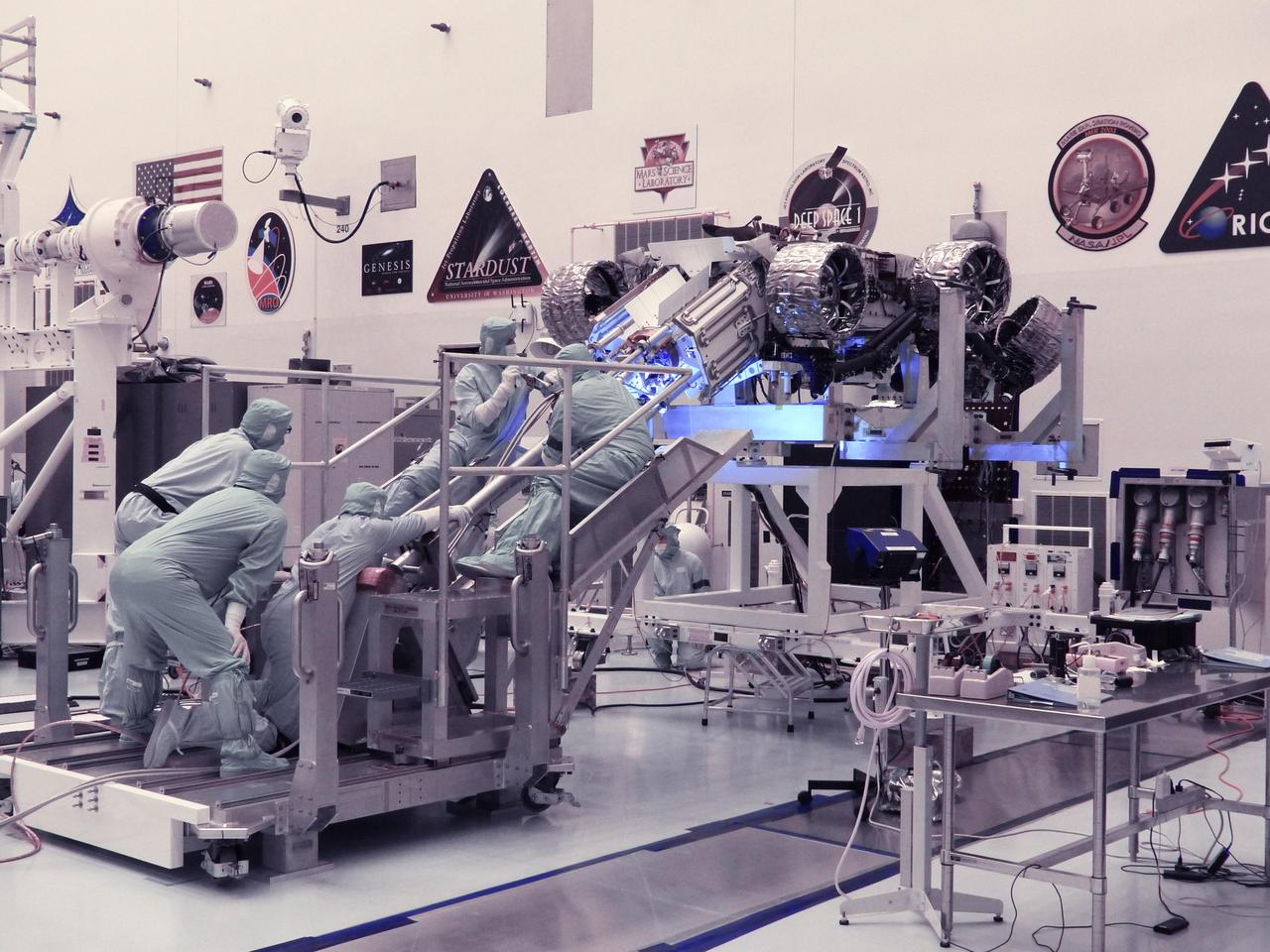
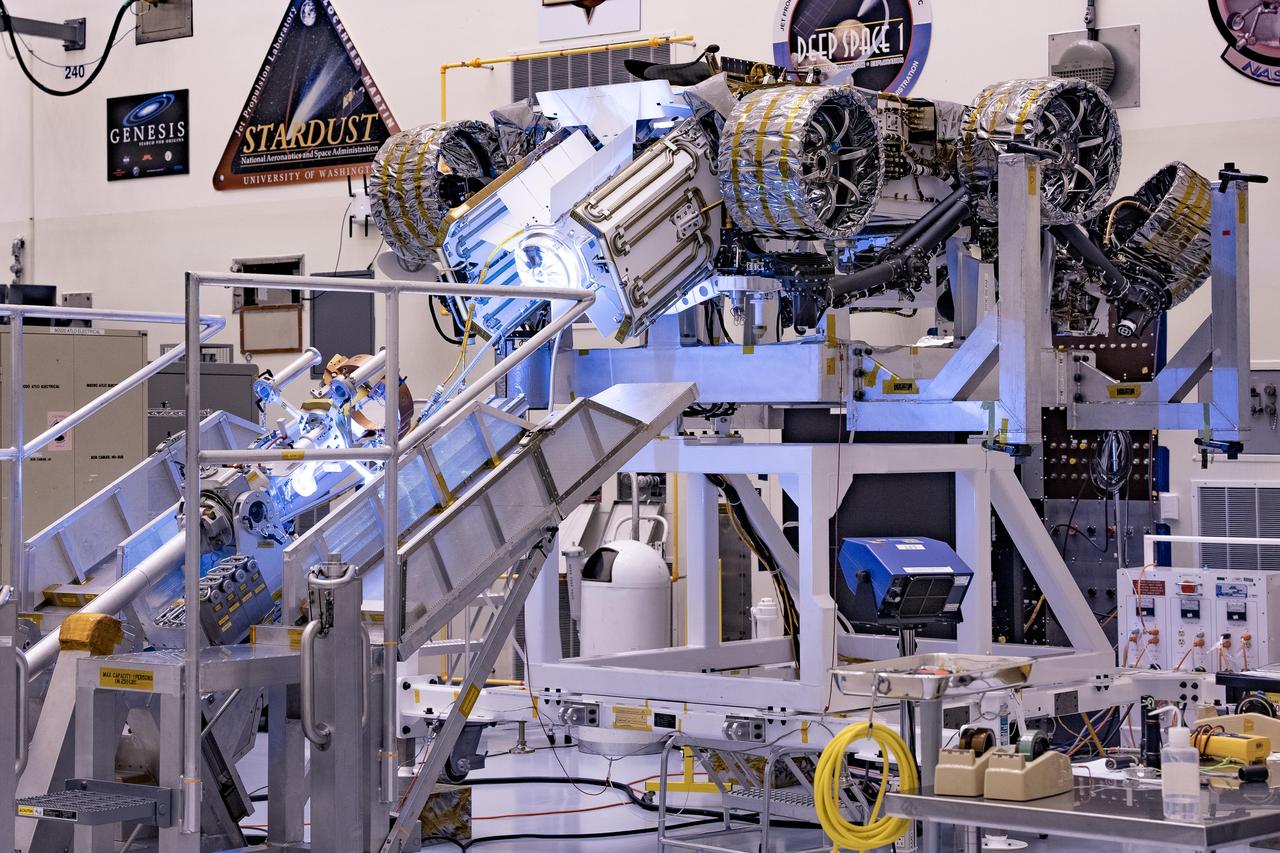
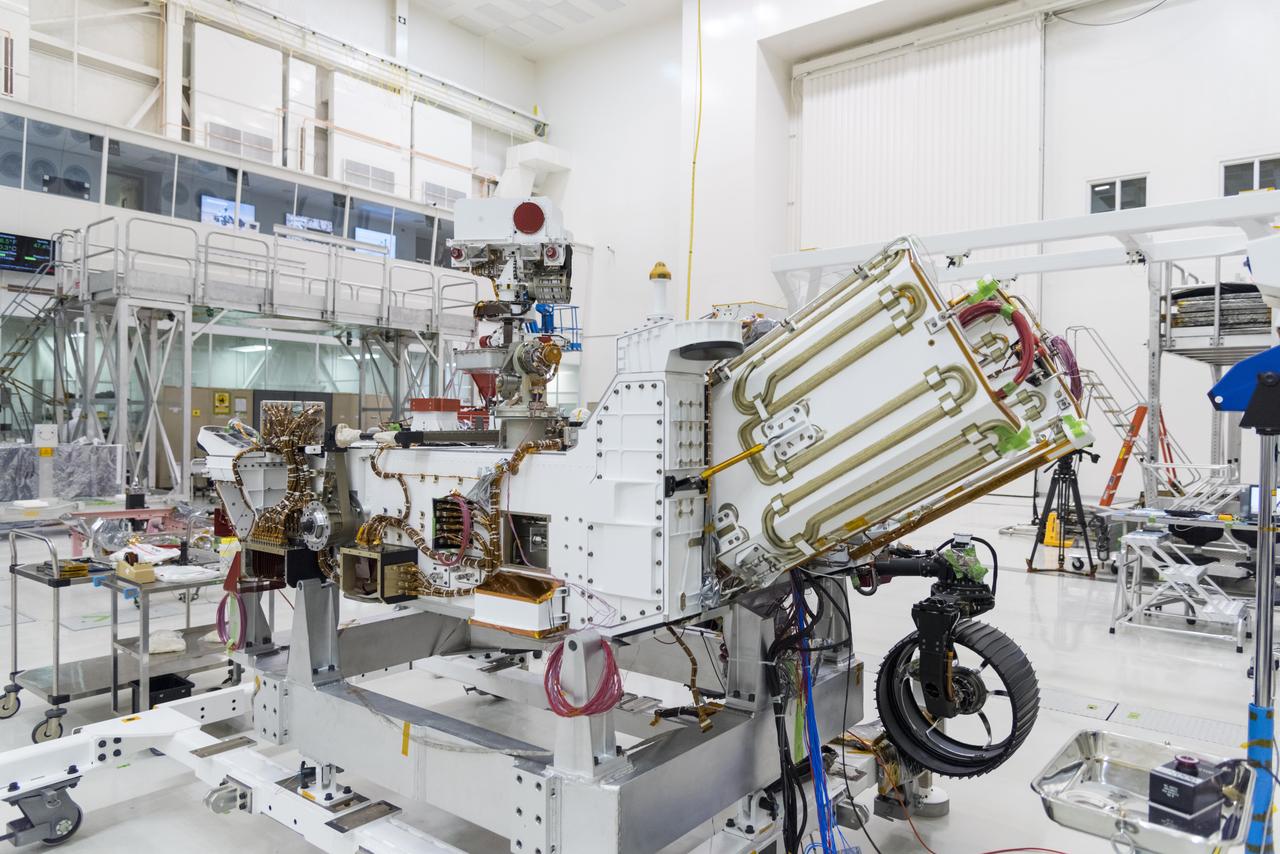
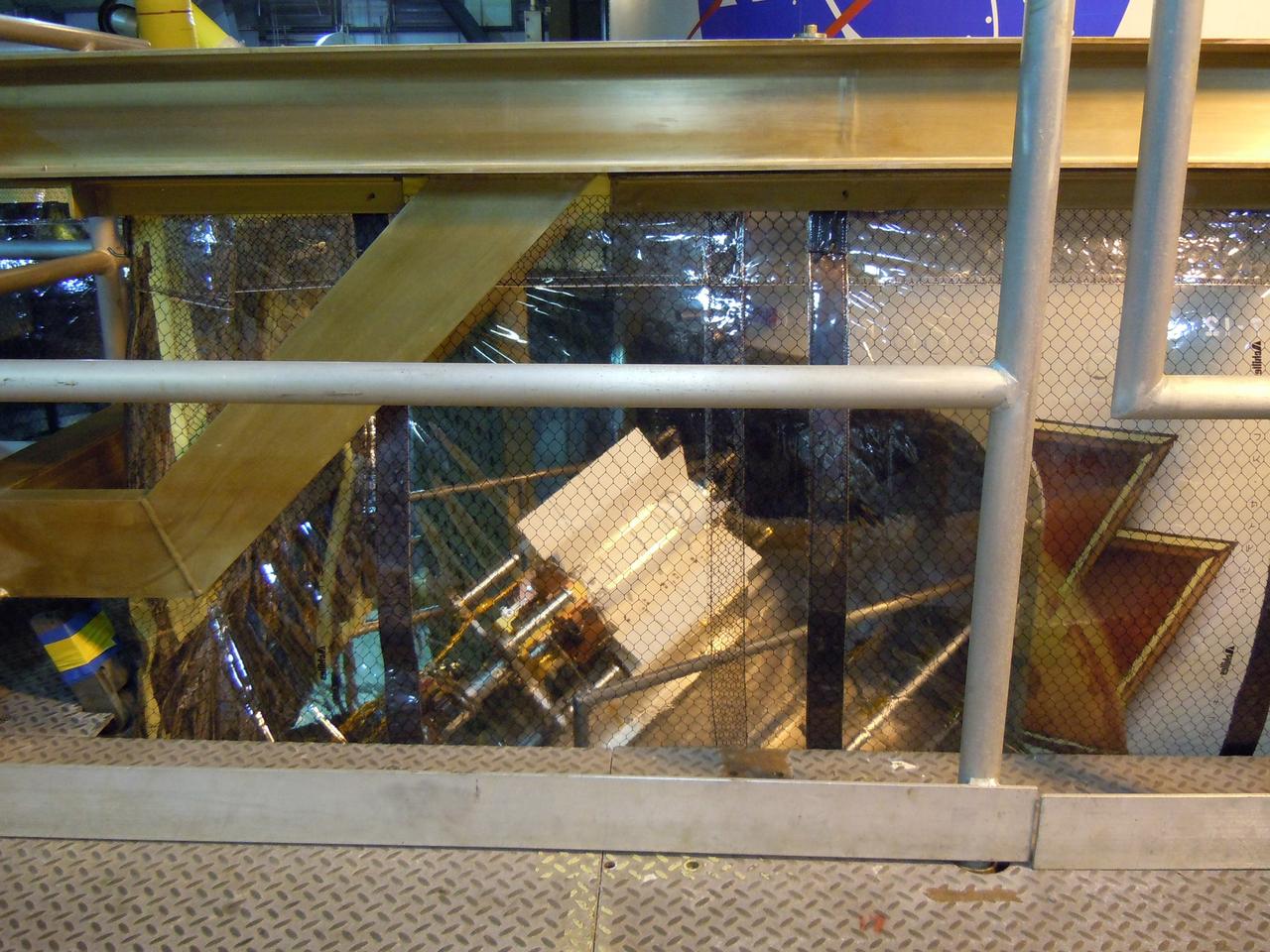
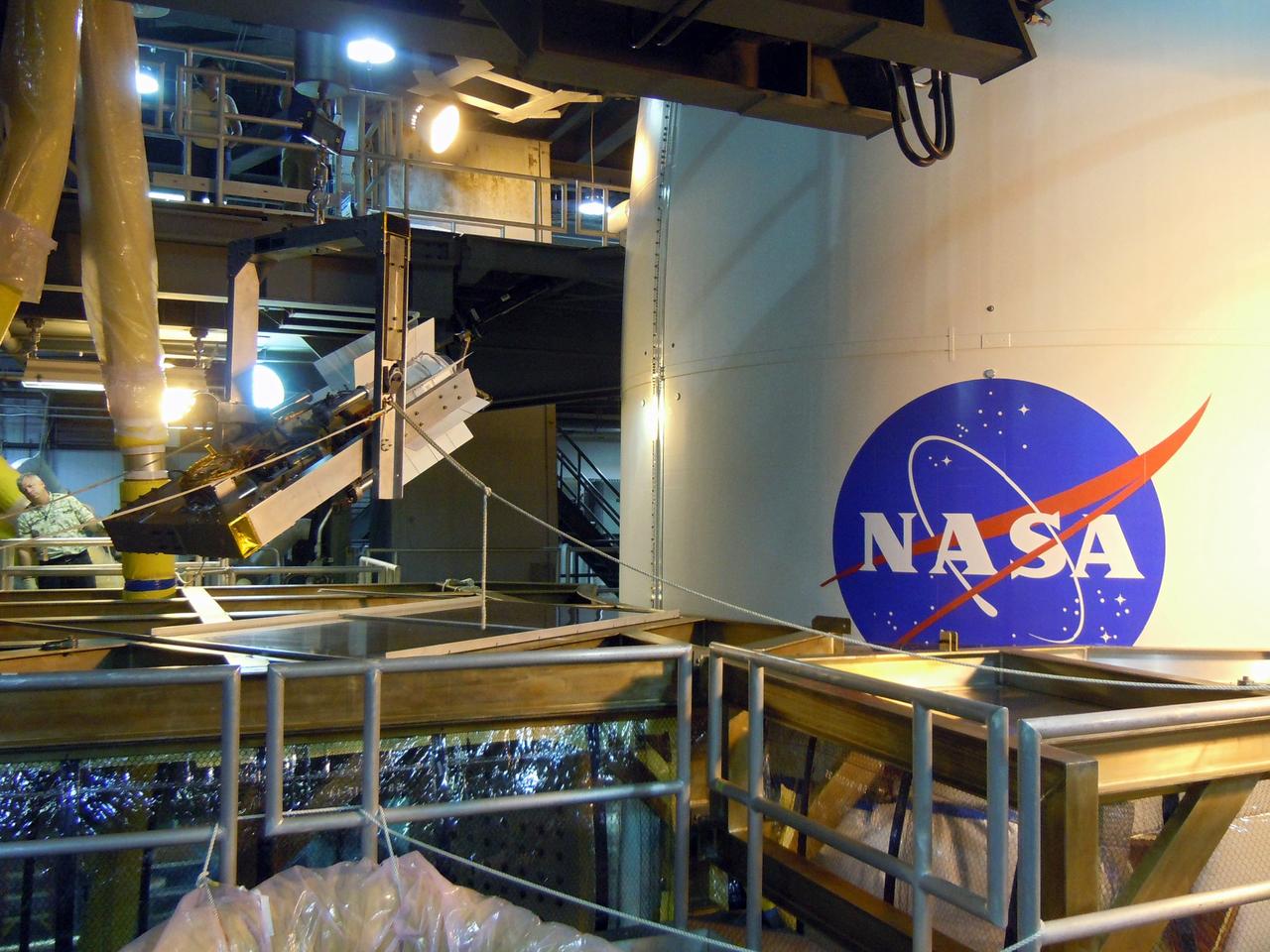
Technicians in the payload processing facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida perform a fit check between NASA'S Mars 2020 Perseverance rover and its Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator on April 16-17, 2020. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is designed and built by the U.S. Department of Energy, and provided to NASA as part of the space agency's Radioisotope Power Systems Program. It arrived at NASA KSC in April 2020 following its final assembly and transport from the Department of Energy's Idaho National Laboratory. The fit check is the first time that the fueled flight generator is connected to the rover. After the successful fit check, the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator was disconnected; it will be connected to the rover for the final time on the launch pad atop the mission's Atlas V launch vehicle in July, before the planned launch of the Mars 2020 mission. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is a space nuclear power system that produces about 110 watts of electrical power to run the rover's systems and science instruments, and extra heat to keep them warm during the frigid Martian nights and winter seasons. It converts the heat from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium dioxide into electricity using thermocouples with no moving parts. The choice of a Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator as the rover's power system gave mission planners significantly more flexibility in selecting the rover's landing site and in planning its surface operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23827
The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator for NASA'S Mars 2020 Perseverance rover is shown during a fit check with the rover in a payload processing facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 16-17, 2020. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is designed and built by the U.S. Department of Energy, and provided to NASA as part of the space agency's Radioisotope Power Systems Program. It arrived at NASA KSC in April 2020 following its final assembly and transport from the Department of Energy's Idaho National Laboratory. The fit check is the first time that the fueled flight generator is connected to the rover. After the successful fit check, the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator was disconnected; it will be connected to the rover for the final time on the launch pad atop the mission's Atlas V launch vehicle in July, before the planned launch of the Mars 2020 mission. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is a space nuclear power system that produces about 110 watts of electrical power to run the rover's systems and science instruments, and extra heat to keep them warm during the frigid Martian nights and winter seasons. It converts the heat from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium dioxide into electricity using thermocouples with no moving parts. The choice of a Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator as the rover's power system gave mission planners significantly more flexibility in selecting the rover's landing site and in planning its surface operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23981

This image shows the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator for NASA'S Mars 2020 Perseverance rover during a fit check with the rover in the payload processing facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 16-17, 2020. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is designed and built by the U.S. Department of Energy, and provided to NASA as part of the space agency's Radioisotope Power Systems Program. It arrived at NASA KSC in April 2020 following its final assembly and transport from the Department of Energy's Idaho National Laboratory. The fit check is the first time that the fueled flight generator is connected to the rover. After the successful fit check, the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator was disconnected; it will be connected to the rover for the final time on the launch pad atop the mission's Atlas V launch vehicle in July, before the planned launch of the Mars 2020 mission. The Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator is a space nuclear power system that produces about 110 watts of electrical power to run the rover's systems and science instruments, and extra heat to keep them warm during the frigid Martian nights and winter seasons. It converts the heat from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium dioxide into electricity using thermocouples with no moving parts. The choice of a Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator as the rover's power system gave mission planners significantly more flexibility in selecting the rover's landing site and in planning its surface operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23982
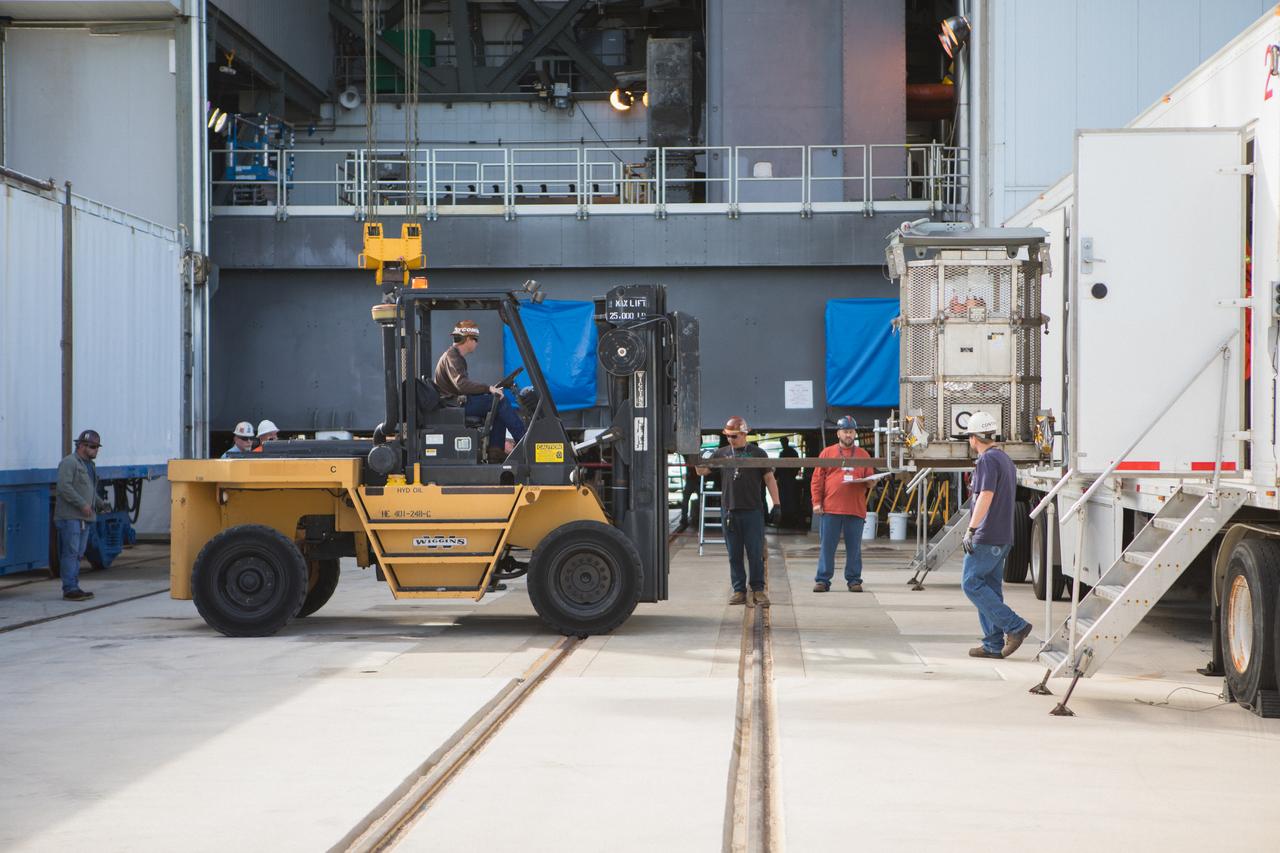

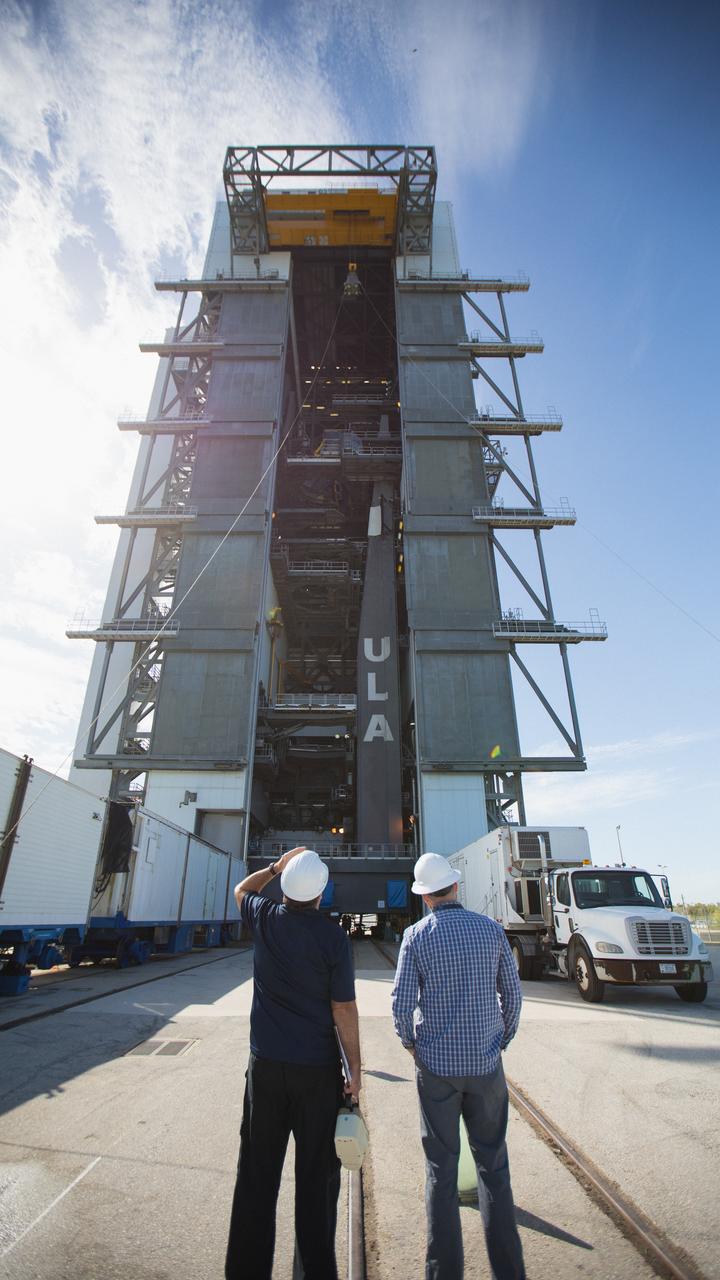
A test version of the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) for NASA’s Mars 2020 mission arrives at the United Launch Alliance Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Feb. 15, 2019. The MMRTG simulator will be used to practice operations and procedures for carefully hoisting it up and into the VIF. The Mars 2020 rover mission is targeted to launch in July 2020 on a ULA Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. Mars 2020 is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars.

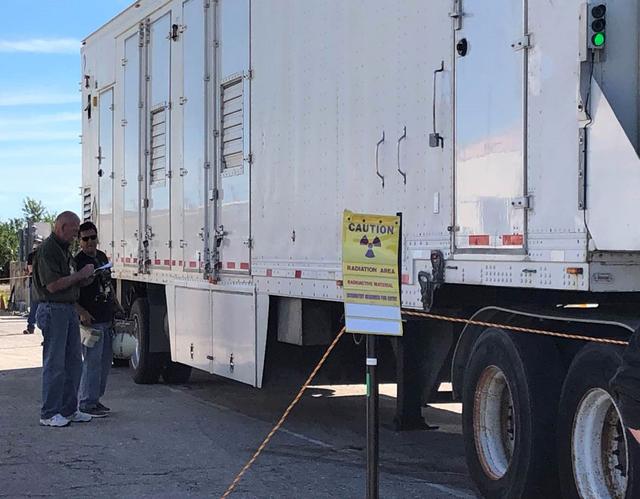
A caution sign marks the presence of a test version of the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) for NASA’s Mars 2020 mission at the United Launch Alliance Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Feb. 15, 2019. The MMRTG simulator will be used to practice operations and procedures for carefully hoisting it up and into the VIF. The Mars 2020 rover mission is targeted to launch in July 2020 on a ULA Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. Mars 2020 is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars.
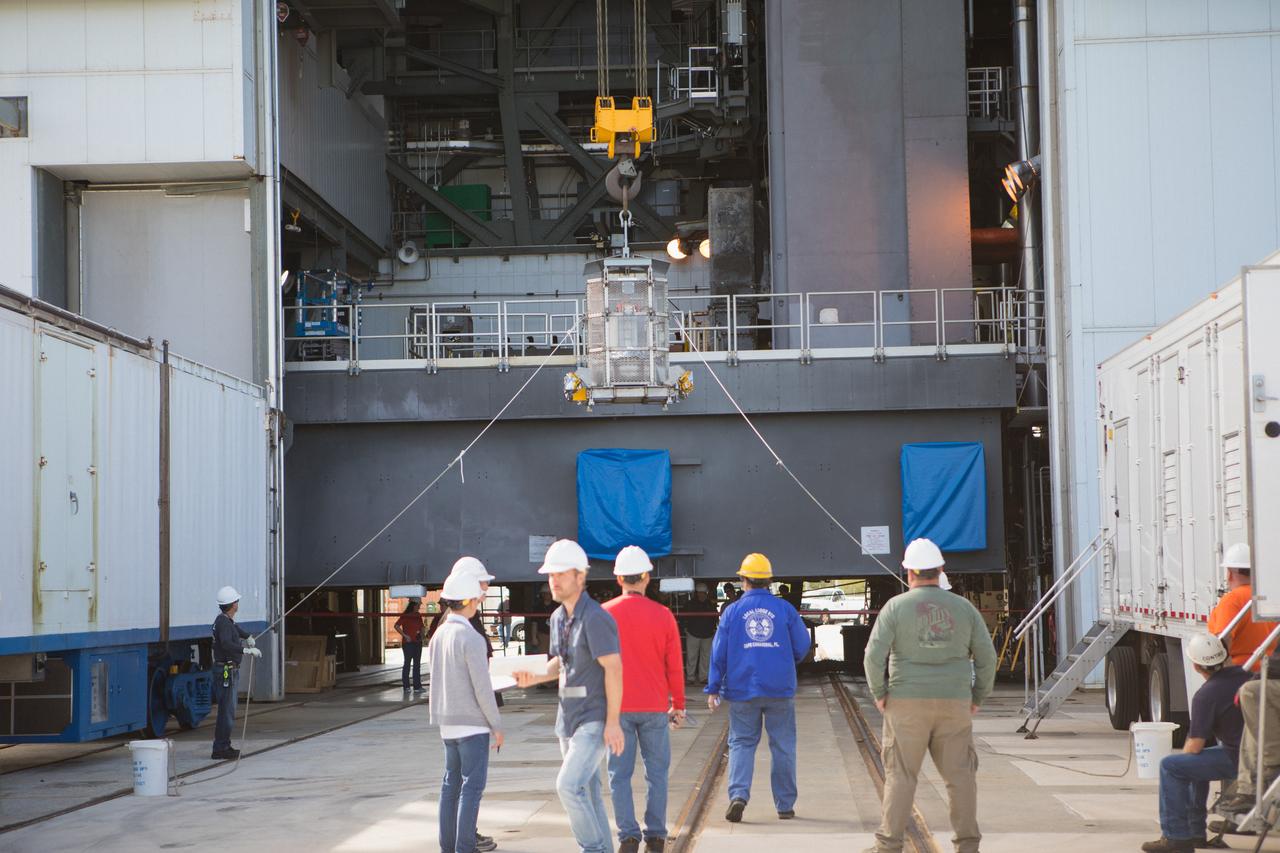

Technicians assist as a crane lifts up a test version of the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) for NASA’s Mars 2020 mission at the United Launch Alliance Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Feb. 15, 2019. The MMRTG simulator is being used to practice operations and procedures for carefully hoisting it up and into the VIF. The Mars 2020 rover mission is targeted to launch in July 2020 on a ULA Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. Mars 2020 is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars.
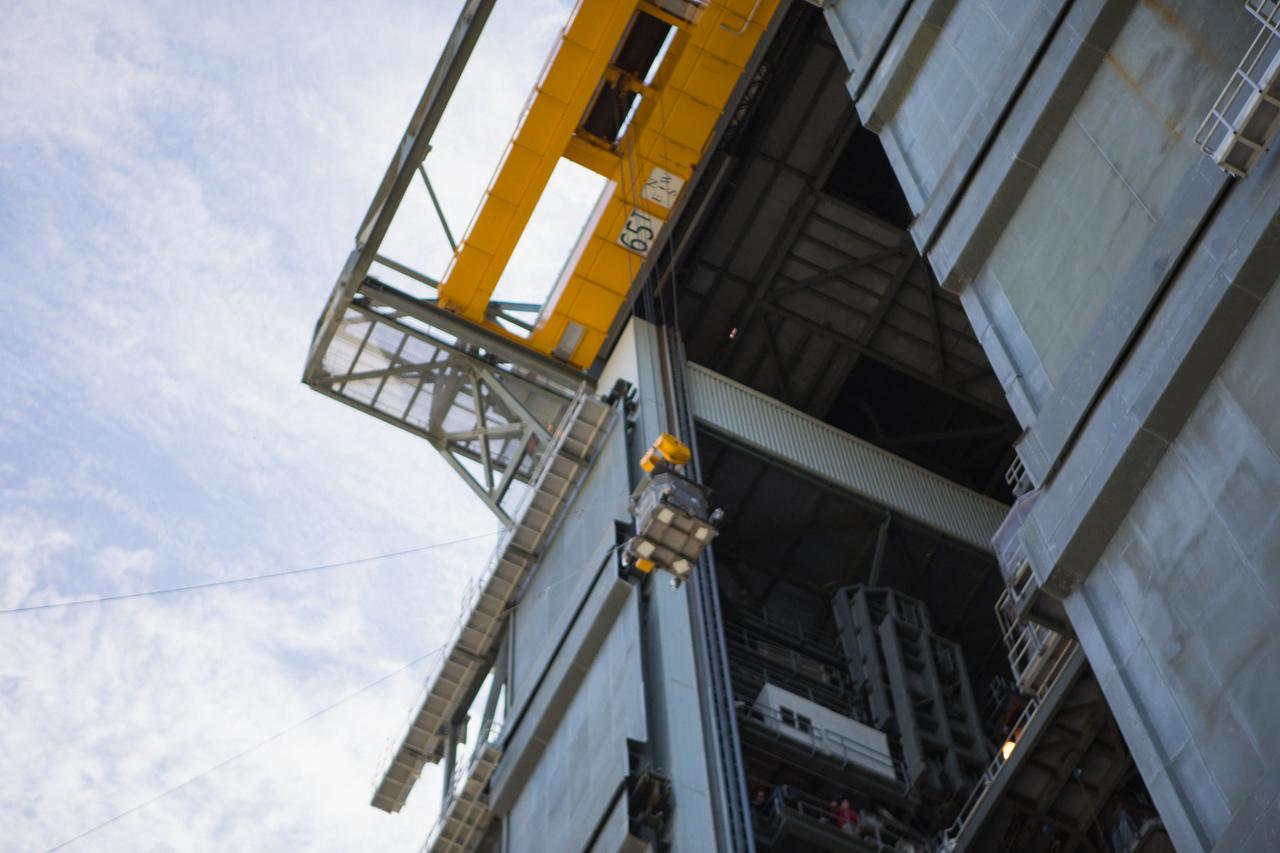

A crane is used to hoist a test version of the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) for NASA’s Mars 2020 mission at the United Launch Alliance Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Feb. 15, 2019. The MMRTG simulator is being used to practice operations and procedures for carefully lifting it up and into the VIF. The Mars 2020 rover mission is targeted to launch in July 2020 on a ULA Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. Mars 2020 is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars.

