
This mosaic from NASA Galileo Probe is of an equatorial hotspot on Jupiter and shows the features of a hazy cloud layer tens of kilometers above Jupiter main visible cloud deck.

NASA Voyager spacecraft was 8.6 million kilometers 5.3 million miles from Neptune when it took this 61 second exposure through the clear filter with the narrow angle camera on August 19, 1989.

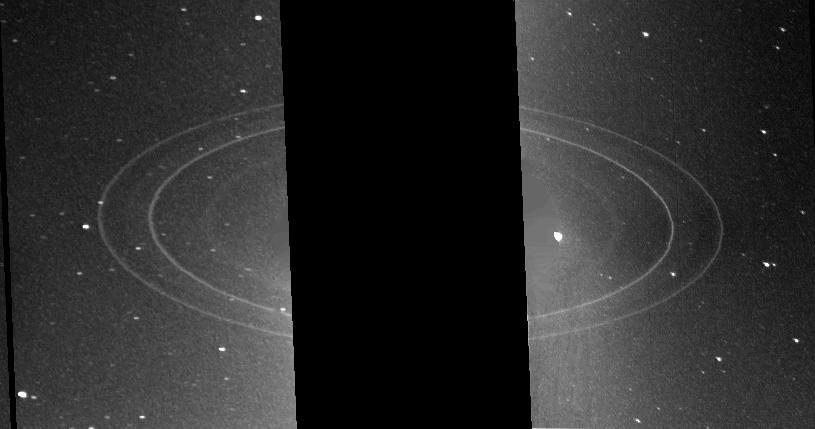
These two 591-second exposures of the rings of Neptune were taken with the clear filter by the NASA Voyager 2 wide-angle camera on Aug. 26, 1989. The two main rings are clearly visible and appear complete over the region imaged.

This wide-angle image from NASA Voyager 2, taken in 1989, was taken through the camera clear filter, and was the first to show Neptune rings in detail.

This 591-second exposure of the rings of Neptune were taken with the clear filter by NASA Voyager 2 wide-angle camera. The two main rings are clearly visible and appear complete over the region imaged.

In this image from NASA's Voyager wide-angle taken on Aug. 23 1989, the two main rings of Neptune can be clearly seen. In the lower part of the frame the originally announced ring arc, consisting of three distinct features, is visible. This feature covers about 35 degrees of longitude and has yet to be radially resolved in Voyager images. From higher resolution images it is known that this region contains much more material than the diffuse belts seen elsewhere in its orbit, which seem to encircle the planet. This is consistent with the fact that ground-based observations of stellar occultations by the rings show them to be very broken and clumpy. The more sensitive wide-angle camera is revealing more widely distributed but fainter material. Each of these rings of material lies just outside of the orbit of a newly discovered moon. One of these moons, 1989N2, may be seen in the upper right corner. The moon is streaked by its orbital motion, whereas the stars in the frame are less smeared. The dark area around the bright moon and star are artifacts of the processing required to bring out the faint rings. This wide-angle image was taken from a range of 2 million kilometers (1.2 million miles), through the clear filter. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00053

N-206 12ft pressure wind tunnel reconstruction, welding and assembly of rings
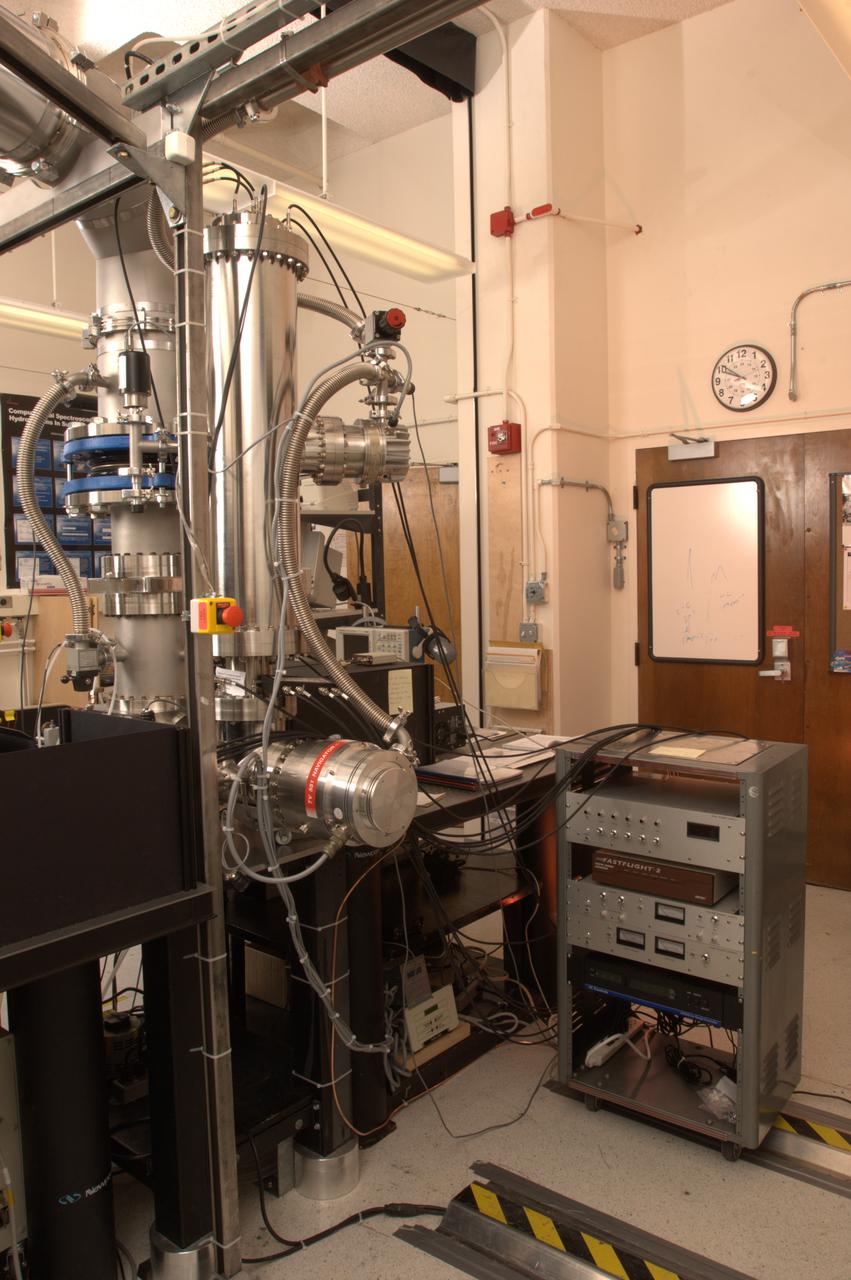

NASA Ames Astrophysics Branch (code-SSA), Pulsed discharge nozzle - Cavity Ring down - Reflection Time of Flight Mass Spectrometer (N-245 rm B-31) (PDN-CRDS-RETOFMS)
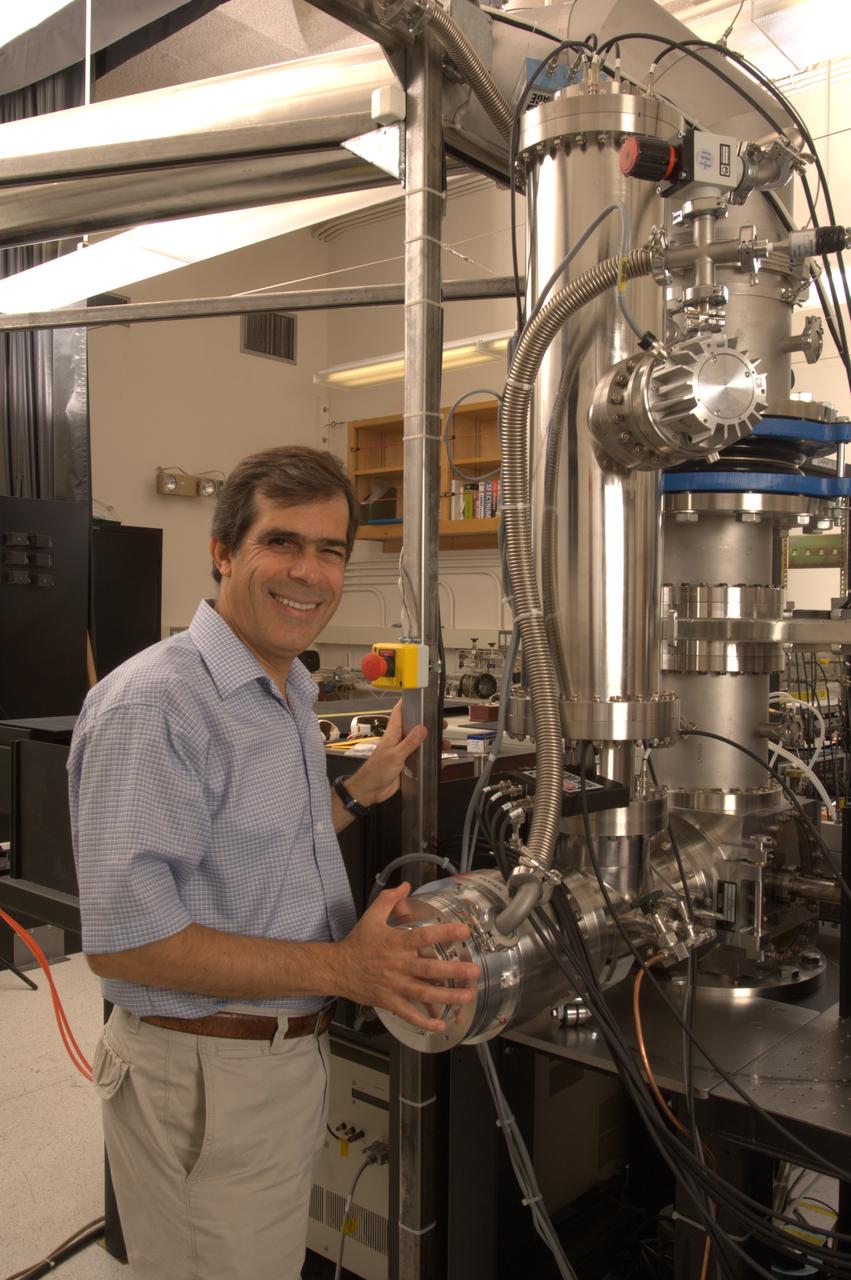

