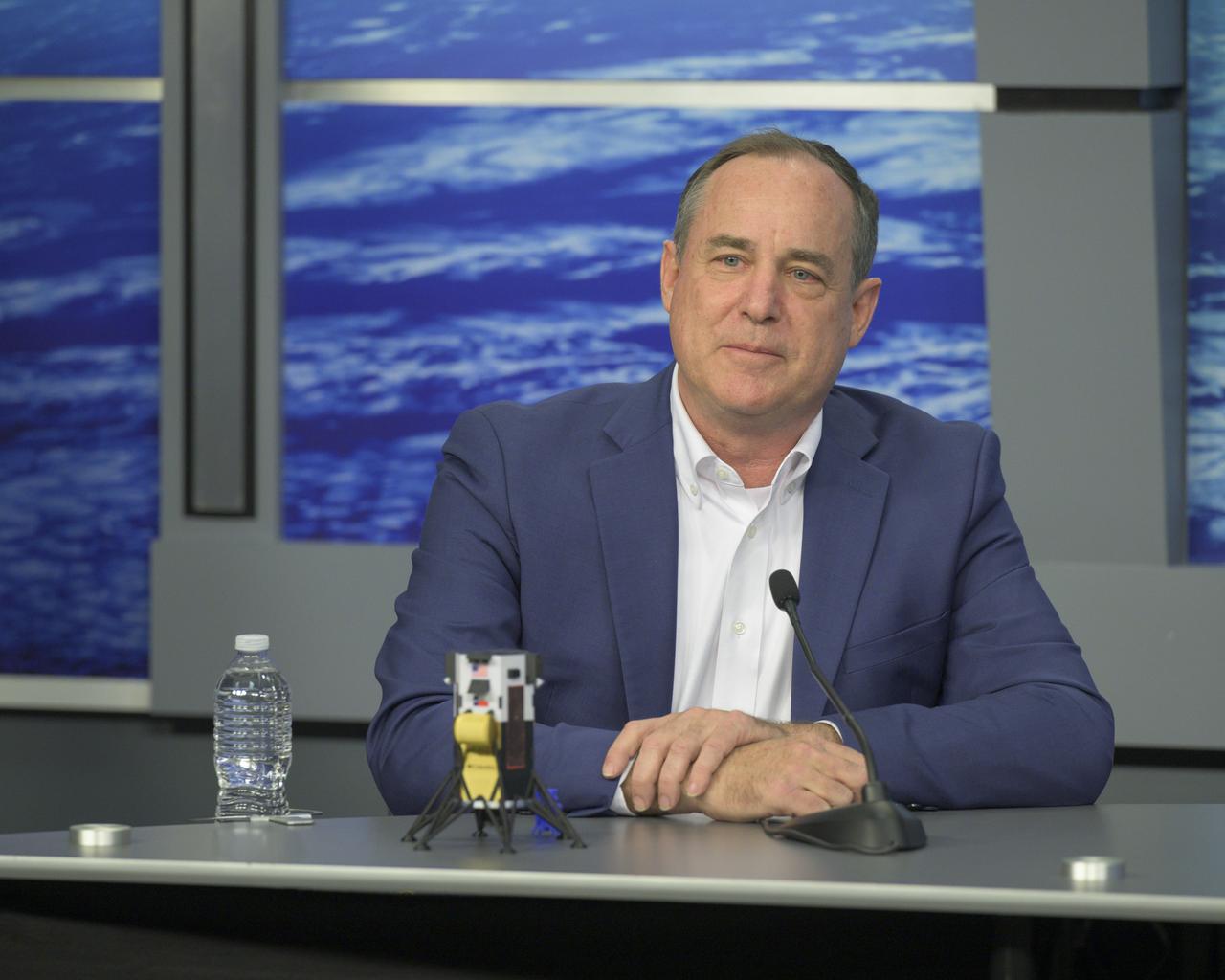

Steve Altemus, chief executive officer and co-founder, Intuitive Machines, participates in a news conference Feb. 23, 2024, at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston to discuss the company’s Nova-C lander, called Odysseus, and its successful soft landing on the Moon Feb. 22, 2024. The mission is the first landing under NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, and the first American lunar landing in more than 50 years.

Prasun Desai, deputy associate administrator, Space Technology Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, participates in a news conference Feb. 23, 2024, at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Desai was on hand to discuss the NASA science and technology aboard the Intuitive Machine’s Nova-C lander, called Odysseus, and its successful soft landing on the Moon Feb. 22, 2024. The mission is the first landing under NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, and the first American lunar landing in more than 50 years.
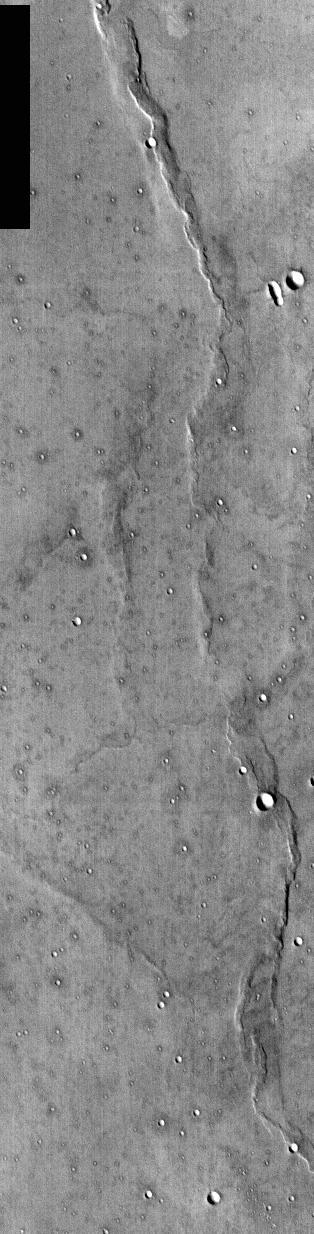
This NASA Mars Odyssey image of NASA Viking 1 landing site was taken to commemorate the anniversaries of NASA Apollo 11 landing on the Moon and Viking 1 landing on Mars -- July 20, 1969 and July 20, 1976, respectively.
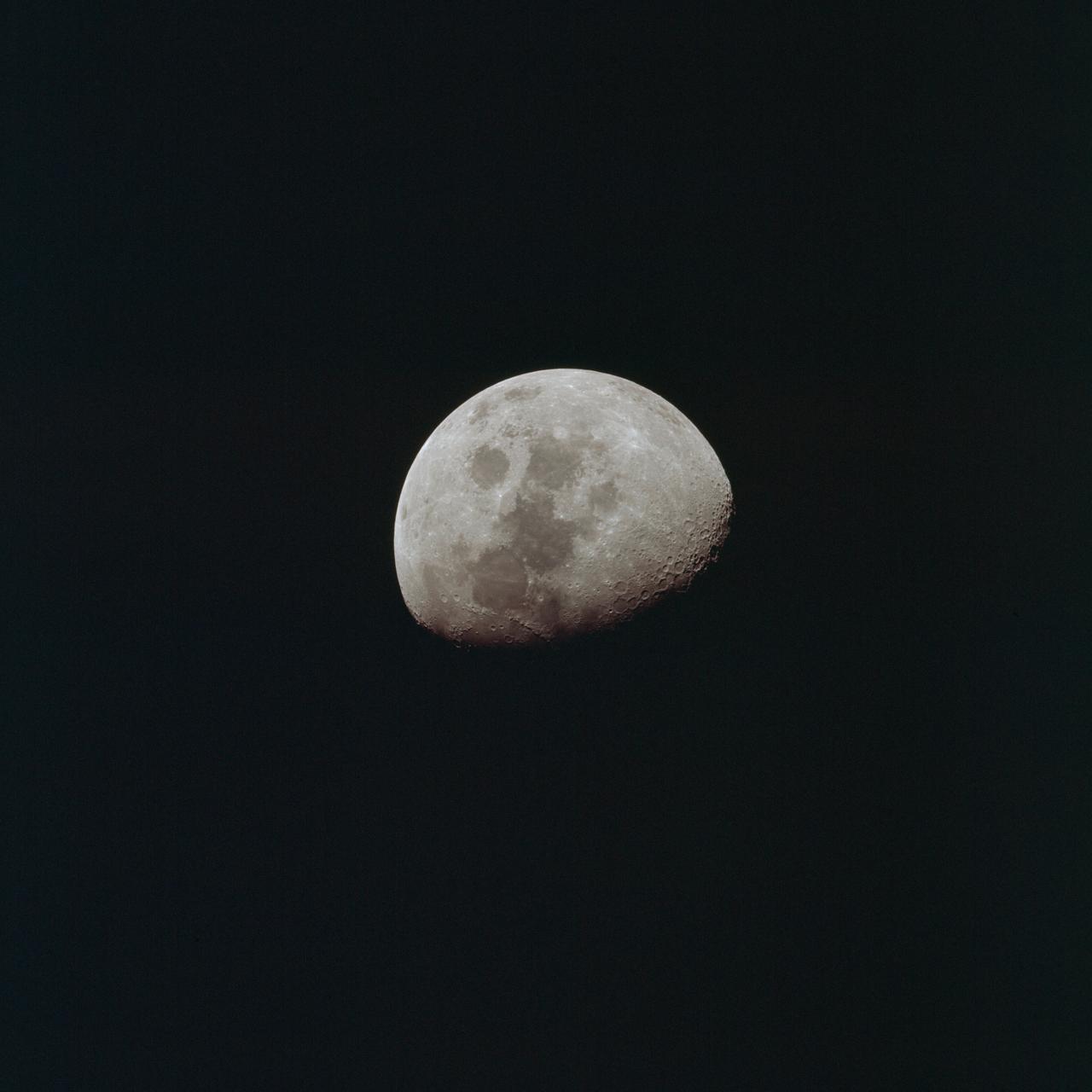

AS10-27-3956 (24 May 1969) --- This photograph of the moon was taken after trans-Earth insertion when the Apollo 10 spacecraft was high above the lunar equator near 27 degrees east longitude. North is about 20 degrees left of the top of the photograph. Apollo Landing Site 3 is on the lighted side of the terminator in a dark area just north of the equator. Apollo Landing Site 2 is near the lower left margin of the Sea of Tranquility (Mare Tranquillitatis), which is the large, dark area near the center of the photograph.
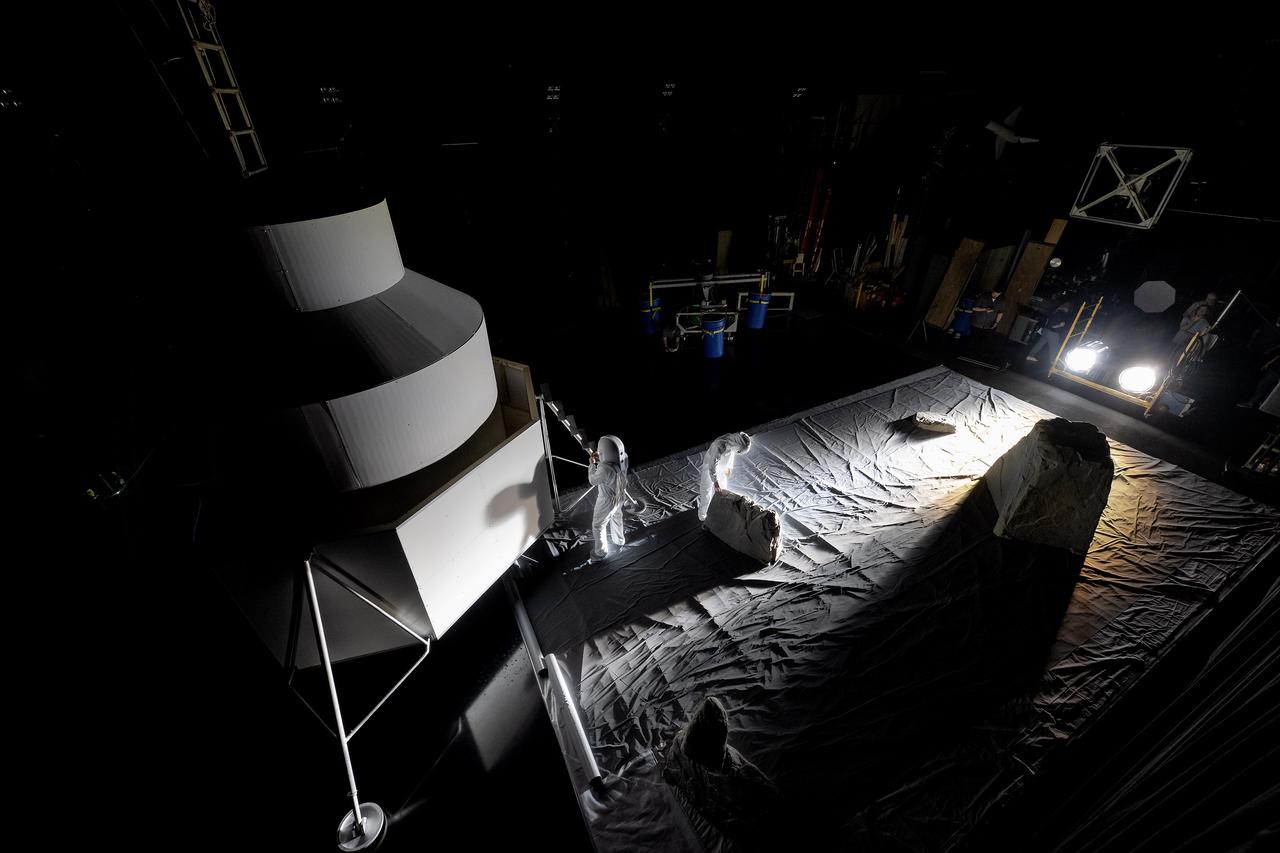