A crane is used to hoist a test version of the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) for NASA’s Mars 2020 mission up and into the United Launch Alliance Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Feb. 15, 2019. The MMRTG simulator is being used to practice operations and procedures for carefully lifting it up and into the VIF. The Mars 2020 rover mission is targeted to launch in July 2020 on a ULA Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. Mars 2020 is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars.
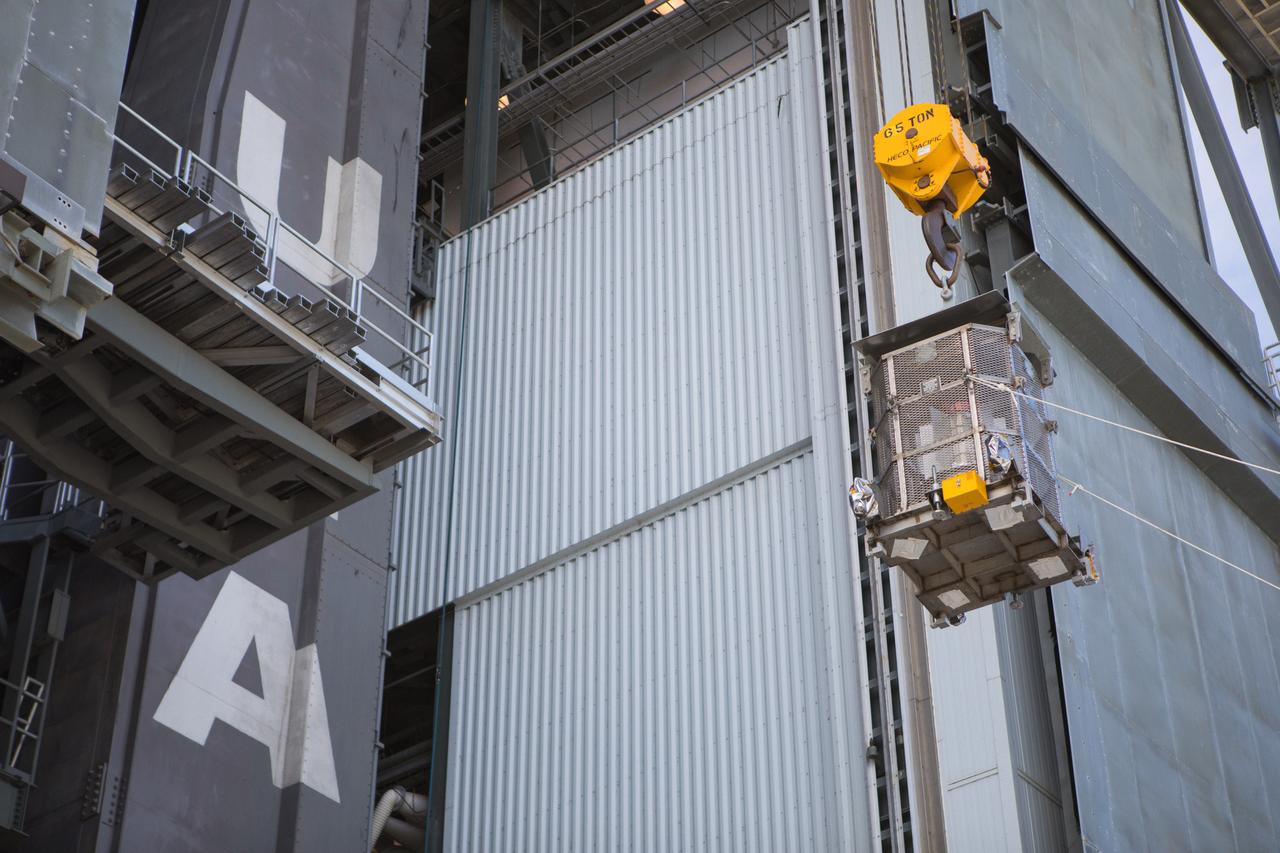

A crane is used to hoist a test version of the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) for NASA’s Mars 2020 mission at the United Launch Alliance Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Feb. 15, 2019. The MMRTG simulator is being used to practice operations and procedures for carefully lifting it up and into the VIF. The Mars 2020 rover mission is targeted to launch in July 2020 on a ULA Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. Mars 2020 is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars.
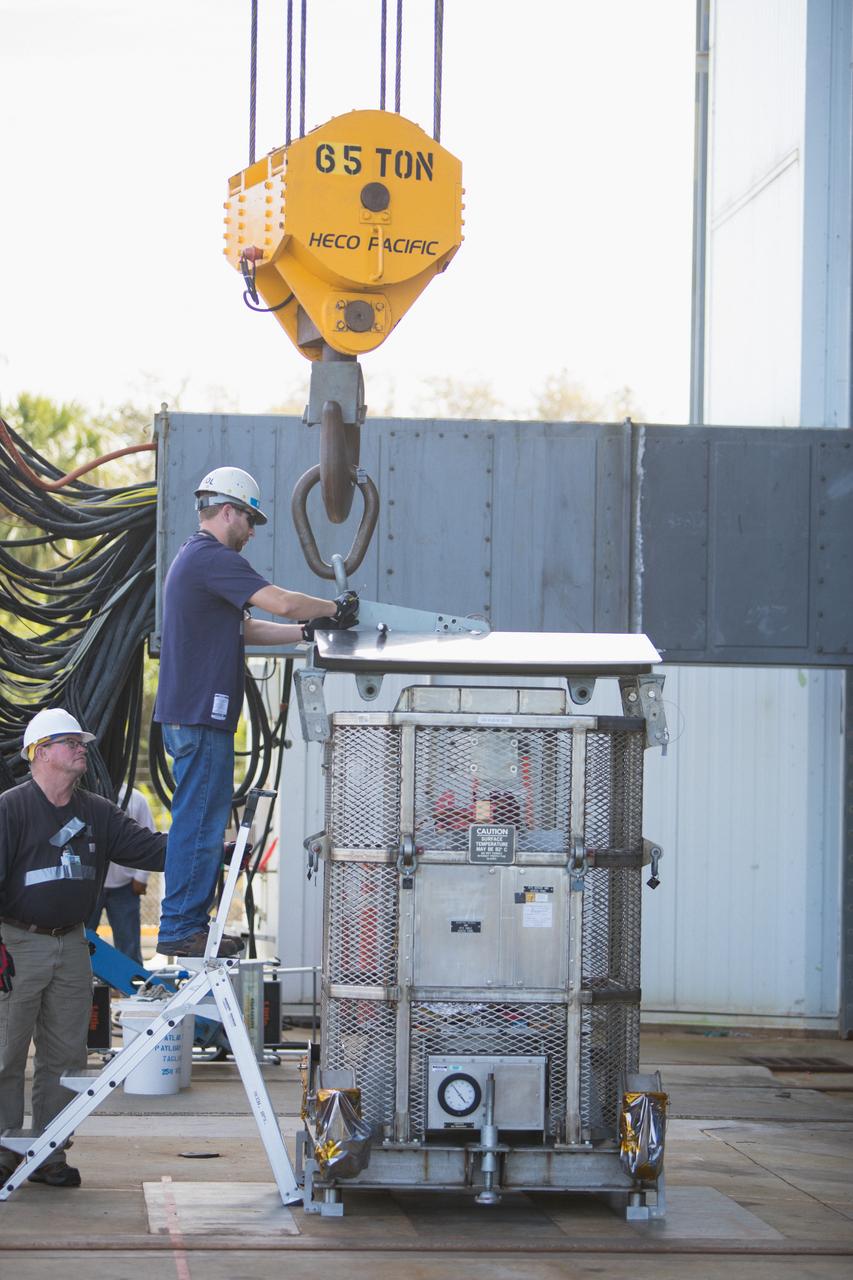

Technicians attach a crane to a test version of the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) for NASA’s Mars 2020 mission at the United Launch Alliance Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Feb. 15, 2019. The MMRTG simulator will be used to practice operations and procedures for carefully hoisting it up and into the VIF. The Mars 2020 rover mission is targeted to launch in July 2020 on a ULA Atlas V rocket from Pad 41. Mars 2020 is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars.

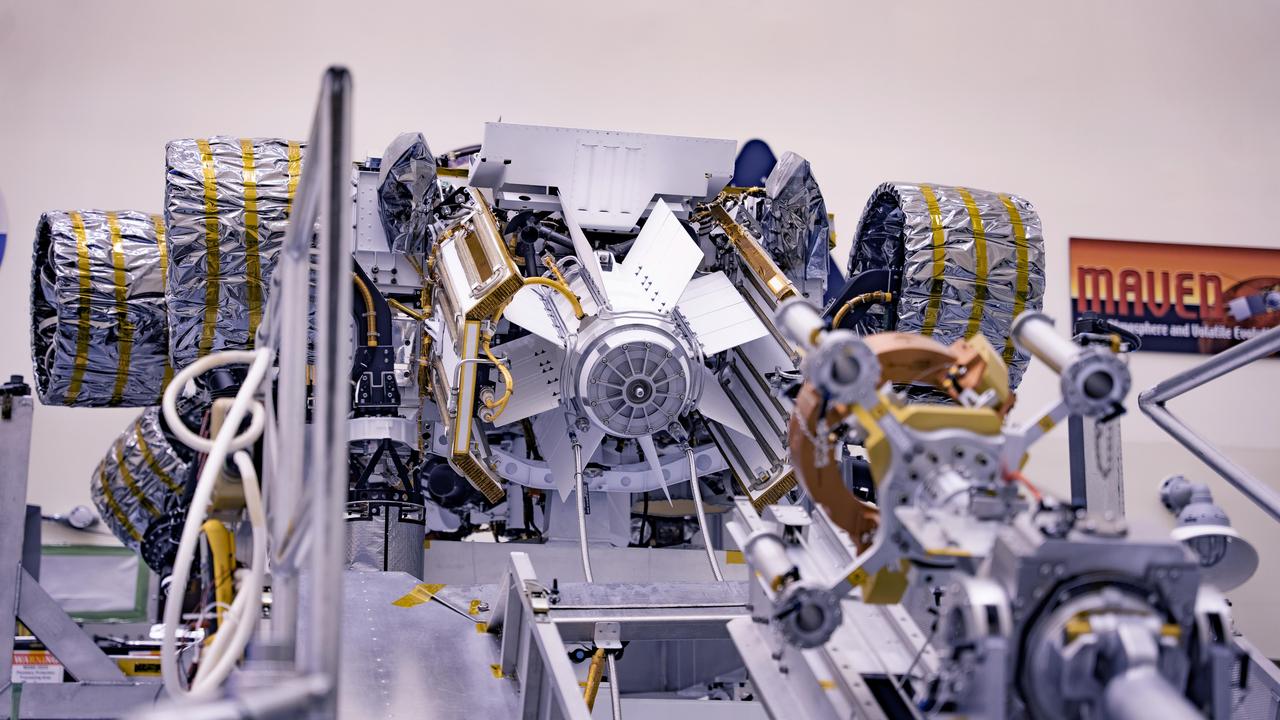
The electricity needed to operate NASA's Mars 2020 rover is provided by a power system called a Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator, or MMRTG. The MMRTG will be inserted into the aft end of the rover between the panels with gold tubing visible at the rear, which are called heat exchangers. Essentially a nuclear battery, an MMRTG uses the heat from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium-238 to generate about 110 watts of electricity at the start of a mission. Besides generating useful electrical power, the MMRTG produces heat. Some of this heat can be used to maintain the rover's systems at the proper operating temperatures in the frigid cold of space and on the surface of Mars. Some of it is rejected into space via the rover's Heat Rejection System. The gold-colored tubing on the heat exchangers form part of the cooling loops of that system. The tubes carry a fluid coolant called Trichlorofluoromethane (CFC-11) that helps dissipate the excess heat. The same tubes are used to pipe some of the heat back into the belly of the rover. MMRTGs are provided to NASA for civil space applications by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE). The radioisotope fuel is inserted into the MMRTG at the DOE's Idaho National Laboratory before the MMRTG is shipped to the launch site. Electrically heated versions of the MMRTG are used at JPL to verify and practice integration of the power system with the rover. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23305
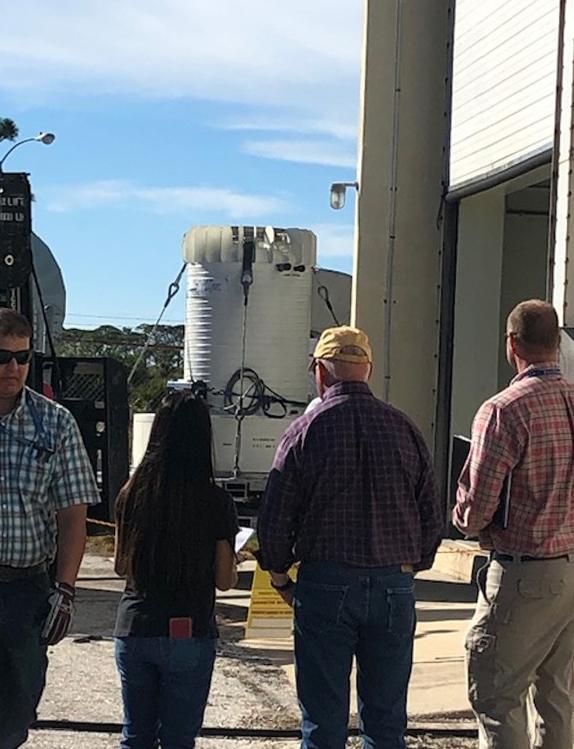

On Feb. 7, 2019, team members with the Test and Operations Support Contract (TOSC) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida offload the cask that will contain the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for the Mars 2020 mission. NASA’s Mars2020 rover will be powered by an MMRTG. The arrival of the MMRTG simulator enables the team to practice radiation control and monitoring protocols, including setting up radiation control points and postings around the trailer prior.

NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Health Physics team sets up a simulated radiation control boundary around the trailer carrying a multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) simulator on Feb. 7, 2019. NASA’s Mars 2020 rover will be powered by an MMRTG. The arrival of the MMRTG simulator enables the team to practice radiation control and monitoring protocols, including setting up radiation control points and postings around the trailer prior.
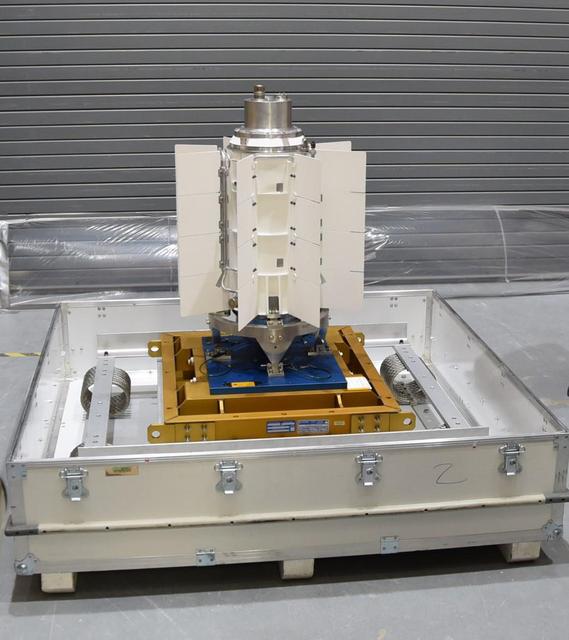

The electricity for NASA's Mars 2020 rover is provided by a power system called a Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator, or MMRTG. Essentially a nuclear battery, an MMRTG uses the heat from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium-238 to generate about 110 watts of electricity at the start of a mission. Besides generating electrical power, the MMRTG produces heat. Some of this heat can be used to maintain the rover's systems at the proper operating temperatures in the frigid cold of space and on the surface of Mars. This device, seen here before fueling and testing at the U.S. Department of Energy's Idaho National Laboratory, has "fins" that radiate excess heat. MMRTGs are provided to NASA for civil space applications by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE). The radioisotope fuel is inserted into the MMRTG at the DOE's Idaho National Laboratory before the MMRTG is shipped to the launch site. Electrically heated versions of the MMRTG are used at JPL to verify and practice integration of the power system with the rover. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23306
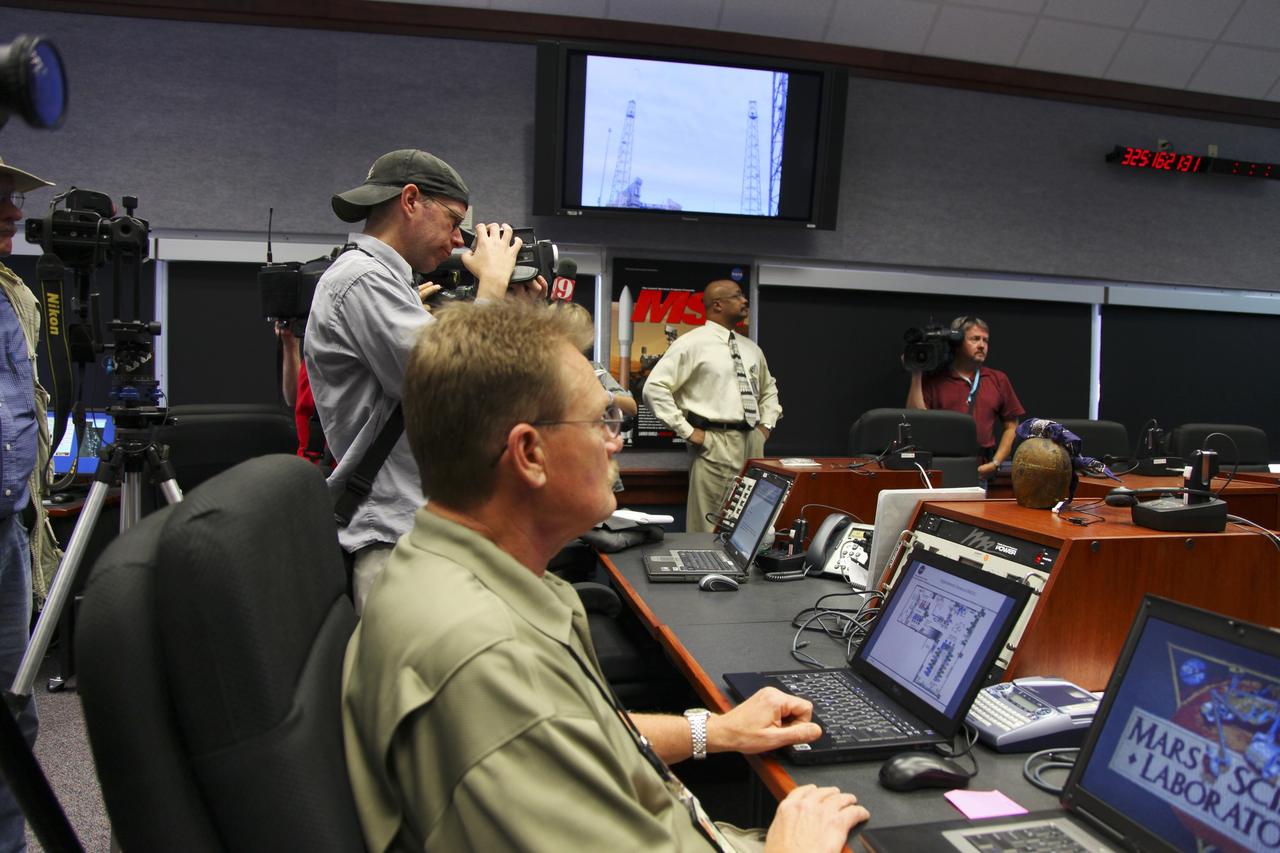

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Members of the media take a tour of the Radiological Control Center (RADCC) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tour focused on safety equipment and procedures for the upcoming launch of the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The MSL spacecraft includes a multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) that will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
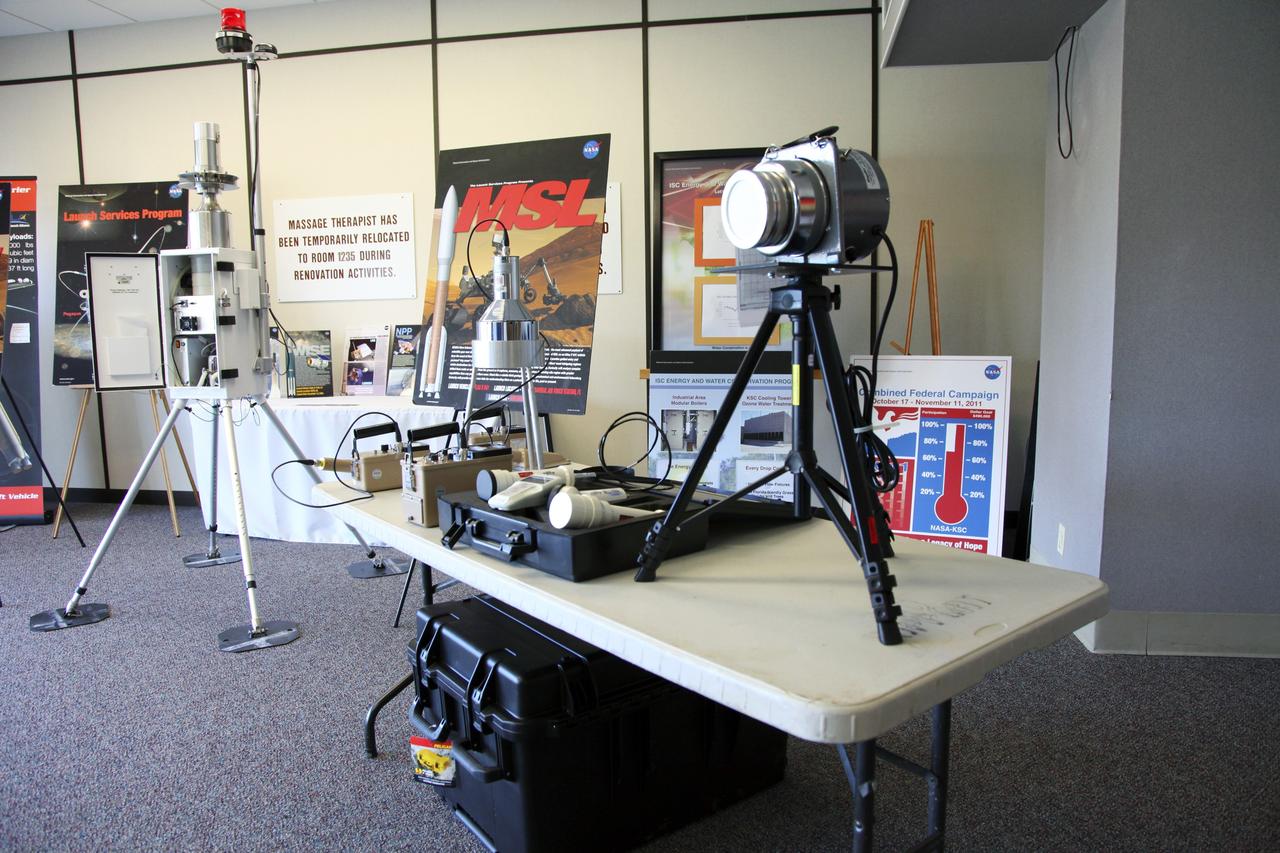

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Several instruments are displayed for the media during a tour of the Radiological Control Center (RADCC) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tour focused on safety equipment and procedures for the upcoming launch of the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The MSL spacecraft includes a multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) that will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
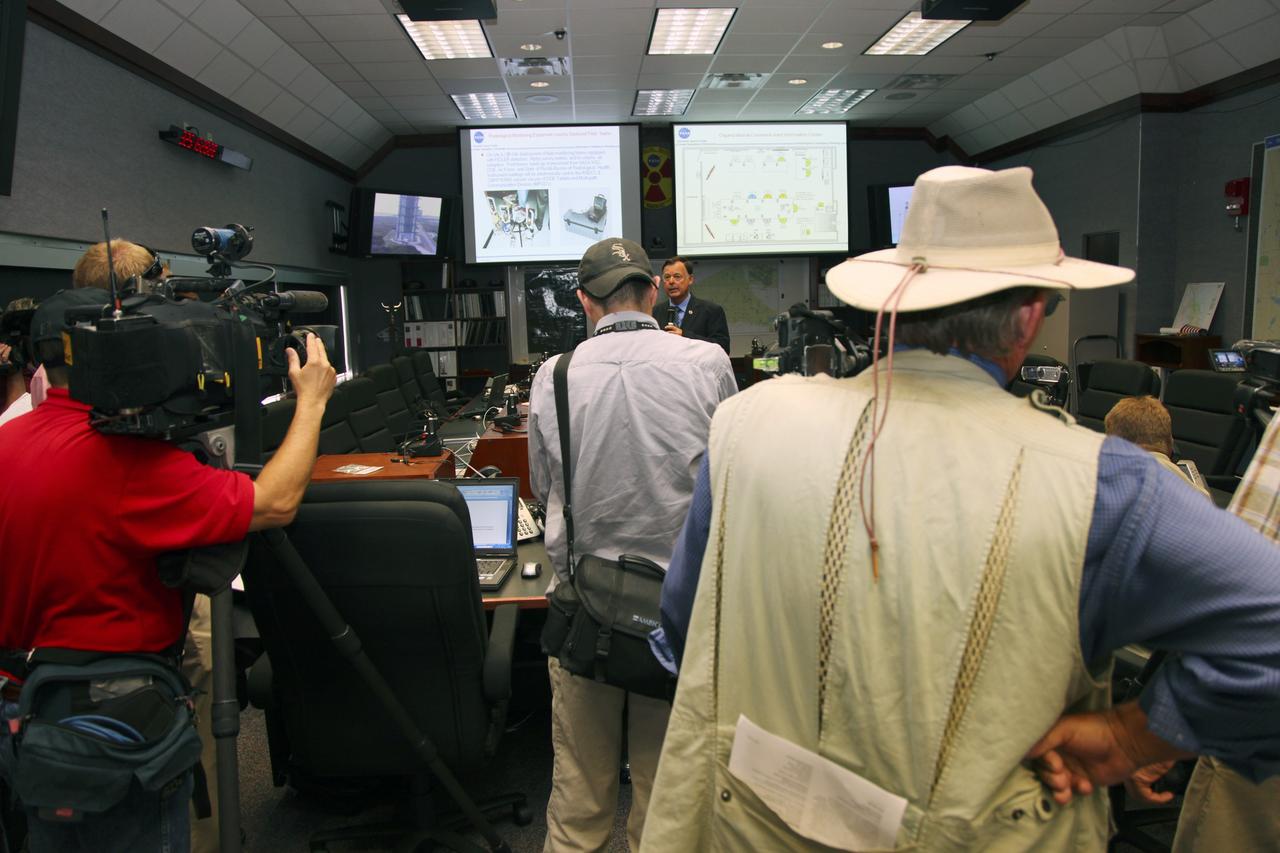

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Members of the media view the Radiological Control Center (RADCC) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a tour regarding safety equipment and procedures for the upcoming launch of the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The MSL spacecraft includes a multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) that will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
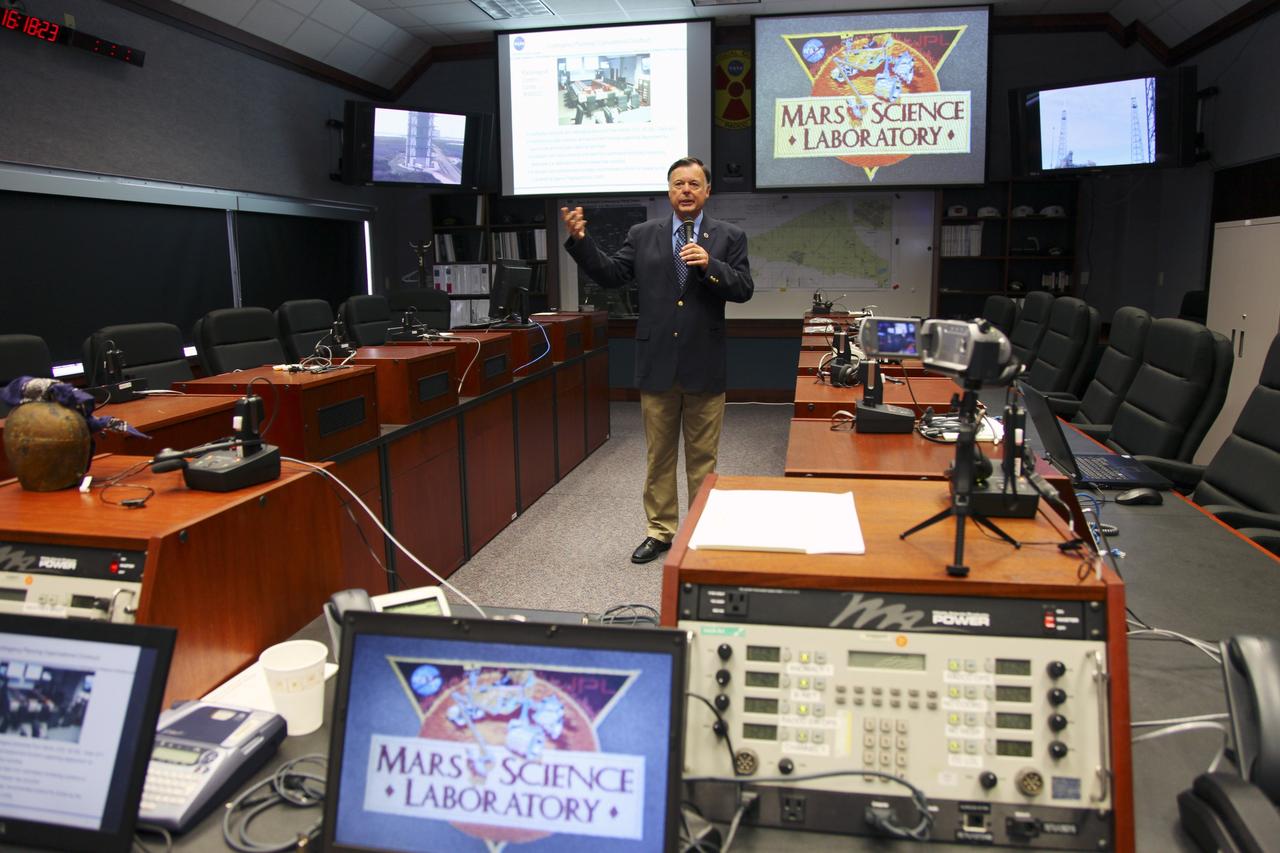

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Surrounded by monitors and consoles, Randy Scott, director of Kennedy Space Center's Radiological Control Center (RADCC), speaks to media during a tour regarding safety equipment and procedures for the upcoming launch of the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The MSL spacecraft includes a multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) that will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
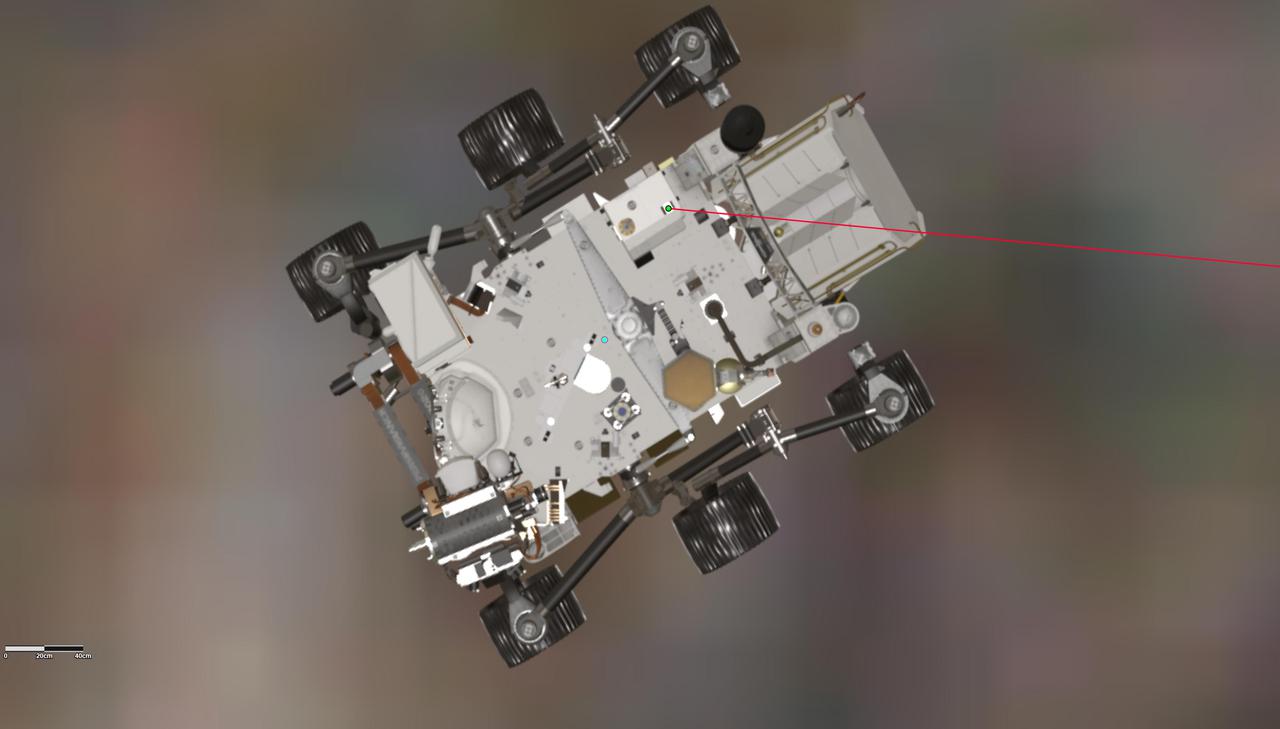
This annotated graphic depicts the orientation of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover during the 17th flight of the agency's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter on Dec. 5, 2021. A green dot on the rover, toward the top center of the frame, indicates the location of the Mars Helicopter Base Station antenna on Perseverance, which sends radio signals to and receives them from the rotorcraft. The red line depicts the line of sight to the helicopter during the final moments of Flight 17. Perseverance's power source, the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG), is at the back of the rover, on the right. It angles above the antenna, impeding direct communications between the rover and helicopter as the rotorcraft descended toward the surface at the end of the flight. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24966

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, secured to a turning fixture, is positioned on the radioisotope power system integration cart (RIC). The MMRTG will be installed on the Curiosity rover with the aid of the RIC. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: Department of Energy/Idaho National Laboratory

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a turning fixture lowers the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission toward the radioisotope power system integration cart (RIC). Once the MMRTG is secured on the cart, it will be installed on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: Department of Energy/Idaho National Laboratory
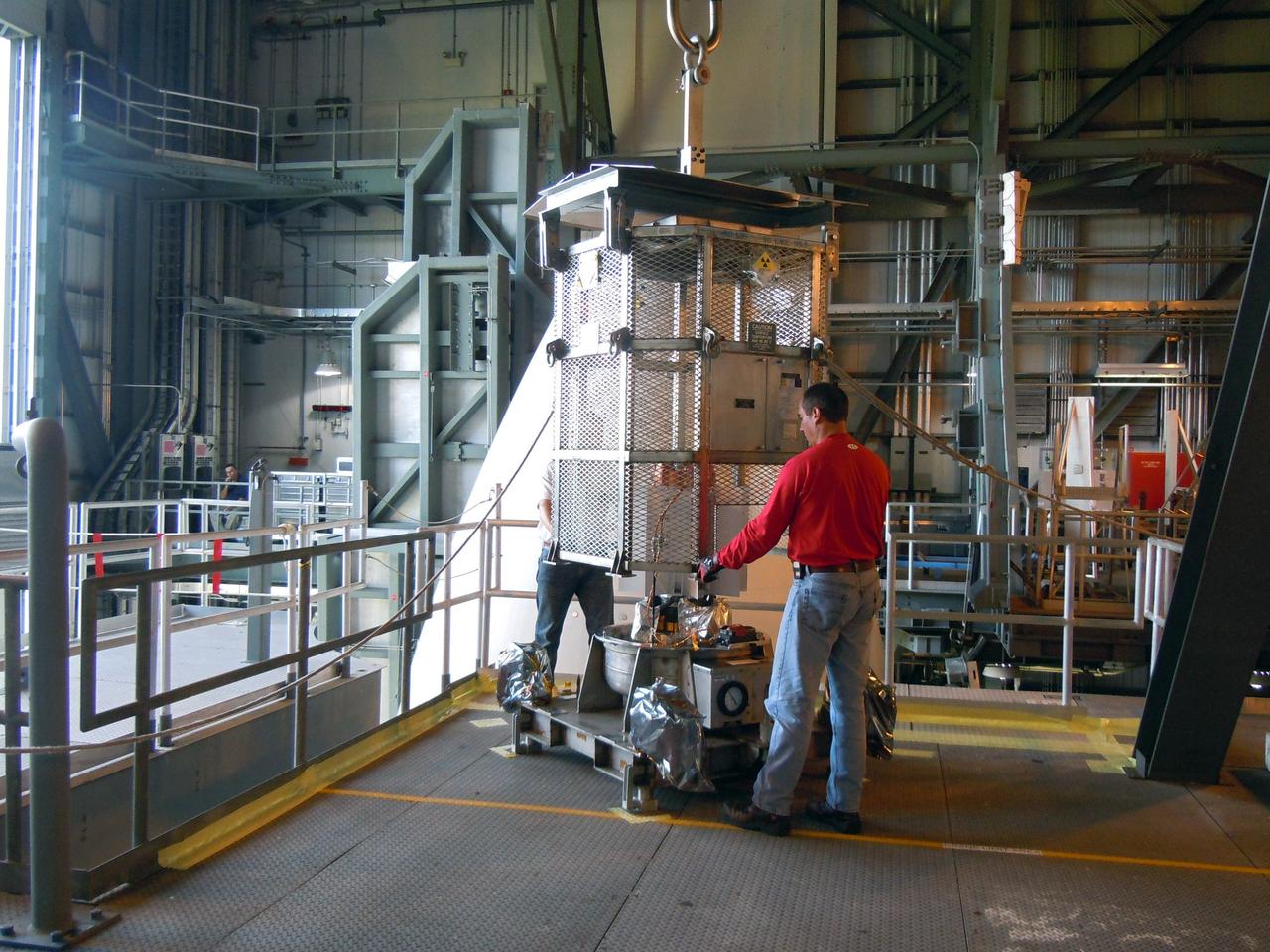

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, spacecraft technicians guide the mesh container protecting the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission as a crane lifts it from around the generator. The container, known as the "gorilla cage," protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. Next, the MMRTG will be installed on MSL's Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: Department of Energy/Idaho National Laboratory
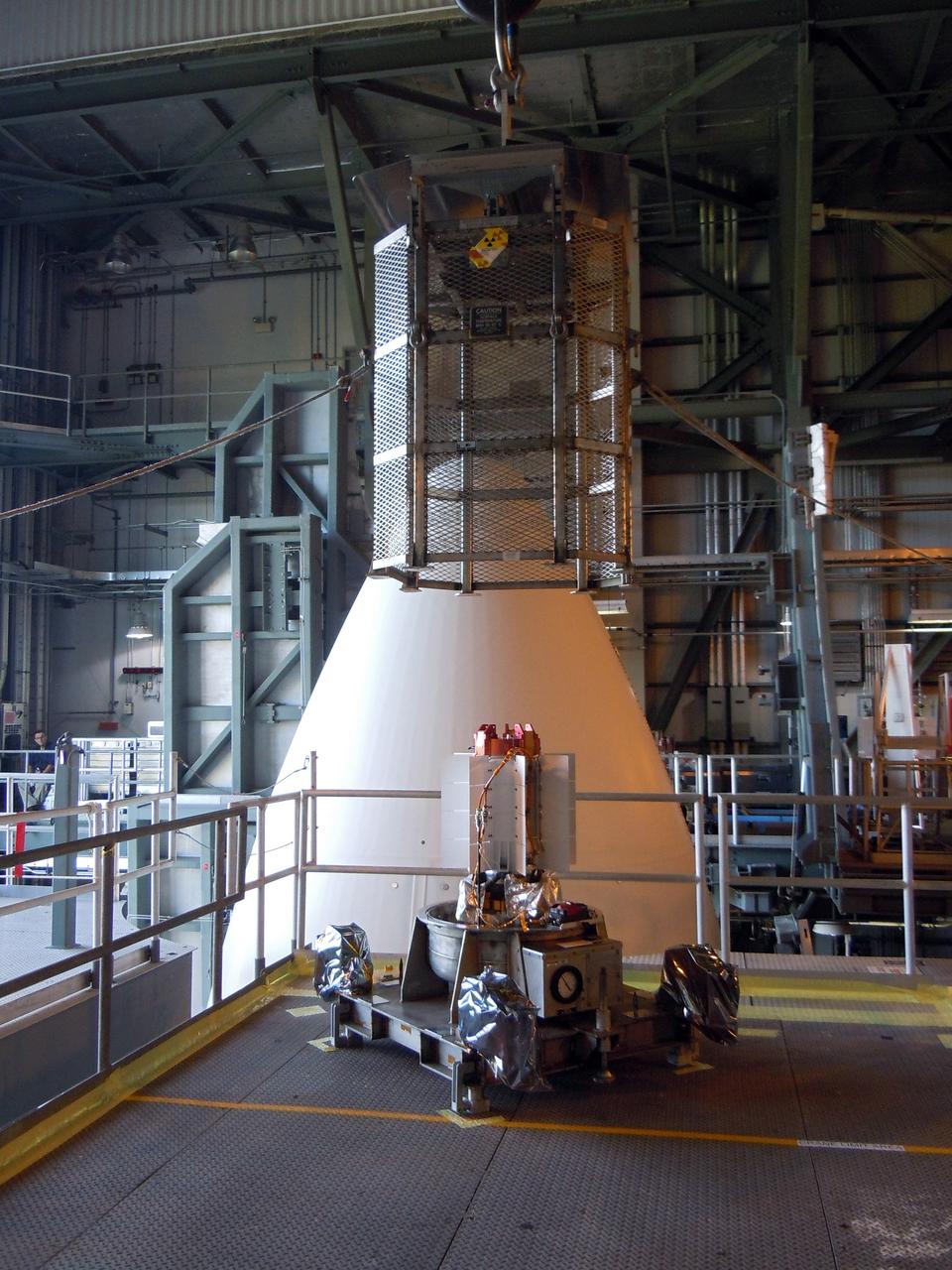