NASA Ames Astrophysics Branch (code-SSA), Pulsed discharge nozzle - Cavity Ring down - Reflection Time of Flight Mass Spectrometer (N-245 rm B-31) (PDN-CRDS-RETOFMS) shown here with Farid Salama
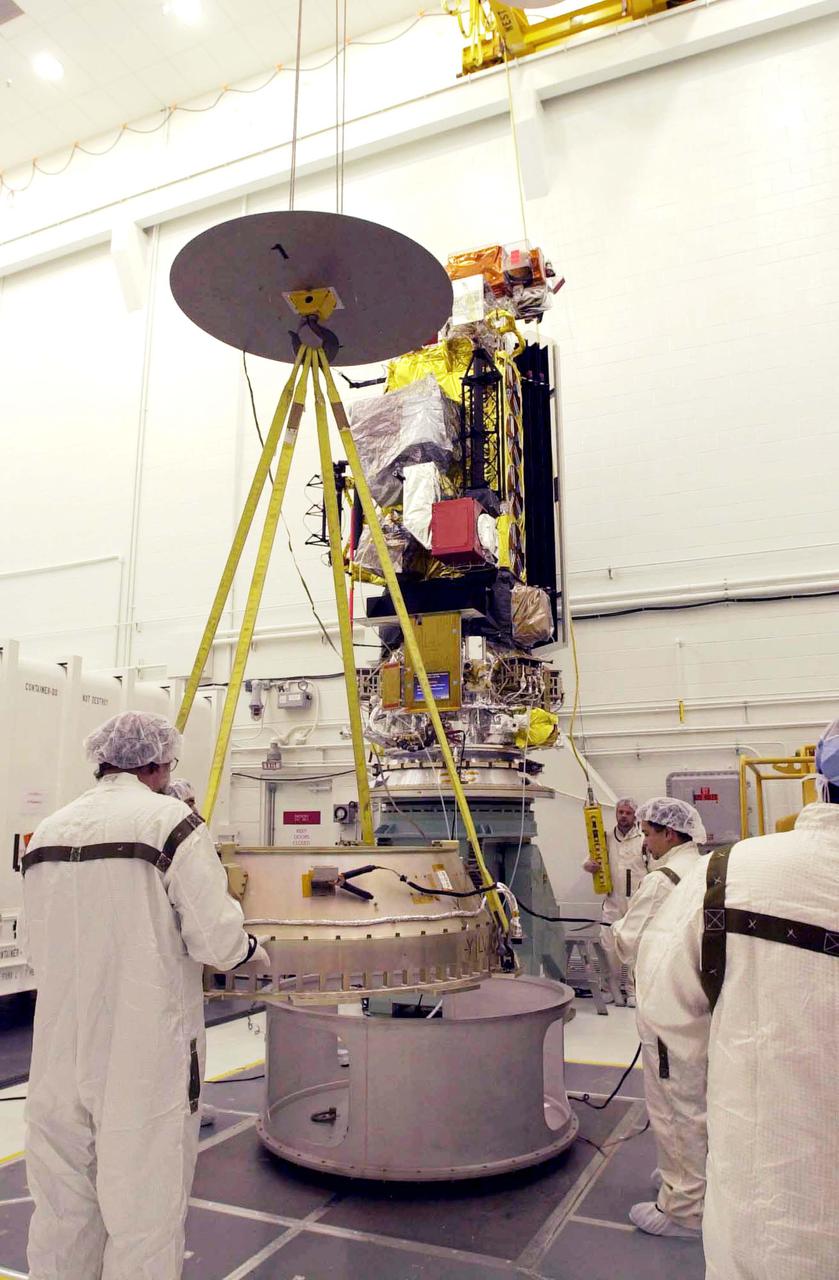

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - Inside the NASA spacecraft processing hangar 1610 located on North Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Lockheed Martin workers maneuver the Boeing Delta II payload attach fitting onto a connecting ring on the floor. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA-N) spacecraft, in the background, will then be mated to the payload attach fitting. Launch of NOAA-N aboard the Boeing Delta II rocket is currently scheduled for May 11, 2005. NOAA-N is the fourth in the series of support dedicated microwave instruments for the generation of temperature, moisture, surface, and hydrological products in cloudy regions where visible and infrared (IR) instruments have decreased capability.
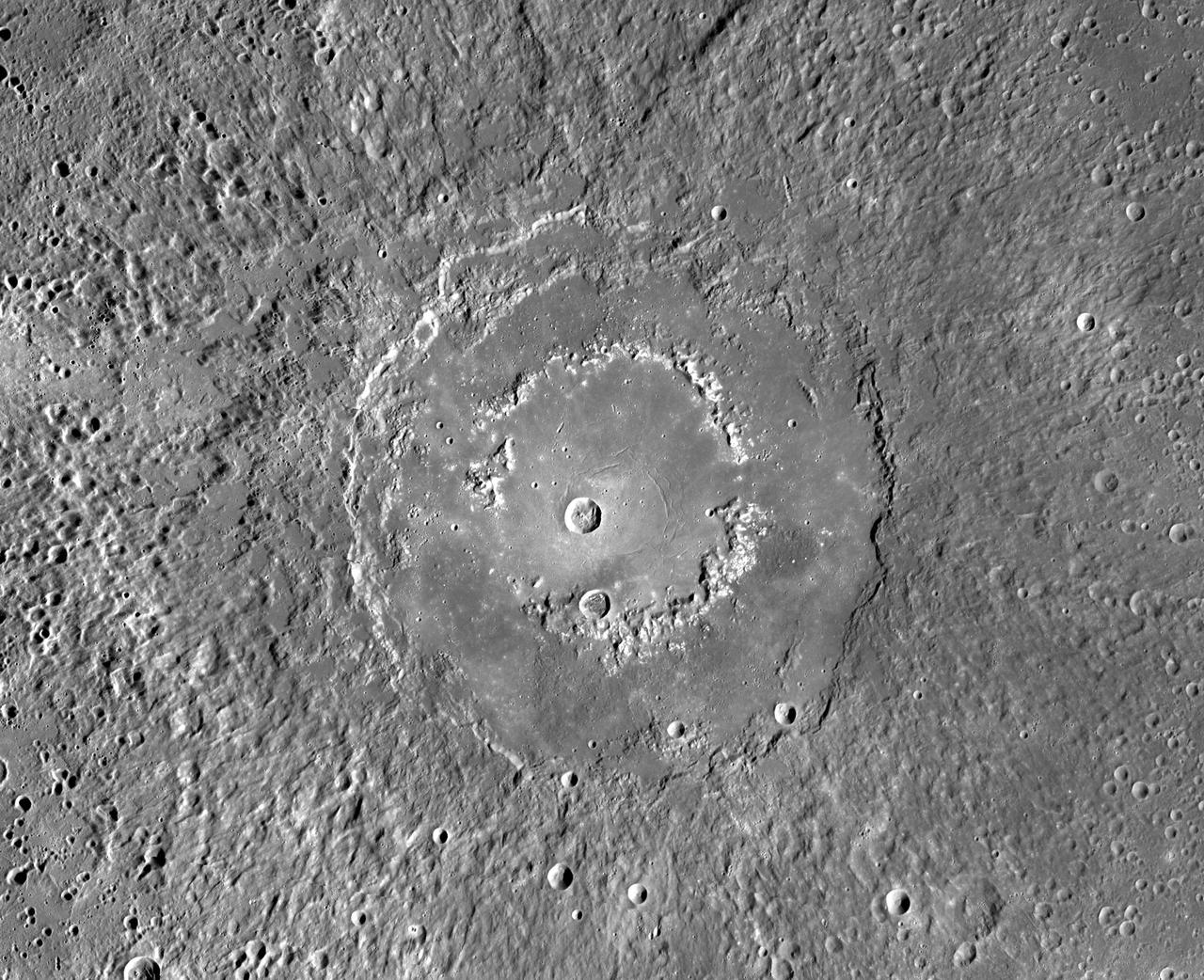
This MDIS mosaic from NASA MESSENGER spacecraft provides a detailed view of the features and structures associated with the peak-ring basin Raditladi. Raditladi, first imaged during MESSENGER's first Mercury flyby and named in April 2008, continues to be an intriguing region of study, with its well-preserved features, relatively young age, exterior impact melt ponds, hollows-covered peak ring, and concentric troughs on its floor. Instrument: Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS) Center Latitude: 27.1° N Center Longitude: 119.2° E Scale: Raditladi has a diameter of 258 kilometers (160 miles) http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19409