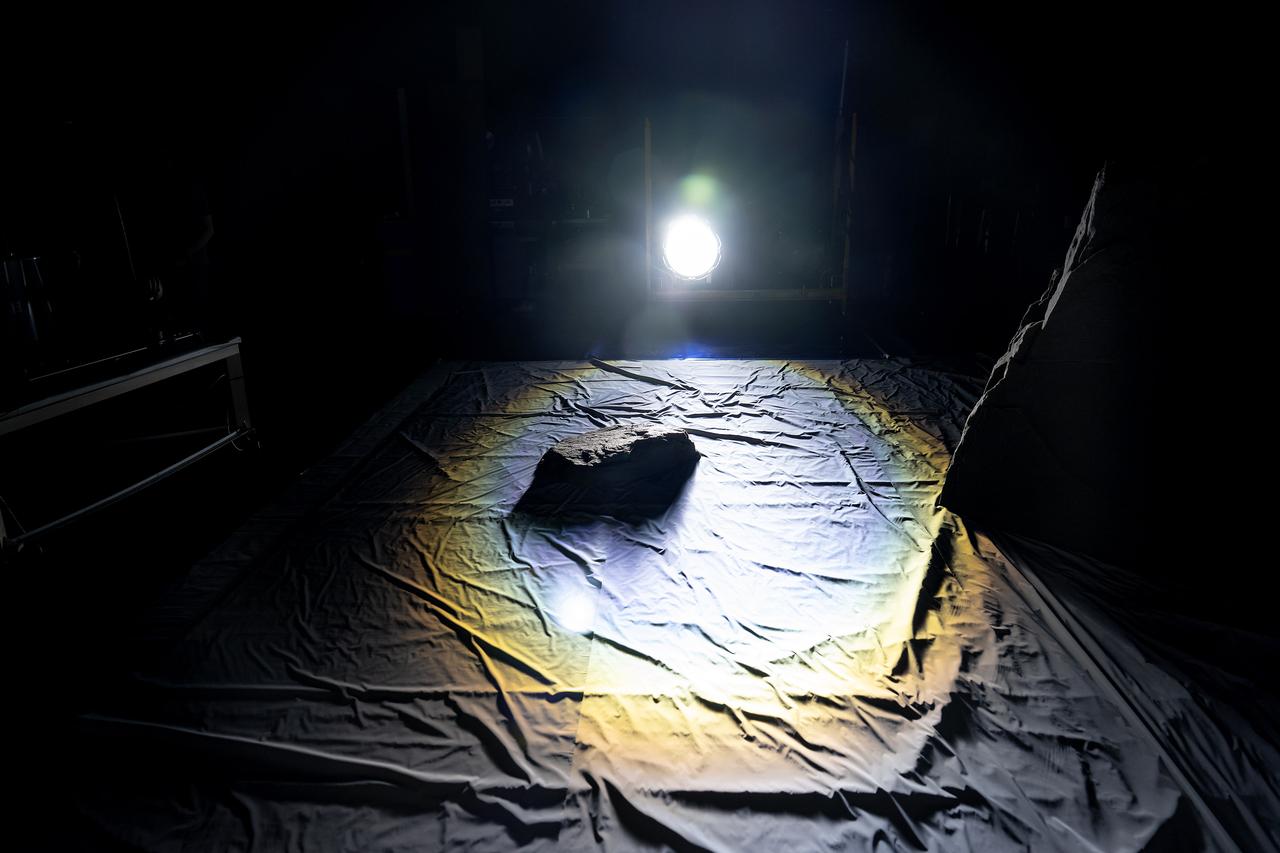
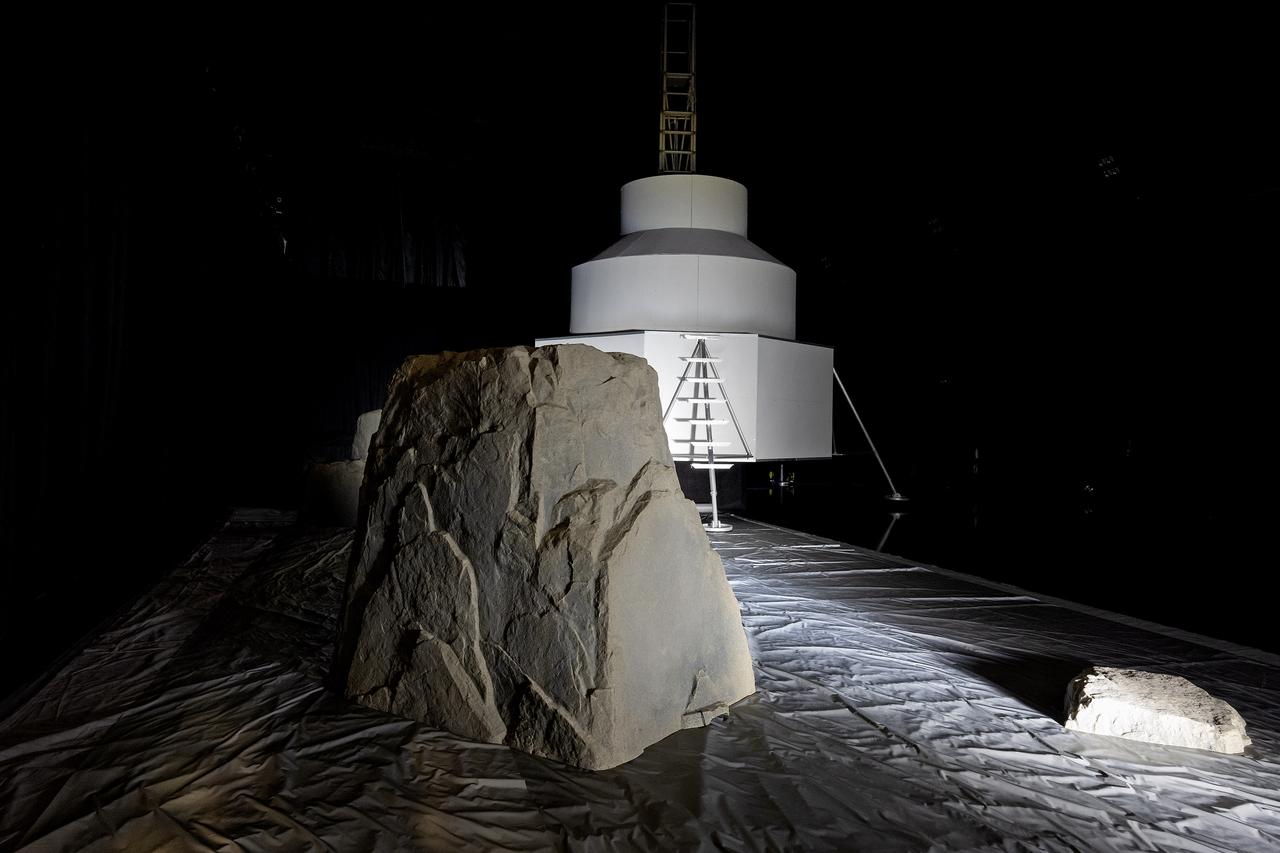
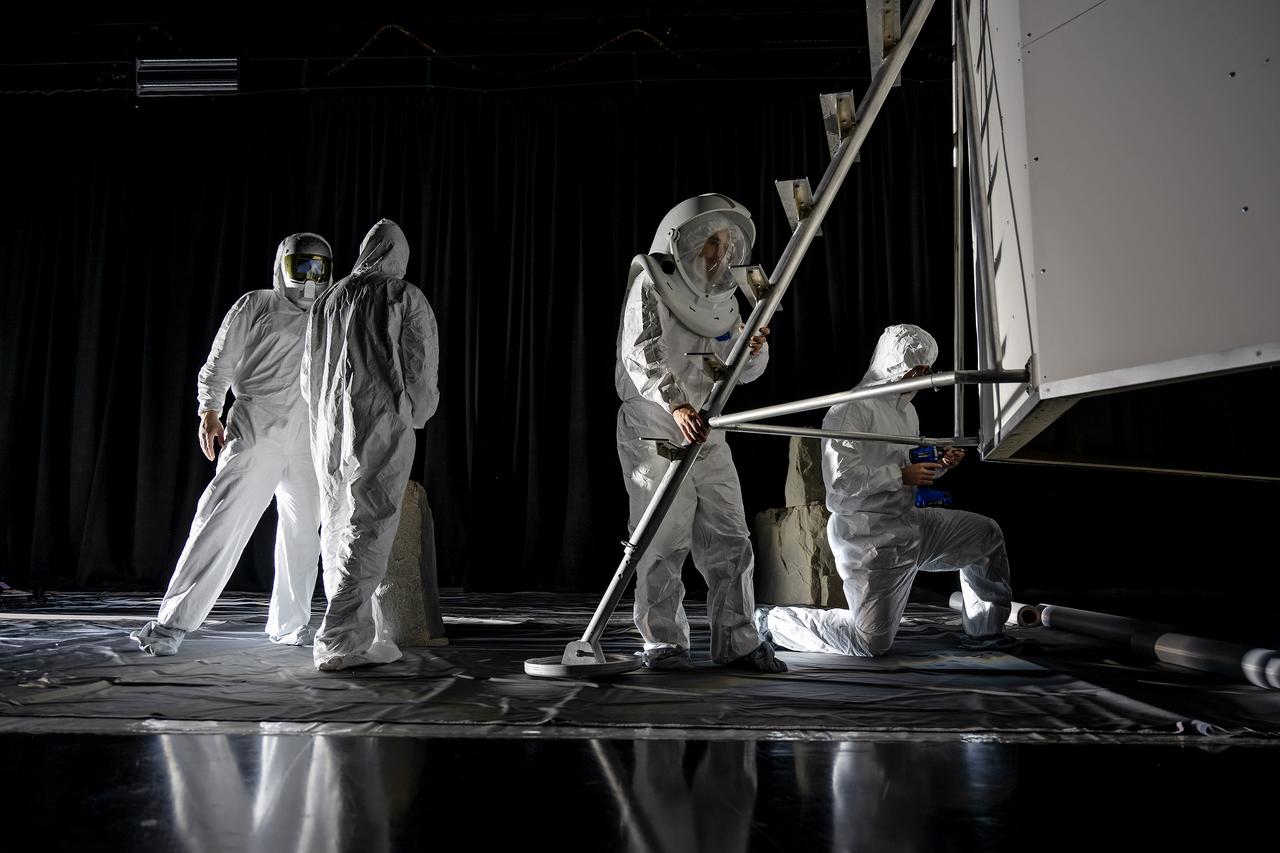
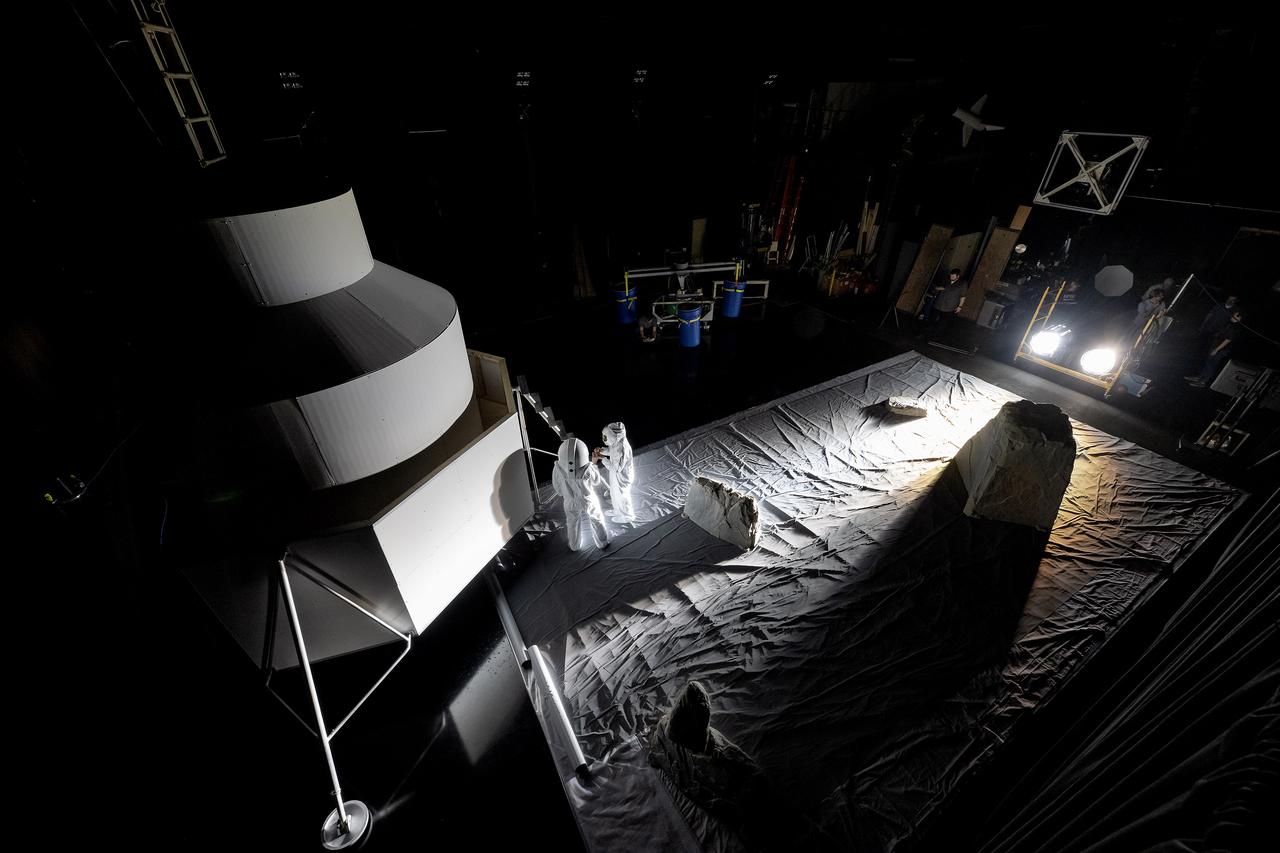
These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
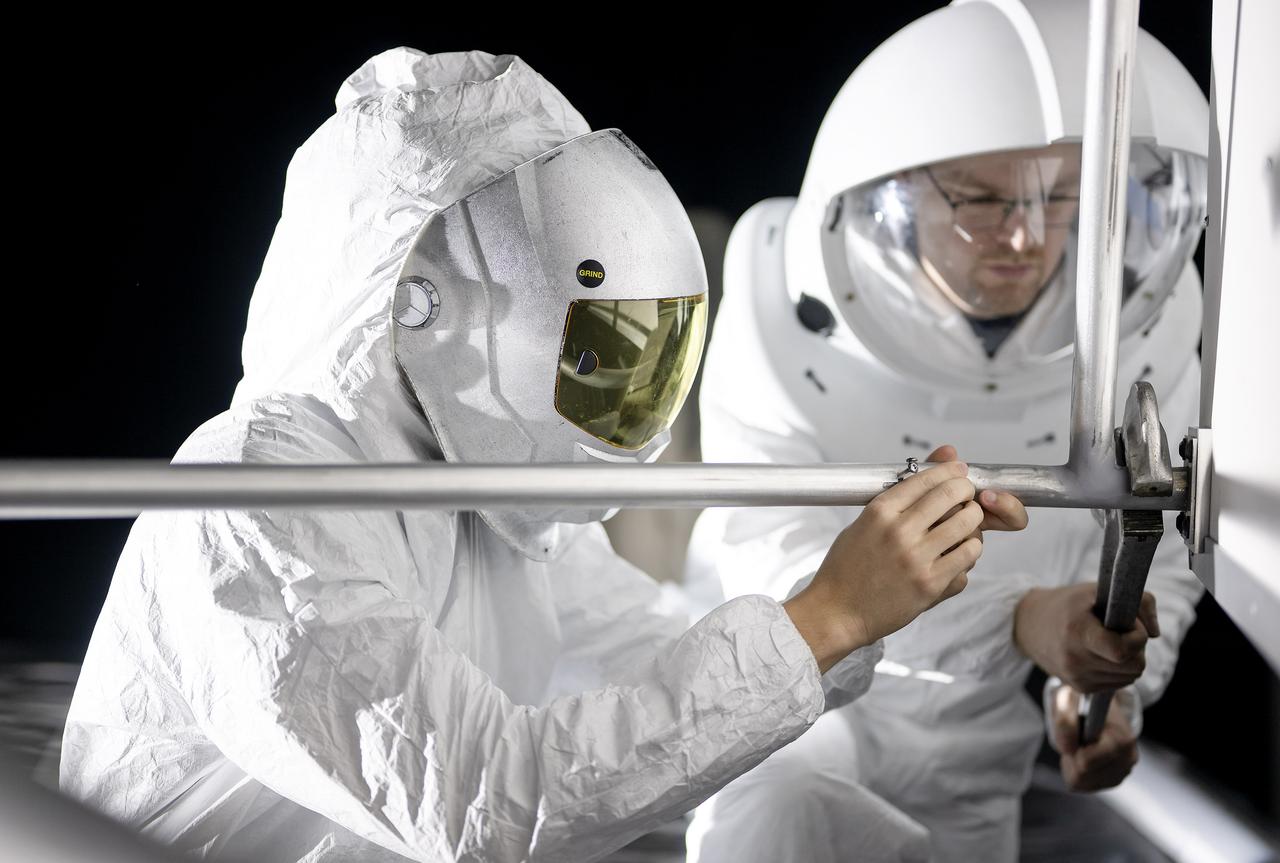

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
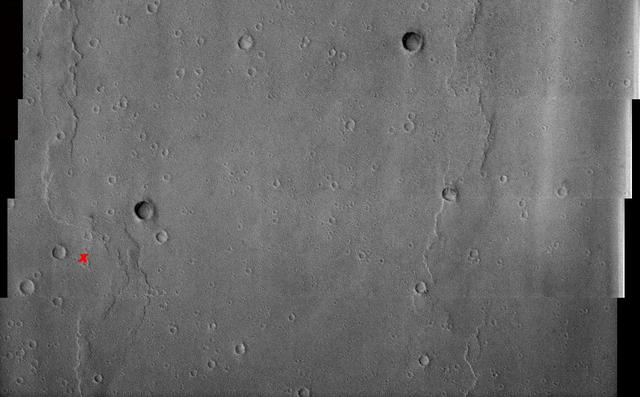
NASA Viking 1 landing site is shown in this commemorative image from NASA Mars Odyssey spacecraft to celebrate the July 20, 1969 and 1976 anniversaries of NASA Apollo 11 and Viking 1 landings on the Moon and Mars, respectively.
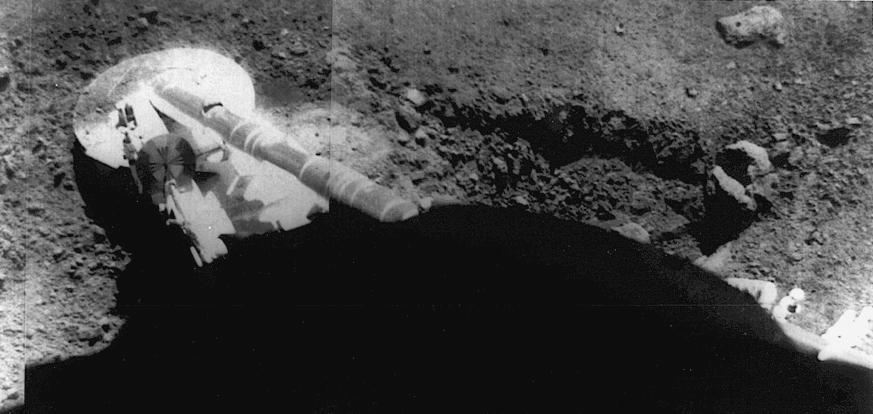

Surveyor 5 image of the footpad resting in the lunar soil. The trench at right was formed by the footpad sliding during landing. Surveyor 5 landed on the Moon on 11 September 1967 at 1.41 N, 23.18E in Mare Tranquillitatis.
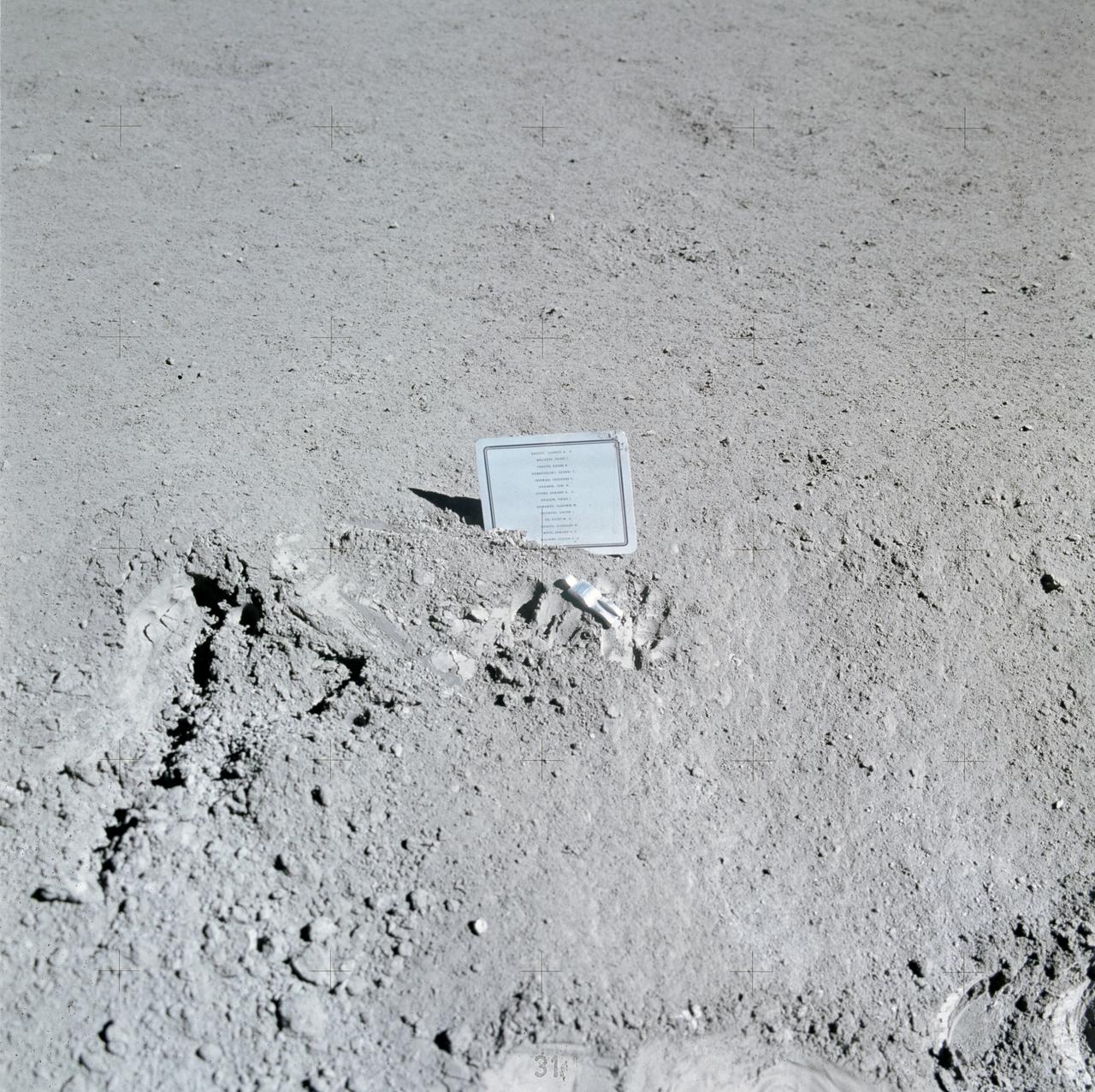

AS15-88-11894 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- A close-up view of a commemorative plaque left on the moon at the Hadley-Apennine landing site in memory of 14 NASA astronauts and USSR cosmonauts, now deceased. Their names are inscribed in alphabetical order on the plaque. The plaque was stuck in the lunar soil by astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, during their Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). The names on the plaque are Charles A. Bassett II, Pavel I. Belyayev, Roger B. Chaffee, Georgi Dobrovolsky, Theodore C. Freeman, Yuri A. Gagarin, Edward G. Givens Jr., Virgil I. Grissom, Vladimir Komarov, Viktor Patsayev, Elliot M. See Jr., Vladislav Volkov, Edward H. White II, and Clifton C. Williams Jr. The tiny, man-like object represents the figure of a fallen astronaut/cosmonaut. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

“INNOVATION IS NOT OPTIONAL,” SAYS DOUGLAS TERRIER, NASA CHIEF TECHNOLOGIST, DURING A TALK ABOUT INNOVATION AT THE AGENCY DEC. 3 IN MORRIS AUDITORIUM AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER. TERRIER SAID THAT NASA MUST CONTINUE TO BE INNOVATIVE TO ACHIEVE THE AGENCY’S MISSIONS AND GOALS FOR THE NEXT 5-10 YEARS, INCLUDING THE 2024 ARTEMIS II MOON LANDING.
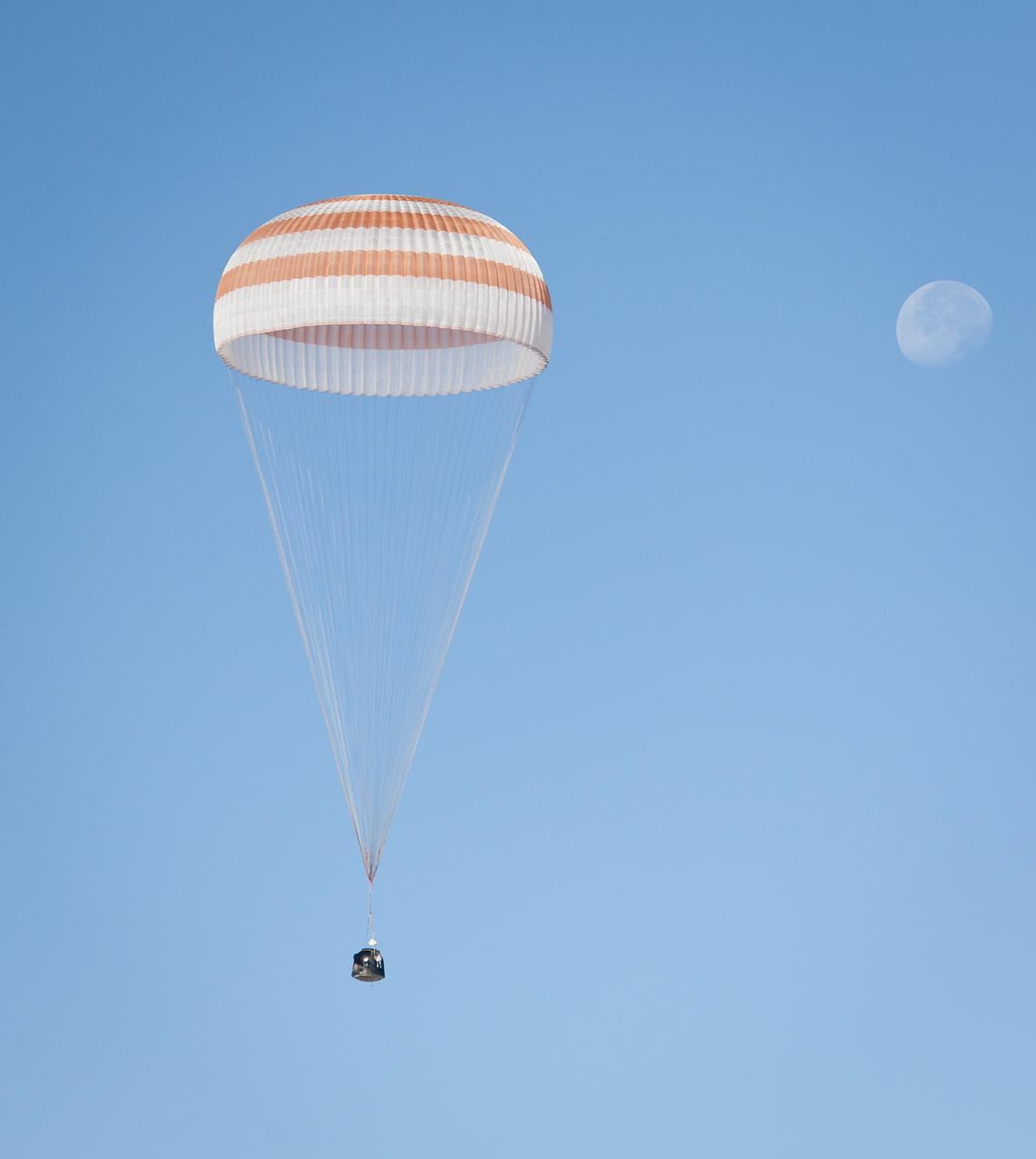