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is uncovered during preparations to install it on MSL's Curiosity rover. The mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," is suspended above the generator as it is lifted off the MMRTG's support base. The cage protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: Department of Energy/Idaho National Laboratory
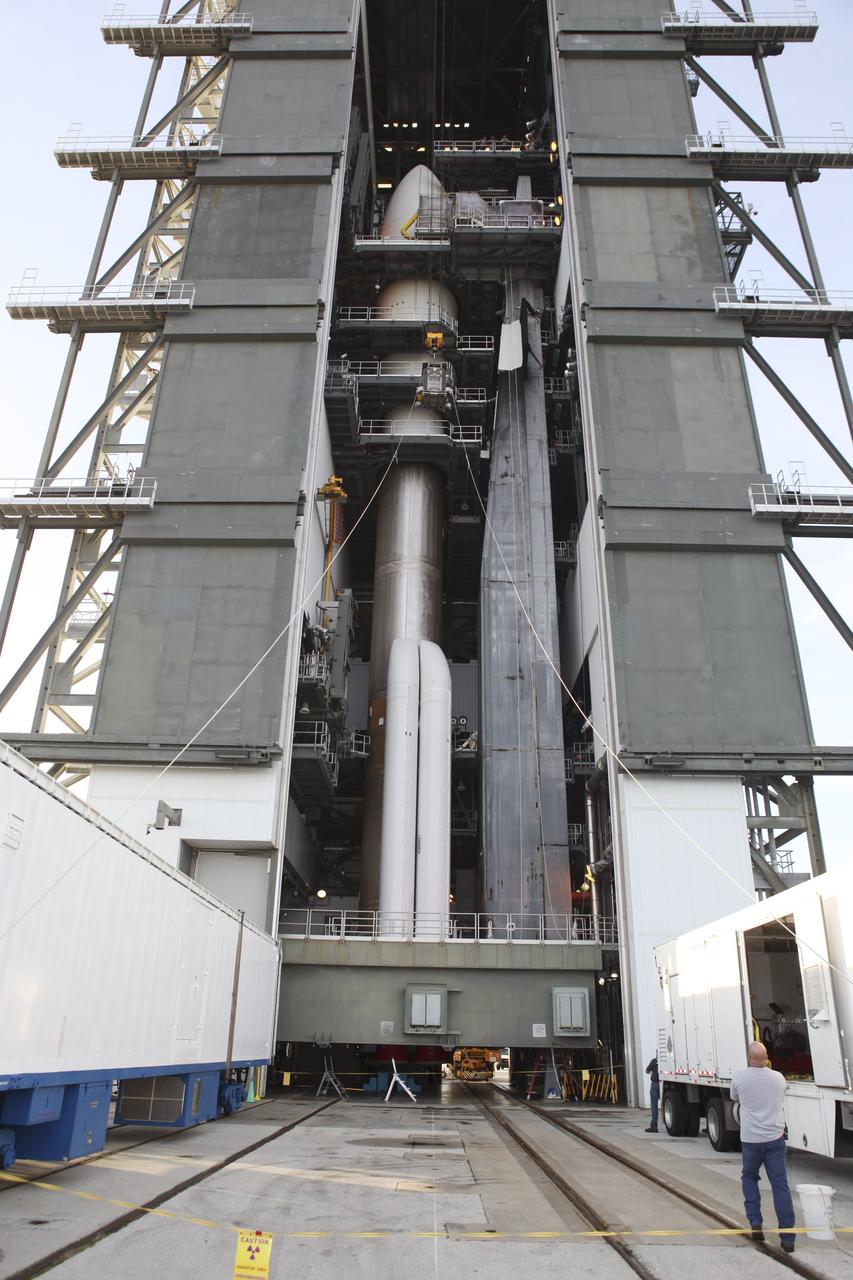

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Enclosed in the protective mesh container known as the "gorilla cage," the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is hoisted up beside the Atlas V rocket standing in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41. The generator will be installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat produced by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
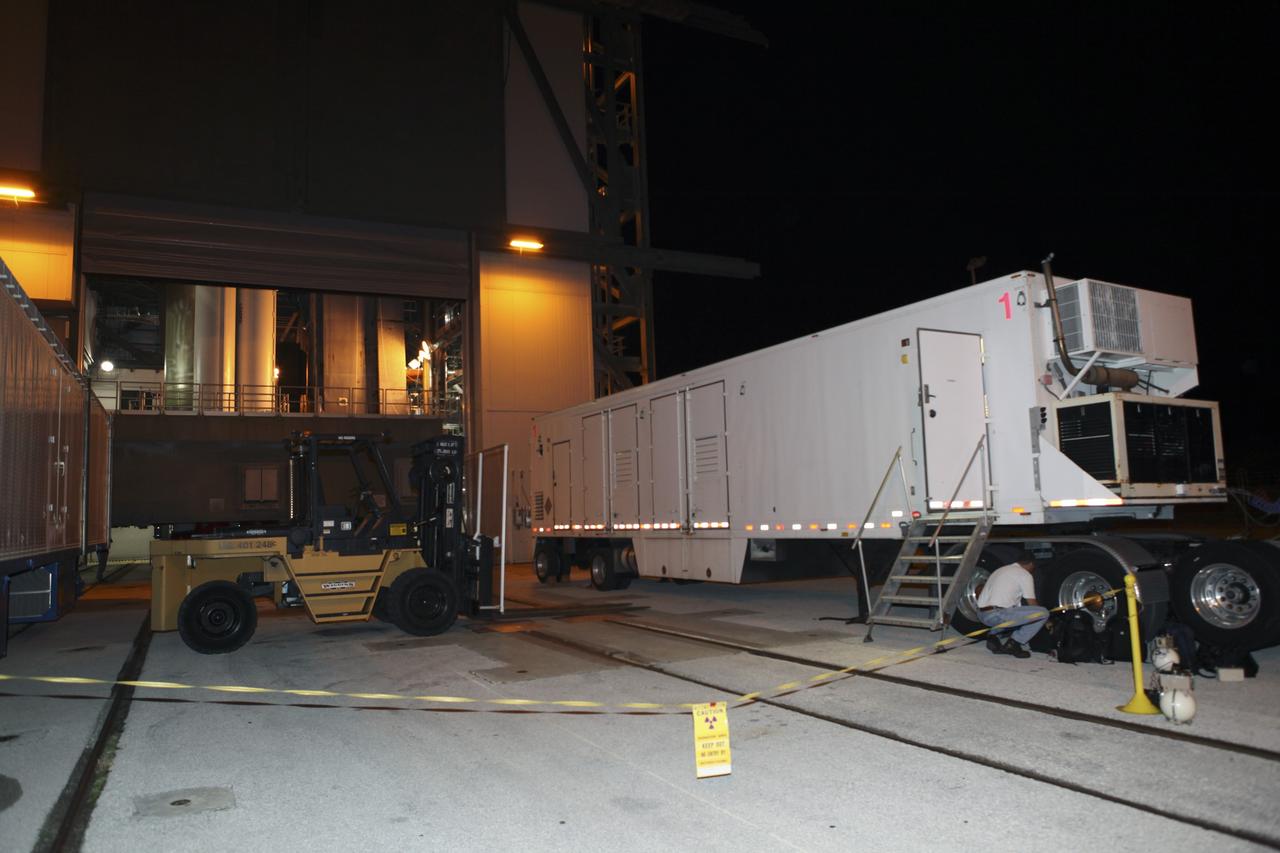

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Outside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41, an area has been cordoned off beside the trailer which has arrived at the pad carrying the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The generator will be lifted up to the top of the rocket and installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat produced by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a forklift positions the protective mesh container enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission onto the floor of the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The container, known as the "gorilla cage," protects the MMRTG and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. In the PHSF, the MMRTG temporarily will be installed on the MSL rover, Curiosity, for a fit check but will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
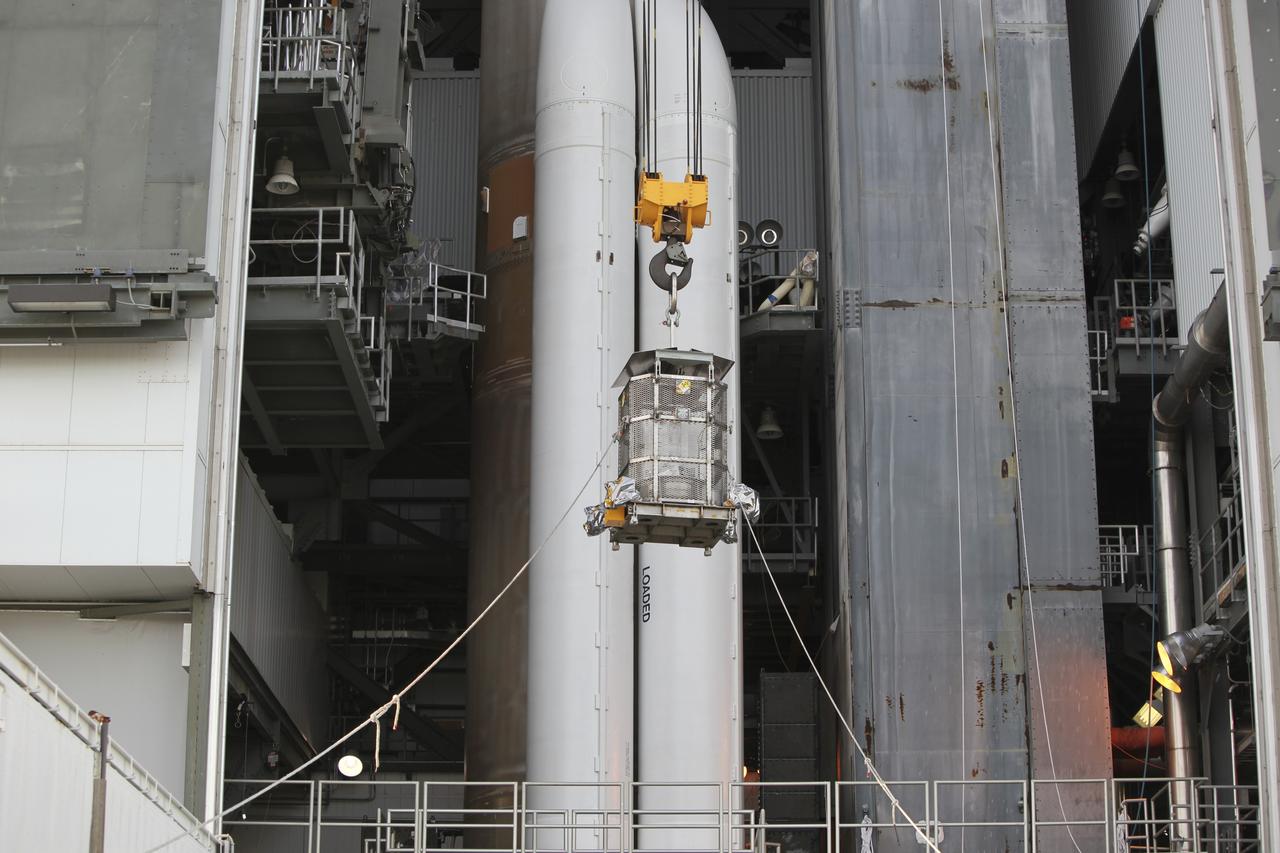

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Enclosed in the protective mesh container known as the "gorilla cage," the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is lifted up the side of the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41. The generator will be hoisted up to the top of the rocket and installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat produced by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
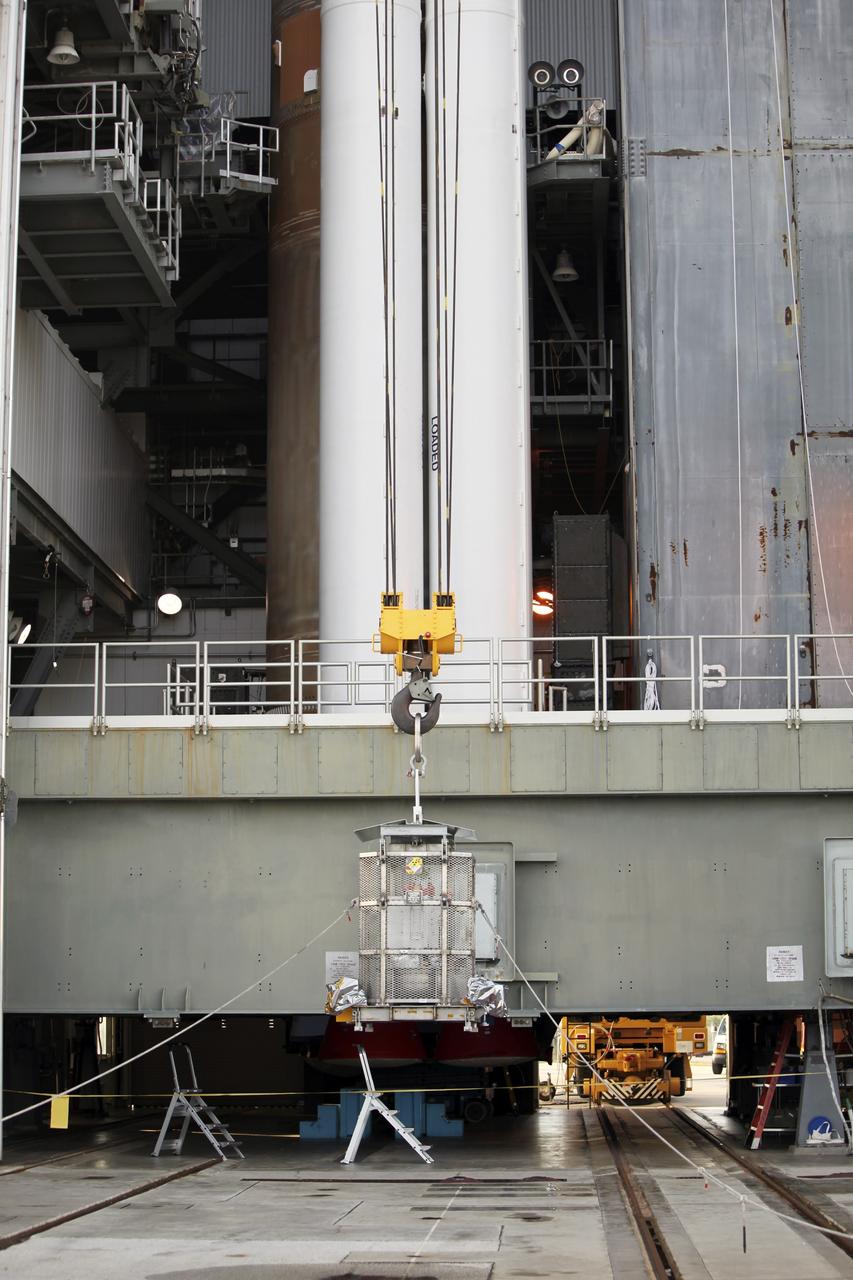

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Enclosed in the protective mesh container known as the "gorilla cage," the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is lifted off the ground at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41. The generator will be hoisted up to the top of the rocket and installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat produced by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
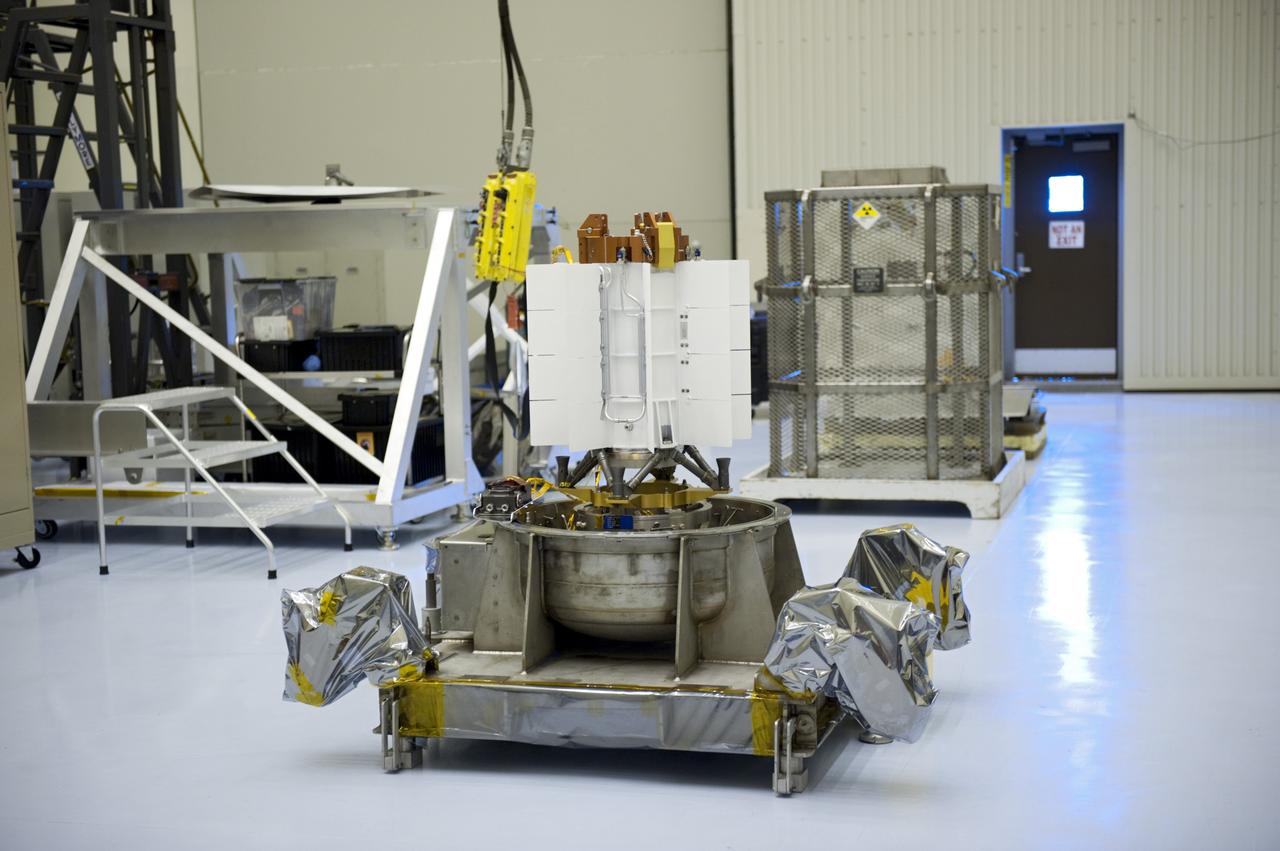
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission rests on its support base in the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover in the high bay. In the background, at right, is the mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," which protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
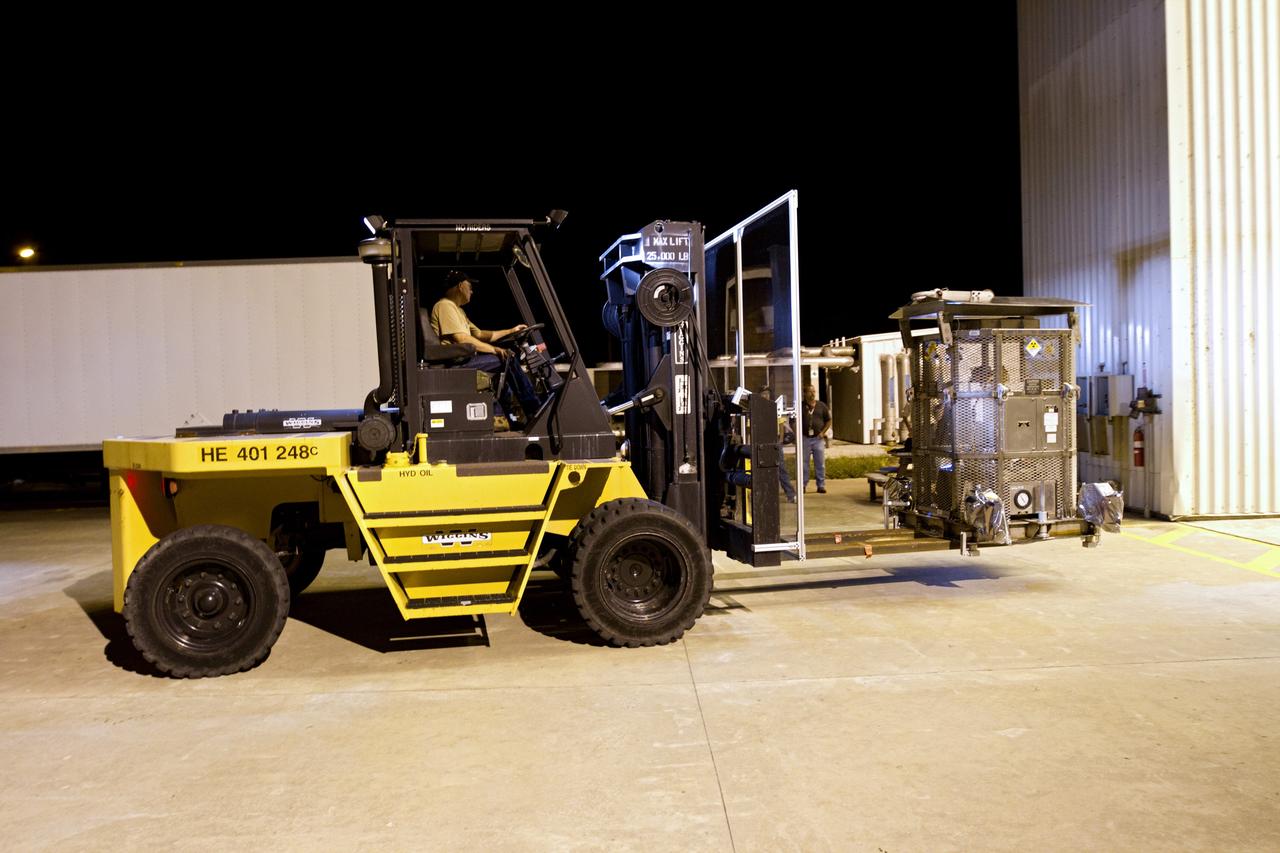

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a forklift carries the protective mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission into the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The cage protects the MMRTG and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. In the PHSF, the MMRTG temporarily will be installed on the MSL rover, Curiosity, for a fit check but will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
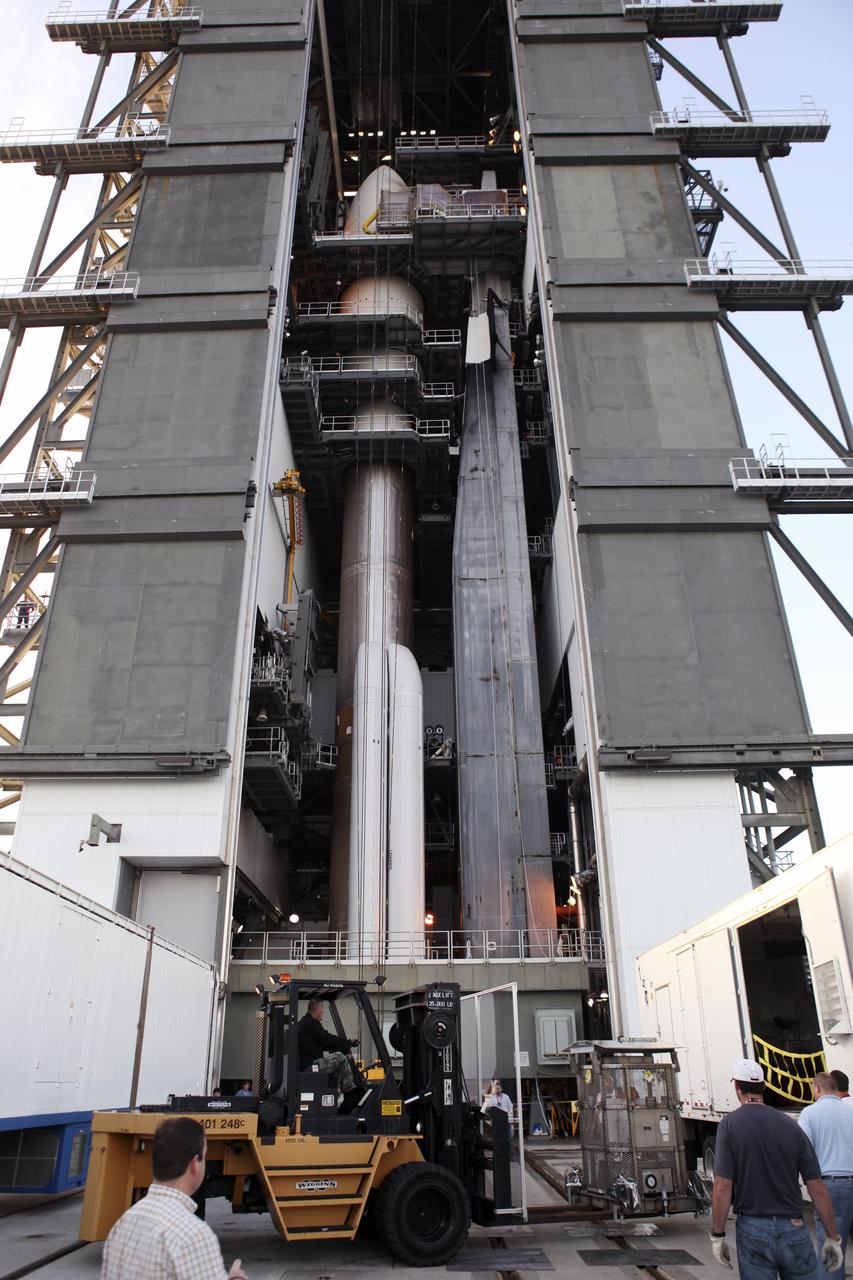

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Backdropped by the Atlas V rocket standing inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, enclosed in the mesh container known as the "gorilla cage," is removed from its trailer. The generator will be lifted up to the top of the rocket and installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat produced by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
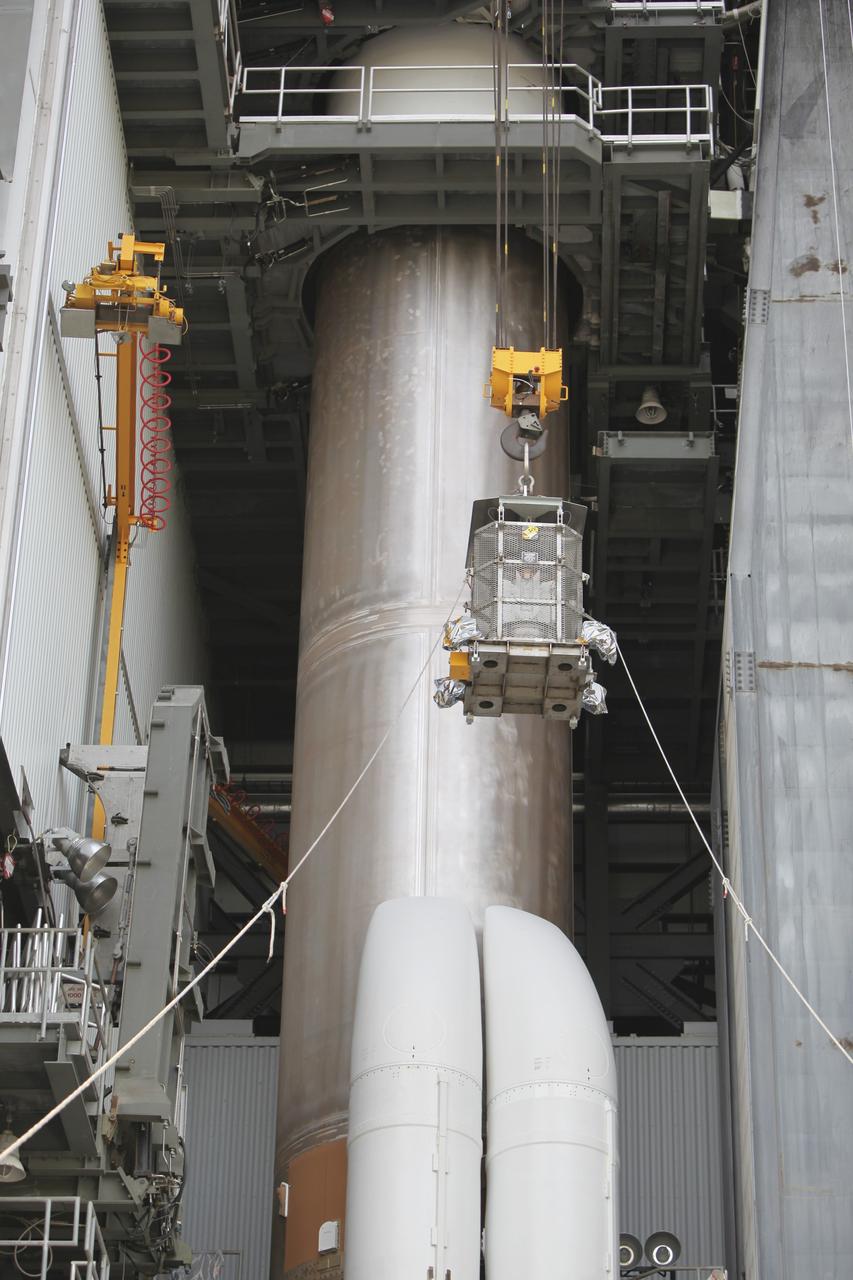

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Enclosed in the protective mesh container known as the "gorilla cage," the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is lifted up the side of the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41. The generator will be installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat produced by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
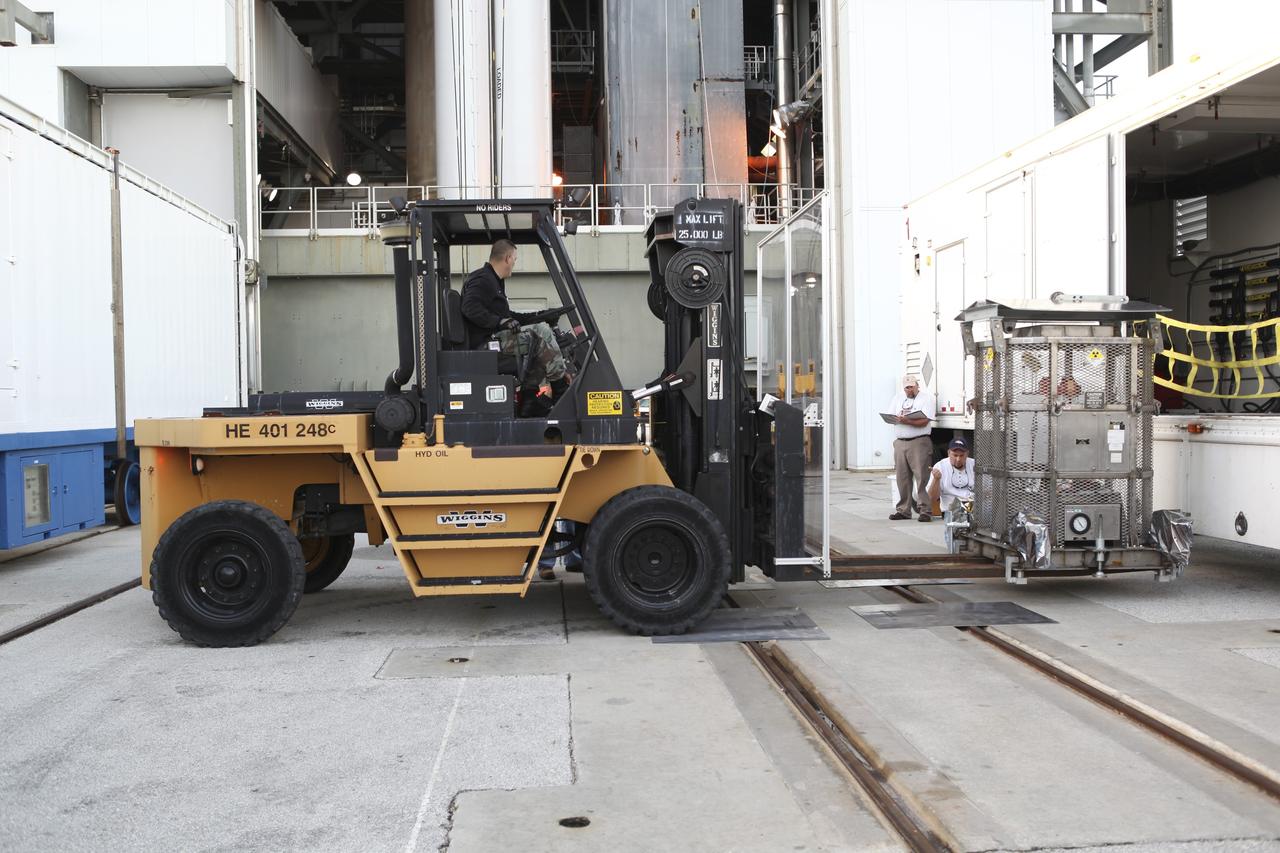

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, enclosed in the mesh container known as the "gorilla cage," is removed from its trailer outside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41. The generator will be lifted up to the top of the rocket and installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat produced by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
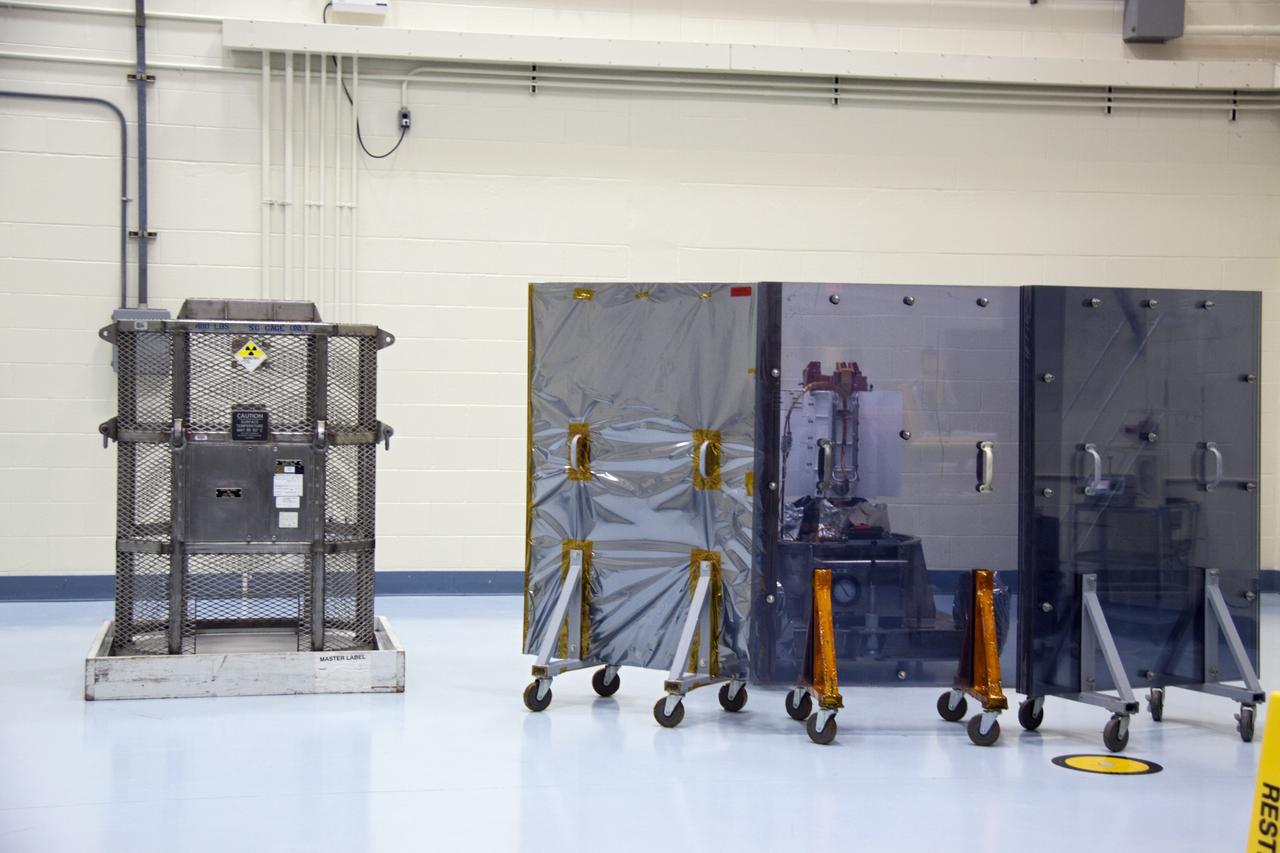

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is position behind mobile plexiglass radiation shields in the high bay of the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MMRTG was returned to the RTGF following a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The generator will remain in the RTGF until is moved to the pad for integration on the rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
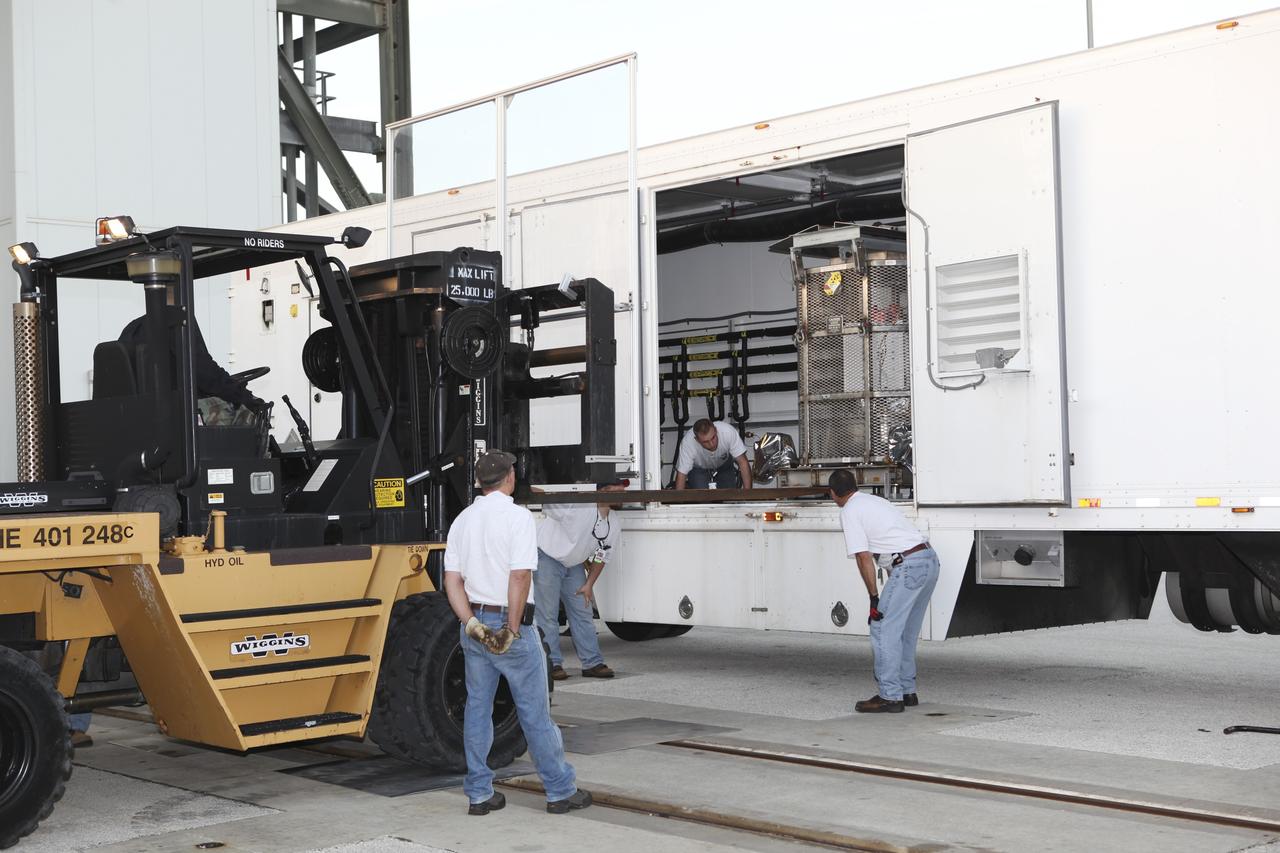