S89-39471 (17 July 1989) --- STS-28 Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, Pilot Richard N. Richards, adjusts launch and entry suit (LES) neck ring after donning launch and entry helmet (LEH). Richards prepares for shuttle emergency egress (bailout) procedures in the Johnson Space Center (JSC) Mockup and Integration Laboratory Bldg 9A.
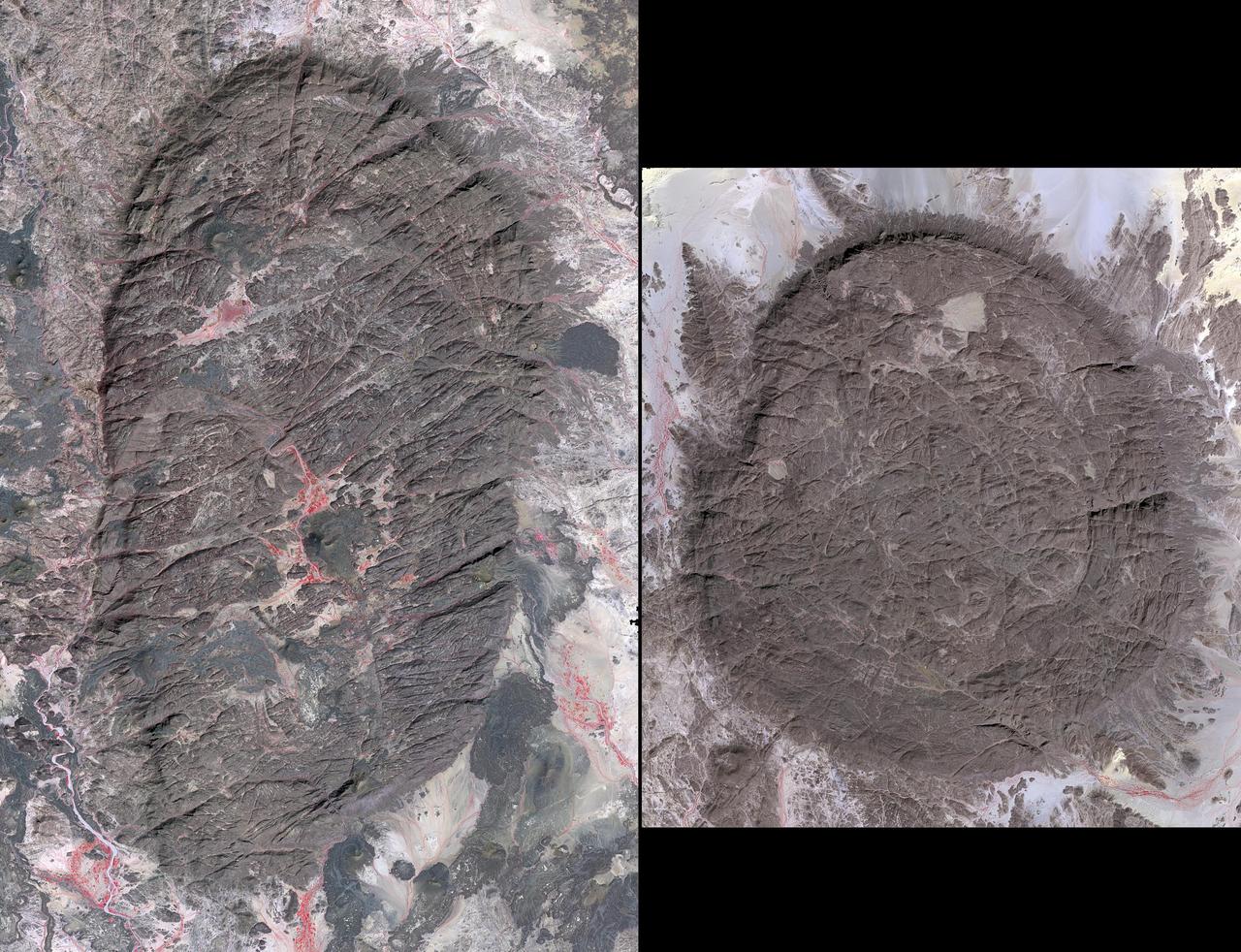

The Air Mountains are located in northern Niger and extend over 84,000 square kilometers within the Sahara Desert. Geologically, the area is notable for its remarkable ring dikes that enclose circular granite massifs. These in turn contain, and are surrounded by, young volcanic features, including cinder cones and lava flows. Two of the massifs are shown here: the oval one includes Mont Idoukal-n-Taghes, Niger's highest point. The montage is made up of images acquired November 5, 2017, covers an area of 45 kilometers north-south, and is located near 18 degrees north, 8.5 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22795
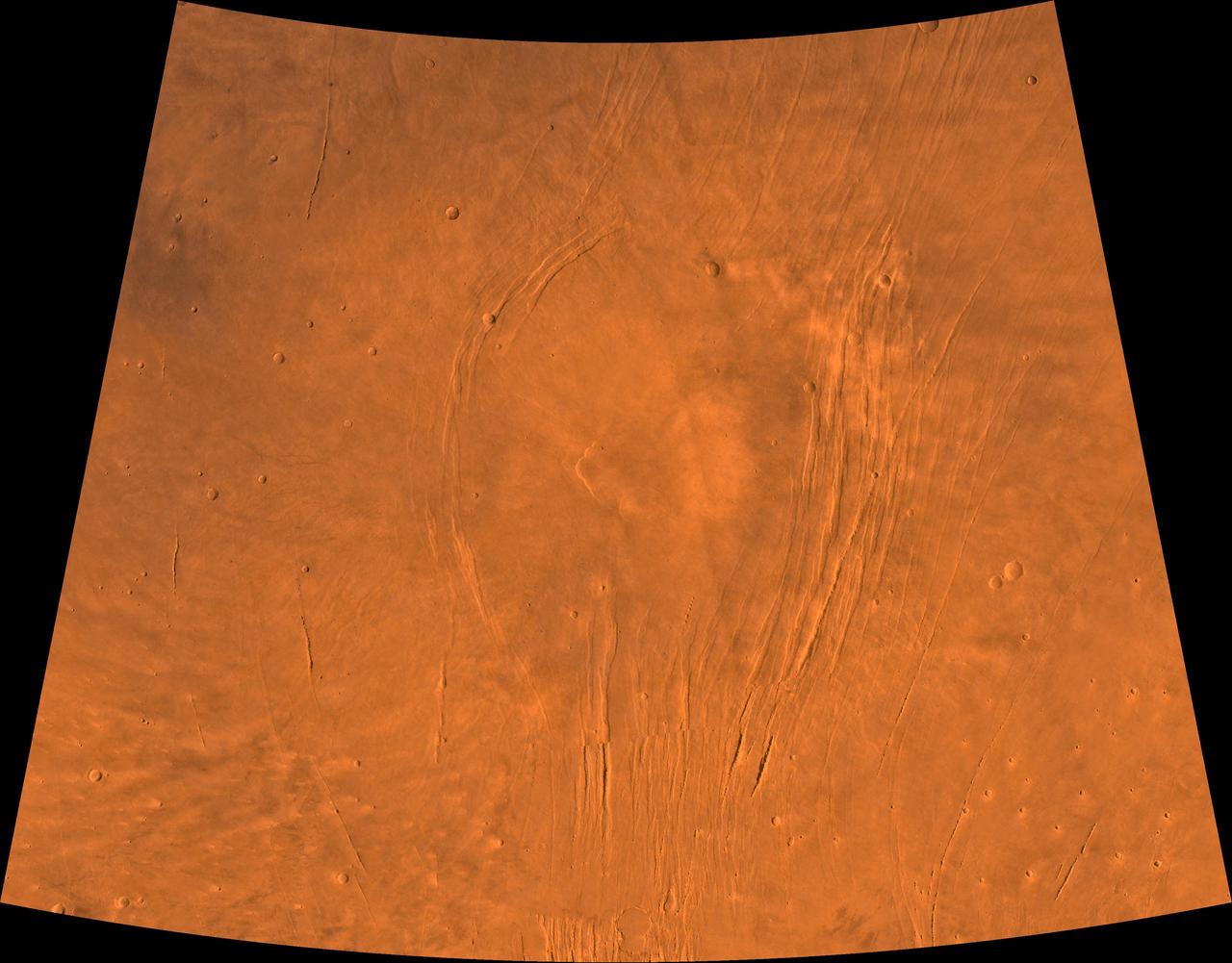
A color image of the Alba Patera region of Mars; north toward top. The scene shows a central circular depression surrounded by splays of fractures, named Alba Fossae (west of Alba Patera) and Tantalus Fossae (east of Alba Patera). A patera (Latin for shallow dish or saucer) is a volcano of broad areal extent with little vertical relief; a fossa is a linear depression. This image is a composite of Viking medium-resolution images in black and white and low-resolution images in color. The image extends from latitude 30 degrees N. to 50 degrees N. and from longitude 95 degrees to 125 degrees; Lambert projection. Alba Patera has a 100-km-diameter caldera at its center surrounded by a fracture ring. In total, the approximately 1,200- km-diameter Alba Patera far exceeds any other known volcano in areal extent; it covers eight times the area of Olympus Mons (the highest volcano in the Solar System) but reaches only about 6 km in height. The patera lies directly north of the Tharsis bulge, which encompasses the most intensely and most recently active volcanic region of the planet. The fossae of the Alba area are fault-bound graben that can be traced south through the Tharsis bulge and therefore likely formed by upwarping of the Tharsis bulge as well as the coeval upwelling of Alba Pateria magma. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00409
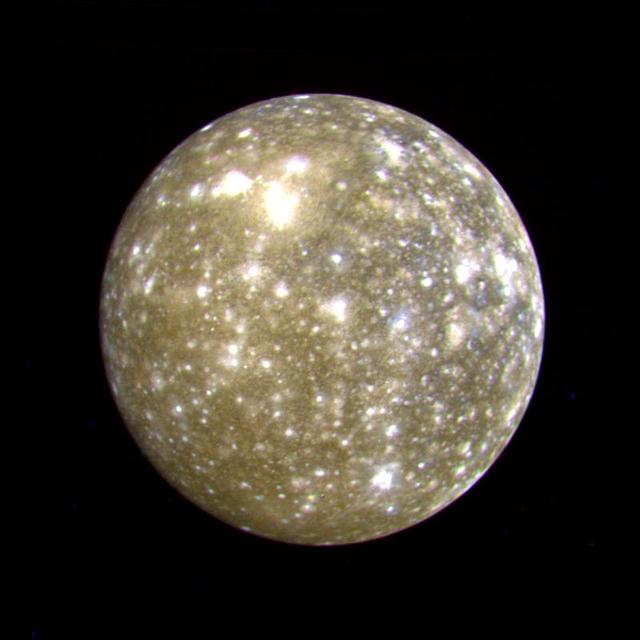

