
NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center marked its 60th anniversary as the aerospace agency's lead center for atmospheric flight research and operations in 2006. In connection with that milestone, hundreds of the center's staff and retirees gathered in nearby Lancaster, Calif., in November 2006 to reflect on the center's challenges and celebrate its accomplishments over its six decades of advancing the state-of-the-art in aerospace technology. The center had its beginning in 1946 when a few engineers from the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics' Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory were detailed to Muroc Army Air Base (now Edwards Air Force Base) in Southern California's high desert to support the joint Army Air Force / NACA / Bell Aircraft XS-1 research airplane program. Since that inauspicious beginning, the center has been at the forefront of many of the advances in aerospace technology by validating advanced concepts through actual in-flight research and testing. Dryden is uniquely situated to take advantage of the excellent year-round flying weather, remote area, and visibility to test some of the nation�s most exciting aerospace vehicles. Today, NASA Dryden is NASA's premier flight research and test organization, continuing to push the envelope in the validation of high-risk aerospace technology and space exploration concepts, and in conducting airborne environmental and space science missions in the 21st century.
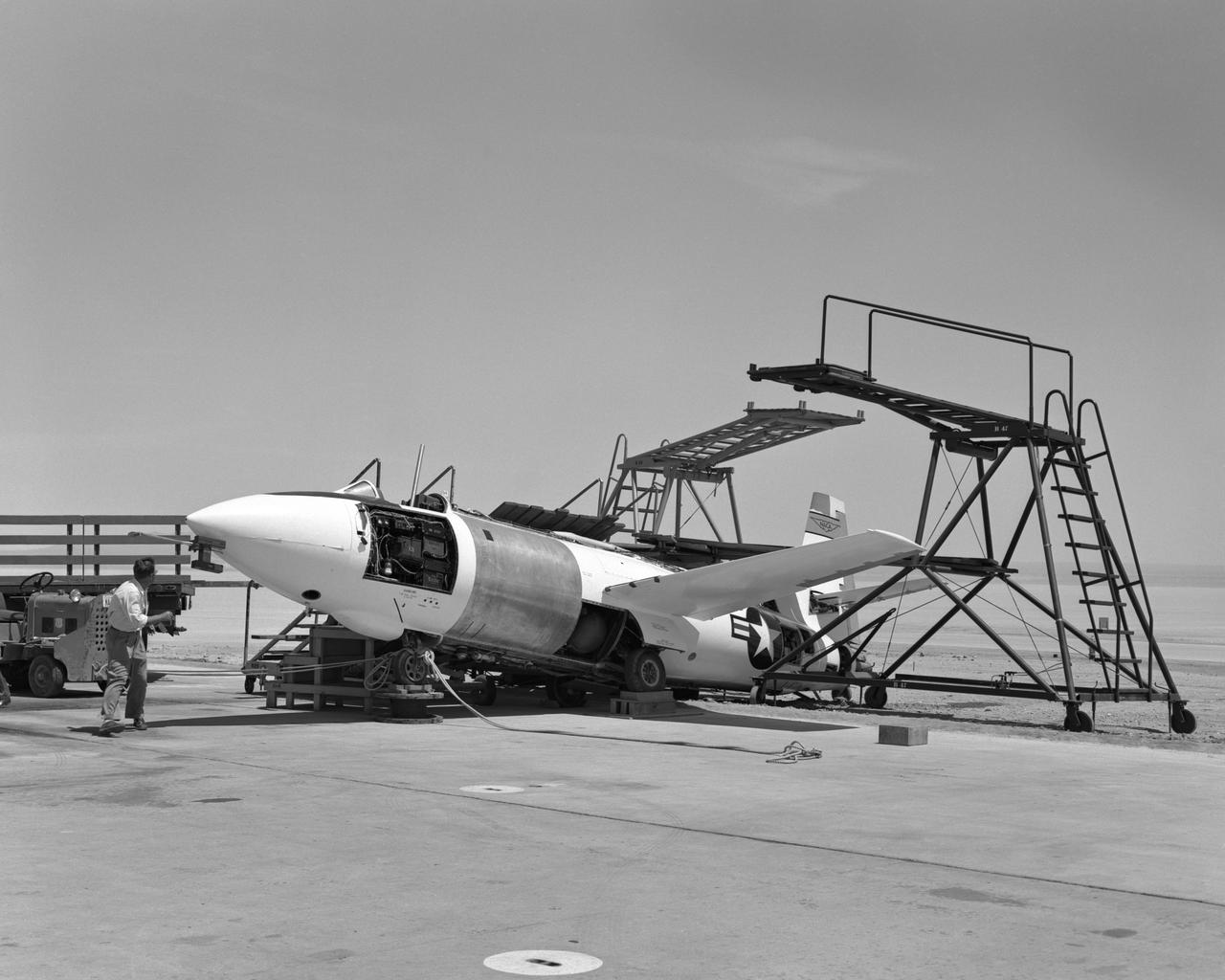

Bell X-1A ejection seat test setup
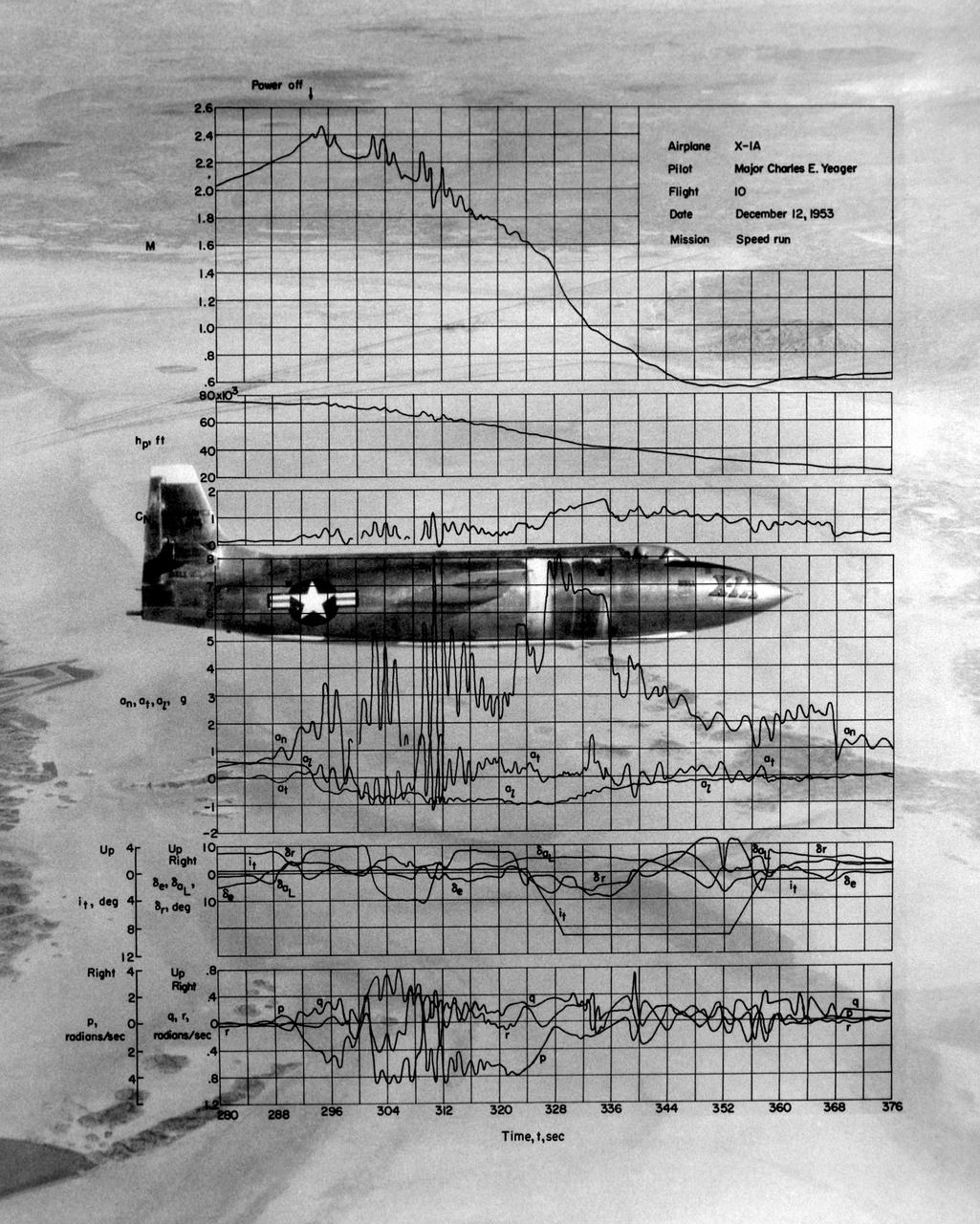
This photo of the X-1A includes graphs of the flight data from Maj. Charles E. Yeager's Mach 2.44 flight on December 12, 1953. (This was only a few days short of the 50th anniversary of the Wright brothers' first powered flight.) After reaching Mach 2.44, then the highest speed ever reached by a piloted aircraft, the X-1A tumbled completely out of control. The motions were so violent that Yeager cracked the plastic canopy with his helmet. He finally recovered from a inverted spin and landed on Rogers Dry Lakebed. Among the data shown are Mach number and altitude (the two top graphs). The speed and altitude changes due to the tumble are visible as jagged lines. The third graph from the bottom shows the G-forces on the airplane. During the tumble, these twice reached 8 Gs or 8 times the normal pull of gravity at sea level. (At these G forces, a 200-pound