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, enclosed in the mesh container known as the "gorilla cage," is about to emerge from its trailer outside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41. The generator will be lifted up to the top of the rocket and installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat produced by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
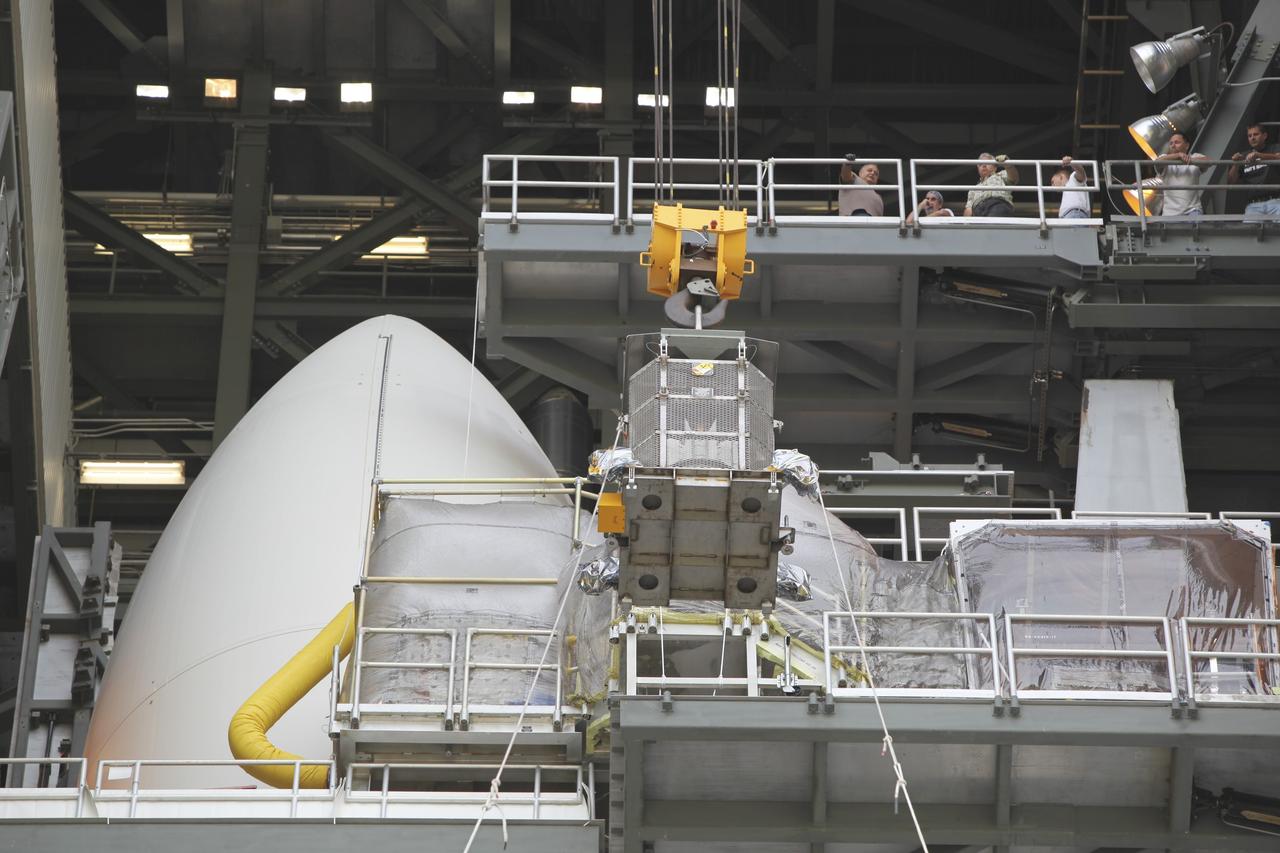

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Employees gathered one level above monitor the progress of the protective mesh container known as the "gorilla cage," holding the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, as it is lifted near the top of the Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41. The generator will be installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat produced by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
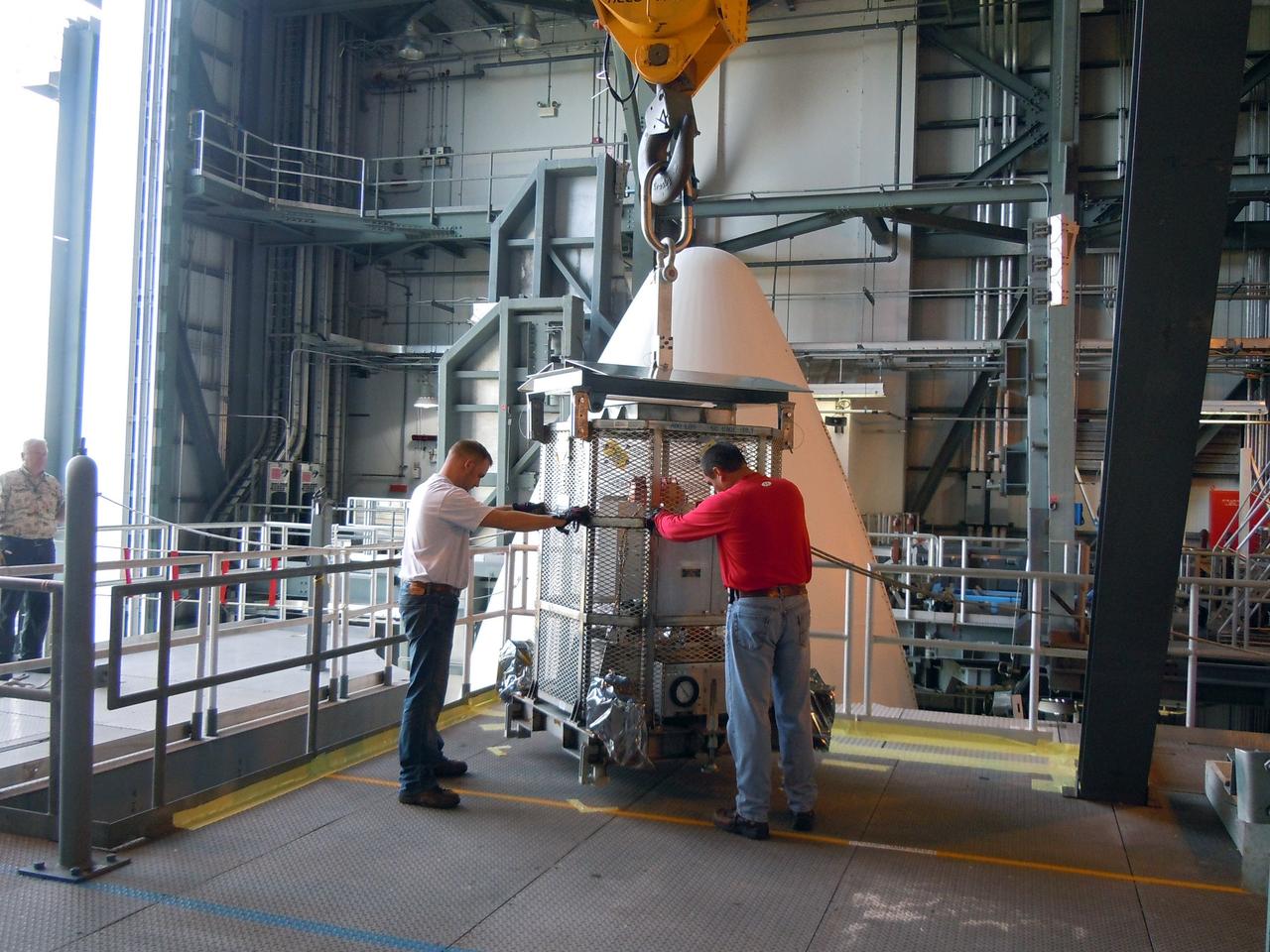

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, spacecraft technicians in the Vertical Integration Facility prepare to install the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG is enclosed in a protective mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," which protects it during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: Department of Energy/Idaho National Laboratory
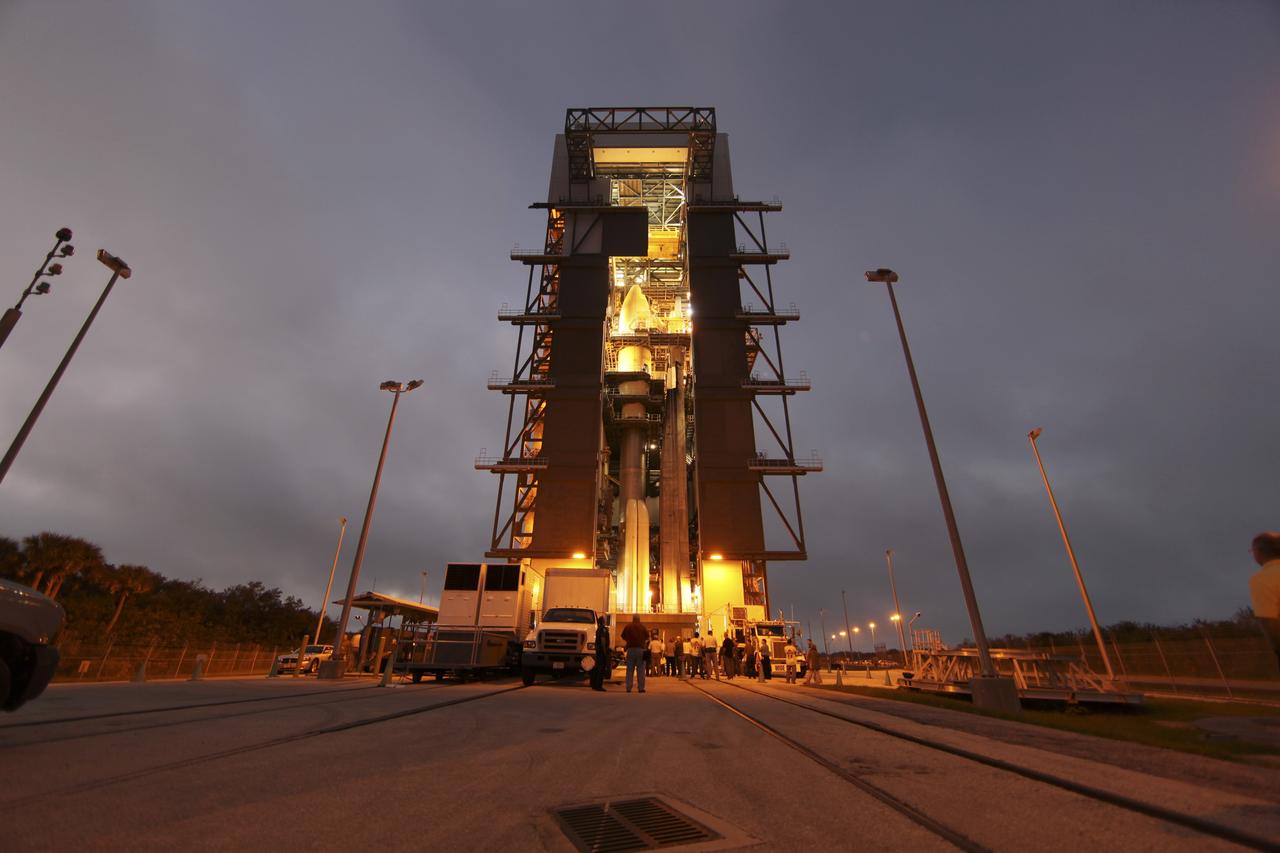

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Atlas V rocket set to launch NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is illuminated inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41, where employees have gathered to hoist the spacecraft's multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG). The generator will be lifted up to the top of the rocket and installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat produced by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
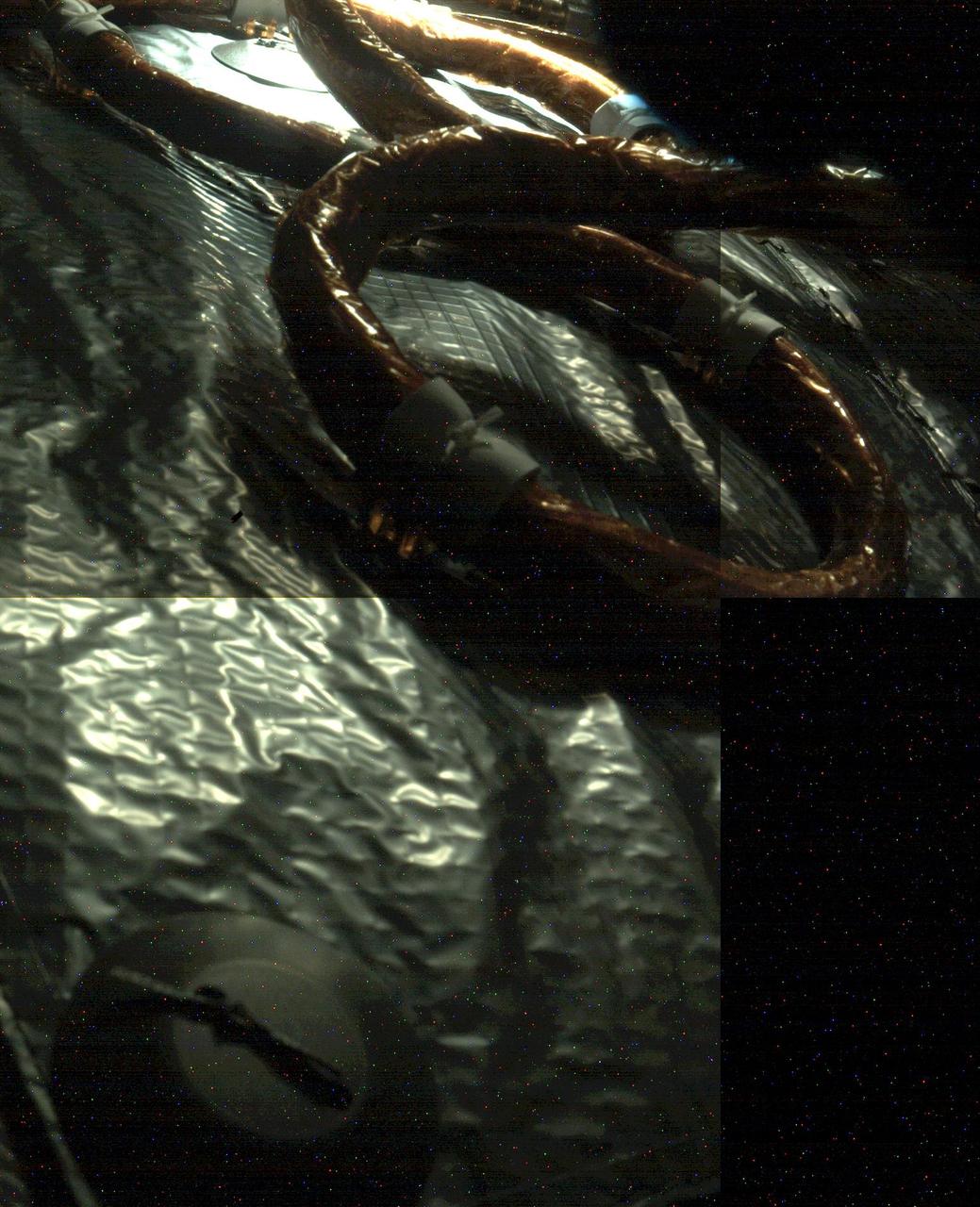

An electrical cable can be seen snaking its way along insulation material in this image of the interior of the Mars 2020 spacecraft at it cruises through interplanetary space to the Red Planet. The cable and insulation are tied to the inside of the spacecraft's heat shield, which will protect the spacecraft from the extreme temperatures generated by friction as it enters the Martian atmosphere on Feb 18, 2021. The light source is the Sun, which likely entered through a vent hole in the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) door. The picture was assembled from three images taken at different times by the Perseverance rover's rear left Hazcam during a systems check on Oct. 19, 2020. The colored pixels seen in the image are due to digital noise from the camera. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24233
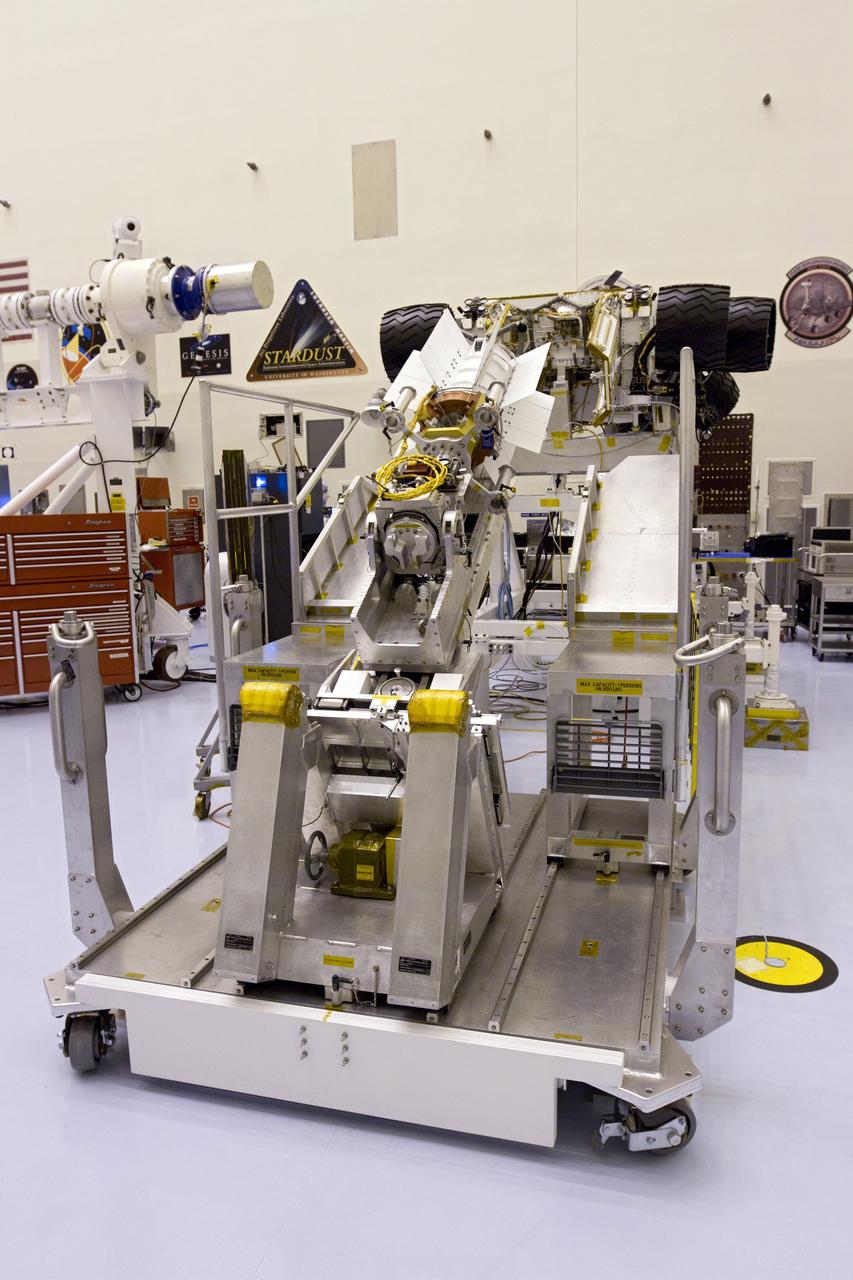

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is attached to the MMRTG integration cart. The cart will be used to install the MMRTG on the Curiosity rover for a fit check. The wheels of the rover appear to stick out on either side of the cart. The MMRTG will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
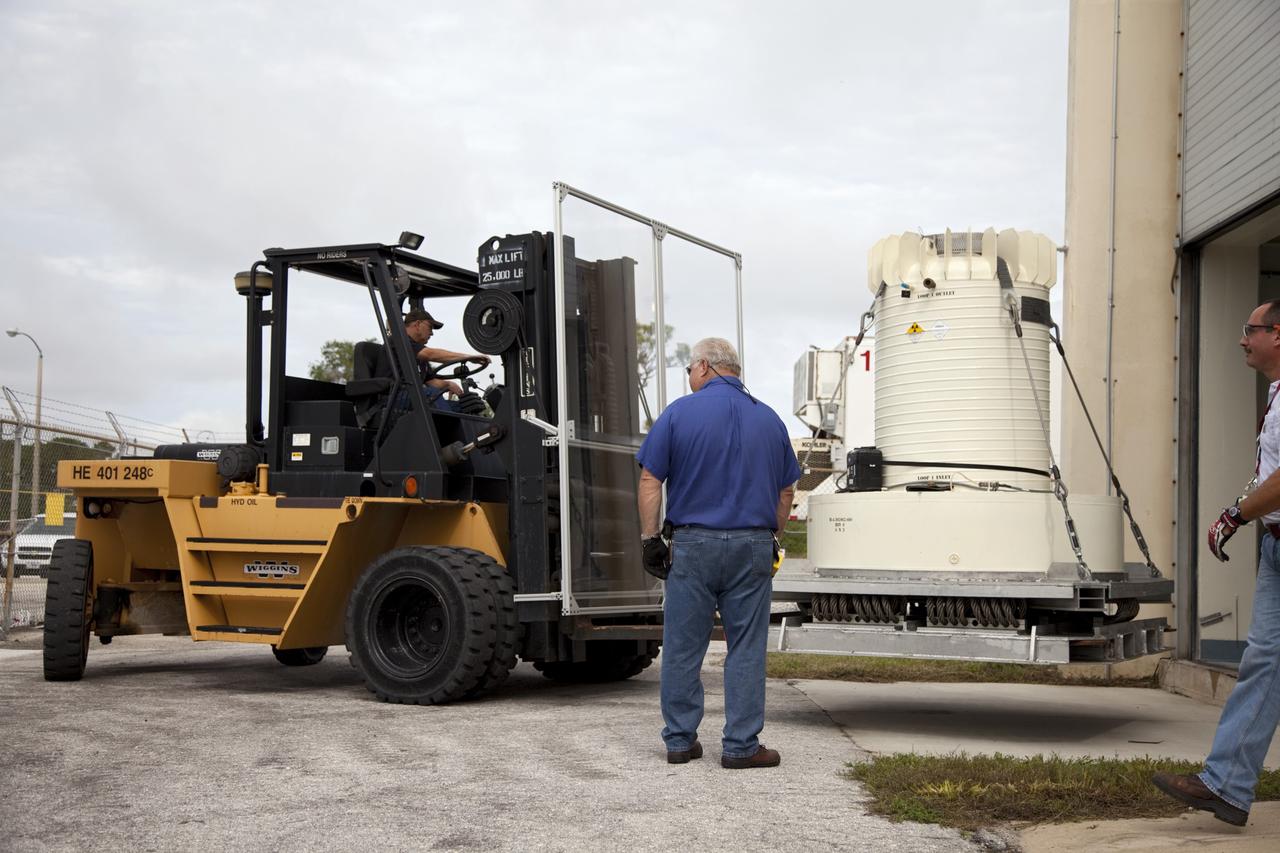

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers use a forklift to transport the shipping cask enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission to the door of the high bay of the RTG storage facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
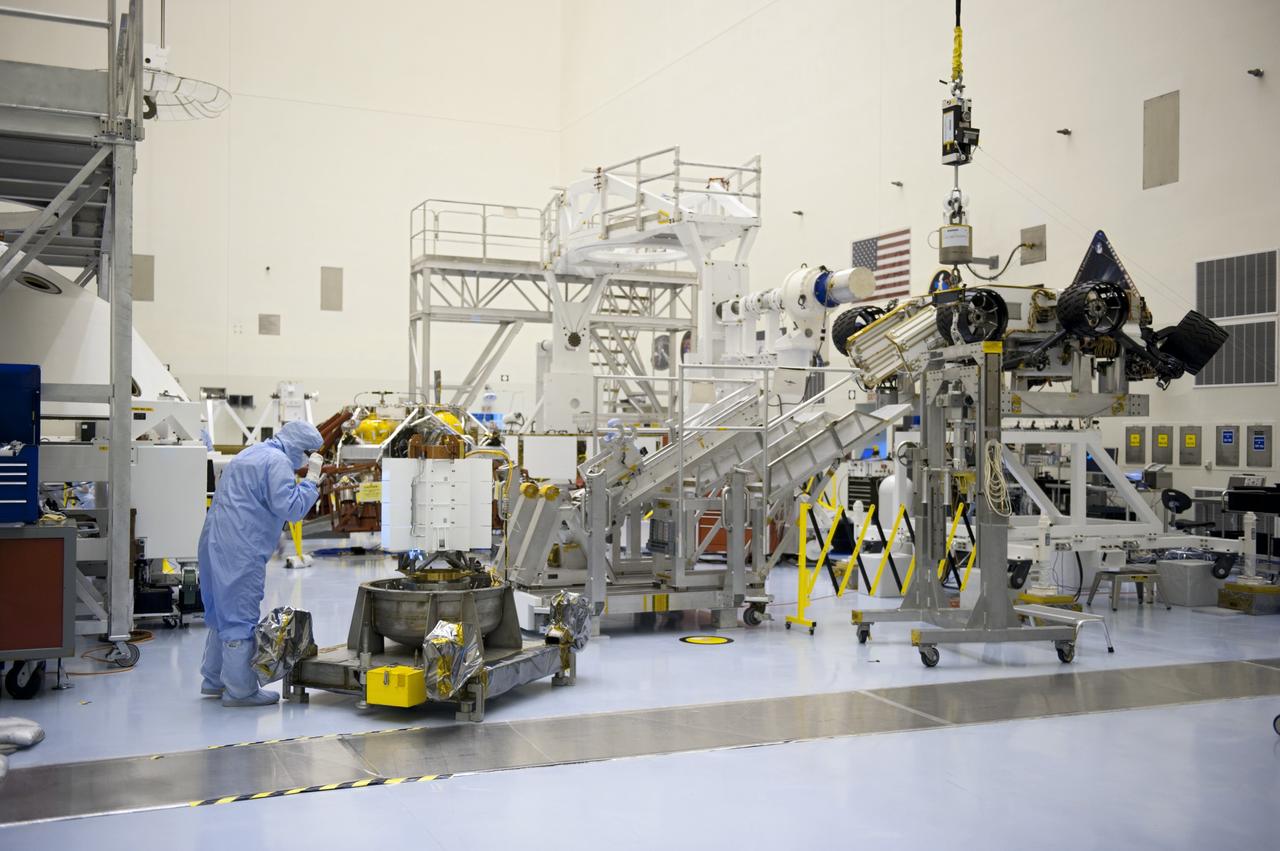

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a spacecraft technician from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory conducts a visual inspection of the cooling tubes on the exterior of the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. At right is the Curiosity rover on an elevated work stand. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
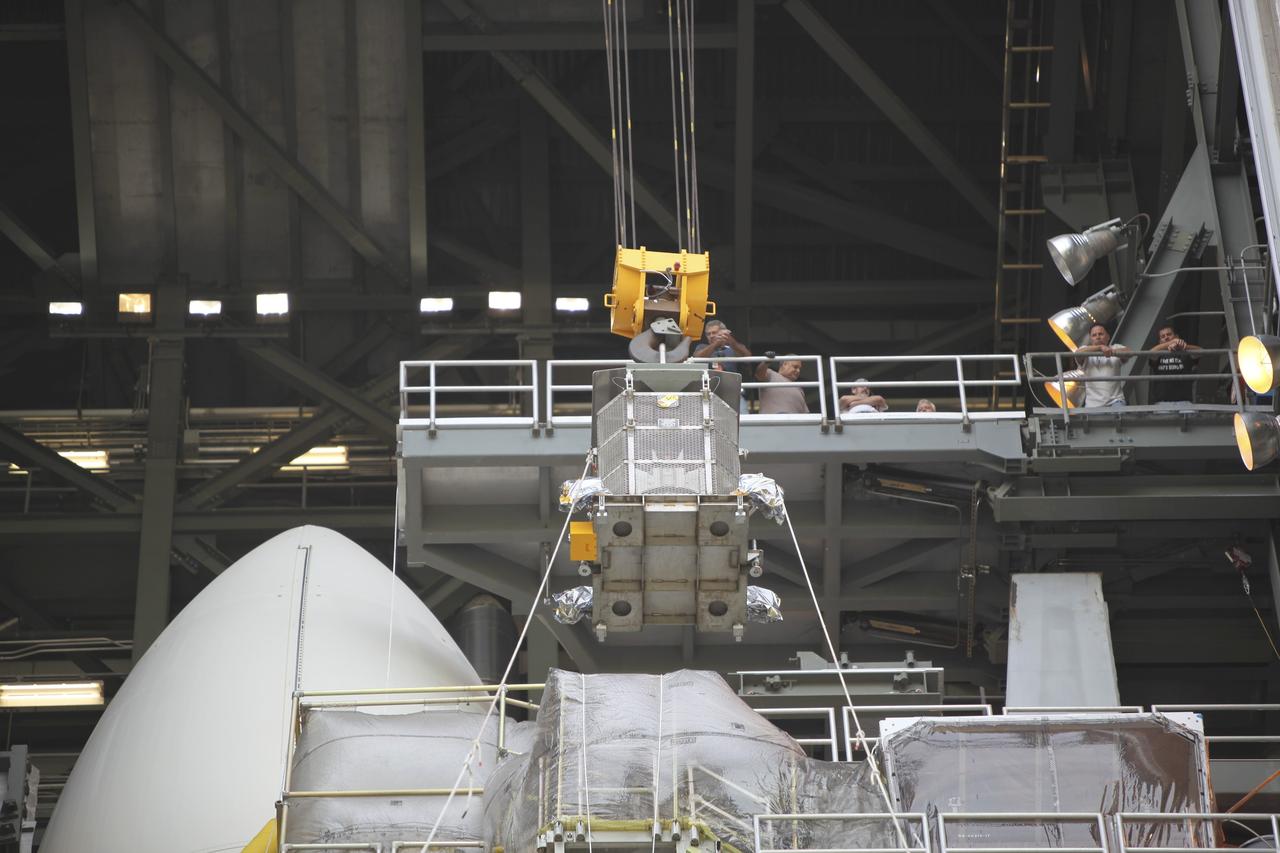

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Employees monitor the progress of the protective mesh container known as the "gorilla cage," holding the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, as it is lifted near the top of the Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41. The MMRTG will be installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat emitted by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are under way to offload the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission from the MMRTG trailer. The MMRTG is returning to the RTGF following a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
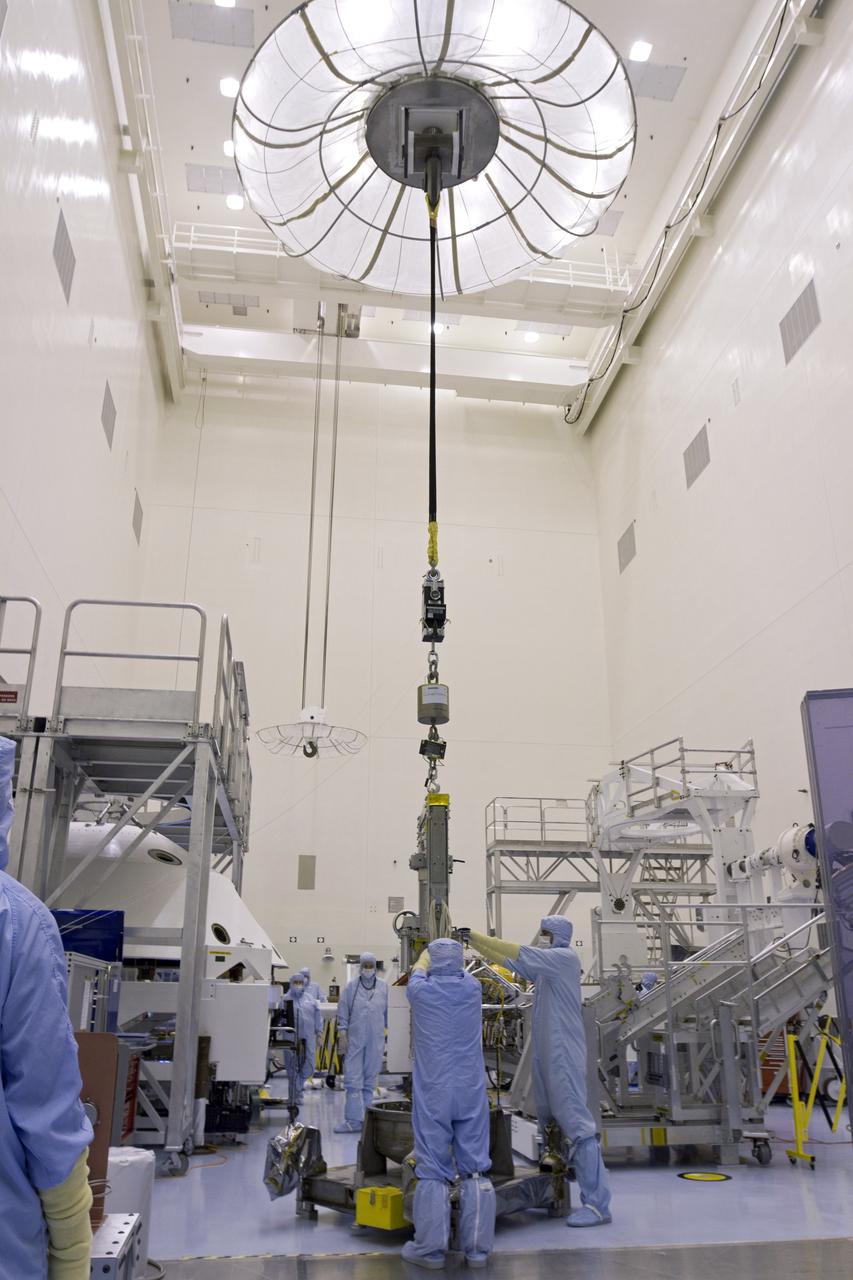

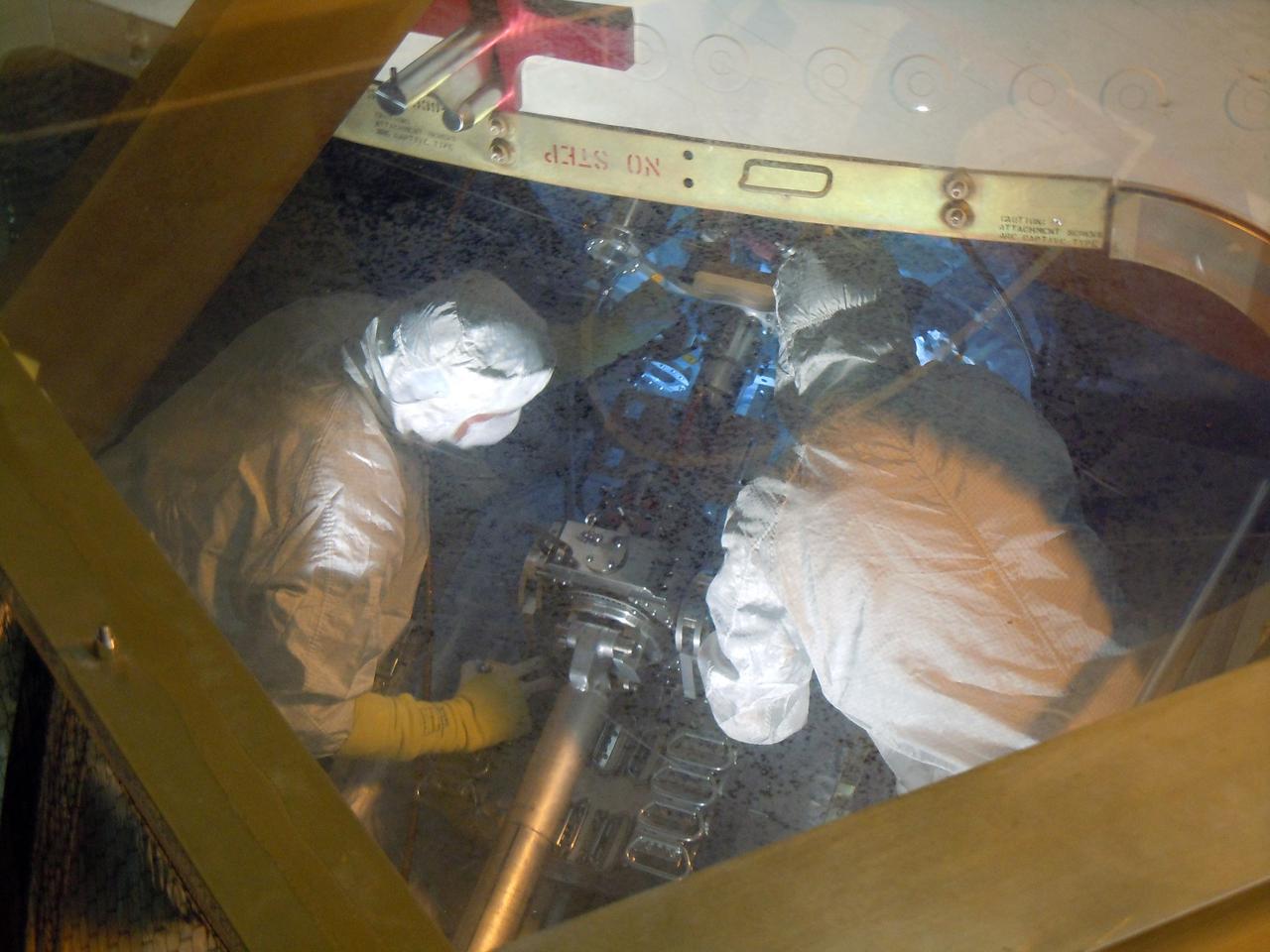
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory connect a crane to a turning fixture connected to the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The fixture will lift and lower the MMRTG onto the MMRTG integration cart. The cart will be used to install the MMRTG on Curiosity for a fit check. The MMRTG will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
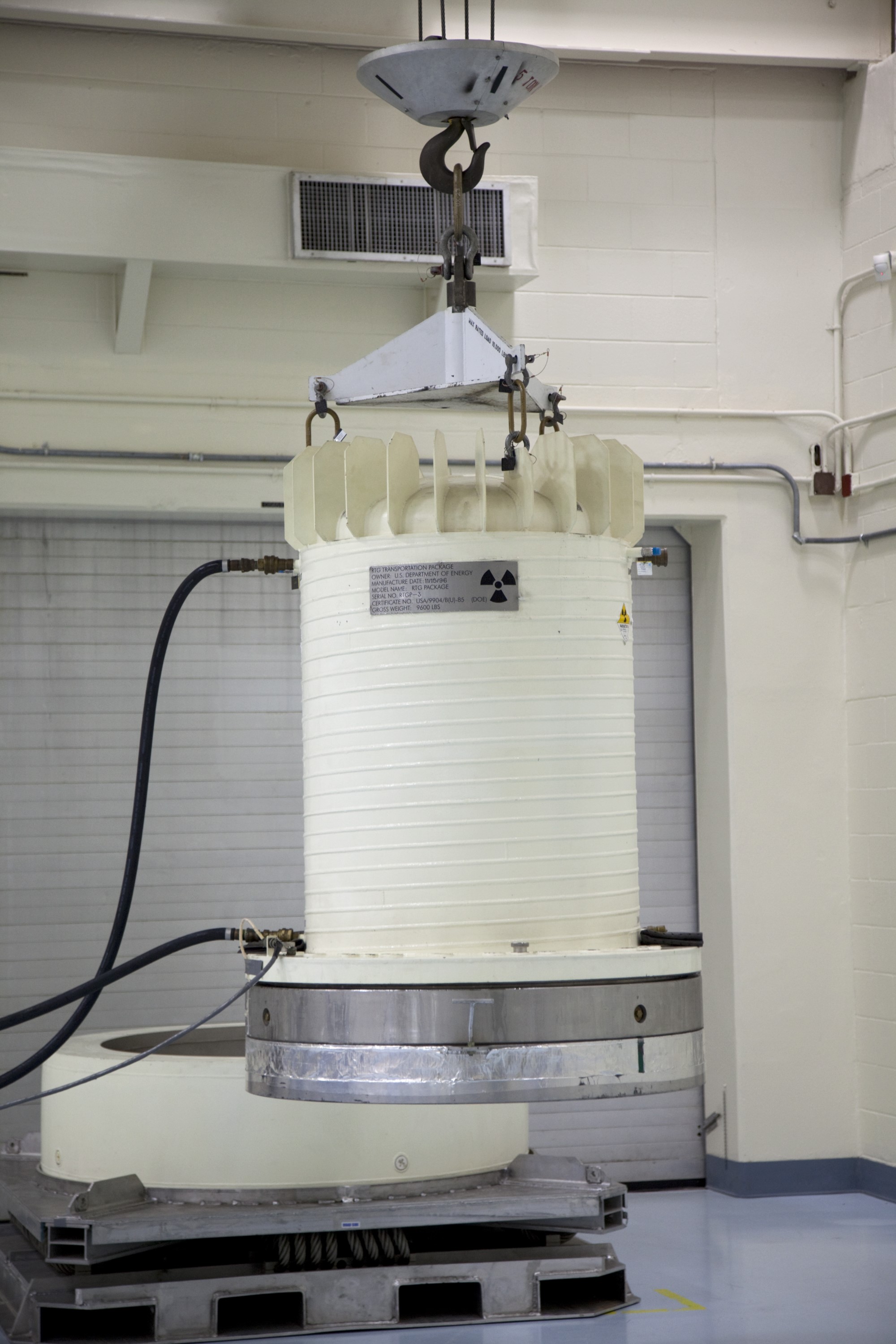