This false color picture of Callisto was taken by NASA's Voyager 2 on July 7, 1979 at a range of 1,094,666 kilometers (677,000 miles) and is centered on 11 degrees N and 171 degrees W. This rendition uses an ultraviolet image for the blue component. Because the surface displays regional contrast in UV, variations in surface materials are apparent. Notice in particular the dark blue haloes which surround bright craters in the eastern hemisphere. The surface of Callisto is the most heavily cratered of the Galilean satellites and resembles ancient heavily cratered terrains on the moon, Mercury and Mars. The bright areas are ejecta thrown out by relatively young impact craters. A large ringed structure, probably an impact basin, is shown in the upper left part of the picture. The color version of this picture was constructed by compositing black and white images taken through the ultraviolet, clear and orange filters. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00457
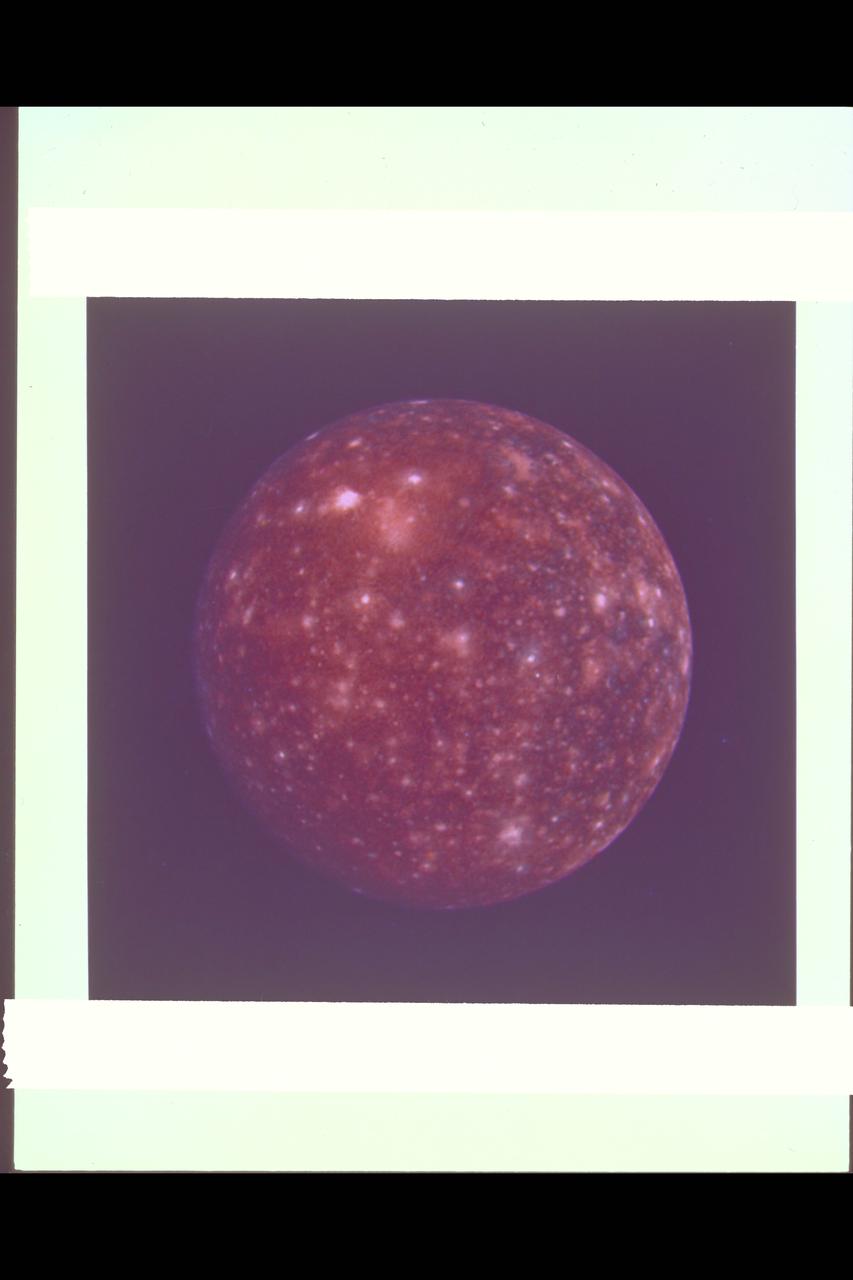

Range : 1,094,666 km (677,000 mi.) This false color picture of Callisto was taken by Voyager 2 and is centered on 11 degrees N and 171 degrees W. This rendition uses an ultraviolet image for the blue component. Because the surface displays regional contrast in UV, variations in surface materials are apparent. Notice in particular the dark blue haloes which surround bright craters in the eastern hemisphere. The surface of Callisto is the most heavily cratered of the Galilean satellites and resembles ancient heavily cratered terrains on the moon, Mercury and Mars. The bright areas are ejecta thrown out by relatively young impact craters. A large ringed structure, probably an impact basin, is shown in the upper left part of the picture. The color version of this picture was constructed by compositing black and white images taken through the ultraviolet, clear and orange filters.
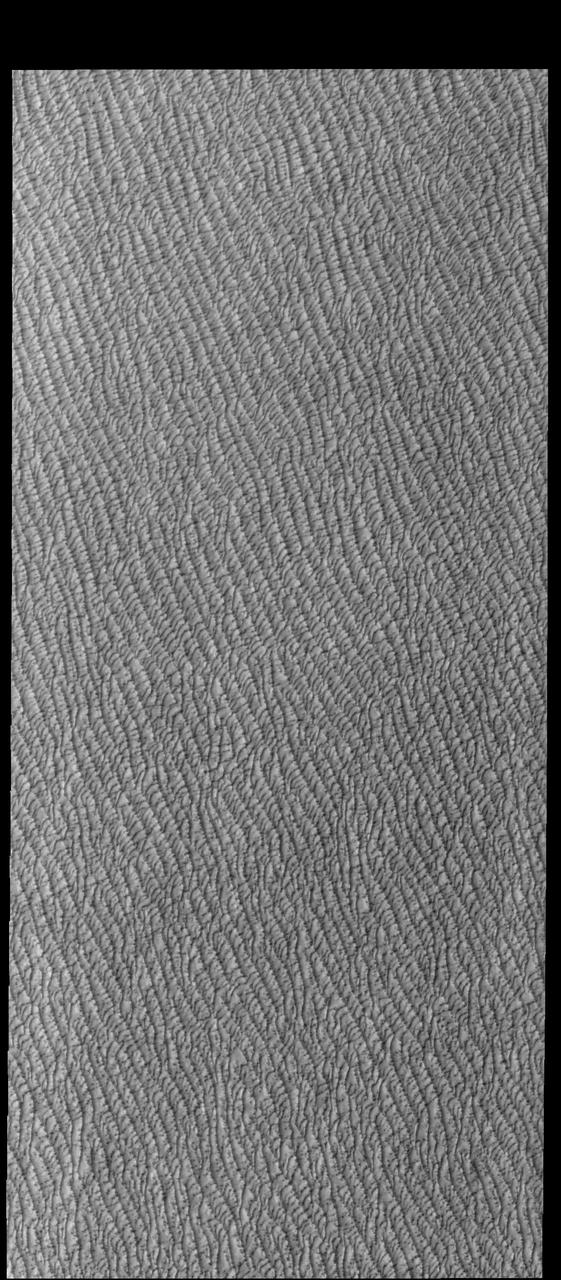

This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected during north polar spring. The dunes are still partially covered by the winter frosts; as the region heats up the frost will dissipate to reveal the dark sand beneath. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. Orbit Number: 94436 Latitude: 80.4194 Longitude: 227.978 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2023-03-30 04:29 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26028

This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected at the very end of north polar spring. As the season changes into summertime, the dune crests have lost all the winter frosts completely revealing the darker sand beneath. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. Orbit Number: 78980 Latitude: 80.645 Longitude: 225.957 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2019-10-04 13:10 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23539

This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected during north polar summer. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. Orbit Number: 80440 Latitude: 80.7922 Longitude: 225.187 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-02-01 18:23 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23833