The Soyuz TMA-21 spacecraft is seen with the Moon in the background as it lands with Expedition 28 Commander Andrey Borisenko, and Flight Engineers Ron Garan, and Alexander Samokutyaev in a remote area outside of the town of Zhezkazgan, Kazakhstan, on Friday, Sept. 16, 2011. NASA Astronaut Garan, Russian Cosmonauts Borisenko and Samokutyaev are returning from more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 27 and 28 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
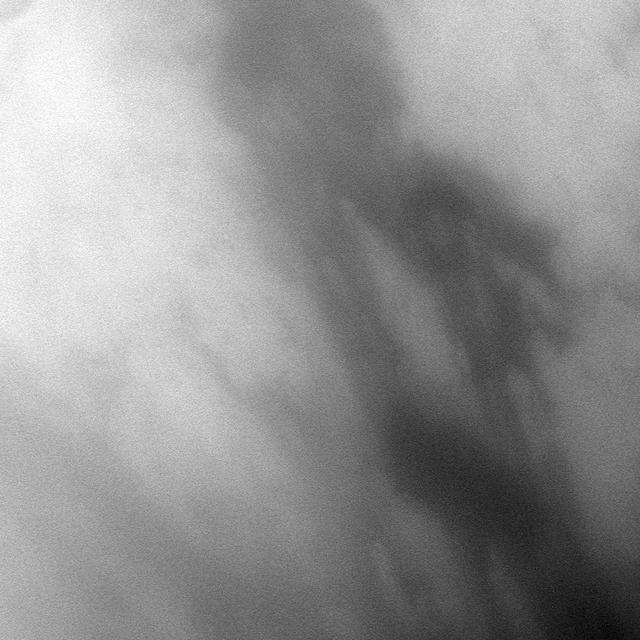

NASA Cassini spacecraft peers through Titan atmosphere at the region called Adiri, west of the landing site of the Huygens probe on the anti-Saturn side of the moon.
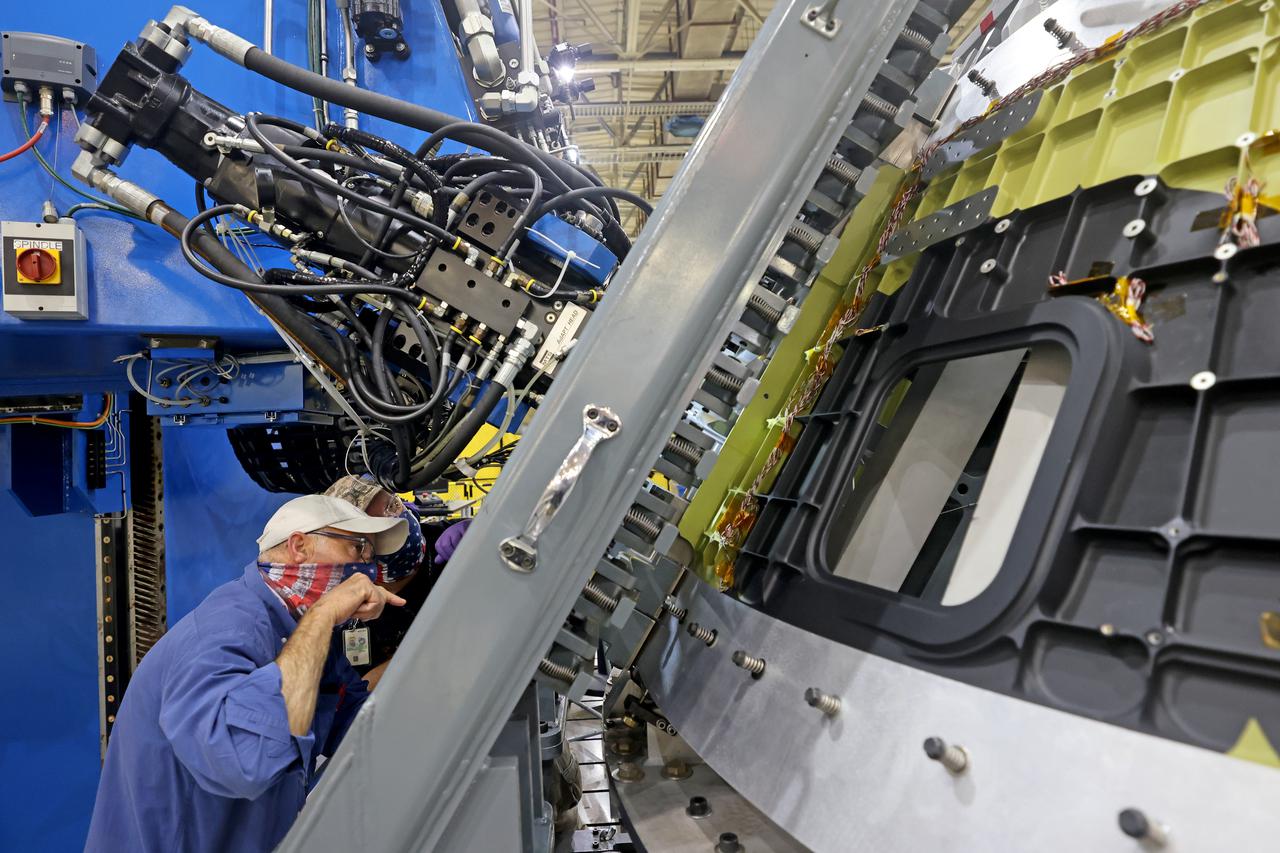

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
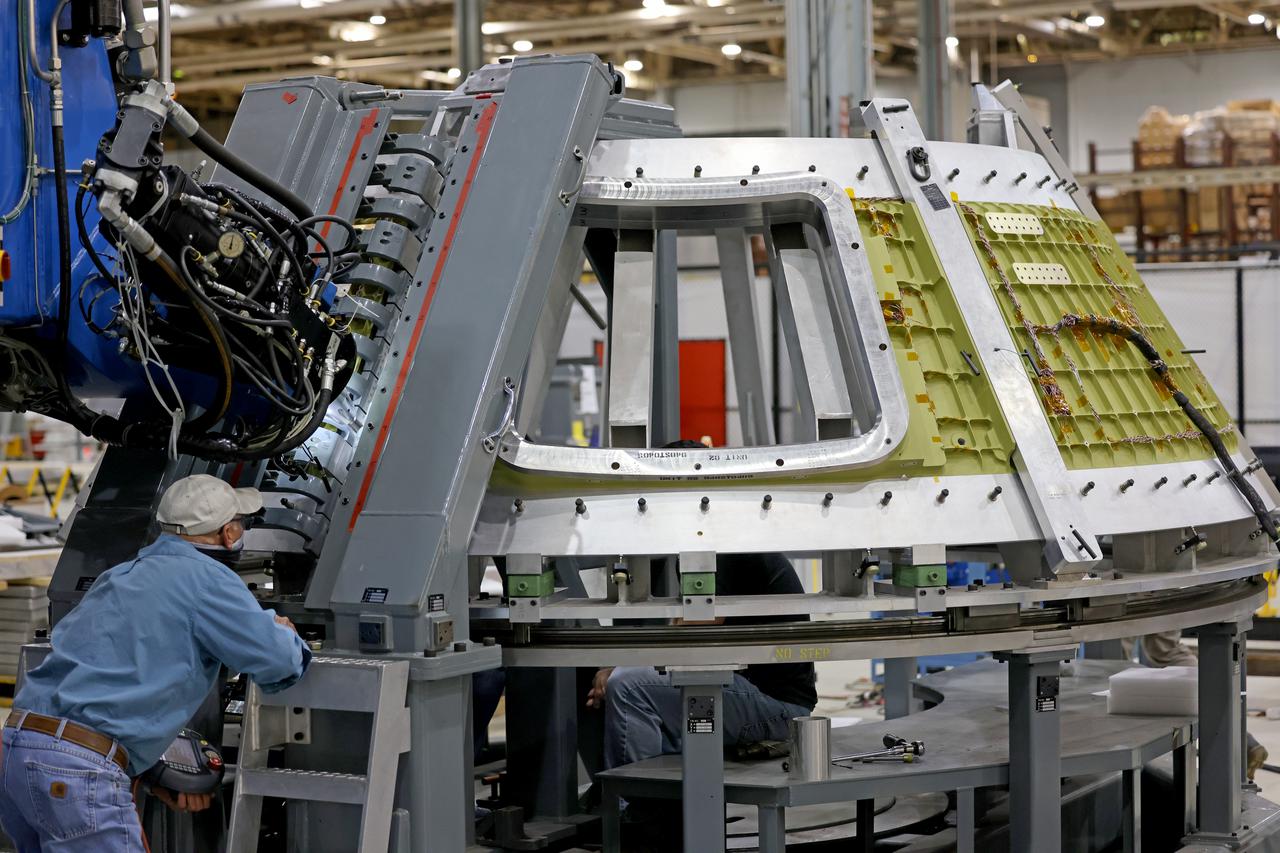
At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
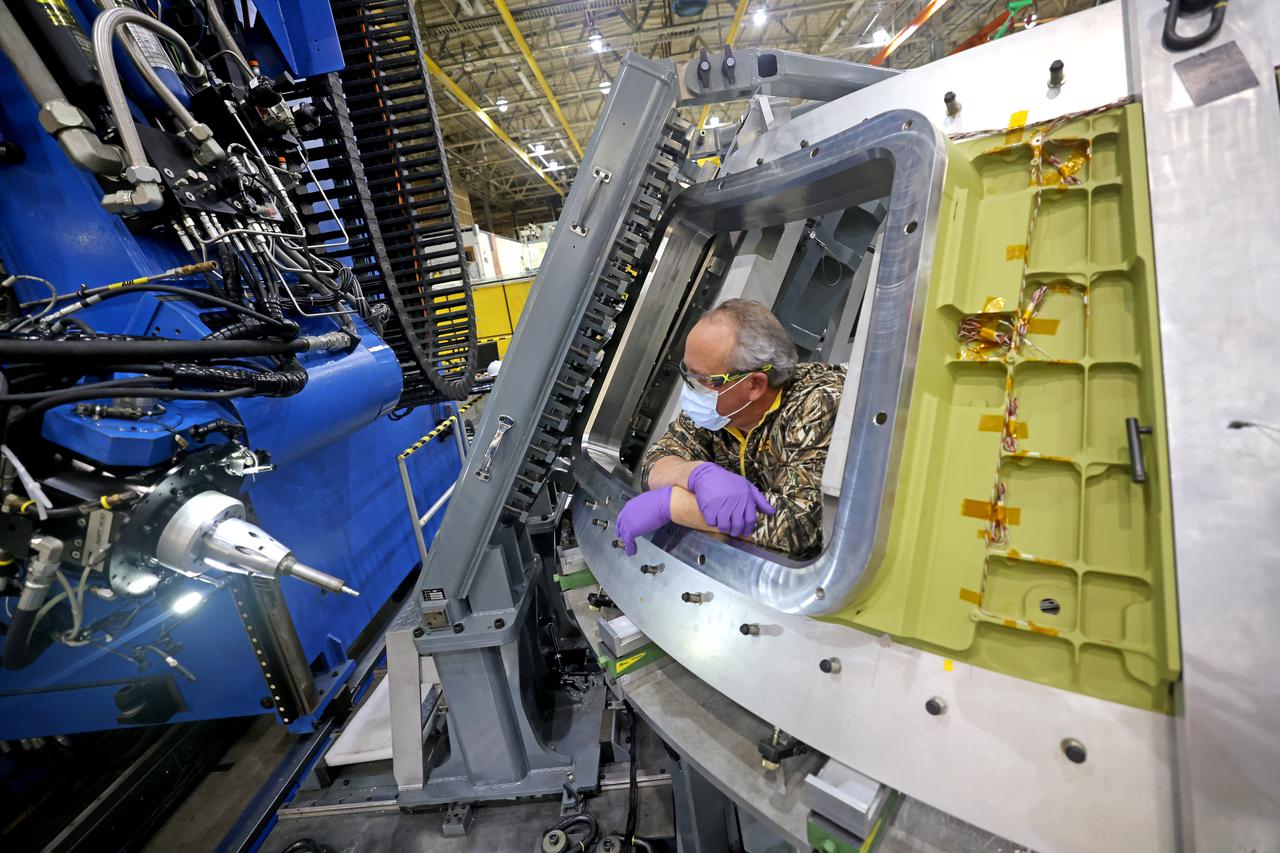

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
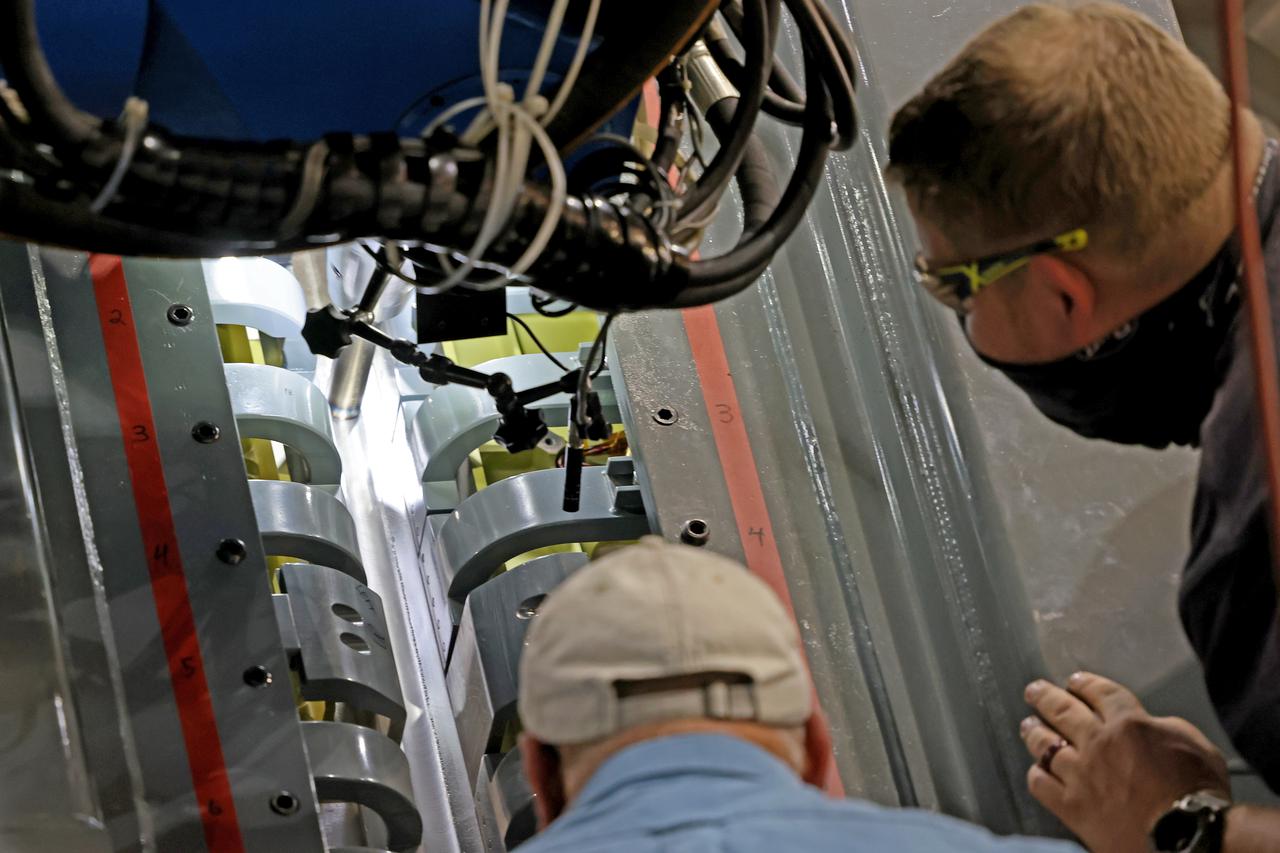

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
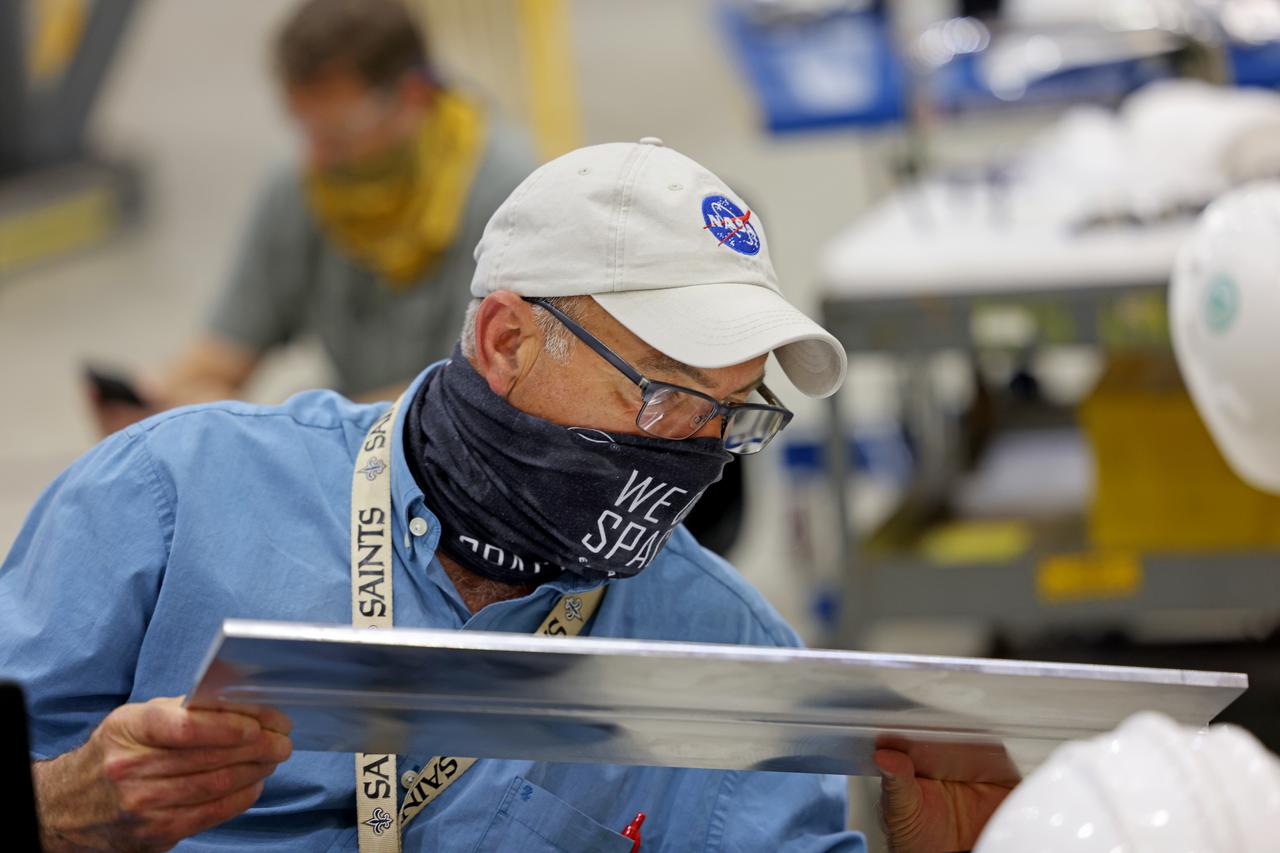