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the RTG storage facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts the shipping cask enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission from its transportation pallet. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

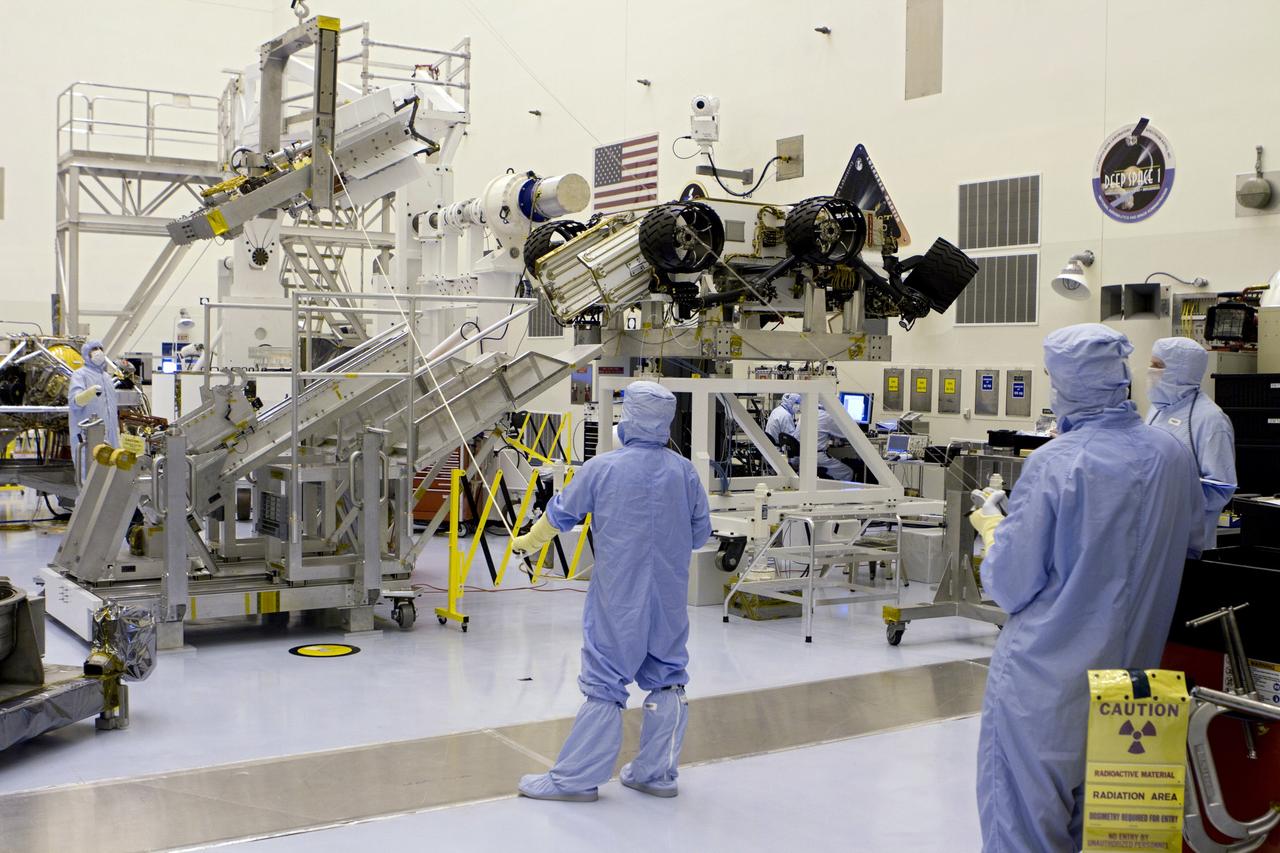
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, spacecraft technicians install the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: Department of Energy/Idaho National Laboratory
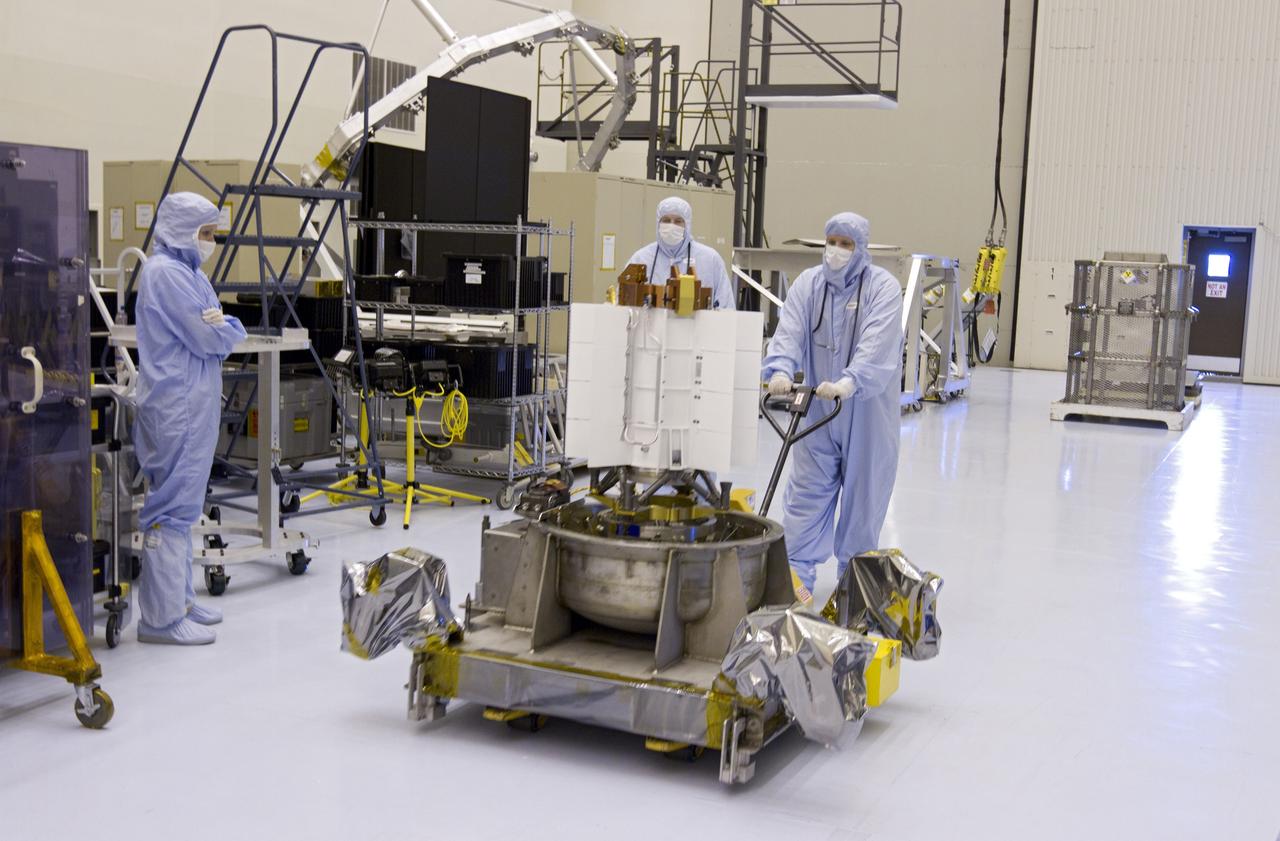

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers dressed in clean room attire, known as bunny suits, transfer the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on its holding base from the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) into the facility's high bay. In the high bay, the MMRTG temporarily will be installed on the MSL rover, Curiosity, for a fit check but will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory position the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on the turning fixture above the MMRTG integration cart. The cart will be used to install the MMRTG on the Curiosity rover for a fit check. The rover is on an elevated work stand, at right. The MMRTG will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
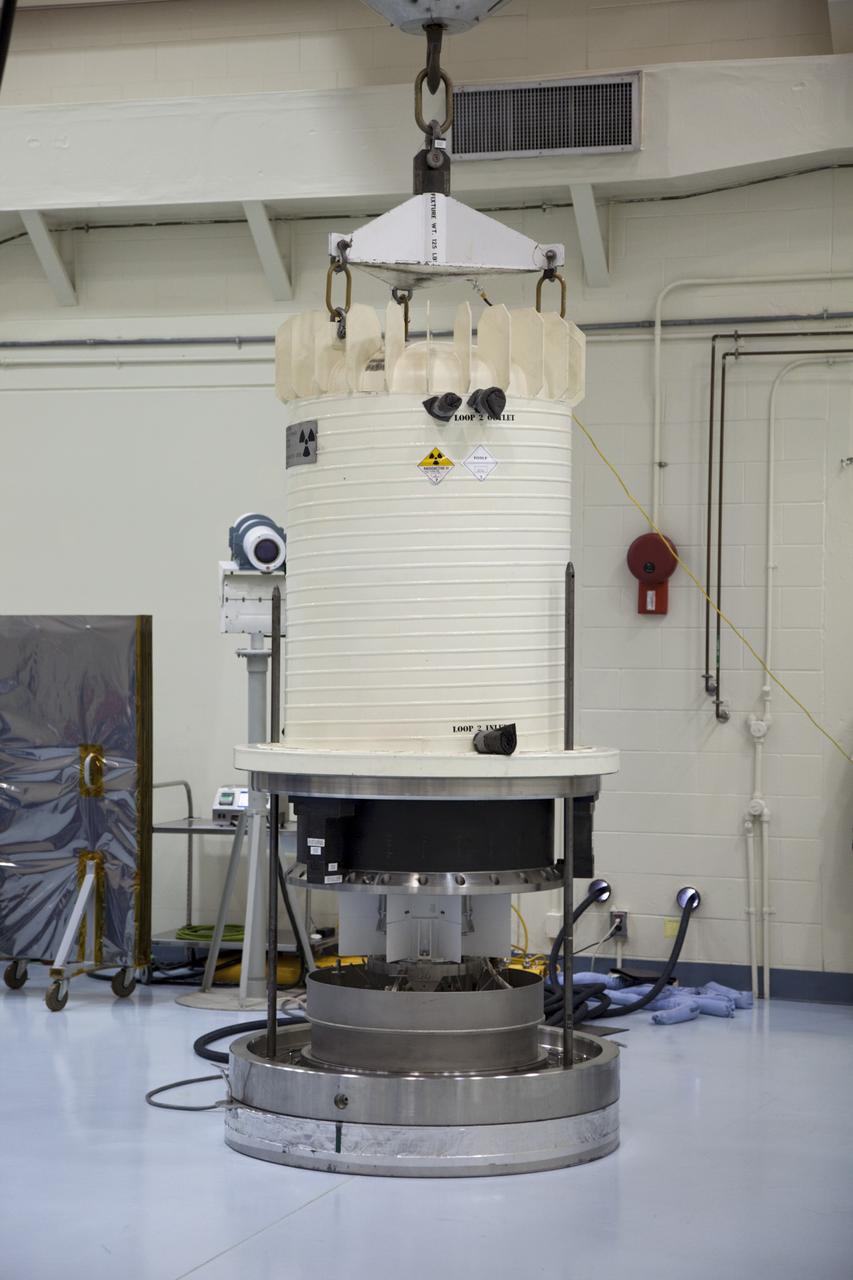

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the RTG storage facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the external and internal protective layers of the shipping cask are lifted from around the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
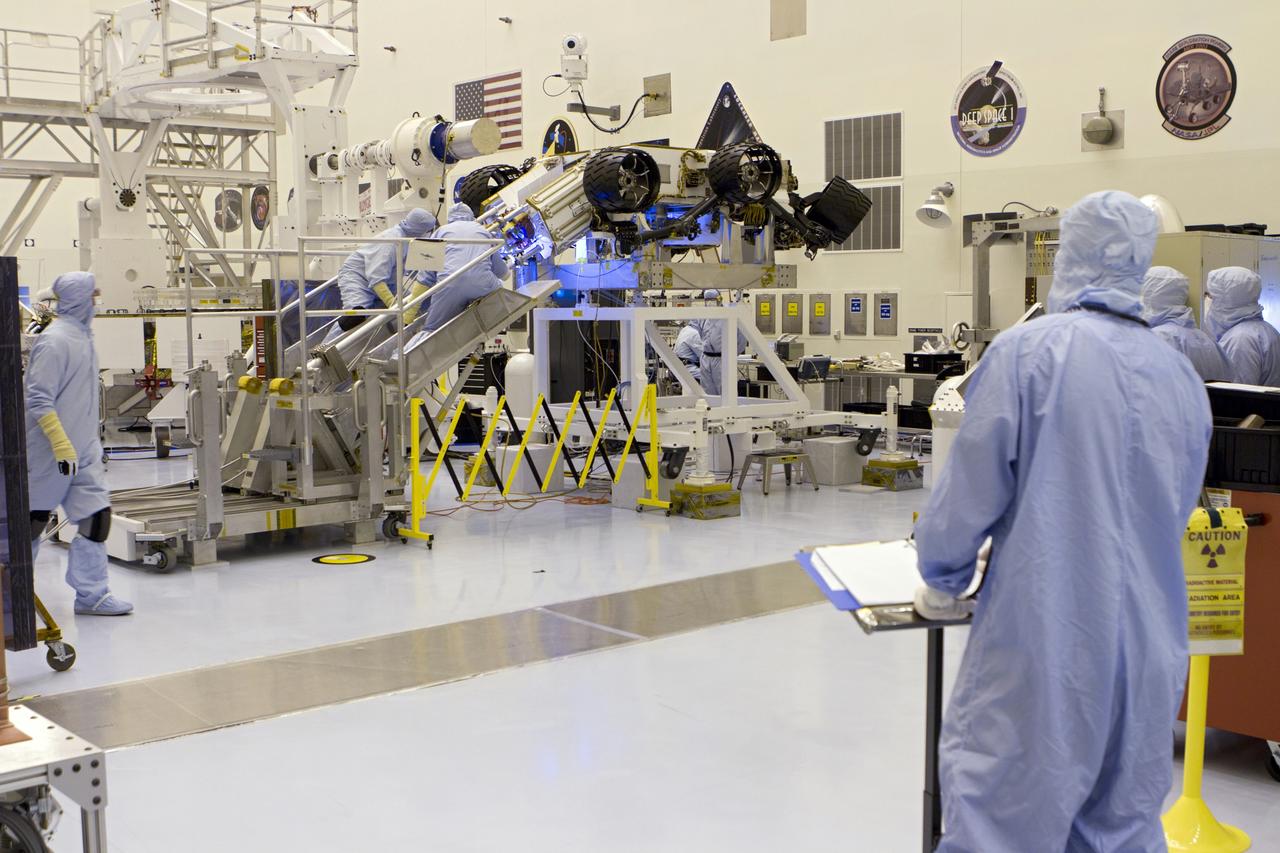

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory transfer the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission onto the aft of the Curiosity rover for a fit check with the aid of the MMRTG integration cart. The MMRTG then will be removed and installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
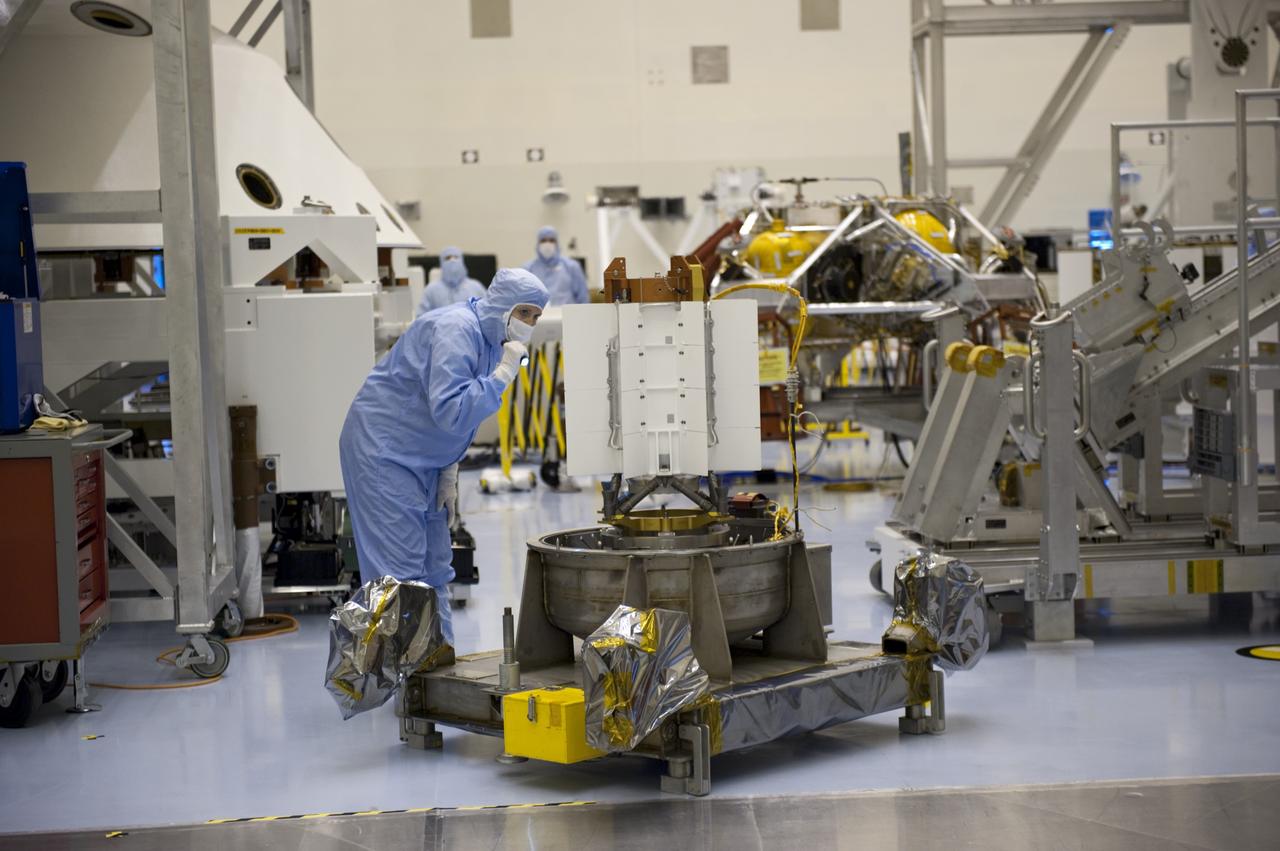

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a spacecraft technician from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory conducts a visual inspection of the cooling tubes on the exterior of the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
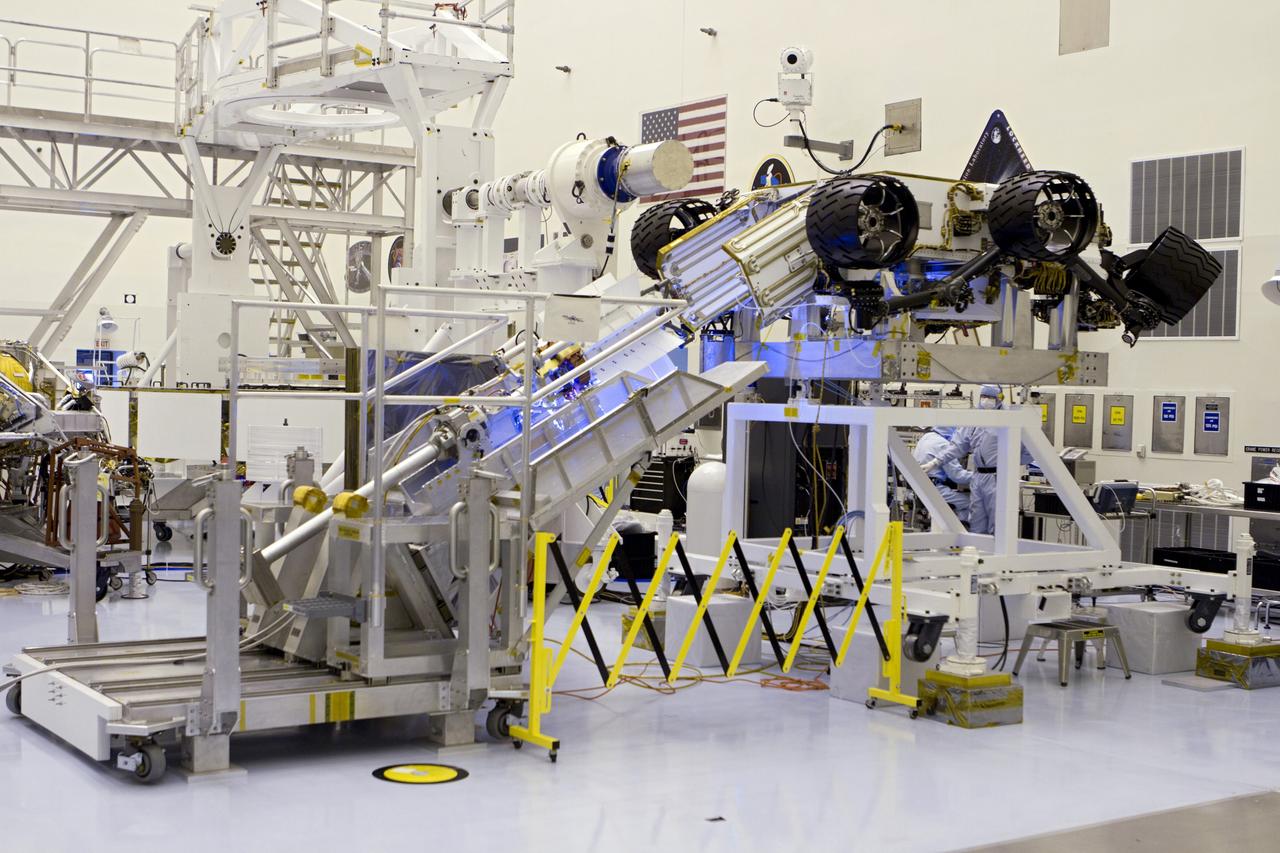

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is attached to the MMRTG integration cart. The cart will be used to install the MMRTG on the Curiosity rover for a fit check. The rover is on an elevated work stand, at right. The MMRTG then will be removed and installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
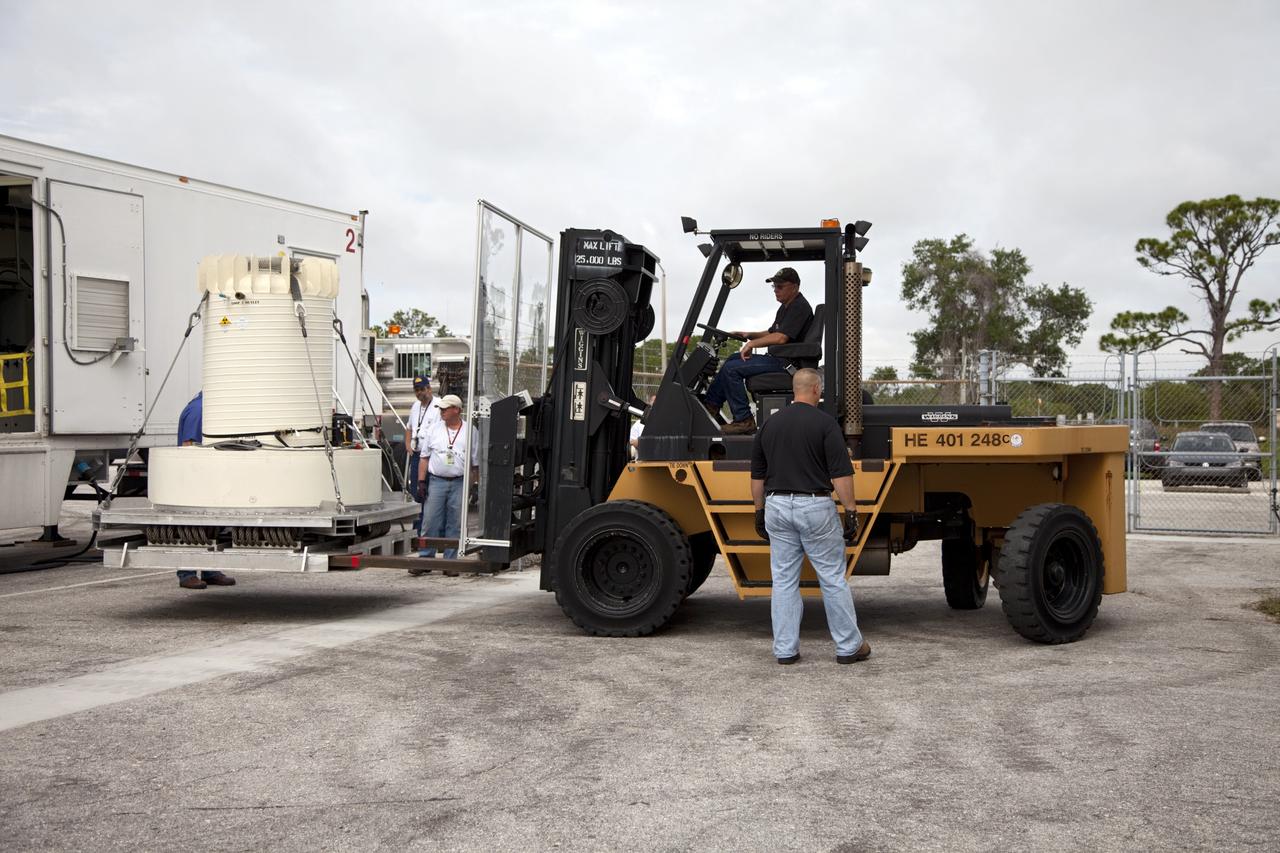

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers use a forklift to offload the shipping cask enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission from the MMRTG trailer that delivered it to the RTG storage facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
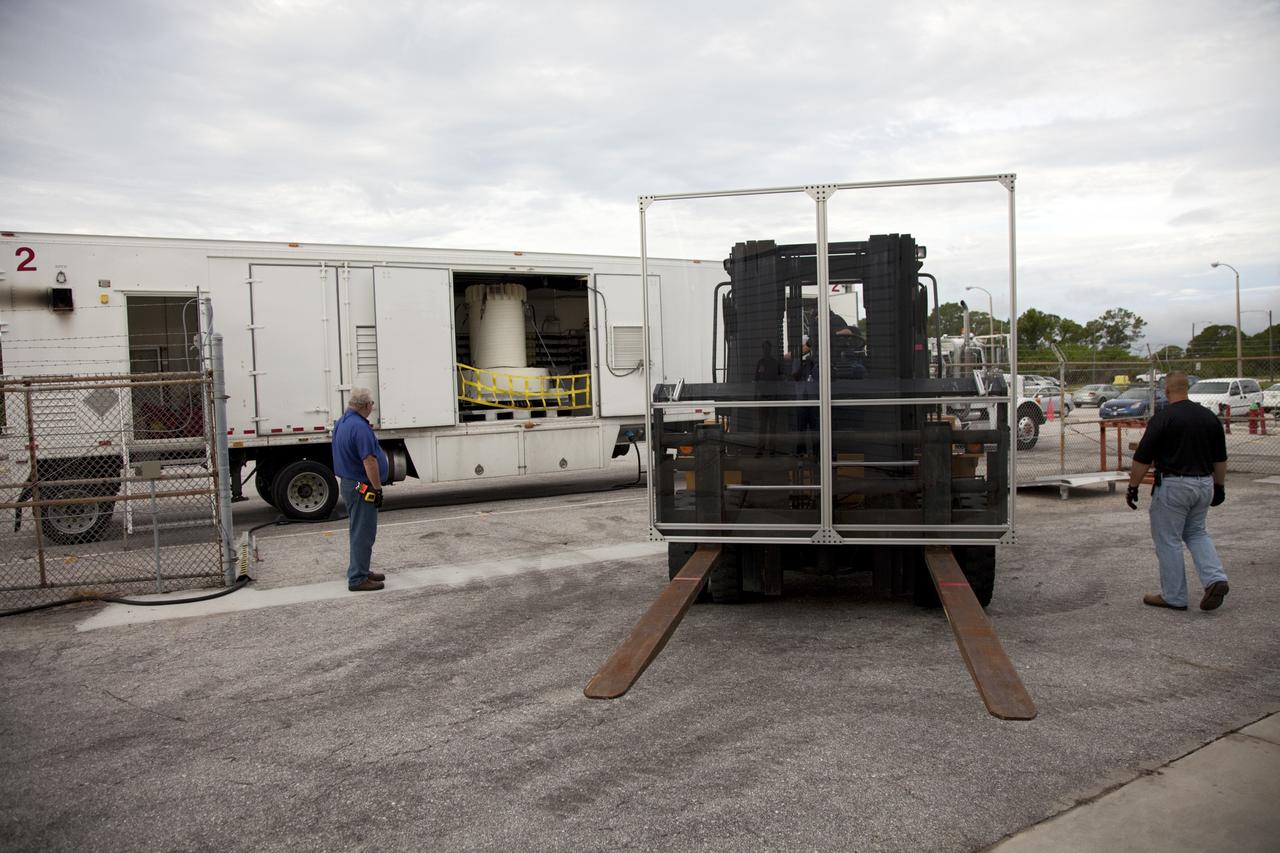

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission, enclosed in a shipping cask, is seen through the open door of the MMRTG trailer that delivered it to the RTG storage facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
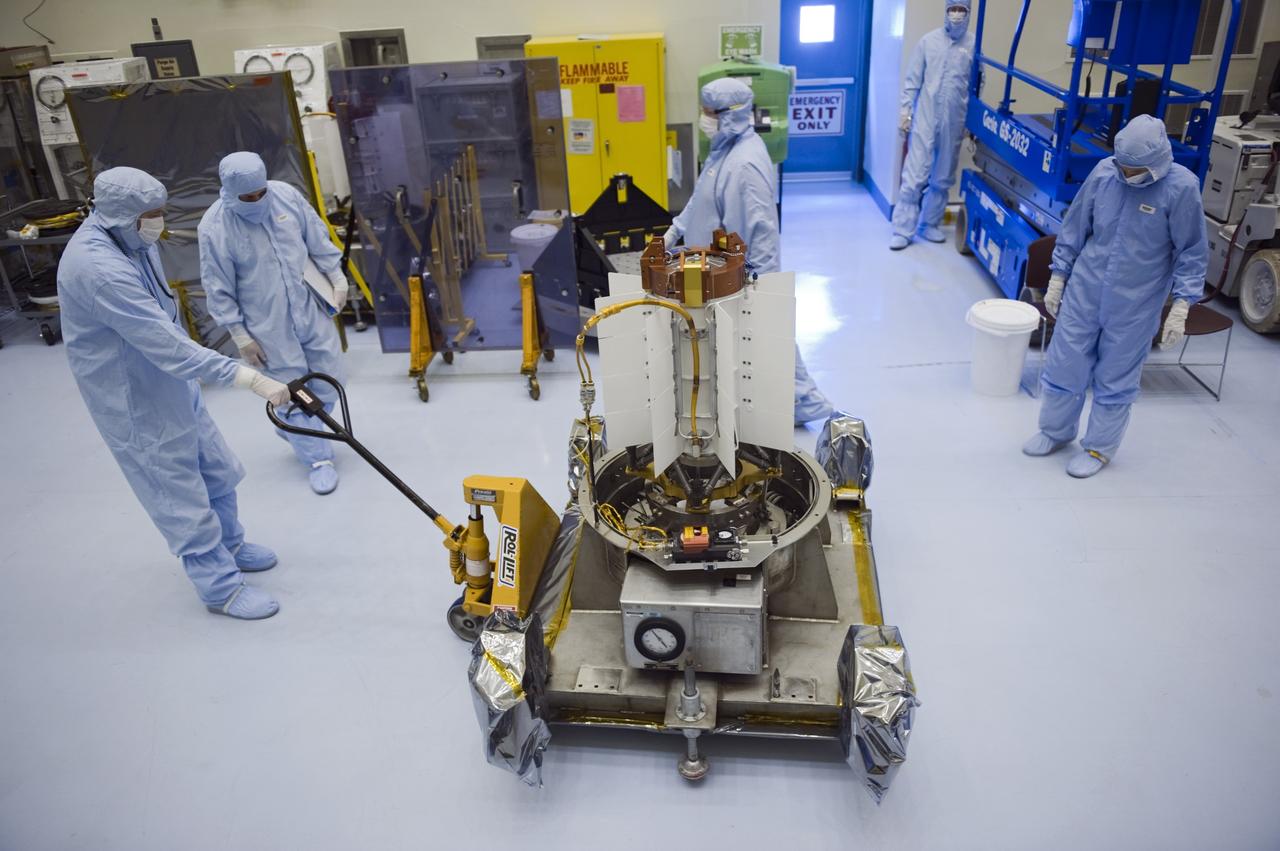

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory park the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on its support base in the airlock following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover in the high bay. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is lowered onto a support base with the aid of a turning fixture following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
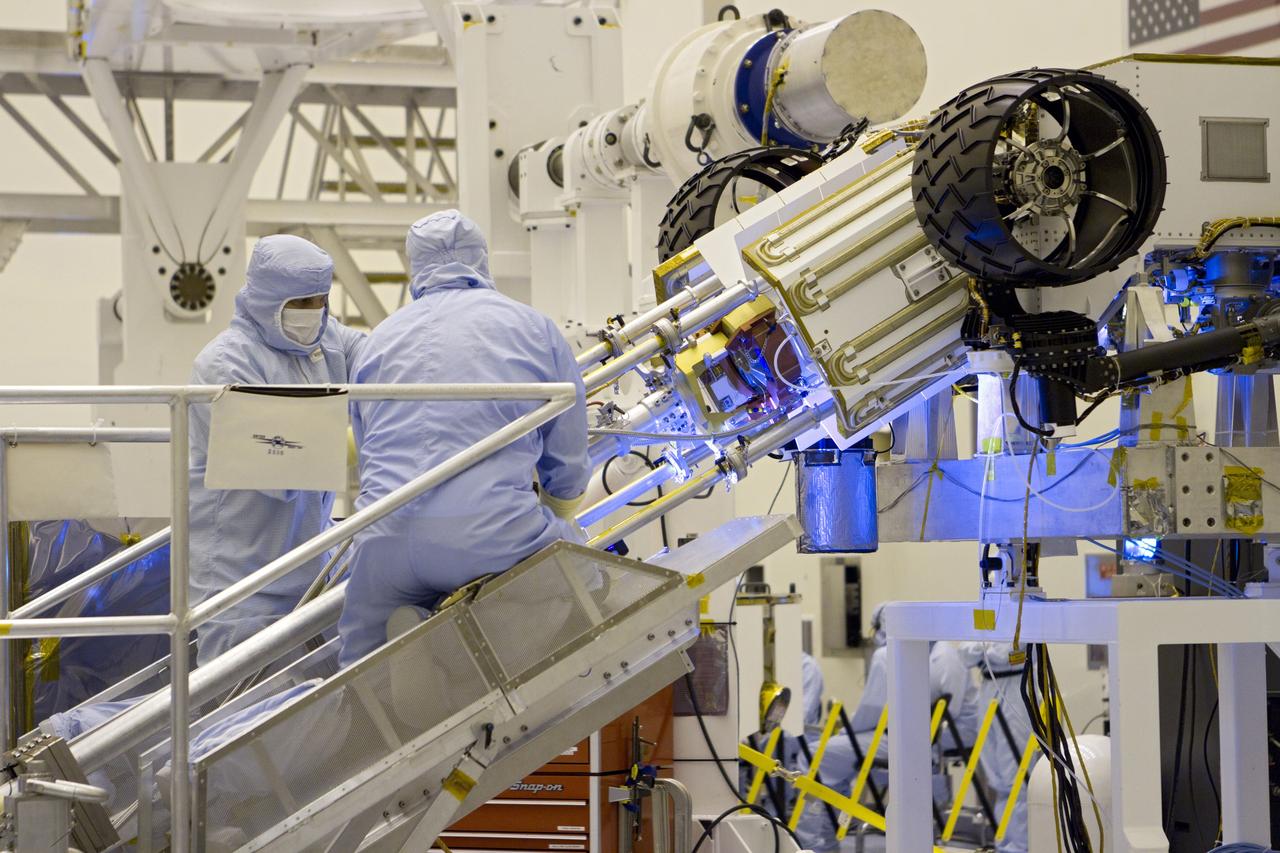

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory use extension tools to attach the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on the MMRTG integration cart onto the aft of the Curiosity rover for a fit check. The MMRTG then will be removed and installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
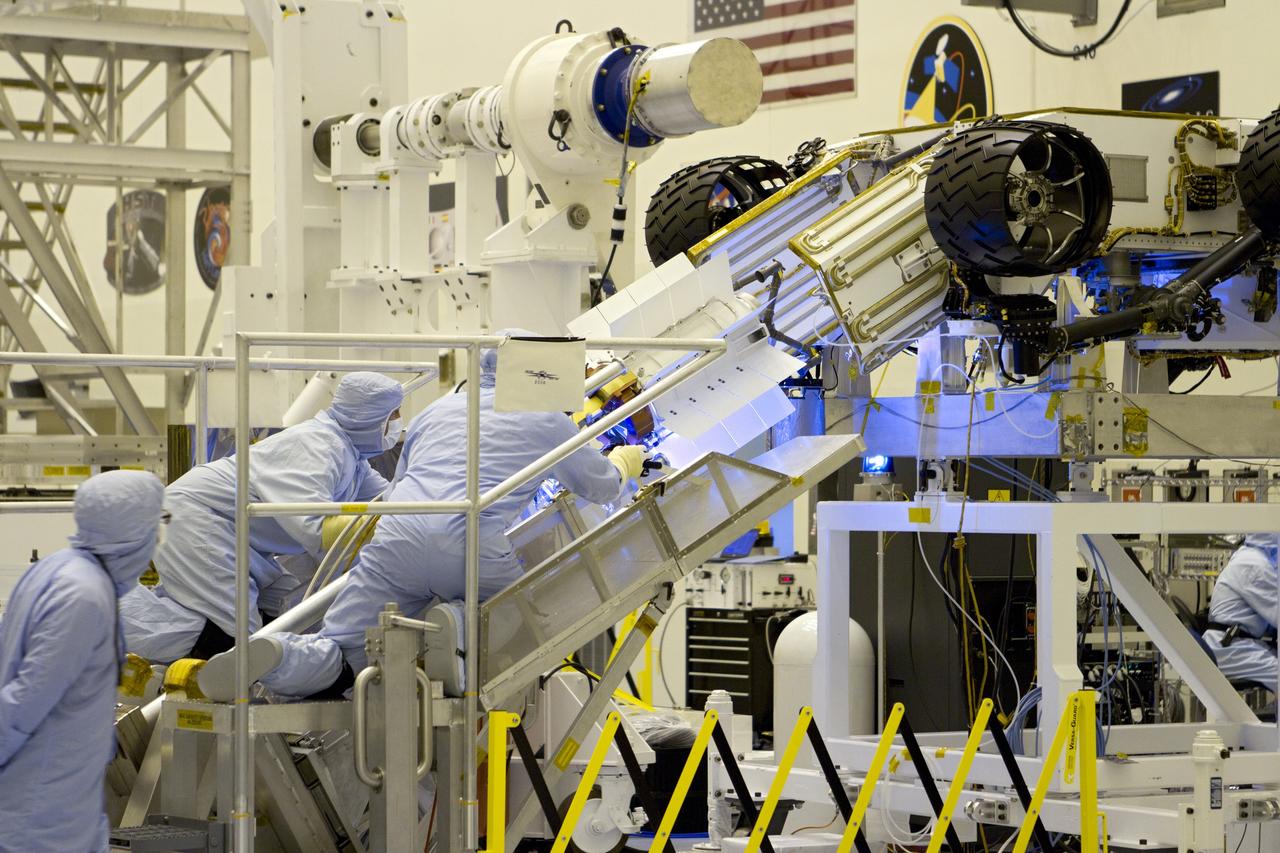