Image released 11 Aug 2011. The "Necklace Nebula" is located 15,000 light-years away in the constellation Sagitta (the Arrow). In this composite image, taken on July 2, 2011, Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 captured the glow of hydrogen (blue), oxygen (green), and nitrogen (red). The object, aptly named the Necklace Nebula, is a recently discovered planetary nebula, the glowing remains of an ordinary, Sun-like star. The nebula consists of a bright ring, measuring 12 trillion miles wide, dotted with dense, bright knots of gas that resemble diamonds in a necklace. <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/necklace-nebula.html" target="_blank" rel="nofollow"></a> <b>Credit:</b> NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
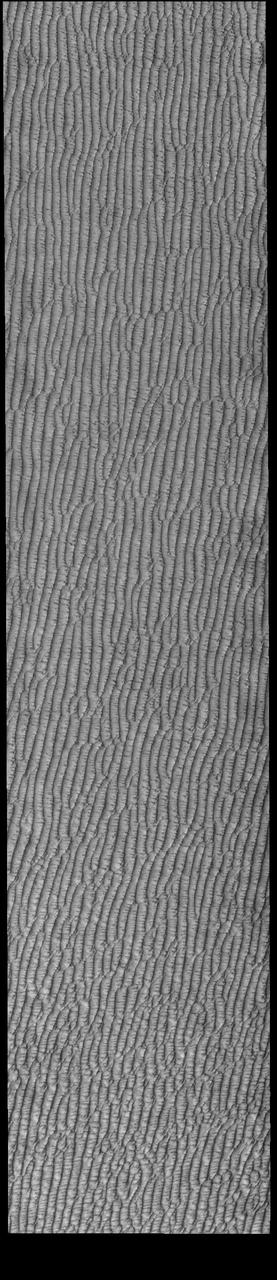
This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected during north polar spring. The dune crests are losing the winter frosts, revealing the dark sand beneath. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. Orbit Number: 94504 Latitude: 81.3452 Longitude: 209.327 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2023-04-04 18:46 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26032
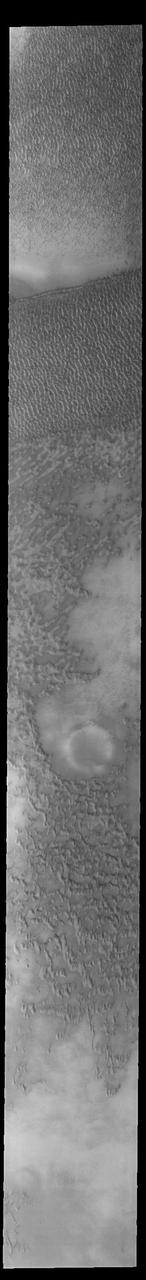
This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected early in north polar spring. The dunes are still covered by the winter frosts; as the region heats up the frost will dissipate to reveal the dark sand beneath. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. Orbit Number: 93727 Latitude: 79.5915 Longitude: 159.786 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2023-01-30 19:25 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25874
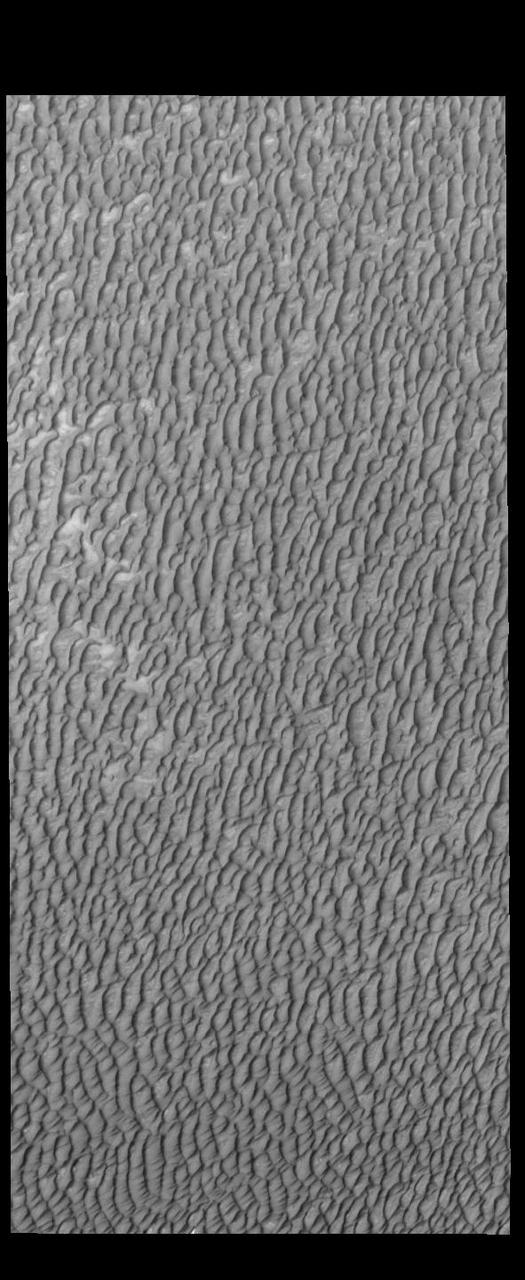

This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected at the middle of north polar summer. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. Orbit Number: 88180 Latitude: 80.9111 Longitude: 135.309 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-10-31 01:32 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25158

This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected during north polar summer. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. Transverse dunes cover the top half of this image. Orbit Number: 80092 Latitude: 81.4474 Longitude: 183.52 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-01-04 02:42 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23751
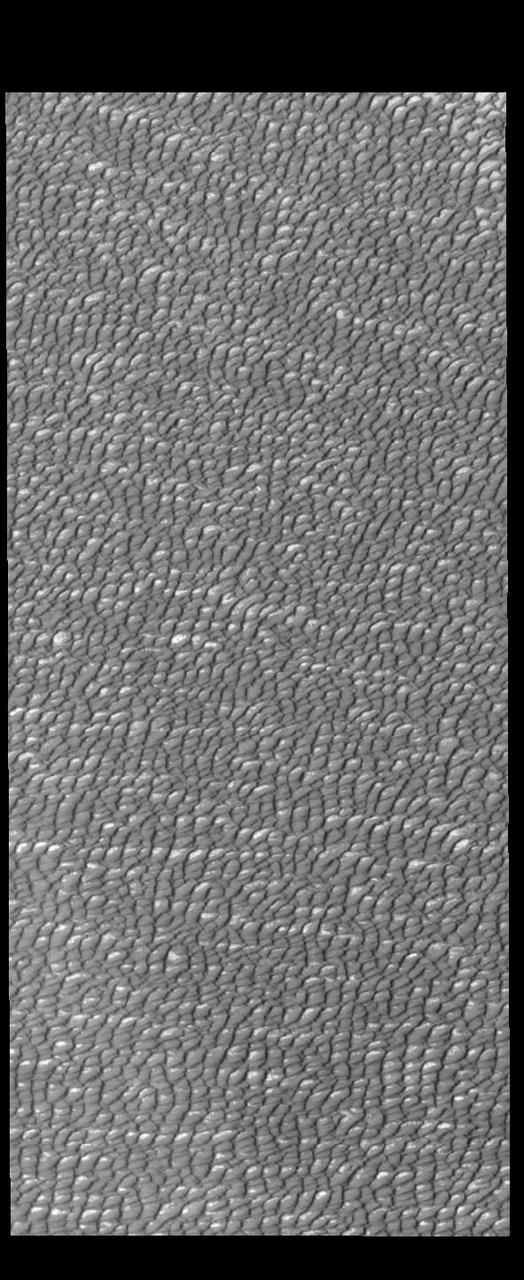

This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected during north polar summer. The dune crests have completely lost the winter frosts, revealing the dark sand. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. Orbit Number: 87767 Latitude: 81.8559 Longitude: 167.732 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-09-27 01:24 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25269

Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 27652 Latitude: 80.983 Longitude: 170.458 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2008-03-09 04:03 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22288
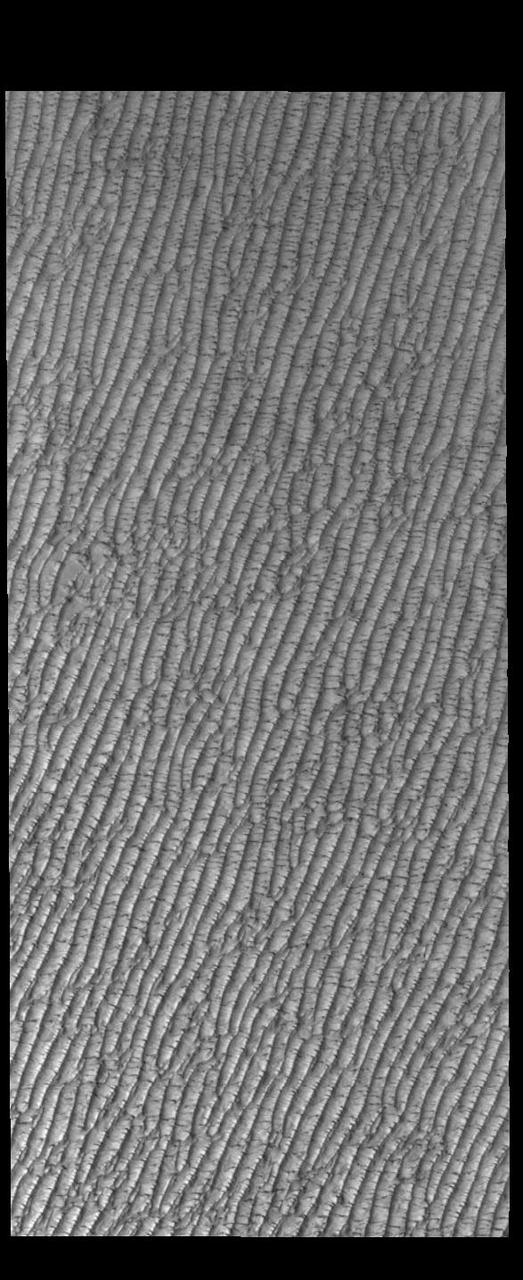

This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected at the beginning of north polar spring. As the season changes into springtime, the dune crests still show most of the winter frosts completely covering the darker sand beneath. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. Orbit Number: 85881 Latitude: 81.5324 Longitude: 216.986 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-04-24 18:26 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24882