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
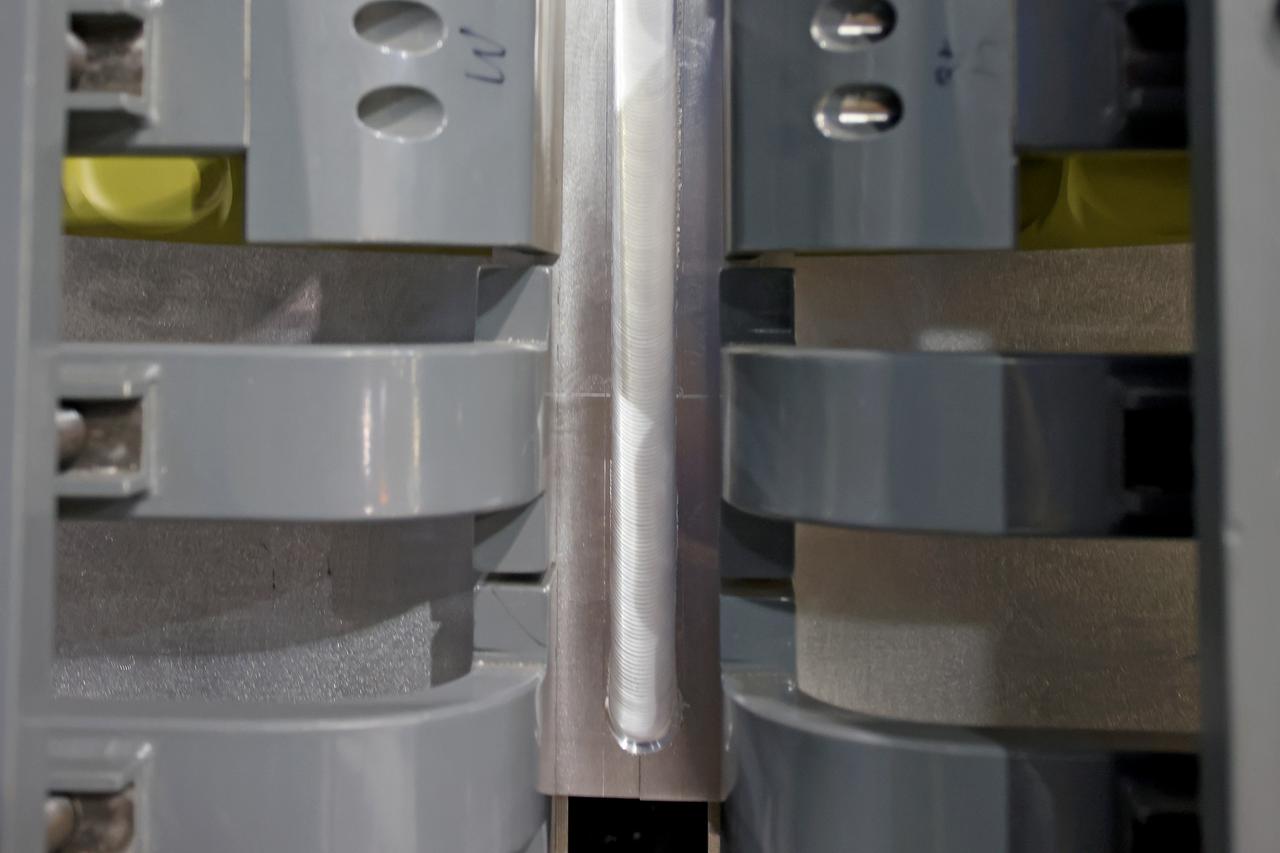

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
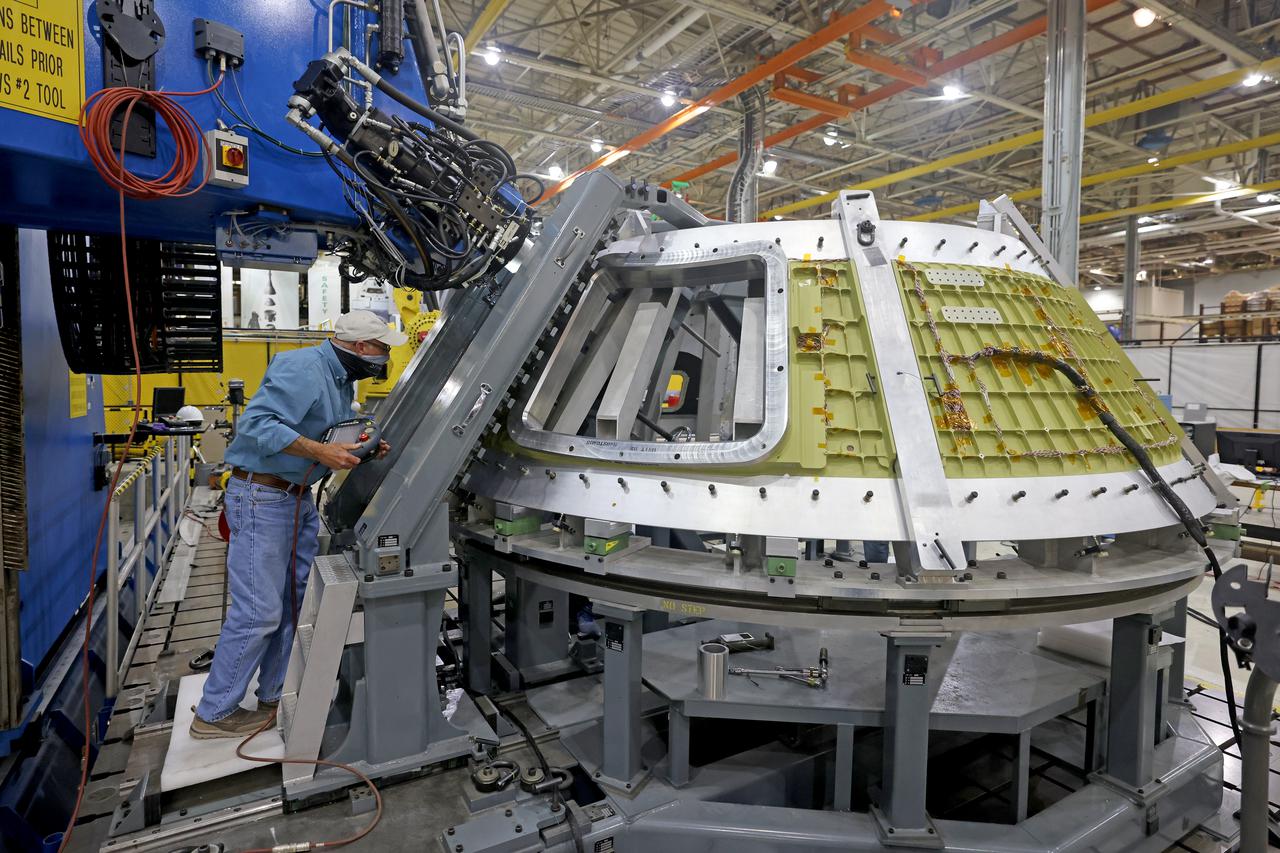

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
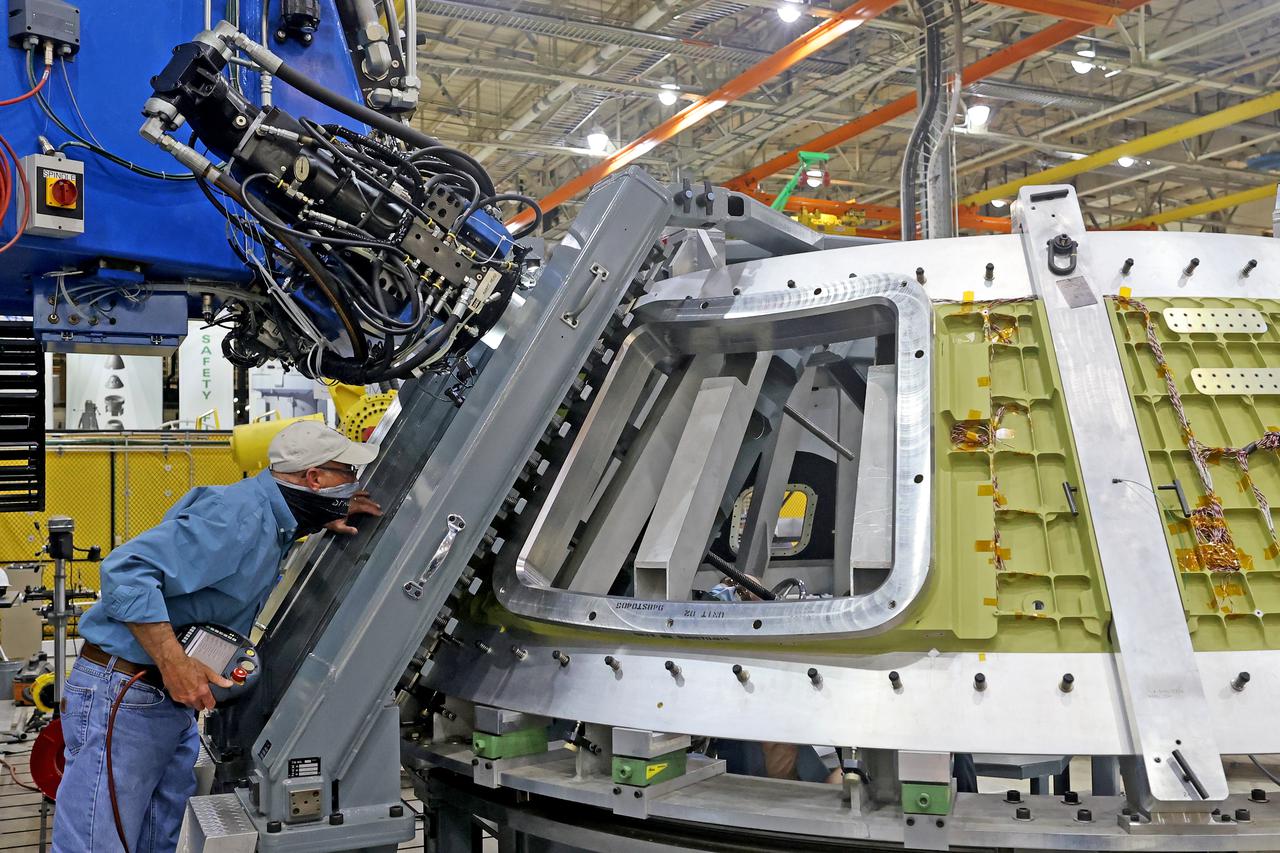

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
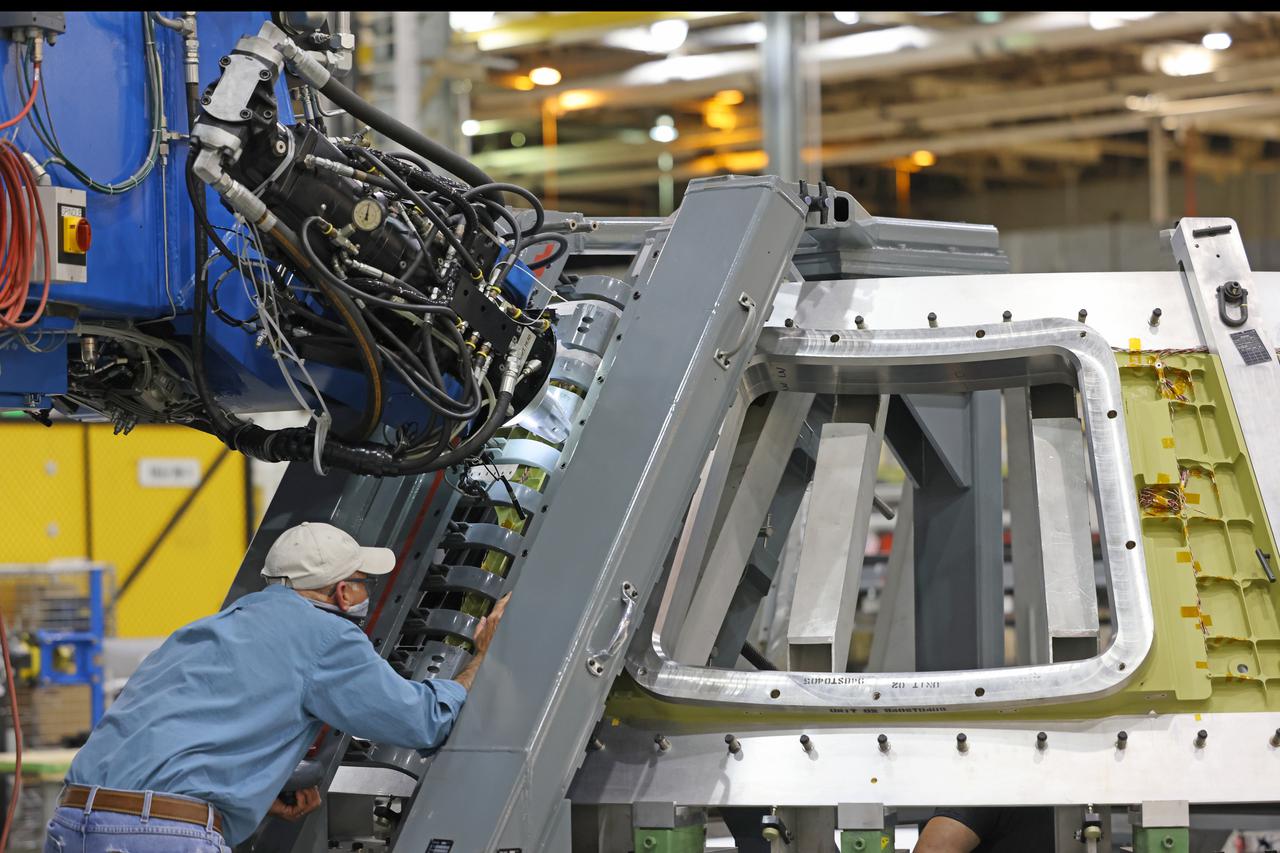

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
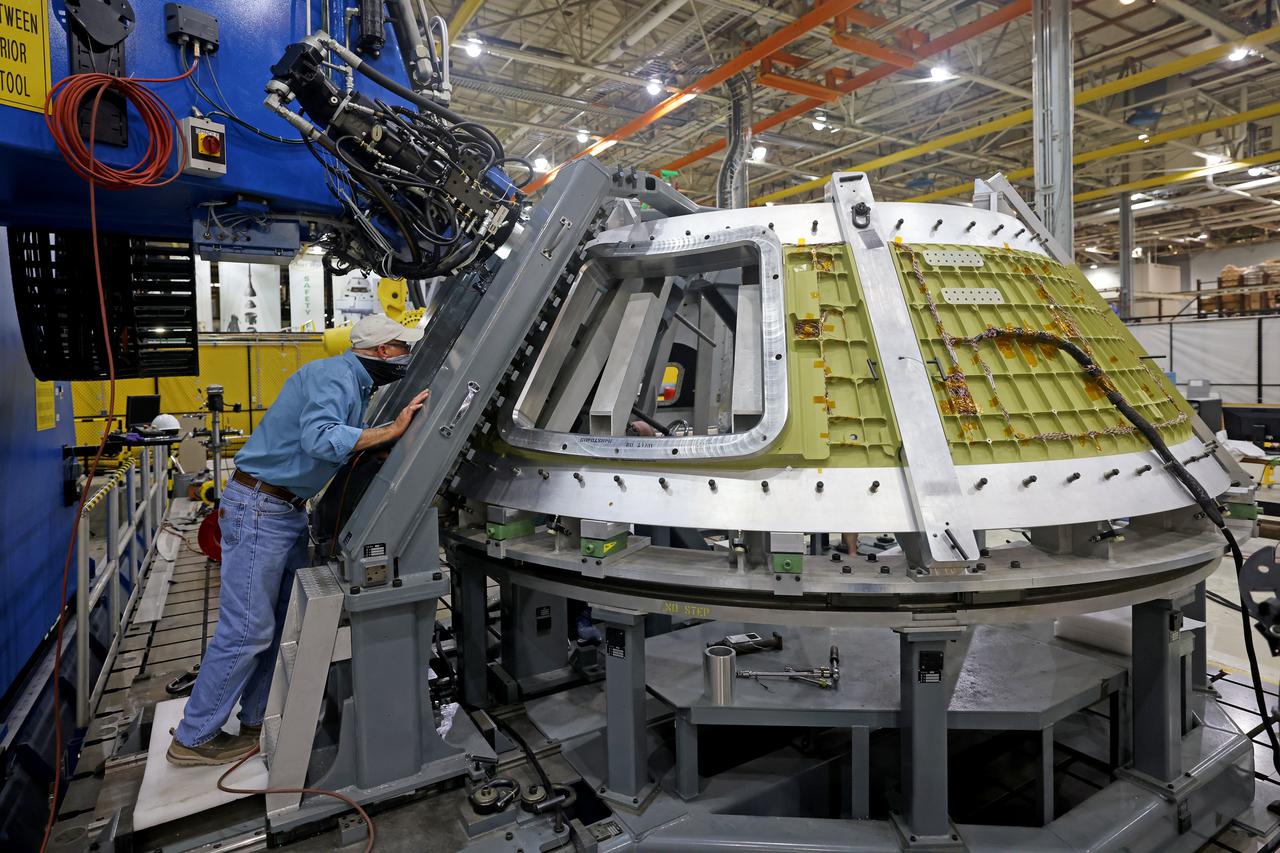