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory transfer the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission onto the aft of the Curiosity rover for a fit check with the aid of the MMRTG integration cart. The MMRTG then will be removed and installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
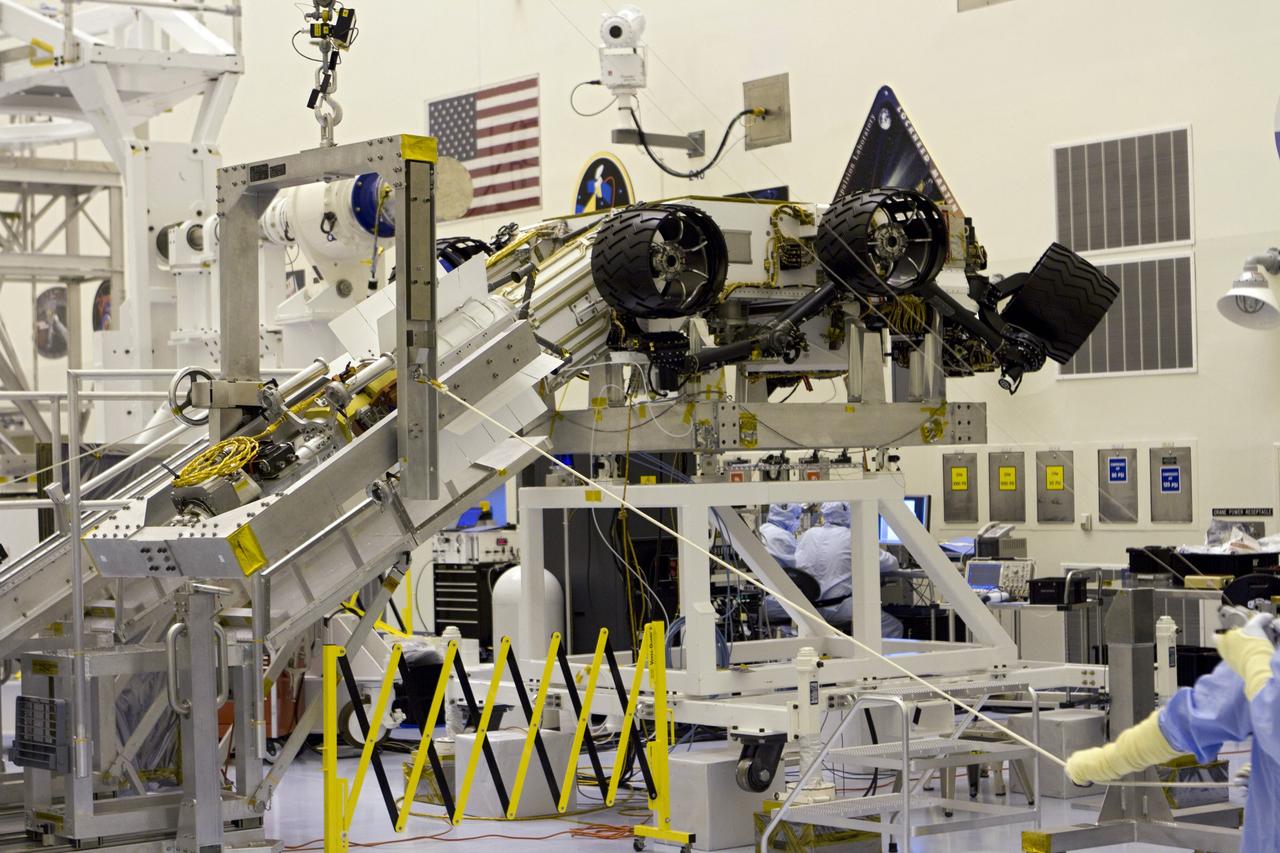

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory guide the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on the turning fixture toward the MMRTG integration cart. The cart will be used to install the MMRTG on the Curiosity rover for a fit check. The rover is on an elevated work stand, at right. The MMRTG will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
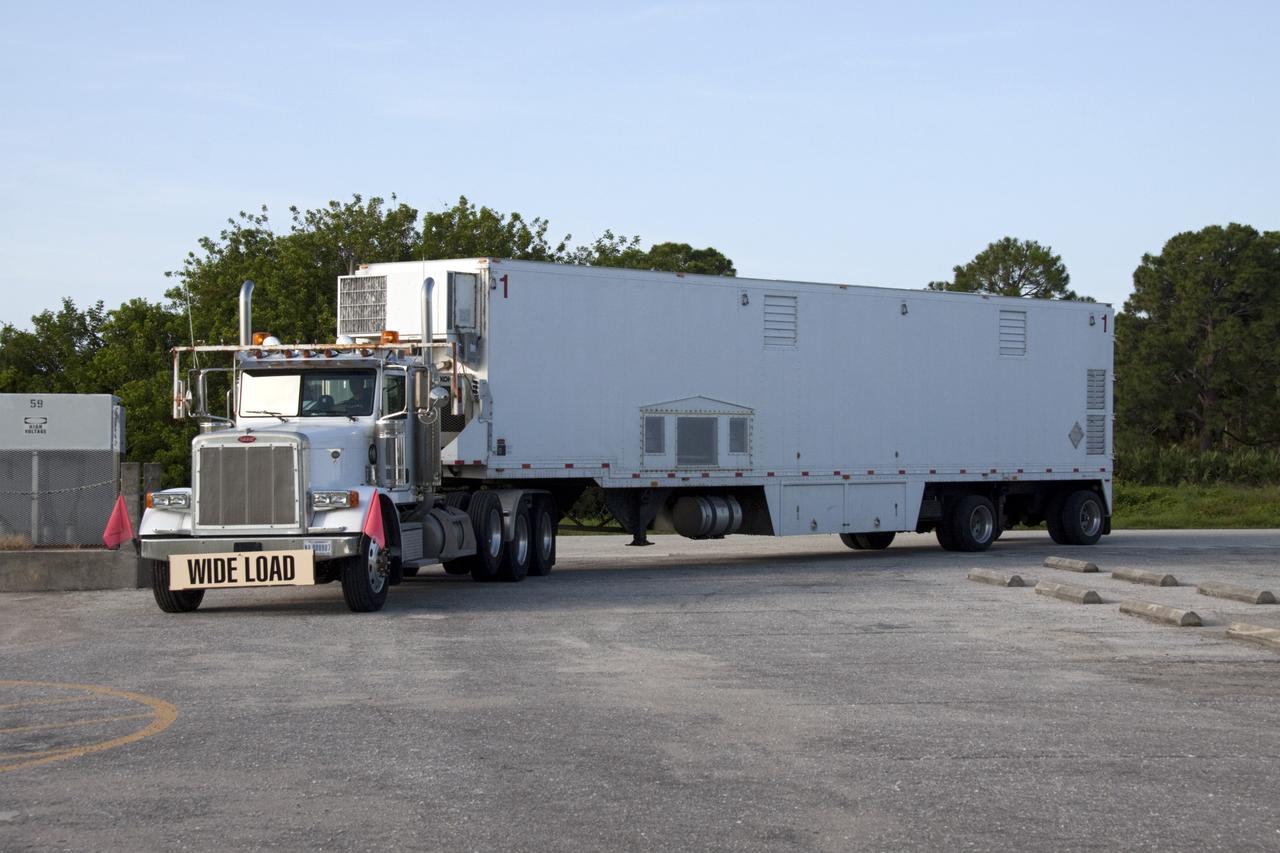

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the trailer transporting the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission arrives at the RTG storage facility (RTGF). The MMRTG is returning to the RTGF following a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
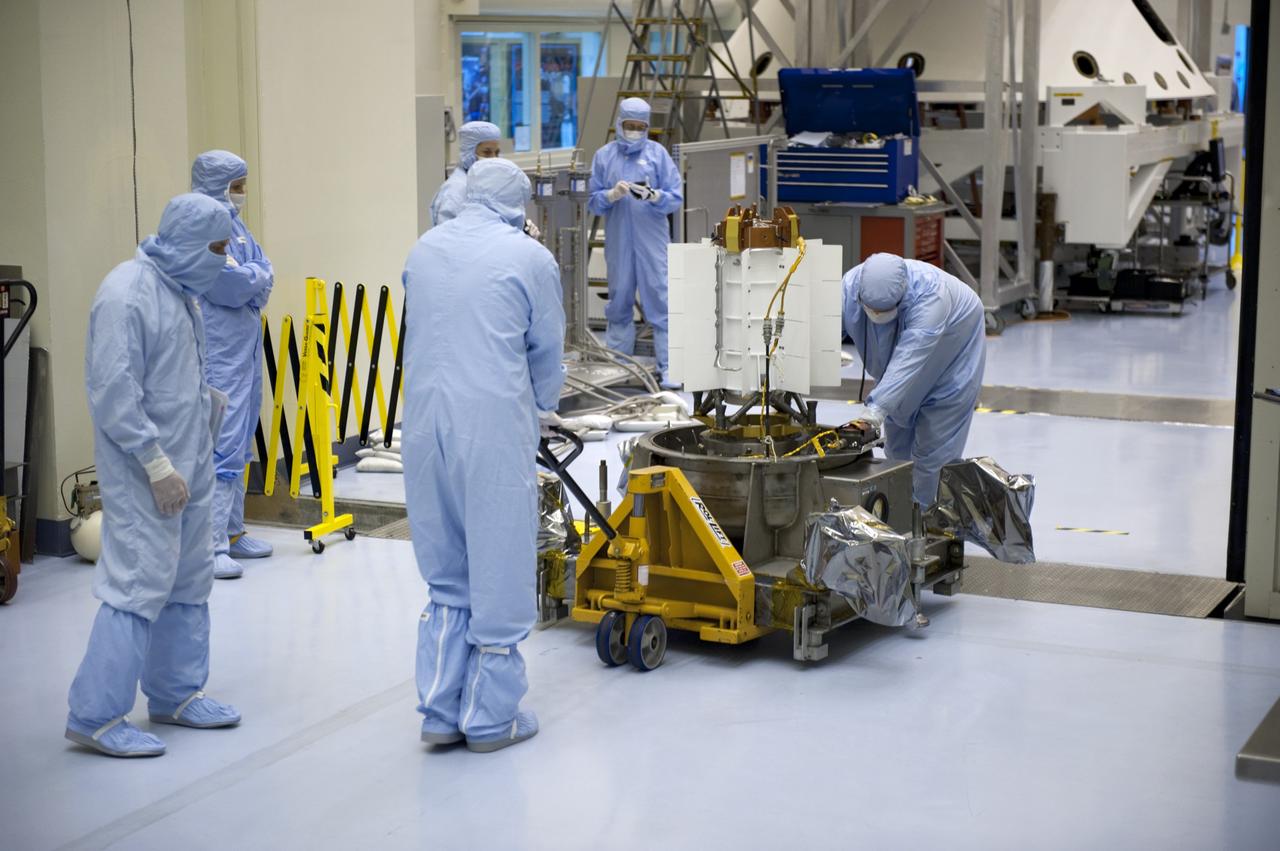

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory roll the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on its support base from the high bay into the airlock following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
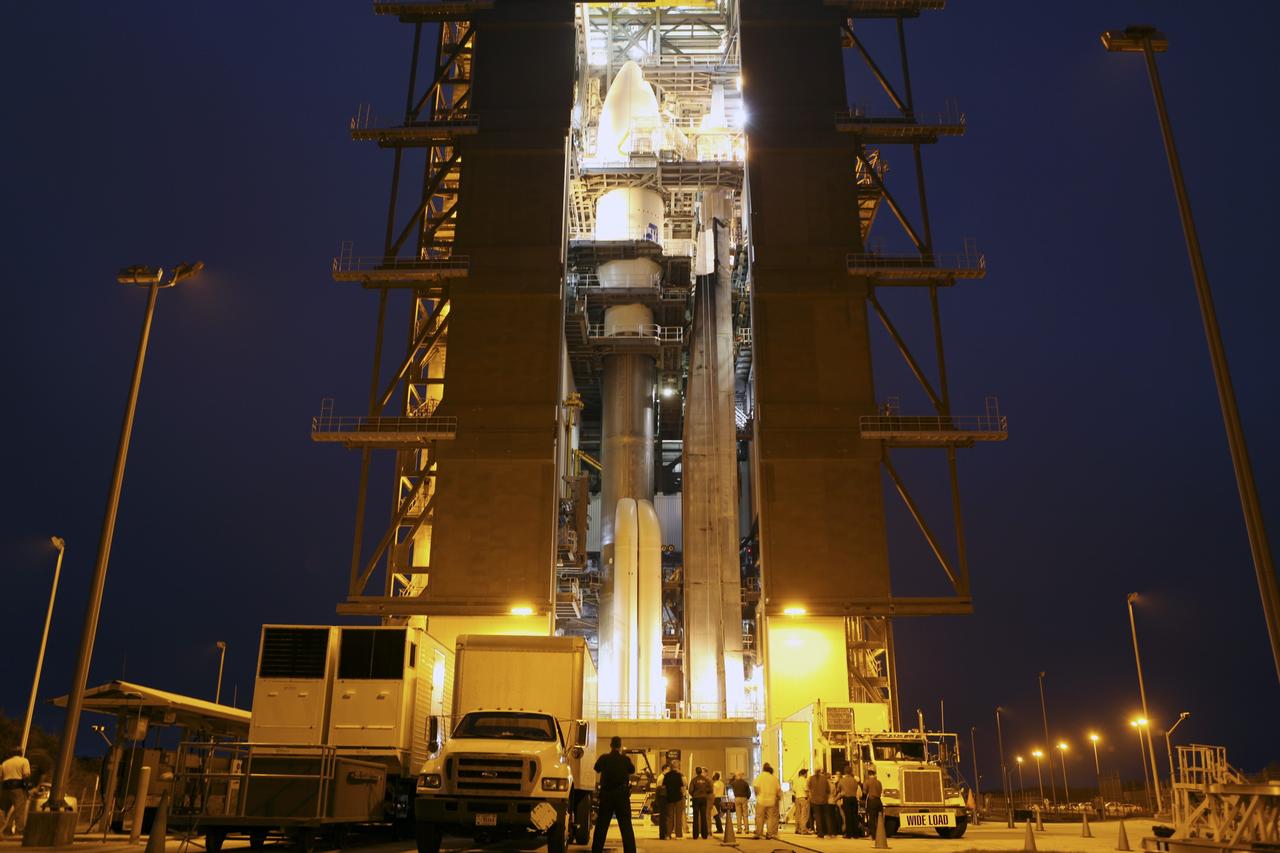

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Atlas V rocket set to launch NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is illuminated inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41, where employees have gathered to hoist the spacecraft's multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG). The MMRTG will be lifted up to the top of the rocket and installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat emitted by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
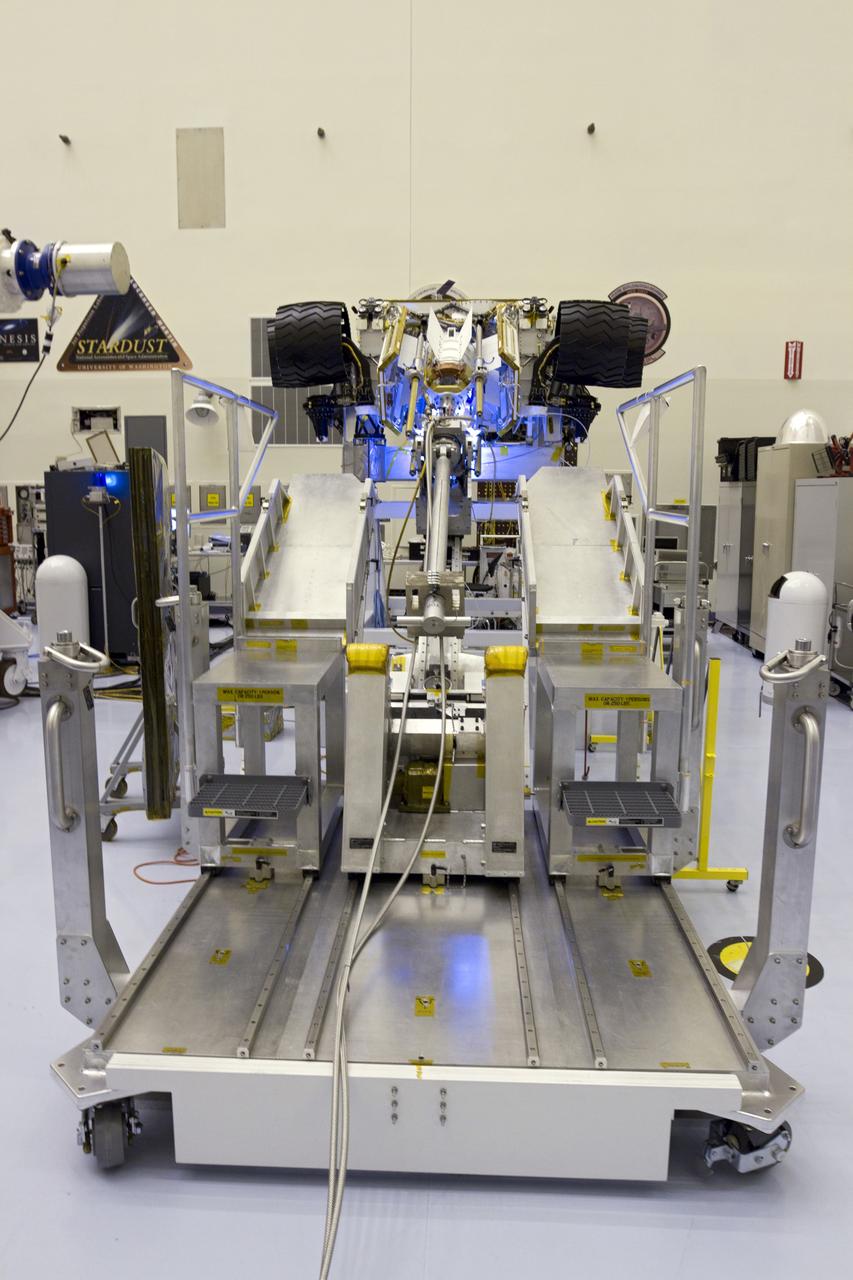

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is detached from the MMRTG integration cart and installed onto the aft of the Curiosity rover for a fit check. Next, the MMRTG will be removed and later installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The "gorilla cage," holding the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, is settled on one of the upper levels above the Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41. The MMRTG will be installed on the MSL spacecraft, encapsulated within the payload fairing. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat emitted by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Heat emitted by the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
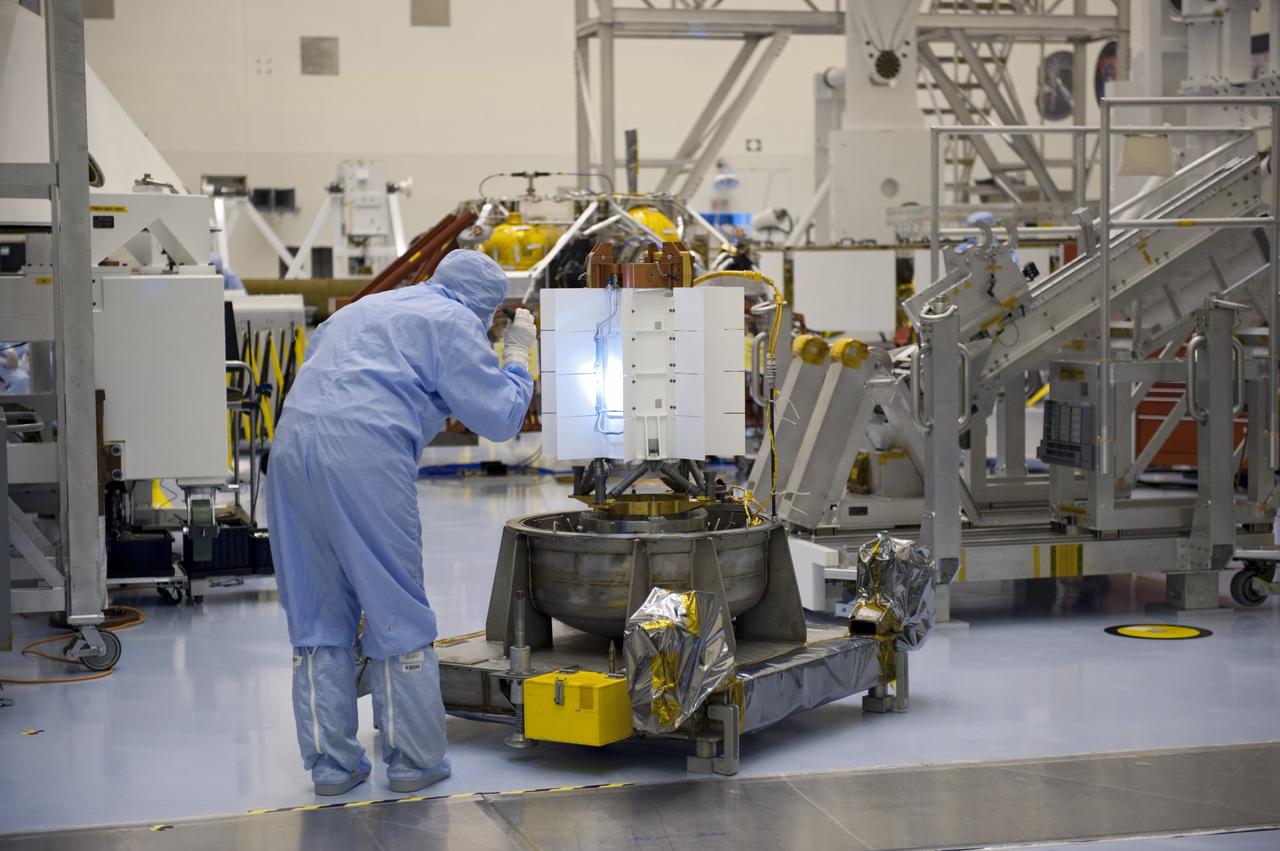

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a spacecraft technician from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory conducts a visual inspection of the cooling tubes on the exterior of the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
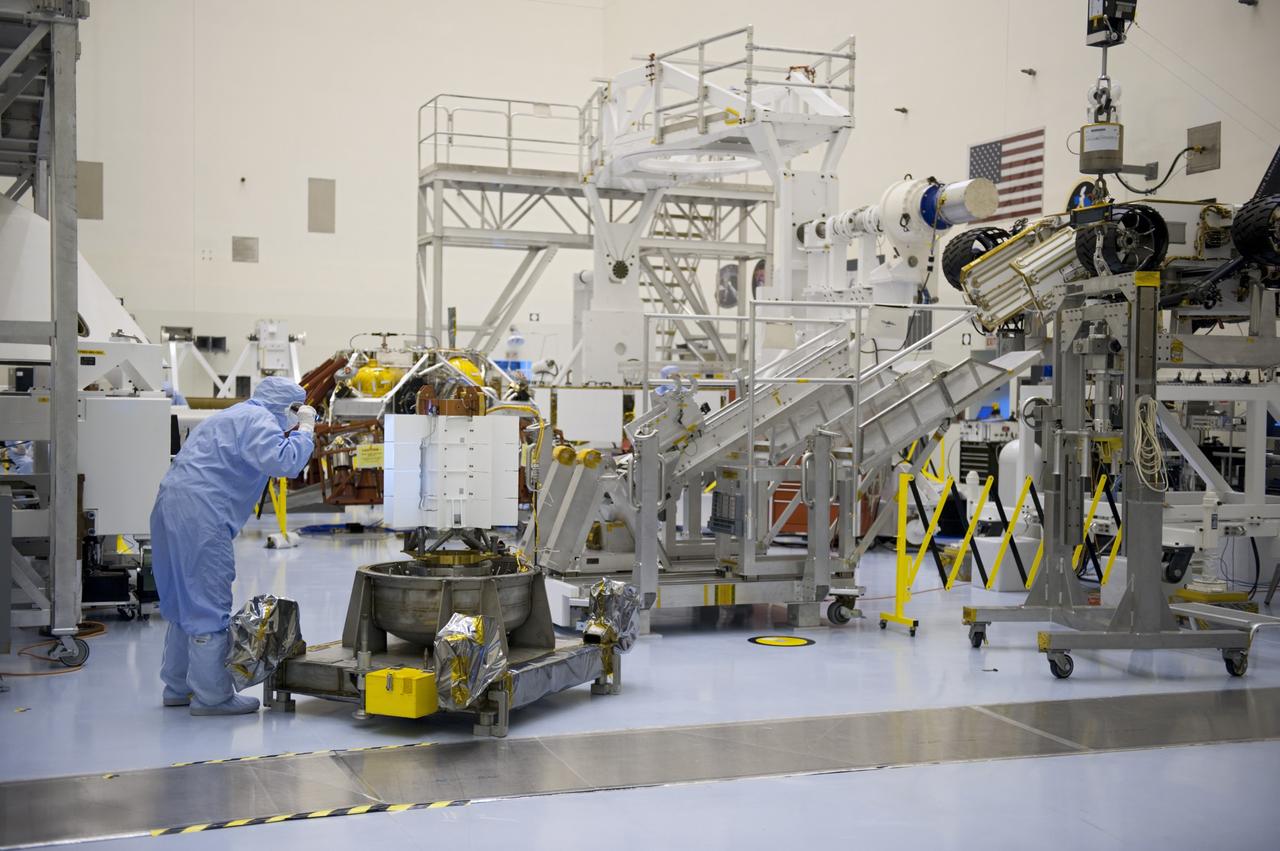

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a spacecraft technician from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory conducts a visual inspection of the cooling tubes on the exterior of the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. At right is the Curiosity rover on an elevated work stand. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
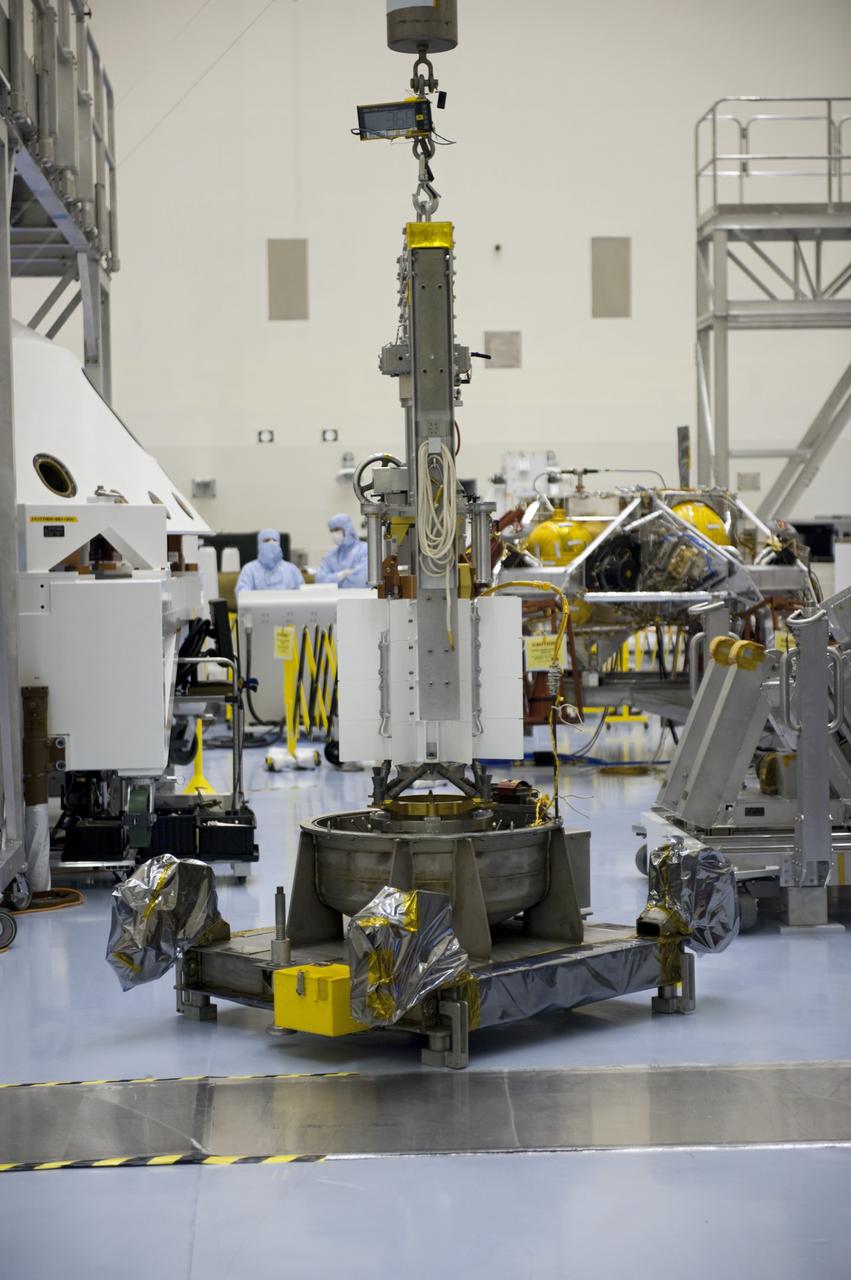

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is positioned on a support base with the aid of a turning fixture following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the descent stage for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission awaits installation on the Curiosity rover, in the background at right. MSL's multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator has been installed onto the aft of the rover for a fit check. The descent stage will cradle the rover and its MMRTG during their approach to the surface of Mars. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Steve Homann, senior advisor for the Department of Energy, speaks to media during a tour of the Radiological Control Center (RADCC) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tour focused on safety equipment and procedures for the upcoming launch of the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The MSL spacecraft includes a multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) that will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Steve Homann, senior advisor for the Department of Energy, speaks to media during a tour of the Radiological Control Center (RADCC) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tour focused on safety equipment and procedures for the upcoming launch of the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The MSL spacecraft includes a multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) that will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
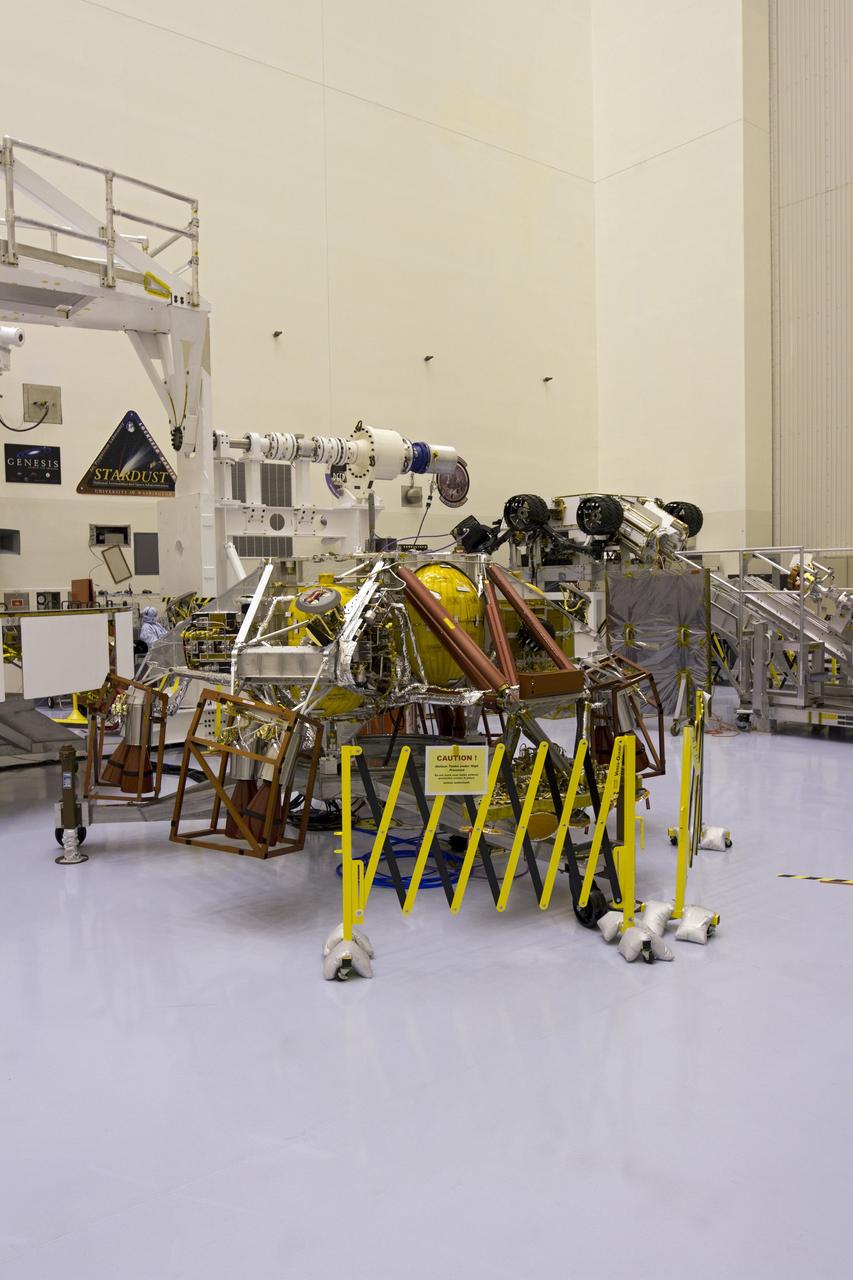

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the descent stage for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission awaits installation on the Curiosity rover, in the background at right. MSL's multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator has been installed onto the aft of the rover for a fit check. The descent stage will cradle the rover and its MMRTG during their approach to the surface of Mars. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
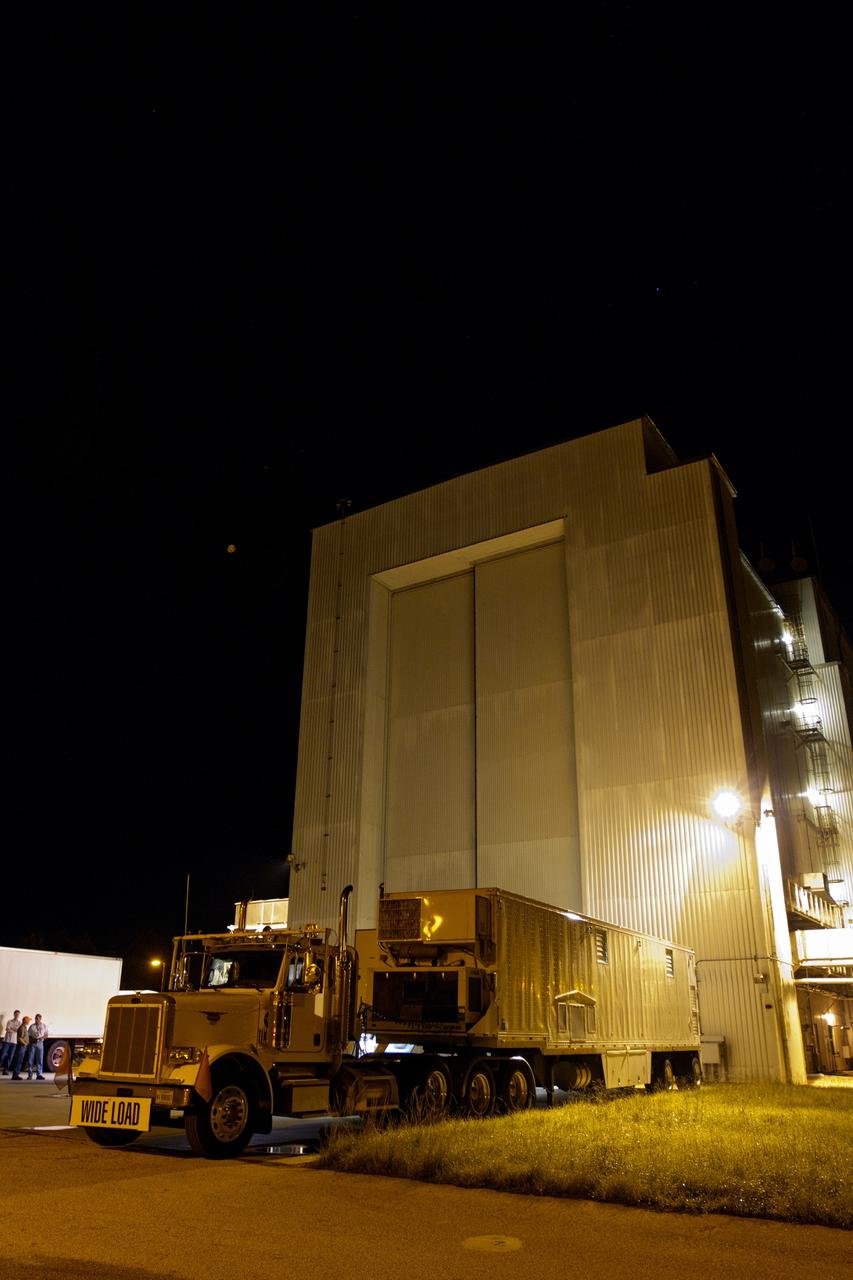

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is delivered to the airlock doors of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida inside the MMRTG trailer. In the PHSF, the MMRTG temporarily will be installed on the MSL rover, Curiosity, for a fit check but will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
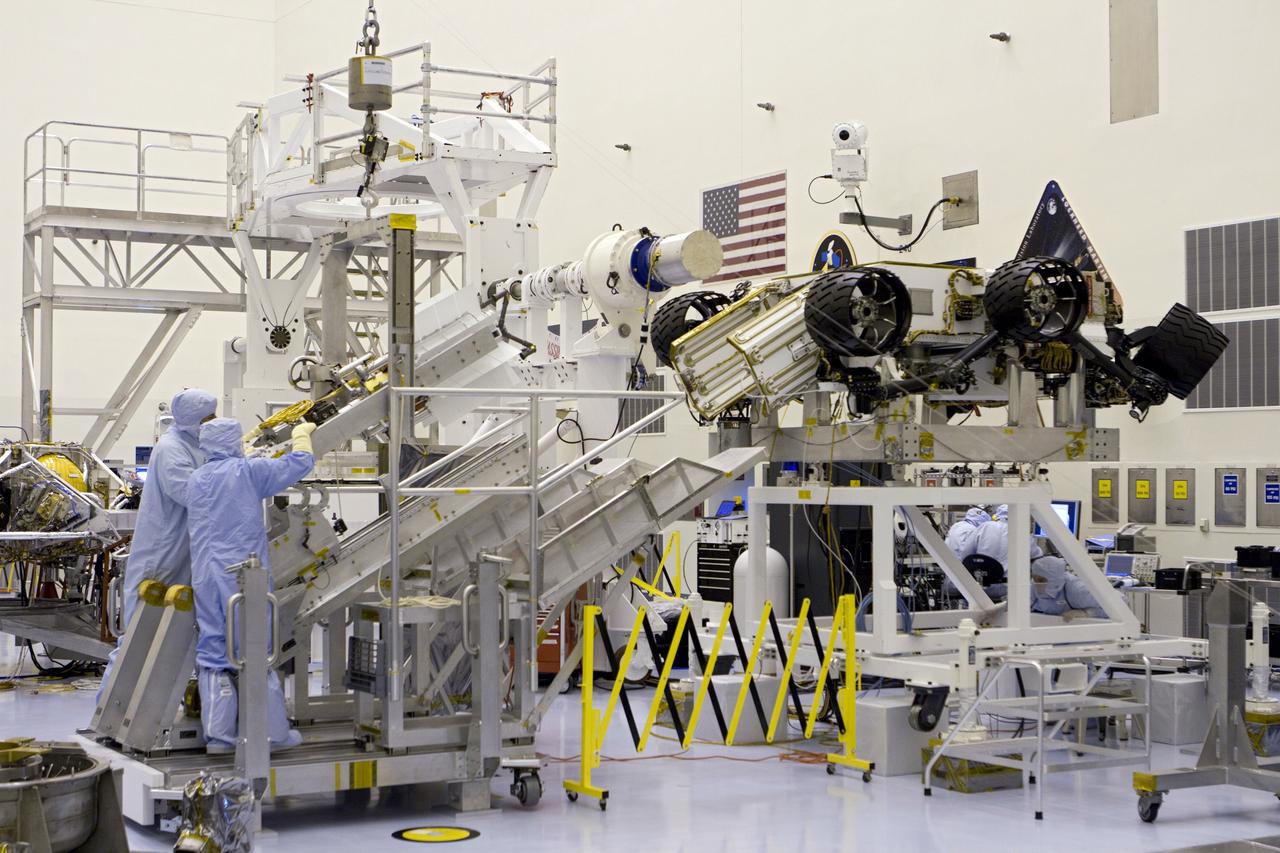