This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected at the start polar spring. As the season changes into springtime, the dune crests are just starting to shed the winter frosts which completely hide the darker sand beneath. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. Orbit Number: 85826 Latitude: 80.894 Longitude: 222.032 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-04-20 05:51 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24878
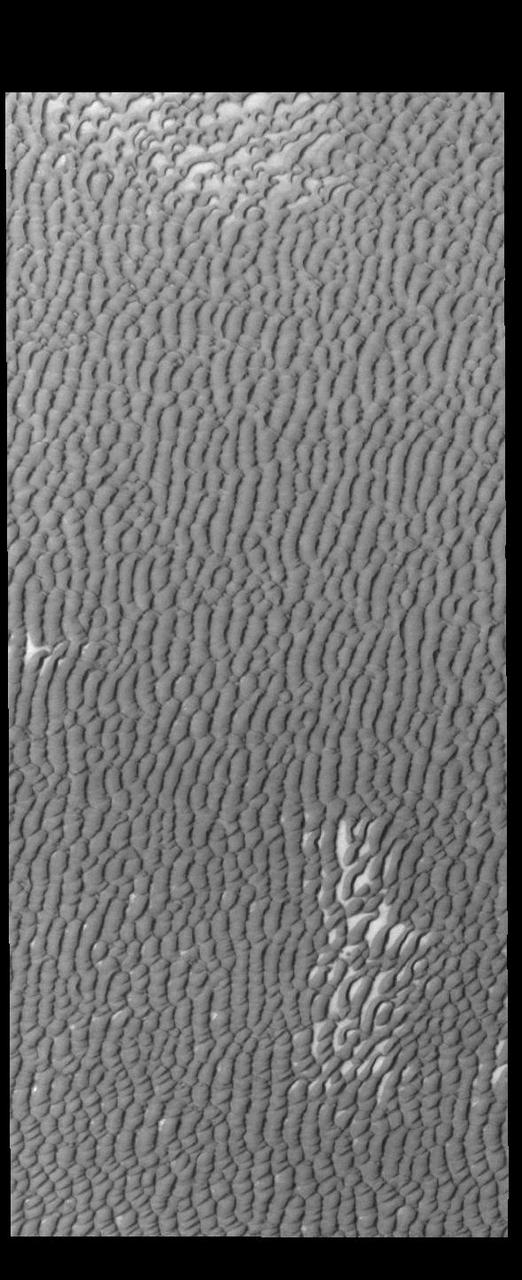
This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected during north polar summer. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. Orbit Number: 88192 Latitude: 81.2425 Longitude: 148.338 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-11-01 01:15 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25192
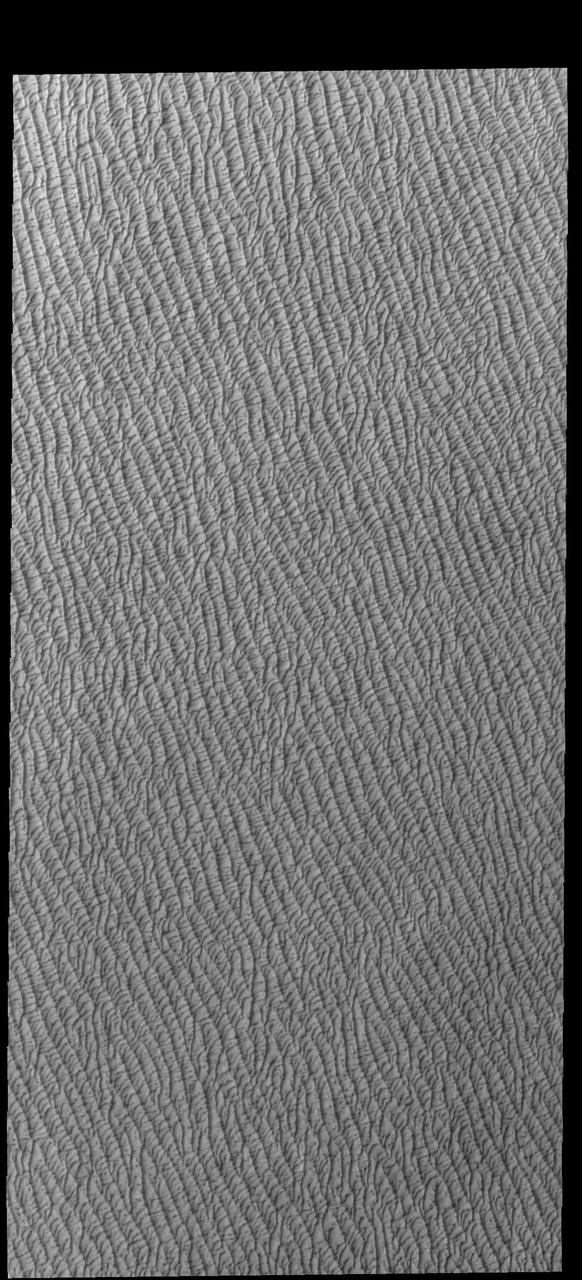

This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected at the middle of north polar spring. As the season changes towards summertime, the dune crests are just starting to lose the winter frosts, revealing the darker sand beneath. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. Orbit Number: 86013 Latitude: 80.6153 Longitude: 226.709 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-05-05 15:23 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24221
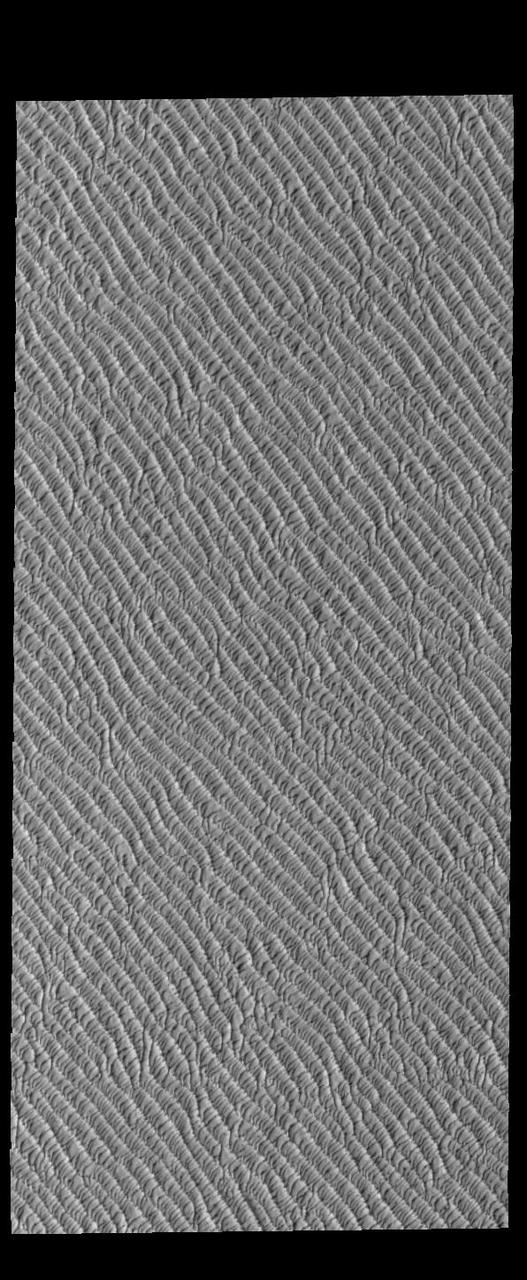

This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected during north polar spring. The dunes are still partially covered by the winter frosts; as the region heats up the frost will dissipate to reveal the dark sand beneath. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. Orbit Number: 94624 Latitude: 80.6784 Longitude: 204.452 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2023-04-14 15:59 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26039
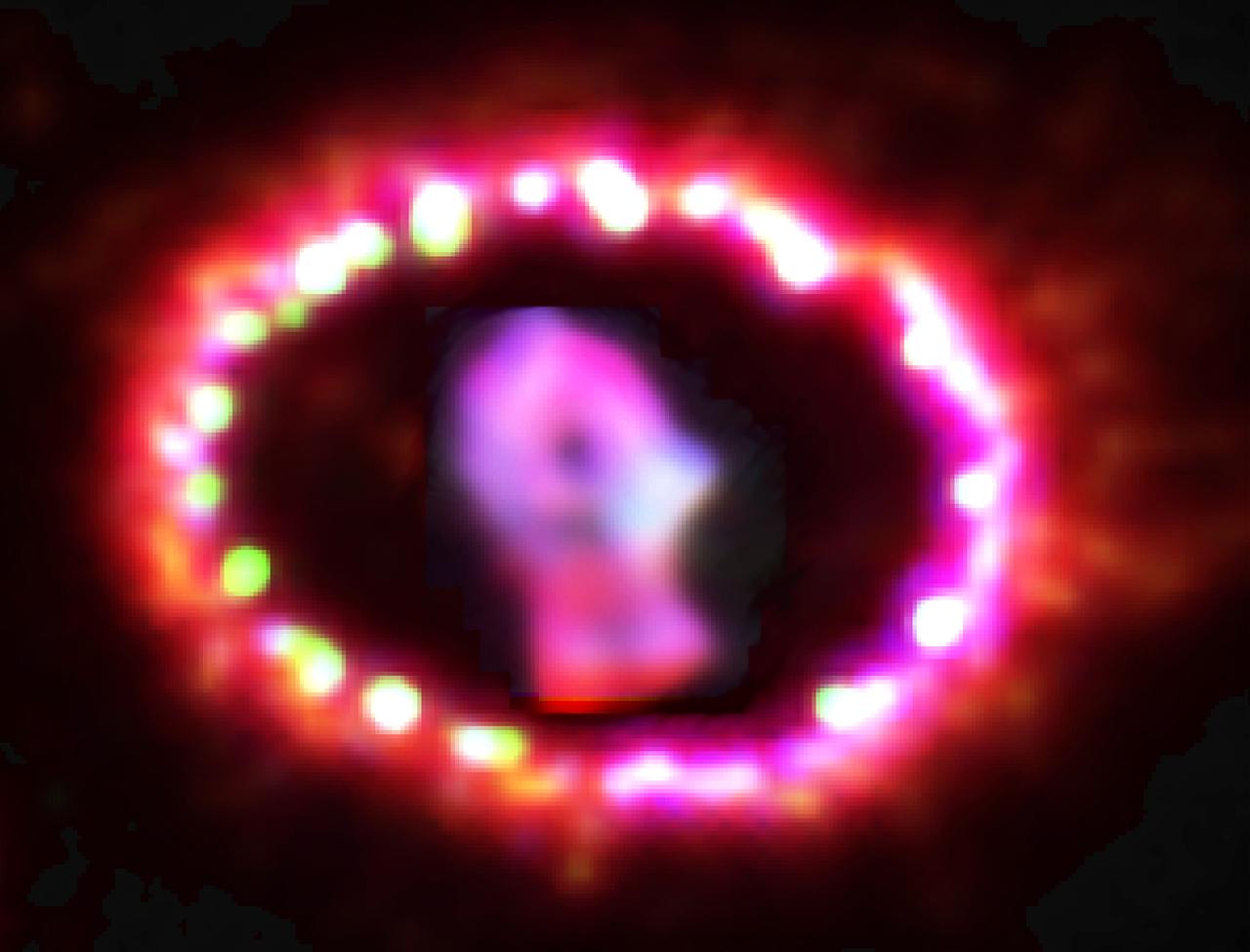
NASA image release June 10, 2011 Astronomers using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope are witnessing the unprecedented transition of a supernova to a supernova remnant, where light from an exploding star in a neighboring galaxy, the Large Magellanic Cloud, reached Earth in February 1987. Named Supernova 1987A, it was the closest supernova explosion witnessed in almost 400 years. The supernova's close proximity to Earth has allowed astronomers to study it in detail as it evolves. Now, the supernova debris, which has faded over the years, is brightening. This means that a different power source has begun to light the debris. The debris of SN 1987A is beginning to impact the surrounding ring, creating powerful shock waves that generate X-rays observed with NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. Those X-rays are illuminating the supernova debris and shock heating is making it glow in visible light. The results are being reported in the June 9, 2011, issue of the journal Nature by a team including Robert Kirshner of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA), who leads a long-term study of SN 1987A with Hubble. Since its launch in 1990, the Hubble telescope has provided a continuous record of the changes in SN 1987A. Credit: NASA, ESA, and P. Challis (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
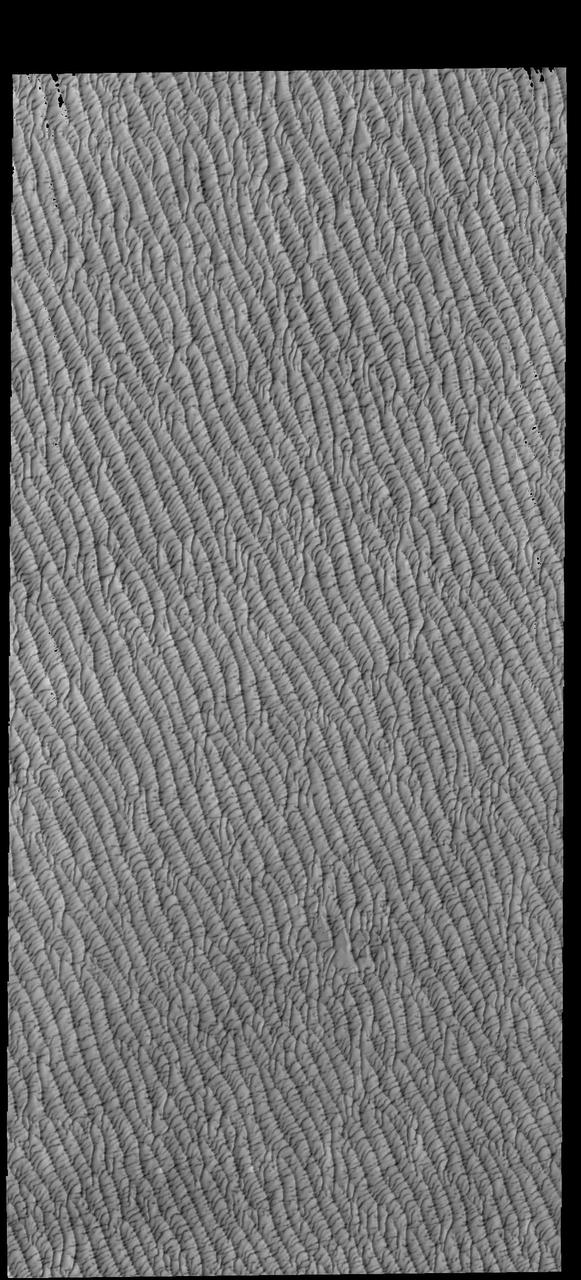