human would, in effect, weigh 1,600 pounds if a scale were placed under him in the direction of the force vector.) Producing these graphs was a slow, difficult process. The raw data from on-board instrumentation recorded on oscillograph film. Human computers then reduced the data and recorded it on data sheets, correcting for such factors as temperature and instrument errors. They used adding machines or slide rules for their calculations, pocket calculators being 20 years in the future.

The Bell Aircraft Corporation X-1-2 aircraft on the ramp at NACA High Speed Flight Research Station located on the South Base of Muroc Army Air Field in 1947. The X-1-2 flew until October 23, 1951, completing 74 glide and powered flights with nine different pilots. The aircraft has white paint and the NACA tail band. The black Xs are reference markings for tracking purposes. They were widely used on NACA aircraft in the early 1950s.
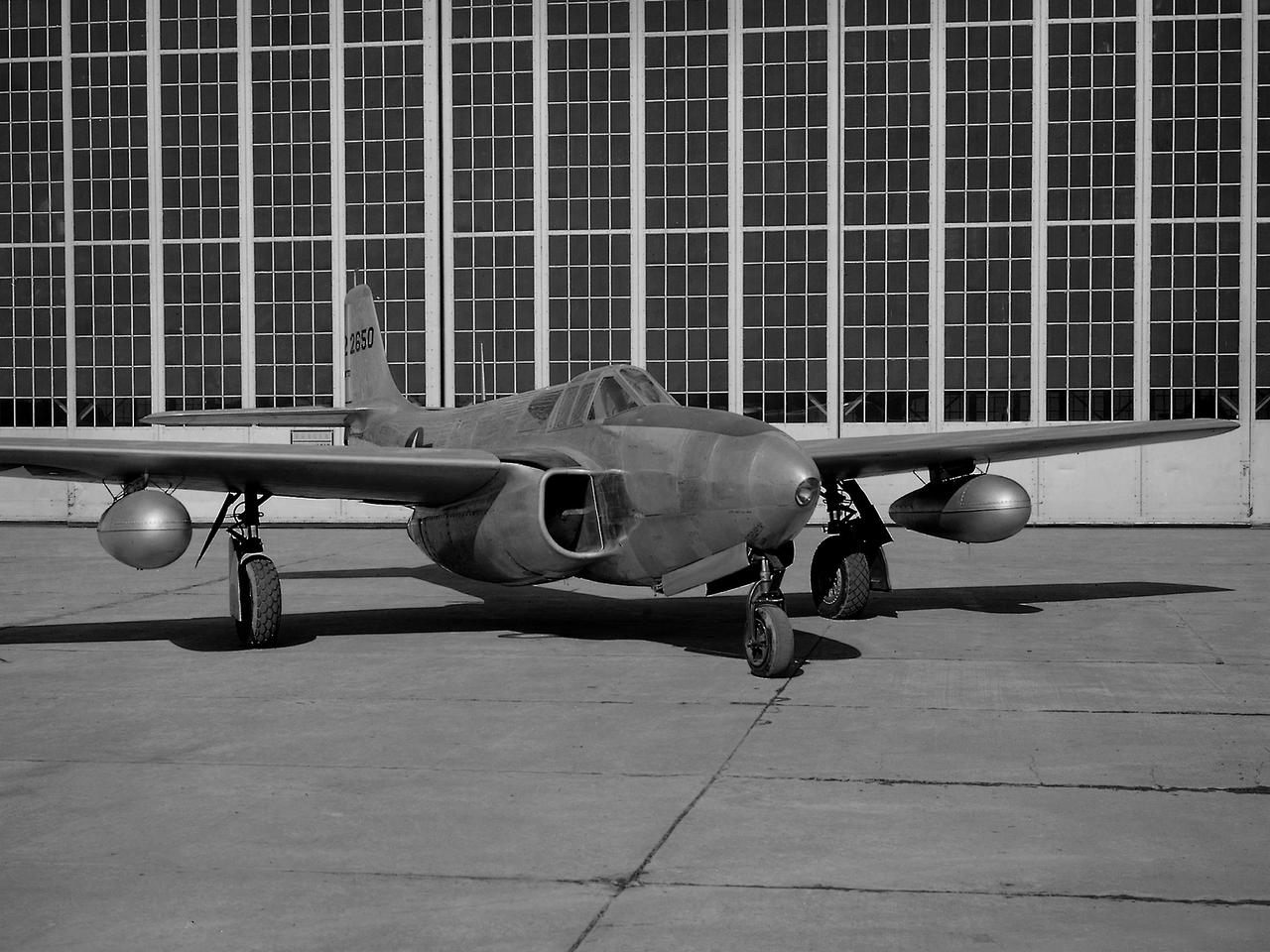

A Bell P-59B Airacomet sits beside the hangar at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. In 1942 the Bell XP-59A Airacomet became the first jet aircraft in the US. The Airacomet incorporated centrifugal turbojet engines that were based on British plans secretly brought to the US in 1941. A Bell test pilot flew the XP-59A for the first time at Muroc Lake, California in October 1942. The General Electric I-16 engines proved to be problematic. In an effort to increase the engine performance, an Airacomet was secretly brought to Cleveland in early 1944 for testing in the Altitude Wind Tunnel. A series of tunnel investigations in February and March resulted in a 25-percent increase in the I-16 engine’s performance. Nonetheless, Bell’s 66 Airacomets never made it into combat. A second, slightly improved Airacomet, a P-59B, was transferred to NACA Lewis just after the war in September 1945. The P-59B was used over the next three years to study general jet thrust performance and thrust augmentation devices such as afterburners and water/alcohol injection. The P-59B flights determined the proper alcohol and water mixture and injection rate to produce a 21-percent increase in thrust. Since the extra boost would be most useful for takeoffs, a series of ground-based tests with the aircraft ensued. It was determined that the runway length for takeoffs could be reduced by as much as 15 percent. The P-59B used for the tests is now on display at the Air Force Museum at Wright Patterson.