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on the turning fixture is lowered onto the MMRTG integration cart. The cart will be used to install the MMRTG on the Curiosity rover for a fit check. The rover is on an elevated work stand, at right. The MMRTG will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
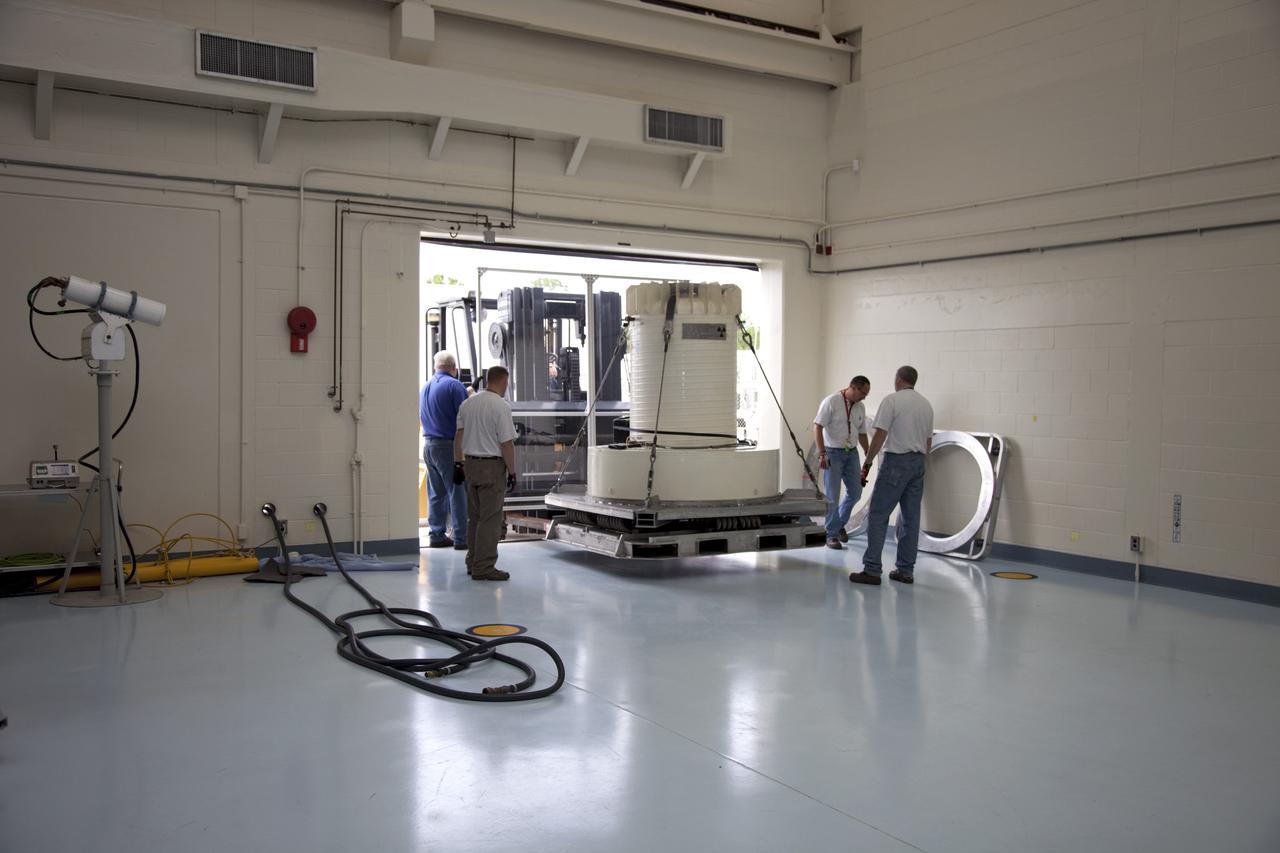

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission, enclosed in a shipping cask, rolls into the high bay of the RTG storage facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
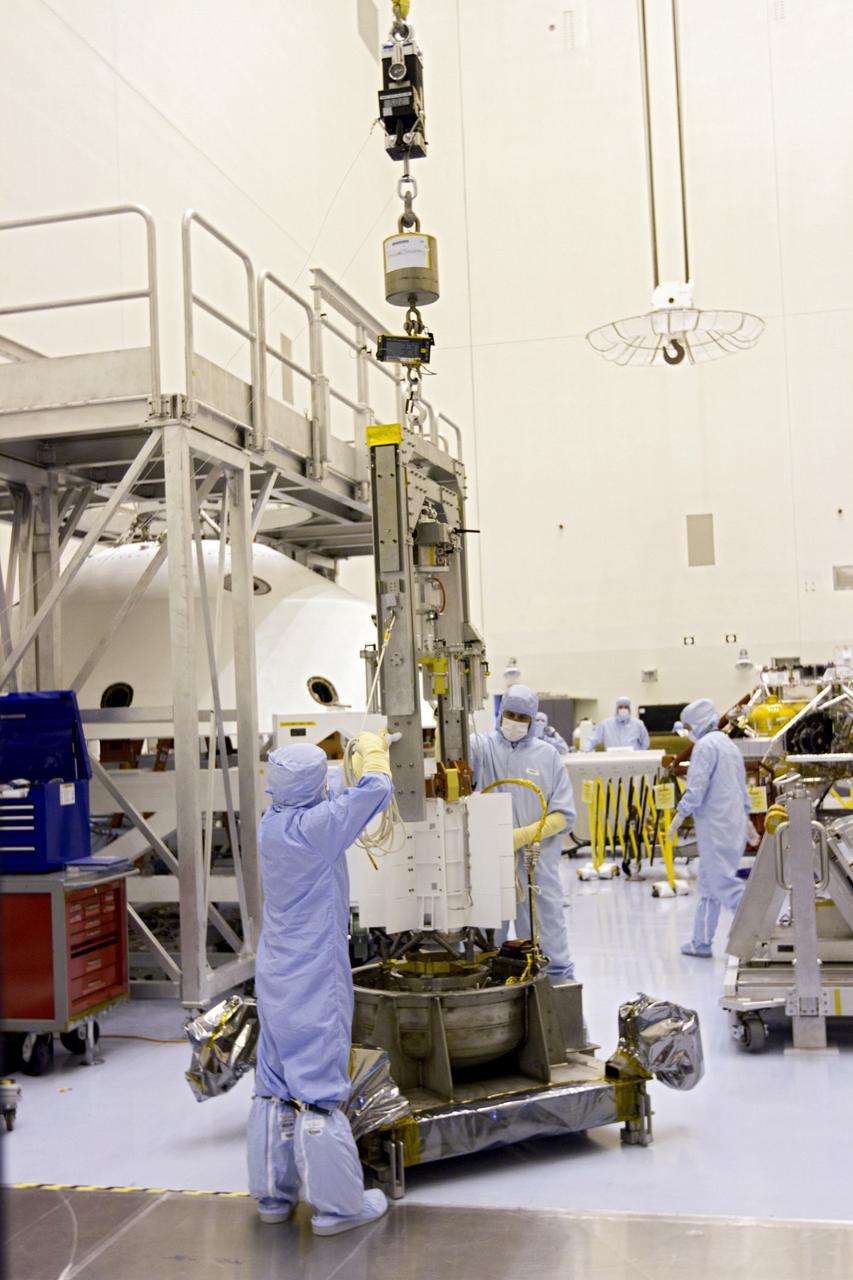

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory guide a turning fixture onto the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The fixture will be used to lift and lower the MMRTG onto the MMRTG integration cart. The cart will be used to install the MMRTG on Curiosity for a fit check. The MMRTG will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
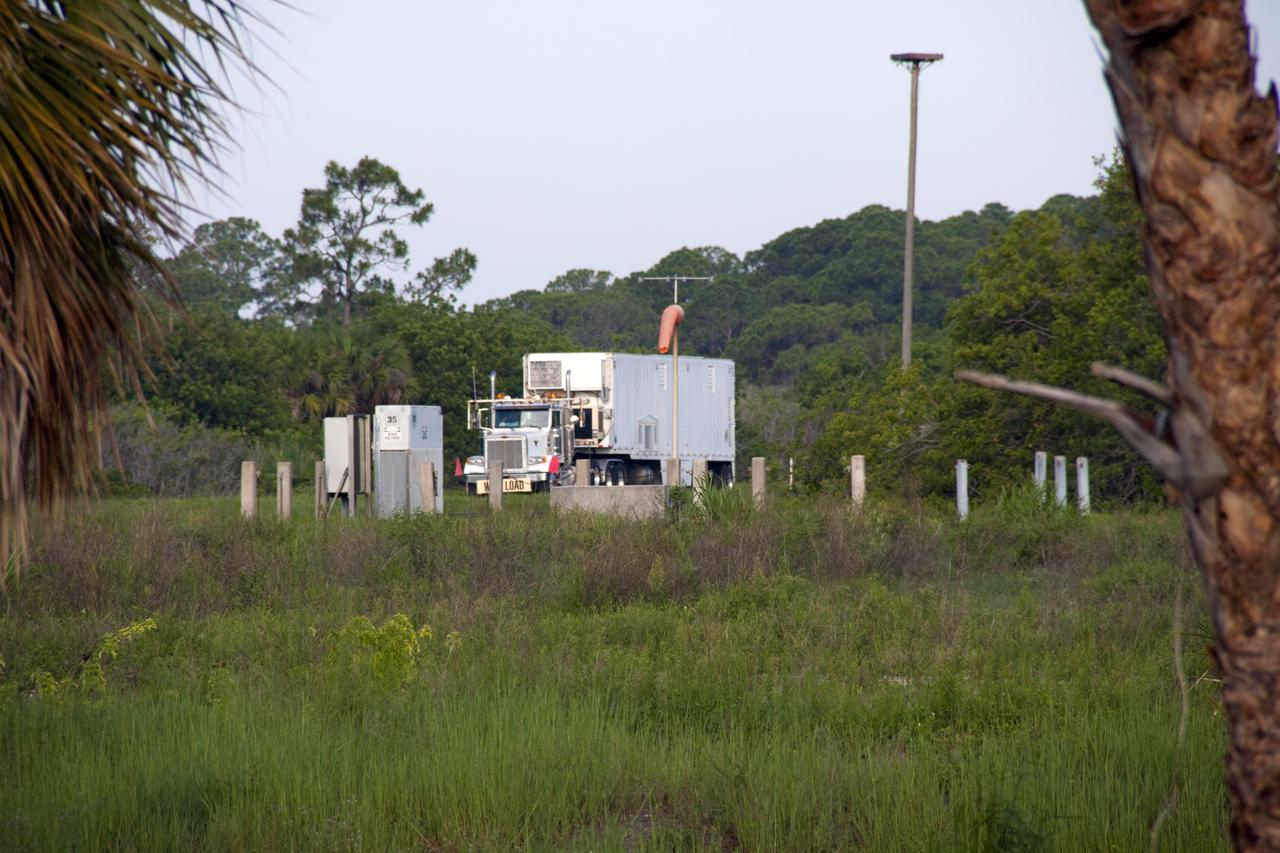

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, secured inside the MMRTG trailer, makes its way between the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) and the RTG storage facility. The MMRTG is being moved following a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the PHSF. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
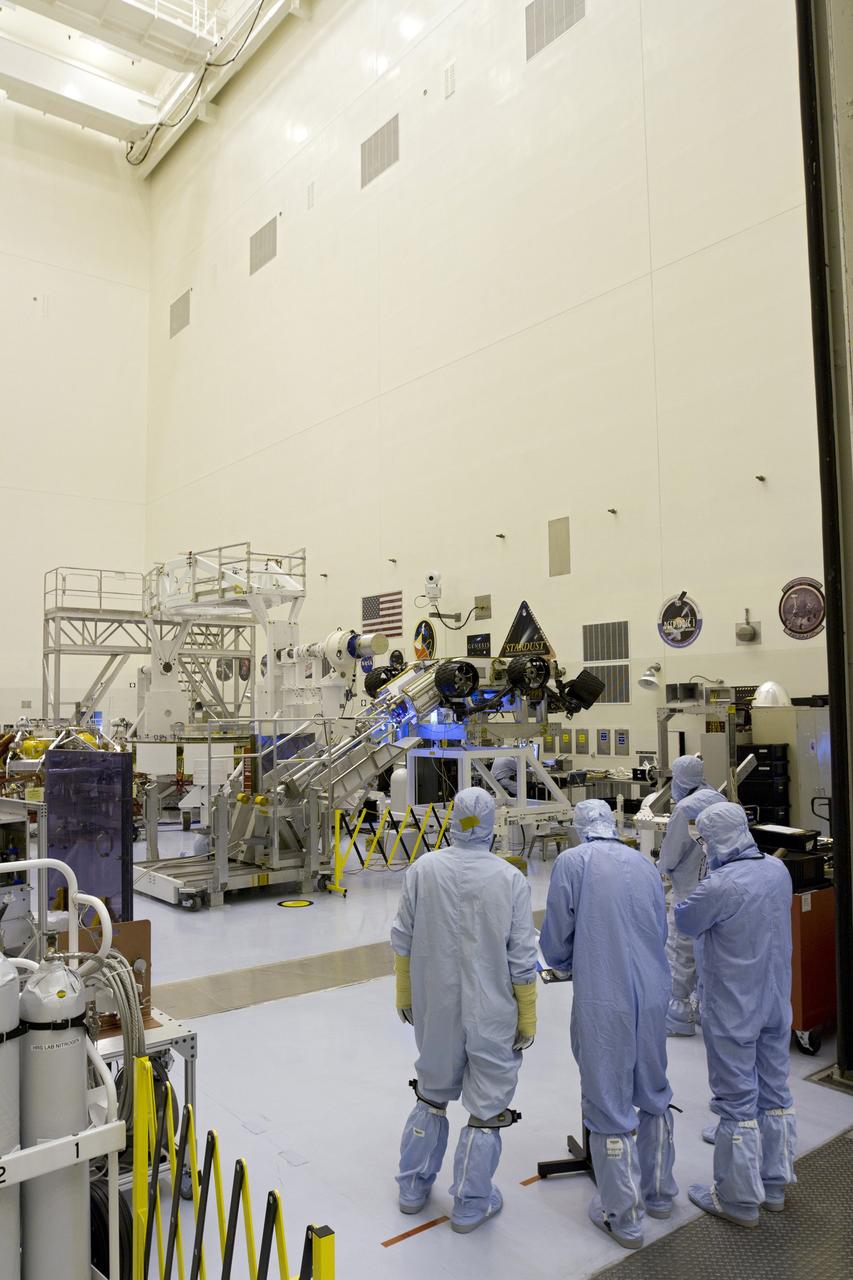

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory prepare to attach the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission onto the aft of the Curiosity rover for a fit check with the aid of the MMRTG integration cart. The MMRTG then will be removed and installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
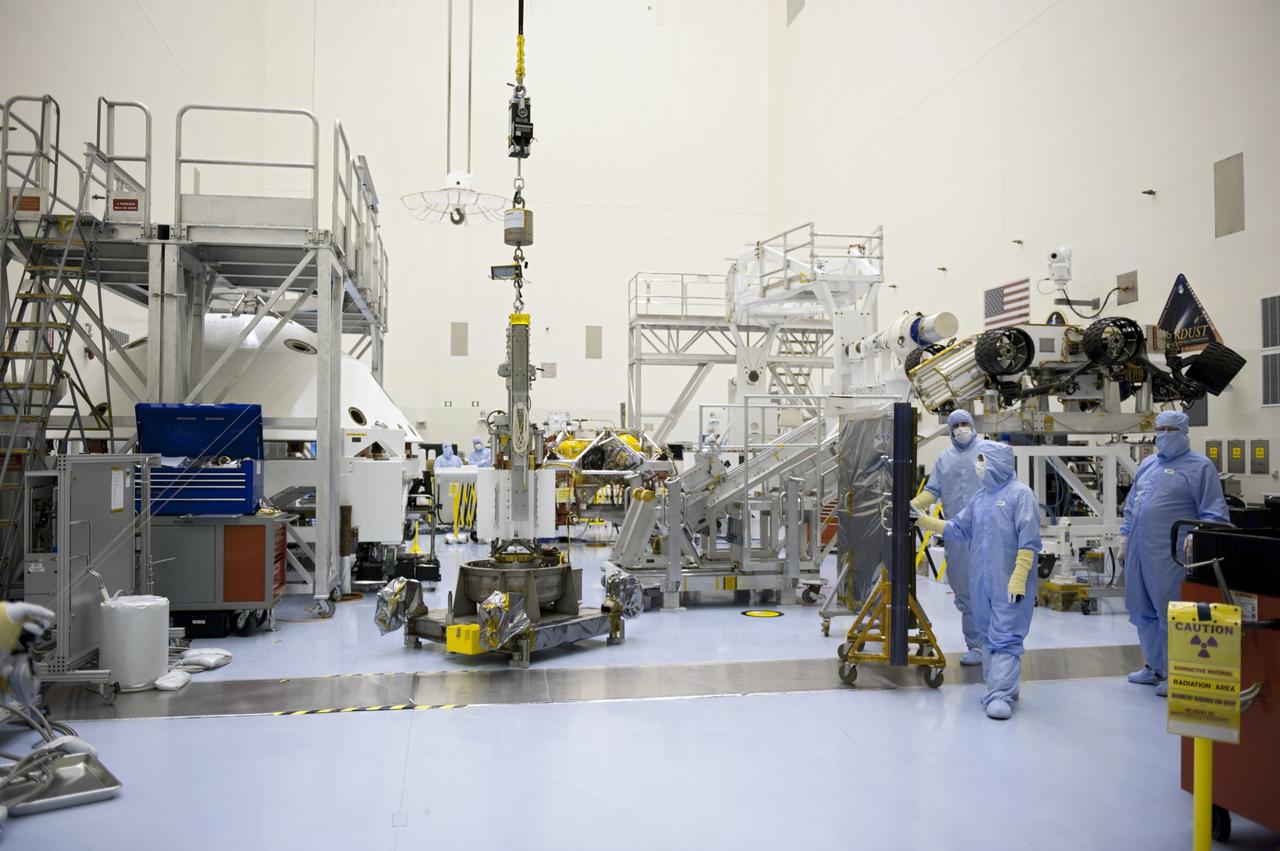

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, still connected to the turning fixture, rests on a support base following the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. A mobile plexiglass radiation shield is in place between the MMRTG and the spacecraft technicians, at right, to help minimize the employees' radiation exposure. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
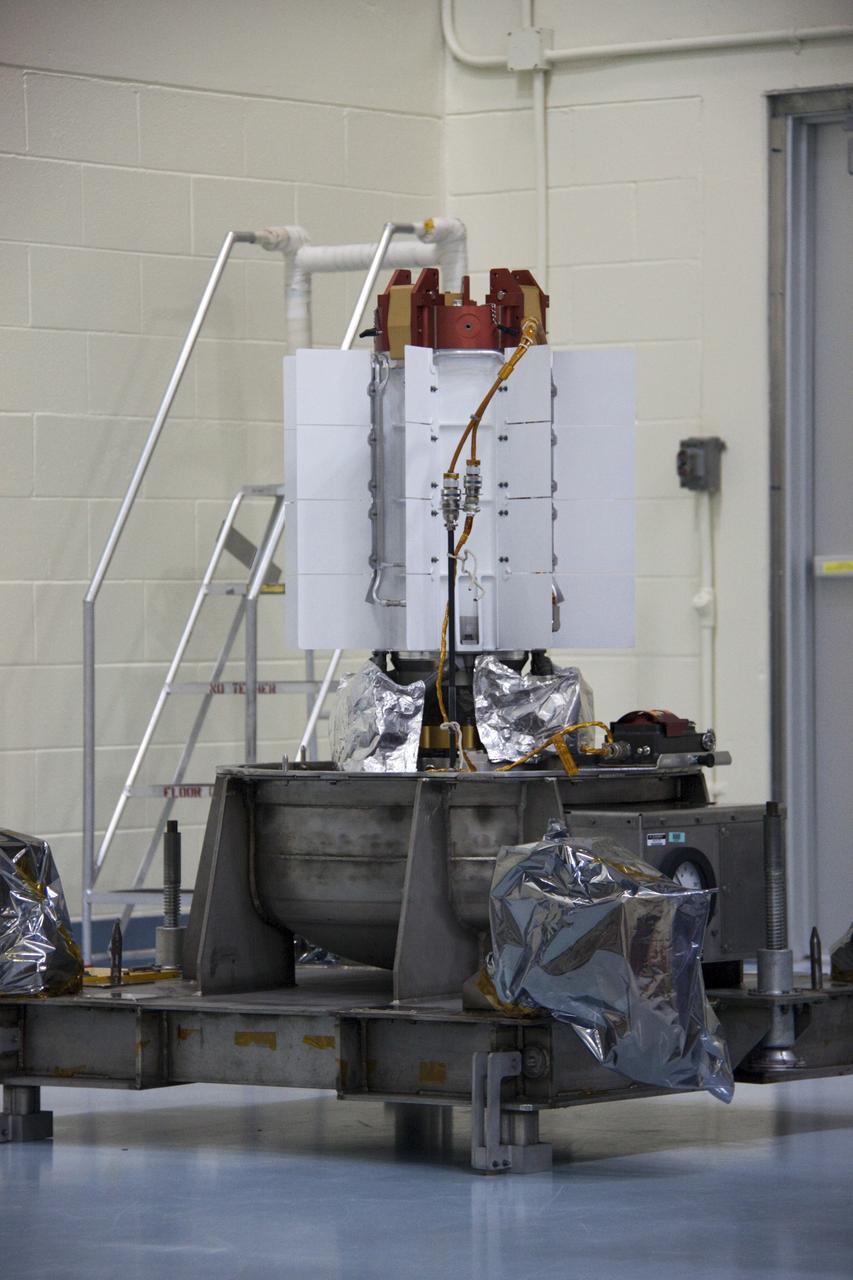

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is uncovered in the high bay of the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MMRTG was returned to the RTGF following a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
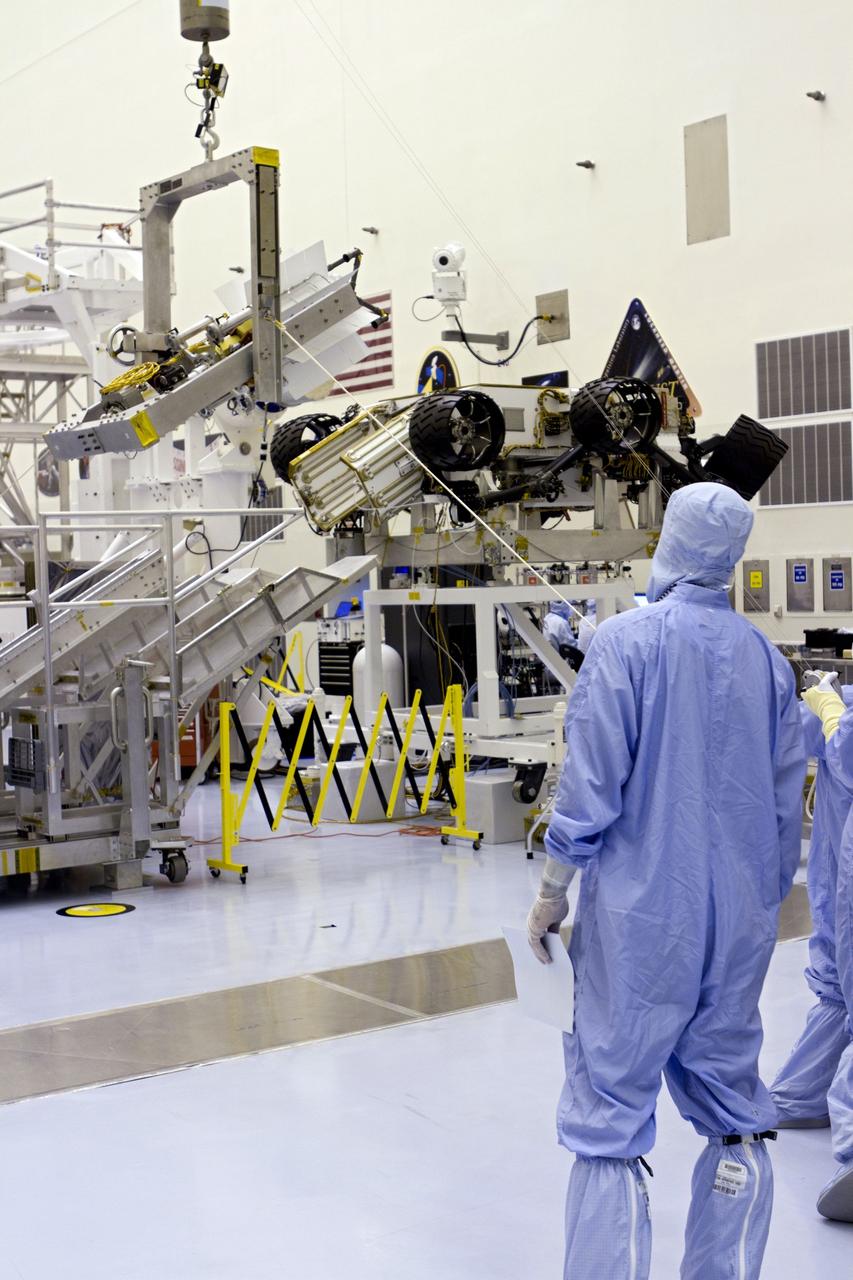

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory guide the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission on the turning fixture toward the MMRTG integration cart. The cart will be used to install the MMRTG on the Curiosity rover for a fit check. The rover is on an elevated work stand, at right. The MMRTG will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission from its support base, at left, toward the MMRTG integration cart behind it. The cart will be used to install the MMRTG on the Curiosity rover for a fit check. The rover appears above the heads of the spacecraft technicians, at right. The MMRTG will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During a tour of the Radiological Control Center (RADCC) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the media listen as Ryan Bechtel of the U.S. Department of Energy explains safety equipment and procedures for the upcoming launch of the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The MSL spacecraft includes a multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) that will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
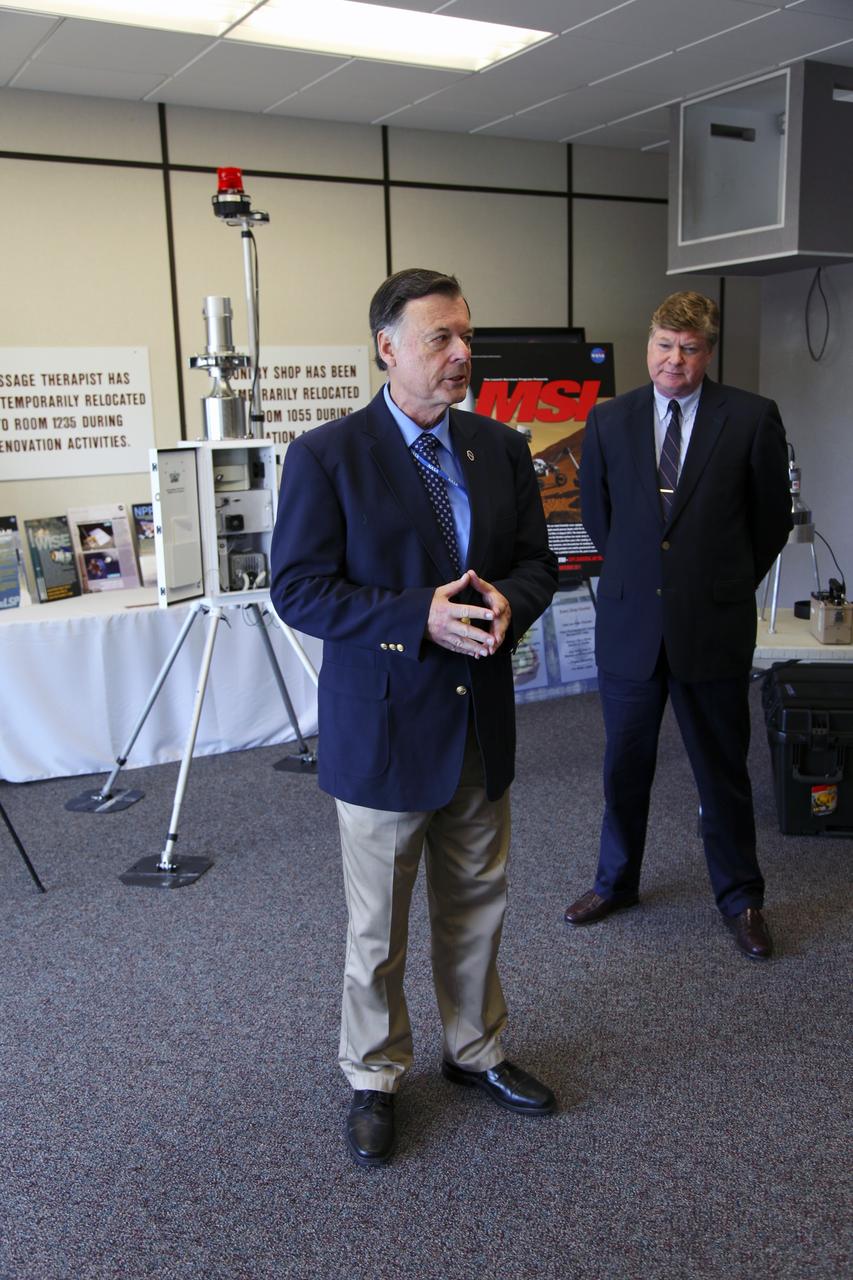

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Randy Scott, director of Kennedy Space Center's Radiological Control Center (RADCC), speaks to media during a tour regarding safety equipment and procedures for the upcoming launch of the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. Behind him is Steve Homann, senior advisor for the Department of Energy. The MSL spacecraft includes a multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) that will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
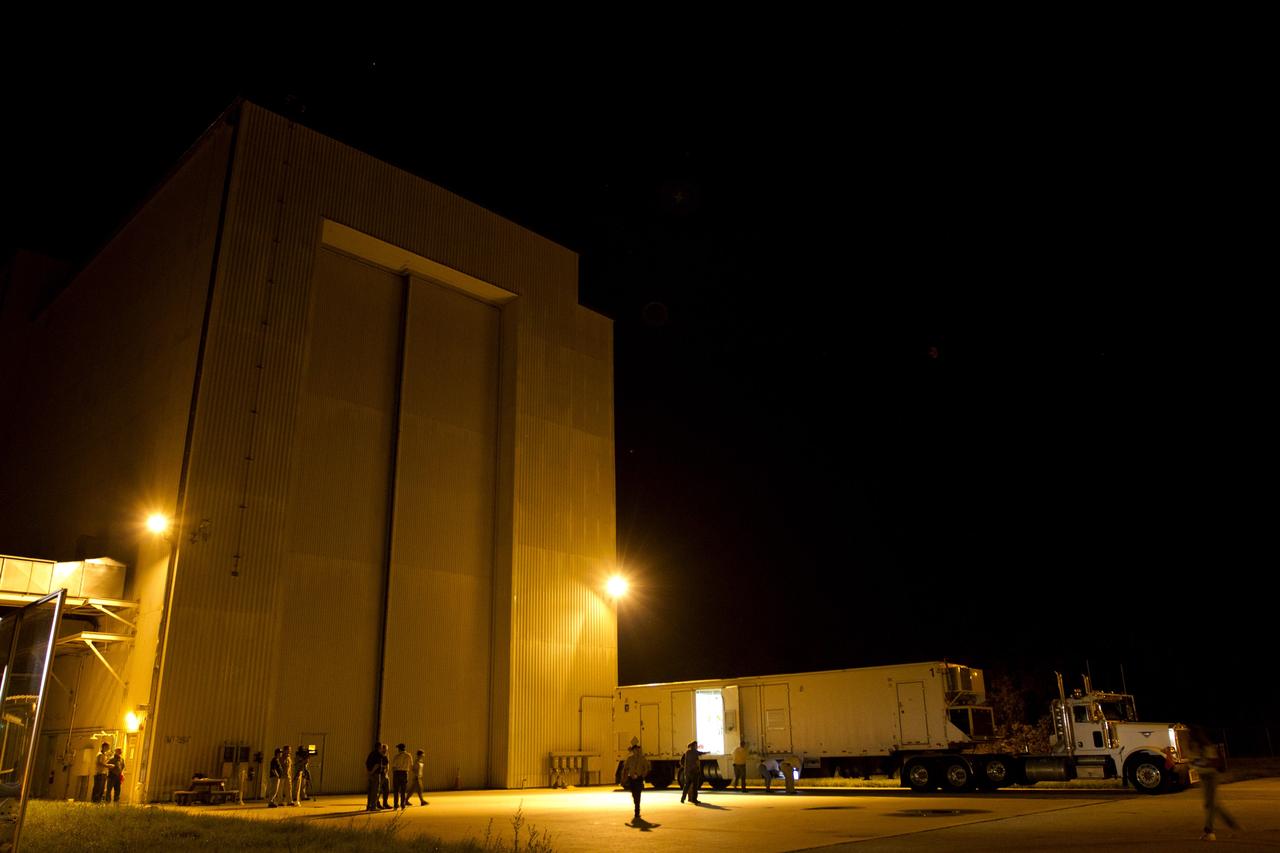

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) trailer backs toward the airlock doors of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MMRTG for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is being transferred into the PHSF, where it will be installed on the MSL rover, Curiosity, for a fit check. The MMRTG will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers use a forklift to offload the shipping cask enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission from the MMRTG trailer that delivered it to the RTG storage facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

Perseverance's Radar Imager for Mars' Subsurface Experiment (RIMFAX) uses radar waves to probe the ground, revealing the unexplored world that lies beneath the Martian surface. Highlighted in blue in this visualization from the interactive tool Learn About Perseverance, the instrument's antenna is externally mounted underneath the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG — the rover's nuclear battery) on the back of the Perseverance. The first ground-penetrating radar set on the surface of Mars, RIMFAX can provide a highly detailed view of subsurface structures down to at least 30 feet (10 meters) underground. In doing so, the instrument will reveal hidden layers of geology and help find clues to past environments on Mars, especially those with conditions necessary for supporting life. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24049

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Outside the RTG storage facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a plexiglass shield has been installed on the forklift enlisted to move the protective mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The shield minimizes the amount of debris dispersed by the wheels of the forklift that can contact the gorilla cage. The cage protects the MMRTG and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The MMRTG is being moved to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) where it temporarily will be installed on the MSL rover, Curiosity, for a fit check but will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
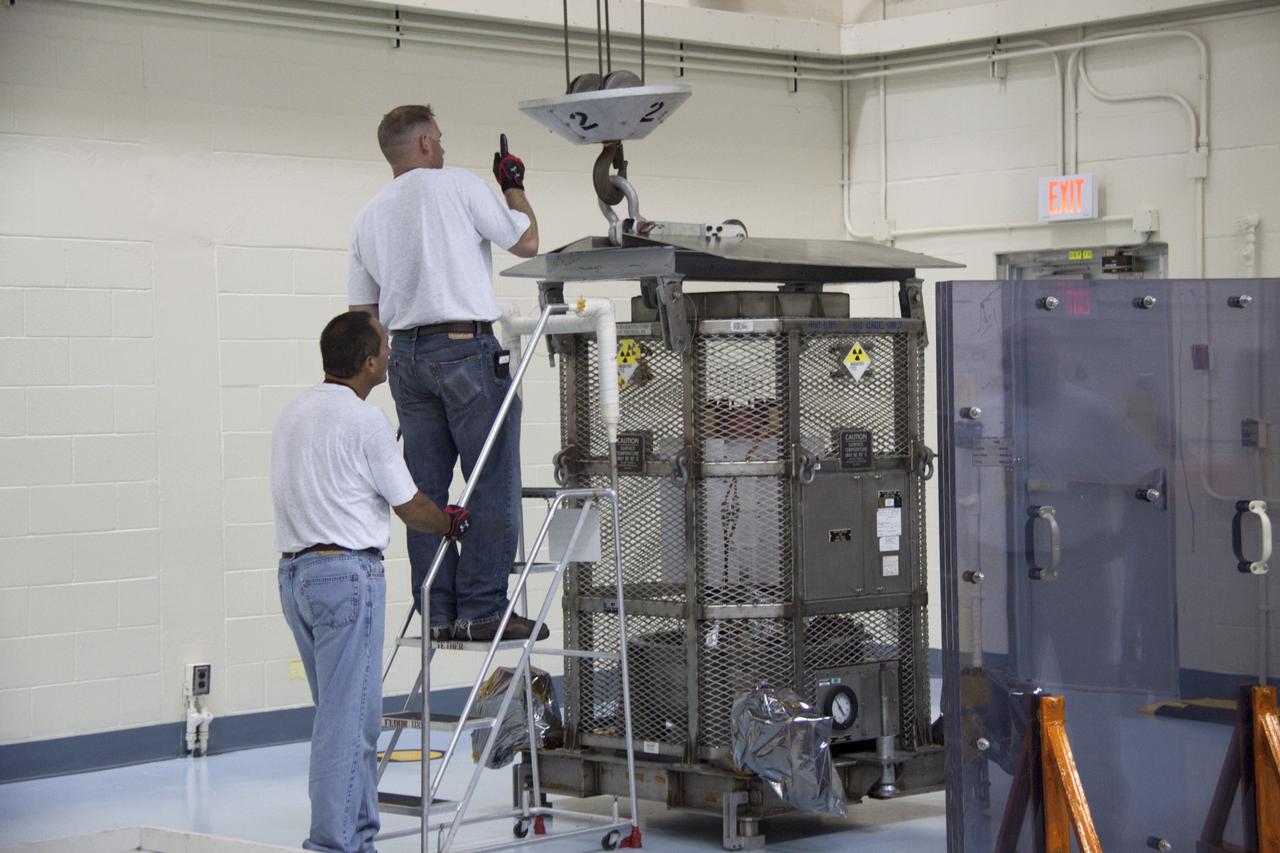