This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected in the middle of north polar spring. As the season changes into summertime, the dune crests will lose all the winter frosts, completely revealing the darker sand beneath. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. Orbit Number: 86712 Latitude: 80.9536 Longitude: 222.236 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-07-02 04:40 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24991
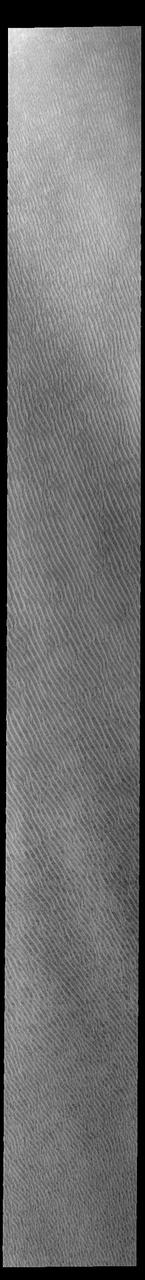
This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected at the start of north polar spring. The dune crests have not yet lost the winter frosts, which still cover the dark sand beneath. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. Orbit Number: 93875 Latitude: 81.2131 Longitude: 213.454 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2023-02-11 23:53 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25908

Image release June 22, 2010 A spectacular new NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image — one of the largest ever released of a star-forming region — highlights N11, part of a complex network of gas clouds and star clusters within our neighbouring galaxy, the Large Magellanic Cloud. This region of energetic star formation is one of the most active in the nearby Universe. The Large Magellanic Cloud contains many bright bubbles of glowing gas. One of the largest and most spectacular has the name LHA 120-N 11, from its listing in a catalogue compiled by the American astronomer and astronaut Karl Henize in 1956, and is informally known as N11. Close up, the billowing pink clouds of glowing gas make N11 resemble a puffy swirl of fairground candy floss. From further away, its distinctive overall shape led some observers to nickname it the Bean Nebula. The dramatic and colourful features visible in the nebula are the telltale signs of star formation. N11 is a well-studied region that extends over 1000 light-years. It is the second largest star-forming region within the Large Magellanic Cloud and has produced some of the most massive stars known. It is the process of star formation that gives N11 its distinctive look. Three successive generations of stars, each of which formed further away from the centre of the nebula than the last, have created shells of gas and dust. These shells were blown away from the newborn stars in the turmoil of their energetic birth and early life, creating the ring shapes so prominent in this image. Beans are not the only terrestrial shapes to be found in this spectacular high resolution image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. In the upper left is the red bloom of nebula LHA 120-N 11A. Its rose-like petals of gas and dust are illuminated from within, thanks to the radiation from the massive hot stars at its centre. N11A is relatively compact and dense and is the site of the most recent burst of star development in the region. Other star clusters abound in N11, including NGC 1761 at the bottom of the image, which is a group of massive hot young stars busily pouring intense ultraviolet radiation out into space. Although it is much smaller than our own galaxy, the Large Magellanic Cloud is a very vigorous region of star formation. Studying these stellar nurseries helps astronomers understand a lot more about how stars are born and their ultimate development and lifespan. Both the Large Magellanic Cloud and its small companion, the Small Magellanic Cloud, are easily seen with the unaided eye and have always been familiar to people living in the southern hemisphere. The credit for bringing these galaxies to the attention of Europeans is usually given to Portuguese explorer Fernando de Magellan and his crew, who viewed it on their 1519 sea voyage. However, the Persian astronomer Abd Al-Rahman Al Sufi and the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci recorded the Large Magellanic Cloud in 964 and 1503 respectively. Credit: NASA, ESA and Jesús Maíz Apellániz (Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía, Spain) To learn more about Hubble go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.

This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected early in north polar spring. The crests of the dunes are light colored, indicative of a frost covering. As the season changes into summertime, the dune crests will lose the frost and reveal the darker sand beneath. The margin of the north polar cap is visible at the top of the image. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 10293 Latitude: 83.0224 Longitude: 174.743 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2004-04-09 22:04 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22289

This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected early in north polar spring. The crests of the dunes are light colored, indicative of a frost covering. As the season changes into summertime, the dune crests will lose the frost and reveal the darker sand beneath. The linear nature of transverse dunes can be seen at the bottom of the image. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 10380 Latitude: 79.7273 Longitude: 176.363 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2004-04-17 02:00 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22290

This VIS image was collected at the height of summer. It is during this season that winds are able to move sand sized particles, slowly modifying the dunes. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 13475 Latitude: 80.7459 Longitude: 177.171 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2004-12-27 21:44 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22297

This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected during north polar spring. The crests of the dunes and other surfaces are light colored, indicative of a frost covering. At the top right of the image is a region of smooth surfaces. This is the ejecta from Jojutla Crater. The ejecta is a higher elevation than the rest of the surface, and dunes are "climbing" or "skirting" the ejecta regions. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time, and, in this case, the presence of different surface elevations. As the season changes into summertime, the dune crests will lose the frost and reveal the darker sand beneath. This loss of frost is just starting to be visible at the bottom of the image. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 27352 Latitude: 80.9139 Longitude: 185.126 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2008-02-13 11:10 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22291
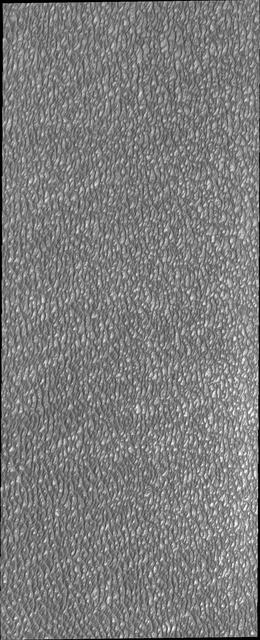
This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected during north polar summer. The dunes are now completely frost free and are dark in color due to being made of basaltic sand. The surface between the dunes, where visible, is a bright tone. In some regions of dense dunes, the bright material may be a deposit on the dunes rather than the underlying surface. The presence of gypsum has been suggested for Olympia Undae, gypsum is a lighter tone than basalt in this filter of the THEMIS VIS camera. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 21125 Latitude: 81.5387 Longitude: 181.591 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2006-09-18 18:07 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22294

This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected during north polar summer. The dunes are now completely frost free and are dark in color due to being made of basaltic sand. The surface between the dunes, where visible, is a bright tone. In some regions of dense dunes, the bright material may be a deposit on the dunes rather than the underlying surface. The presence of gypsum has been suggested for Olympia Undae, gypsum is a lighter tone than basalt in this filter of the THEMIS VIS camera. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 12614 Latitude: 80.8745 Longitude: 174.688 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2004-10-18 00:23 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22293

This VIS image highlights the dune form/dune density aspects of Olypmia Undae. In the center there is a brighter, diagonal region of few dunes. These dunes are the arc or crescent shape of barchan dunes. As more sand becomes available the barchan dunes begin to merge into transverse dunes. The region of dunes surrounding the bright swath still have the underlying surface visible, and the transverse dunes have a lace-like layout. In the regions with a significant abundance of sand have developed the tightly packed transverse dunes with the wave-like distribution. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 13238 Latitude: 80.7247 Longitude: 173.91 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2004-12-08 09:25 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22296
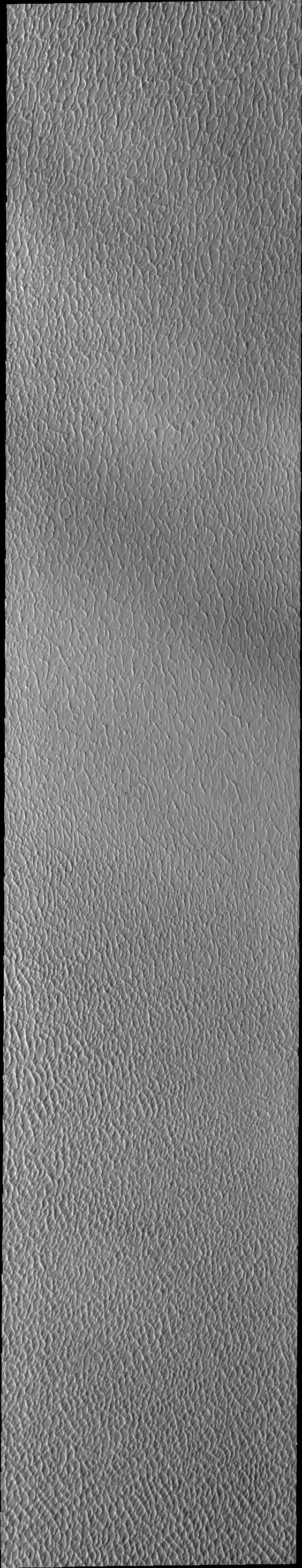

This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected during north polar spring. The crests of the dunes and other surfaces are light colored, indicative of a frost covering. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. As the season changes into summertime, the dune crests will lose the frost and reveal the darker sand beneath. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 27402 Latitude: 81.2035 Longitude: 183.317 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2008-02-17 13:59 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22292
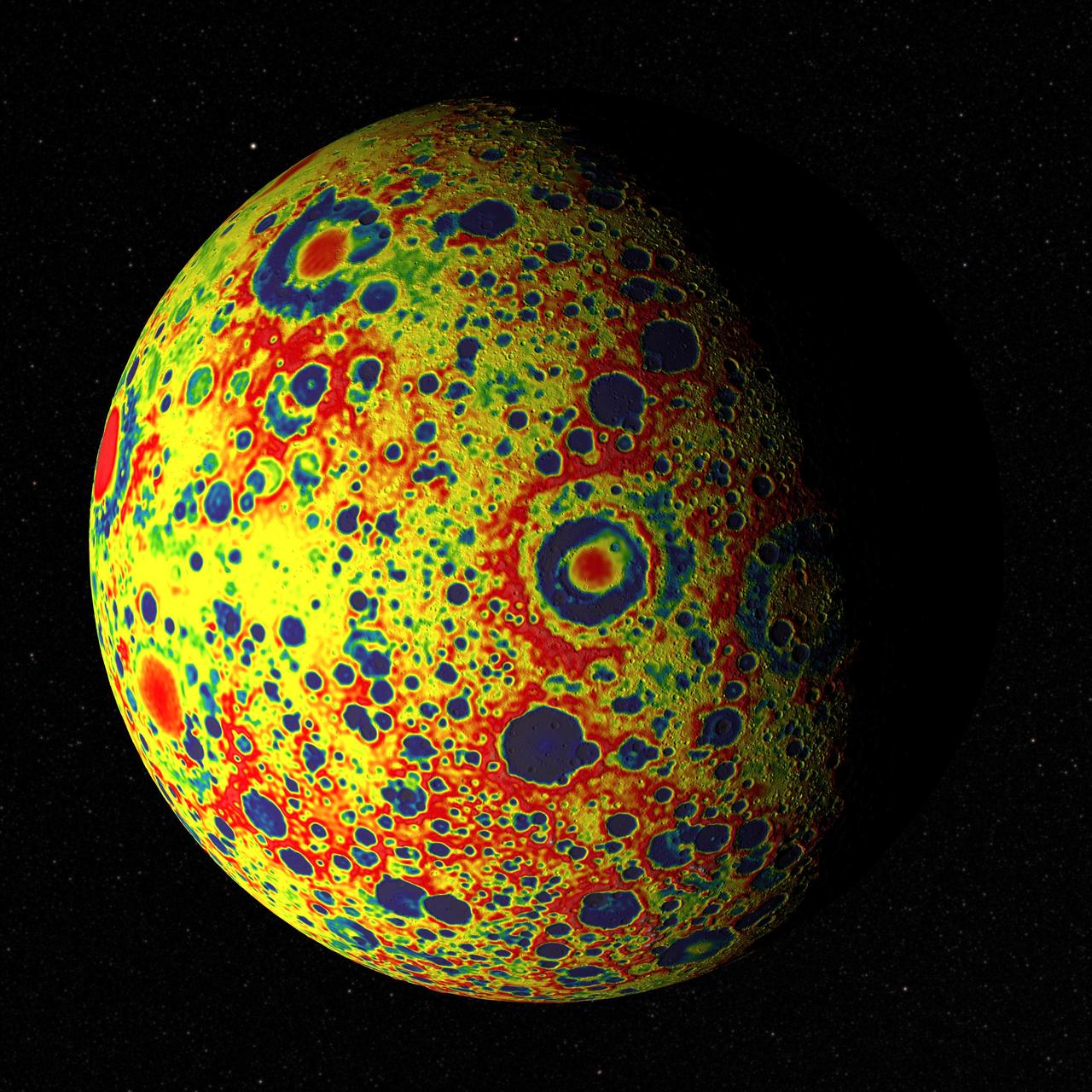
If the Moon were a perfectly smooth sphere of uniform density, the gravity map would be a single, featureless color, indicating that the force of gravity at a given elevation was the same everywhere. But like other rocky bodies in the solar system, including Earth, the Moon has both a bumpy surface and a lumpy interior. Spacecraft in orbit around the Moon experience slight variations in gravity caused by both of these irregularities. The free-air gravity map shows deviations from the mean, the gravity that a cueball Moon would have. The deviations are measured in milliGals, a unit of acceleration. On the map, dark purple is at the low end of the range, at around -400 mGals, and red is at the high end near +400 mGals. Yellow denotes the mean. These views show a part of the Moon's surface that's never visible from Earth. They are centered on lunar coordinates 29°N 142°E. The large, multi-ringed impact feature near the center is Mare Moscoviense. The crater Mendeleev is south of this. The digital elevation model for the terrain is from the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter laser altimeter (LOLA). Merely for plausibility, the sun angle and starry background are accurate for specific dates (December 21, 2012, 0:00 UT and January 8, 2013, 14:00 UT, respectively). To see or download more views go to: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?4041" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?4041</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
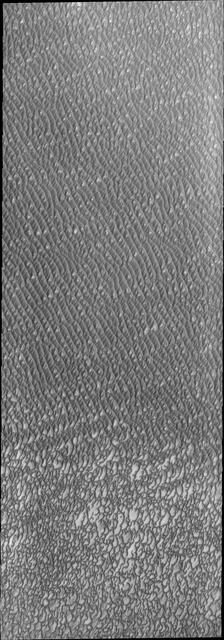
This VIS image of Olympia Undae was collected during north polar summer. The dunes are now completely frost free and are dark in color due to being made of basaltic sand. The surface between the dunes, where visible, is a bright tone. In some regions of dense dunes, the bright material may be a deposit on the dunes rather than the underlying surface. The presence of gypsum has been suggested for Olympia Undae, gypsum is a lighter tone than basalt in this filter of the THEMIS VIS camera. This VIS image hightlights the density of dunes, the bottom third of the image has fewer dunes, spaced farther apart than the top two thirds of the image. The bottom of the image "looks" like lace, while the top with the dense dunes with aligned dune crests "looks" like waves in an ocean. The term used for dune fields on Mar is undae (unda singular). This term translates from Latin as water waves and is used to mean undulatory in planetary nomenclature. All non-Earth dune fields in the solar system are called unda/undae. Olympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of Mars. It consists of a broad sand sea or erg that partly rings the north polar cap from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. The dune field covers an area of approximately 470,000 km2 (bigger than California, smaller than Texas). Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. Olympia Undae is not the only dune field near the north polar cap, several other smaller fields exist in the same latitude, but in other ranges of longitude, e.g. Abolos and Siton Undae. Barchan and transverse dune forms are the most common. In regions with limited available sand individual barchan dunes will form, the surface beneath and between the dunes is visible. In regions with large sand supplies, the sand sheet covers the underlying surface, and dune forms are found modifying the surface of the sand sheet. In this case transverse dunes are more common. Barchan dunes "point" down wind, transverse dunes are more linear and form parallel to the wind direction. The "square" shaped transverse dunes in Olympia Undae are due to two prevailing wind directions. The density of dunes and the alignments of the dune crests varies with location, controlled by the amount of available sand and the predominant winds over time. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 13138 Latitude: 80.8321 Longitude: 178.781 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2004-11-30 03:49 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22295