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
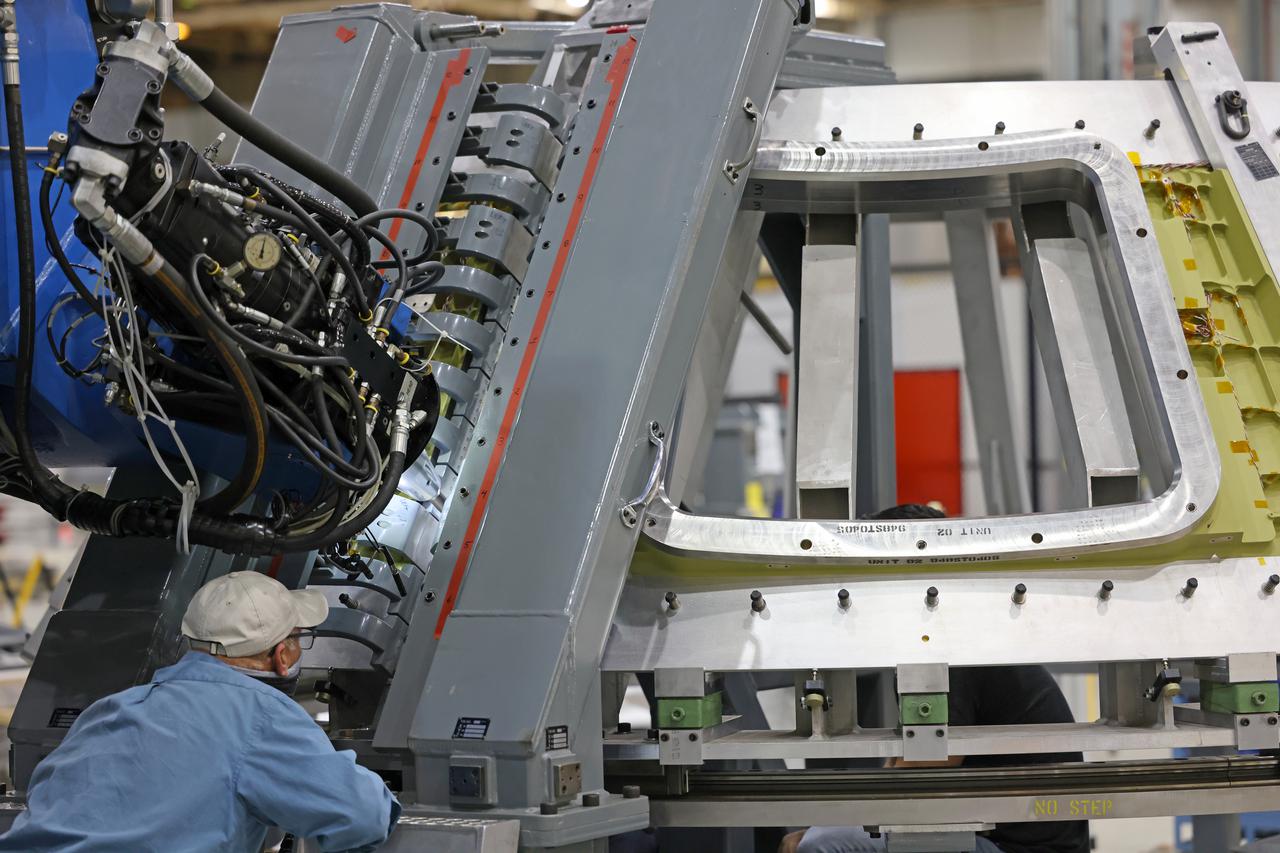
At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
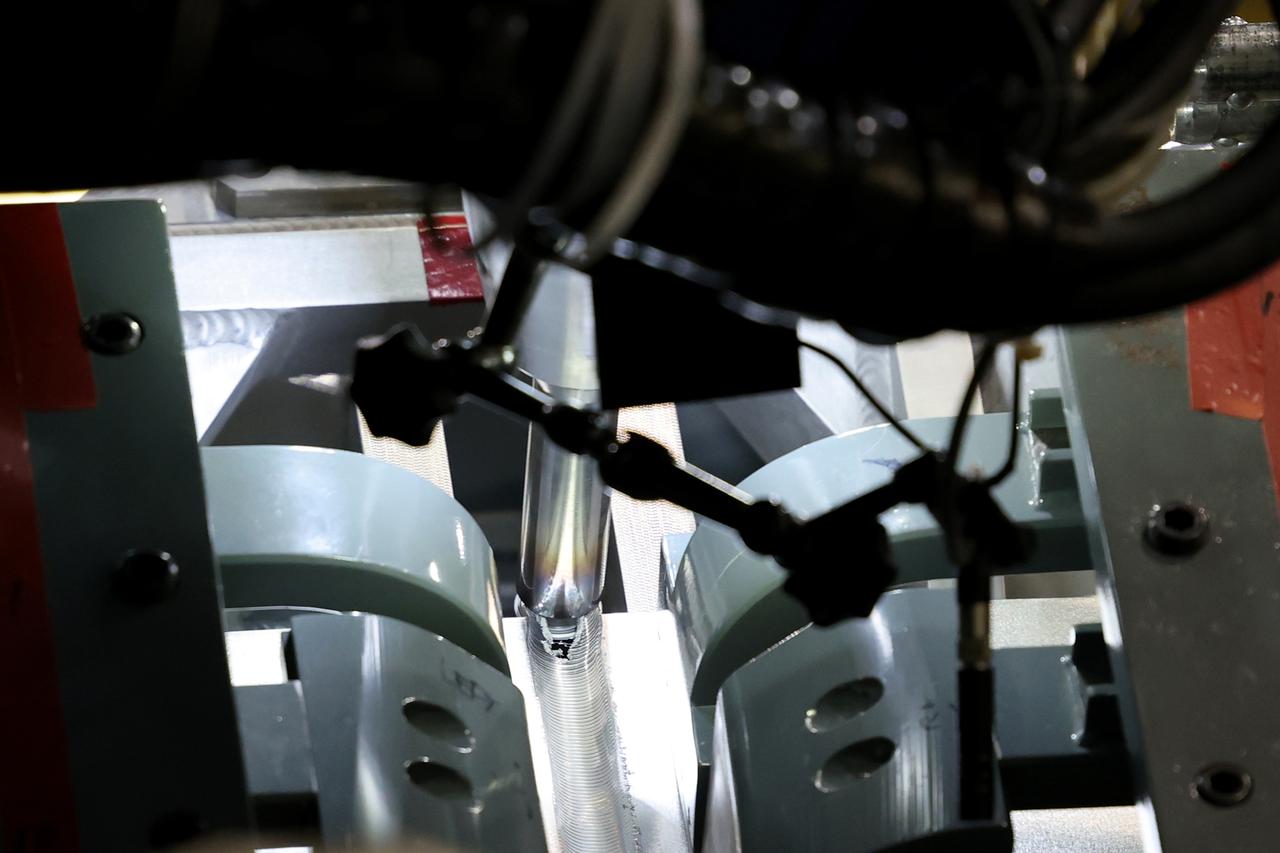

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
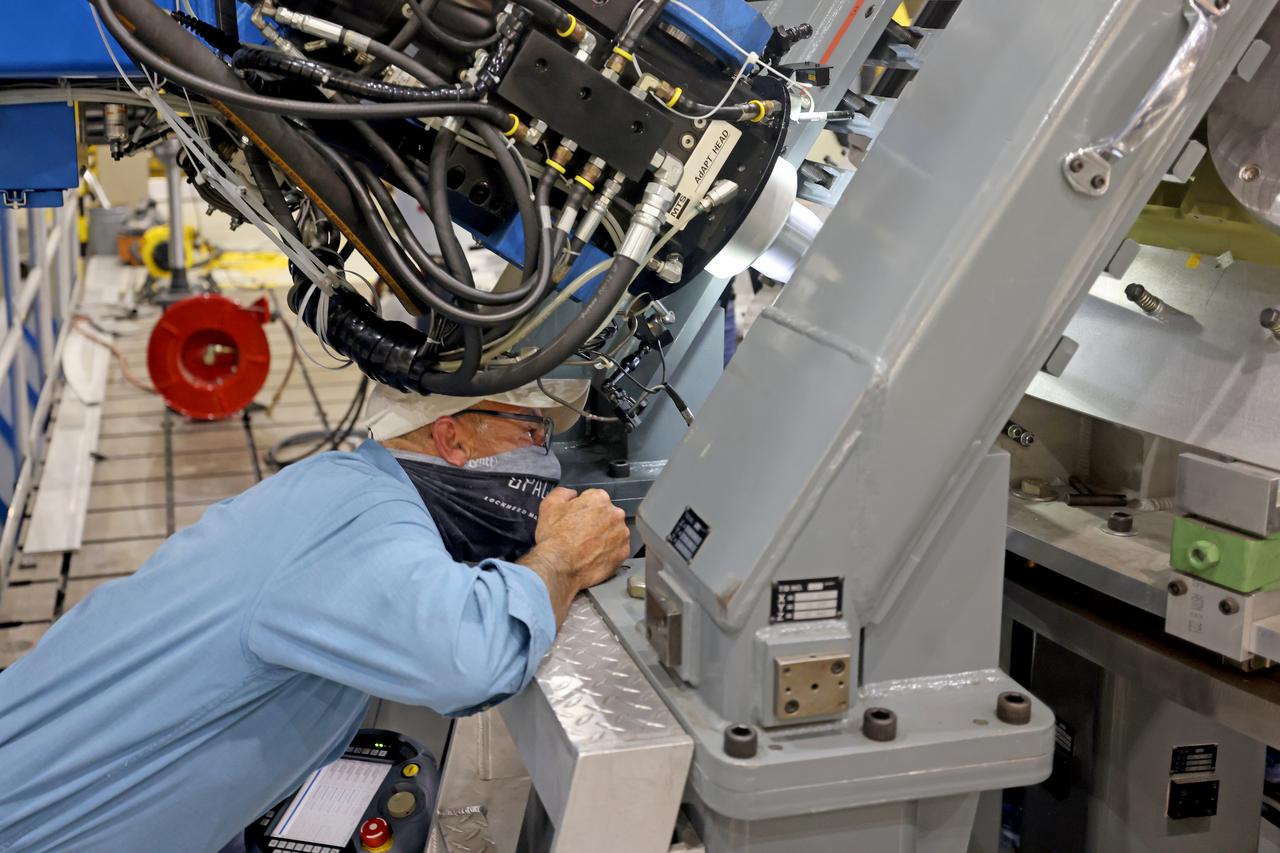

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
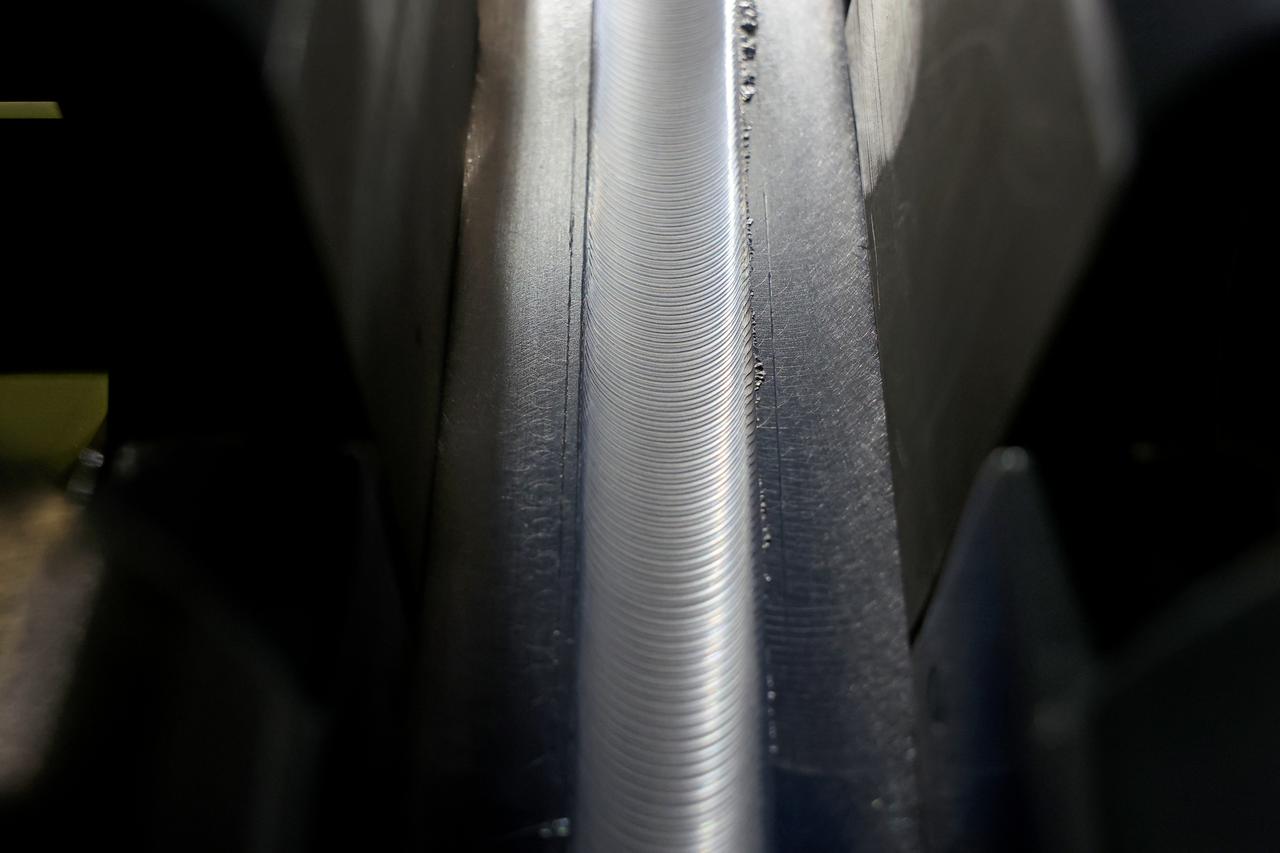

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
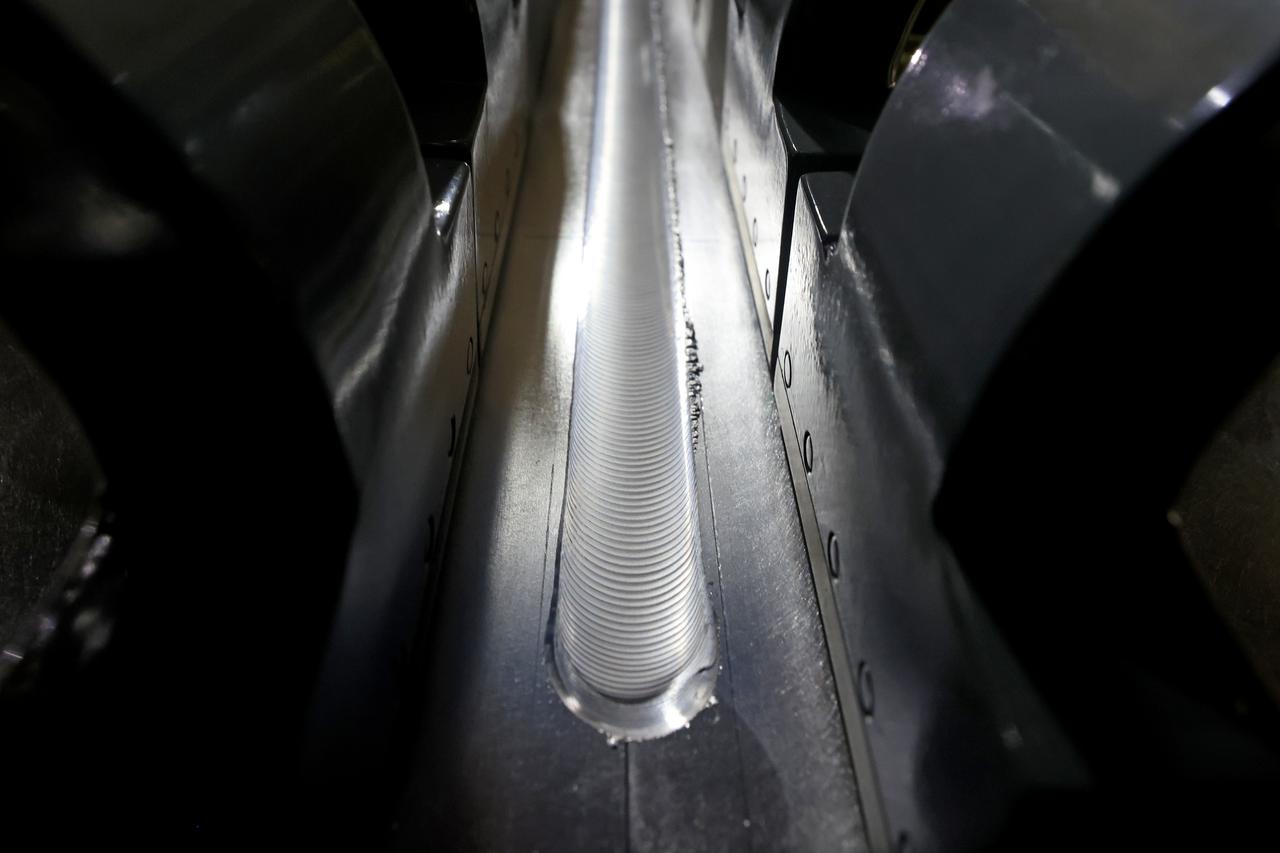

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
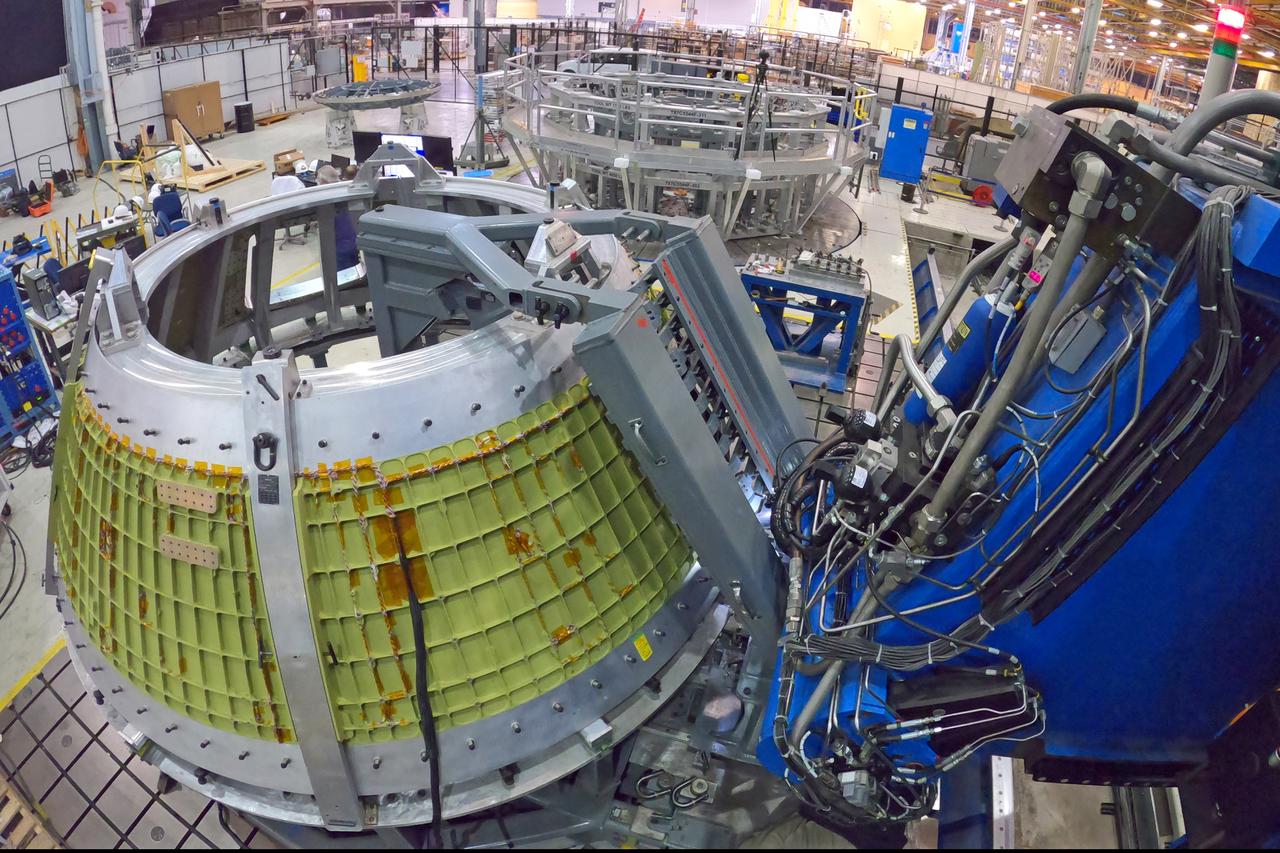
At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
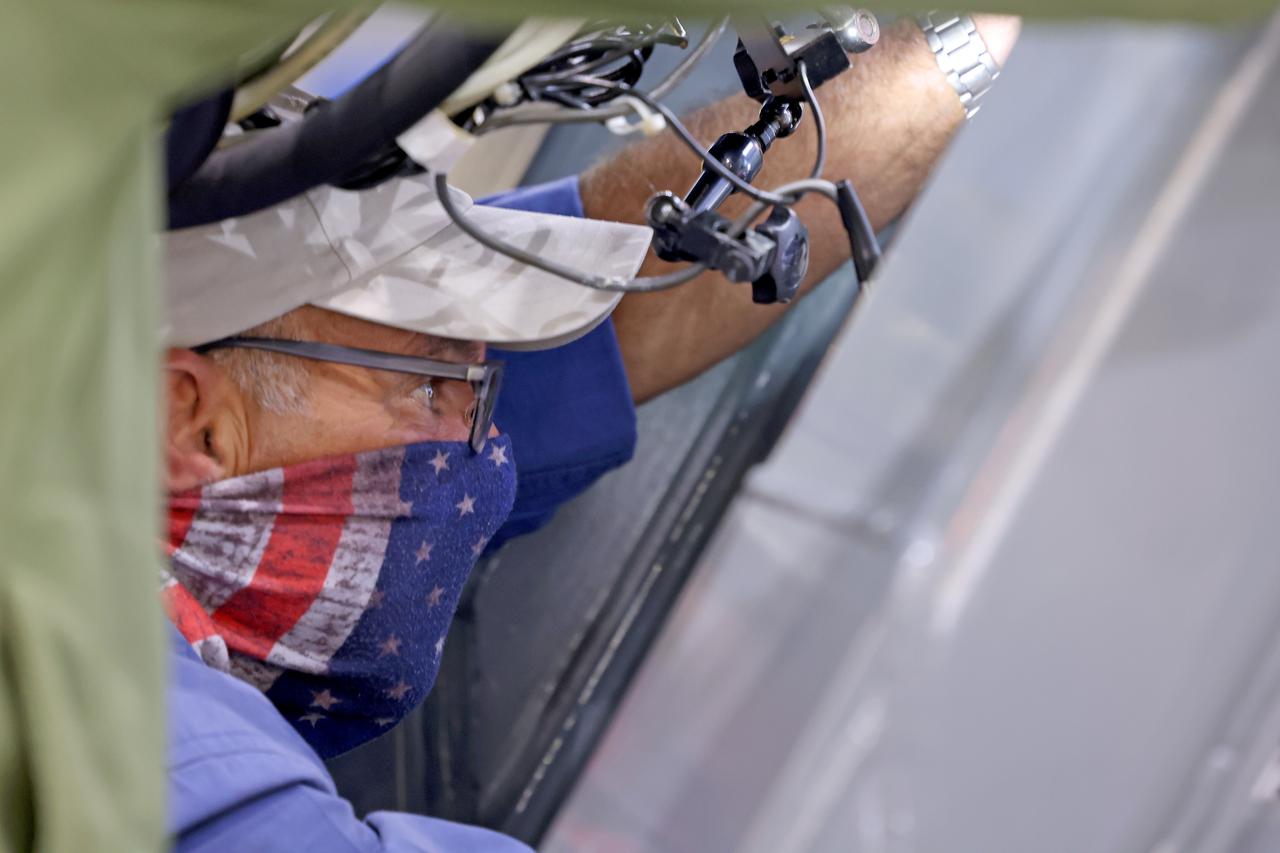

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
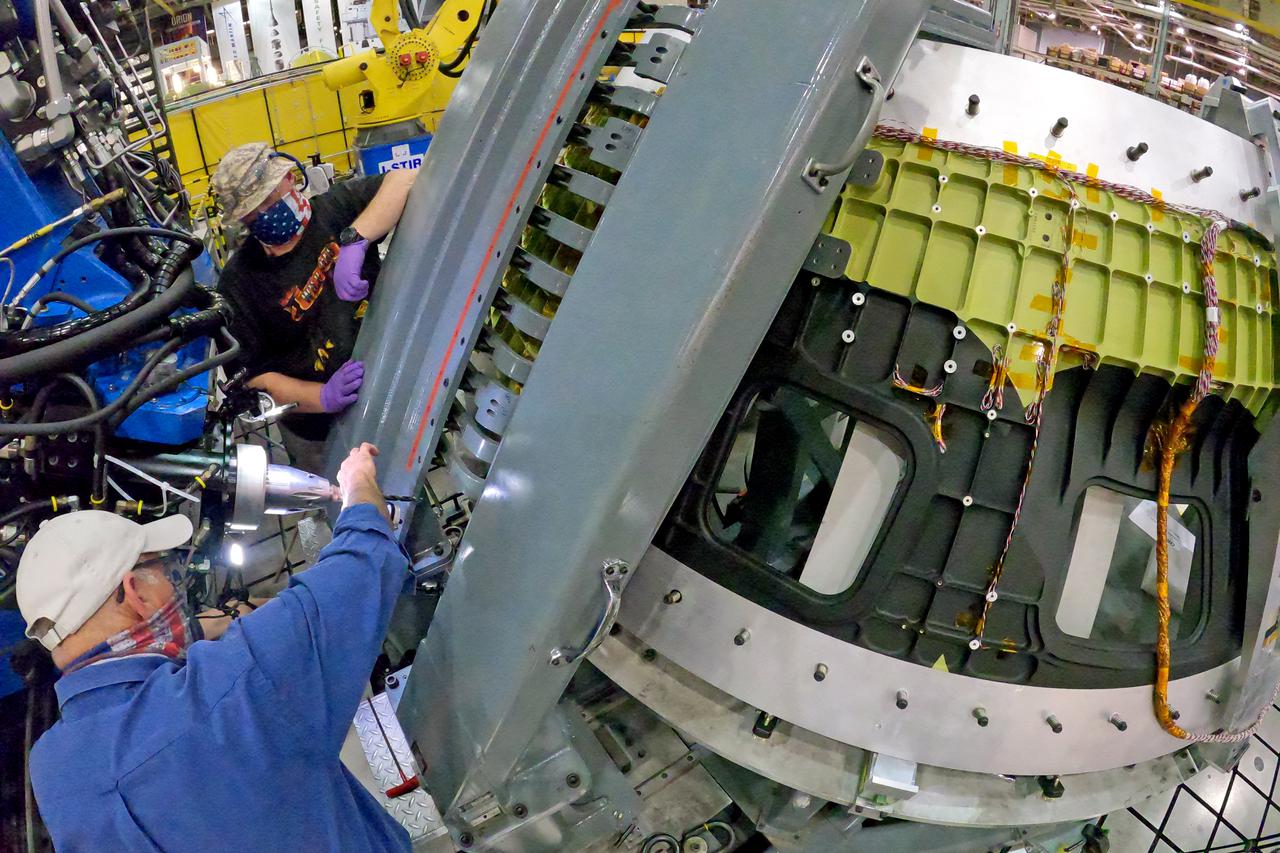

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
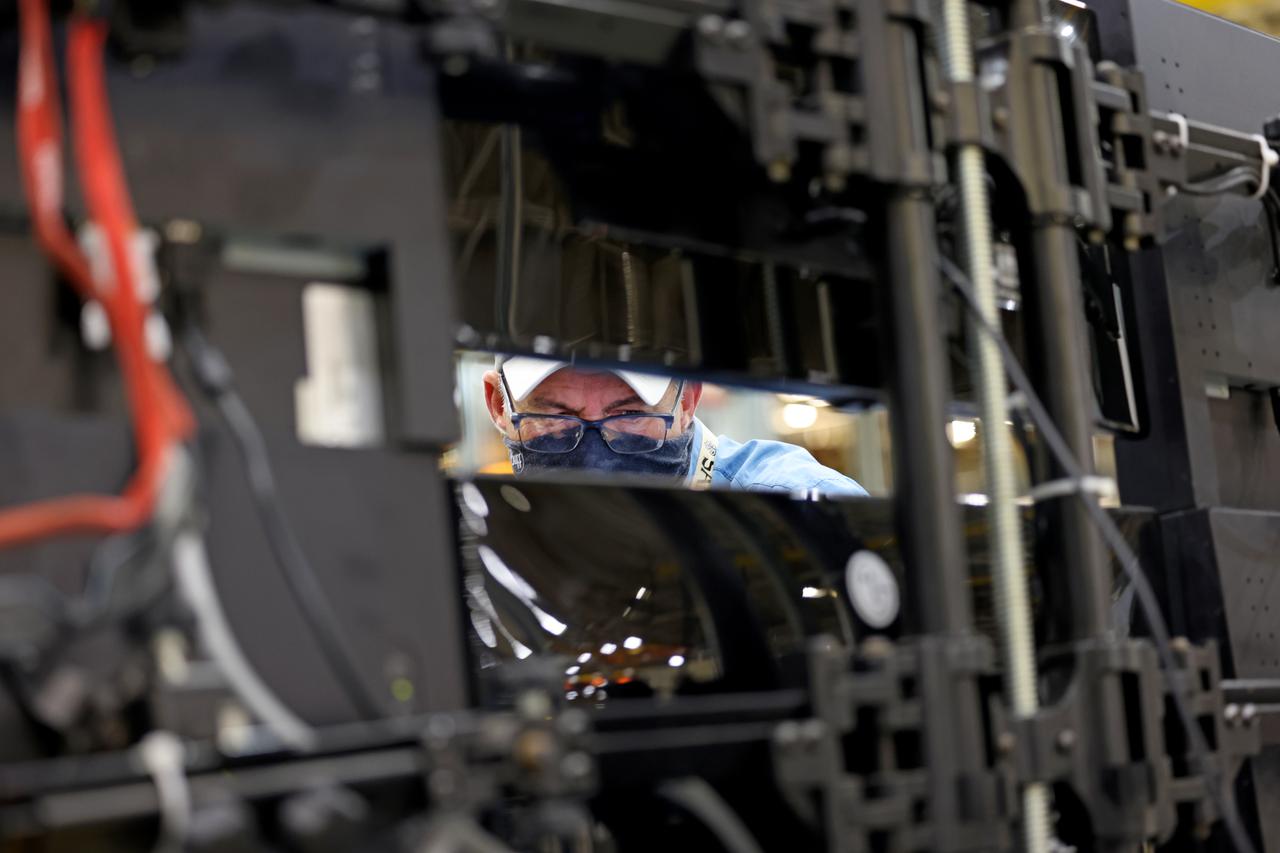

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
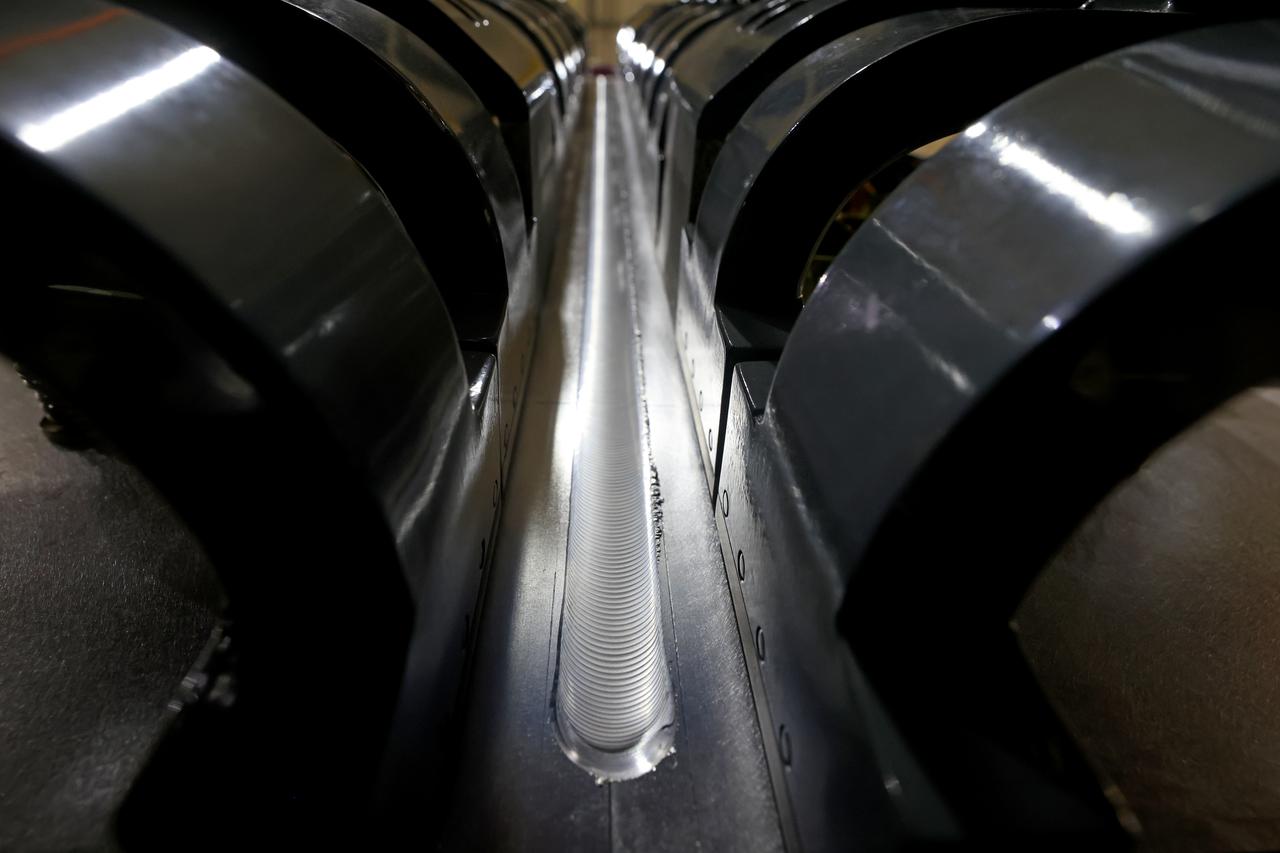

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
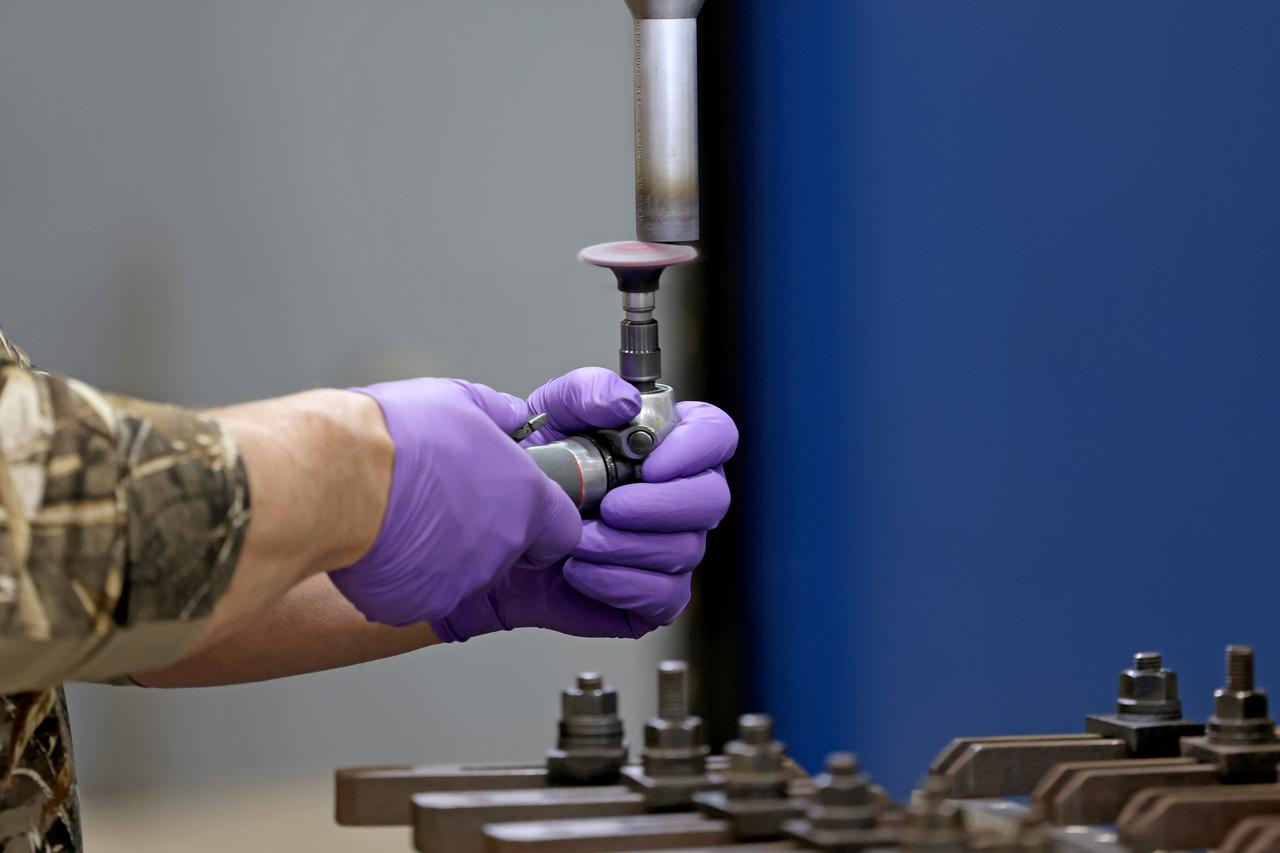

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
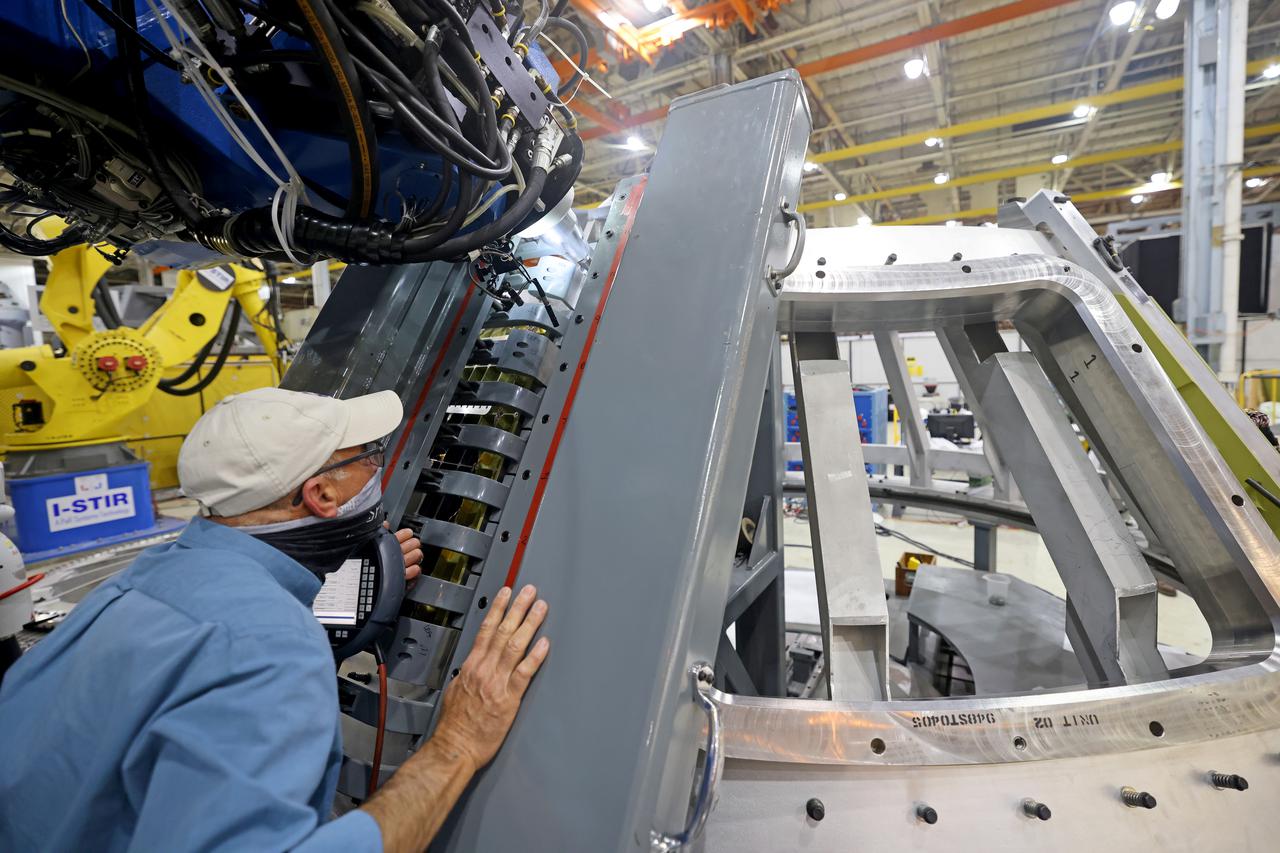

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
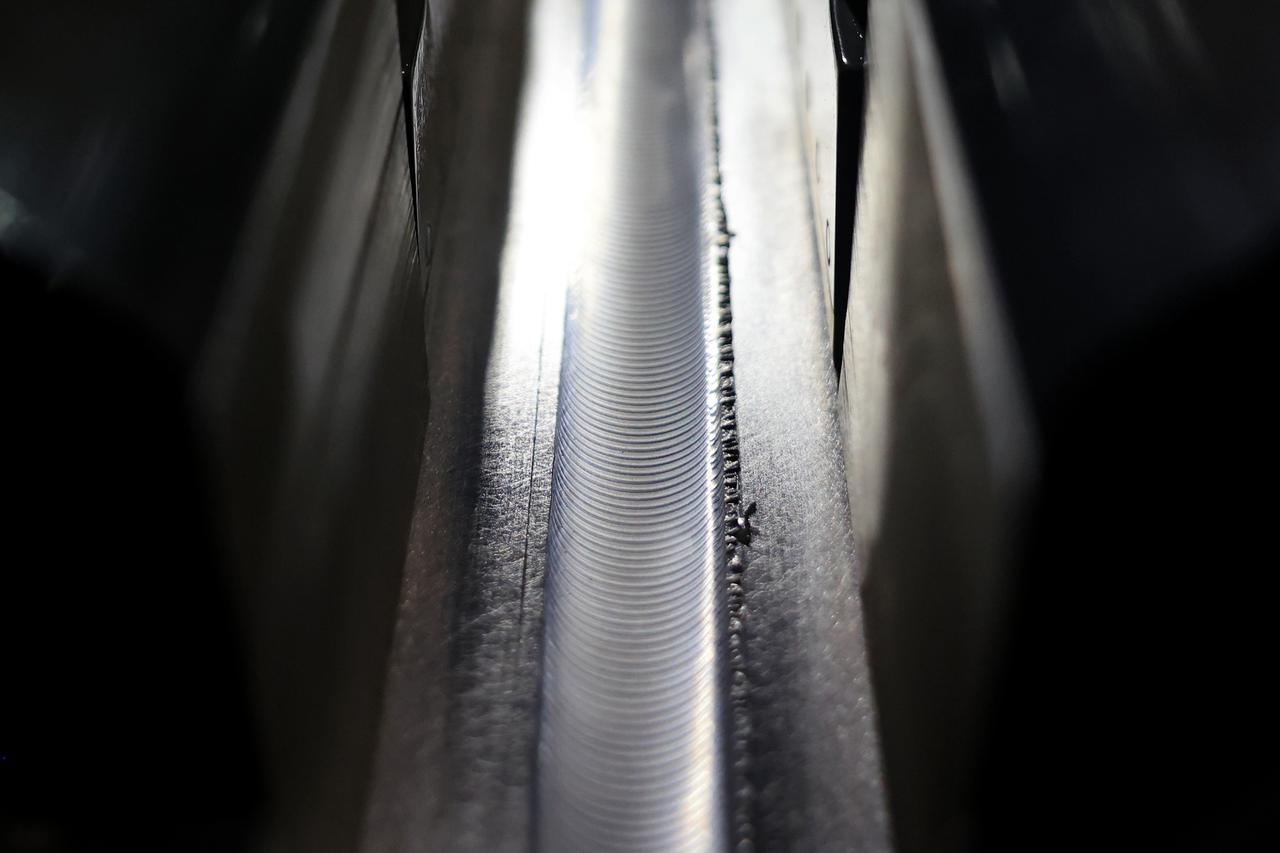

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
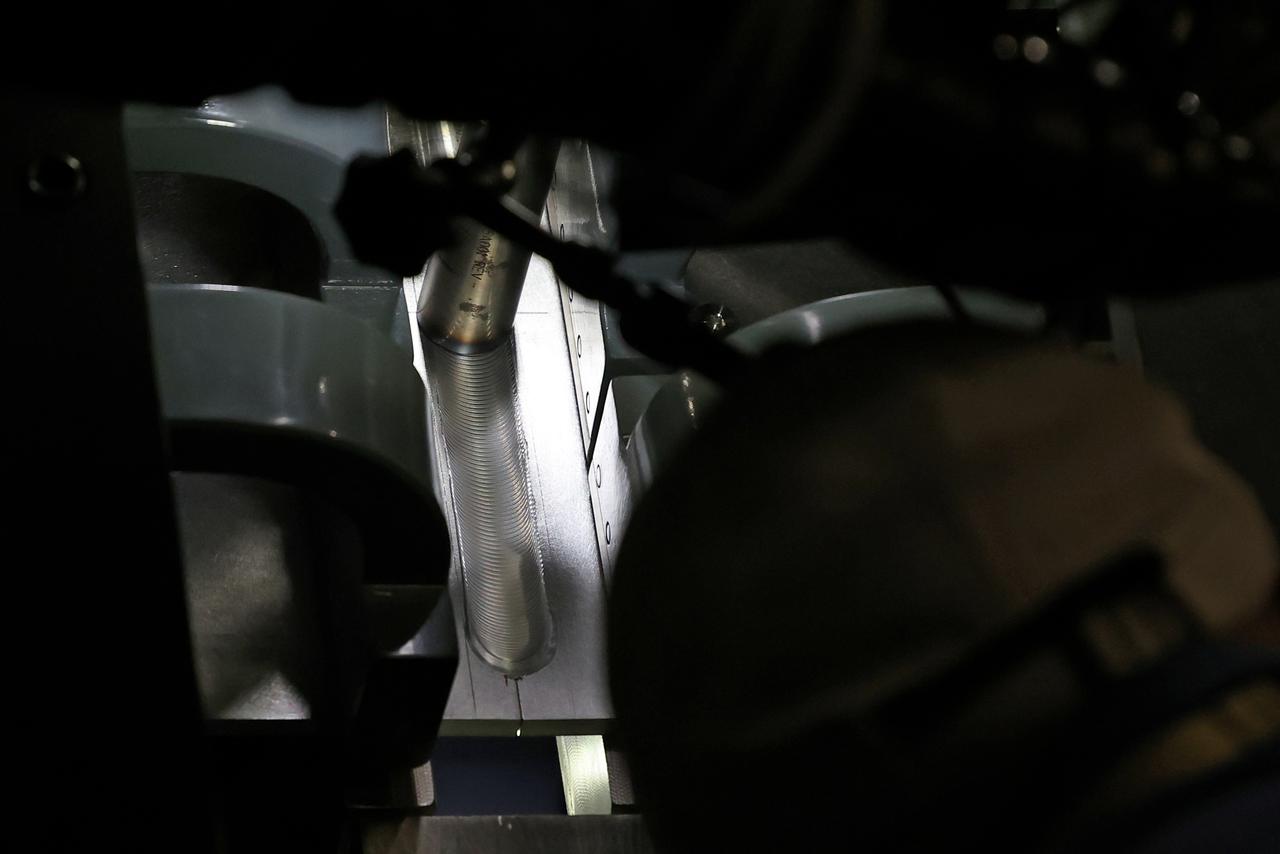

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
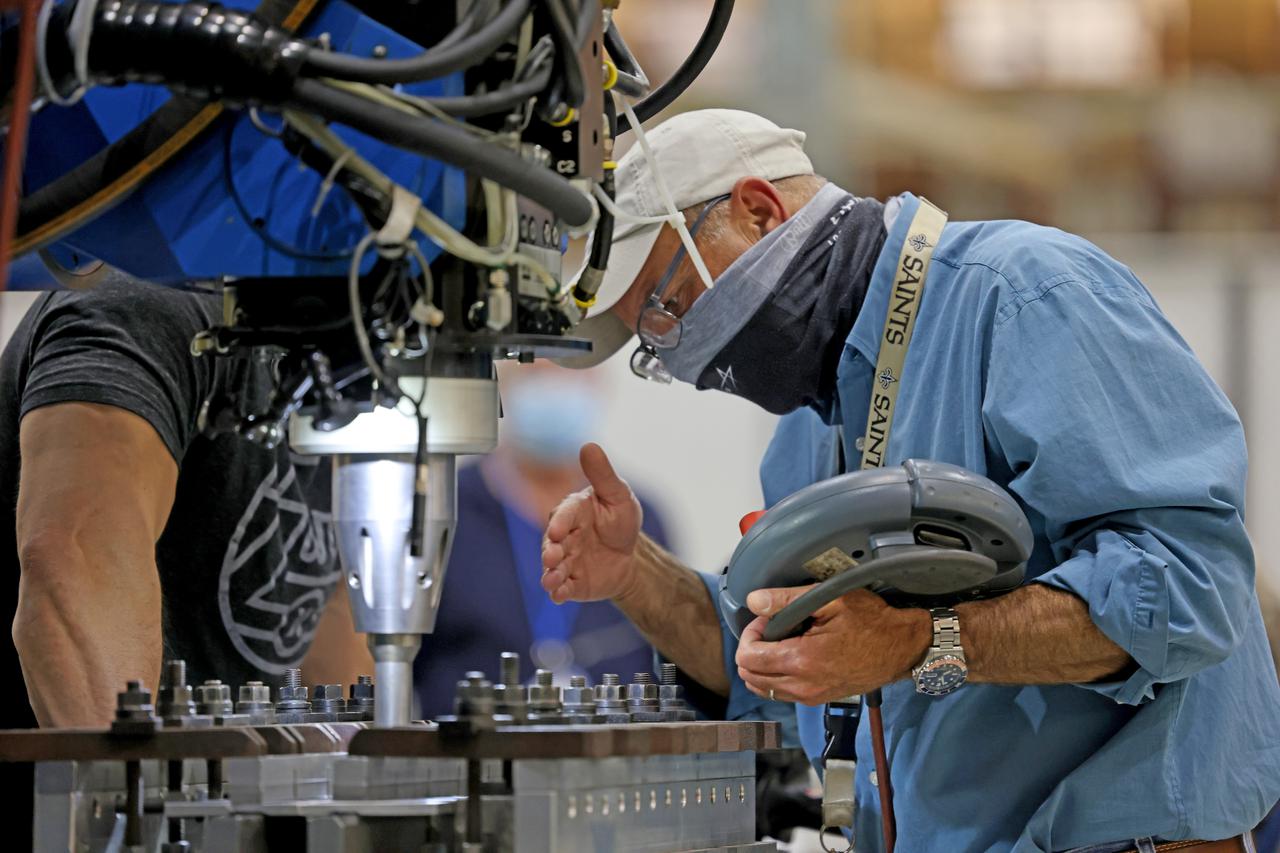

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
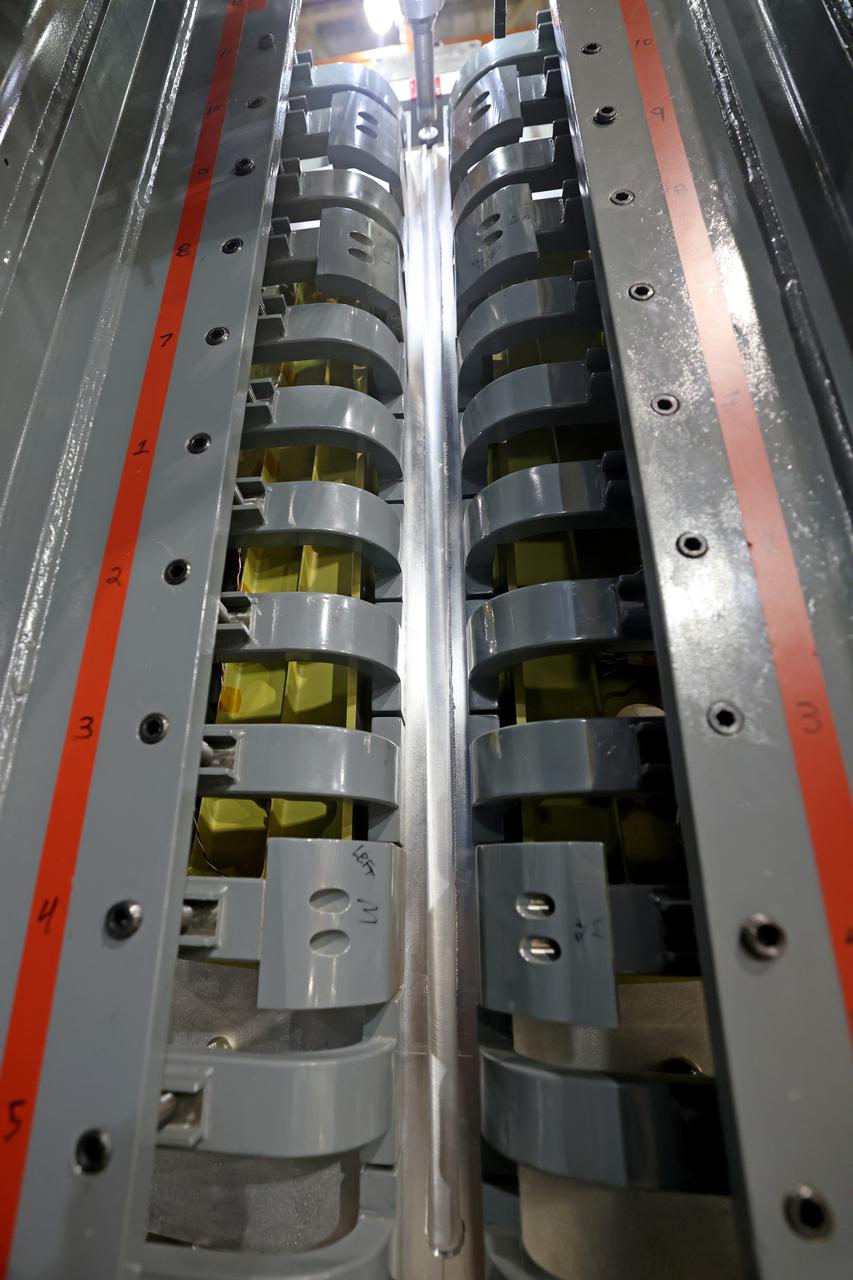

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
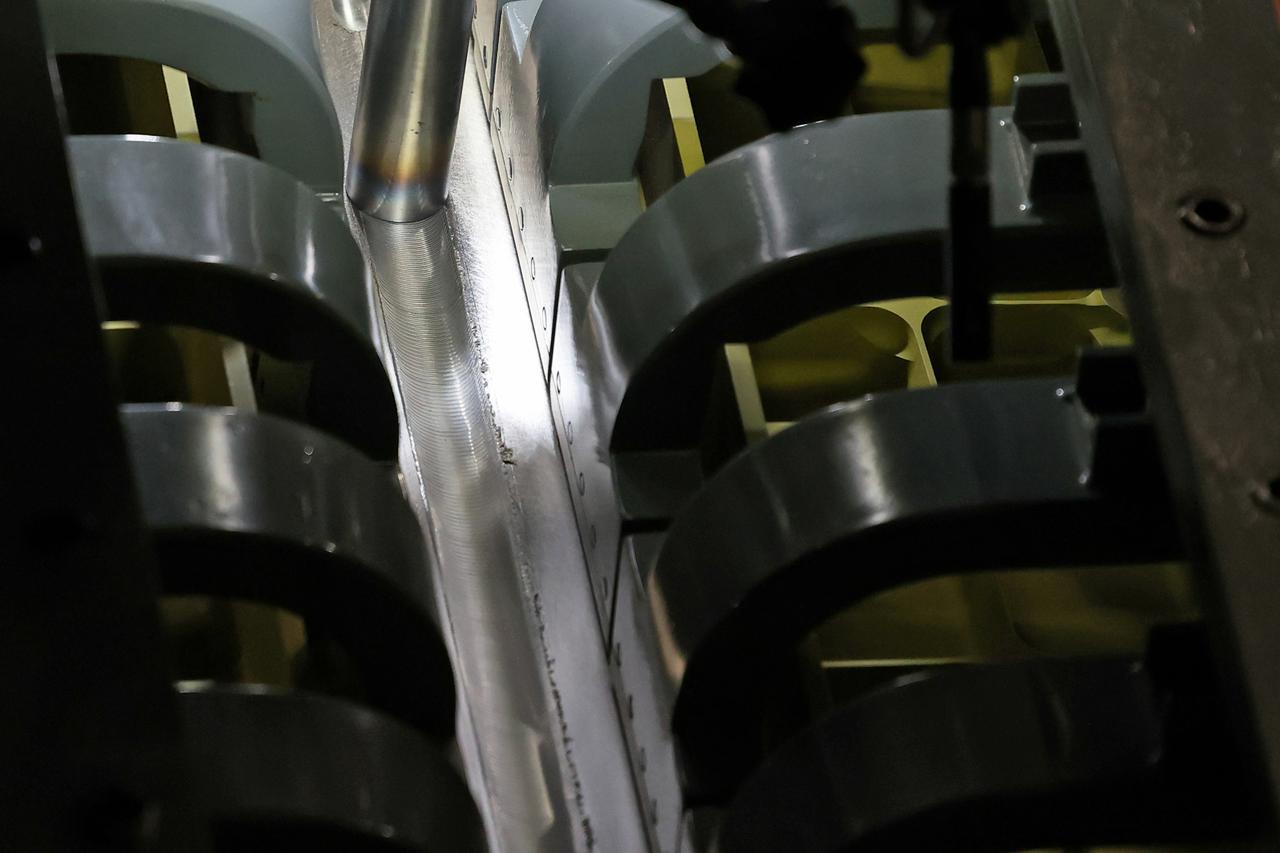

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
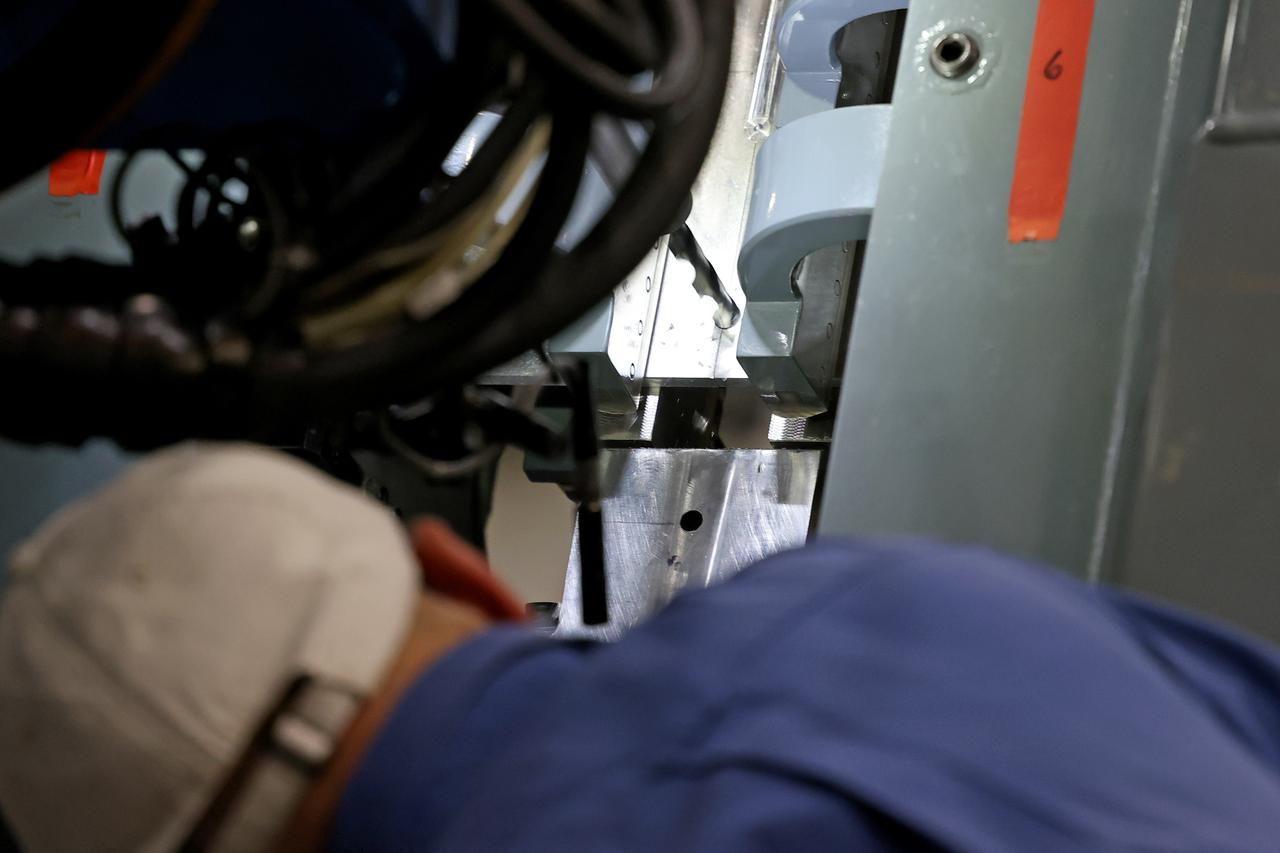

At NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, technicians from Orion prime contractor Lockheed Martin have welded together three cone-shaped panels on Orion’s crew module for the Artemis III mission that will land the first woman and next man on the Moon. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space, and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. Infographic showing the seven pieces of Orion's underlying structure With welding complete on the crew module cone panels – one of which contains windows providing astronauts views of the Moon and Earth – work will begin joining the forward bulkhead to the tunnel to create the top of the spacecraft, followed by the barrel and aft bulkhead join to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
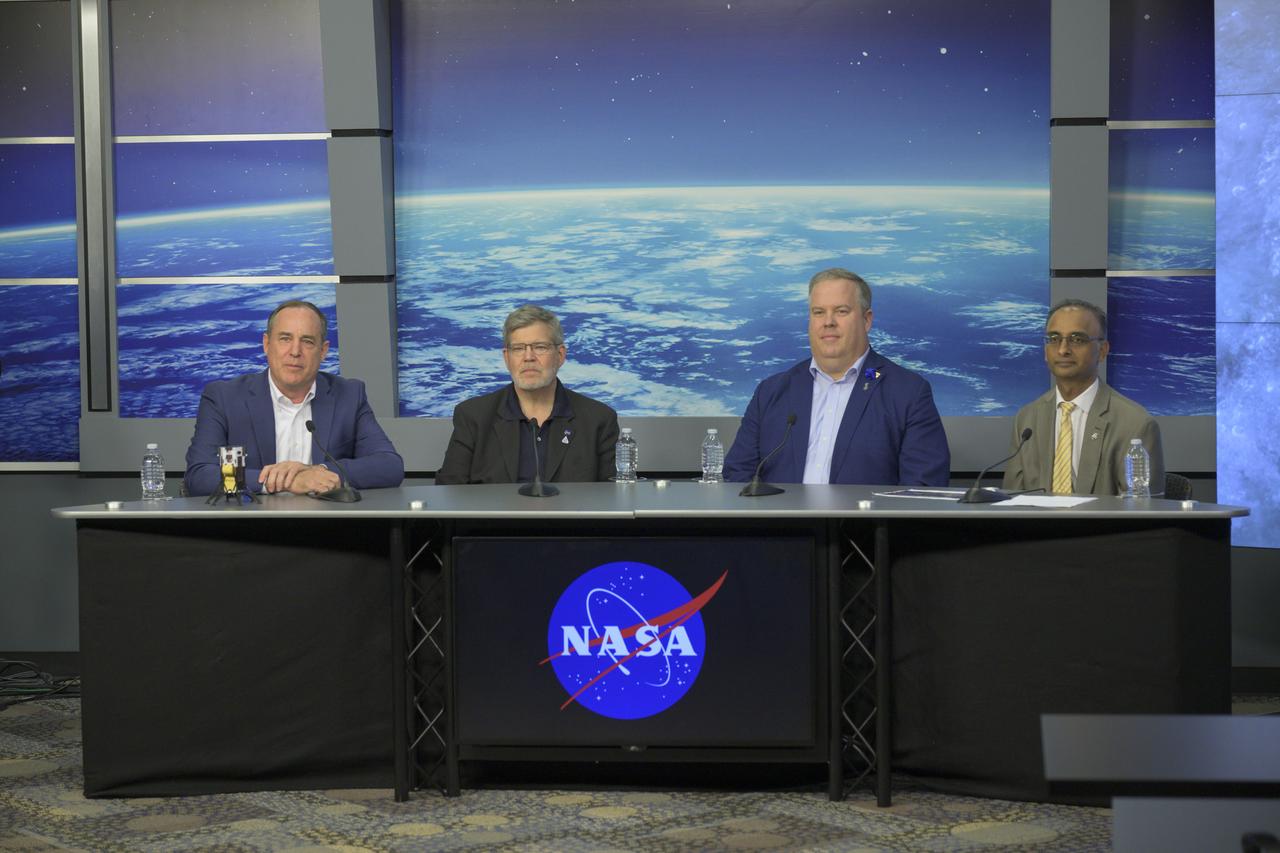

For the first time in more than 50 years, new NASA science instruments and technology demonstrations are operating on the Moon following the first successful delivery of the agency’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. Experts from NASA and Intuitive Machines hosted a news conference Feb. 23, 2024, at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston to discuss the soft landing of the company’s Nova-C lander, called Odysseus. Participants in the briefing included (left to right): Steve Altemus, chief executive officer and co-founder, Intuitive Machines; Joel Kearns, deputy associate administrator for Exploration, Science Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters in Washington; Tim Crain, chief technology officer and co-founder, Intuitive Machines; and Prasun Desai, deputy associate administrator, Space Technology Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters.

AS11-40-5875 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot of the first lunar landing mission, poses for a photograph beside the deployed United States flag during an Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The Lunar Module (LM) is on the left, and the footprints of the astronauts are clearly visible in the soil of the moon. Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm Hasselblad lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM, the "Eagle", to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit. Photo credit: NASA
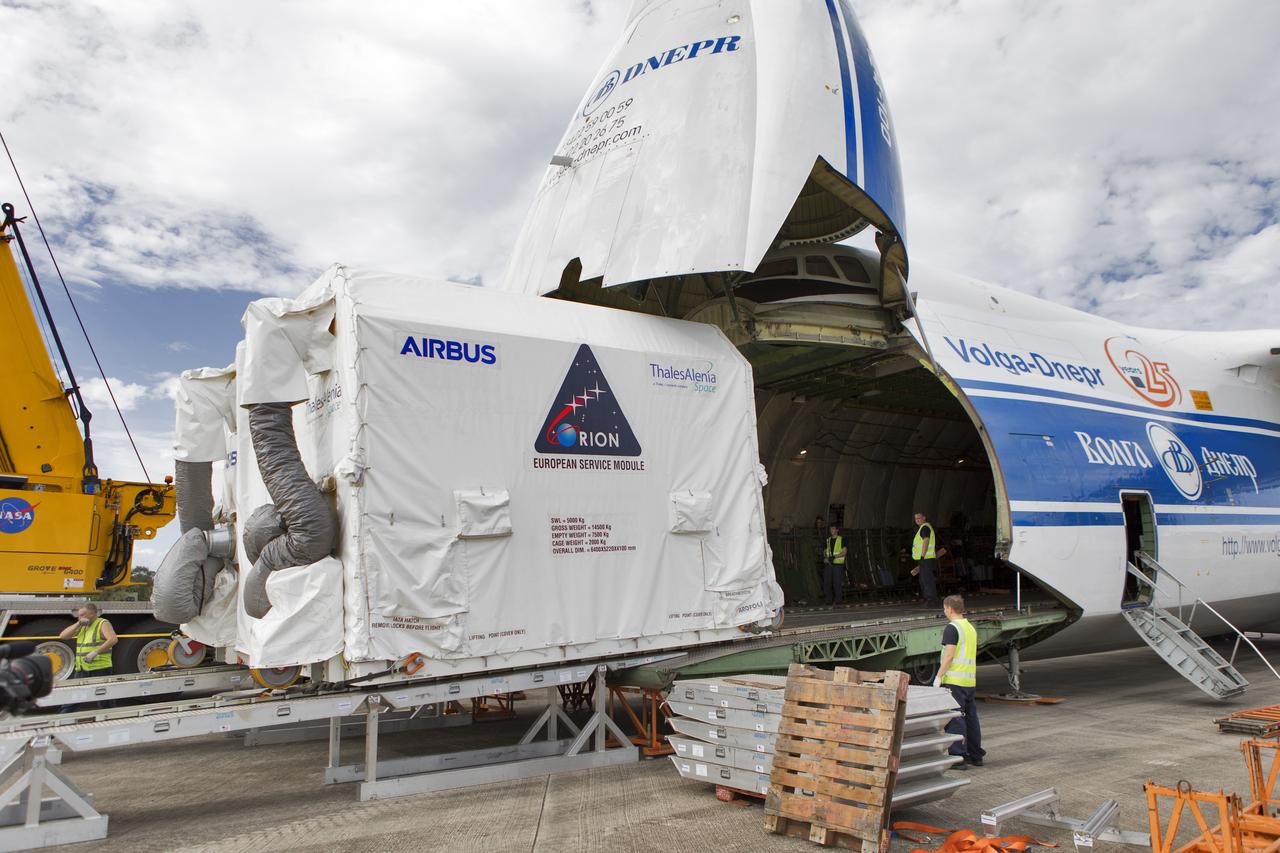

The shipping container holding the European Service Module (ESM) is moved out of the cargo hold of the Antonov cargo aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
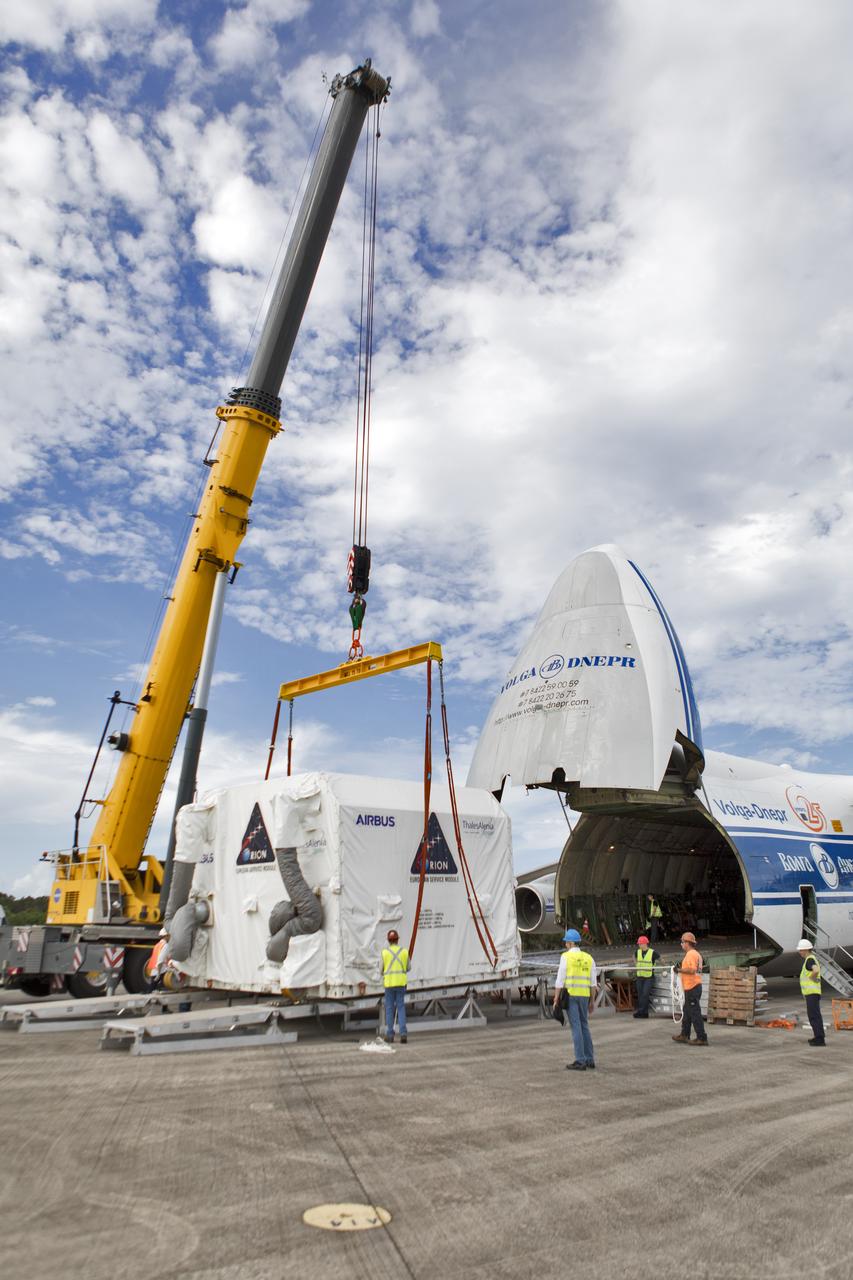

A crane is attached to the shipping container holding the European Service Module (ESM) after it was moved out of the cargo hold of the Antonov cargo aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
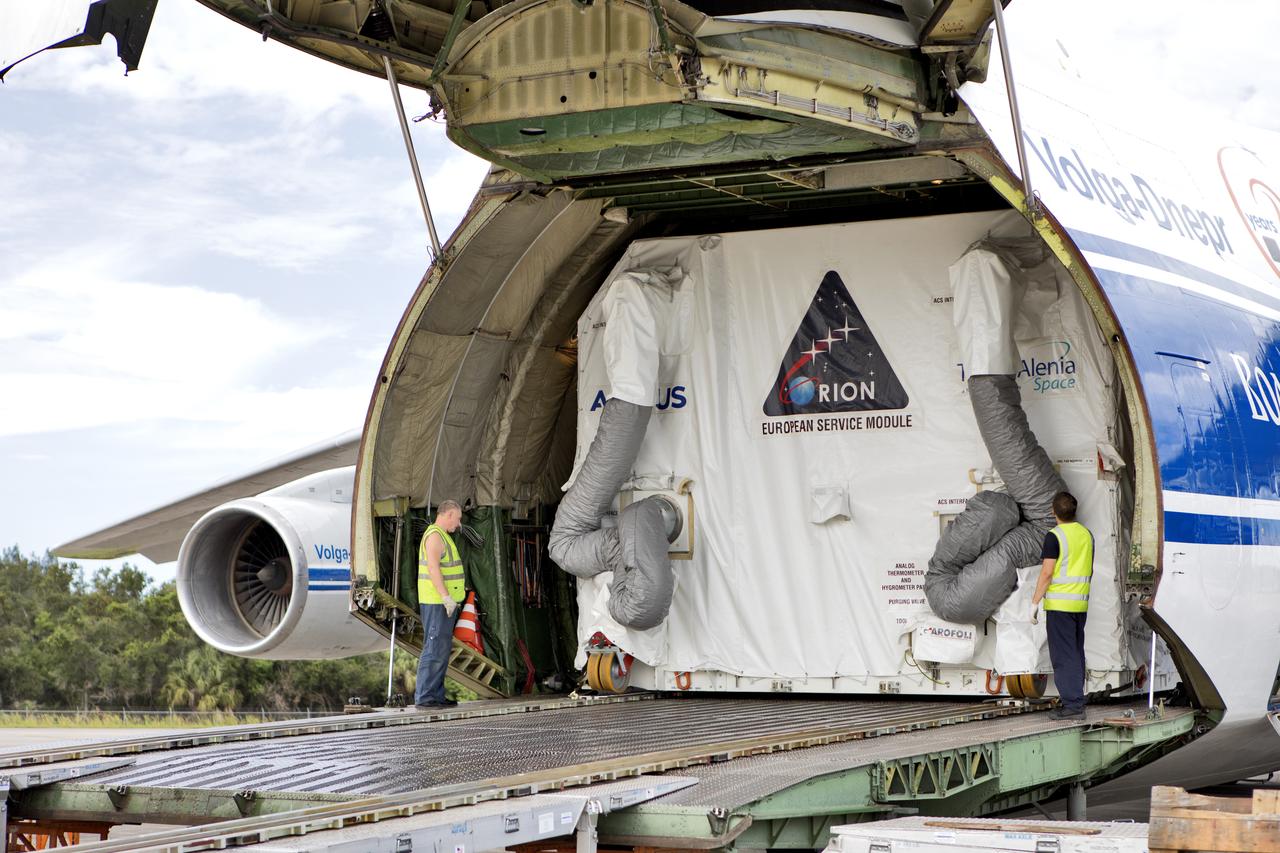

The shipping container holding the European Service Module (ESM) is moved out of the cargo hold of the Antonov cargo aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
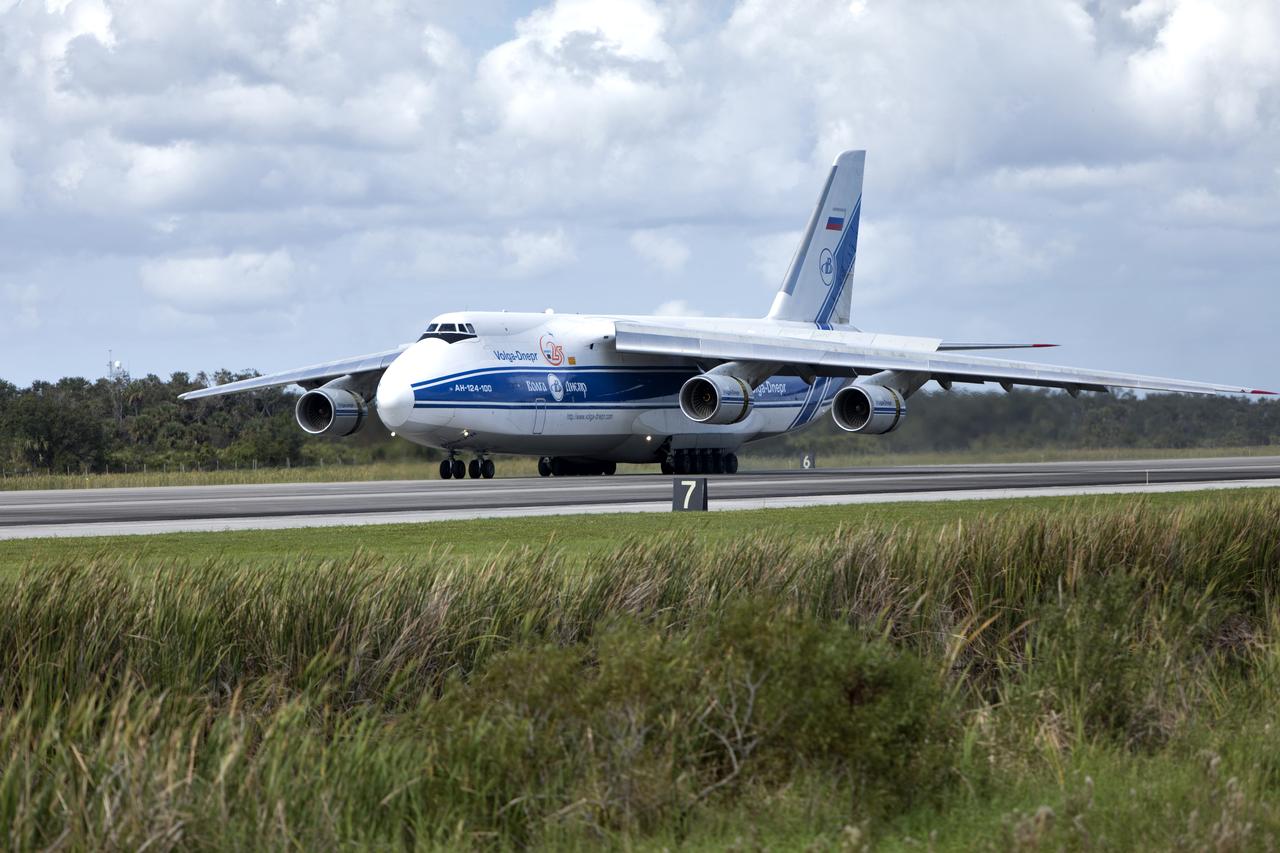

The Antonov cargo aircraft touches down at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018, carrying the European Service Module (ESM) for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.

Technicians operate a forklift to lift the European Service Module (ESM) out of the cargo hold of the Antonov cargo aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
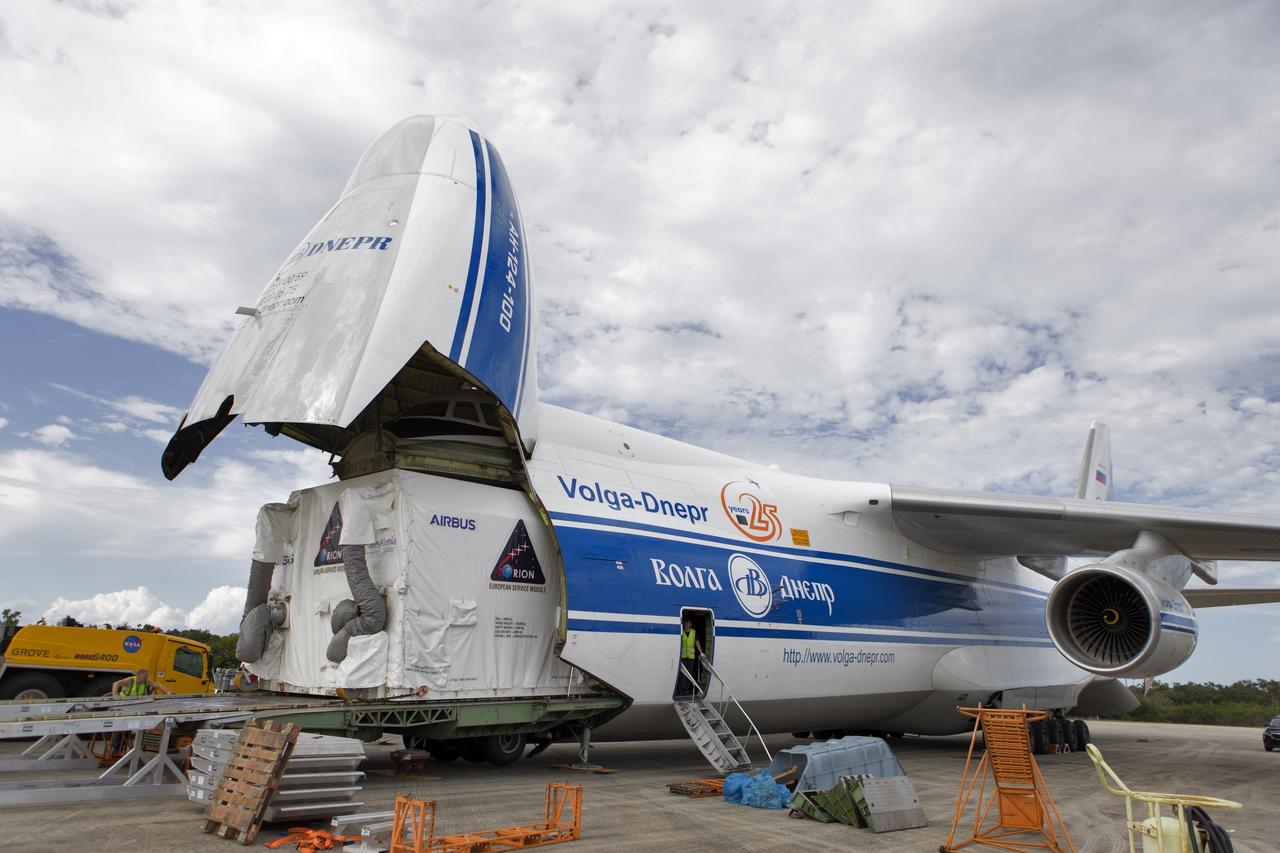

The shipping container holding the European Service Module (ESM) is moved out of the cargo hold of the Antonov cargo aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.