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Department of Energy workers attach a crane to the mesh container enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The container, known as the "gorilla cage," protects it during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The cage is being removed from around the MMRTG following it return to the RTGF from a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
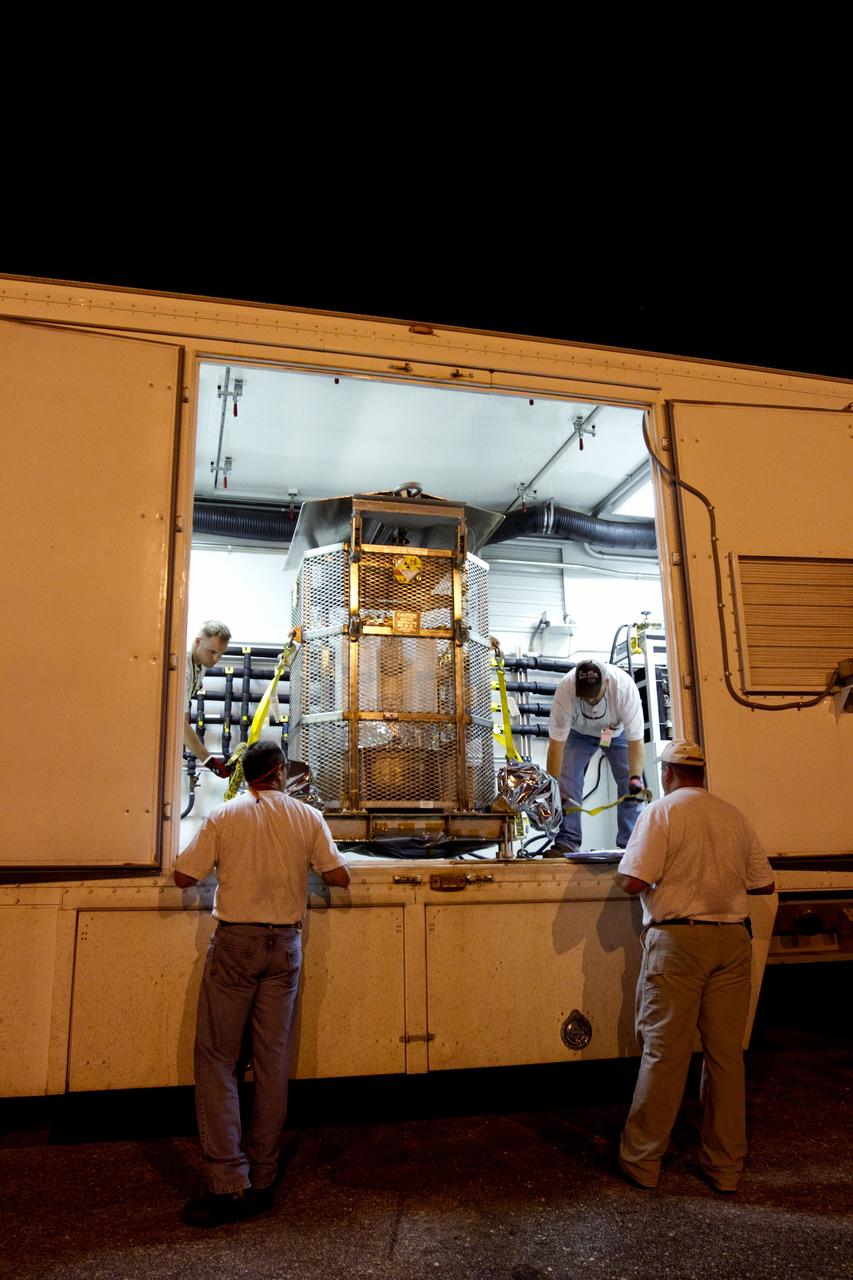

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Outside the RTG storage facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, enclosed in the protective mesh container known as the "gorilla cage," is strapped down inside the MMRTG trailer for transport to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The cage protects the MMRTG and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. In the PHSF, the MMRTG temporarily will be installed on the MSL rover, Curiosity, for a fit check but will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
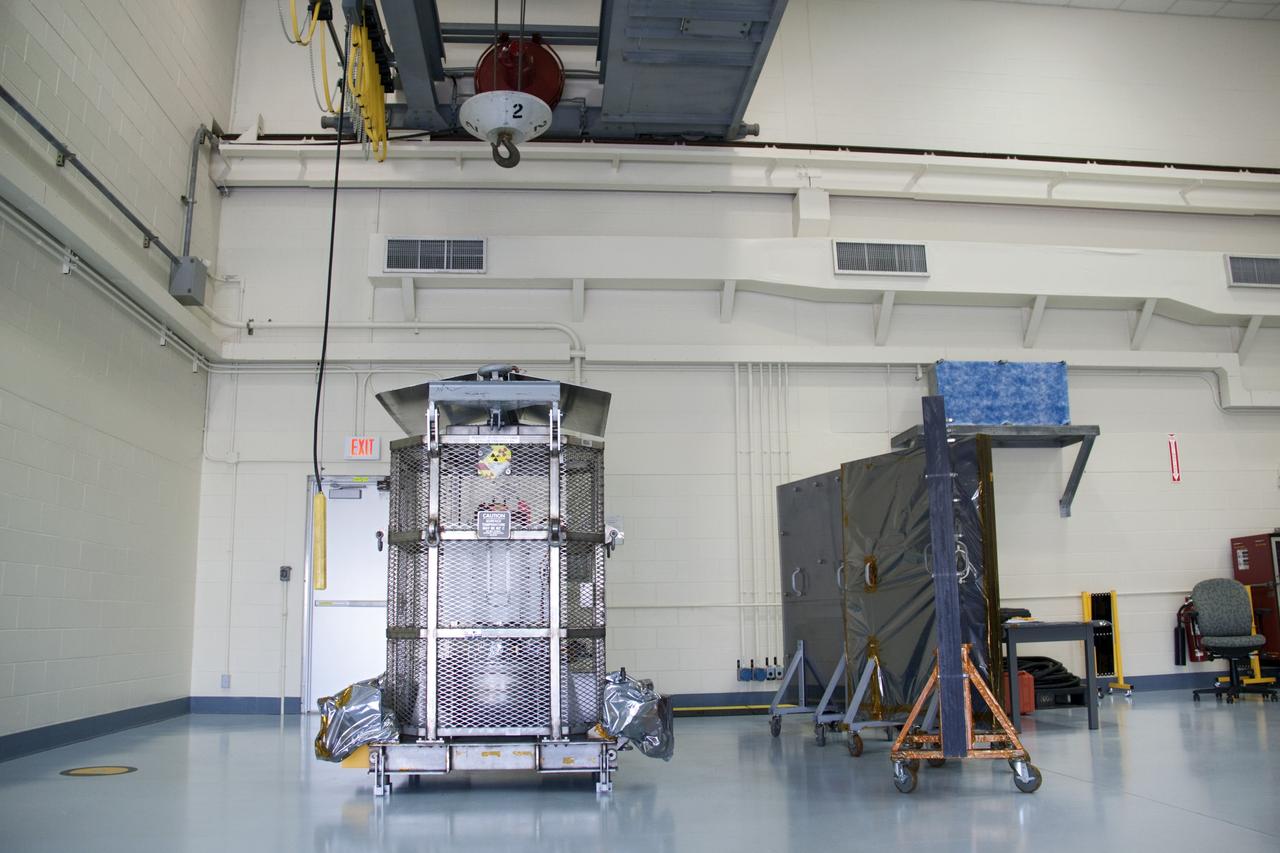

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A crane is positioned over the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission in the high bay of the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Preparations are under way to lift the mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," from the support base on which the MMRTG is resting. The cage protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The MMRTG is returning to the RTGF following a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
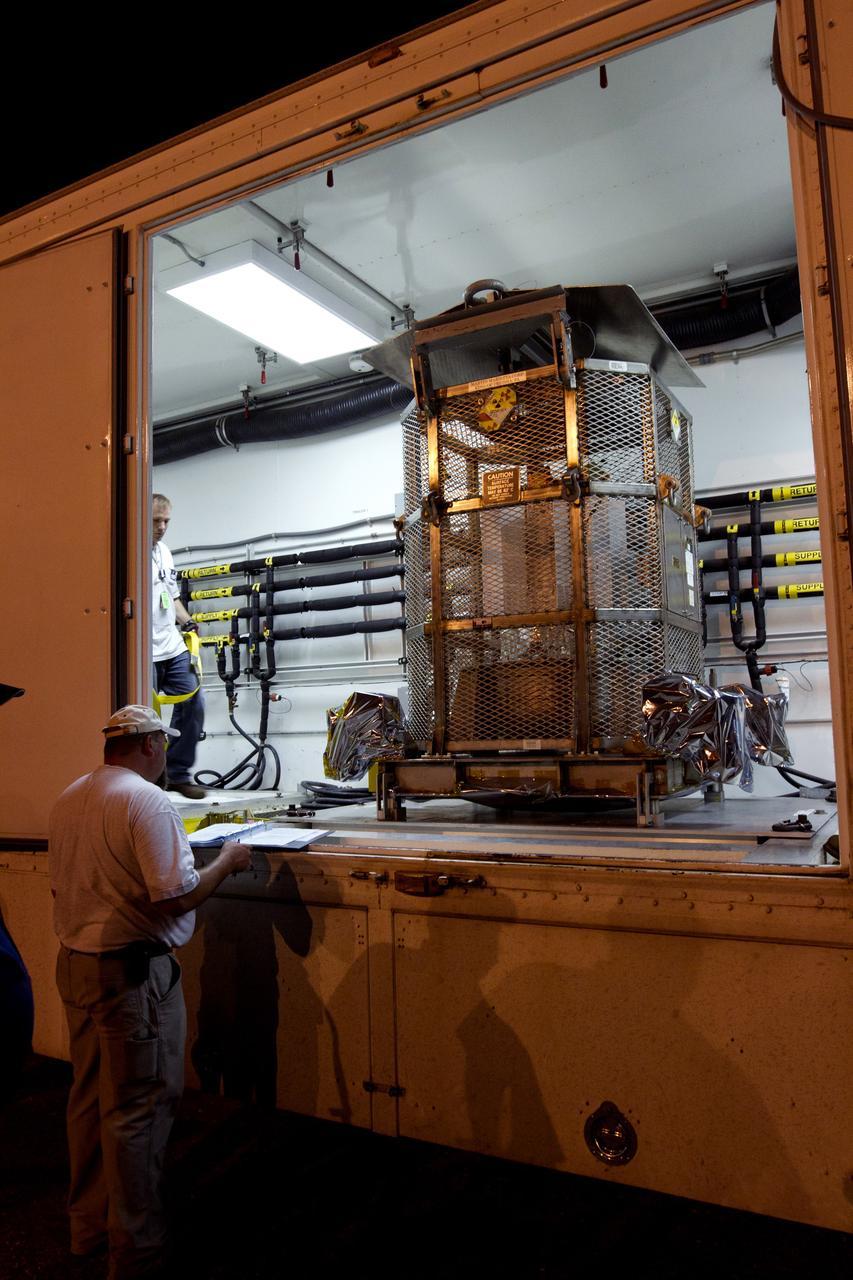

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Outside the RTG storage facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission, enclosed in the protective mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," is positioned inside the MMRTG trailer that will transport it to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The cage protects the MMRTG and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. In the PHSF, the MMRTG temporarily will be installed on the MSL rover, Curiosity, for a fit check but will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
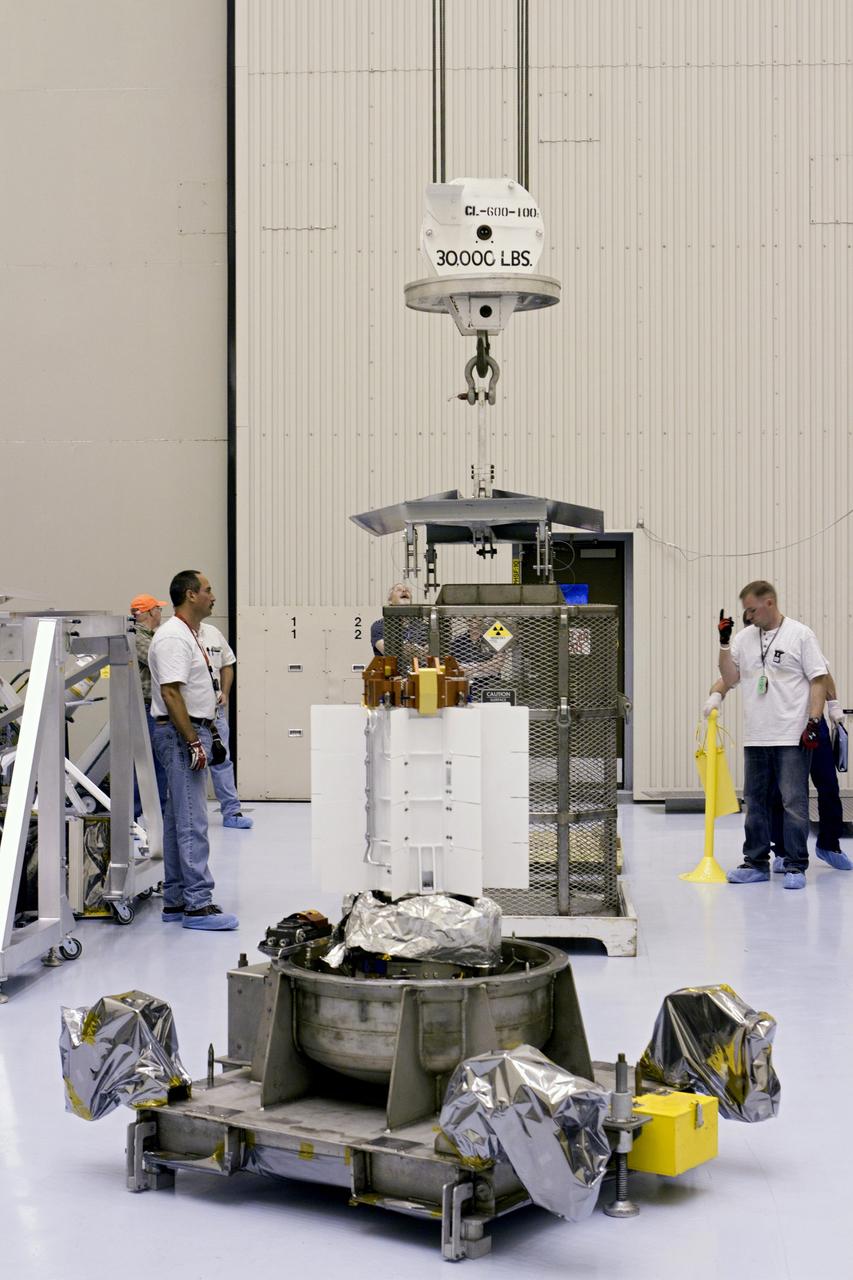

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the protective mesh container enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is lowered to the floor of the airlock beside the MMRTG. The container, known as the "gorilla cage," protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. Next, the airlock will be transitioned into a clean room by purging the air of any particles. In the PHSF, the MMRTG temporarily will be installed on the MSL rover, Curiosity, for a fit check but will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
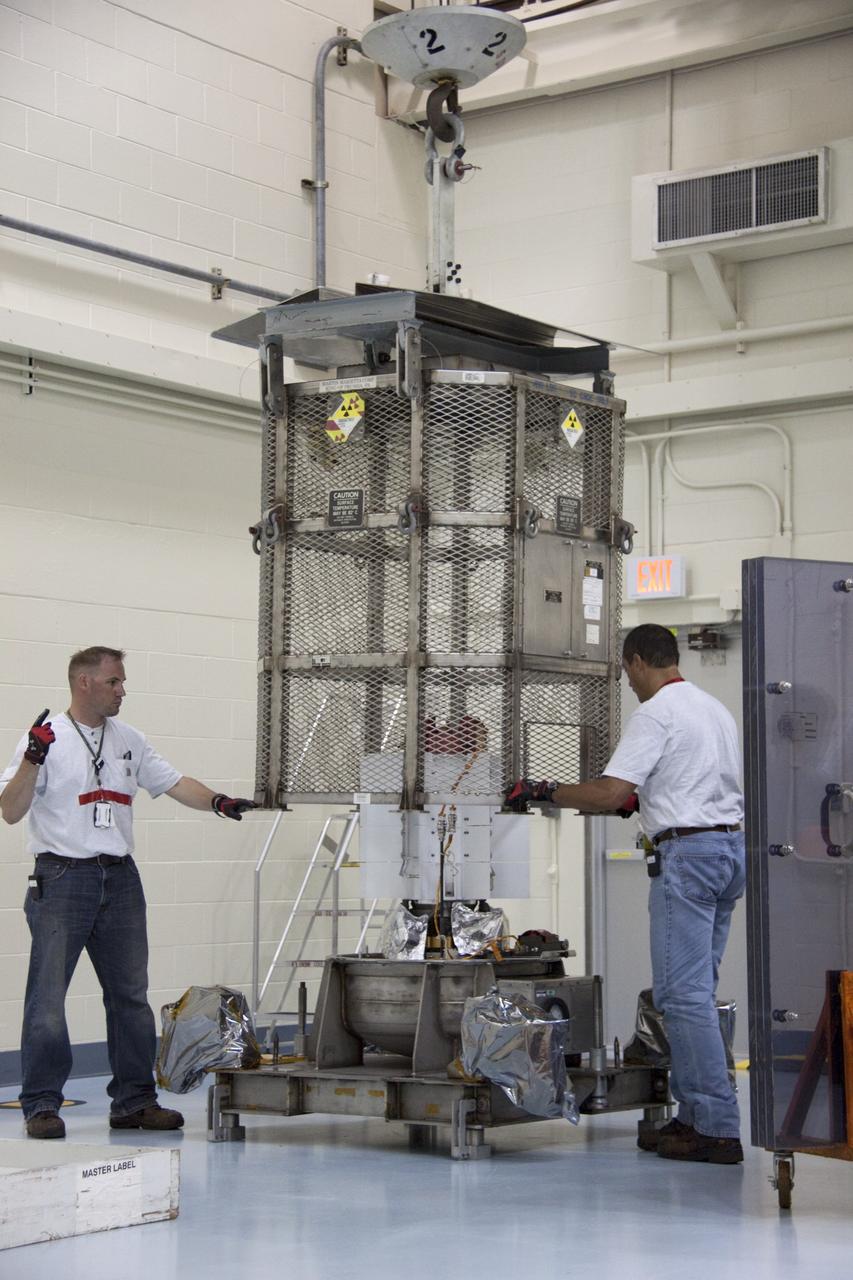

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Department of Energy workers guide the mesh container enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission as it is lifted by a crane. The container, known as the "gorilla cage," protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The cage is being removed from around the MMRTG following it return to the RTGF from a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
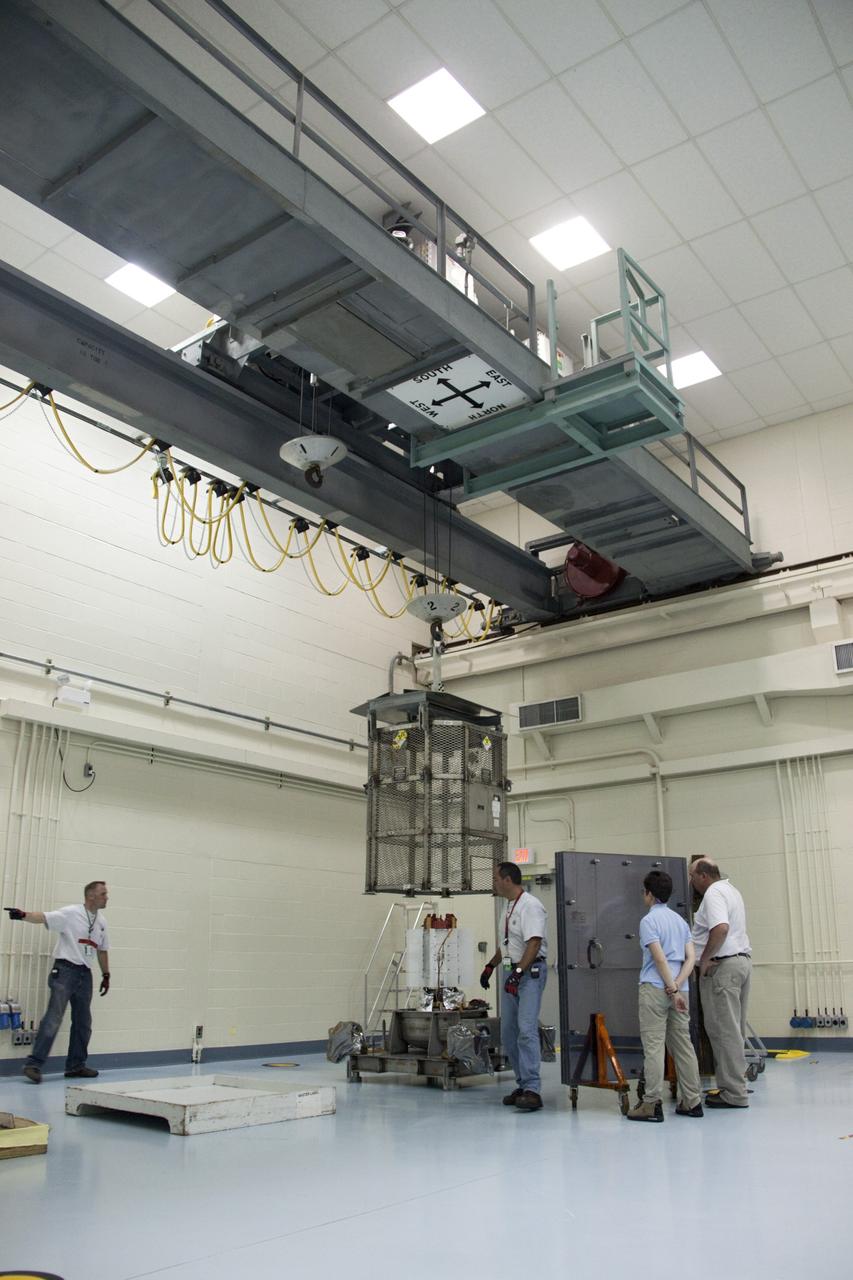

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the mesh container enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is lifted from around the MMRTG. The container, known as the "gorilla cage," protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The cage is being removed following the return of the MMRTG to the RTGF from a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The workers at right are observing the operation from behind a mobile plexiglass radiation shield to minimize their radiation exposure. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
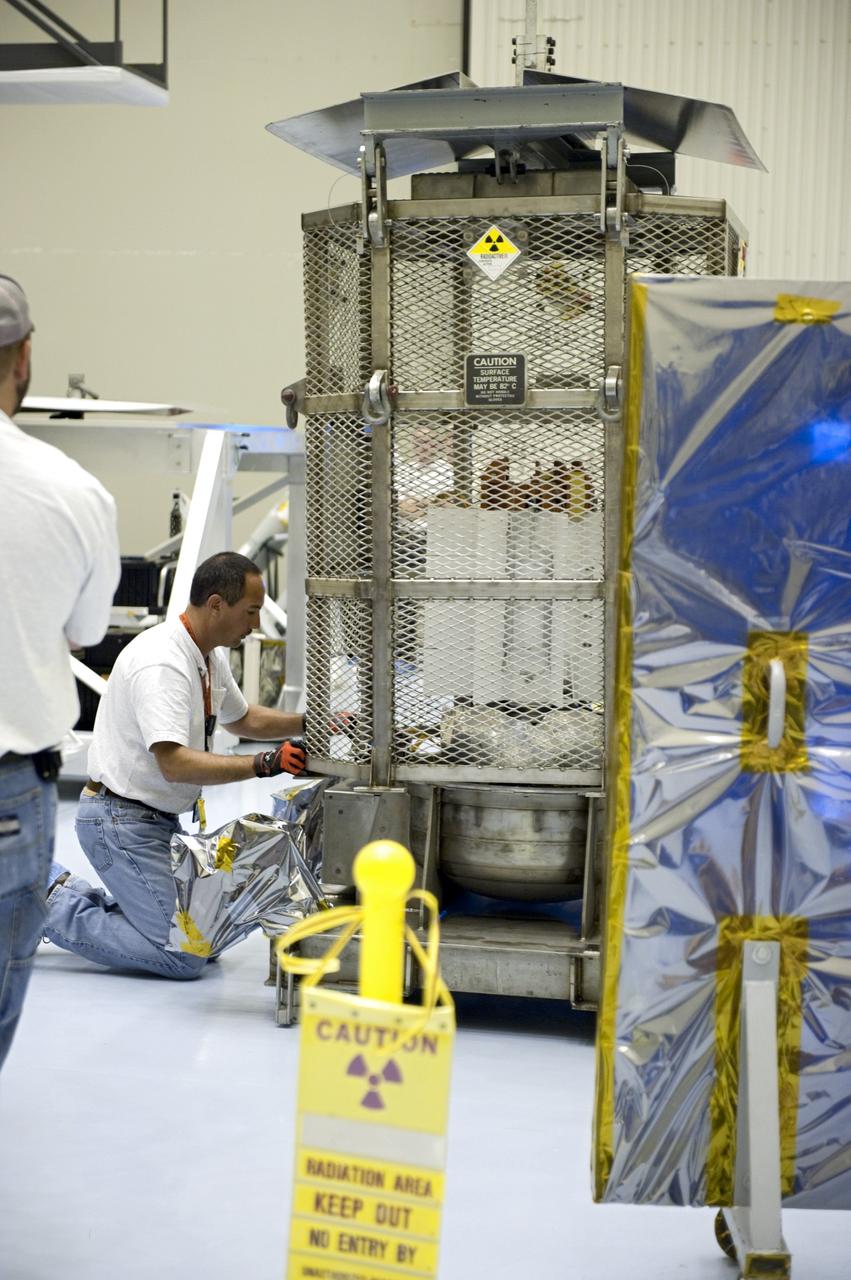

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Department of Energy employee positions the mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," on the support base of the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The mobile plexiglass radiation shields, in the foreground at right, helps minimize the employees' radiation exposure. The cage protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. Transport of the MMRTG to the RTG storage facility follows the completion of the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
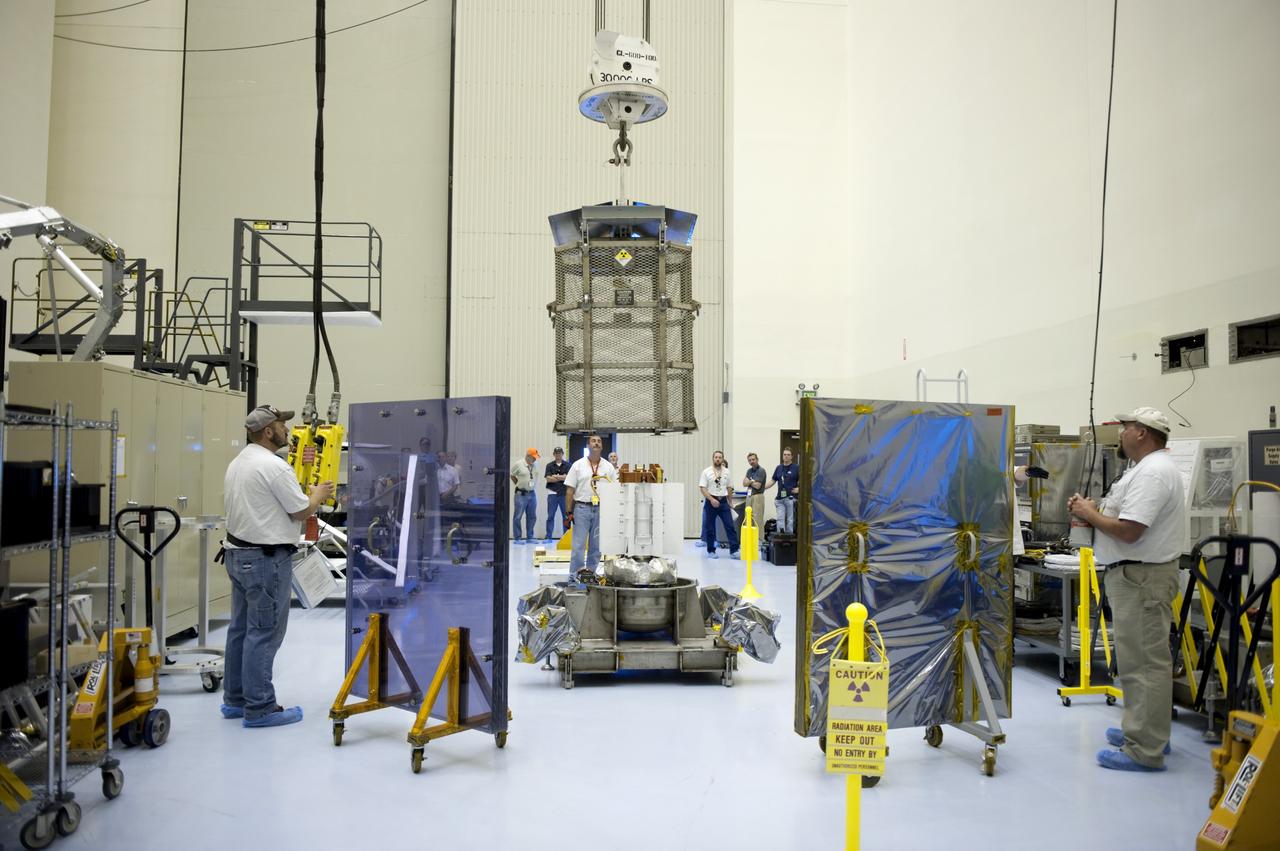

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Department of Energy employees lower the mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," toward the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The employees are standing behind mobile plexiglass radiation shields to help minimize the employees' radiation exposure. The cage protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. Transport of the MMRTG to the RTG storage facility follows the completion of the MMRTG fit check on the Curiosity rover. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
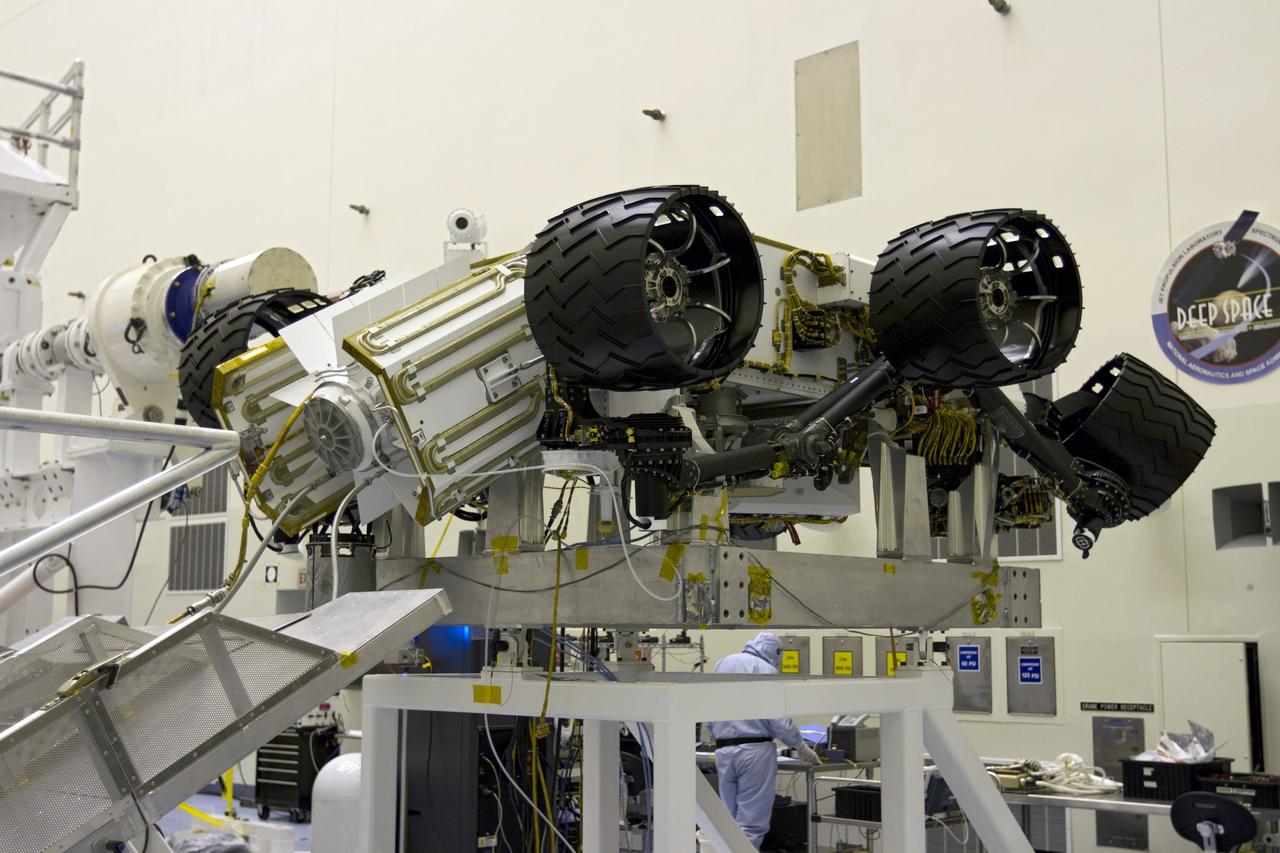

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is installed onto the aft of the Curiosity rover for a fit check. In view are the MMRTG's cooling fins which function like the radiator on a car and will reflect any excess heat generated by the MMRTG to prevent interference with the rover's electronics. Next, the MMRTG will be removed and later installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
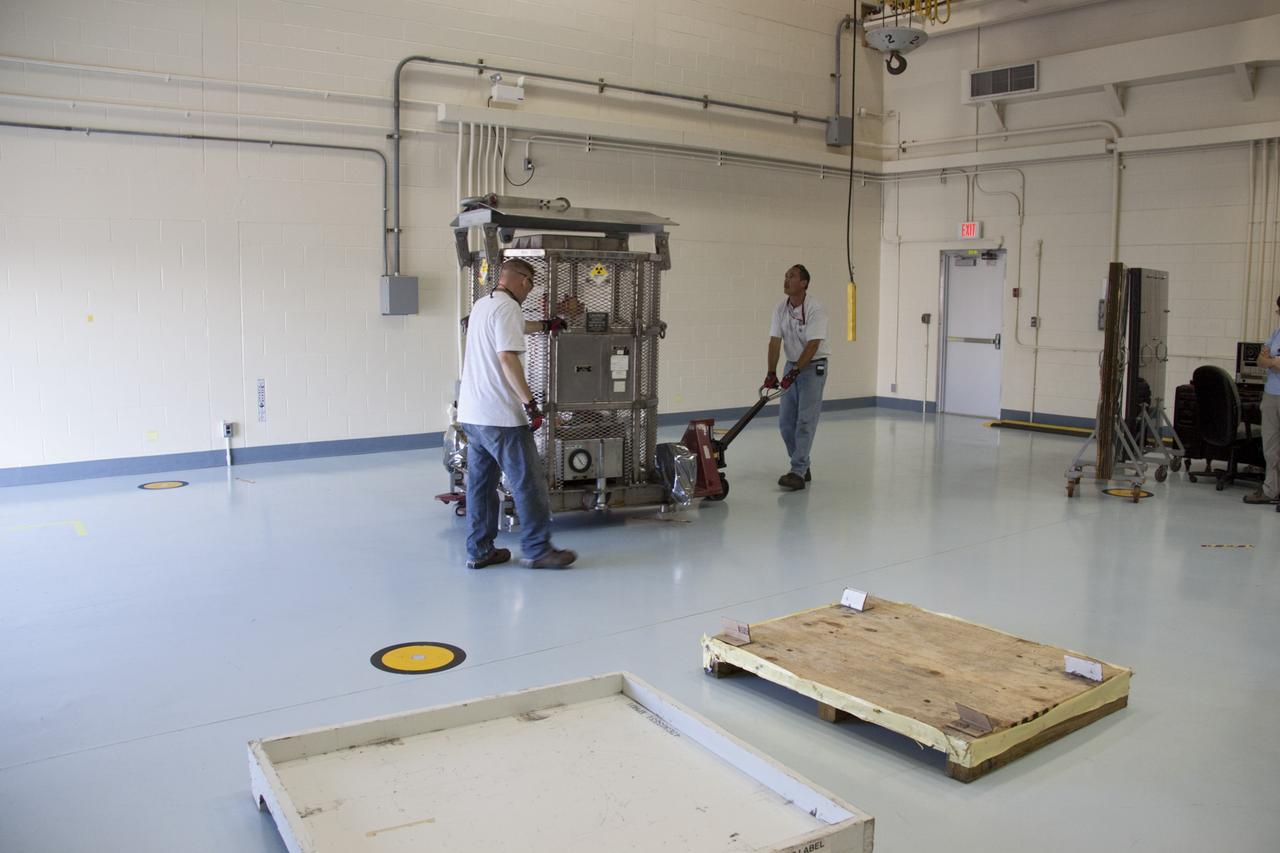

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Department of Energy workers park the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission in the high bay of the RTG storage facility (RTGF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The MMRTG is enclosed in a mesh container, known as the "gorilla cage," which protects it during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. The MMRTG is returning to the RTGF following a fit check on MSL's Curiosity rover in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. MSL's components include a compact car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
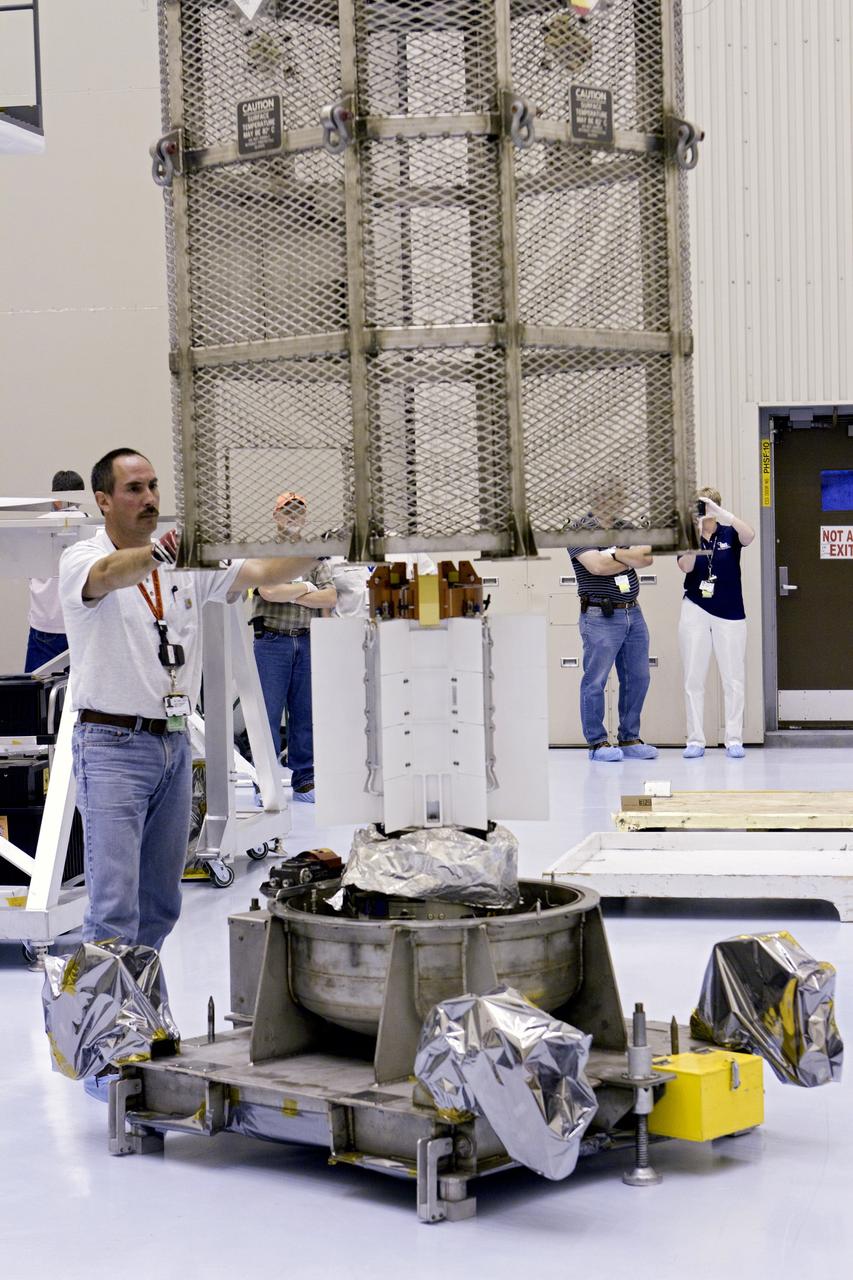

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the airlock of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the protective mesh container enclosing the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission is lifted from around the MMRTG. The container, known as the "gorilla cage," protects the MMRTG during transport and allows any excess heat generated to dissipate into the air. In the PHSF, the MMRTG temporarily will be installed on the MSL rover, Curiosity, for a fit check but will be installed on the rover for launch at the pad. The MMRTG will generate the power needed for the mission from the natural decay of plutonium-238, a non-weapons-grade form of the radioisotope. Heat given off by this natural decay will provide constant power through the day and night during all seasons. Curiosity, MSL's car-sized rover, has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Waste heat from the MMRTG will be circulated throughout the rover system to keep instruments, computers, mechanical devices and communications systems within their operating temperature ranges. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is planned for Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston